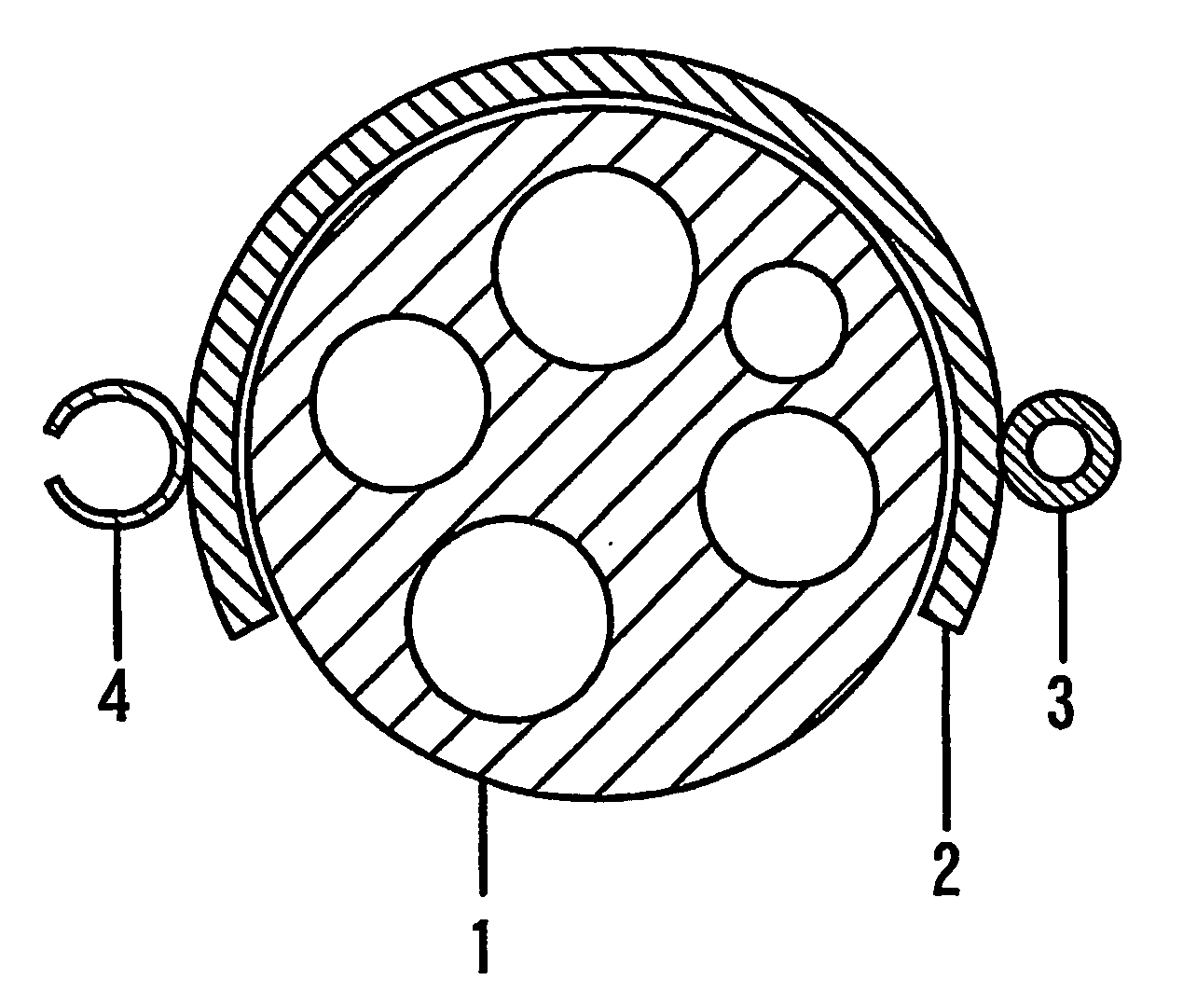
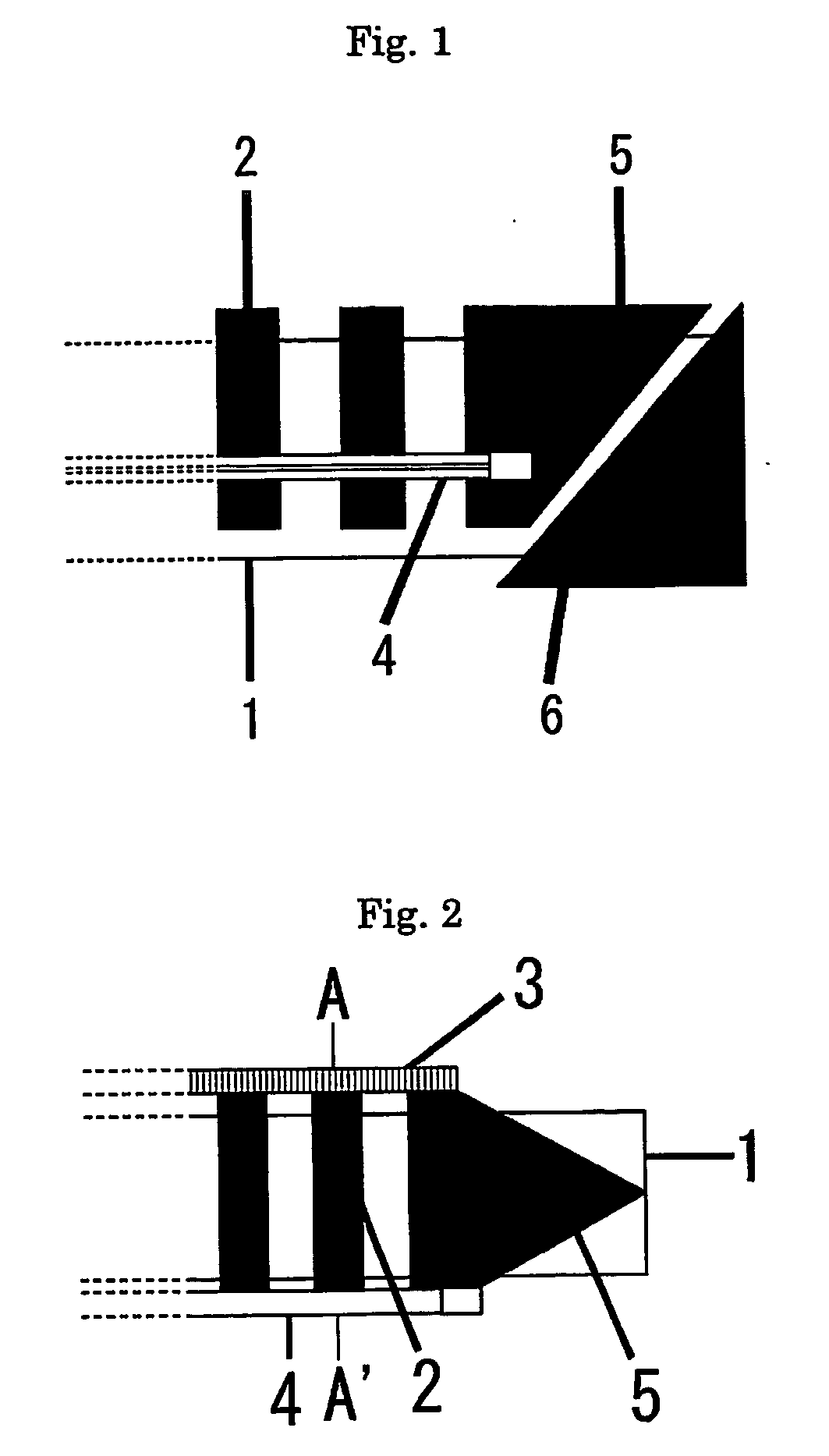
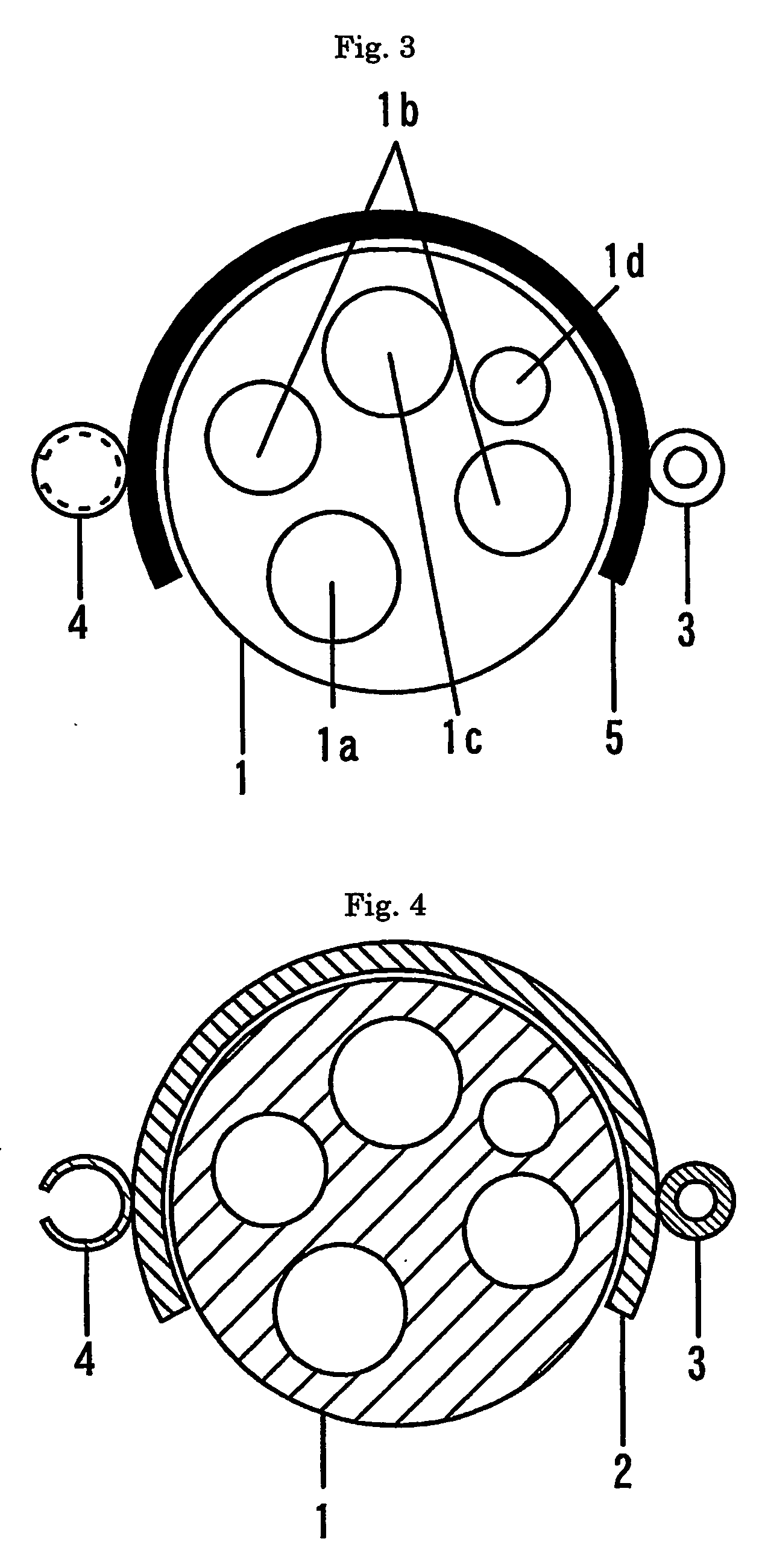
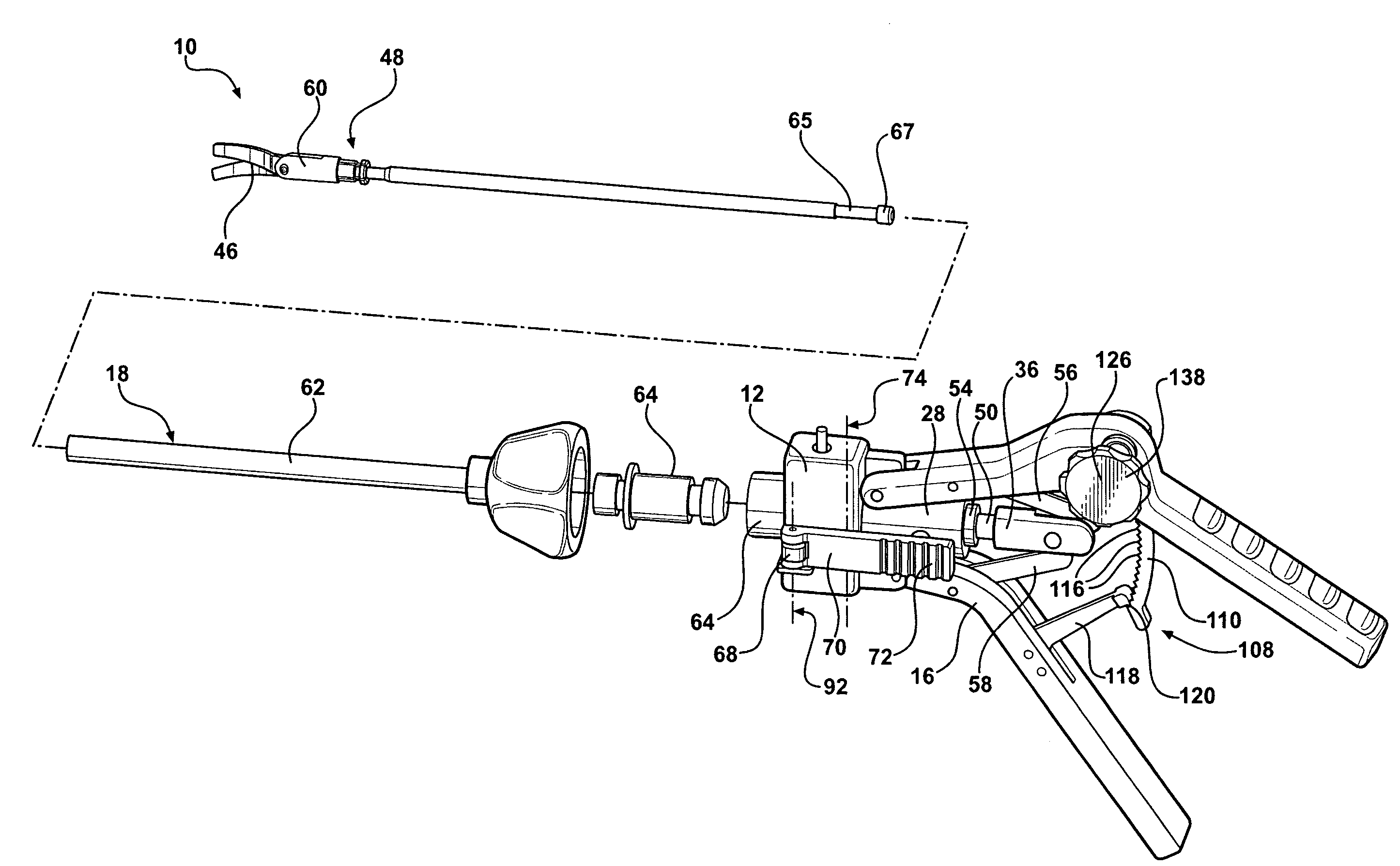
Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
3682 results about "Forceps" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
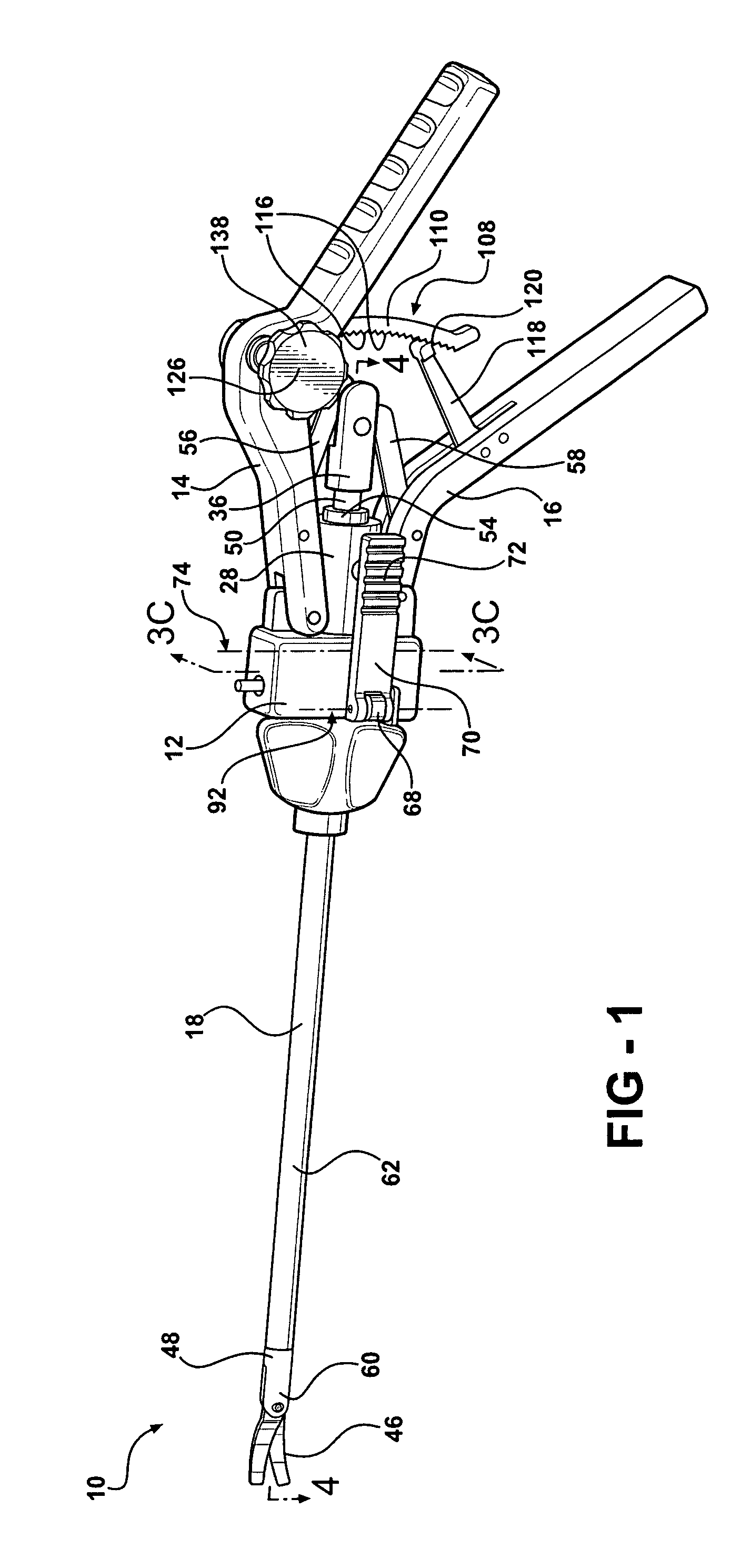
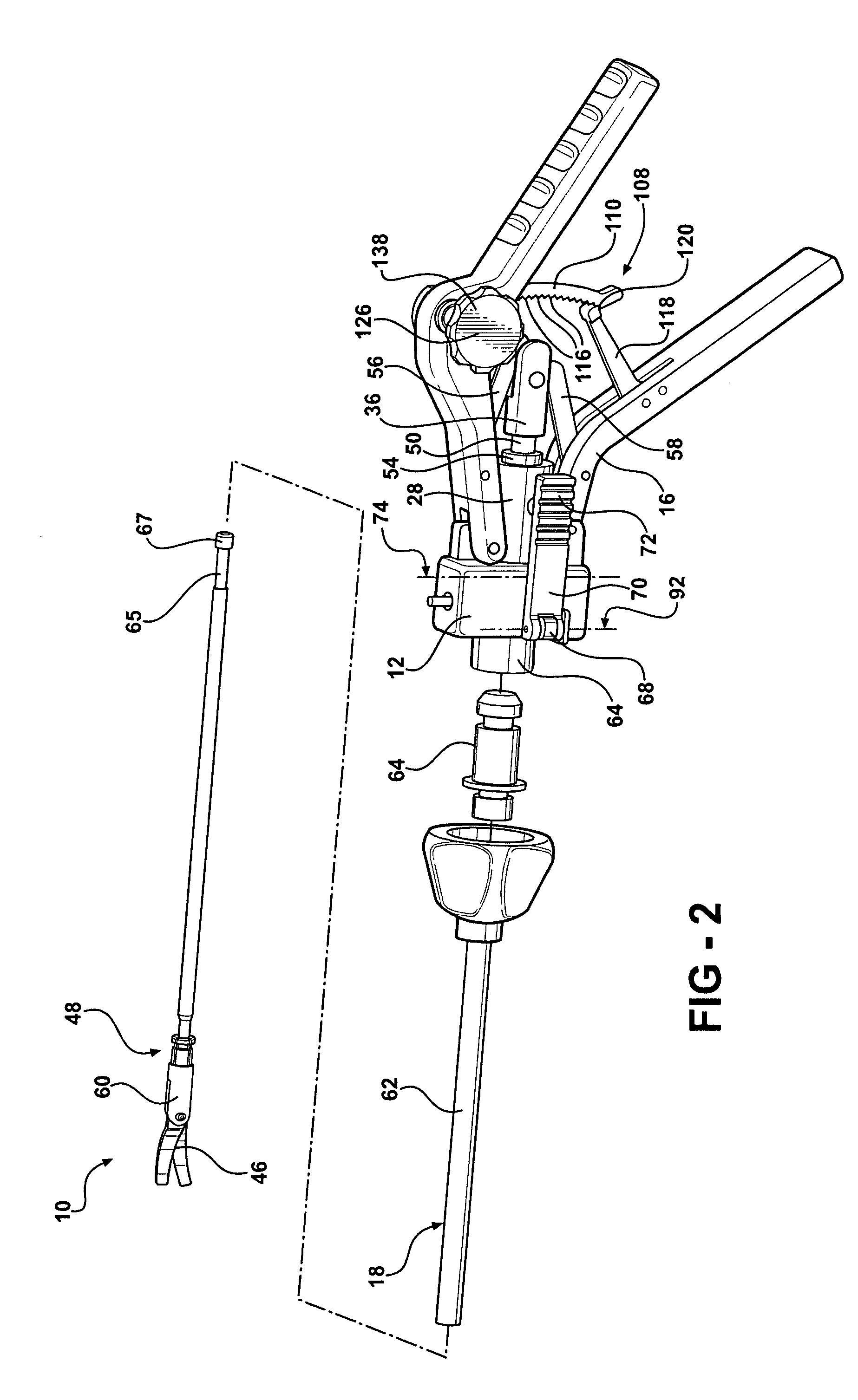
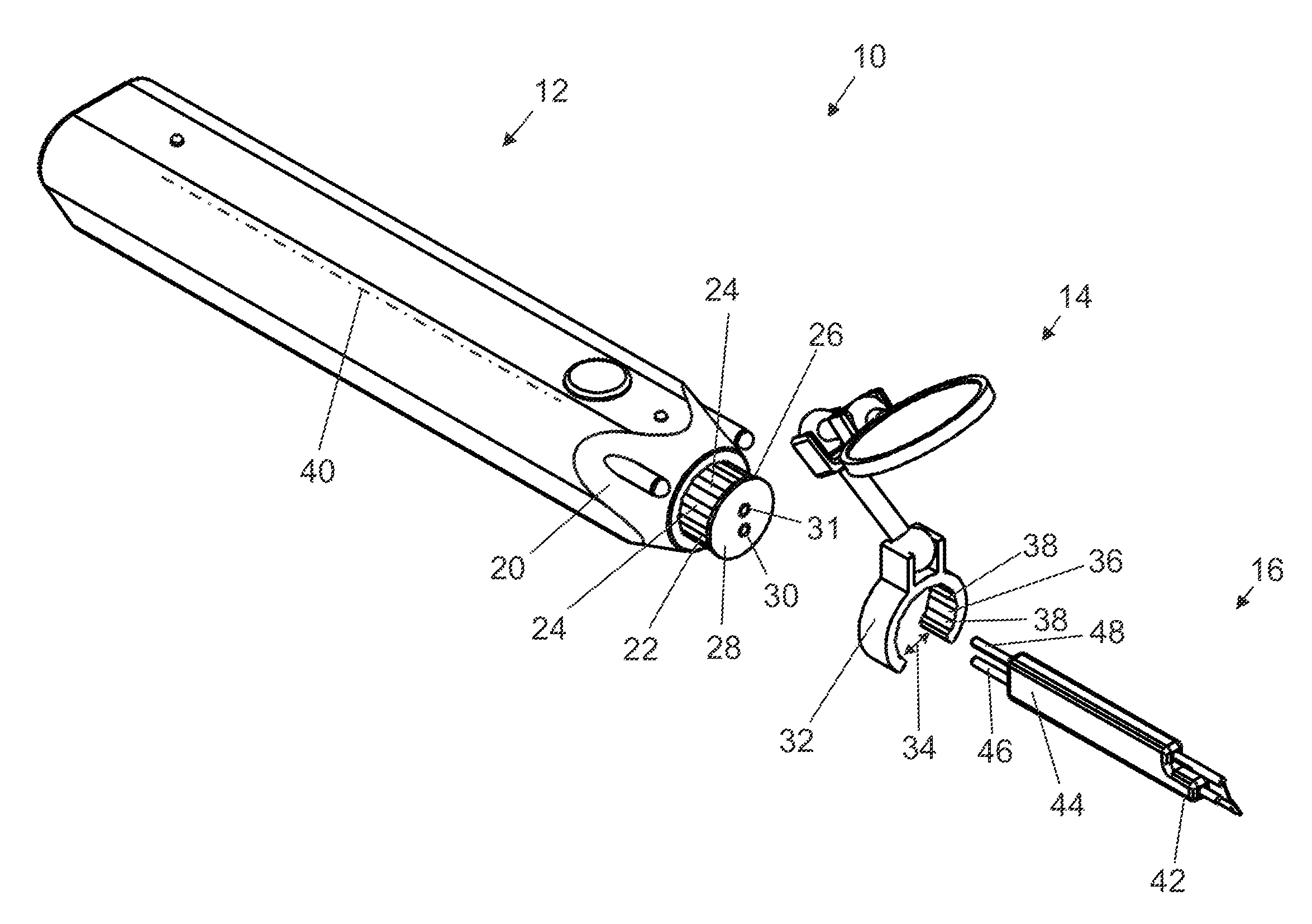
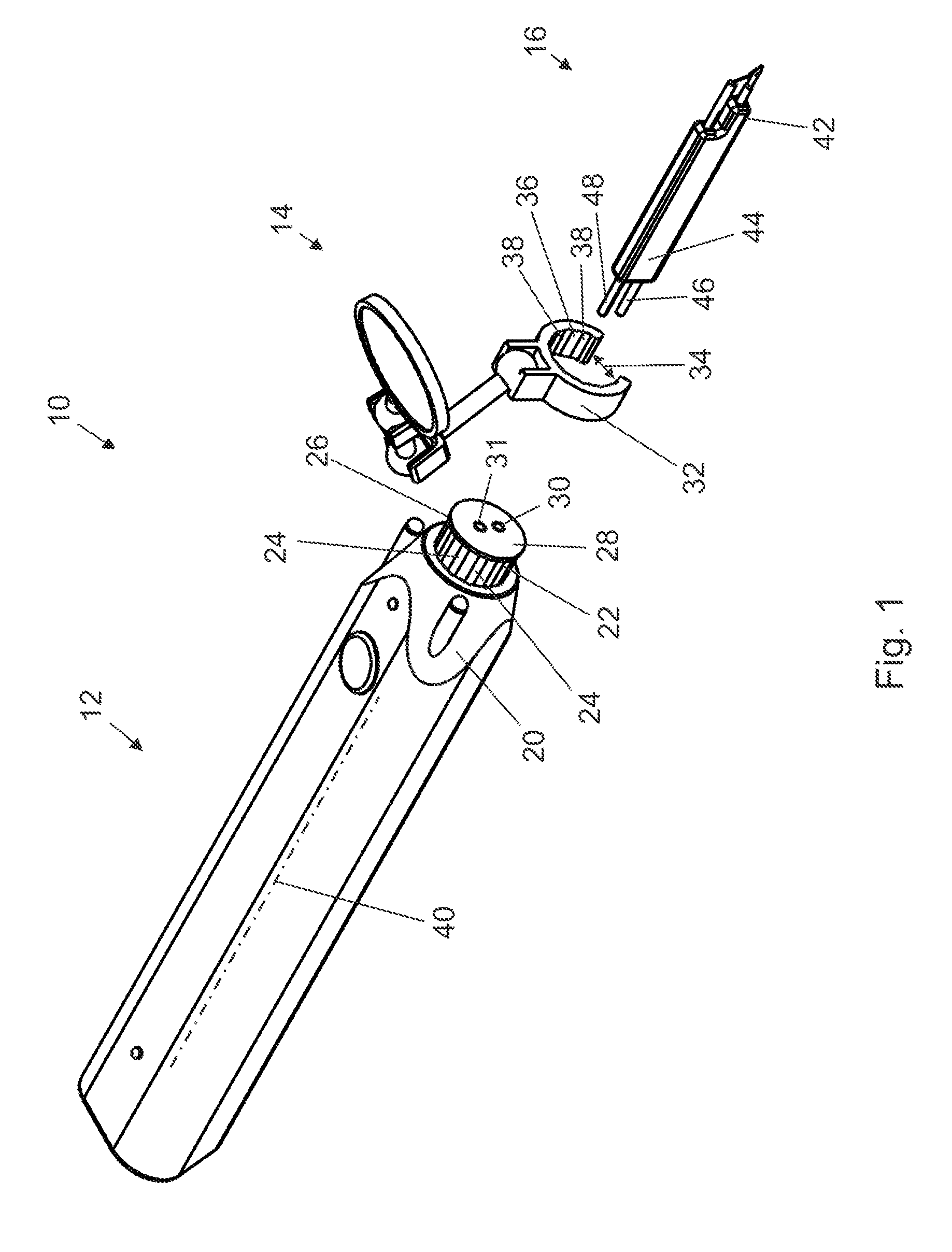
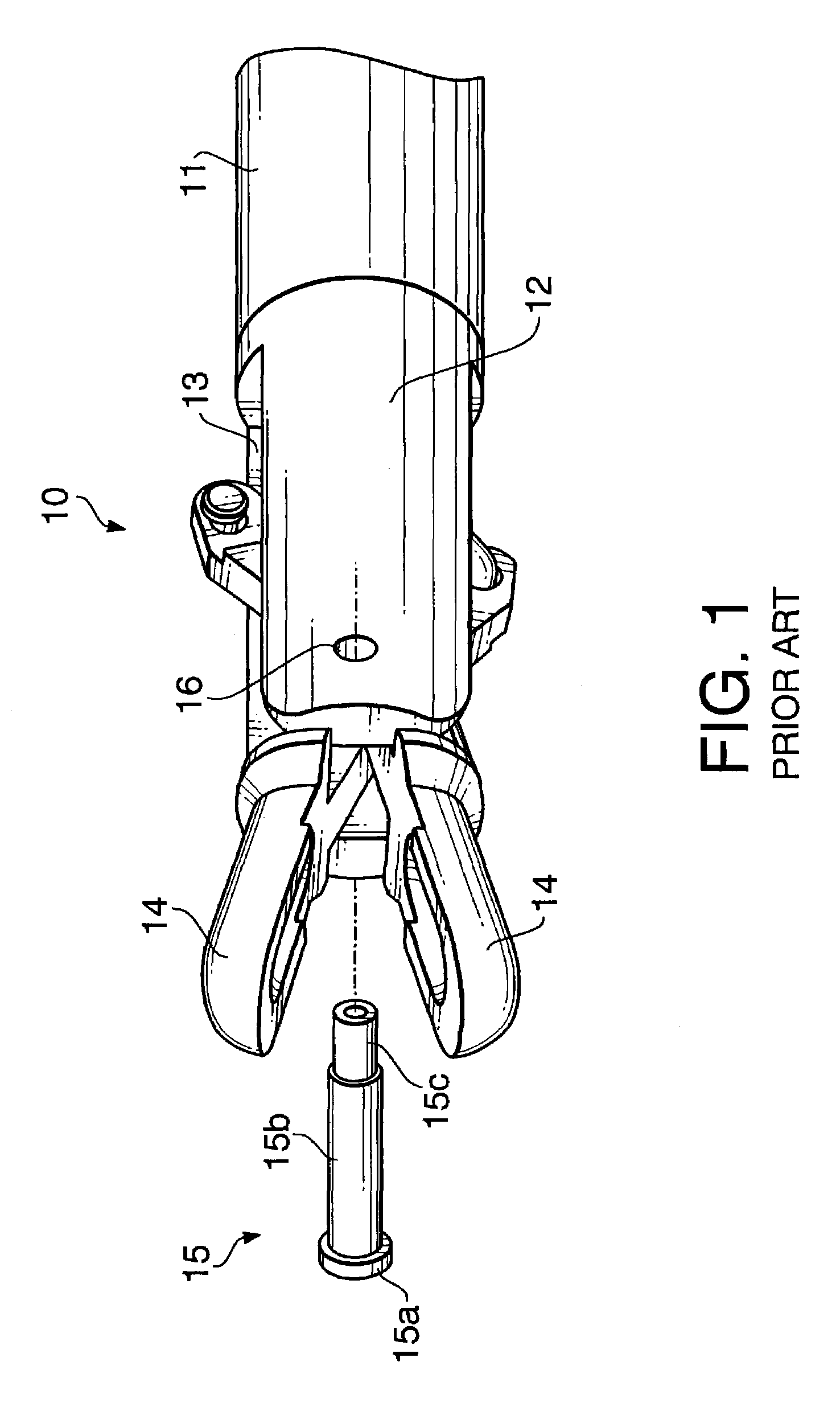
Forceps (plural forceps or considered a plural noun without a singular, often a pair of forceps; the Latin plural forcipes is no longer recorded in most dictionaries) are a handheld, hinged instrument used for grasping and holding objects. Forceps are used when fingers are too large to grasp small objects or when many objects need to be held at one time while the hands are used to perform a task. The term "forceps" is used almost exclusively within the medical field. Outside medicine, people usually refer to forceps as tweezers, tongs, pliers, clips or clamps.
