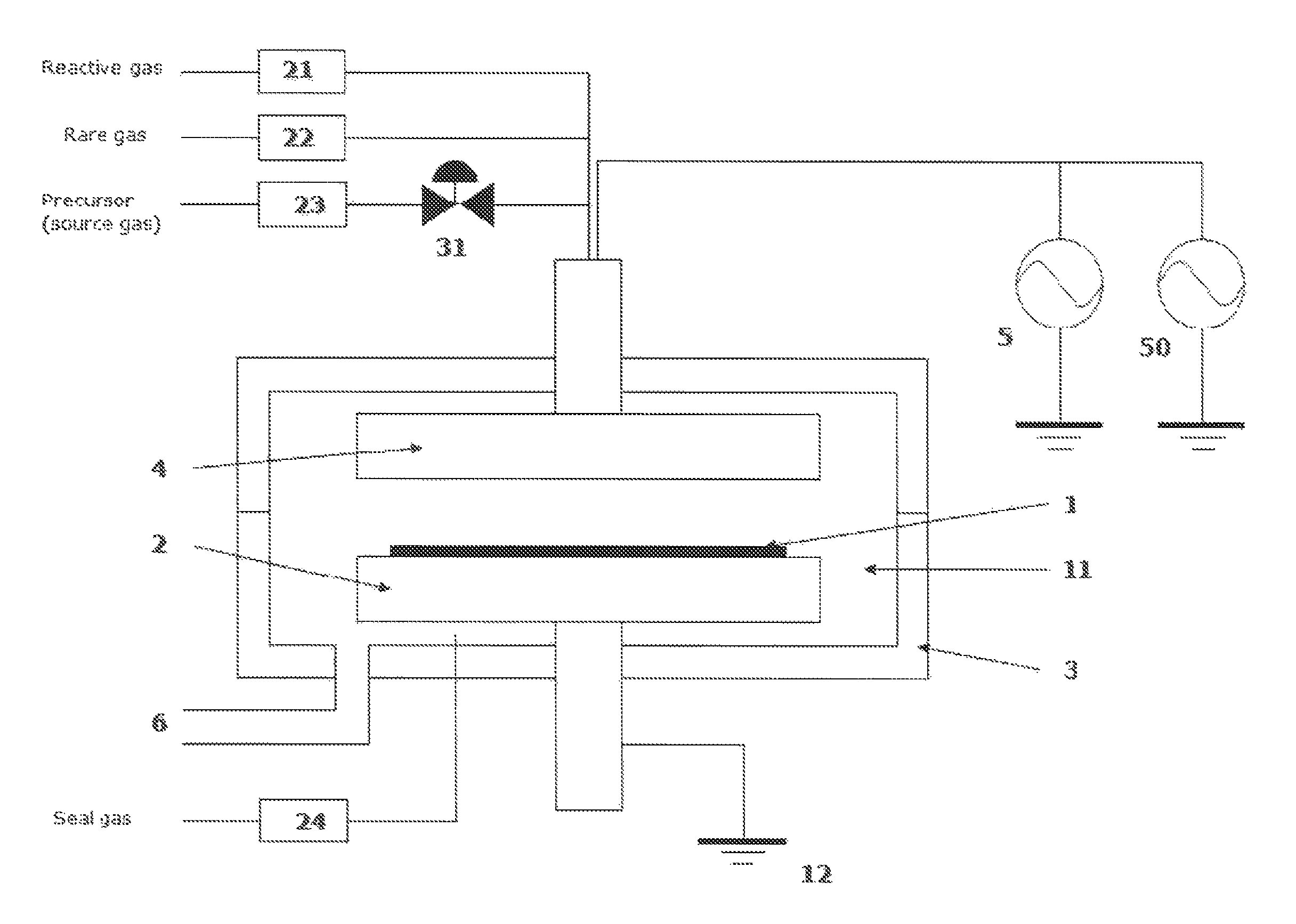Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
2903results about How to "Minimize damage" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
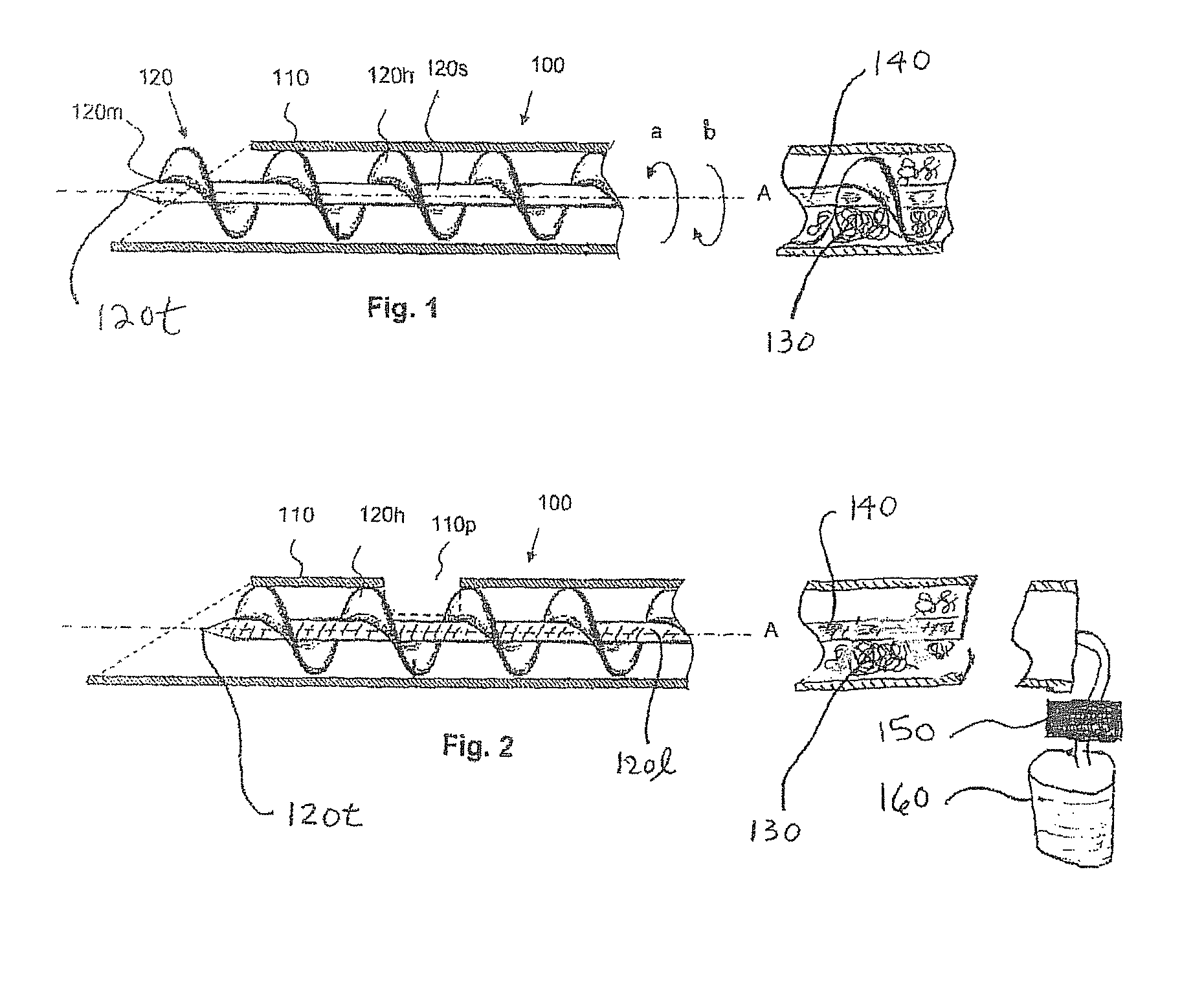
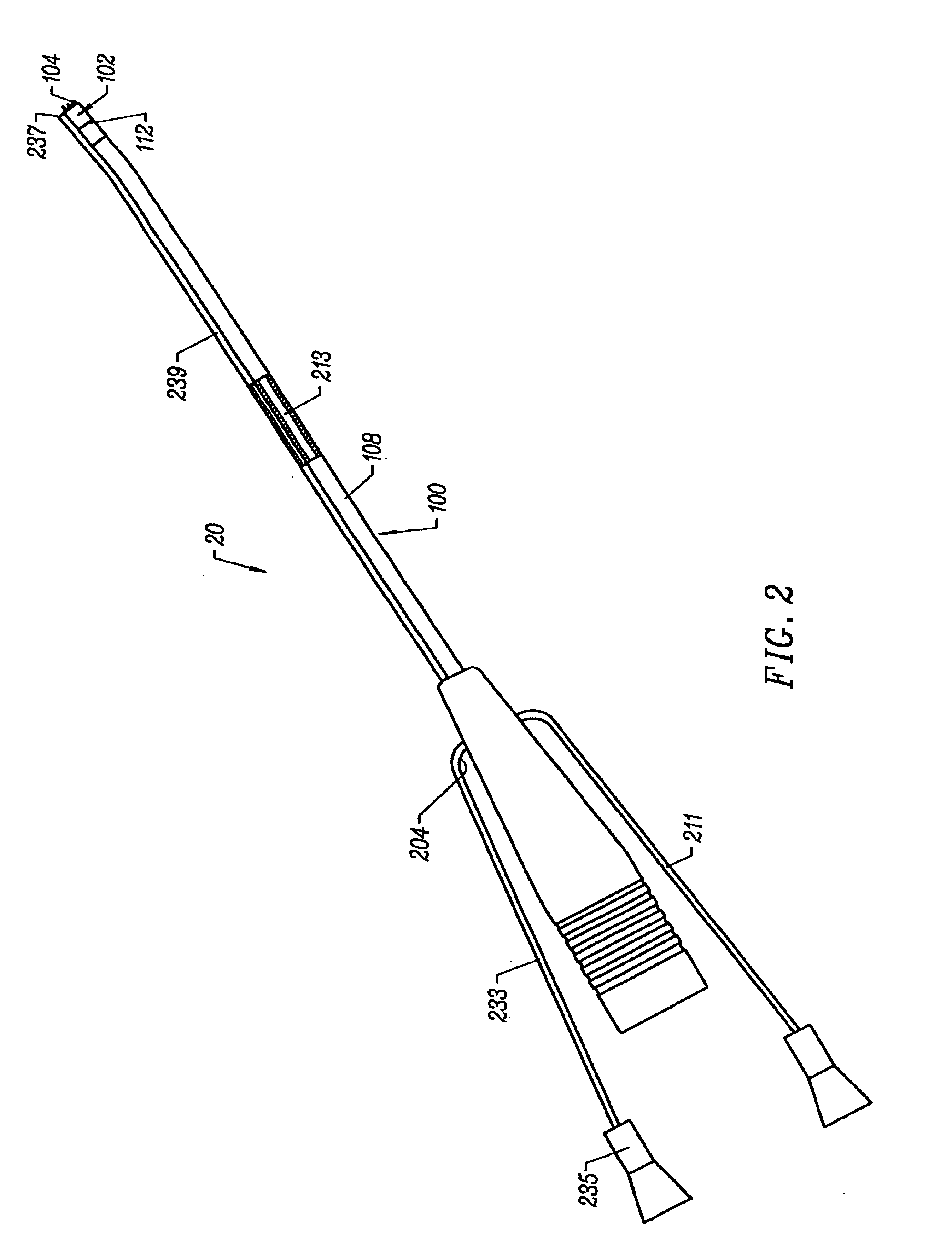
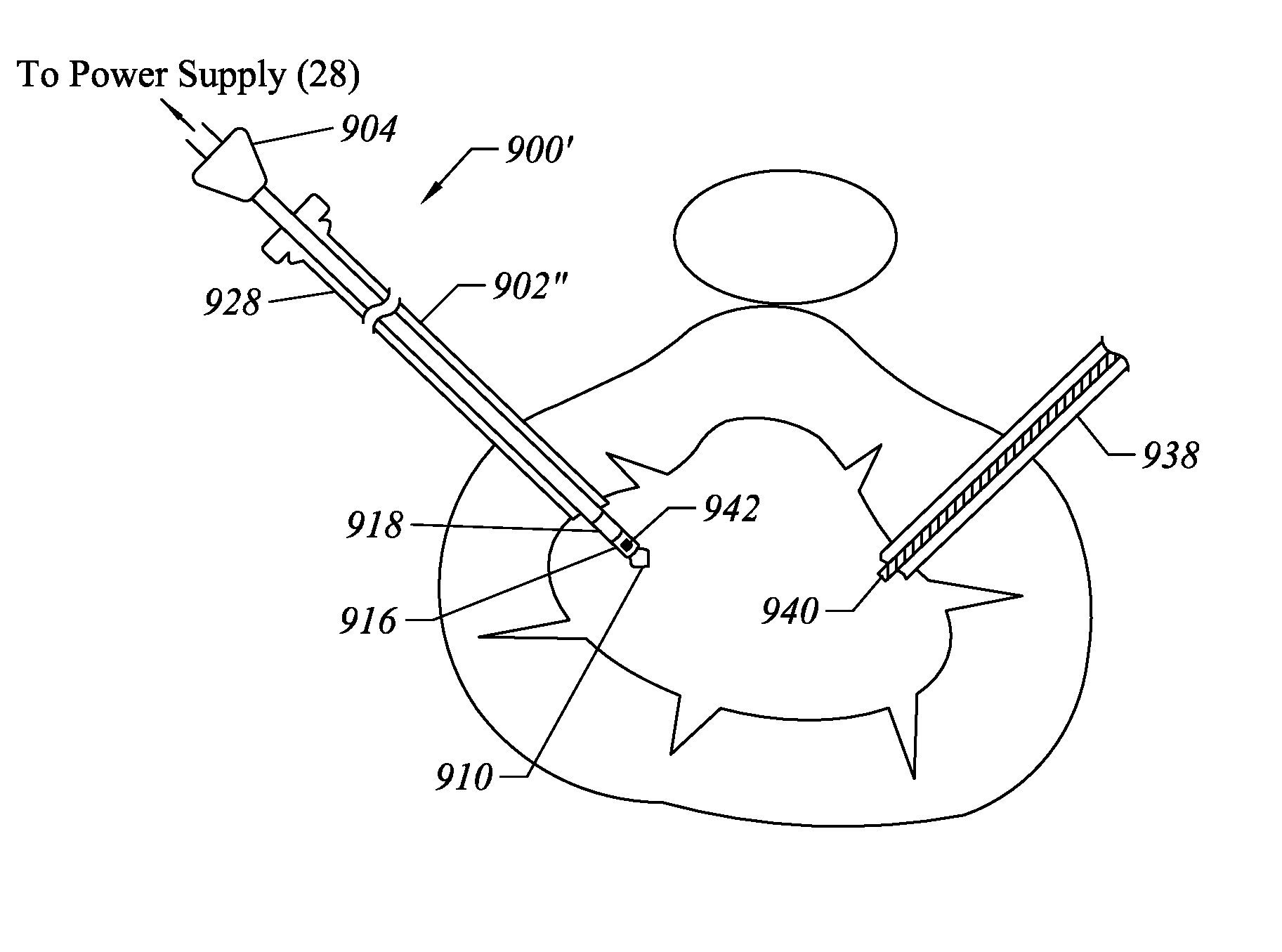
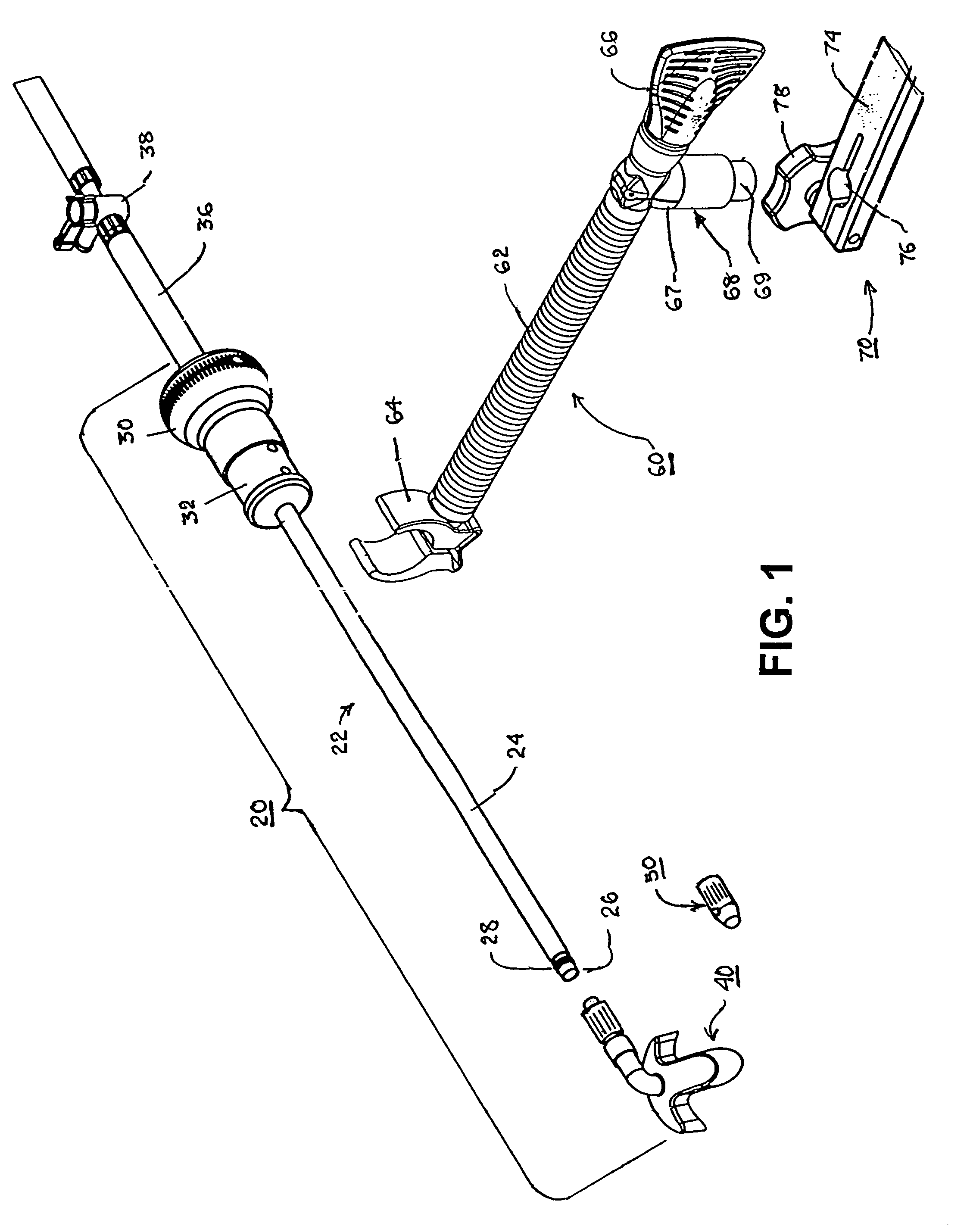
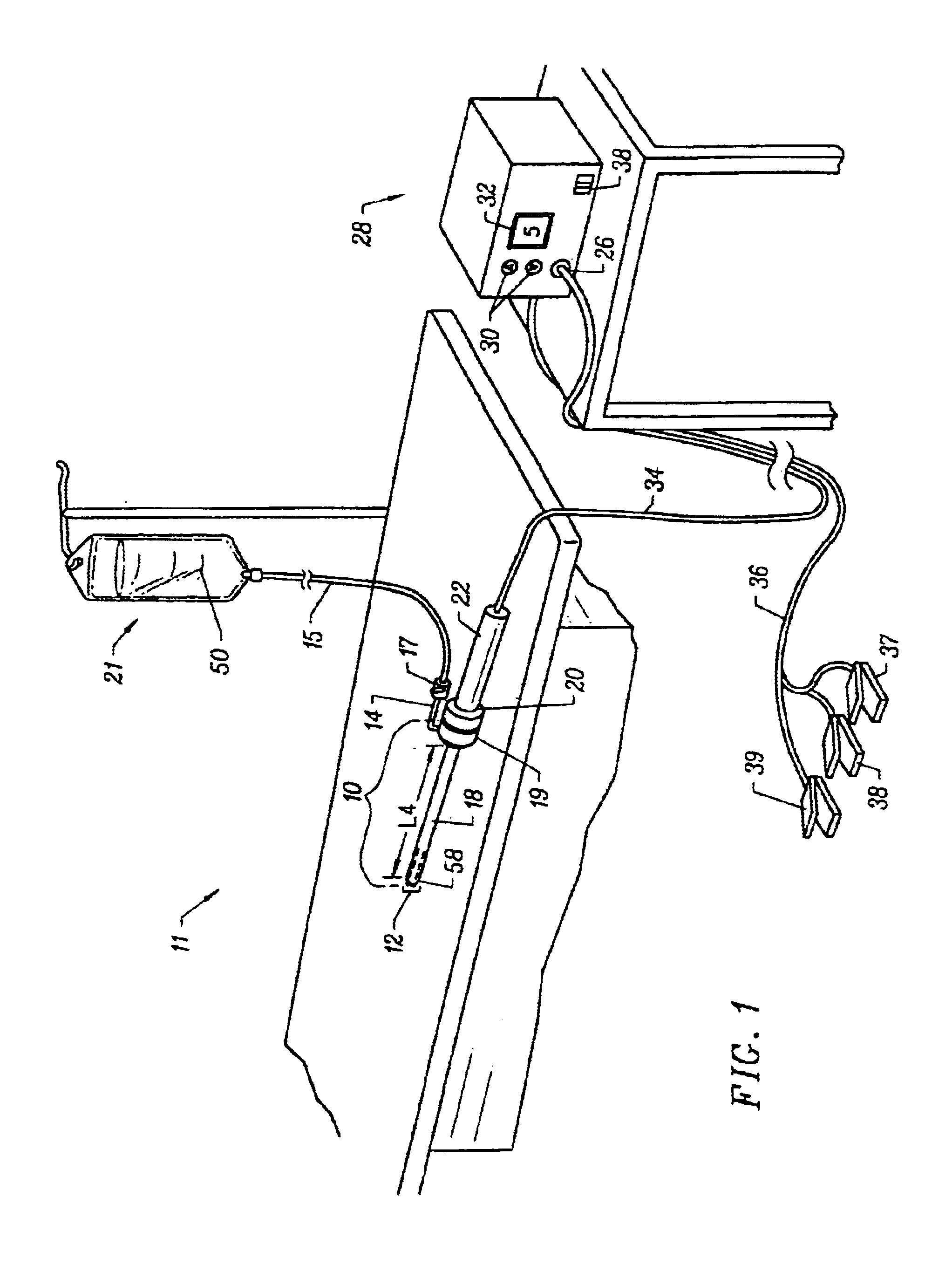
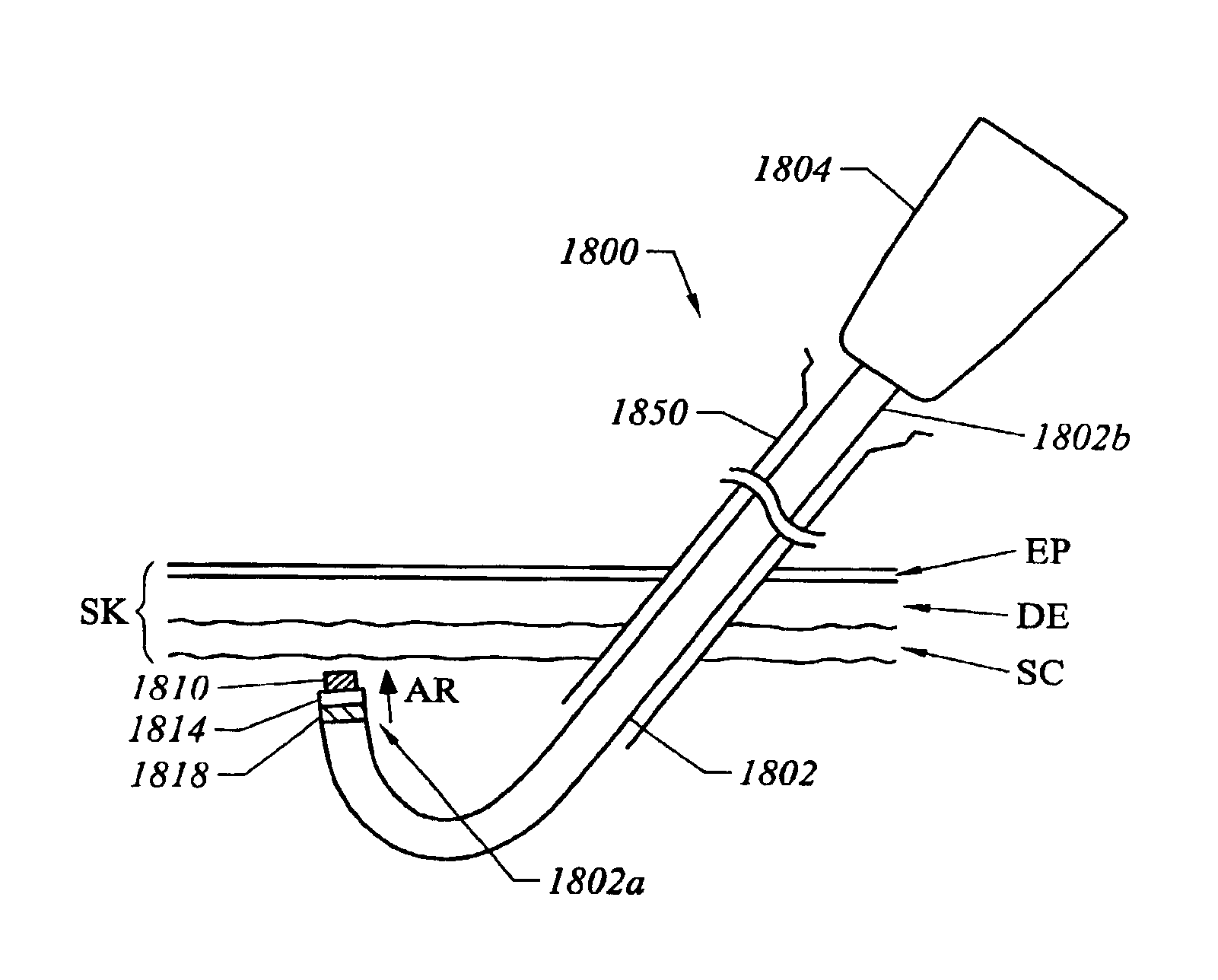
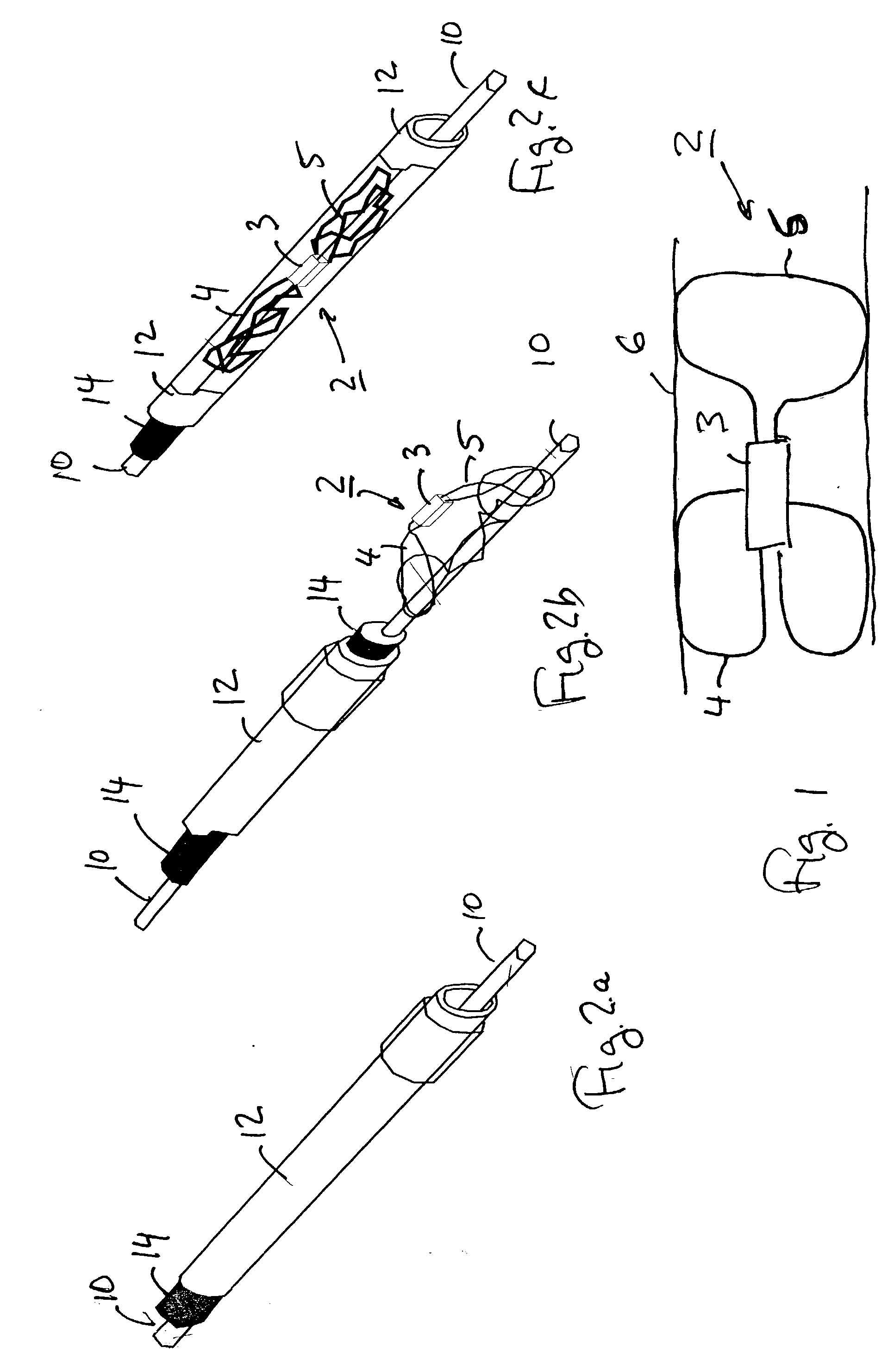
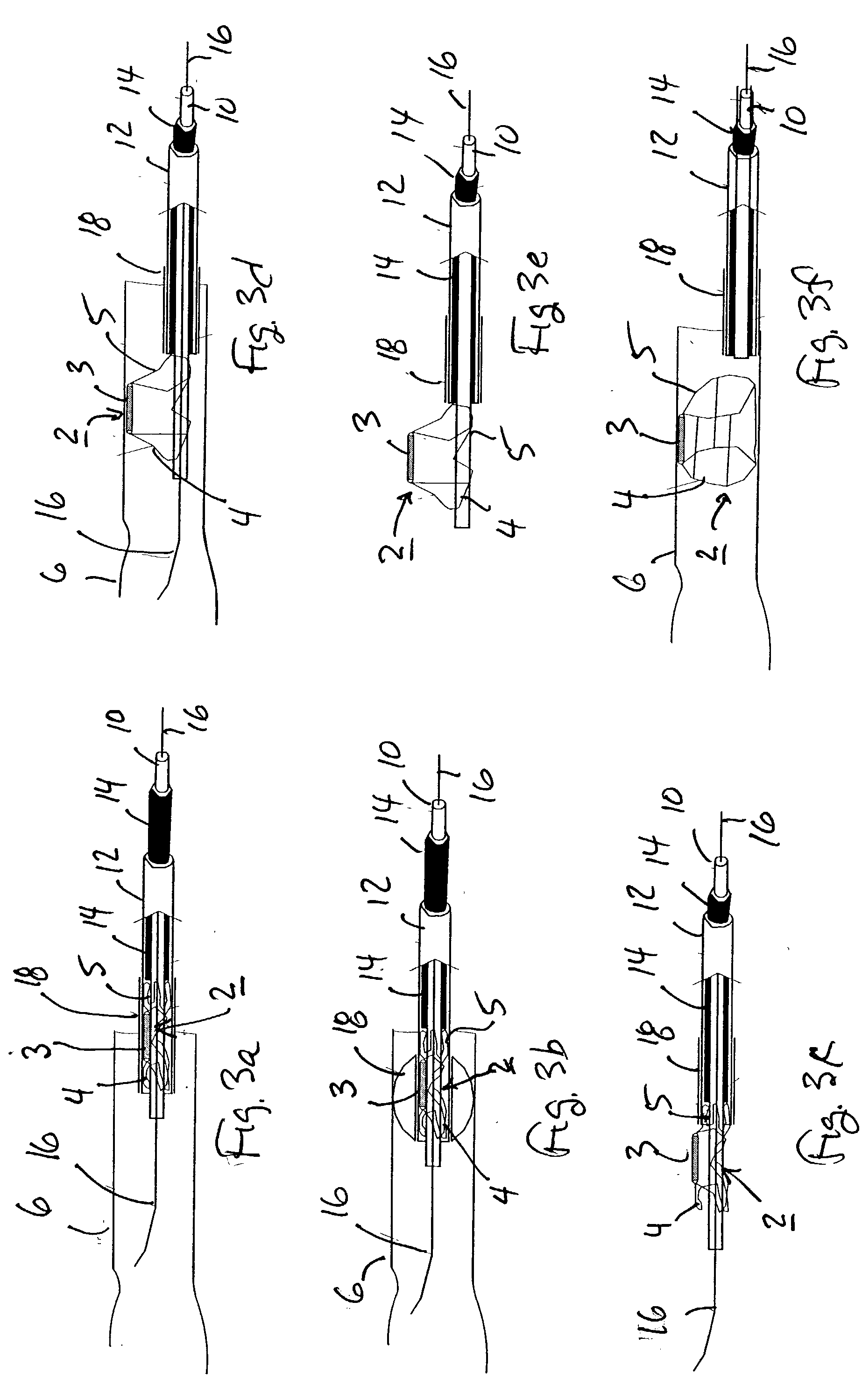
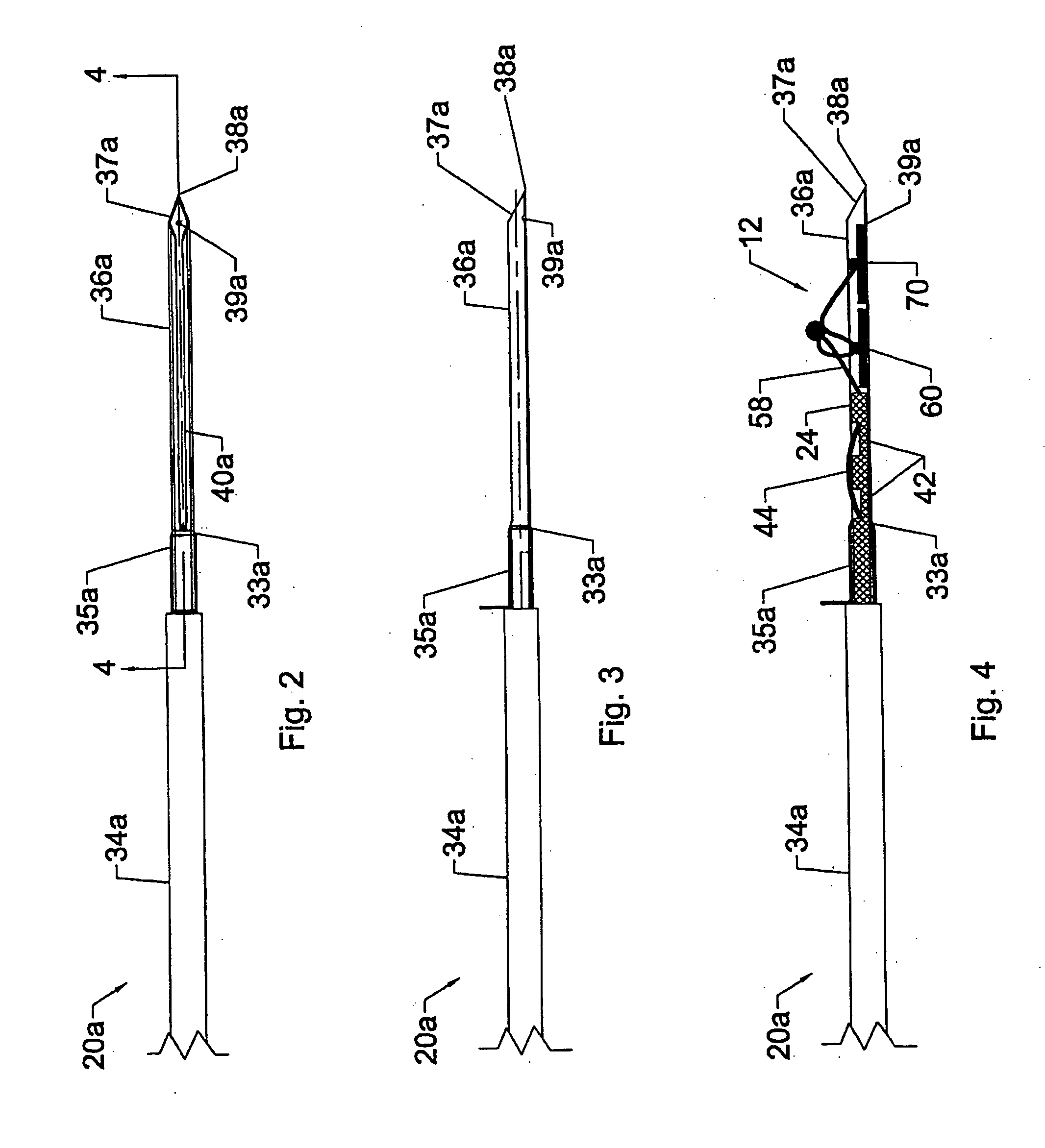
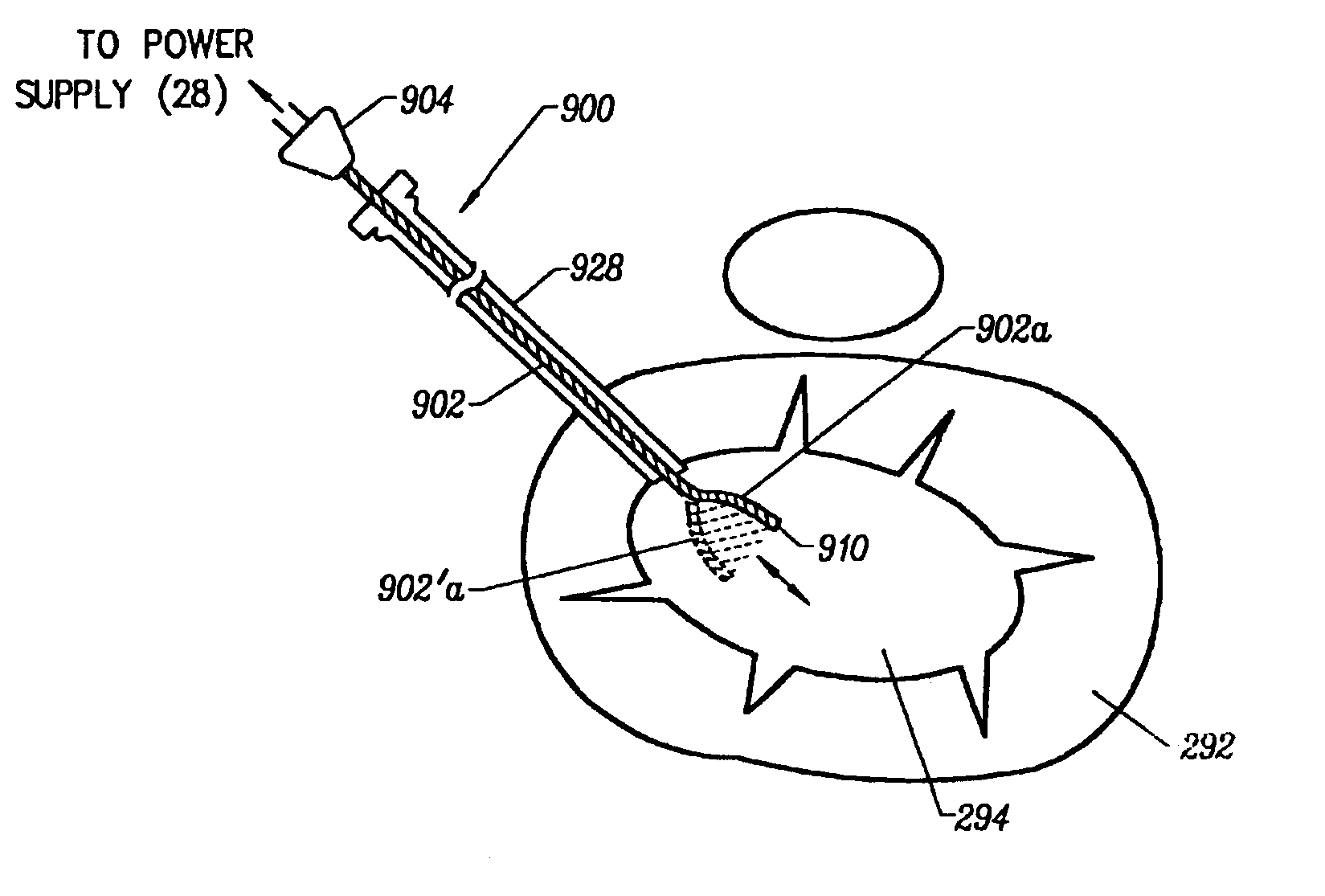
Method and device for tissue removal and for delivery of a therapeutic agent or bulking agent
InactiveUS7806871B2Efficient removalMinimize damageInfusion syringesMedical devicesSurgeryMedical device
According to an aspect of the present invention, a medical device is provided, which comprises the following: (a) a hollow elongate body (e.g., a elongate cylinder, such as a needle) having distal and proximal ends; and (b) a rotatable member comprising a tissue morselizer and an elongate shaft (e.g., an auger-like tissue-drilling bit). The device (i) advances material (e.g., morselated tissue) toward the proximal end of the hollow elongate body when the shaft is rotated in a first direction, and (ii) advances material (e.g., a therapeutic agent and / or a bulking agent) toward the distal end of the hollow elongate body when the shaft is rotated in a second direction that is opposite the first direction. The invention also provides a method of treatment for morselizing and removing tissue from within the patient and creating a void within the patient and introducing a therapeutic agent and / or a bulking agent into the void.
Owner:BOSTON SCI SCIMED INC
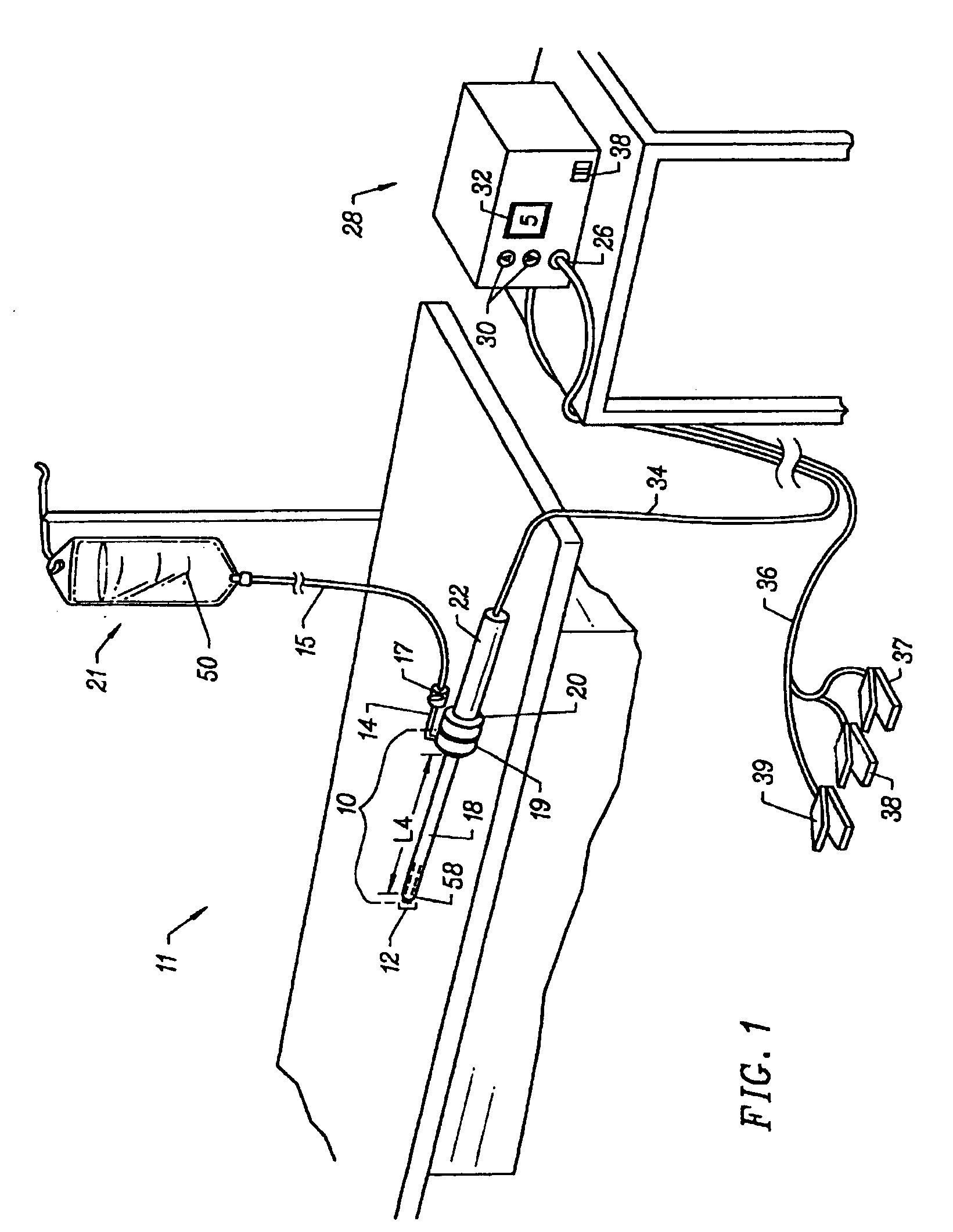
Electrosurgical probe with movable return electrode and methods related thereto
InactiveUS6837888B2Thermal damage is minimizedMinimize damageCannulasEnemata/irrigatorsActive electrodeBiomedical engineering
The present invention provides systems, apparatus, and methods for dissecting, resecting, severing, cutting, contracting, coagulating, or otherwise modifying a tissue or organ of a patient. An apparatus of the invention includes an electrosurgical probe configurable between an open configuration and a closed configuration, the probe including an active electrode terminal, a fixed return electrode disposed proximal to the active electrode terminal, and a movable return electrode configured to move linearly with respect to the active electrode terminal between the open configuration and the closed configuration. A method of the present invention comprises clamping a blood vessel between the active electrode terminal and the movable return electrode, coagulating the clamped blood vessel by application of a first high frequency voltage, and severing the coagulated blood vessel by application of a second high frequency voltage.
Owner:ARTHROCARE
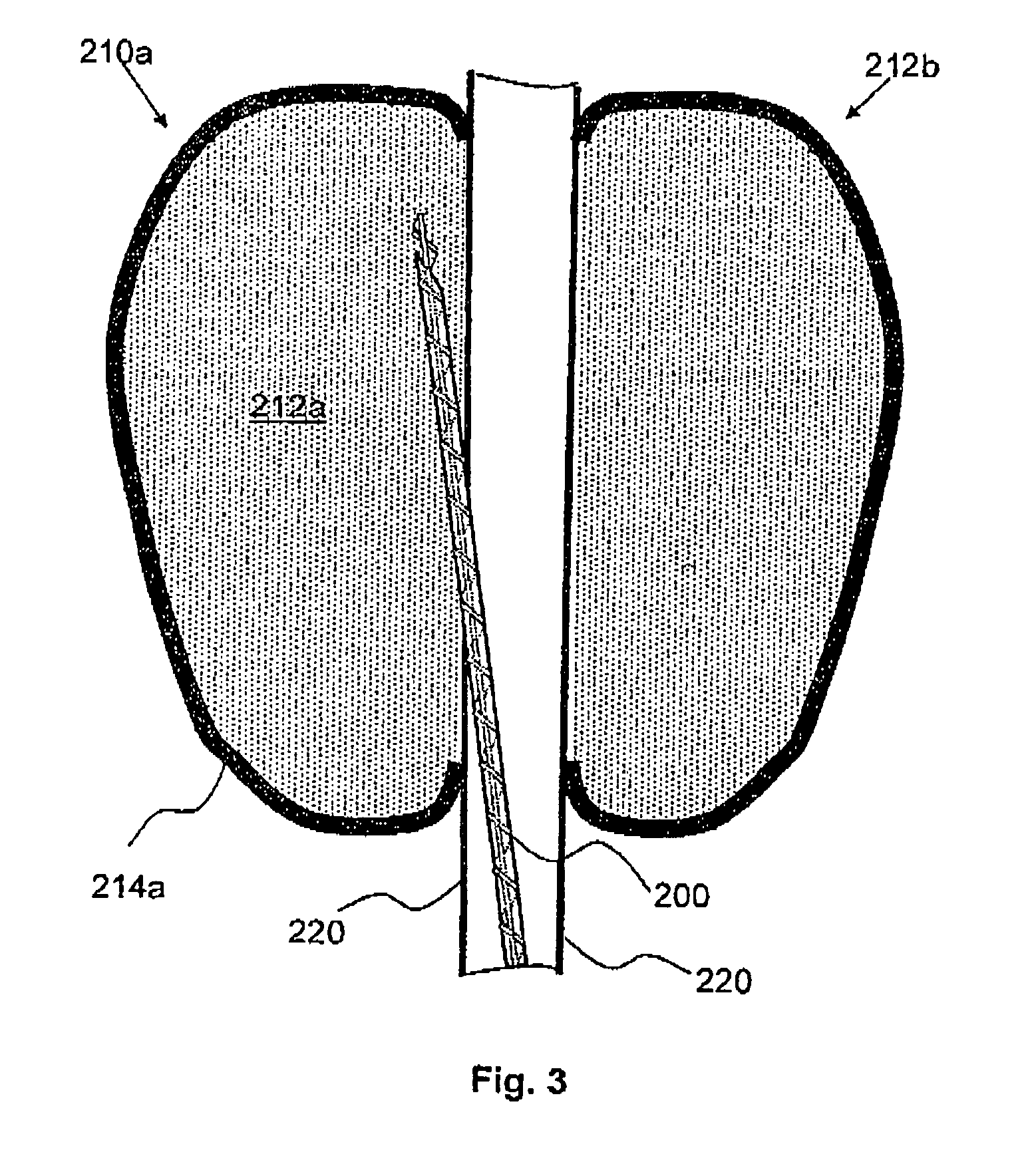
Expandable guide sheath and apparatus with distal protection and methods for use
