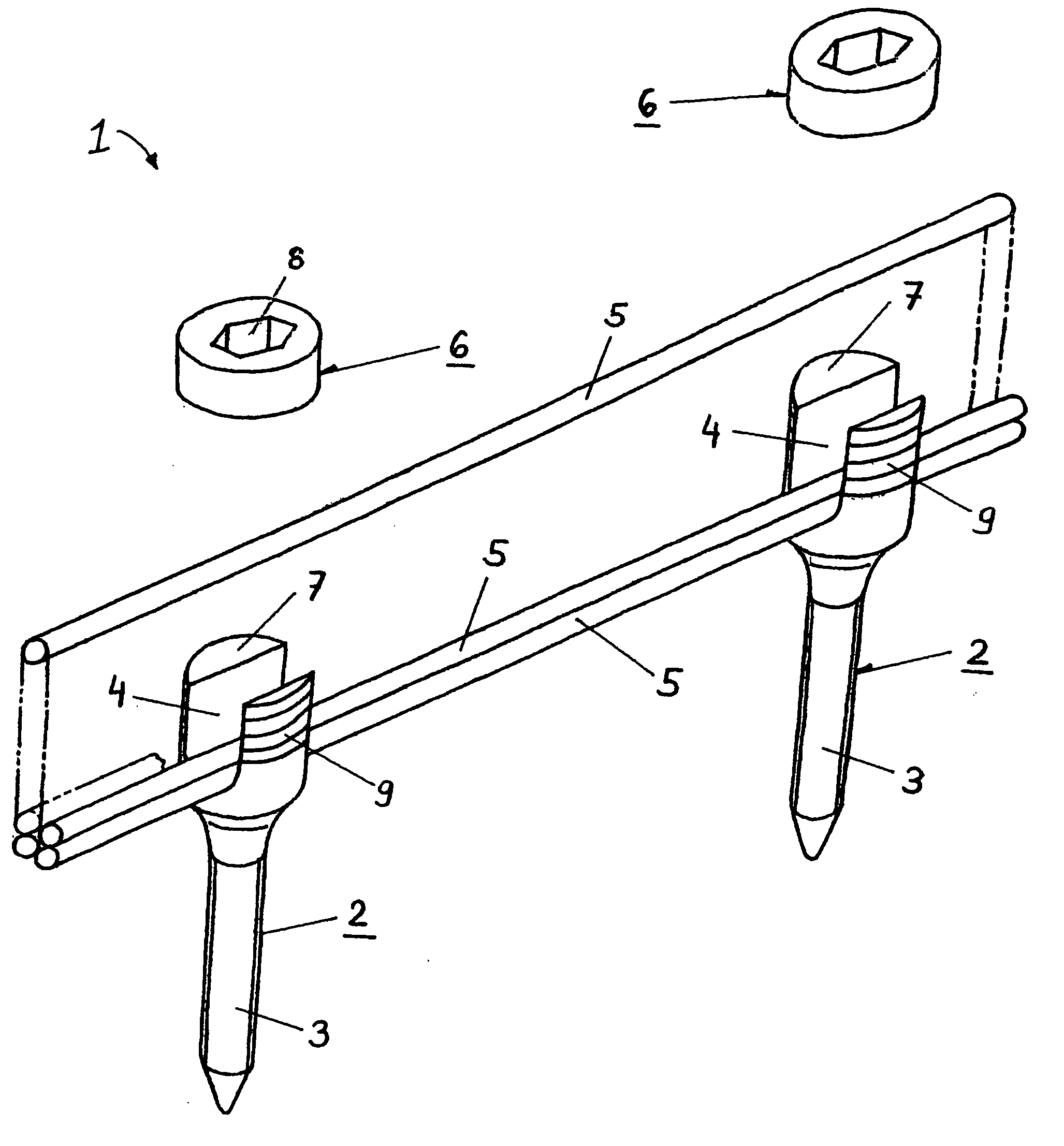
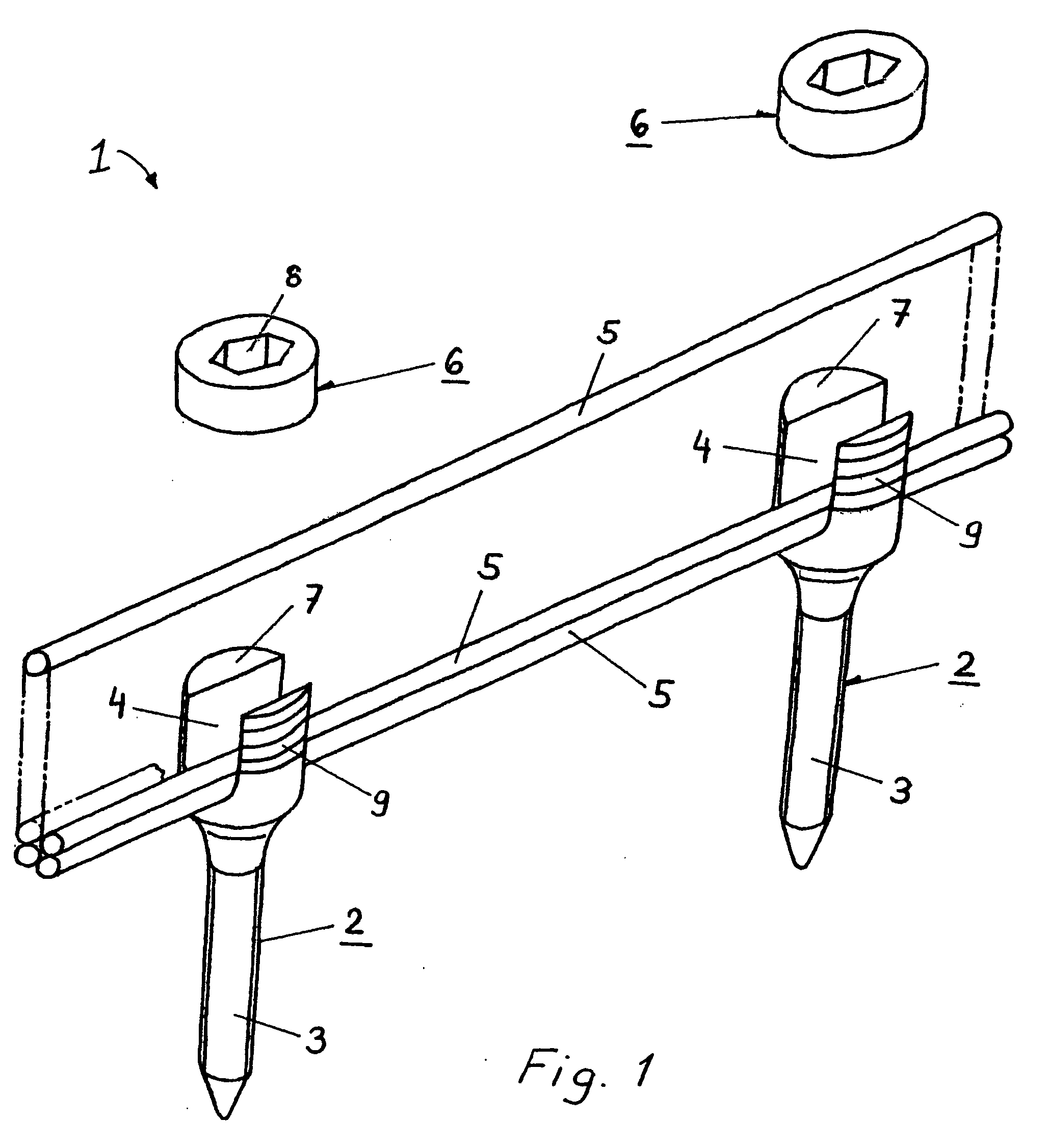
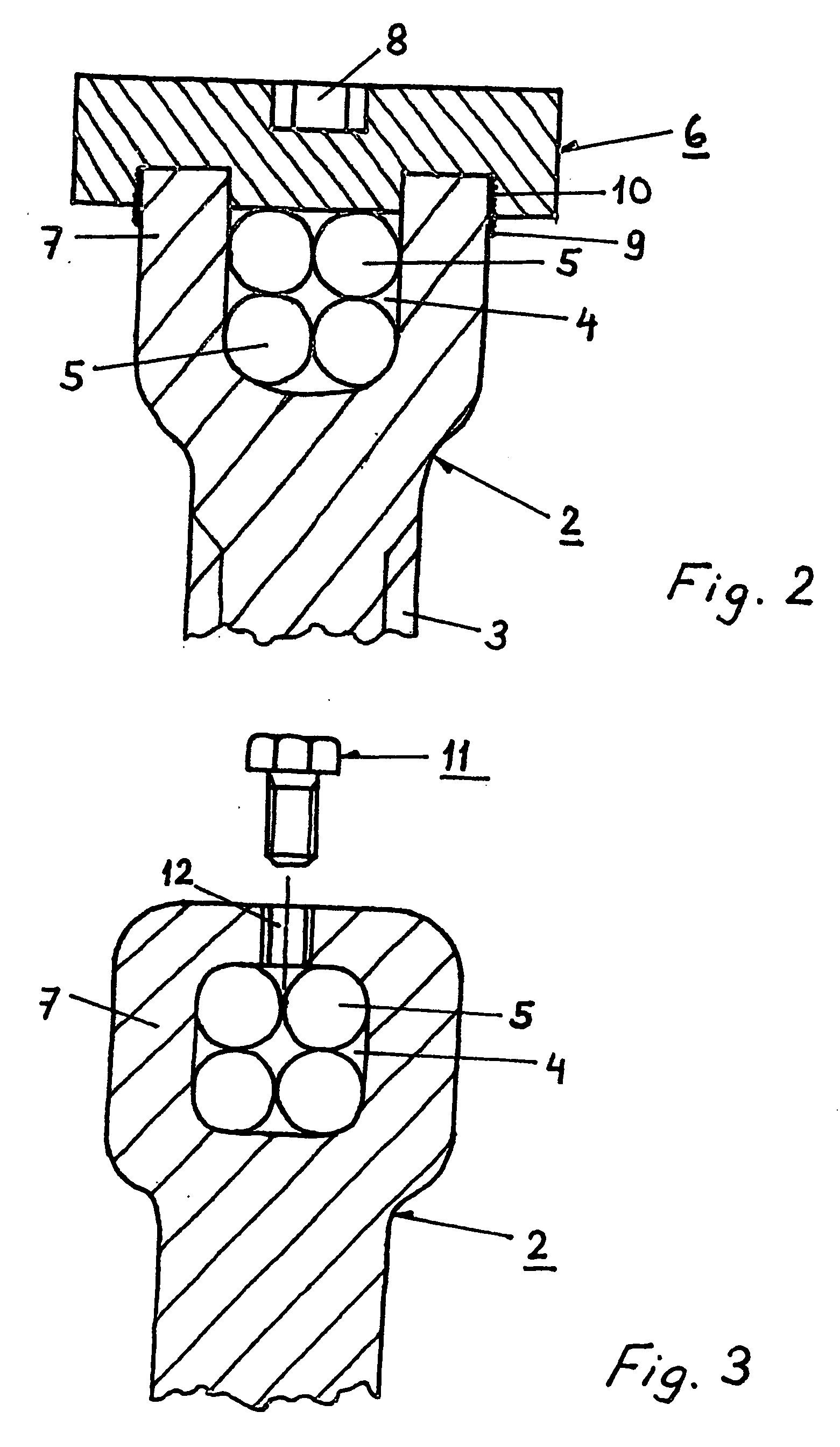
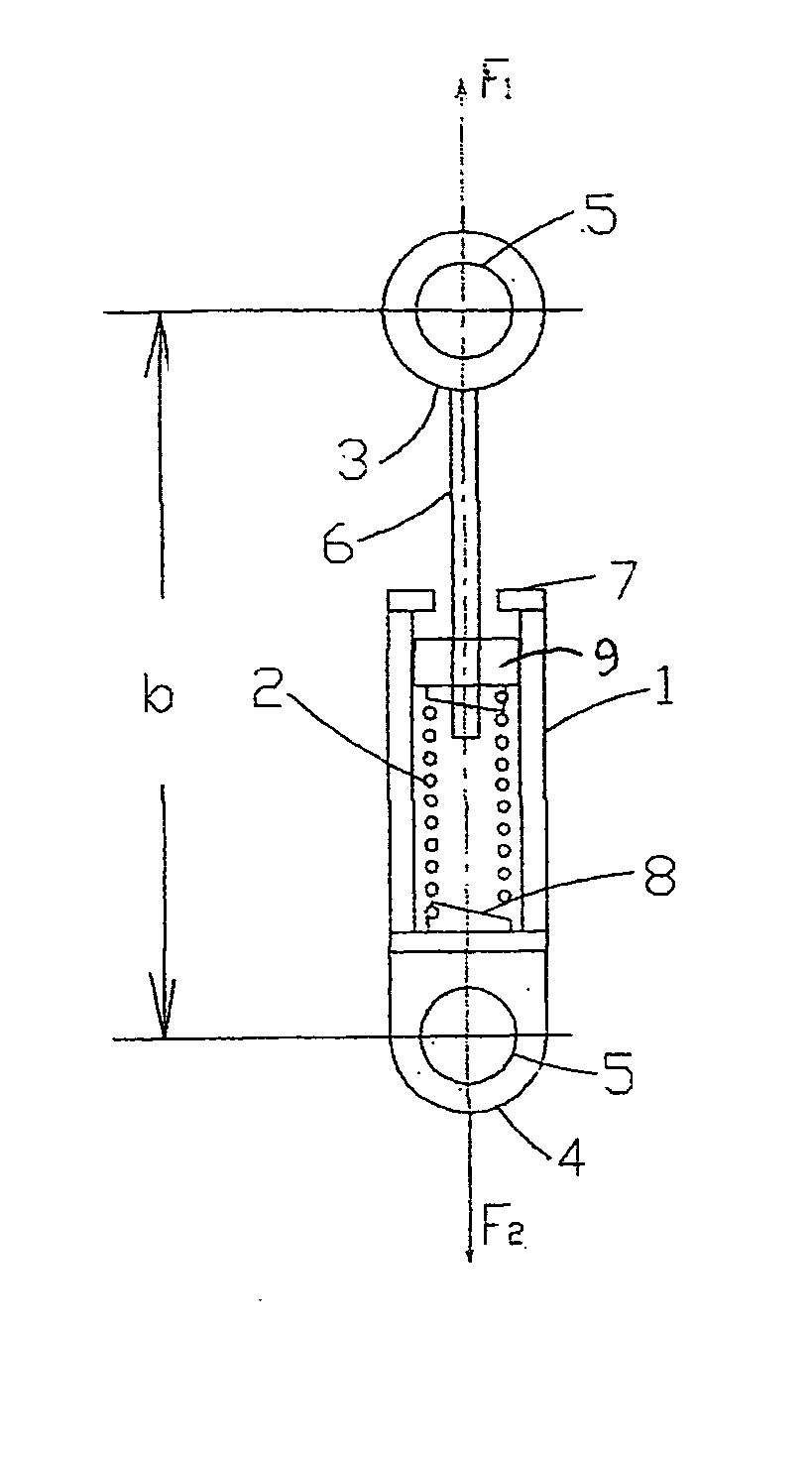
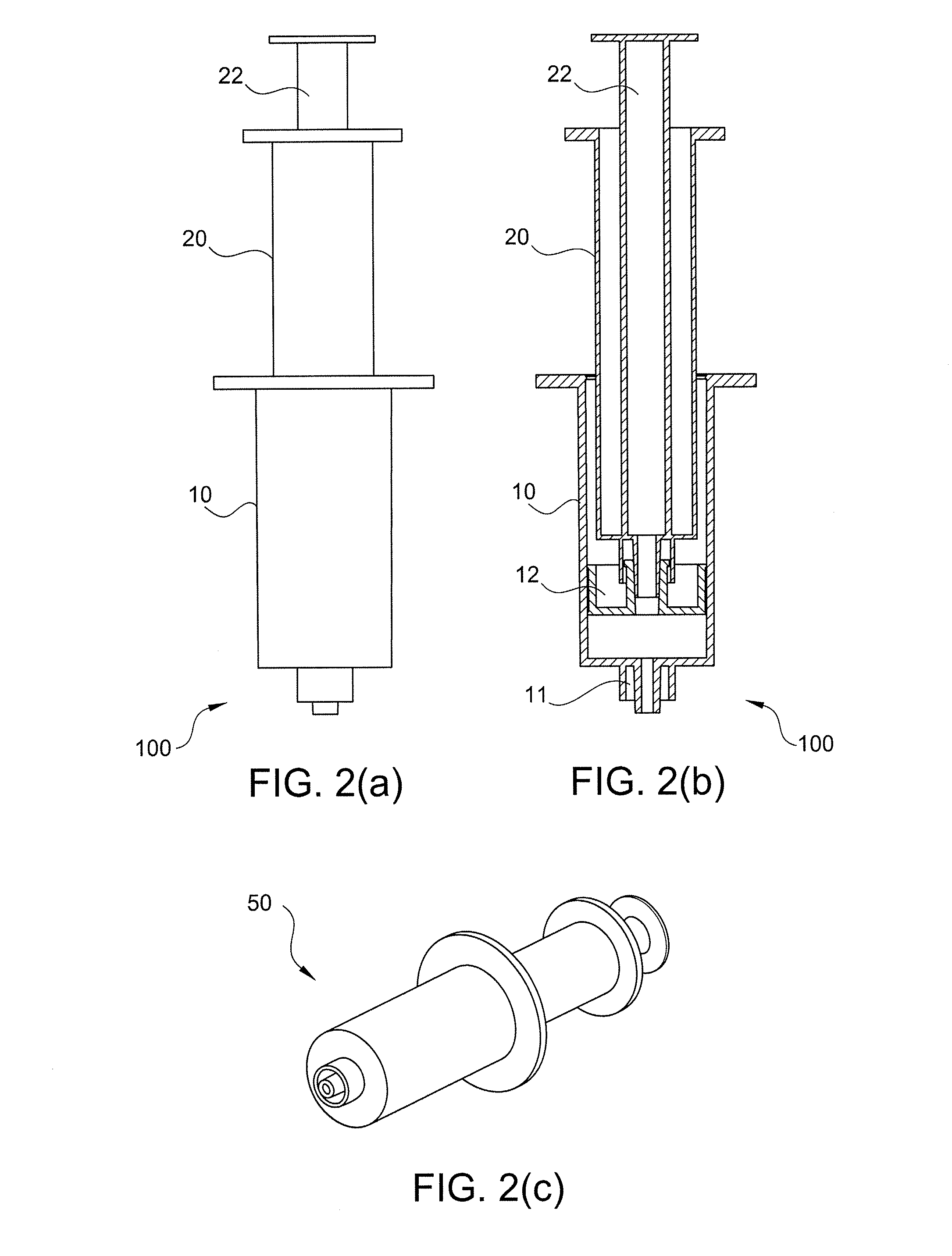
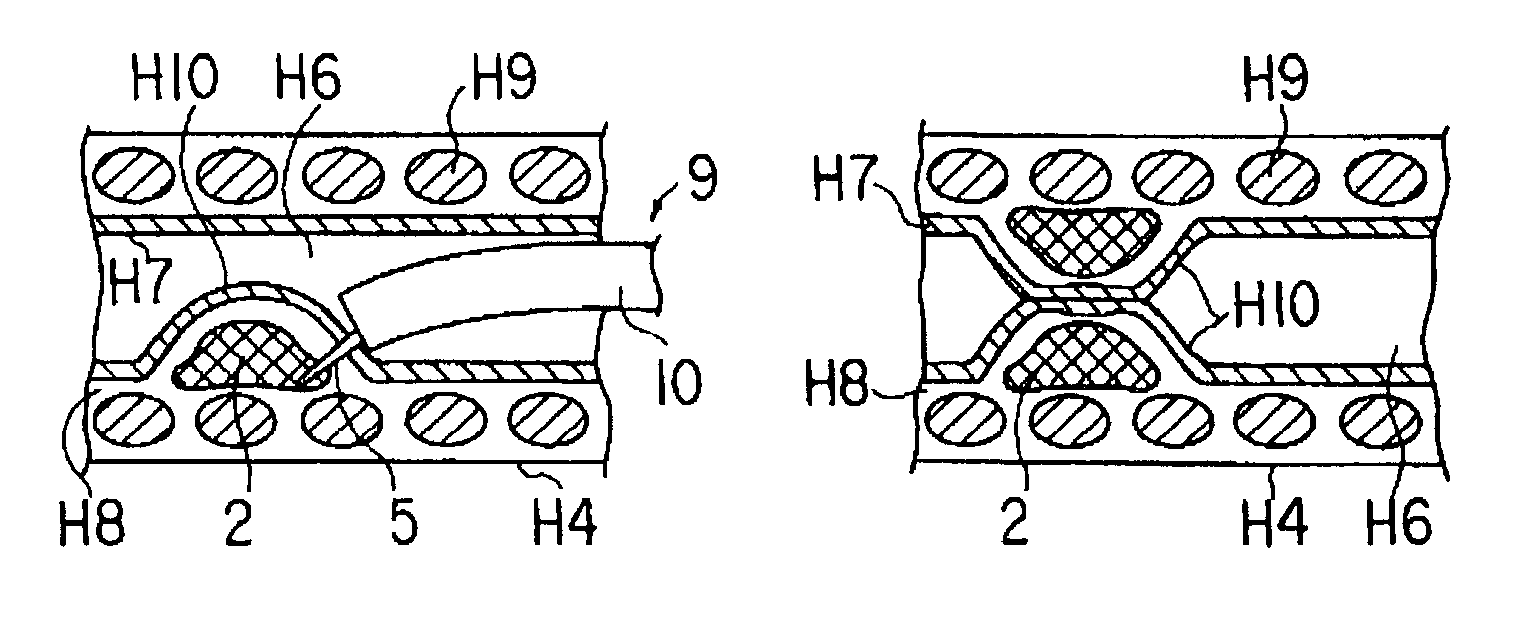
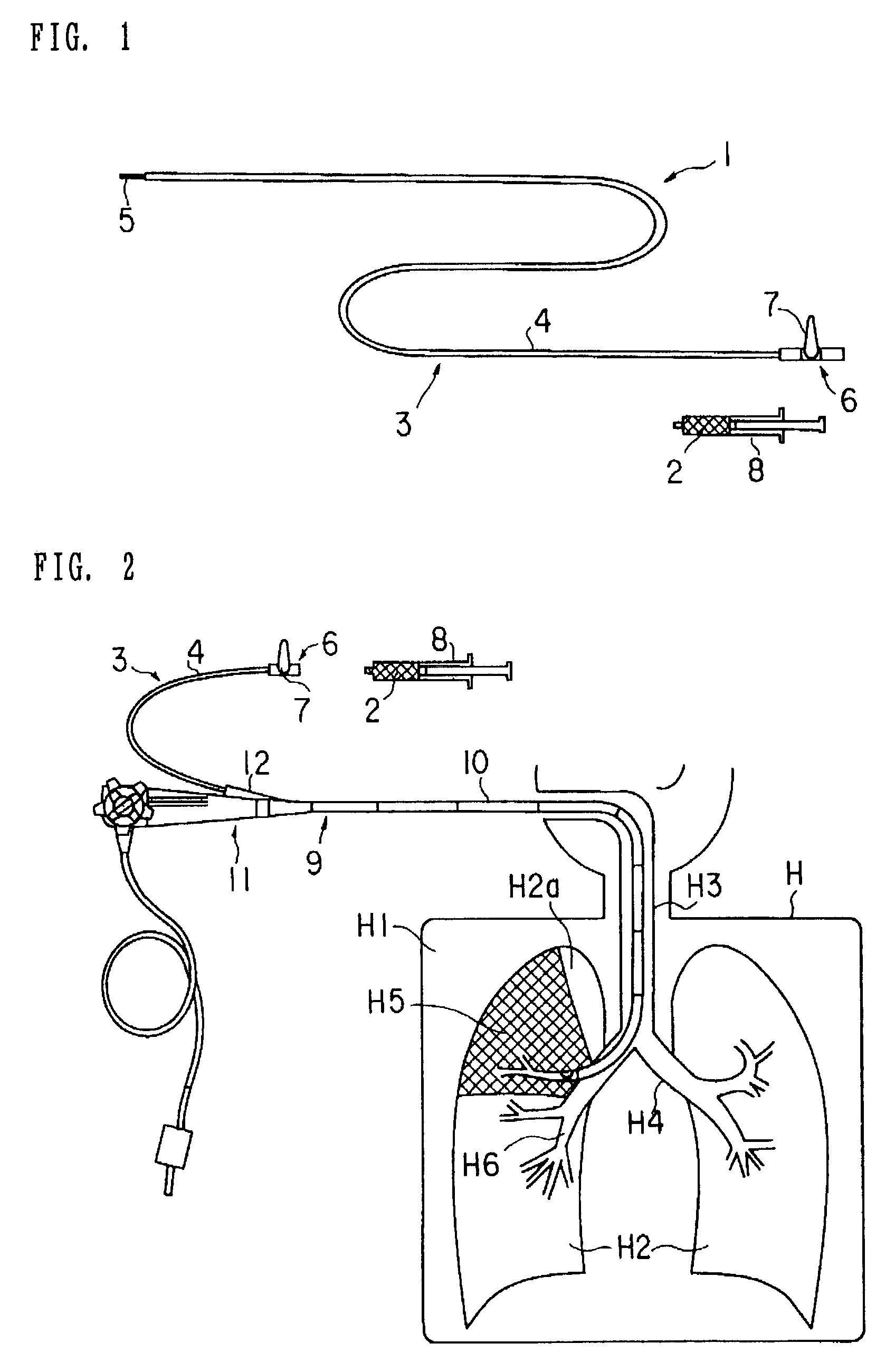
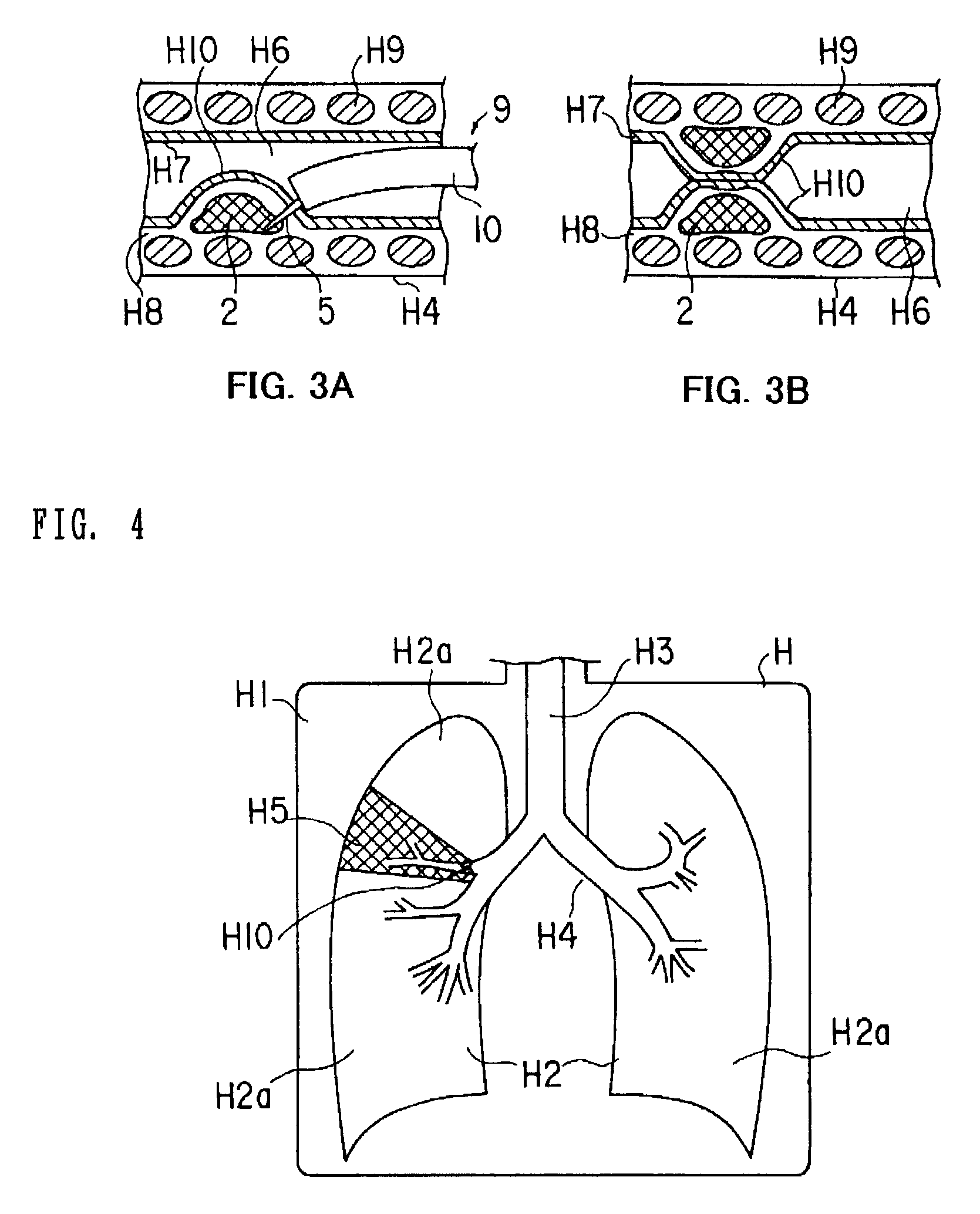
Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
760 results about "Surgical treatment" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Surgical treatment. A surgical intervention performed after the appropriate medical evaluation and diagnostic tests have determined the need for procedure.