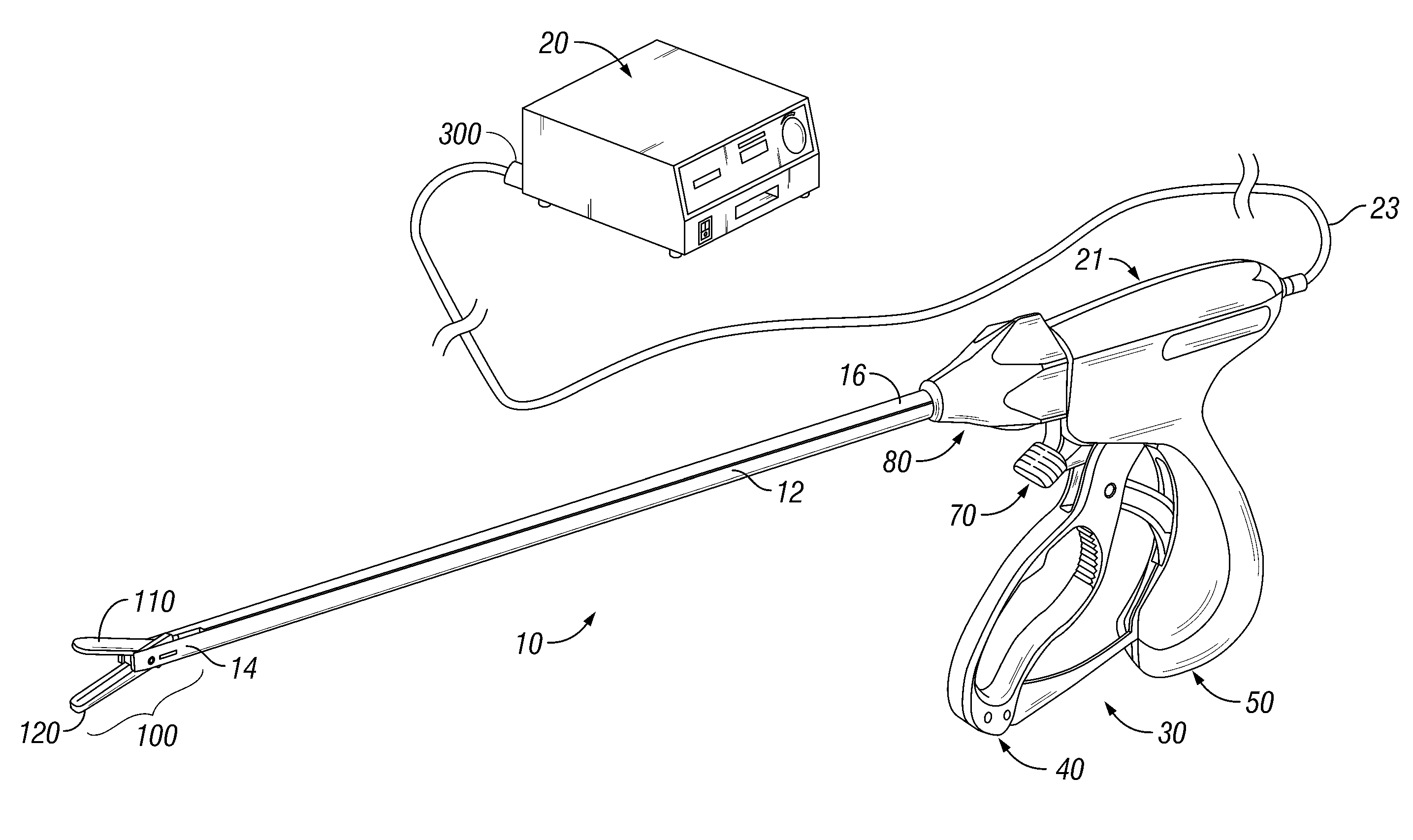
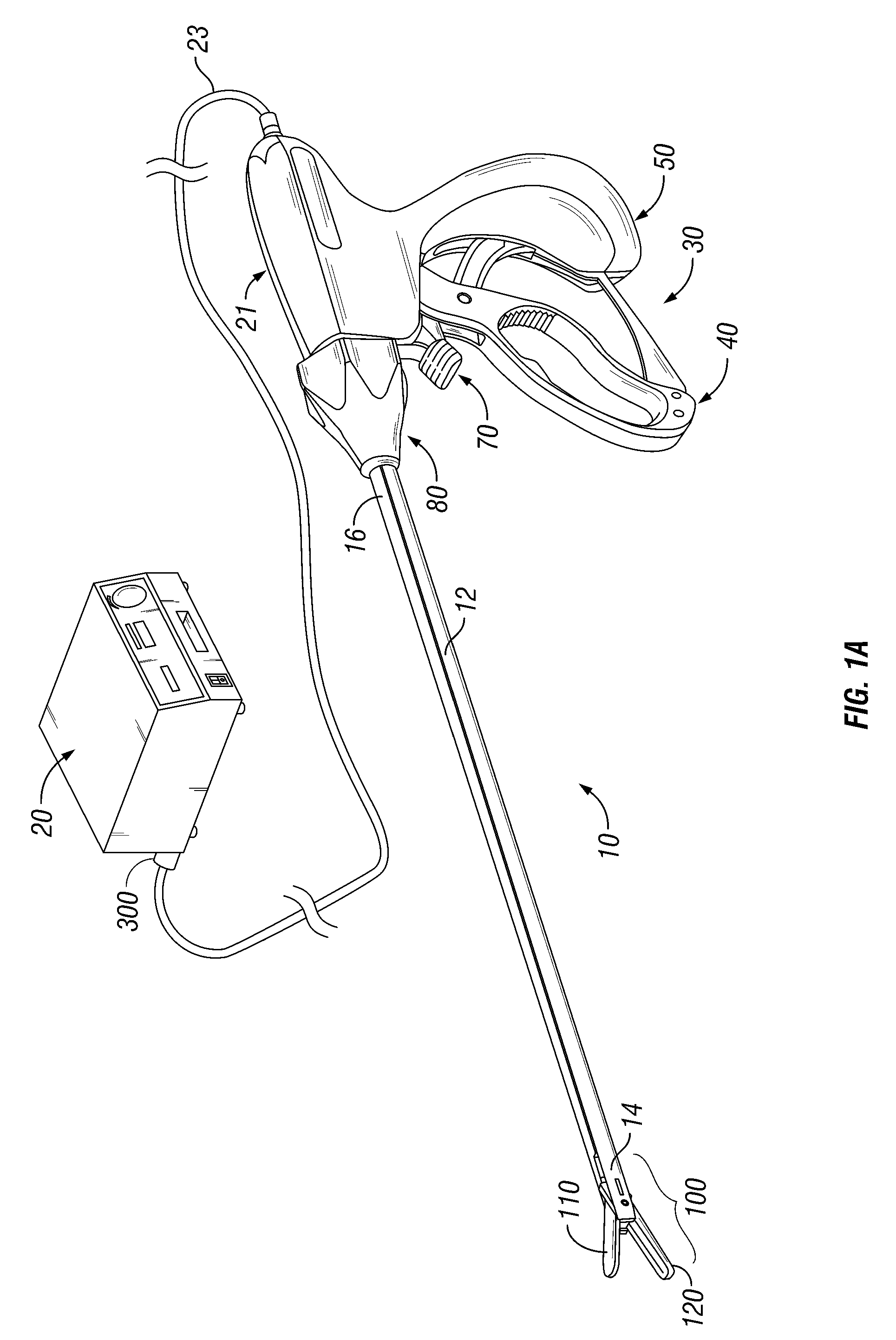
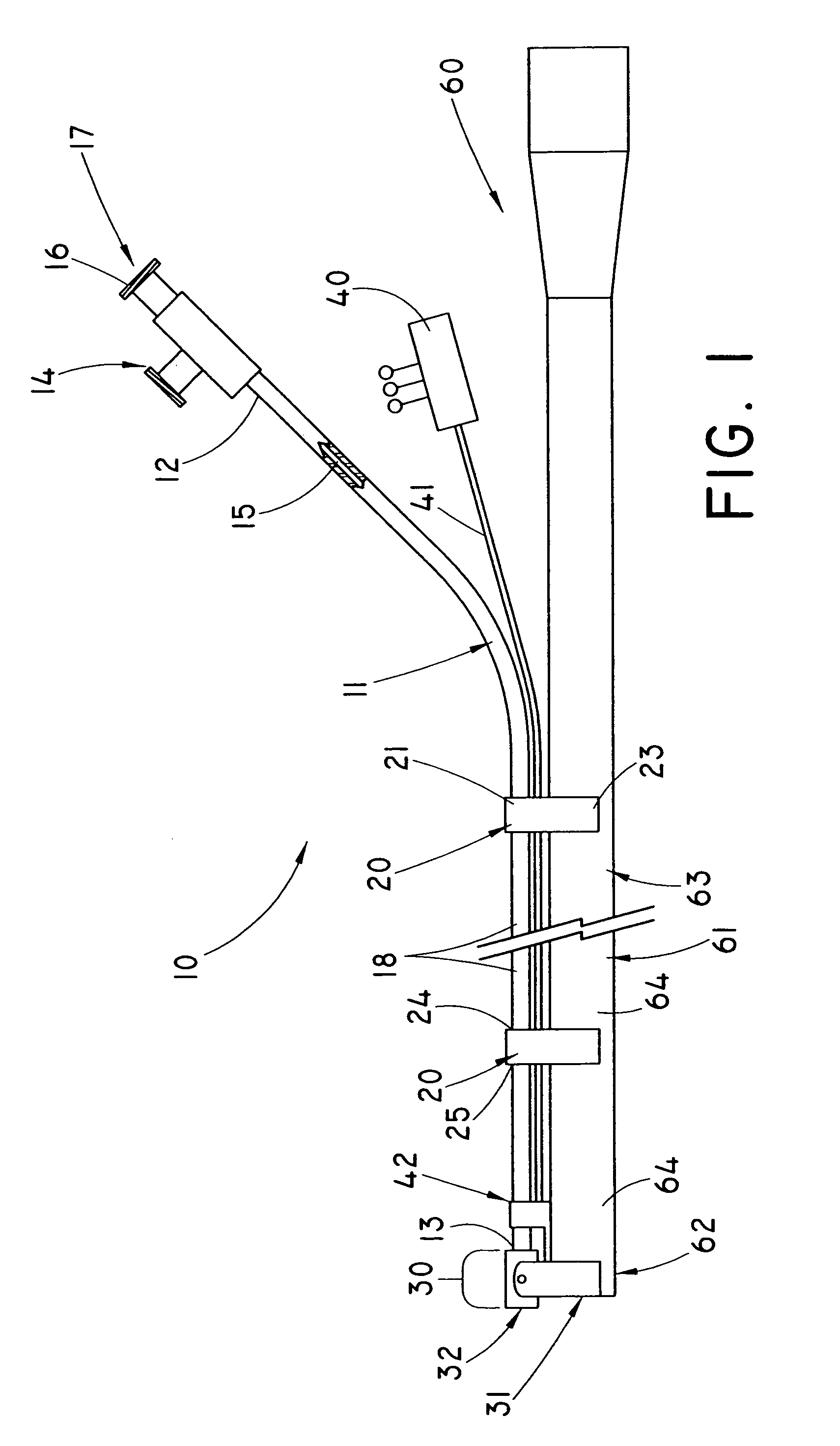
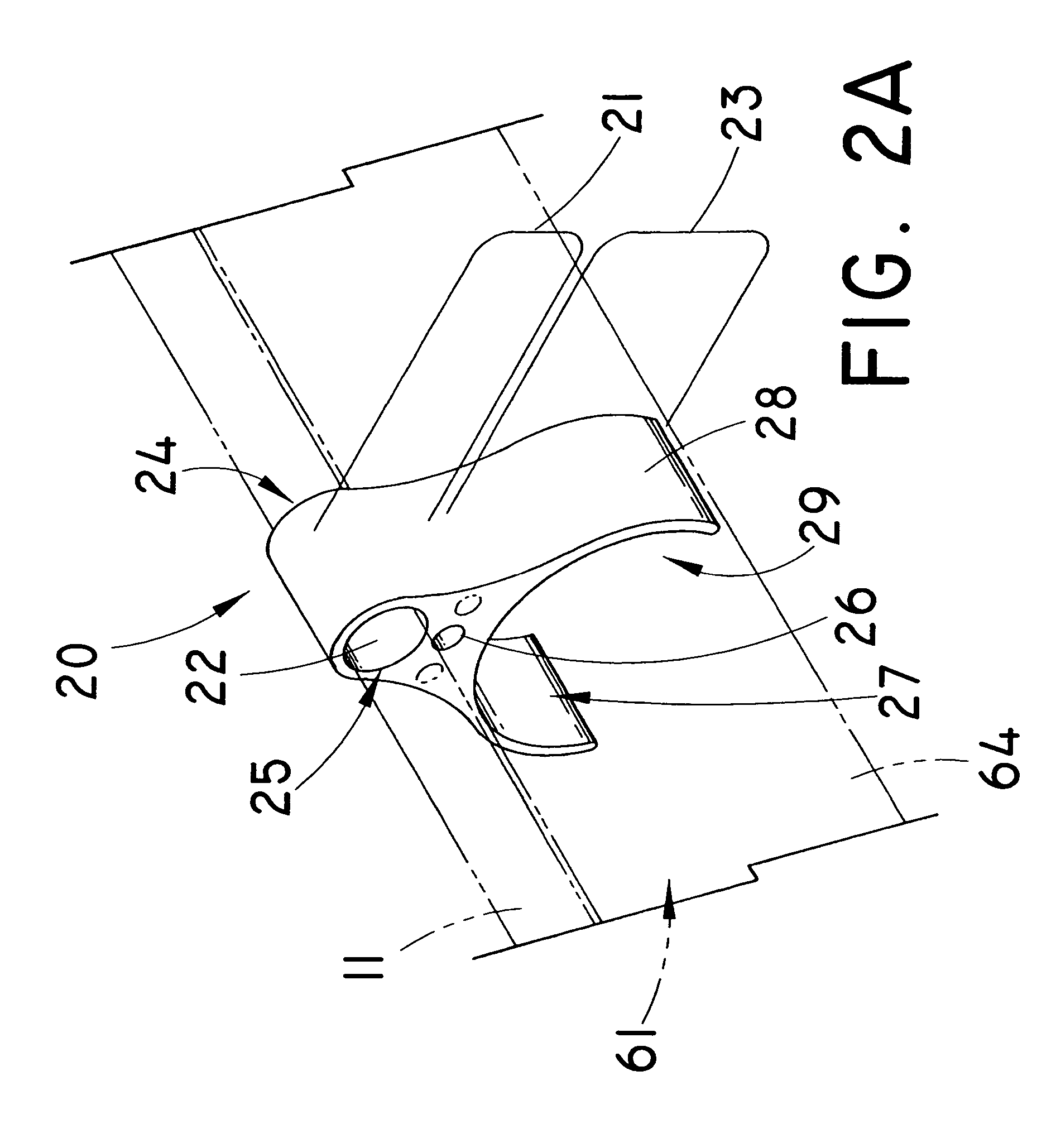
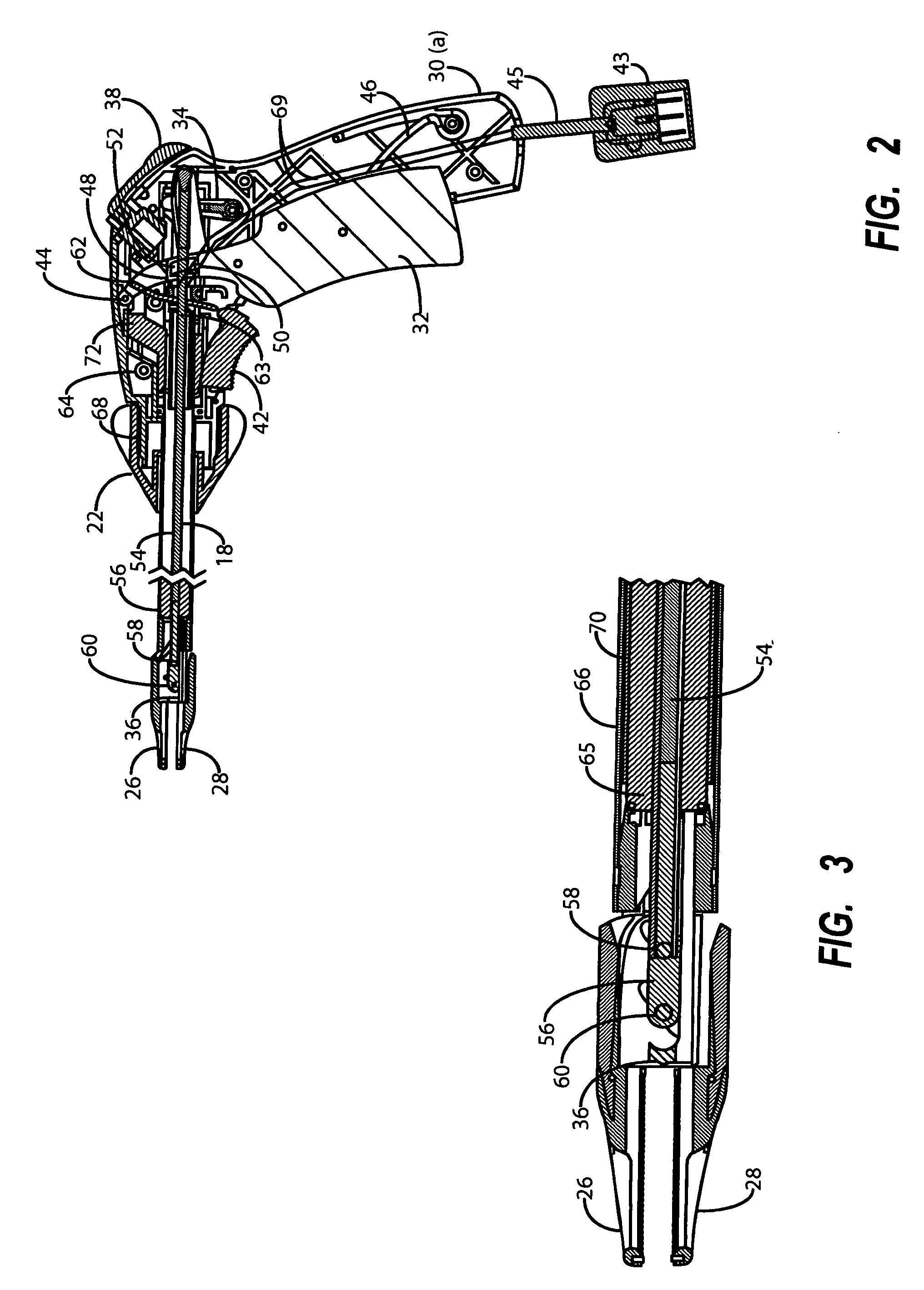
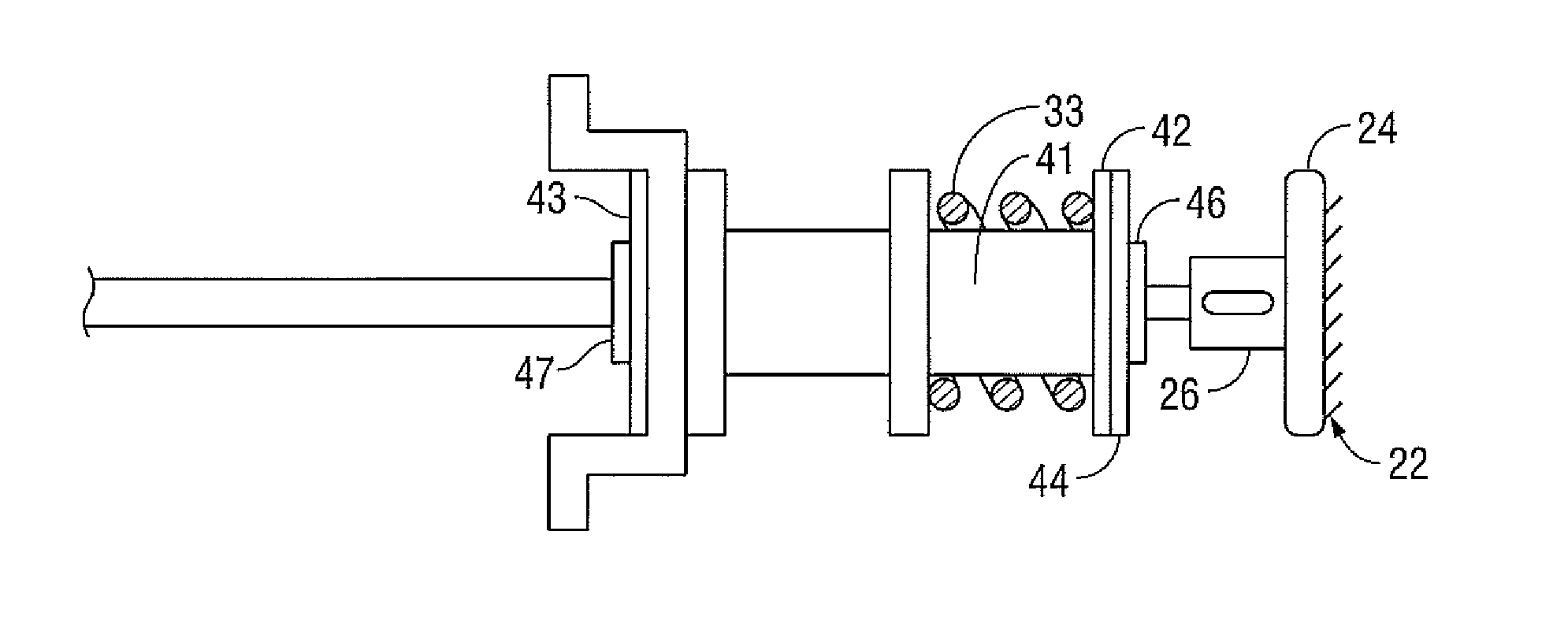
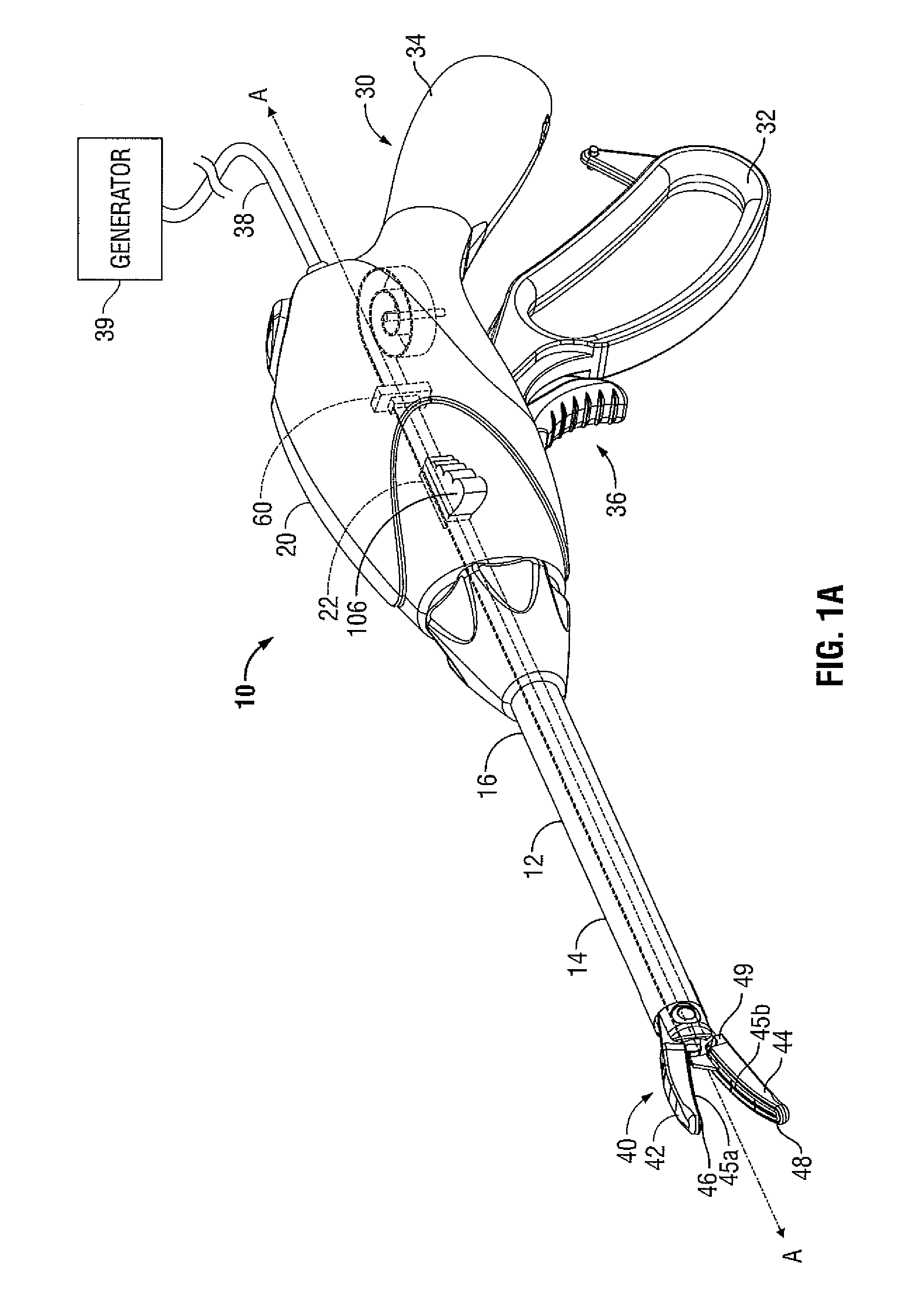
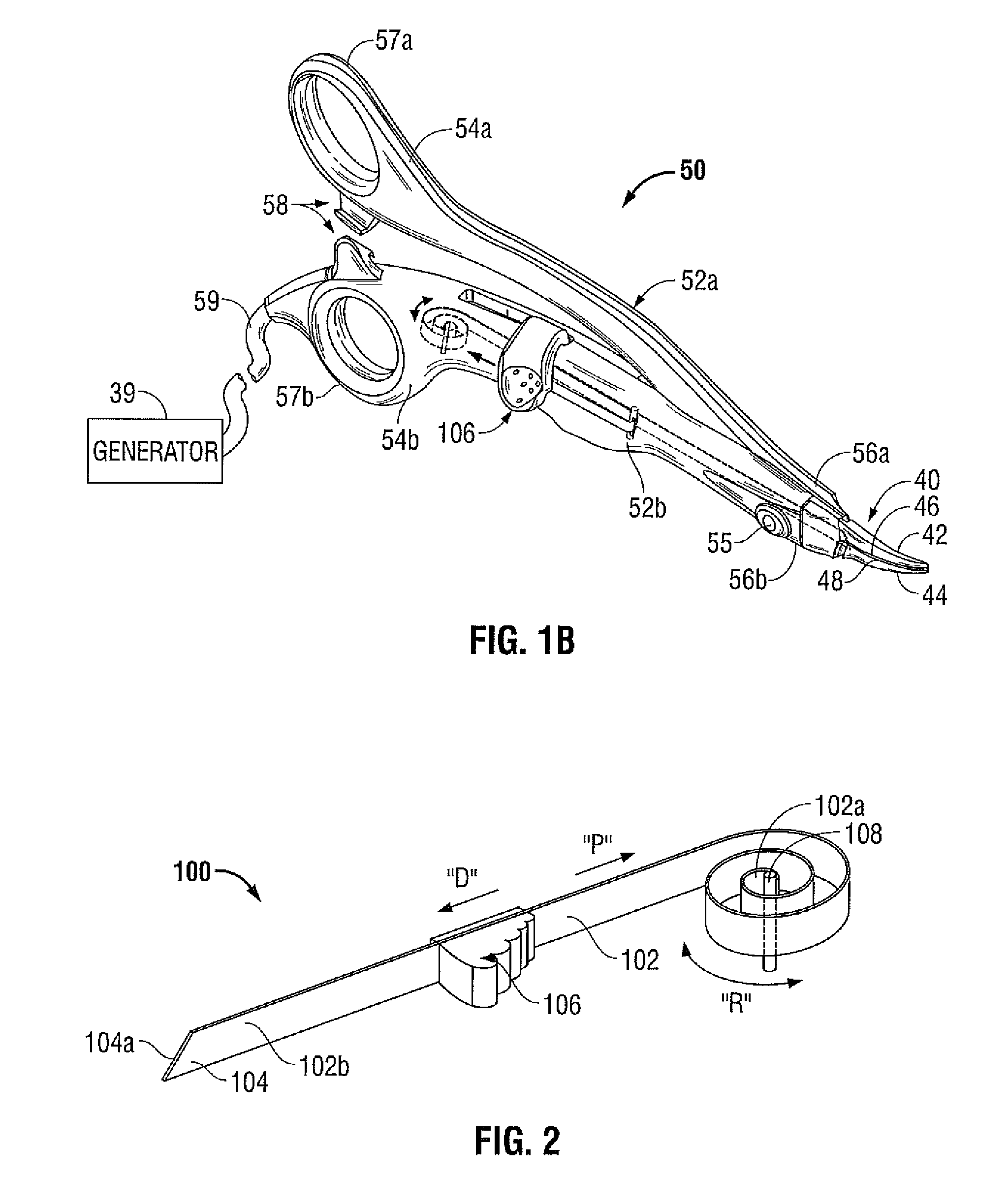
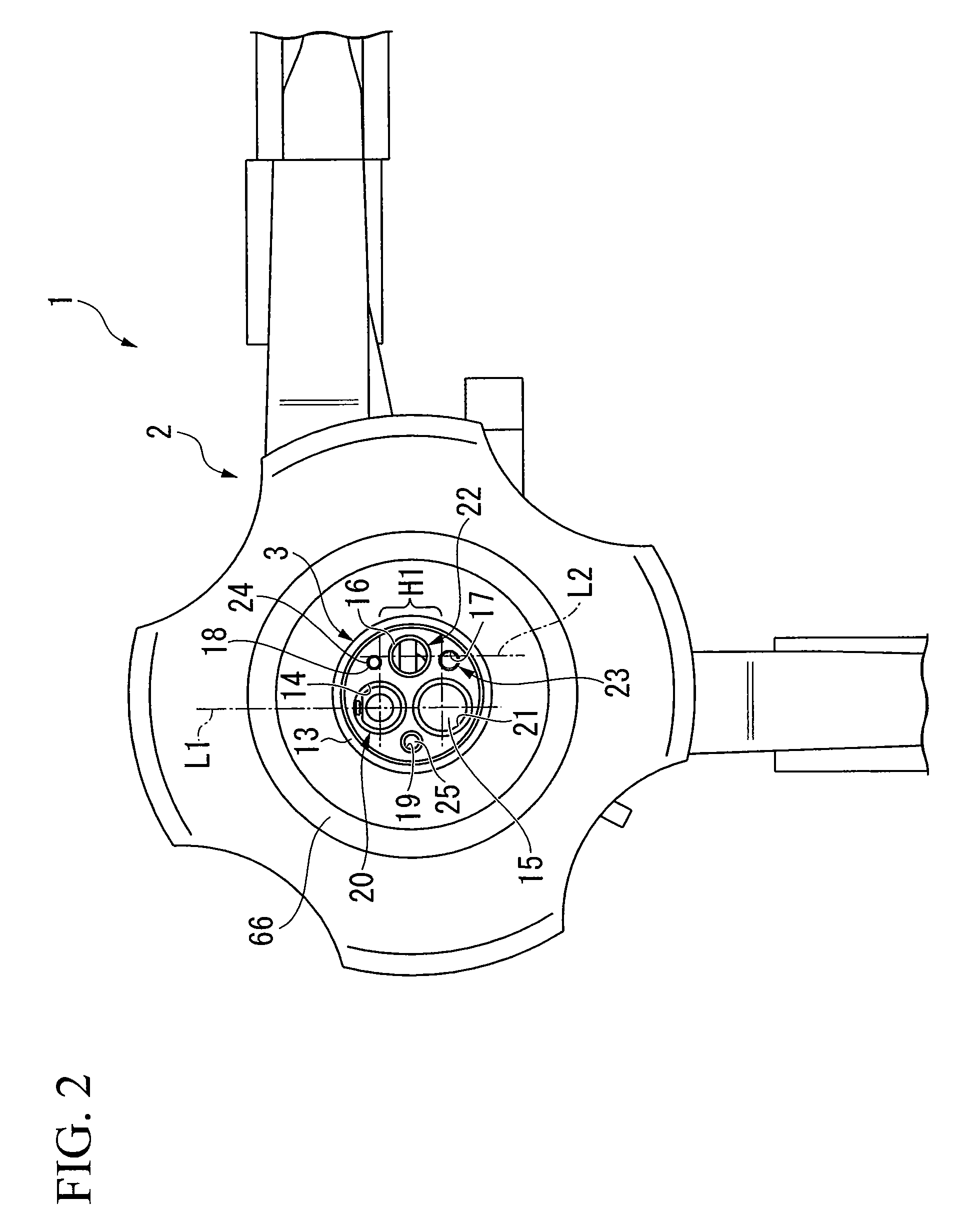
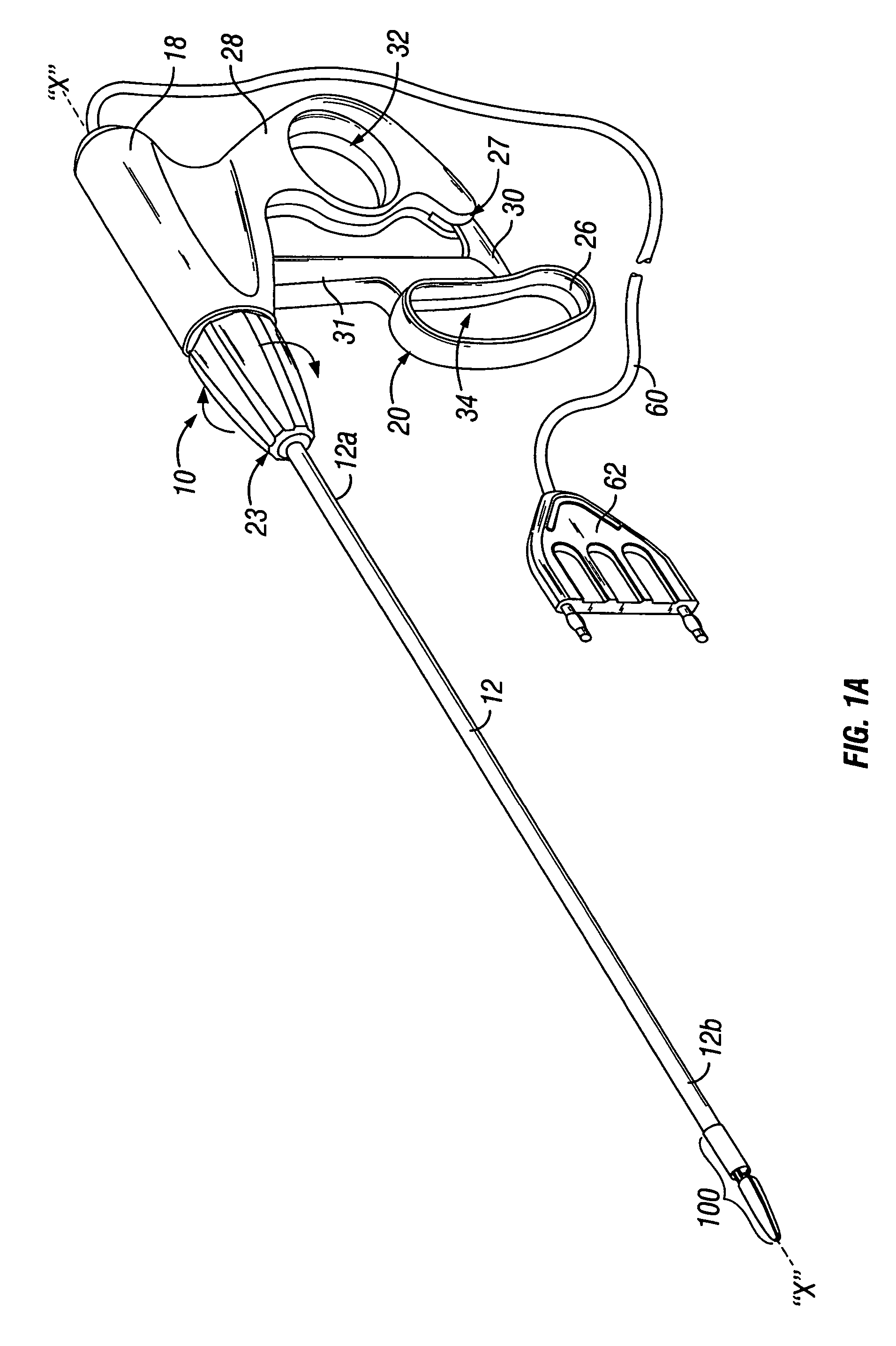
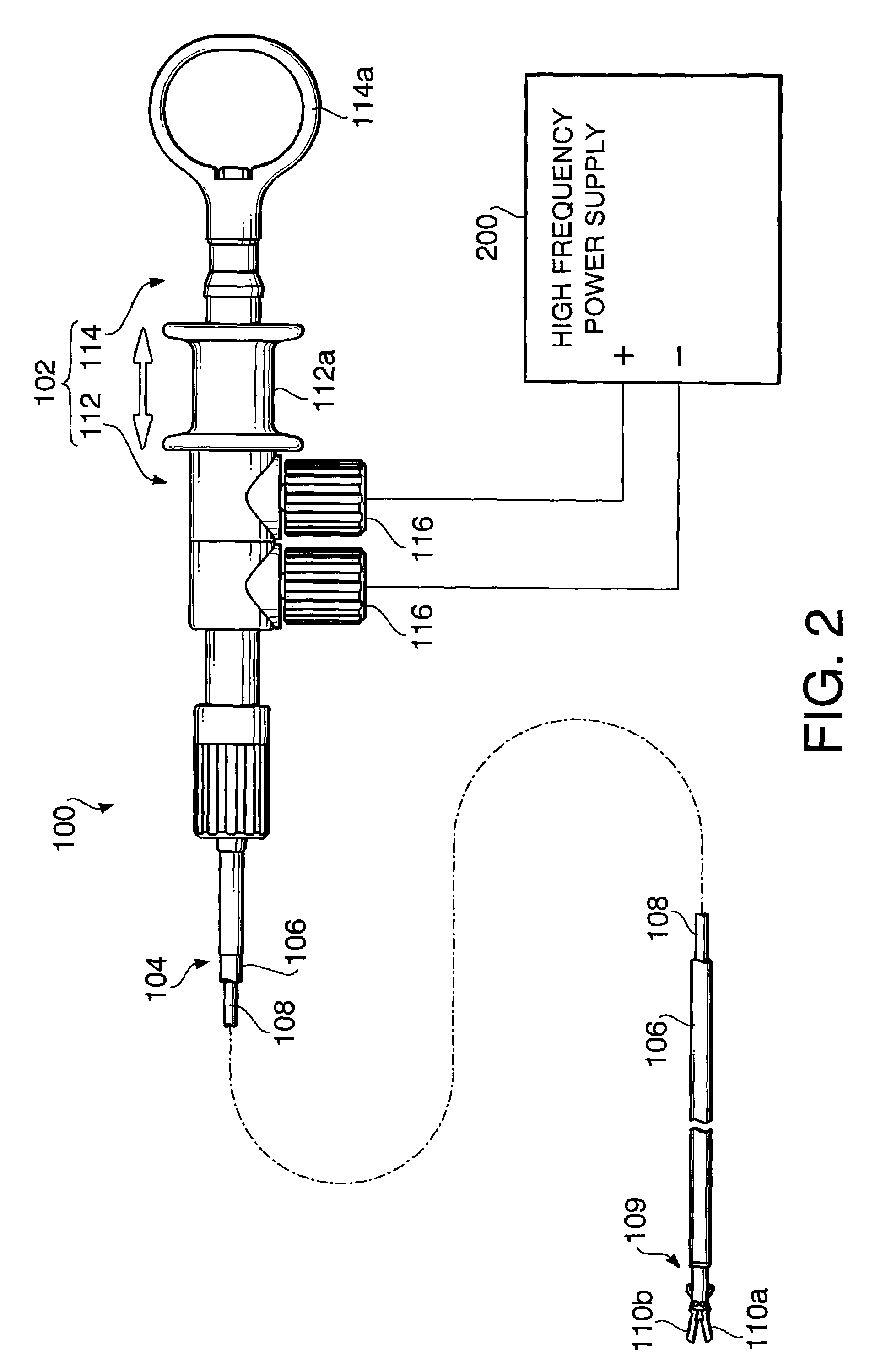
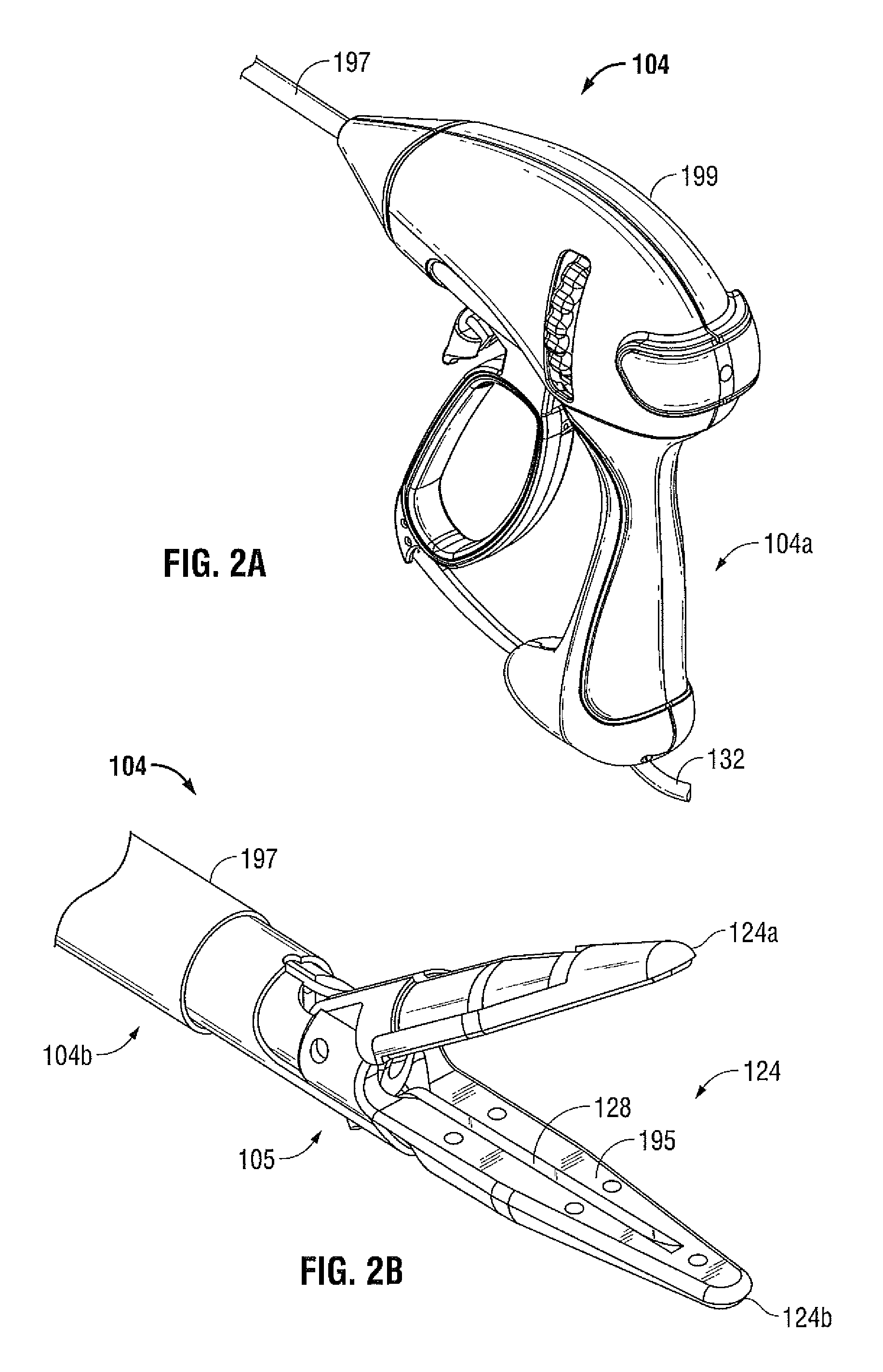
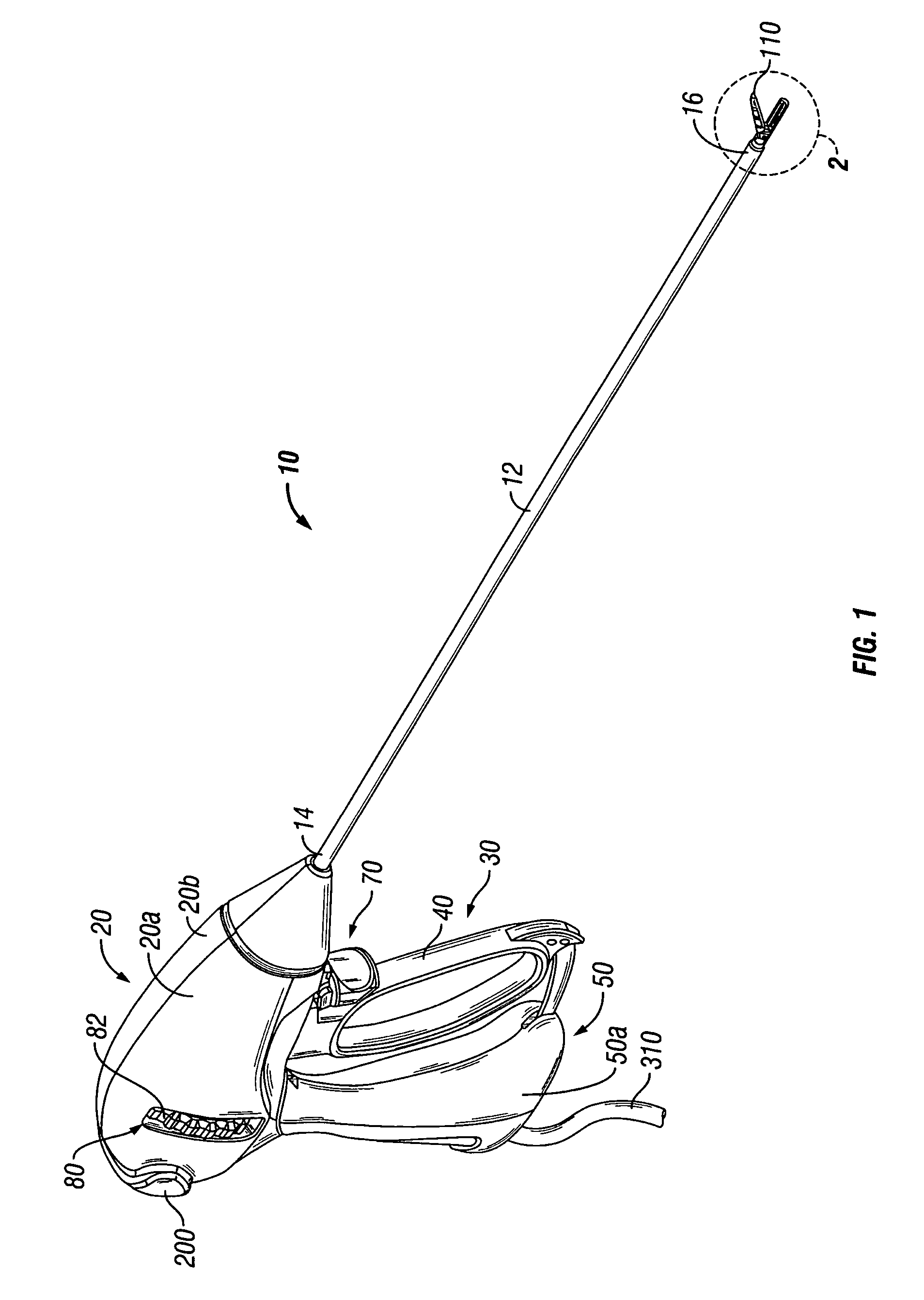
System and method for controlling electrode gap during tissue sealing
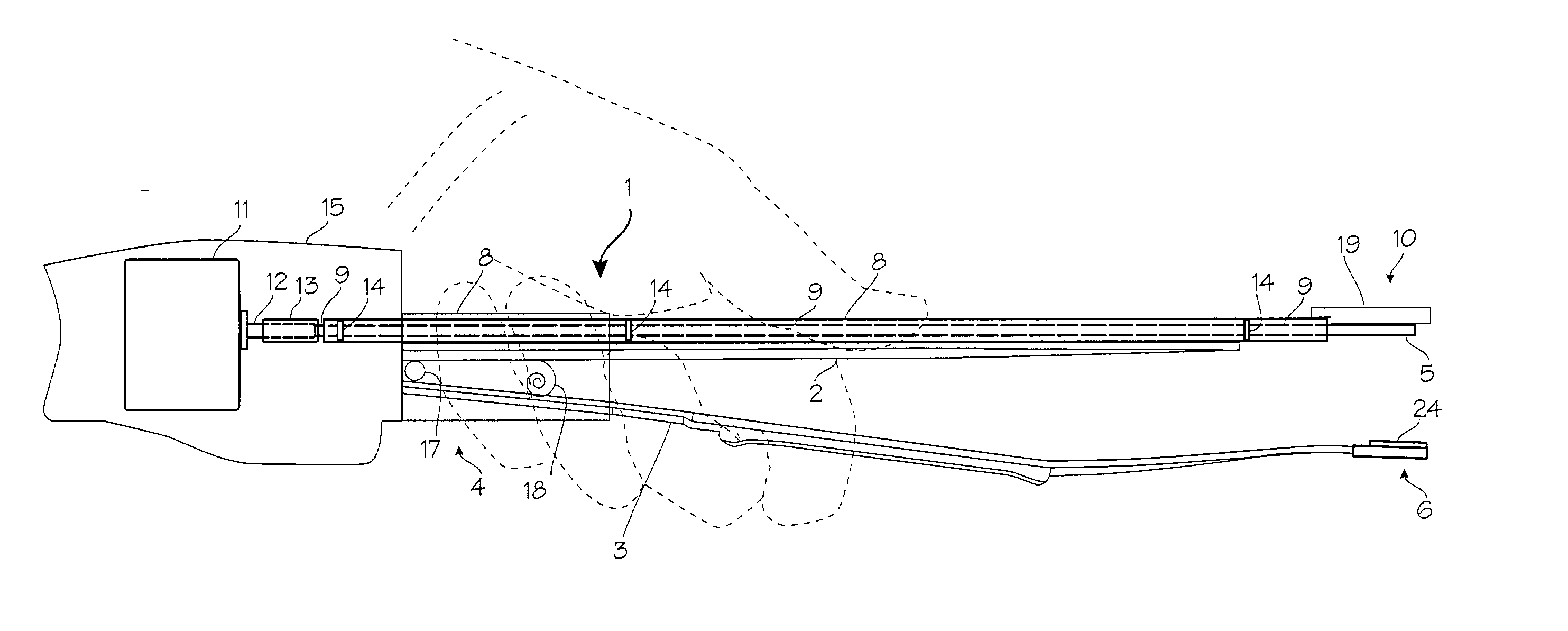
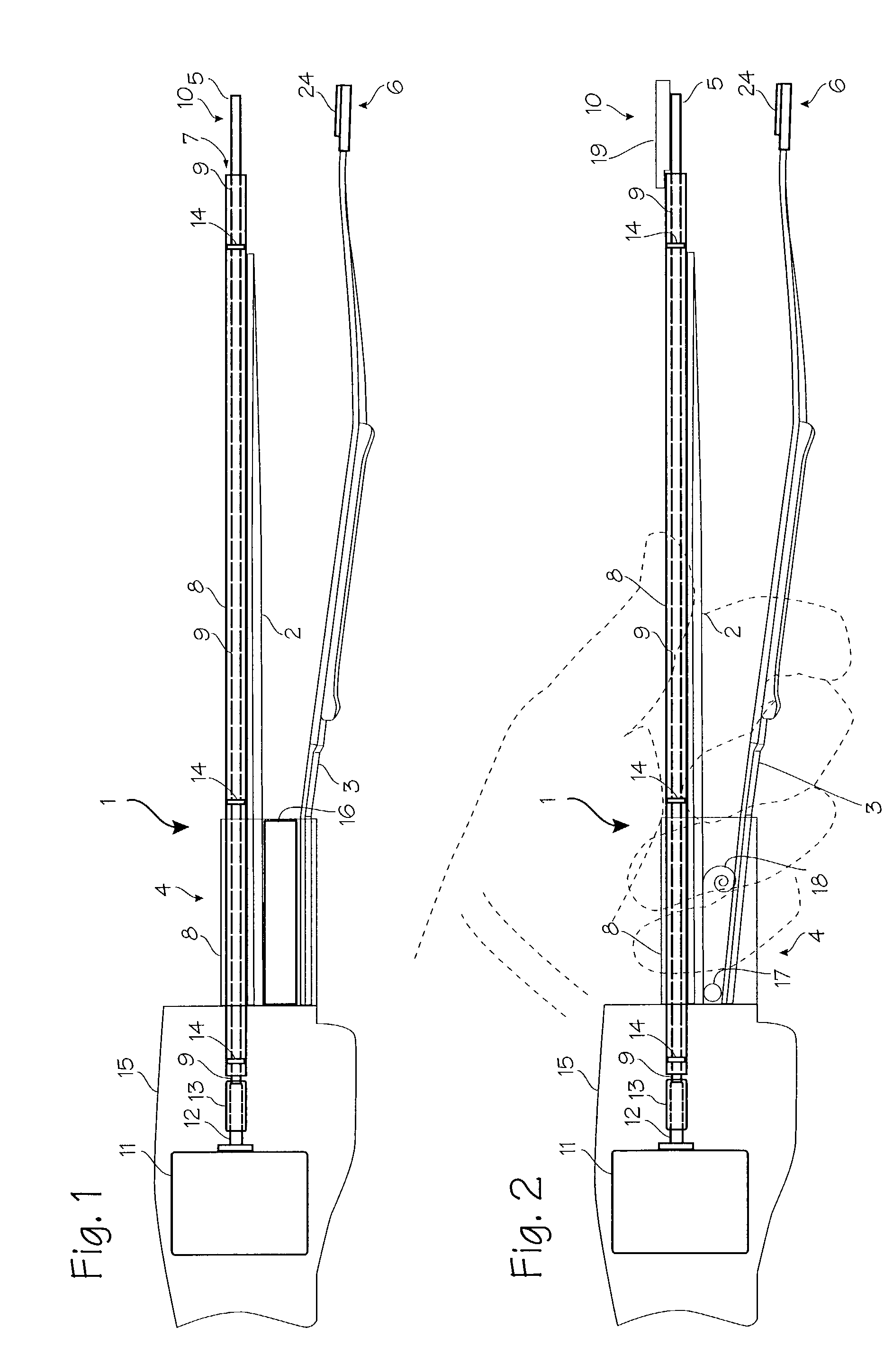
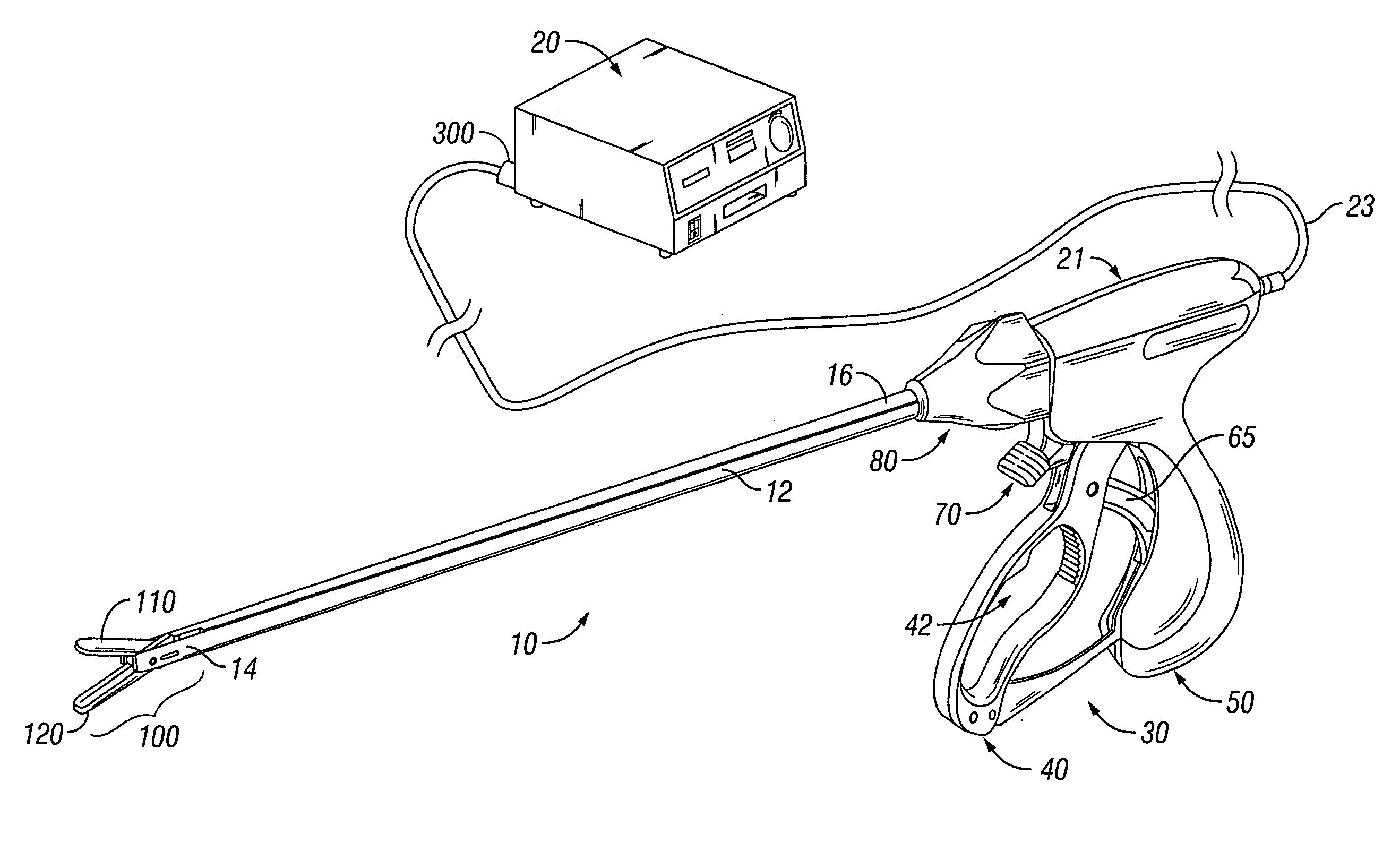
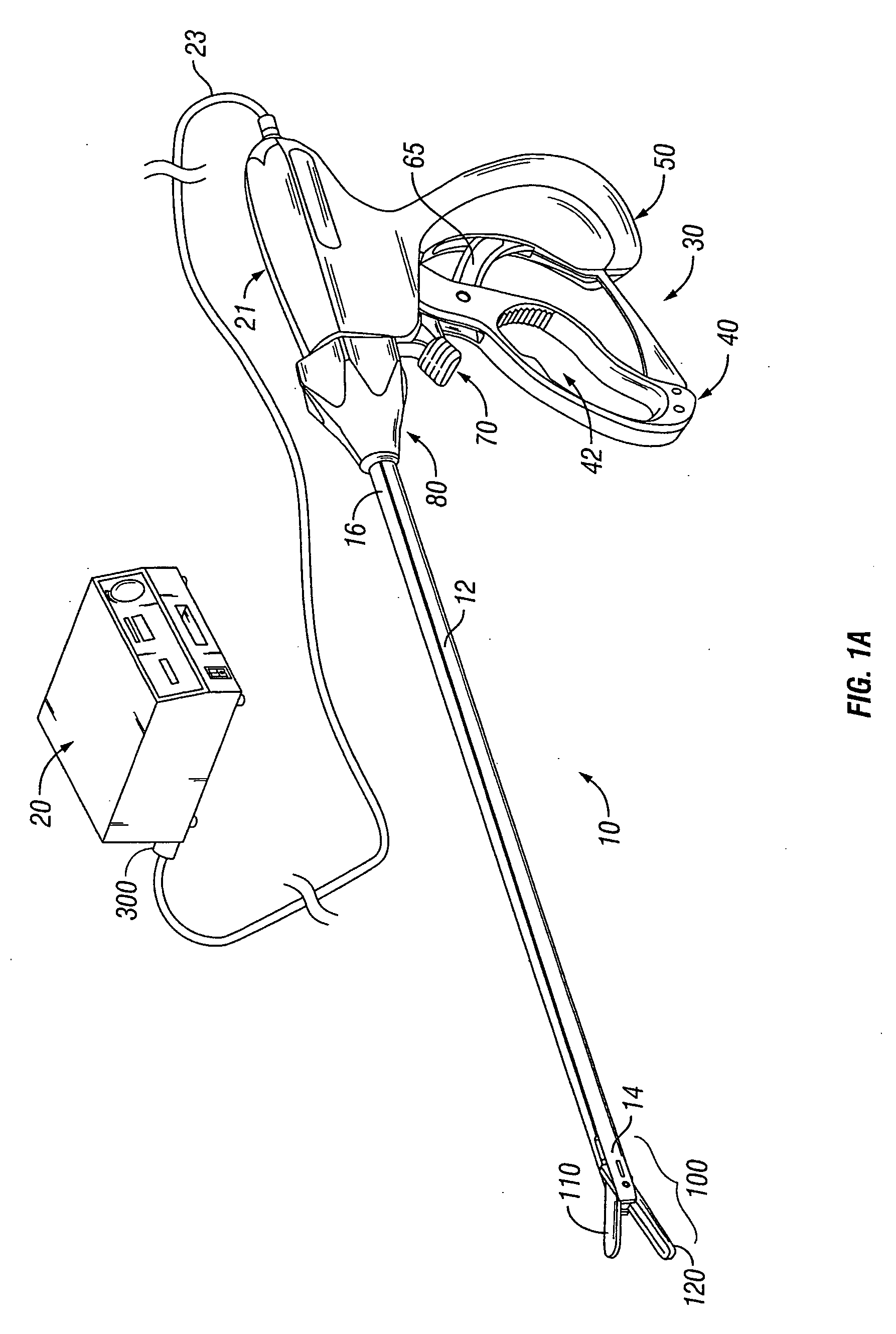
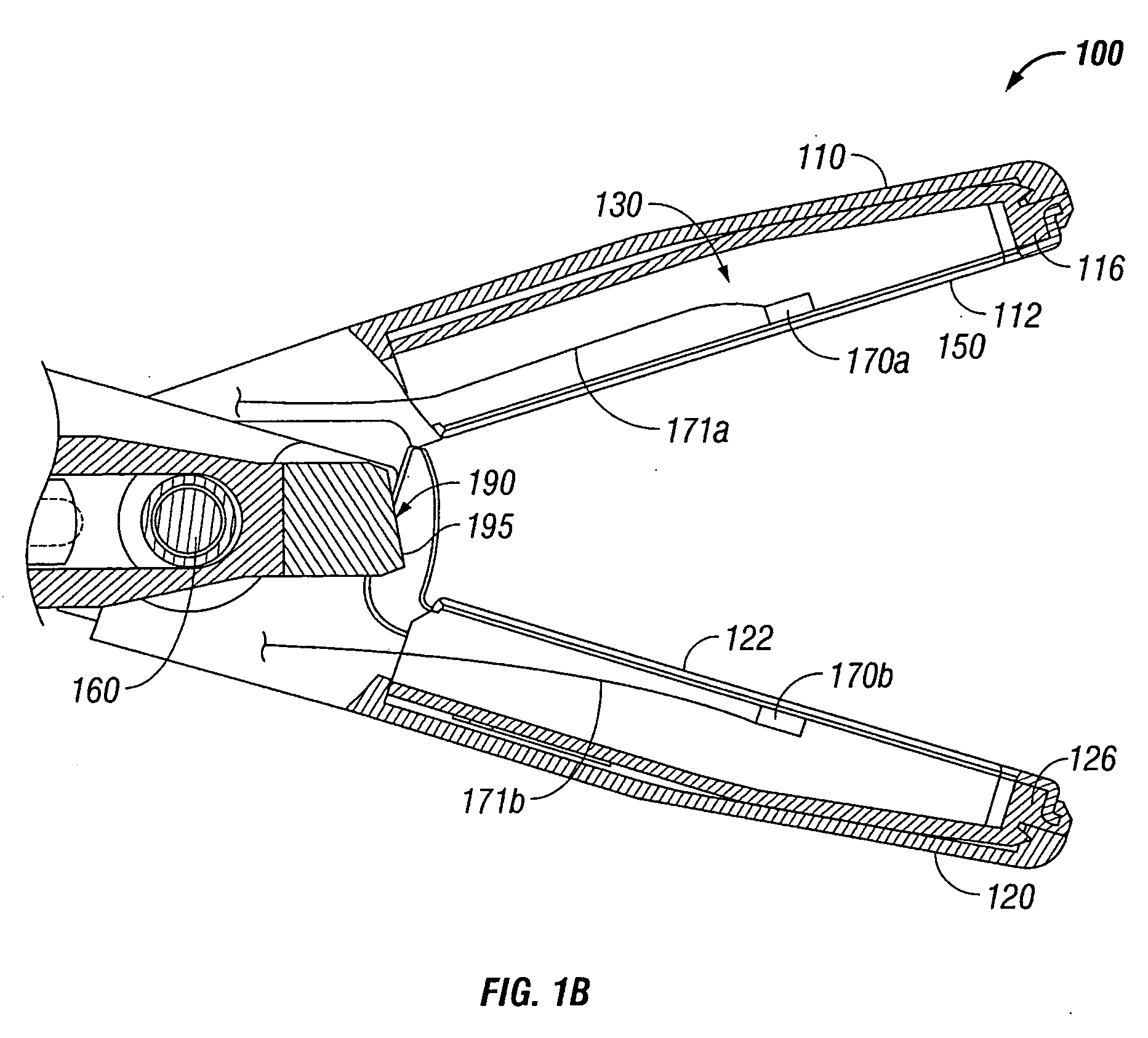
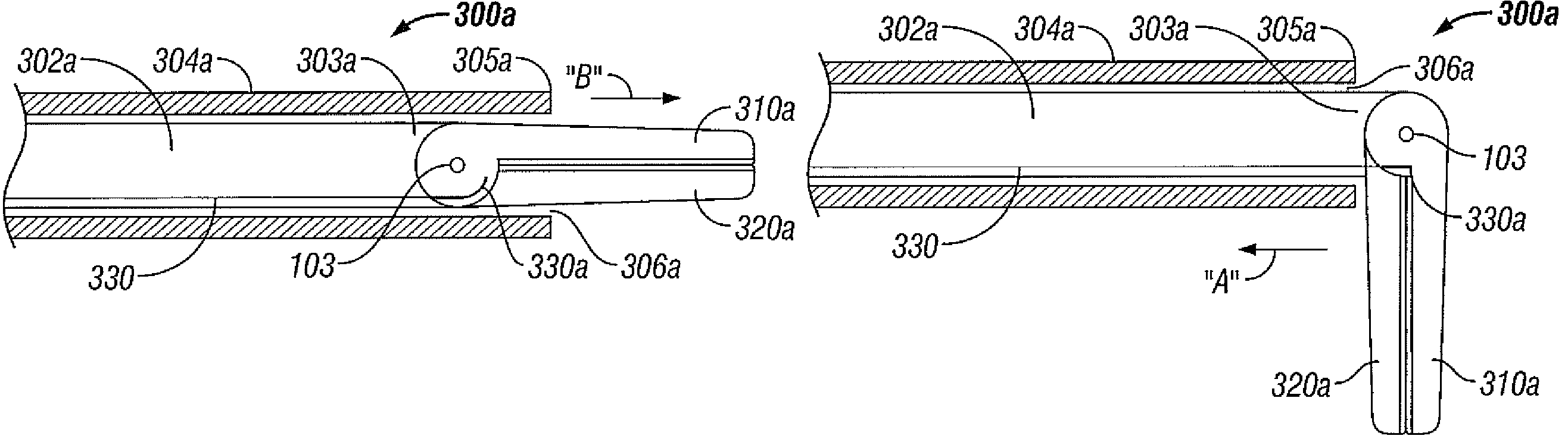
An electrosurgical system for sealing tissue is disclosed that includes an electrosurgical forceps. The forceps includes a drive rod and an end effector assembly coupled to the drive rod at a distal end thereof. The end effector assembly includes jaw members wherein longitudinal reciprocation of the drive rod moves the jaw members from a first position in spaced relation relative to one another to a subsequent position wherein the jaw members cooperate to grasp tissue therebetween. Each of the jaw members includes a sealing plate that communicates electrosurgical energy through tissue held therebetween. The jaw members are adapted to connect to an electrosurgical generator. The system also includes one or more sensors that determine a gap distance between the sealing plates of the jaw members and a pressure applicator coupled to the drive rod. The pressure applicator is configured to move the drive rod in a longitudinal direction. The system further includes a controller adapted to communicate with the sensors and to control the pressure applicator in response to the determined gap distance during the sealing process.
Owner:COVIDIEN AG
Endoscopic surgical access devices and methods of articulating an external accessory channel
Devices and methods for detachably engaging an insertion section of an endoscope and selectively articulating an endoscopic surgical access channel are provided. A device comprises an articulating main body having a stationary first body, an articulatable second body, and coupler having a mounting member and an articulation link member configured to articulatively couple the second body to the first body. The stationary first body has a distal end, a proximal end, and a first longitudinal axis. The articulatable second body has a proximal opening and a distal opening defining an accessory channel member passageway, the distal opening having a second longitudinal axis oriented toward a space exterior to the first body distal end, wherein the second body longitudinal axis is capable of articulating relative to the first body longitudinal axis. The devices and methods, as taught herein, provide control over the position and / or orientation of a diagnostic, monitoring, scope, sewing device, cutting device, suturing device, forceps, grabbing device, instrument, or other tool within the visual field beyond the distal opening of the endoscope.
Owner:COOK MEDICAL TECH LLC
Cutting and coagulating electrosurgical forceps having cam controlled jaw closure
InactiveUS20060271042A1Surgical instruments for heatingSurgical forcepsRange of motionBipolar electrosurgery
