Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
5910 results about "Evaluation system" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
The Performance Evaluation System is a tool used to measure individual performance and to develop employees into high-performing individuals. It applies to all classified employees and the current system is effective July 1, 2012.
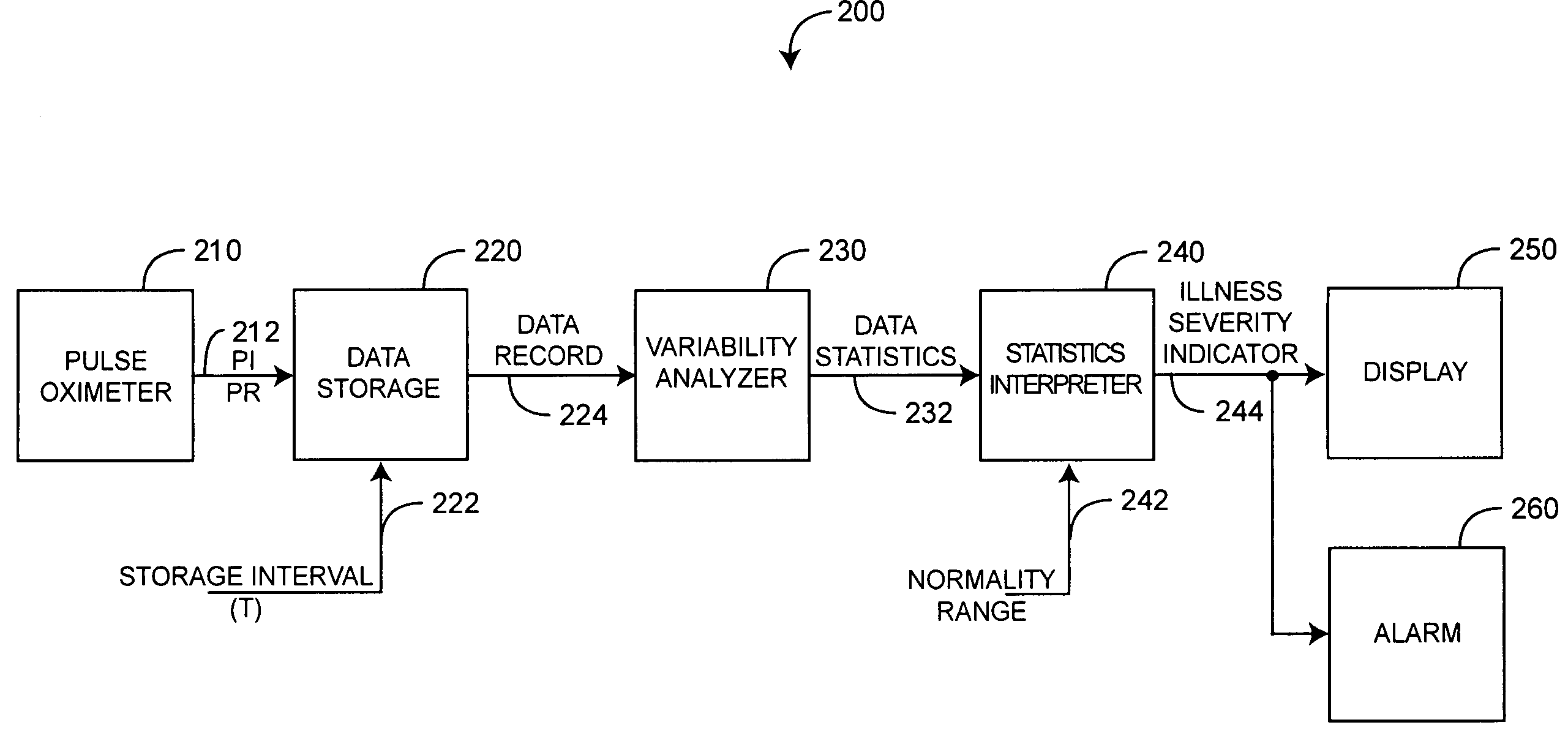
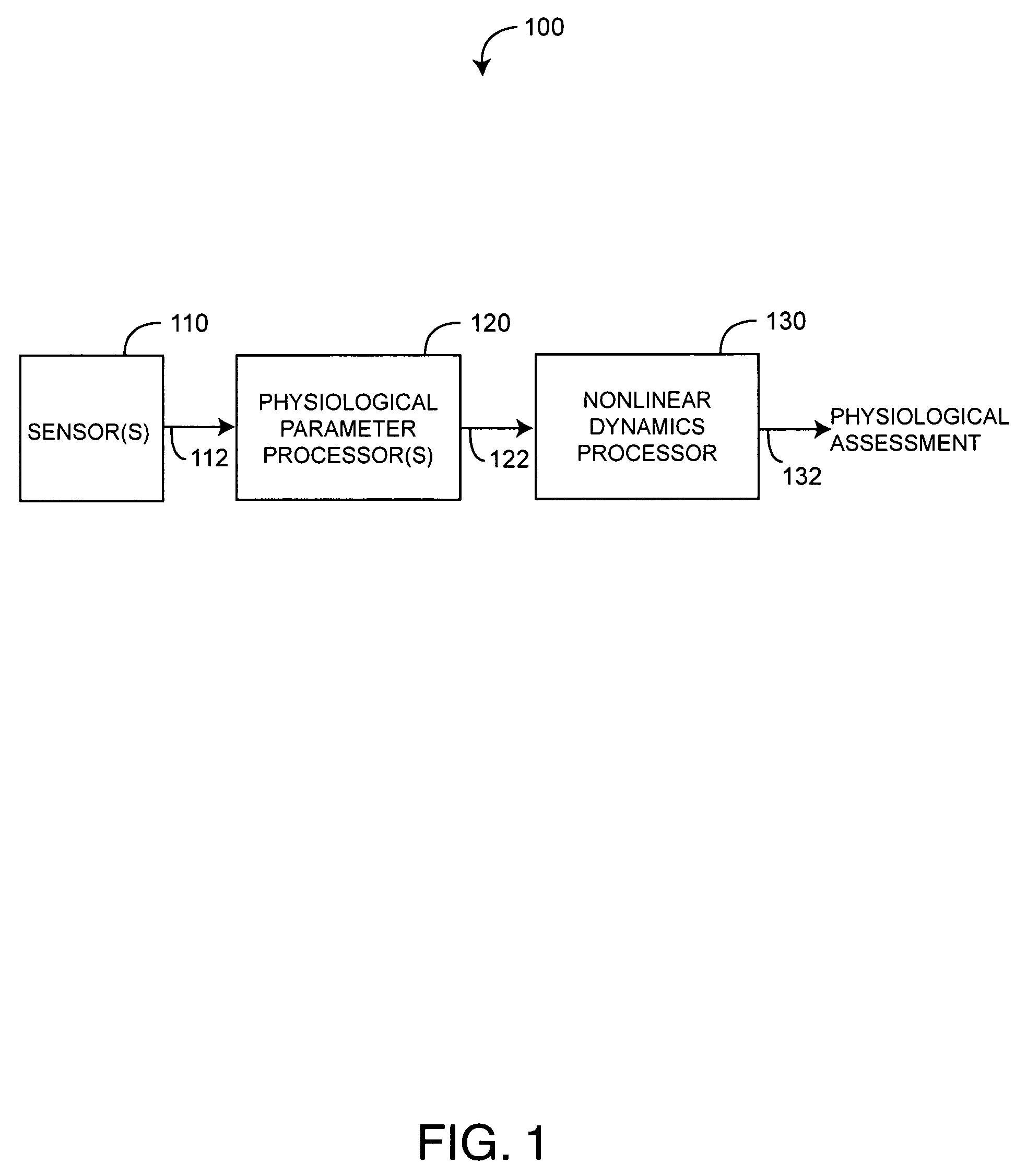
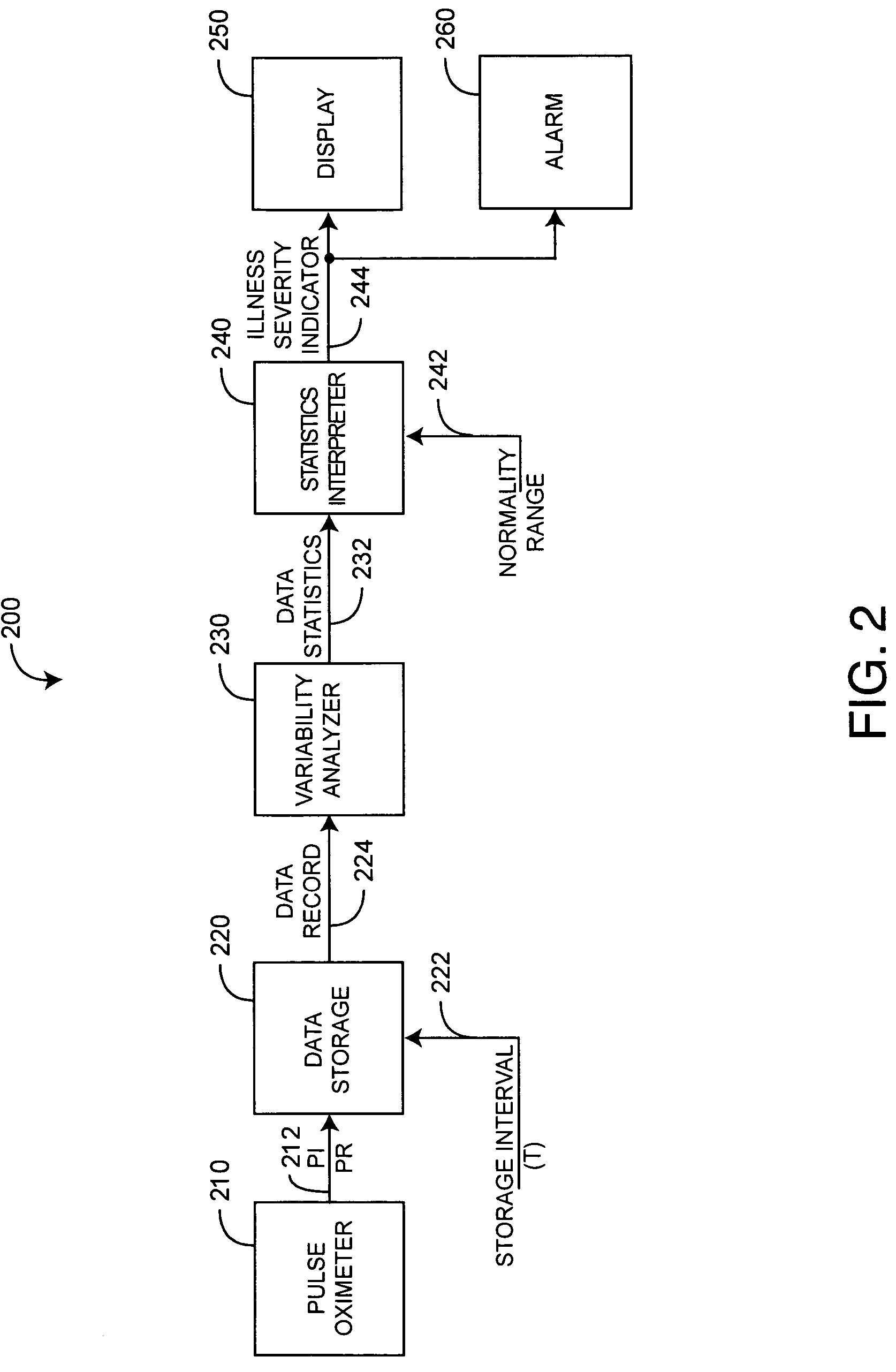
Physiological assessment system
ActiveUS7292883B2Reduce dynamic complexityLow variabilityDiagnostic recording/measuringSensorsBiological bodyMedicine
A physiological assessment system comprises a sensor and first and second processors. The sensor is adapted to generate a signal responsive to a living organism. The first processor is configured to derive a measured parameter from the sensor signal. The second processor is configured to analyze nonlinear dynamics of the measured parameter so as to provide a physiological assessment of the living organism.
Owner:JPMORGAN CHASE BANK NA
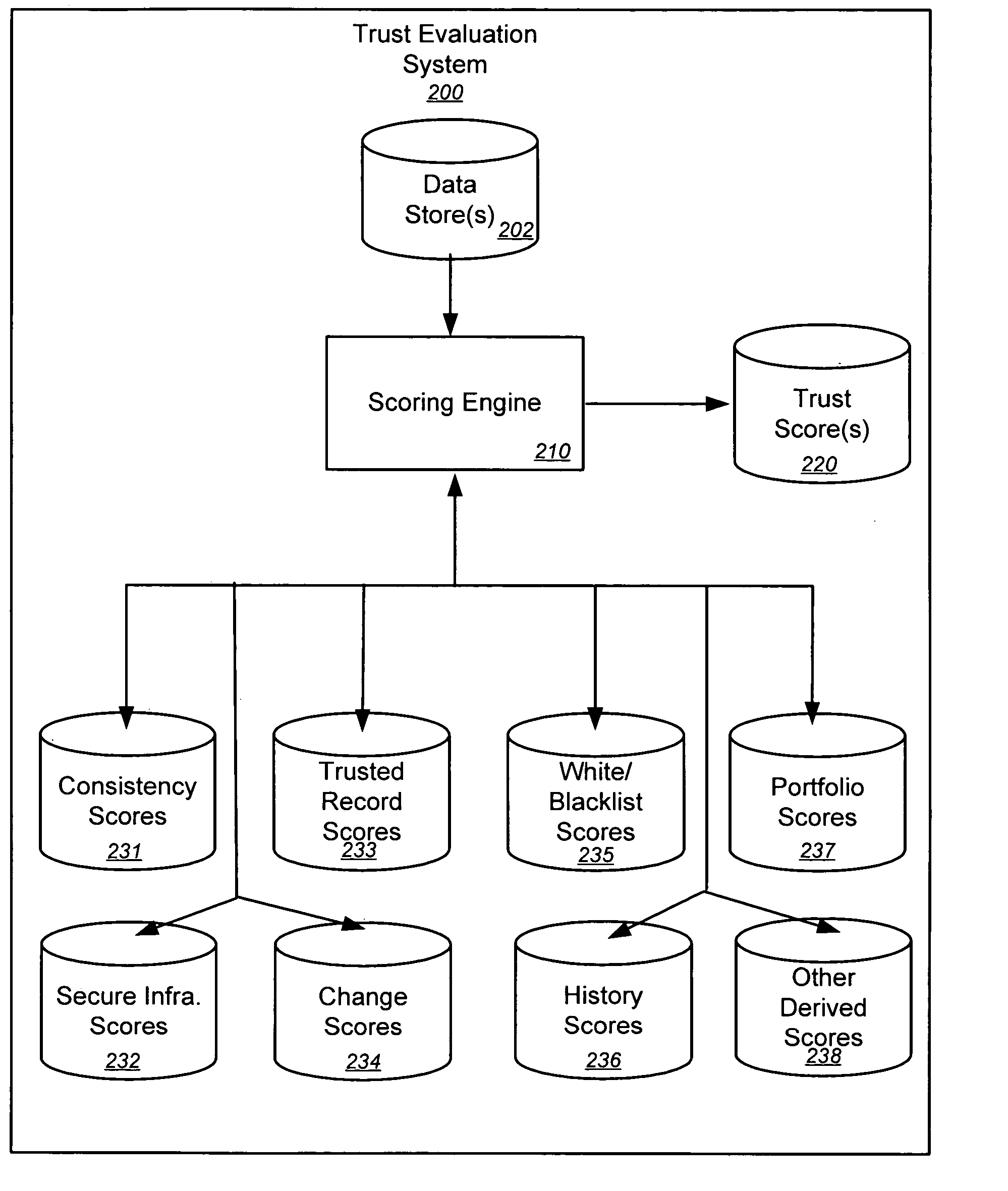
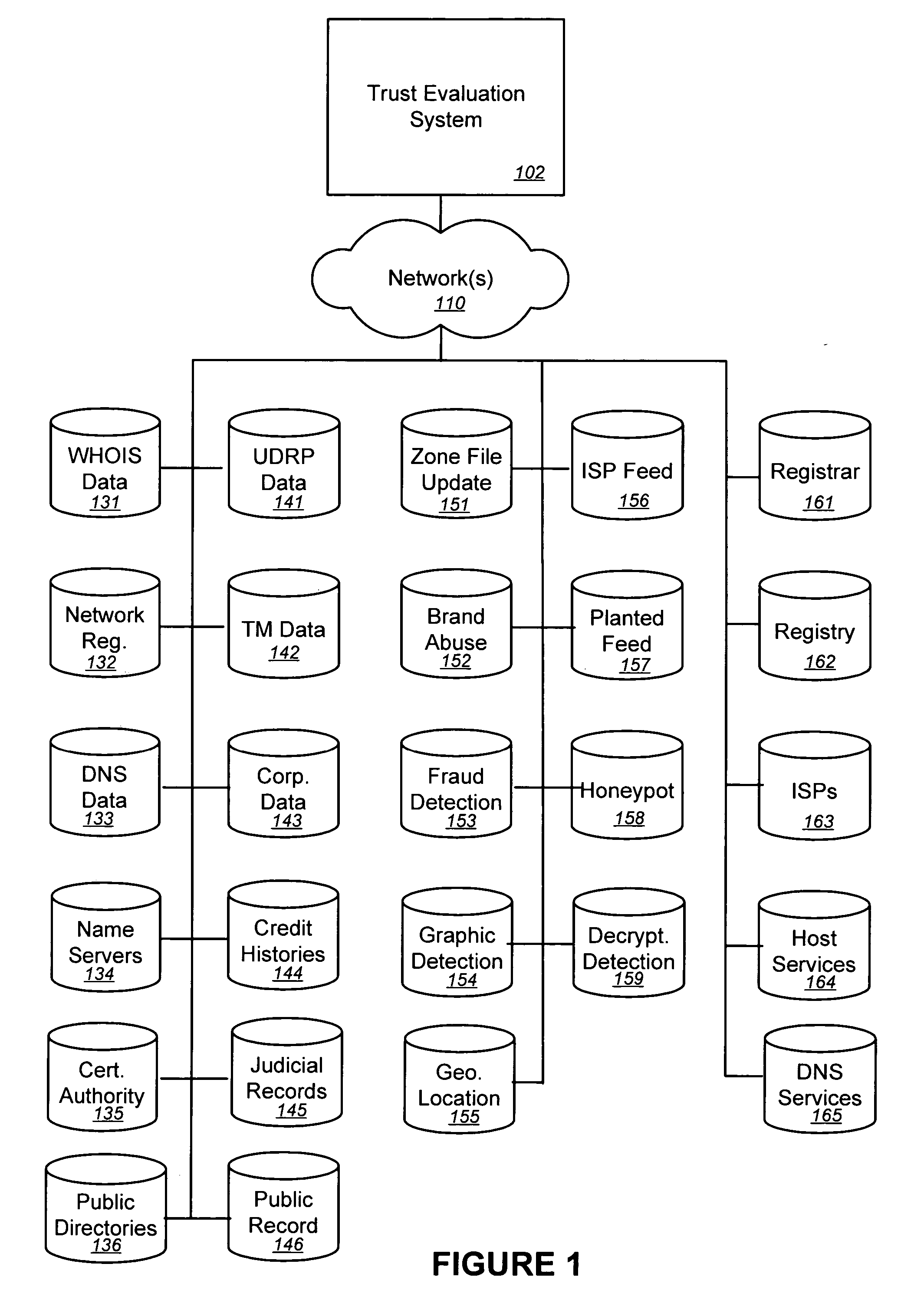
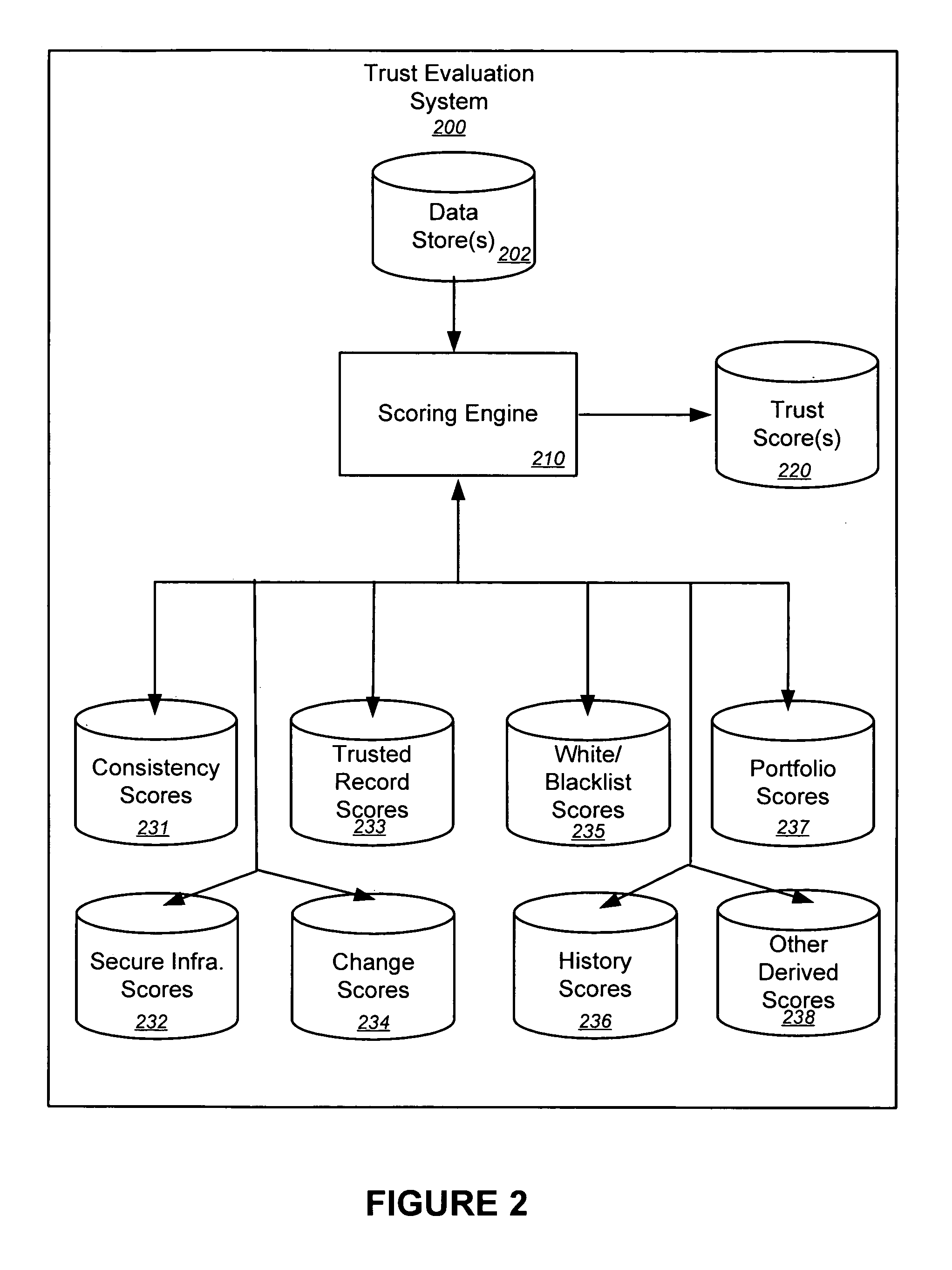
Trust evaluation systems and methods
InactiveUS20060212931A1Digital data processing detailsUser identity/authority verificationData storingEvaluation system
Embodiments of the present invention provide methods, systems, and software for implementing evaluating online entities and / or for providing a trust score for such entities. The trust score may provide an indication of the trustworthiness of the online entity. In some cases, data may be obtained from a variety of sources, and such data may be used to evaluate an online entity and / or to provide a score for the entity. In an aspect of the invention, a plurality of trust scores, each of which related to a behavioral characteristic and / or a category of activity, may be assigned to a particular entity. Such scores may be stored in one or more data stores and / or may be provided to others.
Owner:MARKMONITOR
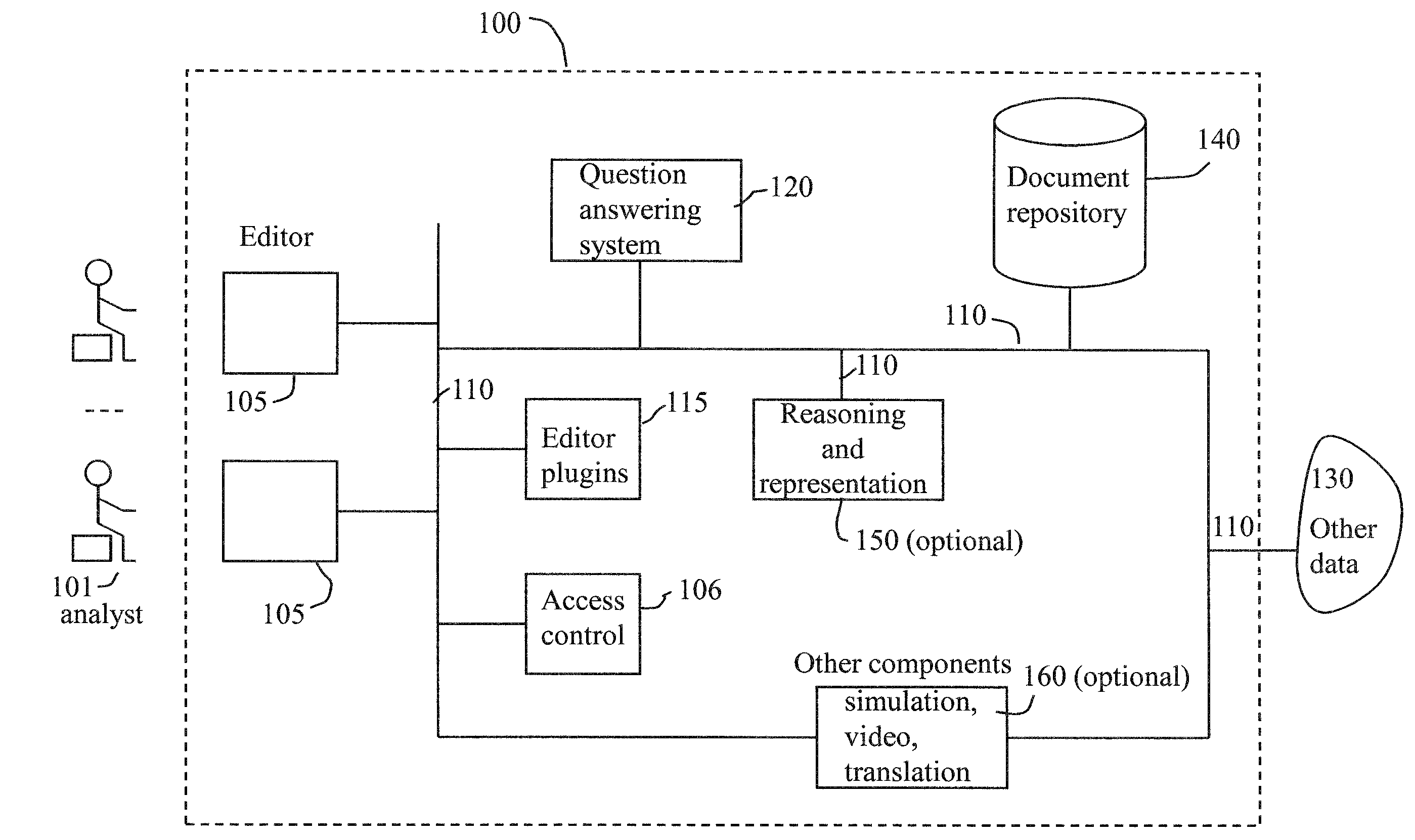
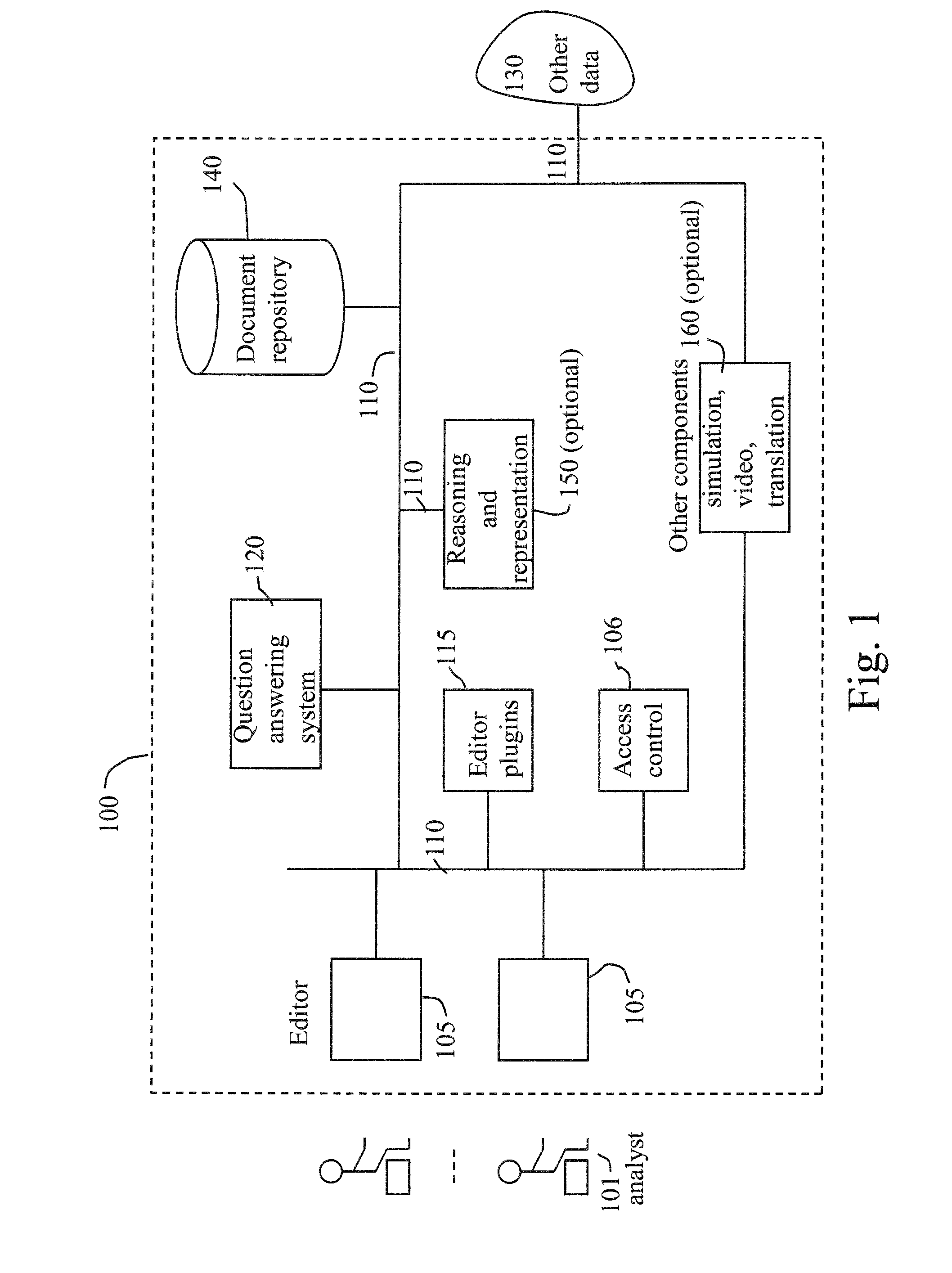
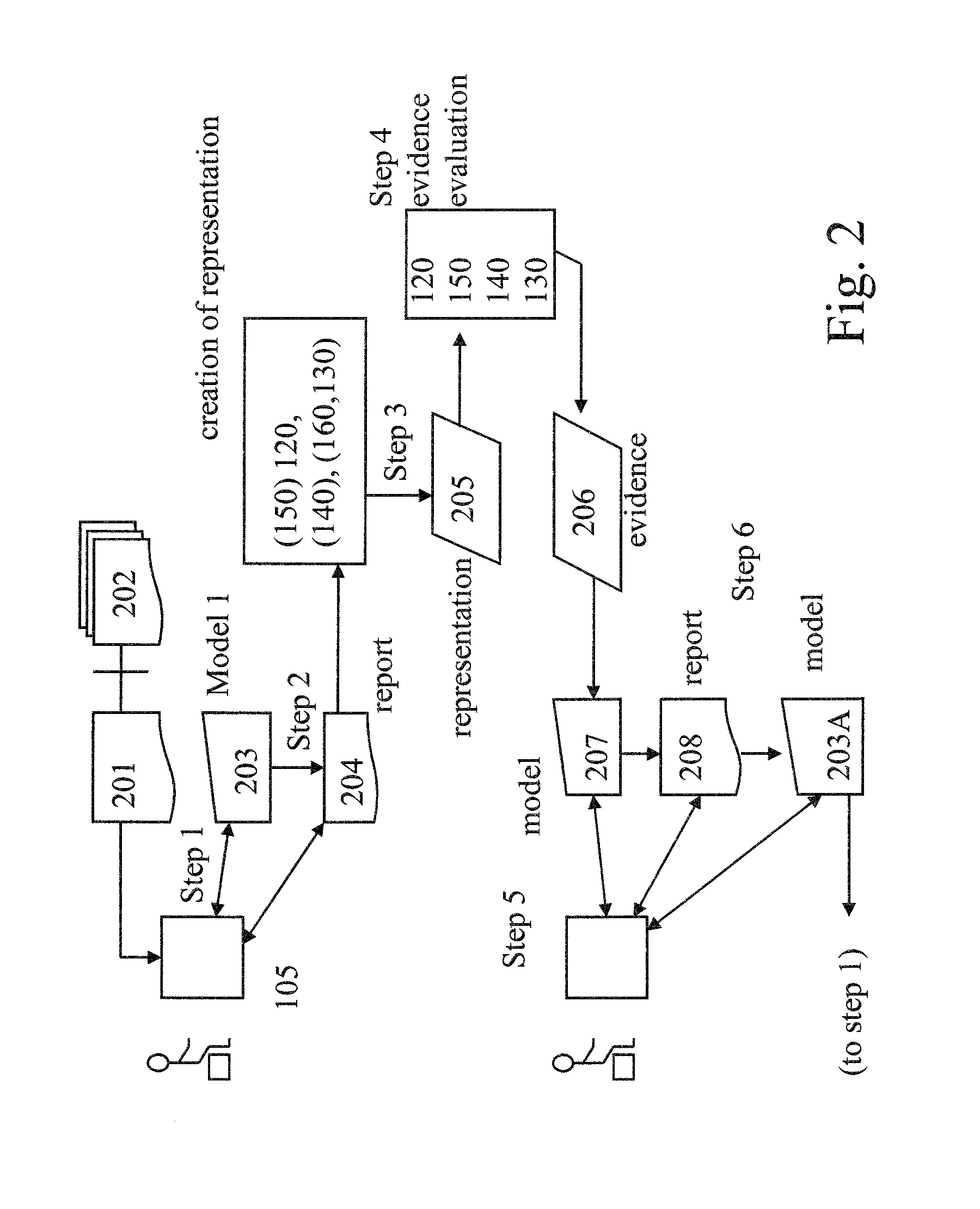
Evidence evaluation system and method based on question answering
An evidence evaluation method and system based on question answering converts a report of analyzed information and / or a model of information into a collection of questions, determines answers for the collection of questions. A fact in the report is marked as being supported if one or more of the answers for the collection of questions support the fact. A fact in the report of analyzed facts is marked as being refuted if one or more of the answers for the collection of questions refute the fact. The method and system also may collect the answers as evidence and add the evidence to the model of information to create an updated model of information. The steps may be repeated using the updated report and updated model.
