Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
145 results about "Arrhythmia detection" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
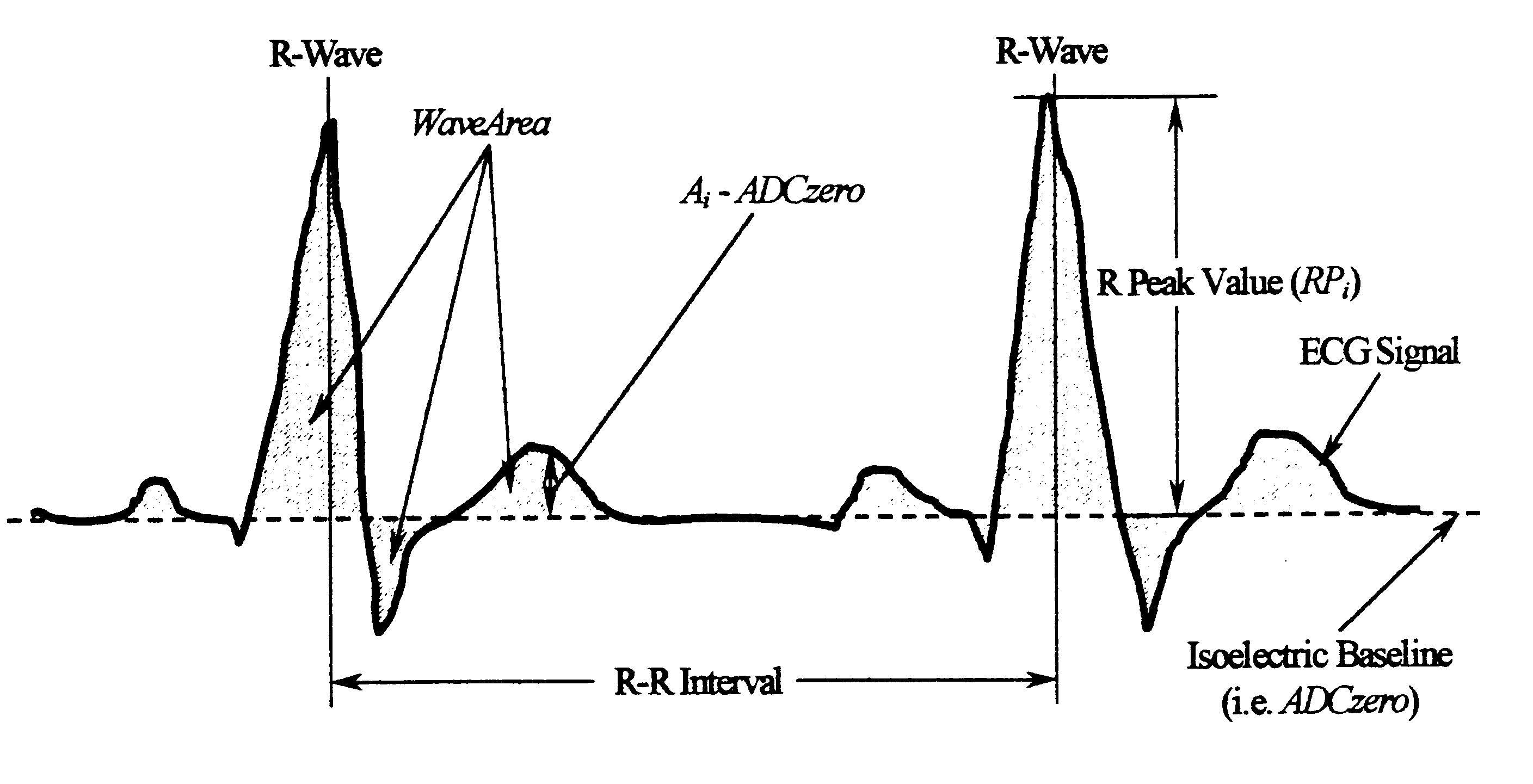
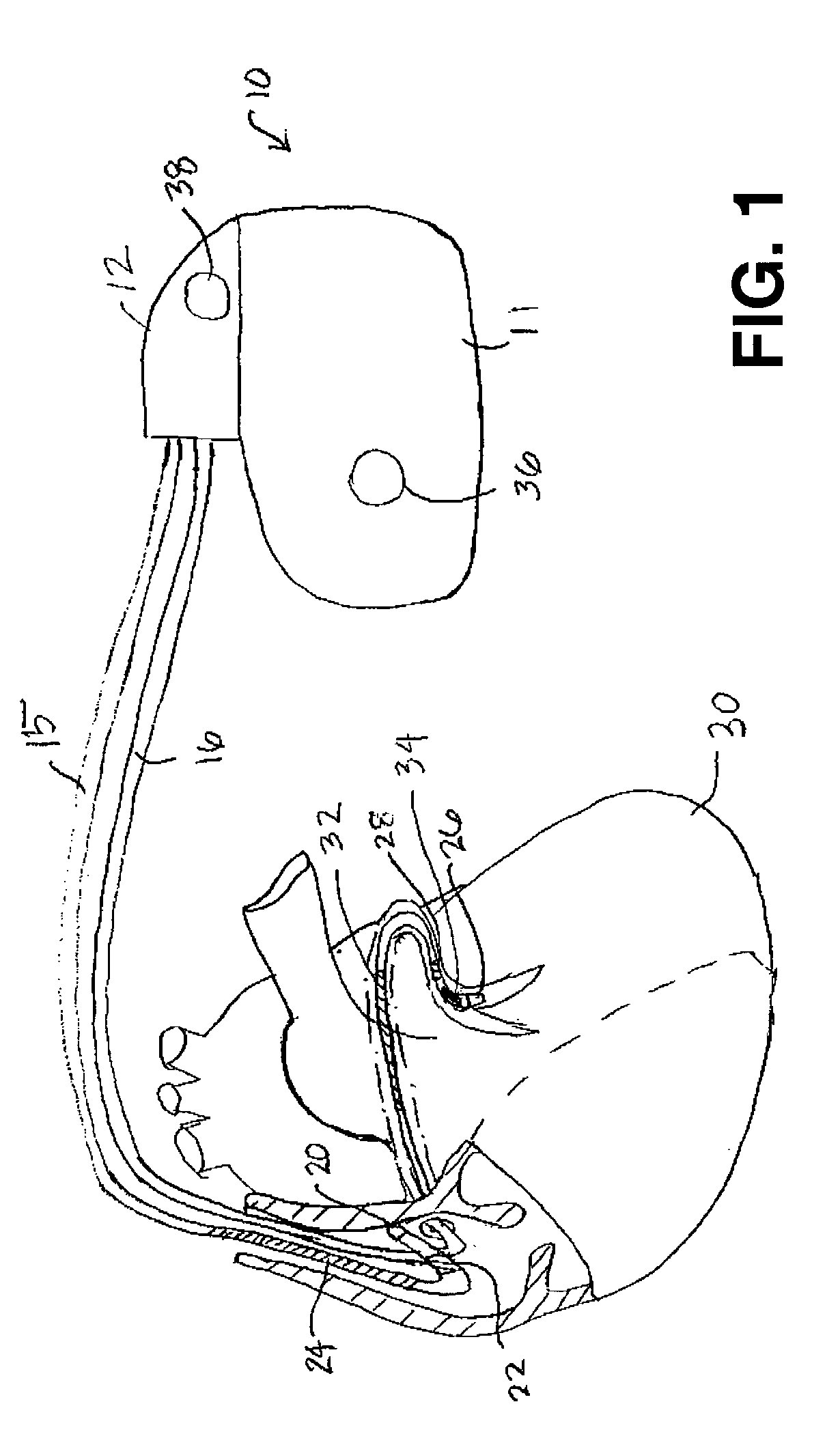
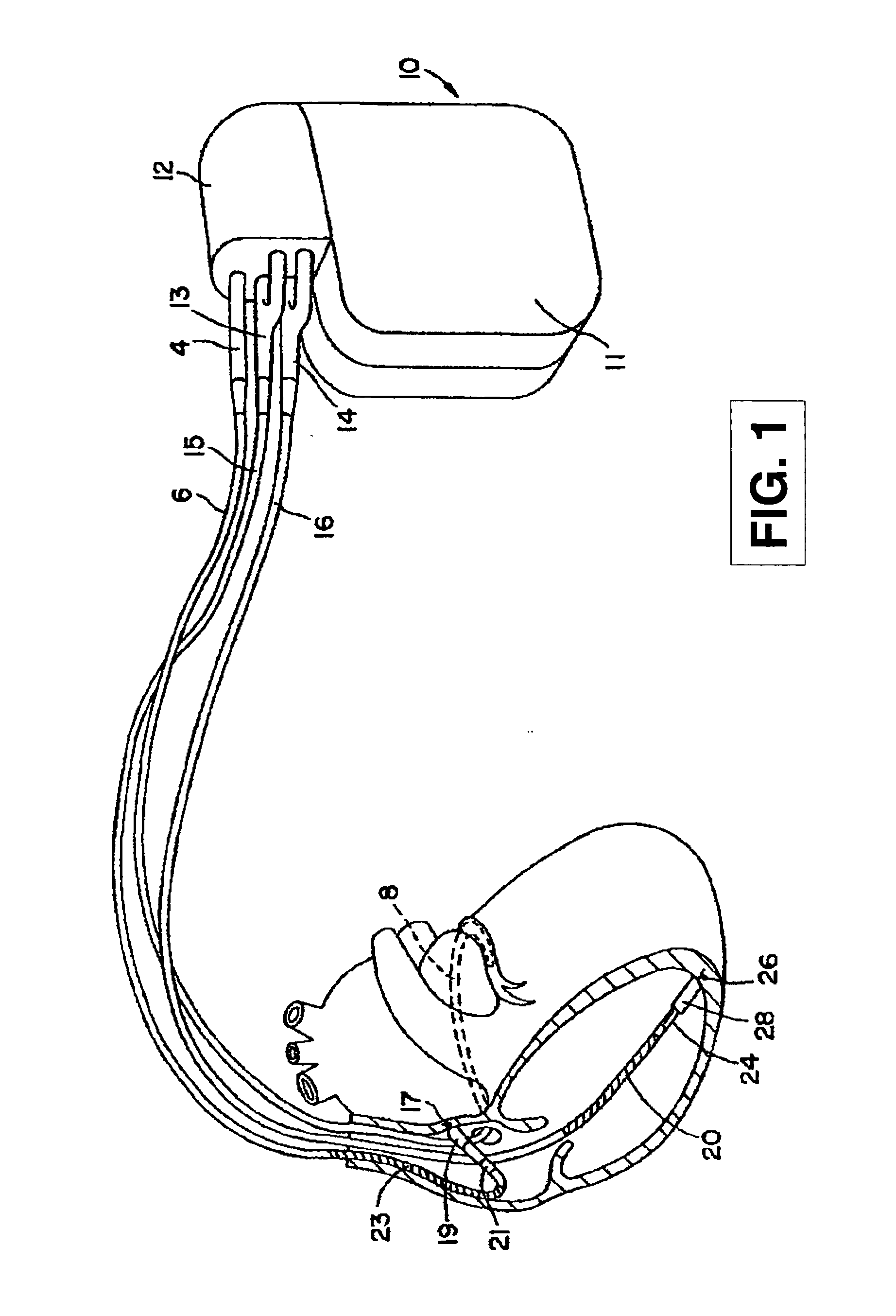
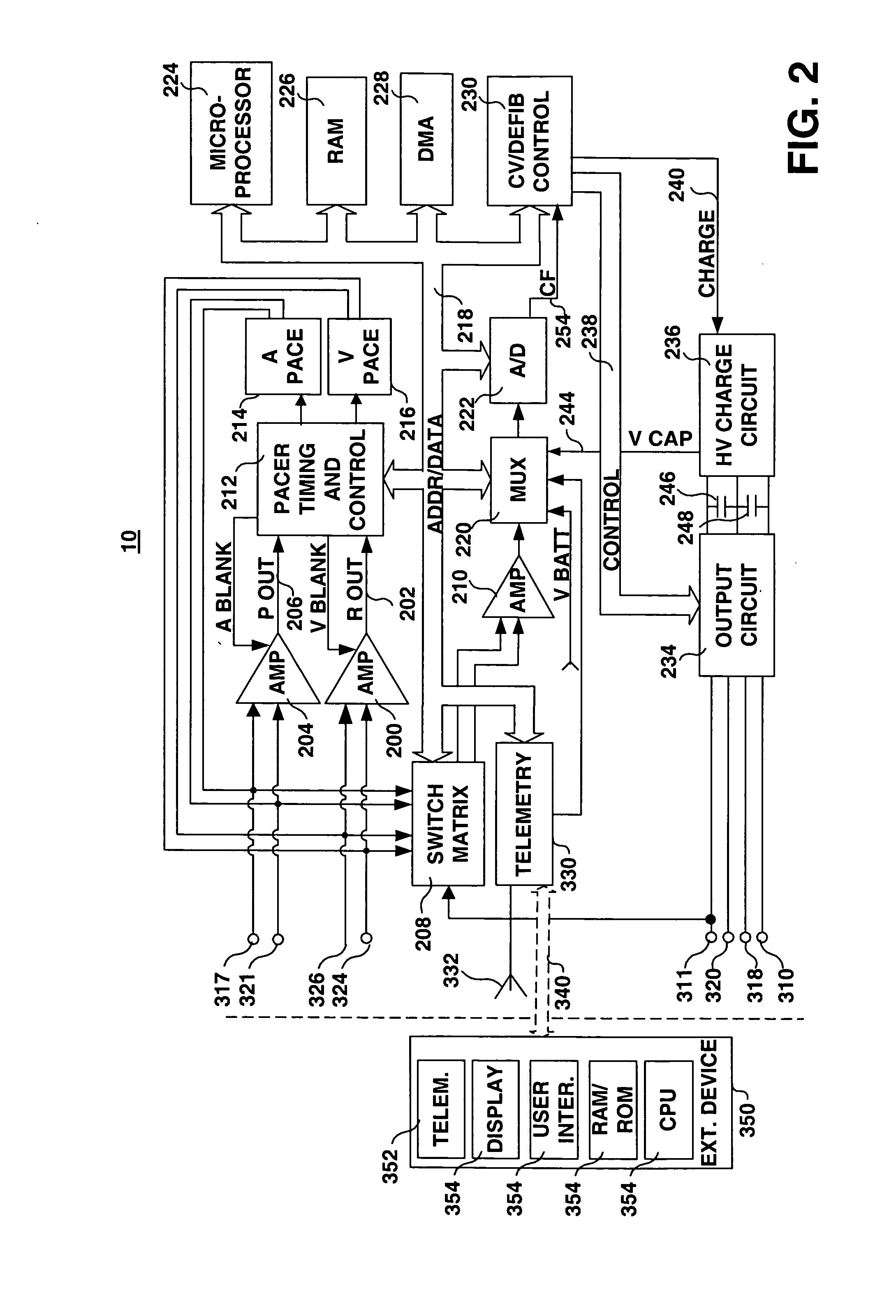
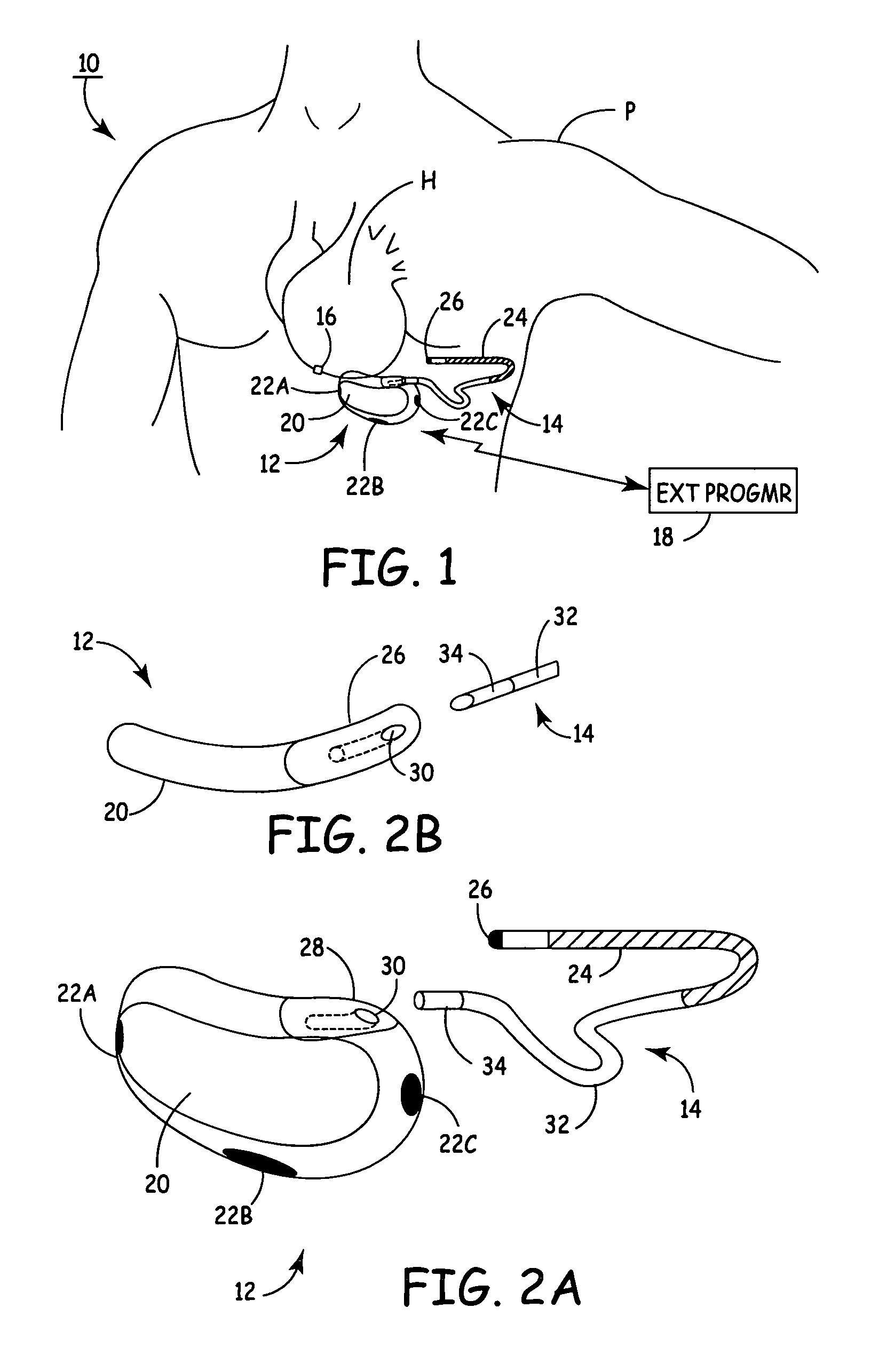
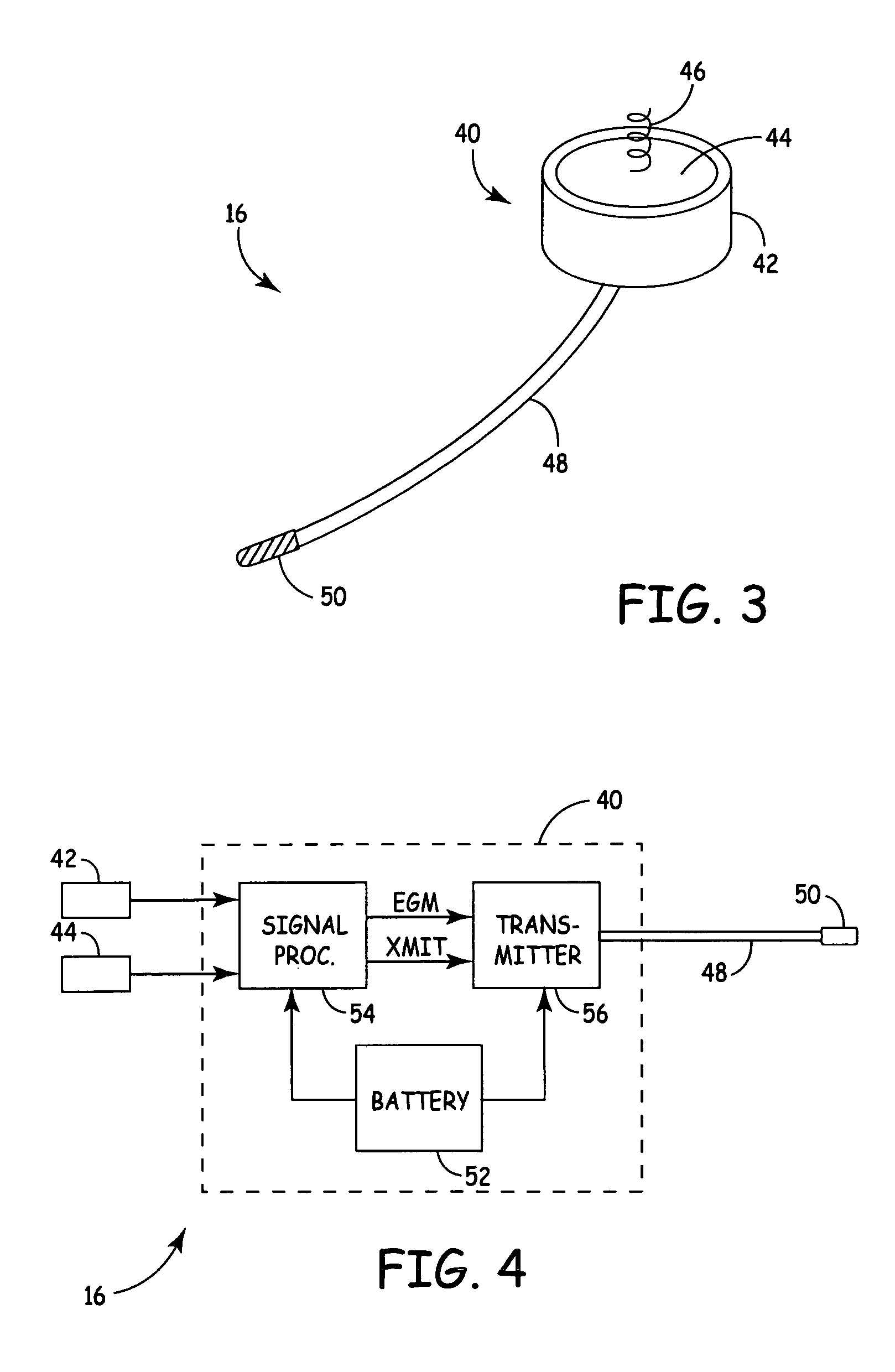
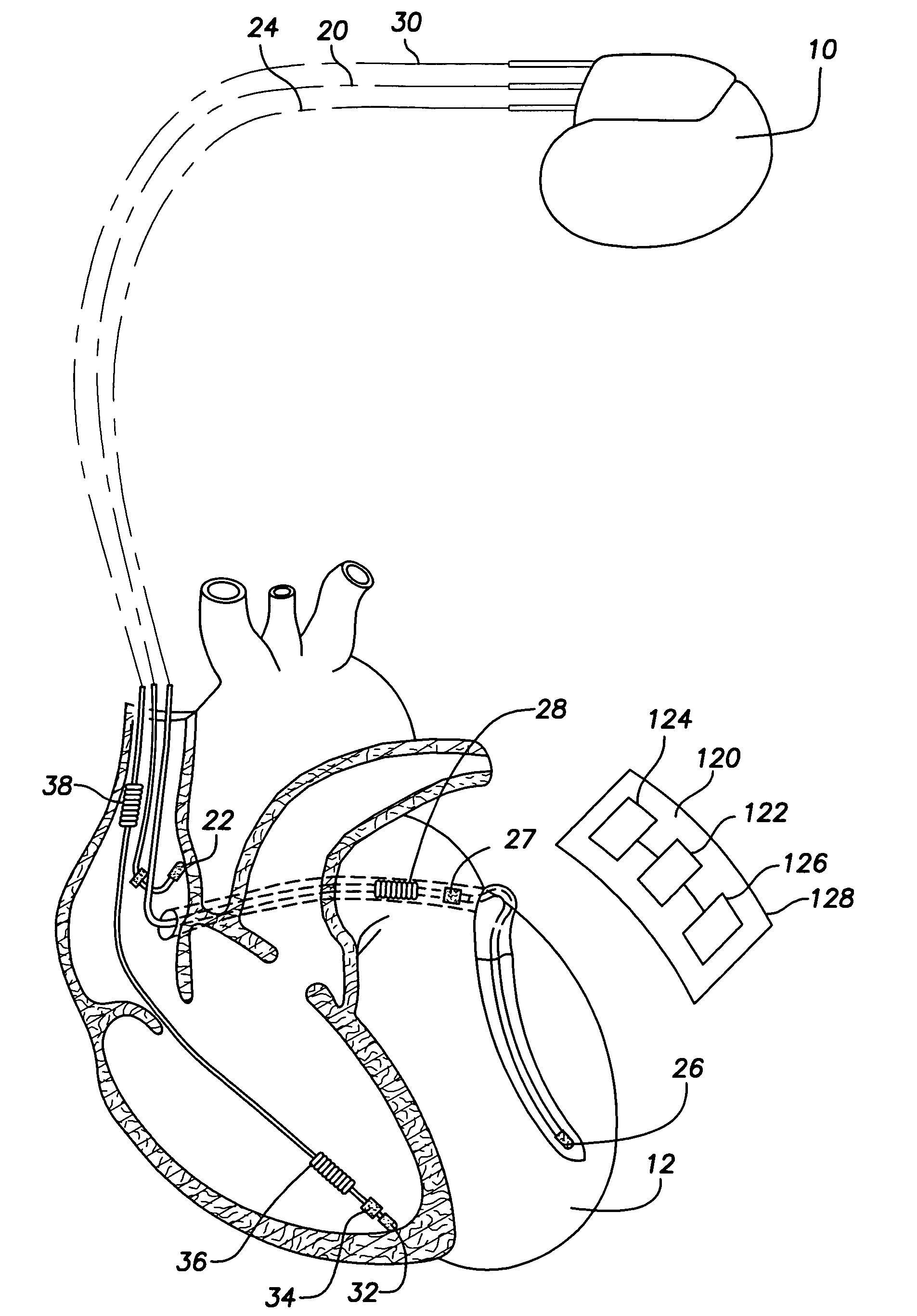
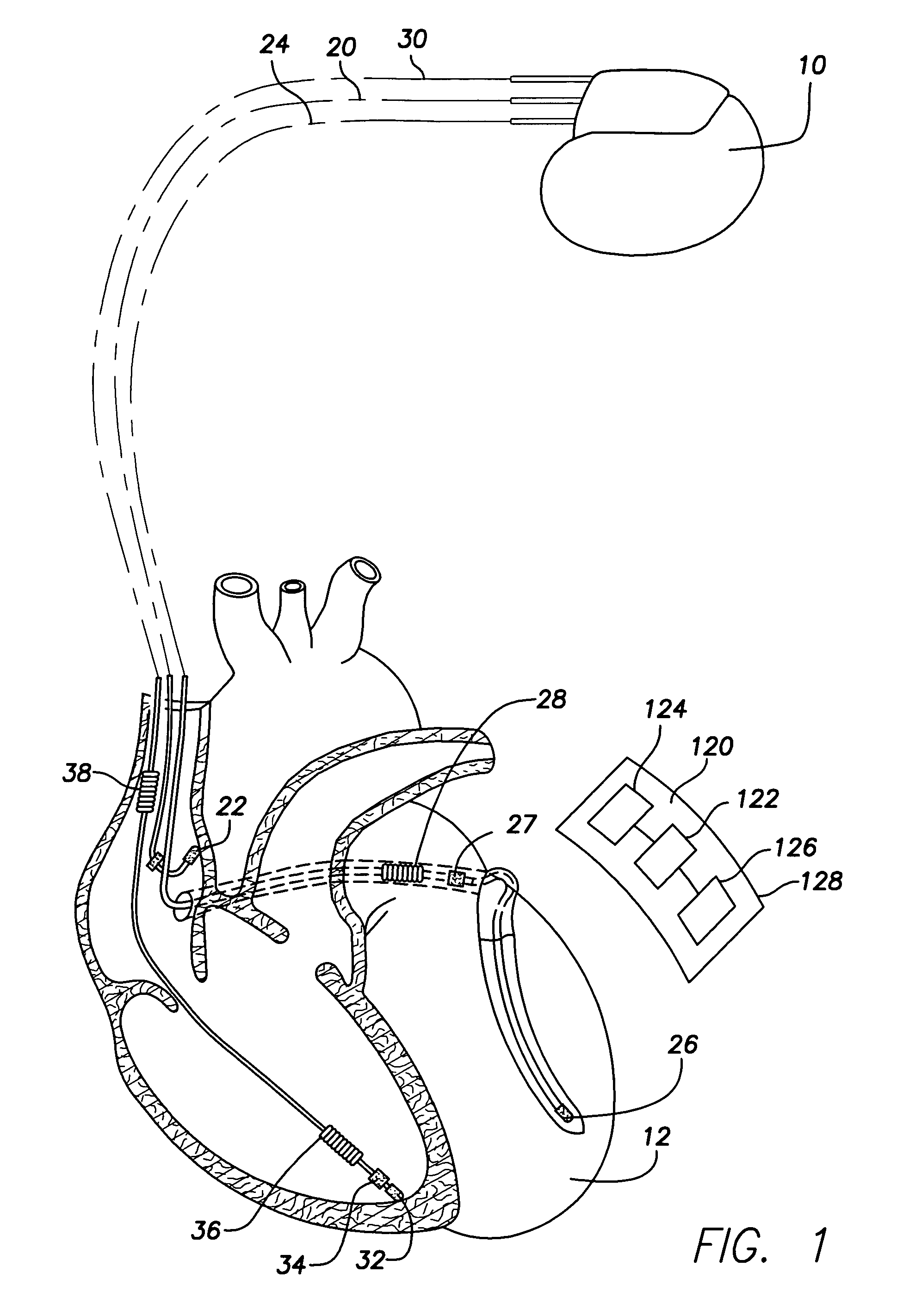
