Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
420 results about "Non linear dynamic" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
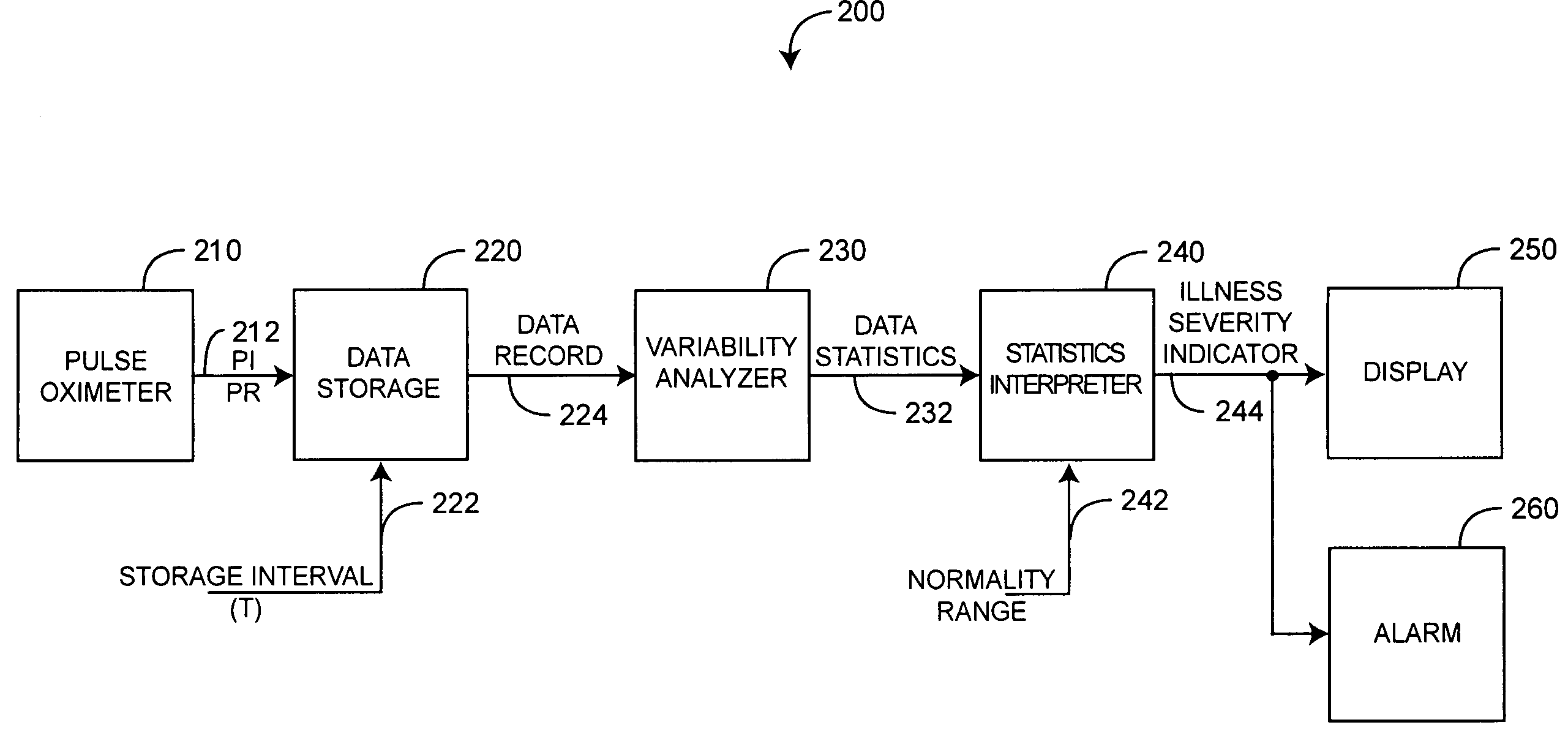
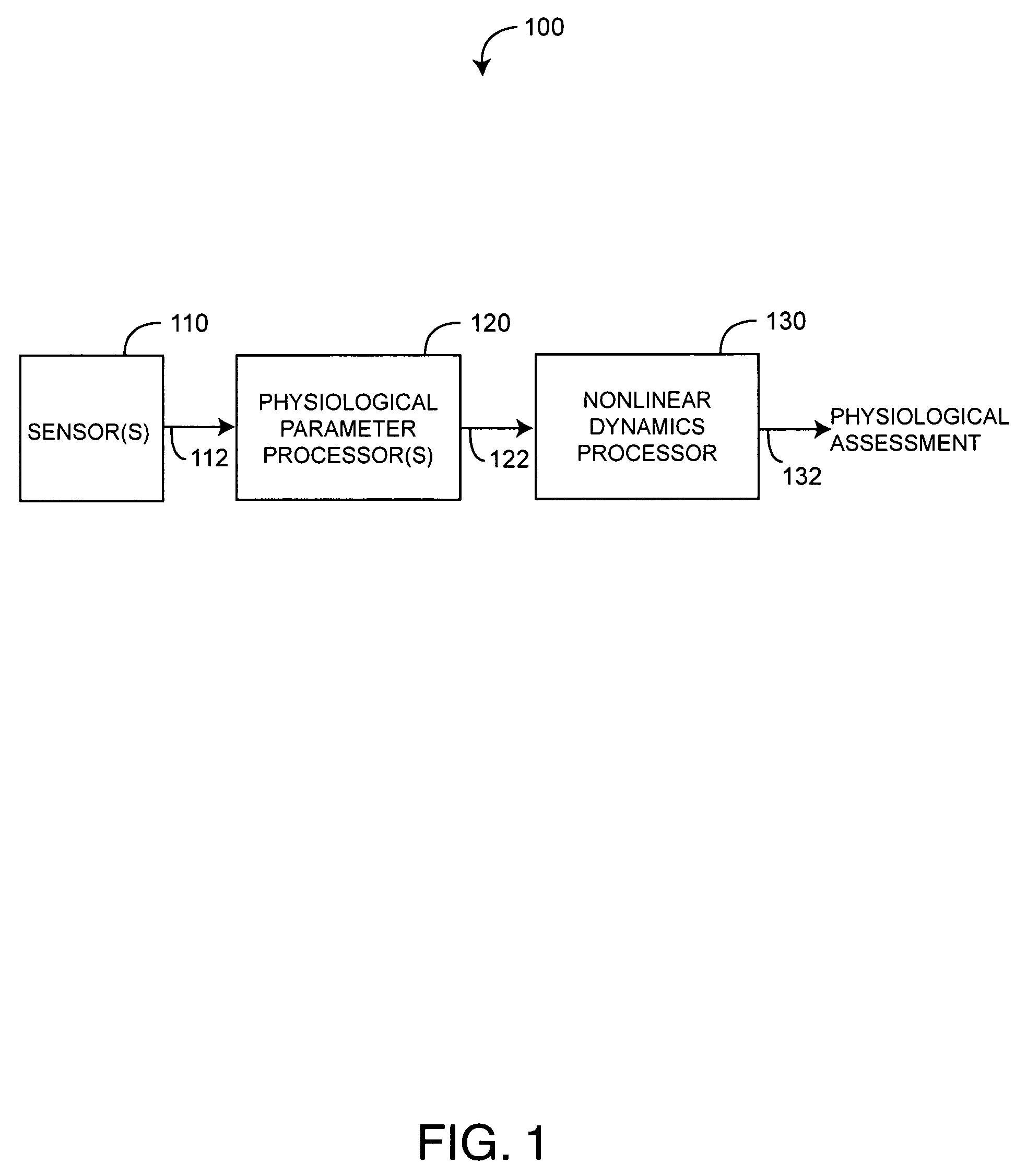
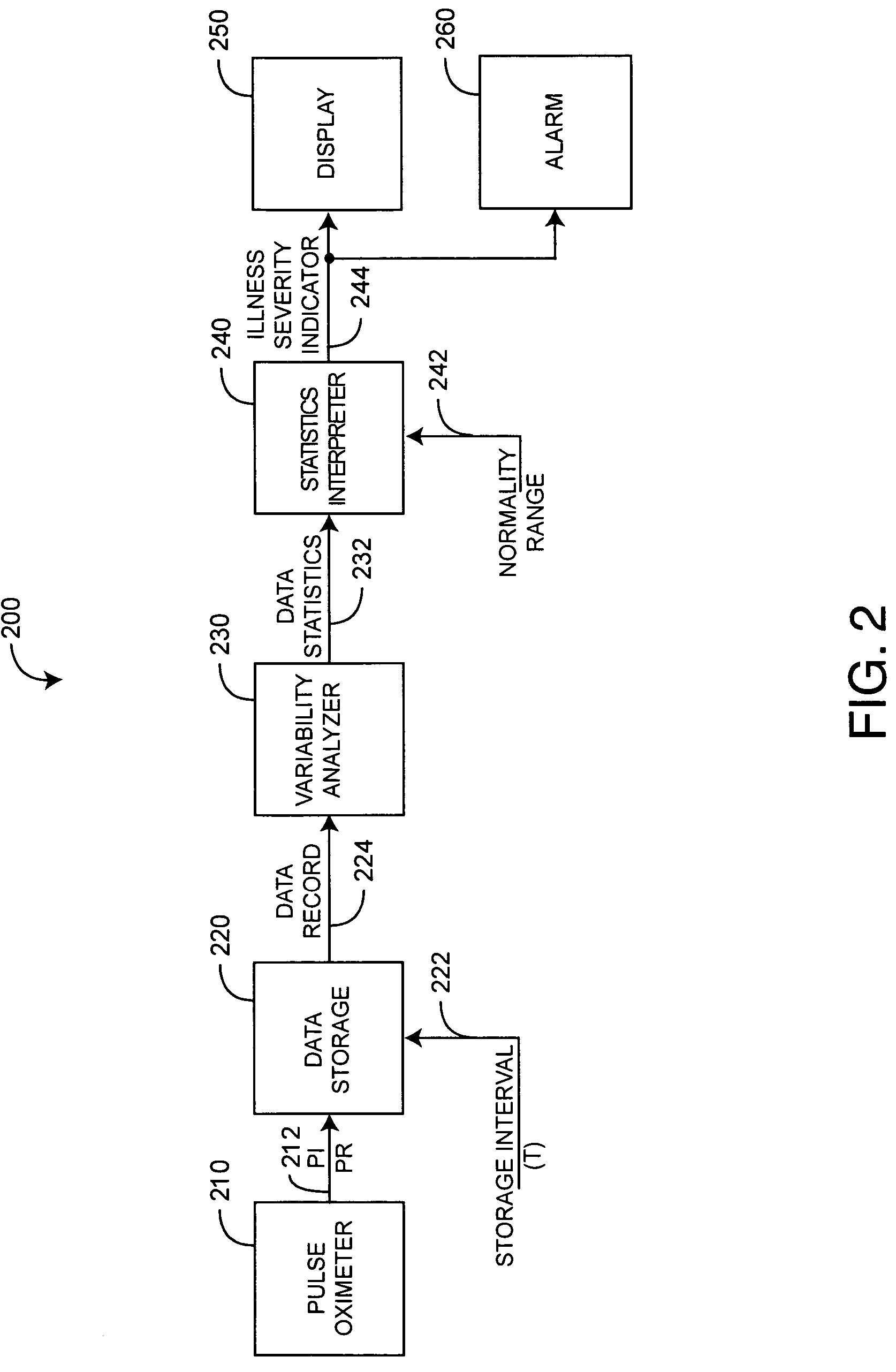
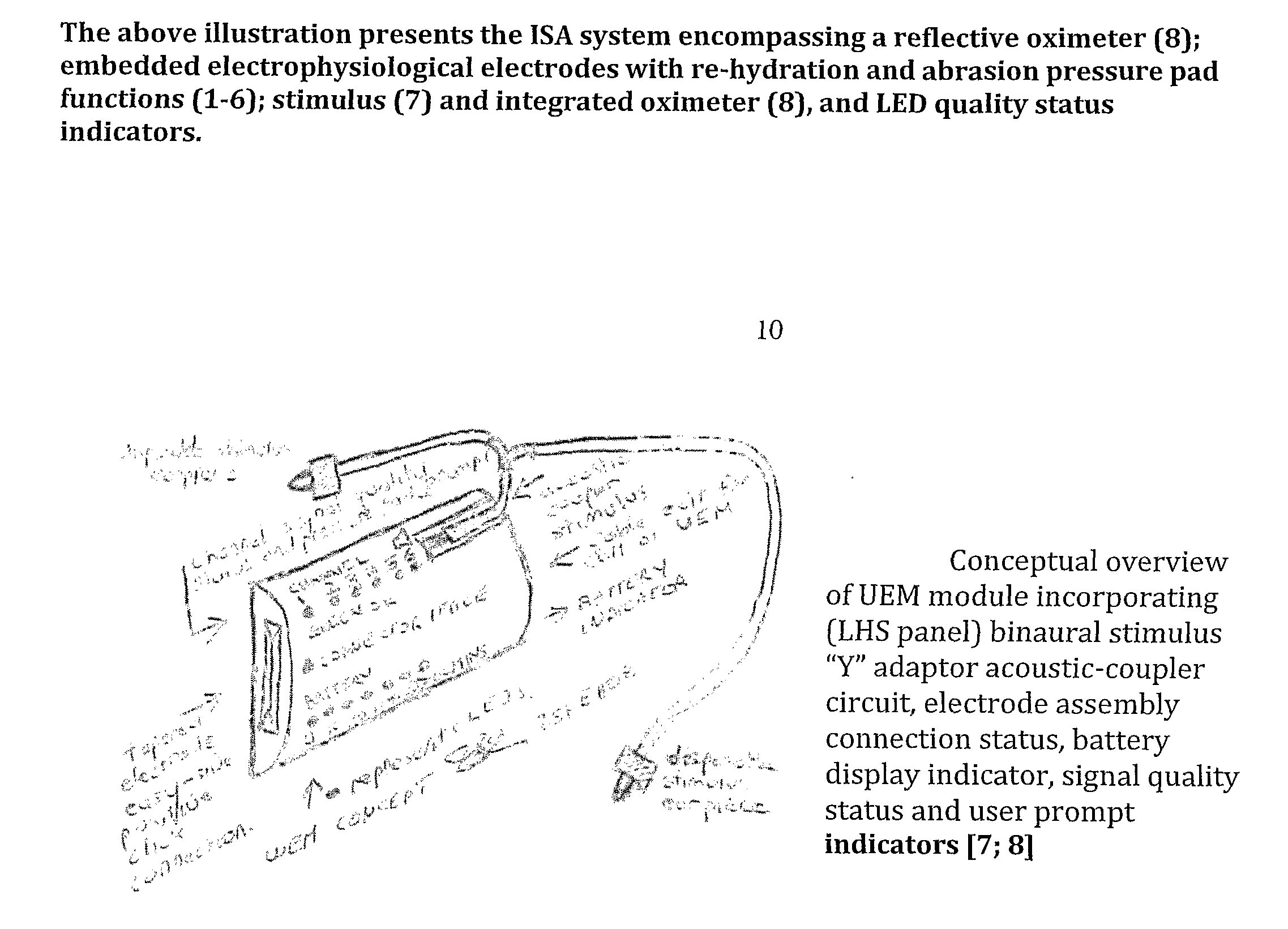
Physiological assessment system
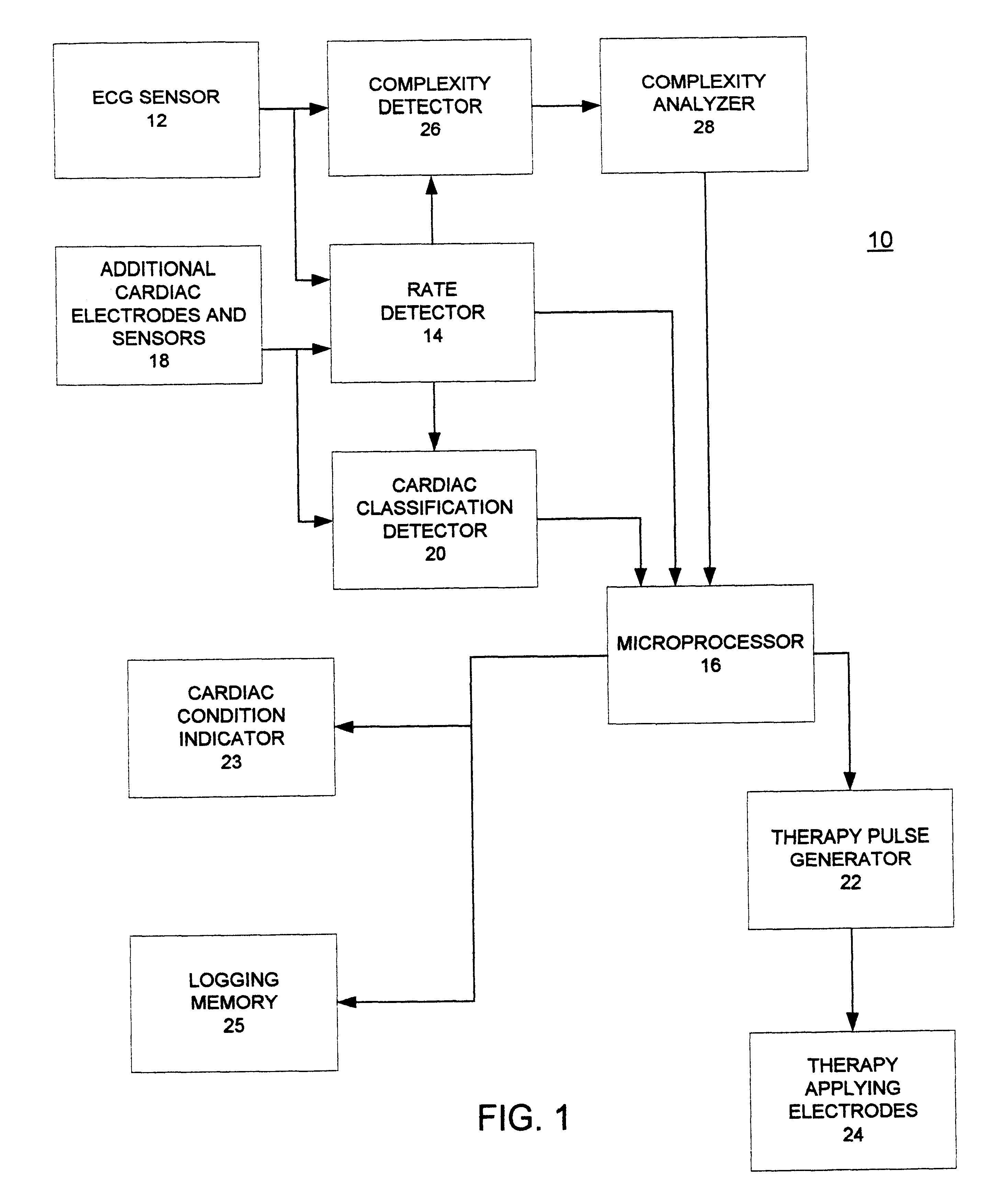
ActiveUS7292883B2Reduce dynamic complexityLow variabilityDiagnostic recording/measuringSensorsBiological bodyMedicine
A physiological assessment system comprises a sensor and first and second processors. The sensor is adapted to generate a signal responsive to a living organism. The first processor is configured to derive a measured parameter from the sensor signal. The second processor is configured to analyze nonlinear dynamics of the measured parameter so as to provide a physiological assessment of the living organism.
Owner:JPMORGAN CHASE BANK NA
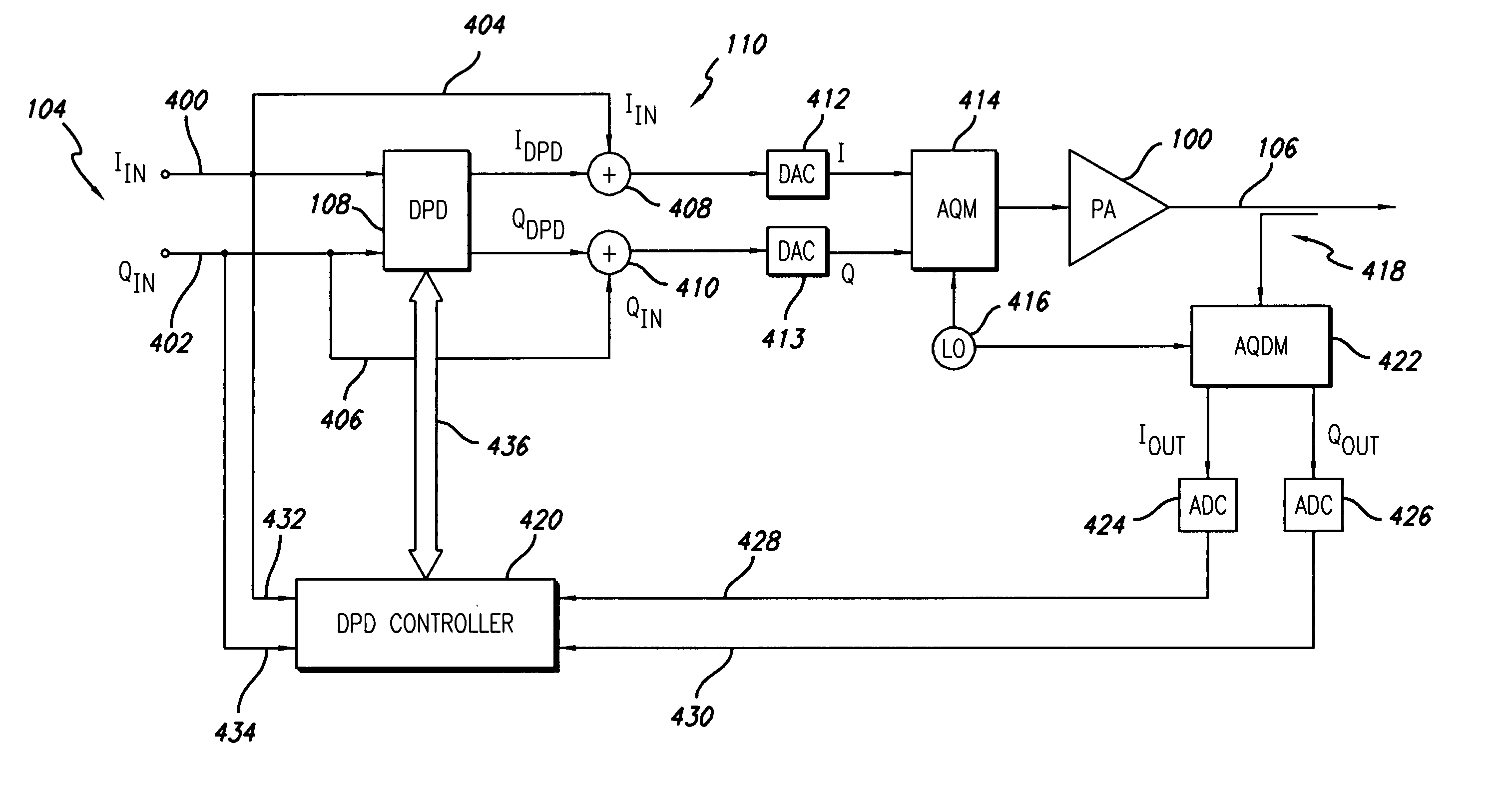
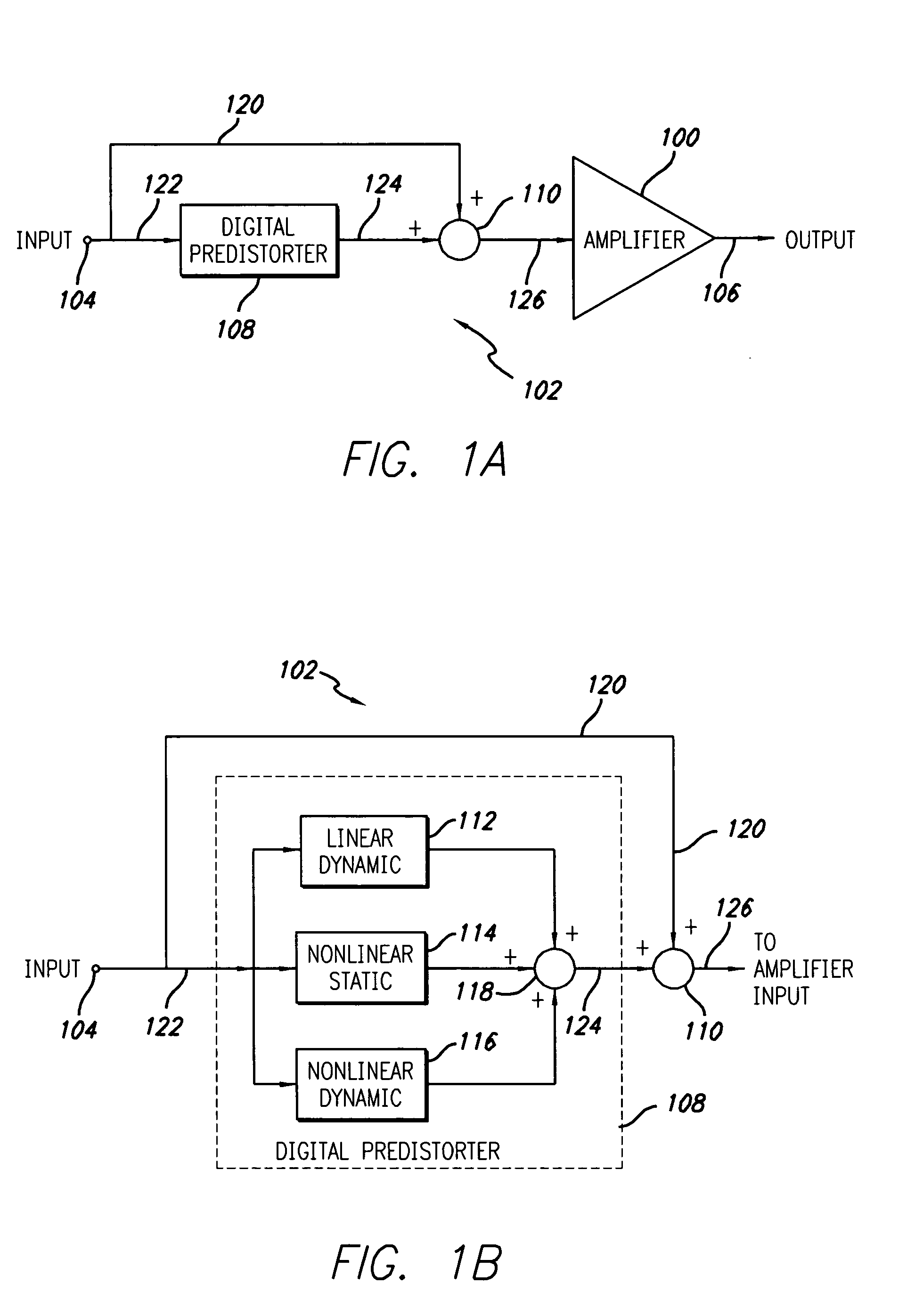
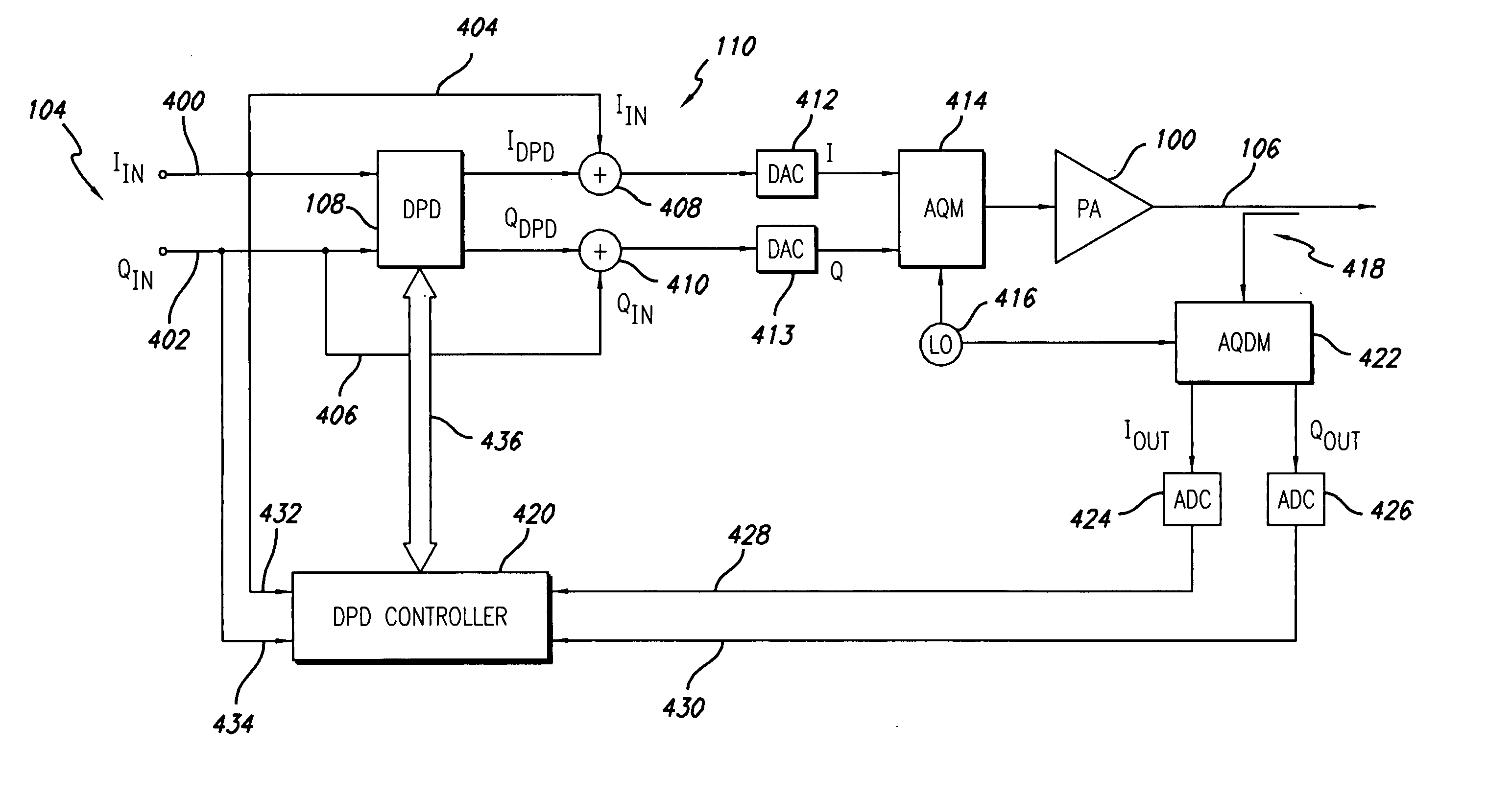
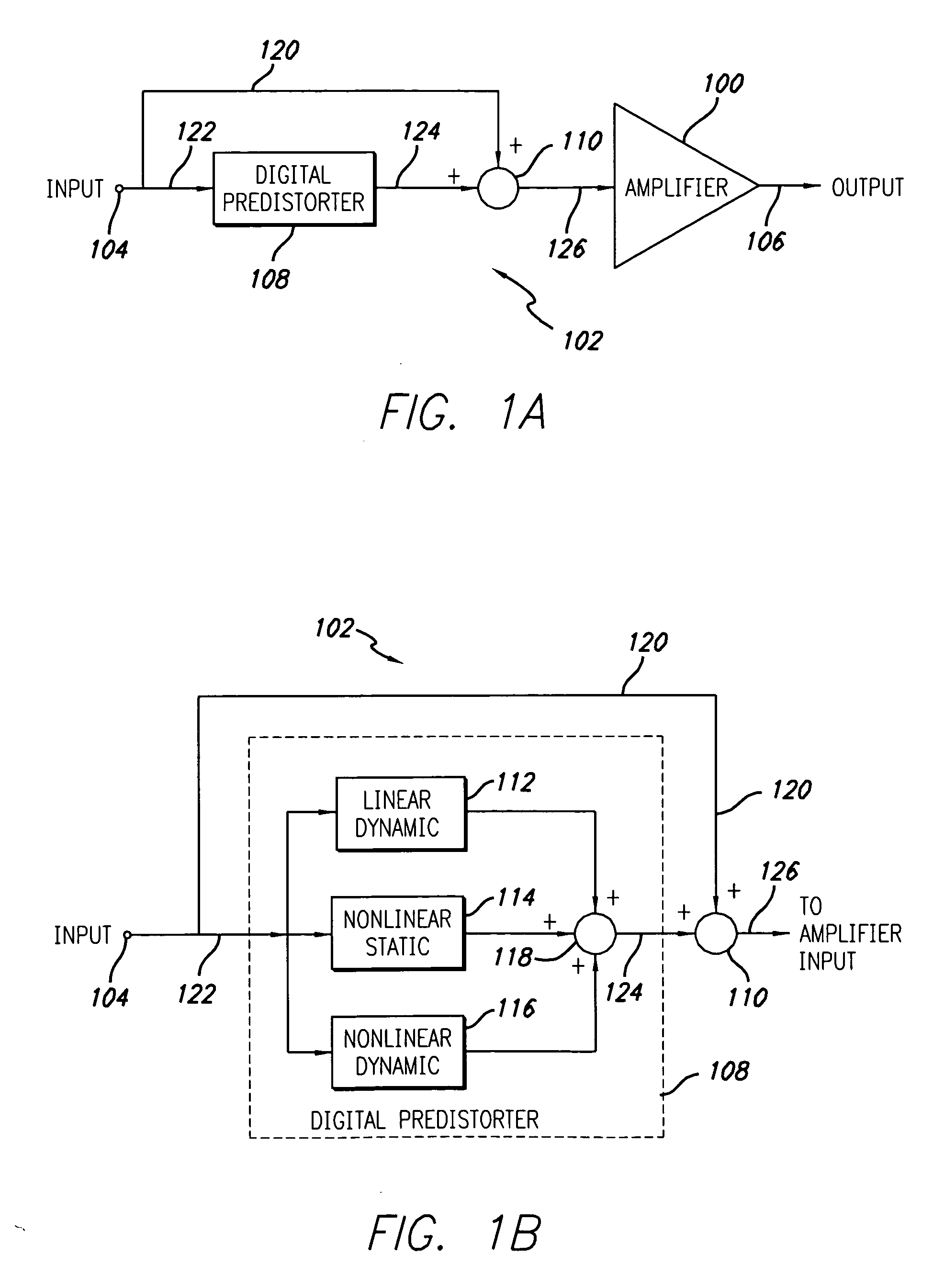
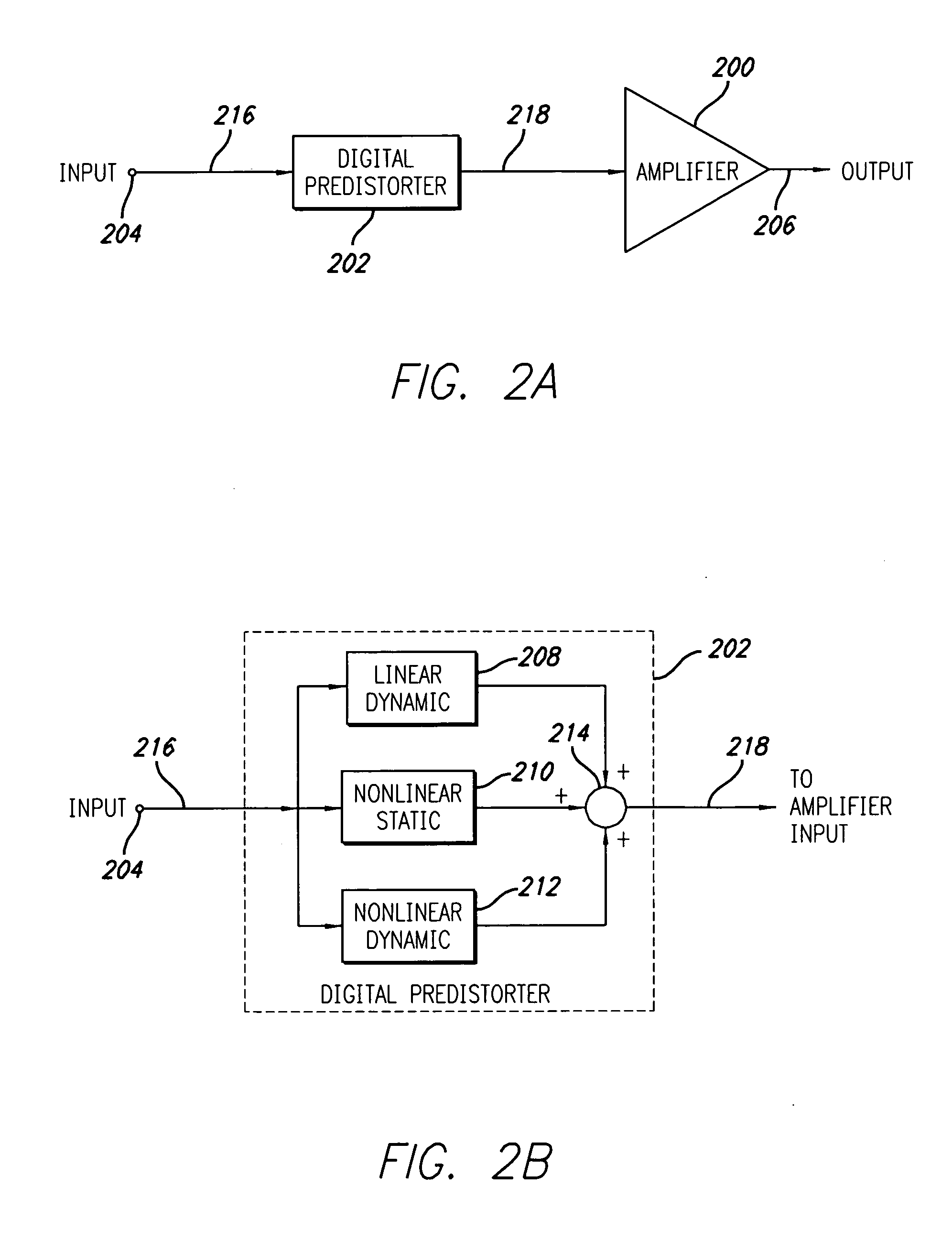
Digital predistortion system and method for high efficiency transmitters
ActiveUS20050195919A1Amplifier modifications to reduce non-linear distortionAmplifiers with memory effect compensationNon linear dynamicEngineering
A system for digitally linearizing the nonlinear behaviour of RF high efficiency amplifiers employing baseband predistortion techniques is disclosed. The system provides additive or multiplicative predistortion of the digital quadrature (I / Q) input signal in order to minimize distortion at the output of the amplifier. The predistorter uses a discrete-time polynomial kernel to model the inverse transfer characteristic of the amplifier, providing separate and simultaneous compensation for nonlinear static distortion, linear dynamic distortion and nonlinear dynamic effects including reactive electrical memory effects. Compensation for higher order reactive and thermal memory effects is embedded in the nonlinear dynamic compensation operation of the predistorter in an IIR filter bank. A predistortion controller periodically monitors the output of the amplifier and compares it to the quadrature input signal to compute estimates of the residual output distortion of the amplifier. Output distortion estimates are used to adaptively compute the values of the parameters of the predistorter in response to changes in the amplifier's operating conditions (temperature drifts, changes in modulation input bandwidth, variations in drive level, aging, etc). The predistortion parameter values computed by the predistortion controller are stored in non-volatile memory and used in the polynomial digital predistorter. The digital predistortion system of the invention may provide broadband linearization of highly nonlinear and highly efficient RF amplification circuits including, but not limited to, dynamic load modulation amplifiers.
Owner:TAHOE RES LTD
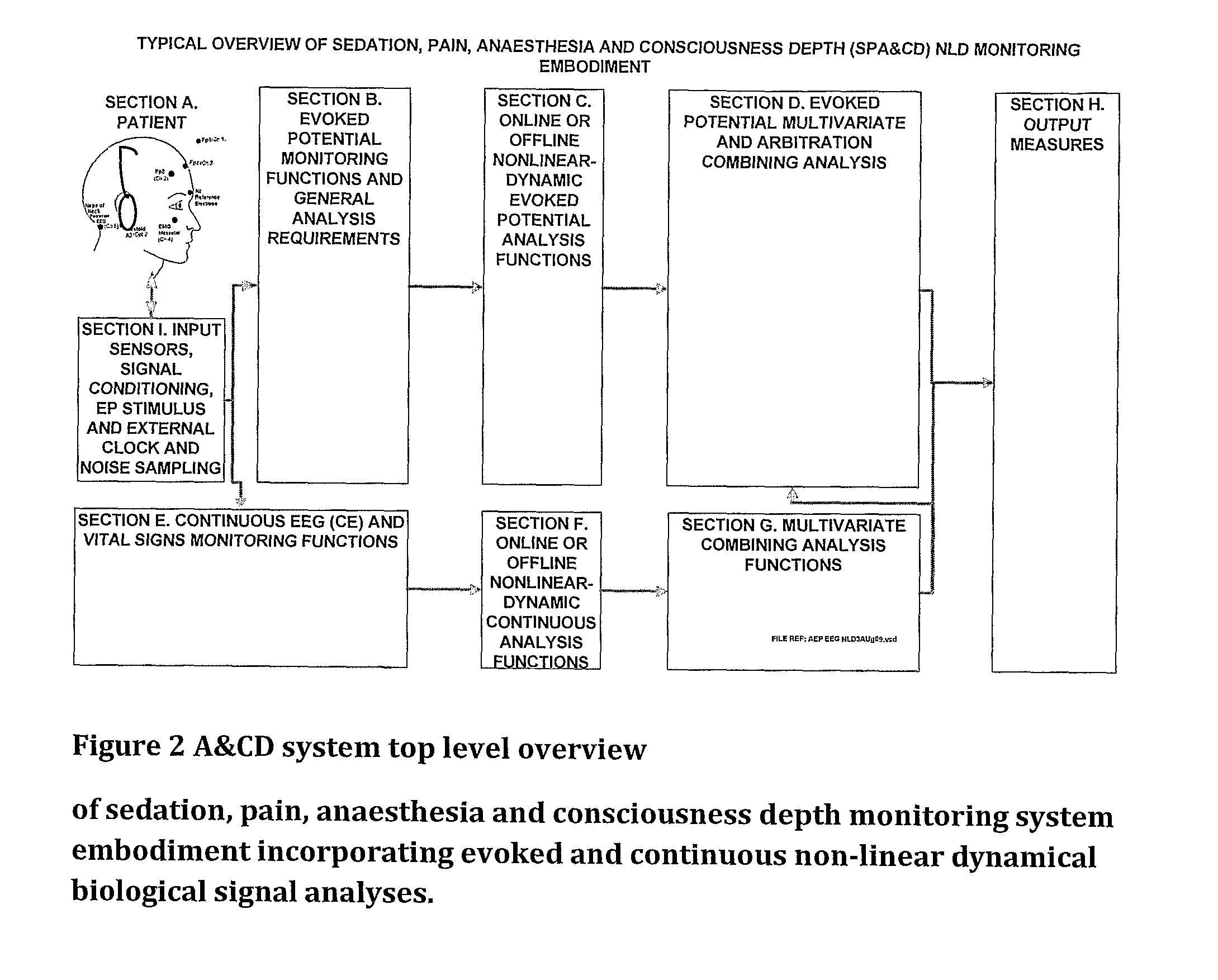
Anaesthesia and consciousness depth monitoring system
ActiveUS20120277548A1Minimize unwanted external signal interferenceGood signalElectroencephalographyElectrocardiographyBiological bodyNervous system
Methods and systems incorporating non-linear dynamic (NLD) analysis such as entropy or other complexity analysis monitoring continuous or evoked signals from a biological subject are presented, where such a system comprises of processing steps including: a) the combination of a biological signal evoked as a result of patient stimulation presented to a biological subject and a non-linear analysis method capable of capturing temporal changes in signal order or regularity; b) any combination of processed evoked or continuous central nervous or peripheral physiological mechanisms b) a means to generate a measure indicative of a patient's level of anaesthesia and consciousness depth (A&CD), sedation or sleep / wake state. Methods and systems incorporating a NLD analysis means to improve the discrimination between different signals origins including any combination of: a) central nervous system (CNS), b) peripheral control or nervous system (PNS), c) autonomic control or nervous system (ANS), d) arousals, and e) artifacts.
Owner:BURTON DAVID
Wideband enhanced digital injection predistortion system and method
ActiveUS20050157814A1Amplifier modifications to reduce non-linear distortionSecret communicationAudio power amplifierNon linear dynamic
