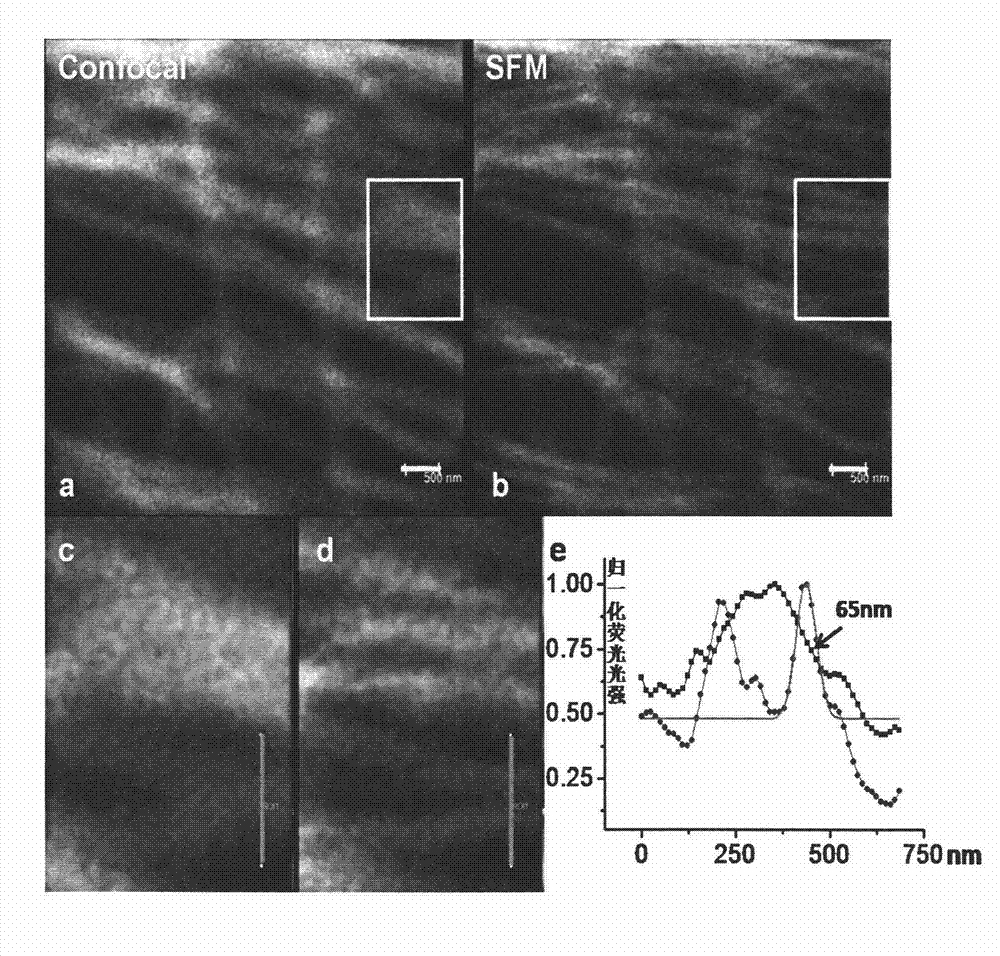
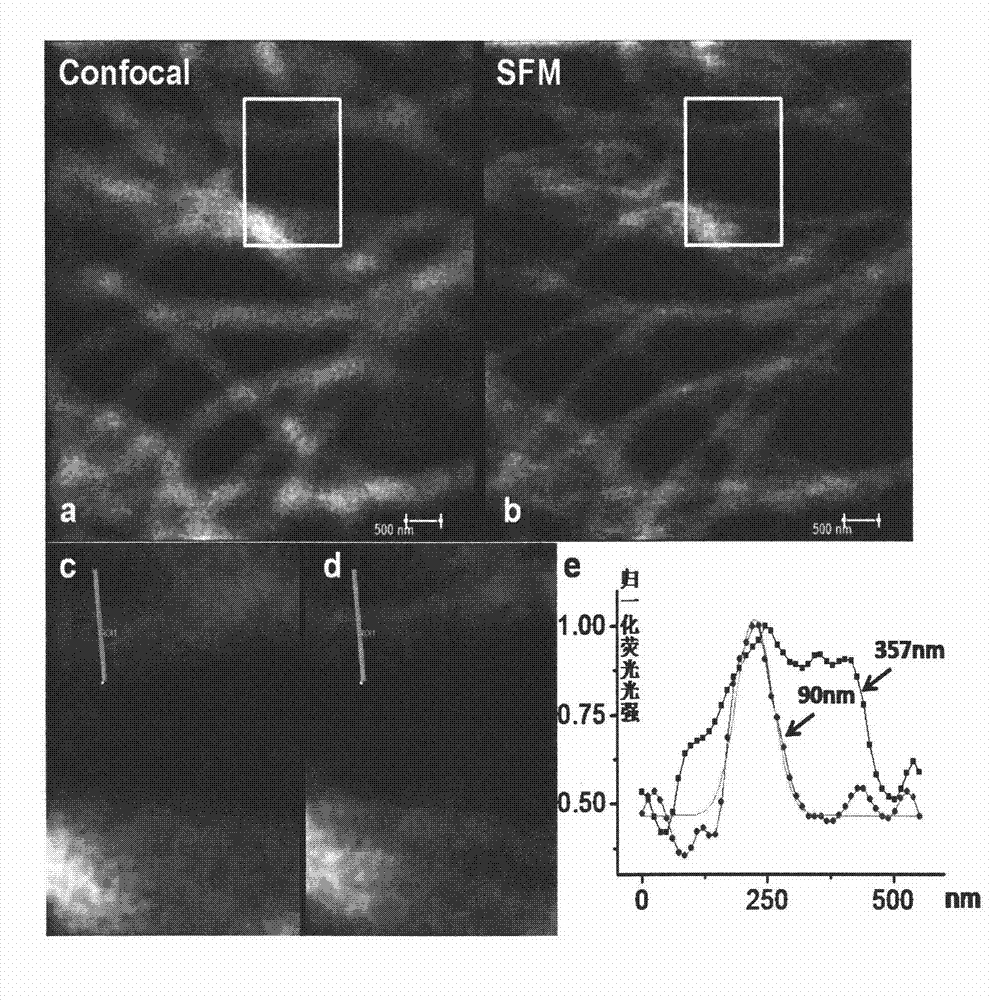
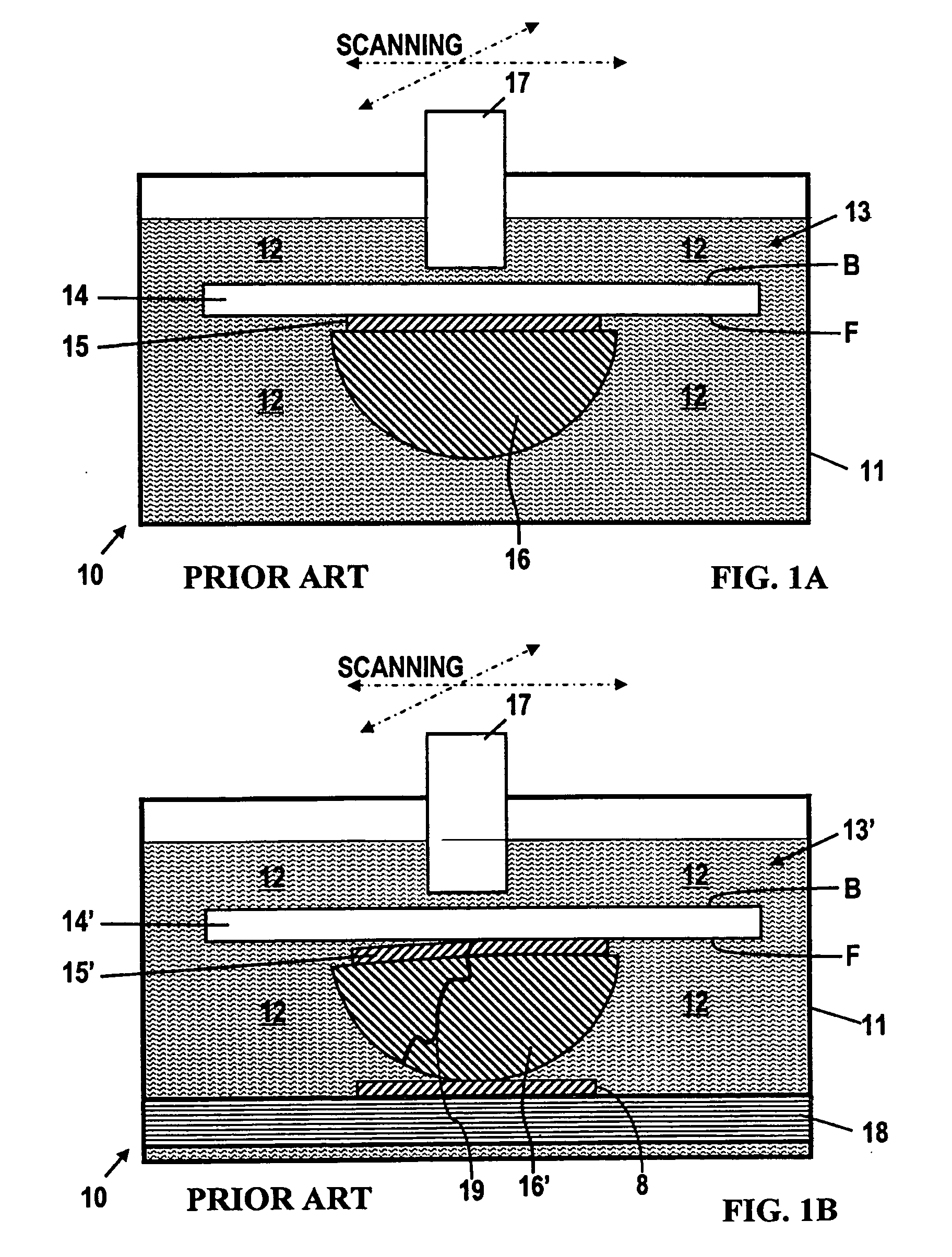
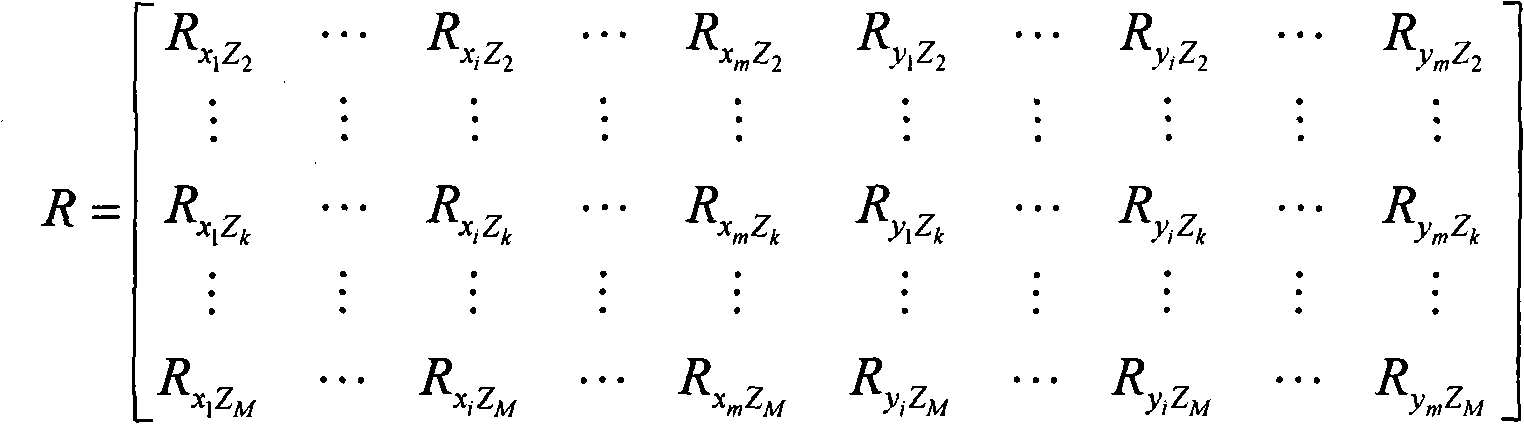Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
384 results about "Microscope imaging" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Microscopy Imaging. The Microscopy Imaging Core at Penn State College of Medicine provides consultation and training in ultra-high-resolution imaging of cells and tissues in fixed or live states. The core also provides expertise in quantitative image analysis and consultations on microscopy-related research projects.
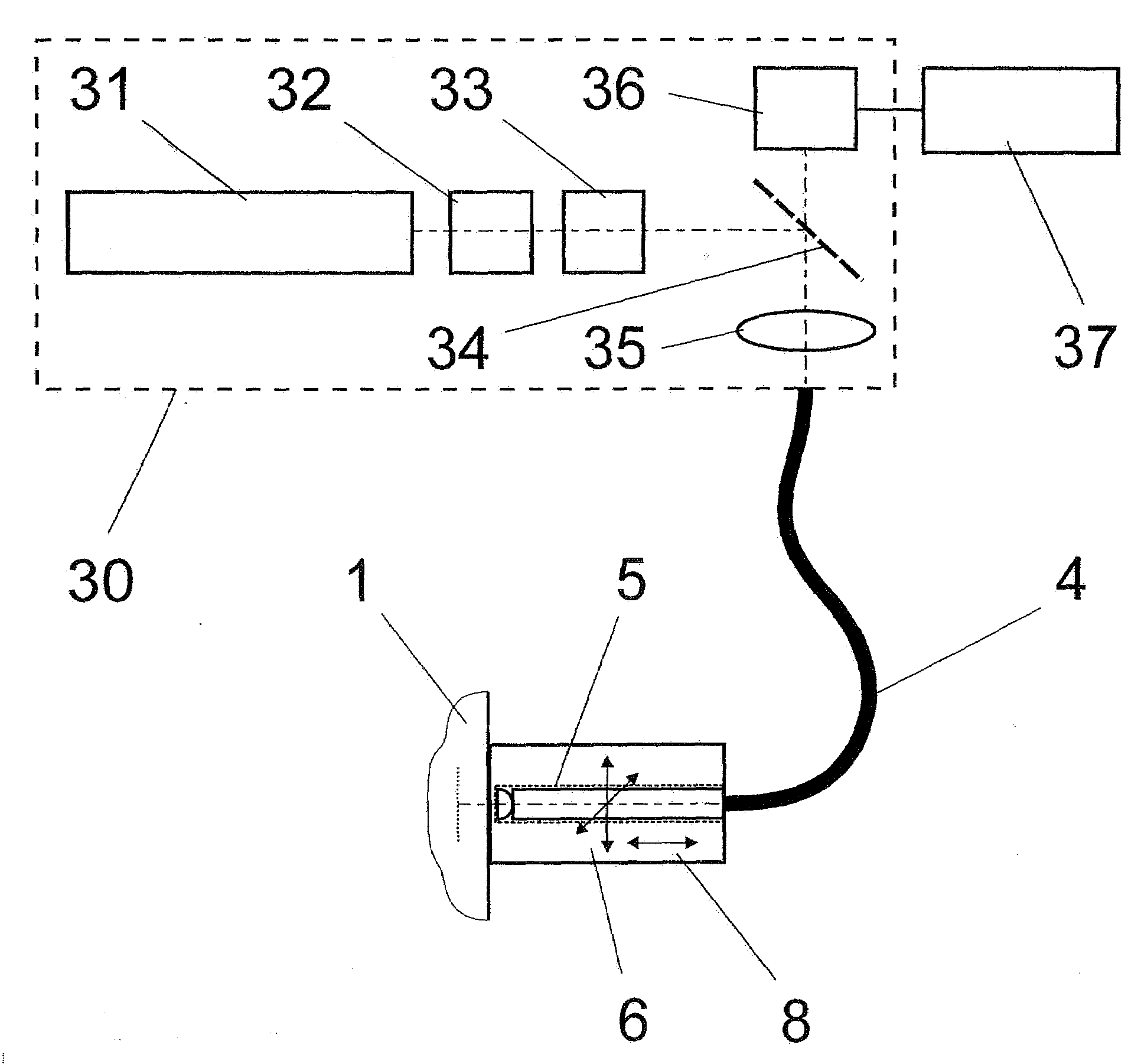
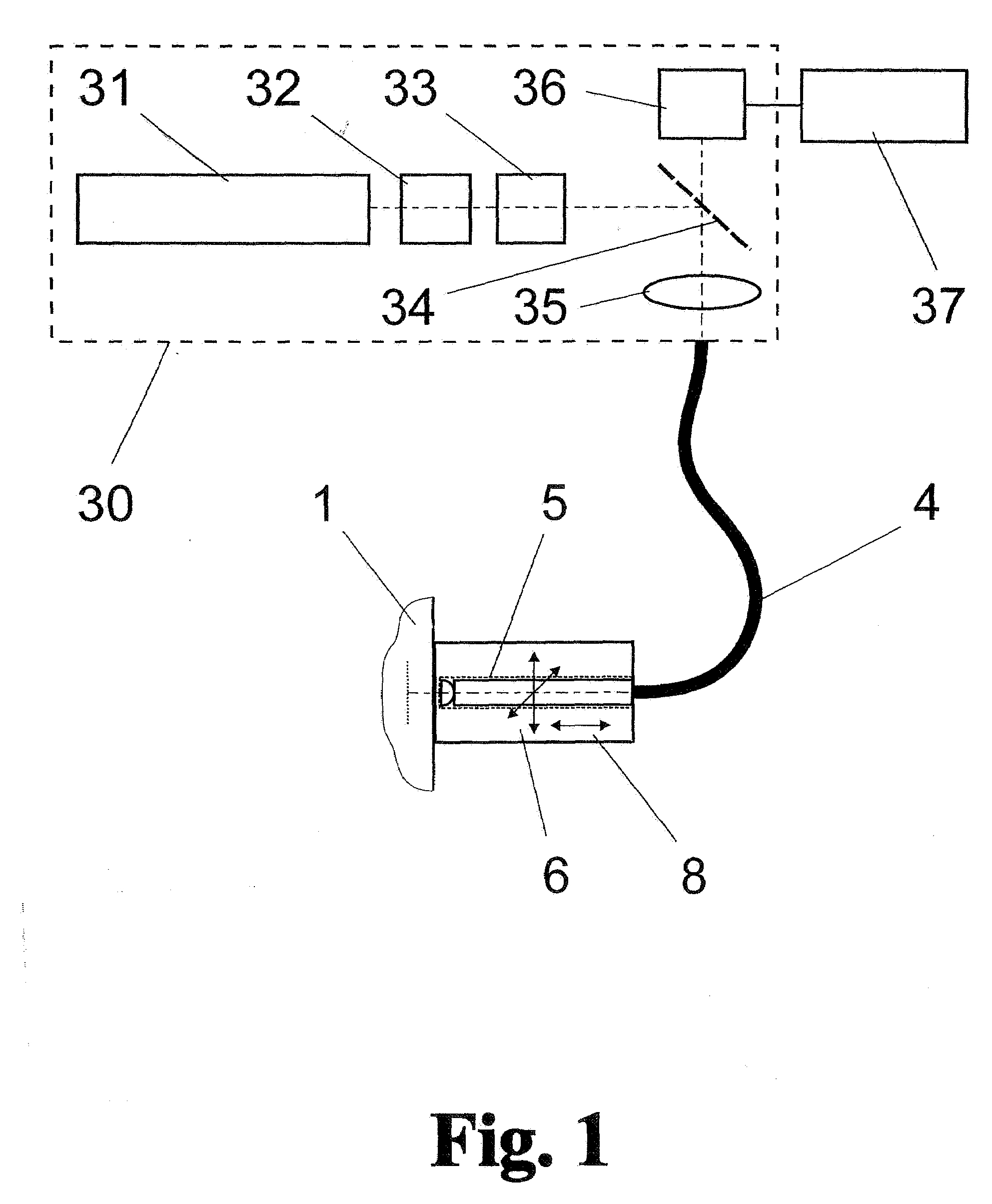
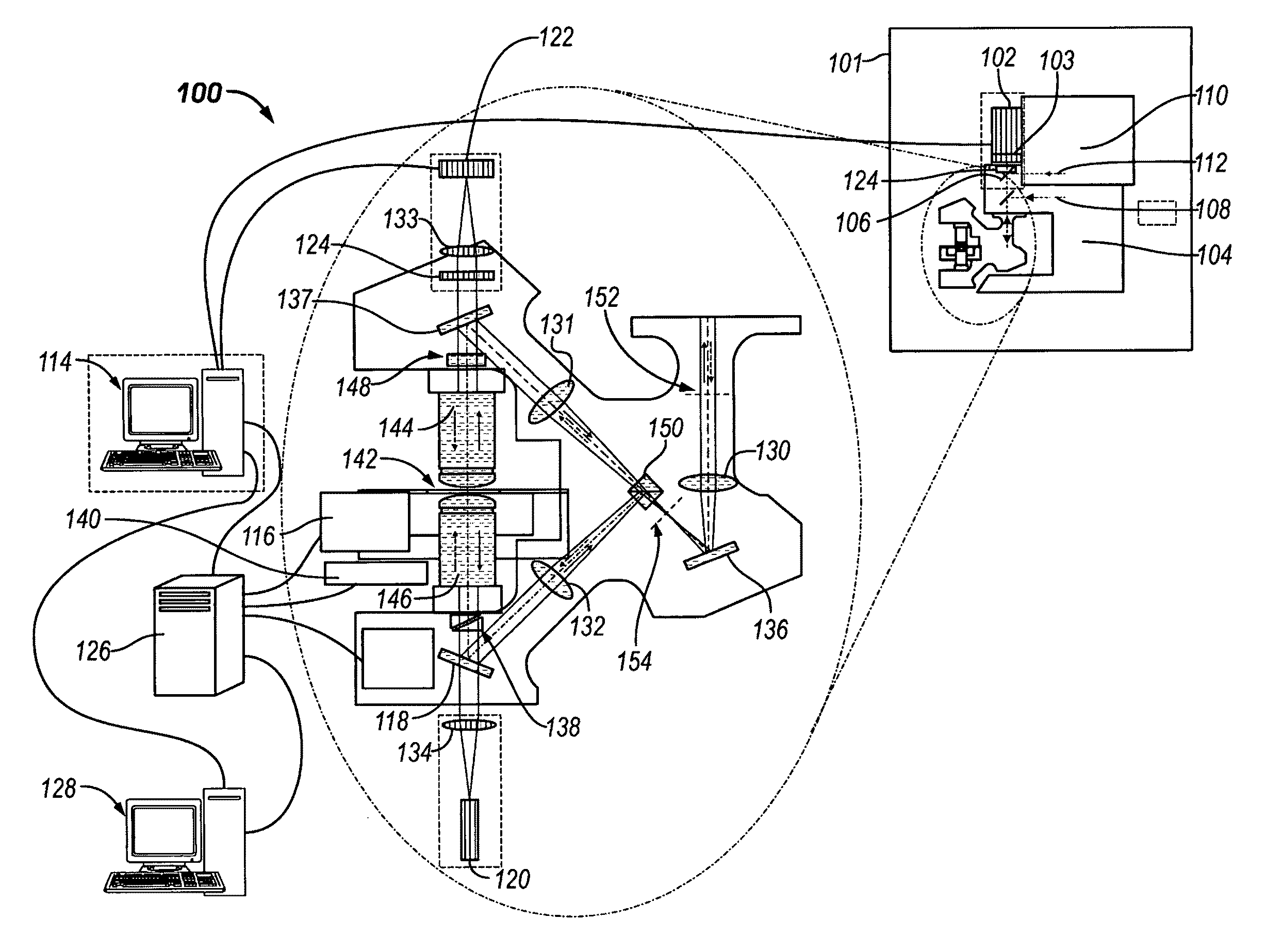
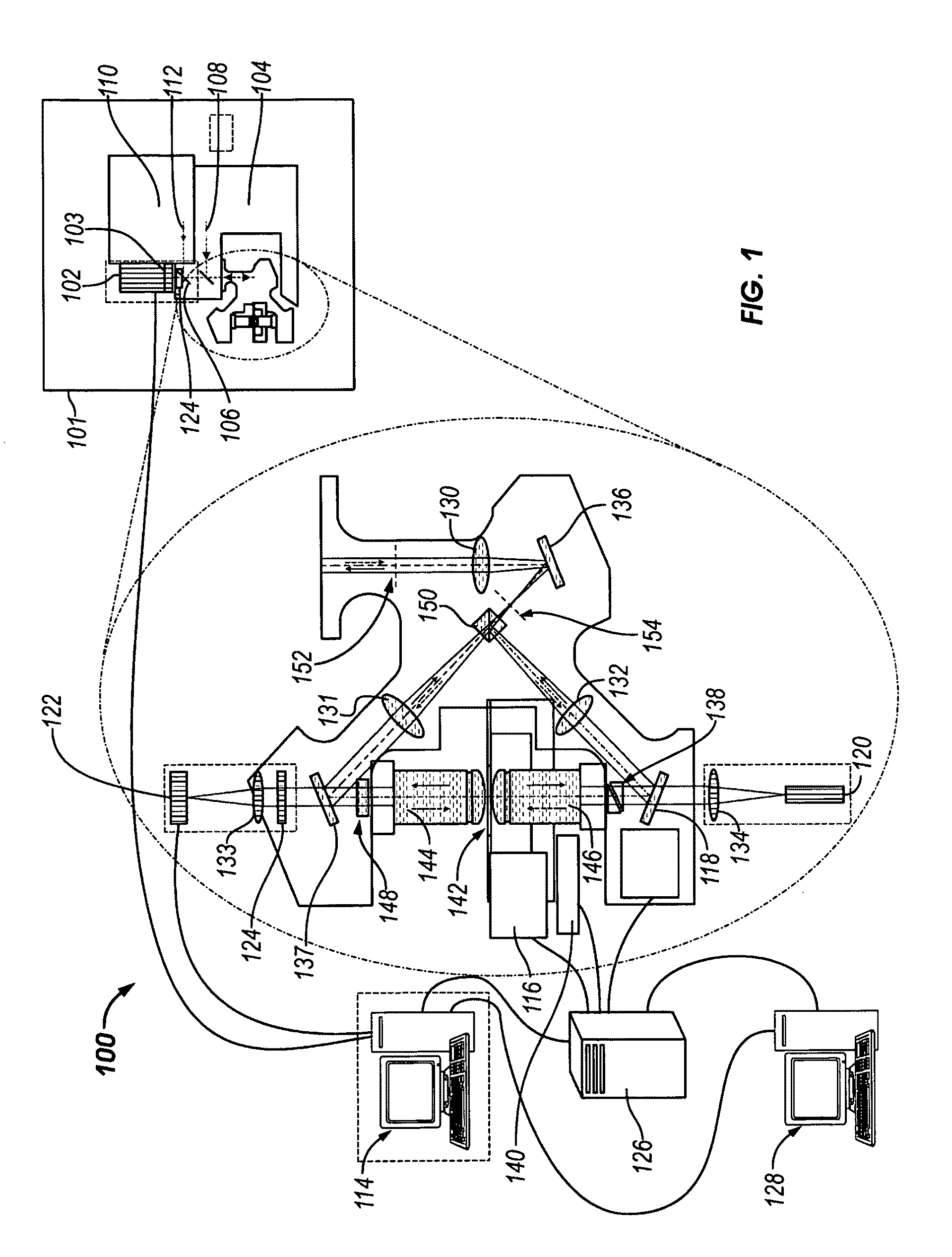
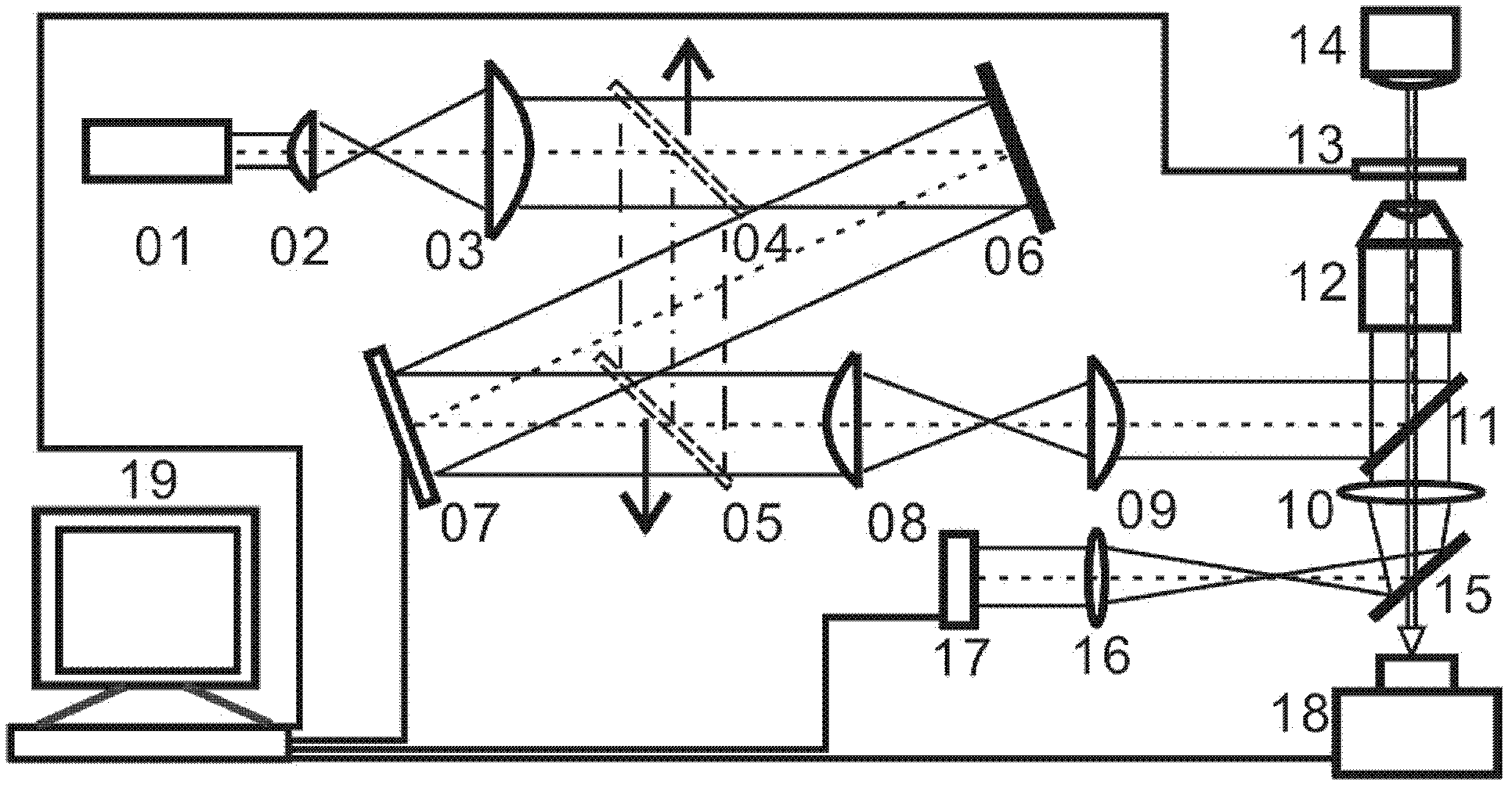
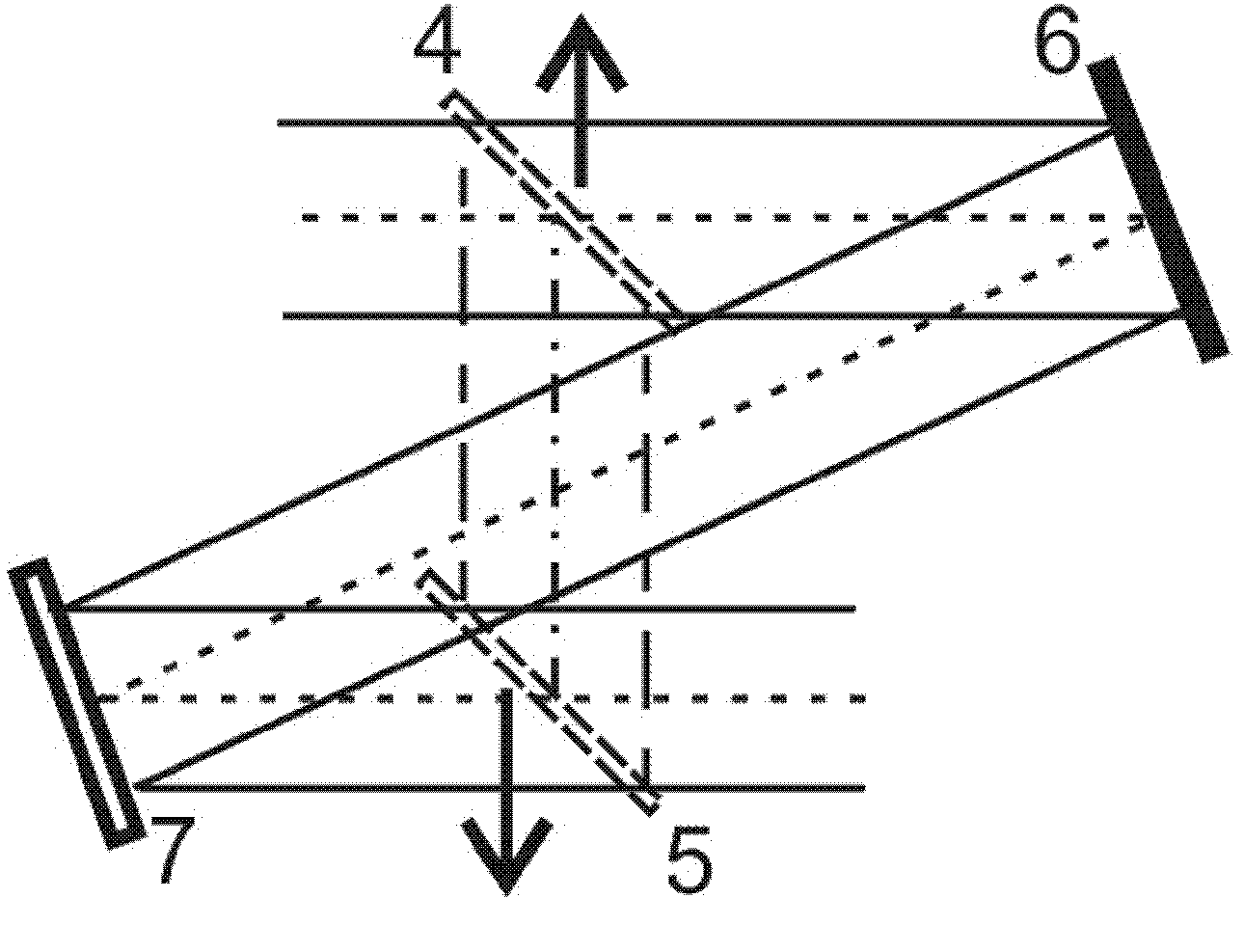
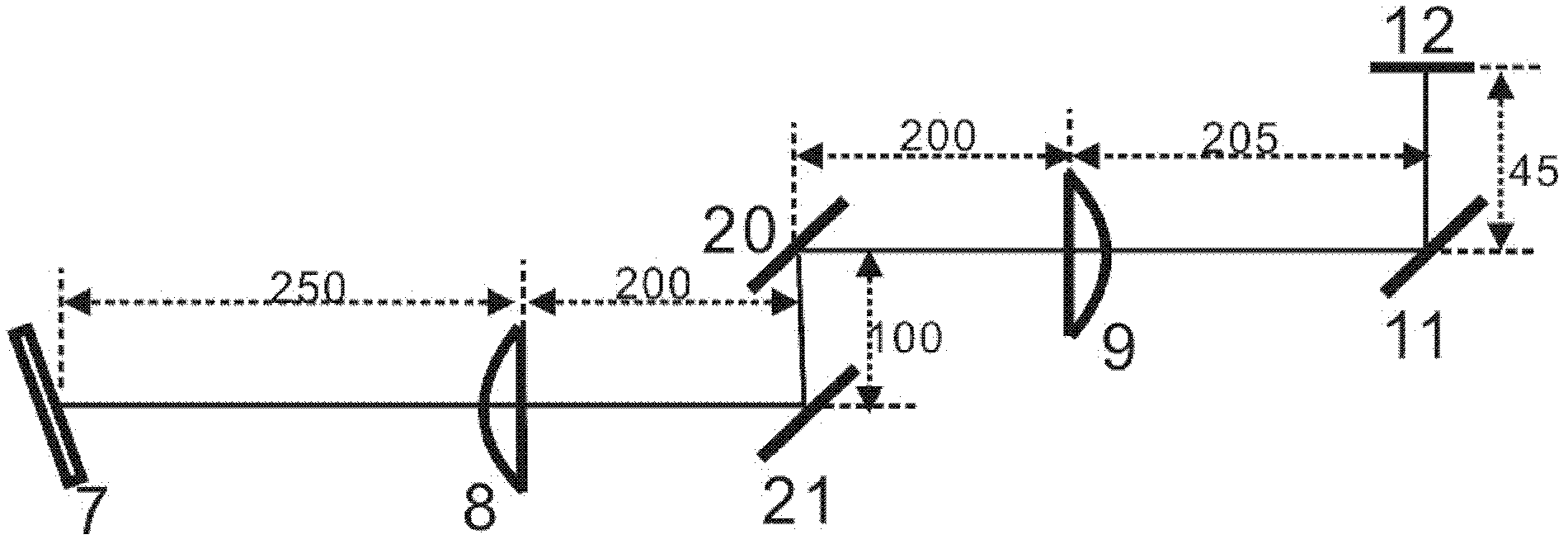
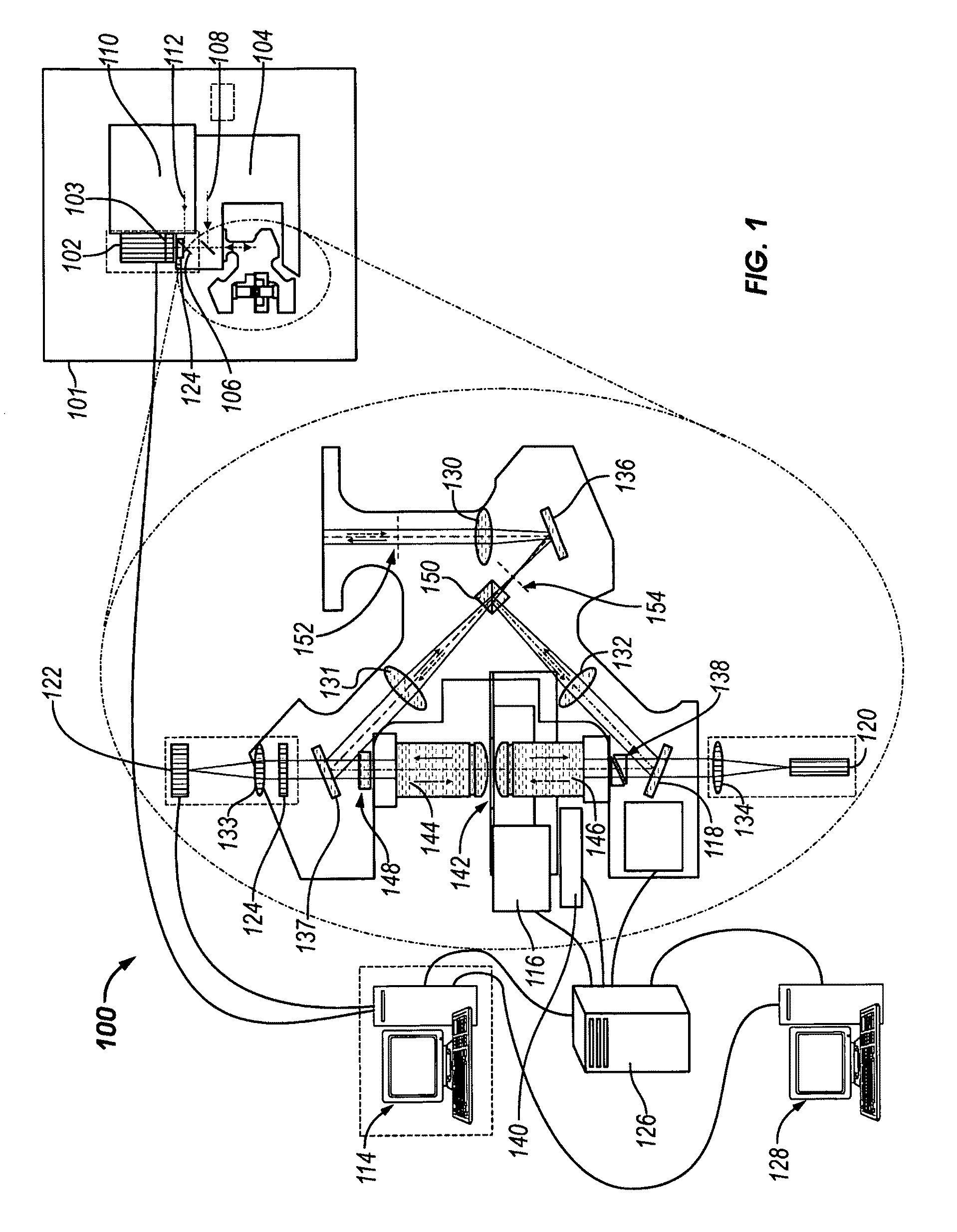
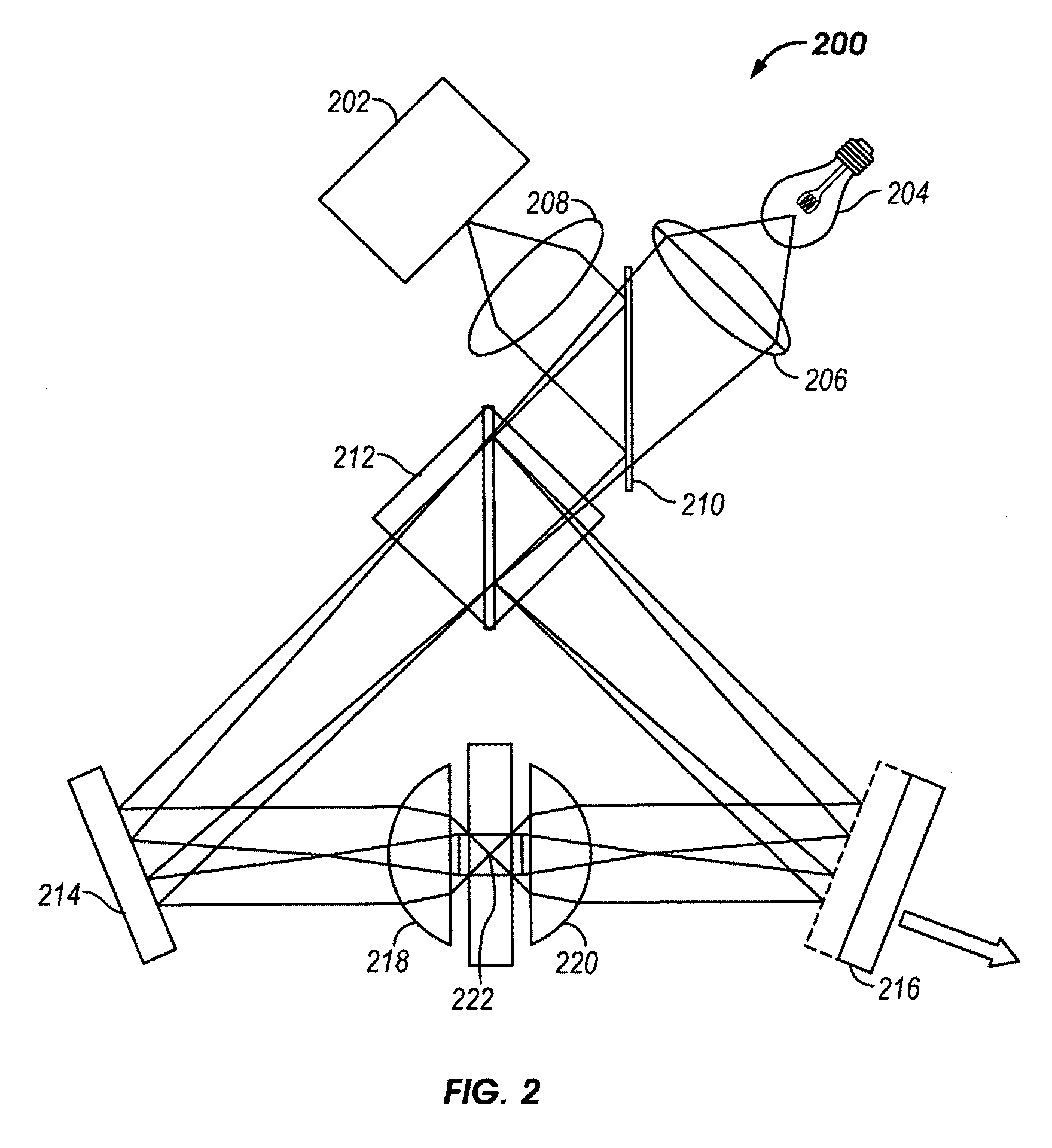
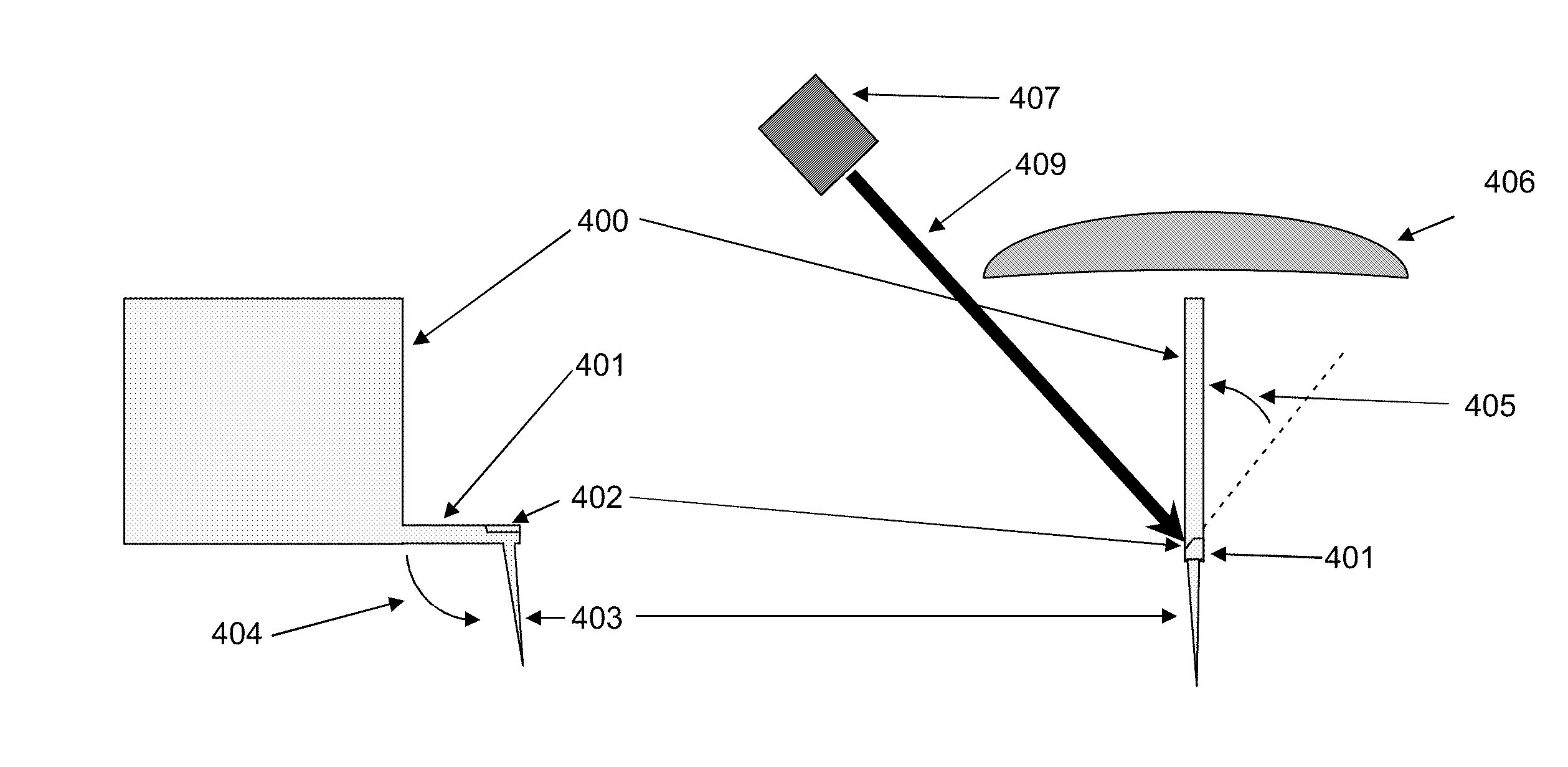
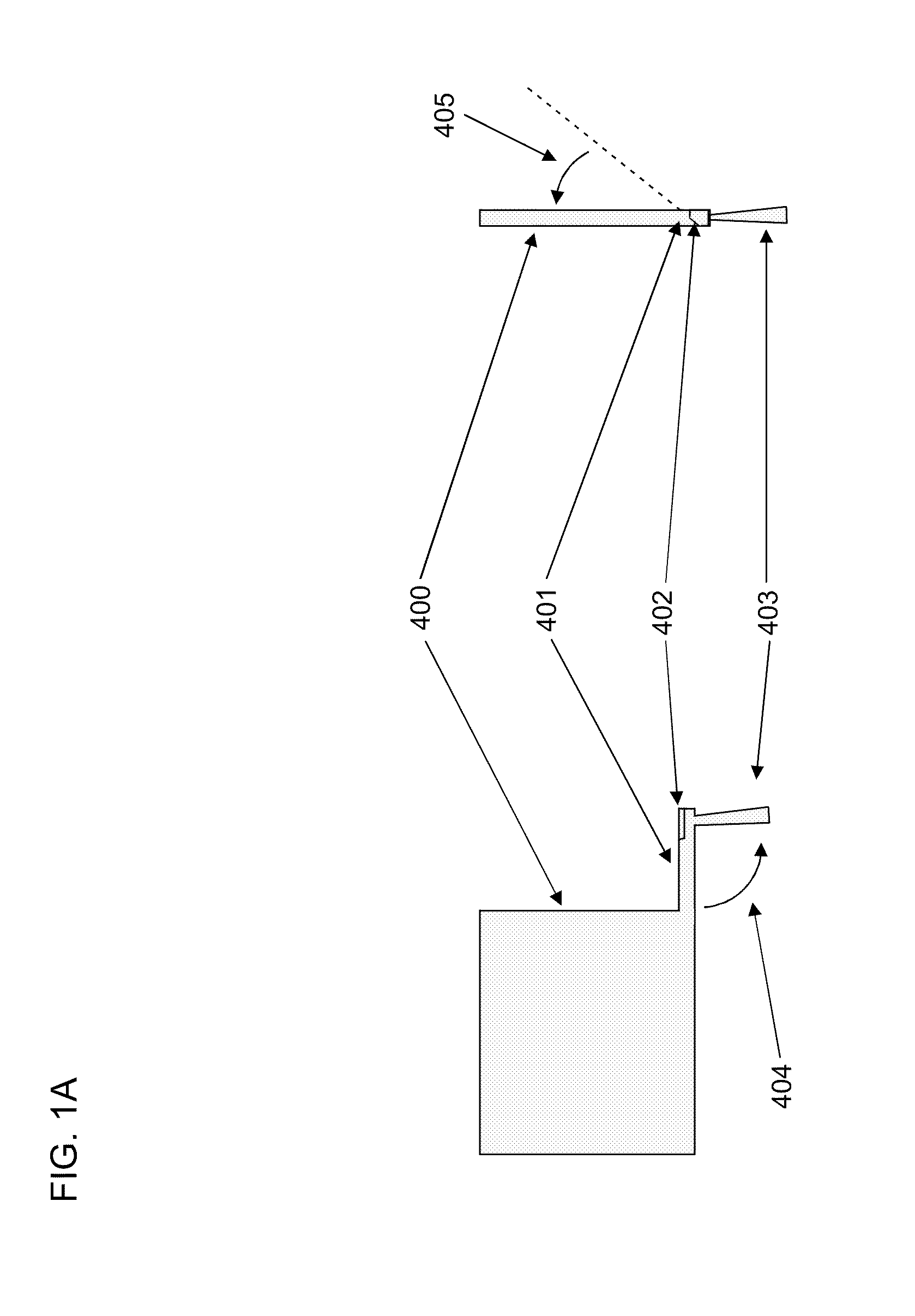
Method and arrangement for high-resolution microscope imaging or cutting in laser endoscopy
ActiveUS20080081950A1Accurate imagingPrecise microcuttingEndoscopesCatheterMicroscopic imageFlexible endoscope