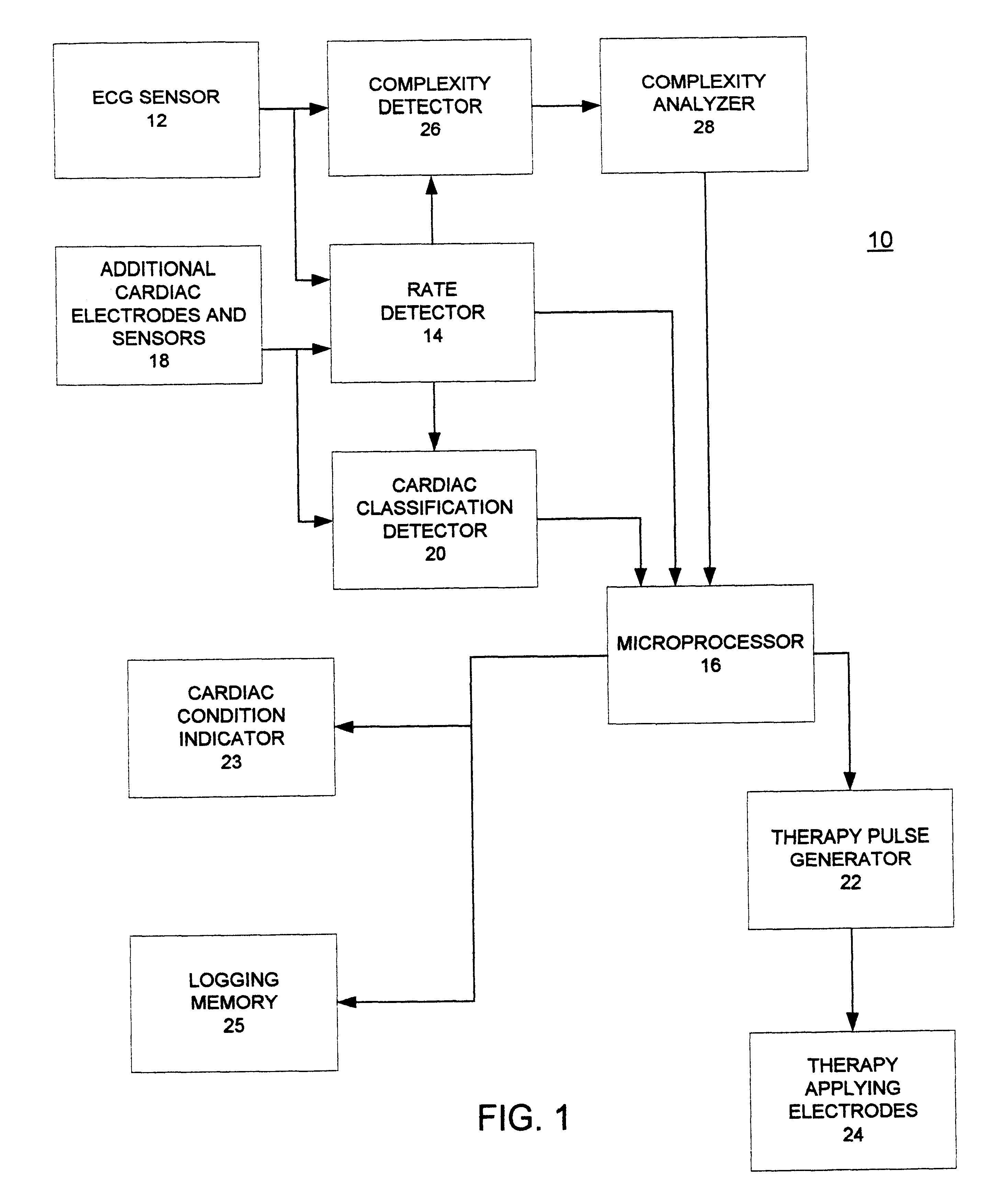
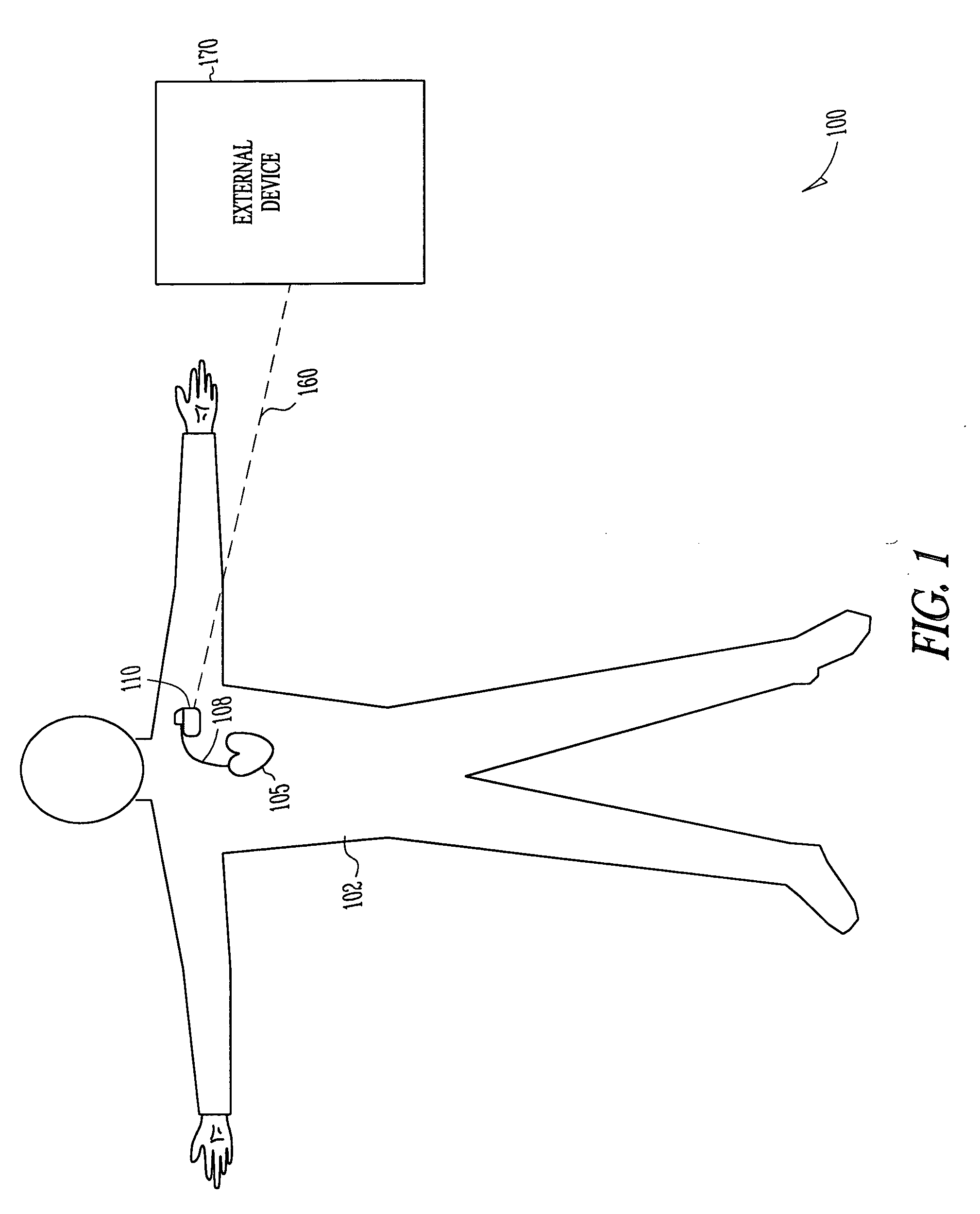
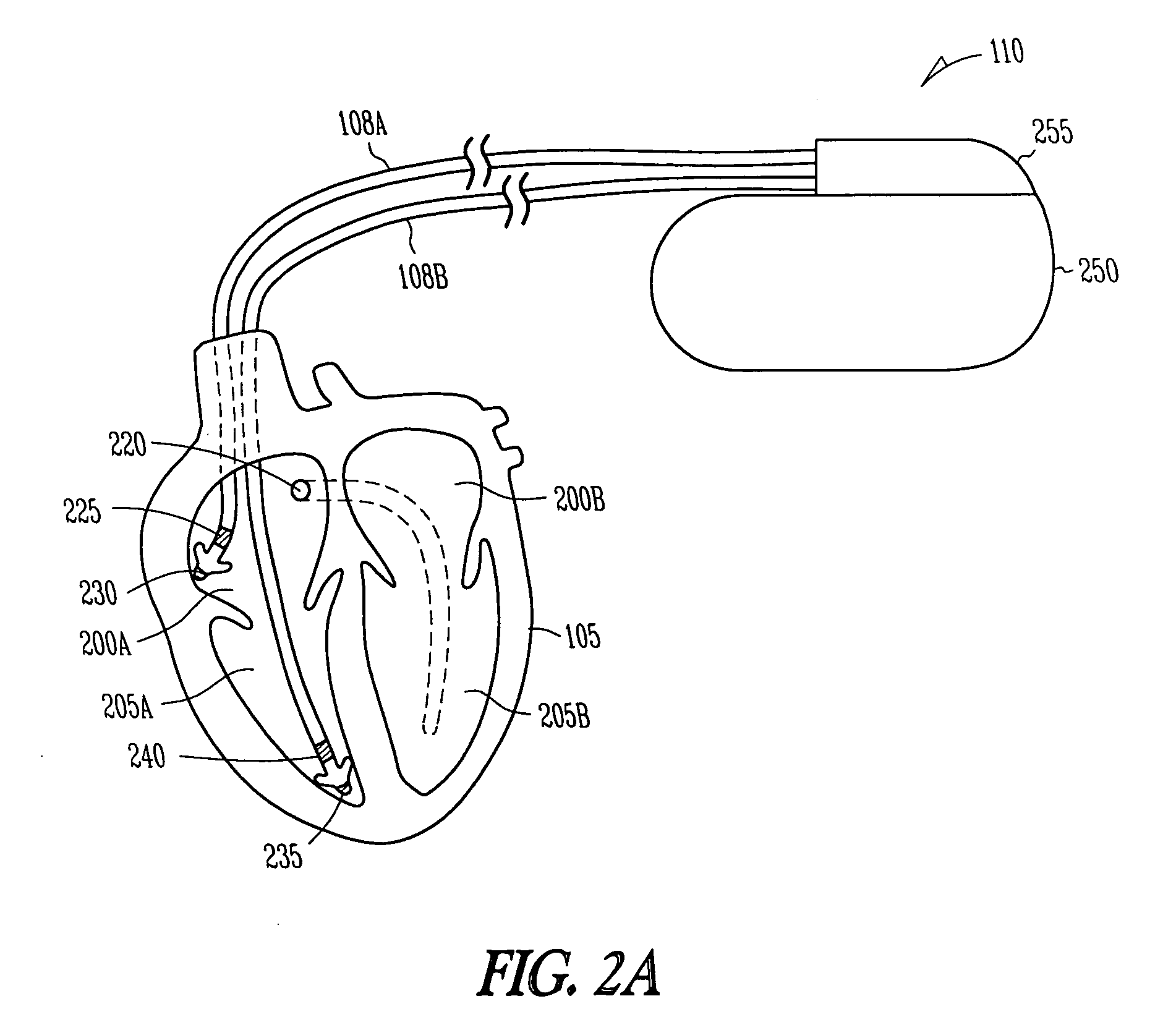
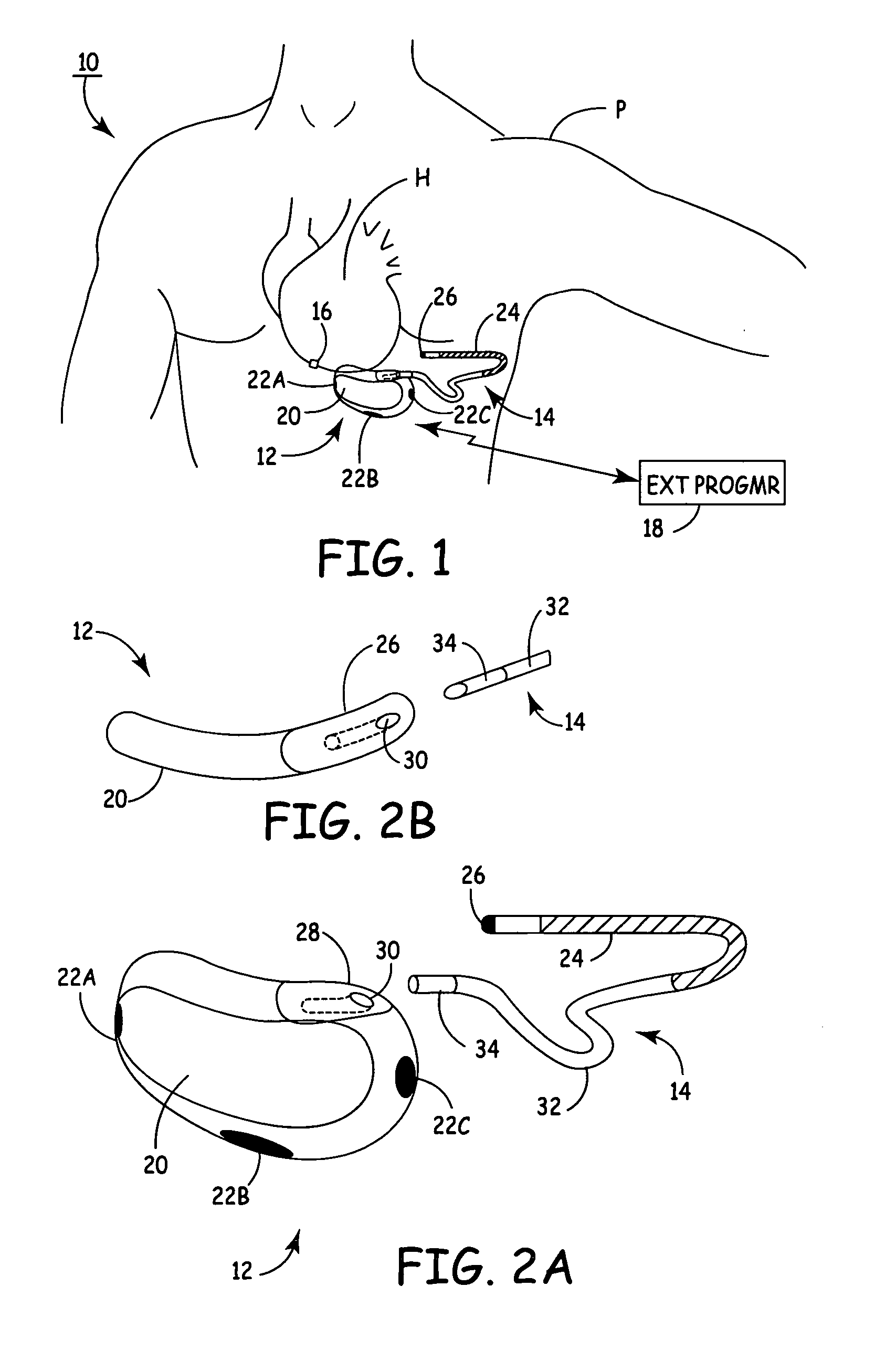
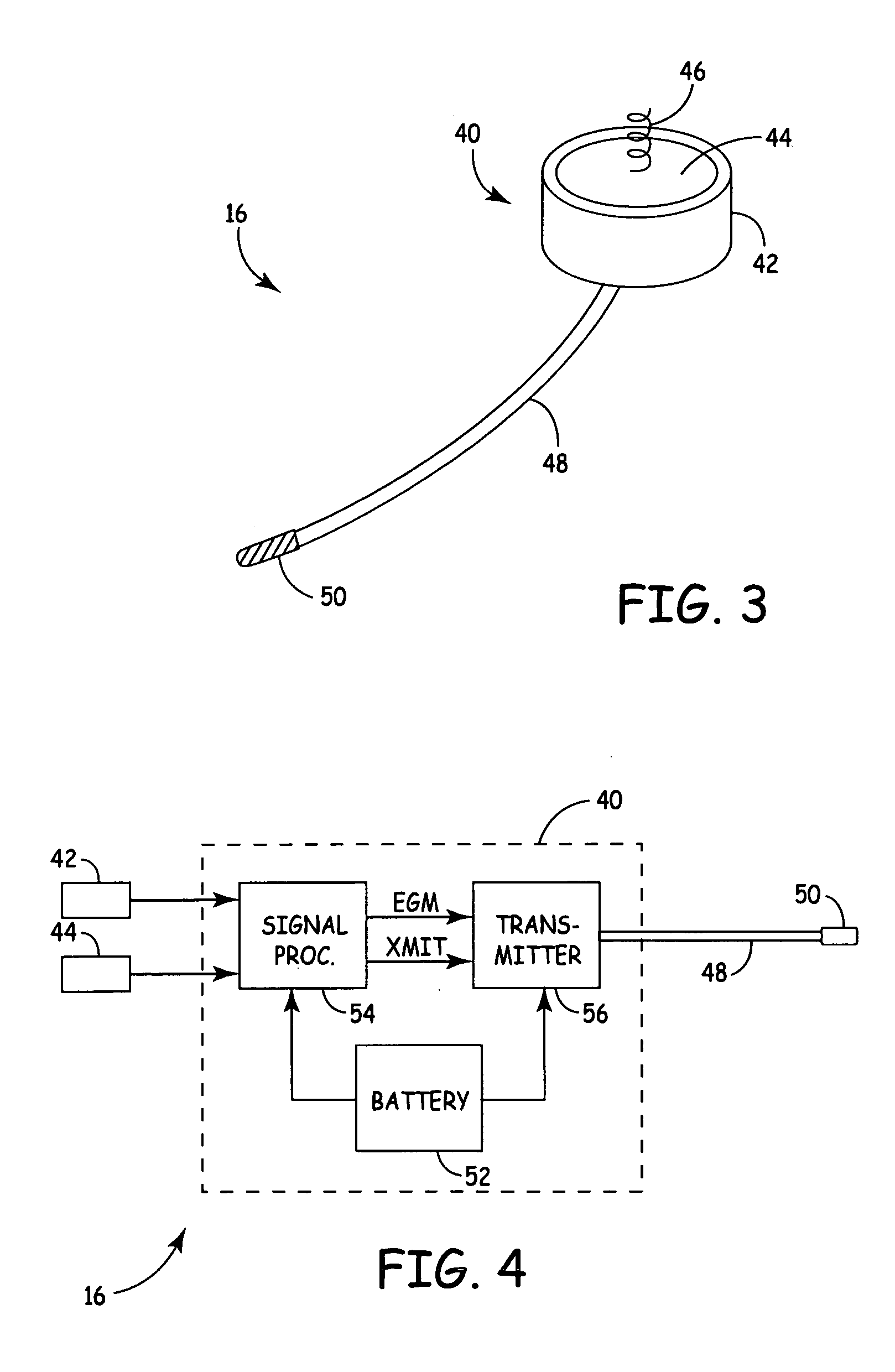
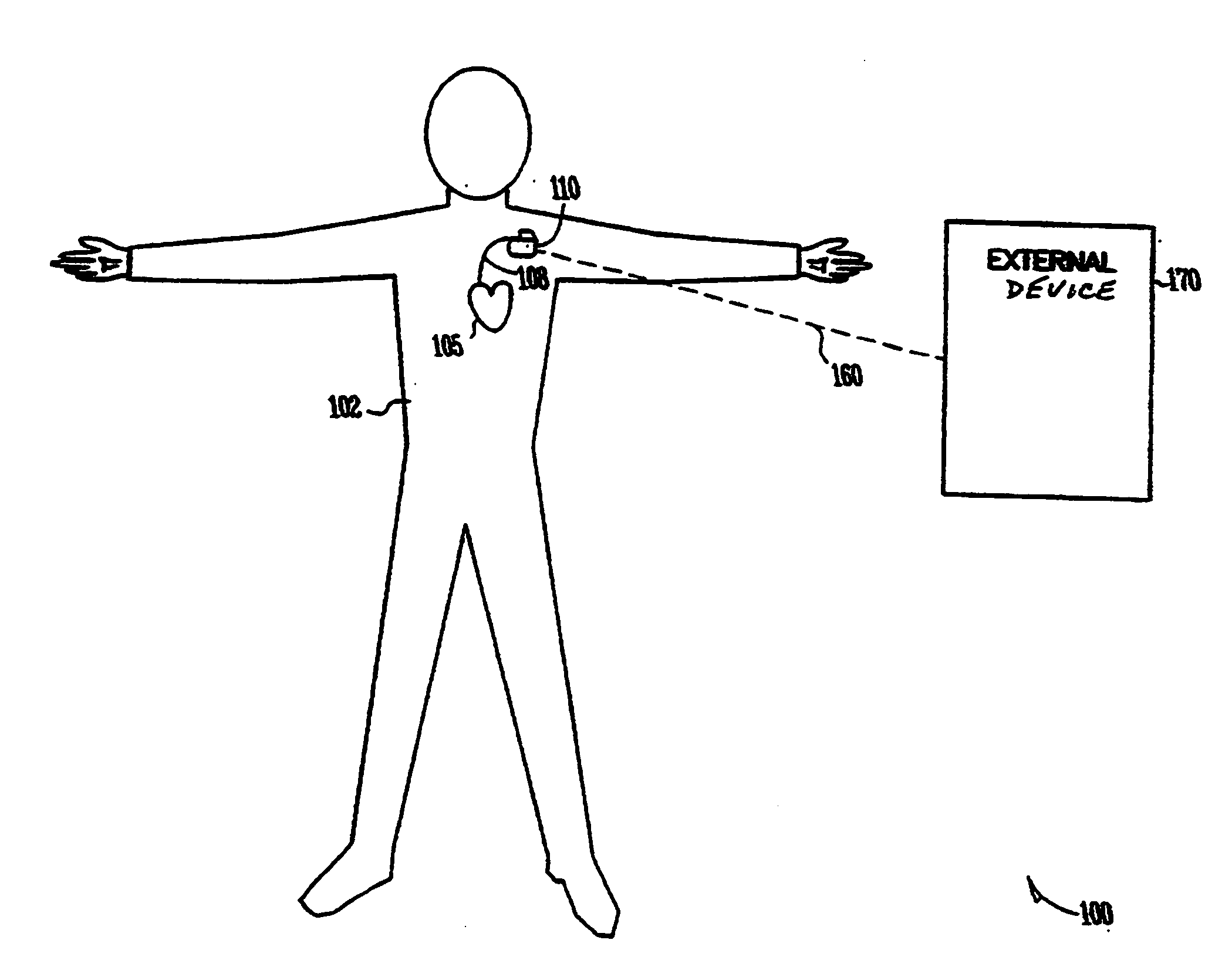
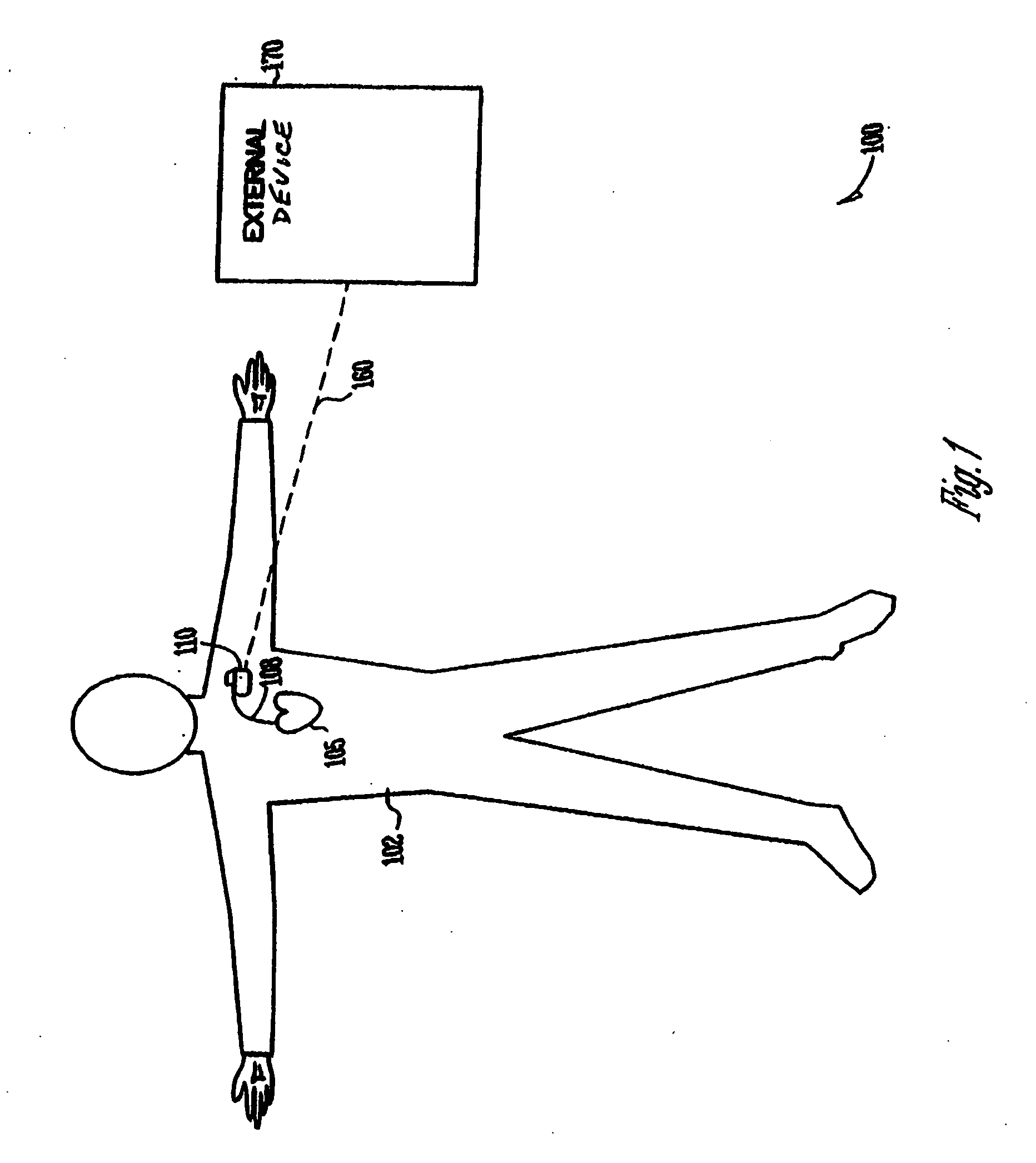
Arrhythmias can be detected using an electrocardiogram (ECG). An ECG provides an electrical readout of the heart’s activity. This is done non-invasively by attaching a set of electrodes to the surface of the skin [8].