A system for digitally linearizing the nonlinear behaviour of RF high efficiency amplifiers employing baseband predistortion techniques is disclosed. The system provides additive or multiplicative predistortion of the digital quadrature (I / Q) input signal in order to minimize distortion at the output of the amplifier. The predistorter uses a discrete-time polynomial kernel to model the inverse transfer characteristic of the amplifier, providing separate and simultaneous compensation for nonlinear static distortion, linear dynamic distortion and nonlinear dynamic effects including reactive electrical memory effects. Compensation for thermal memory effects also is embedded in the nonlinear dynamic compensation operation of the predistorter and is implemented parametrically using an autoregressive dynamics tracking mechanism. A predistortion controller periodically monitors the output of the amplifier and compares it to the quadrature input signal to compute estimates of the residual output distortion of the amplifier. Output distortion estimates are used to adaptively compute the values of the parameters of the predistorter in response to changes in the amplifier's operating conditions (temperature drifts, changes in modulation input bandwidth, variations in drive level, aging, etc). The predistortion parameter values computed by the predistortion controller are stored in non-volatile memory and used in the polynomial digital predistorter. The digital predistortion system of the invention may provide broadband linearization of highly nonlinear and highly efficient RF amplification circuits including, but not limited to, dynamic load modulation amplifiers.
Owner:INTEL CORP
Incorporating video meta-data in 3D models
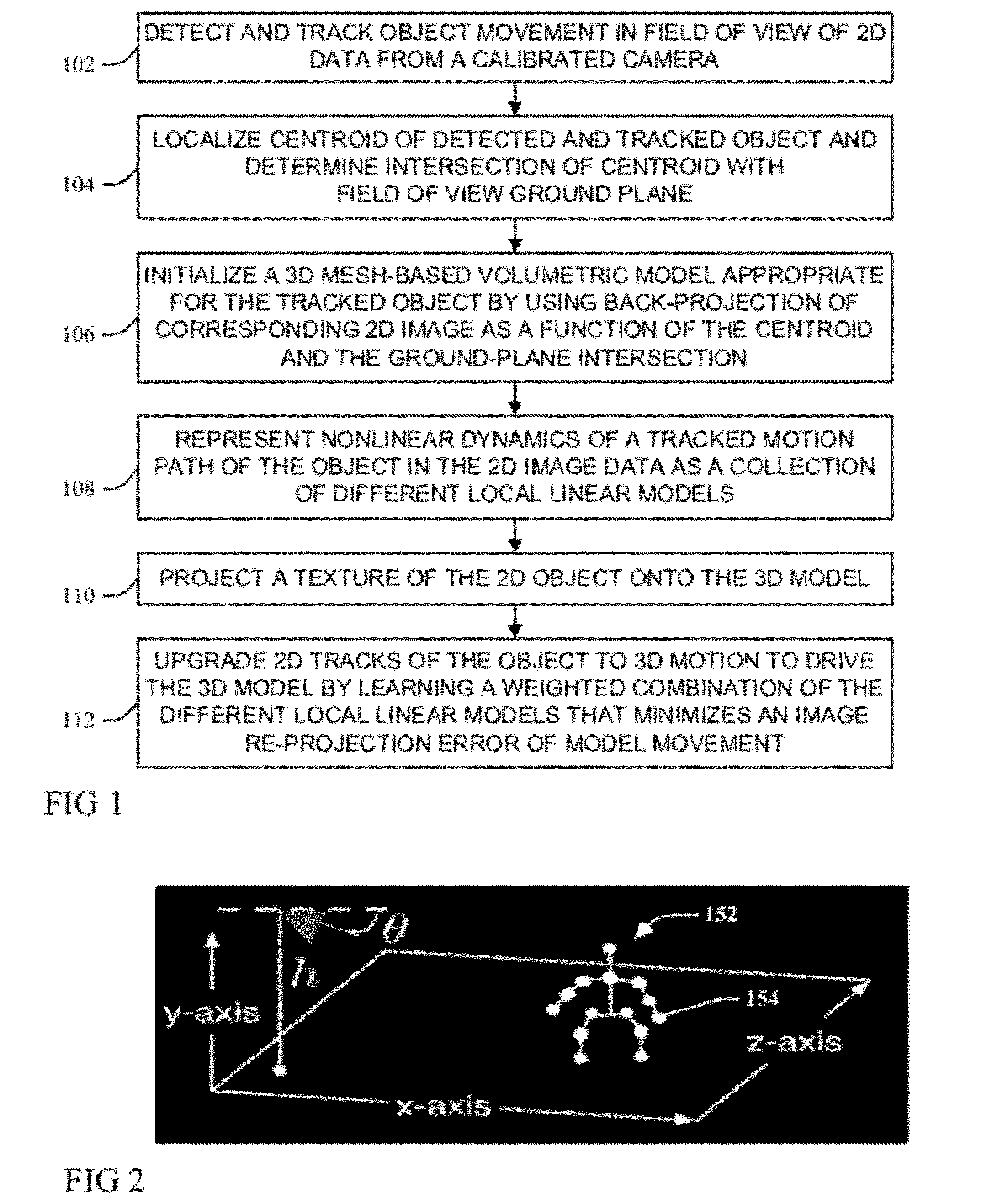
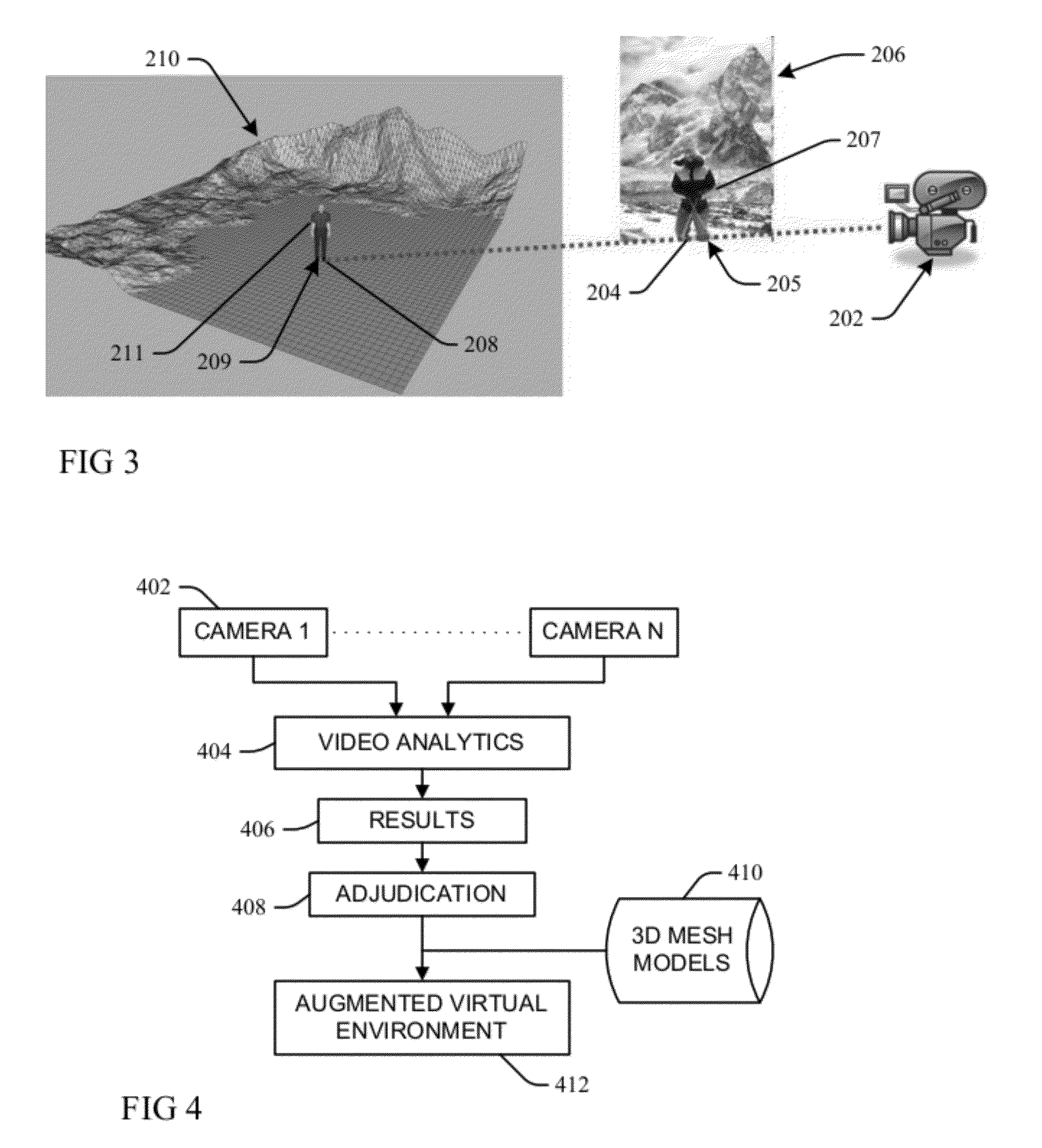
ActiveUS20120281873A1Minimizes an image re-projection error of model movementImaging errorTelevision system detailsImage analysisNon linear dynamicIntersection of a polyhedron with a line
A moving object detected and tracked within a field of view environment of a 2D data feed of a calibrated video camera is represented by a 3D model through localizing a centroid of the object and determining an intersection with a ground-plane within the field of view environment. An appropriate 3D mesh-based volumetric model for the object is initialized by using a back-projection of a corresponding 2D image as a function of the centroid and the determined ground-plane intersection. Nonlinear dynamics of a tracked motion path of the object are represented as a collection of different local linear models. A texture of the object is projected onto the 3D model, and 2D tracks of the object are upgraded to 3D motion to drive the 3D model by learning a weighted combination of the different local linear models that minimizes an image re-projection error of model movement.
Owner:KYNDRYL INC
System and method for complexity analysis-based cardiac tachyarrhythmia detection
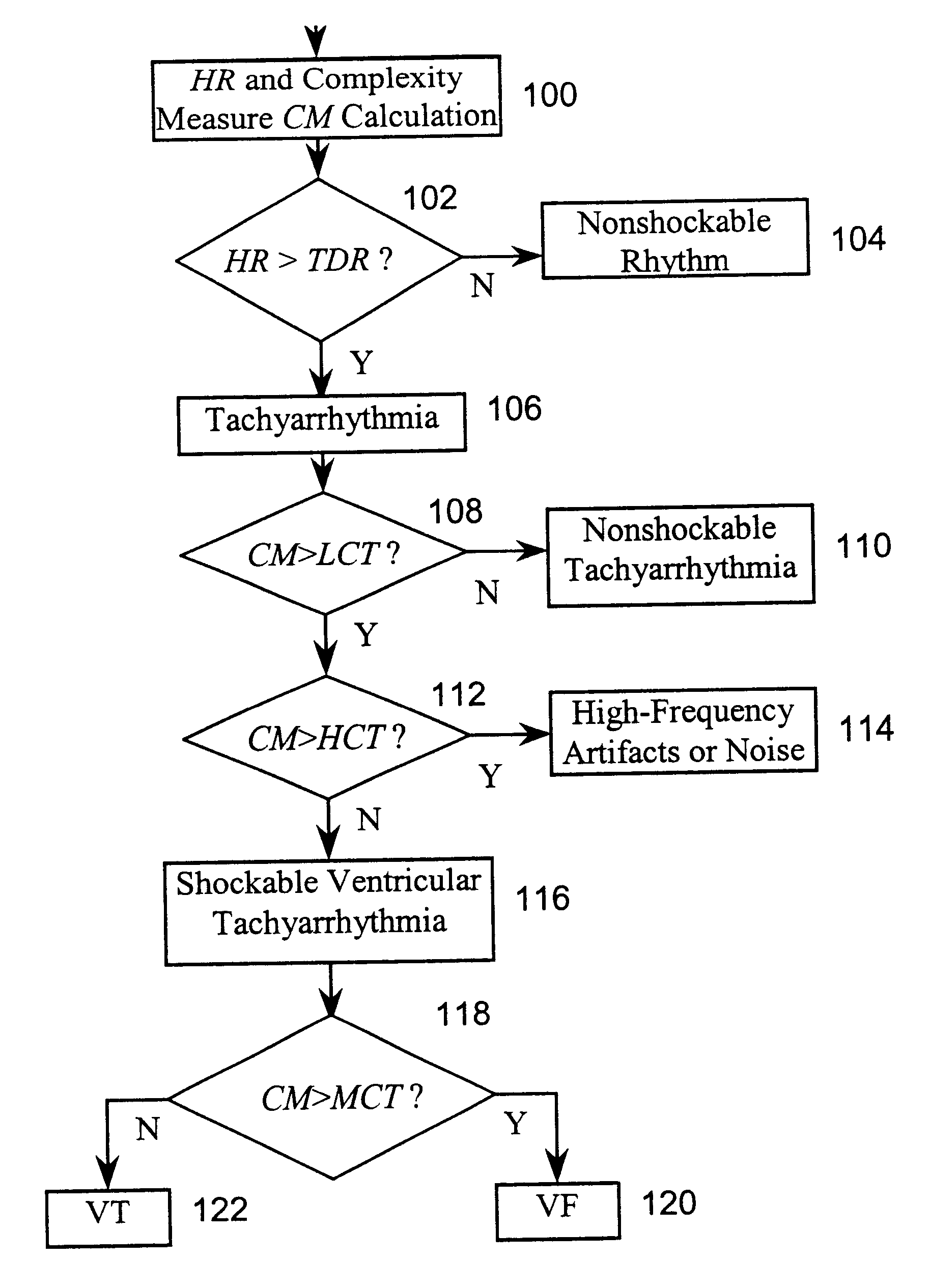
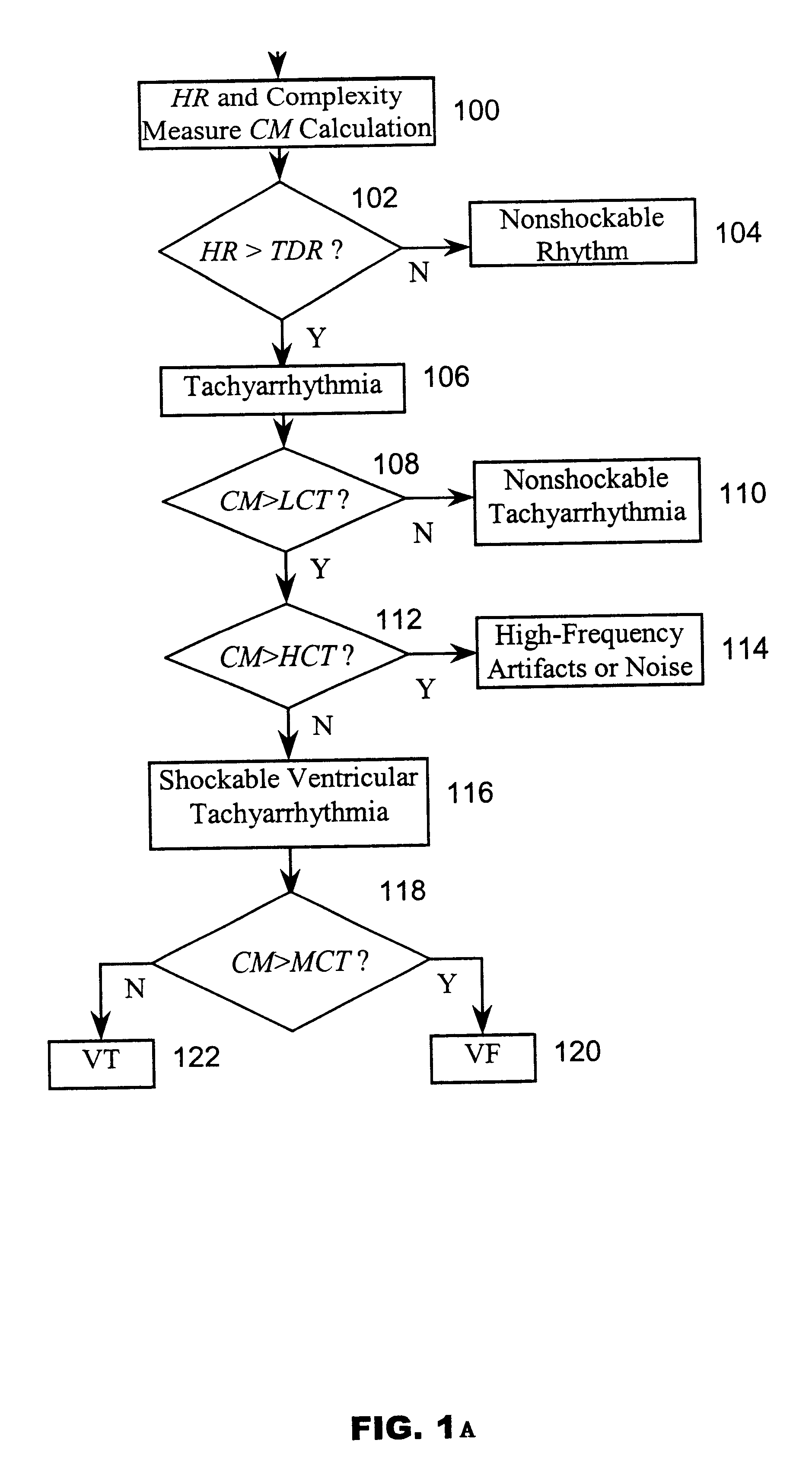
InactiveUS6490478B1Clearer and reliable indicationAvoids possible misidentificationsHeart defibrillatorsHeart stimulatorsEcg signalVentricular tachycardia
A system and method based on electrocardiogram (ECG) complexity analysis for real-time detecting shockable ventricular fibrillation (VF) and ventricular tachycardia (VT), and discriminating them from non-shockable tachyarrhythmia (e.g. supraventricular tachycardia (SVT) and atrial fibrillation (AF)) and high-frequency noise. In the disclosed invention, complexity measure CM (0 to 100), quantitatively characterizing the complexity nature of the non-linear dynamics underlying cardiac arrhythmia, is extracted from the sensed patient ECG signal using ECG complexity analysis. From the calculated complexity measure, by three thresholds (low complexity threshold (LCT), mediate complexity threshold (MCT), and high complexity threshold (HCT)), different kinds of tachyarrhythmia (i.e. heart rate (HR) above a preset rate threshold) and high-frequency noise are discriminated from each other: for non-shockable tachyarrhythmia, CM<=LCT; for VT, LCT<CM<=MCT; for VF, MCT<CM<=HCT; and for high-frequency noise, HCT<CM. The disclosed system and method can be used as a primary cardiac tachyarrhythmia detection scheme or as a backup system to reconfirm arrhythmia detection using conventional techniques.
