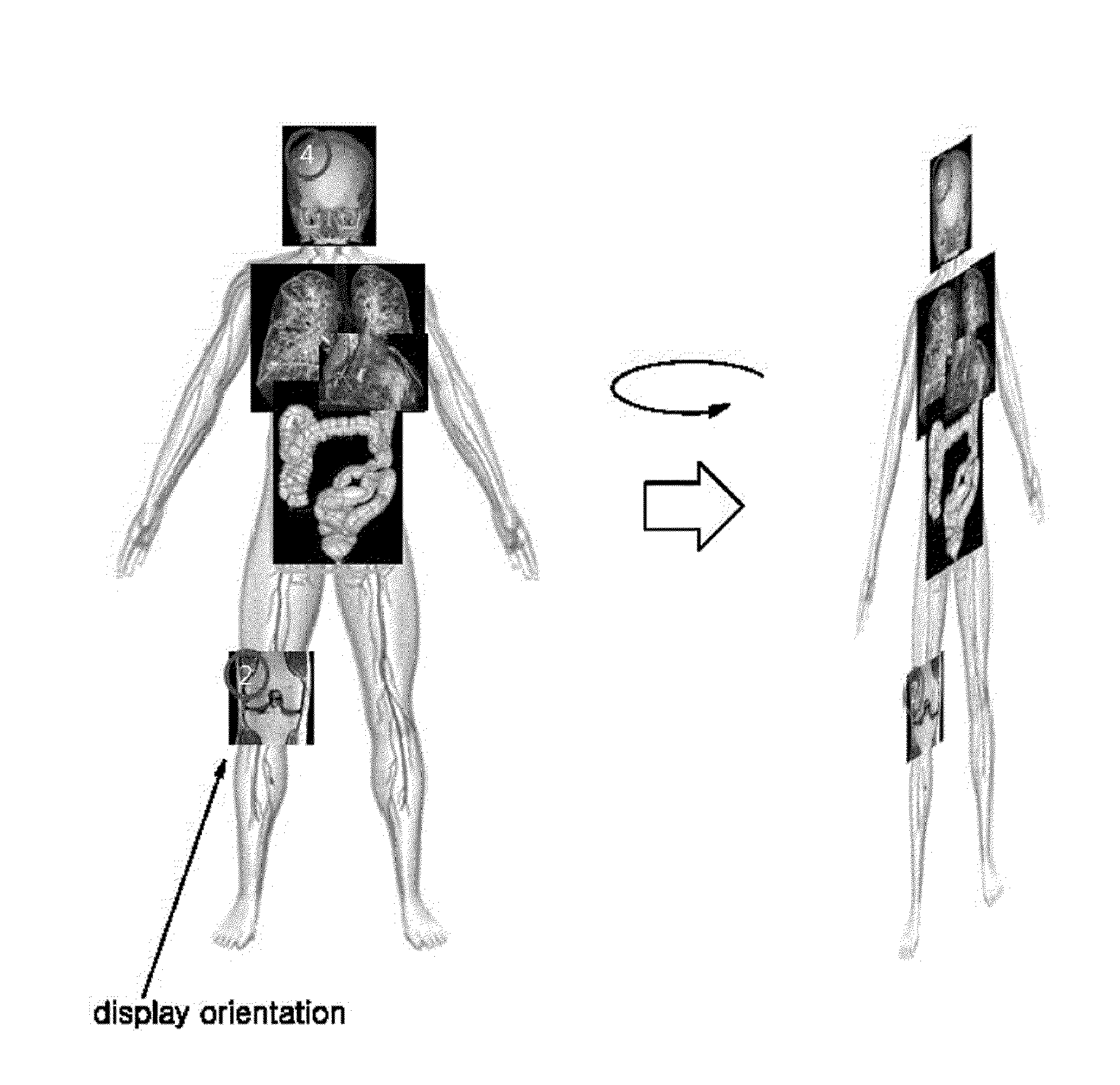Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
78 results about "Virtual patient" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
The term virtual patient is used to describe interactive computer simulations used in health care education. The special focus is targeted on the simulation of clinical processes with virtual patients. Virtual patients combine scientific excellence, modern technologies and the innovative concept of game-based learning. Virtual patients allow the learner to take the role of a health care professional and develop clinical skills such as making diagnoses and therapeutic decisions. Virtual patients have also been considered computer-based simulations designed to complement clinical training. The use of virtual patient programmes is increasing in healthcare, partly in response to increasing demands on health care professionals and education of students but also because they allow opportunity for students to practice in a safe environment. There are many different formats a virtual patient may take. However the overarching principle is that of interactivity—a virtual patient will have mechanisms for the learner to interact with the case and material or information is made available to the learner as they complete a range of learning activities. Interactivity is often included with questions, specific decision-making tasks, text-composition etc. and is non-sequential. Most systems provide quantitative and qualitative feedback.
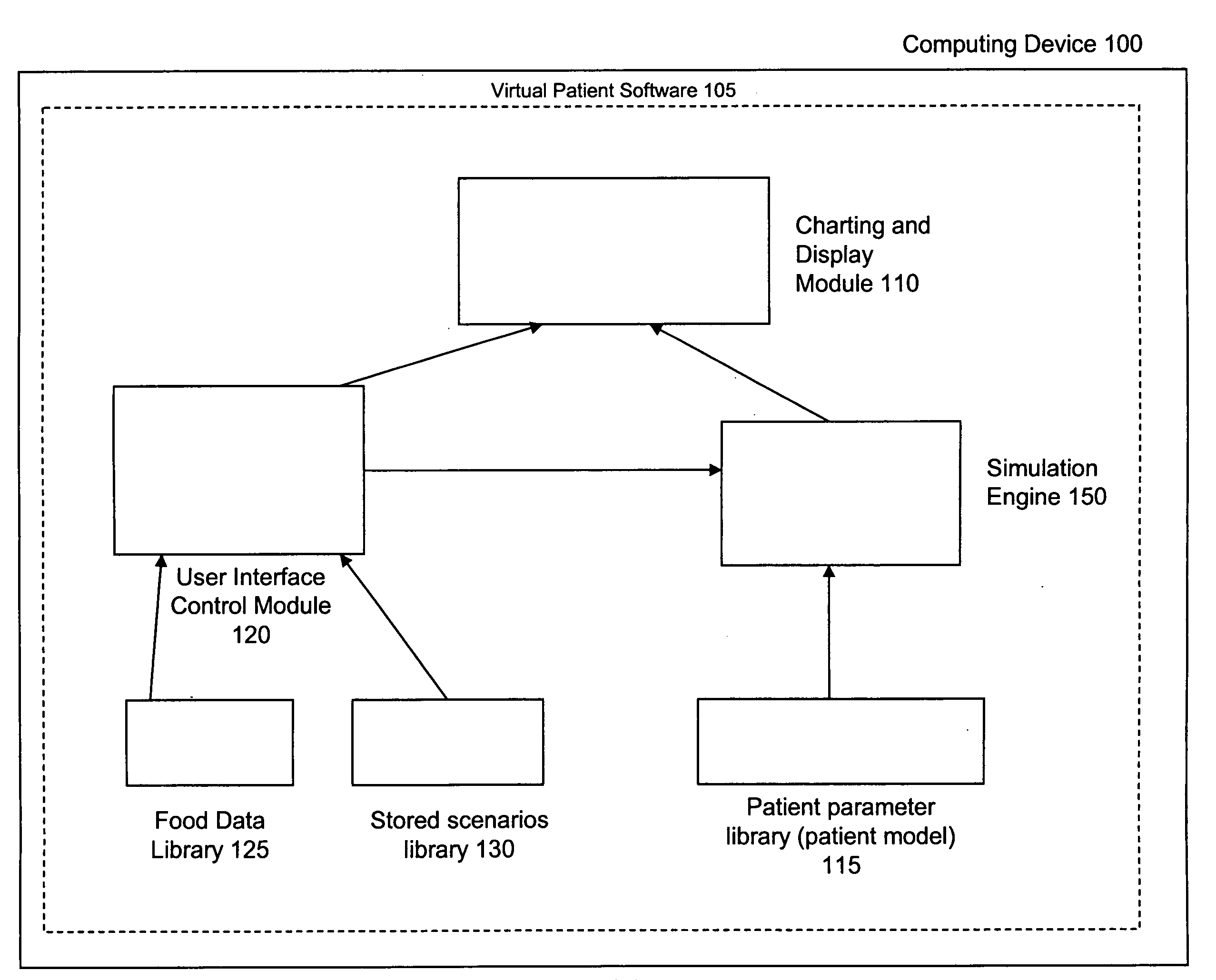
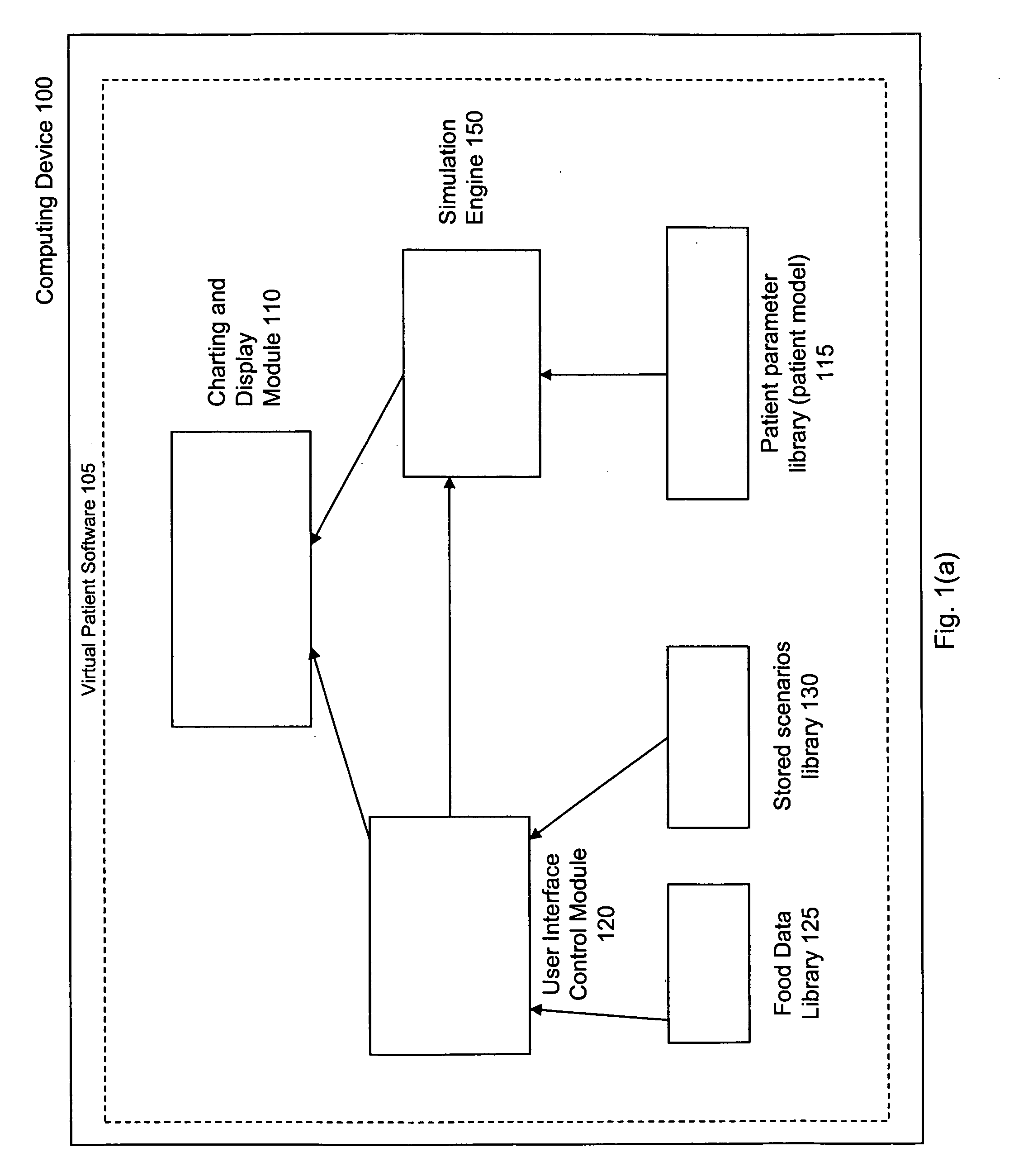
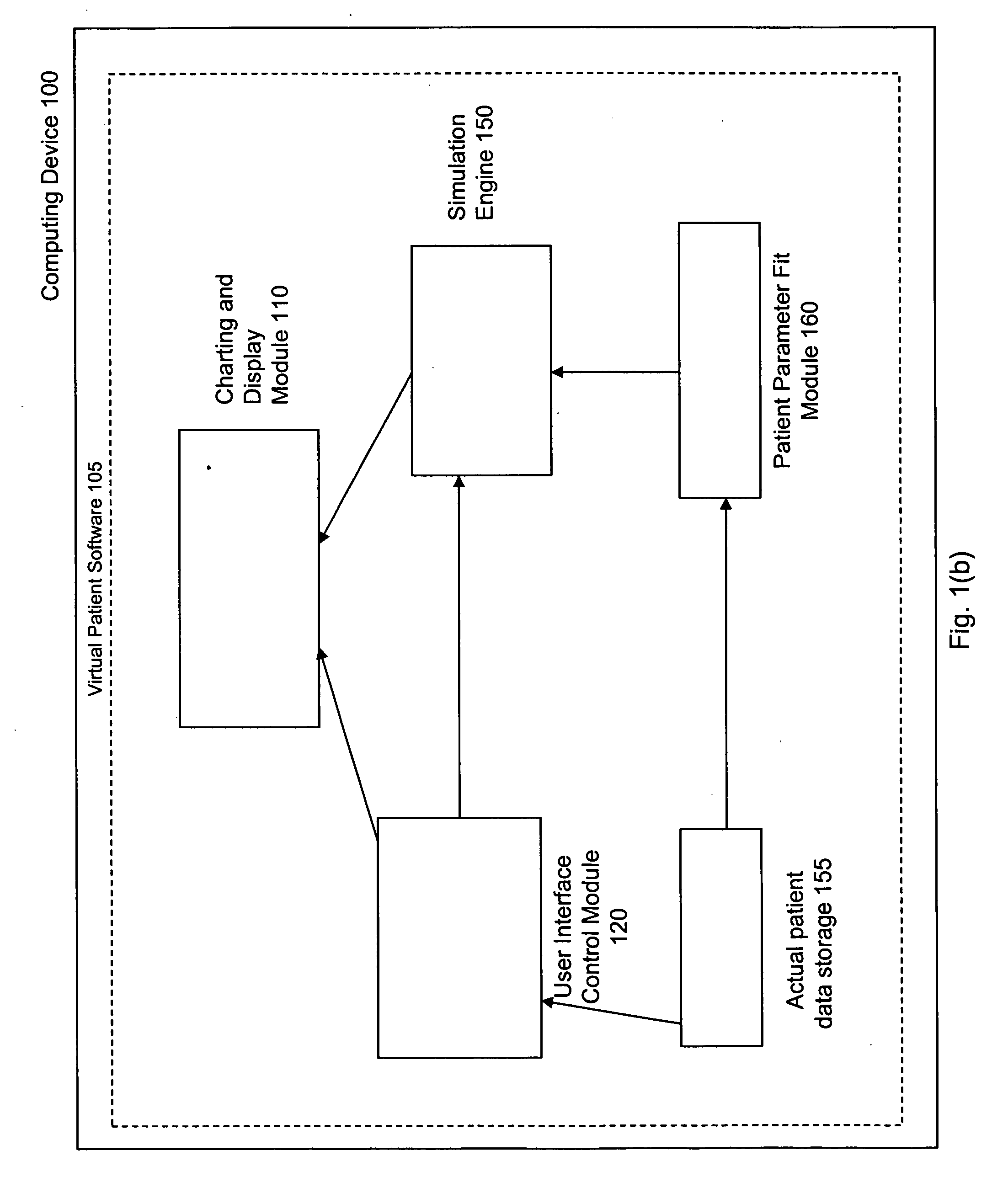
Virtual patient software system for educating and treating individuals with diabetes
A system to assist an individual in developing a therapy in diabetes treatment of a patient includes a user interface control module, a simulation engine, a charting and display module. The user interface control module receives an input related to the patient and captures a current time of the simulation. The simulation engine receives the input, generates a plurality of blood glucose readings for the patient up to the current time of the simulation based on the input, and to transfers the plurality of blood glucose readings. The charting and display module receives the plurality of blood glucose readings and display the plurality of blood glucose readings. The simulation engine receives patient parameters from a patient parameter library based on a selected patient model.
Owner:MEDTRONIC MIMIMED INC
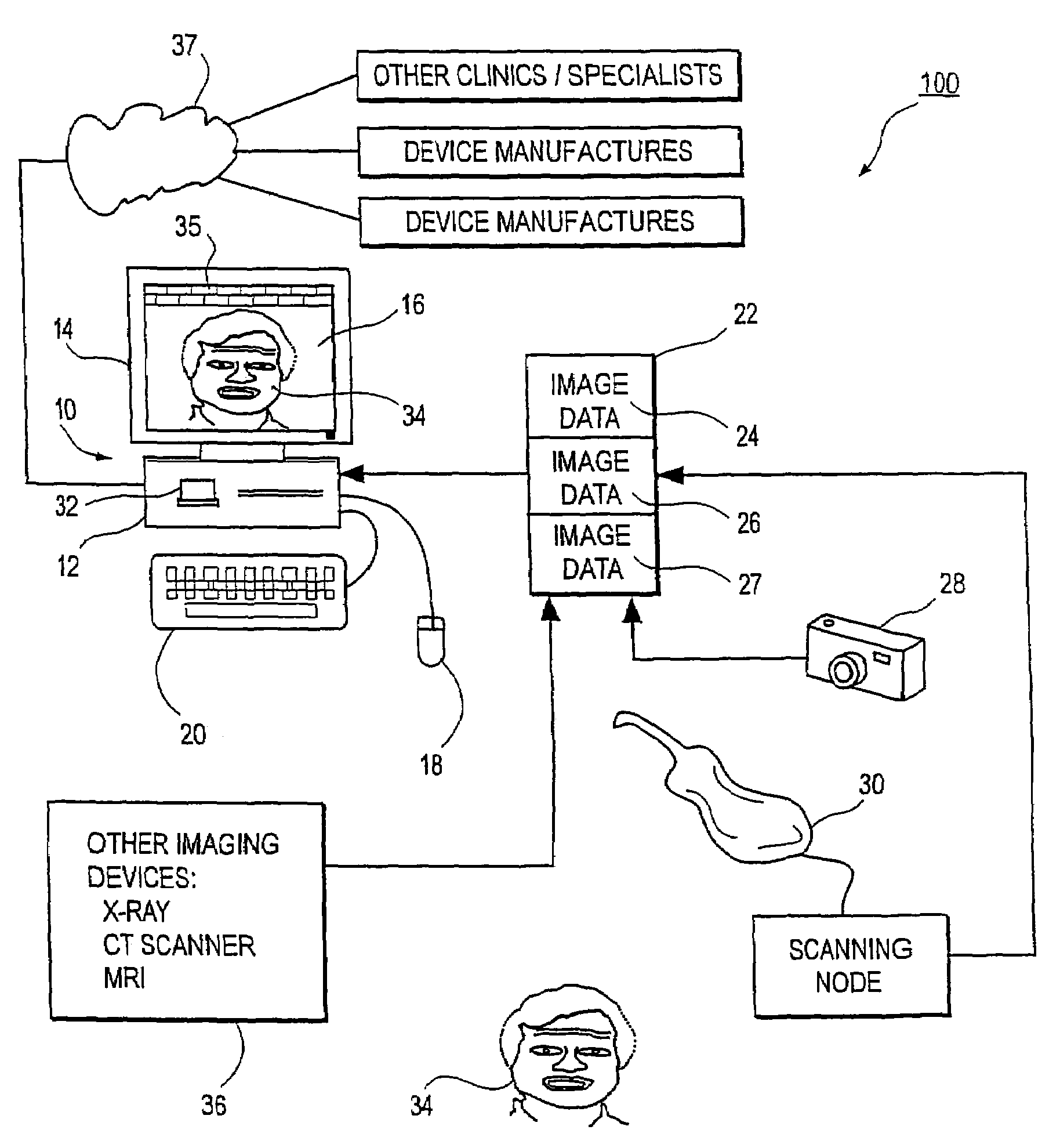
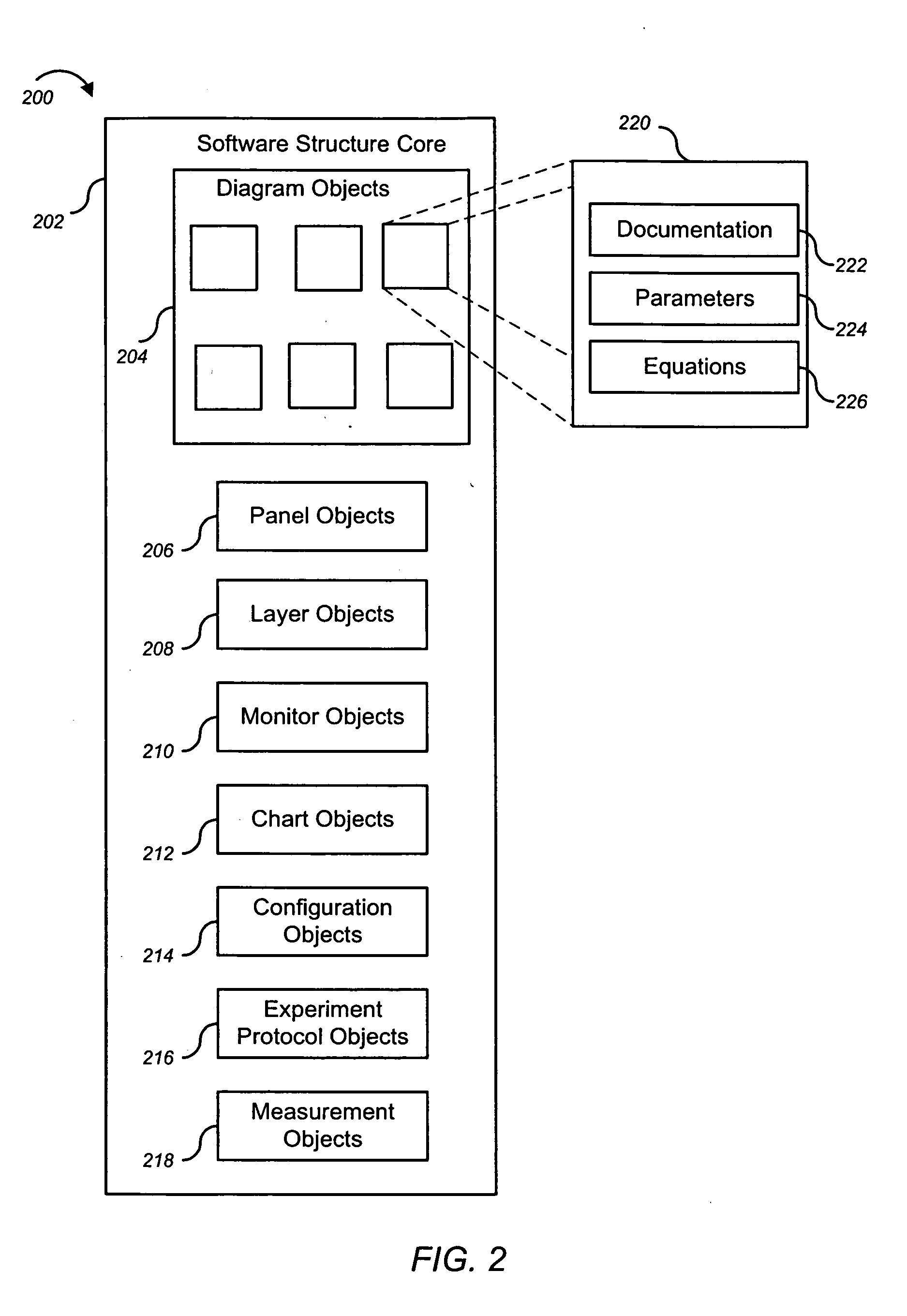
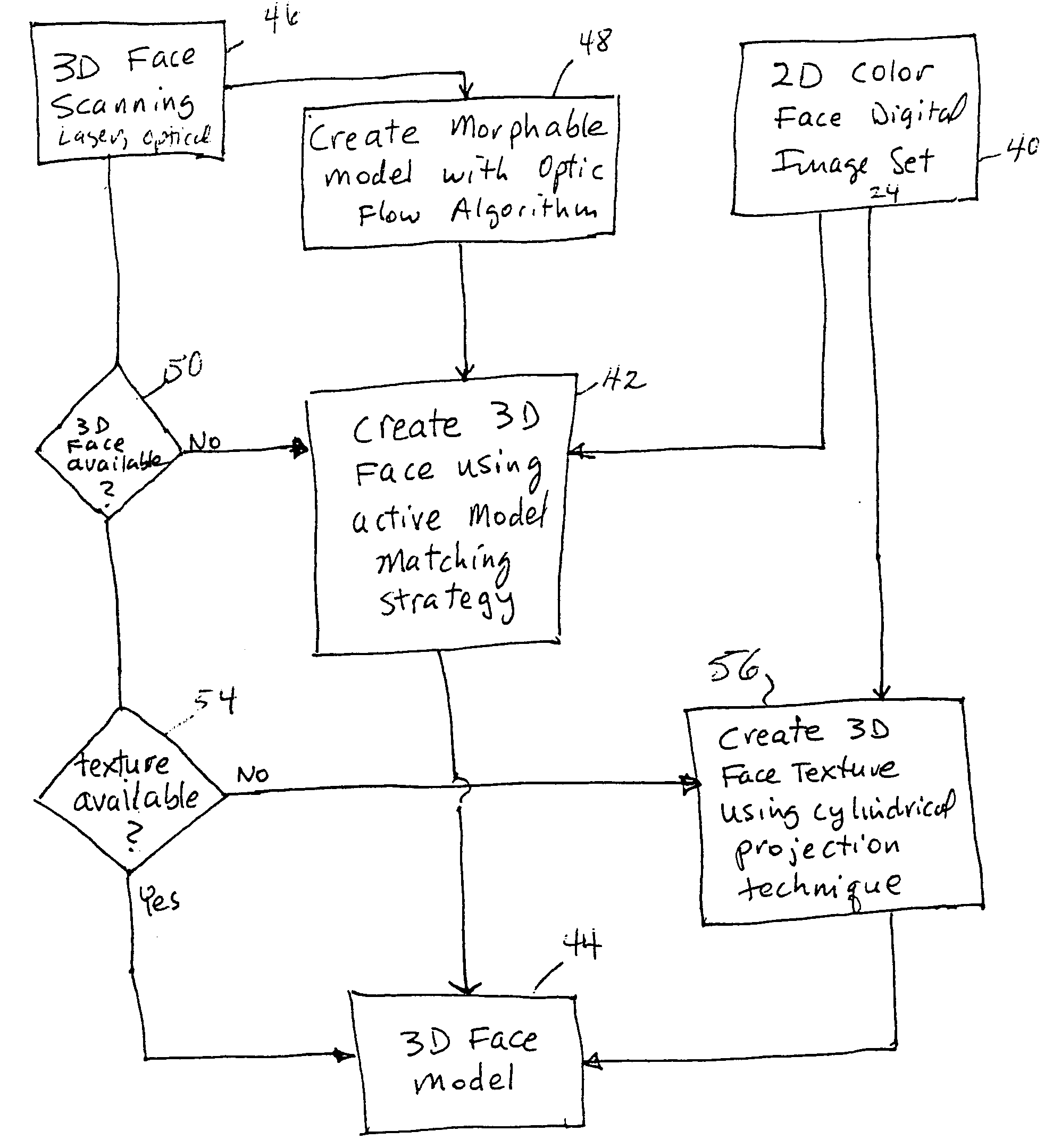
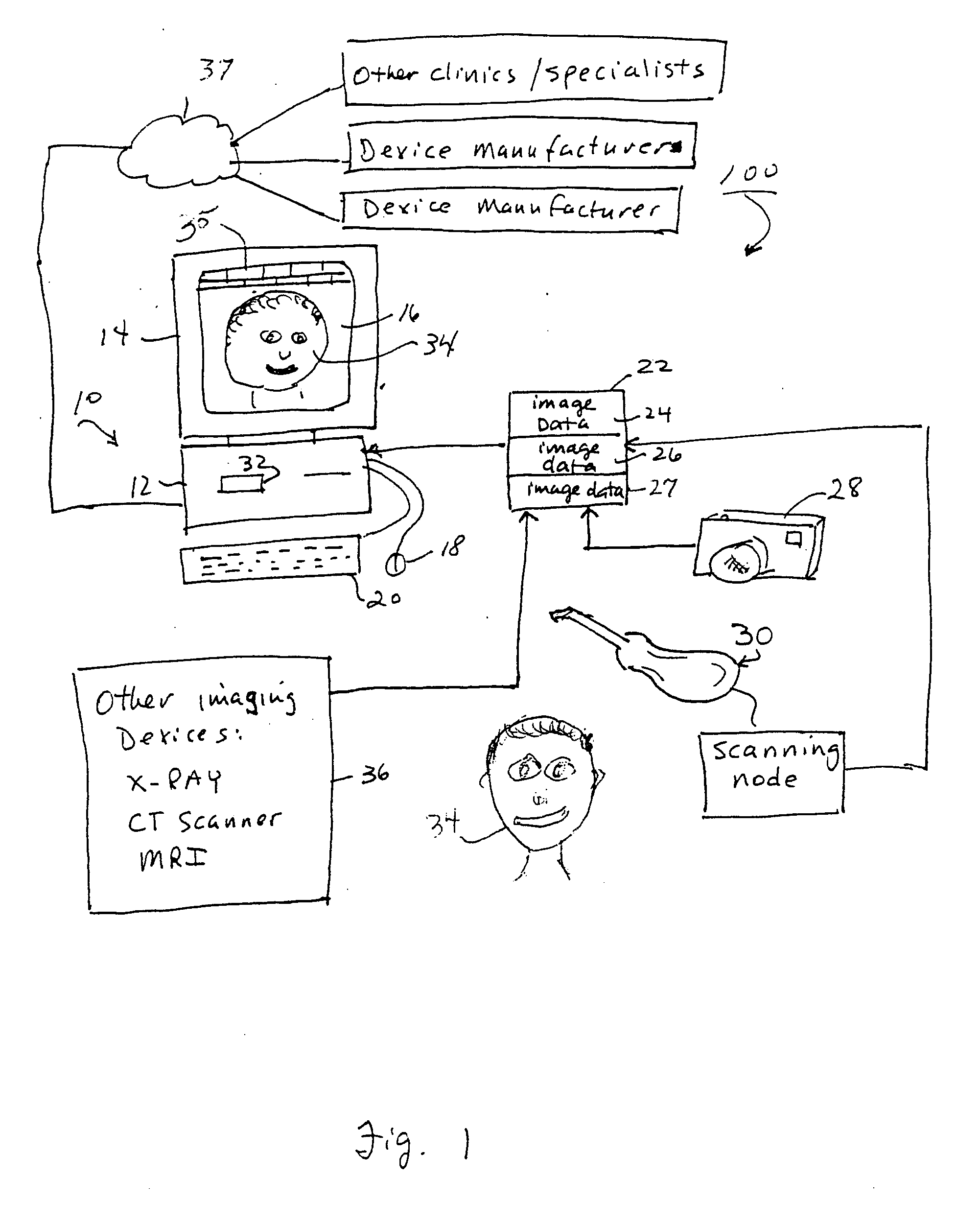
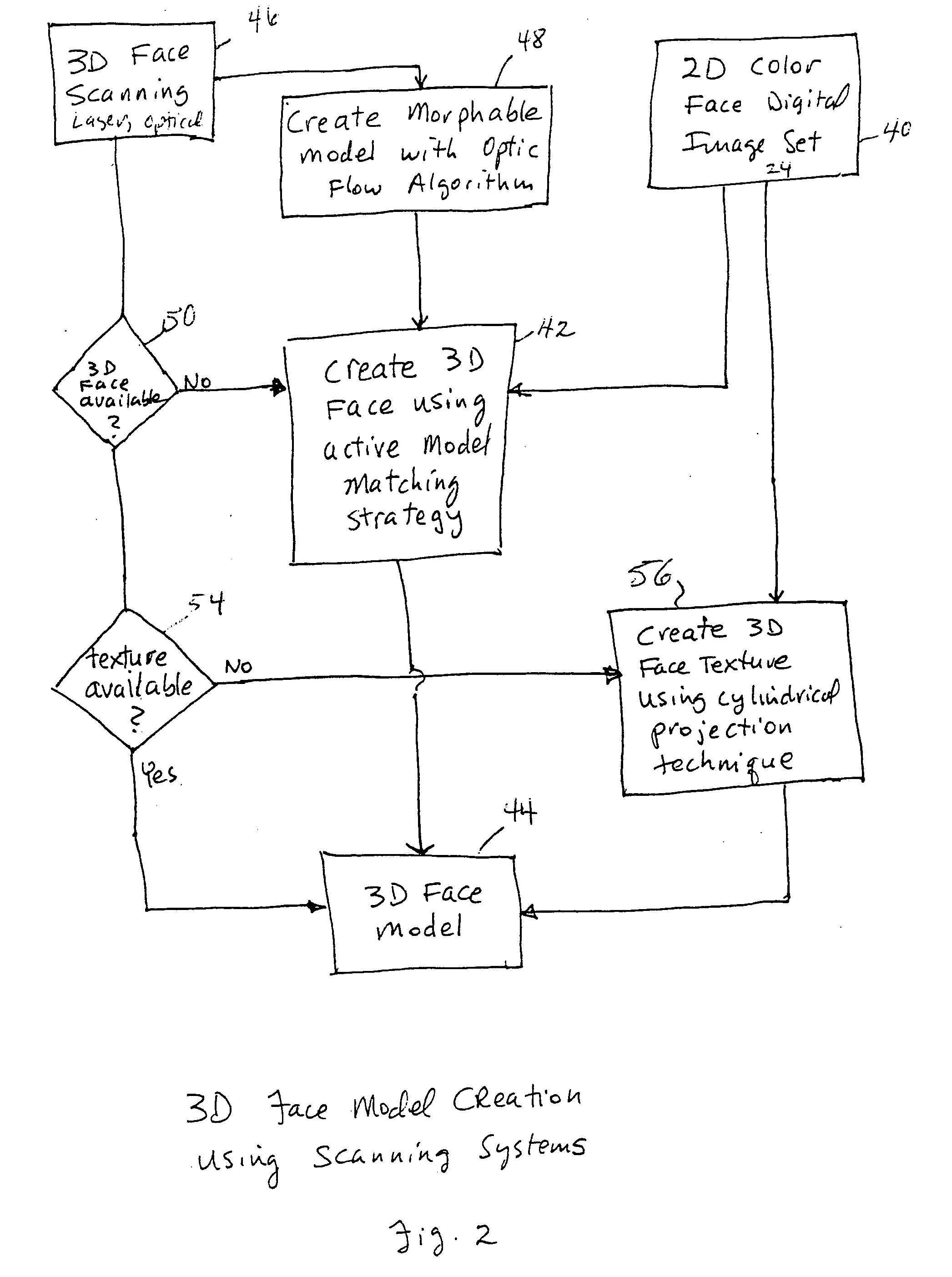
Unified workstation for virtual craniofacial diagnosis, treatment planning and therapeutics
InactiveUS7234937B2Quick analysisPowerful toolDental implantsImpression capsPlan treatmentPatient model
