Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
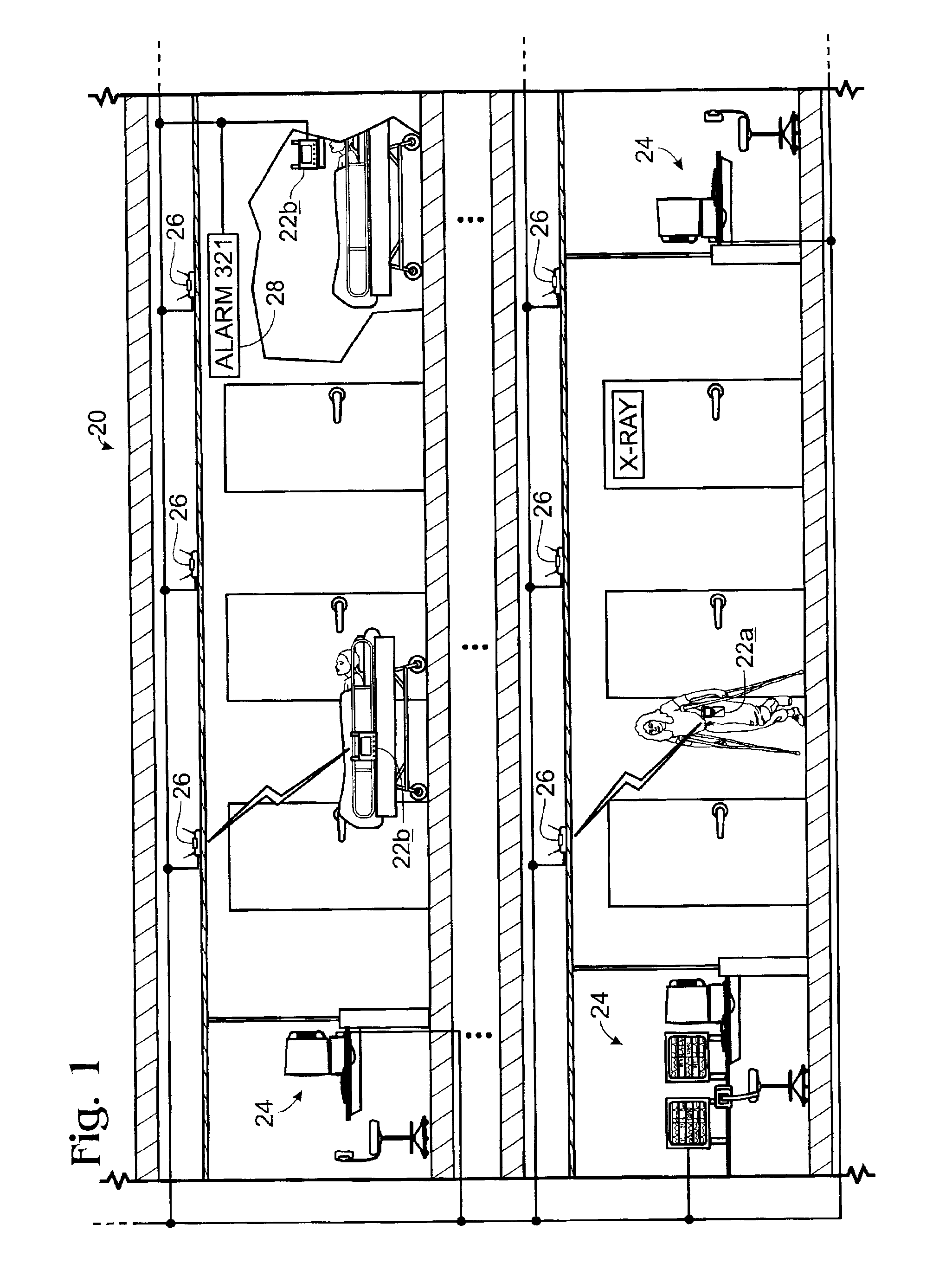
409 results about "Patient monitor" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
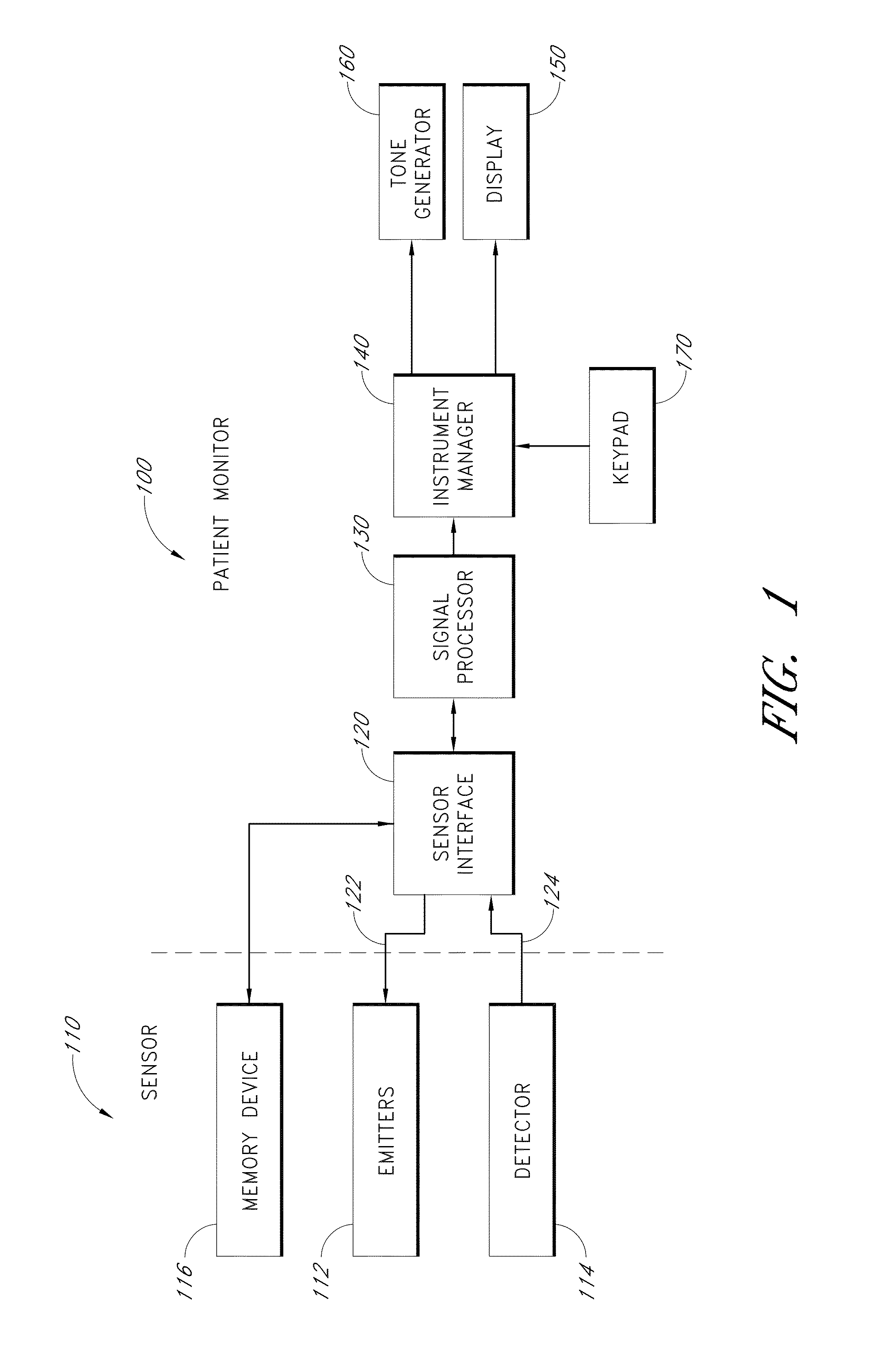
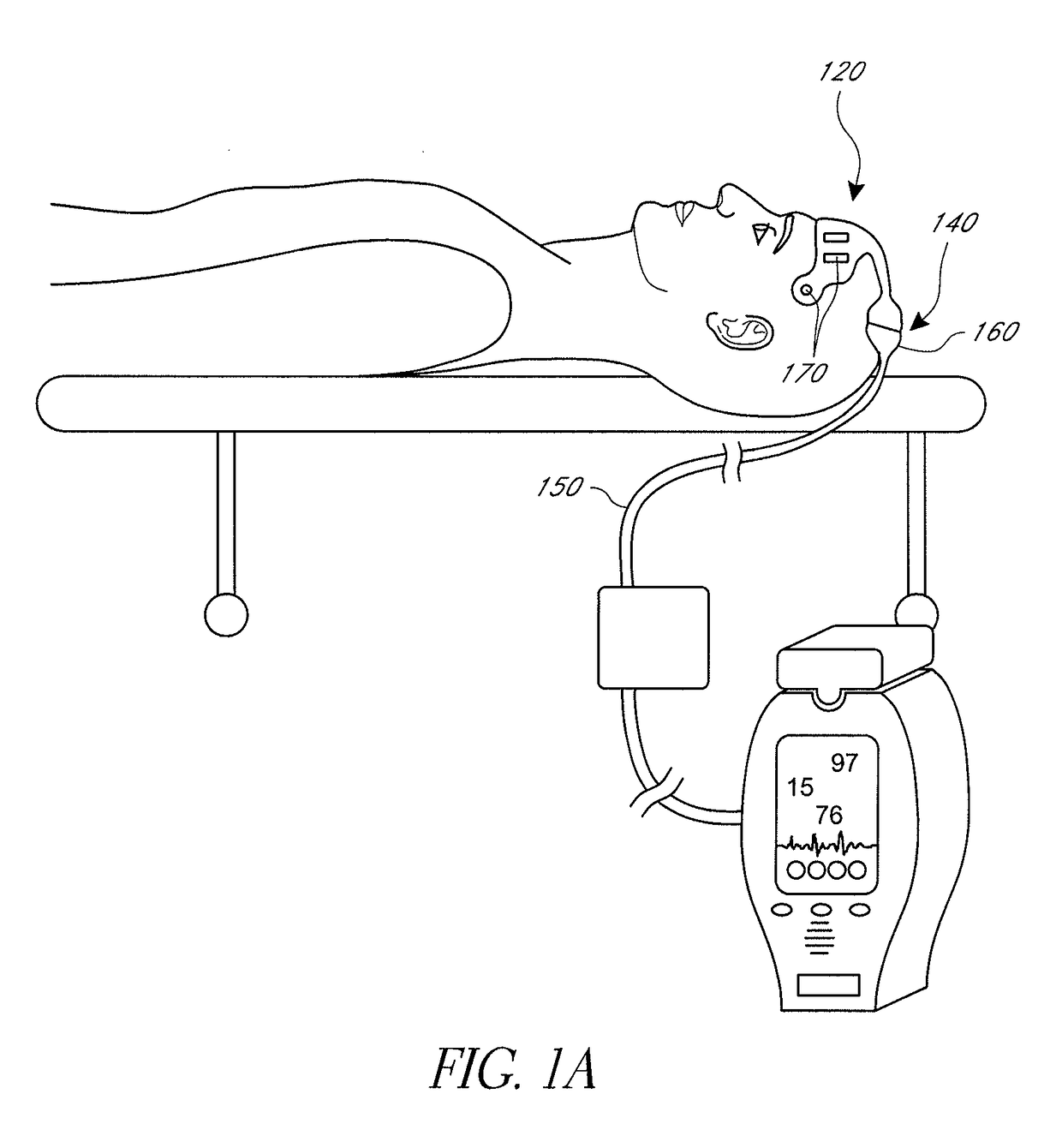
Remote patient monitoring (RPM) is a technology to enable monitoring of patients outside of conventional clinical settings (e.g. in the home), which may increase access to care and decrease healthcare delivery costs.
Manual and automatic probe calibration
InactiveUS7526328B2Complicates designIncreased expenseRadiation pyrometrySpectrum investigationFull Term NeonateEngineering
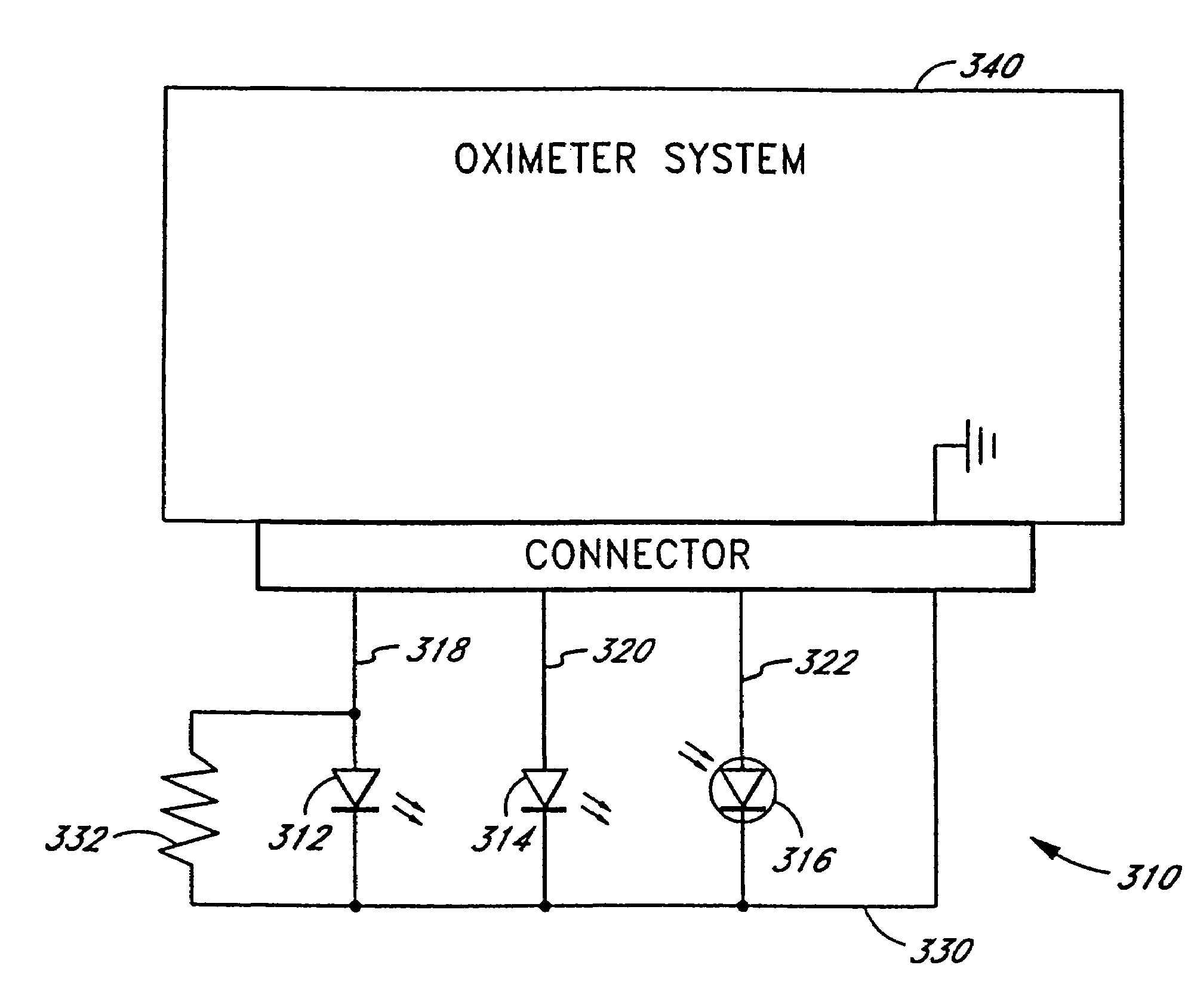
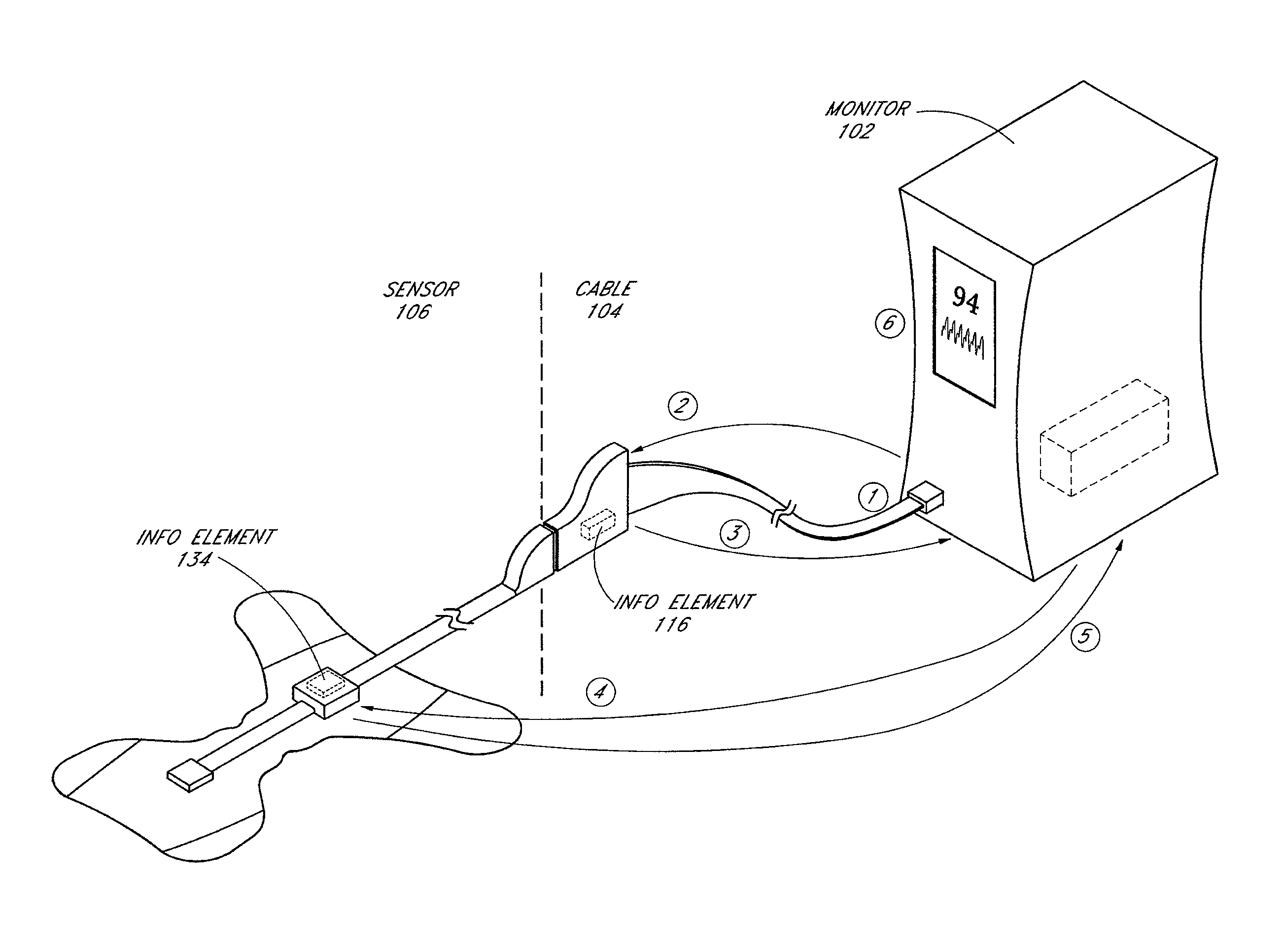
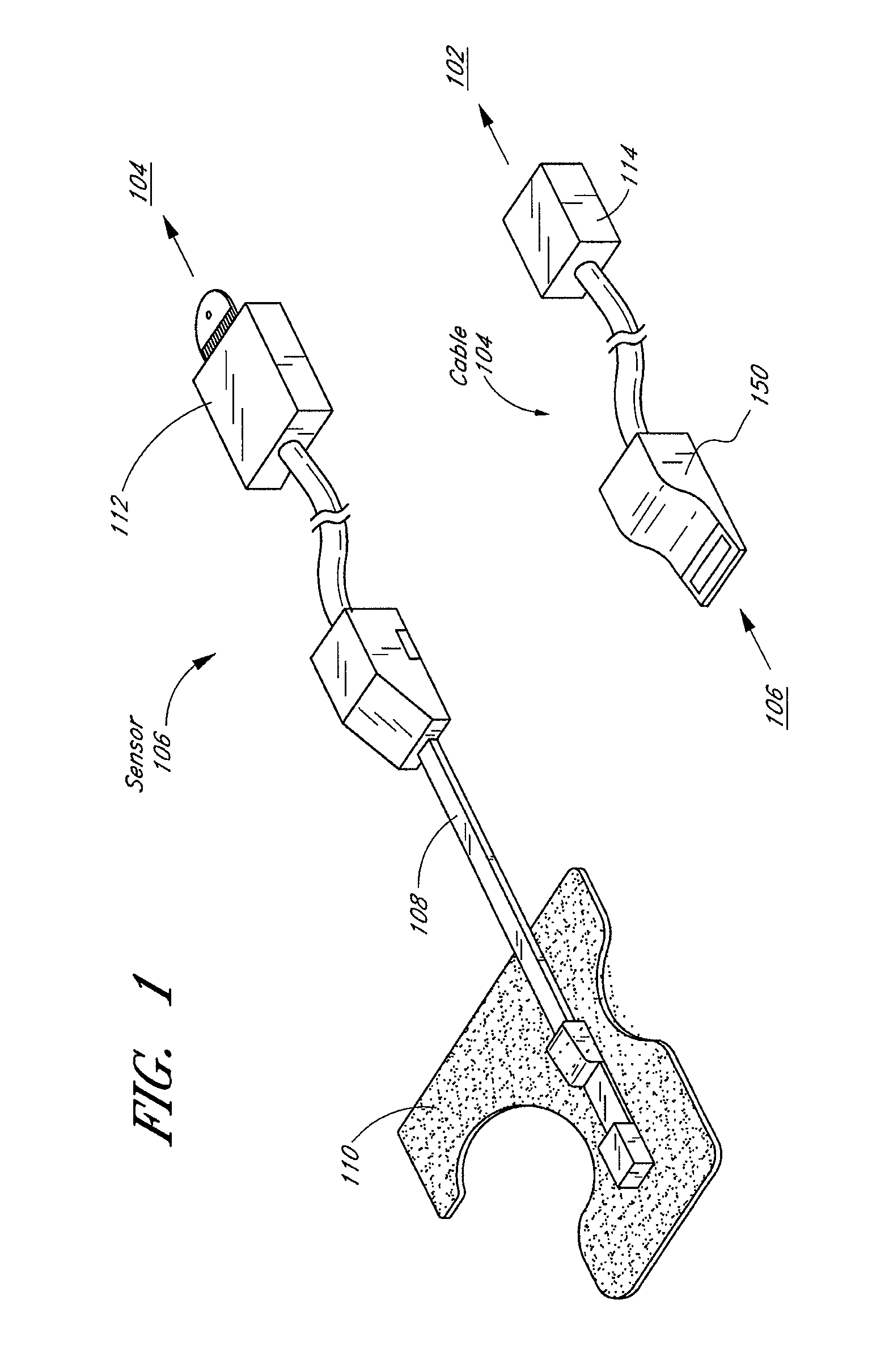
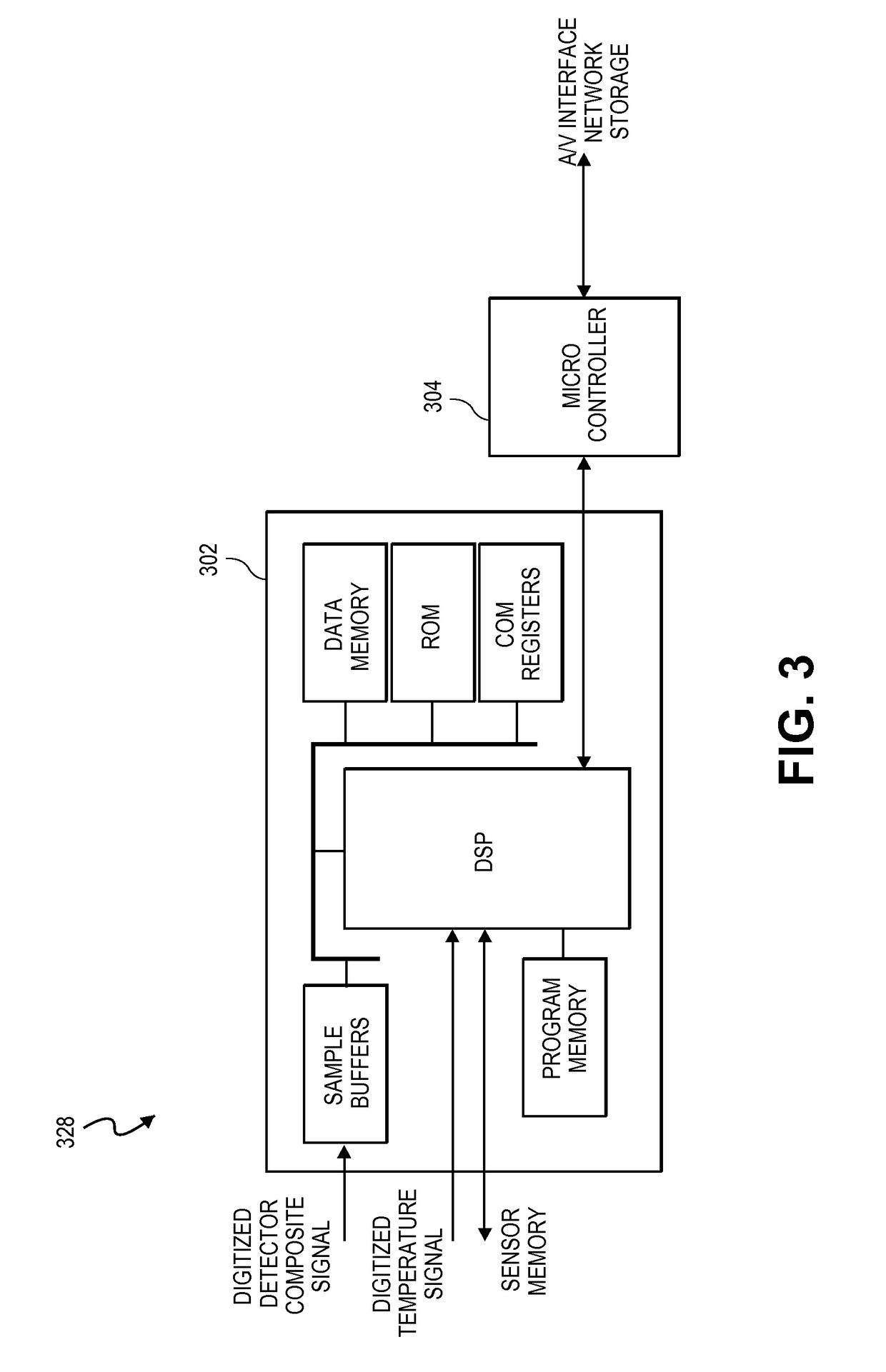
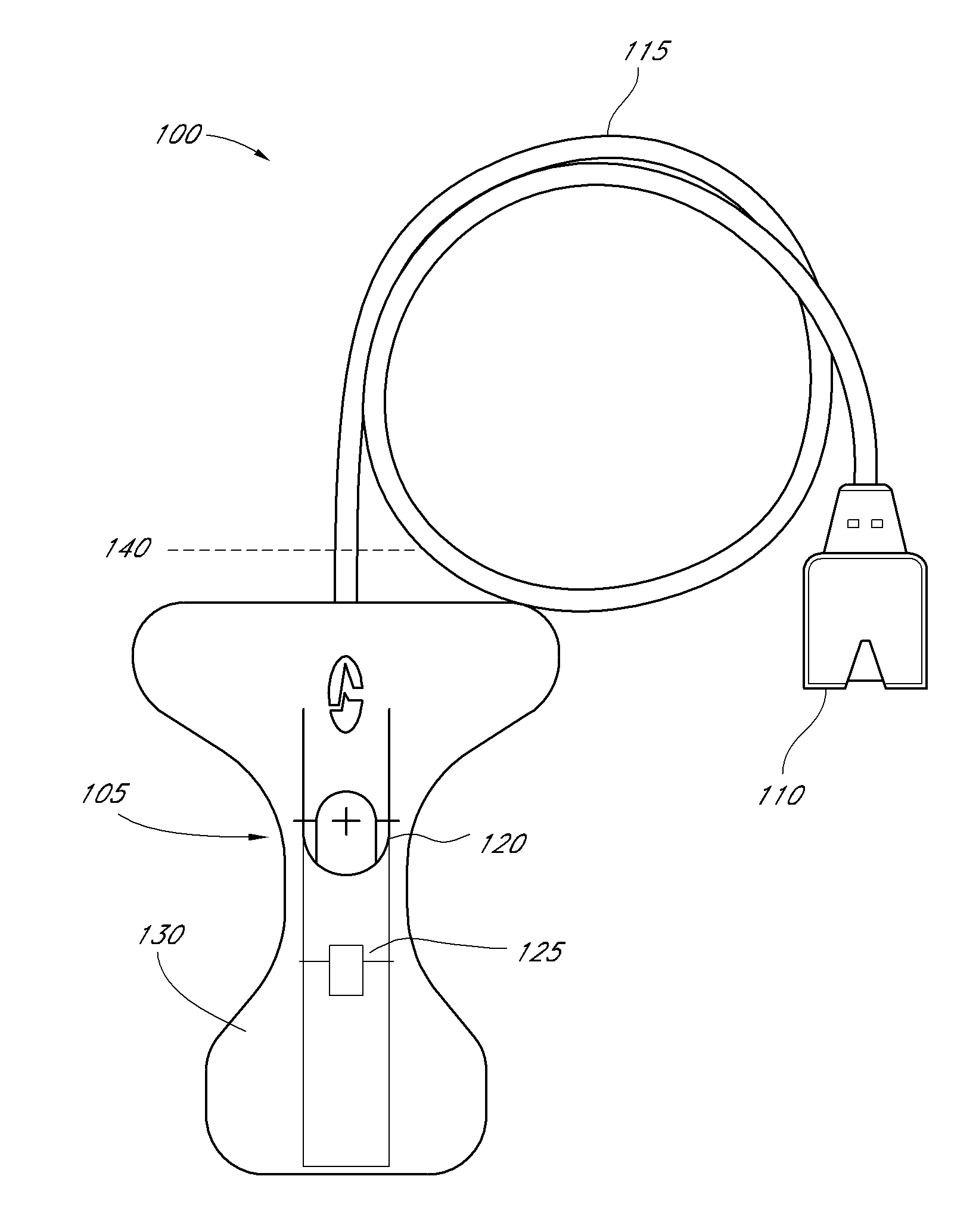
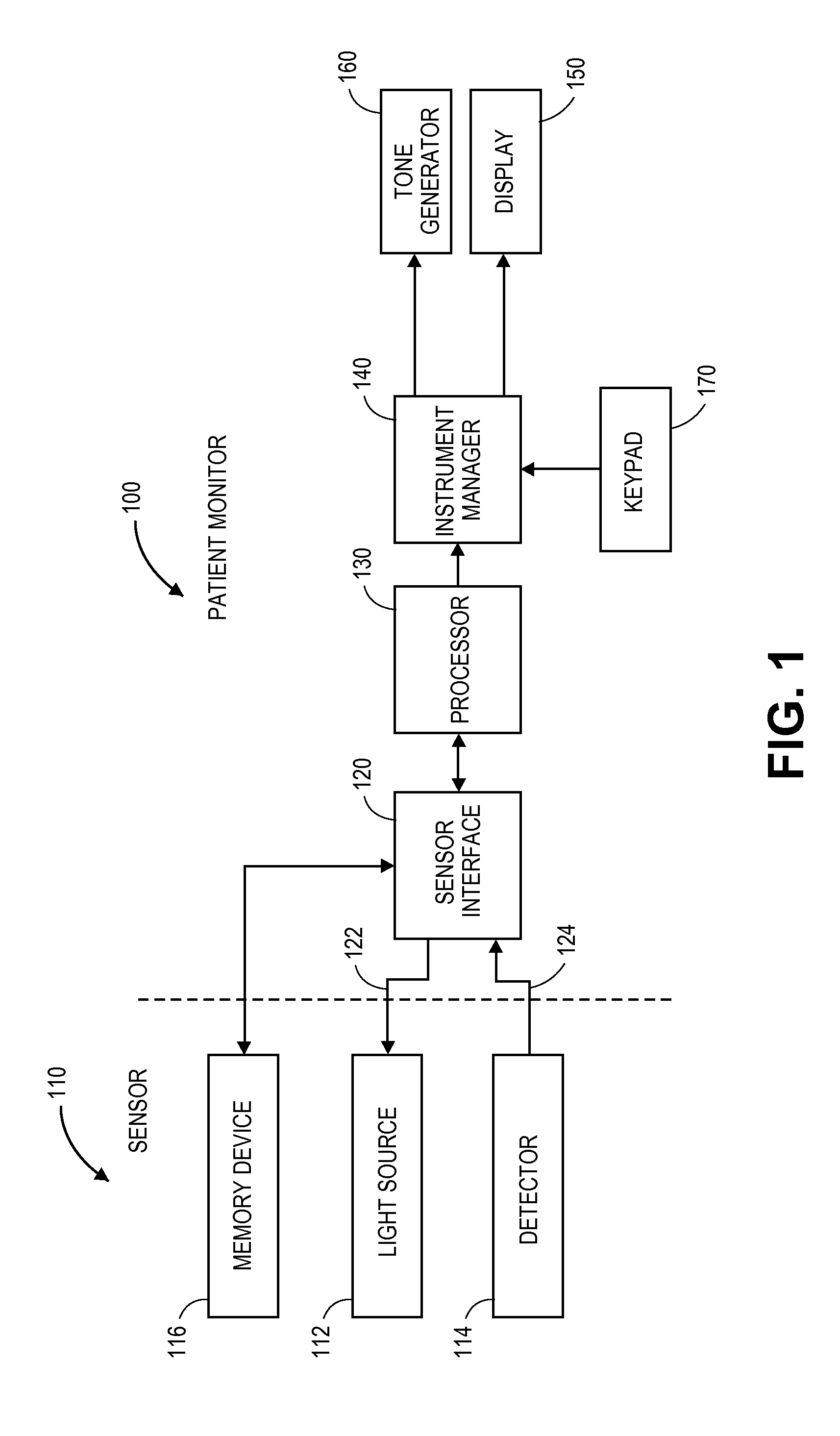
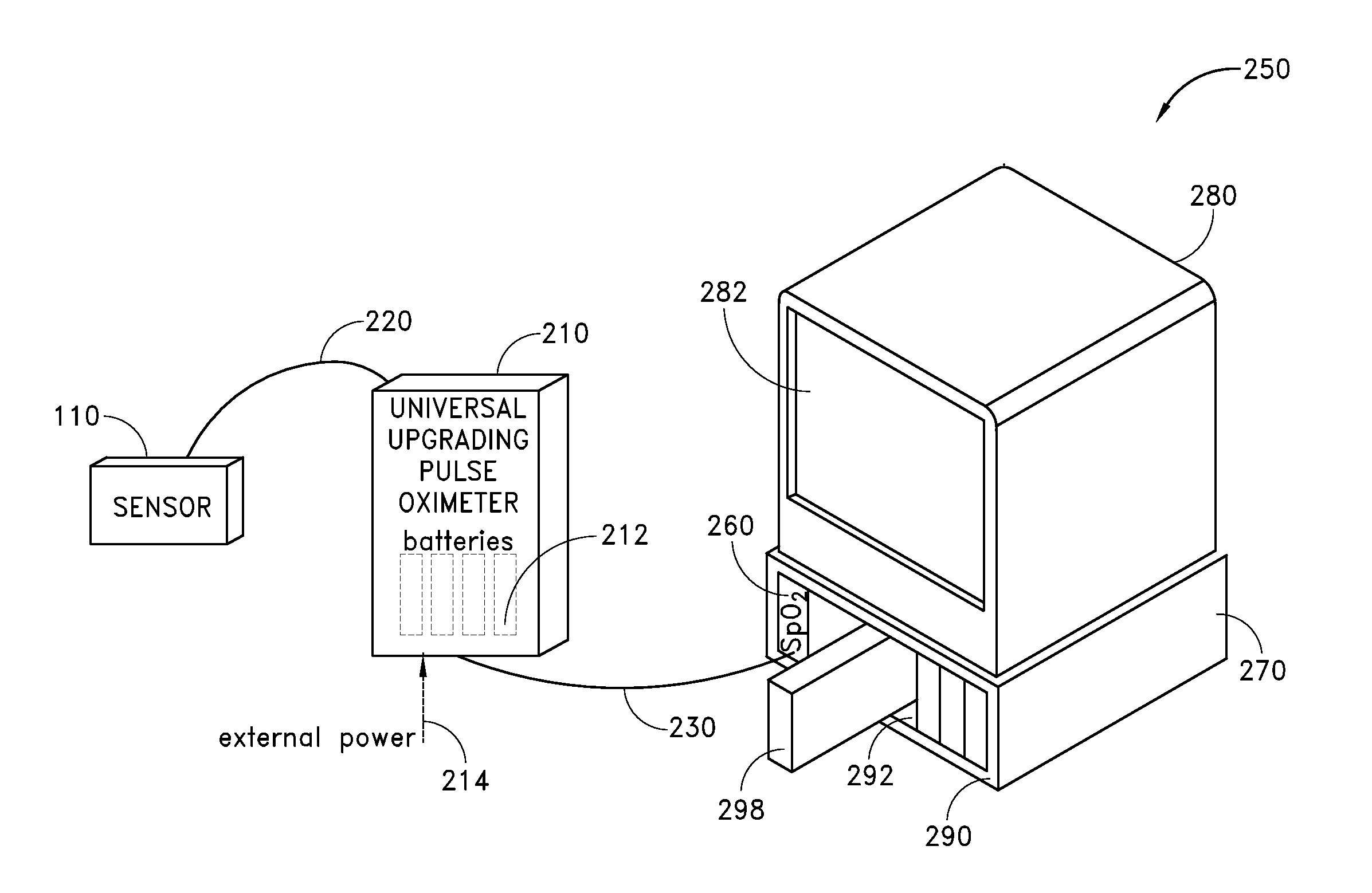
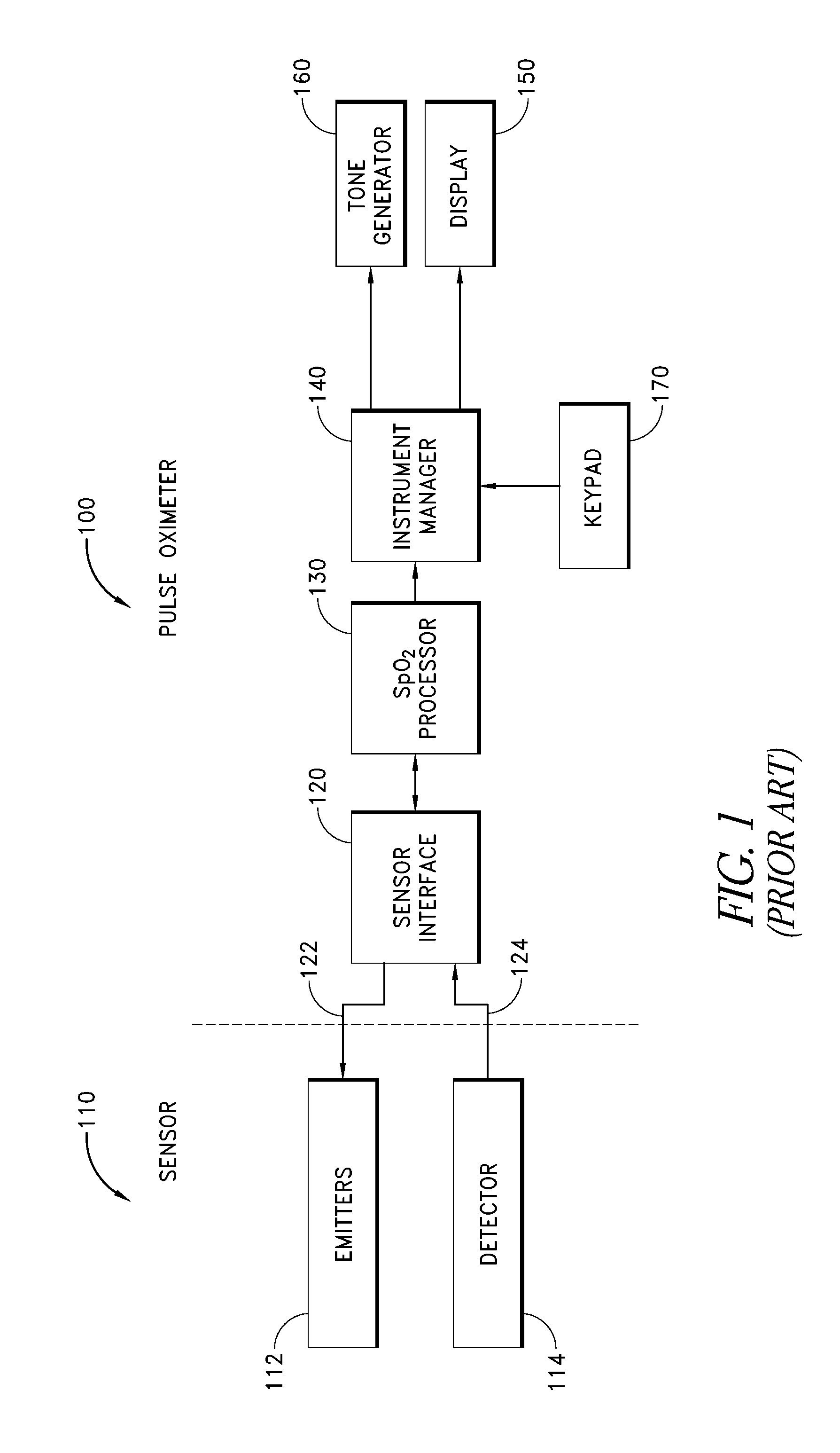
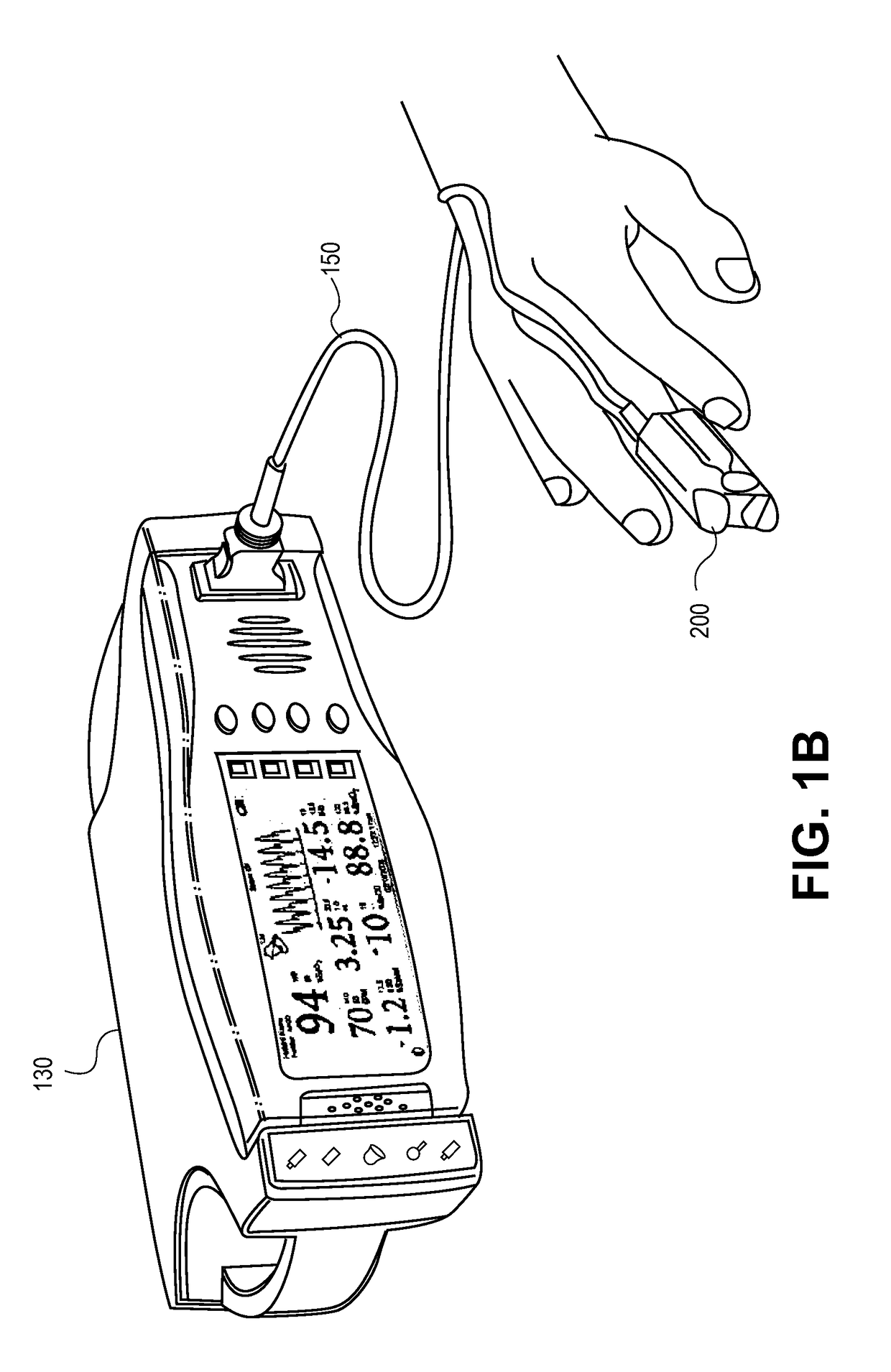
