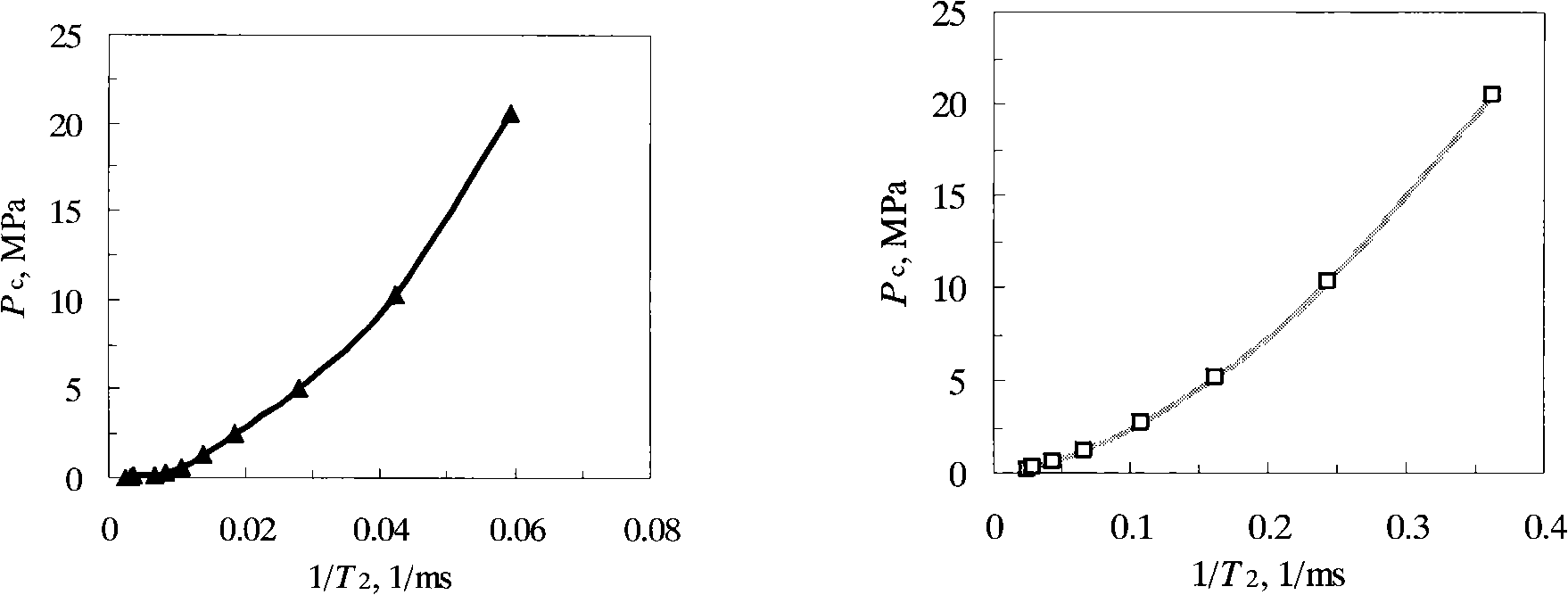Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
1077results about "Detection using electron/nuclear magnetic resonance" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
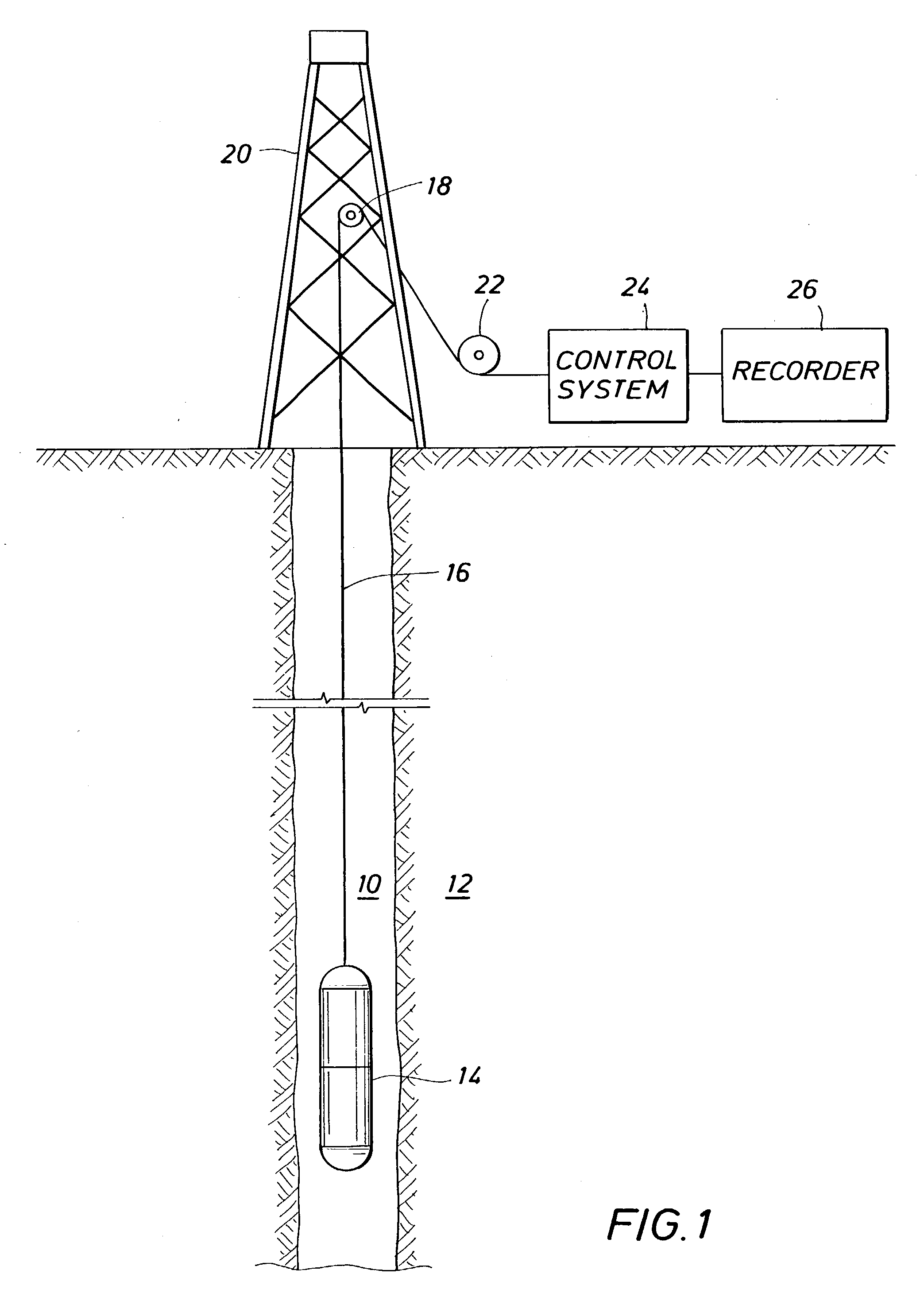
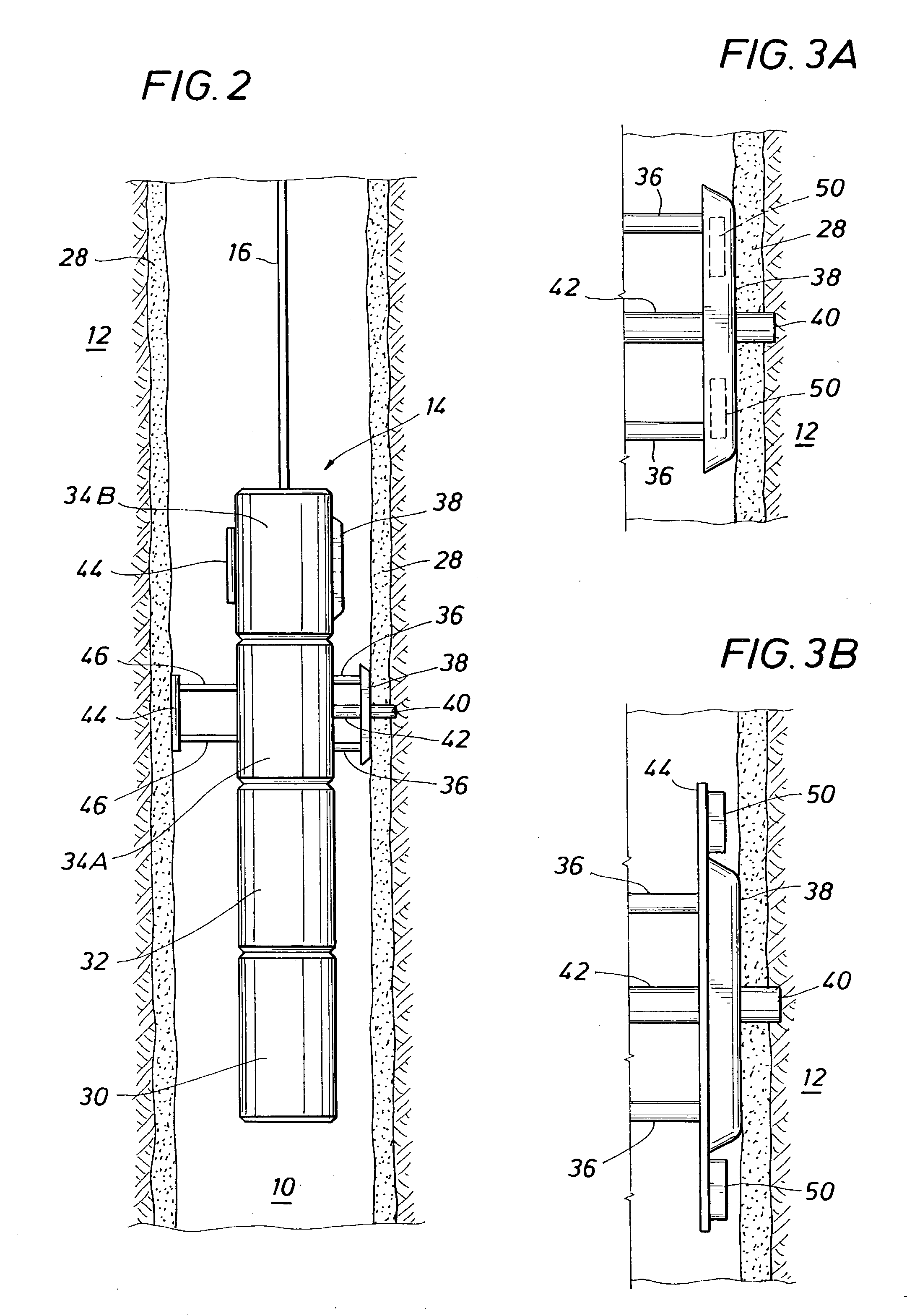
Method and apparatus for subterranean formation flow imaging
InactiveUS6856132B2Accurate measurementAccurately determineElectric/magnetic detection for well-loggingMaterial analysis by using resonanceMri imageGeophysics
The present invention relates to a method and apparatus for measuring a property relating to fluid flow in an earth formation, more specifically to directly measuring formation permeability and other fluid characteristics. The present invention provides a method for determining the permeability of a hydrocarbon bearing earth formation, which method comprises the steps of: locating a tool at a selected position in a borehole penetrating the earth formation; inducing a flow of fluid within the earth formation to said tool; creating at least two MRI images of said fluid while flowing within the earth formation to said tool, said at least two images being created at different times; determining displacement of said fluid within the earth formation between said different times, using the at least two MRI images.
Owner:SHELL OIL CO
Systems and methods for NMR logging
ActiveUS20050030021A1Add depthAccurate estimateElectric/magnetic detection for well-loggingMaterial analysis by using resonanceEngineeringPole piece
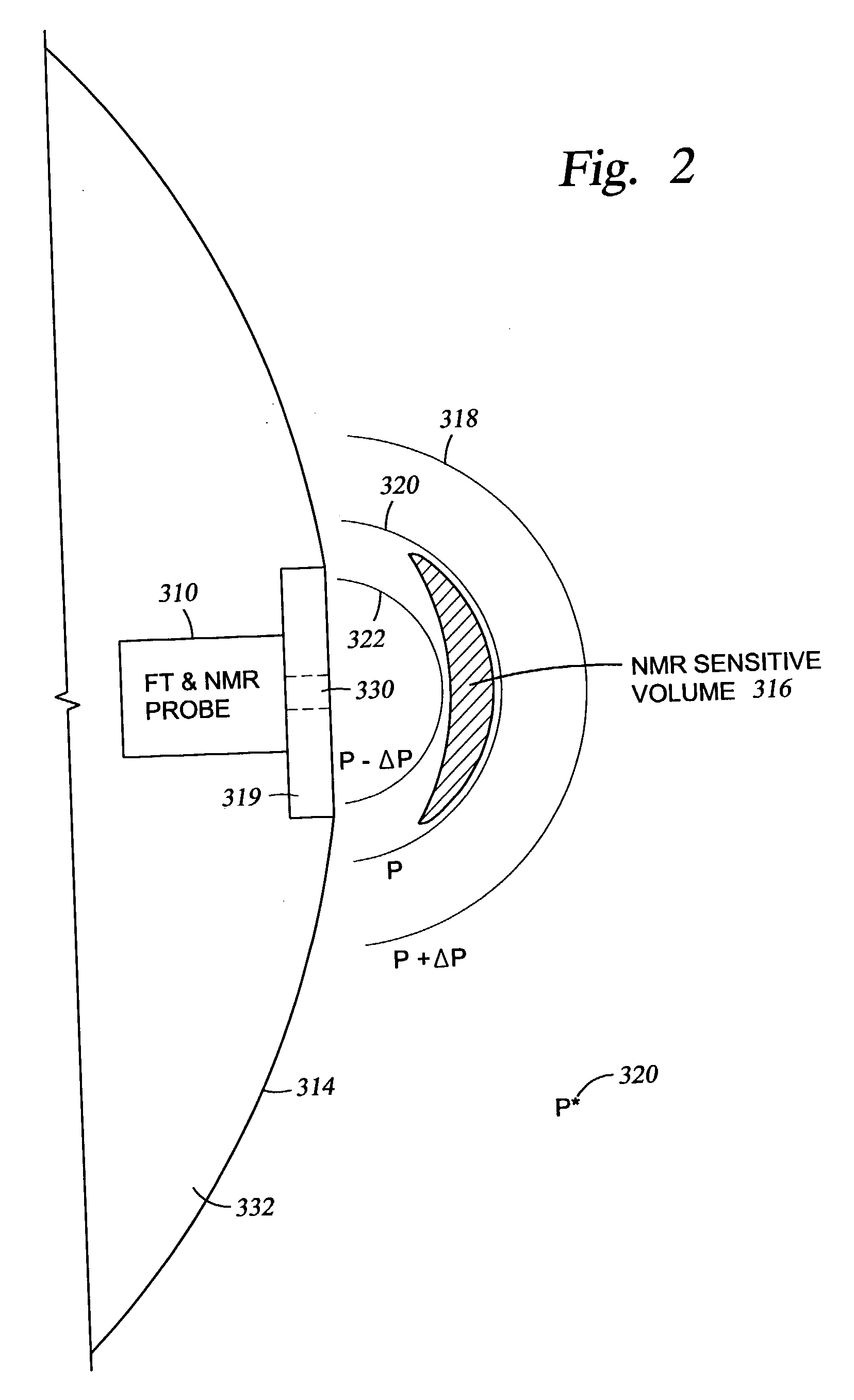
An NMR logging tool for conducting NMR measurements in a plurality of sensitive volumes ranging up to a meter from the tool. The tool comprises a magnetic assembly using one or more permanent magnets and at least one pole piece for extending a magnet pole and shaping the magnetic field to simulate a magnetic monopole in a sensitive volume within the formation. Different embodiments of a segmented antenna enable directional NMR logging. The tool embodiments and methods of their use are suitable for wireline or LWD logging, and can be used for directional drilling.
Owner:HALLIBURTON ENERGY SERVICES INC
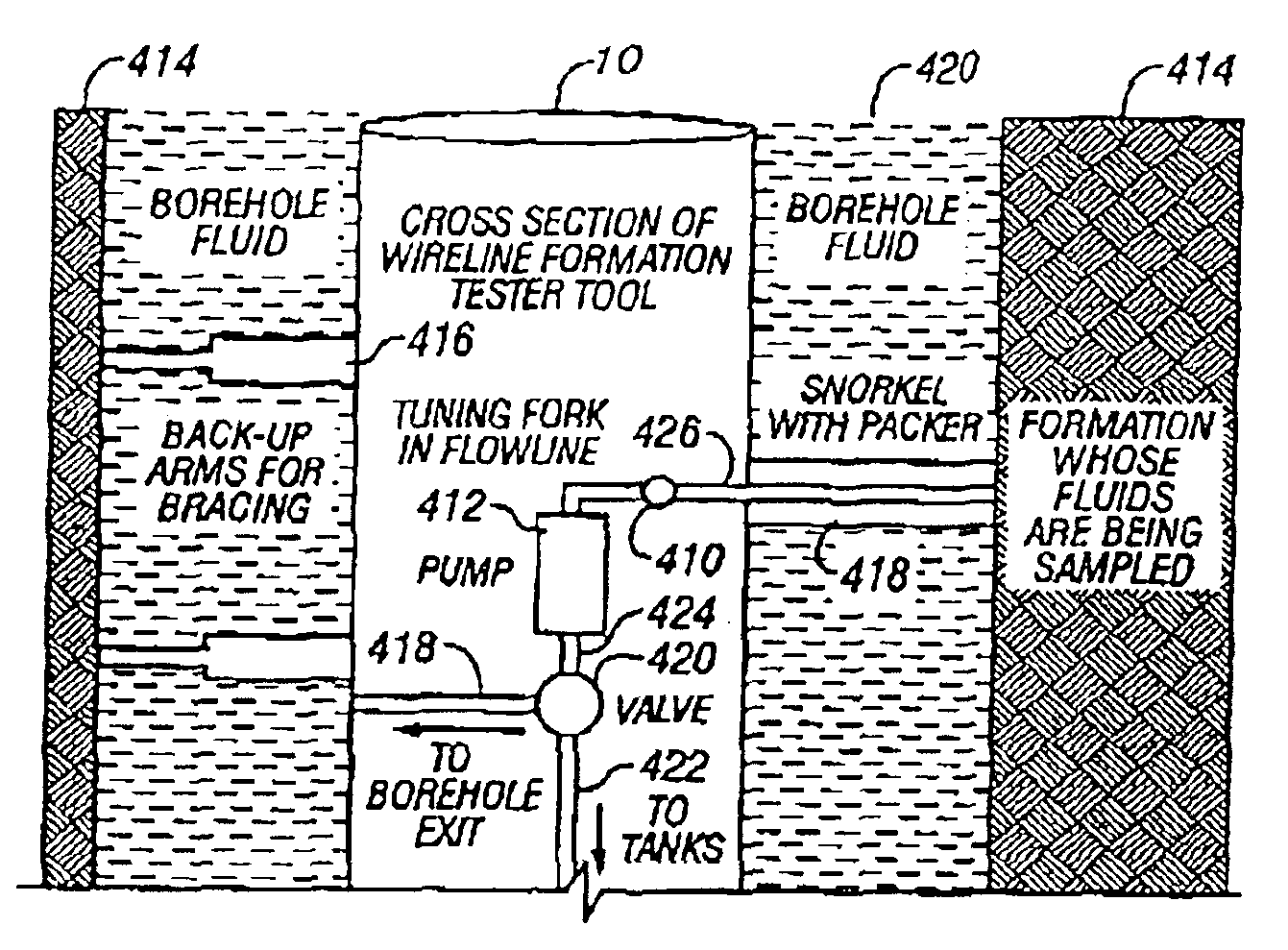
Method and apparatus for downhole fluid characterization using flexural mechanical resonators
InactiveUS20020178805A1Avoid contact corrosionProtection from damageElectric/magnetic detection for well-loggingAnalysing fluids using sonic/ultrasonic/infrasonic wavesTuning forkFormation fluid
The present invention provides a downhole method and apparatus using a flexural mechanical resonator, for example, a tuning fork to provide real-time direct measurements and estimates of the viscosity, density and dielectric constant of formation fluid or filtrate in a hydrocarbon producing well. The present invention additionally provides a method and apparatus for monitoring cleanup from a leveling off of viscosity or density over time, measuring or estimating bubble point for formation fluid, measuring or estimating dew point for formation fluid, and determining the onset of asphaltene precipitation. The present invention also provides for intercalibration of plural pressure gauges used to determine a pressure differential downhole.
Owner:BAKER HUGHES INC
Method and apparatus for subterranean formation flow imaging
InactiveUS20040090230A1Accurately determine formation parameterAccurate measurementElectric/magnetic detection for well-loggingMaterial analysis by using resonanceMri imageGeophysics
The present invention relates to a method and apparatus for measuring a property relating to fluid flow in an earth formation, more specifically to directly measuring formation permeability and other fluid characteristics. The present invention provides a method for determining the permeability of a hydrocarbon bearing earth formation, which method comprises the steps of: locating a tool at a selected position in a borehole penetrating the earth formation; inducing a flow of fluid within the earth formation to said tool; creating at least two MRI images of said fluid while flowing within the earth formation to said tool, said at least two images being created at different times; determining displacement of said fluid within the earth formation between said different times, using the at least two MRI images.
