Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
274 results about "Solid-state nuclear magnetic resonance" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
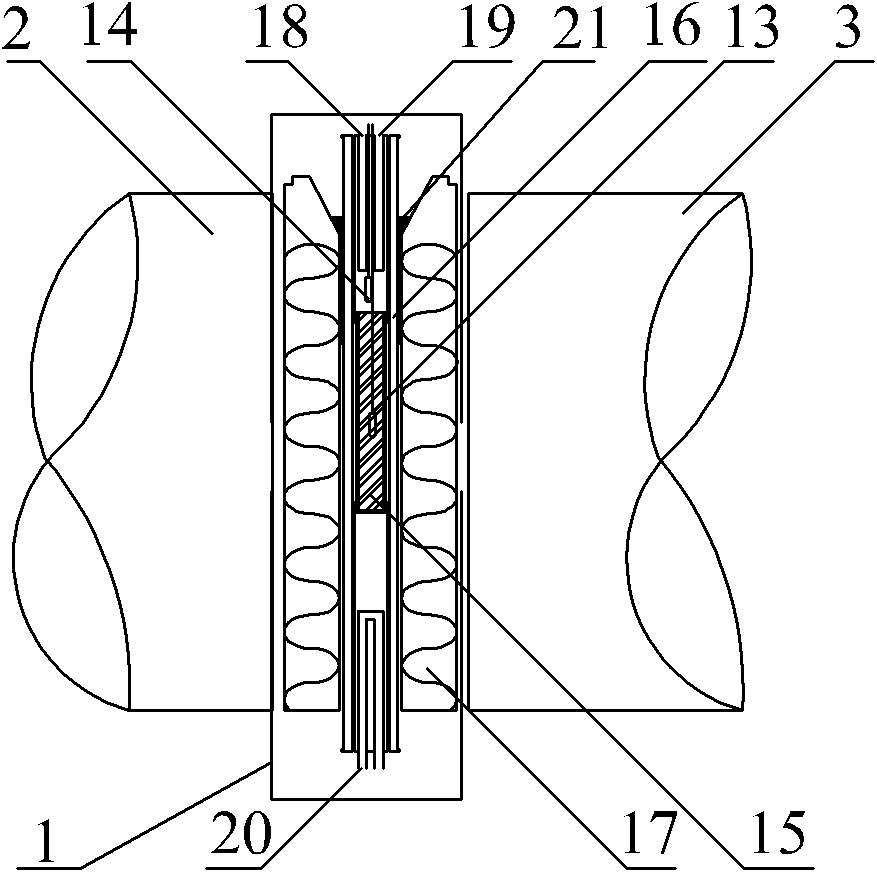
Solid-state NMR (ssNMR) spectroscopy is a special type of nuclear magnetic resonance (NMR) spectroscopy, characterized by the presence of anisotropic (directionally dependent) interactions. Compared to the more common solution NMR spectroscopy, ssNMR usually requires additional hardware for high-power radio-frequency irradiation and magic-angle spinning.
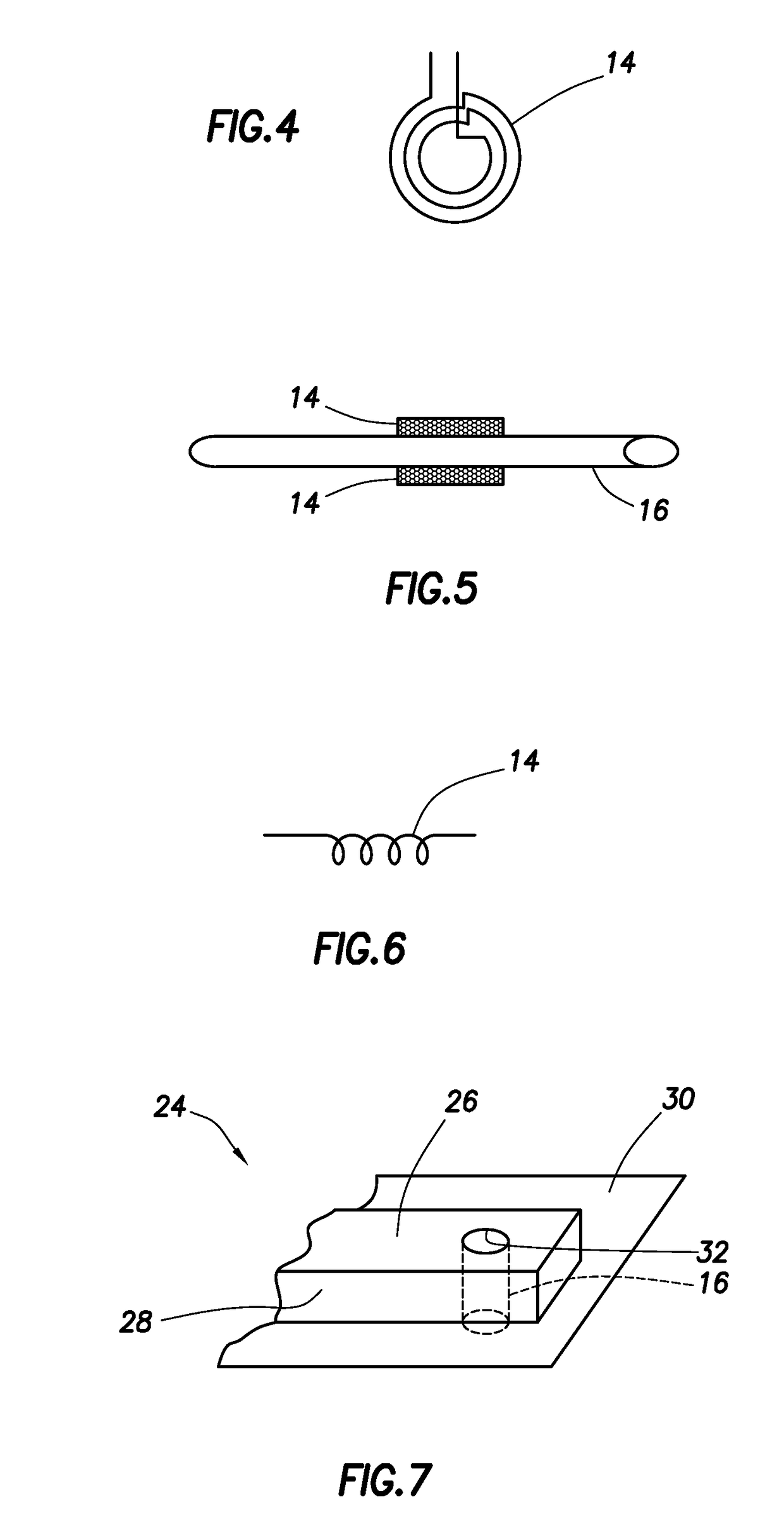
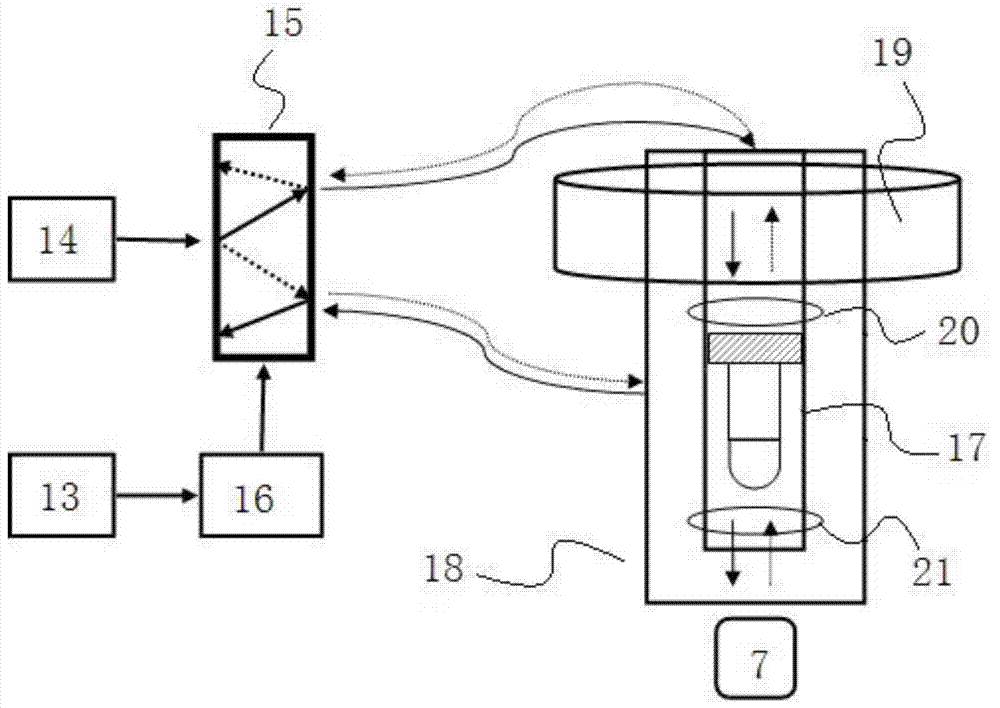
Nuclear magnetic resonance equipment
InactiveUS6958608B2High sensitivityElectric/magnetic detectionMeasurements using magnetic resonanceCapacitanceSpectroscopy
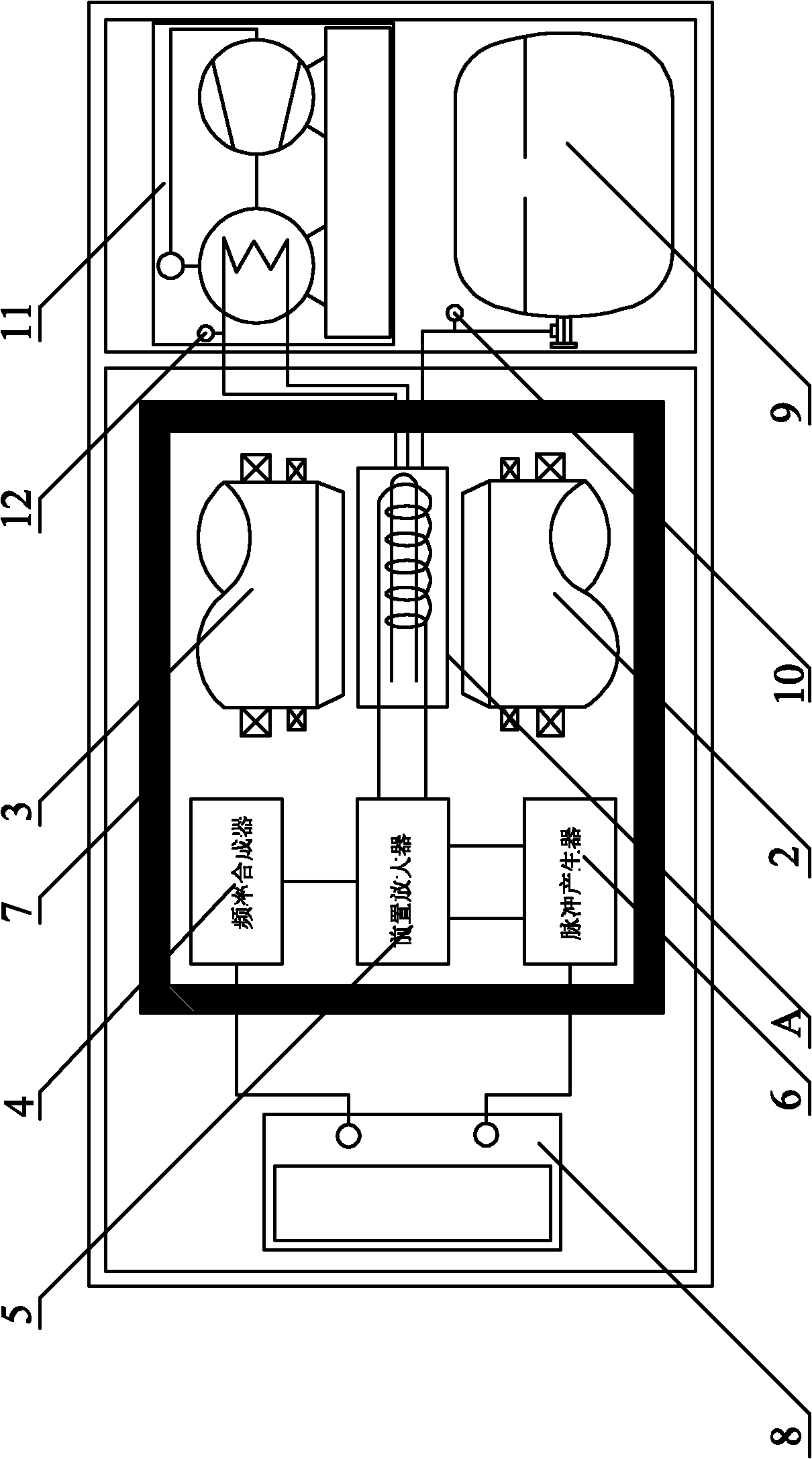
The invention provides nuclear magnetic resonance equipment realizing improved sensitivity of a probe for receiving a free induction decay (FID) signal in nuclear magnetic resonance (NMR) spectroscopy in a high frequency band of 600 MHz or higher. By manufacturing a solenoid coil of a higher filling factor by using a superconductor of extremely low resistance to high frequency current, sensitivity is increased. A superconducting thin film made of magnesium diboride (MgB2) formed on a donut plate-type substrate is disposed so that the film surface becomes parallel with the uniform magnetic field. The object is realized by a probe made by a solenoid coil formed by connecting a plurality of coil parts by capacitive coupling via a normal metal lead.