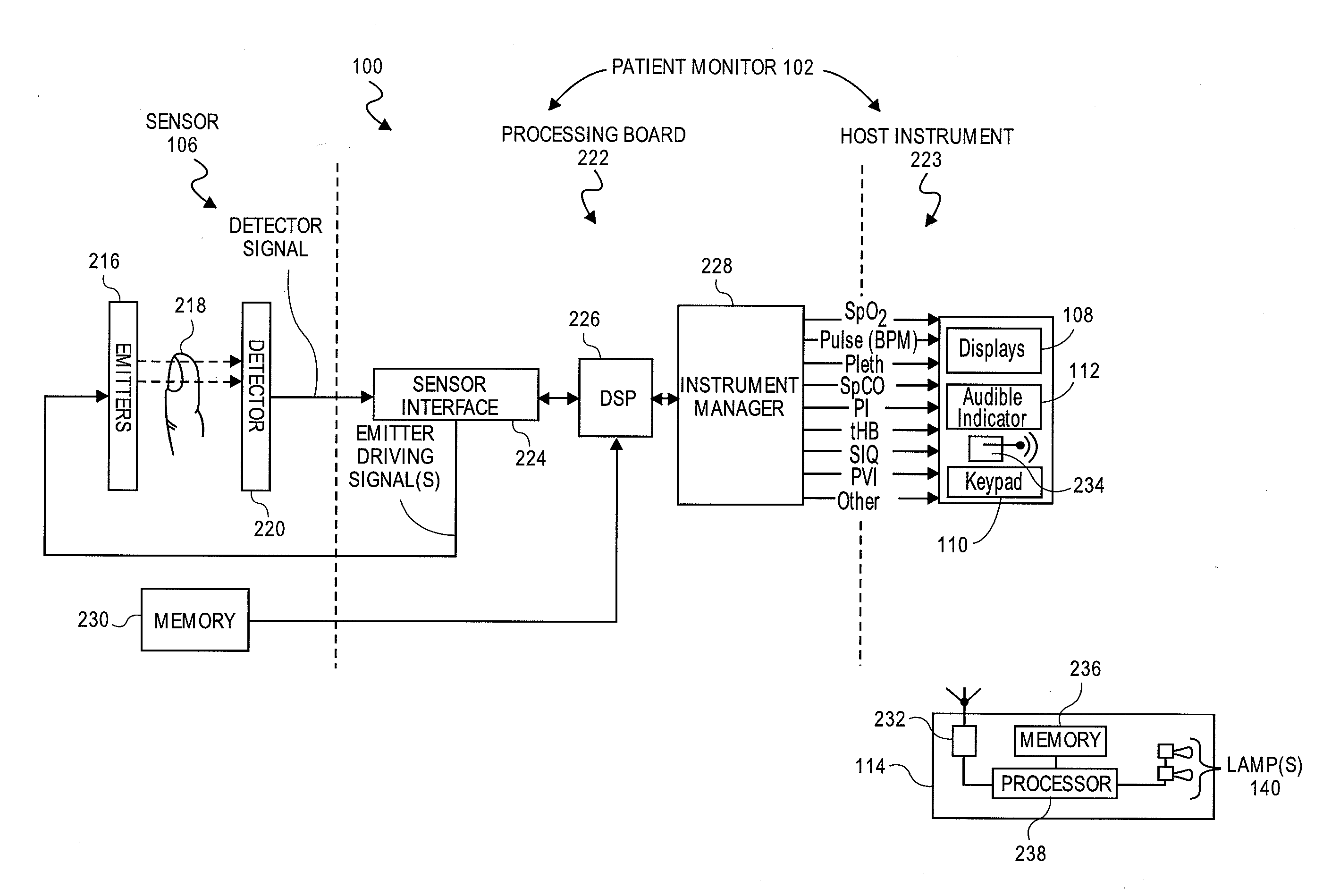
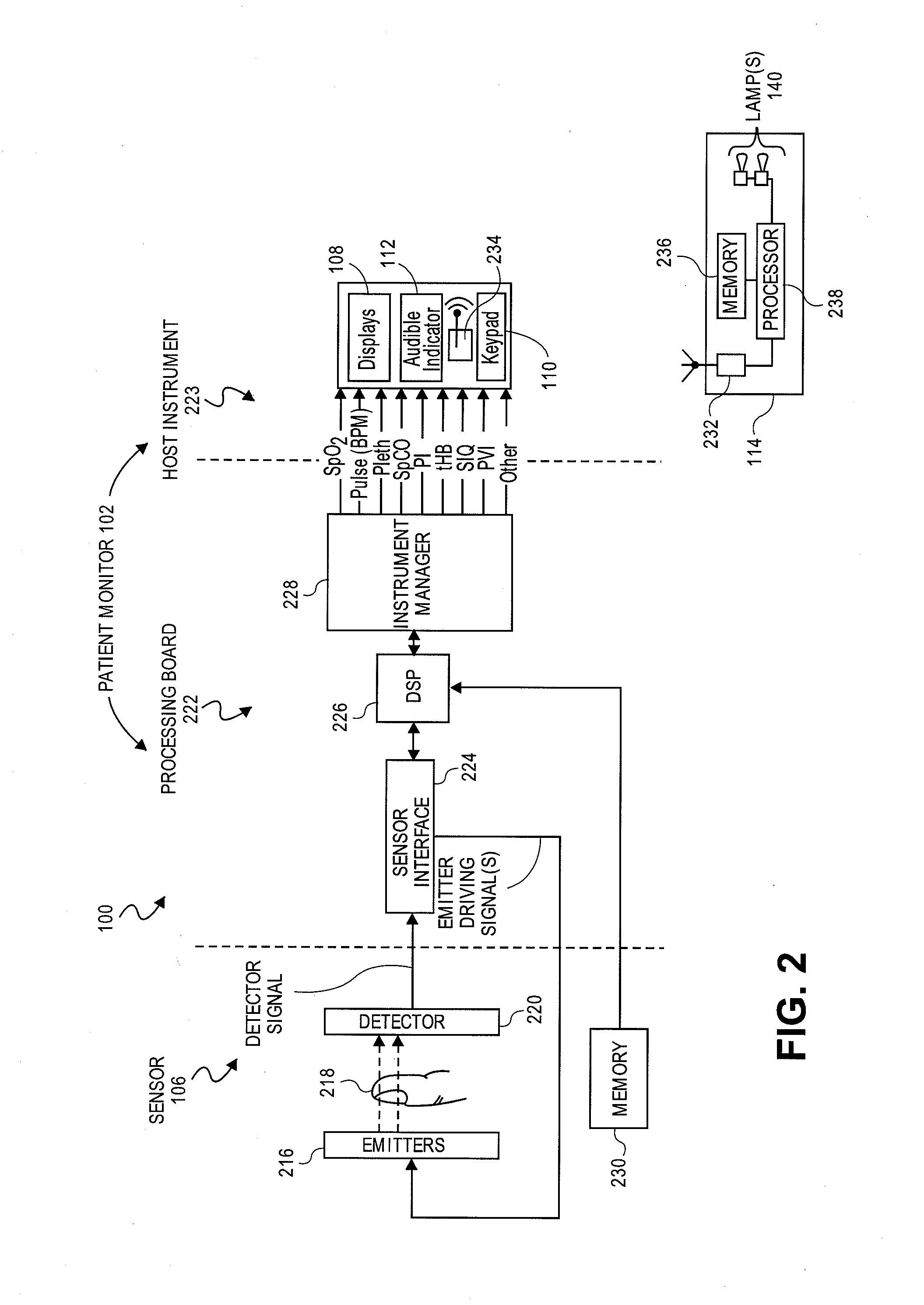
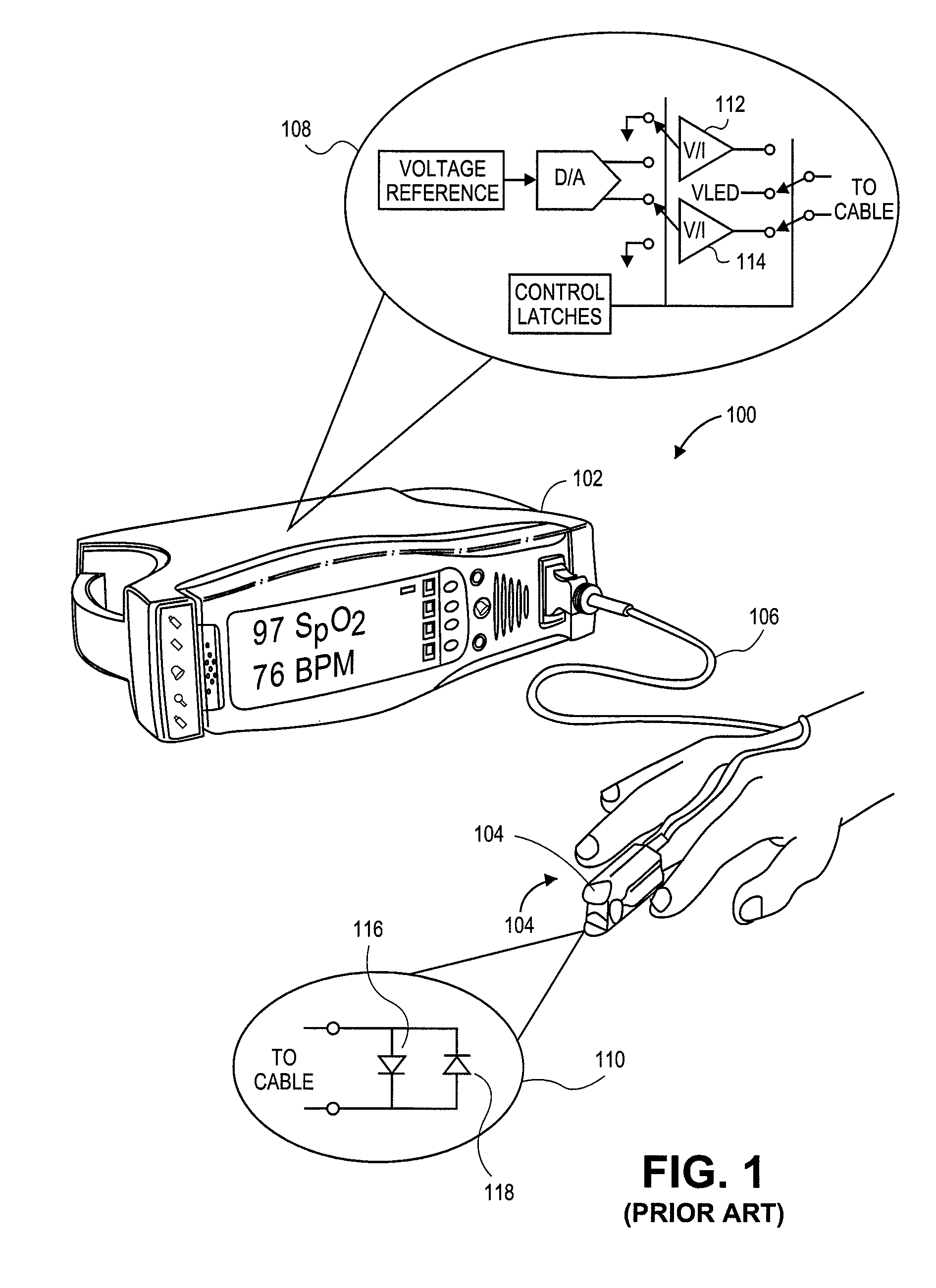
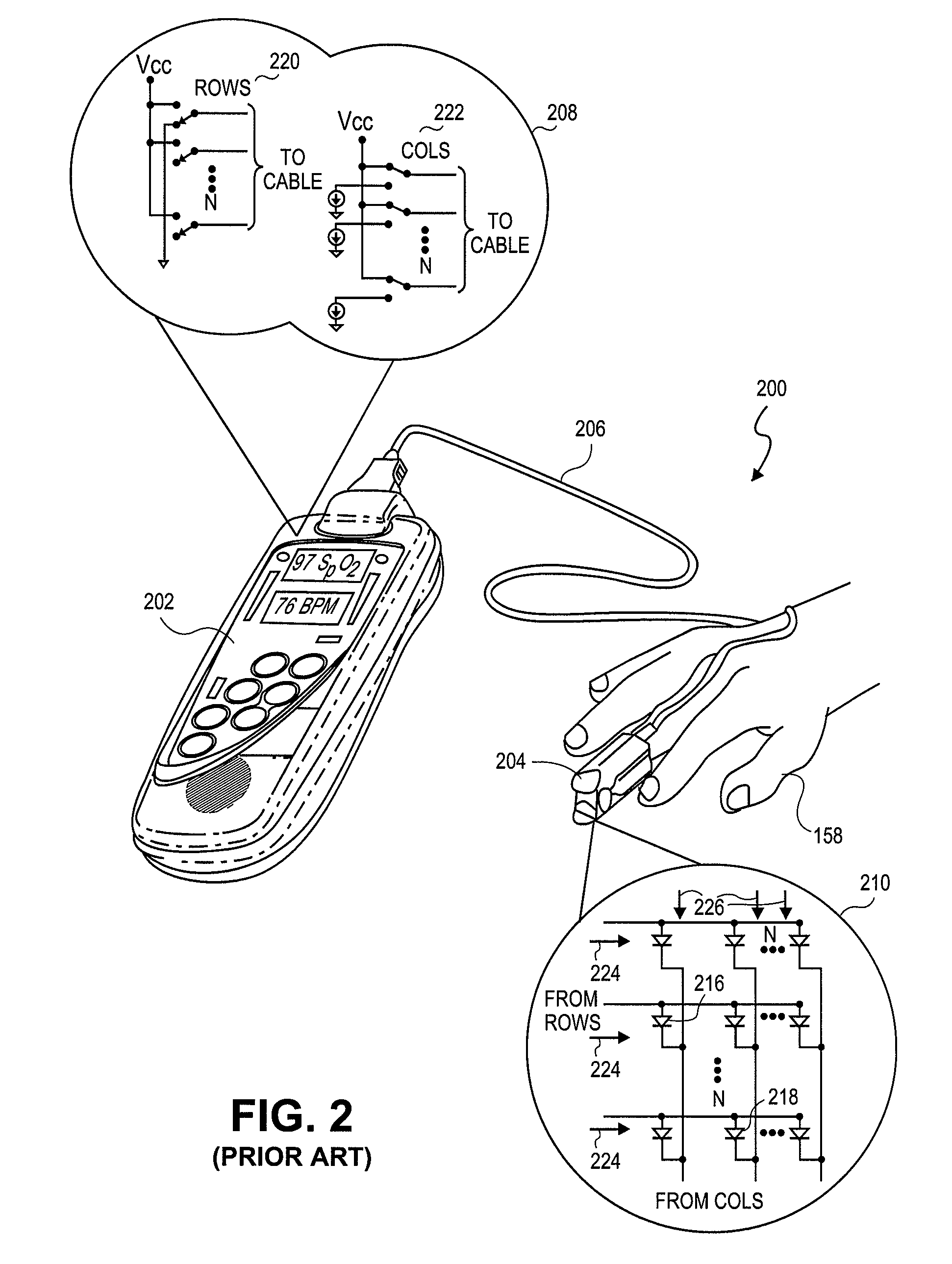
Embodiments of the present disclosure include an optical probe capable of communicating identification information to a patient monitor in addition to signals indicative of intensities of light after attenuation by body tissue. The identification information may indicate operating wavelengths of light sources, indicate a type of probe, such as, for example, that the probe is an adult probe, a pediatric probe, a neonatal probe, a disposable probe, a reusable probe, or the like. The information could also be utilized for security purposes, such as, for example, to ensure that the probe is configured properly for the oximeter, to indicate that the probe is from an authorized supplier, or the like. In one preferred embodiment, coding resistors could be provided across the light sources to allow additional information about the probe to be coded without added leads. However, any device could be used without it being used in parallel.