Apparatus and methods provide distal protection while accessing blood vessels within a patient's vasculature. A flexible sheath and distal protection element, e.g., a balloon or filter, are carried by a stiffening member. The sheath is lubricious and has a relatively thin wall, thereby providing a collapsible / expandable guide for delivering fluids and / or instruments. The sheath is advanced into a blood vessel in a contracted condition, expanded to an enlarged condition to define a lumen, and the distal protection element is deployed within the vessel beyond the sheath. Fluids and / or instruments are introduced into the vessel via the sheath lumen, the distal protection element retaining the fluids and / or capturing emboli released by the instruments. Upon completing the procedure, the sheath, distal protection element, and stiffening member are removed from the vessel.
Owner:MEDTRONIC INC
Methods for targeted electrosurgery on contained herniated discs
InactiveUS7179255B2Reduce pressureReduced neckingEnemata/irrigatorsHeart valvesFibrous ringCorneal ablation
Apparatus and methods for treating an intervertebral disc by ablation of disc tissue. A method of the invention includes positioning at least one active electrode within the intervertebral disc, and applying at least a first high frequency voltage between the active electrode(s) and one or more return electrode(s), wherein the volume of the nucleus pulposus is decreased, pressure exerted by the nucleus pulposus on the annulus fibrosus is reduced, and discogenic pain of a patient is alleviated. In other embodiments, a curved or steerable probe is guided to a specific target site within a disc to be treated, and the disc tissue at the target site is ablated by application of at least a first high frequency voltage between the active electrode(s) and one or more return electrode(s). A method of making an electrosurgical probe is also disclosed.
Owner:ARTHROCARE
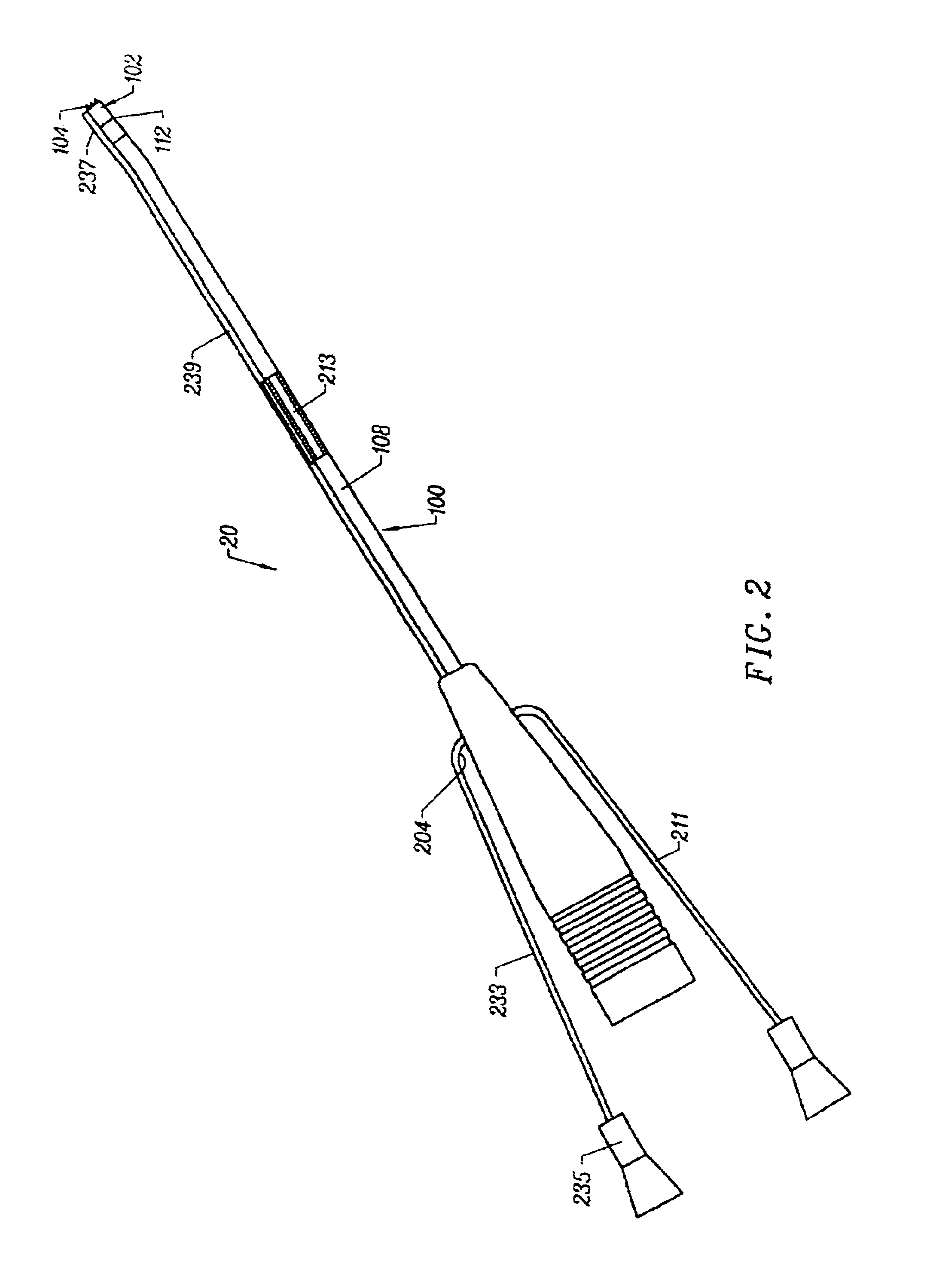
Methods and apparatus providing suction-assisted tissue engagement through a minimally invasive incision
ActiveUS7494460B2Minimize damageEasy to operateDiagnosticsIntravenous devicesSurgical incisionMedicine
Suction-assisted tissue-engaging devices, systems, and methods are disclosed that can be employed through minimal surgical incisions to engage tissue during a medical procedure through application of suction to the tissue through a suction member applied to the tissue. A shaft is introduced into a body cavity through a first incision, and a suction head is attached to the shaft via a second incision. The suction head is applied against the tissue by manipulation of the shaft and suction is applied to engage the tissue while the medical procedure is performed through the second incision. A system coupled to the shaft and a fixed reference point stabilizes the shaft and suction head. When the medical procedure is completed, suction is discontinued, the suction head is detached from the shaft and withdrawn from the body cavity through the second incision, and the shaft is retracted through the first incision.