A bipolar electrosurgical forceps comprises an elongated tubular barrel having a proximal end, a distal end and a lumen extending between these two ends. A handle is provided at the proximal end of the barrel and includes an actuating member for opening and closing a pair of forceps jaws that are mounted at the distal end of the barrel. The forceps jaws include cam slots in a proximal head portion thereof. A coupling member extends between the actuating member on the handle and the pair of forceps jaws. The coupling member includes drive pins that cooperate with the cam slots whereby squeezing of the actuating mechanism first effects pivotal rotation of the pair of forceps jaws over a first range of motion of the actuating member and translation without rotation of the forceps jaws over a second range of motion of the actuating member.
Owner:GYRUS MEDICAL LTD
Surgical instrument
An electrosurgical instrument for use in cutting and / or coagulating tissue includes a dielectric material, the dielectric material being positioned in the current pathway between the tissue-treatment regions of first and second electrodes. This can be achieved by providing one or more electrode surfaces coated with a dielectric material having a reactive impedance of less than 3,000 ohms / sq. mm. at 450 kHz. The dielectric coating acts to couple the RF signal into the tissue primarily by capacitive coupling, providing a more even heating of the tissue and the elimination of “hot spot”. Examples of electrosurgical instruments employing such coated electrodes include forceps, scissors or scalpel blade instruments.
Owner:GYRUS MEDICAL LTD
External forceps channel device for endoscope
The present invention was made in the light of the foregoing backgrounds, and an object thereof is to provide a forceps channel add-on device for an endoscope, provided on an outer periphery of an insertion portion of the endoscope. The forceps channel add-on device for an endoscope is an external forceps channel device for an endoscope, which is capable of providing two forceps channels or more without controlling the luminous intensity and the field of view of the endoscope, capable of extracting a substance larger than the bore diameter of the forceps channel multiple times while using the endoscope in a state of not being drawn out, without imposing a heavy burden on a patient, and also capable of performing examination after an operation as to whether complications are incurred after the evulsion, whether there is any other affected part overlooked, and so forth. An external forceps channel device for an endoscope, provided with an external forceps channel which is capable of being repeatedly inserted and extracted in a way of being guided by a guide provided on an endoscope separately and independently therefrom along an outside of an insertion portion of the endoscope while using the endoscope without drawing it out, the endoscope incorporating an air supply path, a light source, a CCD camera, and a forceps channel and including the insertion portion and an maneuvering portion, characterized in that provided is the external forceps channel capable of repeatedly extracting a foreign substance larger than a bore diameter of the incorporated forceps channel in a way of being guided by the guide along the outside of the endoscope, together with the whole external forceps channel itself in a state where the foreign substance is grasped by forceps inserted through the external forceps channel, and that provided is the external forceps channel capable of being repeatedly inserted in a way of being guided by the guide along the outside of the endoscope in a state where the endoscope is not drawn out.
