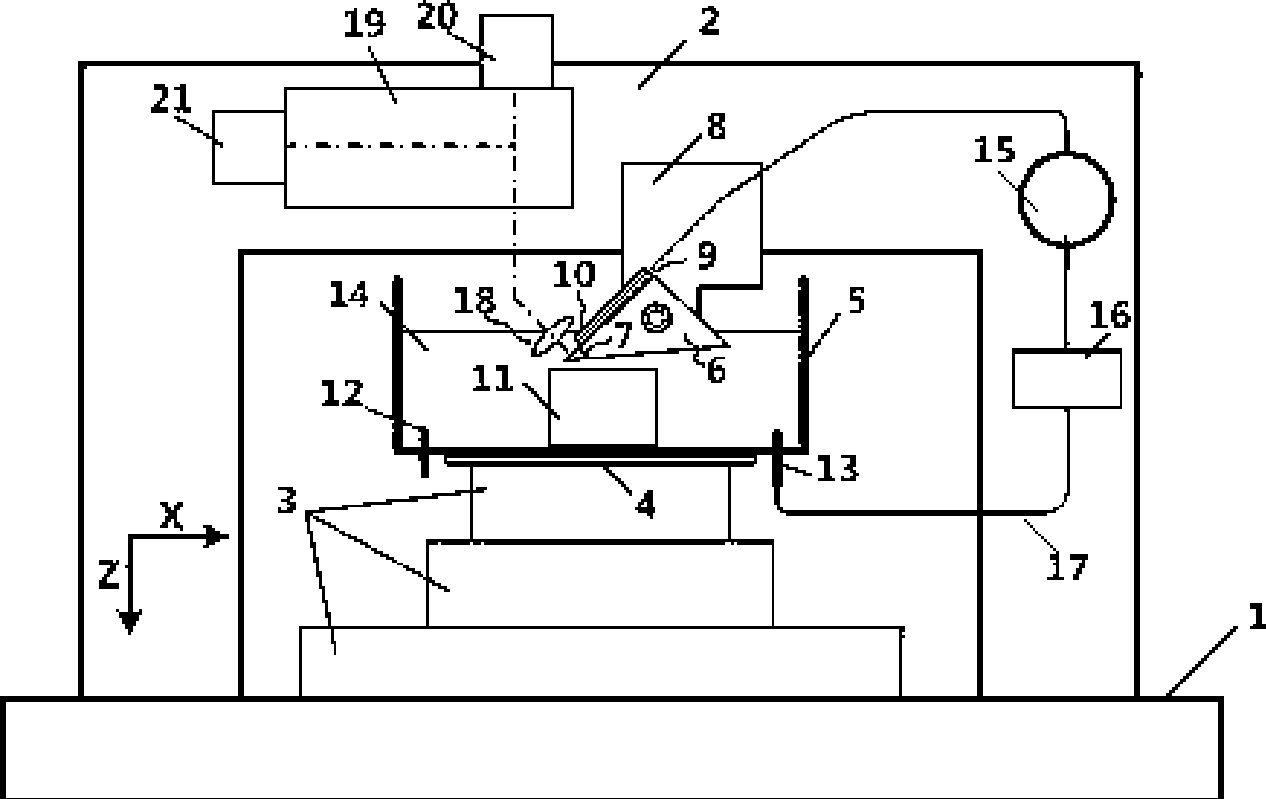
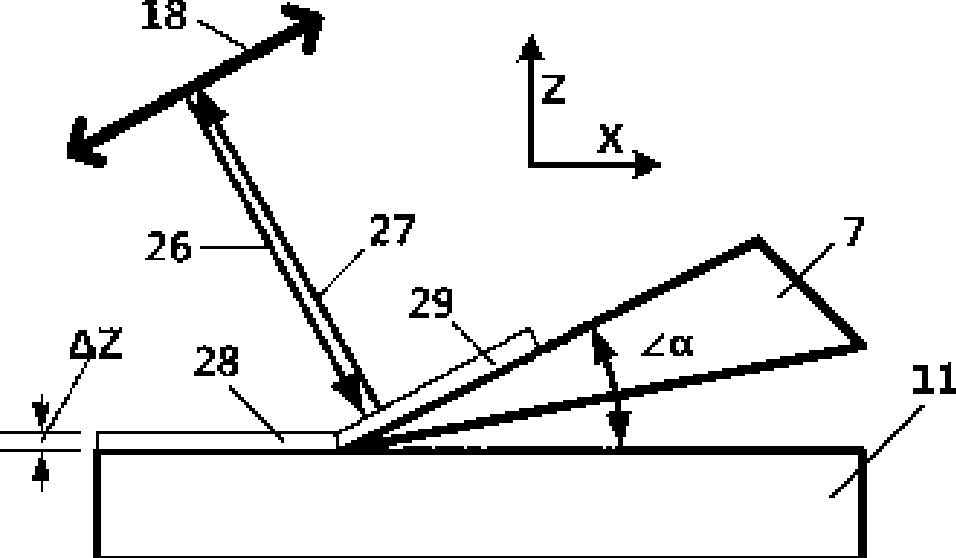
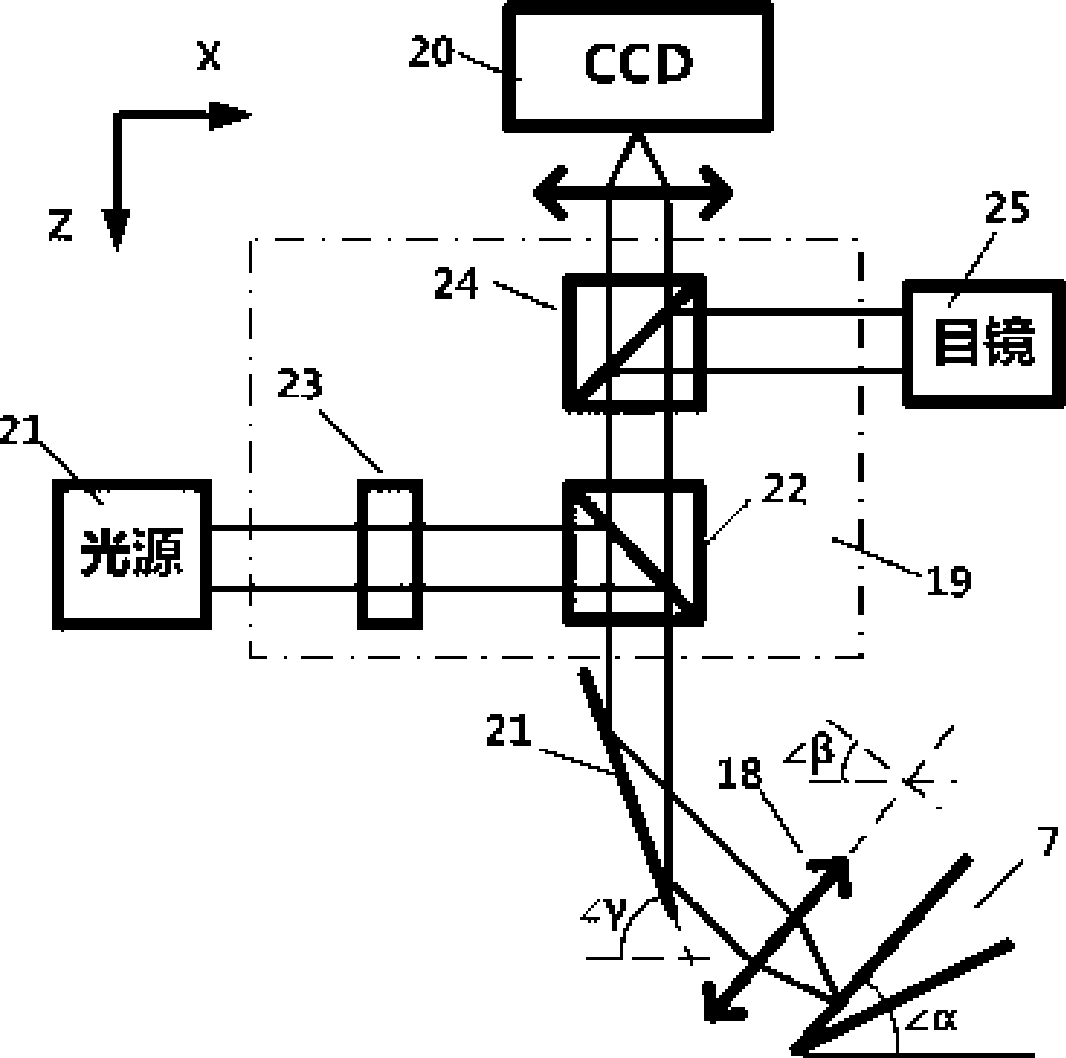
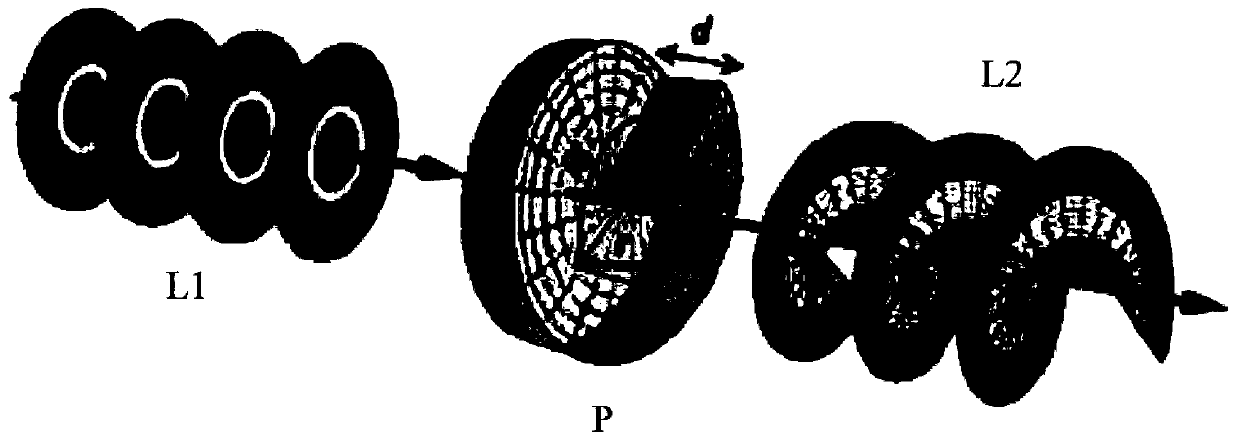
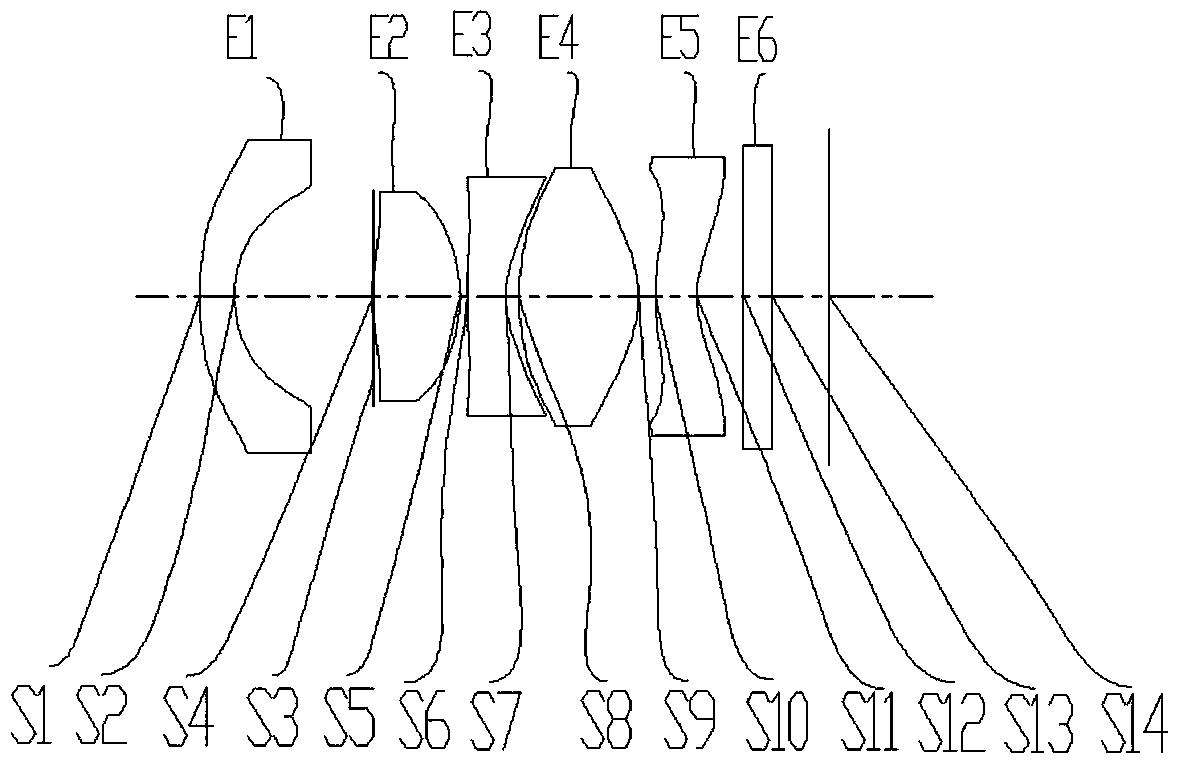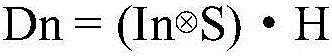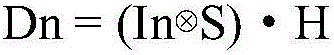Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
861 results about "Micro imaging" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
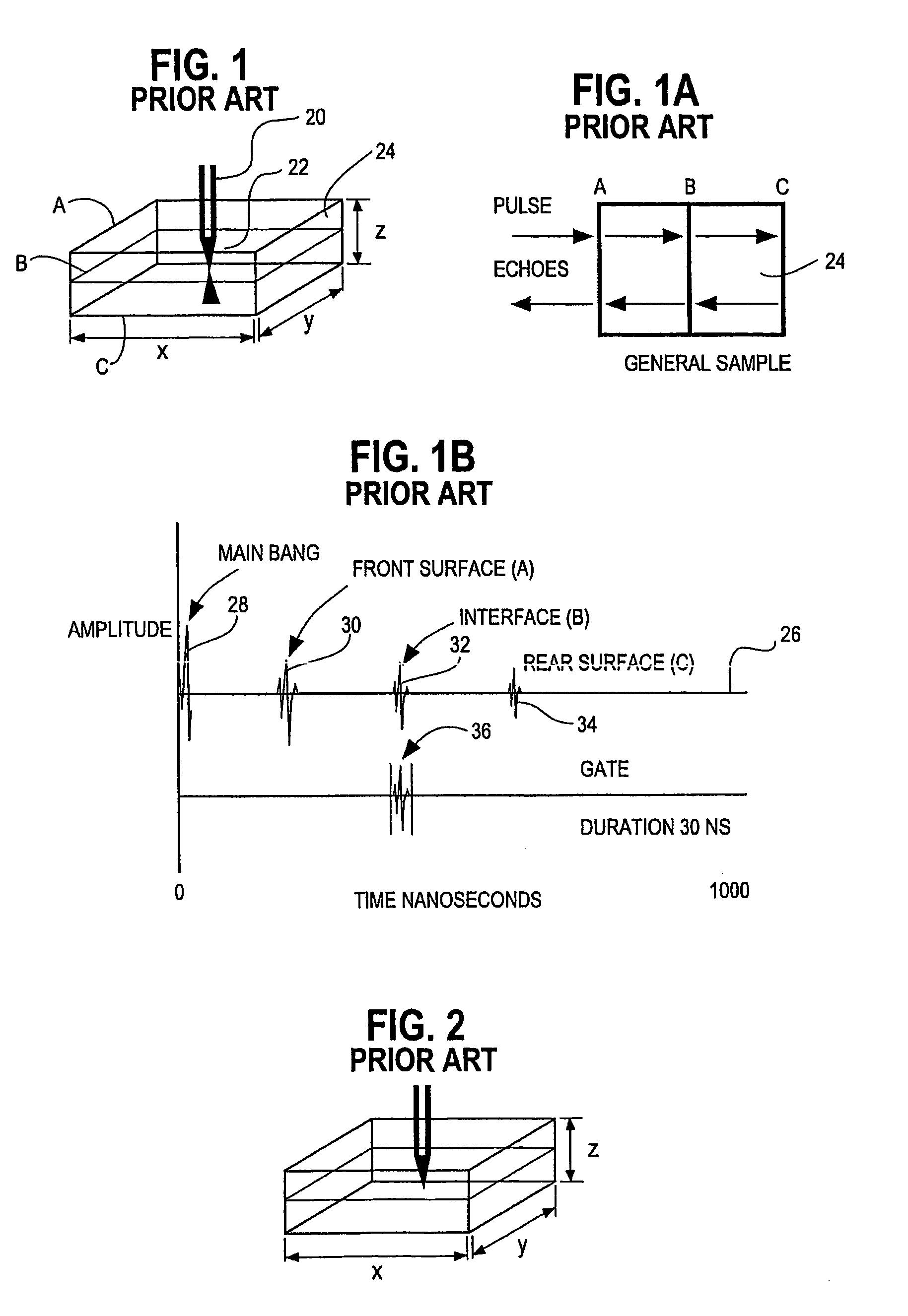
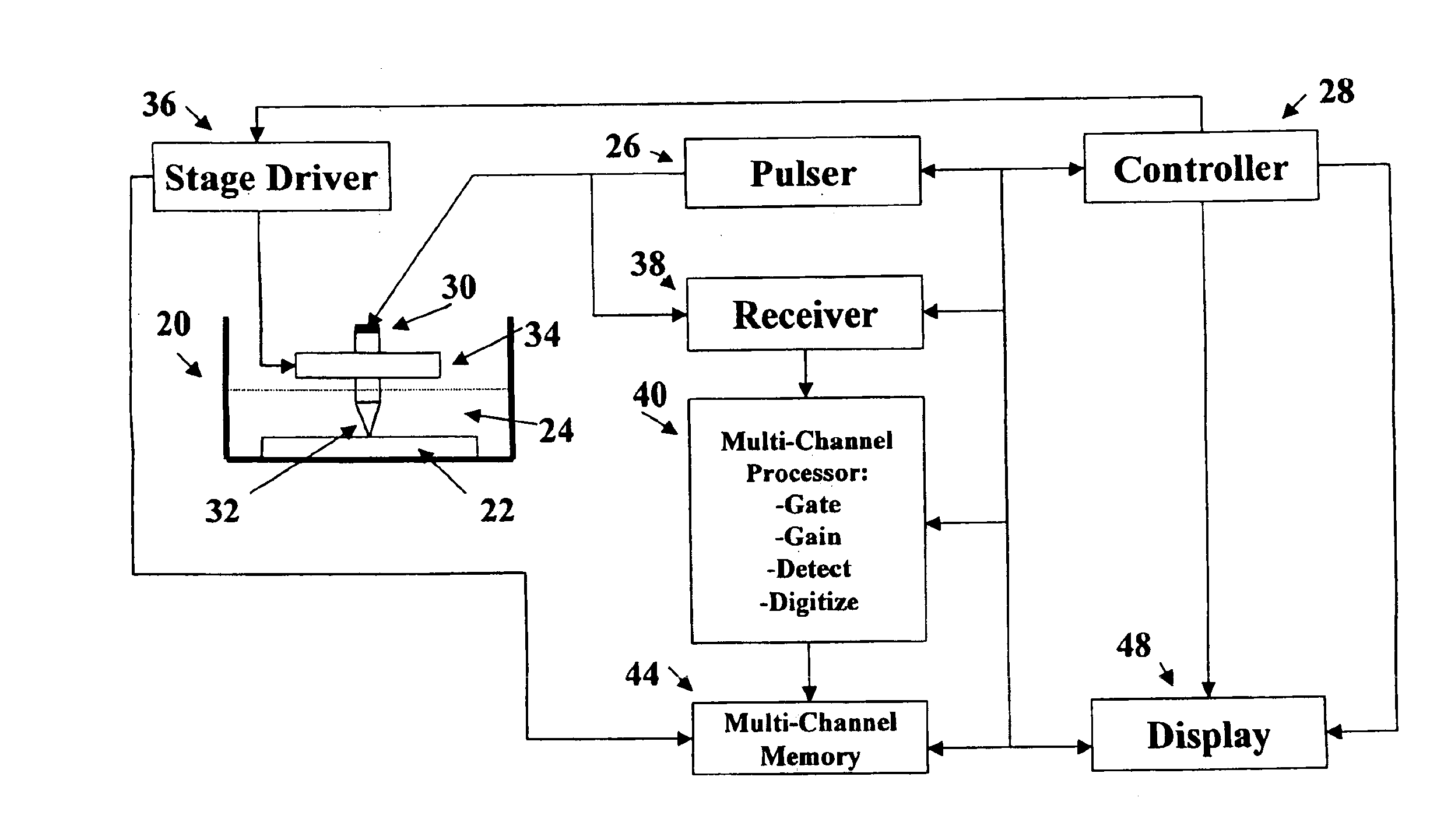
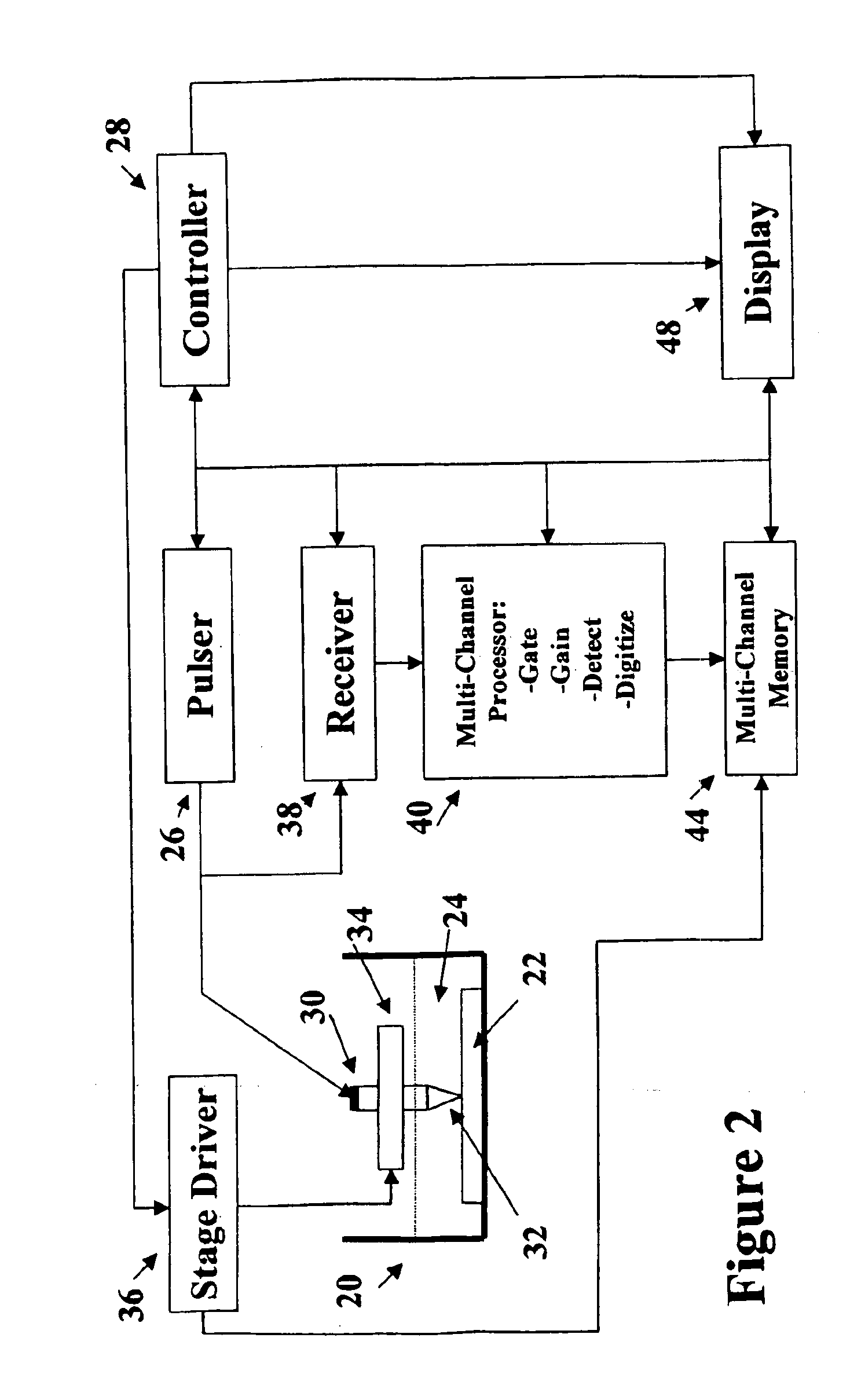
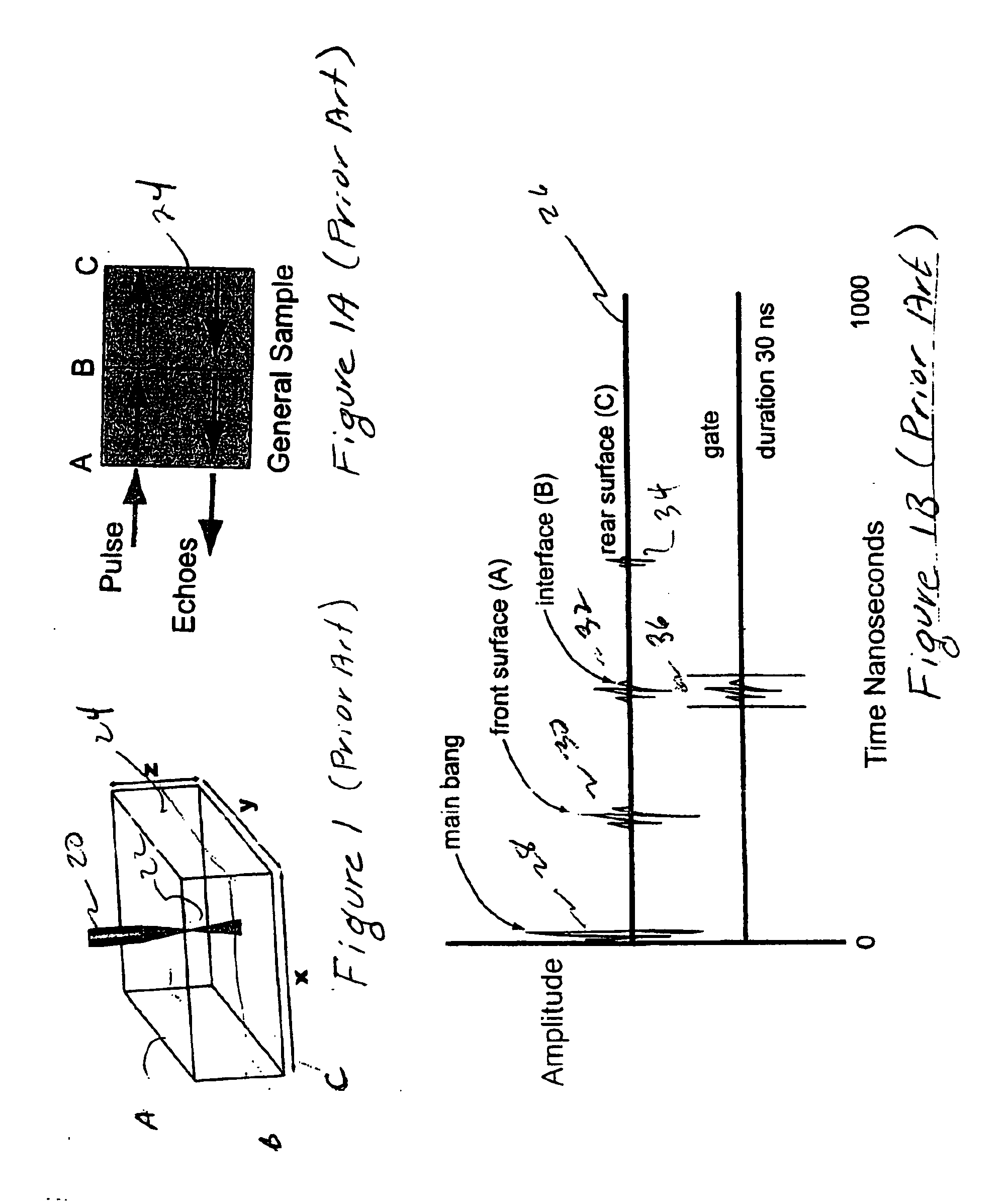
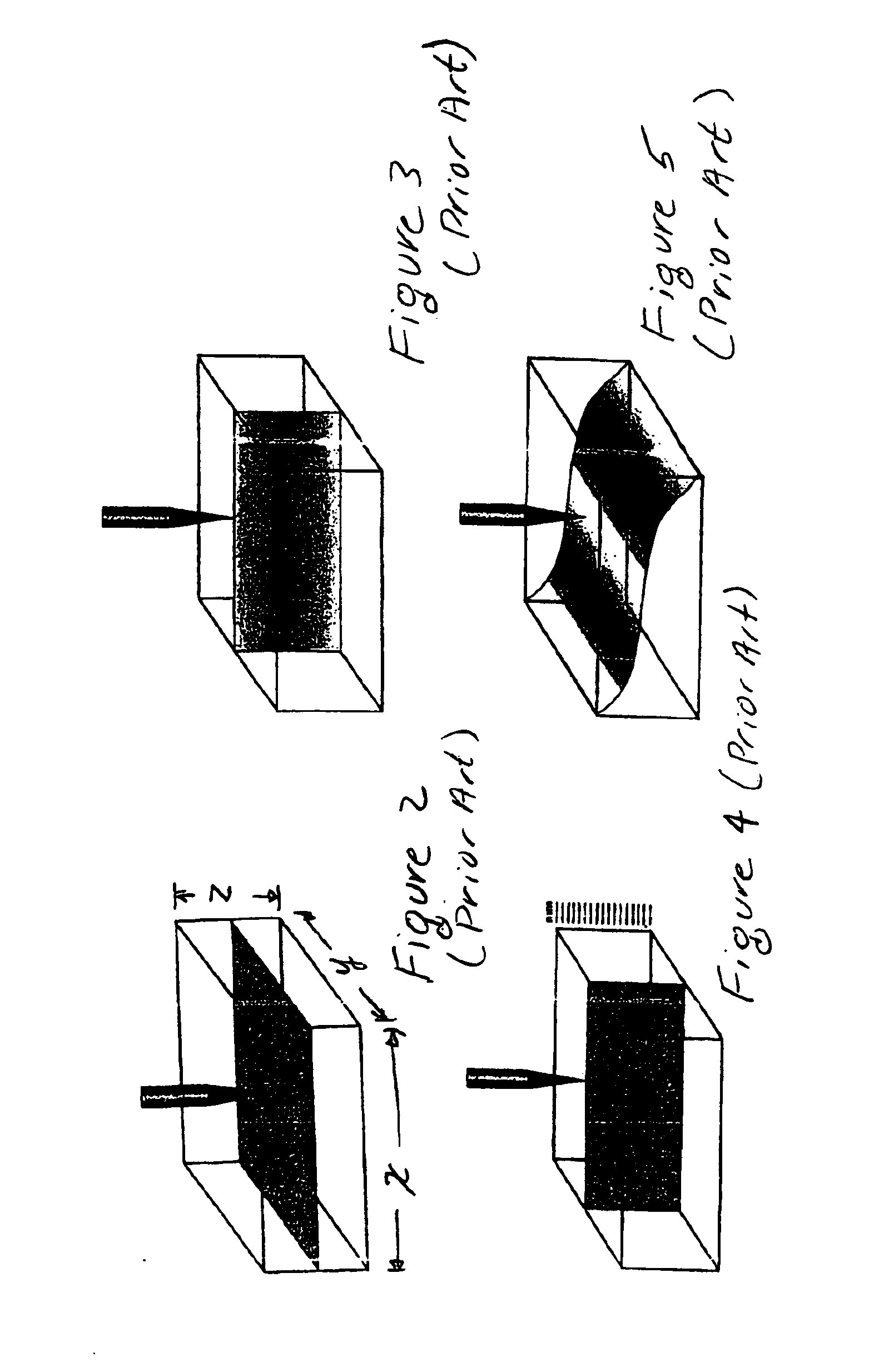
Scanning acoustic micro imaging method and apparatus for non-rectangular bounded files
InactiveUS6981417B1Analysing solids using sonic/ultrasonic/infrasonic wavesWeather/light/corrosion resistanceMicro imagingAcoustic energy
Method and implementing apparatus useful in acquiring data on acoustic features within a sample provides a pulsed acoustic probe and a stage system for effecting relative movement between the sample and the probe. The stage system is commanded such that the probe interrogates a non-rectangularly bounded space on the sample surface or within the volume of the sample. Acoustic energy reflected from or transmitted through the sample is sensed. Amplitude signals are developed from the sensed acoustic energy. Data characterizing the developed amplitude signals are stored for subsequent processing.