Owner:ZOLL MEDICAL CORPORATION
Imaging apparatus, imaging method, integrated circuit, and storage medium
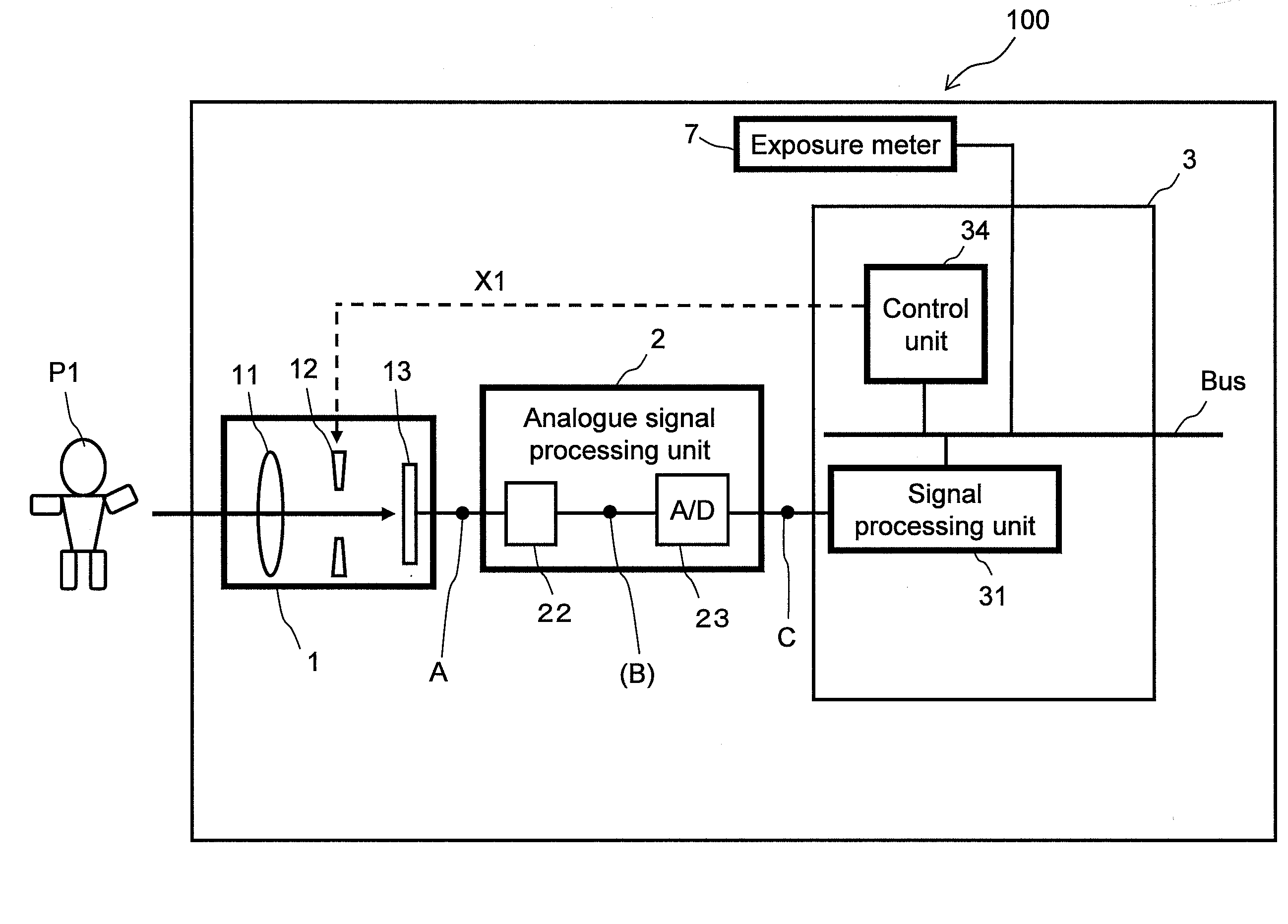
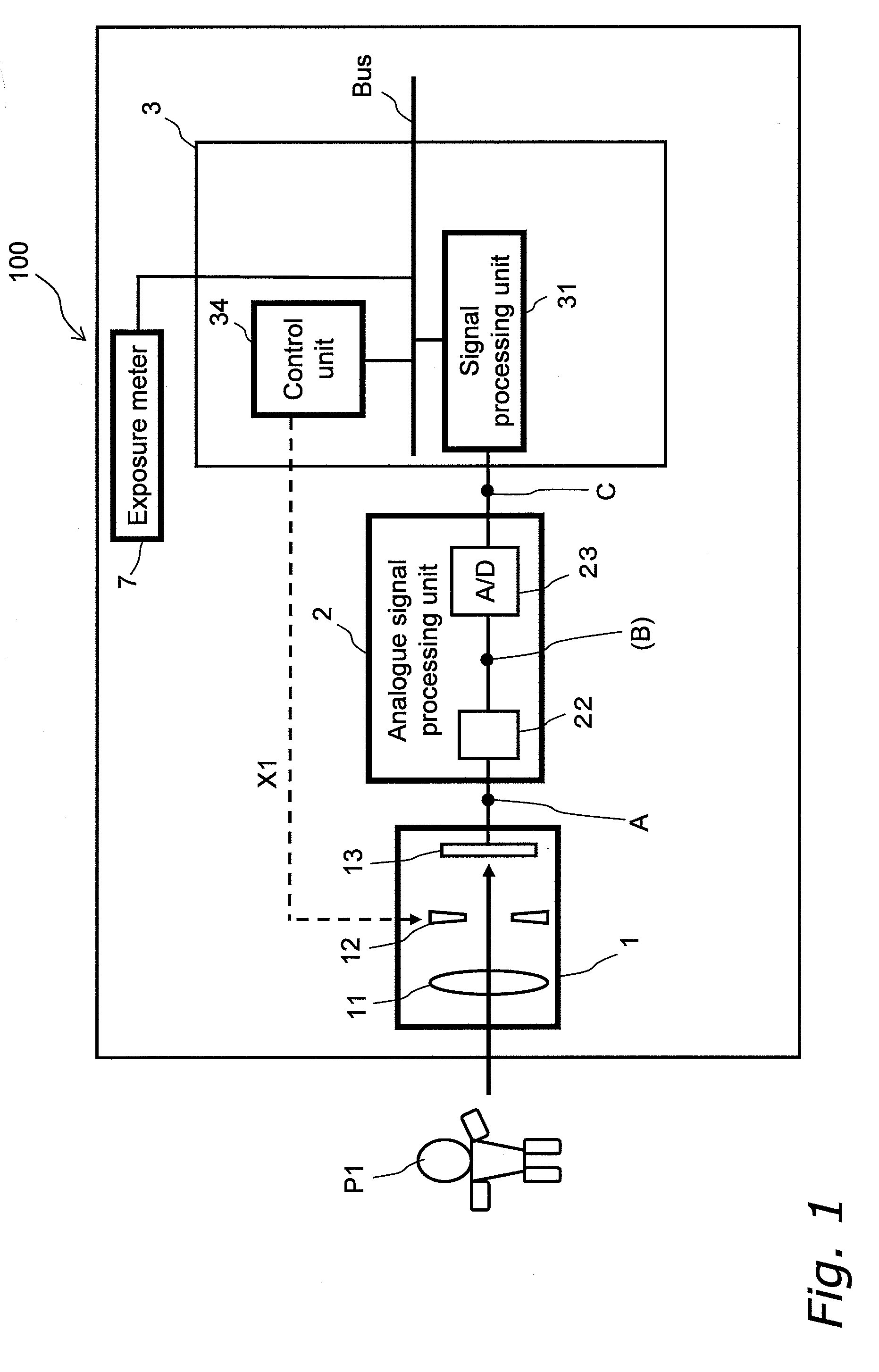
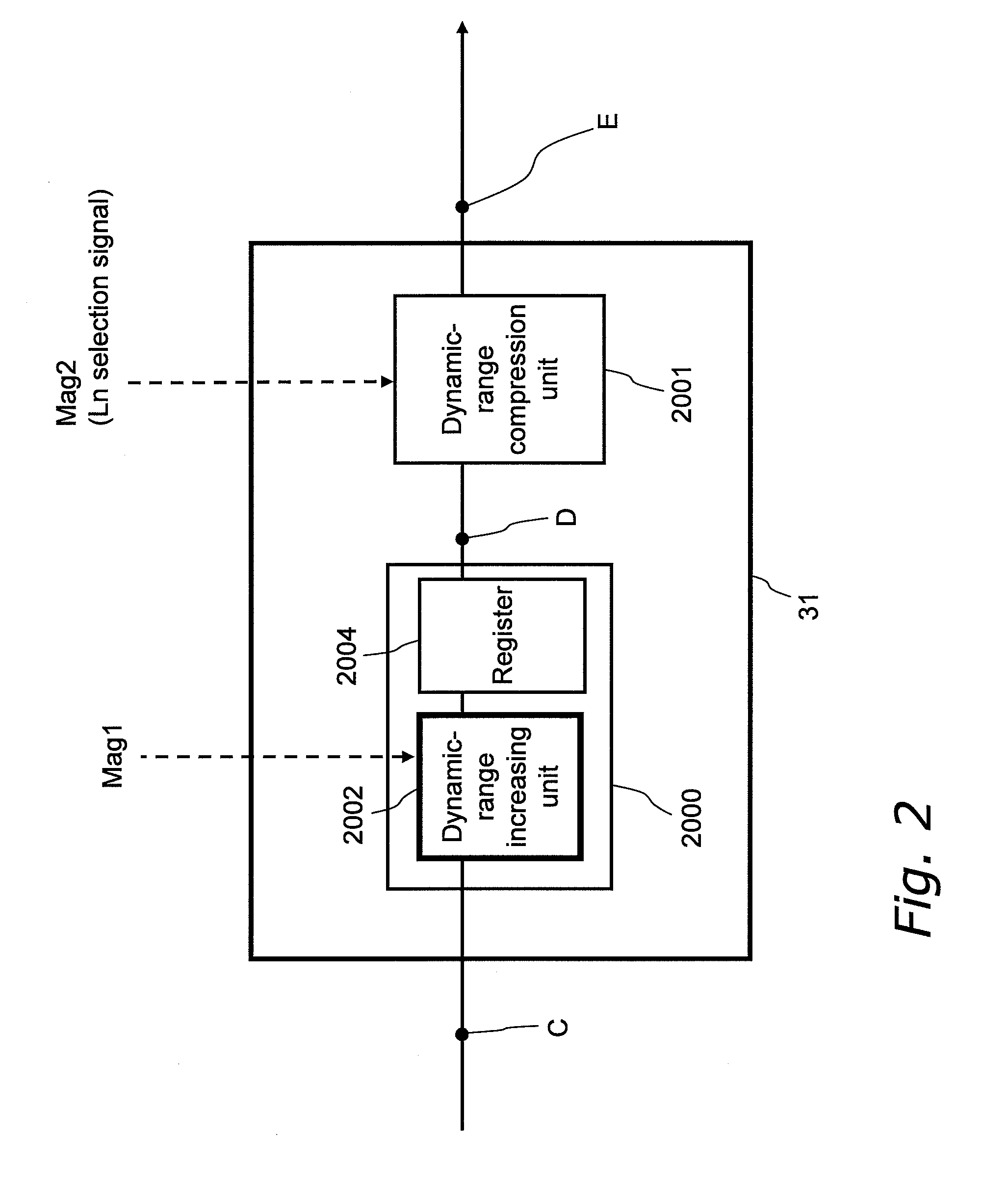
ActiveUS20080259181A1Increase brightnessAppropriately capturedTelevision system detailsColor television detailsNon linear dynamicExposure control
An imaging apparatus appropriately captures a large dynamic range image of even a scene including a backlit person with a blue sky background in a manner that the person's face has an appropriate luminance level without saturating the background sky. In the imaging apparatus, an imaging unit obtains analogue image signals through exposure control that prevents a highlight from being saturated, an A / D converter converts the analogue image signals to digital image signals, and a signal processing unit linearly increases the dynamic range of the digital image signals. The image signals with the increased dynamic range are nonlinearly compressed to have a dynamic range of 100% or less through nonlinear dynamic range compression that intensively compresses a highlight portion. The imaging apparatus with this structure first increases the dynamic range of an image and efficiently compresses the increased large dynamic range of the image.
Owner:PANASONIC INTELLECTUAL PROPERTY CORP OF AMERICA
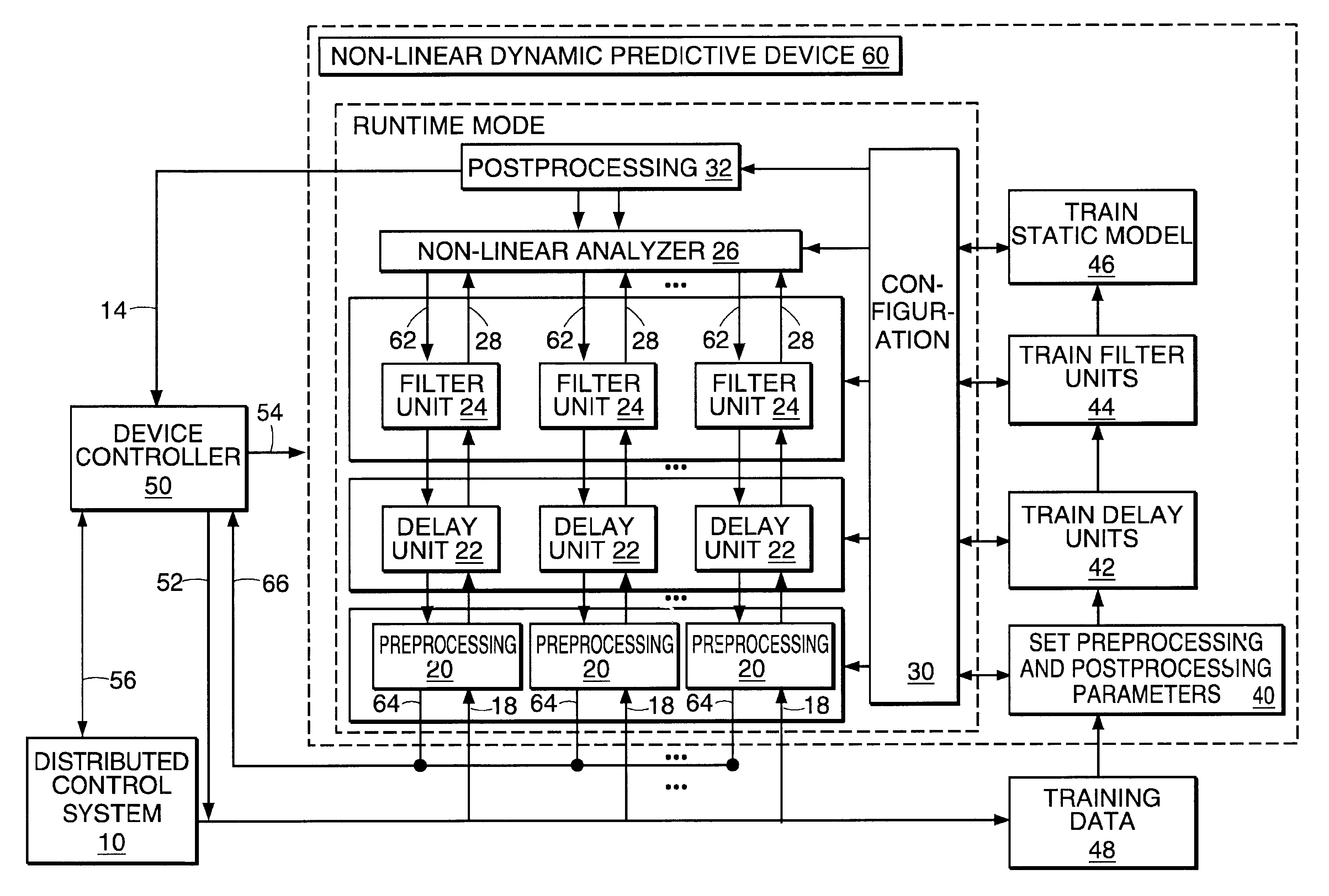
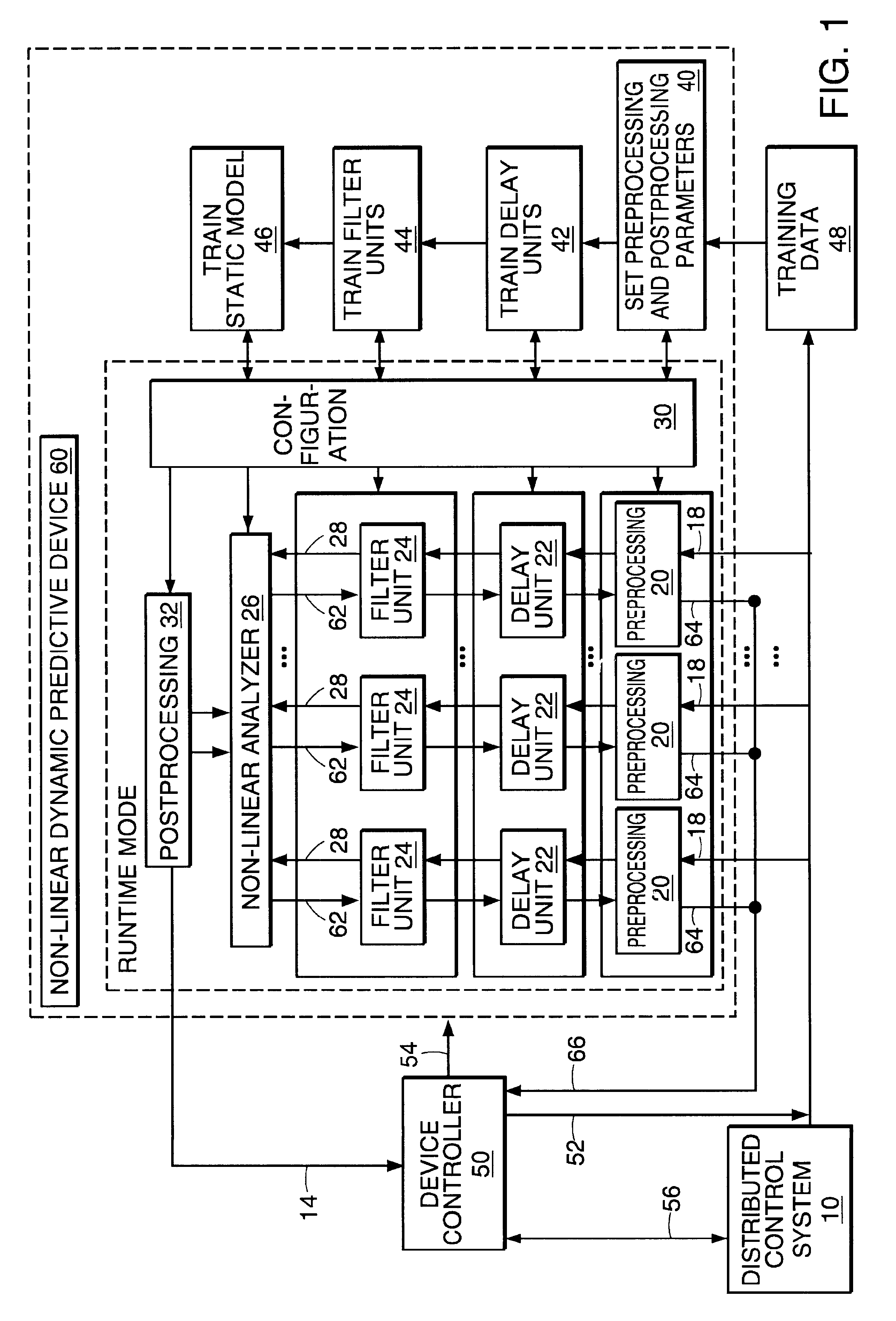
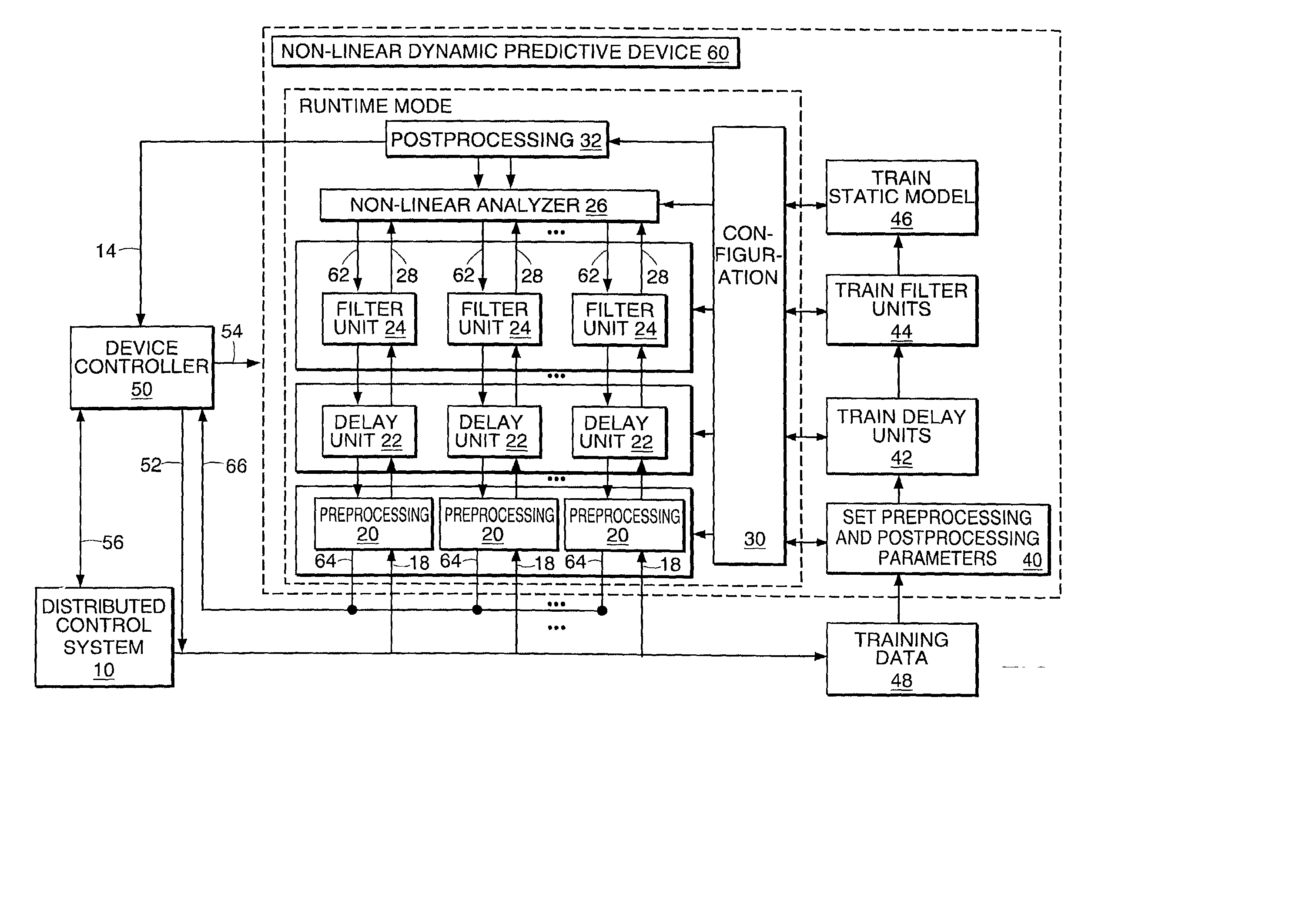
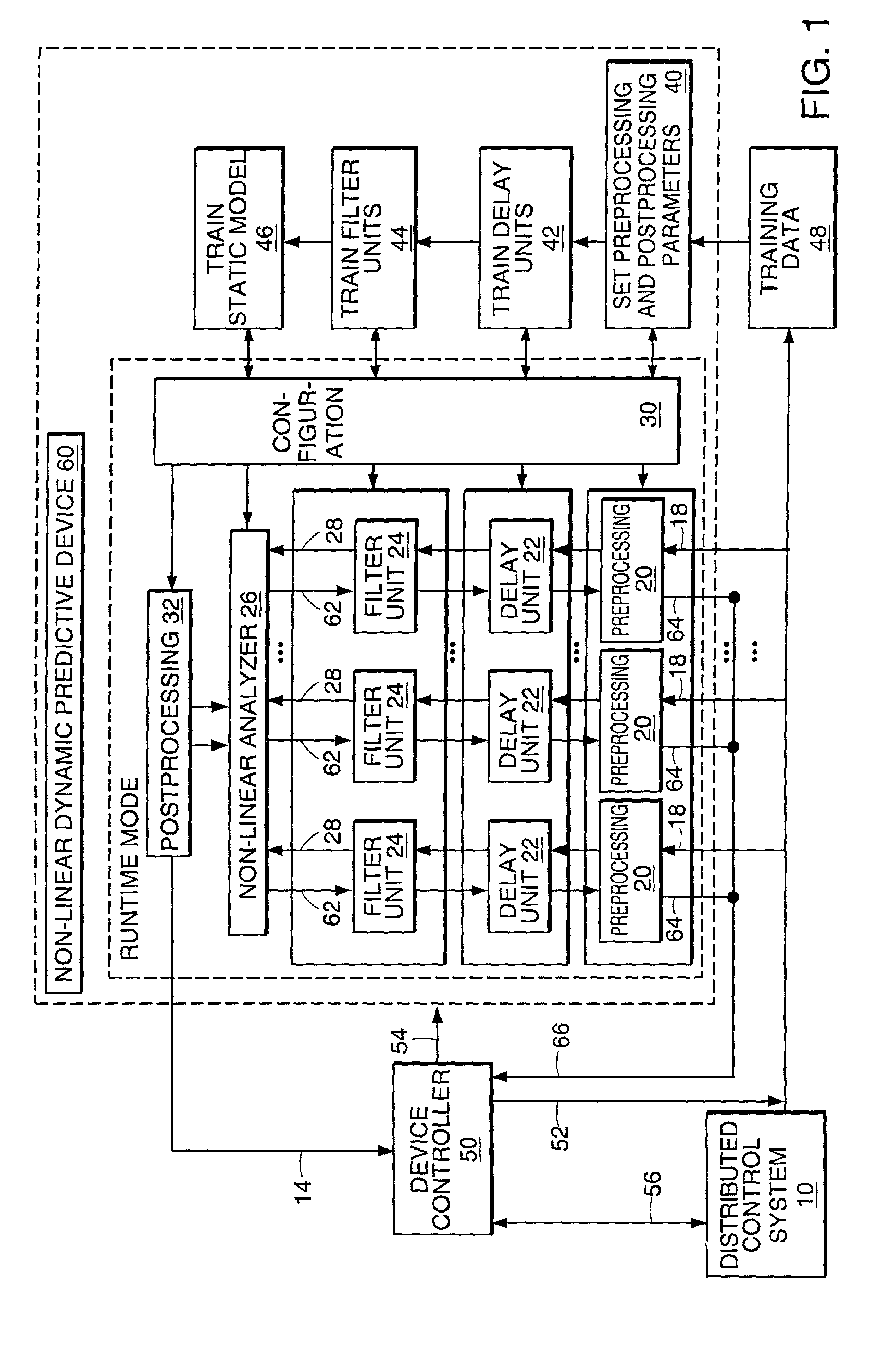
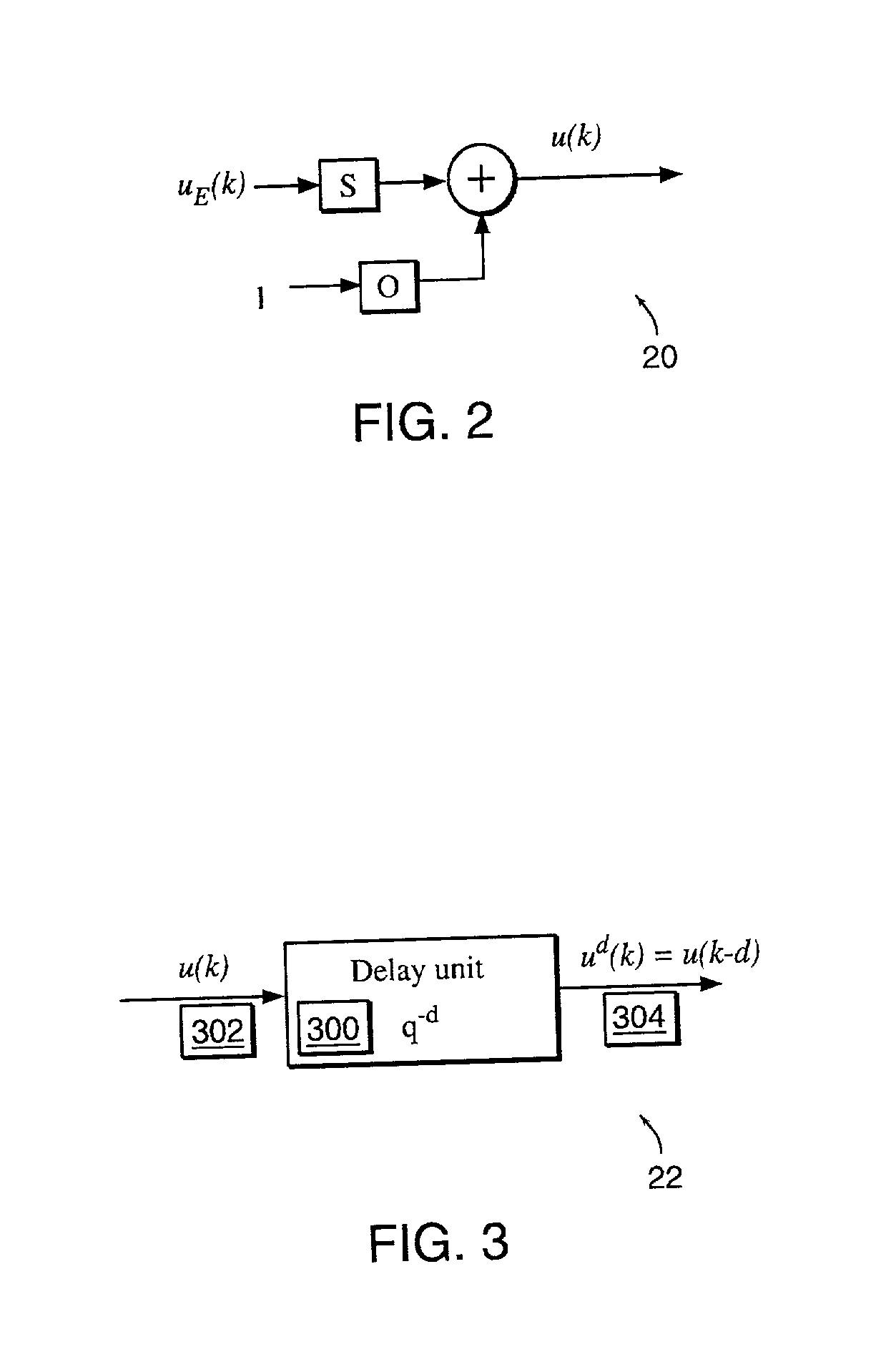
Non-linear dynamic predictive device
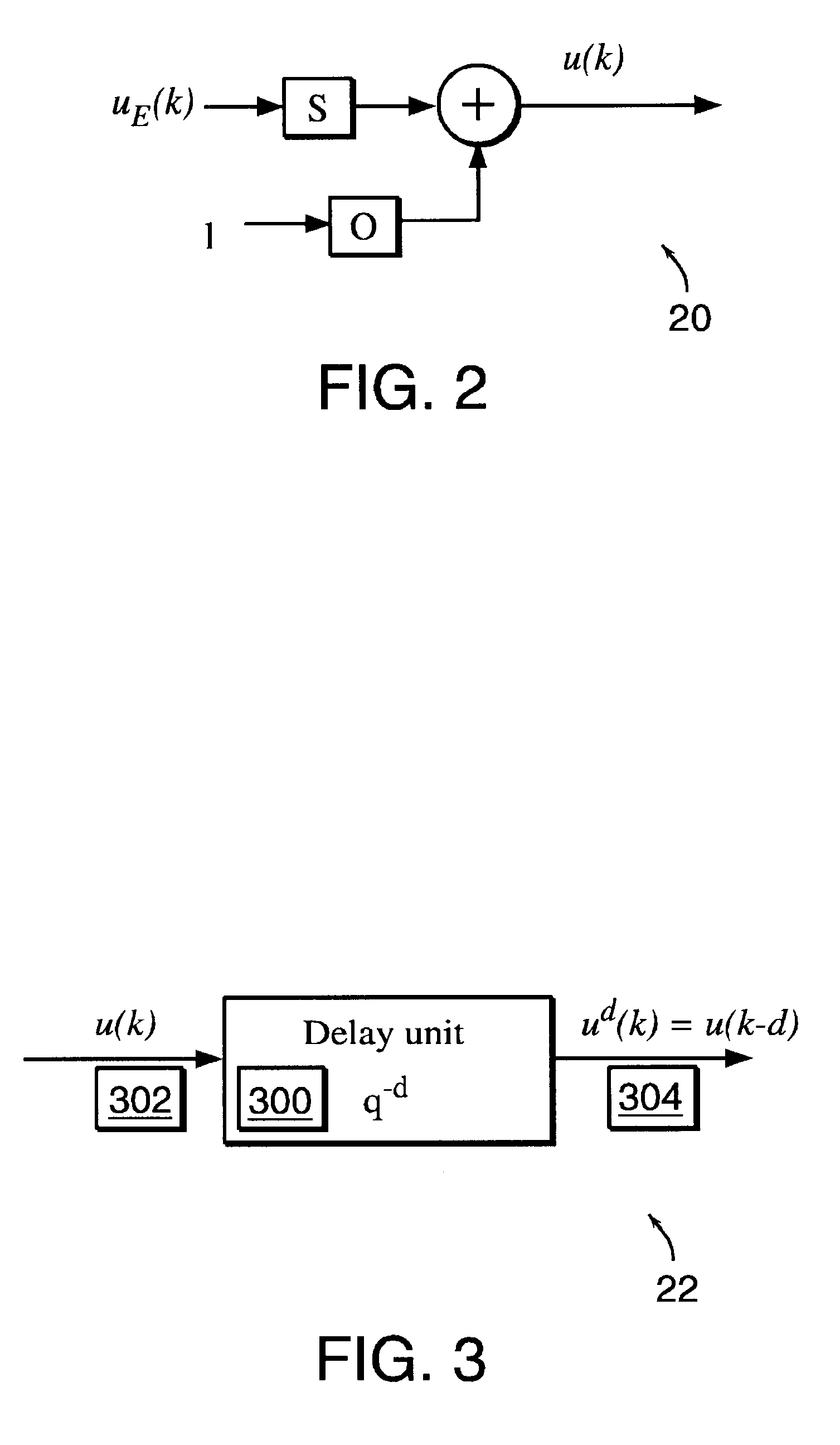
InactiveUS6453308B1Improve accuracyFast computerSimulator controlElectric testing/monitoringHorizonDead time
A non-linear dynamic predictive device (60) is disclosed which operates either in a configuration mode or in one of three runtime modes: prediction mode, horizon mode, or reverse horizon mode. An external device controller (50) sets the mode and determines the data source and the frequency of data. In prediction mode, the input data are such as might be received from a distributed control system (DCS) (10) as found in a manufacturing process; the device controller ensures that a contiguous stream of data from the DCS is provided to the predictive device at a synchronous discrete base sample time. In prediction mode, the device controller operates the predictive device once per base sample time and receives the output from the predictive device through path (14). In horizon mode and reverse horizon mode, the device controller operates the predictive device additionally many times during base sample time interval. In horizon mode, additional data is provided through path (52). In reverse horizon mode data is passed in a reverse direction through the device, utilizing information stored during horizon mode, and returned to the device controller through path (66). In the forward modes, the data are passed to a series of preprocessing units (20) which convert each input variable (18) from engineering units to normalized units. Each preprocessing unit feeds a delay unit (22) that time-aligns the input to take into account dead time effects such as pipeline transport delay. The output of each delay unit is passed to a dynamic filter unit (24). Each dynamic filter unit internally utilizes one or more feedback paths that are essential for representing the dynamic information in the process. The filter units themselves are configured into loosely coupled subfilters which are automatically set up during the configuration mode and allow the capability of practical operator override of the automatic configuration settings. The outputs (28) of the dynamic filter units are passed to a non-linear analyzer (26) which outputs a value in normalized units. The output of the analyzer is passed to a post-processing unit (32) that converts the output to engineering units. This output represents a prediction of the output of the modeled process. In reverse horizon mode, a value of 1 is presented at the output of the predictive device and data is passed through the device in a reverse flow to produce a set of