Owner:SHIMA KIYOTERU +1
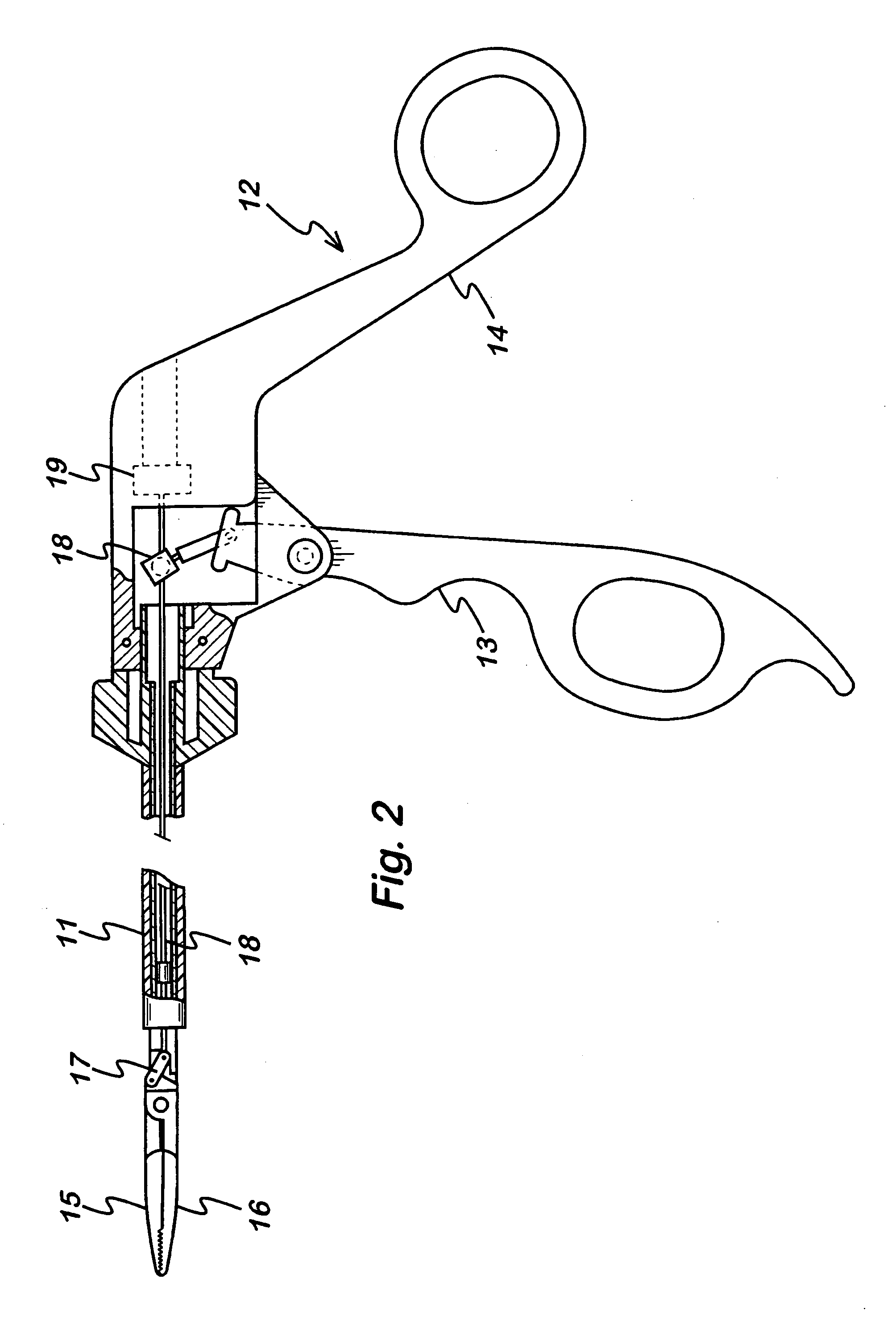
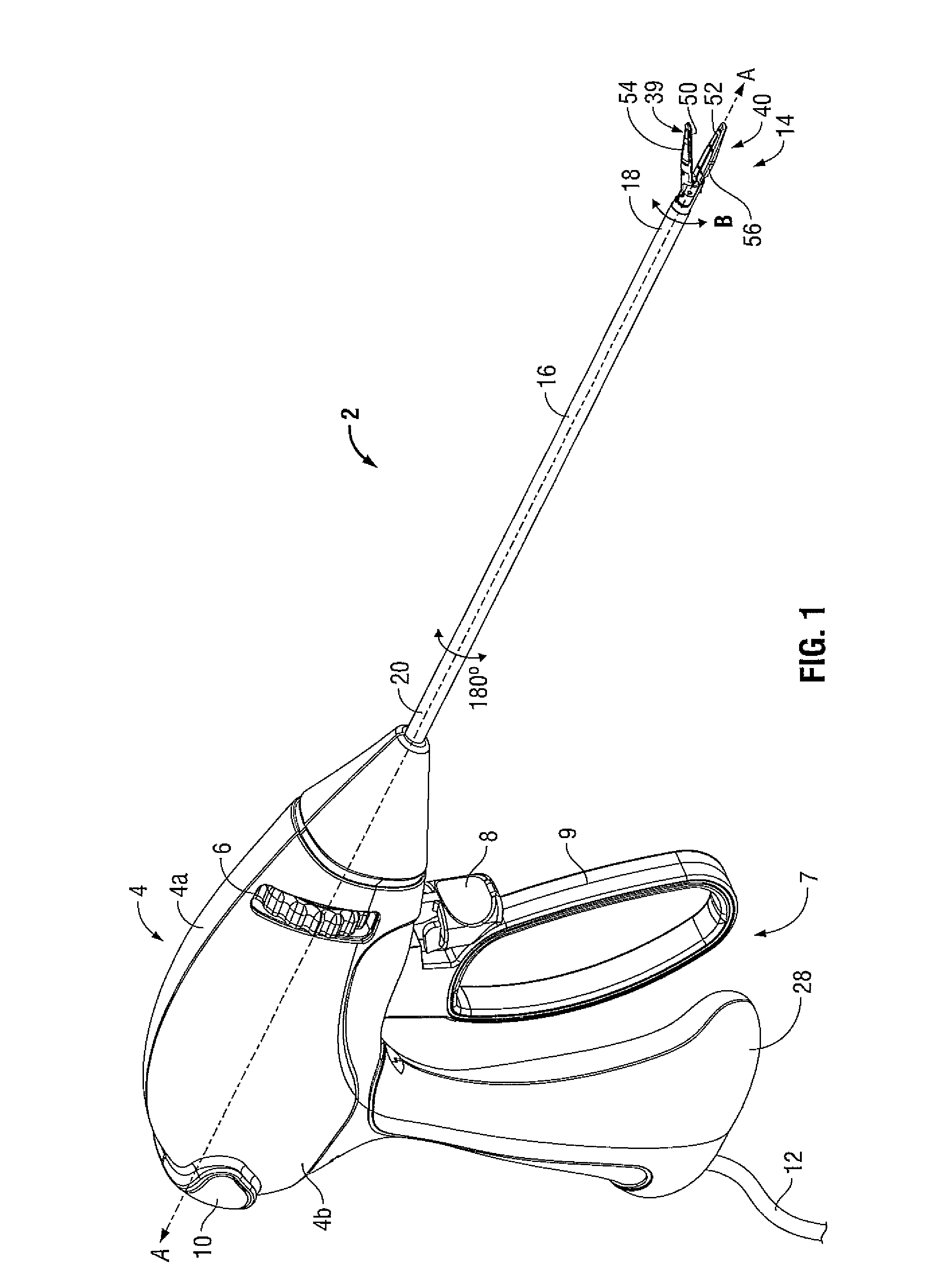
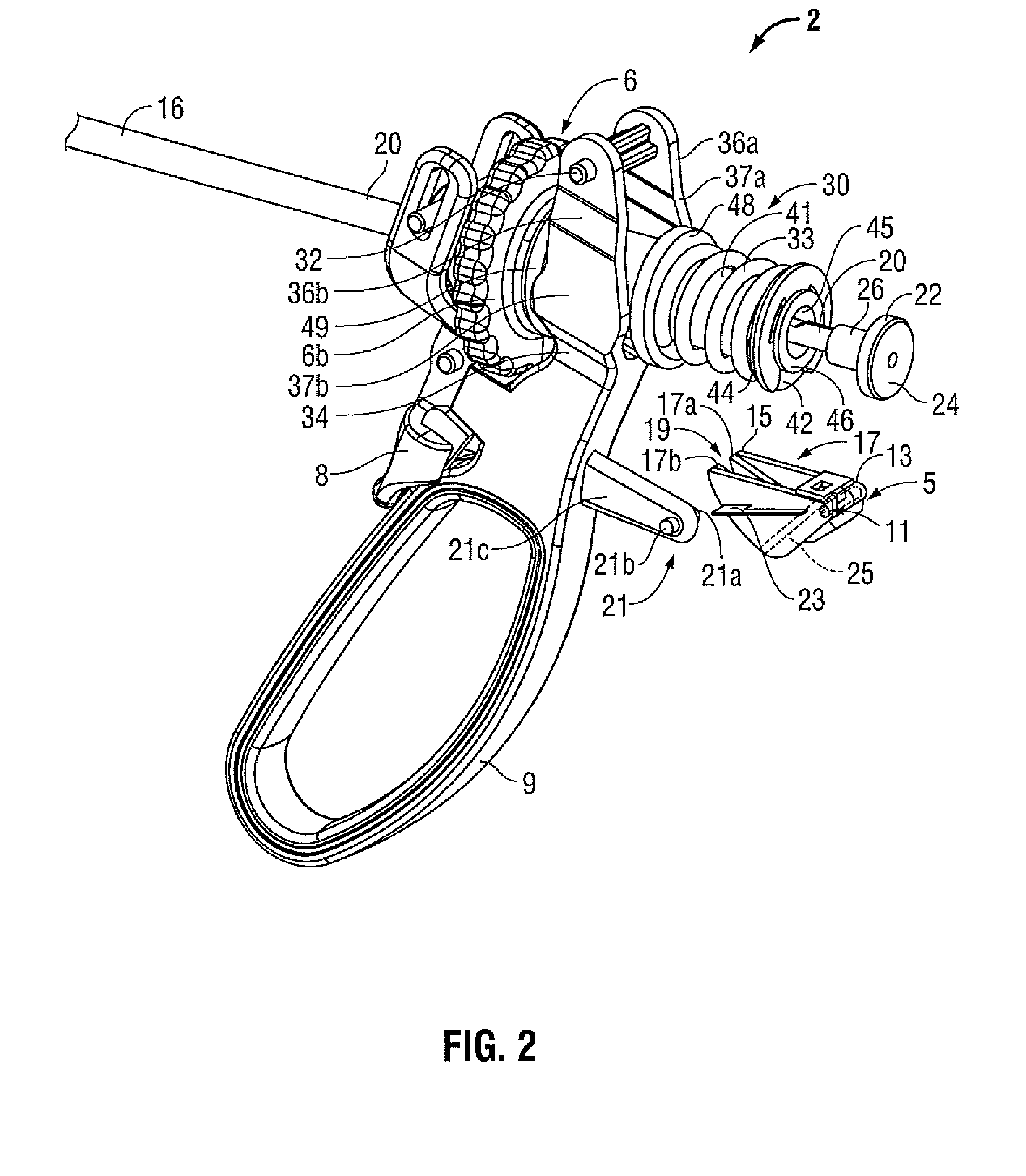
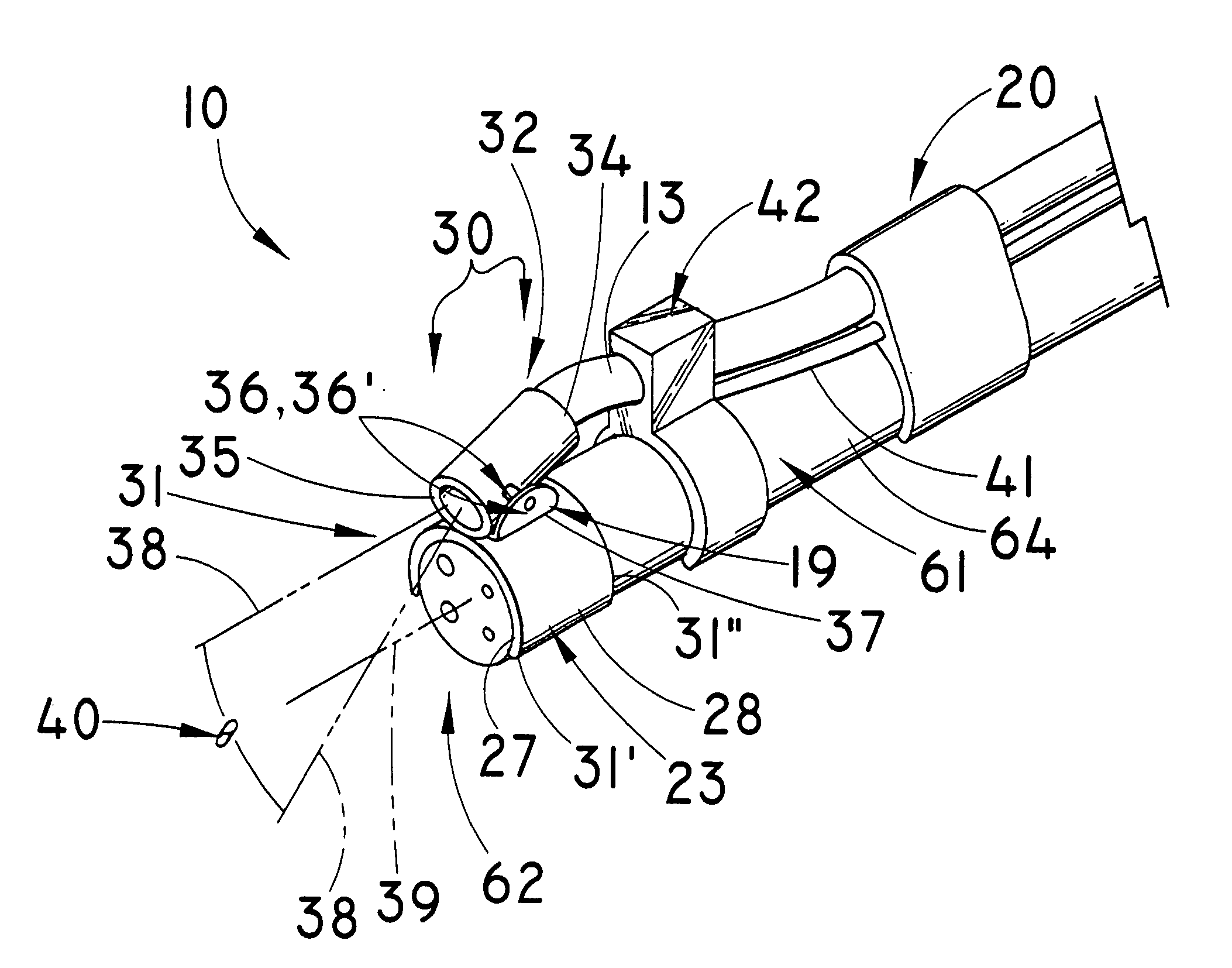
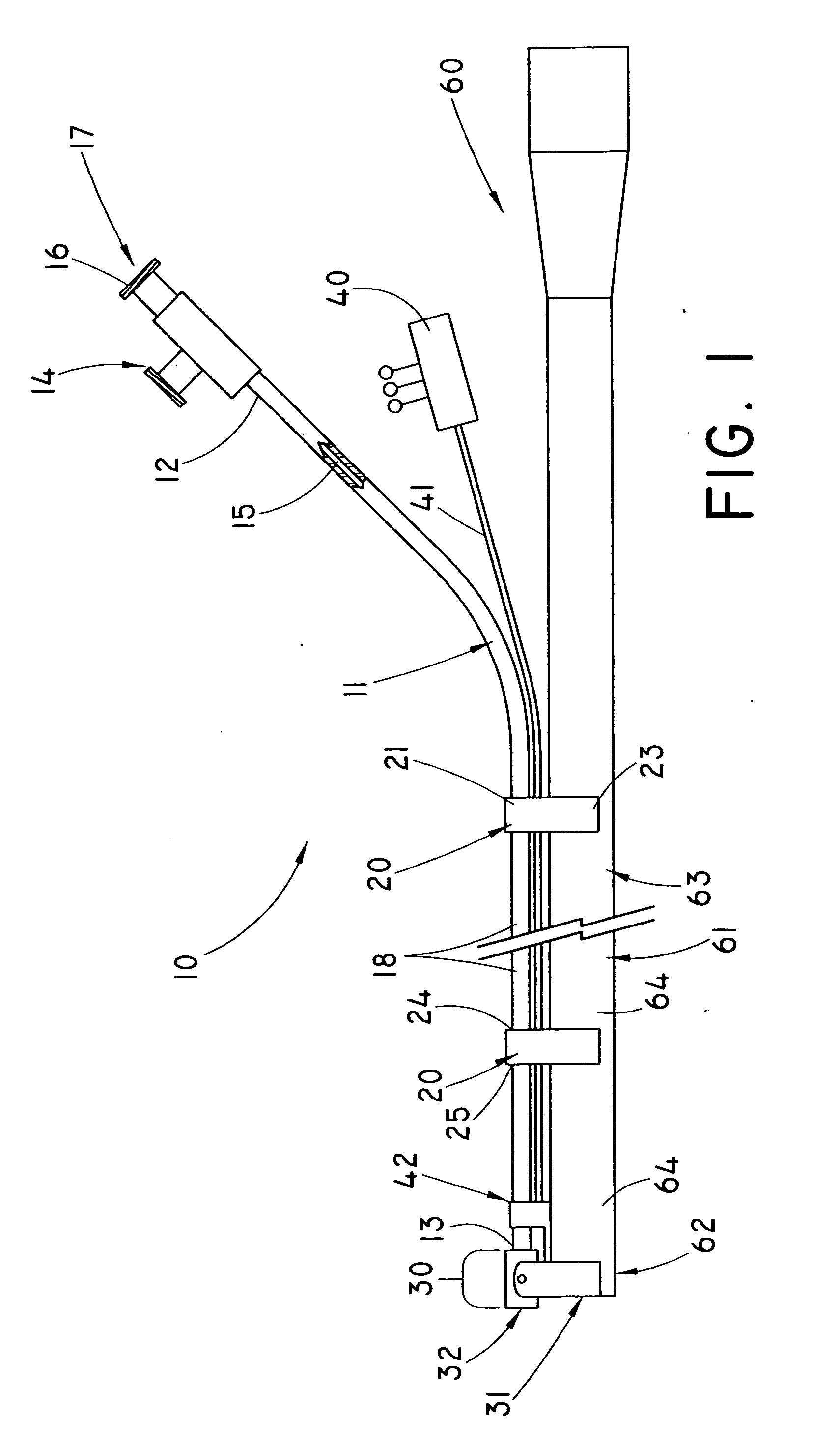
Forceps for performing endoscopic surgery
A surgical instrument for performing surgery includes a housing defining an axial bore. A lock is slidably disposed in the transverse bore to engage and disengage a tube adaptor. A latch extends from the lock to move the latch into and out of the axial bore. The lock and latch allow for interchangeability of tip assemblies inserted into the surgical instrument. A first and second handle are pivotally attached to the housing. A first ratchet member is rotatably attached to the first handle and includes serrated teeth. A second ratchet member extends from the second handle. The second ratchet member including a finger for engagement with the serrated tooth to prevent movement of said first handle relative to the second handle. The first ratchet member is rotatable about the rotational axis to disengage from the second ratchet member and allow the first handle to move relative to the second handle.
Owner:RF KINETICS
Method, apparatus, and kit for thermal suture cutting
InactiveUS7699856B2Reduce tensionMinimize disruptionSuture equipmentsDiagnosticsForcepsRemoval techniques
A novel suture removal instrument, kit and technique are described herein. The invention utilizes a newly designed thermal filament to allow the tip of the suture removal instrument to be slipped under the stitch in order to heat and cut the stitch. Current suture removal techniques utilize scissors, forceps, and / or scalpels. These techniques, which are well known in the art, are problematic because they exert tension on the stitch and are associated with patient discomfort. Small stitches add to the difficulty of suture removal because they have less suture laxity for scissor insertion. The present invention therefore allows for more rapid suture removal with less patient discomfort and at a competitive or lower cost.
Owner:BOVIE MEDICAL CORP
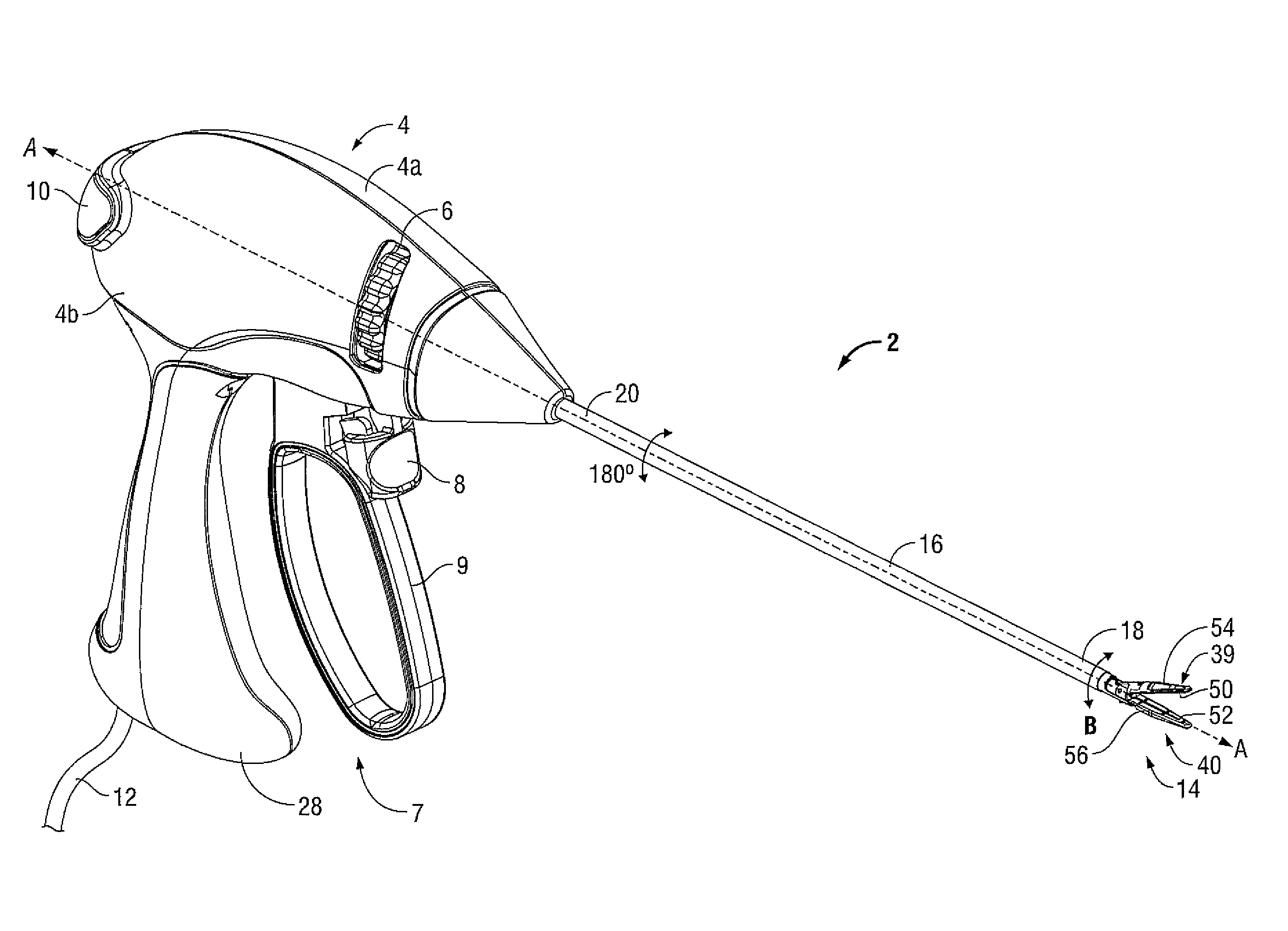
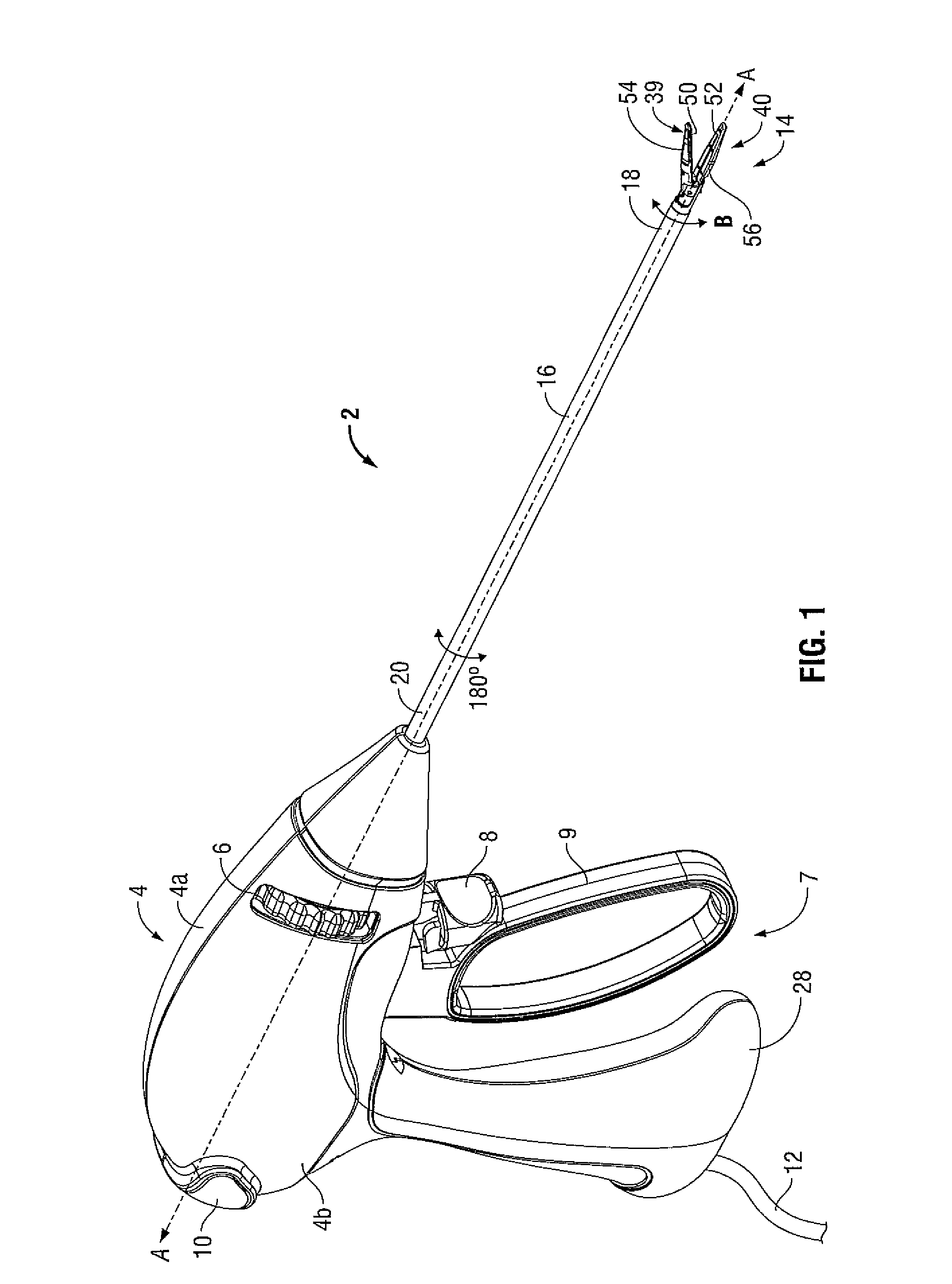
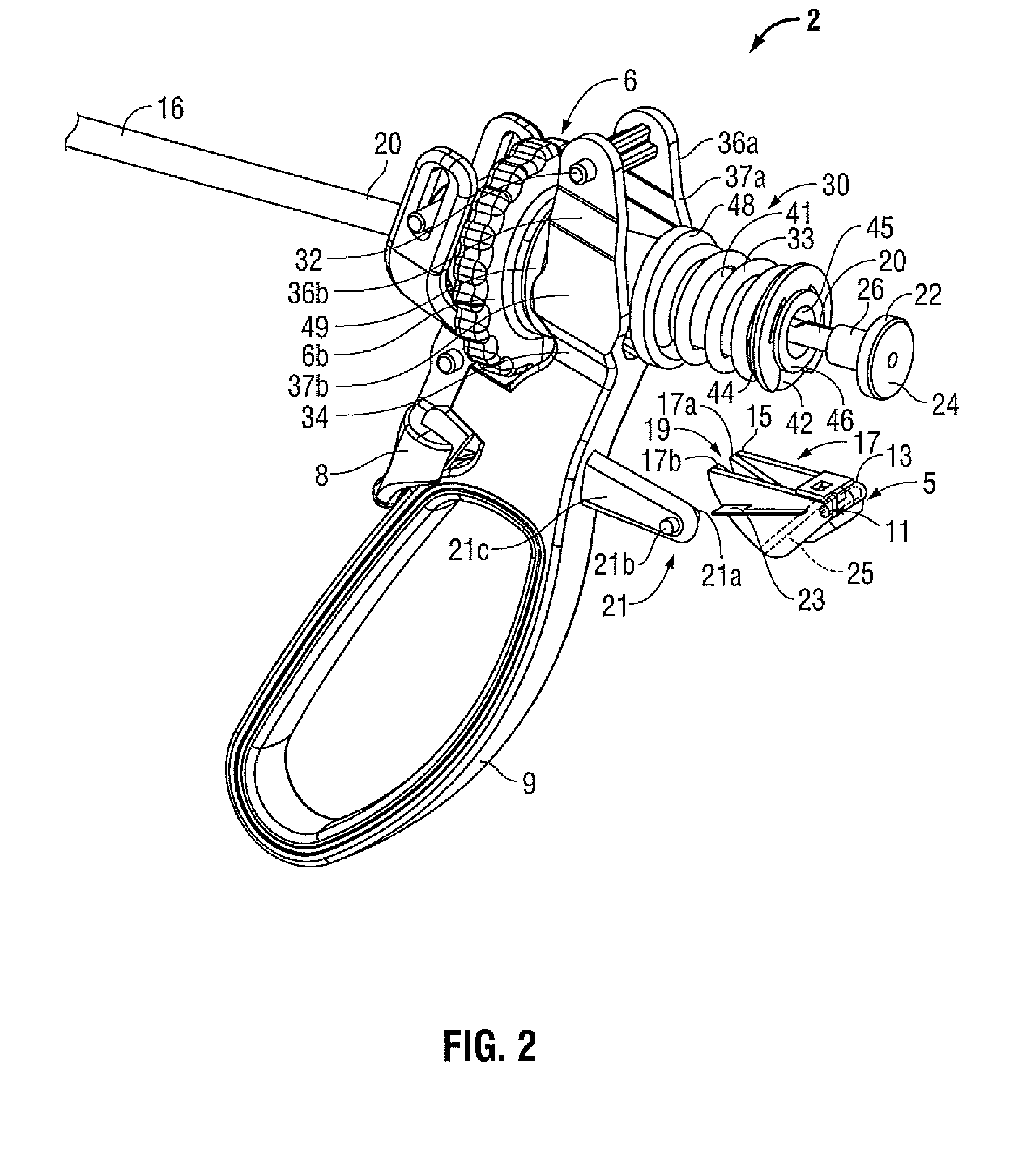
Surgical device
InactiveUS20070208375A1Without requiring lot of skillSimple structureDiagnosticsSurgical manipulatorsForcepsMulti degree of freedom
The invention provides a surgical device which can control a position and an attitude of a multi degree of freedom type grip portion (forceps) in a dummy manner on the basis of an operation of an operator in an operating portion. In a surgical device provided with a leading end joint portion having a leading end grip portion, a near-side joint portion having an operation portion, a handle portion supporting the operation portion, and an arm portion storing a wire for linking motions of the leading end joint portion and the near-side joint portion, the leading end joint portion is moved downward and upward by operating the operation portion and the handle portion upward and downward around the near-side joint portion, and the leading end joint portion is moved rightward and leftward by operating the operation portion and the handle portion leftward and rightward, thereby making the leading end joint portion execute a swing motion, and the leading end grip portion is opened and closed by opening and closing finger rests of the operation portion.