Owner:NORDSON CORP
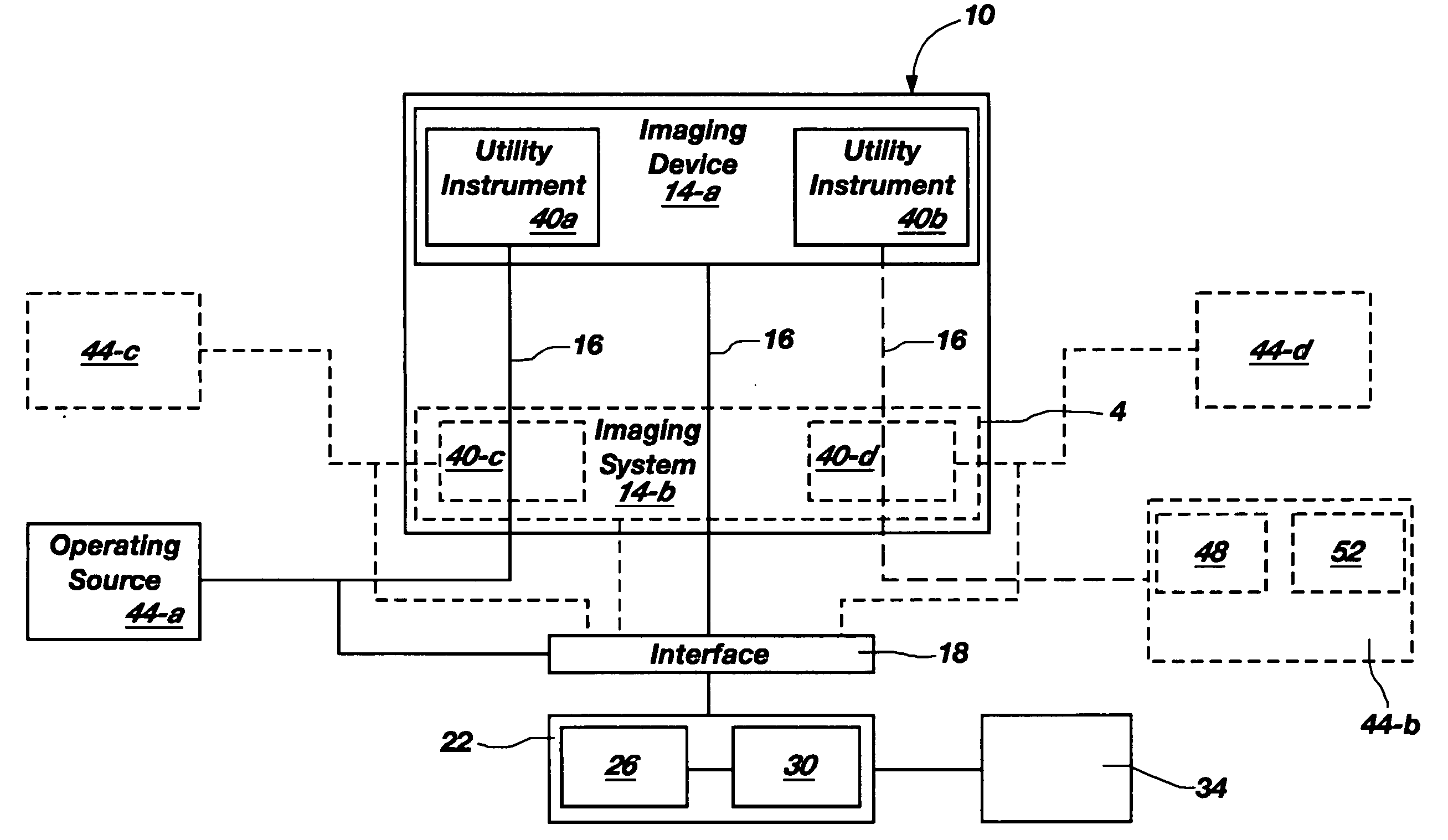
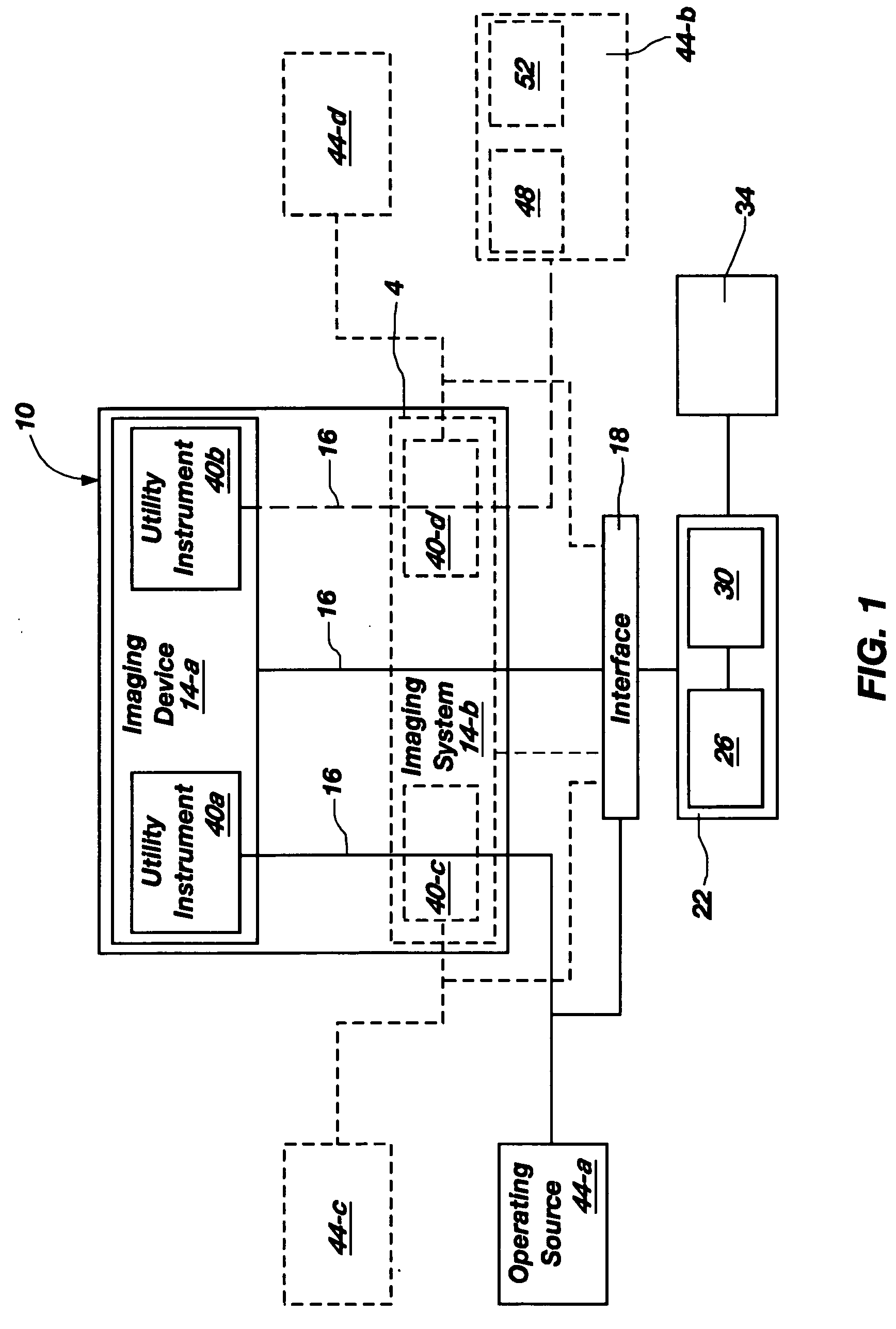
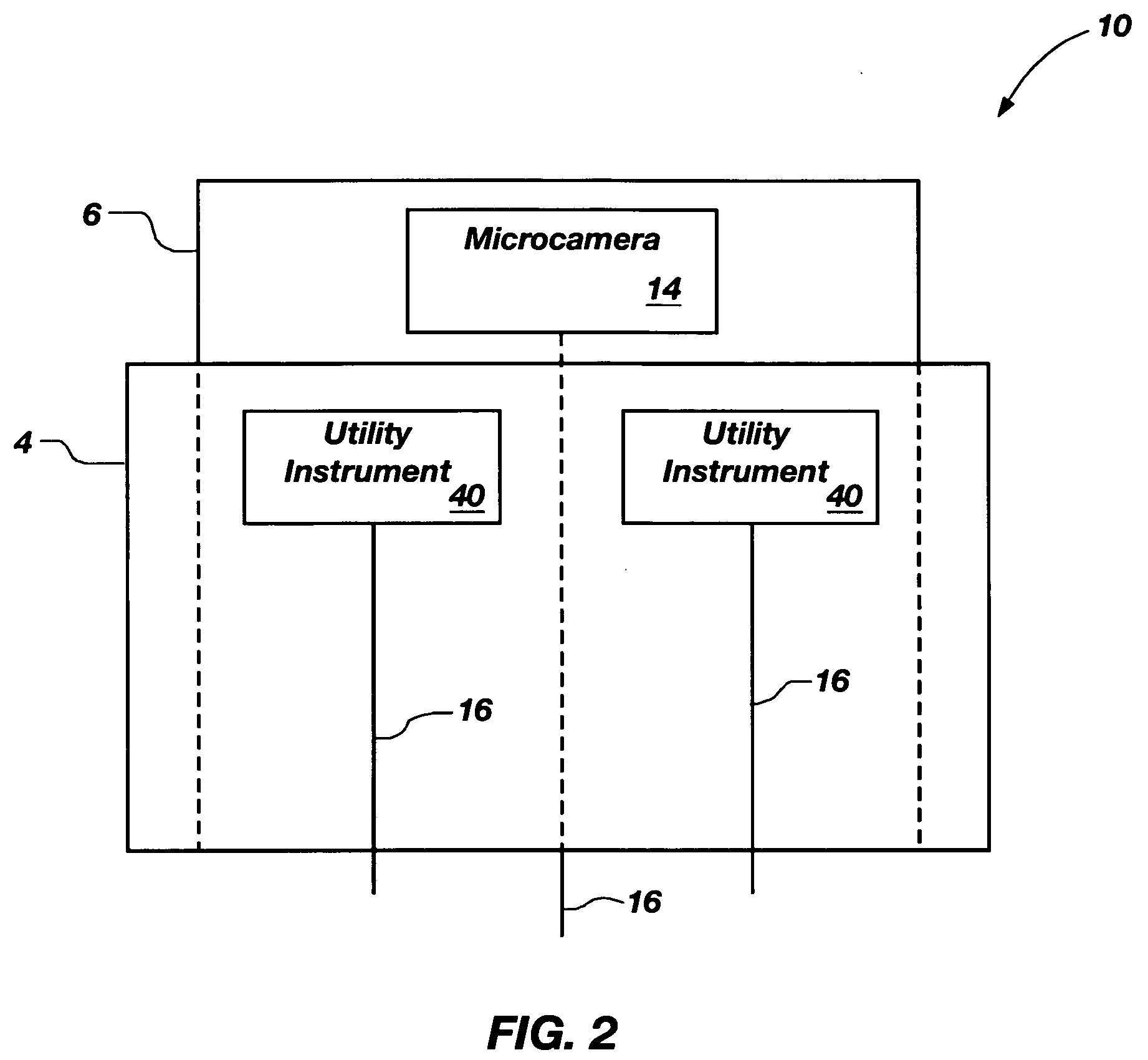
Miniaturized utility device having integrated optical capabilities
InactiveUS20060146172A1High aspect ratioTelevision system detailsEndoscopesMicro imagingCamera image
A miniaturized utility device having integrated optical capabilities for use on a high aspect ratio system, wherein the miniaturized utility device comprises: (a) a micro camera comprising a solid state micro imaging device including, as an integral structure, an imaging array electrically coupled to a conductive pad, wherein the solid state imaging device further includes at least one utility aperture passing therethrough, and a lens optically coupled to the imaging array; and (b) a micro utility instrument configured for coordinated operation with the imaging device at a common local site, wherein the micro utility instrument is configured to perform a designated function viewable, preferably in real-time, via a camera image generated by the micro camera.
Owner:STERLING L C
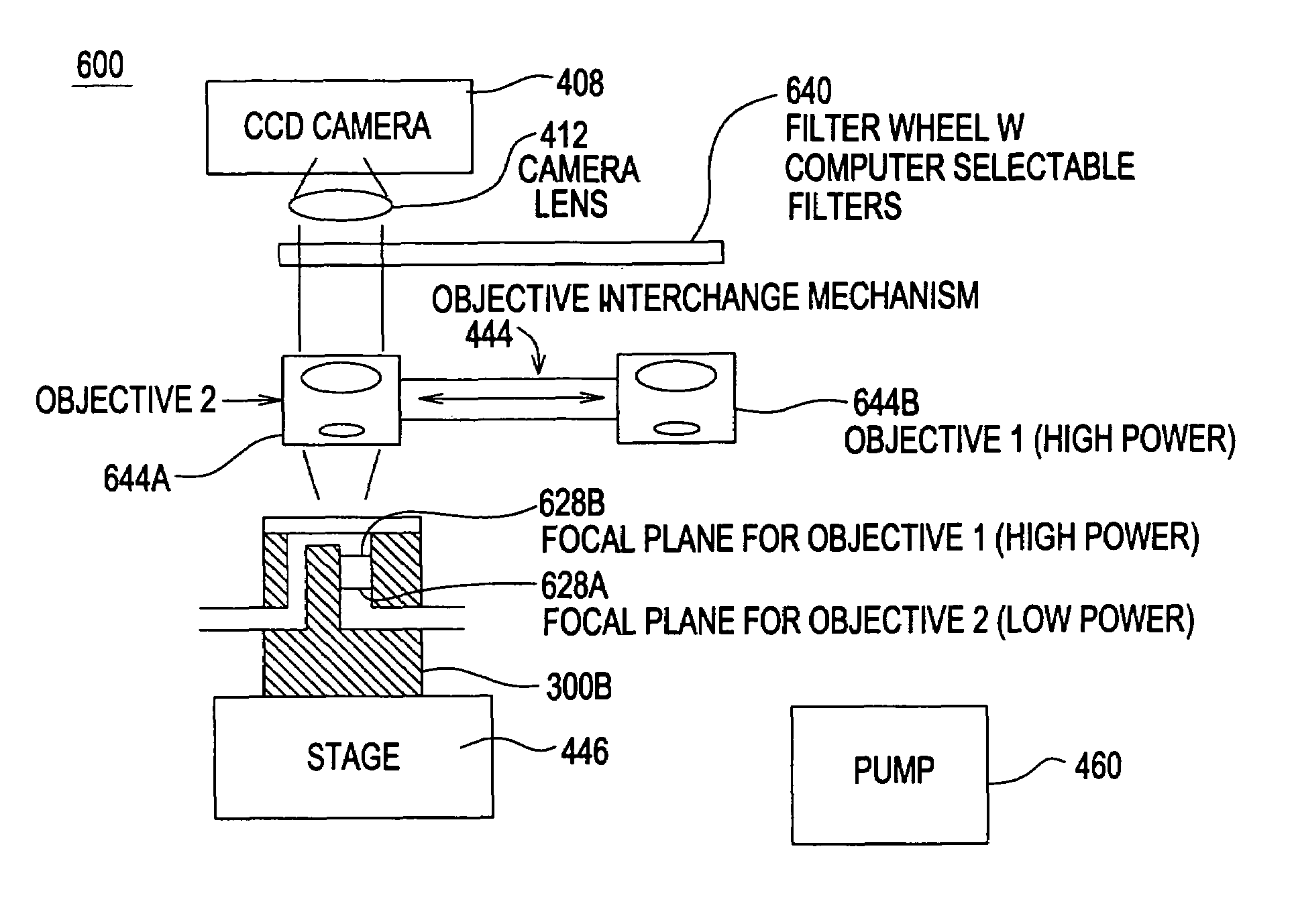
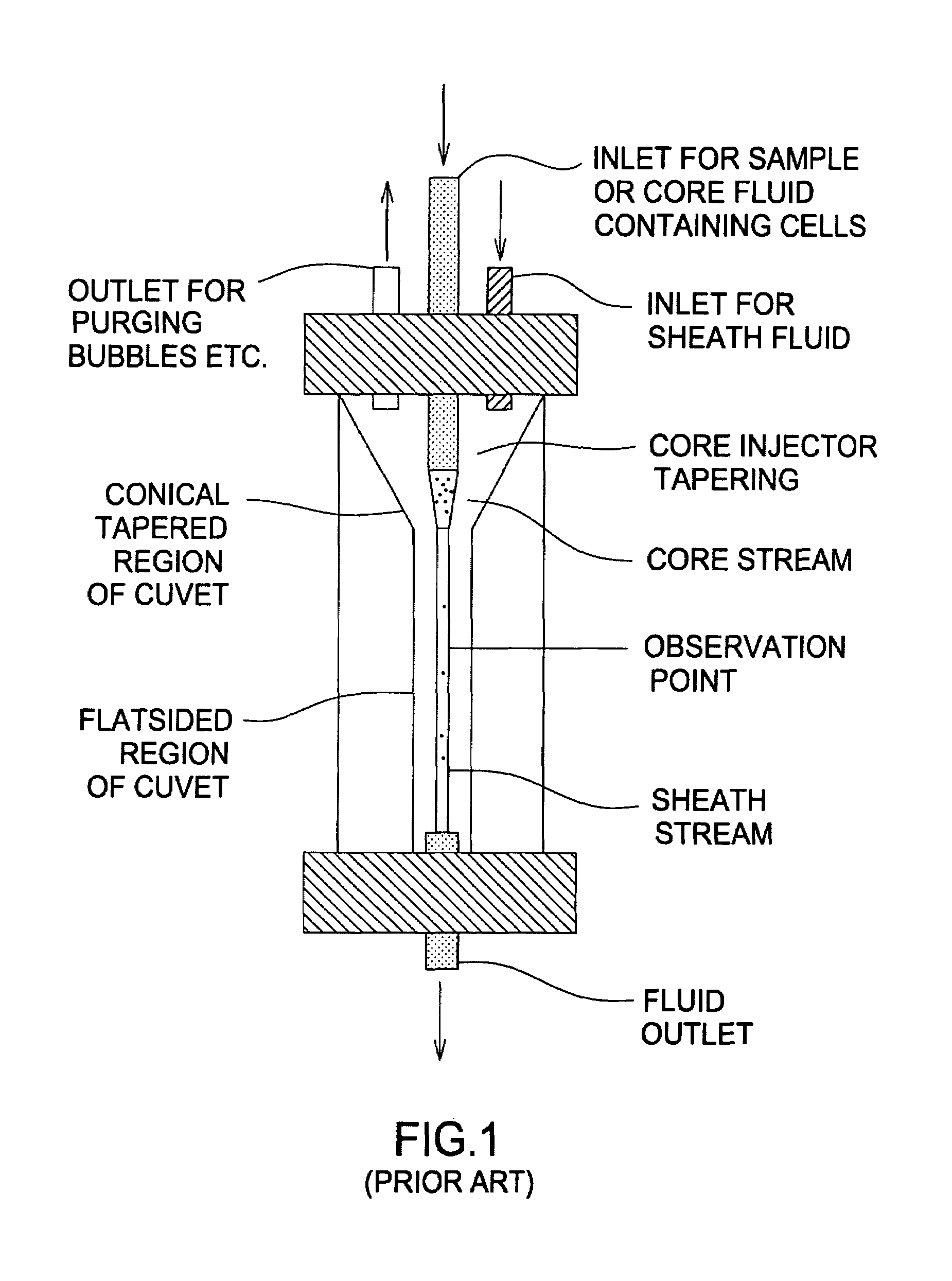
High resolution imaging fountain flow cytometry
InactiveUS7161665B2Improve throughputHigh resolutionWithdrawing sample devicesMaterial analysis by optical meansHigh resolution imagingFlow cell
An imaging fountain flow cytometer allows high resolution microscopic imaging of a flowing sample in real time. Cells of interest are in a vertical stream of liquid flowing toward one or more illuminating elements at wavelengths which illuminate fluorescent dyes and cause the cells to fluoresce. A detector detects the fluorescence emission each time a marked cell passes through the focal plane of the detector. A bi-directional syringe pump allows the user to reverse the flow and locate the detected cell in the field of view. The flow cell is mounted on a computer controlled x-y stage, so the user can center a portion of the image on which to zoom or increase magnification. Several computer selectable parfocal objective lenses allow the user to image the entire field of view and then zoom in on the detected cell at substantially higher resolution. The magnified cell is then imaged at the various wavelengths.