Owner:HITACHI LTD
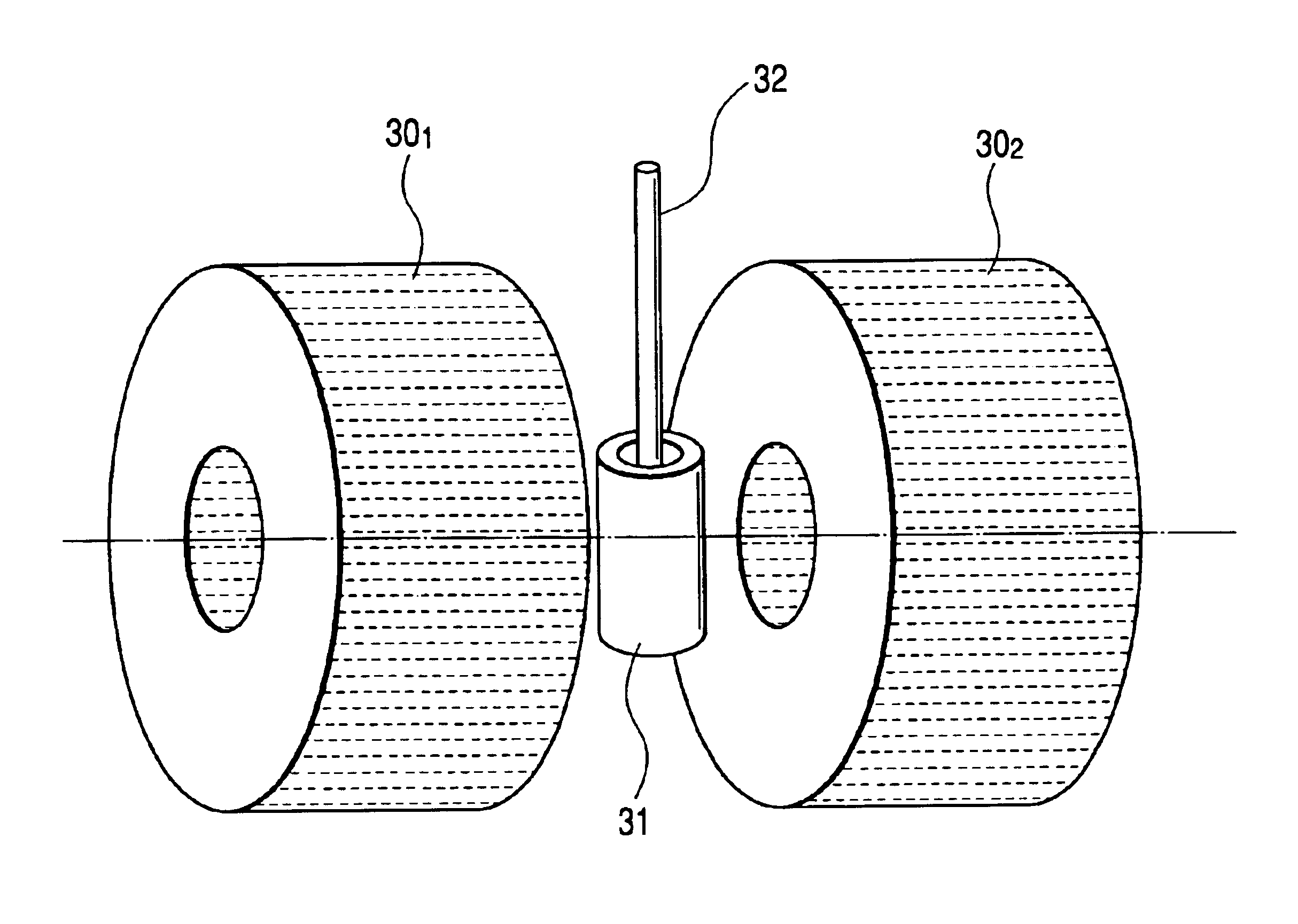
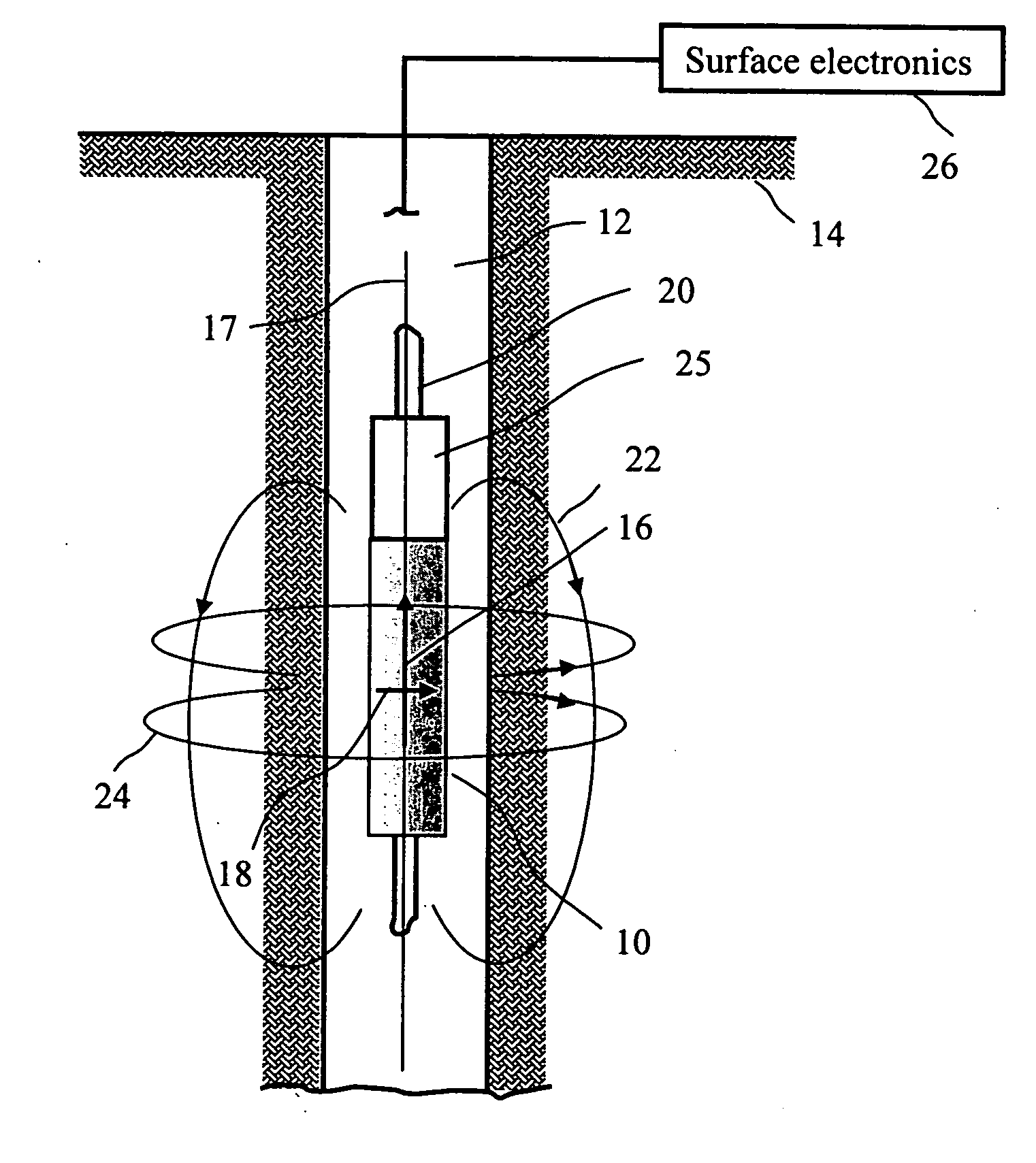
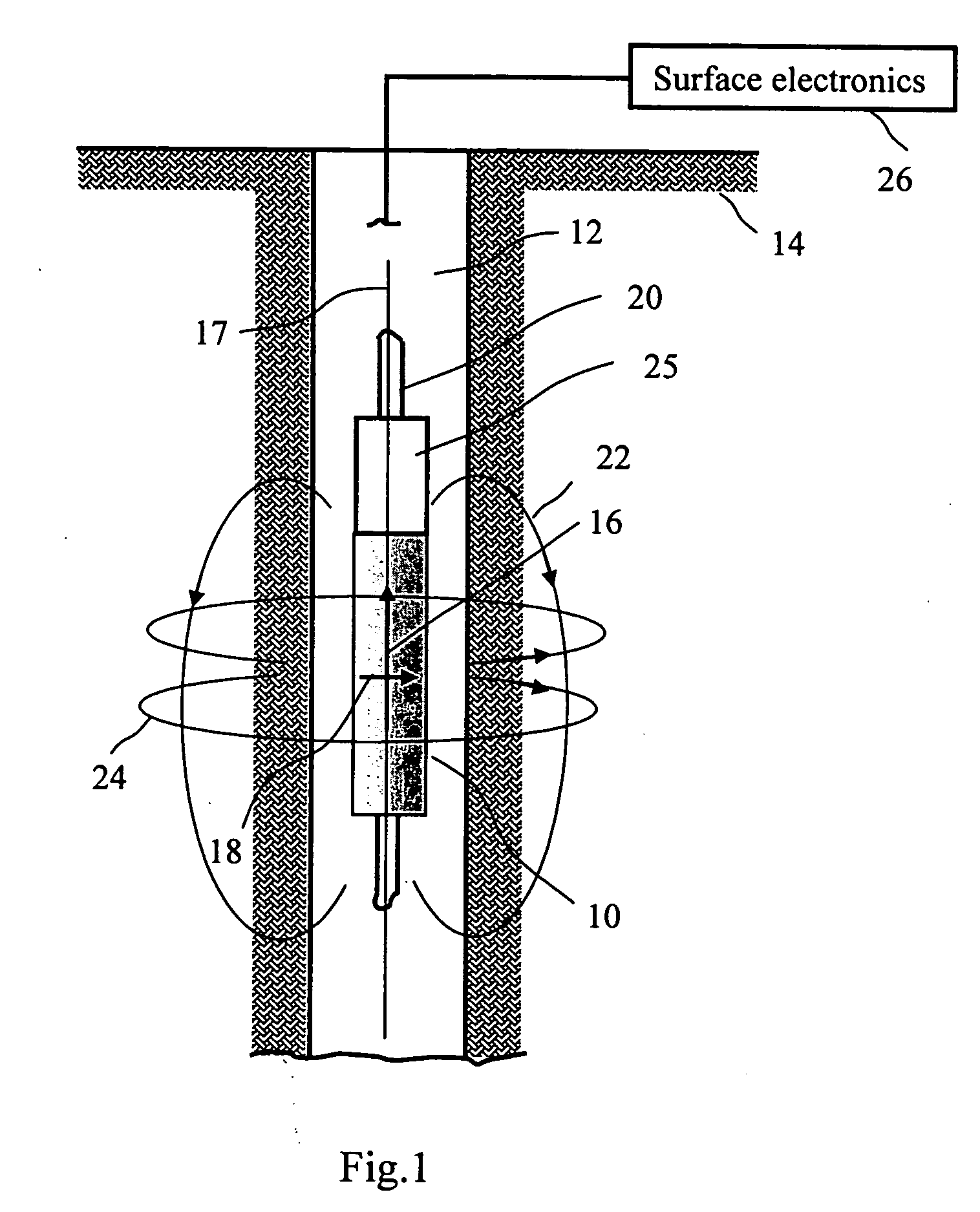
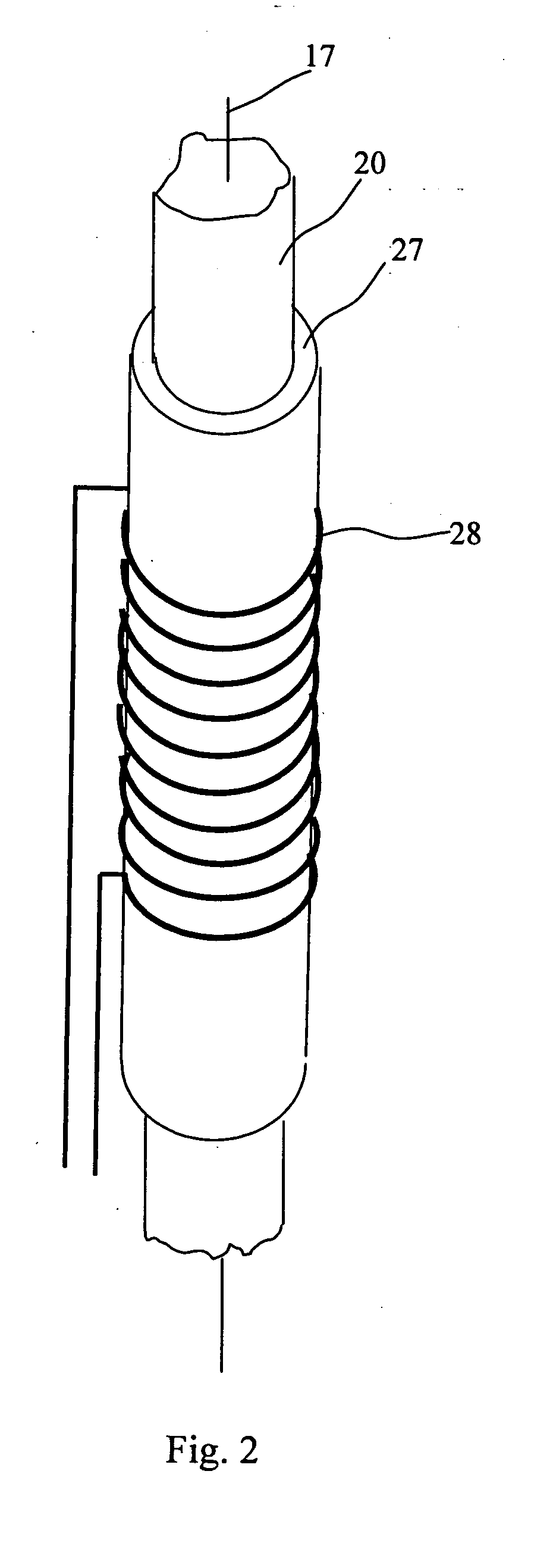
Nuclear magnetic resonance tool using switchable source of static magnetic field
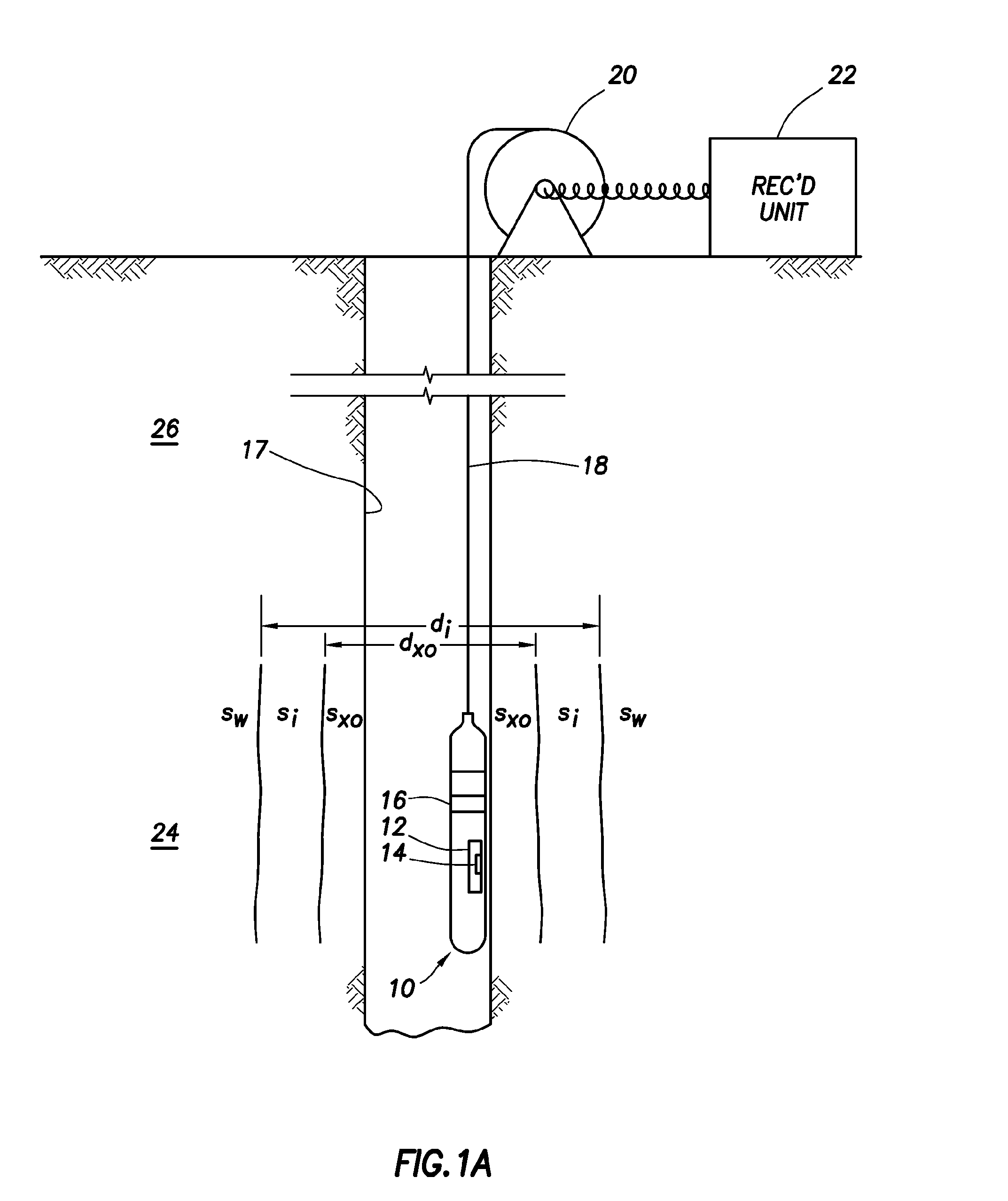
ActiveUS20060255799A1Effective permeability of magneticElectric/magnetic detection for well-loggingMaterial analysis by using resonanceSolid-state nuclear magnetic resonanceSpin magnetic moment
A nuclear magnetic resonance sensing apparatus and method for operating in an earth borehole comprises a source of switchable magnetic field to polarize nuclei in the region of interest, said source comprising a coil wound on a magnetic core having controllable residual magnetization. Maintaining the magnetization of the core during a polarization interval does not require steady current in the coil. Switching intensity and polarity of magnetization of the core causes precession of spin magnetic moments of the nuclei; the precession induces a signal indicative of nuclear magnetic resonance properties of earth formations.
Owner:BAKER HUGHES INC
Nuclear magnetic resonance imaging apparatus and nuclear magnetic resonance imaging method
InactiveUS20130082701A1Avoid sensitivityMeasurements using NMR spectroscopyElectric/magnetic detectionSolid-state nuclear magnetic resonanceIn plane
The present invention has an object to provide a nuclear magnetic resonance imaging apparatus or the like that avoids a region with zero sensitivity of an optical magnetometer and allows imaging by strong magnetic resonance when a common magnetic field is used as a bias field of an optical magnetometer and as a magnetostatic field to be applied to a sample. When a direction of a magnetostatic field application unit applying a magnetostatic field to a sample is a z direction, alkali metal cells of a plurality of scalar magnetometers are arranged so as not to overlap a region to be imaged in a z direction, and so as not to intersect the region to be imaged in an in-plane direction perpendicular to the z direction.