Owner:HITACHI LTD
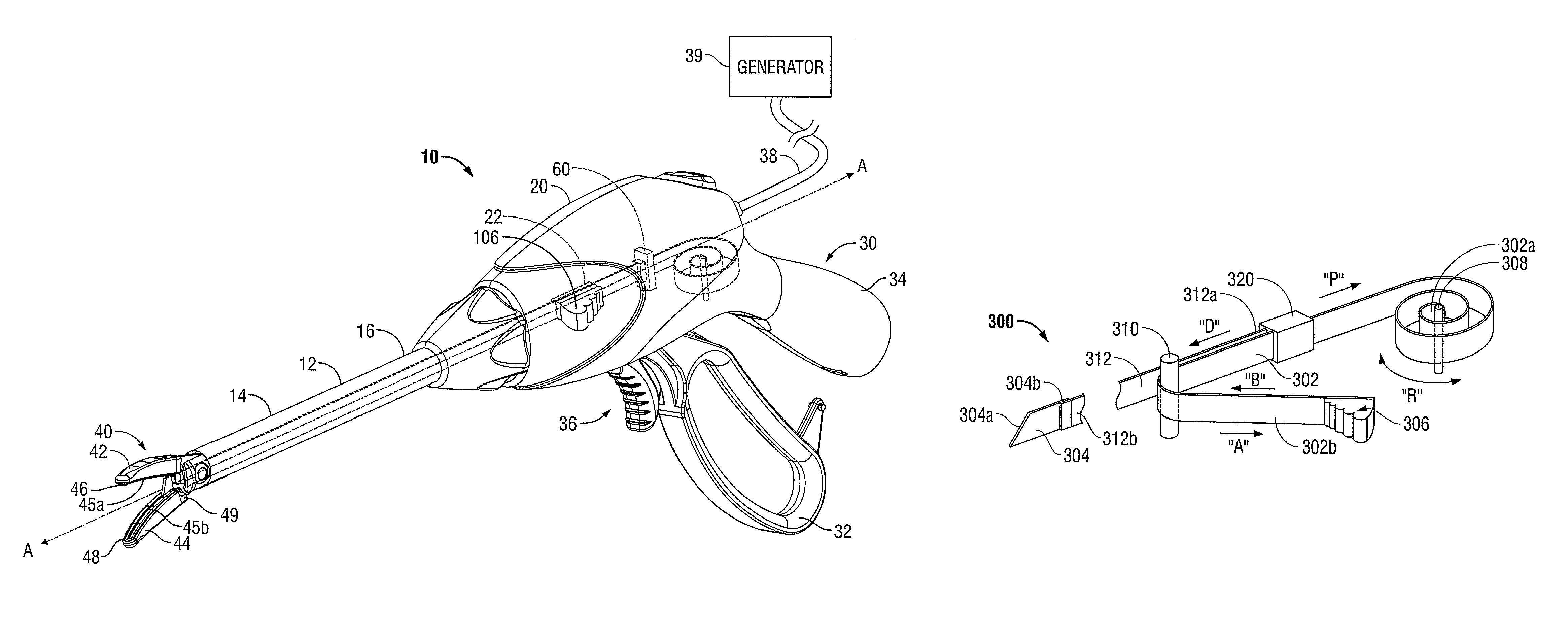
Apparatus for performing an electrosurgical procedure
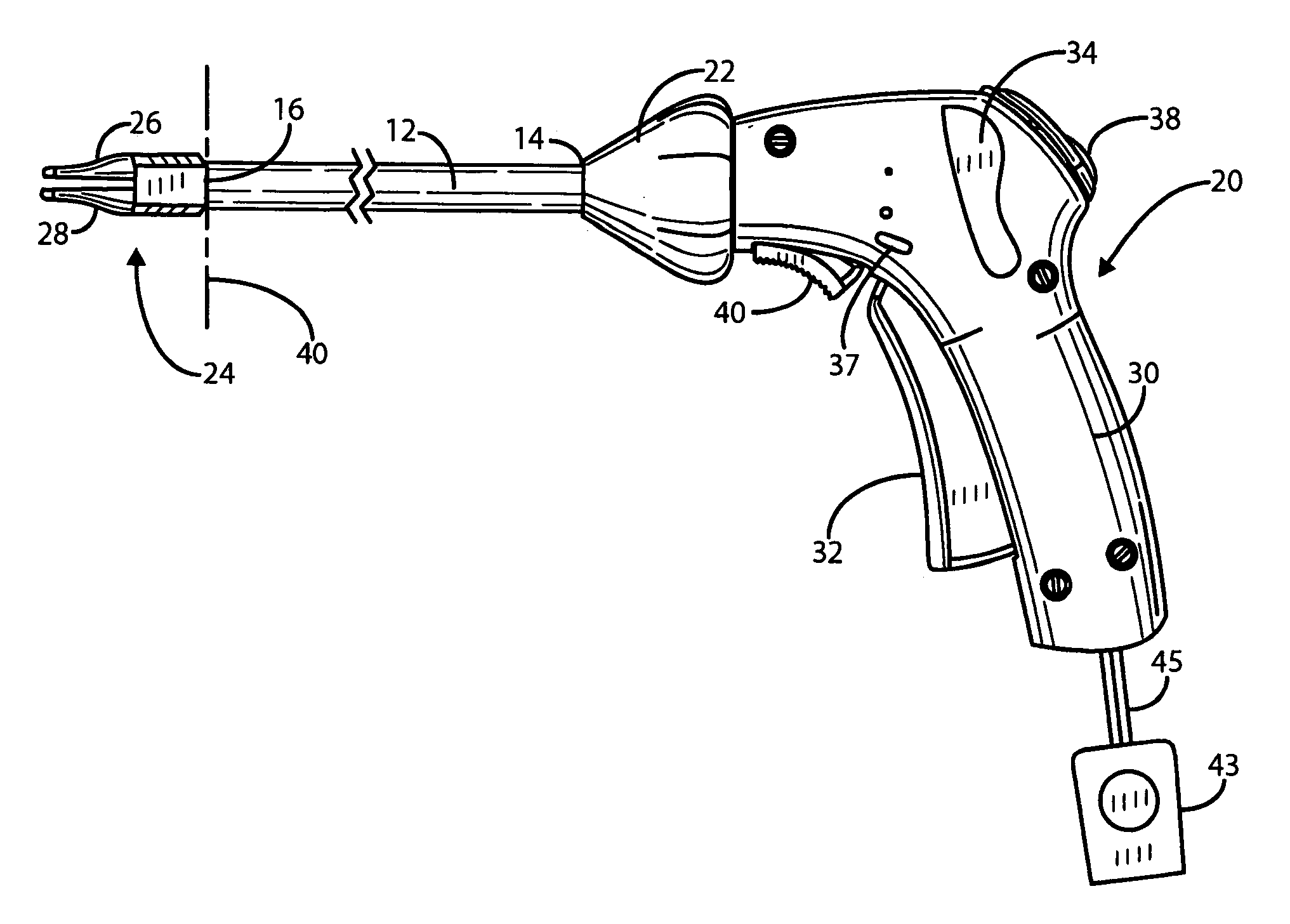
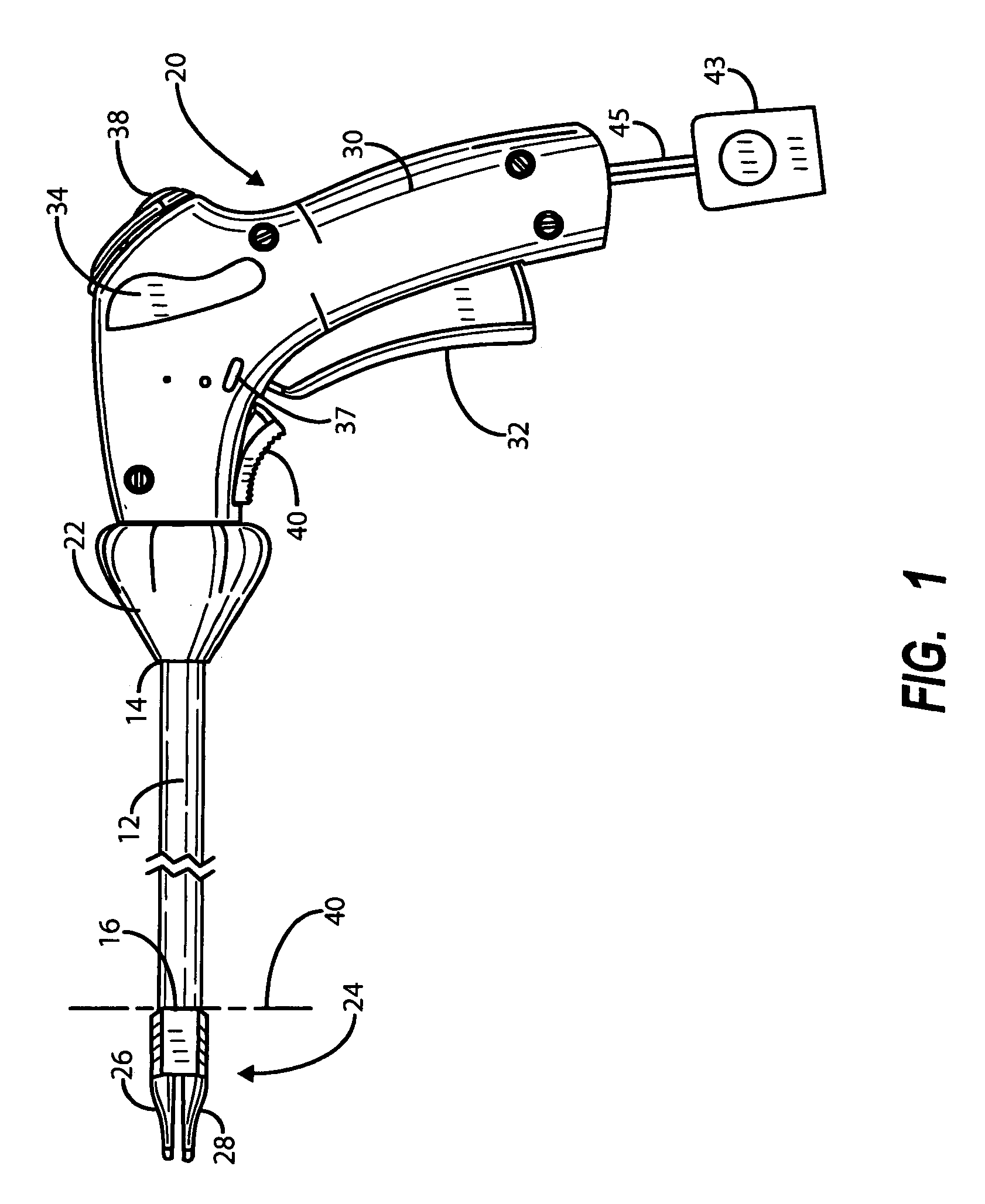
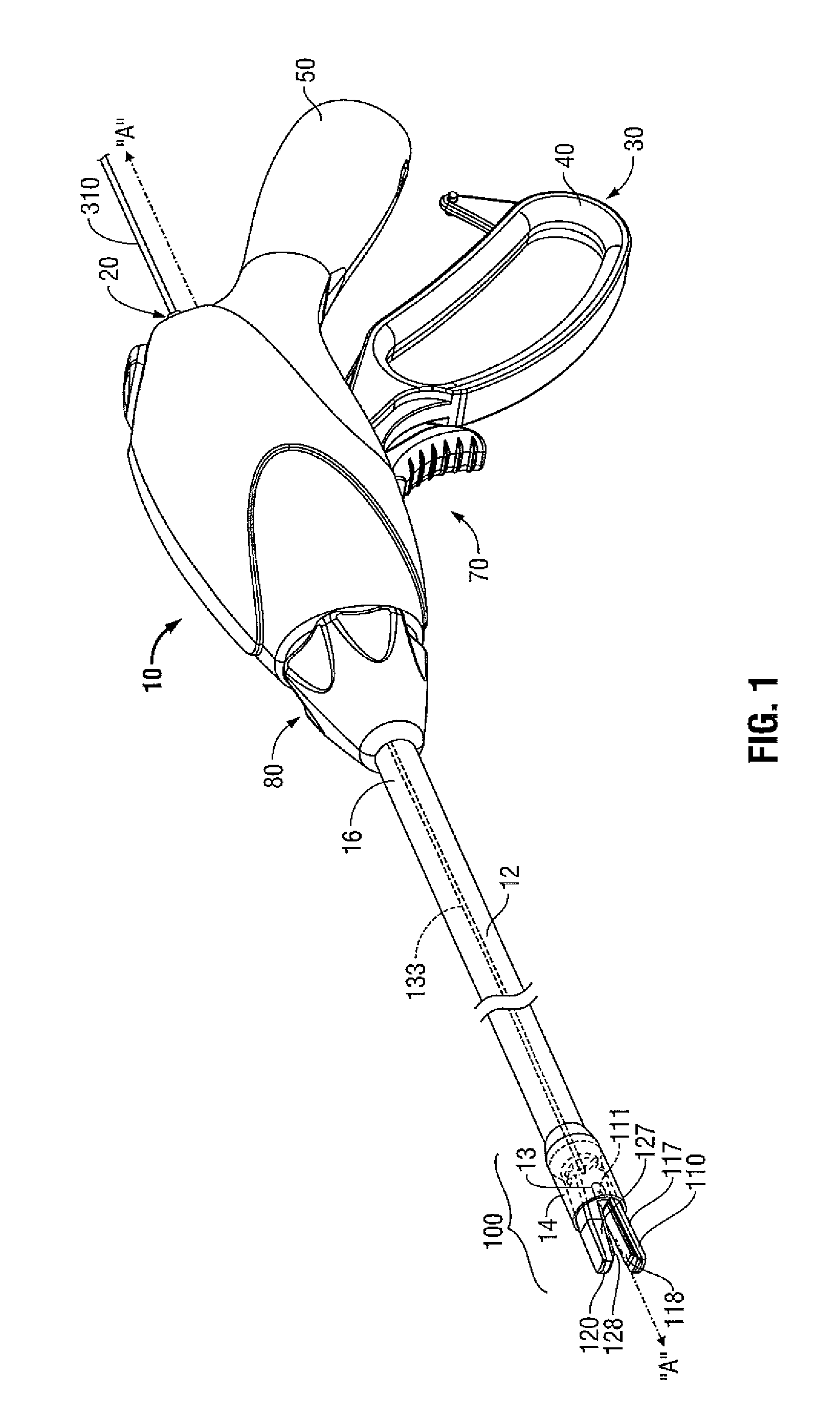
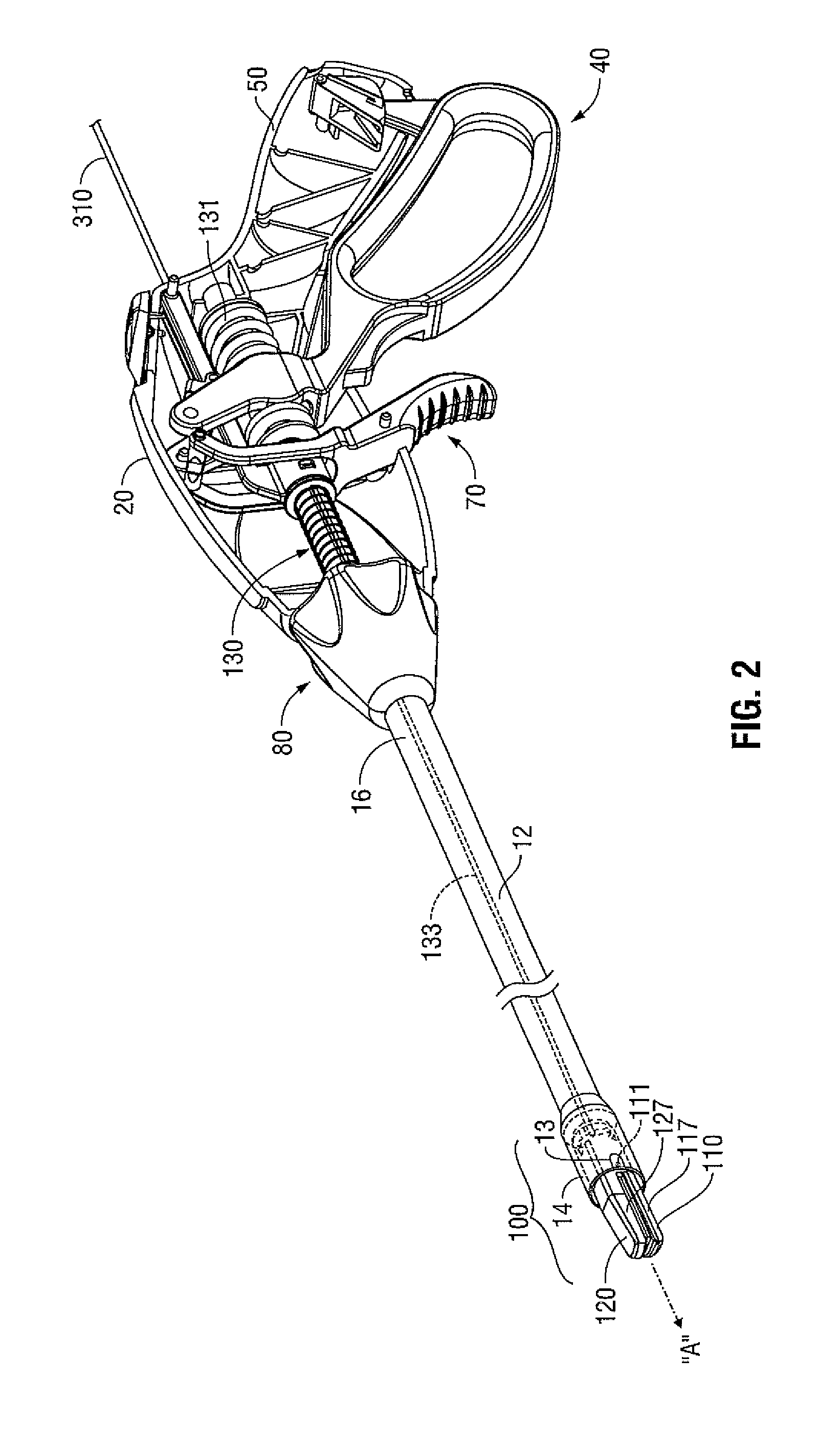
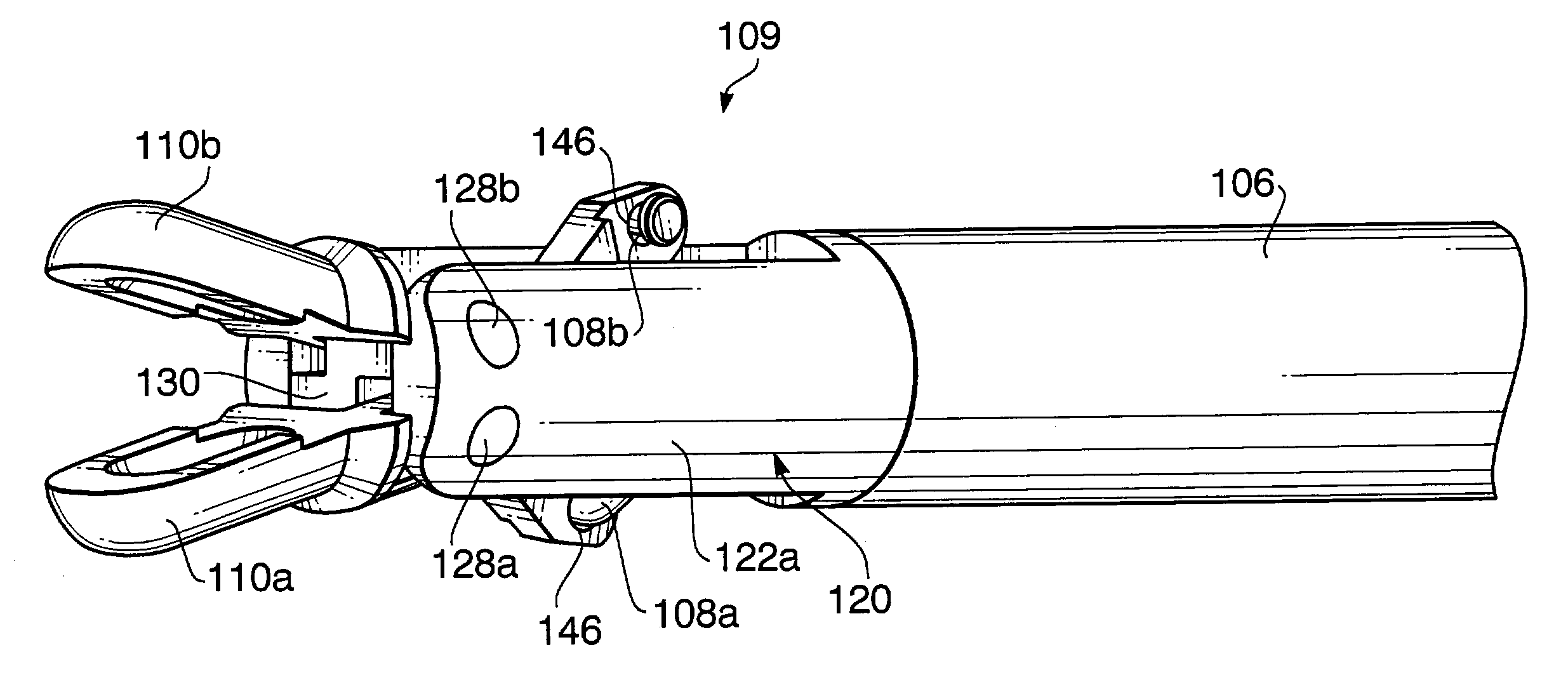
An endoscopic forceps includes a housing having a shaft extending therefrom for treating tissue. A longitudinal axis is defined through the shaft. An end effector assembly is operably coupled to a distal end of the shaft and includes a pair of first and second jaw members. A rotating assembly operably coupled to the shaft is configured to rotate the shaft and the end effector about the longitudinal axis. A drive assembly is configured to selectively and releasably engage the rotating assembly. Engagement of the rotating assembly with the drive assembly couples the rotating assembly to the shaft such that the shaft is rotatable about the longitudinal axis in a predetermined direction when the rotating assembly is rotated. And, disengagement of the rotating assembly from the drive assembly uncouples the rotating assembly from the shaft such that the shaft is non-rotatable about the longitudinal axis when the rotating assembly is rotated.
Owner:TYCO HEALTHCARE GRP LP
Low profile cutting assembly with a return spring
A forceps that includes a housing, a cutting assembly, and an actuator. The housing has a shaft attached thereto that extends therefrom and is configured to support a pair of jaw members at a distal end thereof. The jaw members are movable to grasp tissue therebetween. The cutting assembly includes a spring element that has proximal and distal ends. The proximal end of the spring element is fixed to a boss disposed within the housing and the distal end of the spring element includes a cutting edge. The spring element is coiled at a proximal end thereof to create a spring bias against the boss. The actuator is operably coupled to the spring element and is configured to selectively advance the cutting edge of the spring element into the jaw members against the spring bias to sever tissue disposed therebetween.
Owner:TYCO HEALTHCARE GRP LP
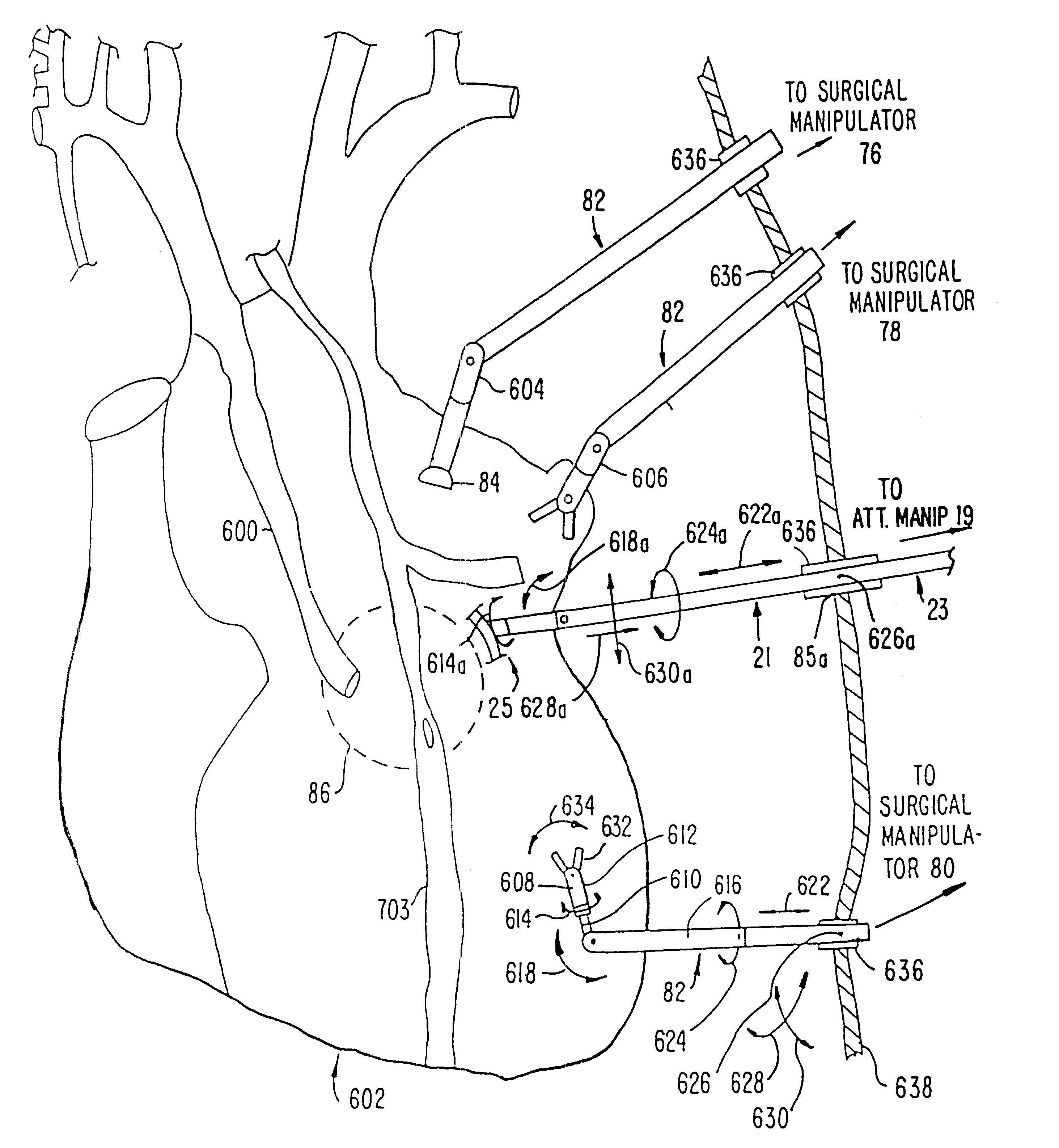
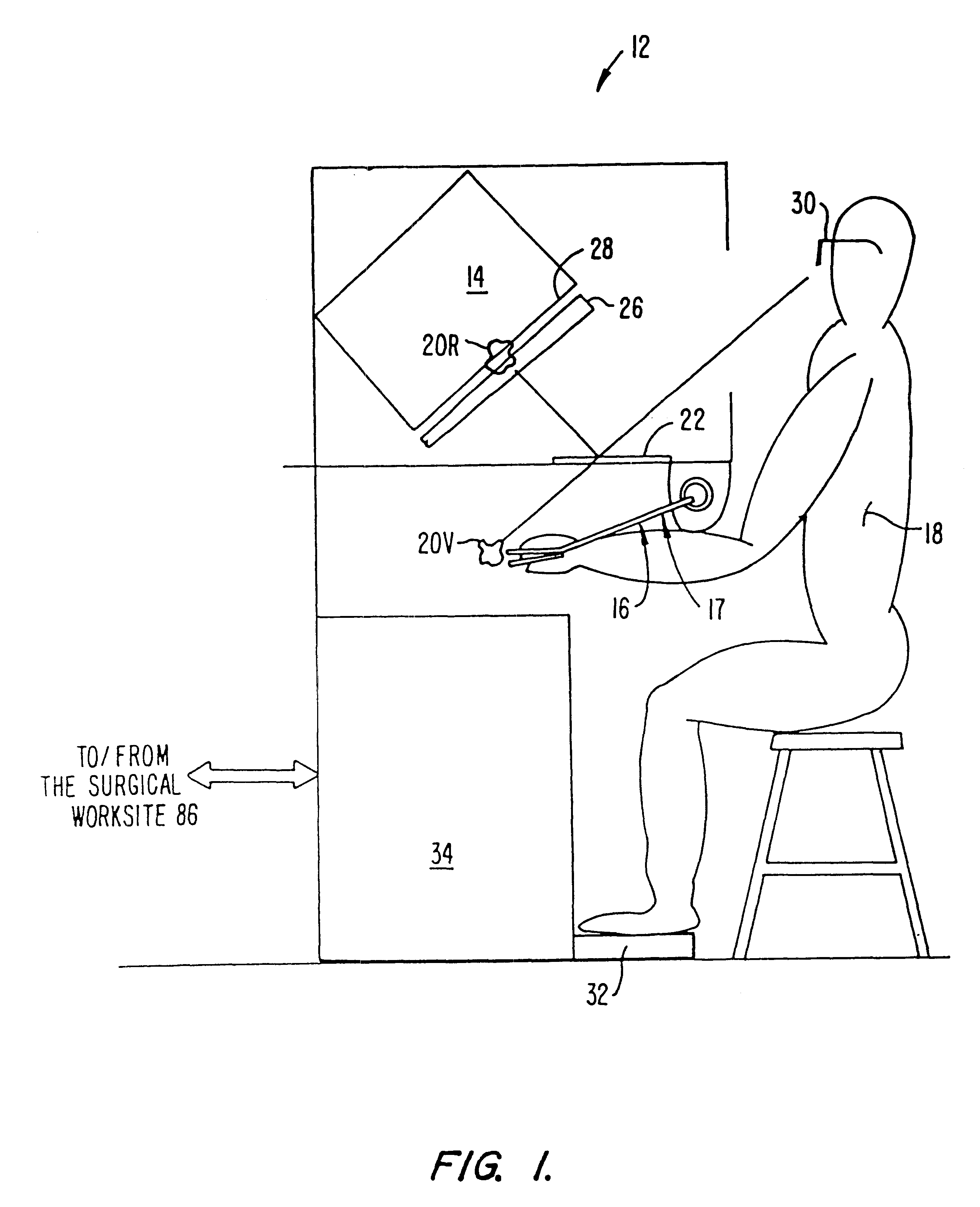
Performing cardiac surgery without cardioplegia
InactiveUS6468265B1Improve abilitiesEasy to controlSuture equipmentsDiagnosticsForcepsMotion tracking system
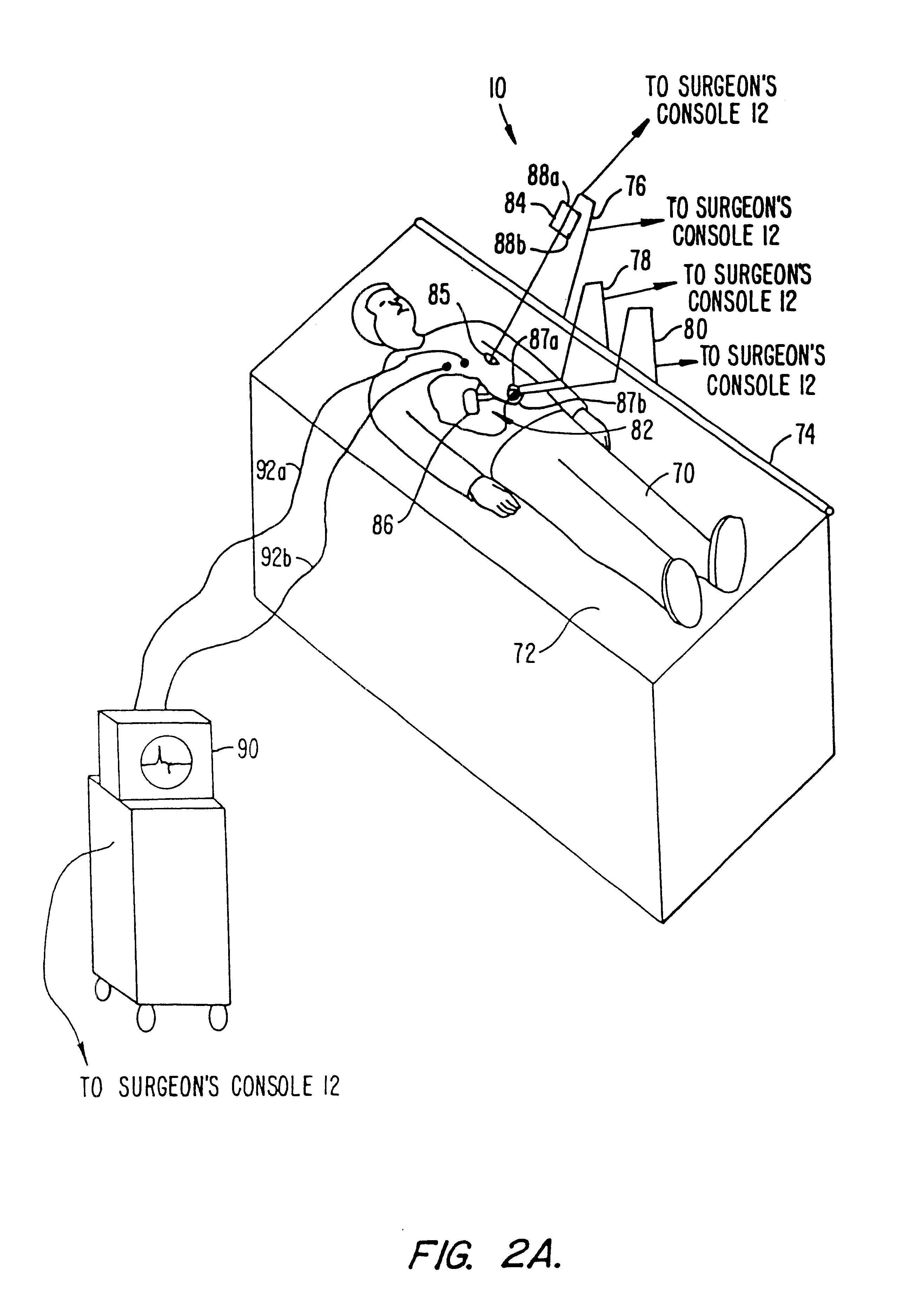
A surgical system or assembly for performing cardiac surgery includes a surgical instrument; a servo-mechanical system engaged to the surgical instrument for operating the surgical instrument; and an attachment assembly for removing at least one degree of movement from a moving surgical cardiac worksite to produce a resultant surgical cardiac worksite. The surgical system or assembly also includes a motion tracking system for gathering movement information on a resultant surgical cardiac worksite. A control computer is engaged to the attachment assembly and to the motion tracking system and to the servo-mechanical system for controlling movement of the attachment assembly and for feeding gathered information to the servo-mechanical system for moving the surgical instrument in unison with the resultant surgical cardiac worksite such that a relative position of the moving surgical instrument with respect to the resultant surgical cardiac worksite is generally constant. A video monitor is coupled to the control computer; and an input system is coupled to the servo-mechanical system and to the control computer for providing a movement of the surgical instrument. The video monitor displays movement of the surgical instrument while the resultant surgical cardiac worksite appears substantially stationary, and while a relative position of the surgical instrument moving in unison with the resultant surgical cardiac worksite, as a result from the movement information gathered by the motion tracking system, remains generally constant. A method of performing cardiac surgery without cardioplegia comprising removing at least one degree of movement freedom from a moving surgical cardiac worksite to produce at least a partially stationary surgical cardiac worksite while allowing a residual heart section, generally separate from the at least partially stationary surgical cardiac worksite, to move as a residual moving heart part. Cardiac surgery is performed on the at least partially stationary cardiac worksite with a surgical instrument such as needle drivers, forceps, blades and scissors.
