Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
31 results about "Discogenic pain" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
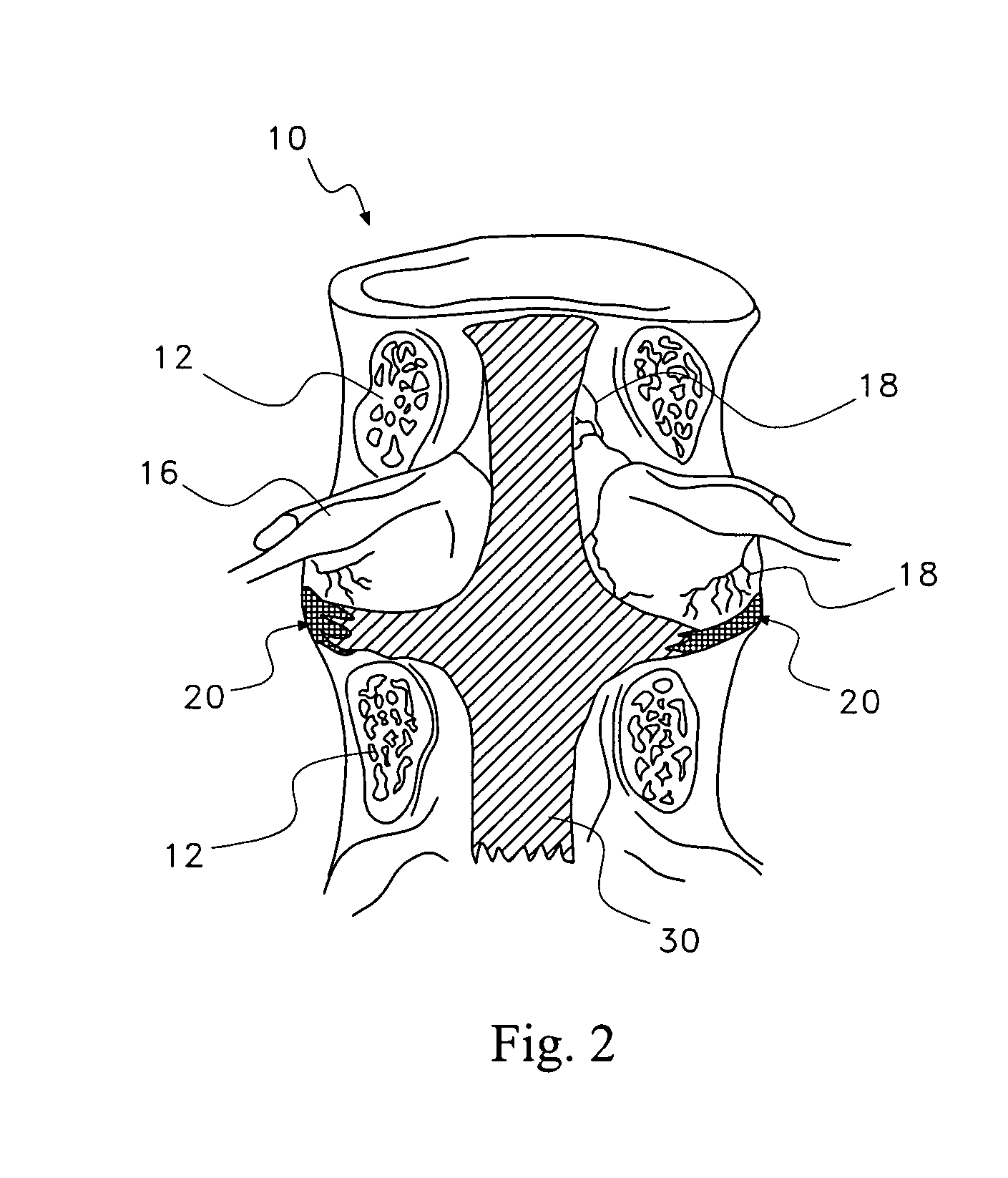
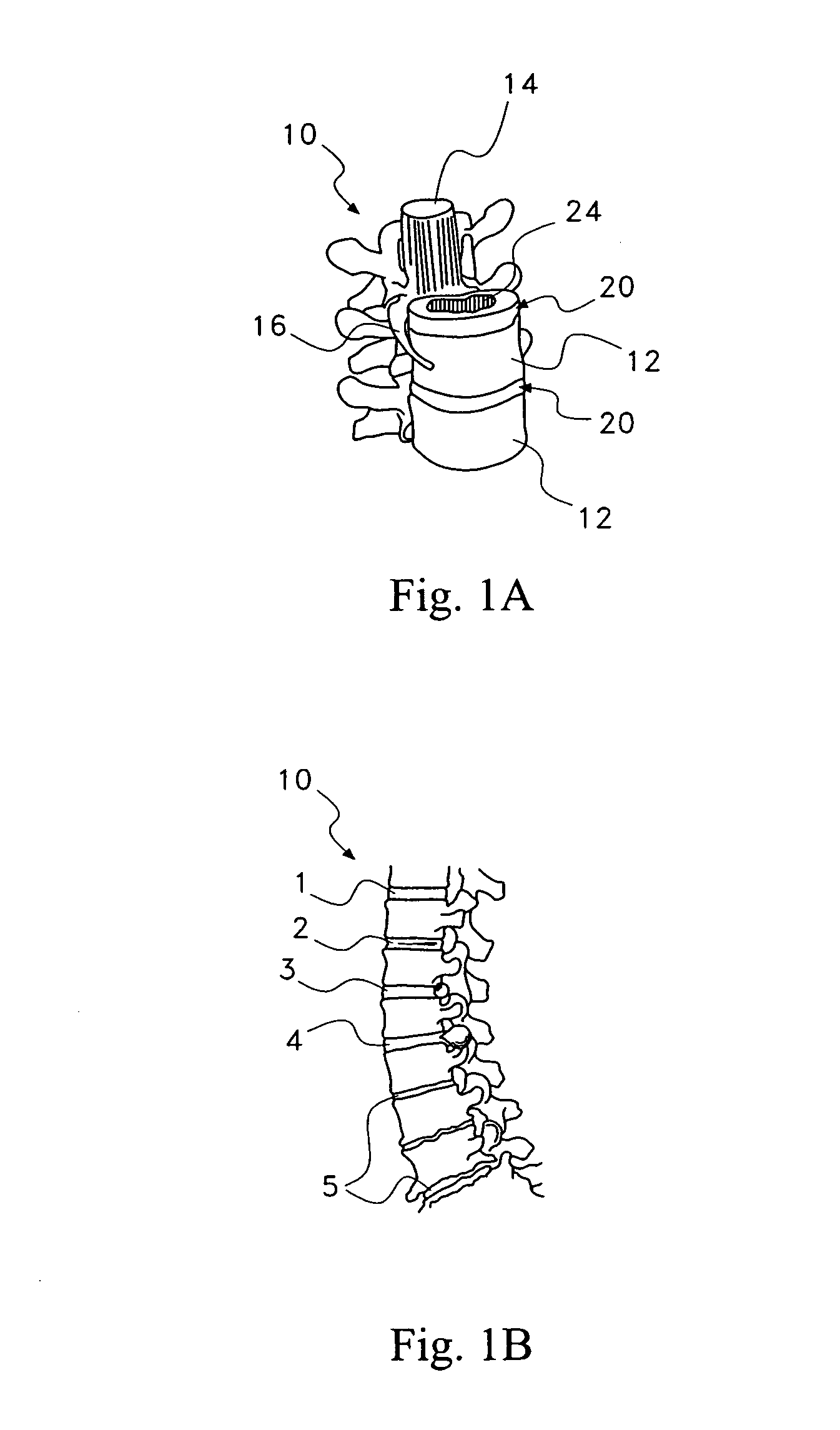
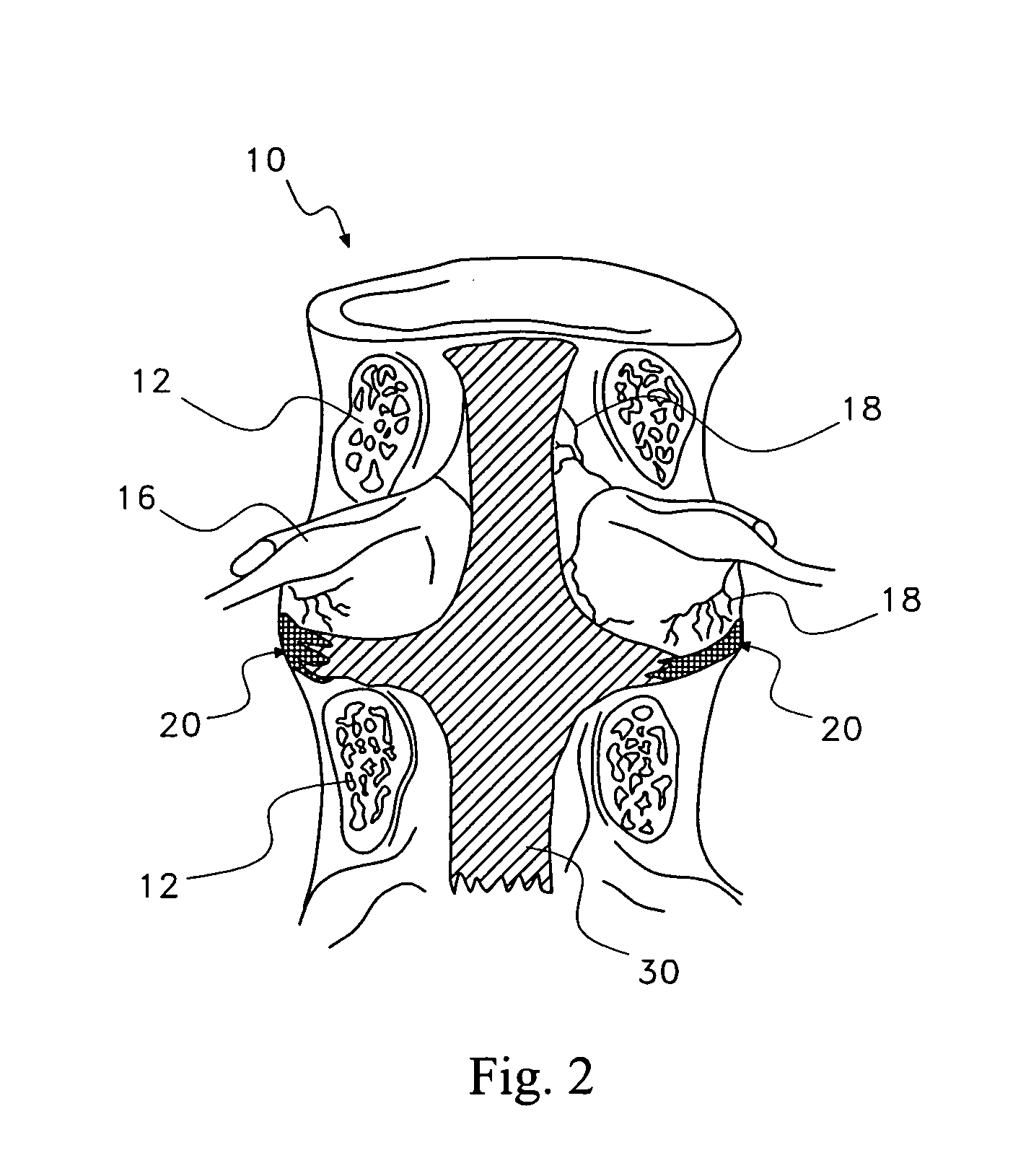
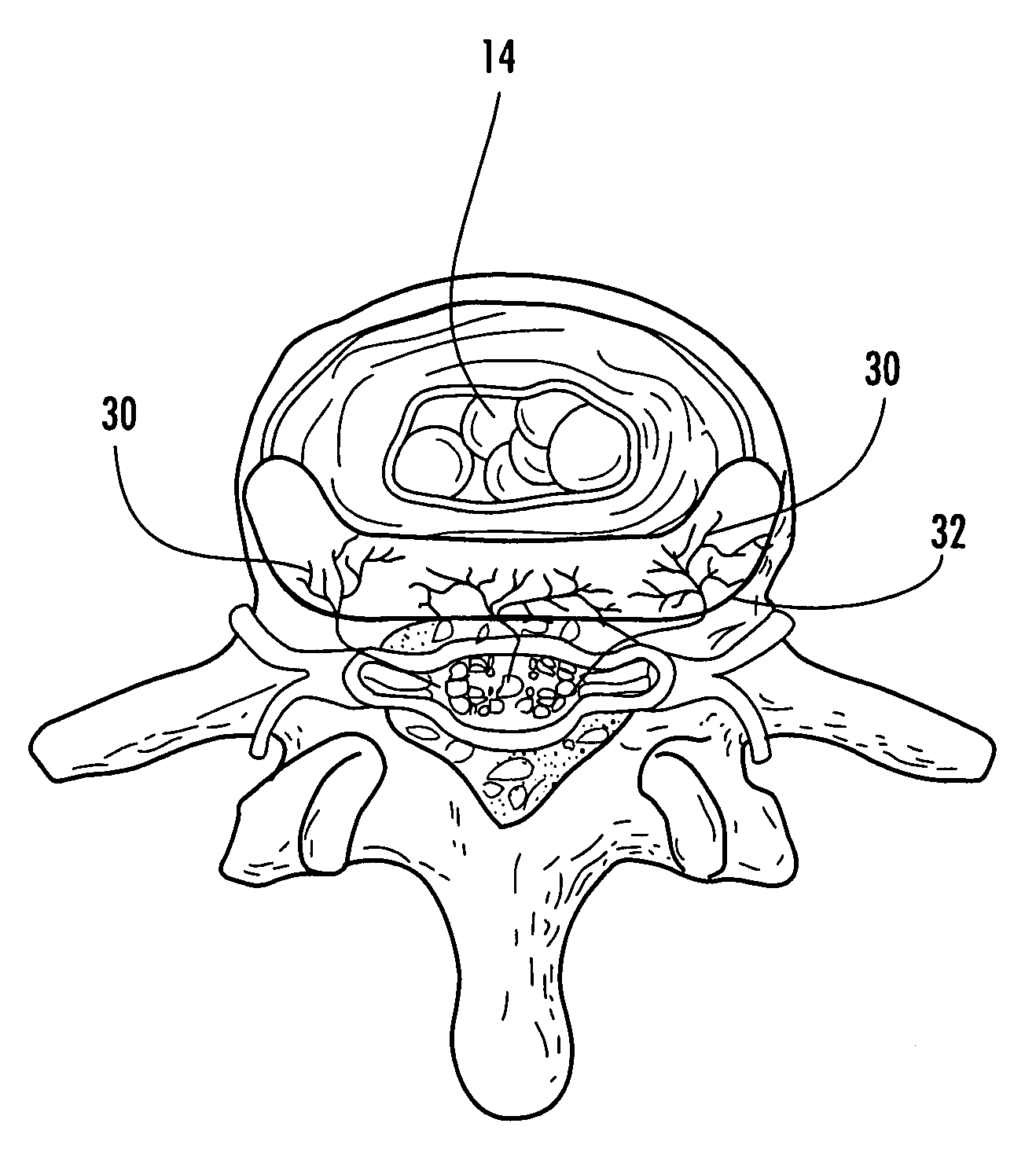
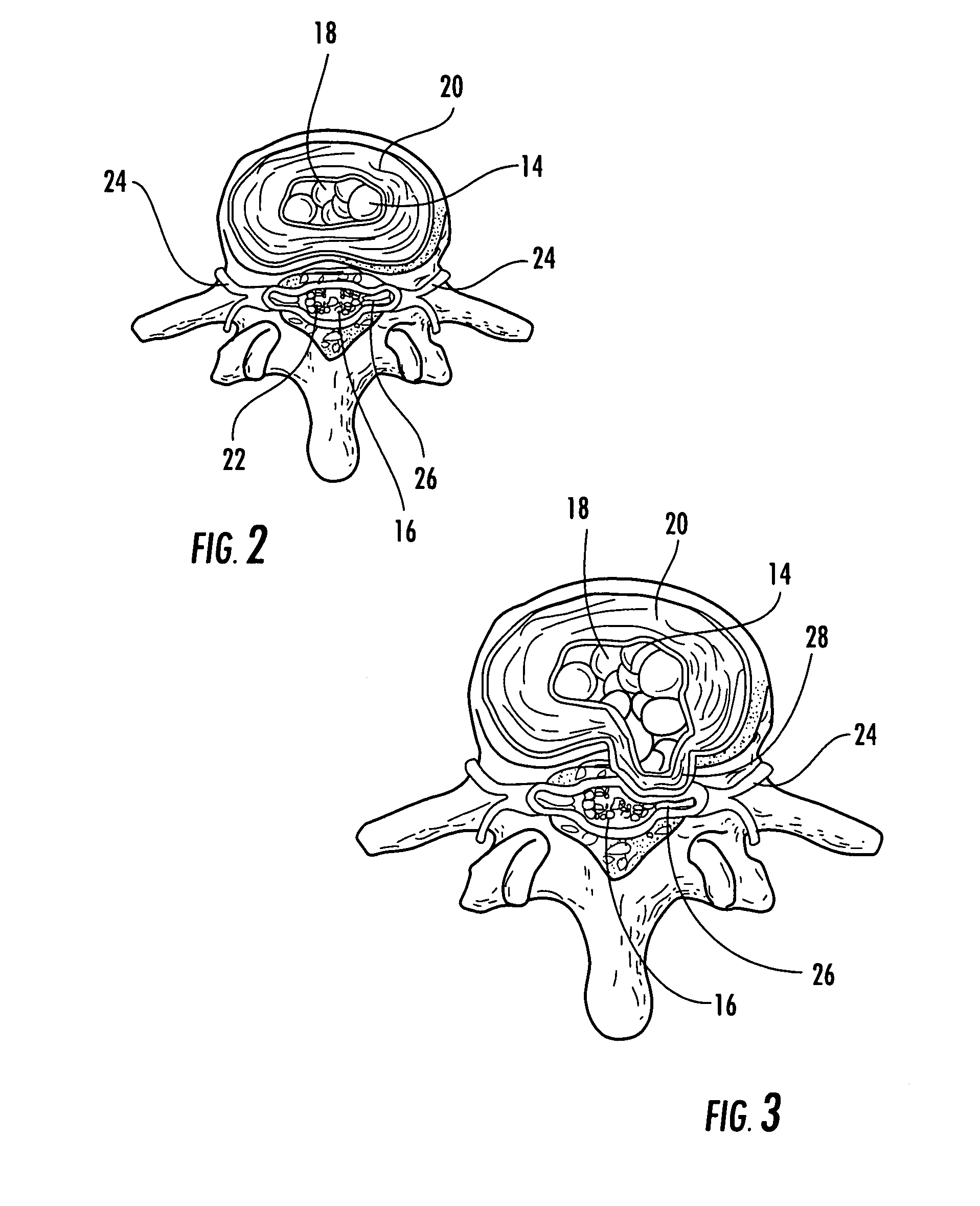
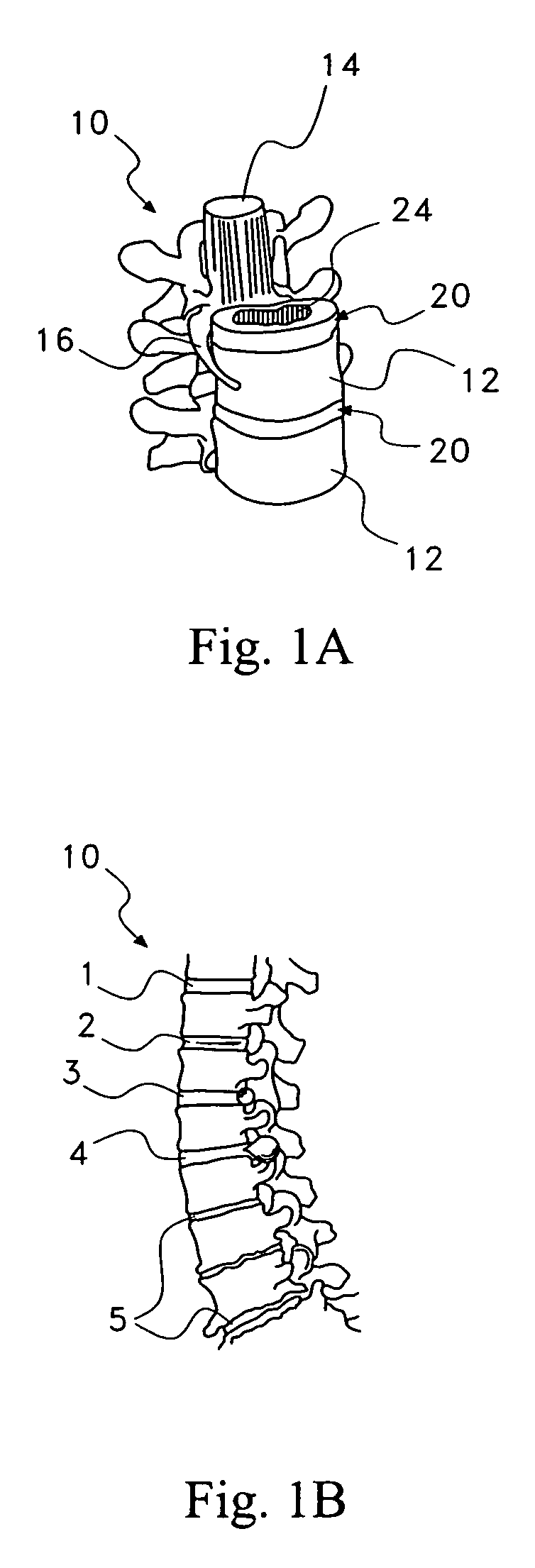
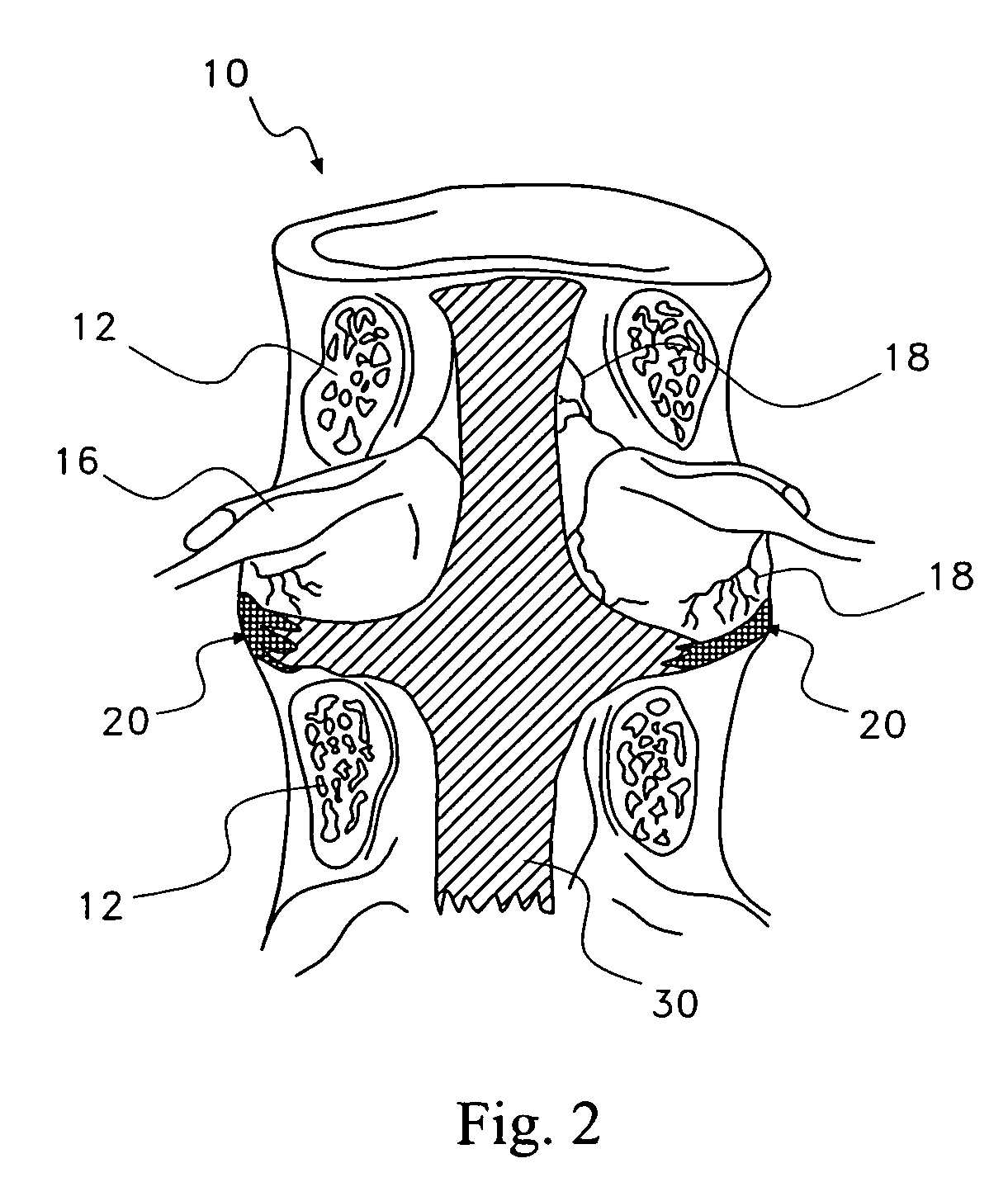
Discogenic pain is pain originating from a damaged vertebral disc, particularly due to degenerative disc disease. However, not all degenerated discs cause pain. Disc degeneration occurs naturally with age.