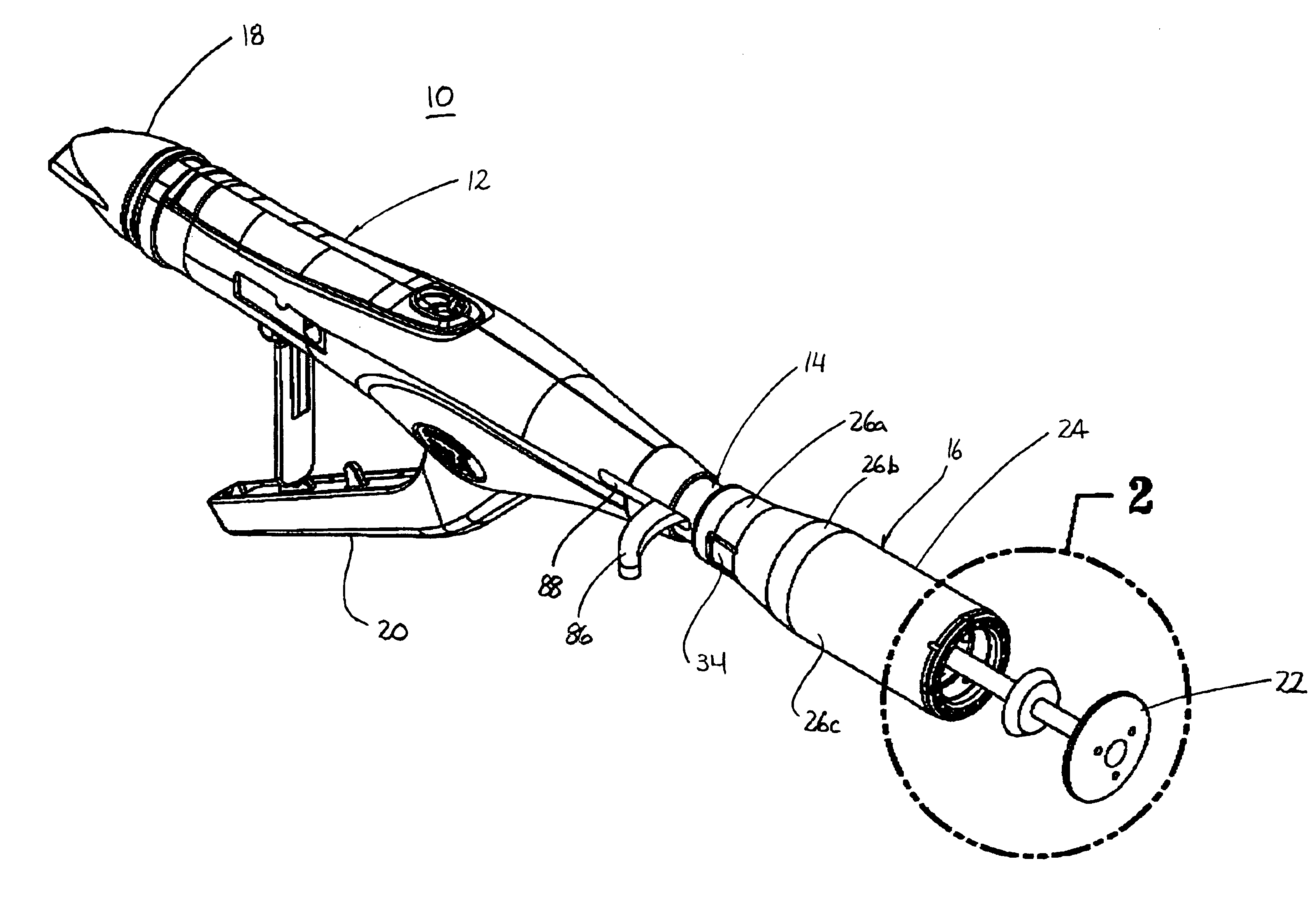
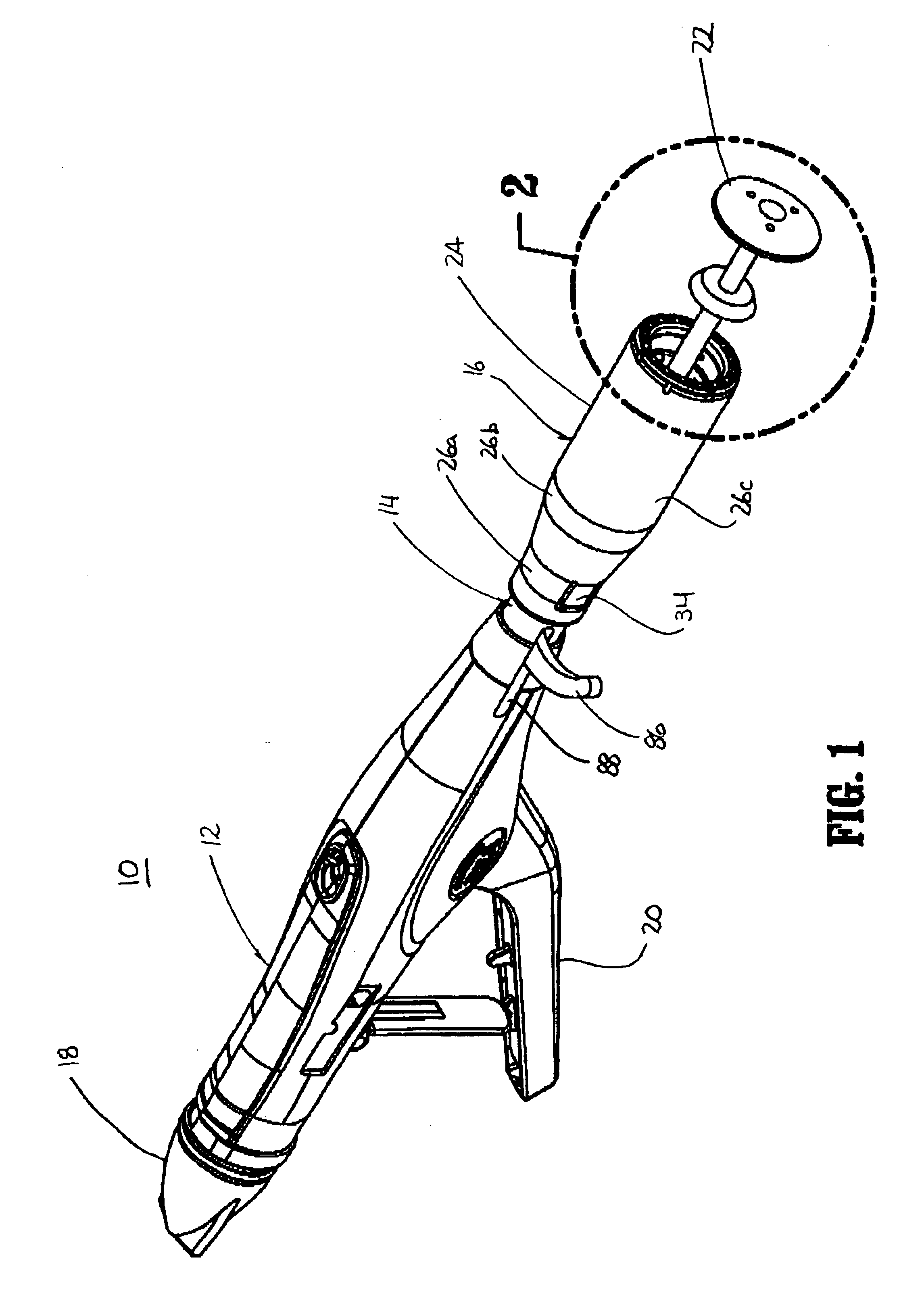
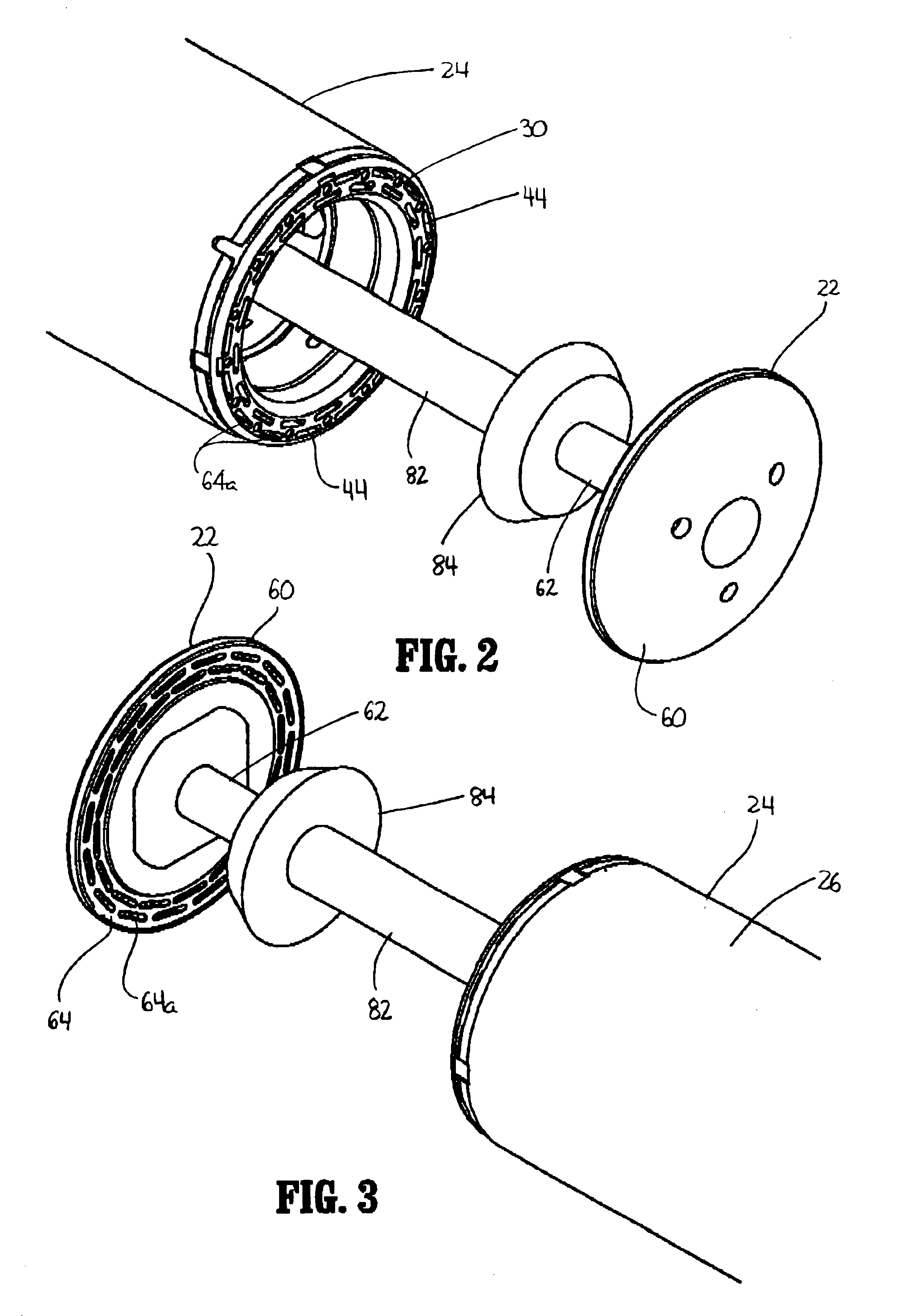
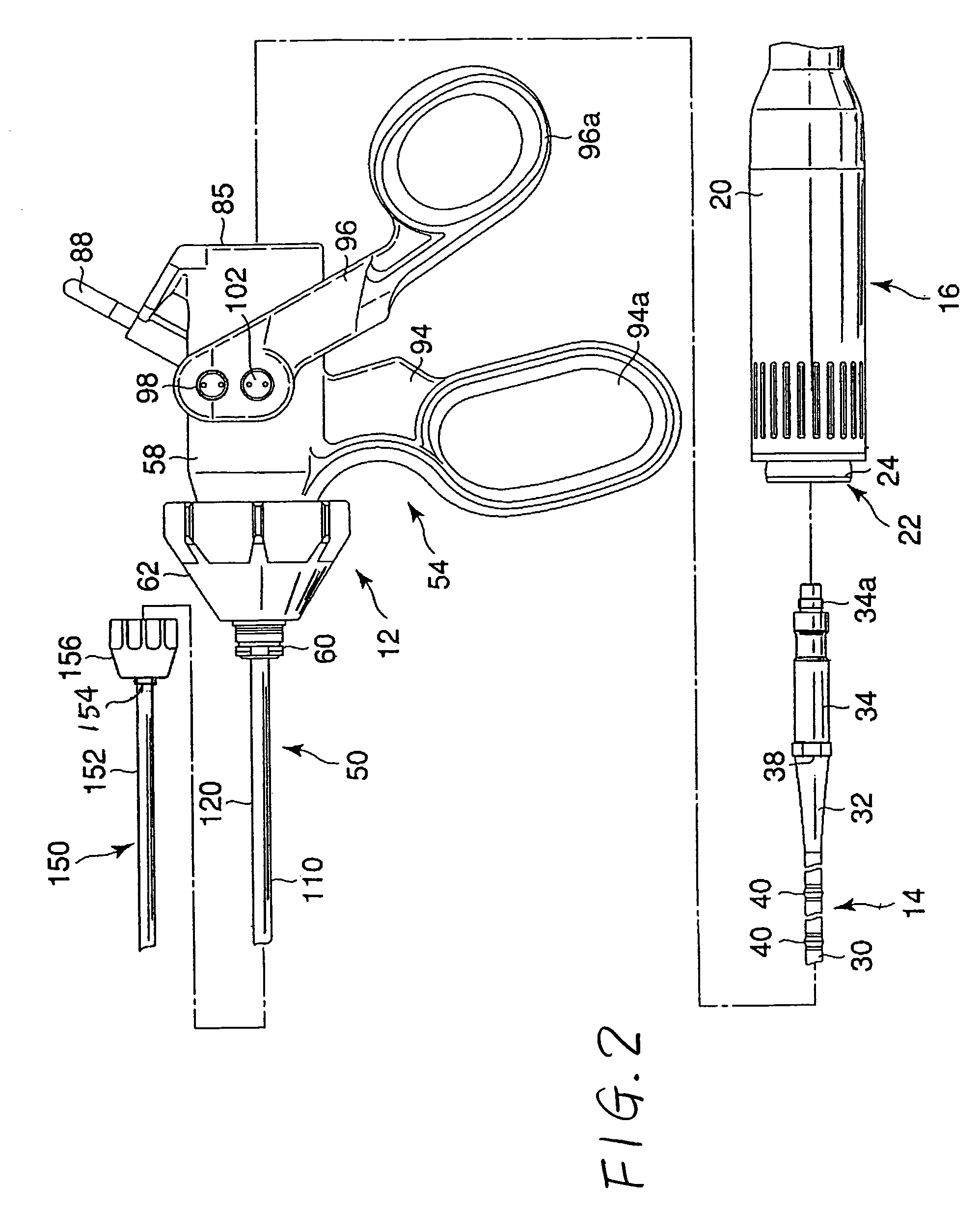
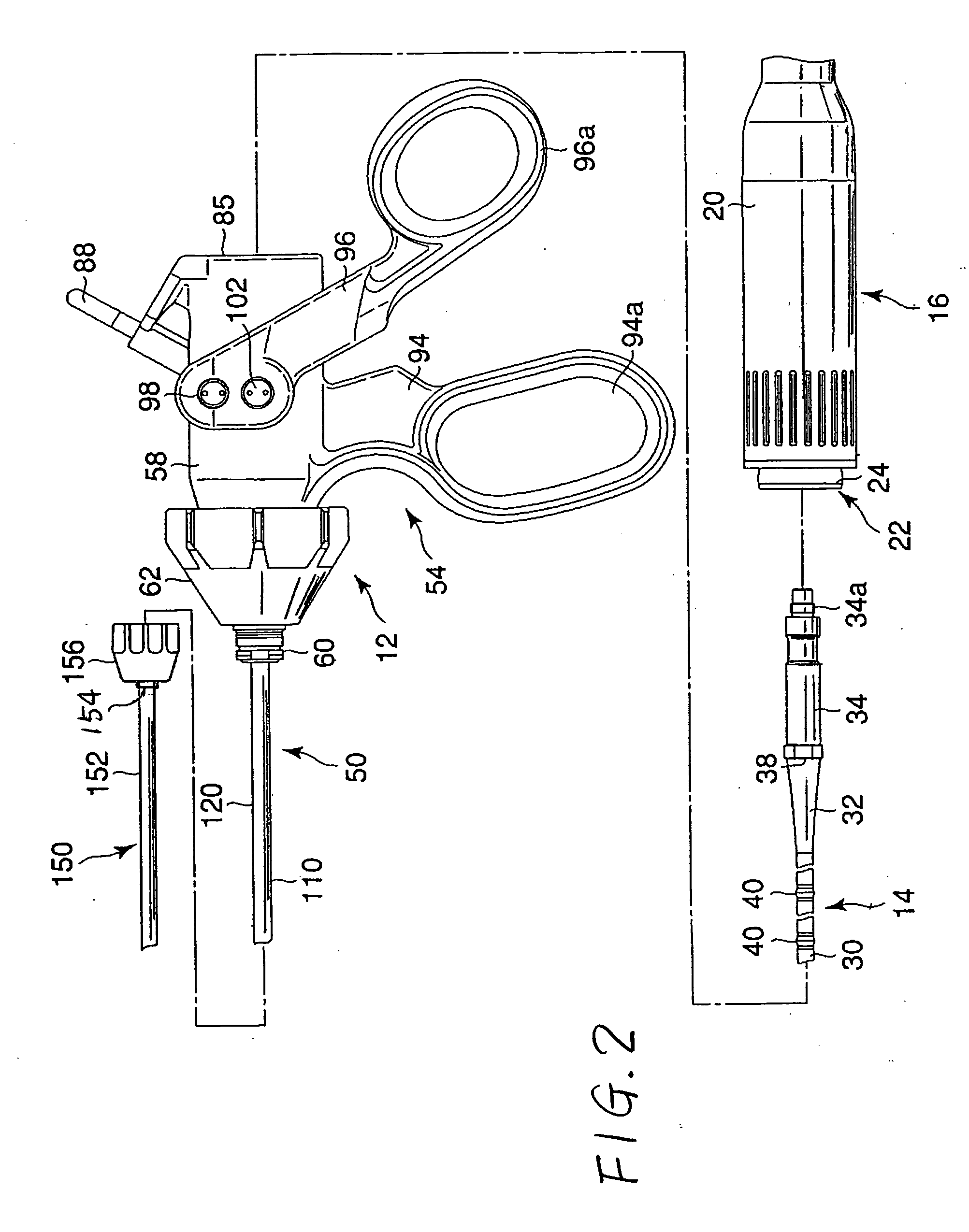
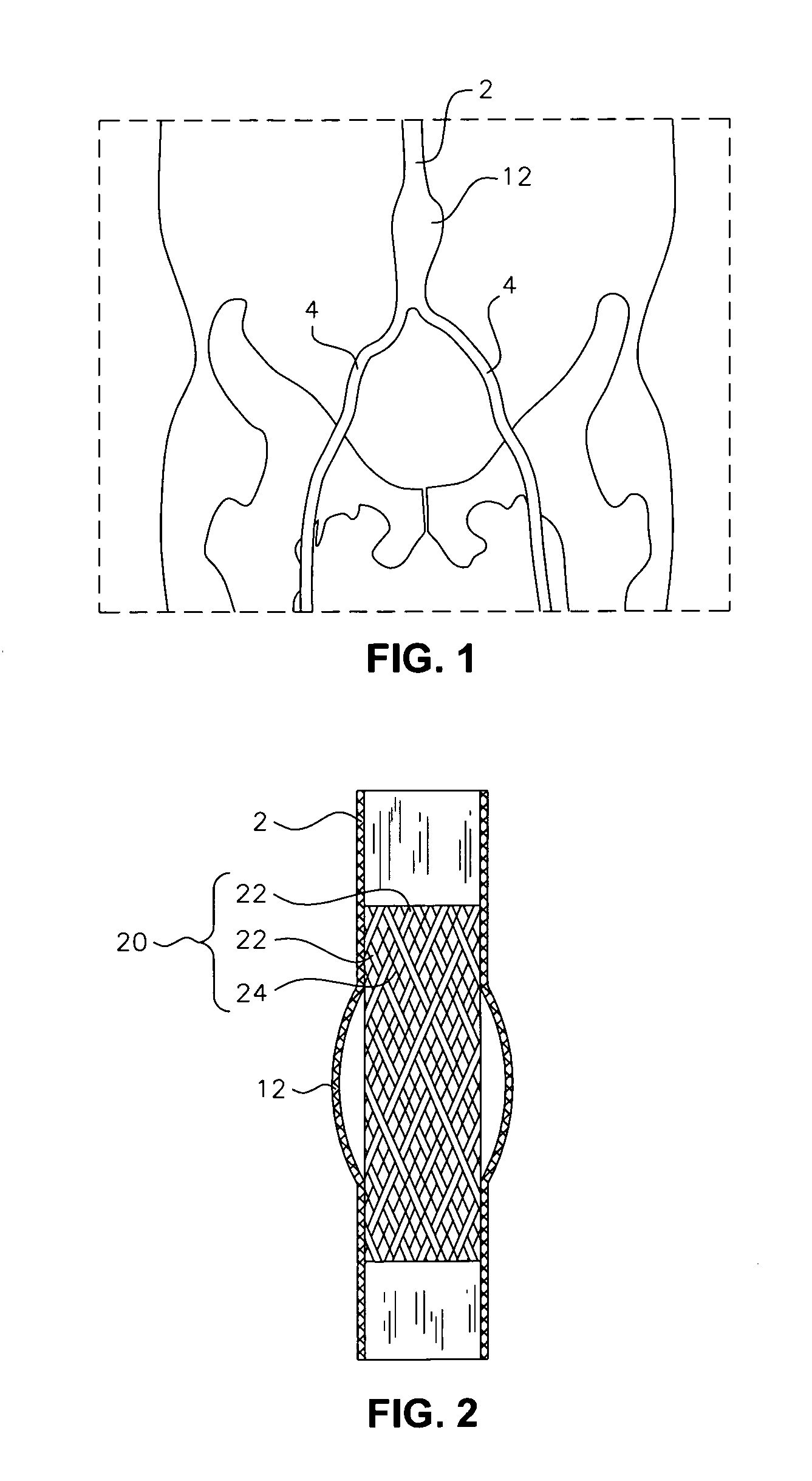
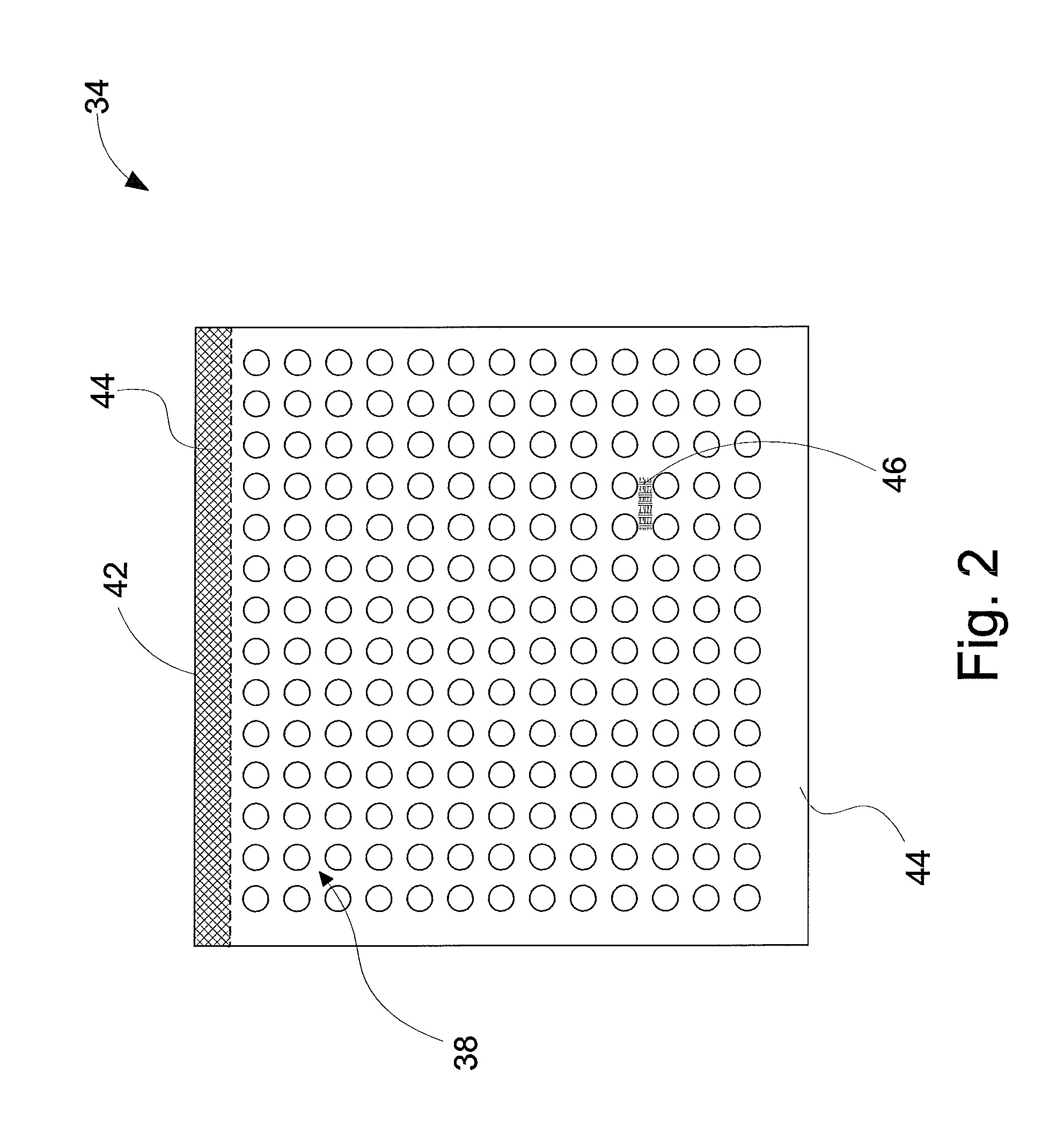
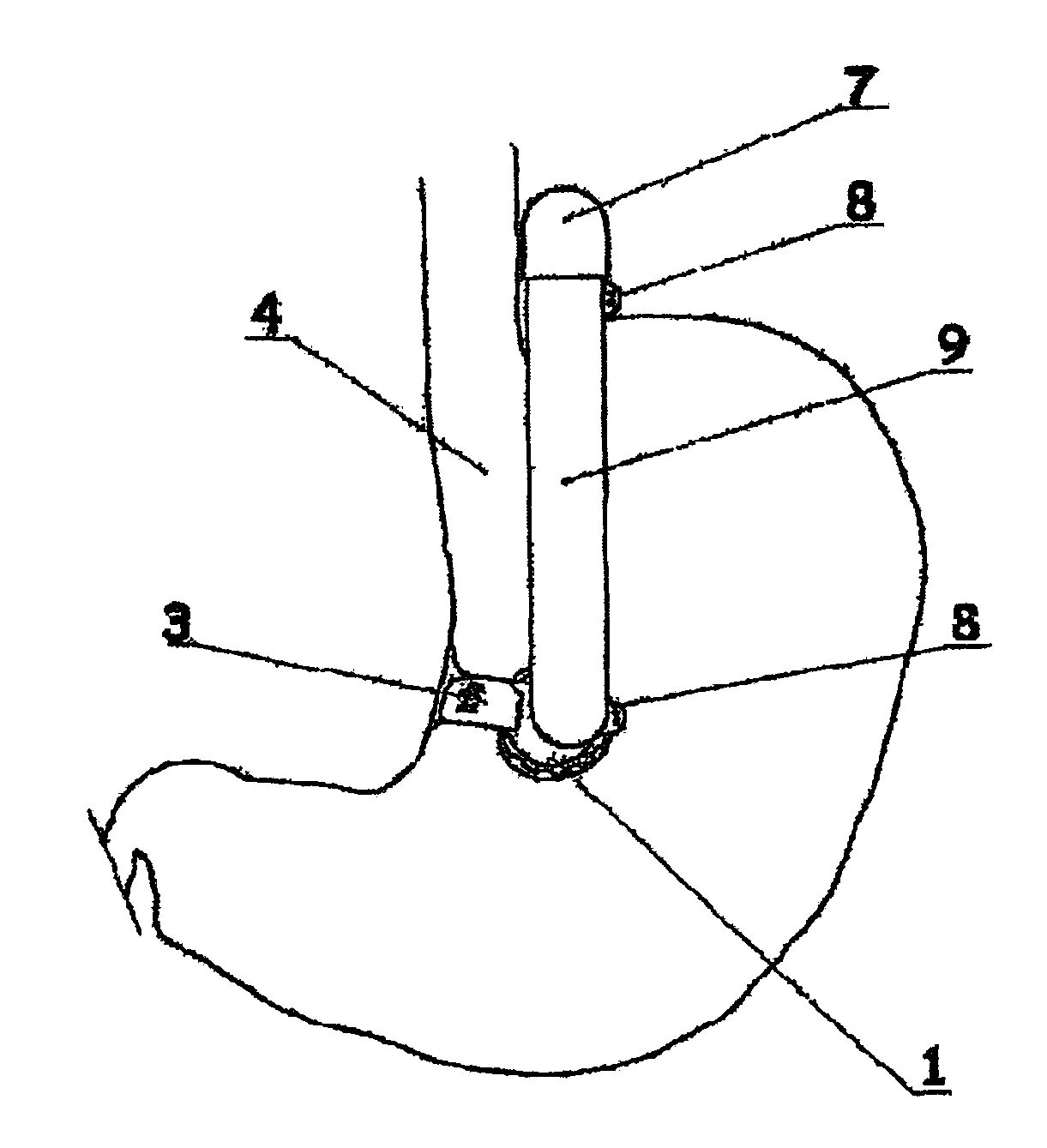
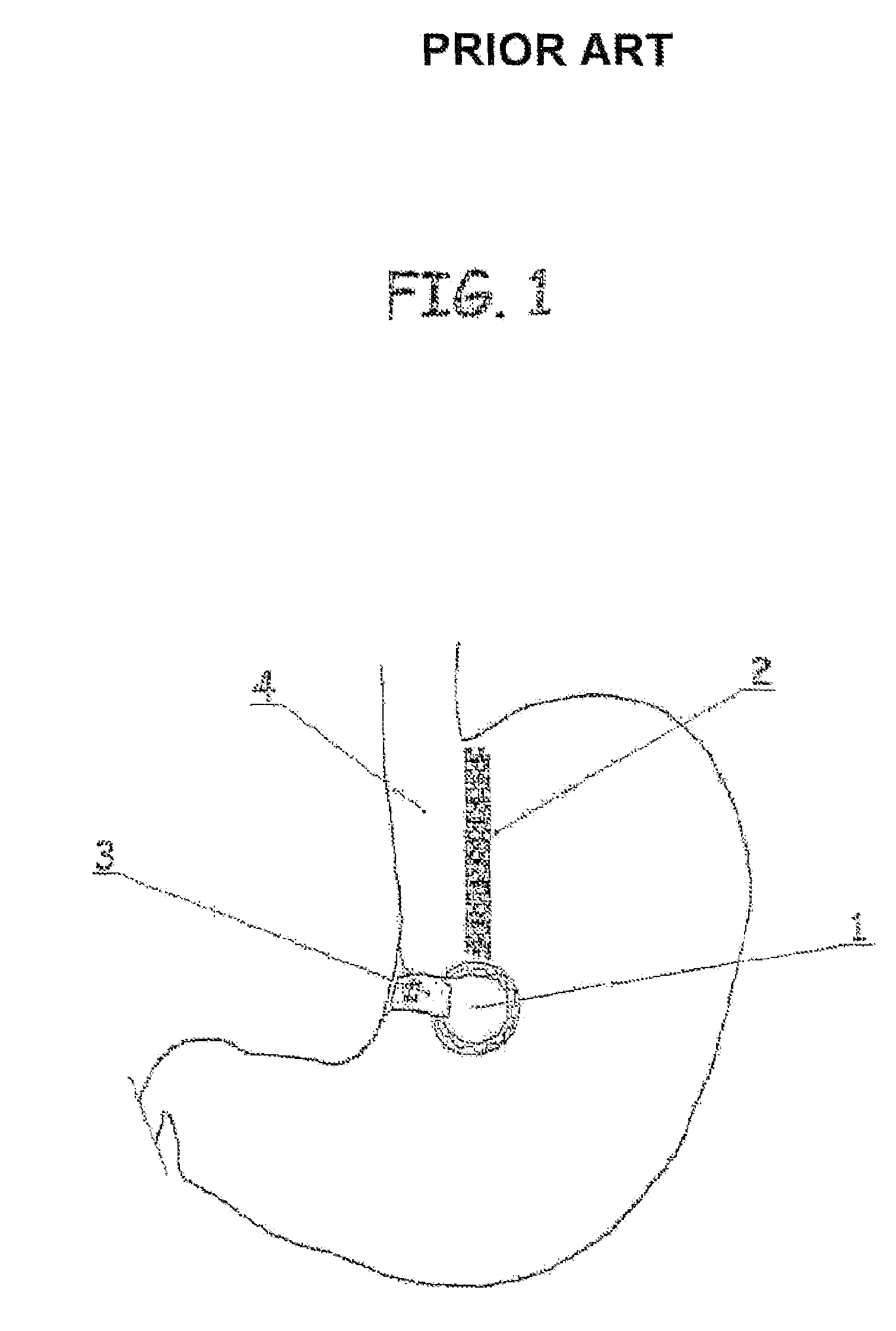
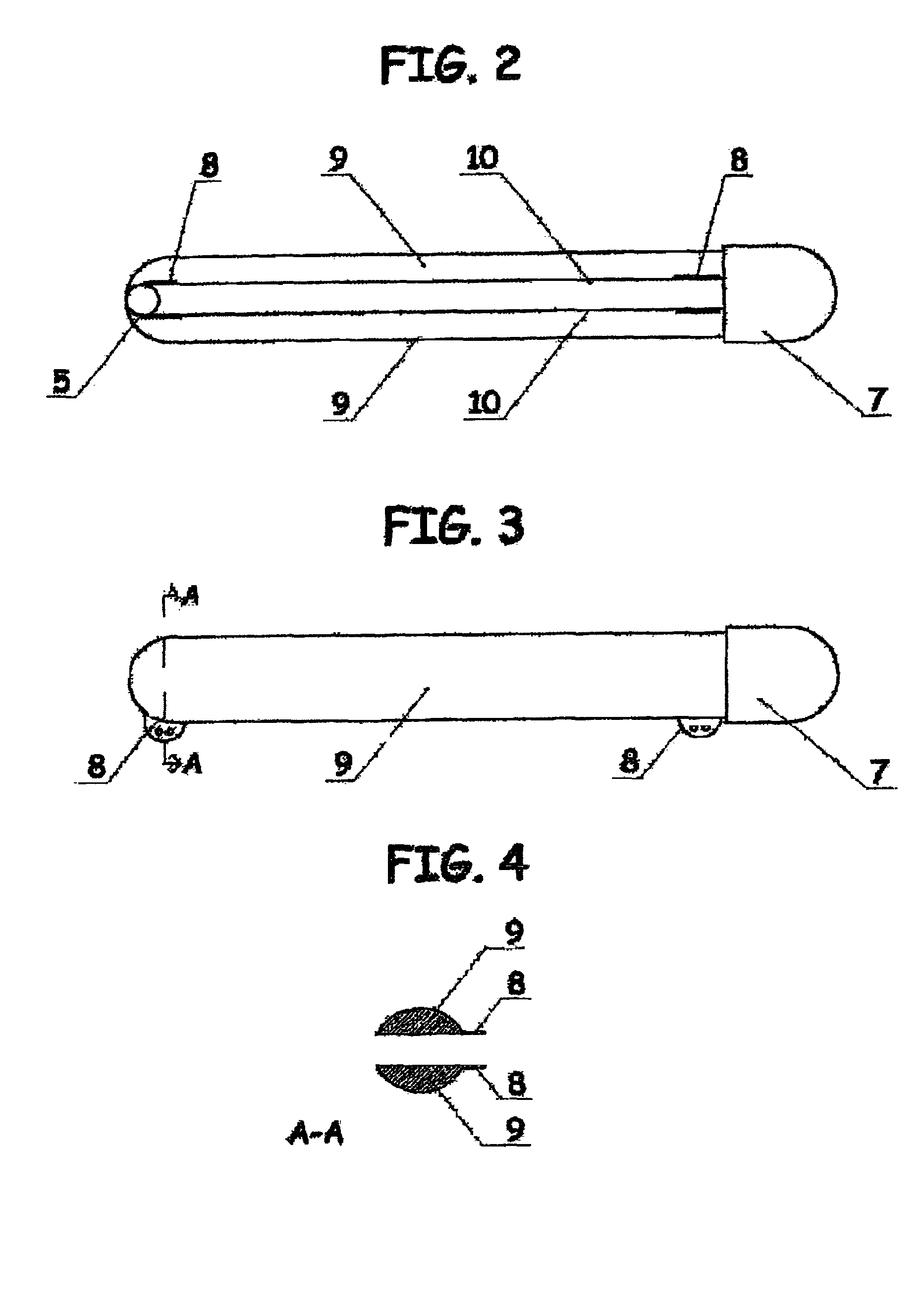
Surgical stapling device with tissue tensioner
A circular stapling device particularly suited for surgical treatment of internal hemorrhoids is provided. The stapling device includes a distal head portion having an anvil and a shell assembly. A tissue tensioner device including a tissue engagement member is movably positioned between the anvil and the shell assembly and is operable via a tensioner trigger to position tissue within a bore defined within the shell assembly.
Owner:TYCO HEALTHCARE GRP LP
Surgical treatment apparatus
A surgical treatment apparatus according to the present invention includes an outer sheath, extending from a base portion subject to an operator's hand to the tip subject to insertion into a body cavity, that is provided with a working channel through which a treatment instrument can be passed; an image pickup device disposed at the tip portion of the outer sheath; and pivotable forceps disposed at the tip portion of the outer sheath, supported on a supporting section protruding in the axial direction via a joint being bent away from the working channel, and having a pair of forceps members arranged so as to be freely opened / closed, wherein the image pickup device is disposed at a position between the axis line of the supporting section and the axis line of the working channel and offset from an imaginary line connecting the two axis lines.
Owner:OLYMPUS CORP
Methods for electrosurgical treatment of spinal tissue
InactiveUS20050004634A1Stiffening the interspinous tissue structureStabilizing the vertebral columnEnemata/irrigatorsHeart valvesThermal energySpinal ligaments
Systems, apparatus, and methods for treating spinal tissue and other body structures in open and endoscopic spine surgery to relieve symptoms, such as neck or back pain. In particular, the present invention provides methods for the controlled heating of various tissues in or around the vertebral column, including various interspinous tissues, such that spinal ligaments and cartilage