Owner:UNIVERSITY OF WYOMING
Laser spectrum analyzer combining confocal micro-Raman spectrometer with laser-induced breakdown spectrometer
ActiveCN103743718AAchieve qualitativeRealize quantitative analysisRaman scatteringMicro imagingHigh resolution imaging
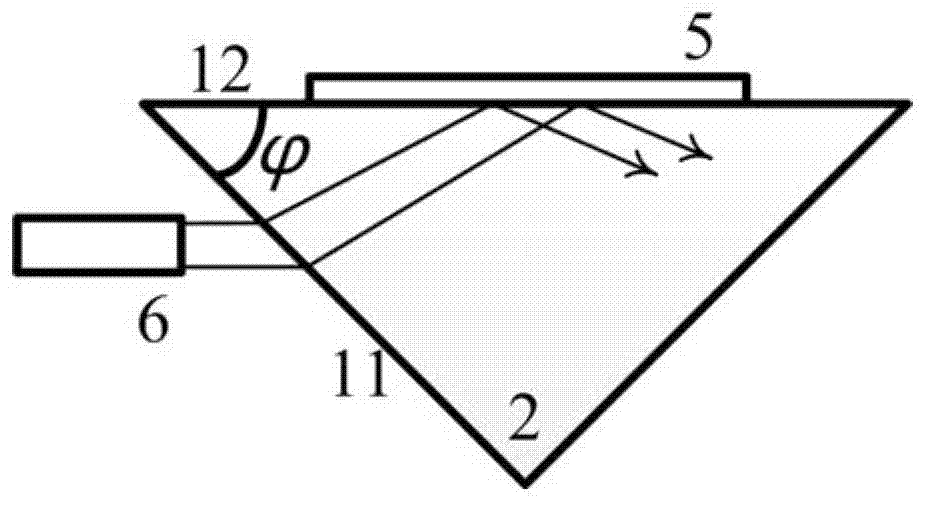
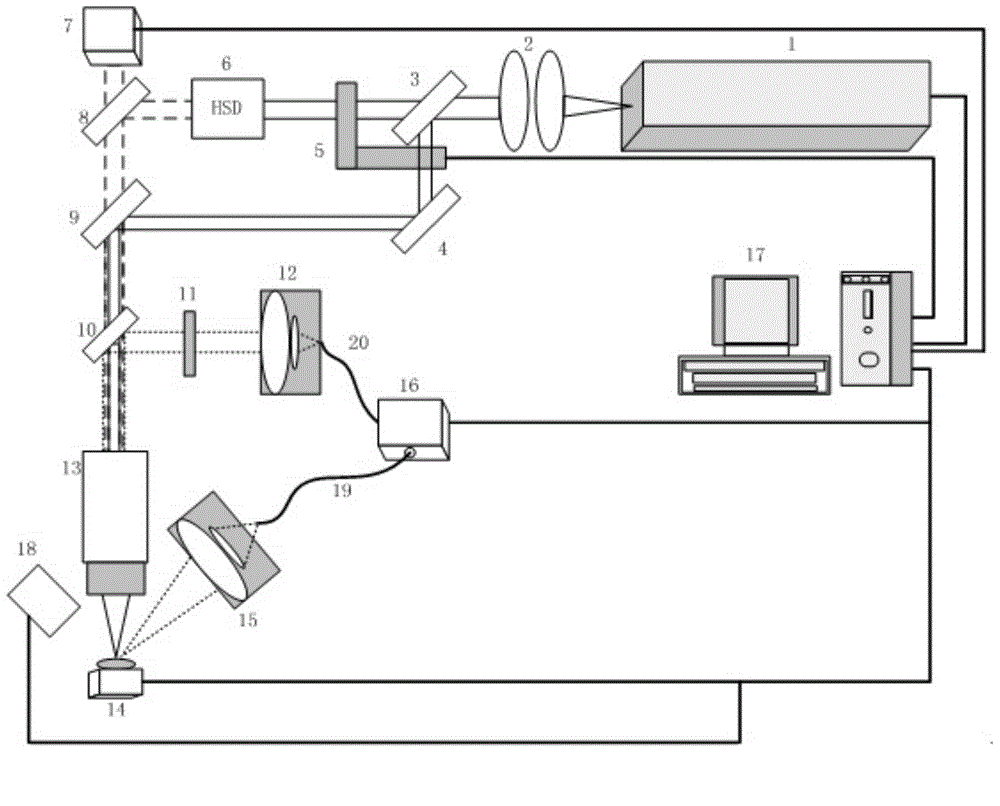
The invention provides a laser spectrum analyzer combining a confocal micro-Raman spectrometer with a laser-induced breakdown spectrometer (LIBS). The analyzer comprises a micro-Raman system, a micro LIBS system, a high resolution micro-imaging system, a confocal micro-light path, and a spectrum receiving system with a time resolution function, and automatically switches into a white light micro-imaging observation mode, an automatic focusing mode, a LIBS spectrum working mode, and a Raman spectrum working mode. The significant characteristics of the invention are that compact combination of Raman with LIBS is realized by a micro confocal system; qualitative and quantitative analysis of substance elements at the same minimal position and molecular structure is realized; with the high-resolution imaging function, element spatial discrimination and substance structure chemical analysis can be carried out in micrometers so as to obtain complete information of spatial distribution images of chemical elements, substance structure and physical conditions of a sample.
Owner:东莞市中科原子精密制造科技有限公司
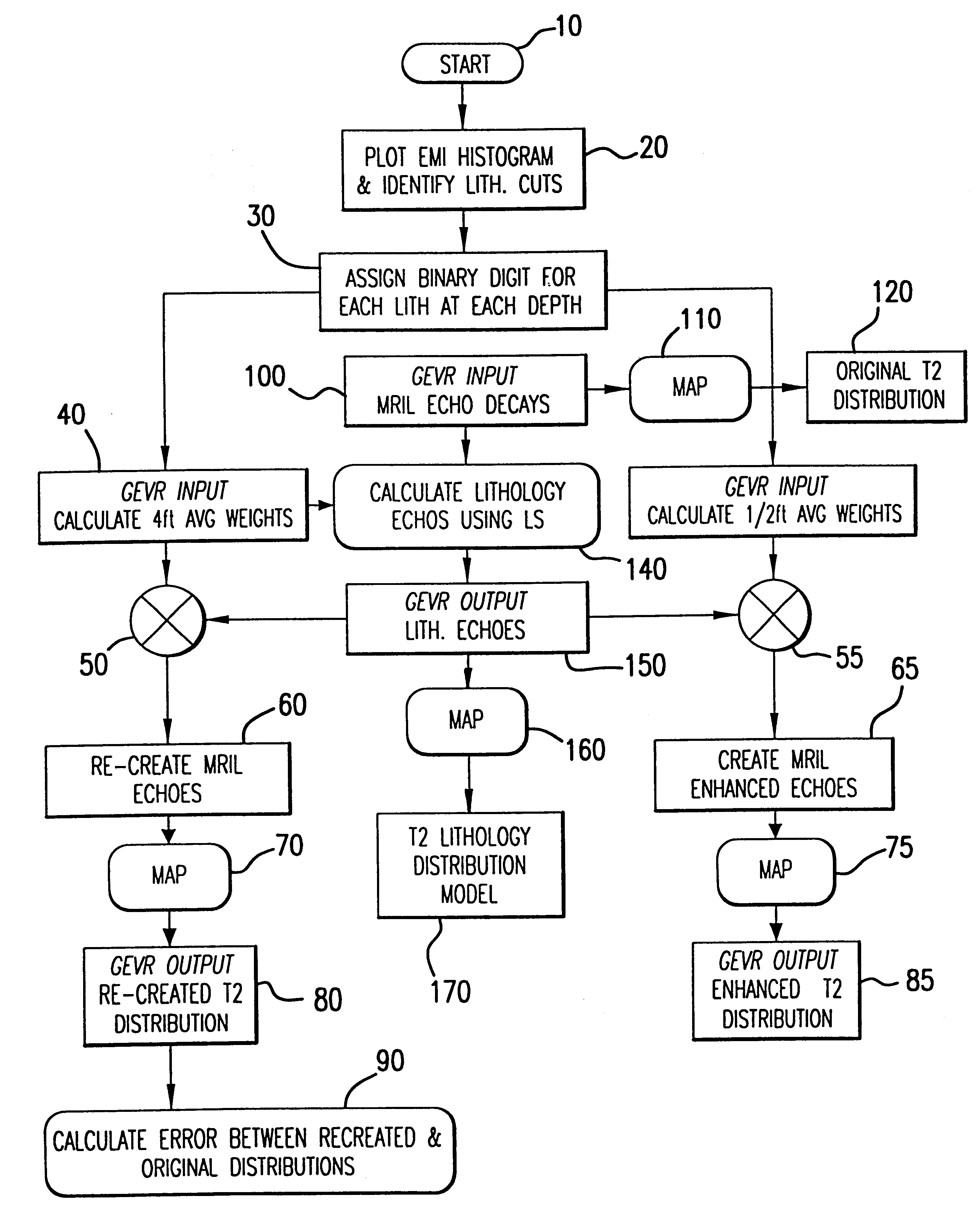
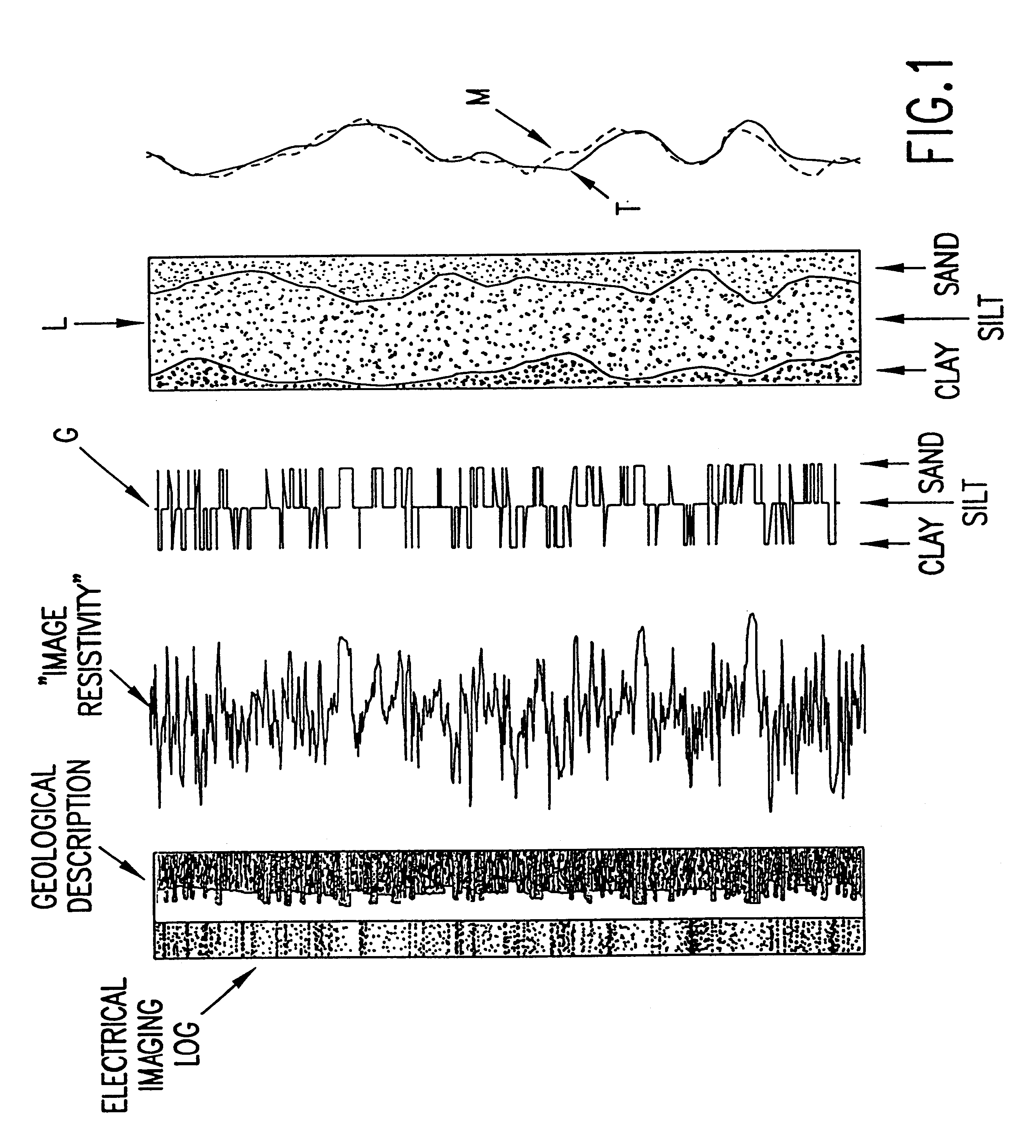
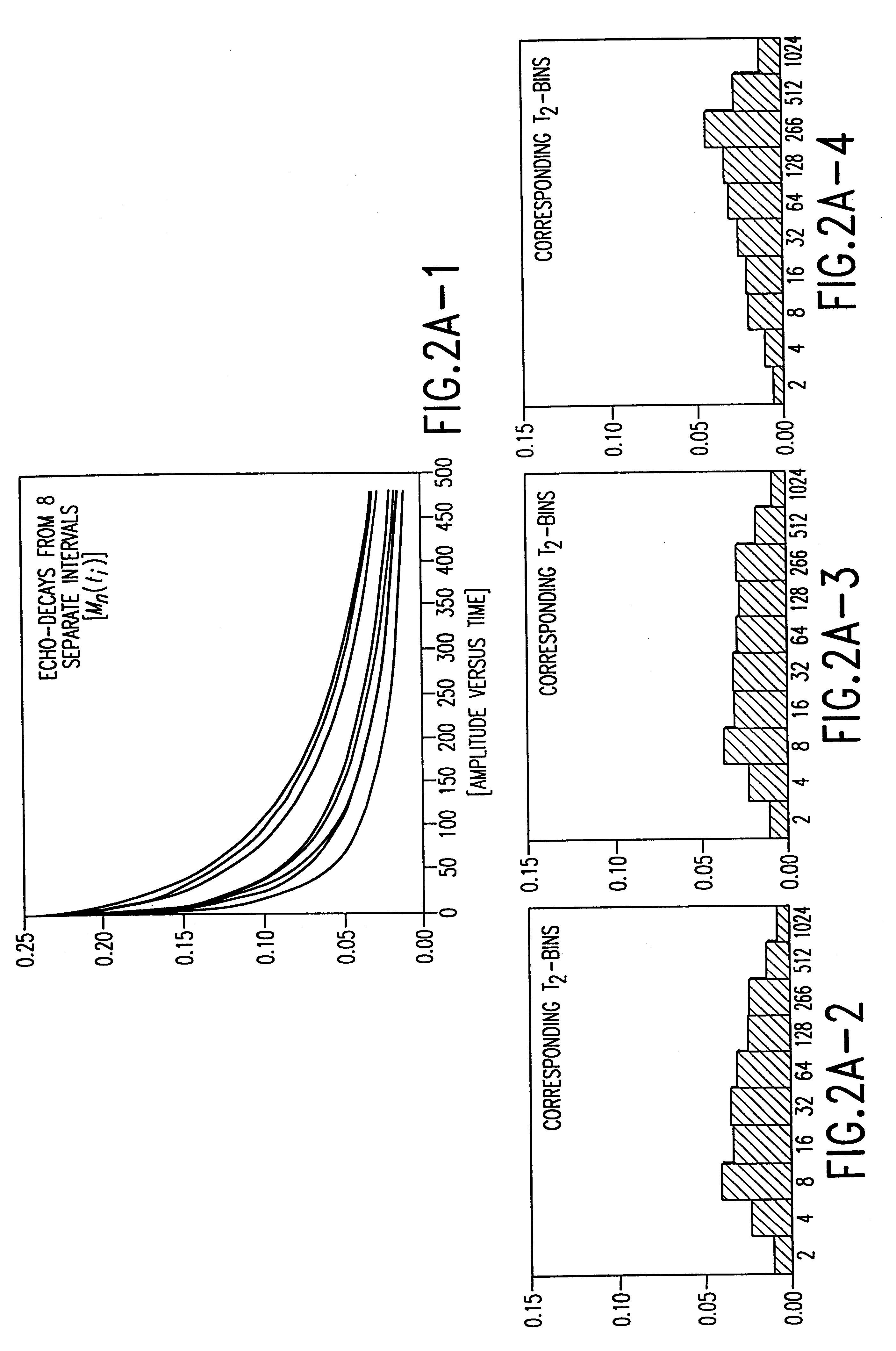
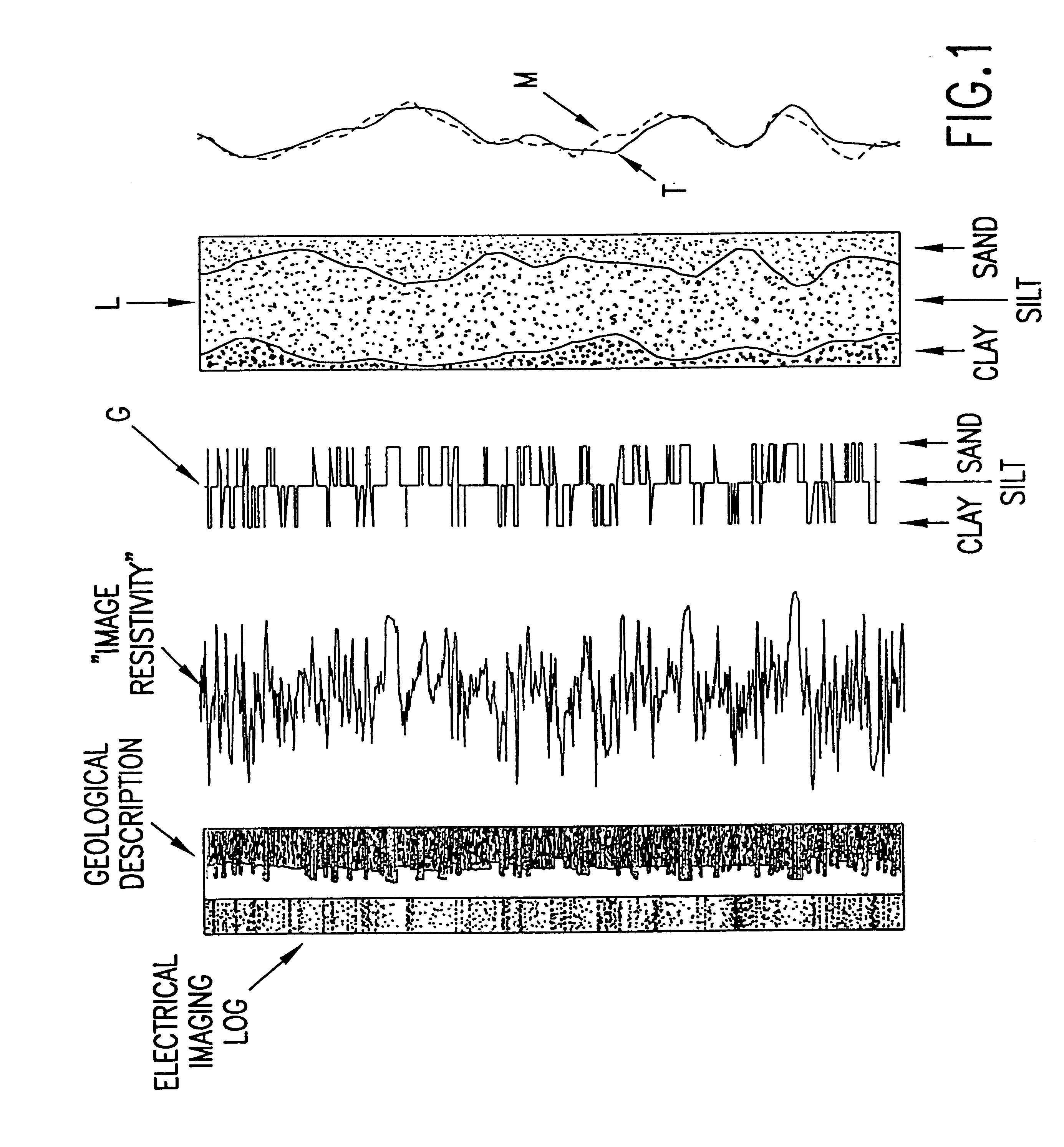
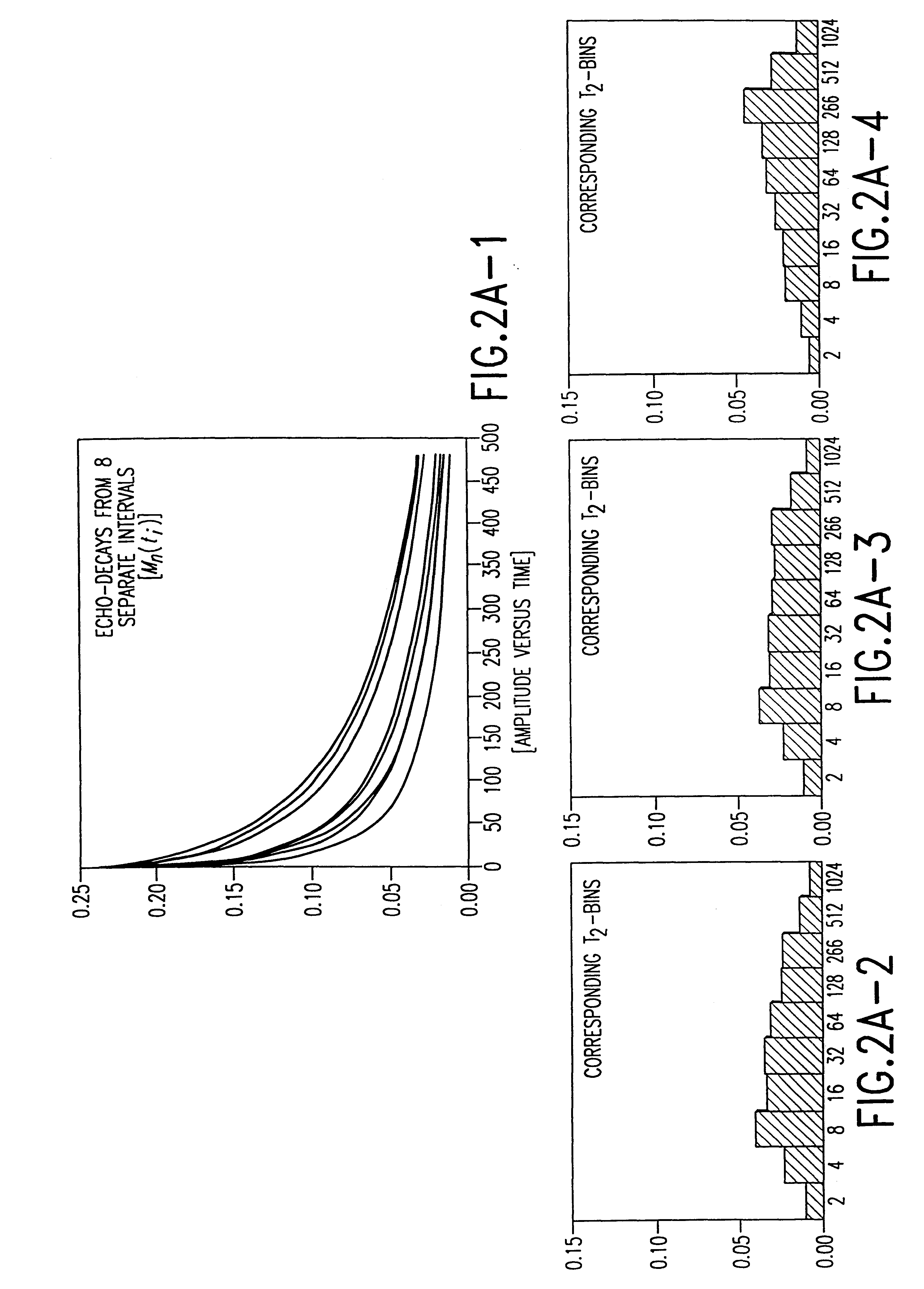
System and method for geologically-enhanced magnetic resonance imaging logs
InactiveUS6255819B1Electric/magnetic detection for well-loggingMeasurements using NMR spectroscopyMicro imagingLithology
An interpretation method and system for NMR echo-train data in thinly laminated sequences. The invention uses geological information obtained at higher vertical resolution, such as using Electric Micro Imaging, to enhance the vertical resolution of echo-train data, and thus avoids log interpretations in which the hydrocarbon potential of the formation can be misread because low resolution logs tend to provide an average description of the formation. Such averaging is especially problematic in thinly laminated sequences that consist of highly permeable and porous sand layers and less permeable silt or essentially impermeable shale layers. In a preferred embodiment, using the additional high-resolution formation information one can estimate the typical T2-spectra of lithological laminae, and significantly enhance the permeability estimate in the laminated sequences. The method and system are applicable to any temporal data from other logging tools, such as the thermal neutron decay log and others. The system and method enable proper evaluation of the high potential of thinly laminated formations, which may otherwise be overlooked as low permeable formations.