Owner:IBM CORP
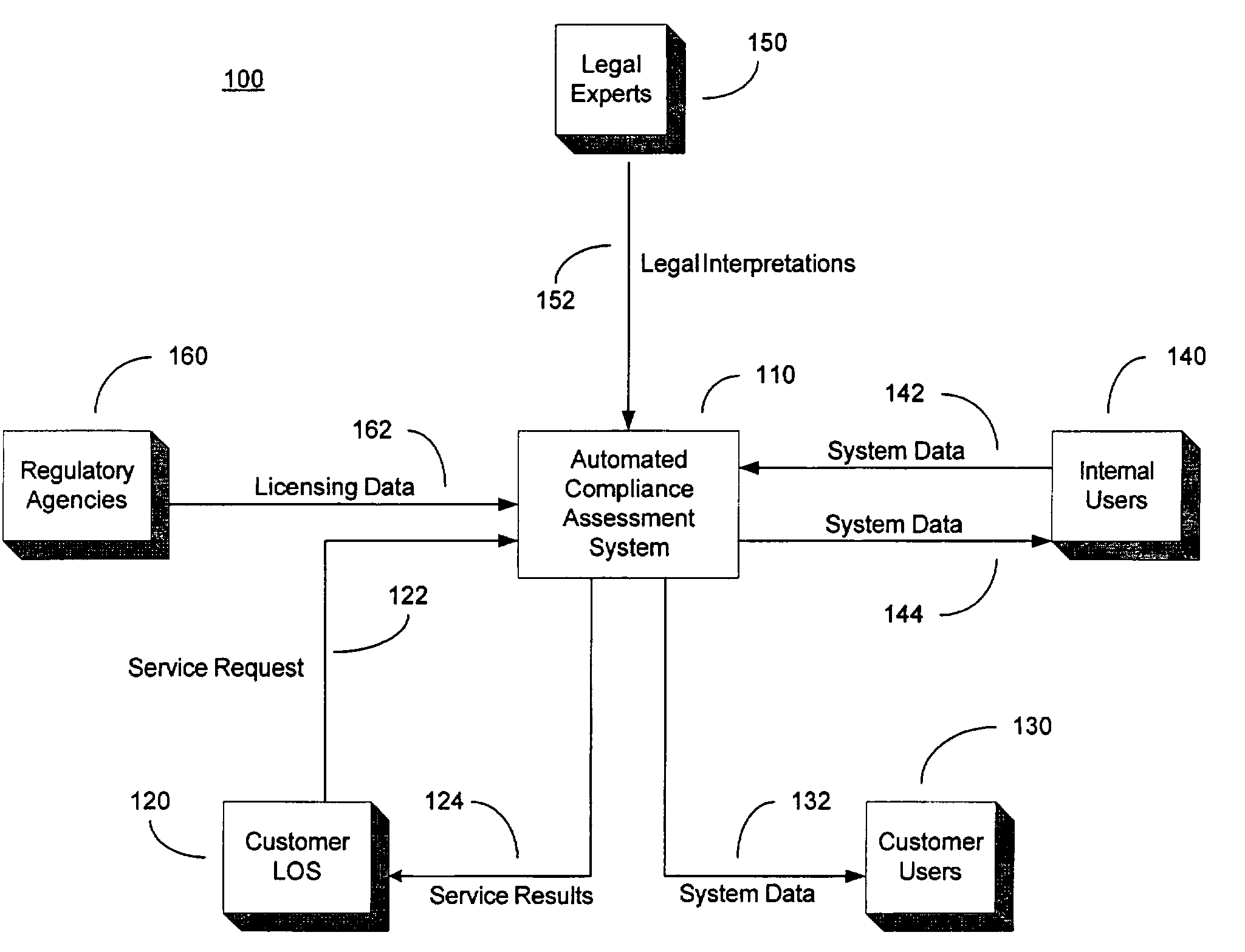
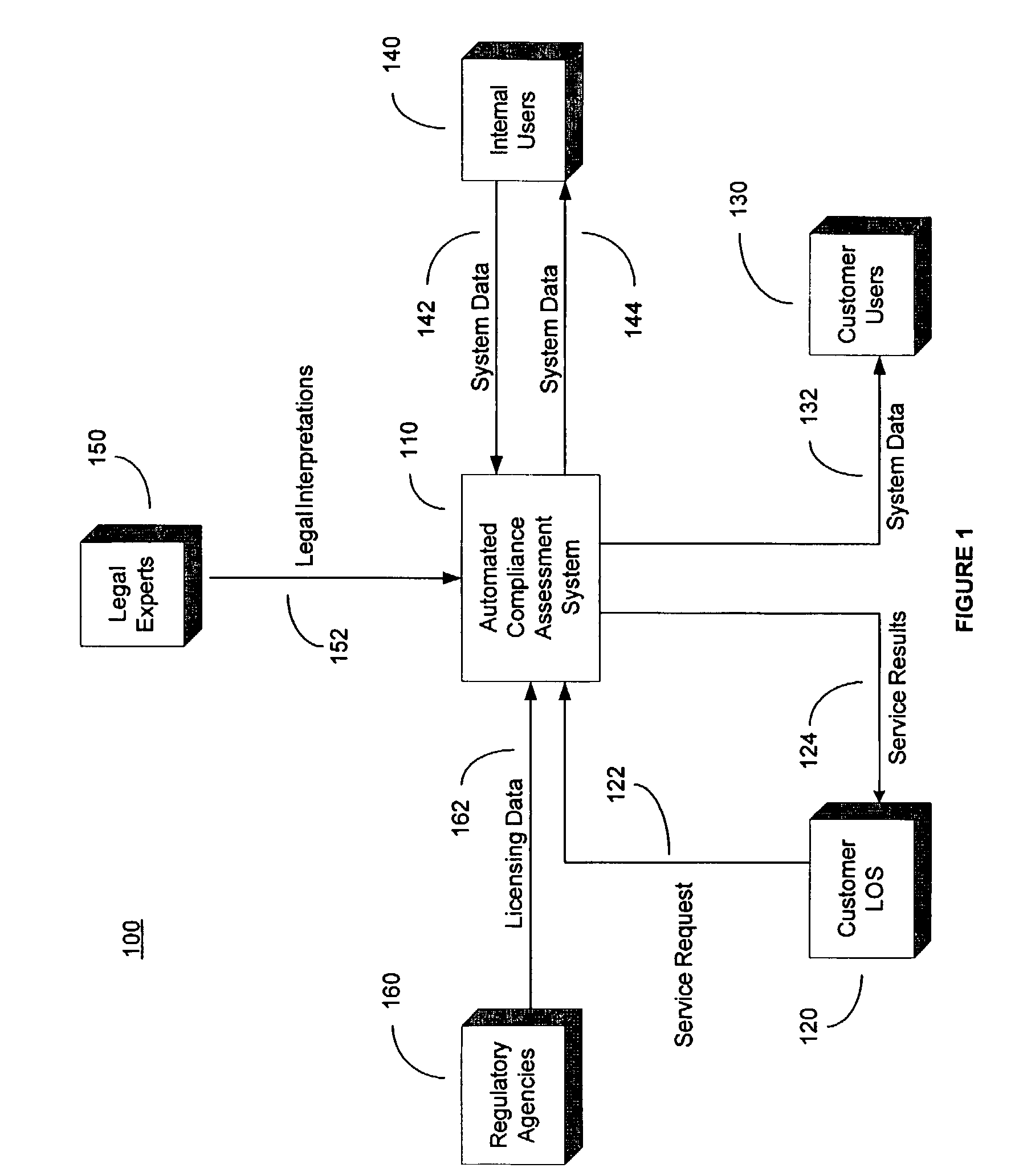
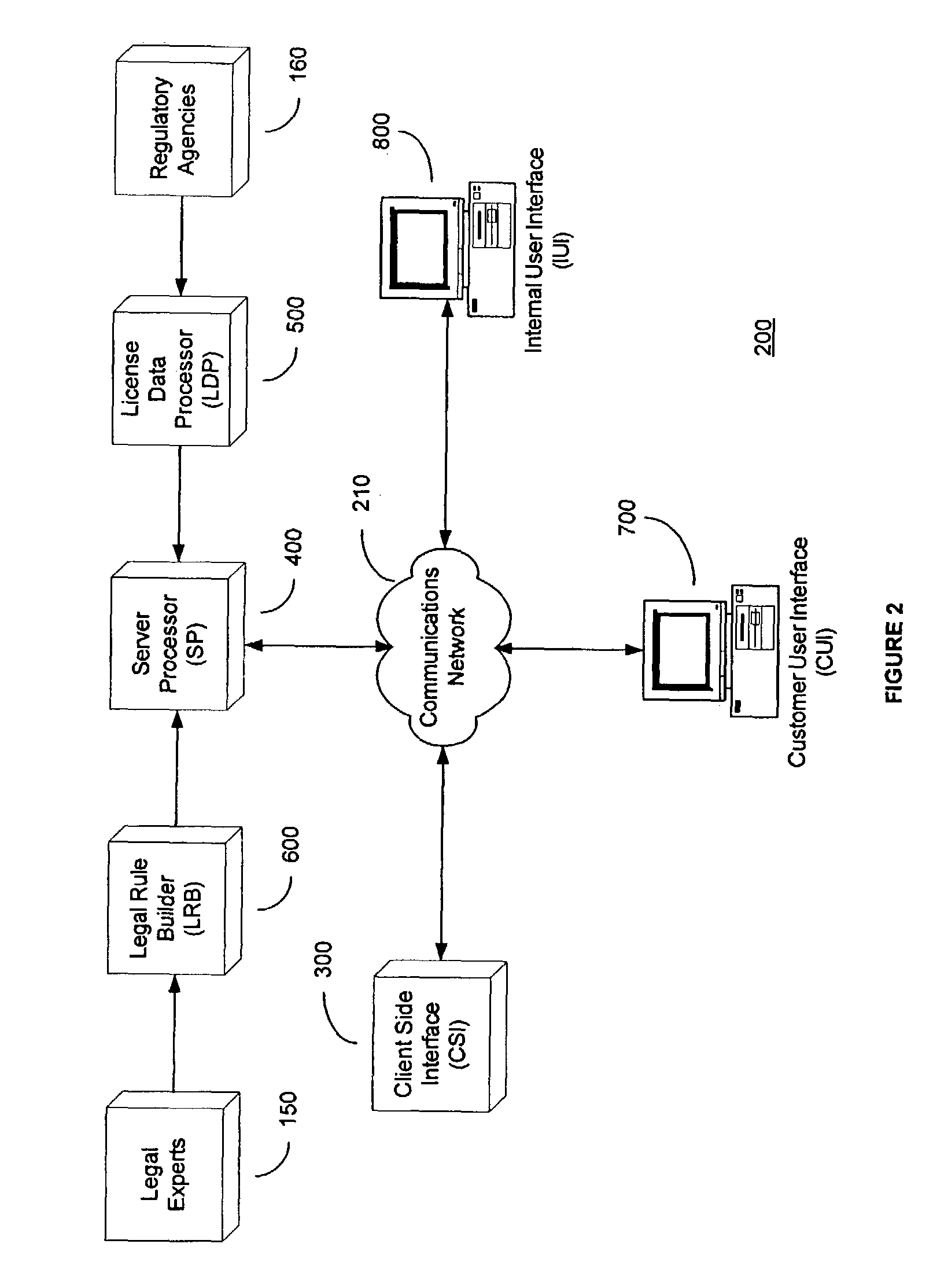
System and method for automated loan compliance assessment
An automated system and method for reviewing and assessing compliance with legal compliance requirements for loan applications. Loan application data is extracted from client loan origination systems and transmitted as a loan information file over a secure communication network to an automated compliance assessment system server where the loan information file is audited for compliance with Federal, state, and local legal compliance requirements. The loan information file is reviewed for legal compliance requirements imposed by Federal, State, and local jurisdictions, as well as licensing requirements that the client loan company and related personnel must satisfy. The results of the audit process are transmitted over a secure communication network to the client loan company, with areas of noncompliance indicated. The automated compliance assessment system server also stores rules data derived from legal compliance requirements, license data derived from regulatory requirements, system setup data and supplemental system application data.
Owner:ICE MORTGAGE TECH INC
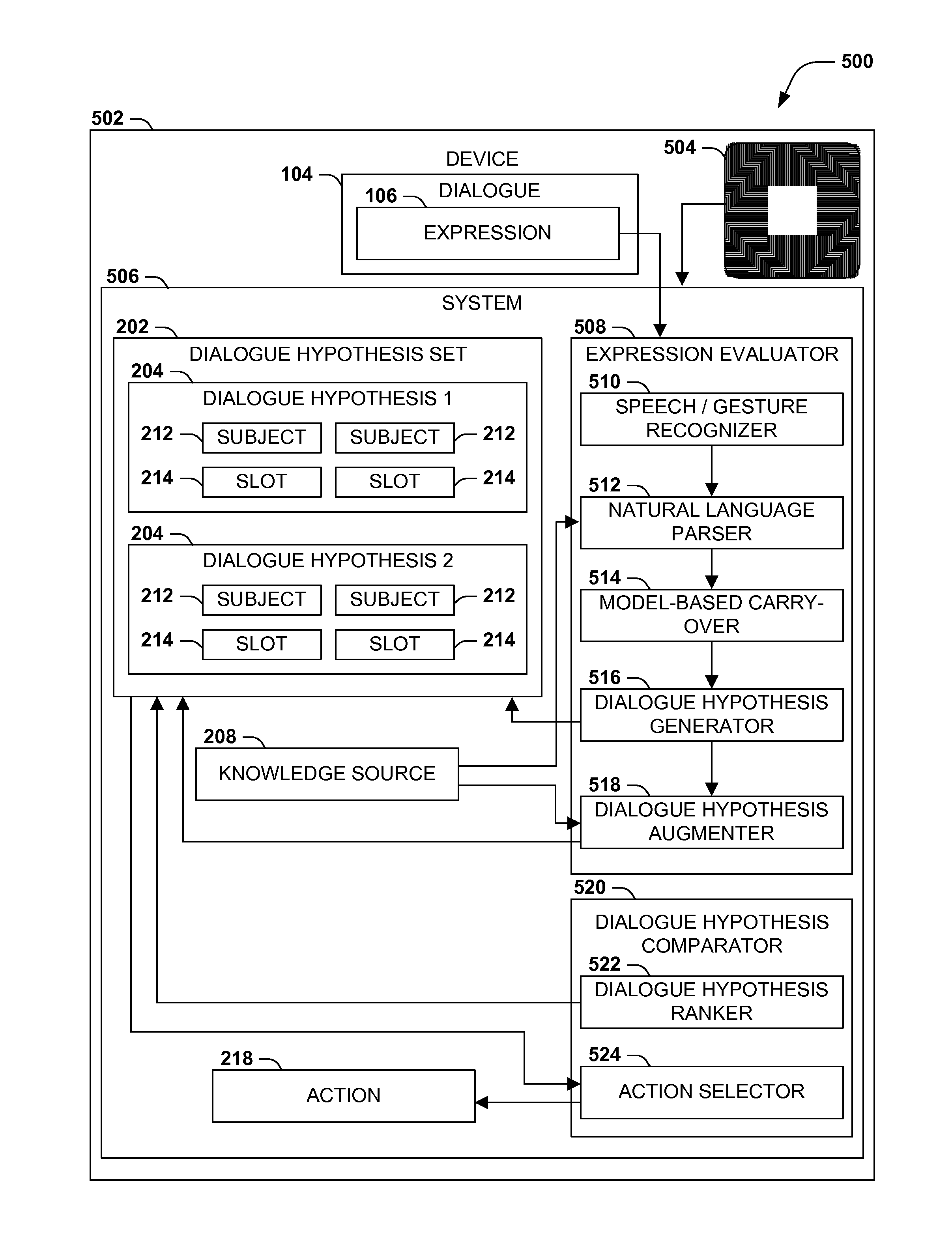
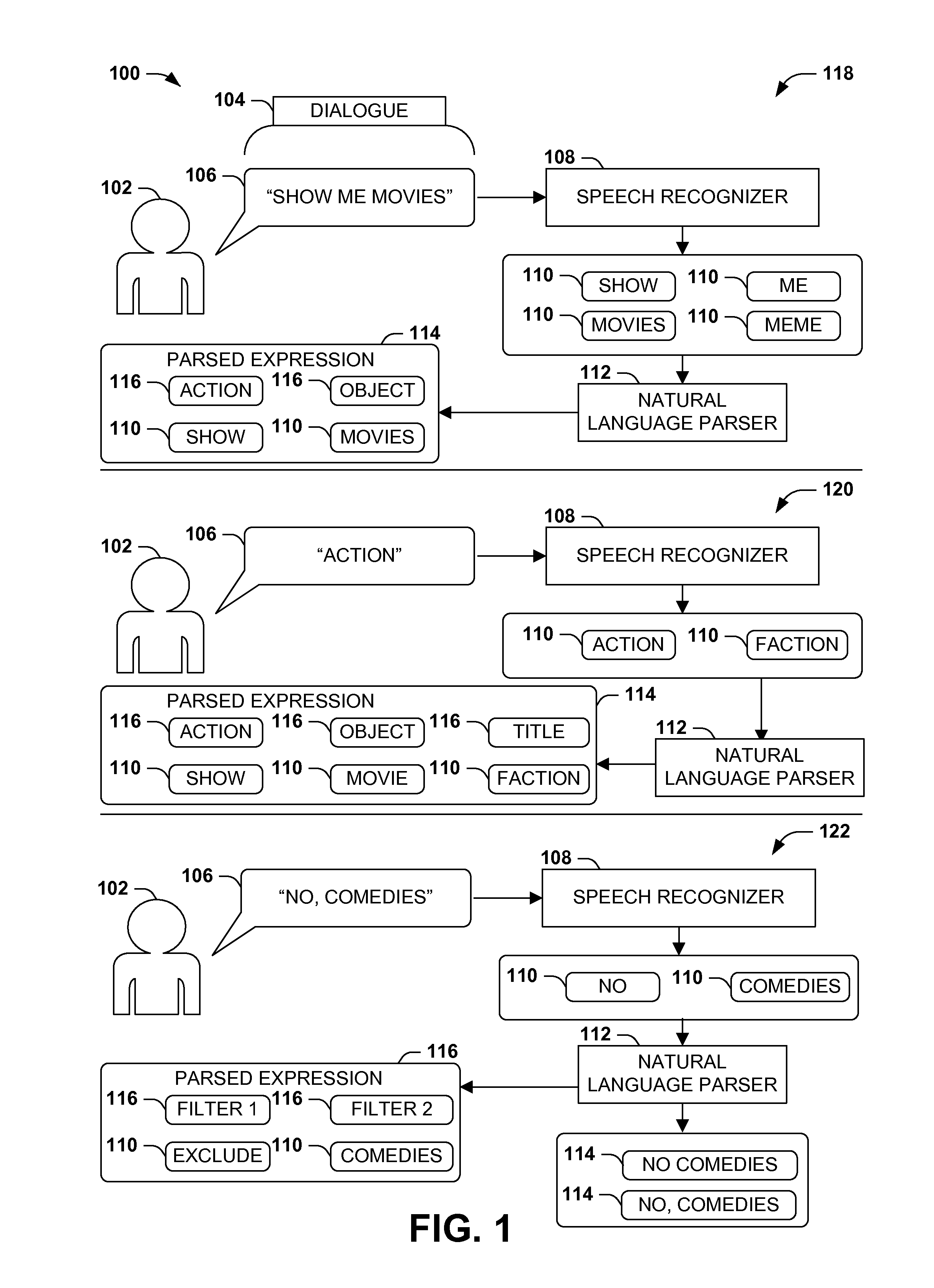
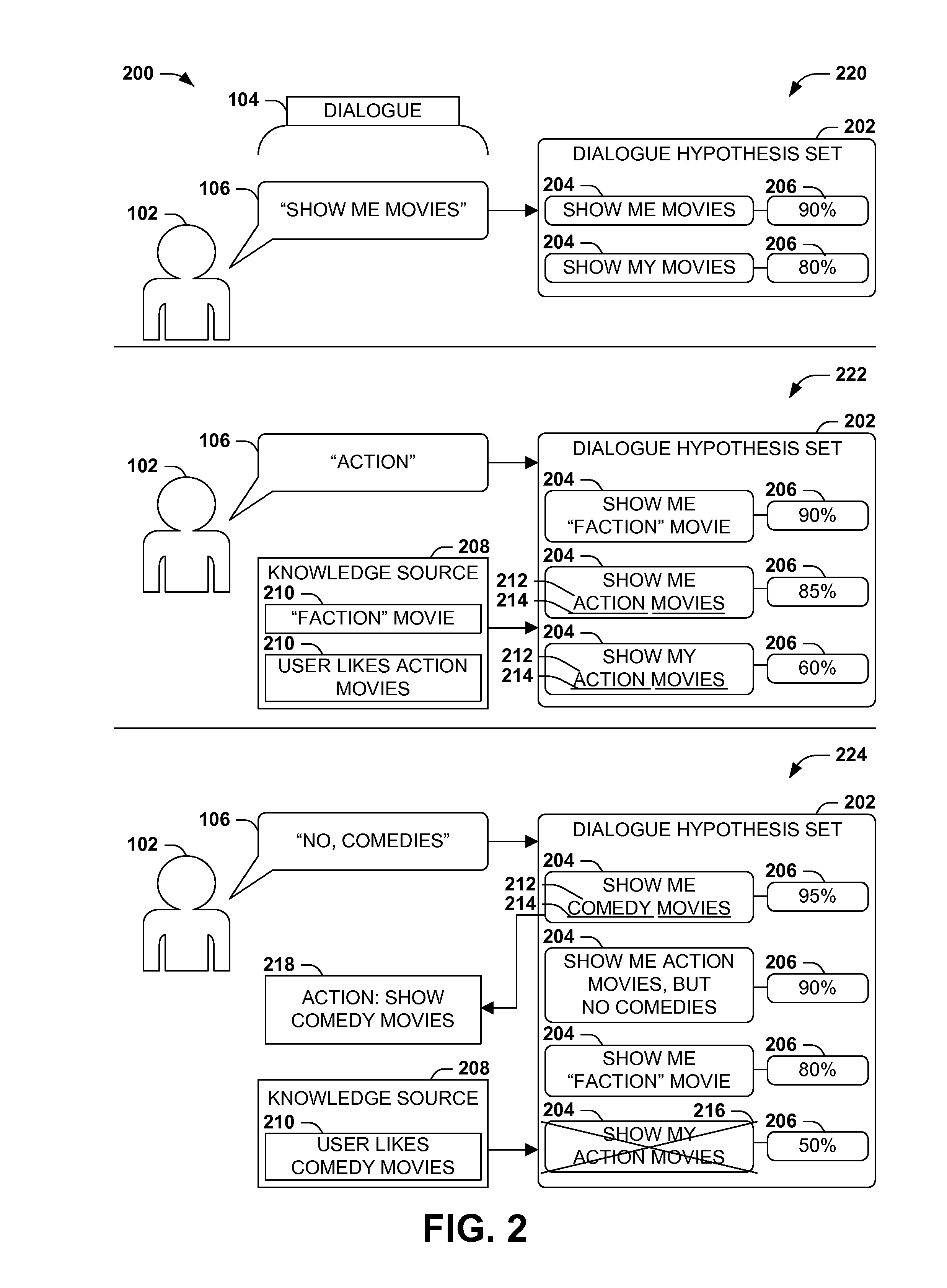
Dialogue evaluation via multiple hypothesis ranking
ActiveUS20150142420A1Reduce settingsNatural language data processingSpeech recognitionKnowledge sourcesMultiple hypothesis
In language evaluation systems, user expressions are often evaluated by speech recognizers and language parsers, and among several possible translations, a highest-probability translation is selected and added to a dialogue sequence. However, such systems may exhibit inadequacies by discarding alternative translations that may initially exhibit a lower probability, but that may have a higher probability when evaluated in the full context of the dialogue, including subsequent expressions. Presented herein are techniques for communicating with a user by formulating a dialogue hypothesis set identifying hypothesis probabilities for a set of dialogue hypotheses, using generative and / or discriminative models, and repeatedly re-ranks the dialogue hypotheses based on subsequent expressions. Additionally, knowledge sources may inform a model-based with a pre-knowledge fetch that facilitates pruning of the hypothesis search space at an early stage, thereby enhancing the accuracy of language parsing while also reducing the latency of the expression evaluation and economizing computing resources.
Owner:MICROSOFT TECH LICENSING LLC
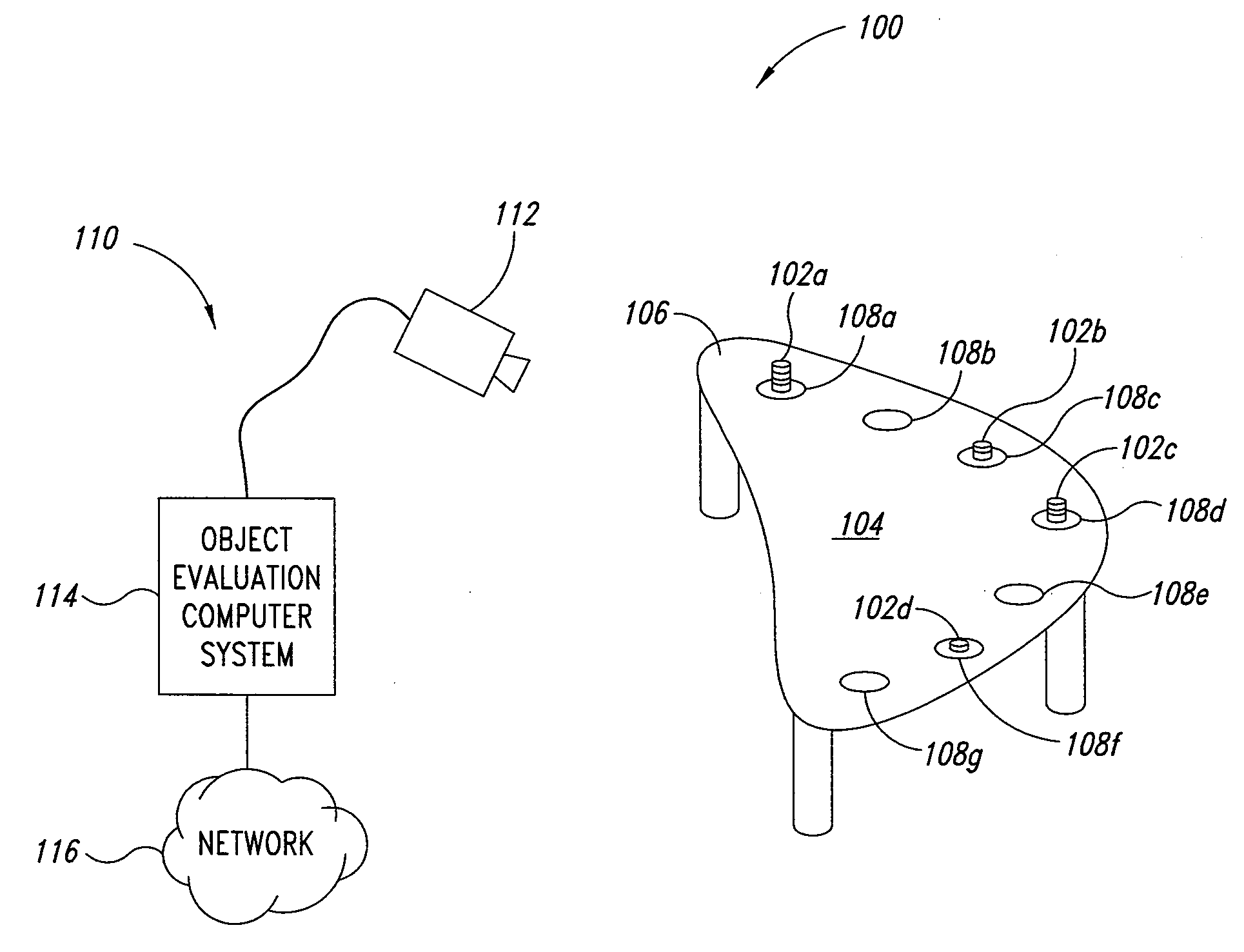
Apparatus, method and article for evaluating a stack of objects in an image
InactiveUS20110052049A1Image analysisCharacter and pattern recognitionPattern recognitionColor image
An object evaluation system may determine a value for a stack of objects that appear in a pixelated color image. To determine the value of the stack of objects, the evaluation system preprocess at least a portion of the pixelated color image to produce a set of two color contour data, processes the two color contour data to identify a location of a top and a bottom of the stack (if any), and locates, for each of the objects in the stack, a respective set of color pixels from the pixelated color image corresponding to each object based on the identified locations of the top and bottom of the stack. Each of the objects in the stack are then classified into a color classification based on the object's respective set of color pixels, and the value of the object is determined based on a known correspondence between the color classification and a value. The cumulative value of the stack is determined by summing the determined values for each of the objects in the stack.