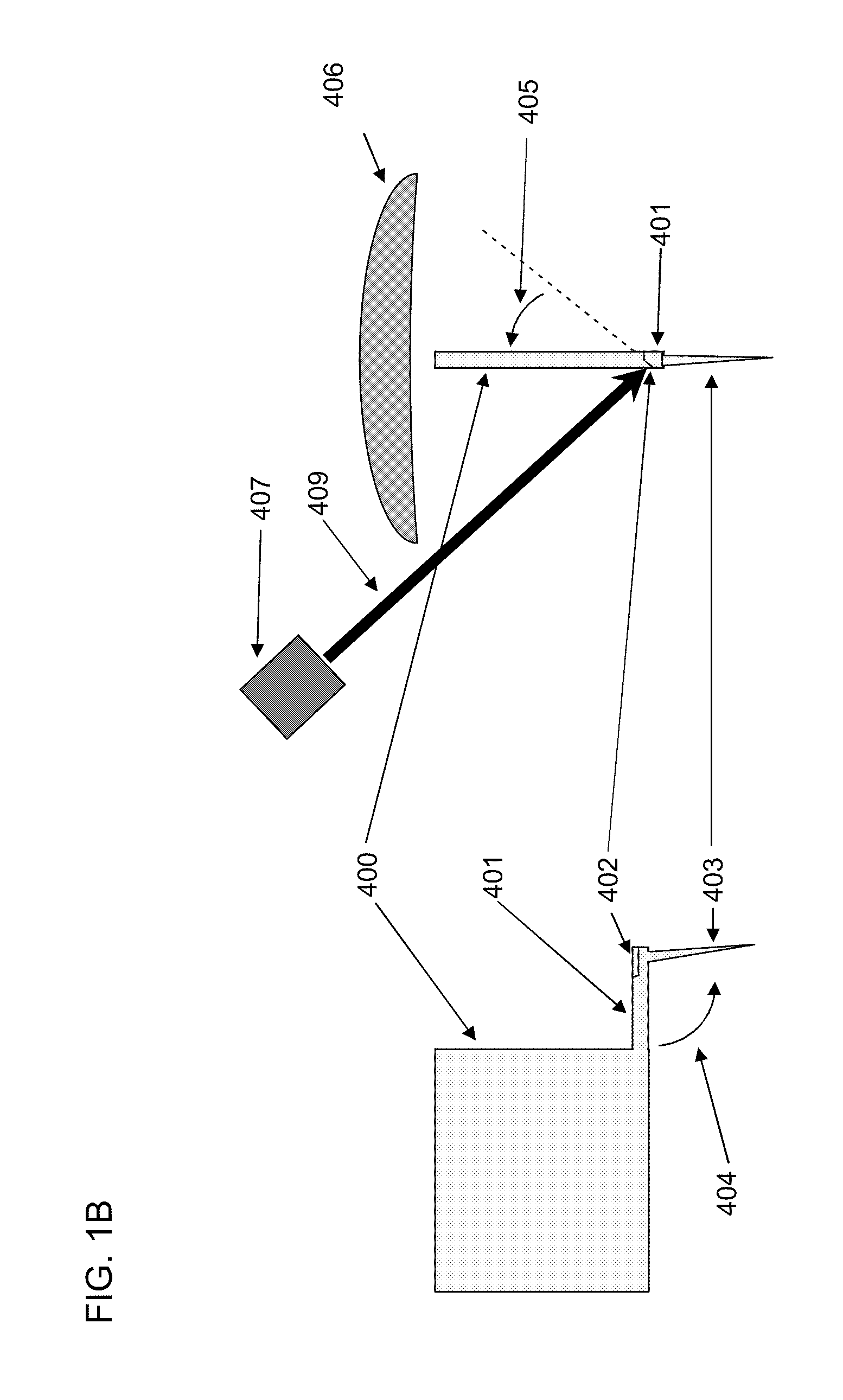
The invention is directed to a method and an arrangement for high-resolution microscopic imaging in laser endoscopy based on laser-induced object reaction radiation and for performing microscopic cuts in biological tissue. In using multiphoton processes for endoscopic applications in biological materials with an accuracy of under one millimeter, radiation of a pulsed femtosecond laser is focused into an object by means of a transmission focusing optics unit comprising a transmission system and miniature focusing optics having a high numerical aperture greater than 0.55 to trigger a local object reaction radiation in the micrometer to nanometer range, and the distal end of the transmission focusing optics unit is moved in at least two dimensions for highly spatially resolved scanning of the object and for transmitting object reaction radiation which is scanned in a locally progressive manner to an image-generating system with a photon detector. In an other embodiment the femtosecond laser radiation is energy enhanced is applied to the same transmission focusing optics unit to perform microendoscopic surgery in biological tissue.