Cardiac arrhythmia detector using ECG waveform-factor and its irregularity
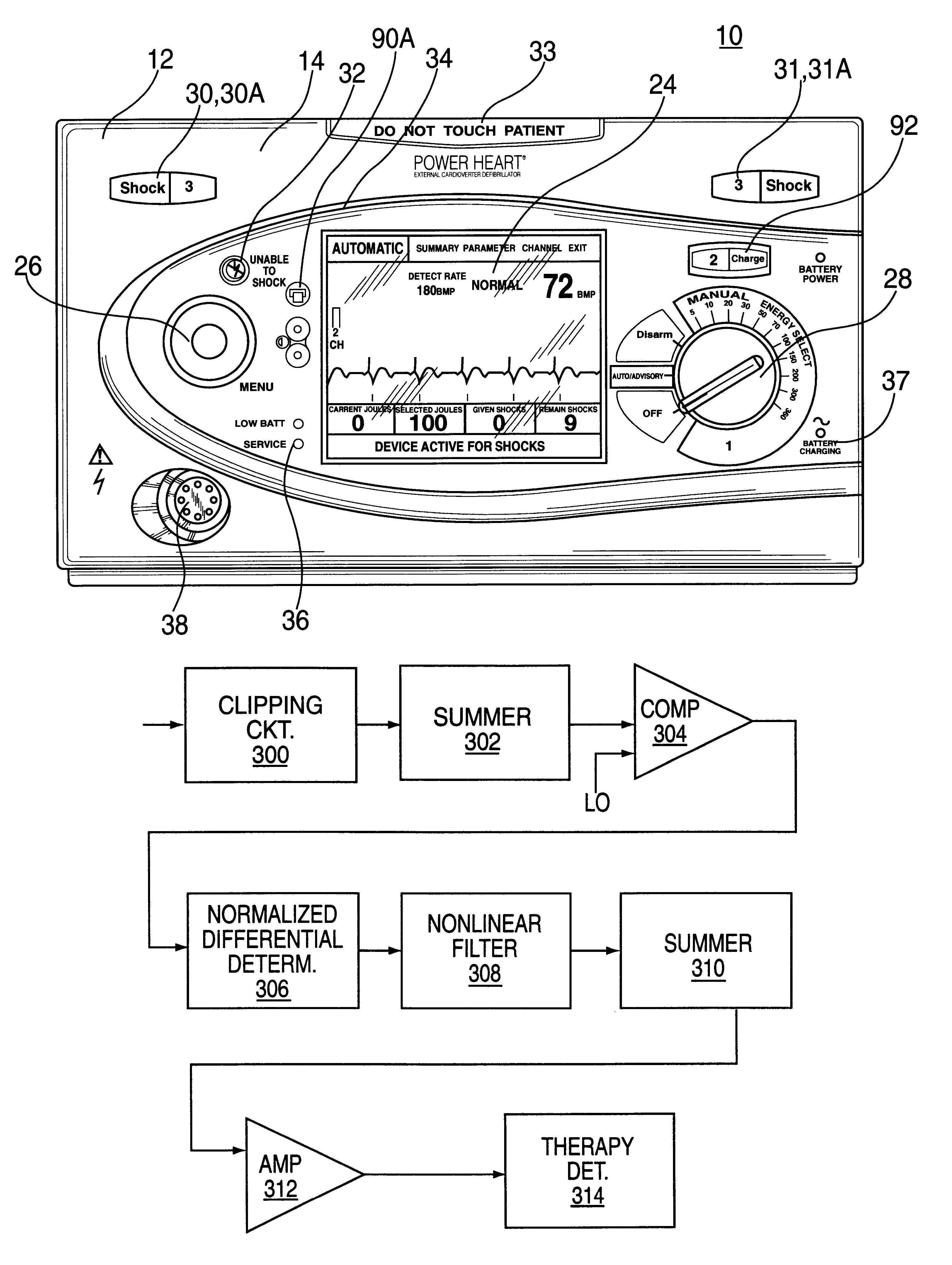
InactiveUS6480734B1Avoiding unnecessary shockSignificant energy savingElectrocardiographyHeart defibrillatorsVentricular tachycardiaCardiac monitoring
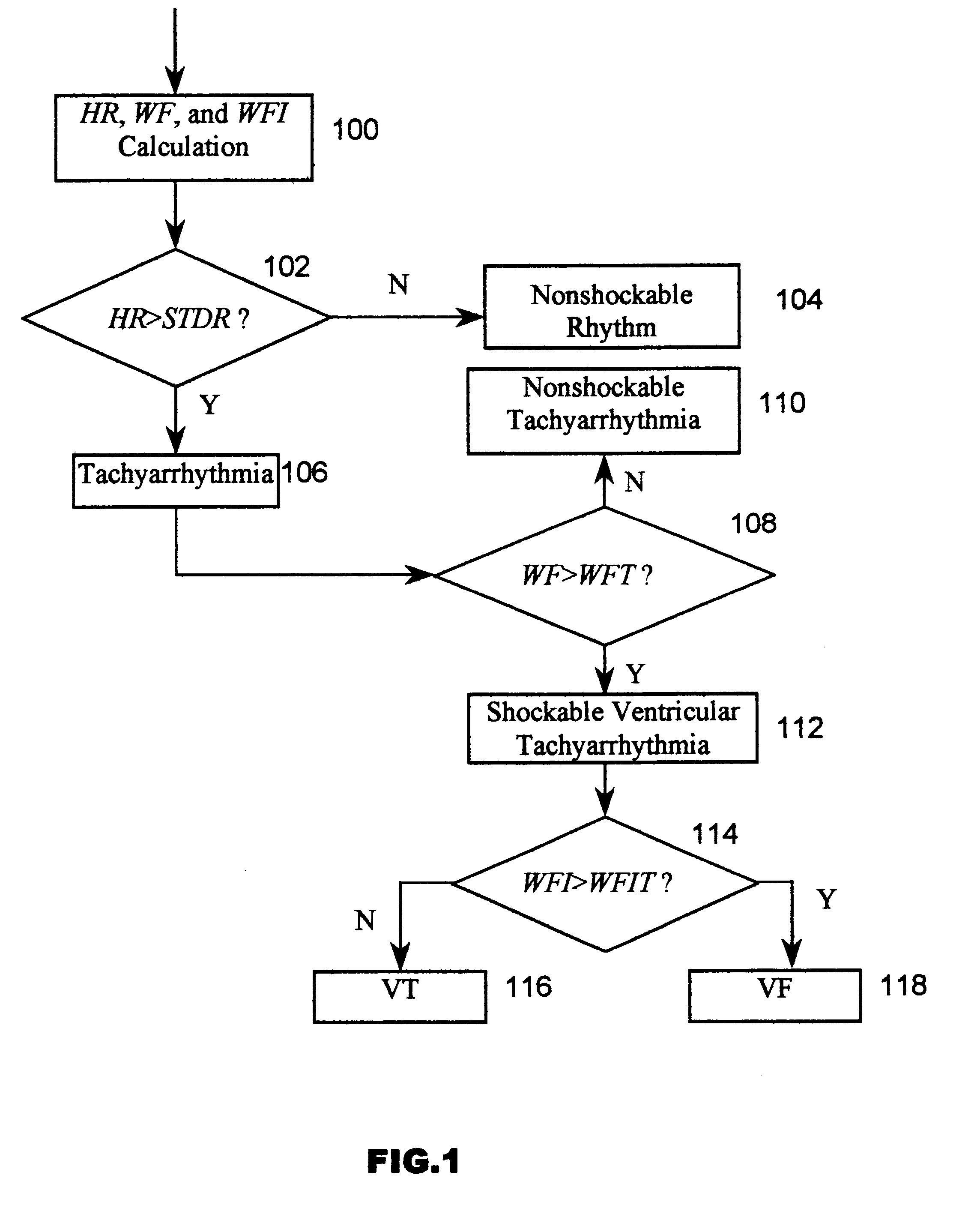
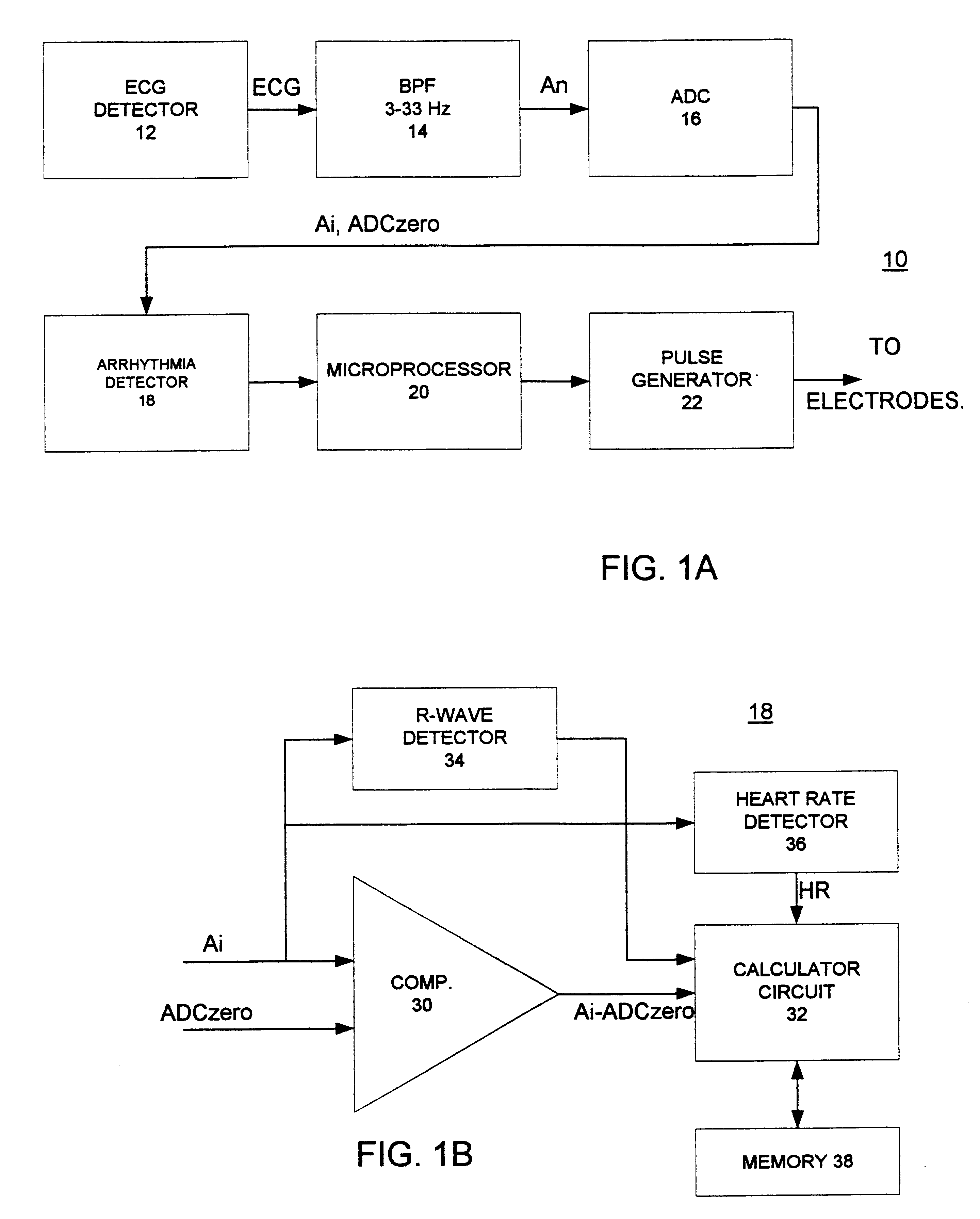
A cardiac monitor is provided that monitors the condition of the heart of a cardiac patient and generates signals indicating one of several conditions, such as supraventricular tachycardia, ventricular tachycardia and ventricular fibrillation. In order to generate these signals, the ECG from the patient is analyzed to determine a cardiac interval and heart rate, as well as a waveform factor and a waveform factor irregularity. The waveform factor is derived from the average of the ECG amplitudes during a cardiac interval and the peak value of the ECG during the same interval. Preferably, a running average is calculated over several intervals. This waveform factor is then used to detect shockable ventricular arrhythmia. The waveform factor irregularity is indicative of the variability of the waveform factor and is used to differentiate between ventricular tachycardia and ventricular defibrillation.
Owner:ZOLL MEDICAL CORPORATION
Use of accelerometer signal to augment ventricular arrhythmia detection
ActiveUS7130681B2Reliable detectionReliable classificationPerson identificationHeart stimulatorsEcg signalVentricular dysrhythmia
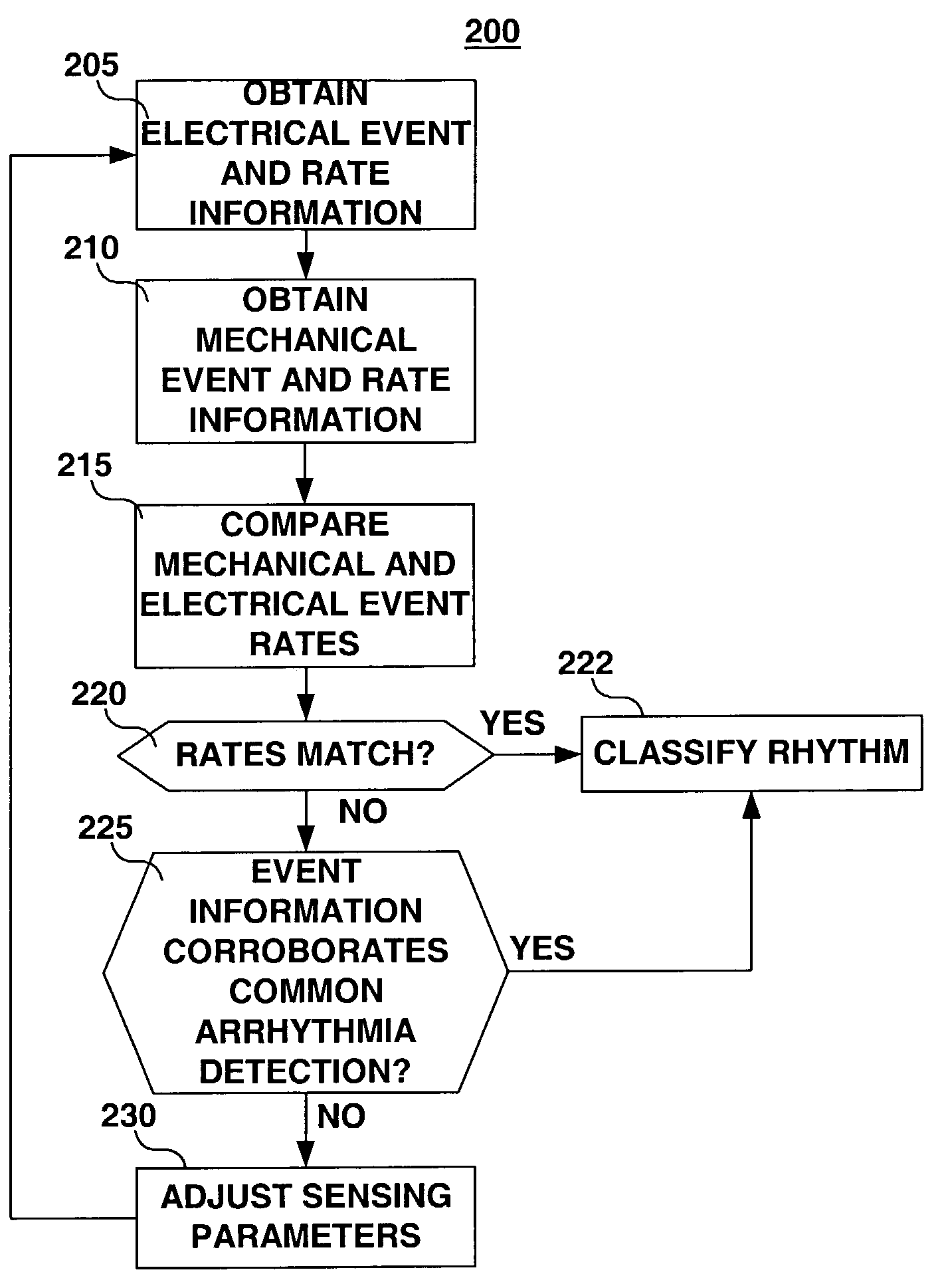
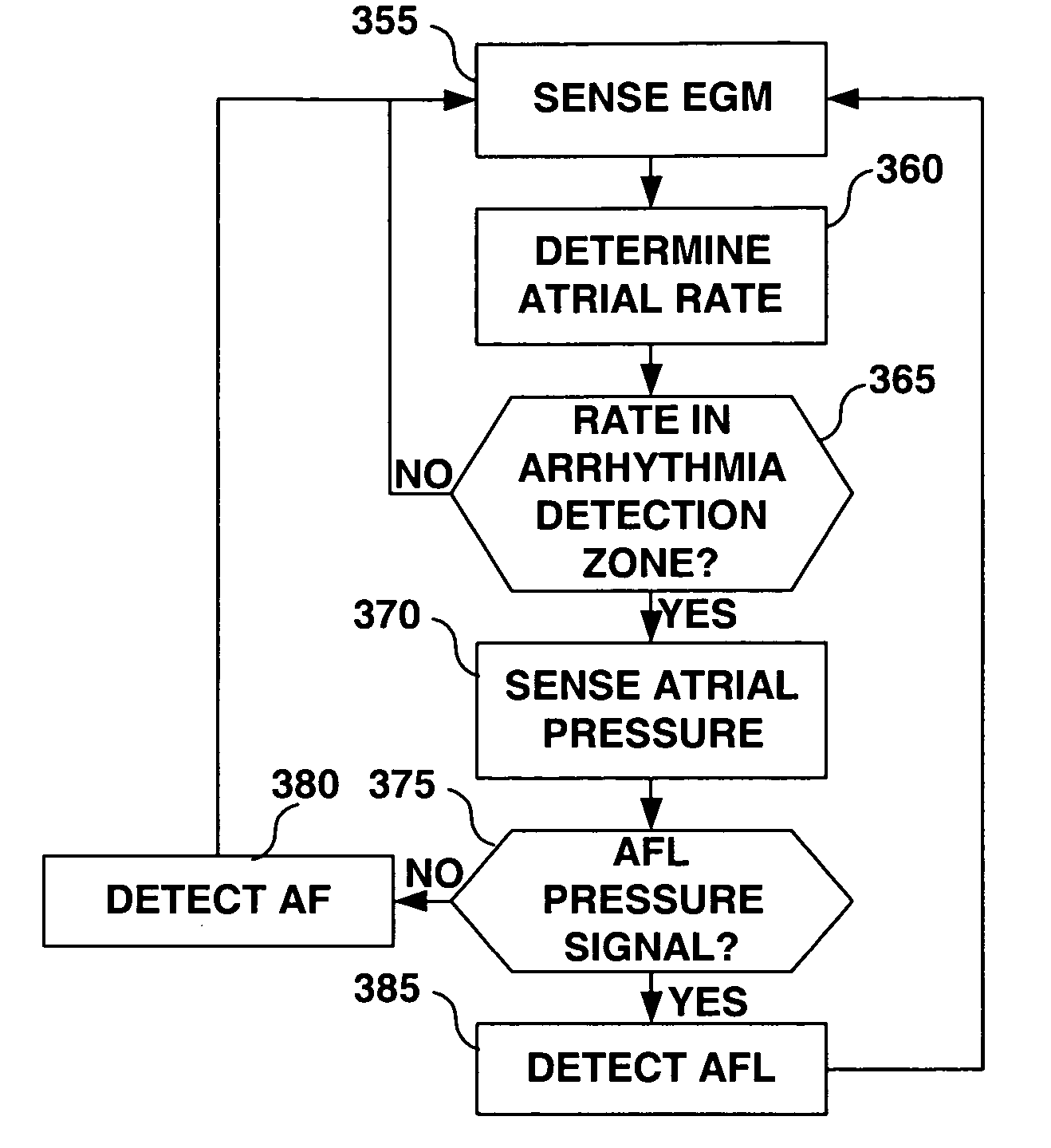
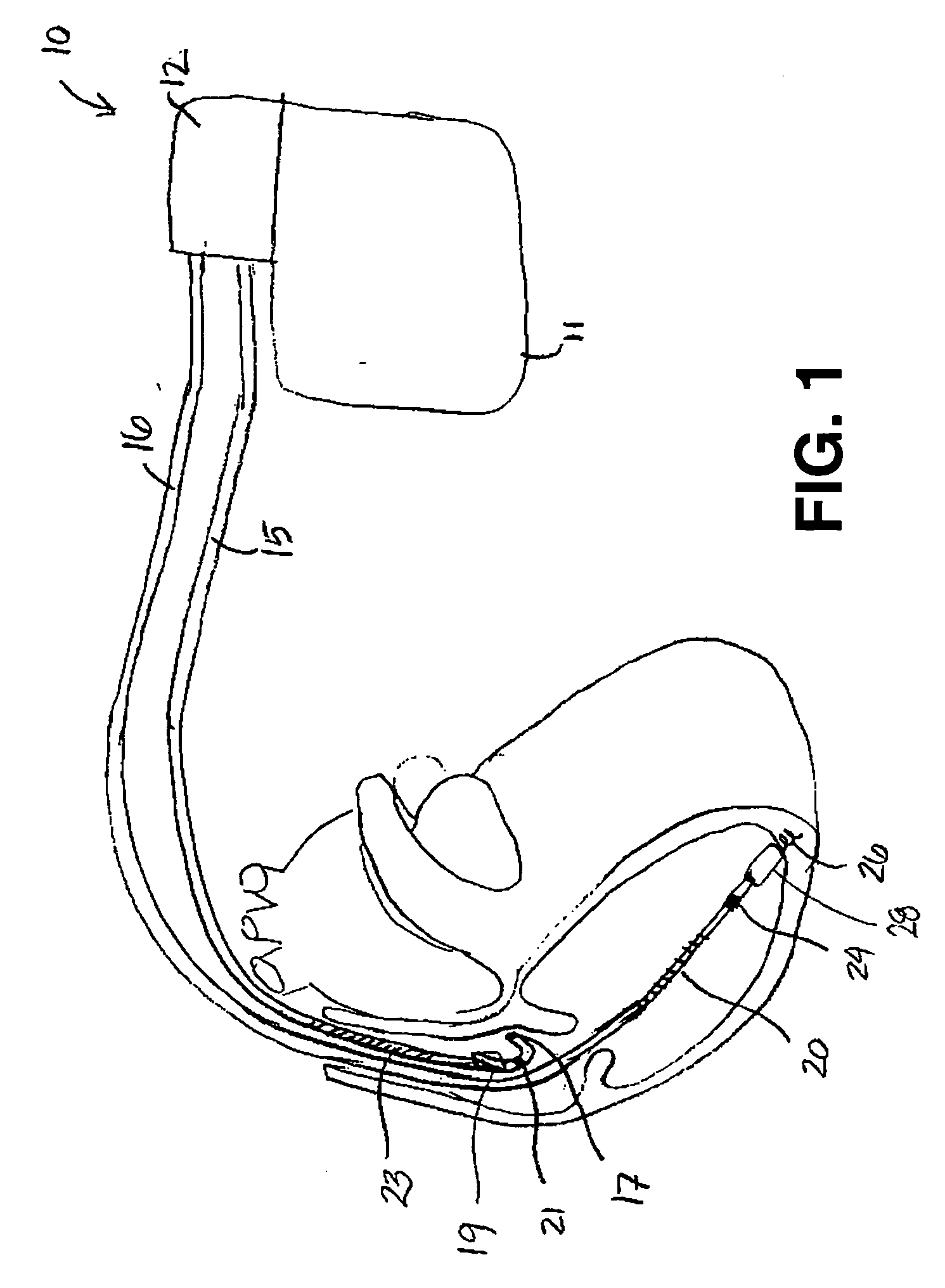
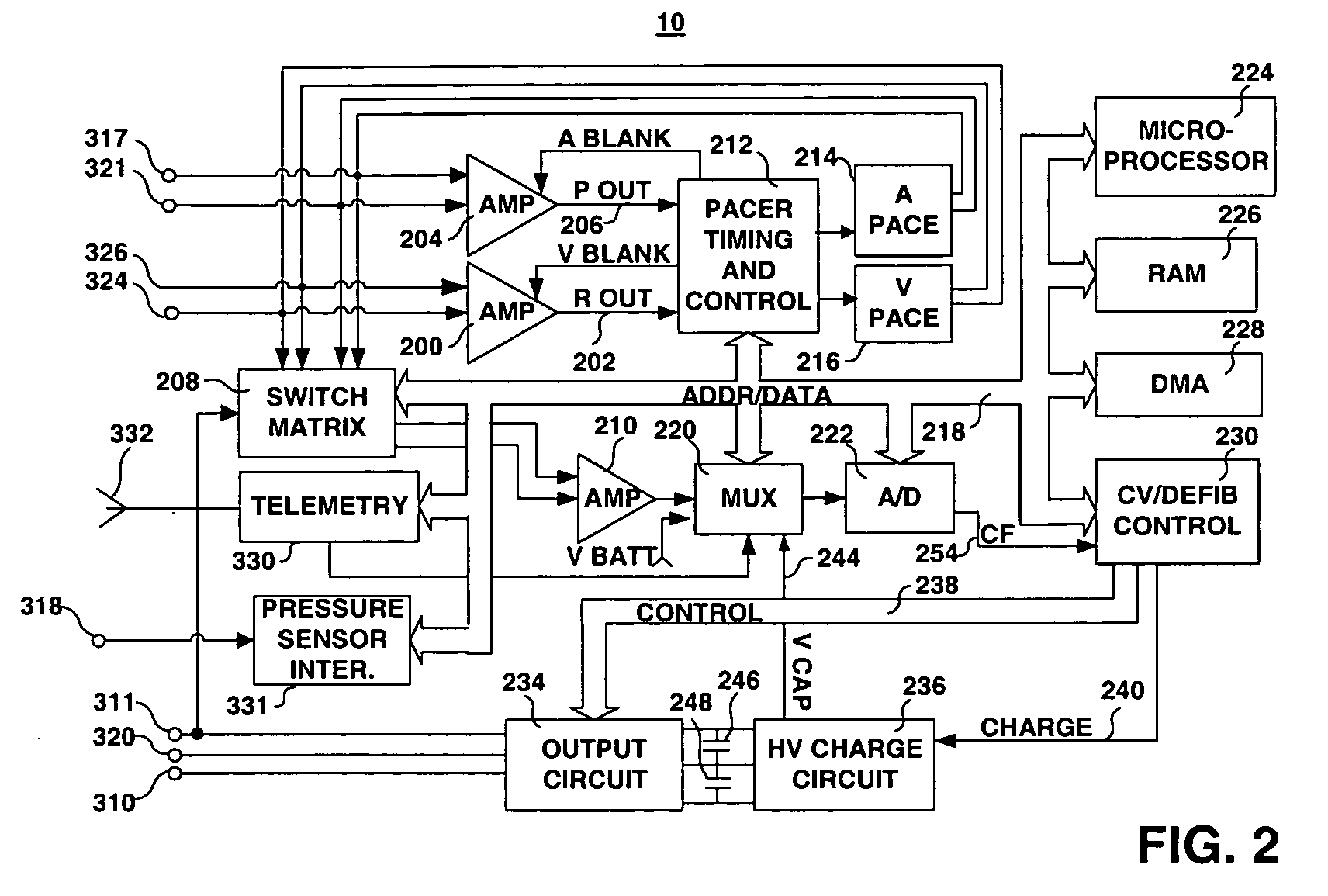
A system and method for detecting and discriminating atrial arrhythmias based on mechanical signals of cardiac wall motion and electrical signals of cardiac depolarizations. A mechanical event rate determined from sensed mechanical events is used to corroborate an electrical event rate determined from sensed EGM or ECG signals to classify the heart rhythm. If the event rates are not correlated, other parameterized data from the mechanical signal and electrical signal are evaluated to detect evidence of an arrhythmia. If electrical and mechanical event data do not corroborate a common arrhythmia condition, electrical and mechanical sensing parameters may be adjusted.
Owner:MEDTRONIC INC
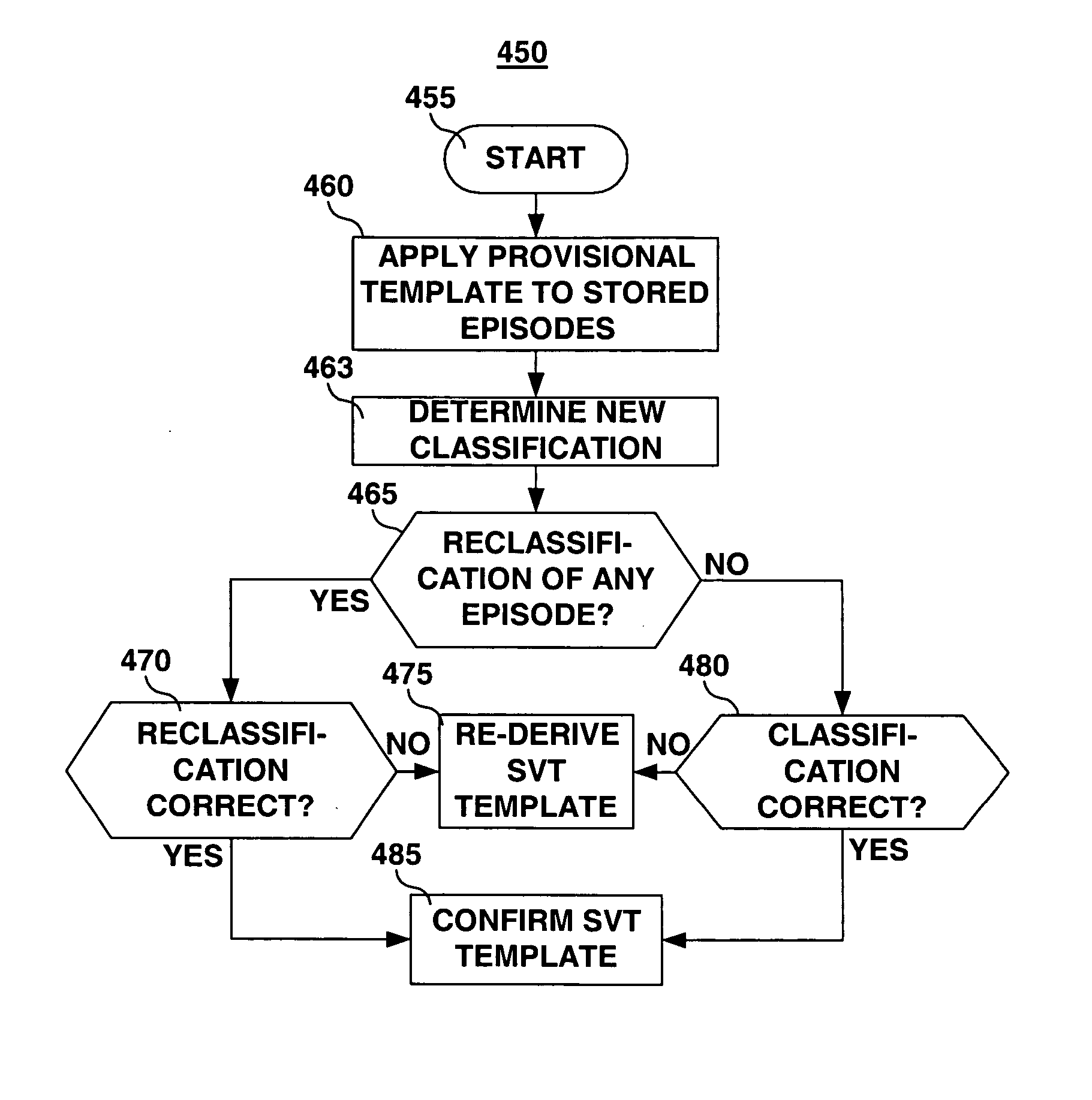
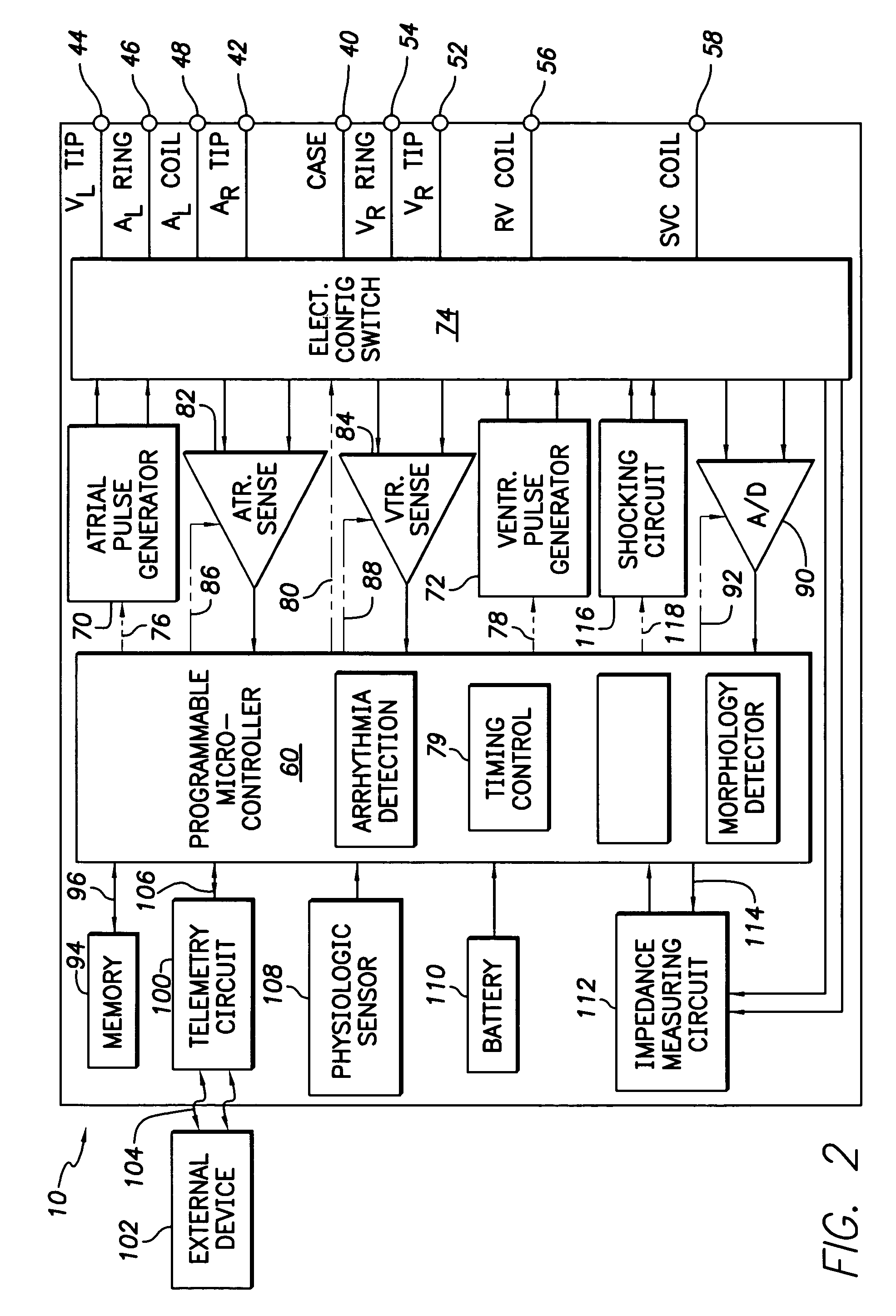
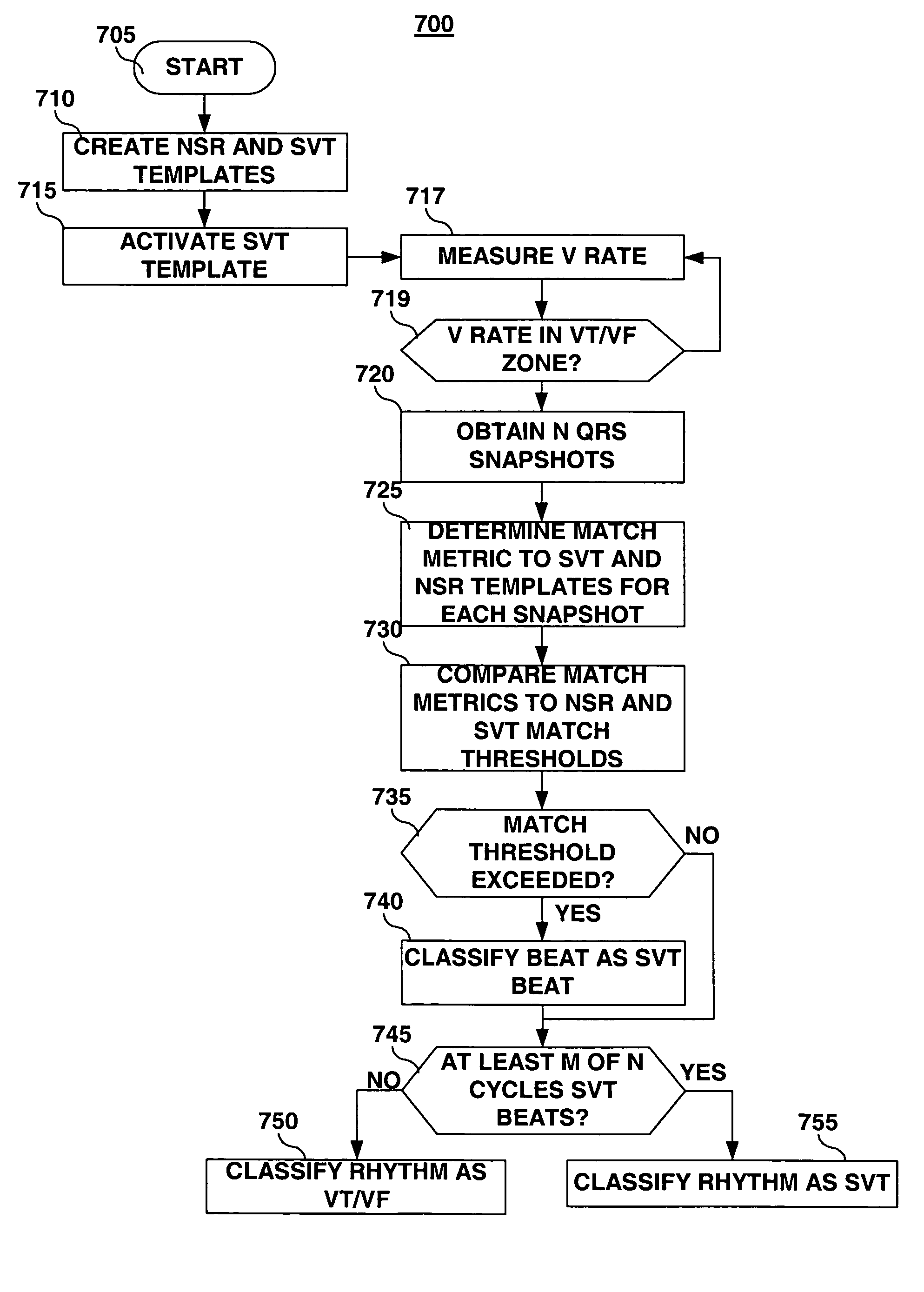
Method and apparatus for generating a template for arrhythmia detection and electrogram morphology classification
An implantable medical device and associated method for automatically generating morphology templates during fast cardiac rhythms, confirming a provisional template as a confirmed template, and using the confirmed template to classify subsequent detected arrhythmias. A provisional SVT template may be created during a fast ventricular rate and activated as a confirmed SVT template upon verification that the fast rate was due to an SVT. The confirmed SVT template may be used to discriminate SVT from VT / VF.