Owner:INTUITIVE SURGICAL OPERATIONS INC
Active forceps
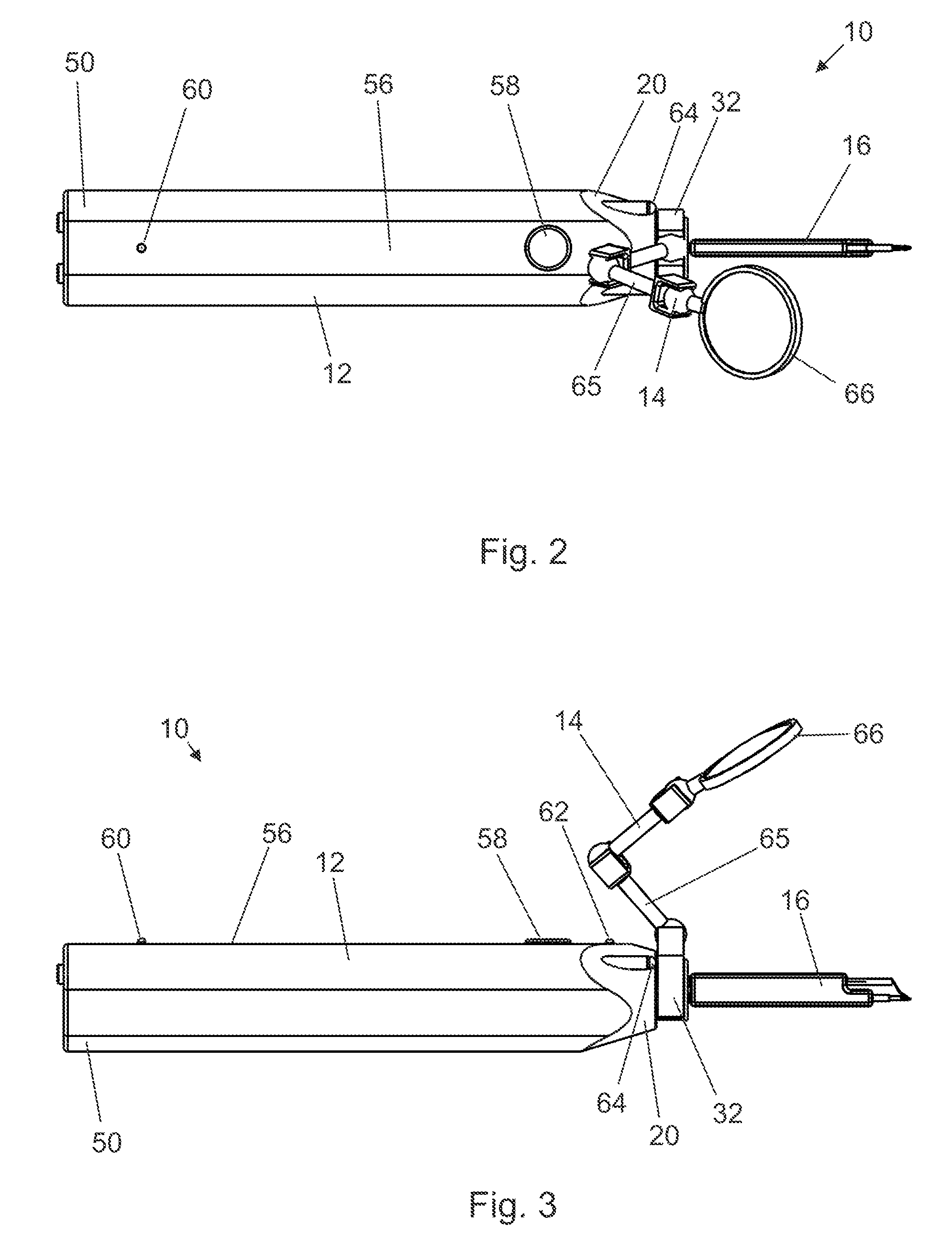
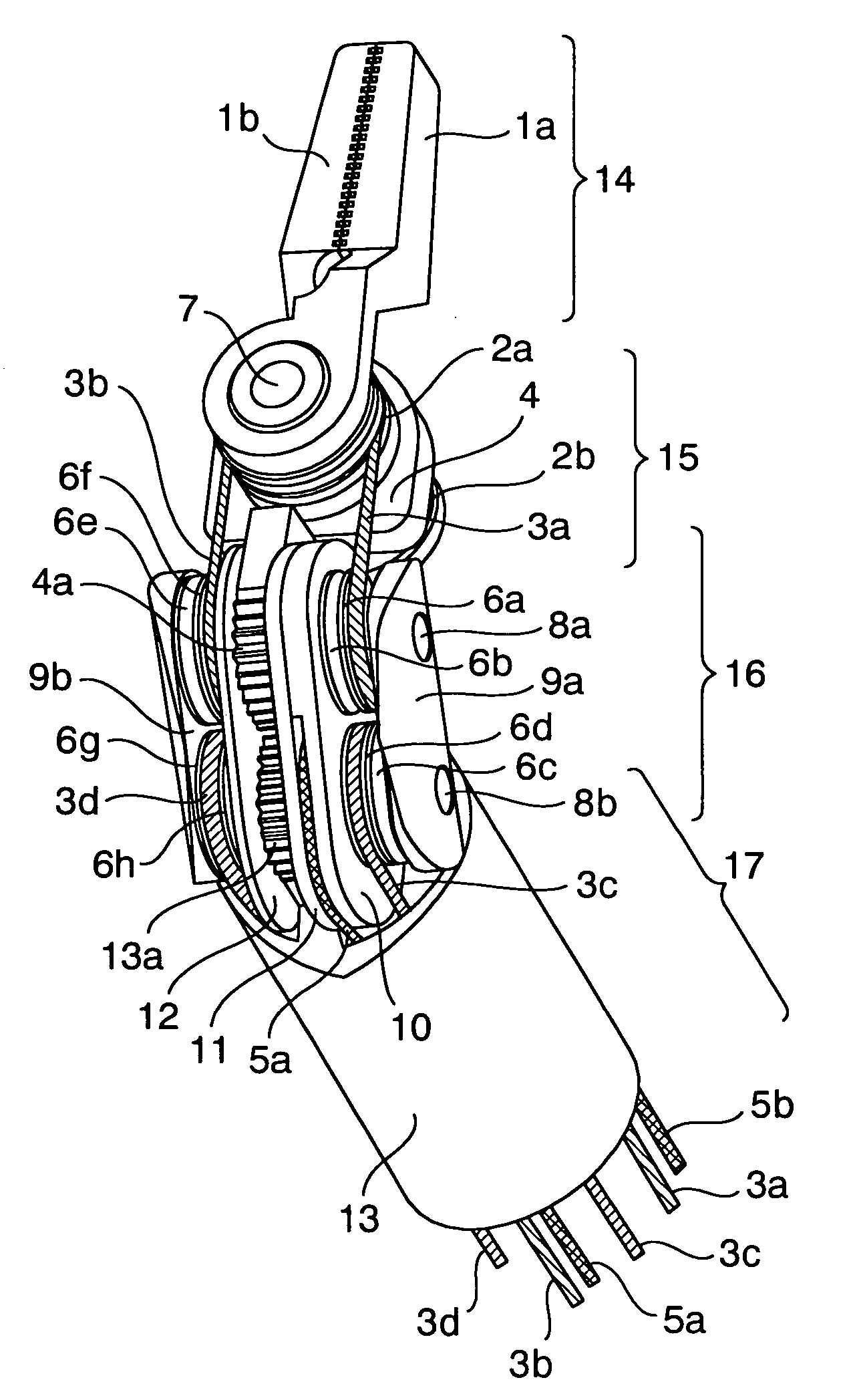
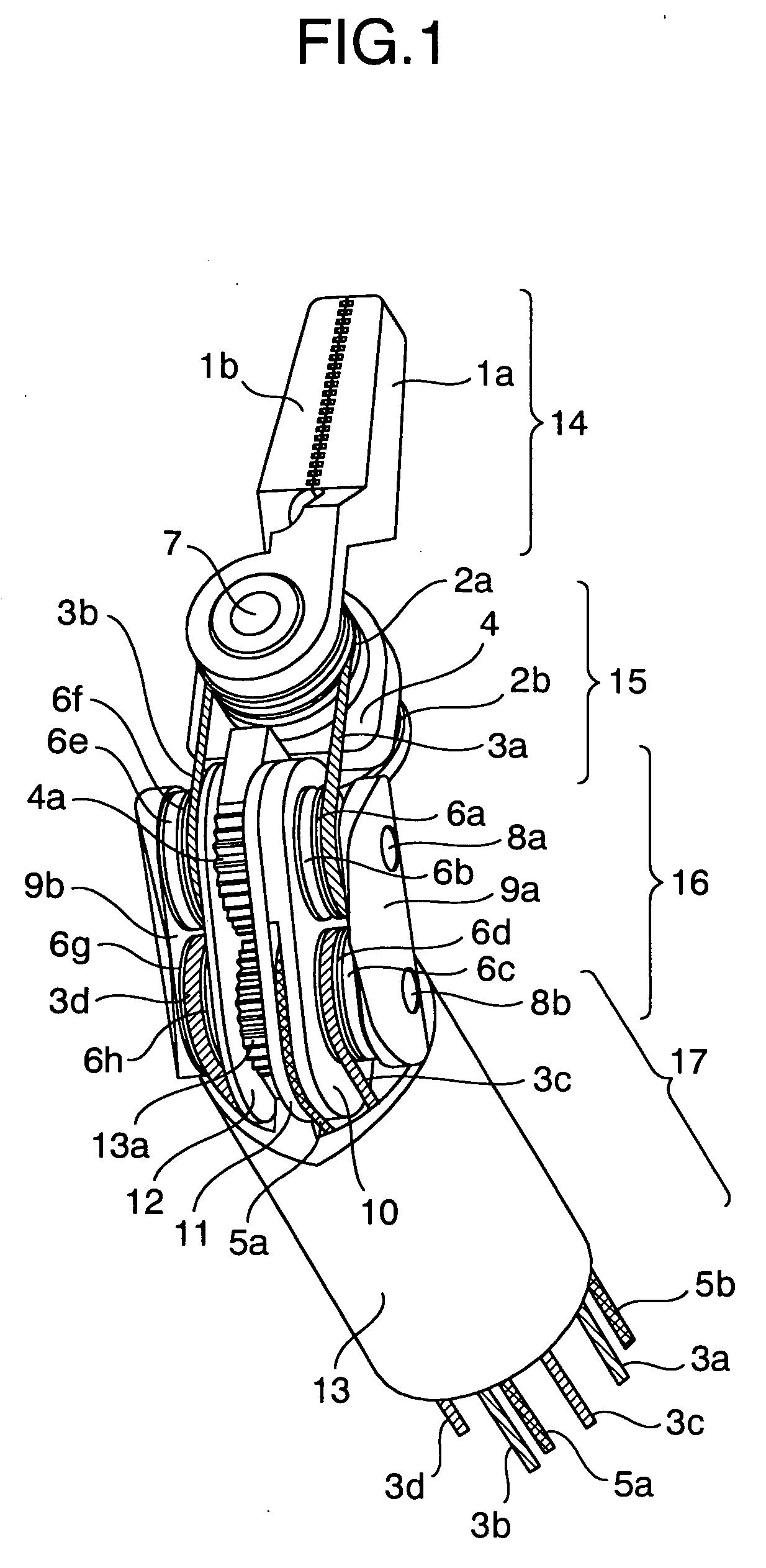
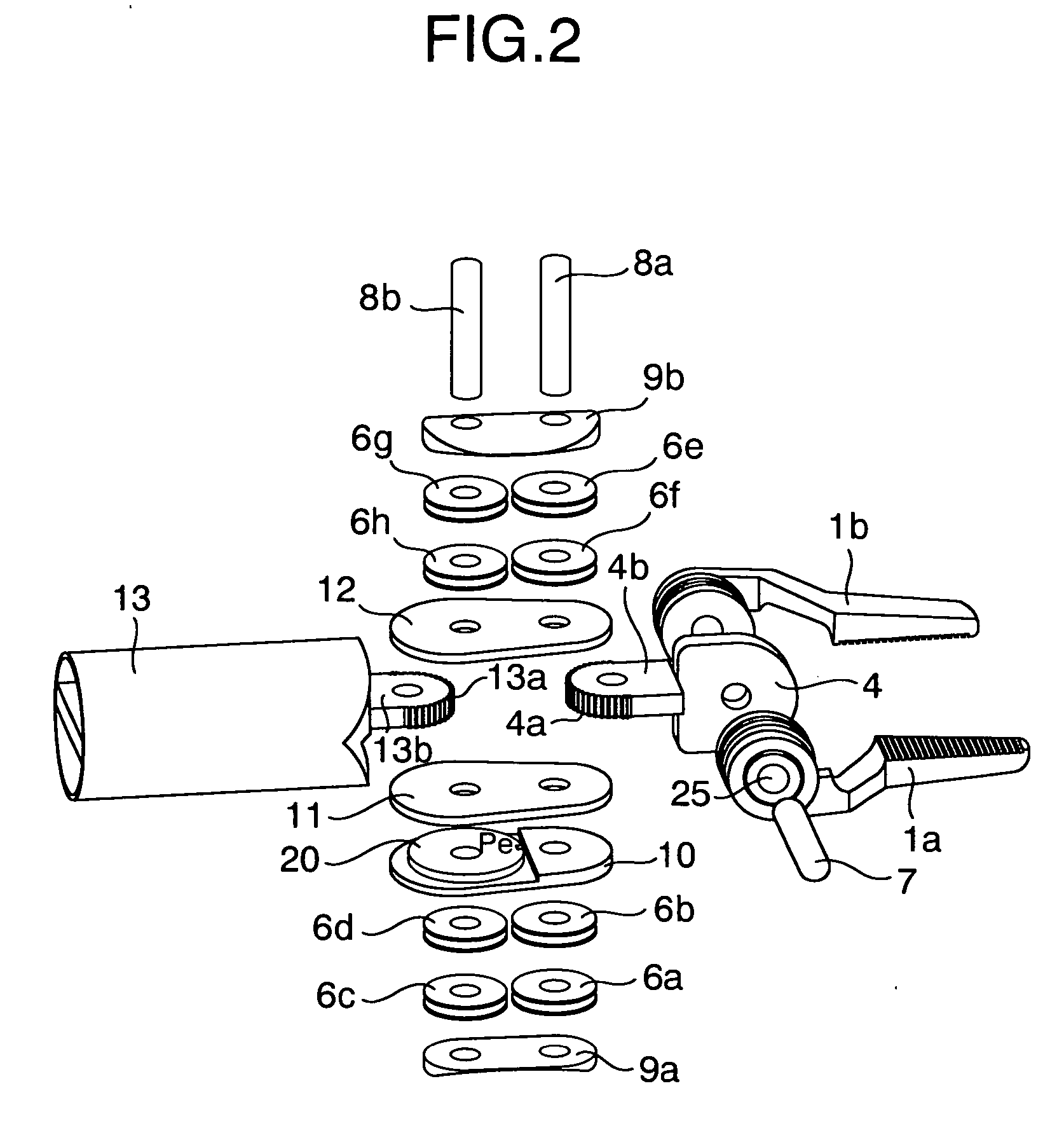
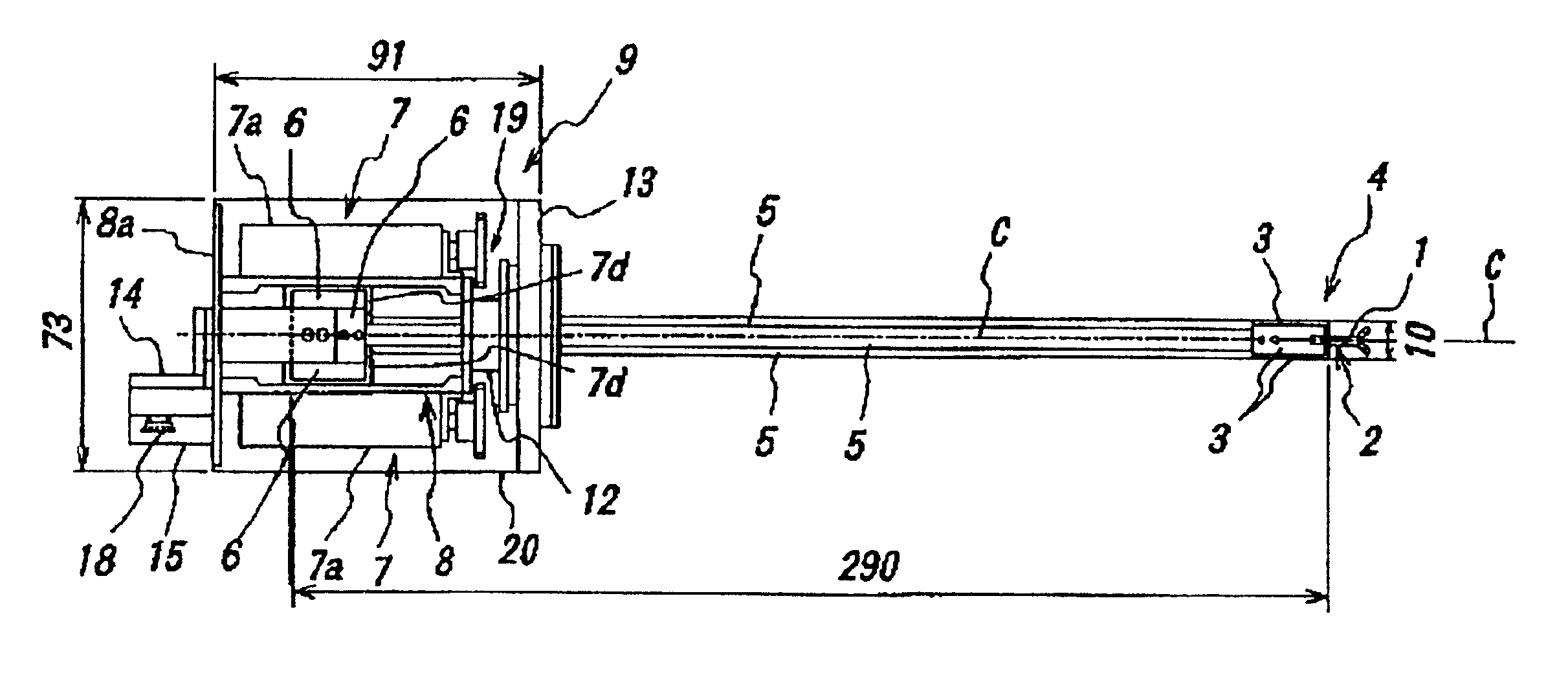
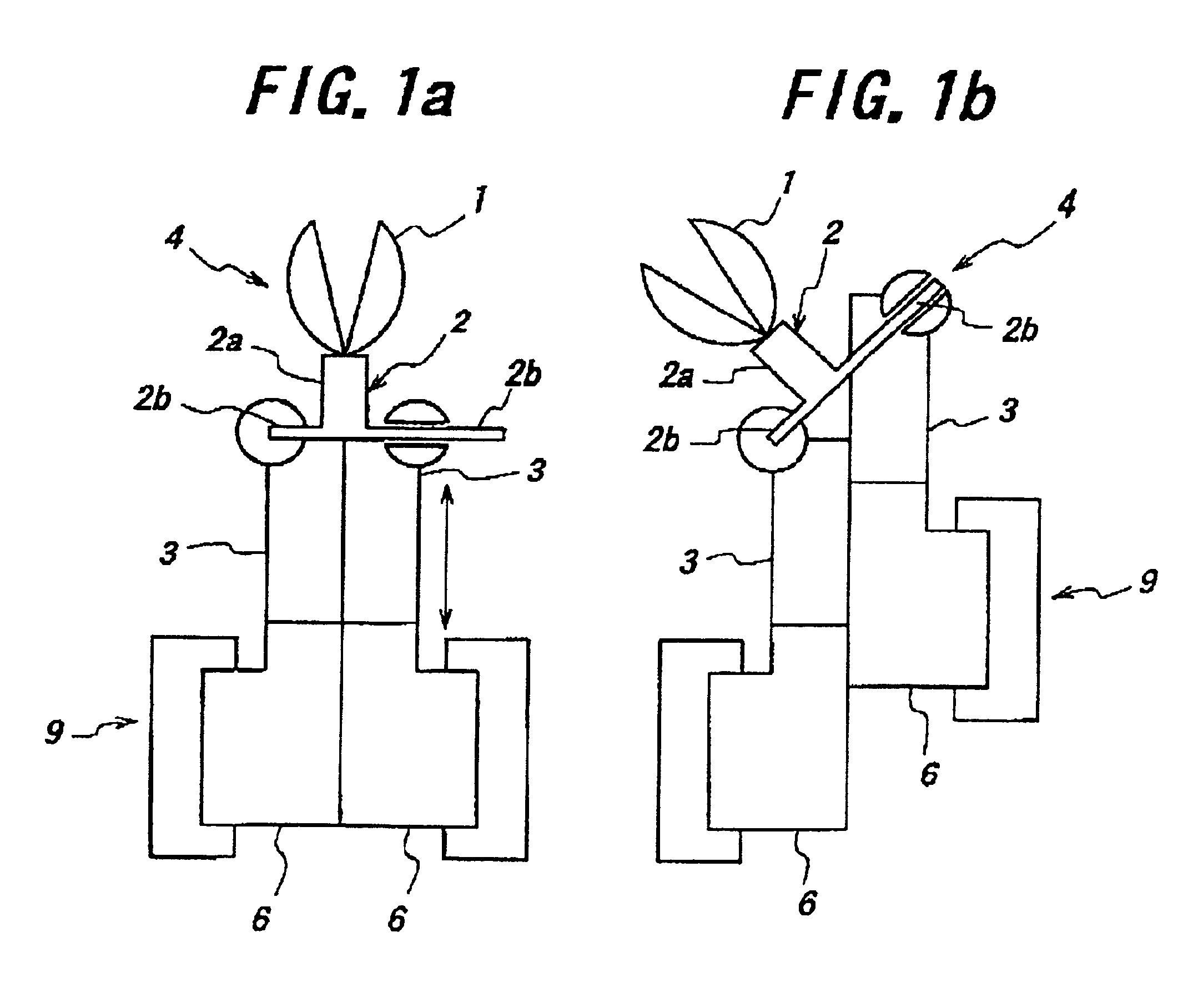
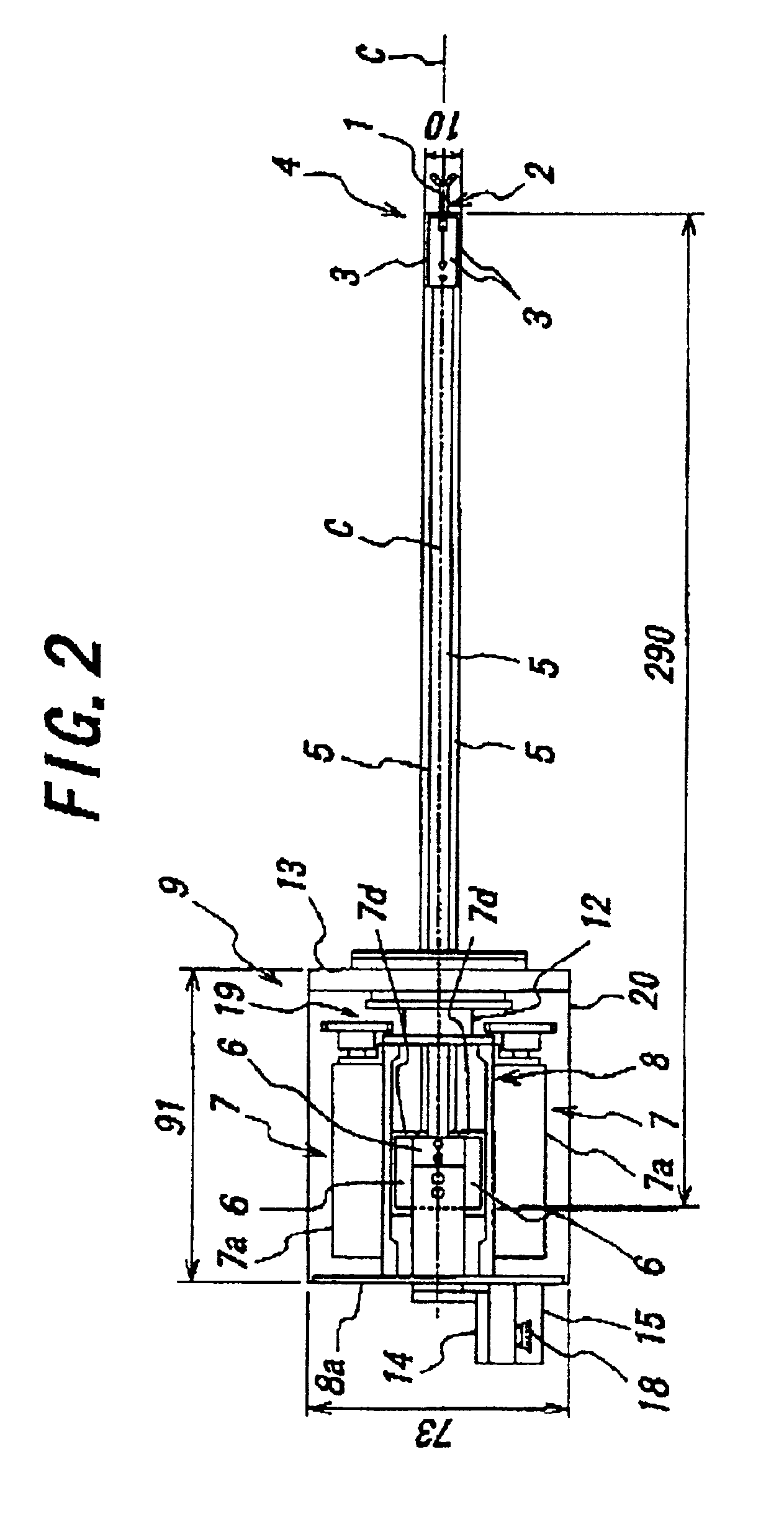
Endoscopic surgical operation such as evisceration has been so far hardly achieved by a medical robot, since it requires high power. The present invention provides a downsized high-flexibility active forceps to enable such an operation, without needing a large space for manipulation to target a limited operative area. An active forceps of the present invention comprises: a tip forceps part 4 having, a tip supporting member 2 to support a forceps tip 1 at a center section 2a with a plurality of arms 2b laterally projected therefrom, and a plurality of tip side advancing and retreating members 3 connected at a front end with the plurality of arms respectively oscillatable while connected to one another relatively movable in directions toward front and rear ends; and a forceps bottom part 9 having, a plurality of bottom side advancing and retreating members 6 each integrally coupled to the plurality of tip side advancing and retreating members 3, while connected to one another relatively movable indirections toward front and rear ends to constitute a link mechanism together with the tip side advancing and retreating members 3 and the tip supporting member 2, and a bottom frame 8 provided with forward and backward actuating means 7 for moving relatively to one another the bottom side advancing and retreating members 6 in directions toward front and rear ends.
Owner:TOKYO UNIV OF THE
Linear suturing and cutting device
Owner:TOUCHSTONE INTERNATIONAL MEDICAL SCIENCE CO LTD
Surgical treatment apparatus
A surgical treatment apparatus according to the present invention includes an outer sheath, extending from a base portion subject to an operator's hand to the tip subject to insertion into a body cavity, that is provided with a working channel through which a treatment instrument can be passed; an image pickup device disposed at the tip portion of the outer sheath; and pivotable forceps disposed at the tip portion of the outer sheath, supported on a supporting section protruding in the axial direction via a joint being bent away from the working channel, and having a pair of forceps members arranged so as to be freely opened / closed, wherein the image pickup device is disposed at a position between the axis line of the supporting section and the axis line of the working channel and offset from an imaginary line connecting the two axis lines.
Owner:OLYMPUS CORP
Apparatus for performing an electrosurgical procedure
An endoscopic forceps is provided and includes a housing having a shaft that extends therefrom. An end effector assembly is operatively connected to a distal end of the shaft and includes a pair of pivotably coupled first and second jaw members. The jaw members are movable relative to one another. A drive mechanism includes a driving structure. A link assembly includes two or more links that are operably coupled to each other and the drive structure. The two or more links are operably coupled to respective ones of the first and second jaw members.
Owner:TYCO HEALTHCARE GRP LP
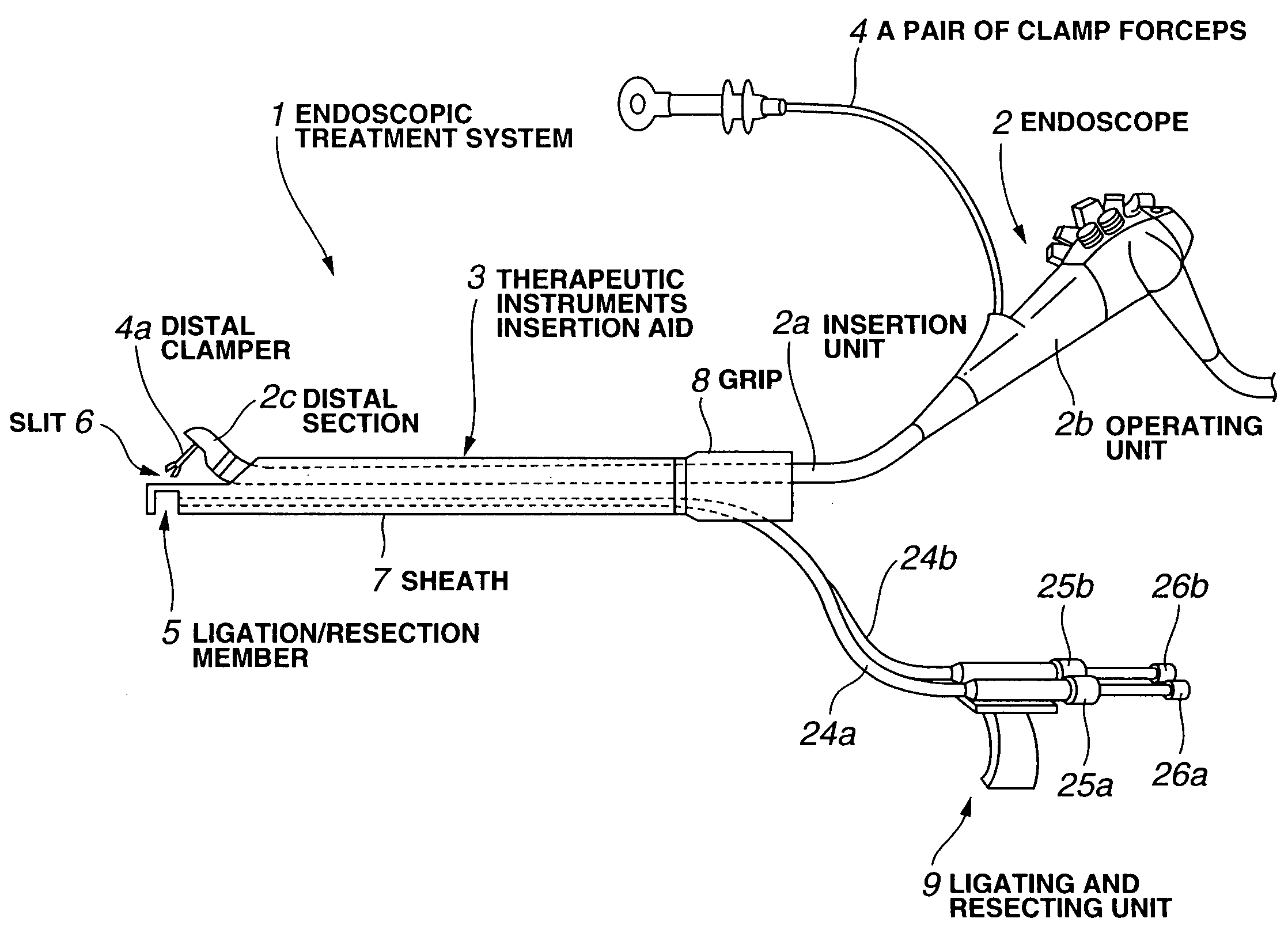
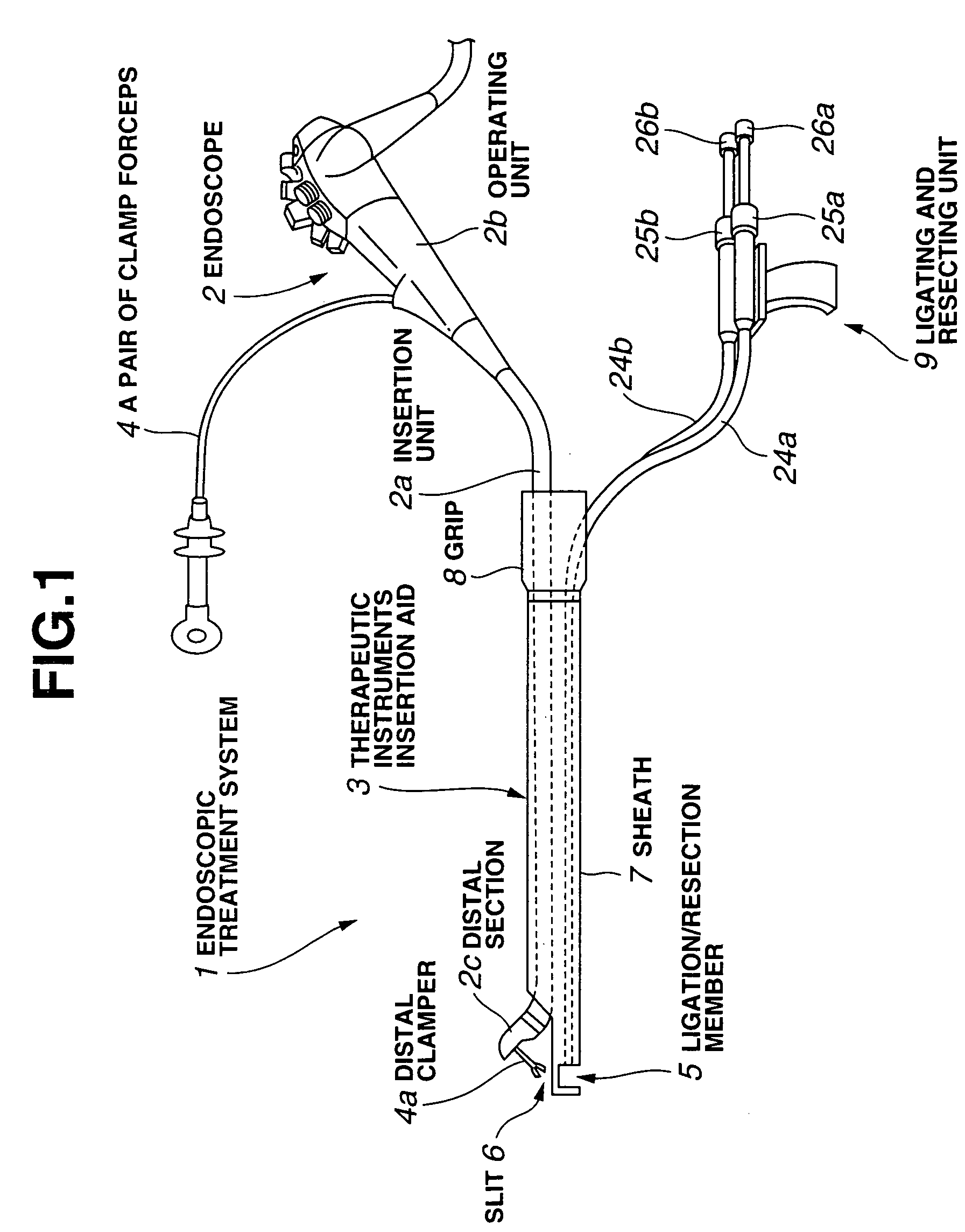
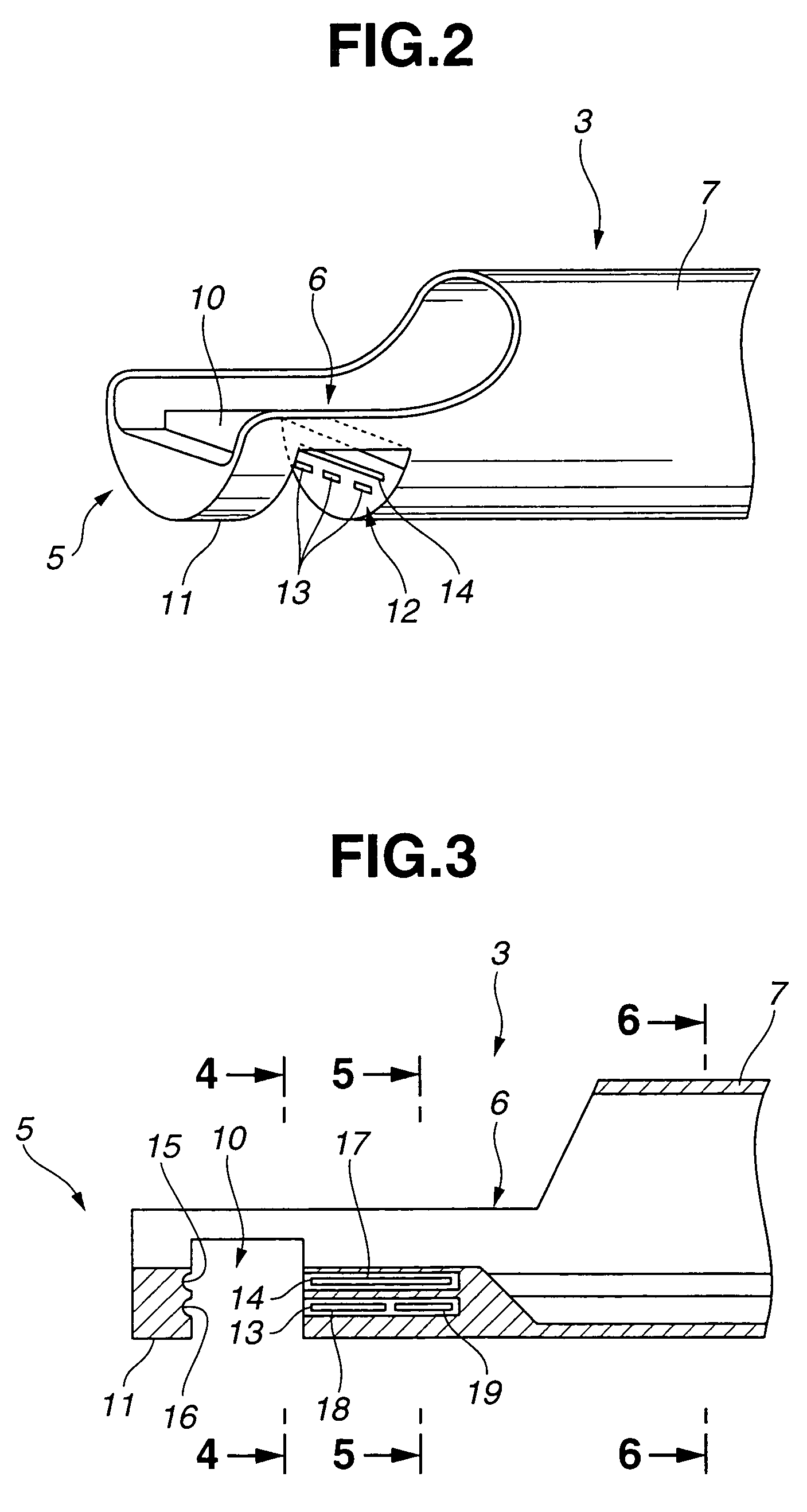
Endoscopic treatment system
InactiveUS7341554B2Reliably suturingReliable resectionSuture equipmentsCannulasBiological bodyEndoscopic treatment
An endoscopic treatment system is designed to suture or resect a lesion while ensuring the ease of insertion into a deep region in the large intestine. The endoscopic treatment system comprises an endoscope and a therapeutic instruments insertion aid into which the endoscope is inserted. The endoscopic treatment system further comprises: a pair of clamp forceps that clamps and lifts a living-body tissue; a lateral hole formed in the therapeutic instruments insertion aid and used to control the position of the living-body tissue clamped and lifted by the pair of clamp forceps or to control the lifting thereof; a ligature used to ligate the living-body tissue whose position or lifting is controlled by the lateral hole; and a cutter used to resect the living-body tissue at a position between a region ligated with the ligature and a region clamped and lifted with the pair of clamp forceps.