surrounding the vertebrae and the facet joints are shrunk or tightened to stabilize the vertebral column of a patient. Thermal energy is applied to the target tissue in a subablation mode of an electrosurgical system to cause shrinkage of the tissue, thereby stiffening the interspinous tissue and stabilizing the vertebral column. In an exemplary embodiment, a high frequency RF voltage can be applied between one or more active electrode(s) and one or more return electrode(s) to heat a target interspinous tissue to within a temperature range at which irreversible shrinkage of the tissue occurs.
Owner:ARTHROCARE
Surgical treatment device
ActiveUS7101378B2Easily approachEffectively unfoldVaccination/ovulation diagnosticsExcision instrumentsSurgical treatmentEngineering
A biotissue excising instrument includes a tubular sheath inserted into a body, manipulator inserted into the sheath through leading end of the manipulator and having a loop portion that can be unfolded and contracted to accommodate biotissue to be excised. A slit is formed leading end the sheath to project and sink loop portion of the treatment portion so that manipulator is advanced or retreated to laterally project or sink the loop portion out of or into the or contract the loop portion, the sheath, and a treatment portion provided at thus excising the biotissue loop portion.
Owner:OLYMPUS CORP
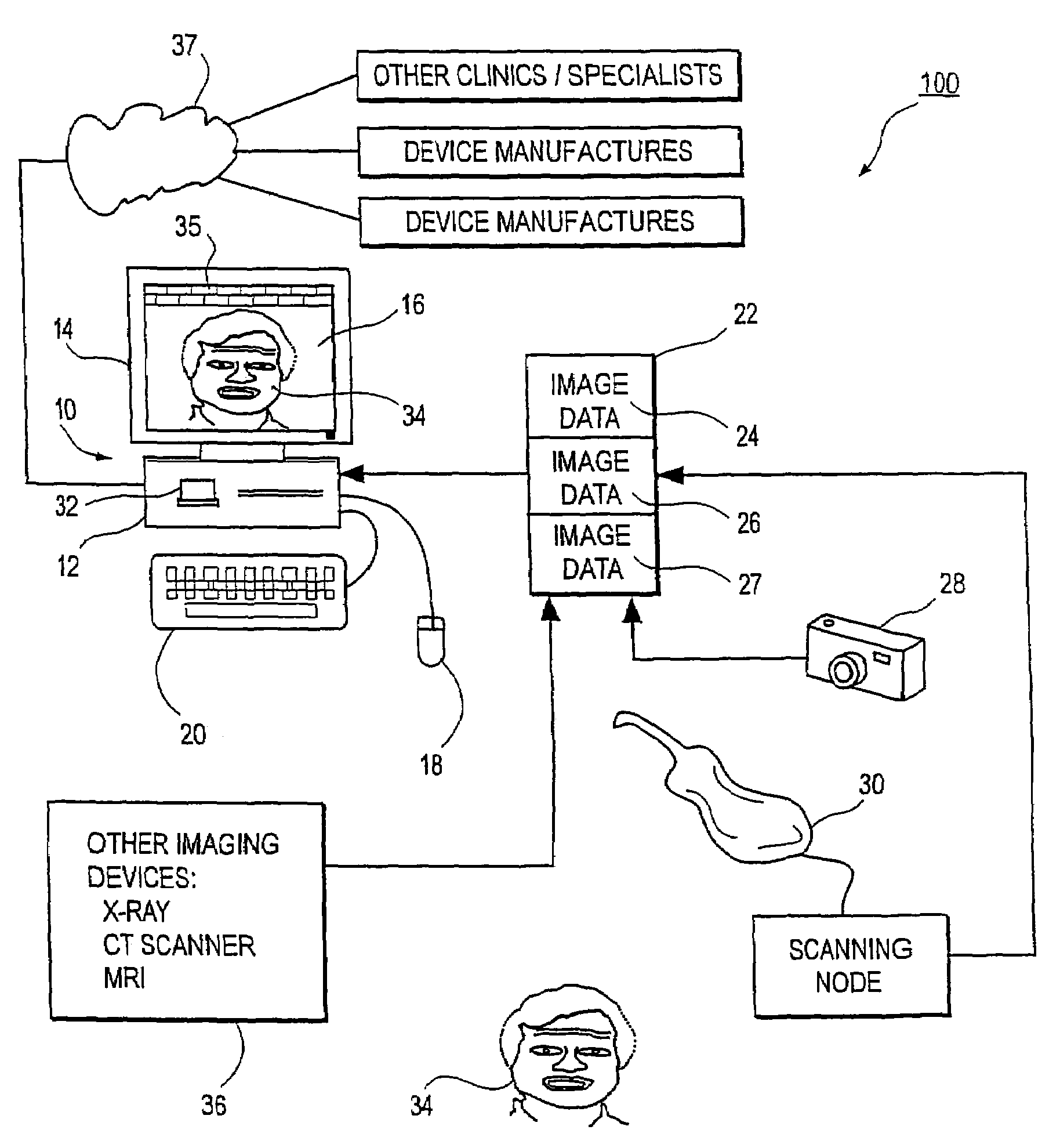
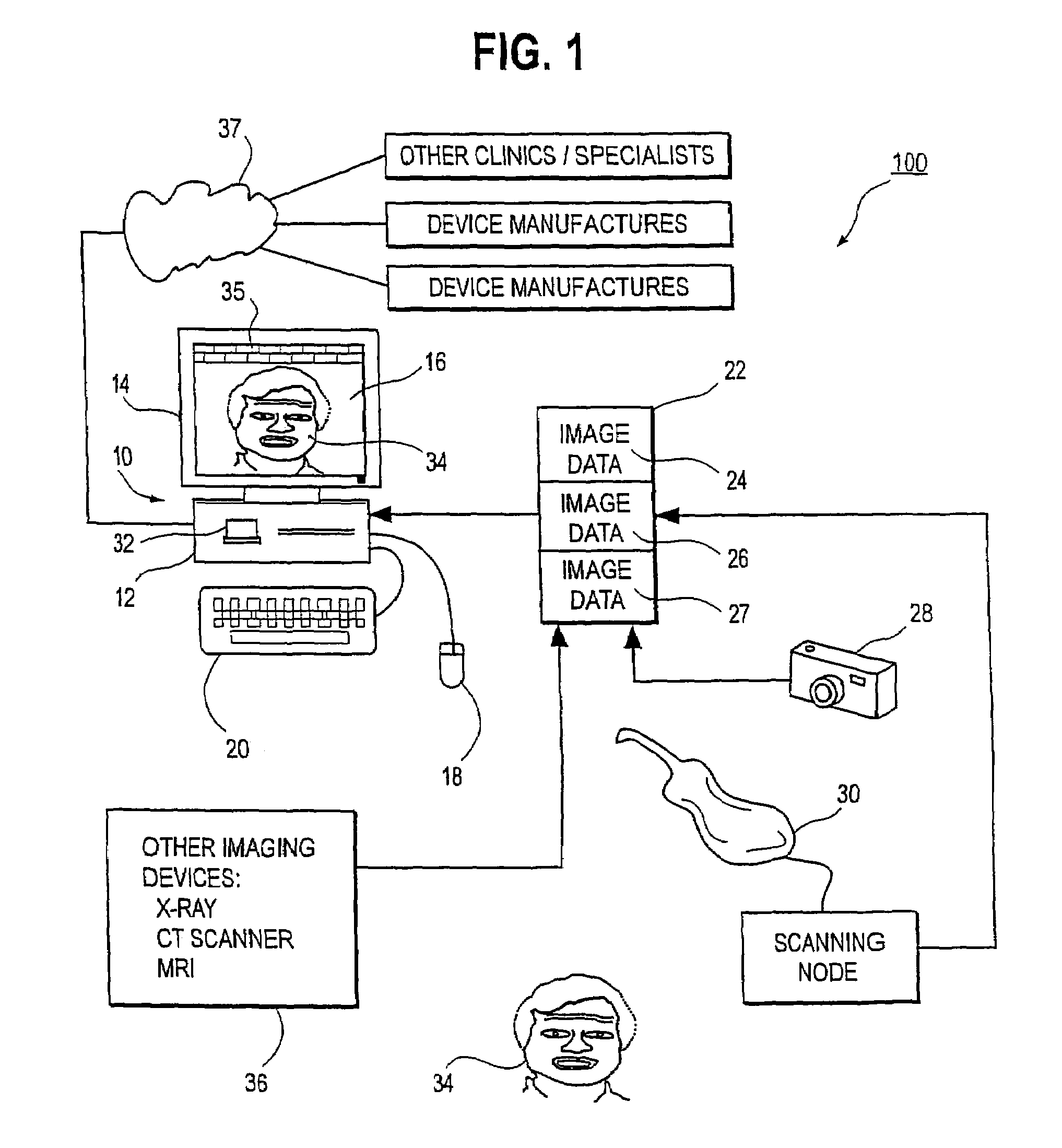
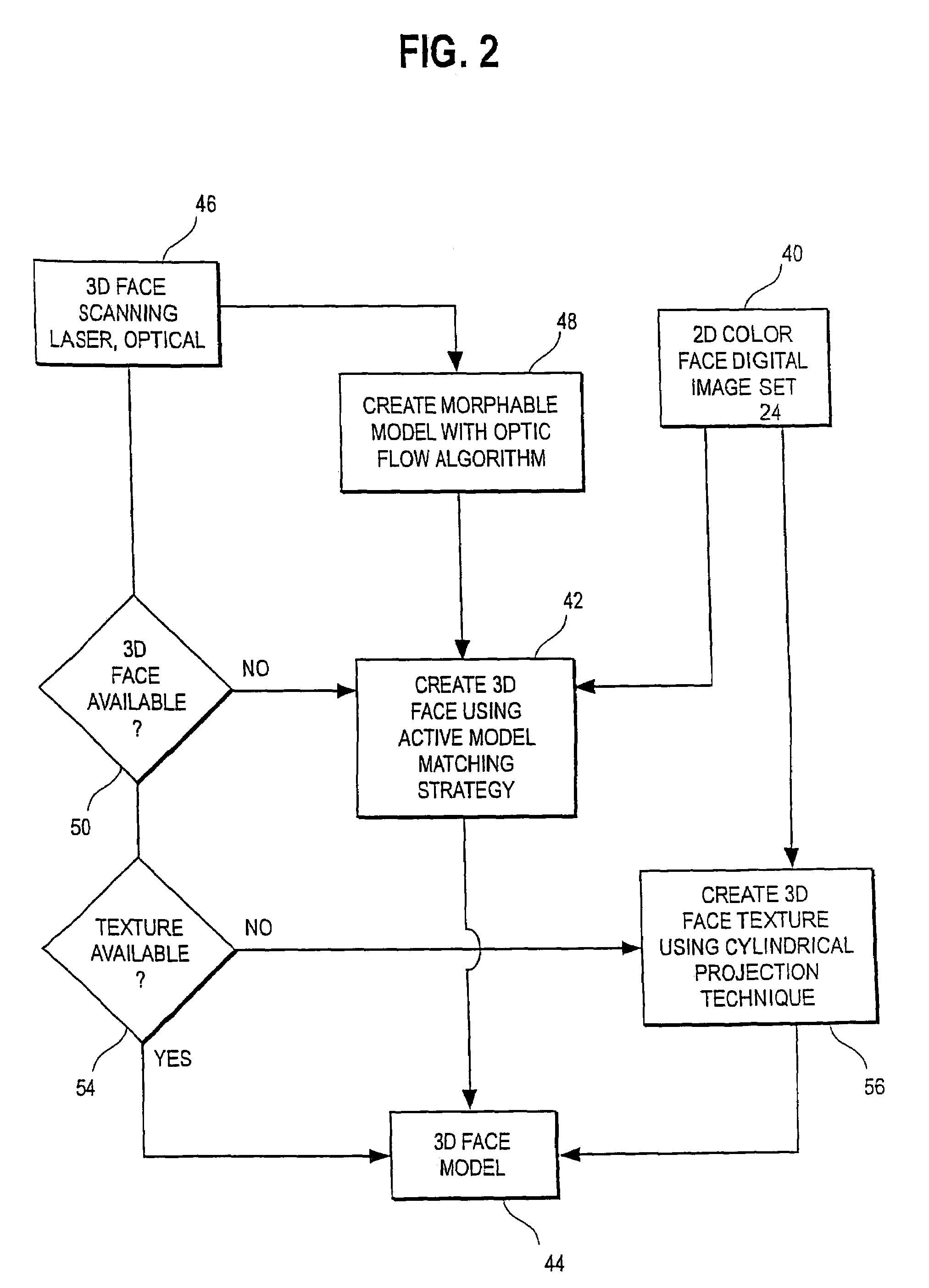
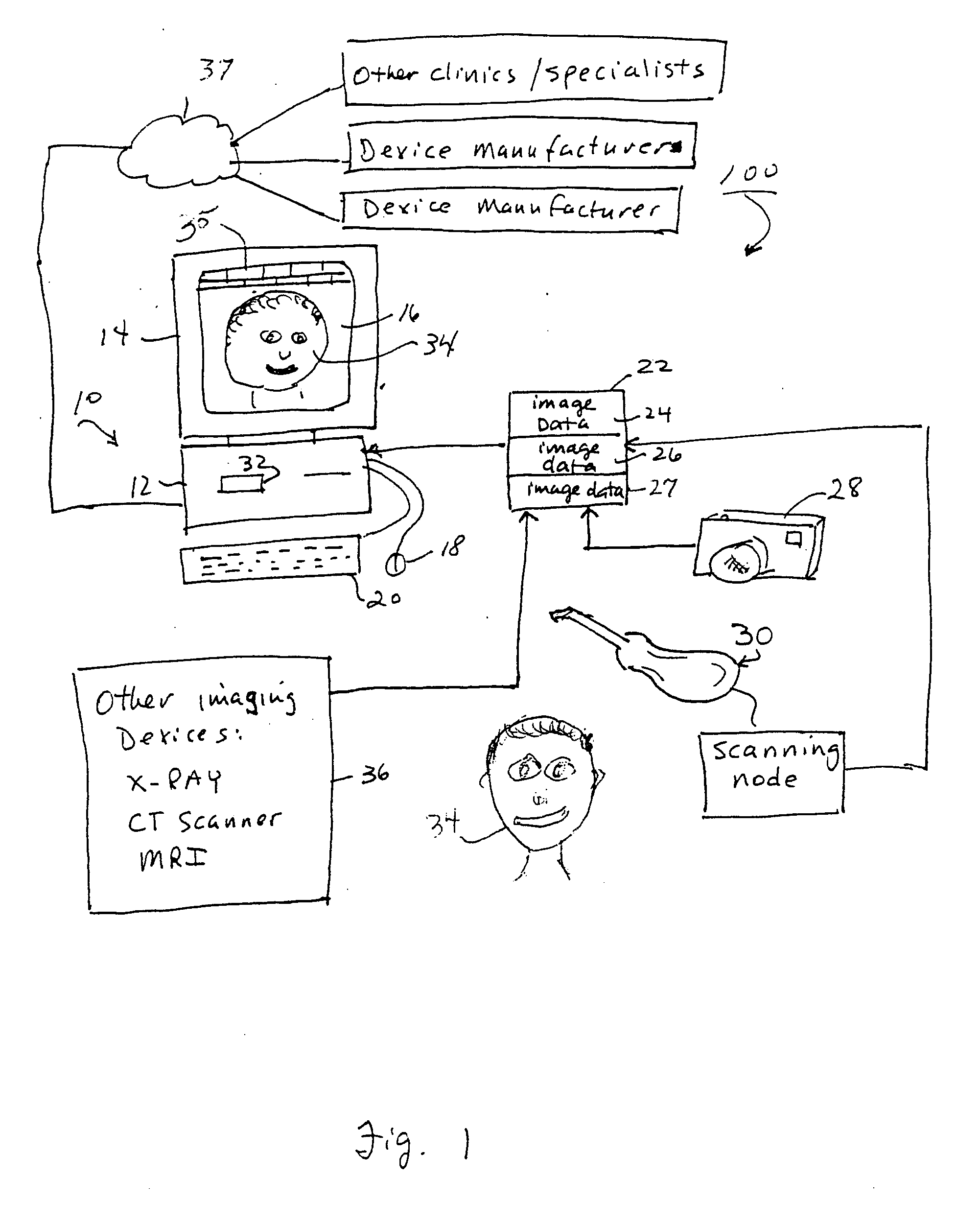
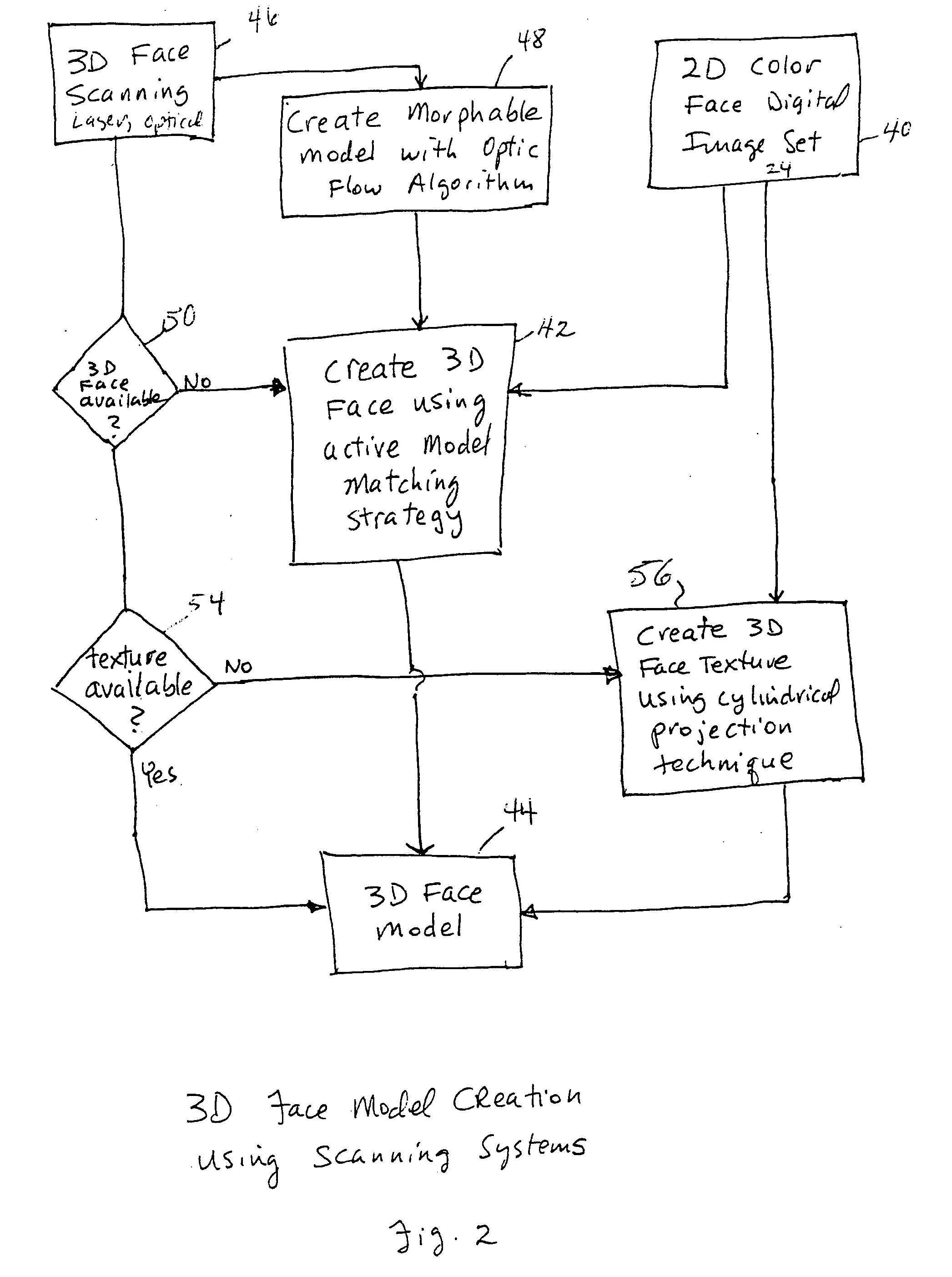
Unified workstation for virtual craniofacial diagnosis, treatment planning and therapeutics
InactiveUS7234937B2Quick analysisPowerful toolDental implantsImpression capsPlan treatmentPatient model
An integrated system is described in which digital image data of a patient, obtained from a variety of image sources, including CT scanner, X-Ray, 2D or 3D scanners and color photographs, are combined into a common coordinate system to create a virtual three-dimensional patient model. Software tools are provided for manipulating the virtual patient model to simulation changes in position or orientation of craniofacial structures (e.g., jaw or teeth) and simulate their affect on the appearance of the patient. The simulation (which may be pure simulations or may be so-called “morphing” type simulations) enables a comprehensive approach