Owner:MEDTRONIC INC
Combination of electrogram and intra-cardiac pressure to discriminate between fibrillation and tachycardia
A system and method for detecting and classifying cardiac arrhythmias based on cardiac pressure signals or the combination of cardiac electrical and cardiac pressure signals. A cardiac electrogram signal is sensed to derive a cardiac rate from which an arrhythmia detection is made when the cardiac rate meets arrhythmia detection criteria. An intracardiac pressure signal is sensed to derive an indicator of tachycardia based on an analysis of the pressure signal in either the time domain or frequency domain. The detected arrhythmia is classified as tachycardia or fibrillation based on the tachycardia indicator wherein the tachycardia indicator is compared to tachycardia detection criteria and the arrhythmia is classified as tachycardia if tachycardia detection criteria are met and the arrhythmia is classified as fibrillation if the tachycardia detection criteria are not met.
Owner:MEDTRONIC INC
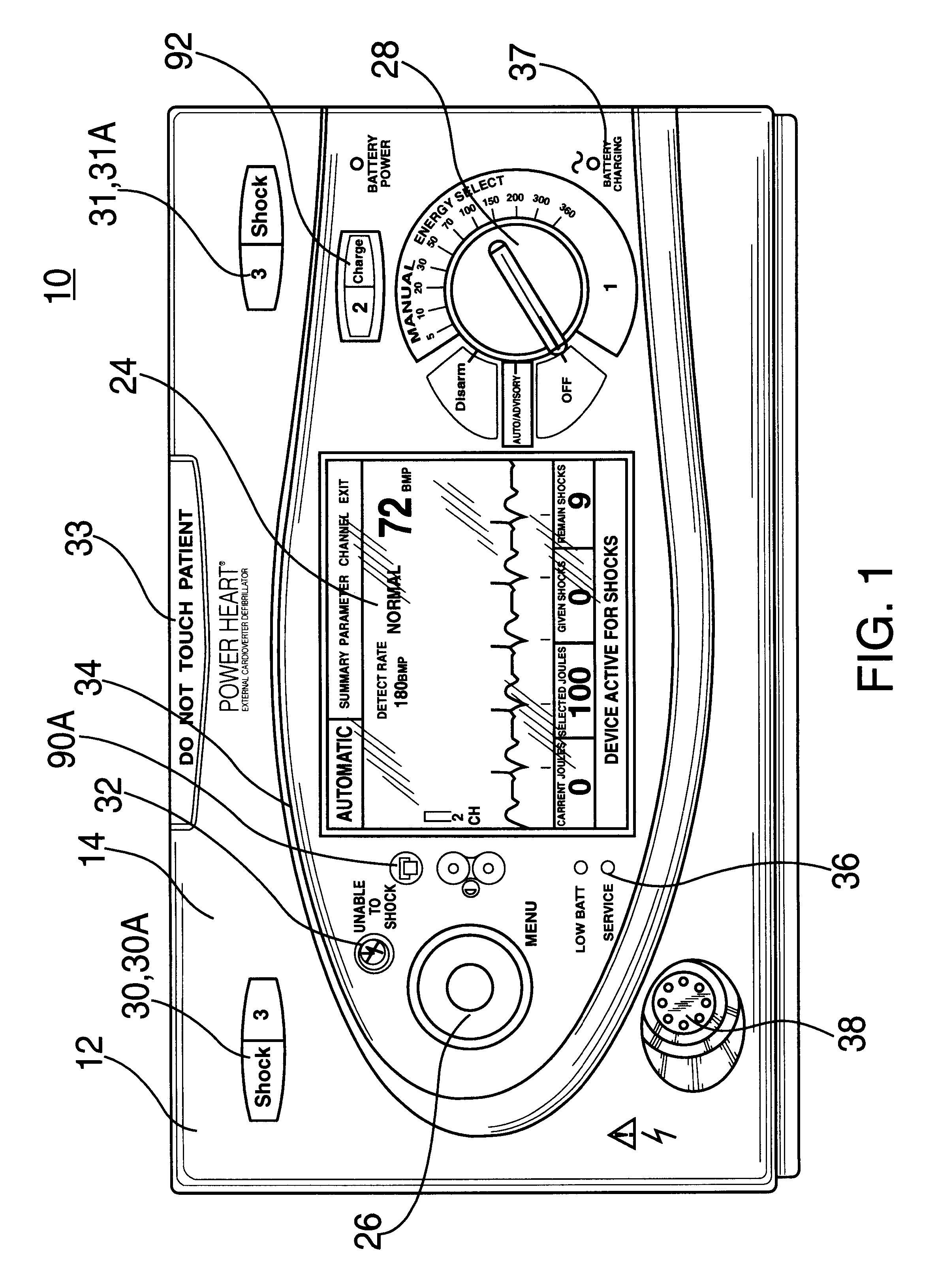
Automatic external cardioverter/defibrillator with tachyarrhythmia detector using a modulation (amplitude and frequency) domain function
InactiveUS6289243B1Reduce probabilityIncrease probabilityHeart defibrillatorsSensorsVentricular TachyarrhythmiasMedical emergency
An external defibrillator includes a detector used to detect a life threatening condition of a patient, a controller operating the defibrillator automatically and a therapy delivery circuit that delivers appropriate therapy. Advantageously a parameter is derived from the cardiac signals sensed in the patient, the parameters being used to differentiate between shockable events such as ventricular tachyarrhythmia and other events such as SVT. The defibrillator is attached to a patient by an attendant and once it is attached, the defibrillator is adapted to monitor the patient and when a life threatening condition is detected, to apply therapy automatically, i.e., without any involvement by the patient or the attendant.
Owner:ZOLL MEDICAL CORPORATION
Subcutaneous ICD with separate cardiac rhythm sensor
Owner:MEDTRONIC INC
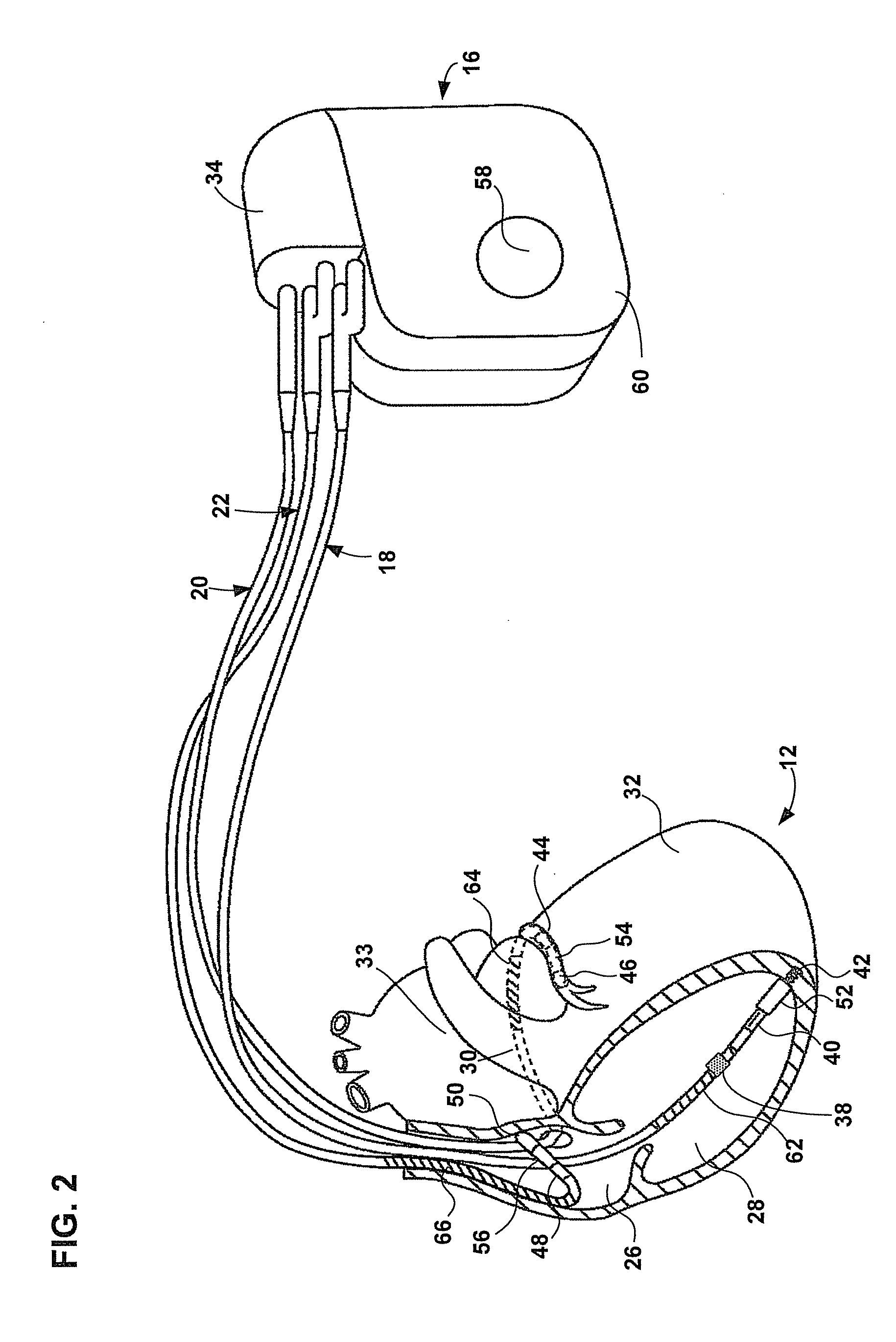
Subcutaneous cardiac stimulation device providing anti-tachycardia pacing therapy and method
An implantable subcutaneous cardiac device includes at least two subcutaneous electrodes adapted for placement external to a heart beneath the skin of a patient. The device further includes an arrhythmia detector that detects a sustained tachyarrhythmia of the heart and a pulse generator that delivers anti-tachycardia pacing pulses to the subcutaneous electrodes in response to detection of a sustained tachyarrhythmia. The pacing pulses preferably have waveforms devoid of any exponential voltage decay and include rounded or substantially constant portions to minimize pain.
Owner:PACESETTER INC
Method and apparatus for generating a template for arrhythmia detection and electrogram morphology classification
Owner:MEDTRONIC INC
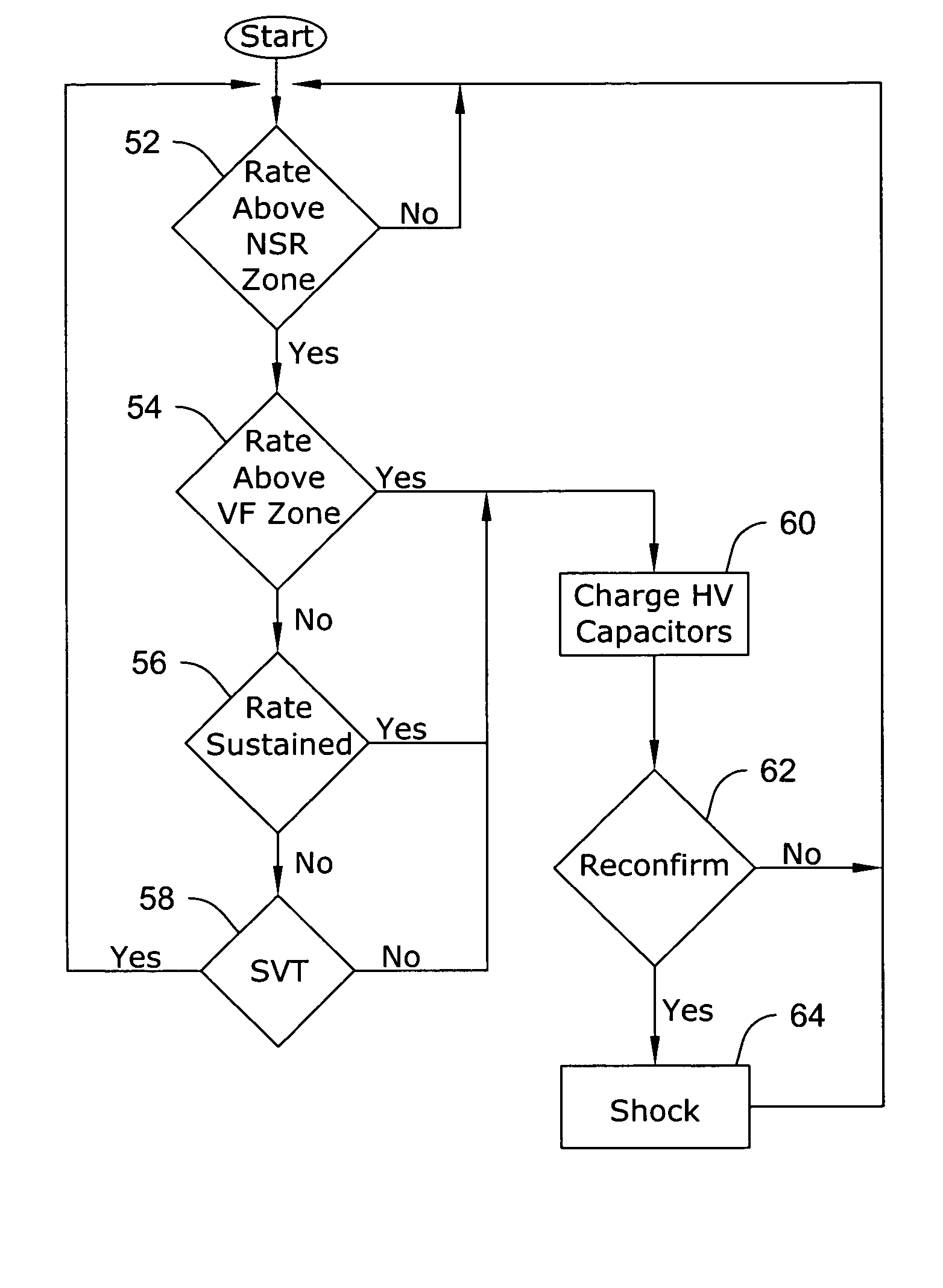
System and method for complexity analysis-based cardiac tachyarrhythmia detection
InactiveUS6490478B1Clearer and reliable indicationAvoids possible misidentificationsHeart defibrillatorsHeart stimulatorsEcg signalVentricular tachycardia
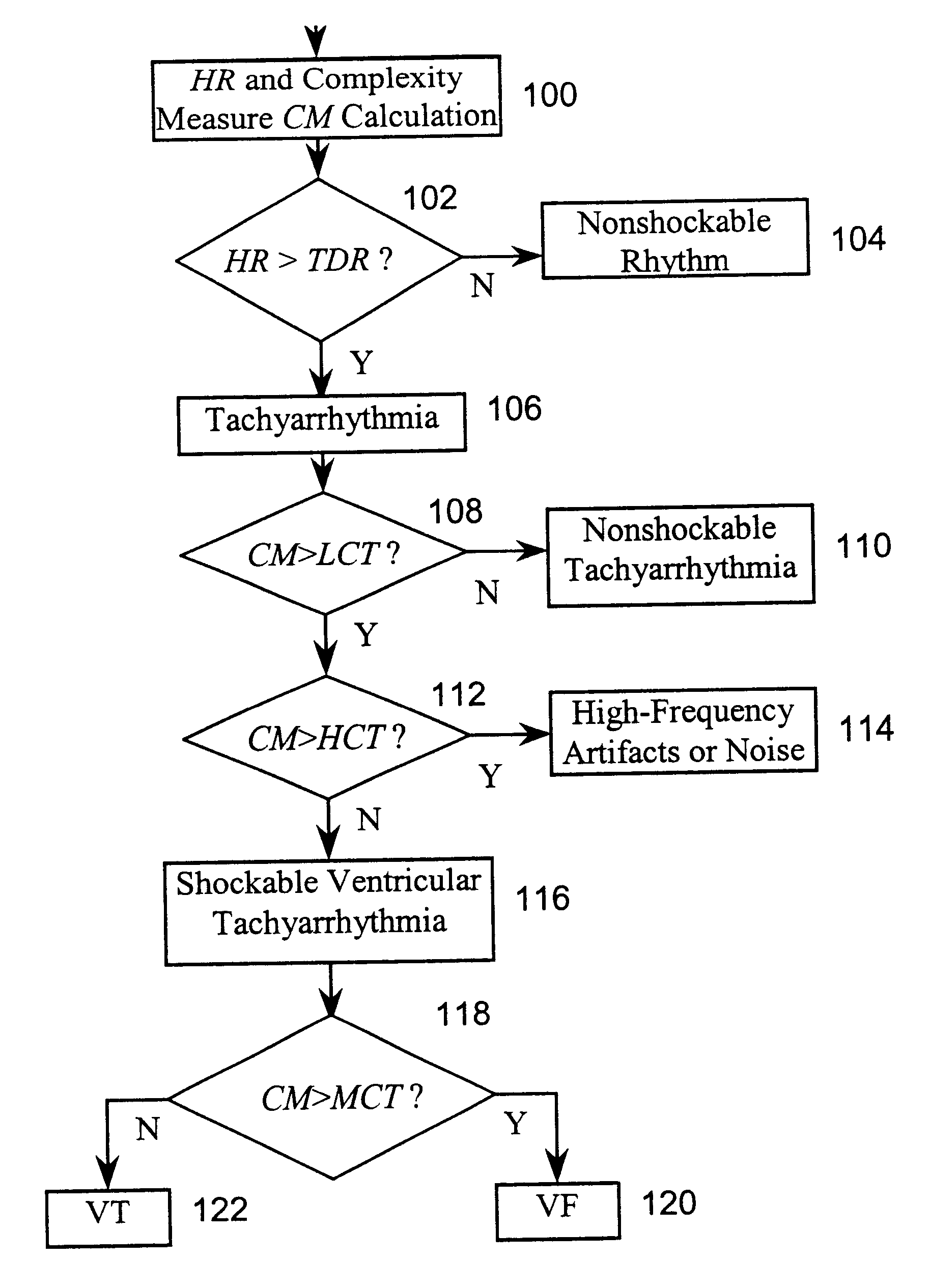
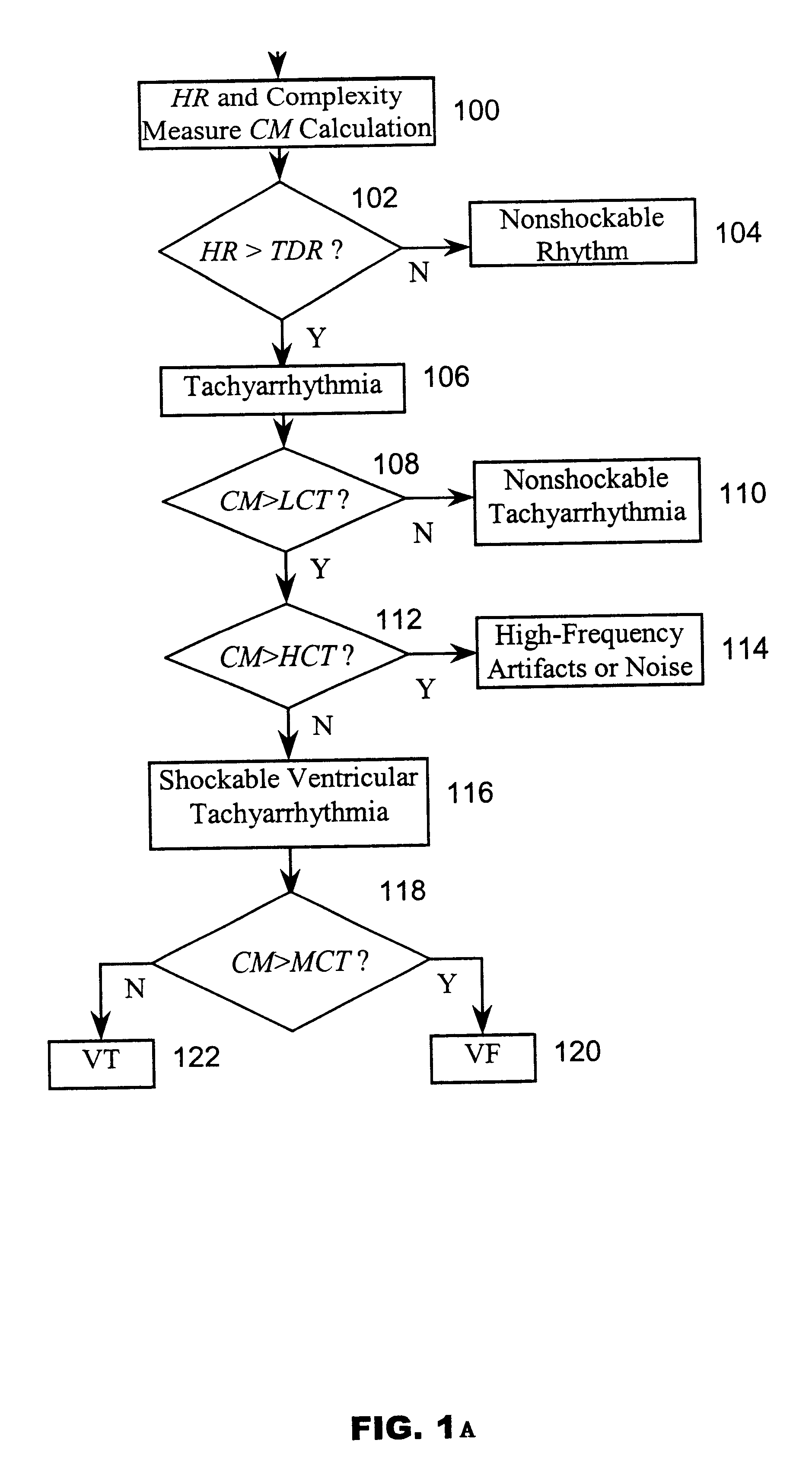
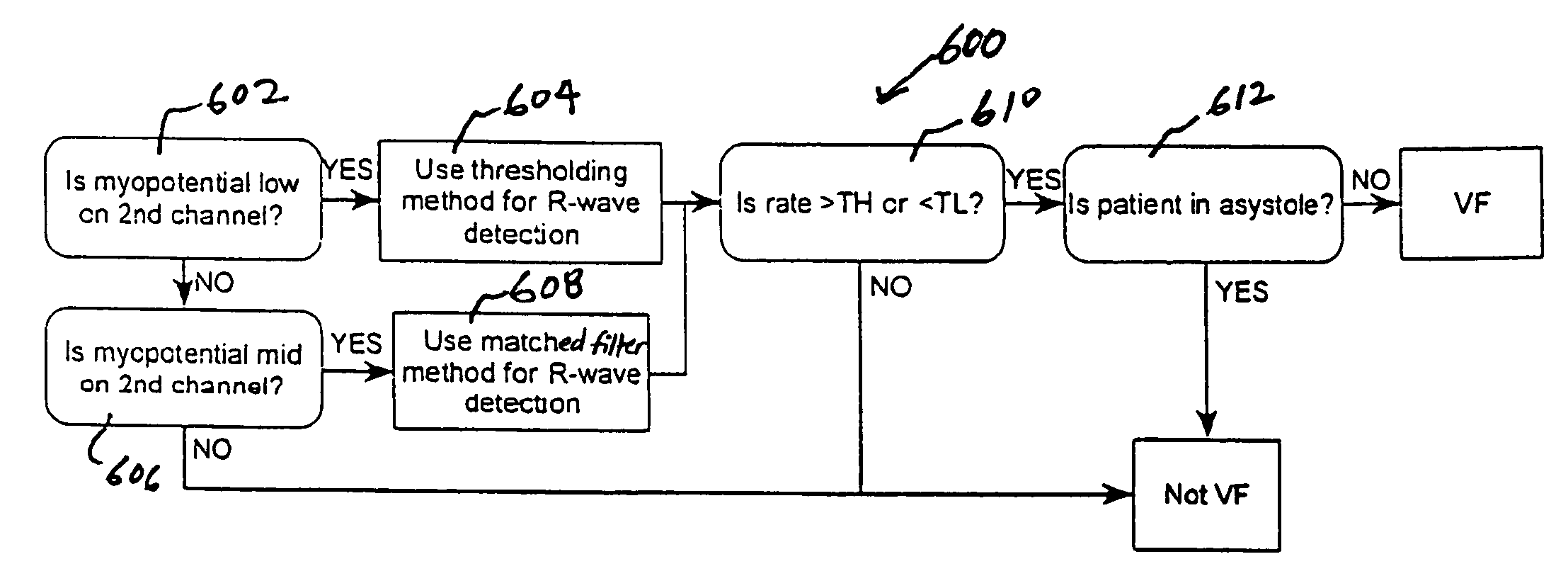
A system and method based on electrocardiogram (ECG) complexity analysis for real-time detecting shockable ventricular fibrillation (VF) and ventricular tachycardia (VT), and discriminating them from non-shockable tachyarrhythmia (e.g. supraventricular tachycardia (SVT) and atrial fibrillation (AF)) and high-frequency noise. In the disclosed invention, complexity measure CM (0 to 100), quantitatively characterizing the complexity nature of the non-linear dynamics underlying cardiac arrhythmia, is extracted from the sensed patient ECG signal using ECG complexity analysis. From the calculated complexity measure, by three thresholds (low complexity threshold (LCT), mediate complexity threshold (MCT), and high complexity threshold (HCT)), different kinds of tachyarrhythmia (i.e. heart rate (HR) above a preset rate threshold) and high-frequency noise are discriminated from each other: for non-shockable tachyarrhythmia, CM<=LCT; for VT, LCT<CM<=MCT; for VF, MCT<CM<=HCT; and for high-frequency noise, HCT<CM. The disclosed system and method can be used as a primary cardiac tachyarrhythmia detection scheme or as a backup system to reconfirm arrhythmia detection using conventional techniques.
