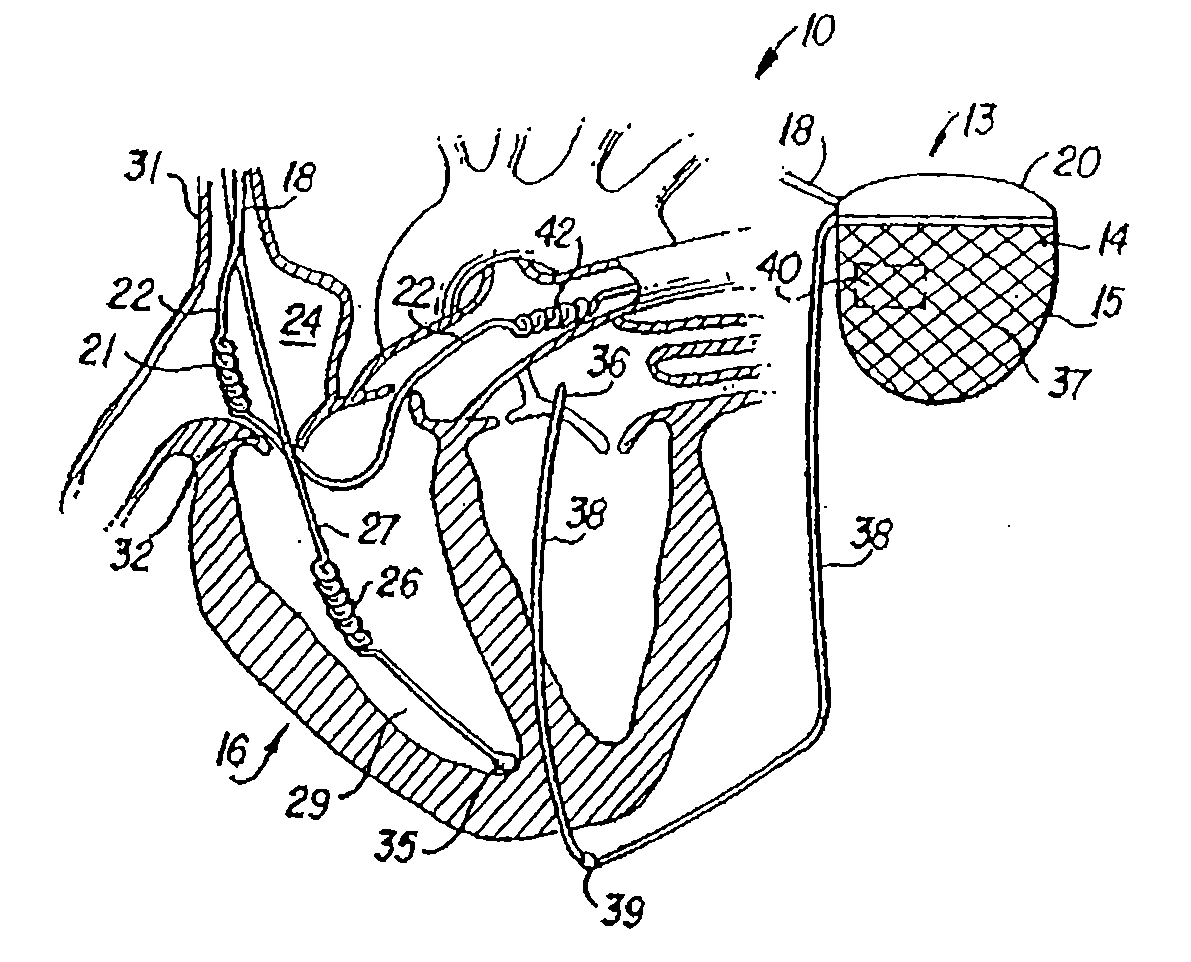
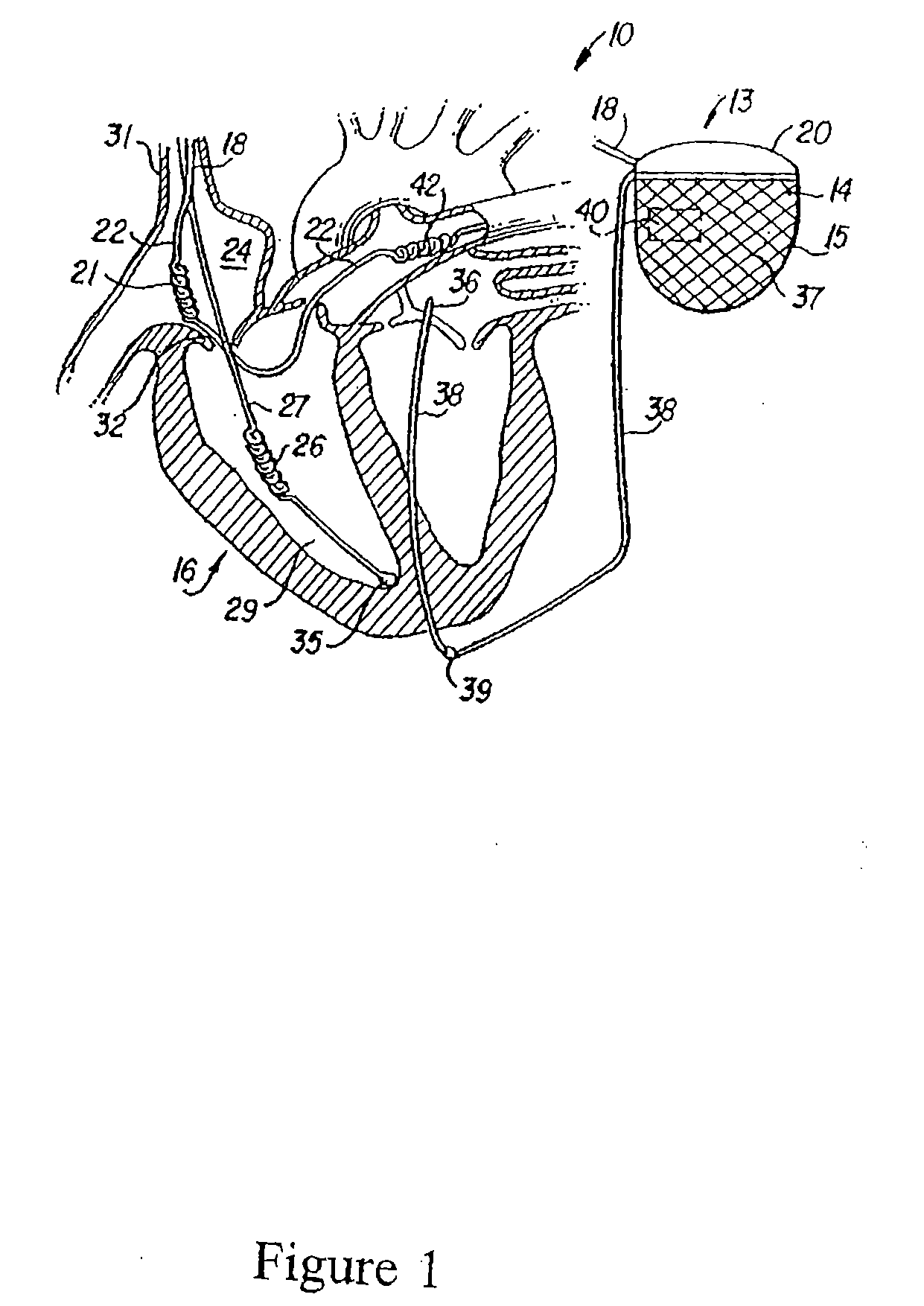
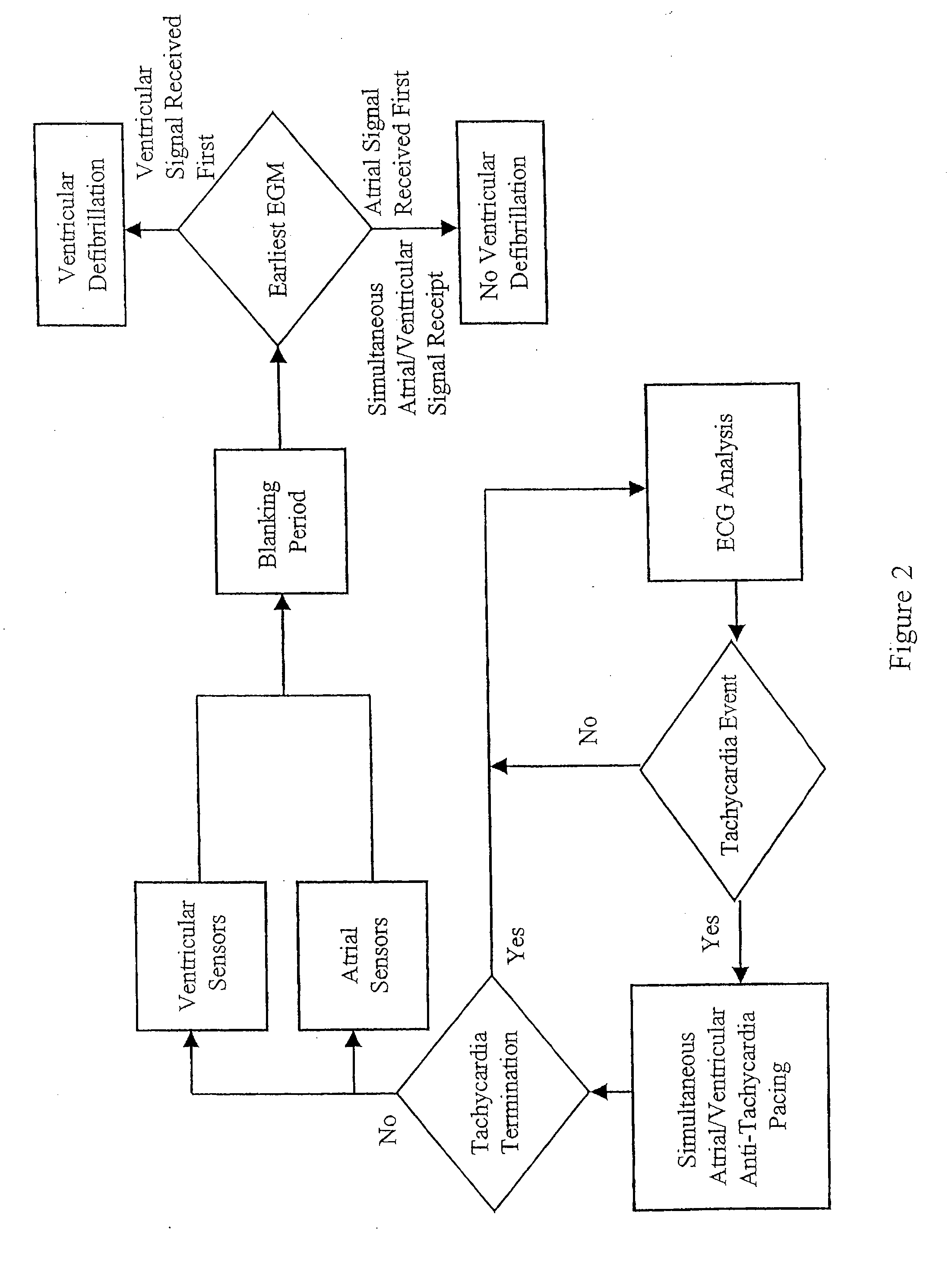
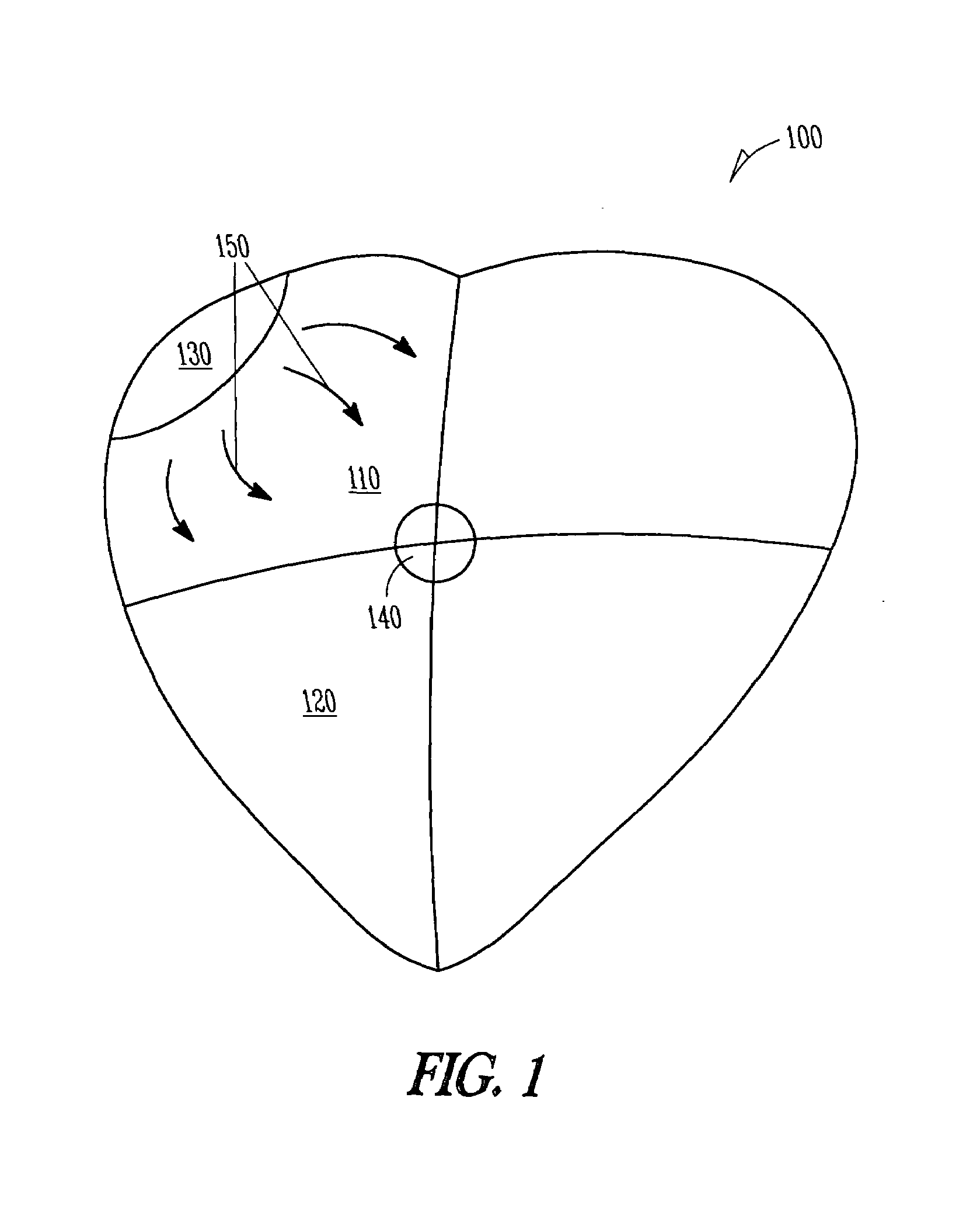
Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
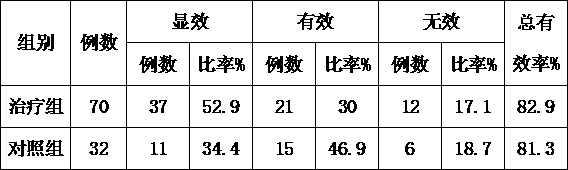
44 results about "Supraventricular tachycardia" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
An abnormally fast heart rhythm due to improper electrical activity in the upper part of the heart.