to planning treatment for the patient. In one embodiment, the treatment may encompass orthodontic treatment. Similarly, surgical treatment plans can be created. Data is extracted from the virtual patient model or simulations thereof for purposes of manufacture of customized therapeutic devices for any component of the craniofacial structures, e.g., orthodontic appliances.
Owner:ORAMETRIX
Apparatus and method for fixation of osteoporotic bone
InactiveUS6887246B2Safely introducedSatisfy safety performance requirementsSurgical needlesJoint implantsSurgical treatmentOsteoporotic bone
A Novel surgical apparatus and method of use in osteoplasty and other methods of injecting materials into a subject for medical purposes. The present invention particularly relates to the surgical treatment of traumatic, pathogenic, or osteoporotic bone conditions of the human and other animal body systems and more particularly, to a novel apparatus and method for injection of a material into a lesion of a vertebral body or other bony structure.
Owner:ZIMMER BIOMET SPINE INC
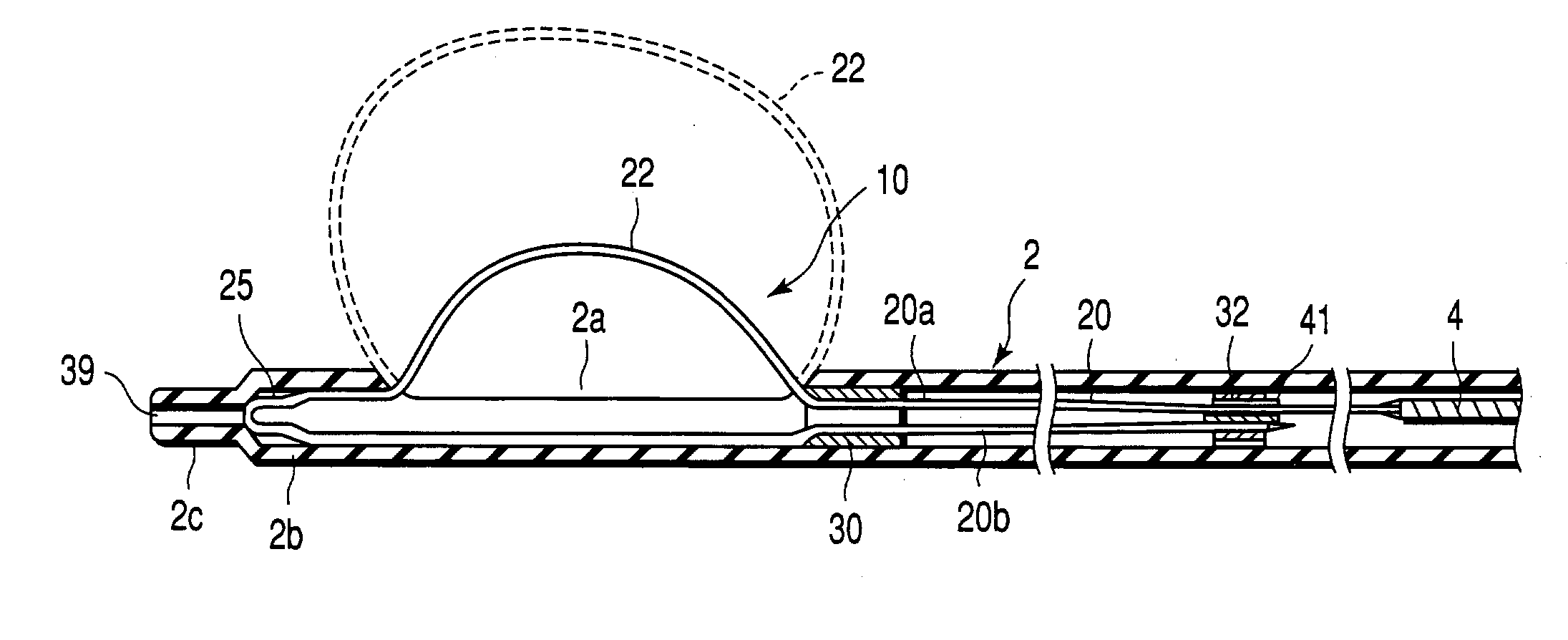
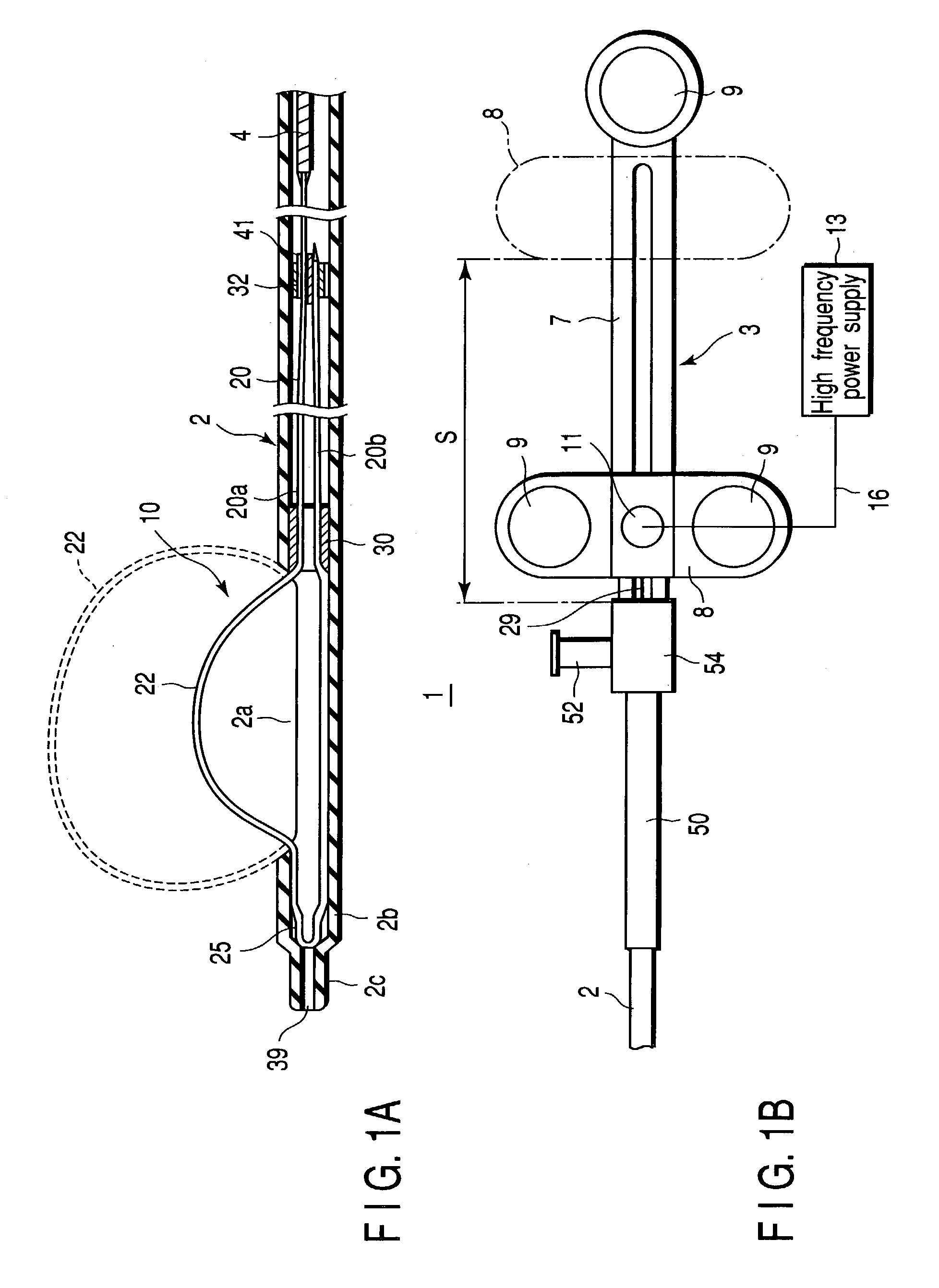
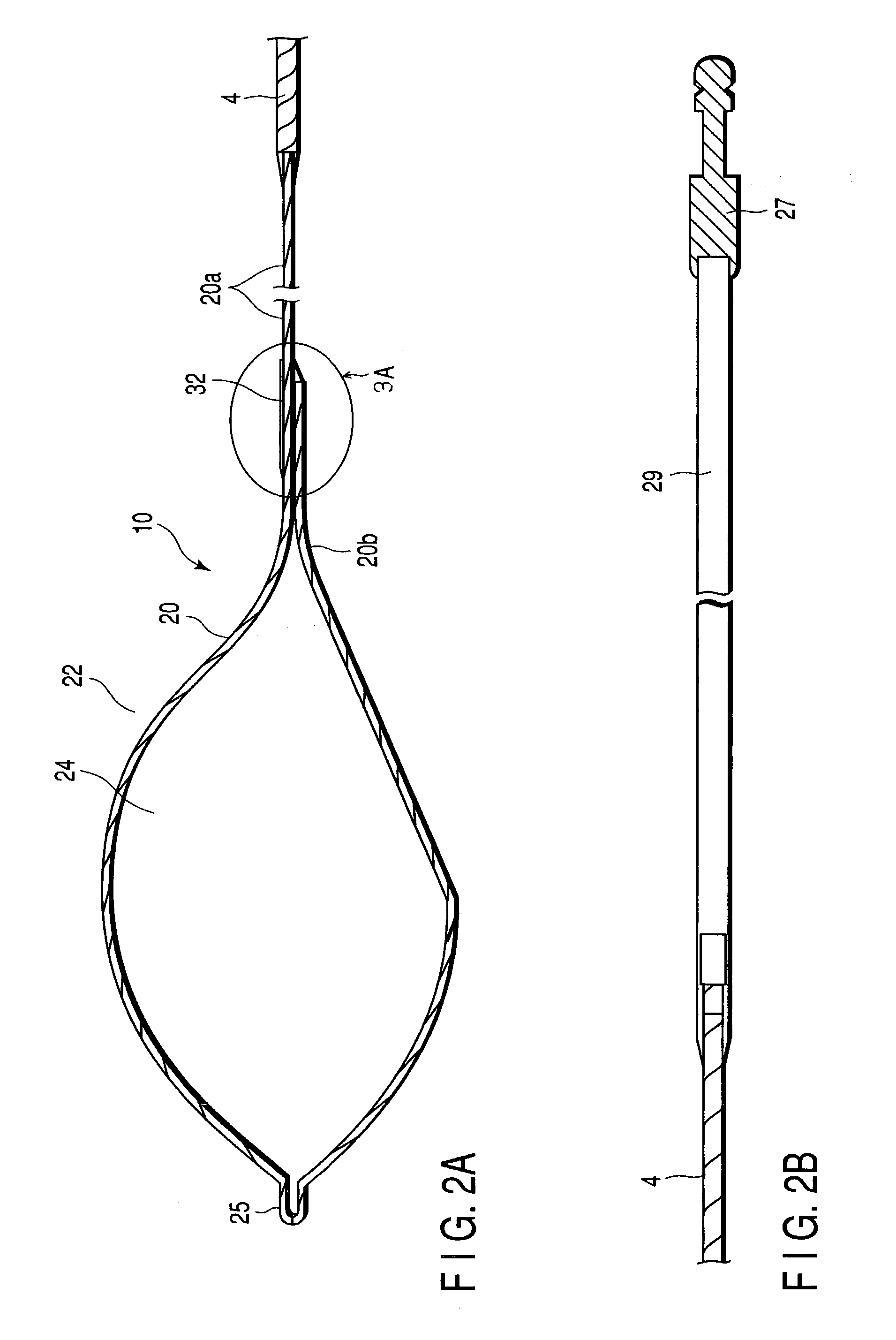
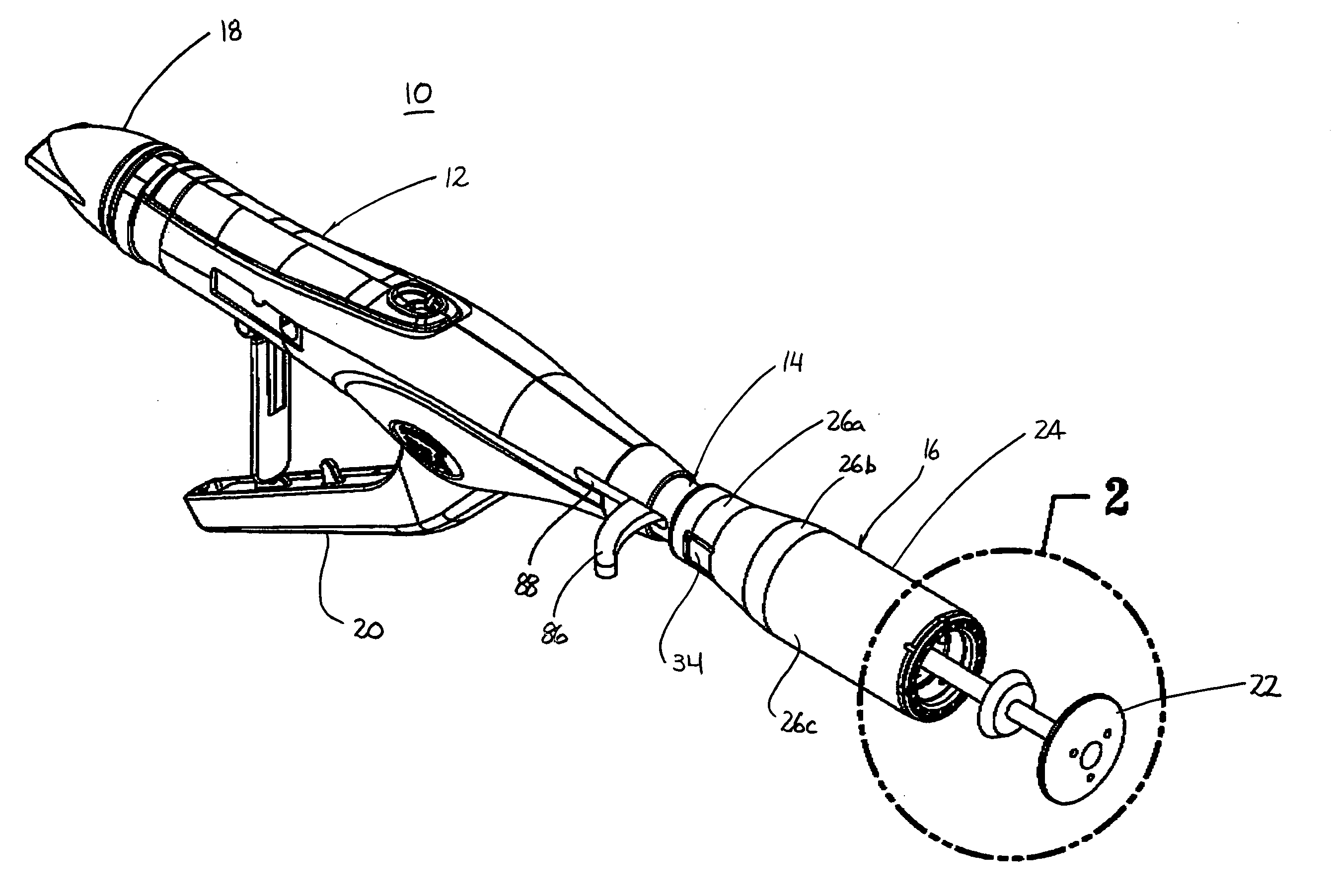
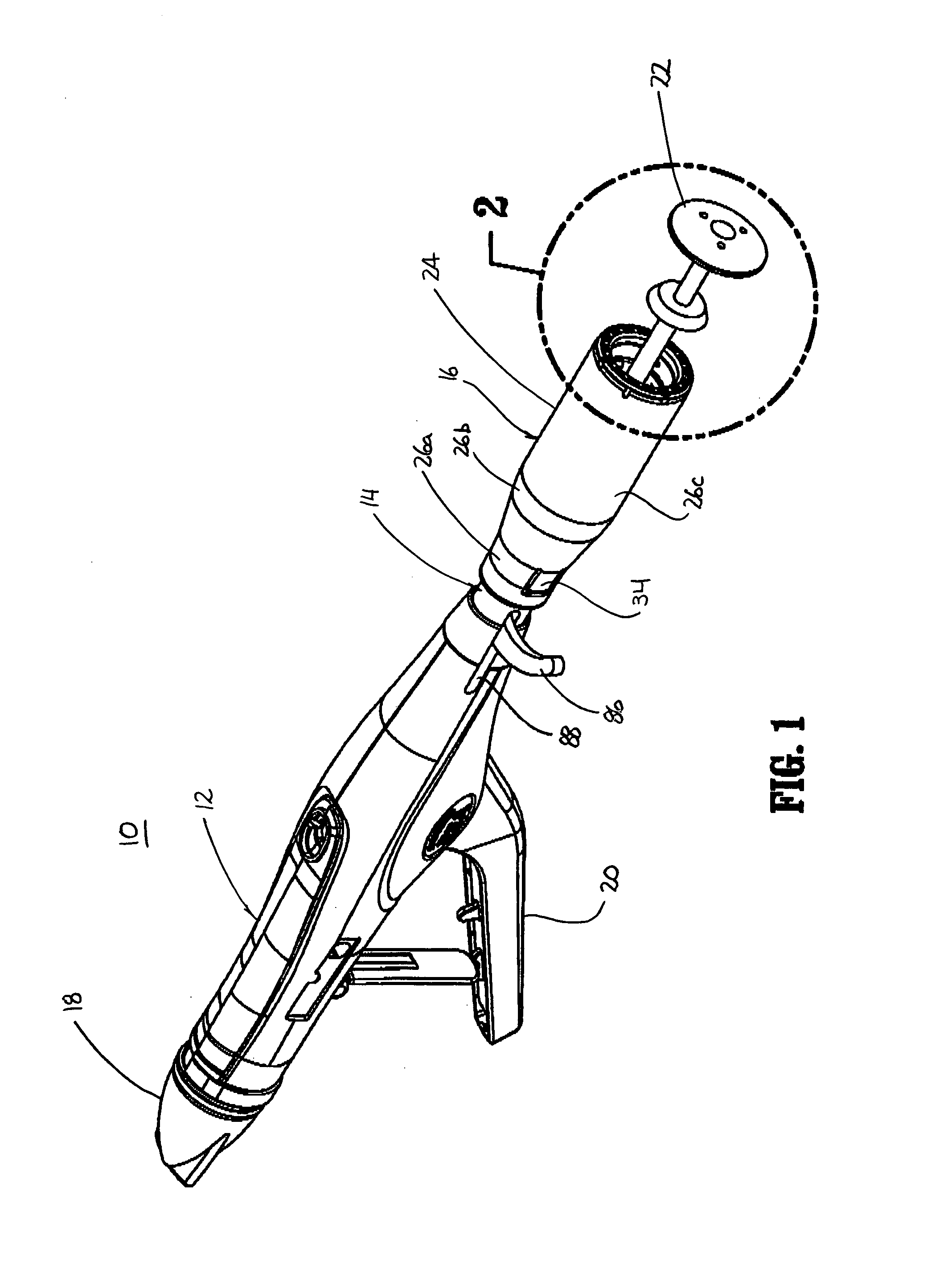
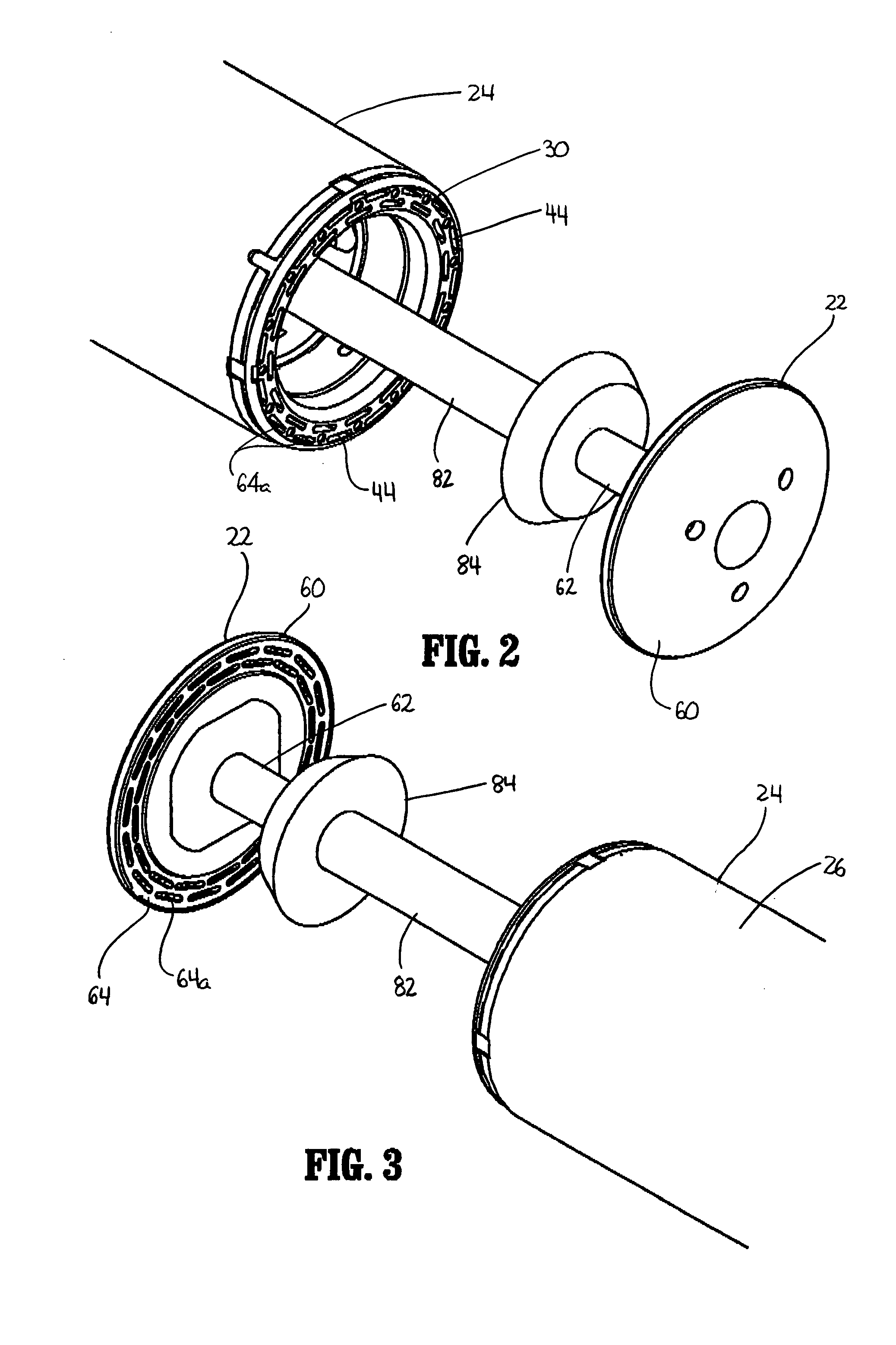
Treatment apparatus and treatment device for surgical treatments using ultrasonic vibration
ActiveUS7799045B2Ultrasonic/sonic/infrasonic diagnosticsInfrasonic diagnosticsSurgical treatmentTransducer
An ultrasonic treatment device comprises a transducer unit, probe unit, and a main unit. The transducer unit comprises an ultrasonic transducer generating ultrasonic vibration in response to supply of power. The probe unit has a treatment member at a distal end thereof. The probe unit is detachably loaded to the transducer unit, and is equipped with an ultrasonic probe transmitting the ultrasonic vibration to the distal end of the treatment member when the transducer unit is loaded to the probe unit. The main unit is manually grasped by an operator. The probe unit with the transducer unit loaded thereto is detachably loaded to the main unit. The main unit has a cylindrical insert through which the ultrasonic probe is inserted to have the treatment member protruded outwardly when the probe unit is loaded. The main unit further has an outer sheath detachably covering an outer surface of the insert.