Owner:CANON KK
Atomic magnetic gradiometer for room temperature high sensitivity magnetic field detection
InactiveUS7573264B2Reduce noiseElectric/magnetic detectionMeasurements using magnetic resonanceProton NMRSingle polarization
A laser-based atomic magnetometer (LBAM) apparatus measures magnetic fields, comprising: a plurality of polarization detector cells to detect magnetic fields; a laser source optically coupled to the polarization detector cells; and a signal detector that measures the laser source after being coupled to the polarization detector cells, which may be alkali cells. A single polarization cell may be used for nuclear magnetic resonance (NMR) by prepolarizing the nuclear spins of an analyte, encoding spectroscopic and / or spatial information, and detecting NMR signals from the analyte with a laser-based atomic magnetometer to form NMR spectra and / or magnetic resonance images (MRI). There is no need of a magnetic field or cryogenics in the detection step, as it is detected through the LBAM.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA
Method for Determining Rock Formation Fluid Interaction Properties Using Nuclear Magnetic Resonance Well Logging Measurements
InactiveUS20130057277A1Electric/magnetic detection for well-loggingDetection using electron/nuclear magnetic resonanceSolid-state nuclear magnetic resonanceDiffusion
A method for determining surface relaxivity of a rock formation in a wellbore includes using measurements of nuclear magnetic resonance properties of the rock formation made from within a wellbore penetrating the rock formations includes determining nuclear magnetic relaxation properties from the measurements of the nuclear magnetic resonance properties. A diffusion property of the rock formation is determined from the measurements of the nuclear magnetic resonance properties. The surface relaxivity of the rock formation is determined from the relaxation properties and the diffusion property. The surface relaxivity and other nuclear magnetic resonance properties are used to infer wettability and / or fluid saturation of the rock formations.
Owner:SCHLUMBERGER TECH CORP
System and method for emulating nuclear magnetic resonance well logging tool diffusion editing measurements on a bench-top nuclear magnetic resonance spectrometer for laboratory-scale rock core analysis
InactiveUS20110234220A1Increase displacementPromote recoveryElectric/magnetic detection for well-loggingMeasurements using NMR imaging systemsWell loggingLaboratory scale
A laboratory NMR methodology (and corresponding laboratory apparatus) defines a sample volume. The method stores downhole tool data corresponding to a hydrocarbon-bearing sample collected from a given subsurface formation. The downhole tool data includes parameters pertaining to magnetic fields used by a downhole tool during a suite of NMR measurements of the given subsurface formation. The sample is positioned in the sample volume of the laboratory apparatus, which applies a static magnetic field in the sample volume. Furthermore, the laboratory apparatus applies a suite of NMR measurements to the sample volume to thereby determine a property of the sample. The NMR measurements of the suite each include a pulse sequence of oscillating magnetic field in conjunction with a pulsed-mode gradient field. The pulsed-mode gradient field is based on the stored downhole tool data corresponding to the sample. A laboratory NMR methodology for optimizing downhole NMR measurements is also described.
Owner:SCHLUMBERGER TECH CORP
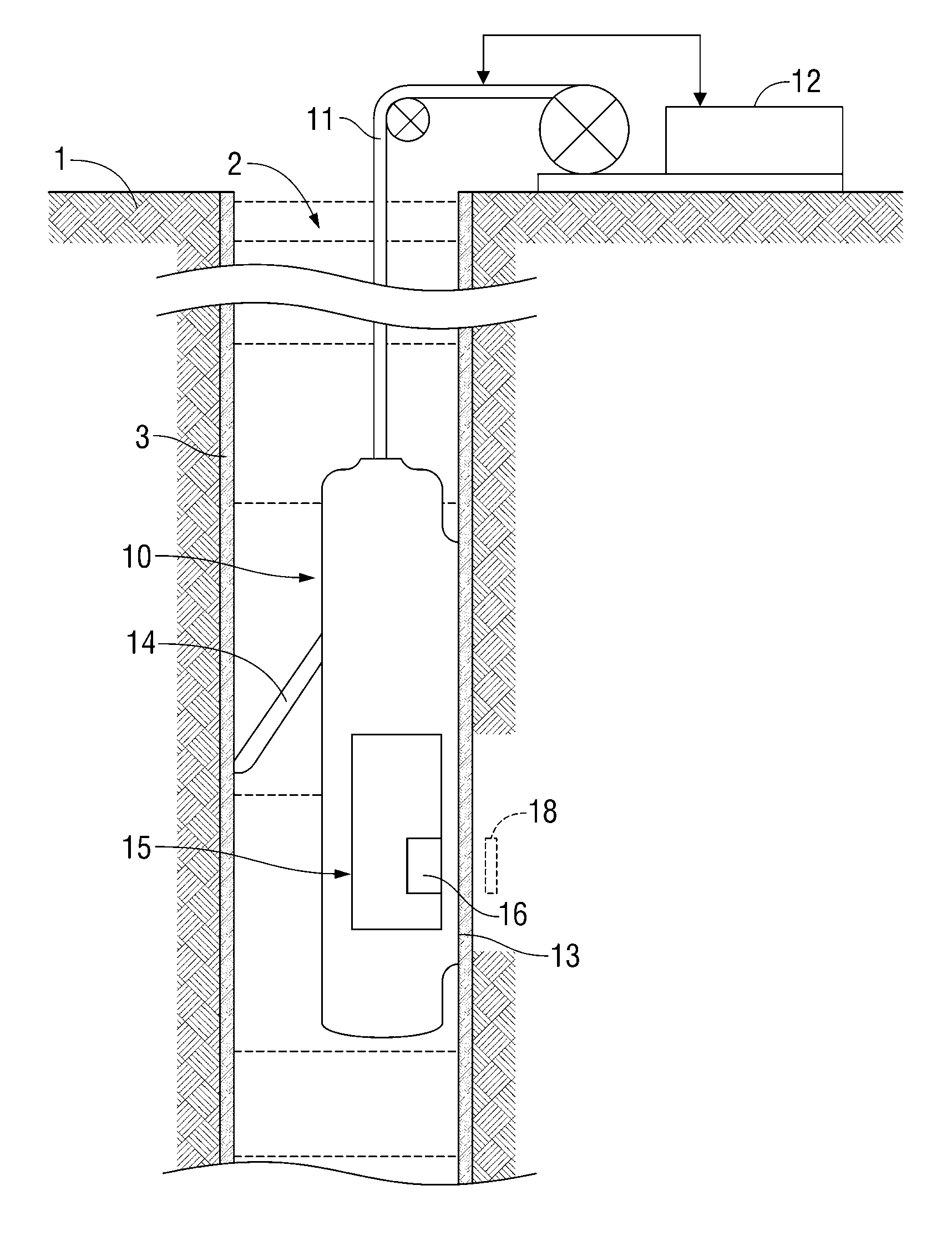
Rock core holder compatible with nuclear magnetic resonance
InactiveCN102507626AAvoid the problem of prone to eddy currentAvoid unsafe factorsAnalysis using nuclear magnetic resonanceSolid-state nuclear magnetic resonanceDiffusion
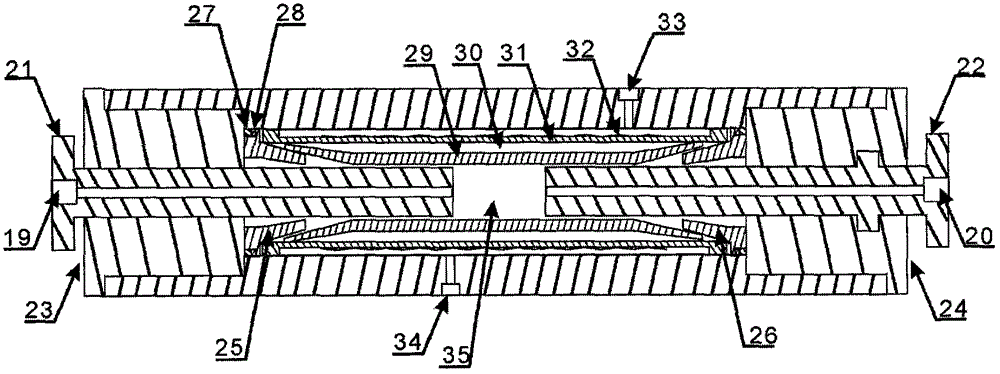
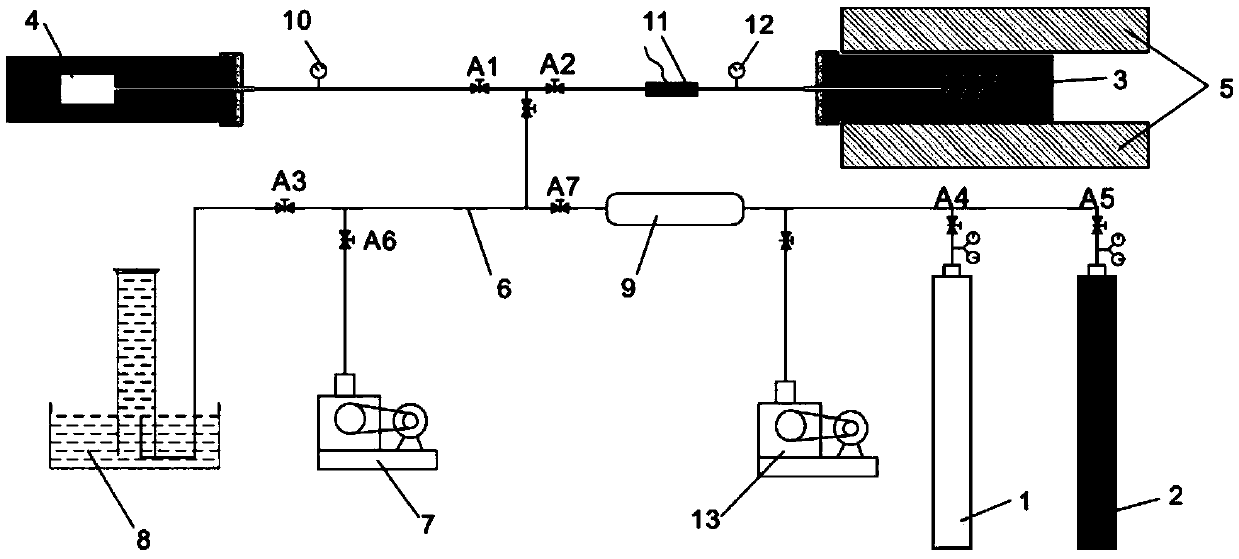
The invention relates to a rock core holder compatible with nuclear magnetic resonance, which can simulate pressures and temperatures of deep reservoirs, perform oil water displacement of a rock core under simulated formation conditions, and simultaneously perform nuclear magnetic resonance on-line measurement. According to the invention, a radio frequency coil is embedded in the rock core holder, and the signal to noise ratio is greatly increased when the rock core holder is compared with a conventional rock core holder. The rock core holder is made of nonmagnetic nonmetal materials, which avoids the damage of the magnetic field uniformity caused by magnetic materials, and also avoids the generation of eddy current in the holder by a pulse gradient. Compared with a conventional rock core holder, the invention not only greatly increases the signal to noise ratio, but also fully ensures the accuracy of nuclear magnetic resonance measurement results at a high temperature and a high pressure. The holder is applicable to on-line measurement of nuclear magnetic resonance relaxation spectra, diffusion-relaxation two-dimensional spectra, and imaging methods during rock core oil water displacement at a high temperature and a high pressure. In addition, the invention performs real-time tracking compensation of temperatures and pressures of ring-crush fluid, and thus ensures the reliability of rock core simulated formation conditions.
Owner:PEKING UNIV
Silica
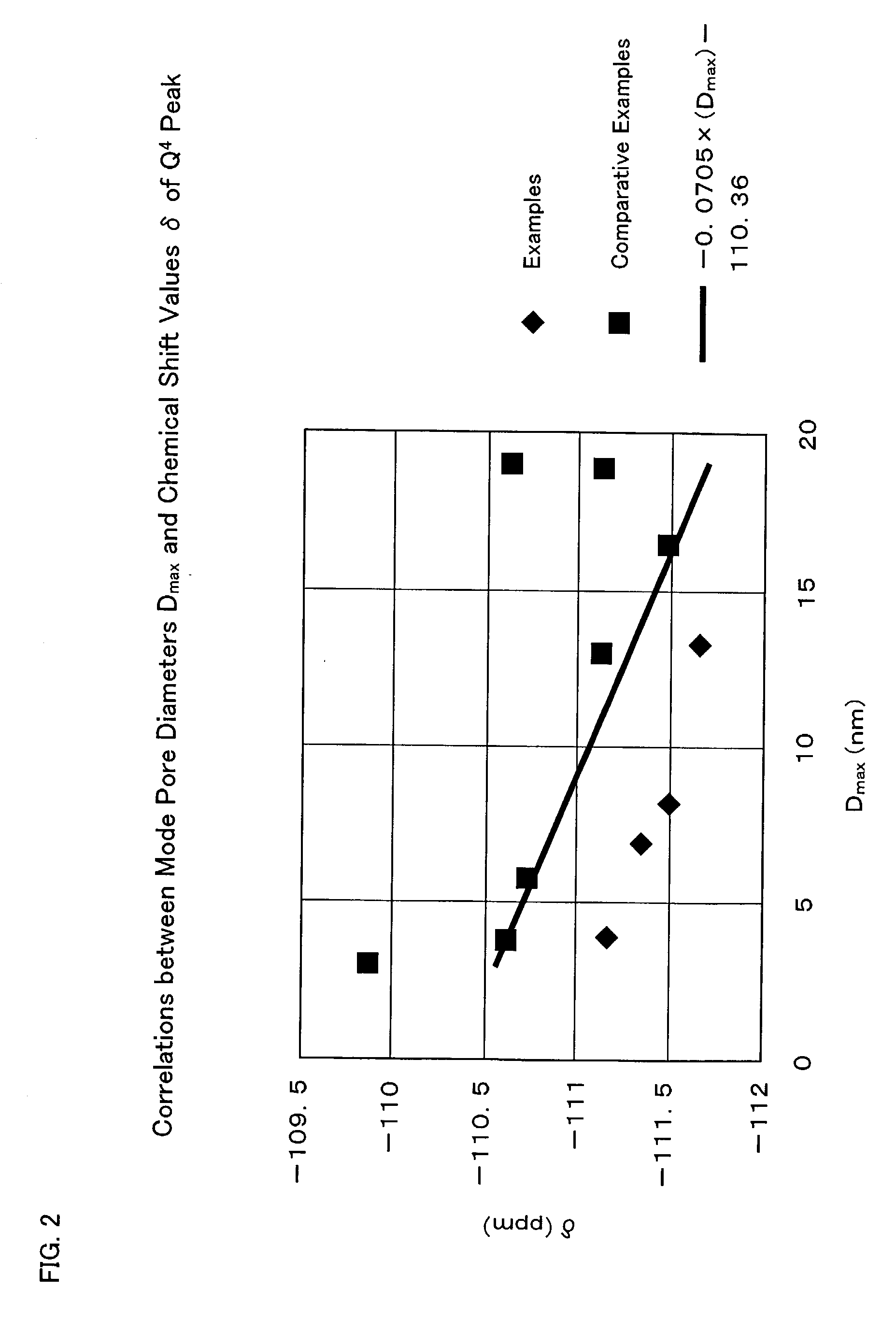
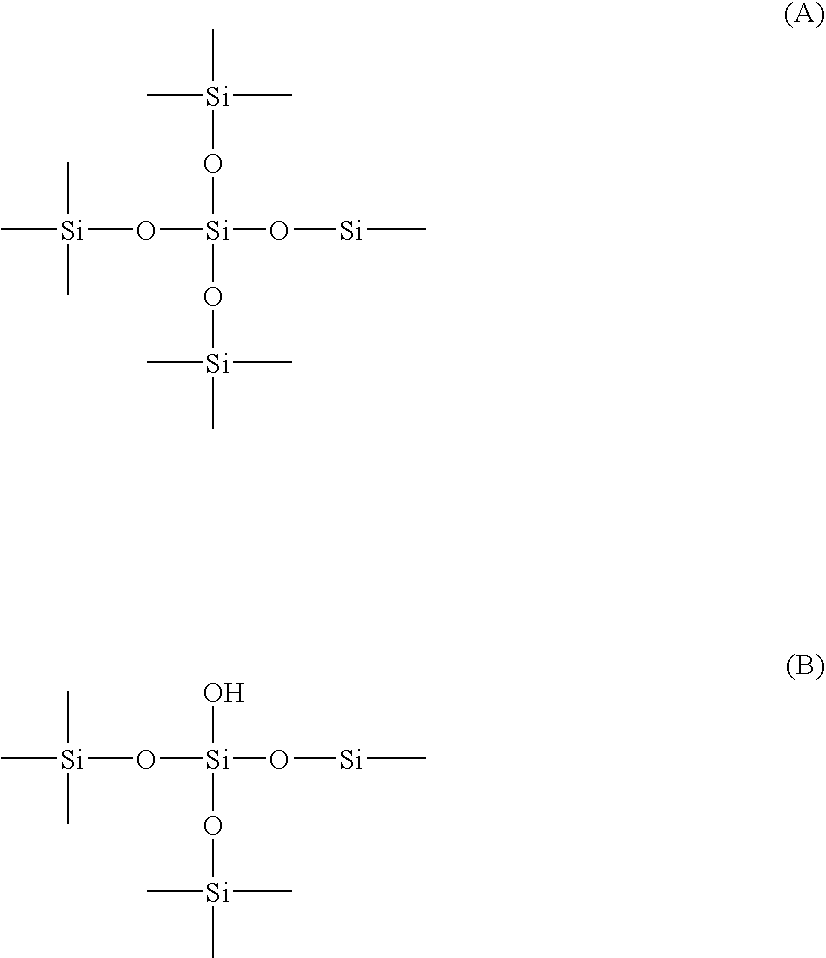
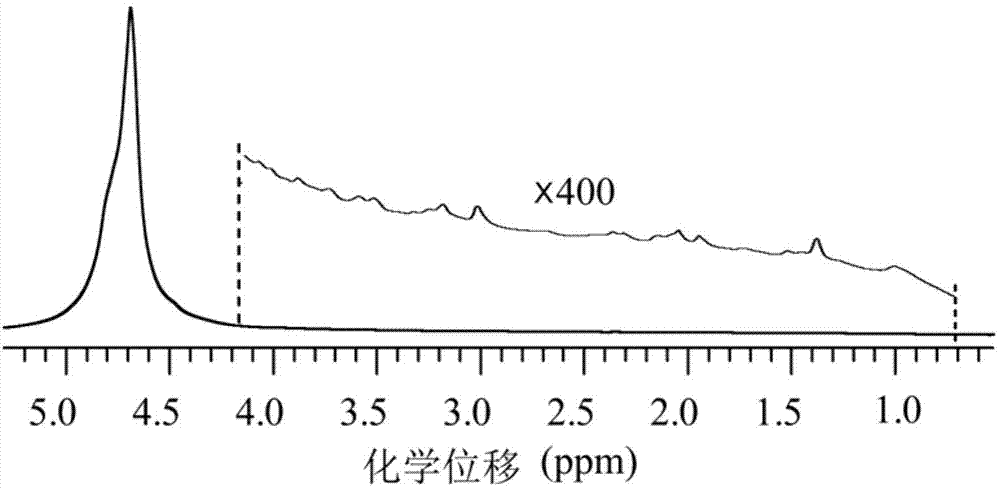
Silica with a large pore volume, a large specific surface area, a narrow pore distribution, low contents of unwanted metal impurities, and excellent physical properties such as high heat-resistance and water-resistance is provided. The silica has a mode pore diameter (Dmax) of 20 nm or less, and a solid-state Si nuclear magnetic resonance (hereinafter called solid-state Si NMR) spectrum of the silica includes a chemical shift (δ ppm) of Q4 peak meeting the following inequality (I). −0.0705×(Dmax)−110.36>δ (I) The silica with such properties can be suitably used in fields of which particularly excellent heat resistance and water resistance are required, and moreover controlled pore properties, and the fact that physical properties scarcely change over a long period of time are required among the above-mentioned applications.