Owner:BALLY GAMING INC
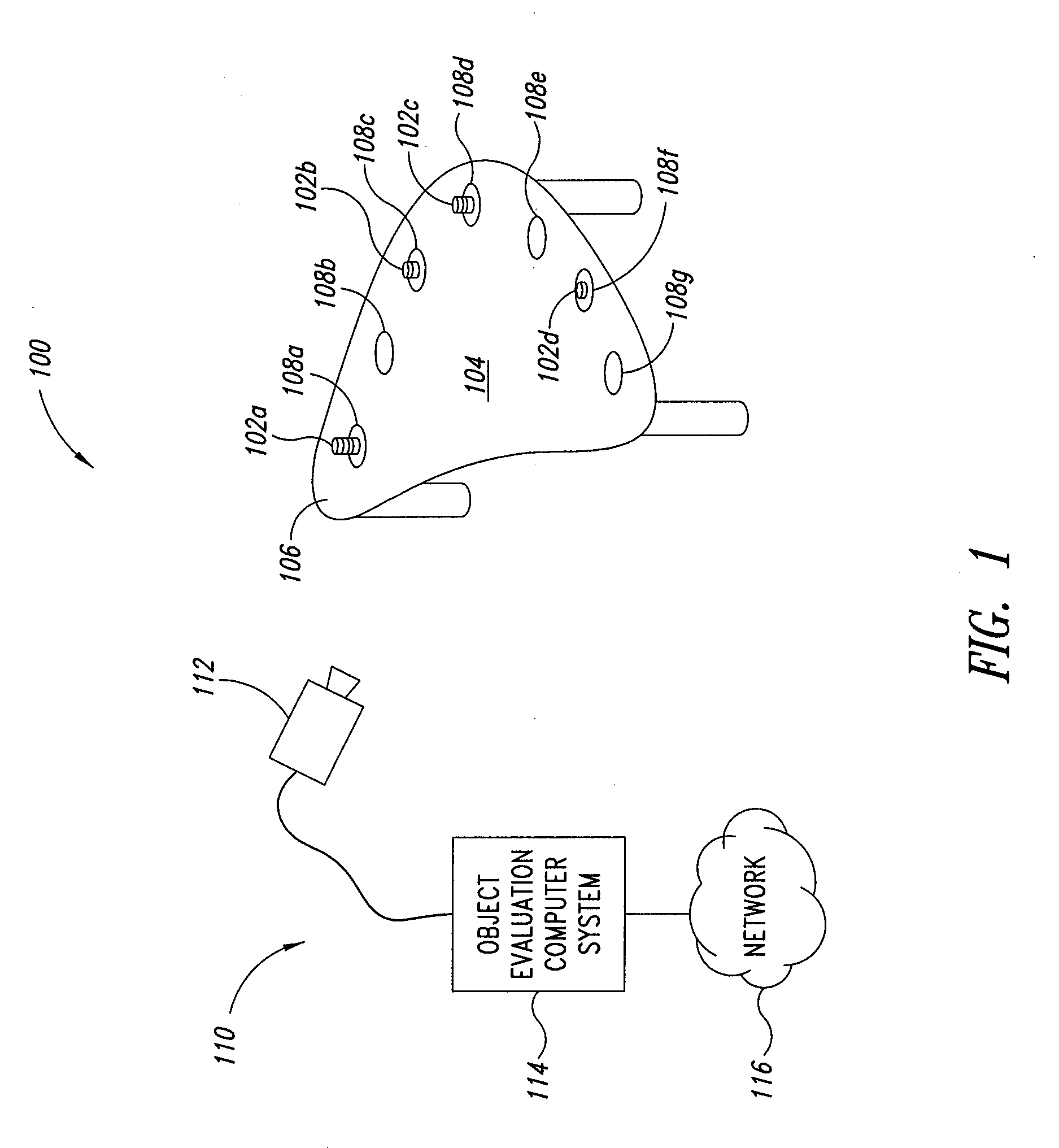
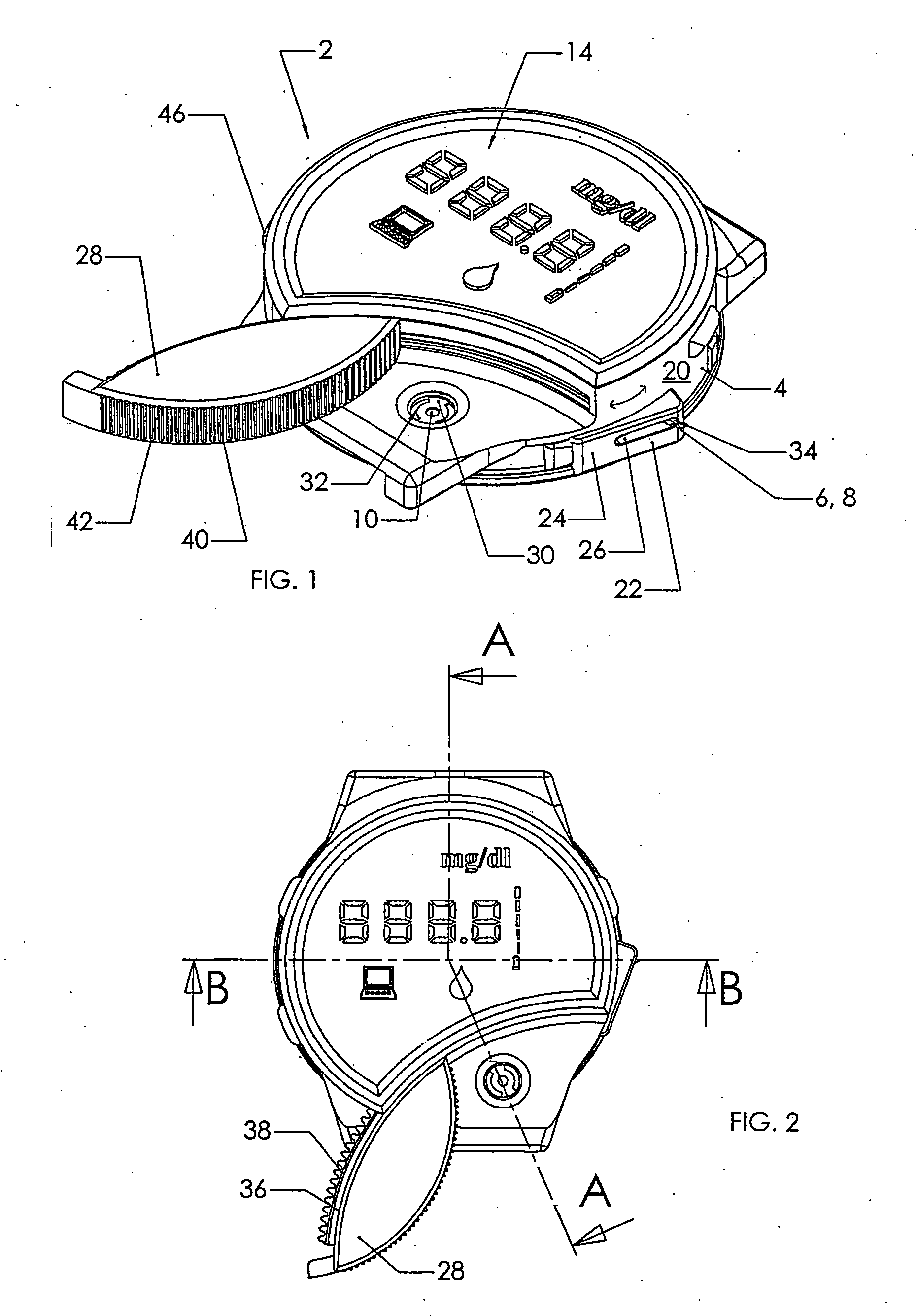
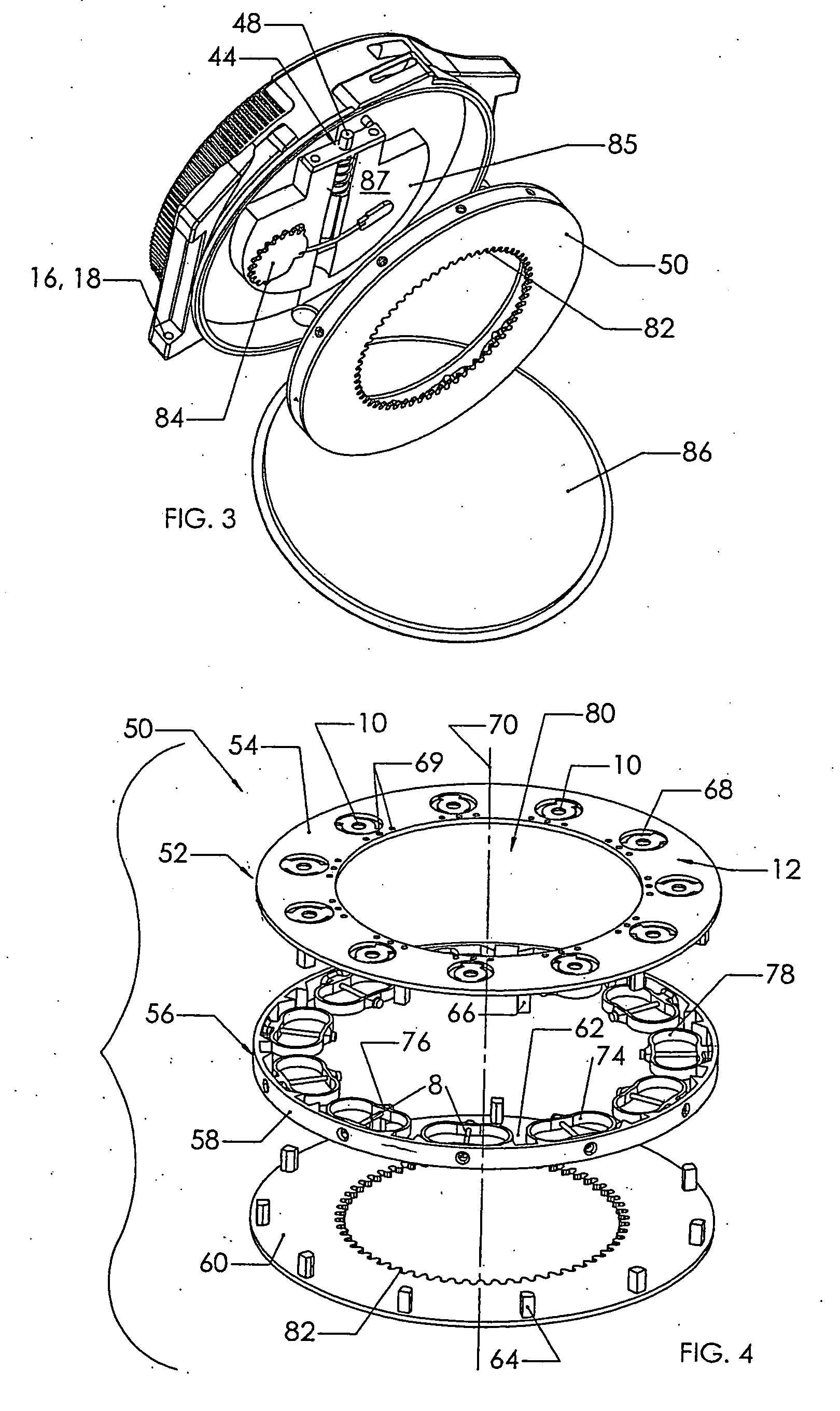
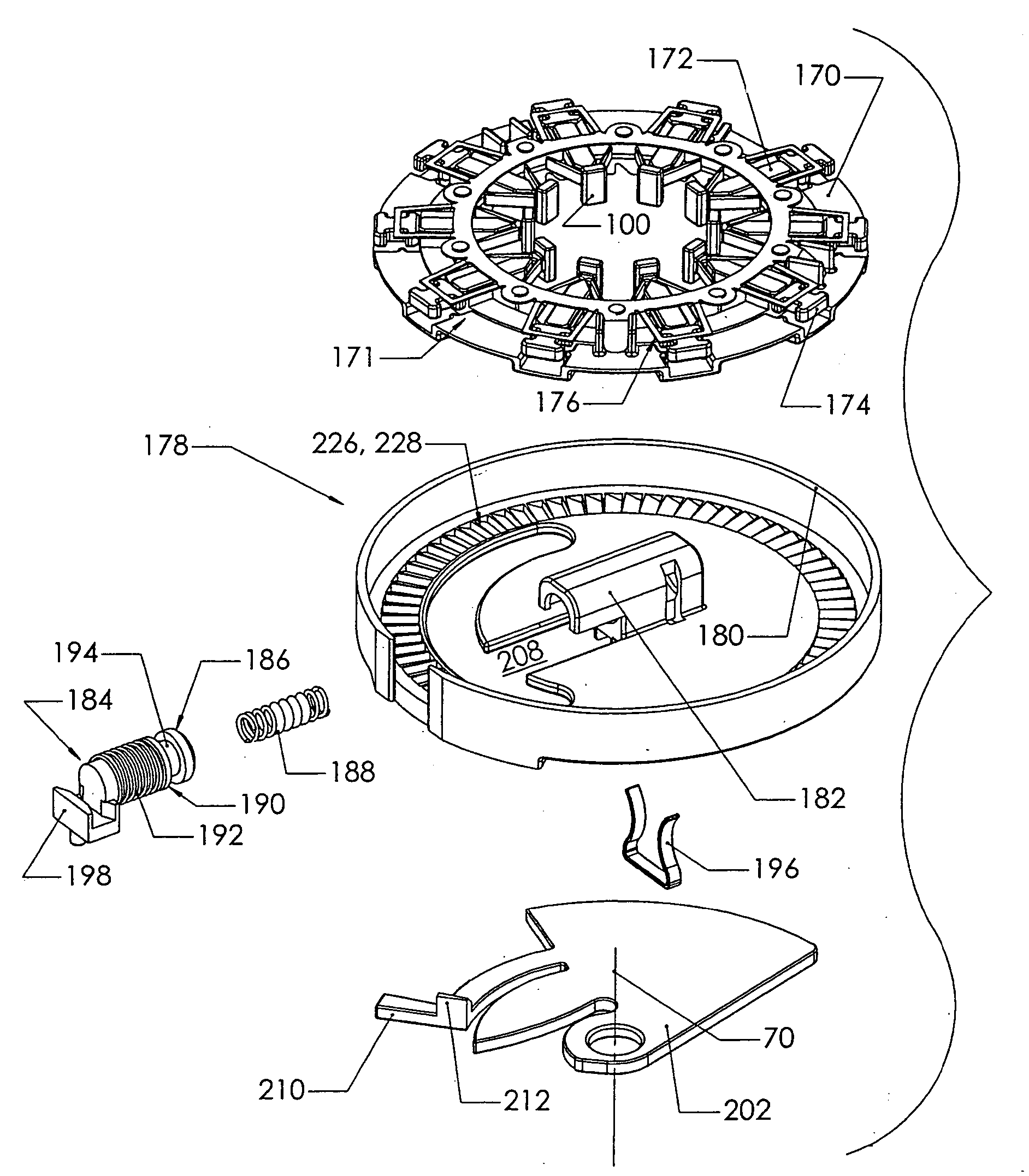
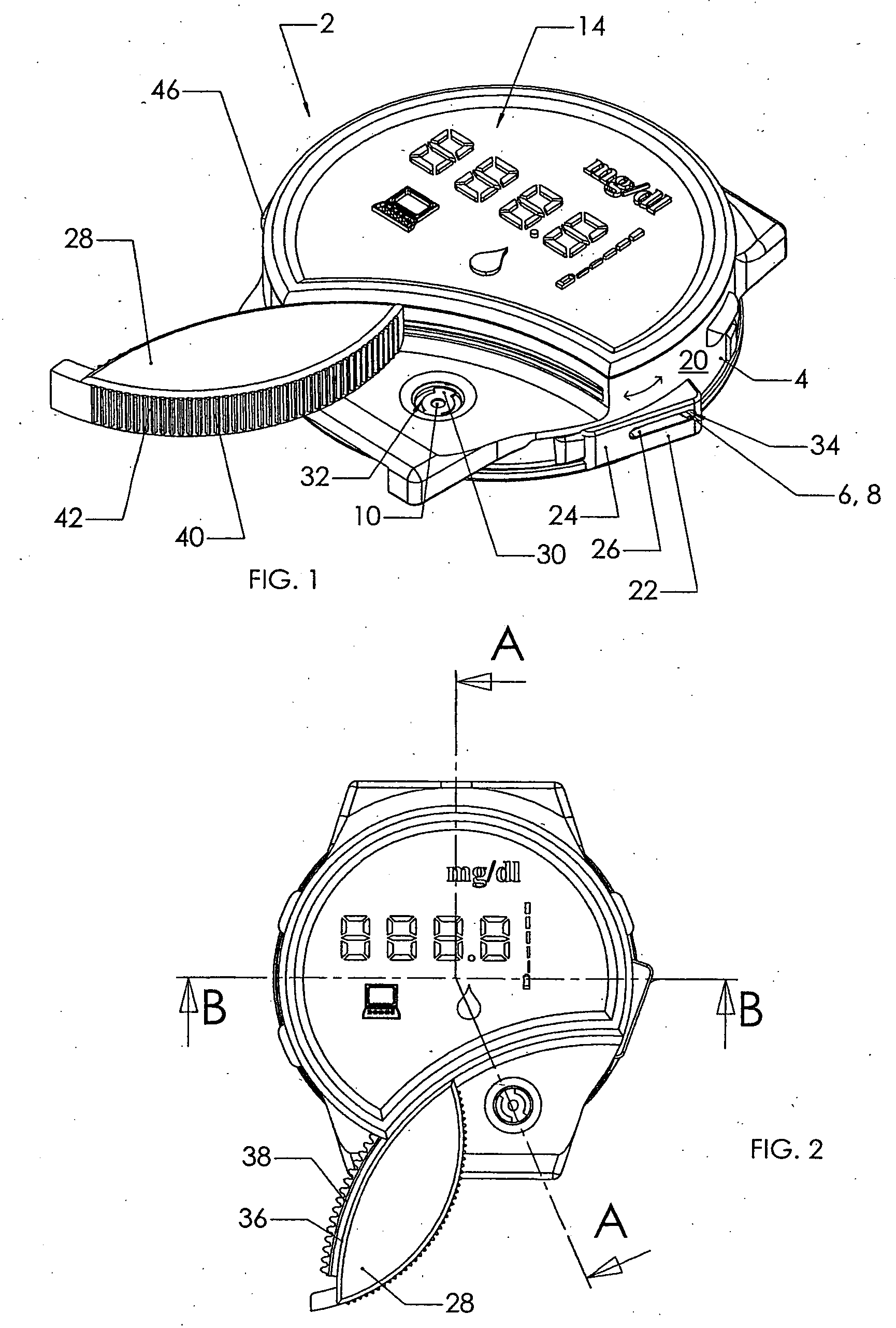
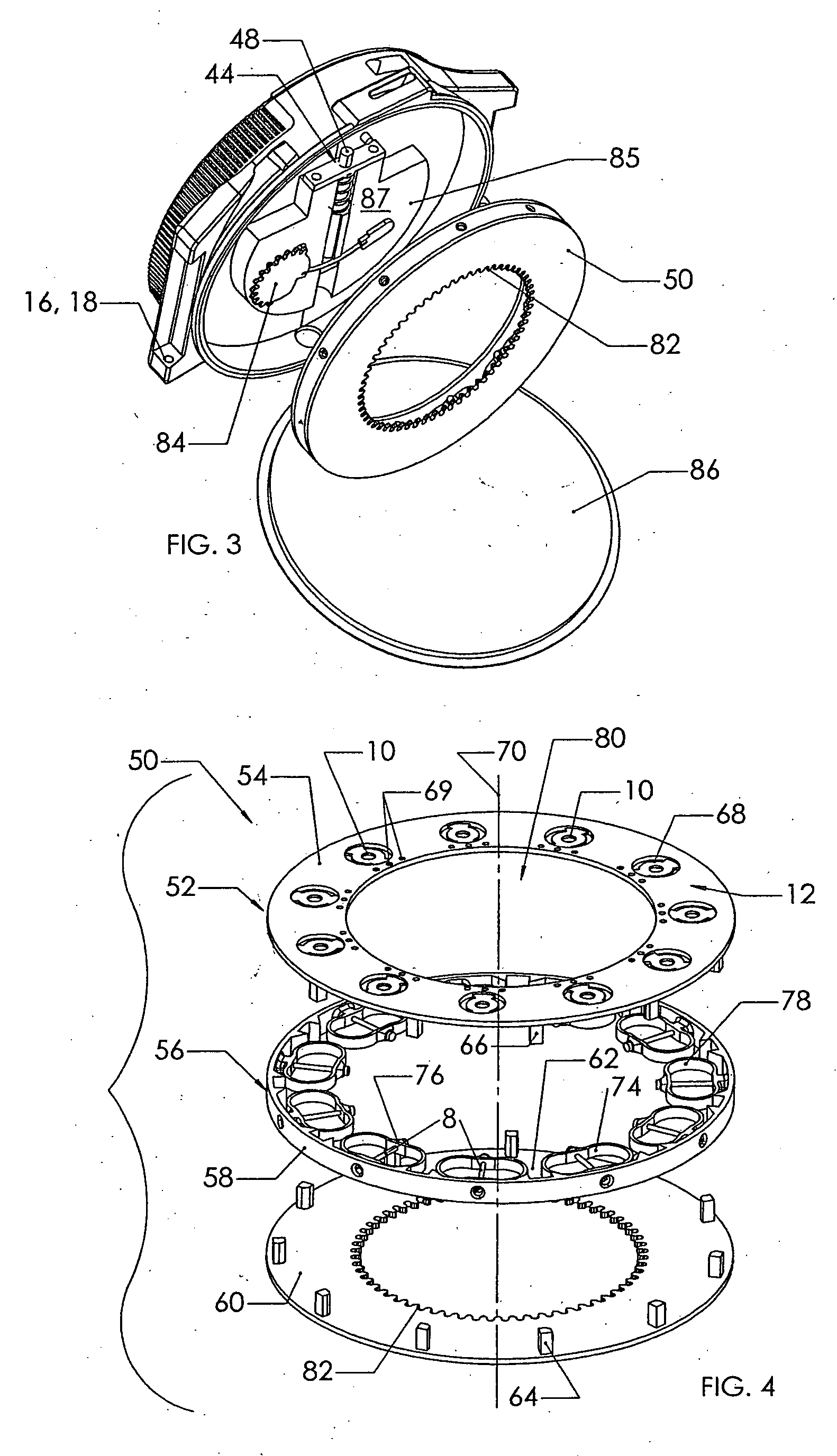
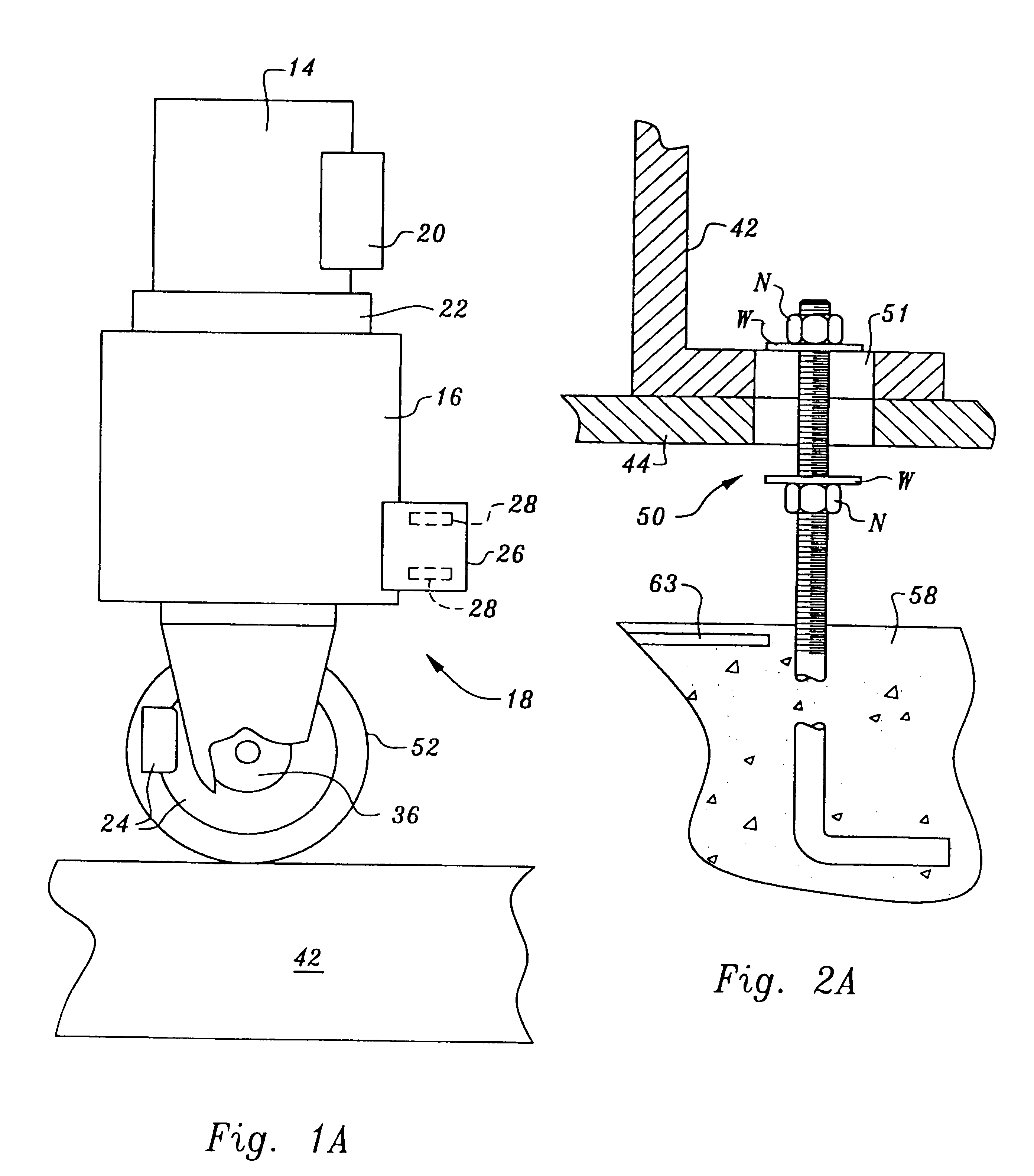
Blood sampling device
A device (302) for sampling and / or analyzing blood or other body fluid of a subject. A housing (306) contains a plurality of lancets (308) and optionally includes test elements (324) to take up a sample of blood, an evaluation system and a display. A complete system that can be handled as a single device, for example in the form of a wristwatch, includes a multiplicity of test elements (324) and lancets (308), which can be brought successively to a working position to perform multiple measurements. A cassette or carrier (320) includes multiple lancets (308) and / or test elements (324), for insertion into the device.
Owner:FACET TECH LLC
Blood sampling device
ActiveUS20040230216A1Preserve sterilityGood removal effectSurgical needlesCatheterDisplay deviceEngineering
A device for sampling and / or analyzing blood or other body fluid of a subject. A housing contains a plurality of lancets and optionally includes test elements to take up a sample of blood, an evaluation system and a display. A complete system that can be handled as a single device, for example in the form of a wristwatch, includes a multiplicity of test elements and lancets, which can be brought successively to a working position to perform multiple measurements. A cassette or carrier includes multiple lancets and / or test elements, for insertion into the device.