Owner:SHELL OIL CO
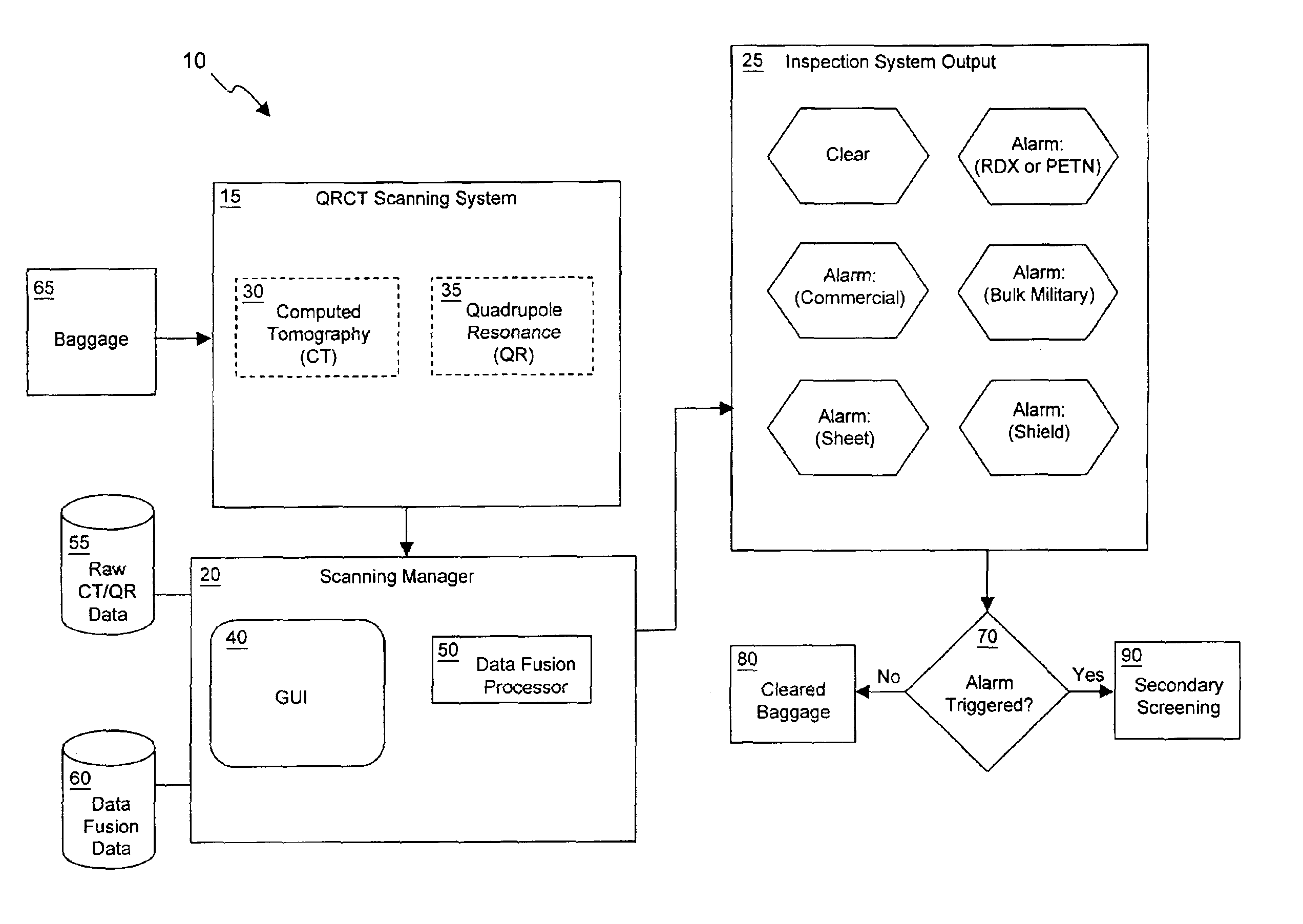
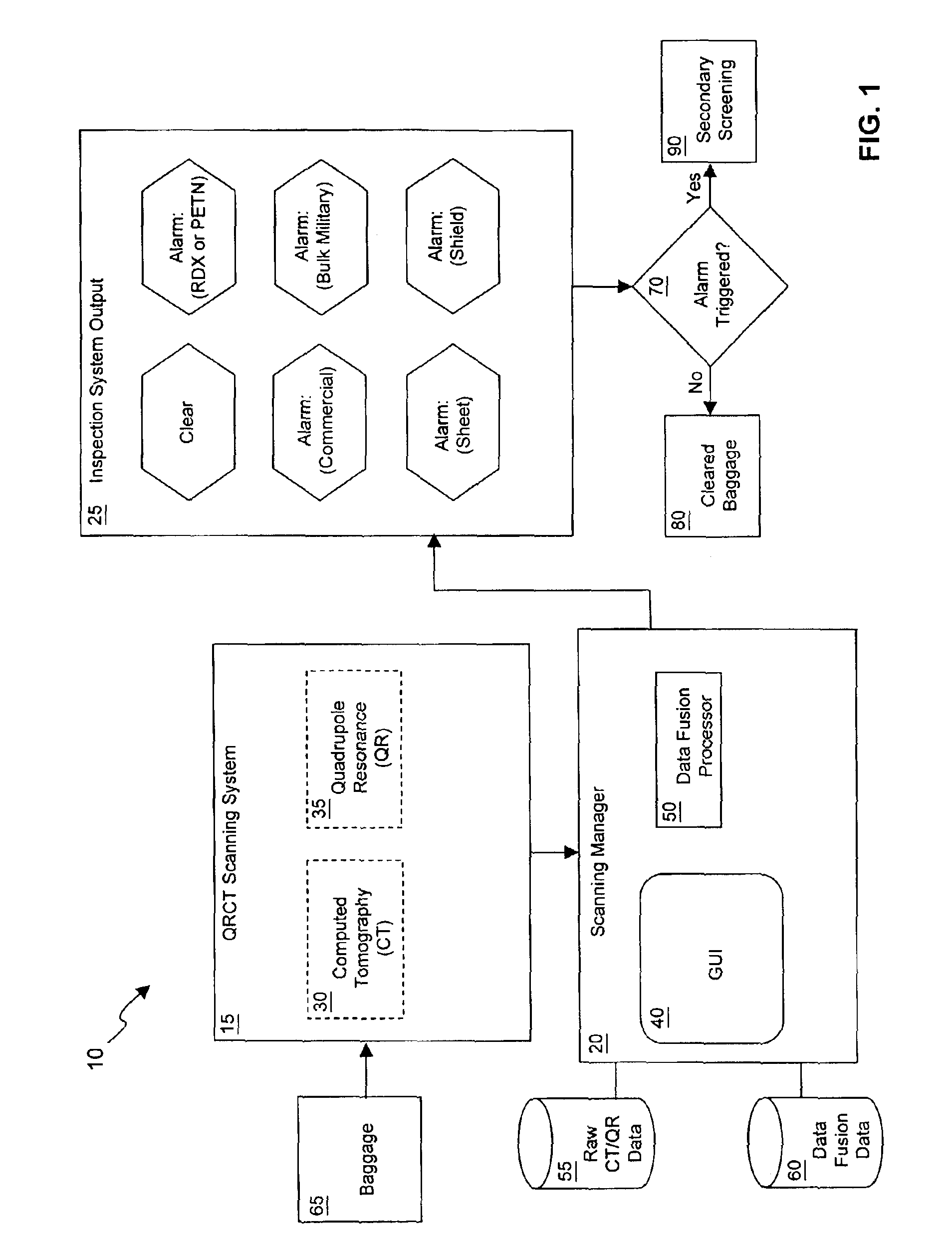
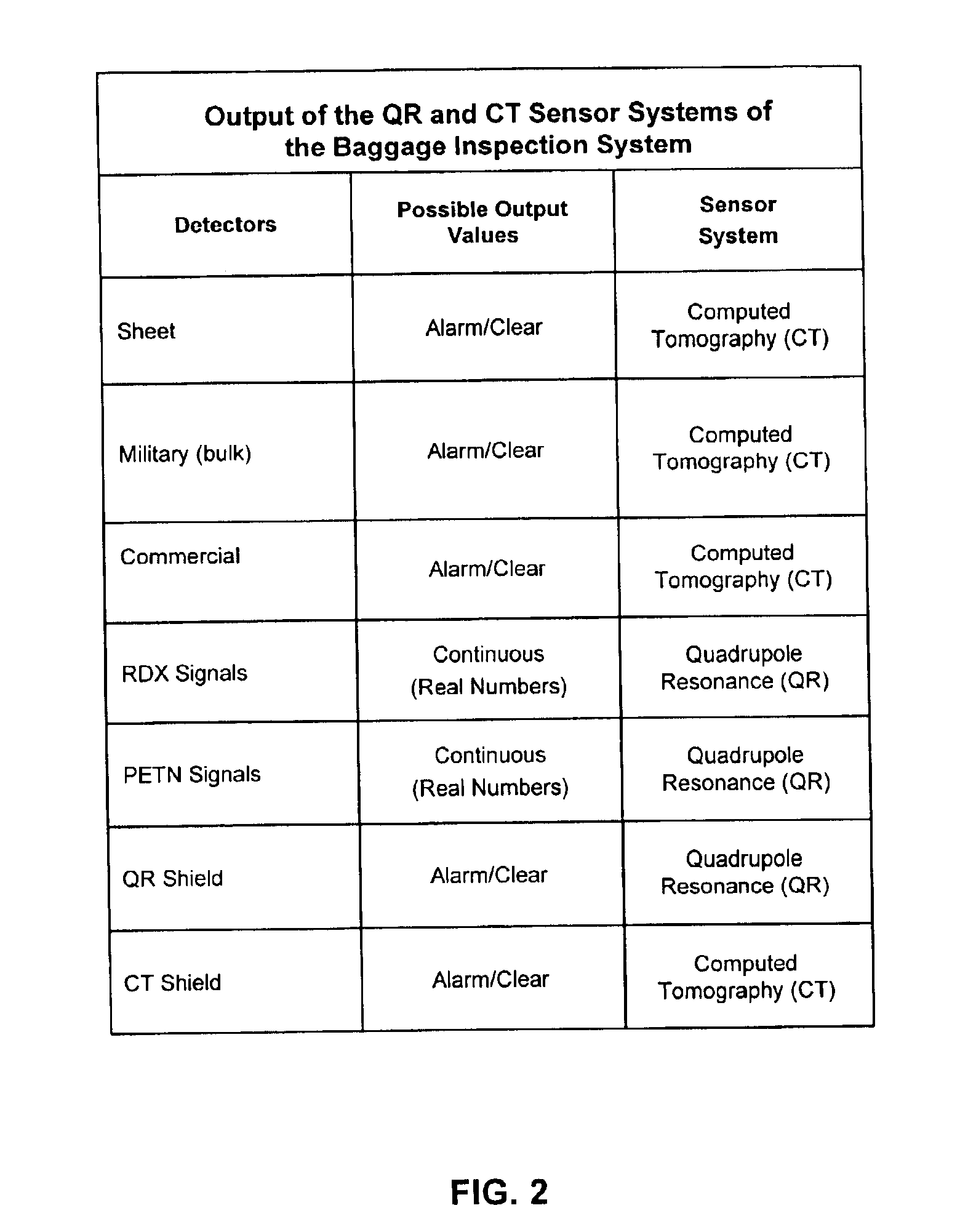
Explosives detection system using computed tomography (CT) and quadrupole resonance (QR) sensors
InactiveUS6922460B2Material analysis by transmitting radiationDetection using electron/nuclear magnetic resonanceResonanceEngineering
An explosives detection system which includes computed tomography (CT) and quadrupole resonance (QR) sensors for identifying particular explosive compounds present in passenger baggage. The CT sensor may be configured to automatically identify the presence or absence of bulk military, commercial, and sheet explosives during CT scanning of the baggage. Similarly, the QR sensor may be configured to responsively generate RDX and PETN signals during QR scanning of the passenger baggage. Using any of a variety of inspection protocols, the explosives detection system may generate an output alarm based upon data obtained from the CT and QR sensors.
Owner:QUANTUM MAGNETICS
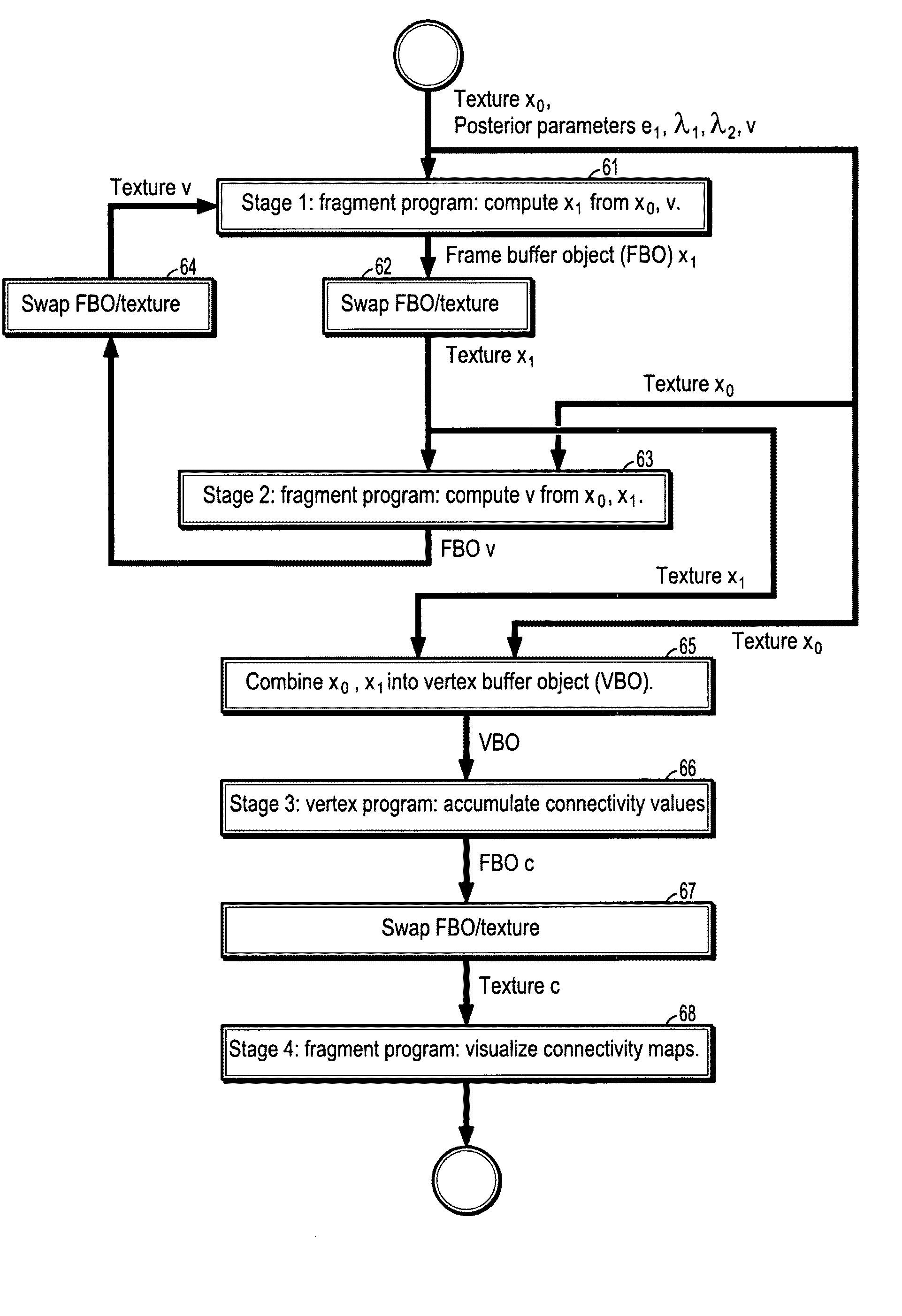
System and method for stochastic DT-MRI connectivity mapping on the GPU
InactiveUS7672790B2Highly parallelizableDrawing from basic elementsMagnetic measurementsGraphicsDiffusion
A graphics processing unit implemented method for fiber tract mapping from diffusion tensor magnetic resonance imaging data includes providing a diffusion tensor magnetic resonance brain image volume, initializing a set of fiber positions in a 3D set of points, fiber displacements, and a posterior distribution for an updated fiber displacement in terms of the initial displacements and diffusion tensors, randomly sampling a set of updated fiber displacements from said posterior distribution, computing a new set of fiber positions from said initial fiber positions and said updated fiber displacements, wherein a fiber path comprises a set of fiber points connected by successive fiber displacements, accumulating connectivity values in each point of said 3D set of points by additive alpha-blending a scaled value if a fiber path has passed through a point and adding zero if not, and rendering said connectivity values.
Owner:SIEMENS MEDICAL SOLUTIONS USA INC
In-situ heavy-oil reservoir evaluation with artificial temperature elevation
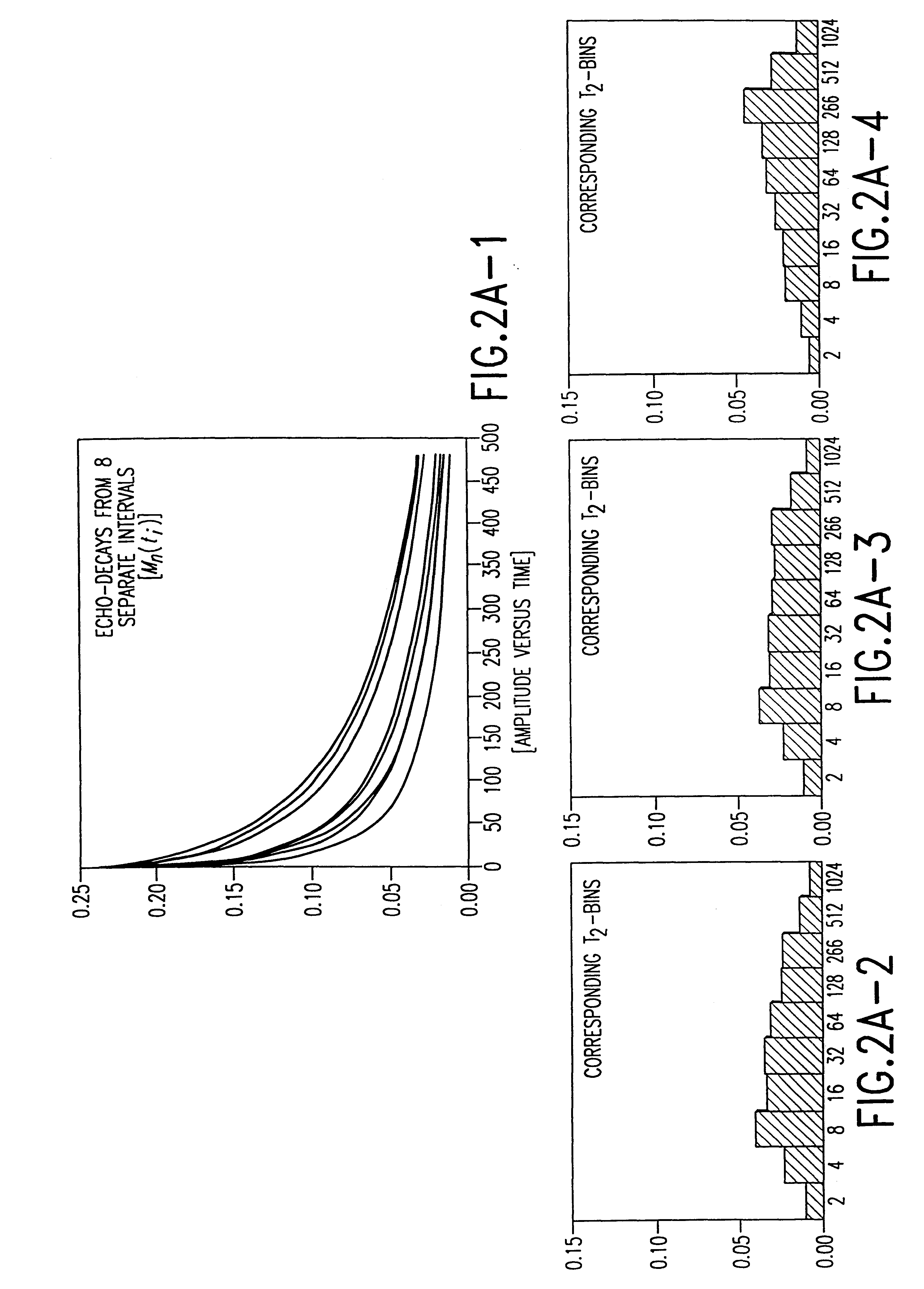
Many reservoirs of interest include heavy oil. In such reservoirs, parti at normal temperatures, many instruments commonly used for formation evaluation may not be able to distinguish between heavy oil and bound water in the formation. Passive or active heating is used to elevate the temperature of the fluids in the formation. At elevated temperatures, distinguishing between heavy oil and bound water is easier. Of particular interest is the increase in the resolvability of the transverse relaxation time T2 of NMR spin echo measurements. Additionally, the dielectric constant and the loss tangents of water and heavy oil show different temperature and frequency dependence.
Owner:BAKER HUGHES HLDG LLC
Method for continuously quantitative evaluation of pore structures of reservoir strata by utilizing nuclear magnetic resonance well logging data
ActiveCN102141637ATo achieve the purpose of classificationElectric/magnetic detection for well-loggingBorehole/well accessoriesThroatPressure curve
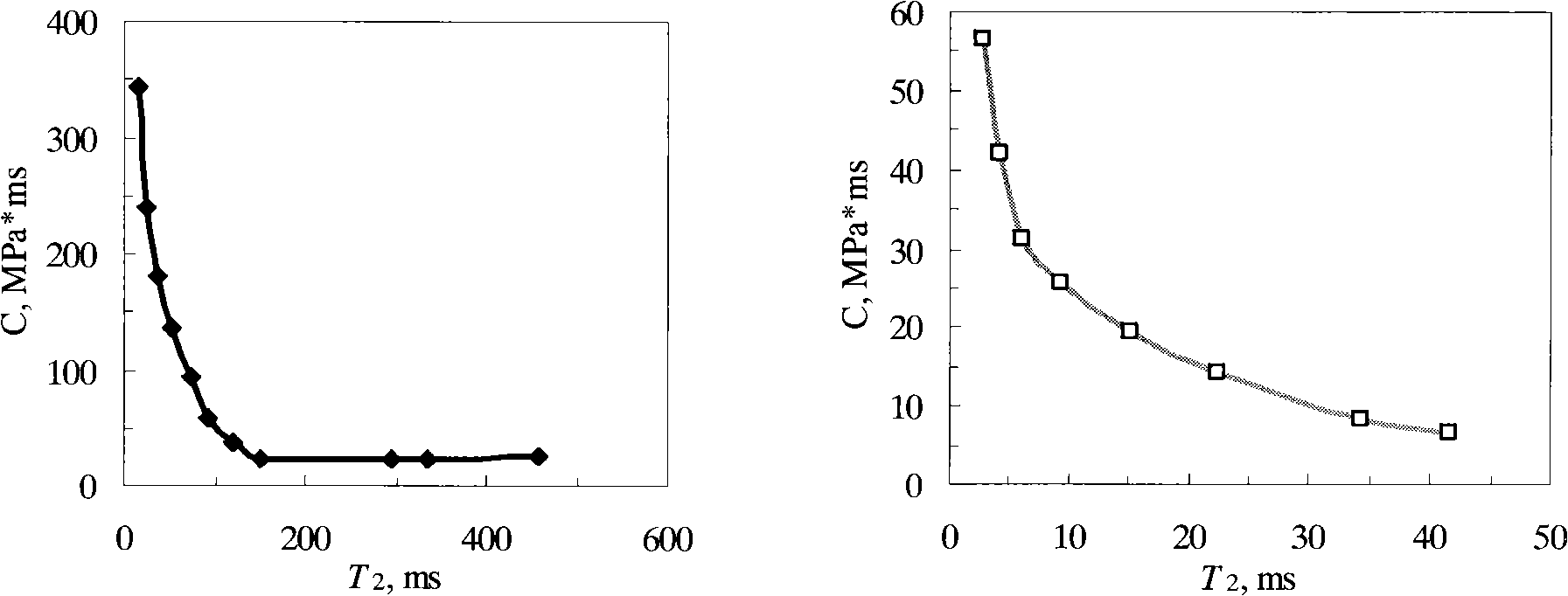
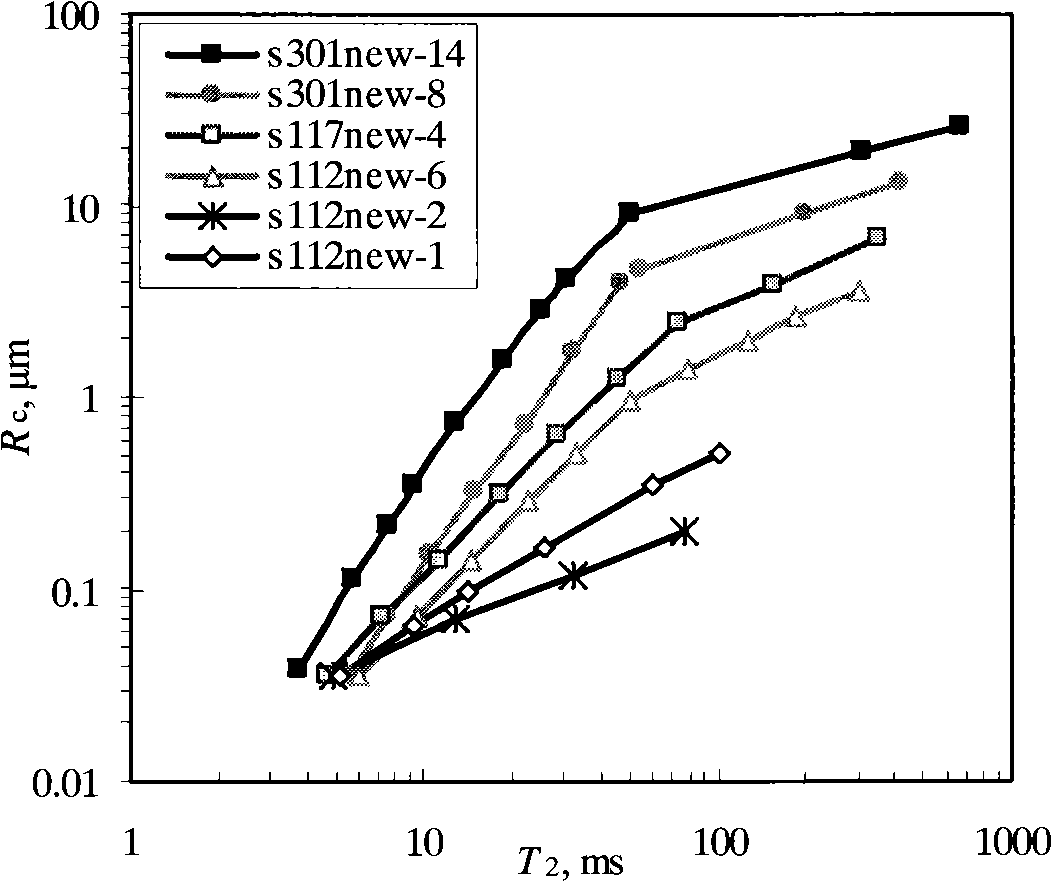
The invention relates to a method for continuously quantitative evaluation of pore structures of reservoir strata by utilizing nuclear magnetic resonance well logging data, so as to divide types of the reservoir strata. The method comprises the following steps of: classifying T2 spectrums according to parameters reflecting differences of reservoir strata, and carrying out a nonlinear calibration method on different T2 spectrums to obtain a continuously distributed capillary pressure curve of the reservoir strata; obtaining continuous reservoir stratum pore throat radius distribution and pore structure parameters by utilizing the nuclear magnetic capillary pressure curve; and evaluating the pore structure of each reservoir stratum on the basis of the nuclear magnetic capillary pressure curve, the features of the reservoir stratum pore throat radius distribution and the pore structure parameters, and dividing types of the reservoir strata. Through the adoption of the method, the nuclear magnetic capillary pressure curve on each depth point can be continuously obtained by utilizing the nuclear magnetic resonance well logging data, the pore structure of each reservoir stratum can be quantitatively evaluated according to the reservoir stratum pore throat radius distribution and the pore structure parameters of the reservoir stratum, and the types of the reservoir strata are classified, therefore, the exploitation and development efficiency of complicated oil-gas reservoir is improved.