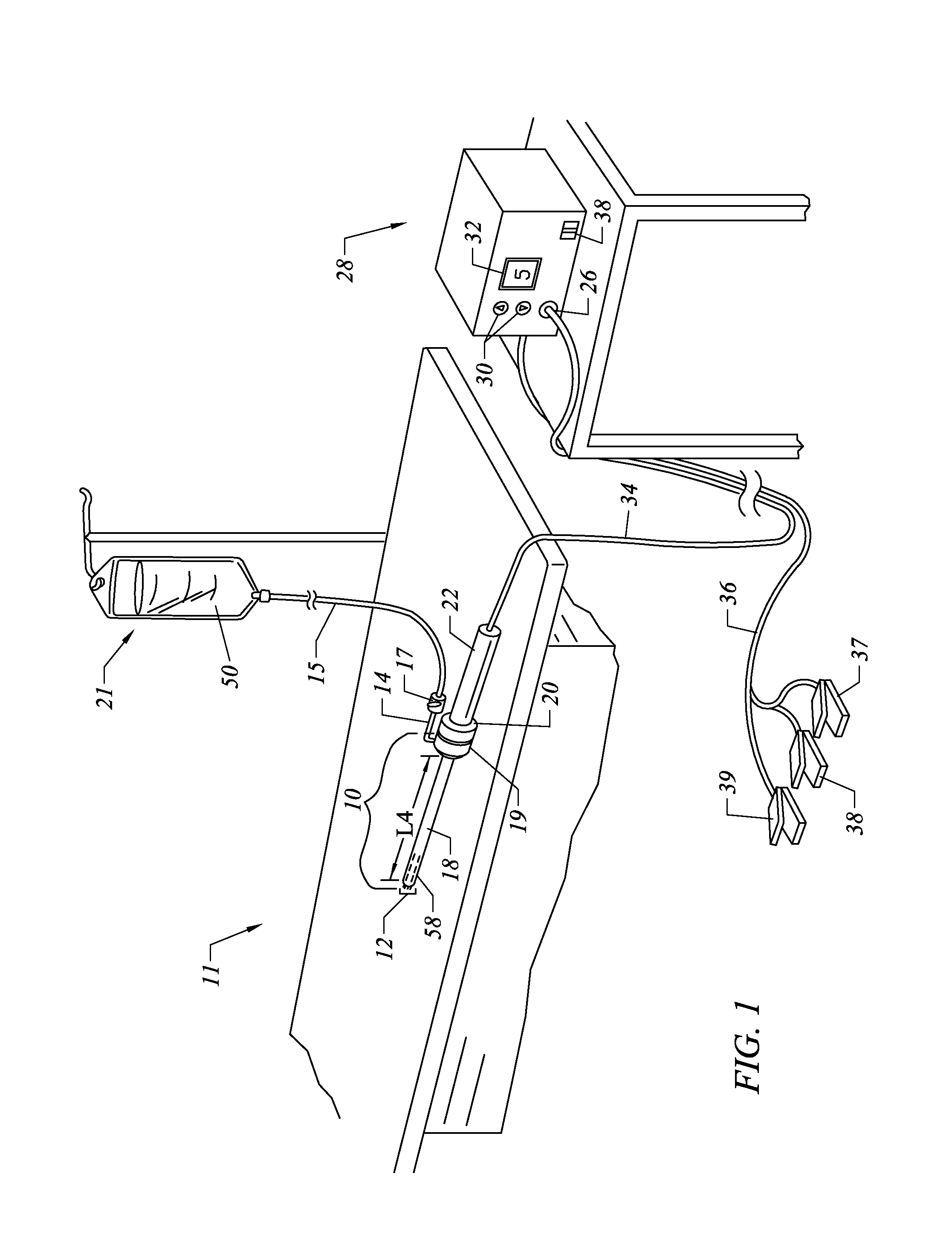
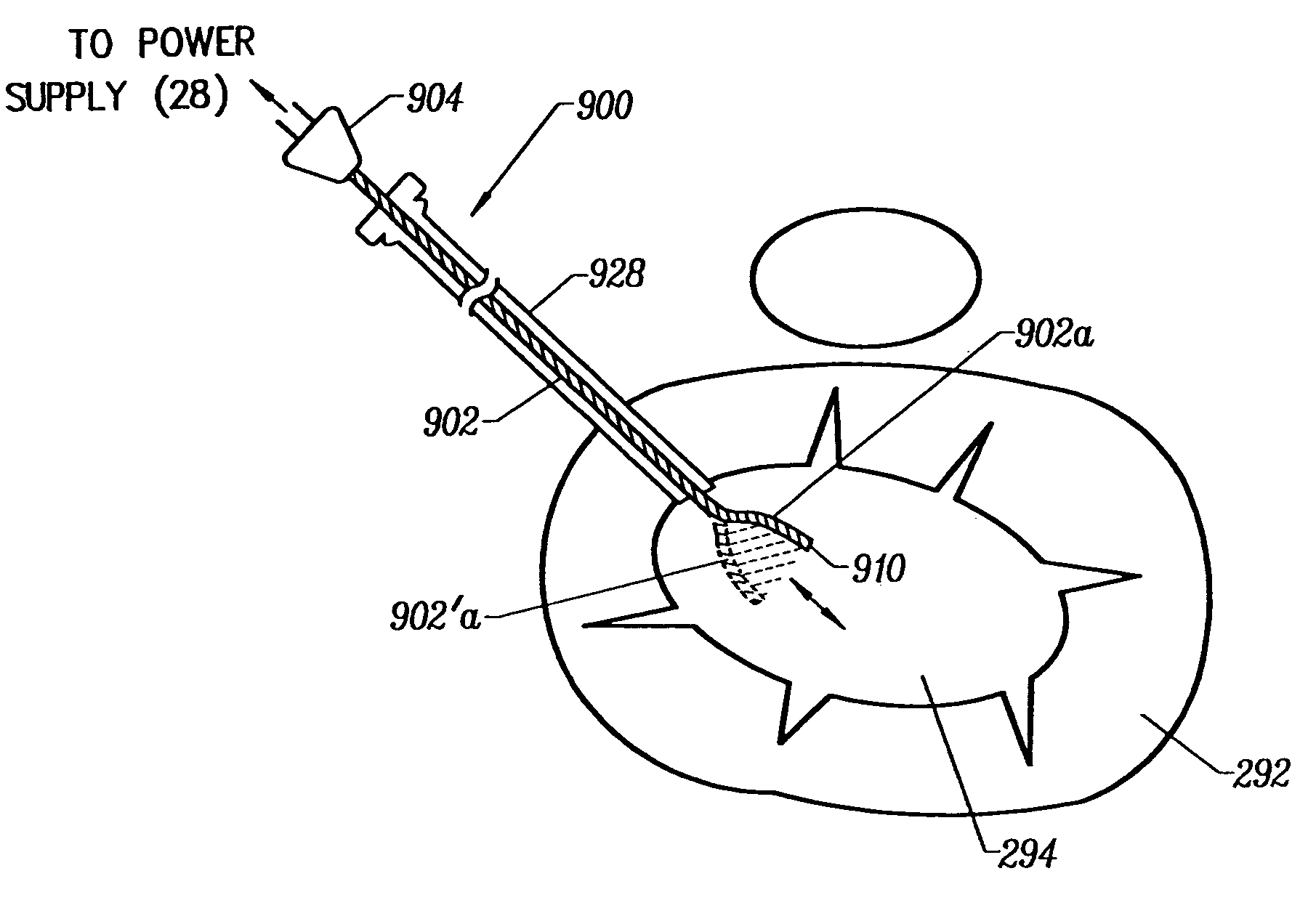
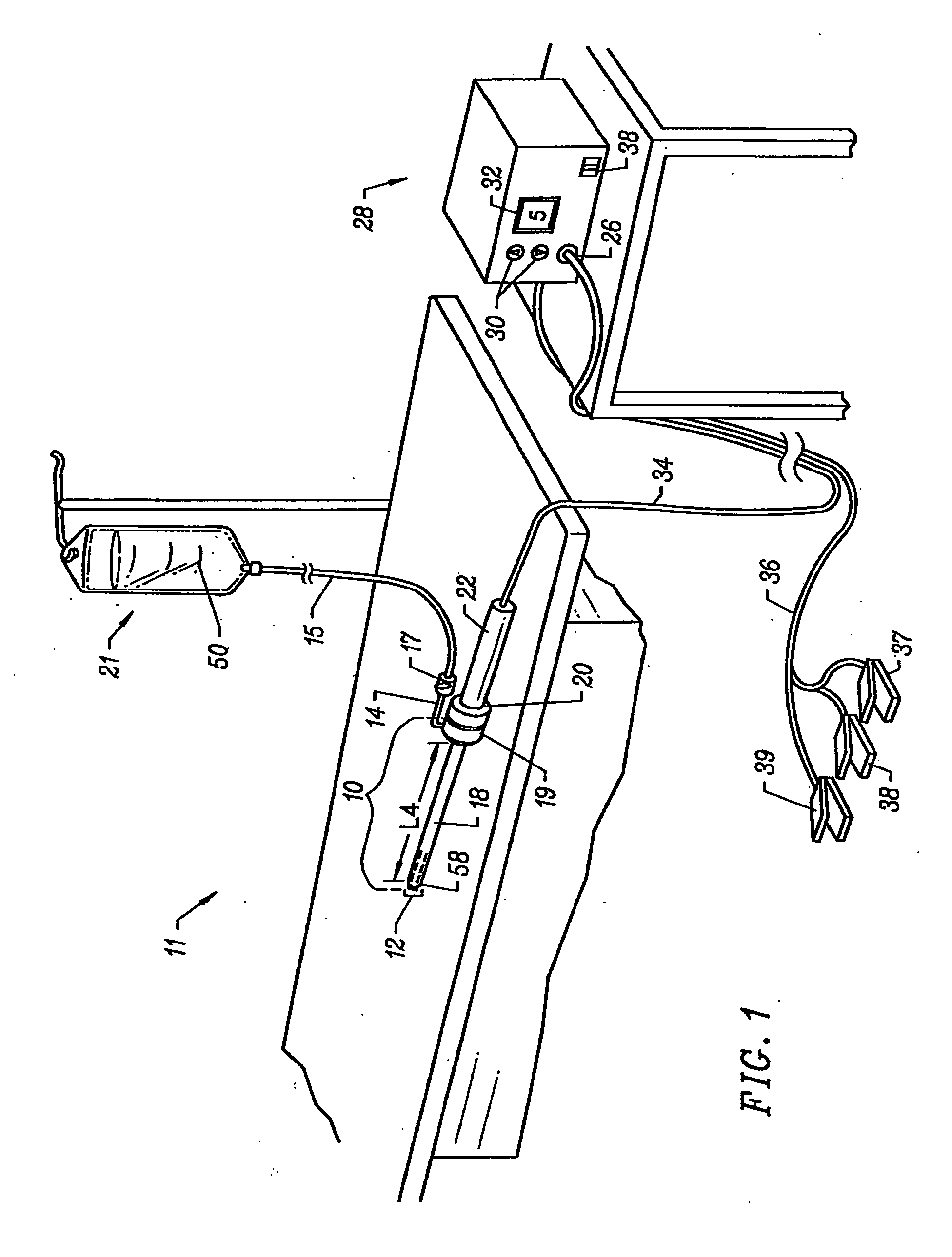
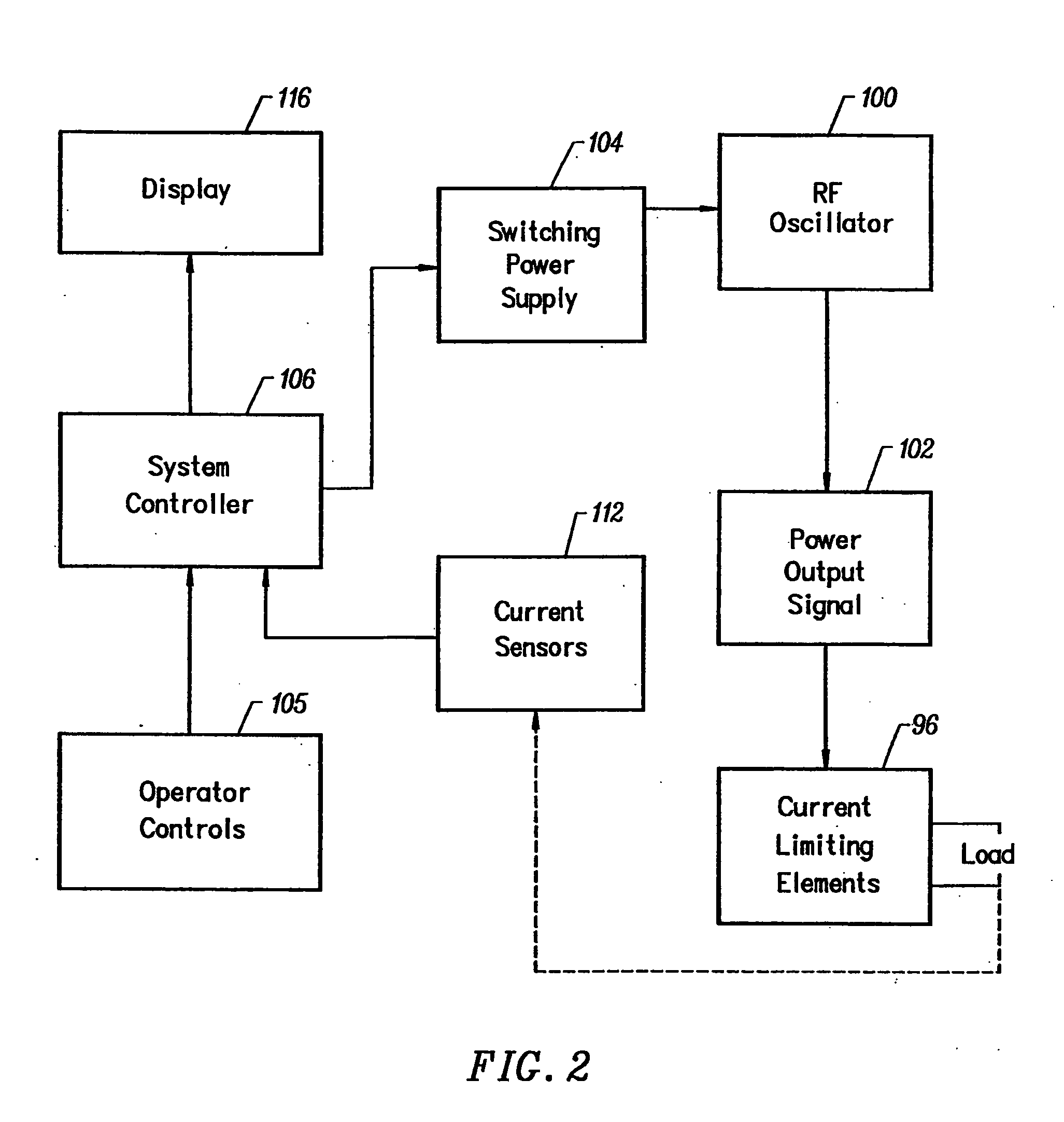
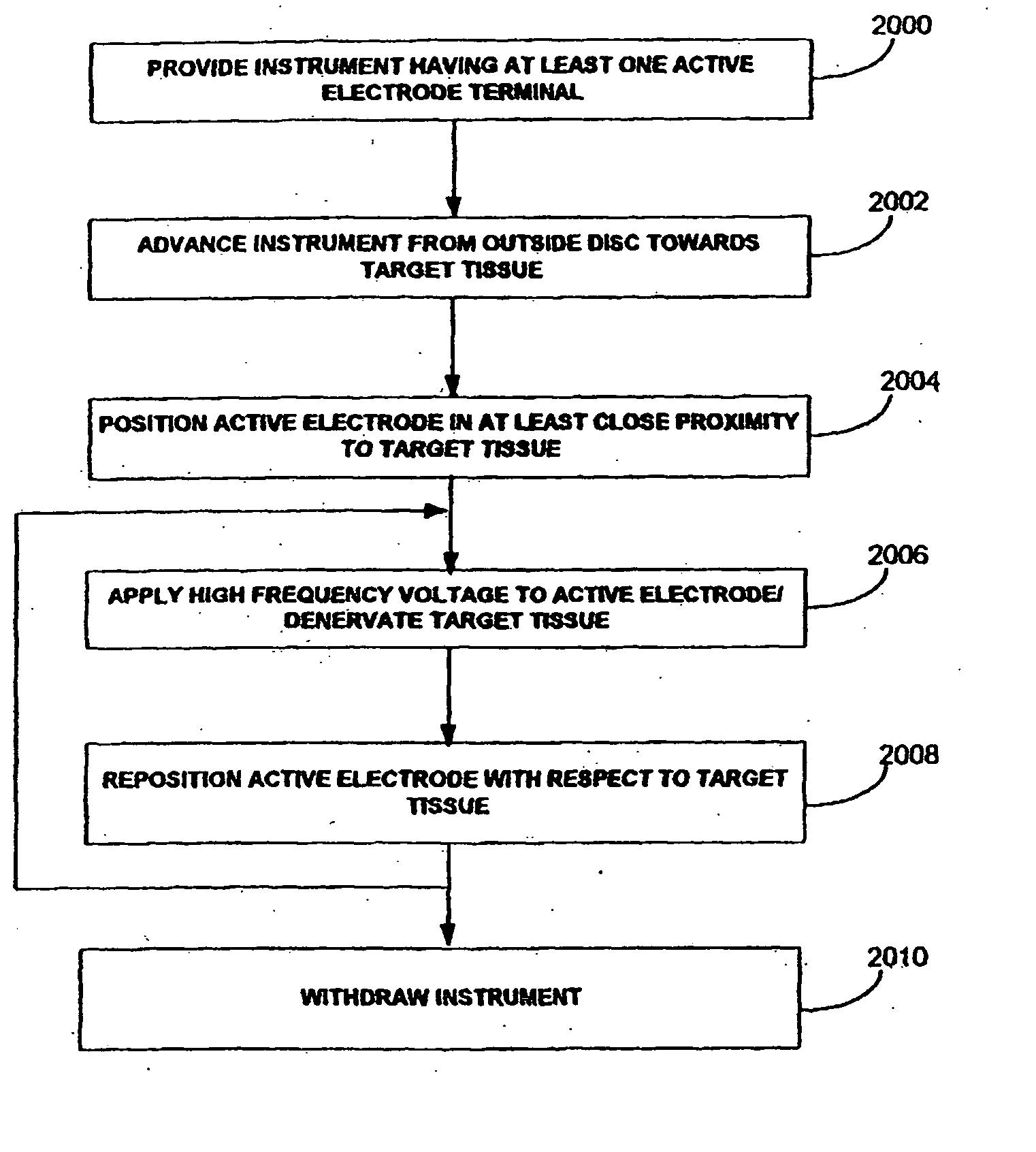
Methods for targeted electrosurgery on contained herniated discs
InactiveUS7179255B2Reduce pressureReduced neckingEnemata/irrigatorsHeart valvesFibrous ringCorneal ablation
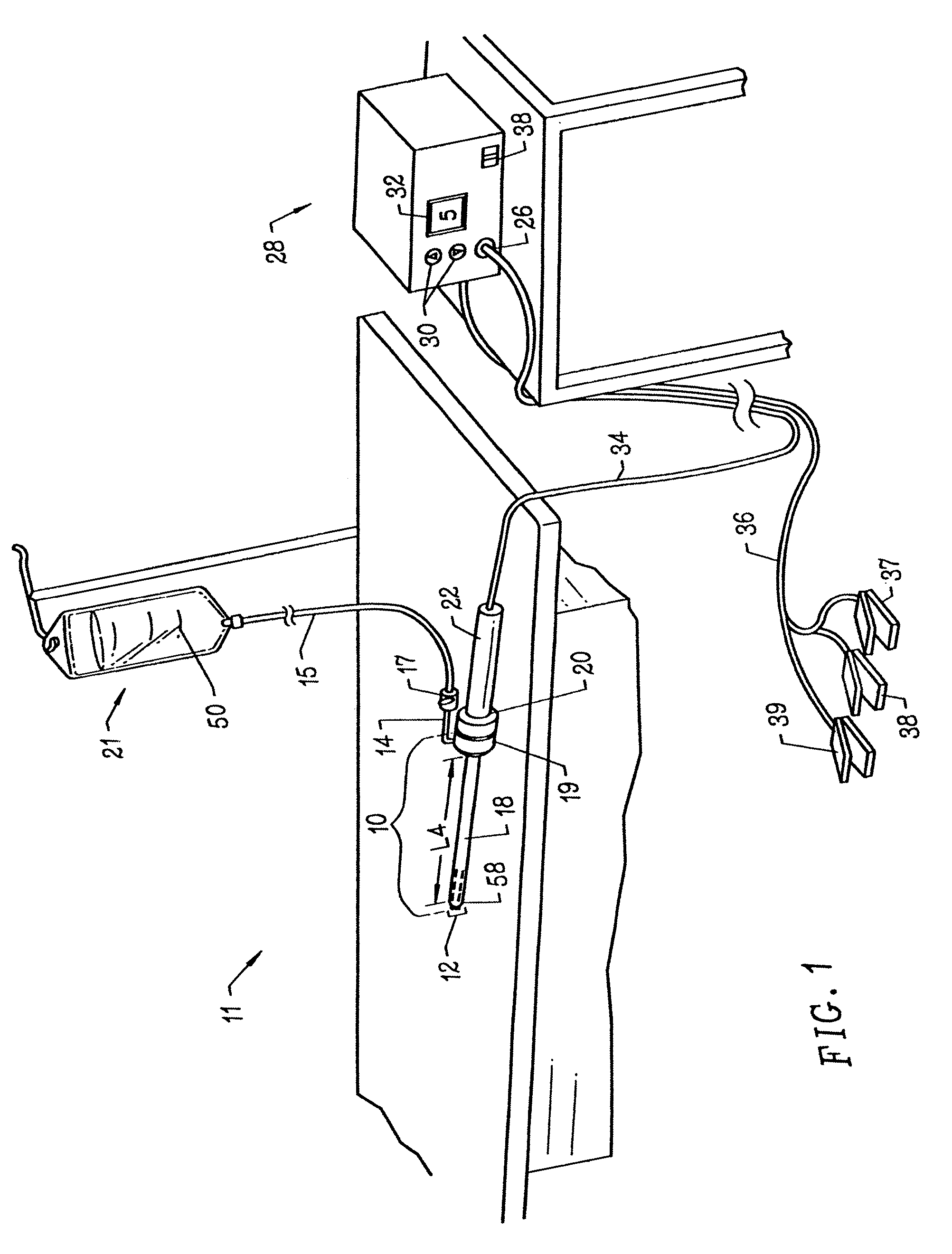
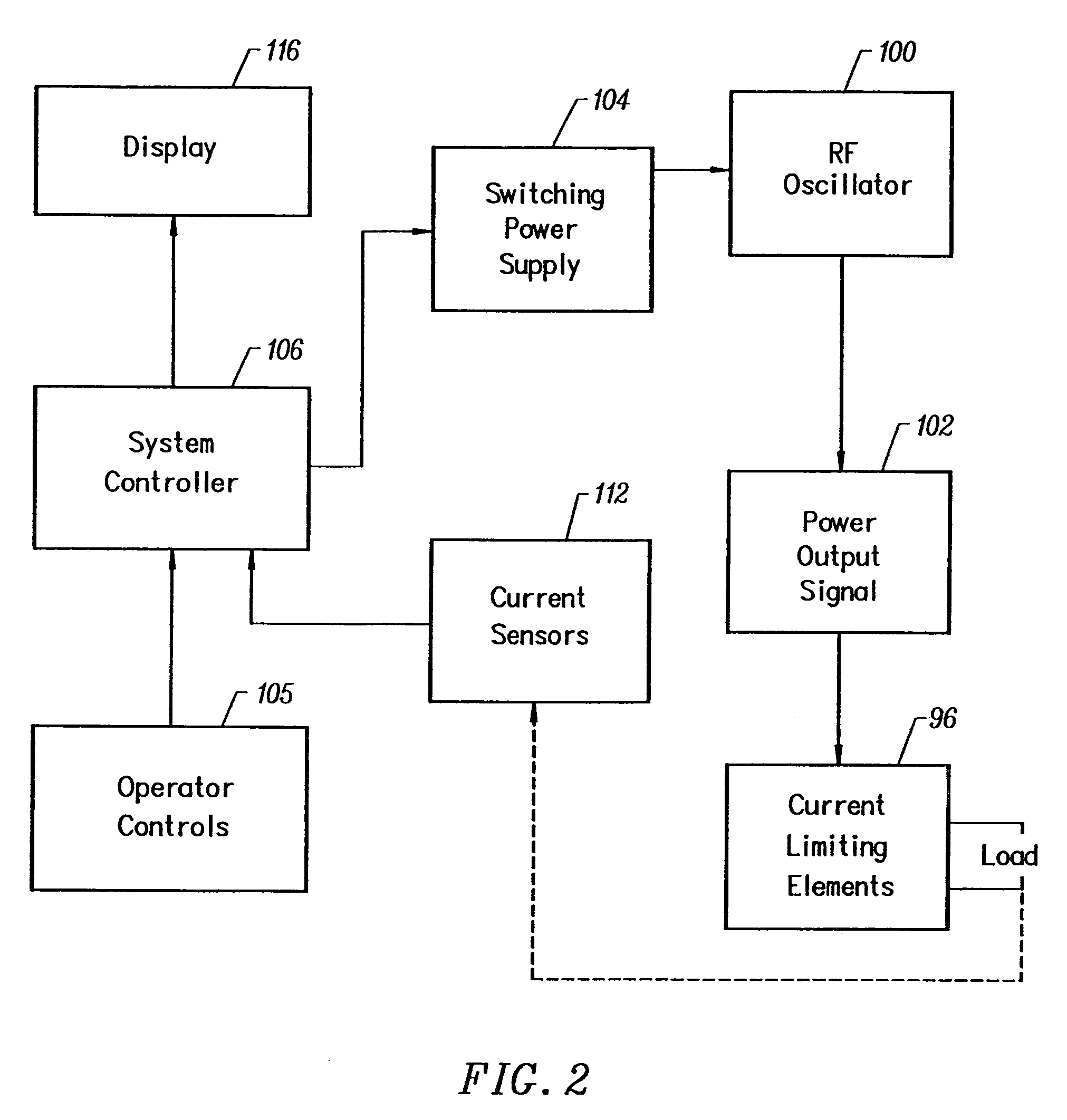
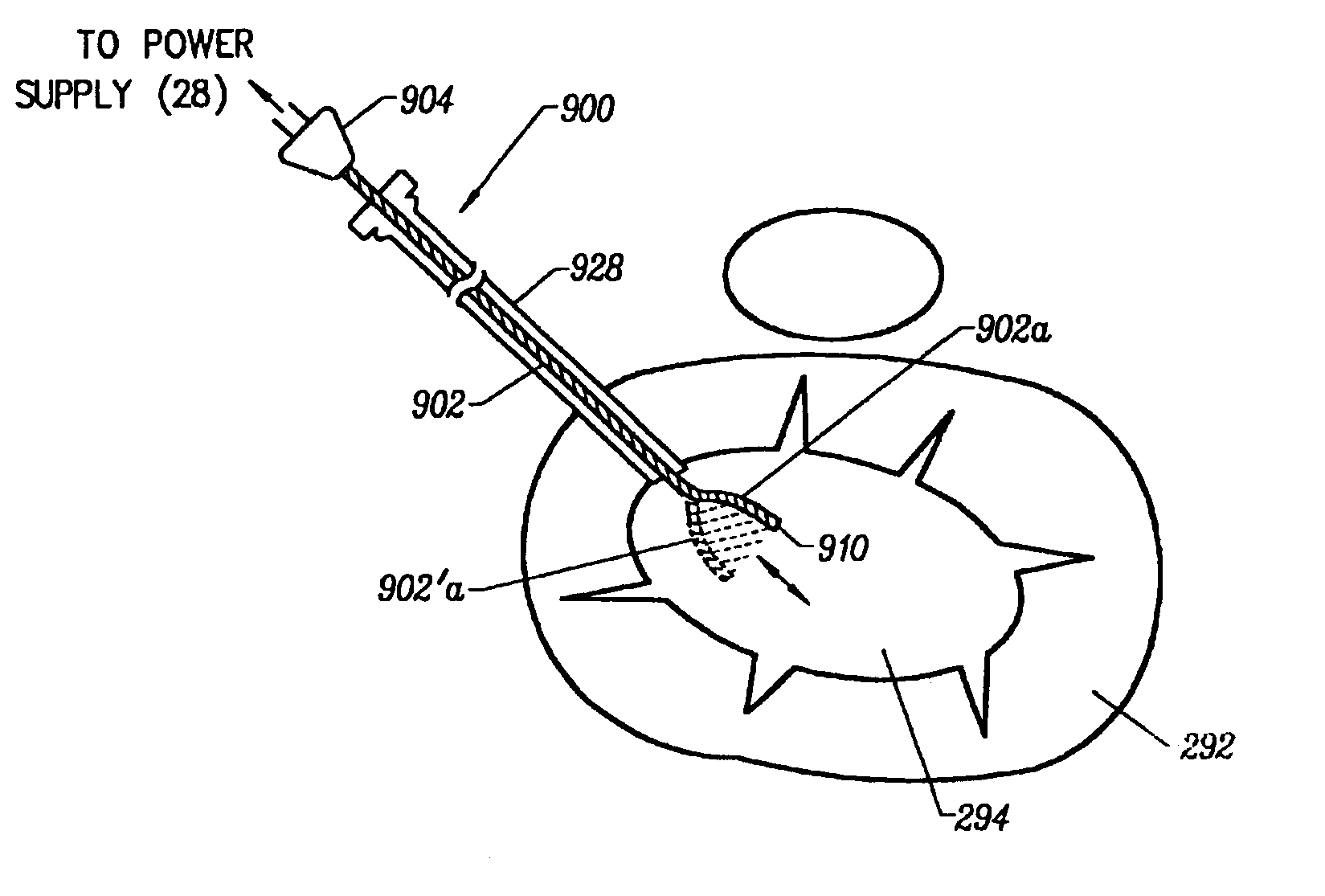
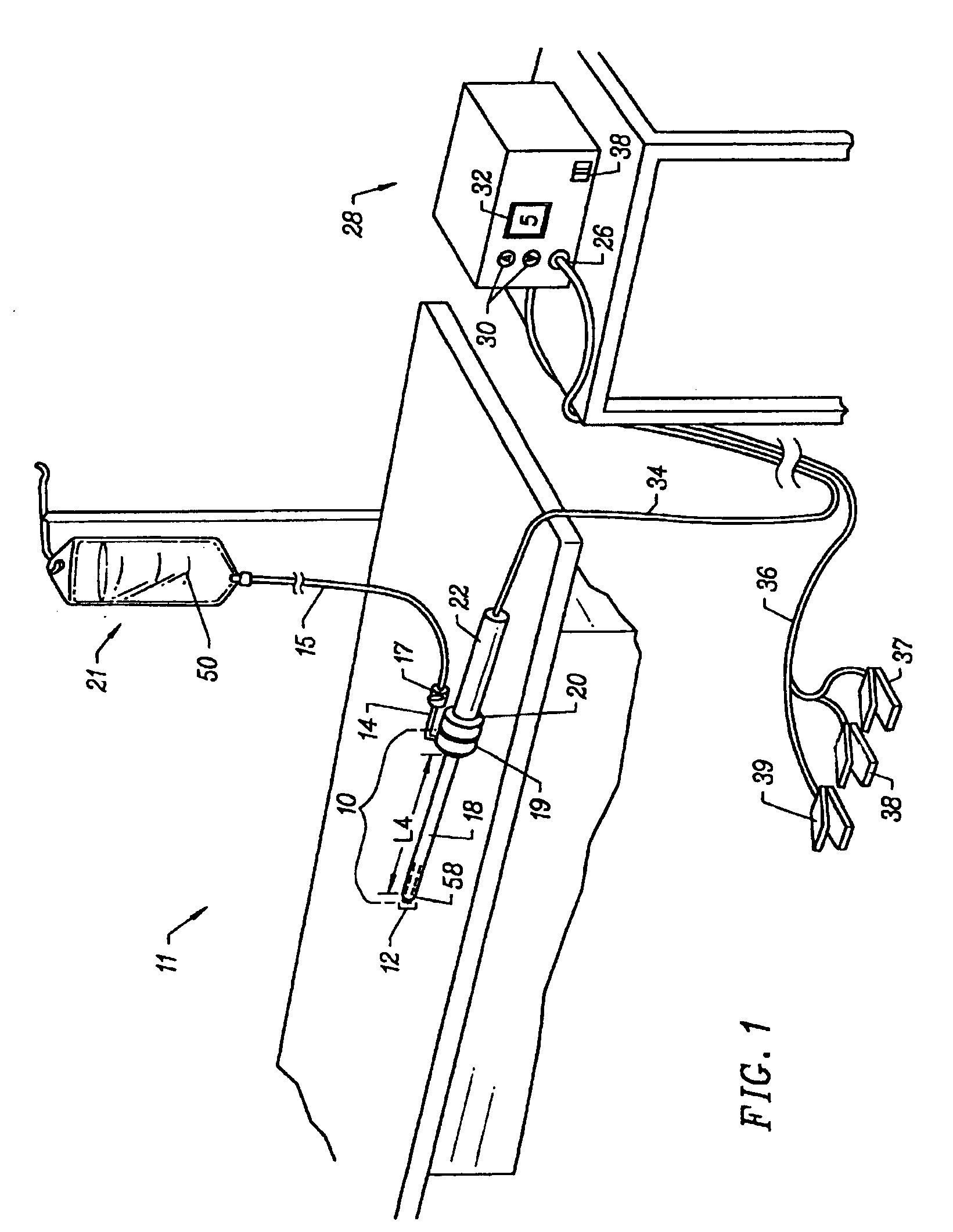
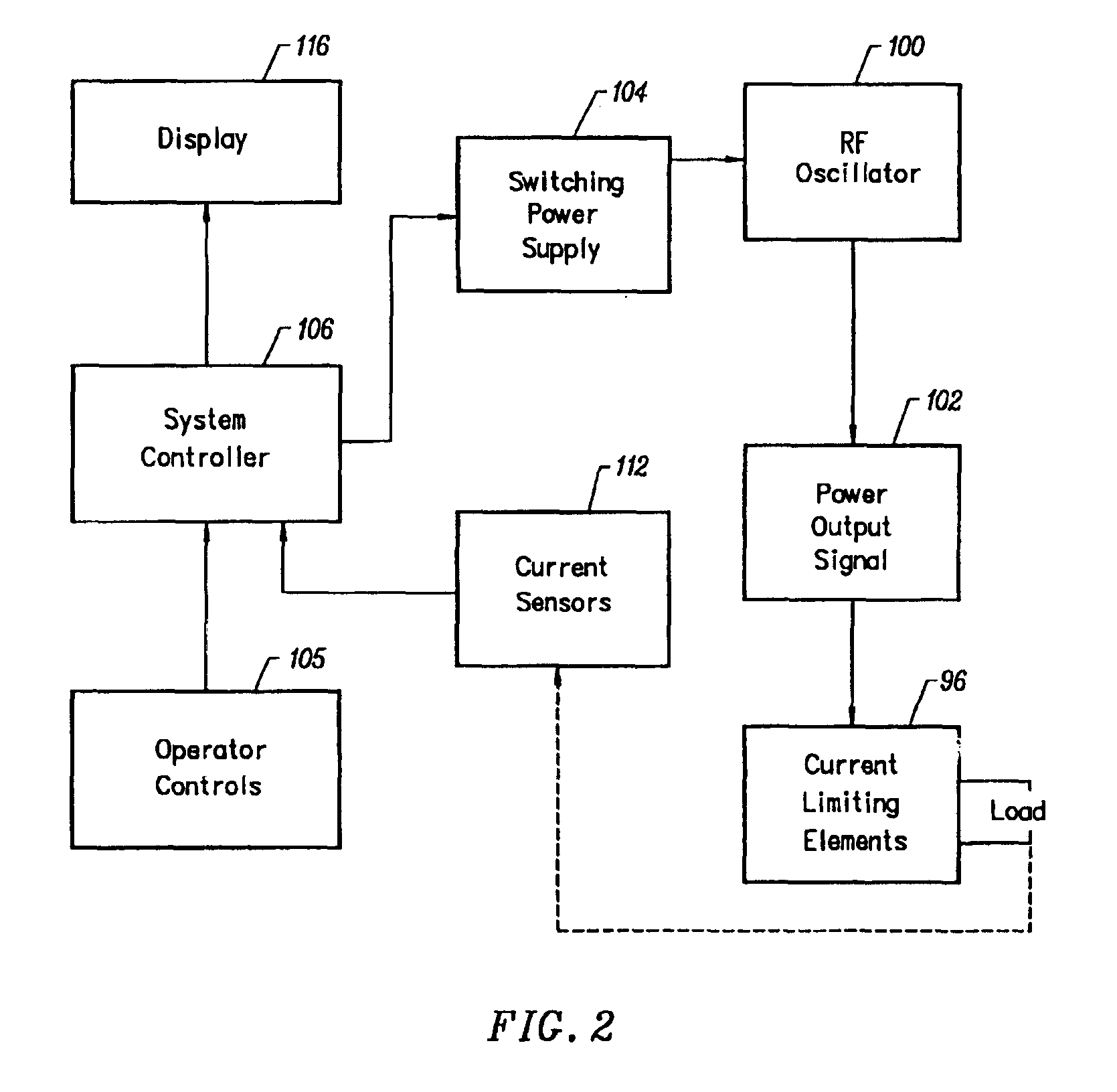
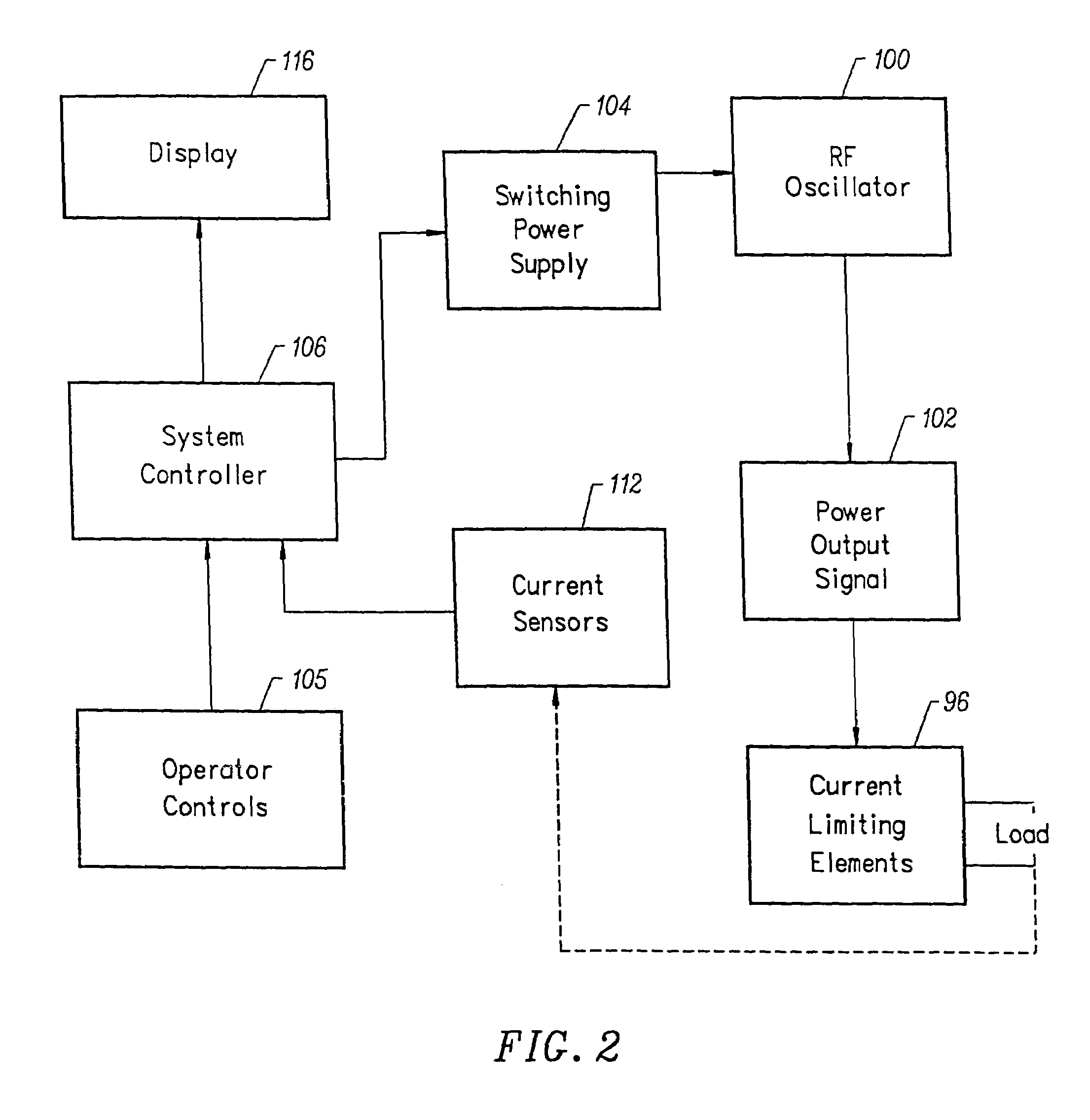
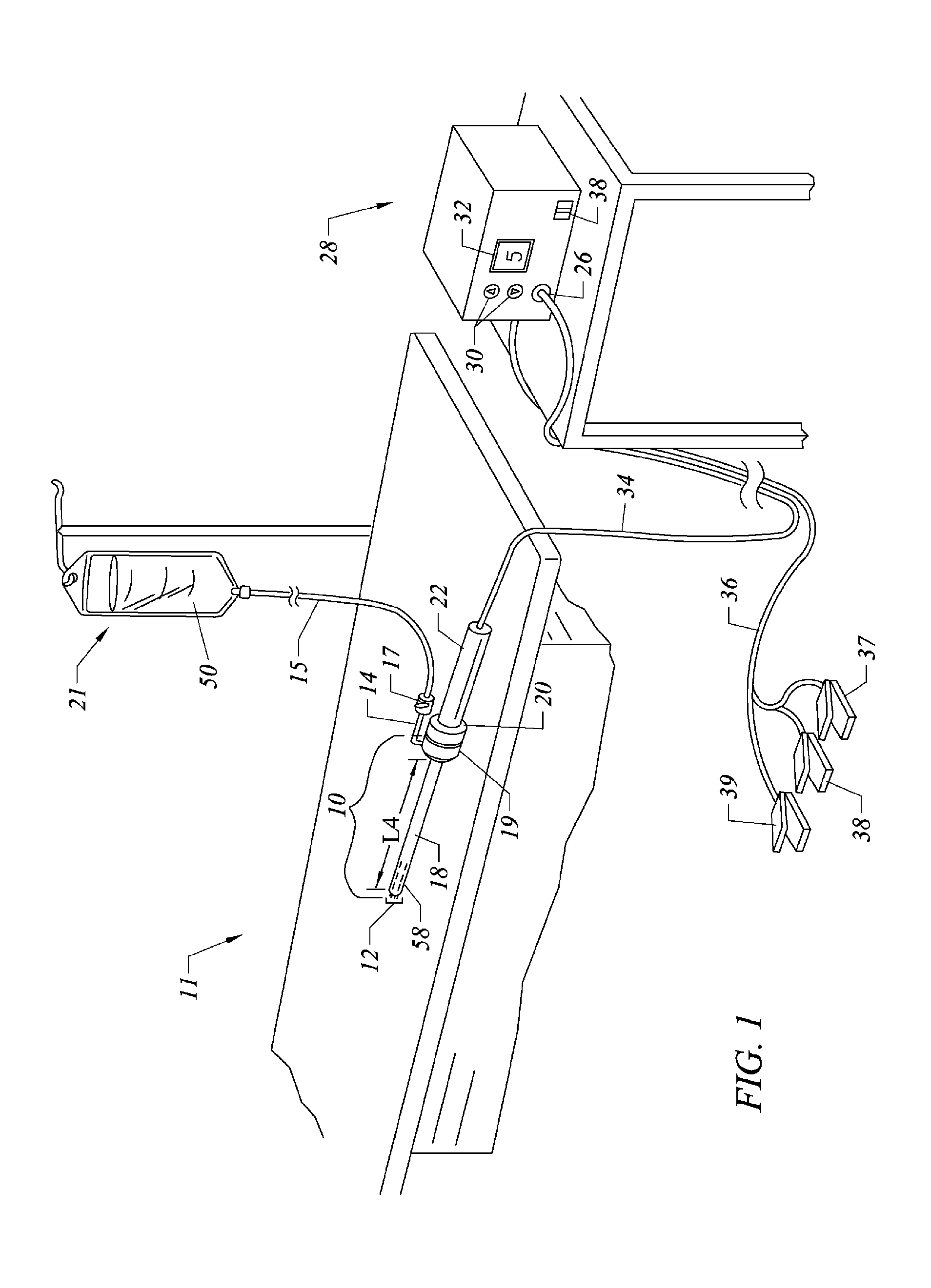
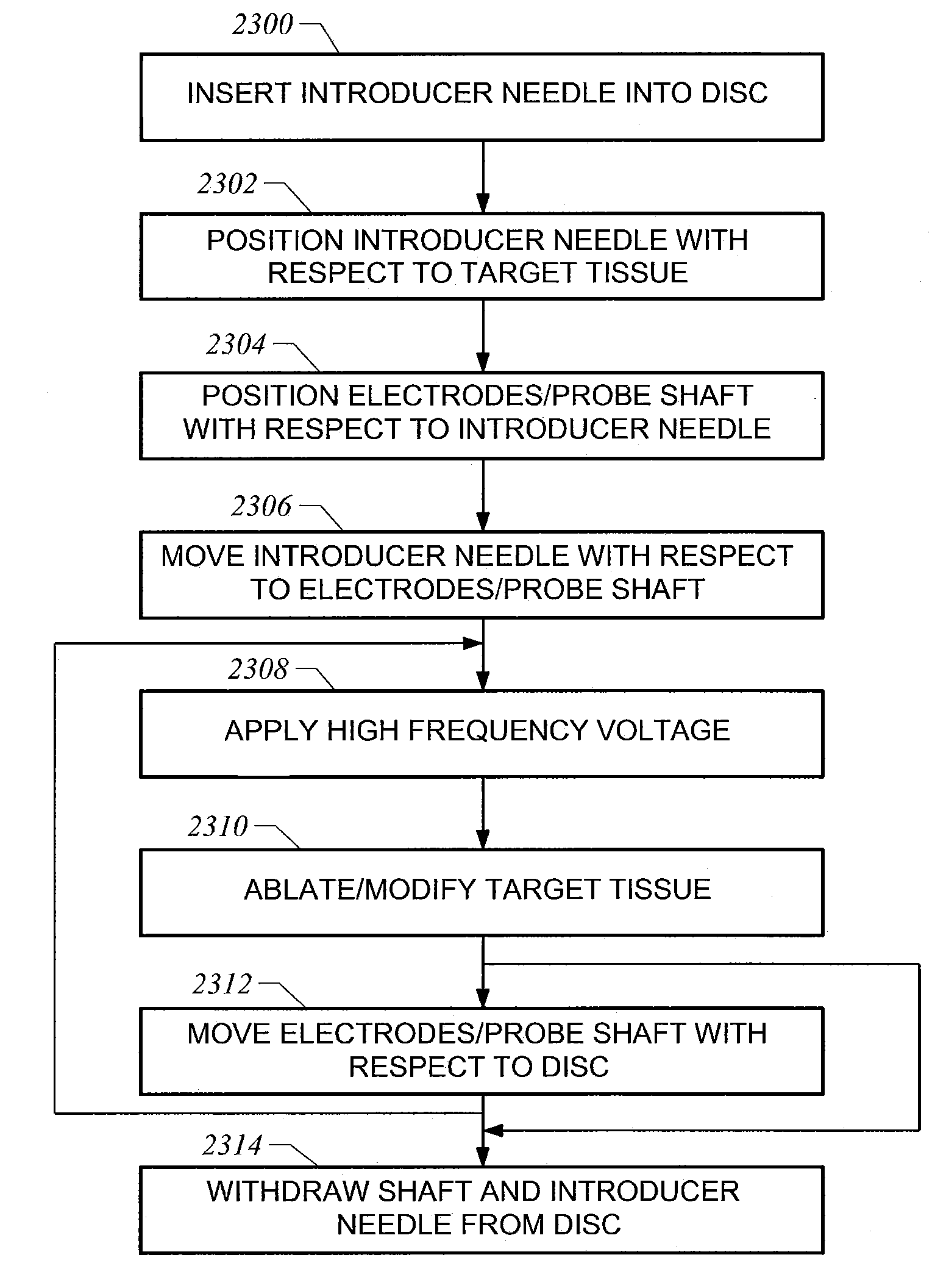
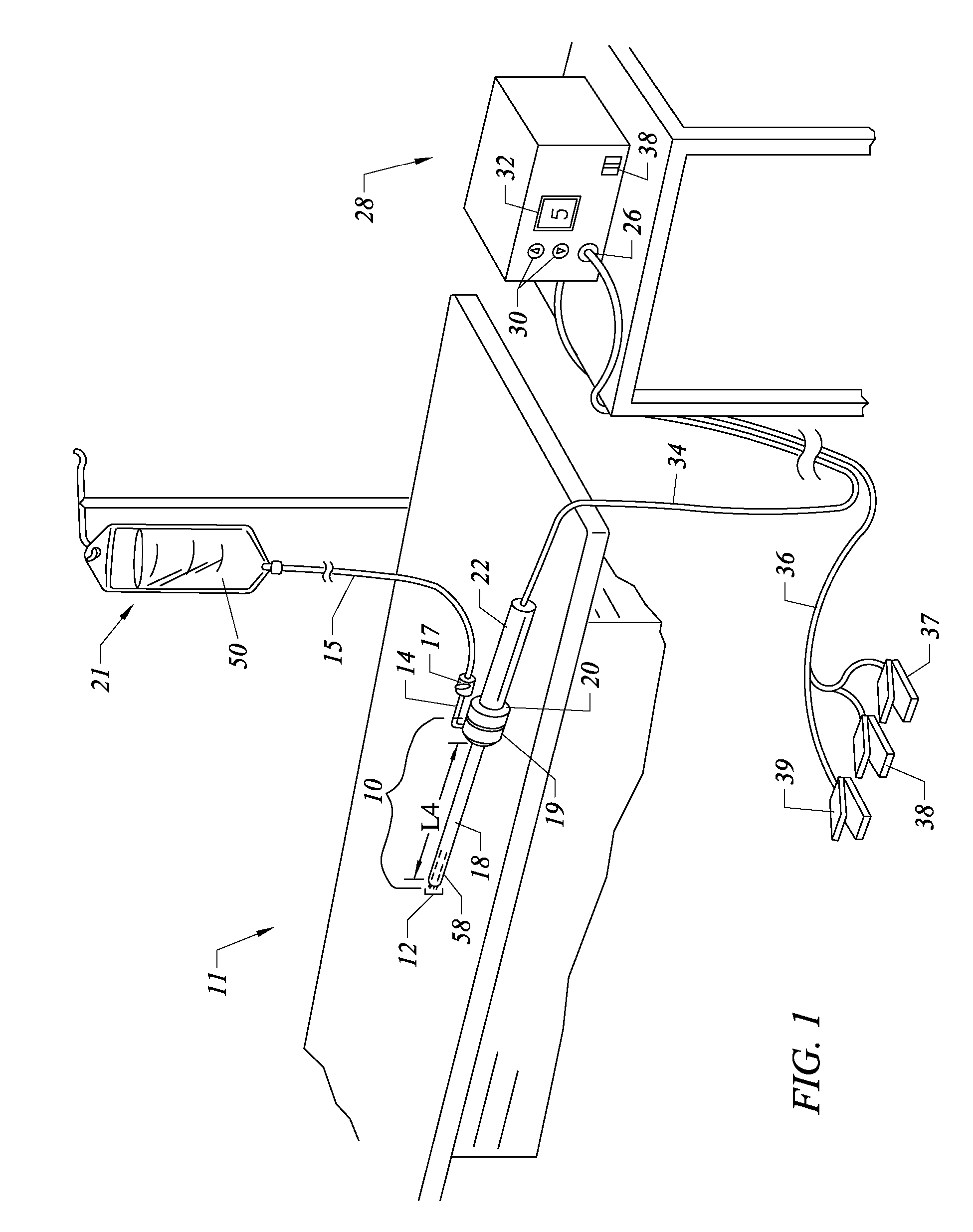
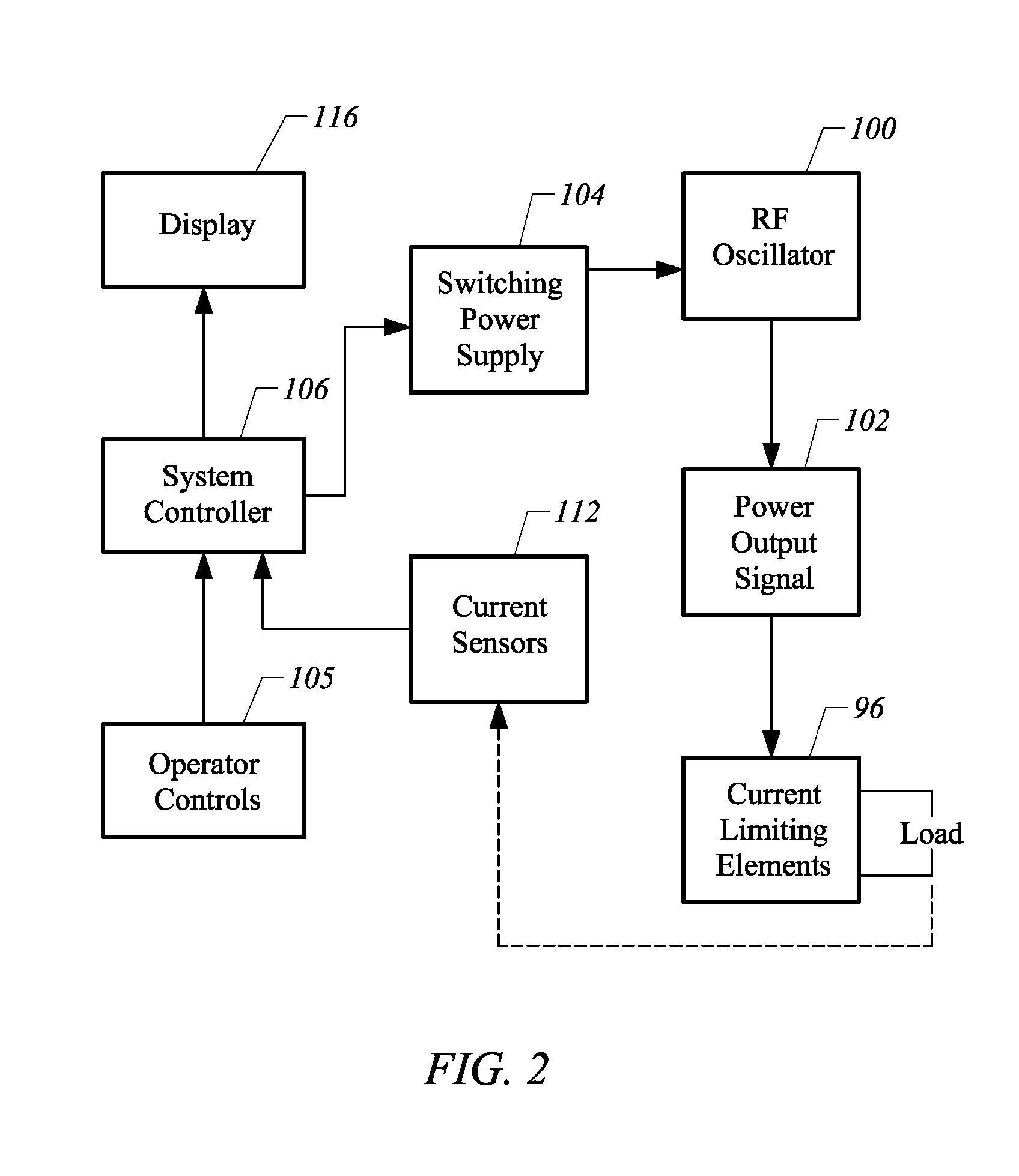
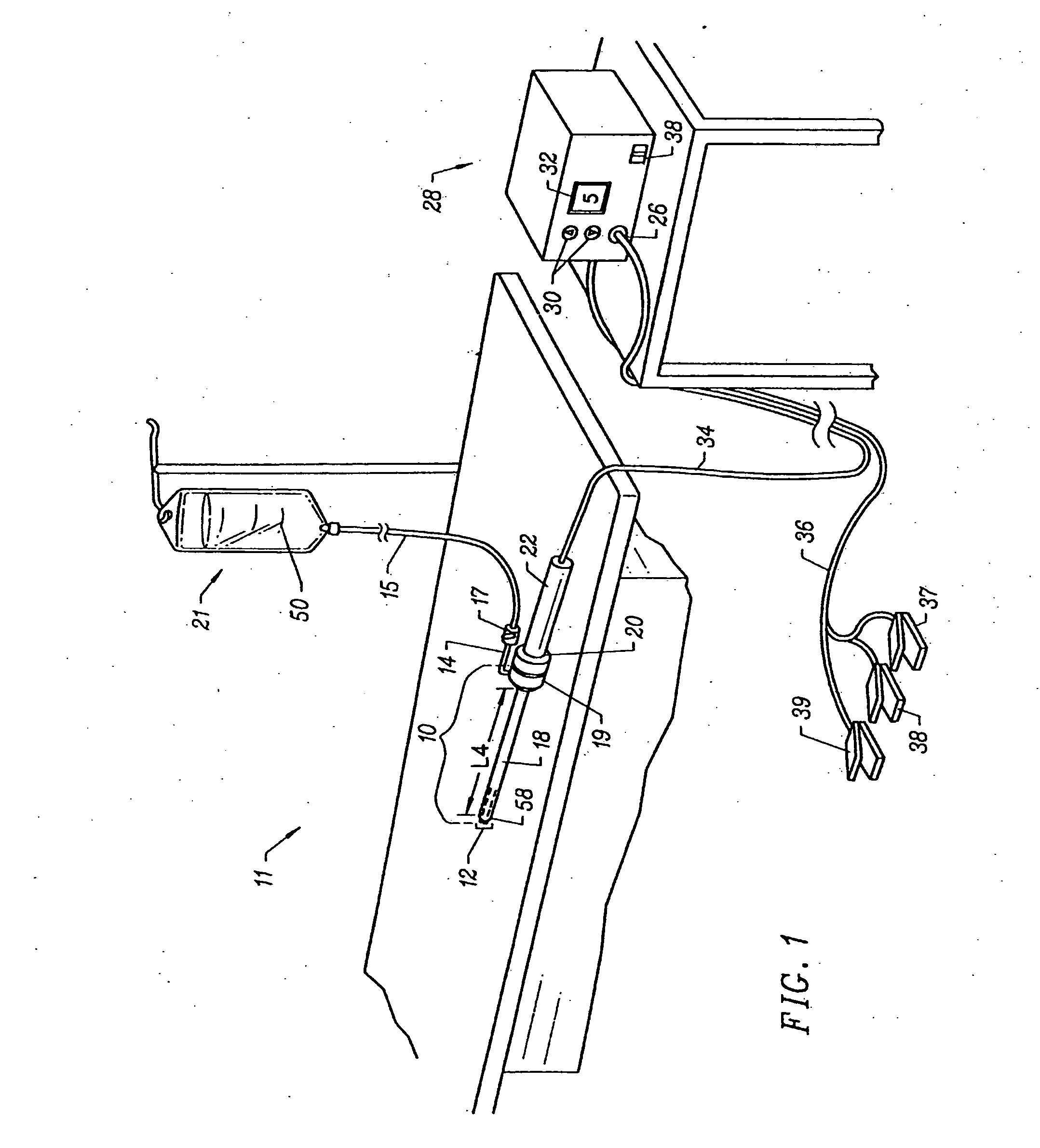
Apparatus and methods for treating an intervertebral disc by ablation of disc tissue. A method of the invention includes positioning at least one active electrode within the intervertebral disc, and applying at least a first high frequency voltage between the active electrode(s) and one or more return electrode(s), wherein the volume of the nucleus pulposus is decreased, pressure exerted by the nucleus pulposus on the annulus fibrosus is reduced, and discogenic pain of a patient is alleviated. In other embodiments, a curved or steerable probe is guided to a specific target site within a disc to be treated, and the disc tissue at the target site is ablated by application of at least a first high frequency voltage between the active electrode(s) and one or more return electrode(s). A method of making an electrosurgical probe is also disclosed.
Owner:ARTHROCARE
Methods for repairing damaged intervertebral discs
InactiveUS7318823B2Reduce internal pressureReduce moistureBiocideOrganic chemistryIntervertebral discActive electrode
Apparatus and methods for treating an intervertebral disc by ablation of disc tissue. A method of the invention includes positioning at least one active electrode within the intervertebral disc, and applying at least a first high frequency voltage between the active electrode(s) and one or more return electrode(s), wherein the volume of the nucleus pulposus is decreased, pressure exerted by the nucleus pulposus on the annulus fibrosus is reduced, and discogenic pain of a patient is alleviated. In other embodiments, a curved or steerable probe is guided to a specific target site within a disc to be treated, and the disc tissue at the target site is ablated by application of at least a first high frequency voltage between the active electrode(s) and one or more return electrode(s). A method of making an electrosurgical probe is also disclosed.