Owner:JENLAB
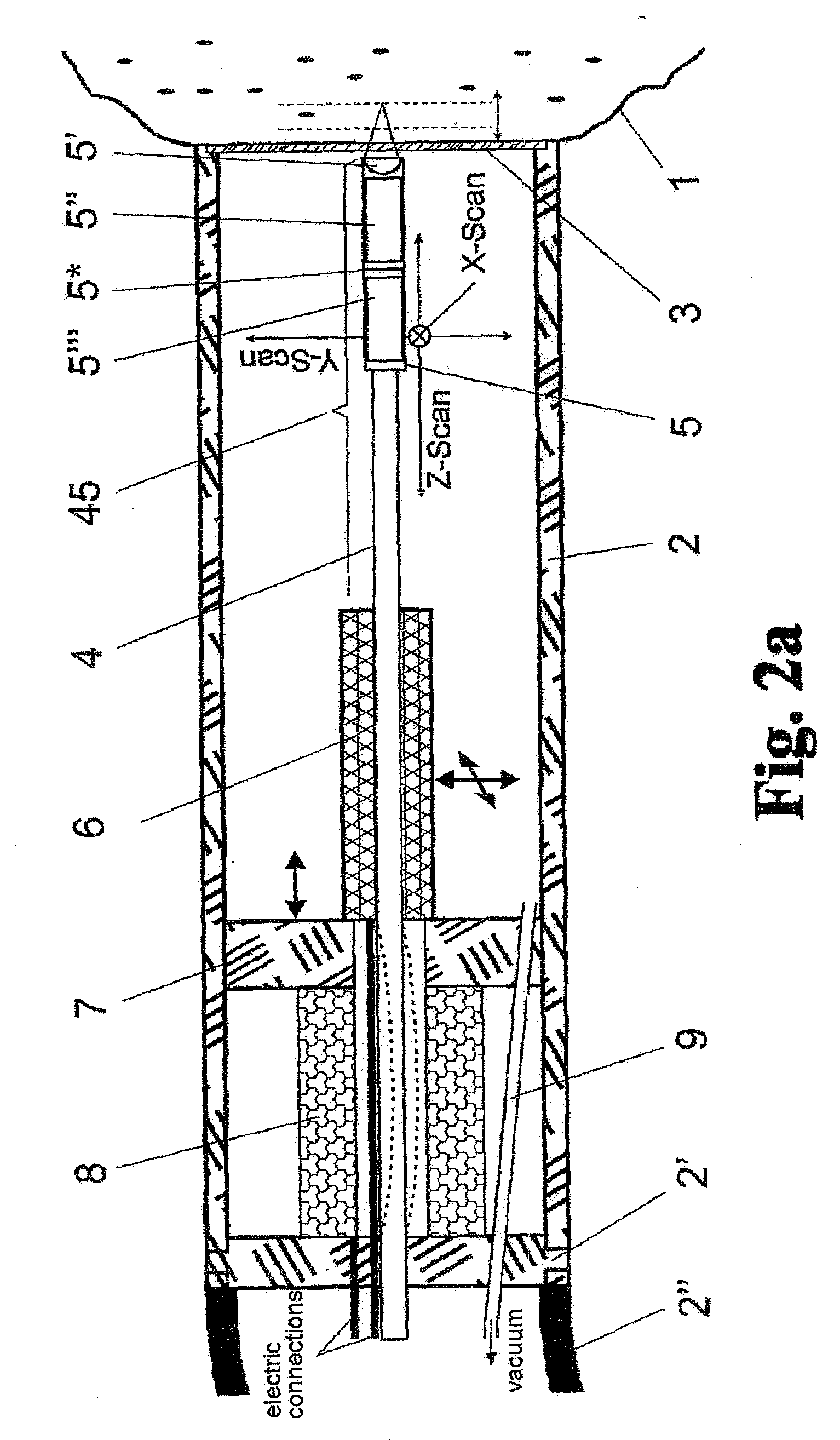
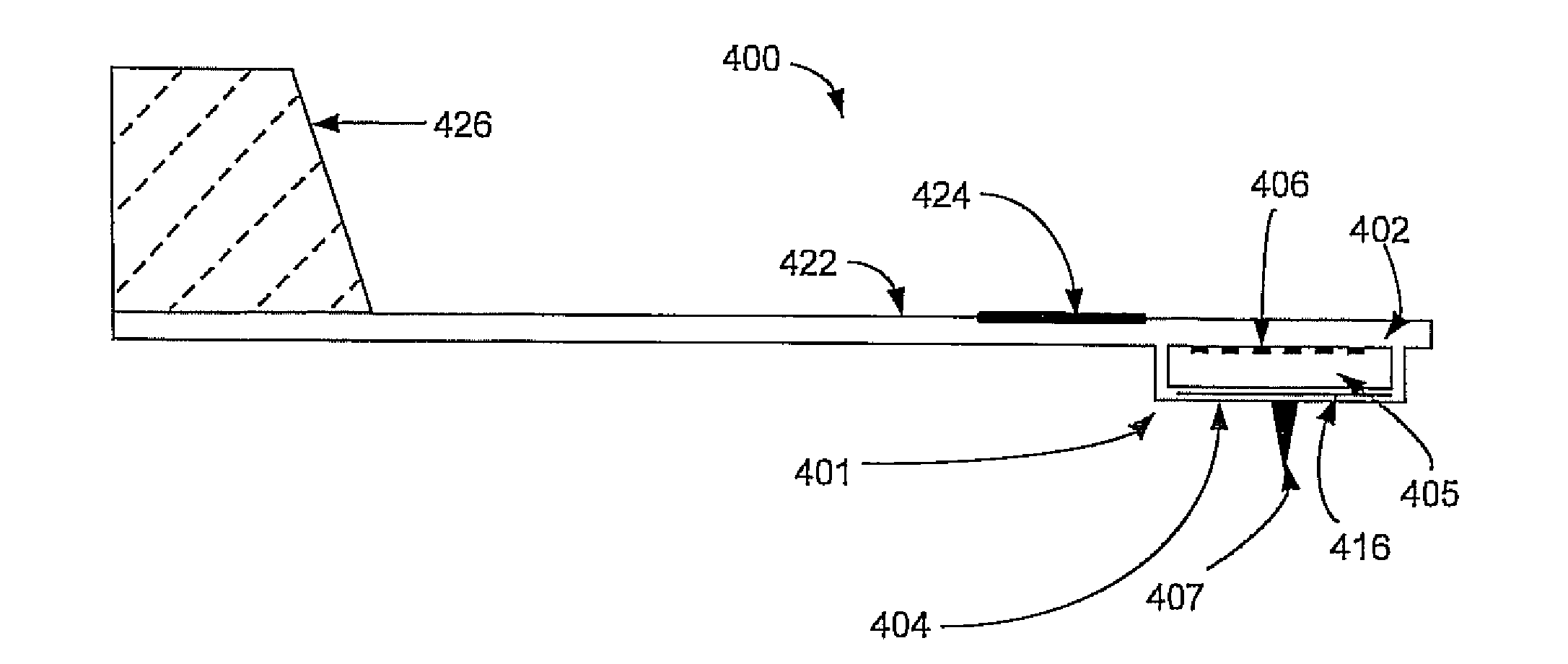
Methods of imaging in probe microscopy
InactiveUS7441447B2NanotechnologyMechanical roughness/irregularity measurementsMethod of imagesEngineering
Owner:GEORGIA TECH RES CORP
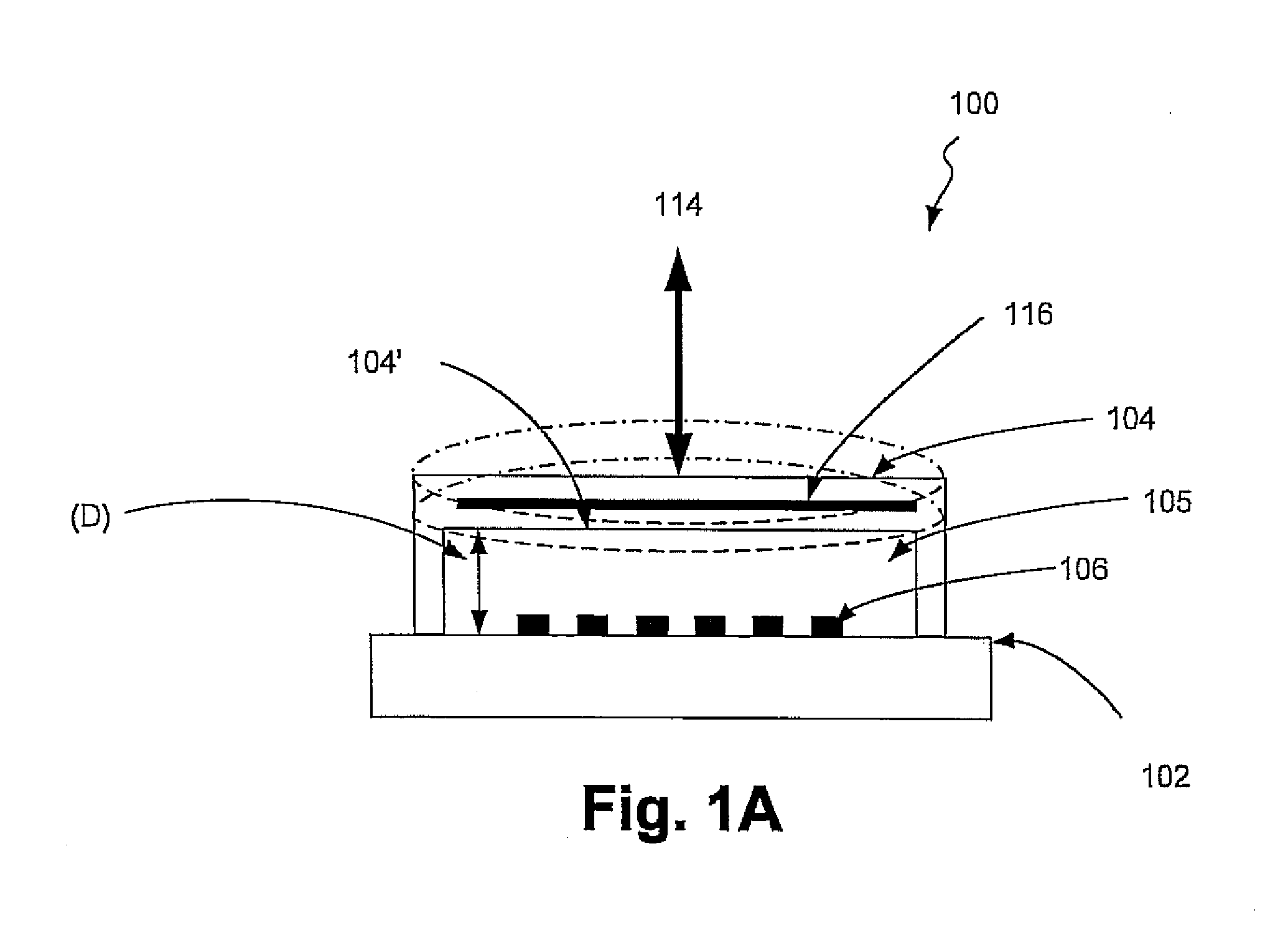
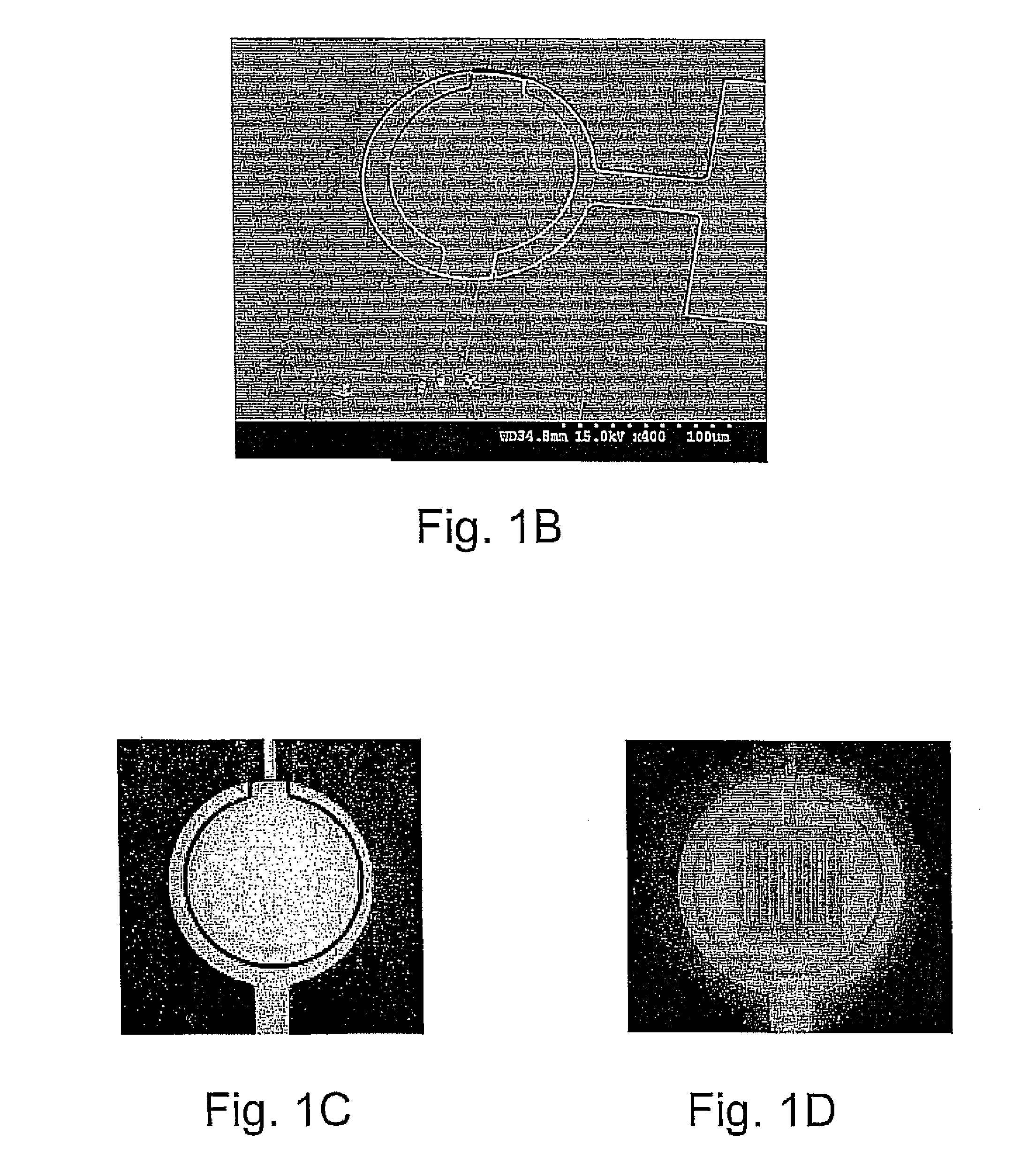
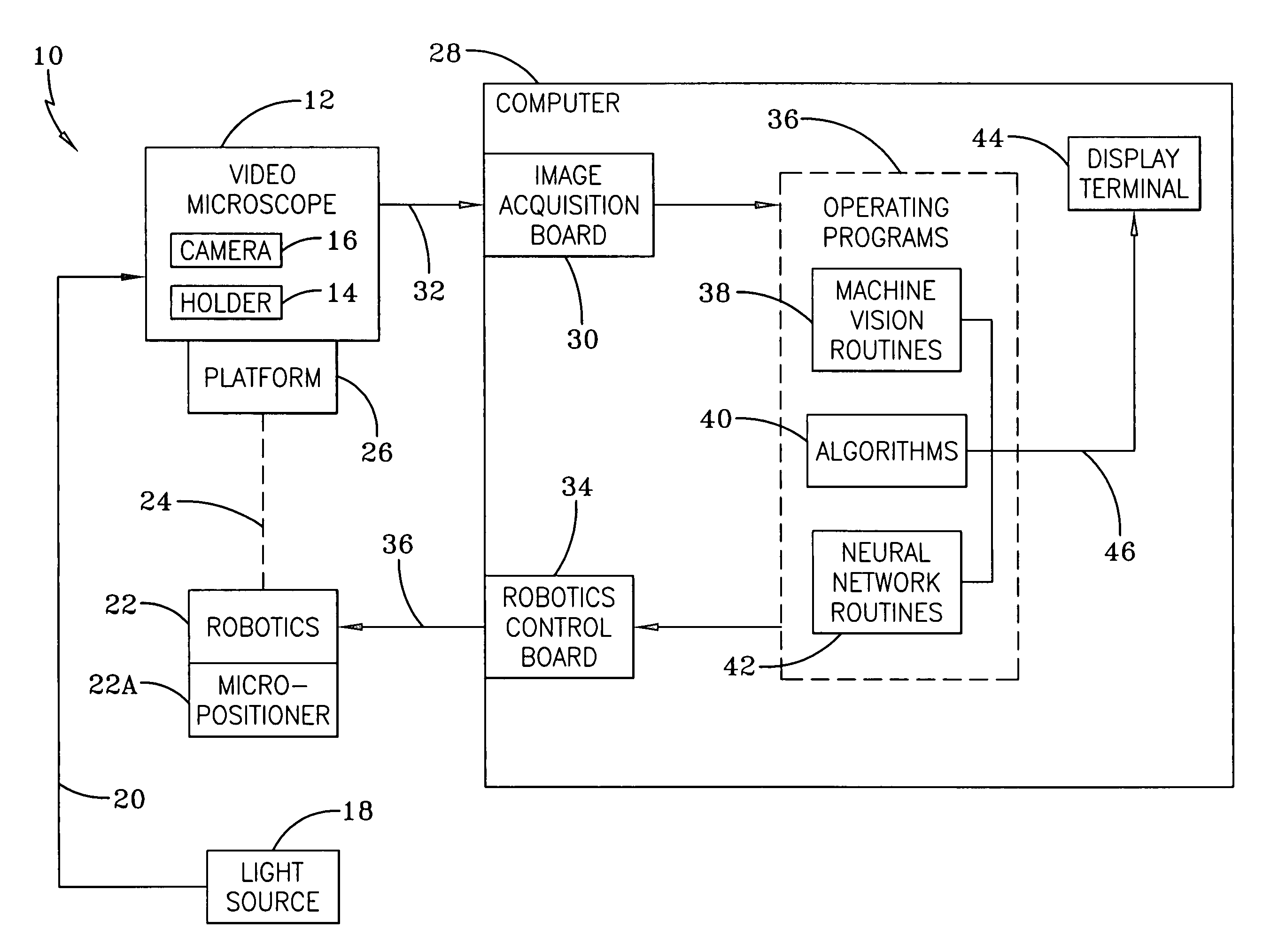
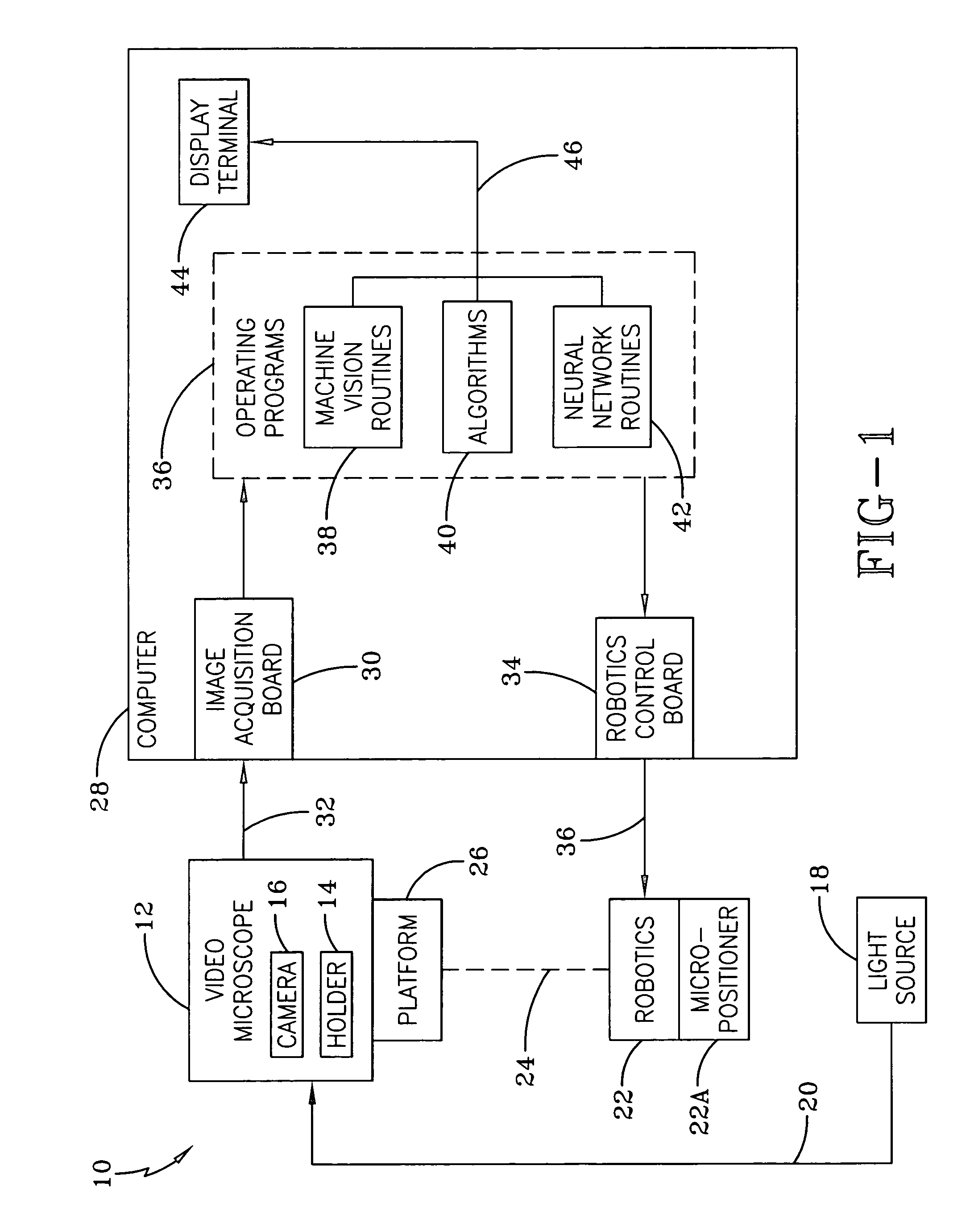
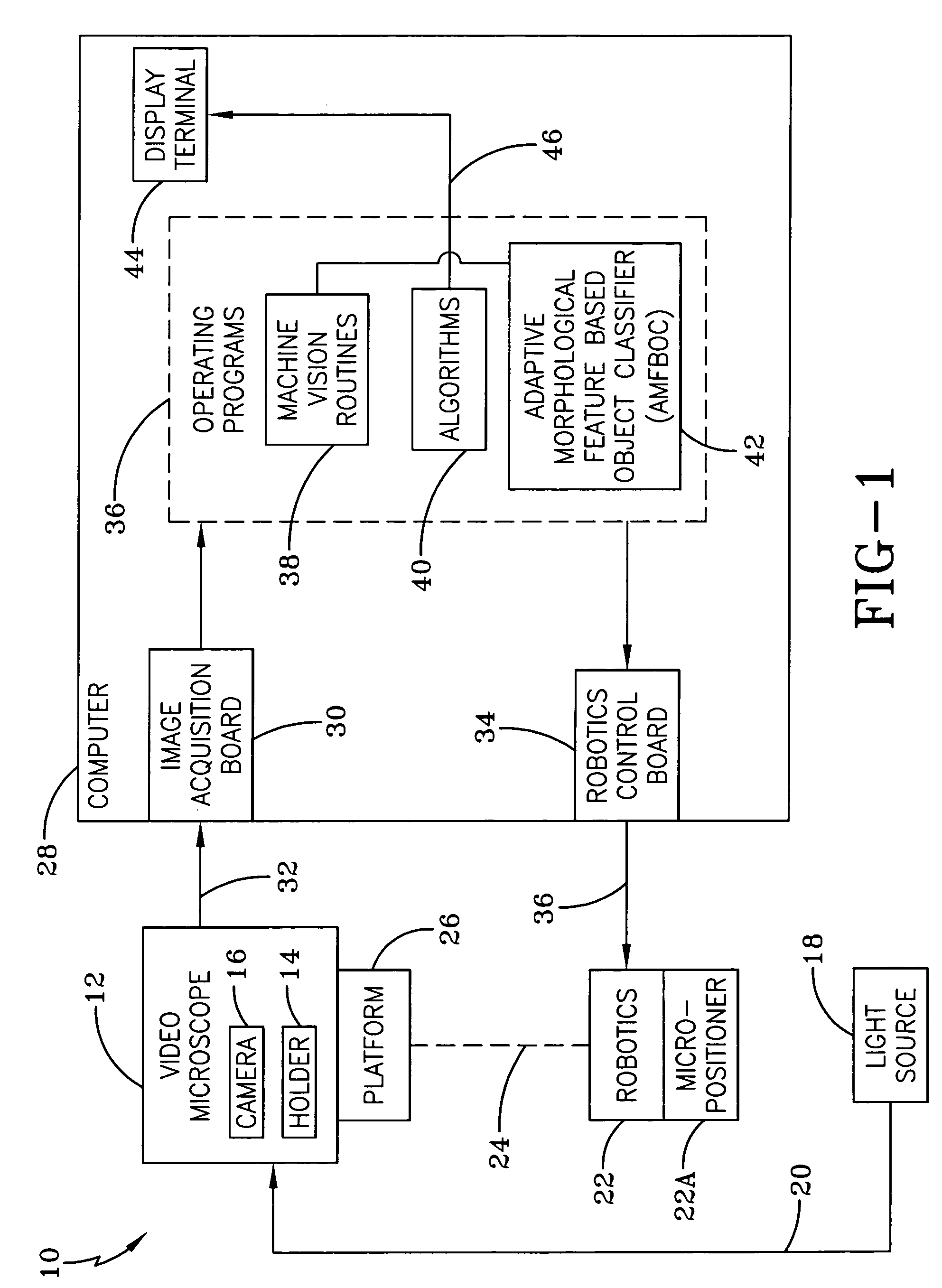
Identification of cells with a compact microscope imaging system with intelligent controls
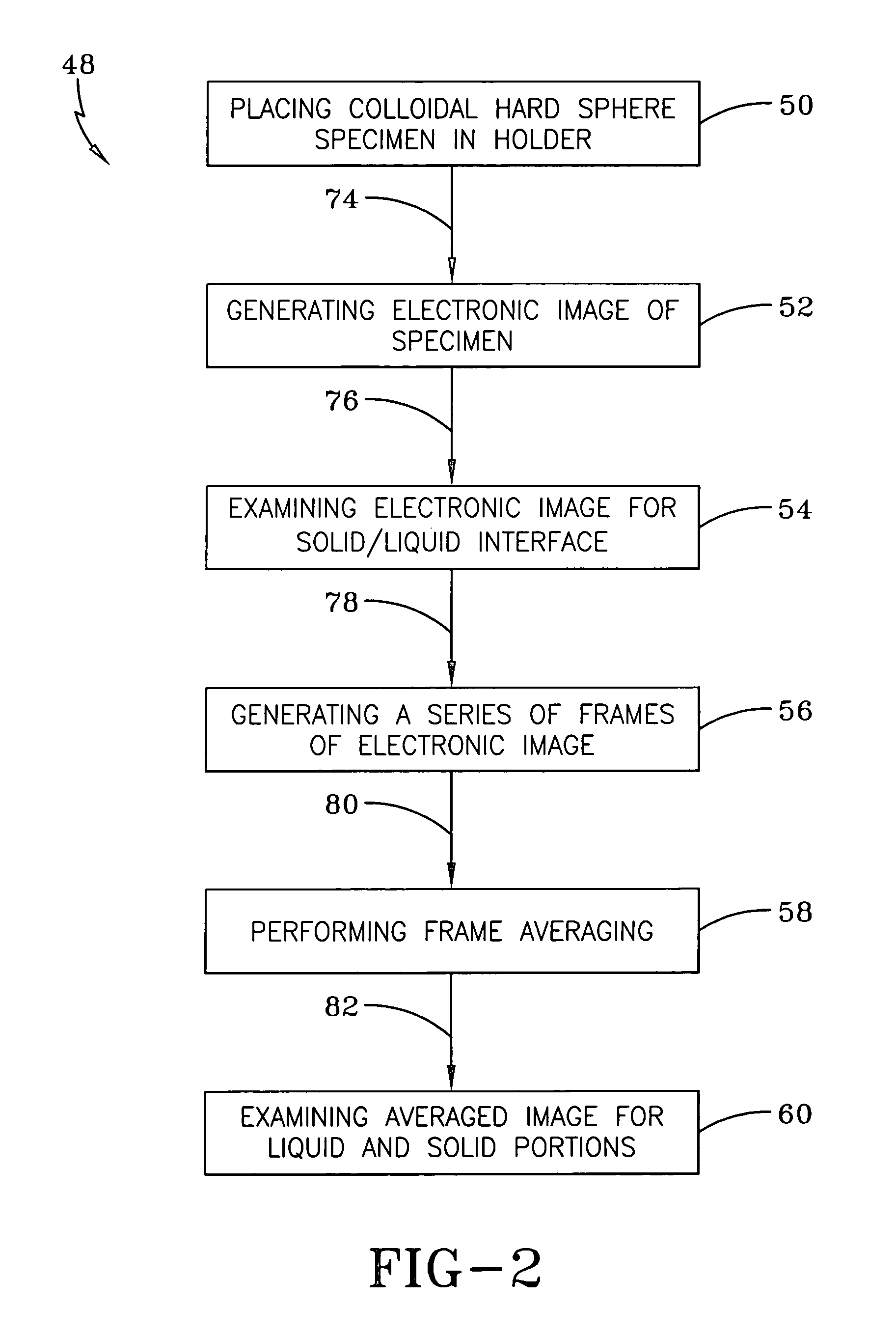
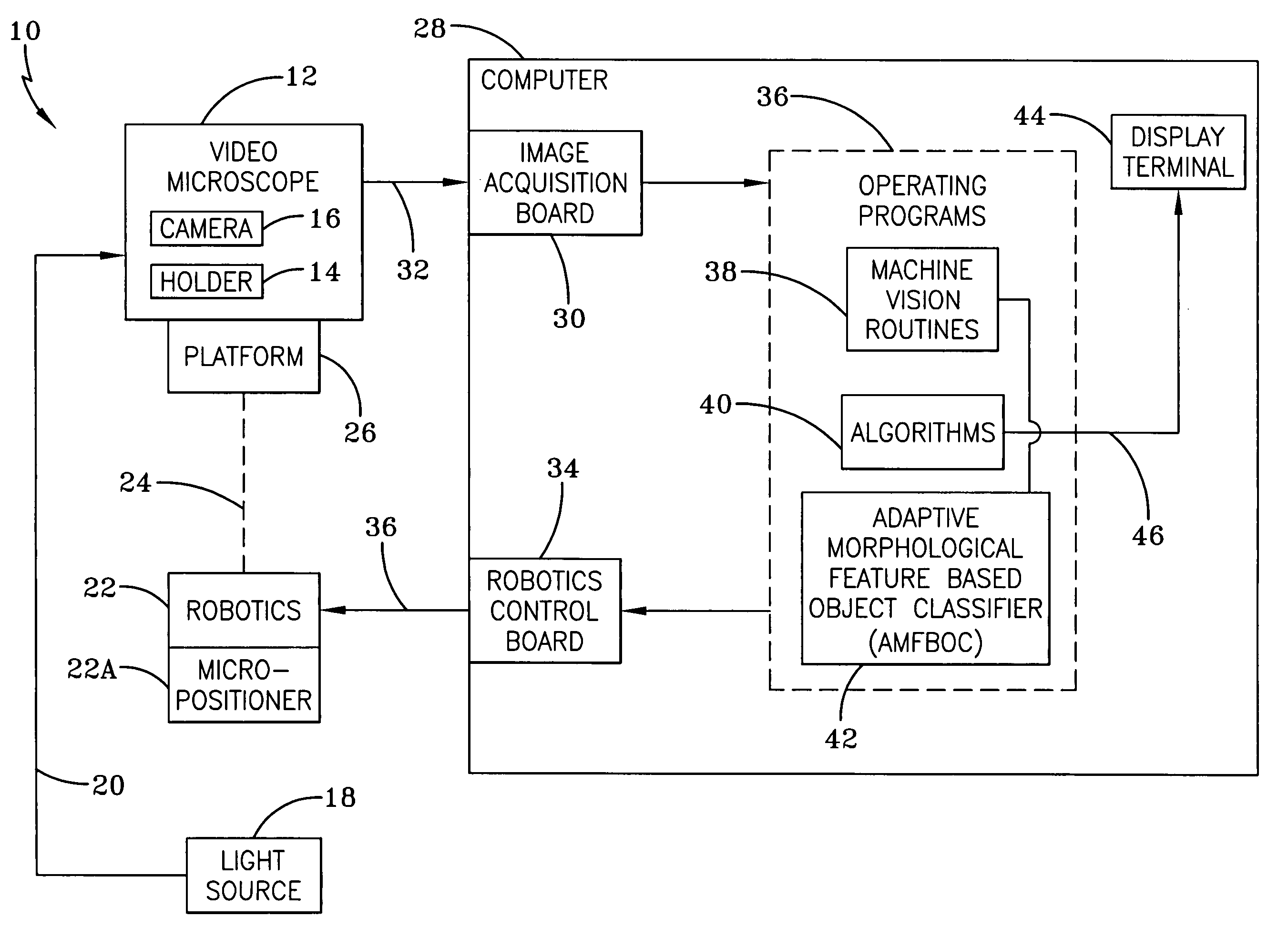
A Microscope Imaging System (CMIS) with intelligent controls is disclosed that provides techniques for scanning, identifying, detecting and tracking microscopic changes in selected characteristics or features of various surfaces including, but not limited to, cells, spheres, and manufactured products subject to difficult-to-see imperfections. The practice of the present invention provides applications that include colloidal hard spheres experiments, biological cell detection for patch clamping, cell movement and tracking, as well as defect identification in products, such as semiconductor devices, where surface damage can be significant, but difficult to detect. The CMIS system is a machine vision system, which combines intelligent image processing with remote control capabilities and provides the ability to auto-focus on a microscope sample, automatically scan an image, and perform machine vision analysis on multiple samples simultaneously.