Owner:PETROCHINA CO LTD +1
System and methods of characterizing a hydrocarbon reservoir
ActiveUS7277796B2Facilitating in performing data processing operationEasy to operateElectric/magnetic detection for well-loggingPermeability/surface area analysisCompressibilityIterative method
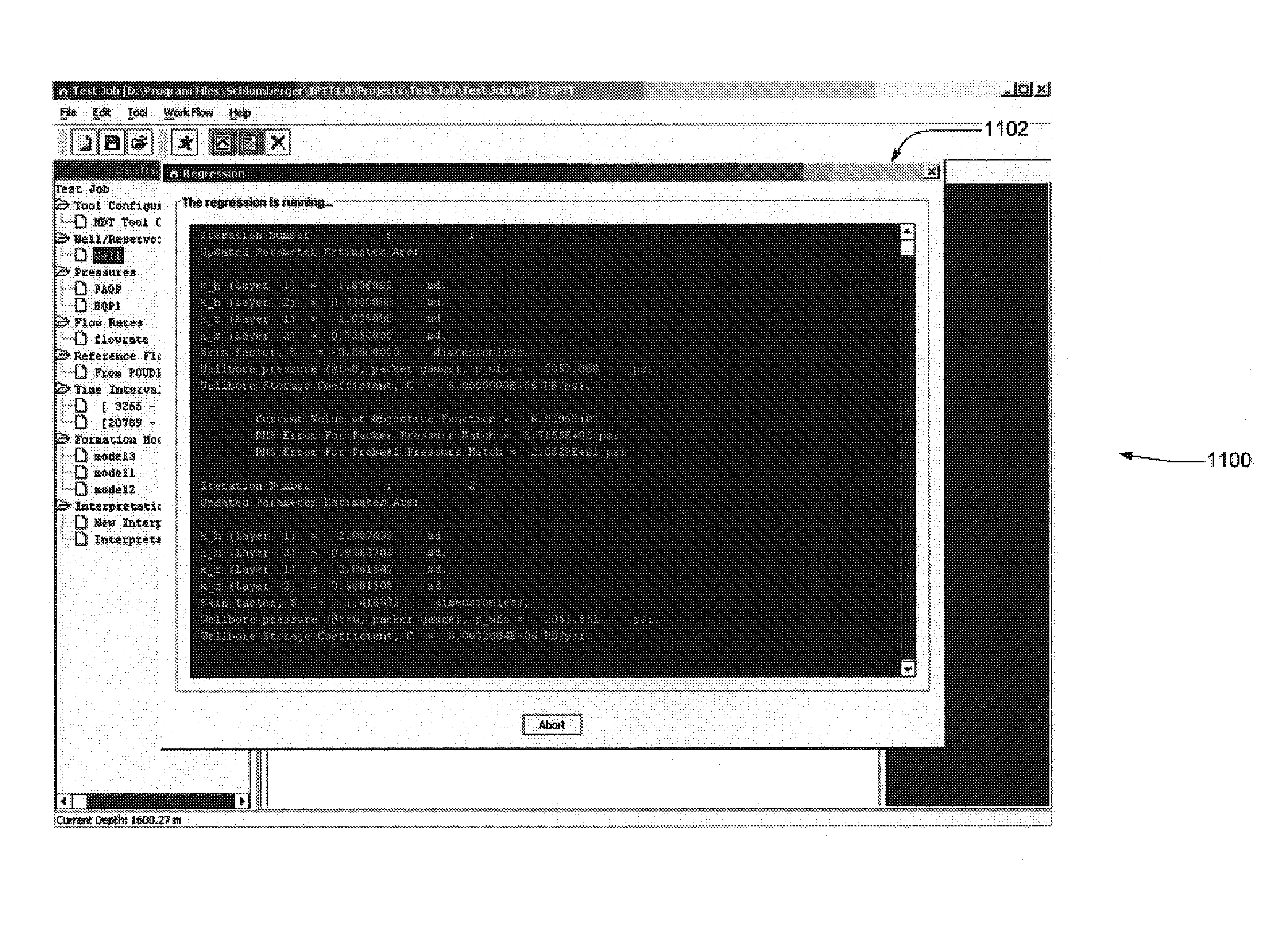
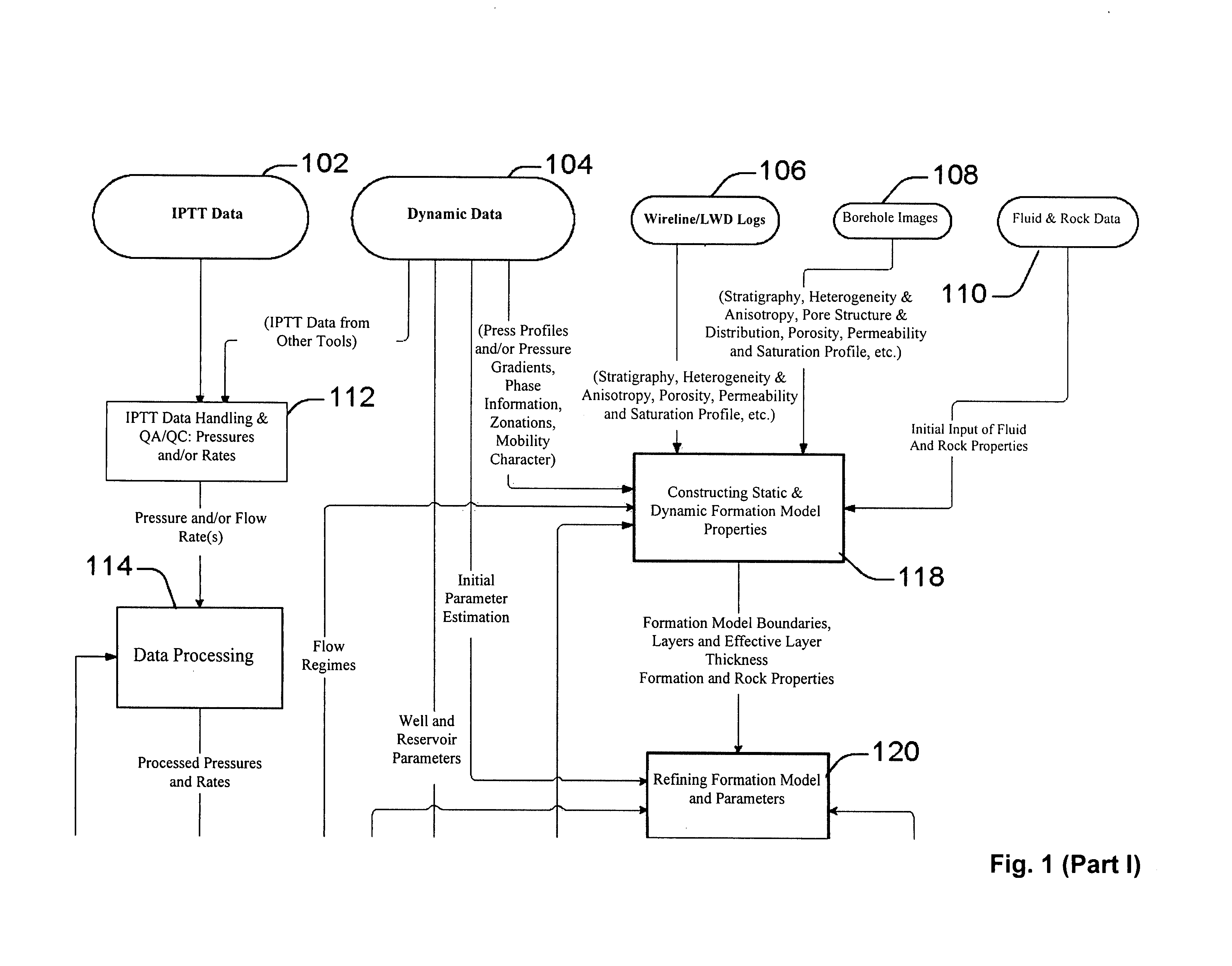
A technique is described for interpretation of IPTT tests. In one implementation, the technique may be configured or designed to standardize the complete interpretation procedure of IPTT in a heterogeneous reservoir, using if available, modern wireline logs (such as, for example, nuclear magnetic resonance and imaging), dynamic data from wireline formation testers and / or any other relevant information (such as, for example, geological description, core data and local knowledge) as constraints on the interpretation. Additionally, an iterative method may be used to define formation layering. An advanced regression technology may also be used to obtain optimized horizontal and vertical permeabilities of reservoir layers. Further a graphical user interface (GUI) based IPTT workflow technique of the present invention provides an integrated user-friendly interpretation platform for analyzing formation testing pressures and flow rate measurements in order to estimate the values and associated uncertainties of local characteristics of a hydrocarbon reservoir such as, for example, local permeability, local reservoir pressure, local compressibility, etc.
Owner:SCHLUMBERGER TECH CORP
Method and apparatus for downhole fluid characterization using flexural mechanical resonators
InactiveUS6938470B2Avoid contact corrosionInversely to viscosityElectric/magnetic detection for well-loggingAnalysing fluids using sonic/ultrasonic/infrasonic wavesTuning forkFormation fluid
Owner:BAKER HUGHES INC
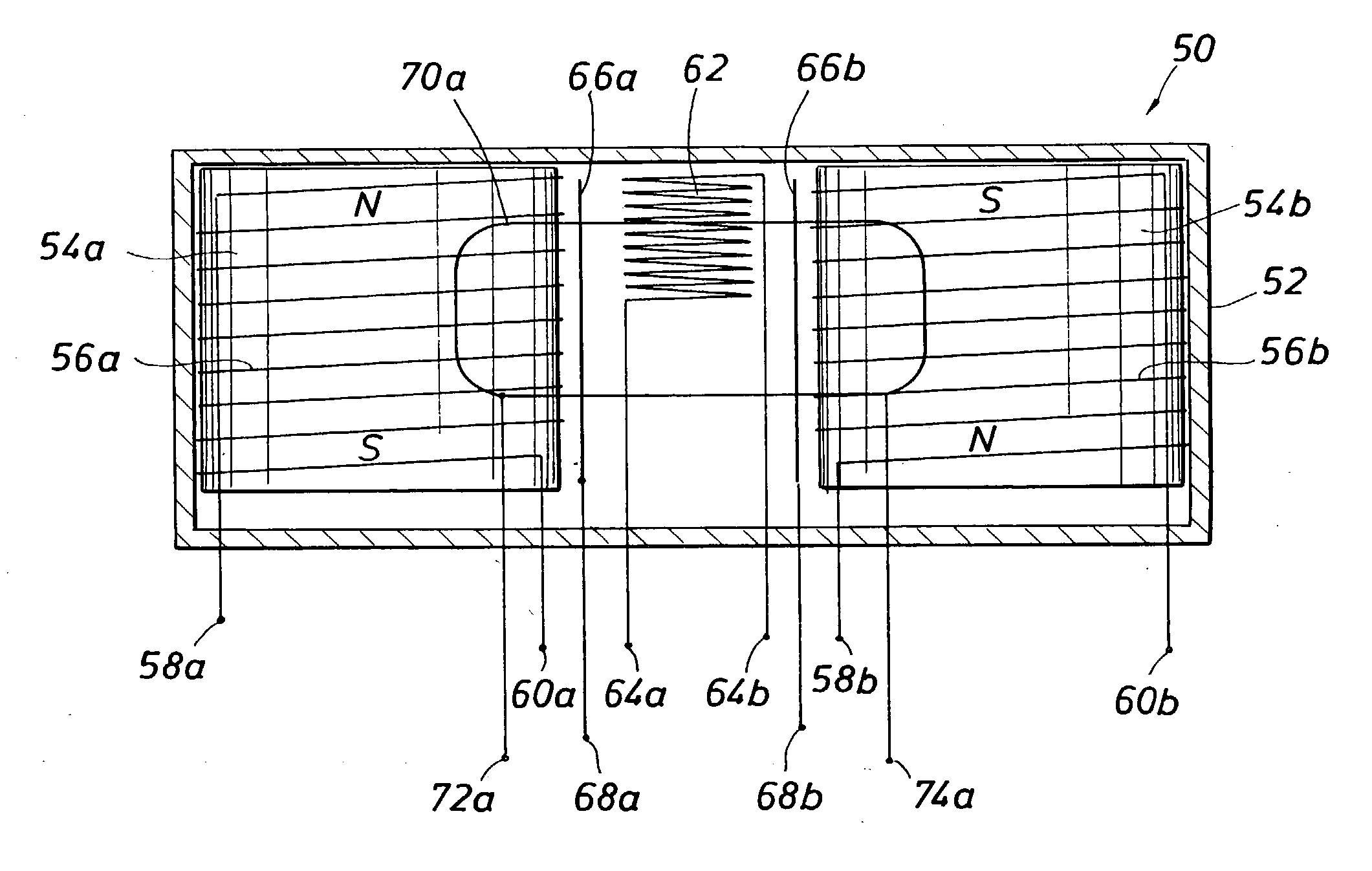
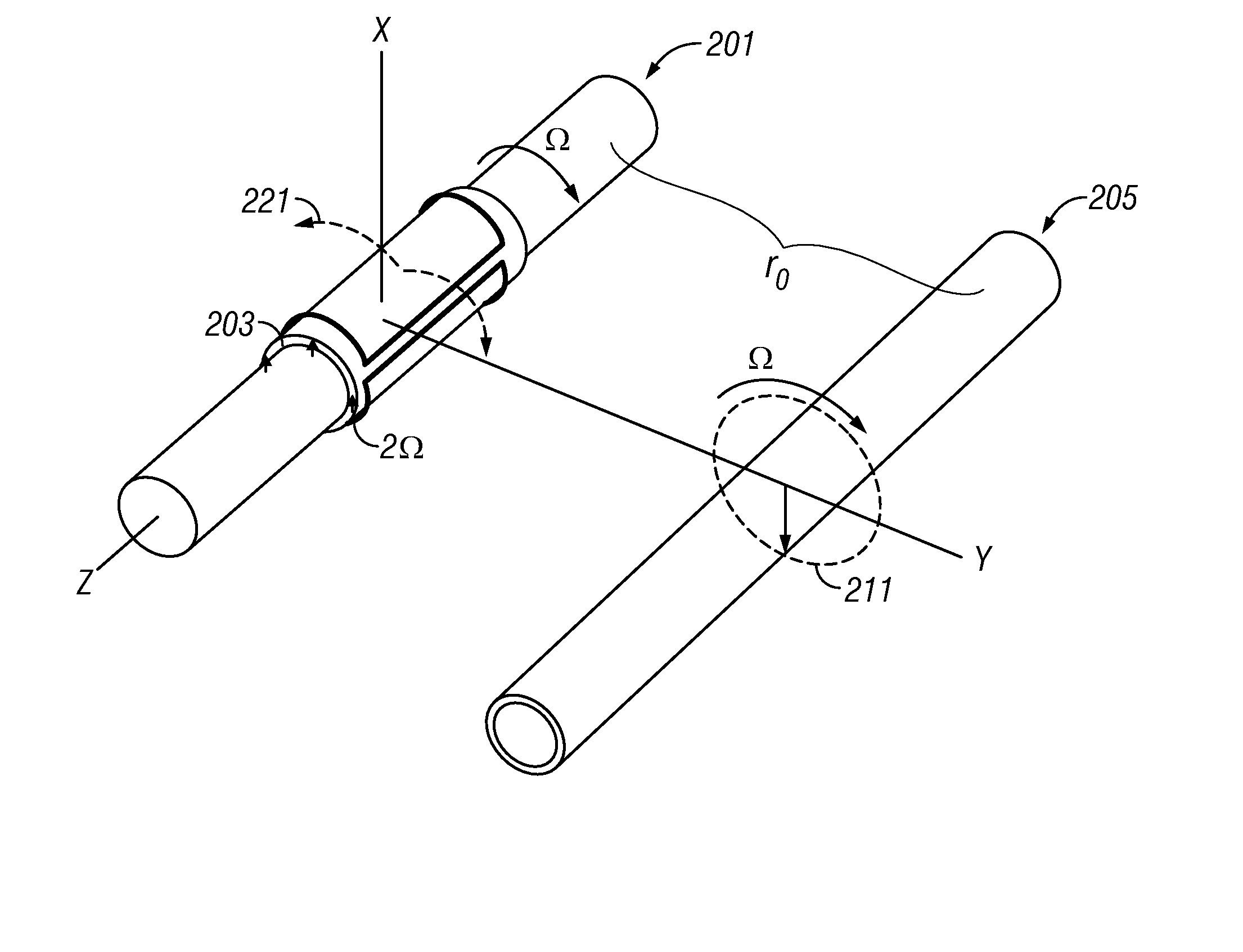
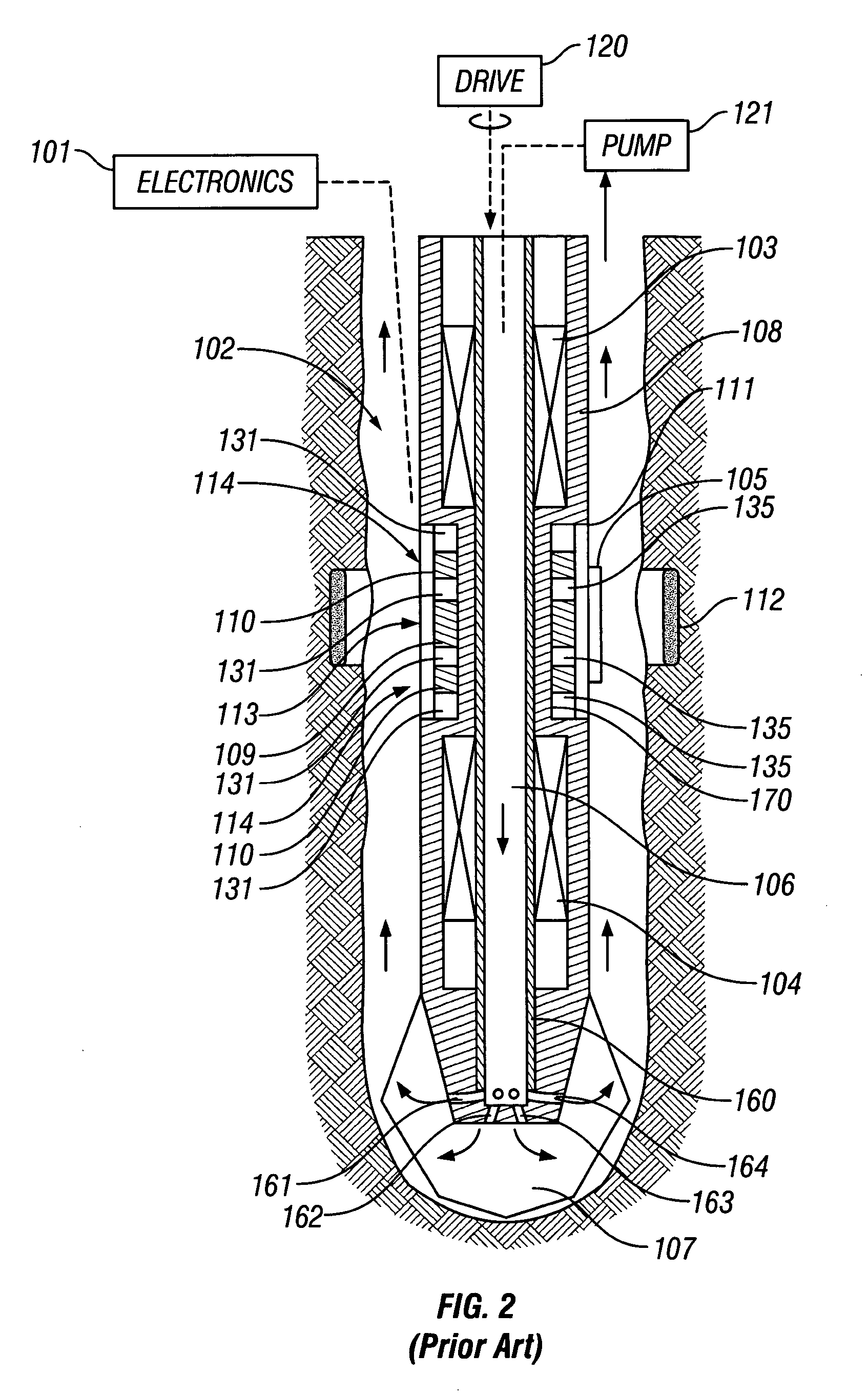
Method and Apparatus for Well-bore Proximity Measurement While Drilling
ActiveUS20080018334A1Eliminate the effects ofElectric/magnetic detection for well-loggingSurveyMagnetizationClassical mechanics
A rotating, transversely magnetized, magnet on a drill collar induces magnetization in a casing of a preexisting well. A coil rotating synchronously with the magnet produces a current at twice the frequency of rotation and having an amplitude that depends upon the distance from the magnet to the preexisting well. Alternatively, a variable magnetic field is produced in the casing using a switchable magnet. It is emphasized that this abstract is provided to comply with the rules requiring an abstract which will allow a searcher or other reader to quickly ascertain the subject matter of the technical disclosure. It is submitted with the understanding that it will not be used to interpret or limit the scope or meaning of the claims.
Owner:BAKER HUGHES INC
Downhole high resolution NMR spectroscopy with polarization enhancement
InactiveUS7126332B2Increase amplitudeElectric/magnetic detection for well-loggingMeasurements using double resonanceSignal onProton NMR
An apparatus and method is discussed for characterizing a fluid sample downhole of aliphatic hydrocarbon compounds, aromatic hydrocarbon compound, or connate mud filtrates containing carbon-13 isotopes using an enhanced nuclear magnetic resonance (NMR) signal on a measurement-while-drilling device. To enhance the carbon-13 NMR signal these nuclei are being hyperpolarized. Either the Overhauser Effect (OE) or the Nuclear Overhauser Effect or optical pumping and the Spin Polarization Induced Nuclear Overhauser Effect (SPINOE) can serve as a mechanism for hyperpolarization of the carbon-13 nuclei.