Owner:JPMORGAN CHASE BANK NA
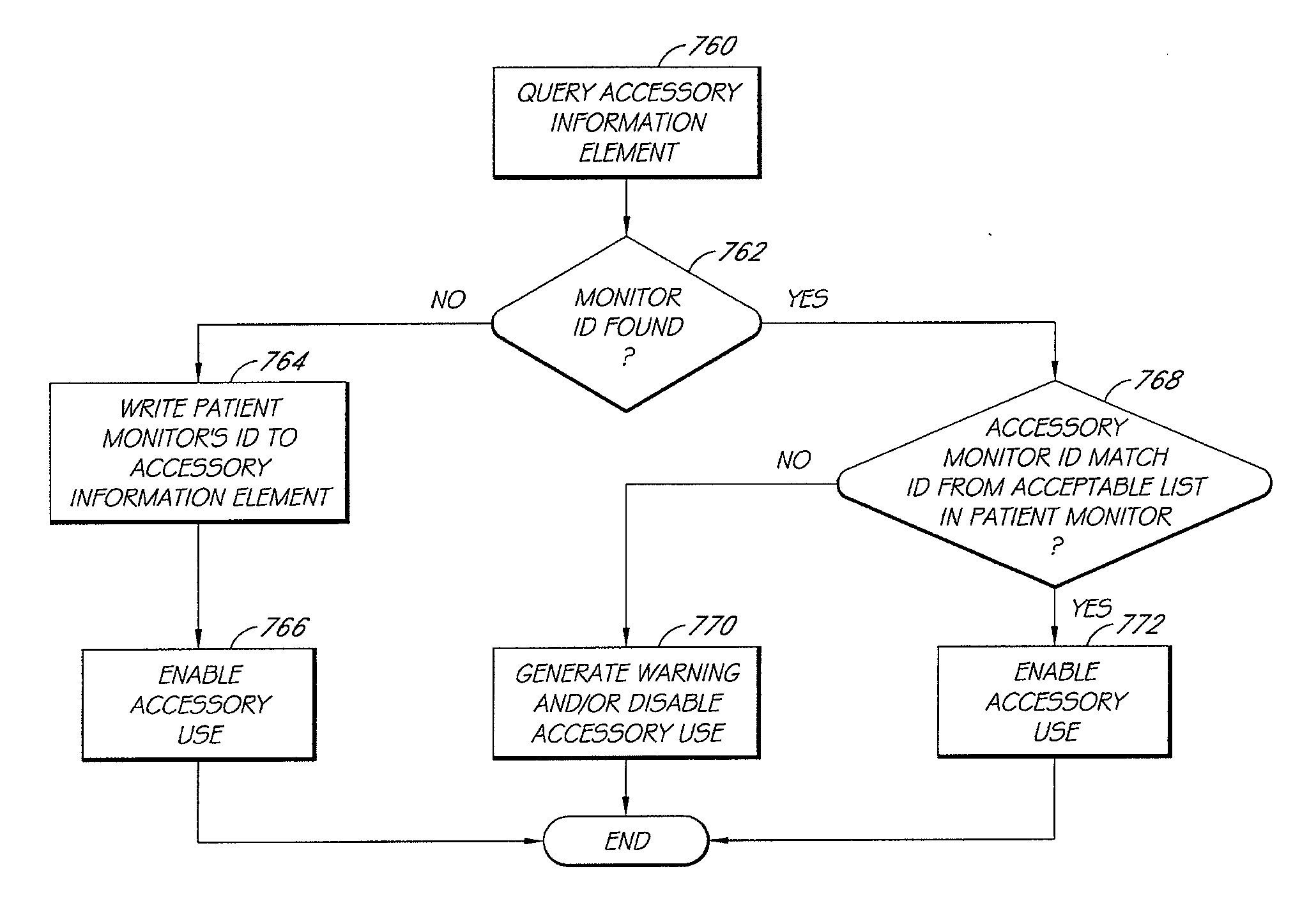
Patient monitor capable of monitoring the quality of attached probes and accessories
ActiveUS8255026B1Reduce capacityReduce the possibilityDiagnostic recording/measuringSensorsQuality controlPulse oximetry
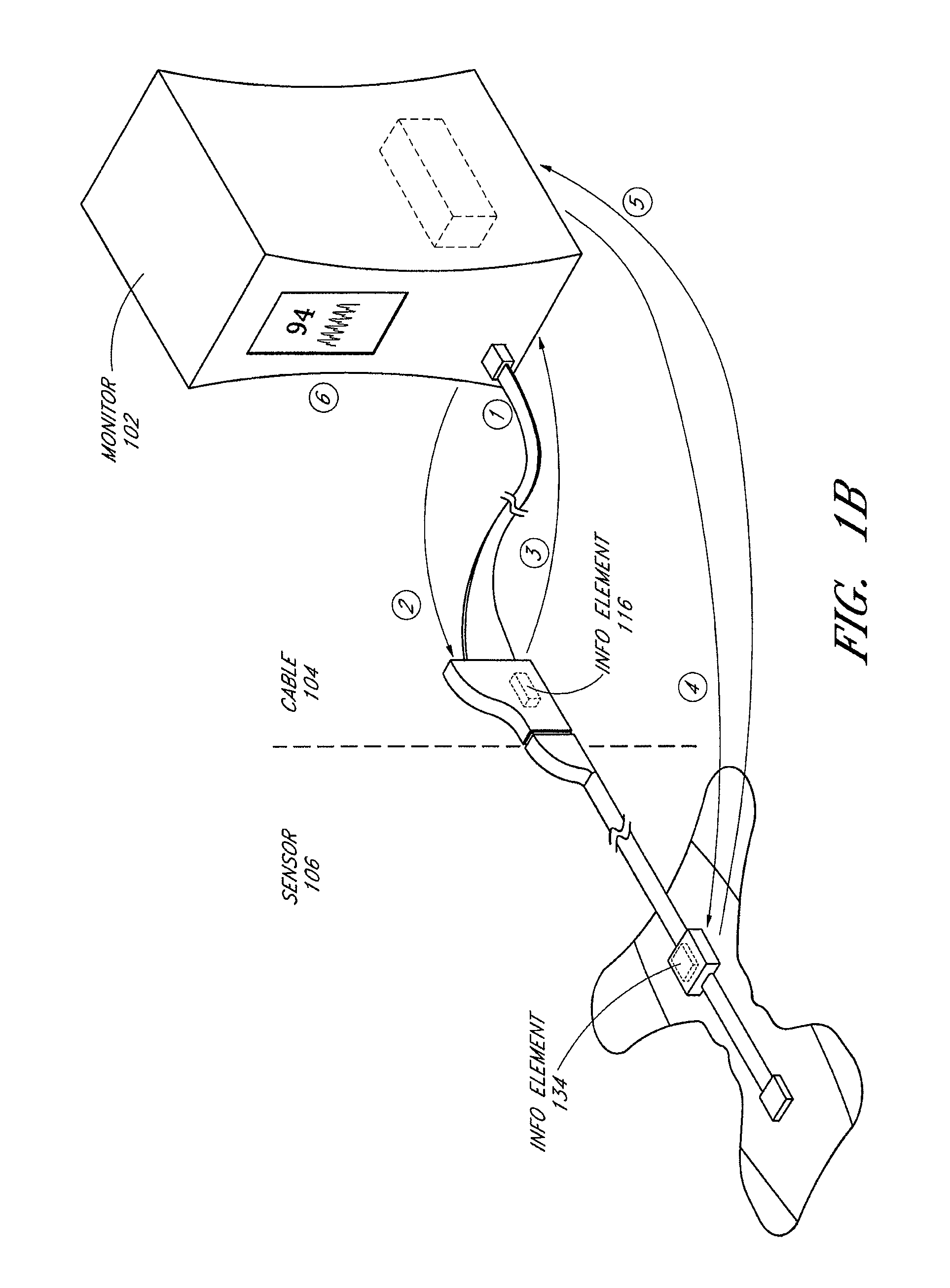
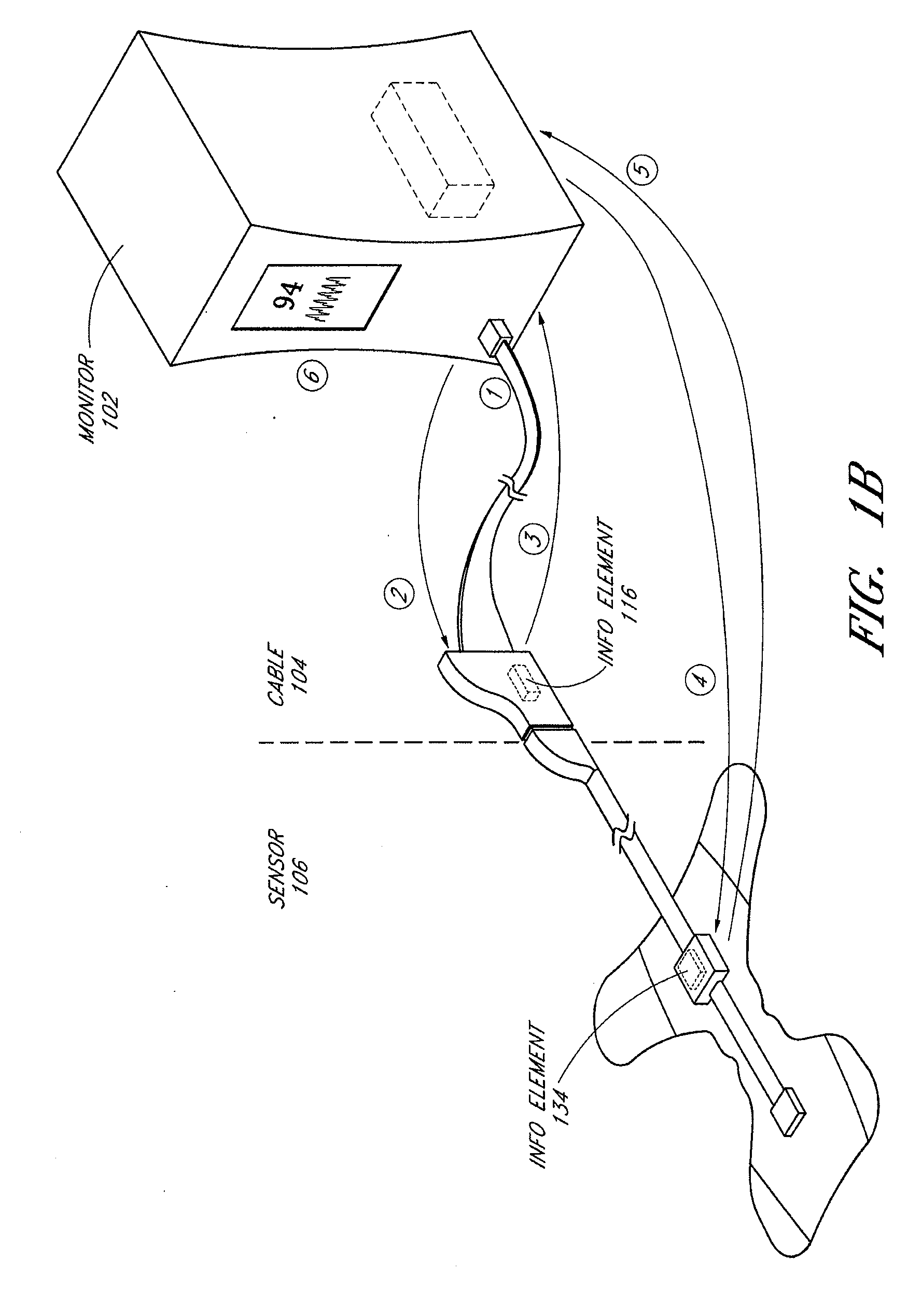
A system and method to help maintain quality control and reduce cannibalization of accessories and attached probes in a highly sensitive patient monitor, such as a pulse oximetry system. One or more attached components may have information elements designed to designate what quality control mechanisms a patient monitor should look to find on that or another component or designate other components with which the one component may properly work. In a further embodiment, such information elements may also include data indicating the appropriate life of the component.