Owner:MEDTRONIC INC
Methods for repairing damaged intervertebral discs
InactiveUS7318823B2Reduce internal pressureReduce moistureBiocideOrganic chemistryIntervertebral discActive electrode
Apparatus and methods for treating an intervertebral disc by ablation of disc tissue. A method of the invention includes positioning at least one active electrode within the intervertebral disc, and applying at least a first high frequency voltage between the active electrode(s) and one or more return electrode(s), wherein the volume of the nucleus pulposus is decreased, pressure exerted by the nucleus pulposus on the annulus fibrosus is reduced, and discogenic pain of a patient is alleviated. In other embodiments, a curved or steerable probe is guided to a specific target site within a disc to be treated, and the disc tissue at the target site is ablated by application of at least a first high frequency voltage between the active electrode(s) and one or more return electrode(s). A method of making an electrosurgical probe is also disclosed.
Owner:ARTHROCARE
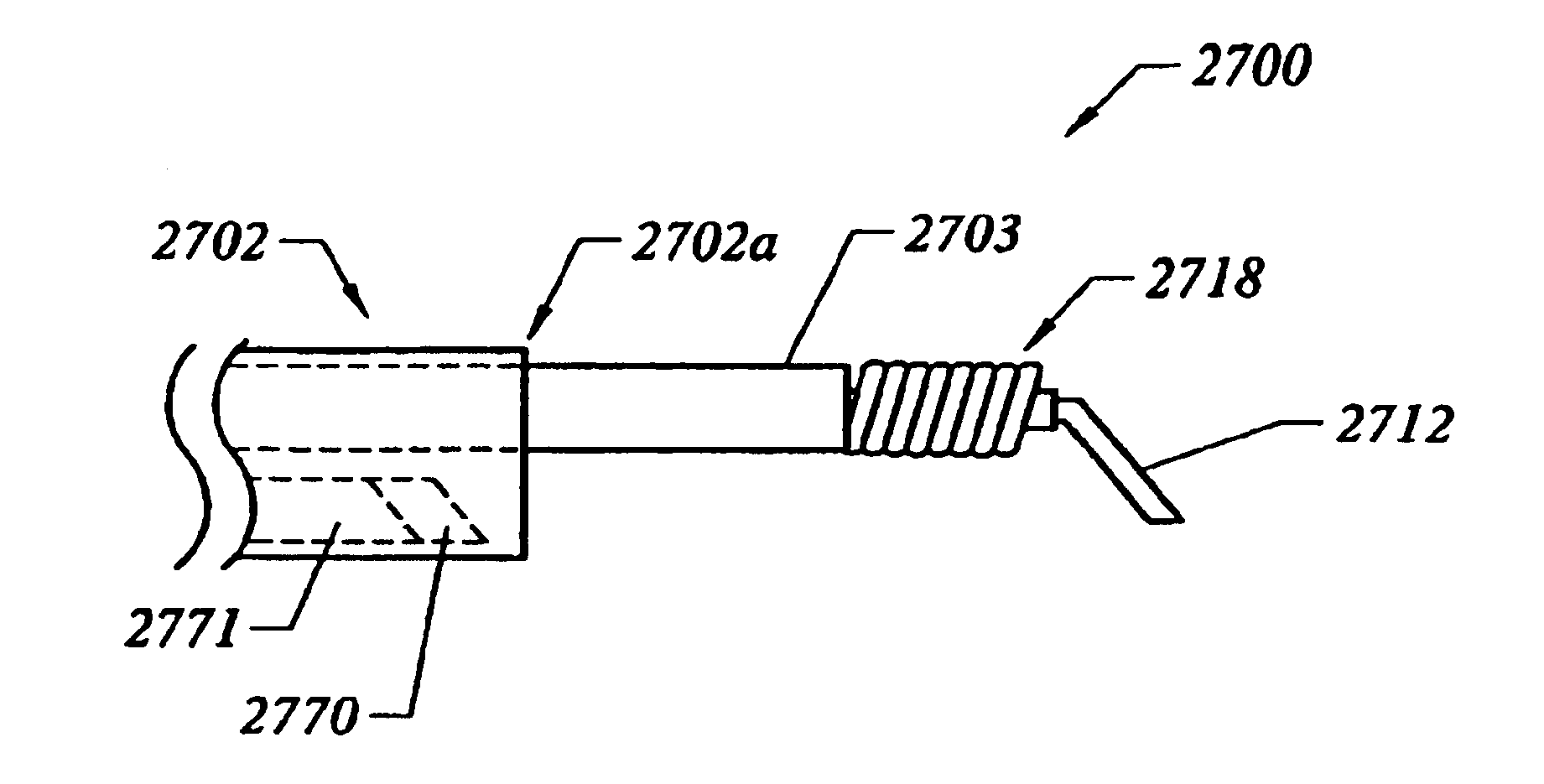
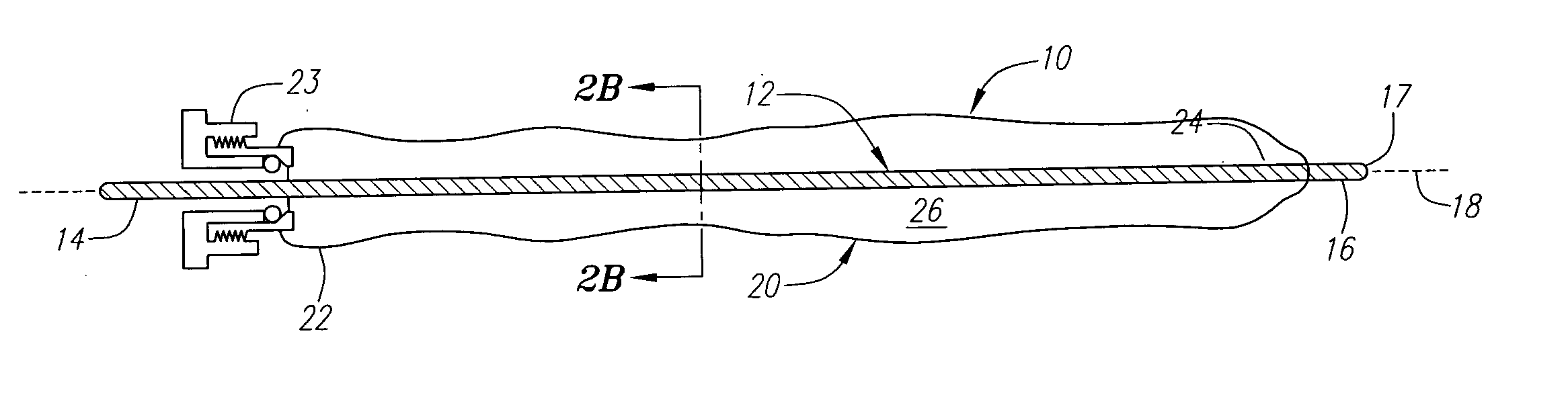
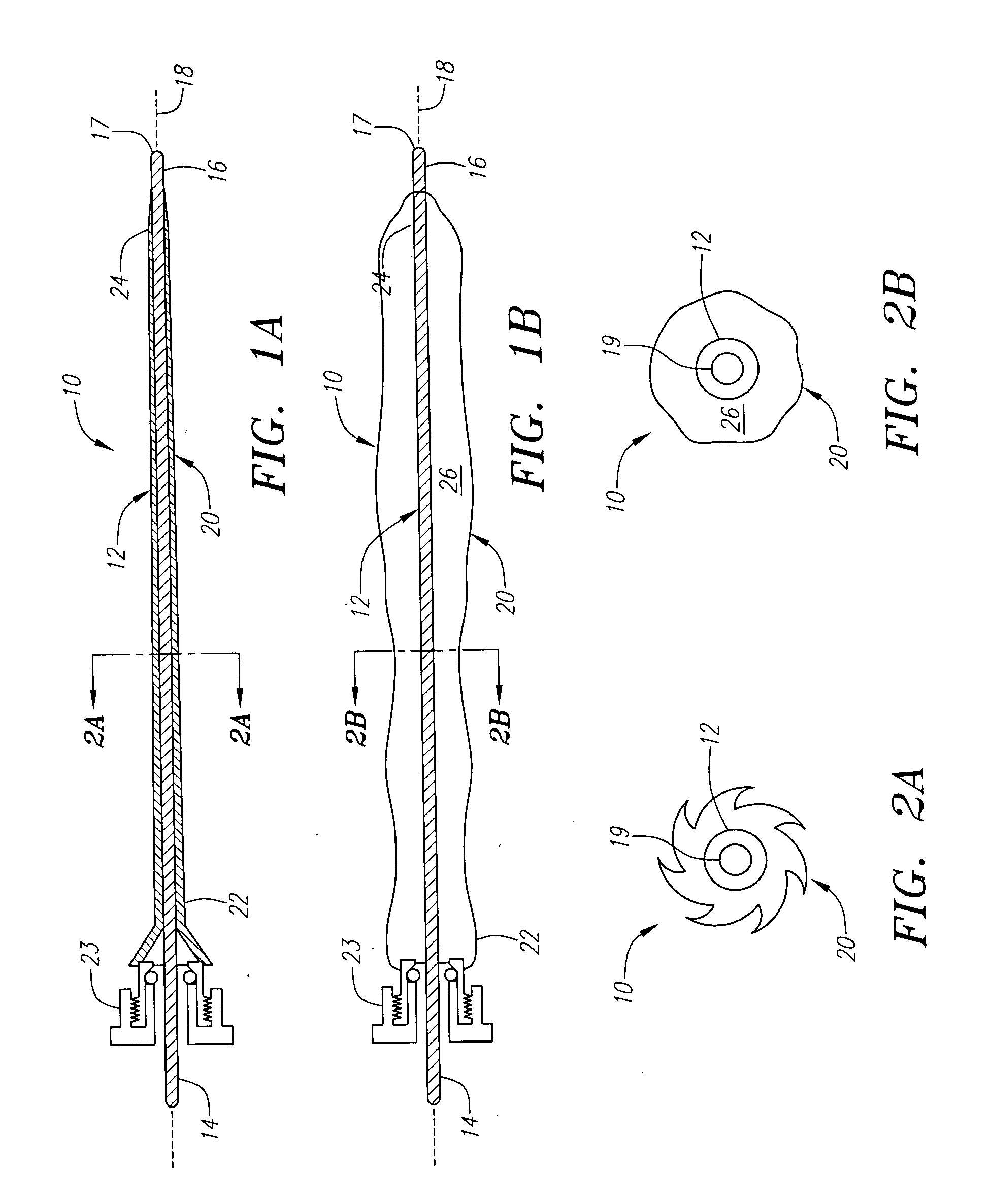
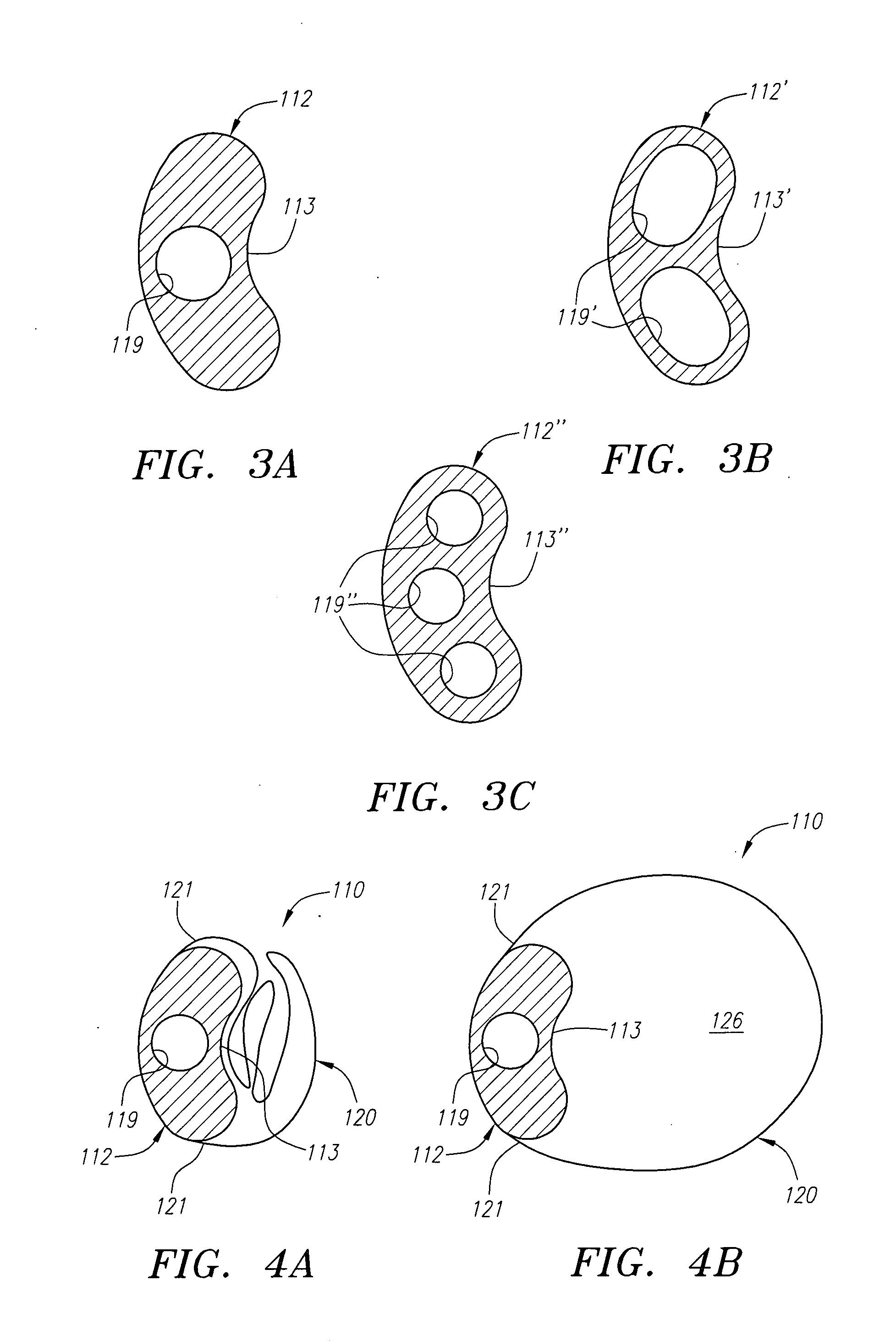
Apparatus and method for tissue removal
InactiveUS20020029055A1Less energyReduce frictionSurgical needlesVaccination/ovulation diagnosticsWood splinterMotion transfer
Percutaneous tissue removal apparatus comprises a flexible drill shaft, a cutting tip mounted on the shaft for placement adjacent a tissue mass for cutting the tissue, means for transmitting motion to the shaft to move the cutting tip against the tissue to cut tissue fragments from the tissue, and means for removing the tissue fragments along the shaft by suction to a location outside the tissue mass while cutting. The apparatus may include means for collecting one or more selected components of the harvested tissue fragments for implantation of the fragments preferably into the body of the patient from whom they were removed. Where the tissue to be cut is bone, a cutting tip is preferably made of a polymeric material which is softer than the cortical portion of the bone, although the cutting tip may be made of a ceramic or a composite material. A second flexible shaft may be provided either within or about the flexible drill shaft. The harvested tissue fragments may be implanted in the donor patient's body.
Owner:BONUTTI SKELETAL INNOVATIONS +2
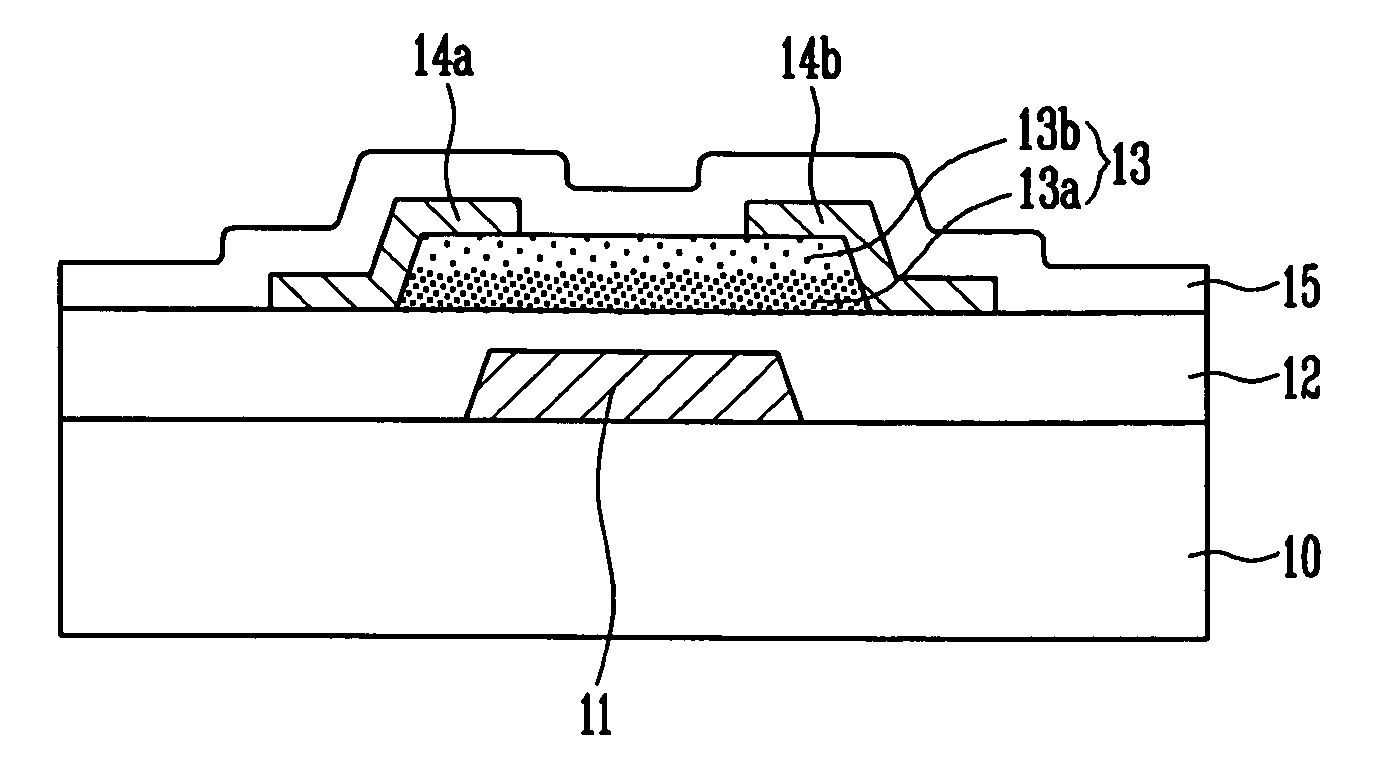
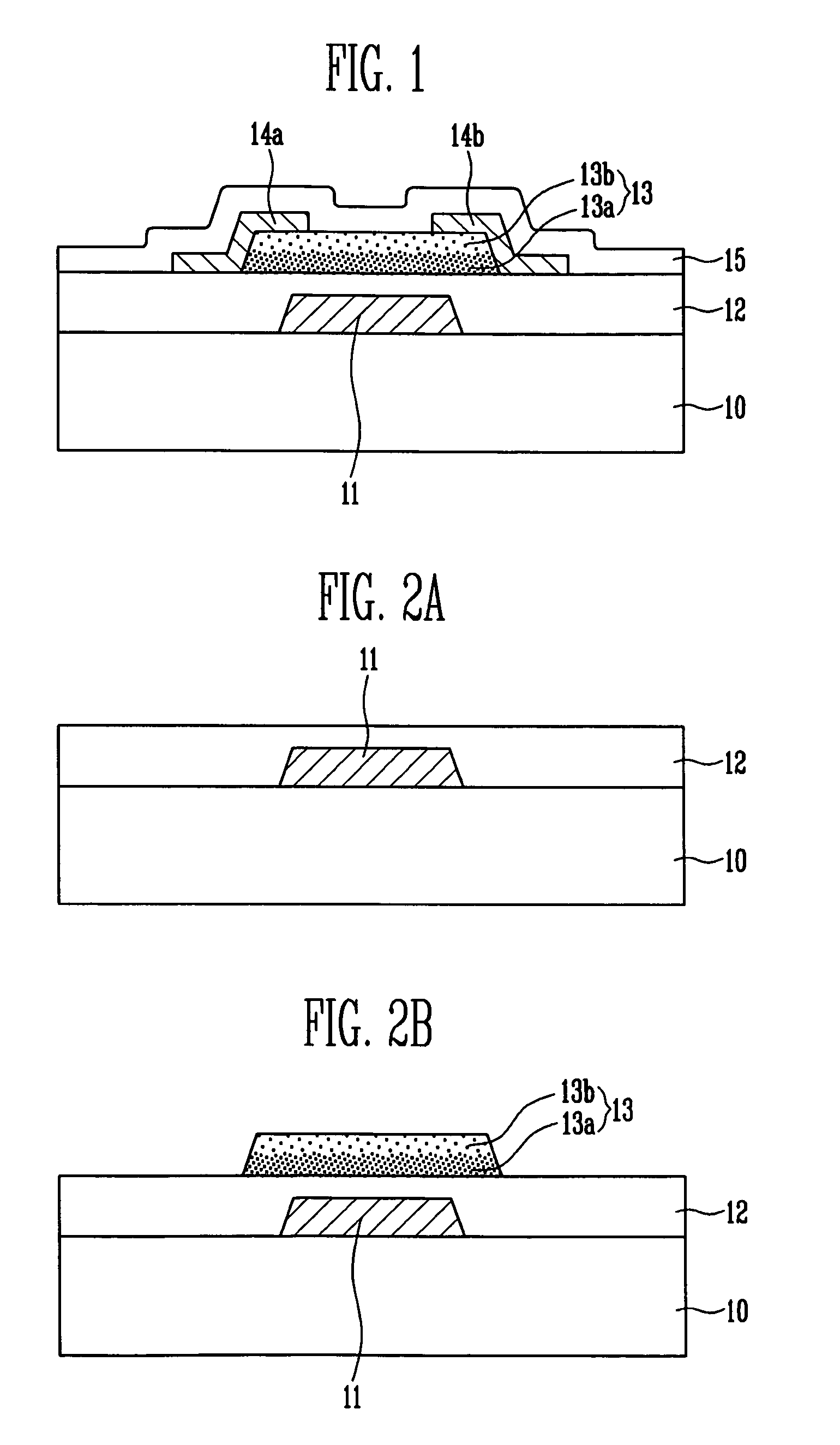
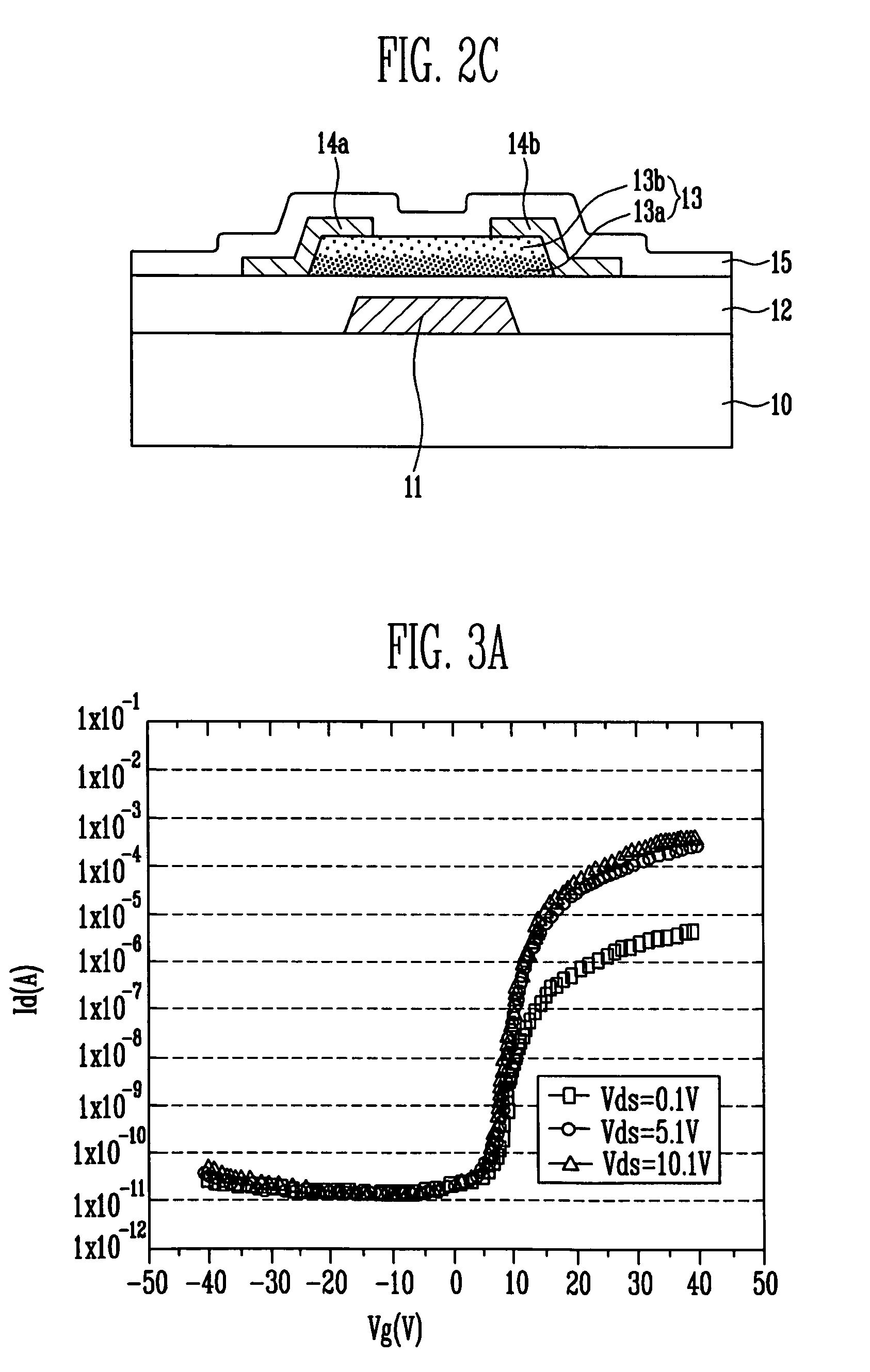
Thin film transistor, display device, including the same, and associated methods
InactiveUS8058645B2Excellent electrical propertiesMinimize damageSolid-state devicesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingIndiumDisplay device
A thin film transistor (TFT), including a substrate, a gate electrode on the substrate, an oxide semiconductor layer including a channel region, a source region, and a drain region, a gate insulating layer between the gate electrode and the oxide semiconductor layer, and source and drain electrodes in contact with the source and drain regions of the oxide semiconductor layer, respectively, wherein the oxide semiconductor layer has a GaInZnO (GIZO) bilayer structure including a lower layer and an upper layer, and the upper layer has a different indium (In) concentration than the lower layer.