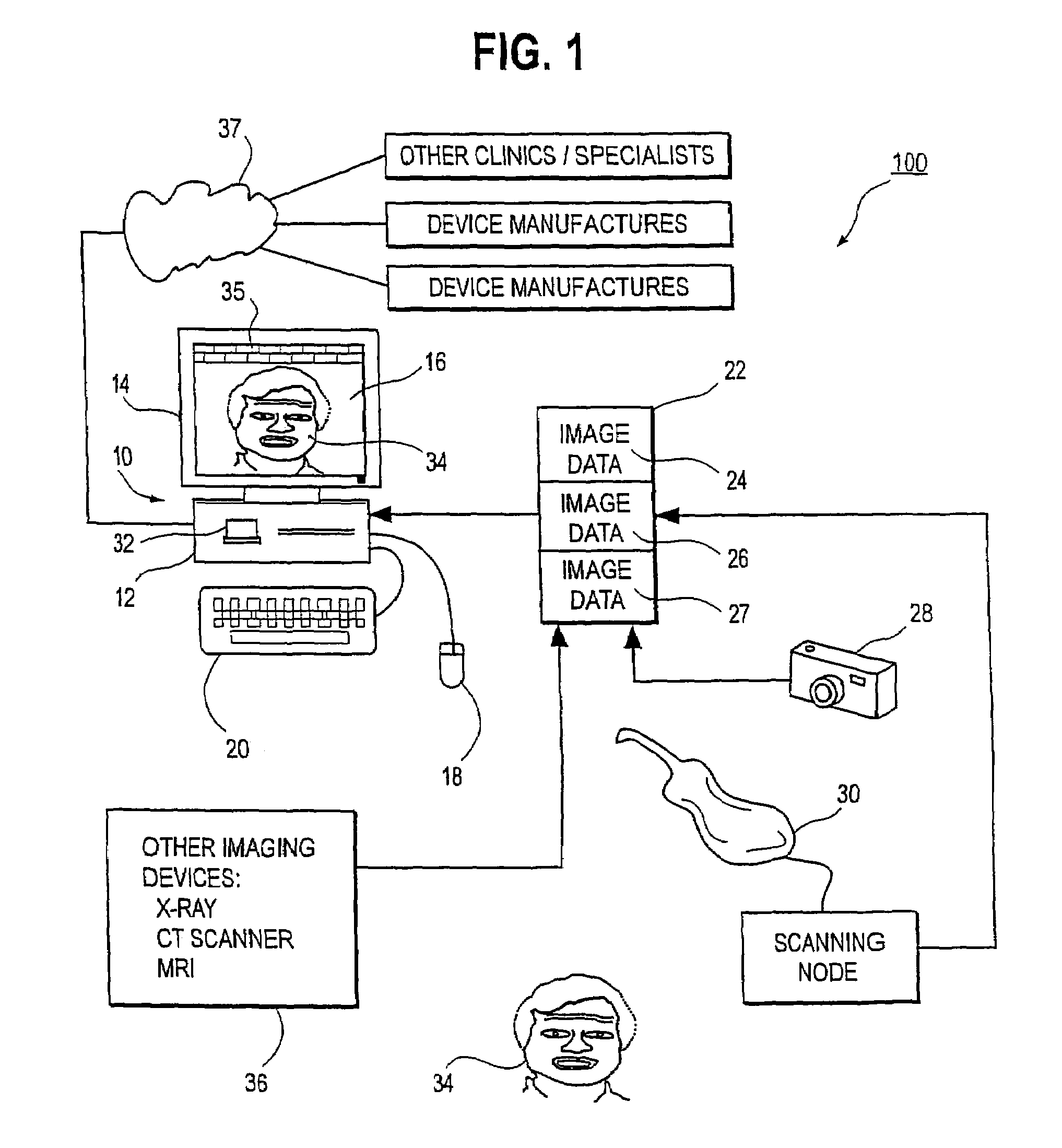
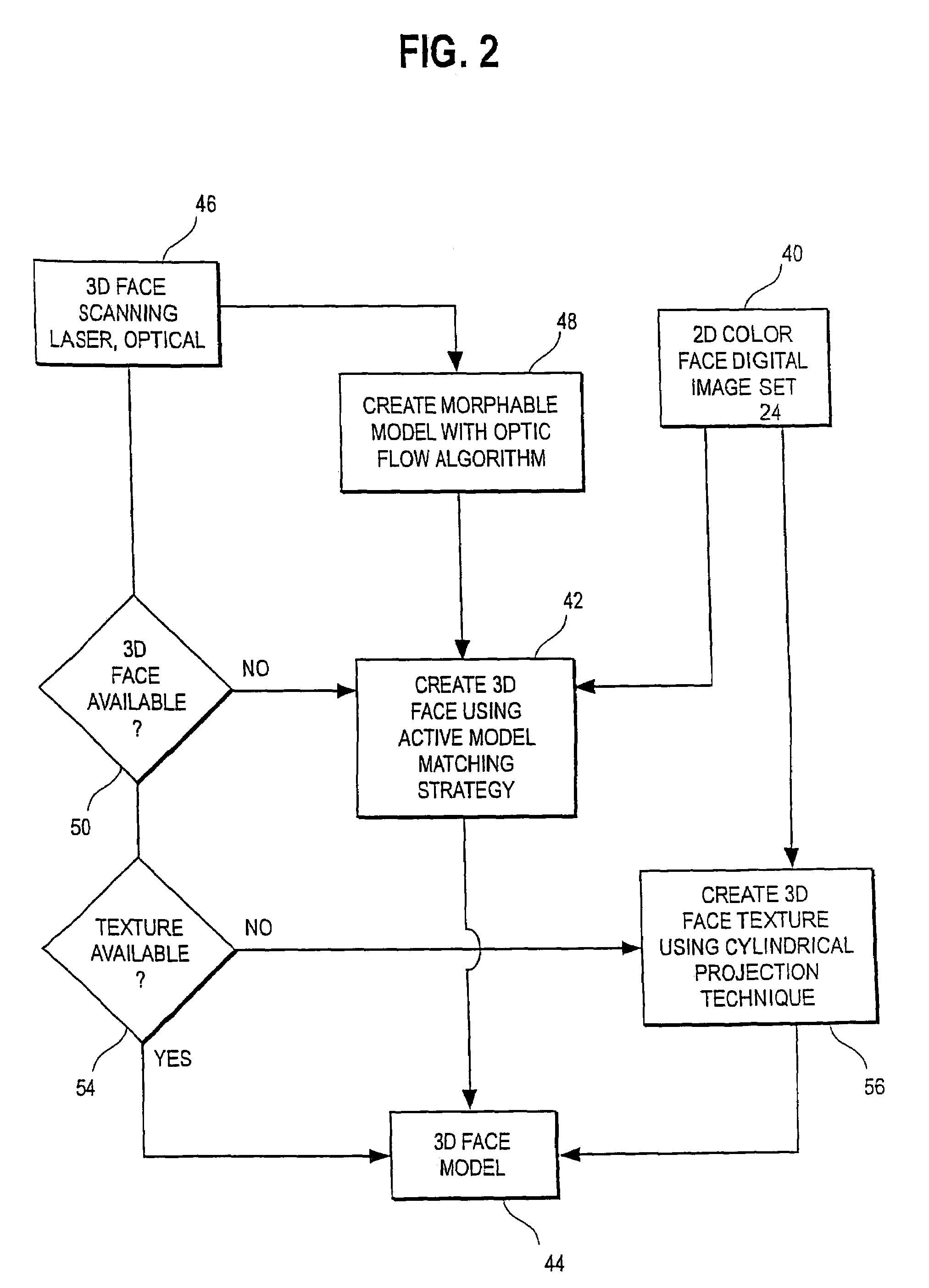
An integrated system is described in which digital image data of a patient, obtained from a variety of image sources, including CT scanner, X-Ray, 2D or 3D scanners and color photographs, are combined into a common coordinate system to create a virtual three-dimensional patient model. Software tools are provided for manipulating the virtual patient model to simulation changes in position or orientation of craniofacial structures (e.g., jaw or teeth) and simulate their affect on the appearance of the patient. The simulation (which may be pure simulations or may be so-called “morphing” type simulations) enables a comprehensive approach to planning treatment for the patient. In one embodiment, the treatment may encompass orthodontic treatment. Similarly, surgical treatment plans can be created. Data is extracted from the virtual patient model or simulations thereof for purposes of manufacture of customized therapeutic devices for any component of the craniofacial structures, e.g., orthodontic appliances.
Owner:ORAMETRIX
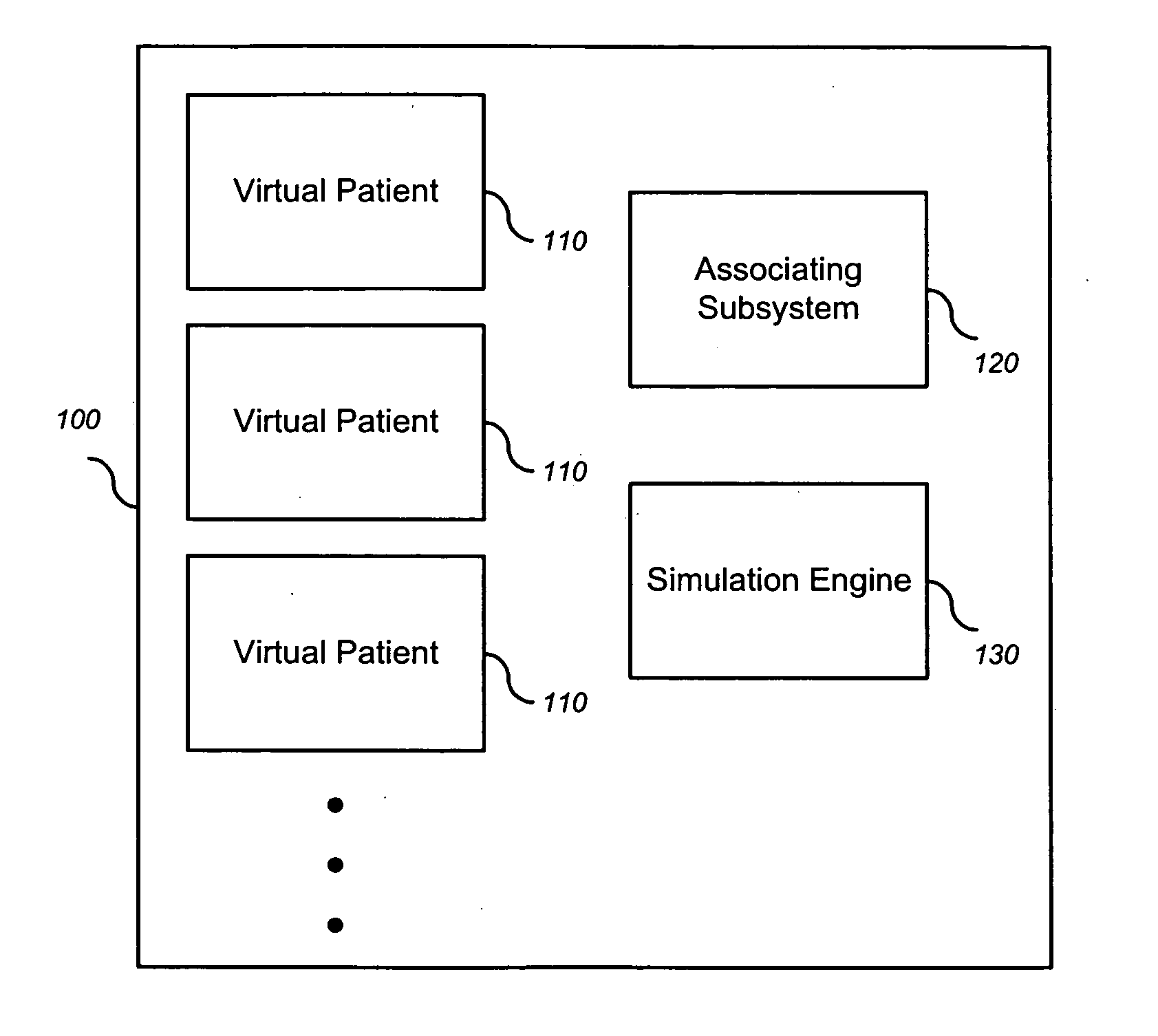
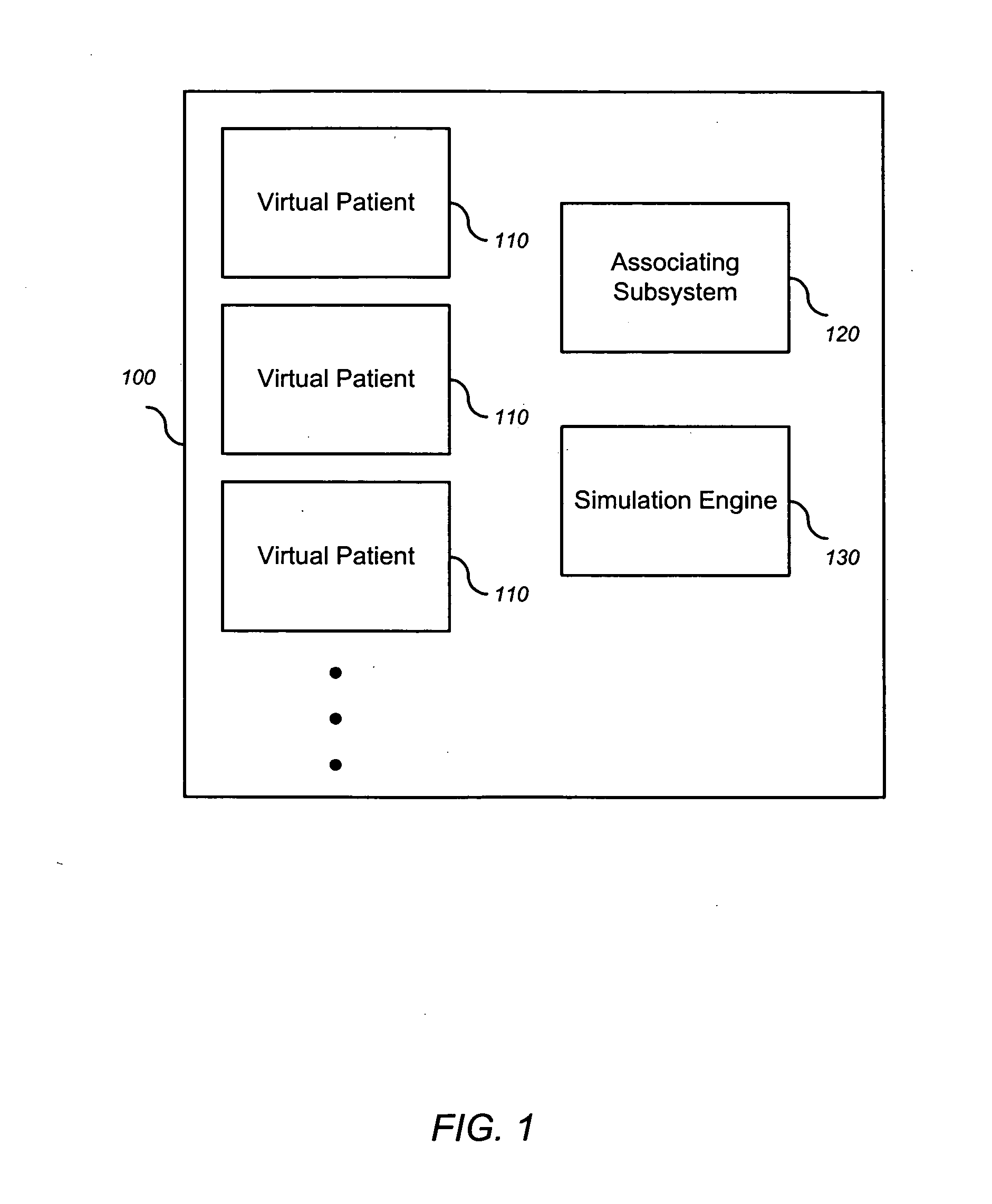
Simulating patient-specific outcomes
InactiveUS20050131663A1Timing is simpleMedical simulationAnalogue computers for chemical processesEfficacyBiomarker (petroleum)
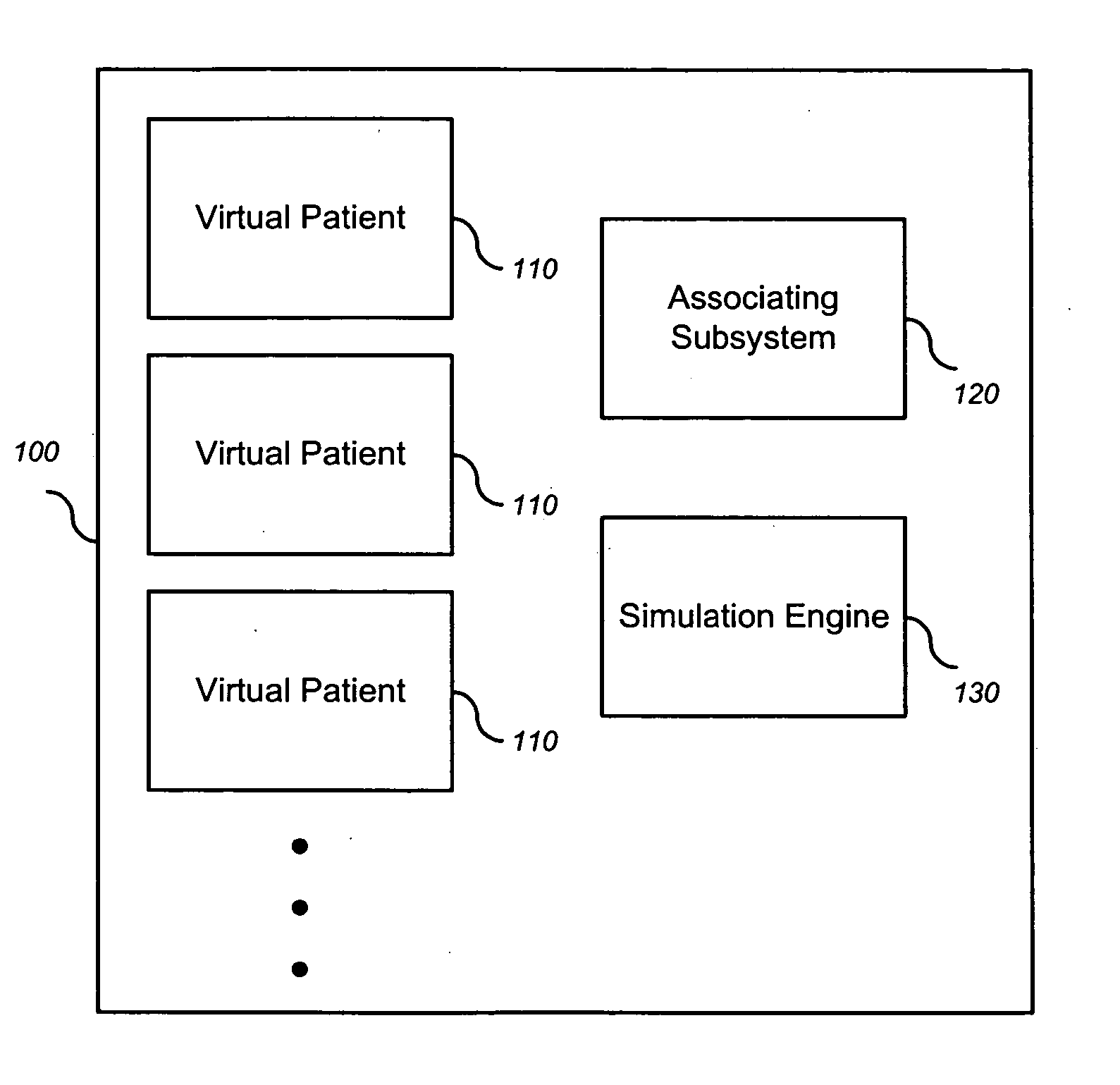
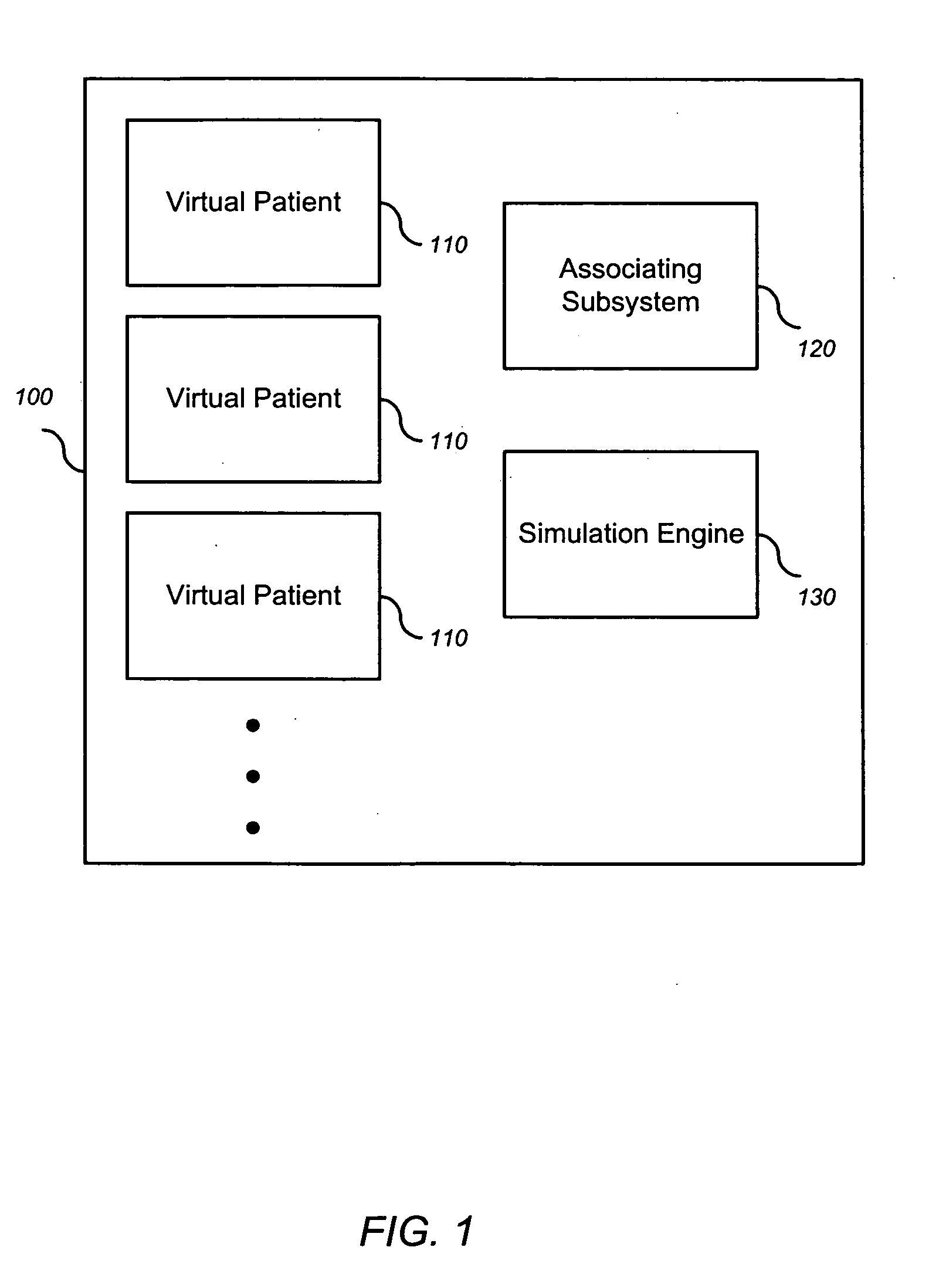
The invention encompasses systems, methods, and apparatus for predicting and monitoring an individual's response to a therapeutic regimen. The invention includes multiple virtual patients, an associating subsystem operable to associate the subject with one or more of the virtual patients, and a simulation engine operable to apply one or more experimental protocols to the one or more virtual patients identified with the subject to generate a set of outputs. The set of outputs can represent therapeutic efficacy, identify biomarkers for monitoring therapeutic efficacy, or merely report the status of the biological system as it represents a particular individual
Owner:ENTELOS HLDG
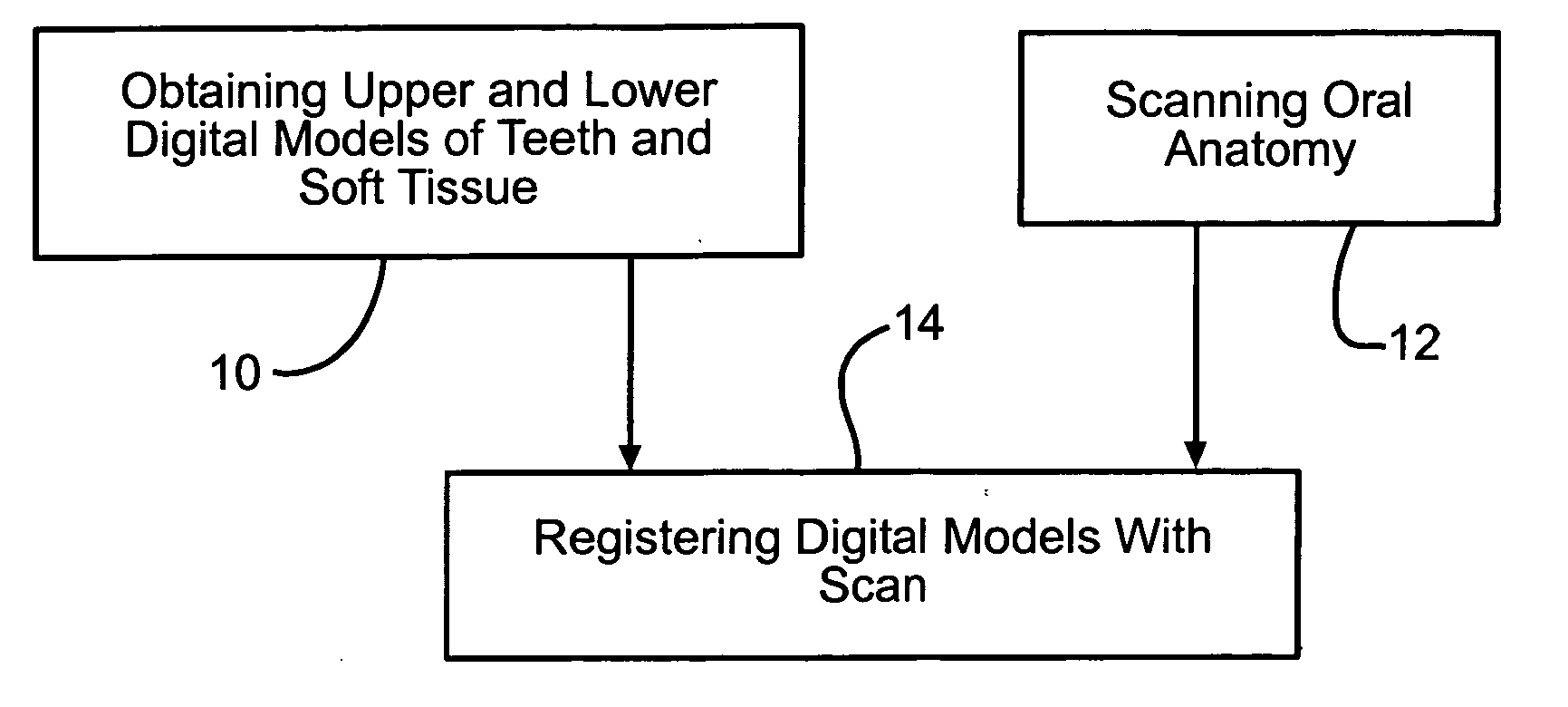
Four dimensional modeling of jaw and tooth dynamics
InactiveUS20070207441A1Impression capsMechanical/radiation/invasive therapiesDimensional modelingTemporomandibular joint
Methods and systems are described to digitally model the 4-dimensional dynamics of jaw and tooth motion using time-based 3-dimensional data. Complete upper and lower digital models are registered to time-based 3-dimensional intra-oral data to produce a true 4-dimensional model. Diagnostic and clinical applications include balancing the occlusion and characterizing the geometry of the temporomandibular joint. The 4-dimensional model is readily combined with conventional imaging methods such as CT to create a more complete virtual patient model.