Owner:ZOLL MEDICAL CORPORATION
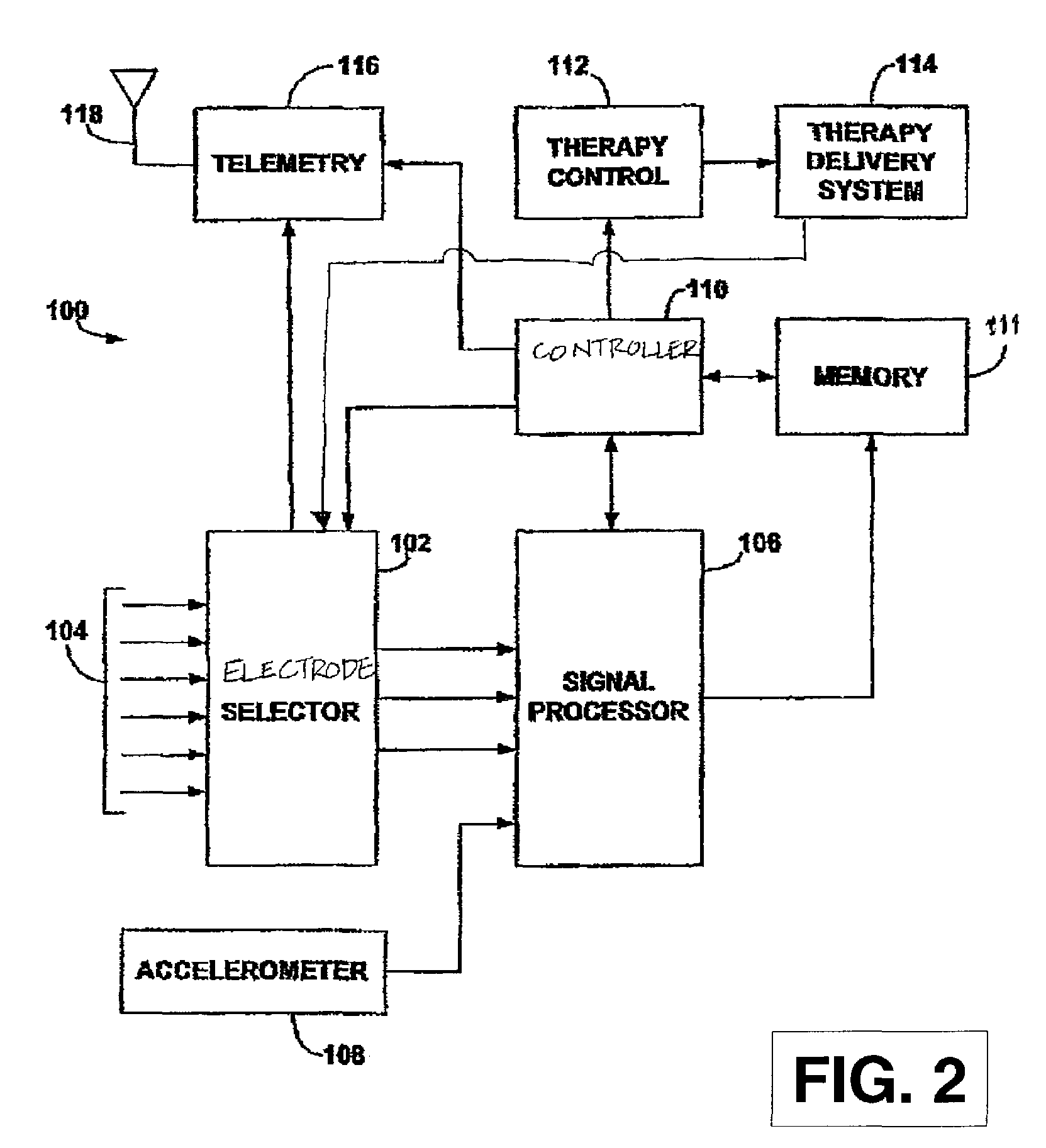
Method and apparatus for arrhythmia detection in a medical device
A method and device for detecting arrhythmias in a patient that includes electrodes positioned subcutaneously within the patient, a microprocessor, coupled to the electrodes, determining one of a sequence of the sensing of cardiac signals by the electrodes and a duration between the sensing of cardiac signals by the electrodes, and control circuitry delivering a therapy in response to one of the determined sequence and the determined duration.
Owner:MEDTRONIC INC
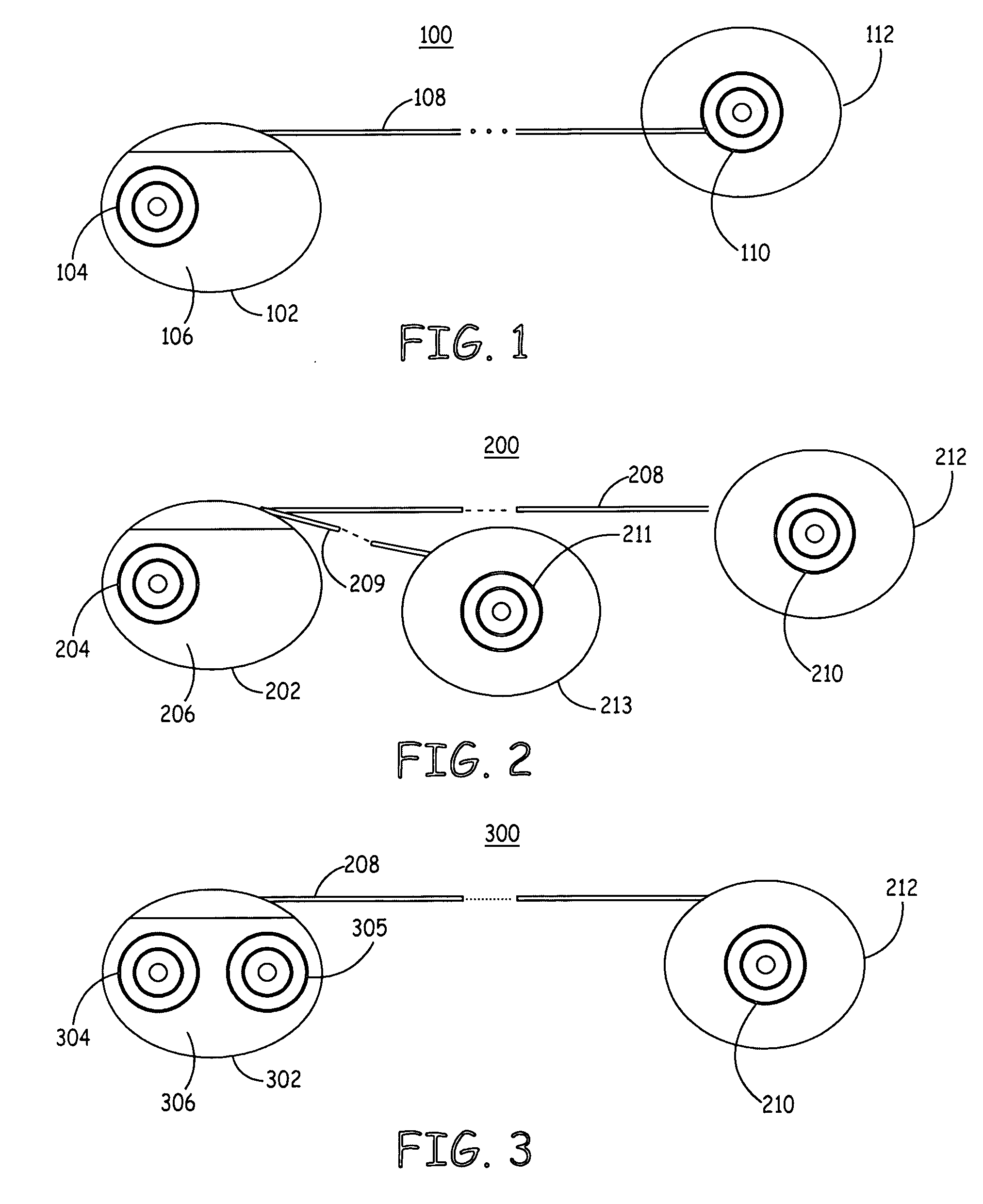
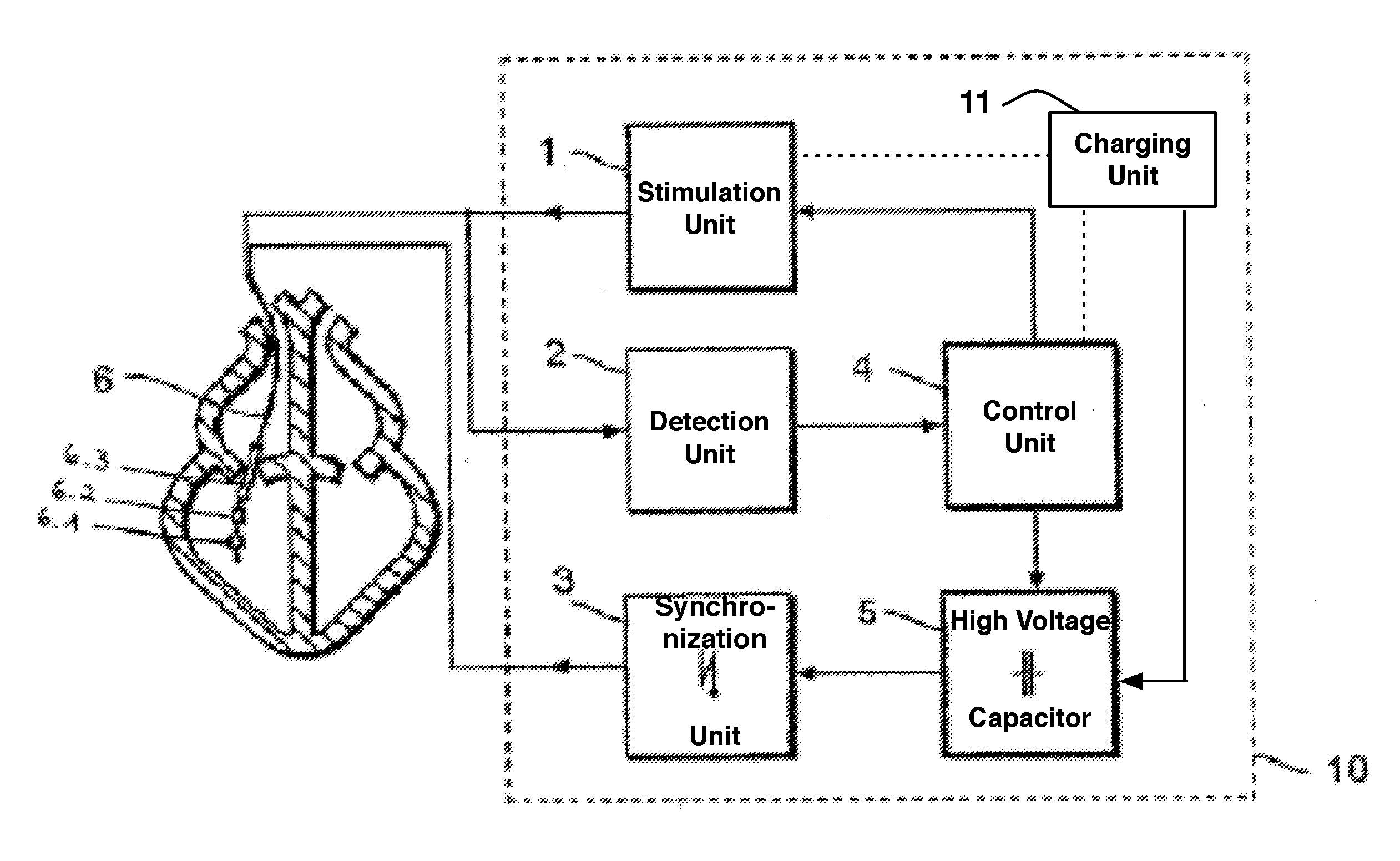
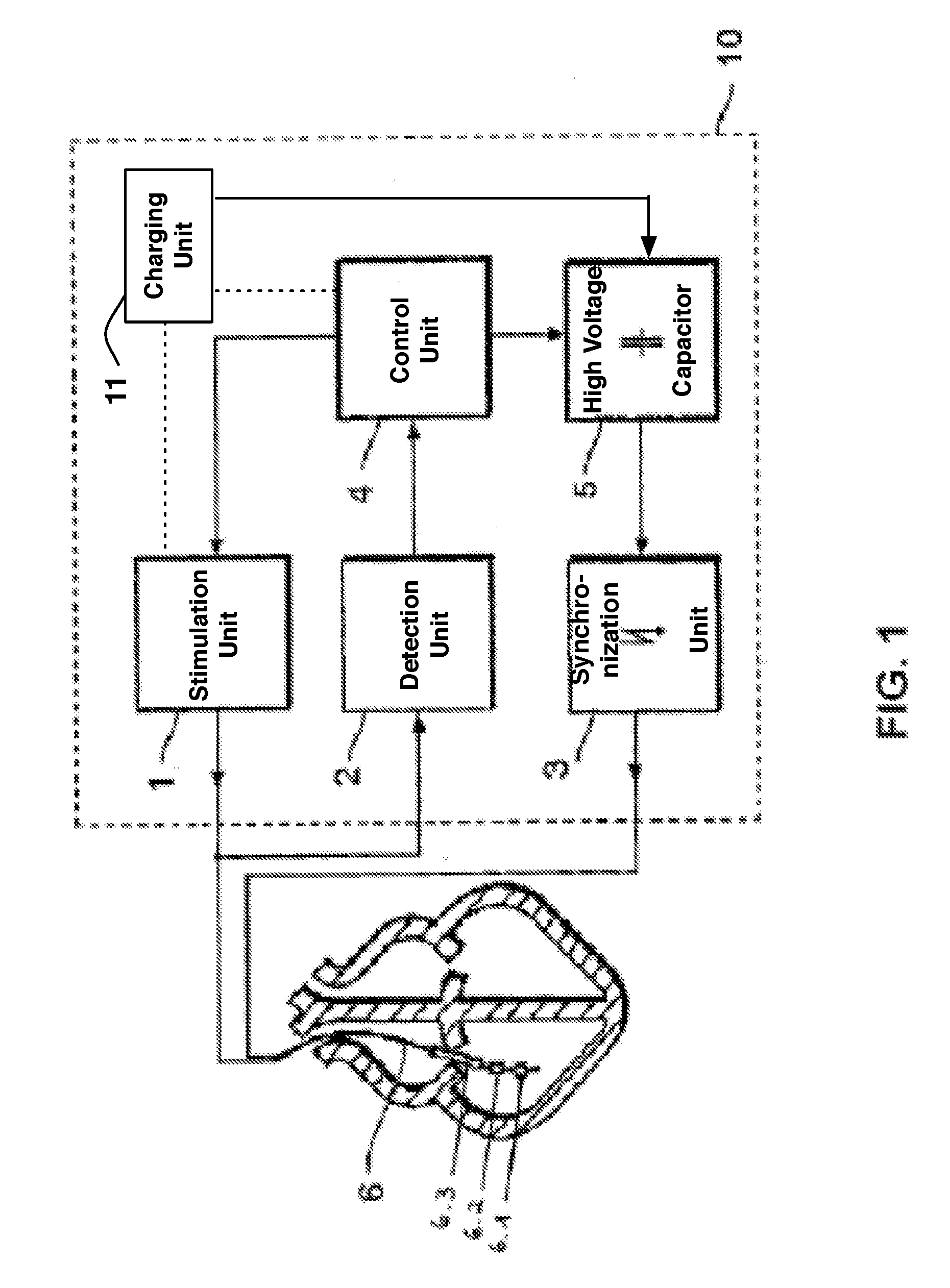
Implantable cardioverter-defibrillator including arrhythmia detection criteria
ActiveUS9393436B2Improve reliabilityLower success rateHeart defibrillatorsMedicineHigh voltage capacitors
An implantable cardioverter-defibrillator system that includes at least one or more stimulation units, one or more detection units, one or more control units, two or more electrode poles and one or more high voltage capacitors. The at least one control unit is connected with the at least one stimulation unit, and the at least one control unit is connected with at the least one detection unit. The two or more electrode poles are in contact with body tissue, and the one or more high voltage capacitors are charged by at least one charging unit, wherein the at least one charging unit is connected to the at least one control unit.
Owner:BIOTRONIK SE & CO KG
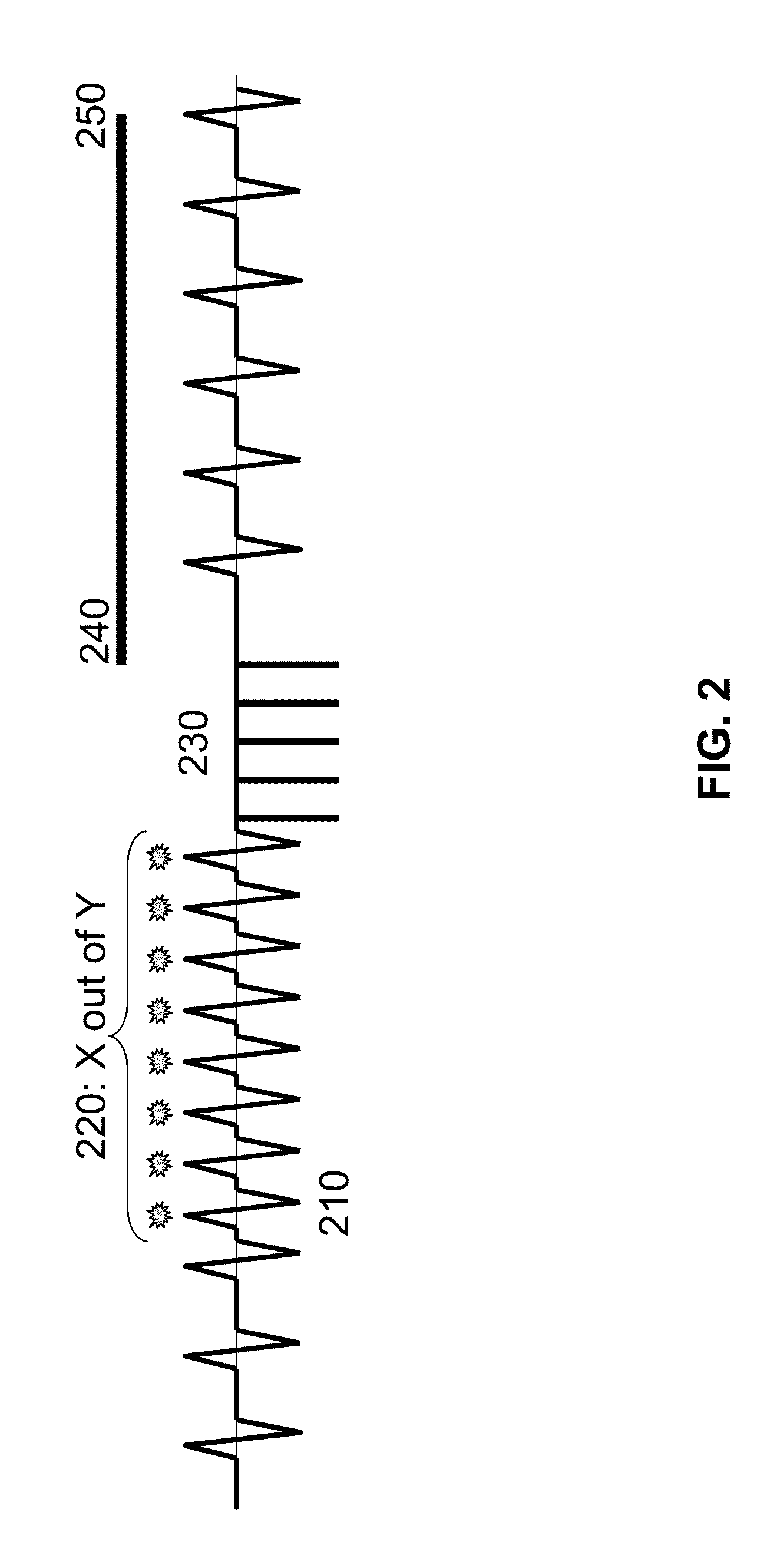
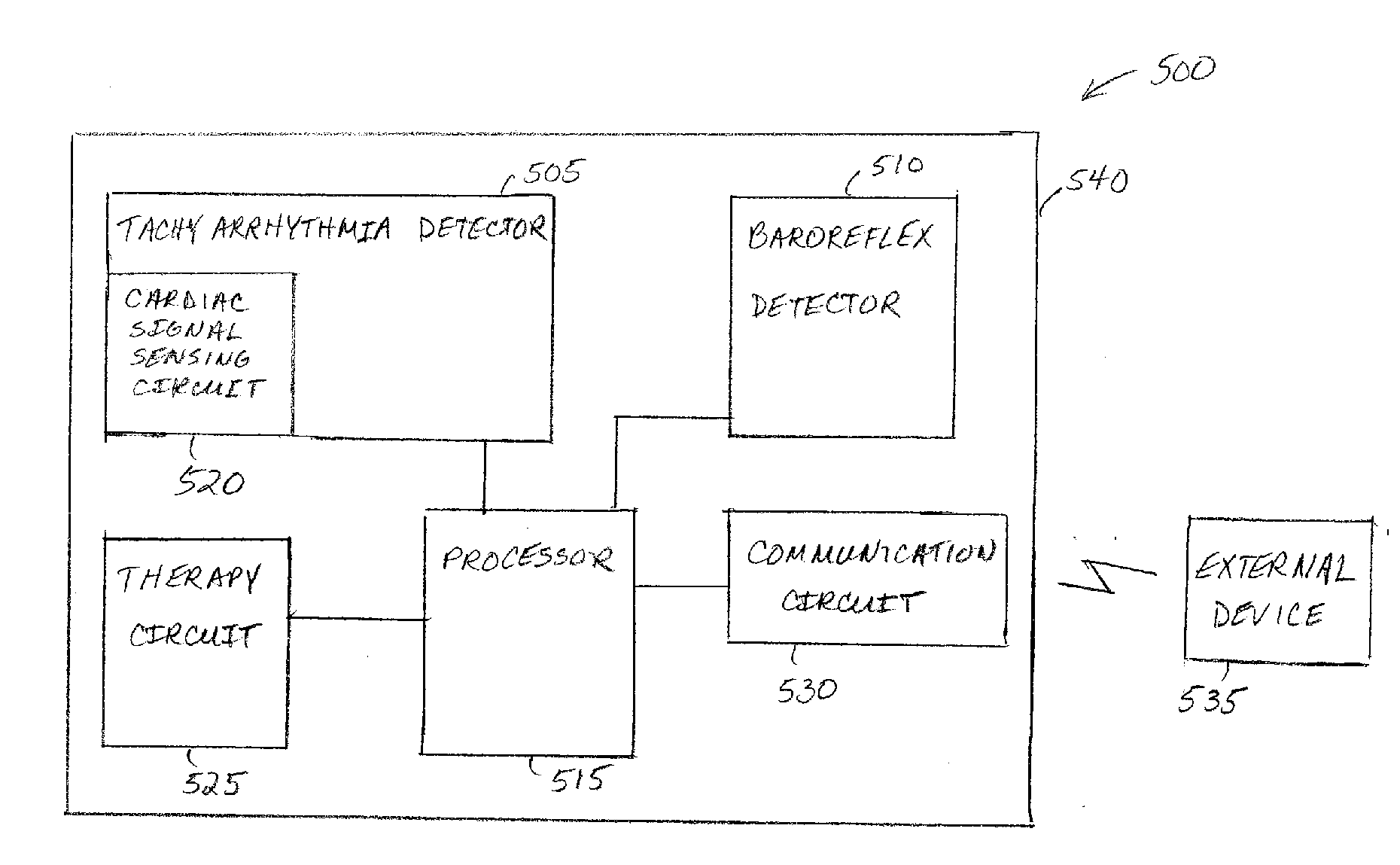
Baroreflex sensitivity monitoring and trending for tachyarrhythmia detection and therapy
A system comprising an implantable medical device (IMD) that includes a tachyarrhythmia detector, a baroreflex detector to obtain baroreflex information, and a processor in communication with the tachyarrhythmia detector and the baroreflex detector. The processor adjusts at least one of a tachyarrhythmia detection parameter of the IMD or a tachyarrhythmia therapy parameter of the IMD using the baroreflex information.
Owner:CARDIAC PACEMAKERS INC
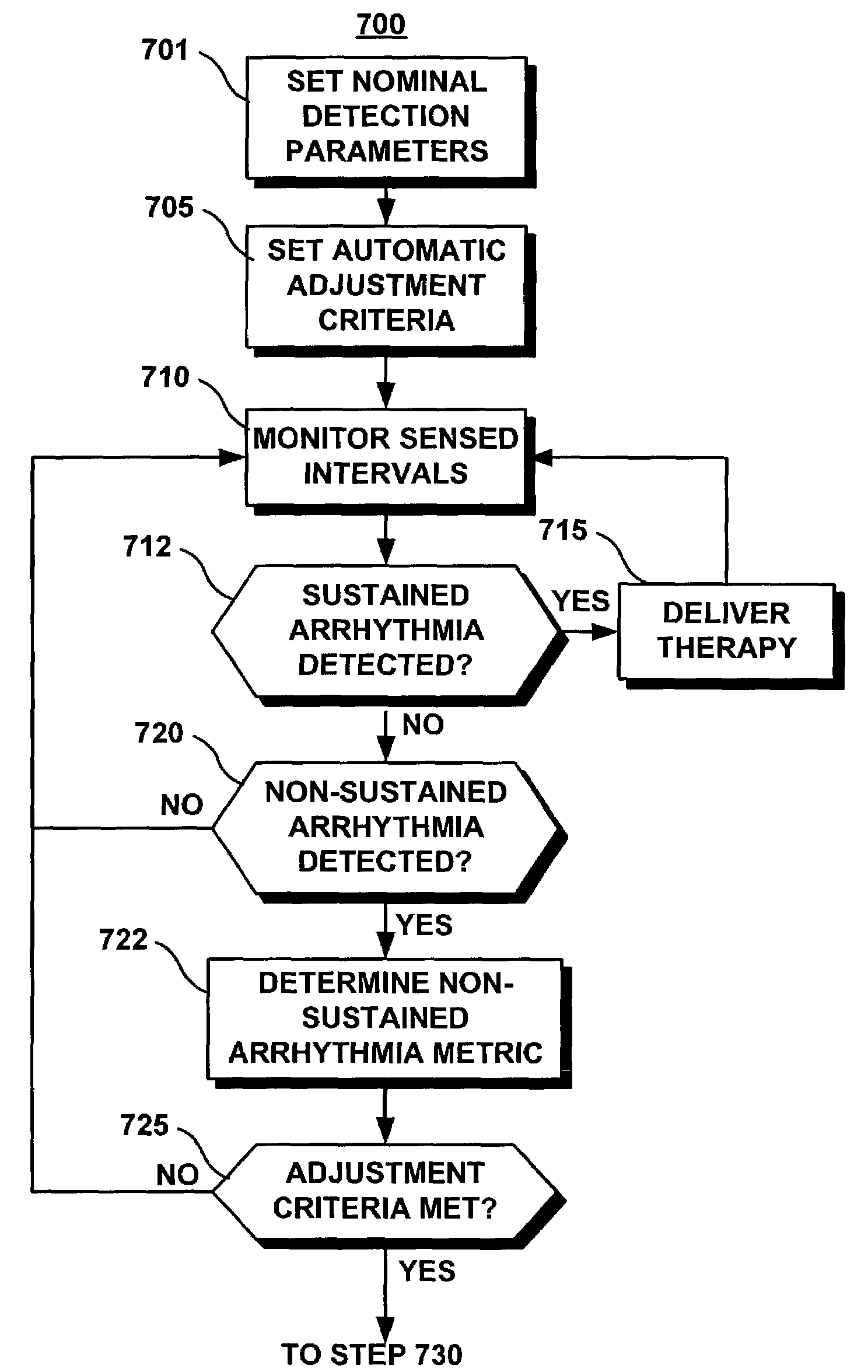
Method for determining a metric of non-sustained arrhythmia occurrence for use in arrhythmia prediction and automatic adjustment of arrhythmia detection parameters
InactiveUS7027856B2Prevent arrhythmiaReduce in quantityElectrocardiographyHeart defibrillatorsMedical deviceMedical treatment
An implantable medical device and associated method are provided for detecting non-sustained arrhythmias and determining a metric of non-sustained arrhythmias. The metric may be used for predicting the occurrence of a sustained arrhythmia or for automatically adjusting the parameters used for detecting a sustained arrhythmia.
Owner:MEDTRONIC INC
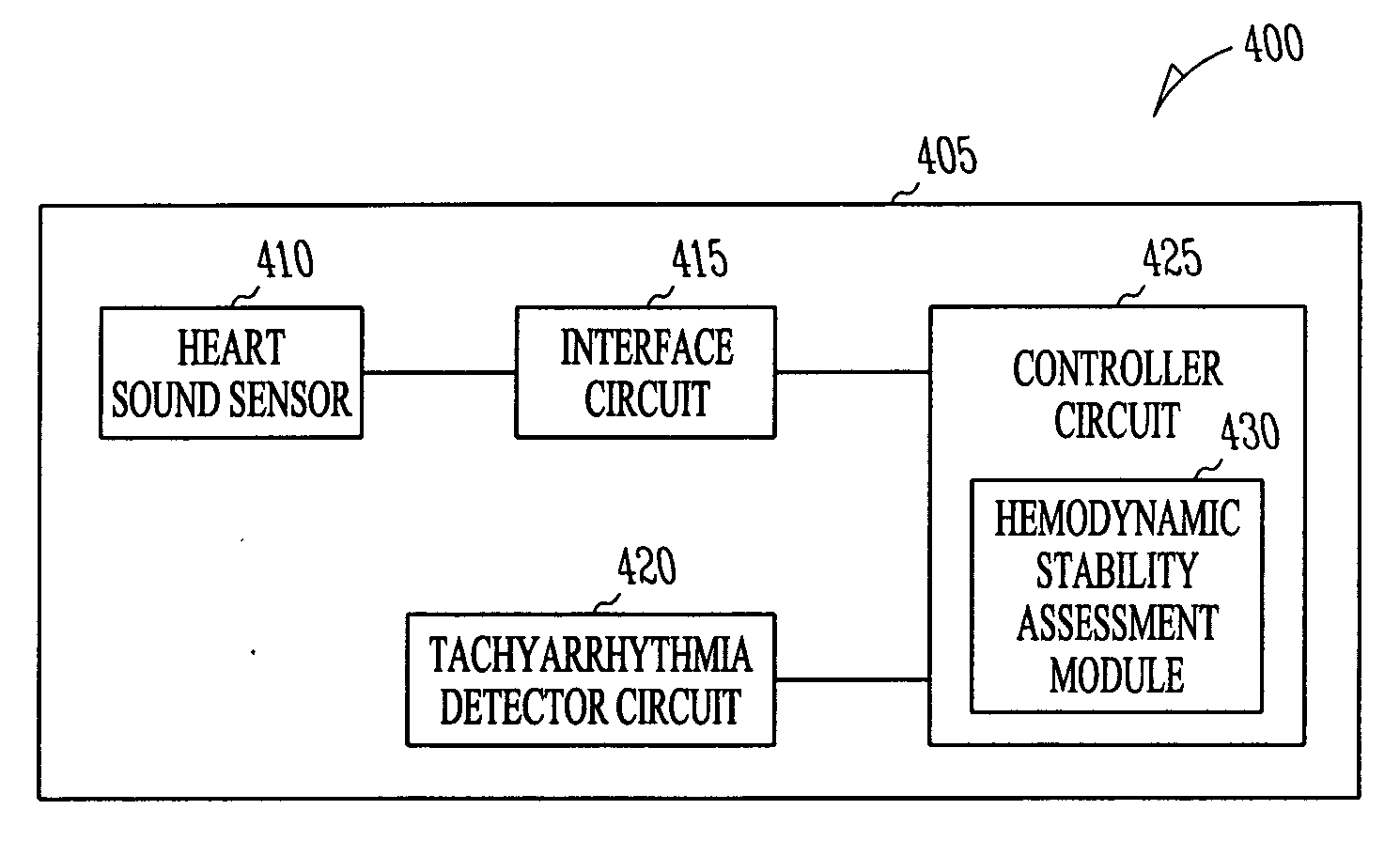
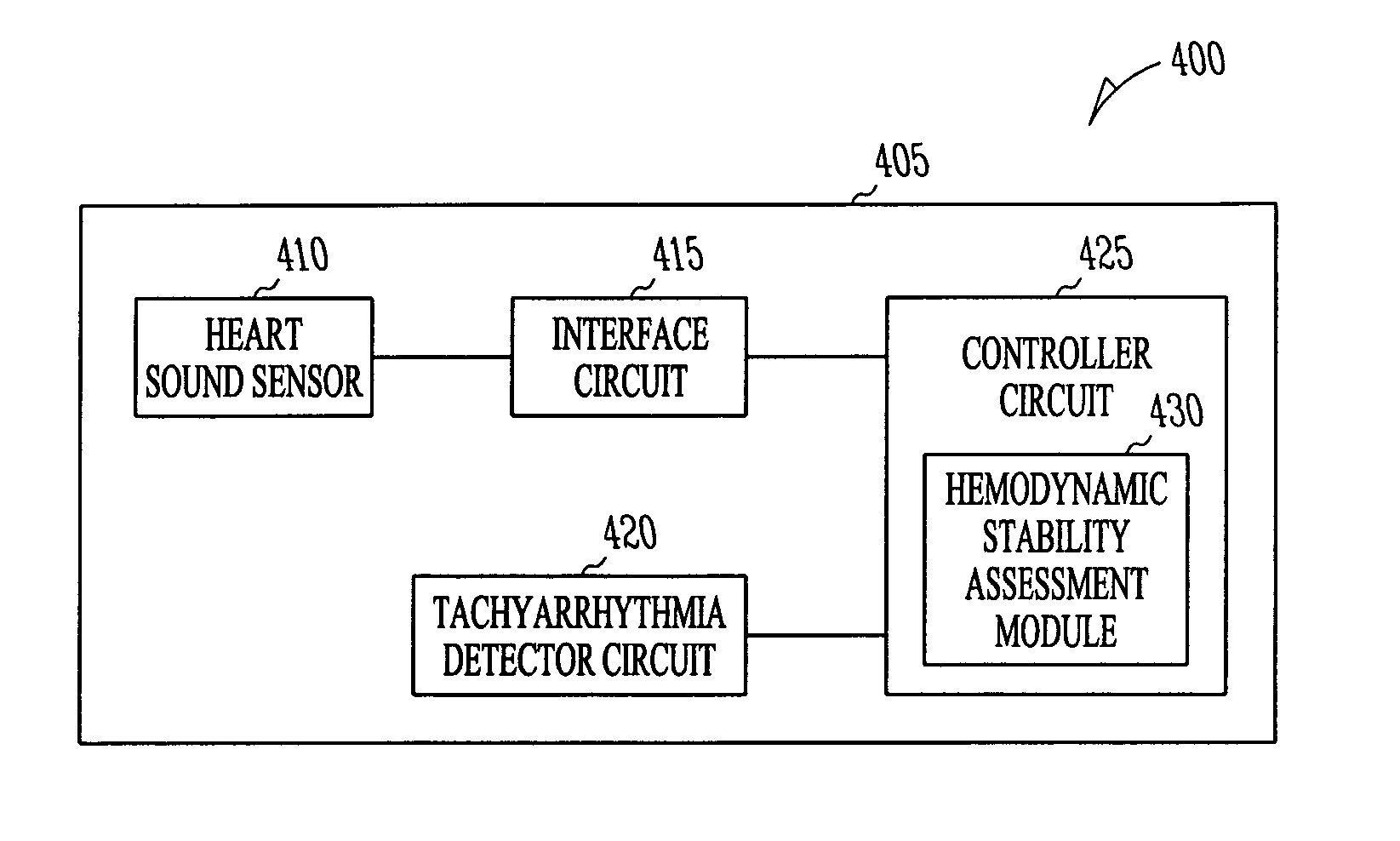
Hemodynamic stability assessment based on heart sounds
ActiveUS20070239218A1Measurement stabilityStethoscopeCatheterVentricular TachyarrhythmiasHeart sounds
A system comprising an implantable medical device (IMD). The IMD includes an implantable sensor operable to produce an electrical signal representative of mechanical activity of a heart of a subject and a controller circuit coupled to the sensor. The IMD also includes a heart sound sensor interface circuit to produce a heart sound signal, a tachyarrhythmia detector, and a controller circuit. The controller circuit includes a hemodynamic stability assessment module configured to determine that at least one episode of ventricular tachyarrhythmia is detected in a subject and obtain a measurement of hemodynamic stability of the ventricular tachyarrhythmia from the heart sound signal.