outputs (64) at the input of the predictive device. These are returned to the device controller through path (66). The purpose of the reverse horizon mode is to provide essential information for process control and optimization. The precise operation of the predictive device is configured by a set of parameters. that are determined during the configuration mode and stored in a storage device (30). The configuration mode makes use of one or more files of training data (48) collected from the DCS during standard operation of the process, or through structured plant testing. The predictive device is trained in four phases (40, 42, 44, and 46) correspo
Owner:ASPENTECH CORP
Non-linearity process failure diagnosis method
InactiveCN101158873AExert grasping abilityUse classification abilityElectric testing/monitoringKernel principal component analysisData acquisition
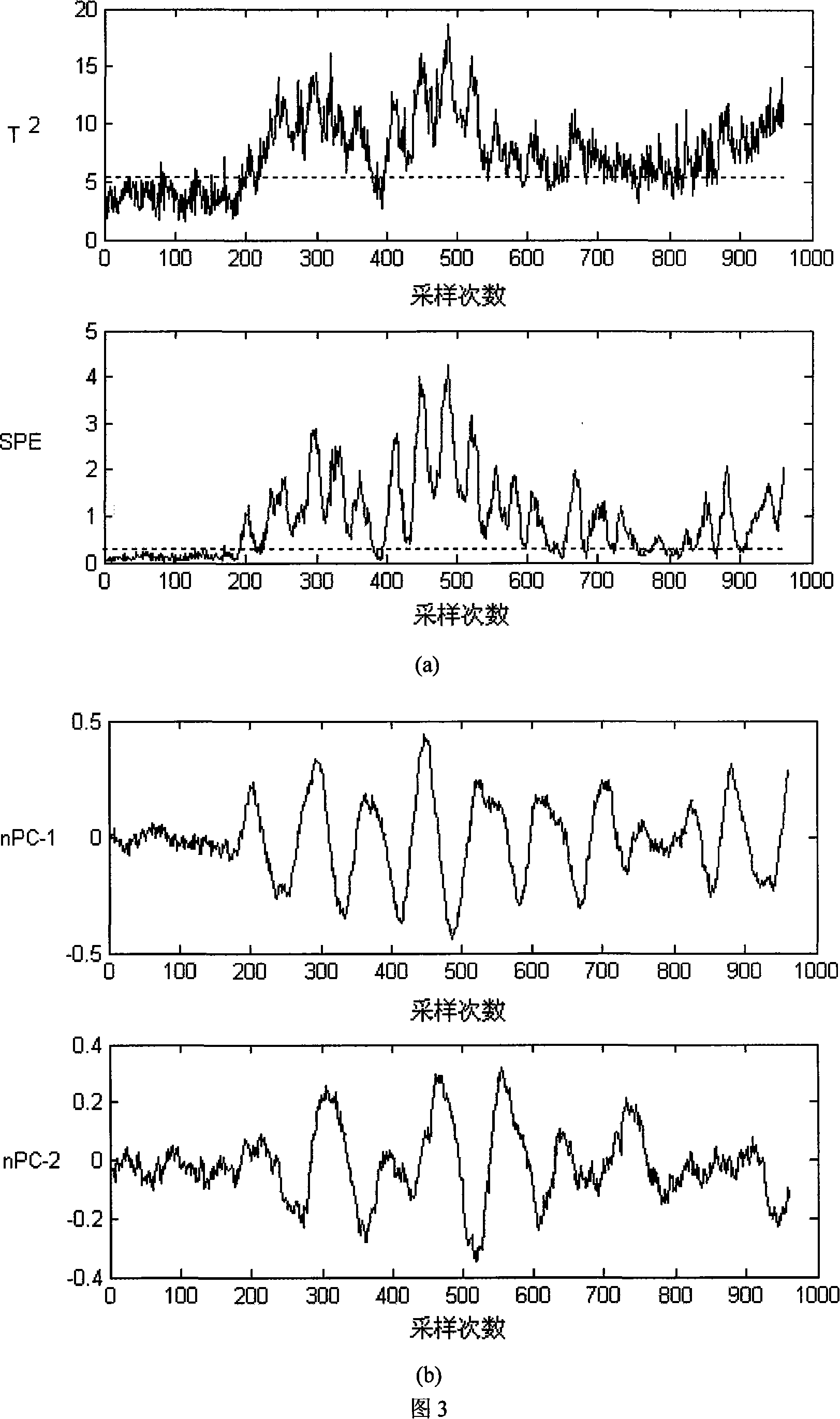
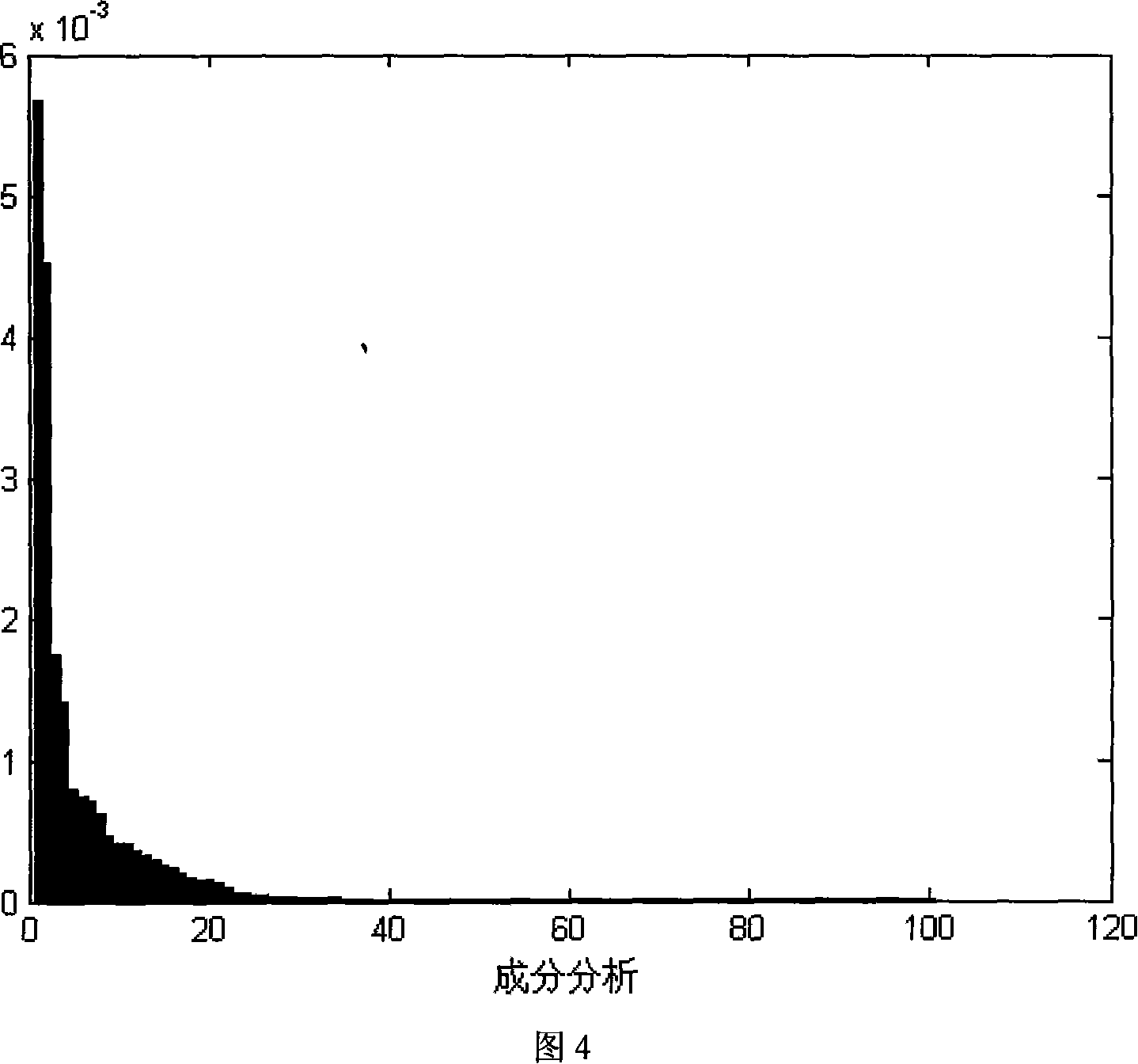
The invention relates to a nonlinear process fault diagnosis method, comprising the steps such as data acquisition, similar analysis, whitening process to the data by utilizing kernel principal component analysis, solving of observation variable z after whitening, independent component exaction by modifying an ICA analysis, and fault detection and diagnosis analysis by utilization of T<2> and SPE statistics and LS-SVM. The invention puts forward the nonlinear dynamic process fault diagnosis technique, combines the advantages of Kernel, ICA and LS-SVM, that is, the exerts the kernel-to-nonlinear express ability, and at the same plays the master ability of ICA to the dynamic characteristic as well as LS - SVM classification ability.
Owner:NORTHEASTERN UNIV
Joint estimation method of travel speed and road attachment coefficient
The invention discloses a joint estimation method of travel speed and a road attachment coefficient. Based on a non-linear dynamic model of a finished automobile and a tire longitudinal force model, the method comprises the following steps: under different road attachment coefficient conditions, respectively establishing a plurality of different Kalman filtering models, and meanwhile, determining an external input quantity and an observed quantity of each Kalman filtering system by utilizing a vehicle-mounted wheel speed and steering wheel angle sensor, and further, interacting different filtering systems through an interactive multi-model algorithm to realize the self-adaptive estimation of the longitudinal speed and the lateral speed of an automobile under different road attachment coefficient conditions, and calculating a model probability of each Kalman filtering model according to the interactive multi-model algorithm so as to realize the real-time estimation of the road attachment coefficient thus achieving the total self-adaptive effect.
Owner:SOUTHEAST UNIV
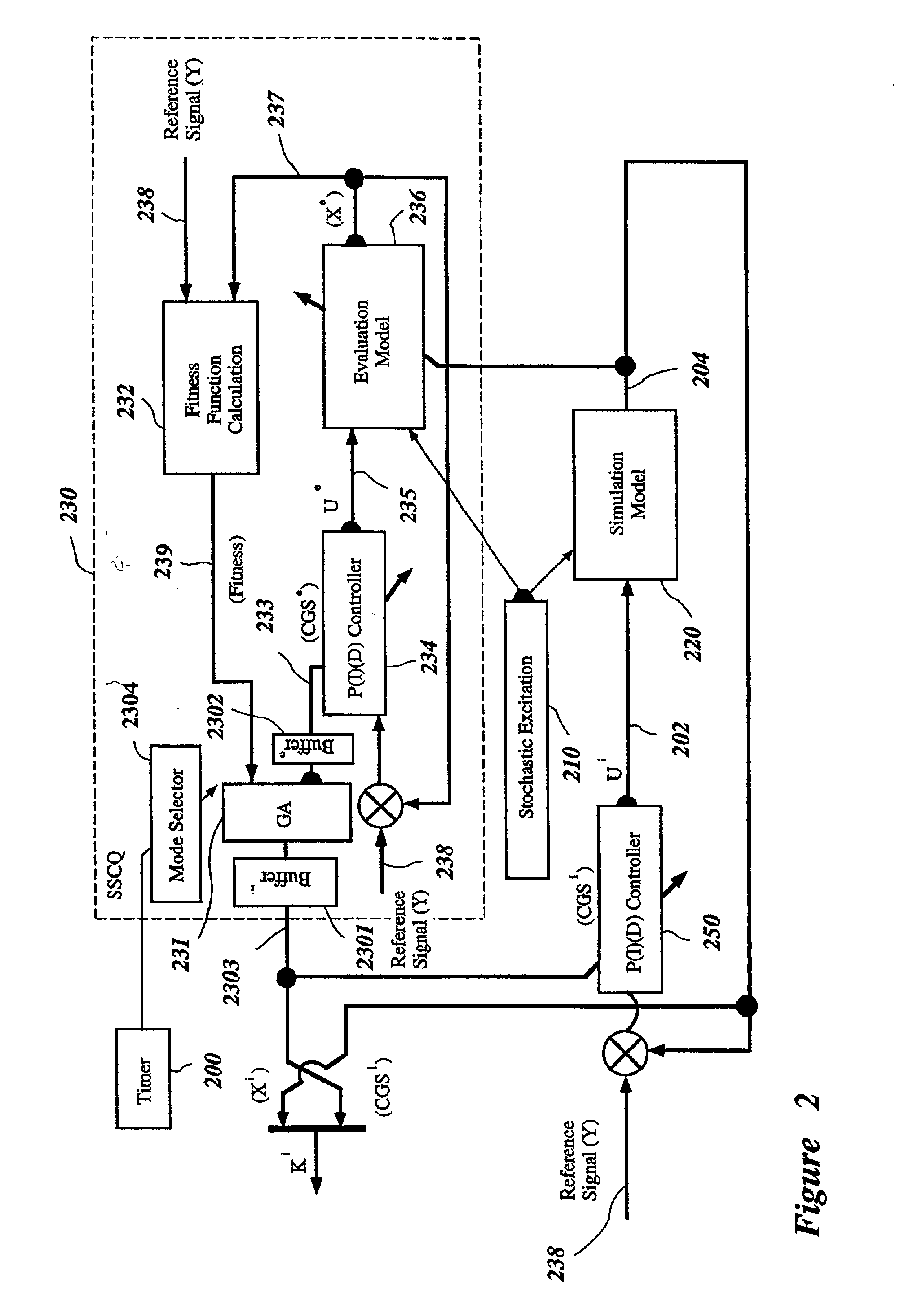
System and method for nonlinear dynamic control based on soft computing with discrete constraints
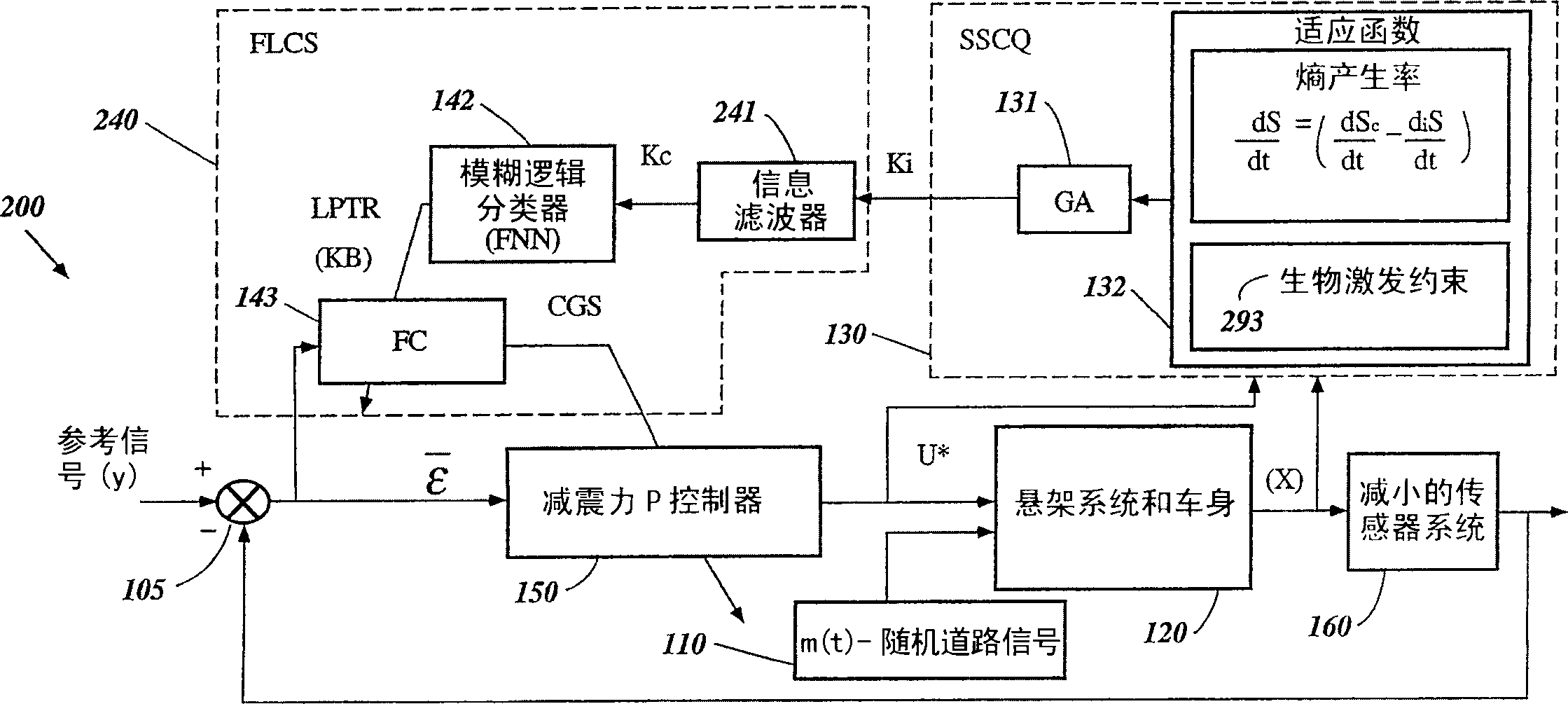
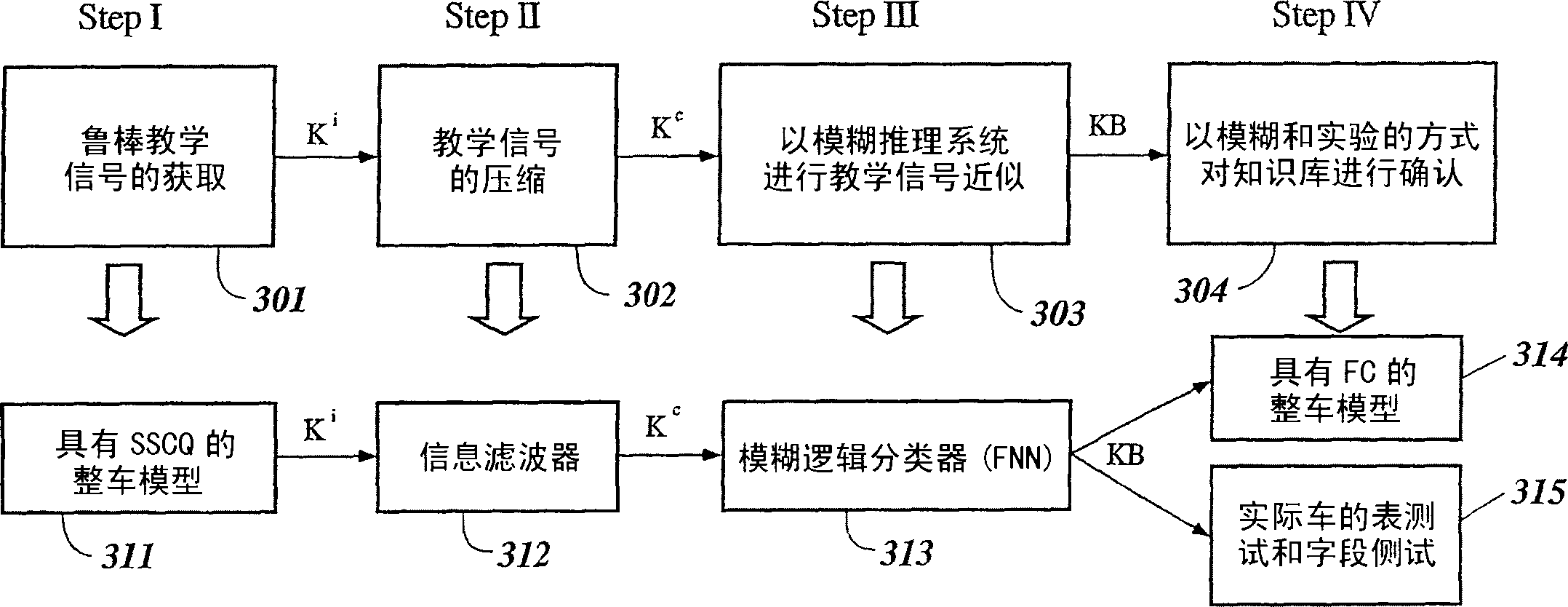
InactiveUS6950712B2Minimizes entropyMaximizes sensor information contentDigital data processing detailsAnimal undercarriagesNon linear dynamicMinimum entropy
A control system using a genetic analyzer based on discrete constraints is described. In one embodiment, a genetic algorithm with step-coded chromosomes is used to develop a teaching signal that provides good control qualities for a controller with discrete constraints, such as, for example, a step-constrained controller. In one embodiment, the control system uses a fitness (performance) function that is based on the physical laws of minimum entropy. In one embodiment, the genetic analyzer is used in an off-line mode to develop a teaching signal for a fuzzy logic classifier system that develops a knowledge base. The teaching signal can be approximated online by a fuzzy controller that operates using knowledge from the knowledge base. The control system can be used to control complex plants described by nonlinear, unstable, dissipative models. In one embodiment, the step-constrained control system is configured to control stepping motors.