Owner:GREAT LAKES ORTHODONTICS
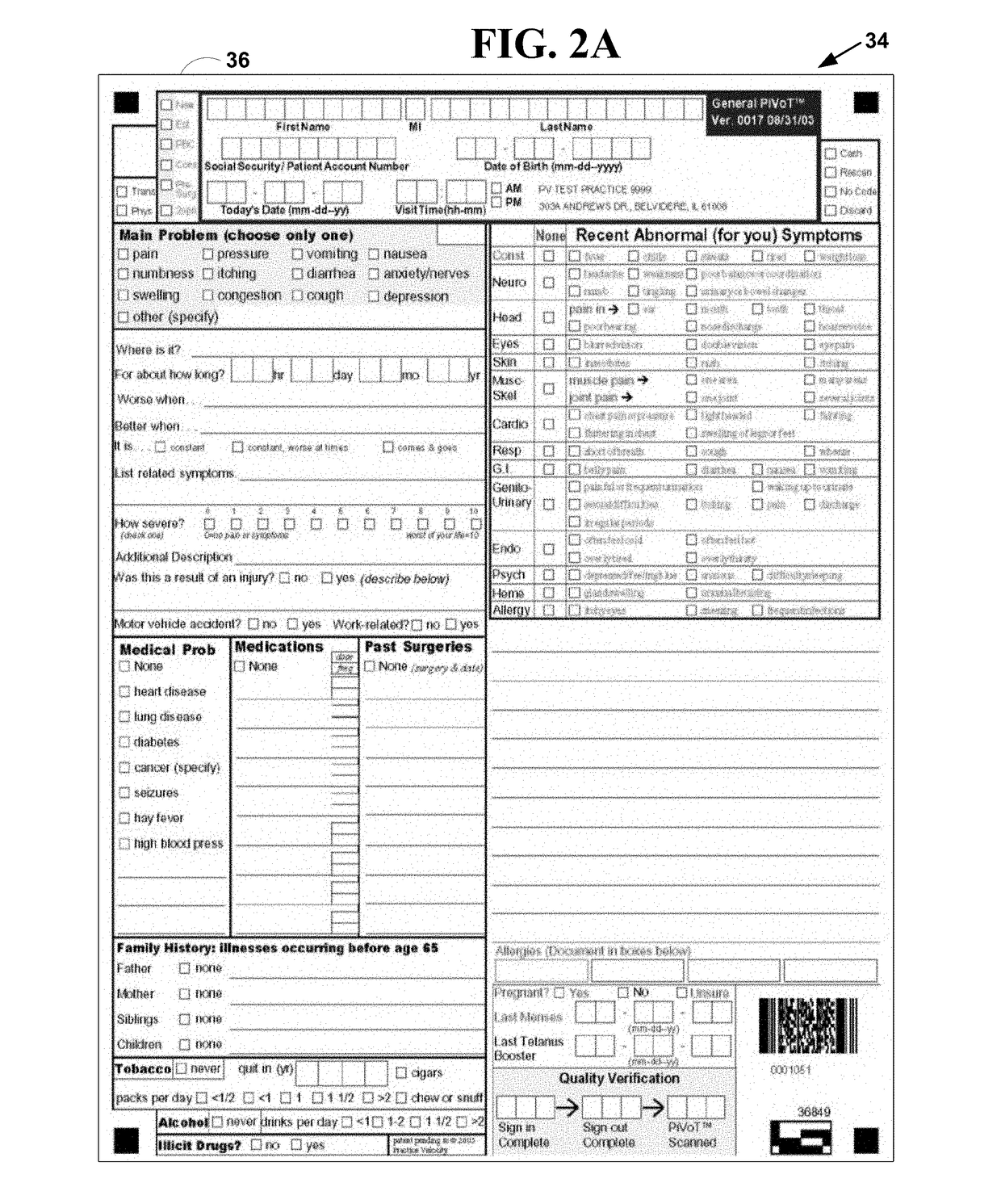
Method and system for automated medical records processing with patient tracking
ActiveUS20180114595A1Reduce complexityReduce riskMedical communicationTransmissionMedical recordMedical diagnosis
A method and system for automated medical records processing with cloud computing including patient tracking for actual and virtual encounters. The method and system includes plural electronic medical templates specifically designed such that they reduce the complexity and risk associated with collecting patient encounter information, creating a medical diagnosis, tracking the patient through the medical processes at the medical facility and generate the appropriate number and type medical codes for a specific type of medical practice when processed. The medical codes and other types of processed actual or virtual patient encounter information are displayed in real-time on electronic medical records and invoices immediately after an actual or virtual patient encounter via a cloud computing network.
Owner:PRACTICE VELOCITY
Unified workstation for virtual craniofacial diagnosis, treatment planning and therapeutics
An integrated system is described in which digital image data of a patient, obtained from a variety of image sources, including CT scanner, X-Ray, 2D or 3D scanners and color photographs, are combined into a common coordinate system to create a virtual three-dimensional patient model. Software tools are provided for manipulating the virtual patient model to simulation changes in position or orientation of craniofacial structures (e.g., jaw or teeth) and simulate their affect on the appearance of the patient. The simulation (which may be pure simulations or may be so-called “morphing” type simulations) enables a comprehensive approach to planning treatment for the patient. In one embodiment, the treatment may encompass orthodontic treatment. Similarly, surgical treatment plans can be created. Data is extracted from the virtual patient model or simulations thereof for purposes of manufacture of customized therapeutic devices for any component of the craniofacial structures, e.g., orthodontic appliances.
Owner:ORAMETRIX
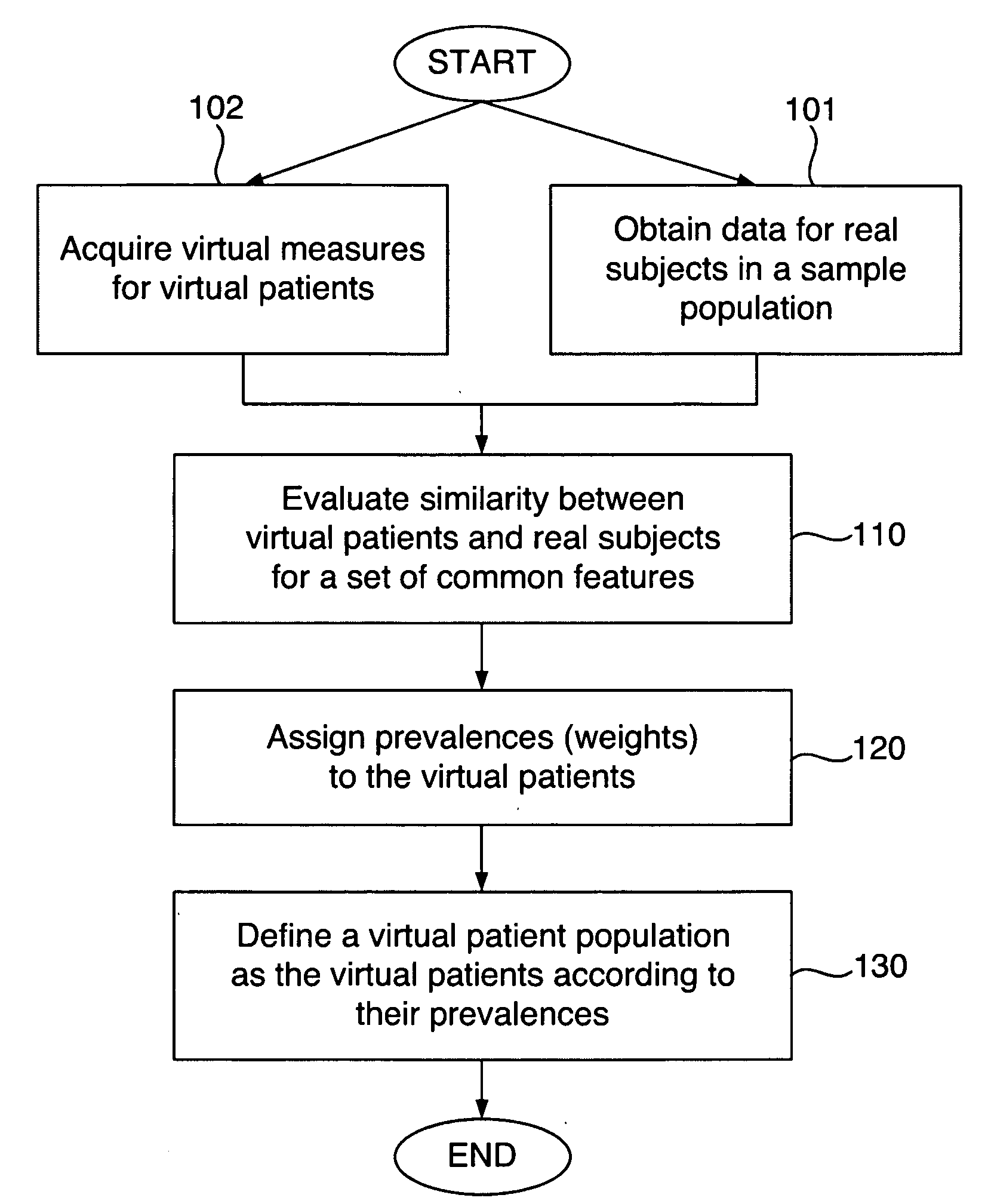
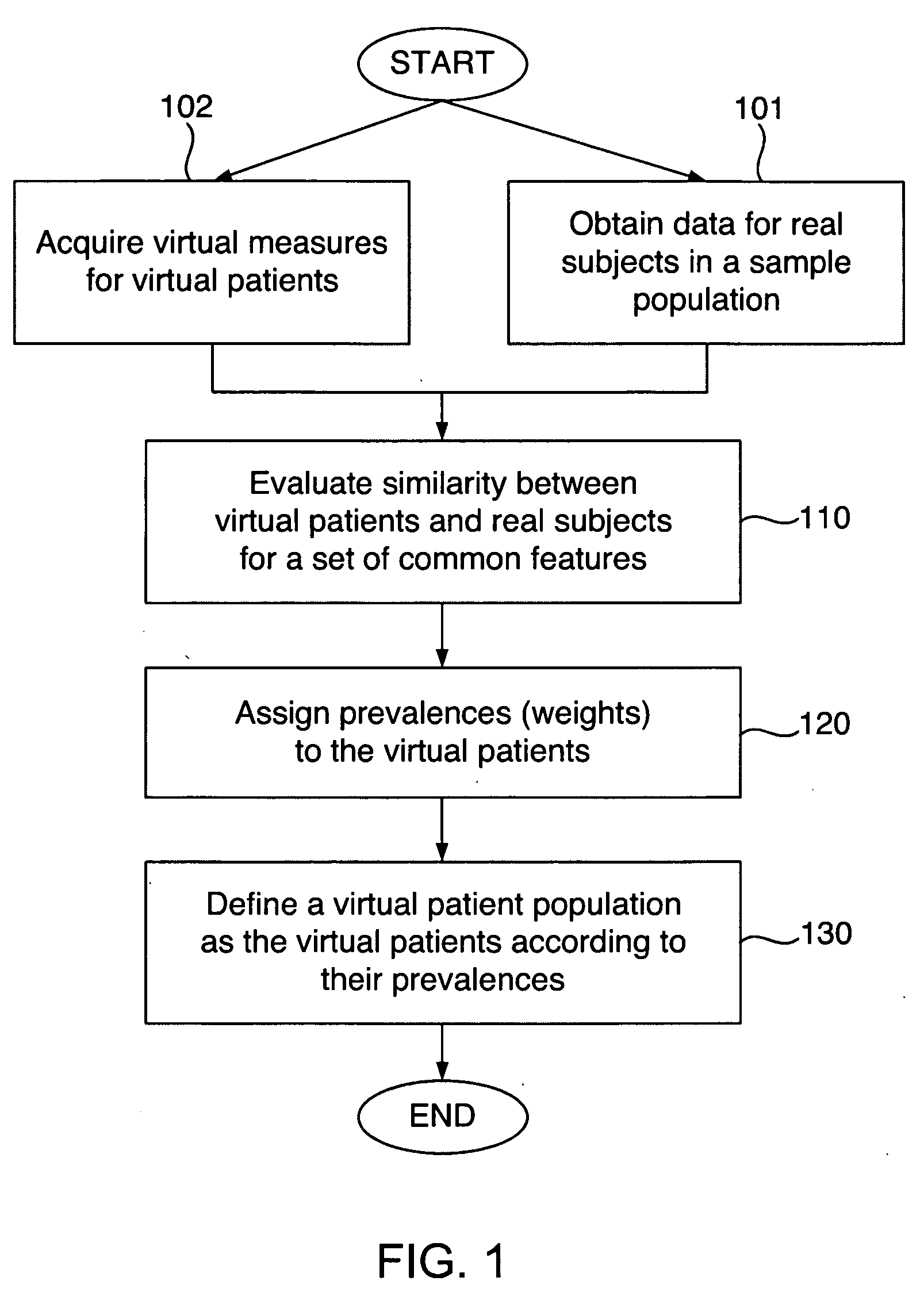
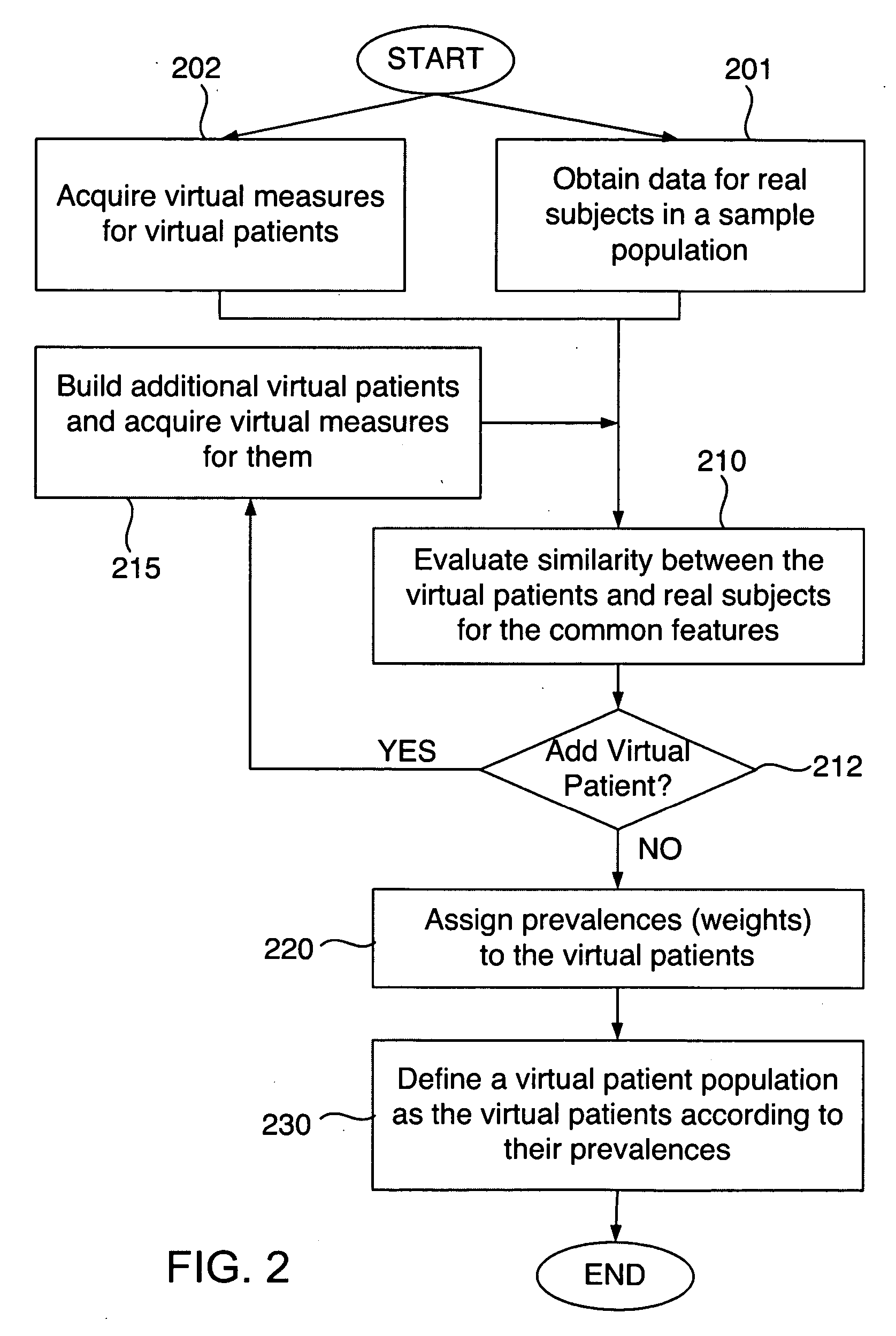
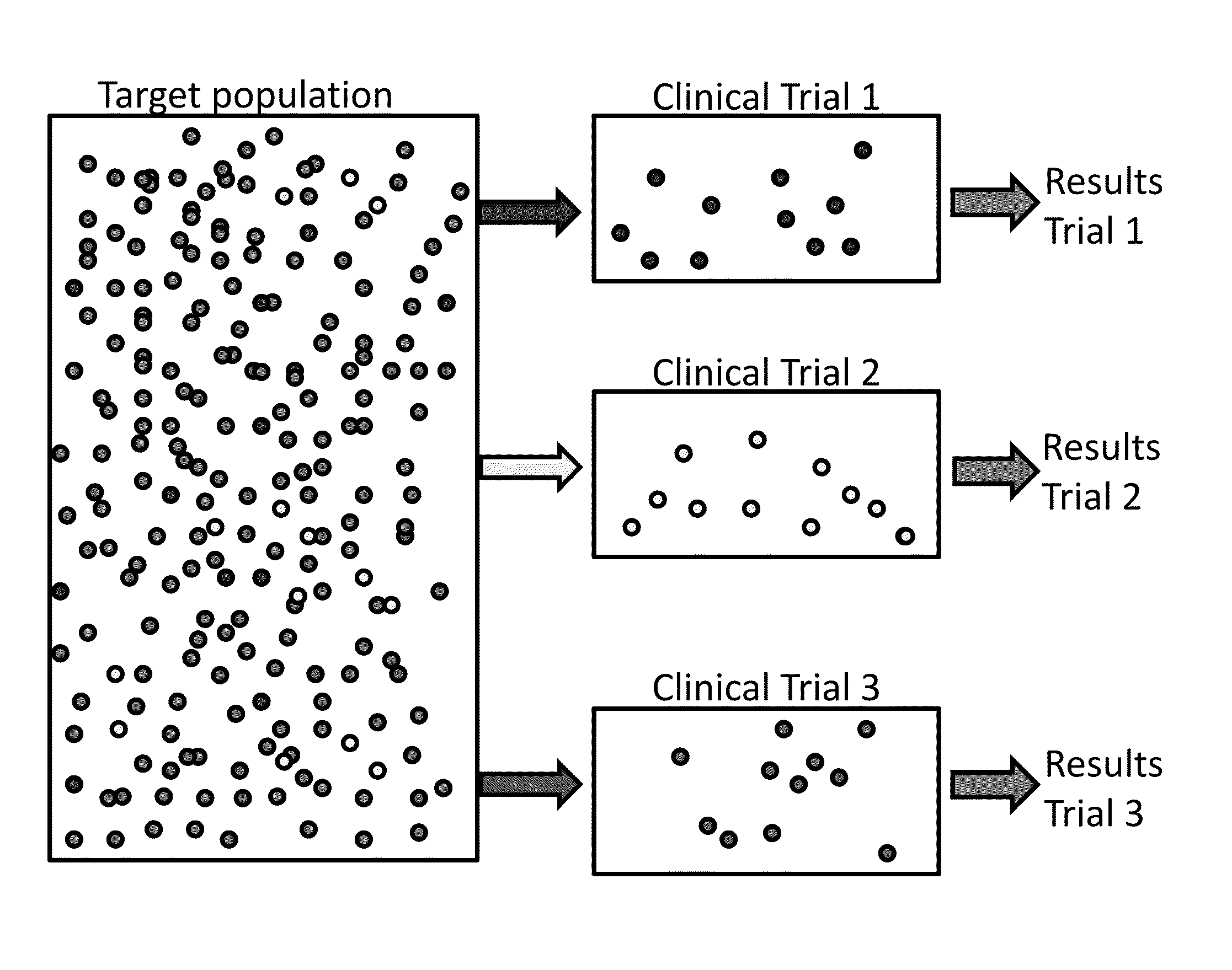
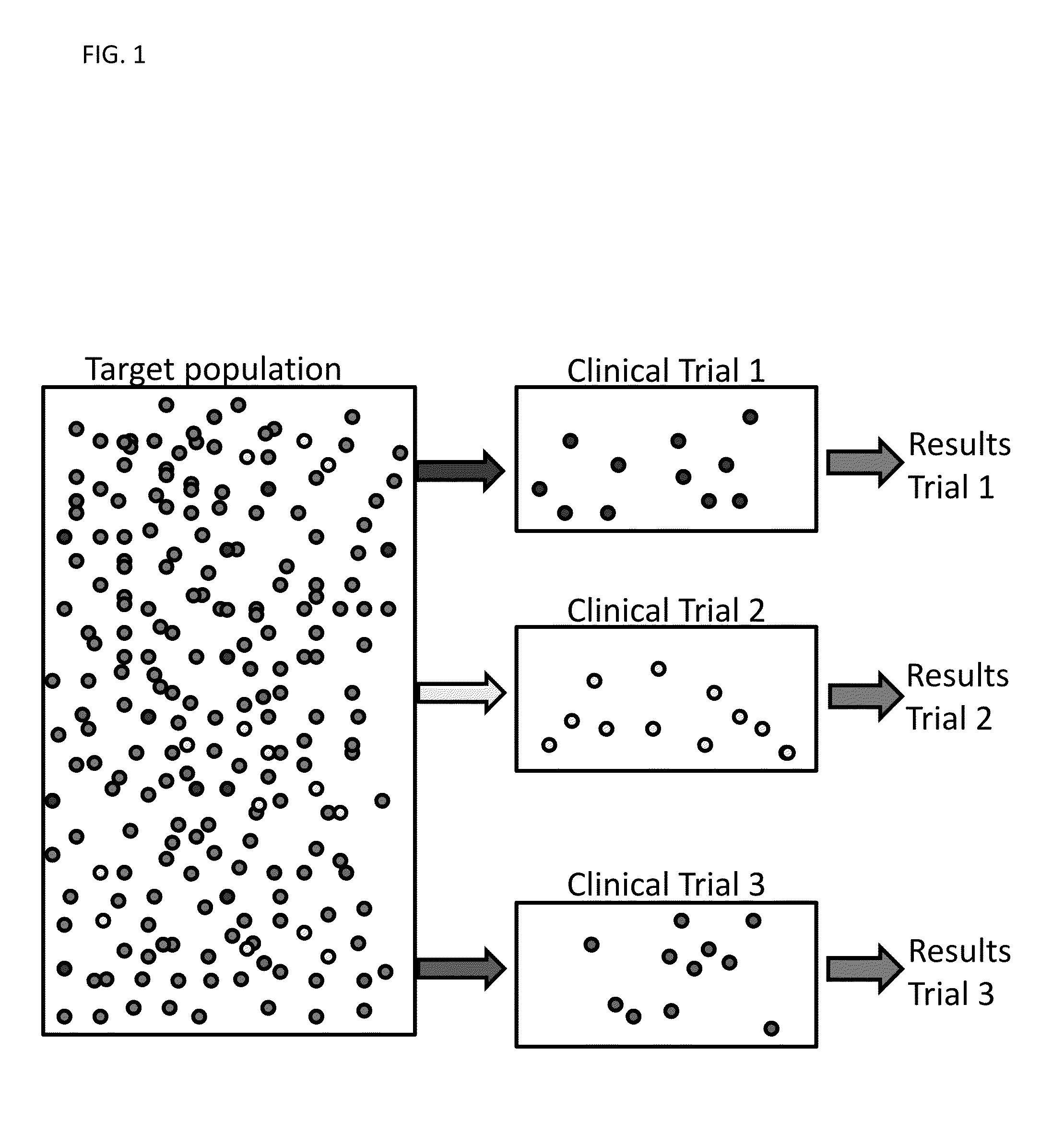
Defining virtual patient populations
InactiveUS20070026365A1Medical simulationData processing applicationsClinical psychologyClinical trial
The invention encompasses methods, including computer-implemented methods, of defining a virtual patient population and mapping the virtual patient population to a population of real patients. The invention utilizes virtual measures from one or more virtual patients, and data representative of multiple real subjects in a sample population, such as data collected from patients in a clinical trial or epidemiological study of a real population. The invention includes evaluating the similarity between the virtual patients and the real subjects, and assigning prevalences to the virtual patients based on the evaluation. The similarity can be assessed using some or all of the virtual measures of the virtual patients and some or all of the data obtained for the real subjects. Any of various goodness-of-fit measures can be used to evaluate the similarity or to help identify prevalences. The virtual patient population is defined as the virtual patients according to their respective prevalences.
Owner:ENTELOS INC
Systems and methods for mixed reality medical training
ActiveUS20180293802A1Radio transmission for post communicationEducational modelsMixed realityMedical treatment
A method for training a student in medical condition identification and intervention. The method can include the step of providing a mixed reality viewing device, providing a computing device, providing a physical object, storing a medical condition scenario in memory of the viewing device, storing the scenario in the memory of the computing device, anchoring a virtual image of at least a portion of a virtual patient on at least a portion of the physical object, selecting the scenario, commanding the processor of the computing device to initiate displaying the virtual image in a selected one of a plurality of stages, controlling one or more states and one or more properties of the physical object, assessing the student's identification of the one or more virtual critical cues; and assessing the student's identification of the one or more physical critical cues.
Owner:UNVEIL LLC
Virtual human interaction system
InactiveUS20080014566A1Overcome disadvantagesImprove realismMedical simulationComputer-assisted treatment prescription/deliveryHuman interactionHuman body
A virtual human interaction system for use on a PC or web-enabled computer facilitates the training and education of medical services practitioners by allowing them to virtually interact with a virtual patient delivered by the system and displayed on the computer screen. The system embodies a plurality of cases, and for each case, there are a number of possible outcomes, depending on the choices made by the medical services practitioner at each stage in a particular case. Together with the virtual patient displayed by the system, also incorporated into the system are a plurality of appearance descriptors which can be applied to the virtual patient by the system so as to cause a change in the appearance based on real-life human conditions which affect the physical appearance of humans generally and which are thus mimicked in the virtual patient. The resulting effect is to provide users with an almost real-time indication of their actions on patients.