Owner:FACET TECH LLC
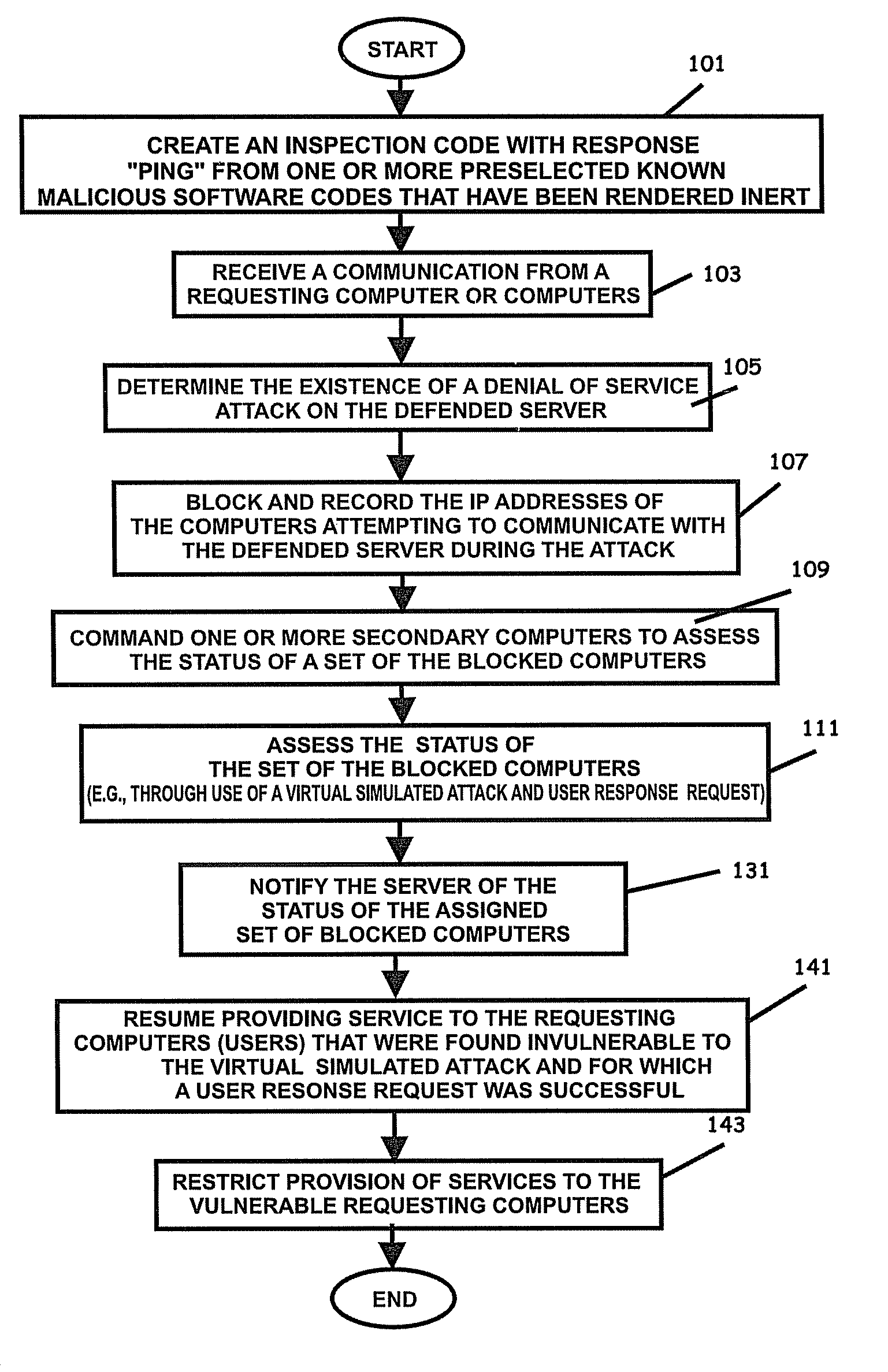
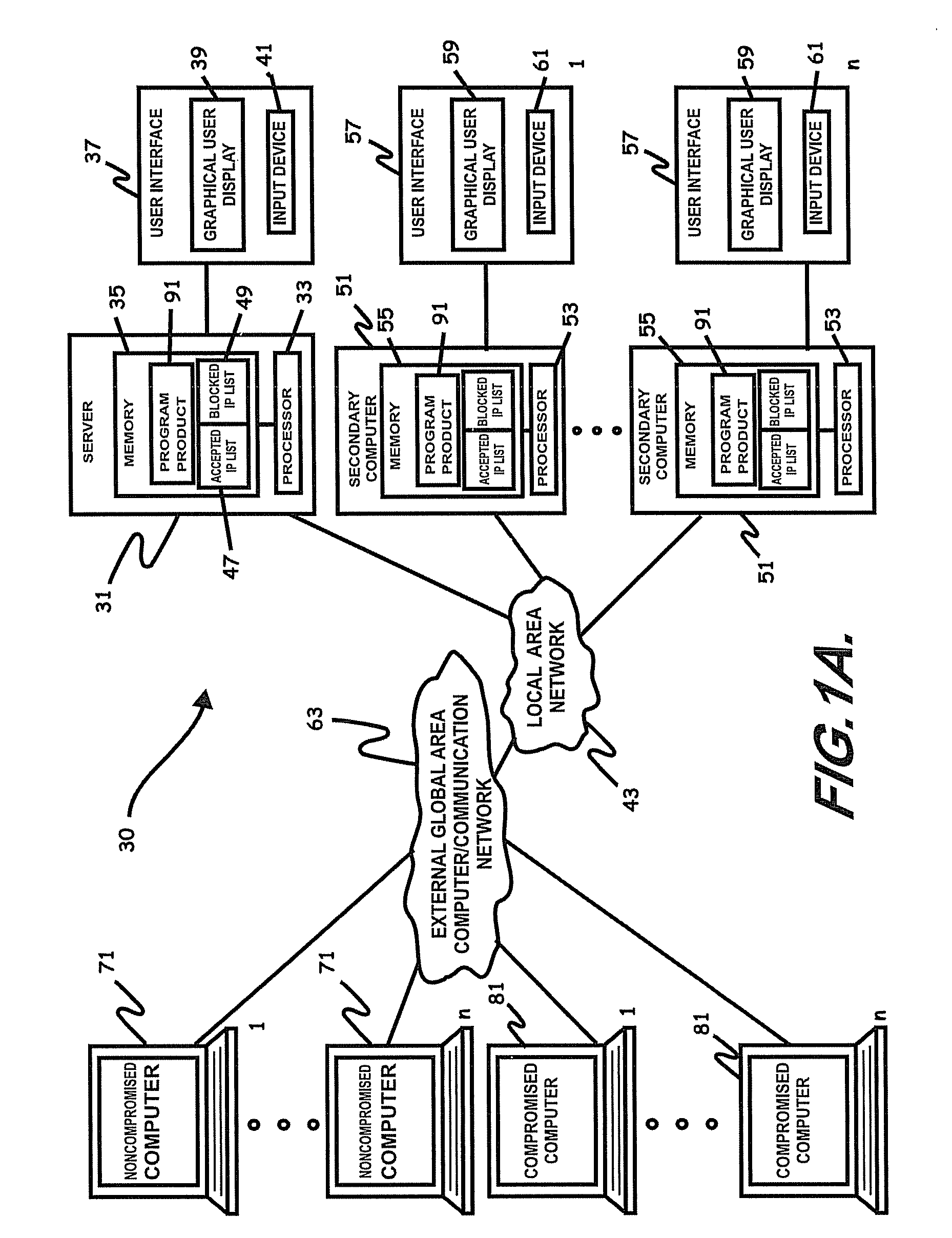
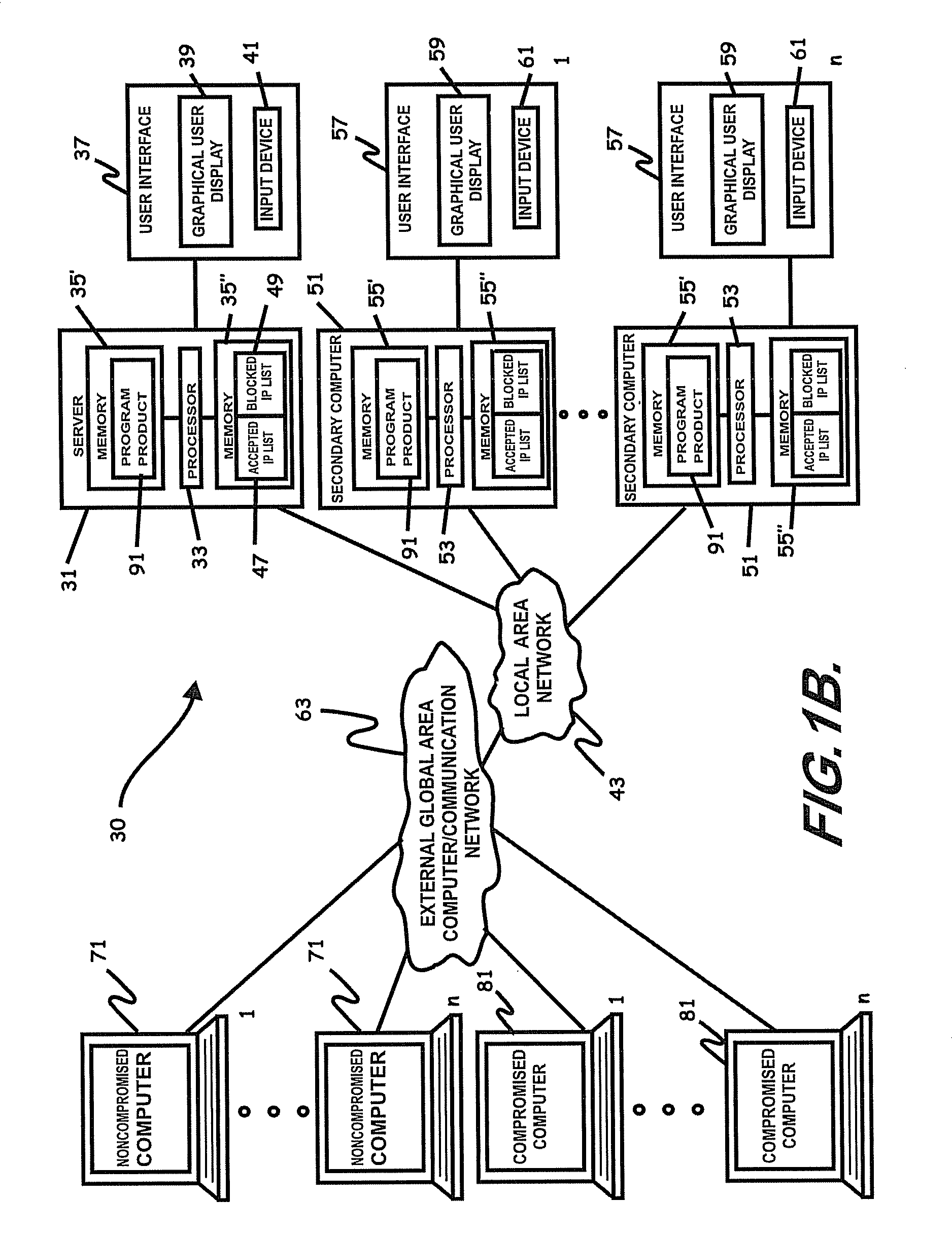
Internet security dynamics assessment system, program product, and related methods
ActiveUS8069471B2Prevent malicious attacksLimited accessMemory loss protectionDigital data processing detailsIp addressThe Internet
Owner:LOCKHEED MARTIN CORP
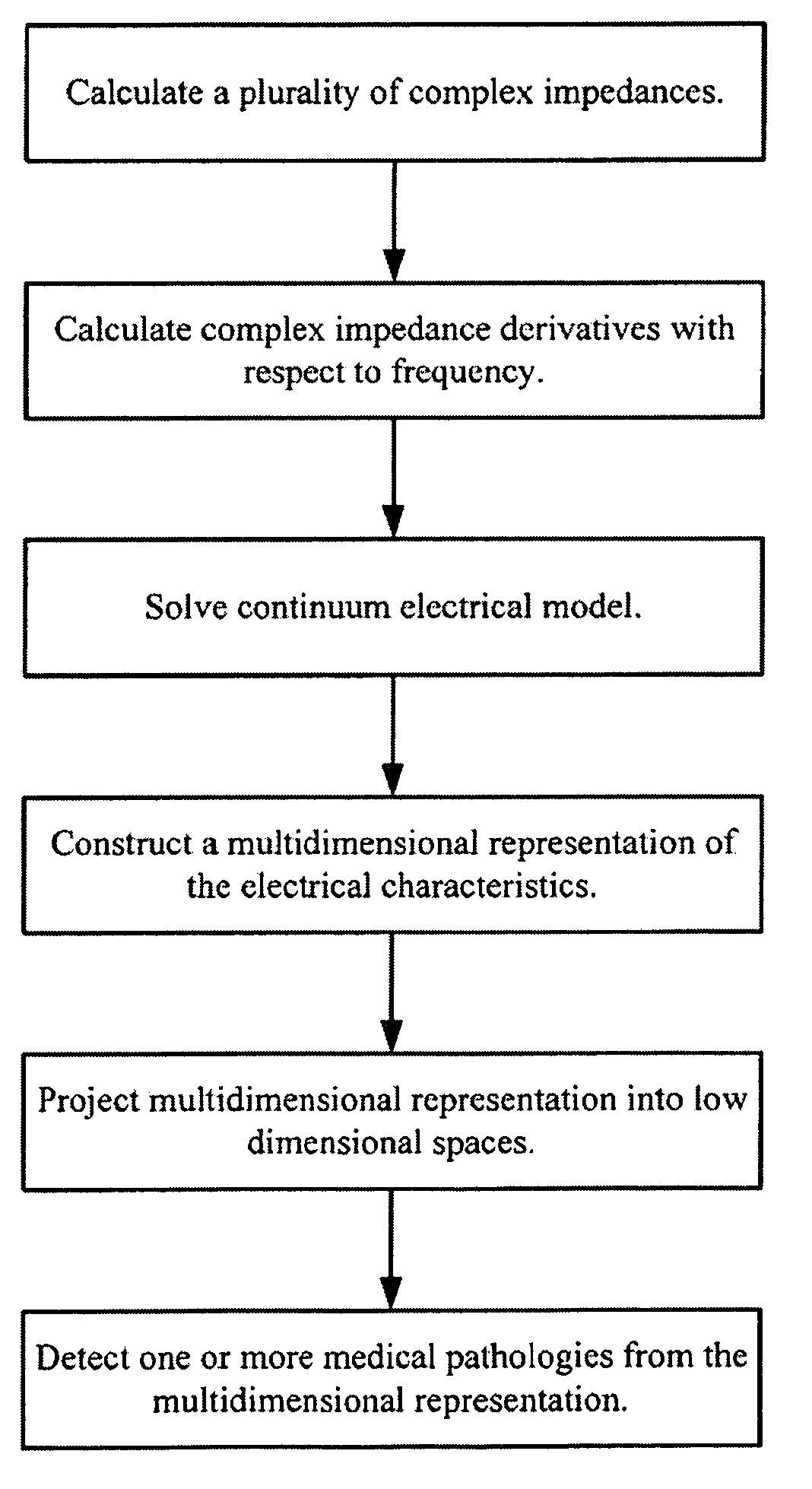
Multidimensional bioelectrical tissue analyzer
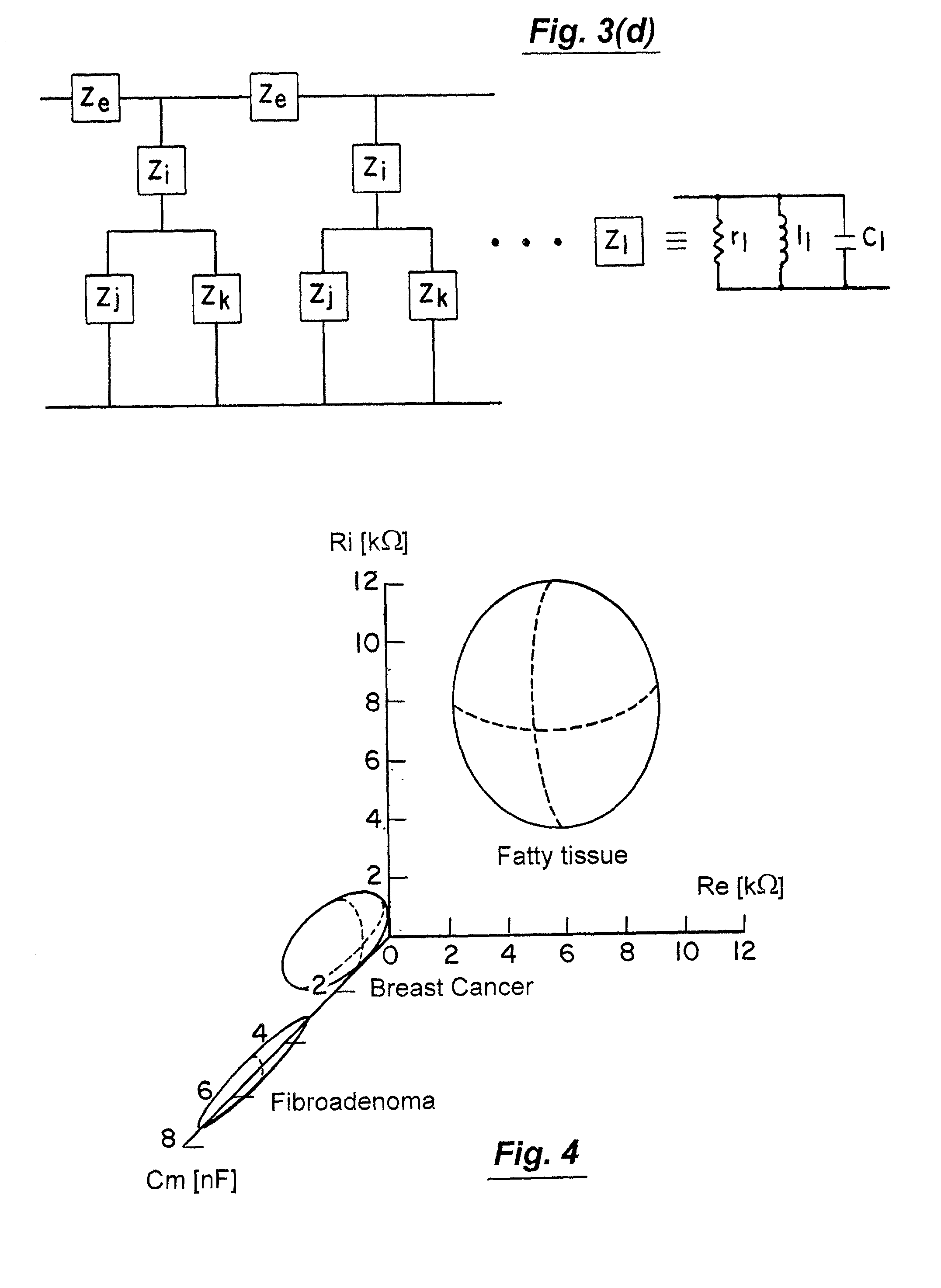
A method and apparatus that use complex impedance measurements of tissue in human or animal bodies for the detection and characterization of medical pathologies is disclosed. An analysis of the complex impedance measurements is performed by a trained evaluation system that uses a nonlinear continuum model to analyze the resistive, capacitive, and inductive measurements collected from a plurality of sensing electrodes. The analysis of the impedance measurements results in the construction of a multidimensional space that defines the tissue characteristics, which the trained evaluation system uses to detect and characterize pathologies. The method and apparatus are sufficiently general to be applied to various types of human and animal tissues for the analysis of various types of medical pathologies.
Owner:DELPHINUS MEDICAL TECH
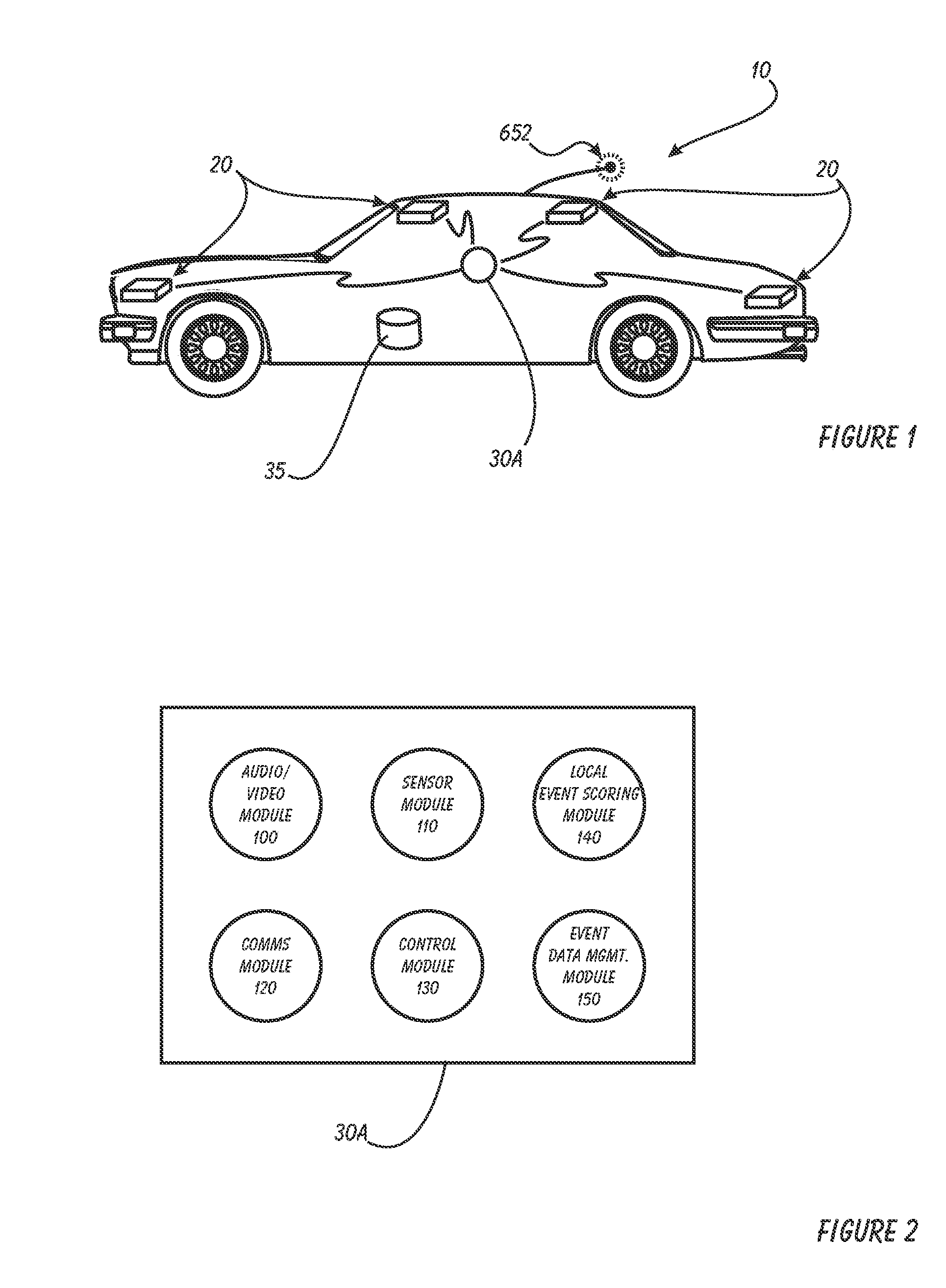
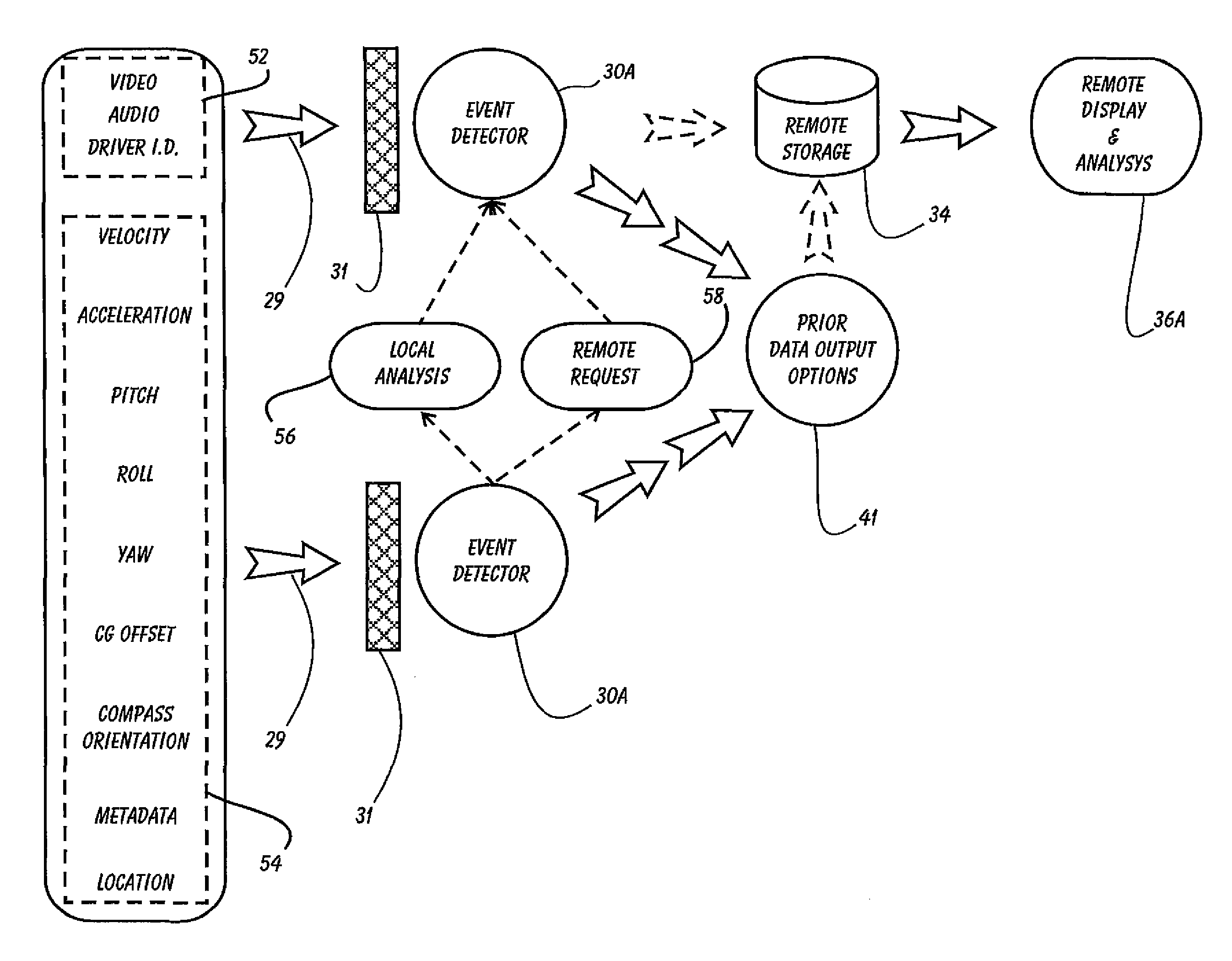
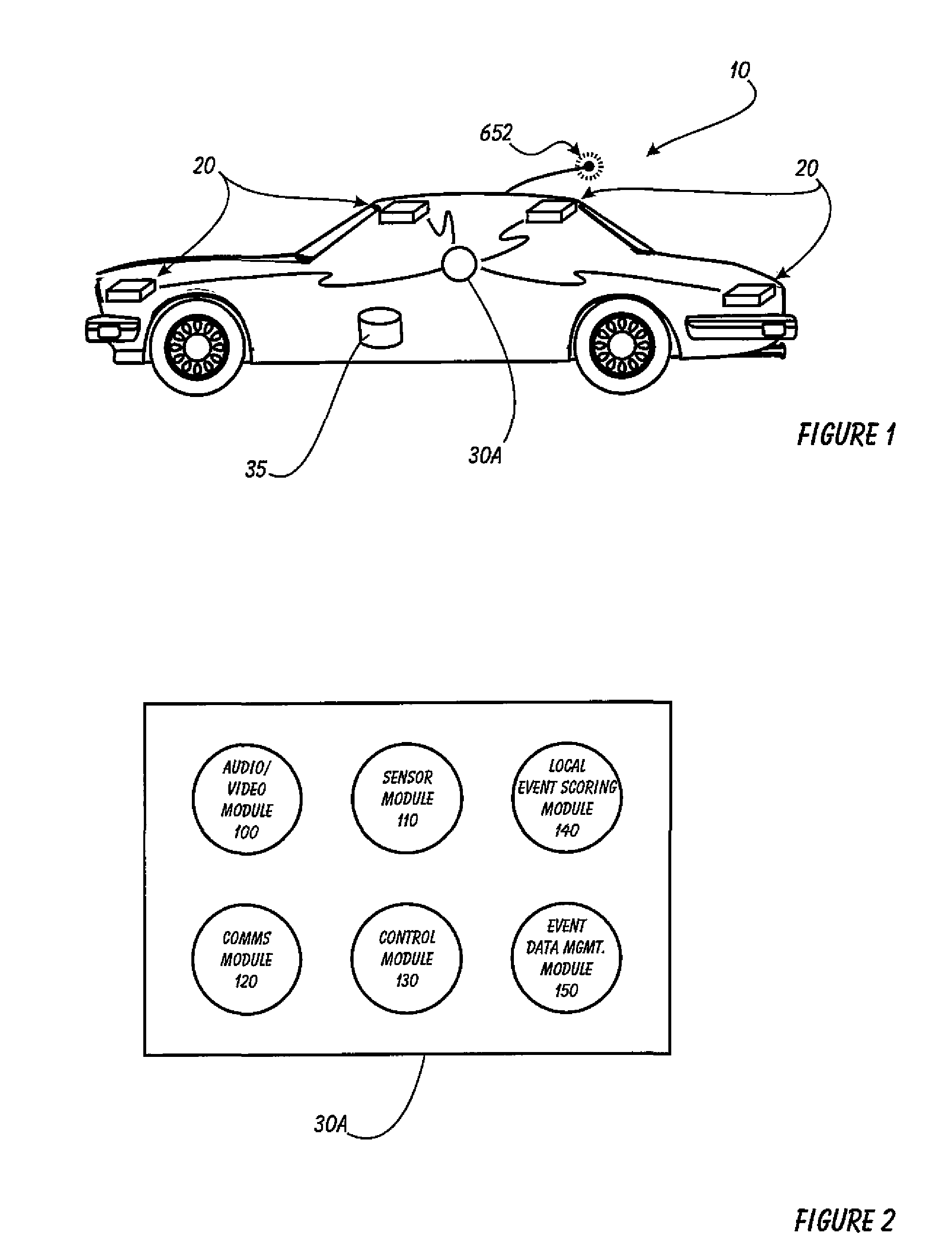
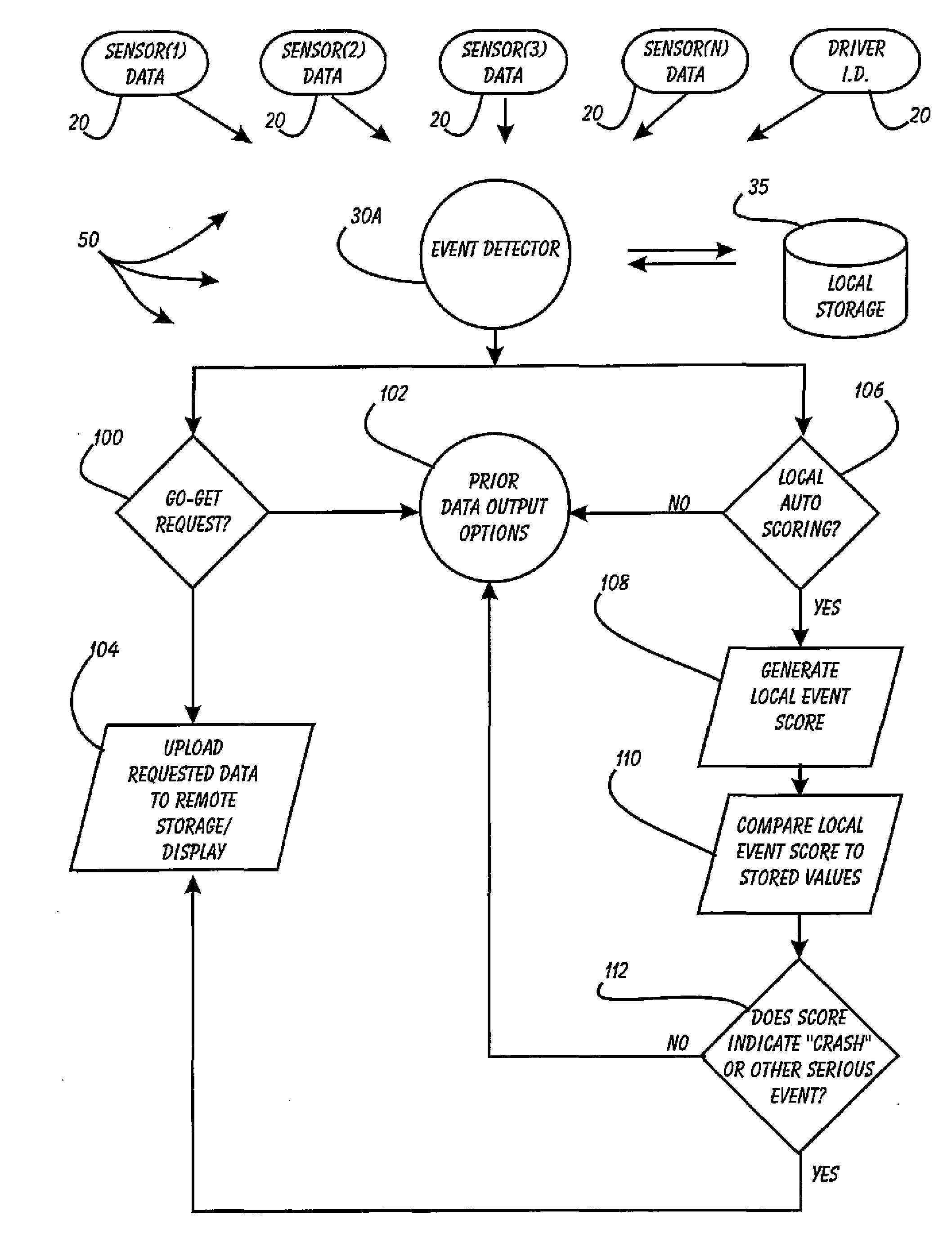
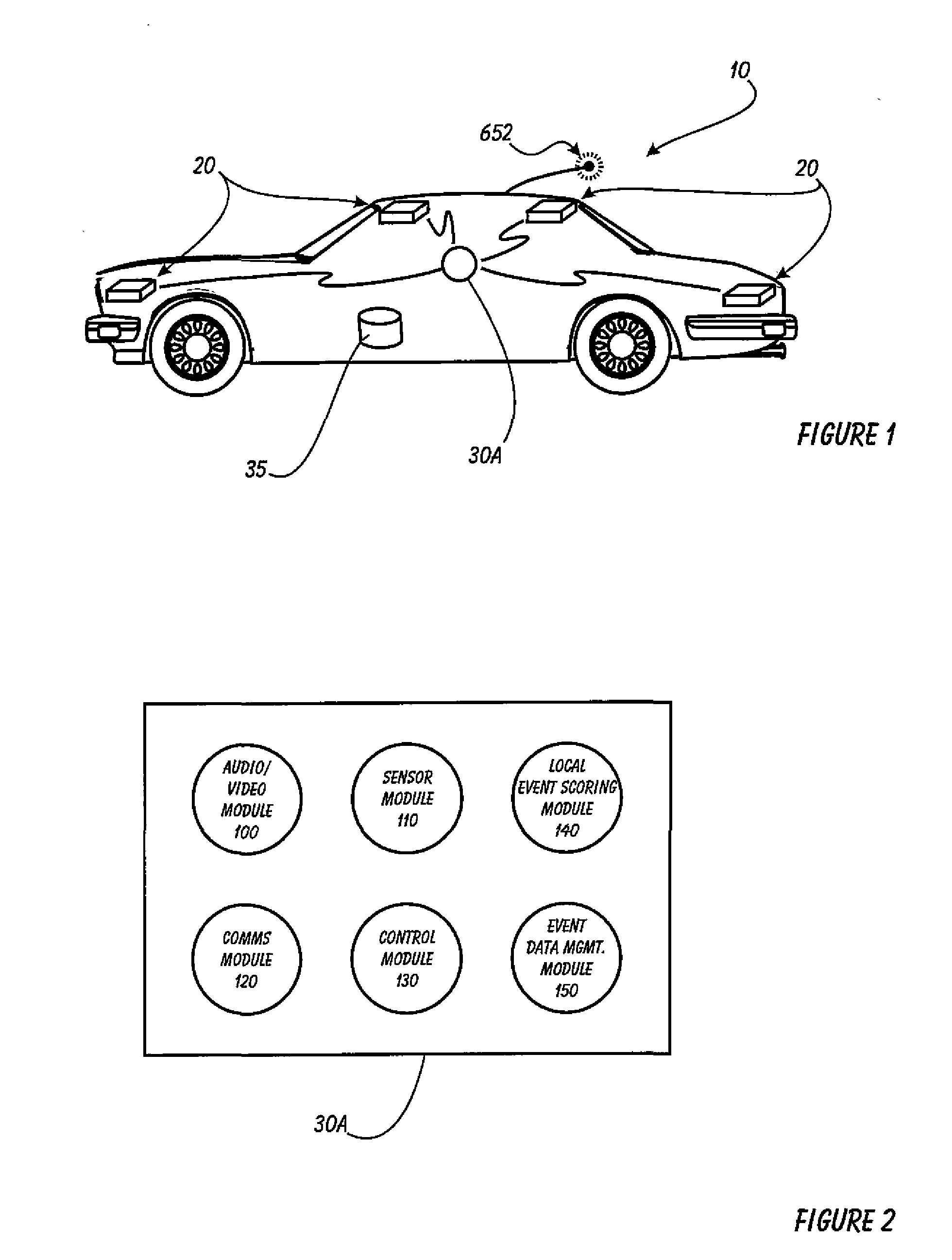
Driver Risk Assessment System and Method Having Calibrating Automatic Event Scoring
ActiveUS20100250021A1Robust and reliable event scoringRobust and reliable and reportingFinanceRegistering/indicating working of vehiclesDriver/operatorDependability
The system and method provides robust and reliable event scoring and reporting, while also optimizing data transmission bandwidth. The system includes onboard vehicular driving event detectors that record data related to detected driving events, selectively store or transfer data related to said detected driving events. If elected, the onboard vehicular system will score a detected driving event, compare the local score to historical values previously stored within the onboard system, and upload selective data or data types to a remote server or user if the system concludes that a serious driving event has occurred. Importantly, the onboard event scoring system, if enabled, will continuously evolve and improve in its reliability by being periodically re-calibrated the ongoing reliability results of manual human review of automated predictive event reports. The system may further respond to independent user requests by transferring select data to said user at a variety of locations and formats.