Owner:SAMSUNG DISPLAY CO LTD
Articulated electrosurgical probe and methods
InactiveUS6837887B2Minimize damageAvoid and minimize currentCannulasEnemata/irrigatorsElectrically conductiveMolecular dissociation
Systems, apparatus and methods for selectively applying electrical energy to body tissue in order to ablate, contract, coagulate, or otherwise modify a target tissue or organ of a patient. An electrosurgical apparatus of the invention includes a shaft having an articulated electrode support at a distal end of the shaft, the electrode support bearing an active electrode on an inferior surface of the electrode support, a return electrode in the form of a tube, and an electrically insulating return tube tray affixed to the tube, the tube adapted for delivering an electrically conductive fluid between the active electrode and the return electrode. The probe can adopt a closed configuration or an open configuration. The closed configuration is adapted for clamping, coagulating, and ablating a target tissue while the apparatus is operating in a sub-ablation mode, while the open configuration is adapted for severing the target tissue via molecular dissociation of tissue components.
Owner:ARTHROCARE
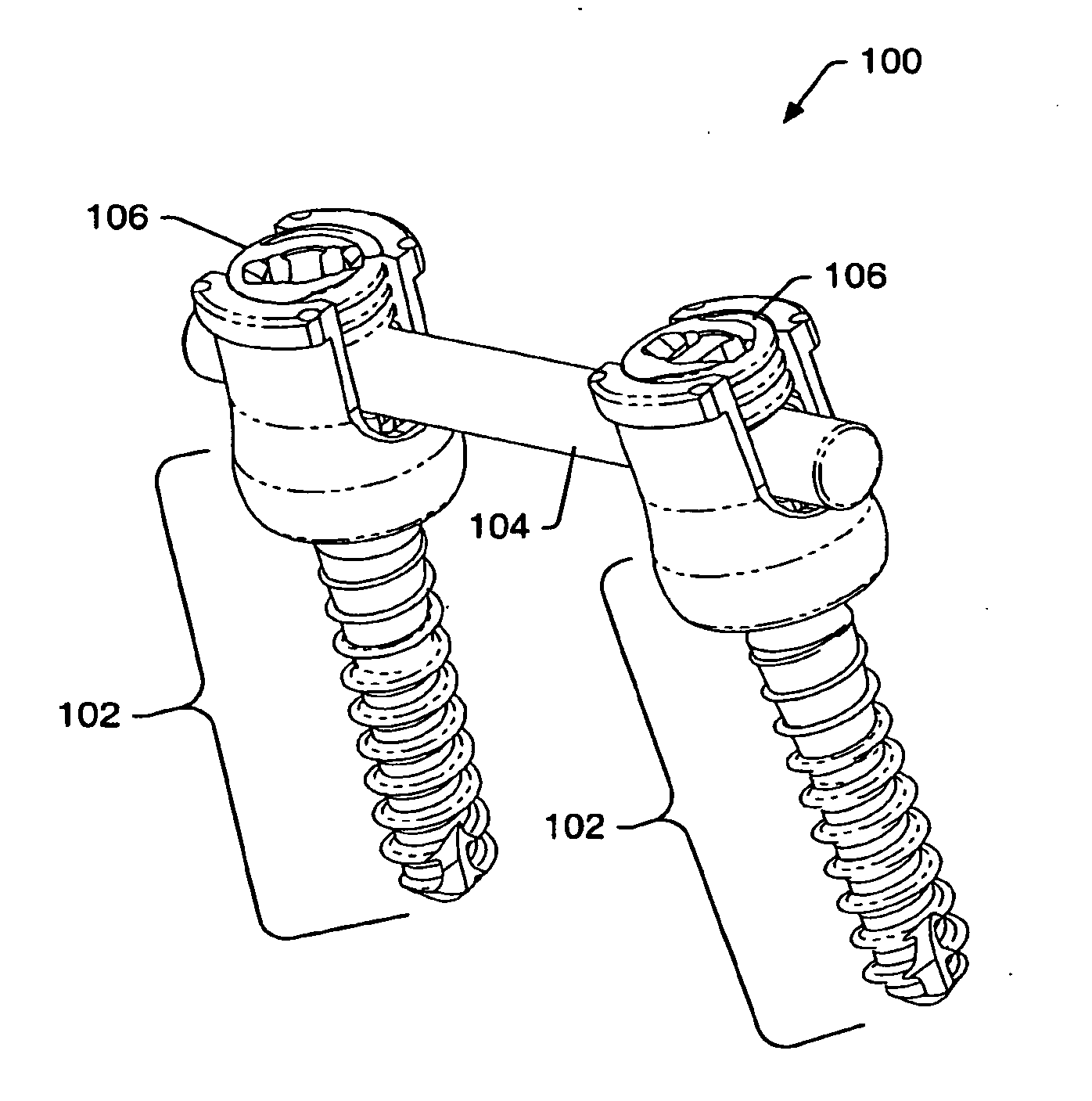
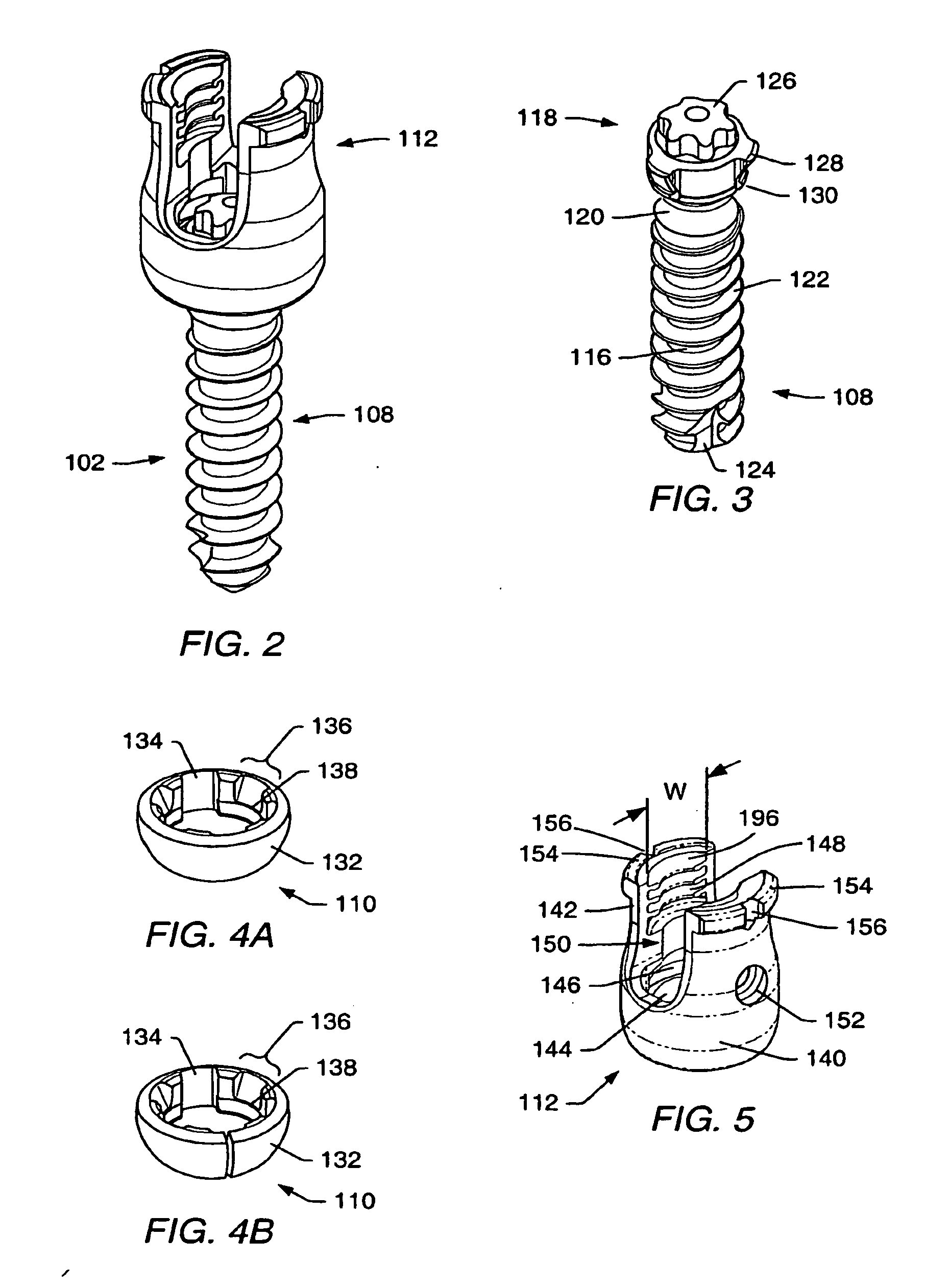
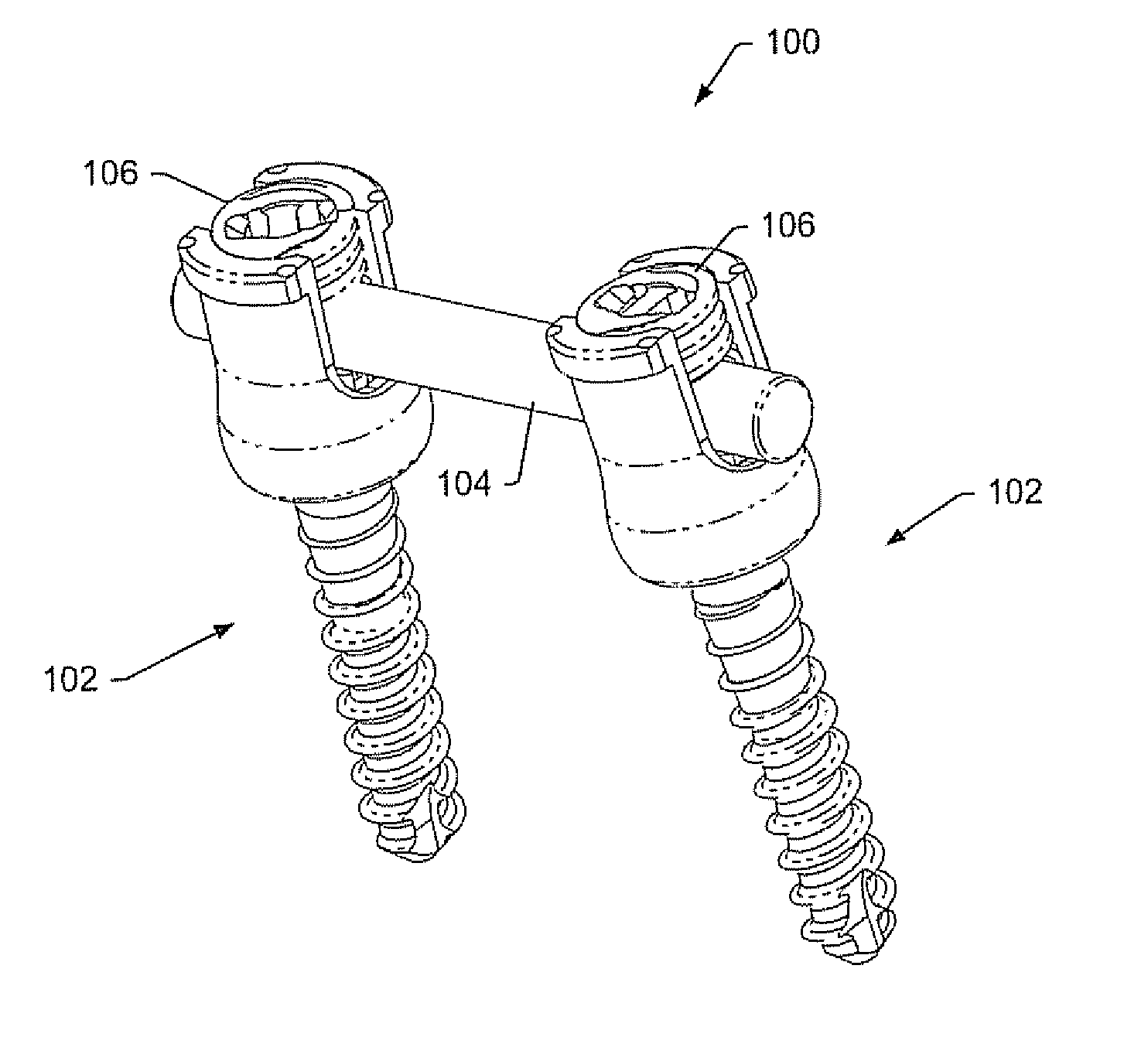
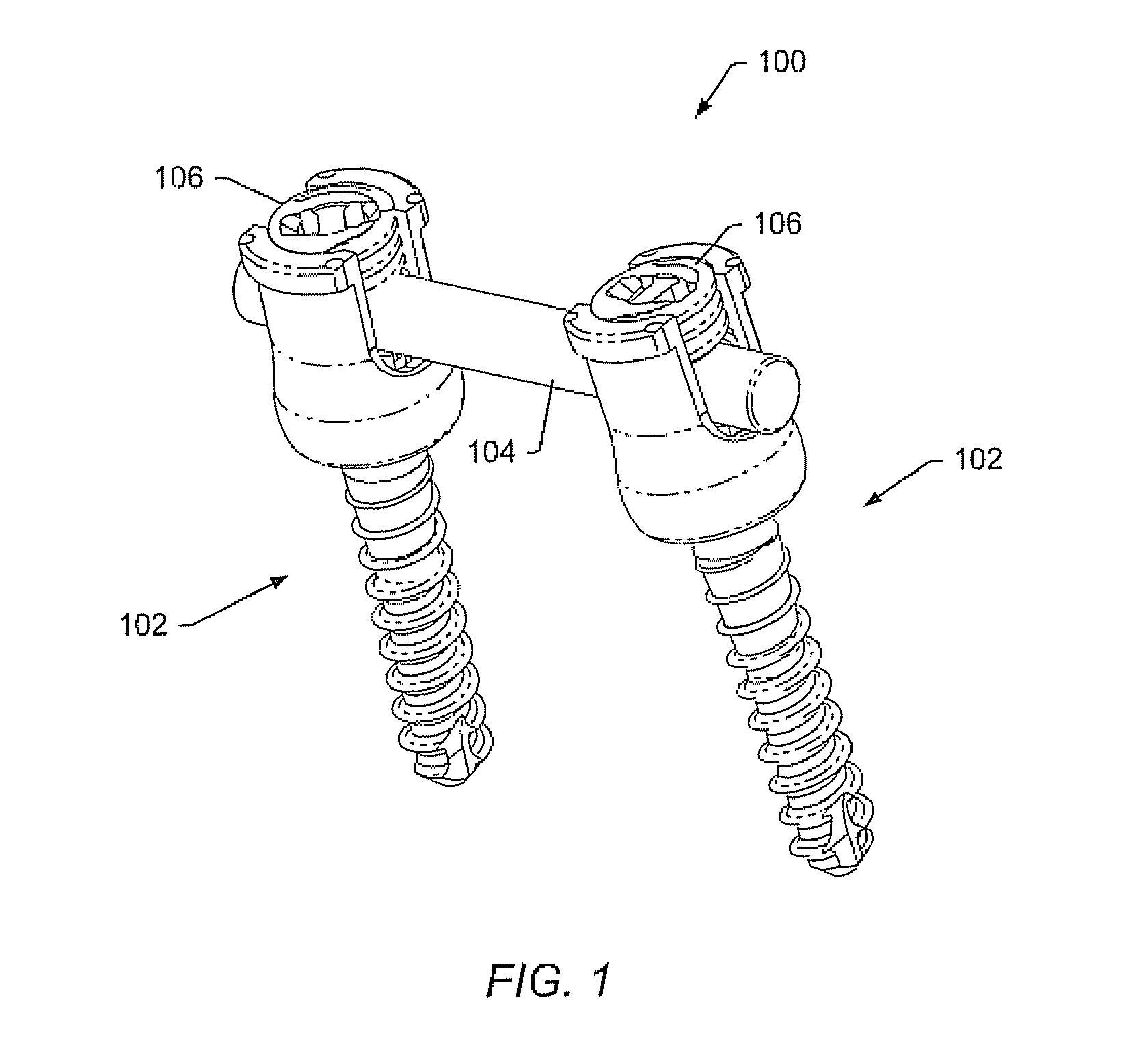
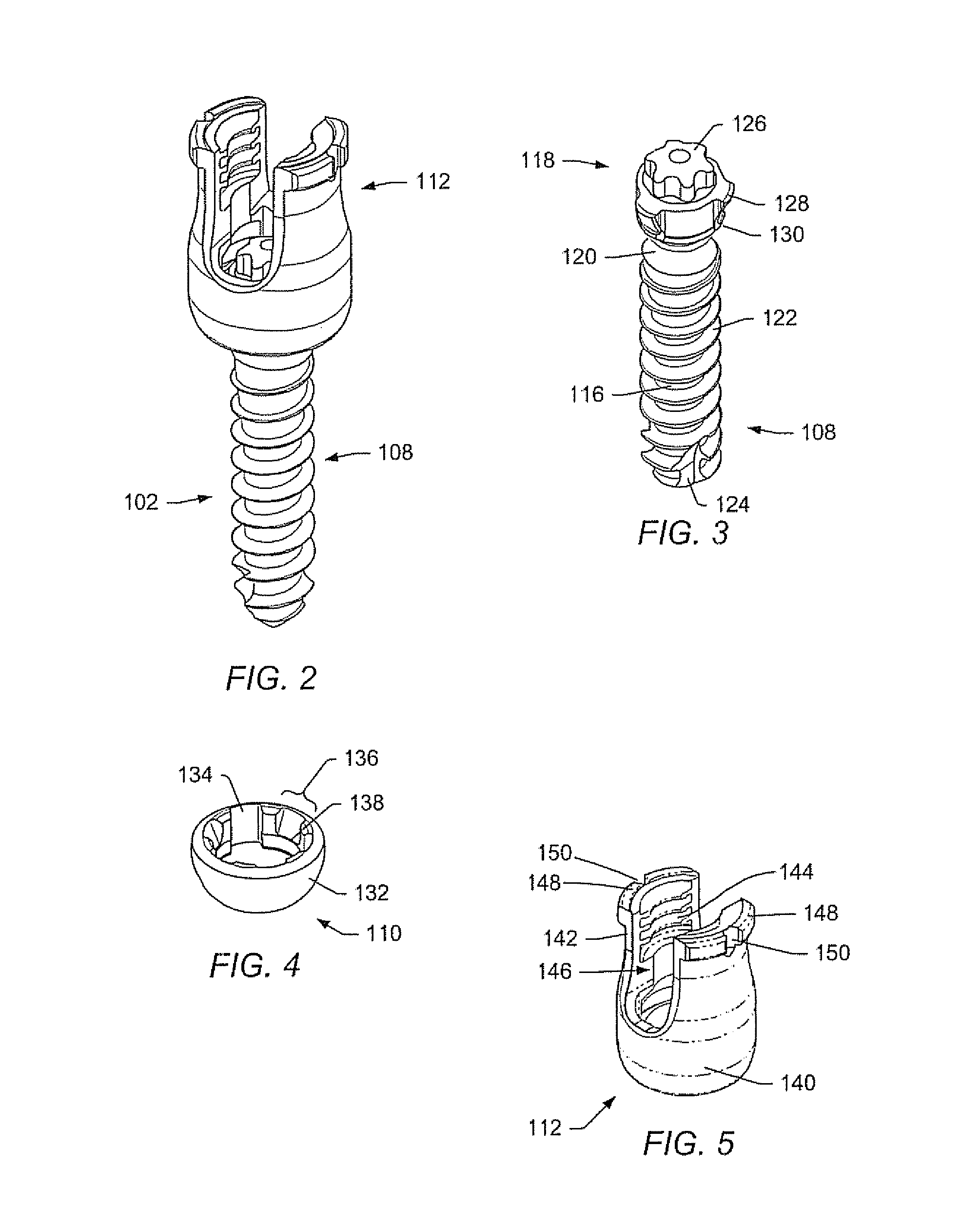
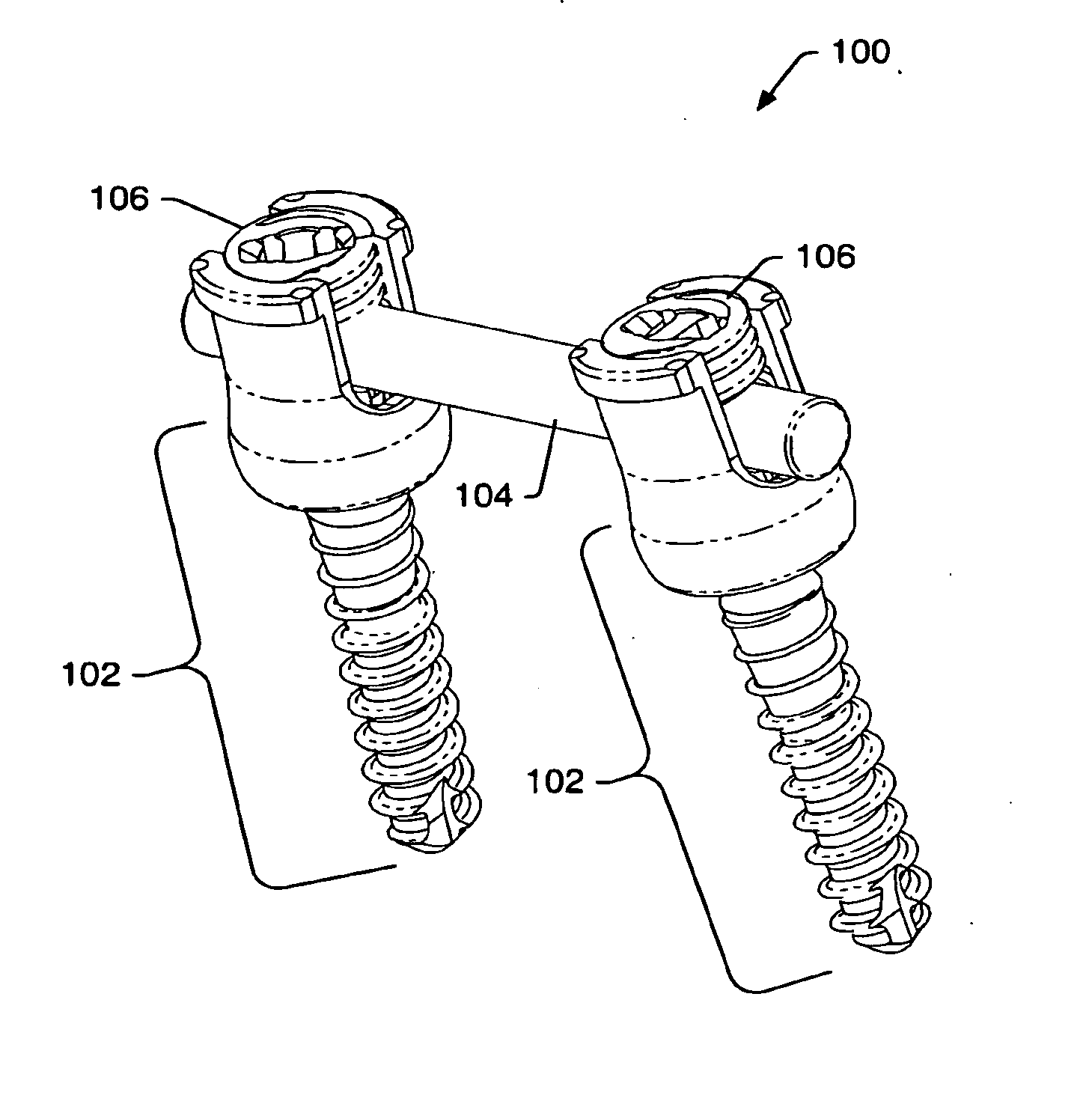
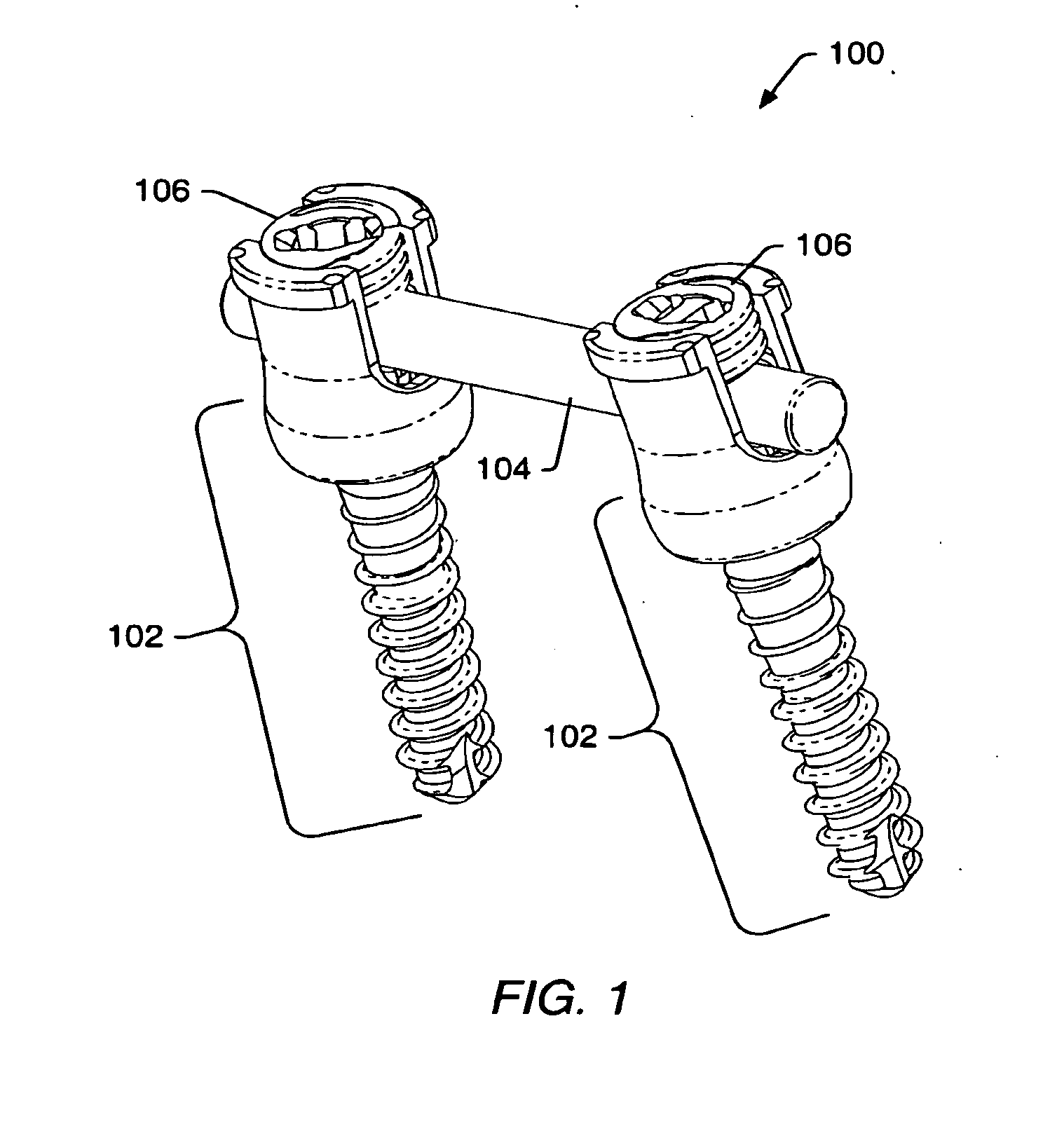
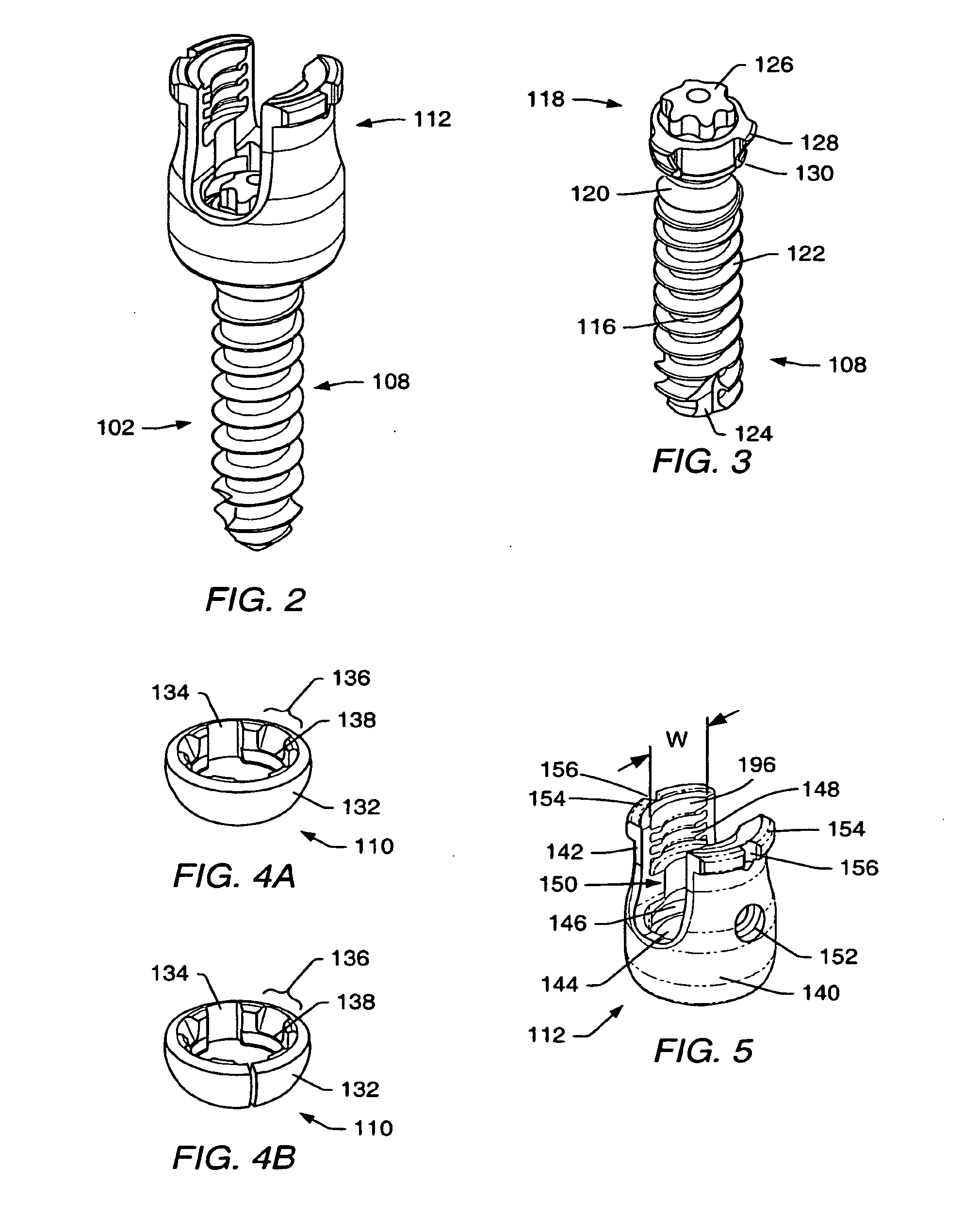
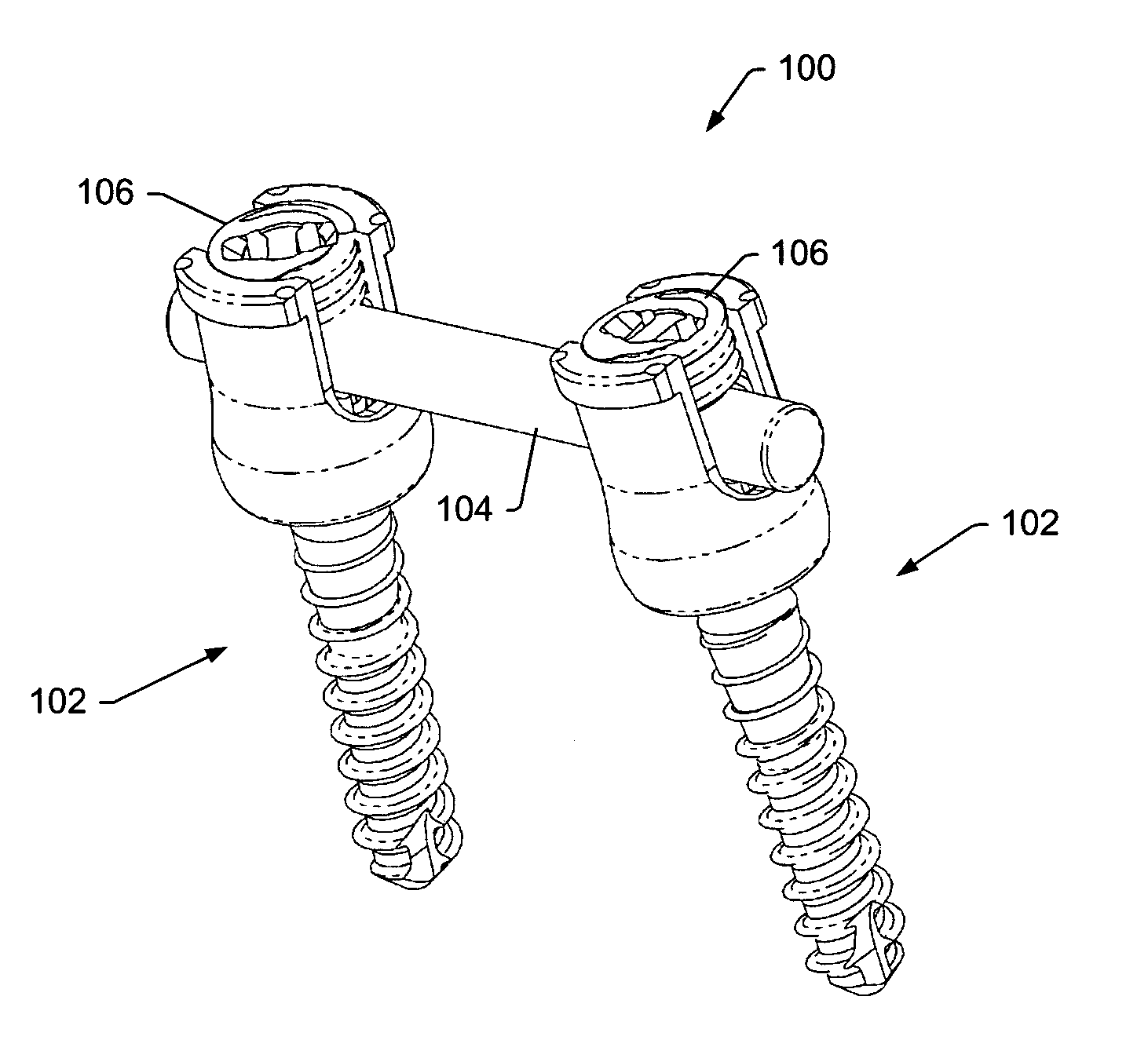
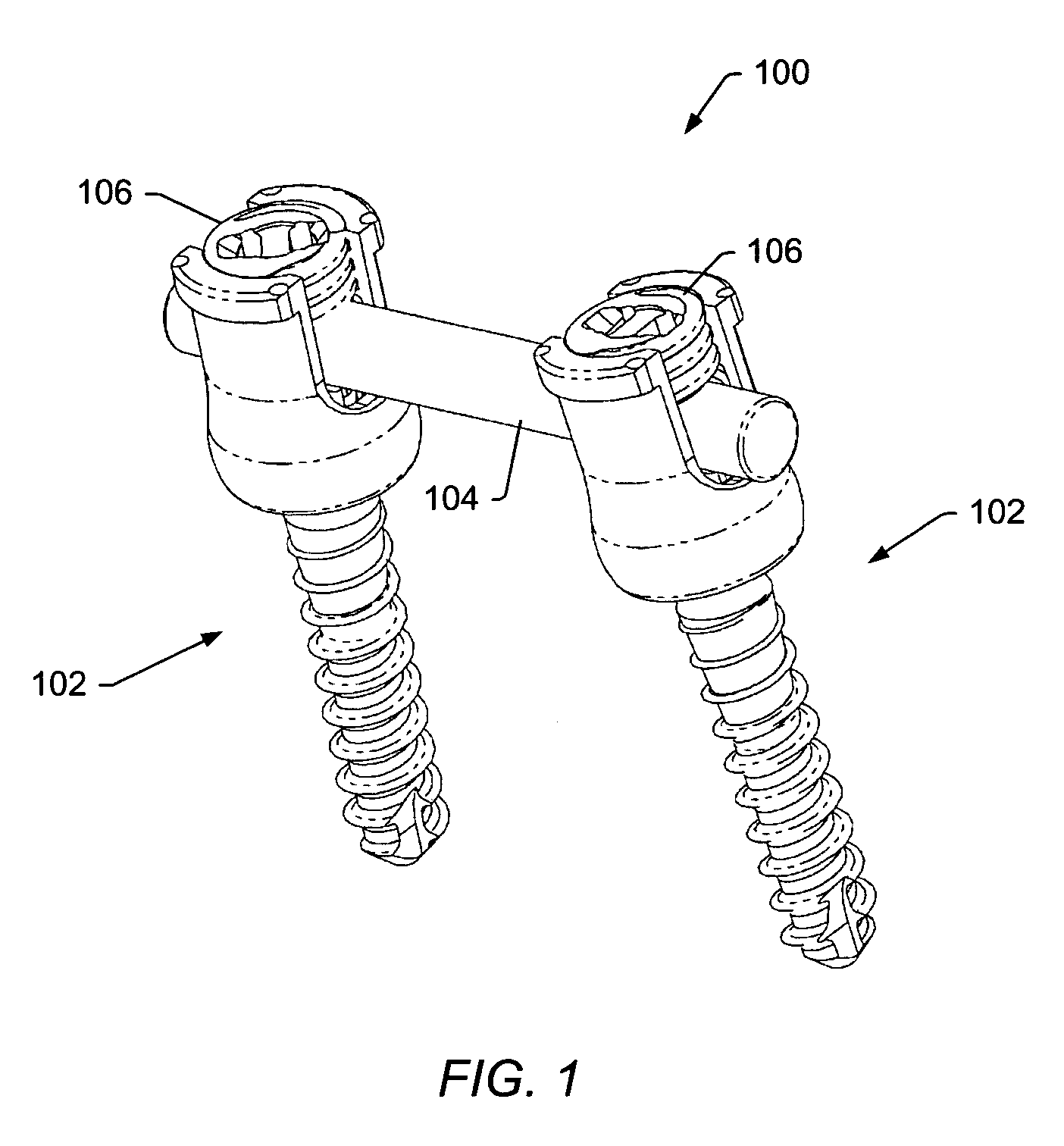
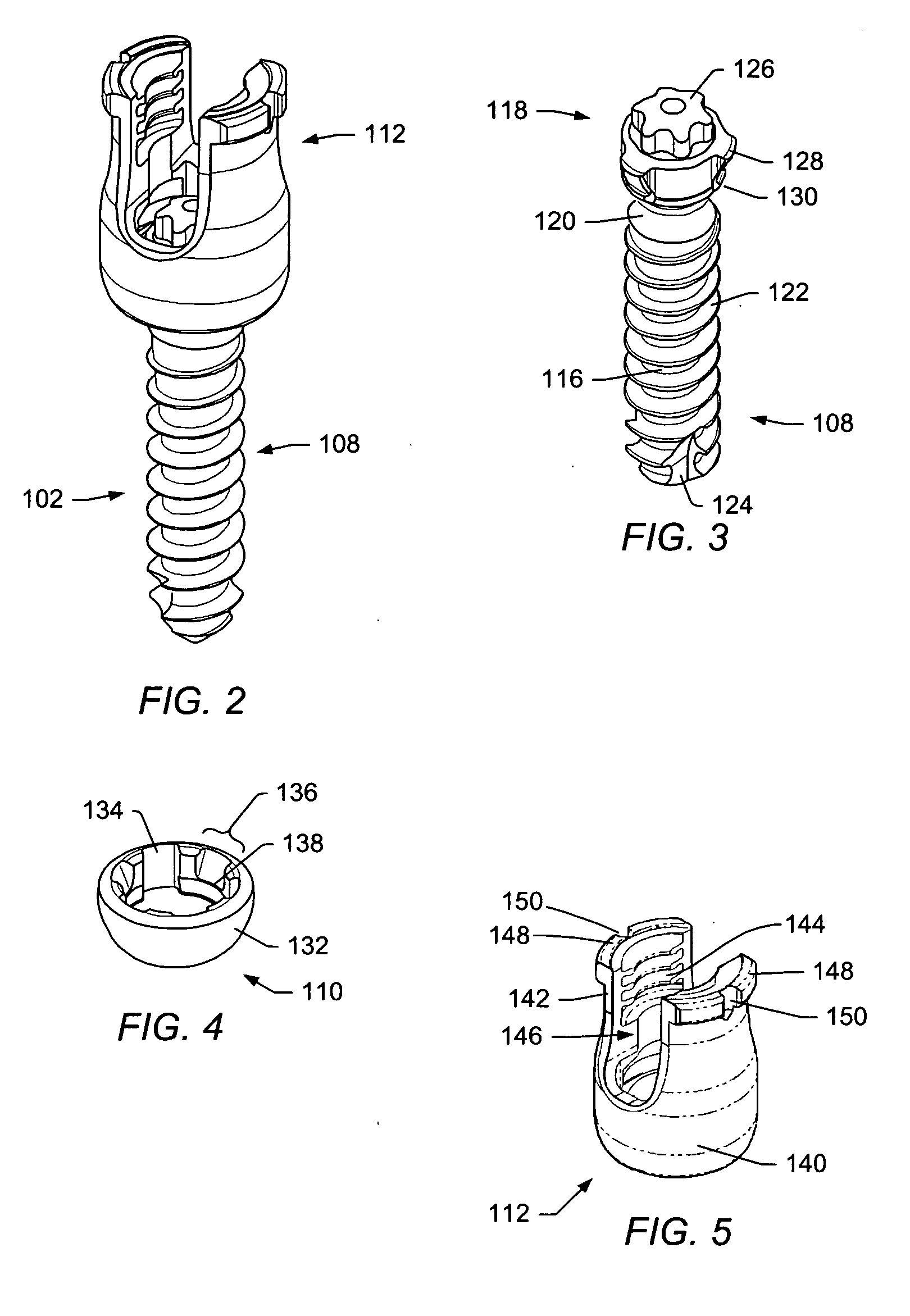
Spinal stabilization systems and methods
ActiveUS20060142761A1Minimize damageProvide stabilityInternal osteosythesisDiagnosticsMinimally invasive proceduresSkin incision
A spinal stabilization system may be formed in a patient. In some embodiments, a minimally invasive procedure may be used to form a spinal stabilization system in a patient. Bone fastener assemblies may be coupled to vertebrae. Each bone fastener assembly may include a bone fastener and a collar. The collar may be rotated and / or angulated relative to the bone fastener. Detachable members may be coupled to the collar to allow for formation of the spinal stabilization system through a small skin incision. The detachable members may allow for alignment of the collars to facilitate insertion of an elongated member in the collars. An elongated member may be positioned in the collars and a closure member may be used to secure the elongated member to the collars.
Owner:ZIMMER BIOMET SPINE INC
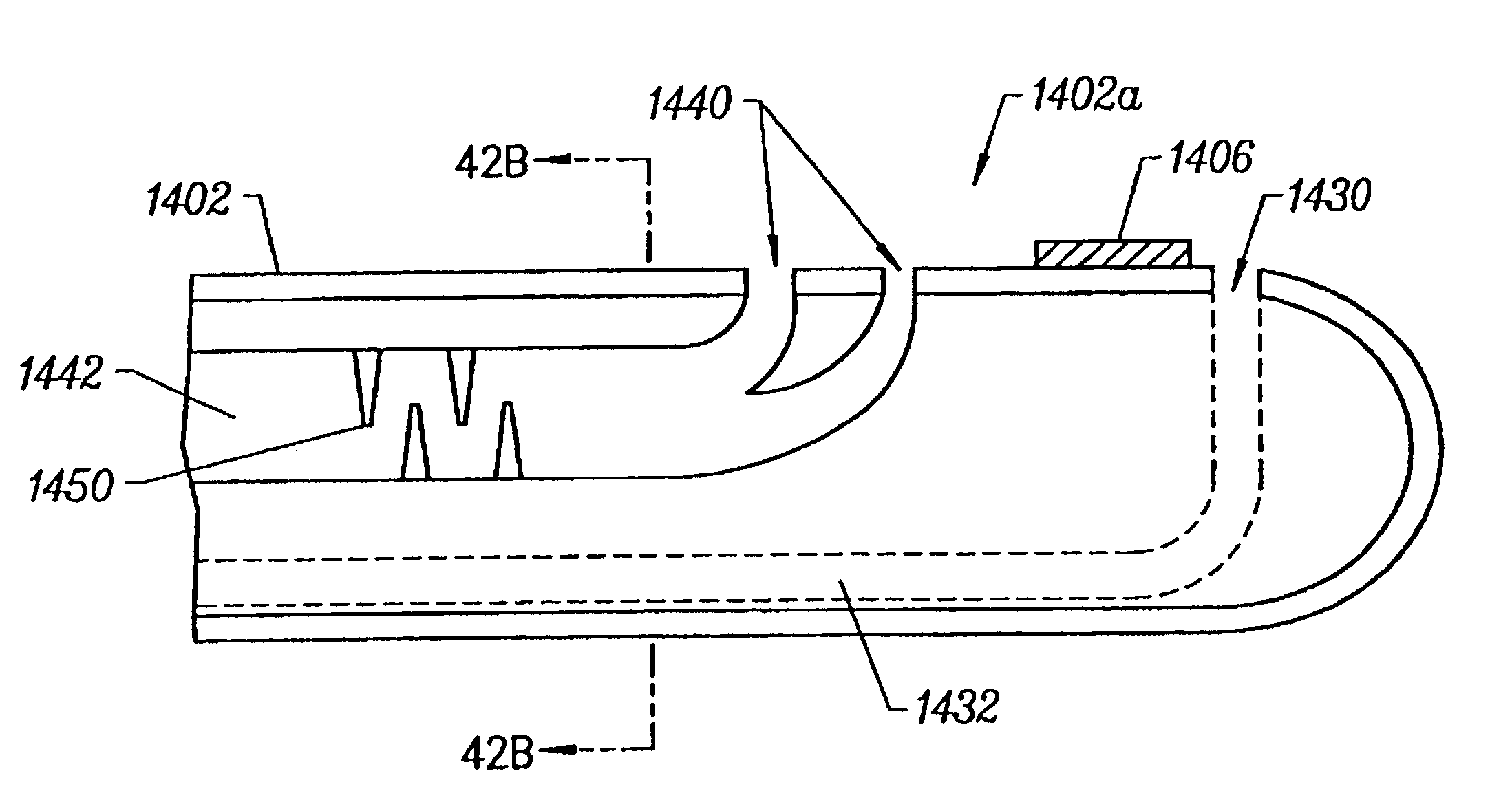
Method and device for tissue removal and for delivery of a therapeutic agent or bulking agent
InactiveUS20060253069A1Efficient removalMinimizing collateral damageMedical devicesVaccination/ovulation diagnosticsSurgeryMedical device
According to an aspect of the present invention, a medical device is provided, which comprises the following: (a) a hollow elongate body (e.g., a elongate cylinder, such as a needle) having distal and proximal ends; and (b) a rotatable member comprising a tissue morselizer and an elongate shaft (e.g., an auger-like tissue-drilling bit). In the devices of the present invention, the elongate shaft is disposed within the hollow elongate body and cooperates with the hollow elongate body to (i) advance material (e.g., morselated tissue) toward the proximal end of the hollow elongate body when the shaft is rotated in a first direction, and (ii) advance material (e.g., a therapeutic agent and / or a bulking agent) toward the distal end of the hollow elongate body when the shaft is rotated in a second direction that is opposite the first direction. According to another aspect of the invention a method of treatment is provided that comprises: (a) inserting the a medical device like that above into the tissue of a patient; (b) morselizing and removing tissue from within the patient while rotating the shaft in a first direction, thereby creating a void within the patient; and (c) introducing a therapeutic agent and / or a bulking agent into the void.