Owner:KEELE UNIVERSITY
Computer architecture and process of user evaluation
ActiveUS20050118557A1Easy to reconfigureDigital computer detailsBiological neural network modelsPrimitive stateComplex system
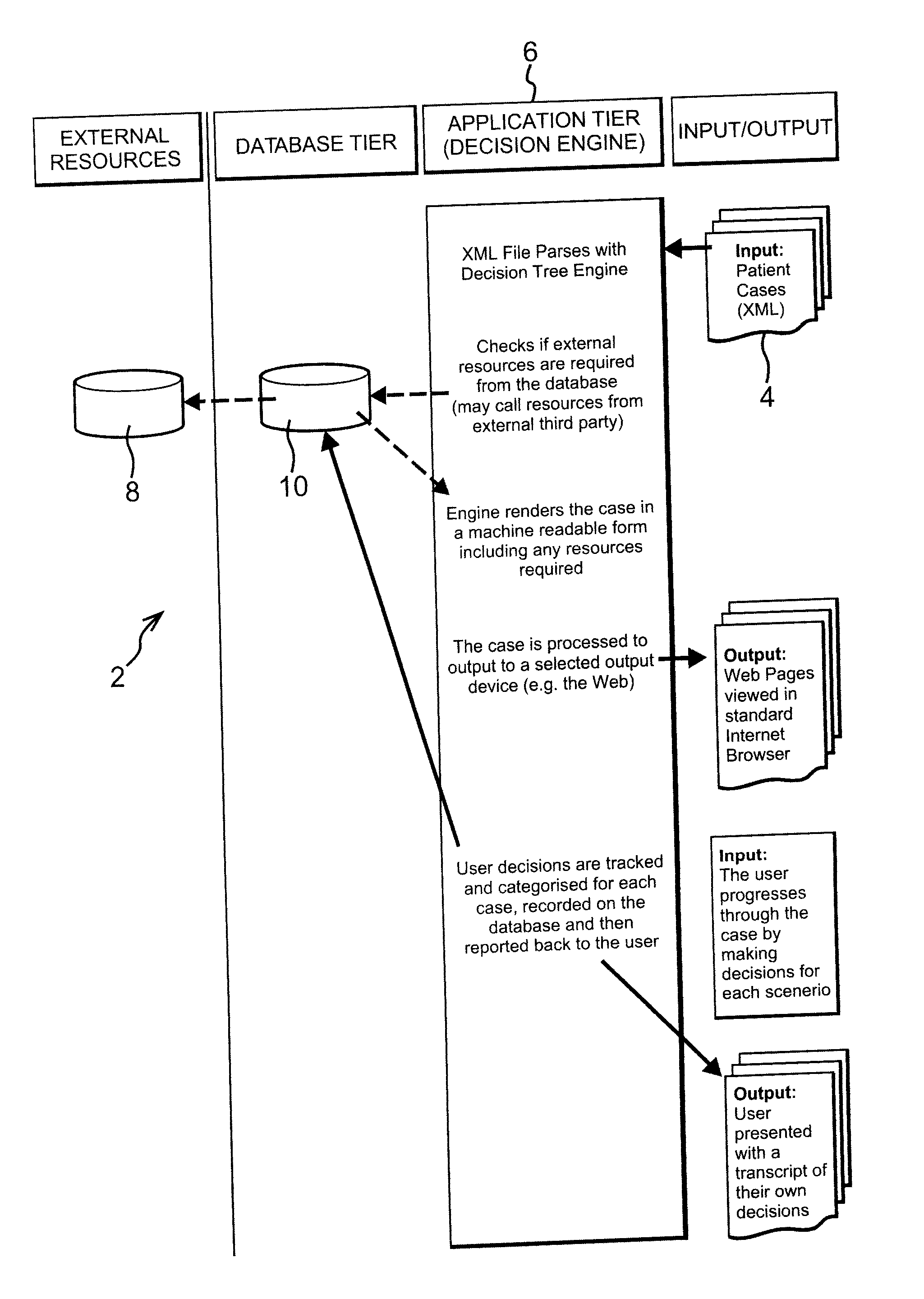
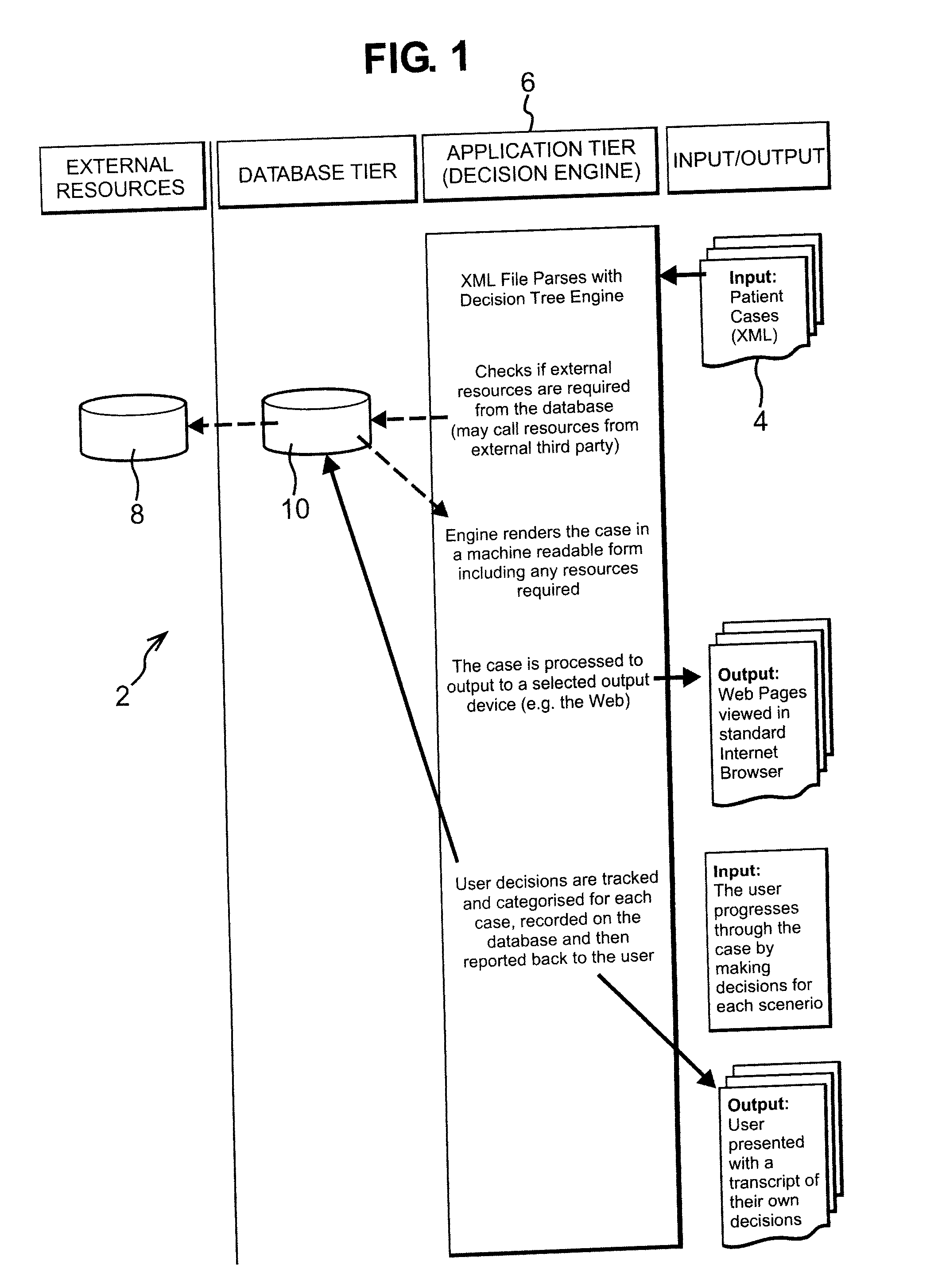
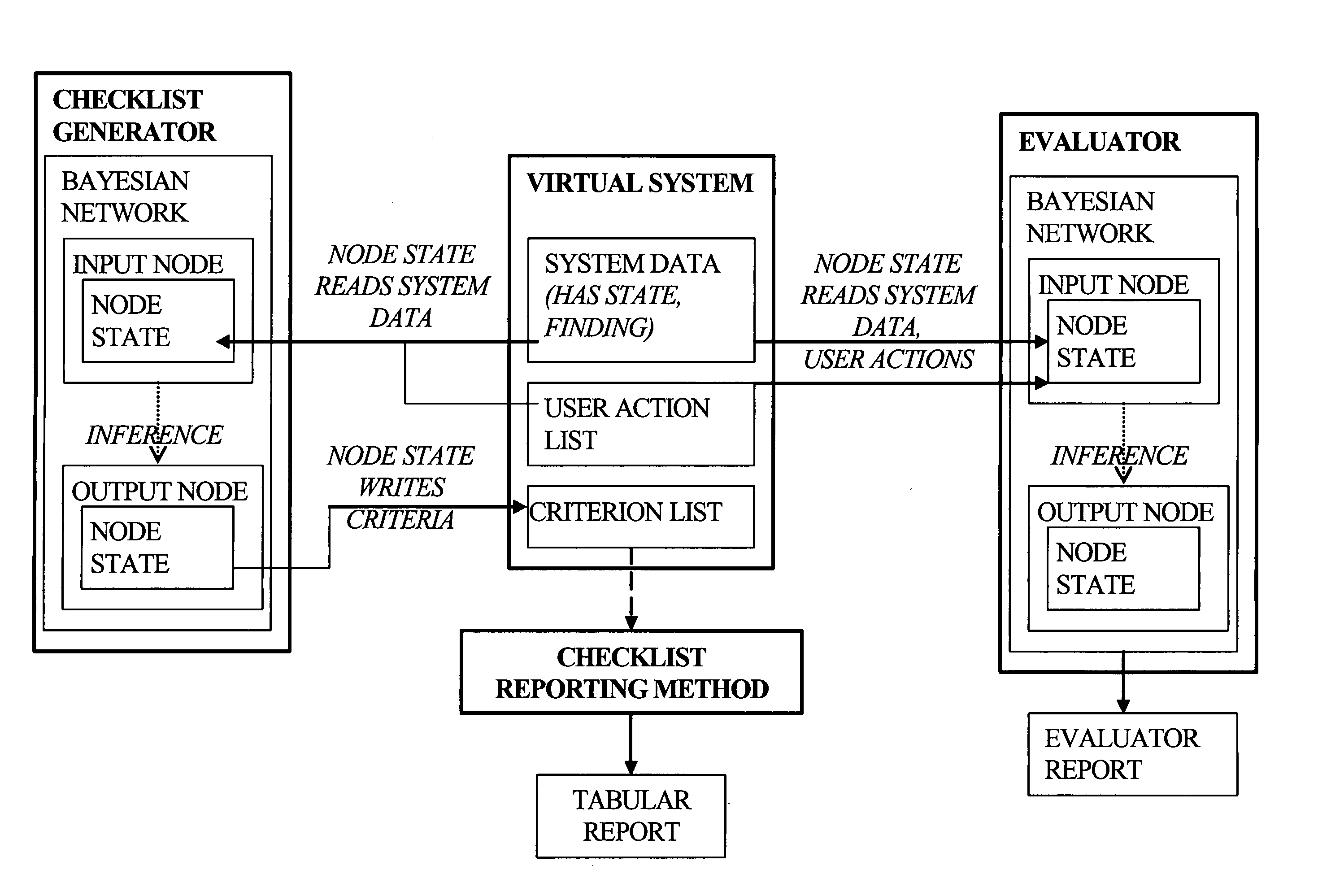
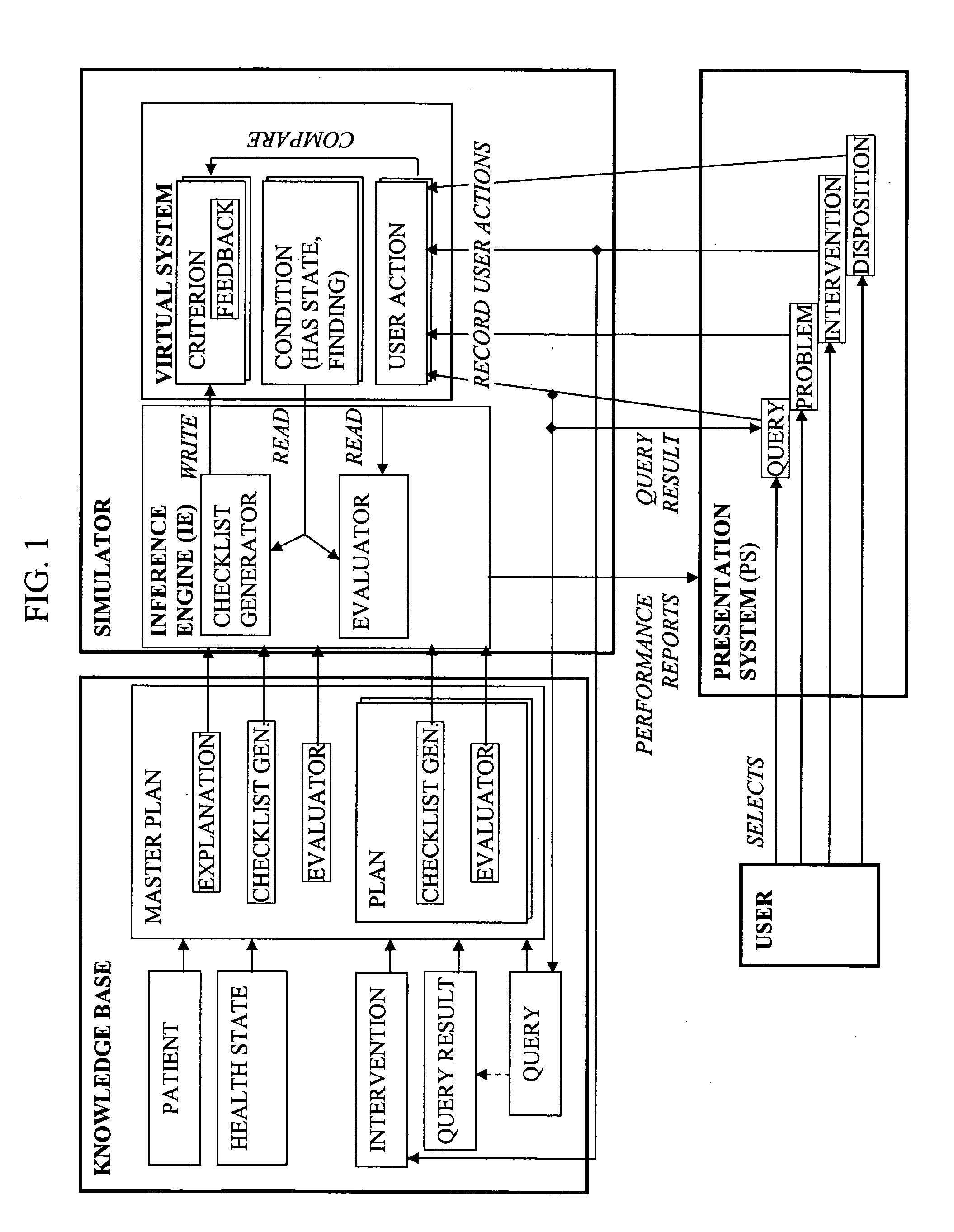
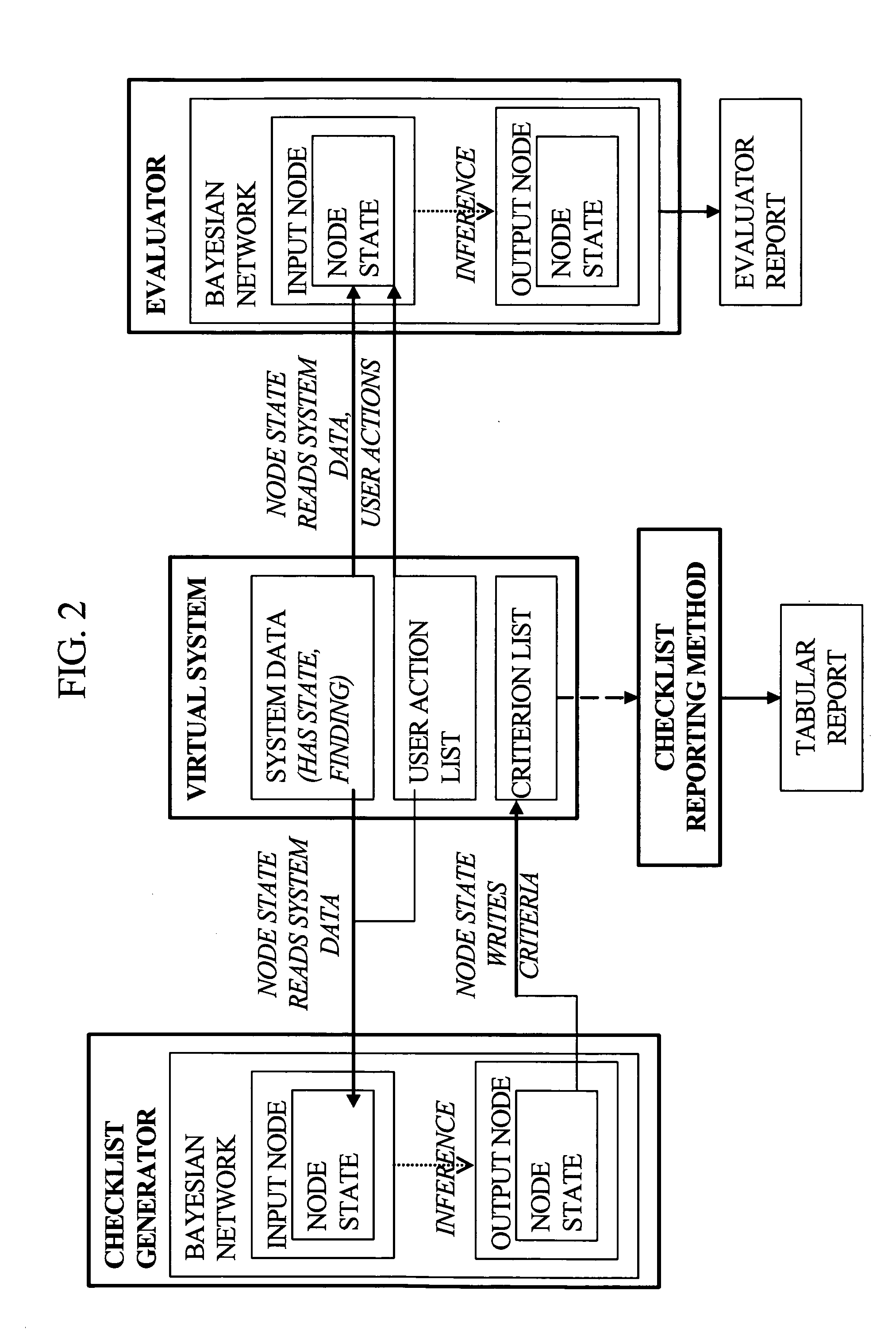
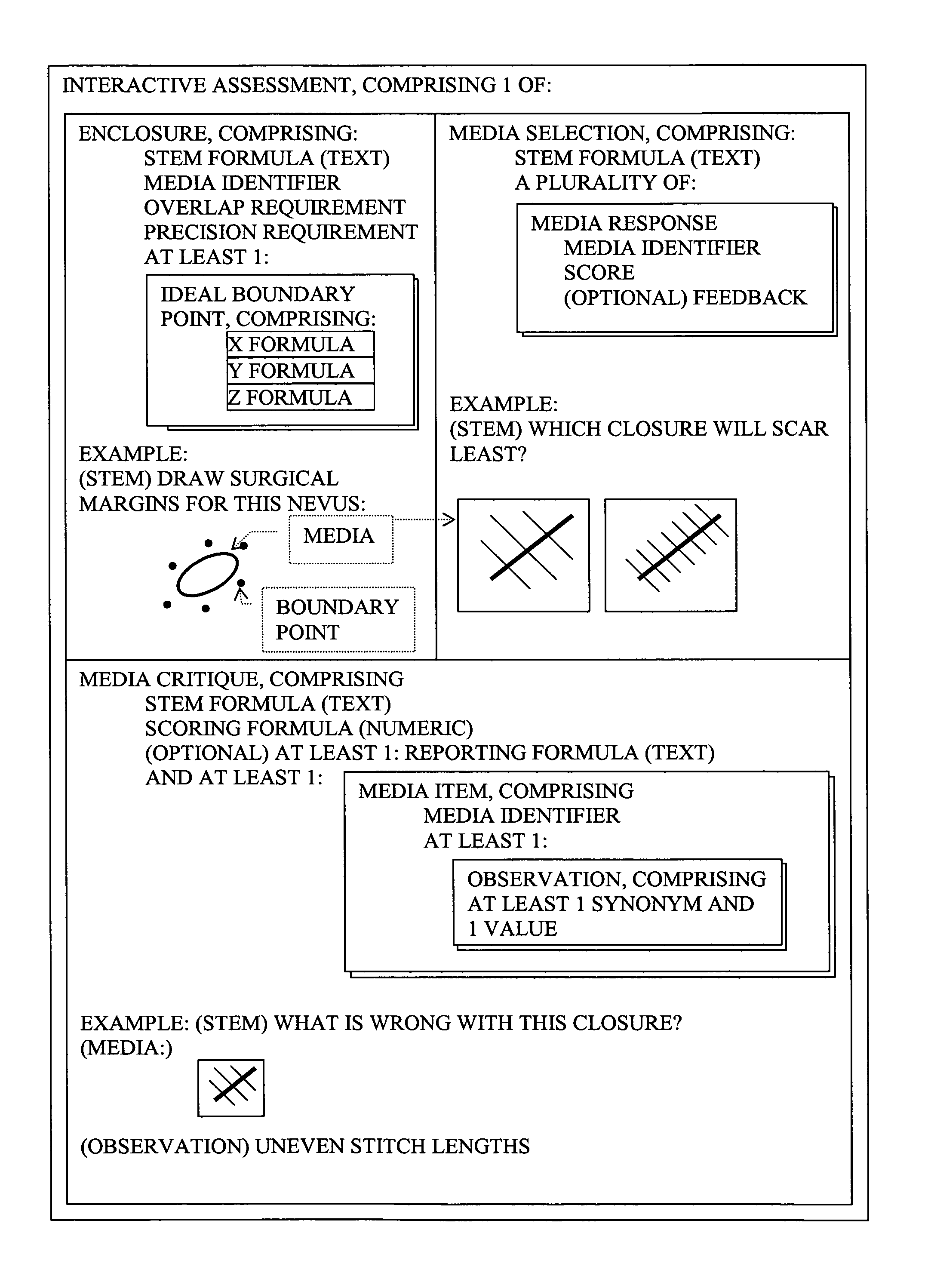
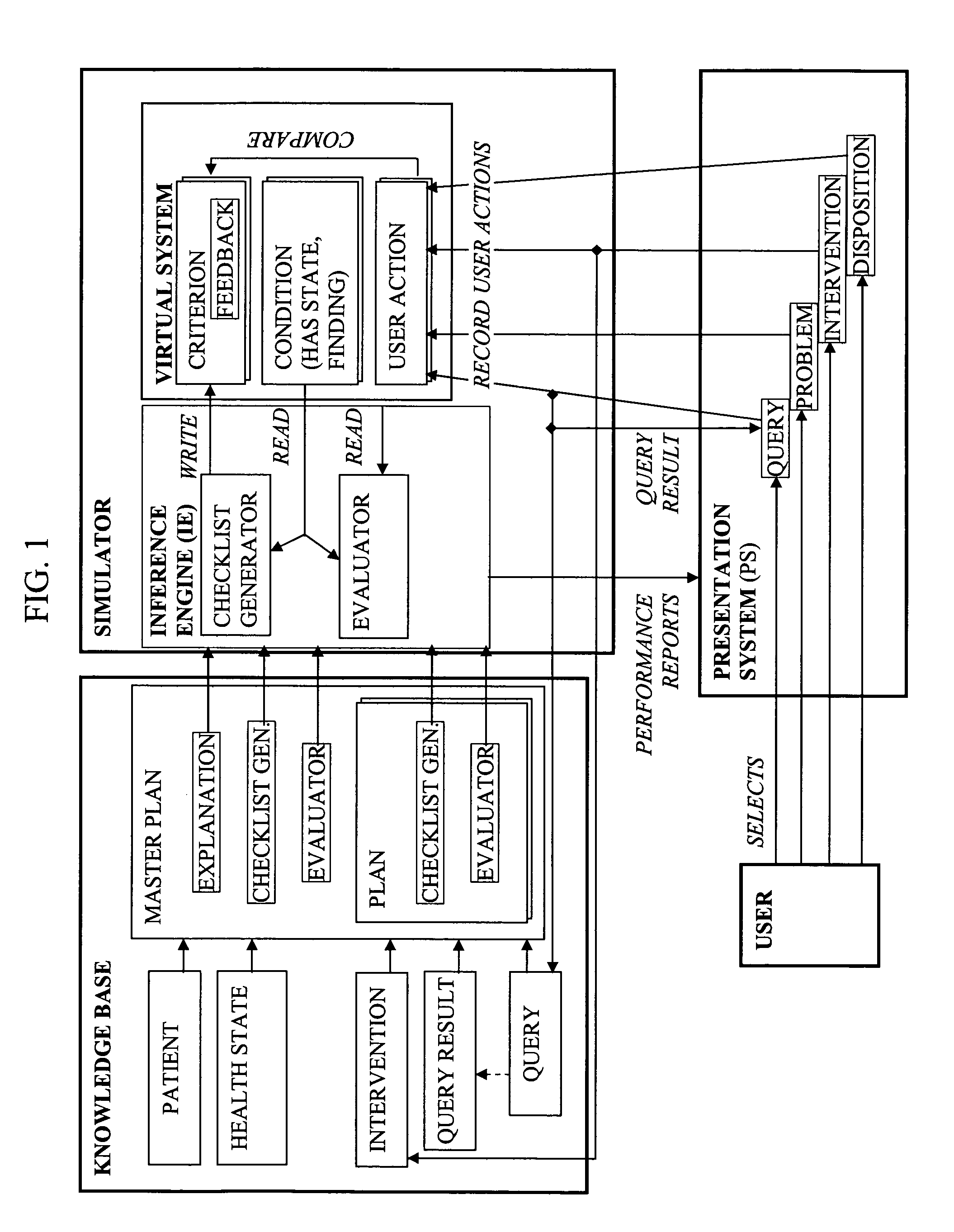
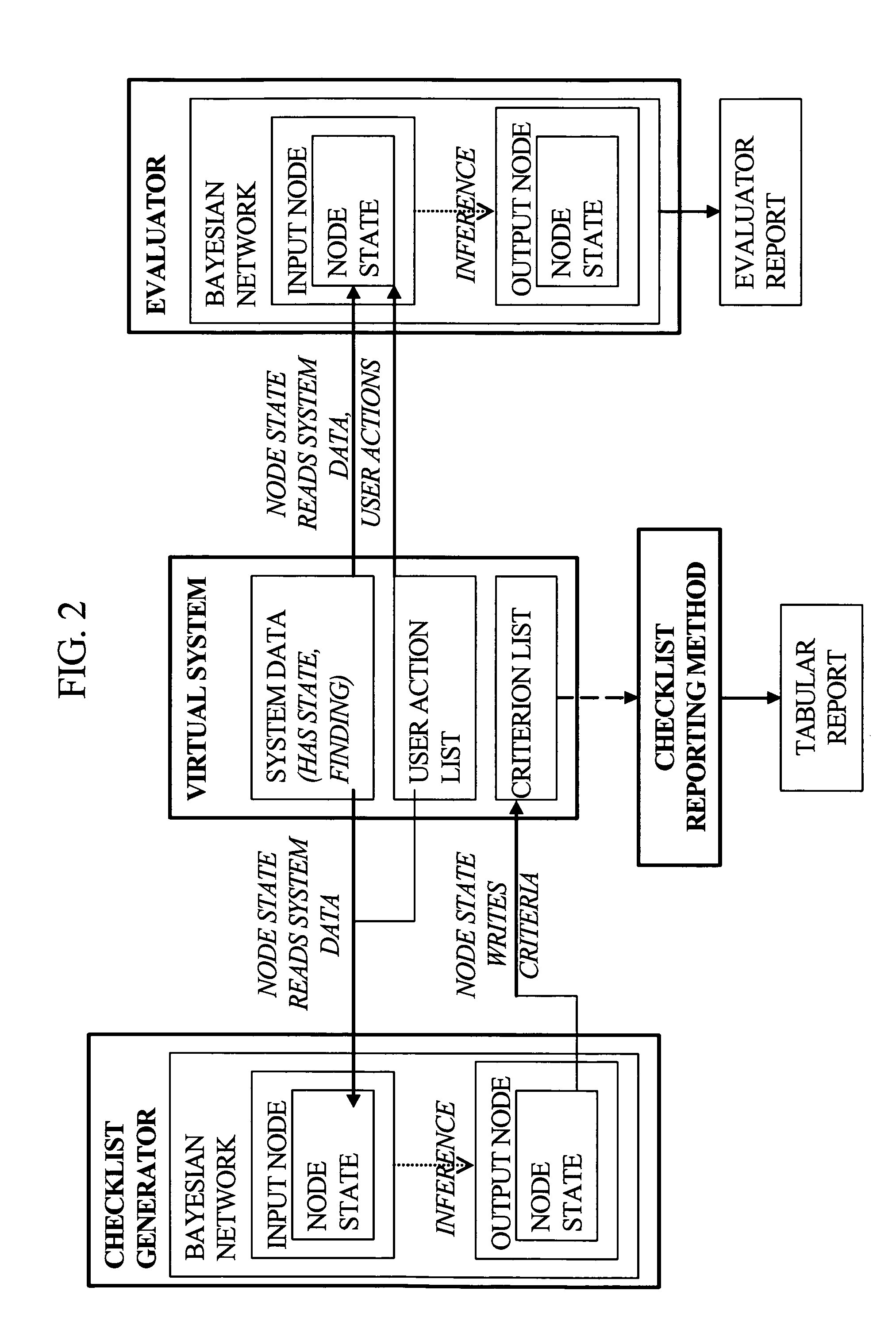
The present invention is generally related to a computer architecture and process for evaluating and reporting on a user's competence in managing a simulation of a complex system modeled in a computer based testing and training system. The simulation may be called a “virtual system.” The method generates evaluation criteria responsive to a user profile, user choices in managing the virtual system, and events that occur during a simulation, in addition to the original state of the system. The method produces summary evaluations responsive to a plurality of characteristics of the simulated system. The implementation may be advantageously employed to evaluate a medical clinician's management of computer-simulated human patients, hereinafter called “virtual patients”. The present invention is also suitable for evaluation of user management of a plurality of complex systems including but not limited to animals, plants, cells, machines, and populations.