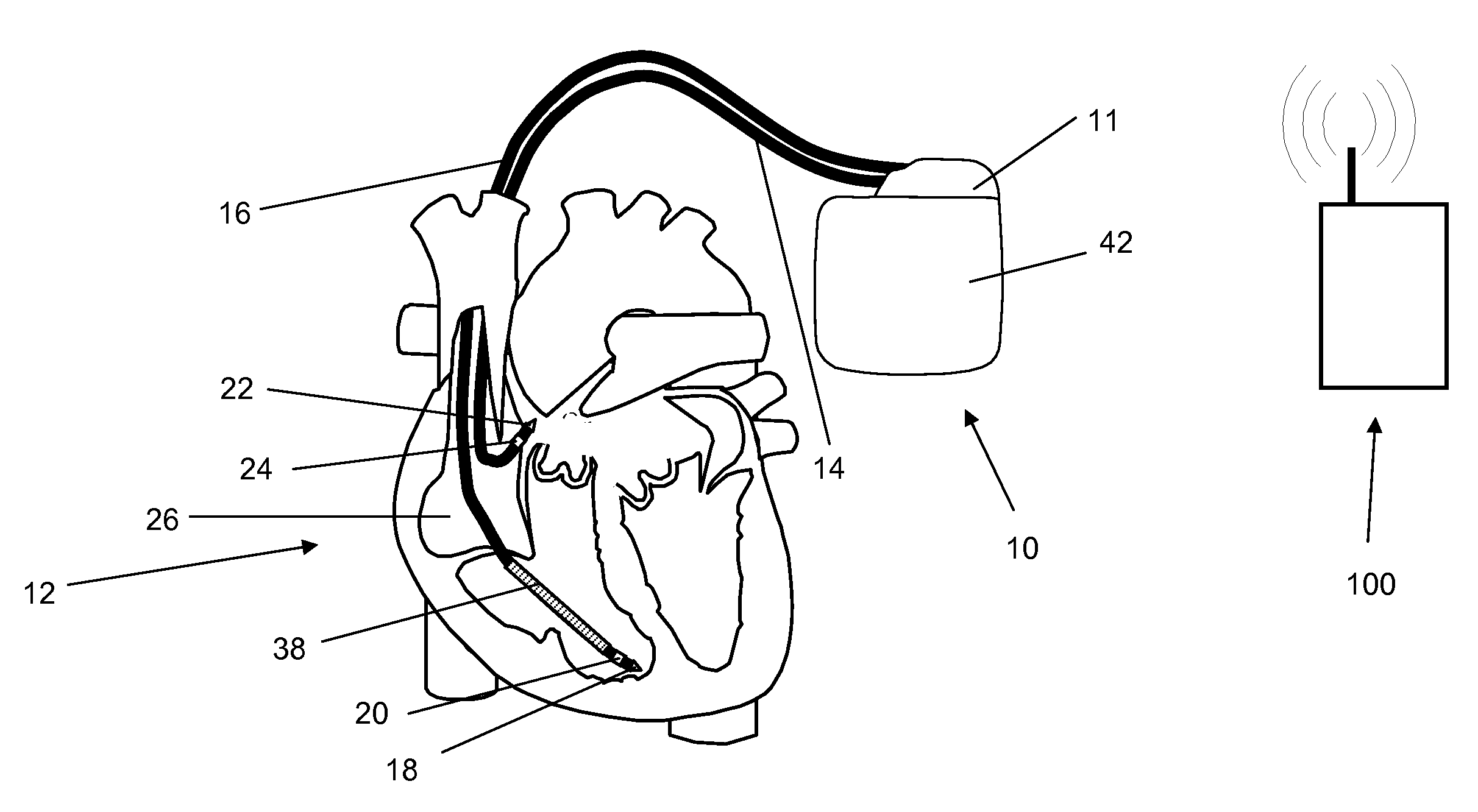
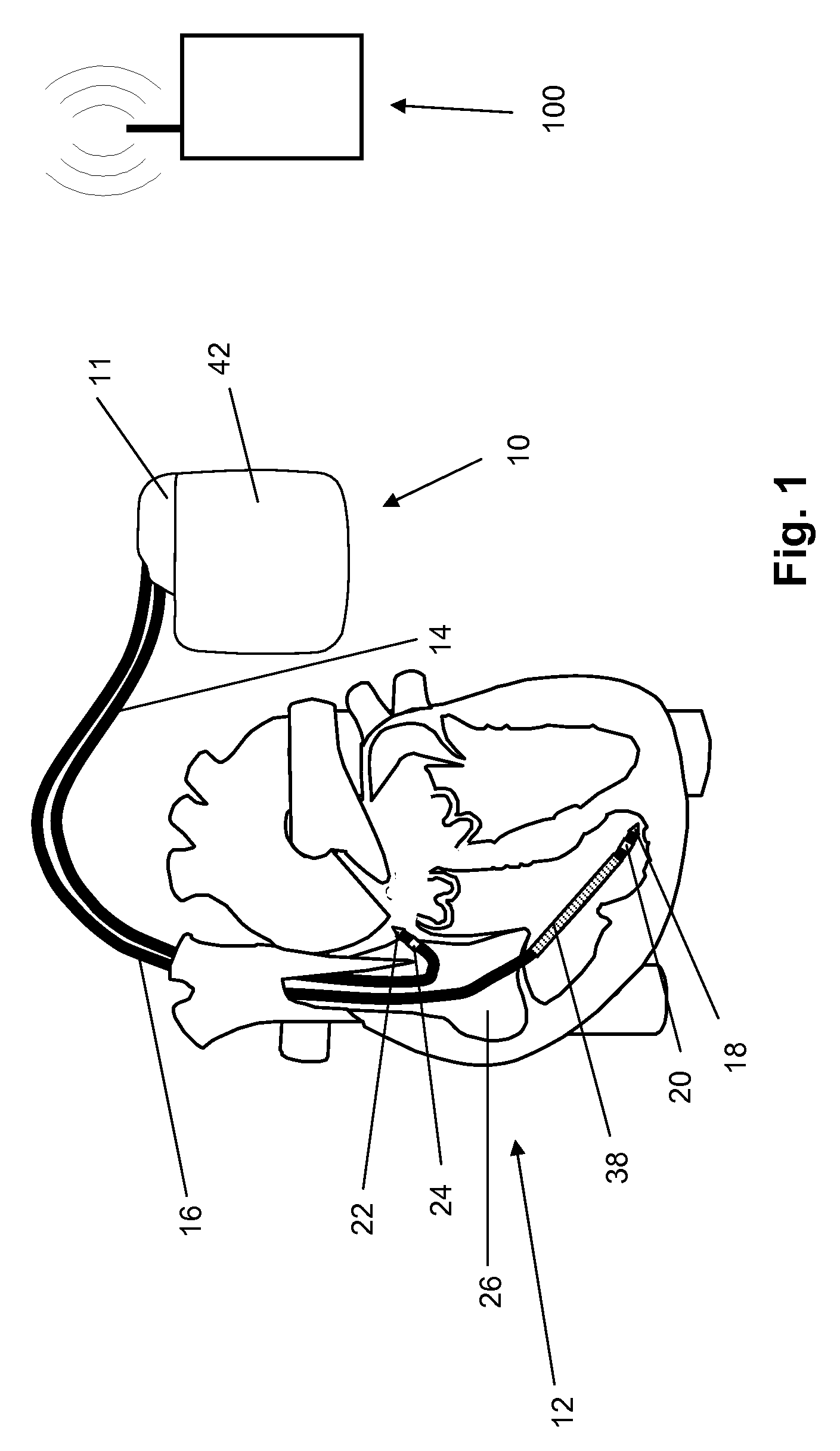
Cardiac arrhythmia detector using ECG waveform-factor and its irregularity
InactiveUS6480734B1Avoiding unnecessary shockSignificant energy savingElectrocardiographyHeart defibrillatorsVentricular tachycardiaCardiac monitoring
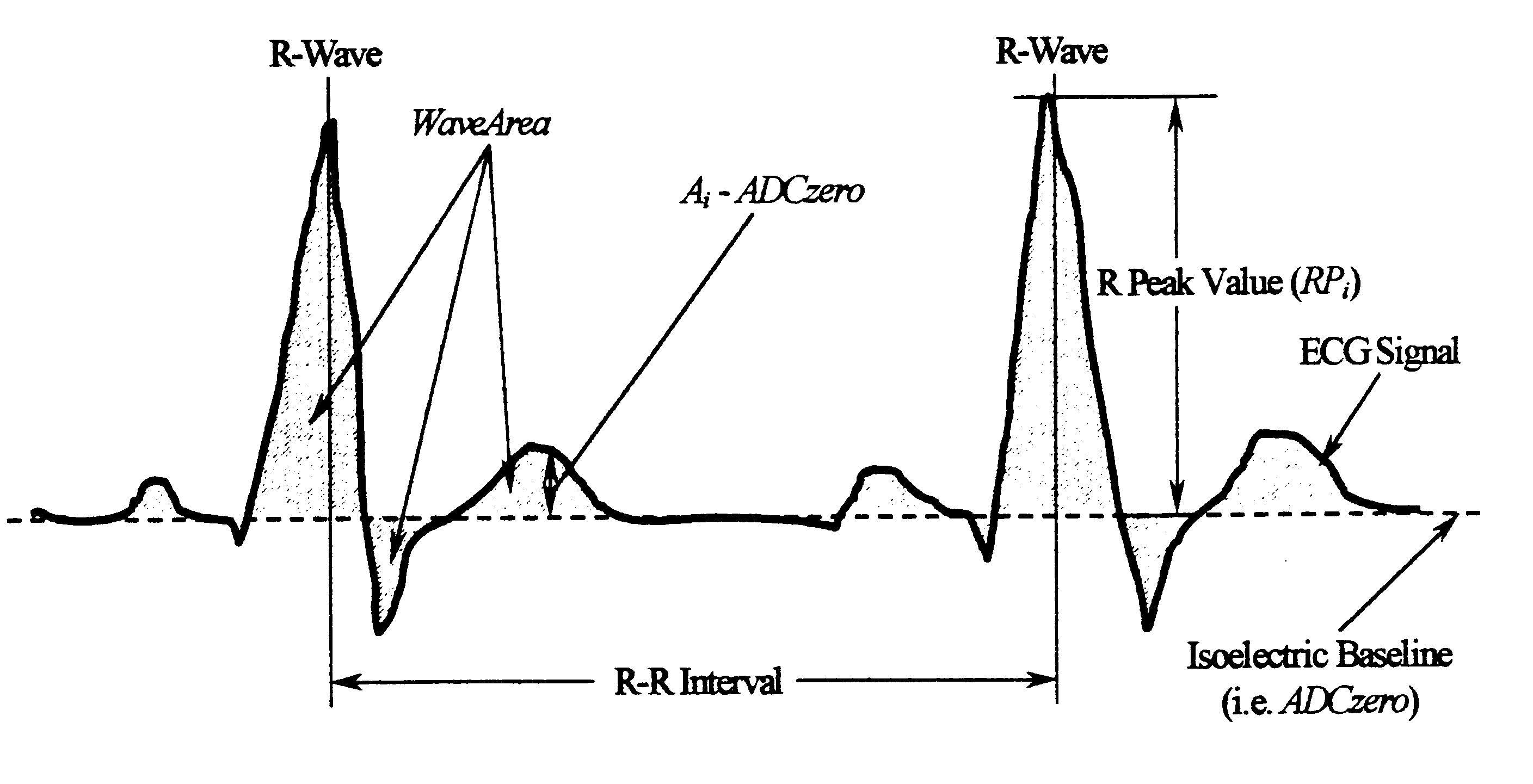
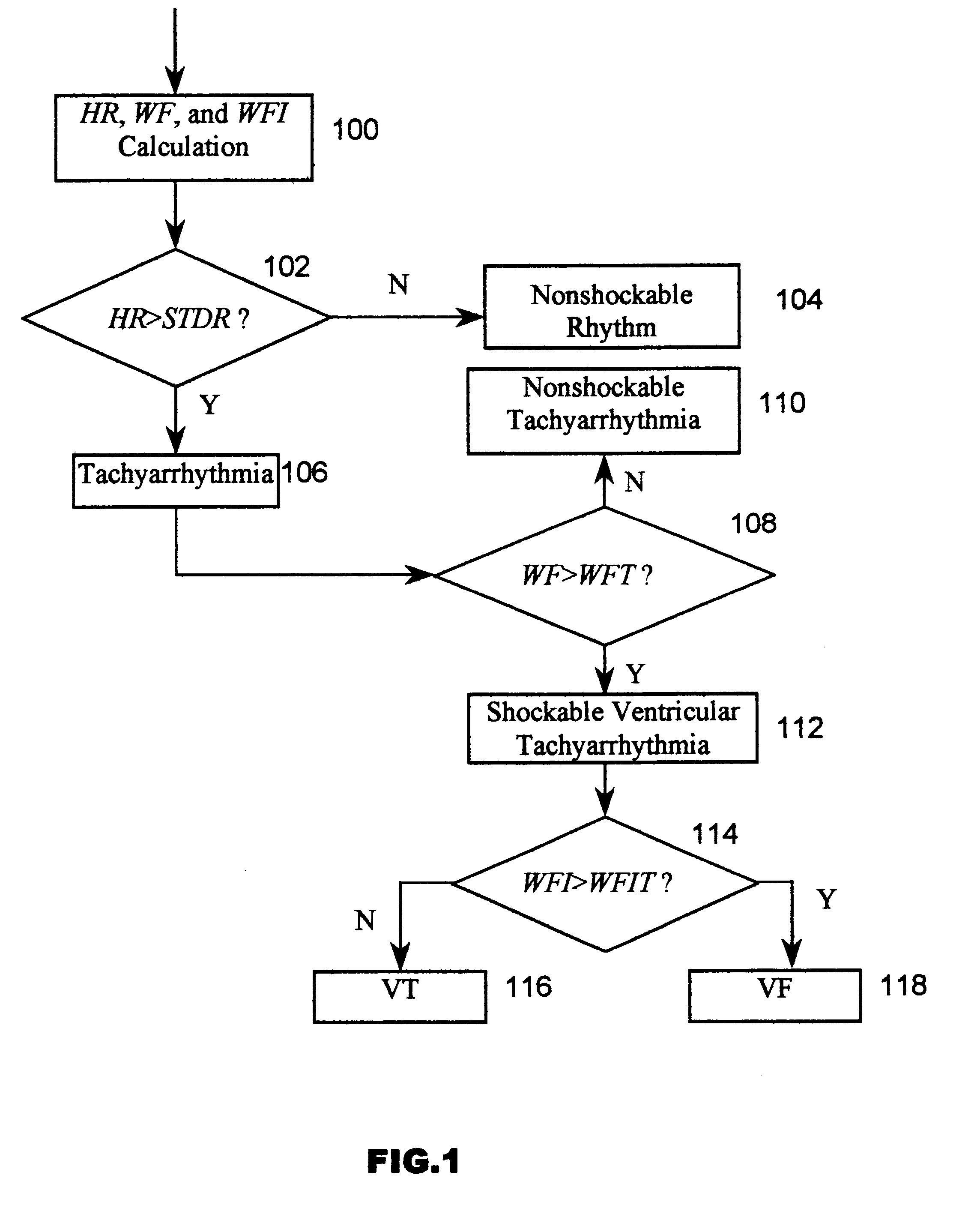
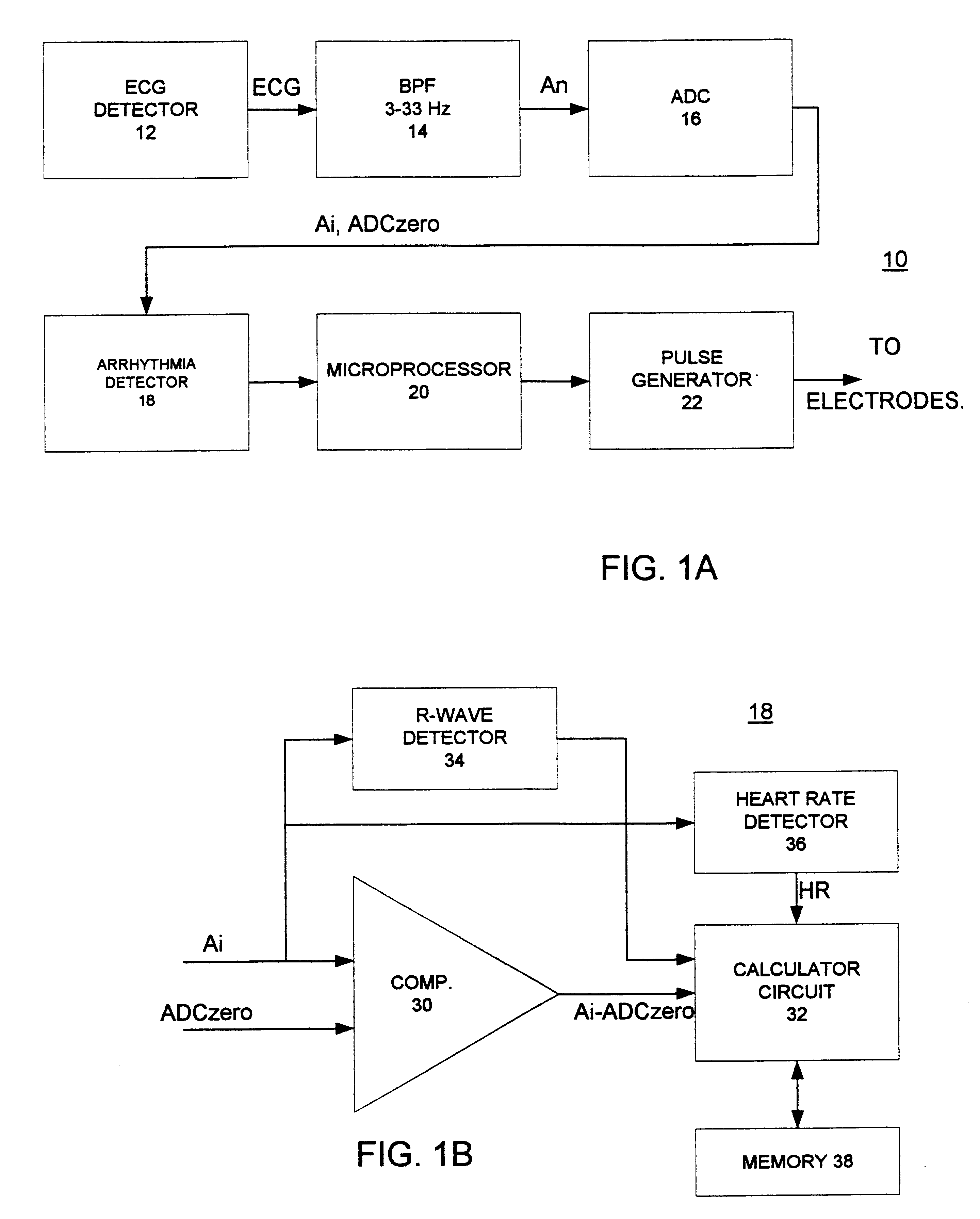
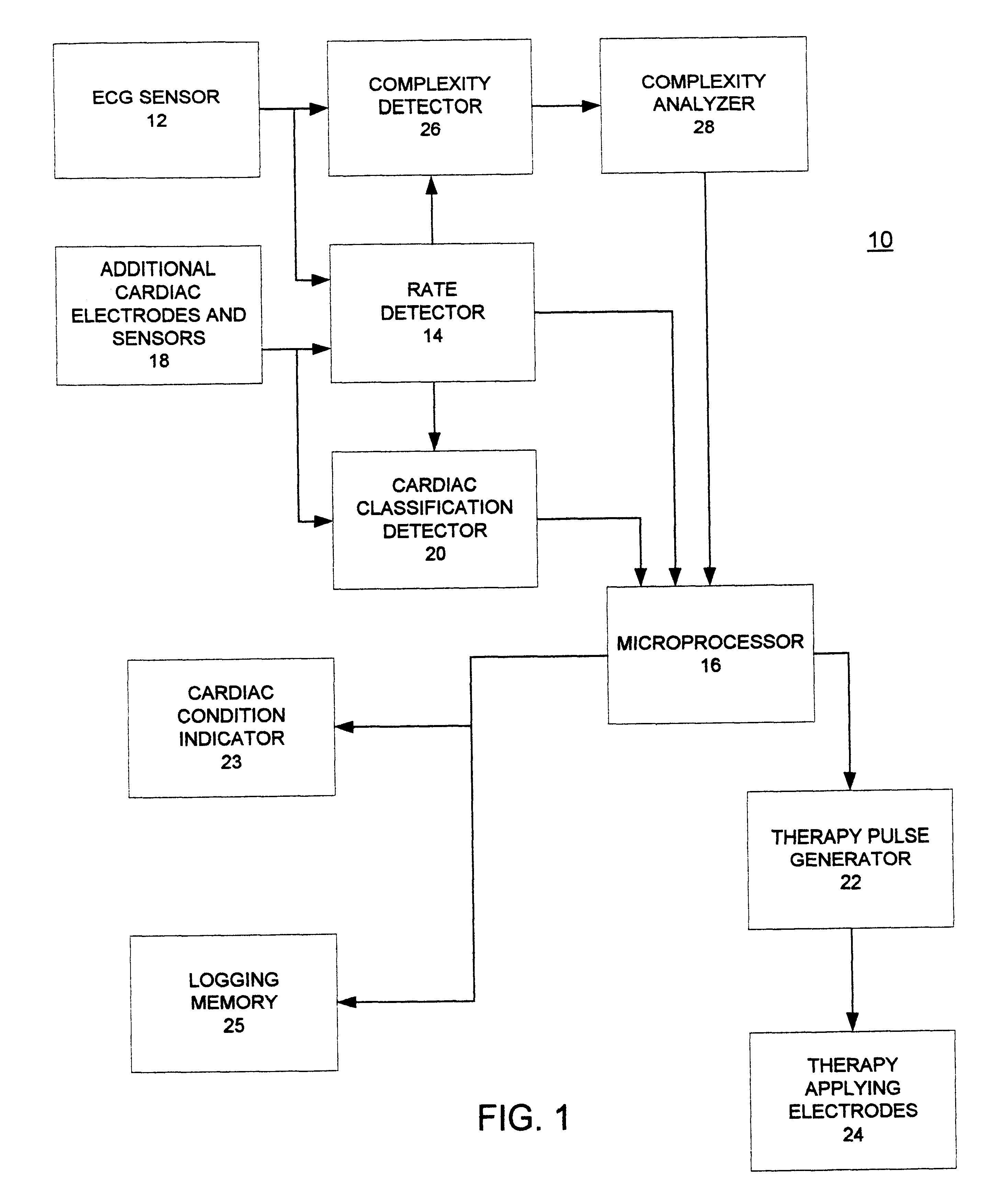
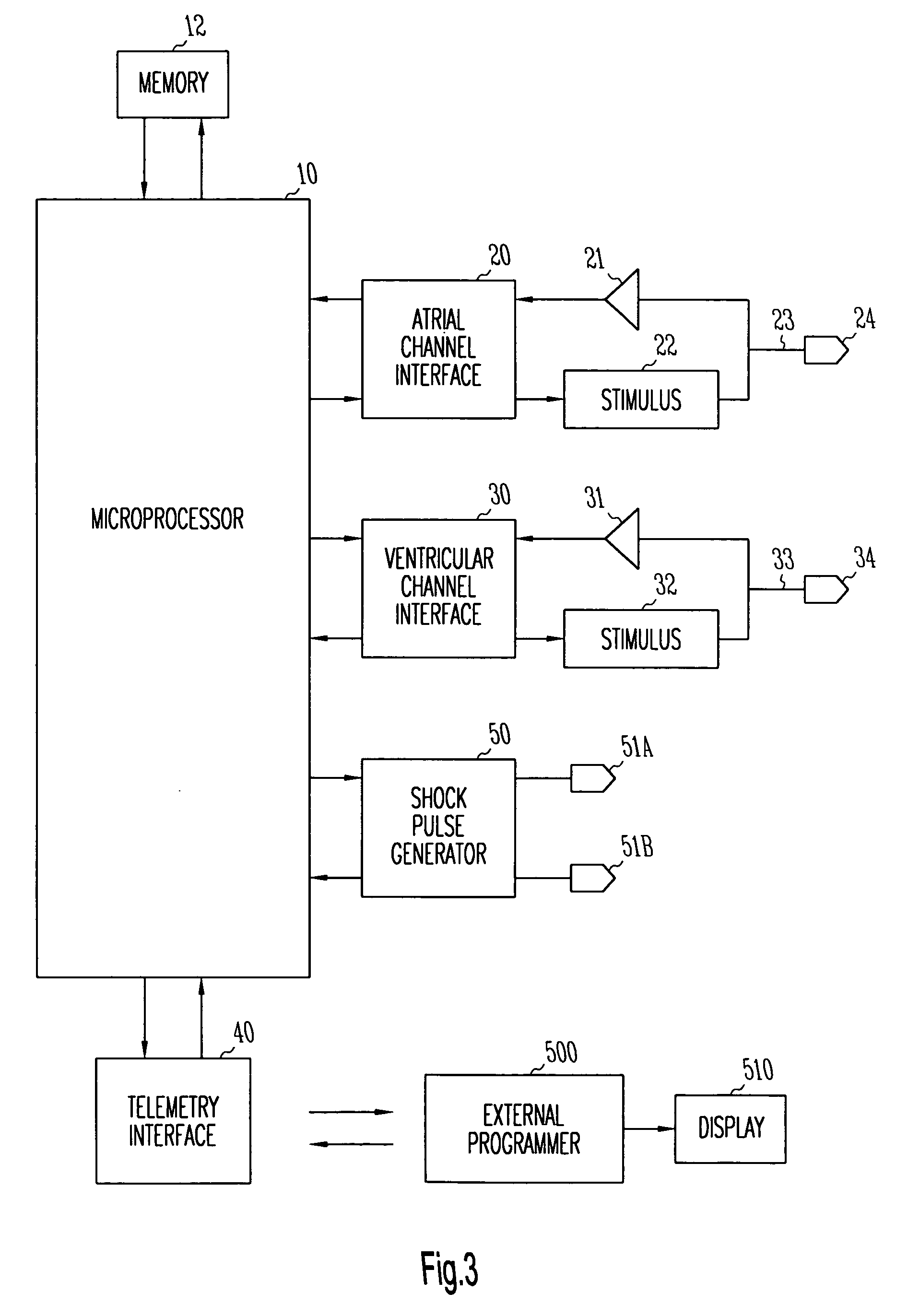
A cardiac monitor is provided that monitors the condition of the heart of a cardiac patient and generates signals indicating one of several conditions, such as supraventricular tachycardia, ventricular tachycardia and ventricular fibrillation. In order to generate these signals, the ECG from the patient is analyzed to determine a cardiac interval and heart rate, as well as a waveform factor and a waveform factor irregularity. The waveform factor is derived from the average of the ECG amplitudes during a cardiac interval and the peak value of the ECG during the same interval. Preferably, a running average is calculated over several intervals. This waveform factor is then used to detect shockable ventricular arrhythmia. The waveform factor irregularity is indicative of the variability of the waveform factor and is used to differentiate between ventricular tachycardia and ventricular defibrillation.