Owner:BAKER HUGHES HLDG LLC
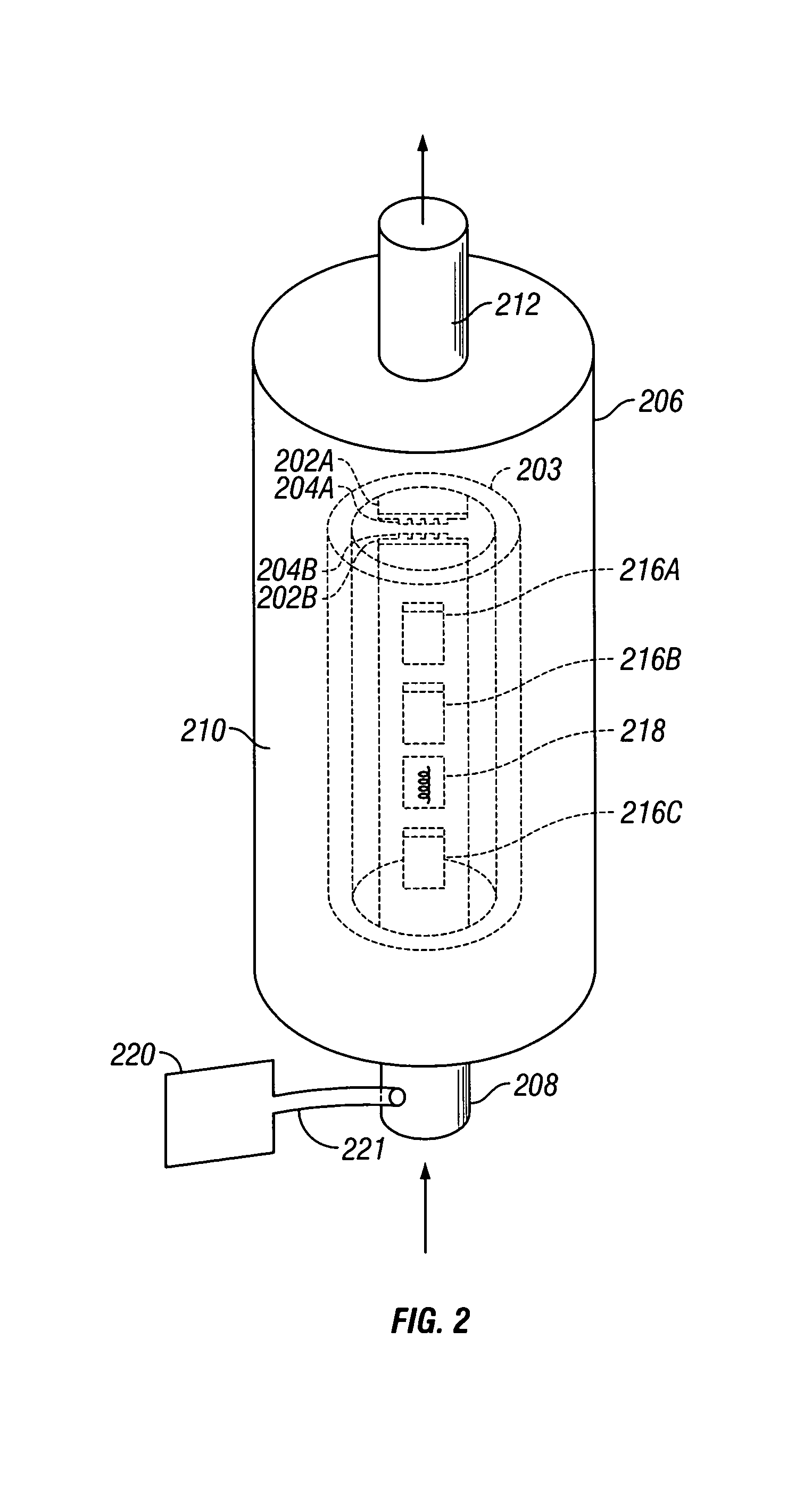
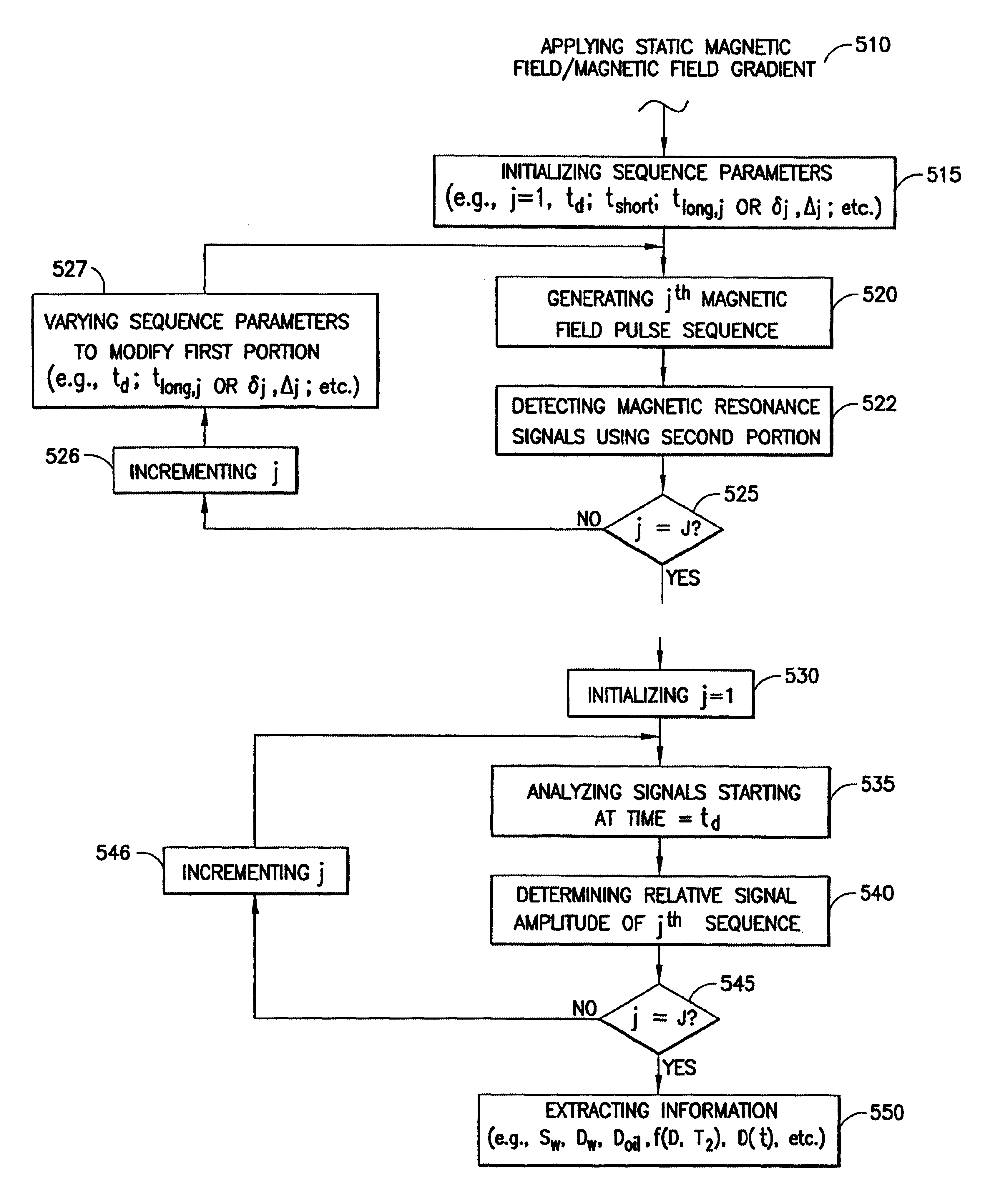
Nuclear magnetic resonance method and logging apparatus for fluid analysis
InactiveUS6891369B2Different sensitivityReadily apparentElectric/magnetic detection for well-loggingMeasurements using electron paramagnetic resonanceDiffusionNMR - Nuclear magnetic resonance
The present invention discloses a diffusion edited pulse technique that allows information about a fluid to be extracted, comprising: a) obtaining a fluid sample; b) generating a sequence of magnetic field pulses in the fluid, the sequence comprising an initial magnetic field pulse, a first portion that follows the initial magnetic field pulse, and a second portion that follows the first portion; c) detecting magnetic resonance signals using the second portion of the sequence; d) modifying the first portion of the sequence, and repeating steps (b) and (c); and e) extracting information about the fluid by determining relaxation and diffusion characteristics and their correlation based on the signals detected in steps (c) and (d). Also disclosed is a logging tool equipped with a processor to implement the diffusion edited pulse technique.
Owner:SCHLUMBERGER TECH CORP
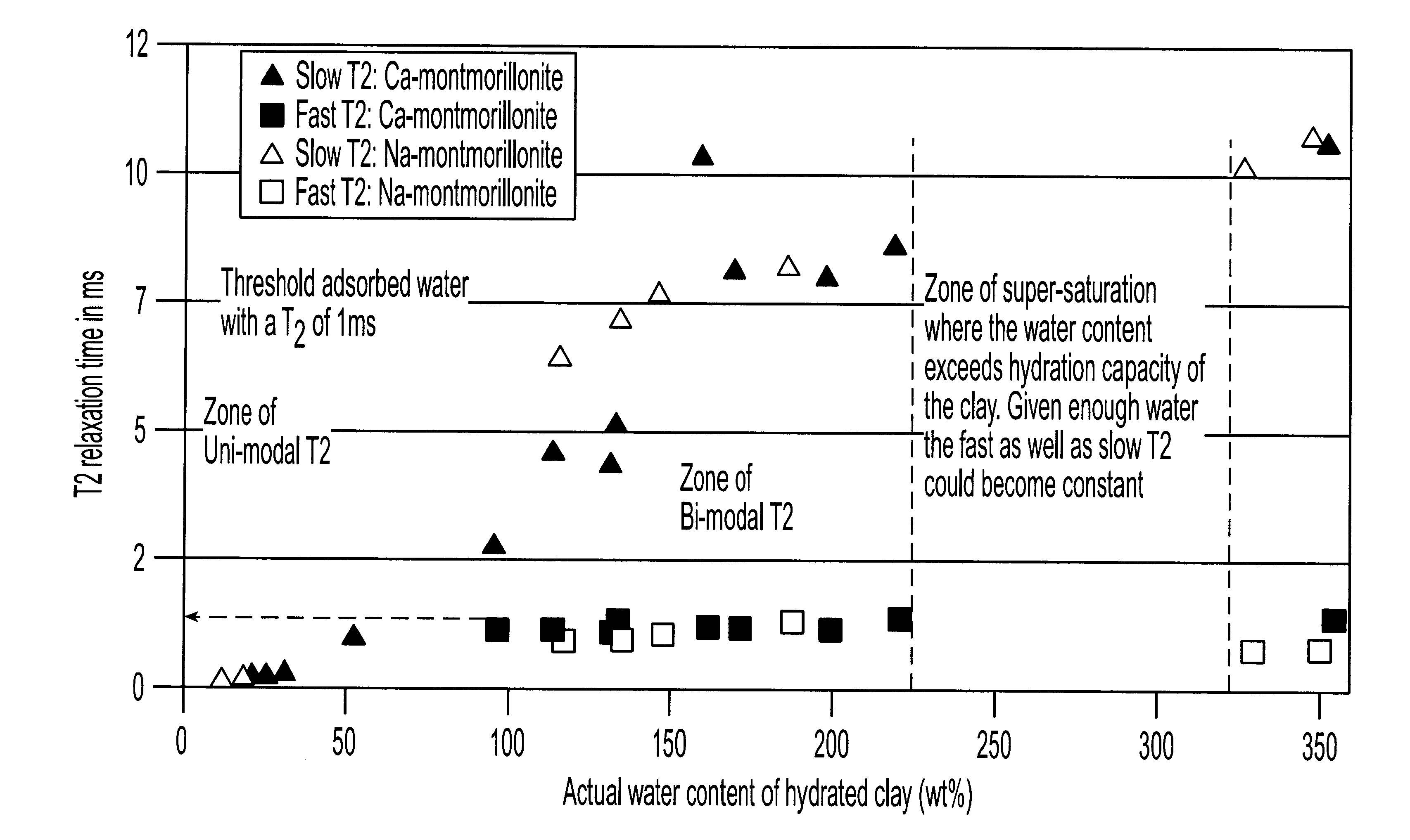
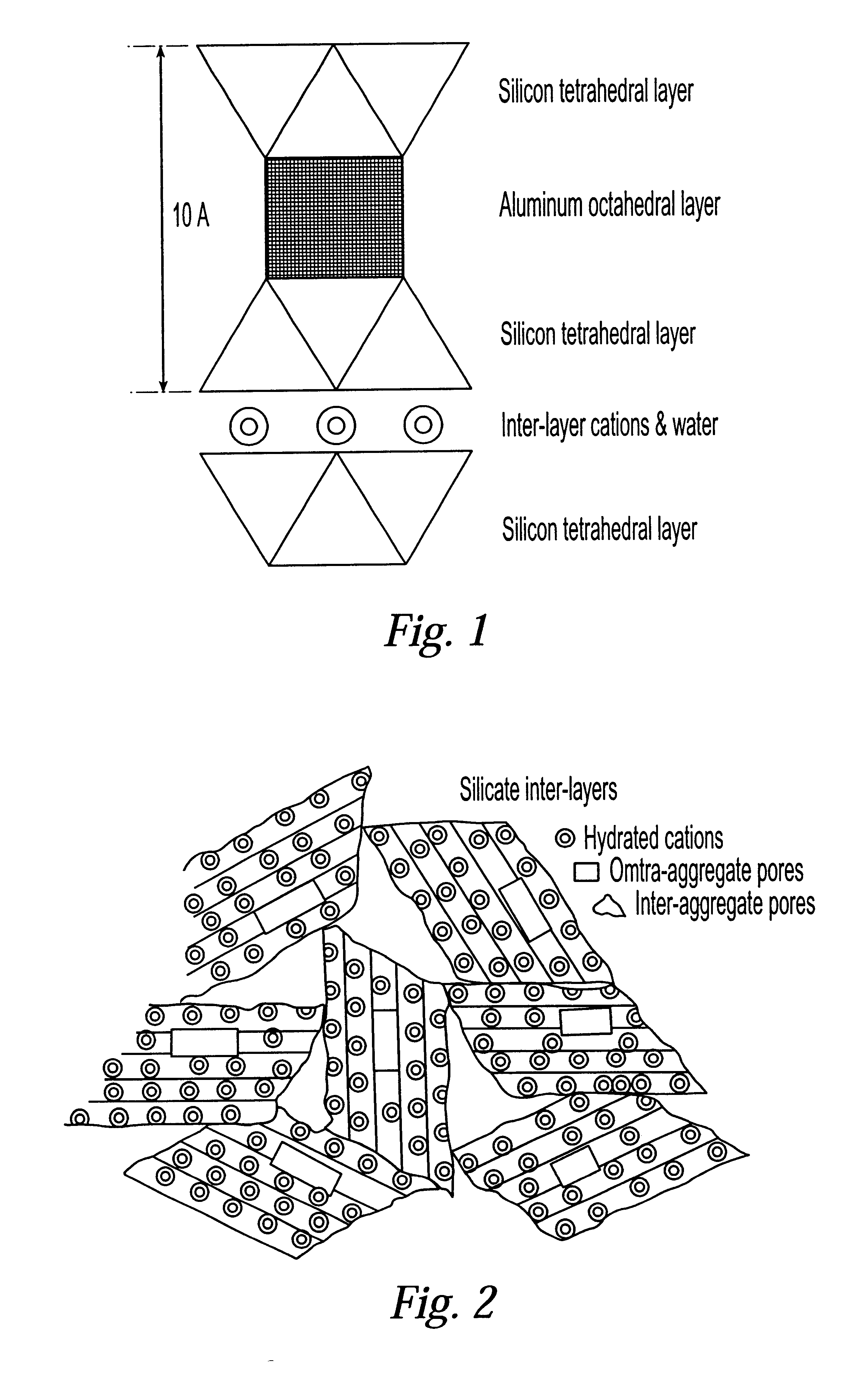
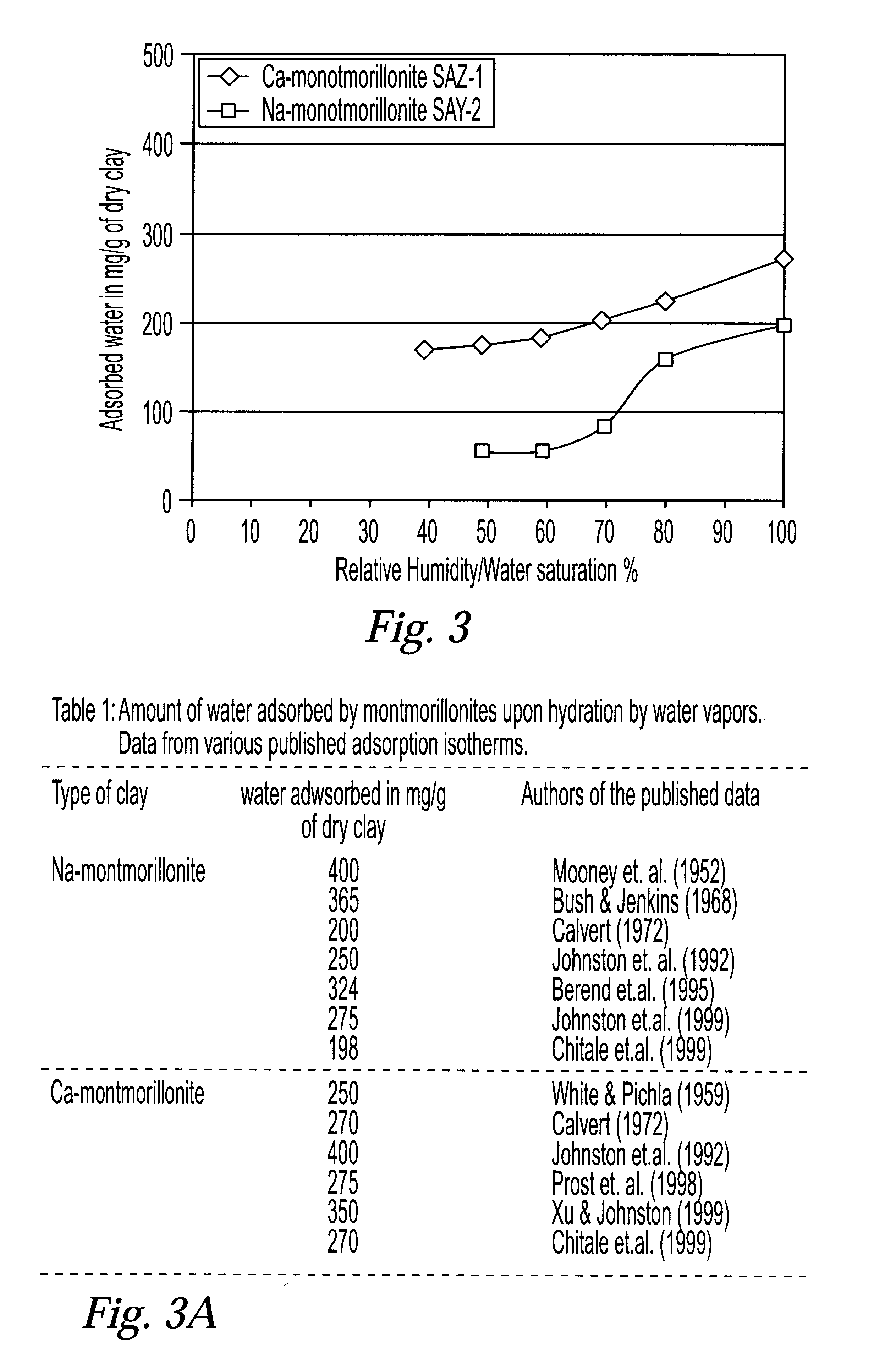
System and method for clay typing using NMR-based porosity modeling
InactiveUS6646437B1Good estimateElectric/magnetic detection for well-loggingSeismology for water-loggingClay mineralsTyping
System and method for characterizing formation properties based on NMR measurements. NMR clay measurements of this invention distinguish between interstitial pore water and the water adsorbed by the clay minerals. The measurements can be used to determine the quantity of adsorbed water in different clays and correct previously available data obtained using conventional density and neutron porosity logs. A new petrophysical parameter wetness clay is defined as an intrinsic parameter for clays, and its value is computed for members of the smectite group of clays, such as montmorillonite. The wet clay values for the density, neutron logs based on the adsorbed water in clays are used to enhance the quality and accuracy of the overall log interpretation.
Owner:HALLIBURTON ENERGY SERVICES INC
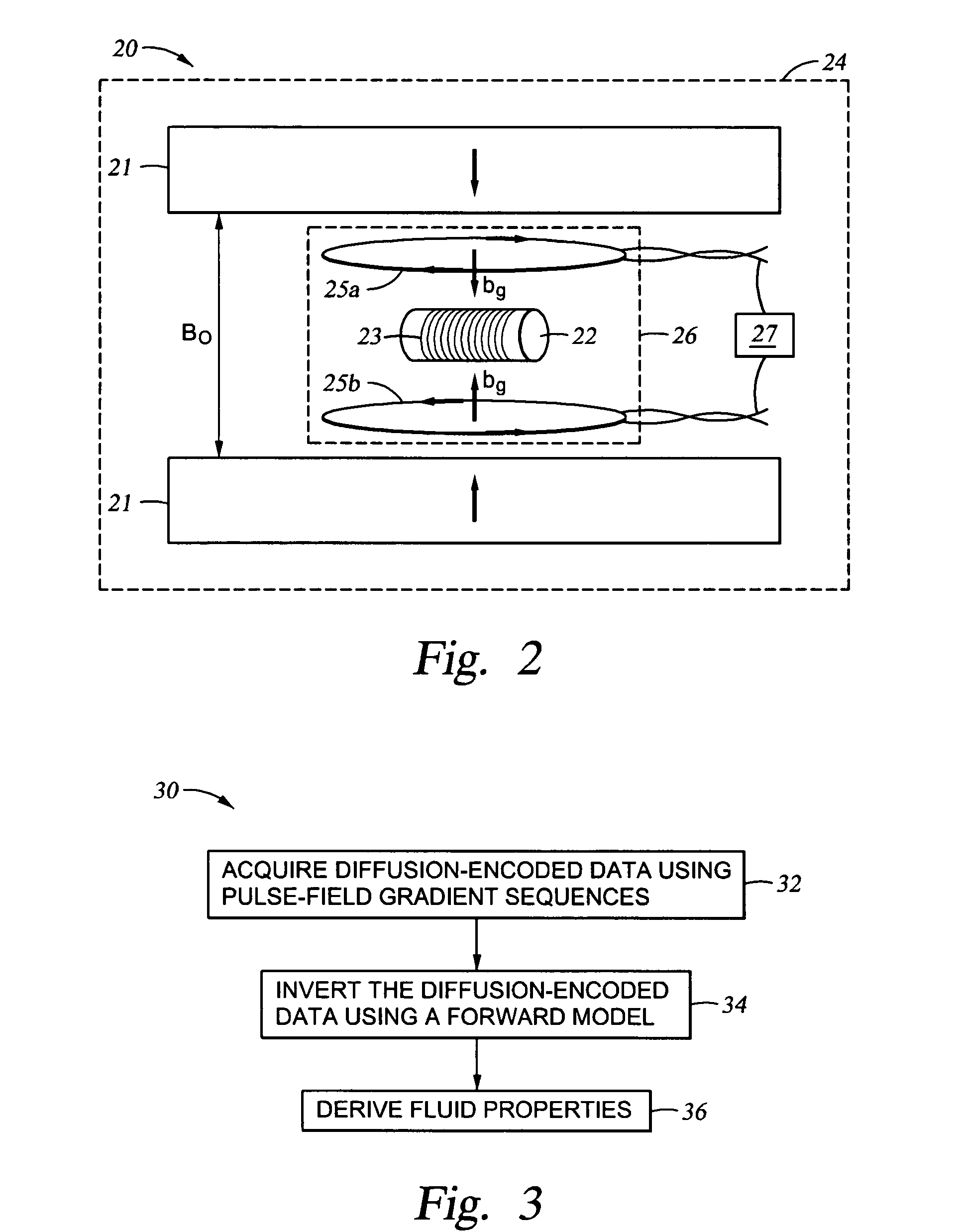
Method and apparatus for using pulsed field gradient NMR measurements to determine fluid properties in a fluid sampling well logging tool
InactiveUS20050270023A1Easy to detectRaise the ratioElectric/magnetic detection for well-loggingSurveyDiffusionNMR - Nuclear magnetic resonance
A method for determining a formation fluid property includes acquiring a suite of nuclear magnetic resonance (NMR) measurements of a fluid sample using a pulse sequence that includes pulsed field gradient pulses for encoding diffusion information, wherein each NMR measurement in the suite is acquired with a different value in a parameter in the pulsed field gradient pulses for producing a different diffusion effect, wherein the acquiring is performed in a formation fluid sampling tool in a borehole; inverting the suite of NMR measurements to produce a distribution function that relates diffusion properties of the fluid sample with an NMR property of the fluid sample; and determining the formation fluid property from the distribution function.