Owner:HALLIBURTON ENERGY SERVICES INC
System and method for enhanced vertical resolution magnetic resonance imaging logs
InactiveUS6337568B1Electric/magnetic detection for well-loggingMeasurements using NMR spectroscopyLithologyMicro imaging
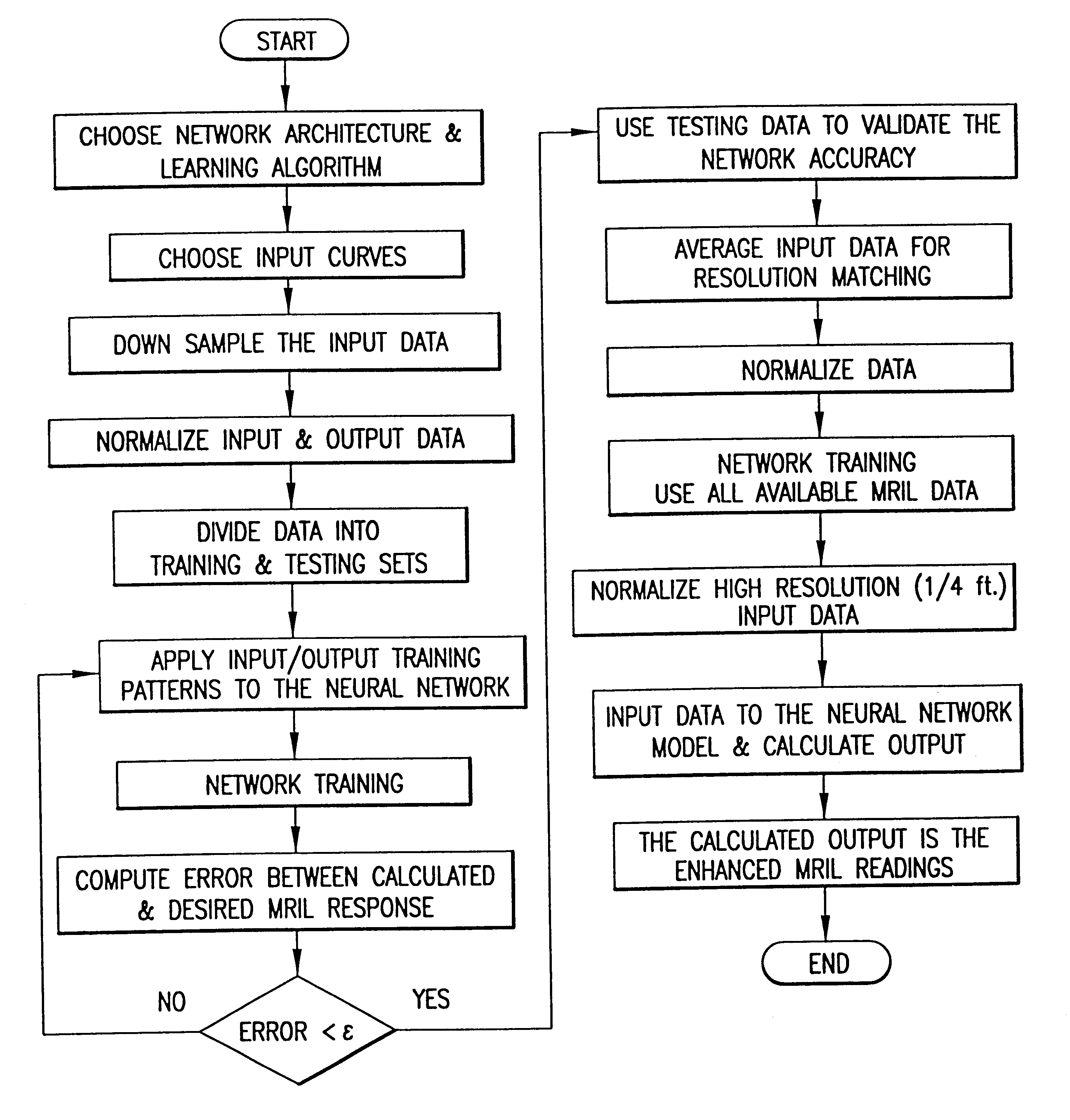
An interpretation method and system for NMR echo-train data in thinly laminated sequences. The invention uses geological information obtained at higher vertical resolution, such as using Electric Micro Imaging, to enhance the vertical resolution of echo-train data, and thus avoids log interpretations in which the hydrocarbon potential of the formation can be misread because low resolution logs tend to provide an average description of the formation. Such averaging is especially problematic in thinly laminated sequences that consist of highly permeable and porous sand layers and less permeable silt or essentially impermeable shale layers. In a preferred embodiment, using the additional high-resolution formation information one can estimate the typical T2-spectra of lithological laminae, and significantly enhance the permeability estimate in the laminated sequences. In another aspect the system and method of the preferred embodiment use neural network(s) to further enhance the resolution of a particular log measurement. The method and system are applicable to any temporal data from other logging tools, such as the thermal neutron decay log and others. The system and method enable proper evaluation of the high potential of thinly laminated formations, which may otherwise be overlooked as low permeable formations.
Owner:HALLIBURTON ENERGY SERVICES INC
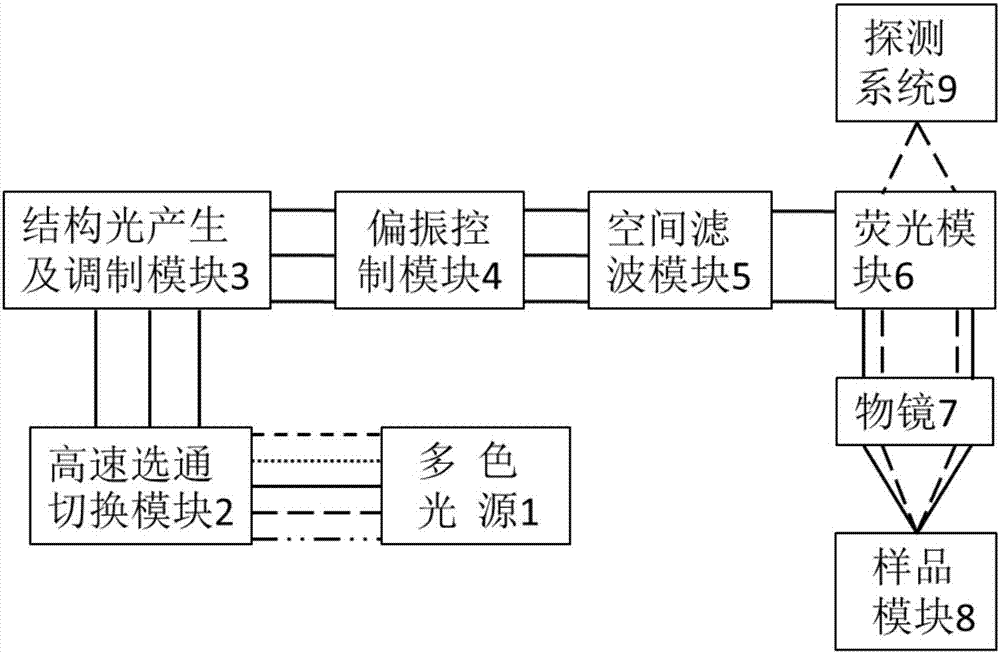
High-speed multicolor and multimode structured light illumination super-resolution microimaging system and method thereof
ActiveCN107389631AIncrease contrastFast imagingFluorescence/phosphorescenceMicro imagingFluorescence
The invention discloses a high-speed multicolor and multimode structured light illumination super-resolution microimaging system. Laser generated by a multicolor light source is incident into a high-speed gating switching module; the high-speed gating switching module selects the laser in one or multiple colors and enables the laser to irradiate a structured light generation and modulation module; the structured light generation and modulation module generates periodically modulated structured light and controls the direction and the phase of the structured light; the modulated laser is transmitted to a polarization control module; the polarization control module adjusts the polarization direction of the laser, so that the structured light illumination stripe is high in contrast, and the laser is transmitted to a space filter module; the space filter module filters out redundant stray light, and then emits the laser to a sample module through a fluorescence module and an objective lens in sequence; signal light emitted by the sample module is collected by the objective lens, and then the fluorescence module separates exciting light from the signal light; finally the signal light is received by a detection module. The system is high in structured light illumination stripe contrast and high in imaging speed, and meanwhile at least 5-color imaging can achieve the optimal performance.
Owner:北京纳析光电科技有限公司
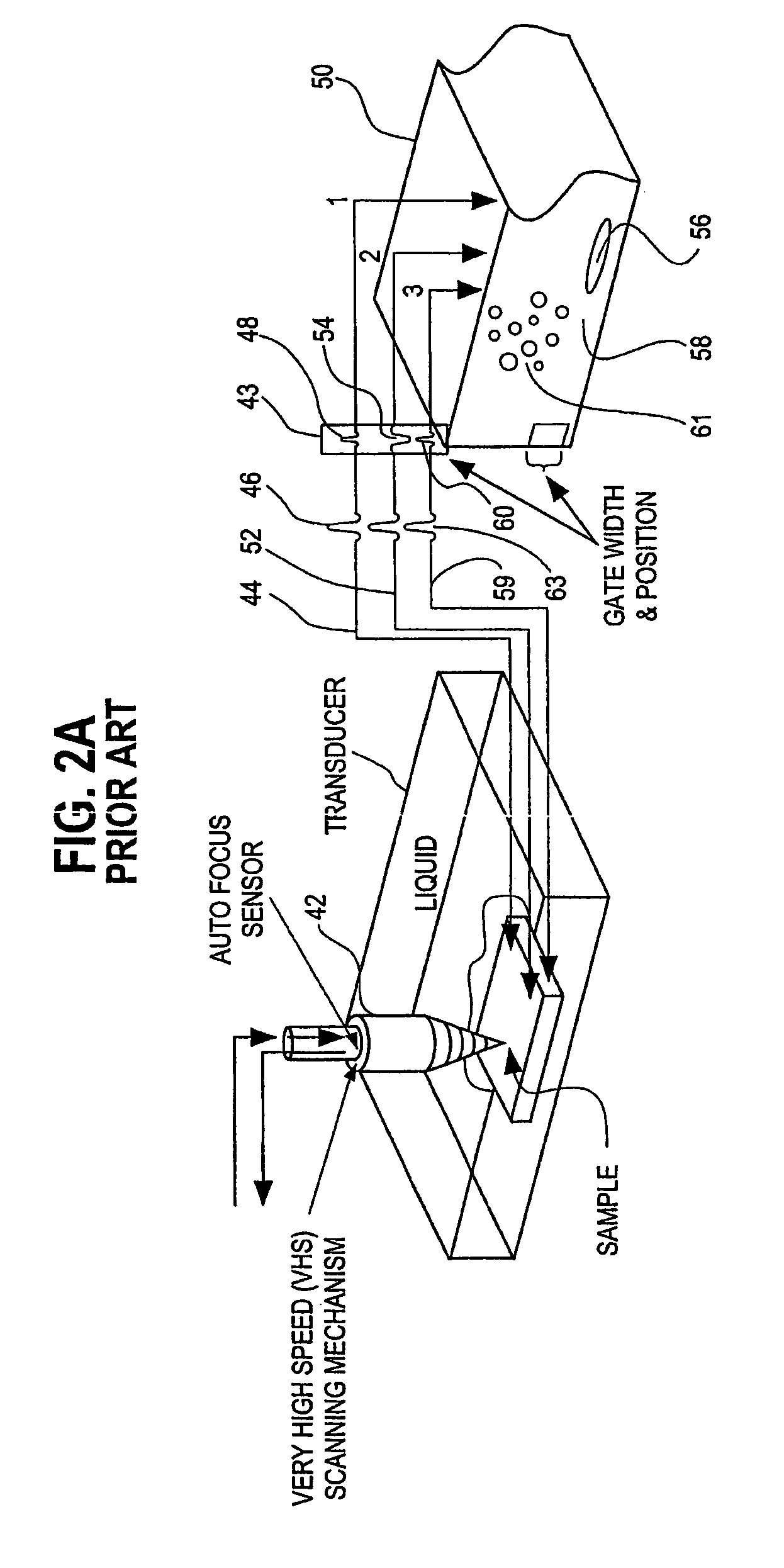
Automated acoustic micro imaging system and method
InactiveUS6460414B1Overcome incompatibilitiesAnalysing solids using sonic/ultrasonic/infrasonic wavesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingEngineeringMicro imaging
An automated acoustic micro imaging system includes a part-storage station favoring a dry environment, a part-transport robot, and a wet-environment inspection station. The wet-environment inspection station has an ultrasonic beam generator, a coupling fluid in which parts are inspected, and a part-retention stage. A moisture barrier is located between the wet-environment inspection station and the part-storage station favoring a dry environment. The inspection station includes a kinematic, quick-change part-retaining chuck and robotic means for interchanging chucks. Automatic acoustic micro imaging methods are disclosed.
Owner:NORDSON CORP
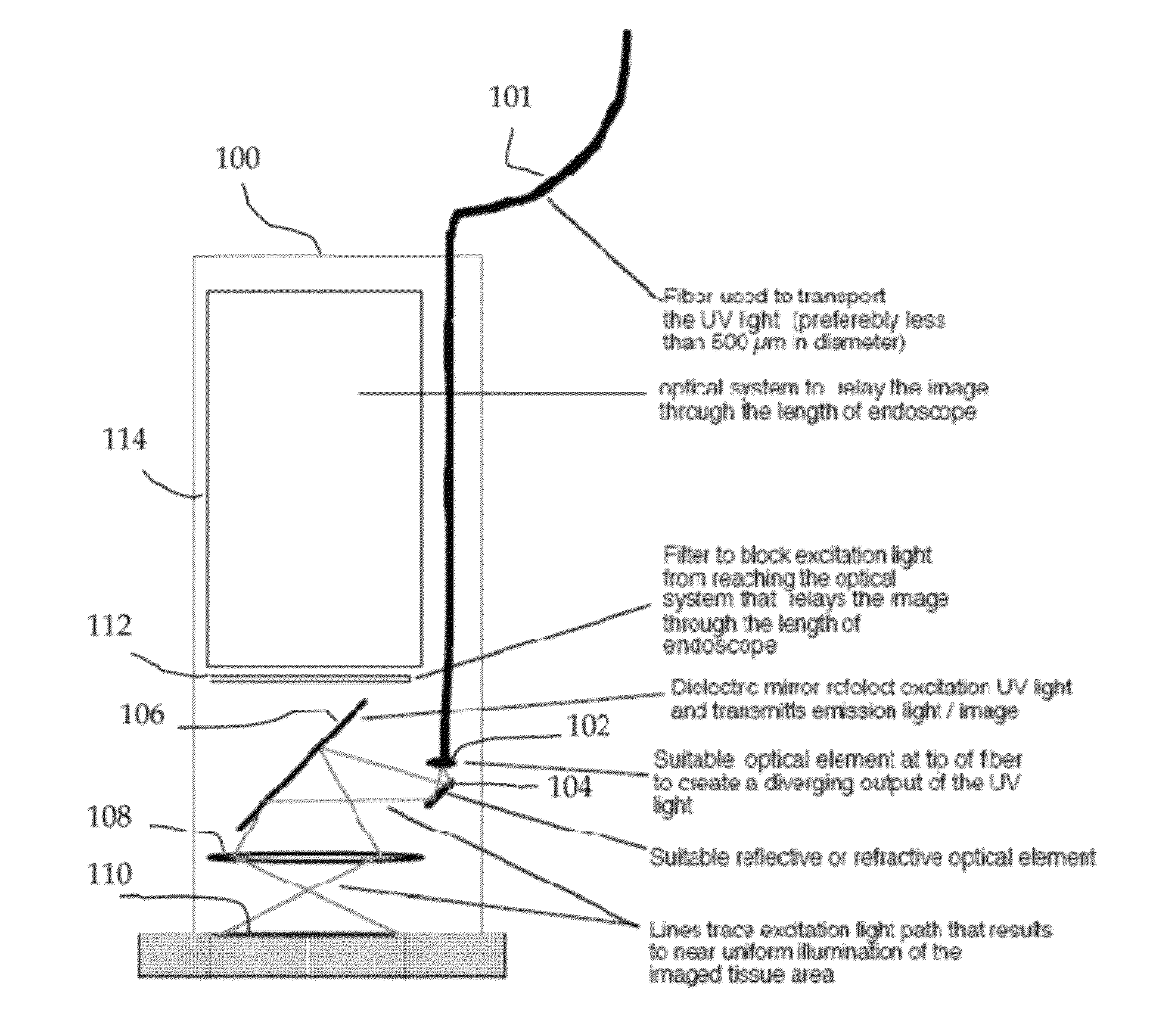
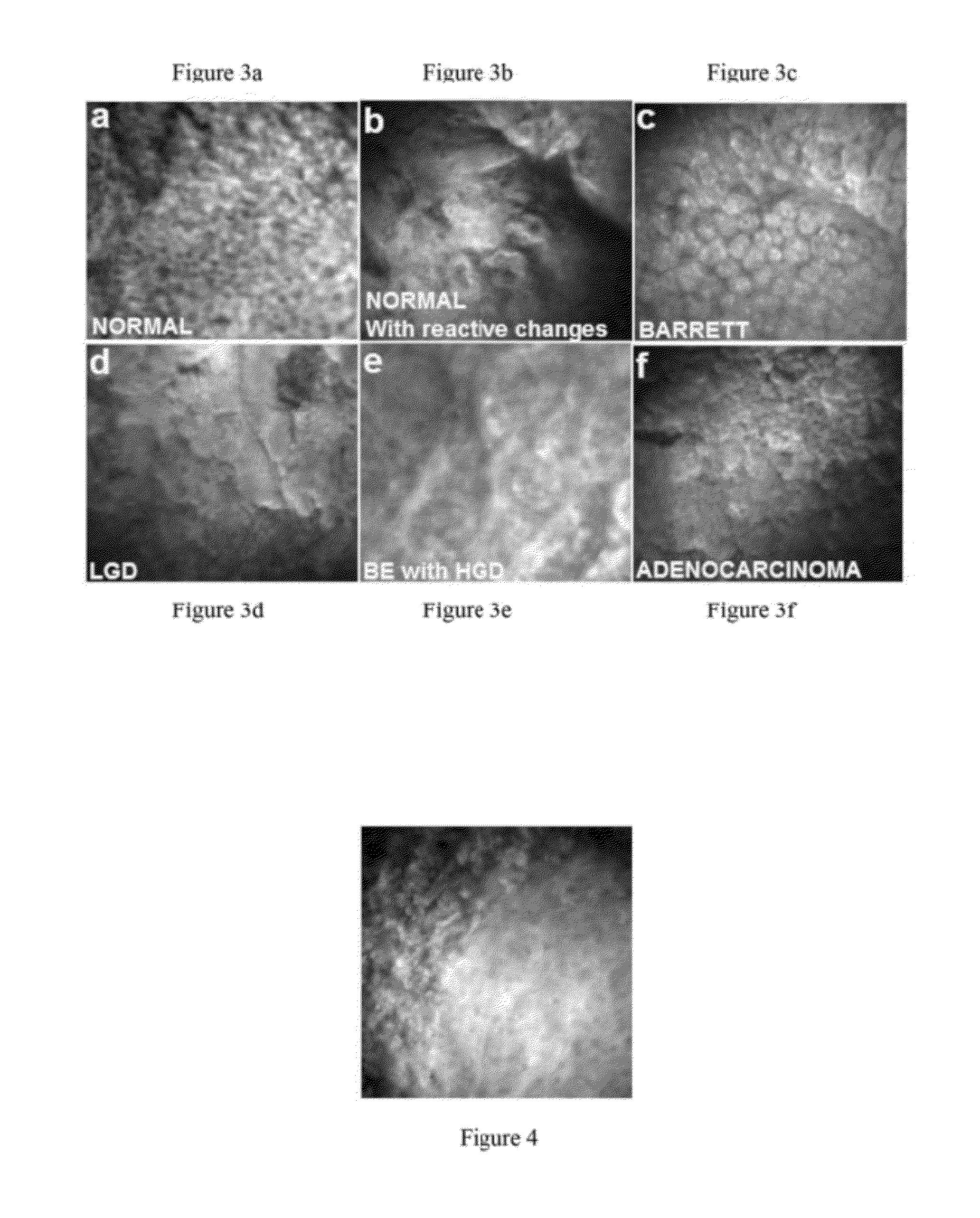
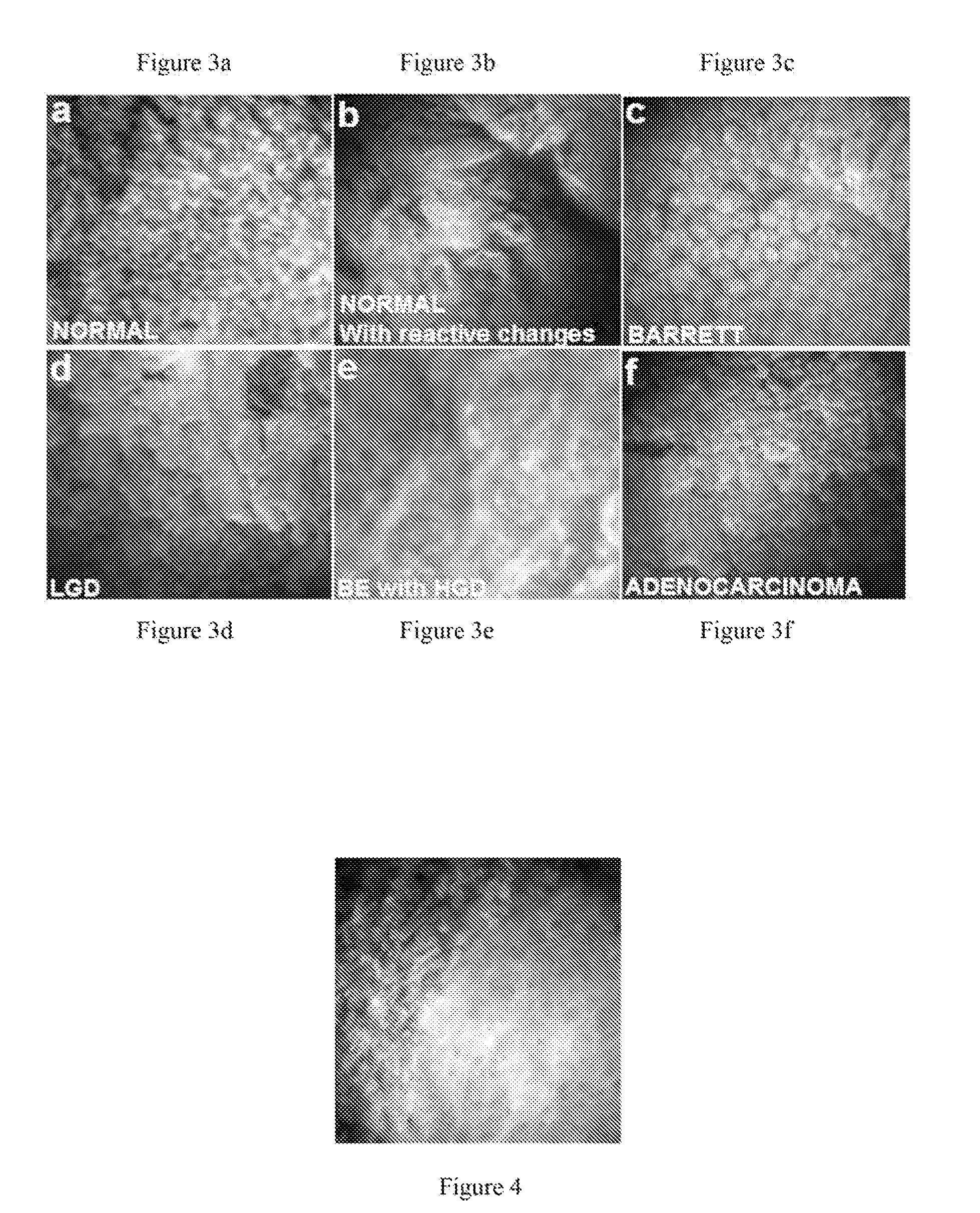
In vivo spectral micro-imaging of tissue
ActiveUS8320650B2Effectively categorizeEffectively visualizeMaterial analysis by optical meansCharacter and pattern recognitionMicro imagingImage resolution
In vivo endoscopic methods an apparatuses for implementation of fluorescence and autofluorescence microscopy, with and without the use of exogenous agents, effectively (with resolution sufficient to image nuclei) visualize and categorize various abnormal tissue forms.
Owner:LAWRENCE LIVERMORE NAT SECURITY LLC +1
In-situ testing machine for microcosmic performance of multi-load and multi-physical-field coupling material
ActiveCN103499483AEfficient combinationSimulate micromechanical propertiesMaterial strength using tensile/compressive forcesInvestigating material hardnessMicro imagingPhysical field
The invention relates to an in-situ testing machine for the microcosmic performance for a multi-load and multi-physical-field coupling material, belonging to the technical field of material mechanics property testing. The in-situ testing machine comprises a micro / nanometer-precision driving / transmission module, a 'mechanical-electric-thermal-magnetic' loading module and a control module, is integrated with a high-field-depth 3D (three dimensional) micro-imaging lens, a Raman spectrometer and a visual in-situ monitoring module and is capable of dynamically monitoring deformational behaviors, damage mechanisms and performance evolvement rules of the material in a loading process. The in-situ testing machine has the advantages that the whole structure is compact, and the space layout is saved; the loads of four manners including 'stretching / compression-torsion-bending-indentation' can be singly loaded, two or more loads can be combined to be loaded as well, and externally-applied physical fields such as heat, electricity, magnetism and the like can be combined to maximally simulate the real working conditions of components of the material, and effective measures and methods are provided for testing the micromechanical performance of the material under a service-approximating condition.