Owner:ZOLL MEDICAL CORPORATION
System and method for complexity analysis-based cardiac tachyarrhythmia detection
InactiveUS6490478B1Clearer and reliable indicationAvoids possible misidentificationsHeart defibrillatorsHeart stimulatorsEcg signalVentricular tachycardia
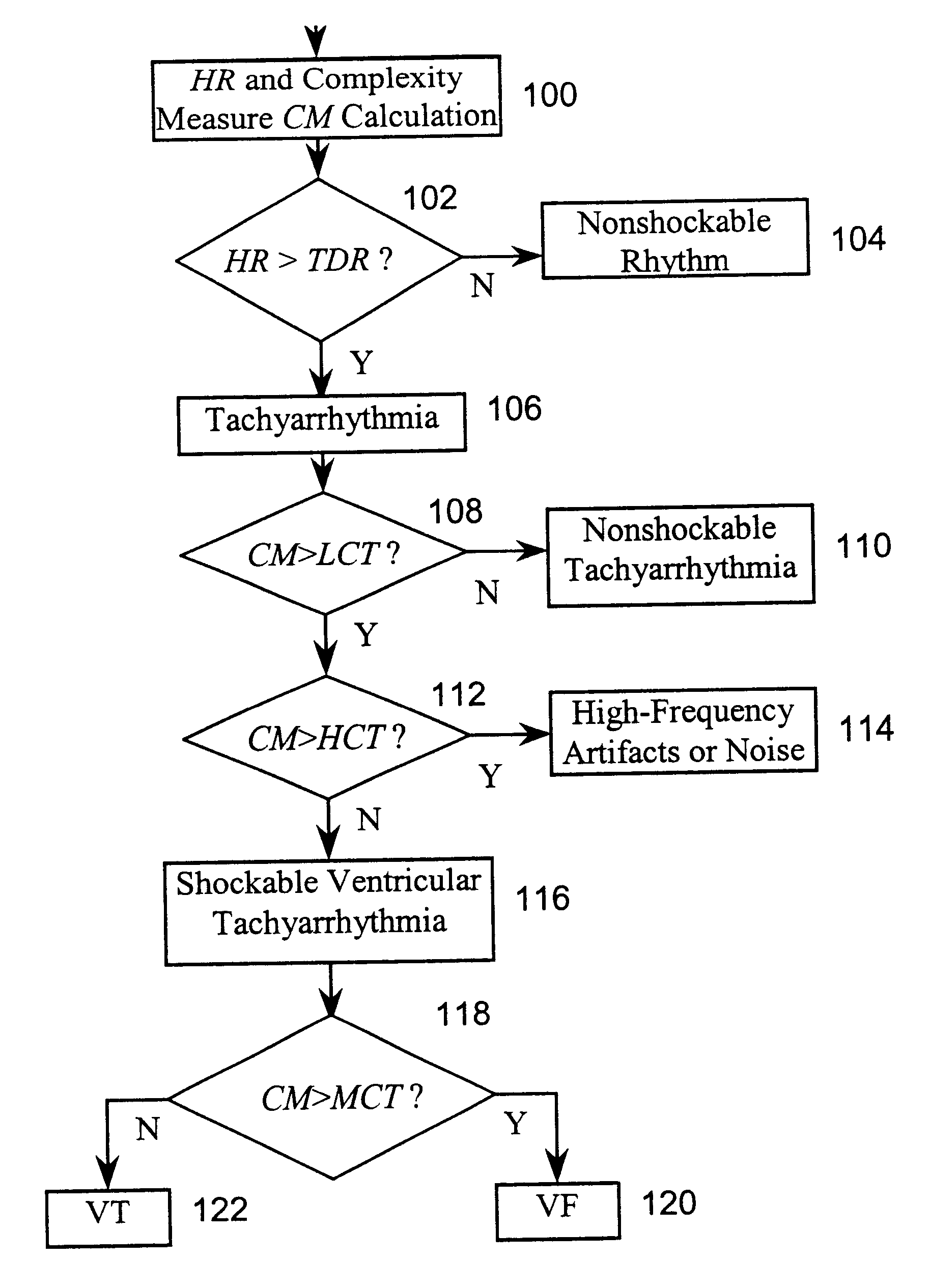
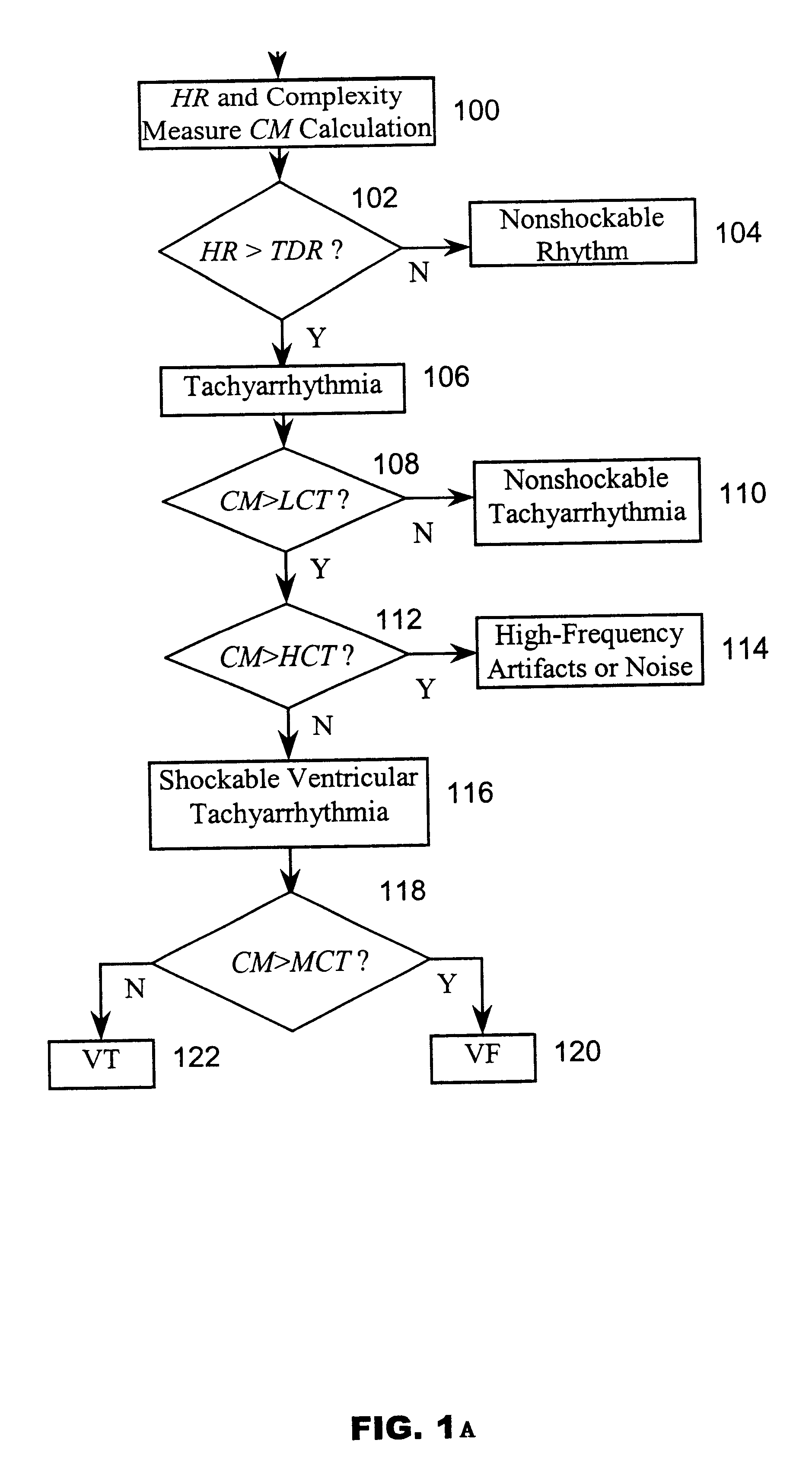
A system and method based on electrocardiogram (ECG) complexity analysis for real-time detecting shockable ventricular fibrillation (VF) and ventricular tachycardia (VT), and discriminating them from non-shockable tachyarrhythmia (e.g. supraventricular tachycardia (SVT) and atrial fibrillation (AF)) and high-frequency noise. In the disclosed invention, complexity measure CM (0 to 100), quantitatively characterizing the complexity nature of the non-linear dynamics underlying cardiac arrhythmia, is extracted from the sensed patient ECG signal using ECG complexity analysis. From the calculated complexity measure, by three thresholds (low complexity threshold (LCT), mediate complexity threshold (MCT), and high complexity threshold (HCT)), different kinds of tachyarrhythmia (i.e. heart rate (HR) above a preset rate threshold) and high-frequency noise are discriminated from each other: for non-shockable tachyarrhythmia, CM<=LCT; for VT, LCT<CM<=MCT; for VF, MCT<CM<=HCT; and for high-frequency noise, HCT<CM. The disclosed system and method can be used as a primary cardiac tachyarrhythmia detection scheme or as a backup system to reconfirm arrhythmia detection using conventional techniques.
Owner:ZOLL MEDICAL CORPORATION
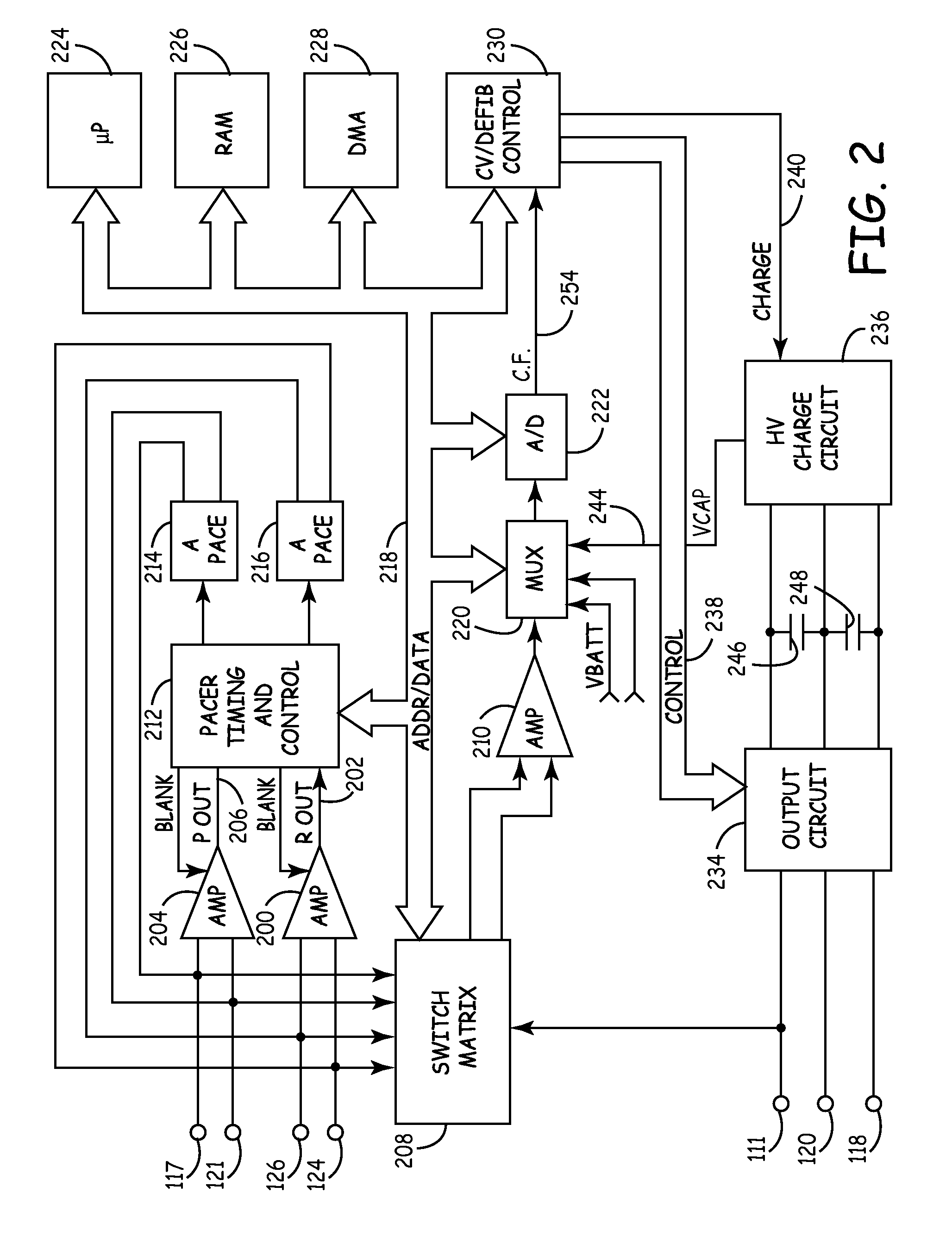
Method and apparatus for using atrial discrimination algorithms to determine optimal pacing therapy and therapy timing
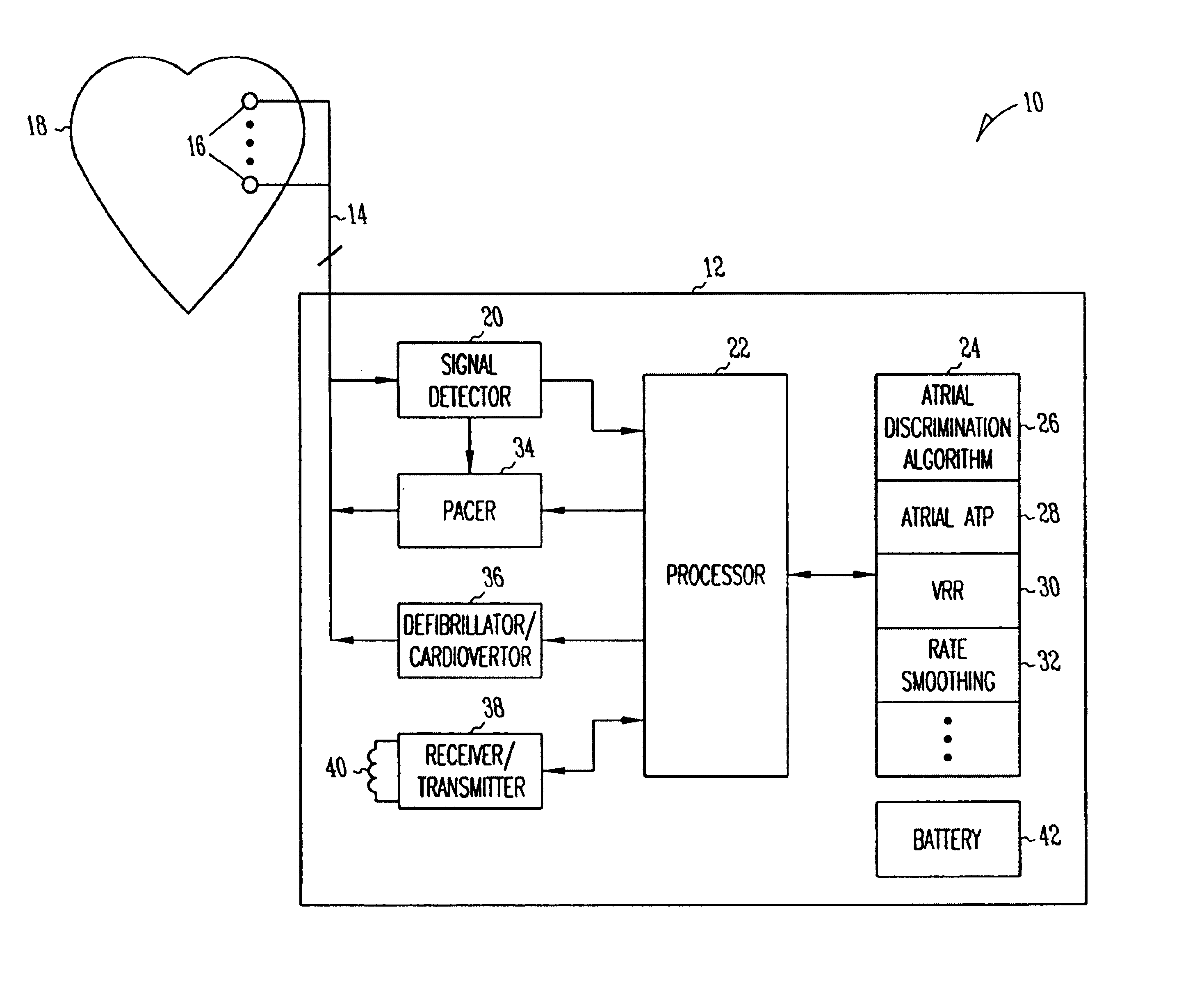
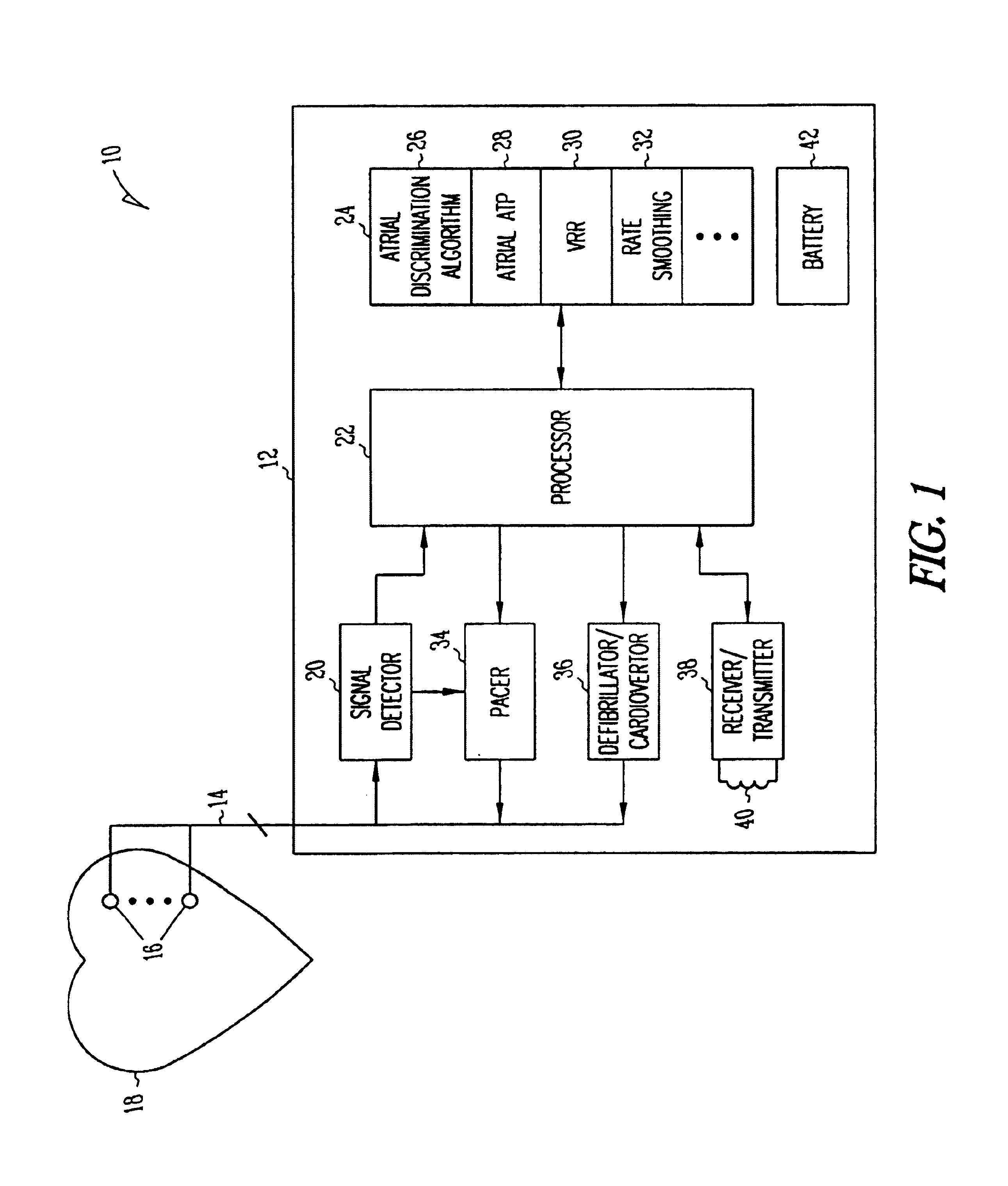
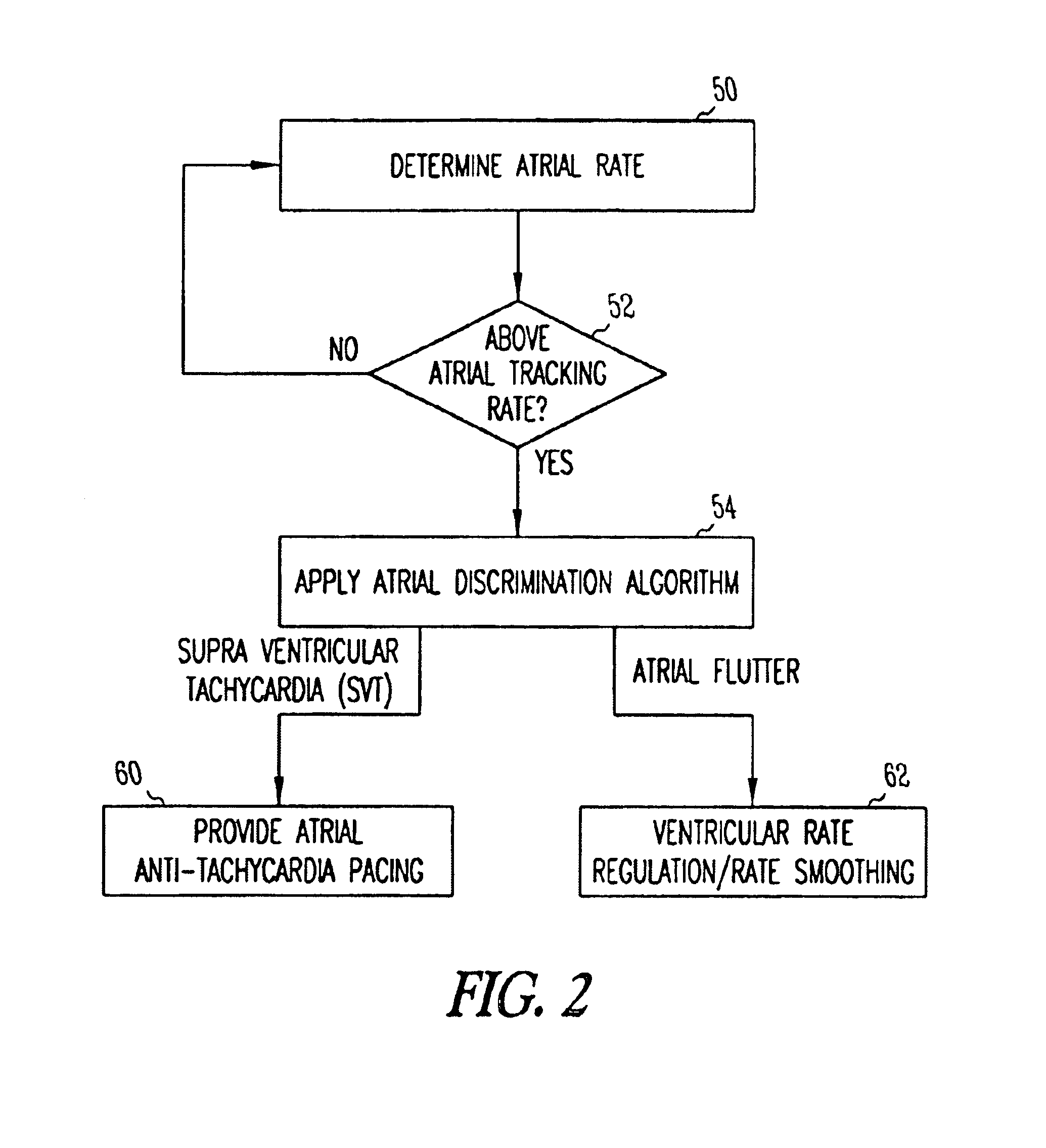
A system and method which employs atrial discrimination algorithms to distinguish between different atrial arrhythmias occurring in a patient for selecting an optimal pacing therapy corresponding to the type of arrhythmia identified. The invention may be implemented in a bradycardia pacemaker or other implantable cardiac device. In response to the detection of an atrial rate above the atrial tracking rate, discrimination criteria are applied to a detected atrial activity signal to distinguish between different types of supraventricular tachycardia, such as fast atrial flutter and other atrial flutter at a relatively slower rate, which may be occurring in the patient. The discrimination criteria may be, for example, rate-based or morphology based. The pacer is controlled to provide pacing therapy to a heart in a manner corresponding to the type of supraventricular tachycardia identified. For example, antitachycardia pacing may be provided to the heart in response to the detection of a relatively lower rate supraventricular tachycardia / other atrial flutter, whereas another pacing control, e.g., ventricular pacing, such as ventricular rate regulation or Rate Smoothing, may be applied if a more rapid rate supraventricular tachycardia / fast atrial flutter is identified. The output of an atrial discrimination algorithm may be tracked and the trend thereof used to improve therapy timing.