Owner:SCHLUMBERGER TECH CORP
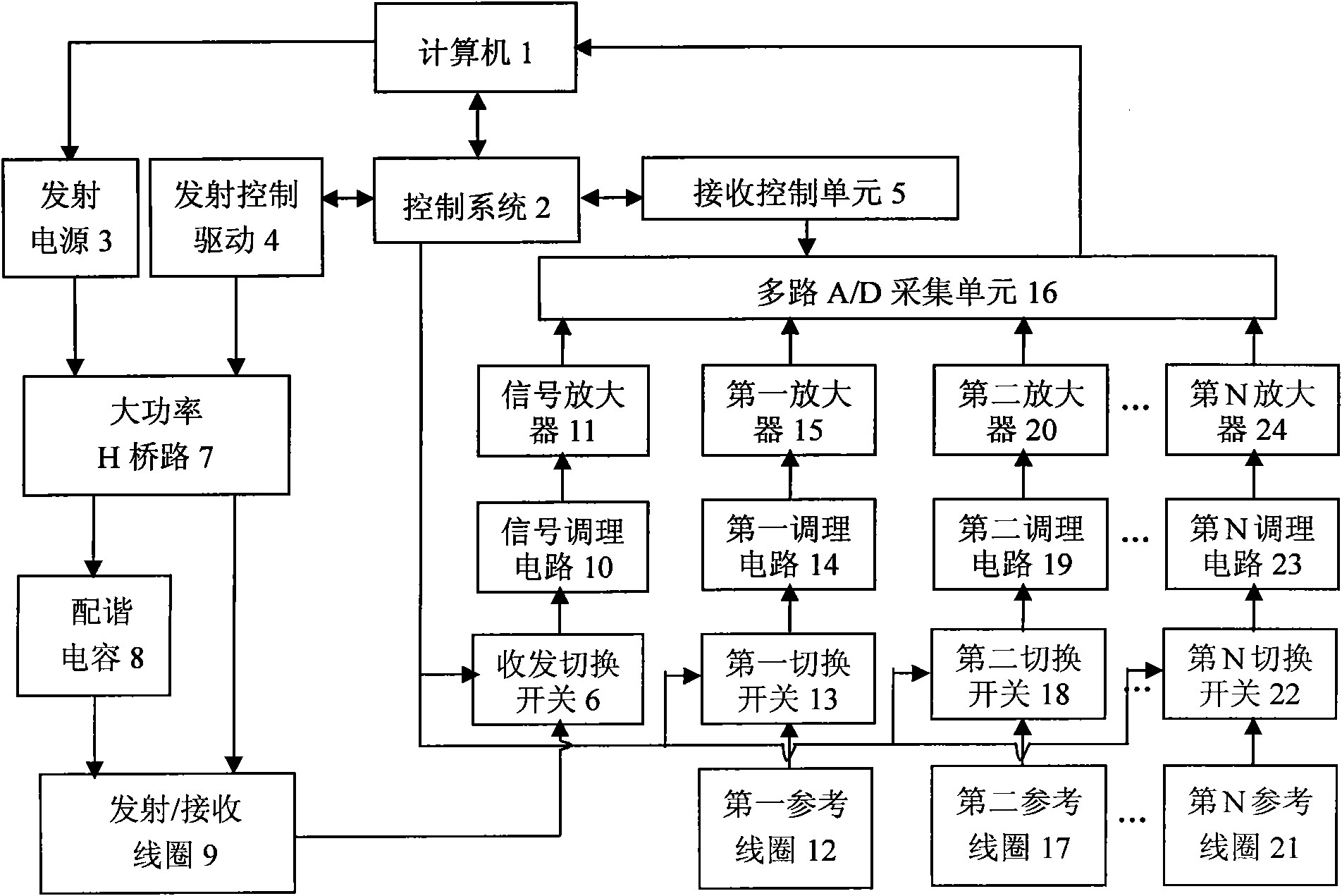
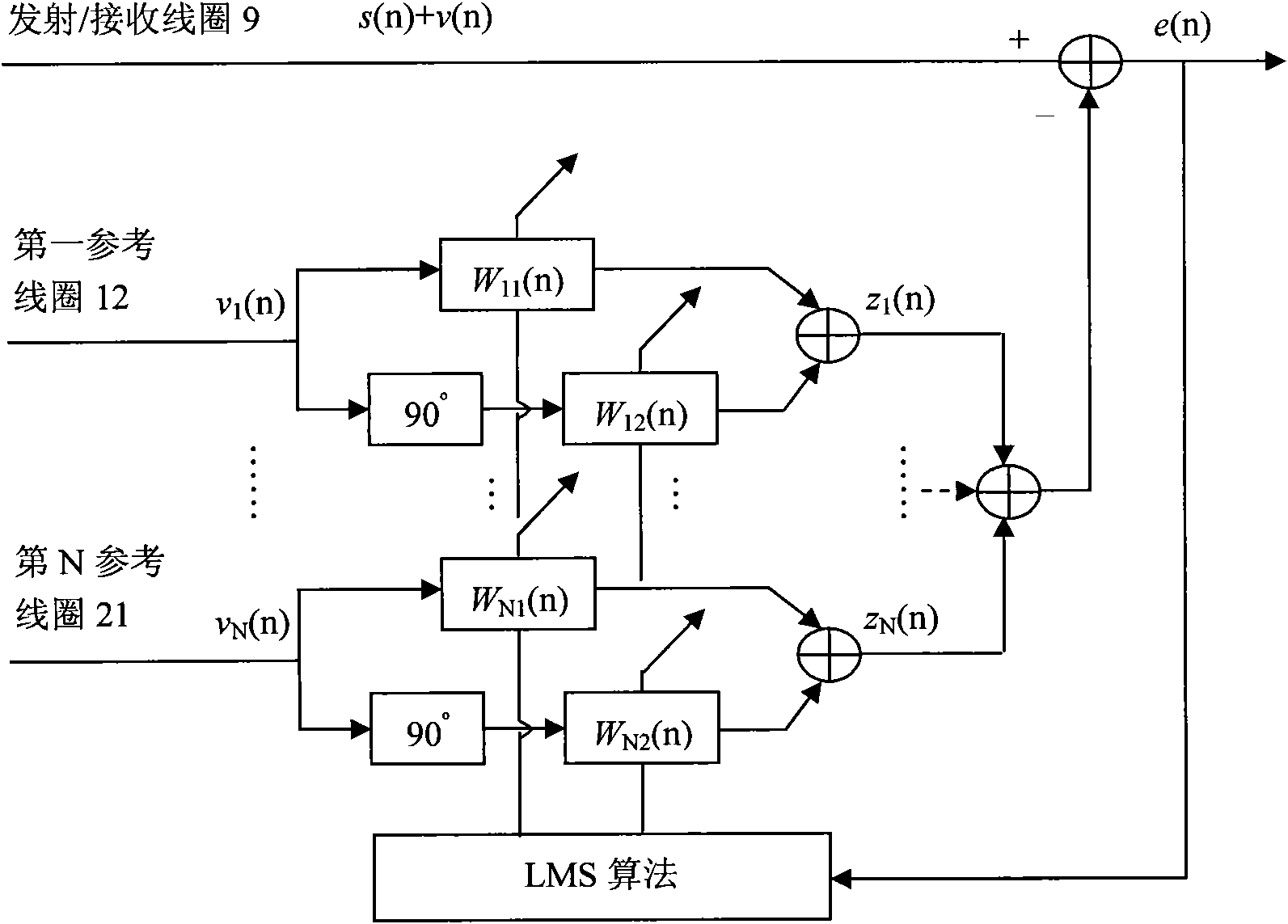
Nuclear magnetic resonance ground water detection system with reference coils and detection method
InactiveCN102053280AEfficient extractionImplement extractionWater resource assessmentDetection using electron/nuclear magnetic resonanceNMR - Nuclear magnetic resonanceInterference resistance
The invention relates to a nuclear magnetic resonance ground water detection system with reference coils and a detection method. All-waveform data of nuclear magnetic resonance signals in a transmitting / receiving coil and noise signals in the reference coils are synchronously acquired through a plurality of paths of A / D acquiring units; the distribution of optimal positions and quantity of the reference coils is realized through calculating the maximum correlation of the noise signals and the nuclear magnetic resonance signals, which are acquired by the reference coils; and under the condition of unknown signal and noise statistical properties, noise in the nuclear magnetic resonance signals obtained by the transmitting / receiving coil is maximally offset by adopting a variable step adaptive algorithm, the nuclear magnetic resonance signals are extracted under the interference of multi-field source complex strong noise, thus the problems of multiple interferences of nuclear magnetic resonance detection near villages and in neighboring regions of cities and difficulty of separating multiple kinds of interference noise data are effectively solved, the interference resistance of instruments is improved, and a reliable detection device and method are provided for searching underground water near villages and in neighboring regions of cities.
Owner:JILIN UNIV
Sensors For Estimating Properties Of A Core
InactiveUS20090105955A1Electric/magnetic detection for well-loggingSurveyEngineeringComputer science
A method for estimating a property downhole is provided, which, in one aspect, may include receiving a core at a receiving end of a downhole tool while removing a portion of the received core distal from the receiving end of the tool, obtaining measurements by a sensor downhole, and processing the measurements to estimate the property of interest.
Owner:BAKER HUGHES INC
Multiple SQUID magnetometer
InactiveUS20070241747A1Avoid complicationsHigh sensitivitySuperconductors/hyperconductorsMagnetic field measurement using superconductive devicesCondensed matter physicsSQUID
Multiple SQUID magnetometers that include at least two SQUID loops, each of which is composed of at least two Josephson Junctions connected in parallel with superconducting wires, are provided. The SQUID loops are fabricated such that they share a common Josephson Junction. Devices and application that employ the multiple SQUID magnetometers are also provided.
Owner:FLORIDA STATE UNIV RES FOUND INC
Systems and methods for deep-looking nmr logging
ActiveUS20090072825A1Add depthAccurate estimateElectric/magnetic detection for well-loggingMaterial analysis by using resonanceNMR - Nuclear magnetic resonanceMagnetic poles
An NMR logging tool for conducting NMR measurements in a plurality of sensitive volumes ranging up to a meter from the tool. The tool comprises a magnetic assembly using one or more permanent magnets and at least one pole piece for extending a magnet pole and shaping the magnetic field to simulate a magnetic monopole in a sensitive volume within the formation. Different embodiments of a segmented antenna enable directional NMR logging. The tool embodiments and methods of their use are suitable for wireline or LWD logging, and can be used for directional drilling.
Owner:HALLIBURTON ENERGY SERVICES INC
System and method for geologically-enhanced magnetic resonance imaging logs
InactiveUS6255819B1Electric/magnetic detection for well-loggingMeasurements using NMR spectroscopyMicro imagingLithology
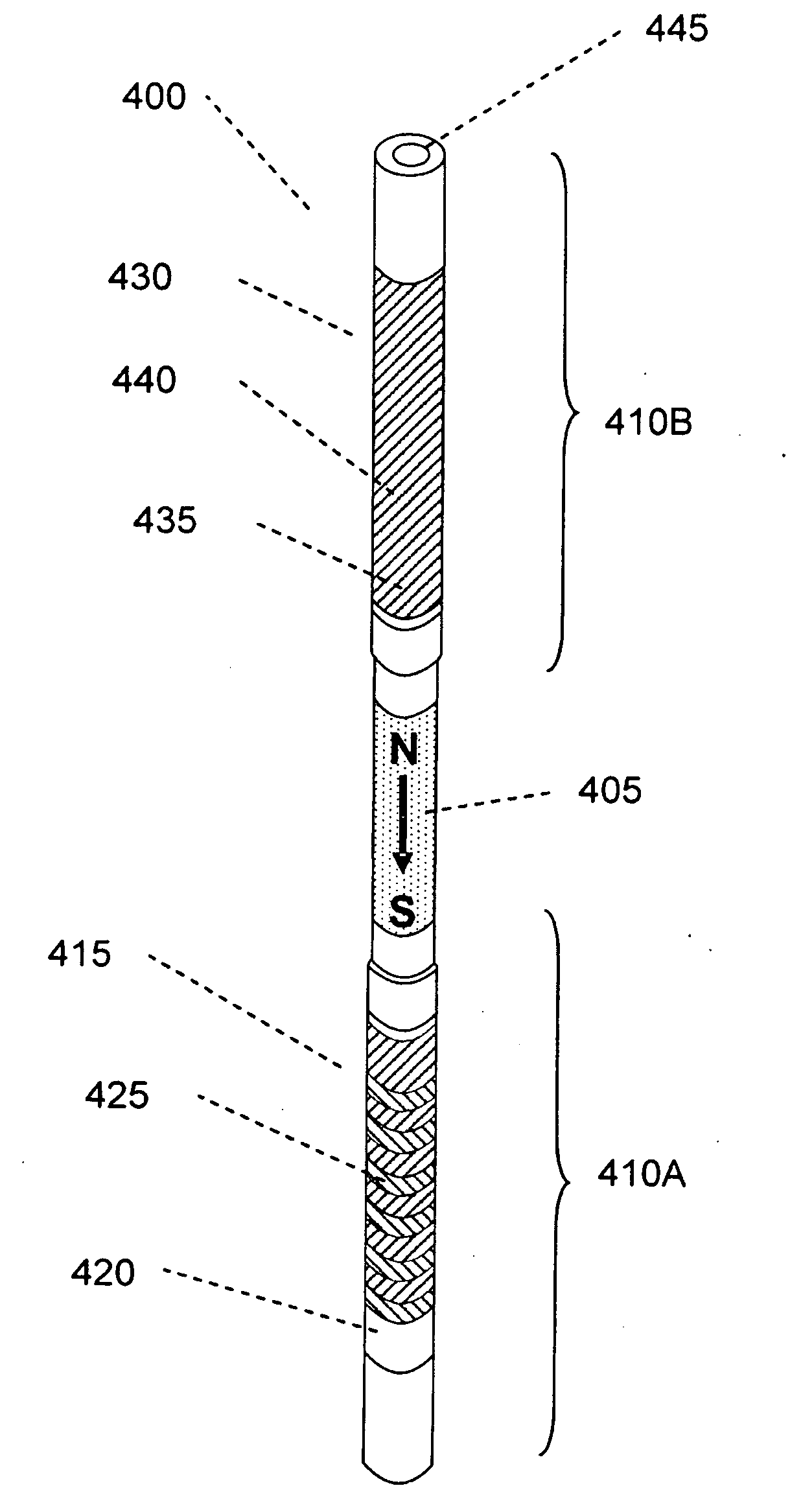
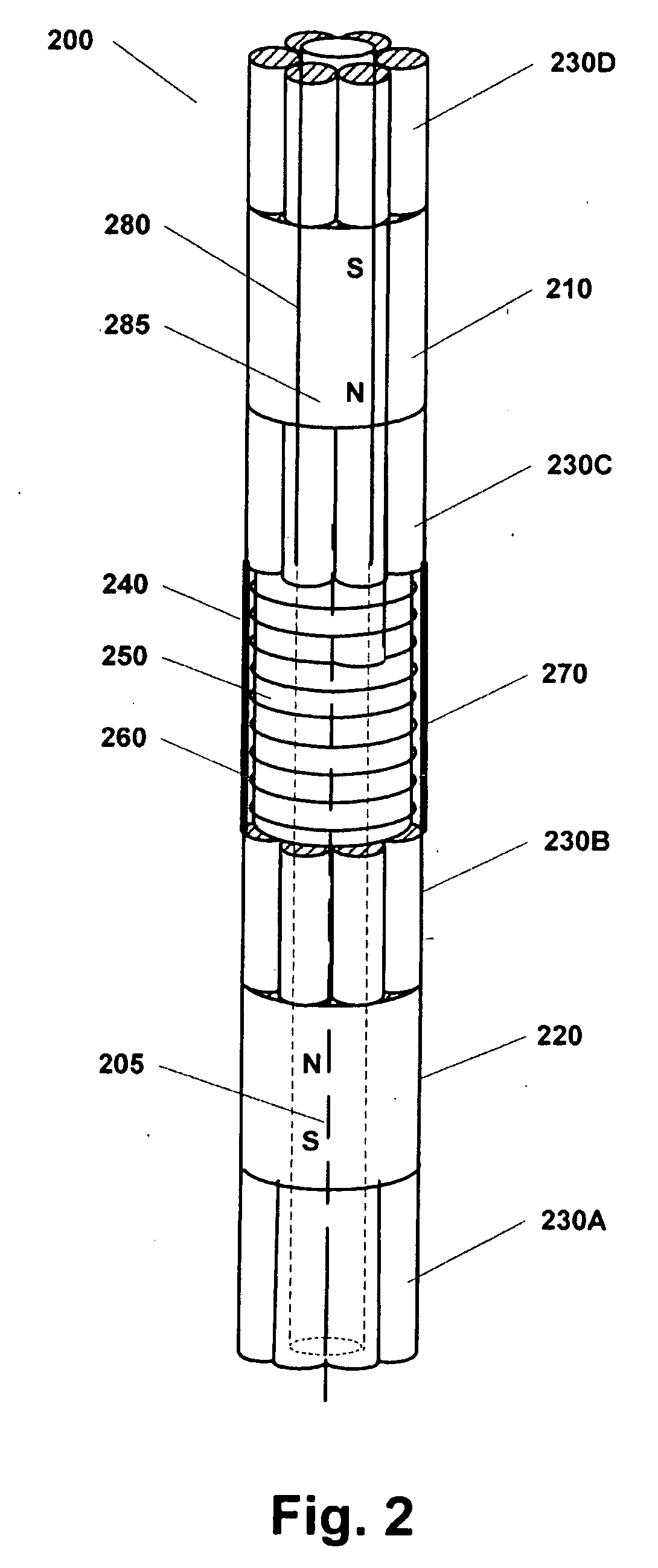
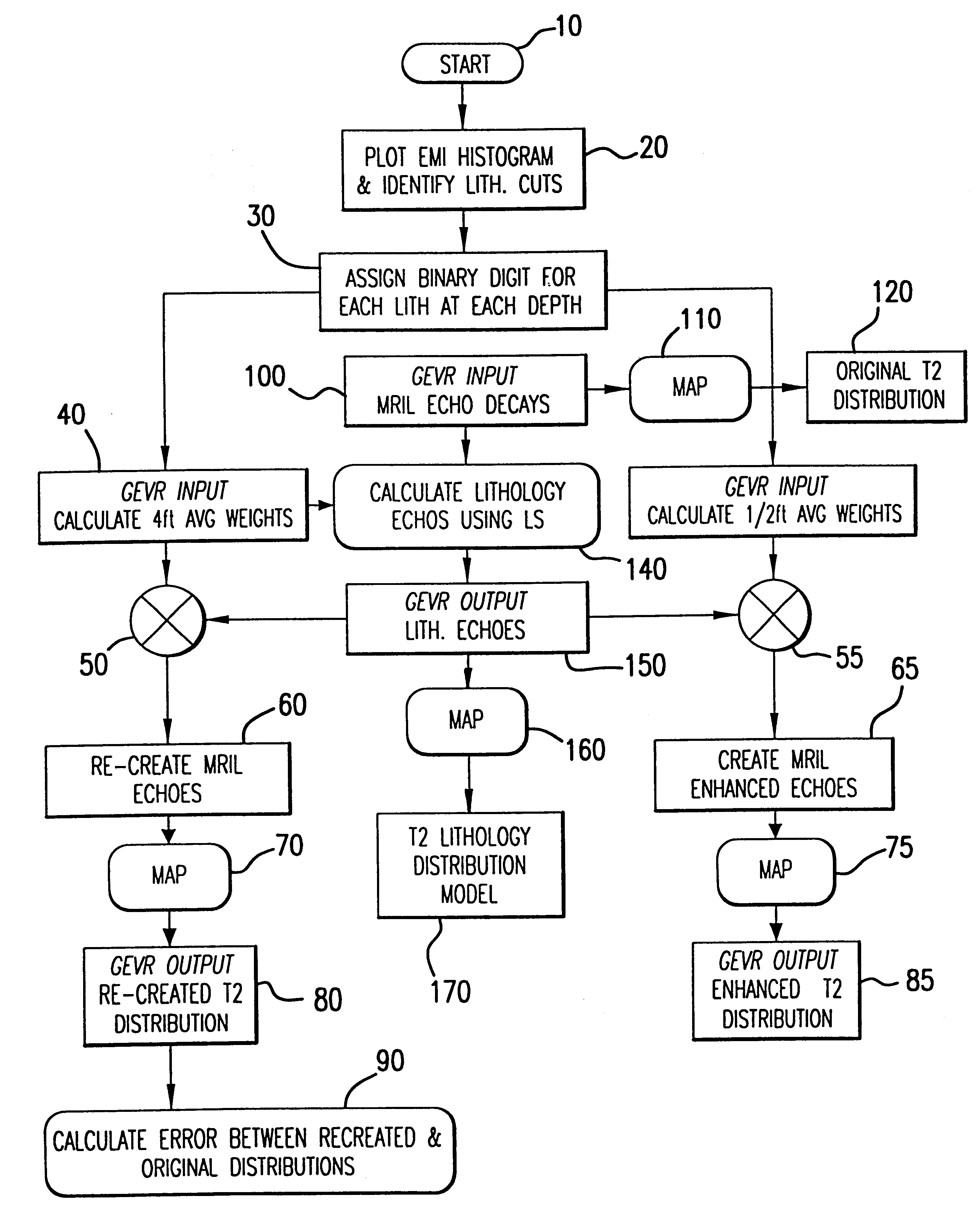
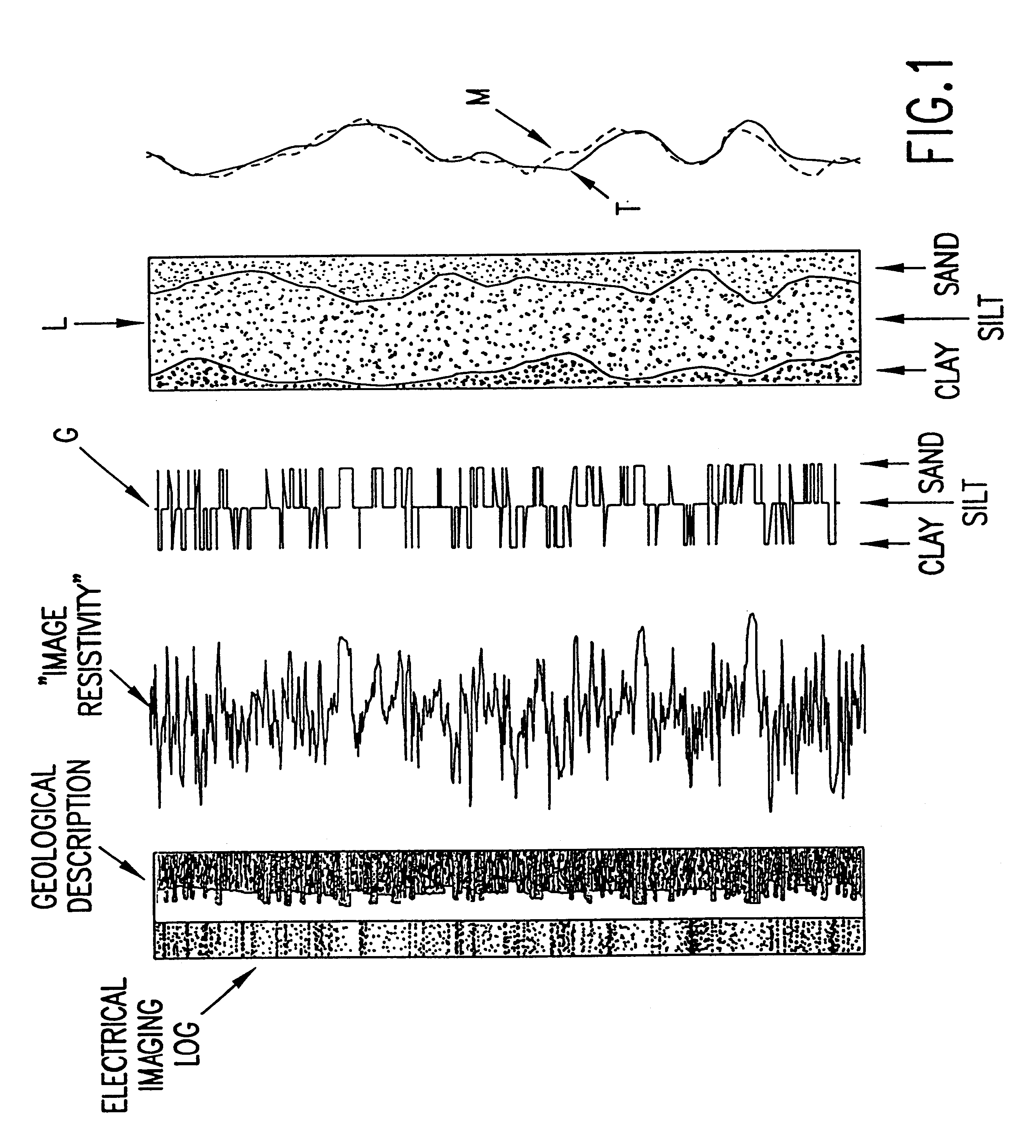
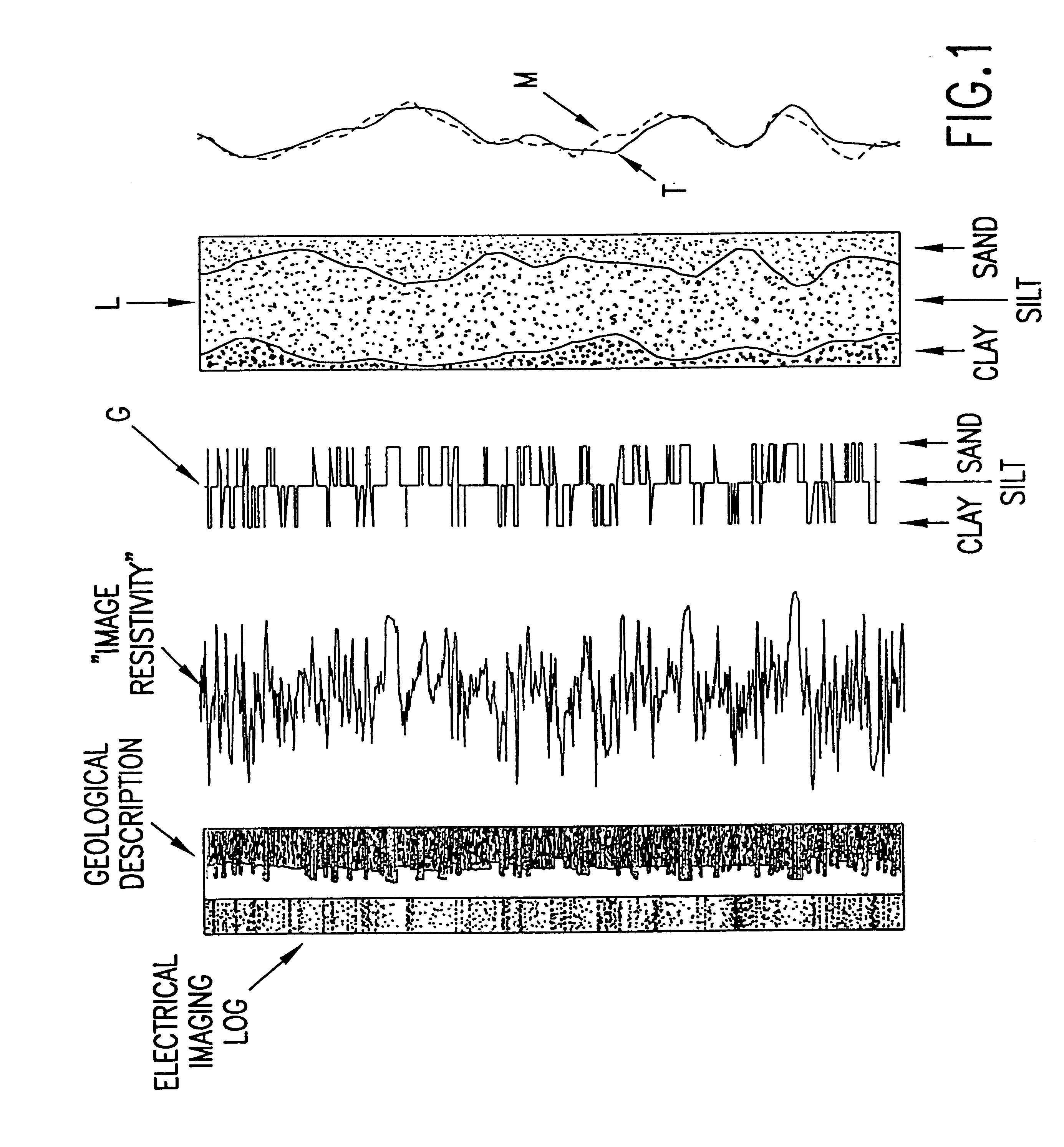
An interpretation method and system for NMR echo-train data in thinly laminated sequences. The invention uses geological information obtained at higher vertical resolution, such as using Electric Micro Imaging, to enhance the vertical resolution of echo-train data, and thus avoids log interpretations in which the hydrocarbon potential of the formation can be misread because low resolution logs tend to provide an average description of the formation. Such averaging is especially problematic in thinly laminated sequences that consist of highly permeable and porous sand layers and less permeable silt or essentially impermeable shale layers. In a preferred embodiment, using the additional high-resolution formation information one can estimate the typical T2-spectra of lithological laminae, and significantly enhance the permeability estimate in the laminated sequences. The method and system are applicable to any temporal data from other logging tools, such as the thermal neutron decay log and others. The system and method enable proper evaluation of the high potential of thinly laminated formations, which may otherwise be overlooked as low permeable formations.