Owner:DRIVECAM
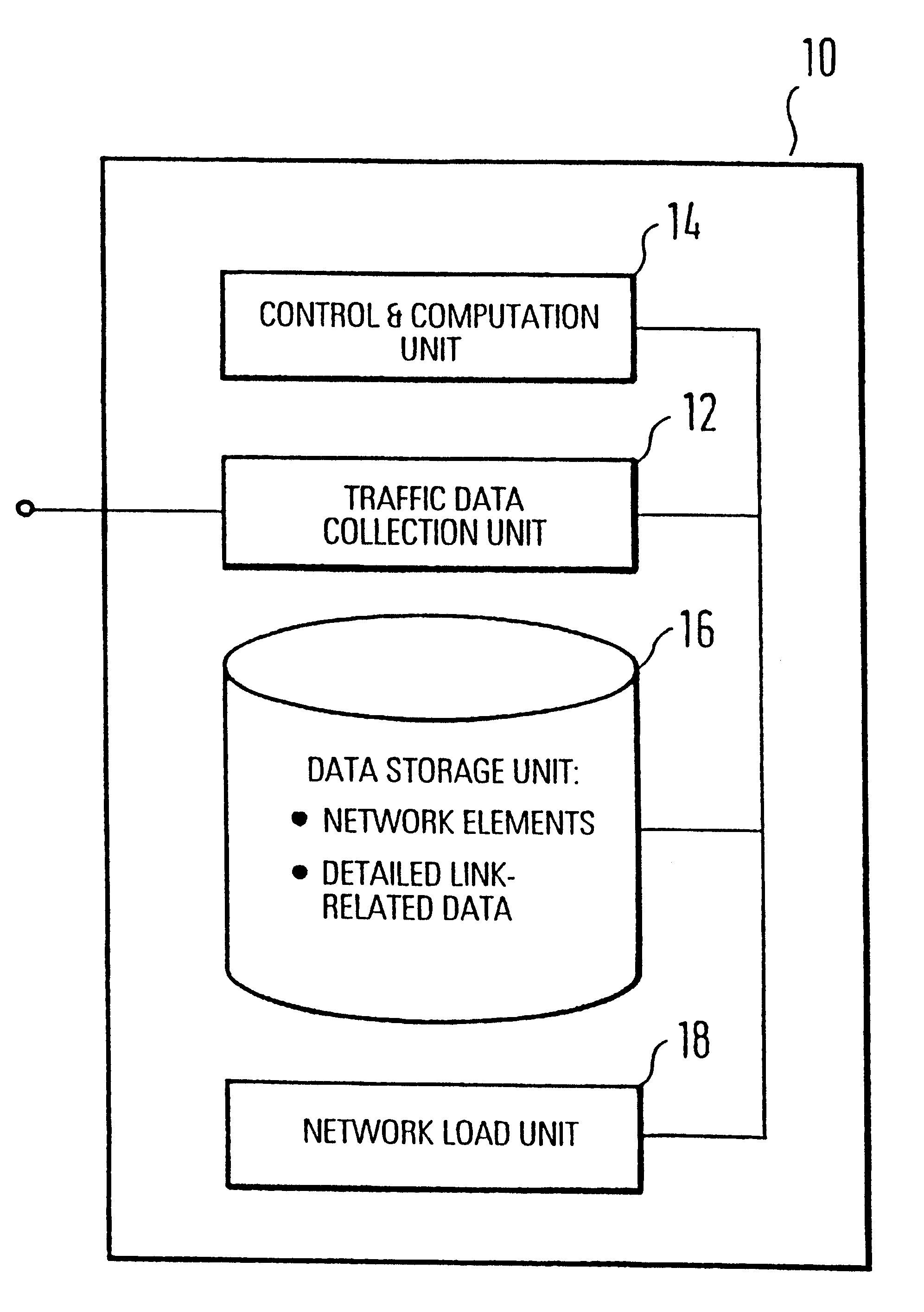
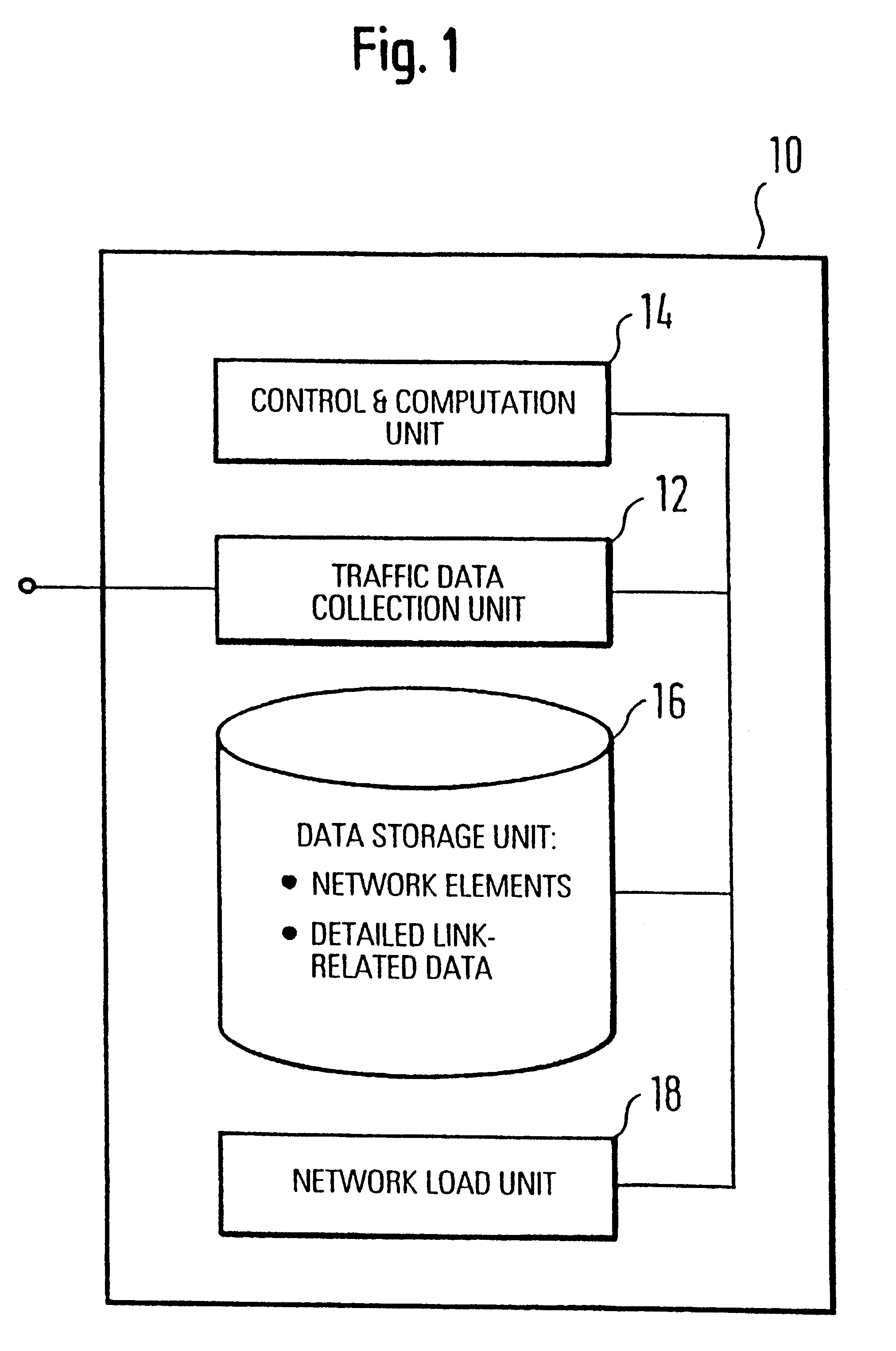
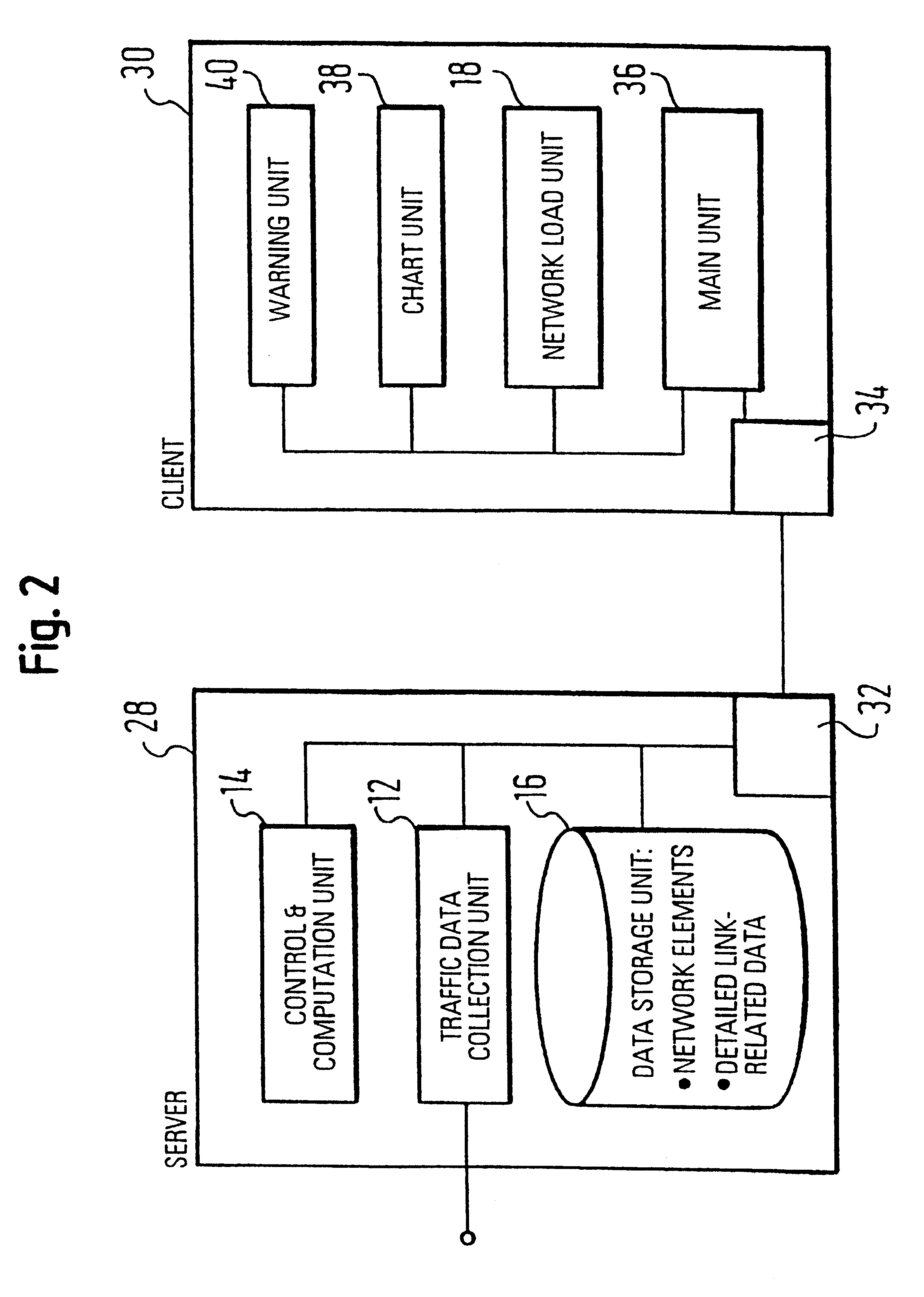
System for traffic data evaluation of real network with dynamic routing utilizing virtual network modelling
InactiveUS6442615B1Multiple digital computer combinationsData switching networksNetwork modelAdaptive routing
To provide an improved approach to traffic data evaluation in a network using dynamic routing there is provided a traffic data evaluation apparatus for a network using dynamic routing comprising traffic data collection means (12) to collect data with respect to a real traffic flow in the network. Further, the traffic data evaluation apparatus comprises a network modelling unit (14, 16) to model the network through a virtual network having virtual links without capacity restrictions imposed thereon. Still further, there is provided a network load evaluation means (18) to map the real traffic flow onto the virtual network assuming optimal routing and to compare the capacity used for each virtual link with the capacity assigned thereto. Thus, it is possible to draw conclusions on the network load by real network measurements also for a network using a dynamic routing protocol.
Owner:TELEFON AB LM ERICSSON (PUBL)
Multidimensional bioelectrical tissue analyzer
Owner:DELPHINUS MEDICAL TECH
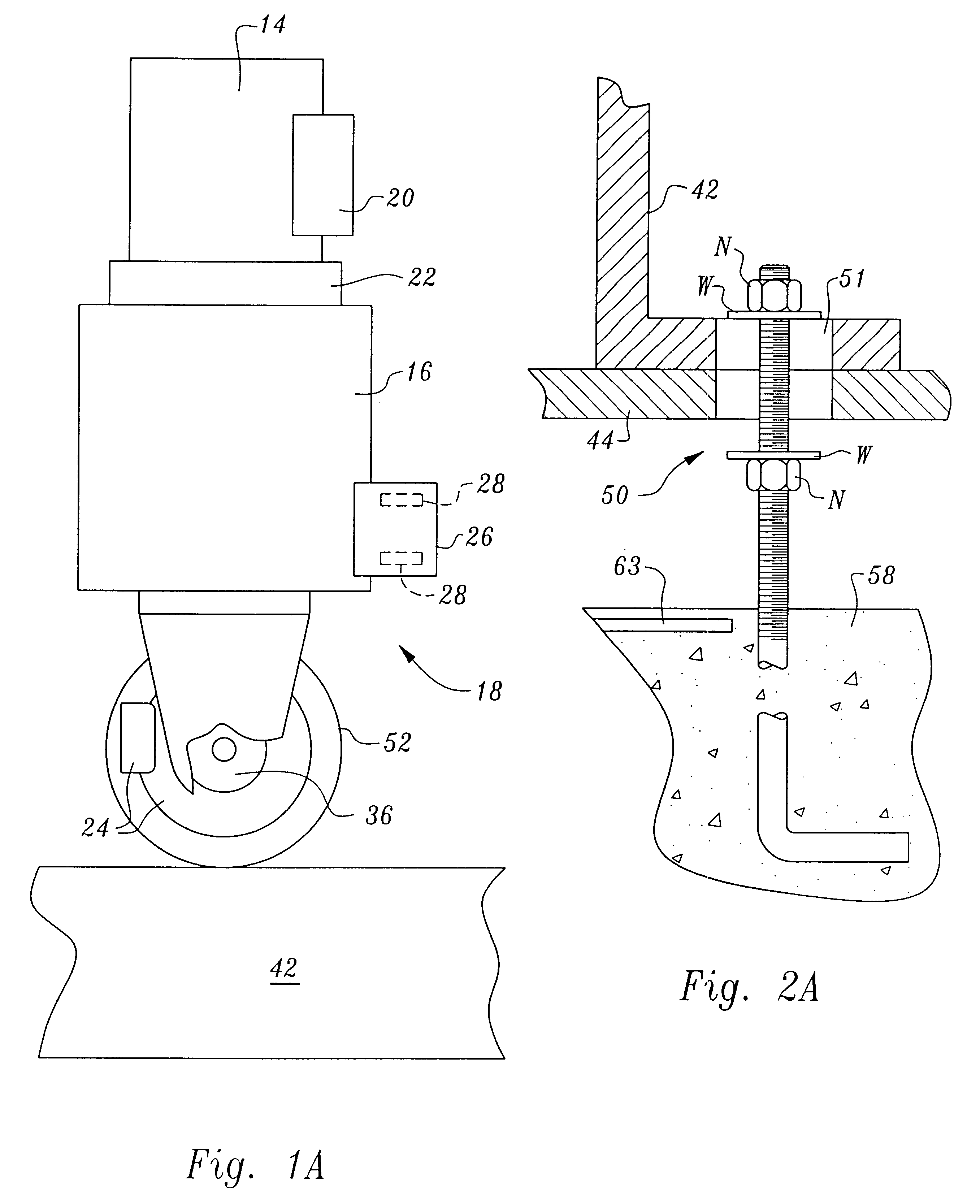
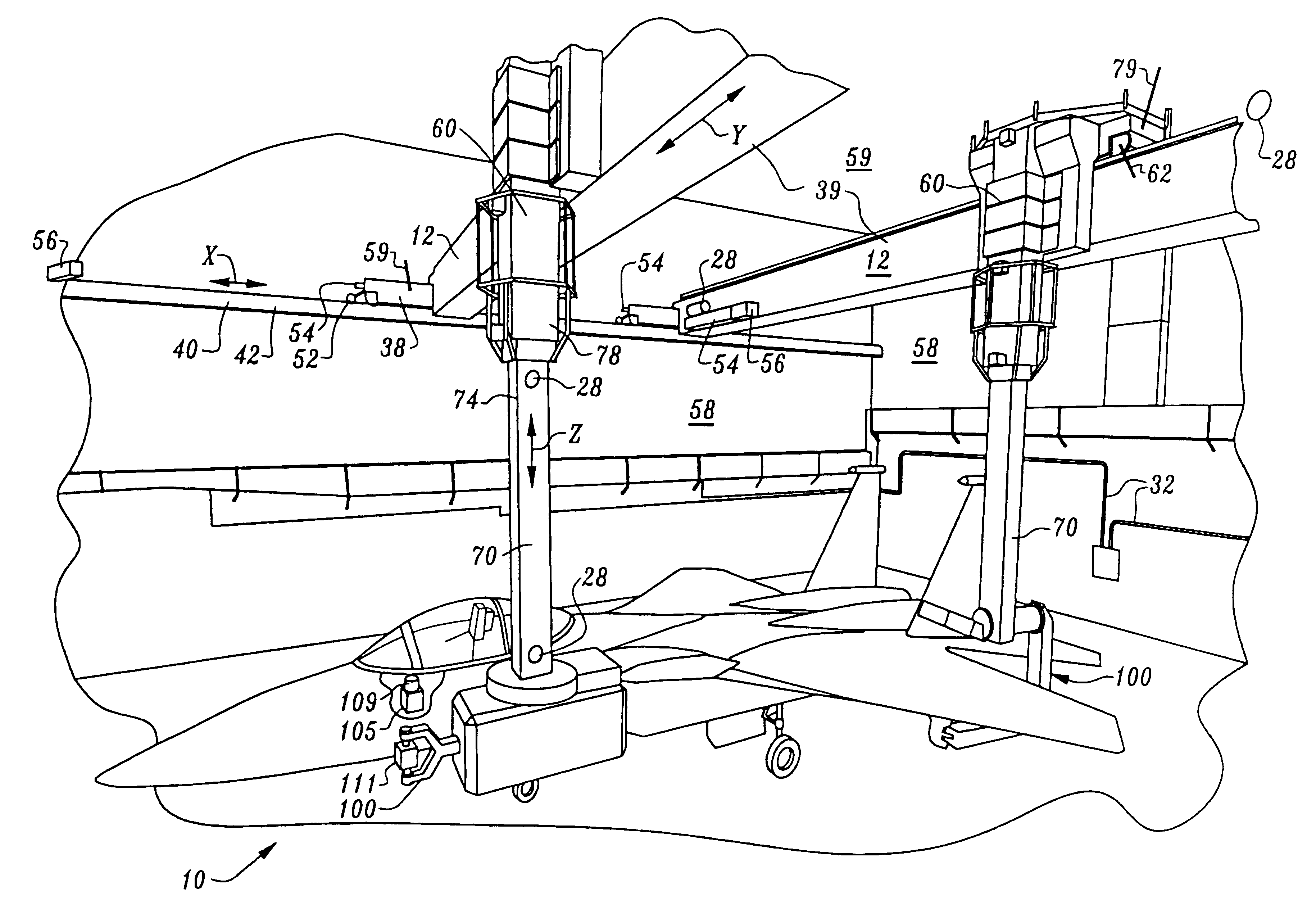
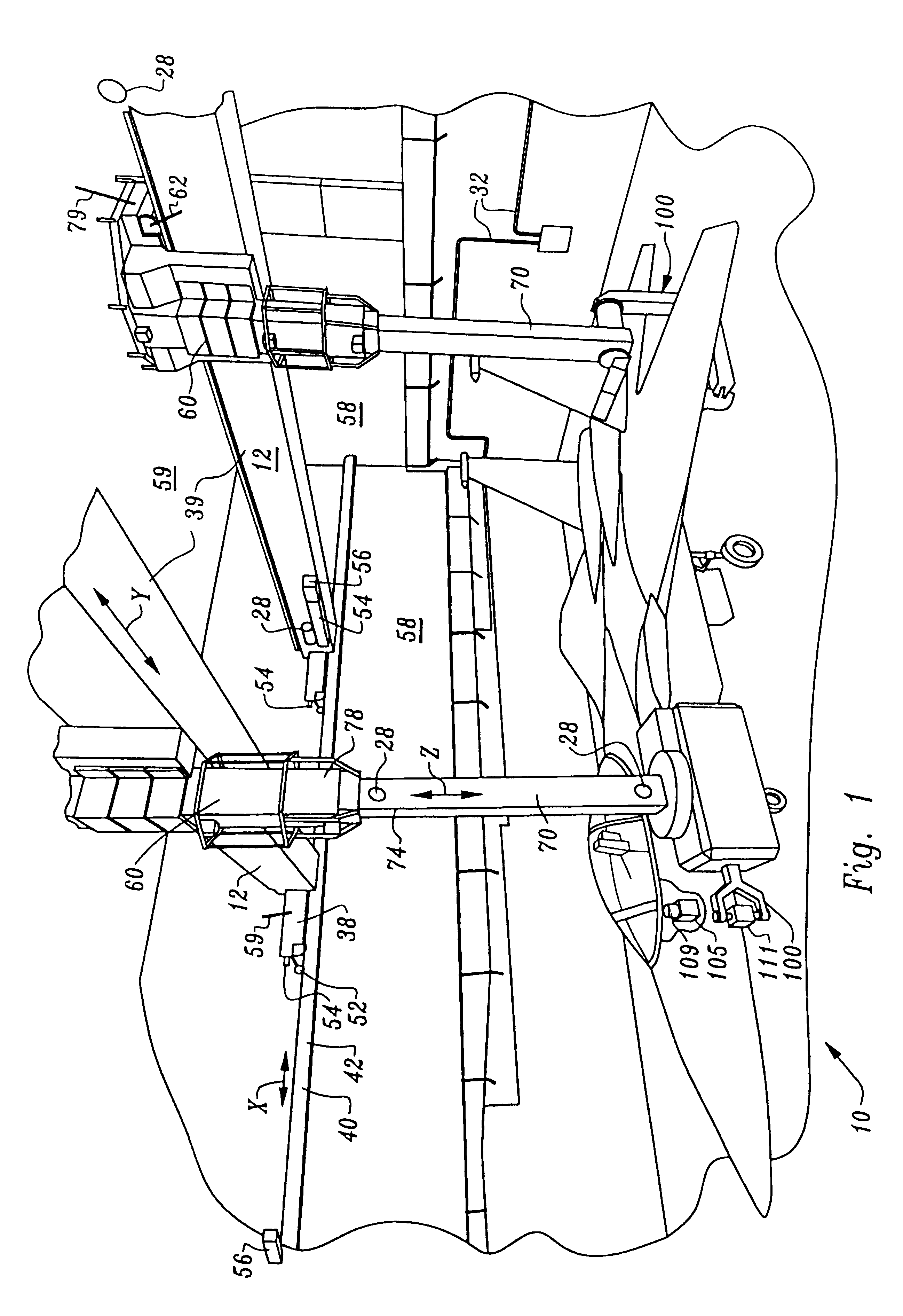
Non-destructive inspection, testing and evaluation systems for intact aircraft and components and method therefore
InactiveUS6637266B1Accurate predictionEasy to useVibration measurement in solidsAnalysing solids using sonic/ultrasonic/infrasonic wavesRadiographic ExamNon destructive
Owner:FROOM DOUGLAS ALLEN
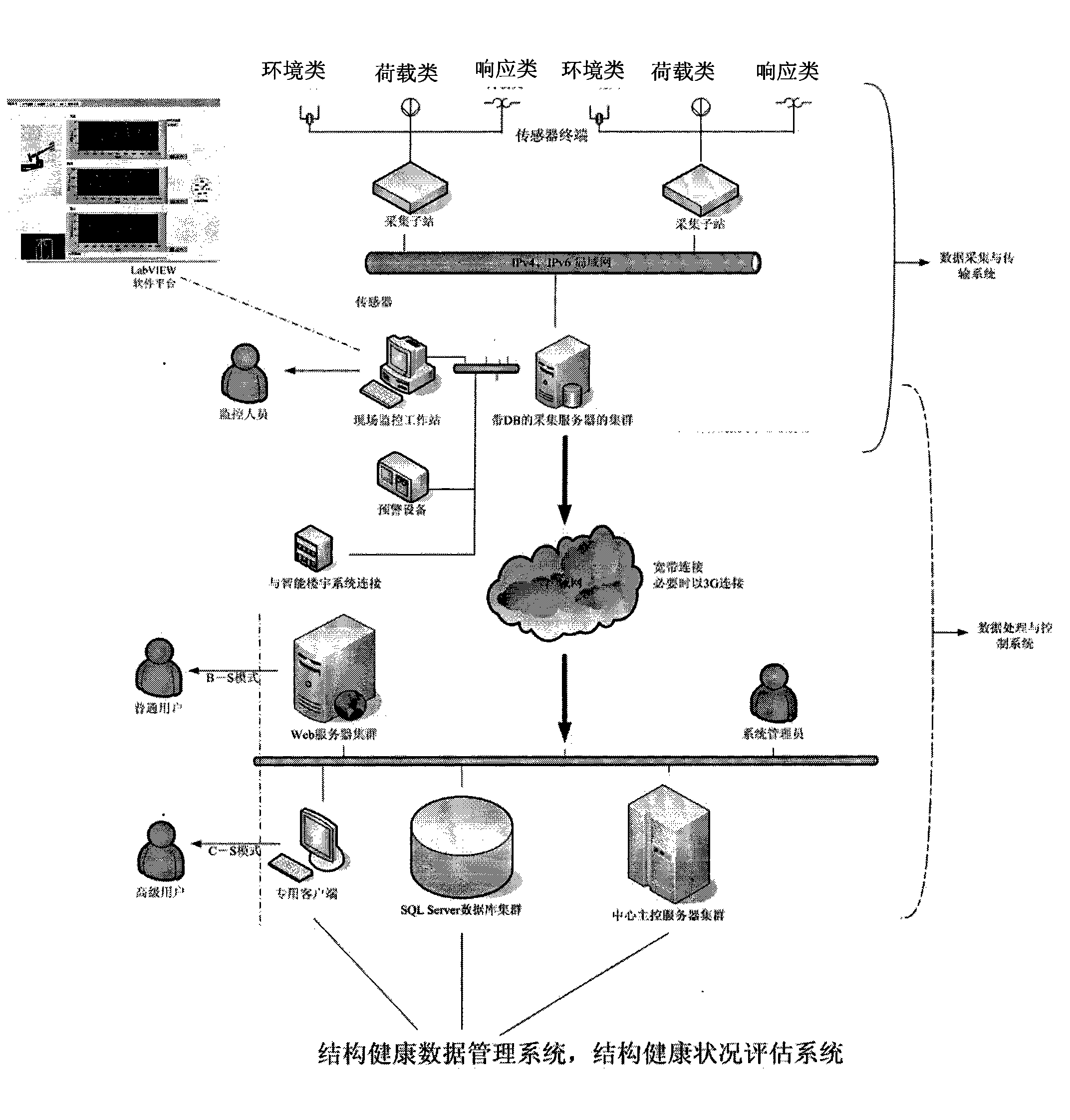
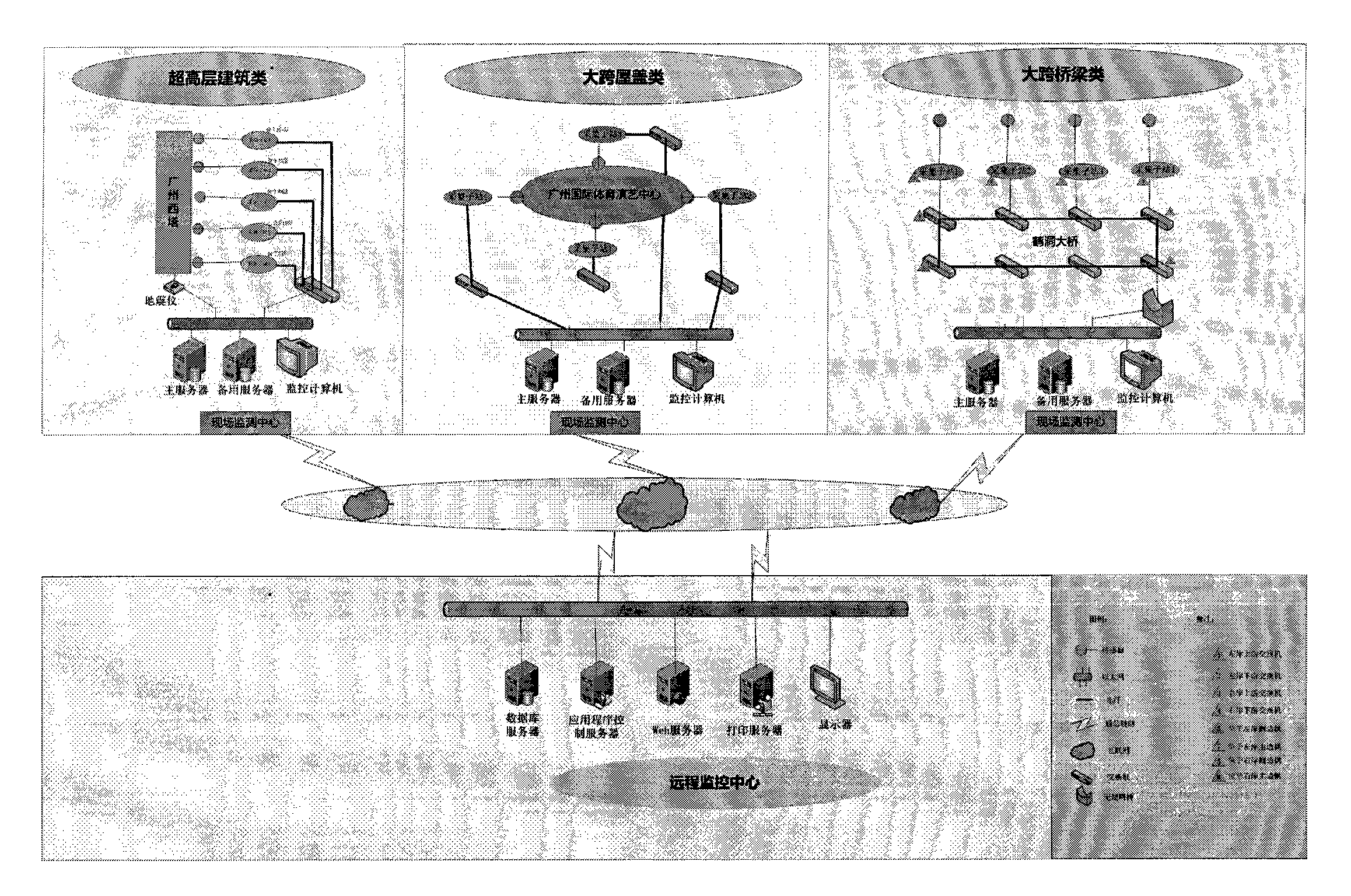
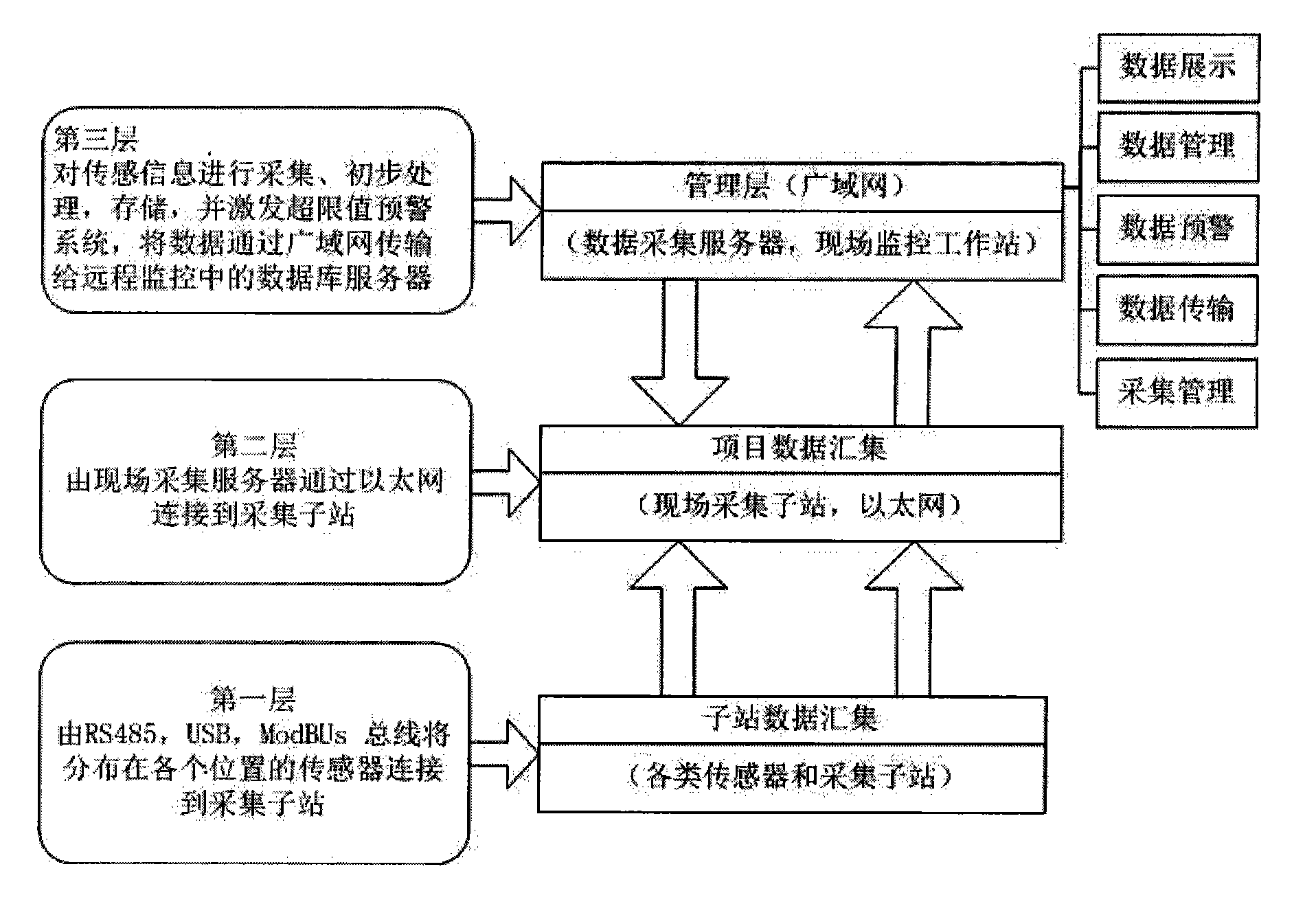
Health monitoring system for structures of great building and bridge
InactiveCN102147597ARealize unified monitoringRealize functionMeasurement devicesComputer controlStructural health monitoringData acquisition
The invention discloses a health monitoring system for structures of a great building and a bridge, which comprises sensor terminals, a data acquisition and transmission system, a data processing and control system, a structural health data management system and a structural health condition evaluation system, wherein the data acquisition and transmission system is a distributed measurement system; a plurality of data acquisition sub-stations read data from the corresponding sensor terminals and transmit the data to a field monitoring work station; the data acquisition and transmission system is connected with the data processing and control system through a network; the data processing and control system is connected to the structural health data management system; and the structural health data management system is connected and interacted with the structural health condition evaluation system. The health monitoring system provides an on-line, dynamic and real-time monitoring mode, improves an automated level of structural health monitoring and the reliability, security and generality of the system, provides technical basis for implementation of health monitoring by using a life cycle of the building as a guidance, and provides an advanced and efficient technical measure for structure monitoring of civil engineering.
Owner:GUANGZHOU UNIVERSITY