Owner:MITSUBISHI CHEM CORP
Inversion method of nuclear magnetic resonance two-dimensional spectrum
InactiveCN103116148AHigh-resolutionImprove execution efficiencyMeasurements using NMR imaging systemsSingular value decompositionData compression
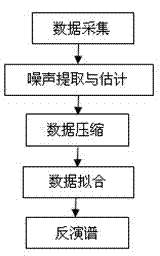
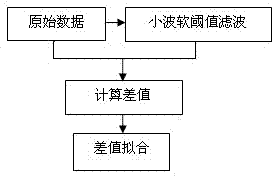
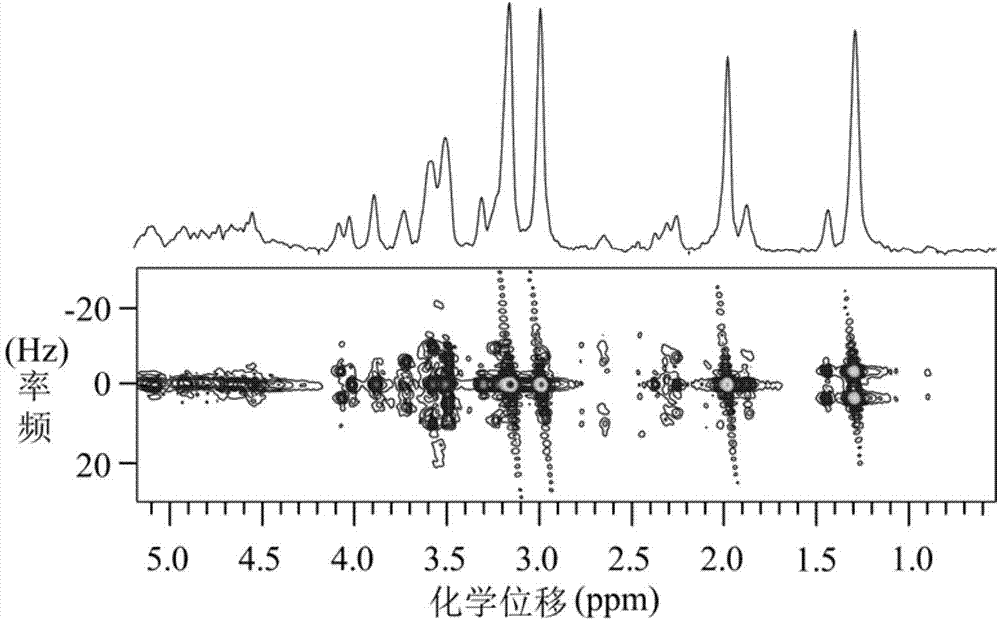
The invention relates to an inversion method of nuclear magnetic resonance two-dimensional spectrum. The method includes firstly, extracting and estimating noise, namely extracting noise in CPMG (Carr-Purcell-Meiboom-Gill) echo string of acquired data and estimating standard deviation of the noise; secondly, compressing data, namely generating an inversion kernel and performing truncated singular value decomposition and reconstruction by sequence of a nuclear matrix to complete data compression; and thirdly, fitting the data, namely subjecting fitting problem of the compressed data to regularization, performing iterative solution to regularization factors and inversion spectrum by newton method with non-exact one-dimensional search so as to obtain the inversion spectrum. Execution efficiency of two-dimensional inversion algorithm and resolution of two-dimensional spectrum are increased greatly, and the inversion method is well robust.
Owner:UNIV OF SHANGHAI FOR SCI & TECH
Nuclear magnetic resonance and transient electromagnetic combined instrument and method
InactiveCN1936621AImprove signal-to-noise ratioOvercoming the small emission currentElectric/magnetic detection for well-loggingMeasurements using NMR imaging systemsSolid-state nuclear magnetic resonanceNMR - Nuclear magnetic resonance
The invention discloses a geophysical exploration device and the method which combines the nuclear magnetic resonance and the transient electromagnetism. First to select the coupled device in the transient electromagnetism mode, and it lays the emission loop and the receiving loop to detect every measuring point in the detecting section and treat the transient electromagnetism data to find the low electrical resistivity point; then it changes to the nuclear magnetic resonance mode and lays the emission loop using the demarcated abnormal detecting point as the center, so it compares the detected data or the figure with the resistivity detected by the transient electromagnetism to judge the true or false of the detected resistivity. The invention can decrease the device cost and improve the detecting efficient and the precision.
Owner:JILIN UNIV
Nuclear magnetic resonance imaging apparatus and nuclear magnetic resonance imaging method
InactiveUS20130082700A1Avoid sensitivityMeasurements using NMR imaging systemsElectric/magnetic detectionSolid-state nuclear magnetic resonanceIn plane
The present invention has an object to provide a nuclear magnetic resonance imaging apparatus or the like that avoids a region with zero sensitivity of an optical magnetometer and allows imaging by strong magnetic resonance when a common magnetic field is used as a bias field of an optical magnetometer and as a magnetostatic field to be applied to a sample. When a direction of a magnetostatic field application unit applying a magnetostatic field to a sample is a z direction, alkali metal cell of a scalar magnetometer is arranged so as not to overlap a region to be imaged in a z direction, and so as not to intersect the region to be imaged in an in-plane direction perpendicular to the z direction.
Owner:CANON KK
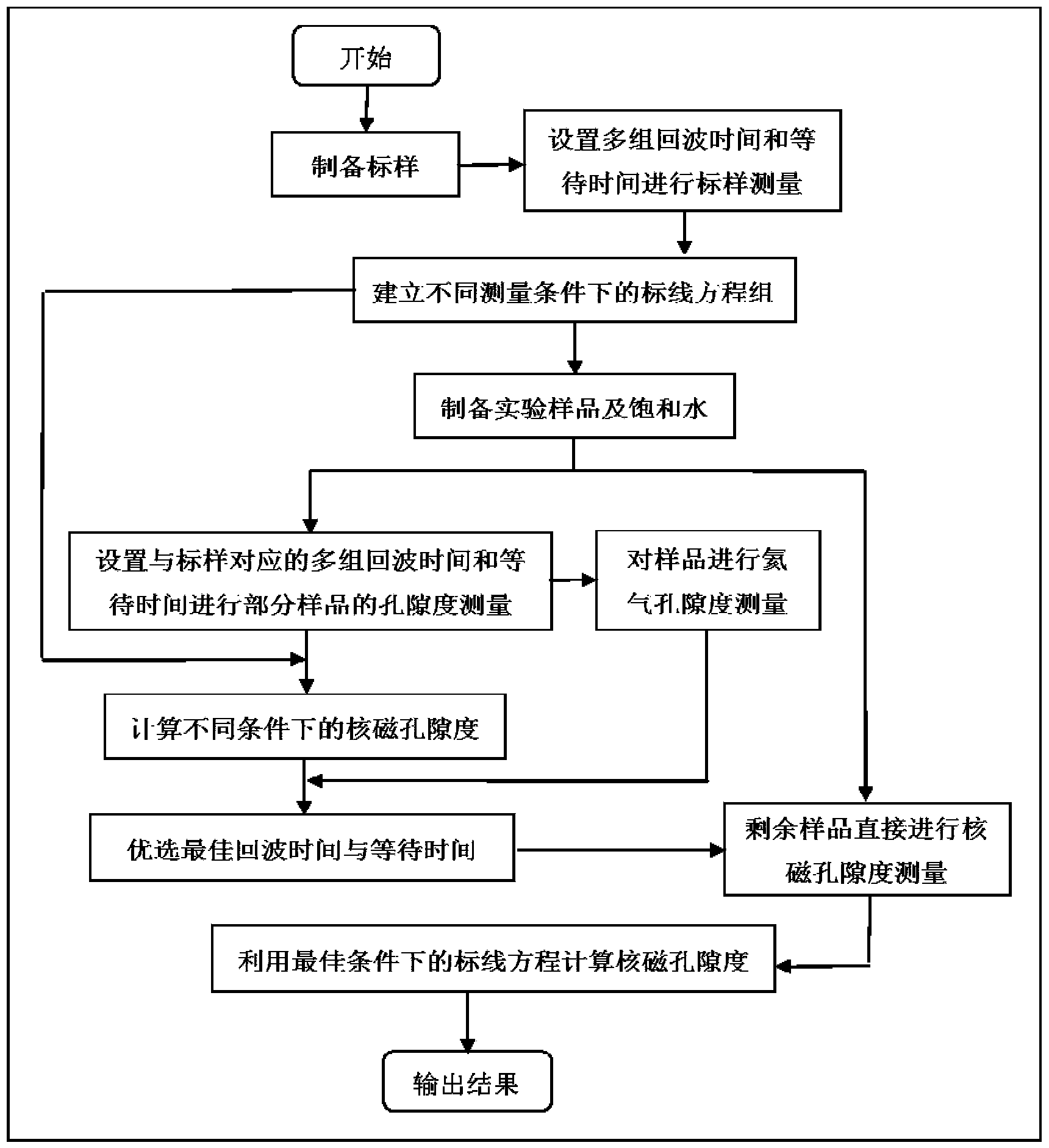
Method for accurately measuring shale porosity by adopting low-field nuclear magnetic resonance
InactiveCN104075974ATest accurateQuick testAnalysis using nuclear magnetic resonancePermeability/surface area analysisSolid-state nuclear magnetic resonancePorosity
The invention discloses a method for accurately measuring shale porosity by adopting the low-field nuclear magnetic resonance. The method comprises the following steps: as for a saturated water column-shaped shale sample, conducting nuclear magnetic porosity measurement in different echo time and waiting time; conducting helium porosity measurement; comprehensively comparing and analyzing the porosity results of the two methods; optimizing the optimal echo time and waiting time for testing to facilitate the accurate testing of follow-up samples. The method solves the problems of how to set reasonable parameters to measure the shale porosity by adopting the low-field nuclear magnetic resonance, and solves the problem that in the actual testing, the nuclear magnetic porosity obtained in different echo time and waiting time is in great disparity, and the comparability of the nuclear magnetic porosity and the helium porosity is relatively poor; compared with the prior art, by adopting the method, the shale porosity can be quickly and nondestructively measured, the accuracy and precision of the shale porosity measurement can be improved, and the operation is convenient.
Owner:CHINA UNIV OF GEOSCIENCES (BEIJING)
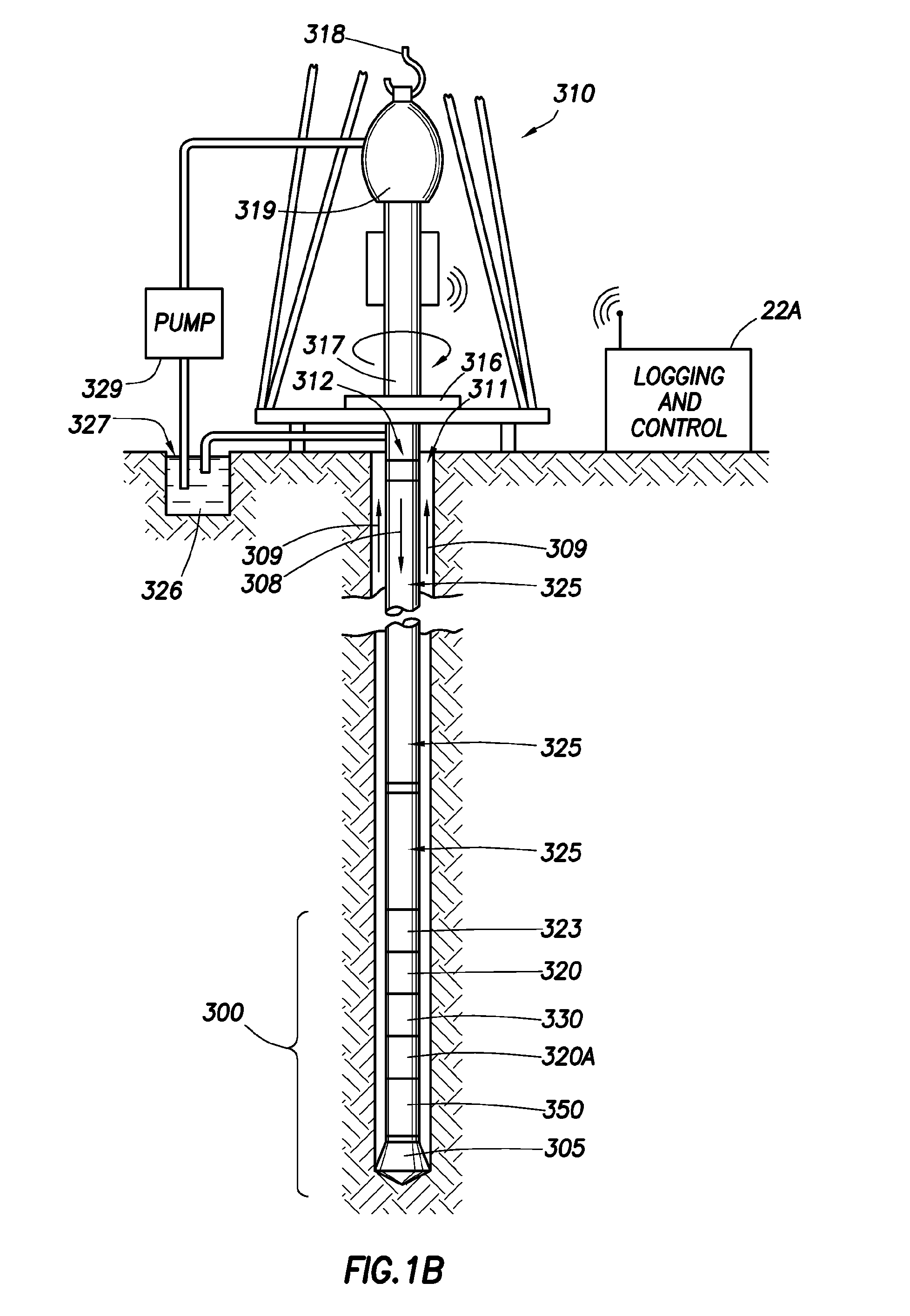
Downhole micro magnetic resonance analyzer
ActiveUS8471559B2Electric/magnetic detection for well-loggingMagnetic property measurementsSolid-state nuclear magnetic resonanceNMR - Nuclear magnetic resonance
A downhole micro MR analyzer for use in a wellbore, having a micro sample tube, a micro RF coil in close proximity to the micro sample tube, and one or more magnets disposed about the micro sample tube is disclosed. The micro MR analyzer can be used for nuclear magnetic resonance or electron spin resonance experiments to ascertain formation properties and chemical compositions.