Owner:JILIN UNIV
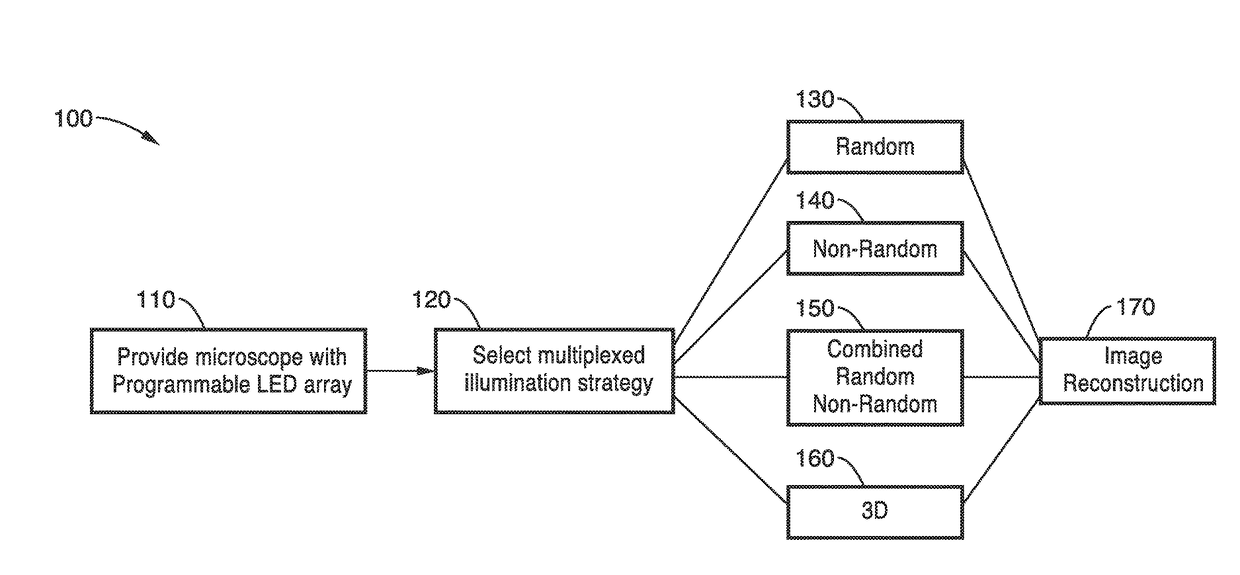
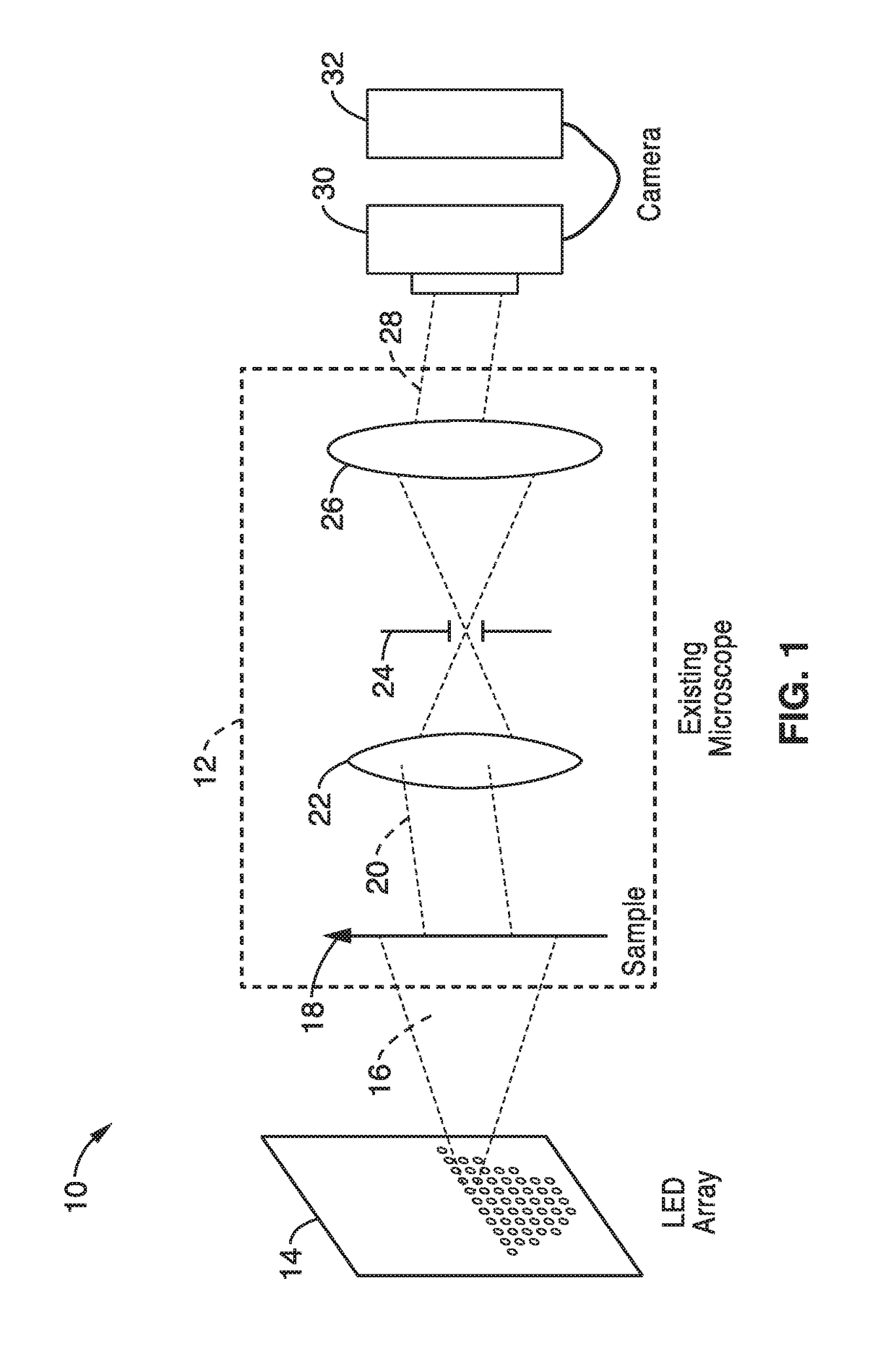
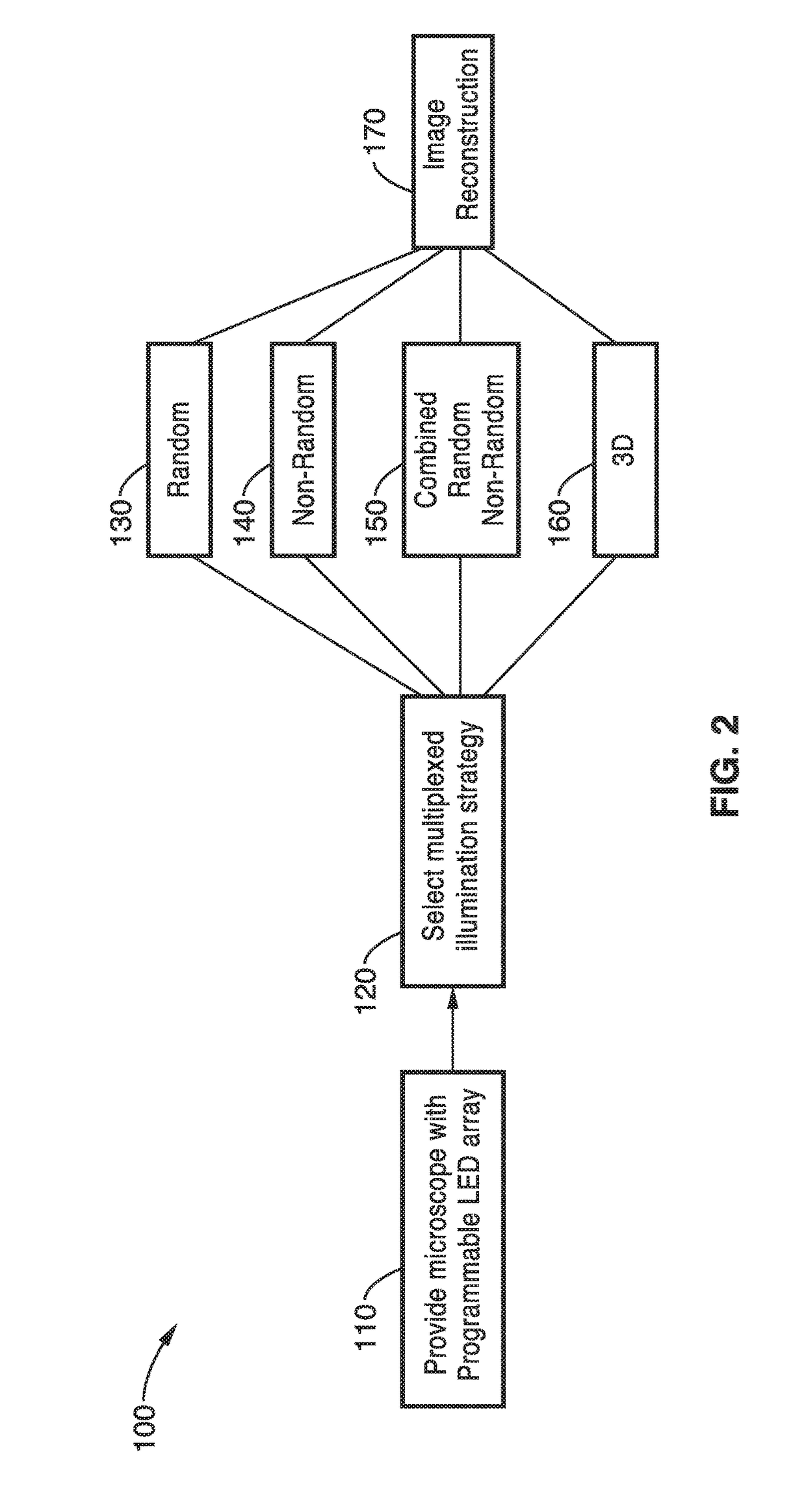
Fourier ptychographic microscopy with multiplexed illumination
InactiveUS20170146788A1Exploits redundancyFaster sample dynamicImage enhancementTelevision system detailsMicroscopic imageWide field
A system and methods for wide field of view, high resolution Fourier ptychographic microscopic imaging with a programmable LED array light source. The individual lights in the LED array can be actuated according to random, non-random and hybrid random and non-random illumination strategies to produce high resolution images with fast acquisition speeds. The methods greatly reduce the acquisition time and number of images captured compared to conventional sequential scans. The methods also provide for fast, wide field 3D imaging of thick biological samples.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA
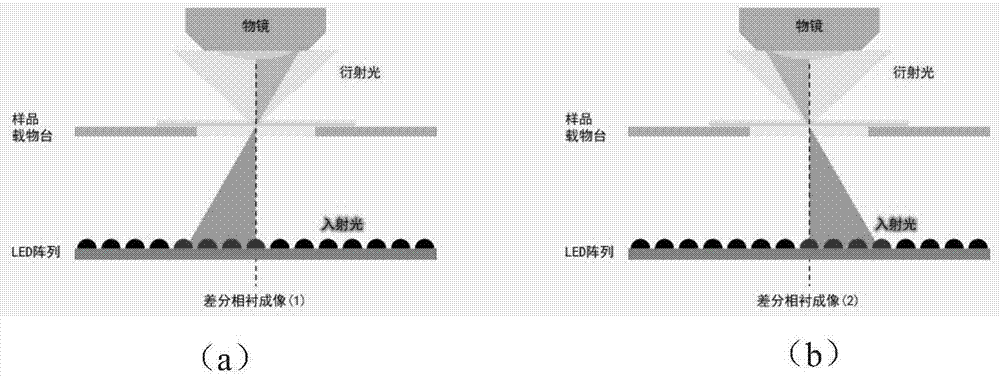
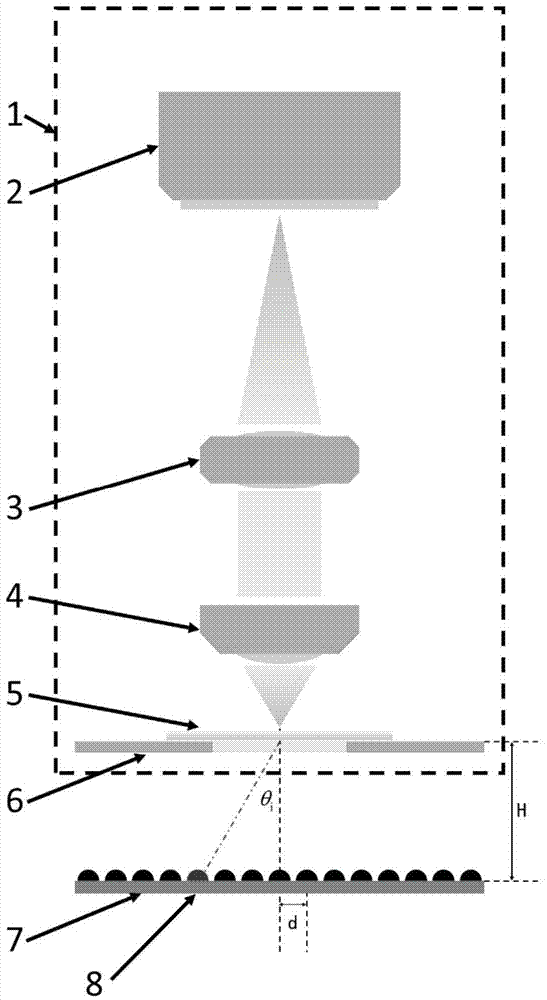
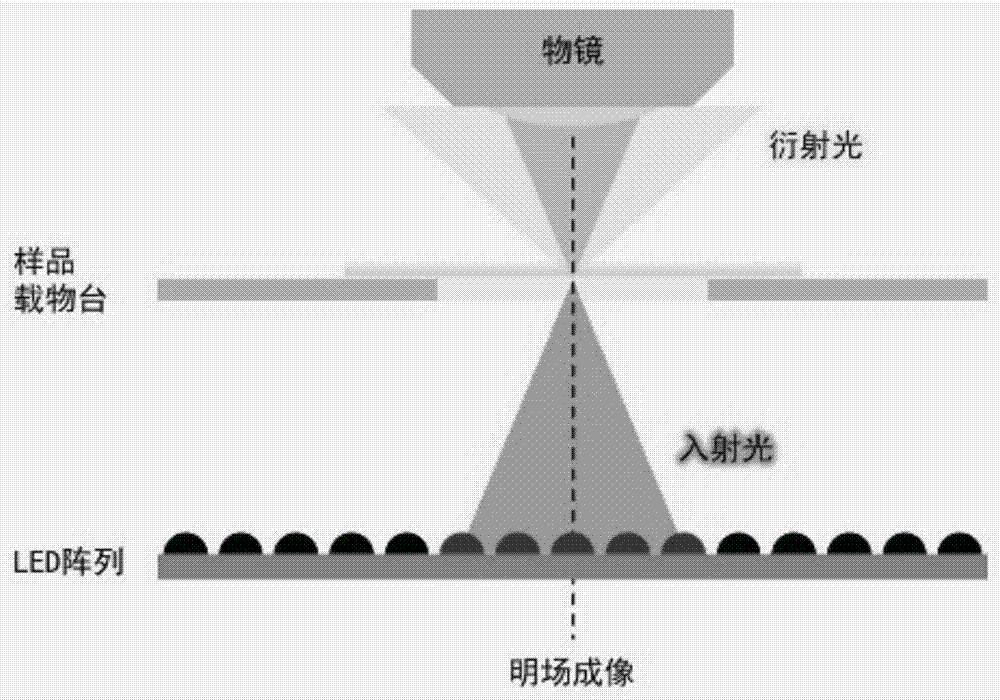
Multi-mode micro-imaging system and method based on LED array
ActiveCN104765138ASolve the problem of complex optical path and difficult operationAccurate measurementMicroscopesMicro imagingLed array
The invention discloses a multi-mode micro-imaging system and method based on an LED array. The LED array serves as a microscope system light source and generates controllable multi-angle illumination light and a controllable illumination pore diameter, and bright field imaging, dark field imaging and difference phase contrast imaging are achieved. The realizable multi-mode imaging includes the three imaging modes of bright field imaging, dark field imaging and difference phase contrast imaging, and while bright field imaging, dark field imaging and difference phase contrast imaging are achieved, it is unnecessary to add any additional optical elements into the imaging path of a traditional microscope; in this way, an optical system is greatly simplified, and the LED array enables the microscope to have the capacity of flexibly adjusting the illumination pore diameter, the illumination angle and light source coherence.
Owner:NANJING UNIV OF SCI & TECH
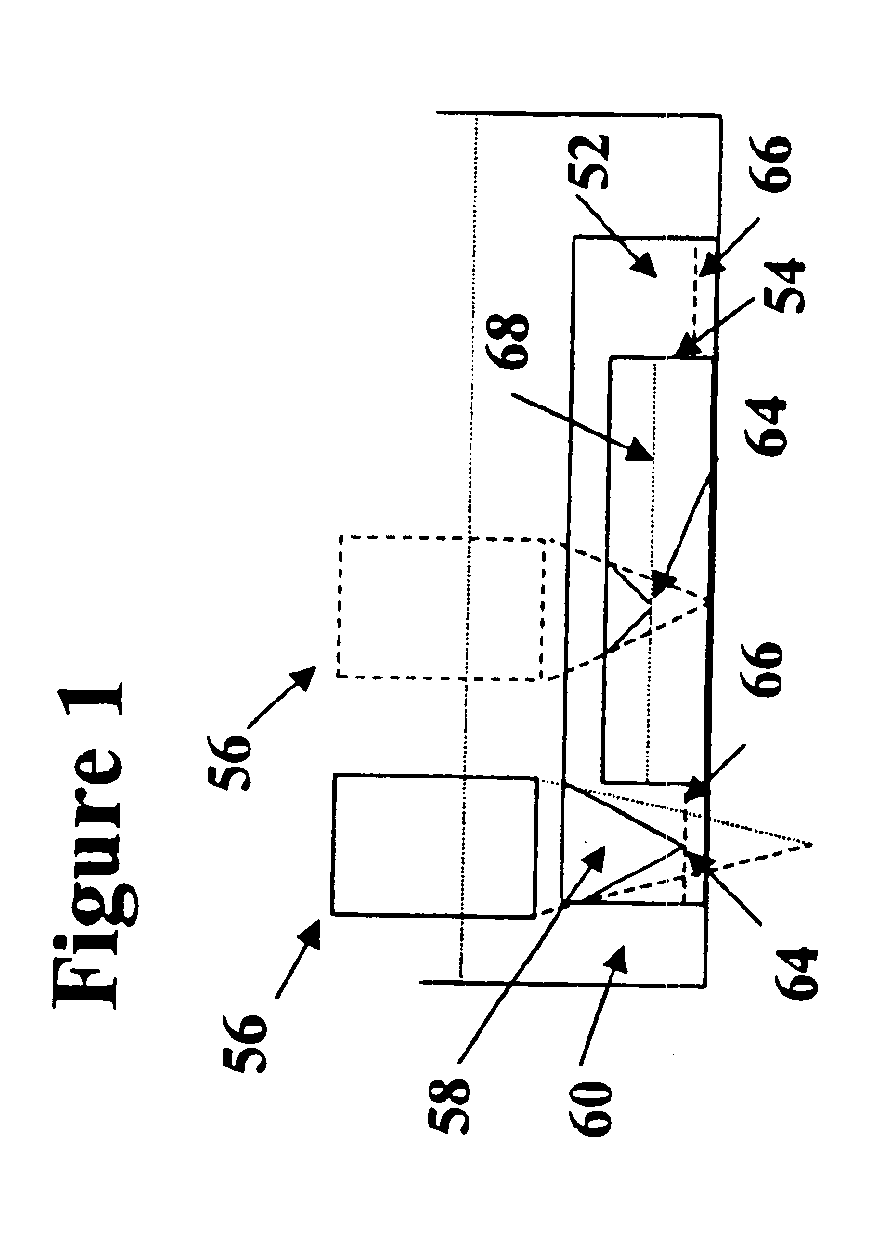
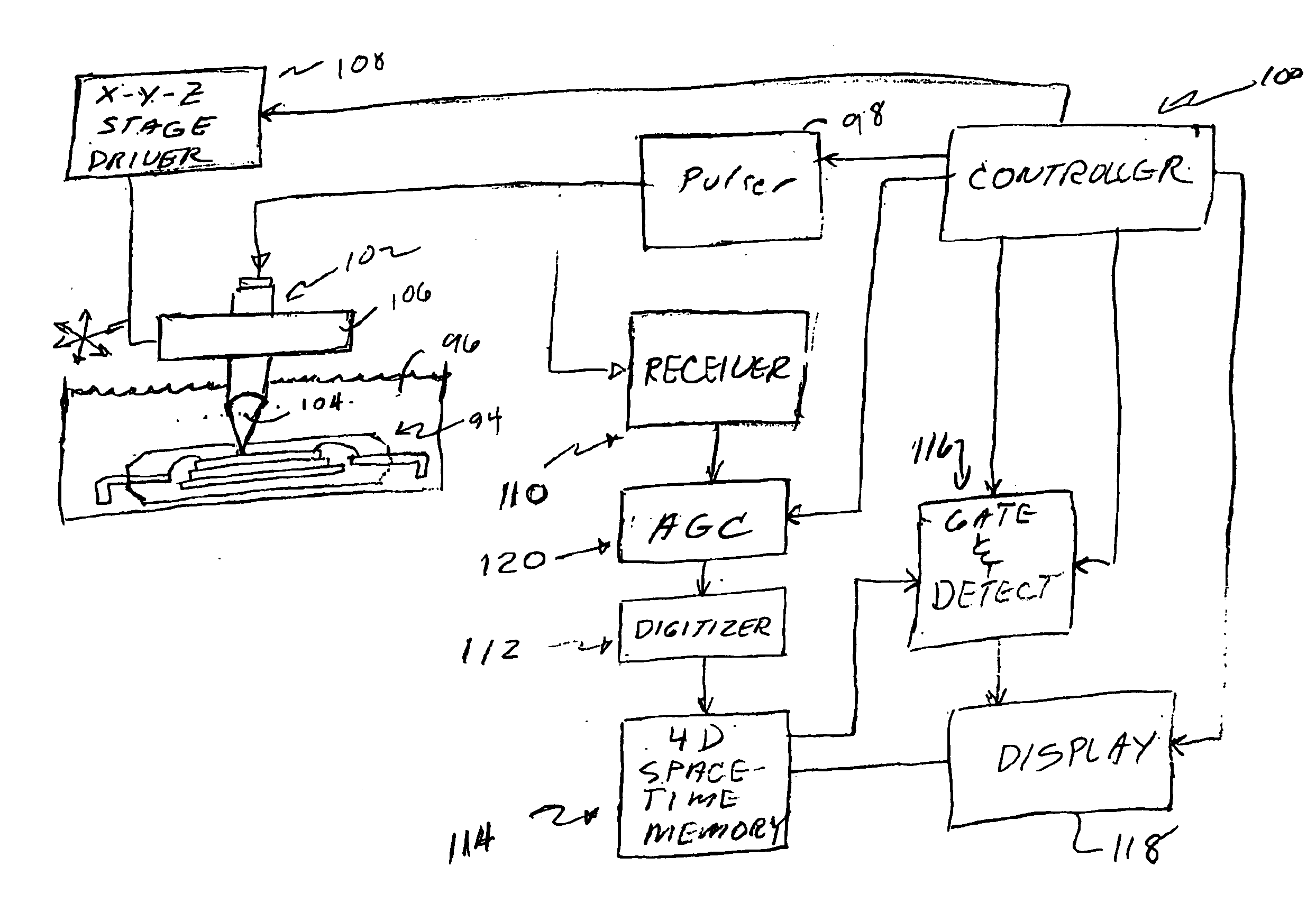
Acoustic micro imaging method providing improved information derivation and visualization
InactiveUS6880387B2Improve understandingEnhanced informationAnalysing solids using sonic/ultrasonic/infrasonic wavesResponse signal detectionMicro imagingX ray image
A method for enhancing information derived from acoustically inspected samples comprises deriving an acoustic image of a sample, and generating a visual superposition of one or more additional images. The additional images are selected from the group consisting of an optical image, a second acoustic image in a different sized field of view form said acoustic image, an infrared image, an X-ray image, and an electron beam image.
Owner:NORDSON CORP
Confocal micro imaging system using dummy pinhole
The invention relates to a confocal imaging system in fields of optical microimaging, it is a confocal microscopic system which uses virtual confocal pinhole to make the system to obtain the longitudinal chromatography capability. It's widely used in the fluorescence microscopy, optical microscopy and so on which possess the microtechnique of three-dimensional imaging capability. The invention includes: light source, collimation lens, beam splitter, microscope objective, objective table, collective lens and CCD. It characterized in that the photosensitive surface of CCD is directly located at the focal plane of the collimation lens, the computer sets the virtual pinhole at the corresponding position of two-dimensional digital image collected by CCD based on the position of the focal point of collimation lens, the signal values of the pixels in the pinhole are accumulated as the signal intensity of current scanning point to eliminate the effect of stray light in non-focal plane to the image quality. The function of virtual confocal pinhole is significant with the physical confocal pinhole and the position, size can be controlled and adjusted by computer, and it possesses the advantages of convenient gauging adjustment.