Owner:JPMORGAN CHASE BANK NA
Interference detector for patient monitor
ActiveUS8471713B2Quickly informedQuickly alertedNoise figure or signal-to-noise ratio measurementElectric testing/monitoringEnvironmental noiseMedical equipment
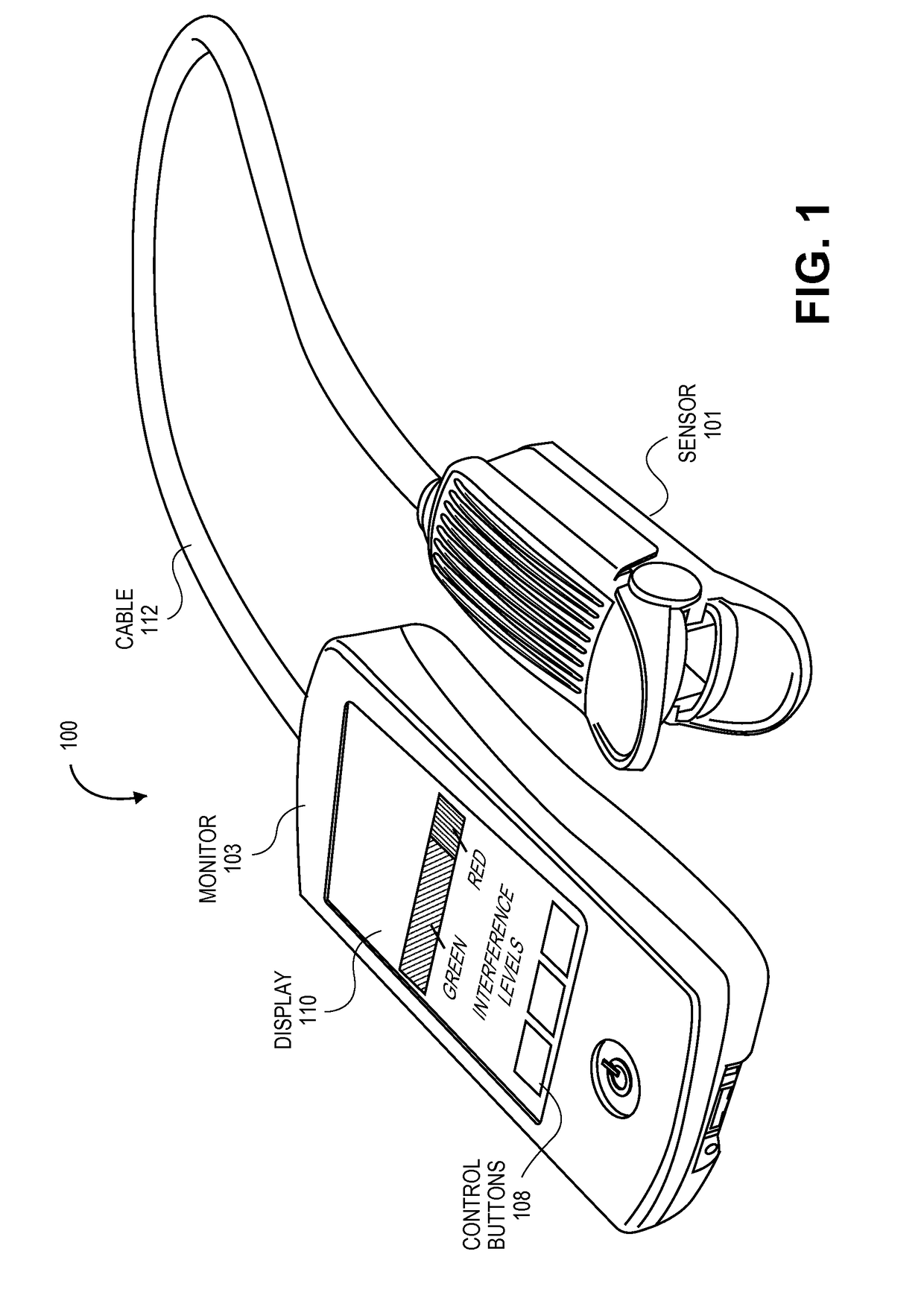
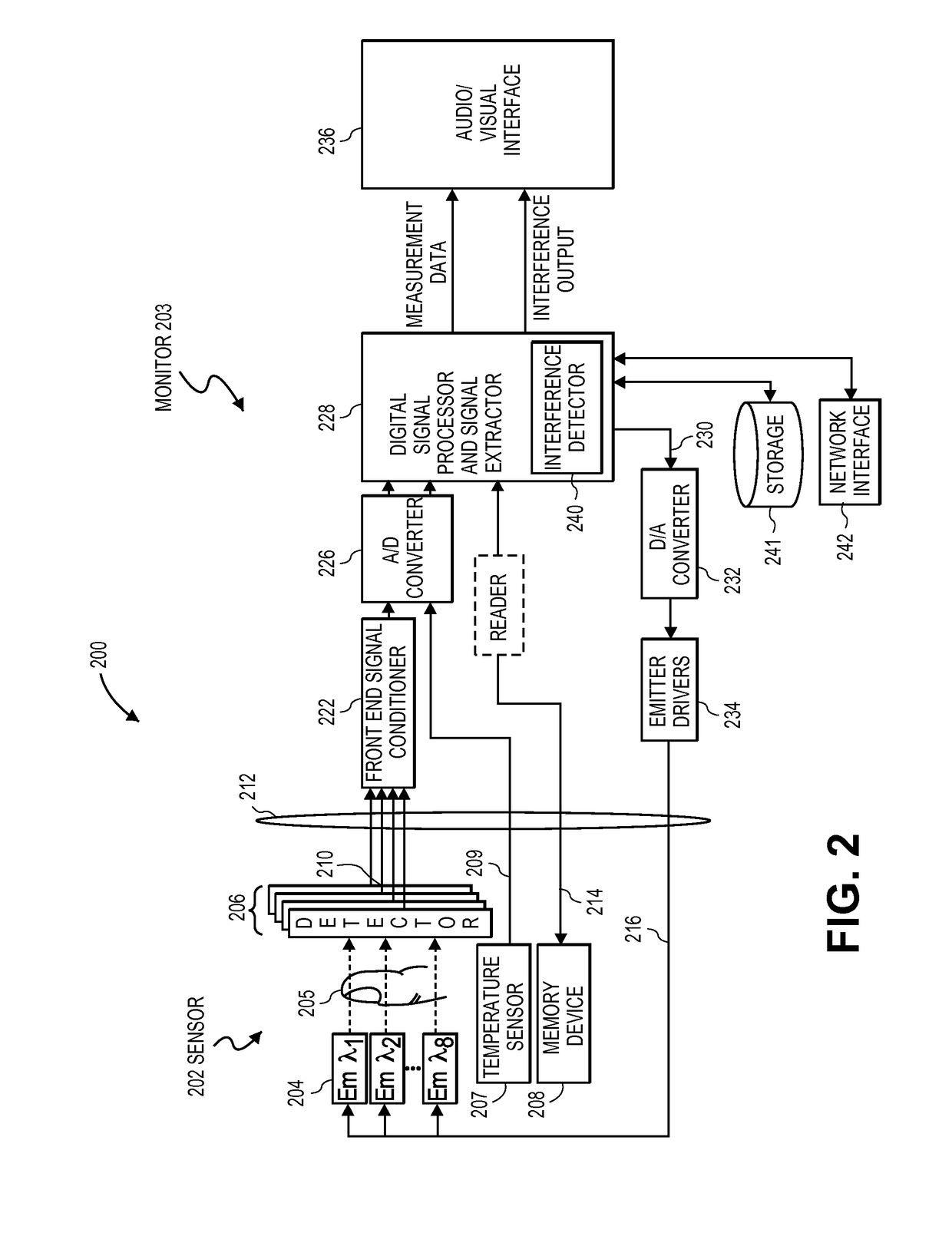
A system is disclosed for detecting and calculating the level of ambient and / or environmental noise, such as electromagnetic interference generated by electric power lines, ambient lights, light dimmers, television or computer displays, power supplies or transformers, and medical equipment. In some embodiments, the system performs frequency analysis on the interference signal detected by light photodetectors and determines the power of the interference signal concentrated in the analyzed frequency bands. The worst-case interference level can be determined by selecting the maximum from the computed power values. In some embodiments, the determined interference signal power can be compared with the noise tolerance of a patient monitoring system configured to reliably and non-invasively detect physiological parameters of a user. The results of the comparison can be presented to the user audio-visually. In some embodiments, the system can be used to perform spot check measurements of electromagnetic interference.
Owner:MASIMO CORP
Congenital heart disease monitor
ActiveUS8457707B2Health-index calculationMedical automated diagnosisUltrasound attenuationOptical radiation
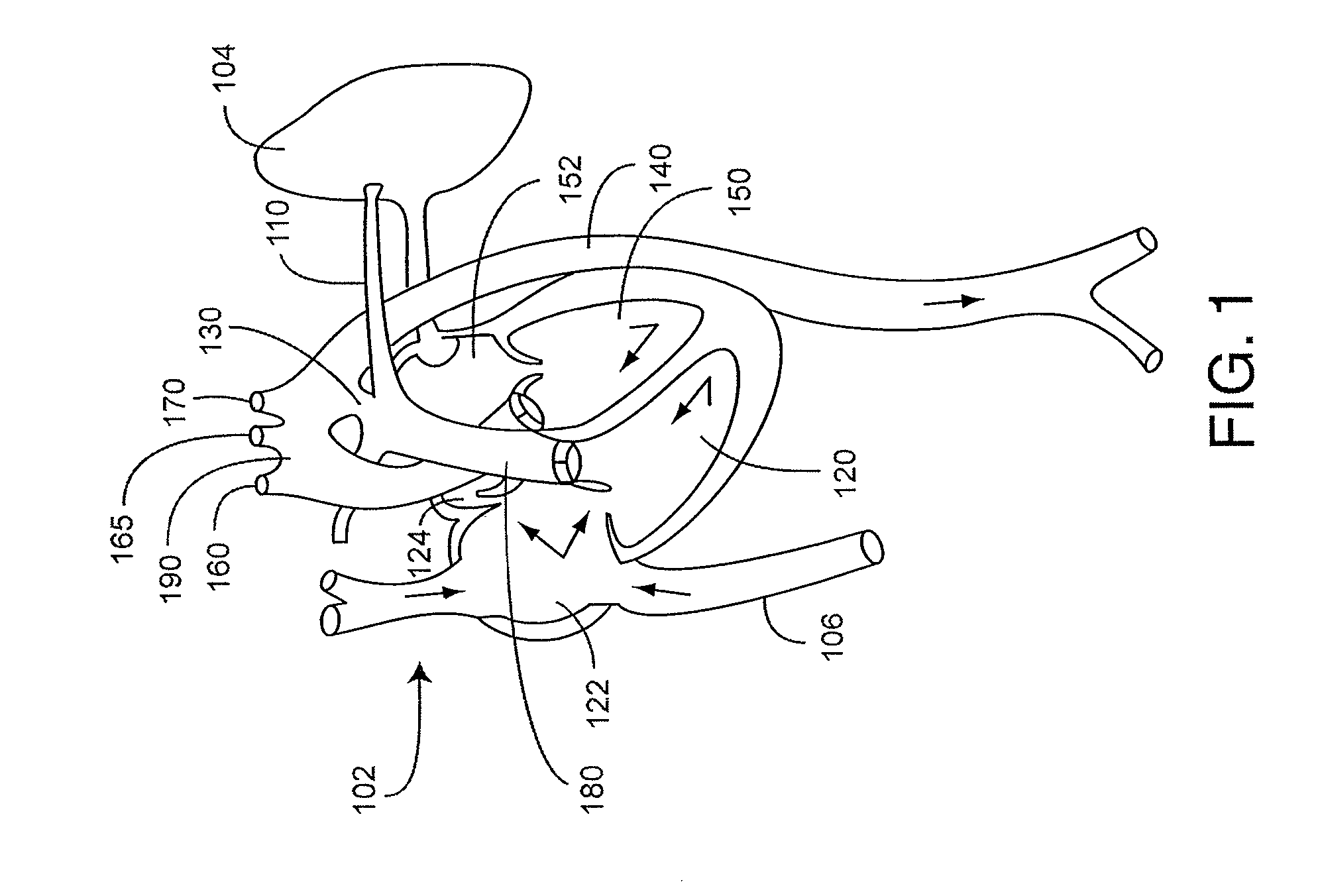
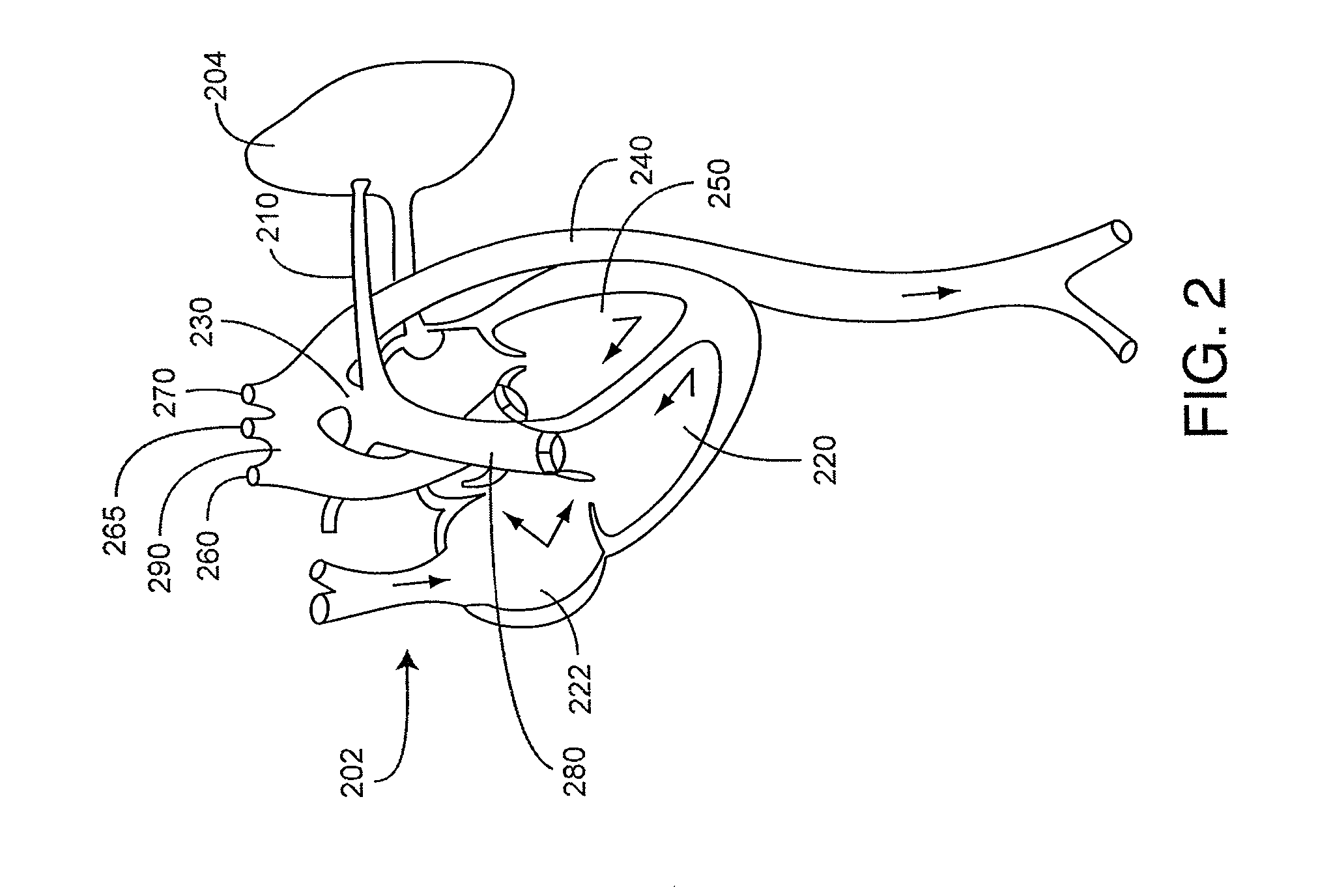
A congenital heart disease monitor utilizes a sensor capable of emitting multiple wavelengths of optical radiation into a tissue site and detecting the optical radiation after attenuation by pulsatile blood flowing within the tissue site. A patient monitor is capable of receiving a sensor signal corresponding to the detected optical radiation and calculating at least one physiological parameter in response. The physiological parameter is measured at a baseline site and a comparison site and a difference in these measurements is calculated. A potential congenital heart disease condition in indicated according to the measured physiological parameter at each of the sites or the calculated difference in the measured physiological parameter between the sites or both.
Owner:JPMORGAN CHASE BANK NA
Sensing system with auxiliary display
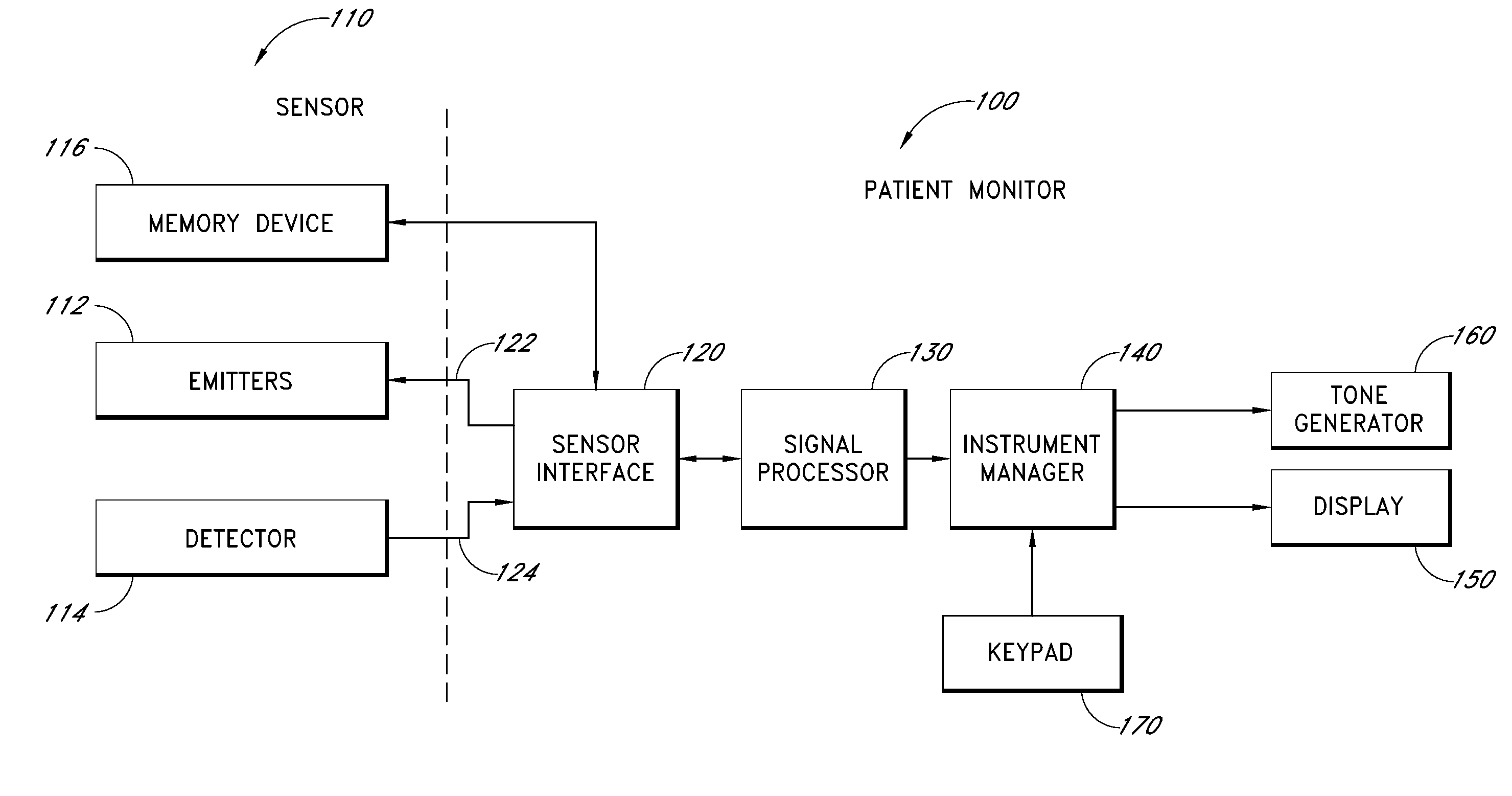
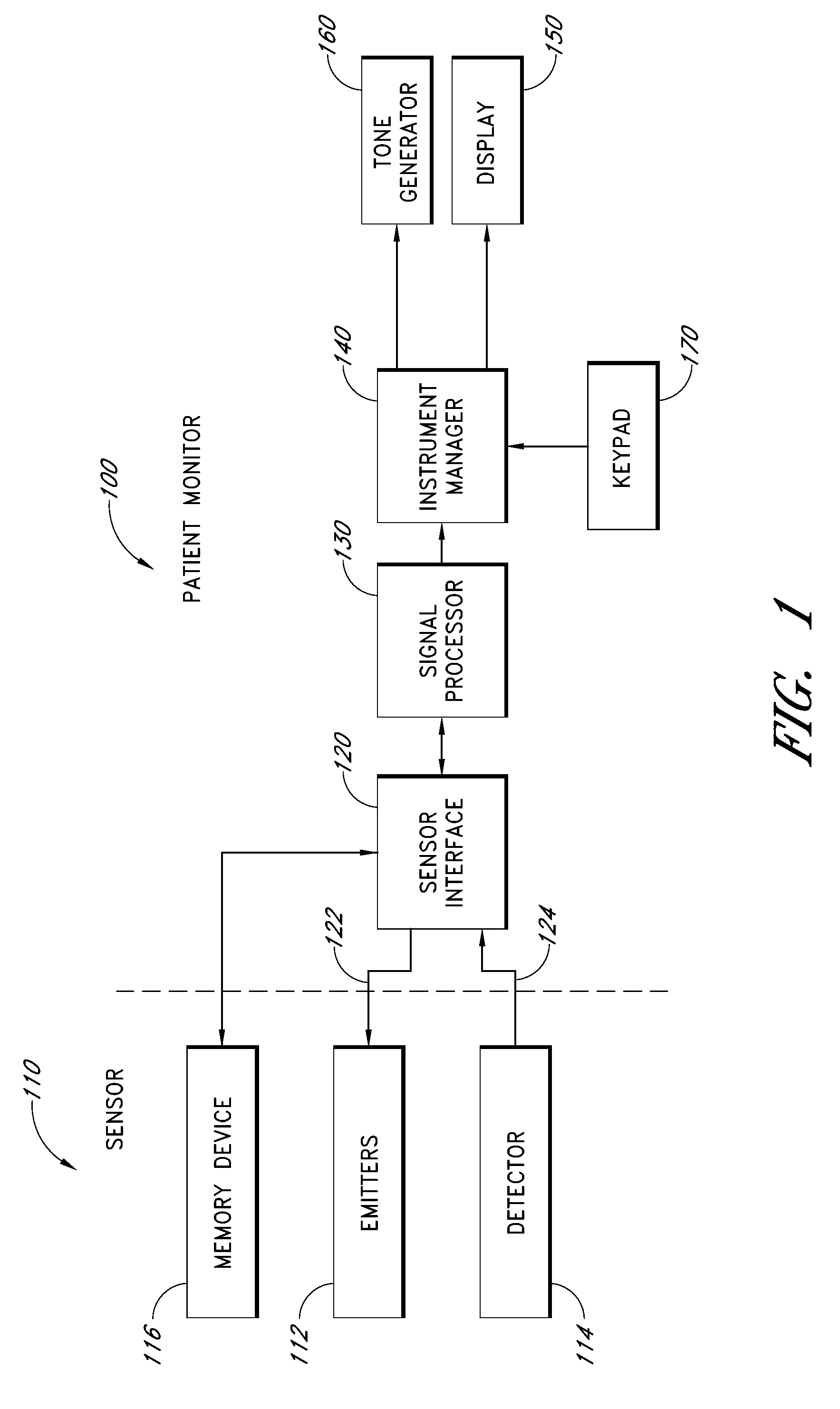
A system is provided for sensing blood glucose data of a patient. The system includes a sensor, user interface, and an optional auxiliary device. If the connection between the sensor and user interface is by a wire, the sensor remains powered when the wire is disconnected. The communication between the sensor and the user interface may be wireless. The auxiliary device can be a patient monitor or other display or signal device, which displays information about the blood glucose data collected by the sensor. The sensor is connected to sensor electronics, which include a sensor power supply, a voltage regulator, and optionally a memory and processor.