Owner:NASA
Multi-mode microimaging method based on programmable LED array illumination
The invention discloses a multi-mode microimaging method based on programmable LED array illumination. An LED array used as an illumination light source of a microimaging system is directly installed below a sample carrying bench of the microimaging system and the center of the LED array is located at an optical axis of the microimaging system, thereby realizing phase contrast, optical field imaging, and optical dyeing imaging modes. With the method, dyeing microimaging can be realized flexibly and no additional optical element like an annular diaphragm, a microlens array, and a phase plate and the like needs to be added in an imaging light path of a microscopic, so that the system structure is simplified and the cost is substantially reduced.
Owner:NANJING UNIV OF SCI & TECH
Optical imaging device and imaging method for microscopy
ActiveUS20100188738A1High magnificationIncrease the number ofMicroscopesTelescopesObject pointLight beam
The present invention relates to an optical imaging device, in particular for microscopy, with a first optical element group and a second optical element group, wherein the first optical element group and the second optical element group, on an image plane, form an image of an object point of an object plane. The first optical element group comprises a first optical element with a reflective first optical surface and a second optical element with a reflective second optical surface. The second optical element group comprises a third optical element with a reflective third optical surface. The first optical element and the second optical element are formed and arranged such that on formation of the image of the object point, in each case a multiple reflection of at least one imaging beam takes place on the first optical surface and the second optical surface.
Owner:CARL ZEISS SMT GMBH
Tracking of cells with a compact microscope imaging system with intelligent controls
A Microscope Imaging System (CMIS) with intelligent controls is disclosed that provides techniques for scanning, identifying, detecting and tracking microscopic changes in selected characteristics or features of various surfaces including, but not limited to, cells, spheres, and manufactured products subject to difficult-to-see imperfections. The practice of the present invention provides applications that include colloidal hard spheres experiments, biological cell detection for patch clamping, cell movement and tracking, as well as defect identification in products, such as semiconductor devices, where surface damage can be significant, but difficult to detect. The CMIS system is a machine vision system, which combines intelligent image processing with remote control capabilities and provides the ability to auto-focus on a microscope sample, automatically scan an image, and perform machine vision analysis on multiple samples simultaneously.
Owner:UNITED STATES OF AMERICA AS REPRESENTED BY THE ADMINISTRATOR NAT AERONAUTICS & SPACE ADMINISTRATION
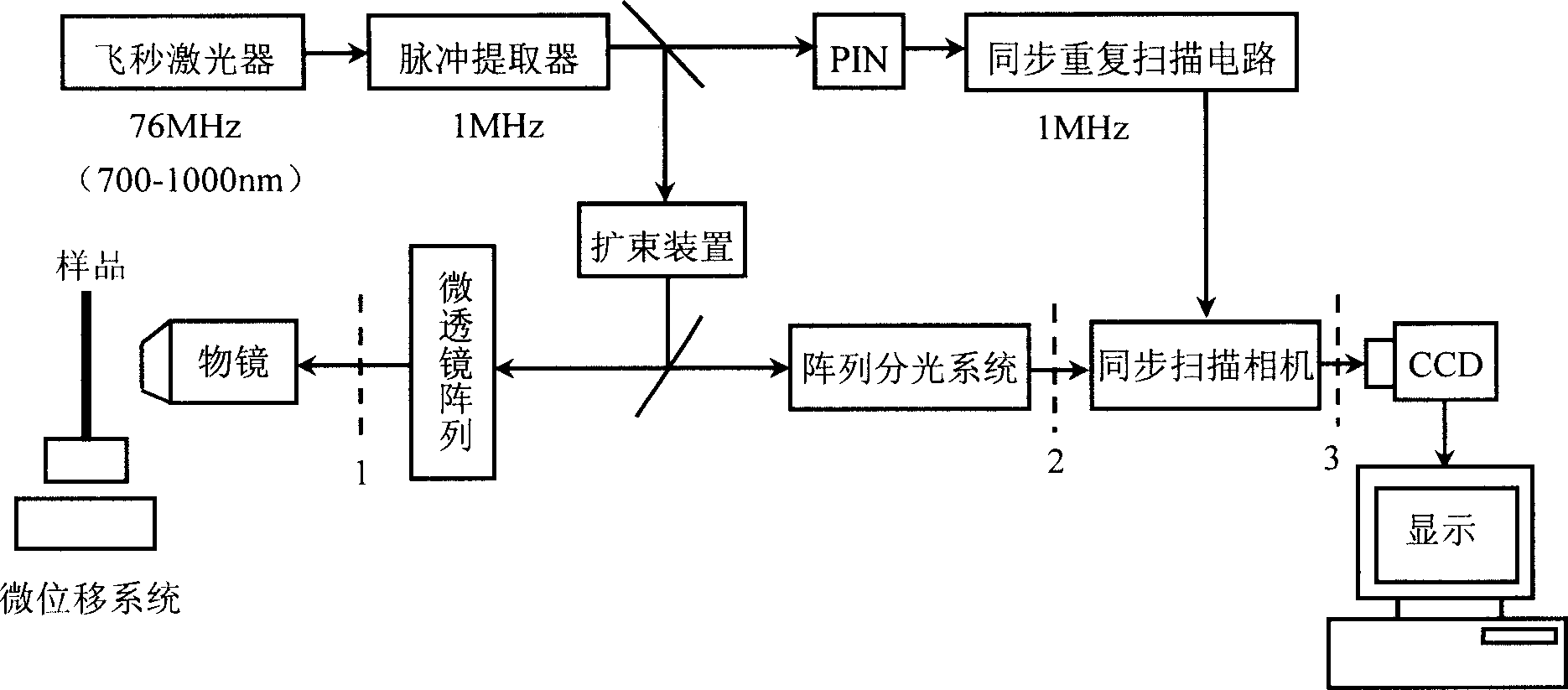
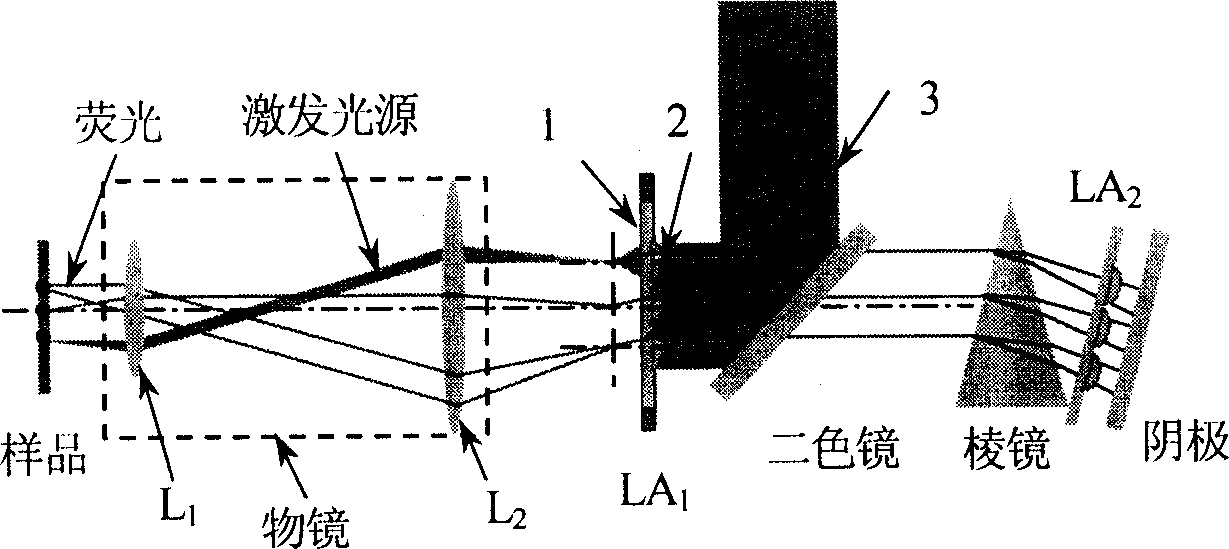
Five-dimensional fluorescent microscope imaging technique
InactiveCN1737536AMeasurable fluorescence lifetimeImprove spatial resolutionColor/spectral properties measurementsFluorescence/phosphorescenceMicroscopic imageFluorescence
This invention relates to one method to acquire biology spectrum information and life information and to realize three-dimensional imaging. The invention is characterized by the following: getting multi-photon or single photon triggering of five-dimensional fluorescent microscope imaging information, that is three-dimensional space, one dimensional time and spectrum. This multi-parameter compound measurement and technique, which can satisfy the needs of different layers in study and can realize the flexible made three-dimensional spectrum for measurement.
Owner:SHENZHEN UNIV
Methods of imaging in probe microscopy
In accordance with an embodiment of the invention, there is a force sensor for a probe based instrument. The force sensor can comprise a detection surface and a flexible mechanical structure disposed a first distance above the detection surface so as to form a gap between the flexible mechanical structure and the detection surface, wherein the flexible mechanical structure is configured to deflect upon exposure to an external force, thereby changing the first distance.
Owner:GEORGIA TECH RES CORP
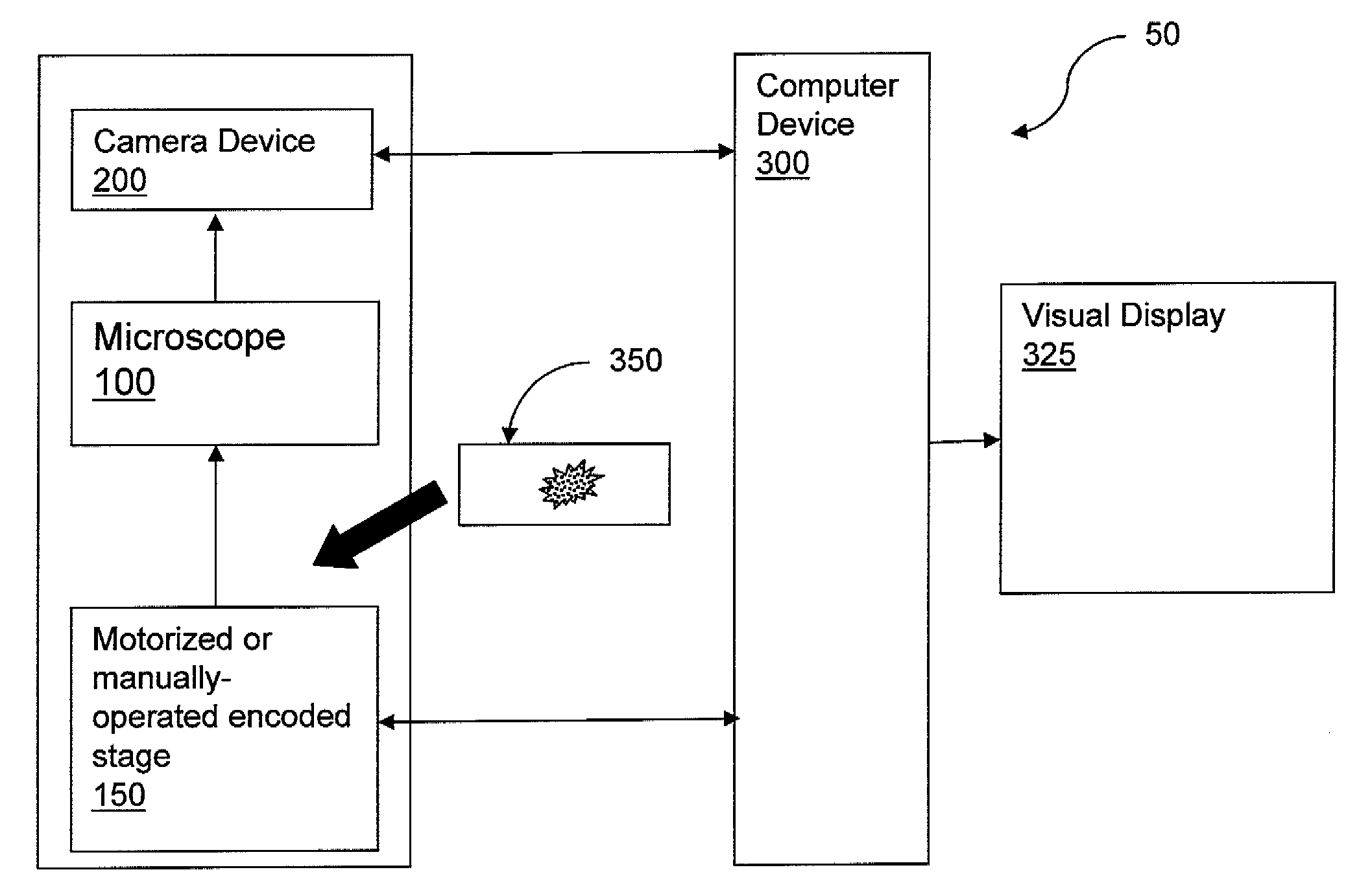
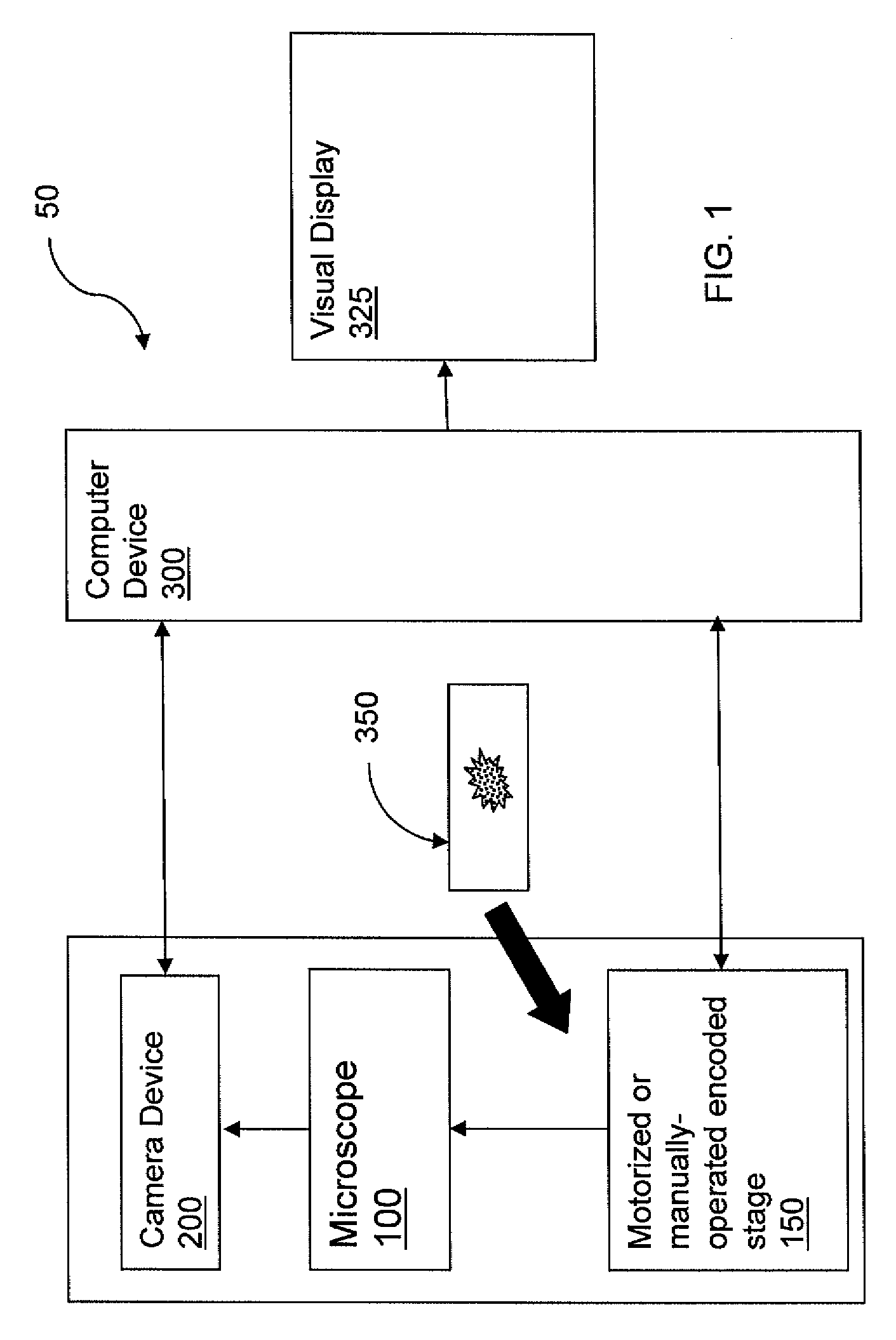
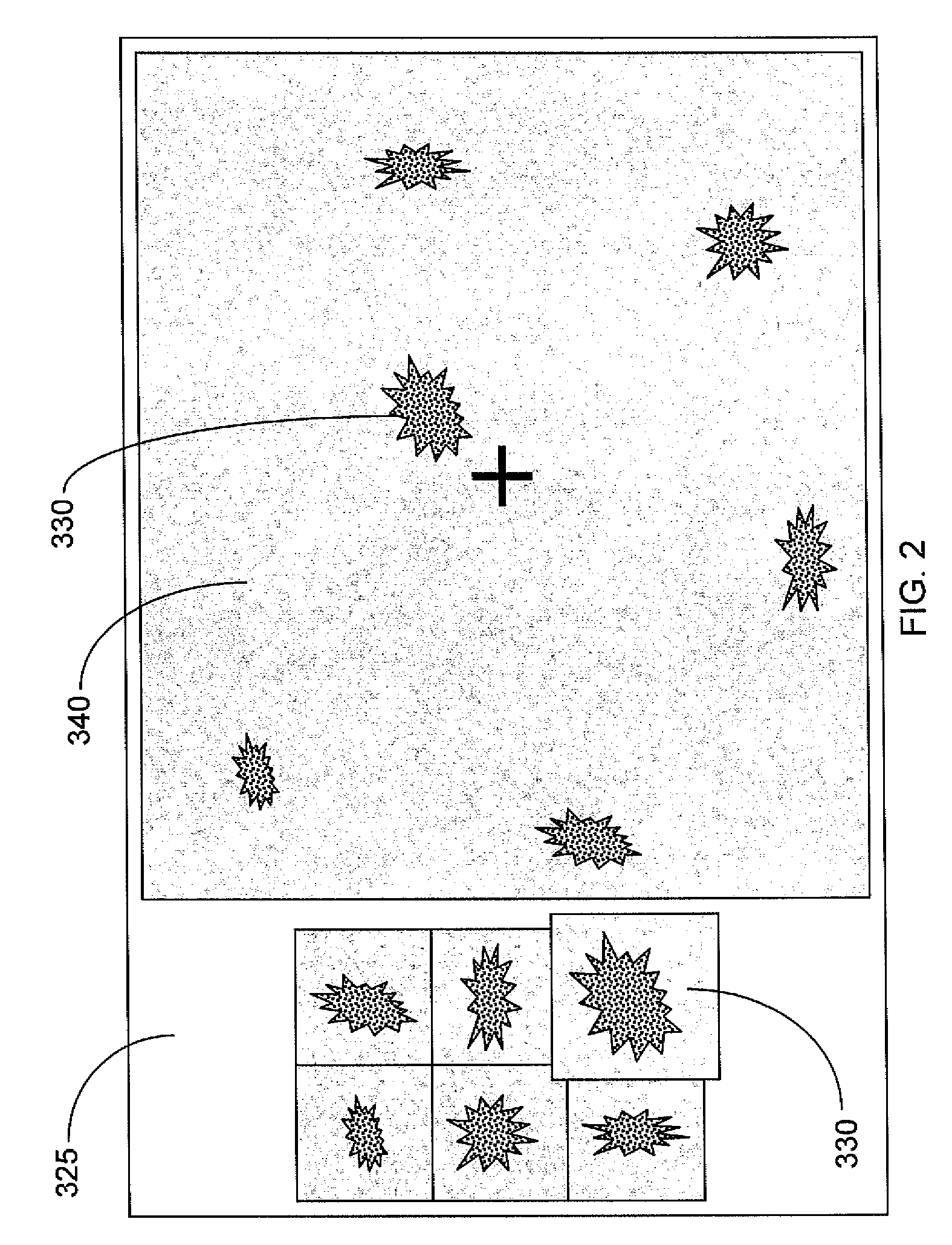
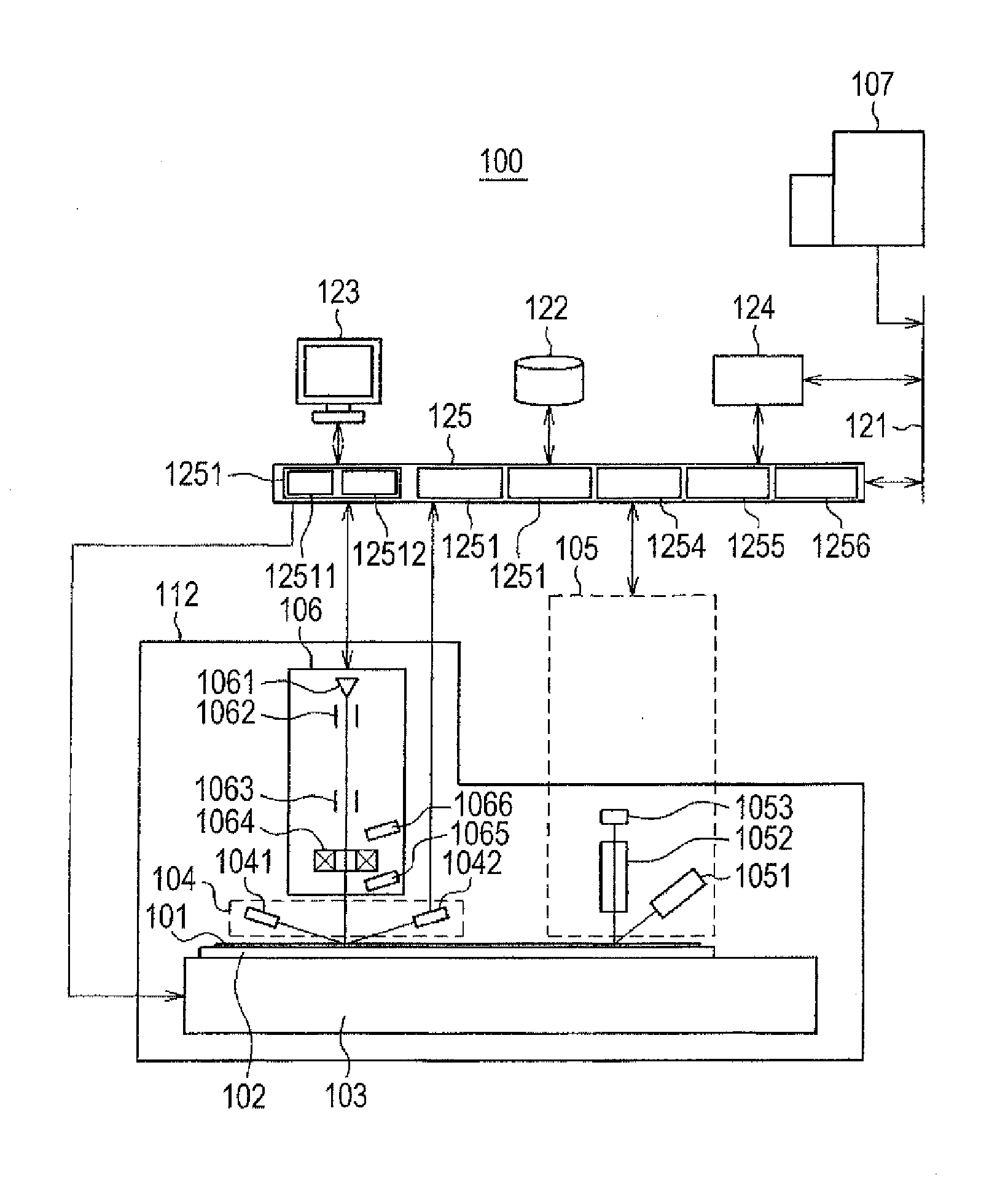
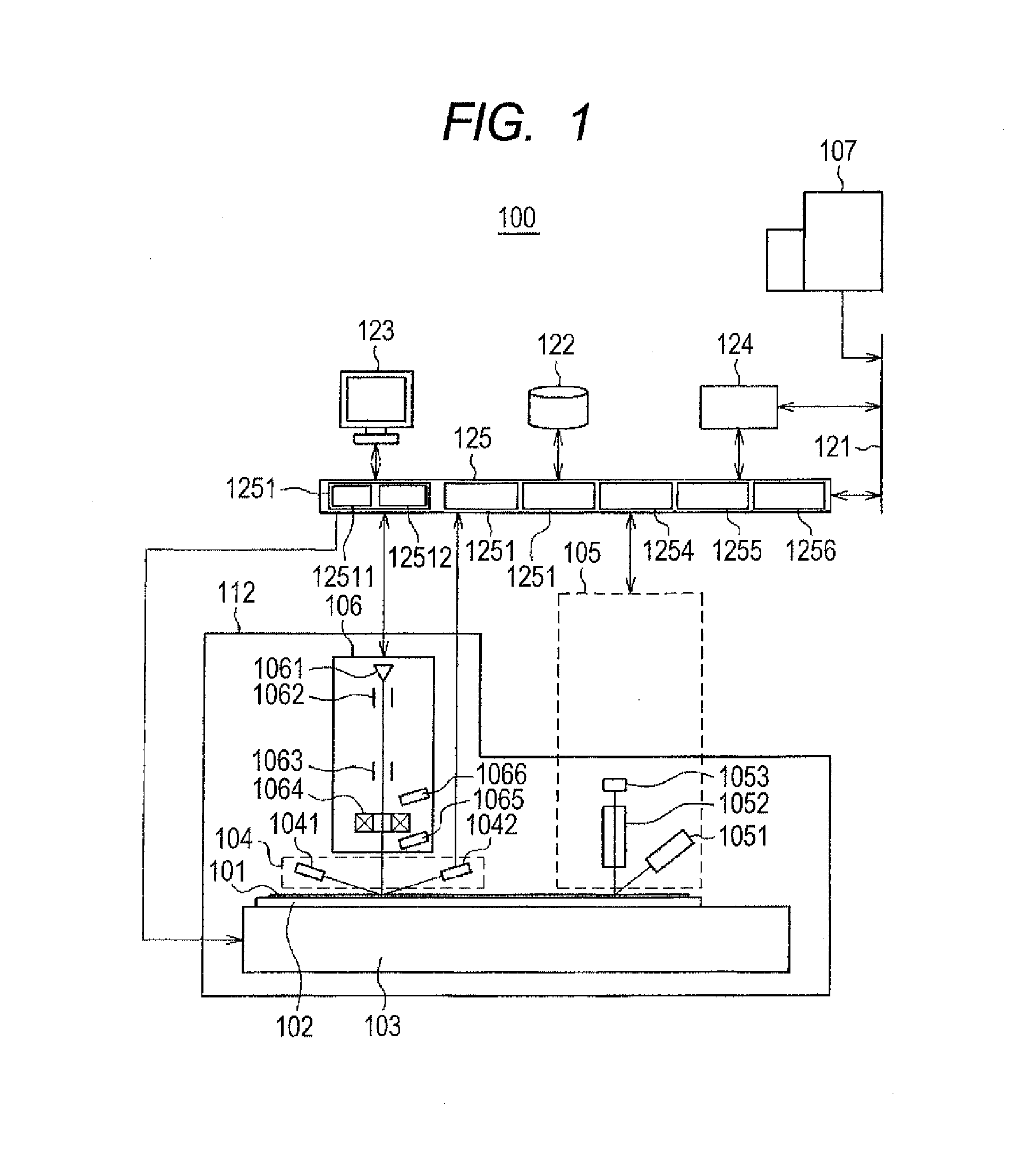
System and Method for Re-locating an Object in a Sample on a Slide with a Microscope Imaging Device
A method of re-locating an object in a sample is provided for a previously-scanned slide having determined objects each with corresponding stored coordinates and a stored image, the objects being mapped relative to each other. The slide is positioned on a microscope stage, stored images of the objects are visually displayed, and a target object is selected. The slide is moved to an estimated coordinate position, corresponding to the coordinates of the target object, and a field-of-view image of the sample is captured for comparison to the stored image of the target. If the target is in the image, an offset between actual coordinates of the located target and the stored coordinates of the corresponding object is determined. The slide is then moved, via the stage, from the estimated coordinate position, according to the offset, to center the target in the image. Associated systems and methods are also provided.