Owner:BOSTON SCI SCIMED INC
Methods and apparatus for skin treatment
InactiveUS6920883B2Thermal damage is minimizedMinimizes and avoids damageDiagnosticsSurgical instruments for heatingDermisFace lifting
Methods and apparatus for electrosurgically treating human skin. The skin may be treated by applying thermal energy to the dermis to shrink the skin following liposuction, or to induce collagen deposition at the site of a wrinkle for wrinkle reduction or removal. In another embodiment, a method involves electrosurgically removing or modifying tissue in the head or neck to provide a face-lift or a neck-lift. In one embodiment, the working end of an electrosurgical instrument is positioned in at least close proximity to the dermis by approaching the dermis from the underside (reverse side) of the skin.
Owner:ARTHROCARE
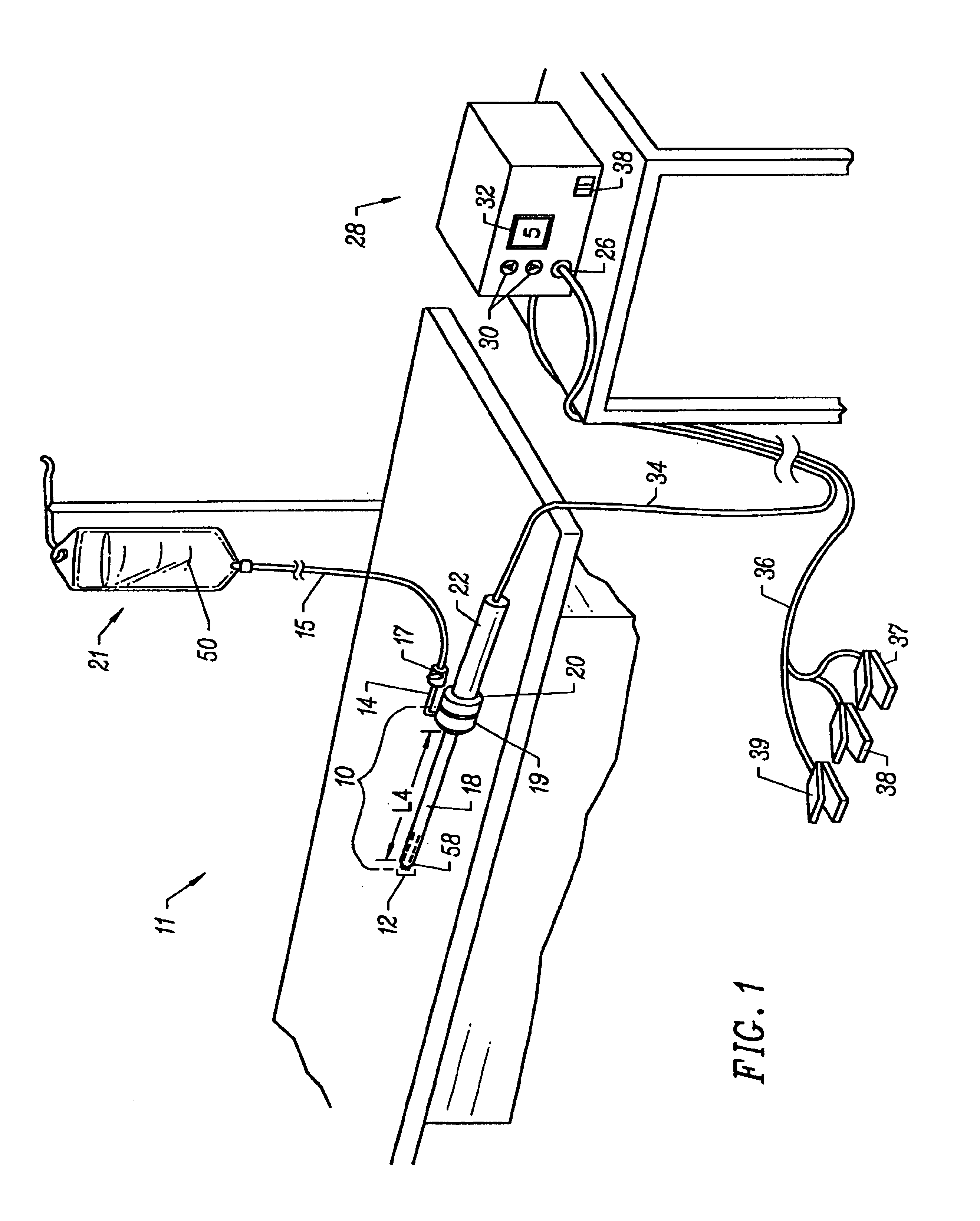
Deployment device, system and method for medical implantation
A deployment device for deploying a self-expansible medical implant at a target location in a body cavity, is provided. While generally, the expansion of self-expansible structures tends to be abrupt, and the impact of expansion may cause injury, a two-stage expansion process of the present invention minimizes the impact of exapnsion. Additionally, an ability to manuever the medical imlant into position, after the first stage of expansion, provides for accurate positioning. Thus the present invention is of a deployment device for precise and well-controlled manner of deployment, so as to minimize damage to the cavity wall and to position the implant accurately at the target location. The deployment device includes: an inner tube; an outer tube; and an implant received on the inner tube and enclosed by the outer tube. The implant has a self-expansible anchoring element which is in a contracted condition when enclosed by the outer tube, expands to a partially-expanded condition when the outer tube is retracted, and expands to a fully-expanded condition when the inner tube is removed.. The implant is deployed by introducing the deployment device to the target location in the body cavity; retracting the outer tube with respect to the implant such that the anchoring element self-expands from its contracted condition to its partially-expanded condition; and withdrawing the inner tube from the implant such that the anchoring element self-expands from its partially-expanded condition to its fully-expanded condition to firmly fix the implant at the target location within the body cavity.
Owner:REMON MEDICAL TECH
Methods and apparatus for treating intervertebral discs
InactiveUS20050010205A1Minimal and collateral damageLower the volumeDiagnosticsSurgical needlesMedicineIntervertebral disc
Apparatus and methods for treating a target tissue by delivering a fluid at a defined temperature to a patient's body. An apparatus of the invention includes a fluid delivery unit for delivering fluid in at least close proximity to the target tissue, an aspiration unit for withdrawing the fluid, and a fluid source unit for providing the fluid at the defined temperature. A method of the invention includes forming a void in at least close proximity to the target tissue, and circulating a preheated fluid through the void, wherein the target tissue undergoes adjustment from body temperature to a treatment temperature due to heat exchange between the fluid and the target tissue.