Owner:NANKAI UNIV
Automatic microscopic imager for detecting cast-off cells and detection method
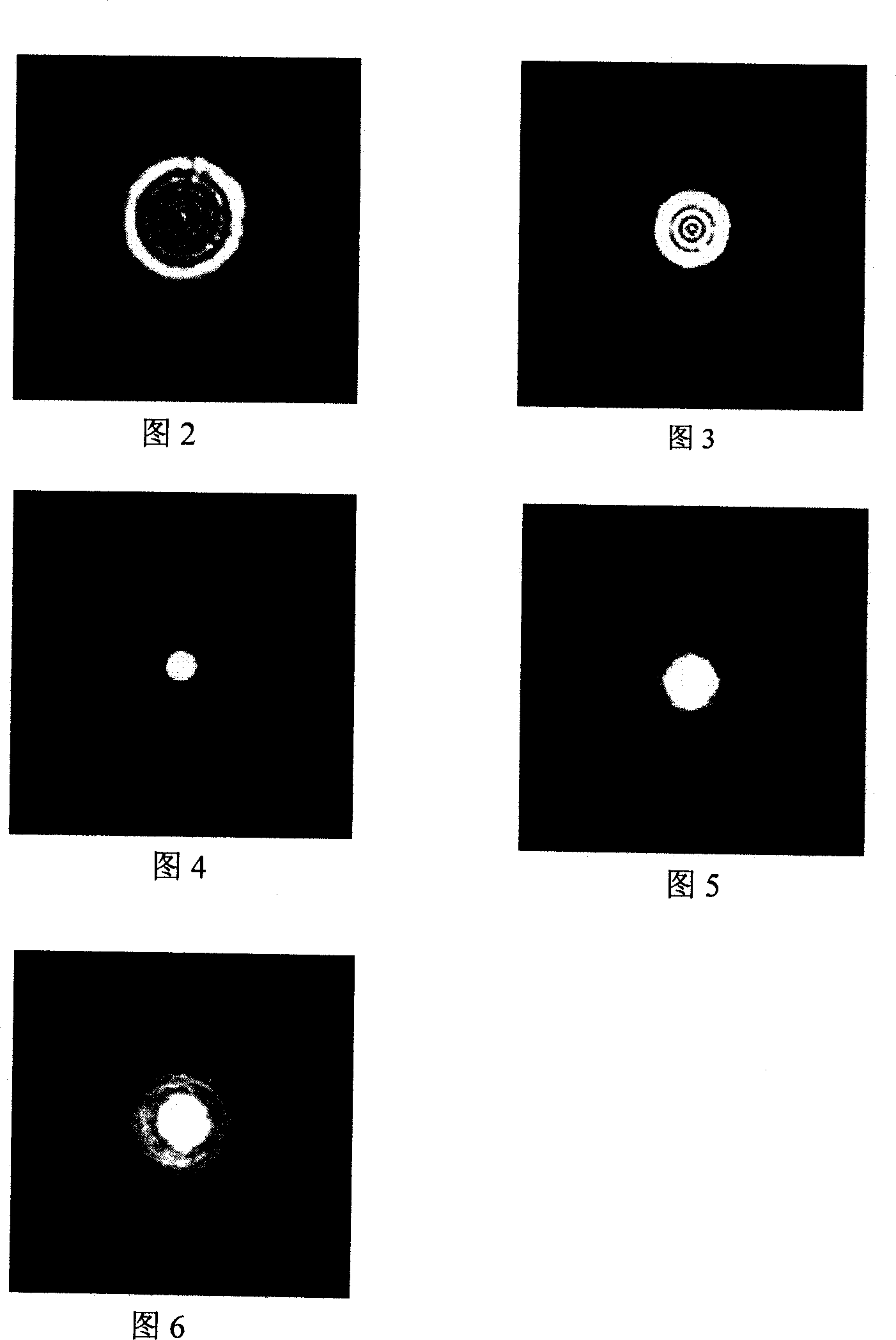
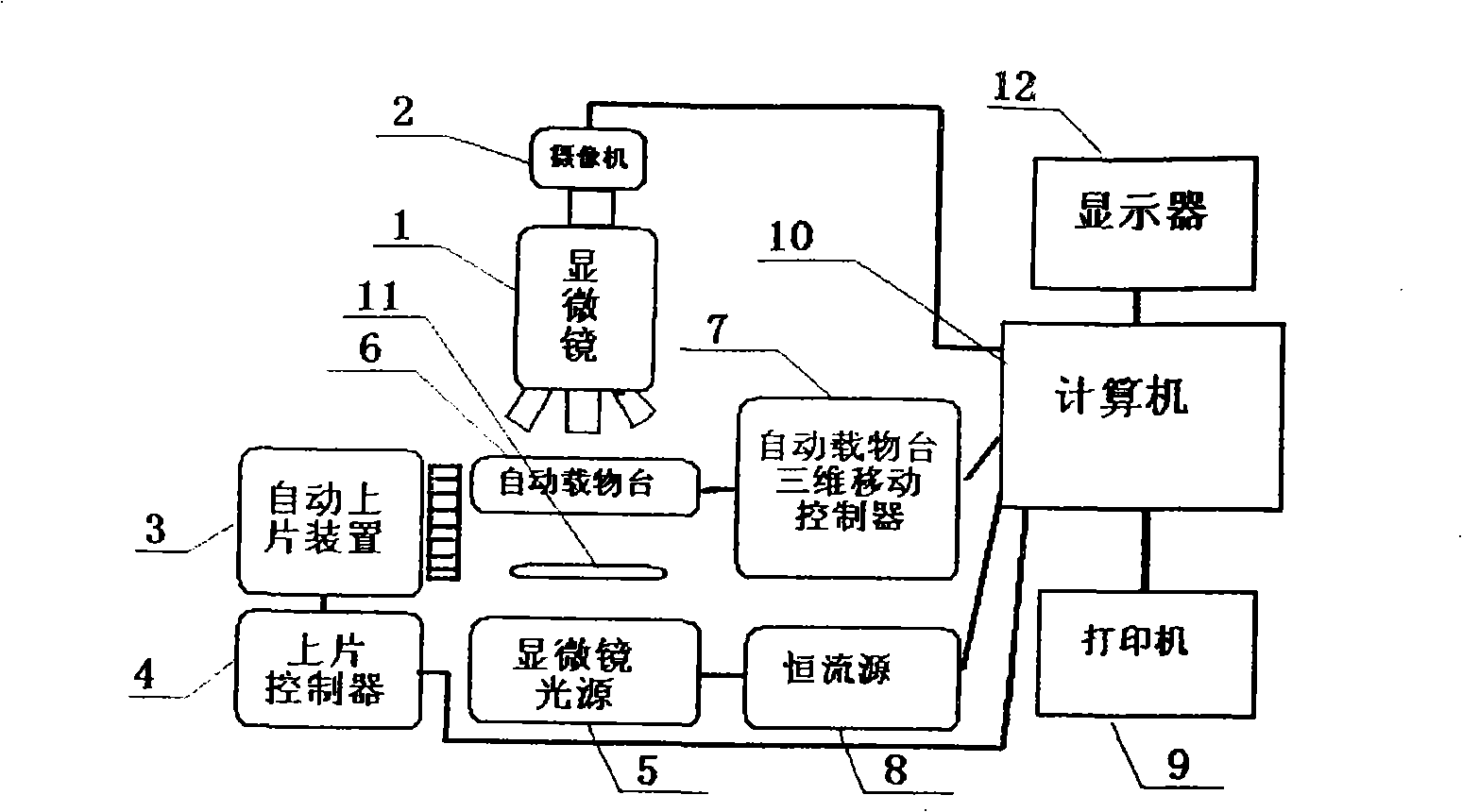
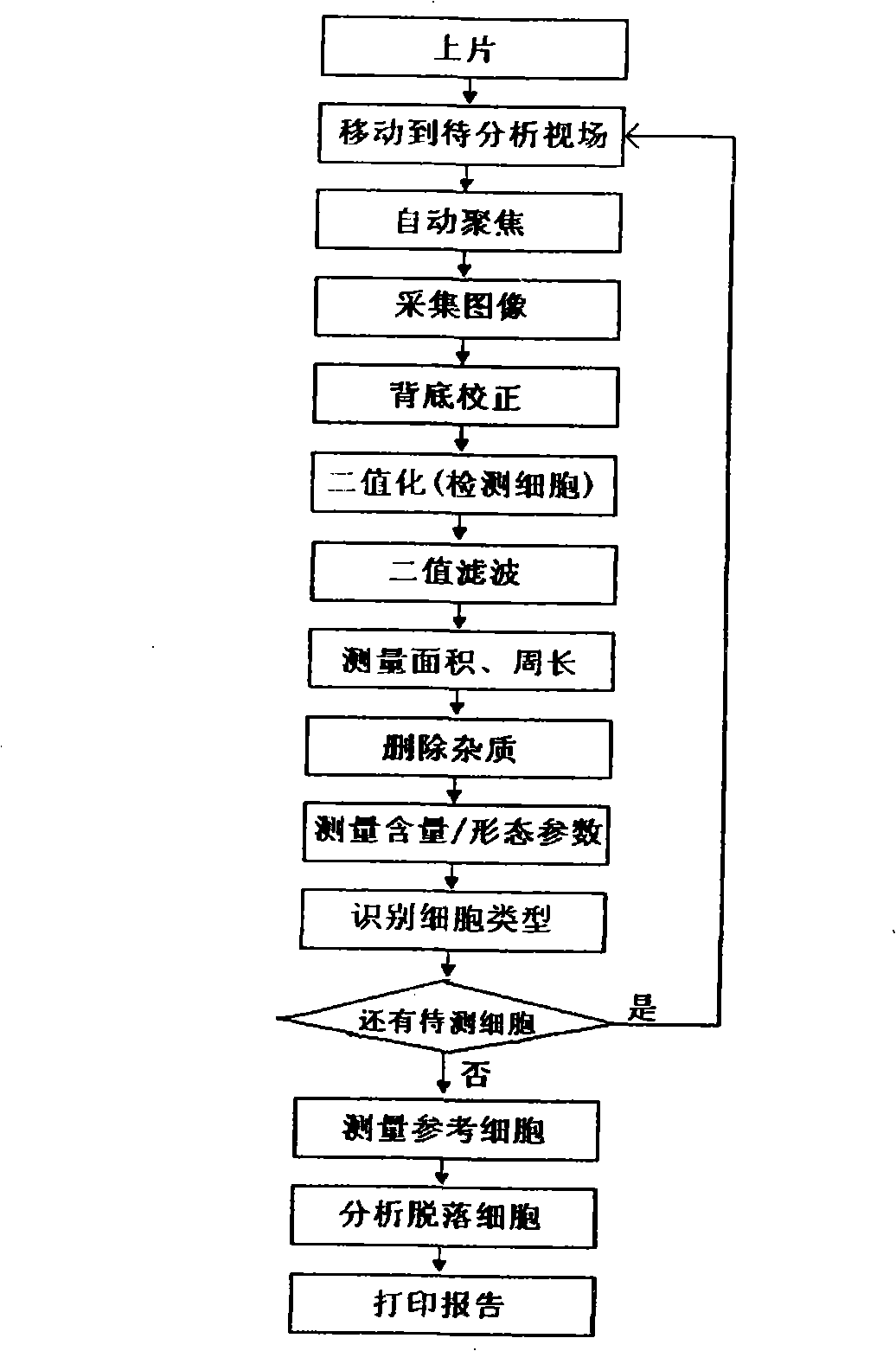
ActiveCN101339185AHigh degree of automationThe analysis result is accurateMaterial analysis by optical meansBiological testingMicro imagingFiltration
The invention relates to an automatic micro imaging instrument used for detecting cast-off cells and a detecting method, in particular to an automatic analysis instrument of a uterine neck cell smear and a detecting method. The instrument comprises a microscope, a three dimensional automatic object stage, an automatic film loading device and a control system thereof, a light system, a stable system, a light filter, a computer, a display and a digital camcorder, etc. The detecting method comprises the following steps: the smear is analyzed and colored, then arranged on the automatic object stage which moves up and down to focus automatically, when the automatic object stage moves horizontally, the smear scanning is realized; cell images are amplified by the microscope, picked up and sent to the computer to carry out image processing and analyzing. The detected cells are filtered by two-value filtration to remove the noises, the area and the perimeter are measured, and the impurity is deleted, then the spectrum and other shape parameters of the cells are measured; the measured cells are classified with a pattern recognition algorithm into the cast-off cells, white blood cells, lymphocyte cells and the impurity; after a viewing field is finished, the cells move down automatically, auxiliary diagnostic data is obtained by the computer. The instrument and the detecting method have the advantages of high degree of automation, accurate analysis results and reliability.
Owner:HEER MEDICAL TECH DEV CO LTD
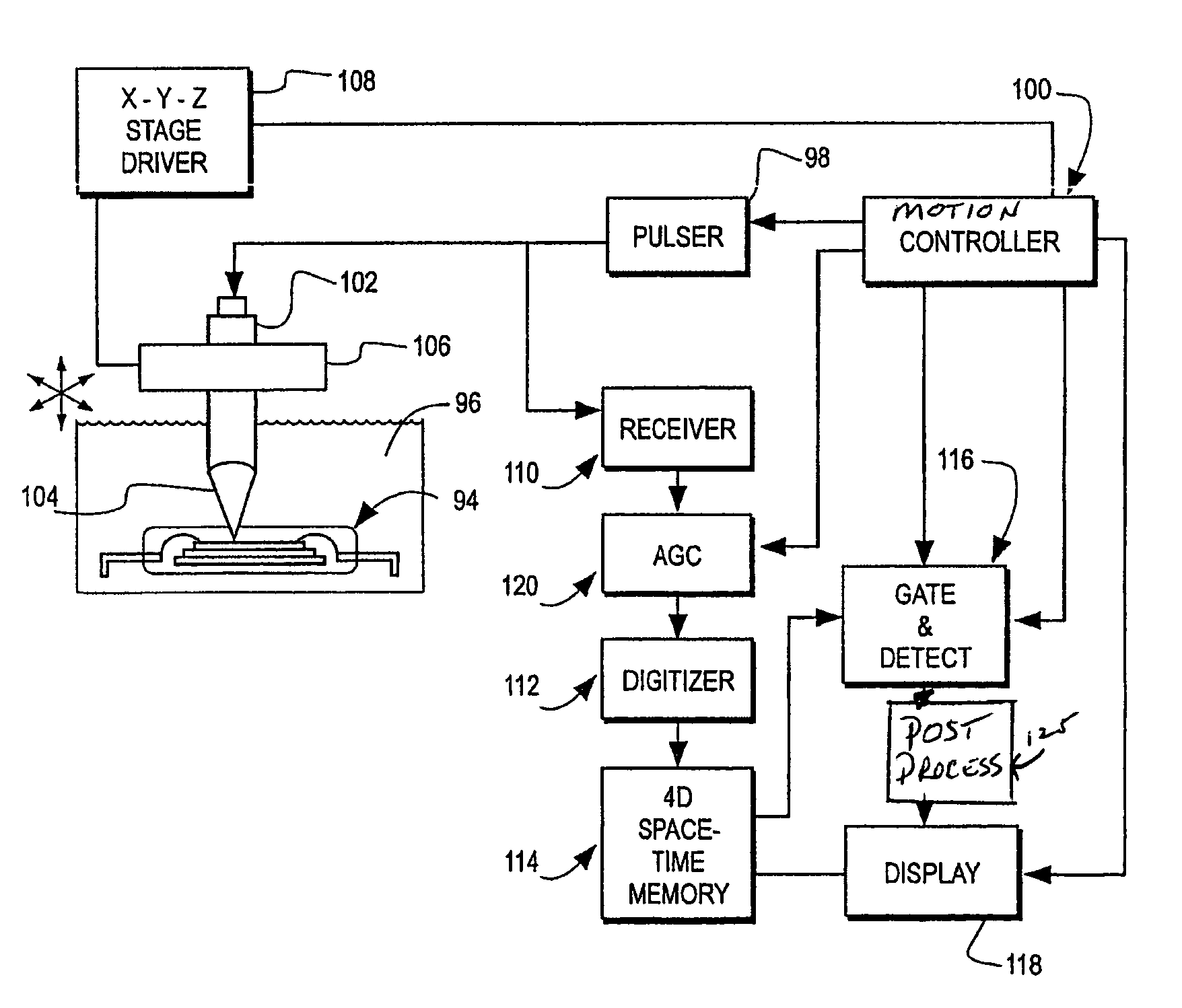
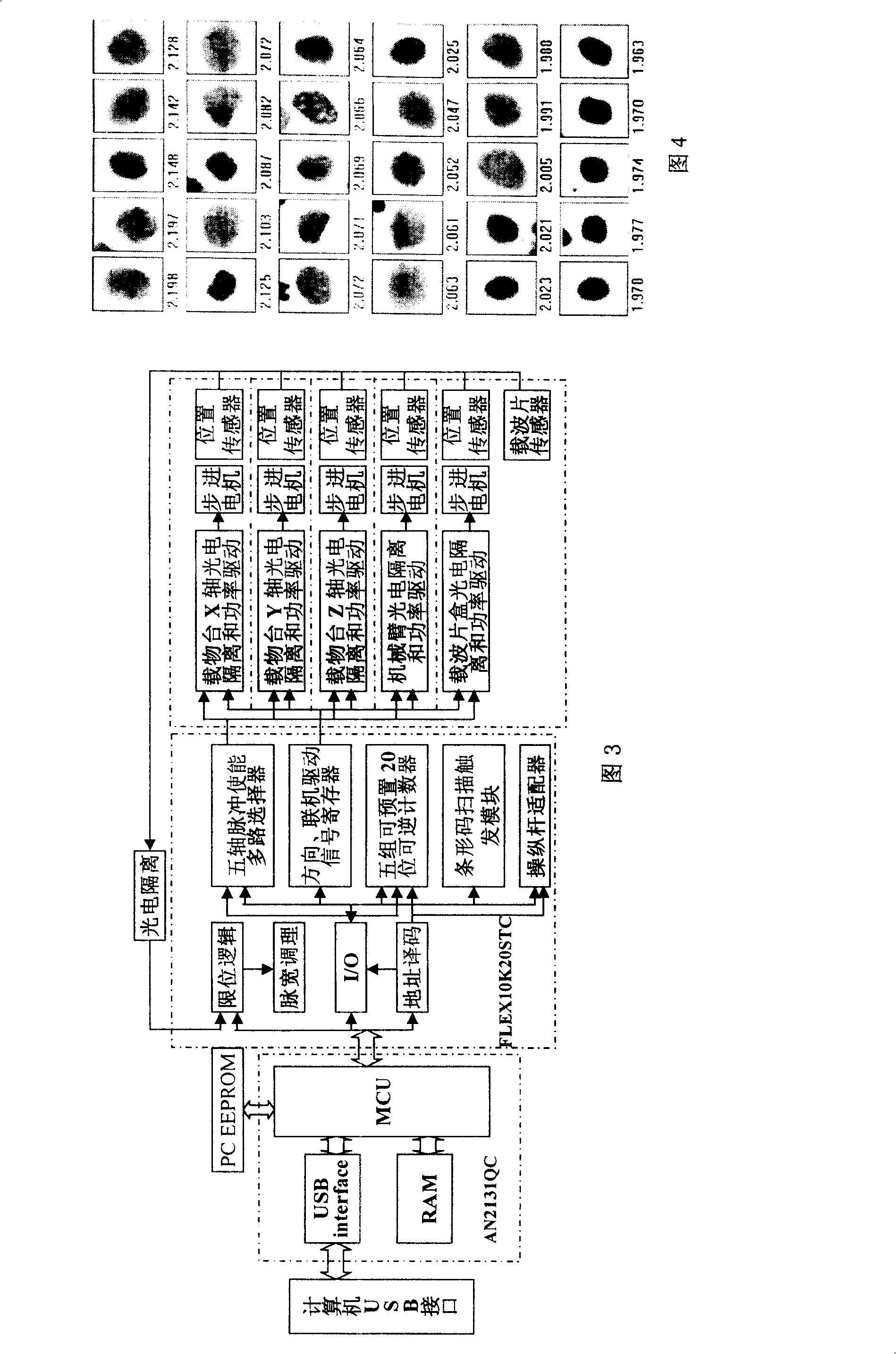
Acoustic micro imaging method and apparatus for capturing 4D acoustic reflection virtual samples
InactiveUS6895820B2Accurate and comprehensive understandingOptimize dataAnalysing solids using sonic/ultrasonic/infrasonic wavesResponse signal detectionMicro imagingVirtual sample
For use in acoustic micro imaging, a method (and implementing apparatus) is disclosed for creating a 4D virtual sample data memory. The method comprises employing a pulsed ultrasonic microscope probe to interrogate a sample at three-dimensionally varied locations in the sample. Data developed by the microscope probe includes for each location interrogated a digitized A-scan for that location. The developed data is stored in a data memory.
Owner:NORDSON CORP
3D interactive lens
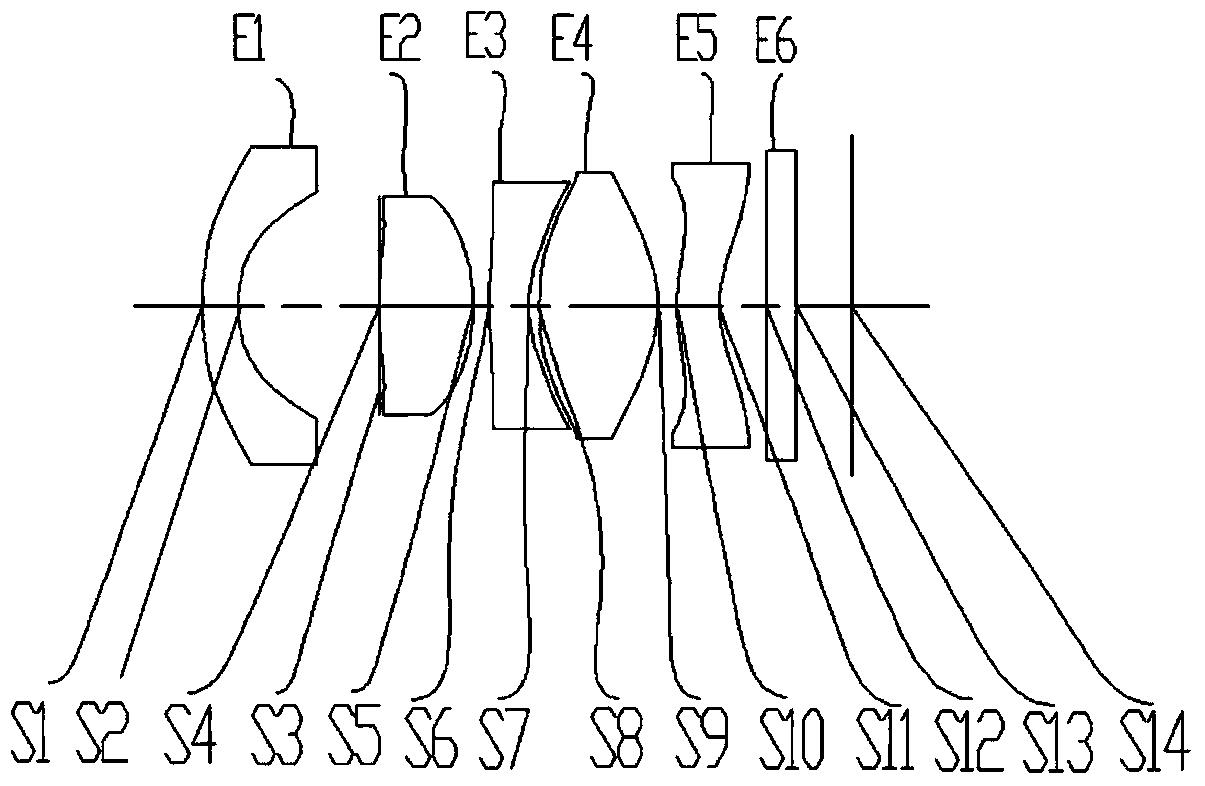
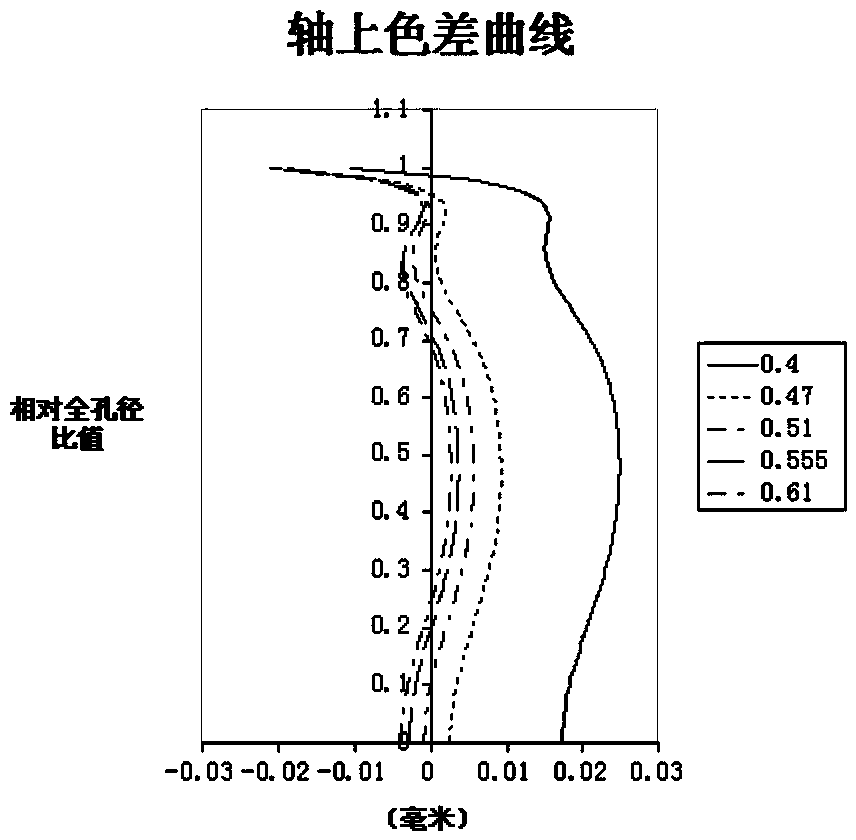
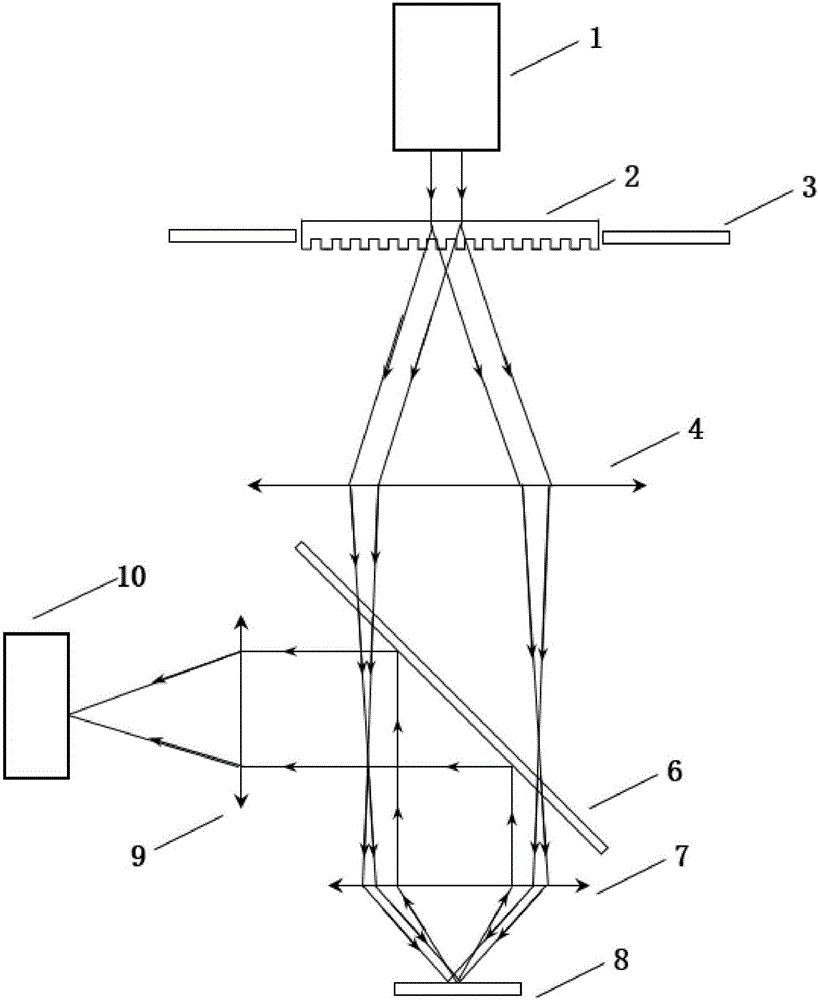
ActiveCN104166220AHigh resolutionLarge resolution under the premise of high resolutionOptical elementsNegative refractionMicro imaging
The invention provides a 3D interactive lens. A micro imaging lens system formed by five groups of lenses is arranged. The 3D interactive lens comprises a first lens, a second lens, a third lens, a fourth lens, a fifth lens from an object side to an image side successively. The first lens has a negative refraction power and the objective side is a convex surface; the second lens has positive fraction power and the image side of the second lens is a convex surface; the third lens has a negative refraction power and the image side of the third lens is a concave surface; the fourth lens has a positive refraction power and the image side of the fourth lens is a convex surface; and the fifth lens has a negative refraction power and the object side of the fifth lens is a convex surface and the image side is a concave surface. The lens meets the relations: 0<(R3+R4) / (R3-R4)<1.2, and 7<T12 / T23<25, wherein R3 and R4 respectively indicate curvature radiuses of the object side and the image side of the second lens, T12 indicates a distance between the first lens and the second lens at the optical axis, and the T23 indicates the distance between the second lens and the third lens at the optical axis. According to the invention, On the basis of configuration of the lens, advantages of small aperture and miniaturization and the like can be realized on the premise that wide angle and high resolution ratio are guaranteed. Meanwhile, the heat difference can be effectively eliminated and distortion can be well corrected.
Owner:ZHEJIANG SUNNY OPTICAL CO LTD
Structure illumination super-resolution microscopy imaging system and imaging method thereof
ActiveCN106770147AReduce in quantityAchieve super resolutionFluorescence/phosphorescenceMicro imagingFrequency spectrum
The invention discloses a structure illumination super-resolution microscopy imaging system and an imaging method thereof. The imaging system comprises an illumination light source, a rotating structure light generator, a first convergent lens, a light splitter, an objective lens, an object stage, a sample, a second convergent lens, a digital imaging device and a computer. An original image is processed through an imaging image reconstruction algorithm; super-resolution can be achieved only by rotating structured light stripes for four times without phase displacement; the imaging image reconstruction algorithm is based on frequency domain processing instead of non-spatial domain processing; a spectrum process of a super-resolution image of a sample is different from a traditional frequency domain method, structured light directions are not analyzed one by one and all directions are merged for analysis; in order to obtain traditional uniform 2-fold resolution improvement in various directions, the theoretical quantity of original images can be reduced to 4 from 9 of a traditional method; the quantity of the original images is further reduced to 3 and uniform 1.5fold resolution improvement in various direction can be theoretically obtained.
Owner:PEKING UNIV
Frequency-shift super-resolution microimaging method and device based on evanescent field illumination
InactiveCN103048272AHigh resolution finenessSimple structureScattering properties measurementsMicroscopic imageMicro imaging
The invention discloses a frequency-shift super-resolution microimaging method based on evanescent field illumination. The method comprises the steps that 1) incident illumination light obliquely irradiates a substrate medium interface, is totally reflected and generates an evanescent field; 2) the evanescent field is used for illuminating the surface of a sample; a strength image of the surface of the sample is received by a microscope; 3) the strength image is subjected to Fourier transformation; a corresponding frequency spectrum is obtained and is restored; a corresponding frequency spectrum restoring image is obtained; 4) the direction of the incident illumination light is changed for many times around the sample till the direction of the incident illumination light covers 0-360 DEG; frequency spectrum restoring images in different directions are obtained; 5) the frequency spectrum restoring images in the different directions are stacked; a complete high frequency spectrum image is obtained; and 6) the complete high frequency spectrum image is subjected to inverse Fourier transformation; and a super-resolution microscopic image of the observed sample is obtained. The invention further discloses a frequency-shift super-resolution microimaging device based on the evanescent field illumination.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV
Laser-induced breakdown-pulsed Raman spectroscopy combined system and using method
ActiveCN104596997ARealize the collectionImprove excitation efficiencyRaman scatteringMicro imagingBeam splitting
The invention discloses a laser-induced breakdown-pulsed Raman spectroscopy combined system which comprises a pulsed laser, a micro-imaging light path, a micro-imaging device, a Raman signal receiving system, a whole-spectrum LIBS signal receiving system, a spectrograph and a sample platform. The wavelength of laser is changed by adopting a half transparent and half reflecting mirror beam-splitting and frequency-doubling module, and the laser-induced breakdown-pulsed Raman spectrum is switched by using a mechanical photochopper. The invention also discloses a using method of the combined system. With the adoption of a pulsed laser, a set of optical system and a set of spectrograph system, two different types of signals excited by two different wavelengths are acquired, no movable lens assembly is arranged in the optical system, the structure is stable, and the performance is high.