Owner:CARDIAC PACEMAKERS INC
Discrimination of supraventricular tachycardia and ventricular tachycardia events
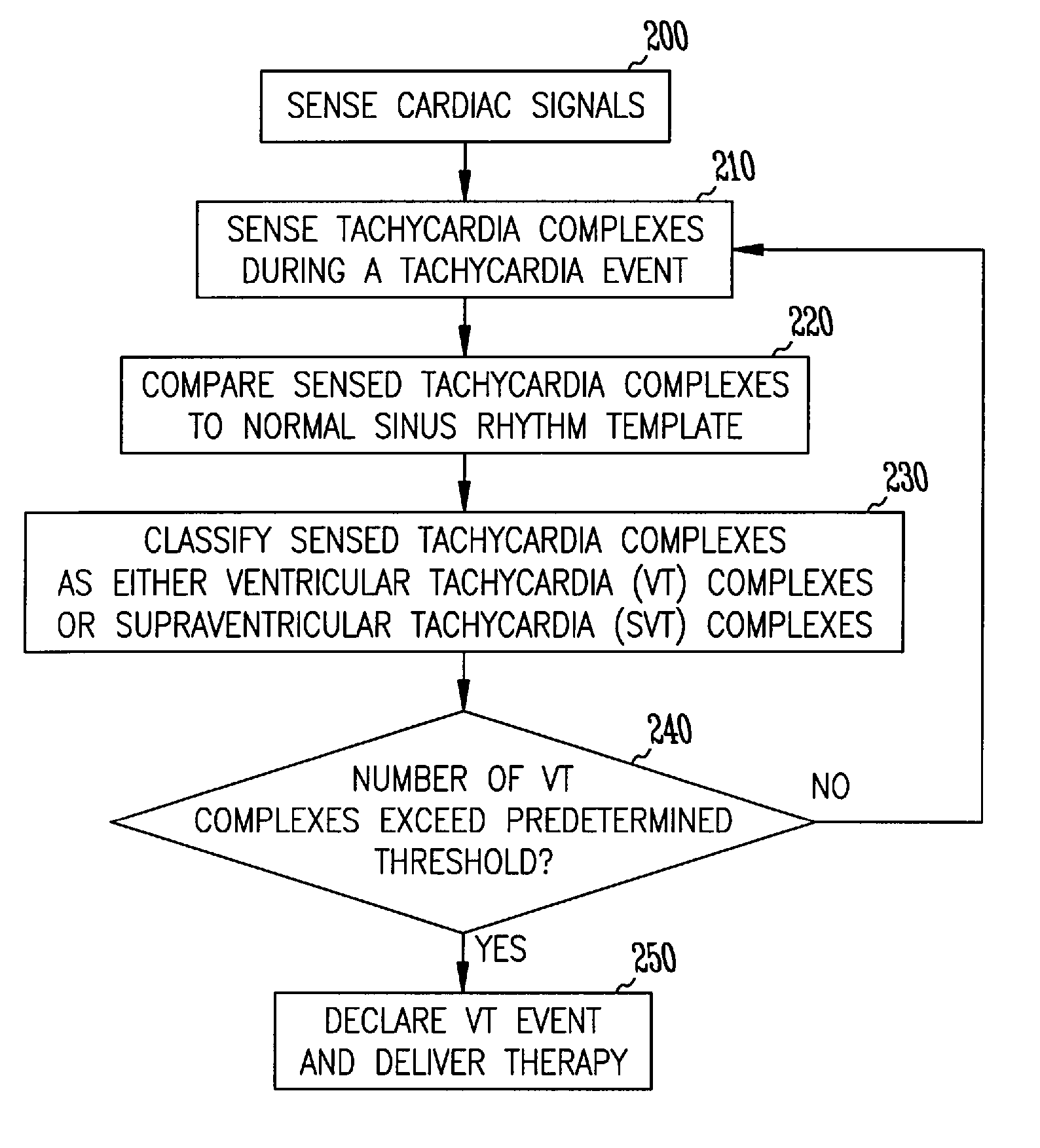
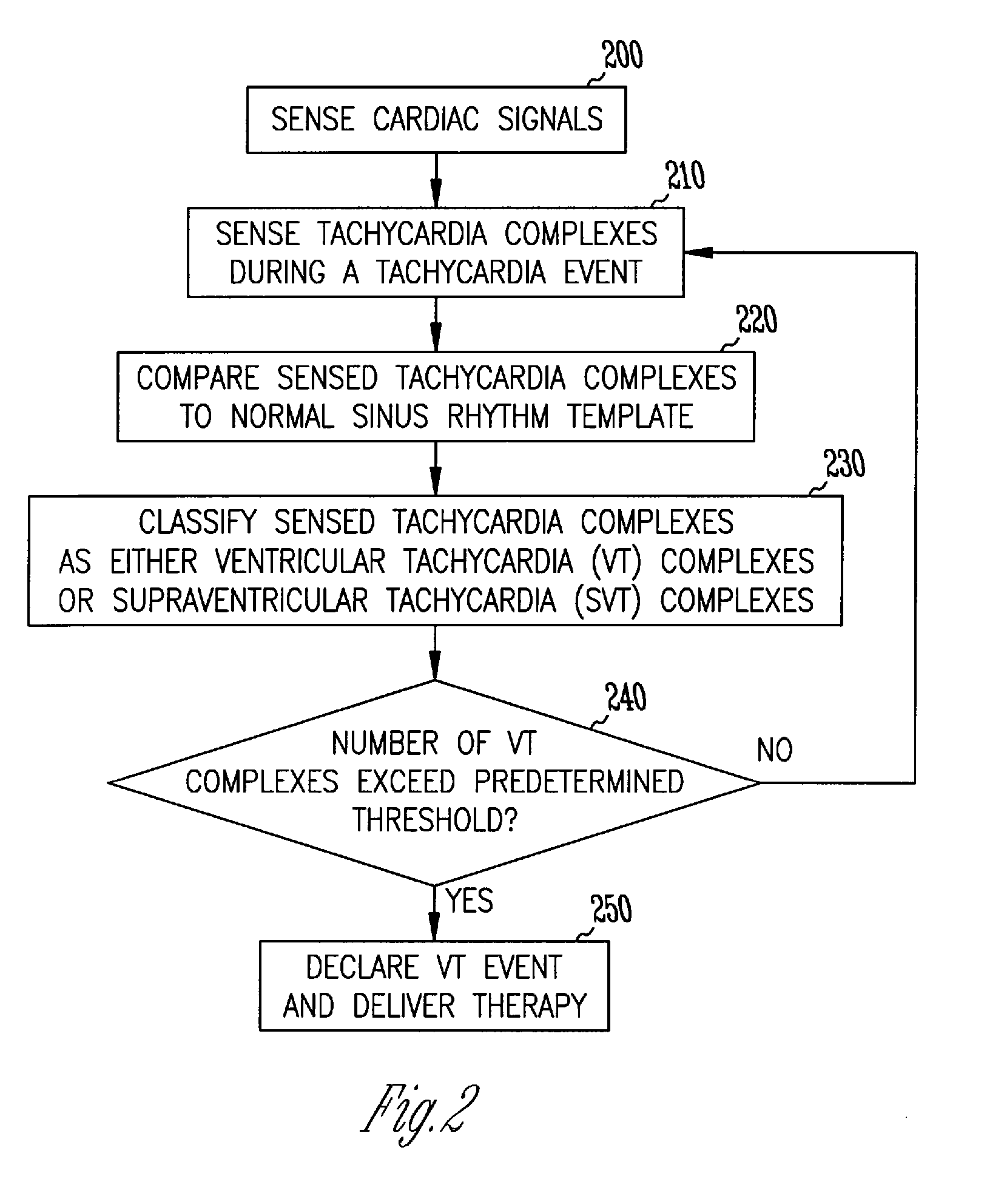
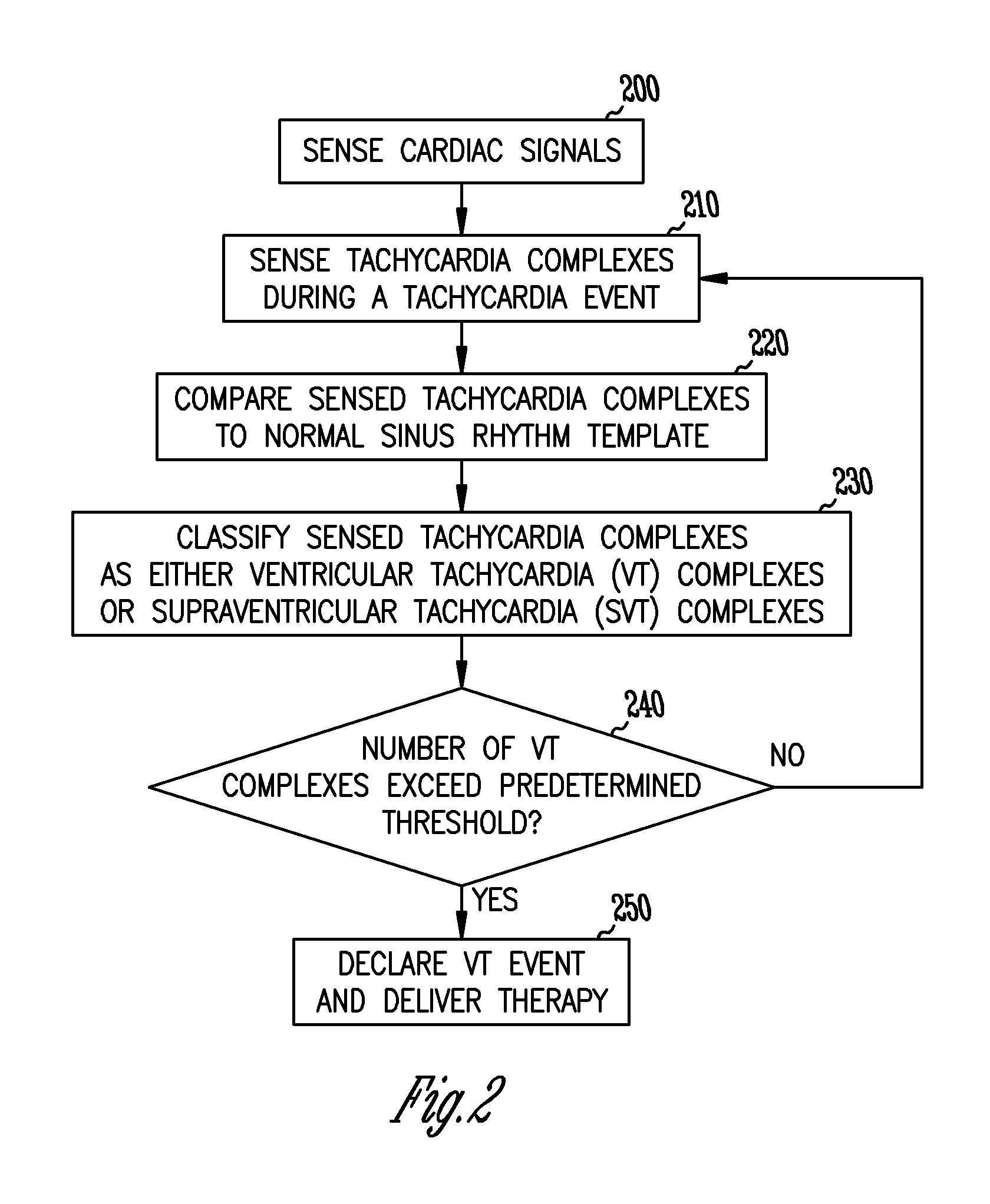
InactiveUS7039463B2Reduce in quantityElectrocardiographyHeart defibrillatorsVentricular tachycardiaNormal Sinus Rhythm
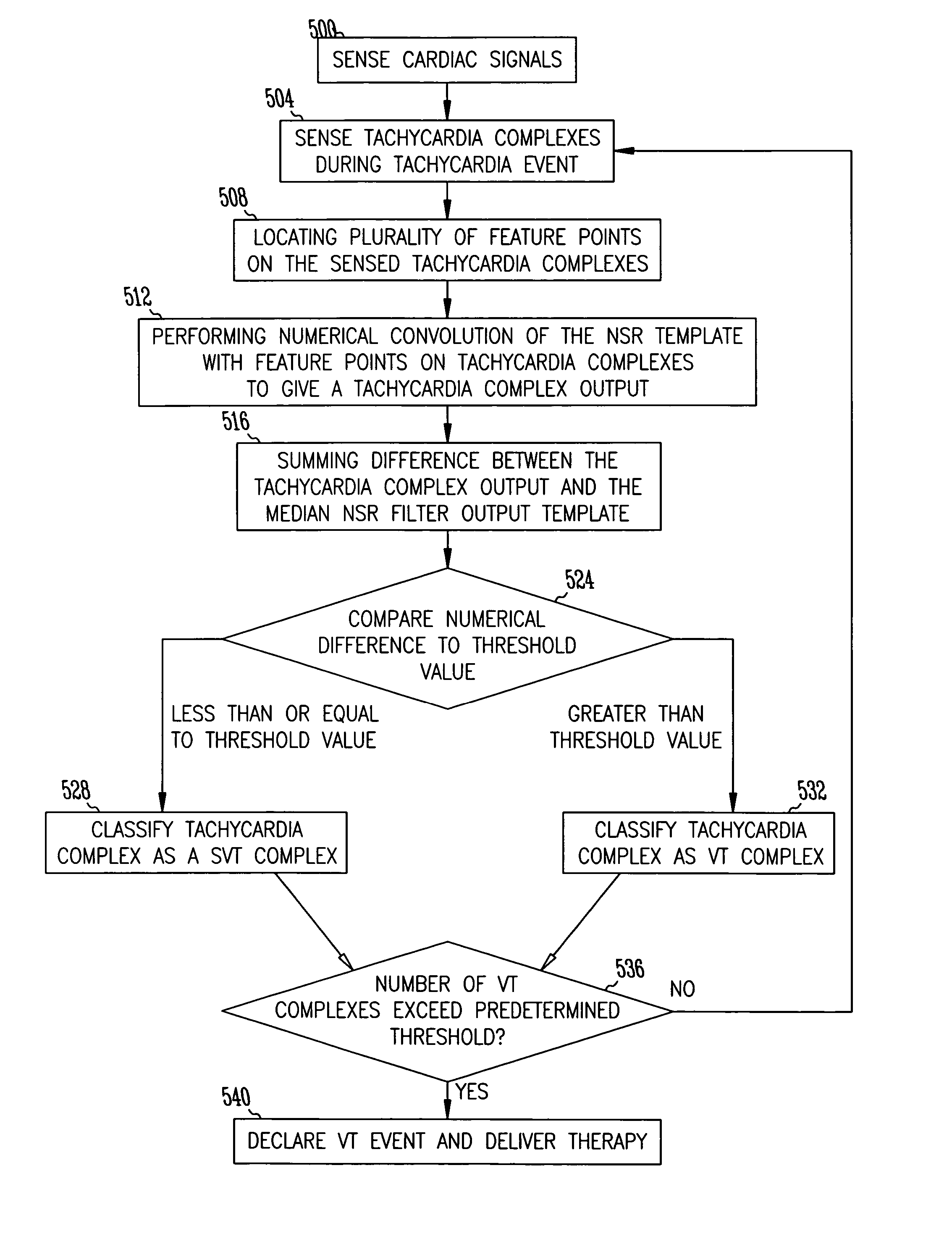
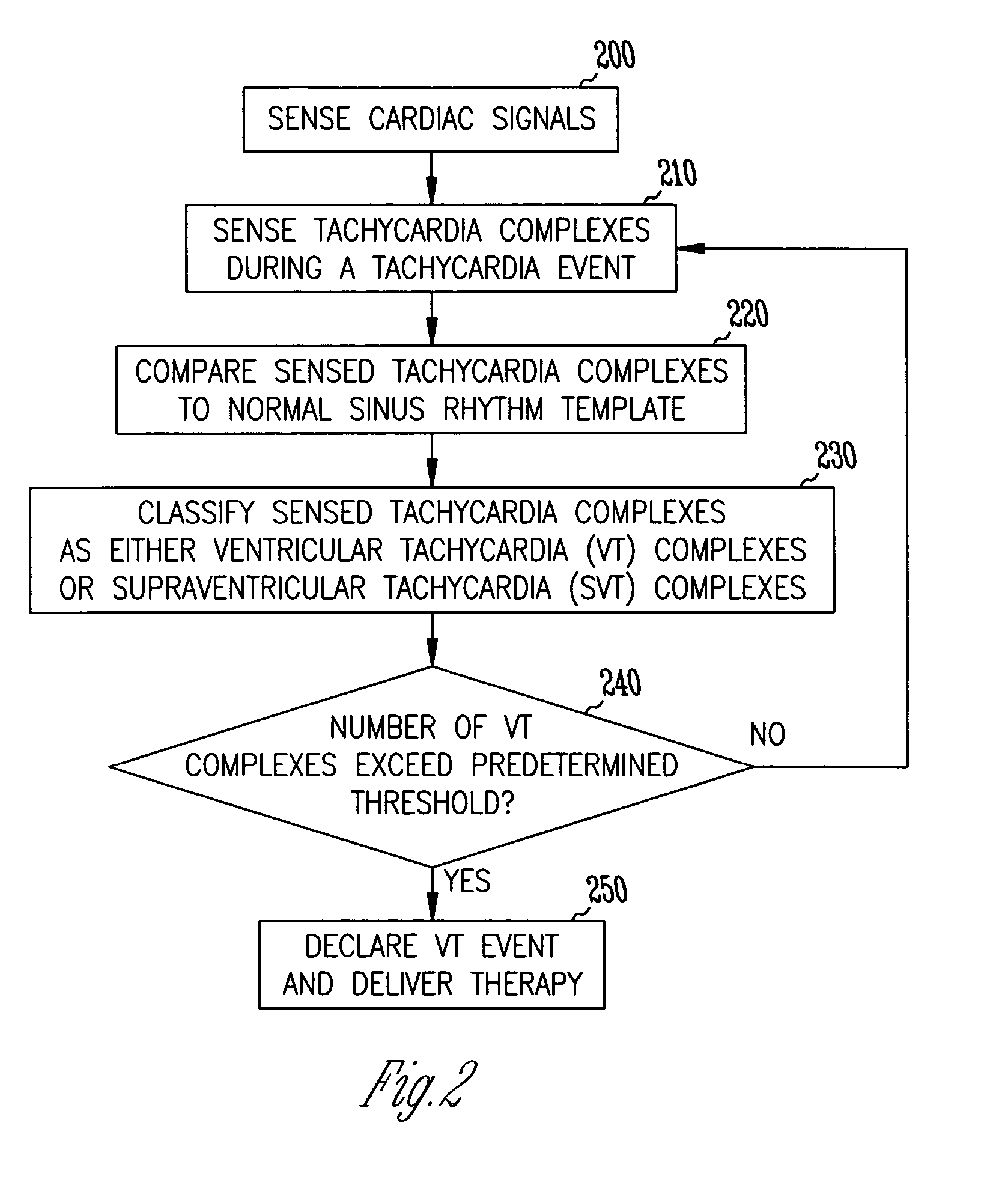
A method and system for discrimination of supraventricular tachycardia and ventricular tachycardia events. Morphological features points are extracted from normal sinus rhythm (NSR) complexes and used to generate a NSR template. A numerical convolution is performed using the NSR template and the feature points for each sensed NSR to give a NSR filter output. Using a plurality of NSR complexes, a median NSR filter output template is determined, where the median NSR filter output template has a median value for each value in the NSR filter output. The median NSR filter output template is then used during a tachycardia event to distinguish tachycardia events as either ventricular tachycardia events or supraventricular tachycardia events.