Owner:TRIPATH IMAGING INC
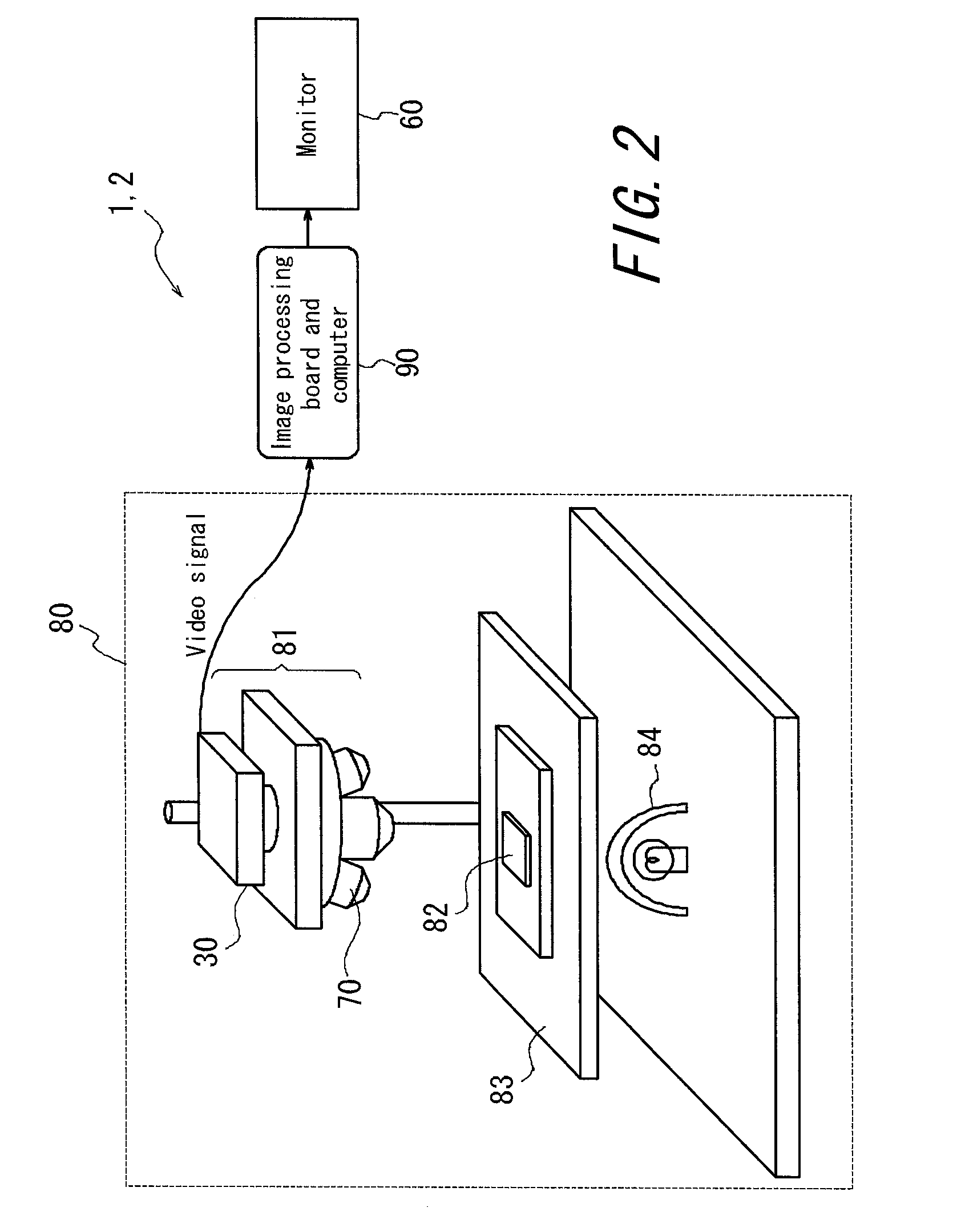
Microscope imaging apparatus and biological-specimen examination system
InactiveUS20060018013A1Material analysis by optical meansMicroscopesSingle imageBrightness perception
A microscope imaging apparatus and a biological-specimen examination system that can accurately carry out measurement even for an object under examination having substantial brightness non-uniformity are provided. The microscope imaging apparatus includes a stage that holds the object under examination, an illumination unit that illuminates the object under examination, an image-acquisition unit that acquires images of the object under examination, and a motion unit that moves the stage and the image-acquisition unit relative to each other. The image-acquisition unit includes an imaging device capable of image acquisition using a time delay integration method. When acquiring a plurality of images of the object under examination, the exposure time during which accumulated charge is produced in the imaging device is made different for each of the acquired images, and the plurality of images are combined into a single image.
Owner:OLYMPUS CORP
Imaging device for microscope
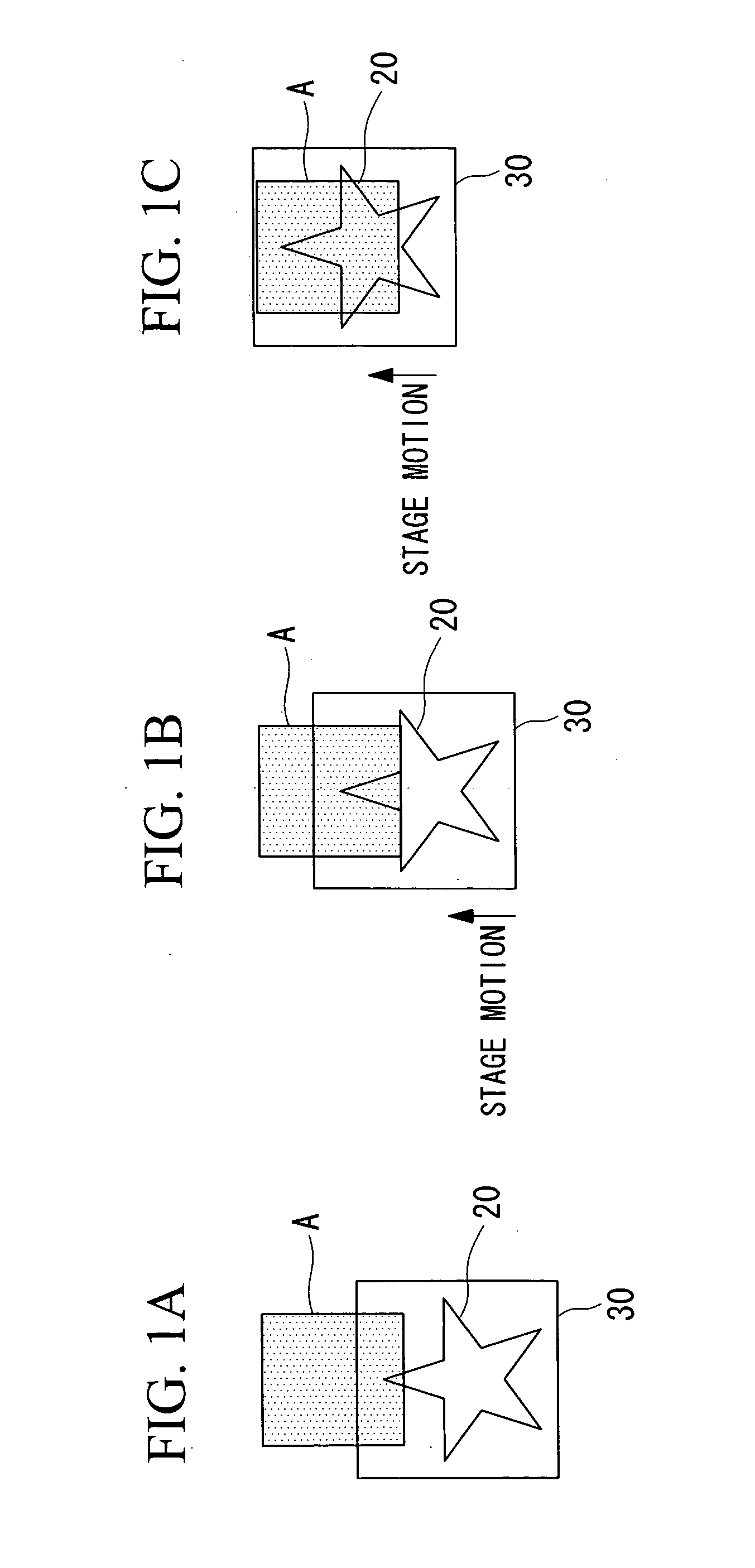
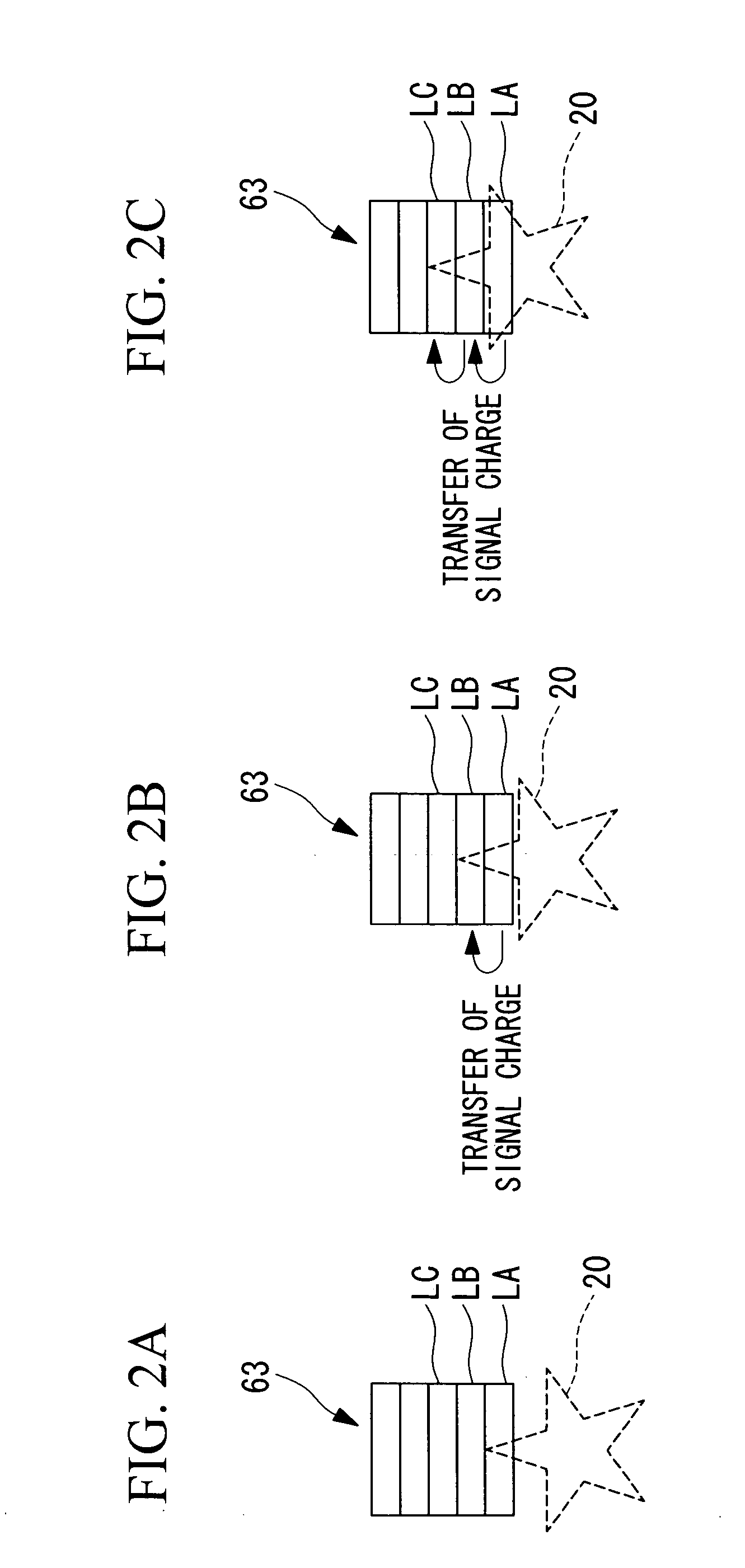
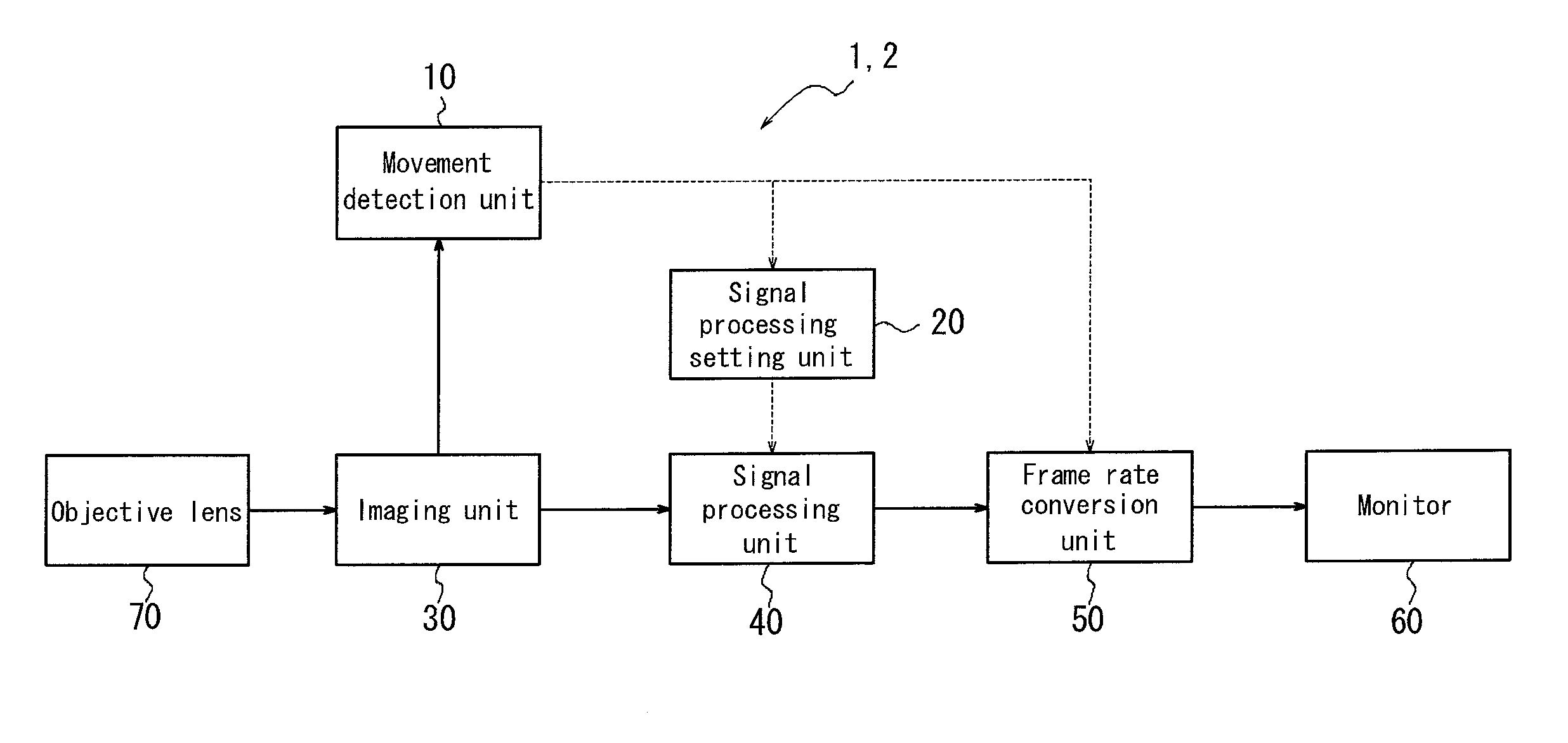
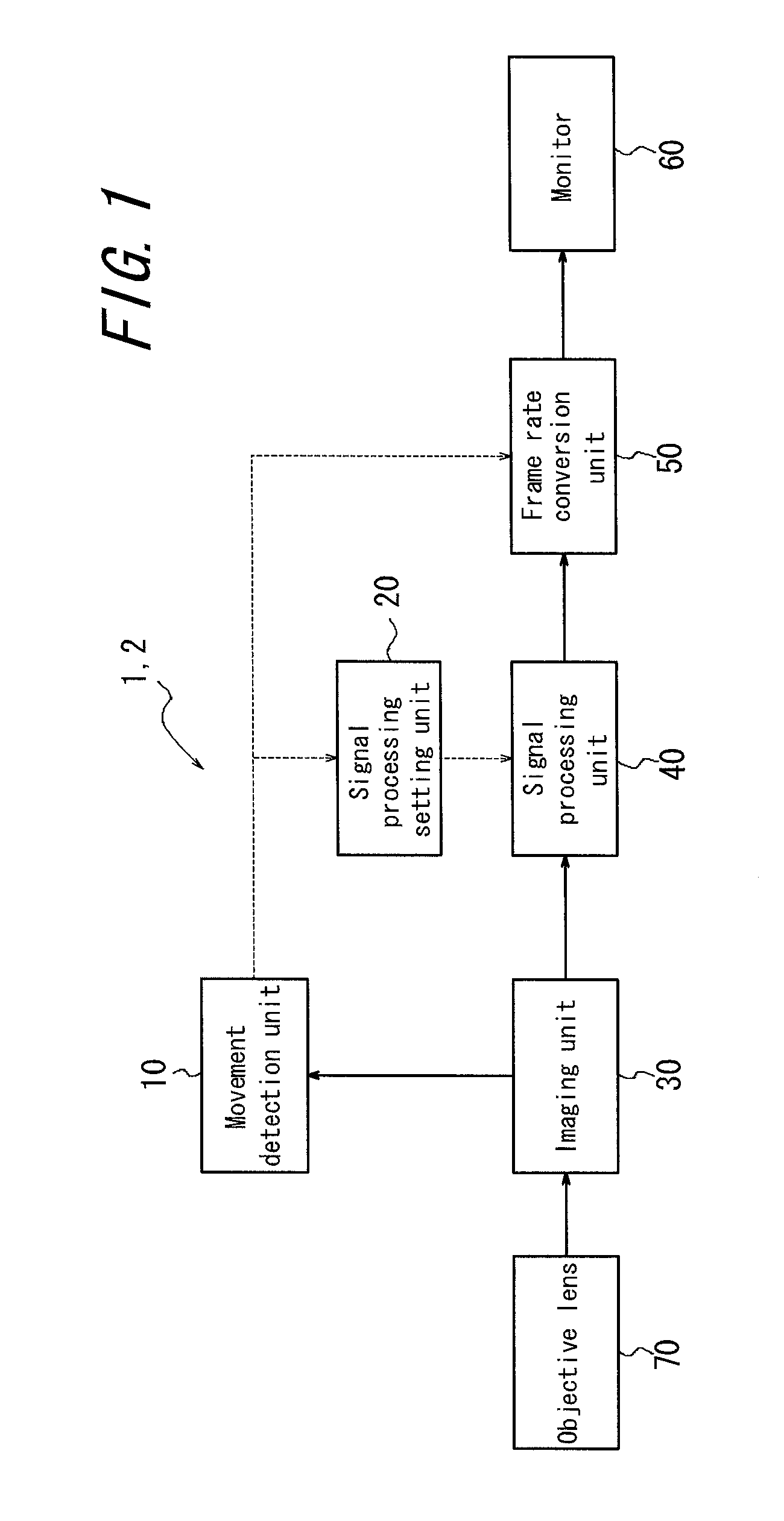
InactiveUS20120069171A1Shorten the timeReduce noiseColor television detailsClosed circuit television systemsOptical axisProcessing element
An imaging device including an imaging unit that obtains a video signal; a signal processing unit that processes the video signal; a movement detection unit that calculates a relative moving speed between the imaging unit and a stage in a first direction perpendicular to an optical axis of the imaging unit; a setting unit that determines a parameter such that time required for the signal processing is reduced where the relative moving speed is more than or equal to a threshold value; and, a frame rate conversion unit that selects between a process of increasing a frame rate of the video signal subjected to the signal processing where the relative moving speed is more than or equal to the threshold value, and a process of maintaining a current frame rate, to apply the selected process, wherein the signal processing unit applies the signal processing in accordance with the parameter.