Owner:HALLIBURTON ENERGY SERVICES INC
System and method for enhanced vertical resolution magnetic resonance imaging logs
InactiveUS6337568B1Electric/magnetic detection for well-loggingMeasurements using NMR spectroscopyLithologyMicro imaging
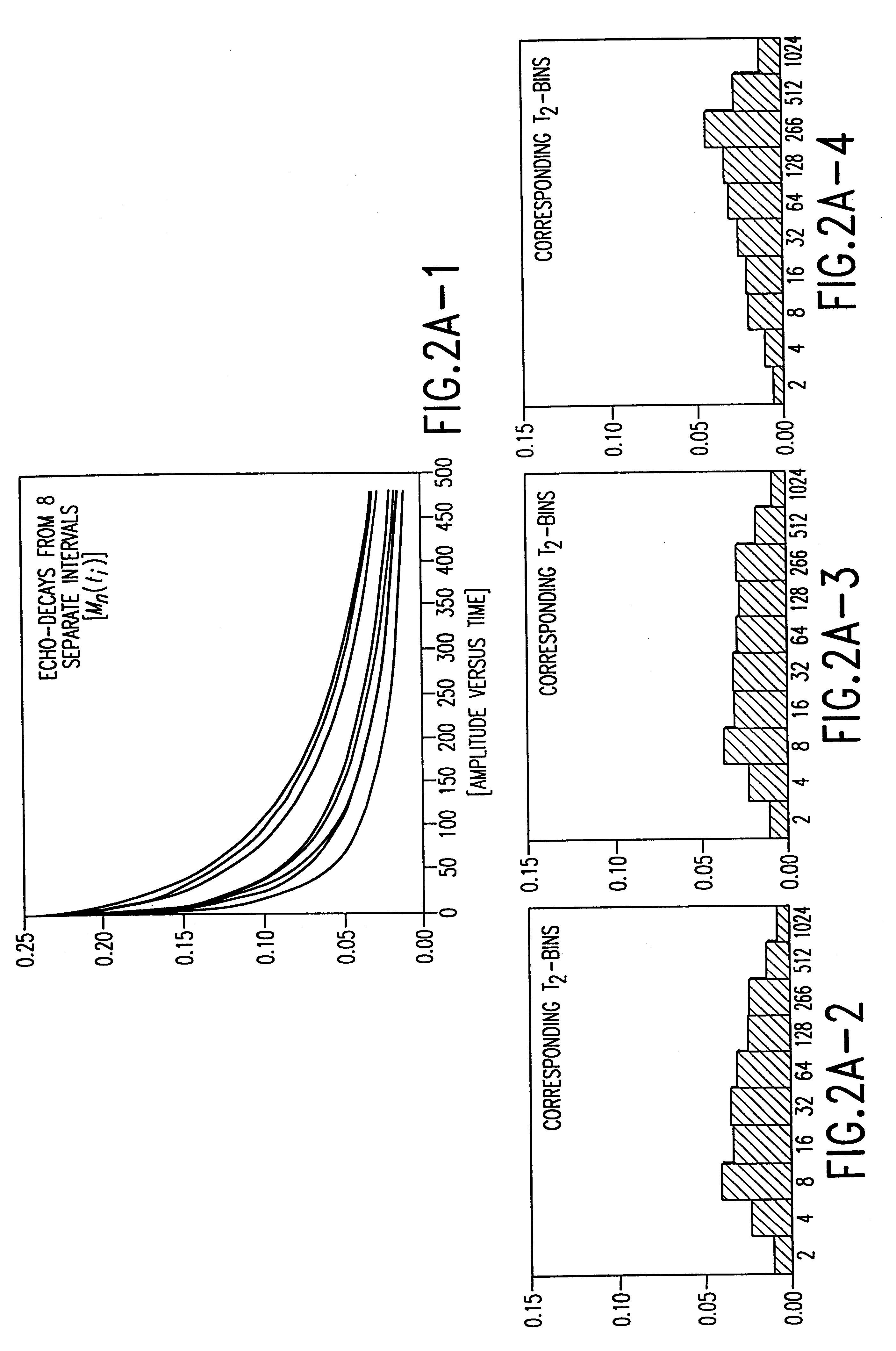
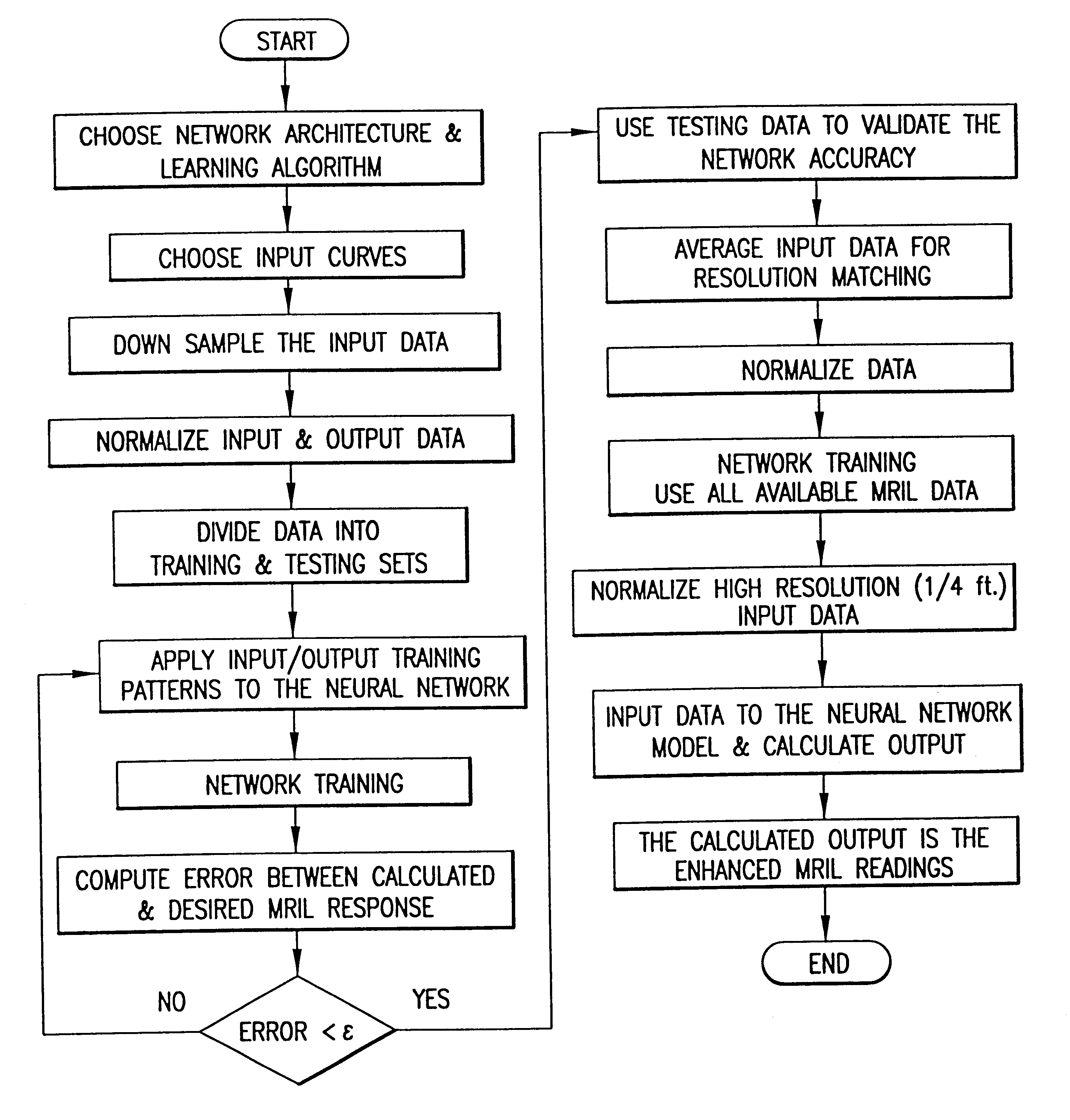
An interpretation method and system for NMR echo-train data in thinly laminated sequences. The invention uses geological information obtained at higher vertical resolution, such as using Electric Micro Imaging, to enhance the vertical resolution of echo-train data, and thus avoids log interpretations in which the hydrocarbon potential of the formation can be misread because low resolution logs tend to provide an average description of the formation. Such averaging is especially problematic in thinly laminated sequences that consist of highly permeable and porous sand layers and less permeable silt or essentially impermeable shale layers. In a preferred embodiment, using the additional high-resolution formation information one can estimate the typical T2-spectra of lithological laminae, and significantly enhance the permeability estimate in the laminated sequences. In another aspect the system and method of the preferred embodiment use neural network(s) to further enhance the resolution of a particular log measurement. The method and system are applicable to any temporal data from other logging tools, such as the thermal neutron decay log and others. The system and method enable proper evaluation of the high potential of thinly laminated formations, which may otherwise be overlooked as low permeable formations.
Owner:HALLIBURTON ENERGY SERVICES INC
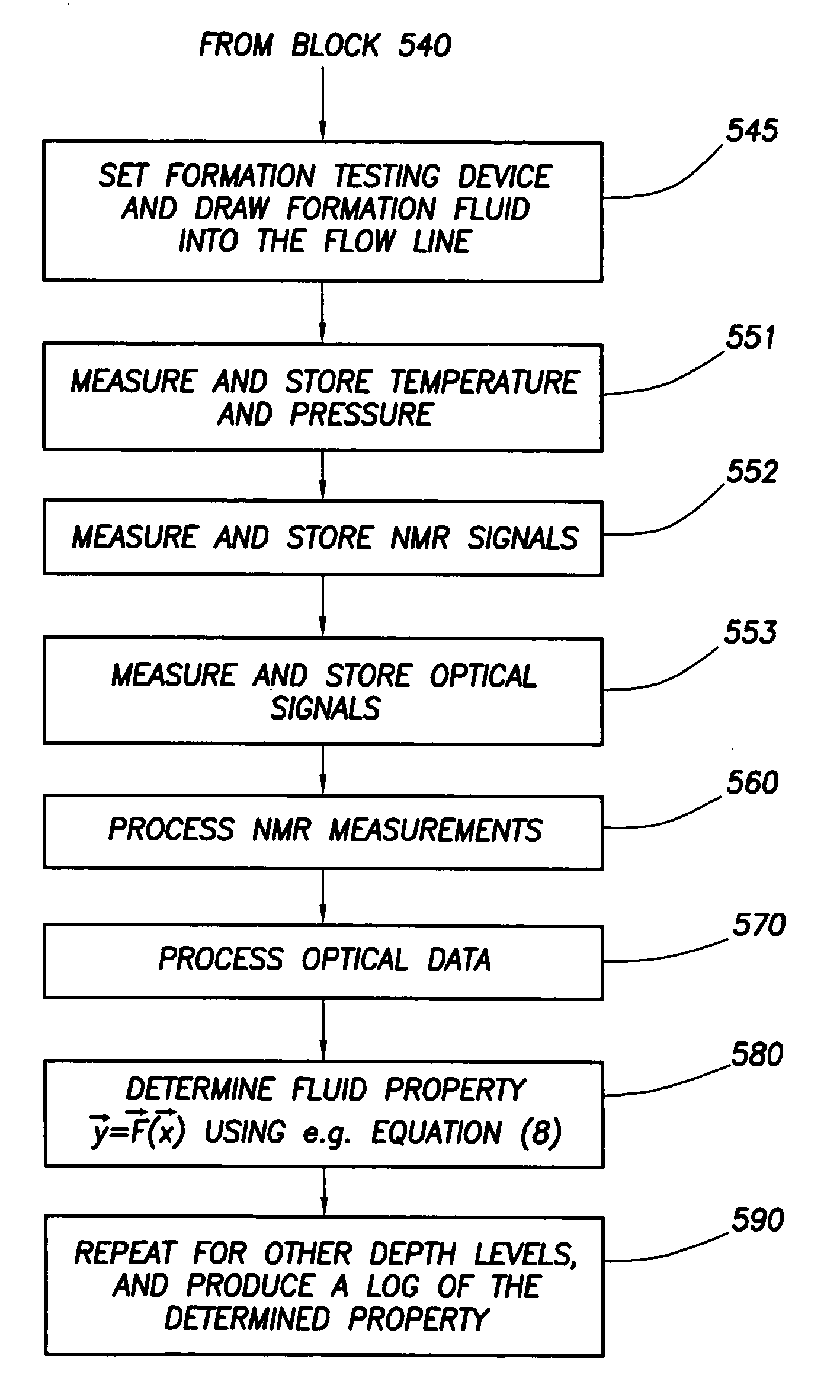
Method and apparatus for combined NMR and formation testing for assessing relative permeability with formation testing and nuclear magnetic resonance testing
InactiveUS20040055745A1Electric/magnetic detection for well-loggingSurveyProduction rateNMR - Nuclear magnetic resonance
Formation testing, resistivity and NMR measurements are used concurrently to determine a relative permeability representative of a formation surrounding the borehole. A method and apparatus is provided for accurate determination of the relative permeability for a formation by measuring saturation levels in a region of interest determined from resistivity or NMR readings versus time during formation draw down pressure testing. The method and apparatus determines and effective permeability over time for various saturation levels to determine the relative permeability for the formation at each saturation level and also enables determination of the efficacy of utilizing completion fluids in the formation to increase formation productivity. The method and apparatus enables more accurate determination of effective permeability and the irreducible saturation level. The method and apparatus also provides for determination of whether a pad is sealed properly against a borehole wall and determines if a probe is clogged.
Owner:BAKER HUGHES INC
Method and apparatus for using pulsed field gradient NMR measurements to determine fluid properties in a fluid sampling well logging tool
InactiveUS7053611B2Easy to detectRaise the ratioElectric/magnetic detection for well-loggingSurveyDiffusionNMR - Nuclear magnetic resonance
A method for determining a formation fluid property includes acquiring a suite of nuclear magnetic resonance (NMR) measurements of a fluid sample using a pulse sequence that includes pulsed field gradient pulses for encoding diffusion information, wherein each NMR measurement in the suite is acquired with a different value in a parameter in the pulsed field gradient pulses for producing a different diffusion effect, wherein the acquiring is performed in a formation fluid sampling tool in a borehole; inverting the suite of NMR measurements to produce a distribution function that relates diffusion properties of the fluid sample with an NMR property of the fluid sample; and determining the formation fluid property from the distribution function.
Owner:SCHLUMBERGER TECH CORP
Apparatus and method for measuring stratum rock physical property by rock NMR relaxation signal
InactiveCN1763563ACalculation speedHigh precisionAnalysis using nuclear magnetic resonanceDetection using electron/nuclear magnetic resonanceFluid saturationNMR - Nuclear magnetic resonance
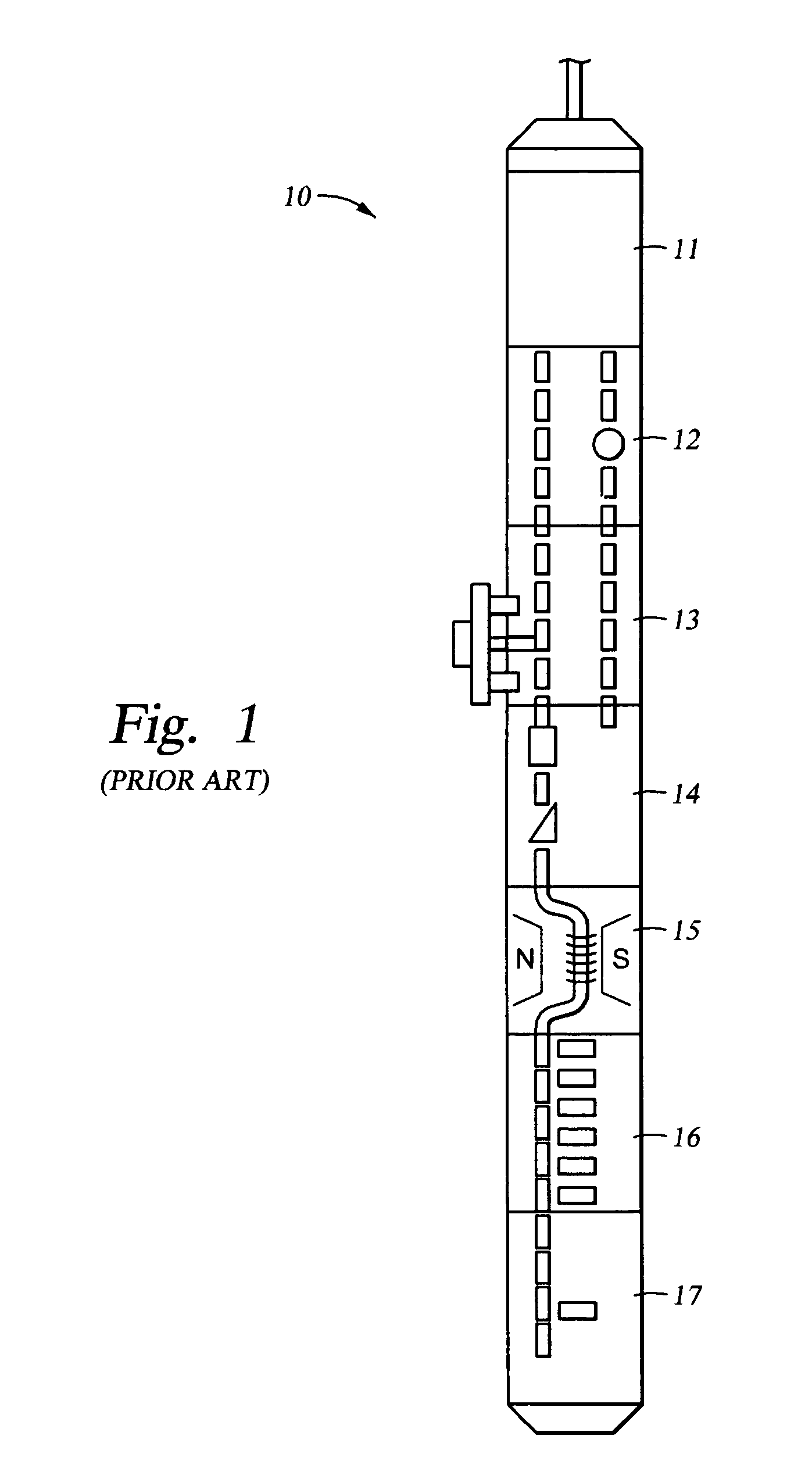
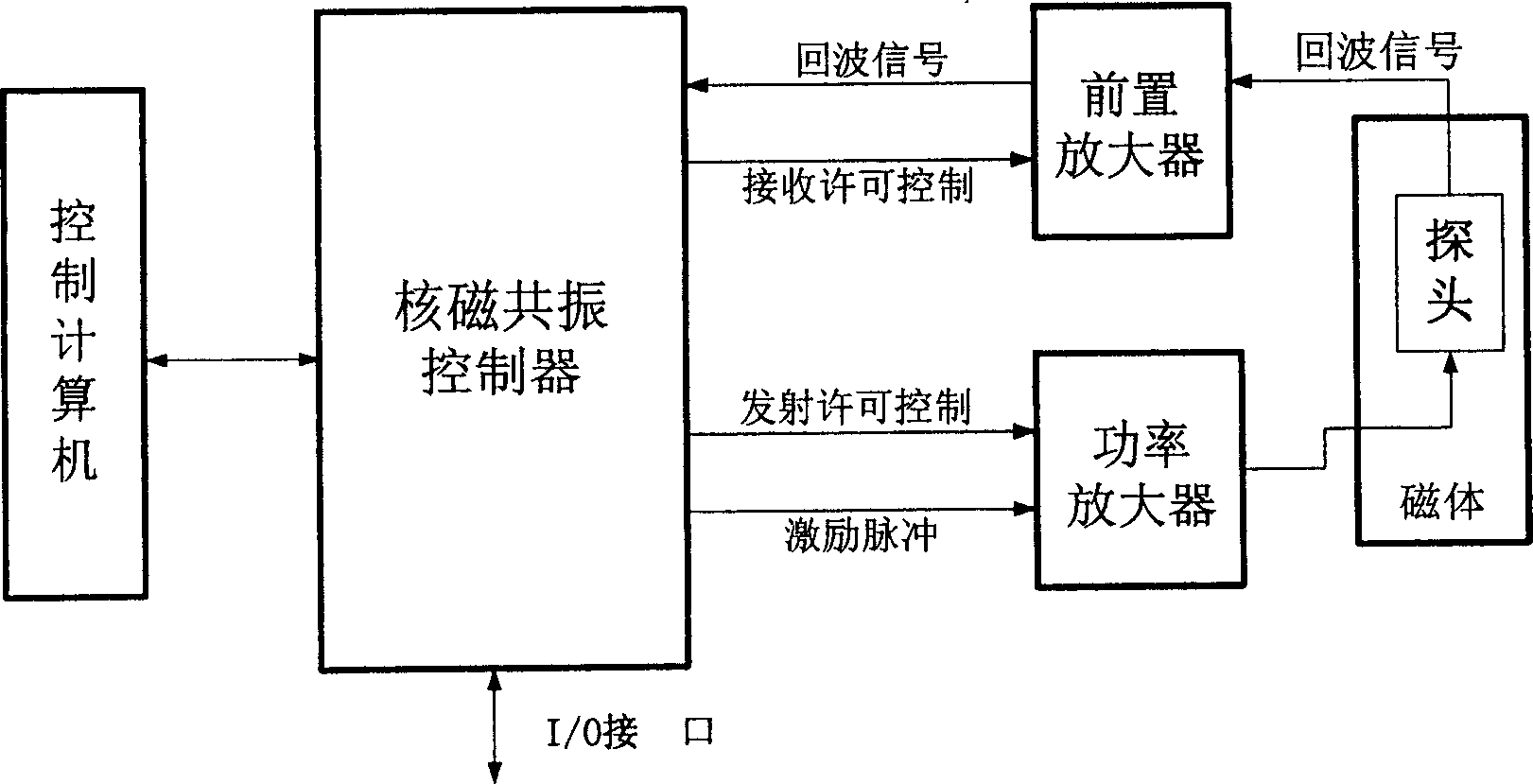
The invention discloses a rock nuclear magnetic resonance relaxation signal measuring device of formation rock matter property, which comprises the following parts: magnet, probe, preposition amplifier, power amplifier, nuclear magnetic resonance controller and control computer, wherein the nuclear magnetic resonance controller generates specific frequency and waveshape radio frequency actuation impulse, which is sent to the nuclear magnetic resonance probe in the magnet after magnified; the rock sample is set in the exciting probe, which generates nuclear magnetic resonance backward wave signal; the nuclear magnetic resonance probe receives the backward wave signal and sends to the nuclear magnetic resonance controller after magnified, which is sent to the computer finally. The invention can generate the parameter for usage directly, which can be applied in the oil field nuclear magnetic resonance well.