Owner:YAMAHA MOTOR CO LTD
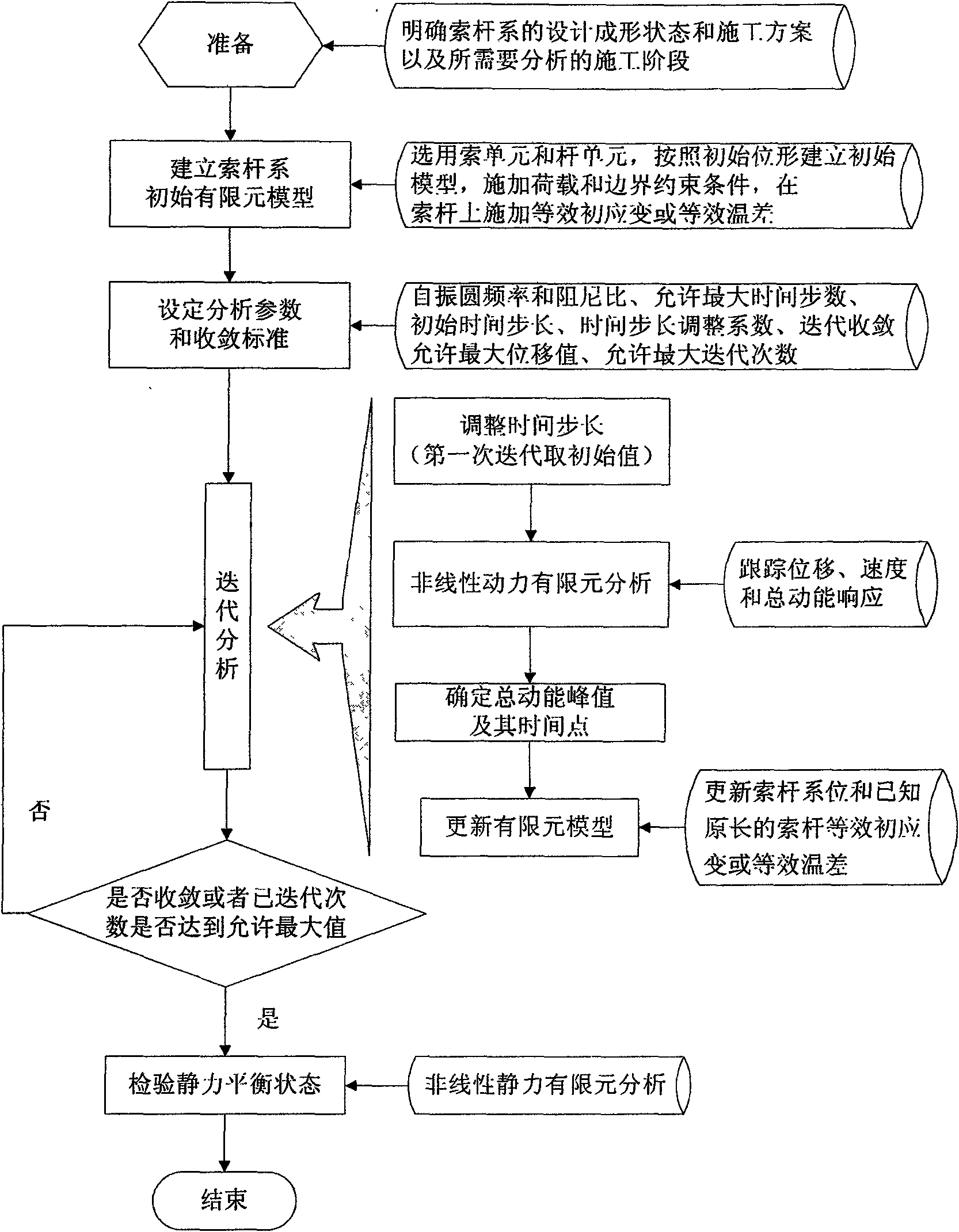
Non-linear dynamic finite element method for determining cable-strut system static balancing state
ActiveCN101582095ASolve the form-finding problemHolisticSpecial data processing applicationsViscous dampingDynamic balance
The invention relates to a non-linear dynamic finite element method for determining cable-strut system static balancing state. In the construction processes of traction mounting and stretch-draw forming, a cable-strut system as a mechanism has super large displacement, mechanism displacement and guy cable looseness, and a conventional linear dynamic finite element method cannot obtain the static balancing state in the construction stage. The non-linear dynamic finite element method adopts form-finding analysis to establish a non-linear dynamic finite element equation by introducing inertia force and viscous damping force so as to change a static problem which is difficult to solve into a dynamic problem which is easy to solve, and gradually converge the dynamic balancing state of the cable-strut system into a static balancing state through iteration updating of the configuration of the cable-strut system. The cable-strut system is in a static unbalancing state before analysis, is in the dynamic balancing state in the analysis, and reaches the static balancing state after the convergence, namely the cable-strut system discontinuously moves (non-continuous movement) from the initial static unbalancing state to the stable static balancing state.
Owner:SOUTHEAST UNIV
Non-linear dynamic predictive device
InactiveUS20020178133A1Fast computerImprove accuracySimulator controlElectric testing/monitoringNonlinear approximationDead time
A non-linear dynamic predictive device (60) is disclosed which operates either in a configuration mode or in one of three runtime modes: prediction mode, horizon mode, or reverse horizon mode. An external device controller (50) sets the mode and determines the data source and the frequency of data. In the forward modes (prediction and horizon), the data are passed to a series of preprocessing units (20) which convert each input variable (18) from engineering units to normalized units. Each preprocessing unit feeds a delay unit (22) that time-aligns the input to take into account dead time effects. The output of each delay unit is passed to a dynamic filter unit (24). Each dynamic filter unit internally utilizes one or more feedback paths that provide representations of the dynamic information in the process. The outputs (28) of the dynamic filter units are passed to a non-linear approximator (26) which outputs a value in normalized units. The output of the approximator is passed to a post-processing unit (32) that converts the output to engineering units. This output represents a prediction of the output of the modeled process. In reverse horizon mode, data is passed through the device in a reverse flow to produce a set of outputs (64) at the input of the predictive device. These are returned to the device controller through path (66). The purpose of the reverse horizon mode is to provide information for process control and optimization. The predictive device approximates a large class of non-linear dynamic processes. The structure of the predictive device allows it to be incorporated into a practical multivariable non-linear Model Predictive Control scheme, or used to estimate process properties.
Owner:ASPENTECH CORP
Non-linear dynamic characteristic monitoring system and method of vehicle tyre
InactiveCN101710027AImprove measurement accuracyImprove calculation accuracyVehicle tyre testingInformation processingNerve network
The invention discloses non-linear dynamic characteristic monitoring system and method of a vehicle tyre. The system comprises an acceleration sensor, a gyroscope sensor, a tyre air pressure sensor, a tyre temperature sensor, a tyre rotation speed sensor, a vehicle speed sensor, a communication module, an information processing module, a learning module and a learning knowledge base module. The method comprises the following steps of: collecting signals obtained by a plurality of sensors by the communication module, and compiling, converting and storing data through the information processing module; dividing the data of the sensor into a parameter, an independent variable and a dependent variable through the information processing module, and uploading the parameter into the learning module; operating an improved genetic algorithm by the learning module to carry out parameter identification on a tyre nerve network model and describing the dynamic property of the tyre; finally uploading the independent variable data to the learning module through the information processing module, and calculating a dependent variable value by the learning module according to a pre-established dynamic property model; and storing the dependent variable value into the learning knowledge base module and simultaneously extracting useful information to other systems of the vehicle to share by the communication module.
Owner:JIANGSU UNIV
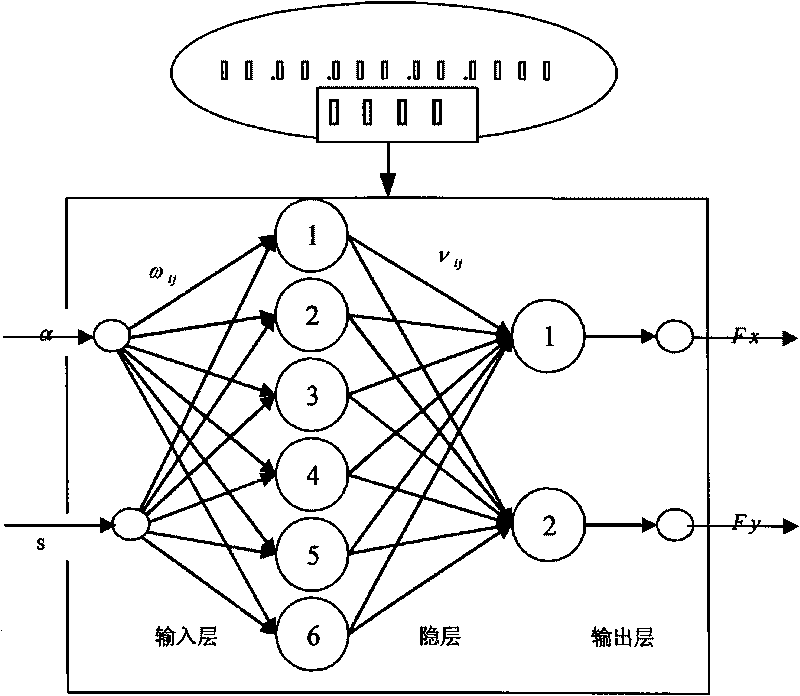
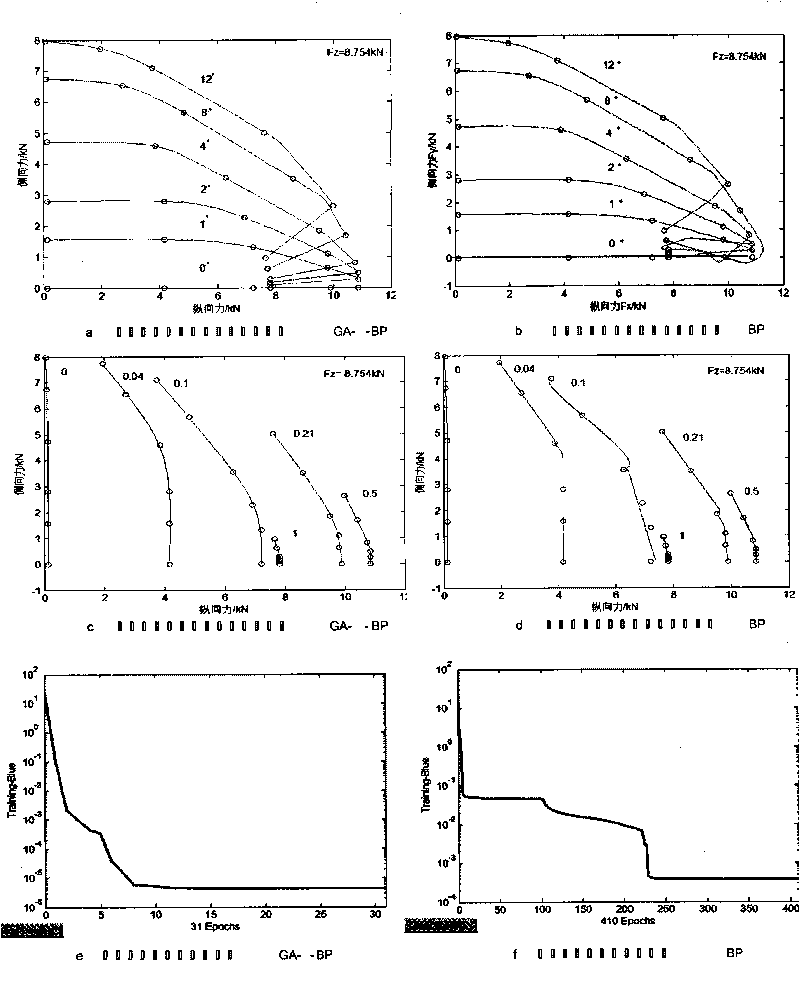
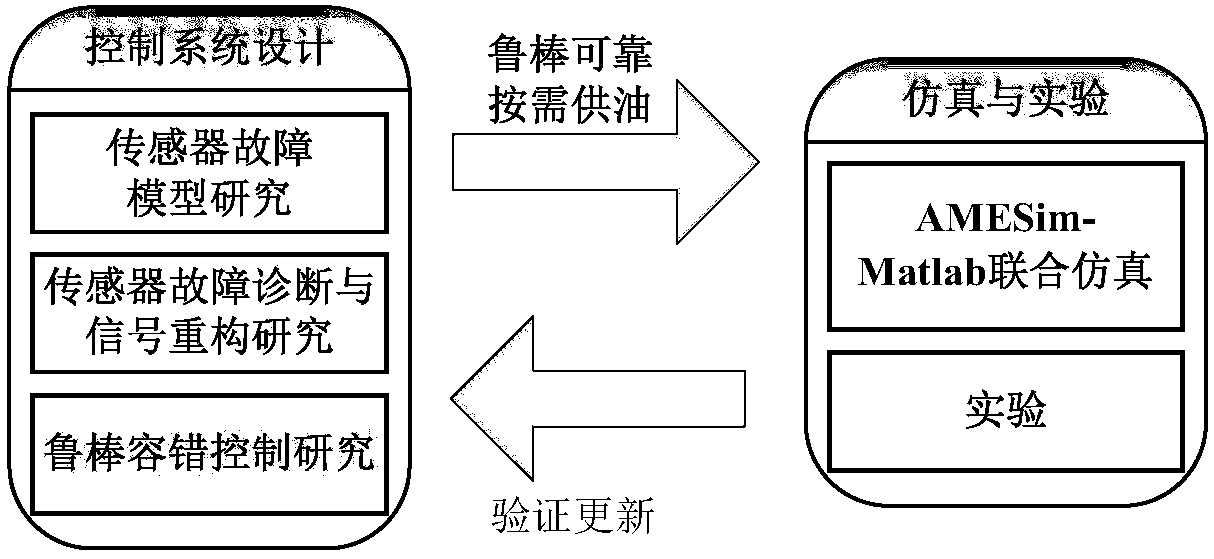
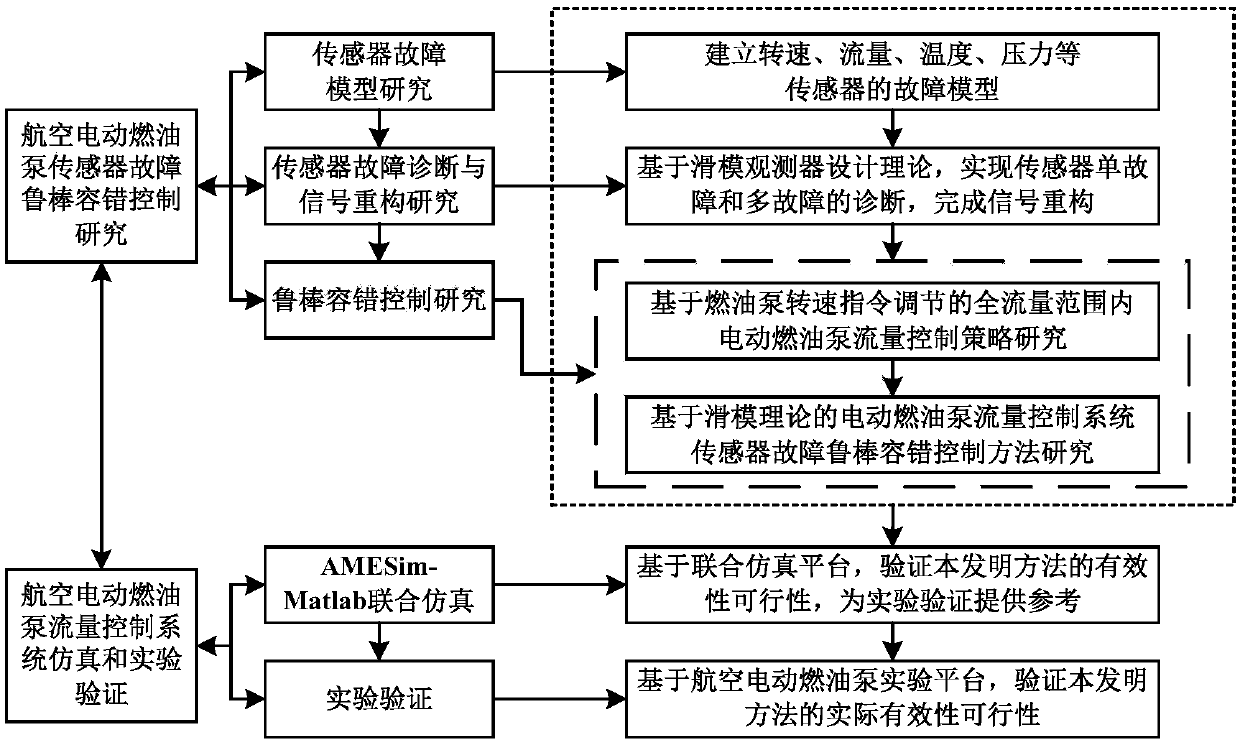
Robust fault tolerance method of sensor fault of flow control system of aircraft electric fuel pump
InactiveCN107942653AWide range of fuel adjustmentSafe and reliable oil supply on demandSimulator controlAdaptive controlFault toleranceControl system
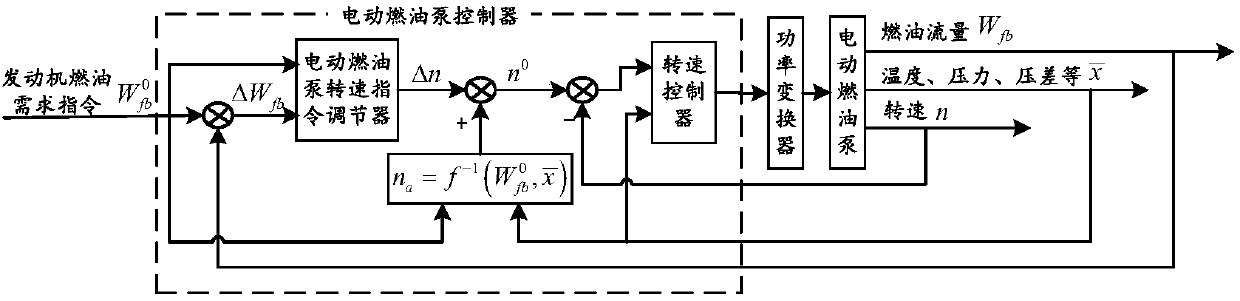
The invention discloses a robust fault tolerance method of a sensor fault of a flow control system of an aircraft electric fuel pump. A rotating speed instruction adjustment part and a rotating speedcontrol part are arranged. The rotating speed instruction adjustment part provides a proper electric fuel pump rotating speed instruction suitable for an all flow range for the control system based onan engine fuel demand instruction, a fuel flow non-linear steady-state model and an output fuel flow of an electric fuel pump. The rotating speed control part is mainly used for minimizing an error between an actual rotating speed and a rotating speed instruction; and under the circumstance that the uncertainty and the sensor failure are considered, on the basis of an adaptive combined nonlineardynamic model of the electric fuel pump, a sliding mode fault estimator and a sliding mode rotating speed controller are designed comprehensively based on a sliding mode theory, so that the rotating speed response of the electric fuel pump is done quickly and the expected rotating speed is reached accurately; and thus on-demand oil supply for the aero-engine by the electric fuel pump is realized safely, reliably, quickly, and precisely.
Owner:NANJING UNIV OF AERONAUTICS & ASTRONAUTICS
Method and apparatus for detecting and tracking faint target of high frequency ground wave radar
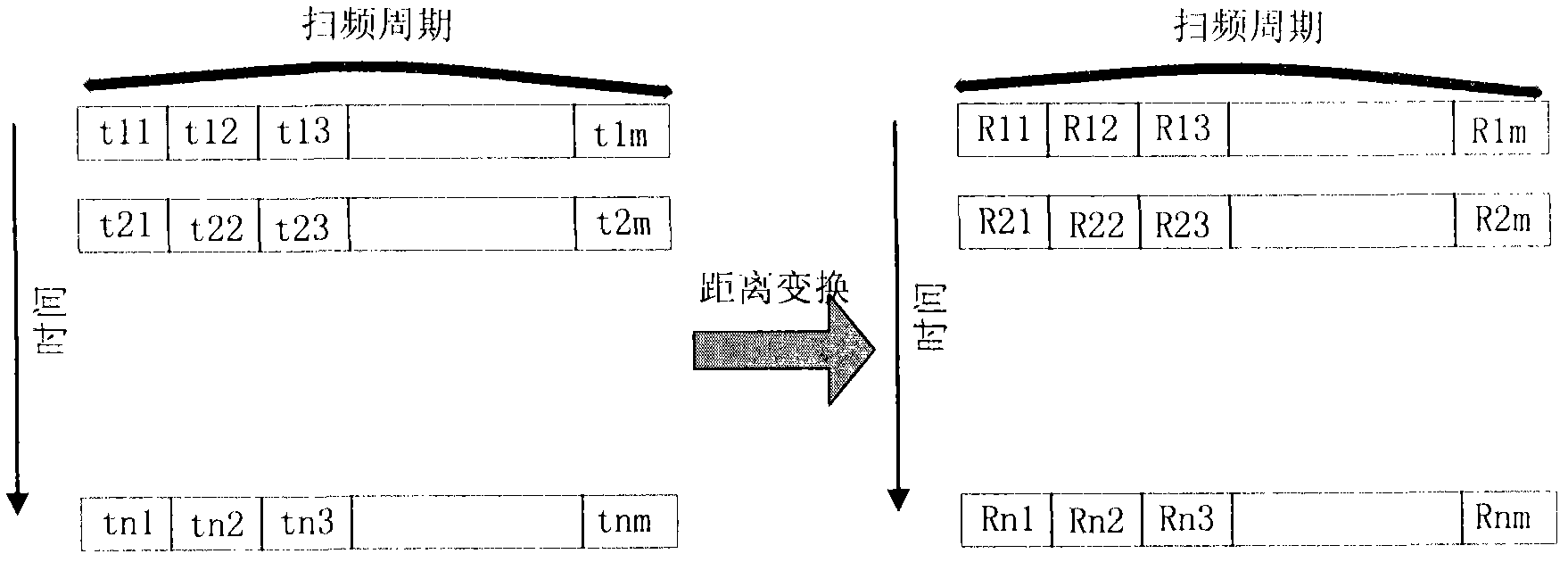
The invention discloses a method for detecting and tracking a faint target of a high frequency ground wave radar with a non-linear dynamics characteristic of a wave echo. The method comprises the following steps: recording intermediate frequency data in an echo signal in real time; canceling impact interference and the first-order data of an echo; establishing a chaotic dynamics forecasting model of the wave echo; and executing detection and tracking of the faint target, wherein the steps of canceling are as follows: implementing distance conversion and speed conversion to the intermediate frequency data; eliminating impact interference on a speed spectral domain through a spline wavelet filter, and eliminating a strong sea clutter through a track matrix wave of a reconstructing attractor. In addition, the invention discloses an apparatus for detecting and tracking a faint target of a high frequency ground wave radar with a non-linear dynamics characteristic of a wave echo.
Owner:HARBIN INST OF TECH +1
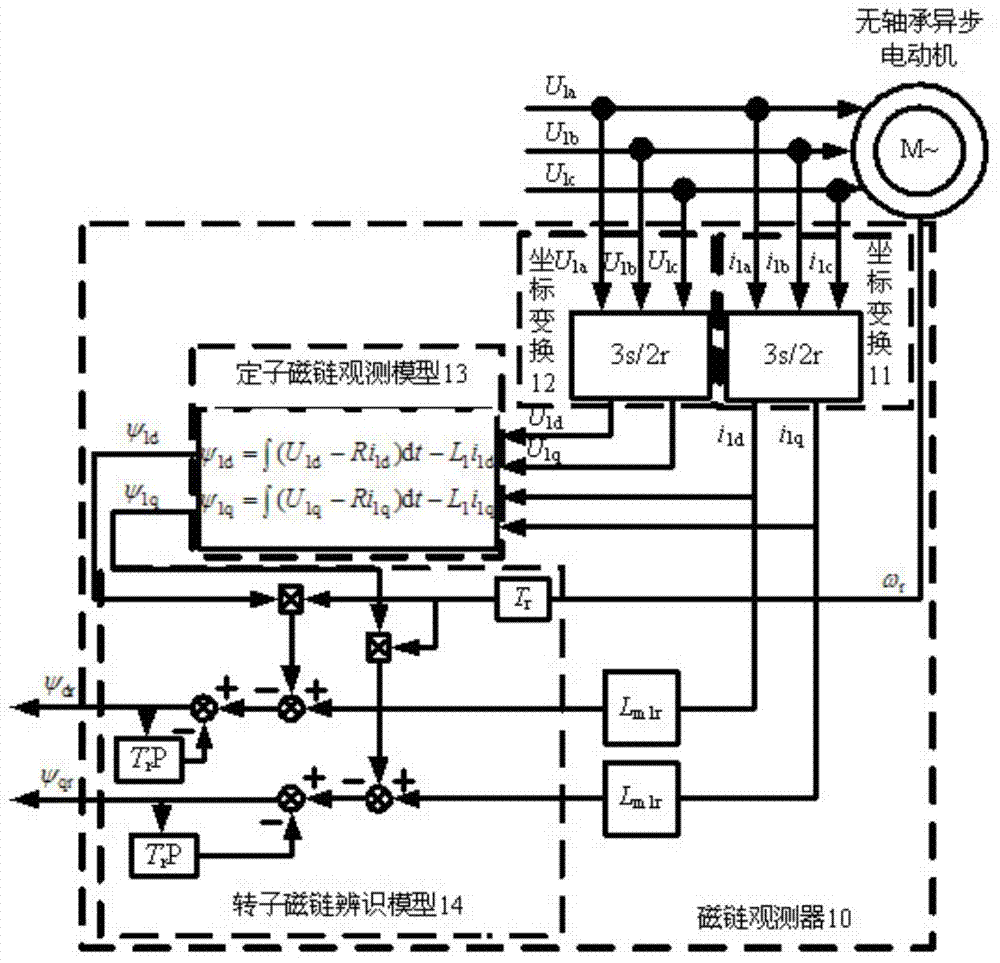
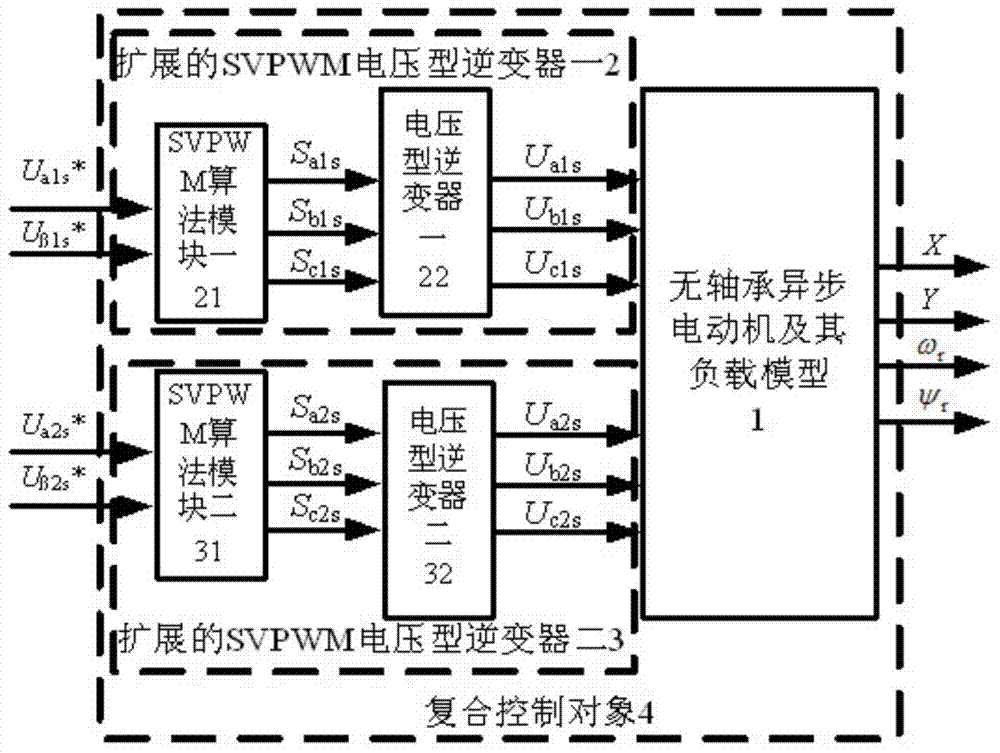
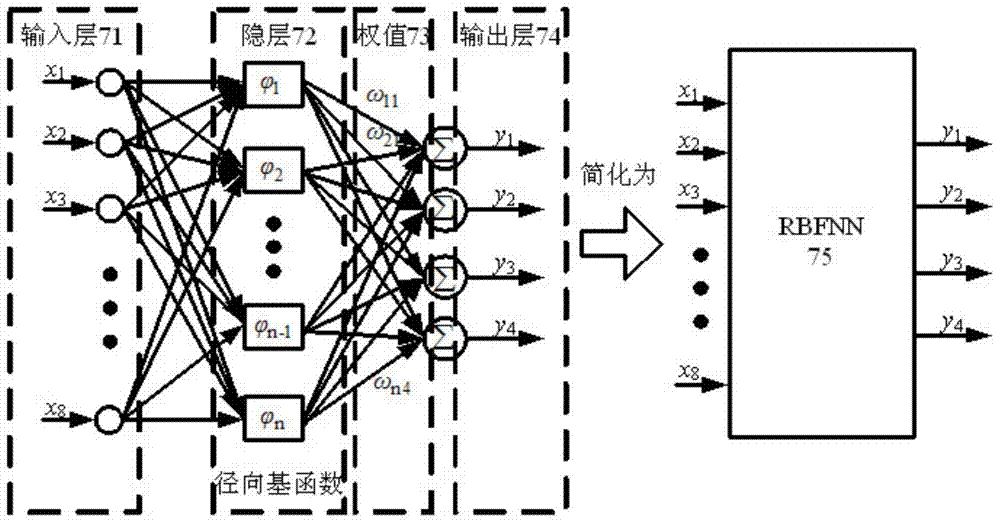
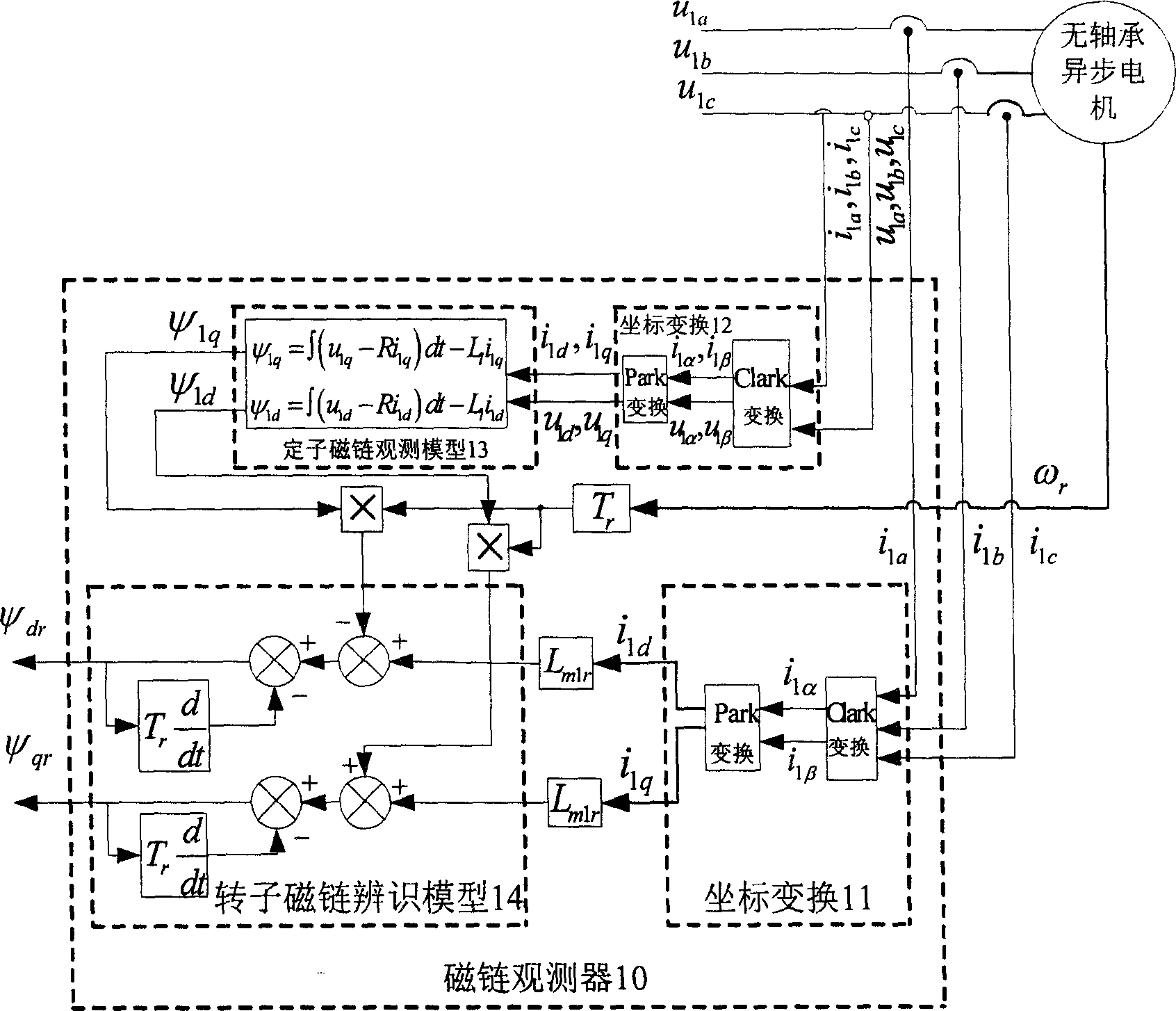
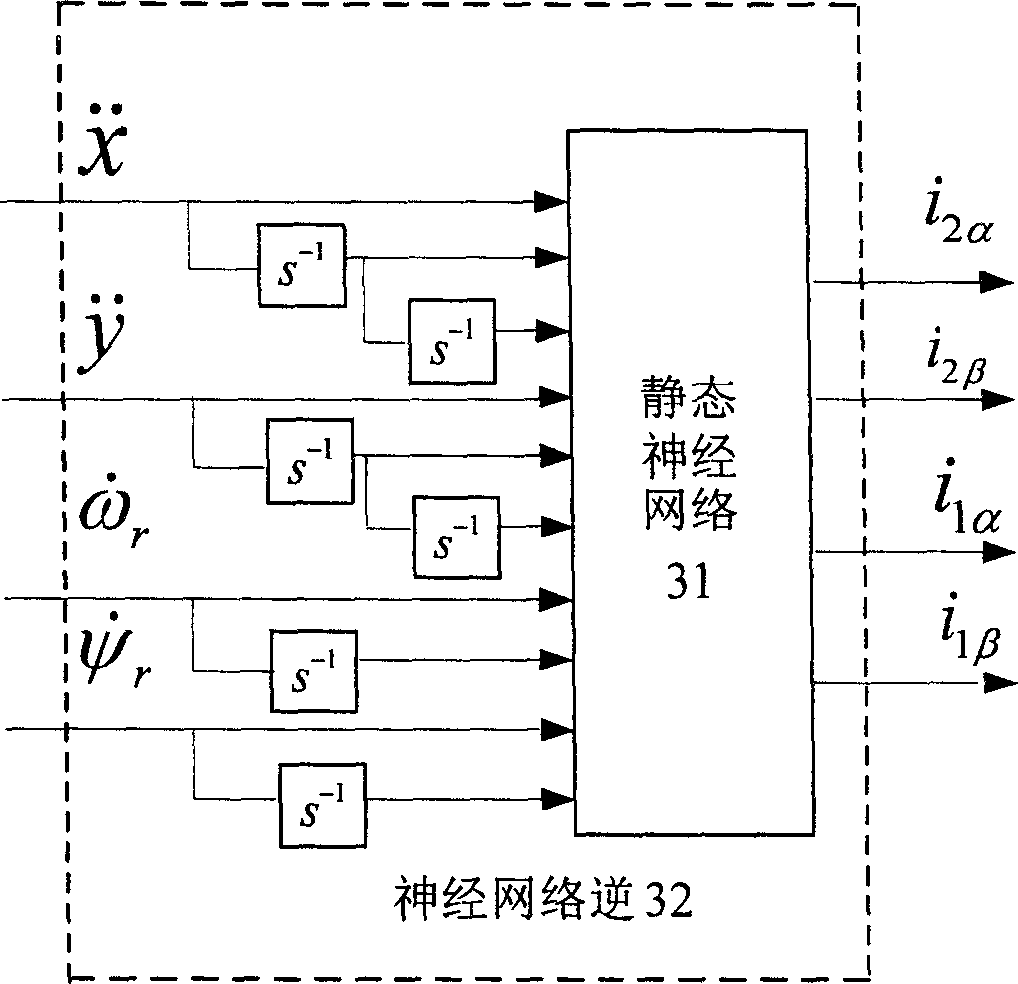
Bearing-free asynchronous motor RBF neural network self-adaptive inverse decoupling control and parameter identification method
InactiveCN104767449AFrictionlessNo wearElectronic commutation motor controlVector control systemsRadial basis function neuralVoltage inverter
The invention discloses a bearing-free asynchronous motor RBF neural network self-adaptive inverse decoupling control and parameter identification method. An SVPWM module, a voltage inverter, a bearing-free asynchronous motor and a load of the bearing-free asynchronous motor form a whole serving as a composite controlled object. Two radial basis function neural networks are adopted to achieve inverse control and parameter identification conducted on the composite controlled object. A self-adaptive inverse controller is formed by using an RBF neural network through learning, and is serially connected in front of the composite controlled object, errors of a feedback signal and a given signal are input into an inverse controller, and accordingly closed-loop control is formed, then a self-adaptive parameter identifier is formed by using one RBF neural network through learning and identifies output quantity speed and displacement of the composite controlled object, speed-less and displacement-free sensor control is achieved, online learning of an estimation signal is aided by means of a learning algorithm, and non-linear dynamic decoupling control of the bearing-free asynchronous motor is achieved. The bearing-free asynchronous motor RBF neural network self-adaptive inverse decoupling control and parameter identification method is high in control speed and higher in identification accuracy, and a control system is excellent.