Owner:MEDTRONIC MIMIMED INC
Reprocessing of a physiological sensor
ActiveUS8584345B2Low reliabilityReduce material costsWave amplification devicesManufacture of electrical instrumentsReprocessorEngineering
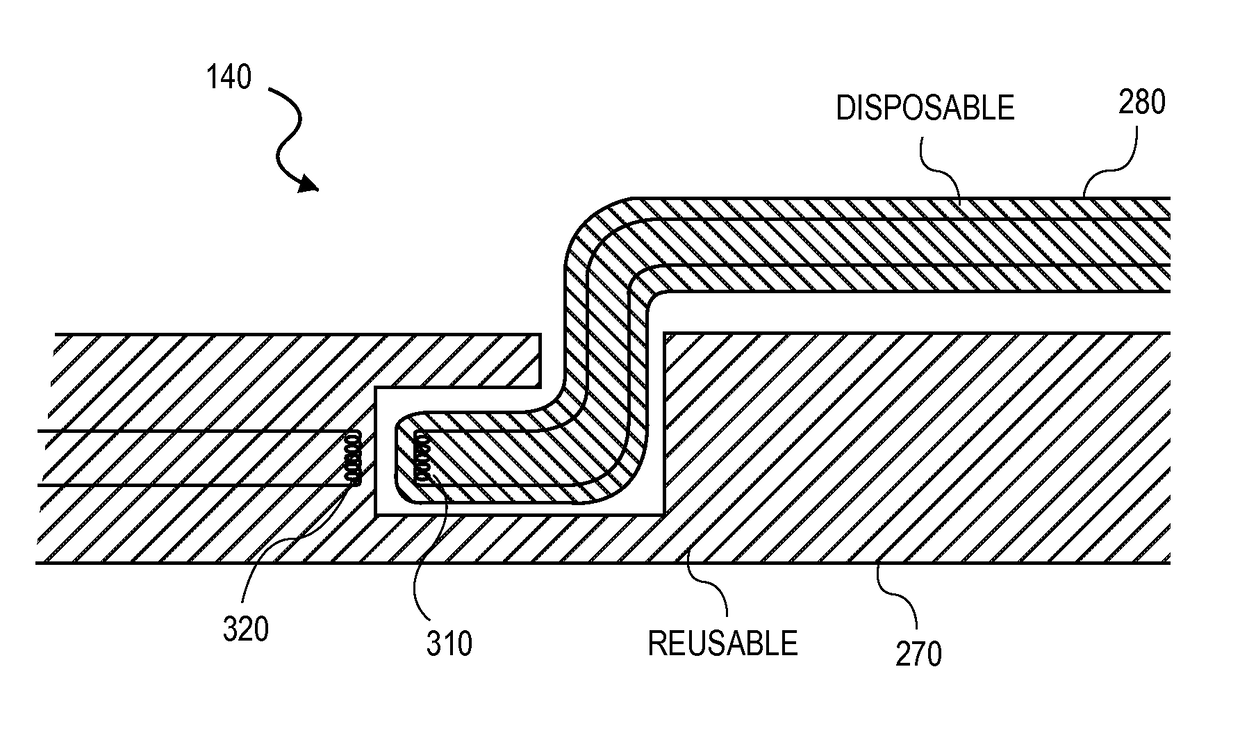
Because reprocessing or refurbishing of physiological sensors reuses large portions of an existing sensor, the material costs for refurbishing sensors is significantly lower than the material costs for making an entirely new sensor. Typically, existing reprocessors replace only the adhesive portion of an adhesive physiological sensor and reuse the sensing components. However, re-using the sensing components can reduce the reliability of the refurbished sensor and / or reduce the number of sensors eligible for refurbishing due to out-of-specification sensor components. It is therefore desirable to provide a process for refurbishing physiological sensors that replaces the sensing components of the sensor. While sensing components are replaced, generally, sensor cable and / or patient monitor attachments are retained, resulting in cost savings over producing new sensors.
Owner:JPMORGAN CHASE BANK NA
Wireless optical communication between noninvasive physiological sensors and patient monitors
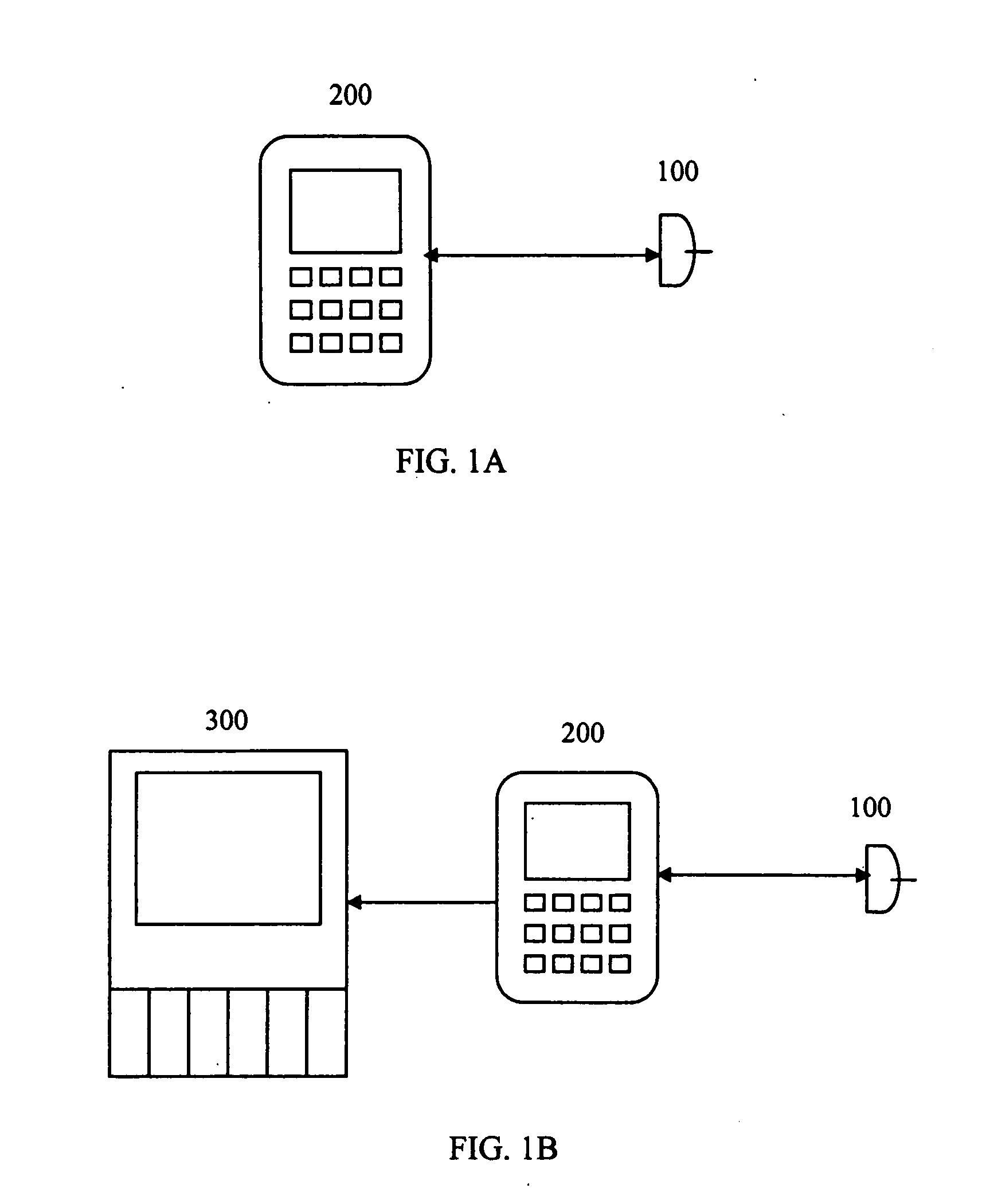
InactiveUS20140275871A1Reduced portabilityReduce compactnessClose-range type systemsDiagnostic recording/measuringPatient monitorComputer science
Embodiments of the disclosure include a noninvasive physiological patient sensor and a patient monitor capable of wireless communication with one another. An optical communication path can be used to provide the communication path between the noninvasive physiological patient sensor and the patient monitor. The path can be maintained by one or more light sources and detectors traditionally associated with noninvasive optical sensors or by one or more additional dedicated light sources and detectors.
Owner:MASIMO CORP
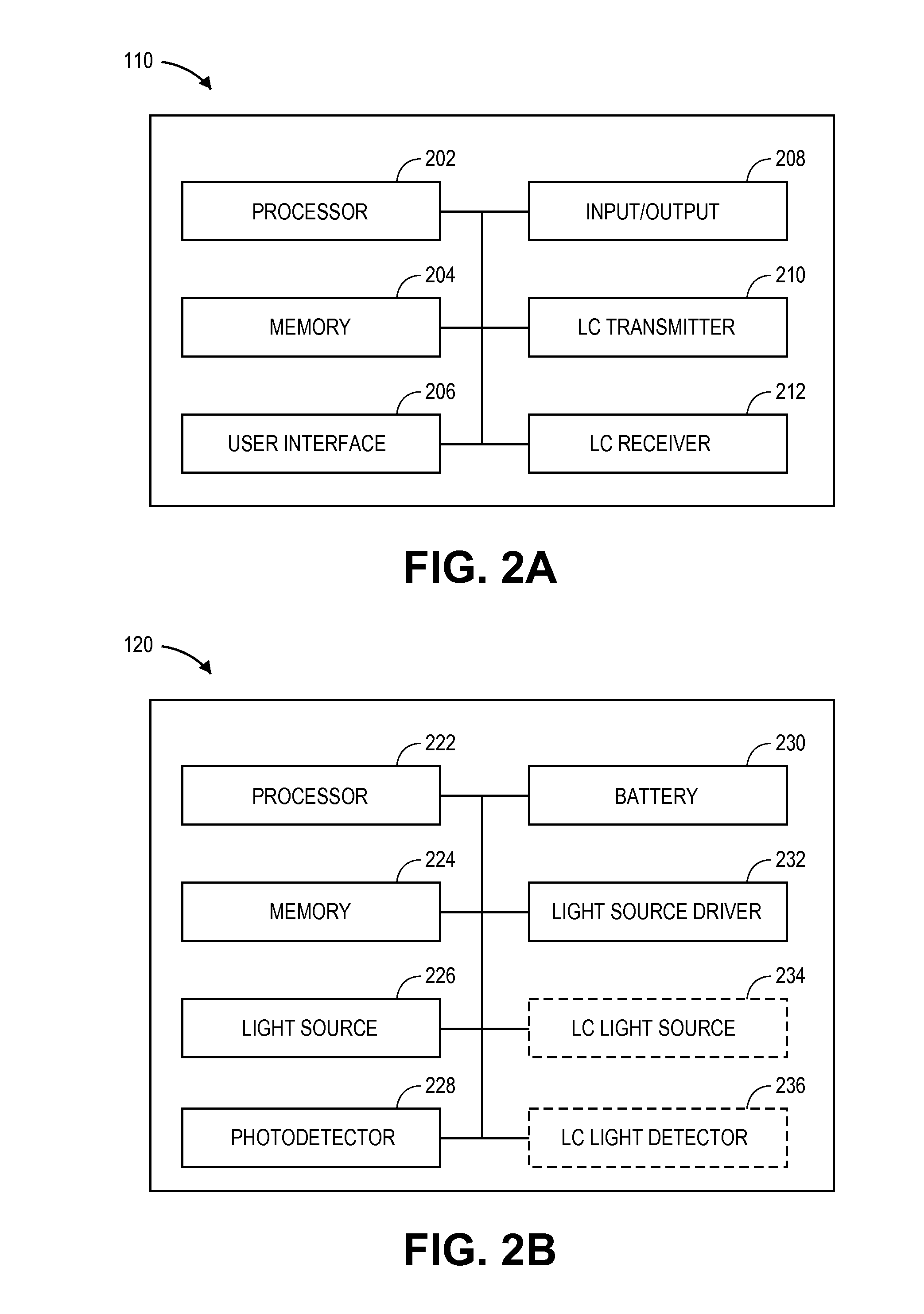
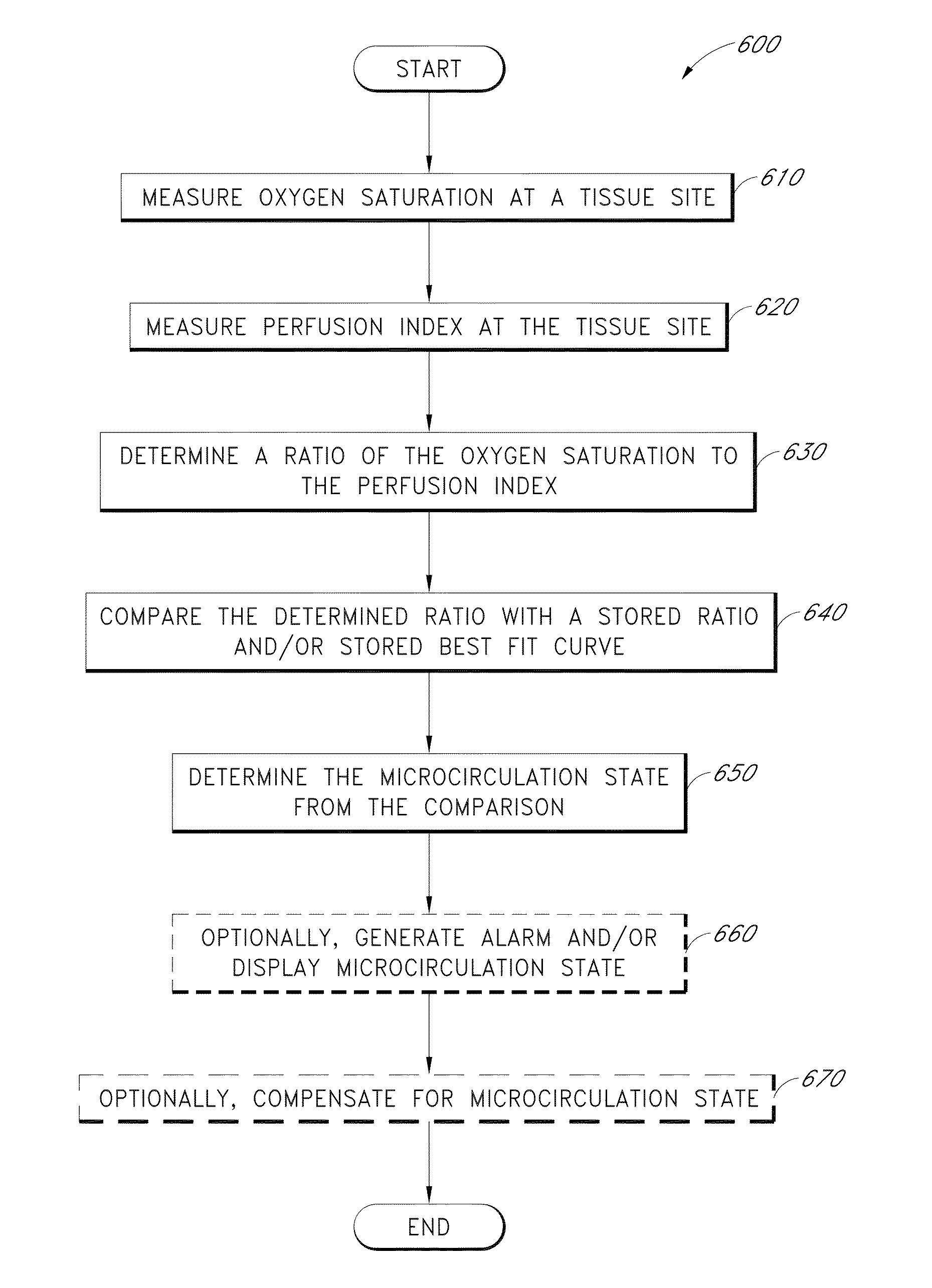
Patient monitor for determining microcirculation state
As placement of a physiological monitoring sensor is typically at a sensor site located at an extremity of the body, the state of microcirculation, such as whether vessels are blocked or open, can have a significant effect on the readings at the sensor site. It is therefore desirable to provide a patient monitor and / or physiological monitoring sensor capable of distinguishing the microcirculation state of blood vessels. In some embodiments, the patient monitor and / or sensor provide a warning and / or compensates a measurement based on the microcirculation state. In some embodiments, a microcirculation determination process implementable by the patient monitor and / or sensor is used to determine the state of microcirculation of the patient.
Owner:MASIMO CORP
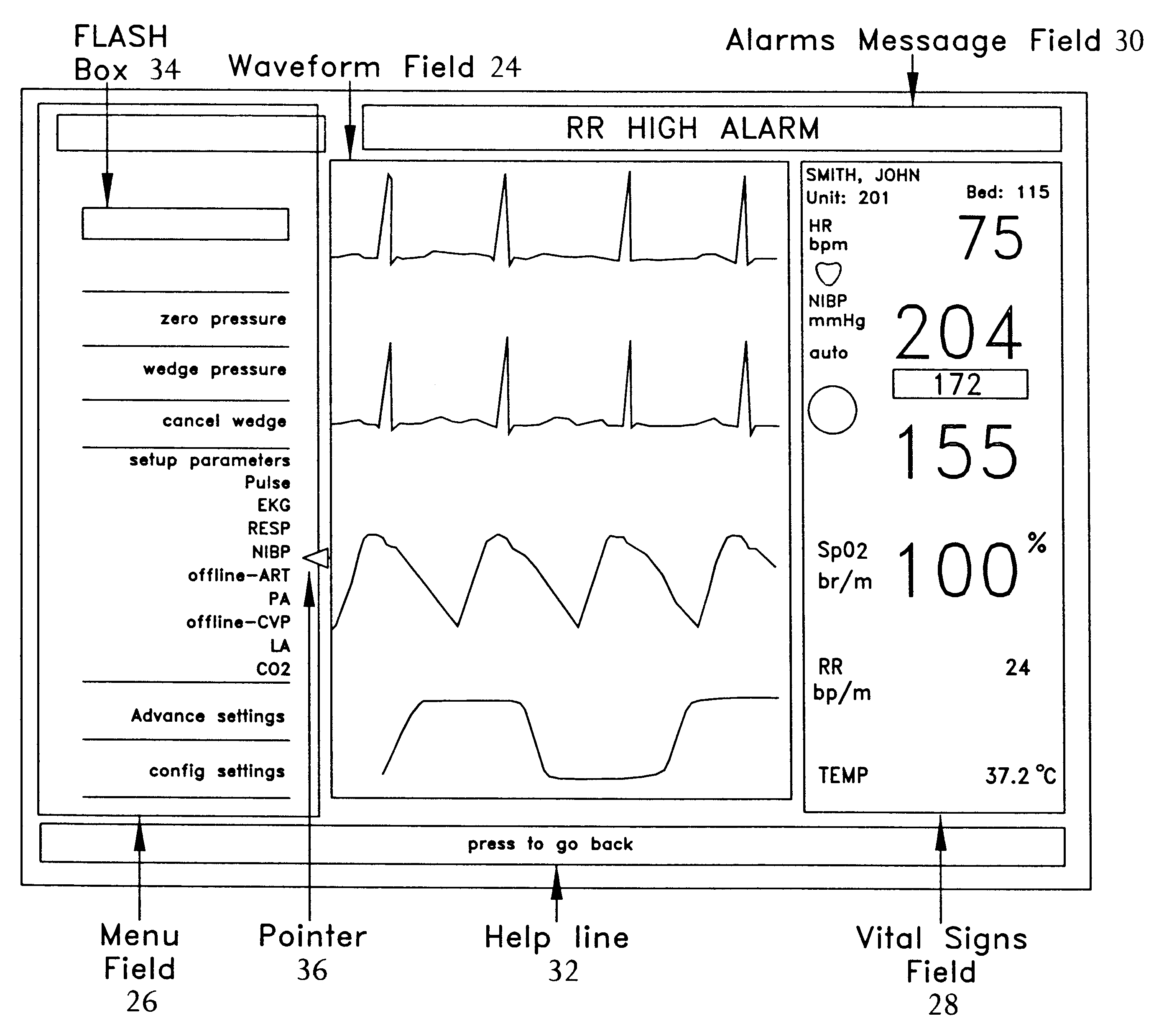
Reconfigurable user interface for modular patient monitor
InactiveUS6188407B1Maximize useMinimizing navigationData processing applicationsElectrocardiographyOperational systemModularity
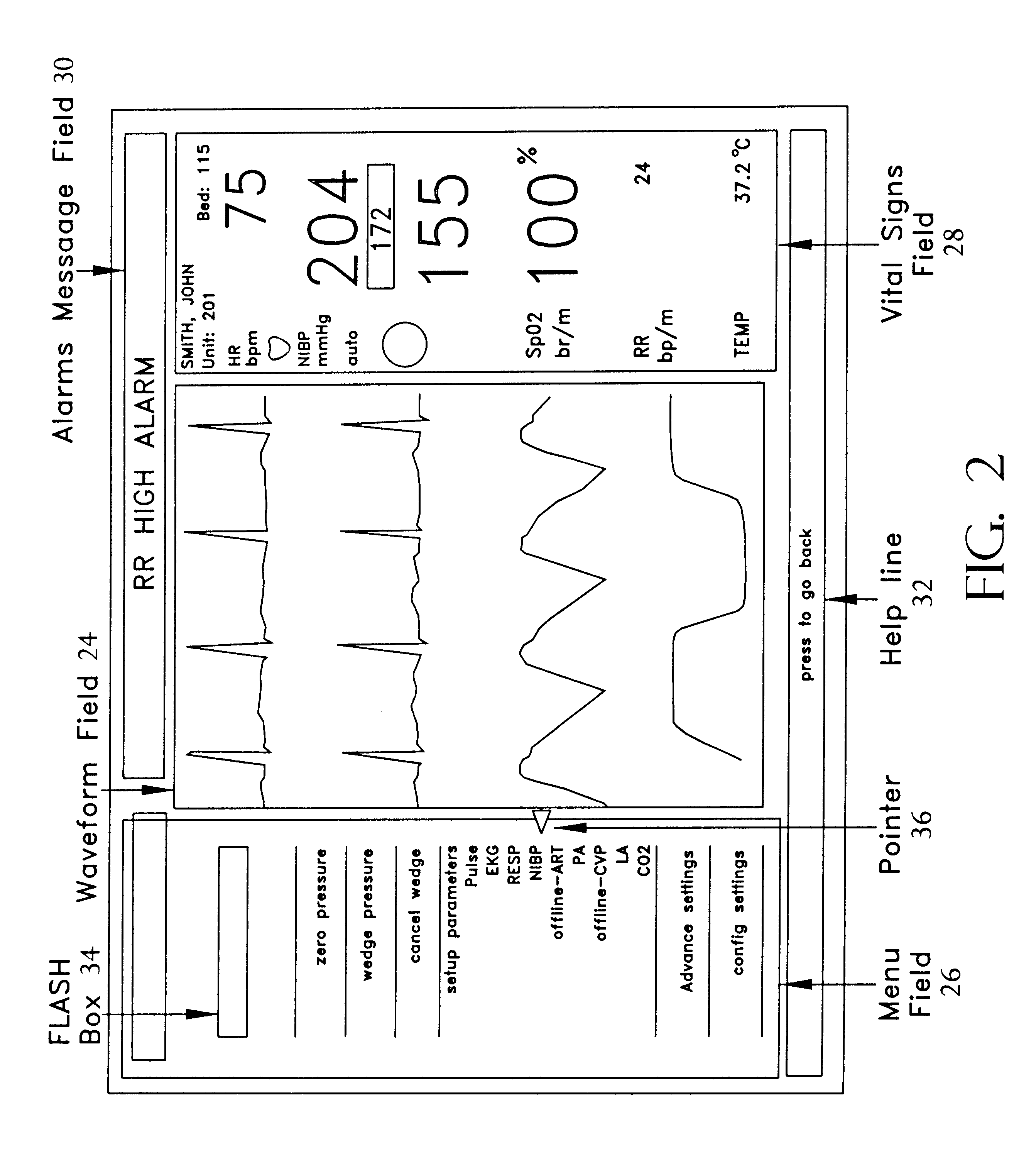
A reconfigurable user interface for a modular patient monitor which selectively populates menus for operator selection based on the parameters which are available at any given time. Due to event processing, when a parameter module is added or removed from the system, the reconfigurable user interface is updated immediately to reflect the addition or subtraction of the associated parameter. A flash box in each menu provides shortcuts to the most likely menu option in response to asynchronous events such as alarms and the like. The flash box also assists the operator with the particular steps that must be followed to properly setup or operate a particular feature of the system. Since the menus are not modal, an operator may navigate the menus without making any selections or changing the state of the device.