Owner:PEKING UNIV
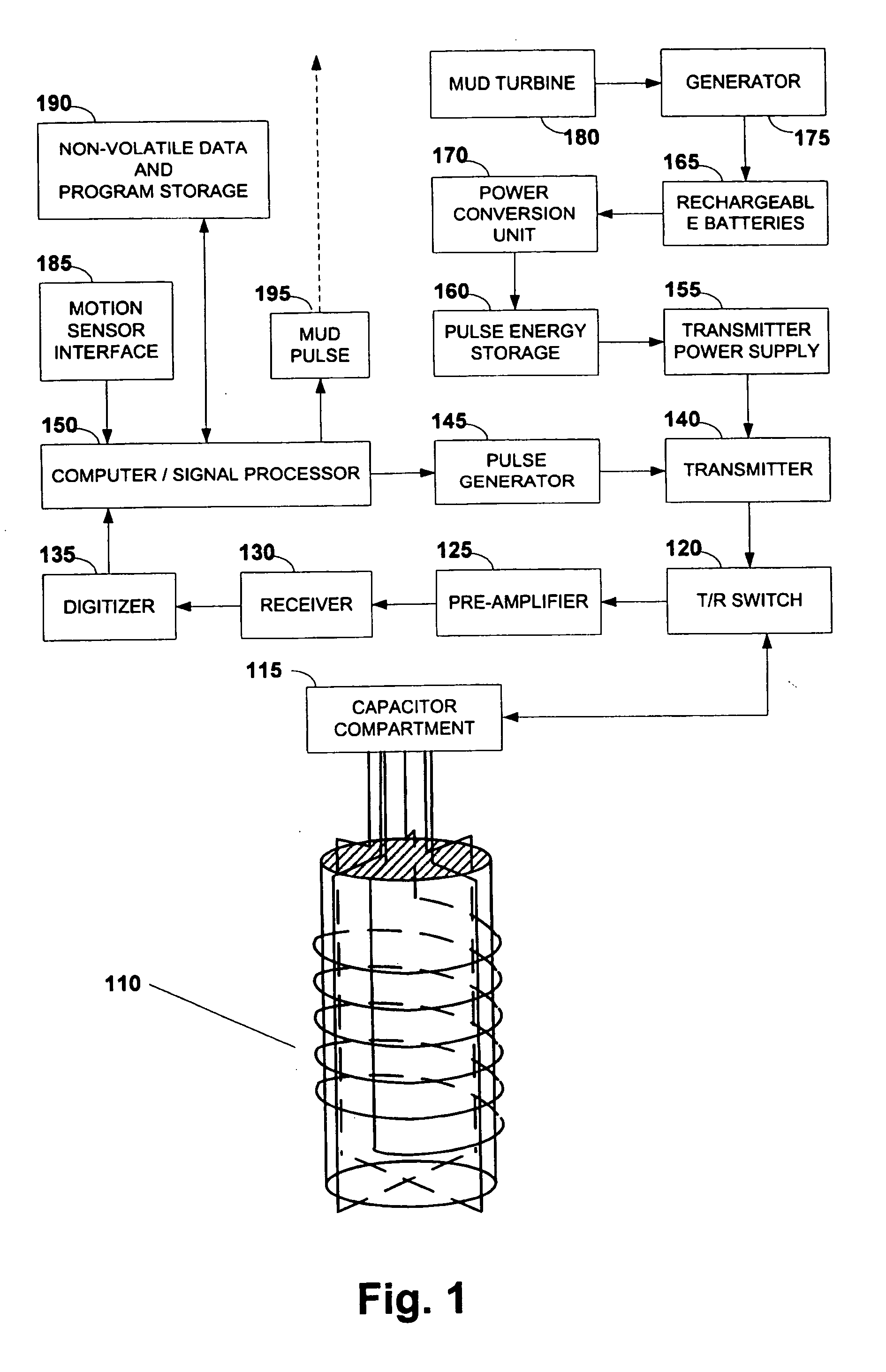
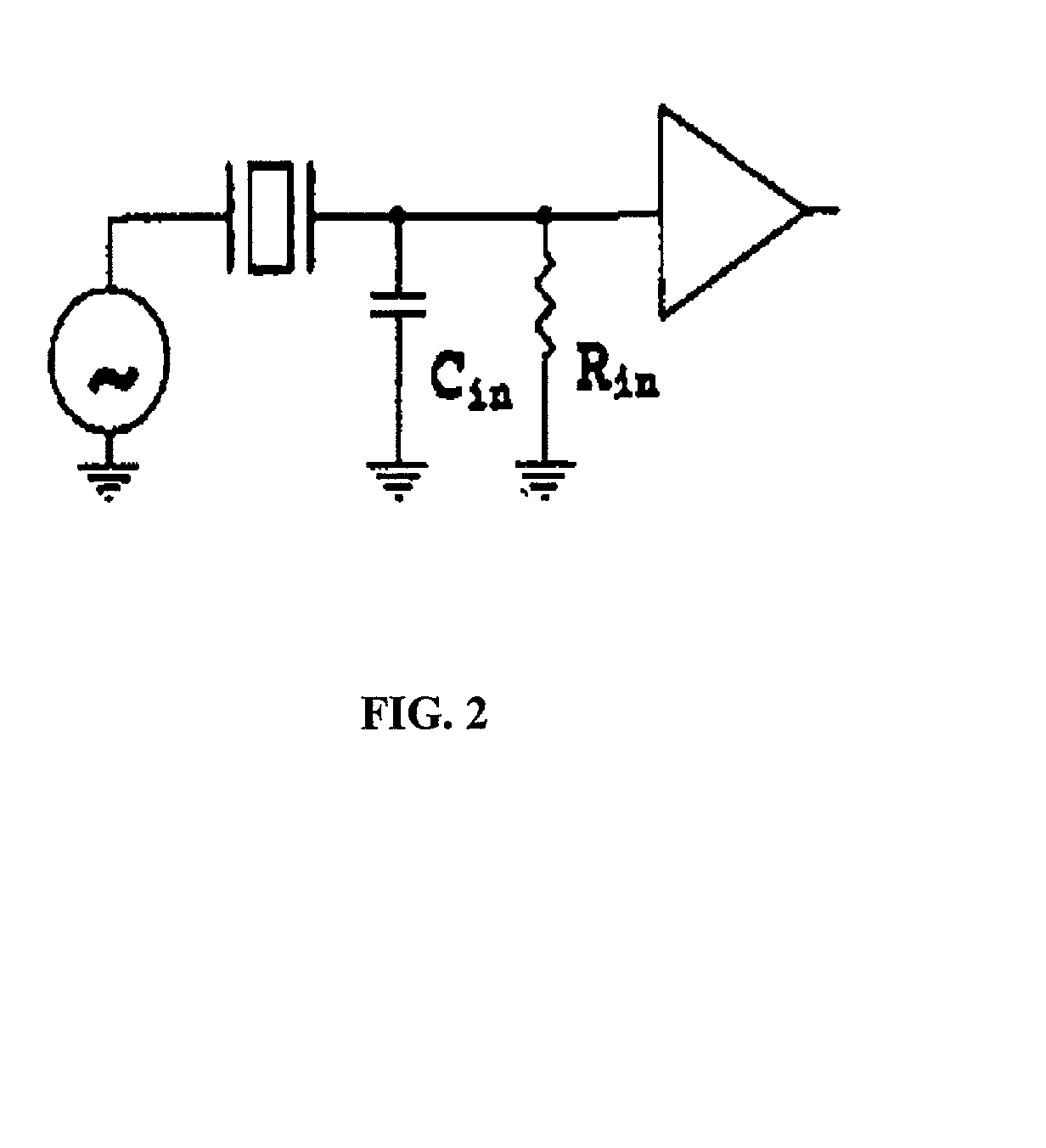
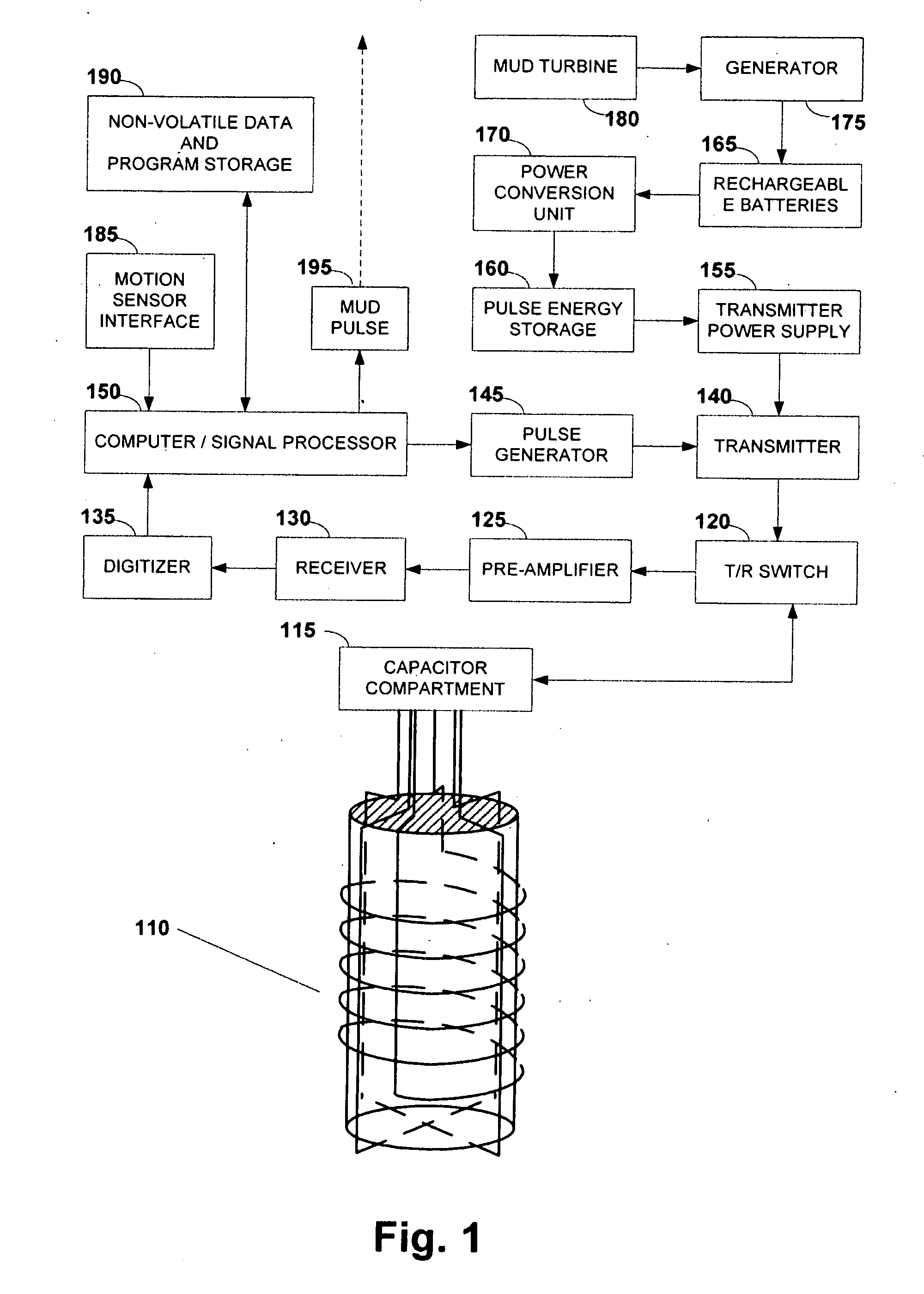
Active signal conditioning circuitry for well logging and monitoring while drilling nuclear magnetic resonance spectrometers
InactiveUS6603309B2Electric/magnetic detection for well-loggingMaterial analysis by using resonanceNMR - Nuclear magnetic resonanceWell logging
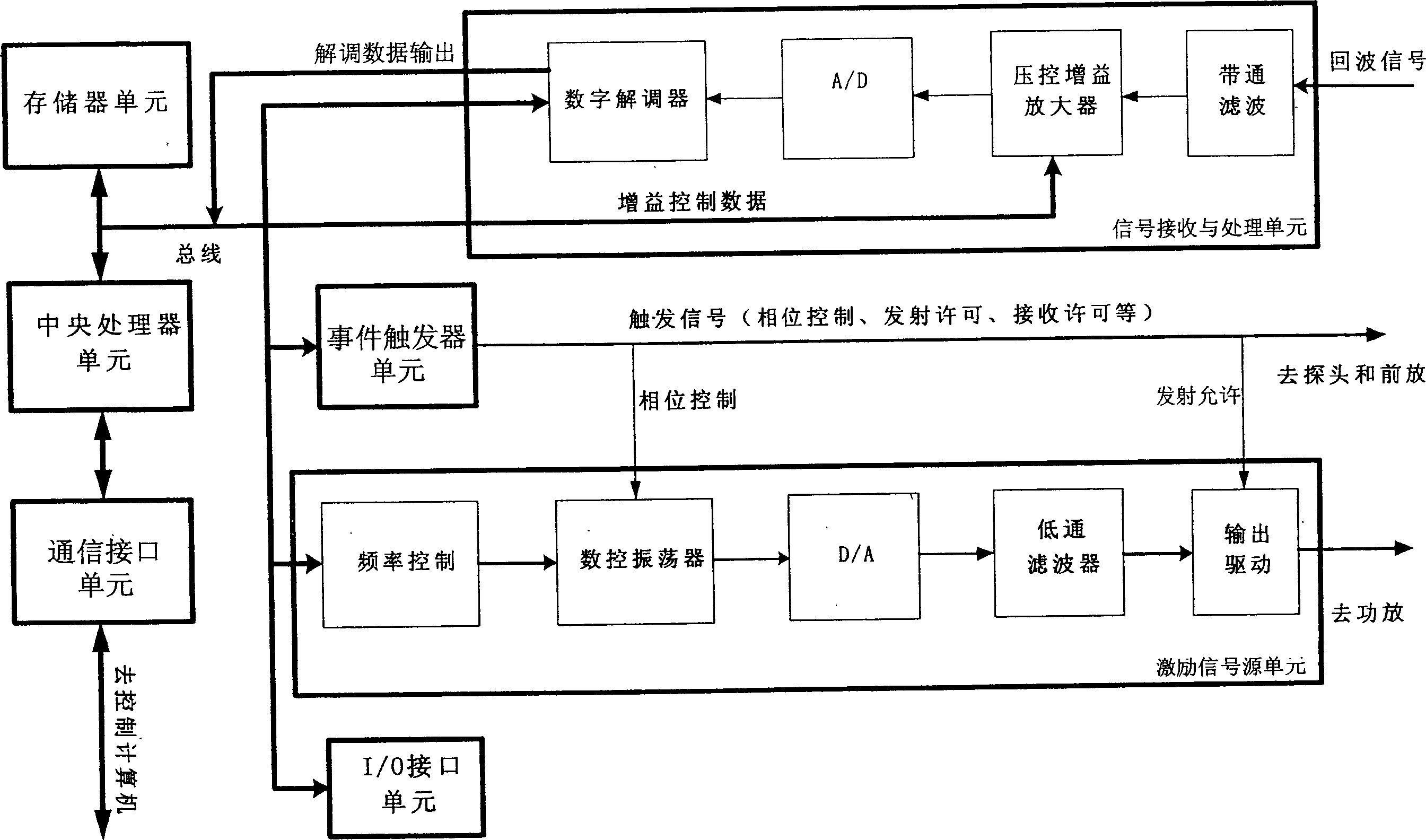
NMR transmitter / receiver antenna active signal conditioning circuitry that enables receiver antenna circuit protection from high voltage RF transmitter pulses, provides energy dumping for the entire antenna in successive stages and eliminates re-tuning during sweeping of the antenna frequency.
Owner:BAKER HUGHES INC
Nuclear magnetic resonance detection device and method for advanced detection of water bodies in front
ActiveCN102062877ASmall footprintEnsure construction safetyDetection using electron/nuclear magnetic resonanceCapacitanceEngineering
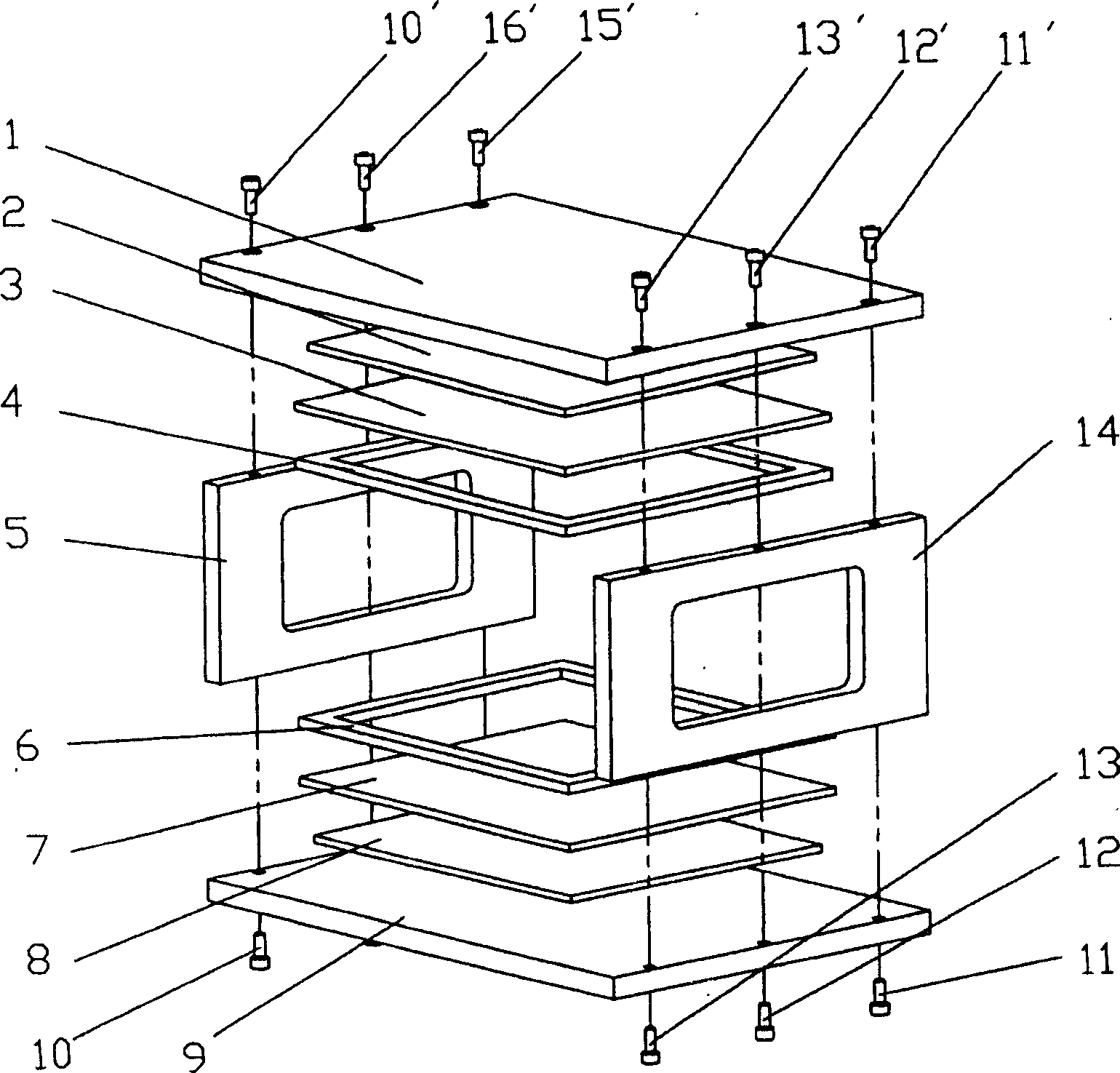
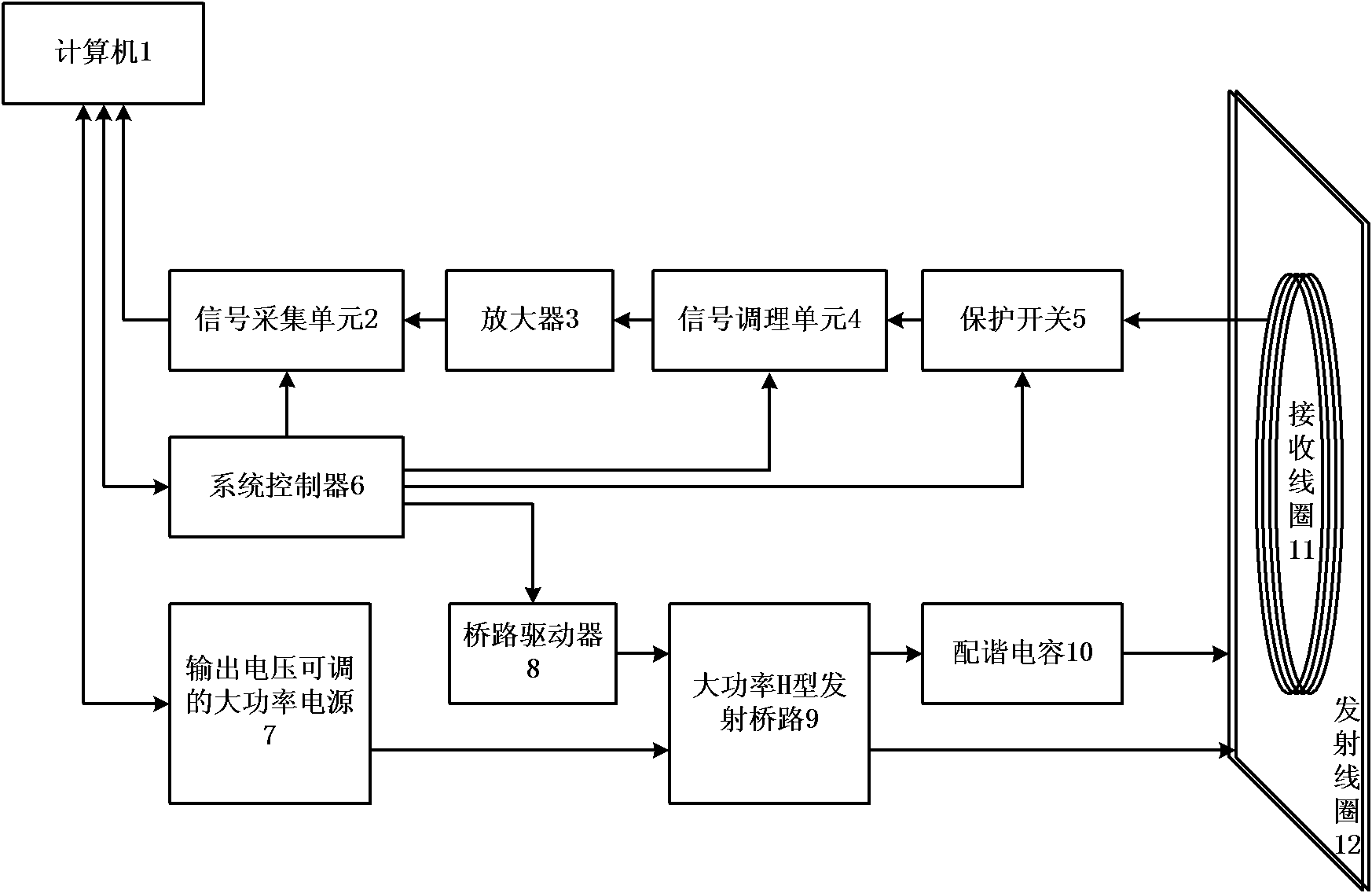
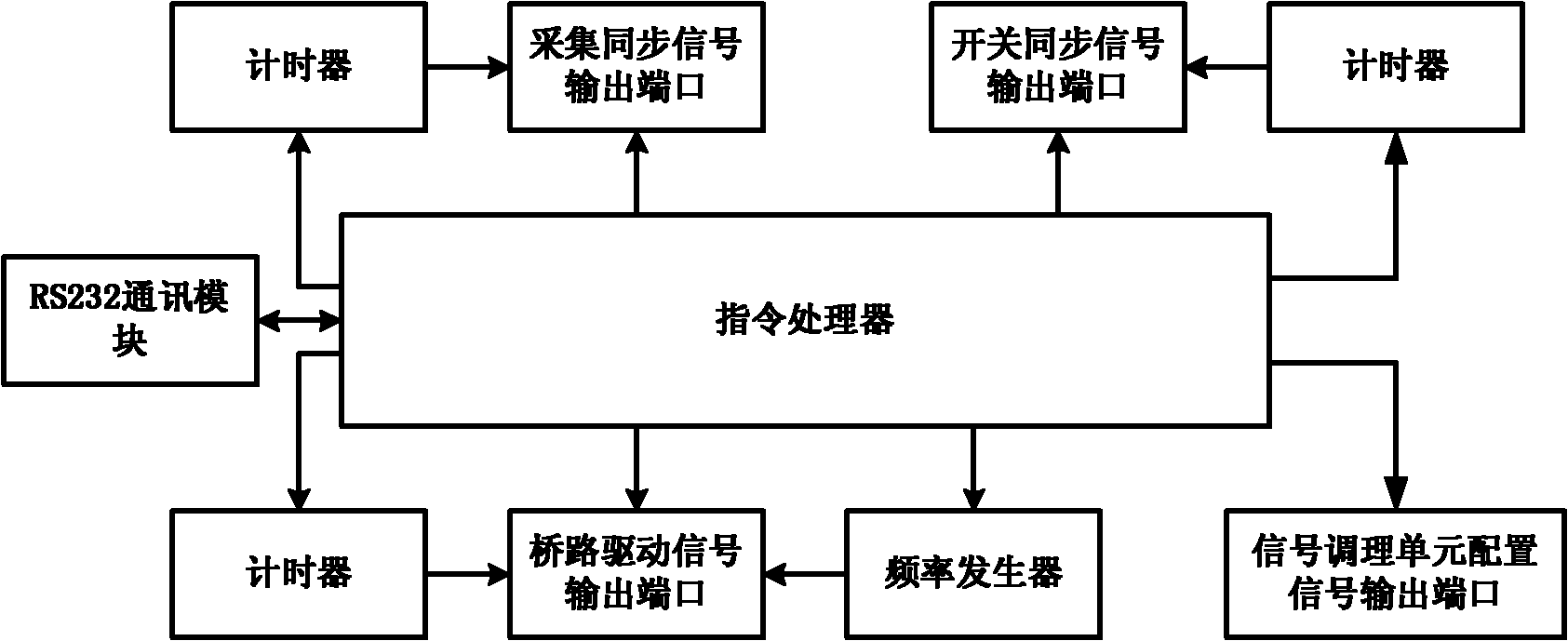
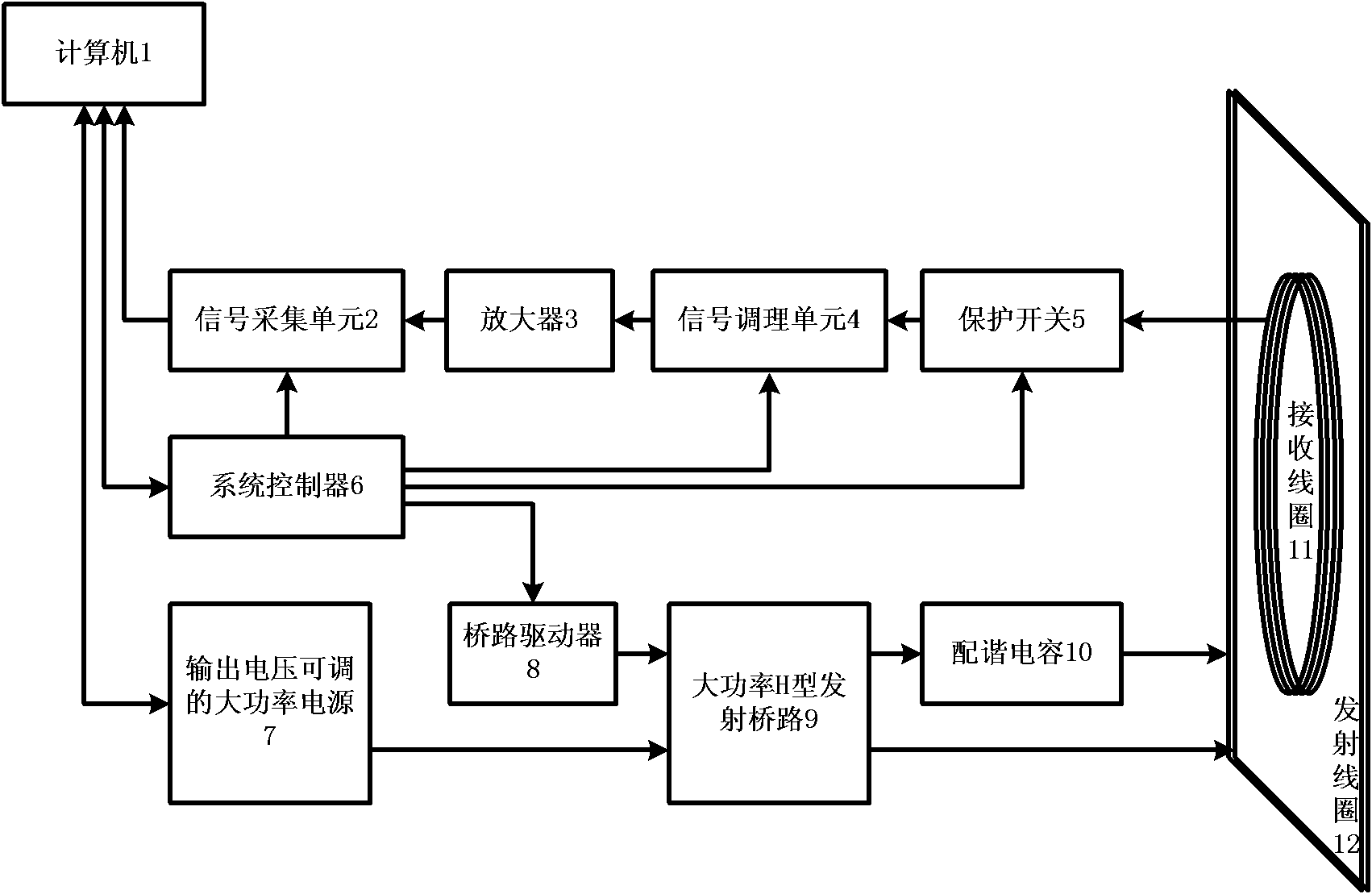
The invention relates to a nuclear magnetic resonance detection device and a nuclear magnetic resonance detection method for the advanced detection of a water bodies in the front. In the device, a computer is connected with a system controller, a high-power power supply and a signal acquisition unit by a serial port bus respectively; and the system controller is formed by connecting a bridge circuit driver, a high-power H-shaped transmitting bridge circuit, a resonant capacitor and a transmitting coil. Compared with the prior art, the device can detect important information such as the existence of water-bearing bodies in the front, the water content of the water-bearing bodies and the like accurately and effectively. The occupied area of the coil is reduced effectively by a mode of arranging the coil vertically, so that the device can perform exploration in narrow space. The device can detect the underground geological condition within a certain distance in the front directly and accurately in production fields of coal fields and mines or construction sites of tunnels so as to reduce mine accidents caused by geological disasters such as water burst, mud gushing and the like due to unclear geological conditions in the front or various incidents caused by the geological disasters in the process of tunnel construction.