Owner:OLYMPUS CORP
Surgical stapling device with tissue tensioner
ActiveUS20050021053A1Promote sportsSuture equipmentsStapling toolsSurgical treatmentSurgical department
A circular stapling device particularly suited for surgical treatment of internal hemorrhoids is provided. The stapling device includes a distal head portion having an anvil and a shell assembly. A tissue tensioner device including a tissue engagement member is movably positioned between the anvil and the shell assembly and is operable via a tensioner trigger to position tissue within a bore defined within the shell assembly.
Owner:TYCO HEALTHCARE GRP LP
Bone fixation device
InactiveUS20060069390A1Complicated and activityInjury can be limitedSuture equipmentsInternal osteosythesisSpinal columnSurgical treatment
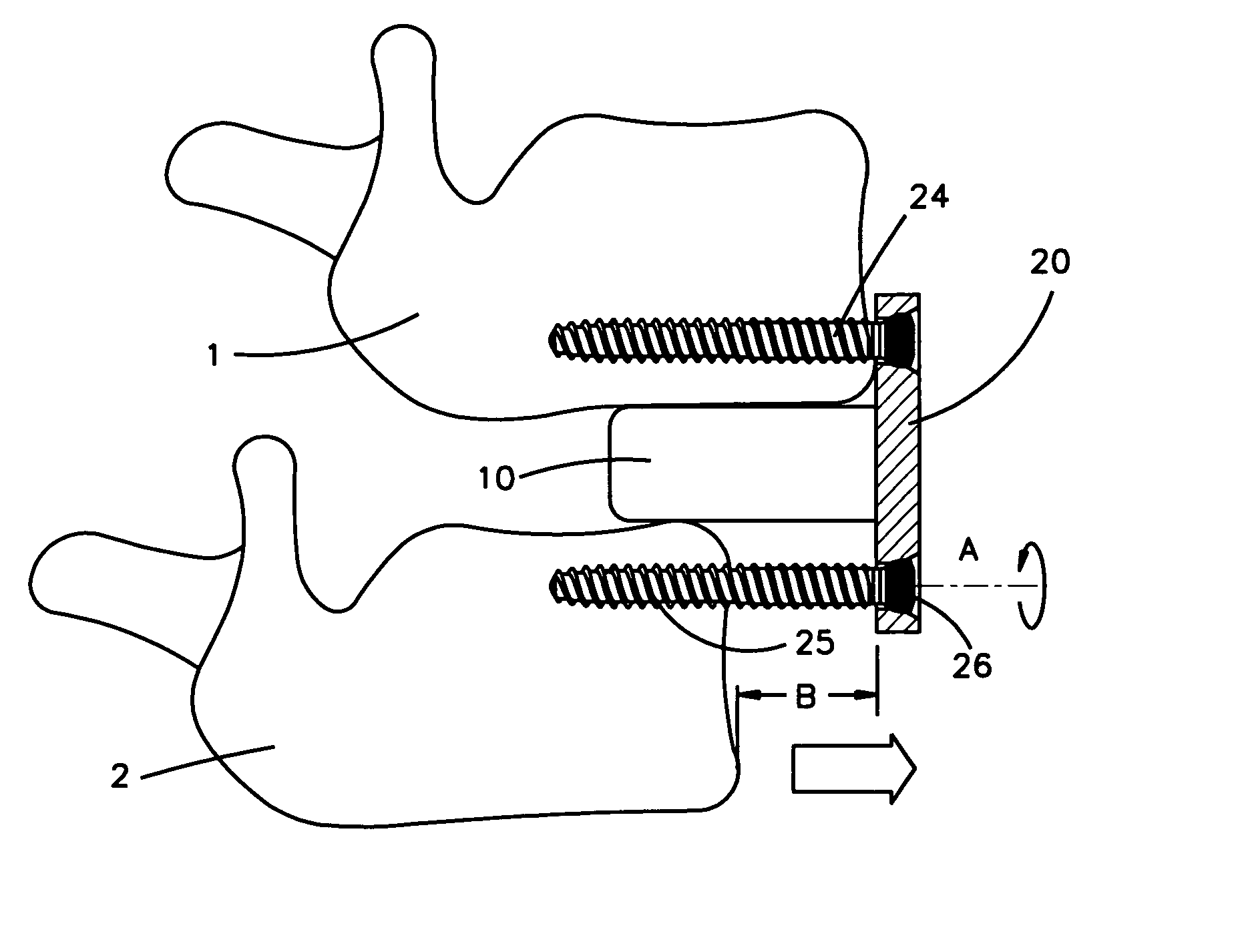
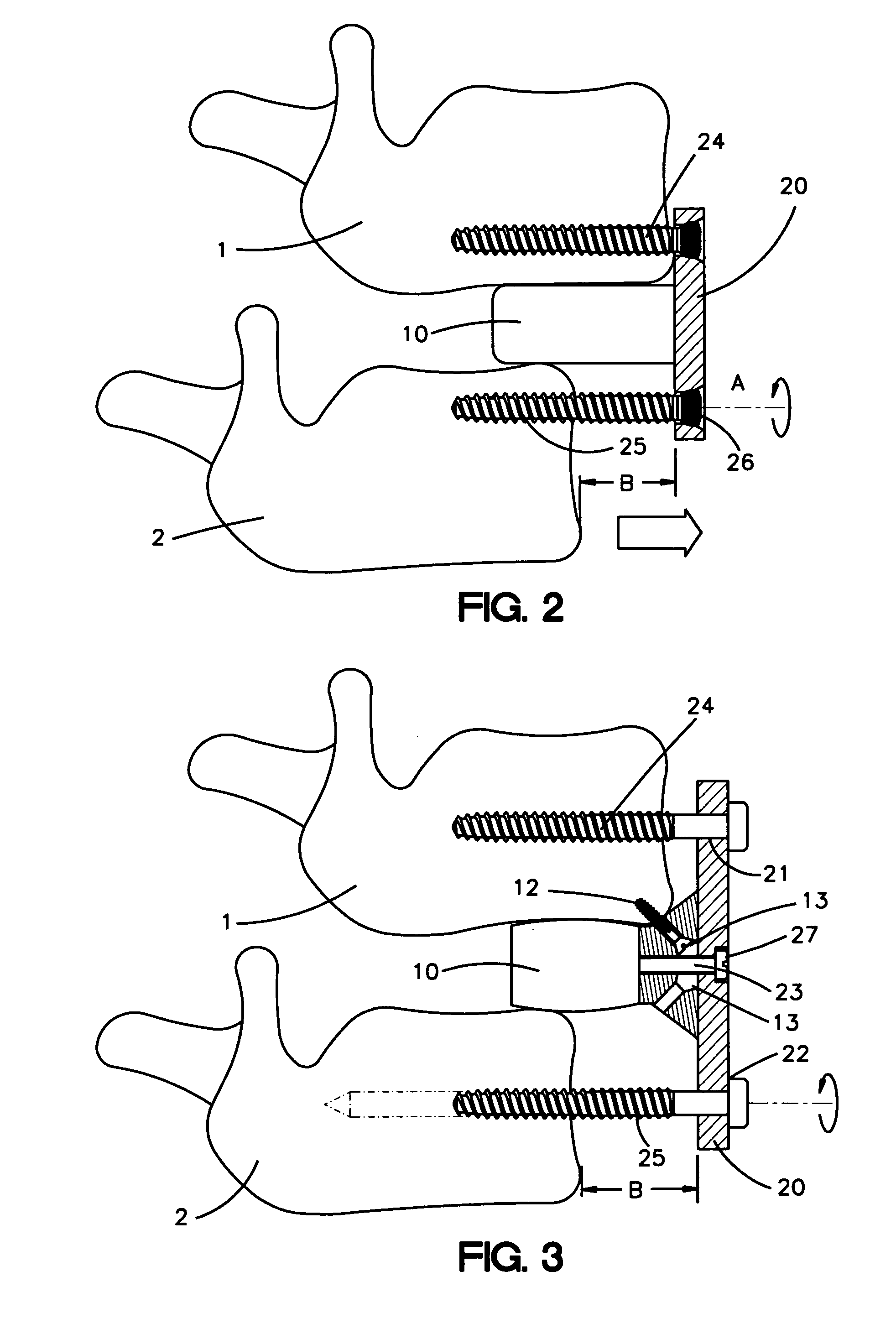
A bone fixation device for use in, for example, spinal column surgery, includes at least two bone fixation elements that each have a passage and a portion to be anchored on or in the bone. The device also includes at least two longitudinal, flexible connecting members that can be inserted and fastened in the passages of two adjacent fixation elements. The device can flexibly adapt to a patient's anatomy and to desired surgical results during the implantation of the device, and can then be rendered entirely rigid by simply blocking the fixation elements relative to one another. In addition, use of the device in the surgical treatment of the spinal column is minimally invasive.
Owner:SYNTHES USA
Device for providing a combination of flexibility and variable force to the spinal column for the treatment of scoliosis
Non-surgical treatments for idiopathic scoliosis include muscle stimulation therapy, chiropractic care, and the application of a variety of braces (orthotics). Surgical intervention frequently employs rigid metallic braces that prevent further flexing of the spine where applied. This invention allows flexing of the spine with long term correction of the scoliosis by application of small variable forces to supplant and counter the unbalance of the pertinent muscles. This invention may be applied to other spine problems in addition to idiopathic scoliosis as this invention permits and accommodates flexing of the spine and simultaneously supplies correcting and straightening forces.
Owner:LEWIS DAVID WARREN
Methods for electrosurgical treatment of spinal tissue
InactiveUS20060095026A1Stiffening the interspinous tissue structureStabilizing the vertebral columnEnemata/irrigatorsHeart valvesSpinal ligamentsSpinal column
Owner:ARTHROCARE
Method of surgically treating scoliosis
InactiveUS6837904B2Broaden applicationFacilitate sameInternal osteosythesisDiagnosticsSurgical treatmentScoliosis
A surgical treatment for restoring a proper anatomical spacing and alignment to vertebral bones of a scoliosis patient, the treatment including determining an angular misalignment associated with at least one pair of adjacent bones, adjusting the intervertebral space between adjacent vertebral bones to restore proper spacing, and inserting a tapered spacer to restore proper anatomical misalignment of the vertebral bones.
Owner:HOWMEDICA OSTEONICS CORP
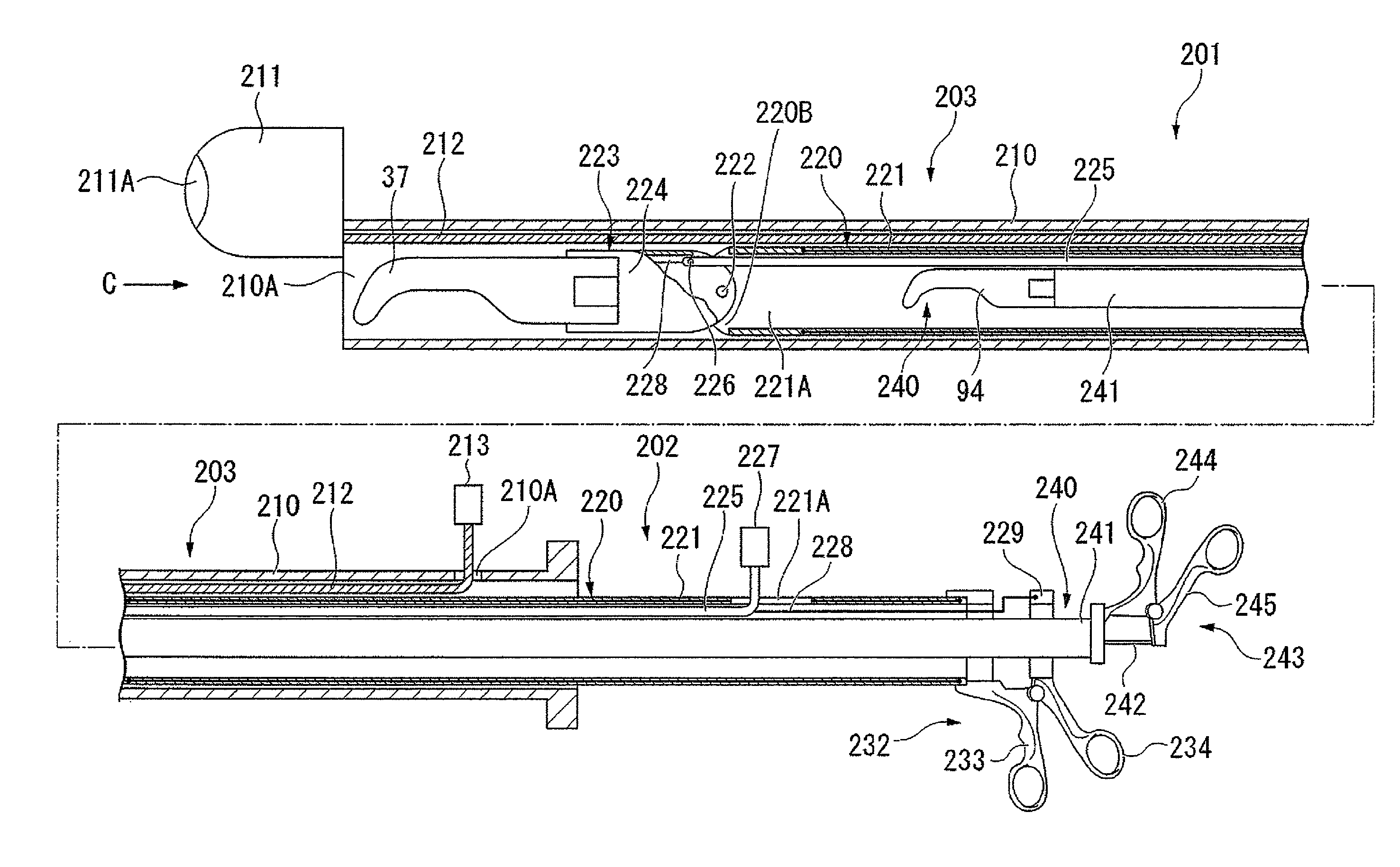
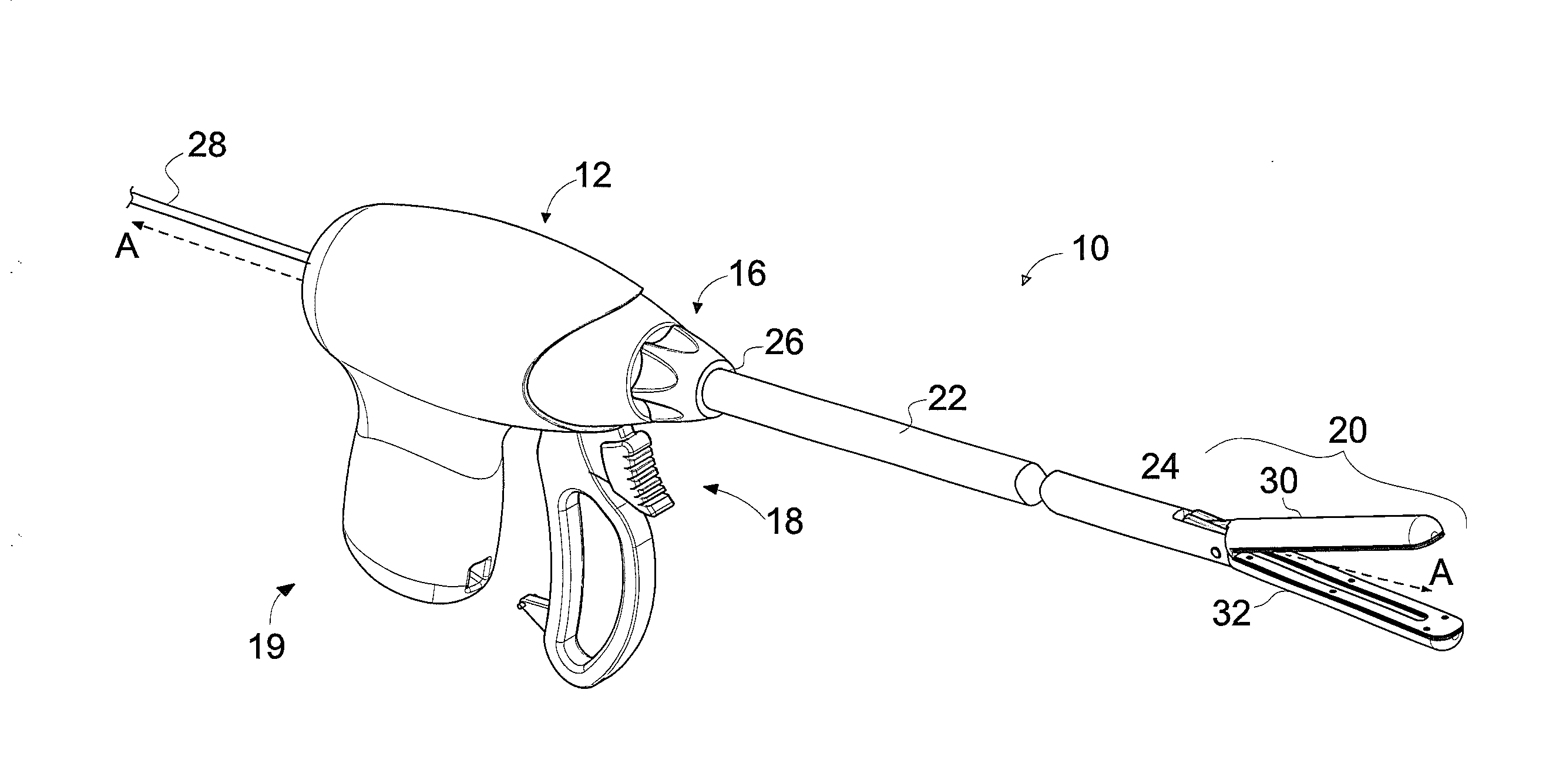
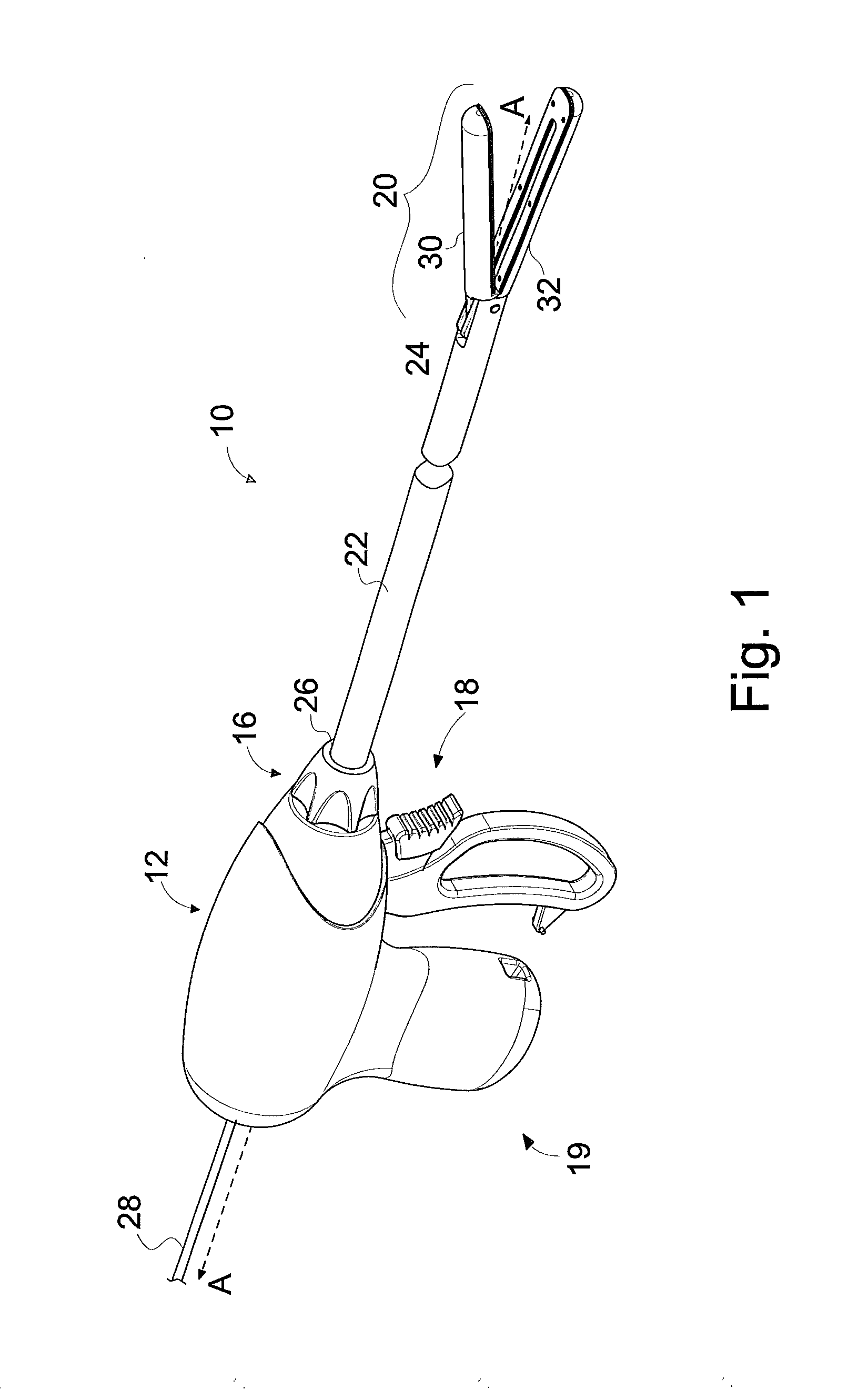
Medical treating instrument
InactiveUS7297106B2Easy to switchReduce the overall heightCannulasDiagnosticsSurgical treatmentForceps
There is provided a surgical treatment instrument in which the mode can be easily switched between a treatment under a pneumoperitoneum condition and a treatment outside the peritoneal cavity, and forceps can be manipulated under the pneumoperitoneum condition, and when taking out a cancer-affected part, an incision in the abdominal wall is protected, and the incision is free from infection. The surgical treatment instrument includes a tubular portion which has a first fixing member provided at a near end-side open portion thereof, and also has a second fixing member provided at a remote end-side open portion thereof. At least two tension belts are mounted on the second fixing member, and fixing means for adjusting the length of the tension belts to position the first fixing member is provided at the first fixing member.