Owner:OLYMPUS CORP
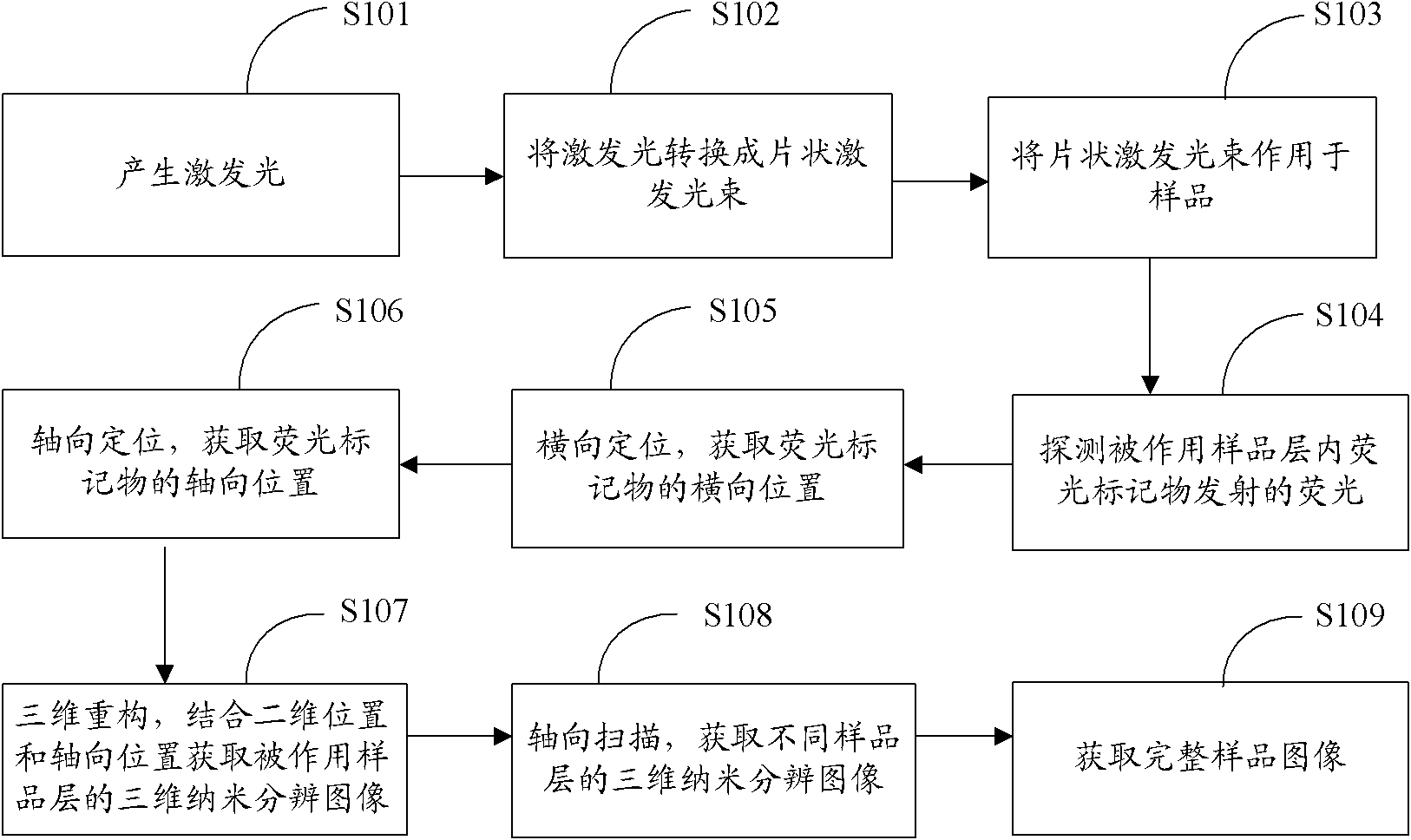
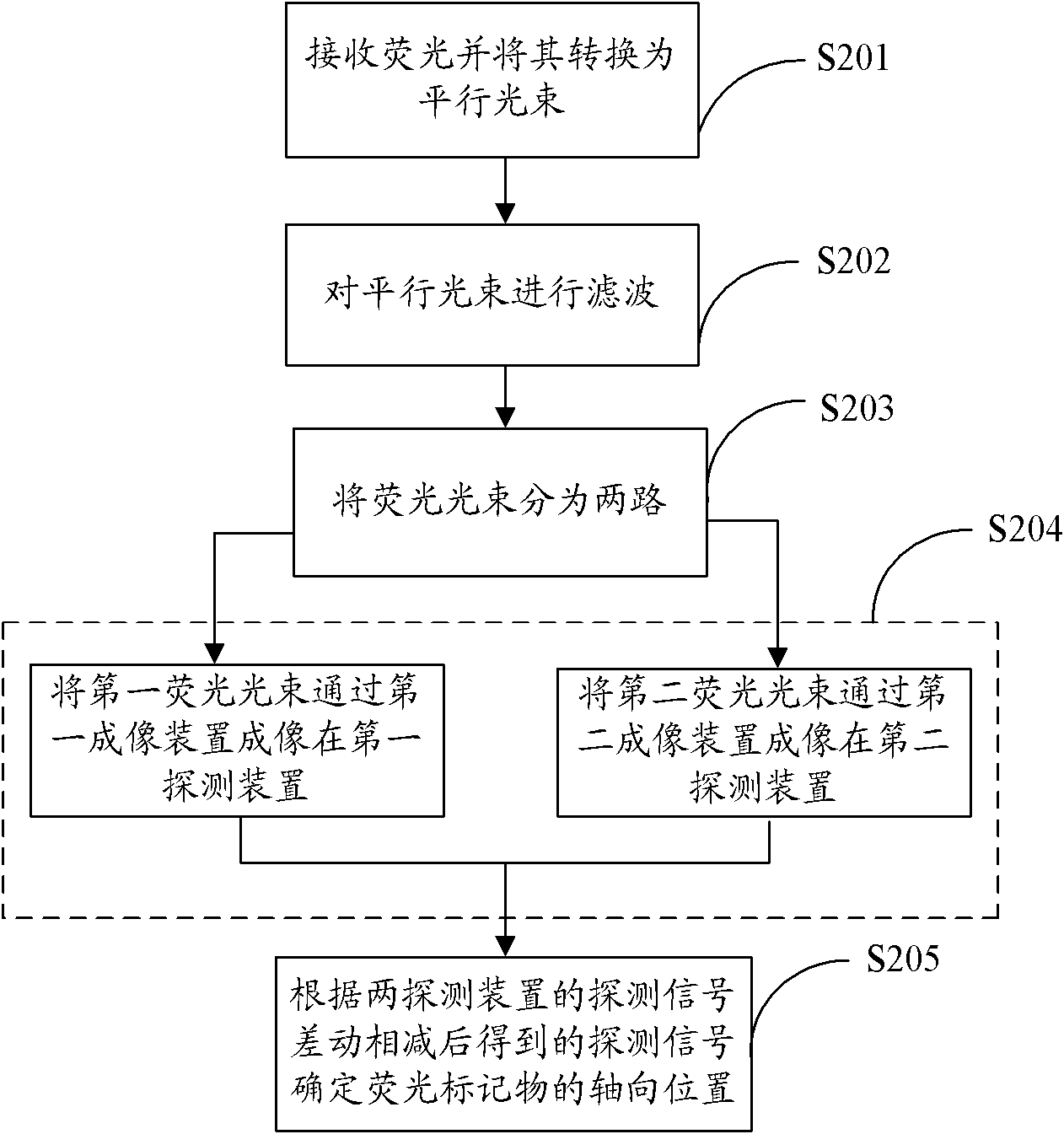
Three-dimensional fluorescence nano microscope imaging method and system, and image equipment
ActiveCN101963582AAvoid crosstalkReduce out-of-focus background noiseFluorescence/phosphorescenceMicro imagingLight beam
The invention is suitable for the field of microscope imaging, and provides a three-dimensional fluorescence nano microscope imaging method and a three-dimensional fluorescence nano microscope imaging system, and image equipment. The method comprises the following steps of: producing exciting light; converting the exciting light into a laminar exciting beam; making the laminar exciting beam act on a sample; detecting a fluorescent light emitted by a fluorescent label in the sample layer on which the laminar exciting beam acts; transversely positioning to acquire the two-dimensional position of the fluorescent label; axially positioning to acquire the axial position of the fluorescent label; three-dimensionally reconstructing, combining the two-dimensional position with the axial position to acquire a three-dimensional nano resolution image of the sample layer on which the laminar exciting beam acts; axially scanning to acquire the three-dimensional nano resolution images of different sample layers; and acquiring the three-dimensional nano resolution image of the complete sample. Through the three-dimensional fluorescence nano microscope imaging method and the three-dimensional fluorescence nano microscope imaging system, and the image equipment, the high-precision three-dimensional nano microscope imaging is realized by taking the laminar light beam as the exciting light, and combining with axial scanning, and the method, system and equipment are suitable for three-dimensional microscope imaging of the thick sample, such as cells in the biological field and the like, and solve the problems that the positioning accuracy of molecules in the thick sample is low and the sample is difficult to observe.
Owner:SHENZHEN UNIV
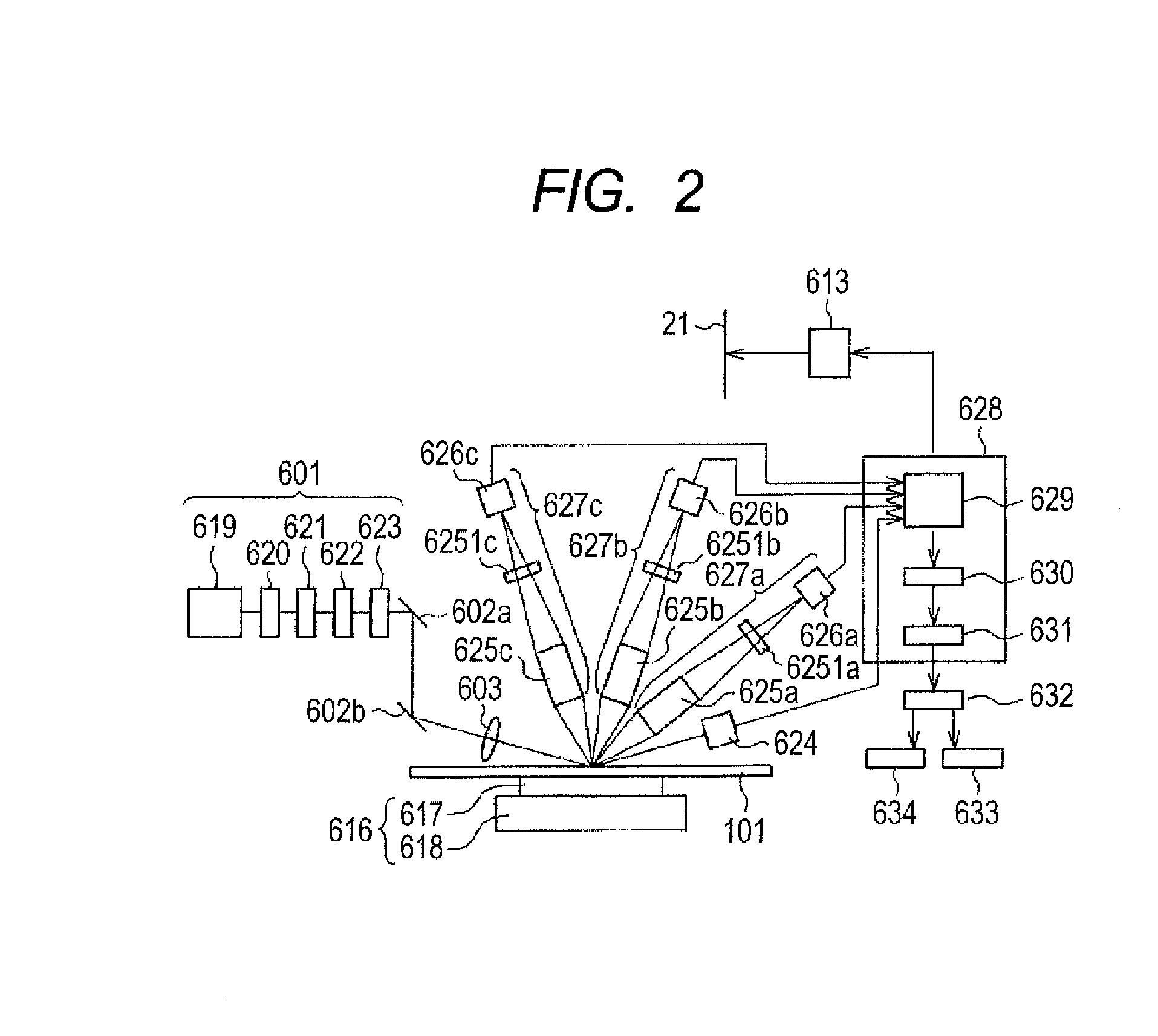
Optical scanning zoom microscope with high magnification and a large field of view
InactiveUS20060291042A1Easy accessEffective enlarged viewing areaMicroscopesFluorescence microscopeHigh resolution image
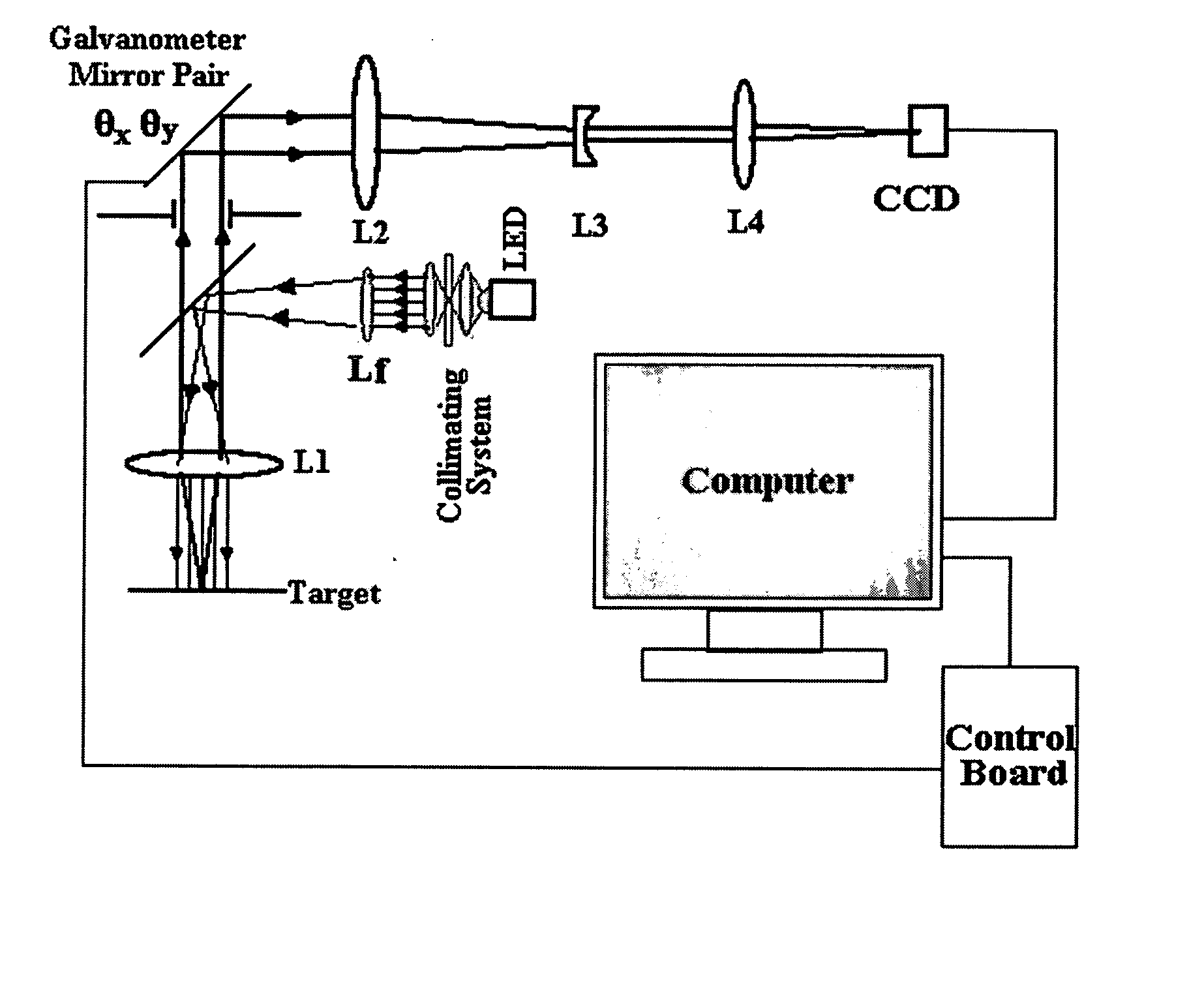
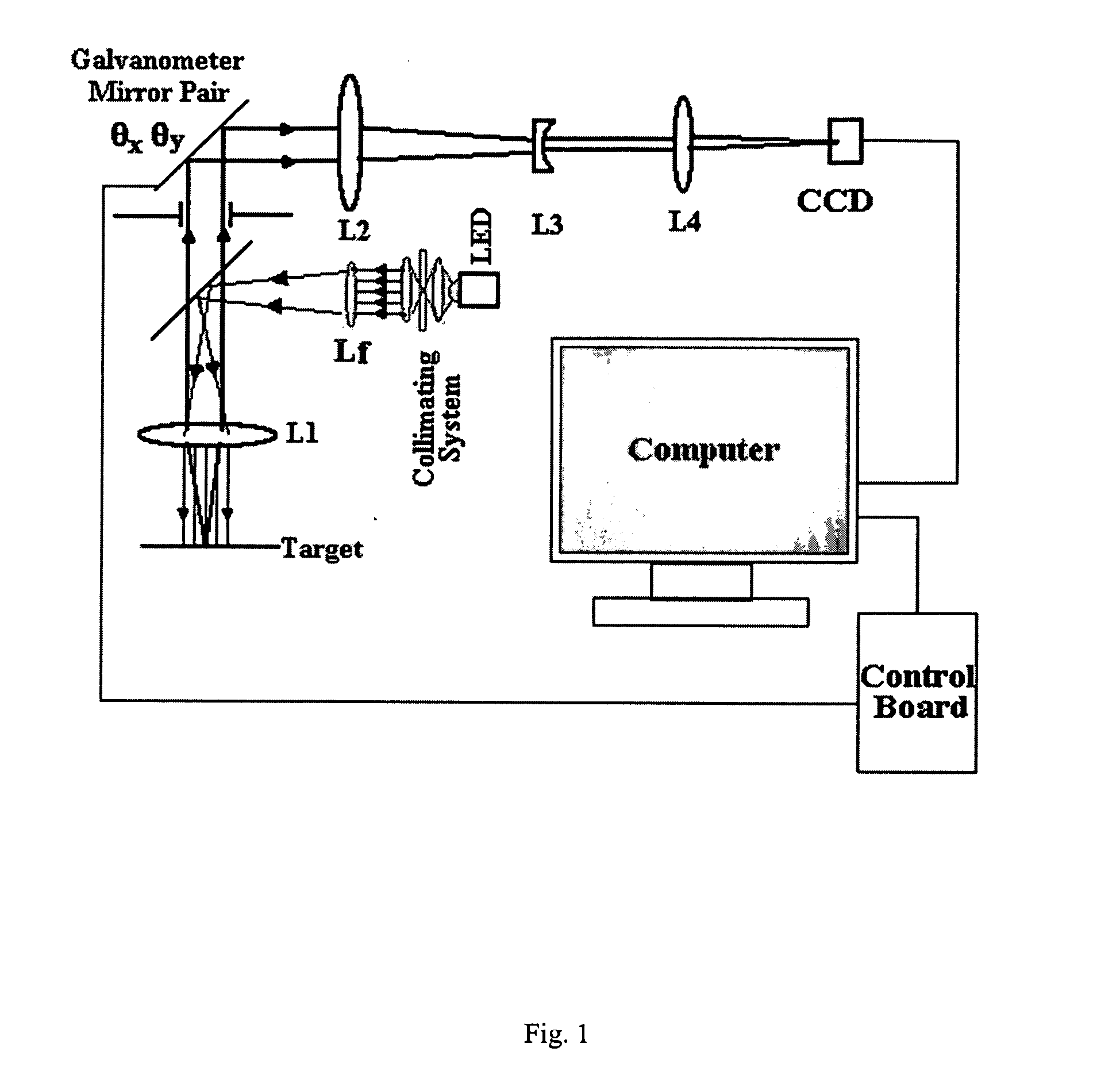
The computer-controlled optical scanning high magnification microscope imaging system with a large field of view disclosed herein overcomes a previous inability to achieve simultaneous high magnification and large field of view in microscopes. The subject imaging system includes galvanometer scanners, a CCD camera and high brightness LED sources at different wavelengths for rapid acquisition of a large number of high-resolution segmented tile images with a magnification of 800× each. The numerous segmented tiles combine to form a larger viewing field of the target, resulting in a compound image with an effective enlarged viewing area of 1.6×1.2 mm2. The speed and sensitivity of the system make it suitable for high resolution image monitoring of a small segmented area of dimensions 320×240 μm2 with a 4 μm resolution. The microscope can zoom in on each segment of the target without lost of resolution to attain a great degree of spatial detail. With its special capacities, this microscope would be beneficial to medicine, biology, semiconductor inspection, device analysis and quality control, as well as with multiphoton and fluorescence microscopes to image large fields with high resolution.
Owner:ALFANIX TECH
Sensor for microscopy
ActiveUS20120287256A1Efficient change of focus depthColor television detailsClosed circuit television systemsX-CoordinateMicroscopy
This invention pertains to a method for microscopically imaging a sample, with a digital scanner comprising a sensor including a 2D array of pixels and to a digital scanning microscope carrying out this method. It is notably provided a method for microscopically imaging a sample with a scanner comprising a sensor including a 2D array of pixels in an XY coordinate system, the axis Y being substantially perpendicular to the scan direction, wherein the scanner is arranged such that the sensor can image an oblique cross section of the sample, and wherein the method comprises the steps of: • activating a first sub-array of the 2D array of pixels, the first sub-array extending mainly along the Y axis at a first X coordinate (X1), • creating a first image by imaging a first area of the sample by means of the first sub-array of pixels. According to aspects of the invention, it is further proposed a scanner carryout this method and using the same 2D array sensor for imaging and auto-focusing purpose.
Owner:KONINKLIJKE PHILIPS ELECTRONICS NV
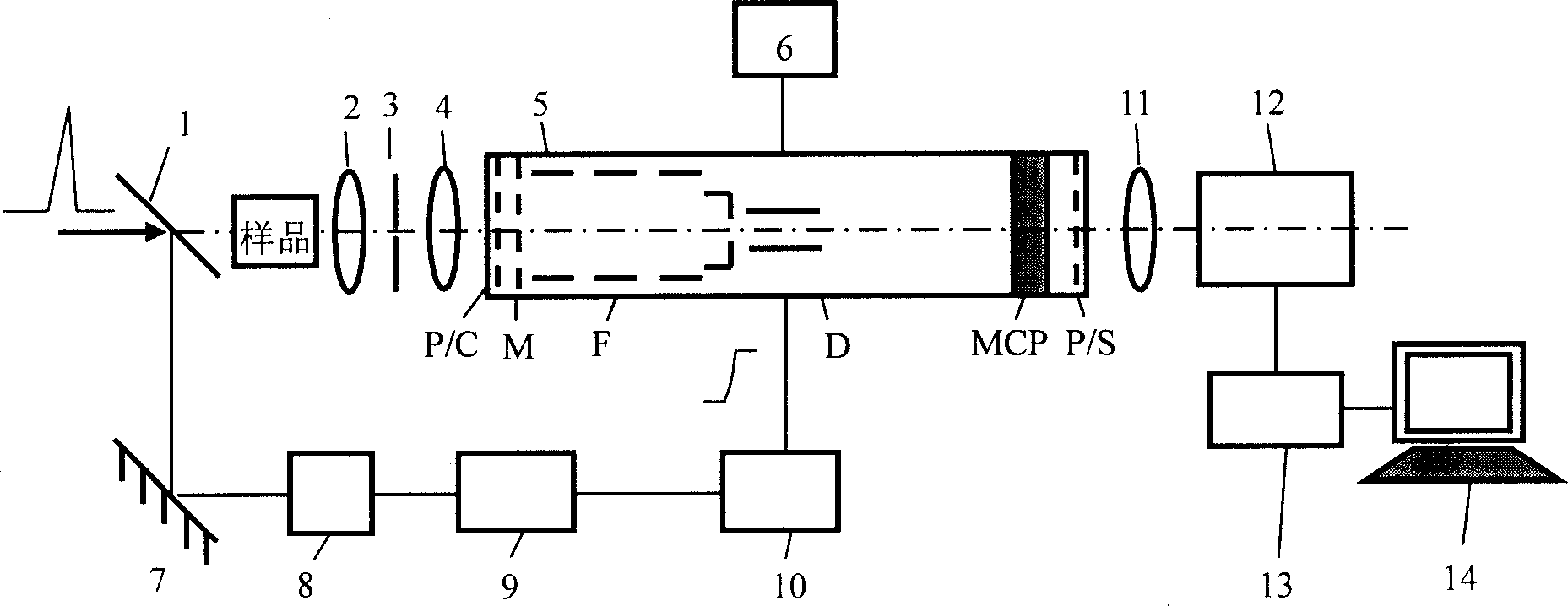
Microscopic imaging techniques
A method of performing 3D photoactivation microscope imaging includes providing a sample having a plurality of probes, each of the plurality of probes including a photo-activatable material. Probes from the plurality of probes are activated to form a sparse subset of probes, the sparse subset of probes having probes that are spatially separated by at least a microscope resolution. The sample is illuminated with a readout light source, and light emitted from activated probes is detected. Based on the light emission detected from the activated probes, localized three-dimensional positions of the activated probes are obtained.
Owner:JACKSON LAB THE +1
Method and system of laser scanning phase-microscope imaging
InactiveCN102841083AEnabling label-free imagingReduce complexityMicroscopesFluorescence/phosphorescenceLaser scanningGalvanometer
The invention relates to a method and a system of laser scanning phase-microscope imaging. The system comprises a fluorescence microscope, a laser confocal laser scanning system and a photoelectric detection system, wherein the laser confocal laser scanning system is arranged in a light inlet hole of the fluorescence microscope; the photoelectric detection system is arranged at a light outlet direction of the laser confocal laser scanning system; an angle between each adjacent optical elements is regulated; a sample slice is arranged on a testing table; a fluorescence medium is added on the top of a glass slide; after being focused and in beam expansion through a dichroscope, an X-directional scanning galvanometer, a Y-directional scanning galvanometer, a scanning mirror and a tube lens, exciting light generated by the laser launches to an object lens and is focused on a biological sample; the exciting light focused on the biological sample launches to the fluorescence medium through the biological sample; the fluorescence medium is excited by the exciting light so as to launch fluorescence; the fluorescence shines and returns along the original light path through the biological sample; the emergent fluorescence launches to a filter and is focused through a convergent lens so as to enter a needle hole; the fluorescence exited by the needle hole is received and processed through the photoelectric detection system so as to obtain a relief structure of the biological sample. The method and system provided by the invention can be widely used in an imaging process of the biological sample.
Owner:PEKING UNIV
Ultra-high resolution optical microscope imaging method and device
InactiveCN102033308AIncrease contrastHigh resolutionScattering properties measurementsTransmissivity measurementsMicroscopic imageMicro nano
The invention discloses an ultra-high resolution optical microscope imaging method and device. In the technical scheme, a special lighting illumination and microscope imaging method combining narrow-band filtering, annular aperture and dark-filed illumination is adopted, and annular transmitting apertures with different numerical apertures, transmittances and filtering characteristics are designed, so that the ultra-high resolution and high-contrast microscope imaging on a micro-nano-sized substance can be realized. The device comprises a high-resolution optical microscope system consisting of an LED (light-emitting diode) lighting source, a light barrier, an annular transmitting hole, a condensing lens, a sample platform, a light-shading wafer, a microscope objective and a microscope image collecting and processing system, wherein the microscope image collecting and processing system consists of a CCD (Charge Coupled Device) image sensor, an imaging collecting card and a computer. The invention can maintain the real-time, direct and non-scanned imaging observation way of conventional optical microscopes, and also embodies excellent resolution and imaging contrast.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV
Defect observation method and device therefor
InactiveUS20140204194A1Semiconductor/solid-state device testing/measurementSolid-state devicesRefractive indexScanning electron microscope
This invention relates to a method for performing an analysis of defective material and the refractive index, and a three-dimensional analysis of very small pattern shapes including the steps of imaging by a scanning electron microscope to acquire an image of the position of a defect under observation using information of inspection results obtained by an optical inspection device, creating a model of the defect by using the acquired image of the defect under observation, calculating the values detected by the detector when reflected and scattered light emitted from a defect model is received by the detector when light is irradiated onto the defect model thus created, comparing the detection values thus calculated and the values detected by the detector, which has received light actually reflected and scattered from the sample, to obtain information relating to the height of the defect under observation, the material, or the refractive index.
Owner:HITACHI HIGH-TECH CORP
Living cell laser scanning co-focusing microscope imaging system
InactiveCN102621117ACompact structureHigh precisionMicroscopesFluorescence/phosphorescenceFluorescenceLaser scanning
The invention relates to a living cell laser scanning co-focusing microscope imaging system, which is characterized by comprising a laser scanning co-focusing microscope and a fluorescent signal collecting device, wherein the fluorescent signal collecting device comprises a culture dish, a converging lens and a reflecting type narrow-band light filter, the converging lens and the reflecting type narrow-band light filter are arranged in the culture dish, the bottom of the culture dish is provided with a culture dish bottom plate used for placing cells to be tested, the converging lens is fixedly arranged on the culture dish through a lens clamping frame, the cells to be tested on the culture dish bottom plate are positioned on the focal plane of the converging lens, the reflecting type narrow-band light filter is positioned right above the converging lens, and an objective lens of the laser scanning co-focusing microscope is positioned right under the culture dish bottom plate. The living cell laser scanning co-focusing microscope imaging system has the advantages that the structure is compact, the precision is high, the fluorescent signal collection efficiency of the laser scanning co-focusing microscope can be effectively improved, the phototoxicity and the light bleaching degree are reduced, and a technical means is provided for obtaining reliable experiment results.