Owner:JIANGSU UNIV
Intelligent mechatronic control suspension system based on quantum soft computing
InactiveCN1672171AGood precisionImprove reliabilityQuantum computersNanoinformaticsQuantum search algorithmMinimum entropy
A control system for optimizing a shock absorber having a non-linear kinetic characteristic is described. The control system uses a fitness (performance) function that is based on the physical laws of minimum entropy and biologically inspired constraints relating to mechanical constraints and / or rider comfort, driveability, etc. In one embodiment, a genetic analyzer is used in an off-line mode to develop a teaching signal. The teaching signal can be approximated online by a fuzzy controller that operates using knowledge from a knowledge base. A learning system is used to create the knowledge base for use by the online fuzzy controller. In one embodiment, the learning system uses a quantum search algorithm to search a number of solution spaces to obtain information for the knowledge base. The online fuzzy controller is used to program a linear controller.
Owner:YAMAHA MOTOR CO LTD
Under-actuated water surface ship control method satisfying preset tracking performance
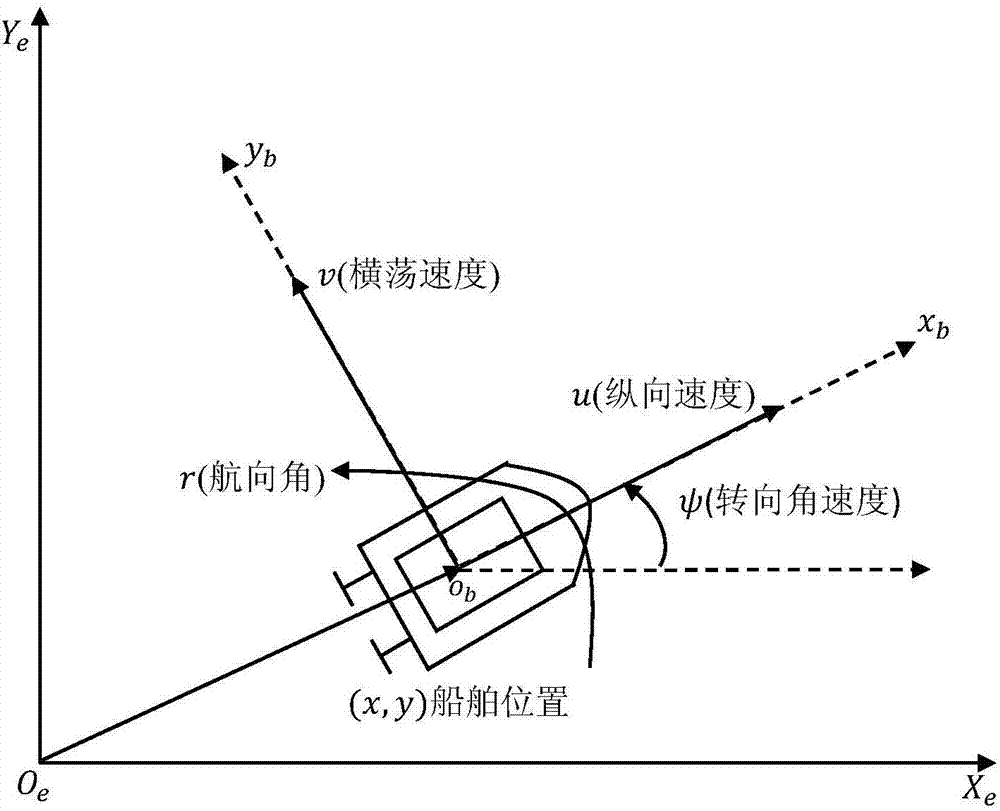
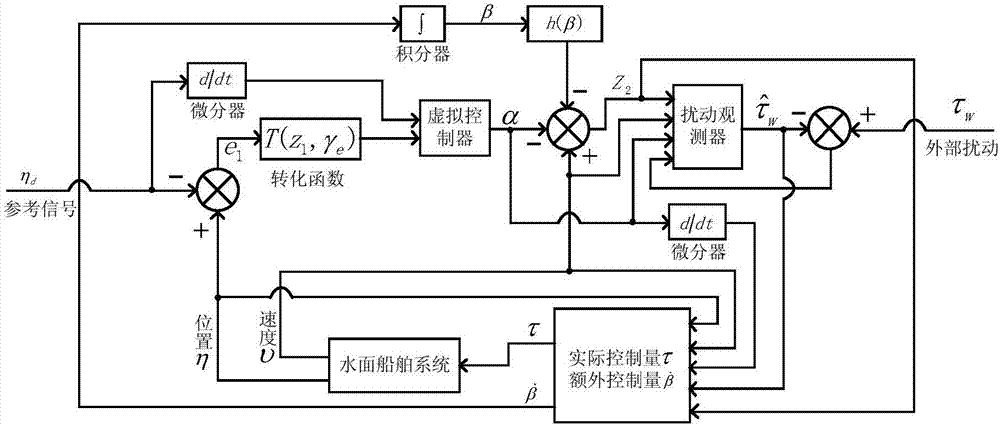
ActiveCN107015562AEasy to troubleshoot system stability issuesImprove performancePosition/course control in two dimensionsDynamic modelsNon linear dynamic
The invention discloses an under-actuated water surface ship control method satisfying preset tracking performance. Aiming at an under-actuated water surface ship nonlinear dynamic model, tracking error steady state precision and a transient state performance index are designed, a transverse function is built to introduce extra control input, and design of a tracking controller is completed, thereby ensuring that a tracking error of a closed-loop control system converges to a preset arbitrarily small area, and ensuring that the convergence rate and overshoot satisfy preset requirements. The method specifically includes the following steps: establishing an under-actuated water surface ship dynamic model; designing steady state performance and transient state performance requirements of a control system; designing a speed error equation to introduce extra control; designing a disturbance observer to compensate external time-varying disturbance; and designing a state feedback tracking controller. The control method designed by the invention can solve the problem of under-actuated water surface ship motion control, realize tracking control of any smooth reference trajectory, and improve tracking error steady state performance and transient state performance of the control system.
Owner:SOUTH CHINA UNIV OF TECH
Non-affine uncertain system self-adaptive control method with range restraint
The present invention relates to a non-affine uncertain system self-adaptive control method with a range restraint. In combination with the characteristic that system input and states are subject to the range restraint, based on a mean value theorem, a non-affine system is converted into a time varying system (a strict feedback system) with a linear structure, and a varying interval of time-varying uncertain parameters of the time varying system is obtained. On the basis, a parameter adaptive projection technique is utilized to carry out online estimation on bounded uncertain time-varying parameters and external disturbances, and a parameter estimation error is compensated by using the nonlinear dynamic damping technology. Based on the nonlinear mapping technology, a restraint amount is mapped to the whole real number space to solve a state restraint problem of the system, thus to ensure the state is always within a restraint range. A hyperbolic tangent function and the Nussbaum gain technology are simultaneously utilized to solve the problem that system input is subject to the range restraint or the problem of input saturation and the potential problem of singular values of a controller, and the controller is designed in combination with a method of inversion, thereby solving the problem of self-adaptive control of the non-affine uncertain system with the range restraint.
Owner:NANCHANG HANGKONG UNIVERSITY
Strong tracking Kalman filer method for target tracking
InactiveCN104408744AAddressed issue where tracking performance was affected by target mutationsEasy to implementImage enhancementImage analysisKaiman filterNon linear dynamic
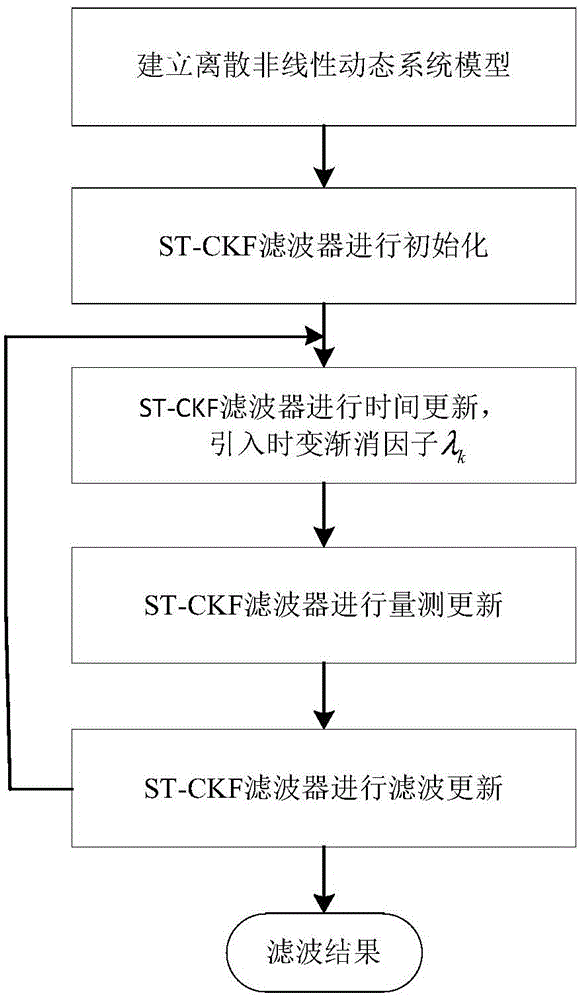
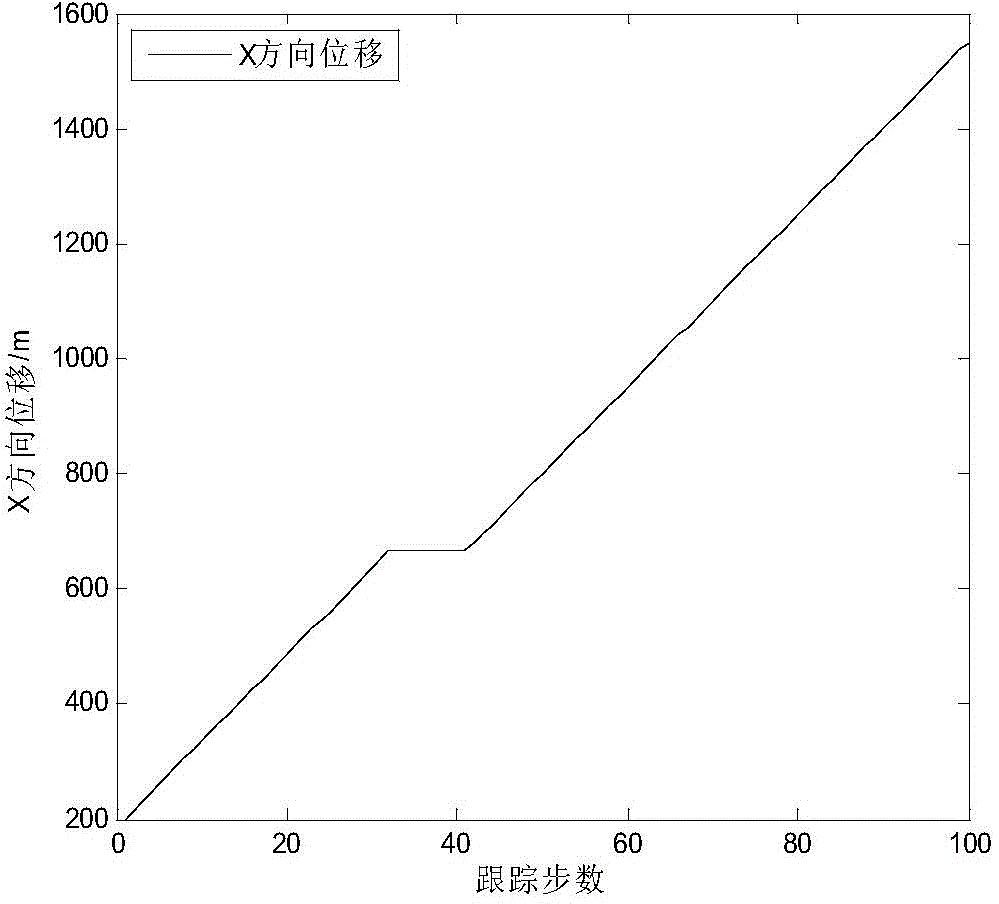
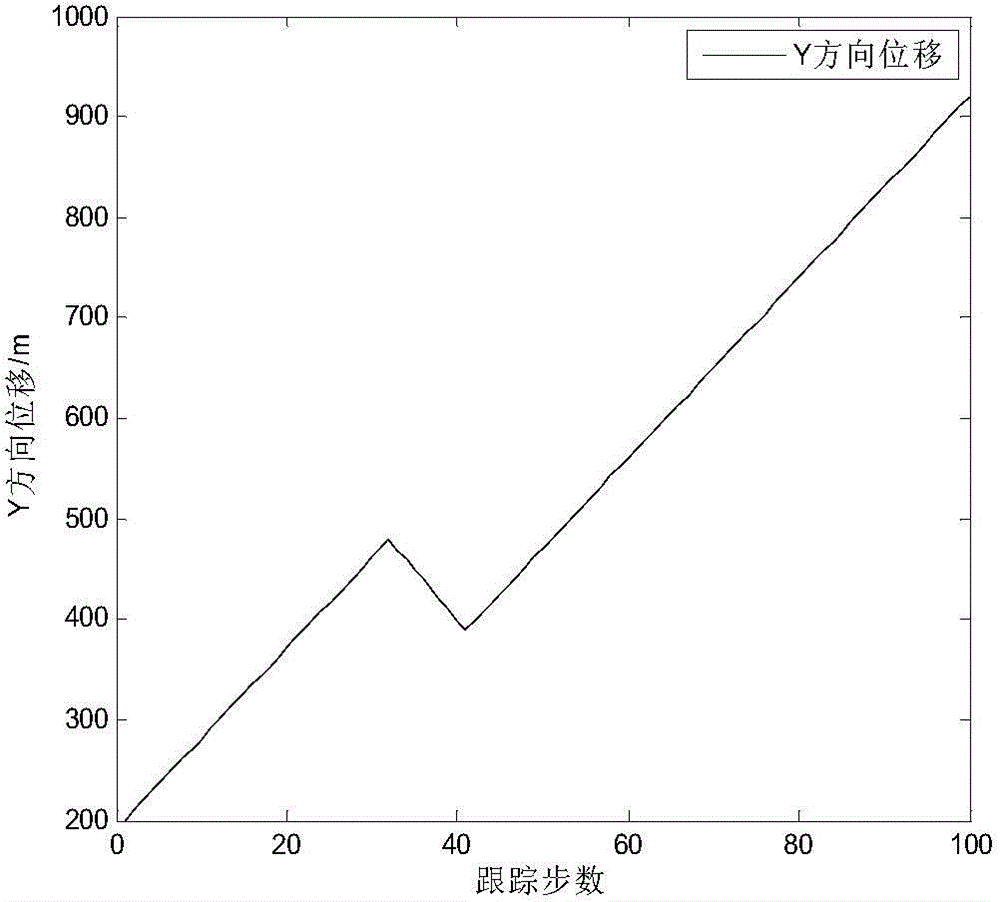
The invention discloses a strong tracking Kalman filter method for target tracking, belongs to the field of target tracking, and relates to a maneuvering target method based on a strong tracking Kalman filter. The method comprises the steps of building a disperse nonlinear dynamic system model; carrying out system initialization; carrying out time updating, and introducing a time varying and fading factor [lambda k]; measuring and updating; and finally carrying out filtering updating. According to the method, the time varying and fading factor is introduced into a Kalman filter, therefore, the method has the advantages that the Kalman filter is simple to realize and high in filter precision; meanwhile, the strong tracking Kalman filter has a real-time tracking capacity on the sudden change of the system.
Owner:UNIV OF ELECTRONICS SCI & TECH OF CHINA
Method for controlling bearing-less AC asynchronous motor neural network inverse decoupling controller
InactiveCN1845449ARealize dynamic decouplingImprove anti-interference abilityMotor parameters estimation/adaptationObserver controlIntegratorSystems design
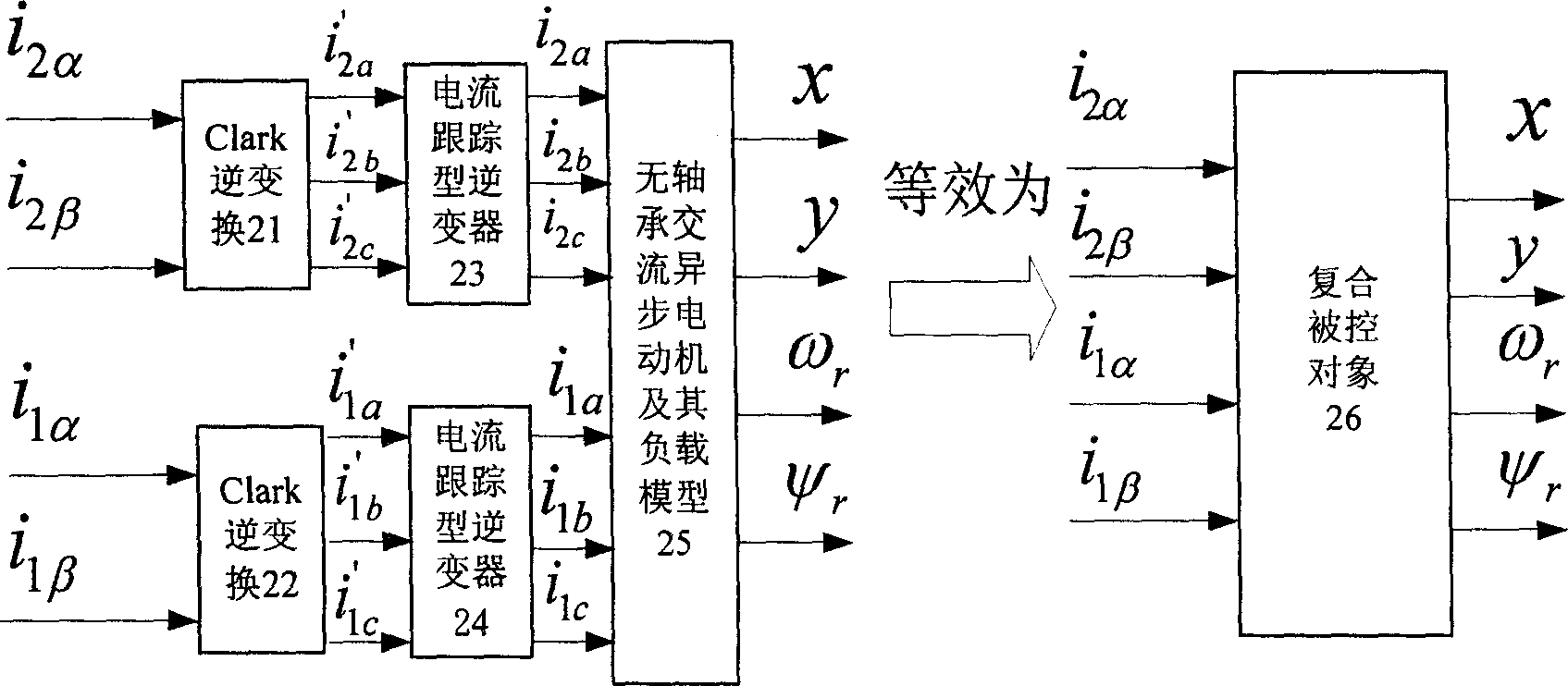
The control method for a NN reverse decoupling controller of bearingless ac asynchronous motor comprises: composing the controlled target with two Clark inverse transforms, two current track inverters, the said motor and its load; according to corresponding inverse system, making up the NN inverse by a static NN and an integrator with learning algorithm to series connect between composite targets and form the pseudolinear system; designing linear close-loop controller as the method on linear system; finally, connecting the controller and NN inverse to form the objective controller with former transforms and inverters. This invention has well control performance.