Owner:AMERICAN BOARD OF FAMILY MEDICINE
Techniques for delivering medical care by improving decision-making skills of medical personnel
ActiveUS20050170323A1Improve decision makingSimple designEducational modelsRequest - actionSkill sets
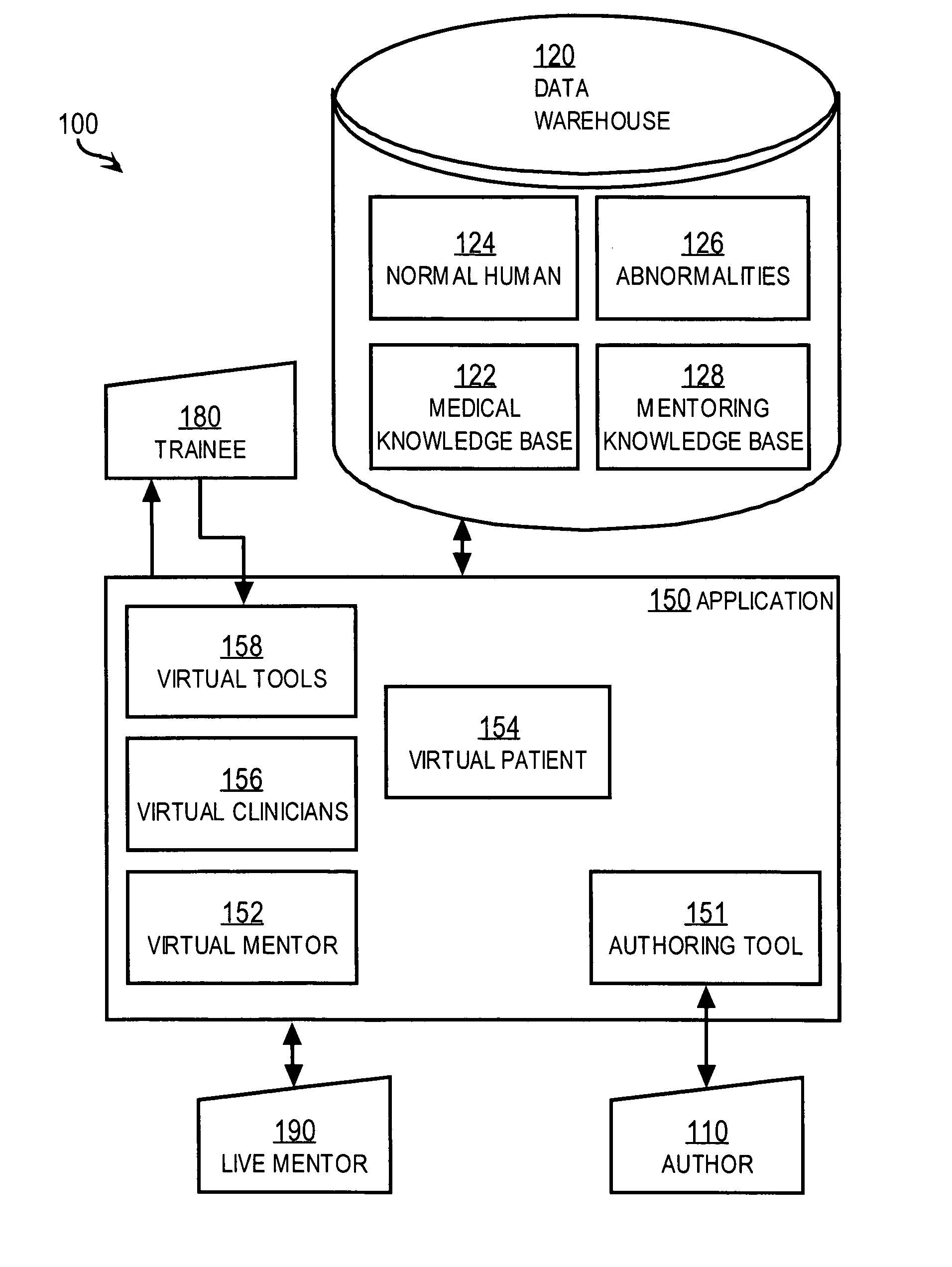
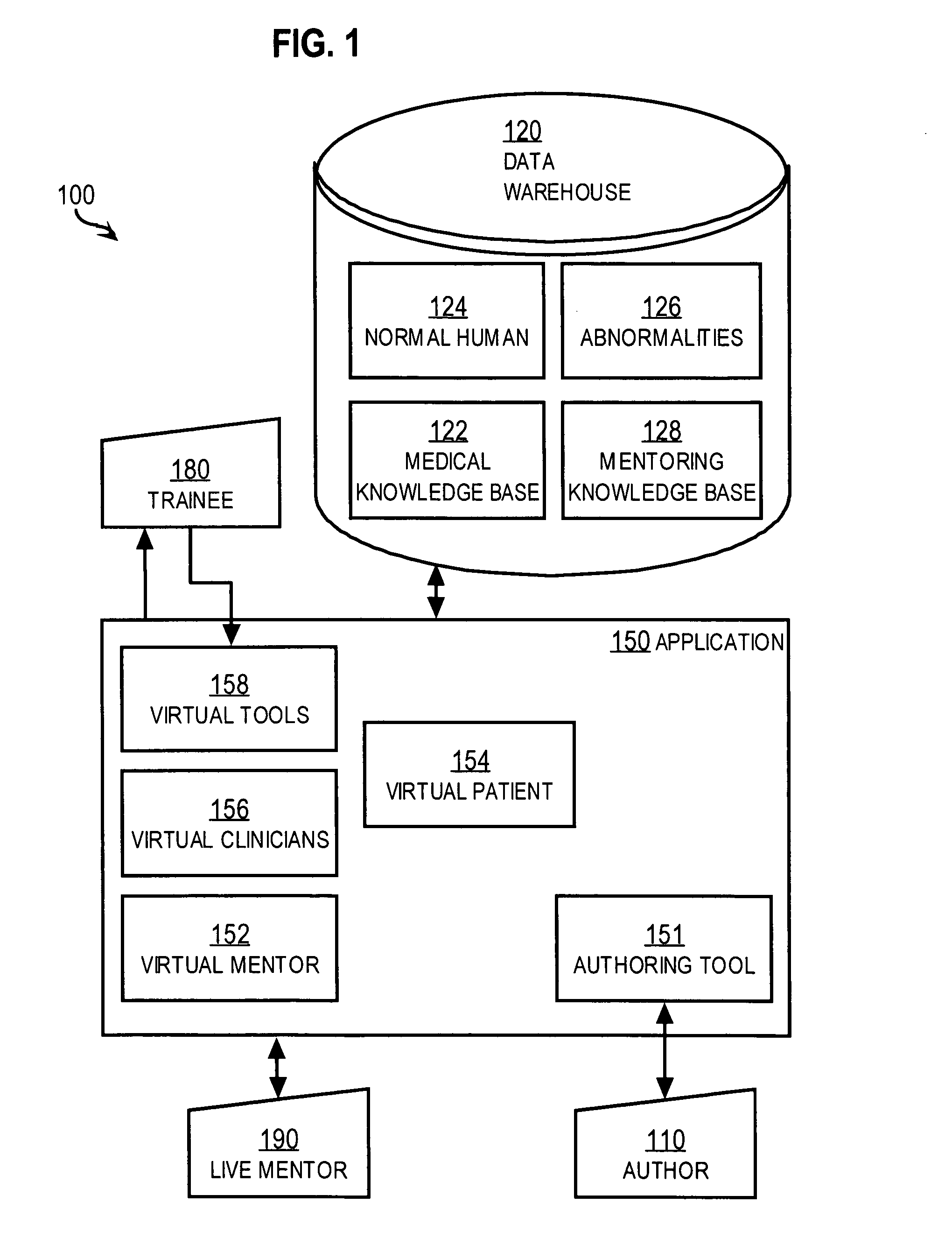
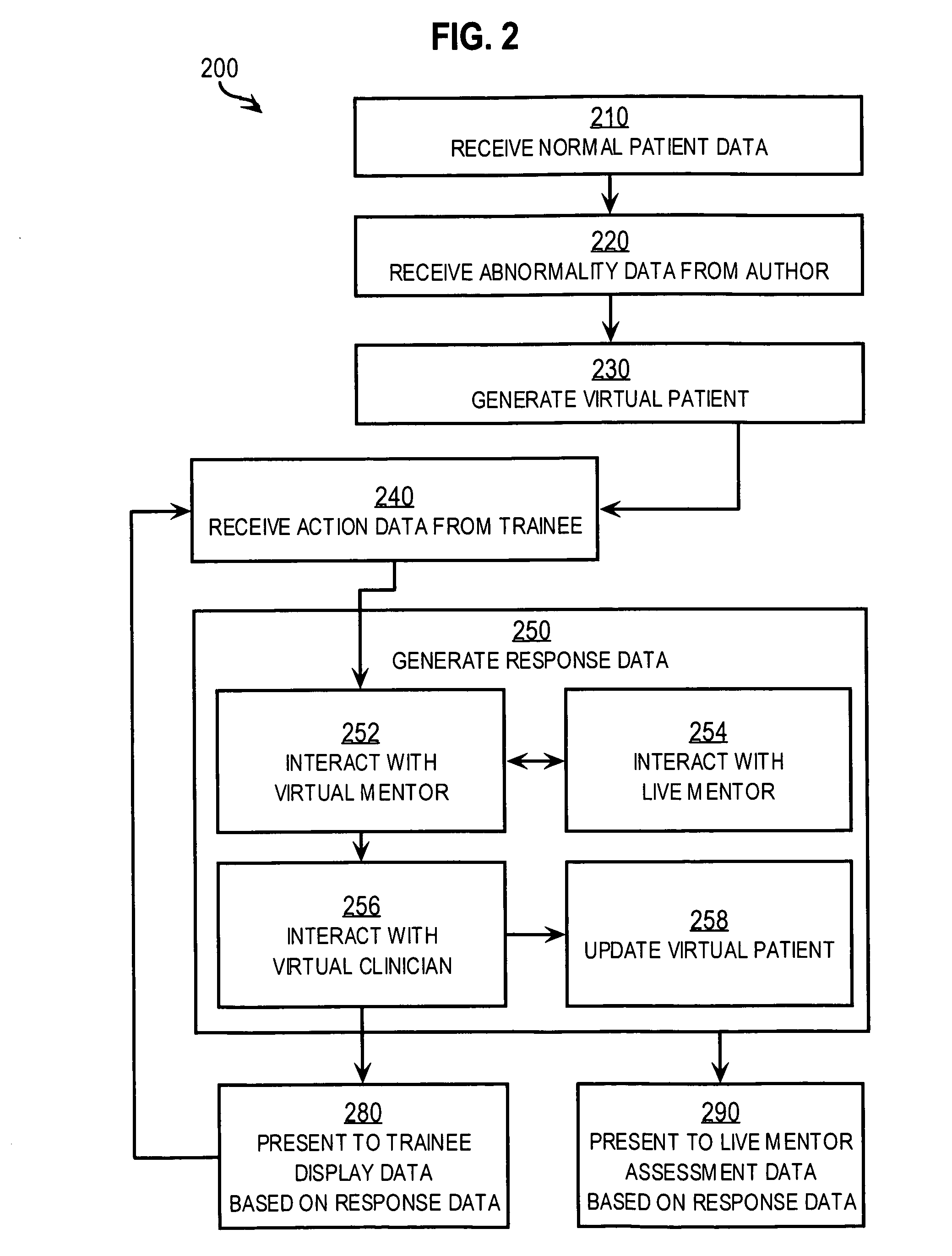
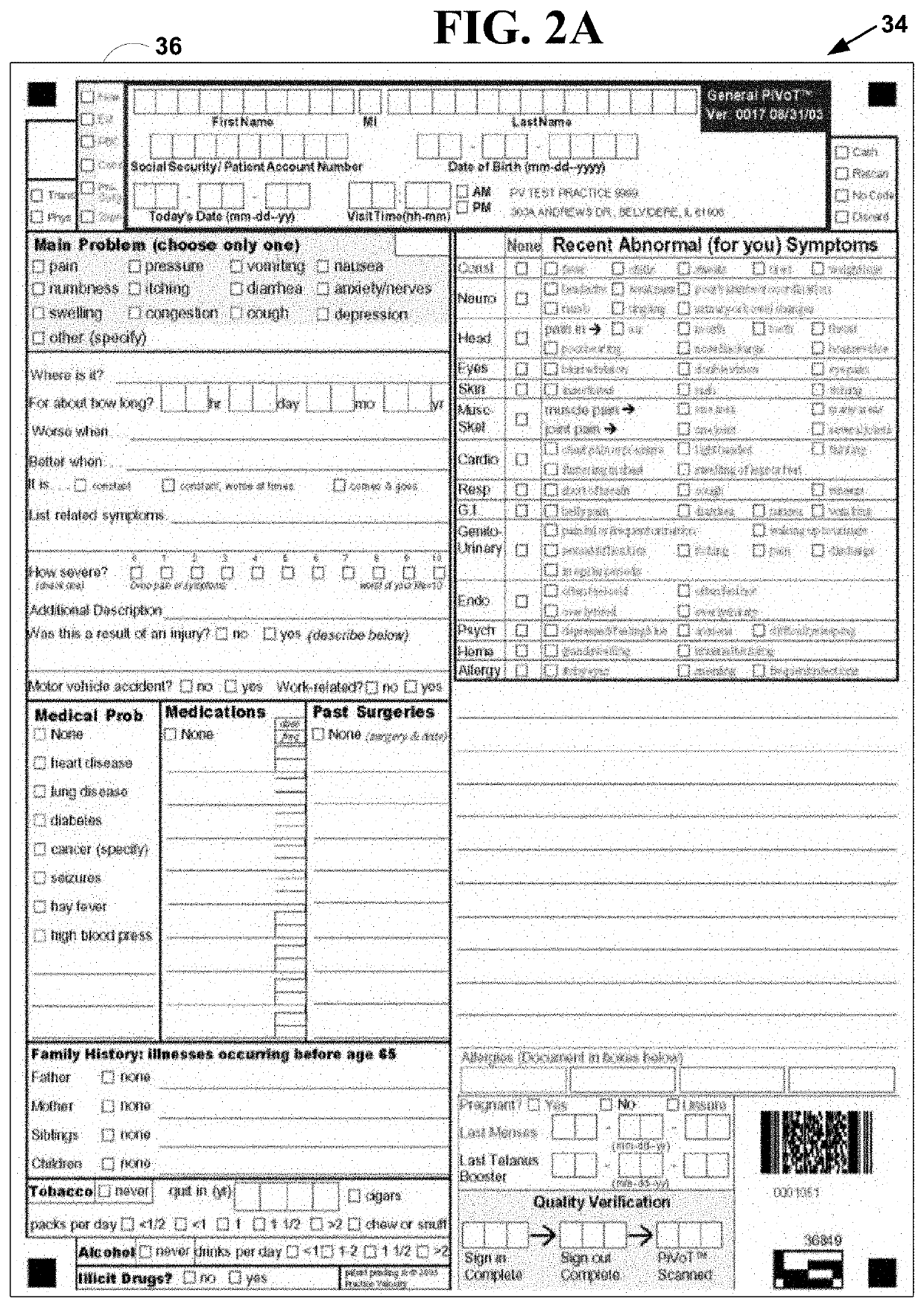
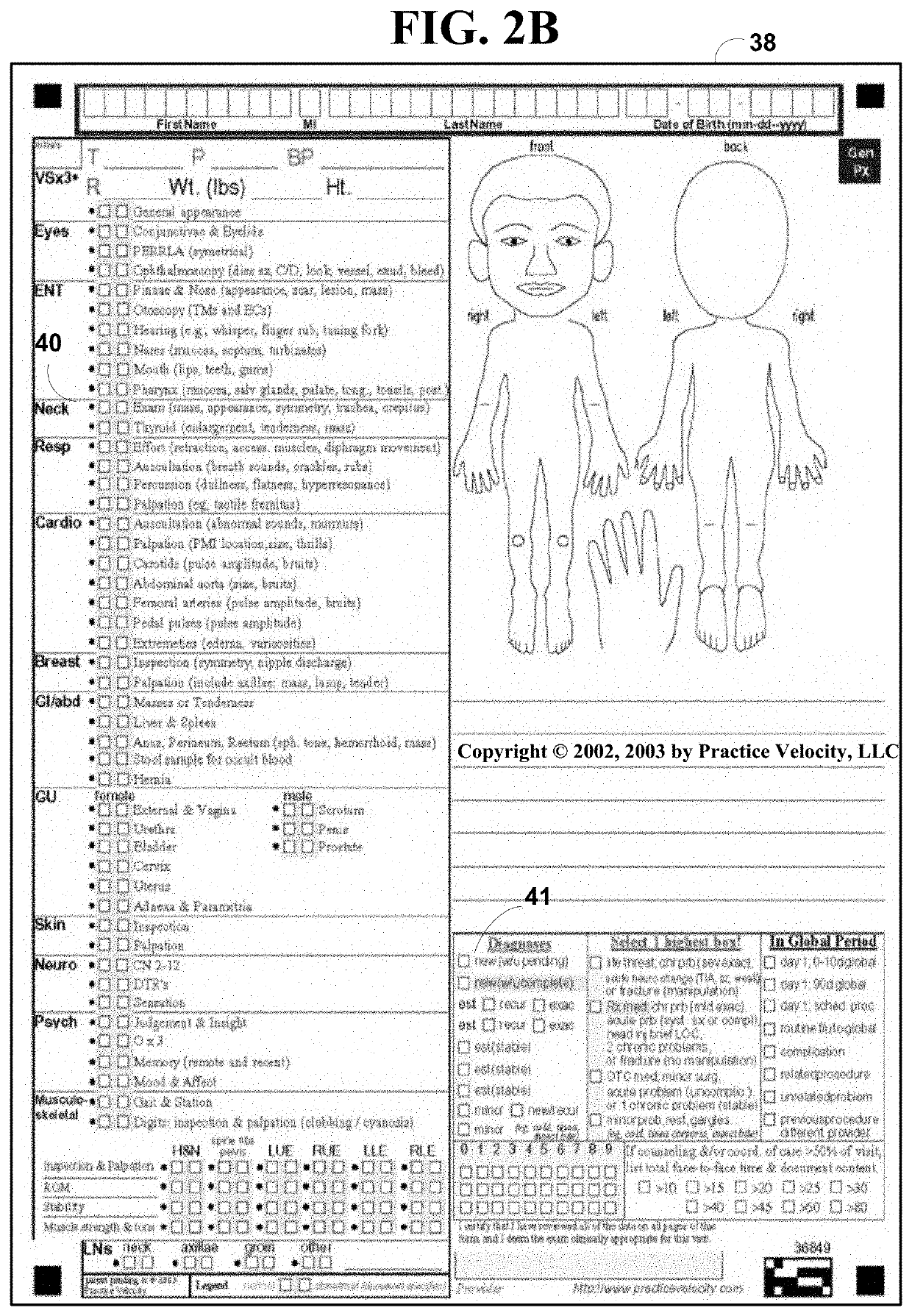
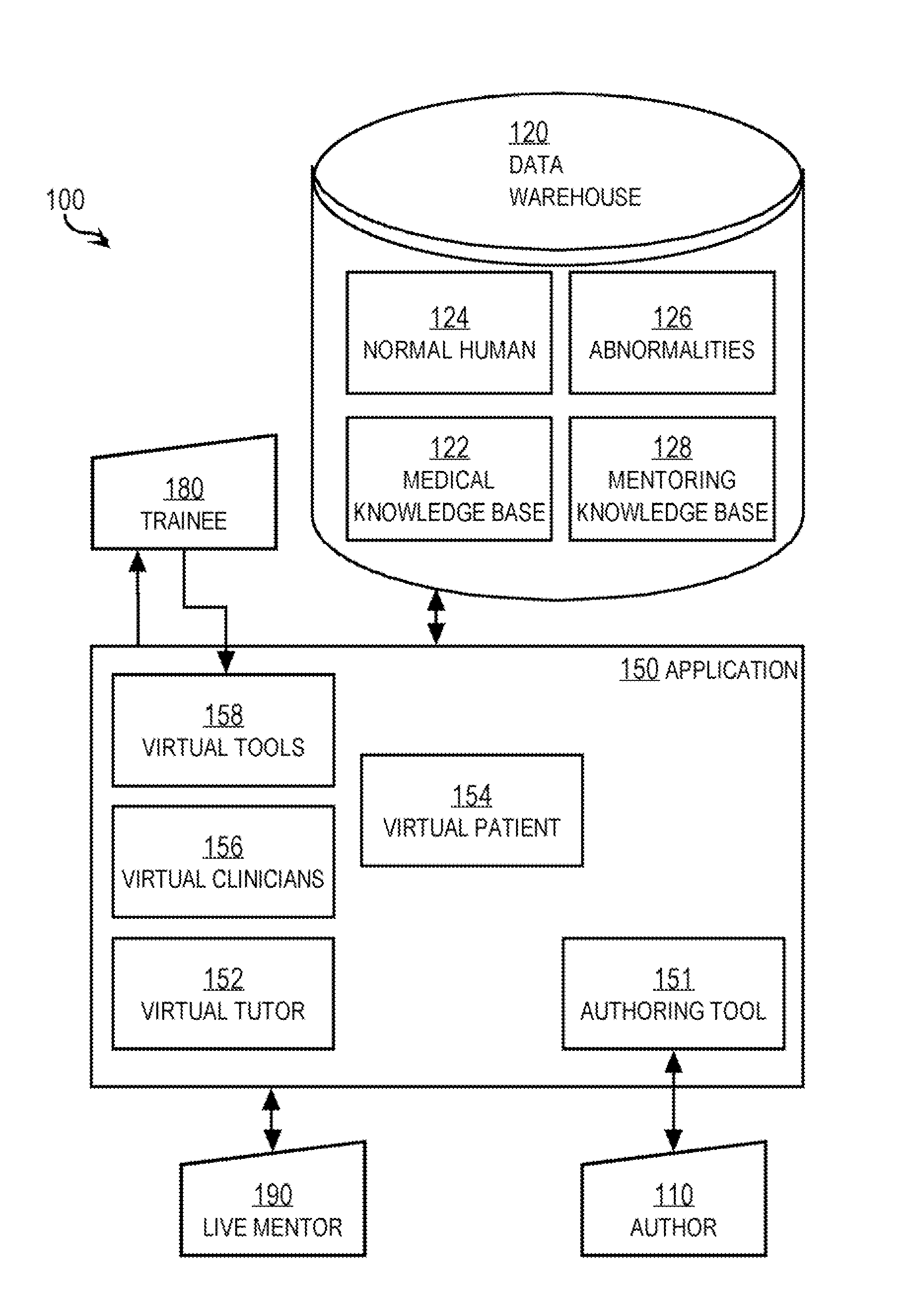
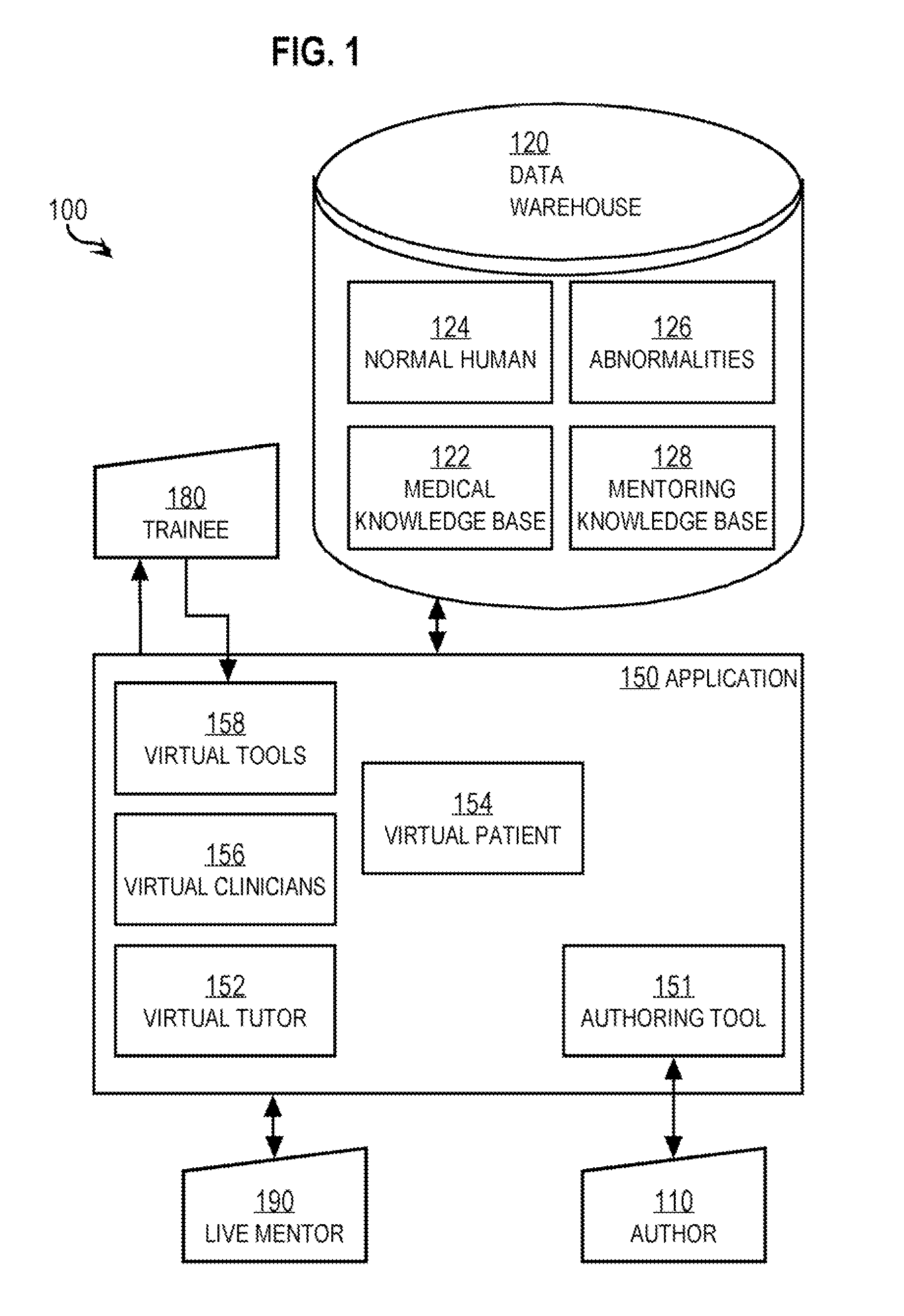
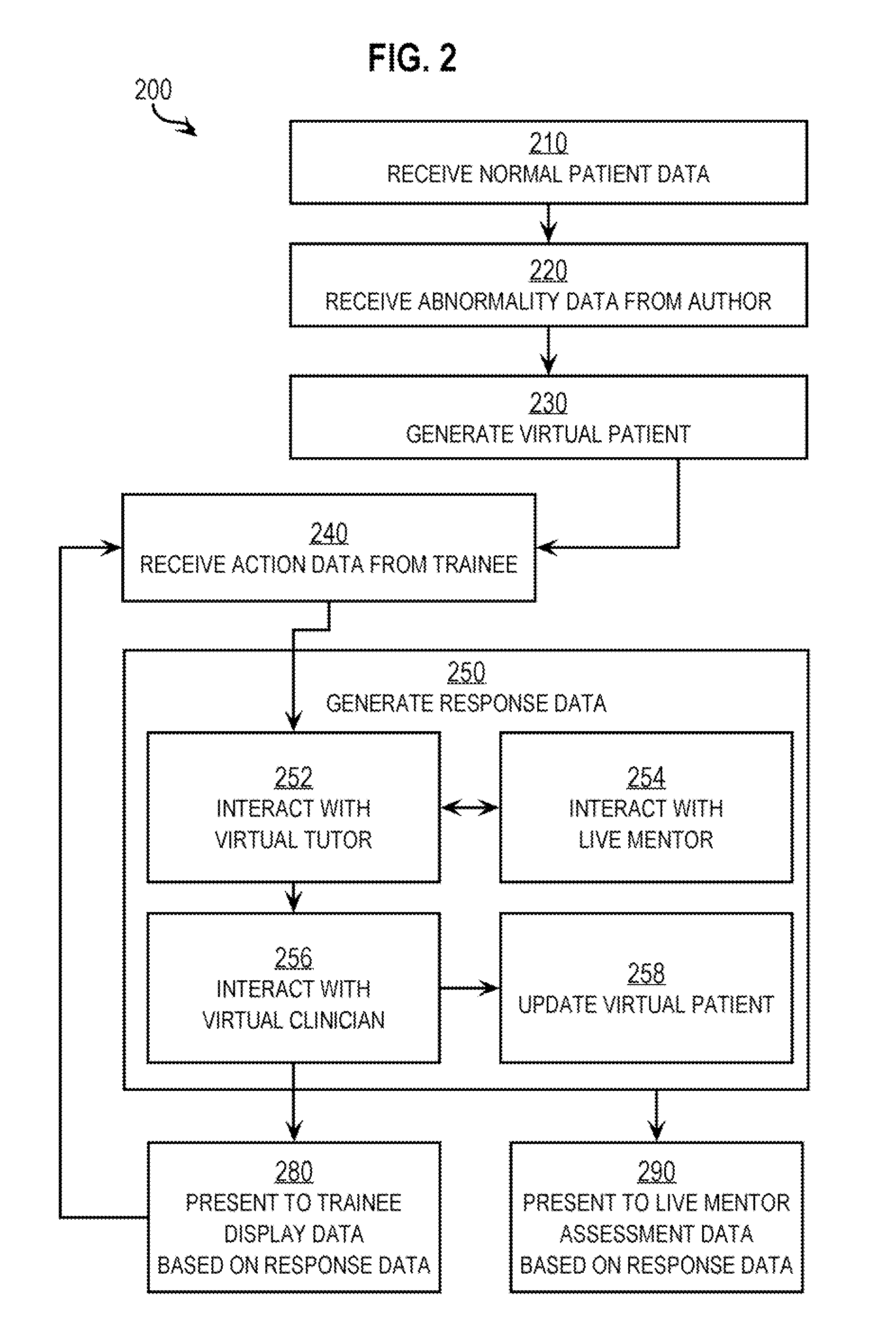
Techniques for delivering medical care by improving decision making skills of medical personnel who deliver the care include receiving normal data that indicates normal conditions in a patient. Abnormality data is received from an author and indicates an abnormal condition in a patient. An instance of a virtual patient is generated based on the normal data and the abnormality data. The instance describes a sufficiently comprehensive physical state of a patient having the abnormal condition to simulate clinical measurements of the patient's condition. Action data is received from a trainee who is different from the author. Action data indicates a requested action relevant to dealing with the instance. Response data is generated based on the action data and the instance. Display data is presented to the trainee based on the response data. The display data indicates information about the instance available as a result of the requested action.
Owner:UNIV OF MARYLAND
Communication System for Remote Patient Visits and Clinical Status Monitoring
InactiveUS20100128104A1Television conference systemsHospital data managementDiagnostic Radiology ModalityHospitalized patients
Disclosed embodiments include a telemedicine communication system designed to make possible “virtual” patient visits by approved visitors such as the spouse, family, and friends of the hospitalized patient having the appropriate digital certificate and visitation / communication permissions. According to one embodiment, the system enables relatives to visit hospitalized patients using audiovisual communication modalities selected according to the severity and health status of the patient. Additionally, the system provides functionality to enable approved relatives to follow the health status of the patient according to their permissions.
Owner:INNOVATEC
Prescription management system
InactiveUS7574370B2Easy to solveQuality improvementFinanceDigital data processing detailsPoint of careCost savings
An electronic prescription creation system for use by professional prescribers at the point of care has a prescription division subsystem permitting creation of a single prescription to be automatically divided into two components for fulfillment of one portion quickly and locally at higher cost and of another portion by remote mail order taking more time but providing a cost saving for a major part of the prescription. The prescription creation system has an ability to access remote source databases for system presentation to the prescriber of relevant, authorized and current drug, drug formulary and patient history information, with dynamic creation of a transient virtual patient record, the information being presented to the prescriber before completion of the prescription, permitting enhancement of the quality of prescribing decisions.