Owner:SICHUAN UNIV
Three-dimensional fluorescence nano microscope imaging method and system, and image equipment
ActiveCN101963582AAvoid crosstalkReduce out-of-focus background noiseFluorescence/phosphorescenceMicro imagingLight beam
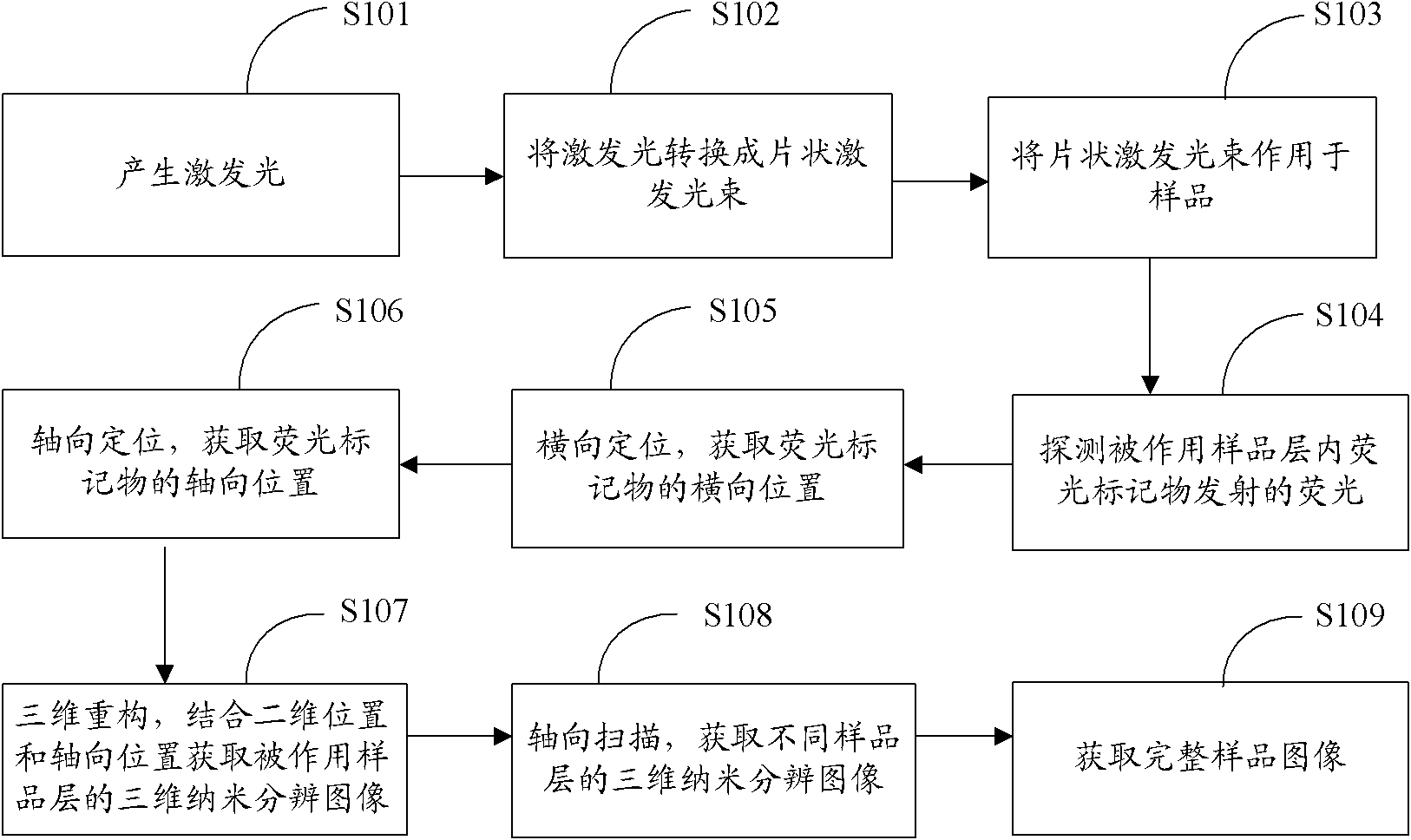
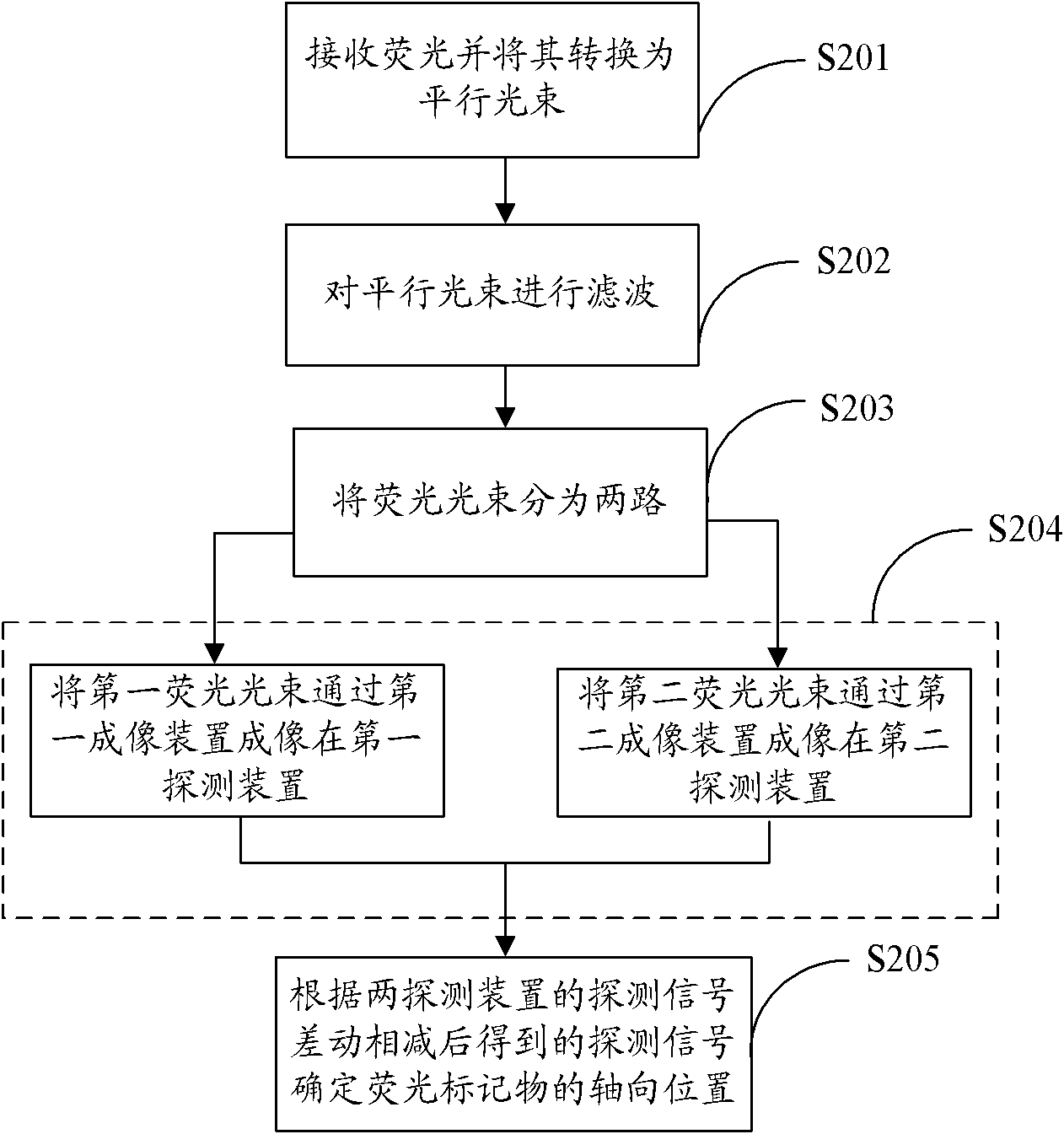
The invention is suitable for the field of microscope imaging, and provides a three-dimensional fluorescence nano microscope imaging method and a three-dimensional fluorescence nano microscope imaging system, and image equipment. The method comprises the following steps of: producing exciting light; converting the exciting light into a laminar exciting beam; making the laminar exciting beam act on a sample; detecting a fluorescent light emitted by a fluorescent label in the sample layer on which the laminar exciting beam acts; transversely positioning to acquire the two-dimensional position of the fluorescent label; axially positioning to acquire the axial position of the fluorescent label; three-dimensionally reconstructing, combining the two-dimensional position with the axial position to acquire a three-dimensional nano resolution image of the sample layer on which the laminar exciting beam acts; axially scanning to acquire the three-dimensional nano resolution images of different sample layers; and acquiring the three-dimensional nano resolution image of the complete sample. Through the three-dimensional fluorescence nano microscope imaging method and the three-dimensional fluorescence nano microscope imaging system, and the image equipment, the high-precision three-dimensional nano microscope imaging is realized by taking the laminar light beam as the exciting light, and combining with axial scanning, and the method, system and equipment are suitable for three-dimensional microscope imaging of the thick sample, such as cells in the biological field and the like, and solve the problems that the positioning accuracy of molecules in the thick sample is low and the sample is difficult to observe.
Owner:SHENZHEN UNIV
Devices, methods, and systems relating to super resolution imaging
The devices, methods, and systems of the present disclosure provide for spectroscopic super-resolution microscopic imaging. In some examples, spectroscopic super-resolution microscopic imaging may be referred to or comprise spectroscopic photon localization microscopy (SPLM), a method which may employ the use of extrinsic labels or tags in a test sample suitable for imaging. In some examples spectroscopic super-resolution microscopic or spectroscopic photon localization microscopy (SPLM) may not employ extrinsic labels and be performed using the intrinsic contrast of the test sample or test sample material.Generally, spectroscopic super-resolution microscopic imaging may comprise resolving one or more non-diffraction limited images of an area of a test sample by acquiring both localization information of a subset of molecules using microscopic methods known in the art, and simultaneously or substantially simultaneously, acquiring spectral data about the same or corresponding molecules in the subset. This method maybe useful to detect a variety of features in cellular material for the molecular characterization of cells and disease.
Owner:NORTHWESTERN UNIV
Single photon counting formatter
InactiveCN101387548AStitching is not requiredHigh sensitivityTelevision system detailsColor television detailsMicro imagingPhotocathode
The invention relates to a single photon counting and imaging detection device. A high-voltage power supply of the device is connected with a micro-imaging reinforced tube through a high tension lead; a display, an image processing device and a printer are connected with a computer respectively; an anode collector is arranged between the micro-imaging reinforced tube and a preamplifier; the anode collector comprises a substrate, an electrode plated on the substrate and a signal lead; an anode is connected with the preamplifier through the signal lead; and the micro-imaging reinforced tube comprises a photocathode and a microchannel plate connected with the photocathode which are arranged sequentially along a light path. The device has the characteristics that the device can read out a time mark for arriving time and a general image of integral in a period, realize the single photon counting and two-dimensional imaging detection of an extremely-weak object, has the function of single photon counting, and can perform two-dimensional imaging on the extremely-weak luminous object. The device has the advantages of large area array, high sensitivity, low dark count, high resolution factor, good imaging linearity and the real-time measurement and processing.
Owner:陕西光电子先导院科技有限公司
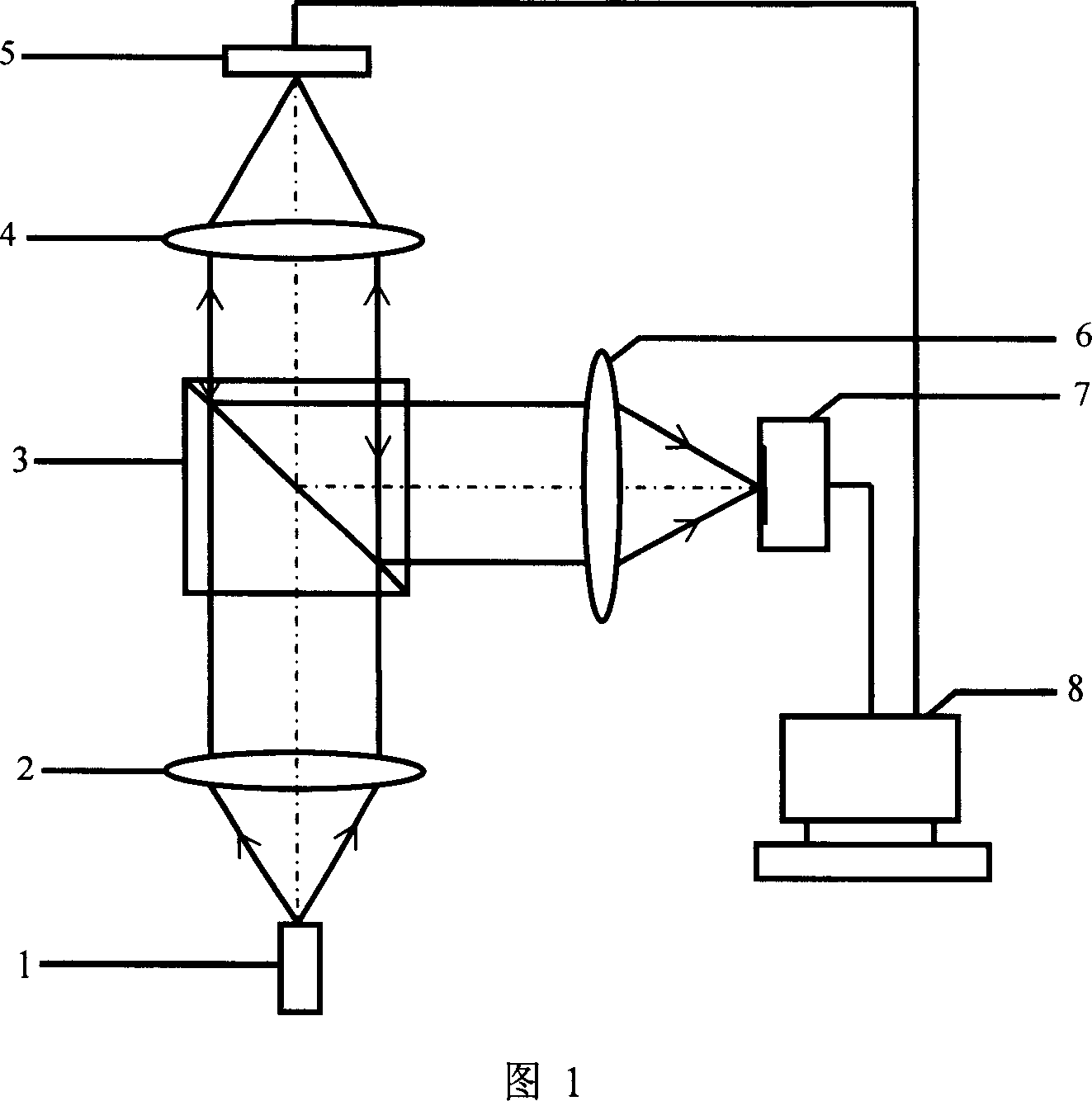
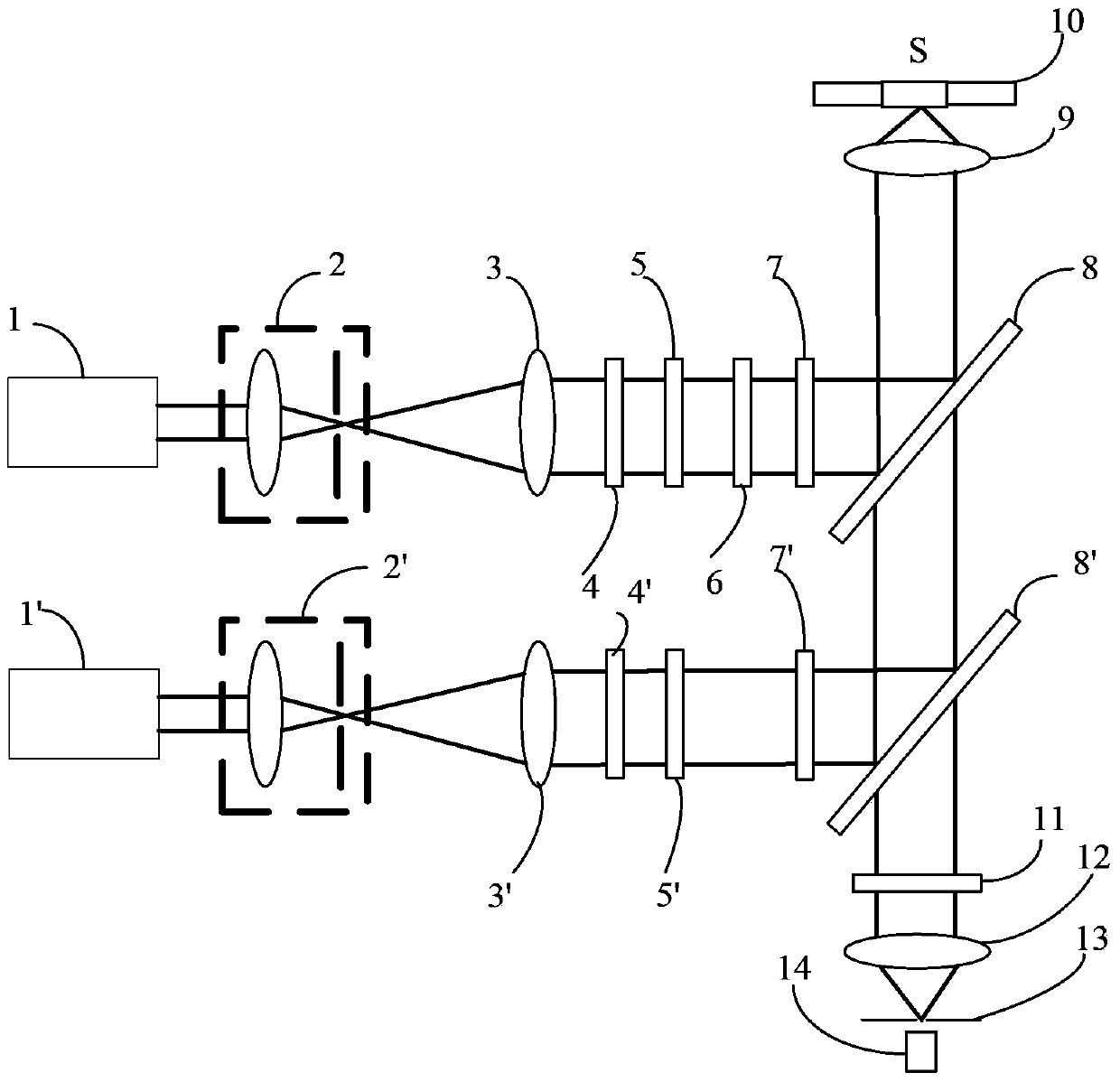
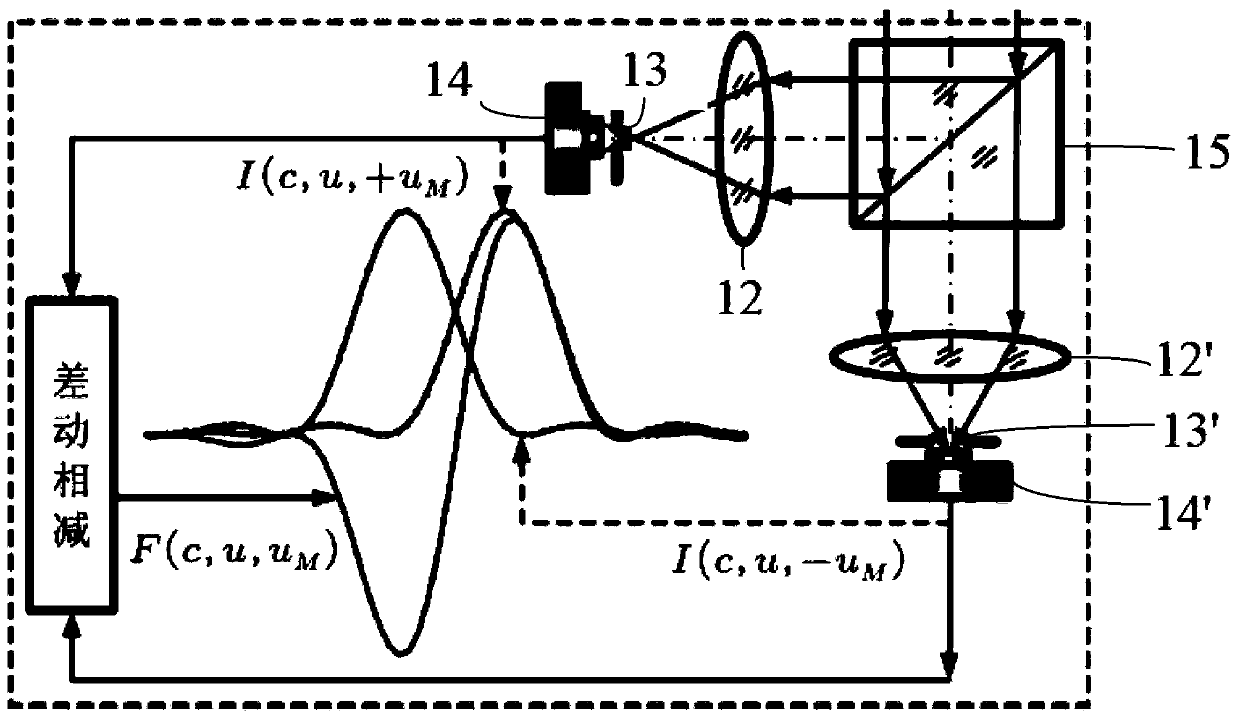
Laser Differential Confocal Mapping-Spectrum Microscopic Imaging Method and Device
ActiveUS20150346101A1Improve spatial resolutionSize of the detection area of the sample to be controllableRadiation pyrometrySpectrum investigationBeam splittingImage resolution
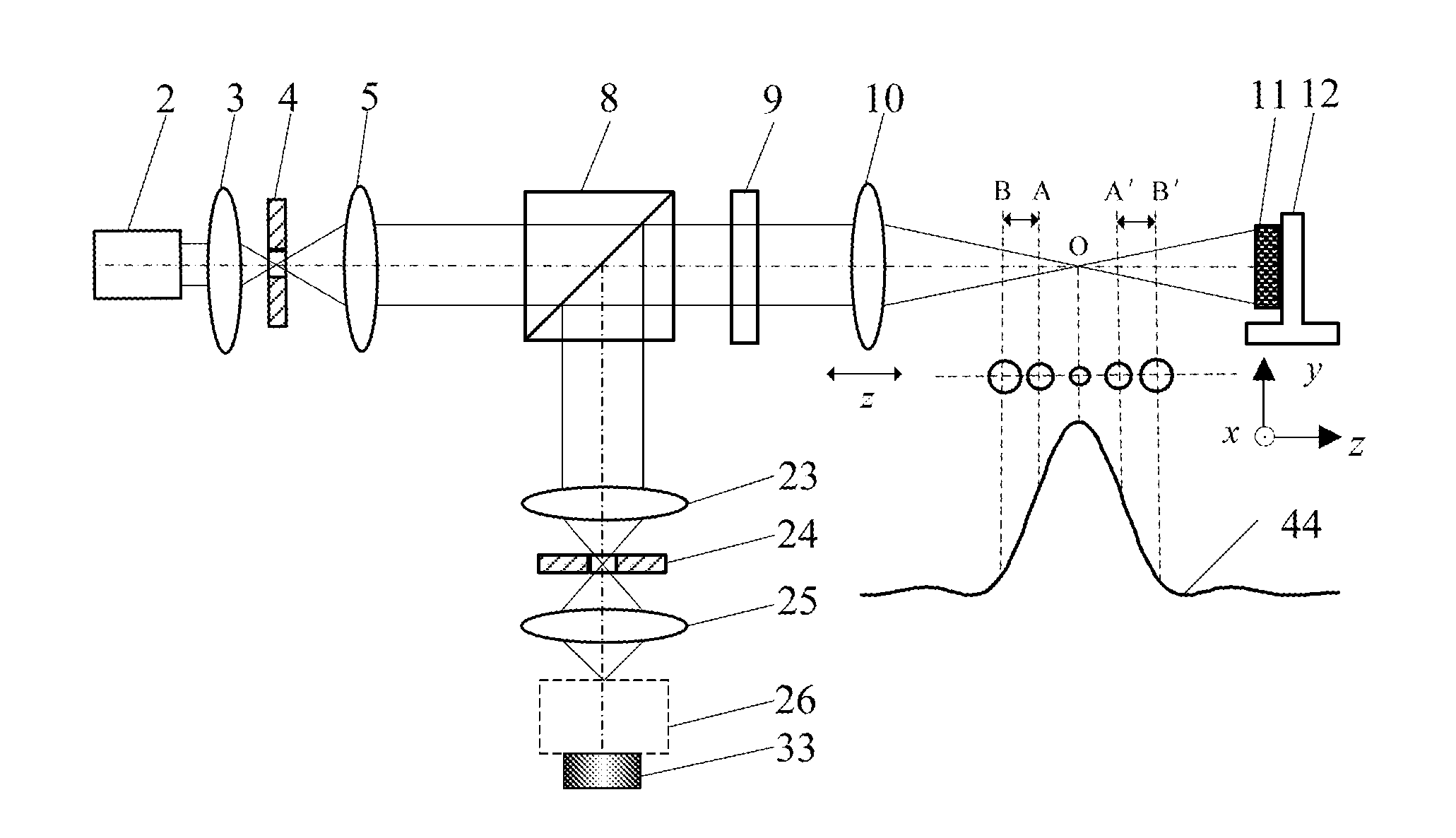
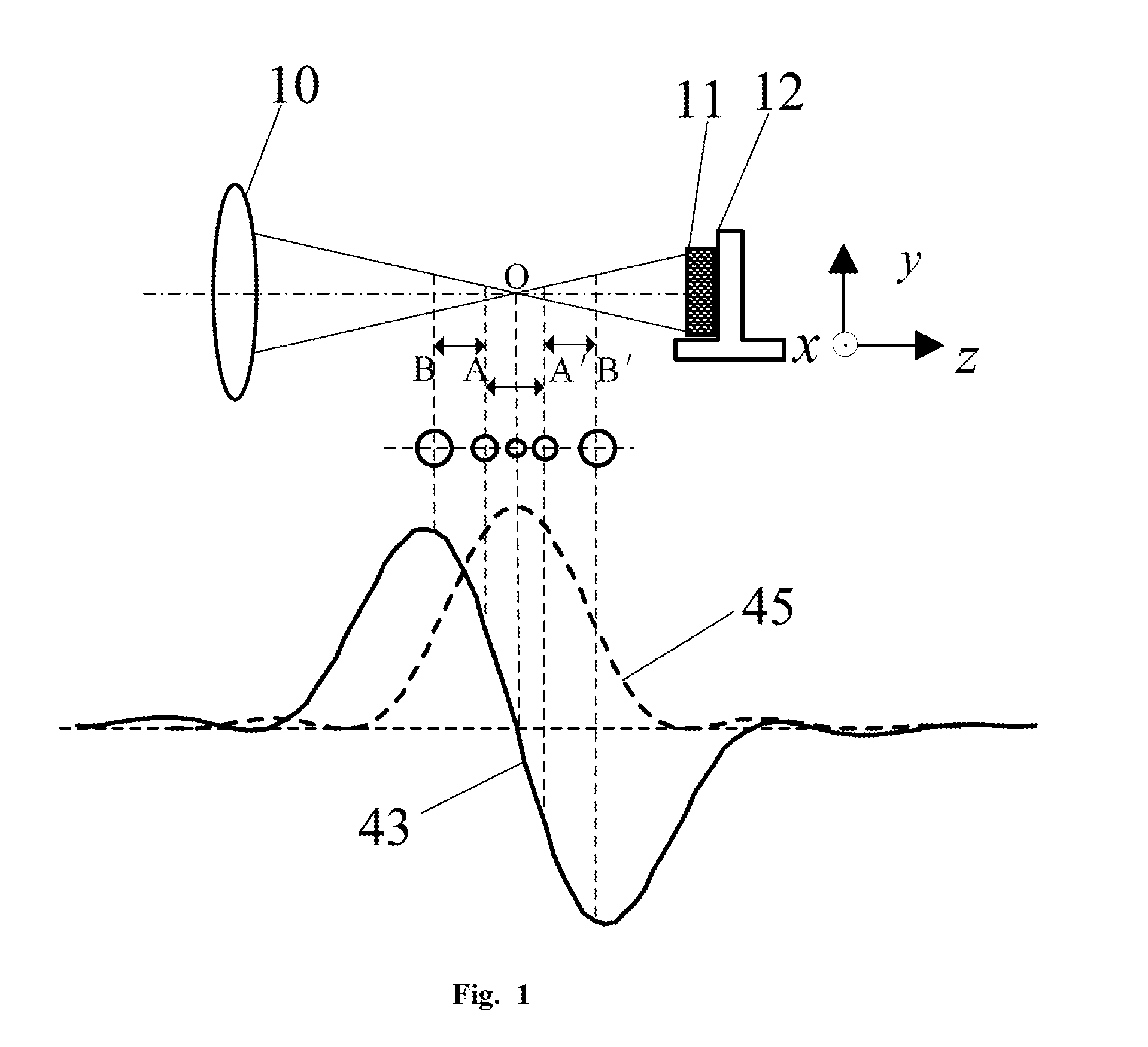
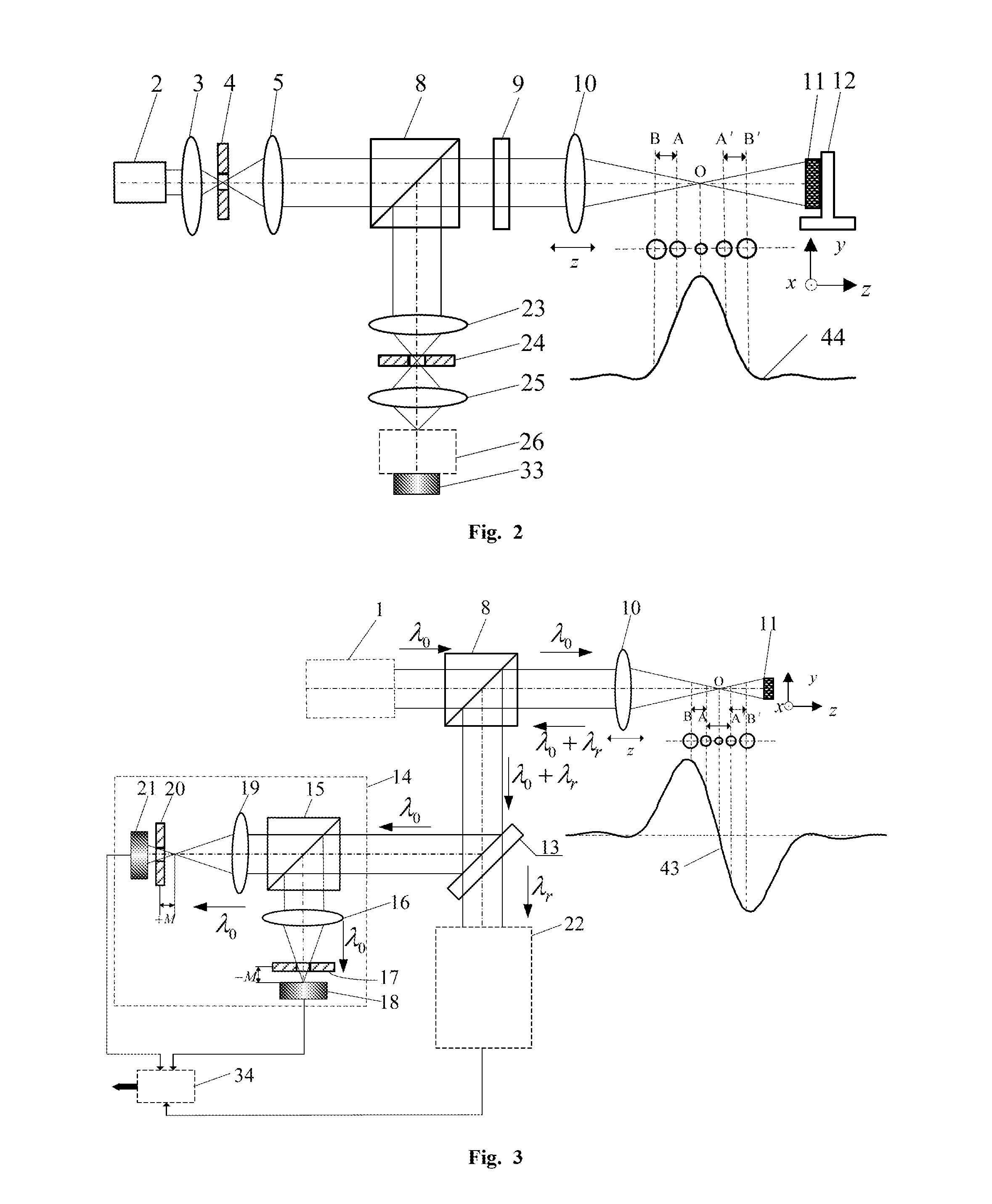
The present invention belongs to a technical field of optical microscopic imaging and spectral measurement, and discloses a laser differential confocal mapping-spectrum microscopic imaging method and device. The core concept of the present invention is to combine the differential confocal detection and the spectrum detection techniques and use a dichroic beam splitting system (13) to separate the Rayleigh light for geometric position detection from the Raman scattering light for spectrum detection, by mean of the property that the zero-cross point of the differential confocal curve (43) accurately corresponds to the focus of the objective, the spectral information at focus of the excitation spot being accurately captured by the zero trigger to accomplish the spectrum detection with high spatial resolution. Therefore, the present invention provides a method and device that may be able to accomplish the spectrum detection with high spatial resolution to a micro-area of a sample.