Owner:SCHLUMBERGER TECH CORP
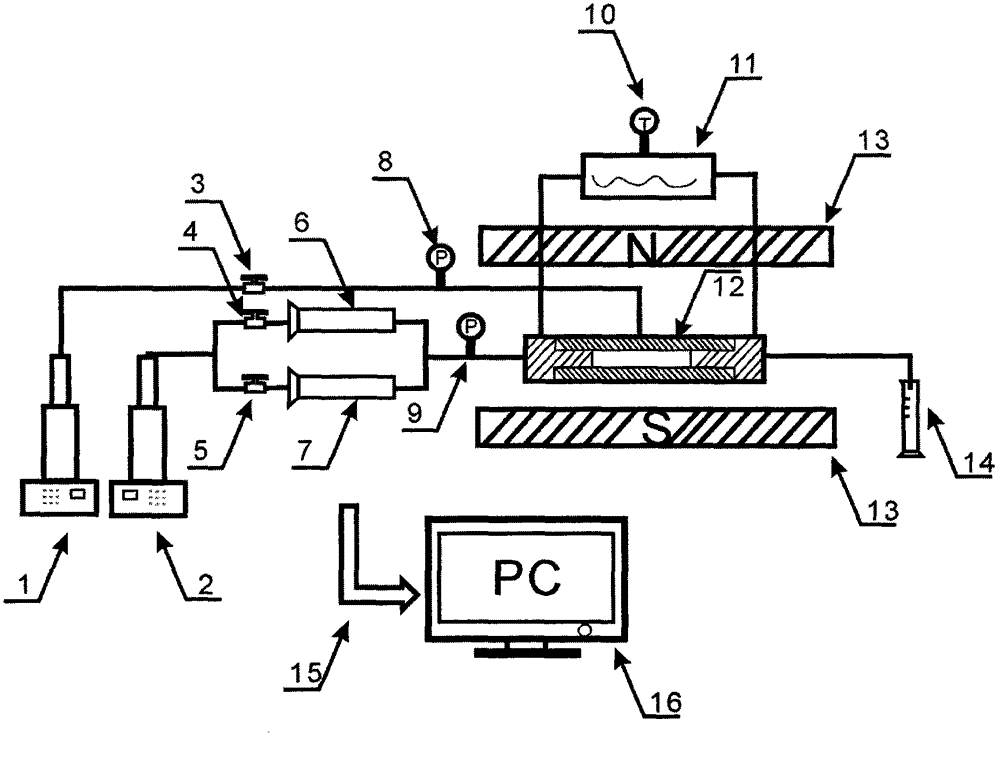
On-line testing device for high temperature and high pressure rock physical property and percolation mechanism nuclear magnetic resonance
The invention relates to an on-line testing device for high temperature and high pressure rock physical property and percolation mechanism nuclear magnetic resonance. The on-line testing device comprises a nuclear magnetic resonance on-line testing module, a rock fluid displacement module (comprising core holder compatible with nuclear magnetic resonance tests) and a computer control and data processing module, a nuclear magnetic resonance testing system and a rock fluid displacement system are combined into a whole through computer control, formation temperature and pressure are simulated, rock displacement tests are carried out under high temperature and high pressure conditions, and real-time nuclear magnetic resonance signals are measured on line to obtain rich rock parameters (porosity, permeability, reservoir forming critical pressure, wettability and the like). The on-line testing device serves as a device for oil gas reservoir forming geological research and oil gas target assessment, and the purposes of analyzing core physical properties and percolation mechanism from micro perspective are achieved.
Owner:PEKING UNIV
Shale gas reservoir pore structure quantitative calculation method based on nuclear magnetic resonance
InactiveCN108169099AThe calculation result is accuratePracticalAnalysis using nuclear magnetic resonancePermeability/surface area analysisPore distributionHigh pressure
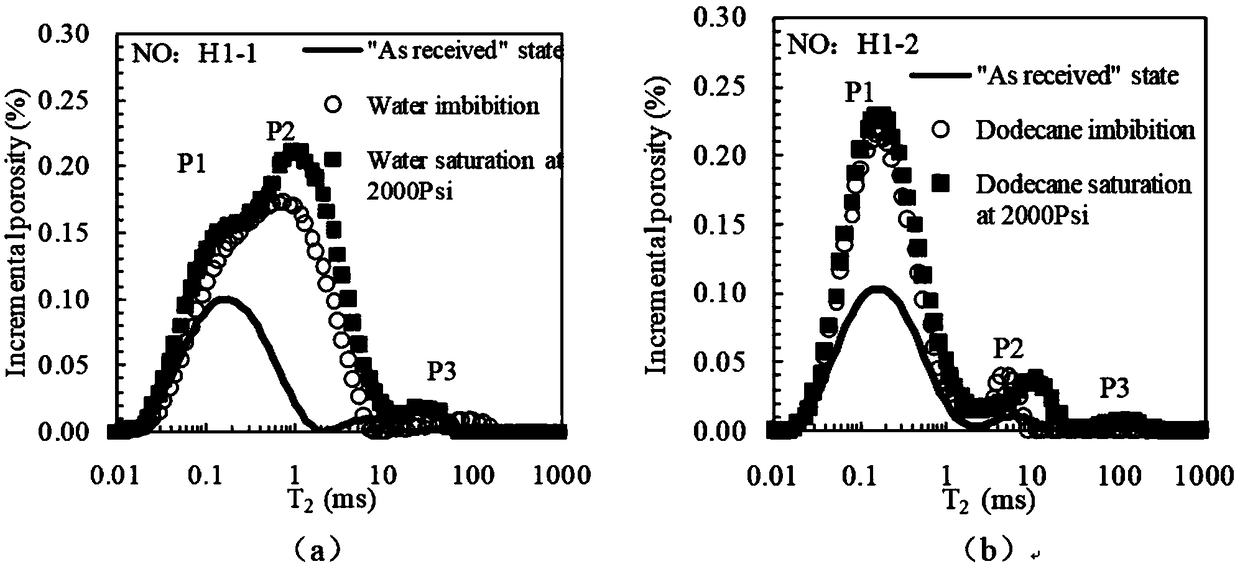
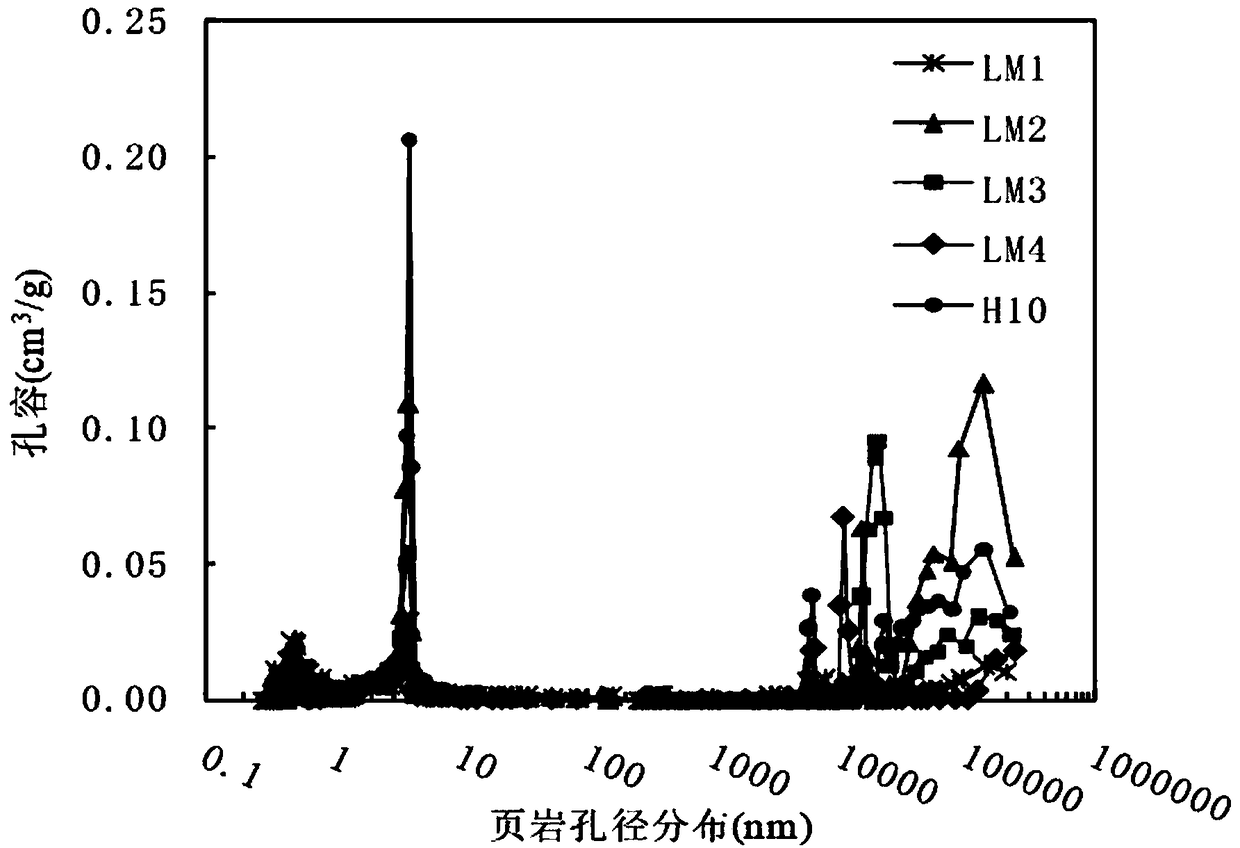
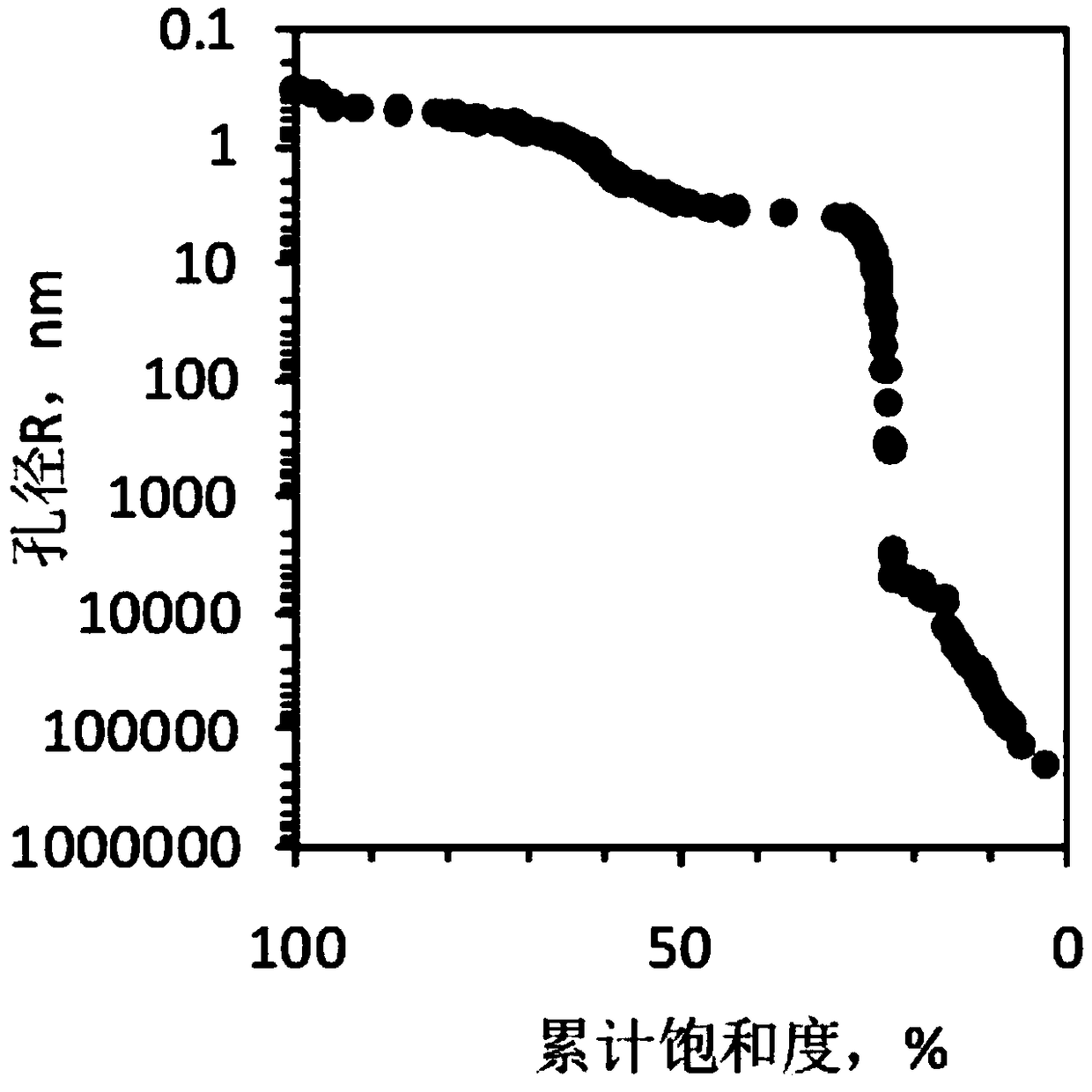
The invention discloses a shale gas reservoir pore structure quantitative calculation method based on nuclear magnetic resonance. The shale gas reservoir pore structure quantitative calculation methodcomprises the following steps: collecting cores; drilling parallel samples, carrying out oil and water self-adsorption nuclear magnetic resonance experiment measurement; contrastively analyzing the difference of a parallel sample oil and water nuclear magnetic resonance T2 spectrum, and determining the distribution of different wetting pore types on the nuclear magnetic resonance T2 spectrum; obtaining a shale gas reservoir full-pore distribution curve according to high-pressure pressurized mercury, nitrogen adsorption and carbon dioxide adsorption; furthermore, obtaining an intersection plate of pore diameters and corresponding T2 time; and according to the intersection plate of different pore types of pore diameters and corresponding T2 time, establishing a quantitative calculation model of the pore diameters according to the pore types. The method has the advantages that a shale gas reservoir pore full-pore distribution curve can be quantitatively calculated through the technology;simultaneously, the nuclear magnetism measurement is quick, simple and loss-free, and is higher in practicability by compared with high-pressure pressurized mercury, nitrogen adsorption and carbon dioxide adsorption; and compared with a conventional method, the calculation result is more accurate.
Owner:SOUTHWEST PETROLEUM UNIV
Metabolite detection using magnetic resonance
InactiveUS20080081375A1Material analysis using wave/particle radiationMagnetic measurementsMetaboliteDisease cause
Methods using magnetic resonance, such as nuclear magnetic resonance (NMR) spectroscopy or magnetic resonance imaging (MRI), are provided for detecting metabolites in a sample. The methods are useful for the diagnosis or prognosis of a disease such as cancer and can also be used to determine or monitor a treatment protocol. The methods are useful in characterizing speciation in biological samples where mixtures are often encountered and chemical shifts of the same structural group of similar molecules can produce complicated overlapping resonances.