Owner:CYBEAR
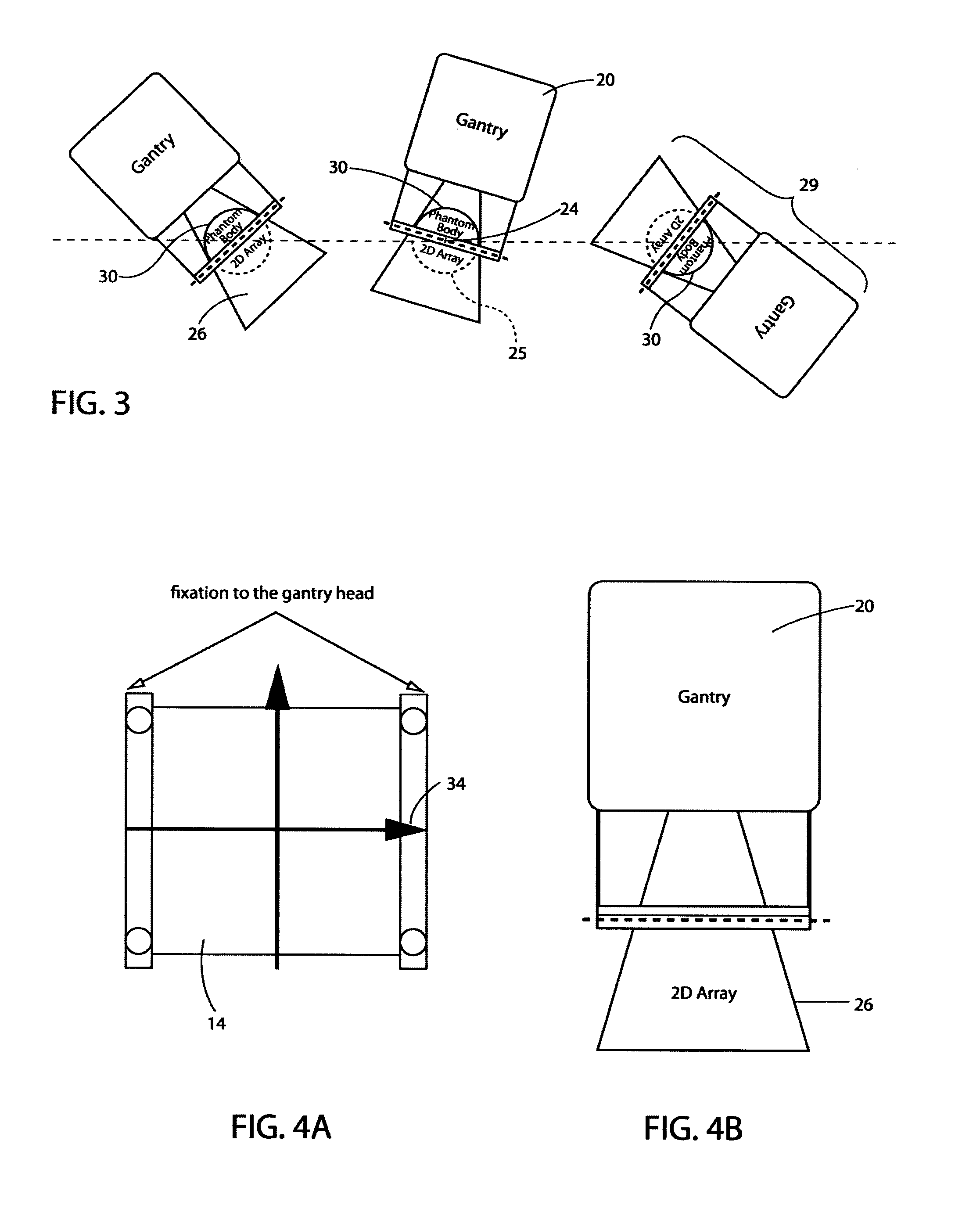
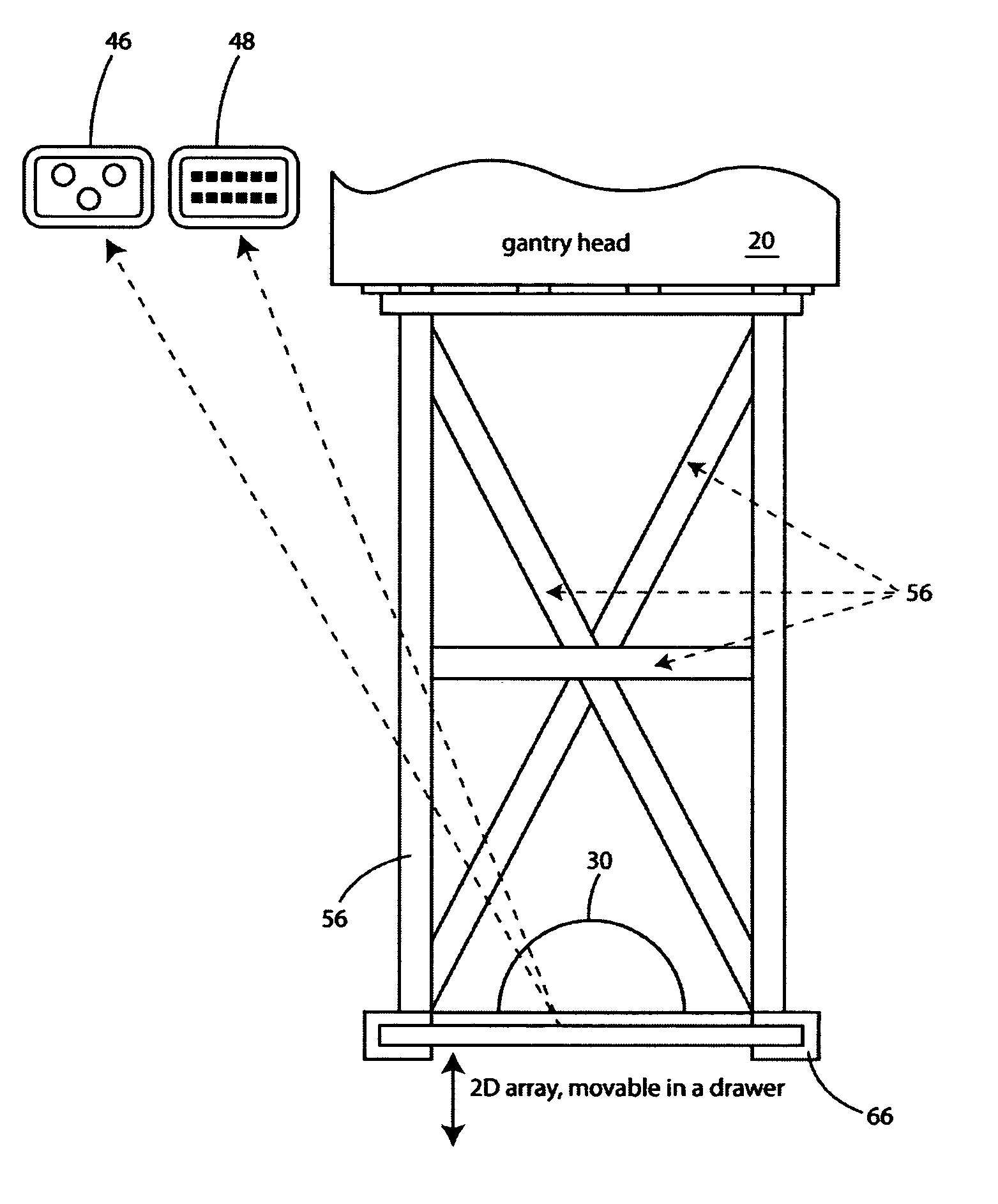
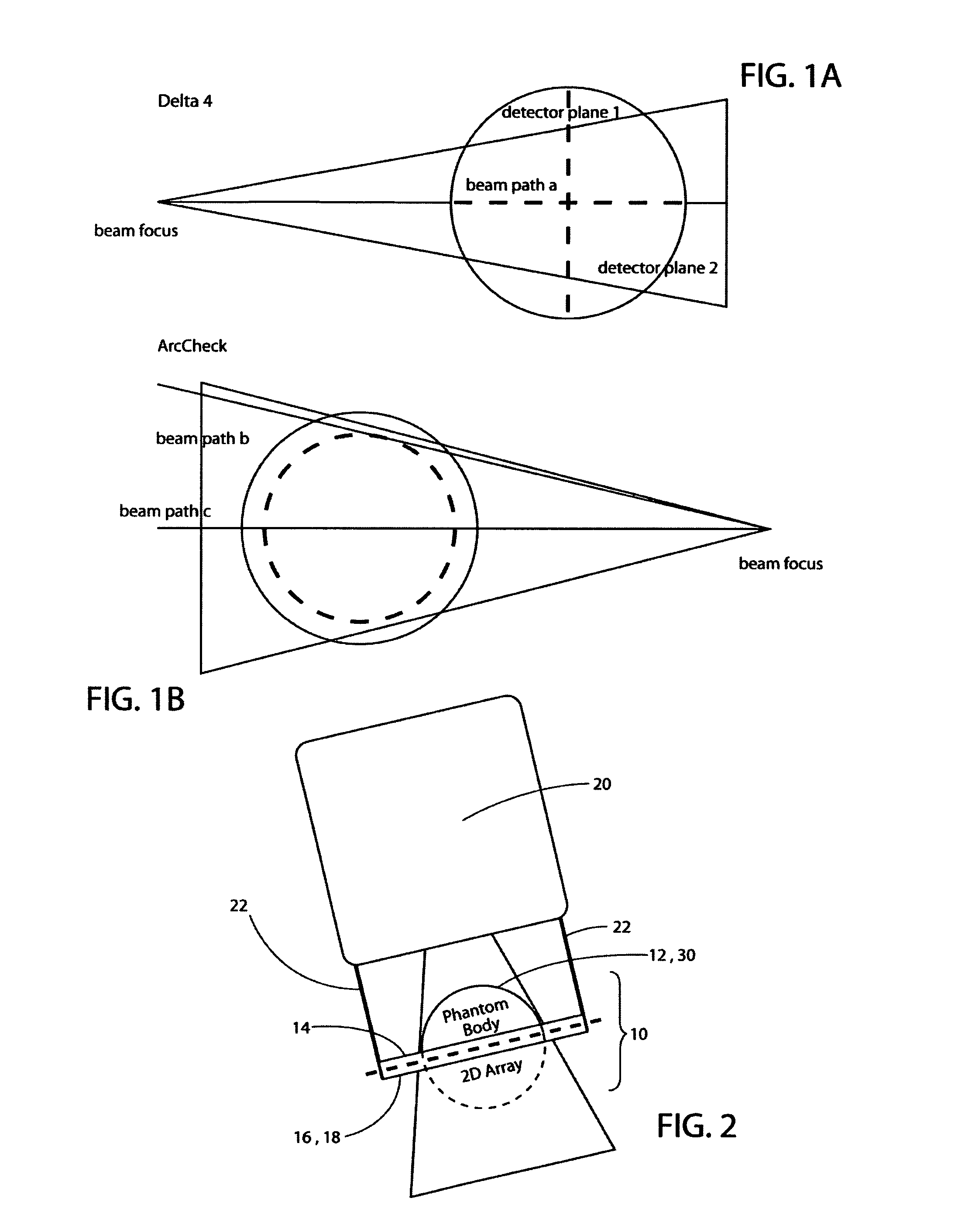
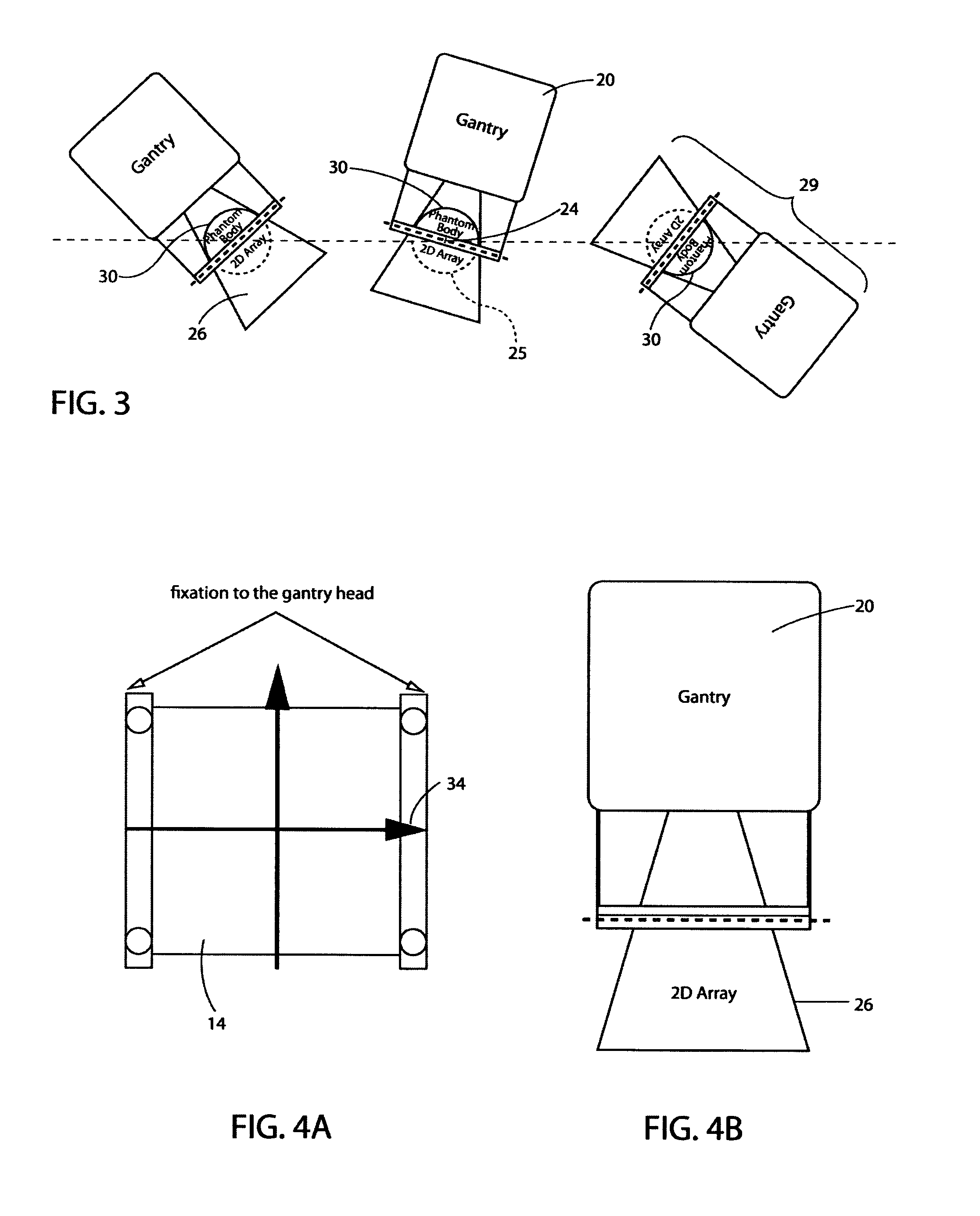
Rotationally symmetrical coherent verification phantom (virtual patient) with a flat detector disposed on a rotary axis integrated in a multi purpose qc-accessory
InactiveUS20120305793A1Without loss of accuracyMaterial analysis by optical meansPhotometry using electric radiation detectorsRotational axisTwo dimensional detector
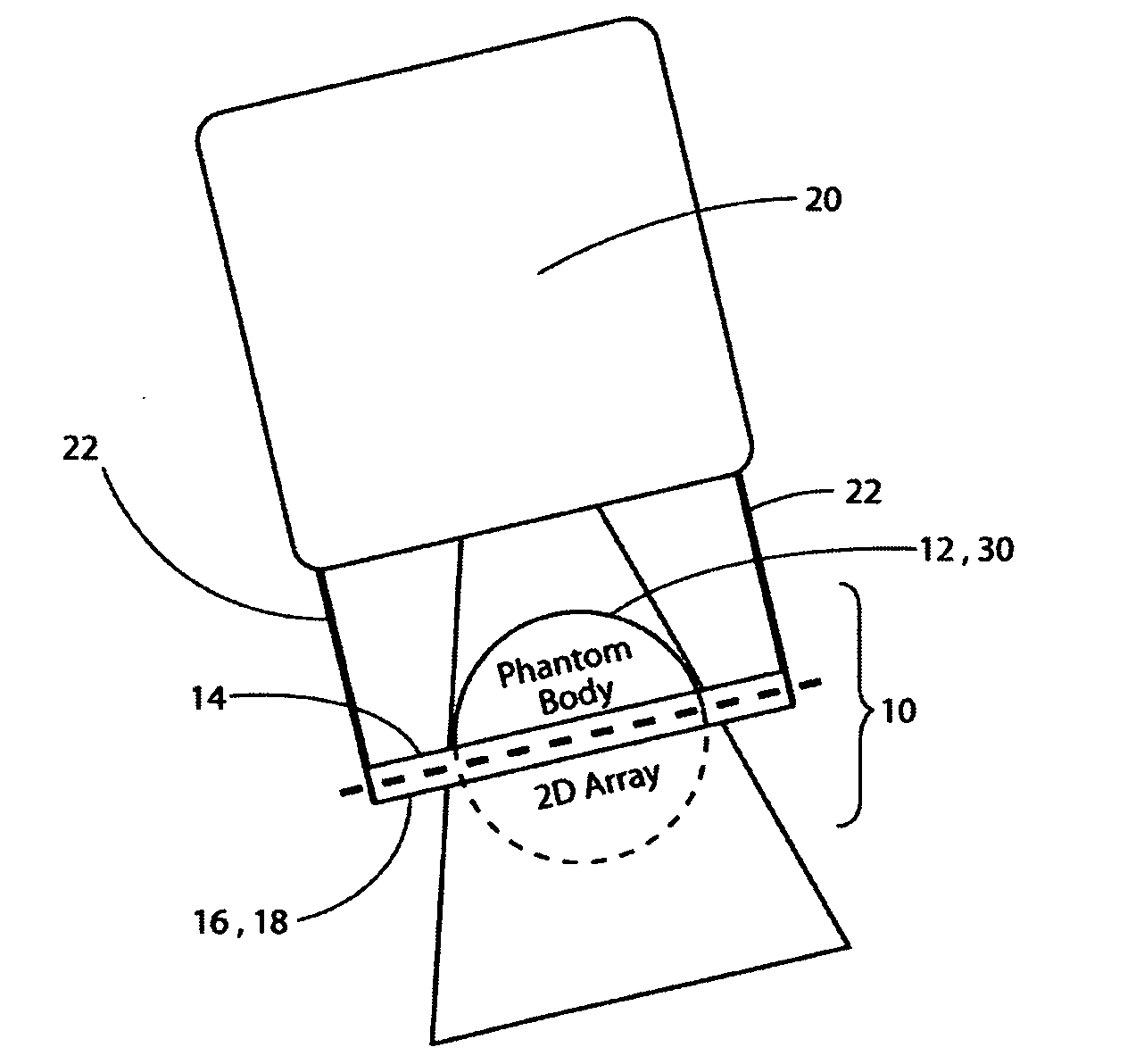
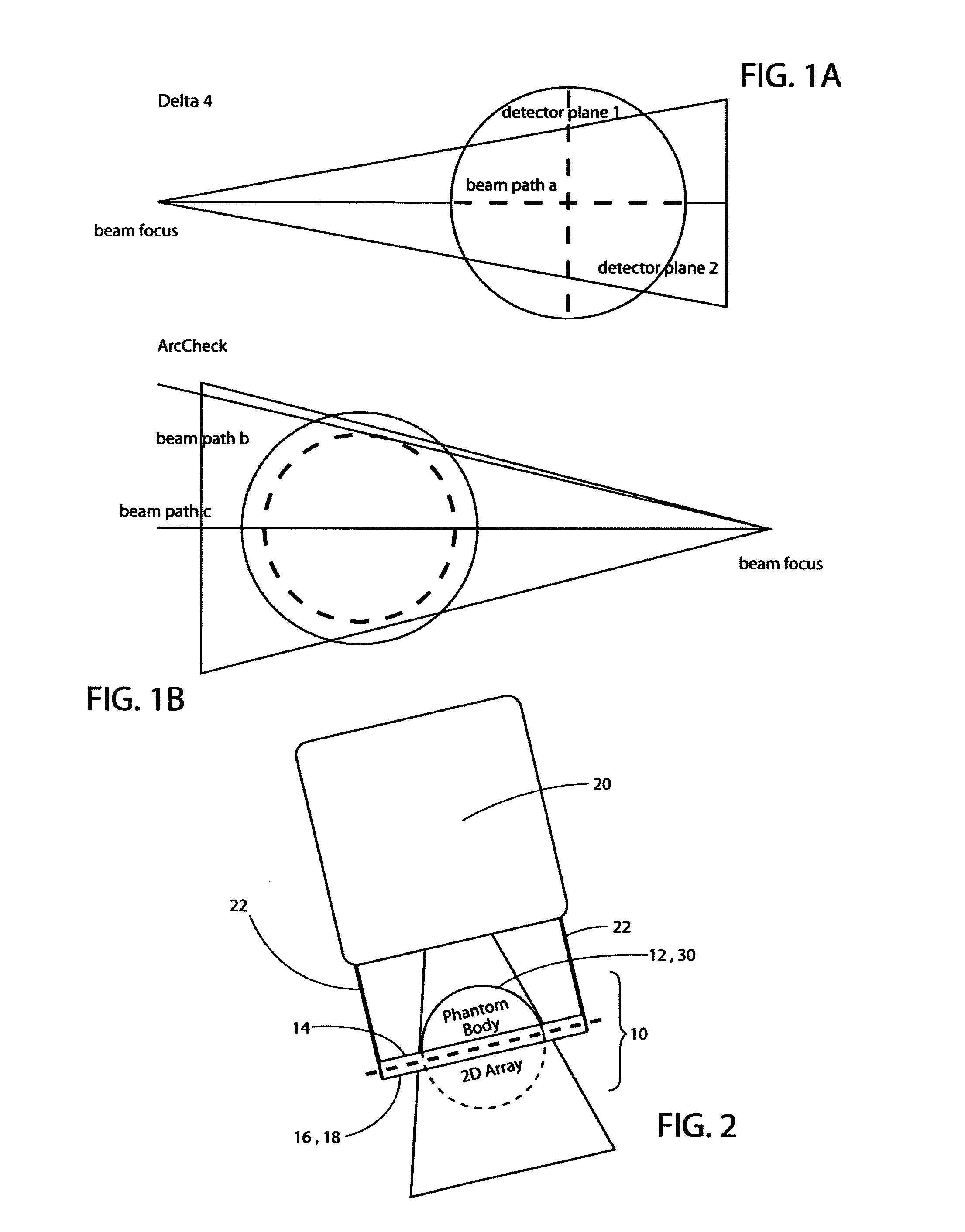
A quality control accessory (QC accessory) is provided which is adapted for use in linear accelerator quality control or in verification of an arbitrary isocentric radiation treatment plan of a patient or radiation sensitive body. The accessory includes an absorber, a detector and an optional orientation device. The absorber is rotationally symmetric, preferably spherical or hemispherical. The detector is adapted to be fixed in a stationary spatial relationship with respect to the absorber. The optional orientation device is adapted to maintain the two dimensional detector (2d detector) and the absorber in a fixed relative spatial relationship with respect to the beam focus of the linear accelerator, when the gantry is rotated, so that the central axis of the beam is essentially orthogonal to the 2d detector and the phantom axis of symmetry is parallel to or aligned with the central axis of the gantry rotation axis.
Owner:MOETTELI JOHN BRENT
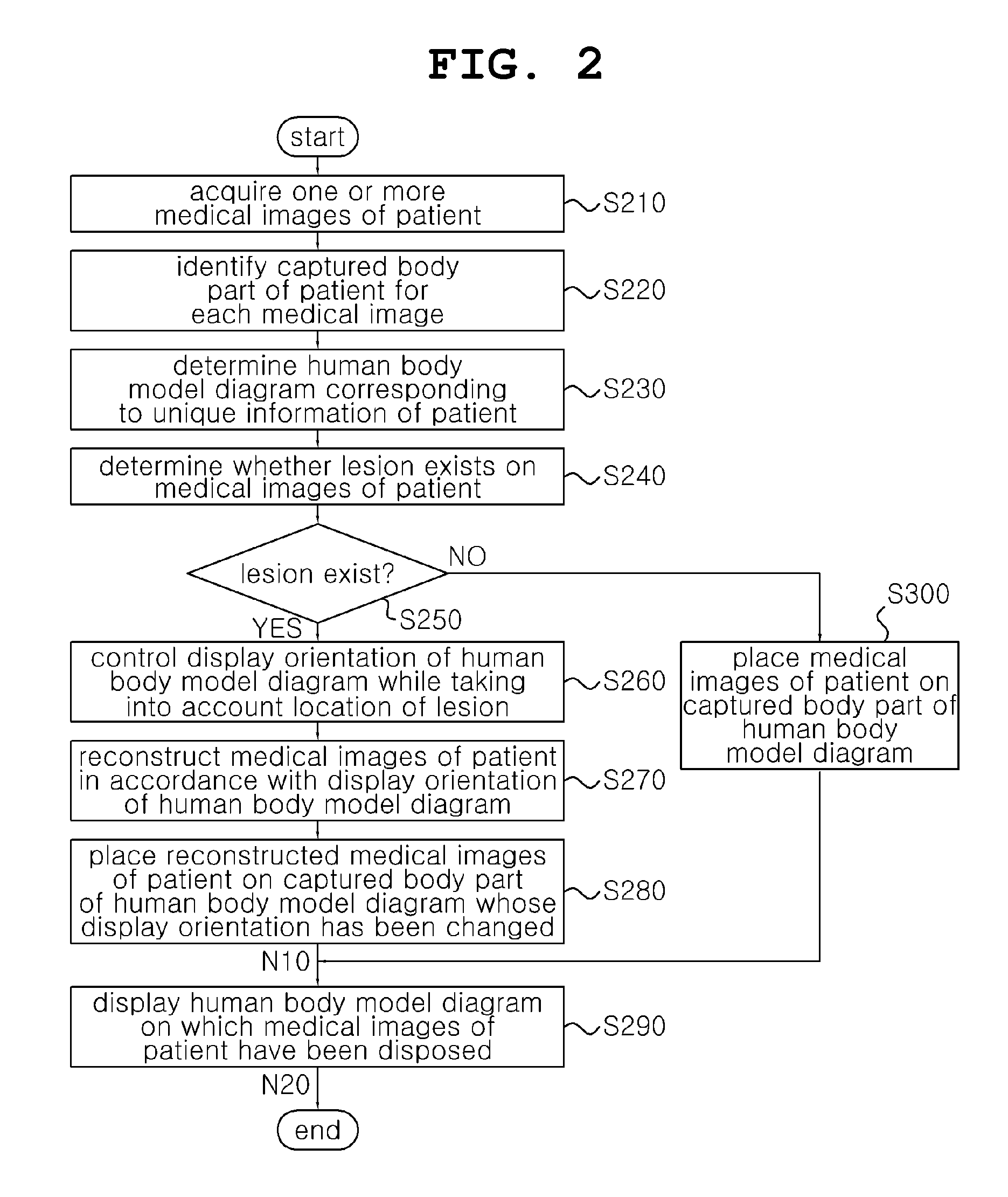
Medical image display method using virtual patient model and apparatus thereof
InactiveUS20140104311A1Clear visionSure easyCathode-ray tube indicatorsComputerised tomographsComputer scienceHuman-body model
Disclosed herein are a method and apparatus for displaying medical images using a virtual patient model. The apparatus includes a processor, the processor includes an image acquisition unit, a captured body part determination unit, a determination unit, and a display (control) unit. The image acquisition unit acquires one or more medical images of a patient. The captured body part determination unit determines the captured body part of each of the acquired one or more medical images. The determination unit determines a human body model diagram corresponding to unique information of the patient among a plurality of predetermined human body model diagrams. The display unit places and displays the one or more medical images on the determined captured body parts of the determined human body model diagram.
Owner:INFINITT HEALTHCARE CO LTD
Simulating patient-specific outcomes
InactiveUS20100324874A9Timing is simpleMedical simulationAnalogue computers for chemical processesEfficacyBiomarker (petroleum)
The invention encompasses systems, methods, and apparatus for predicting and monitoring an individual's response to a therapeutic regimen. The invention includes multiple virtual patients, an associating subsystem operable to associate the subject with one or more of the virtual patients, and a simulation engine operable to apply one or more experimental protocols to the one or more virtual patients identified with the subject to generate a set of outputs. The set of outputs can represent therapeutic efficacy, identify biomarkers for monitoring therapeutic efficacy, or merely report the status of the biological system as it represents a particular individual
Owner:ENTELOS HLDG
Method and system for automated medical records processing with telemedicine
ActiveUS20200342966A1Reduce complexityReduce riskBilling/invoicingOffice automationMedical recordMedical diagnosis
A method and system for automated medical records processing with telemedicine is presented. The method and system includes plural electronic medical templates specifically designed such that they reduce the complexity and risk associated with collecting virtual patient encounter information, creating a medical diagnosis, tracking the patient through the medical processes during a telemedicine session and generate the appropriate number and type medical codes for a specific type of medical practice when processed. The medical codes and other types of processed virtual patient encounter information are displayed in real-time on electronic medical records and invoices immediately after a virtual patient encounter from a telemedicine visit.
Owner:PRACTICE VELOCITY
Techniques for implementing virtual persons in a system to train medical personnel
ActiveUS8317518B2Improve decision makingReduce deliveryMedical simulationData processing applicationsRequest - actionNormal conditions
Techniques for delivering medical care include receiving normal data that indicates normal conditions in a patient. Abnormality data is received and indicates an abnormal condition, if any, in a patient. An instance of a virtual patient is generated based on the normal data and the abnormality data. The instance includes a physiological component that describes a sufficiently comprehensive physical state of a patient having the abnormal condition to simulate clinical measurements of the patient's condition. The instance also includes a cognitive component that describes a patient's awareness of symptoms, history of behavior and ability to convey information in response to queries. Action data is received from a trainee. Response data is generated based on the action data and the instance. Display data is presented based on the response data, and indicates information about the instance available as a result of the requested action.