Owner:JIANGSU UNIV
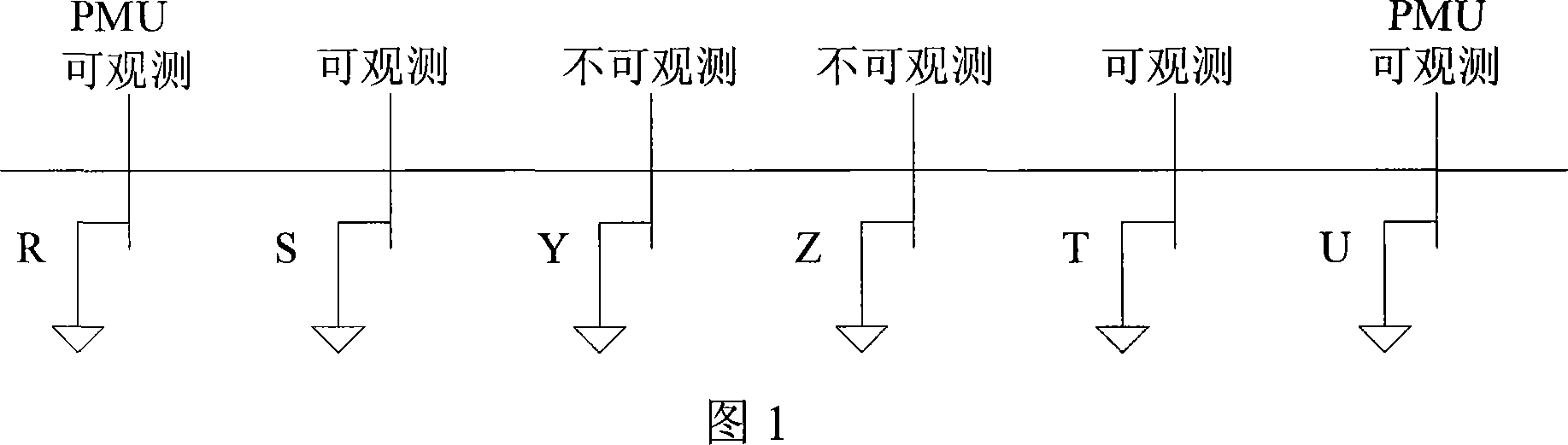
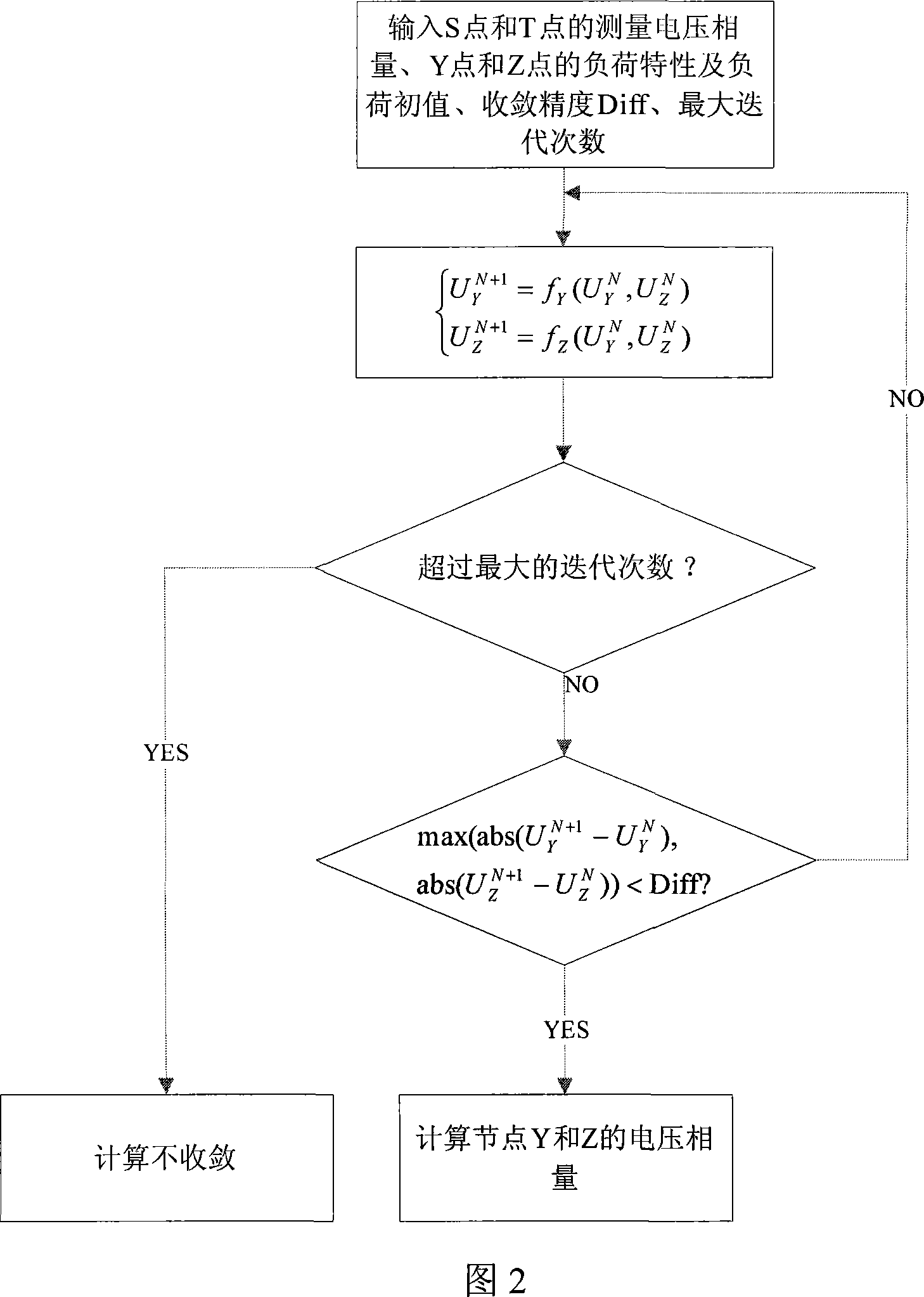
Method for evaluating non-linear dynamic state with loading voltage characteristics
InactiveCN101075741AAchieve estimatesSpeed up the solutionData processing applicationsCurrent/voltage measurementEstimation methodsNonlinear systems of equations
This is a nonlinear dynamic state estimation method based combined measurement by PMU and SCADA. A static module is established on the history data of SCADA. In case of non-measurement for part of nodes, conduct an accurate measure on adjacent nodes by PMU. An estimation on the non-measured nodes is made by Gauss-Seidel method.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV
Prediction system and method of circulating fluidized bed household garbage incineration boiler NOx discharge
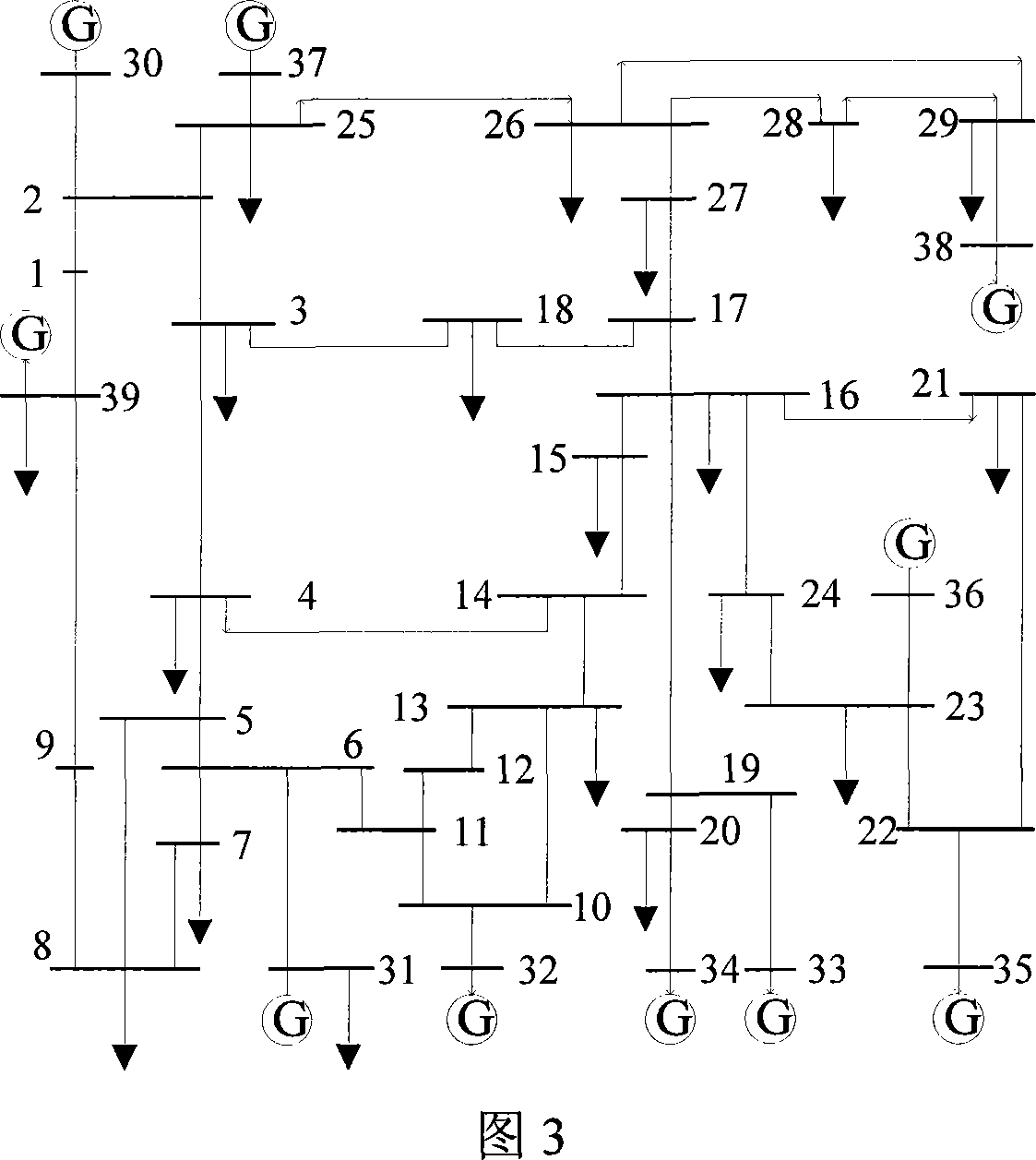
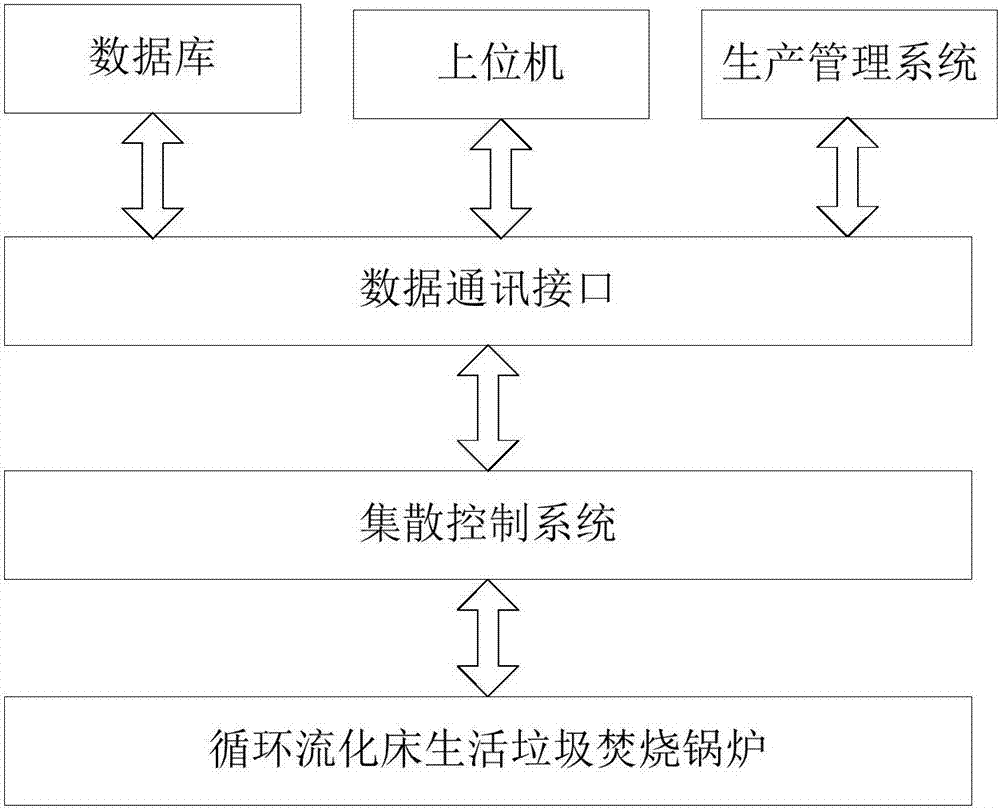
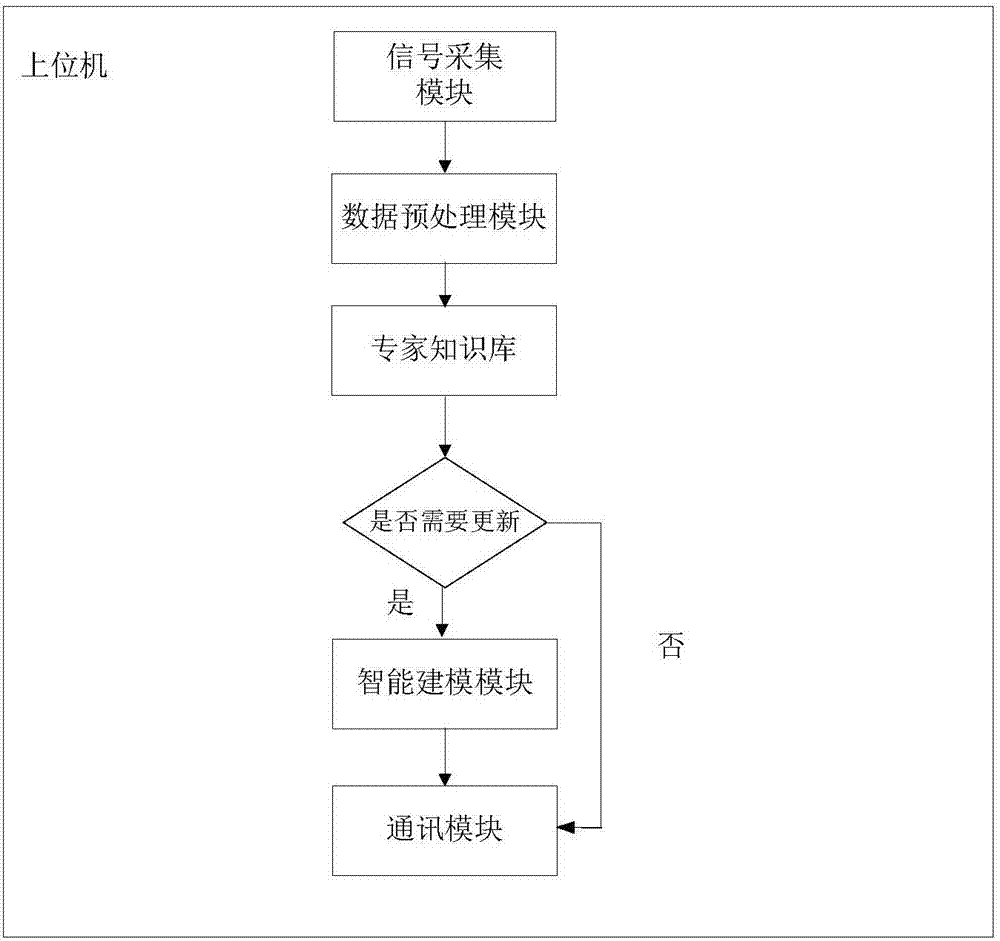
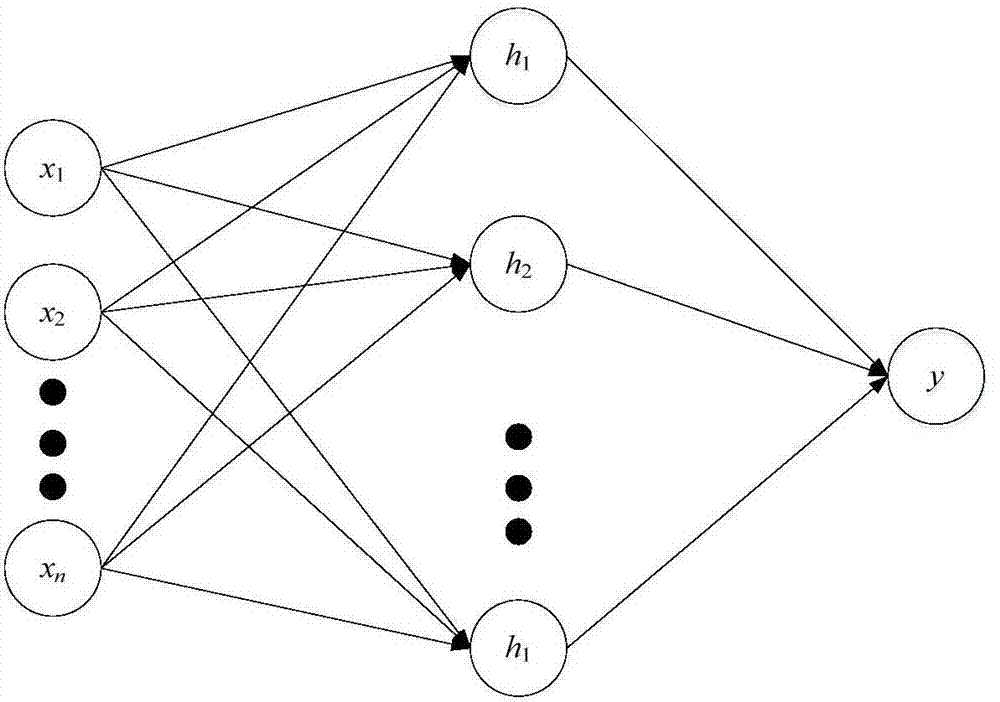
ActiveCN106931453AImprove local optimization abilityImprove build efficiencyBiological neural network modelsForecastingNon linear dynamicEngineering
The invention discloses a prediction system and a method of circulating fluidized bed household garbage incineration boiler NOx discharge. An integrated modeling method of a BP neural network algorithm and a multi-swarm particle swarm optimization algorithm introducing a simplex operator is adopted to construct a rapid economic self-adaptive updating system and a method for carrying out real time prediction on the boiler flue gas NOx discharge, so that the tedious complex mechanism modeling work is avoided. A dynamic change characteristic of NOx discharge is represented by utilizing the non-linear dynamic characteristic, the generalization ability and the real time prediction ability of the BP neural network algorithm; an initial weight value and a threshold value of the BP neural network are optimized by utilizing the particle swarm optimization algorithm, and the possibility of reaching a local optimum of the BP neural network in a training process is reduced; the simplex operator and the multi-population migration mechanism are introduced, so that the diversity of the particle swarm optimization algorithm and the local searching ability are improved, and the possibility of reaching the local optimum of the particle swarm optimization algorithm is reduced.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV
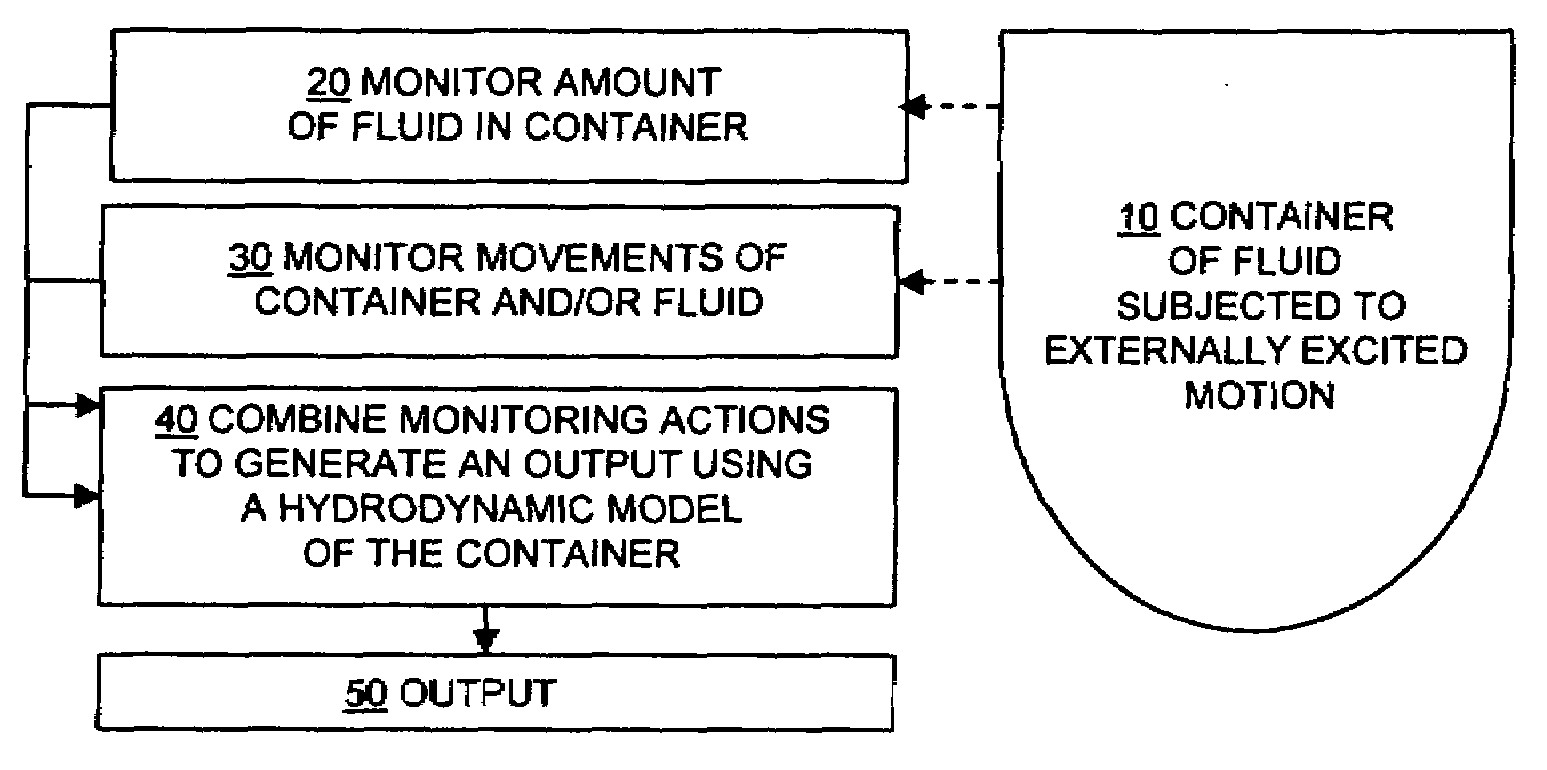
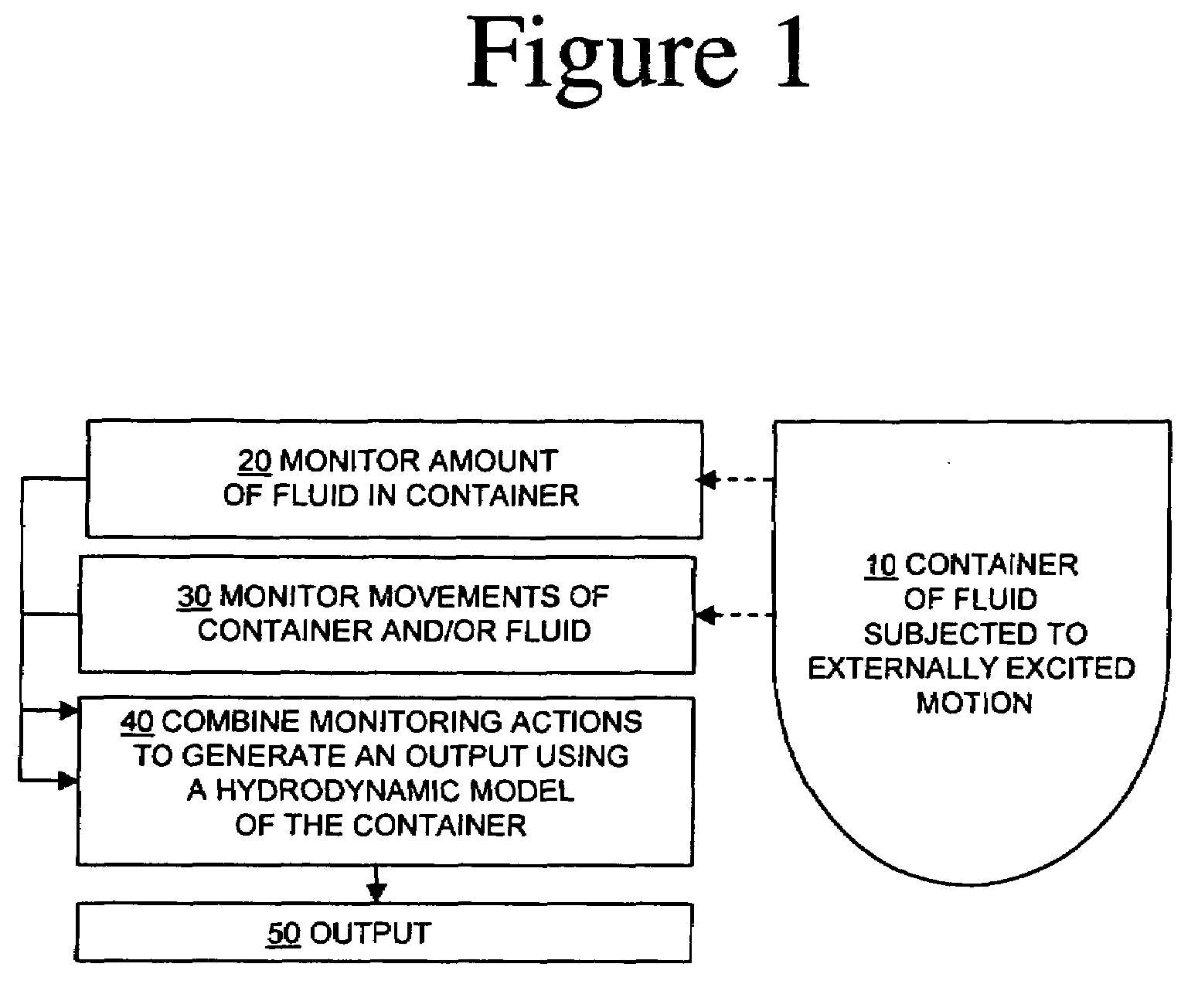
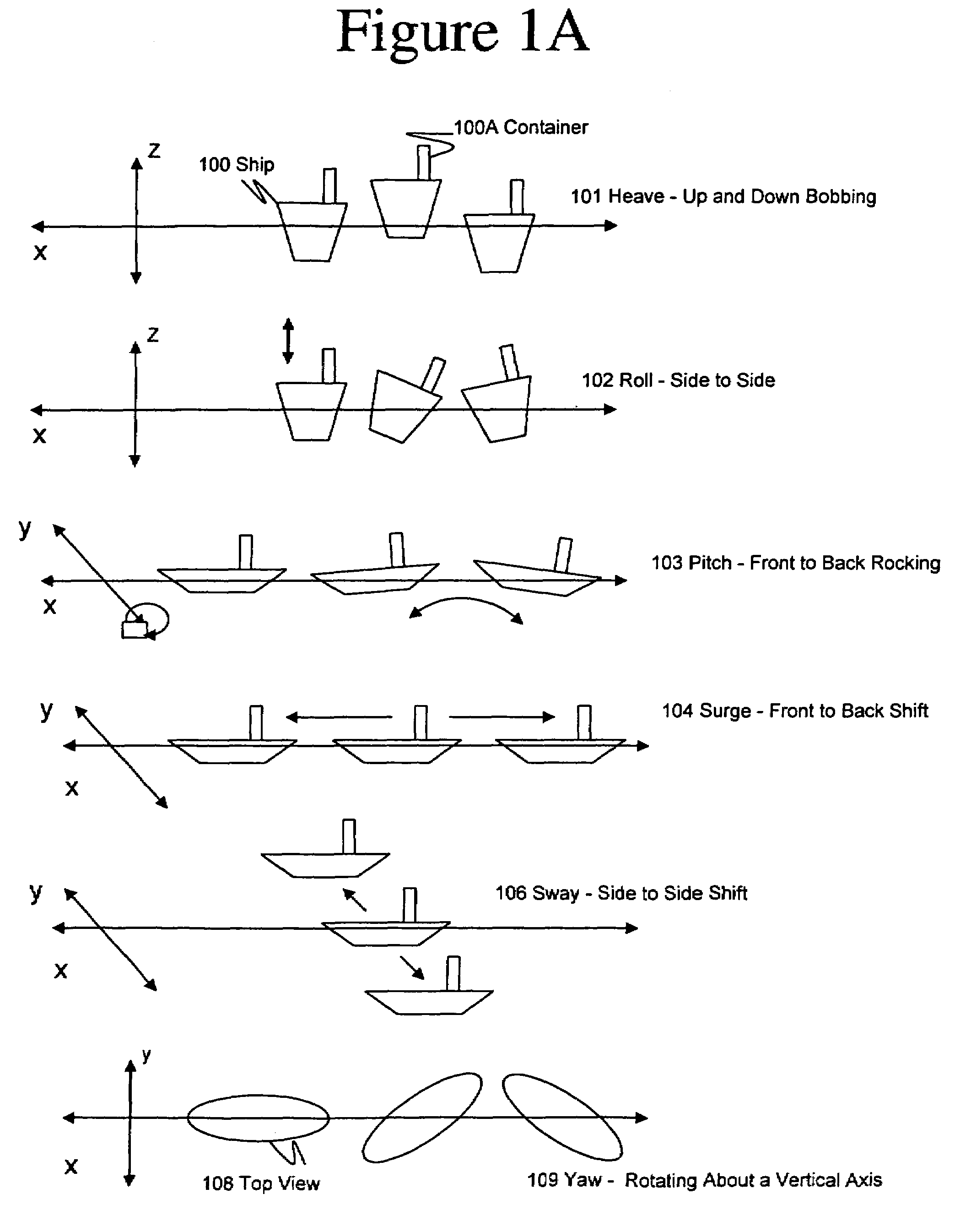
Process control architecture with hydrodynamic correction
InactiveUS20080084783A1Provide stabilityControlling ratio of multiple fluid flowsTesting/calibration apparatusDynamic modelsSea waves
Methods and systems for controlling processes related to the amount of fluid in a container subjected to externally-excited motions. Fluid level sensor measurements in processing tanks on-board boats are confused by ocean waves and swells. A hydrodynamic model of a fluid in a tank can be constructed using non-linear dynamic model algorithms with inputs such as multi-axis accelerations, fluid viscosity, and apparent level measurements. The model can be used to filter-out boat motion disturbances to obtain a corrected level of the fluid in the tank. The corrected fluid level signal can be further processed using a dynamic model of the tank and associated input and output flow rates in a closed loop observer. The methods and systems are especially advantageous for offshore equipment such as cementing and fracturing ships.
Owner:HALLIBURTON ENERGY SERVICES INC
Robot simulation learning method based on dynamic system model
The invention discloses a robot simulation learning method based on a dynamic system model. Simulation of teaching movement of the robot is achieved through learning, specifically, the demonstration motion is modeled into a nonlinear dynamic system model through a gaussian mixture model, in addition, the stability of the motion model is guaranteed through the method with the additional stability constraint conditions, the parameter learning problem of the motion model is converted into a constraint optimization problem, so that a complete description of the motion model is obtained, and finally, the motion model obtained through learning is used as a control strategy to guide the robot to imitate the teaching motion. The method is used for teaching motion of target point fixation, the method has good stability, all the generated motion trails are converged to a target point, and has good expression capacity for simple and complex teaching movement, the generalization ability of the motion model is good, a motion track which is smooth and can be converged to a target can be generated outside the teaching movement range.