Owner:OKLAHOMA MEDICAL RES FOUND
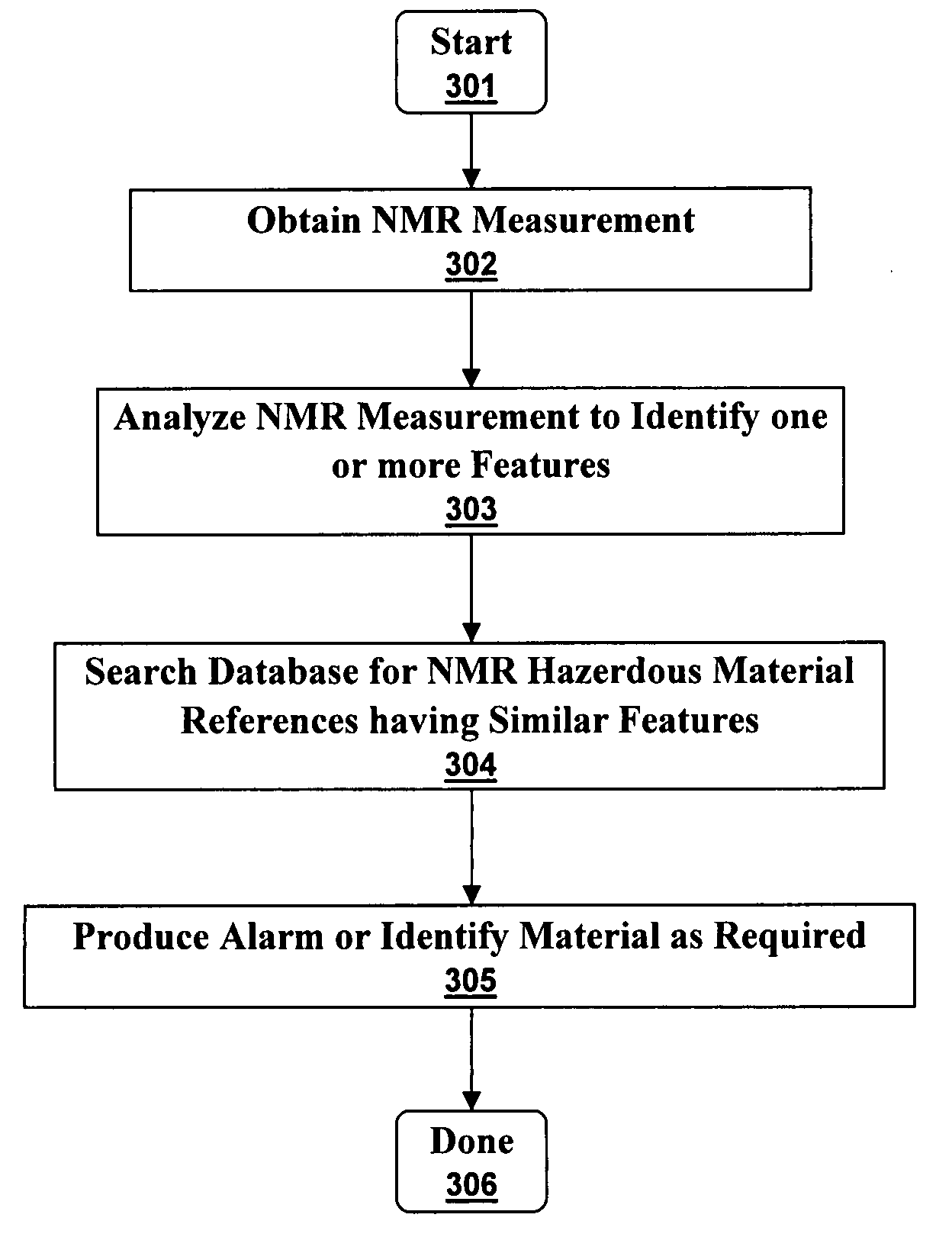
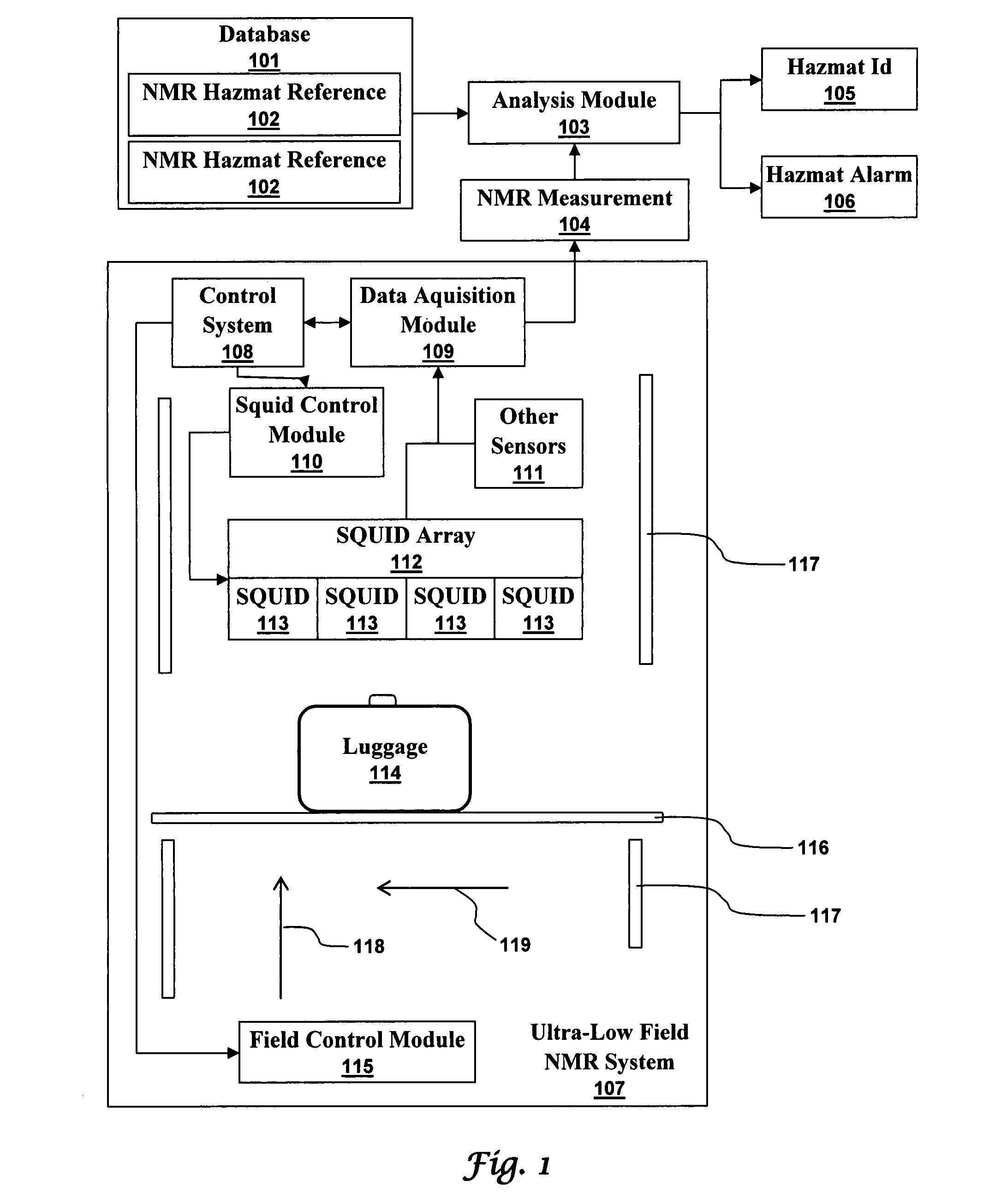
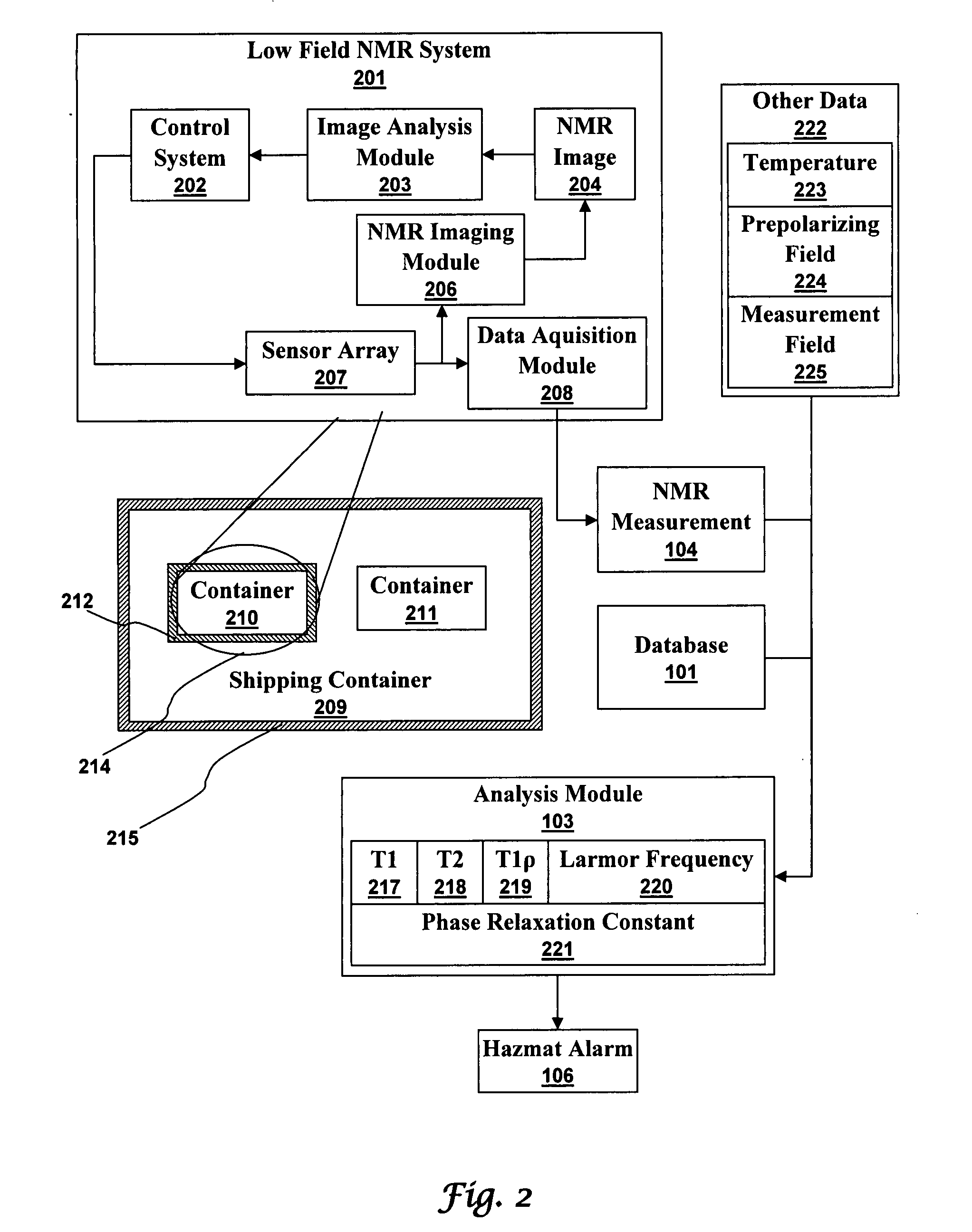
Ultra-low field nuclear magnetic resonance and magnetic resonance imaging to discriminate and identify materials
InactiveUS20080284433A1Increased signal noiseMeasurements using NMR imaging systemsAnalysis using nuclear magnetic resonanceLow field nuclear magnetic resonanceProton NMR
An ultra-low magnetic field NMR system can non-invasively examine containers. Database matching techniques can then identify hazardous materials within the containers. Ultra-low field NMR systems are ideal for this purpose because they do not require large powerful magnets and because they can examine materials enclosed in conductive shells such as lead shells. The NMR examination technique can be combined with ultra-low field NMR imaging, where an NMR image is obtained and analyzed to identify target volumes. Spatial sensitivity encoding can also be used to identify target volumes. After the target volumes are identified the NMR measurement technique can be used to identify their contents.
Owner:TRIAD NAT SECURITY LLC
Method for obtaining nuclear magnetic resonance two-dimensional J-resolved spectroscopy in non-uniform magnetic field
Owner:XIAMEN UNIV
Cross-correlation-based nuclear magnetic resonance full wave signal noise filtering method
ActiveCN104898172AImprove detection depthSmall amount of calculationDetection using electron/nuclear magnetic resonanceFull waveRandom noise
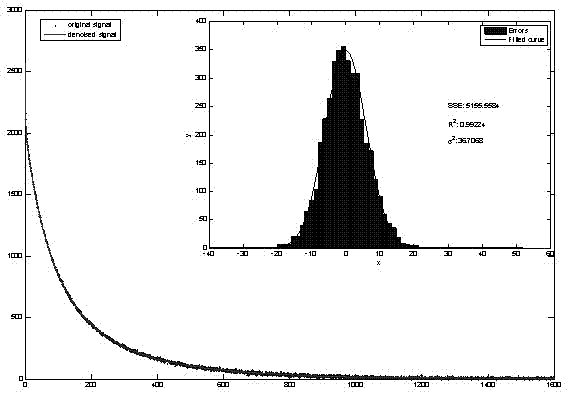
The invention relates to a cross-correlation-based nuclear magnetic resonance full wave signal noise filtering method. Based on characteristics that noise is irrelevant to the sinusoidal signals of Larmor frequency but FID amplitude attenuation sinusoidal signals are relevant to the sinusoidal signals of Larmor frequency, the method comprises steps of filtering noise via cross-correlation operation, then fitting envelope of related wave forms, reconstituting correlation wave forms without noise and at last extracting FID signals in nuclear magnetic resonance full wave data by use of the deconvolution algorithm. According to the invention, calculated amount of operation data is small; power frequency, noise of harmonic waves, random noise and peak noise can be simultaneously suppressed; signal to noise ratio of the nuclear magnetic resonance full wave data is remarkably increased, thereby facilitating application range and detection depth of a nuclear magnetic resonance water explorer; additional reference noise eliminating devices are not required, so cost is reduced; and ideal filtering effects of the full wave data which are acquired at a time can be achieved via cross correlation, so measuring time is saved.
Owner:JILIN UNIV
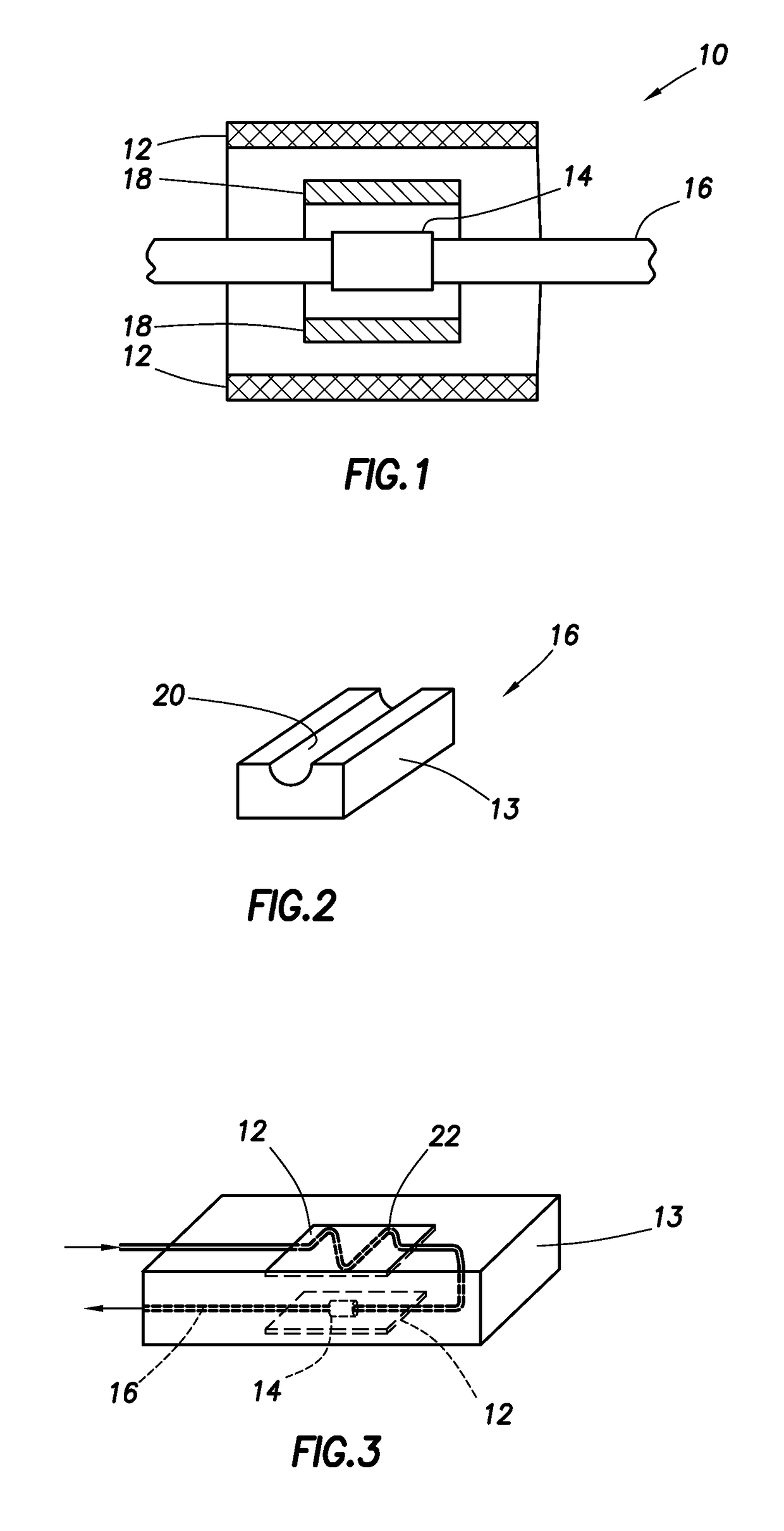
Capillary toroid cavity detector for high pressure NMR
InactiveUS7268552B1Reduced line shape distortionReduce shape distortionMagnetic measurementsAnalysis using nuclear magnetic resonanceSolid-state nuclear magnetic resonanceChemical reaction
A Toroid Cavity Detector (TCD) is provided for implementing nuclear magnetic resonance (NMR) studies of chemical reactions under conditions of high pressures and temperatures. A toroid cavity contains an elongated central conductor extending within the toroid cavity. The toroid cavity and central conductor generate an RF magnetic field for NMR analysis. A flow-through capillary sample container is located within the toroid cavity adjacent to the central conductor to subject a sample material flowing through the capillary to a static magnetic field and to enable NMR spectra to be recorded of the material in the capillary under a temperature and high pressure environment.