Owner:UNIV OF MARYLAND BALTIMORE COUNTY +1
System of preoperative planning and provision of patient-specific surgical aids
A method of preoperative planning and provision of patient-specific surgical aids includes creating a virtual model of a native patient tissue. A virtual device is placed into a predetermined device orientation relative to the virtual model of the native patient tissue. At least one predetermined landmark orientation is specified for placement of at least one virtual landmark relative to the native patient tissue. A virtual patient-specific template containing the predetermined landmark orientation and having a landmark guiding feature is generated. At least one virtual patient-specific placement guide configured to interact simultaneously with at least one previously placed virtual landmark and the virtual device when the virtual device is in the predetermined device orientation is generated. A physical patient-specific template is created as a tangible representation of the virtual patient-specific template. A physical patient-specific placement guide is created as a tangible representation of the virtual patient-specific placement guide.
Owner:THE CLEVELAND CLINIC FOUND
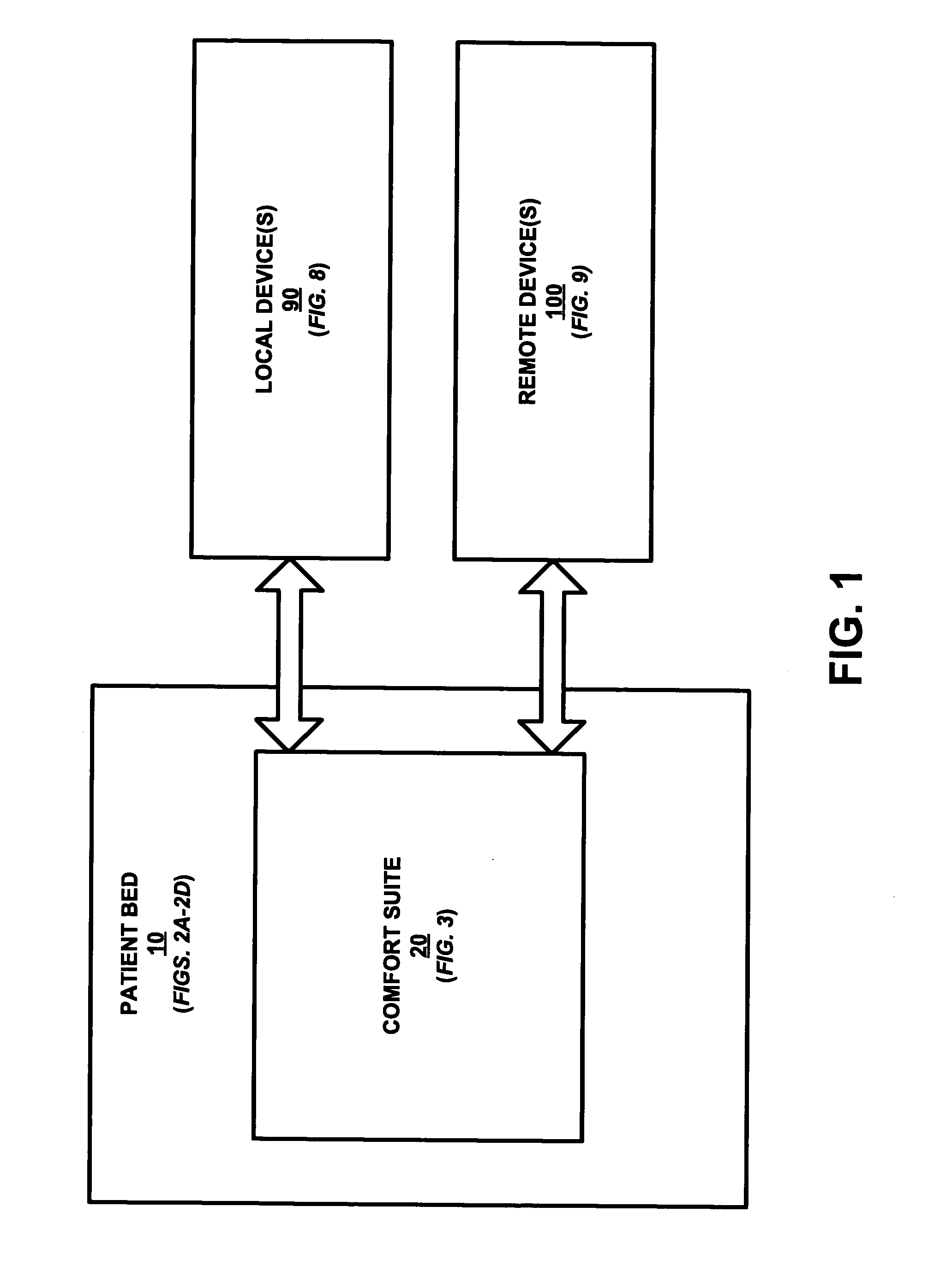
Comfort suite for an intelligent patient bed
InactiveUS20060235283A1Maximum degree of comfortGreat degreePhysical therapies and activitiesData processing applicationsEnvironmental SettingElectricity
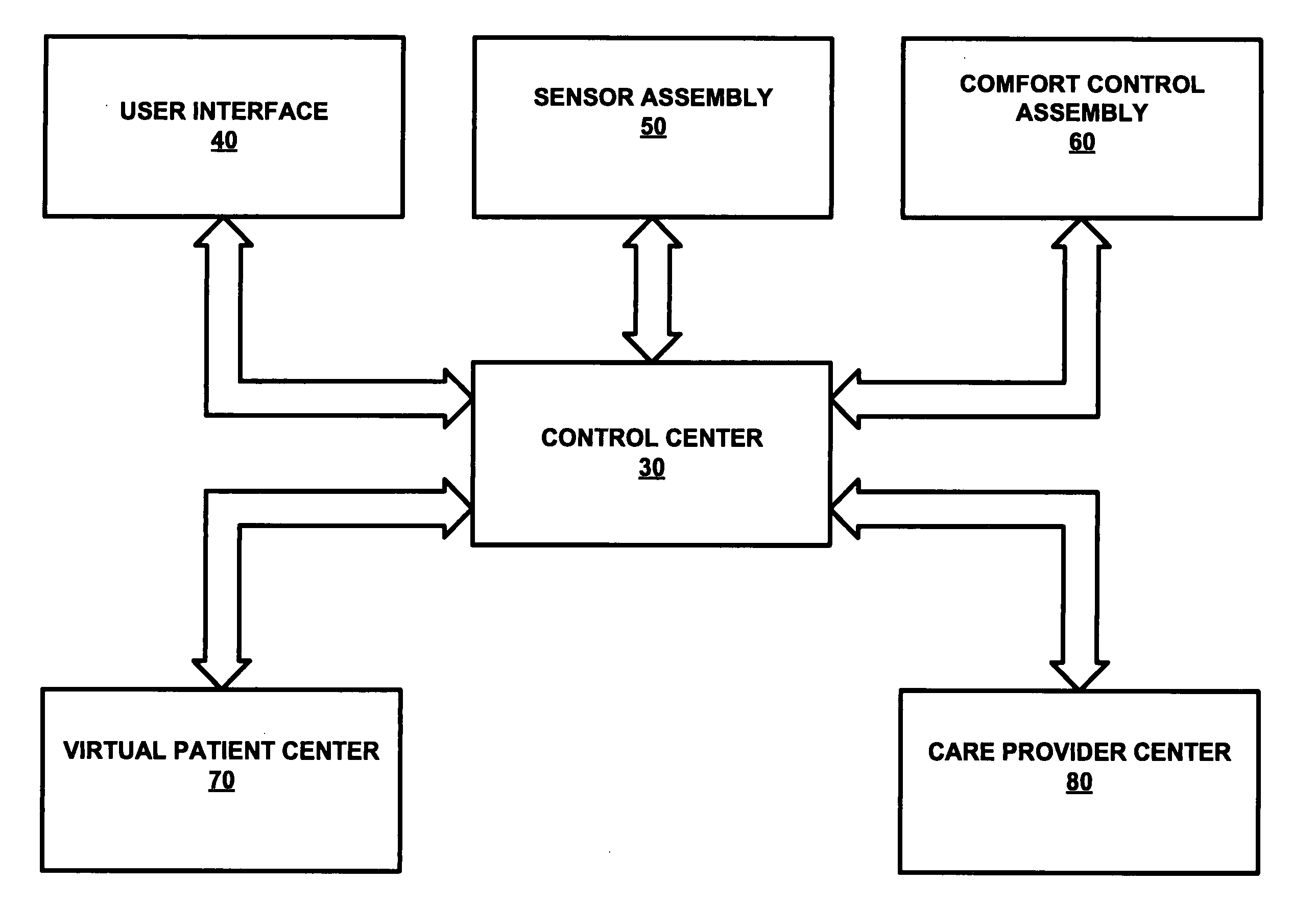
An intelligent patient bed includes a patient bed equipped with a comfort suite employing a control center in electrical communication with a user interface, a sensor assembly, a comfort control assembly and a virtual patient center for providing comfort to a patient laying on the patient bed as well as an industrious environmental setting for the patient. The control center is also in electrical communication with a care provider center for providing an optimal degree of patient monitoring.
Owner:TREVI WIRELESS
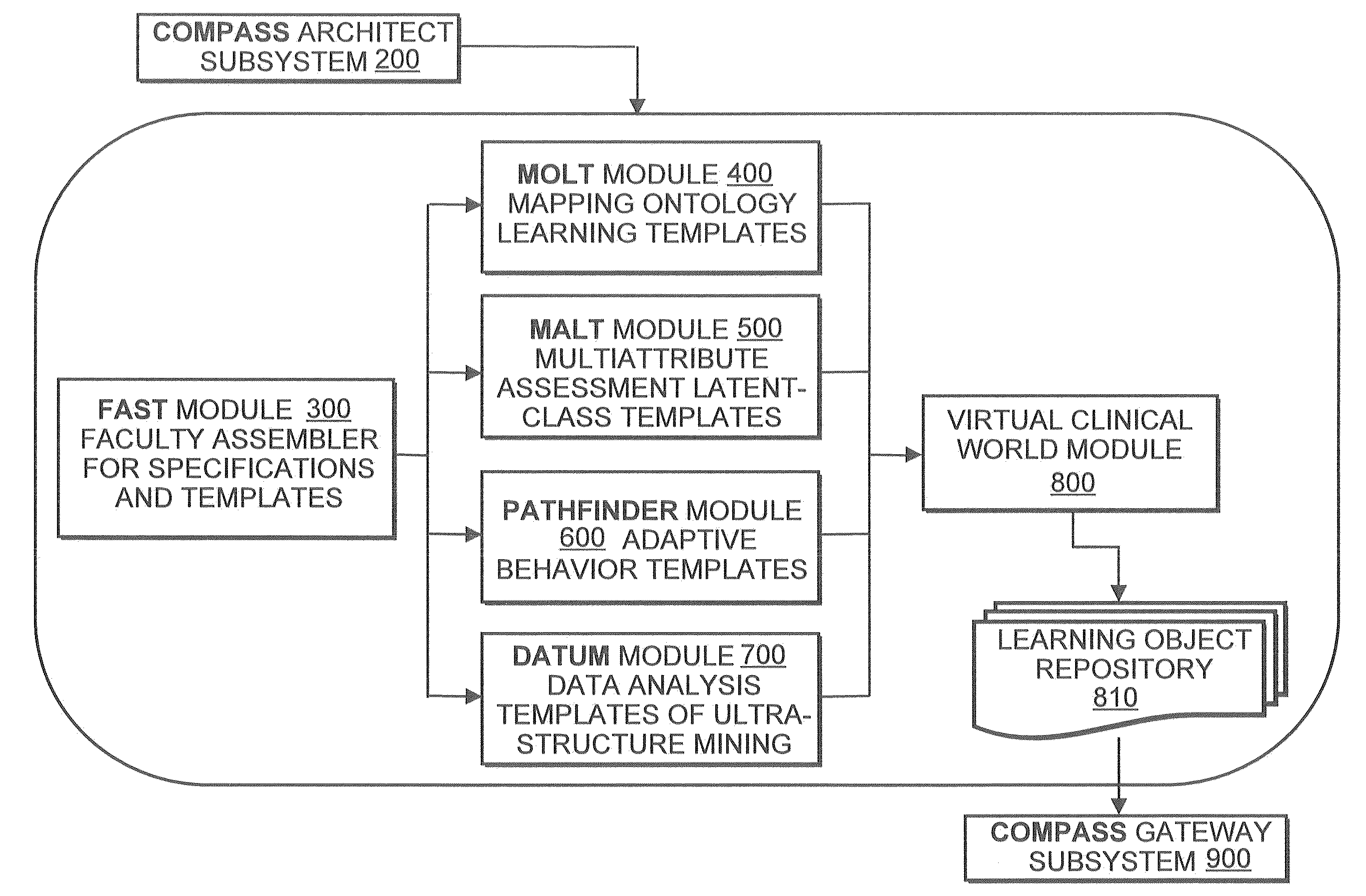
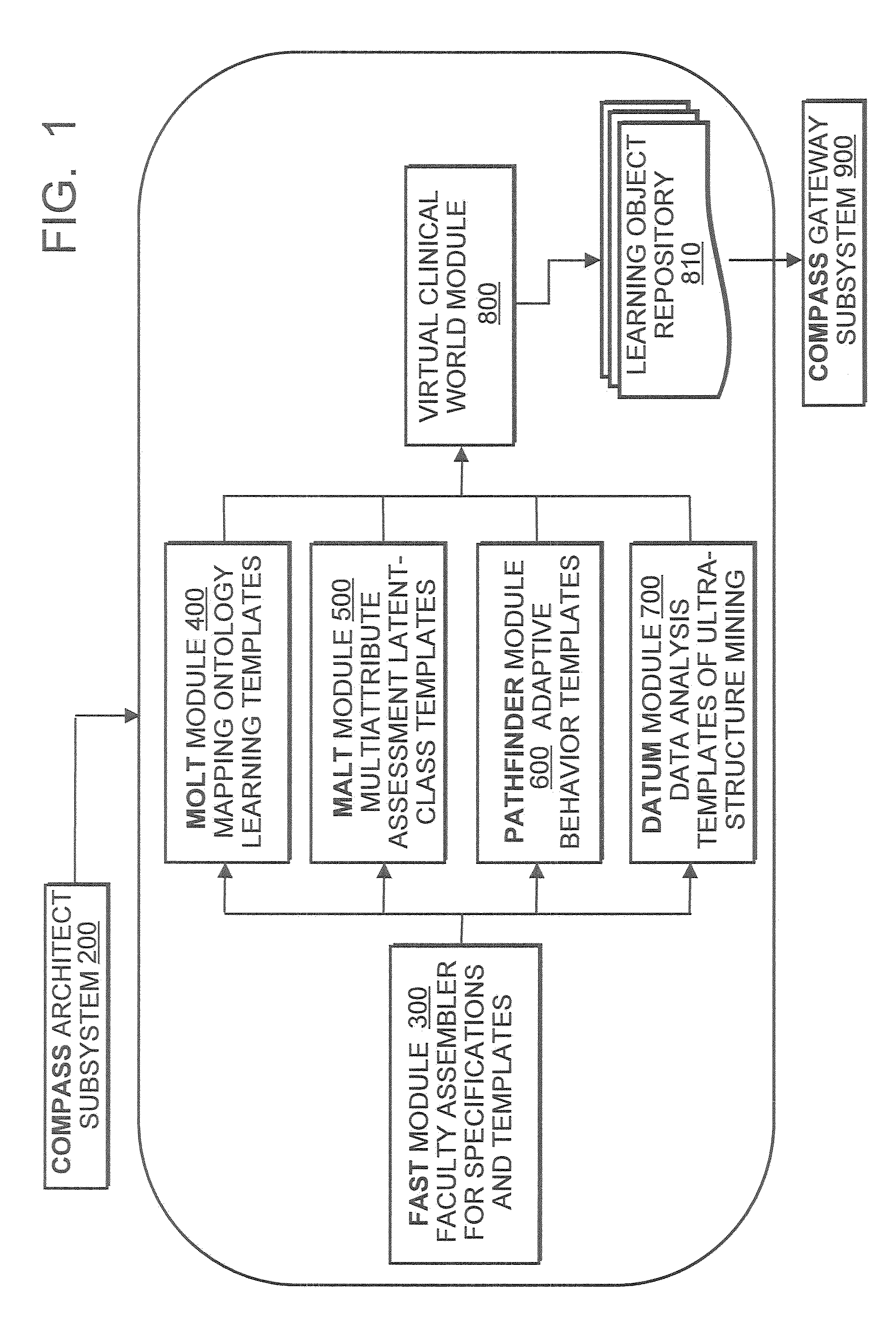
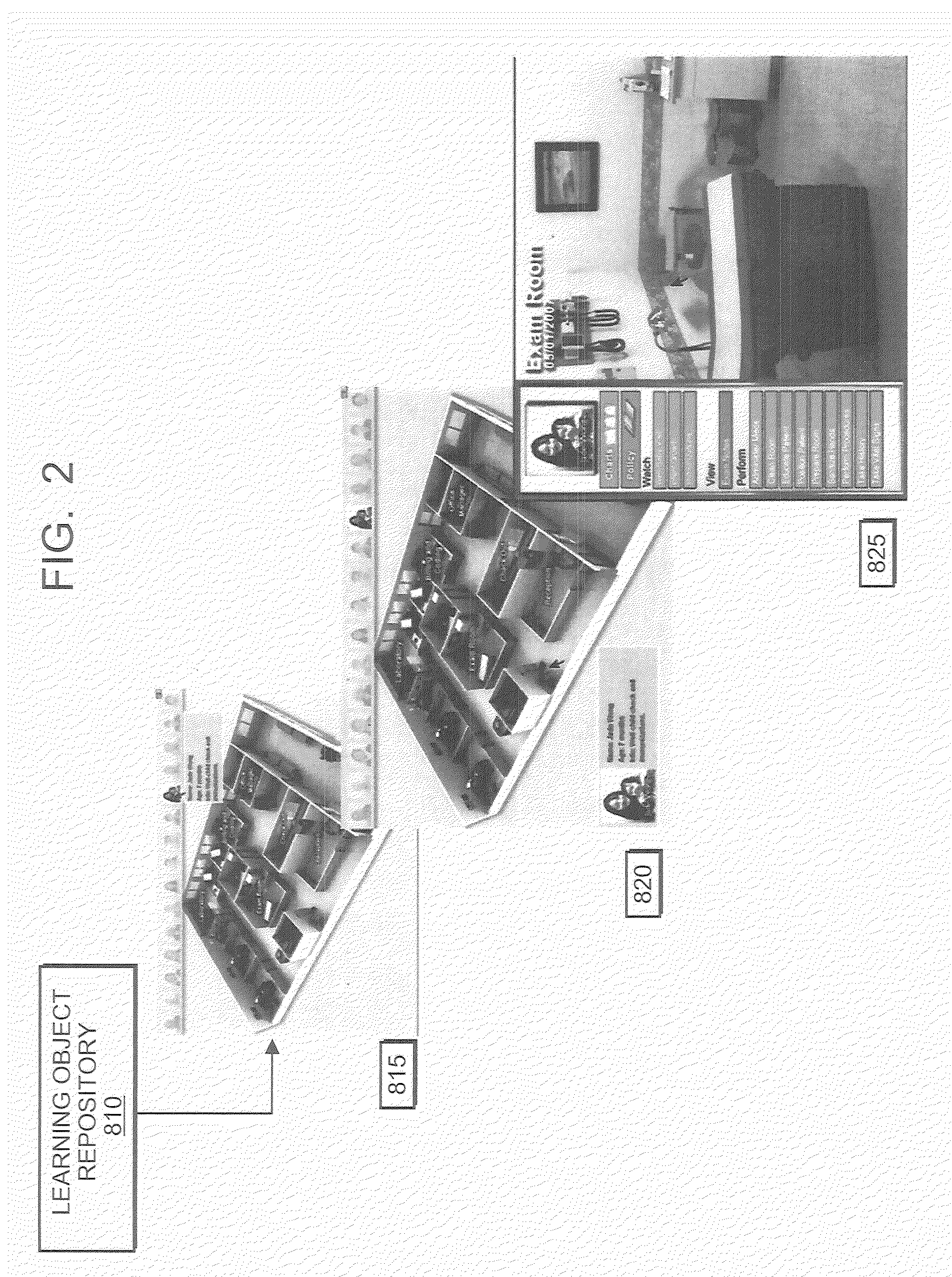
Method for competency assessment of healthcare students and practitioners
A method to assess the competency of a healthcare practitioner, wherein the method provides a learning object repository comprising a plurality of previously-created virtual objects, creates a first template and a second template by the second module, wherein the first template comprises one or more previously-defined learning objectives, and wherein the second template comprises one or more previously-defined competency assessments related to the one or more selected learning objectives. The method provides the first template and the second template to the learning object repository. The method displays on a visual display device a virtual clinical world comprising a plurality of virtual objects retrieved from the learning object repository. Further according to the method, a practitioner selects a virtual patient from the virtual clinical world, selects a series of interactions with the patient, and selects patient data. The method tracks the selected patient interactions, and the selected patient data.
Owner:TASHIRO JAY SHIRO +2
Dynamic Differential Diagnosis Training and Evaluation System and Method for Patient Condition Determination
A dynamic differential diagnosis training and evaluation system incorporates a beginner student learning mode, a beginner student test mode, an advanced student learning mode, and an advanced student test mode for training, nurturing, and evaluating dynamic differential diagnosis (dynamic DDx) reasoning skills for patient condition determination. In a preferred embodiment of the invention, the dynamic differential diagnosis training and evaluation system incorporates one or more computerized user interfaces for displaying, choosing, and interacting with a simulated virtual patient, hypotheses selections for the patient condition determination, simulated physical exam selections, simulated medical test selections, simulated medical test results, a computerized expert's feedback and answers, and an iterative differential diagnosis (DDx) list modification and refinement process that simulates real-life dynamic differential diagnosis (dynamic DDx). Furthermore, the dynamic differential diagnosis training and evaluation system can also incorporate healthcare education contents generated from a healthcare content authoring platform.
Owner:KAPLAN
Rotationally symmetrical coherent verification phantom (virtual patient) with a flat detector disposed on a rotary axis integrated in a multi purpose QC-accessory
InactiveUS8921766B2Television system detailsMaterial analysis by optical meansTwo dimensional detectorAxis of symmetry
A quality control accessory (QC accessory) is provided which is adapted for use in linear accelerator quality control or in verification of an arbitrary isocentric radiation treatment plan of a patient or radiation sensitive body. The accessory includes an absorber, a detector and an optional orientation device. The absorber is rotationally symmetric, preferably spherical or hemispherical. The detector is adapted to be fixed in a stationary spatial relationship with respect to the absorber. The optional orientation device is adapted to maintain the two dimensional detector (2d detector) and the absorber in a fixed relative spatial relationship with respect to the beam focus of the linear accelerator, when the gantry is rotated, so that the central axis of the beam is essentially orthogonal to the 2d detector and the phantom axis of symmetry is parallel to or aligned with the central axis of the gantry rotation axis.
Owner:MOETTELI JOHN BRENT
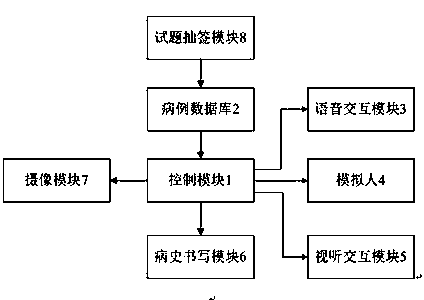
Standardized patient simulation system based on artificial intelligence
InactiveCN108053886AMedical simulationInput/output for user-computer interactionTest questionPatient simulation
Provided is a standardized patient simulation system based on artificial intelligence. The system includes a control module and a case history database, the case history database is connected with thecontrol module, stores various types of case history data and information, and sends the case history data and information corresponding to test questions selected by participants to the control module; the system also includes a voice interaction module, the voice interaction module is connected with the control module, and based on the case history data and information, the voice interaction module conducts interactive question answering with the participants and simulates scenes of diagnosis through interrogation; the system also includes a simulation person, the simulation person is connected with the control module, and simulates signs of patients on case histories according to the case history data and information, and the participants conduct physical examinations on the stimulation person; the system also comprises an audio-visual interaction module, the audio-visual interaction module is connected with the control module, and according to the case history data and information, the audio-visual interaction module simulates movements and voices of various signs of the patients on the case histories. According to the system, the questions of the participants can be recognized and understood, and feedbacks are made according to data and information recorded in the case history database; the voices of various signs and the movements of virtual patients can be simulated; anexisting teaching mode which uses a real person as a standardized patient can be replaced.
Owner:SHANGHAI GEMMA MEDICAL SCI & TECH CO LTD
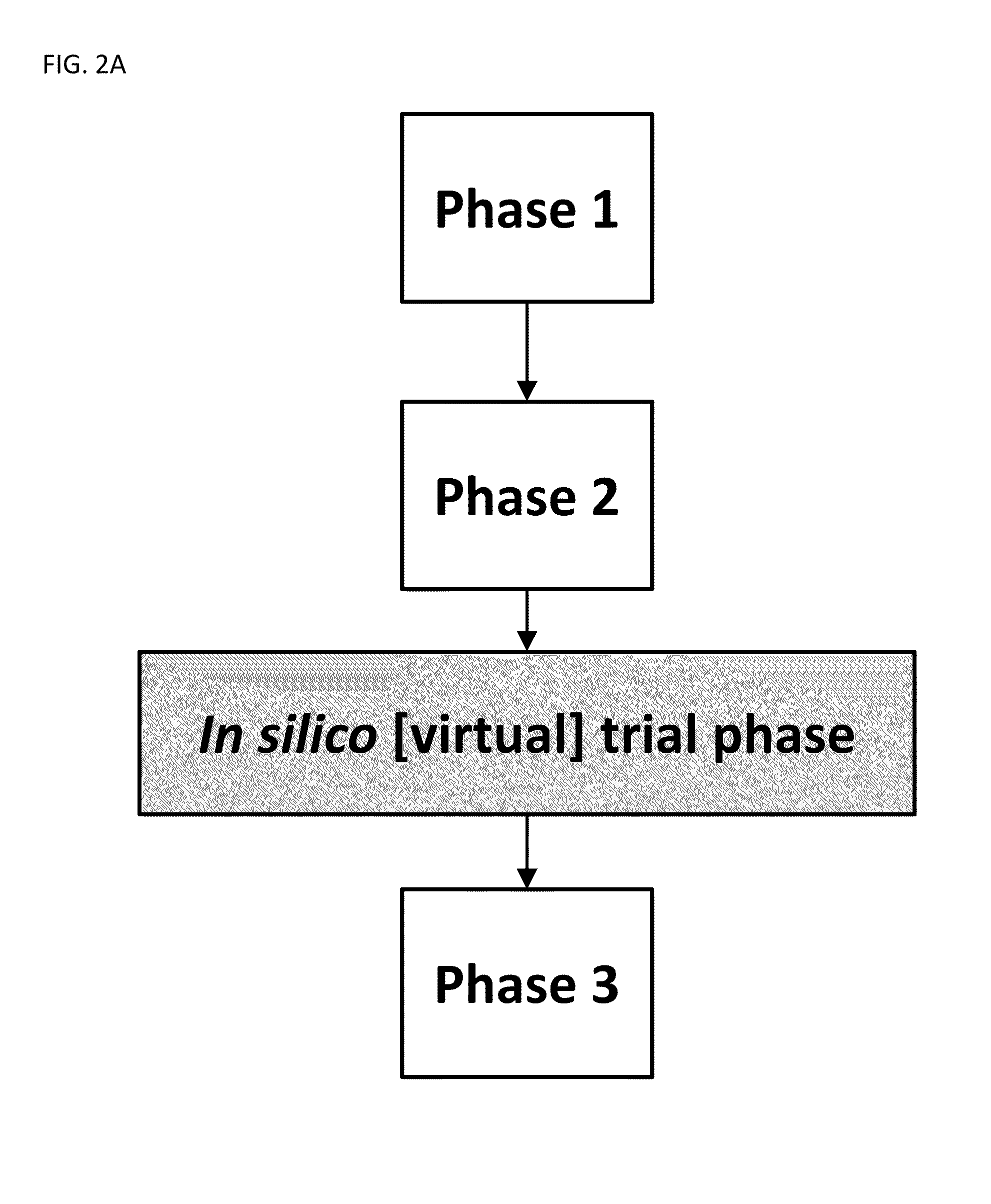
System And Method Of Conducting In Silico Clinical Trials
ActiveUS20160180053A1Medical simulationData processing applicationsIn silico clinical trialsClinical trial
Described herein are computer systems and methods for generating, in silico, one or more virtual patients. The one or more virtual patients can be used, for example, to conduct a virtual clinical trial, such as to determine an efficacy of a therapy or medical device. The one or more virtual patients mathematically represent a physiological system in an actual patient for a health condition. Also, the one or more virtual patients can be used, for example, to determine an adverse effect from a therapy or any other deviation from a therapy, or compliance of a patient suffering from a health condition on a therapeutic protocol.