Owner:OLYMPUS CORP
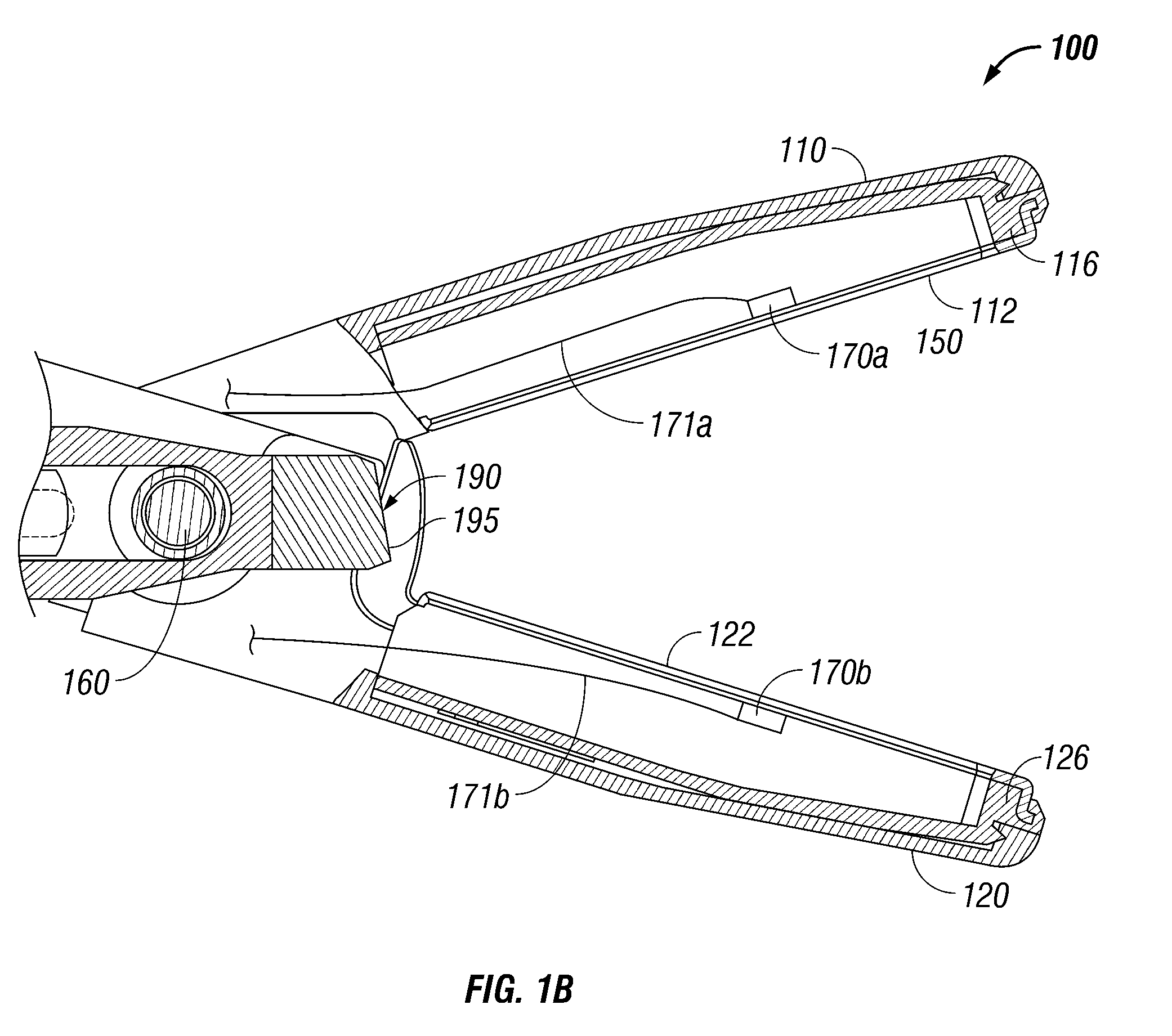
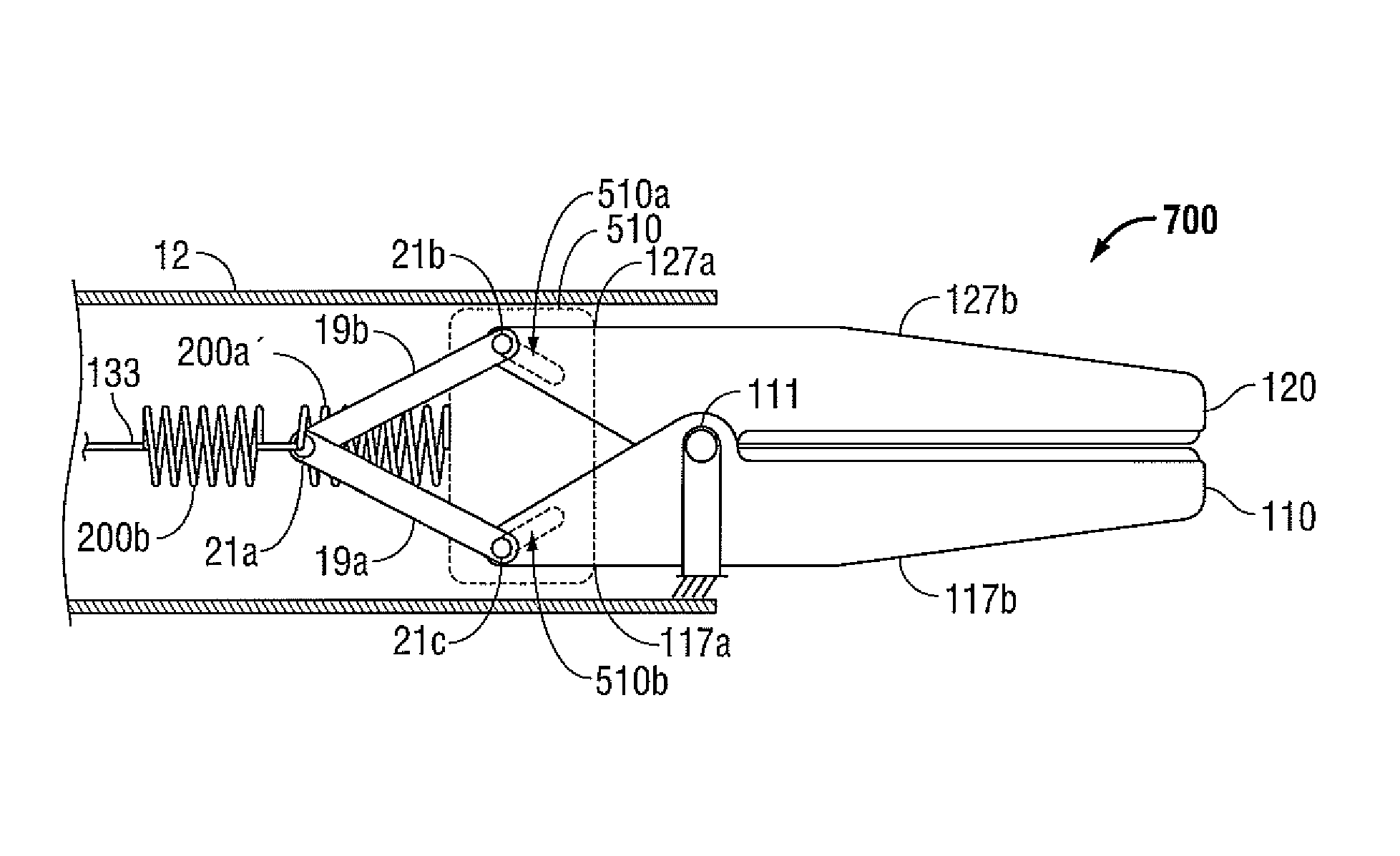
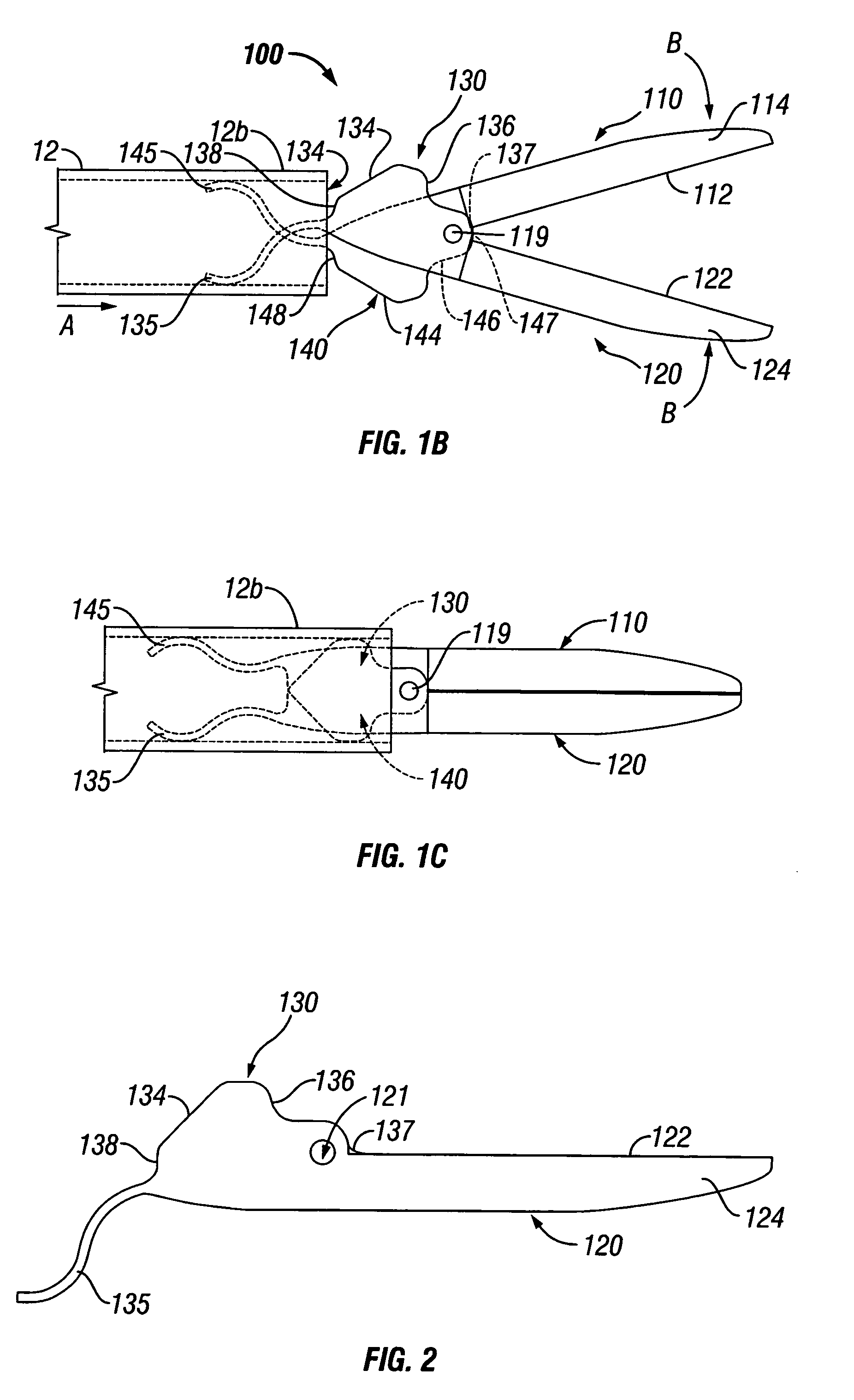
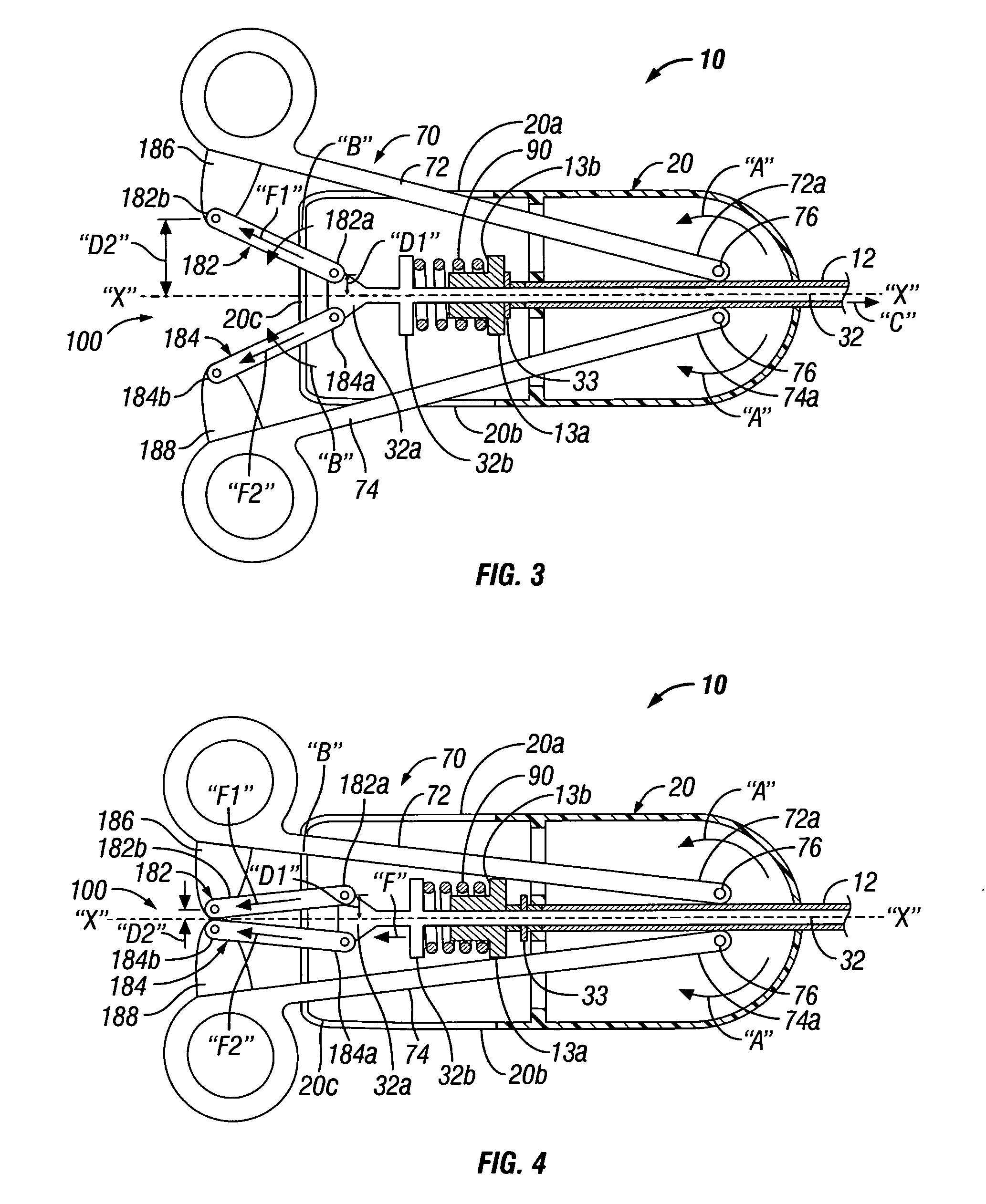
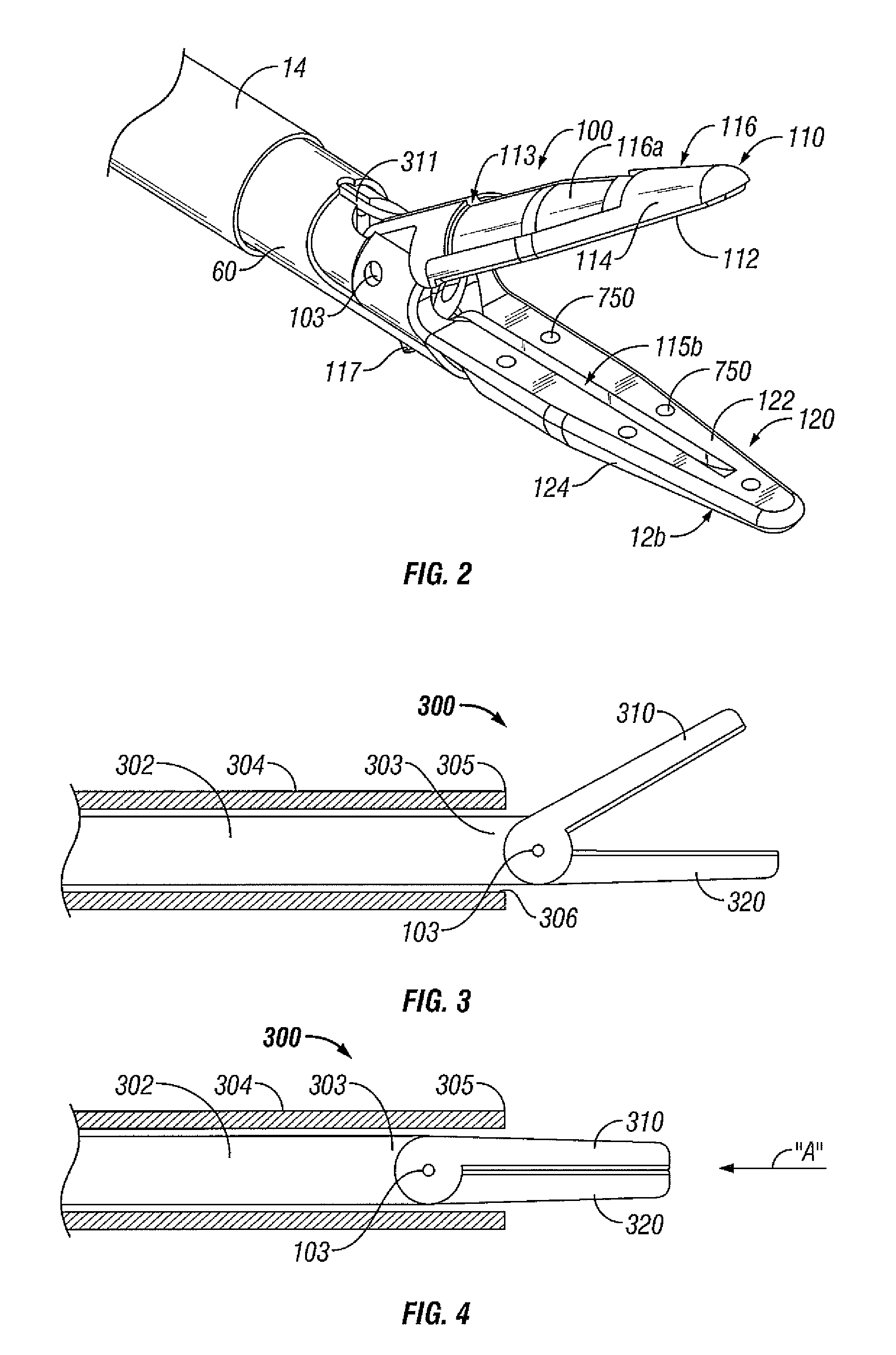
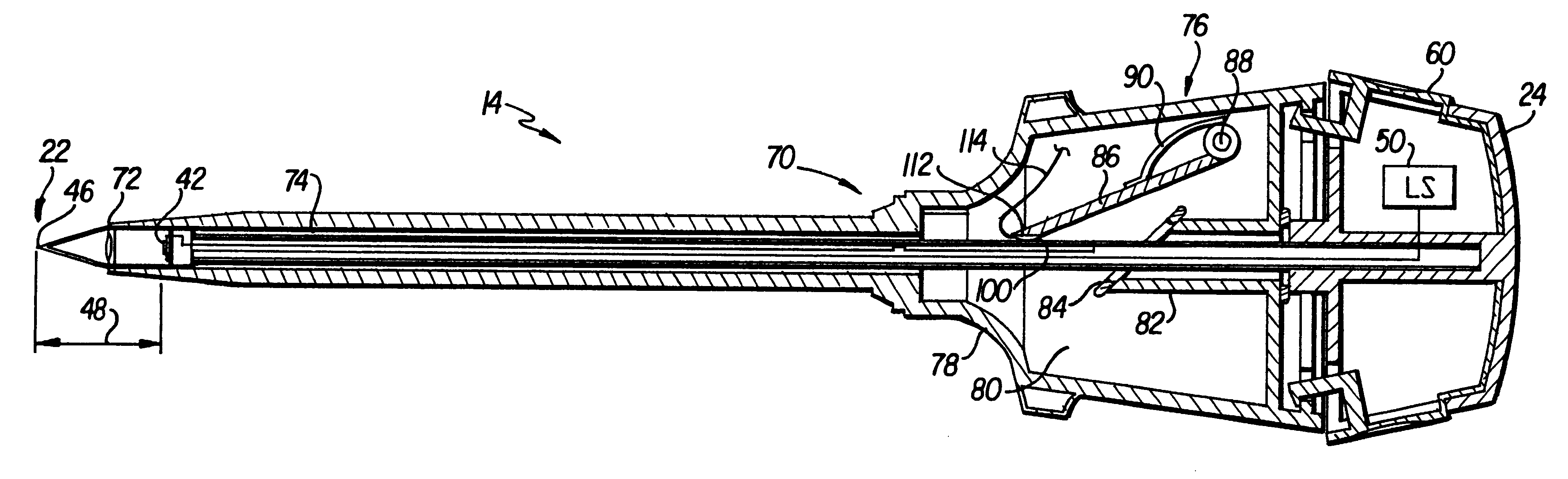
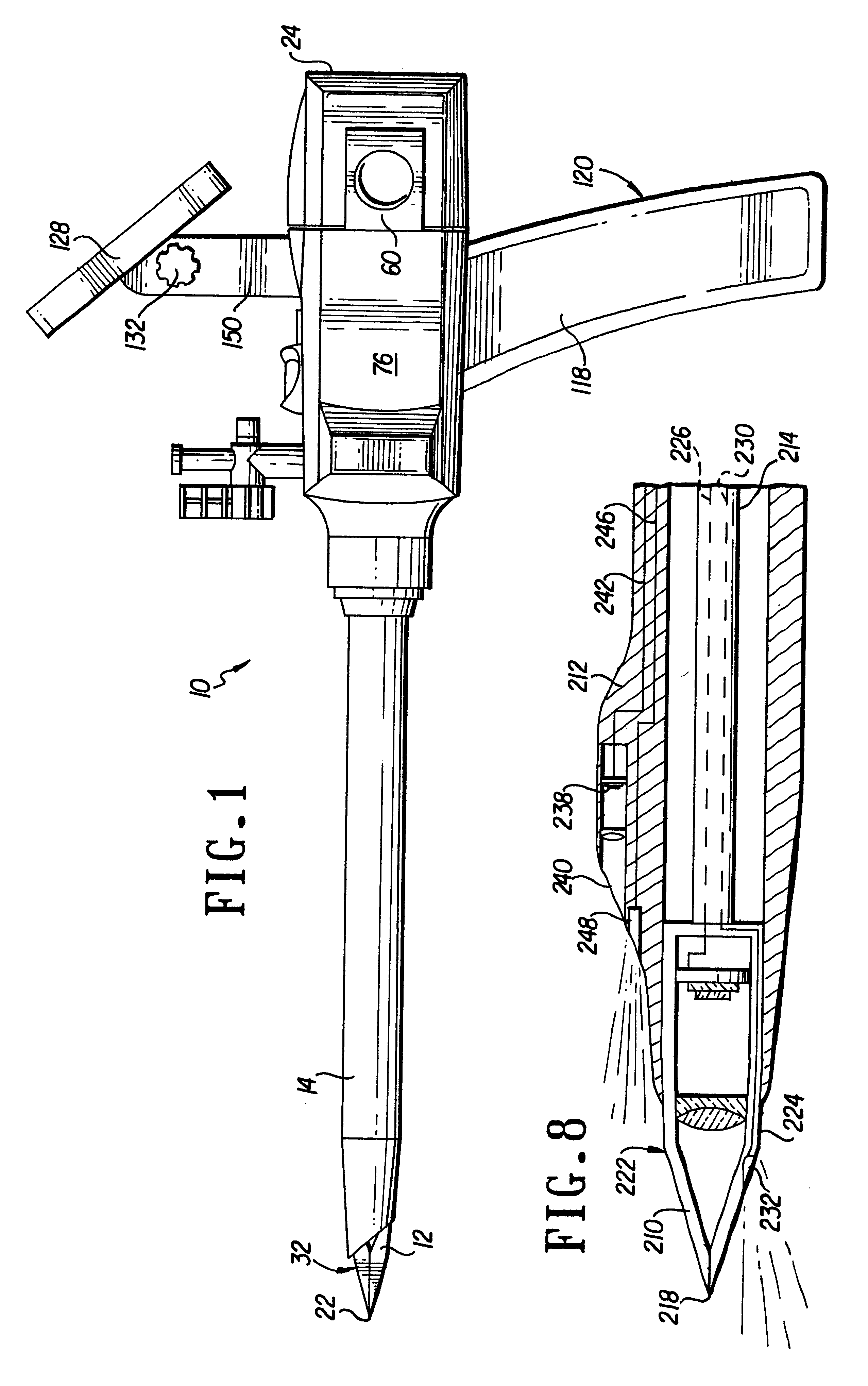
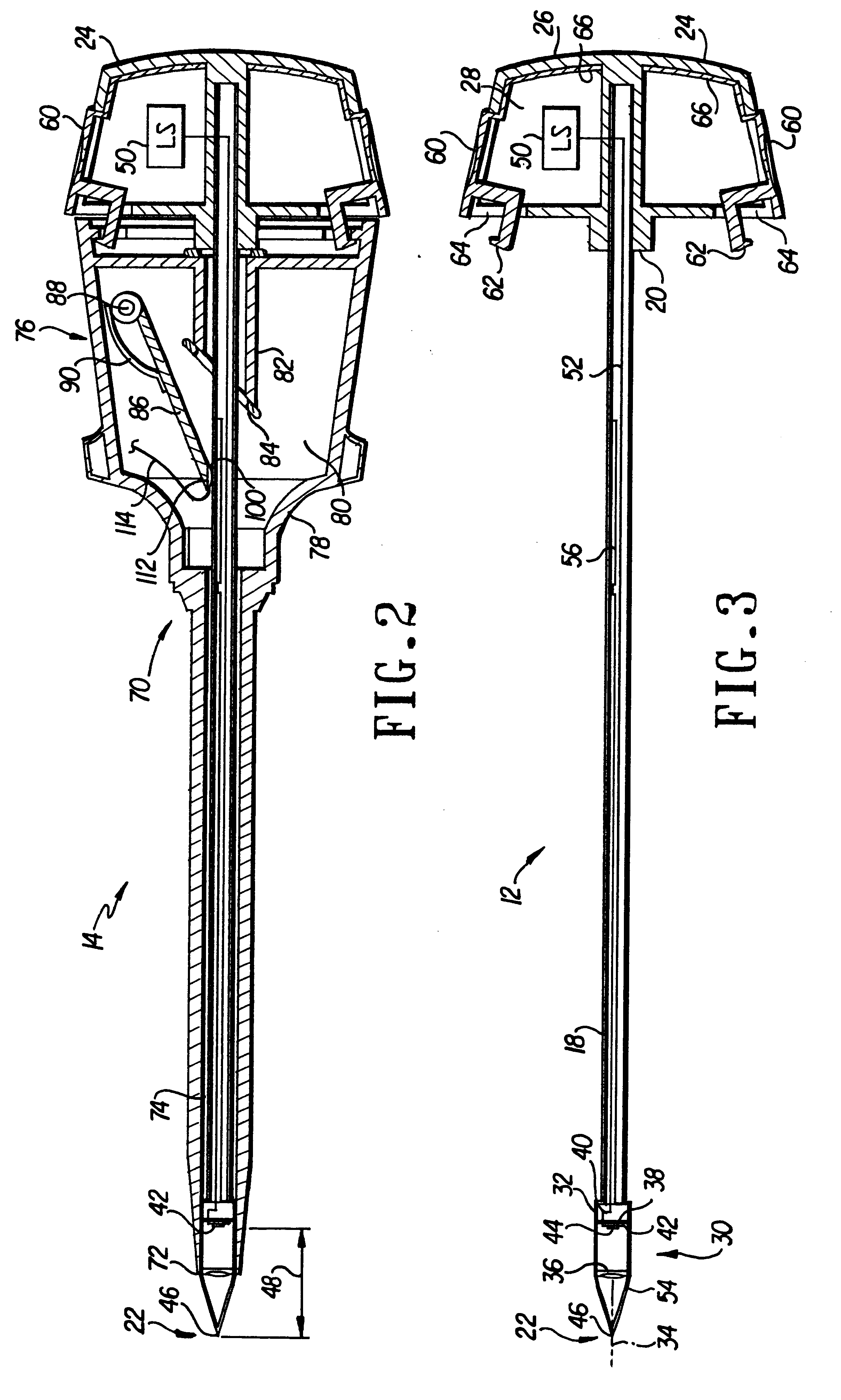
Forceps with spring loaded end effector assembly
ActiveUS7195631B2Effectively seal applicationSurgical instruments for heatingTherapeutic coolingForcepsEngineering
An endoscopic forceps for treating tissue includes a handle assembly having a elongated shaft extending therefrom which is movable relative to the handle assembly by an actuator. The forceps also including an end effector assembly attached to a distal end of the shaft which has first and second jaw members which are movable about a pivot from a first position in spaced relation relative to one another to a second position for clamping tissue. Each of the jaw members include: an insulative outer housing having an electrically conductive, inwardly facing tissue contacting surface and a proximal flange with a camming surface. The proximal flange being provided with a spring-like tail which mounts within the distal end of the elongated shaft to bias the jaw members in an open configuration. The actuator is movable relative to the handle to actuate the elongated shaft to cam the proximal flanges to pivot the jaw members toward the second position to clamp tissue.
Owner:COVIDIEN AG
Linear Suture Cutting Device
The invention discloses a linear suturing and cutting device. The linear suturing and cutting device comprises an upper forceps holder and a lower forceps holder which can be closed and opened mutually. The upper forceps holder comprises a nail anvil, the lower forceps holder comprises a nail cartridge rack, the nail cartridge rack is detachably provided with a nail cartridge, and the inside of the nail cartridge is sequentially provided with a nail cartridge hole which penetrates the surface of the nail cartridge and a nail pushing sheet which is arranged inside the nail cartridge and can slide relative to the nail cartridge hole; the inside of the nail cartridge is also slidingly provided with a trigger sheet, the trigger sheet is provided with a wedge-shaped nail pushing unit which can drive the nail pushing sheet to slide inside the nail cartridge hole, and the nail cartridge hole is inclined to the far end of the nail cartridge. Therefore, when the nail pushing sheet inside the nail cartridge sheet is pushed, the stress direction of the nail pushing sheet is identical to the extension direction of the nail cartridge hole, relatively high friction force between the nail pushing sheet and the inner wall of the nail cartridge hole can be avoided, so that the nail pushing sheet can be pushed more smoothly, and further the surgical difficulty can be reduced.
Owner:TOUCHSTONE INTERNATIONAL MEDICAL SCIENCE CO LTD
Ultrasonic forceps
Ultrasonic forceps adapted for use in open surgical forceps. The device is provided in the form of traditional open surgery forceps or tweezers, and the transmitting rod which transmits ultrasonic vibration from a proximally located transducer to the distally mounted welding horn runs through a lumen in one of the arms of the forceps.
Owner:STARION INSTR
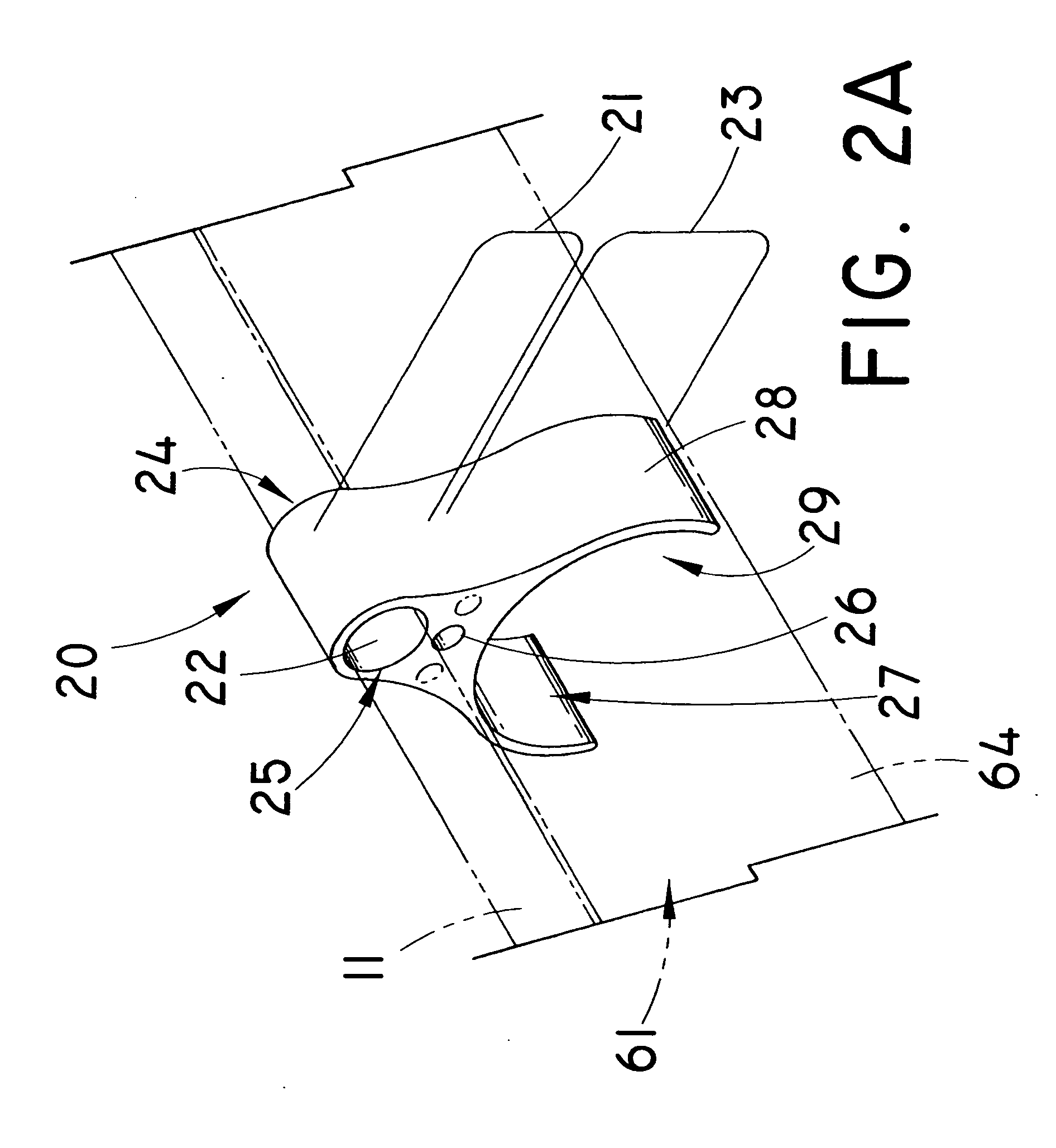
Endoscopic forceps instrument
An endoscopic forceps instrument has an inserting portion to be inserted into a body cavity through an endoscope, a clevis, a pair of rivets, and a pair of opposing jaws. The clevis is coupled to a distal end of the inserting portion. The pair of rivets is coupled to the clevis. Each of the rivets has a tip end that is swaged in order to fix the rivet to the clevis. The pair of opposing jaws is pivotably coupled to respective rivets so as to be movable between an open position and a closed position. The pair of rivets is arranged in parallel to each other. Further, the pair of rivets is arranged such that the tip ends thereof, which are swaged and therefore having relatively low mechanical strength, are located and swaged at opposite sides of the clevis.