Owner:FUJIAN NORMAL UNIV
Total reflection near-field microscope combining with magnetic forceps for observing biomacromolecule
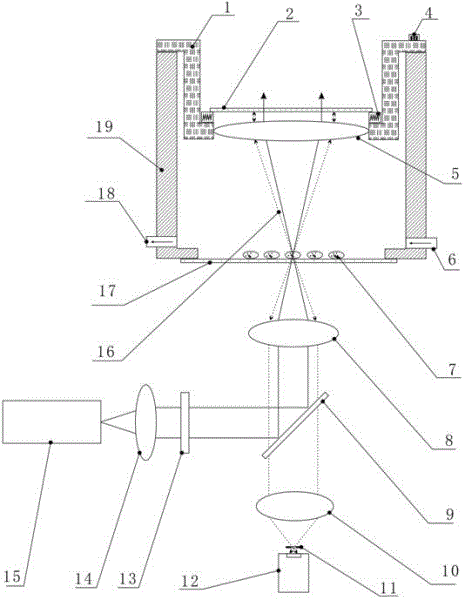
InactiveCN101042326AHigh measurement accuracyReduce sizeSurface/boundary effectMaterial analysis by optical meansProcess systemsForceps
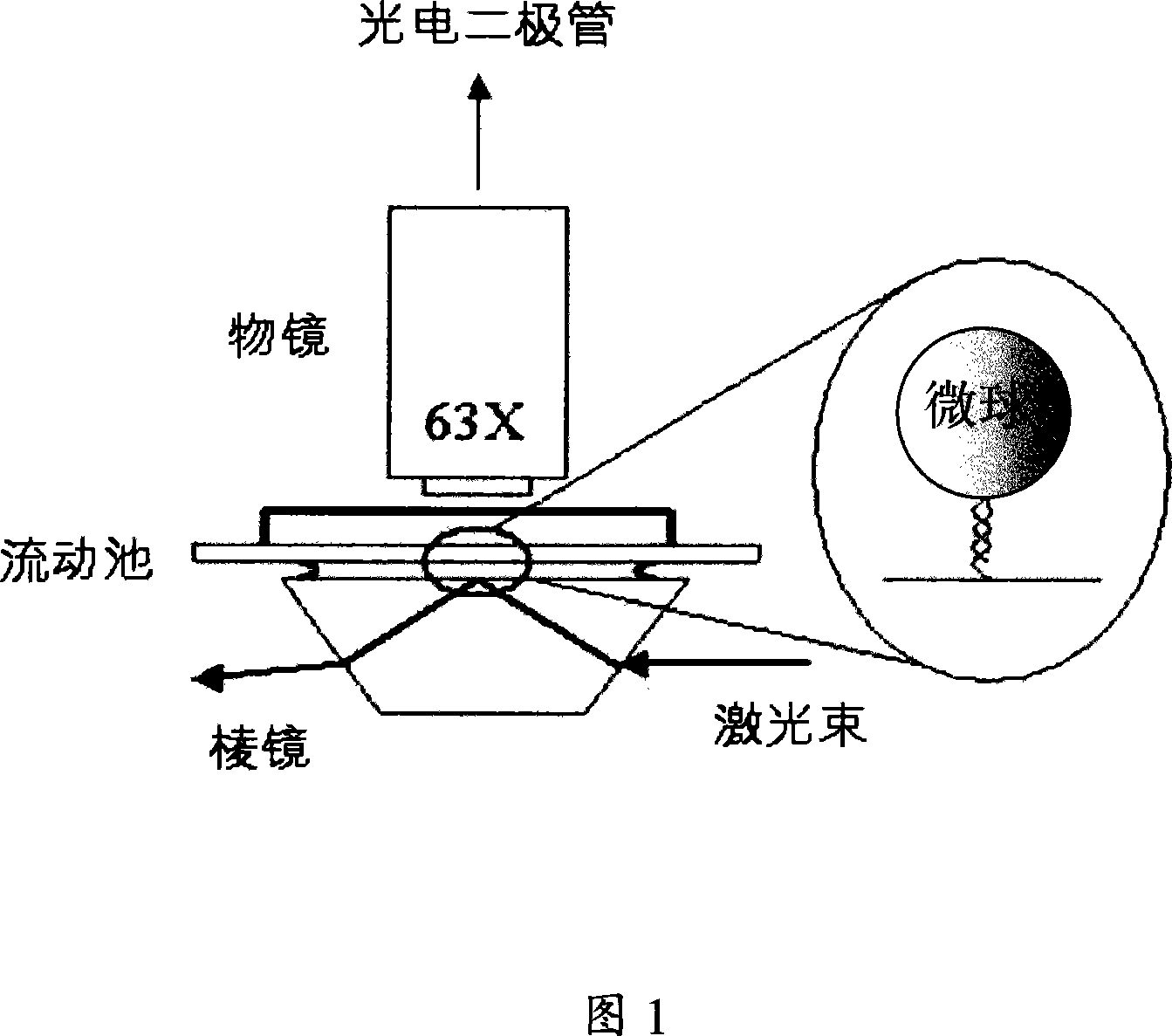
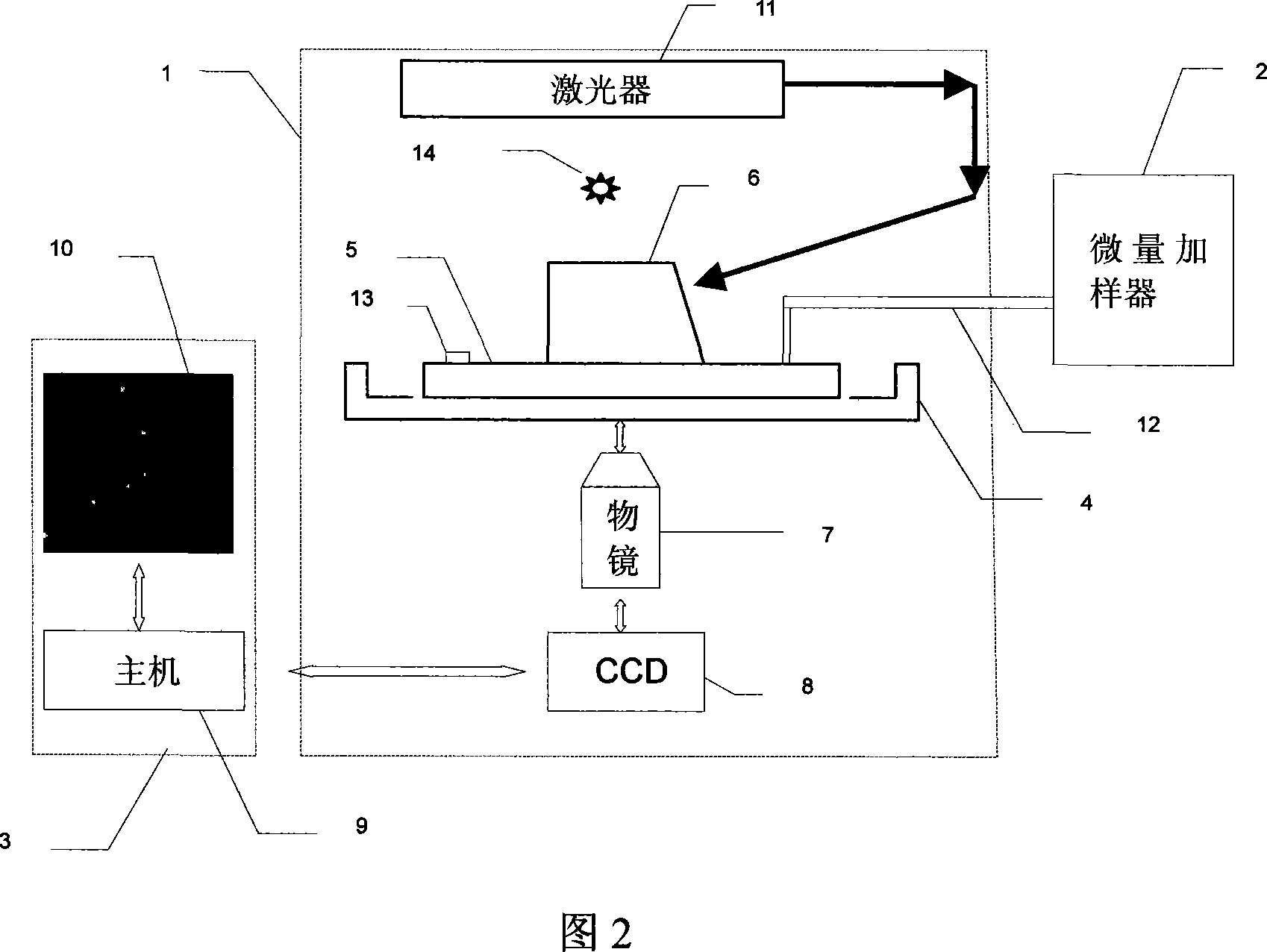
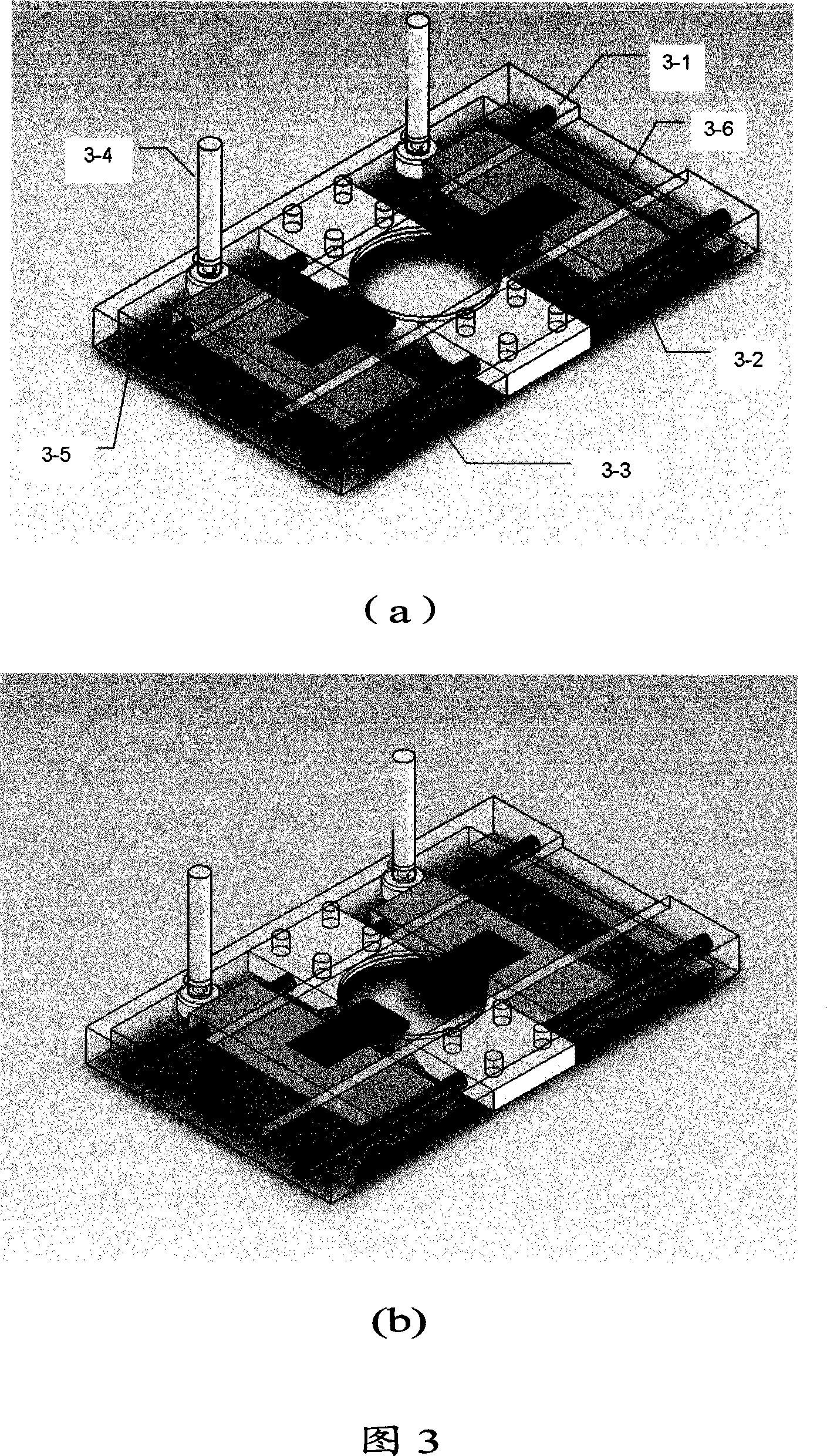
This invention relates to one whole reflection near field microscope to observe biology molecule, which comprises microscope lens imaging system, micro adding device, central process system, magnetic nipper control bench and sample reaction tank, wherein, the control bench comprises main sample bench, slide block, magnetic nipper, slide block control handle, slide axis and middle concave tank; the bench is fixed with magnetic nipper and control device and its middle concave tank is to fix sample reaction tank; the sample reaction tank is set on transparent closed system with both ends opened with sample supply; the inner biology large molecule one end is connected to upper surface and with other end connected with magnetic ball.
Owner:INST OF PHYSICS - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Laser scanning confocal microscope imaging system
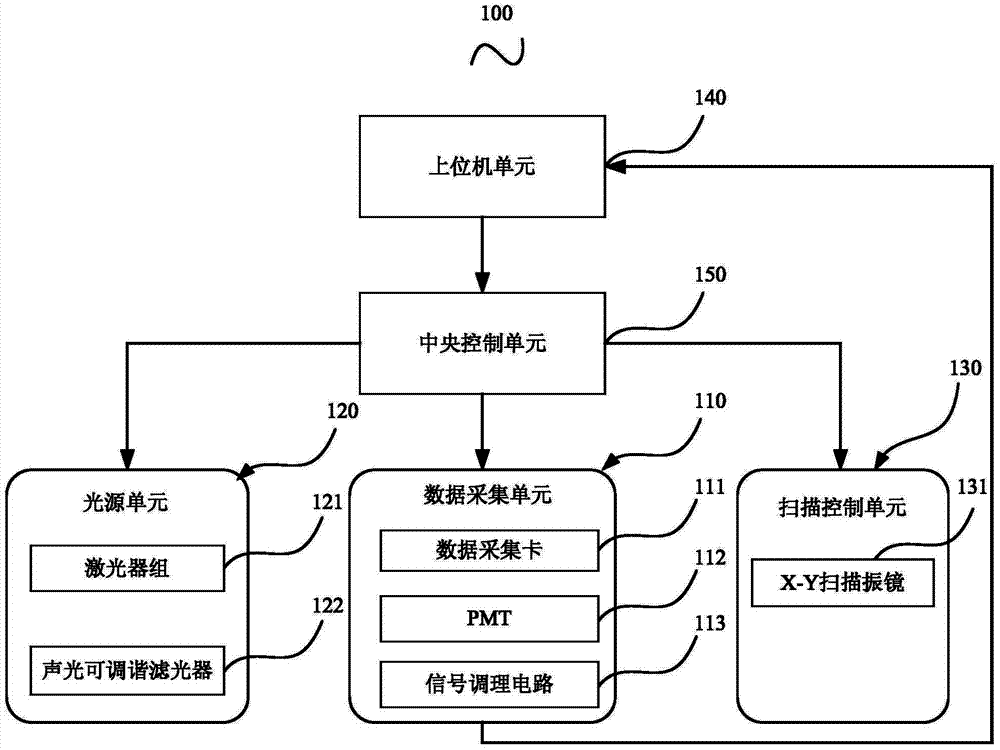
ActiveCN103616760ARealize scanning imagingSatisfactory signal to noise ratioMicroscopesFluorescence/phosphorescenceSignal-to-noise ratio (imaging)Imaging quality
The invention provides a laser scanning confocal microscope imaging system which comprises a data collecting unit, a light source unit, a scanning control unit, an upper computer unit and a central control unit. By means of the upper computer unit, fluorescence intensity data are collected and scanning parameter of the imaging system are calculated according to the fluorescence intensity data, the central control unit generates a control signal of the data collecting unit, the light source unit and the scanning control unit according to the scanning parameters sent by the upper computer unit, and scanning and imaging of a sample to be detected are achieved. Accordingly, a scanned image with a satisfying signal-to-noise ratio is obtained, and imaging quality is improved.
Owner:SUZHOU INST OF BIOMEDICAL ENG & TECH CHINESE ACADEMY OF SCI
Super-resolution imaging method based on fluorescence resonance energy transfer
ActiveCN102830101ASuper-resolution imaging methods are fastSuper-resolution imaging method is simpleMicroscopesFluorescence/phosphorescenceLuminous intensityLaser scanning
The invention discloses a super-resolution imaging method based on fluorescence resonance energy transfer (FRET). The super-resolution imaging method comprises the following steps: 1) marking a sample to be detected with a fluorescent probe having high FRET efficiency, wherein the fluorescent probe having high FRET efficiency has a marked FRET molecule pair, the FRET molecule pair includes a first fluorophore (a donor) and a second fluorophore (a receptor), and the first fluorophore can exert FRET on the second fluorophore; and 2) carrying out laser scanning confocal microscope imaging at an excitation light threshold with an excitation light intensity capable of allowing the FRET molecule pair in the step 1) to generate FRET. A super resolution technology based on saturated FRET in the invention can realize super resolution imaging of a biological sample on an ordinary laser confocal microscope, and the method provided by the invention has high resolution.
Owner:SHANGHAI INST OF APPLIED PHYSICS - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Universal liquid crystal adaptive aberration correcting retina imaging system
The invention belongs to the technical field of microscope imaging, relates to a high-order aberration correcting optical design for high-ametropia human eyes, and discloses a universal liquid crystal adaptive aberration correcting retina imaging system. An LCD screen is adopted for displaying a sighting target point light source, and the sighting target is designed into an E shape so that the self-adjusting effect of visibility is enhanced; and meanwhile, E-shaped micro displacement is easily controlled on the LCD screen so that the position of an imaging area can be quantitatively changed. Through the sign of a plurality of key devices, the universality of the liquid crystal adaptive system in fundus imaging is improved, the problem of difficult clear imaging of the fundus adaptive imaging technology under the condition of over 800-degree myopia or 200-degree astigmatism can be solved, and the system can acquire a high-resolution retina image on the human eye of 200-degree astigmatism.
Owner:CHANGCHUN INST OF OPTICS FINE MECHANICS & PHYSICS CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Imaging thin film structures by scanning acoustic microscopy
InactiveUS20080022774A1Avoid interior spacesIncrease contrastAnalysing solids using sonic/ultrasonic/infrasonic wavesSpecific gravity measurementAcoustic transmissionSemiconductor
A method and apparatus for Scanning Acoustic Microscopy (SAM) for testing of a semiconductor device having a first surface and a second surface with bonding features secured to said first surface are provided. An impervious fixture comprising a dam or a tank retains acoustic transmission fluid in contact with the second surface. Acoustic transmission fluid is excluded from admission to the space surrounding the bonding features where an atmosphere of gas or a vacuum is provided by isolating the first surface from the acoustic transmission fluid either by providing a sealed chamber protecting the first surface or by providing a dam surrounding the second surface.
Owner:IBM CORP
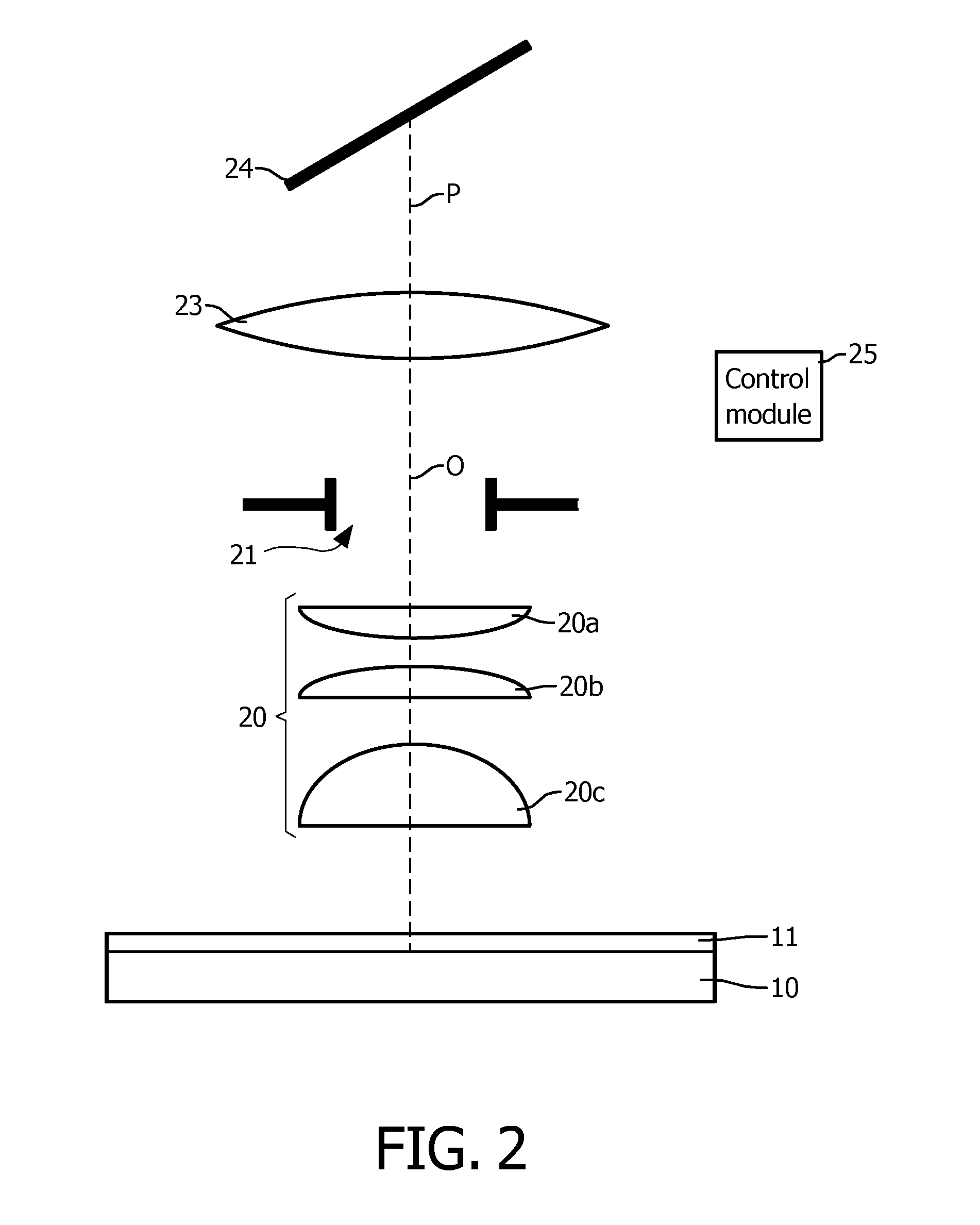
Objective table device for rapidly focusing microscope
The invention discloses an objective table device for rapidly focusing a microscope. The objective table device is composed of an upper objective table, a base, piezoelectric ceramic executors, a pre-tightening spring, a control unit and the like. According to the objective table device for rapidly focusing the microscope, independent or synchronization telescope movements of the three piezoelectric ceramic executors which are fixedly arranged between the upper objective table and the base are controlled to change the horizontal degree or the height of the objective table; the control unit is used for driving the radial displacement of the piezoelectric ceramic executors by adjusting current voltage, changing an inclined direction and an inclined angle of the upper objective table and ascending and descending the upper objective table. The objective table device for rapidly focusing the microscope can be used for various optical microscopes including biological microscopes, integrated type microscopes and the like and can be used as a microscope auxiliary appliance; the imaging effect of the microscope is improved and the difficulty of focusing operation is reduced. The piezoelectric ceramic executors are adopted so that the movement precision of the objective table reaches a 0.1-micron grade, a focusing speed reach an ms grade, and the change of an accurate focusing range which is more than 50 microns is easy to realize. The objective table device for rapidly focusing the microscope has the characteristics of simple structure, easiness for operation and the like; a precision, rapid and accurate focusing scheme is provided for high-magnification microscopic observation.
Owner:JILIN UNIV
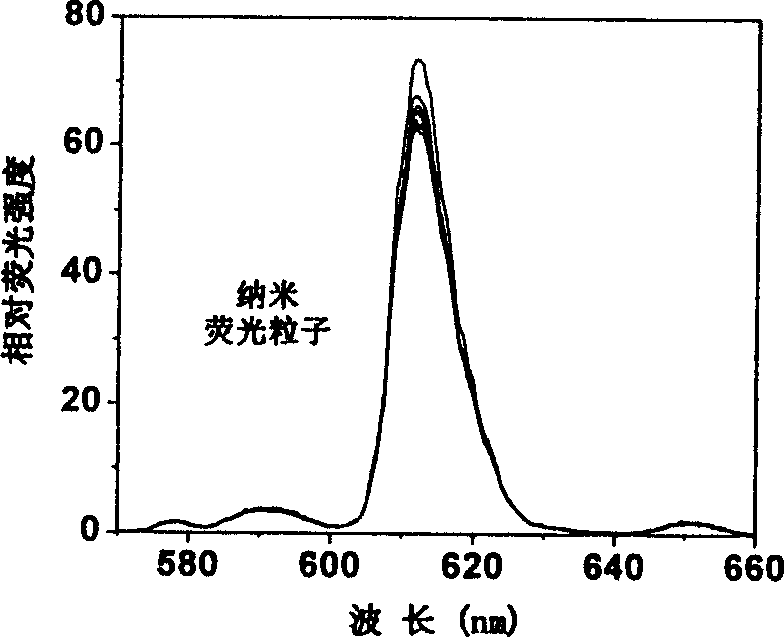
Beta-diketone-trivalent europium complex nano fluorescent probe, its preparation and use thereof
InactiveCN1566954AImprove photostabilityAvoid the phenomenon of "concentration extinction"Biological testingFluorescence/phosphorescenceRare earthFunction group
This invention relates to a kind of beta- diketone-triatomic europium complex nanometer fluorescent probe and its preparation and application. Its steps are the following: the monomer which can copolymarized with silicate ester takes conjugated bonding reaction with beta- diketone-triatomic europium complex in organic solvent and then takes copolymerization with silicate ester to form functional nanometer rare earth fluorescence particles. The said triatomic europium ion, beta - diketone organic complex and the monomer and silicate ester take the mol proportion as 1 : 2-3 : 10-100 : 350-450. The particles is of higher fluorescence and stability and has in its surface with active function group directly used for biological marking and is free of interference of scattered light and short light when used for detecting time-resolution fluorescent. This invention is of high value in fields of time-resolution fluorescent immune detecting, cell chemistry, microscope forming, DNA crossing detecting and biological chip detecting.
Owner:DALIAN INST OF CHEM PHYSICS CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
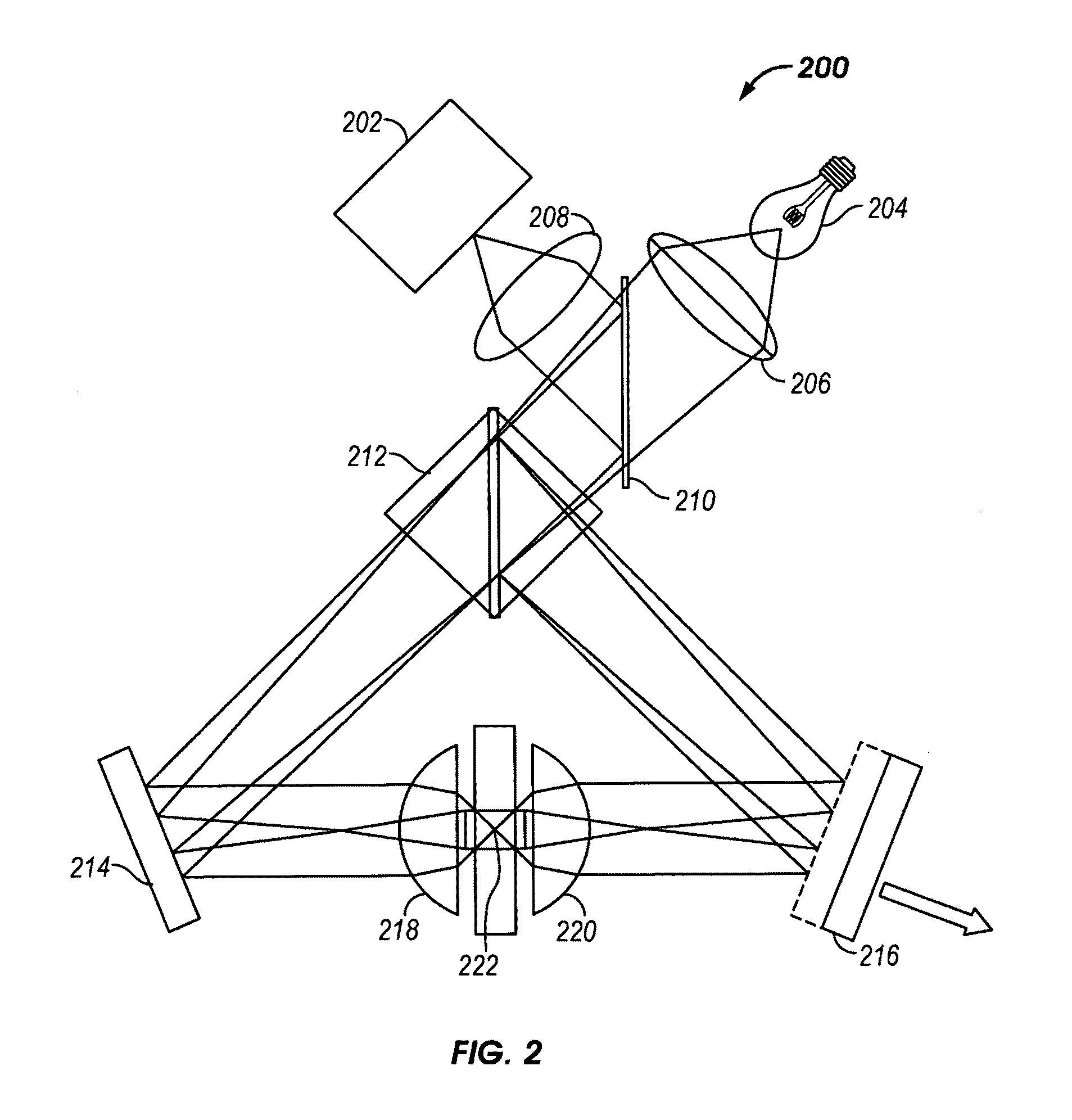
Soft matter comprehensive measuring device based on novel hybrid optical tweezers
InactiveCN102519862AAchieve shapingRestoring Fluorescence Imaging CapabilitiesHydrodynamic testingMicroscopesMeasurement deviceImaging lens
The invention discloses a soft matter comprehensive measuring device based on novel hybrid optical tweezers, comprising a laser, a first planoconvex spotlight, a second planoconvex spotlight, a first reversible reflector, a first reflector, a liquid crystal spatial light modulator, a second reversible reflector, a third planoconvex spotlight, a fourth planoconvex spotlight, a first dichroic mirror, a microscope objective, a two-dimensional electric platform, a halogen lamp, a microscope imaging tube mirror, a second dichroic mirror, a position detector imaging lens, a position detector, a camera and a computer, wherein the device can effectively work in the modes of high precision single optical tweezers and holographic optical tweezers, and the computer is respectively connected with theliquid crystal spatial light modulator, the camera and a position sensor signal inception system through signal lines. According to the invention, the measurement of simultaneous capture operation and interaction of a plurality of particles in liquid phase can be realized, and the measurement of broadband rheology characteristics of a microfluid by using a single particle probe can be realized.