Non-destructive inspection, testing and evaluation system for intact aircraft and components and method therefore
InactiveUS6378387B1Accurate predictionEasy to useProcessing detected response signalDigital computer detailsRadiographic ExamNon destructive
A non-destructive inspection, testing and evaluation system and process is provided for the review of aircraft components. The system provides for a structure configured to contain an inspection and testing apparatus and the aircraft components under inspection. The structure is lined with shielding to attenuate the emission of radiation to the outside of the structure and has corbels therein to support the components that constitute the inspection and testing apparatus. The inspection and testing apparatus is coupled to the structure, resulting in the formation of a gantry for supporting a carriage and a mast is mounted on the carriage. The inspection and testing equipment is mounted on the mast which forms, in part, at least one radiographic inspection robot capable of precise positioning over large ranges of motion. The carriage is coupled to the mast for supporting and allowing translation of the equipment mounted on the mast. The mast is configured to provide yaw movement to the equipment.
Owner:AEROBOTICS
Driver risk assessment system and method having calibrating automatic event scoring
ActiveUS8508353B2Stable and reliableOptimizing data transmission bandwidthFinanceRegistering/indicating working of vehiclesEngineeringDependability
A Driver Risk Assessment System and Method Having Calibrating Automatic Event Scoring is disclosed. The system and method provide robust and reliable event scoring and reporting, while also optimizing data transmission bandwidth. The system includes onboard vehicular driving event detectors that record data related to detected driving events and selectively store or transfer data related to said detected driving events. If elected, the onboard vehicular system will score a detected driving event, compare the local score to historical values previously stored within the onboard system, and upload selective data or data types to a remote server or user if the system concludes that a serious driving event has occurred. Importantly, the onboard event scoring system, if enabled, will continuously evolve and improve in its reliability by being periodically re-calibrated with the ongoing reliability results of manual human review of automated predictive event reports. The system may further respond to independent user requests by transferring select data to said user at a variety of locations and formats.
Owner:DRIVECAM
Orientation and motion sensing in athletic training systems, physical rehabilitation and evaluation systems, and hand-held devices
ActiveUS7383728B2Improve accuracyHigh sensitivityPerson identificationInertial sensorsObject basedAthletic training
Owner:NOKIA TECH LTD
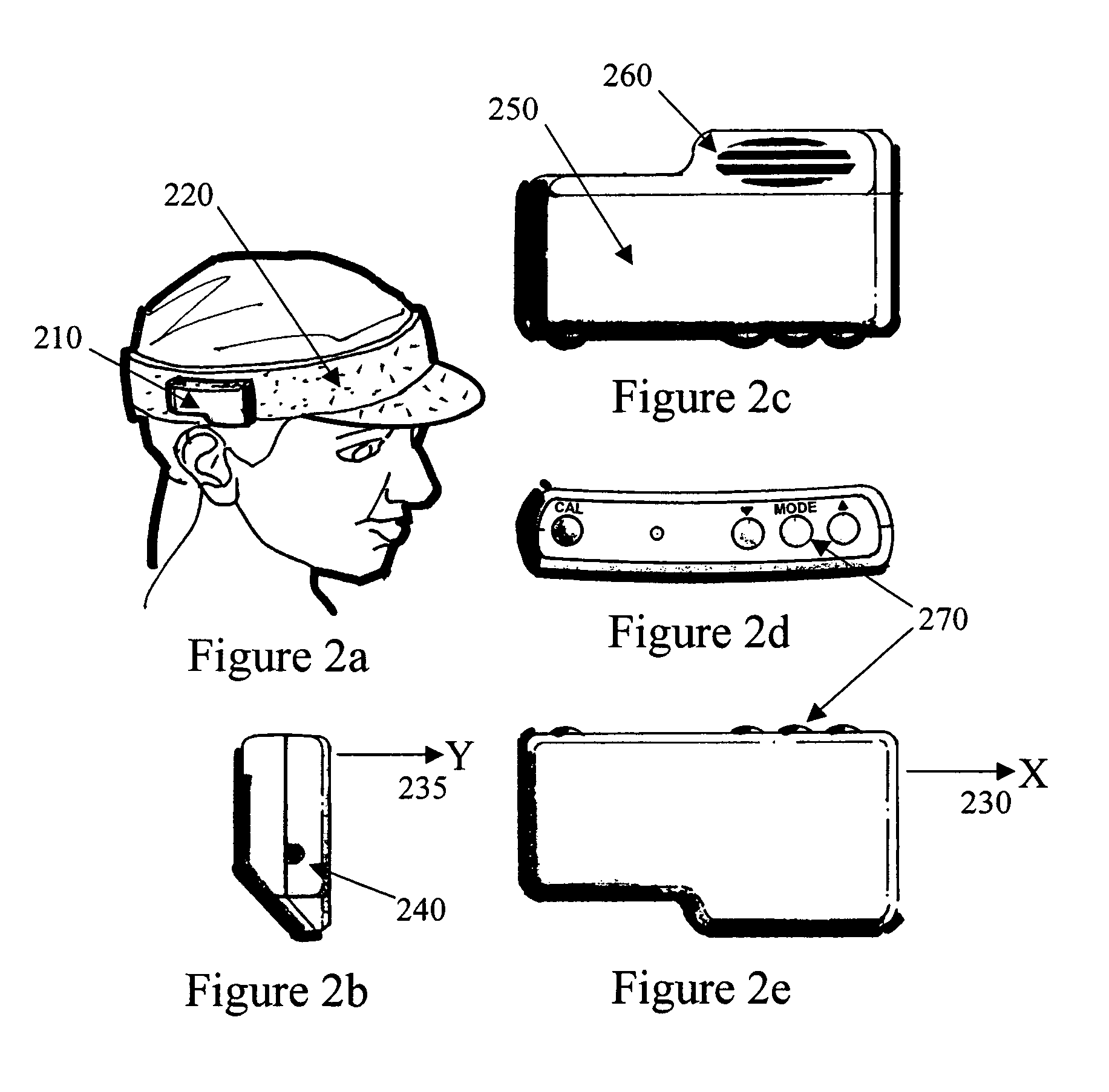
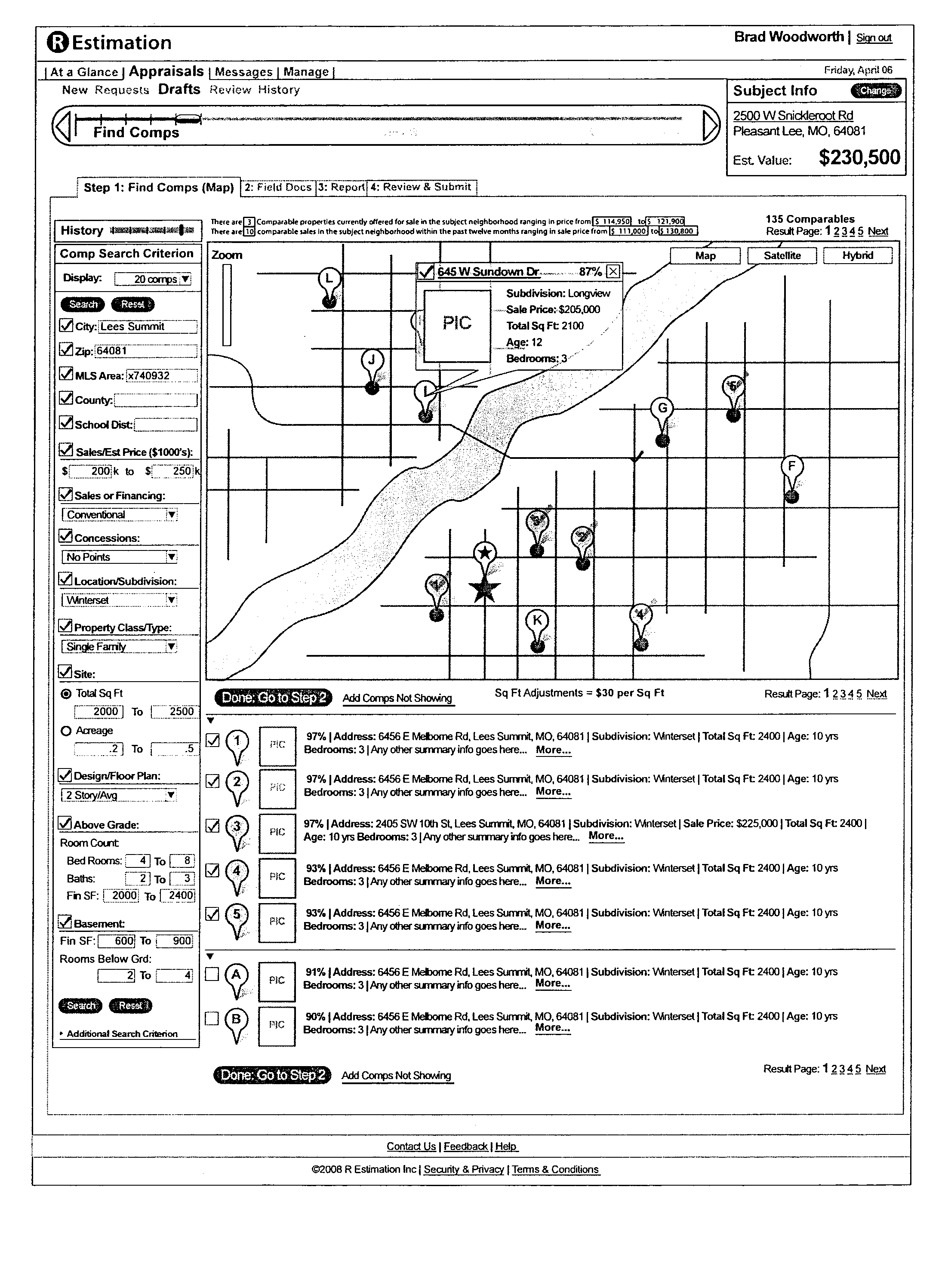
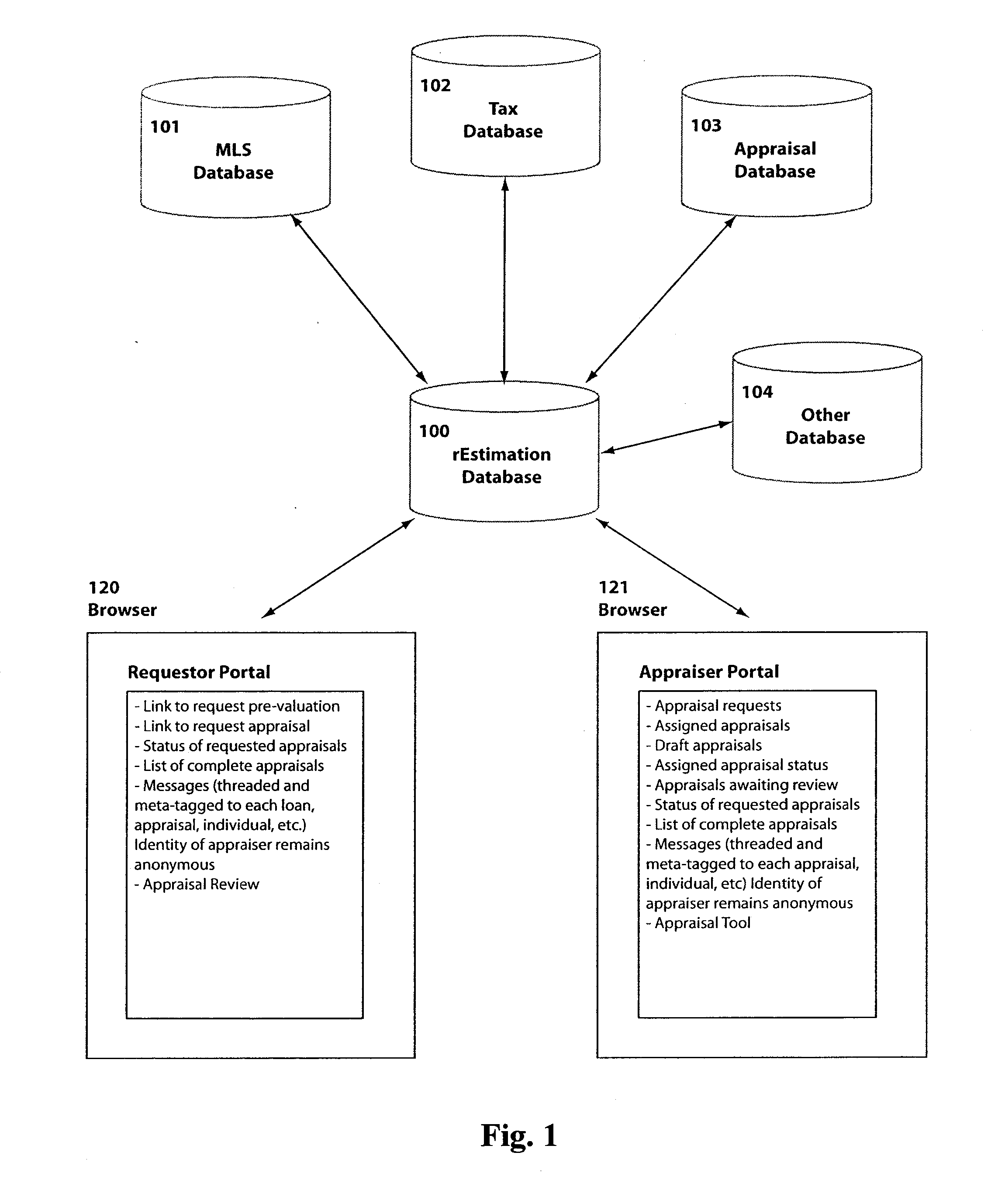
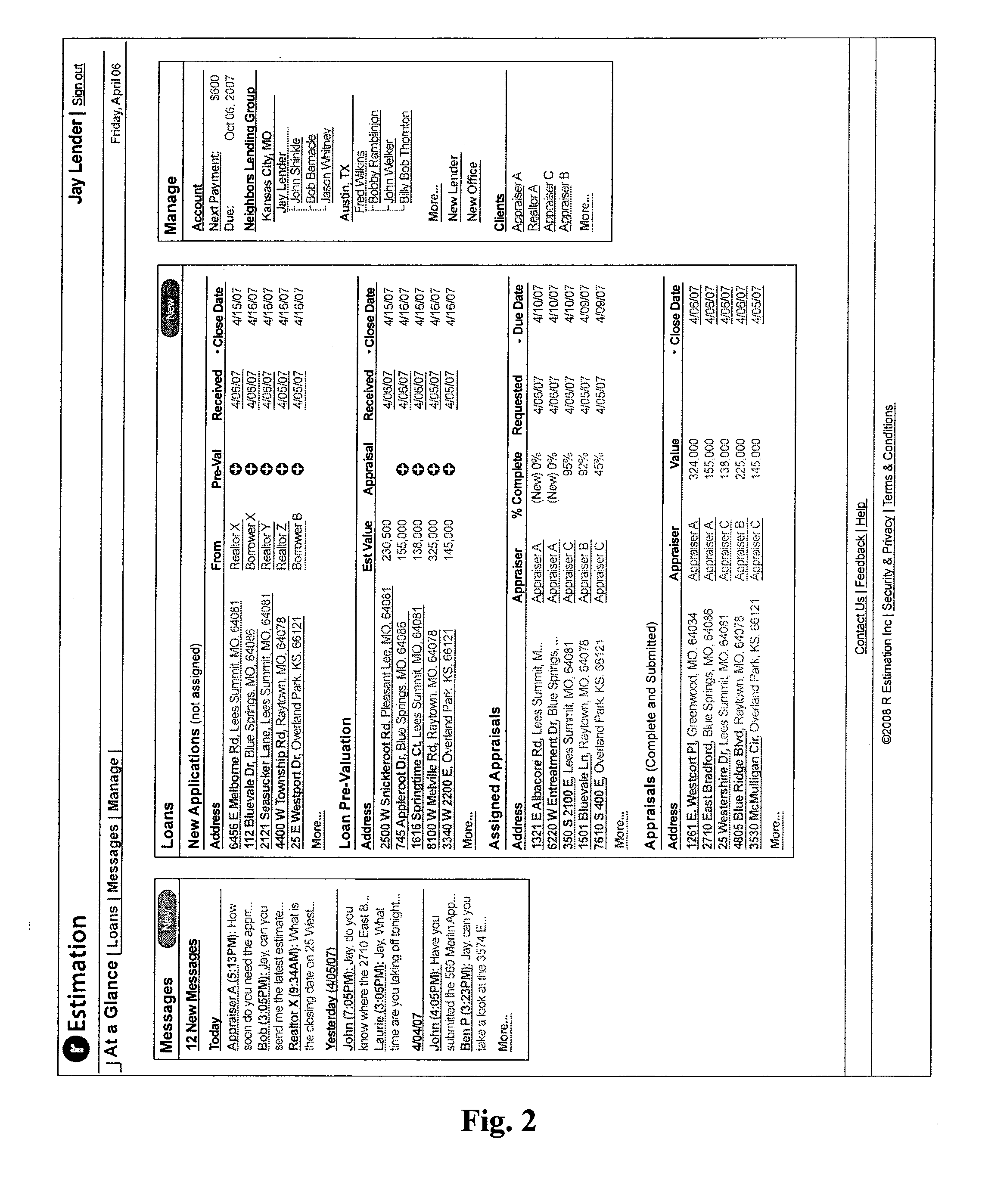
Real estate appraisal system and method
InactiveUS20090234775A1Facilitate entry of real estate dataImprove accuracyFinanceUnauthorized memory use protectionProperty valueEvaluation system
The present general inventive concept provides a system and method to facilitate entry of real estate data related to property value, store the real estate data, and track any manipulation thereof, thereby providing secure real estate data with increased accuracy.