Owner:HOYA CORP
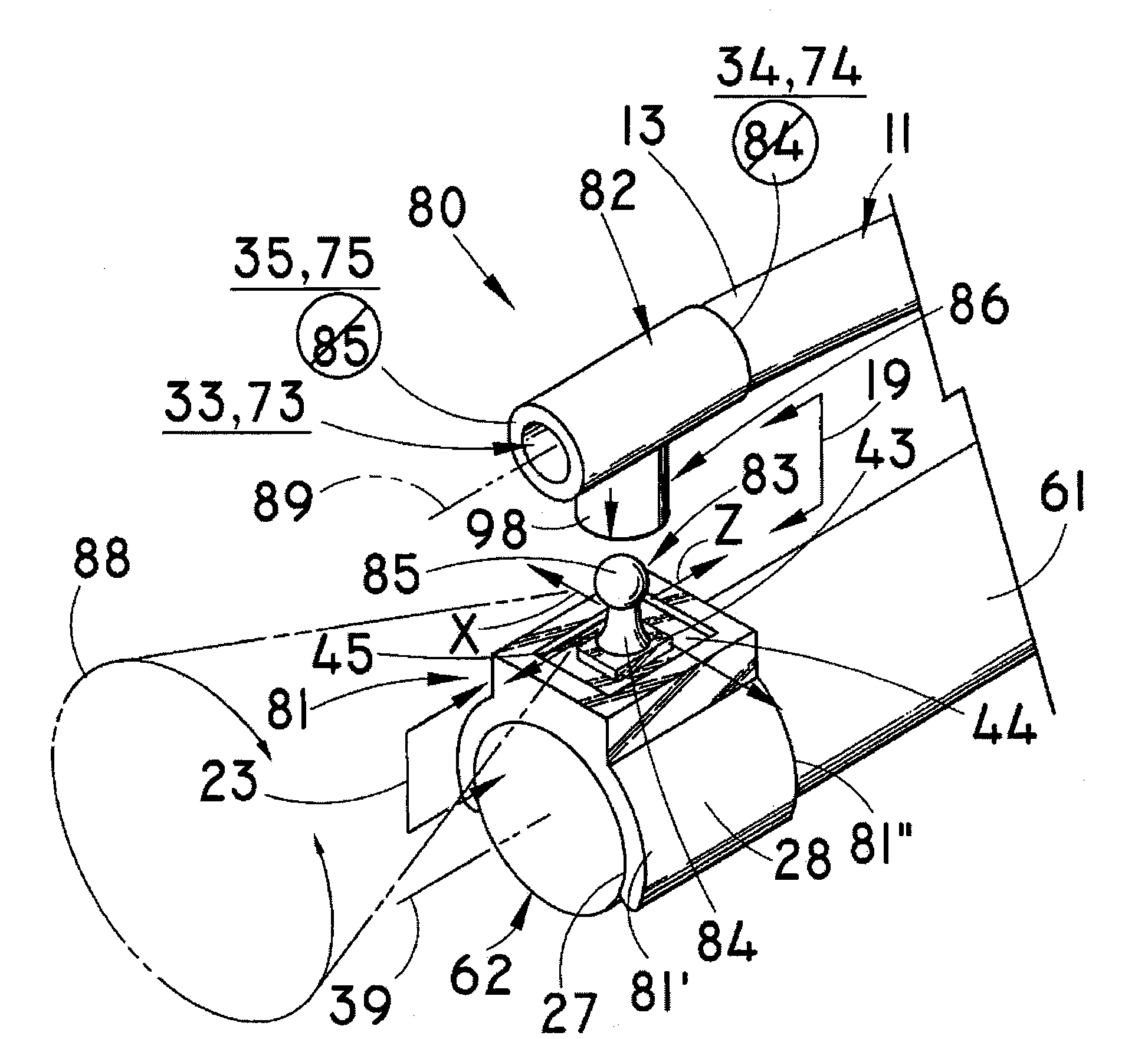
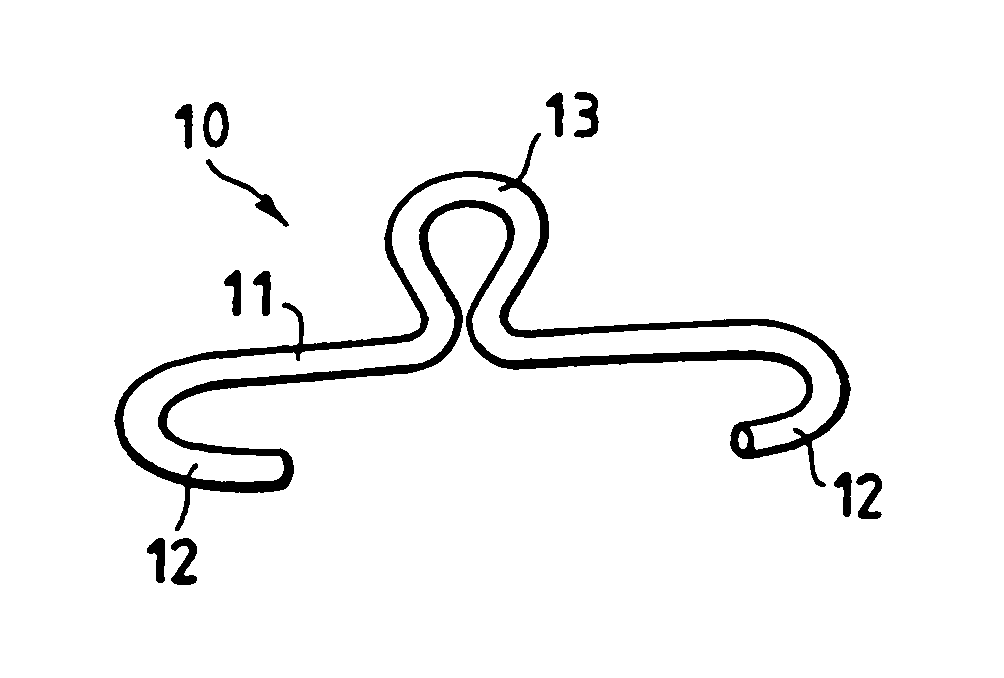
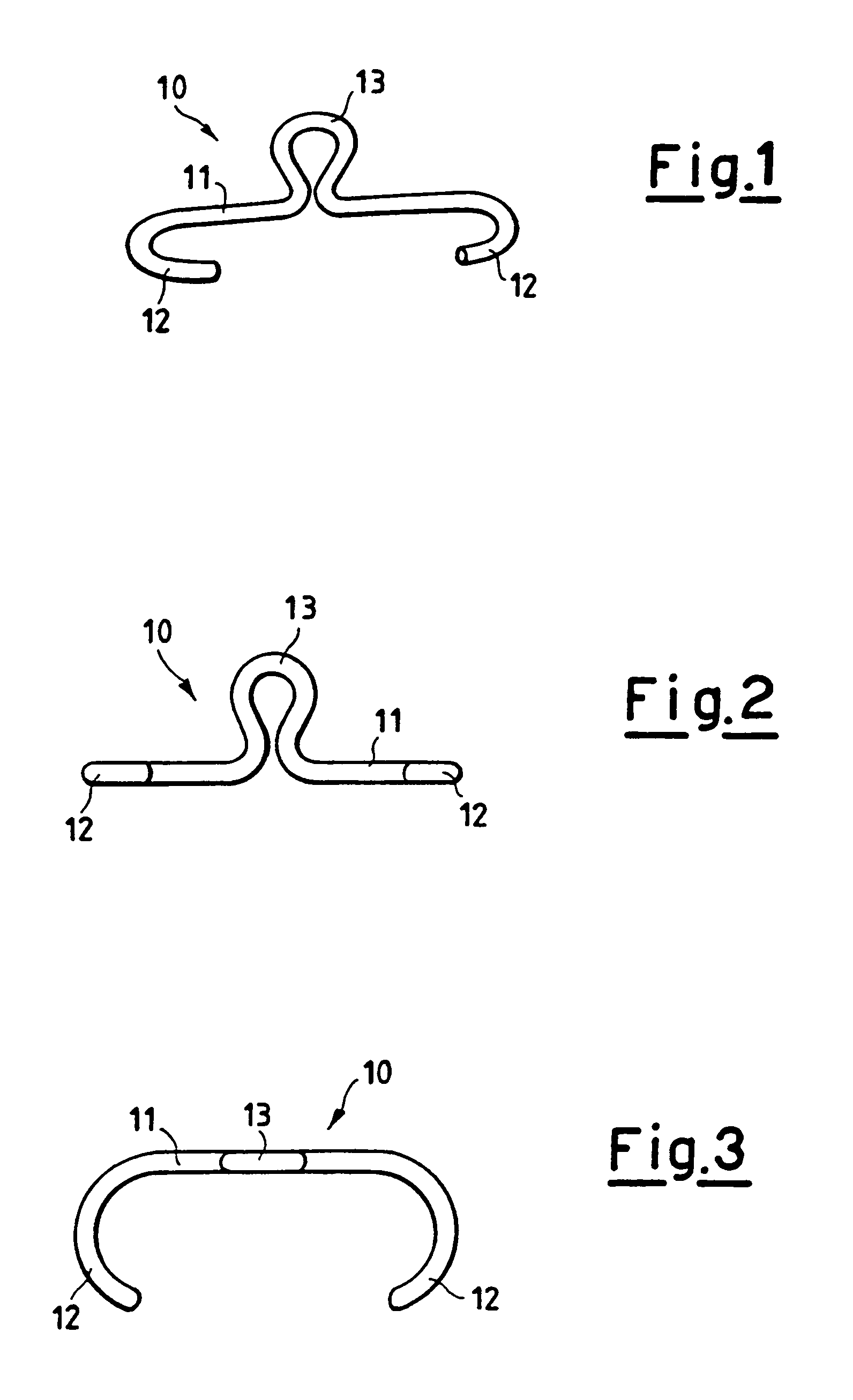
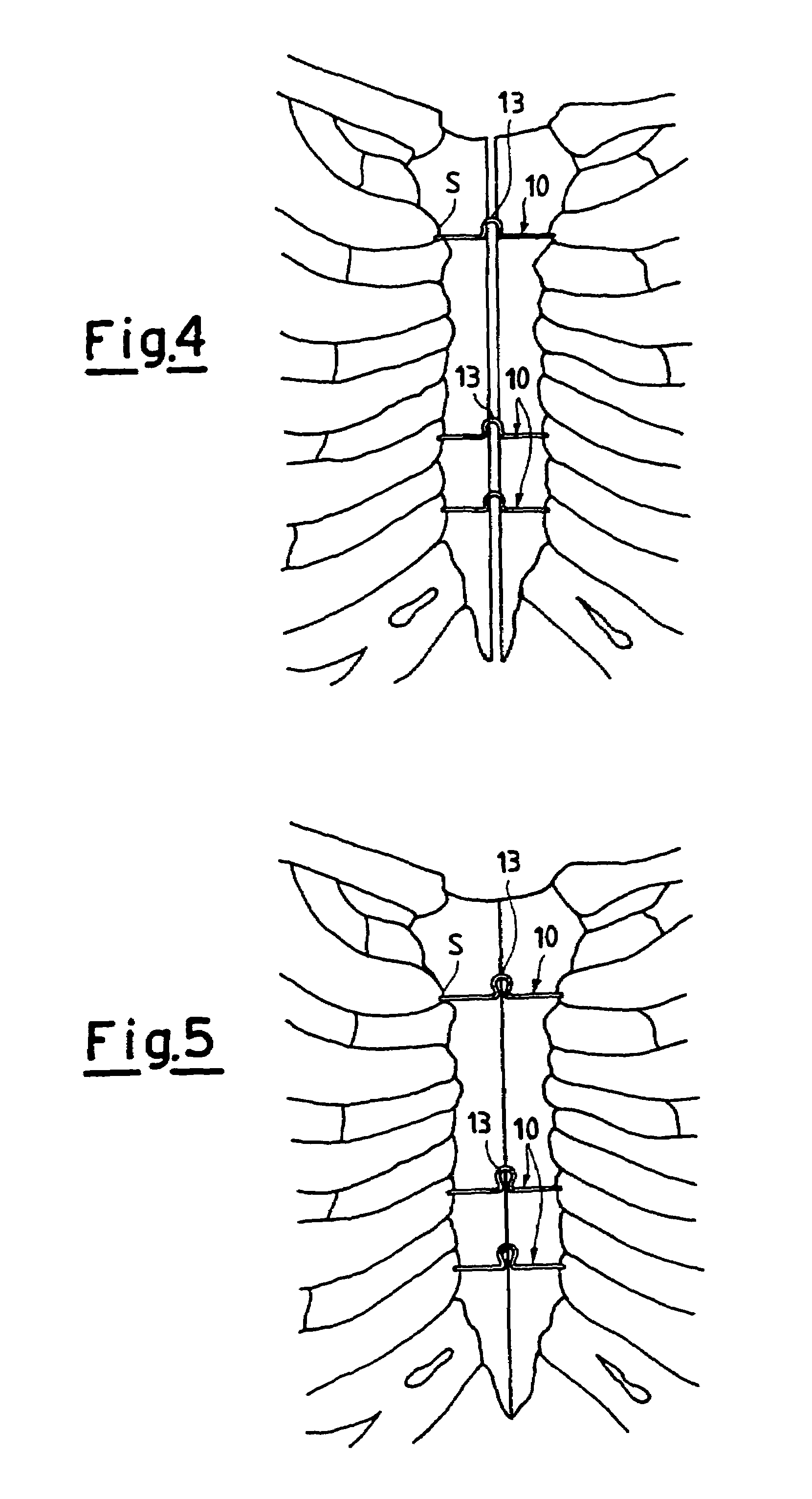
Semi-rigid compressive clamp for use in sternotomy, and forceps for its application
A clamp designed for use in the heart-surgery field for osteosynthesis following on sternotomy has a roughly C-shaped configuration with a core (11) terminating at opposite ends with hooks (12) set opposite to one another. In the centre, the said core (11) extends vertically according to a plane which is substantially perpendicular to the one on which the end hooks (12) lie, with a loop (13) which is elastically compliant. The said clamp is made of a so-called “shape-memory” metallic alloy, i.e., an alloy which is malleable at a low temperature and which re-acquires its original form at body temperature, exerting a semi-rigid compression on the ends or edges of the bones requiring synthesis.
Owner:PRAESIDIA
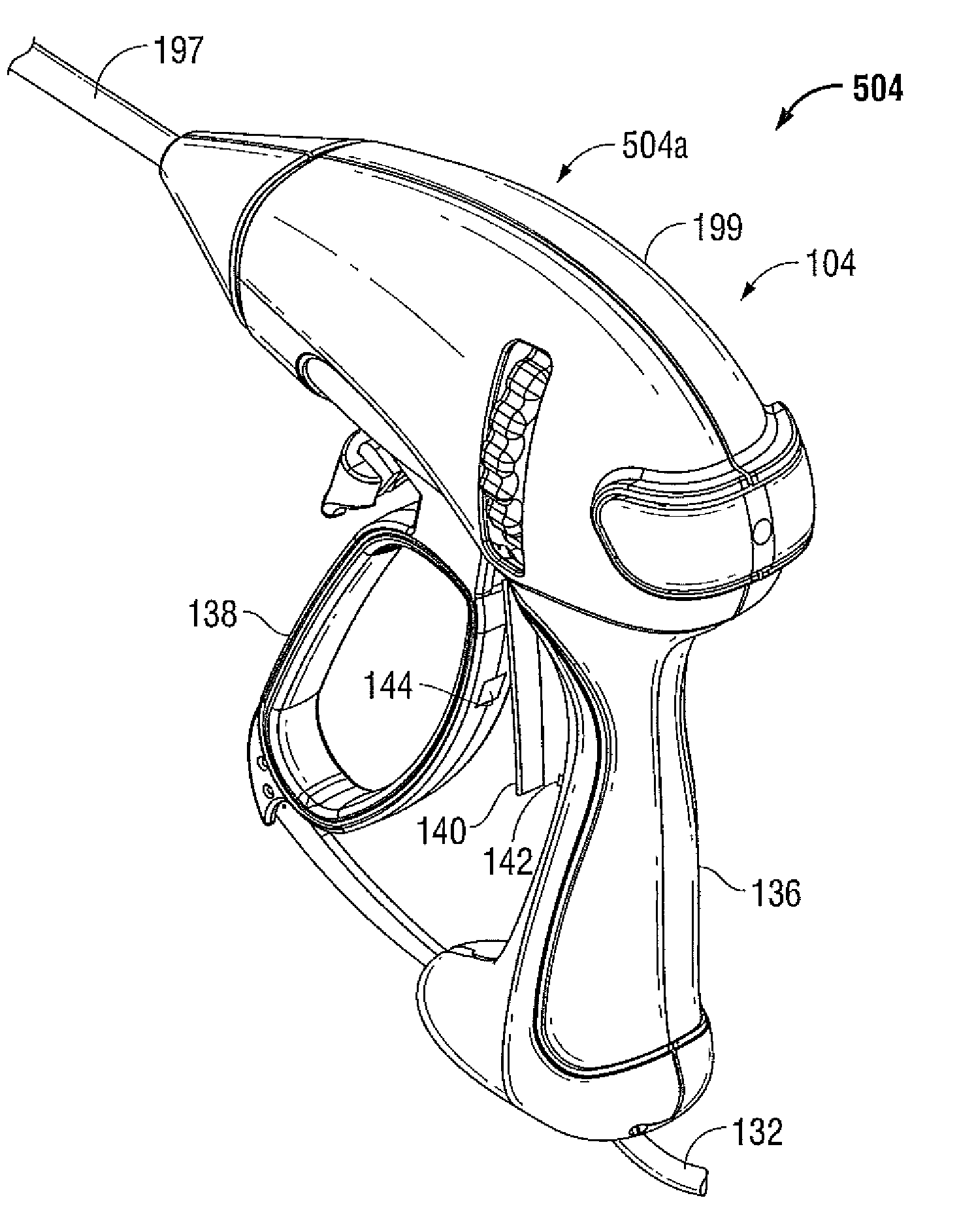
Vessel sealer and divider with blade deployment alarm
ActiveUS8251994B2DiagnosticsSurgical instruments for heatingElectrical resistance and conductanceElectricity
An electrosurgical forceps includes a selectively advanceable knife and a knife deployment alarm configured to emit a signal under predetermined conditions. An alarm is configured to emit a signal when the cutting blade moves relative to the blade channel. A series of resistances are arranged so that a shorting of each resistor is indicative of a predetermined operating condition triggering the alarm to emit a signal. Pressure sensors, optical measurement devices, and electrical contacts are envisioned for determining blade or trigger actuation or translation.
Owner:TYCO HEALTHCARE GRP LP
Medical devices for minimally invasive surgeries and other internal procedures
InactiveUS20060020167A1Minimize unnecessary damageImprove eyesightSuture equipmentsSurgical needlesForcepsReoperative surgery
Minimally invasive surgical devices and related tools are provided. The devices include image acquisition devices and forceps, scissors, clamps, ultrasound probes, lasers, cautery devices, staplers, knives, suturing devices, rivet drivers, ligation devices, aspiration devices, injection devices, biopsy devices, radiotherapy devices; and radioactive emitter loading devices. Other devices useful for internal procedures in a patient's body or for facilitating such procedures are also provided.
Owner:BIOARTTIS
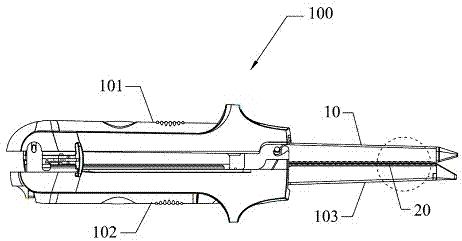
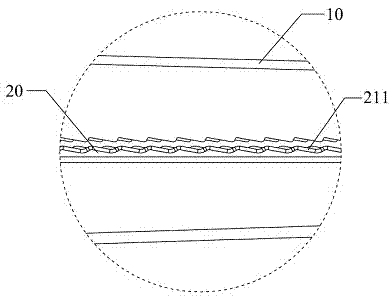
Latching mechanism for forceps
The present disclosure relates to a surgical instrument that includes a slidable shaft having a proximal and a distal end and a housing coupled to the shaft. The instrument includes an actuation assembly having a first lever and a second lever, each of the first and second levers being pivotably connected to the shaft. The instrument further includes an end effector assembly coupled to the distal end of the shaft, the end effector assembly having a pair of opposing jaw members. The instrument may have a drive rod disposed within the shaft and connected to a housing connection, the drive rod being operable by the actuation assembly to actuate the opposing jaw members between open and closed positions. A latching mechanism is operatively associated with the actuation assembly and drive rod for maintaining the jaw members in the closed position, the latching mechanism including a biasing member housed between a spring collar and a spring mandrel.
Owner:SHERWOOD SERVICES AG
Apparatus for Performing an Electrosurgical Procedure
An endoscopic forceps includes a housing having a shaft extending therefrom for treating tissue. A longitudinal axis is defined through the shaft. An end effector assembly is operably coupled to a distal end of the shaft and includes a pair of first and second jaw members. A rotating assembly operably coupled to the shaft is configured to rotate the shaft and the end effector about the longitudinal axis. A drive assembly is configured to selectively and releasably engage the rotating assembly. Engagement of the rotating assembly with the drive assembly couples the rotating assembly to the shaft such that the shaft is rotatable about the longitudinal axis in a predetermined direction when the rotating assembly is rotated. And, disengagement of the rotating assembly from the drive assembly uncouples the rotating assembly from the shaft such that the shaft is non-rotatable about the longitudinal axis when the rotating assembly is rotated.
Owner:TYCO HEALTHCARE GRP LP
System and method for controlling electrode gap during tissue sealing
An electrosurgical system for sealing tissue is disclosed that includes an electrosurgical forceps. The forceps includes a drive rod and an end effector assembly coupled to the drive rod at a distal end thereof. The end effector assembly includes jaw members wherein longitudinal reciprocation of the drive rod moves the jaw members from a first position in spaced relation relative to one another to a subsequent position wherein the jaw members cooperate to grasp tissue therebetween. Each of the jaw members includes a sealing plate that communicates electrosurgical energy through tissue held therebetween. The jaw members are adapted to connect to an electrosurgical generator. The system also includes one or more sensors that determine a gap distance between the sealing plates of the jaw members and a pressure applicator coupled to the drive rod. The pressure applicator is configured to move the drive rod in a longitudinal direction. The system further includes a controller adapted to communicate with the sensors and to control the pressure applicator in response to the determined gap distance during the sealing process.
Owner:COVIDIEN AG
Flexible endoscopic catheter with ligasure
An endoscopic forceps is disclosed including an end effector assembly having two jaw members movable from a first position in spaced relation relative to one another to at least a second position closer to one another for grasping tissue therebetween. Each of the jaw members is connectable to an electrosurgical energy source for conducting energy through tissue held therebetween. The jaw members are biased to the first position. The end effector assembly of the endoscopic forceps further includes a wire snare having a proximal end connectable to an electrosurgical energy source and a distal end translatably extending out of one of the jaw members and operatively associated with the other of the jaw members. In use, withdrawal of the proximal end of the wire snare results in movement of the jaw members from the first position to a second position and clamping of the tissue between the jaws.
Owner:COVIDIEN AG
Endoscopic surgical access devices and methods of articulating an external accessory channel
Devices and methods for detachably engaging an insertion section of an endoscope and selectively articulating an endoscopic surgical access channel are provided. A device comprises an articulating main body having a stationary first body, an articulatable second body, and coupler having a mounting member and an articulation link member configured to articulatively couple the second body to the first body. The stationary first body has a distal end, a proximal end, and a first longitudinal axis. The articulatable second body has a proximal opening and a distal opening defining an accessory channel member passageway, the distal opening having a second longitudinal axis oriented toward a space exterior to the first body distal end, wherein the second body longitudinal axis is capable of articulating relative to the first body longitudinal axis. The devices and methods, as taught herein, provide control over the position and / or orientation of a diagnostic, monitoring, scope, sewing device, cutting device, suturing device, forceps, grabbing device, instrument, or other tool within the visual field beyond the distal opening of the endoscope.
Owner:COOK MEDICAL TECH LLC
Penetrating endoscope and endoscopic surgical instrument with CMOS image sensor and display
A penetrating endoscope provides visualization of organ or tissue structures or foreign objects in a body. The penetrating endoscope includes an elongate penetrating member, a complementary metal dioxide semiconductor (CMOS) image sensor and an objective lens. The CMOS image sensor is substantially planar and includes a plurality of pixels with a pixel signal processing circuit for generating a color image ready signal. The CMOS image sensor converts image light energy into electrical color image ready signal energy for transmission out of the body. The color image ready signal is viewed on a color image display. The CMOS image sensor is carried on the elongate penetrating member adjacent a distal end of the elongate penetrating member. The objective lens is also carried on the distal end of the elongate penetrating member on an optical axis and focuses an image corresponding to an endoscope field of view at an image plane intersecting the optical axis. The CMOS image sensor is mounted with the CMOS image sensor pixels disposed substantially in the image plane and on the optical axis. The penetrating endoscope may include end effectors such as cutters and forceps.
Owner:YOON INBAE
Medical ultrasound instrument with articulated jaws
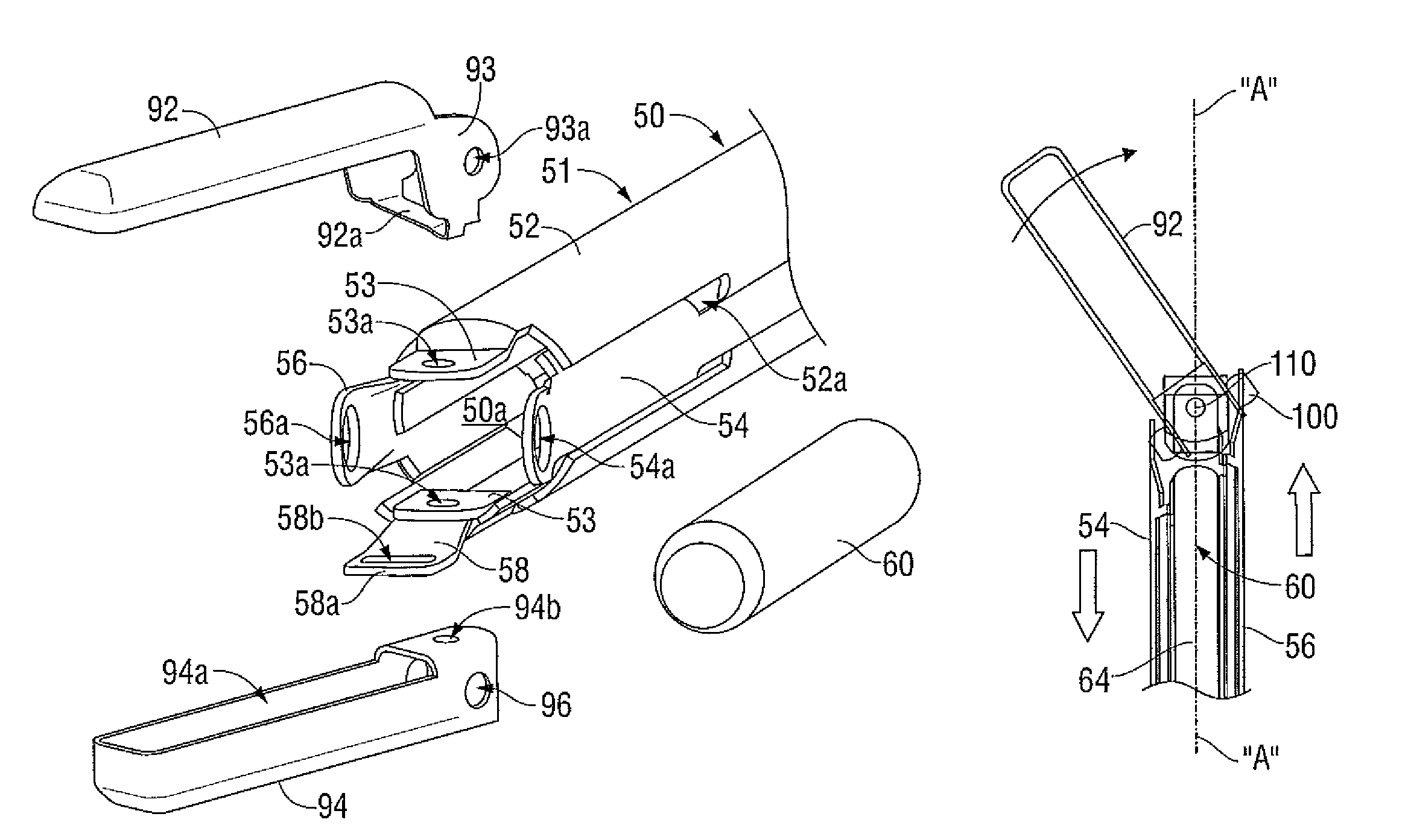
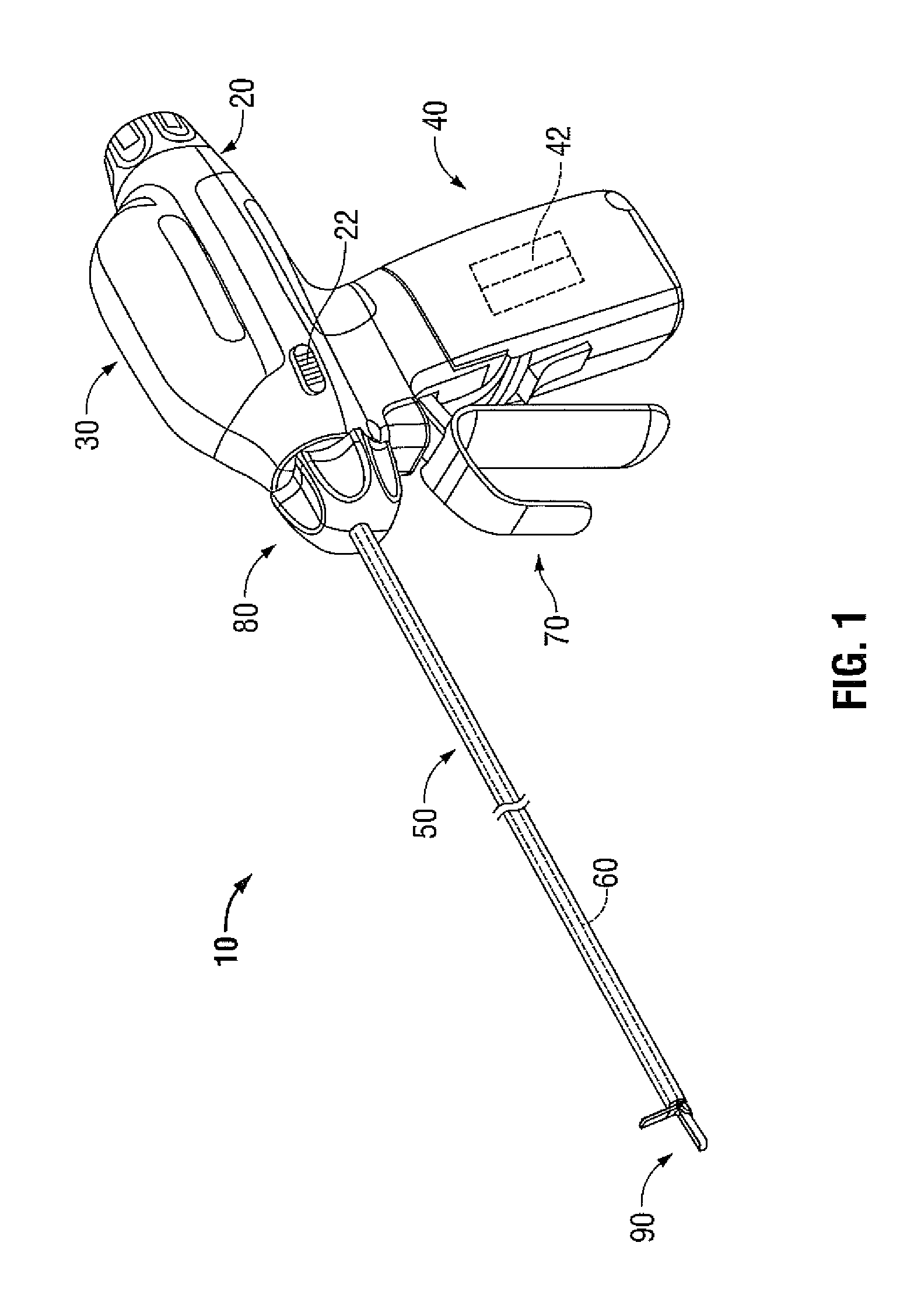
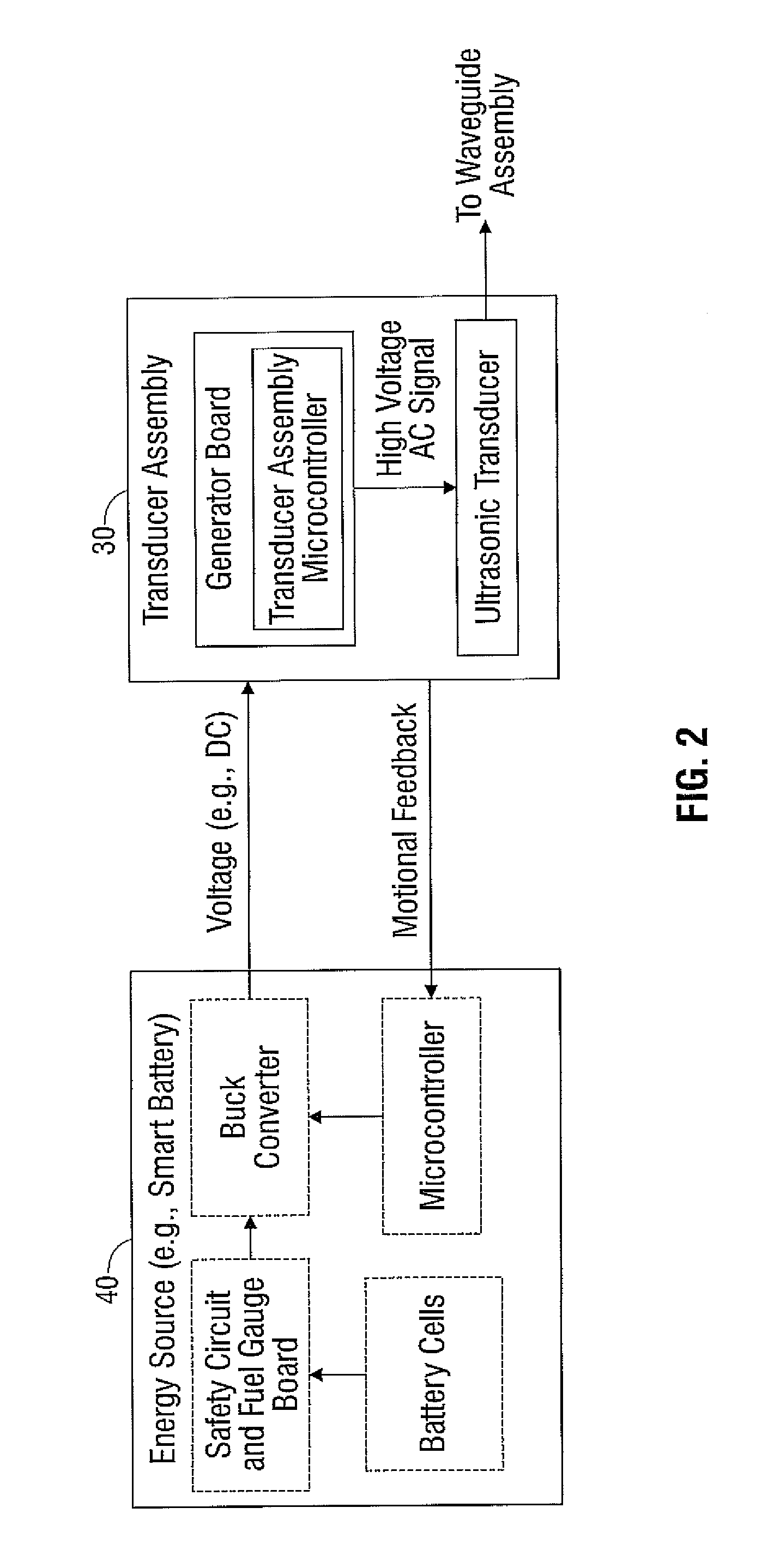
A forceps includes a housing, a shaft assembly, an end effector assembly, and a waveguide assembly. The housing has one or more transducers that generate a mechanical vibration in response to energy transmitted thereto from an energy source. The shaft assembly extends from the housing and includes one or more articulating and clamping members and a longitudinal axis defined therethrough. The end effector assembly is disposed at a distal end of the shaft assembly and includes a pair of opposing jaw members pivotable between approximated and unapproximated configurations in response to movement of the one or more clamping members. The articulating members articulate the jaw members relative to the longitudinal axis of the shaft assembly. The waveguide assembly is positioned within the shaft assembly and receives the mechanical vibration generated by the transducer. The waveguide assembly is positionable within one or both of the jaw members.
Owner:TYCO HEALTHCARE GRP LP
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com