Owner:BEIJING UNIV OF TECH
Methods for managing flow control valves in process systems
InactiveUS20080183336A1Amount of signal is lostLose amountTesting/monitoring control systemsRatio controlProcess systemsNon linear dynamic
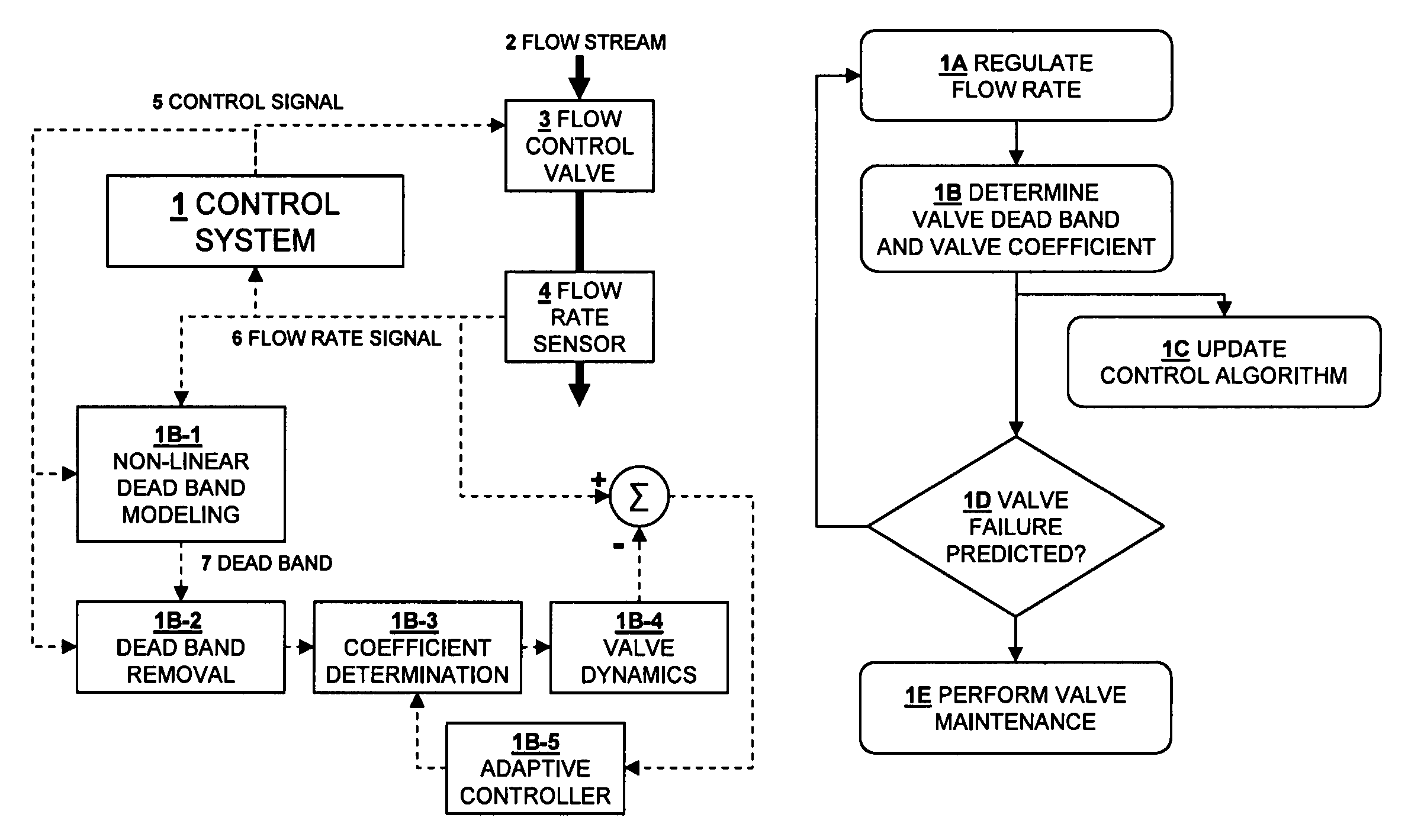
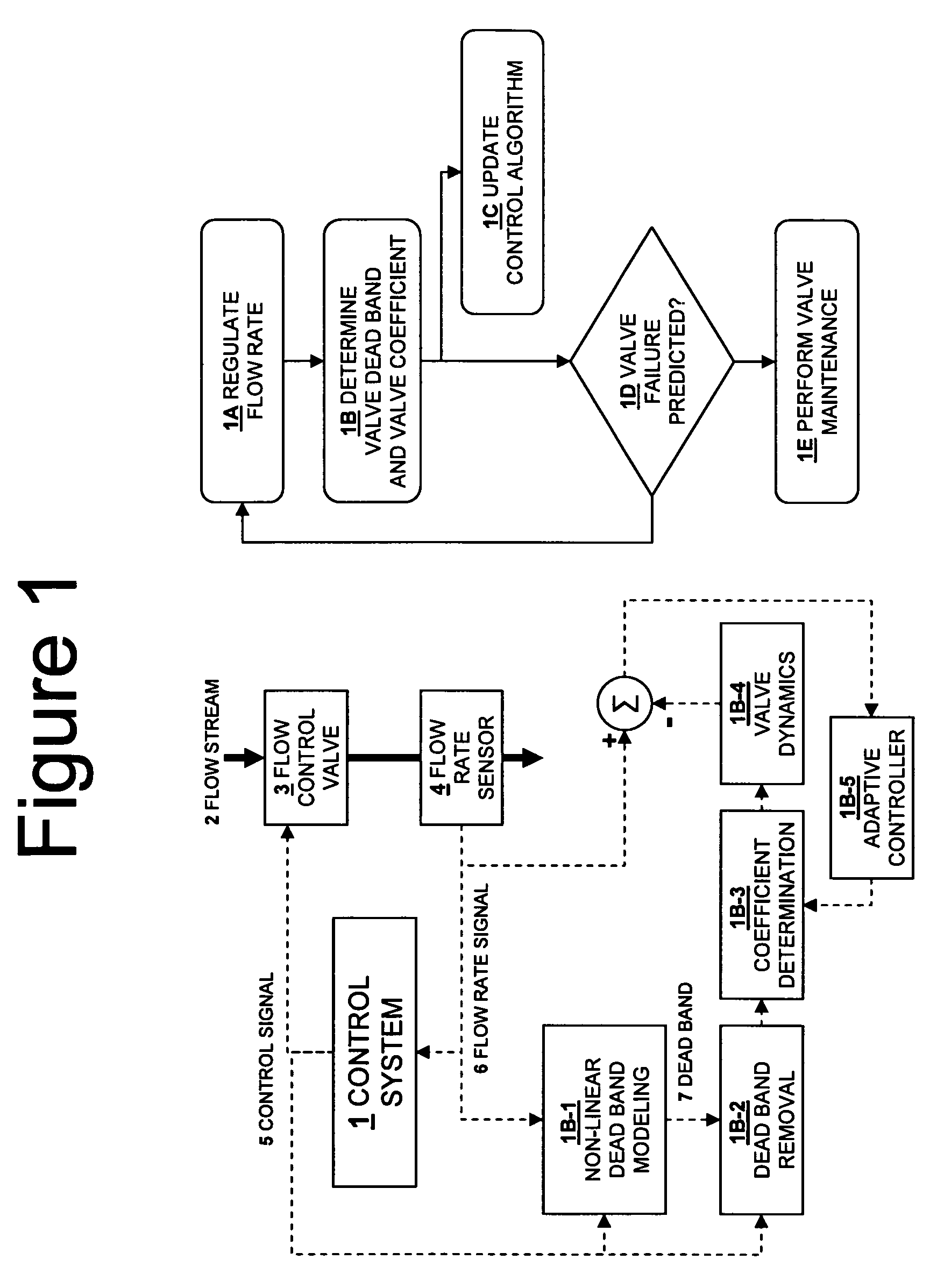
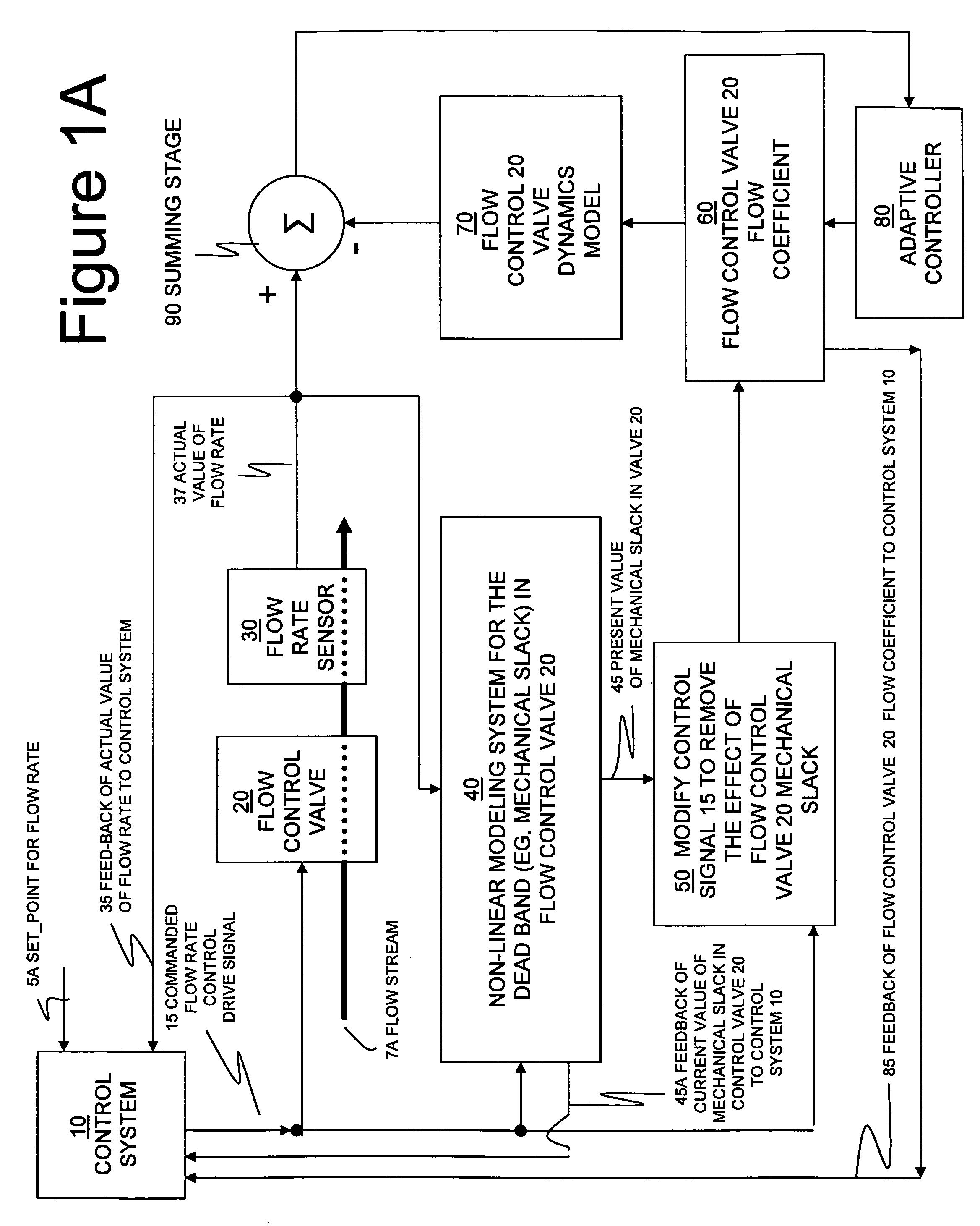
Methods for managing the operational condition of flow control valves in process systems. As a control valve experiences mechanical wear during operation, the physical changes to the valve can alter its dead band and flow coefficient. A non-linear dynamic model determines the present dead band by modeling the relationship between the actual flow through the valve and the commanded drive signal to the valve. The present valve flow coefficient can be determined by removing the dead band from the drive signal and using that modified signal in a flow rate model for the valve to adaptively find the flow coefficient value which matches the predicted flow from the flow rate model to the present measured flow from a flow rate sensor. The present dead band and flow coefficient can be used to update valve control algorithms and to make valve maintenance decisions.
Owner:HALLIBURTON ENERGY SERVICES INC
Novel practical method frangibility index method for evaluating seam floor water inrush
InactiveCN101699451ASolve the difficult problem of water inrush prediction and evaluationSpecial data processing applicationsMaterial defectCoupling
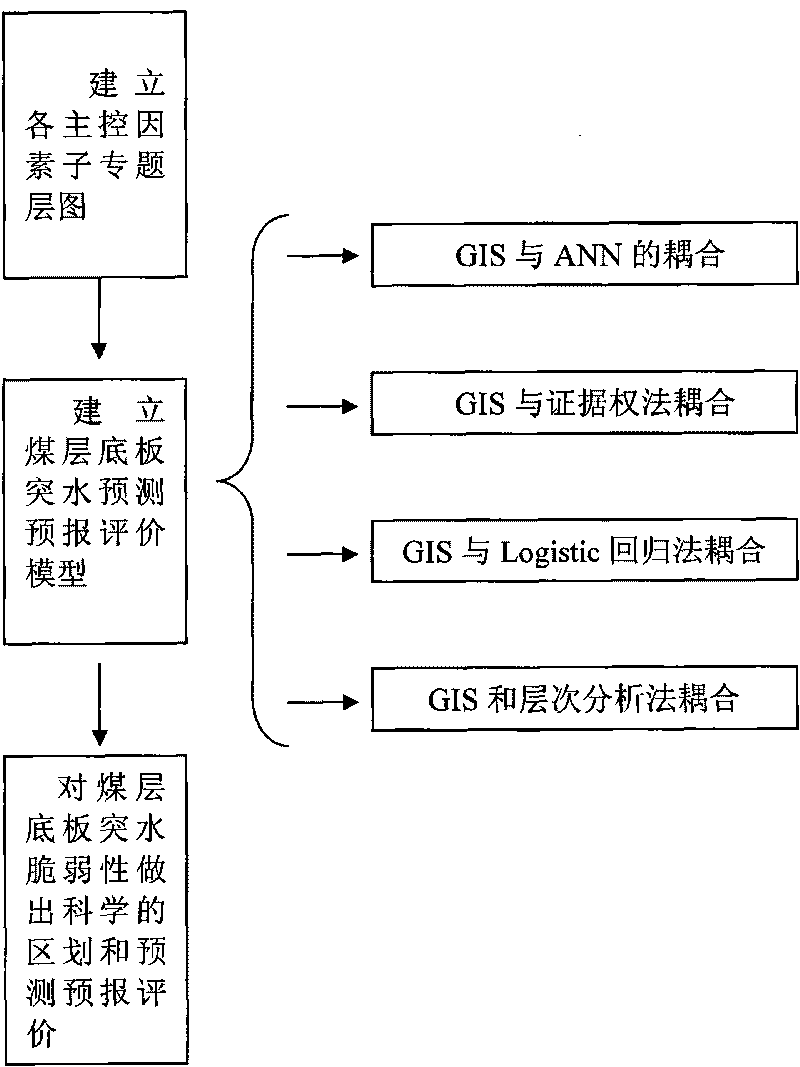
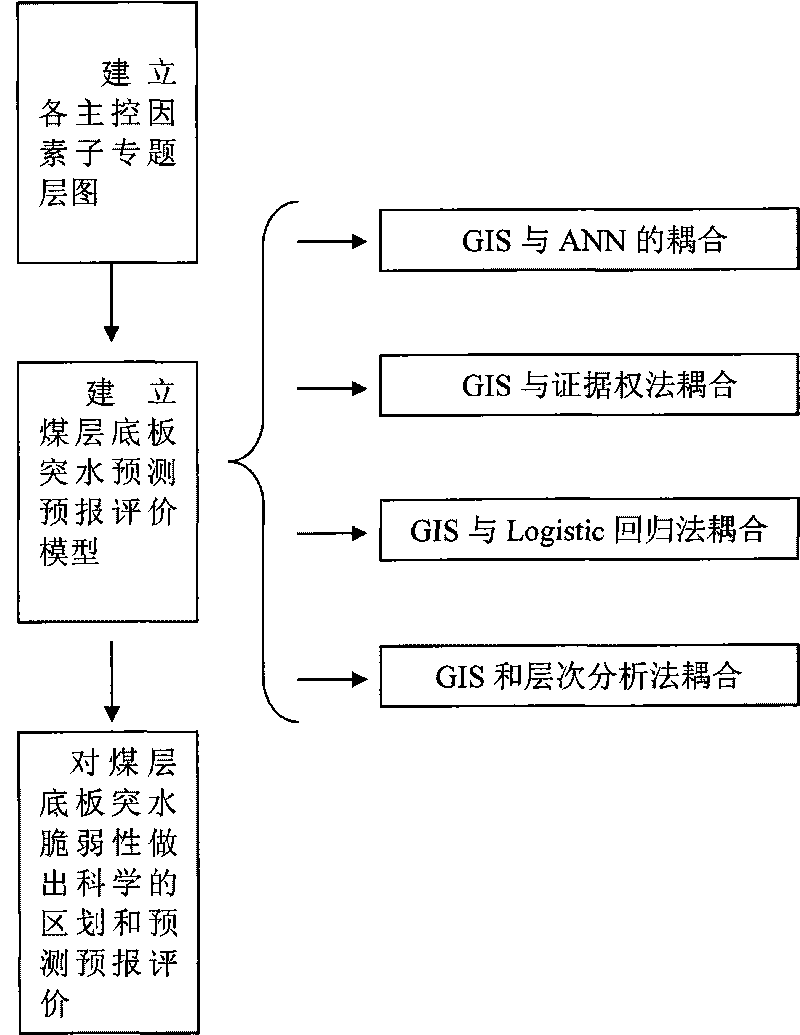
The invention relates to a frangibility index method for evaluating seam floor water inrush, which comprises the following steps: determining main control factors of the seam floor water inrush by taking GIS as an operating platform based on a multi-source information fusion theory, and establishing a sub-subject layer diagram for each main control factor through data acquisition, analysis and processing; determining the 'contribution' or the 'weight' of each main control factor to a complex water inrush process and establishing a forecast evaluation model for the seam floor water inrush through the inversion identification or the learning training of the model by applying a multi-source geoscience data composite superposition principle and adopting a modern linear or non-linear mathematical method; and reasonably determining a subarea threshold value of the water inrush frangibility according to the analysis of a frequency histogram of water inrush frangibility indexes calculated by each unit in a research area and finally making a scientific division and a forecast evaluation on the seam floor water inrush frangibility. The method well overcomes the difficulty of the forecast evaluation on the seam floor water inrush, breaks through the restriction by significant deficiencies that the conventional water inrush coefficient method for the seam floor water inrush evaluation can only consider two control factors and has no influence 'weight' concept and the like, and adopts the GIS and the modern non-linear mathematical coupling method to truly depict the non-linear dynamic process of the seam floor water inrush which is controlled by a plurality of factors and has a very complicated formation mechanism.
Owner:CHINA UNIV OF MINING & TECH (BEIJING)
Mutual-inspection and temporal fusion method for surface subsidence monitoring result of PSInSAR for lifting track
InactiveCN104111457AAchieving Timing FusionRestoring nonlinear dynamic processesHeight/levelling measurementRadio wave reradiation/reflectionStart timeRadar
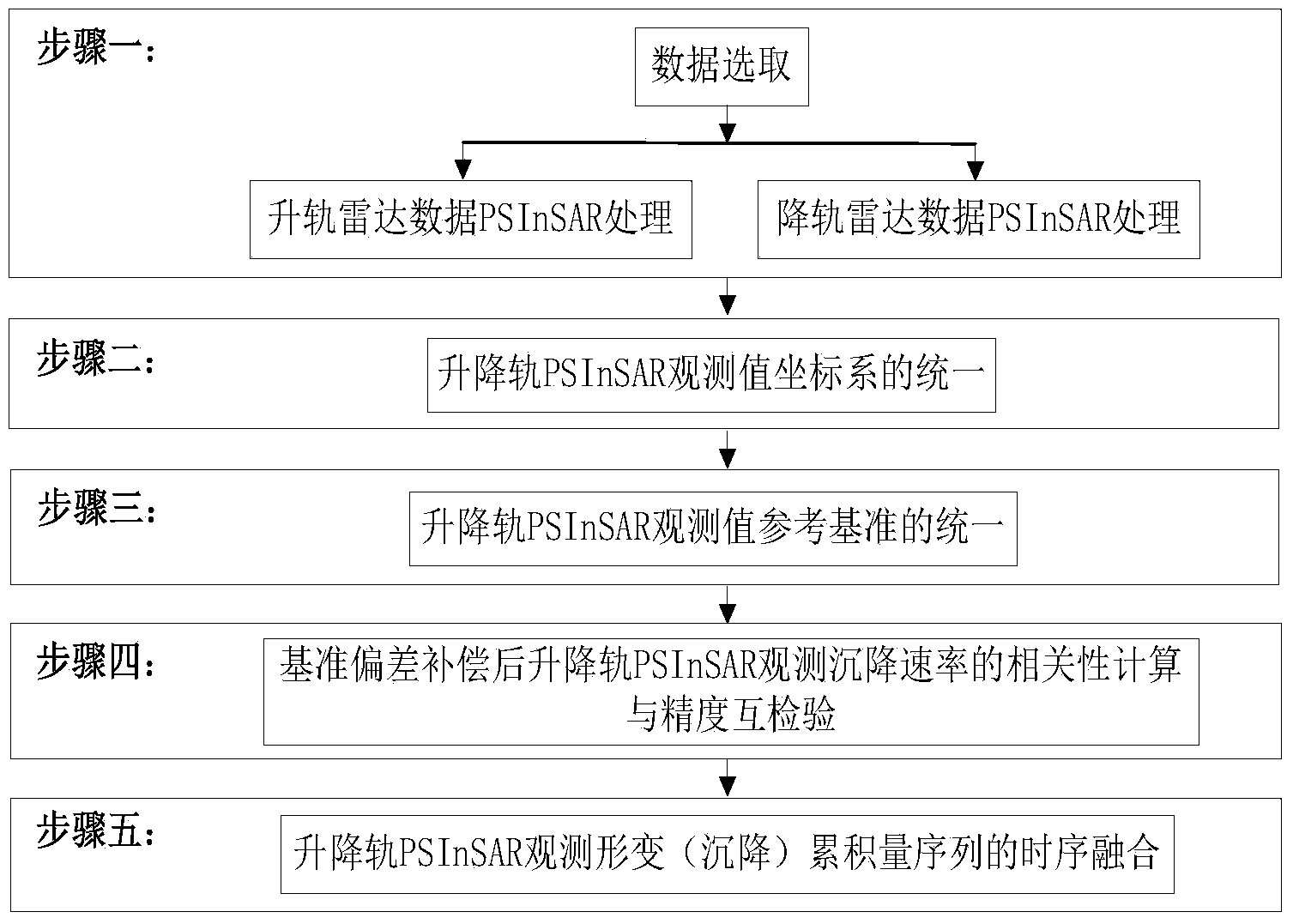
The invention discloses a mutual-inspection and temporal fusion method for surface subsidence monitoring result of PSInSAR for a lifting track. The mutual-inspection and temporal fusion method for the surface subsidence monitoring result of the PSInSAR for the lifting track includes steps that 1, selecting data and carrying out PSInSAR treatment on lifting track radar data; 2, unifying PSInSAR observation value coordinate systems of the lifting track; 3, unifying PSInSAR observation value basis references of the lifting track; 4, after compensating the reference deviation, carrying out correlation calculation and mutual-precision inspection on PSInSAR observation sedimentation rates of the lifting track; 5, carrying out temporal fusion on the PSInSAR observation deformation (sedimentation accumulation sequence). The mutual-inspection and temporal fusion method for the surface subsidence monitoring result of the PSInSAR for the lifting track realizes the temporal fusion for the PSInSAR observation deformation accumulation data of main and auxiliary tracks through calculating the whole deviation of main and auxiliary track observation sequences and deformation accumulation difference caused by starting time difference and encrypts the observation deformation sequences of the PSInSAR of a research area so as to precisely and subtly restore the nonlinear dynamic change process of the surface subsidence of the research area.
Owner:CHINA AERO GEOPHYSICAL SURVEY & REMOTE SENSING CENT FOR LAND & RESOURCES
System and Method to Simulate the Impact of Leadership Activity
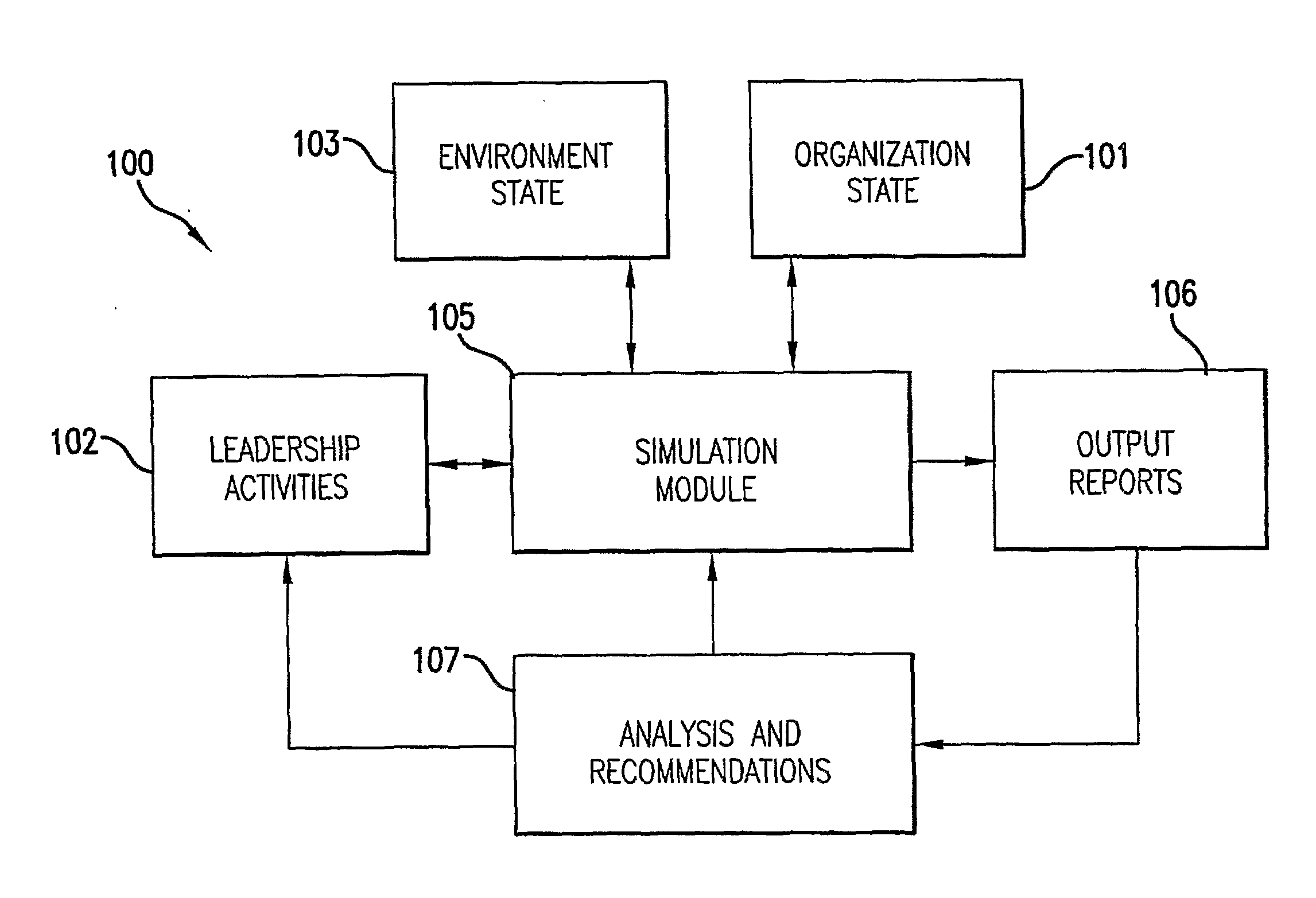
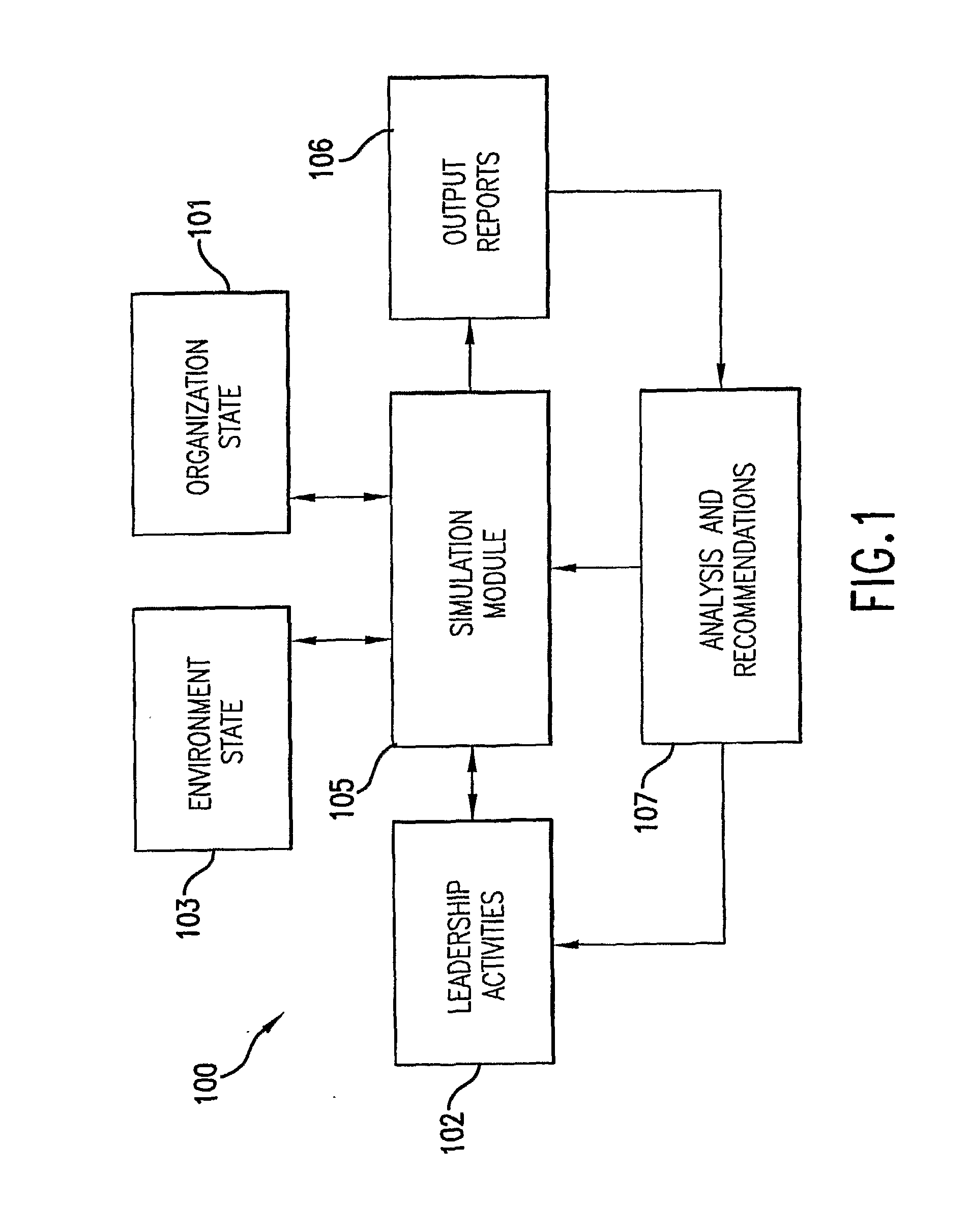
A system and method to simulate the impact of leadership activity for individuals in leader and / or manager roles to be able to model their organization as a system and to simulate a plurality of actions that might be taken and their impact on the non-linear dynamics of the organization, its functions, capabilities, processes and outcomes. The system includes an Organization State component, a Leadership Activities component, an Environment State component, and a Simulation Module component. The Simulation Module component takes in initial conditions defined for the Organization State, Leadership Activities and the Environment State, iterates the functions and process of the organization through time, simulates the interactions of the various variables described in the Organization State, the Leadership Activities and the Environment State and the interactive effects among them and provides outputs of a plurality of measures for each time step.
Owner:HAZY JAMES K
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com