Owner:ARTHROCARE
Methods for repairing damaged intervertebral discs
InactiveUSRE40156E1Reduce internal pressureReduce moistureBiocideOrganic chemistryIntervertebral discActive electrode
Apparatus and methods for treating an intervertebral disc by ablation of disc tissue. A method of the invention includes positioning at least one active electrode within the intervertebral disc, and applying at least a first high frequency voltage between the active electrode(s) and one or more return electrode(s), wherein the volume of the nucleus pulposus is decreased, pressure exerted by the nucleus pulposus on the annulus fibrosus is reduced, and discogenic pain of a patient is alleviated. In other embodiments, a curved or steerable probe is guided to a specific target site within a disc to be treated, and the disc tissue at the target site is ablated by application of at least a first high frequency voltage between the active electrode(s) and one or more return electrode(s). A method of making an electrosurgical probe is also disclosed.
Owner:ARTHROCARE
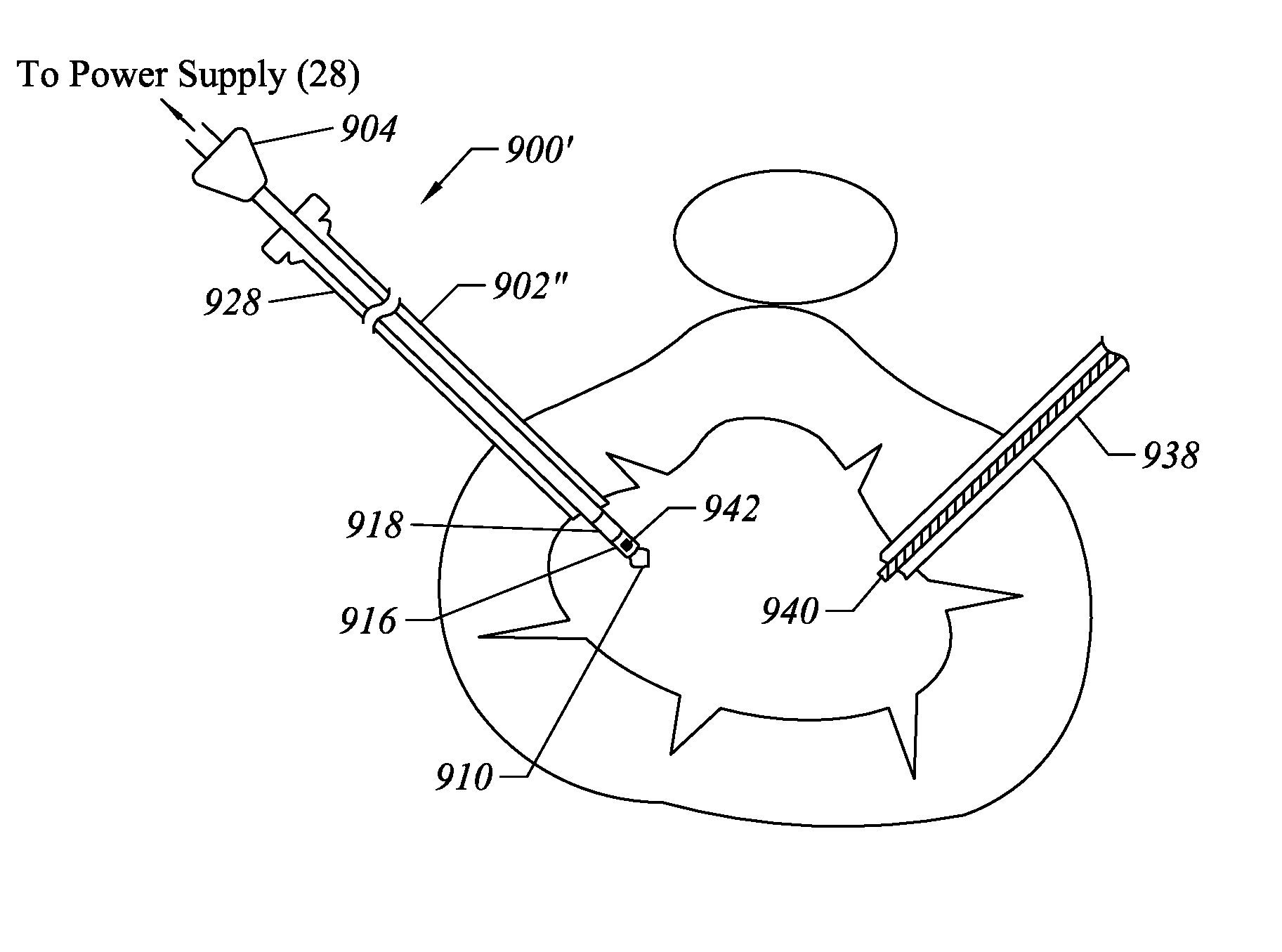
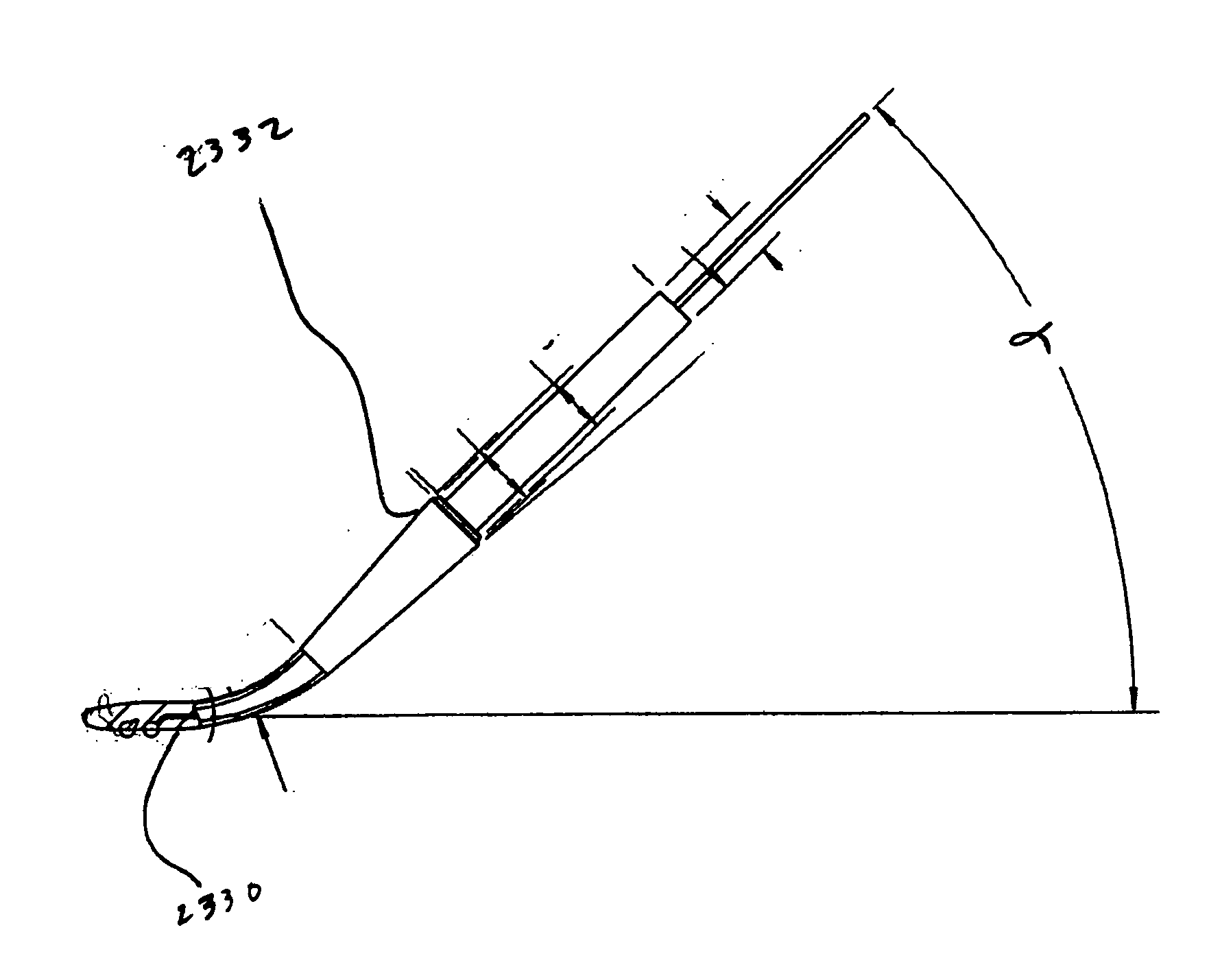
Electrosurgical apparatus having a curved distal section
InactiveUS7070596B1Reduce pressureReduced neckingDiagnosticsSurgical needlesIntervertebral discActive electrode
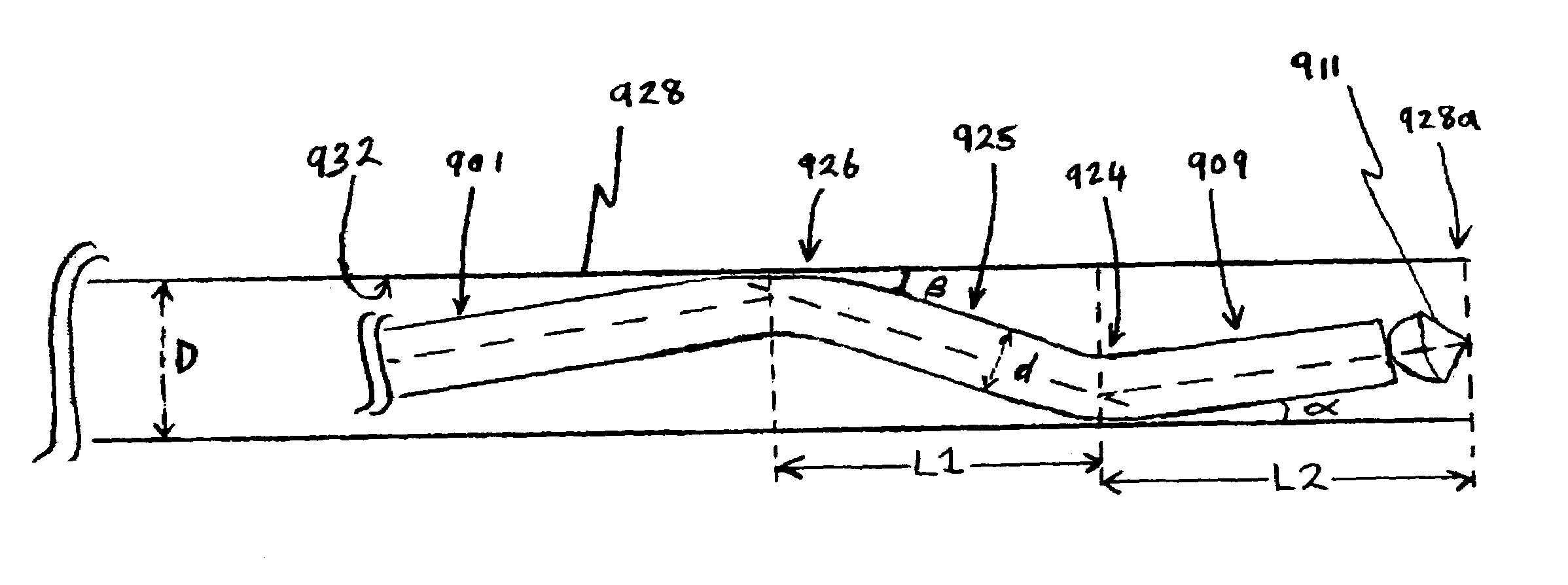
Apparatus and methods for advancing and retracting a medical instrument within an introducer device, wherein the instrument includes a distal tip, a distal linear portion, a first distal curve, a substantially linear inter-curve portion, and a second proximal curve. The length of the distal linear portion and the angle of the first curve determine the position of the distal tip within a lumen of the introducer device, such that the distal tip occupies a substantially central transverse location within the lumen and the distal tip avoids contact with the introducer device. The length of the inter-curve portion and the angle of the second curve determine deflection of the distal tip from a longitudinal axis of the shaft when the second curve is extended distally beyond a distal end of the introducer device. Also, methods and apparatus for treating an intervertebral disc by ablation of disc tissue. A method of the invention includes positioning at least one active electrode within the intervertebral disc, and applying at least a first high frequency voltage between the active electrode(s) and one or more return electrode(s), wherein the volume of the nucleus pulposus is decreased, pressure exerted by the nucleus pulposus on the annulus fibrosus is reduced, and discogenic pain of a patient is alleviated. In other embodiments, a curved or steerable probe is guided to a specific target site within a disc to be treated, and the disc tissue at the target site is ablated by application of at least a first high frequency voltage between the active electrode(s) and one or more return electrode(s). A method of making an electrosurgical probe is also disclosed.
Owner:ARTHROCARE
Methods and apparatus for treating back pain
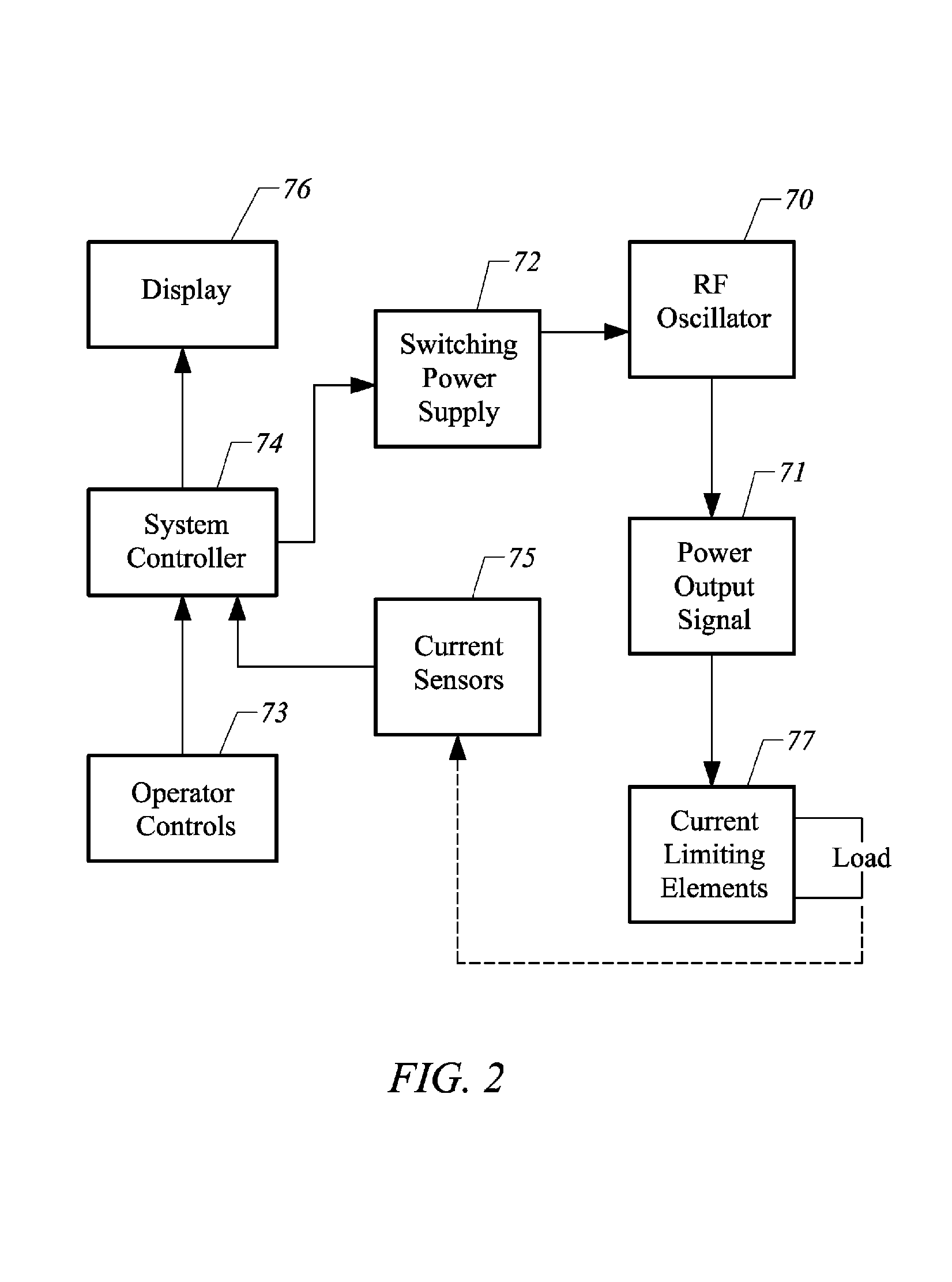
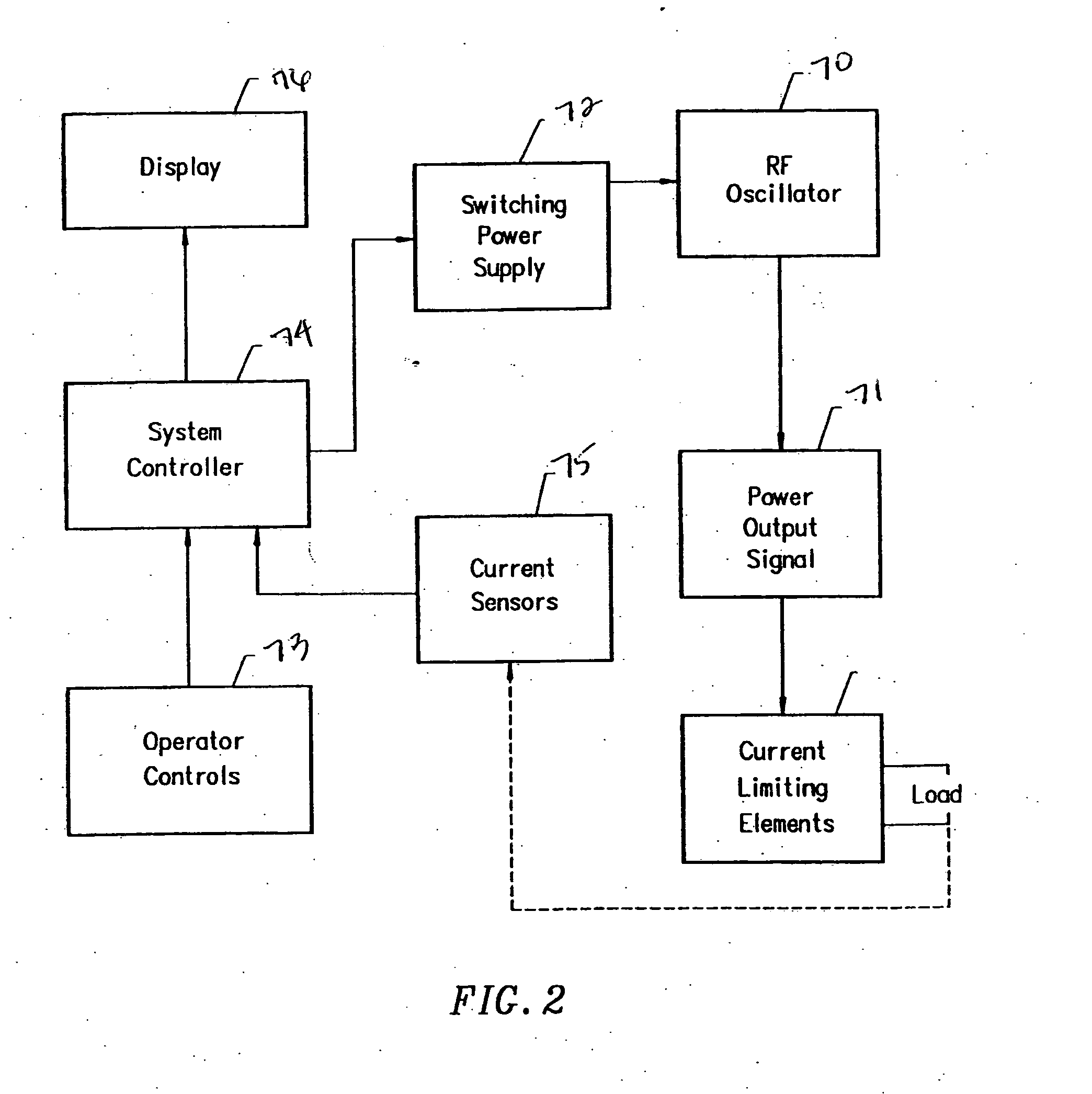
Apparatus and methods for treating back pain of a patient by denervation of an intervertebral disc or a region of the posterior longitudinal ligament by the controlled application of heat to a target tissue. In one embodiment, the invention may include a procedure combining both decompression of a disc, and denervation of the annulus fibrosus. In one embodiment, a method of the invention includes positioning an active electrode of an electrosurgical instrument in at least close proximity to an intervertebral disc, and applying at least a first high frequency voltage between the active electrode and a return electrode, wherein nervous tissue within the annulus fibrosus is inactivated, and discogenic pain of the patient is alleviated. In one embodiment, the invention includes positioning a first electrode of a dual-shaft electrosurgical instrument at a first location in relation to a target disc, positioning a second electrode of the instrument at a second location, and applying a high frequency voltage between the first and second electrodes, wherein the first and second electrodes are disposed on separate shafts of the instrument.