Owner:SUMITOMO BAKELITE CO LTD
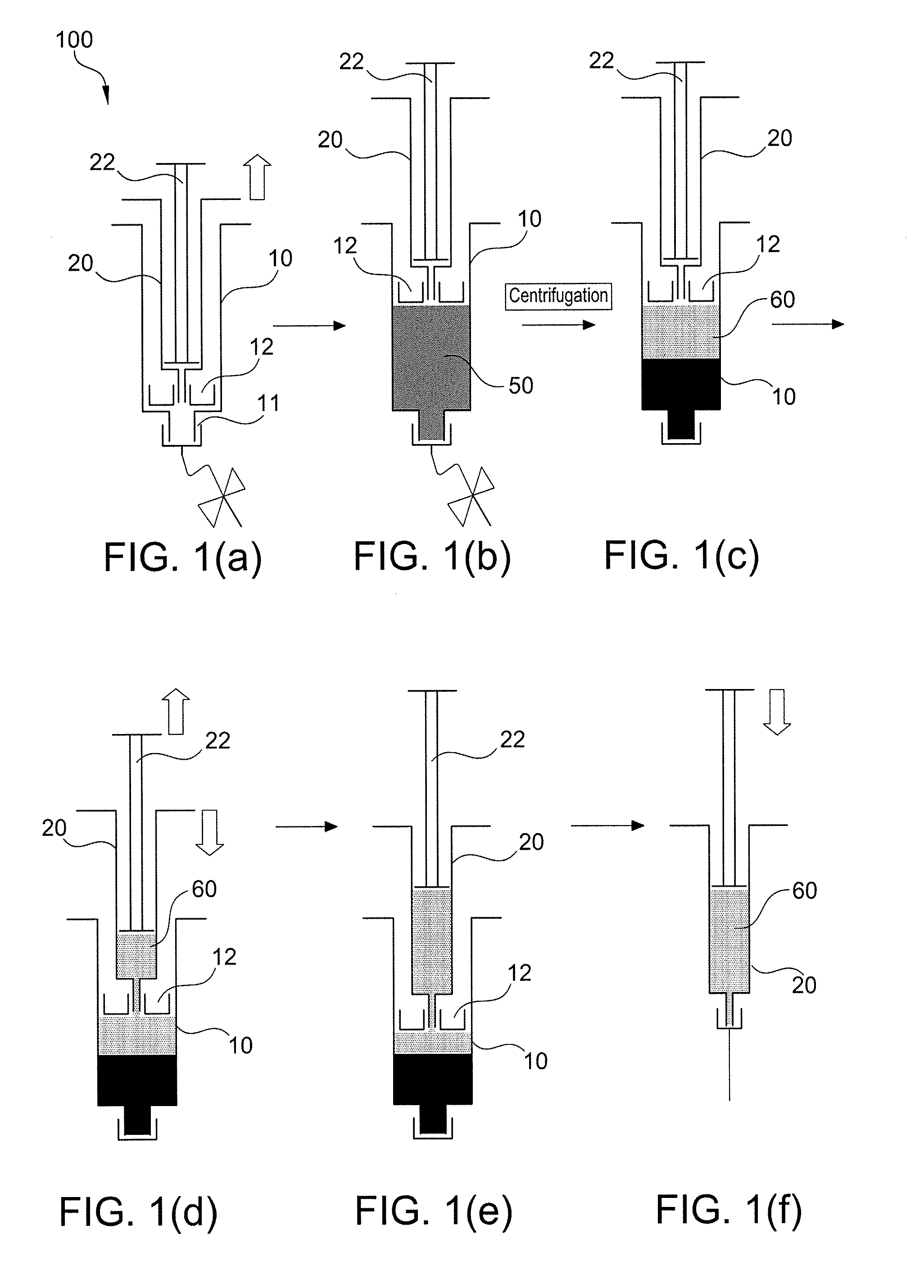
Method of surgical treatment using autologous conditioned plasma
A method of providing autologous conditioned plasma (ACP) for treatment of connective tissue injuries. The method comprises the steps of: (i) providing an apparatus comprising a centrifuge and a double syringe, the double syringe including an inner syringe body and an outer syringe body; (ii) drawing autologous blood into the outer syringe body; (iii) subjecting the autologous blood to at least one centrifugation step to obtain an autologous conditioned plasma (ACP); (iv) removing, with the inner syringe body, at least a portion of autologous conditioned plasma (ACP) from the outer syringe body; and (v) inject ACP for treatment of various cartilage or tendon damage or diseases.
Owner:ARTHREX
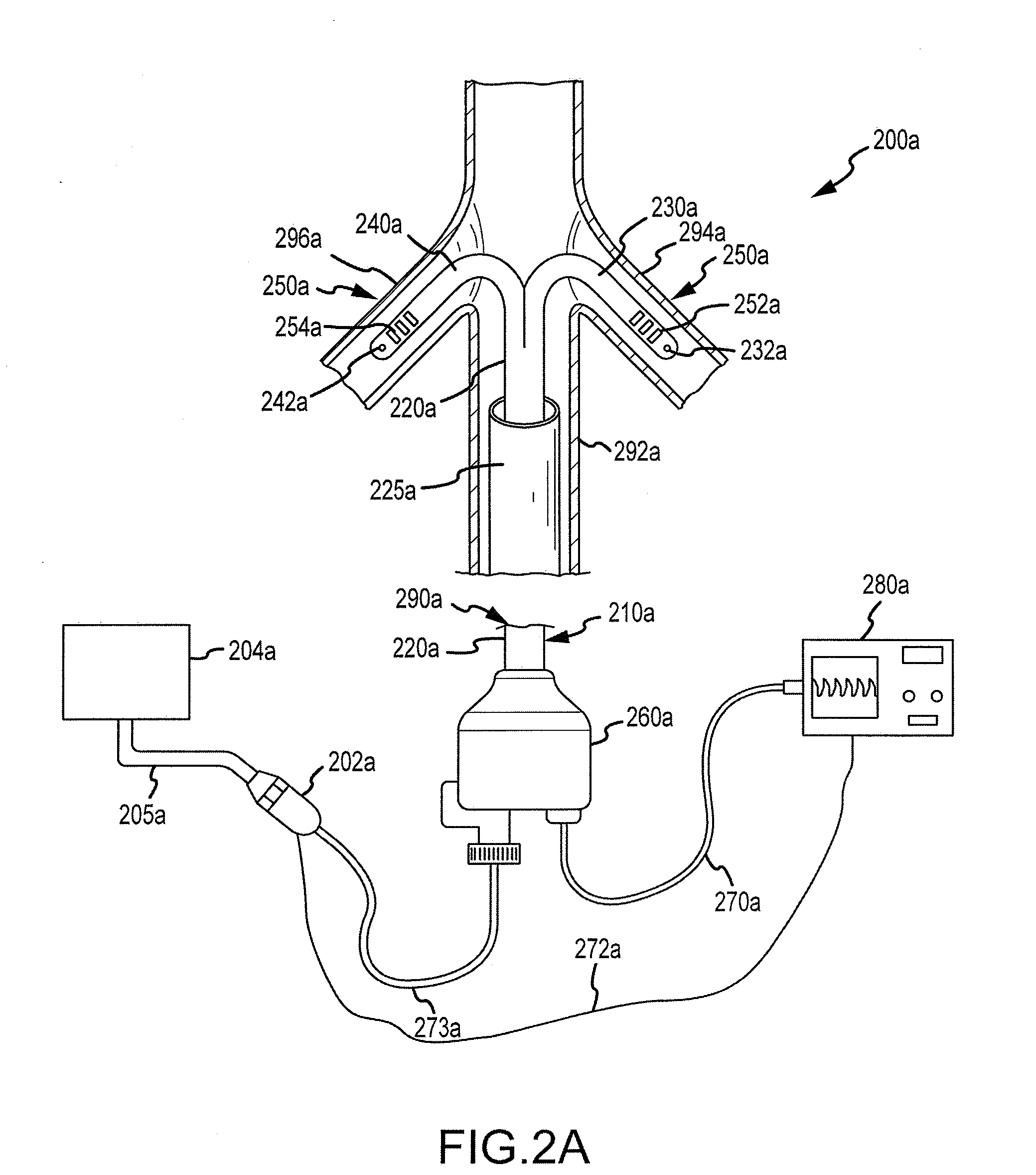
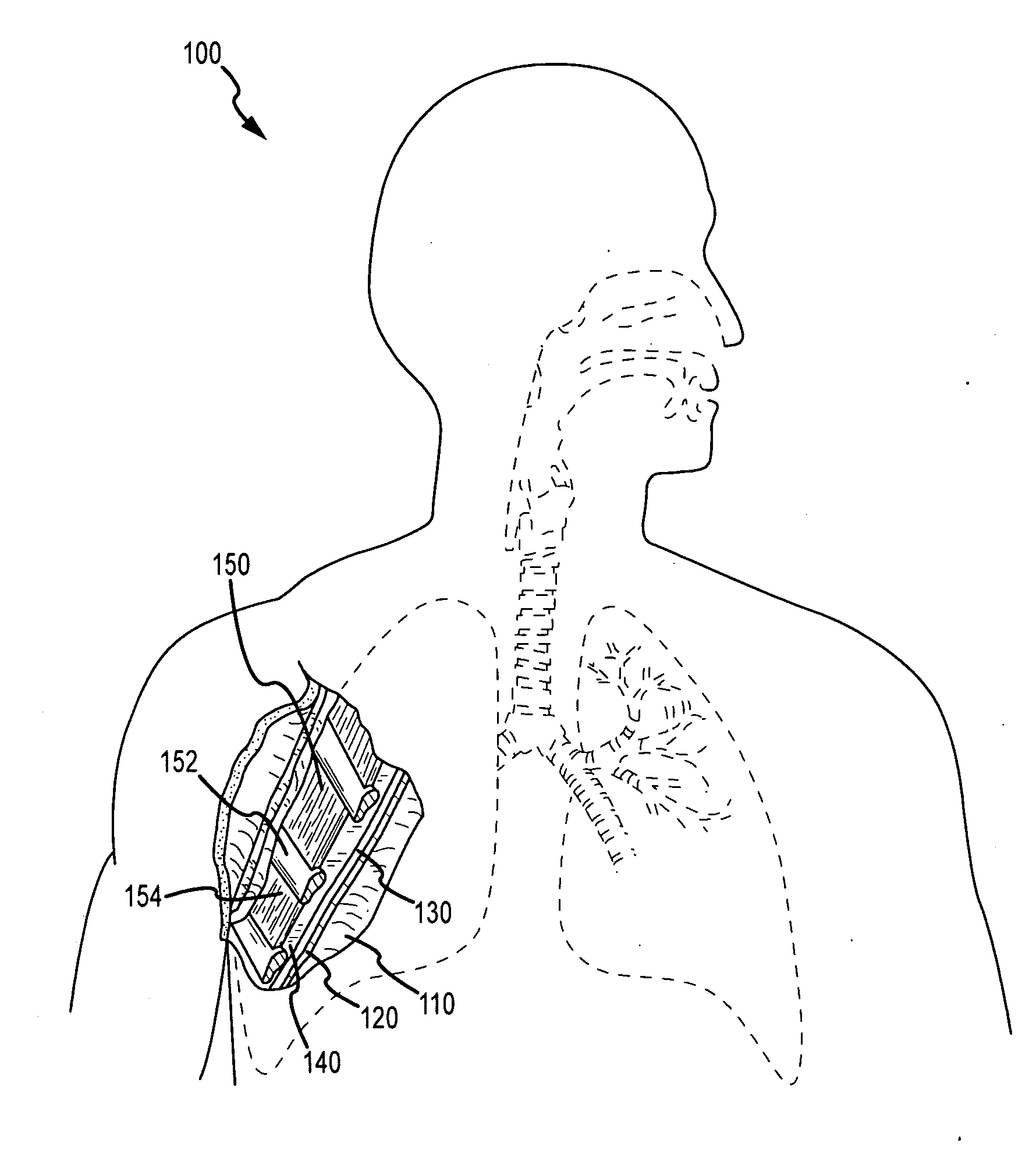
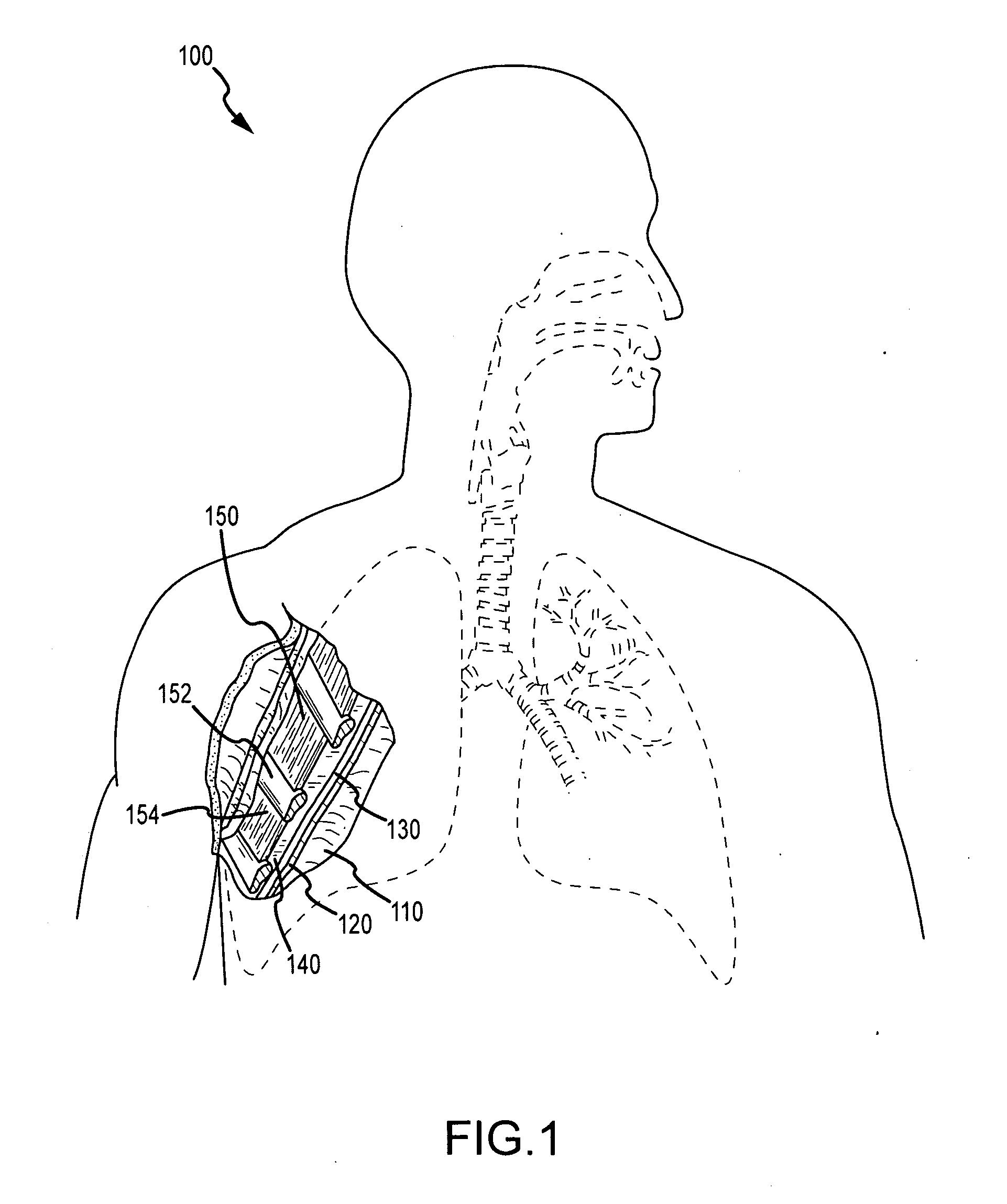
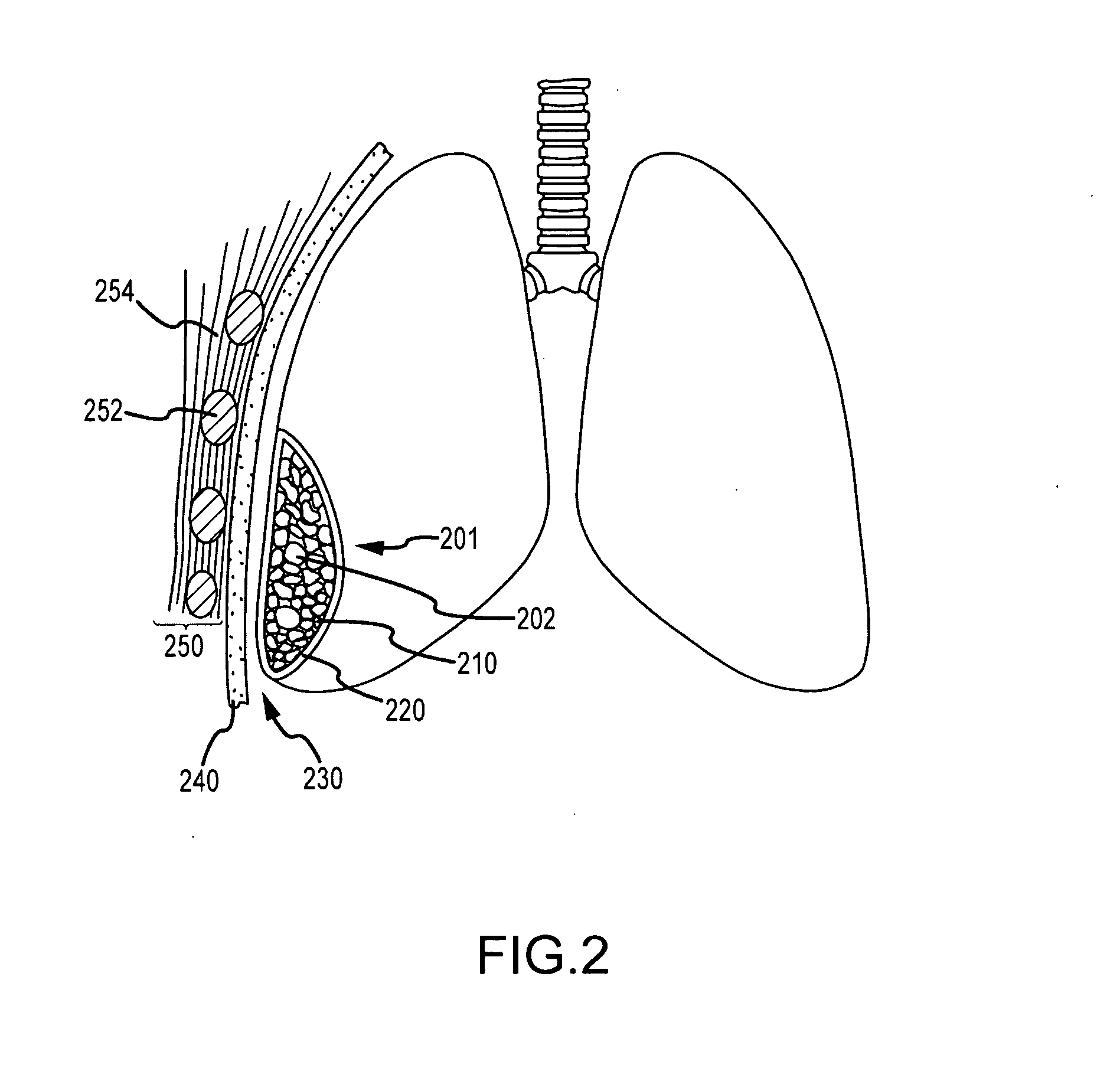
Medical device and method of embolizing bronchus or bronchiole
ActiveUS7357795B2Maintaining swellingGood biocompatibilityDiagnosticsDilatorsSurgical treatmentBronchial submucosa
To provide a medical device and a method both of which can suitably embolize a bronchus in a target part by embolizing the bronchus with (at least a part of) a living tissue during surgical treatment of lung emphysema. For example, an injection material is injected into a submucosa by the use of a syringe, and in the injected part, a swelling swollen into the internal cavity of the bronchus is formed to tightly seal the living tissue of the bronchus or a bronchiole, thereby embolizing a target bronchus.
Owner:OLYMPUS CORP
Method and instruments to treat spondylolisthesis by an anterior minimally invasive approach of the spine
InactiveUS20070123989A1Reducing surgical morbidityReduce morbidityInternal osteosythesisSpinal implantsSurgical treatmentLumbar vertebrae
A method for intra-operative surgical treatment of spondylolisthesis by an anterior minimally invasive approach of the lumbar spine includes inserting an interbody spacer between two vertebrae, attaching an anatomically designed reduction plate to at least one of the two vertebrae, and attaching the interbody spacer to the reduction plate by a fastening means through a central borehole of the reduction plate and the interbody spacer. The interbody spacer may be attached to the anteriorly positioned vertebra by at least bone screw. The upper and lower parts may be attached to the upper and lower vertebra by at least one bone screw to stabilize the displaced vertebral segment of the spine.