Owner:CARDIAC PACEMAKERS INC
Automated Assessment Of Atrioventricular And Ventriculoatrial Conduction
ActiveUS20090143832A1Restore normal sinus rhythmHeart defibrillatorsHeart stimulatorsVentricular dysrhythmiaInappropriate shock
A method discriminates between ventricular arrhythmia and supraventricular arrhythmia by determining the direction of an electrical signal conducted through the atrioventricular node. An implantable cardiac defibrillator provides atrioventricular and ventriculoatrial pacing bursts to determine if an arrhythmia with a 1:1 atrial to ventricular relationship is due to ventricular tachycardia or supraventricular tachycardia. This discrimination capability reduces the incidence of inappropriate shocks from dual-chamber implantable cardiac defibrillators to near zero and provides a method to differentially diagnose supraventricular tachycardia from ventricular tachycardia.
Owner:UNIVERSITY OF PITTSBURGH
System and method for classifying tachycardia arrhythmias having 1:1 atrial-to-ventricular rhythms
An implantable cardioverter / defibrillator includes a tachycardia detection system that detects one-to-one (1:1) tachycardia, which is a tachycardia with a one-to-one relationship between atrial and ventricular contractions. When the 1:1 tachycardia is detected, the system discriminates ventricular tachycardia (VT) from supraventricular tachycardia (SVT) based on analysis of a cardiac time interval. Examples of the cardiac time interval include an atrioventricular interval (AVI) and a ventriculoatrial interval (VAI). A template time interval is created during a known normal sinus rhythm. The system measures a tachycardia time interval after detecting the 1:1 tachycardia, and indicates a VT detection if the tachycardia time interval differs from the template time interval by at least a predetermined percentage of the template time interval.
Owner:CARDIAC PACEMAKERS INC
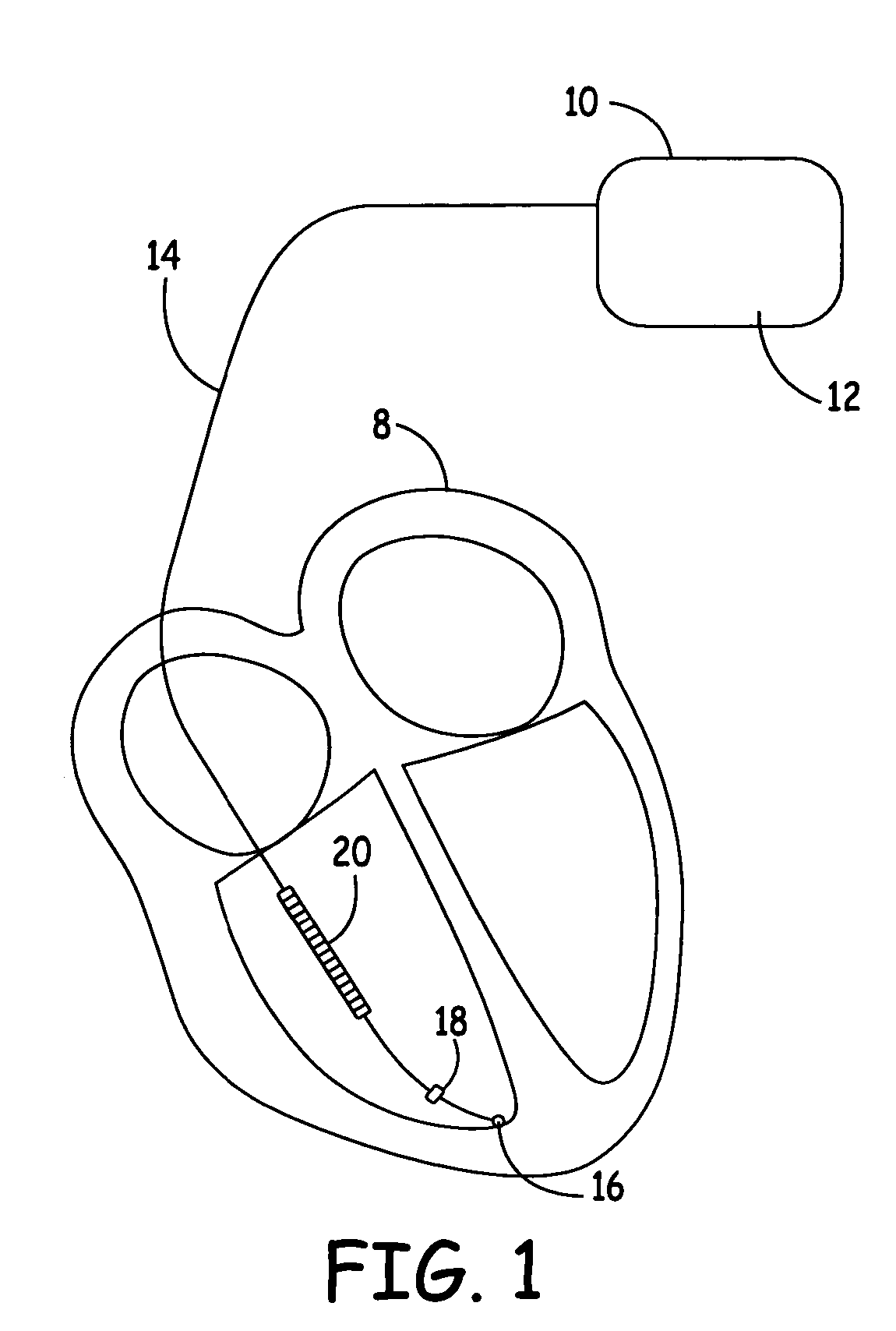
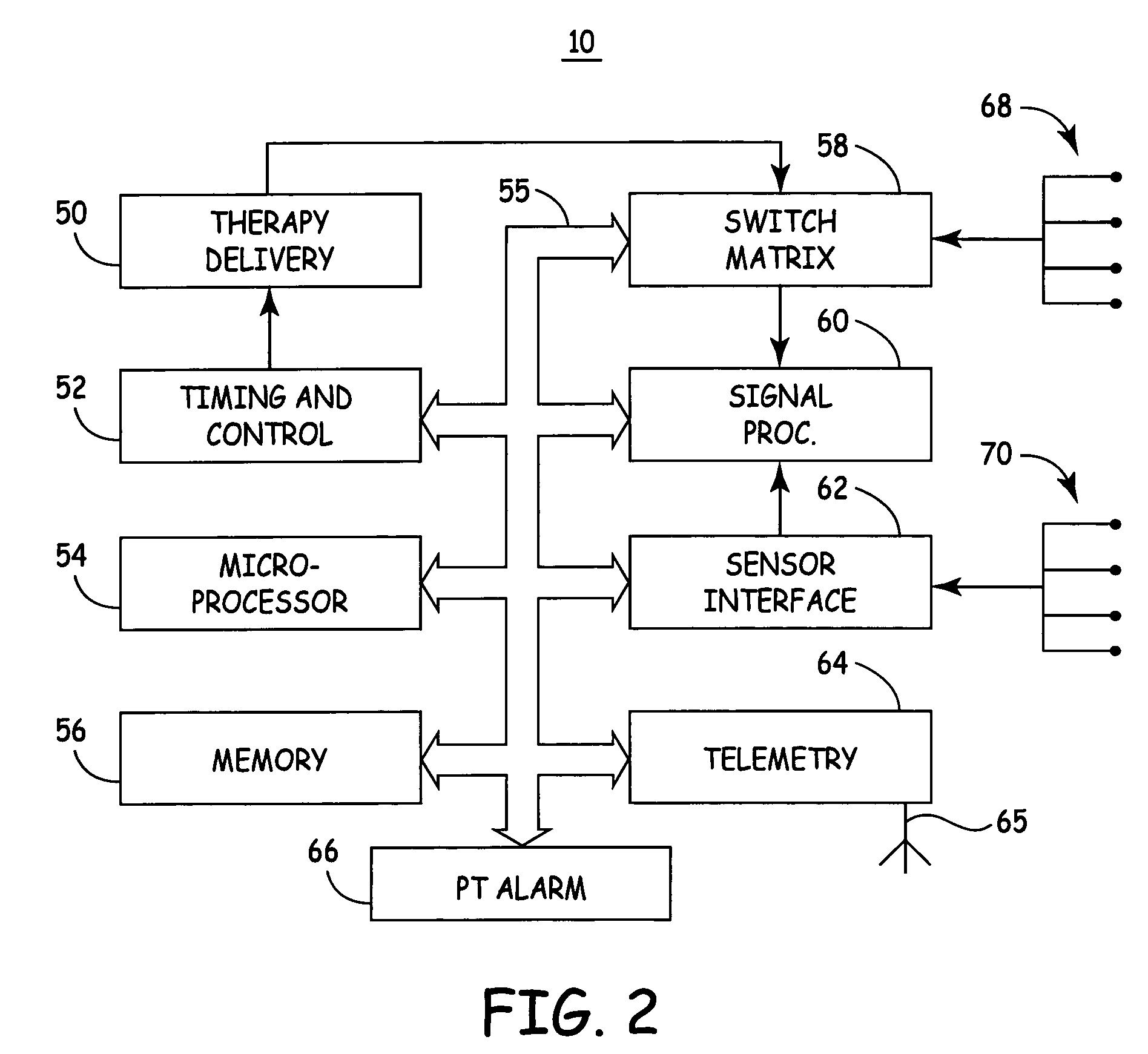
Cardiac rhythm monitoring device
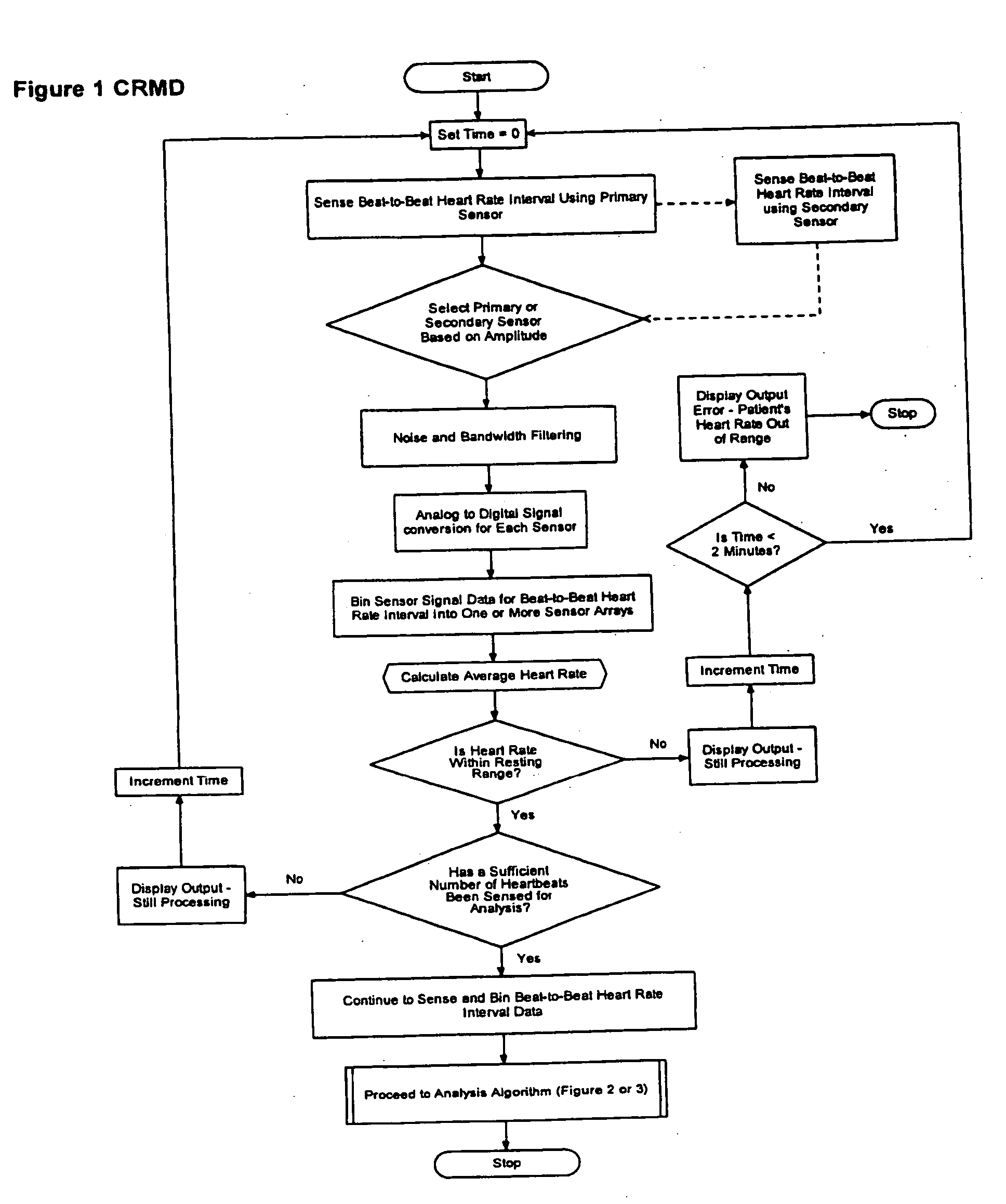
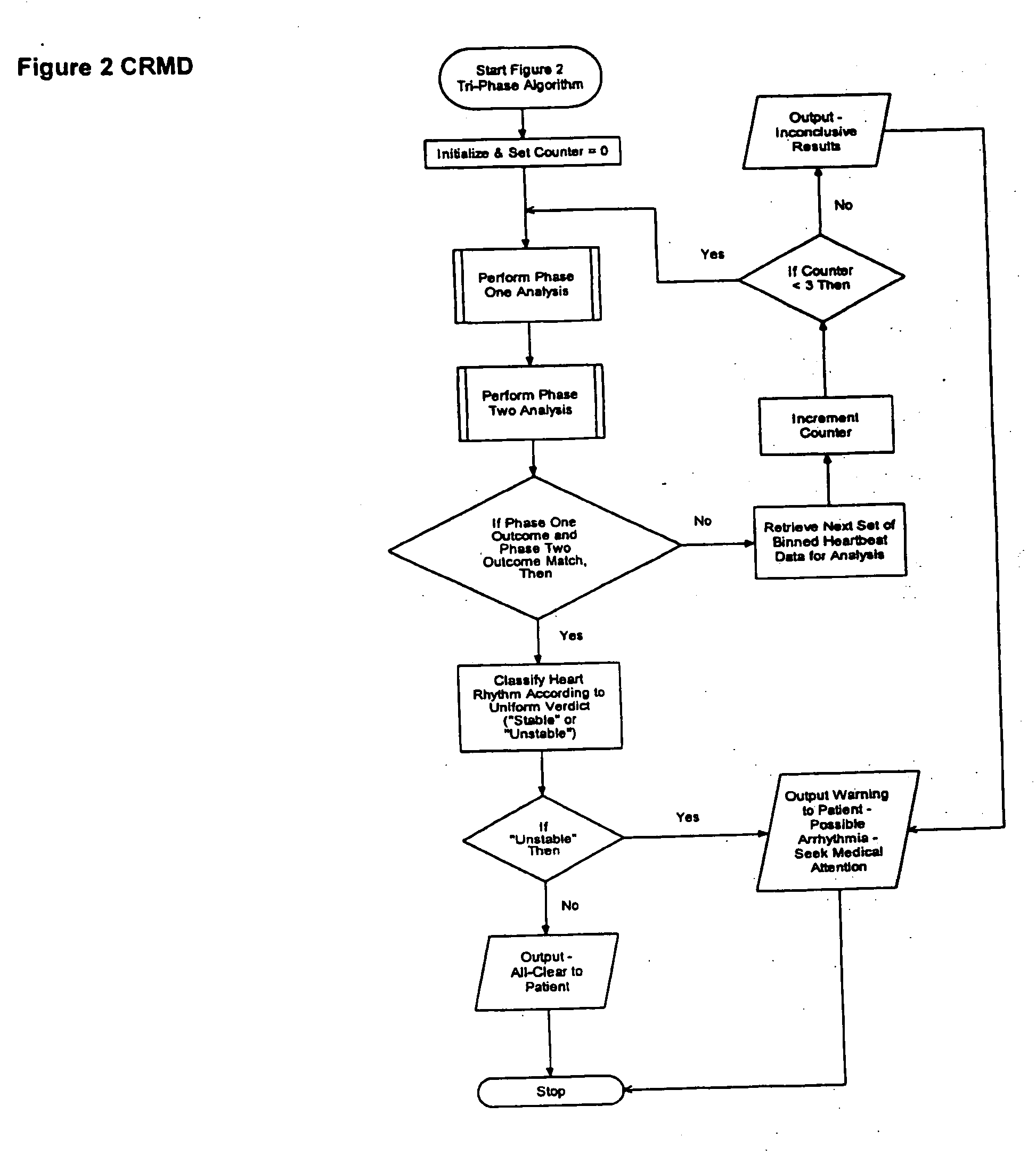
The present invention is a cardiac rhythm-monitoring device, which allows patients to perform a preliminary screening for supraventricular arrhythmia. The device detects beat-to-beat heart rhythms (i.e. the R-R interval between individual heart beats) and performs a screening test to determine if there are indications of arrhythmia. The test looks for variance in the R-R interval that is outside of the normal range, either using a pre-constructed chart based upon general population studies to determine the normal range of variance or using normal distribution analysis of the patient's own heart rhythm to determine the normal range of variance for determining irregular heartbeats, and if there are multiple irregularities within the sensed time frame, the patient is warned of potential supraventricular arrhythmia. By sensing both electrical impulses form the heart and mechanical responses to the heartbeat, the device may augment its analysis.
Owner:BISCHOFF EDWARD T +1
Cardiac rhythm monitoring device
Owner:BISCHOFF EDWARD T +1
Discrimination of supraventricular tachycardia and ventricular tachycardia events
InactiveUS20060122527A1Reduce in quantityElectrocardiographyHeart defibrillatorsVentricular tachycardiaNormal Sinus Rhythm
A method and system for discrimination of supraventricular tachycardia and ventricular tachycardia events. Morphological features points are extracted from normal sinus rhythm (NSR) complexes and used to generate a NSR template. A numerical convolution is performed using the NSR template and the feature points for each sensed NSR to give a NSR filter output. Using a plurality of NSR complexes, a median NSR filter output template is determined, where the median NSR filter output template has a median value for each value in the NSR filter output. The median NSR filter output template is then used during a tachycardia event to distinguish tachycardia events as either ventricular tachycardia events or supraventricular tachycardia events.