Owner:ARTHROCARE
Intervertebral disc repair
InactiveUS20040097927A1Alleviate nerve impingementMinimize segmental instabilitySuture equipmentsInternal osteosythesisAtrophySpinal stenosis
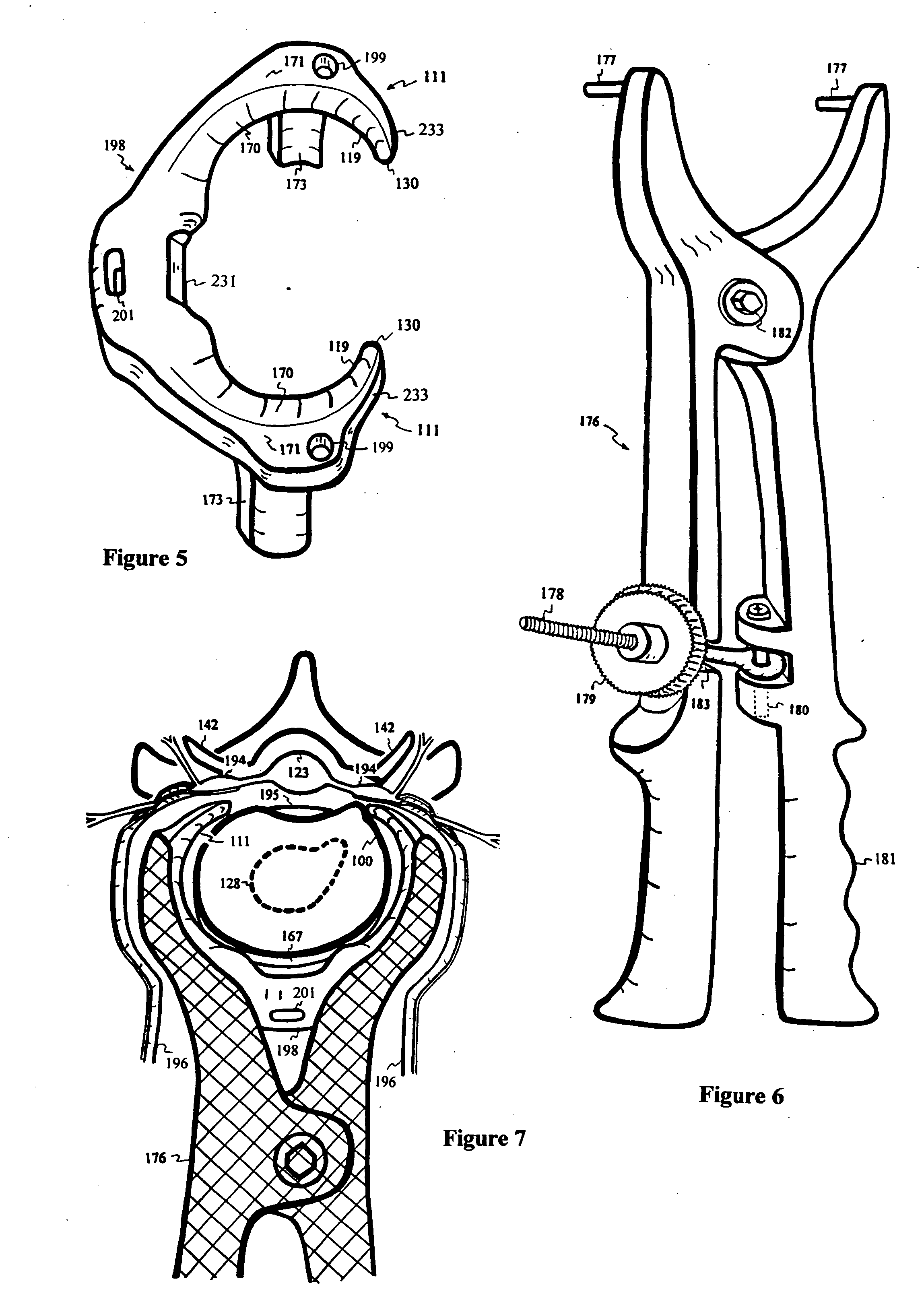
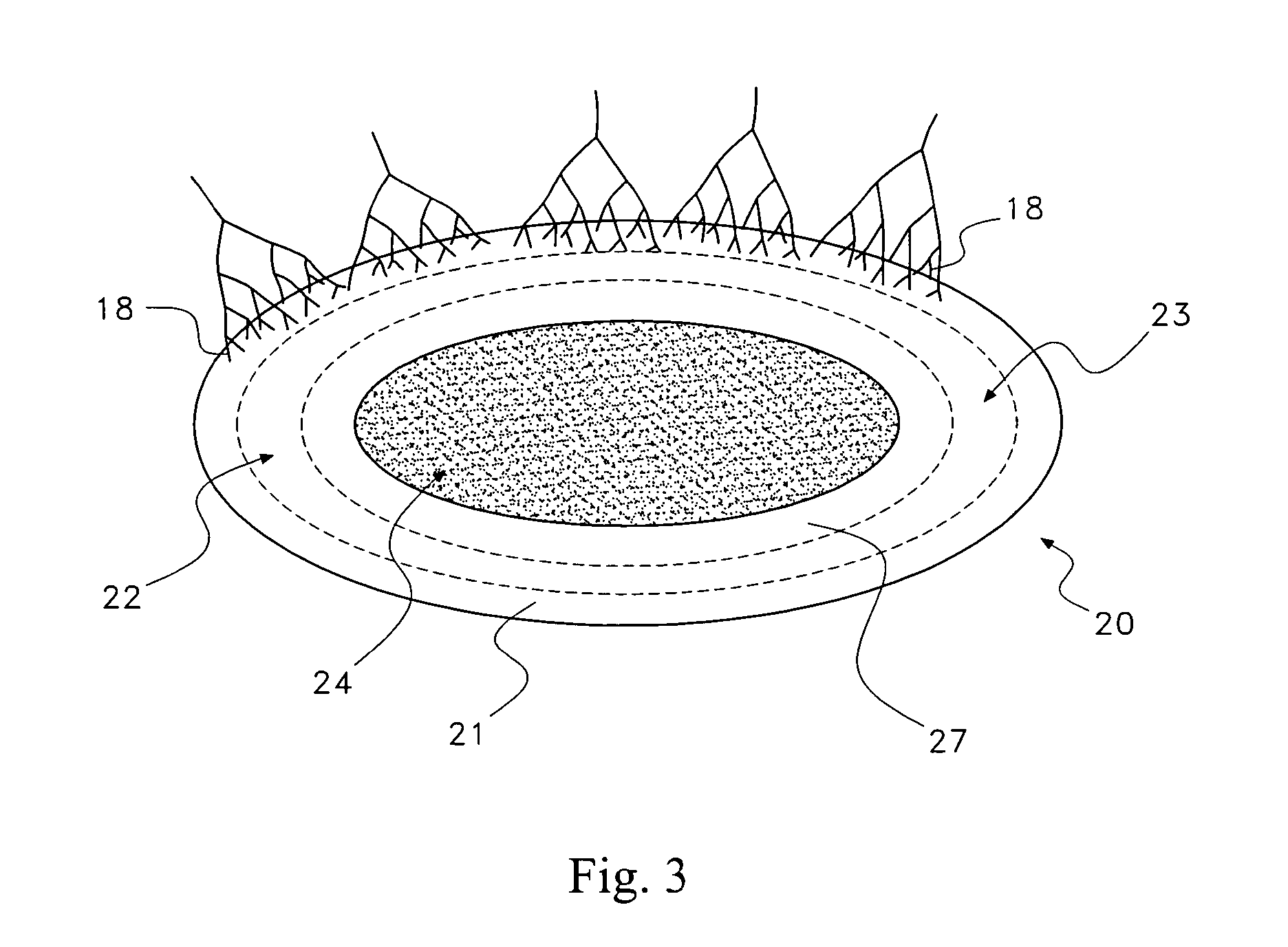
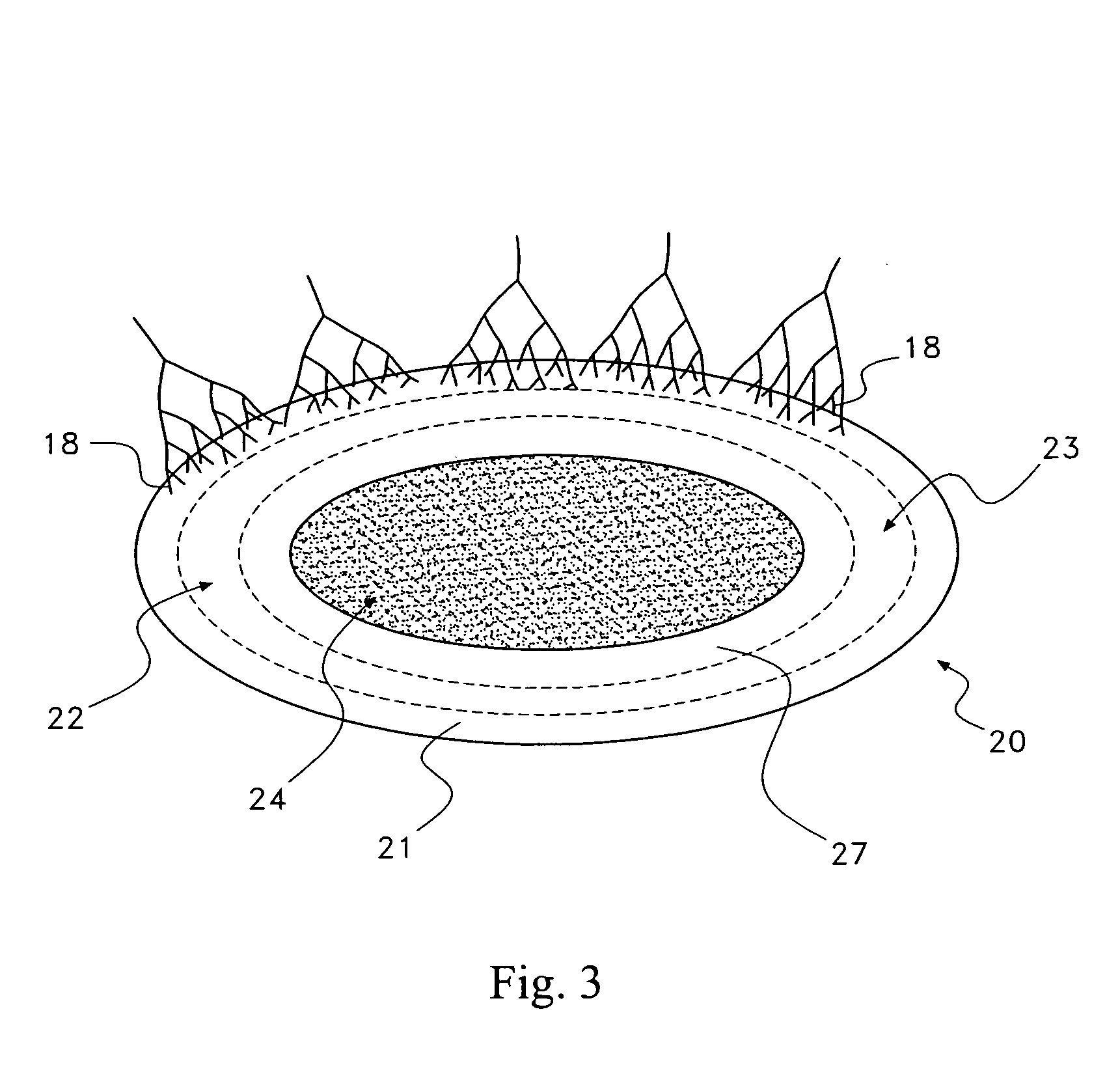
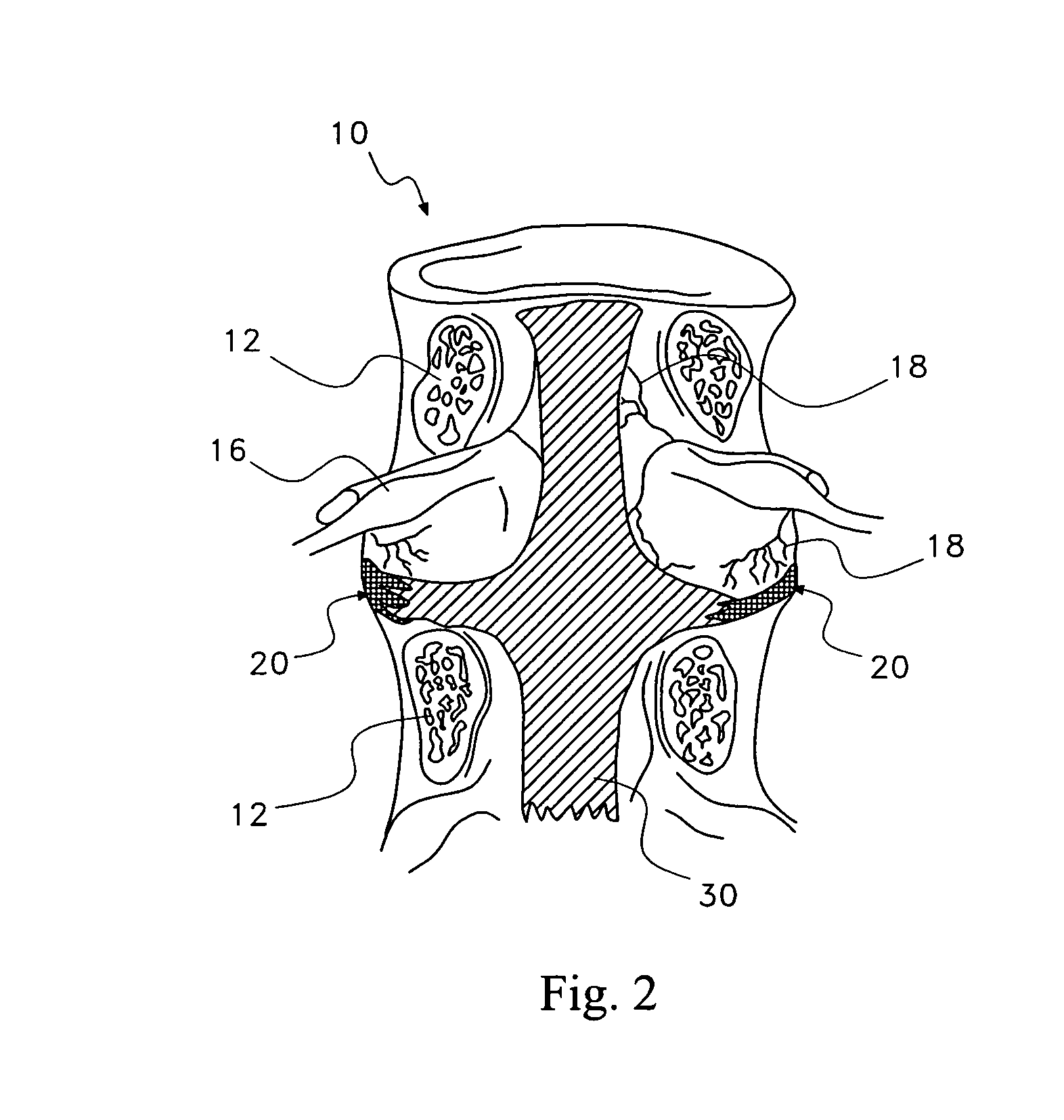
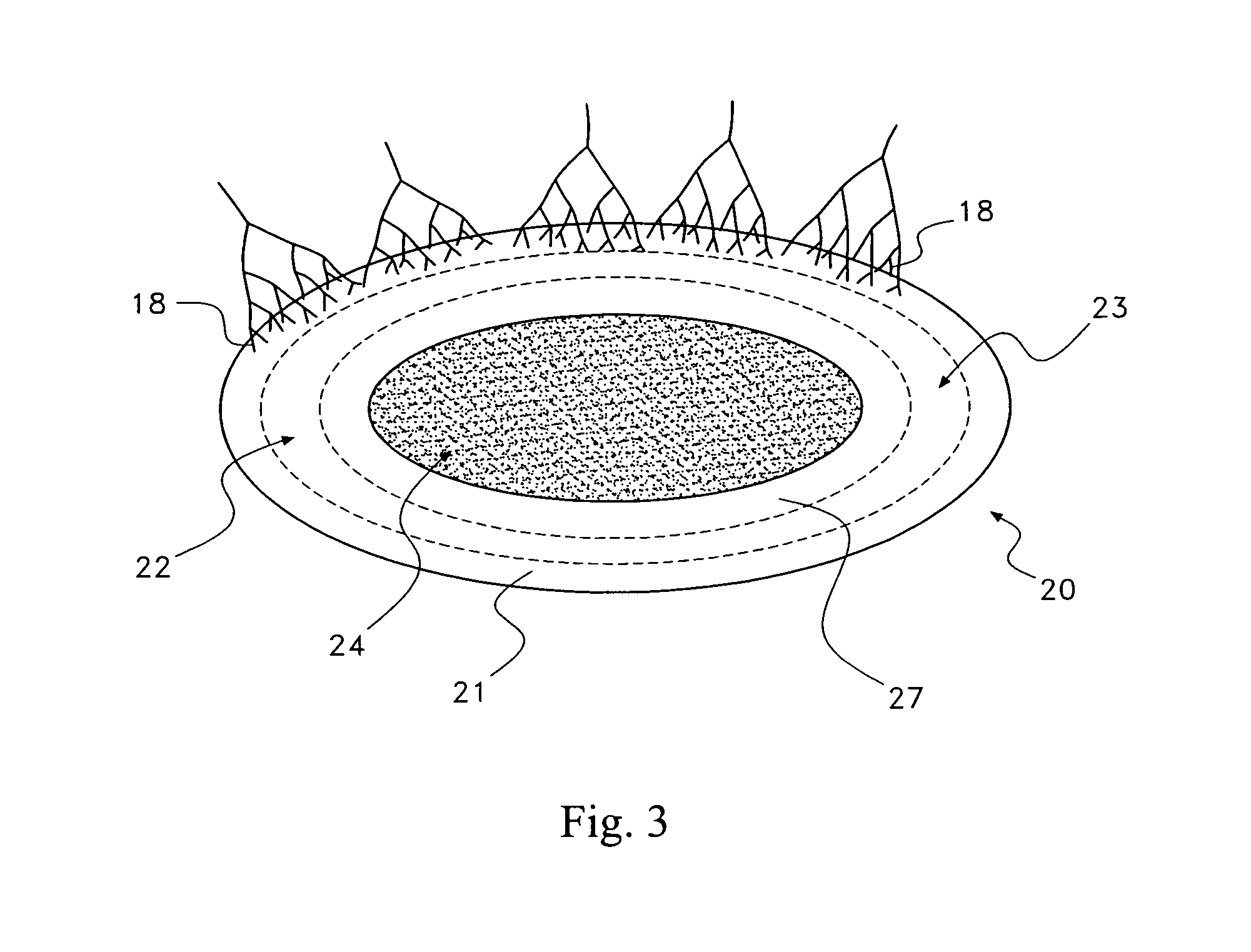
A saddle-shaped compression device and methods of fastening a dysfunctional intervertebral disc are used to (1) compress a protrusion to alleviate nerve impingement, (2) fortify the annulus to stabilize a motion segment, (3) minimize the inward / outward bulging and delamination of the annulus, (4) atrophy the nerve to treat discogenic pain, (5) correct the curvature of spinal deformities, (6) elevate the disc space to treat spinal stenosis, and (7) seal the seepage of nucleus pulposus from a herniated disc.
Owner:YEUNG JEFFREY E +1
Apparatus and methods for treating cervical inter-vertebral discs
InactiveUS7393351B2Reduce the overall diameterAvoid arcingCannulasEnemata/irrigatorsMedicineActive electrode
Apparatus and methods for treating an inter-vertebral disc by ablation, coagulation, shrinking, stiffening, or other treatment of disc tissue. A method of the invention includes positioning at least one active electrode within the inter-vertebral disc, and applying at least a first high frequency voltage between the active electrode(s) and one or more return electrode(s), wherein the volume of the nucleus pulposus is decreased, pressure exerted by the nucleus pulposus on the annulus fibrosus is reduced, and discogenic pain of a patient is alleviated. An apparatus of the invention includes an electrosurgical probe, an introducer needle adapted for passing the distal end of the probe therethrough, and a positioning unit for monitoring a position of the probe in relation to the introducer needle.
Owner:ARTHROCARE
Methods and apparatus for treating back pain
InactiveUS20050261754A1Relieve back painSurgical instruments for heatingTherapeutic coolingIntervertebral discBACK DISCOMFORT
Apparatus and methods for treating back pain of a patient by denervation of an intervertebral disc or a region of the posterior longitudinal ligament by the controlled application of heat to a target tissue. In one embodiment, the invention may include a procedure combining both decompression of a disc, and denervation of the annulus fibrosus. In one embodiment, a method of the invention includes positioning an active electrode of an electrosurgical instrument in at least close proximity to an intervertebral disc, and applying at least a first high frequency voltage between the active electrode and a return electrode, wherein nervous tissue within the annulus fibrosus is inactivated, and discogenic pain of the patient is alleviated. In one embodiment, the invention includes positioning a first electrode of a dual-shaft electrosurgical instrument at a first location in relation to a target disc, positioning a second electrode of the instrument at a second location, and applying a high frequency voltage between the first and second electrodes, wherein the first and second electrodes are disposed on separate shafts of the instrument.
Owner:ARTHROCARE
Methods and apparatus for treating back pain
Apparatus and methods for treating back pain of a patient by denervation of an intervertebral disc or a region of the posterior longitudinal ligament by the controlled application of heat to a target tissue. In one embodiment, the invention may include a procedure combining both decompression of a disc, and denervation of the annulus fibrosus. In one embodiment, a method of the invention includes positioning an active electrode of an electrosurgical instrument in at least close proximity to an intervertebral disc, and applying at least a first high frequency voltage between the active electrode and a return electrode, wherein nervous tissue within the annulus fibrosus is inactivated, and discogenic pain of the patient is alleviated. In one embodiment, the invention includes positioning a first electrode of a dual-shaft electrosurgical instrument at a first location in relation to a target disc, positioning a second electrode of the instrument at a second location, and applying a high frequency voltage between the first and second electrodes, wherein the first and second electrodes are disposed on separate shafts of the instrument.
Owner:ARTHROCARE
Pharmaceutical removal of vascular and/or neuronal extensions form a degenerating disc
ActiveUS20070253930A1Suppression and reduction of sensitivitySuppression and reduction of and activityOrganic active ingredientsPeptide/protein ingredientsMedicineWhole body
The invention provides a method for alleviating discogenic pain by administering a therapeutic agent that disrupts neuronal and / or vascular elements in the disc, which is typically a degenerated disc. Disruption of neuronal elements in the disk includes destroying nerve endings without substantially affecting the central body of the nerve, suppressing activation of the nerve endings, and inhibiting the growth of nerve endings into the disk. Disruption of vascular elements includes causing the vascular extensions to retract from the disk, or suppressing the formation of such extensions. The therapeutic agent may be administered locally via an interbody pump, a bolus or a depot, or may be administered systemically.
Owner:WARSAW ORTHOPEDIC INC
Methods and devices for the treatment of intervertebral discs
Owner:WARSAW ORTHOPEDIC INC
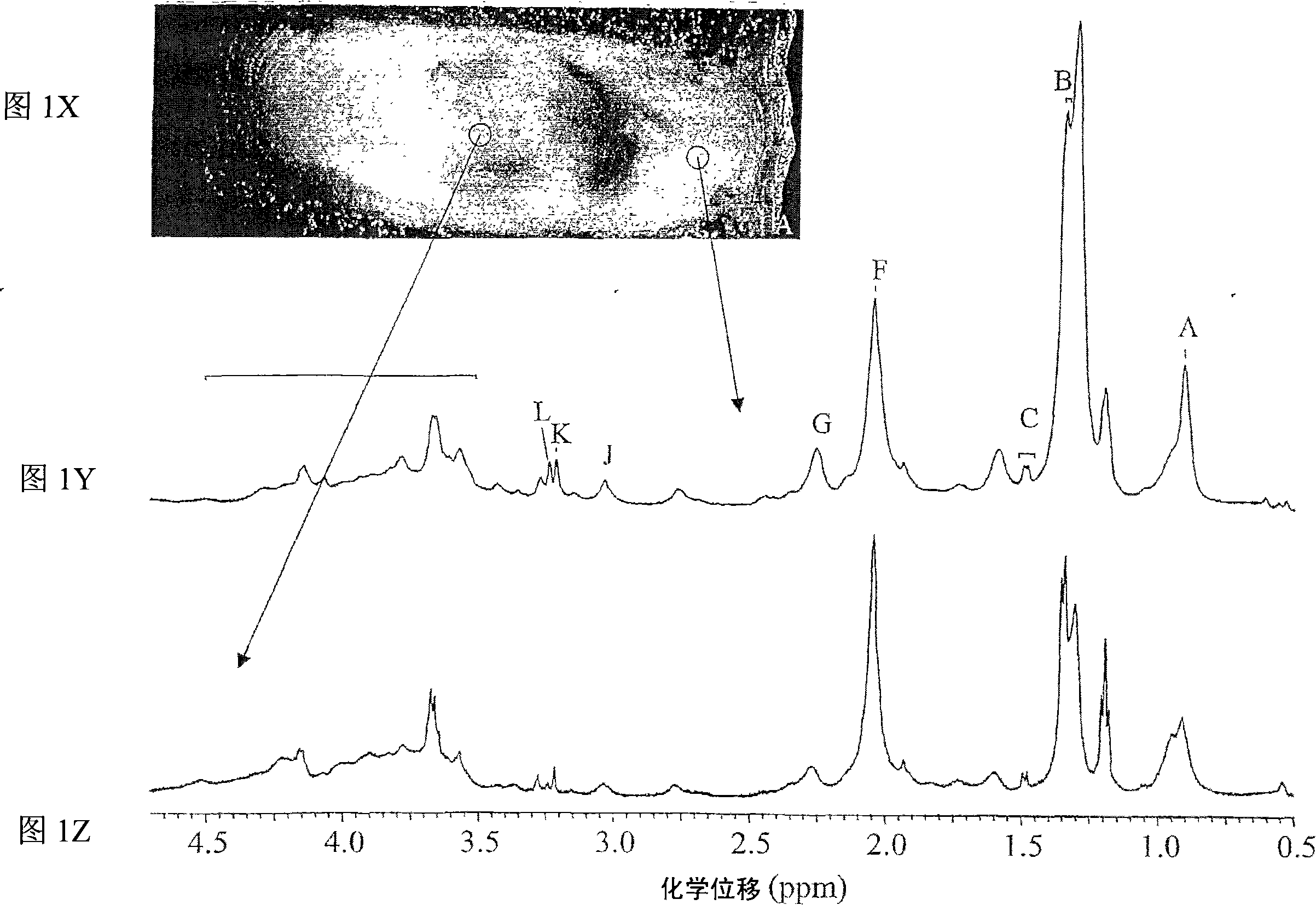
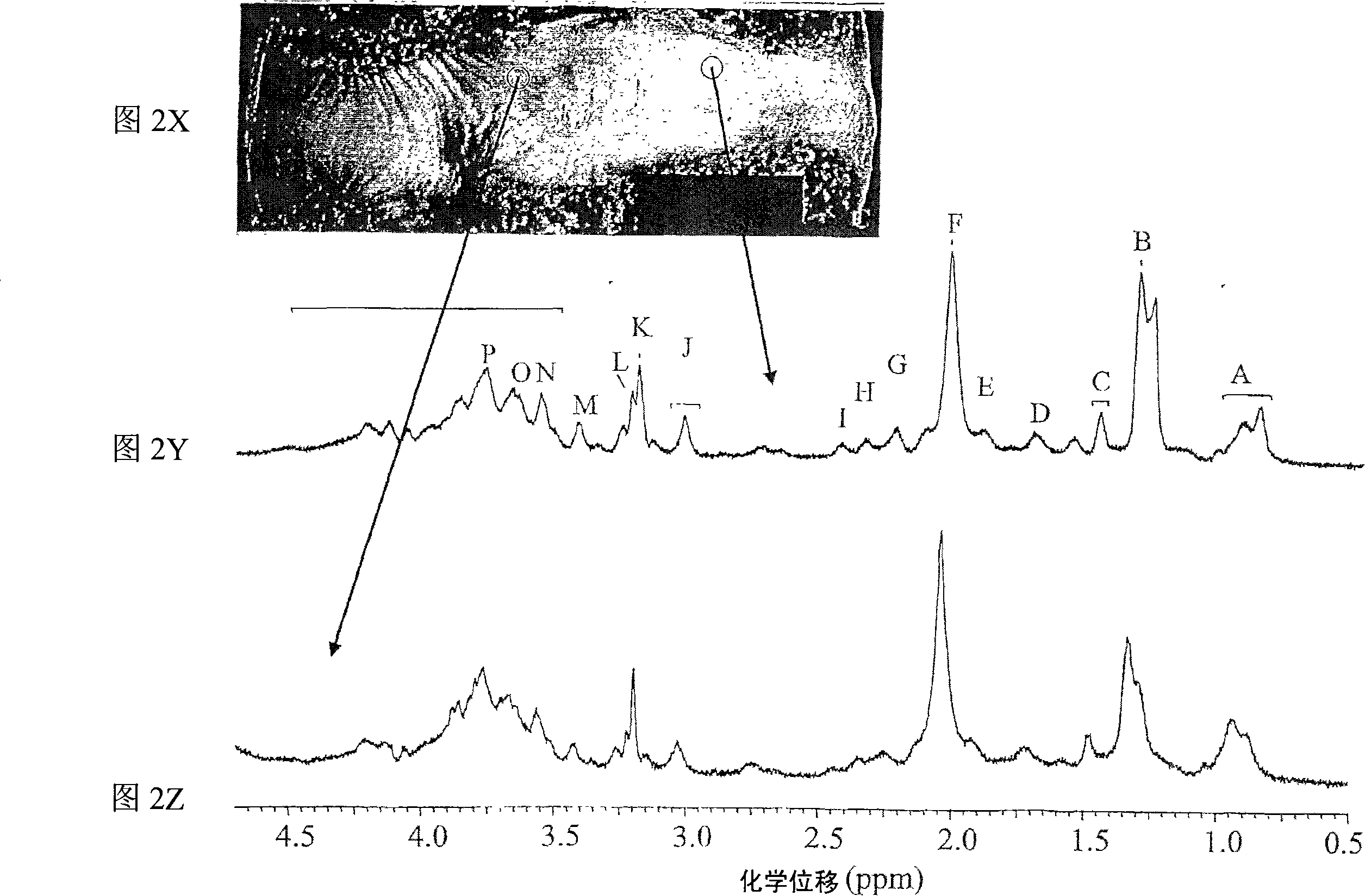
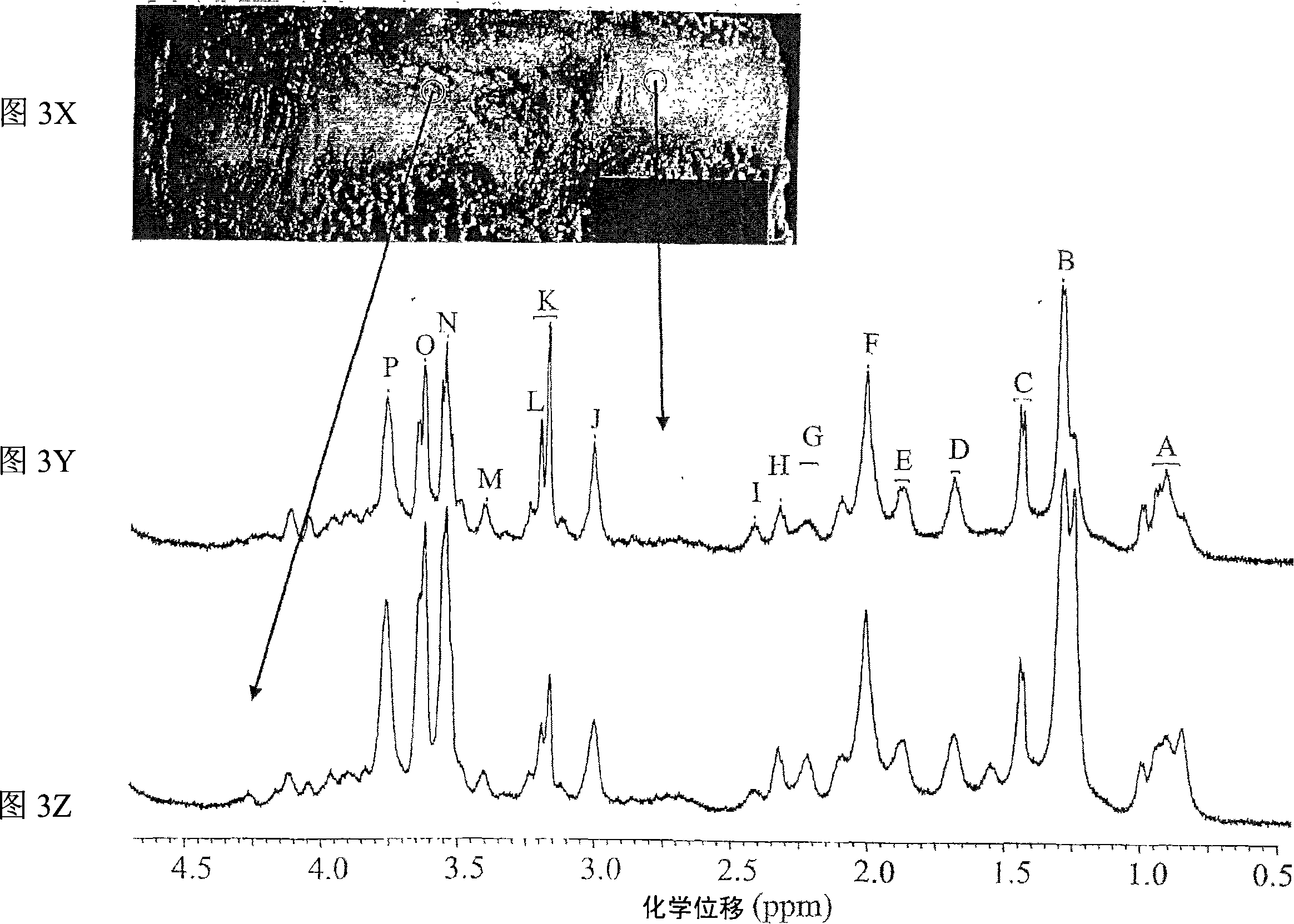
Systems and methods using nuclear magnetic resonance (NMR) spectroscopy to evaluate pain and degenerative properties of tissue
ActiveUS8344728B2Minimal overlapIncreasing Thompson gradeMeasurements using NMR spectroscopyDiagnostic recording/measuringAnatomical structuresSolid-state nuclear magnetic resonance
NMR spectroscopy is performed on intervertebral disc tissue. Extent of degeneration is determined based on the NMR spectroscopy. Correlation between NMR spectral regions and at least one of tissue degeneration and pain are made. Accordingly, NMR spectroscopy is used to determine location and / or extent of at least one of degeneration or pain associated with a region of tissue, such as for example in particular disc degeneration, or discogenic pain. NMR spectral peak ratios, such as between N-Acetyl / cho and cho / carb, are readily acquired and analyzed to predict degree of tissue degeneration and / or pain for: tissue samples using HR-MAS spectroscopy; and larger portions of anatomy such as joint segments such as a spine, using clinical 3 T MRI systems with surface head or knee coils; and tissue regions such as discs within spines of living patients using 3 T MRI systems with a surface spine coil, thus providing a completely non-invasive diagnostic toolset and method to image and localize degeneration and / or pain.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA
Methods for diagnosing and treating pain in the spinal cord
The present invention provides methods, reagents and kits for the diagnosis and treatment of spinal-related pain, e.g., radiculopathic pain, facet pain and discogenic pain. Cytokine biomarkers, e.g., IFNγ can be used to diagnose spine-related injury. It is also a finding of the present invention that spinal-related pain can be alleviated by administering therapeutic agents to the site of diagnostic presence of the cytokine biomarker. This invention further provides methods for extraction of samples from the spine, e.g., disc space samples, epidural samples and facet joint samples.
Owner:CYTONICS CORP
Pharmaceutical removal of vascular extensions from a degenerating disc
InactiveUS20070253960A1Suppression and reduction of sensitivitySuppression and reduction of and activityPeptide/protein ingredientsAntibody ingredientsAnesthesiaDiscogenic pain
The invention provides a method for alleviating discogenic pain by administering a therapeutic agent that disrupts neuronal and / or vascular elements in the disc, which is typically a degenerated disc. Disruption of neuronal elements in the disc includes destroying nerve endings without substantially affecting the central body of the nerve, suppressing activation of the nerve endings, and inhibiting the growth of nerve endings into the disc. Disruption of vascular elements includes causing the vascular extensions to retract from the disc, or suppressing the formation of such extensions. The therapeutic agent may be administered locally via an interbody pump, a bolus or a depot, or may be administered systemically.