Owner:CARDIAC PACEMAKERS INC
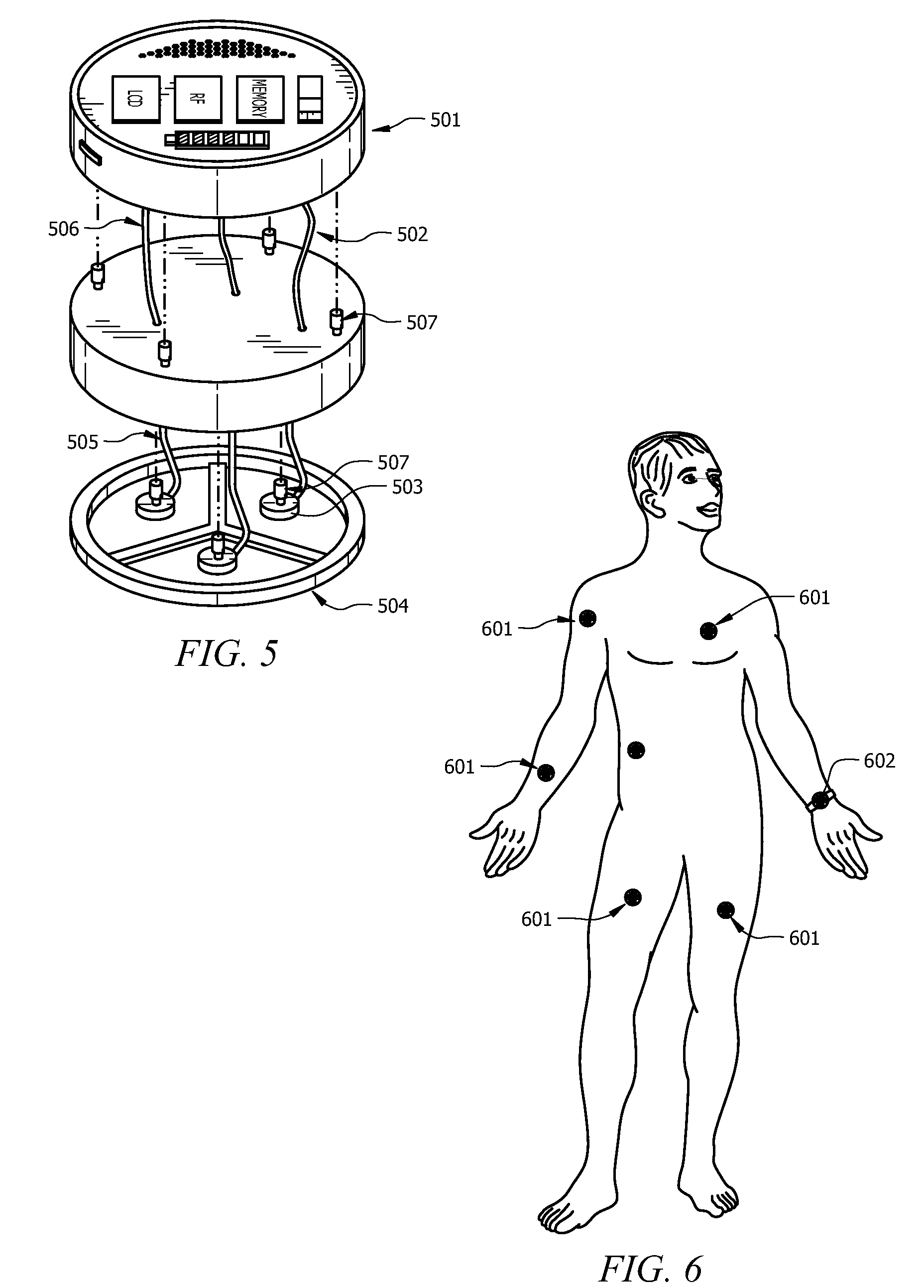
Diagnostic device for remote sensing and transmitting biophysiological signals
InactiveUS20100042012A1Noise minimizationMaximize signalElectrocardiographySensorsSpatially resolvedWireless transmission
A diatrophic, bio-physiological interface is self-contained with onboard intensification, filtering, and signal processing and is wirelessly enabled (idio-electrode), with multiple sensory system for bio-physiological measurements, described herein utilizes spatially resolved potential profiles from a cluster of mini electrodes to form constituent sets comprising mini sensorial electrodes. The sets of sub electrodes containing the clusters are jointly optimized to attain measurable gradient of some diagnostic value. The present invention provides a distinct lead-free single electrode that is rotationally invariant with onboard Digital Signal Processor for arrhythmia detection, source encoding, and passive and active wireless transmission. Additionally, in one aspect of the present invention the lead-free idio-electrode bio-physiological adapter allows for utmost clinical operational freedom and dramatically obviates the needs for leads of any length that invariably encumber the acquisition and performance of electrocardiogram recordings of any sort.
Owner:ALHUSSINY KARIM
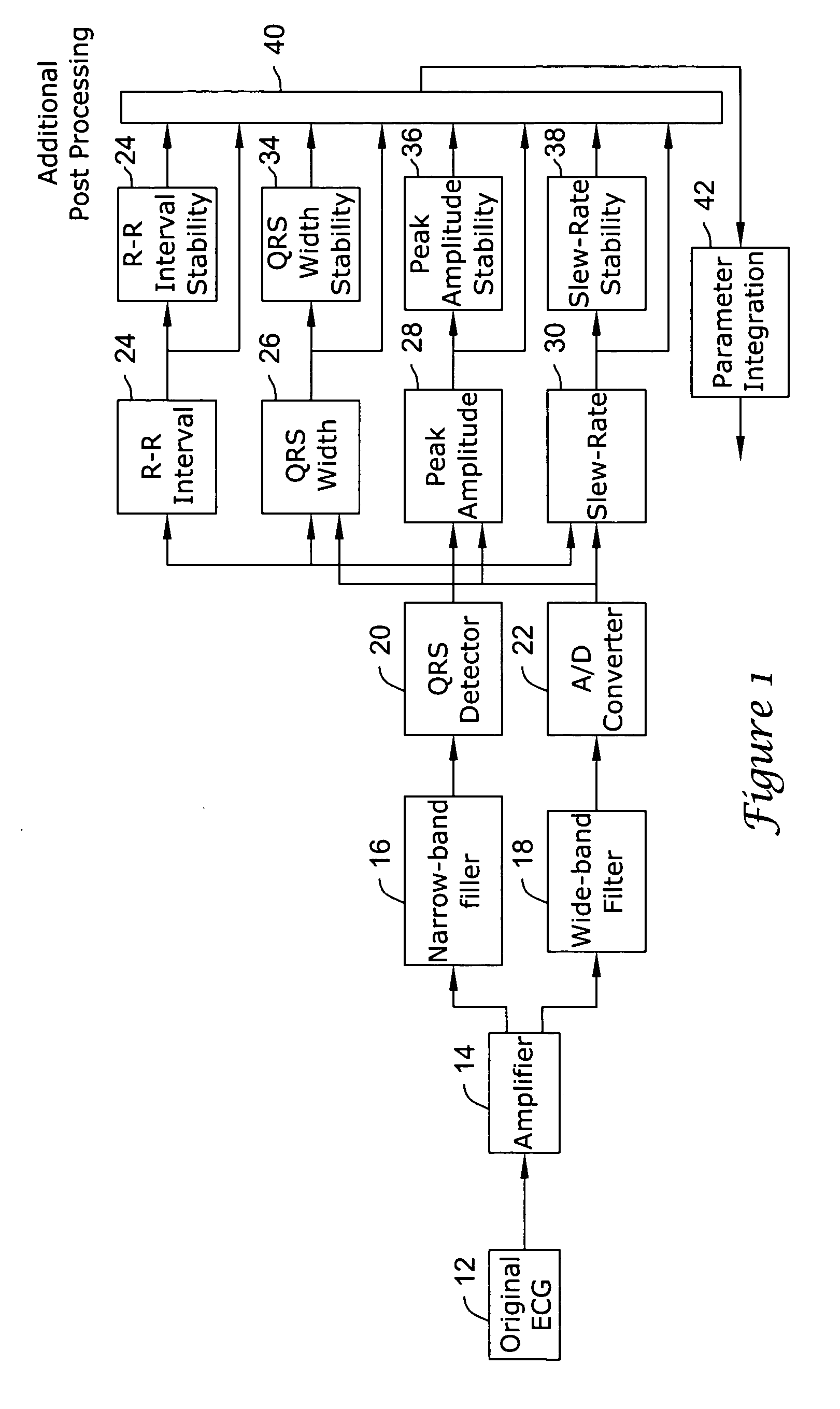
Apparatus and method of arrhythmia detection in a subcutaneous implantable cardioverter/defibrillator
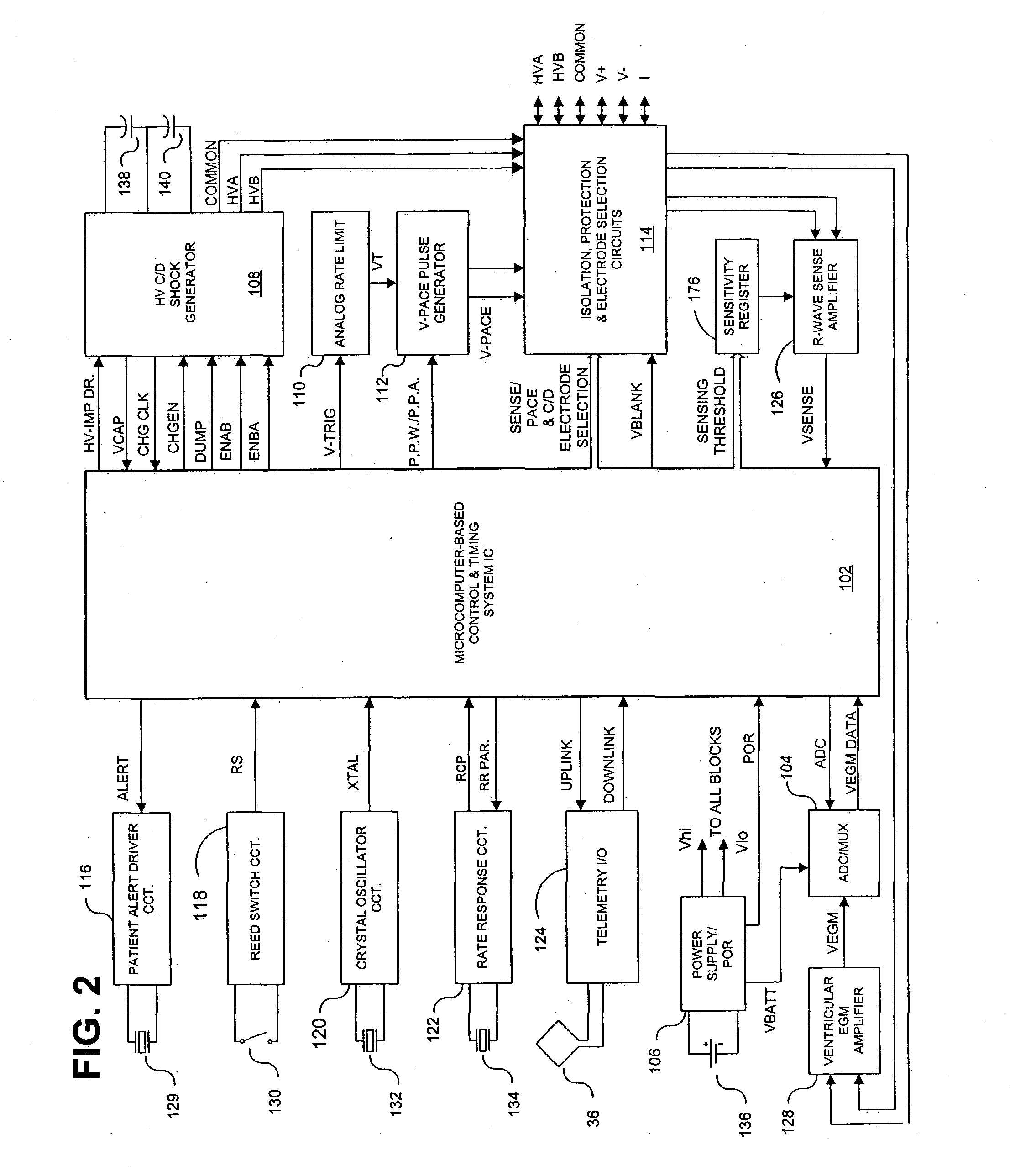
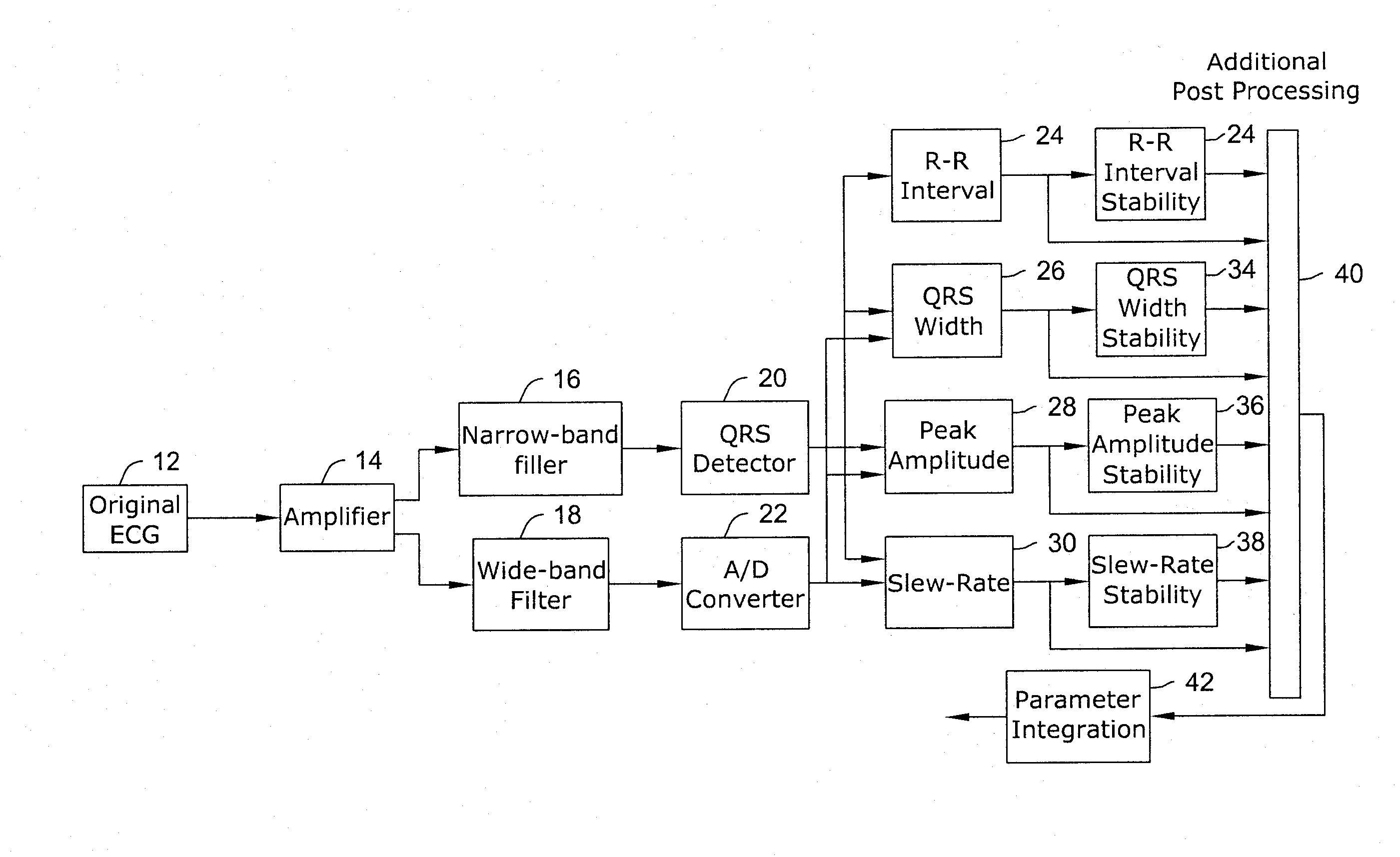
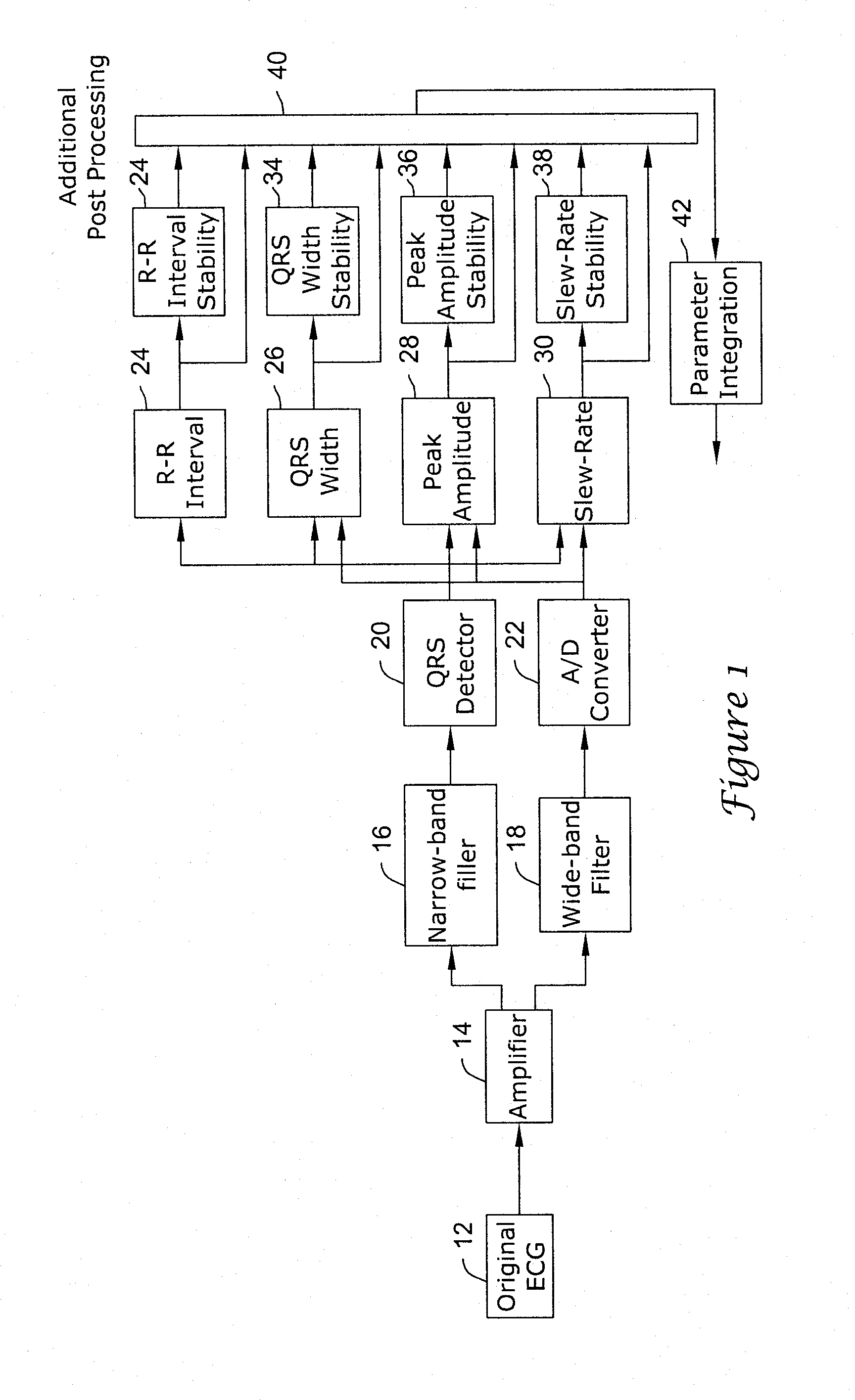
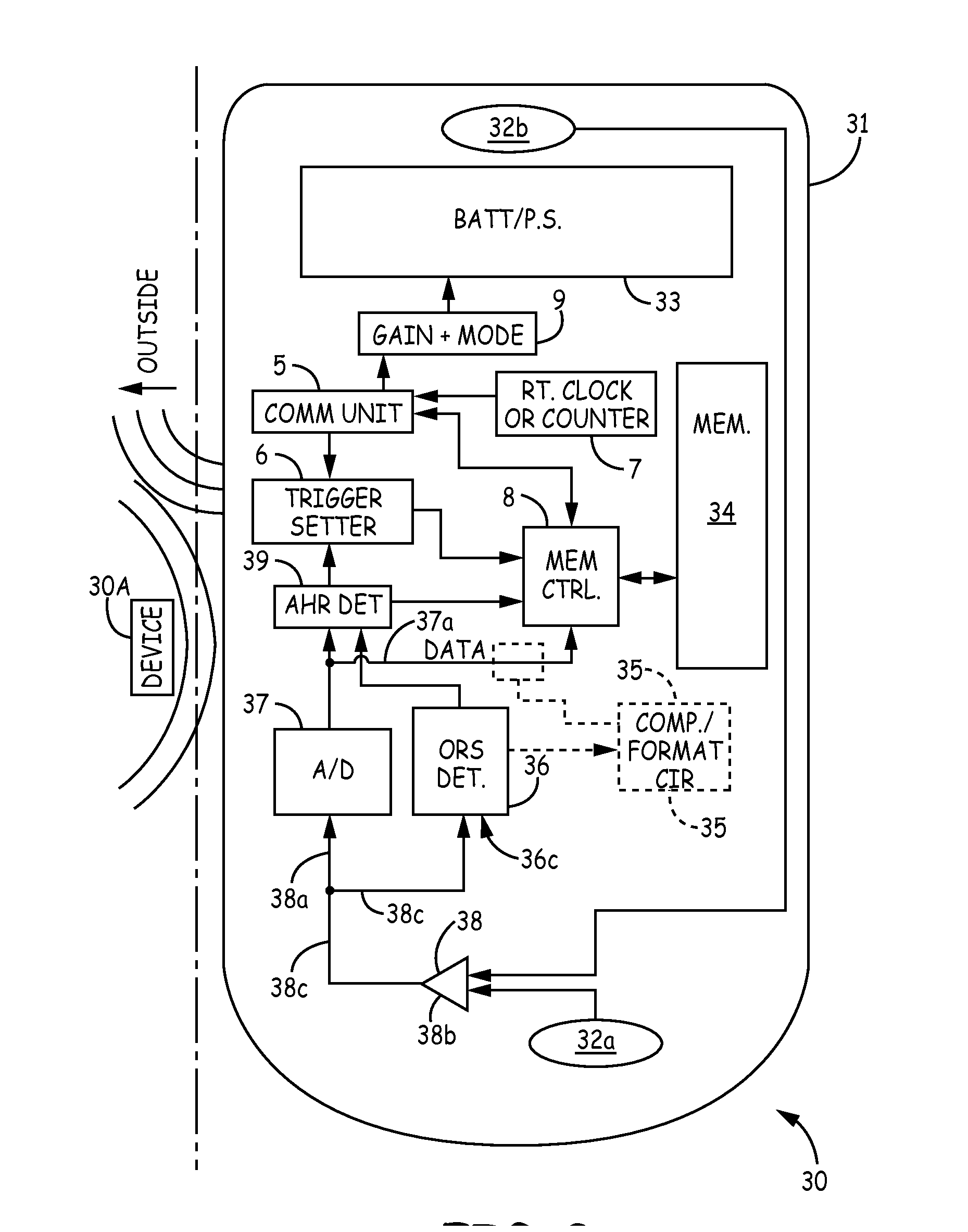
In a subcutaneous implantable cardioverter / defibrillator, cardiac arrhythmias are detected to determine necessary therapeutic action. Cardiac signal information is sensed from far field electrodes implanted in a patient. The sensed cardiac signal information is then amplified and filtered. Parameters such as rate, QRS pulse width, cardiac QRS slew rate, amplitude and stability measures of these parameters from the filtered cardiac signal information are measured, processed and integrated to determine if the cardioverter / defibrillator needs to initiate therapeutic action.
Owner:CAMERON HEALTH
Subcutaneous cardiac sensing and stimulation system employing blood sensor
Owner:CARDIAC PACEMAKERS INC
Automatic EGM amplitude measurements during tachyarrhythmia episodes
InactiveUS20040260350A1ElectrocardiographyHeart stimulatorsAudio power amplifierVentricular Tachyarrhythmias
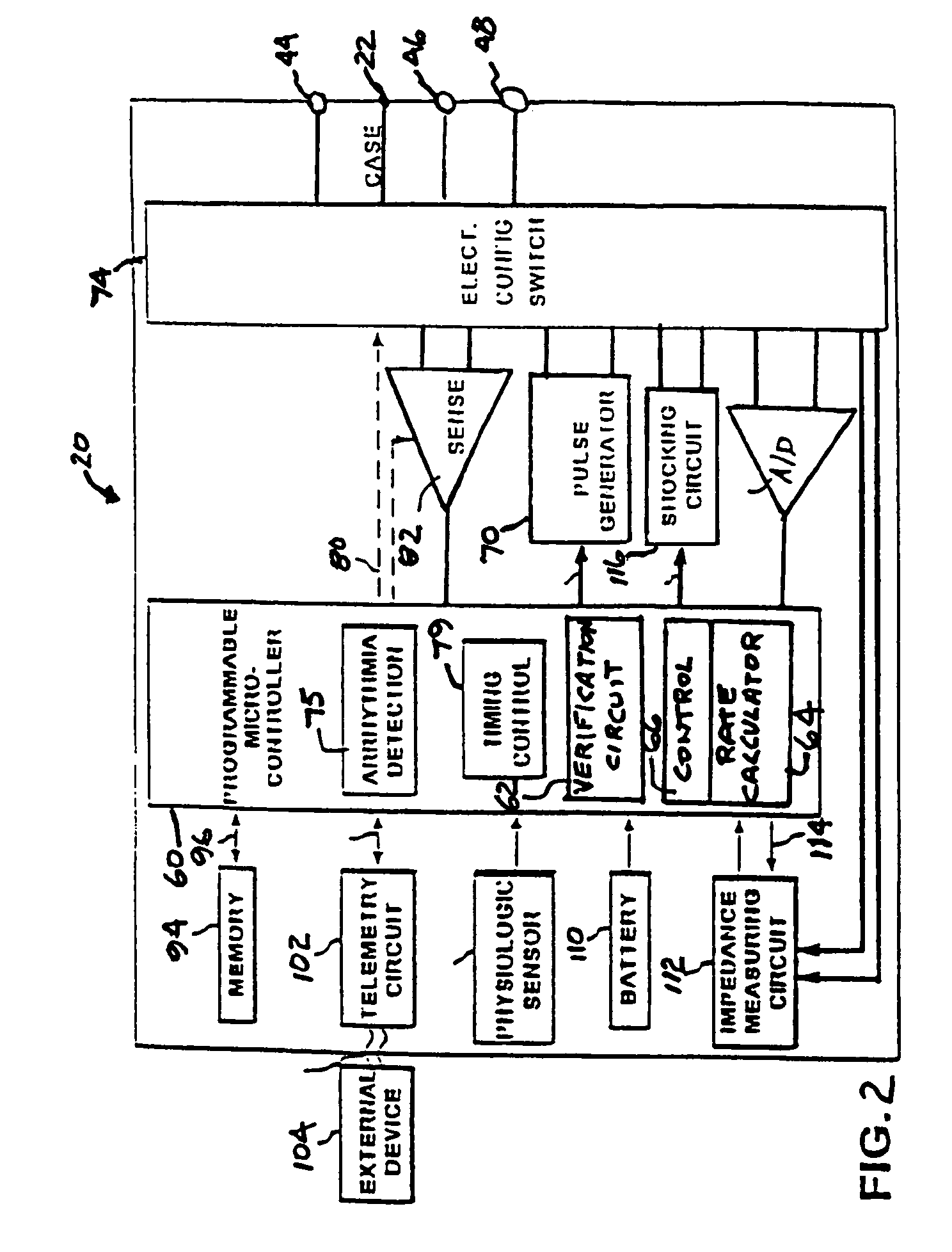
In an IMD, when tachyarrhythmia detection criterion are satisfied or a high intrinsic heart rate is detected, a peak amplitude detection circuit is enabled to detect the peak amplitude of the cardiac signal of interest, i.e., the P-wave in the case of atrial tachyarrhythmias and the R-wave in case of ventricular tachyarrhythmias. Peak amplitude data is accumulated for subsequent use in setting sensing thresholds and / or gain of a sense amplifier to reduce undersensing of lower amplitude cardiac signals during such tachyarrhythmias.