Owner:THE UNITED STATES AS REPRESENTED BY THE DEPARTMENT OF ENERGY
System and method for measuring unfrozen water content in frozen soil by pulse nuclear magnetic resonance (NMR)
InactiveCN102004115AImprove measurement efficiencyNo side effectsAnalysis using nuclear magnetic resonancePulse nuclear magnetic resonanceMagnetization
The invention relates to a system and a method for measuring unfrozen water content in frozen soil by pulse NMR, aiming at the problems that, in the measurement of unfrozen water content, measuring procedures are complex, operators need relatively high electromagnetism theoretical basis, and operations are difficult; a plurality of test pieces are needed under multi-temperature and multi-pressure working conditions, and the test pieces are exposed in normal temperature to influence measurement precision. The system is characterized in that a soil testing tube is disposed in a ceramic tube; a temperature signal input end of a temperature sensor is disposed in the soil testing tube; a temperature signal output end of the temperature sensor is connected to the temperature signal input end of a temperature control valve. The method is characterized in that different relaxation time of solid water, combined water and free water in attenuation process are stipulated when free attenuation signals of magnetization intensity are fitted, so that the magnetic field intensity value corresponding to the free attenuation signals of magnetization intensity during the relaxation time can be obtained. The system and method of the present invention measure the unfrozen water content in frozen soil.
Owner:HARBIN INST OF TECH
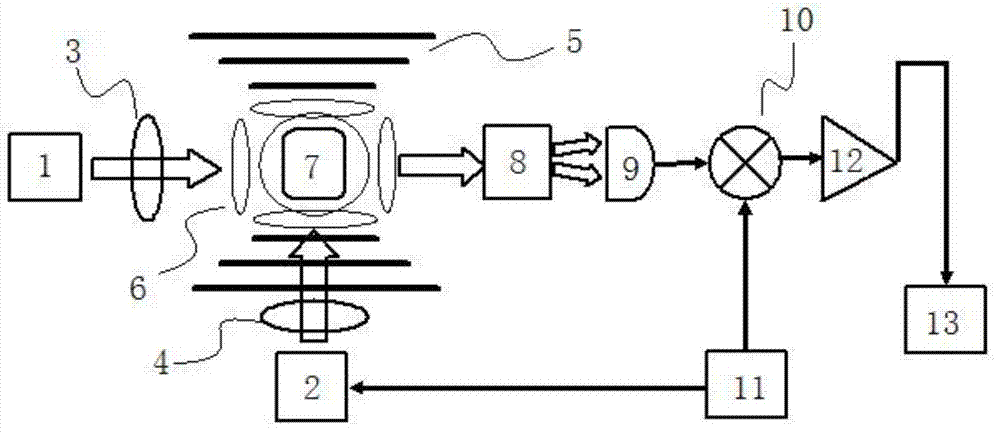
Nuclear magnetic resonance spectroscopy using light with orbital angular momemtum
InactiveUS20100327866A1Less noisyHigh resolutionLaser detailsAnalysis using optical pumpingTwo-dimensional nuclear magnetic resonance spectroscopySpectroscopy
The present invention relates to a device capable of producing a high resolution chemical analysis of a sample, such as fluid, based upon nuclear magnetic resonance (NMR) spectroscopy, where the nuclear magnetic polarizations of the sample are generated by sequentially illuminating the sample with a focused beam of light carrying angular orbital angular momentum (OAM) and possibly momentum (spin). Unlike in usual NMR used for magnetic nuclear resonance imaging (MRI) or spectroscopy, the invention does not make use of a strong magnet.
Owner:KONINKLIJKE PHILIPS ELECTRONICS NV
Method for measuring coal sample methane adsorbing capacity through low-field nuclear magnetic resonance
ActiveCN103424421AShort measurement timeHigh speedAnalysis using nuclear magnetic resonanceUnit massLow field nuclear magnetic resonance
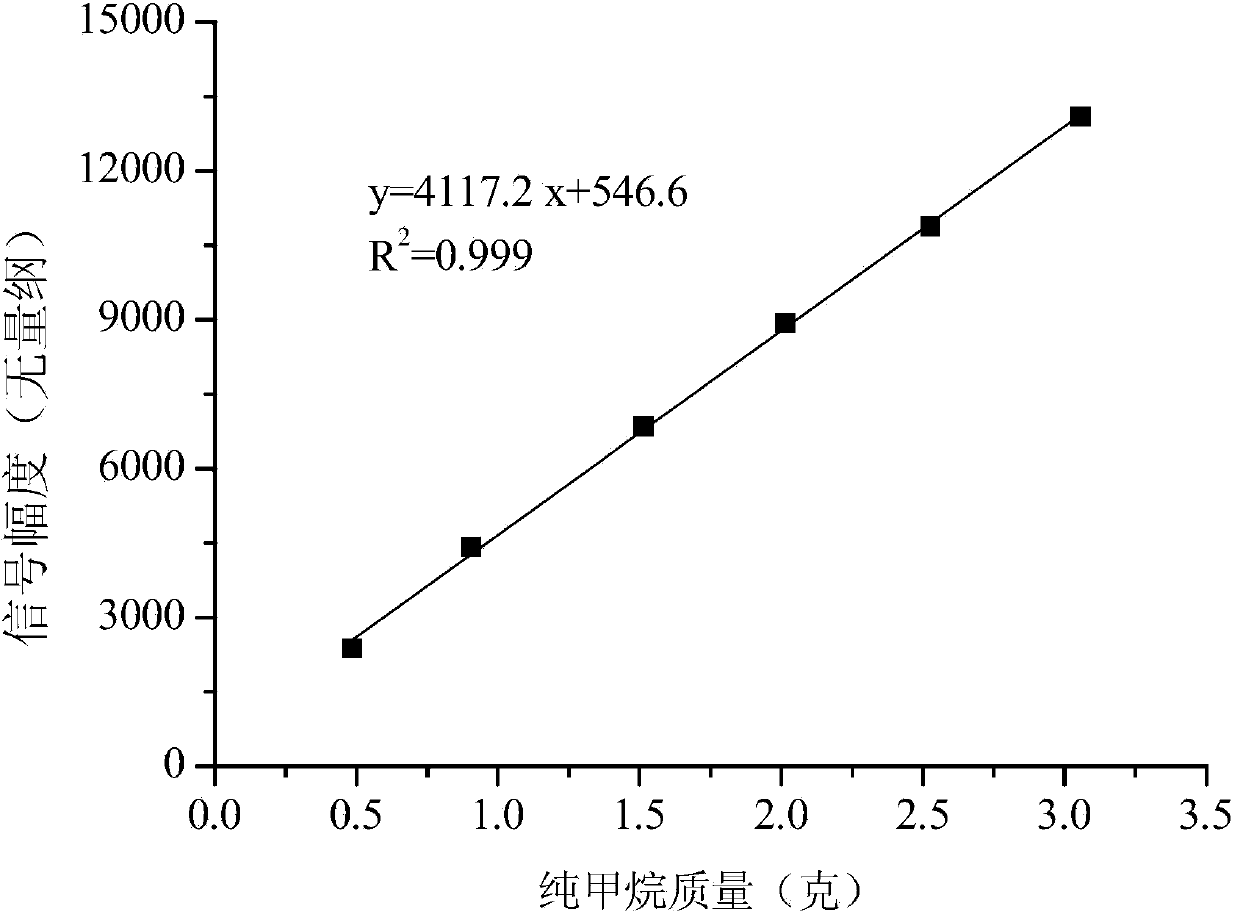
The invention discloses a method for measuring coal sample methane adsorbing capacity through low-field nuclear magnetic resonance. According to the method, selected measuring parameters are used for carrying out low-field nuclear magnetic resonance measurement on powder coal samples after methane adsorption balance under set pressure, the nuclear magnetism T2 spectrum of methane in the coal samples is obtained, then signal amplitude integrals of the first spectrum peak (in the range of 0.1-4ms spectrum) on the left of the T2 spectrum are substituted to a hydrogen content index reticle equation of methane under the standard condition built through an experiment, the standard condition size of methane adsorbed by the coal samples is obtained, and therefore the methane adsorbing capacity of unit mass of coal under the set pressure is obtained. According to the method, the scale relation of methane mass and nuclear magnetic resonance 1H nuclear signals is built, the quantitative assay of methane adsorbing capacity under the same temperature and different pressures is achieved, and the novel method can be used for measuring coal methane absorbing capacity in a real-time, home-position and dynamic mode.
Owner:CHINA UNIV OF GEOSCIENCES (BEIJING)
Nuclear magnetic resonance (NMR) device and measurement method based on laser atomic magnetometer
ActiveCN102830381AHigh detection sensitivityLow running costMeasurements using NMRHelmholtz coilProton NMR
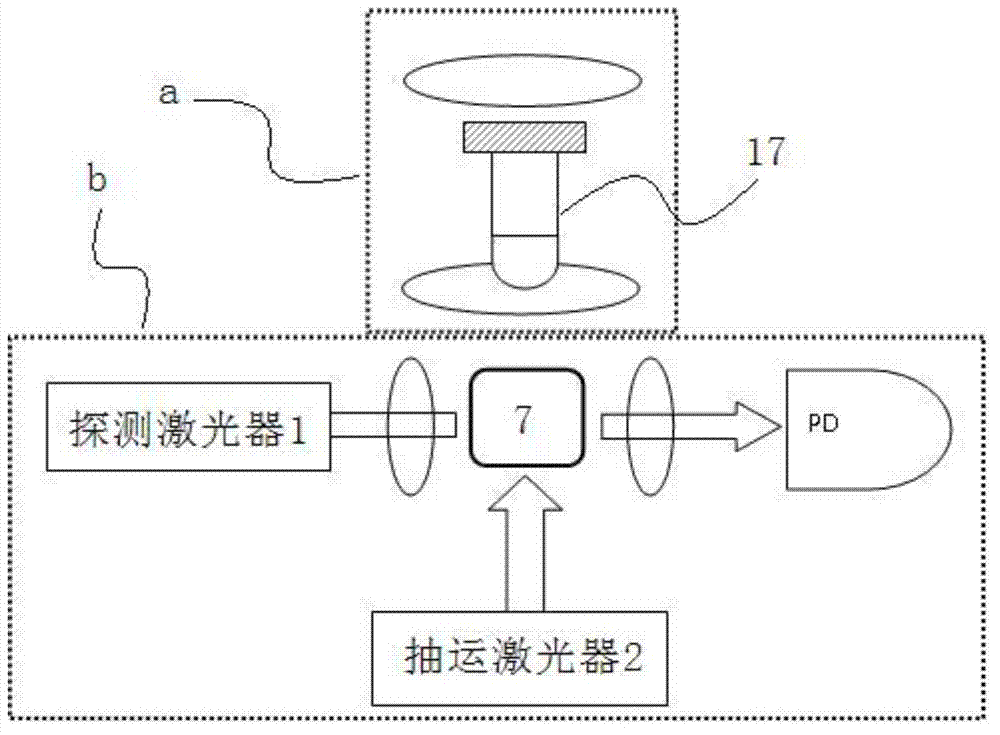
The invention discloses a nuclear magnetic resonance (NMR) device based on a laser atomic magnetometer, and the NMR device comprises a cesium atom vapor bubble, a magnetic shielding bushing which is sleeved on the cesium atom vapor bubble, three groups of Helmholtz coils which are arranged inside the magnetic shielding bushing, a polarization device which is used for polarizing cesium atoms inside the cesium atom vapor bubble, a laser transmitting device which is used for transmitting detection laser to the cesium atom vapor bubble, a detection device which is used for detecting an NMR signal of the detection laser penetrating the cesium atom vapor bubble and a pneumatic sample feeding device which is used for pre-polarizing a sample to be detected and can place the pre-polarized sample on the cesium atom vapor bubble. The invention also discloses a measurement method of an NMR based on the laser atomic magnetometer. The device and the method are high in detection sensitivity, free from needing low-temperature refrigeration, low in running cost and lower in working temperature.