Owner:WARSAW ORTHOPEDIC INC
Pharmaceutical removal of neuronal extensions from a degenerating disc
The invention provides a method for alleviating discogenic pain by administering a therapeutic agent that disrupts neuronal and / or vascular elements in the disc, which is typically a degenerated disc. Disruption of neuronal elements in the disk includes destroying nerve endings without substantially affecting the central body of the nerve, suppressing activation of the nerve endings, and inhibiting the growth of nerve endings into the disk. Disruption of vascular elements includes causing the vascular extensions to retract from the disk, or suppressing the formation of such extensions. The therapeutic agent may be administered locally via an interbody pump, a bolus or a depot, or may be administered systemically.
Owner:WARSAW ORTHOPEDIC INC
Intrathecal administration of mesenchymal stem cells and derivatives thereof for treatment of pain
InactiveUS20180036348A1Pharmaceutical delivery mechanismUnknown materialsWharton's jellyIntrathecal use
The invention discloses means of treating pain through administration of mesenchymal stem cells or derivatives thereof via an intrathecal manner at a concentration and frequency sufficient to reduce pain. In one embodiment of the invention, treatment of discogenic pain is provided by administration of mesenchymal stem cells intrathecally that are derived from the Wharton's Jelly. In another embodiment the invention teaches administration of supernatants from mesenchymal stem cells, in one embodiment said supernatants comprising of concentrated microvesicles.
Owner:AIDAN RES & CONSULTING
Probe and device for detecting abnormality of intervertebral disc
InactiveUS20120136251A1Accurate judgmentRapidly and easily determinedUltrasonic/sonic/infrasonic diagnosticsDiagnostics using vibrationsIntervertebral discMedicine
The present invention relates to a probe and a device for detecting abnormality of an intervertebral disc. More particularly, the present invention relates to a probe and a device for detecting abnormality of an intervertebral disc that gives vibration stimulation to the inner part of the intervertebral disc and obtains an ultrasonic image in order to sense the abnormality of the intervertebral disc causing discogenic pains and inspects whether the intervertebral disc is abnormal by measuring impedance in the intervertebral disc.The present invention provides a probe for detecting abnormality of an intervertebral disc including: a shaft connector; a vibration generator connected to the shaft connector; and an inspector connected to the vibration generator, wherein the vibration generator vibrates the inspector by using a piezoelectric element and a device for detecting abnormality of an intervertebral disc.
Owner:GWANGJU INST OF SCI & TECH
Pharmaceutical removal of neuronal extensions from a degenerating disc
The invention provides a method for alleviating discogenic pain by administering a therapeutic agent that disrupts neuronal and / or vascular elements in the disc, which is typically a degenerated disc. Disruption of neuronal elements in the disk includes destroying nerve endings without substantially affecting the central body of the nerve, suppressing activation of the nerve endings, and inhibiting the growth of nerve endings into the disk. Disruption of vascular elements includes causing the vascular extensions to retract from the disk, or suppressing the formation of such extensions. The therapeutic agent may be administered locally via an interbody pump, a bolus or a depot, or may be administered systemically.
Owner:WARSAW ORTHOPEDIC INC
Method and apparatus for treatment of discogenic pain
Owner:SPINAL GENERATIONS
System and method for electrical modulation of the posterior longitudinal ligament
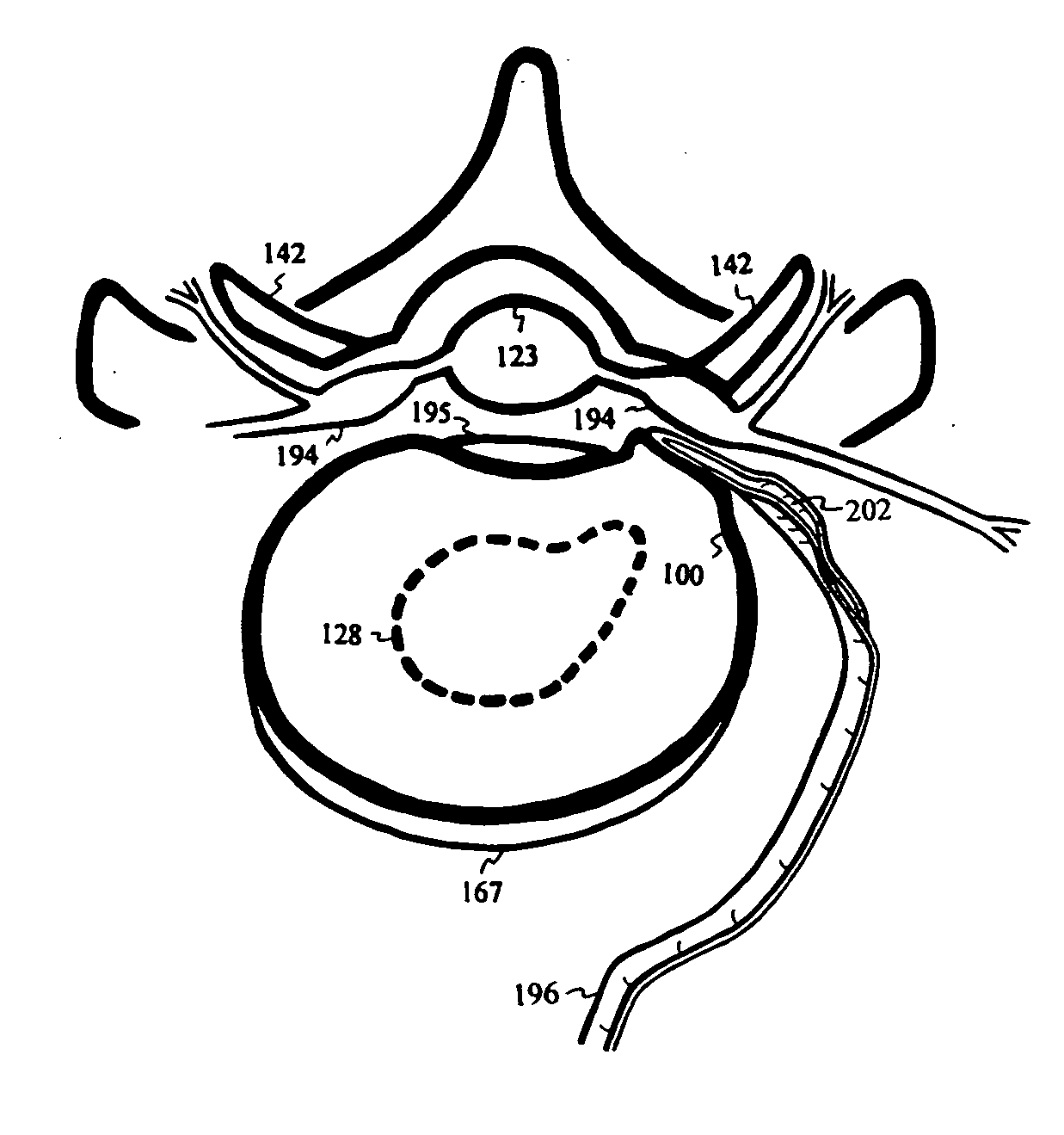
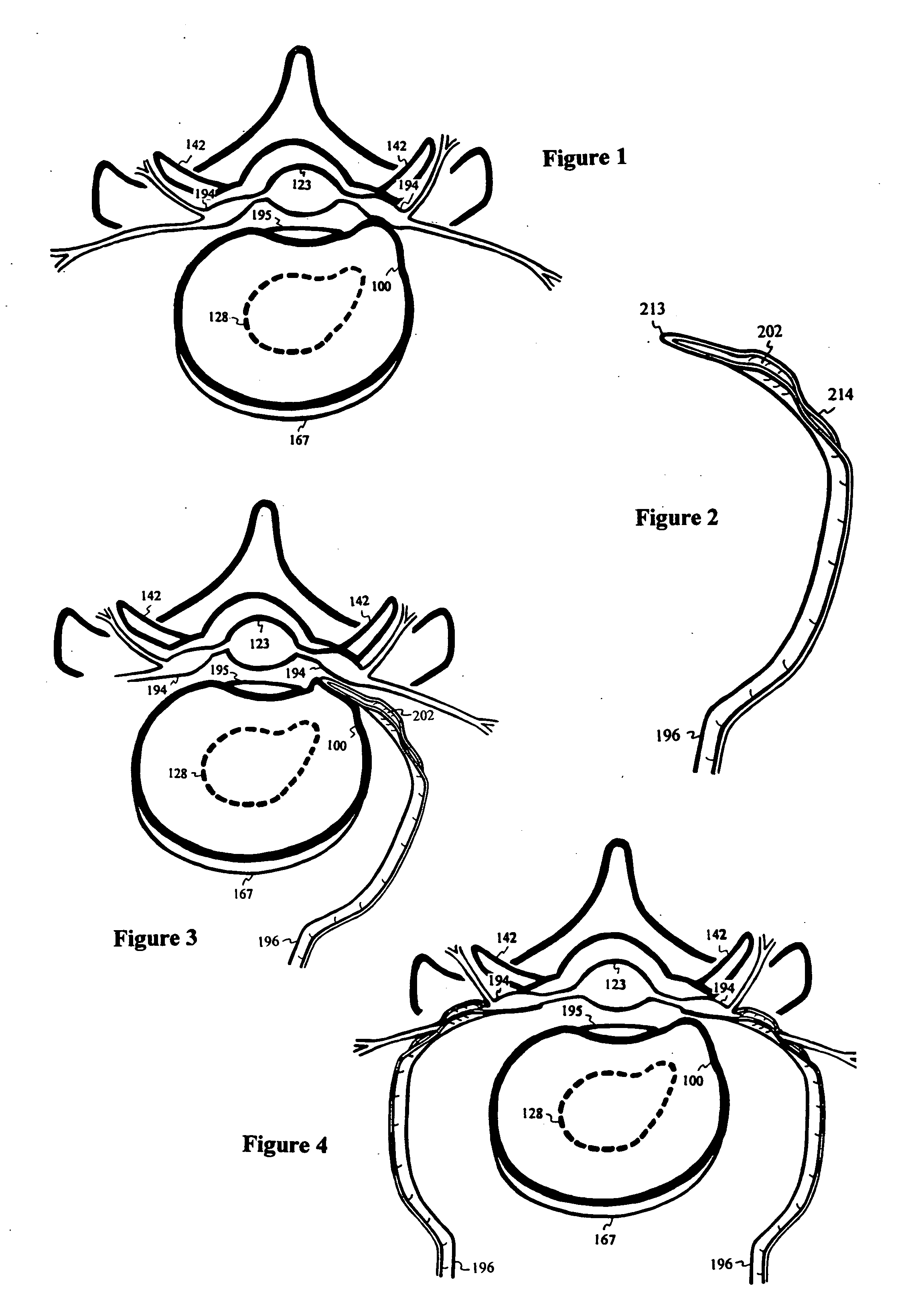
ActiveUS20120290059A1Prevent travelSpinal electrodesExternal electrodesSpinal columnLigament structure
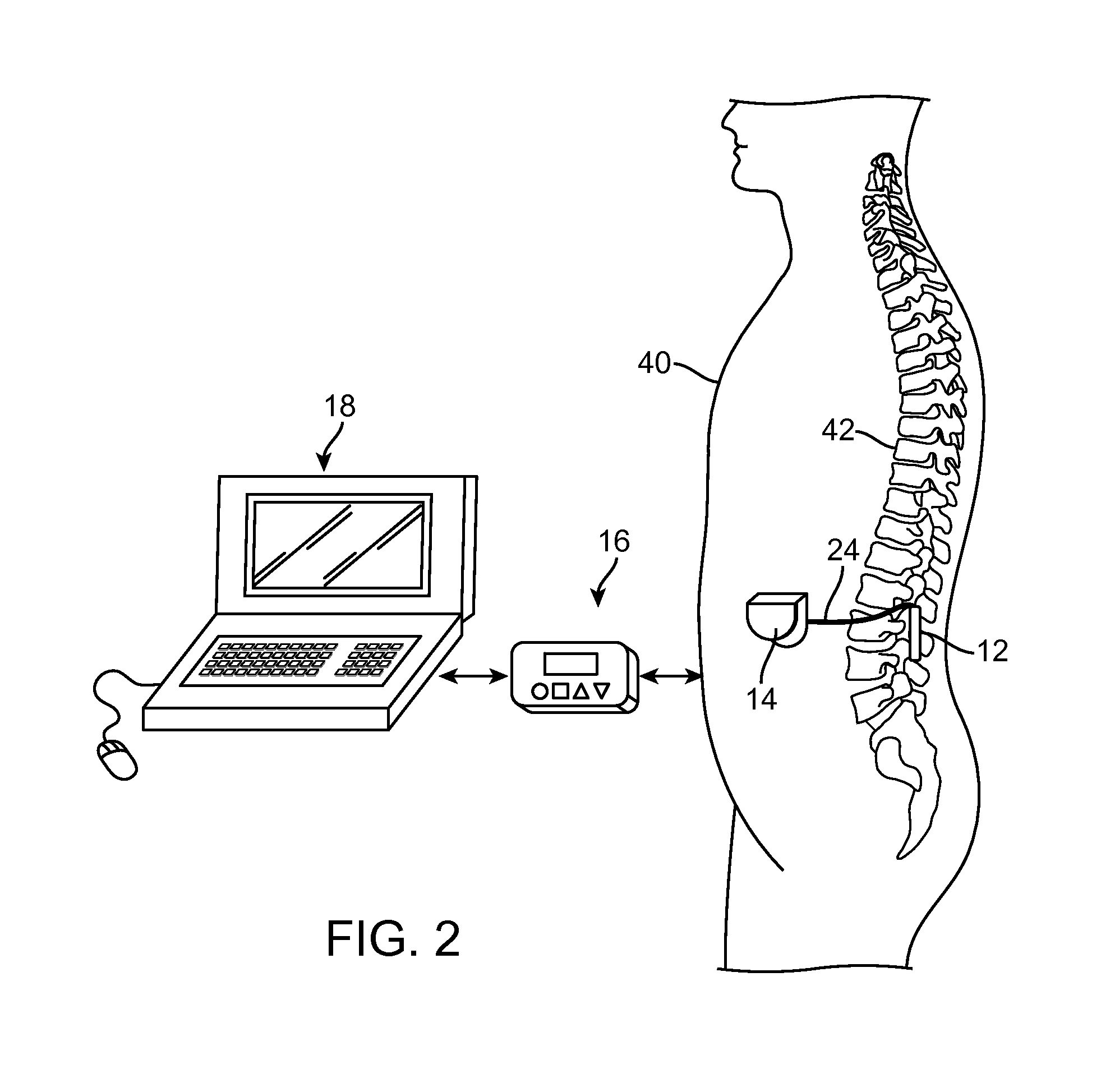
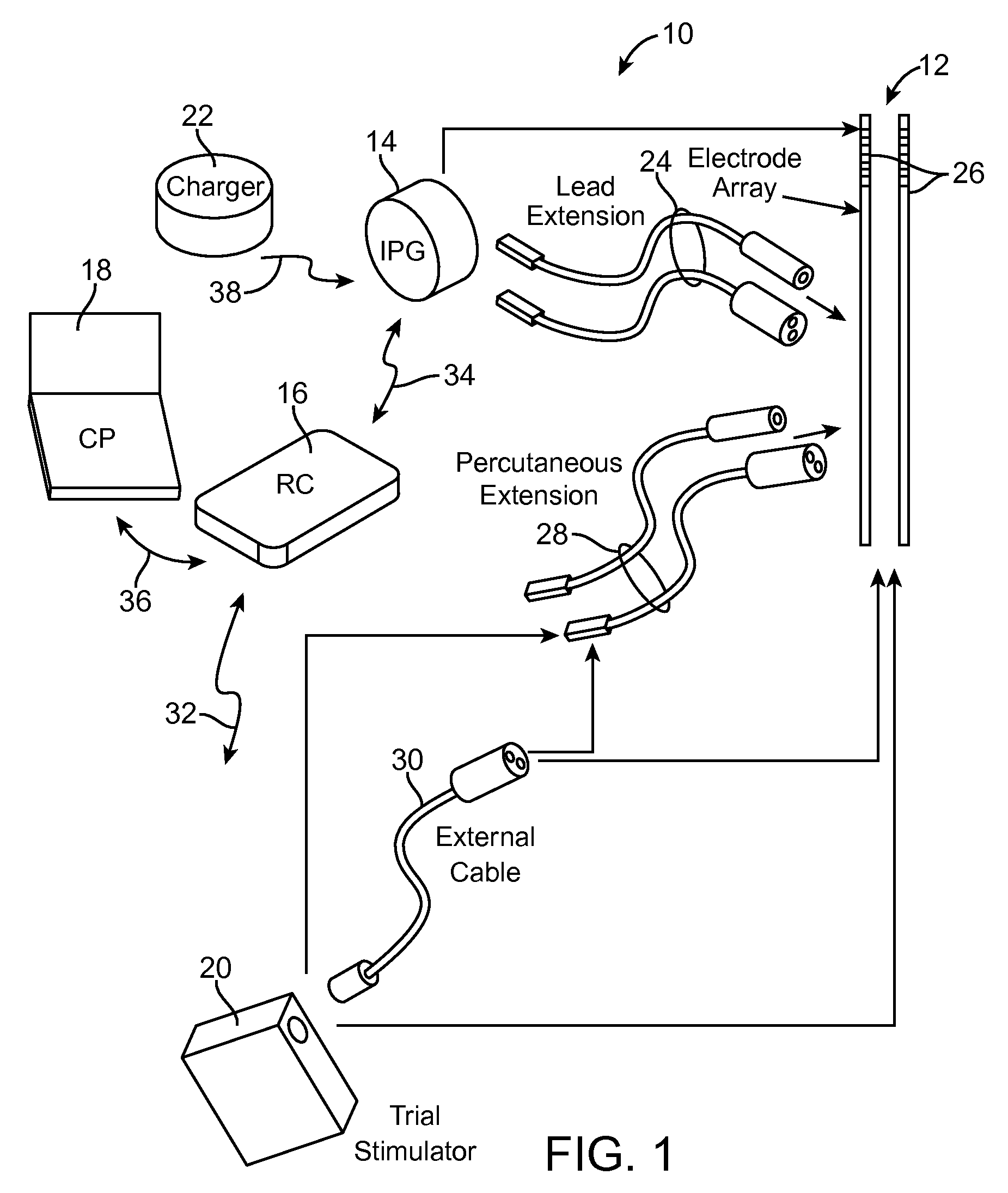
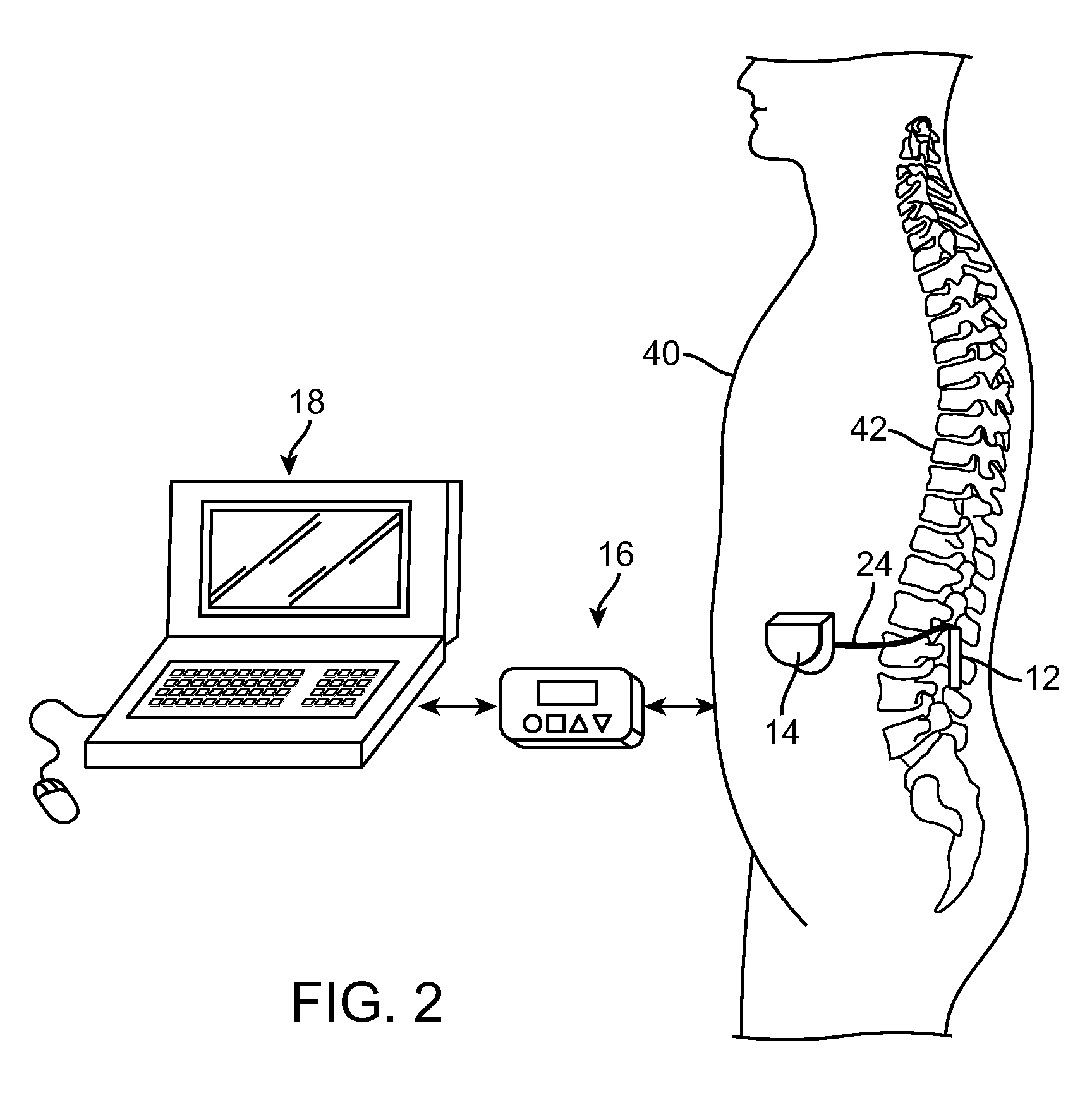
A method for treating a patient having discogenic pain includes implanting a neurostimulation lead within an anterior portion of the epidural space adjacent to the posterior longitudinal ligament. A plurality of electrodes is attached to the lead and the lead is implanted with at least a portion of the electrodes facing the posterior longitudinal ligament. The lead may be implanted in the lumbar region of the patient's spine, posterior and parallel to the posterior longitudinal ligament. Electrical stimulation energy applied to the patient through the electrode lead implanted in this manner inhibits the pain signals traveling within the posterior longitudinal ligament. Thus, the applied electrical stimulation energy has an anesthetic effect on the pain fibers adjacent to the posterior longitudinal ligament.
Owner:BOSTON SCI NEUROMODULATION CORP
Methods for treating back or neck pain caused by NGF using a therapeutic agent consisting of ReN-1820, ALE-0540 and capsaicin
The invention provides a method for alleviating discogenic pain by administering a therapeutic agent that disrupts neuronal and / or vascular elements in the disc, which is typically a degenerated disc. Disruption of neuronal elements in the disk includes destroying nerve endings without substantially affecting the central body of the nerve, suppressing activation of the nerve endings, and inhibiting the growth of nerve endings into the disk. Disruption of vascular elements includes causing the vascular extensions to retract from the disk, or suppressing the formation of such extensions. The therapeutic agent may be administered locally via an interbody pump, a bolus or a depot, or may be administered systemically.