Owner:MEDTRONIC INC
Apparatus and Method of Arrhythmia Detection in a Subcutaneous Implantable Cardioverter/Defibrillator
In a subcutaneous implantable cardioverter / defibrillator, cardiac arrhythmias are detected to determine necessary therapeutic action. Cardiac signal information is sensed from far field electrodes implanted in a patient. The sensed cardiac signal information is then amplified and filtered. Parameters such as rate, QRS pulse width, cardiac QRS slew rate, amplitude and stability measures of these parameters from the filtered cardiac signal information are measured, processed and integrated to determine if the cardioverter / defibrillator needs to initiate therapeutic action.
Owner:CAMERON HEALTH
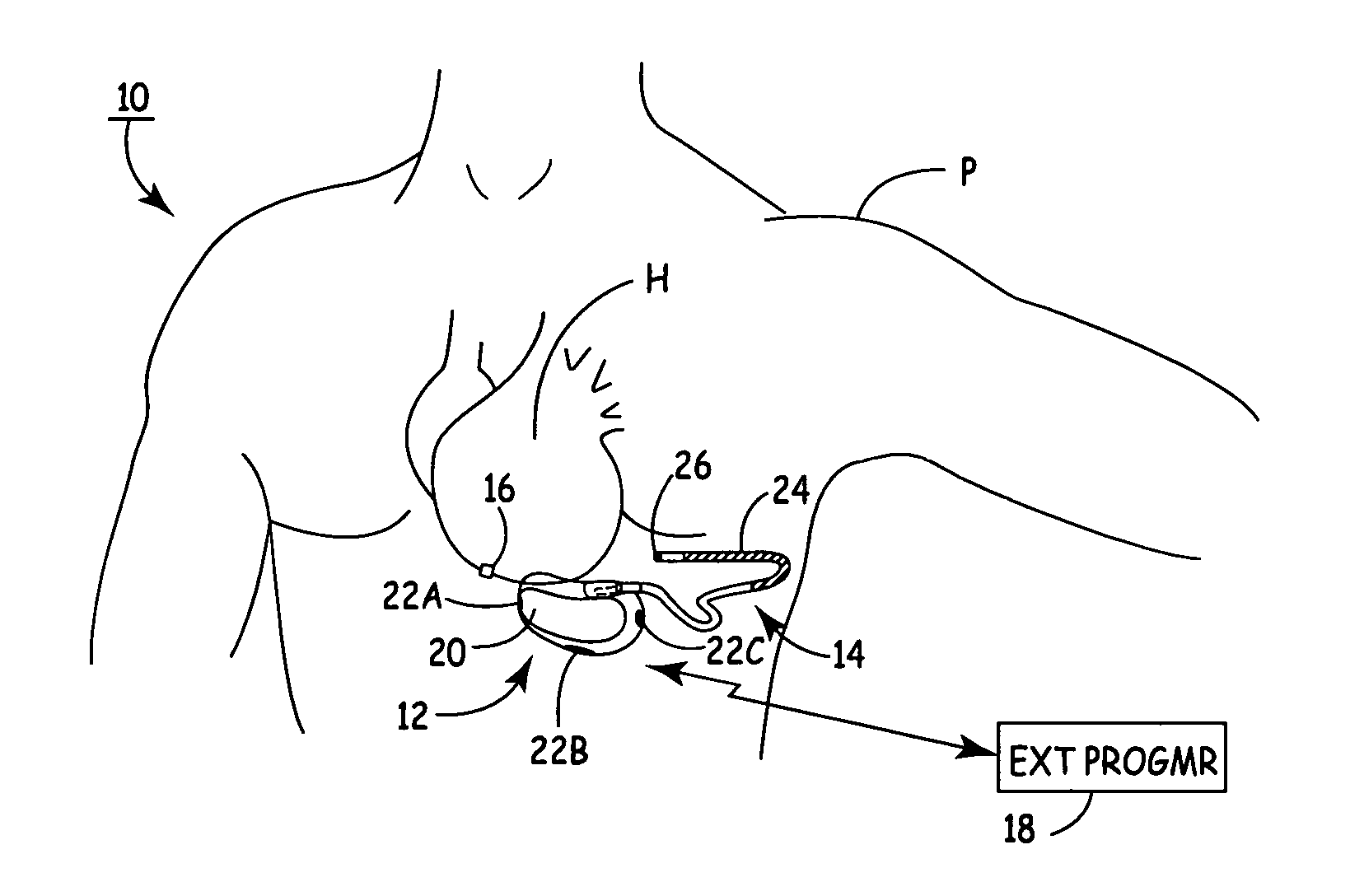
Subcutaneous ICD with separate cardiac rhythm sensor
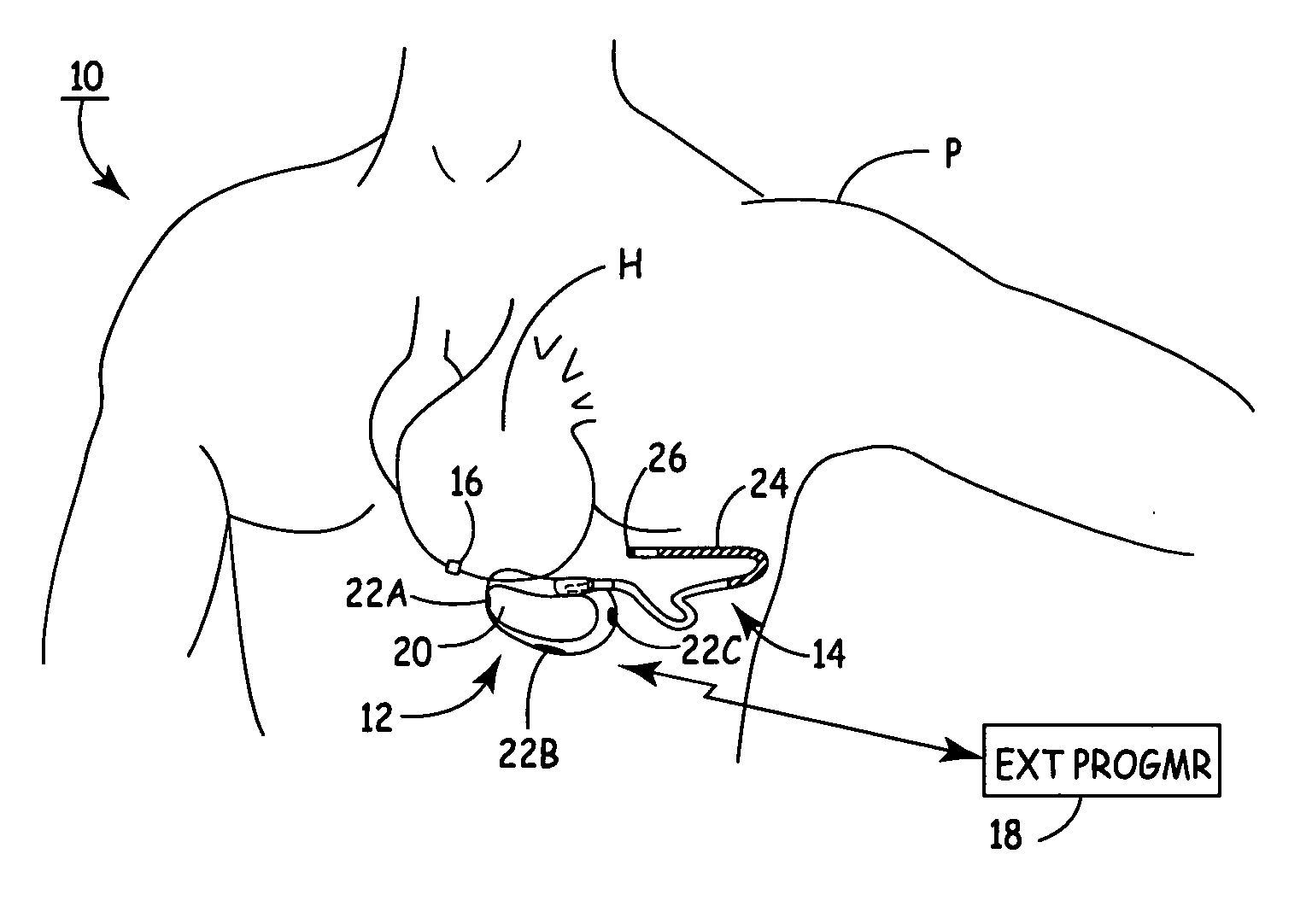
A cardiac rhythm sensor positioned on or close to the heart senses electrical or mechanical activity and transmits a cardiac rhythm signal wirelessly to a subcutaneous ICD. Arrhythmia detection and delivery of therapy are performed by the SubQ ICD based upon the cardiac rhythm signal received from the sensor.
Owner:MEDTRONIC INC
Zoneless tachyarrhythmia detection with real-time rhythm monitoring
A system including an implantable medical device (IMD). The IMD includes a ventricular contraction sensing circuit that provides a sensed ventricular contraction signal, a timer circuit that provides a ventricular time interval between ventricular contractions, and a controller circuit coupled to the timer circuit, the controller circuit determines the ventricular contraction rate using the ventricular time interval. The controller circuit further includes a tachyarrhythmia detection module that declares tachyarrhythmia, in response to detecting a sudden rate increase, without comparing a ventricular rate or time interval to a respective tachyarrhythmia detection rate or time interval threshold.
Owner:CARDIAC PACEMAKERS INC
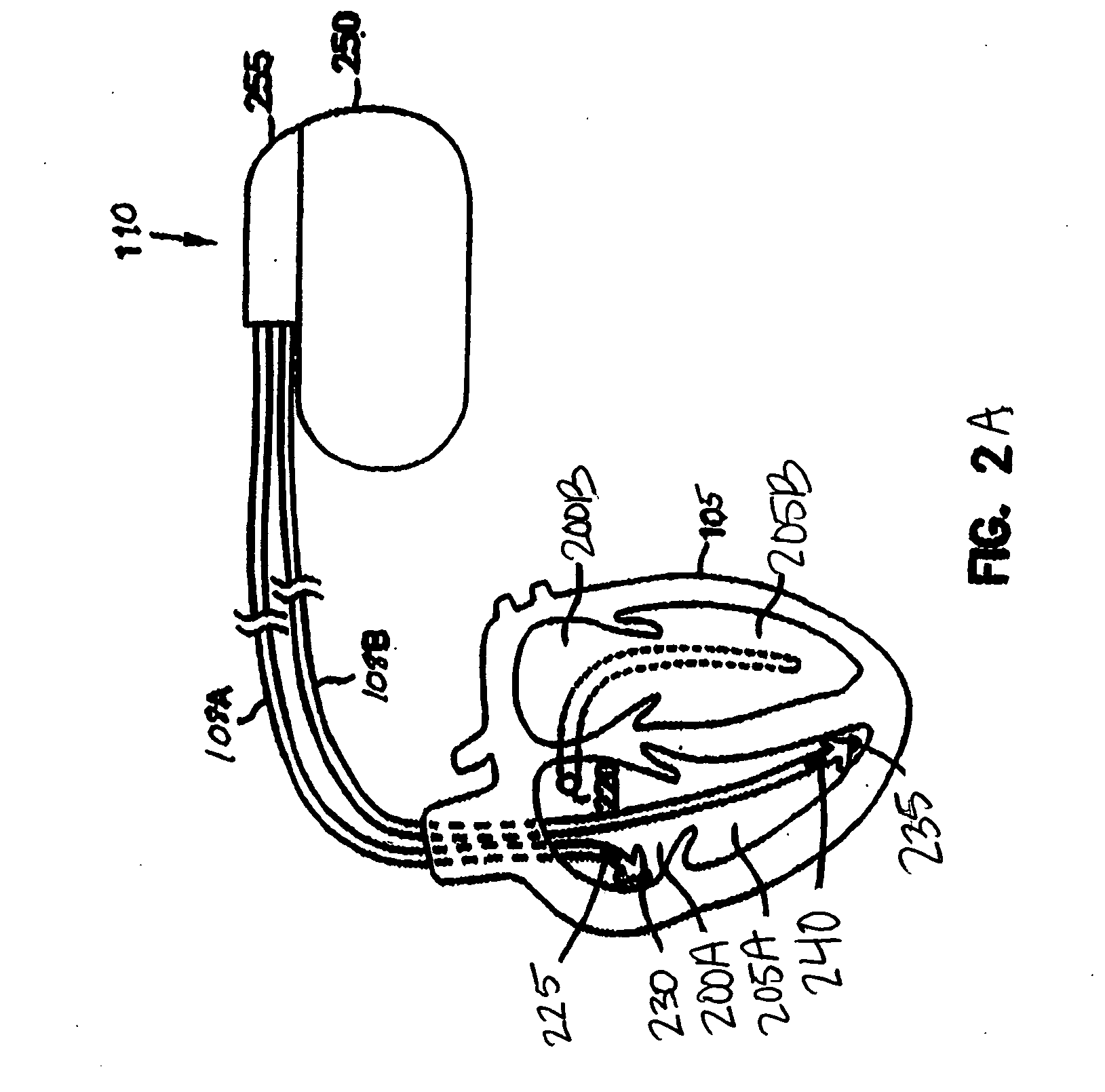
Subcutaneous cardiac stimulation device, system, and method providing accelerated arrhythmia detection verification and transient rate compensation
A subcutaneous cardiac stimulation system verifies accelerated arrhythmia detection before delivering accelerated arrhythmia therapy to the heart. The stimulation system includes a verification circuit that verifies detection of the accelerated arrhythmia with each of first and second sense channels utilizing first and second electrode configurations. The therapy circuit delivers the stimulation therapy to the heart if the accelerated arrhythmia detection is verified with each of the first and second electrode configurations. The system also compensates for transient rate changes during the detection of the accelerated arrhythmia.
Owner:PACESETTER INC
Method and apparatus for automatic configuration of implantable medical devices
ActiveUS20150088216A1Implantation is simpleImprove the level ofPhysical therapies and activitiesHeart stimulatorsMedicineImplanted device
A system including a programmable implantable monitoring device and a programmer for programming the device and a method of use thereof. The programmer may be configured to transmit programming commands responsive to entry of a reason for monitoring to the implantable device including a prioritization of an arrhythmia storage criterion. The implantable may be configured to thereafter store and / or transmit records of the arrhythmia according to the prioritization. The programmer may be configured to transmit the patient's age to the implantable device and the implantable may be configured to thereafter apply arrhythmia detection criteria based upon the patient's age.
Owner:MEDTRONIC INC
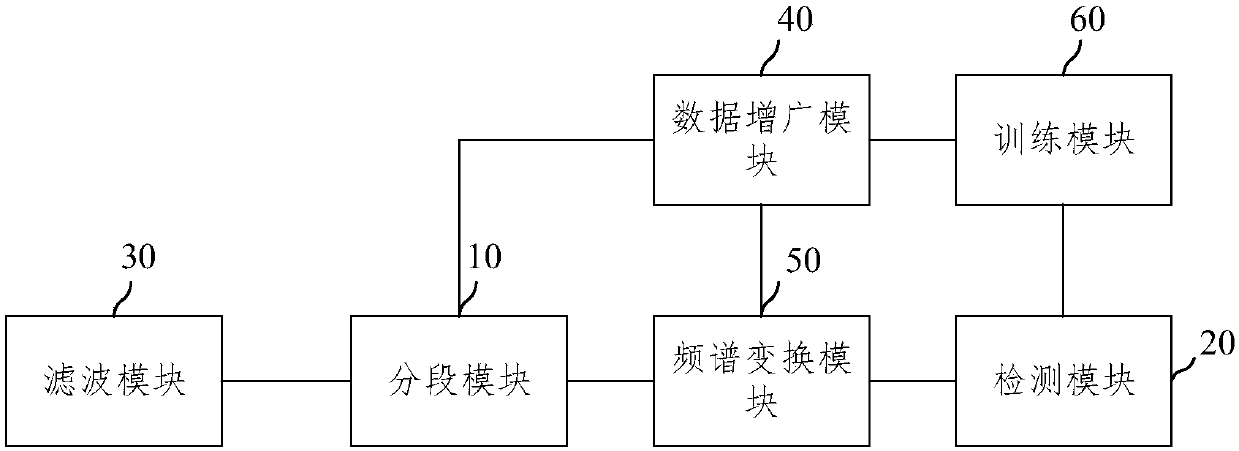
Detection system of arrhythmias based on convolutional neural network
InactiveCN108030488AHigh reliability predictionImprove accuracyMedical imagingDiagnostic recording/measuringData segmentFeature extraction
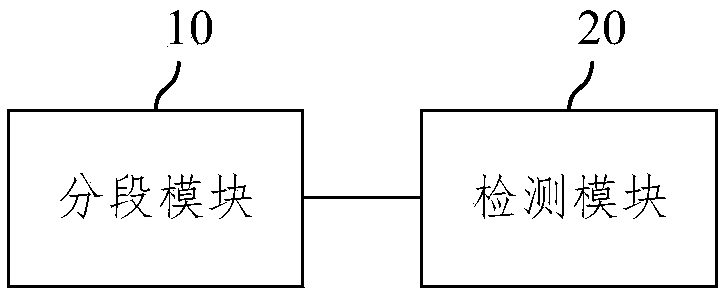
The invention provides a detection system of arrhythmias based on a convolutional neural network. The system comprises a segmentation module and a detection module; the segmentation module is used forsegmenting the obtained K-lead electrocardiogram data of a first patient in chronological order, multiple K-lead electrocardiogram data segments are obtained, the length of each K-lead electrocardiogram data segment is equal, and K is a positive integer; the detection module is used for inputting the multiple K-lead electrocardiogram data segments into a trained convolutional neural network modelin chronological order, and a type of arrhythmia in the first patient is obtained. According to the provided detection system of arrhythmias based on the convolutional neural network, by combining the convolutional neural network with the electrocardiogram data, feature extraction and classification of arrhythmia are integrated into one step, multiple leads and timing sequence information of electrocardiogram are fully excavated, a high reliable prediction of a case can be made, and thus the accuracy of arrhythmia detection is improved.
Owner:北京医拍智能科技有限公司
Hemodynamic stability assessment based on heart sounds
A system comprising an implantable medical device (IMD). The IMD includes an implantable sensor operable to produce an electrical signal representative of mechanical activity of a heart of a subject and a controller circuit coupled to the sensor. The IMD also includes a heart sound sensor interface circuit to produce a heart sound signal, a tachyarrhythmia detector, and a controller circuit. The controller circuit includes a hemodynamic stability assessment module configured to determine that at least one episode of ventricular tachyarrhythmia is detected in a subject and obtain a measurement of hemodynamic stability of the ventricular tachyarrhythmia from the heart sound signal.
Owner:CARDIAC PACEMAKERS INC
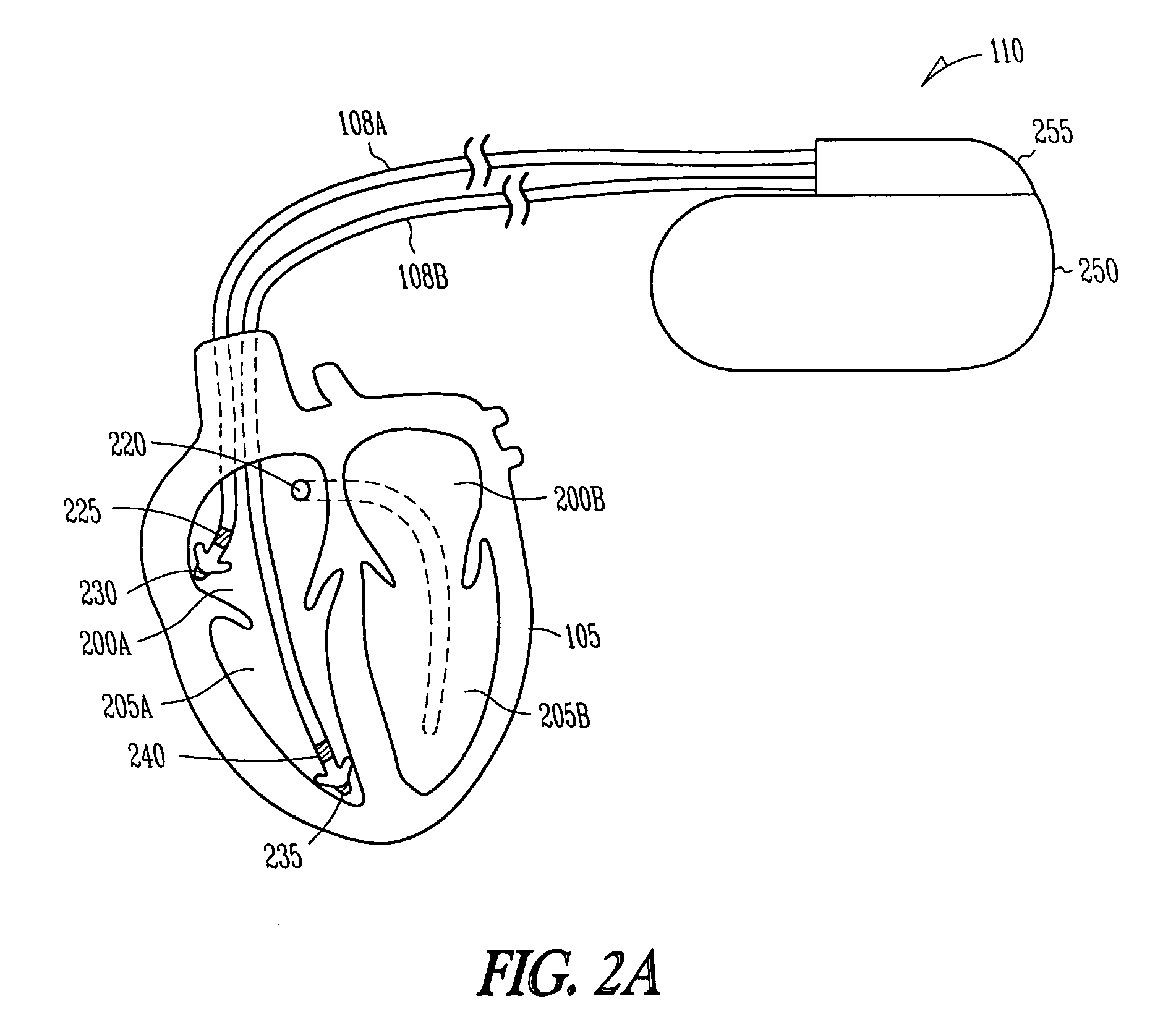
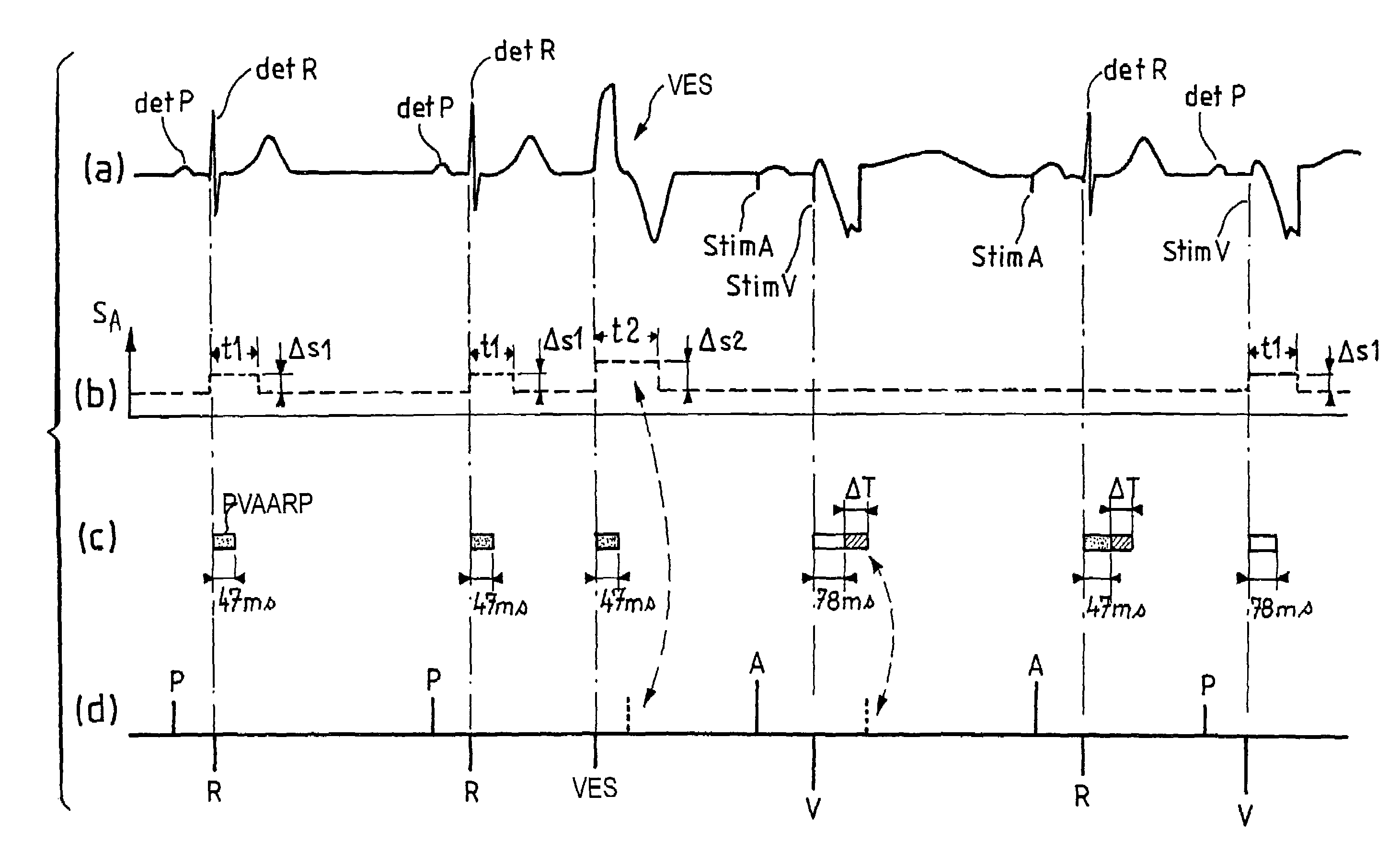
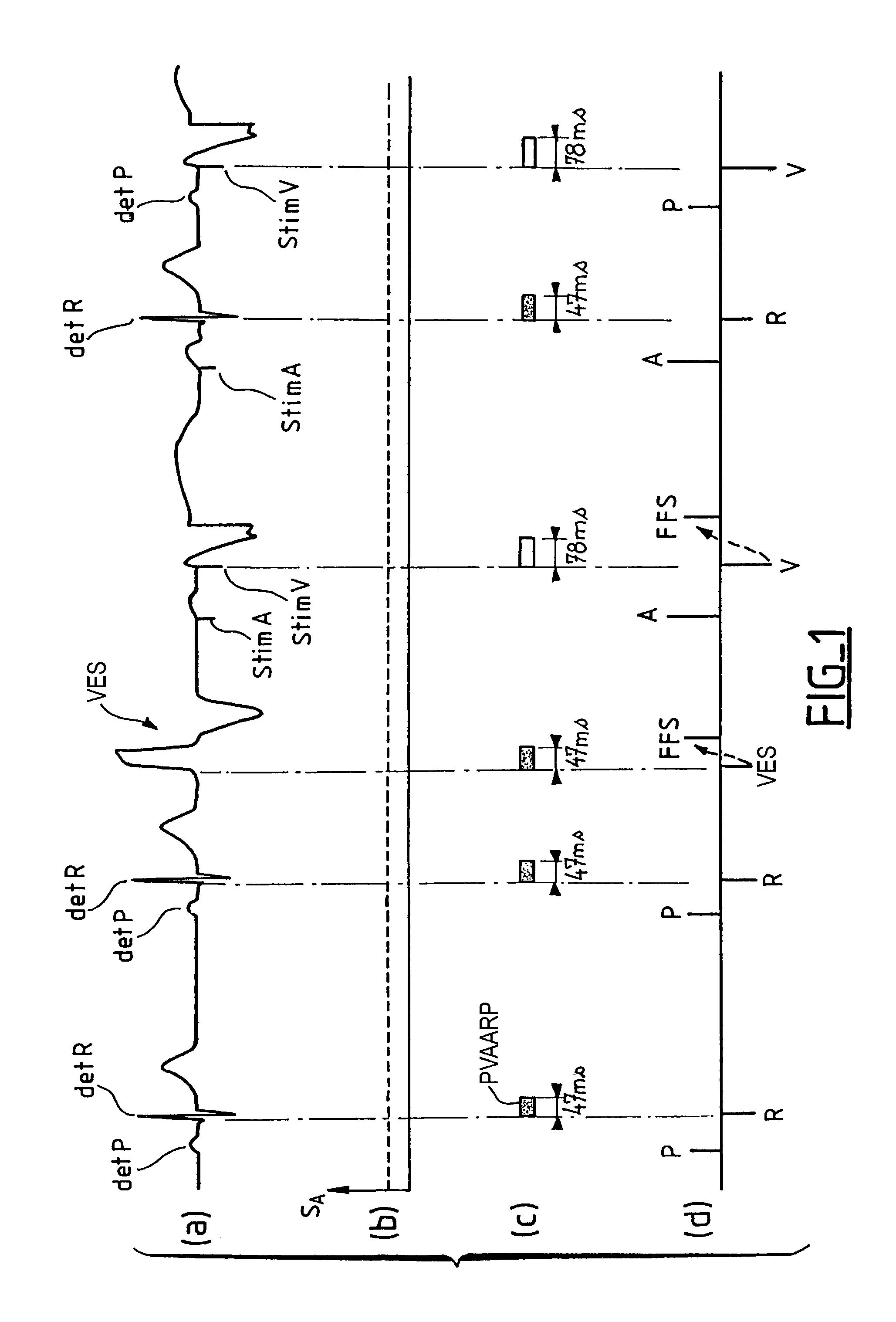
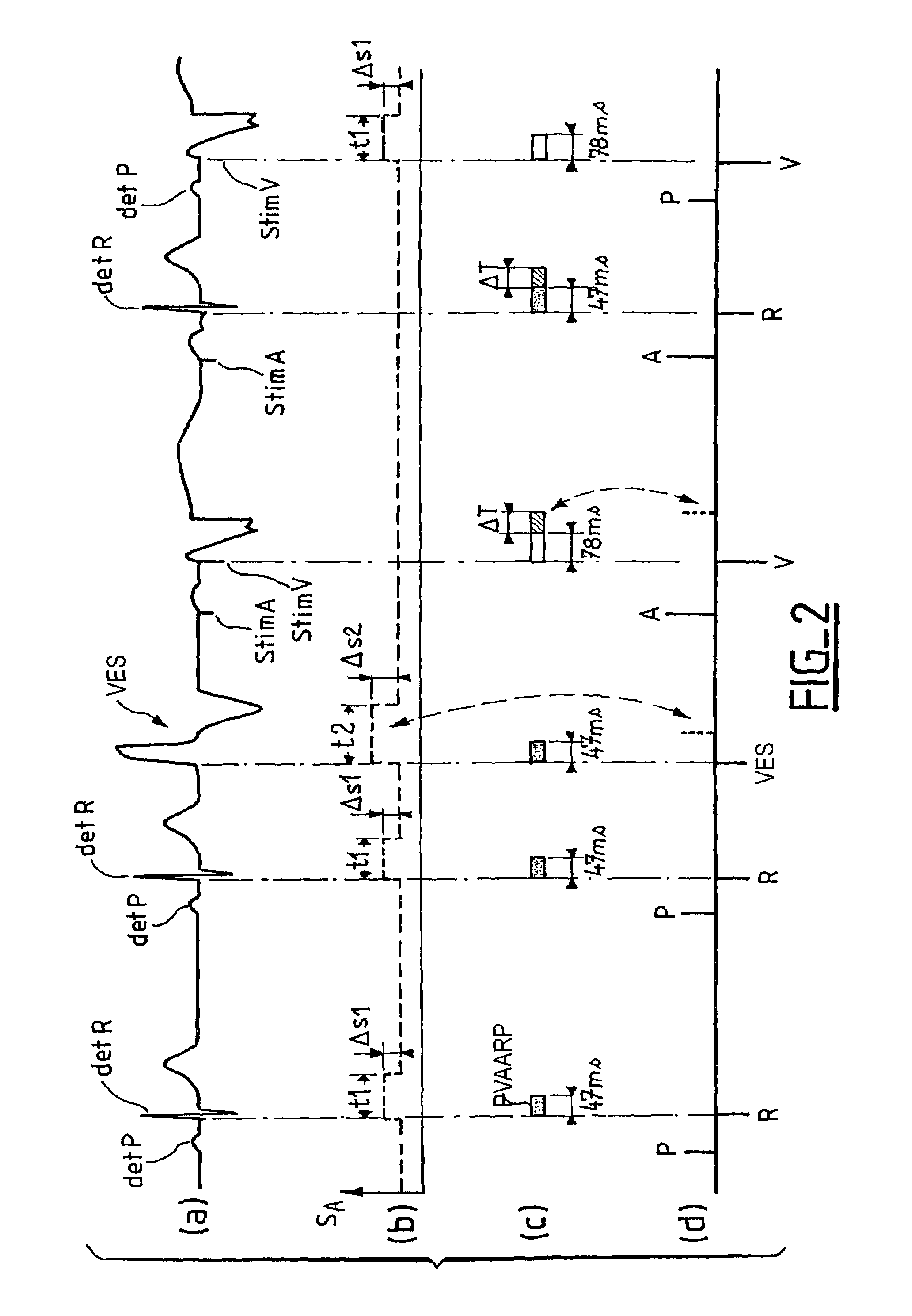
Atrial arrhythmia detection for an active implantable medical device
ActiveUS7113826B2Avoid detectionHeart stimulatorsDiagnostic recording/measuringAtrial cavityCardiac pacemaker electrode
Apparatus for detecting atrial arrhythmias in the treatment of disorders of the heartbeat rate in active implantable medical devices of the pacemaker, cardioverter, defribillator and / or multisite type. This device includes conventional systems, circuits and control algorithm for detecting spontaneous and stimulated ventricular events (R, V) and atrial events (P, A), indicating the delivery of a ventricular and / or atrial event, and inhibiting the detection of atrial events after detection of a ventricular event throughout a post-ventricular atrial absolute refractory period (PVAARP). Detecting atrial events includes protecting against the detection of atrial signals that do not correspond to an atrial event that has actually occurred, in particular protecting against atrial detection of far-field signals caused by a ventricular event. The protection operates by a dynamic adjustment of the sensitivity of detection by temporarily raising (t1, t2) a detection threshold (ΔS1, ΔS2) after detection of a ventricular event without detection of a preceding (spontaneous or stimulated) atrial event during the same cardiac cycle.