Owner:ARTHROCARE
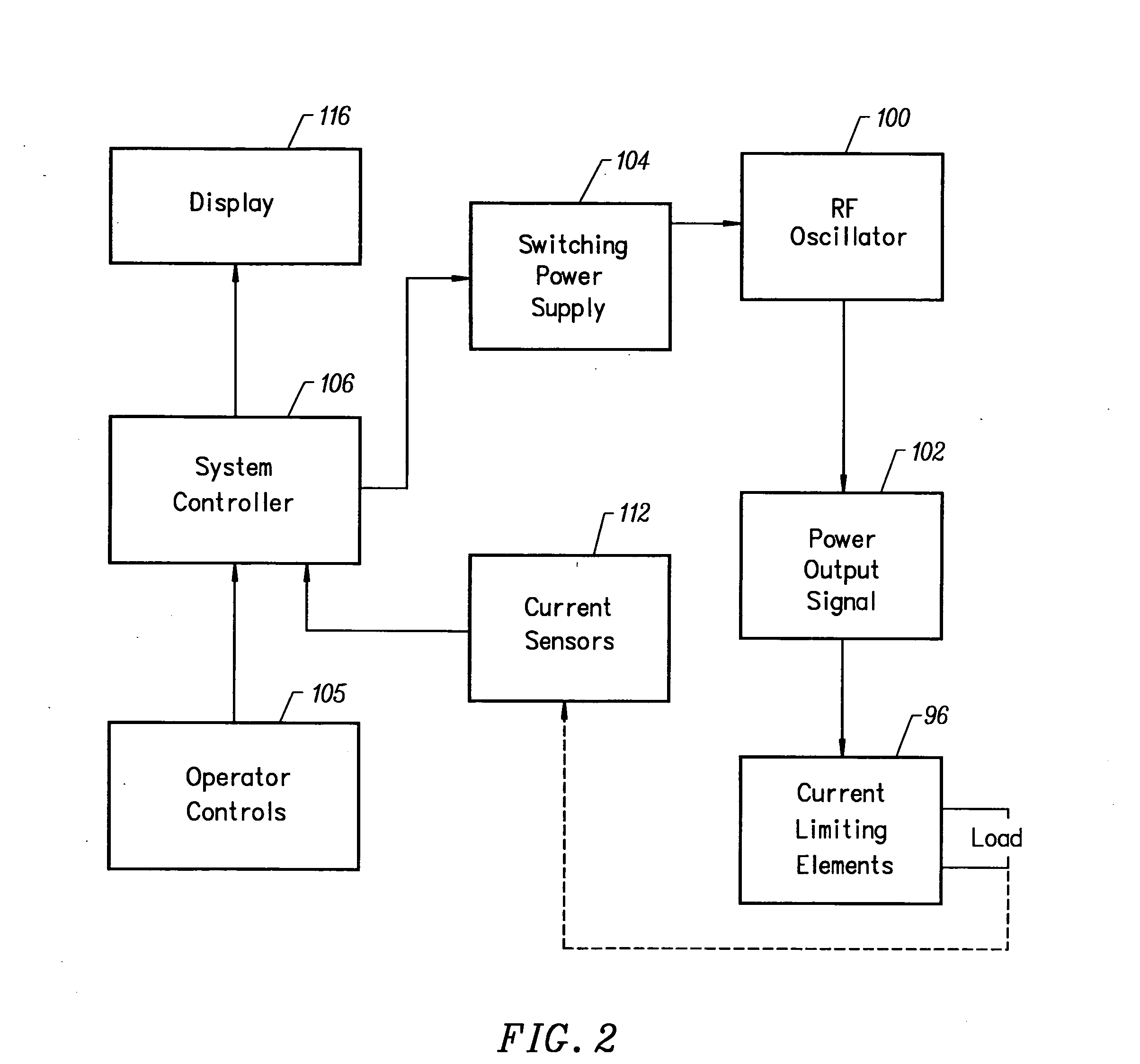
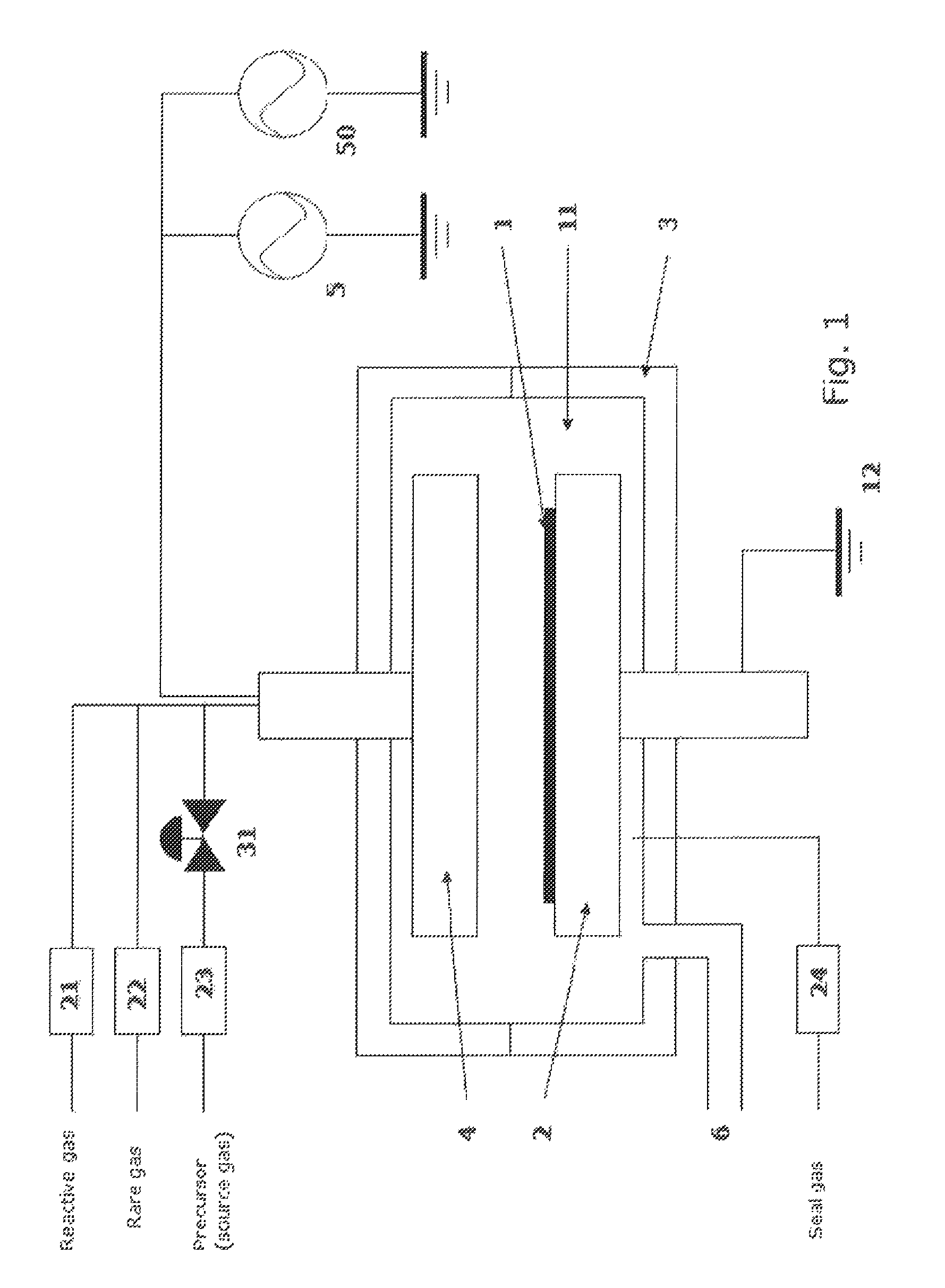
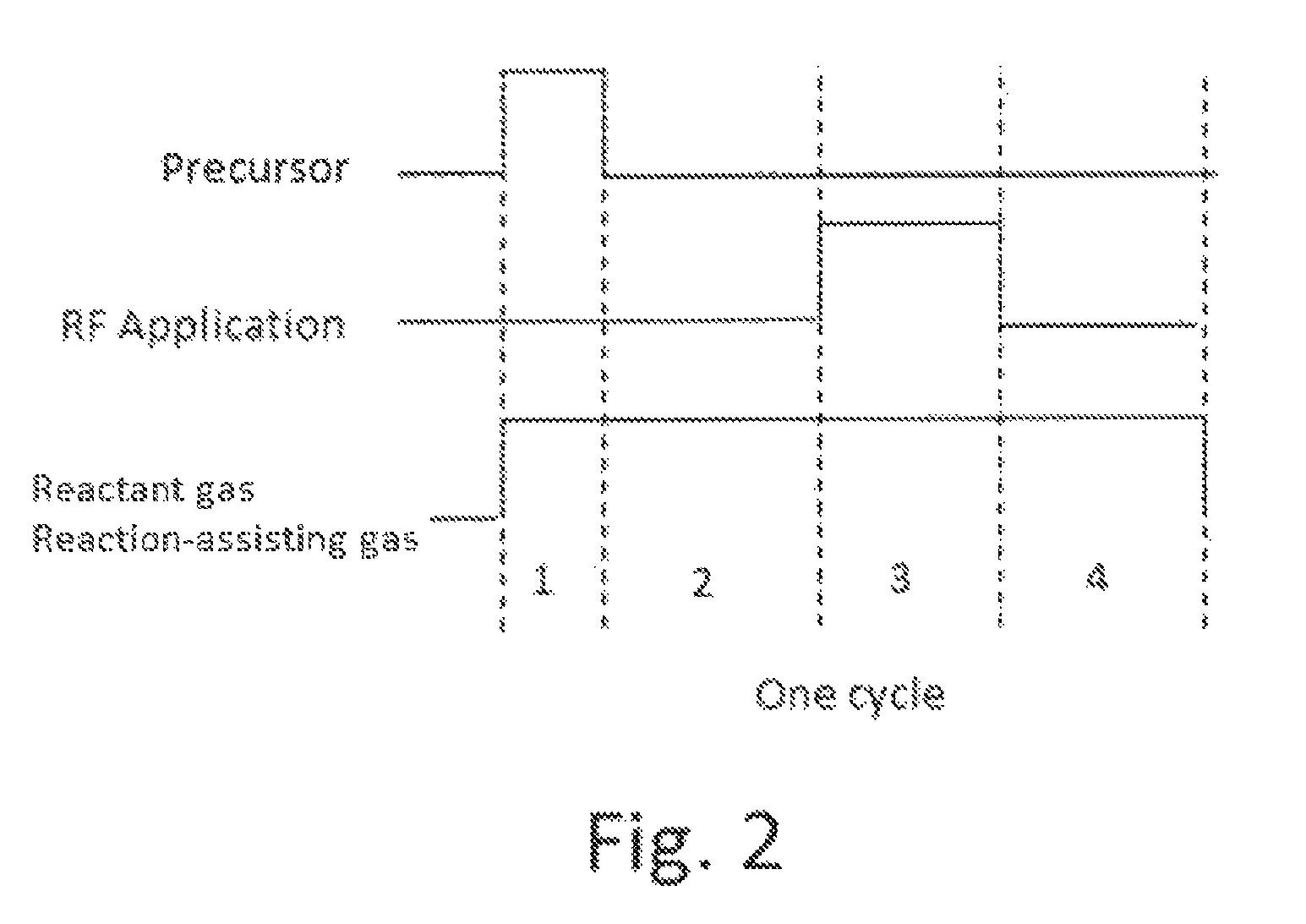
Method for forming aluminum oxide film using Al compound containing alkyl group and alkoxy or alkylamine group
ActiveUS8784950B2Safety with regard to handling and storage of the precursor can be ensuredDamage is causedChemical vapor deposition coatingPlasma techniqueProduct gasPhotochemistry
A method for forming a conformal film of aluminum oxide on a substrate having a patterned underlying layer by PEALD includes: adsorbing an Al precursor containing an Al—C bond and an Al—O—C or Al—N—C bond; providing an oxidizing gas and an inert gas; applying RF power to the reactant gas and the reaction-assisting gas to react the adsorbed precursor with the reactant gas on the surface, thereby forming a conformal film of aluminum oxide on the patterned underlying layer of the substrate, wherein the substrate is kept at a temperature of about 200° C. or lower.
Owner:ASM IP HLDG BV
Substrate support
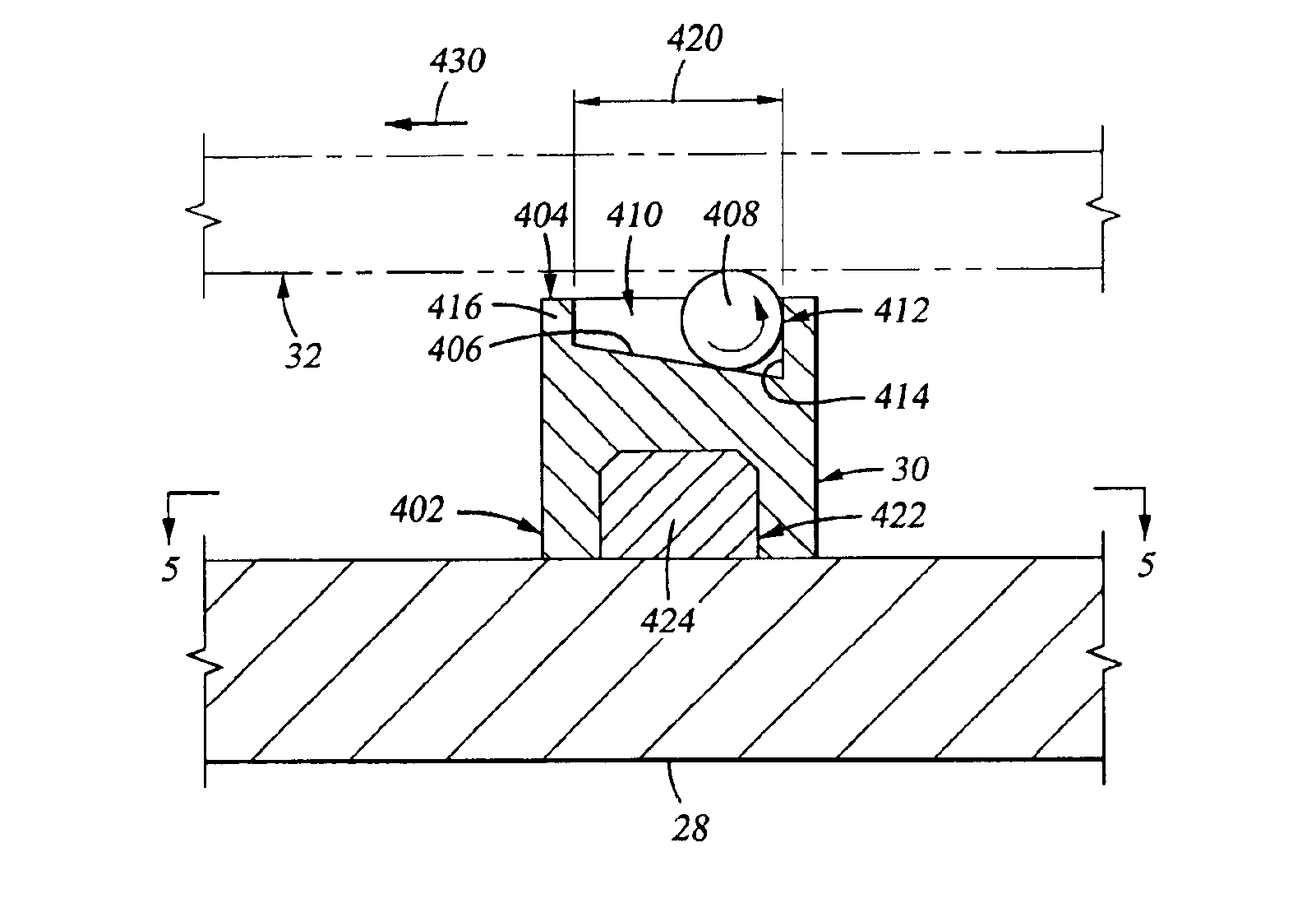
InactiveUS6917755B2Minimize damageProvide spaceDrying solid materials with heatMuffle furnacesSupport surfaceEngineering
An apparatus for supporting a substrate is described that has a ball adapted to minimize damage between the substrate support and the substrate supported thereon. In one embodiment, an apparatus for supporting a substrate includes ball disposed on an inclined ball support surface. The ball support surface is adapted to bias the ball toward one side of the ball support surface thereby providing space for the ball to roll as the substrate supported thereon changes in length when exposed to thermal influences. In another embodiment, the apparatus further comprises a cage adapted to capture the ball to the ball support surface.
Owner:APPLIED MATERIALS INC
Instruments and methods for reduction of vertebral bodies
ActiveUS20080009864A1Minimize damageProvide stabilityInternal osteosythesisJoint implantsMinimally invasive proceduresReducer
A spinal stabilization system may be formed in a patient. In some embodiments, a minimally invasive procedure may be used to form a spinal stabilization system in a patient. Bone fastener assemblies may be coupled to vertebrae. Each bone fastener assembly may include a bone fastener and a collar. The collar may be rotated and / or angulated relative to the bone fastener. Extenders may be coupled to the collar to allow for formation of the spinal stabilization system through a small skin incision. The extenders may allow for alignment of the collars to facilitate insertion of an elongated member in the collars. An elongated member may be positioned in the collars and a closure member may be used to secure the elongated member to the collars. A reducer may be used to achieve reduction of one or more vertebral bodies coupled to a spinal stabilization system.
Owner:ZIMMER BIOMET SPINE INC
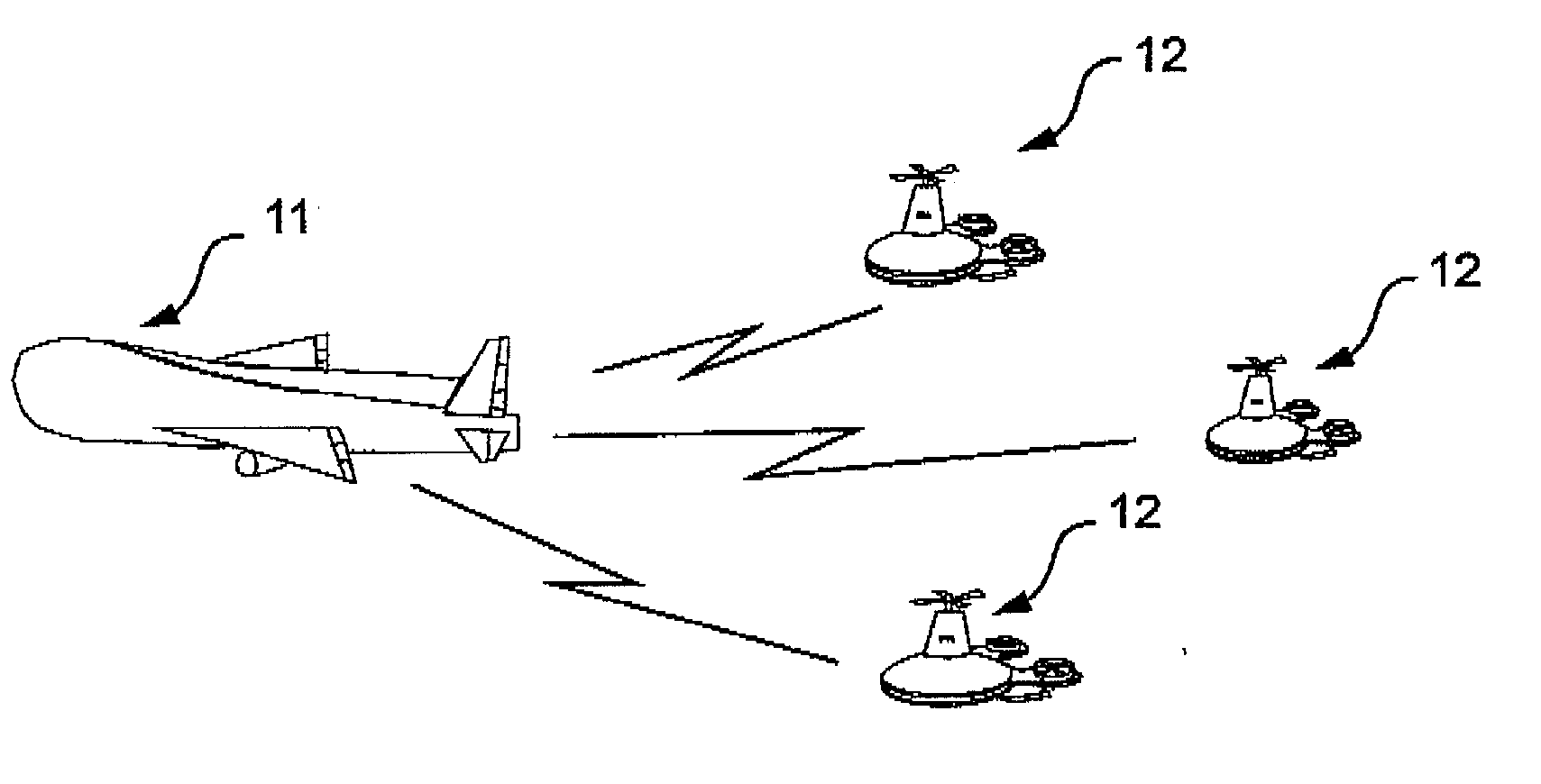
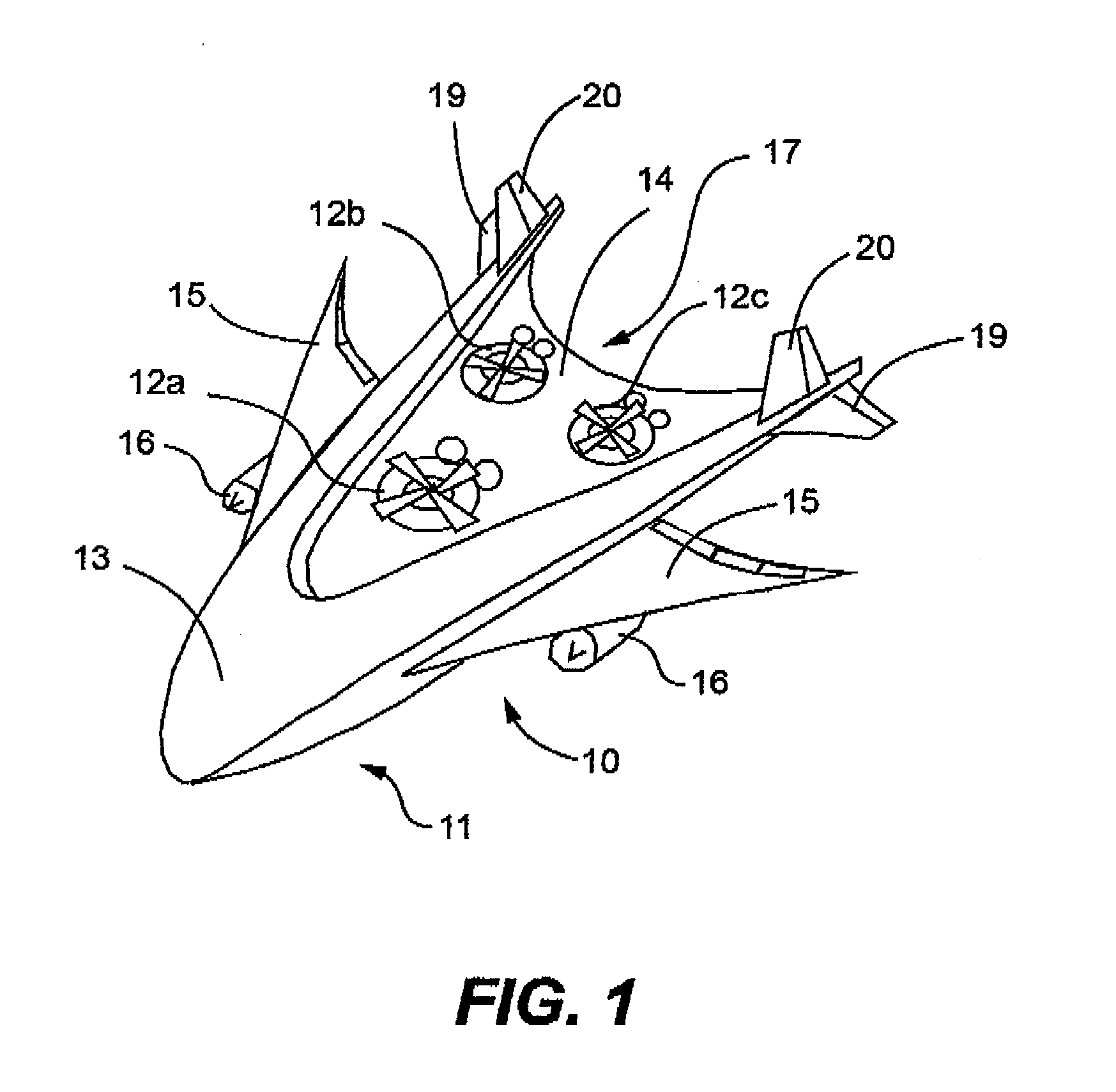
Combination of unmanned aerial vehicles and the method and system to engage in multiple applications
InactiveUS20160214717A1Minimize damageEasy landingAircraft componentsRemote controlled aircraftRemote controlUncrewed vehicle
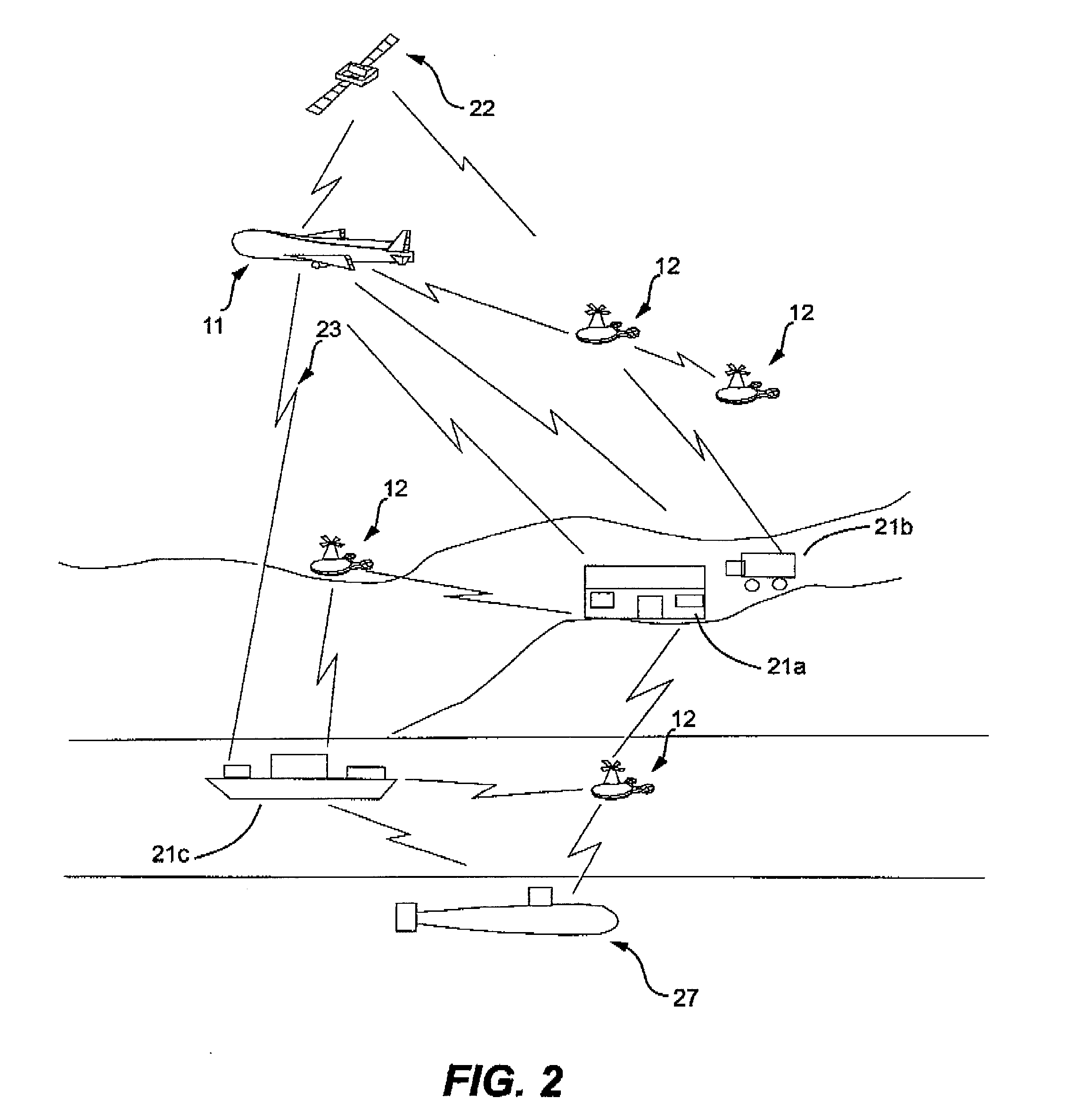
This invention relates to an Unmanned Aerial Vehicle hereinafter called “Mother UAV” member (11) capable of carrying modules of Sub Unmanned Aerial Vehicle members (12) hereinafter called “Sub UAV” member. More particularly, the method and system that is capable of communicating via satellite and remote control technology wherein ejecting said Sub UAV members (12) from the Mother UAV member (11) wherein Sub UAV members (12) autonomously fly in sequence in a coordinated manner with the Mother UAV member (11), and capable of engaging in multiple missions in high, medium, low altitude, and surface, also communication with under sea submarines (27). Further, comprises of a method and system that the Sub UAV members (12) are able to return back to the Mother UAV member (11) after the mission is completed and be firmly secured to the flatbed (14) of the Mother UAV member (11). The present invention is specifically designed for multifunctional and multipurpose applications where humans and other vehicles are unable to access, for civil, commercial and military purposes.