Owner:WARSAW ORTHOPEDIC INC
Systems and methods using nuclear magnetic resonance (NMR) spectroscopy to evaluate pain and degenerative properties of tissue
ActiveCN101150983ADiagnostic recording/measuringSensorsSolid-state nuclear magnetic resonanceNMR - Nuclear magnetic resonance
NMR spectroscopy is performed on intervertebral disc tissue. Extent of degeneration is determined based on the NMR spectroscopy. Correlation between NMR spectral regions and pain are made. Accordingly, NMR spectroscopy is used to determine location and / or extent of at least one of disc degeneration, or discogenic pain.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA
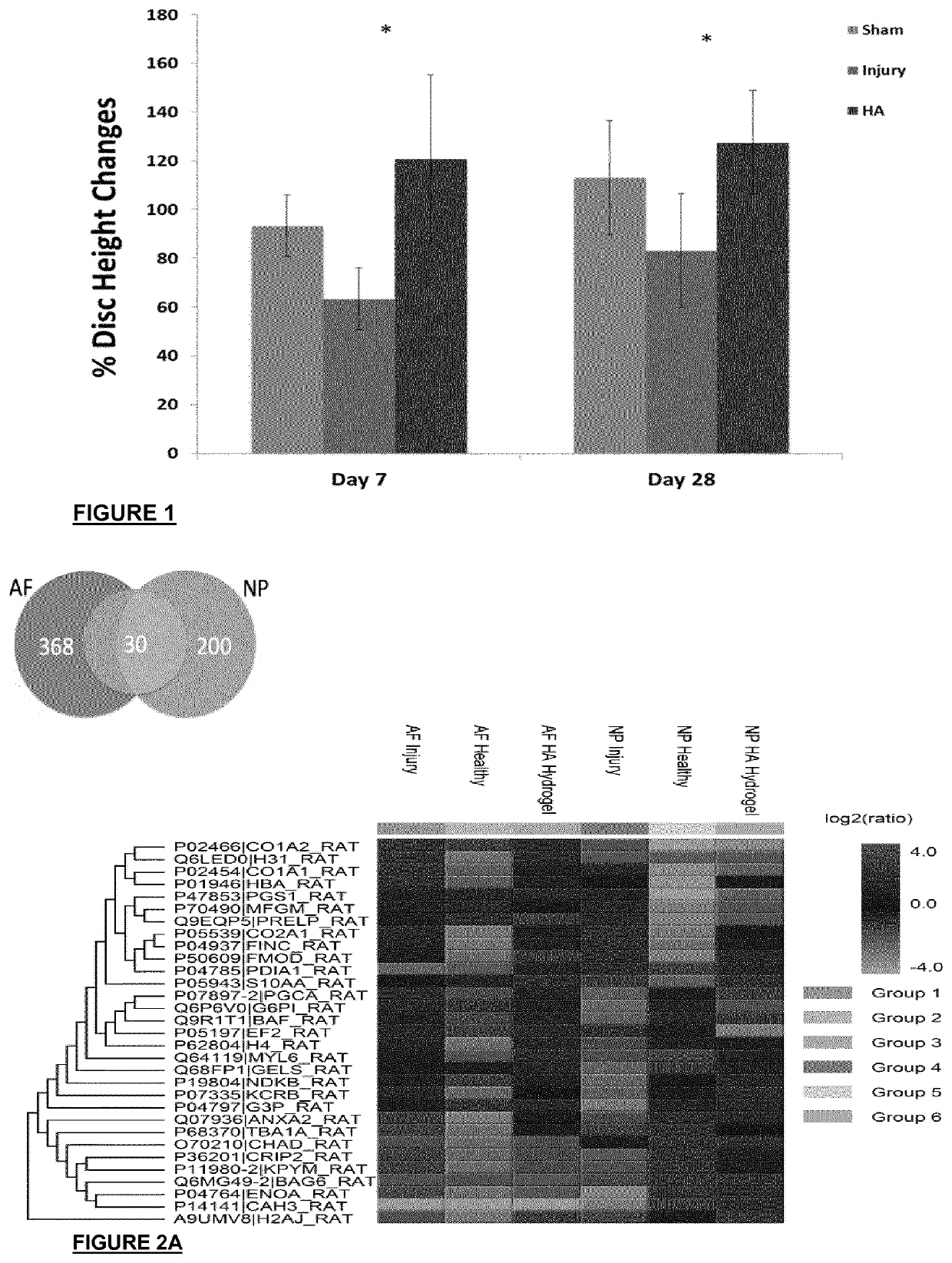
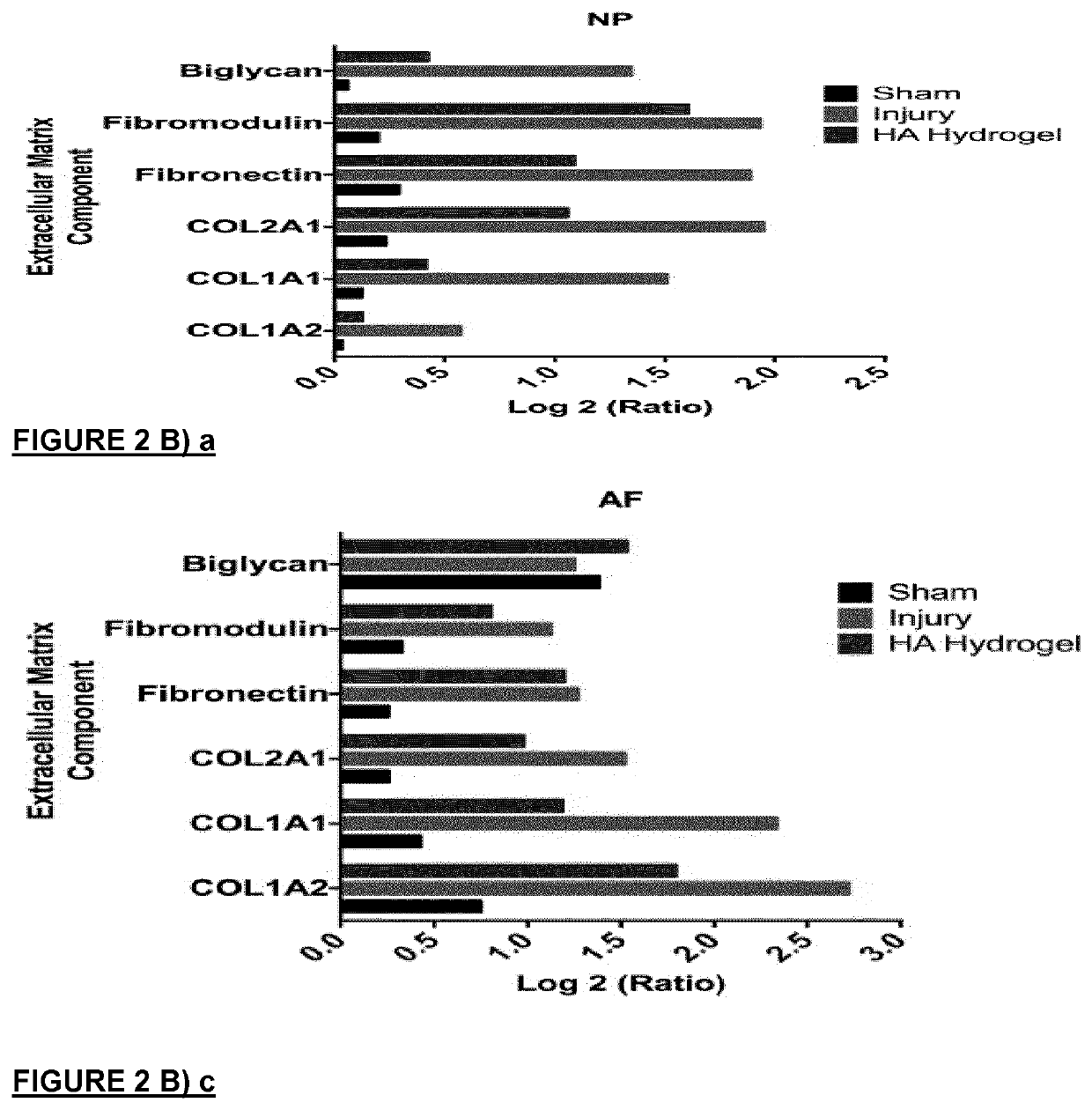
Regeneration of diseases intervertebral discs
InactiveUS20200038551A1Reduce the overall heightRelieve painNervous disorderPharmaceutical delivery mechanismDiseaseEngineering
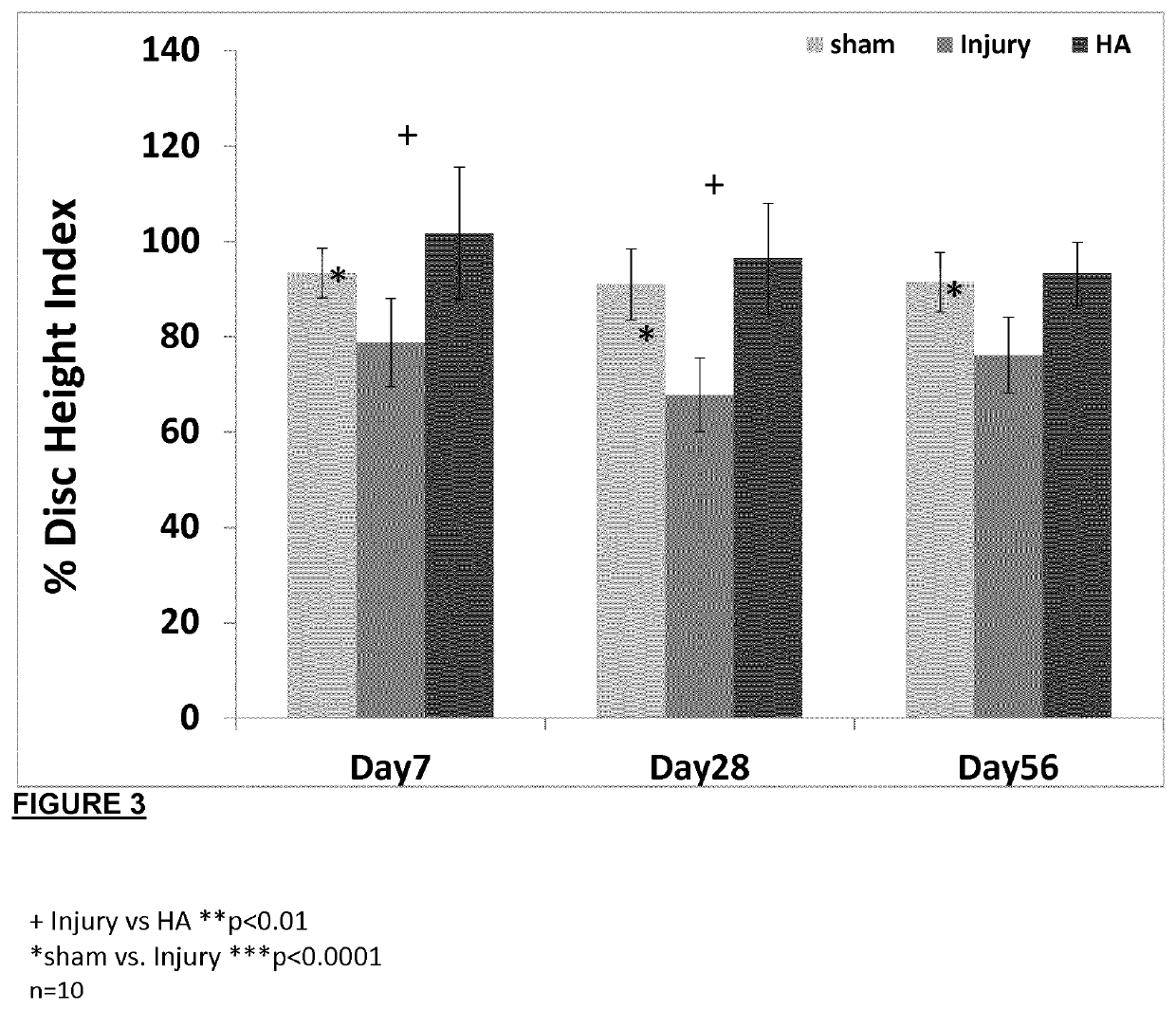
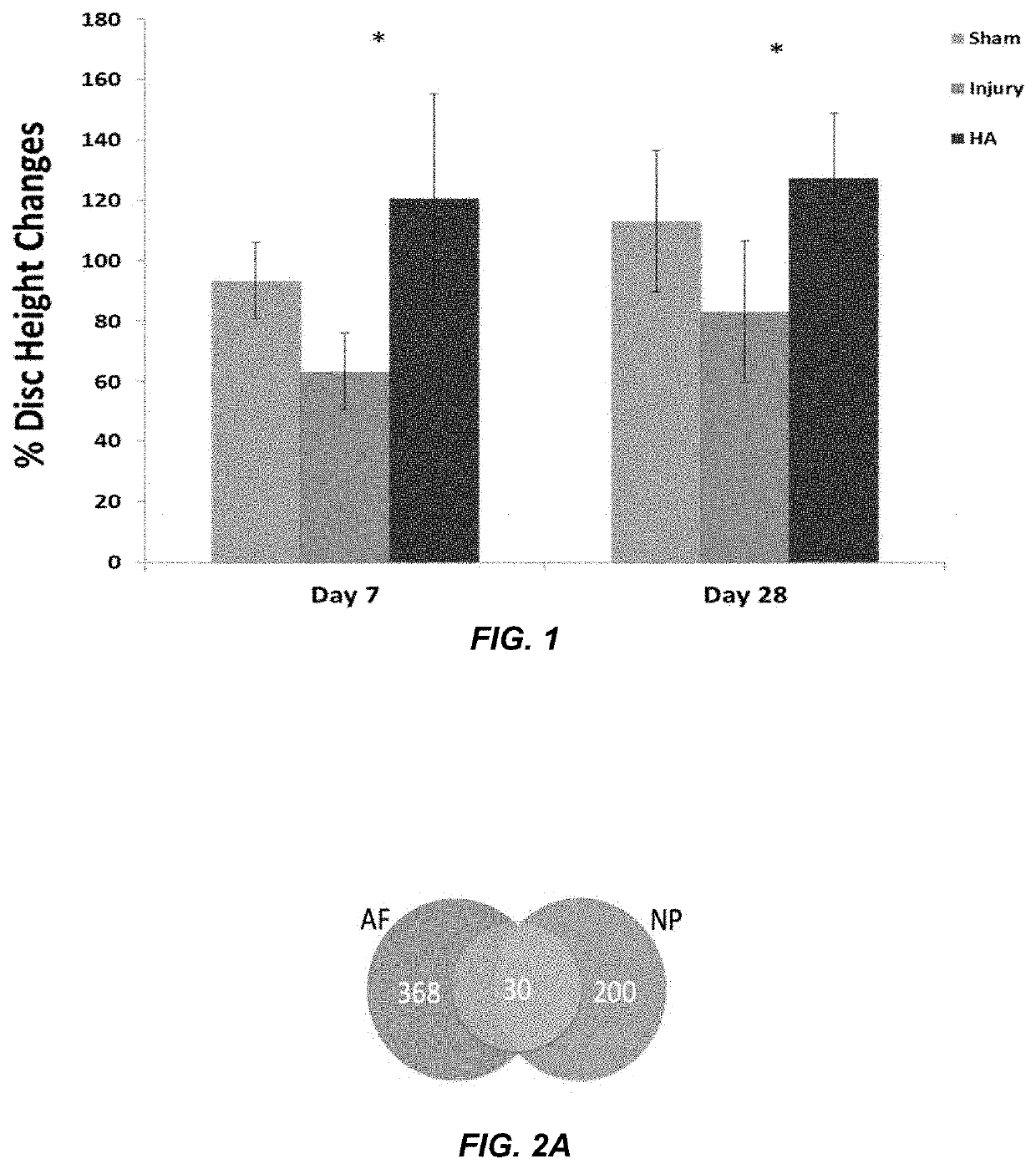
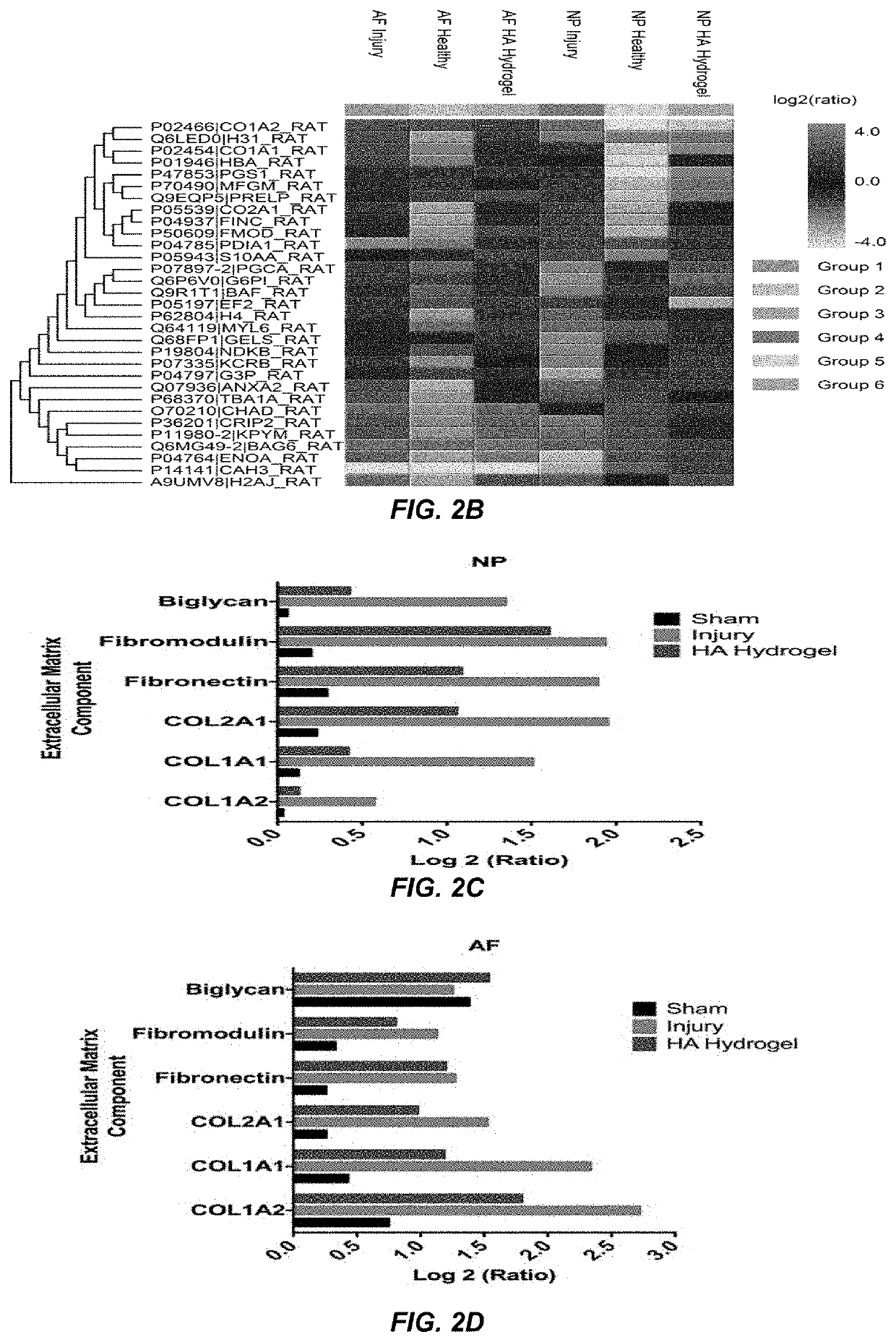
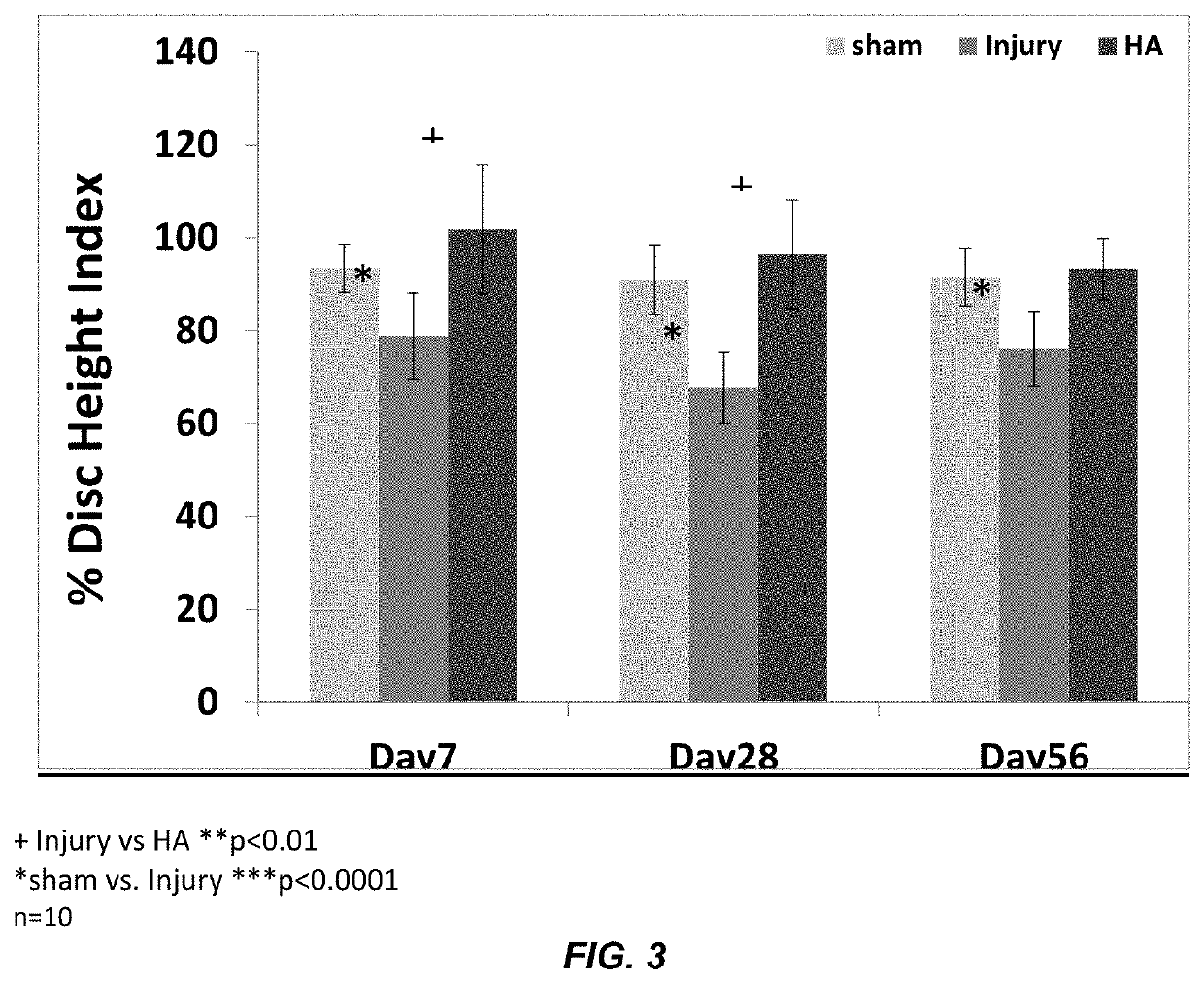
A hydrogel composition for use in a method of regeneration of an intervertebral disc, or suppression of discogenic pain, in a mammal with intervertebral disc degeneration isdescribed. The hydrogel composition comprises cross-linked high molecular weight hyaluronan. The hydrogel composition is implanted in the mammal at a site of intervertebral disc degeneration.
Owner:NATIONAL UNIVERSITY OF IRELAND
Imaging biomarkers for the diagnosis and prognosis of back pain and related conditions
The present invention teaches novel methods of diagnosing and prognosing conditions associated with tissue degeneration and / or pain, including intervertebral disc degeneration, discogenic pain, osteoarthritis, rheumatoid arthritis, and articular cartilage injury. Using the inventive noninvasive imaging methods, the diagnosis and prognosis of back pain and related conditions can be quickly and accurately determined by detecting one or more biomarkers disclosed herein.
Owner:CEDARS SINAI MEDICAL CENT
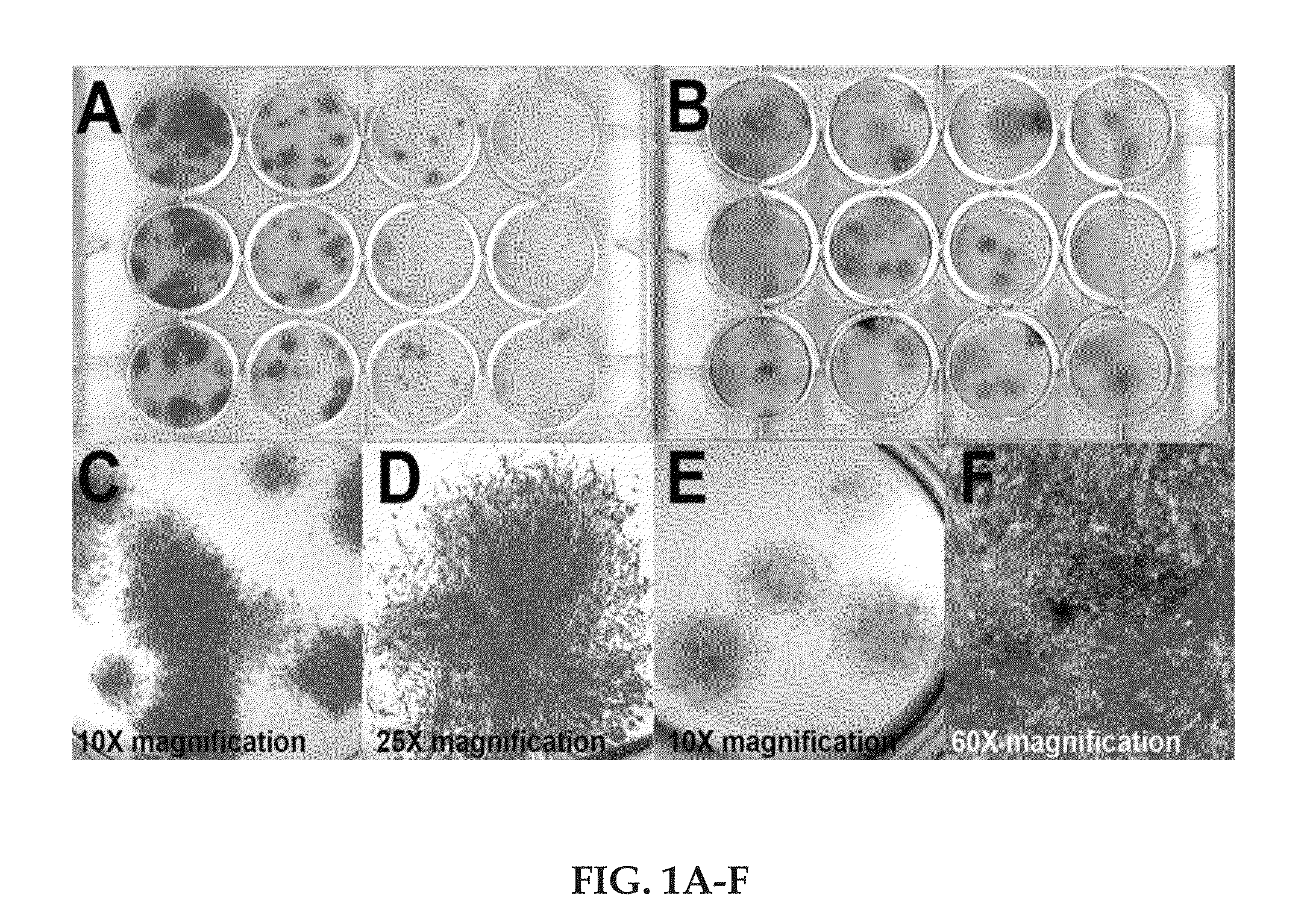
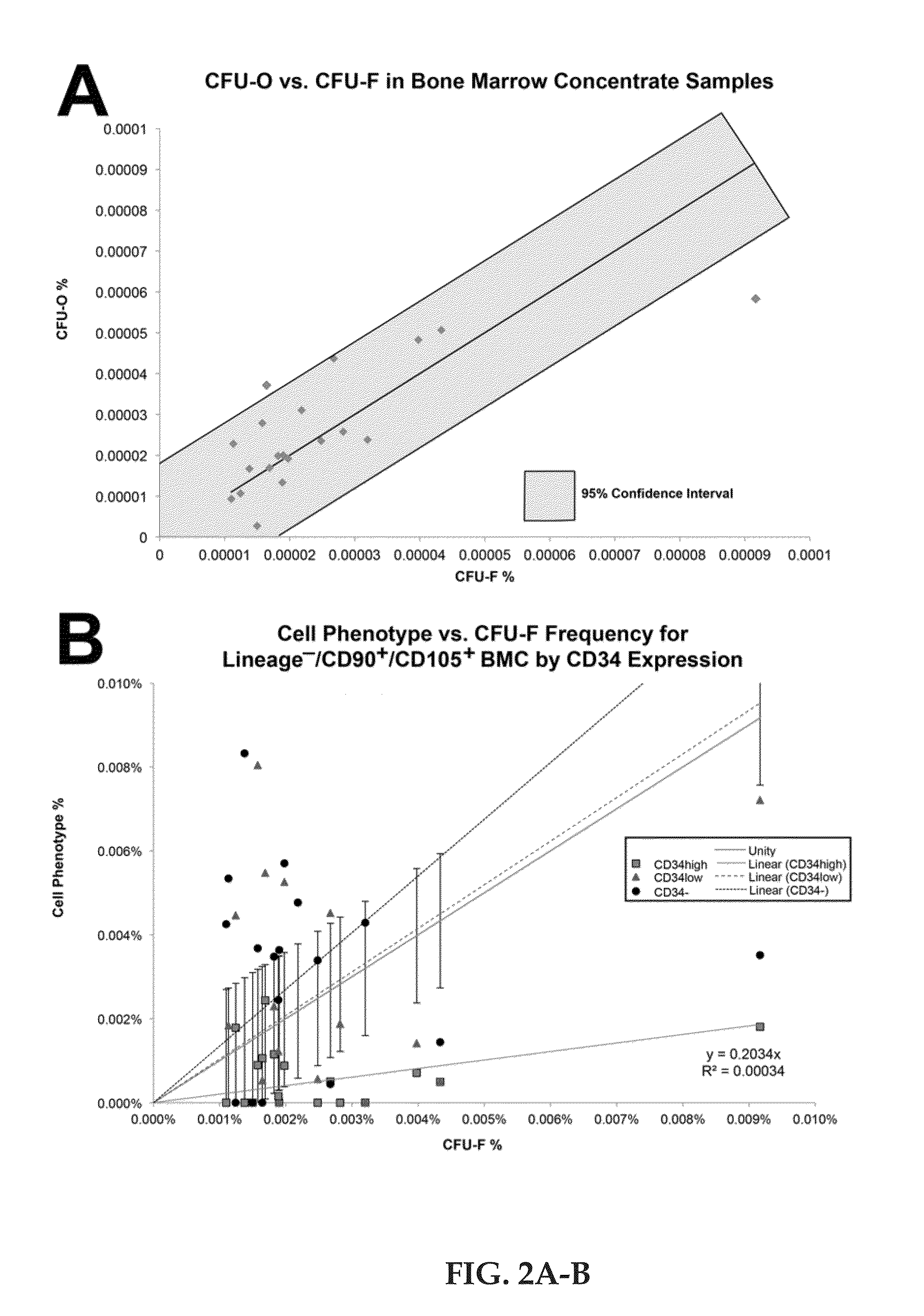
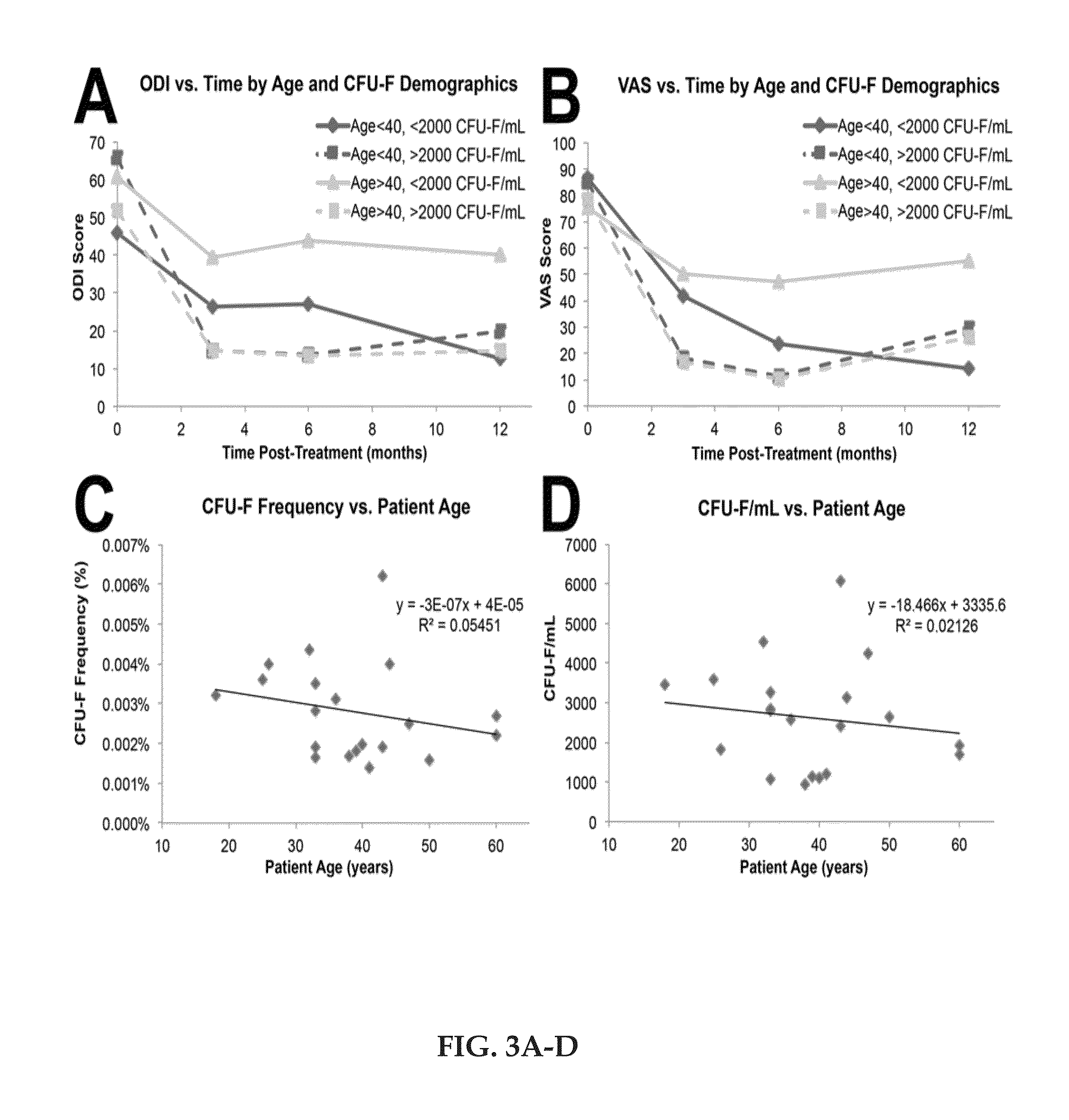
Regenerative autologous bone marrow cell therapies and methods for their use in the treatment of joint pain
The present novel technology relates to an autologous cell therapy that comprises a pre-determined amount of a processed bone marrow cellular matrix with a pre-determined amount of pre-mixture, where the pre-mixture includes quantities of anticoagulant solution, dextrose and phosphate buffered saline, and methods for production. The present novel technology further relates to a method of using the composition to reduce discogenic pain in humans.