Owner:DEPUY SYNTHES PROD INC
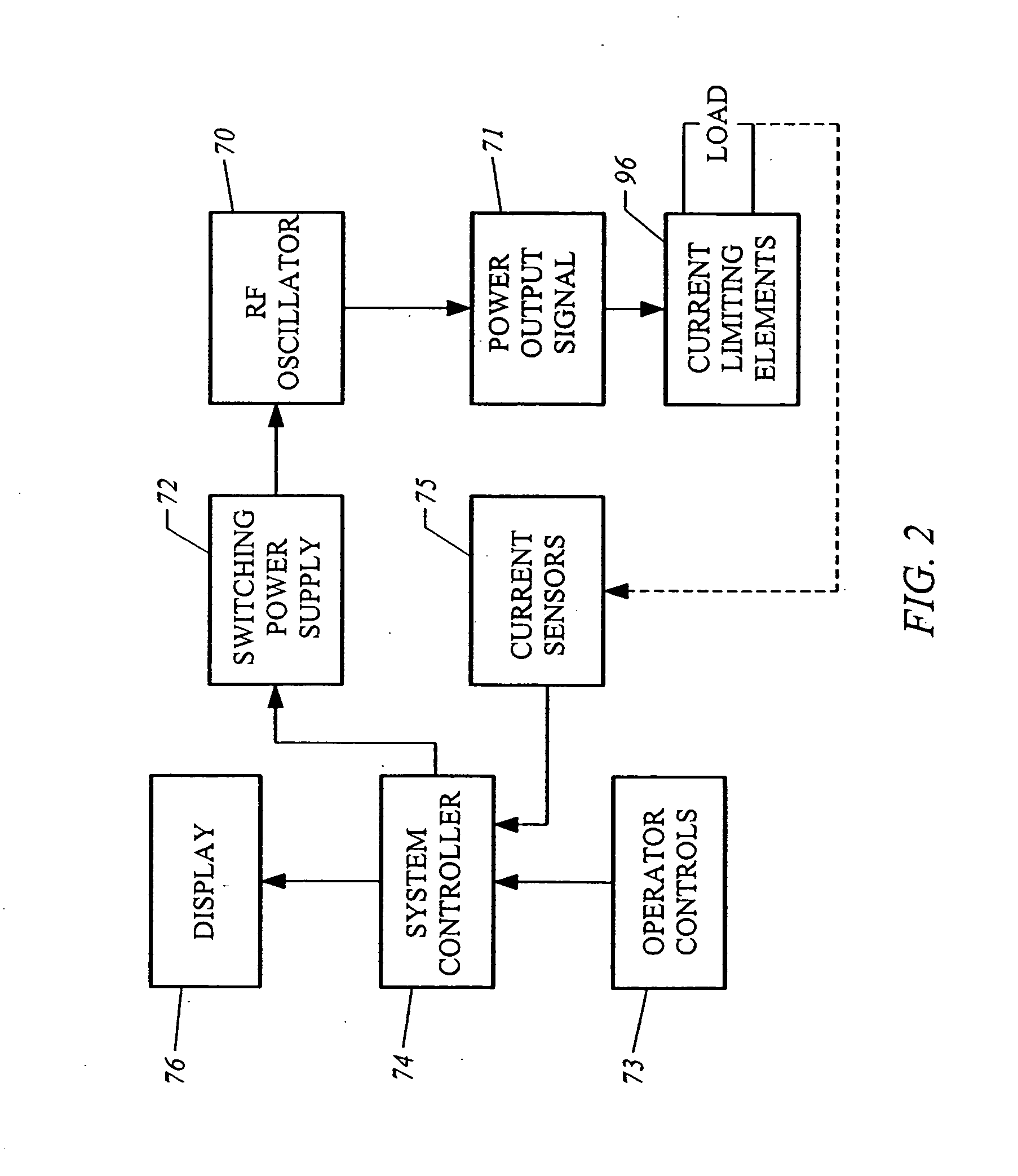
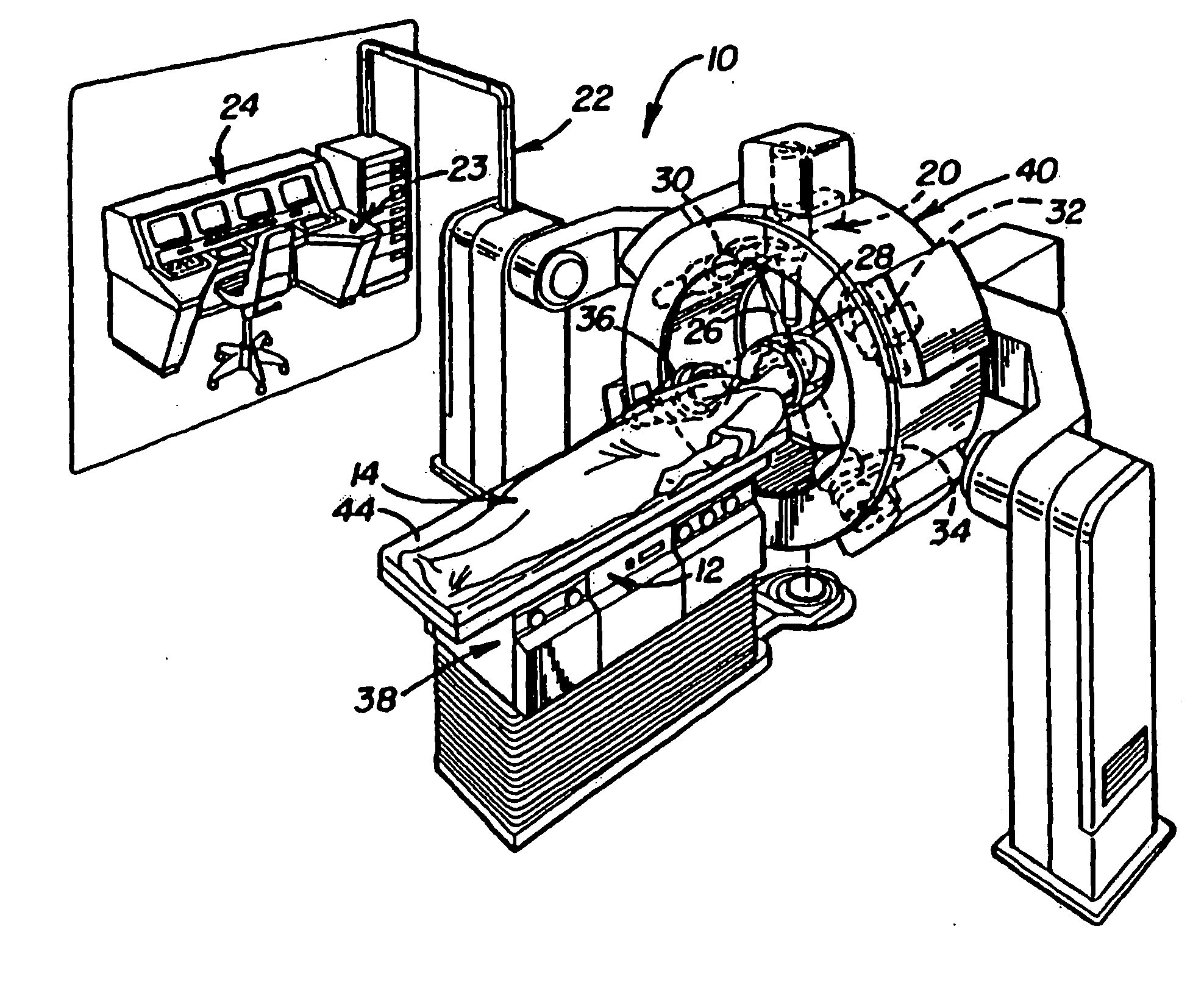
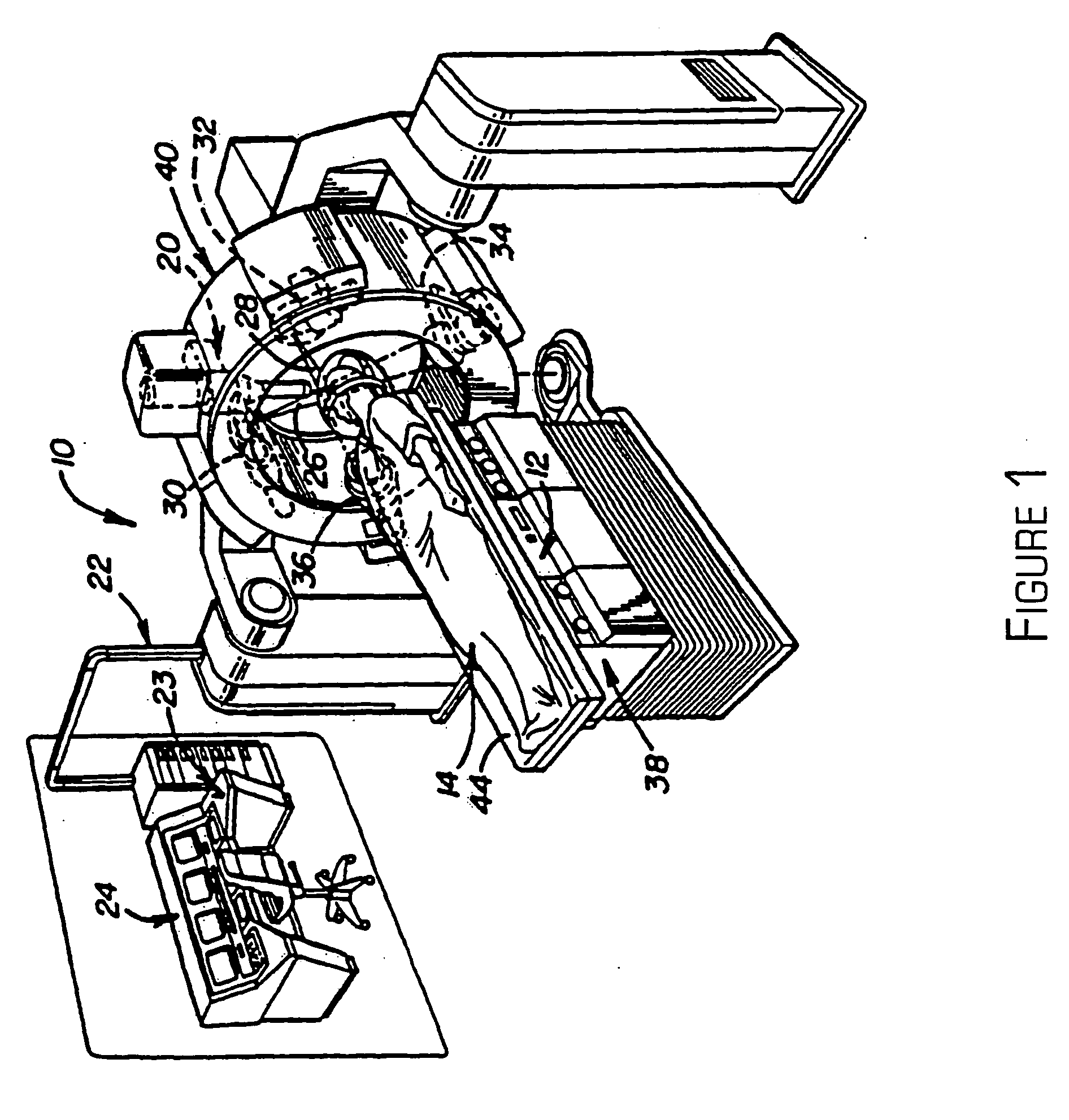
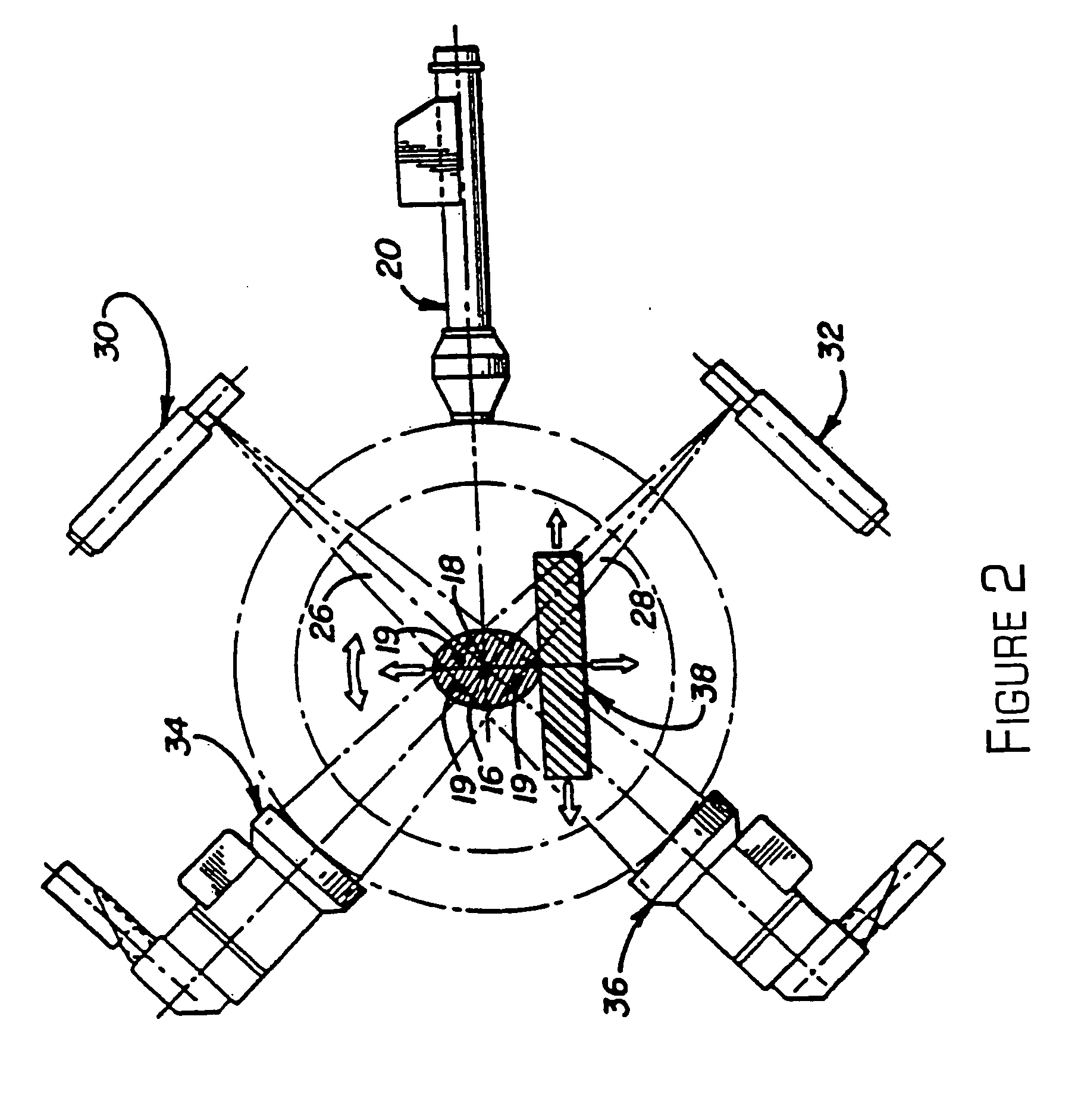
Kilovoltage delivery system for radiation therapy
A small tabletop stationary five-degree of freedom device such as a “robot” is used to define the treatment region by tracing the region under direct visualization and then to precisely deliver the treatment plan created by an automatic planning system by positioning a single low energy radiation source, or a plurality of low energy sources connected to each other in a predetermined parallel or similar geometry, each source equipped with blocking and attenuation mechanisms, at a plurality of positions in a planar fashion across or through a selected treatment field, thereby delivering a plurality of parallel overlapping beams indexed on a millimeter or submillimeter grid such that a concentration of dose is achieved at a variable depth in tissue relative to the dose where the radiation first enters the tissue and can be used to treat regions on or below the surface of tissue, in a cavity and underlying region created following a surgical resection, on or below the surface of an internal cavity, hollow viscus, or lumen, or deep in tissue adjacent to an inserted probe or conduit or catheter. By generating a plurality of overlapping beams indexed on a millimeter or submillimeter grid that converge on a target volume loaded with gold nanoparticles, a tumorcidal dose of radiation can be delivered in as little as a single session to tumor cells but not to normal cells within or outside the treatment volume. This approach also makes it possible to deliver serial radiosurgical treatments.
Owner:CAROL MARK PHILIP
Treatment apparatus and treatment device for surgical treatments using ultrasonic vibration
ActiveUS20050234338A1Easy to cleanUltrasonic/sonic/infrasonic diagnosticsInfrasonic diagnosticsSurgical treatmentUltrasonic sensor
An ultrasonic treatment device comprises a transducer unit, probe unit, and a main unit. The transducer unit comprises an ultrasonic transducer generating ultrasonic vibration in response to supply of power. The probe unit has a treatment member at a distal end thereof. The probe unit is detachably loaded to the transducer unit, and is equipped with an ultrasonic probe transmitting the ultrasonic vibration to the distal end of the treatment member when the transducer unit is loaded to the probe unit. The main unit is manually grasped by an operator. The probe unit with the transducer unit loaded thereto is detachably loaded to the main unit. The main unit has a cylindrical insert through which the ultrasonic probe is inserted to have the treatment member protruded outwardly when the probe unit is loaded. The main unit further has an outer sheath detachably covering an outer surface of the insert.
Owner:OLYMPUS CORP
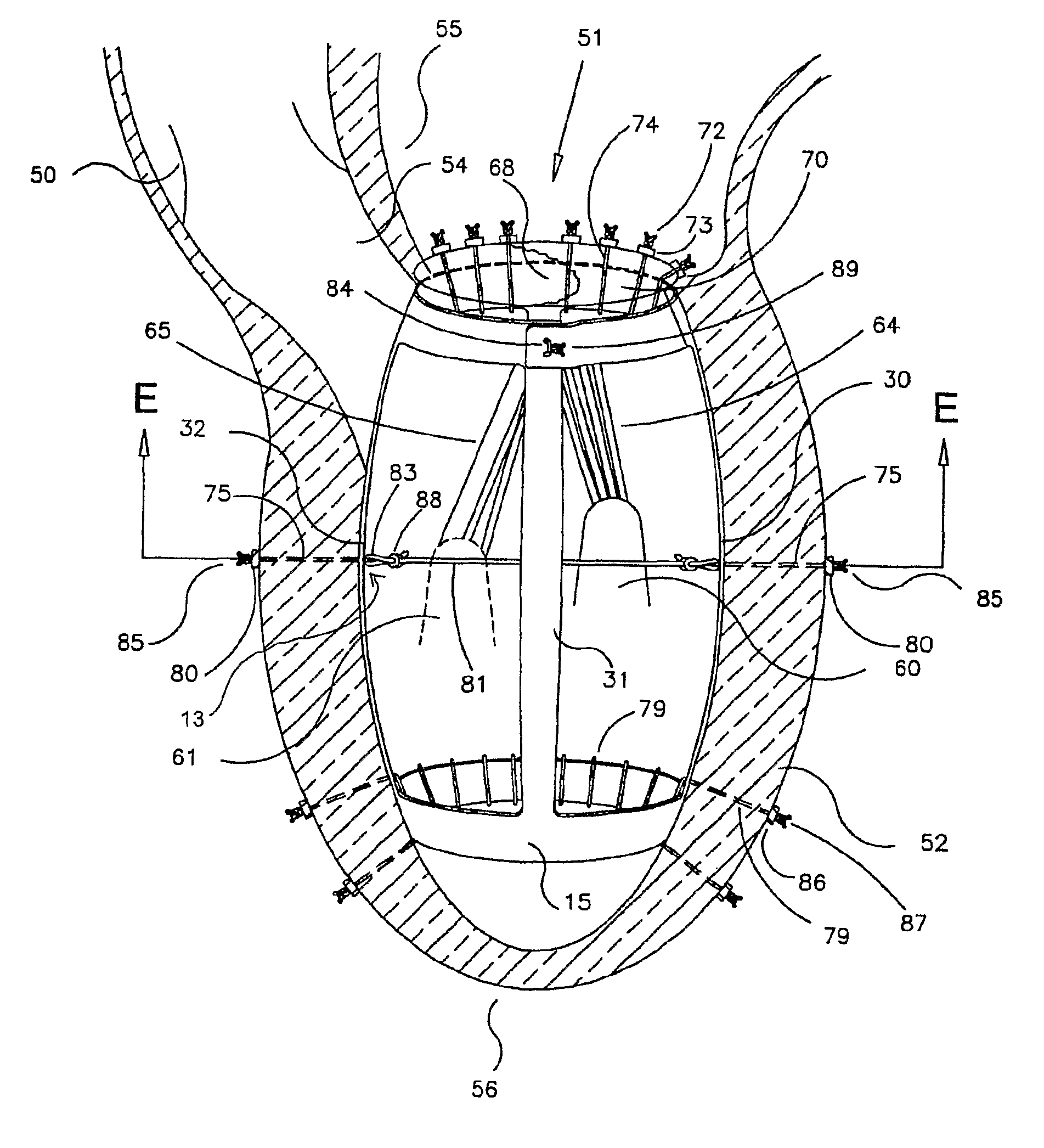
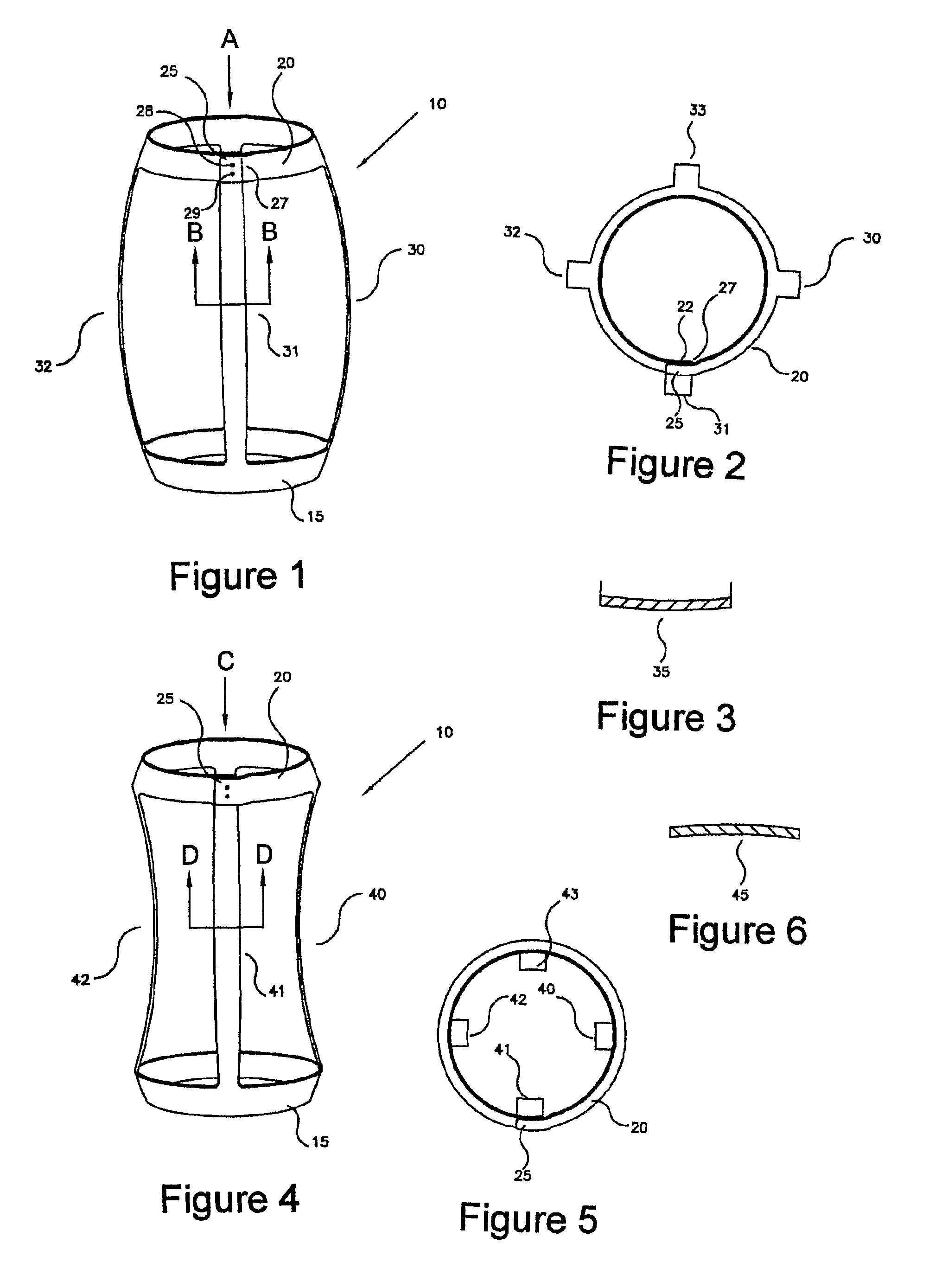
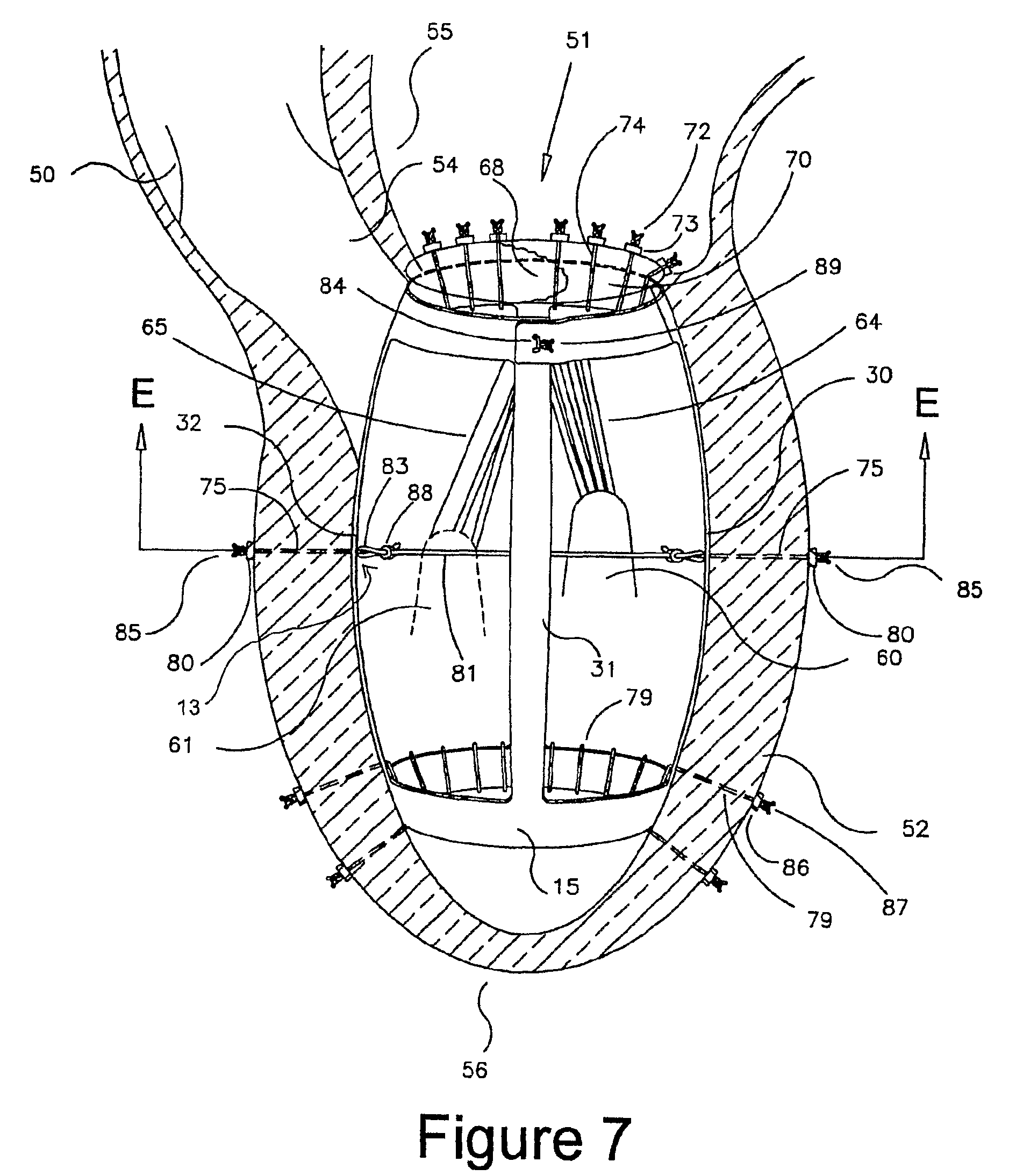
Artificial disc
InactiveUS6913622B2Increase temperatureStay flexibleBone implantJoint implantsSurgical treatmentImplanted device
An implant device for surgical treatment of spinal disc damage or injury is formed as a resilient body comprising porous TiNi; the body is internally mobile such that it resiliently expands and contracts in response to variation in forces applied externally on the body.
Owner:BIORTHEX
Unified workstation for virtual craniofacial diagnosis, treatment planning and therapeutics
An integrated system is described in which digital image data of a patient, obtained from a variety of image sources, including CT scanner, X-Ray, 2D or 3D scanners and color photographs, are combined into a common coordinate system to create a virtual three-dimensional patient model. Software tools are provided for manipulating the virtual patient model to simulation changes in position or orientation of craniofacial structures (e.g., jaw or teeth) and simulate their affect on the appearance of the patient. The simulation (which may be pure simulations or may be so-called “morphing” type simulations) enables a comprehensive approach to planning treatment for the patient. In one embodiment, the treatment may encompass orthodontic treatment. Similarly, surgical treatment plans can be created. Data is extracted from the virtual patient model or simulations thereof for purposes of manufacture of customized therapeutic devices for any component of the craniofacial structures, e.g., orthodontic appliances.