Owner:WHITNEY JASON +3
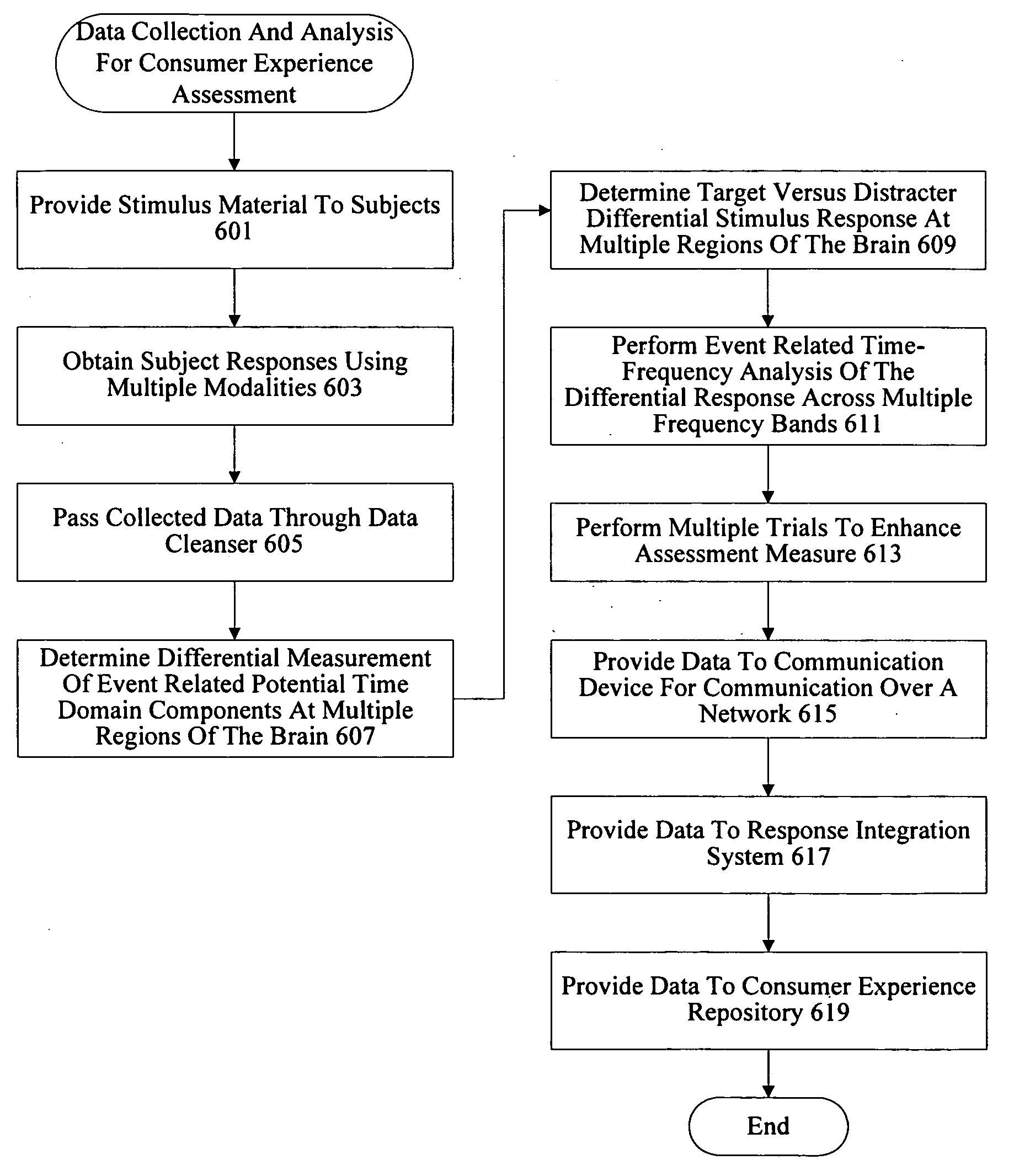
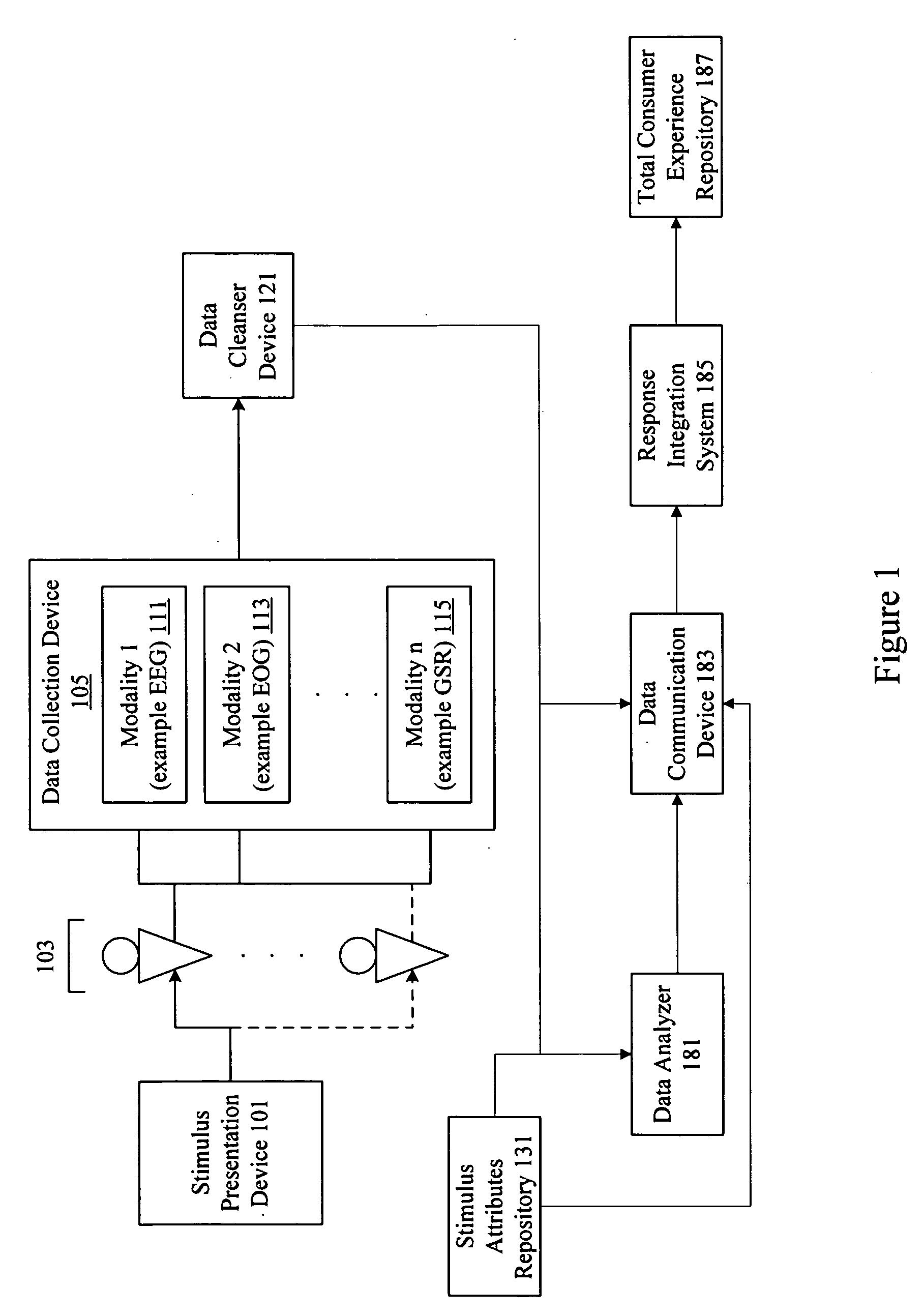
Consumer experience assessment system
ActiveUS20090063255A1ElectroencephalographyElectrocardiographyEeg electroencephalographyEvaluation system
A system assesses consumer experience by evaluating neuro-response measurements for a consumer exposed to products, services, offerings, and stimulus. Examples of neuro-response measurements include Electroencephalography (EEG), Galvanic Skin Response (GSR), Electrocardiograms (EKG), Electrooculography (EOG), eye tracking, and facial emotion encoding measurements. Components of a consumer experience are analyzed to assess neuro-response measurements specific to each component. In many instances, neuro-response data is combined with other data and analyzed to determine total consumer experience.
Owner:NIELSEN CONSUMER LLC
Devices, systems and methods for the containment and use of liquid solutions
The present invention includes devices, systems and methods for containing and using liquid solutions. The devices include liquid containment structures and packages of such liquid containment structures for containing single doses of a liquid solution for subsequent use. The systems include at least one subject containment structure or package of containment structures and the liquid solution for which they are intended to contain. The liquid solutions may comprise any type of agent, reagent or control solution. The subject methods involve the use of the liquid containment structures and packages thereof as well as methods of providing a control solution for use to evaluate a system's performance.
Owner:LIFESCAN IP HLDG LLC
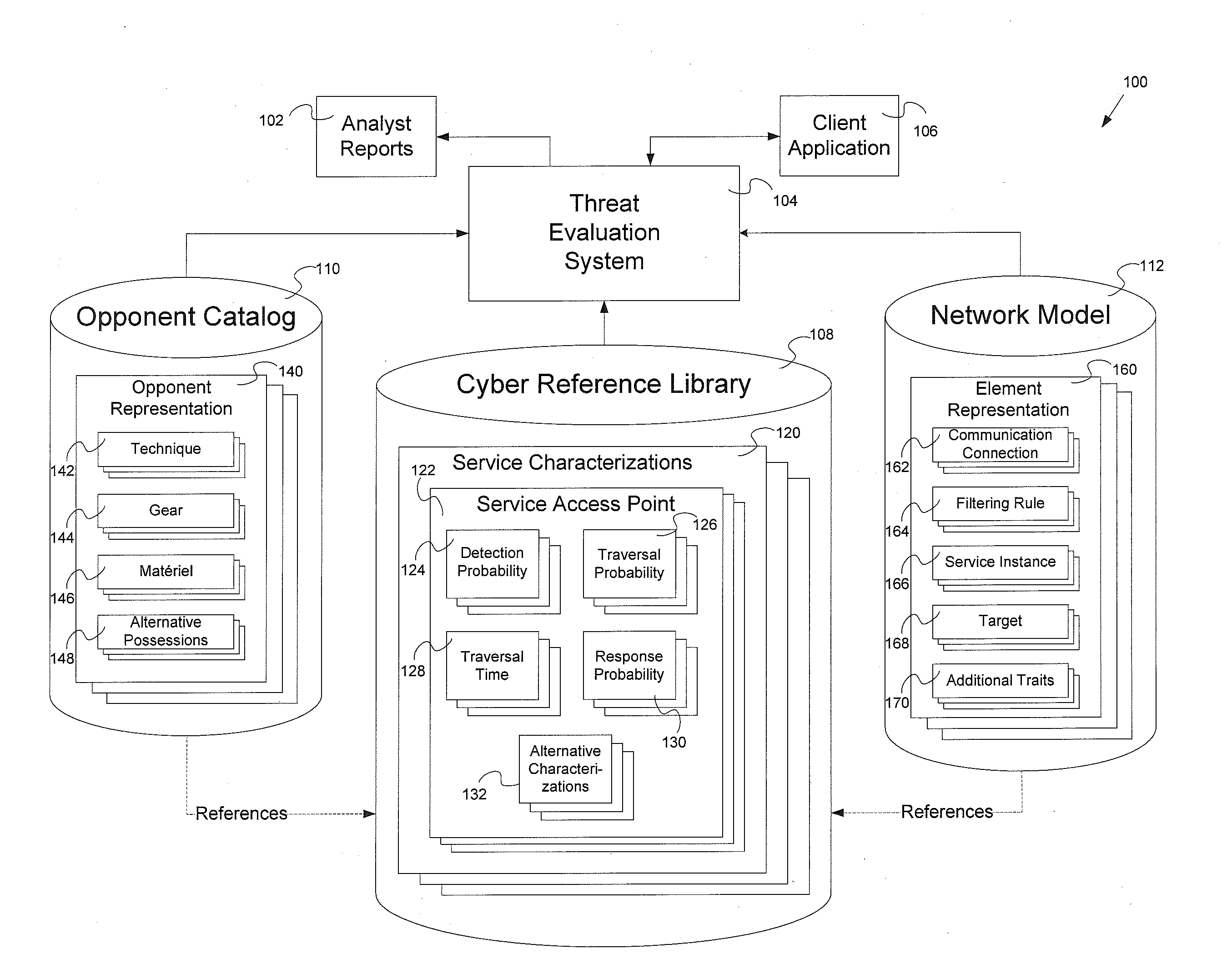
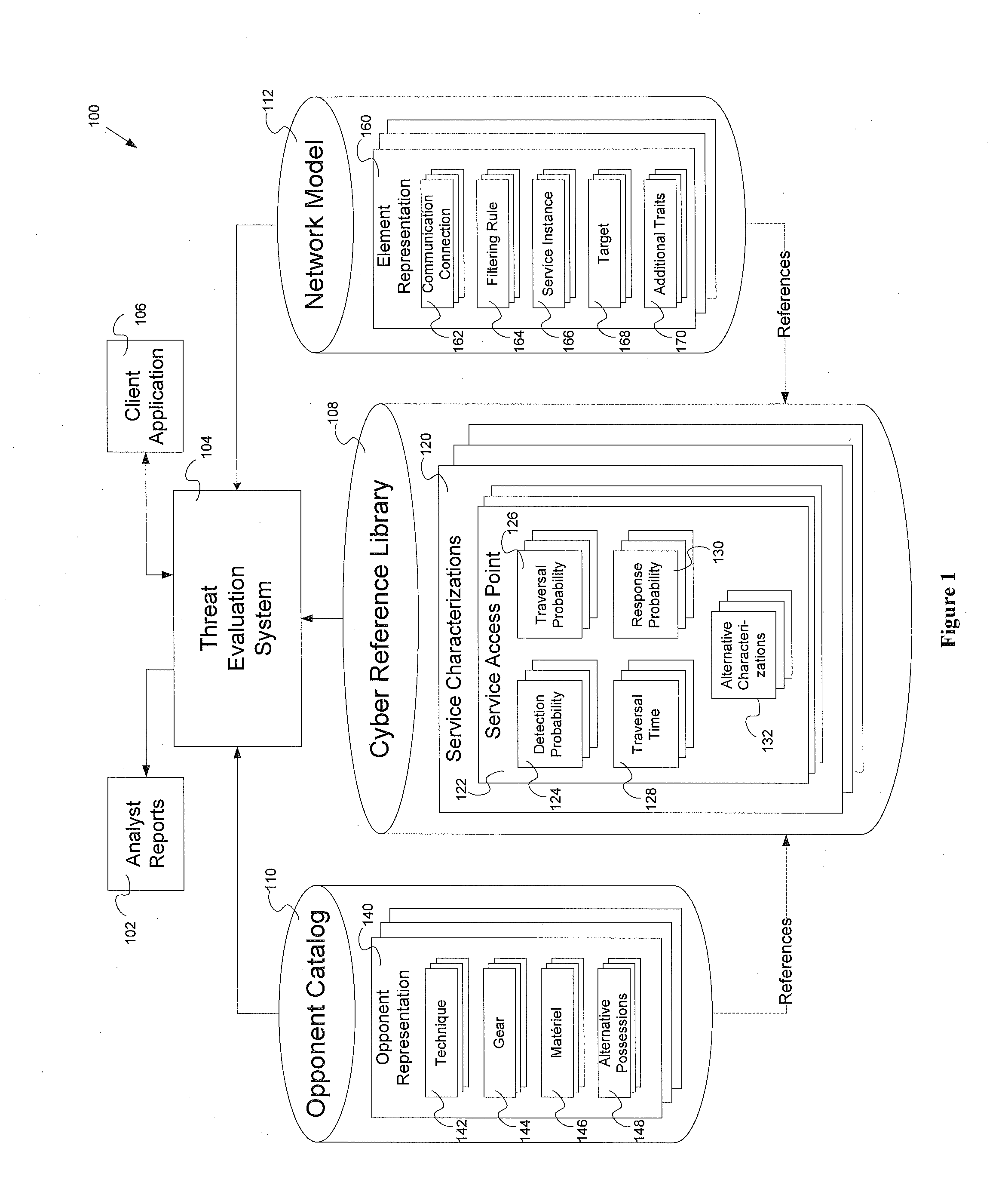
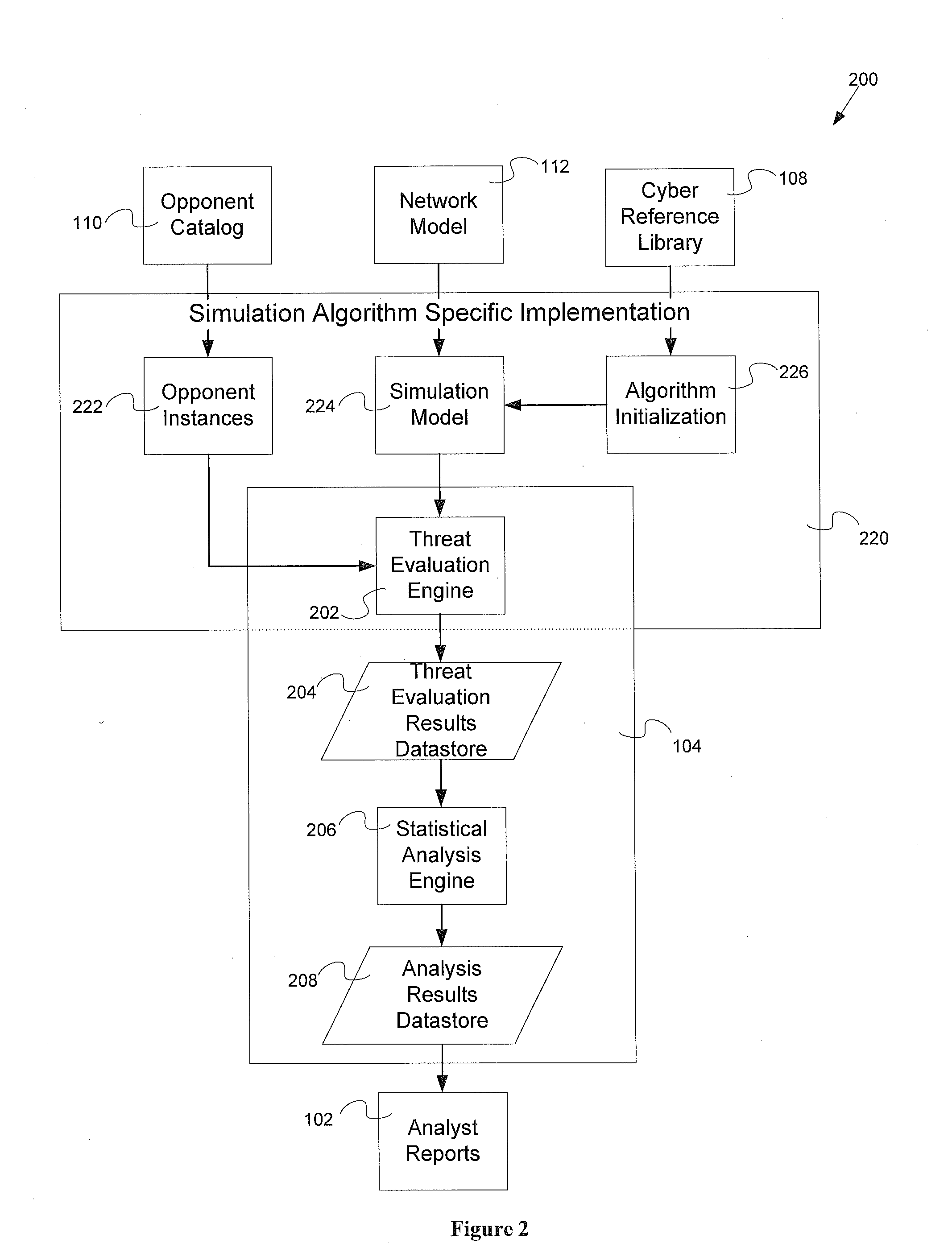
Threat evaluation system and method
InactiveUS20130347116A1Memory loss protectionError detection/correctionStatistical analysisNetwork model
Systems and methods of evaluation of threats to elements of a client computer application having a cyber reference library, an opponent catalog and a network model. The systems and methods produce a set of analyst reports evaluating the threats to the client computer application. One embodiment of the system for evaluating at least one threat to a client computer application has a threat evaluation engine which performs a plurality of algorithms, where each algorithm of has implementation specific needs for input into the individual algorithm, a threat evaluation results data store, a statistical analysis engine, and an analysis results data store.
Owner:OPPLEO SECURITY
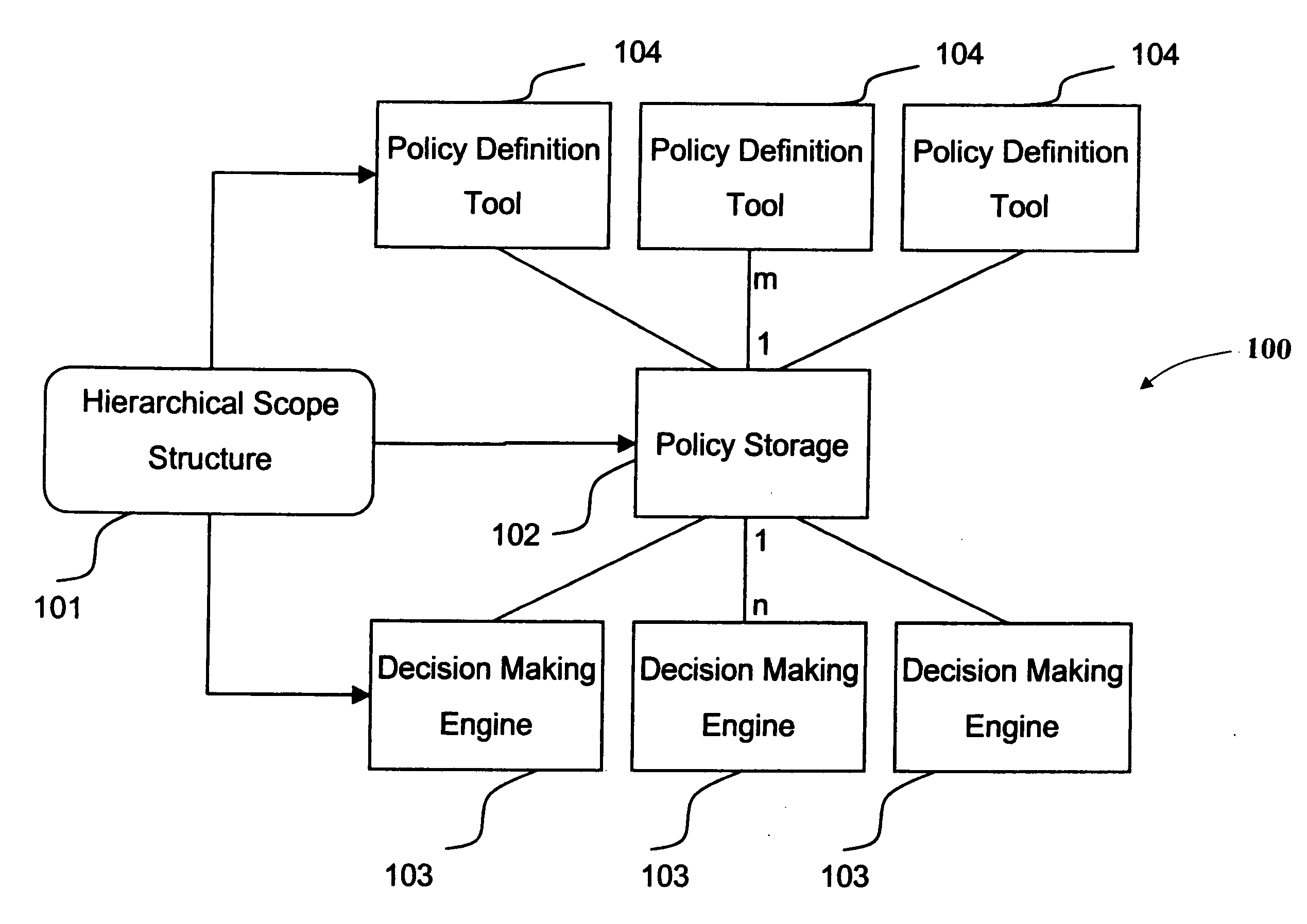
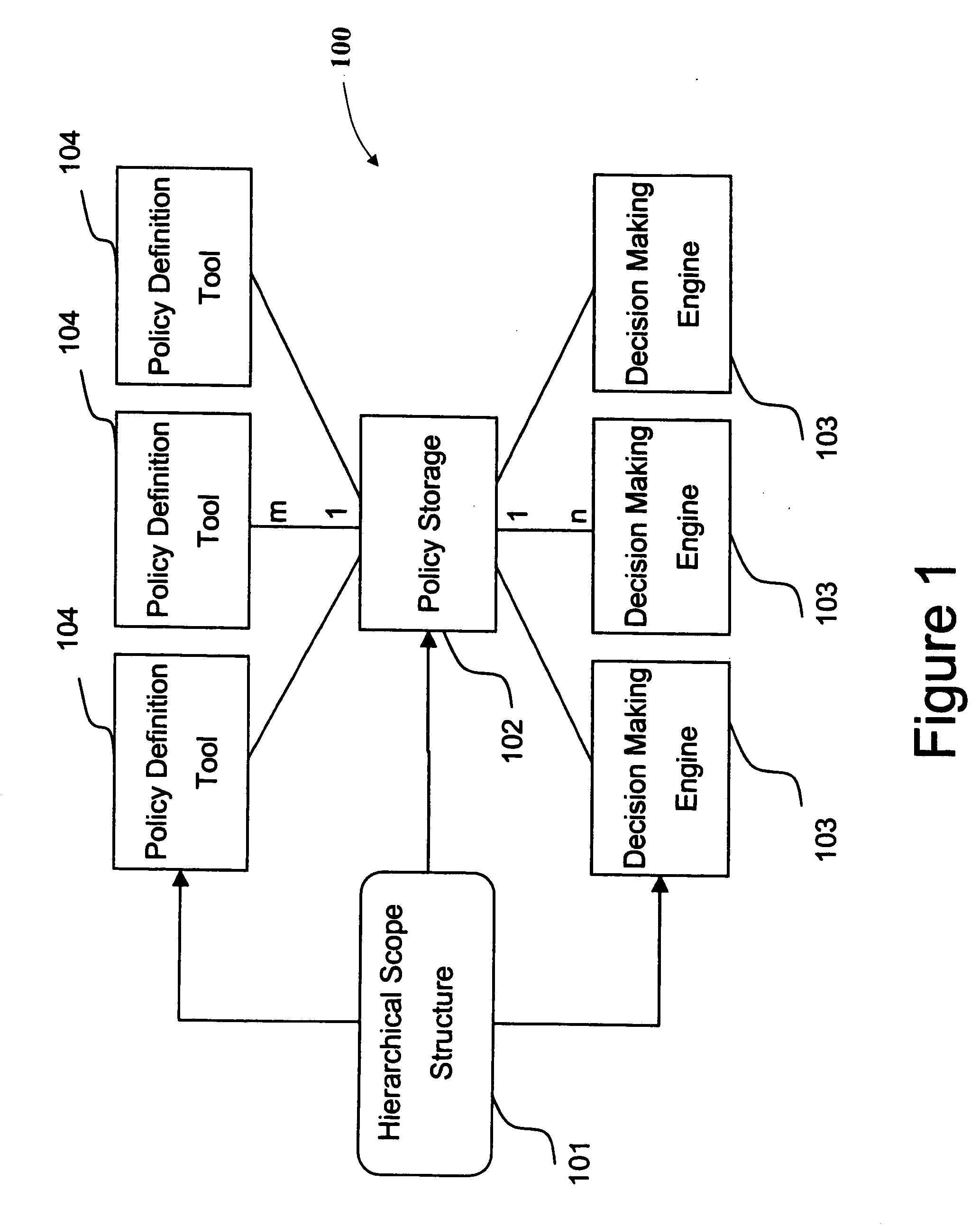
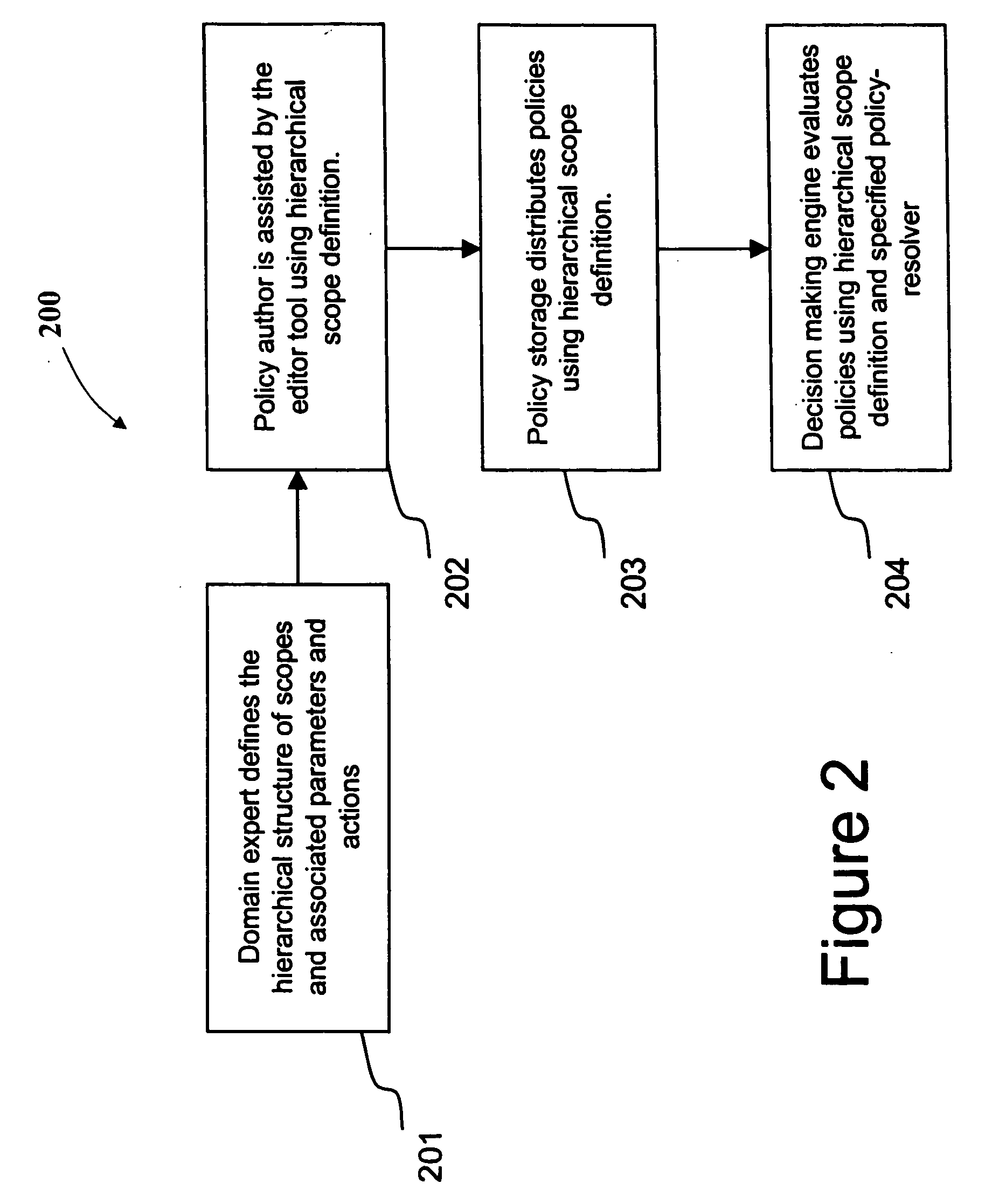
System of hierarchical policy definition, dissemination, and evaluation
InactiveUS20070255769A1Wide applicabilityResourcesSpecial data processing applicationsDecision systemEvaluation system
A system for defining, disseminating, and evaluating policies in a policy-based decision system includes a unit for defining a hierarchy of policy groups, a unit for associating a group of orthogonal parameters with at least one policy group, a unit for defining at least one policy for one or more policy groups in said hierarchy, a unit for disseminating policies to one or more decision making component for at least one policy group in said hierarchy, and a unit for evaluating policies for at least one policy groups in the hierarchy.
Owner:IBM CORP
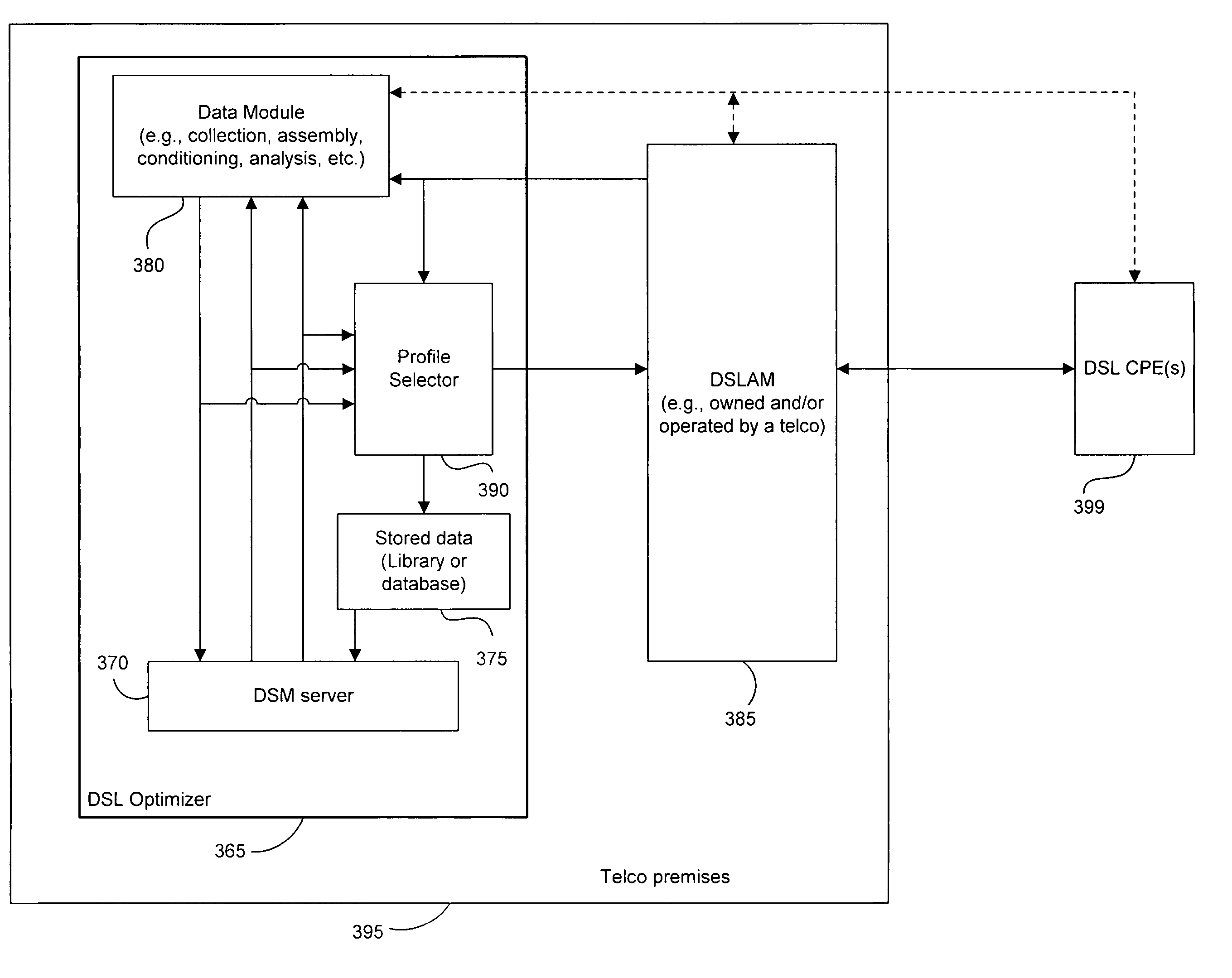
DSL system estimation including known DSL line scanning and bad splice detection capability
InactiveUS20060098725A1Improve accuracyImprove performanceSupervisory/monitoring/testing arrangementsSubstation equipmentSystem elementElectronic mail
Estimates of a communication system configuration, such as a DSL system, are based on operational data collected from a network element management system, protocol, users and / or the like. The operational data collected from the system can include performance-characterizing operational data that typically is available in an ADSL system via element-management-system protocols. Generated estimates and / or approximations can be used in evaluating system performance and directly or indirectly dictating / requiring changes or recommending improvements in operation by transmitters and / or other parts of the communication system. Data and / or other information may be collected using “internal” means or may be obtained from system elements and components via email and / or other “external” means. The likelihood of a model's accuracy can be based on various data, information and / or indicators of system performance, such as observed normal operational data, test data and / or prompted operational data that shows operating performance based on stimulation signals. One example of such prompted data uses frequency carrier masks to approximate the Hlog of a given channel, including information regarding bridged taps, attenuation, etc. Scanning, wherein a number of line profiles are used in connection with DSL loops having known configurations, can be used to generate a database or library of loop configuration information. One or more of the line profiles can be used with an unknown DSL loop to generate operational data from the unknown DSL loop that is compared to the loop configuration information in the database, allowing identification of loop configuration information pertaining to the unknown DSL loop. The unknown DSL loop operational data also can be used to determine whether one or more bad splices are present on the unknown DSL loop and, in some cases, the approximate or exact bad splice(s) location(s).