Owner:UNIV OF SCI & TECH OF CHINA
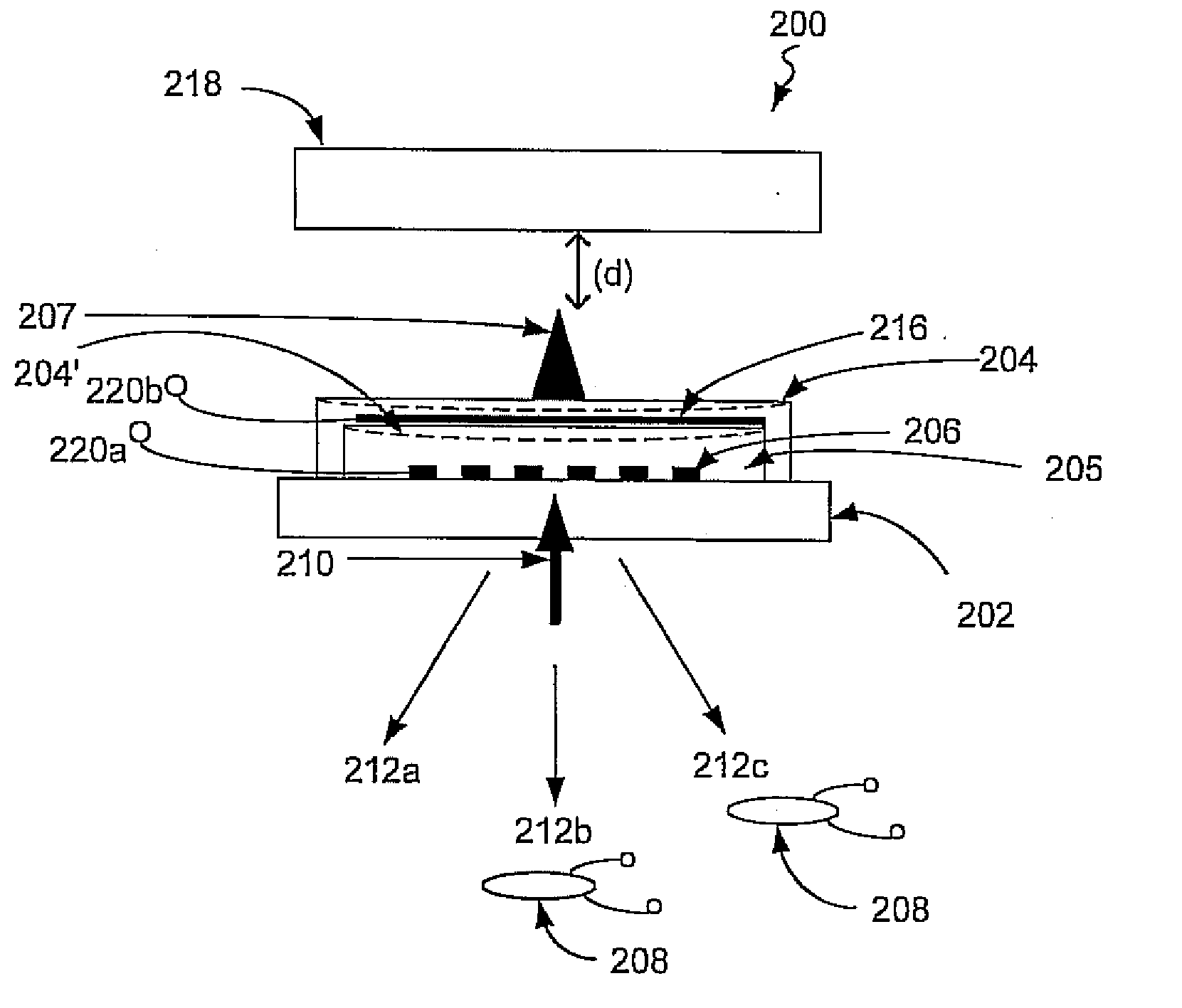
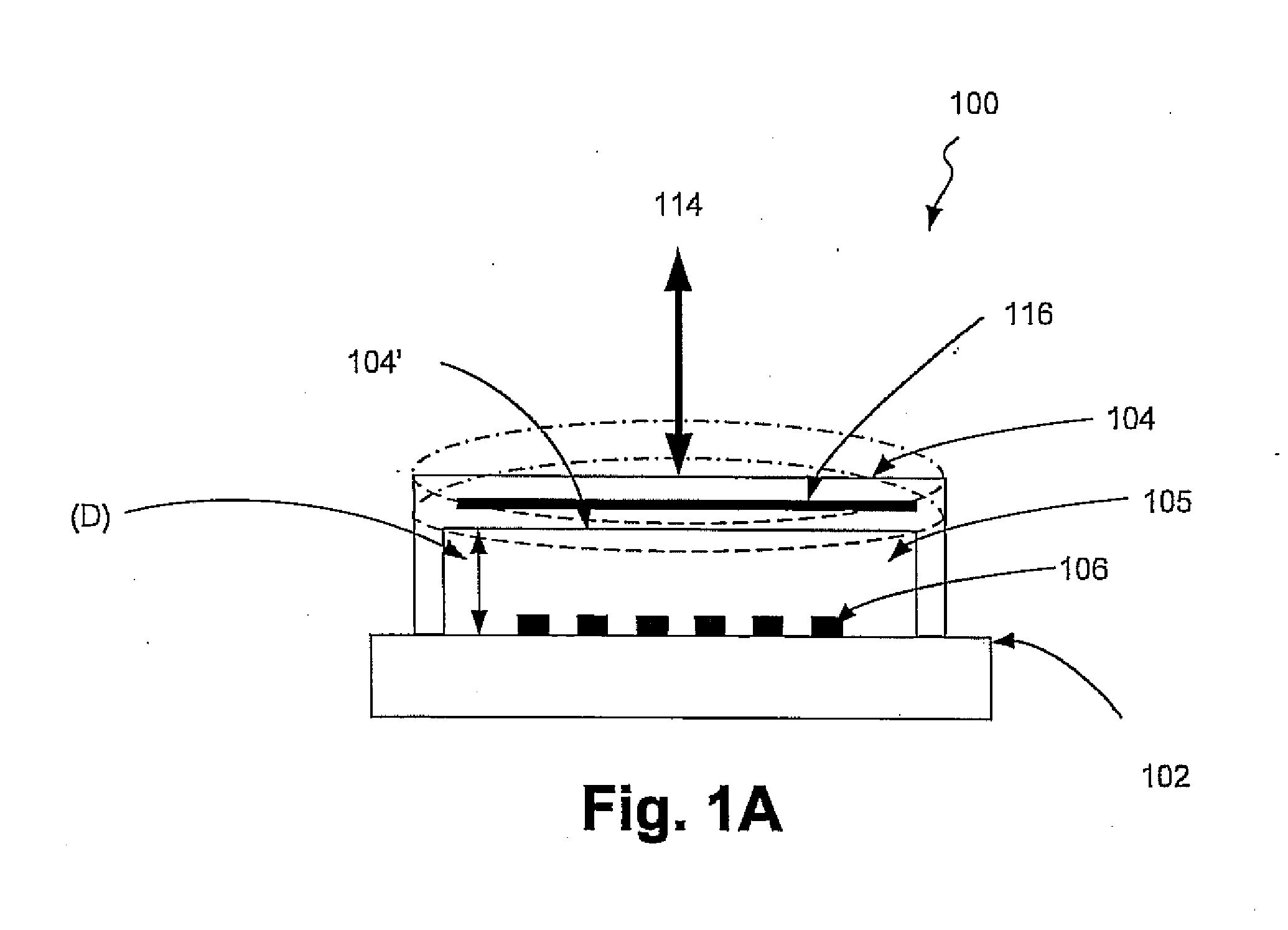
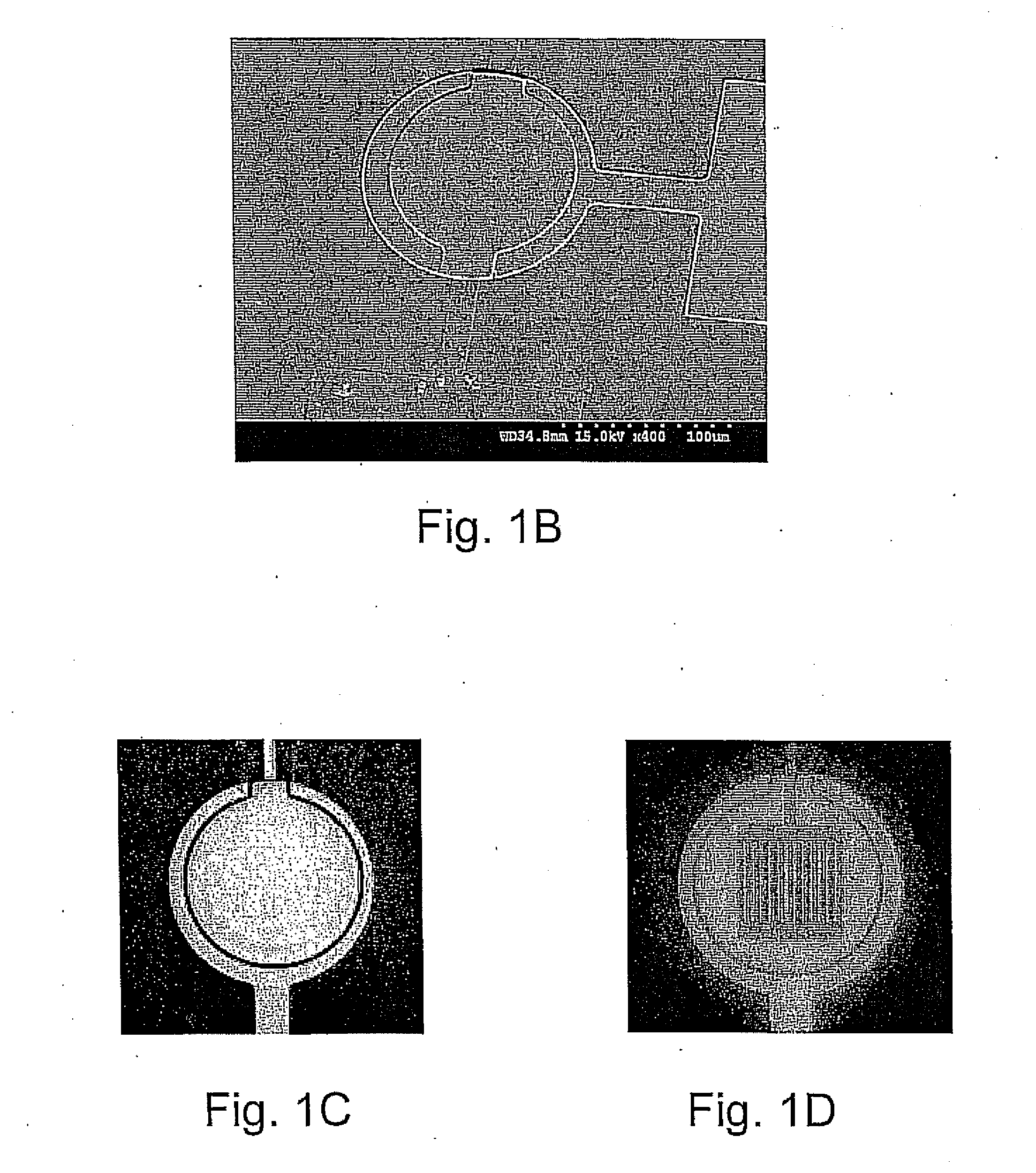
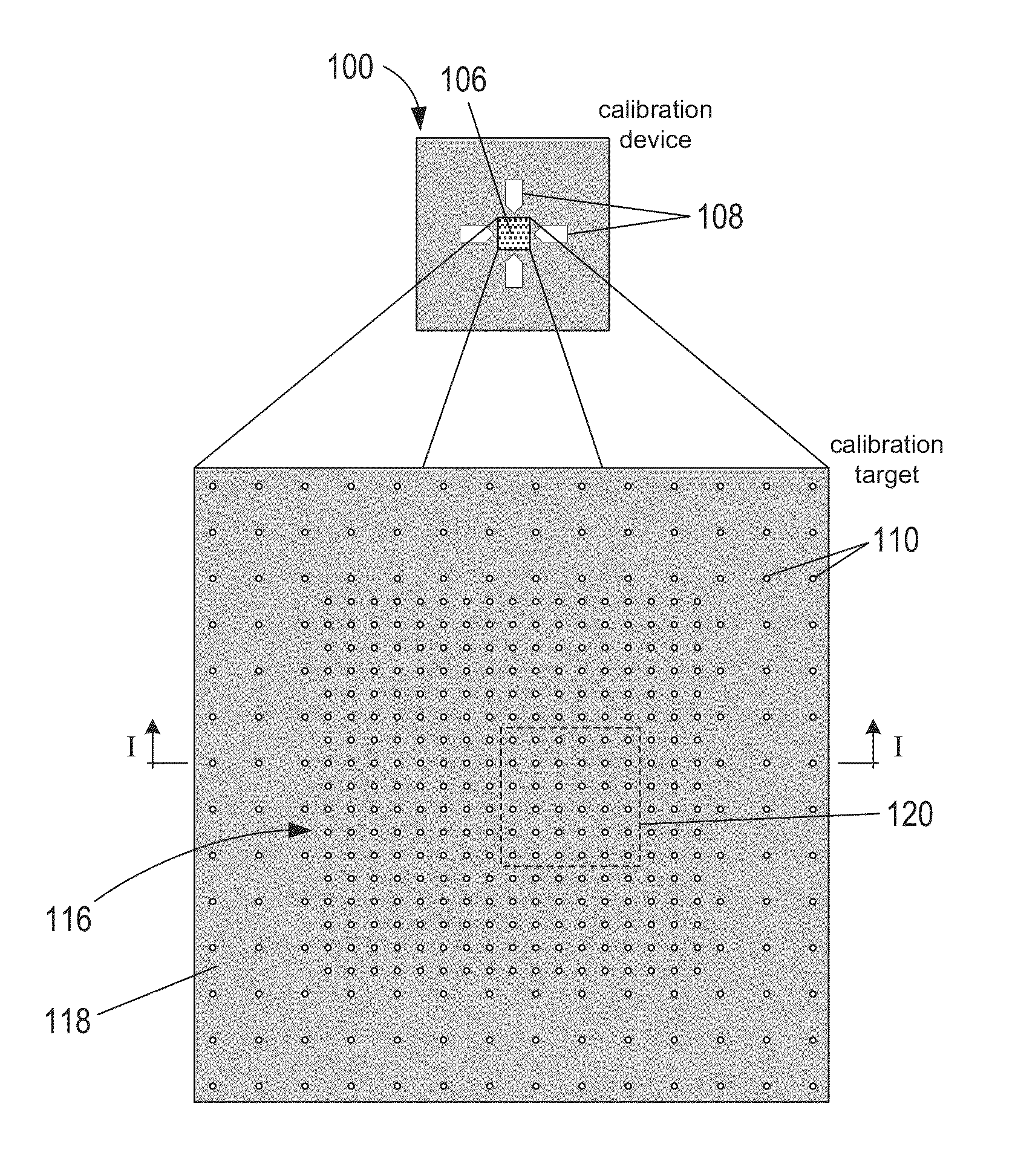
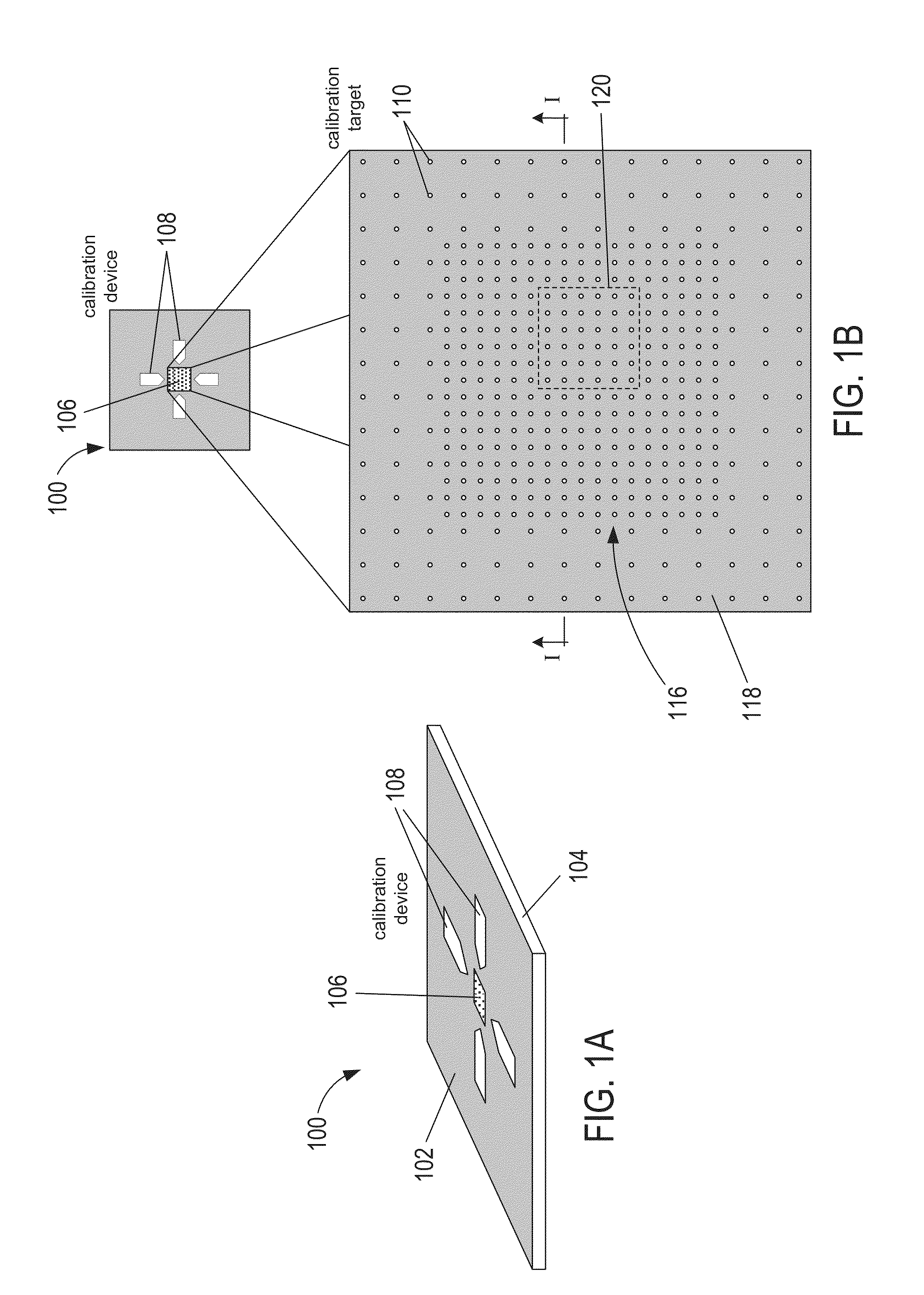
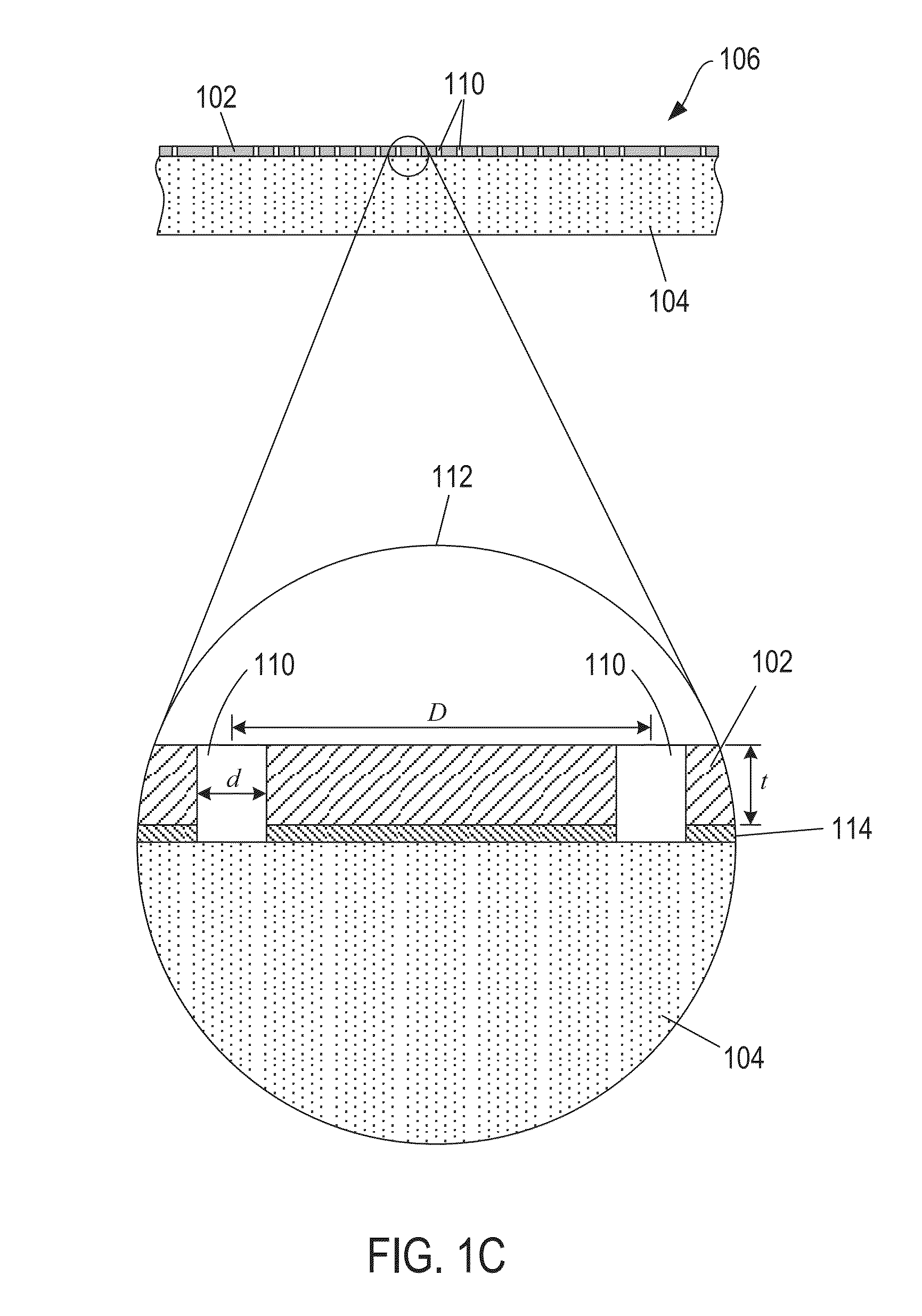
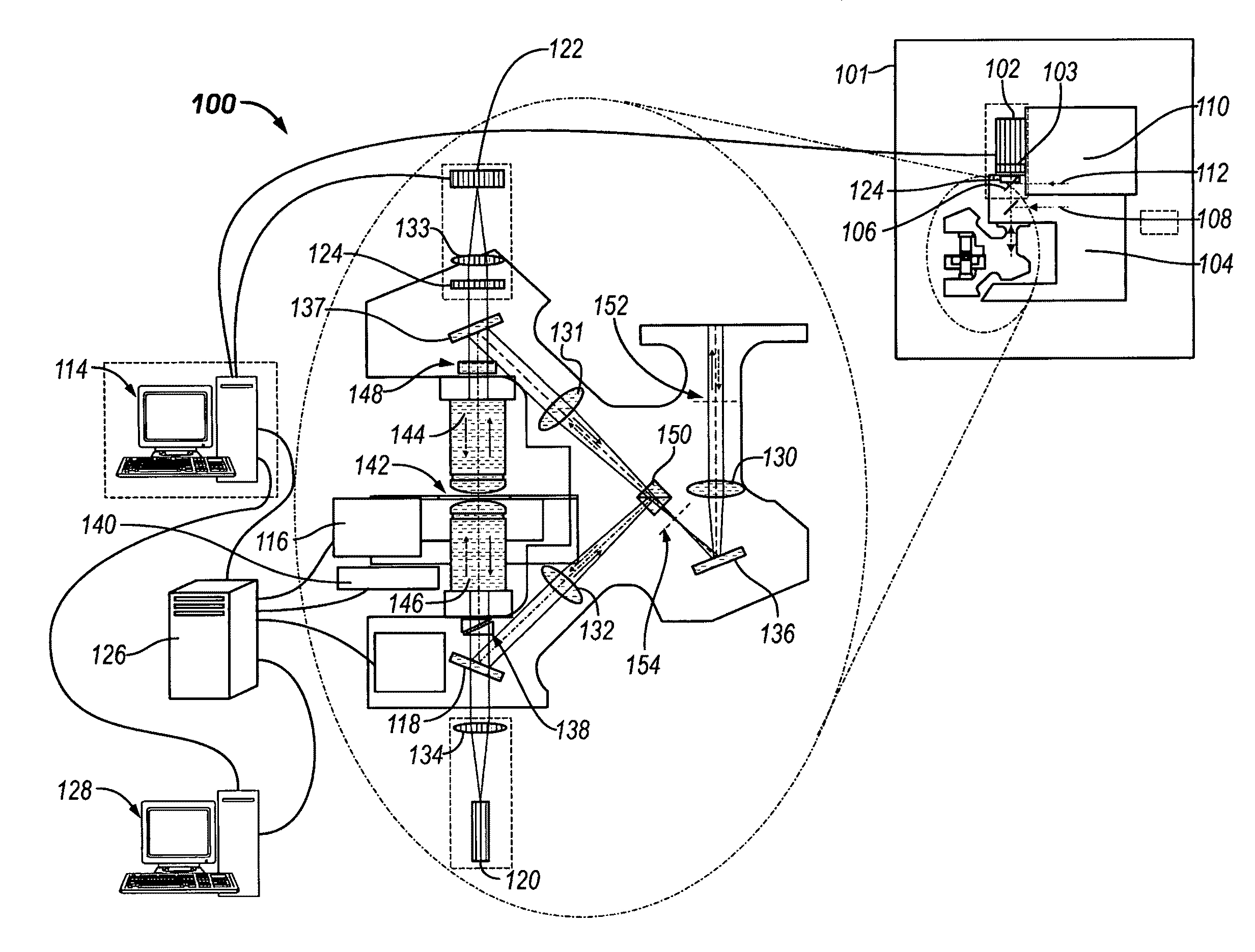
Calibration targets for microscope imaging
ActiveUS20130188035A1Color television detailsClosed circuit television systemsMagnificationImage processing
This disclosure is directed to optical microscope calibration devices that can be used with optical microscopes to adjust the microscope imaging parameters so that images of samples can be obtained below the diffraction limit. The microscope calibration devices include at least one calibration target. Each calibration target includes a number of features with dimensions below the diffraction limit of a microscope objective. Separate color component diffraction limited images of one of the calibration targets are obtained for a particular magnification. The color component images can be combined and image processed to obtain a focused and non-distorted image of the calibration target. The parameters used to obtain the focused and non-distorted image of the calibration target can be used to obtain focused and non-distorted images of a sample for the same magnification by using the same parameters.
Owner:LEICA MICROSYSTEMS CMS GMBH
Microscopic imaging techniques
A method of performing 3D photoactivation microscope imaging includes providing a sample having a plurality of probes, each of the plurality of probes including a photo-activatable material. Probes from the plurality of probes are activated to form a sparse subset of probes, the sparse subset of probes having probes that are spatially separated by at least a microscope resolution. The sample is illuminated with a readout light source, and light emitted from activated probes is detected. Based on the light emission detected from the activated probes, localized three-dimensional positions of the activated probes are obtained.
Owner:JACKSON LAB THE +1
Tool Tips with Scanning Probe Microscopy and/or Atomic Force Microscopy Applications
InactiveUS20100031405A1Large lengthControl shapeConfectioneryCeramic shaping apparatusAtomic force microscopyEngineering
A micro-object is affixed to a mounting structure at a desired relative orientation. The micro-object may be a tool tip optimized to work with particular microscope objectives permitting the tip to be imaged along with the object surface and used to make measurements or modifications through a travel range along the microscope imaging axis equal to or nearly equal to the working distance of the given objective. The tool tip may have a lengths exceeding 80 microns, say up to several millimeters; even the longest tips can have widths of tens of microns.
Owner:KLEY VICTOR B
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com