Owner:GE MEDICAL SYST INFORMATION TECH
Patient monitor for monitoring microcirculation
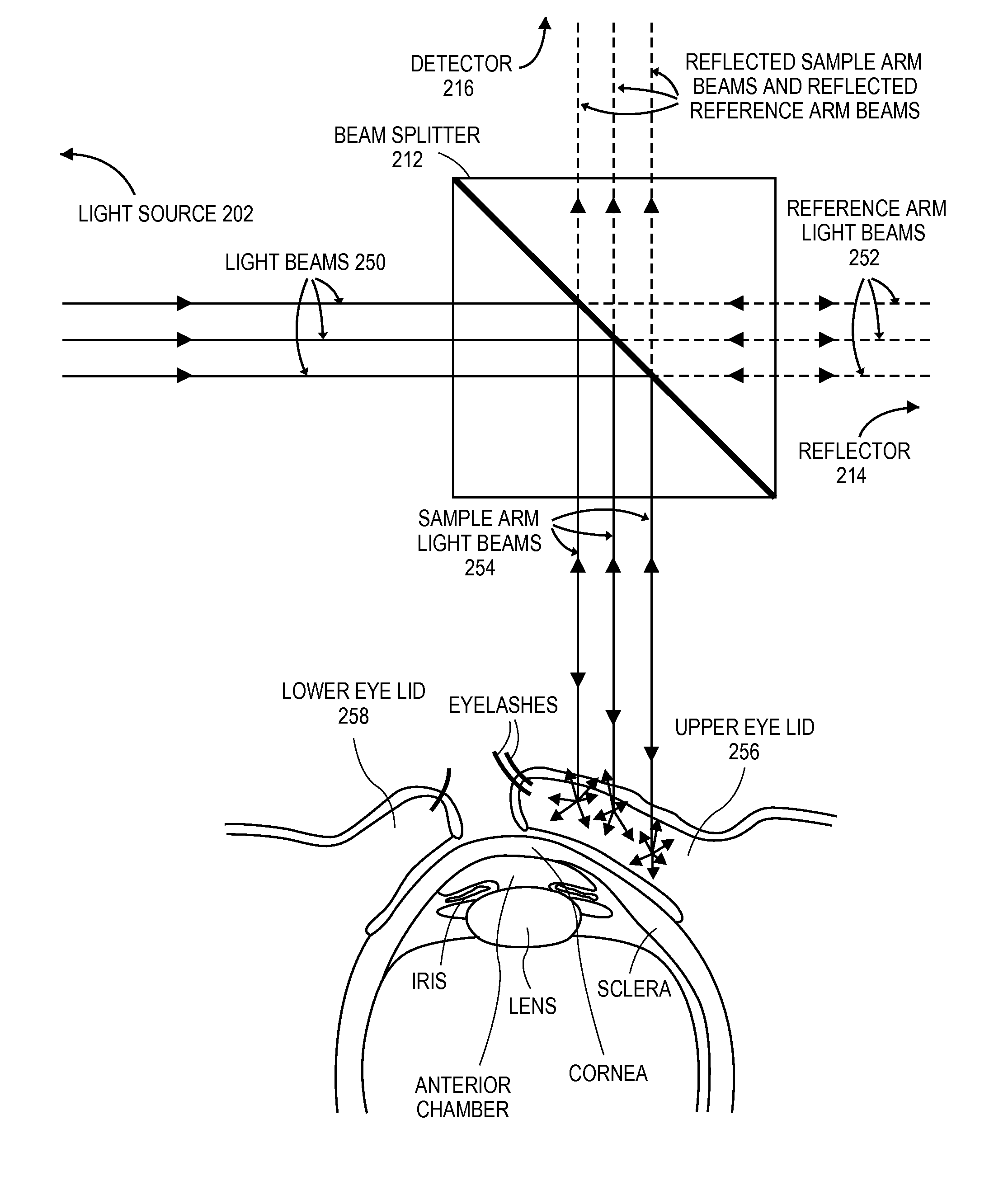
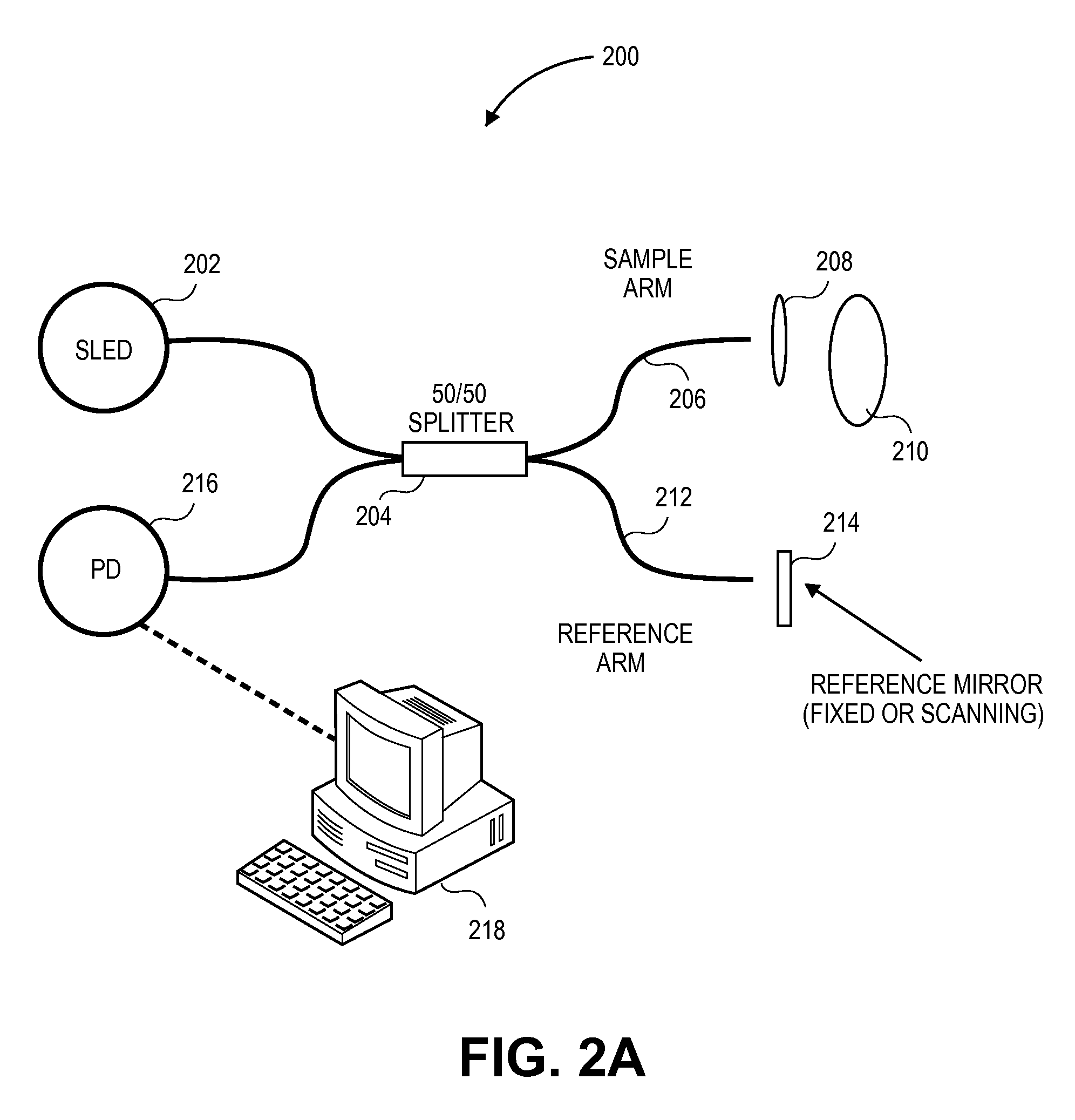
A patient monitor capable of measuring microcirculation at a tissue site includes a light source, a beam splitter, a photodetector and a patient monitor. Light emitted from the light source is split into a reference arm and a sample arm. The light in the sample arm is directed at a tissue site, such as an eyelid. The reflected light from the tissue site is interfered with the light from the reference arm. The photodetector measures the interference of the light from both the sample arm and the reference arm. The patient monitor uses the measurements from the photodetector to calculate the oxygen saturation at the tissue site and monitor the microcirculation at the tissue site.
Owner:MASIMO CORP
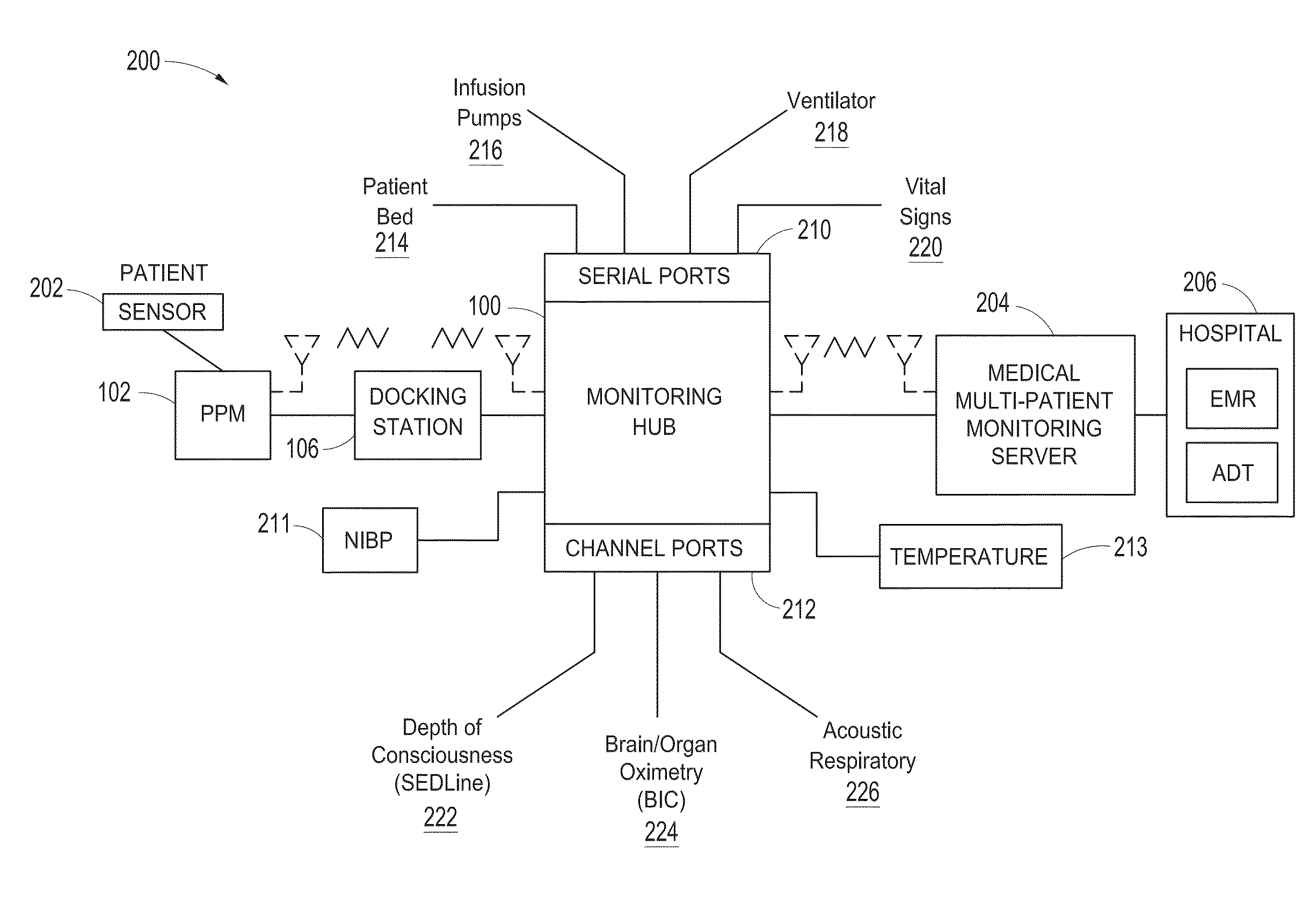
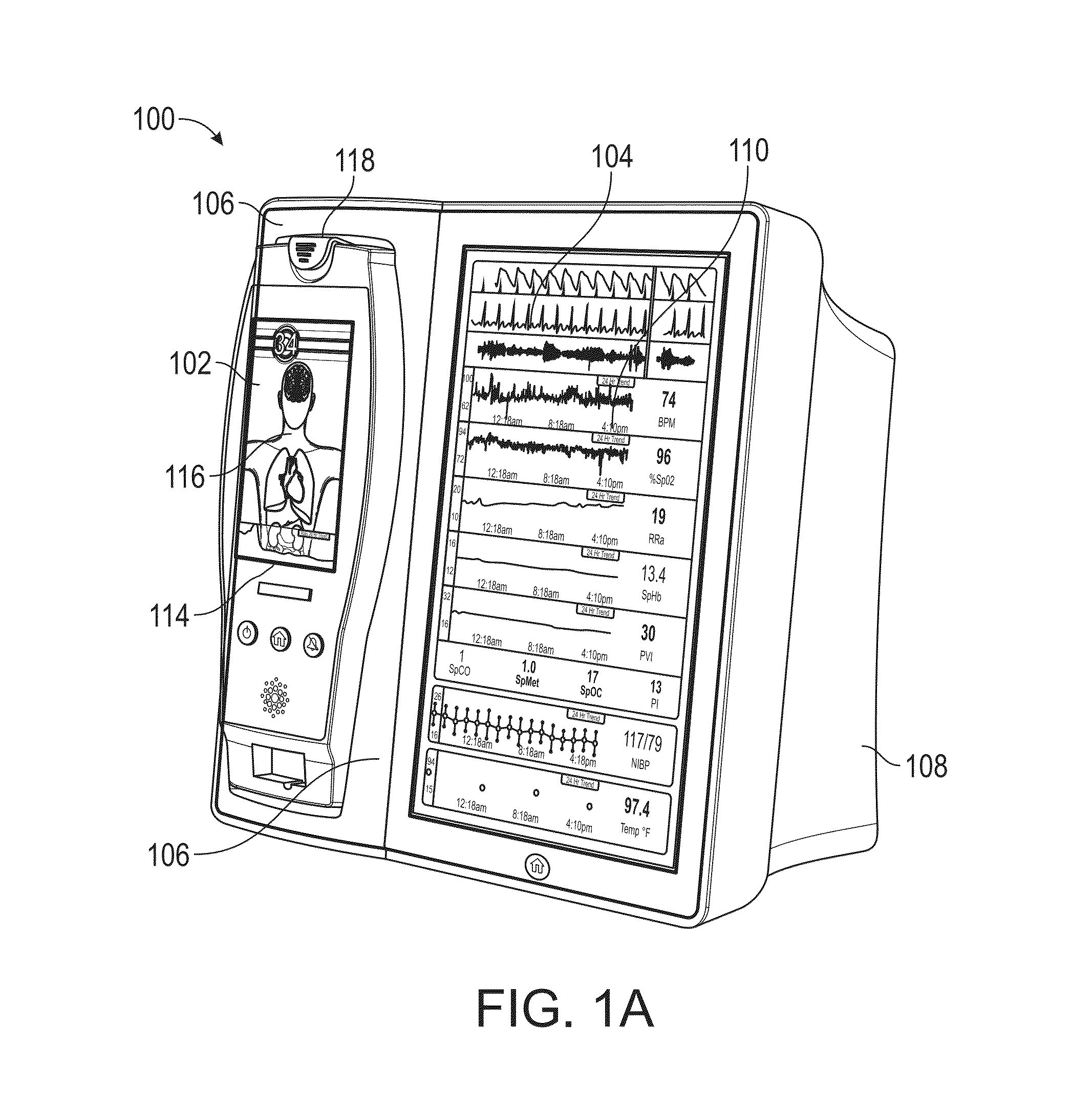
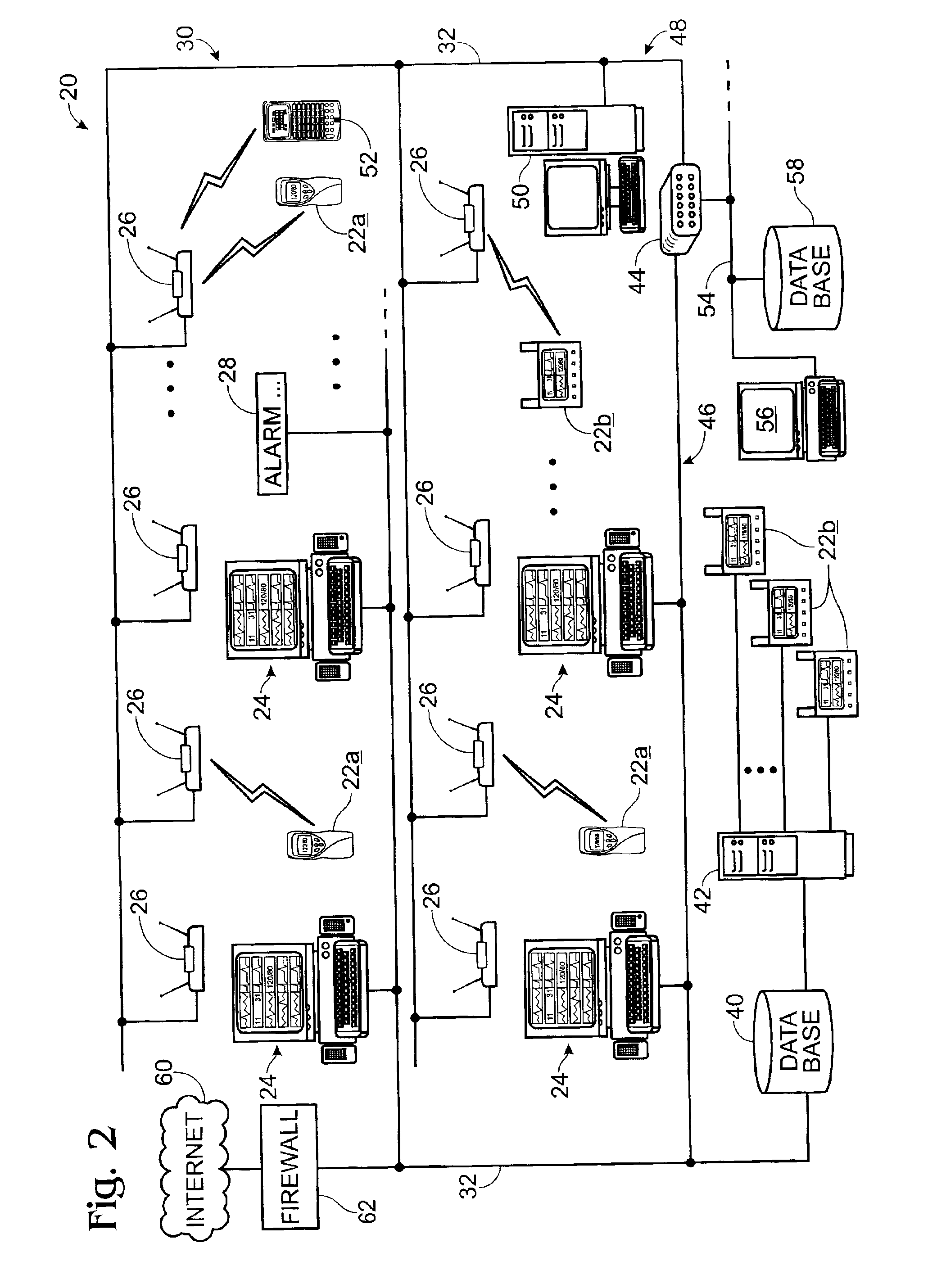
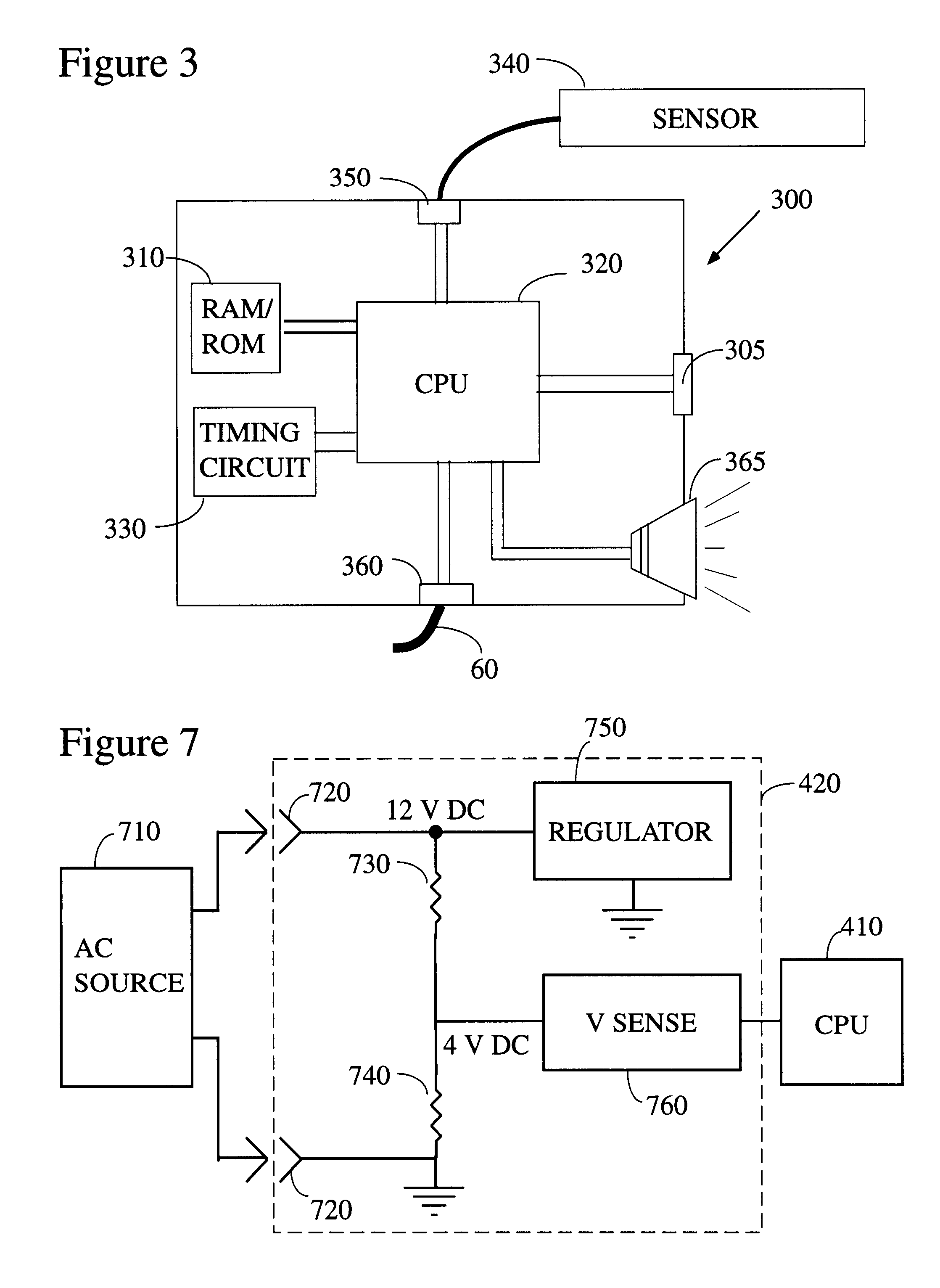
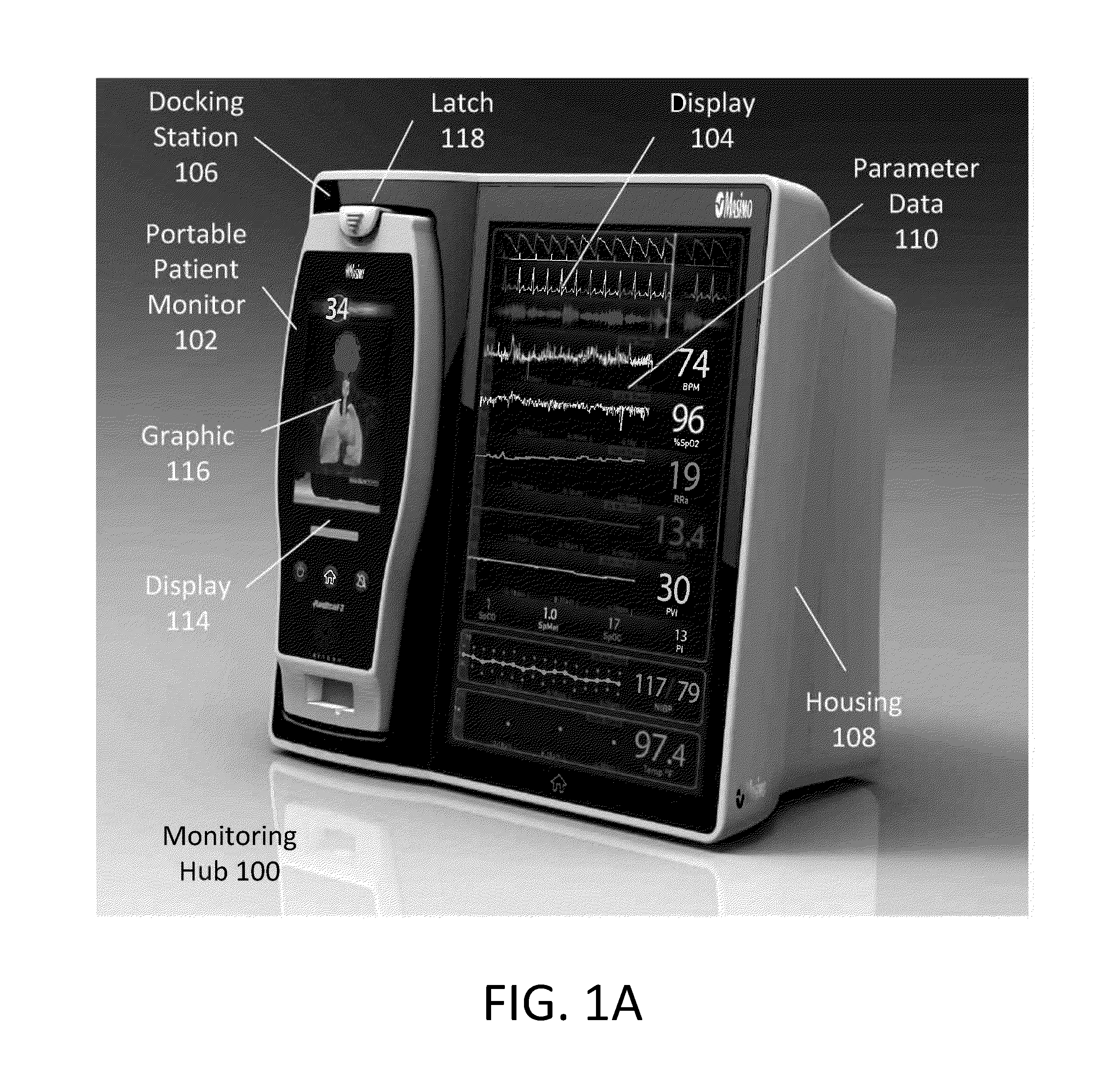
Medical monitoring hub
The present disclosure includes a medical monitoring hub as the center of monitoring for a monitored patient. The hub includes configurable medical ports and serial ports for communicating with other medical devices in the patient's proximity. Moreover, the hub communicates with a portable patient monitor. The monitor, when docked with the hub provides display graphics different from when undocked, the display graphics including anatomical information. The hub assembles the often vast amount of electronic medical data, associates it with the monitored patient, and in some embodiments, communicates the data to the patient's medical records.