Owner:CARDIAC PACEMAKERS INC
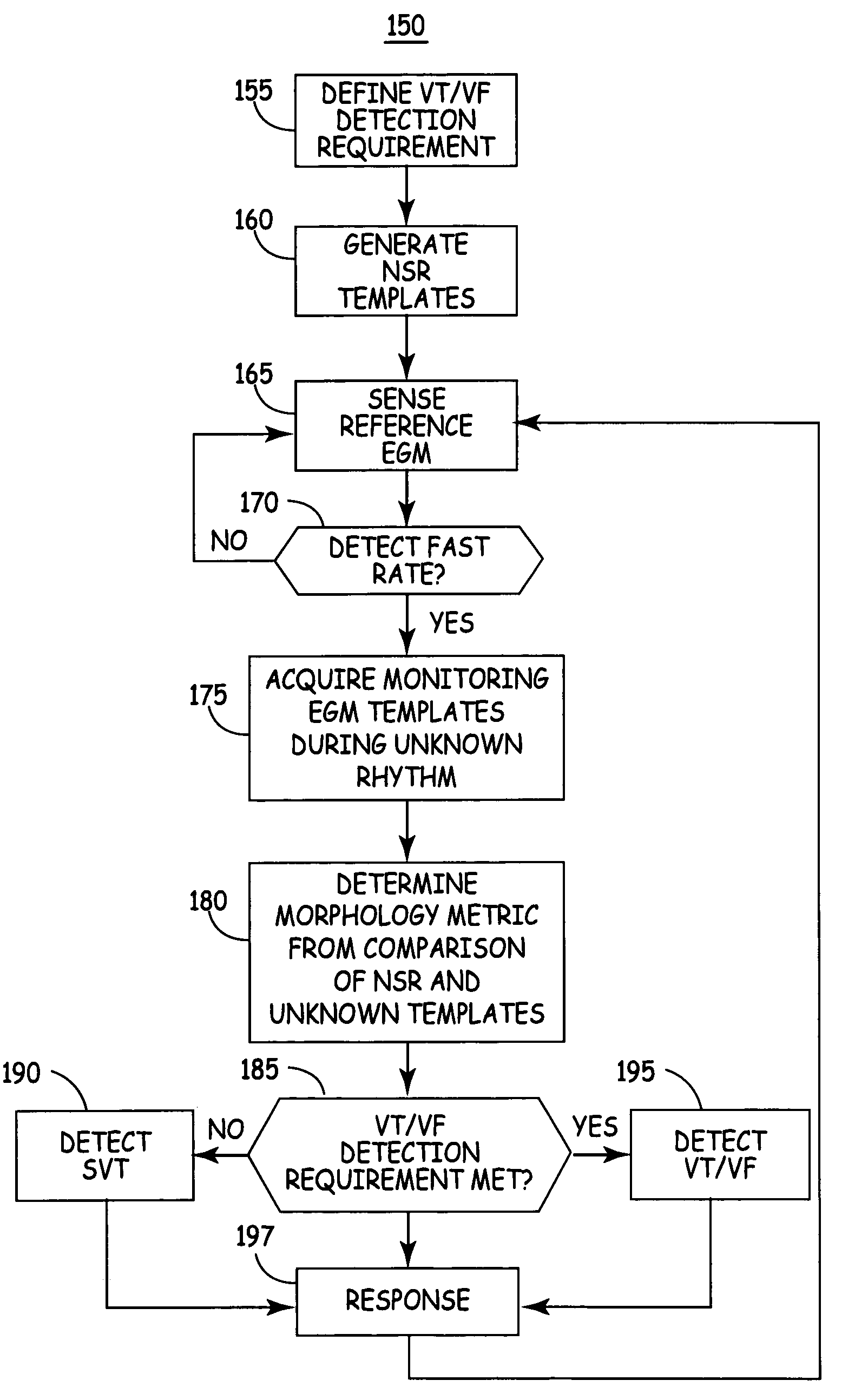
Method and apparatus for discriminating ventricular and supraventricular tachyarrhythmias
A system and method are provided for discriminating supra-ventricular tachycardia (SVT) from ventricular tachycardia (VT). A monitoring EGM signal is acquired during a sensing window timed according to the time of R-wave detection on a reference EGM signal. A normal sinus rhythm (NSR) template is generated using the monitoring EGM signal during the time-referenced sensing window. During an unknown rhythm, the monitoring EGM signal sensed during the time-referenced sensing window is compared to the NSR template for use in computing a morphology metric. The morphology metric is compared to a VT / VF detection threshold for discriminating SVT from VT / VF.
Owner:MEDTRONIC INC
Cardiac rhythm monitoring device
The present invention is a cardiac rhythm-monitoring device, which allows patients to perform a preliminary screening for supraventricular arrhythmia. The device detects beat-to-beat heart rhythms (i.e. the R-R interval between individual heart beats) and performs a screening test to determine if there are indications of arrhythmia. The test looks for variance in the R-R interval that is outside of the normal range, either using a pre-constructed chart based upon general population studies to determine the normal range of variance or using normal distribution analysis of the patient's own heart rhythm to determine the normal range of variance for determining irregular heartbeats, and if there are multiple irregularities within the sensed time frame, the patient is warned of potential supraventricular arrhythmia. By sensing both electrical impulses form the heart and mechanical responses to the heartbeat, the device may augment its analysis.
Owner:BISCHOFF EDWARD T +1
Cardio mapping system and method for cardio mapping
A method and system for determining the mechanism of cardiac arrhythmia in a patient is disclosed. The method basically entails measuring the impedance of cardiac tissue in a portion of the patient's heart using a catheter during an episode of supraventricular tachycardia to produce an iso-impedance map of that cardiac tissue on a video display and analyzing the pattern of the iso-impedance map to differentiate focal arrhythmia caused by a circumscribed region of focal firing and reentrant arrhythmia caused by a macroreentrant circuit. The method can also be used to identify regions of coherent rapidly conducting tissue e.g., Bachman's bundle or the inferoposterior pathway insertion points, to identify focal “mother rotors” throughout the left atrium that may participate in the generation and maintenance of atrial fibrillation and to identify areas of CAFE (complex atrial / fractionated electrograms) that truly reflect these mother rotors.
Owner:ALBERT EINSTEIN HEALTHCARE NETWORK
Method and apparatus for detecting and treating tachyarrhythmias incorporating diagnostic/therapeutic pacing techniques
ActiveUS20090259269A1Well formedElectrocardiographyMedical automated diagnosisVentricular tachycardiaPassive detection
An implantable medical device (IMD) and methods of operating the same to treat a tachyarrhythmia are disclosed herein. In accordance with this method, an arrhythmia of the heart is classified based on one or more supraventricular tachycardia (SVT) rejection rules, which differentiate between a first group of heart rhythms that do not require treatment and a second group of heart rhythms that possibly require treatment. Diagnostic / therapeutic pacing can then be performed to further discriminate the second group of heart rhythms as being within a first sub-group of heart rhythms and a second sub-group of heart rhythms which are to be treated by applying a ventricular tachycardia (VT) / ventricular fibrillation (VF) therapy sequence. In another implementation, the order in which the IMD performs diagnostic / therapeutic pacing and analyzes passive detection and classification criteria can be reversed.
Owner:MEDTRONIC INC
Method and apparatus for using atrial discrimination algorithms to determine optimal pacing therapy and therapy timing
A system and method which employs atrial discrimination algorithms to distinguish between different atrial arrhythmias occurring in a patient for selecting an optimal pacing therapy corresponding to the type of arrhythmia identified. In response to the detection of an atrial rate above the atrial tracking rate, discrimination criteria are applied to a detected atrial activity signal to distinguish between different types of supraventricular tachycardia, such as fast atrial flutter and other atrial flutter at a relatively slower rate, which may be occurring in the patient. The pacer is controlled to provide pacing therapy to a heart in a manner corresponding to the type of supraventricular tachycardia identified. The output of an atrial discrimination algorithm may be tracked and the trend thereof used to improve therapy timing. Various embodiments are disclosed herein.
Owner:CARDIAC PACEMAKERS INC
Algorithm for discrimination of 1:1 tachycardias
InactiveUS7174209B2Heart stimulatorsDiagnostic recording/measuringVentricular tachycardiaSupraventricular tachycardia
Owner:CARDIAC PACEMAKERS INC
Implementable medical equipment with ventricular tachycardia diagnosis function
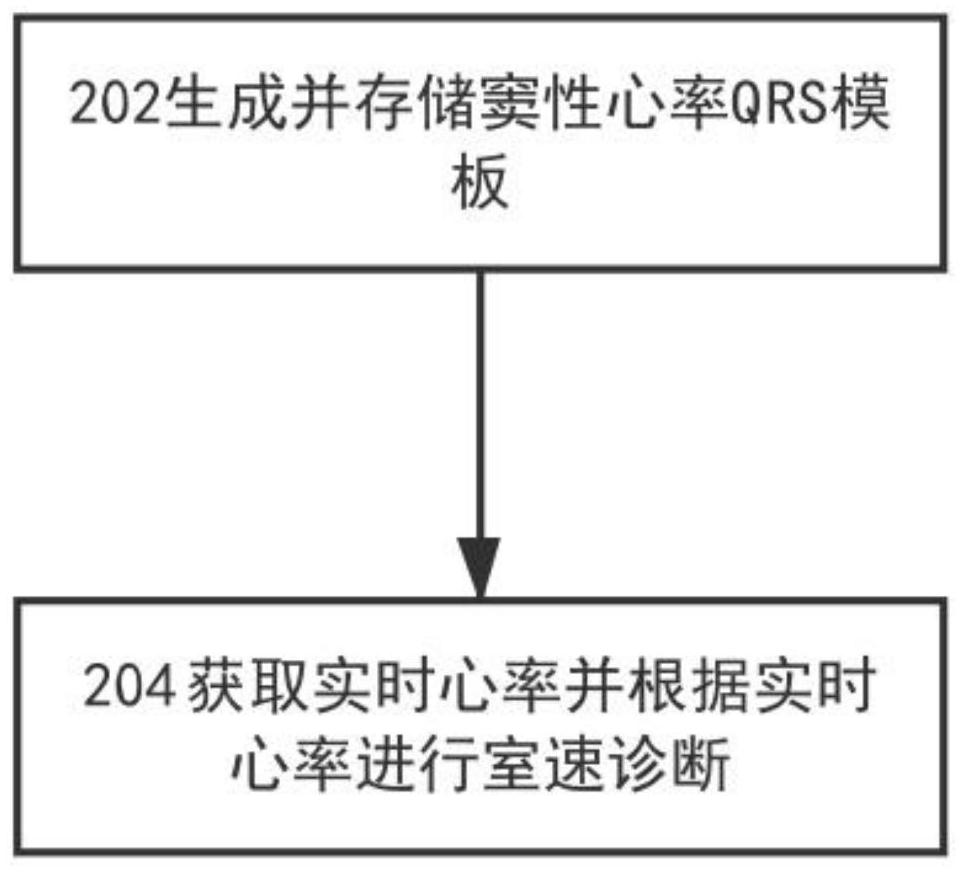
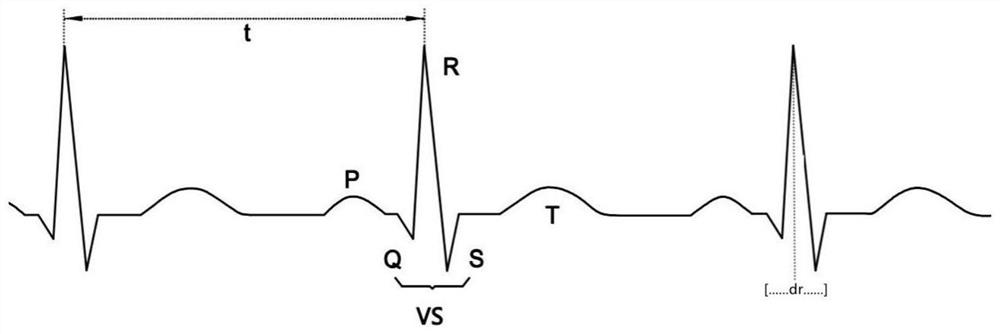
The invention relates to implementable medical equipment with a ventricular tachycardia diagnosis function. According to the implementable medical equipment with the ventricular tachycardia diagnosisfunction, ventricular tachycardia counting and template matching algorithms are combined, and heart rate suddenness judgement and multistage ventricular tachycardia counting thresholds are set; ventricular tachycardia counting is conducted if a sudden heart rate is acquired, and when a ventricular tachycardia count value reaches a sampling threshold, QRS waveform sampling is conducted; when the ventricular tachycardia count value reaches a matching threshold, sampled real-time heart rate QRS waveforms match sinus heart rate QRS waveform templates; and when the ventricular tachycardia count value reaches a diagnosis threshold, if the number of sampled QRS waveforms which cannot match QRS waveform templates reaches a ventricular tachycardia threshold, ventricular tachycardia is diagnosed. Bymeans of the scheme, supraventricular tachycardia and ventricular tachycardia can be distinguished, so that therapeutic errors are prevented.
Owner:苏州无双医疗设备有限公司
Av nodal stimulation during atrial tachyarrhythmia to prevent inappropriate therapy delivery
ActiveCN103517734AHeart stimulatorsArtificial respirationVentricular rateVentricular Tachyarrhythmias
The disclosure describes techniques for delivering electrical stimulation to decrease the ventricular rate response during an atrial tachyarrhythmia, such as atrial fibrillation. AV nodal stimulation is employed during an atrial tachyarrhythmia episode with rapid ventricular conduction to distinguish ventricular tachyarrhythmia from supraventricular tachycardia and thereby prevent delivering inappropriate therapy to a patient.
Owner:MEDTRONIC INC
Discrimination of supraventricular tachycardia and ventricular tachycardia events
InactiveUS20110034817A1Reduce in quantityElectrocardiographyHeart defibrillatorsVentricular tachycardiaNormal Sinus Rhythm
A method and system for discrimination of supraventricular tachycardia and ventricular tachycardia events. Morphological features points are extracted from normal sinus rhythm (NSR) complexes and used to generate a NSR template. A numerical convolution is performed using the NSR template and the feature points for each sensed NSR to give a NSR filter output. Using a plurality of NSR complexes, a median NSR filter output template is determined, where the median NSR filter output template has a median value for each value in the NSR filter output. The median NSR filter output template is then used during a tachycardia event to distinguish tachycardia events as either ventricular tachycardia events or supraventricular tachycardia events.
Owner:CARDIAC PACEMAKERS INC
Episode classifier algorithm
The present disclosure is directed to the classification of cardiac episodes using an algorithm. In various examples, an episode classification algorithm evaluates electrogram signal data from a near-field channel and a far-field channel. The episode classification algorithm classifies the cardiac episode based on the evaluation of the electrogram signal data for at least one of the near-field and far-field channels. In some examples, a cardiac episode being classified may be an episode that resulted in treatment being provided by an implantable medical device. Possible classifications of the cardiac episode may include, for example, unknown, inappropriate, appropriate, supraventricular tachycardia, ventricular tachycardia, ventricular fibrillation or ventricular over-sensing.
Owner:MEDTRONIC INC
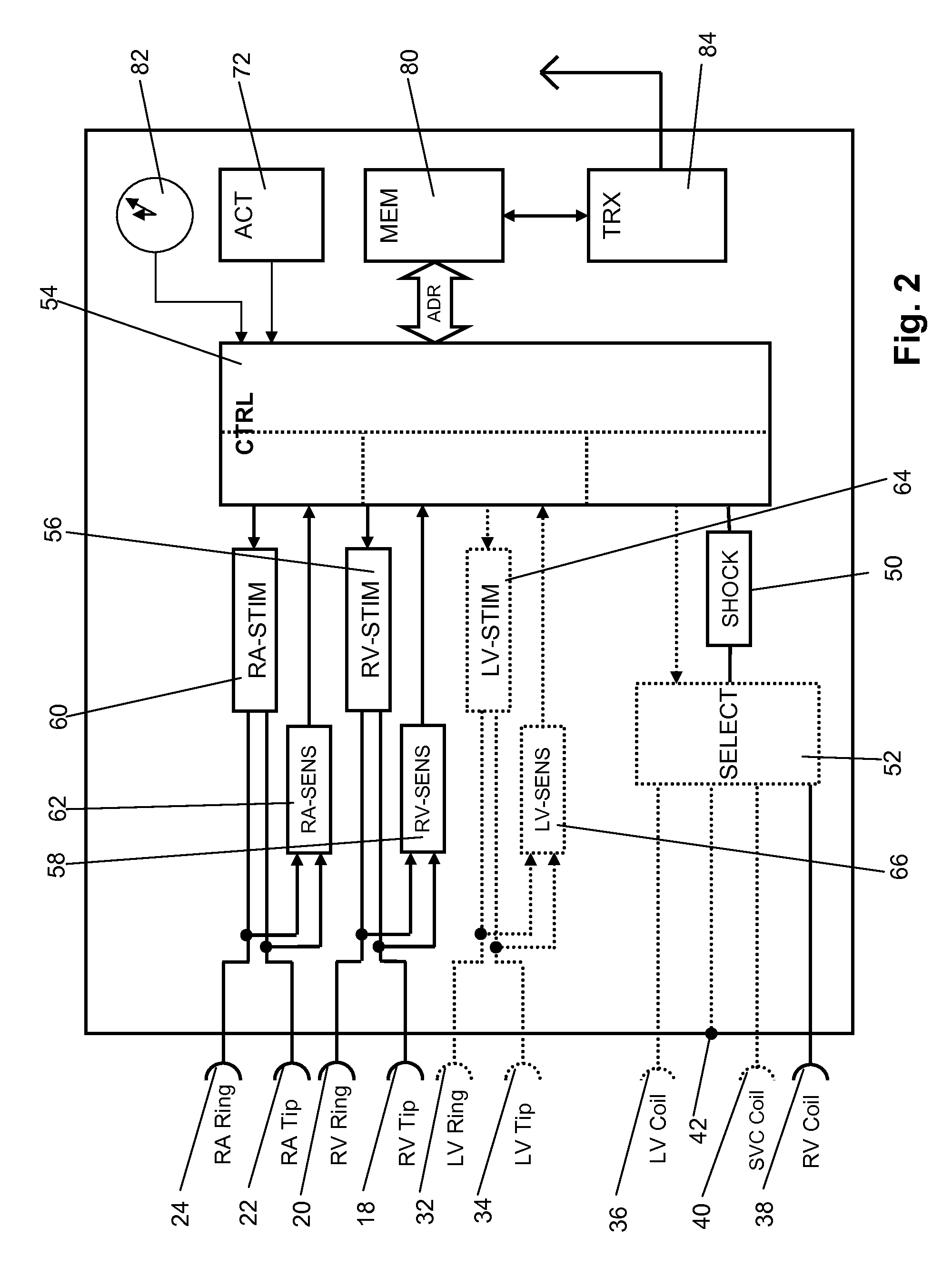
Antitachycardiac heart stimulator
An implantable cardiac stimulator includes a cardioversion / defibrillation unit connected to at least one electrode pair for generation and delivery of cardioversion or defibrillation shocks; an atrial sensing unit detecting atrial contraction, and outputting an atrial sensing signal indicating a atrial event when an atrial contraction is detected; a ventricular sensing unit detecting ventricular contraction, and outputting a ventricular sensing signal when a ventricular contraction is detected; a tachycardia detection unit connected to the atrial and ventricular sensing units and detecting a tachycardia, and classifying it as a ventricular tachycardia (VT) or as a supraventricular tachycardia (SVT); and a treatment control unit designed to trigger at least one atrial cardioversion shock when a ventricular rhythm detected by the ventricular sensing unit is faster than a programmed frequency limit, and the tachycardia detection unit classifies an SVT as an atrial fibrillation (AFib).