Owner:BEIJING INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGYGY
High microspectrum imaging system
InactiveCN1563947AMain indicators are highMature technologyColor/spectral properties measurementsMicro imagingData acquisition
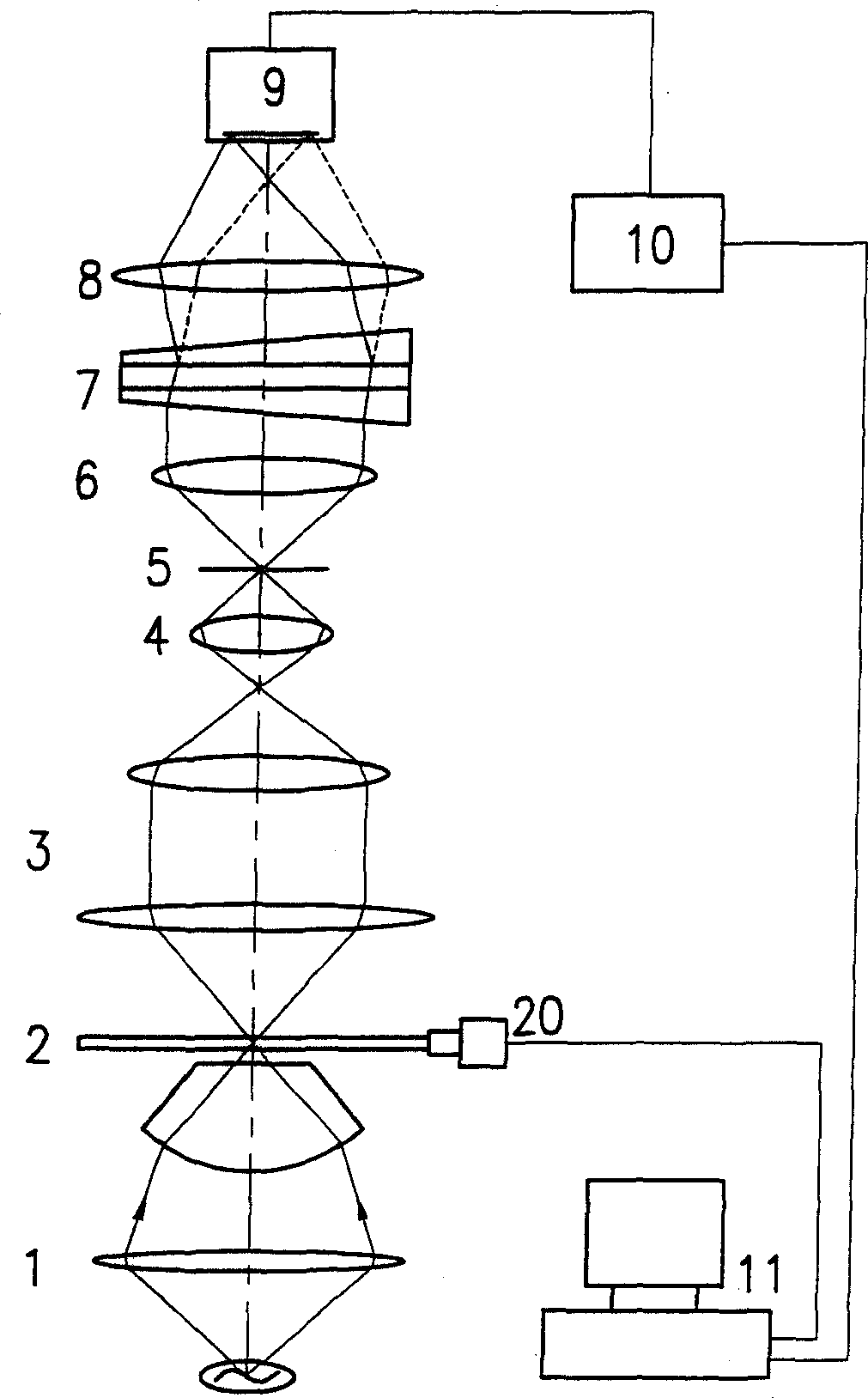
Disclosed system as an integrated system integrates micro imaging system with high spectrum imaging system, including optical microscope, spectroscope, area array CCD camera and dedicated software of data acquisition and treatment. The disclosed system provides microcosmic spectrogram combining image with spectrum, applicable to clinical medicine, biology, materials science and microelectronics.
Owner:SHANGHAI INST OF TECHNICAL PHYSICS - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Coherent anti-stokes Raman scattering spectrum detection and microimaging system and method
InactiveCN106226284ARapid Simultaneous ImagingSimple structureRaman scatteringMicro imagingBandpass filtering
The invention relates to the field of optics, and provides a coherent anti-stokes Raman scattering spectrum detection and microimaging system which comprises a femtosecond pulse laser device, a beam divider, a pohotonic crystal fiber, a narrow bandpass filter, a delay unit, a beam combiner and a detector, wherein the beam divider is used for dividing femtosecond pulse laser into a first light beam and a second light beam; the pohotonic crystal fiber is used for pumping the first light beam to output super-continuum spectrum laser of which the pulse width is picosecond grade as Stokes light; the narrow bandpass filter is used for filtering the second light beam to increase the pulse width to be approximate to that of the super-continuum spectrum laser as pumping light and detection light; the delay unit is used for synchronizing the stokes light, the pumping light and the detection light; the beam combiner is used for combining the Stokes light, the pumping light and the detection light into a third light beam; the detector is used for detecting a correlated anti-Stokes Raman scattered spectrum. By adopting the coherent anti-stokes Raman scattering spectrum detection and microimaging system, simultaneous imaging of multiple chemical bands can be rapidly achieved, a super-continuum spectrum light source is lowly required, a complete CARS (Coherent Anti-Stokes Raman Scattering) spectrum can be obtained, the light beam utilization efficiency can be maximized, and the spectral resolution of CARS imaging can be improved.
Owner:SHENZHEN UNIV
Micro-optical scanning tomography device
The invention relates to a three-dimensional micro-optical imaging device and aims to provide an imaging method of micro-optical scanning chromatography. The method comprise that: a large sample is sliced up layer by layer through precise mechanical processing technique; and the slice is scanned and imaged while performing the mechanical processing so as to acquire a complete faultage image data set of the sample. The system comprises a mechanical processing module, an imaging module and a data acquiring module, wherein the mechanical processing module is used for realizing scanning type slicing on the sample; the imaging module is used for imaging the sample near a cutter edge; and the data acquiring module is used for scanning and recording the imaging of the sample. The three modules coordinate to realize the functions of a micro-optical scanning chromatography imaging device. The imaging device adopts a synchronous mode of slicing and imaging, the automation degree of the whole process is extremely high, the problem that pictures between different layers are difficult to match does not exist, and the acquisition efficiency of the whole data is high.
Owner:WUHAN OE BIO CO LTD
STED (stimulated emission depletion) micro imaging method and device based on radially polarized vortex beam
A super-resolution STED micro imaging method based on a radially polarized vortex beam comprises the steps as follows: a stimulation beam is aligned, and a first parallel beam is obtained; the first parallel beam is converted into a first radially polarized beam; the first radially polarized beam is modulated and focused on a sample of a focal plane, and a focus solid light spot is obtained; a restraint beam is aligned, and a second parallel beam is obtained; the second parallel beam is converted into a second radially polarized beam; the second radially polarized beam is converted into the radially polarized vortex beam; the radially polarized vortex beam is modulated and focused on the sample of the focal plane, and a focus hollow light spot is obtained, wherein the center of the focus hollow spot and the center of the focus solid light spot are overlapped, so that only a middle point located in the middle position and having a size smaller than a diffraction limit emits fluorescence; and a detector detects the fluorescence emitted by the middle point.
Owner:BEIJING INFORMATION SCI & TECH UNIV
In vivo spectral micro-imaging of tissue
ActiveUS20100134605A1Increase contrastImprove image contrastMaterial analysis by optical meansCatheterMicro imagingImage resolution
In vivo endoscopic methods an apparatuses for implementation of fluorescence and autofluorescence microscopy, with and without the use of exogenous agents, effectively (with resolution sufficient to image nuclei) visualize and categorize various abnormal tissue forms.
Owner:LAWRENCE LIVERMORE NAT SECURITY LLC +1
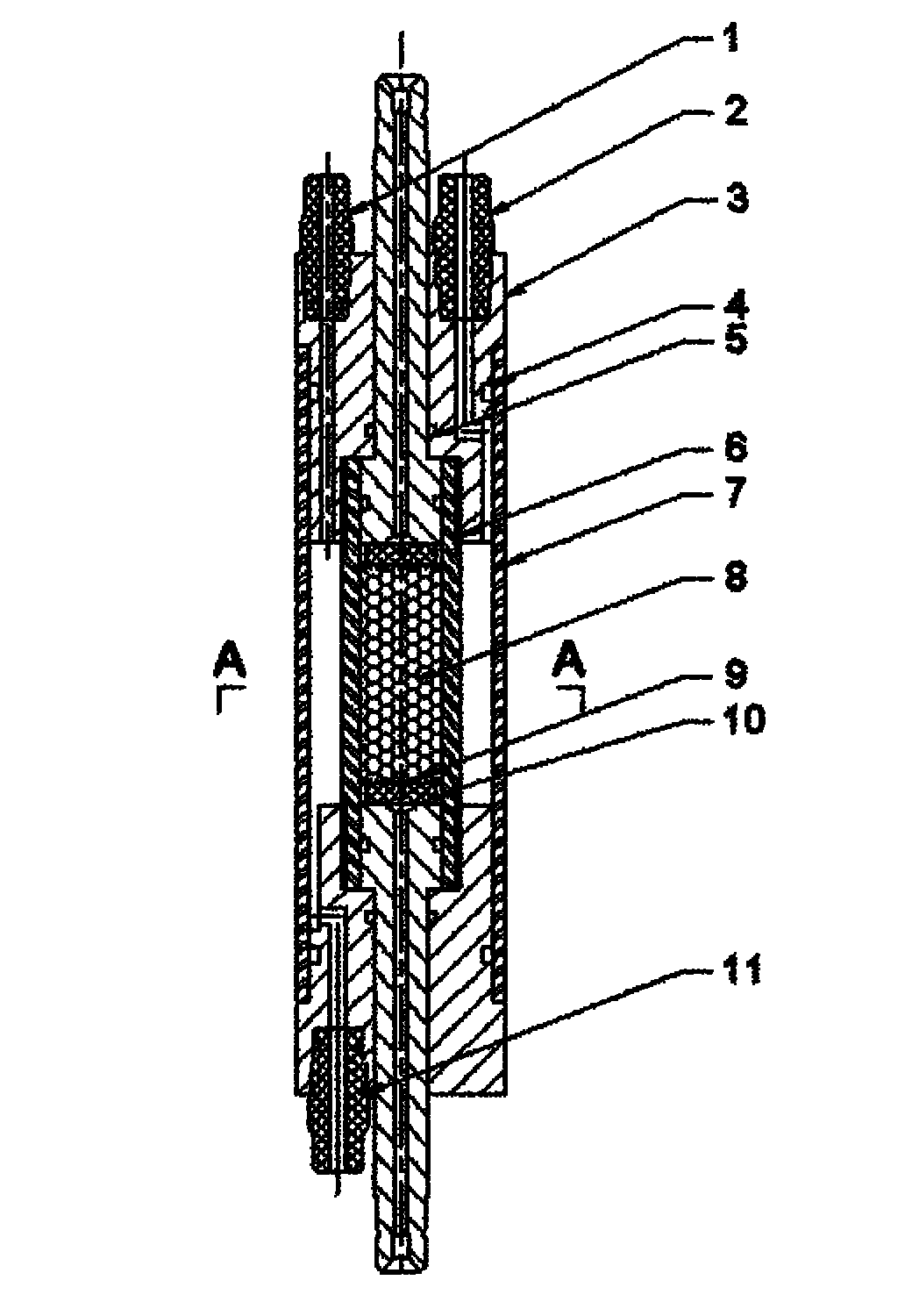
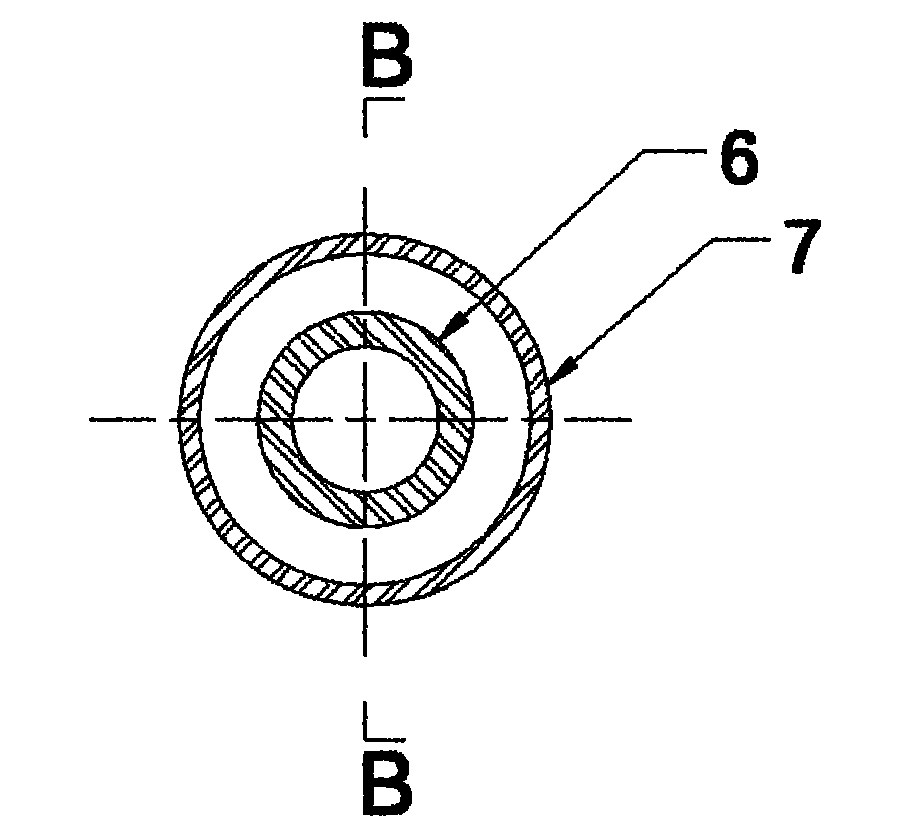
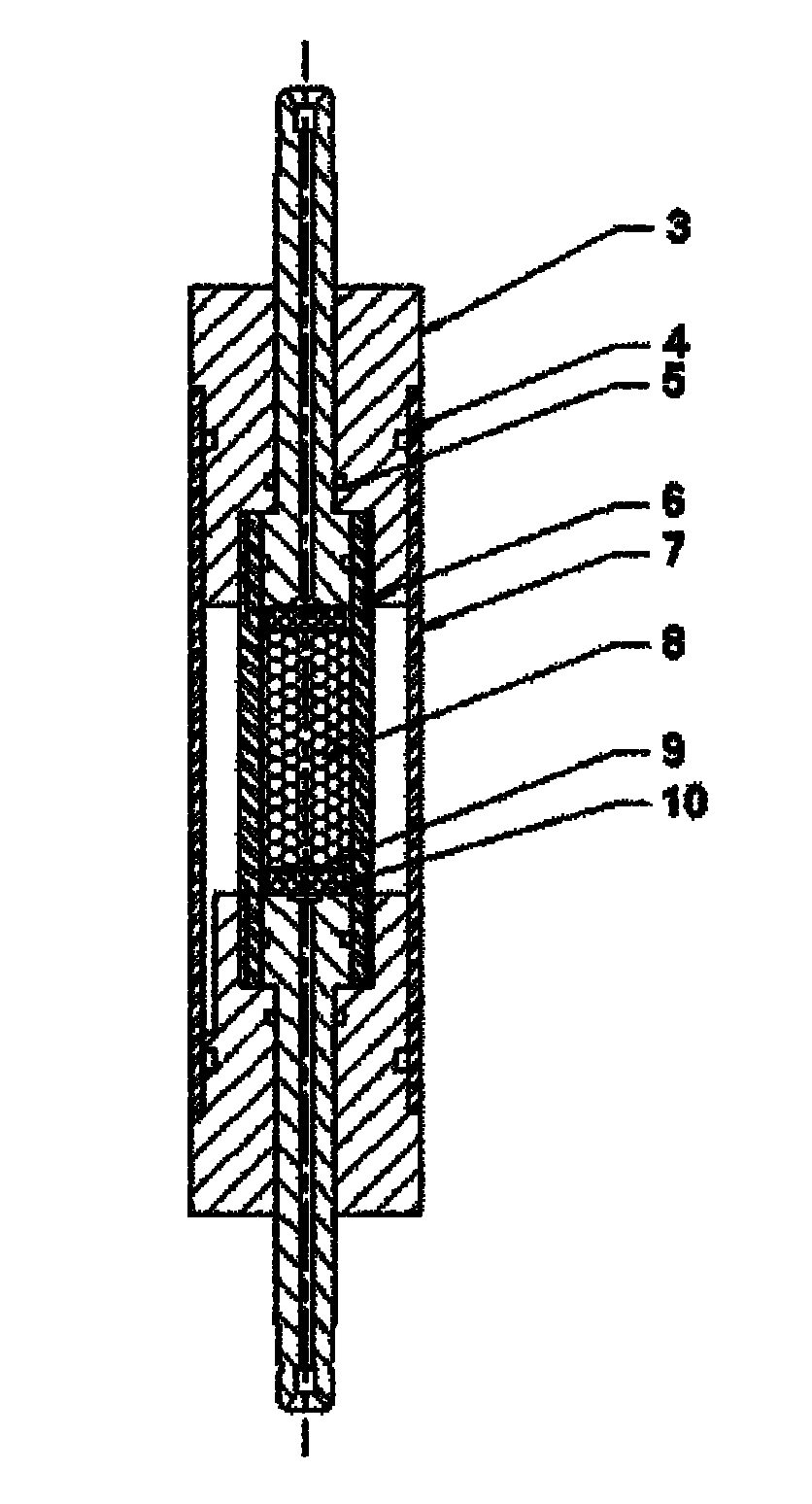
Sand-filling type clamp fastener for nuclear magnetic resonance imaging
InactiveCN102062742AEasy to meet high temperature and high pressure requirementsCompact designAnalysis using nuclear magnetic resonancePermeability/surface area analysisMicro imagingImide
The invention relates to a sand-filling type clamp fastener for nuclear magnetic resonance imaging, which belongs to the technical field of scientific research apparatuses for petroleum. The sand-filling type clamp fastener is vertically inserted into a micro-imaging probe of a nuclear magnetic resonance imager, the design pressure is 0-15MPa, and the design temperature is 0-70 DEG C. The sand-filling type clamp fastener can be used for carrying out indoor experiment research on the seepage and transport properties of a multi-phase multi-component fluid in an analog core. Besides a seal ring, all components of the sand-filling type clamp fastener are made from a polyamide-imide material which does not have magnetism, meets the high-temperature high-pressure requirements and has no effect on nuclear magnetic signals. The sand-filling type clamp fastener has the advantages of compact design structure, multiple times of filling, repeatability of use, convenience of operation in an experiment process, simplicity and applicability.
Owner:DALIAN UNIV OF TECH
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com