Owner:JPMORGAN CHASE BANK NA +1
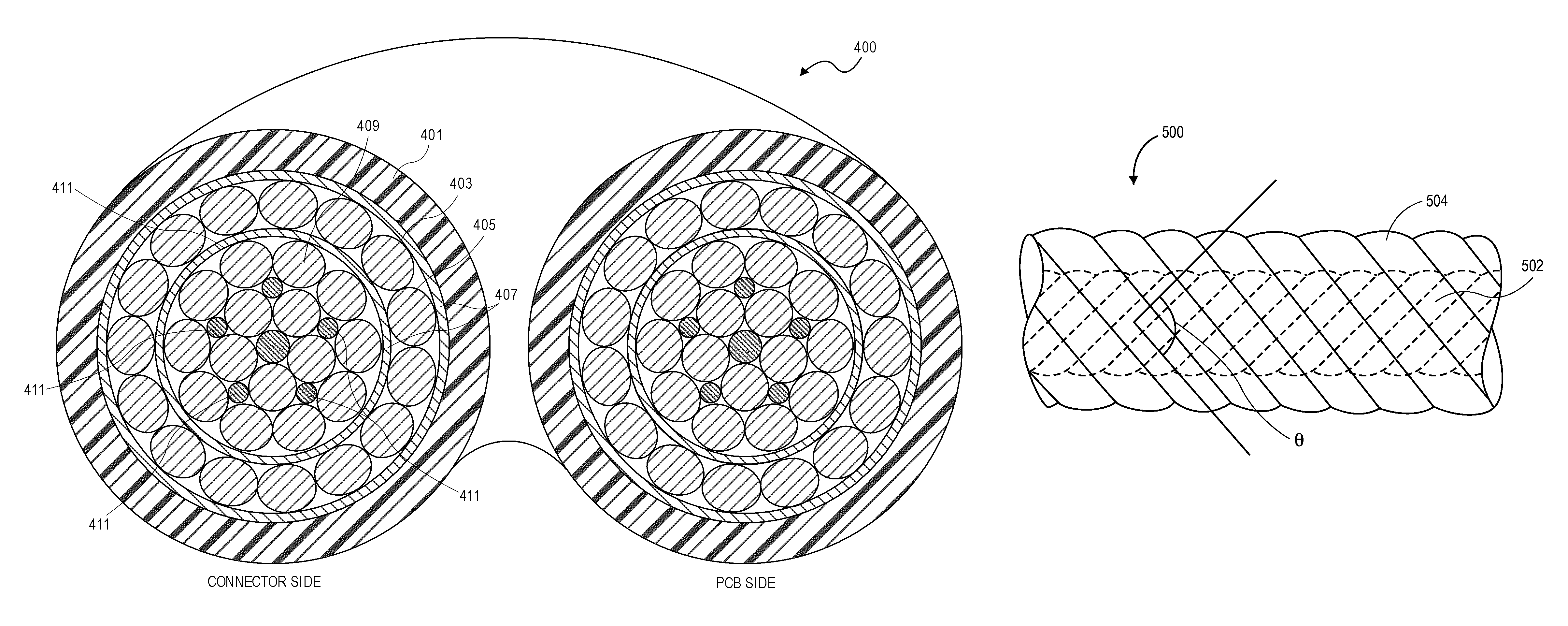
Low noise cable providing communication between electronic sensor components and patient monitor
ActiveUS9245668B1Reduce crosstalkNot hindering sensor placementDiagnostics using lightConductive materialLow noiseEngineering
A physiological measurement system can include a low noise patient cable that connects a monitor and a noninvasive optical sensor. The cable has a plurality of emitter wires configured to communicate a drive signal between the monitor and at least one emitter. The cable also has a plurality of detector wires configured to communicate a physiological signal between at least one detector responsive to the emitter and the monitor. The emitter and detector wires are orthogonally disposed so that crosstalk between the two functionally different wires is mitigated.
Owner:MASIMO CORP
Dual-mode patient monitor
InactiveUS20140012100A1Easy to disassembleElectroencephalographyElectrocardiographyDual modeMonitoring system
A portable patient monitor has an integrated mode in which it operates as a plug-in module for a multiparameter patient monitoring system (MPMS). The patient monitor also has a portable mode in which it operates separately from the MPMS as a battery-powered handheld or standalone instrument. The patient monitor has a sensor port that receives a signal indicative of physiological parameters as input to an internal processor. The patient monitor processes this sensor signal to derive patient measurements. In the portable mode, this information is provided on its display. In the integrated mode, the patient monitor provides patient measurements to the MPMS to be displayed on a MPMS monitor.
Owner:JPMORGAN CHASE BANK NA
Patient monitor capable of monitoring the quality of attached probes and accessories
ActiveUS20120319816A1Reduce capacityReduce the possibilityProgramme controlElectric signal transmission systemsQuality controlPulse oximetry
A system and method to help maintain quality control and reduce cannibalization of accessories and attached probes in a highly sensitive patient monitor, such as a pulse oximetry system. One or more attached components may have information elements designed to designate what quality control mechanisms a patient monitor should look to find on that or another component or designate other components with which the one component may properly work. In a further embodiment, such information elements may also include data indicating the appropriate life of the component.
Owner:JPMORGAN CHASE BANK NA
Magnetic electrical connector for patient monitors
ActiveUS9775545B2Reduce the risk of contaminationImprove efficiency and benefitElectroencephalographySensorsElectricityMonitoring system
The present disclosure relates to an electrical connector for providing signal isolation between various components of a physiological monitoring system. In an embodiment, the electrical connector is placed between a sensor and associated monitoring system and includes a physical barrier and inductive components.
Owner:JPMORGAN CHASE BANK NA
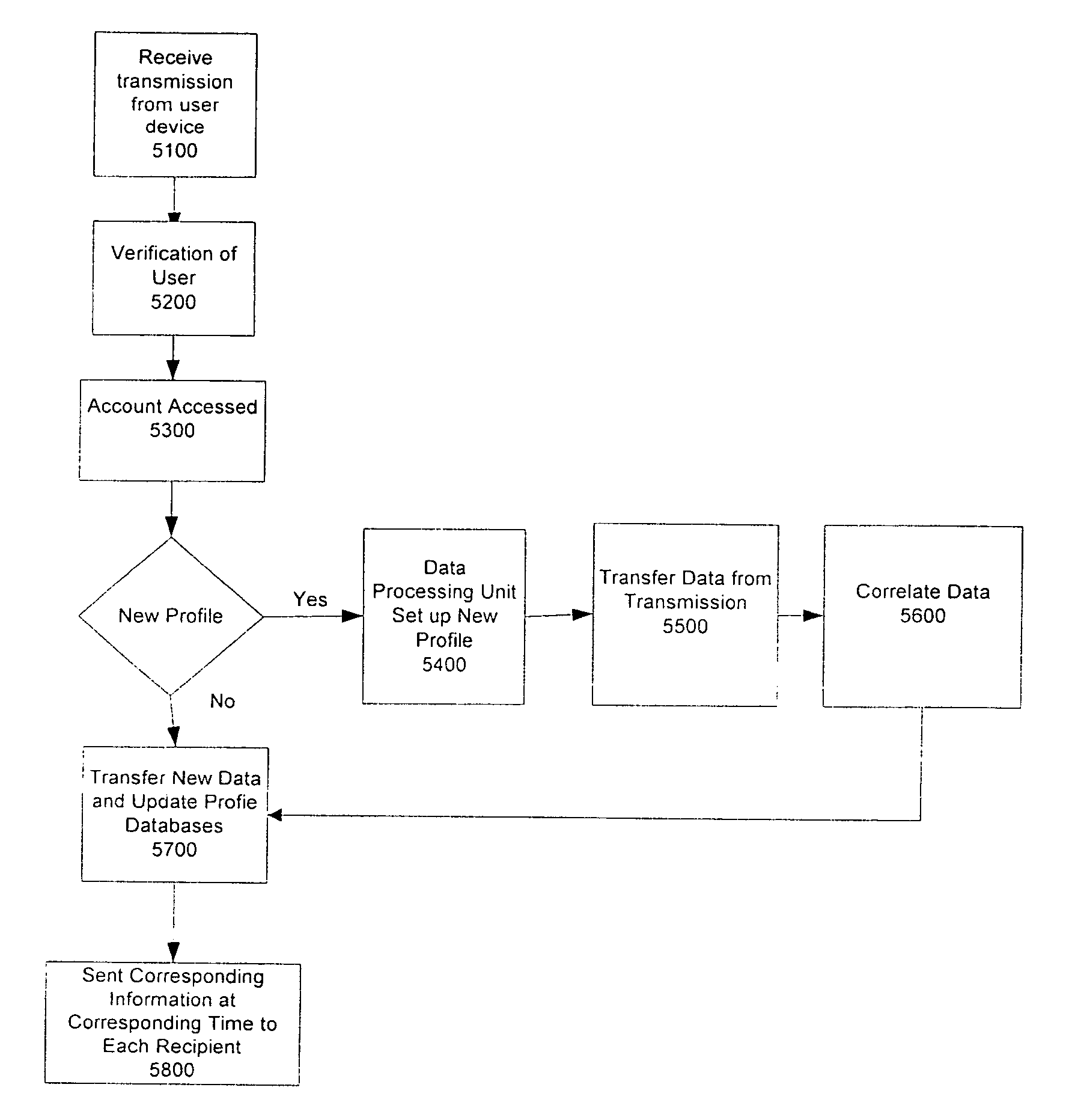
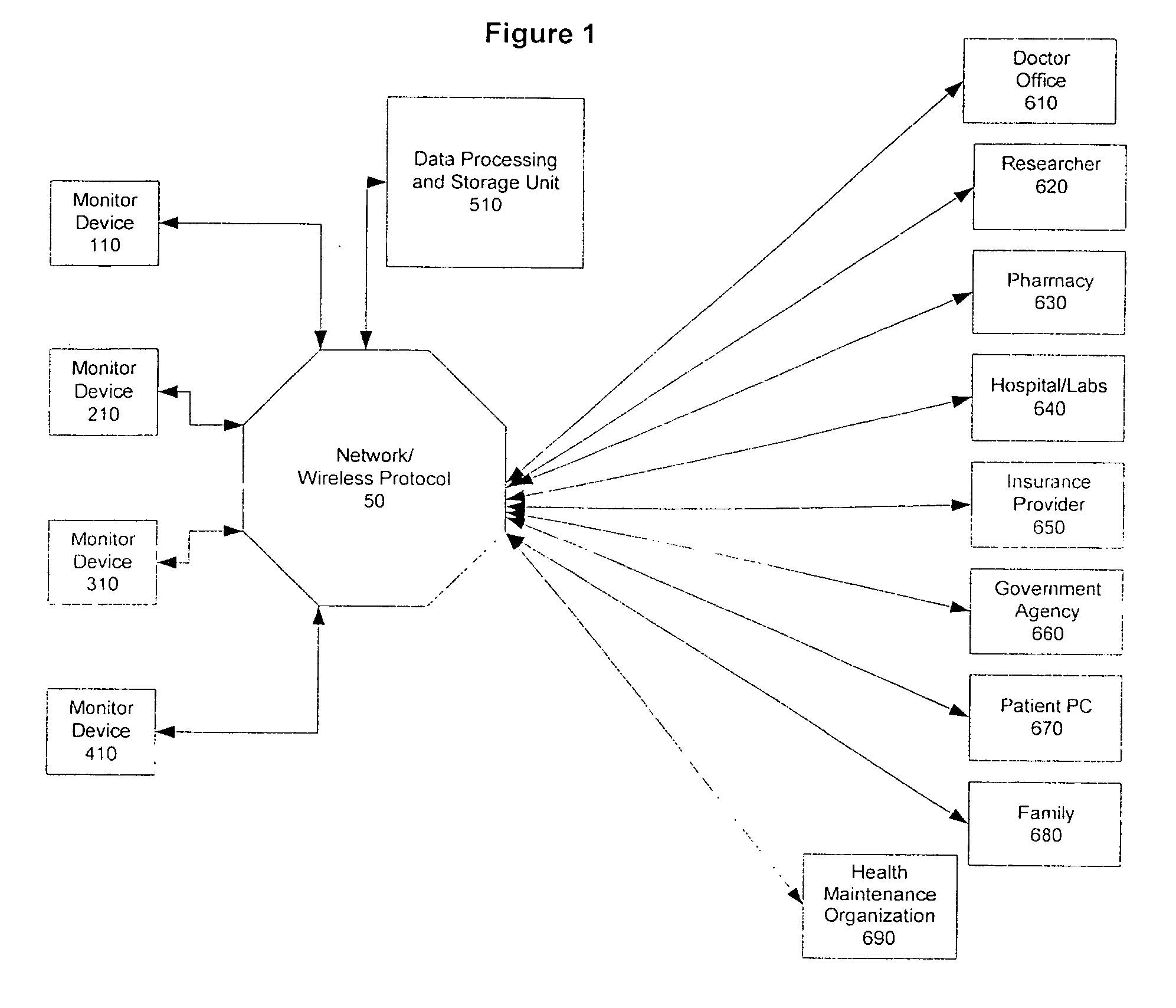
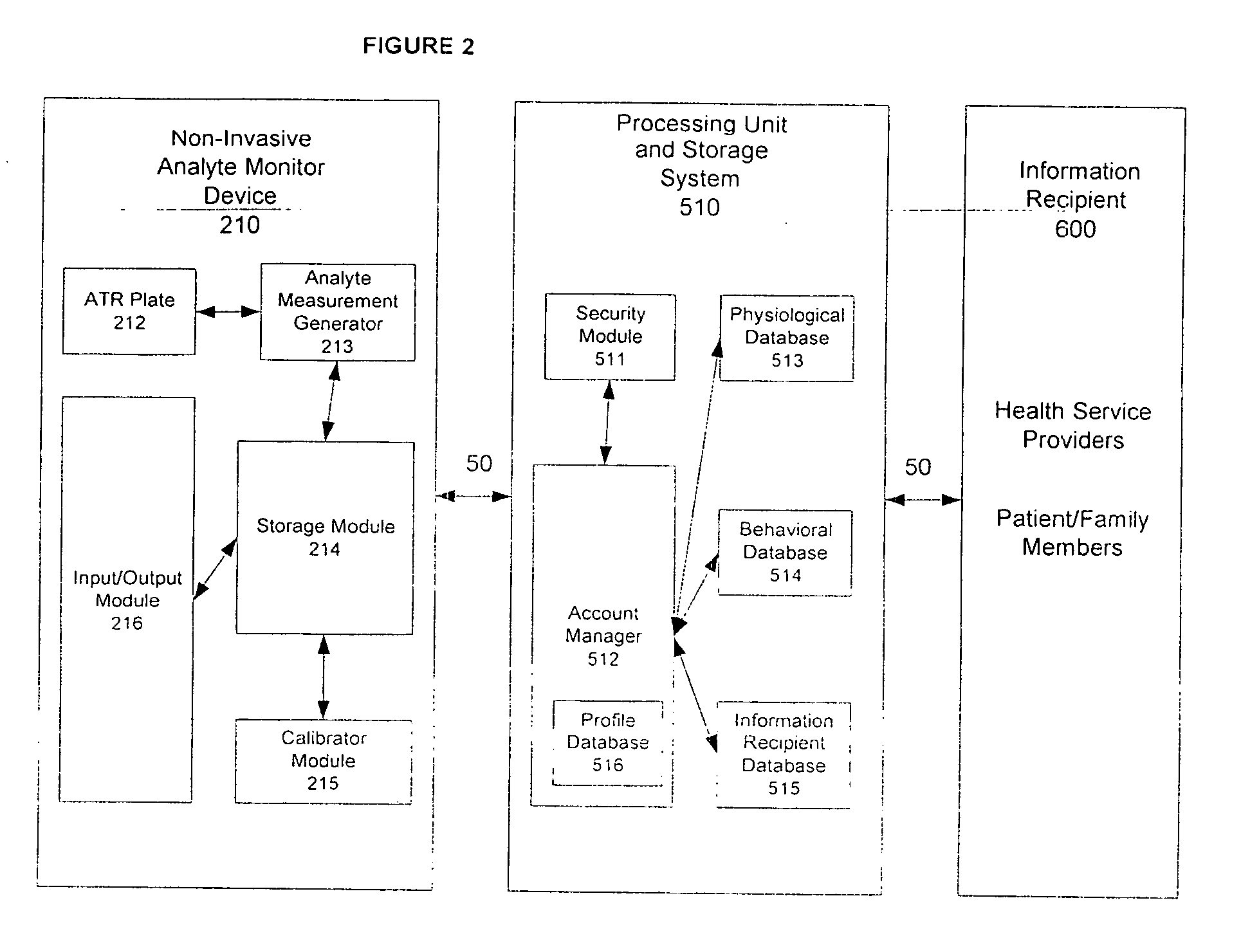
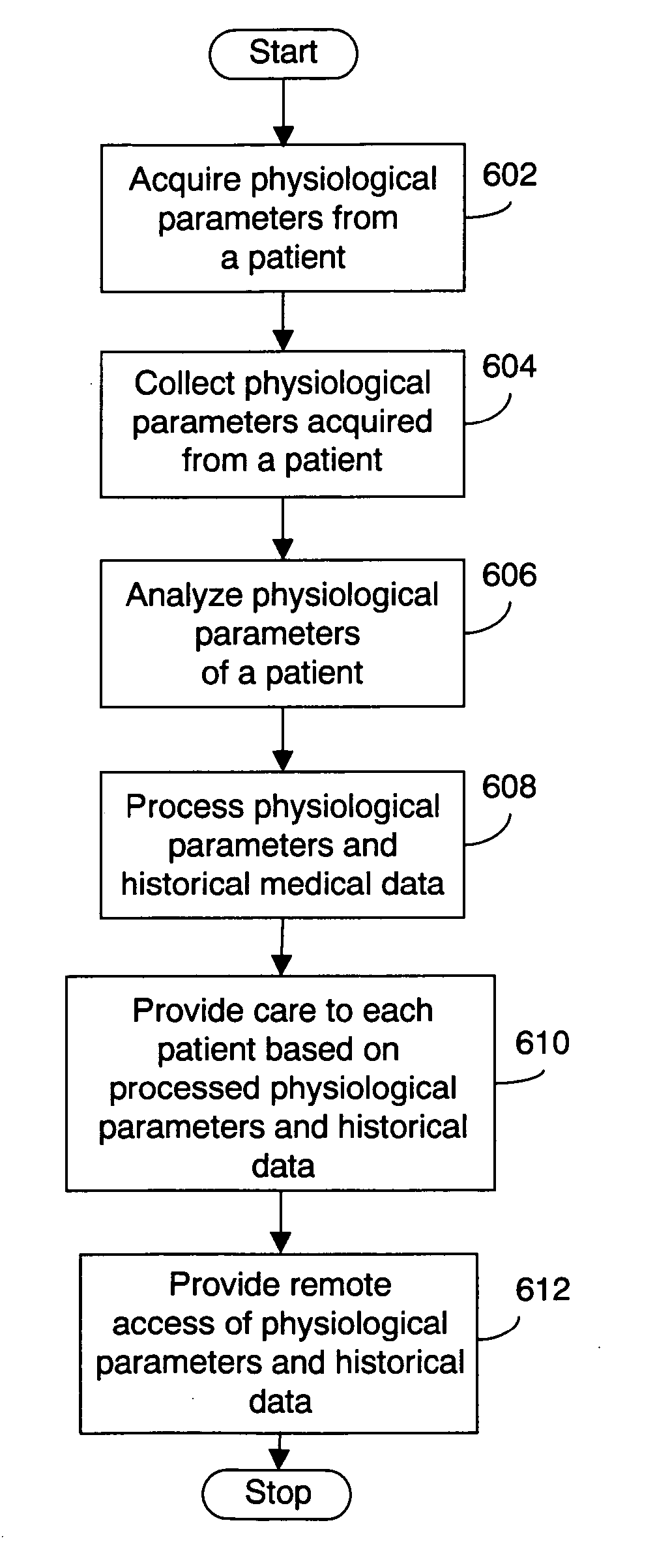
Method and system of monitoring a patient
A patient monitor system implemented by a service provider for users via recording a patients analytes measurements by an attenuated total reflection (ATR) infrared total spectroscopy method. The system comprises an input module that provides a non-invasive method in measuring analytes in a patient, such as a measurement of the glucose level and other blood analytes. The measurement is shared among a plurality of output devices such as computers, personal digital assistants (PDAs), cellular phones, and pagers that are stationed or held by various users such as doctors, patients, researchers, pharmacies, labs, and health insurers. In addition behavioral attributes are recorded and correlated with the analytes measurements to generate a profile. The profile is selectively sent to output devices based on the user profile corresponding to the output device. Also, access to the profile is monitored by a security module that encrypts the profile to prevent access by un-authorized users.