Owner:HLDG PEN LLC
System and method for electrical modulation of the posterior Longitudinal ligament
A method for treating a patient having discogenic pain includes implanting a neurostimulation lead within an anterior portion of the epidural space adjacent to the posterior longitudinal ligament. A plurality of electrodes is attached to the lead and the lead is implanted with at least a portion of the electrodes facing the posterior longitudinal ligament. The lead may be implanted in the lumbar region of the patient's spine, posterior and parallel to the posterior longitudinal ligament. Electrical stimulation energy applied to the patient through the electrode lead implanted in this manner inhibits the pain signals traveling within the posterior longitudinal ligament. Thus, the applied electrical stimulation energy has an anesthetic effect on the pain fibers adjacent to the posterior longitudinal ligament.
Owner:BOSTON SCI NEUROMODULATION CORP
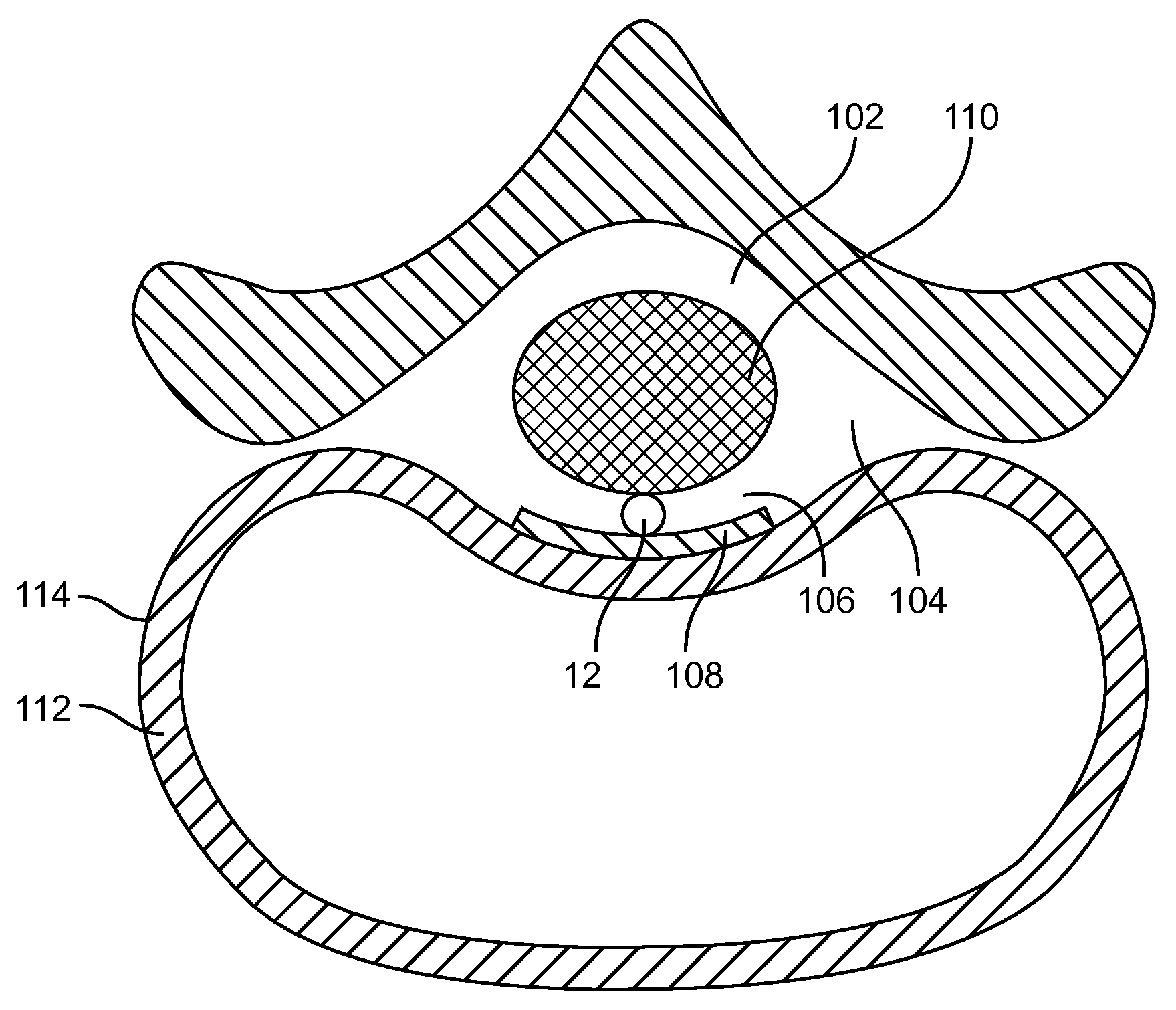
Method for relieving pain and regenerating intervertebral disc
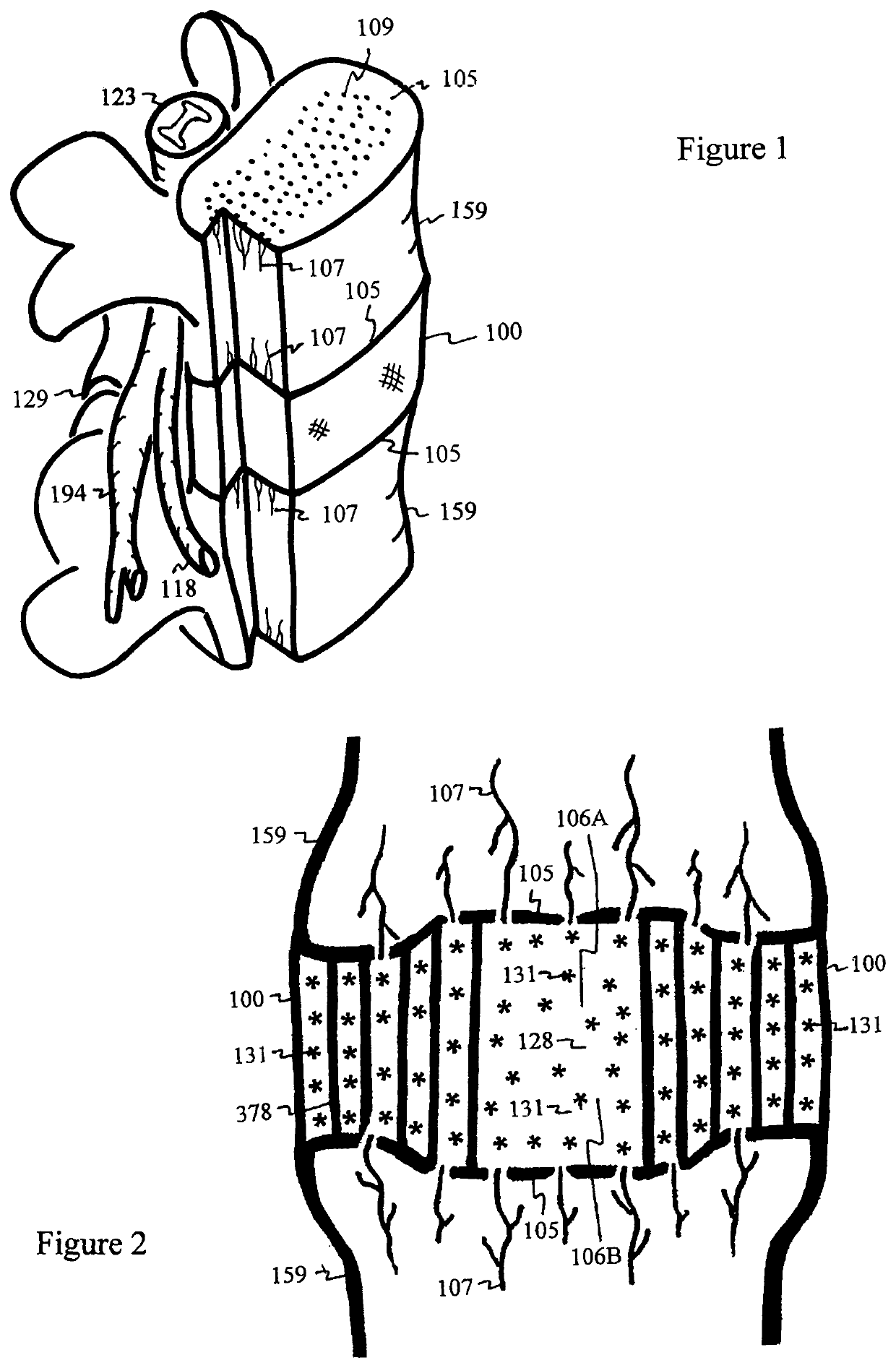
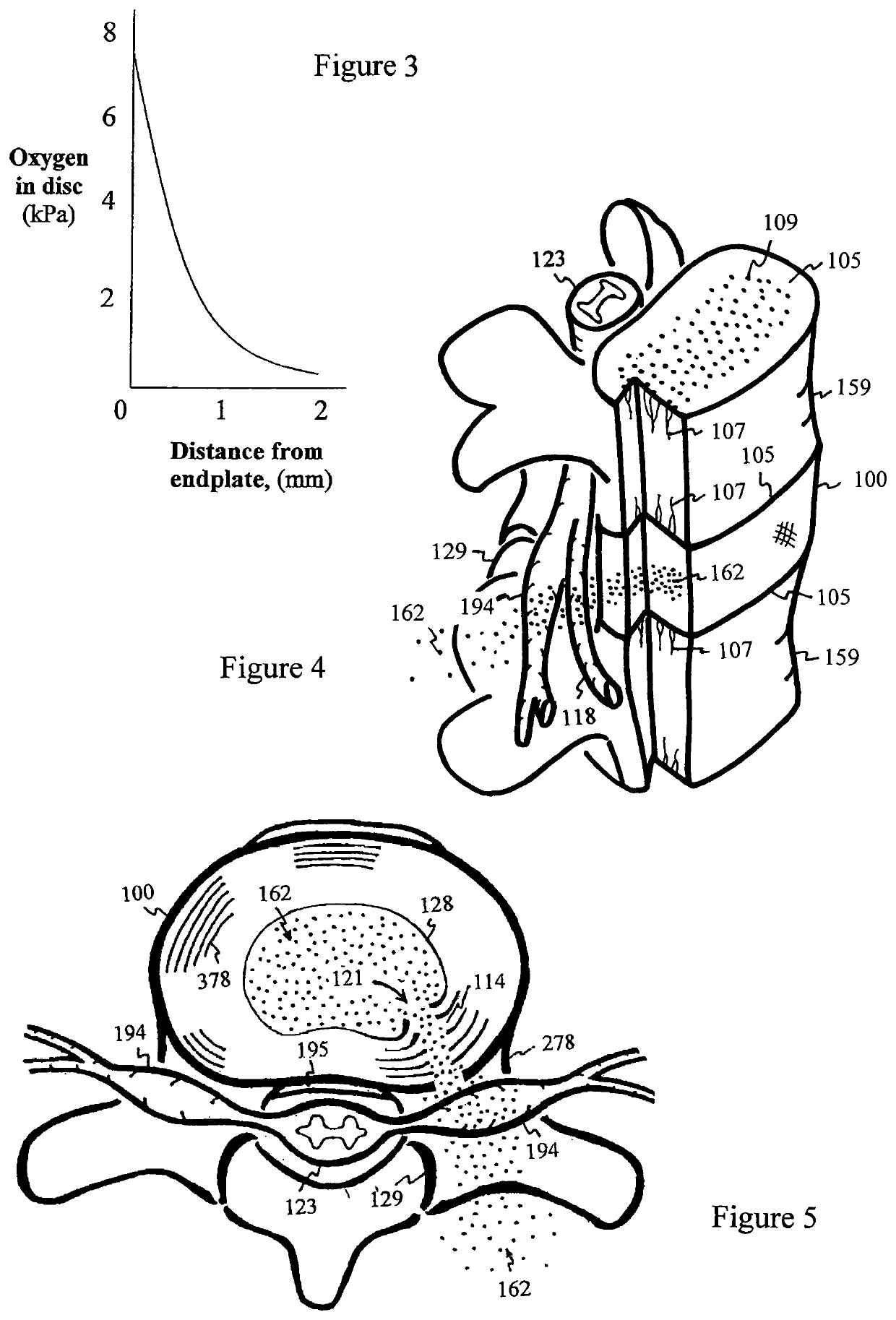
ActiveUS10561503B2Relieve the discogenic painInhibit inflammationJoint implantsSpinal implantsNutritionBACK DISCOMFORT
Disc degeneration and chronic back pain are caused by a transport hindrance of oxygen, nutrients and pH buffer from capillaries in endplates into mid-layer of the intervertebral disc. A fluid absorbing conduit is inserted into the intervertebral disc, drawing and delivering the oxygen, nutrients and pH buffer in fluid of body circulation from capillaries at endplates into the mid-layer of the disc. The disc undergoes thousands of relaxation and compression cycles each day from daily activity of the patient. During relaxation phase, the fluid of body circulation containing oxygen, nutrients, and pH buffer is infused into the fluid absorbing conduit. During compression phase, the oxygen, nutrients, and pH buffer in the fluid absorbing conduit is dispersed into the mid-layer of the disc. The pH buffer, bicarbonate, neutralizes the lactic acid to relieve the discogenic pain. Oxygen inhibits hypoxic inflammation and production of lactic acid to further reduce the discogenic pain. Nutrients nourish the disc cells to rebuild or regenerate the disc matrix.Therapeutic agents can be added into the fluid absorbing conduit or injected into the disc implanted with the fluid absorbing conduit to expedite pain relief and disc regeneration. The therapeutic agents can be pH buffering agent, antibiotic, anti-inflammatory drug, anesthetic, antacid, nutrient, sulfate, anti-depressant, calcium channel blocker, growth factor, cells or other.
Owner:ALEEVE MEDICAL INC
Application of inhibitor and pharmaceutical composition
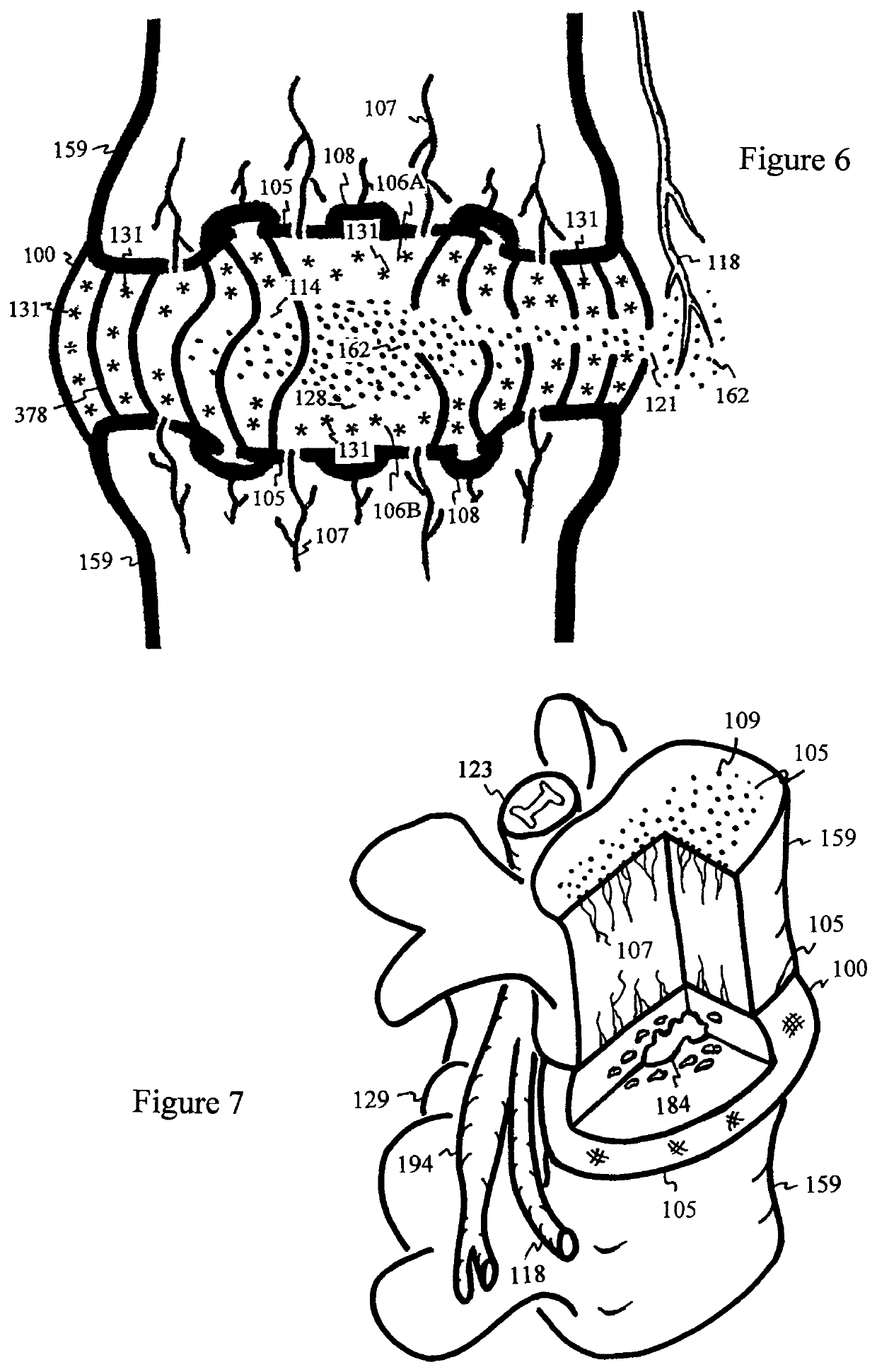
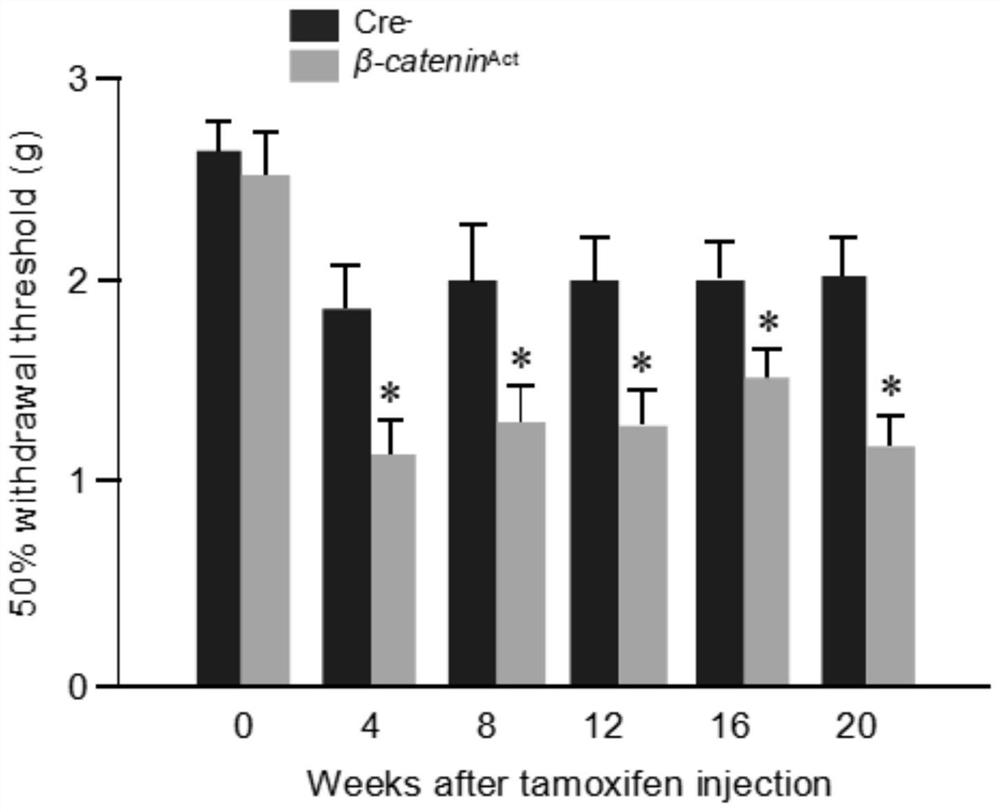
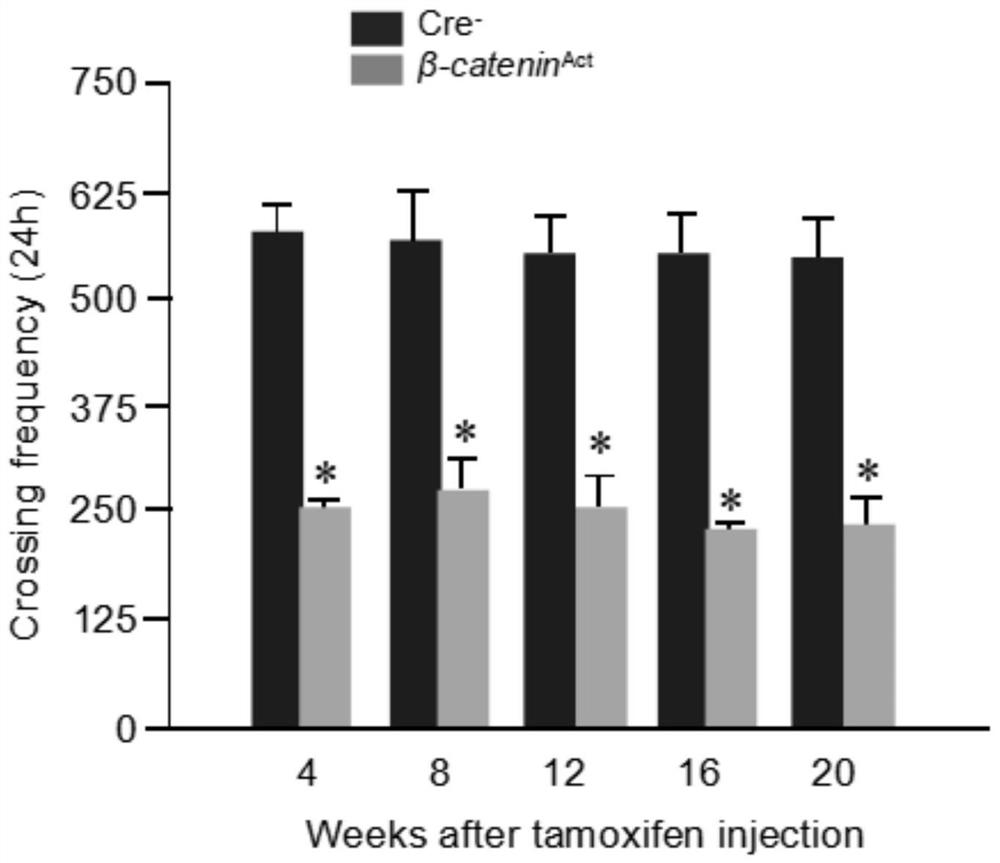
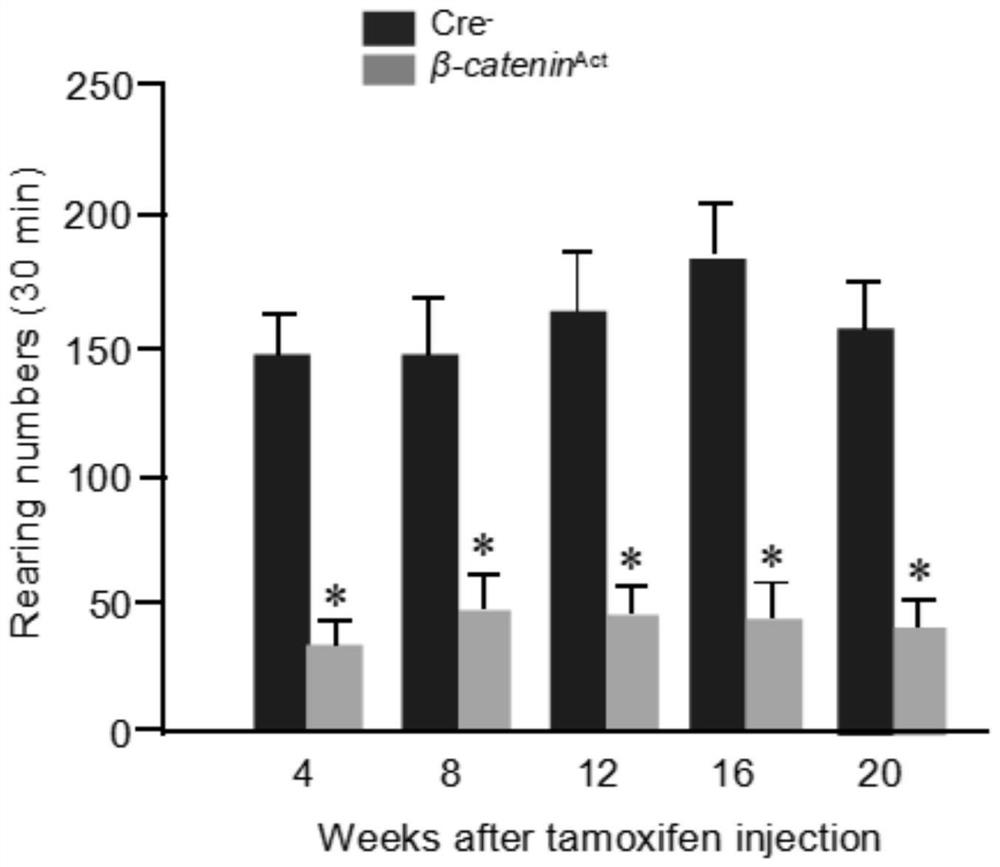
The invention discloses application of an inhibitor in preparation of a medicine for treating discogenic pain and a medicine composition. The pharmaceutical composition is a beta-catenin protein and TCF7 transcription factor binding inhibitor and / or a Wnt / beta-catenin signal channel inhibitor. In combination with data of an embodiment part, the beta-catenin protein and TCF7 transcription factor binding inhibitor and / or the Wnt / beta-catenin signal channel inhibitor can achieve the effect of treating the discogenic pain based on the inhibition of the Wnt / beta-catenin signal channel.
Owner:SHENZHEN INST OF ADVANCED TECH +1
Regeneration of diseases intervertebral discs
InactiveUS20210236692A1Reduce the overall heightRelieve painNervous disorderPharmaceutical delivery mechanismDiseaseIntervertebral disc
A hydrogel composition for use in a method of regeneration of an intervertebral disc, or suppression of discogenic pain, in a mammal with intervertebral disc degeneration is described. The hydrogel composition comprises cross-linked high molecular weight hyaluronan. The hydrogel composition is implanted in the mammal at a site of intervertebral disc degeneration.
Owner:NATIONAL UNIVERSITY OF IRELAND
Probe and device for detecting abnormality of intervertebral disc
InactiveUS8900160B2Rapidly and easily determinedUltrasonic/sonic/infrasonic diagnosticsDiagnostics using vibrationsIntervertebral discBiomedical engineering
The present invention relates to a probe and a device for detecting abnormality of an intervertebral disc. More particularly, the present invention relates to a probe and a device for detecting abnormality of an intervertebral disc that gives vibration stimulation to the inner part of the intervertebral disc and obtains an ultrasonic image in order to sense the abnormality of the intervertebral disc causing discogenic pains and inspects whether the intervertebral disc is abnormal by measuring impedance in the intervertebral disc. The present invention provides a probe for detecting abnormality of an intervertebral disc including: a shaft connector; a vibration generator connected to the shaft connector; and an inspector connected to the vibration generator, wherein the vibration generator vibrates the inspector by using a piezoelectric element and a device for detecting abnormality of an intervertebral disc.
Owner:GWANGJU INST OF SCI & TECH
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com