Owner:WUHAN INST OF PHYSICS & MATHEMATICS CHINESE ACADEMY OF SCI
Systems and methods using nuclear magnetic resonance (NMR) spectroscopy to evaluate pain and degenerative properties of tissue
ActiveUS8344728B2Minimal overlapIncreasing Thompson gradeMeasurements using NMR spectroscopyDiagnostic recording/measuringAnatomical structuresSolid-state nuclear magnetic resonance
NMR spectroscopy is performed on intervertebral disc tissue. Extent of degeneration is determined based on the NMR spectroscopy. Correlation between NMR spectral regions and at least one of tissue degeneration and pain are made. Accordingly, NMR spectroscopy is used to determine location and / or extent of at least one of degeneration or pain associated with a region of tissue, such as for example in particular disc degeneration, or discogenic pain. NMR spectral peak ratios, such as between N-Acetyl / cho and cho / carb, are readily acquired and analyzed to predict degree of tissue degeneration and / or pain for: tissue samples using HR-MAS spectroscopy; and larger portions of anatomy such as joint segments such as a spine, using clinical 3 T MRI systems with surface head or knee coils; and tissue regions such as discs within spines of living patients using 3 T MRI systems with a surface spine coil, thus providing a completely non-invasive diagnostic toolset and method to image and localize degeneration and / or pain.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA
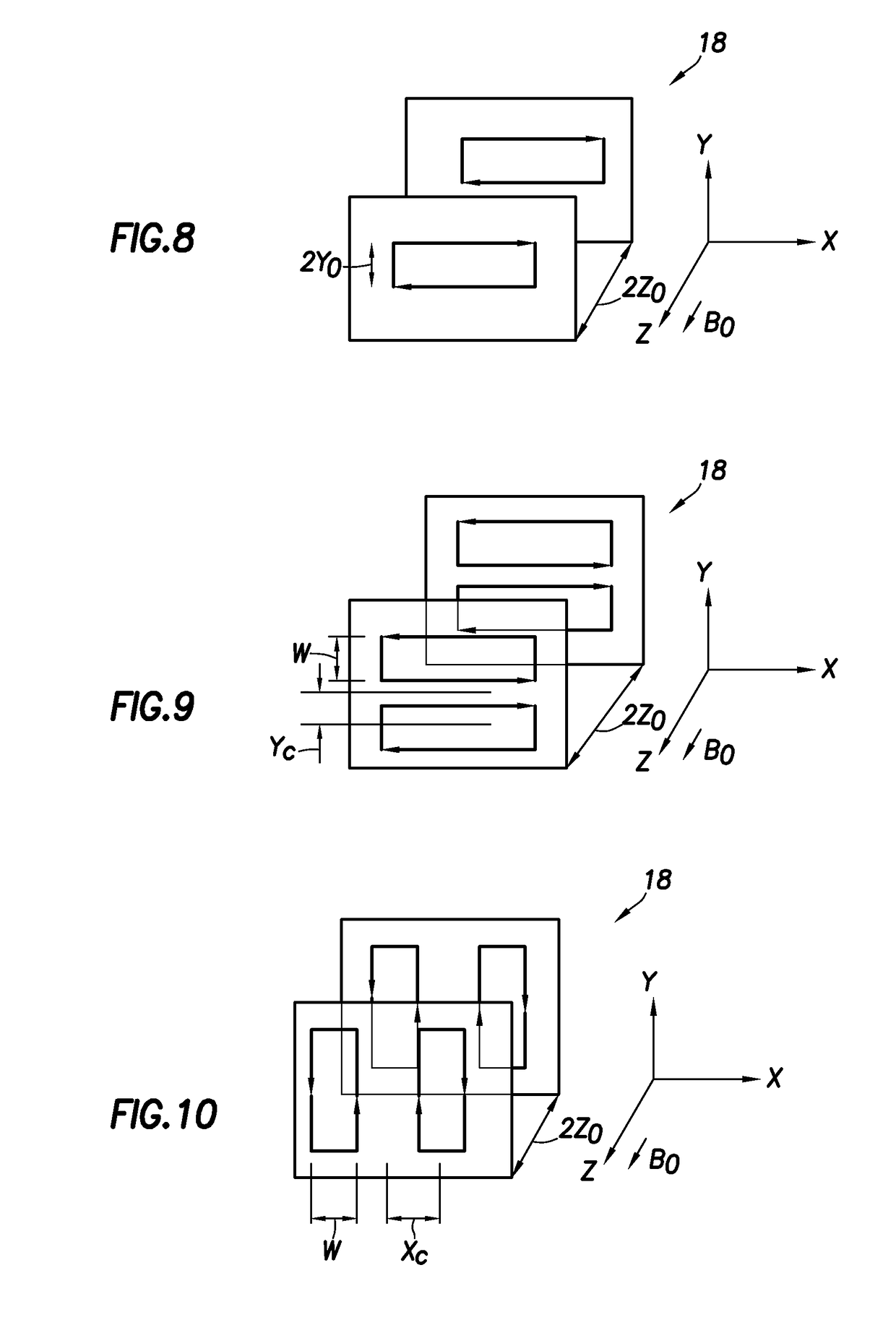
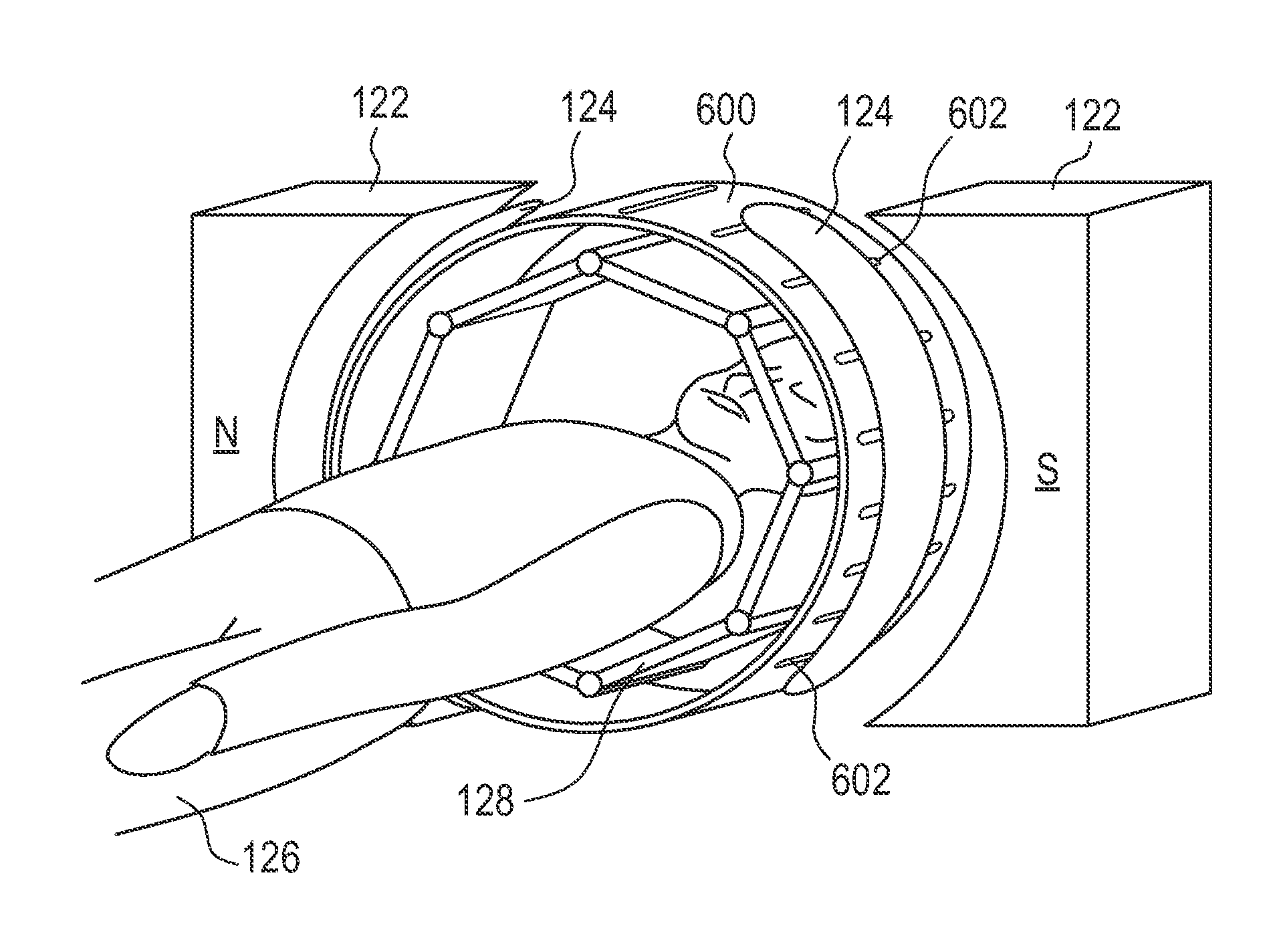
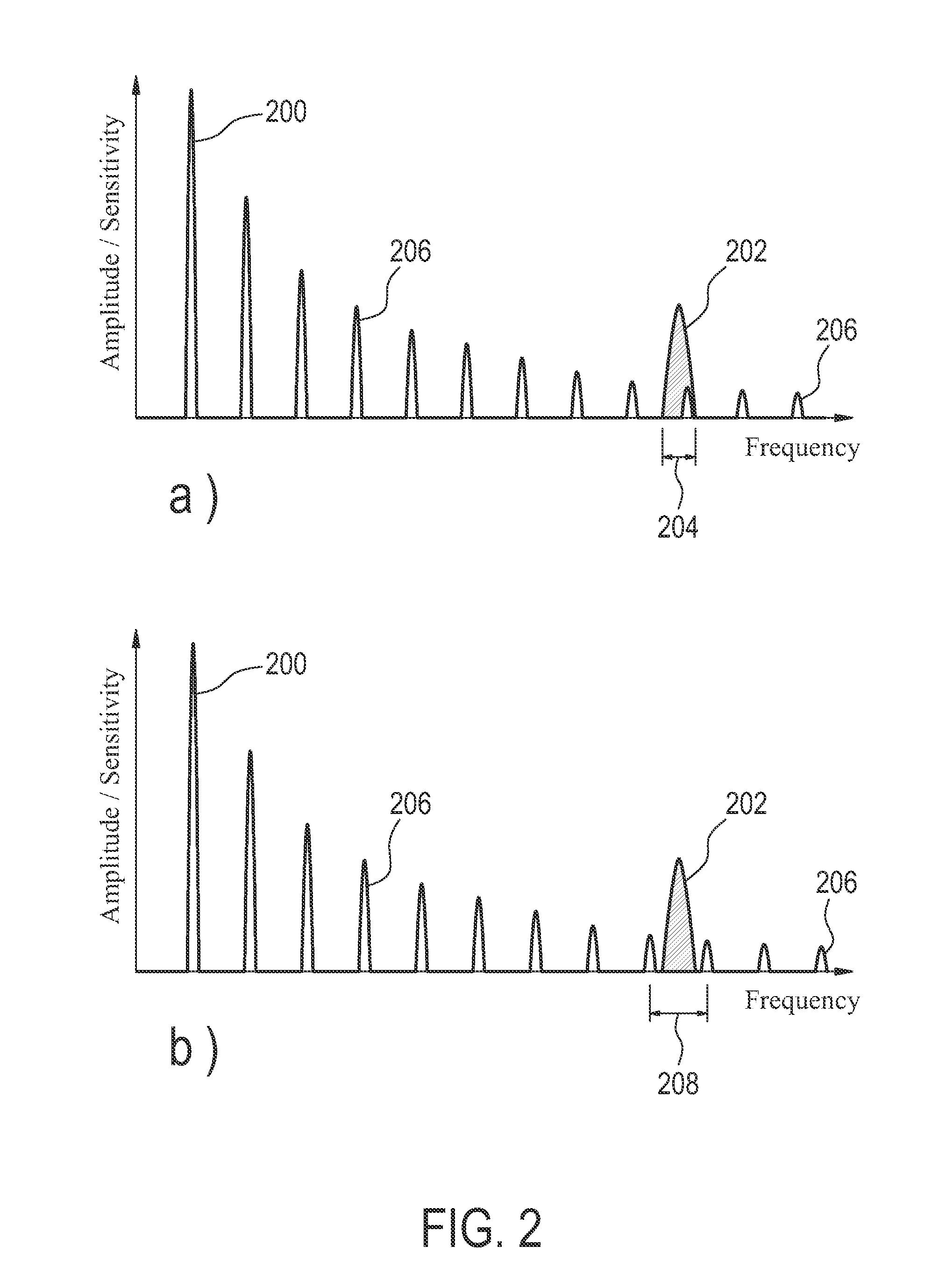
Inductively powered electric component of an MRI apparatus
ActiveUS20110084694A1Disturbances due to improper selection of the operating frequency of the inductive power transfer system are avoidedElectric/magnetic detectionMeasurements using NMRElectric power transmissionElectric power system
The invention relates to a nuclear magnetic resonance imaging apparatus comprising: a main magnet (122) adapted for generating a main magnetic field; at least one radio frequency receiver coil unit (144) for acquiring magnetic resonance signals in a receiver coil radio frequency band (202) from an examined object (124); means (140) for inductively (wirelessly) supplying electric power to an electric component of the apparatus, wherein the electric component is adapted to be powered by inductively supplied electric power, wherein the power transfer frequency (200) and the higher-harmonics (206) of the power transfer frequency (200) for inductively supplying the electric power are located outside the receiver coil radio frequency band (202).
Owner:KONINKLIJKE PHILIPS ELECTRONICS NV
Method for obtaining nuclear magnetic resonance two-dimension spin echo related spectrum under uneven magnetic field
ActiveCN103744042AOvercoming the influence of uneven magnetic fieldMagnetic measurementsLine widthPulse sequence
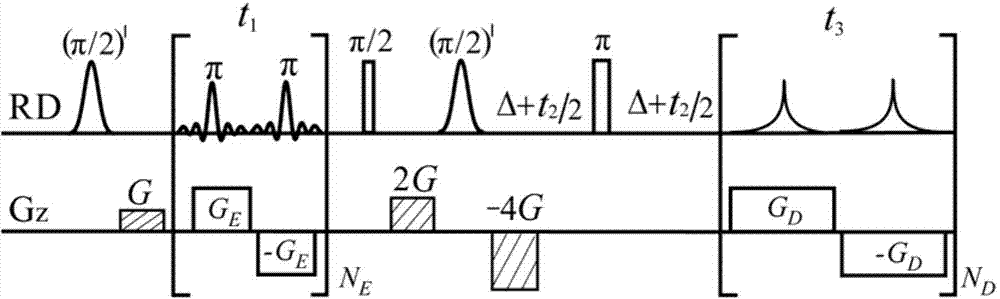
A method for obtaining a nuclear magnetic resonance two-dimension spin echo related spectrum under an uneven magnetic field relates to a nuclear magnetic resonance wave spectrum detection method and comprises the steps of using a normal one-dimension pulse sequence to sample a one-dimension spectrum, obtaining the line width of spectral lines, and providing a basis for spectrum width parameter setting, wherein the line width value also reflects the uniformity condition of a magnetic field; introducing well precompiled two-dimension spin echo related spectrum pulse sequences onto a nuclear magnetic resonance spectrometer; opening a multi-quantum coherent signal selection module, a three-dimension sampled indirect dimension evolution period t1 combination and indirect dimension evolution period t2 combination and an echo delay module among the two-dimension spin echo related spectrum pulse sequences; setting each experiment parameter of the two-dimension spin echo related spectrum pulse sequences; executing the two-dimension spin echo related spectrum pulse sequences, of which the experiment parameters are set, for data sampling; after the data sampling is finished, performing related data postprocessing to obtain the two-dimension spin echo related spectrum uninfluenced by the uneven magnetic field. The method has no need of shimming operation and is simple, convenient and effective.
Owner:XIAMEN UNIV
Method for simultaneously quantitatively analyzing water and oil in oily sludge through low-field NMR (nuclear magnetic resonance)
InactiveCN104807847AFast testThe test result is accurateAnalysis using nuclear magnetic resonanceCorrection algorithmSludge
The invention relates to a method for simultaneously quantitatively analyzing water and oil in oily sludge through low-field NMR (nuclear magnetic resonance). The method comprises steps as follows: deionized water and crude oil are taken as standard samples to perform low-field NMR measurement, and calibration curves of water and oil are established; a to-be-measured sample which is uniformly stirred is divided into two parts and put in containers respectively, a reagent capable of realizing signal partition of oil and water is added to one part, and the mixture is uniformly stirred to form a sample a; the other part keeps unchanged and is taken as a sample b; the two samples are subjected to low-field NMR measurement to obtain an echo attenuation curve, and transverse relaxation time T2 curves of the two samples are obtained through inversion with a joint iterative correction algorithm; the transverse relaxation time T2 curves of the two samples are subjected to area integration and calculation to obtain integral areas of a water peak and an oil peak, and the calibration curves of water and oil are substituted to calculate water content and oil content of the to-be-measured sample b. The method can be suitable for measurement of content of water and oil in various kinds of oily sludge, and the measurement result is high in accuracy and good in repeatability and consumes short time.
Owner:UNIV OF SHANGHAI FOR SCI & TECH
Downhole micro magnetic resonance analyzer
ActiveUS20090219019A1Material analysis by using resonanceElectric/magnetic detectionSolid-state nuclear magnetic resonanceNMR - Nuclear magnetic resonance
A downhole micro MR analyzer for use in a wellbore, having a micro sample tube, a micro RF coil in close proximity to the micro sample tube, and one or more magnets disposed about the micro sample tube is disclosed. The micro MR analyzer can be used for nuclear magnetic resonance or electron spin resonance experiments to ascertain formation properties and chemical compositions.
Owner:SCHLUMBERGER TECH CORP
Shale pore structure detection method based on nuclear magnetic resonance
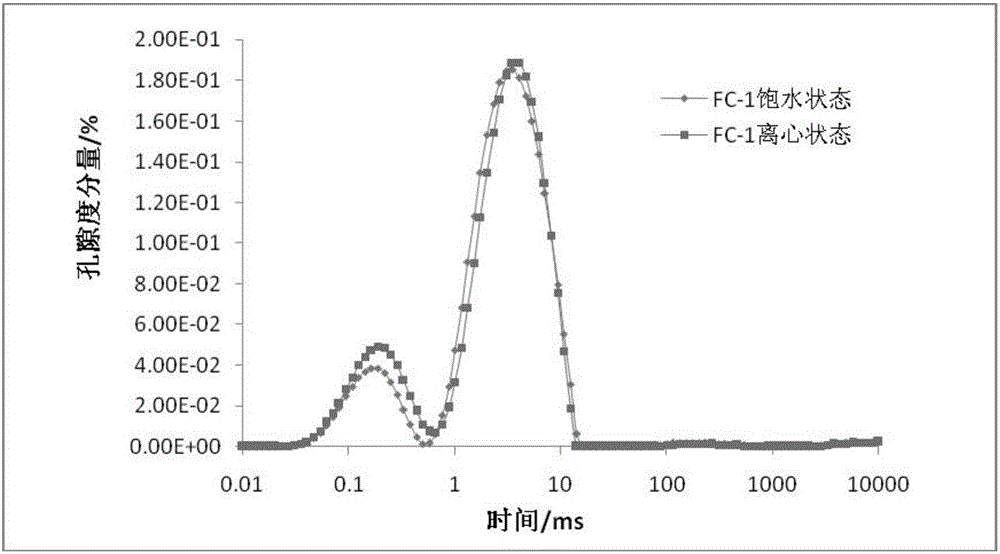
InactiveCN106249306AClearly understand the changes in the size of poresAchieving Crack PredictionWater resource assessmentDetection using electron/nuclear magnetic resonancePore distributionWater state
The invention provides a shale pore structure detection method based on nuclear magnetic resonance. The method comprises the steps that a sample is processed into a cylinder; the sample is saturated with water at normal pressure for 12h, and then is taken out; CPMG pulse sequence test is carried out on the sample to acquire a spin-echo-series attenuation signal; the spin-echo-series signal is inversed to acquire a T2 spectrum distribution diagram and the details of each peak; and the T2 spectrum of acquired same sample under water saturation and centrifugation is analyzed in a coordinate system to acquire the change of the volume and quantity of pores of the sample. The shale pore structure is mainly studied in a saturated water state in the prior art of nuclear magnetic resonance, and the problems that the study angle is single and limited; only pore distribution can be studied; and fracture prediction cannot be carried out are solved. The method provided by the invention belongs to the technical field of petroleum exploration and development.
Owner:GUIZHOU UNIV
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com