Owner:BIOTRONIK SE & CO KG
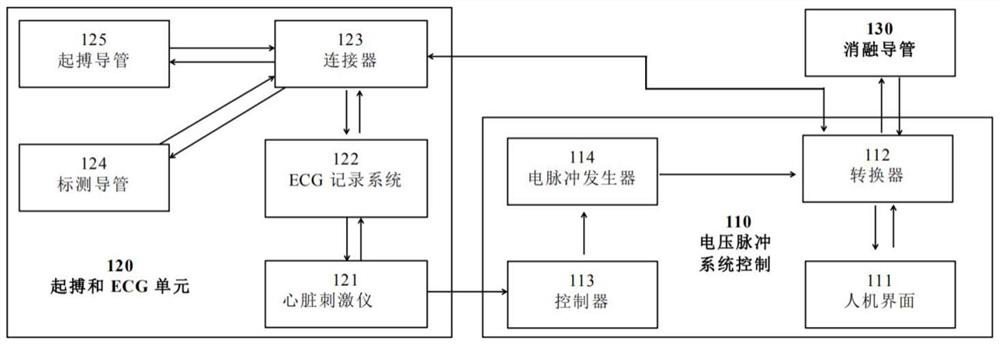
System for treating arrhythmia by adopting pulsed electric field ablation technology
PendingCN111728693AImprove ablation efficiencyEasy to fixSurgical instrument detailsVoltage pulseCardiac cycle
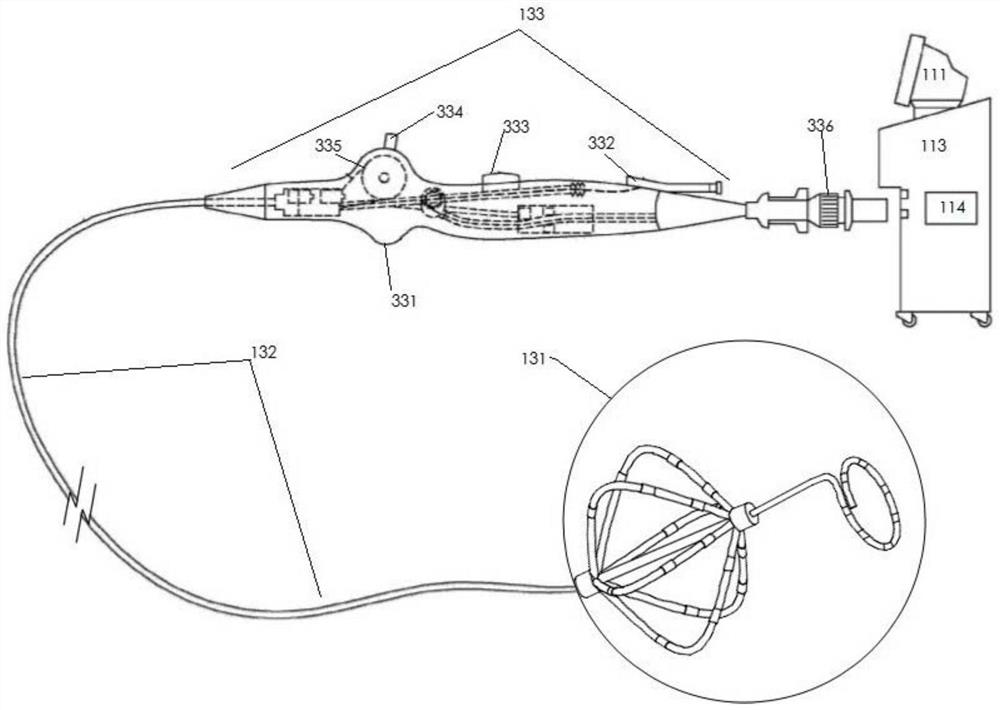
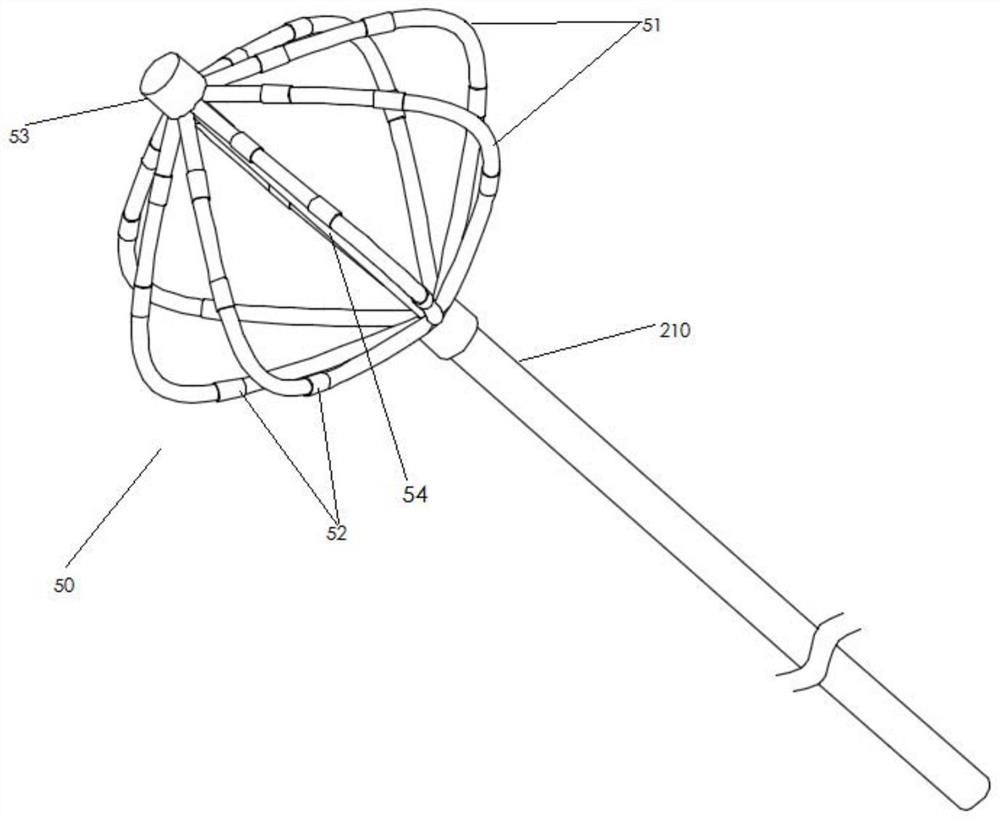
The invention provides a system for treating arrhythmia by adopting a pulsed electric field ablation technology. The system comprises a voltage pulse system console, a pace-making and ECG unit and anablation catheter. The voltage pulse system console comprises an electrical pulse generator, a controller, a human machine interface and a converter. The pace-making and ECG unit comprises an ECG recorder, a pace-making catheter, a cardiac stimulator and a mapping catheter, and pace-making electric signals are synchronously transmitted to the voltage pulse system console. The ablation catheter isconnected to the system console through the converter, delivers a voltage pulse waveform within the refractory period of the cardiac cycle based on a pacing signal, and delivers pulsed electric fieldenergy to the ablated tissue through electrodes on the ablation catheter. The ablation catheter comprises a spline basket, an annular catheter entering the pulmonary vein is further arranged at the far end of the spline basket, and large-area irreversible injuries which are locally, linearly, annularly or evenly distributed can be formed, so that the purpose of treating arrhythmia diseases such asatrial repair, supraventricular tachycardia and atrial fibrillation is achieved.
Owner:SHANGHAI OPTIPULSE BIOTECH CO LTD
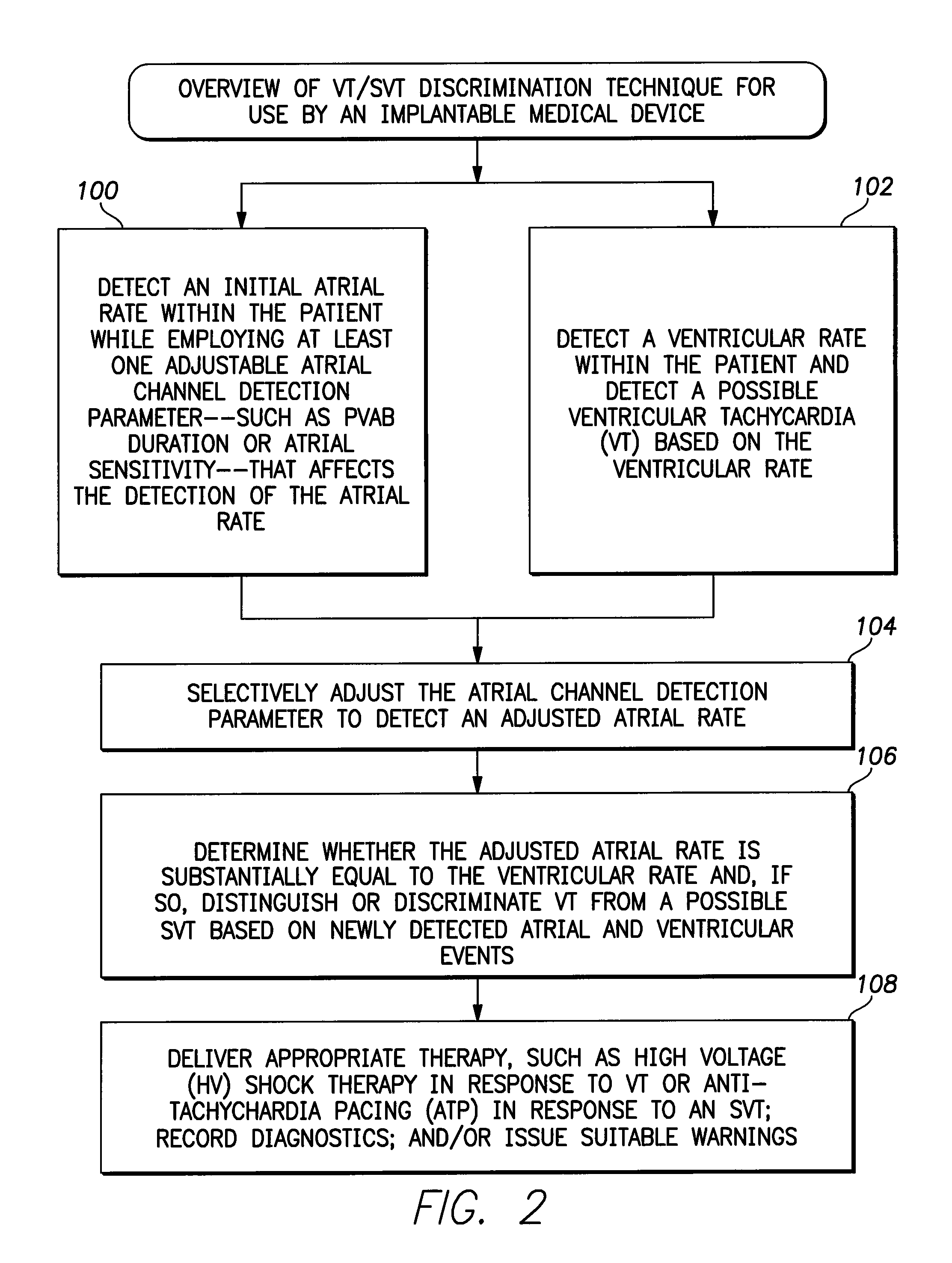
Systems and methods for use with an implantable medical device for discriminating vt and svt be selectively adjusting atrial channel sensing parameters
ActiveUS20110282405A1Increase chanceAssessment of atrioventricular (AV) association stabilityElectrocardiographyHeart defibrillatorsVentricular rateVentricular tachycardia
Techniques are described for discriminating ventricular tachycardia (VT) from supraventricular tachycardia (SVT) in circumstances when the ventricular rate exceeds the atrial rate (i.e. V>A). In one example, an initial atrial rate is detected while employing adjustable atrial channel detection parameters that can affect the detection of the true atrial rate—such as a post-ventricular atrial blanking (PVAB) interval or an atrial channel sensitivity level. If the ventricular rate exceeds a VT rate zone threshold with V>A, the device does not immediately deliver high voltage shock therapy as done in other devices. Rather, the device instead selectively adjusts the atrial channel detection parameter(s) to determine if the true atrial rate is equal to the ventricular rate. If so, then such is an indication that the arrhythmia might be SVT rather than VT and various discrimination procedures are employed to distinguish SVT from VT before therapy is delivered.
Owner:PACESETTER INC
Antitachycardiac stimulator
ActiveUS20090264947A1Prevent inadequate shock therapyExtend detection timeHeart defibrillatorsInternal electrodesNodal rhythmSupraventricular tachycardia
Implantable cardiac stimulator, with chamber stimulation unit connectable to left / right ventricular stimulation electrode to generate / deliver chamber stimulation pulses for stimulation of ventricle; ventricular sensing unit (VSU) to detect respective chamber contraction and deliver ventricular sensing signal when chamber contraction detected; optional atrial stimulation unit, connectable to atrial stimulation electrode to generate atrial stimulation pulses to stimulate atrium; atrial sensing unit, to detect atrial contraction, deliver atrial sensing signal indicating respective atrial event; tachycardia detection unit, connected to VSU to detect and categorize ventricular / supraventricular tachycardia; treatment control unit (TCU), triggers chamber stimulation unit to deliver antitachycardiac stimulation (ATP); analyzer unit, connected to atrial sensing unit and TCU. Analyzes atrial events from sensing unit before / during / after delivering antitachycardiac stimulation for atrial rhythm pattern during ventricular ATP by comparison atrial rhythm pattern immediately before ATP and to trigger TCU as function of ATP response signal representing comparison result for selection of the following antitachycardiac treatment.
Owner:BIOTRONIK SE & CO KG
Vascular radio-frequency ablation electrode catheter provided with claw-shaped catheter branches
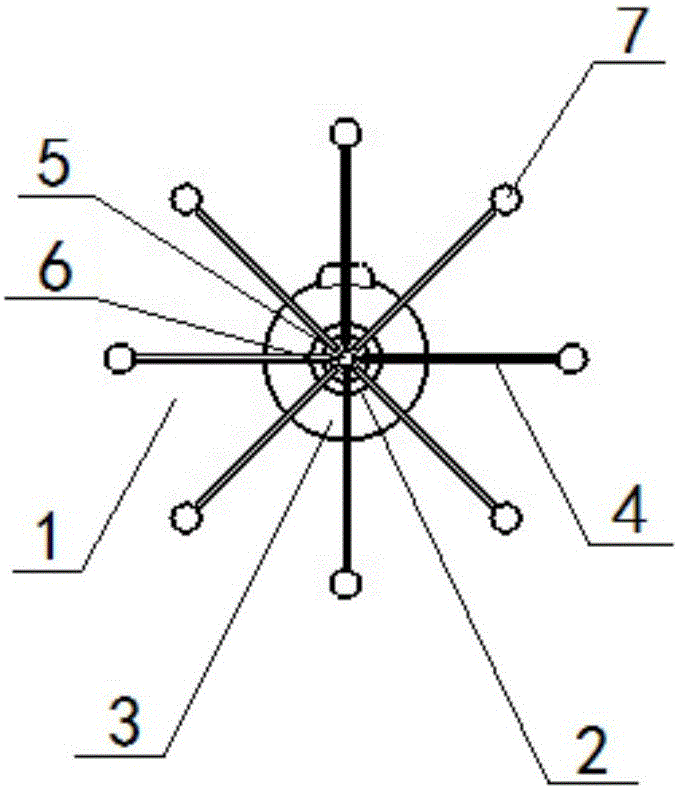
The invention relates to the technical field of medical apparatuses, and in particular to a vascular radio-frequency ablation electrode catheter provided with claw-shaped catheter branches; a radio-frequency ablation working section is arranged on the front section of the vascular radio-frequency ablation electrode catheter , a catheter body section is arranged on the middle section of the vascular radio-frequency ablation electrode catheter and a control handle section is arranged on the rear section of the vascular radio-frequency ablation electrode catheter; the eight radio-frequency catheter branches extend from a peripheral direction of the radio-frequency ablation working section; the eight radio-frequency catheter branches are integrally represented as claw-shaped structures; and at least one ablation electrode is connected to the head end of each radio-frequency catheter branch. The vascular radio-frequency ablation electrode catheter provided by the invention has the beneficial effects that in practical clinical treatment, the vascular radio-frequency ablation electrode catheter provided with the claw-shaped catheter branches provided by the invention can be applied to various blood vessels differing in diameter and can be used for conducting radio-frequency ablation therapy on cardiac muscle tissues in a complex part, such as for vascular ablation of such diseases as paroxysmal atrial tachycardia, supraventricular tachycardia, atrial flutter, atrial fibrillation, resistant hypertension and the like.
Owner:汤敬东 +2
Antitachycardiac stimulator
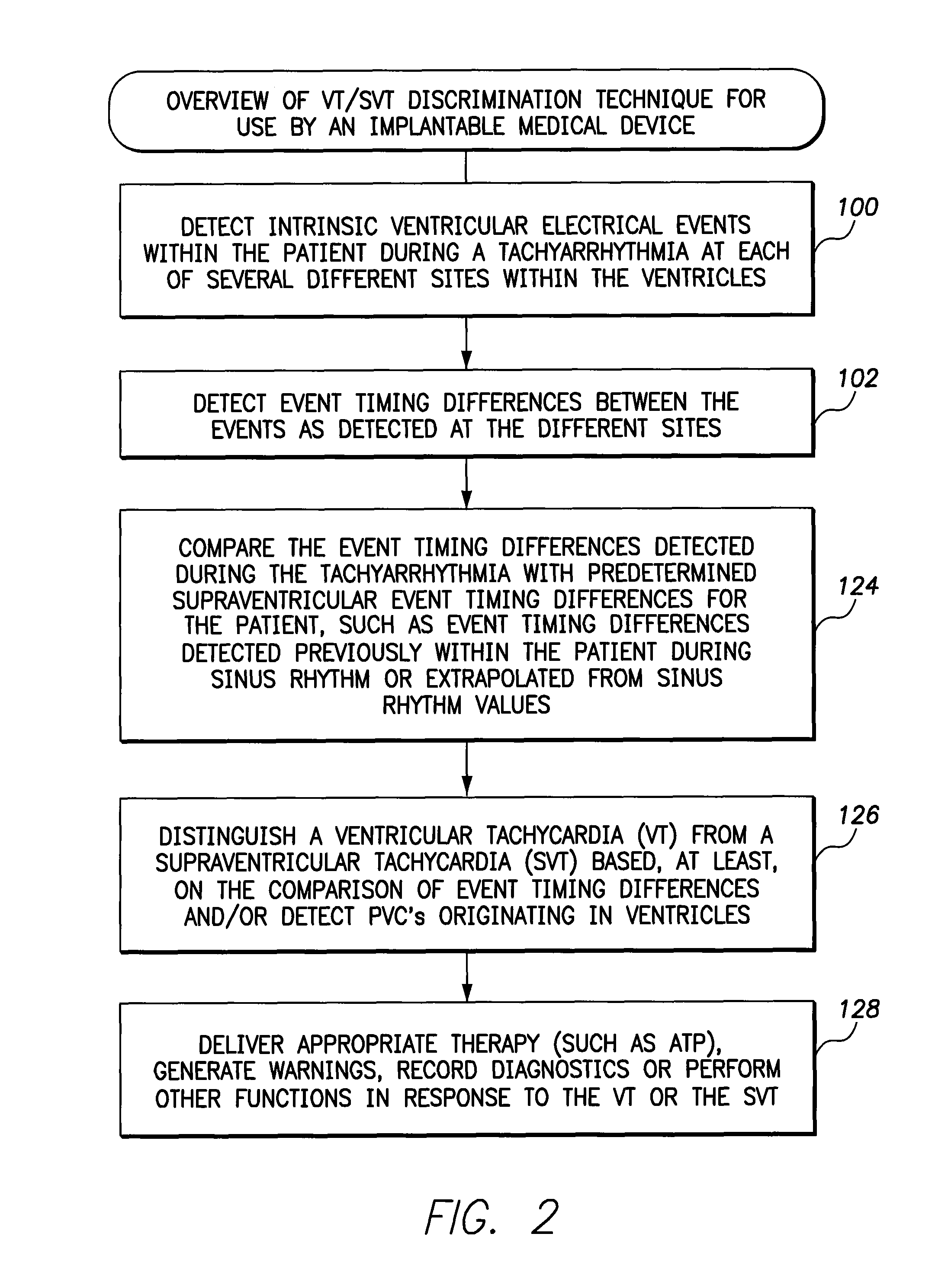
InactiveUS7983752B2Extend detection timeStrong specificityHeart stimulatorsNodal rhythmSupraventricular tachycardia
Implantable cardiac stimulator, with chamber stimulation unit connectable to left / right ventricular stimulation electrode to generate / deliver chamber stimulation pulses for stimulation of ventricle; ventricular sensing unit (VSU) to detect respective chamber contraction and deliver ventricular sensing signal when chamber contraction detected; optional atrial stimulation unit, connectable to atrial stimulation electrode to generate atrial stimulation pulses to stimulate atrium; atrial sensing unit, to detect atrial contraction, deliver atrial sensing signal indicating respective atrial event; tachycardia detection unit, connected to VSU to detect and categorize ventricular / supraventricular tachycardia; treatment control unit (TCU), triggers chamber stimulation unit to deliver antitachycardiac stimulation (ATP); analyzer unit, connected to atrial sensing unit and TCU. Analyzes atrial events from sensing unit before / during / after delivering antitachycardiac stimulation for atrial rhythm pattern during ventricular ATP by comparison atrial rhythm pattern immediately before ATP and to trigger TCU as function of ATP response signal representing comparison result for selection of the following antitachycardiac treatment.