Owner:长春国地探测仪器工程技术股份有限公司
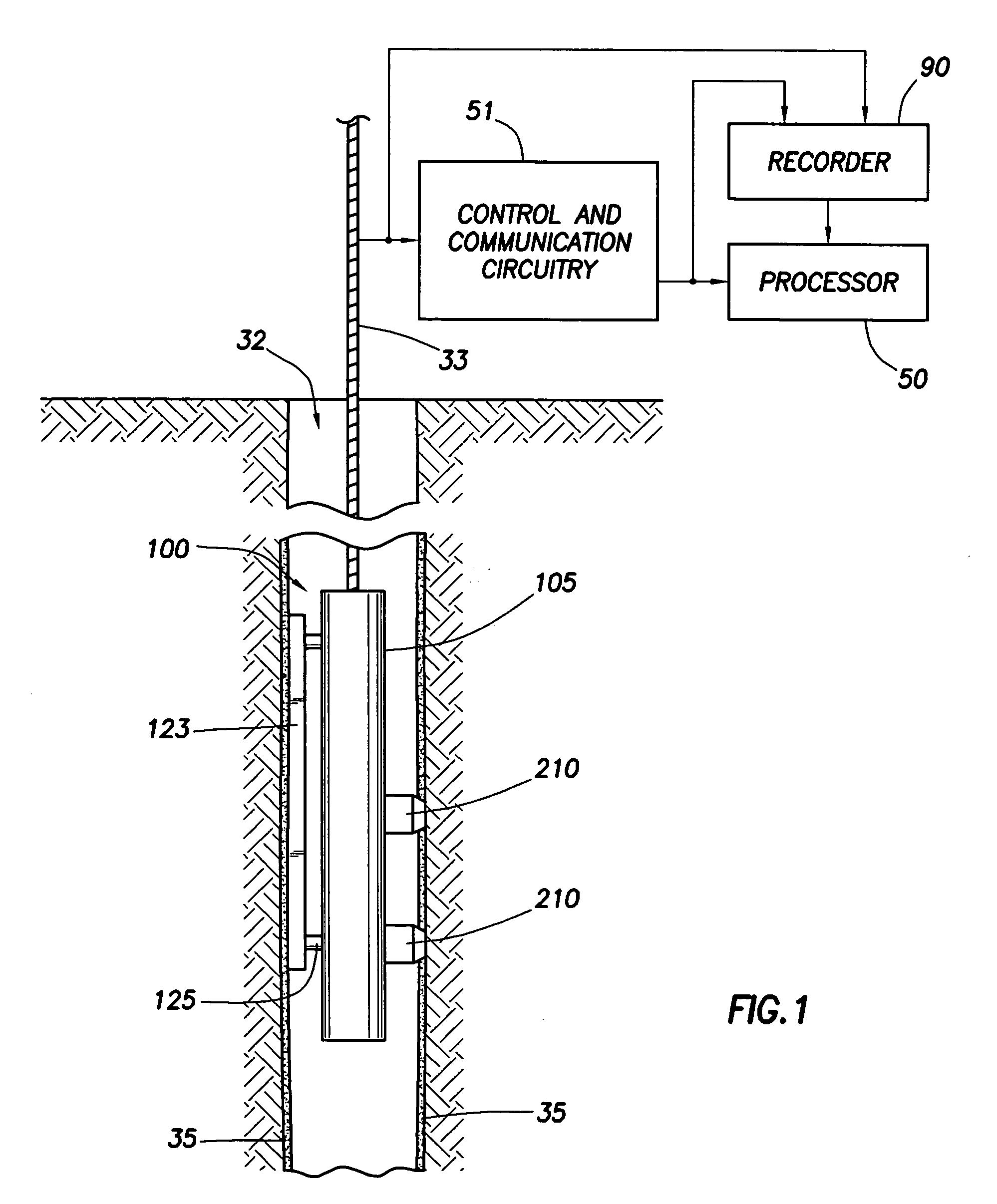
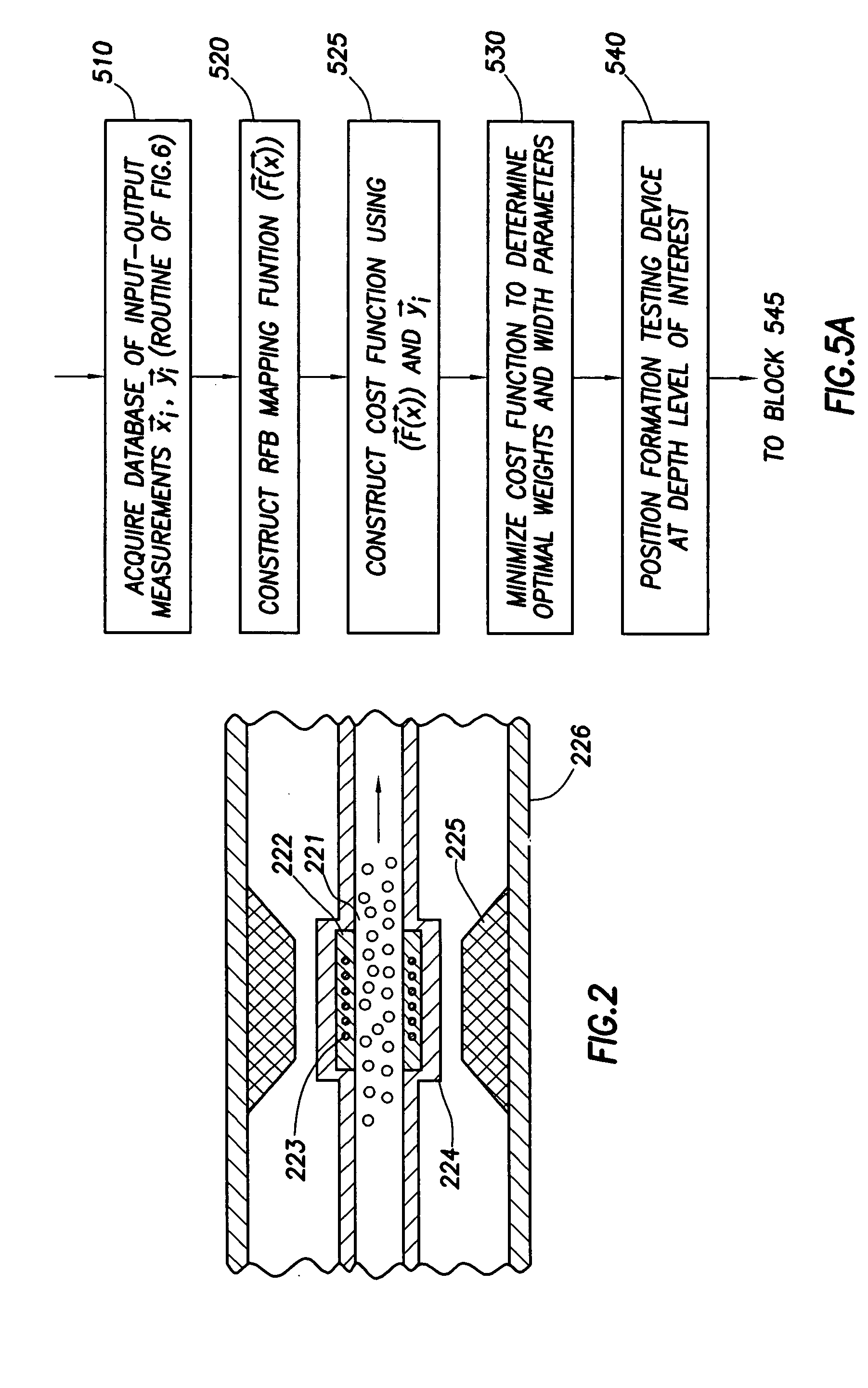
Method for determining properties of formation fluids
ActiveUS20050242807A1Minimize cost functionElectric/magnetic detection for well-loggingSurveyFormation fluidRadial basis function interpolation
A method for determining a property of fluids in formations surrounding an earth borehole includes the following steps: producing, from measurements on a multiplicity of fluid samples, a database of stored fluid property training values related to stored fluid measurement training values; deriving, from the database, radial basis function parameters; deriving formation fluid measurement values; and determining, using radial basis function interpolation, the property of formation fluids from values in the database, the parameters, and the derived formation fluid measurement values.
Owner:SCHLUMBERGER TECH CORP
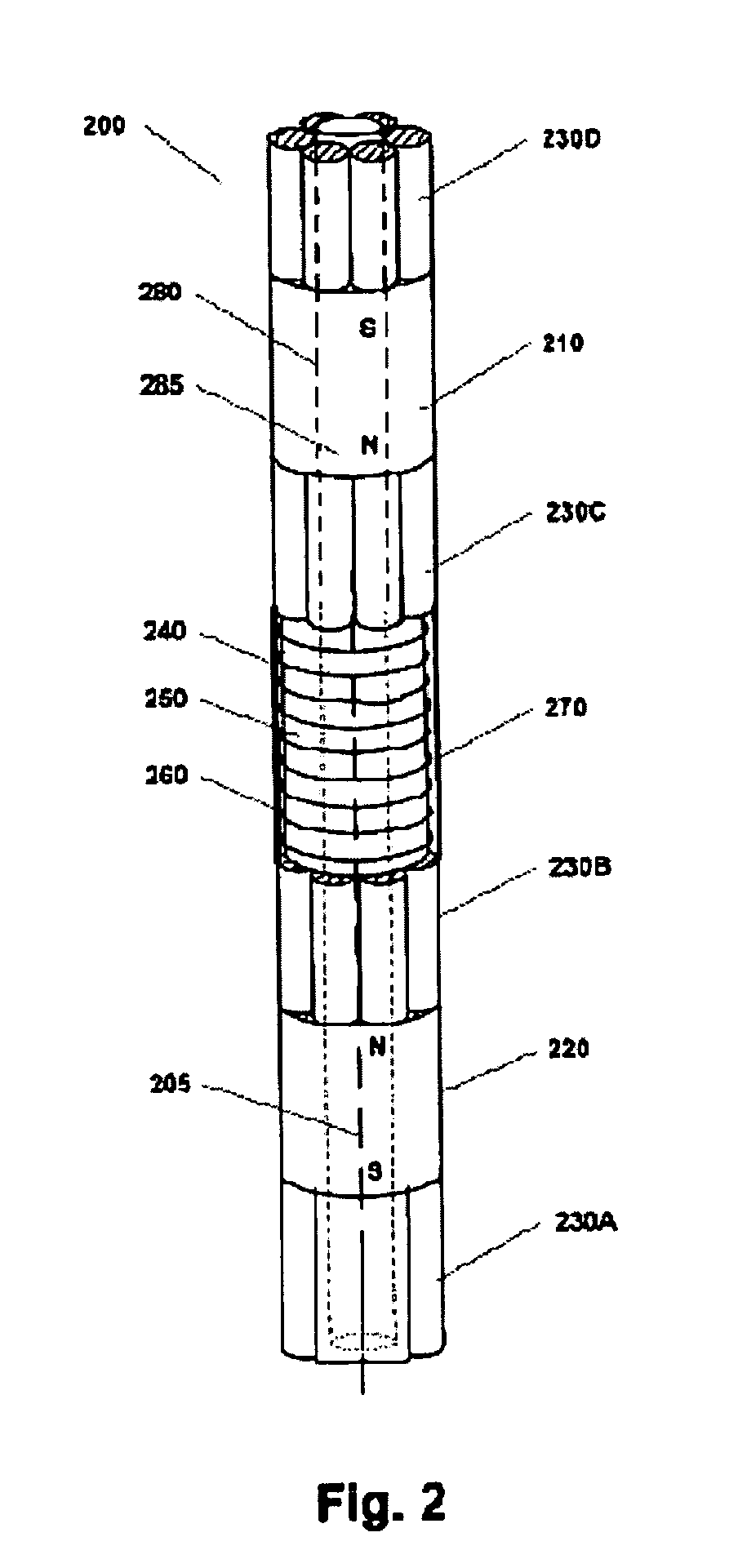
Nuclear magnetic resonance tool using switchable source of static magnetic field
ActiveUS20060255799A1Effective permeability of magneticElectric/magnetic detection for well-loggingMaterial analysis by using resonanceSolid-state nuclear magnetic resonanceSpin magnetic moment
A nuclear magnetic resonance sensing apparatus and method for operating in an earth borehole comprises a source of switchable magnetic field to polarize nuclei in the region of interest, said source comprising a coil wound on a magnetic core having controllable residual magnetization. Maintaining the magnetization of the core during a polarization interval does not require steady current in the coil. Switching intensity and polarity of magnetization of the core causes precession of spin magnetic moments of the nuclei; the precession induces a signal indicative of nuclear magnetic resonance properties of earth formations.
Owner:BAKER HUGHES INC
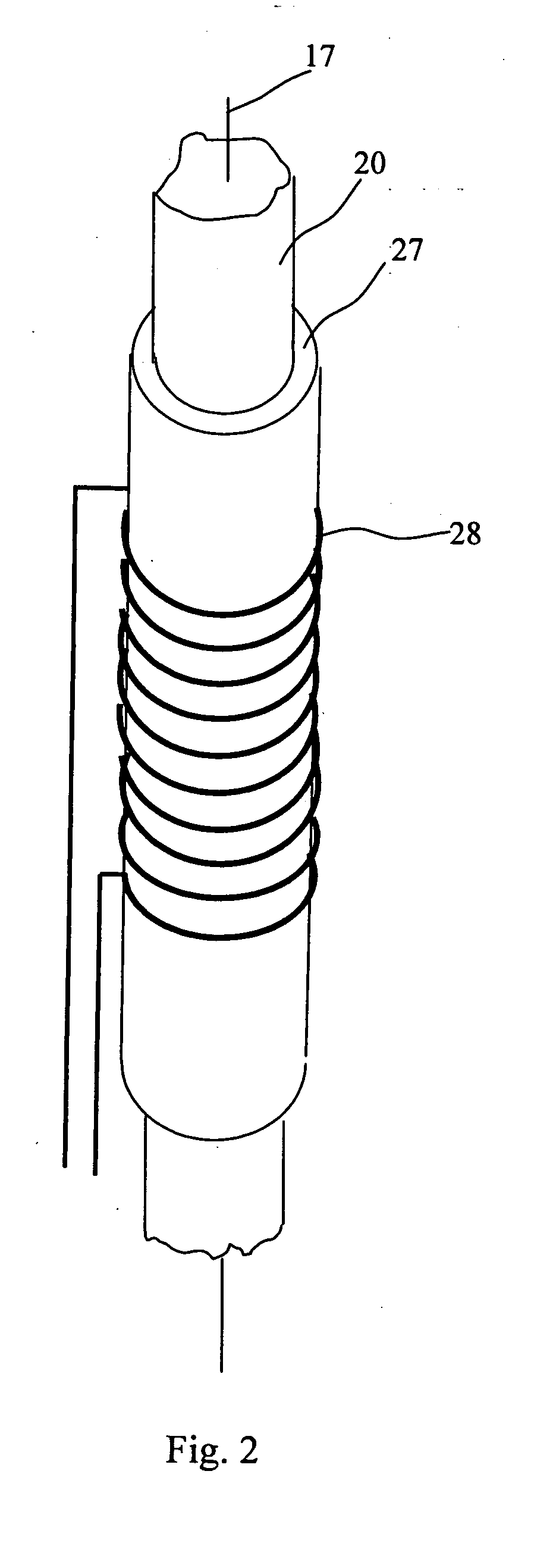
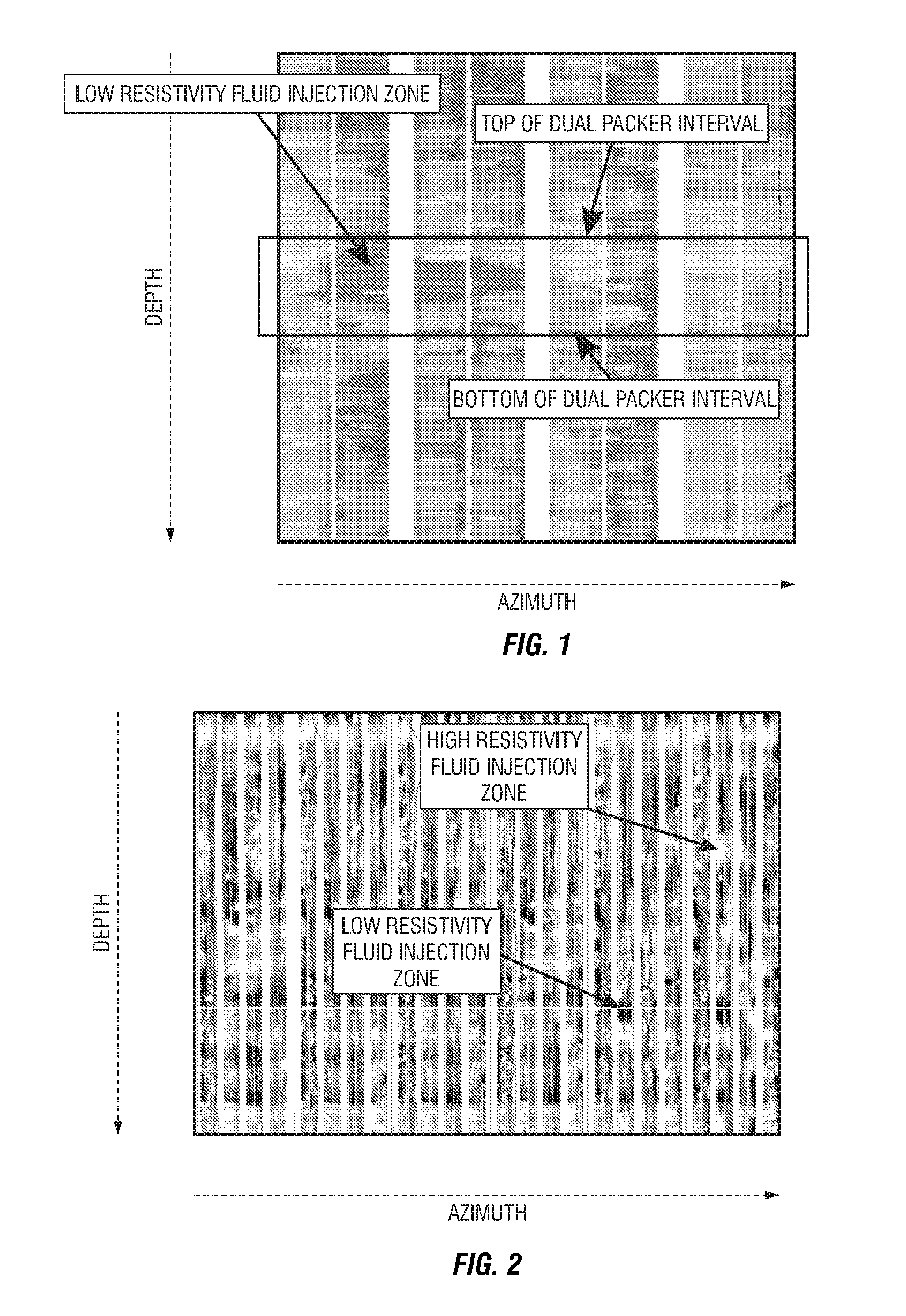
Formation testing and evaluation using localized injection
ActiveUS20100264915A1Electric/magnetic detection for well-loggingFluid removalProximateLocal injection
Evaluating a formation by lowering a downhole tool in a wellbore penetrating the formation, injecting a fluid into the formation at an injection zone via the downhole tool, and using a formation evaluation sensor to perform a measurement at each of a plurality of locations in the wellbore each proximate the injection zone. At least two of the plurality of measurements are compared, and a formation property is determined based on the comparison.
Owner:SCHLUMBERGER TECH CORP
Reduction of motion artifacts in NMR
ActiveUS20050248342A1Different sensitivityElectric/magnetic detection for well-loggingDetection using electron/nuclear magnetic resonanceMagnetic fluxMotion artifacts
NMR spin echo signals, acquired on a MWD logging tool, are susceptible to errors magnetic flux density has a gradient and the magnet on the logging tool is moving relative to the earth. The errors can be corrected by having the excitation pulse cover a smaller or a larger volume than the refocusing pulses. Correction may also be made by selective saturation, or by echo averaging.
Owner:BAKER HUGHES INC
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com