Owner:ORAMETRIX
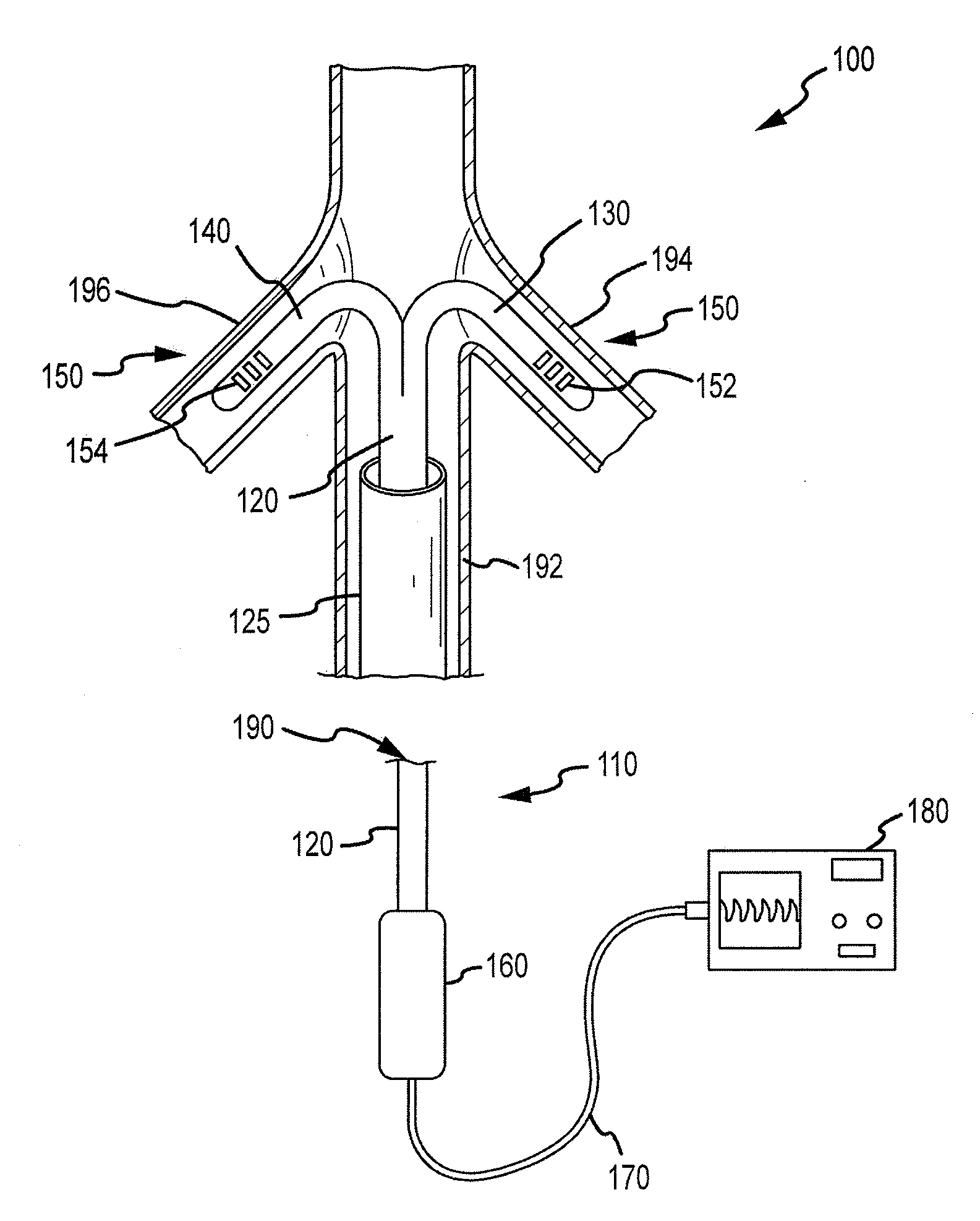
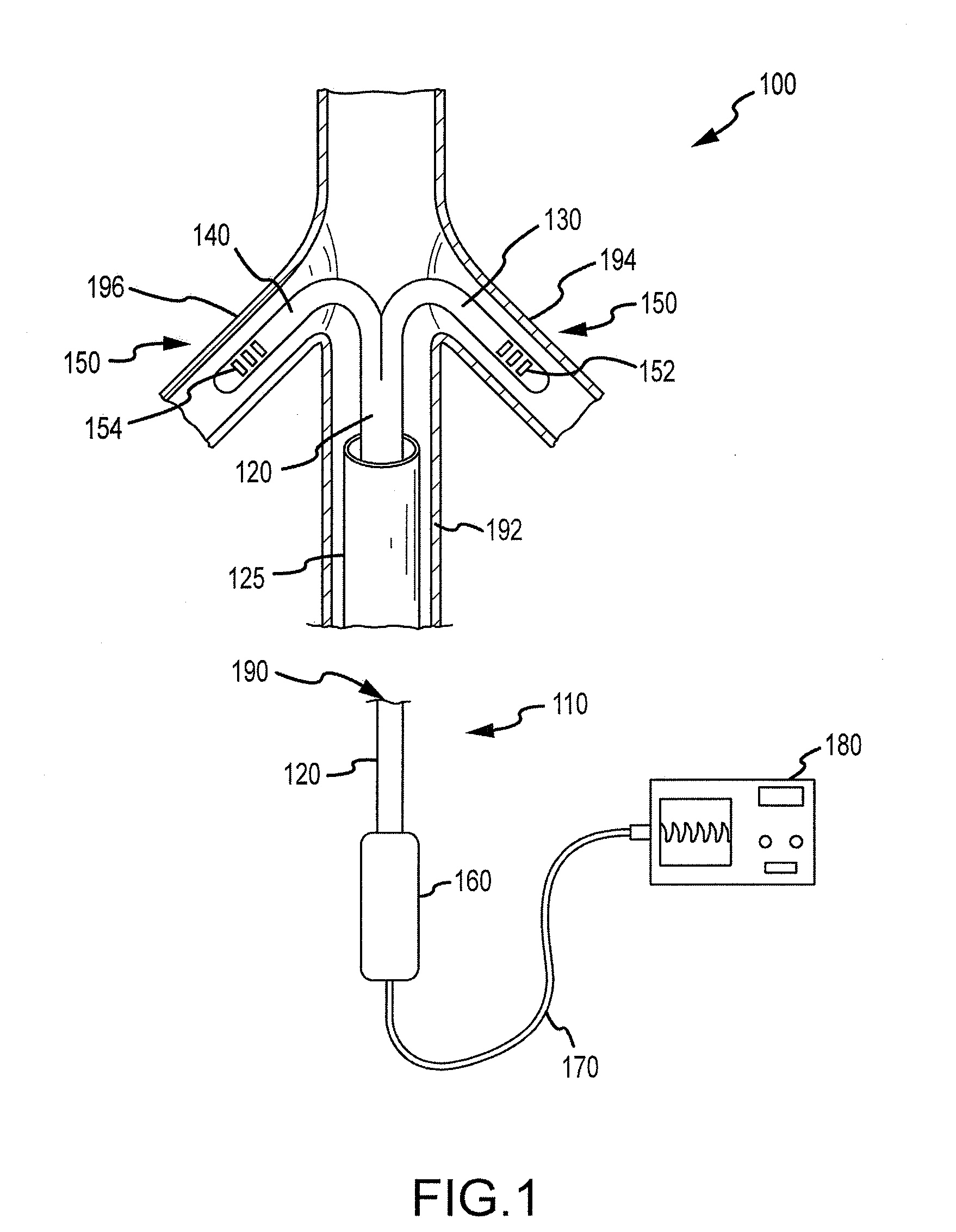
Renal assessment systems and methods
Techniques for assessing a physiological profile of a patient include advancing a catheter shaft of a bifurcated renal catheter system into an aorta of the patient, deploying branches of the bifurcated renal catheter system into the renal arteries of the patient, detecting a renal arterial physiological parameter with a sensing mechanism, and assessing the physiological profile of the patient based on the physiological parameter. Related techniques include modifying or initiating pharmacological or surgical treatments for the patient based on the assessment.
Owner:FLOWMEDICA
Use of a regenerative biofunctional collagen biomatrix for treating visceral or parietal defects
ActiveUS20090142396A1Avoiding and inhibiting persistent tissue leakImprove lung functionPowder deliveryPeptide/protein ingredientsSurgical treatmentTissue defect
Techniques for treating visceral or parietal membrane and tissue defects include the application of a collagen biomatrix to the defect to repair and regenerate a visceral or parietal membrane, for example in patients suffering tissue defects or undergoing visceral or parietal surgical treatment. Such approaches avoid persistent tissue leaks and their consequences such as fluid leaks and air leaks. The use of collagen biomatrix, optionally in conjunction with a fibrin sealant, an anti-adhesive, or both, can minimize tissue leaks or fluid leaks in injured patients suffering tissue defects or subjects undergoing surgery such as visceral or parietal resections and other operations.
Owner:BAXTER INT INC +1
Method for Depositing Radiation in Heart Muscle
InactiveUS20080177280A1Improved radiosurgical treatment of tissueReduce arrhythmiaComputer-aided planning/modellingDiagnostic recording/measuringX-raySurgical department
Radiosurgical treatment of tissues of the heart to mitigate arrhythmias such as atrial fibrillation or the like. Radiosurgical targeting of the relatively rapid movement of heart tissues may be enhanced by generating a moving model volume using a time-sequence of three dimensional acquired tissue volumes. A digitally reconstructed radiograph (DRR) may be generated from the model at a desired cardiac and / or respiration motion phase and compared to an X-ray or the like taken immediately before or during treatment. When a series of radiation beams will be directed to a heart tissue to alleviate an arrhythmia, the treatment system may alter the radiation beam series in response to the type of the arrhythmia.
Owner:CYBERHEART
Devices and methods for AAA management
A device is provided for endoluminal delivery of a luminary graft. As applied in the vascular system, the device comprises a catheter configured to be advanced endovascularly to a graft location. A generally tubular temporary stent having a distal end and a proximal end is tapered and attached to the catheter at the proximal end. The temporary stent comprises helically braided thread members that expand radially outwardly to a maximum diameter in a resting state. The temporary stent terminates in discrete ends temporarily affixed to the graft at the distal end. A tubular sheath selectively and reversibly radially constrains the temporary stent. The sheath is configured to be longitudinally moveable relative the temporary stent to constrain and reconstrain the temporary stent when positioned over the temporary stent, and to release the temporary stent when withdrawn from over the temporary stent. Optionally, a perfusion balloon may be combined with the temporary stent to stabilize the graft during vascular surgical treatment.
Owner:LIFESHIELD SCI
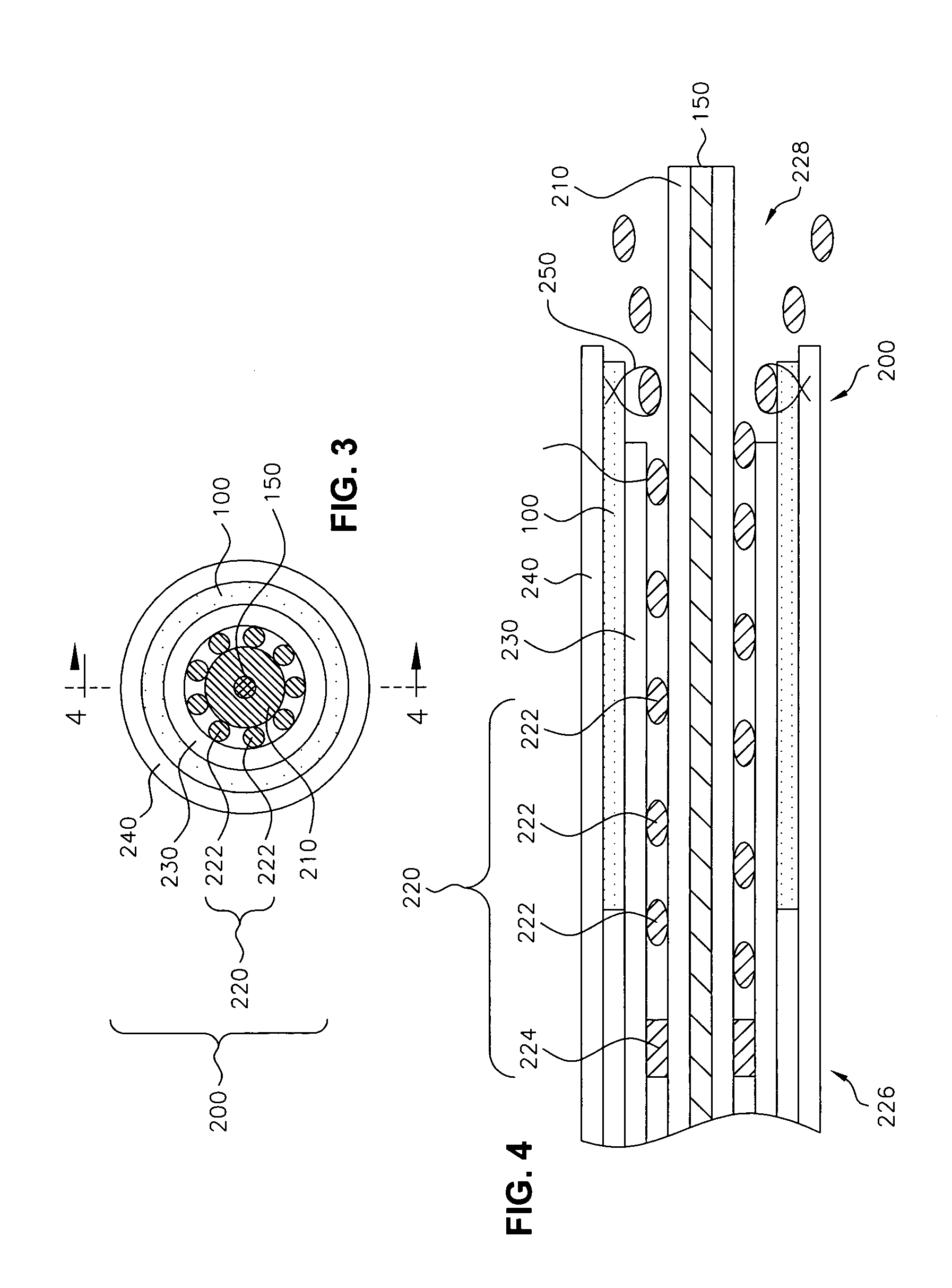
Vessel corset for use with electrosurgical forceps
InactiveUS20150032106A1Reduced cross sectionSurgical instruments for heatingSurgical forcepsSurgical treatmentForceps
A system for treating tissue is provided. The system includes a forceps having opposing jaw members at a distal end thereof configured to treat tissue. A corset is configured to be wrapped around tissue and stretched to reduce an overall cross section of tissue and allow the jaw members to grasp the tissue for surgical treatment thereof
Owner:TYCO HEALTHCARE GRP LP
Device for removing tissue
A device for removing tissue by means of laparoscopy or thoracoscopy with an operating part and an optionally partially open hollow tube with a guide for operating a removing part. The removing part has the form of a zeppelin with one or more ribs. The removing part is provided on the upper side with longitudinal connecting elements.Further described is an application of such a device in a surgical treatment wherein, by use of the operating part, the removing part with the form of a zeppelin is opened out, the removed tissue is collected in the expanded bag of the removing part, and the removing part with tissue is pulled optionally at least partially into the open part of the hollow tube. The connecting elements of the removing part can then be brought together and snapped or zipped closed.
Owner:JANSEN ANTON
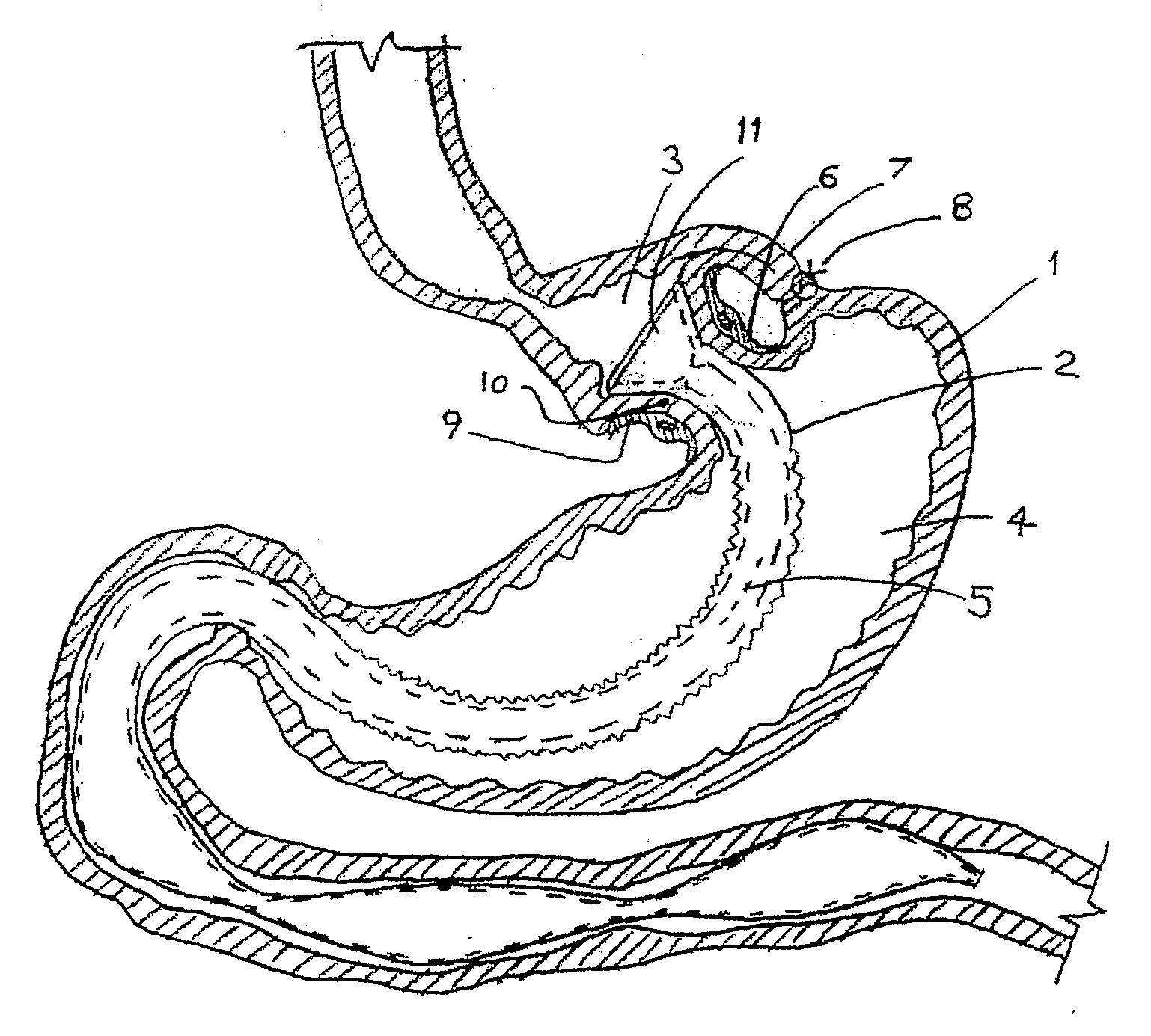
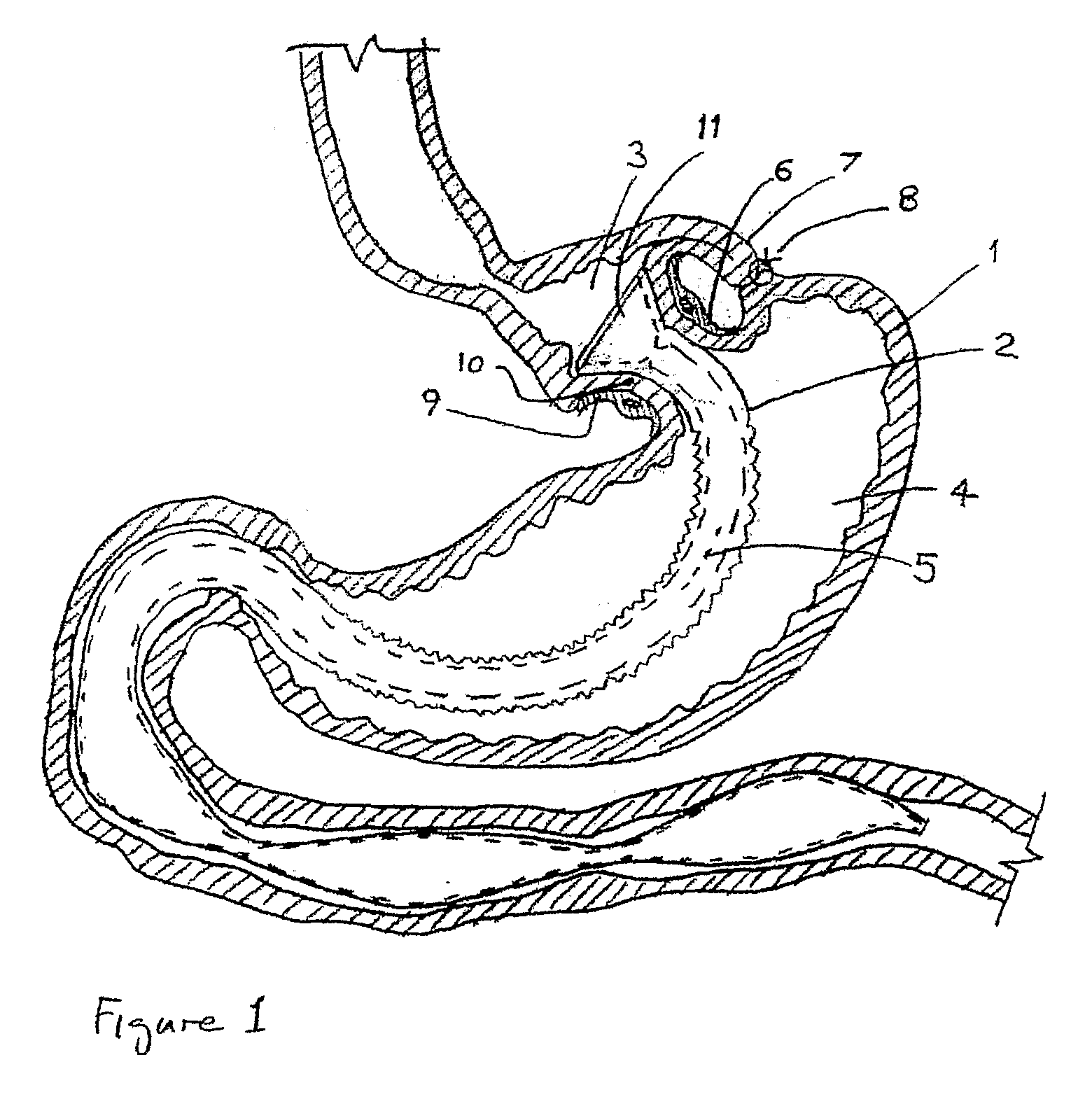
Gastric clamp for performing vertical band gastroplasty and a gastric bypass with lesser curvature
InactiveUS7288100B2Efficient compressionNon-surgical orthopedic devicesObesity treatmentSurgical treatmentStomach walls
The invention relates to the production of a vertical gastric reservoir for the surgical treatment of morbid obesity. The reservoir consists of a clamp having two plates articulated at the lower end thereof and an automatic closing system in the upper part thereof, reinforced with a sealing system. Both plates are provided with two extensions (one at each end of the instrument) on the right-hand edge thereof. Both extensions are provided with two openings that are used to fix the instrument to the stomach wall. Application of the instrument and the technical solution provided are as follows: the substitution of metal staples which are subsequently eliminated in between 15% and 20% of patients and which result in failure of the vertical band gastroplasty operation. The instrument could also be used for producing small gastric reservoirs used for gastric bypass with minor curvature instead of metal staples.
Owner:SURGICAL IOC
Frameless radiosurgery treatment system and method
InactiveUS20050027194A1Precision therapyFewer healthy cells and tissueUltrasonic/sonic/infrasonic diagnosticsSurgical needlesSurgical treatmentRadiology
Owner:ADLER JOHN R +1
Gastric bypass prosthesis fixation system and method for treatment of obesity
InactiveUS20090216337A1Facilitate rapidFacilitate early weight lossIntravenous devicesTubular organ implantsSurgical treatmentGastric bypass
An improved gastric bypass prosthetic (GBP) device and an improved GBP fixation device, as well as a GBP kit for the surgical treatment of obesity. In one form, a gastric bypass prosthetic (GBP) device of the invention includes a optional flexible tube extending along a central axis from a proximal end to a distal end, and having a tubular tissue fixation portion at or near said proximal end. The tissue fixation portion extends along the central axis between a proximal end and a distal end of the tissue fixation portion, and has an annular outer surface between the proximal end and the distal end of the tissue fixation portion.
Owner:GASTRX MEDICAL
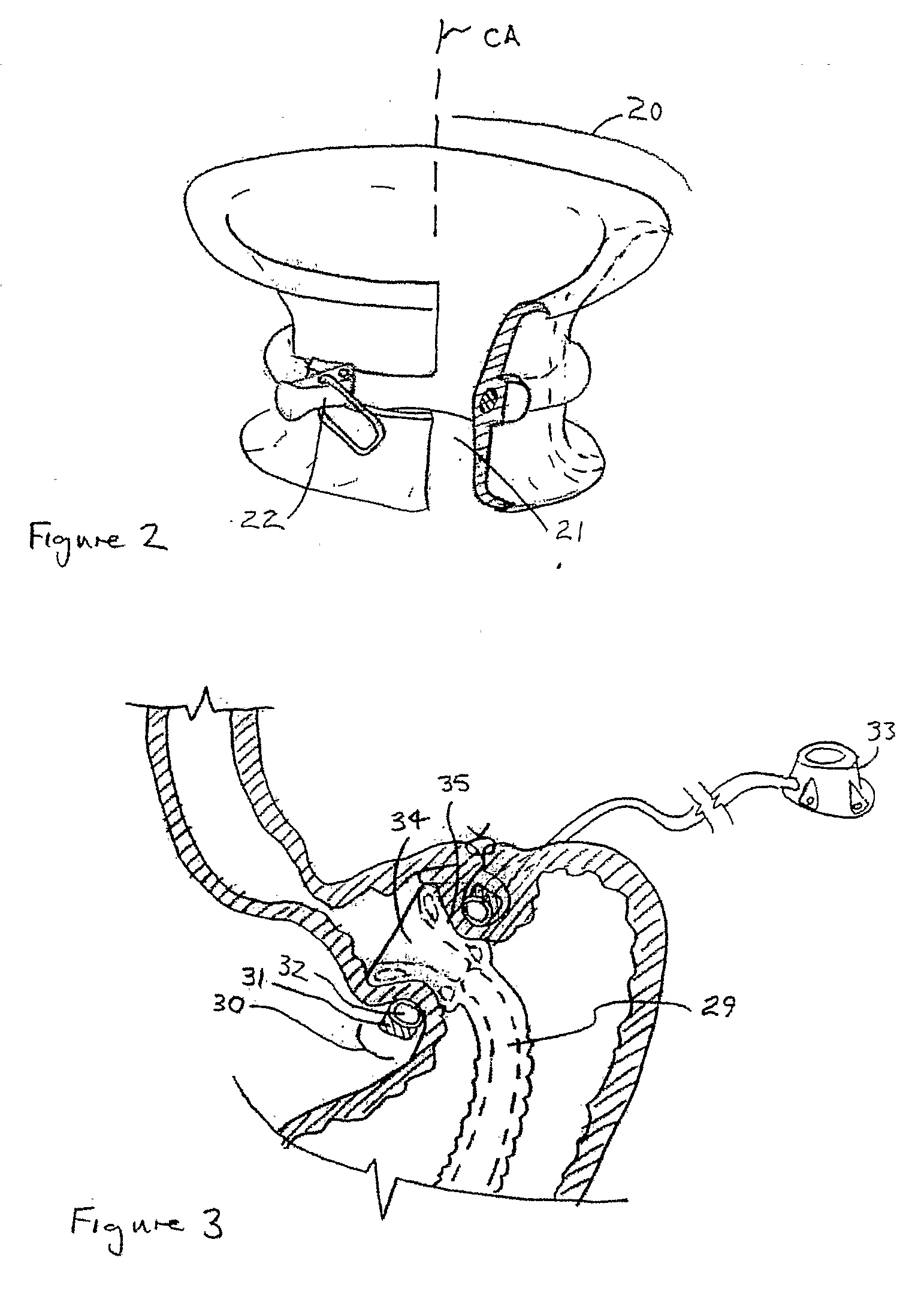
Method and apparatus for the surgical treatment of congestive heart failure
ActiveUS7758491B2Effective of treatingReduce manufacturing costSuture equipmentsAnnuloplasty ringsSurgical treatmentSystole
An apparatus implantable in a heart ventricle includes a frame configured to engage an inner circumferential periphery of the ventricle and to expand and contract between an expanded state corresponding to a desired end diastolic diameter of the ventricle and a contracted state corresponding to a desired end systolic diameter of the ventricle. A bistable structure is operatively associated with the frame. The bistable structure mechanically assists movement of the ventricle toward both an end systolic diameter during systole and an end diastolic diameter during diastole. The bistable structure may be integrally formed of the frame. A method of implanting the apparatus in a heart ventricle includes surgically accessing a ventricle, inserting the apparatus in the ventricle and attaching the device to a portion of myocardium defining an inner circumferential periphery of the ventricle.
Owner:GENESEE BIOMEDICAL
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com