Owner:FRESENIUS MEDICAL CARE HLDG INC
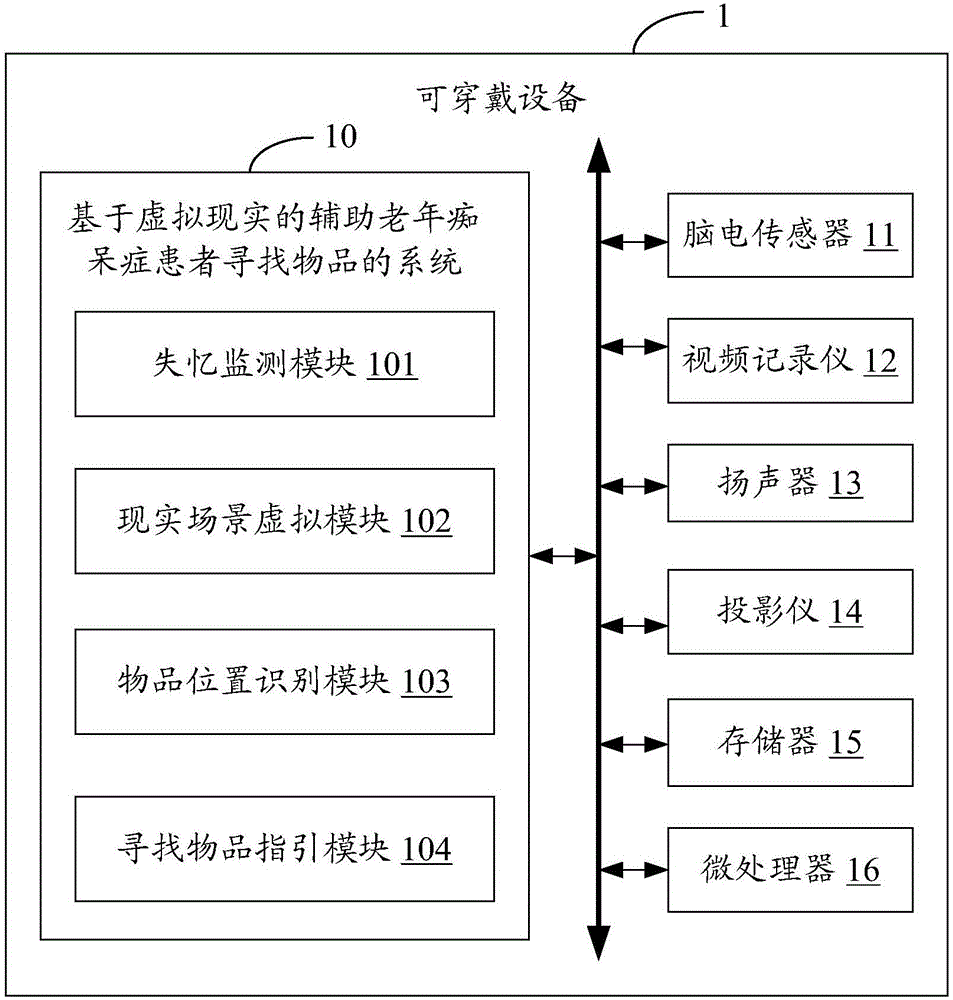
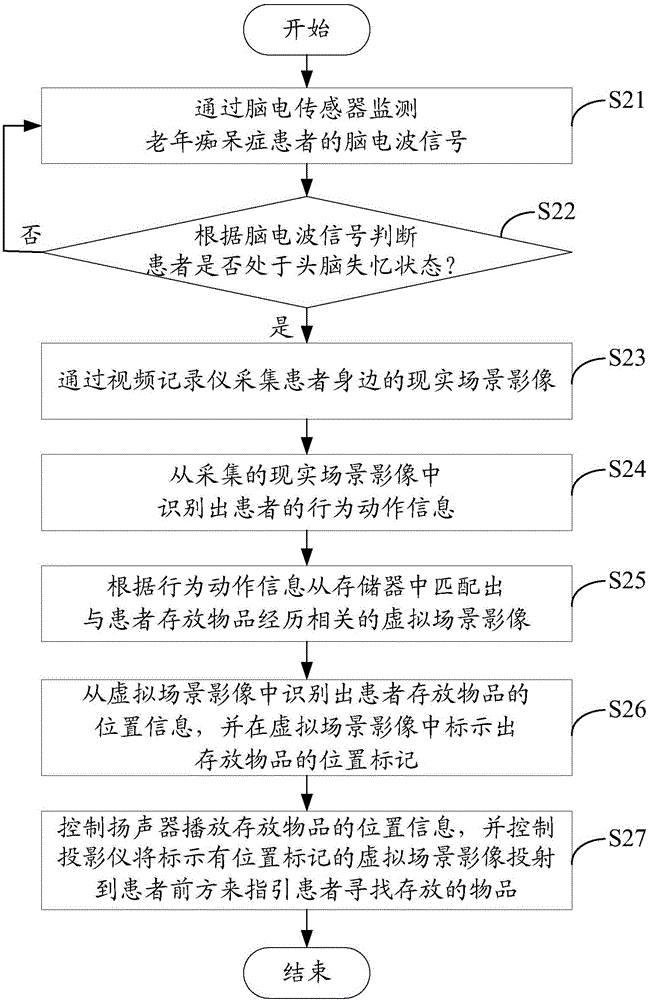
System and method for assisting Alzheimer's disease patient in searching object based on virtual reality
InactiveCN106293073AFind quicklyInput/output for user-computer interactionDiagnostic recording/measuringPattern recognitionObject based
The invention discloses a system and method for assisting an Alzheimer's disease patient in searching object based on virtual reality. The system and the method can be applied to a wearable device. The method comprises the steps of monitoring an electroencephalogram signal of the Alzheimer's disease patient through an electroencephalogram sensor; judging whether the patient is in a brain memory loss state or not according to the electroencephalogram signal; collecting reality scene images around the patient through a video recorder when the patient is in the brain memory loss state; identifying behavior action information of the patient from the collected reality scene images; matching virtual scene images related to object storage experiences of the patient from a memory according to the behavior action information; identifying the object storage location information of the patient from the virtual scene images; and controlling a loudspeaker to play the object storage location information, thereby guiding the patient to search stored objects. Through application of the method and the system, the patient is assisted in searching required objects rapidly through virtualizing the virtual scene images related to object storage experiences of the patient.
Owner:ANYCHECK INFORMATION TECH
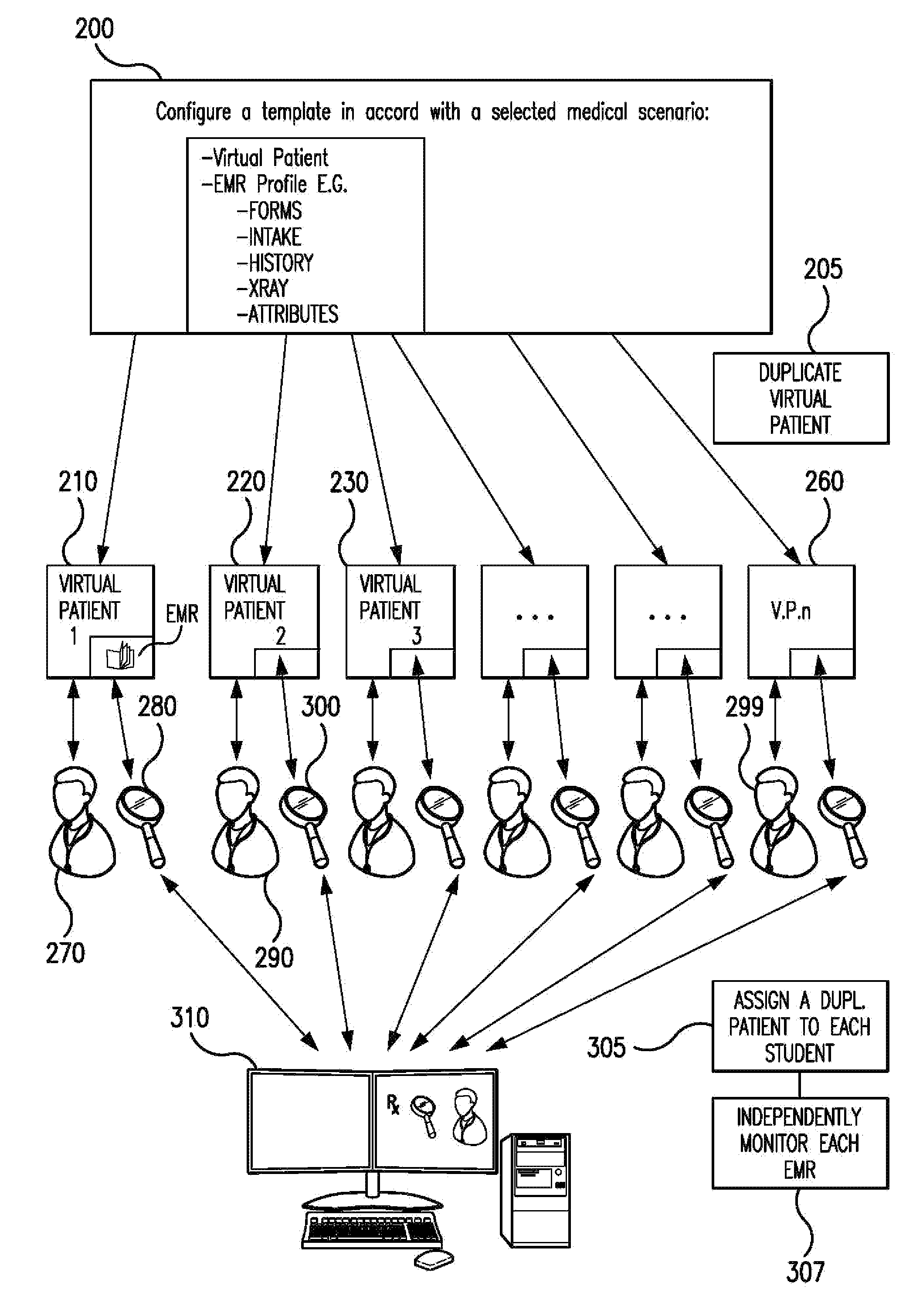
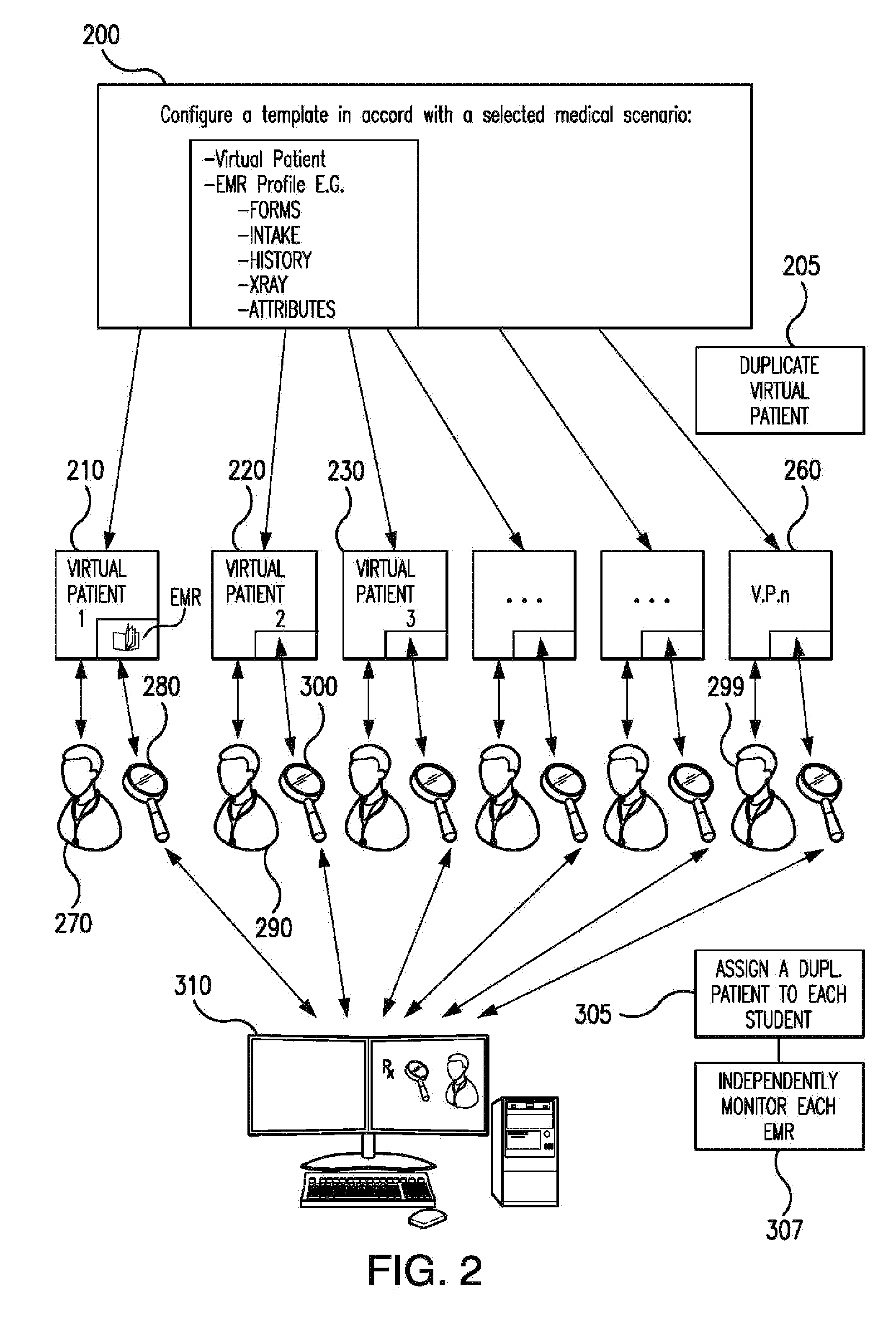
System and method for clinical patient care simulation and evaluation
An evaluation system and method are provided for simulating clinical care of a virtual patient. A database of electronic medical records (EMRs) is established, with at least one EMR including a plurality of EMR items collectively profiling the virtual patient. A simulation management unit coupled to the database includes a plurality of selectively executable control modules. At least one control module defines a simulation scenario; and, at least one other control module generates a duplicate EMR of the virtual patient for each of a plurality of simulation participants. At least one evaluator station establishes interactive interface for an evaluator. A plurality of participant stations establish interactive access for the simulation participants to a corresponding one of the duplicate EMRs during a simulated clinical encounter with the virtual patient. The simulation management unit independently updates the duplicate EMRs for the simulation participants responsive to clinical actions respectively taken by those participants.
Owner:EDUCATION MANAGEMENT SOLUTIONS +1
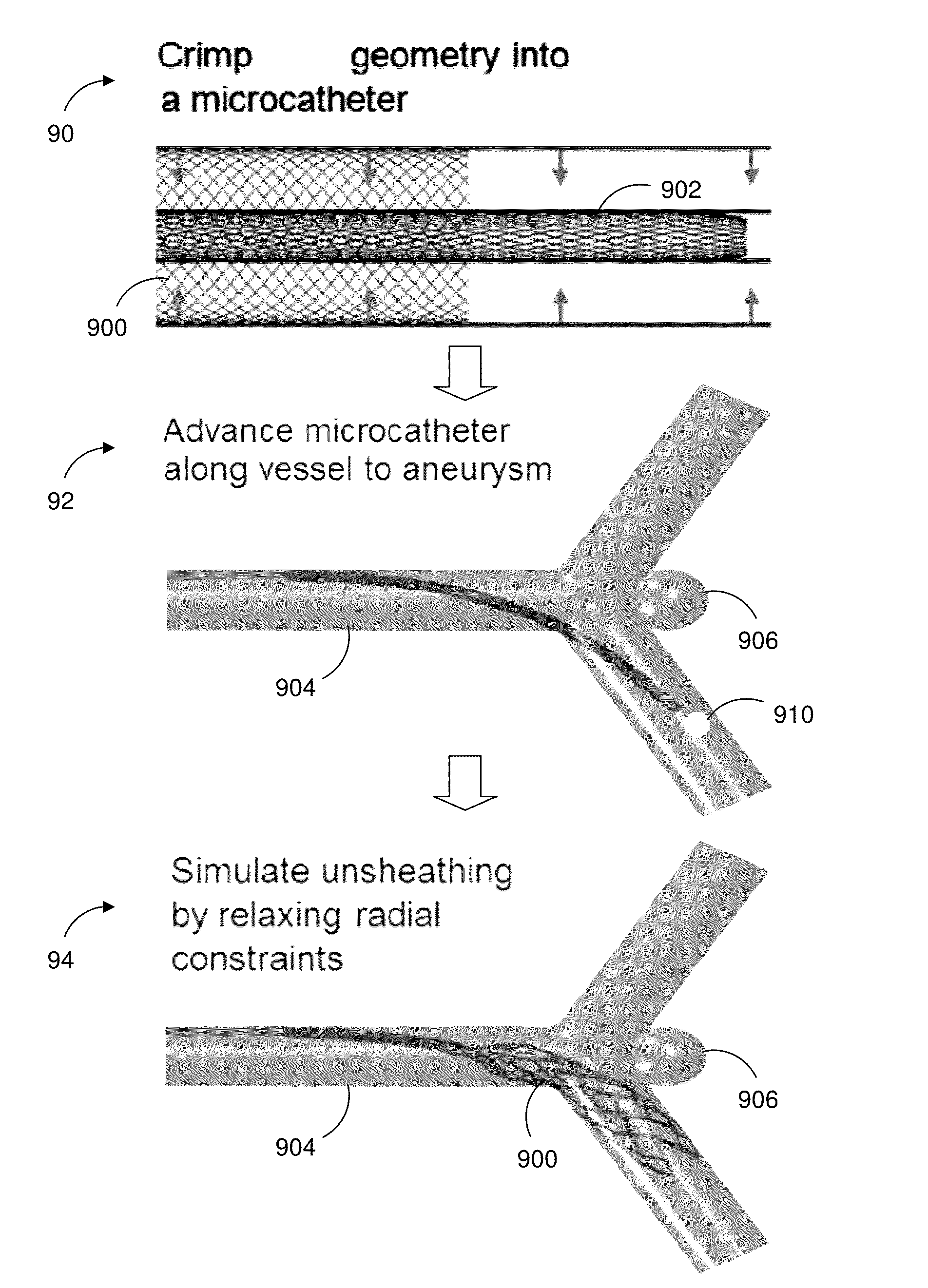
Device specific finite element models for simulating endovascular treatment
ActiveUS20150235569A1Educational modelsElectrical appliancesAnatomical structuresEndovascular treatment
Systems and methods provide a novel computational approach to planning the endovascular treatment of cardiovascular diseases. In particular, the invention simulates medical device deployment and hemodynamic outcomes using a virtual patient-specific anatomical model of the area to be treated, high-fidelity finite element medical device models and computational fluid dynamics (CFD). In an embodiment, the described approach investigates the effects of coil packing density, coil shape, aneurysmal neck size and parent vessel flow rate on aneurysmal hemodynamics. A processor may receive patient clinical data used to construct the relevant anatomical structure model. The processor may access medical device models constructed using finite element analysis and three dimensional beam analysis, and simulates the deployment of selected medical devices in the anatomical structure model. The selected medical device models and the anatomical structure model mesh, allowing the processor to simulate hemodynamic outcomes using computational fluid dynamics.
Owner:MAYO FOUND FOR MEDICAL EDUCATION & RES +1
Computer architecture and process of user evaluation
ActiveUS8096811B2Digital computer detailsBiological neural network modelsTechnical standardComplex system
The present invention is generally related to a computer architecture and process for evaluating and reporting on a user's competence in managing a simulation of a complex system modeled in a computer based testing and training system. The simulation may be called a “virtual system.” The method generates evaluation criteria responsive to a user profile, user choices in managing the virtual system, and events that occur during a simulation, in addition to the original state of the system. The method produces summary evaluations responsive to a plurality of characteristics of the simulated system. The implementation may be advantageously employed to evaluate a medical clinician's management of computer-simulated human patients, hereinafter called “virtual patients”. The present invention is also suitable for evaluation of user management of a plurality of complex systems including but not limited to animals, plants, cells, machines, and populations.
Owner:AMERICAN BOARD OF FAMILY MEDICINE
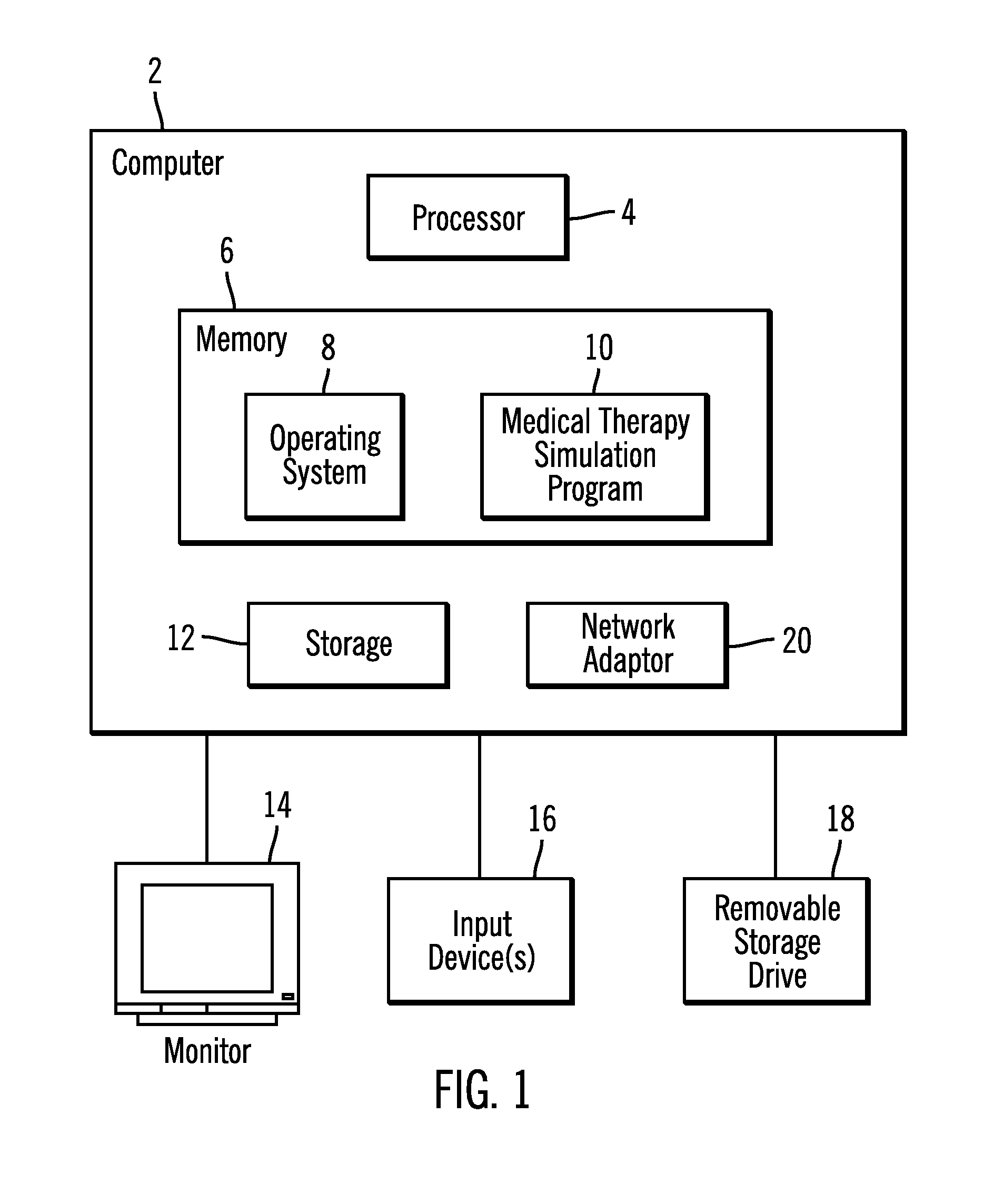
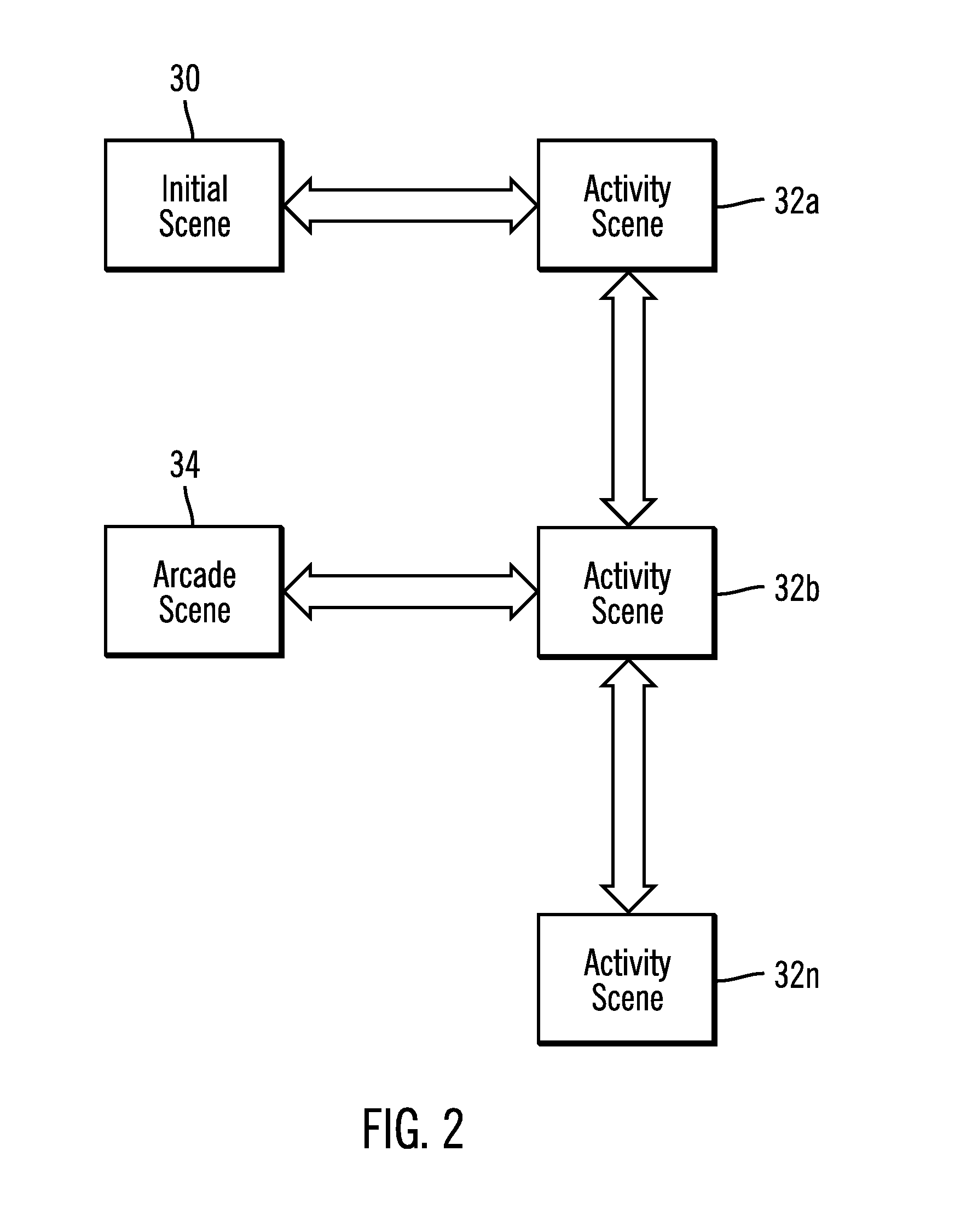
Method, system, and program for using a virtual environment to provide information on using a product
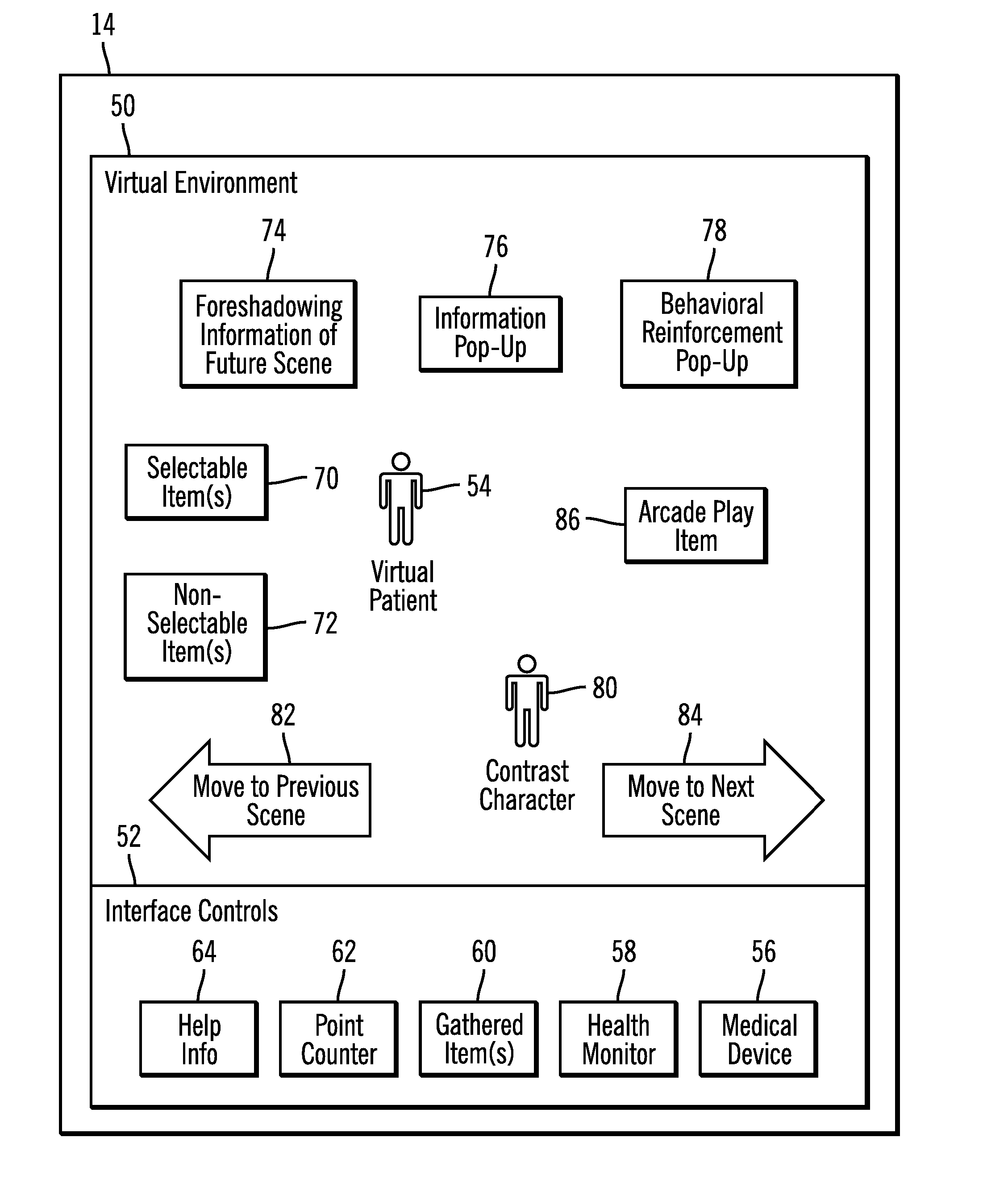
Provided are a method, system, and article of manufacture for providing information to a user of the computer program on using a medical therapy to treat a medical condition. A virtual environment is displayed and a user controlled virtual patient is displayed within the virtual environment. The user controlled virtual patient is simulating receiving the medical therapy and simulating real life activity in the virtual environment. Input control signals are received from the user controlling movement of the user controlled virtual patient through the virtual environment and interactions are rendered between the user controlled virtual patient and the virtual environment in response to the input control signals to enable the user to virtually engage in a simulated daily activity through the actions of the user controlled virtual patient. The simulated daily activity is other than simulated receiving of the simulated medical therapy. Information is displayed on how the simulated medical therapy positively impacts the user controlled virtual patient engaged in the daily activity to promote the medical therapy. Other embodiments are described and claimed.
Owner:MEDTRONIC MIMIMED INC
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com