Owner:SORIN CRM
Automatic electrocardiosignal classification method based on single channel
ActiveCN109077715ARelieve pressureOvercoming ECG specificity issuesDiagnostic recording/measuringSensorsFeature vectorEcg signal
The invention provides an automatic electrocardiosignal classification method based on single channel. The method comprises the steps that a limb channel electrocardiosignal is received through Web socket; a wavelet median threshold method is adopted to perform electrocardiosignal denoising; a Pan-Tompkins method is used for conducting R wave detection, the electrocardiosignal is segmented based on R wave to resolve RR period characteristics, corresponding characteristics vectors are obtained by sequentially conducting empirical mode decomposition, Gaussian random projection matrix, polynomialfitting and interval extremum on obtained electrocardiogram segments; normalization is conducted on obtained characteristic features to allow the characteristic features to be conformed to standardized normal distribution, the standardized characteristic vectors are input to a trained XGboost model, and a corresponding detecting value is output. By means of the method, the problem of personal electrocardiosignal specificity is solved, the method is run at a server end, the pressure on a client is relieved, and the method has higher reference value on N and V type arrhythmias detection results.
Owner:BEIJING UNIV OF TECH
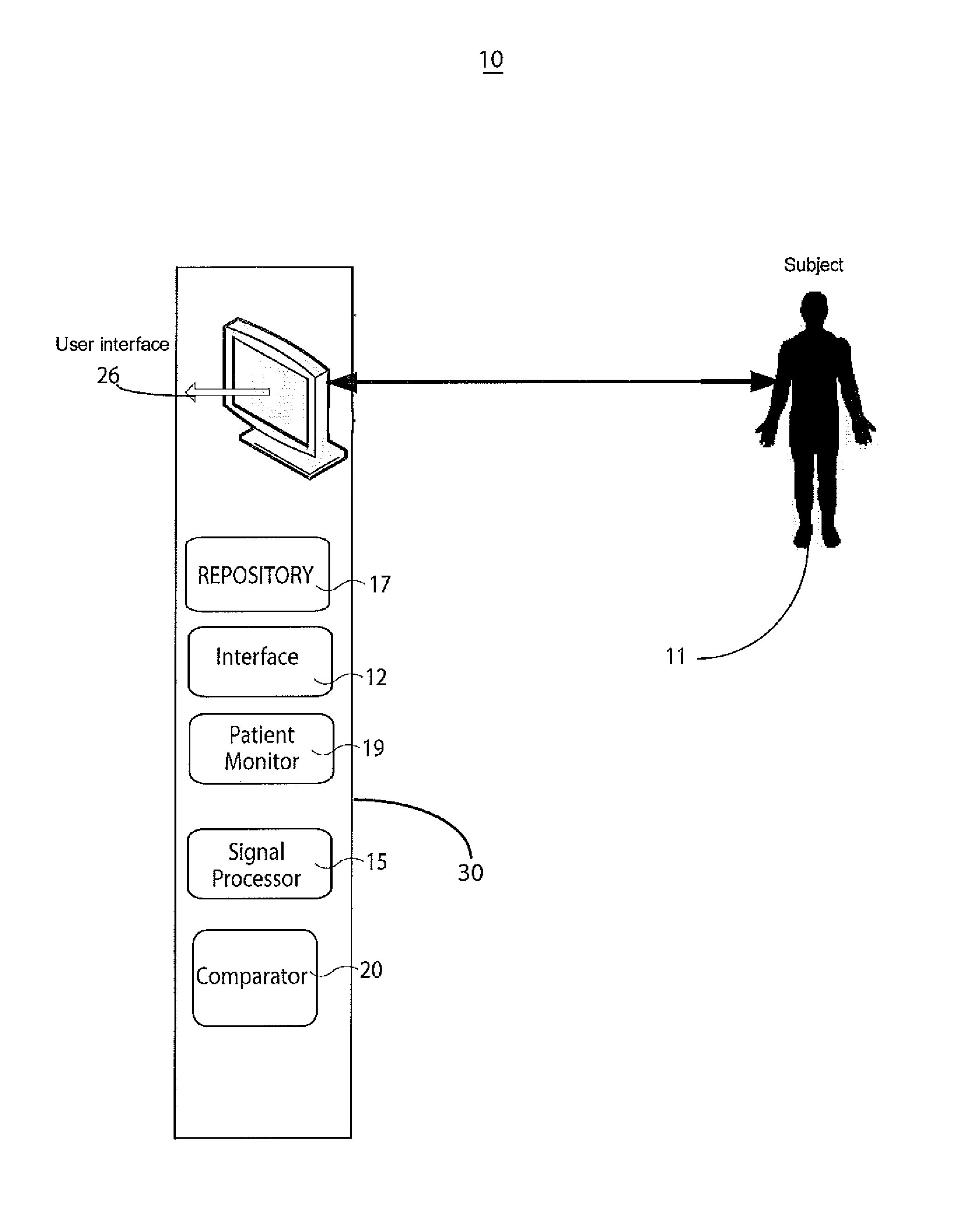
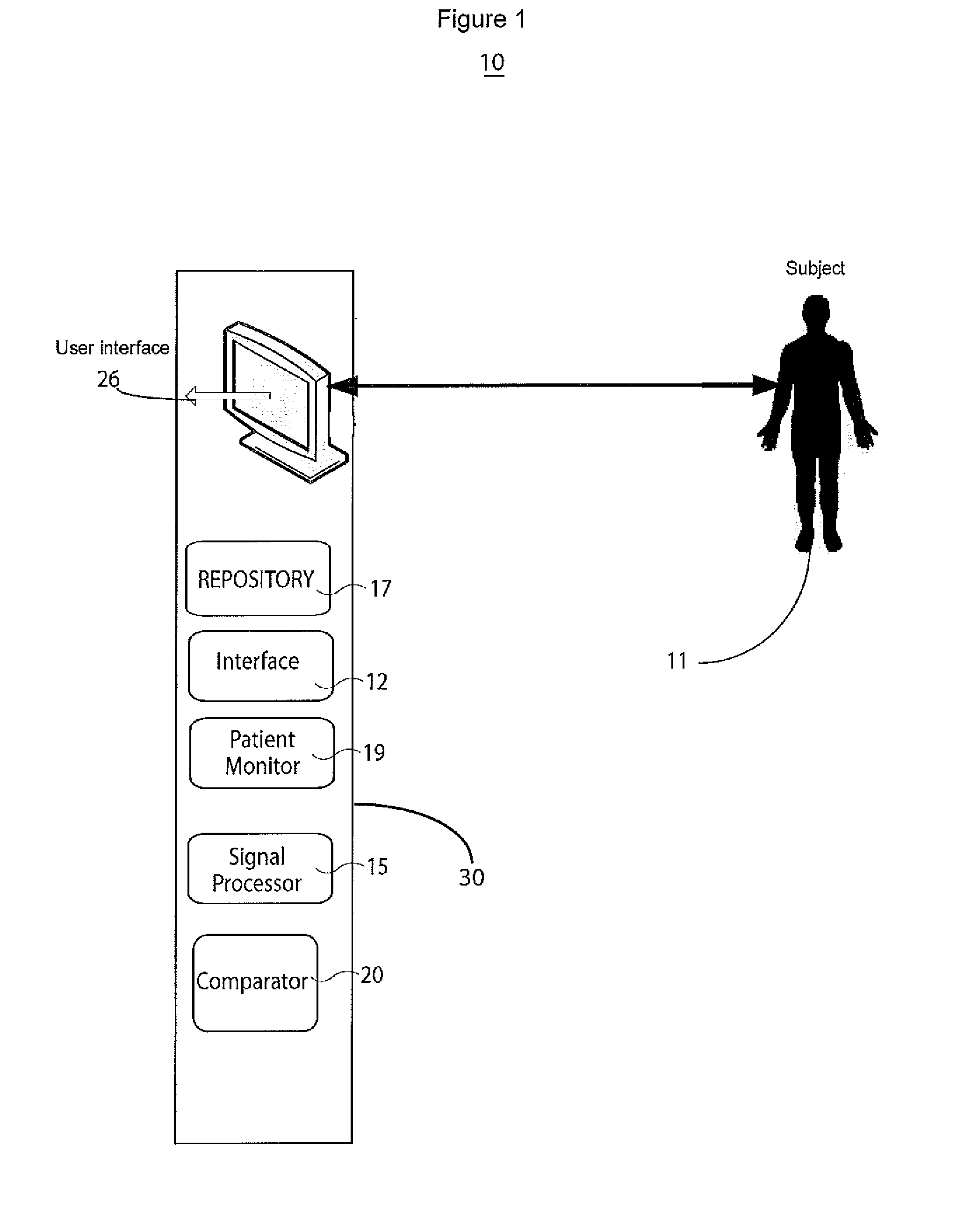
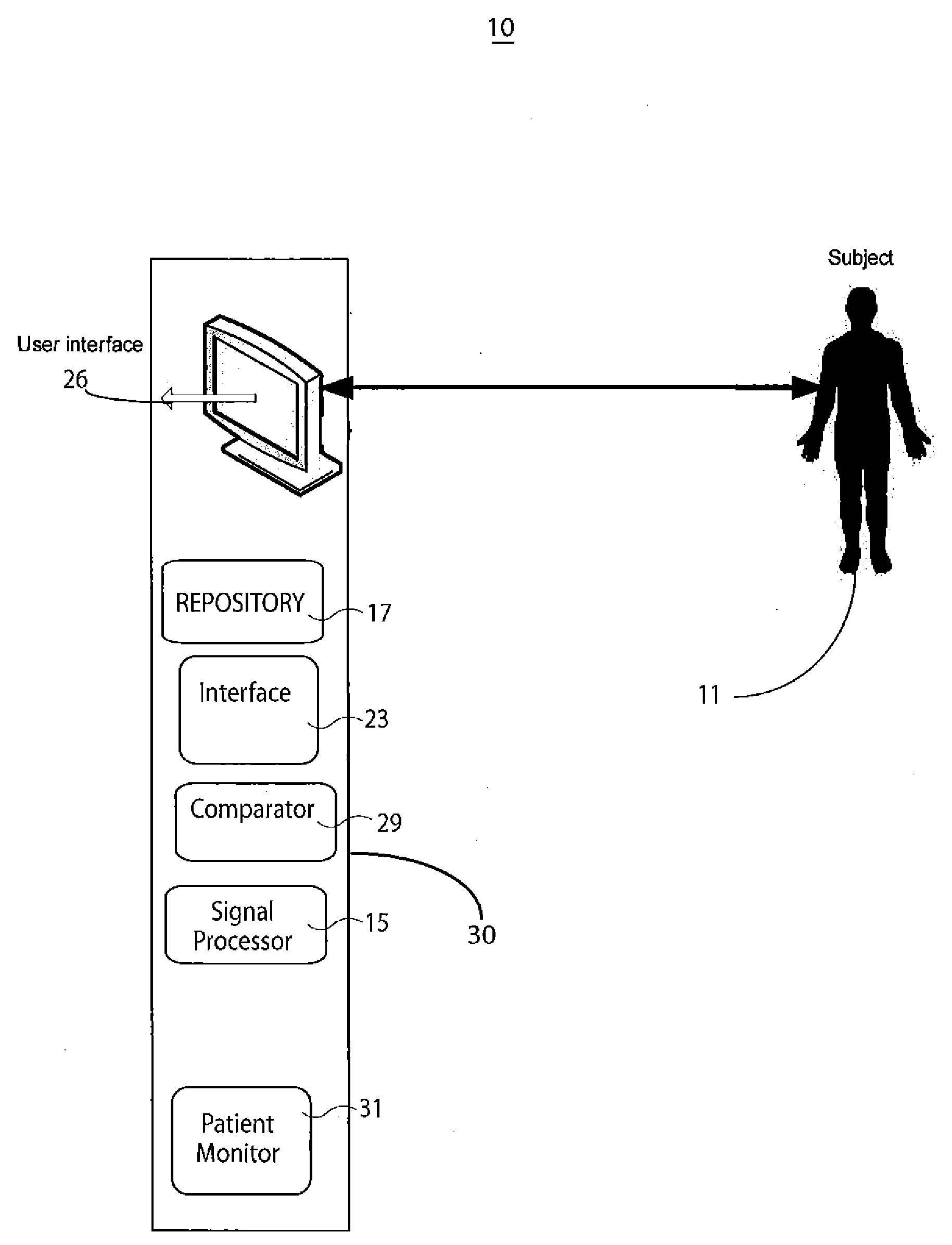
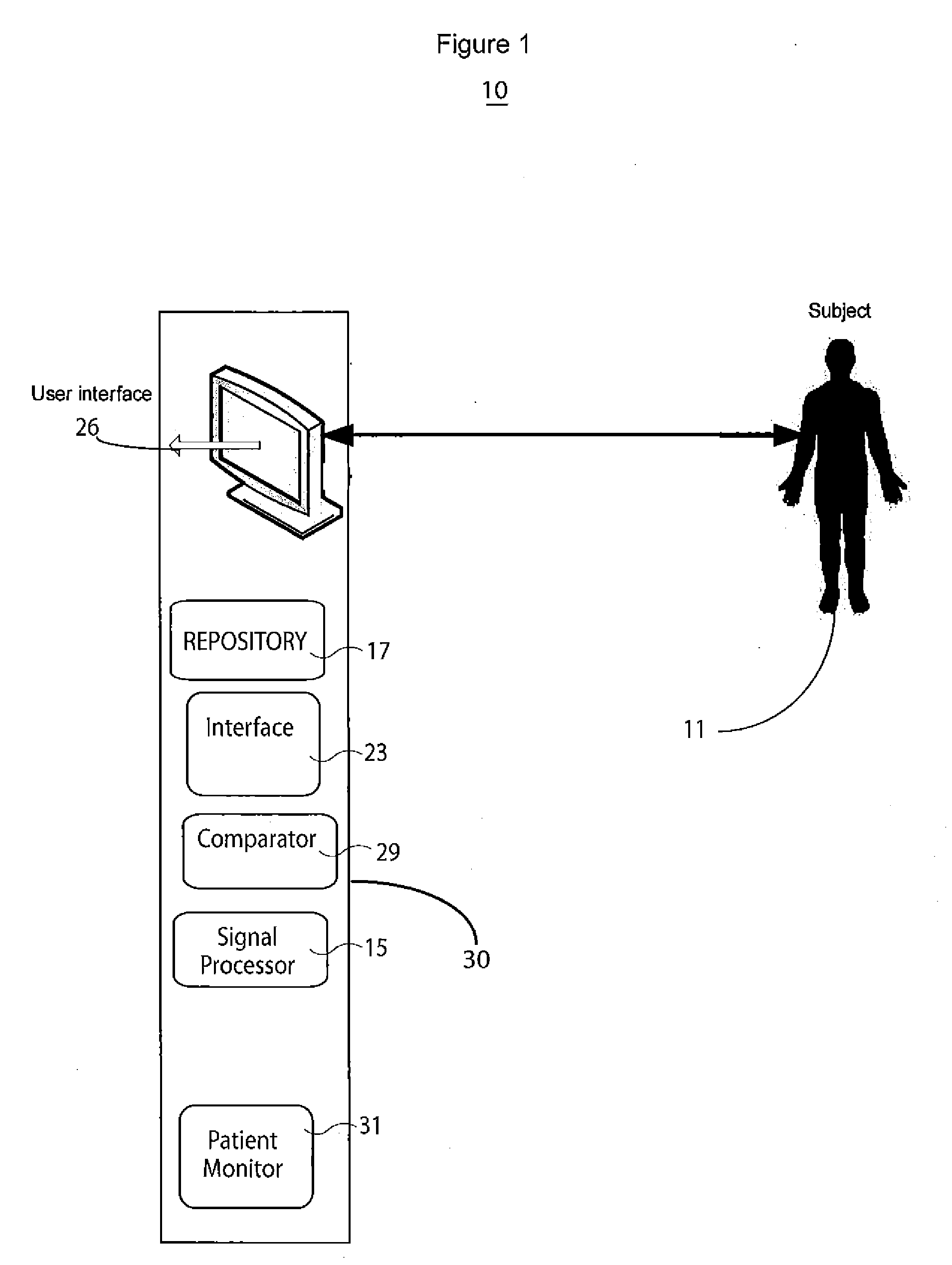
System for cardiac arrhythmia detection and characterization
A system for heart performance characterization and abnormality detection includes an interface that receives a signal representing electrical activity of a patient heart occurring during individual heart cycles of multiple sequential heart cycles. A signal processor decomposes the received signal into multiple signals comprising a heart cycle signal primary wave and one or more heart cycle signal wavelets occurring at corresponding successively higher frequencies. The signal processor determines multiple amplitude representative values of the heart cycle signal primary wave and the one or more heart cycle signal wavelets. A comparator compares the multiple amplitude representative values with corresponding multiple predetermined threshold values to provide comparison indicators. A patient monitor in response to the comparison indicators indicating at least one of the amplitude representative values exceeds a respective predetermined threshold value, generates an alert message associated with the respective predetermined threshold.
Owner:PIXART IMAGING INC
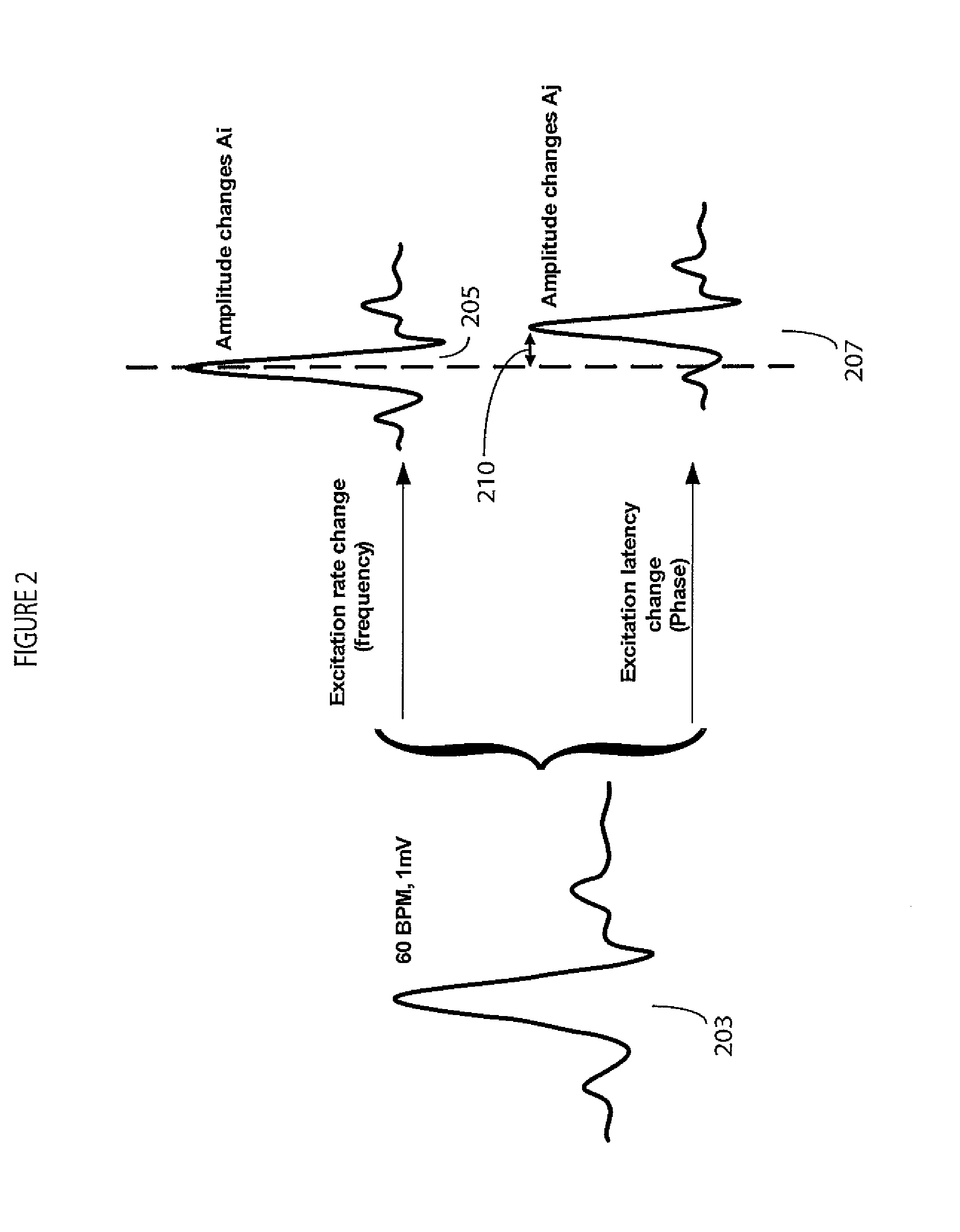
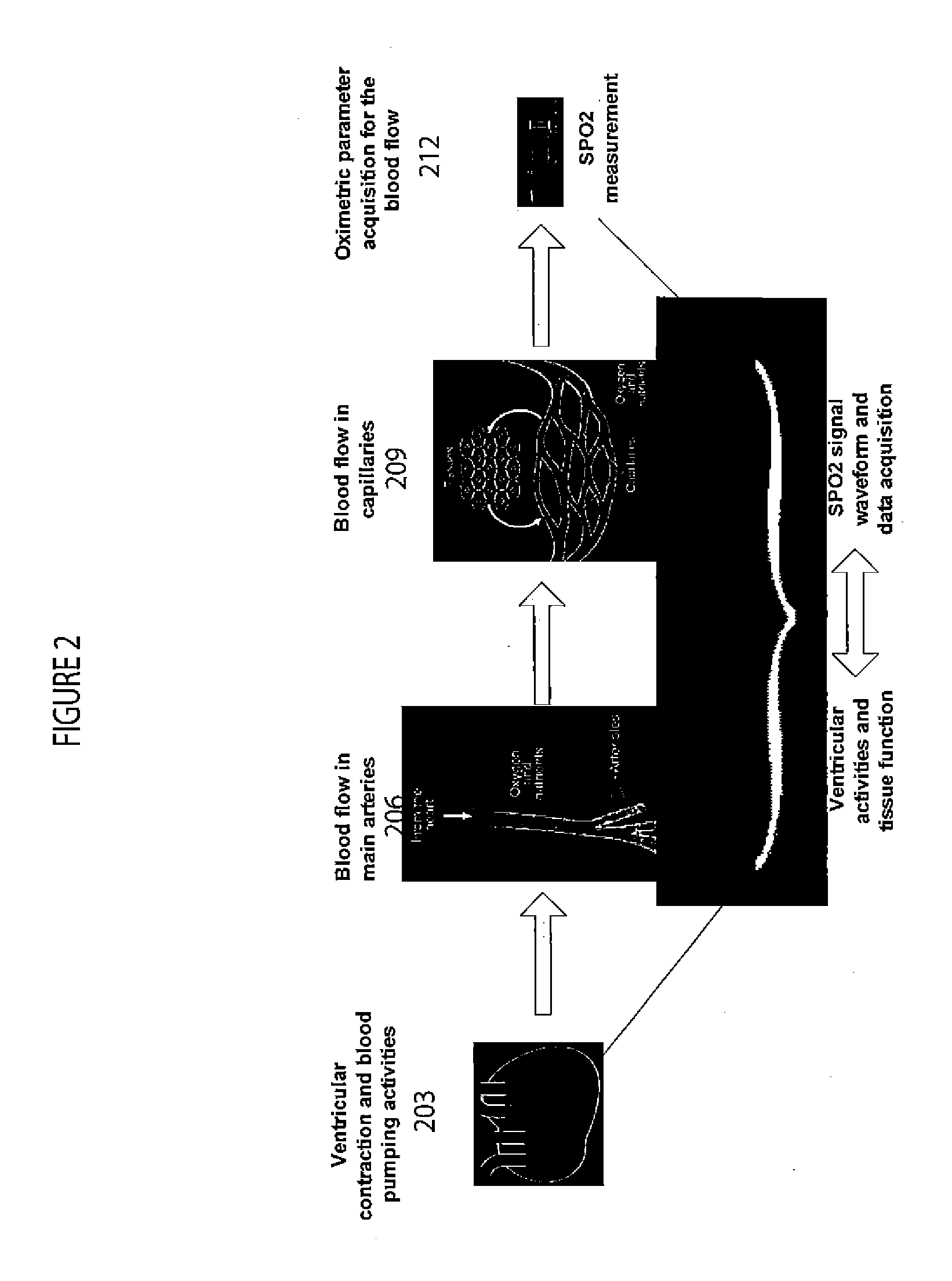
System for Ventricular Arrhythmia Detection and Characterization
A system for heart performance characterization and abnormality detection detects peaks and at least one of, a valley and a baseline comprising a substantially zero voltage level, of received signal data representing oxygen content of blood in a patient vessel over multiple heart beat cycles. The signal processor determines signal parameters including at least one of, (a) a signal amplitude magnitude between a maximum peak and minimum valley, of the received signal data, (b) a signal amplitude magnitude between a maximum peak and a baseline, of the received signal data and (c) a signal amplitude magnitude between a second highest maximum peak and minimum valley, of the received signal data. The system compares a determined signal parameter or value derived from the determined signal parameter, with a threshold value and generates an alert message associated with the threshold, in response to the comparison.
Owner:PIXART IMAGING INC
Automatic adjustment of arrhythmia detection parameters
InactiveUS20120109240A1ElectrocardiographyHeart defibrillatorsCardiac arrhythmiaArrhythmia detection
Methods and / or devices for initiating an automatic adjustment of arrhythmia detection parameters (e.g., upon delivery of cardiac therapy after detection of VT / VF).
Owner:MEDTRONIC INC
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com