Owner:DE SILVA SHELTON GAMINI
Lighting devices and methods of installing light engine housings and/or trim elements in lighting device housings
ActiveUS20080106907A1Easy to useReduce and eliminate tendency for sagging-thatPicture framesPoint-like light sourceElectricityElectrical connection
A lighting device, comprising a housing and at least one mounting clip. The housing comprises an electrical connection region engageable in an electrical receptacle. The mounting clip is pivotable from a first position, where an end region of the mounting clip does not extend beyond a periphery of the housing, to a second position, where the end region extends beyond the housing periphery. Also, a lighting device, comprising a housing, a trim element and at least one mounting clip. The mounting clip is pivotable, such that if the mounting clip is in a second position and then the trim element is rotated, the mounting clip will pivot to a third position, where the mounting clip engages the housing such that the trim element is biased toward a ceiling or other structure in which the lighting device is mounted. Also, methods of installing housings and / or trim elements.
Owner:IDEAL IND LIGHTING LLC
Electrosurgical apparatus having digestion electrode and methods related thereto
InactiveUS6896674B1High trafficAvoid and minimize current shortingHeart valvesEndoscopesHigh frequency powerDigestion
Methods and apparatus for resecting and ablating tissue at a target site of a patient, the apparatus including a probe having an elongate shaft. The shaft includes a shaft distal end portion and a shaft proximal end portion, and a resection unit located at the shaft distal end portion. The resection unit includes a resection electrode support and at least one resection electrode arranged on the resection electrode support. The at least one resection electrode includes a resection electrode head. The probe and resection electrode head are adapted for concurrent electrical ablation and mechanical resection of target tissue. The shaft may include at least one digestion electrode capable of aggressively ablating resected tissue fragments. At least one fluid delivery port on the shaft distal end portion may provide an electrically conductive fluid to the resection unit or to the target site. The shaft may include at least one aspiration port, located proximal to the resection unit, for aspirating excess or unwanted fluids and resected tissue fragments from the target site. The at least one aspiration port is coupled to an aspiration lumen. The at least one digestion electrode may be arranged within the aspiration lumen for ablation of tissue fragments therein. In use, the digestion and resection electrodes of the probe are coupled to a high frequency power supply. A surgical kit comprising the probe is also disclosed, together with a method of making the probe.
Owner:ARTHROCARE
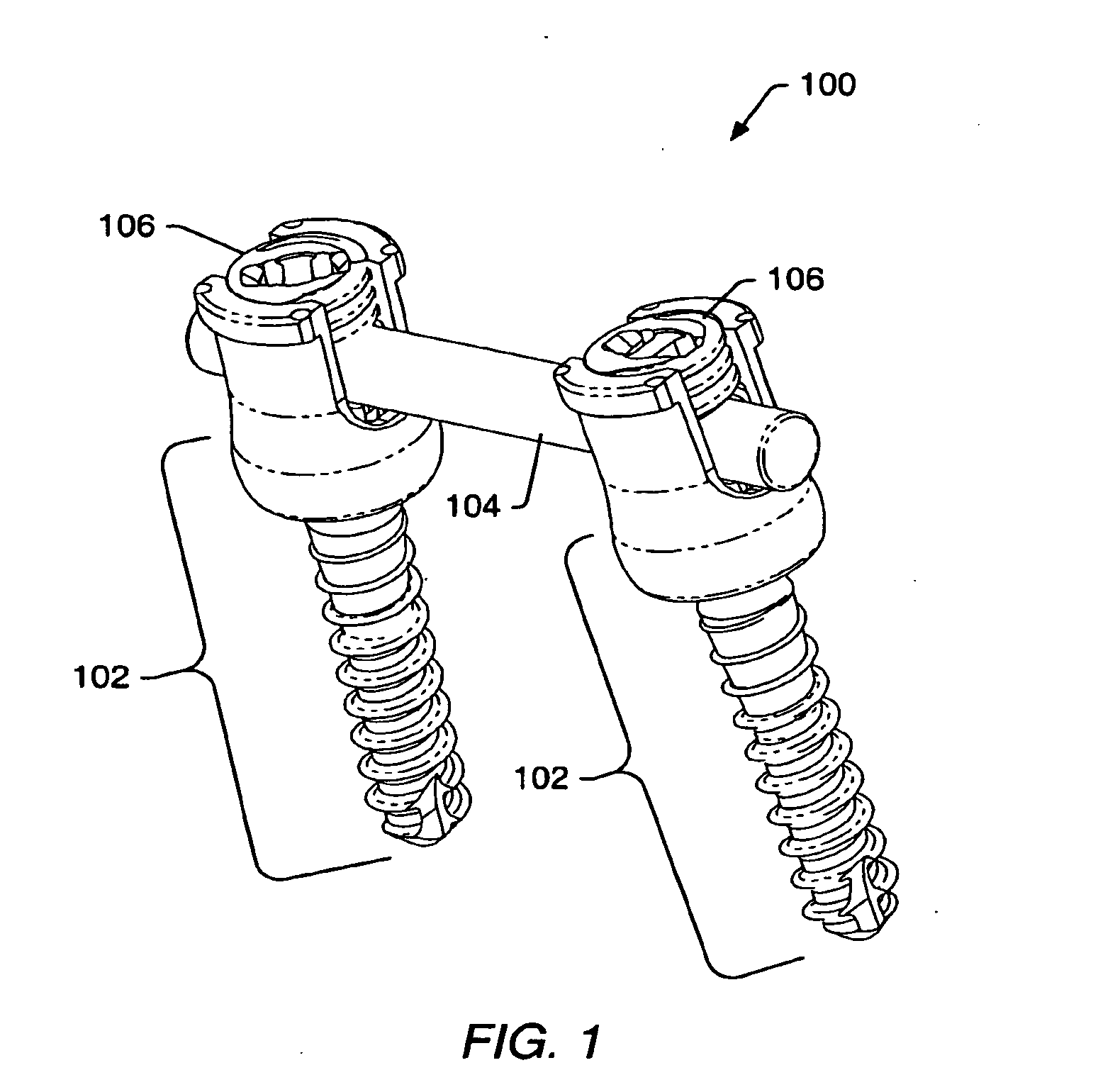
Spinal stabilization systems and methods
ActiveUS20060084993A1Minimize damageProvide stabilityInternal osteosythesisDiagnosticsMinimally invasive proceduresSkin incision
A spinal stabilization system may be formed in a patient. In some embodiments, a minimally invasive procedure may be used to form a spinal stabilization system in a patient. Bone fastener assemblies may be coupled to vertebrae. Each bone fastener assembly may include a bone fastener and a collar. The collar may be rotated and / or angulated relative to the bone fastener. Detachable members may be coupled to the collar to allow for formation of the spinal stabilization system through a small skin incision. The detachable members may allow for alignment of the collars to facilitate insertion of an elongated member in the collars. An elongated member may be positioned in the collars and a closure member may be used to secure the elongated member to the collars.
Owner:ZIMMER BIOMET SPINE INC
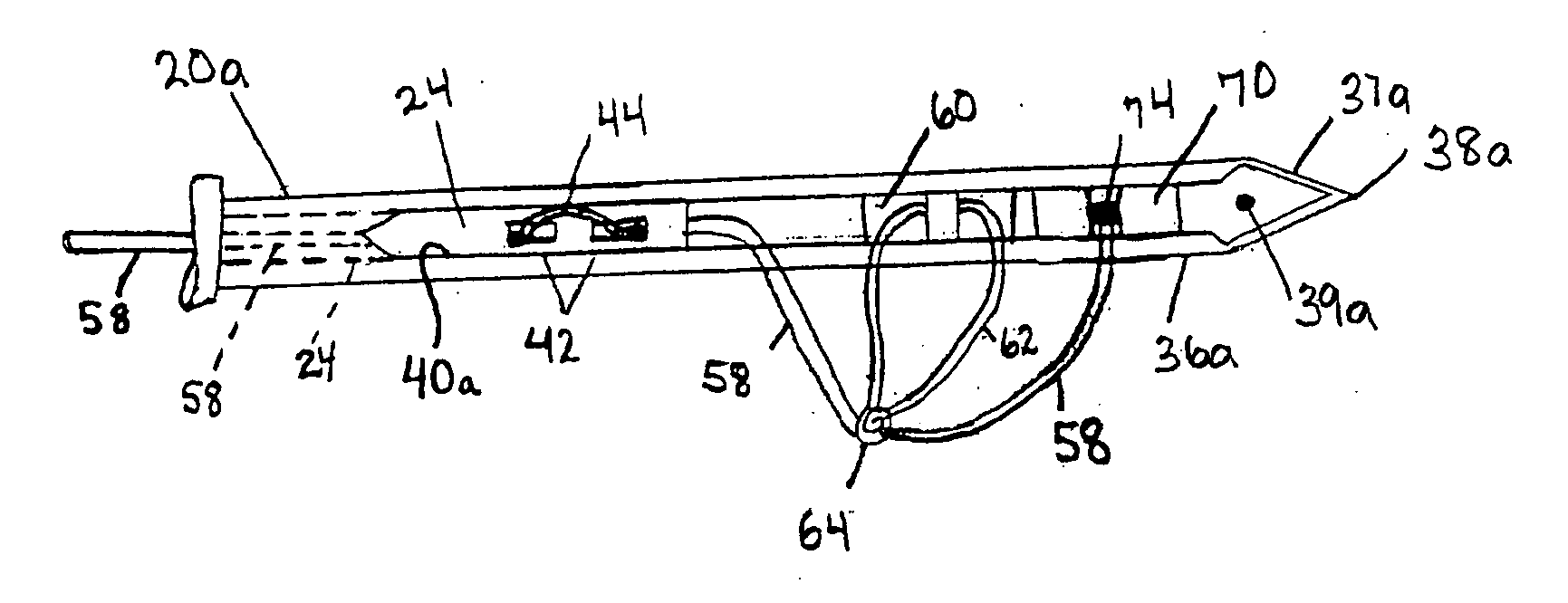
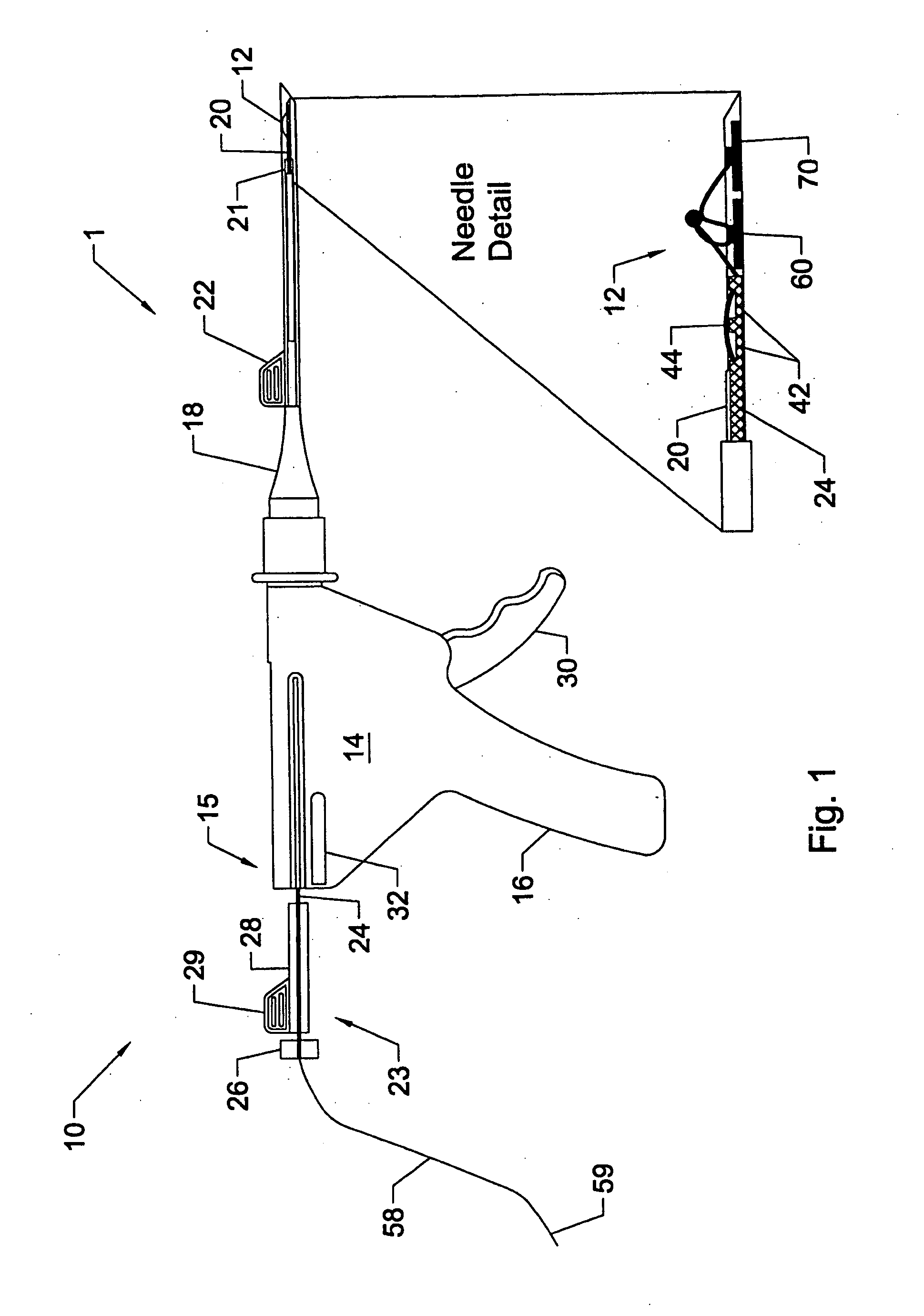
System and method for all-inside suture fixation for implant attachment and soft tissue repair
A system for repairing a meniscus includes a suture that includes a first anchor, a second anchor, and a flexible portion connecting the first anchor and the second anchor. The flexible portion includes a self-locking slide knot between the first anchor and the second anchor. The system also includes a needle having a longitudinal extending bore and an open end. The bore is configured to receive the first anchor and the second anchor. The system further includes a body portion operatively connected to the needle at a distal end of the body portion. The body portion has a lumen. The system also includes a pusher configured to rotate and slide within the lumen of the body portion and the longitudinal extending bore of the needle. The pusher has first and second stop surfaces, each of which is constructed and arranged to engage a proximal end of the body portion.
Owner:STRYKER CORP
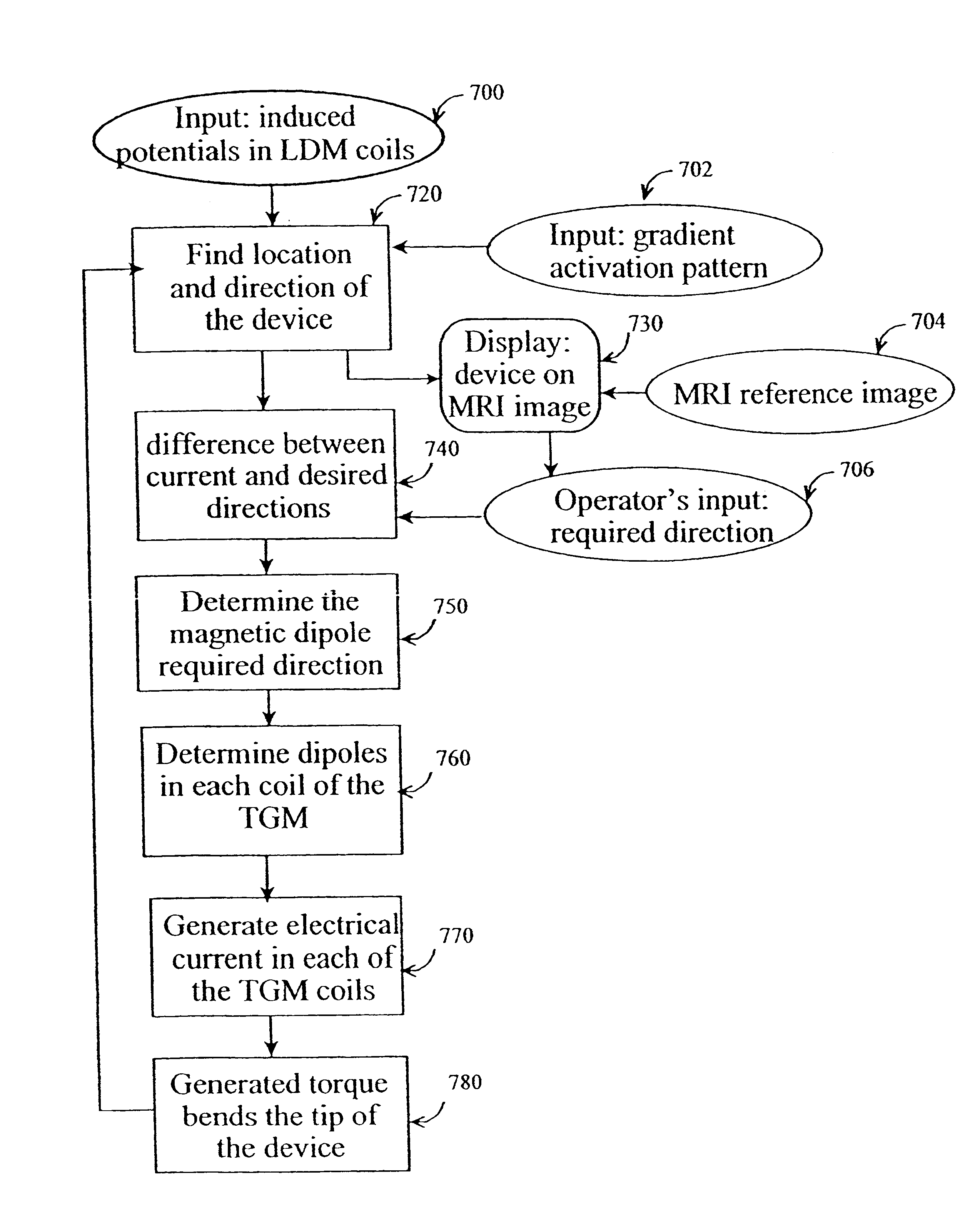
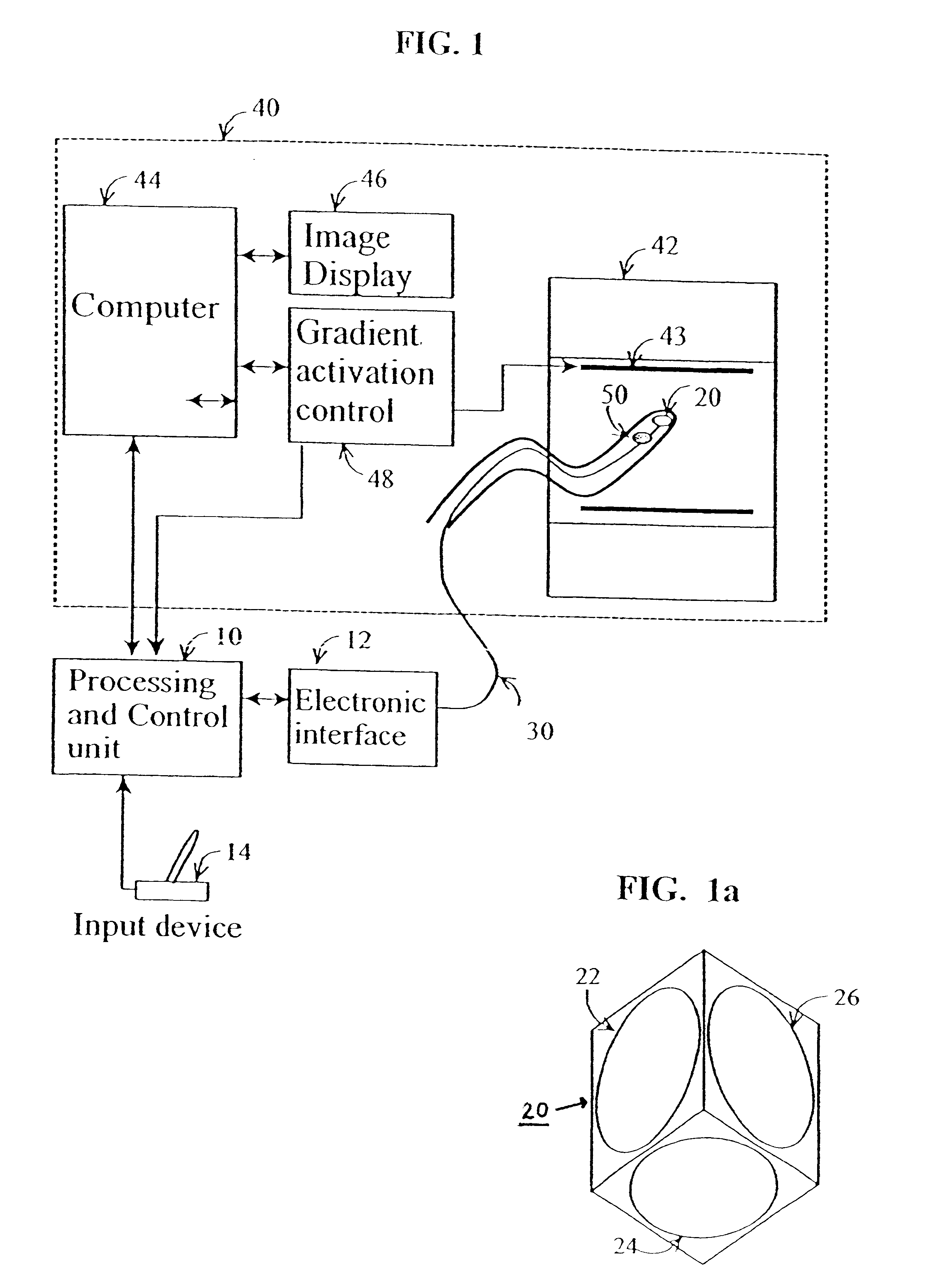
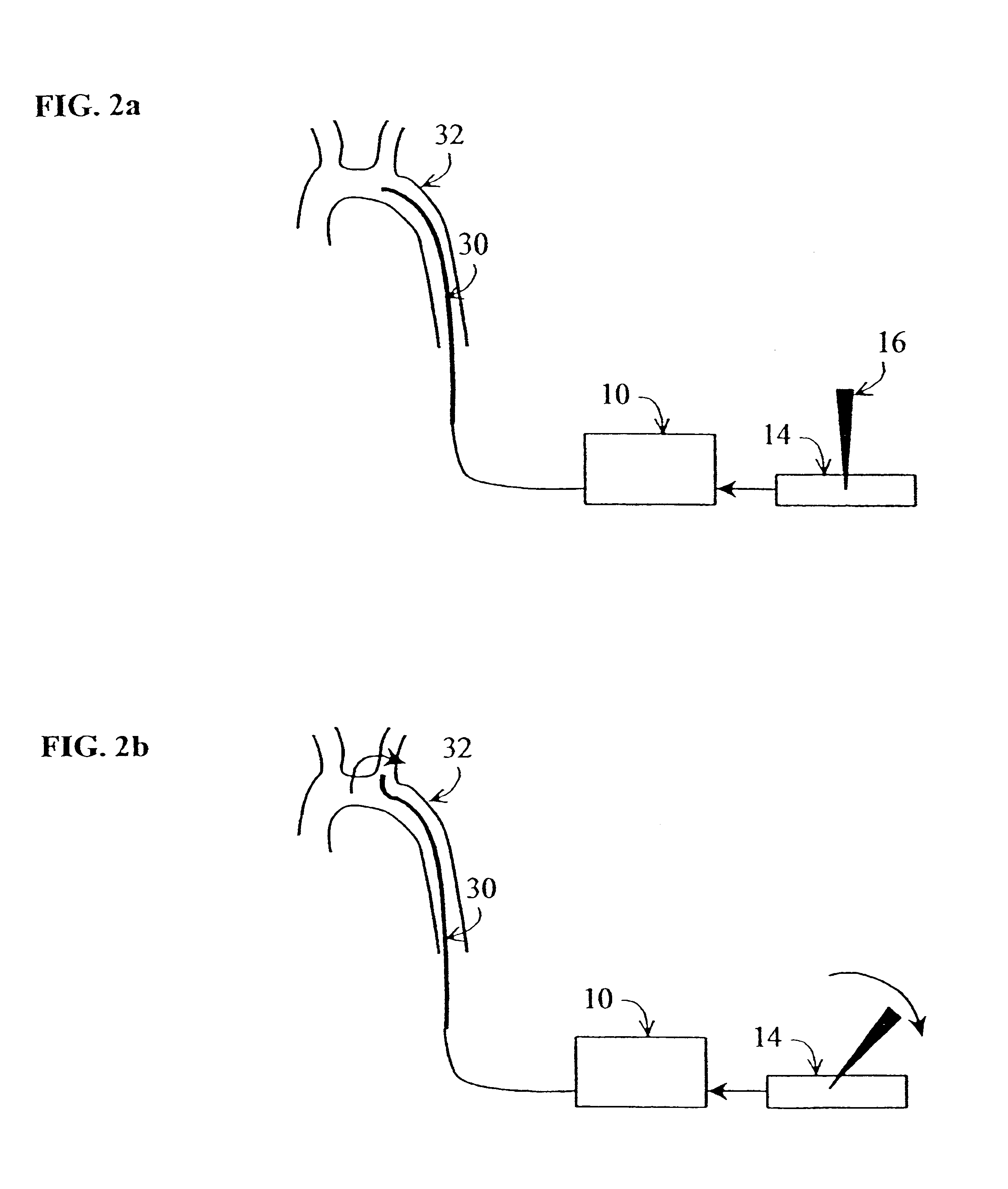
Method and apparatus for generating controlled torques on objects particularly objects inside a living body
A method and apparatus for generating a controlled torque of a desired direction and magnitude in an object within a body, particularly in order to steer the object through the body, such as a catheter through a blood vessel in a living body, by producing an external magnetic field of known magnitude and direction within the body, applying to the object a coil assembly including preferably three coils of known orientation with respect to each other, preferably orthogonal to each other, and controlling the electrical current through the coils to cause the coil assembly to generate a resultant magnetic dipole interacting with the external magnetic field to produce a torque of the desired direction and magnitude.