Owner:ASSIA SPE LLC CO THE CORP TRUST CO
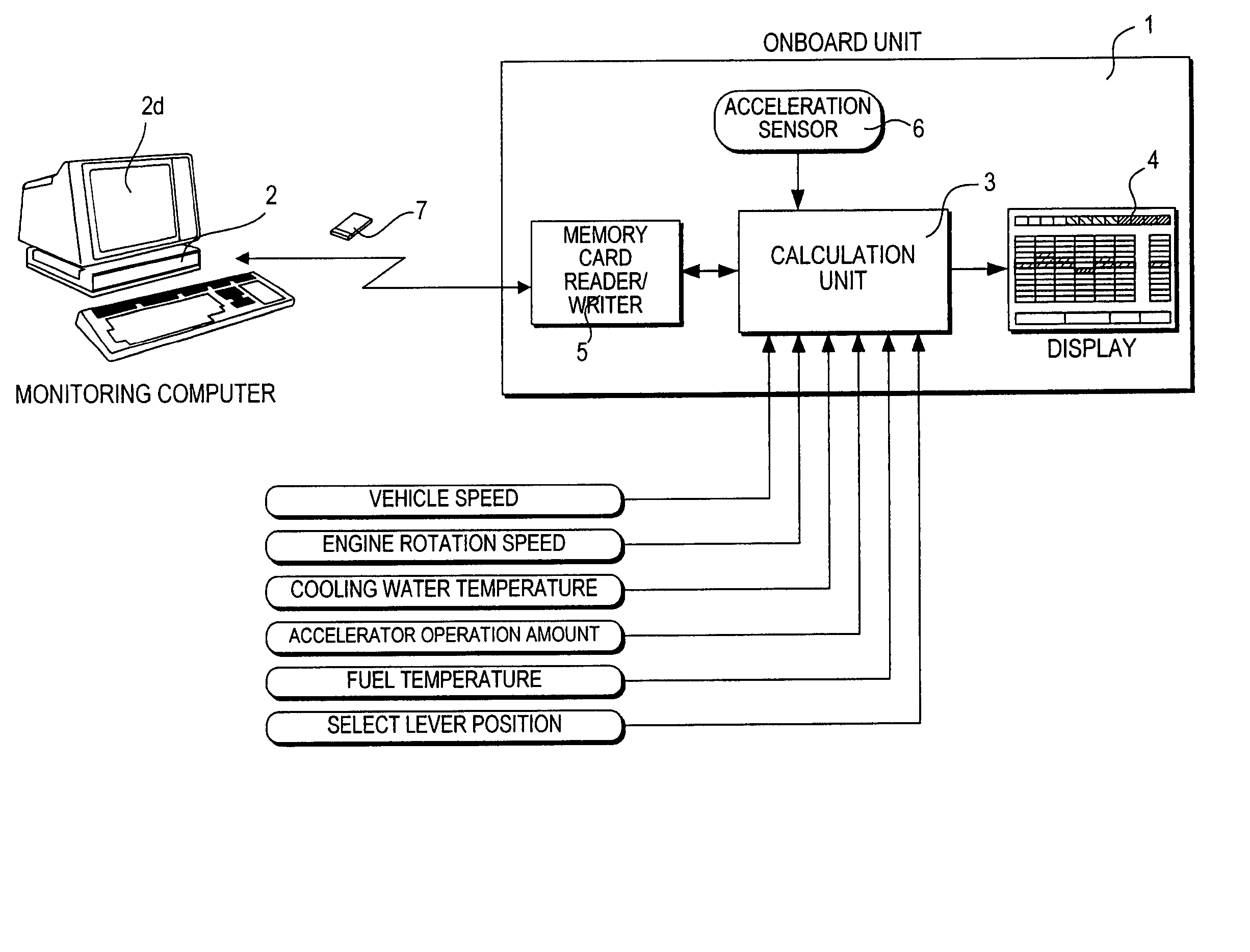
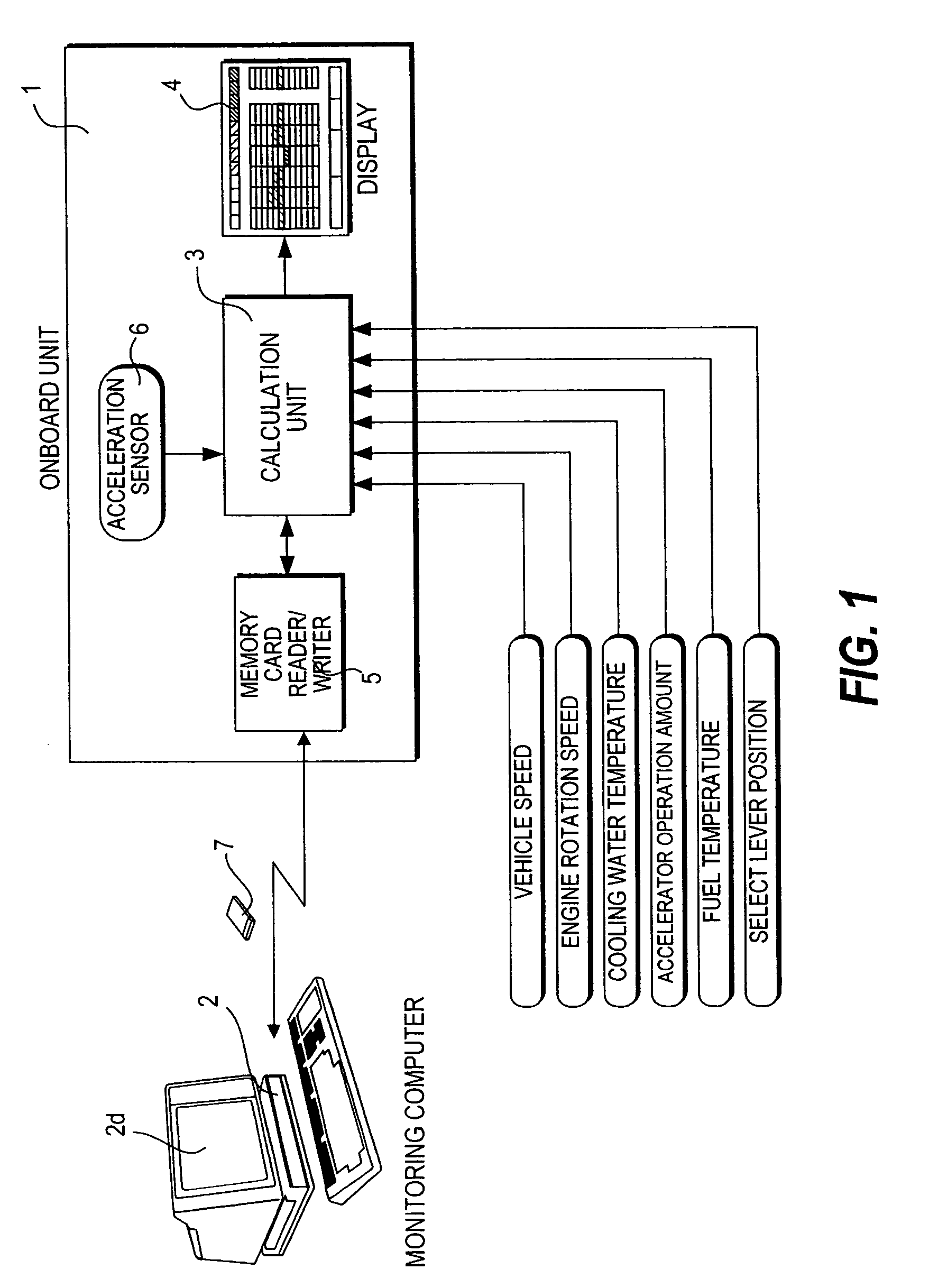
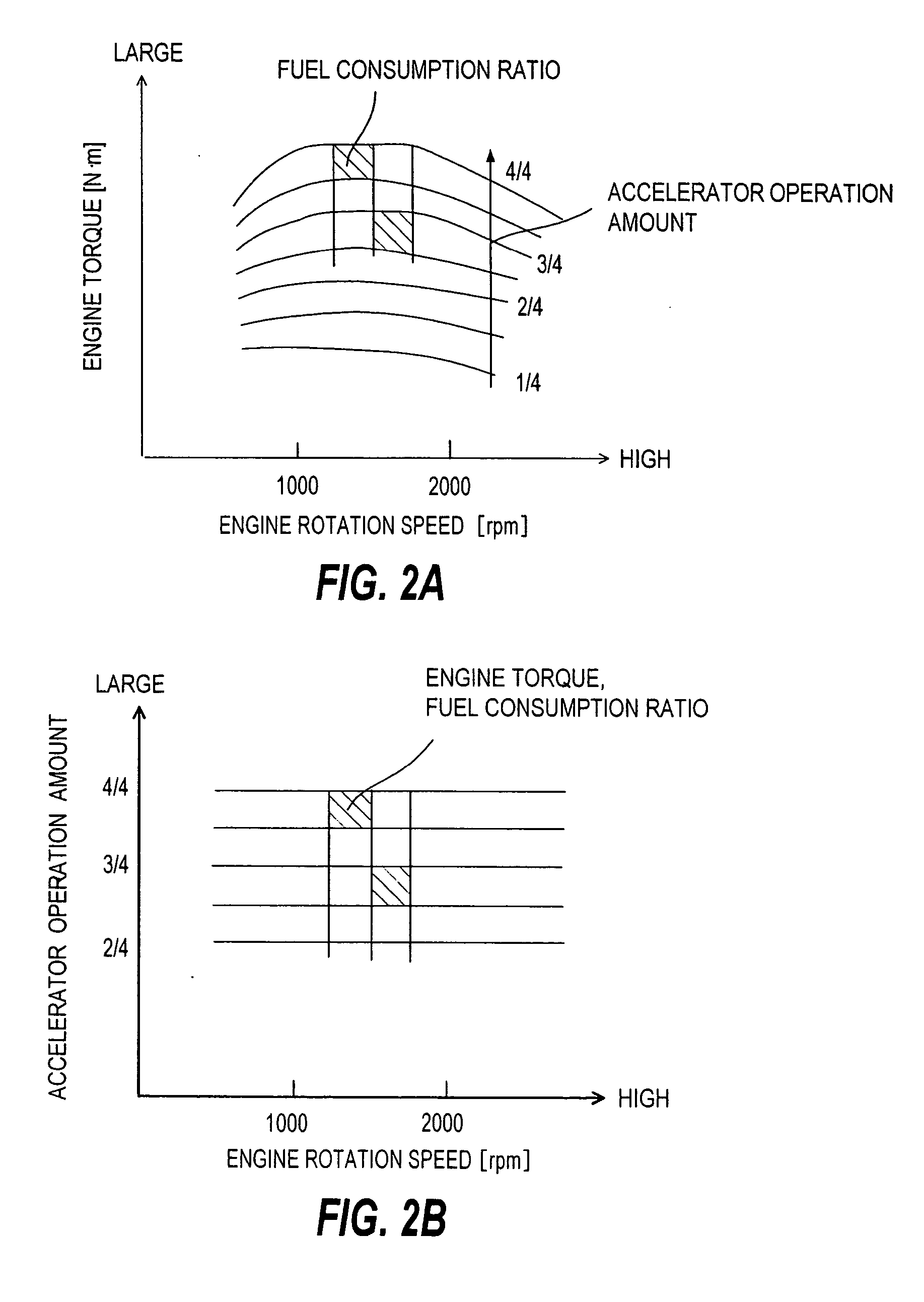
Evaluation system for vehicle operating conditions and evaluation method thereof
InactiveUS20050021222A1Improve fuel economyImprove economyVehicle testingAnalogue computers for vehiclesDisplay deviceEvaluation system
Owner:MIYAMA
Driver risk assessment system and method employing selectively automatic event scoring
ActiveUS8849501B2Stable and reliableOptimizing data transmission bandwidthVehicle testingRegistering/indicating working of vehiclesDriver/operatorEngineering
A Driver Risk Assessment System and Method Employing Selectively Automatic Event Scoring. The system and method provides robust and reliable event scoring and reporting, while also optimizing data transmission bandwidth. The system includes onboard vehicular driving event detectors that record data related to detected driving events, selectively store or transfer data related to said detected driving events. If elected, the onboard vehicular system will score a detected driving event, compare the local score to historical values previously stored within the onboard system, and upload selective data or data types to a remote server or user if the system concludes that a serious driving event has occurred. The system may further respond to independent user requests by transferring select data to said user at a variety of locations and formats.
Owner:DRIVECAM
Driver Risk Assessment System and Method Employing Selectively Automatic Event Scoring
ActiveUS20100191411A1Robust and reliable event scoringRobust and reliable and reportingVehicle testingRegistering/indicating working of vehiclesDriver/operatorEngineering
A Driver Risk Assessment System and Method Employing Selectively Automatic Event Scoring. The system and method provides robust and reliable event scoring and reporting, while also optimizing data transmission bandwidth. The system includes onboard vehicular driving event detectors that record data related to detected driving events, selectively store or transfer data related to said detected driving events. If elected, the onboard vehicular system will score a detected driving event, compare the local score to historical values previously stored within the onboard system, and upload selective data or data types to a remote server or user if the system concludes that a serious driving event has occurred. The system may further respond to independent user requests by transferring select data to said user at a variety of locations and formats.
Owner:DRIVECAM
System for restoring organic contaminated soil through in-situ electrical heating and treatment method
ActiveCN108311535AUniversalPull out in timeCombination devicesContaminated soil reclamationTreatment effectSoil properties
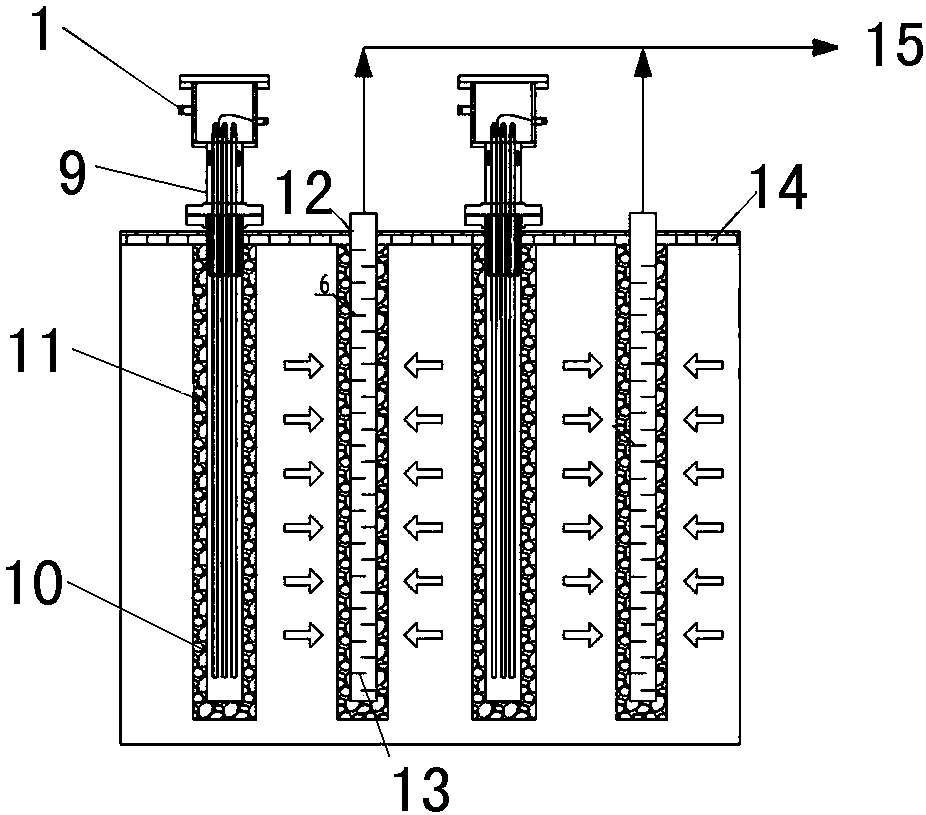
The invention provides a system for restoring organic contaminated soil through in-situ electrical heating. The system comprises an infrastructure technology, an electronic control system, a gas treatment system, a monitoring and data acquisition system and a repairing effect comprehensive assessment system. The infrastructure technology comprises heating well and extraction well construction, ground compaction and insulating layer construction technologies; heating wells are distributed on a contaminated site according to a triangle arrangement principle and a proximity principle, and the extraction well is arranged in the geometric center of the layout of the heating well; the gas treatment system is composed of a pre-cooling adsorption sledge, an extraction sledge and a treatment sledge, and is used for completing gas extraction and treatment and achieving the tail gas discharging requirement; and the repairing effect comprehensive assessment system evaluates the temperature risingeffect of the contaminated soil in the restoring process and the treatment effect of the contaminated soil. According to the system, the technological route is complete, the soil property applicability is wide, the heating temperature can reach 500 DEG C or above, and volatile and difficult-to-volatilize organic contaminant can be treated at the same time.
Owner:BEIJING MUNICIPAL RES INST OF ENVIRONMENT PROTECTION +1
Simulation training device for manual arc welding rod-moving operation, and arc welding rod-moving detection method
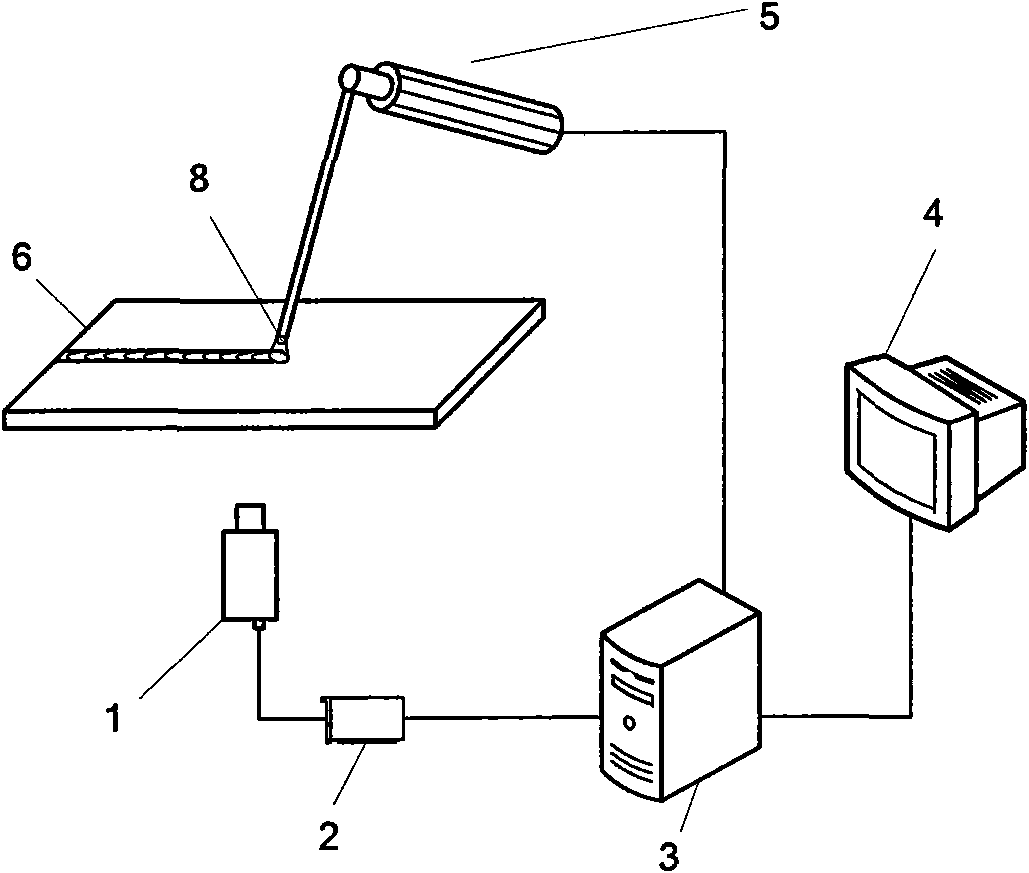
InactiveCN101587659ARealize high-precision detectionImprove learning efficiencyUsing optical meansTeaching apparatusShielded metal arc weldingImage detection
The invention provides a simulation training device for manual arc welding rod-moving operation, and an arc welding rod-moving detection method, which is used for the introduction, improvement and enhancement training of welders in welding rod-moving operation. The device comprises a simulated welding torch, a simulated test plate, an image detection module, a dip-angle sensor, a master control computer and an evaluation system. Through the reasonable choice and layout of sensors and efficient data processing, high-precision detection and evaluation of real-time positions of simulated welding rods operated by the welders are realized. The device can record the arc striking, rod moving, ending and a series of operation of welding students during operation, and allows operation tracks to reappear after the operation is completed so as to improve learning efficiency and learning effects.
Owner:XI AN JIAOTONG UNIV
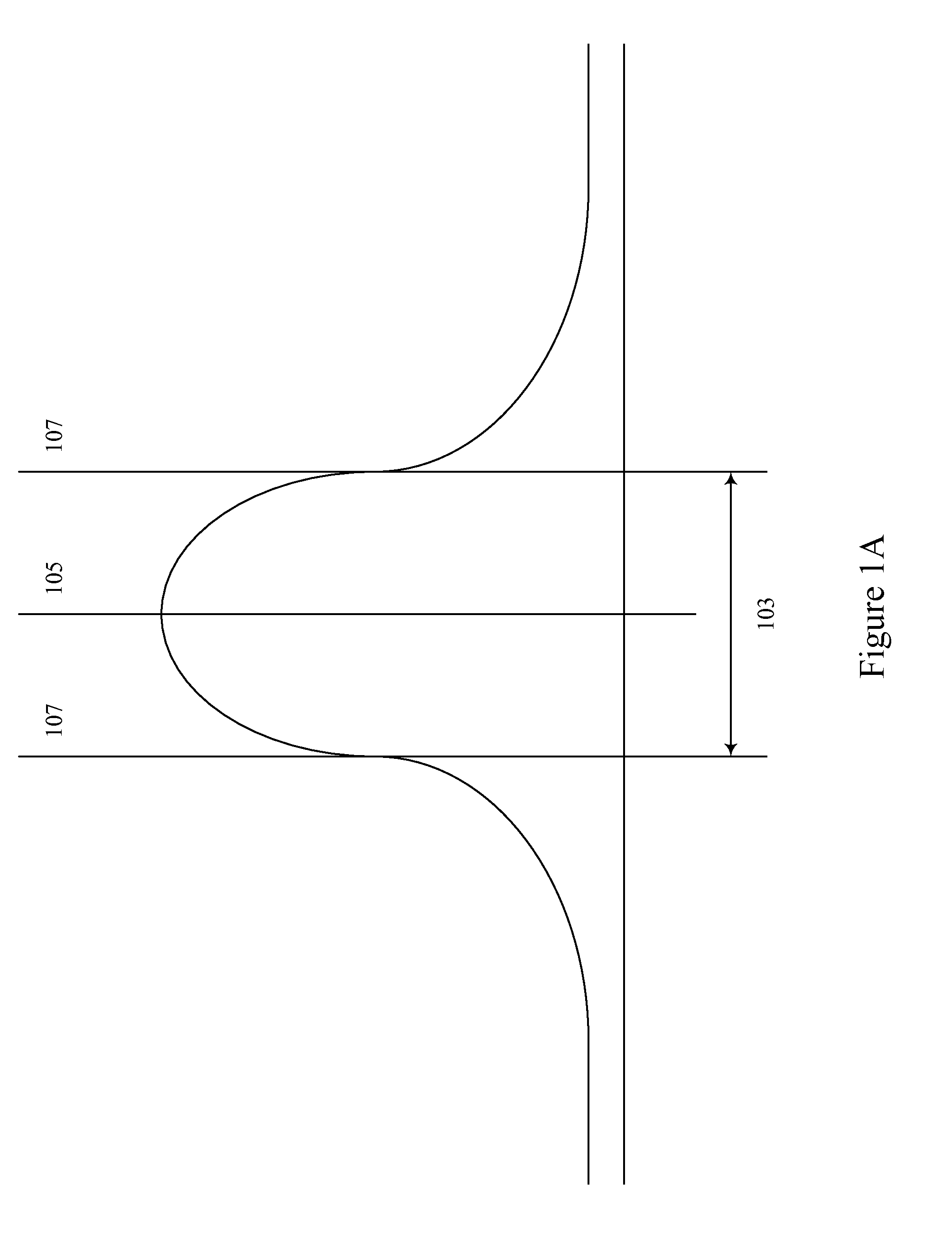
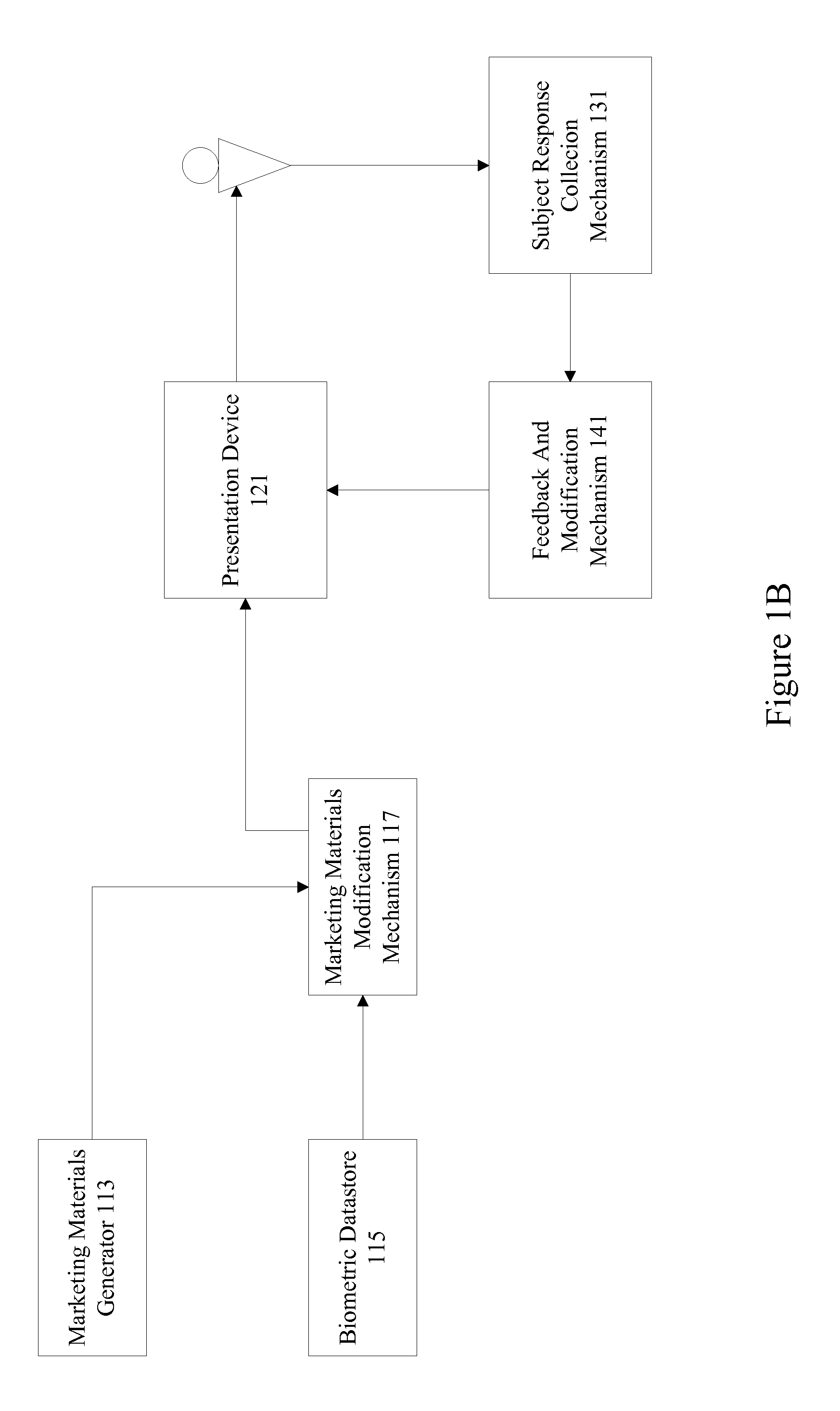
Biometric aware content presentation
InactiveUS20120072289A1CommerceSpecial data processing applicationsSubject matterChemical sensitivity
A content generation, presentation, and evaluation system identifies biometric factors to improve the effectiveness of content presented to subjects. Biometric factors include subject visual acuity ranges, color sensitivity spectrums, audio sensitivity spectrums, chemical sensitivity ranges, etc. Content is generated and / or modified to benefit from subject visual acuity ranges, spectral sensitivities, tactile sensitivities, etc. In particular examples, content is tailored and / or modified for particular individuals and groups based on acuity and sensitivity profiles of those individuals or groups. Neuro-response data can be analyzed to determine the effectiveness of biometric aware content and further enhance content generation.
Owner:THE NIELSEN CO (US) LLC
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com