Owner:BIOTRONIK SE & CO KG
Systems and methods for use with an implantable medical device for discriminating VT and SVT based on ventricular depolarization event timing
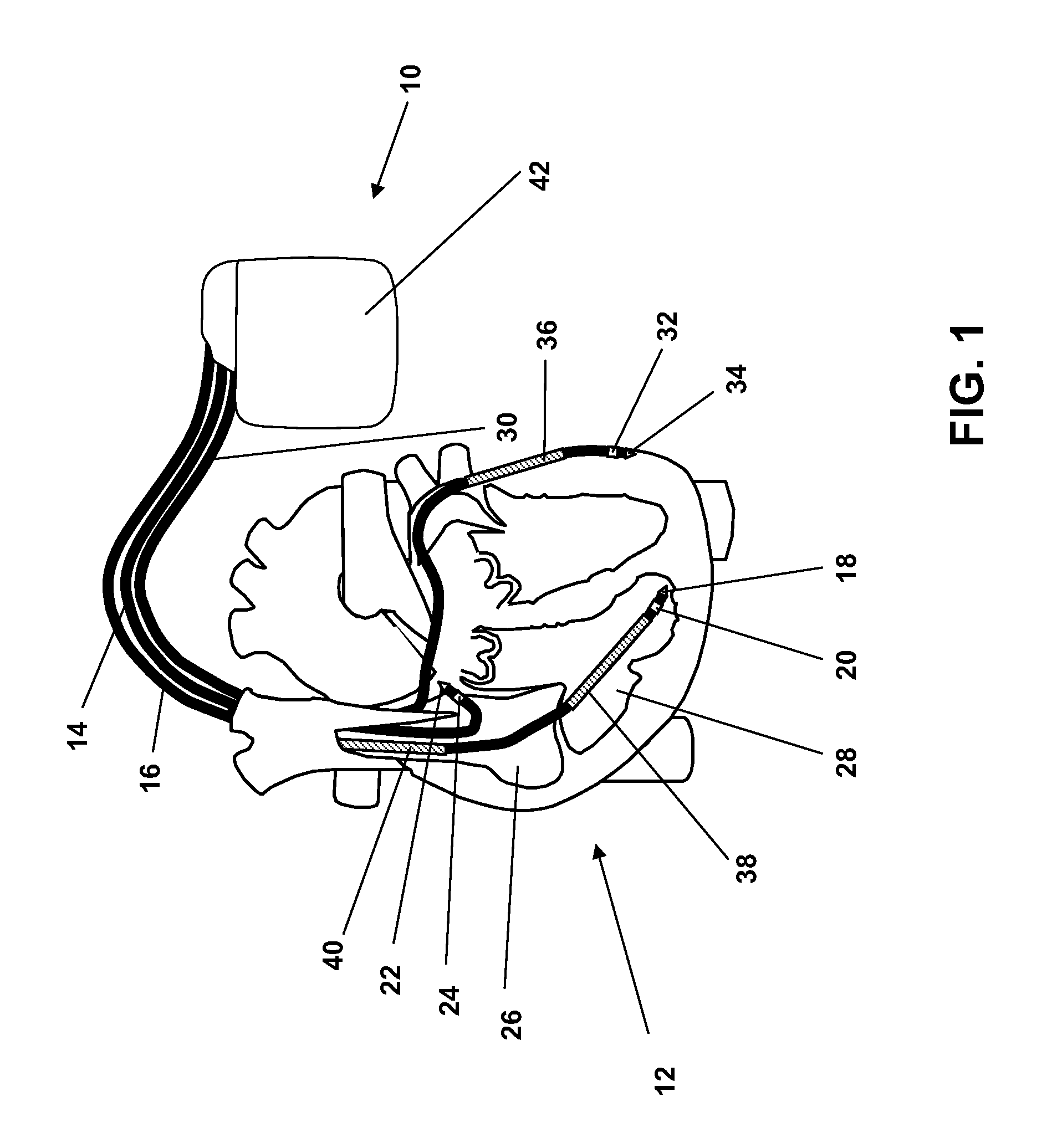
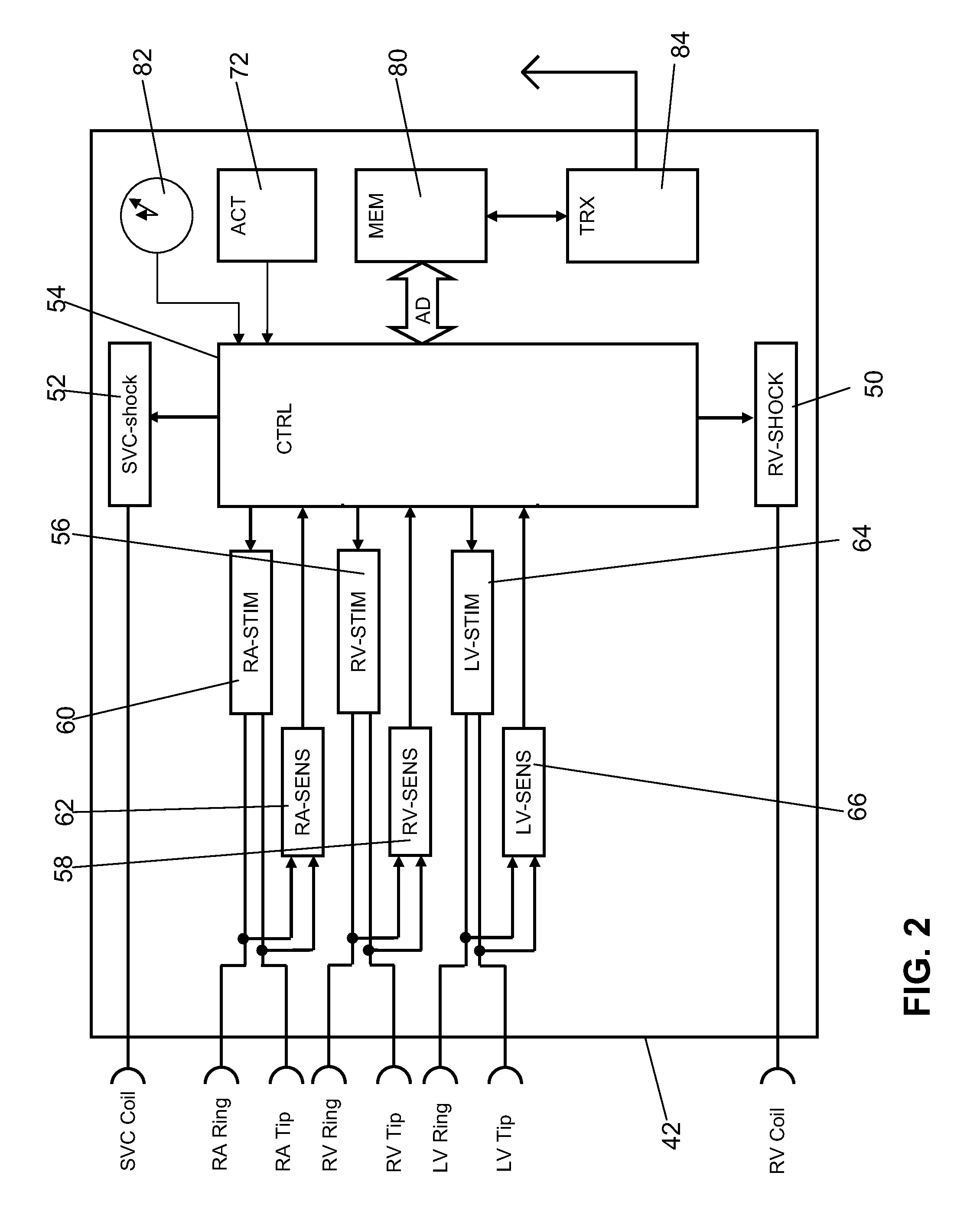
ActiveUS8165675B2Efficiently and reliably distinguishedElectrotherapyElectrocardiographyMulti siteWaveform analysis
Techniques are described for discriminating ventricular tachycardia (VT) from supraventricular tachycardia (SVT) using an implantable medical device capable of multi-site ventricular sensing. In one example, ventricular depolarization events are detected within a patient by the implantable device during a tachyarrhythmia, at both a left ventricular sensing site and a right ventricular sensing site. Ventricular event timing differences are then ascertained. The device compares the ventricular event timing differences detected during the tachyarrhythmia with predetermined supraventricular event timing differences for the patient, such as event timing differences previously detected within the patient during sinus rhythm or extrapolated from sinus rhythm values. The device then distinguishes VT from SVT based on the comparison of the event timing differences detected during the tachyarrhythmia with the predetermined supraventricular event timing differences. Morphological waveform analysis can also be performed, when needed, to further distinguish VT from SVT.
Owner:PACESETTER INC
Traditional Chinese medicine for treating tachyarrhythmia
ActiveCN111298019AGood clinical efficacyImprove securityAnthropod material medical ingredientsInanimate material medical ingredientsDiseaseRadix Ophiopogonis
The invention relates to a traditional Chinese medicine composition for treating tachyarrhythmia. The traditional Chinese medicine composition contains the following traditional Chinese medicines in parts by weight: 18-22 parts of radix pseudostellariae, 14-16 parts of radix astragali, 9-11 parts of radix ophiopogonis, 9-11 parts of fructus schisandrae chinensis, 14-16 parts of parched wild jujubeseeds, 9-11 parts of rhizoma polygonati, 9-11 parts of radix glycyrrhizae preparata, 9-11 parts of bombyx batryticatus, 14-16 parts of herba taxilli, 9-11 parts of gynostemma pentaphylla, 14-16 partsof radix sophorae flavescentis, 9-11 parts of rhizoma coptidis, 9-11 parts of radix salviae miltiorrhizae, 9-11 parts of fructus corni, 28-32 parts of ossa draconis and 28-32 parts of concha ostreae.The traditional Chinese medicine composition is capable of treating multiple tachyarrhythmia diseases such as ventricular, supraventricular and atrial premature beats caused due to deficiency of bothvital energy and yin and lack of heart and spirit nourishment as well as nodal tachycardia, supraventricular tachycardia and the like.
Owner:河北省中医药科学院
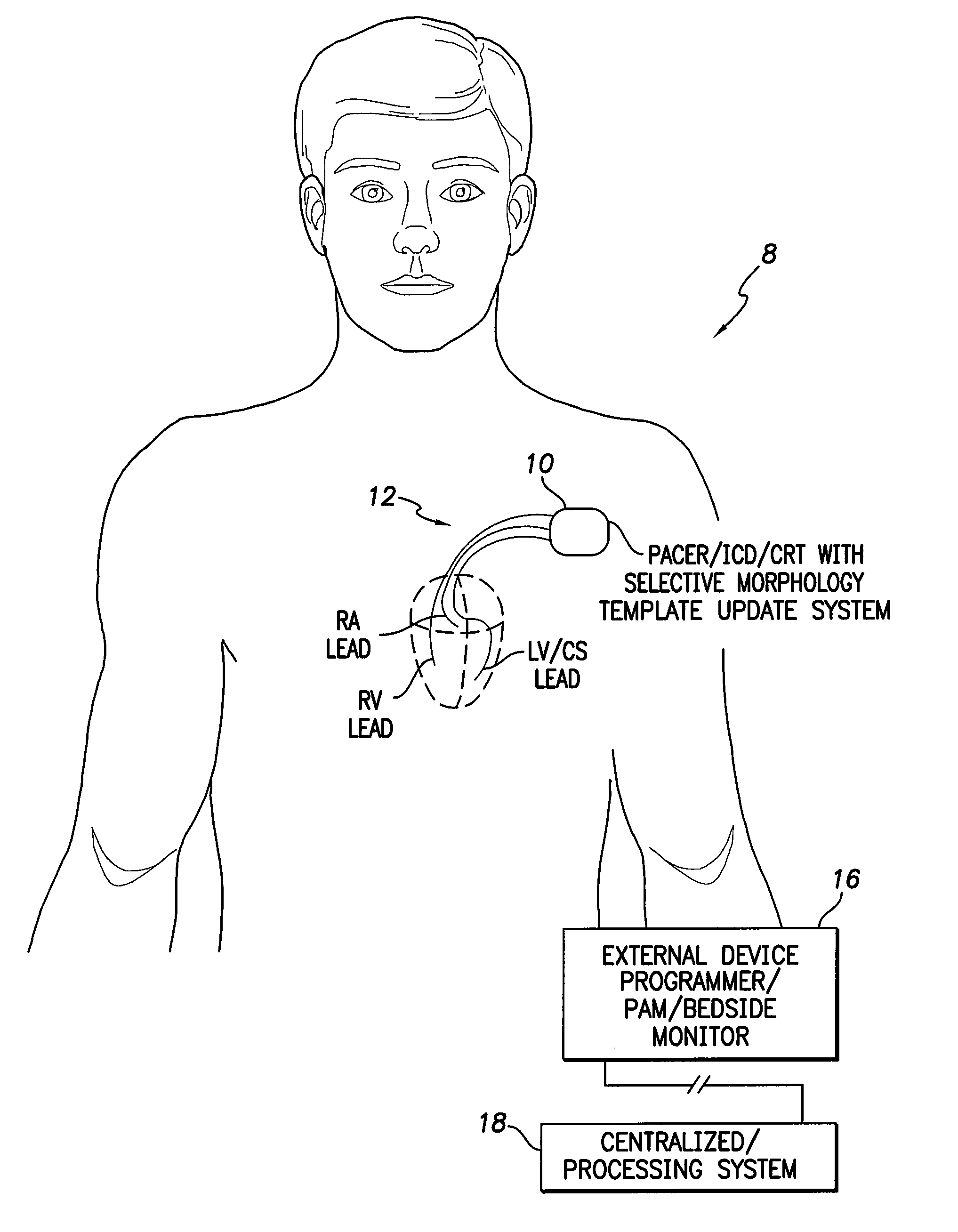
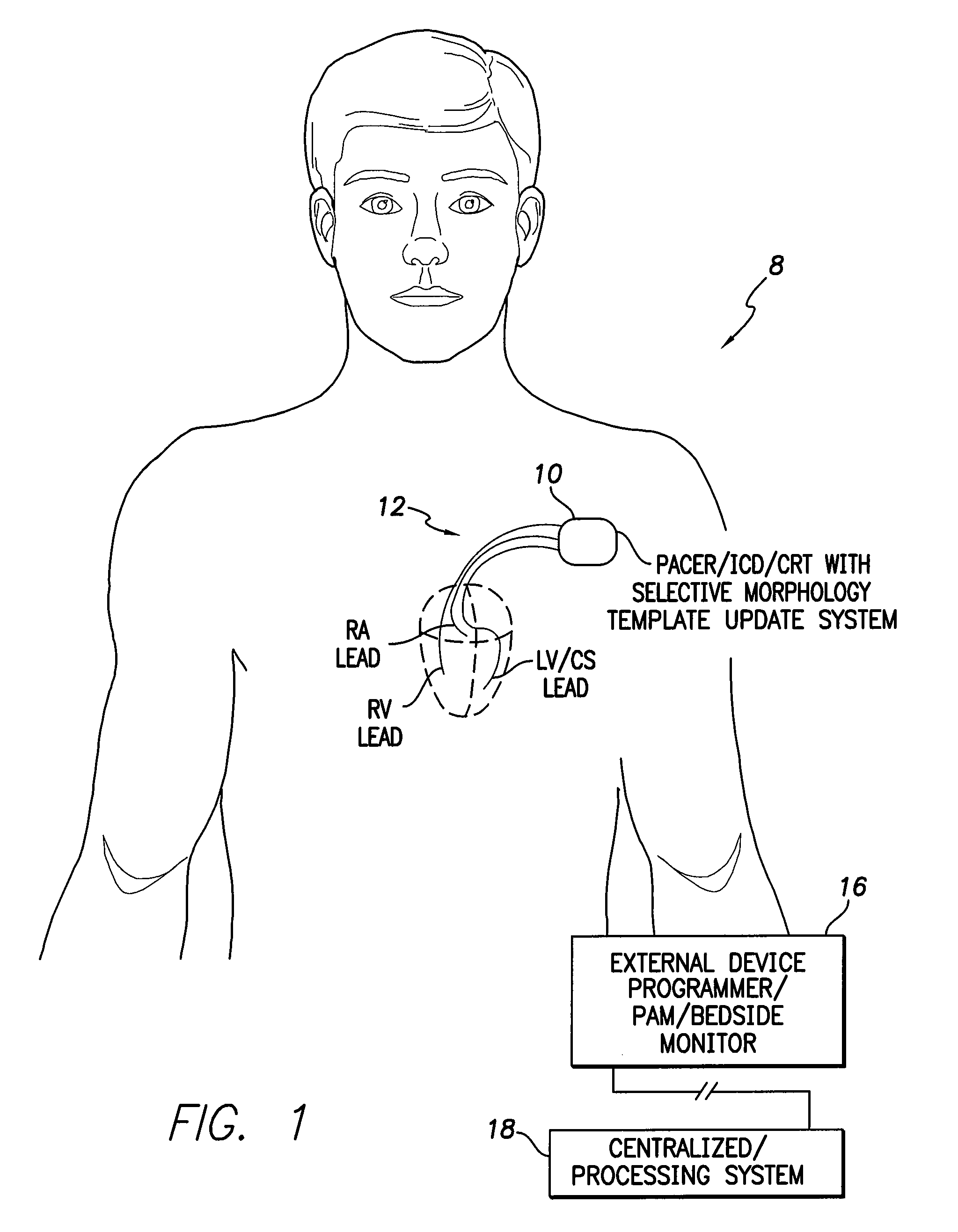
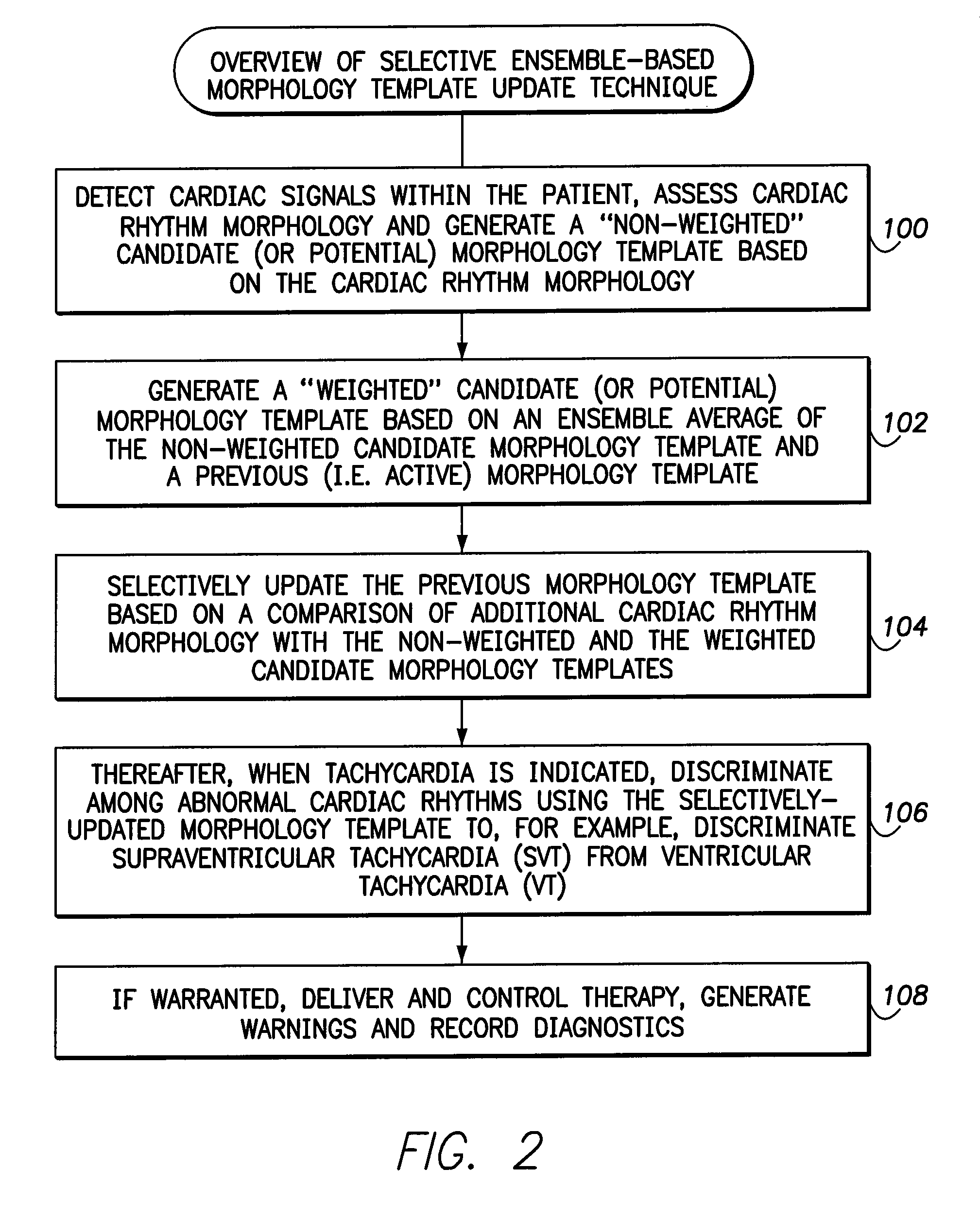
Systems and methods for selectively updating cardiac morphology discrimination templates for use with implantable medical devices
ActiveUS9220434B2Reliably obtainedAppropriate deliveryElectrocardiographyHeart defibrillatorsVentricular tachycardiaTemplate based
Techniques are provided for updating a morphology template used to discriminate abnormal cardiac rhythms. In one example, a non-weighted candidate morphology template is generated based on far-field R-wave morphology. A weighted candidate morphology template is generated based on an ensemble average of the non-weighted candidate morphology template and a previous (i.e. active) morphology template. The previous morphology template is then selectively updated based on a comparison of additional R-waves against both the non-weighted and the weighted candidate templates. Thereafter, abnormal cardiac rhythms such as ventricular tachycardia and supraventricular tachycardia are discriminated using the updated morphology template based on newly-detected far-field R-waves. These techniques provide a method for updating the morphology discrimination template in response to long-term changes in morphology due to cardiac remodeling or cardiac disease progression.
Owner:PACESETTER INC
Systems and methods for use with an implantable medical device for discriminating vt and svt based on ventricular depolarization event timing
ActiveUS20110106194A1Efficiently and reliably distinguishedElectrocardiographyInertial sensorsMulti siteWaveform analysis
Techniques are described for discriminating ventricular tachycardia (VT) from supraventricular tachycardia (SVT) using an implantable medical device capable of multi-site ventricular sensing. In one example, ventricular depolarization events are detected within a patient by the implantable device during a tachyarrhythmia, at both a left ventricular sensing site and a right ventricular sensing site. Ventricular event timing differences are then ascertained. The device compares the ventricular event timing differences detected during the tachyarrhythmia with predetermined supraventricular event timing differences for the patient, such as event timing differences previously detected within the patient during sinus rhythm or extrapolated from sinus rhythm values. The device then distinguishes VT from SVT based on the comparison of the event timing differences detected during the tachyarrhythmia with the predetermined supraventricular event timing differences. Morphological waveform analysis can also be performed, when needed, to further distinguish VT from SVT.
Owner:PACESETTER INC
Systems and methods for use with an implantable medical device for discriminating VT and SVT be selectively adjusting atrial channel sensing parameters
ActiveUS8271081B2Increase chanceAssessment of atrioventricular (AV) association stabilityElectrocardiographyCatheterVentricular rateVentricular tachycardia
Techniques are described for discriminating ventricular tachycardia (VT) from supraventricular tachycardia (SVT) in circumstances when the ventricular rate exceeds the atrial rate (i.e. V>A). In one example, an initial atrial rate is detected while employing adjustable atrial channel detection parameters that can affect the detection of the true atrial rate—such as a post-ventricular atrial blanking (PVAB) interval or an atrial channel sensitivity level. If the ventricular rate exceeds a VT rate zone threshold with V>A, the device does not immediately deliver high voltage shock therapy as done in other devices. Rather, the device instead selectively adjusts the atrial channel detection parameter(s) to determine if the true atrial rate is equal to the ventricular rate. If so, then such is an indication that the arrhythmia might be SVT rather than VT and various discrimination procedures are employed to distinguish SVT from VT before therapy is delivered.
Owner:PACESETTER INC
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com