Owner:ROBIN MEDICAL
Methods for repairing damaged intervertebral discs
InactiveUSRE40156E1Reduce internal pressureReduce moistureBiocideOrganic chemistryIntervertebral discActive electrode
Apparatus and methods for treating an intervertebral disc by ablation of disc tissue. A method of the invention includes positioning at least one active electrode within the intervertebral disc, and applying at least a first high frequency voltage between the active electrode(s) and one or more return electrode(s), wherein the volume of the nucleus pulposus is decreased, pressure exerted by the nucleus pulposus on the annulus fibrosus is reduced, and discogenic pain of a patient is alleviated. In other embodiments, a curved or steerable probe is guided to a specific target site within a disc to be treated, and the disc tissue at the target site is ablated by application of at least a first high frequency voltage between the active electrode(s) and one or more return electrode(s). A method of making an electrosurgical probe is also disclosed.
Owner:ARTHROCARE
Instruments and methods for reduction of vertebral bodies
InactiveUS20060095035A1Minimize damage amountProvide stabilityInternal osteosythesisFractureMinimally invasive proceduresReducer
A spinal stabilization system may be formed in a patient. In some embodiments, a minimally invasive procedure may be used to form a spinal stabilization system in a patient. Bone fastener assemblies may be coupled to vertebrae. Each bone fastener assembly may include a bone fastener and a collar. The collar may be rotated and / or angulated relative to the bone fastener. Extenders may be coupled to the collar to allow for formation of the spinal stabilization system through a small skin incision. The extenders may allow for alignment of the collars to facilitate insertion of an elongated member in the collars. An elongated member may be positioned in the collars and a closure member may be used to secure the elongated member to the collars. A reducer may be used to achieve reduction of one or more vertebral bodies coupled to a spinal stabilization system.
Owner:ZIMMER SPINE INC
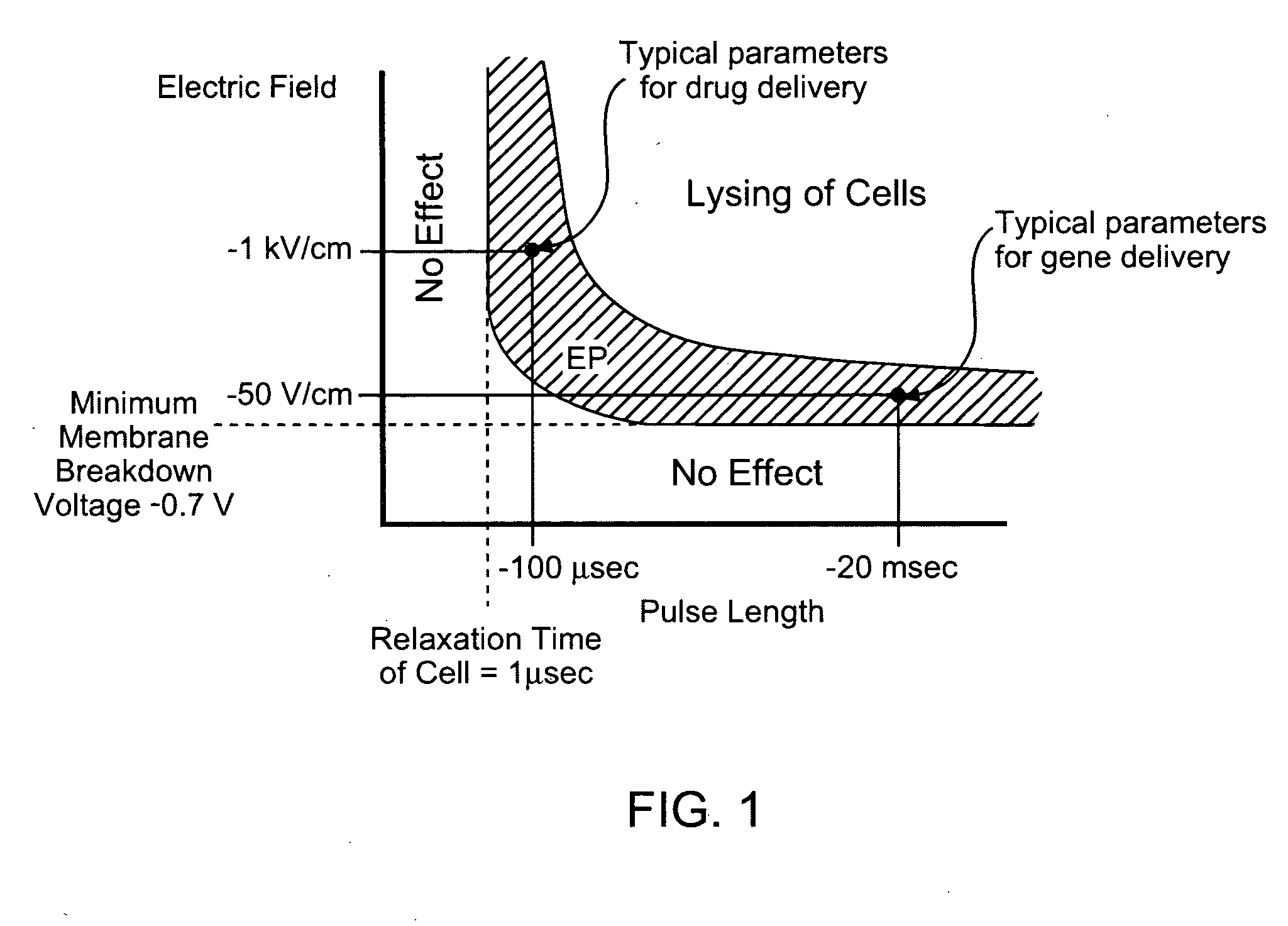
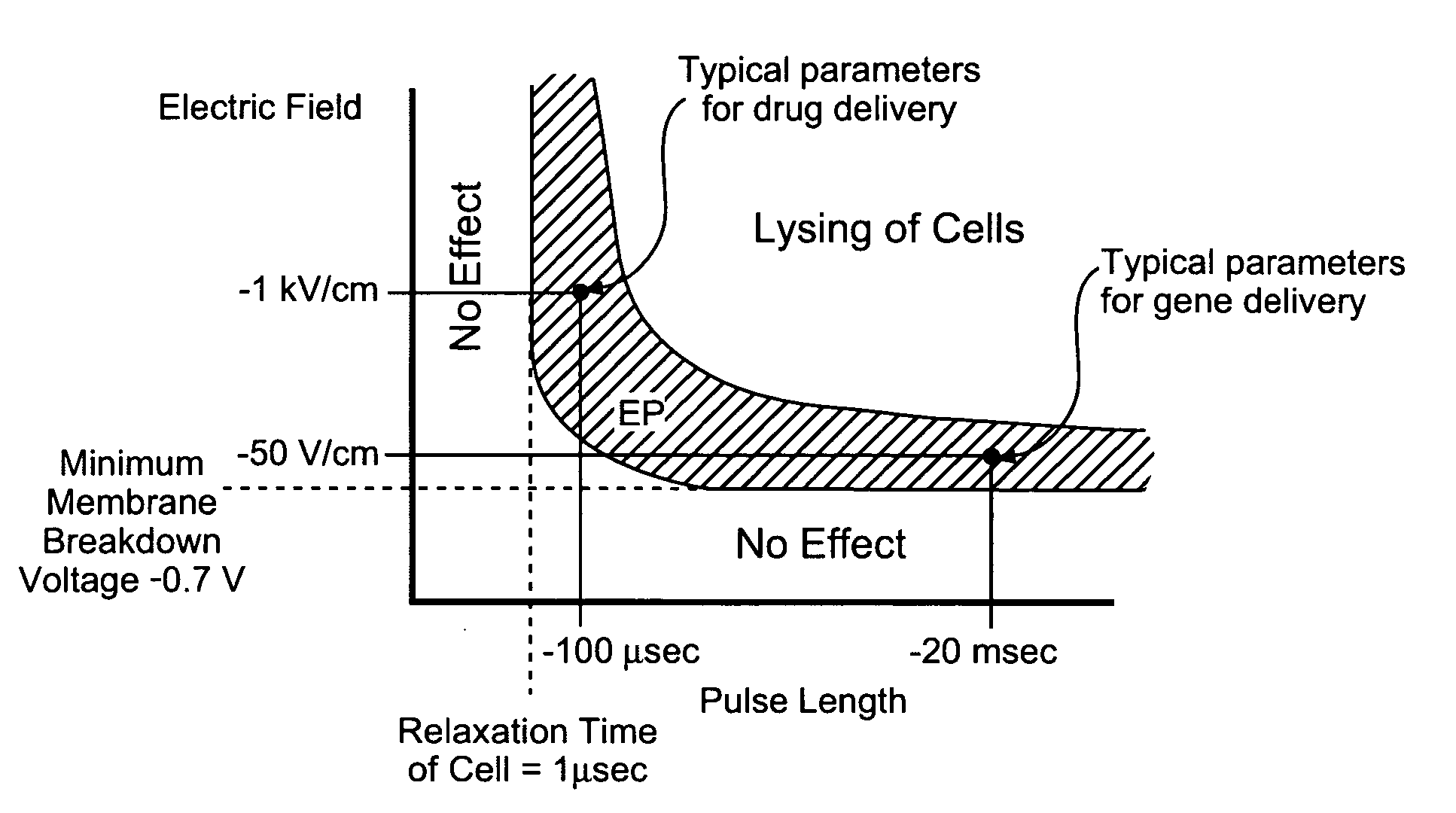
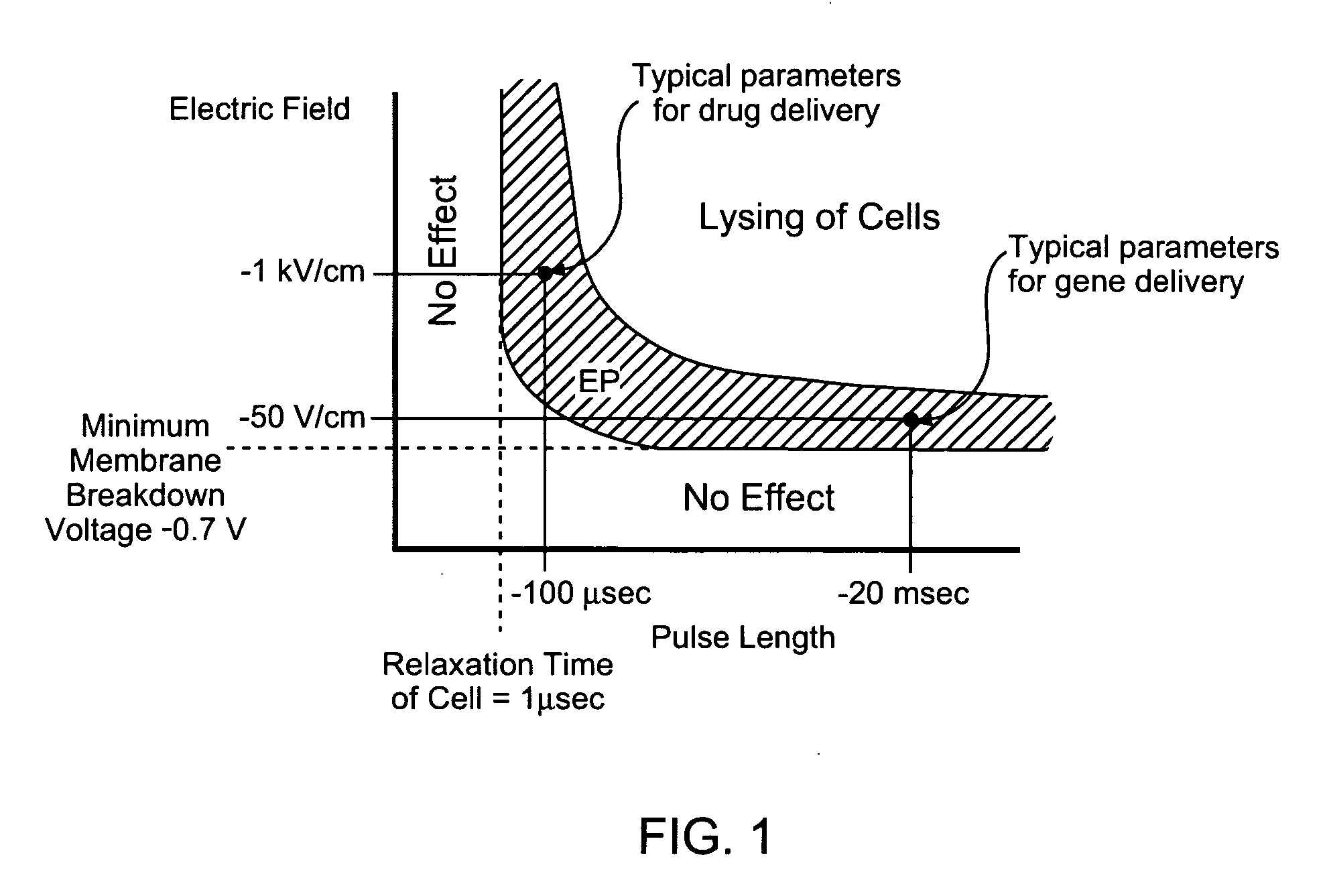
Electroporation to interrupt blood flow
InactiveUS20050171574A1High level of controlRestricted blood flowSurgical needlesInternal electrodesAbnormal tissue growthBlood flow
A method for disrupting blood flow to undesirable tissue such as cells of a cancerous or non-cancerous tumor is disclosed. It involves the placement of electrodes into or near the vicinity of vessels supplying blood to the undesirable tissue and through the application of electrical pulses causing blood flow disruption. The electric pulses irreversibly permeate the cell membranes, thereby invoking cell death. The irreversibly permeabilized cells are left in situ and are removed by the body immune system. The process may further comprise monitoring blood flow and / or infusion of a material such as a chemotherapeutic agent or marker into the blood.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA
Dual mode electrosurgical clamping probe and related methods
InactiveUS6974453B2Minimize damageAvoid and minimize currentCannulasEnemata/irrigatorsDual modeSurgical department
The present invention provides systems, apparatus and methods for selectively applying electrical energy to body tissue in order to ablate, contract, coagulate, or otherwise modify a target tissue or organ of a patients. An electrosurgical apparatus of the invention includes a shaft having a shaft distal end bearing an active electrode and a return electrode. At least one of the active electrode and the return electrode is moveable such that the shaft distal end can adopt a closed configuration or an open configuration. The apparatus can operate in an ablation mode or a sub-ablation mode. The closed configuration is adapted for clamping and coagulating a target tissue while the apparatus is operating in the sub-ablation mode, while the open configuration is adapted for ablating the target tissue via molecular dissociation of tissue components. A method of the present invention comprises clamping a target tissue or organ with an electrosurgical probe. A first high frequency voltage is applied between the active electrode and the return electrode to effect coagulation of the clamped tissue. Thereafter, a second high frequency voltage is applied to effect localized molecular dissociation of the coagulated tissue. The present invention allows the ablation or modification of the target tissue with minimal or no damage to surrounding, non-target tissue.
Owner:ARTHROCARE
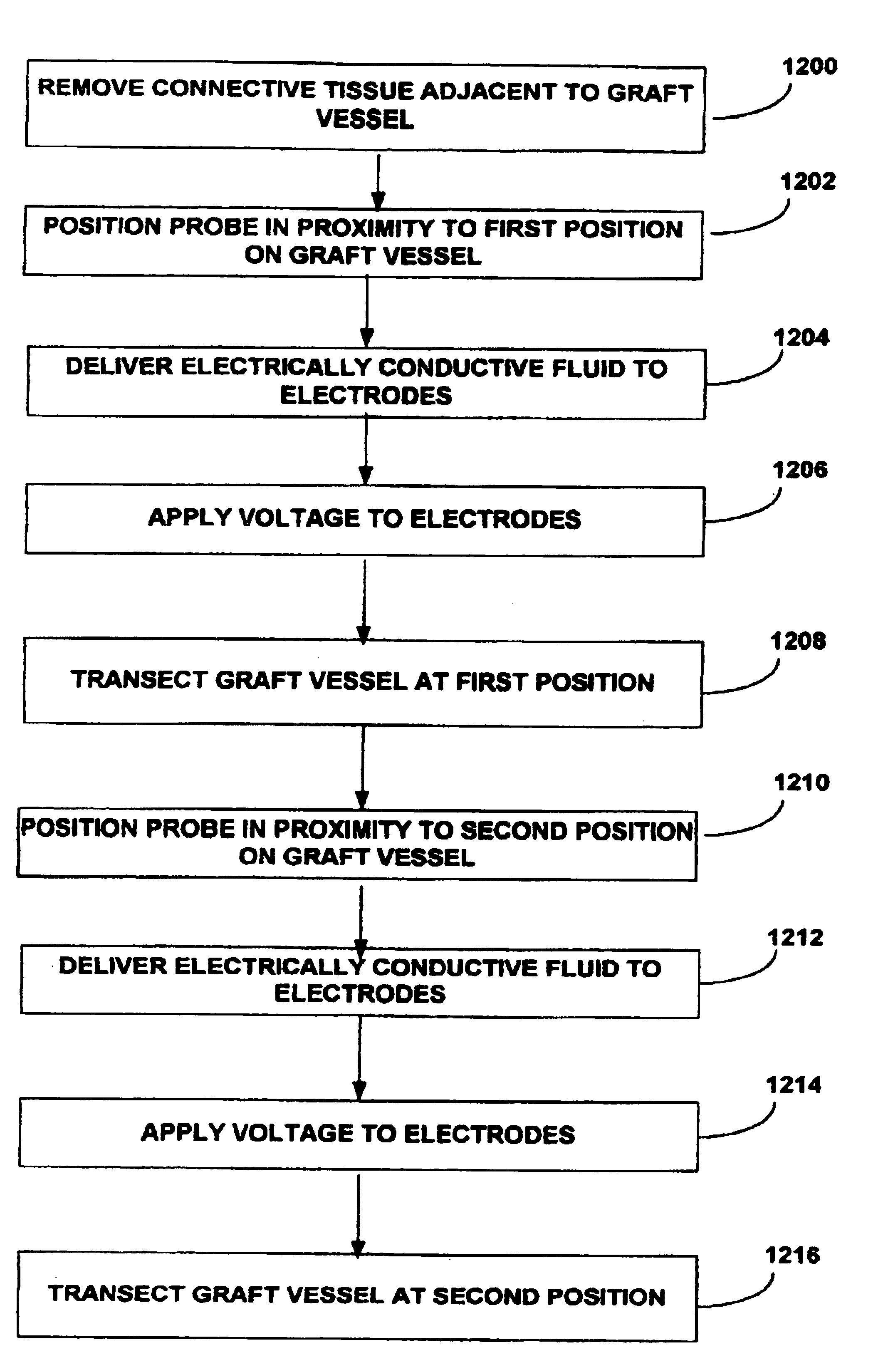
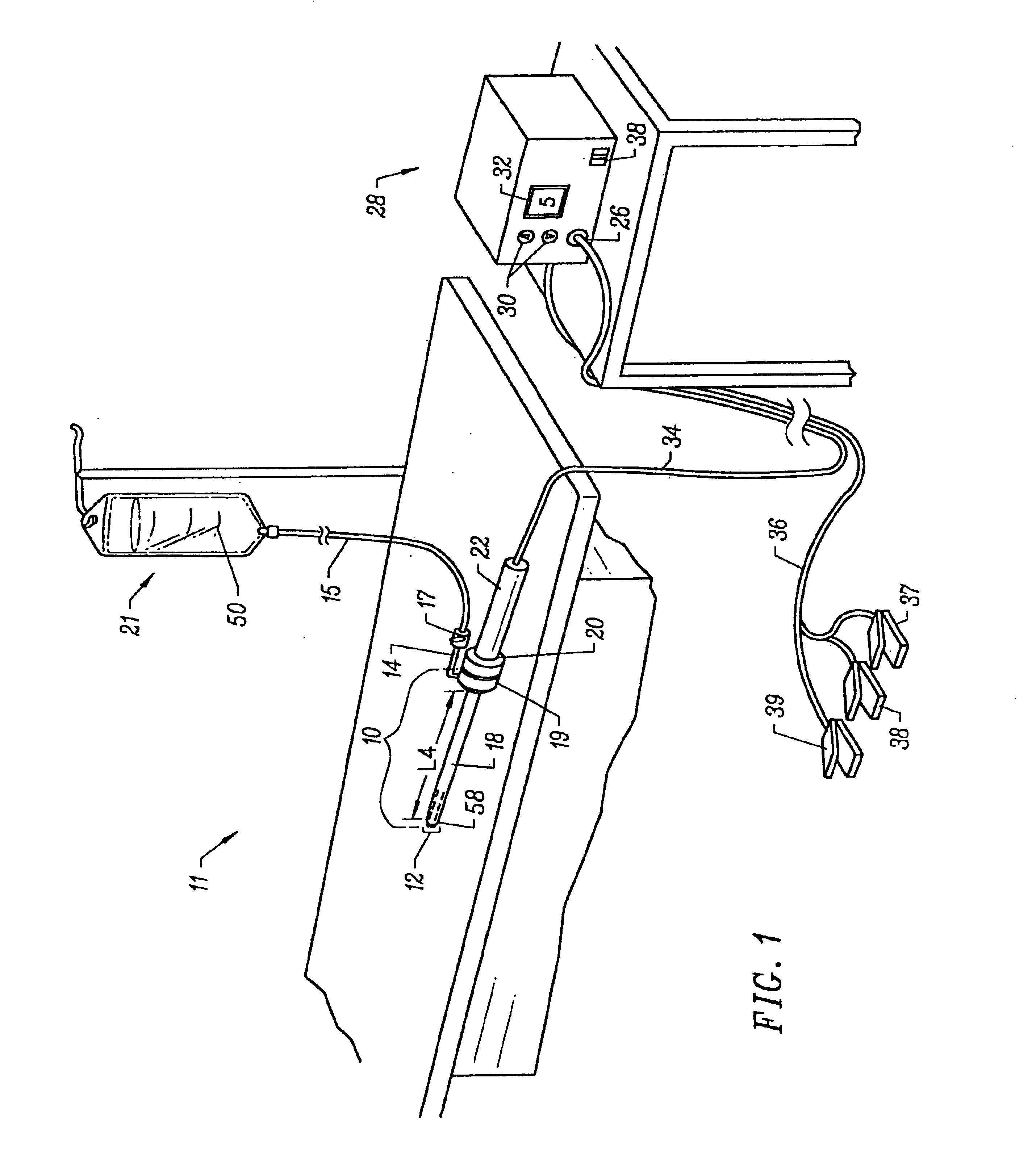
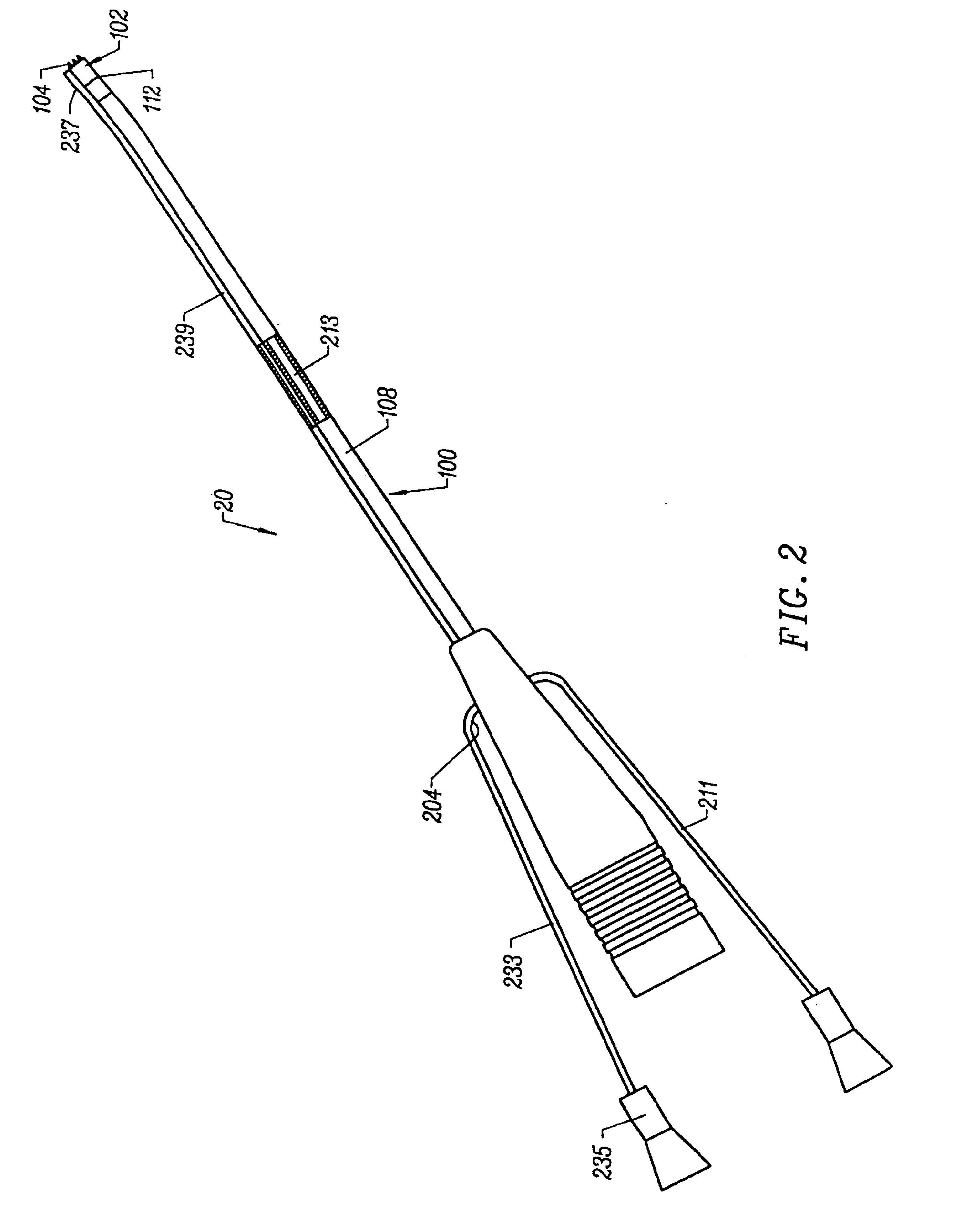
Method for harvesting graft vessel
InactiveUS6915806B2Improves surgeon 's viewThermal damage is minimizedCannulasEnemata/irrigatorsSaphenous veinsMammary artery
The present invention provides systems, apparatus and methods for selectively applying electrical energy to body tissue in order to incise, dissect, harvest or transect tissues or an organ of a patient. The electrosurgical systems and methods are useful, inter alia, for accessing, dissecting, and transecting a graft blood vessel, such as the internal mammary arteries (IMA) or the saphenous vein, for use in a by-pass procedure. A method of the present invention comprises positioning an electrosurgical probe adjacent the target tissue so that one or more active electrode(s) are brought into at least partial contact or close proximity with a target site in the presence of an electrically conductive fluid. A high frequency voltage is then applied between the active electrode and one or more return electrode(s). During application of the high frequency voltage, the electrosurgical probe may be translated, reciprocated, or otherwise manipulated such that the active electrode is moved with respect to the tissue. The present invention volumetrically removes the tissue at the point of incision, dissection, or transection in a cool ablation process that minimizes thermal damage to surrounding, non-target tissue.
Owner:ARTHROCARE
Irreversible electroporation to control bleeding
InactiveUS20050171523A1High level of controlMinimize damageSurgical needlesInternal electrodesCell membraneMedicine
A method of stopping or controlling bleeding by the placement of electrodes into or near the vicinity of vessels is disclosed. Then the application of electrical pulses causing irreversible electroporation of vessel and blood cells throughout the entire area of current flow the bleeding is stopped or controlled. The electric pulses irreversibly permeate the cell membranes, thereby invoking cell death. The irreversibly permeabilized cells are left in situ and are removed by the body immune system. Through the use of irreversible electroporation bleeding can be stopped or controlled without inducing thermal damage.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com