Owner:VIVOMEDICAL INC
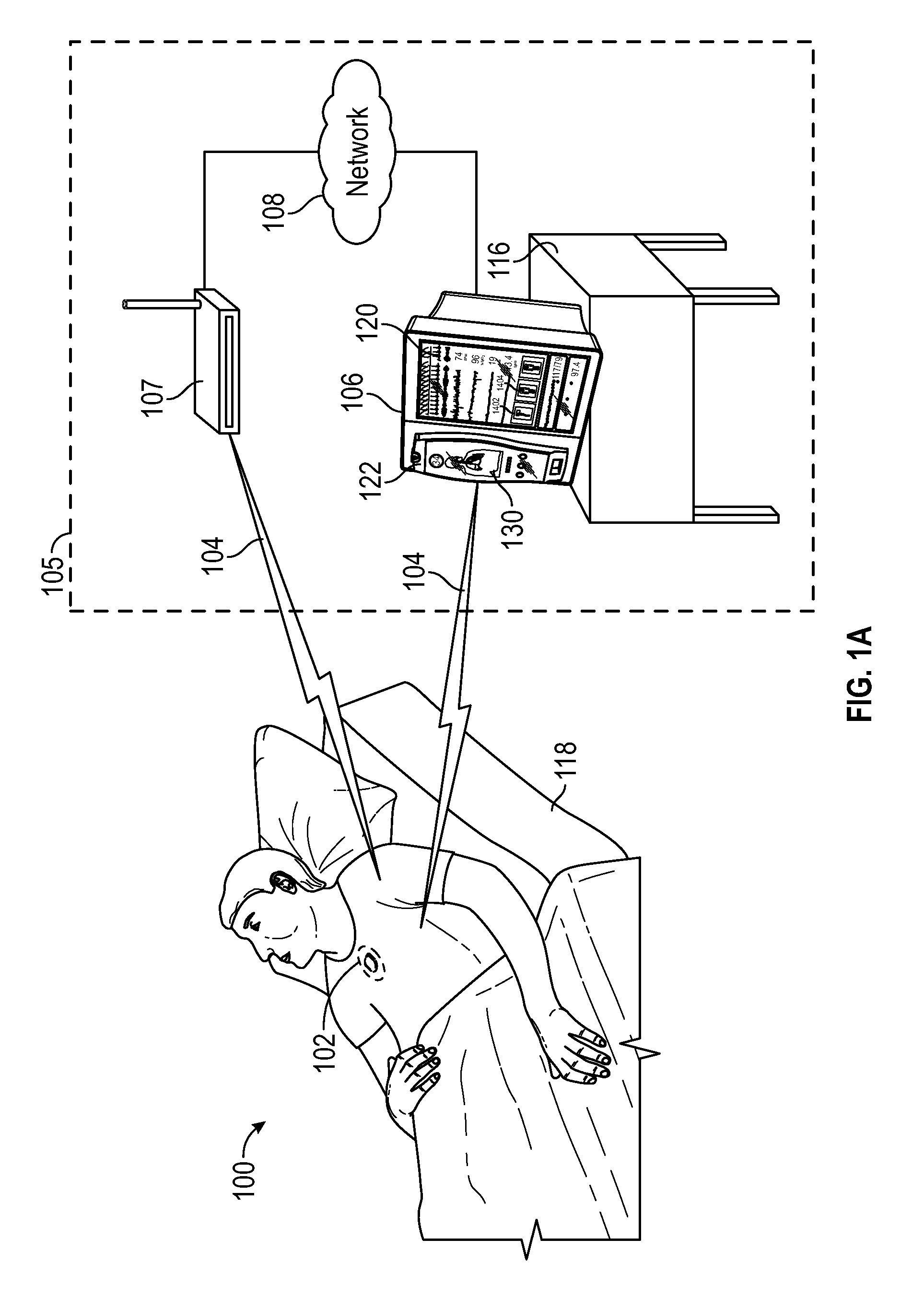
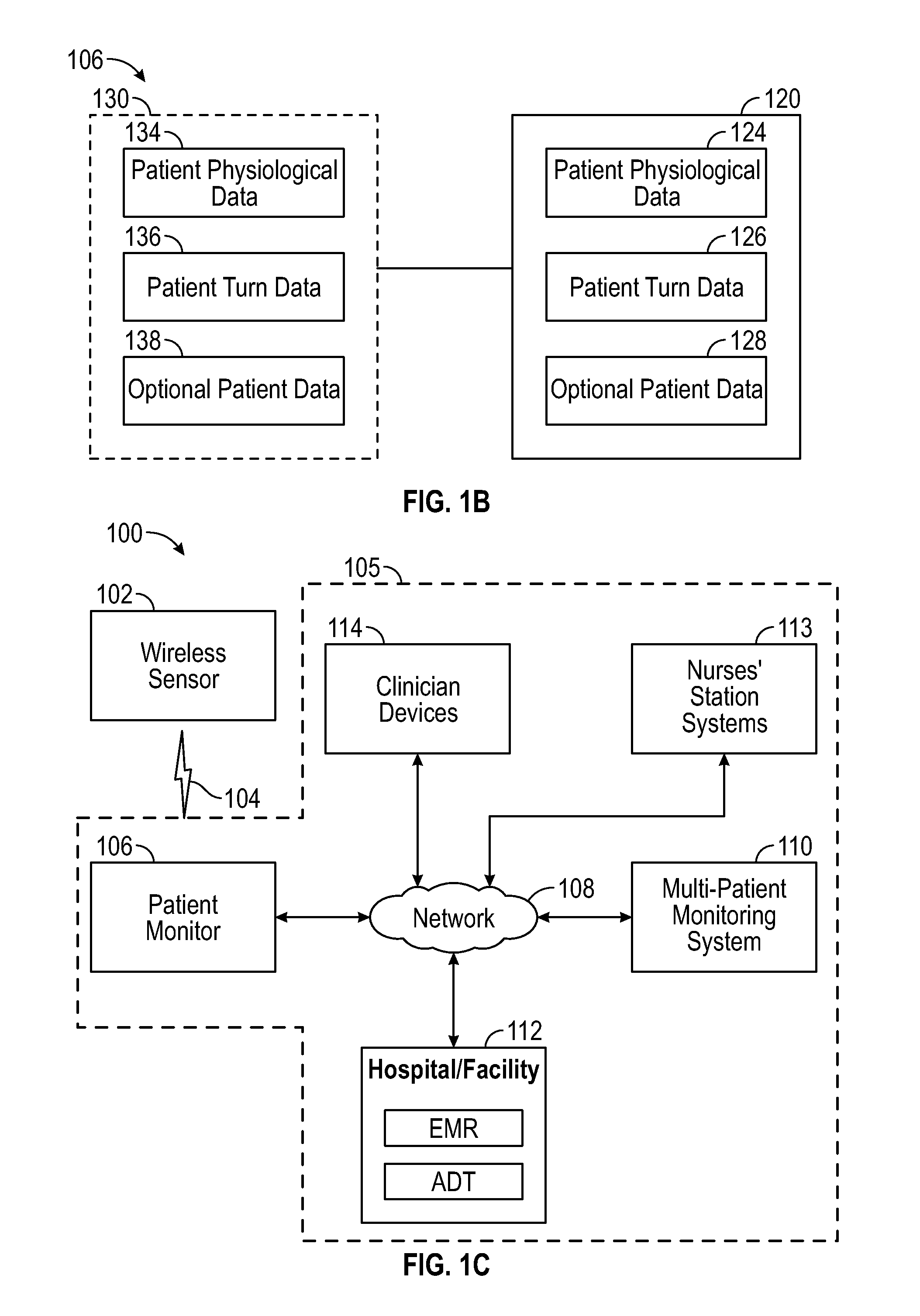
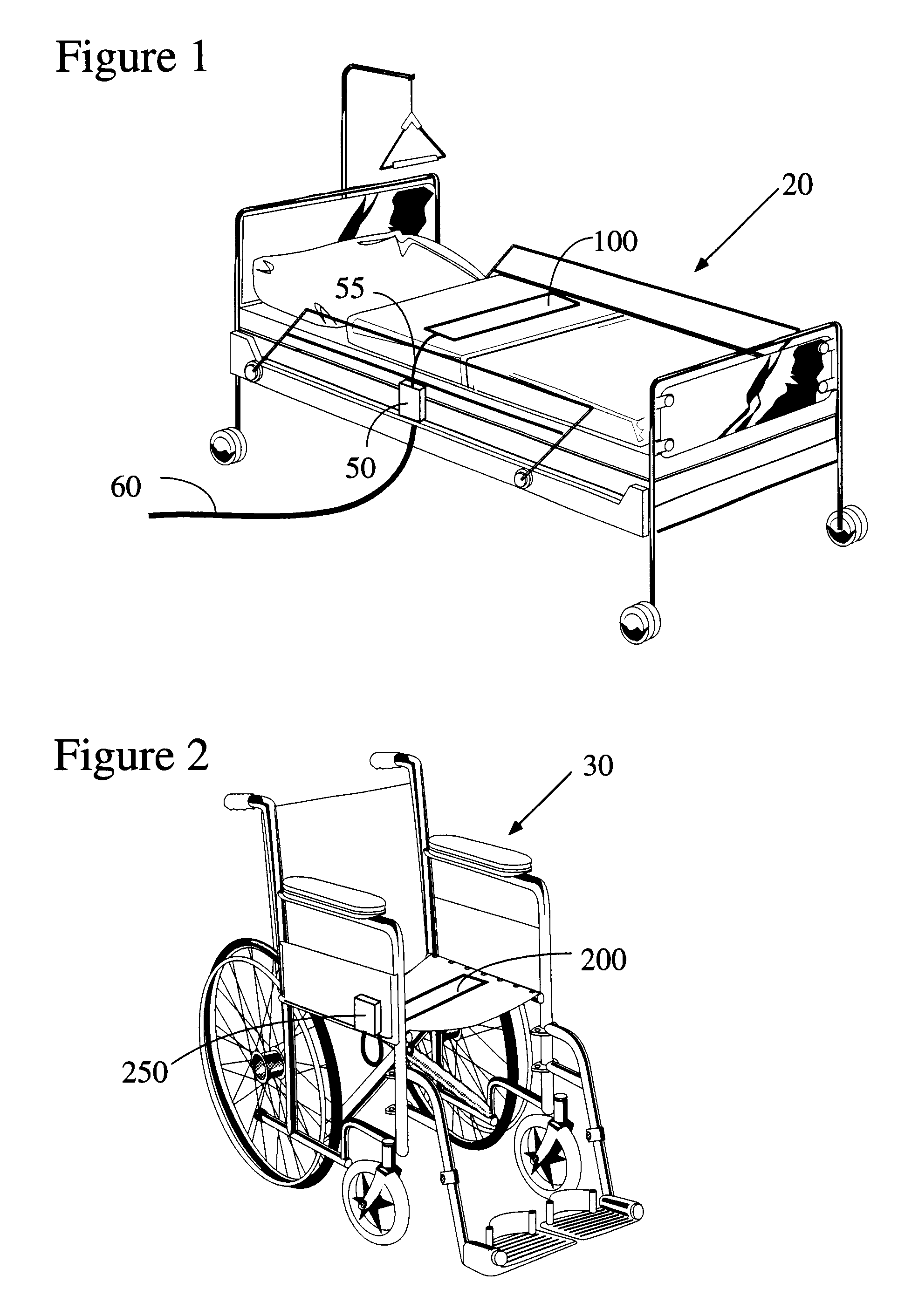
Wireless patient monitoring systems and methods
A patient monitoring system to help manage a patient that is at risk of forming one or more pressure ulcers is disclosed. The system includes a patient-worn wireless sensor that senses the patient's orientation and wirelessly transmits information indicative of the sensed orientation to a patient monitor. The patient monitor receives, stores, and processes the transmitted information. It also displays and transmits information indicative of the patient's orientation to help caregivers manage the patient's risk of formation of one or more pressure ulcers. The system can identify the present orientation of the patient and determine how long the patient has been in the present orientation. If the patient remains in an orientation beyond a predefined duration, the system can notify the patient and / or caretakers that the patient is due to be repositioned.
Owner:MASIMO CORP
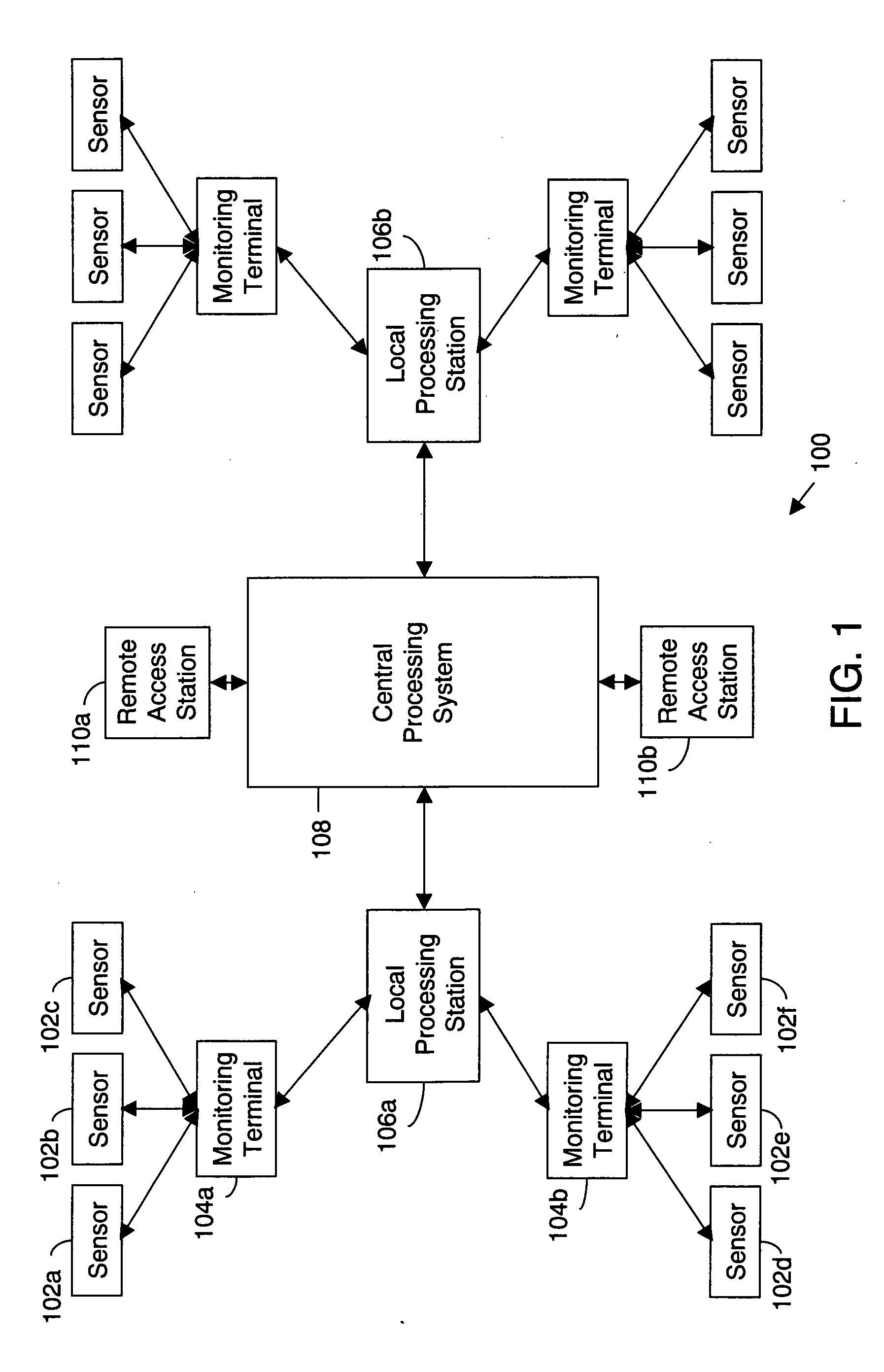
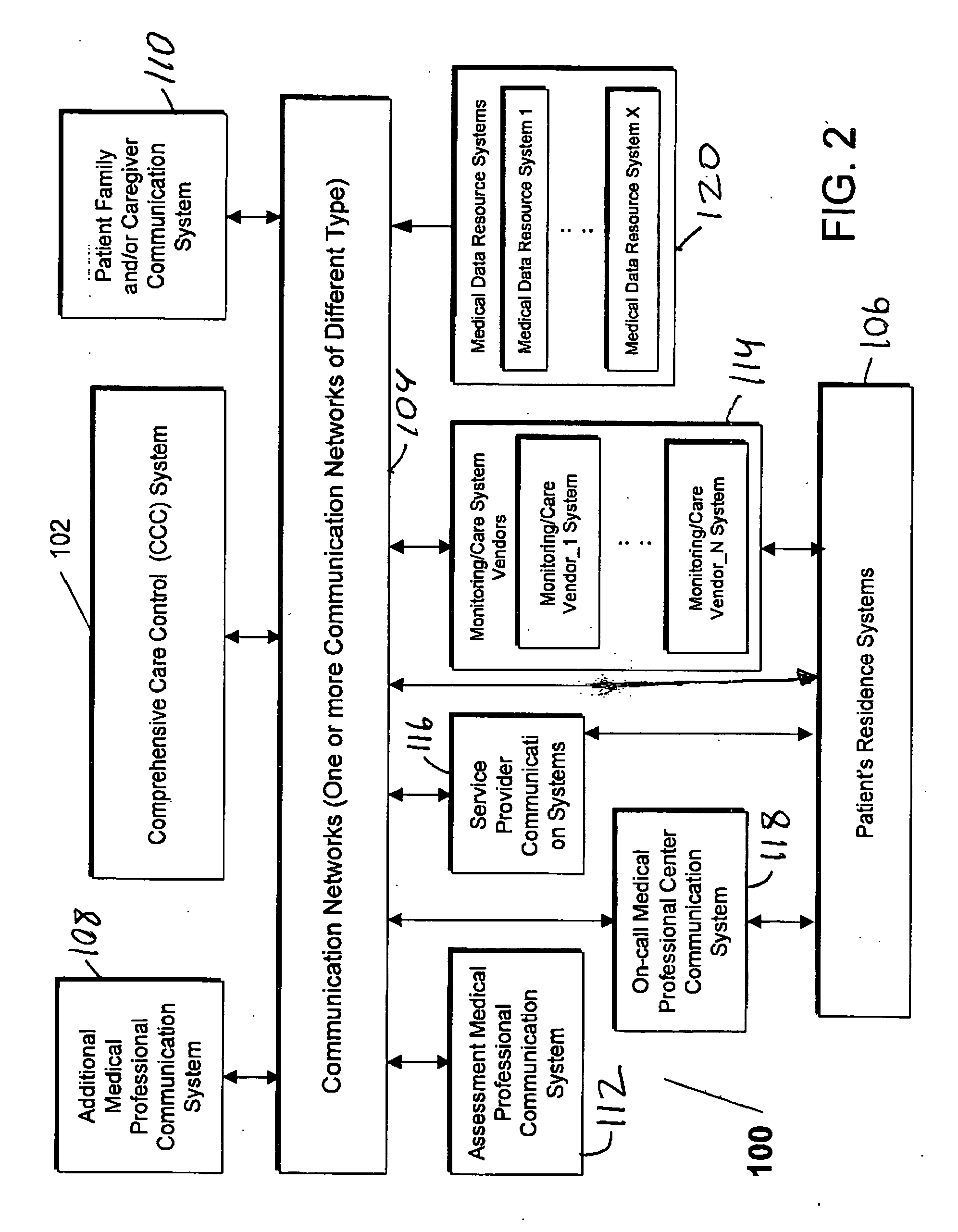
Distributed architecture for remote patient monitoring and caring
The present invention provides a system and method for remote patient monitoring and caring, wherein the system has a distributed architecture. The system comprises sensors for measuring real-time physiological parameters, such as ECG and SpO2, from patients. The system also comprises a monitoring terminal for monitoring these parameters. A local processing station analyzes the real-time physiological parameters. A central processing system processes the real-time physiological parameters and their analysis, in combination with the relevant historical medical data, for each patient. The medical staff uses this processed data to provide required medical care to the patients. Further, the system provides remote access of patients' data, via remote access stations
Owner:SKANDA SYST
Patient monitor using radio frequency identification tags
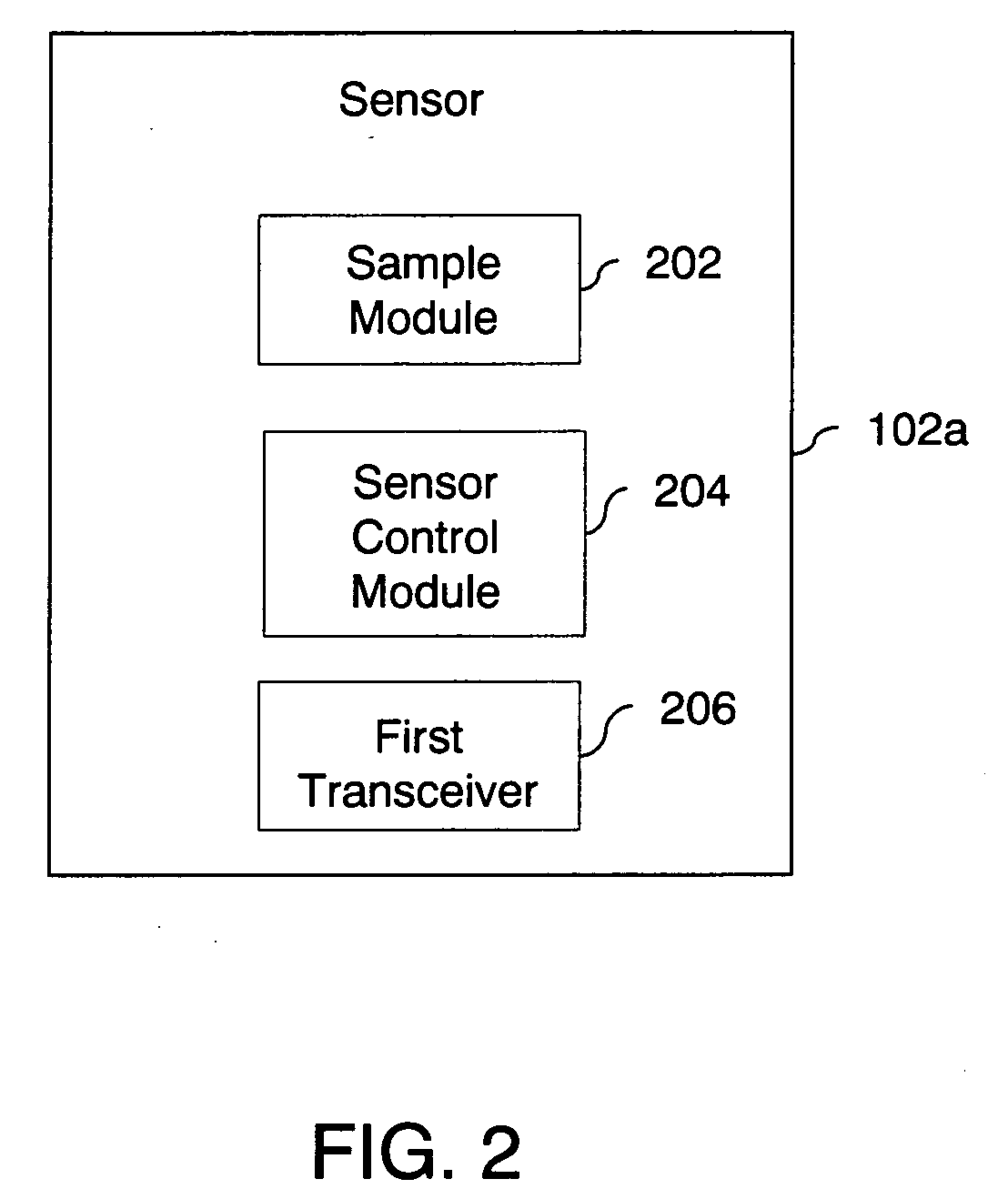
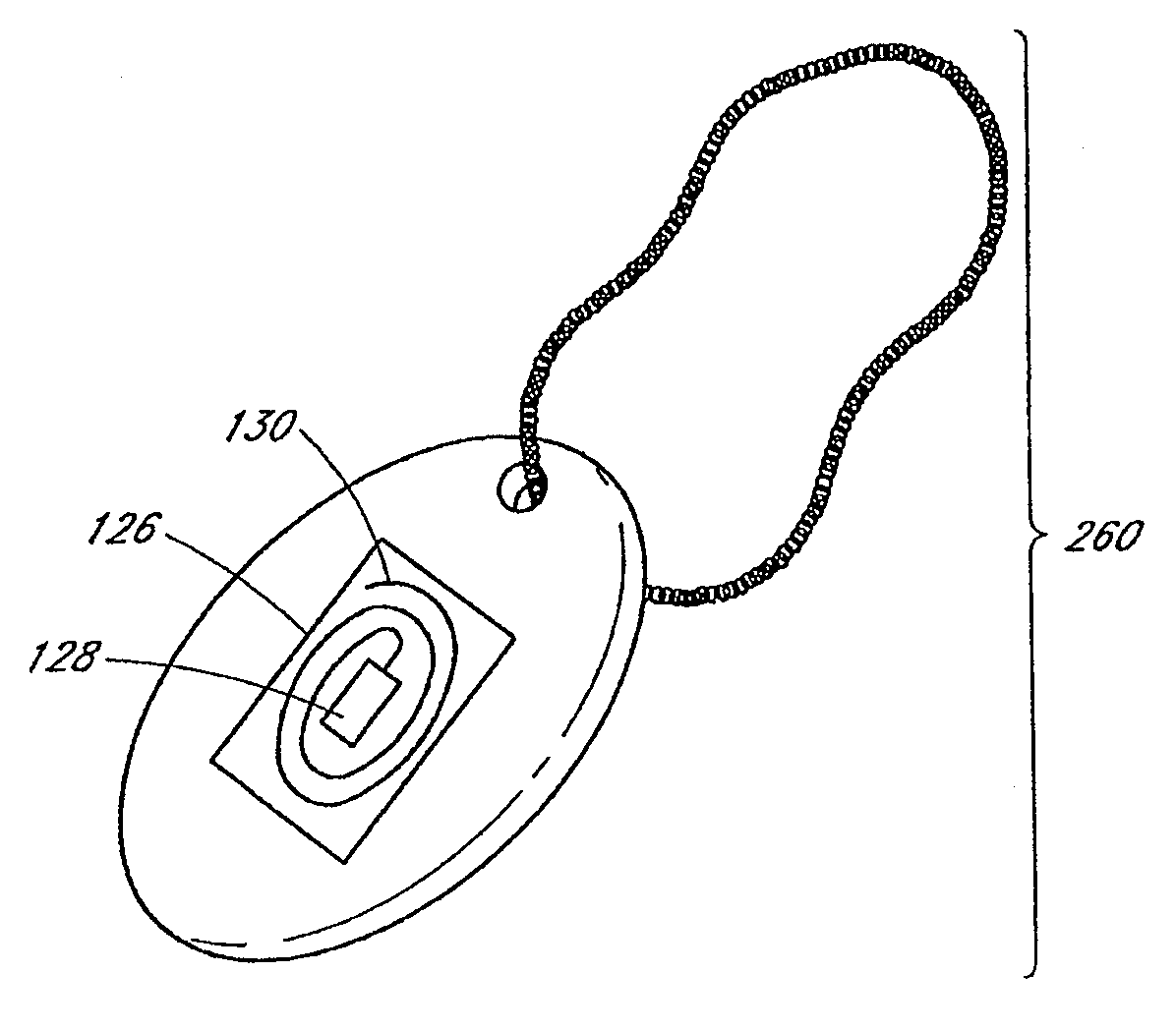
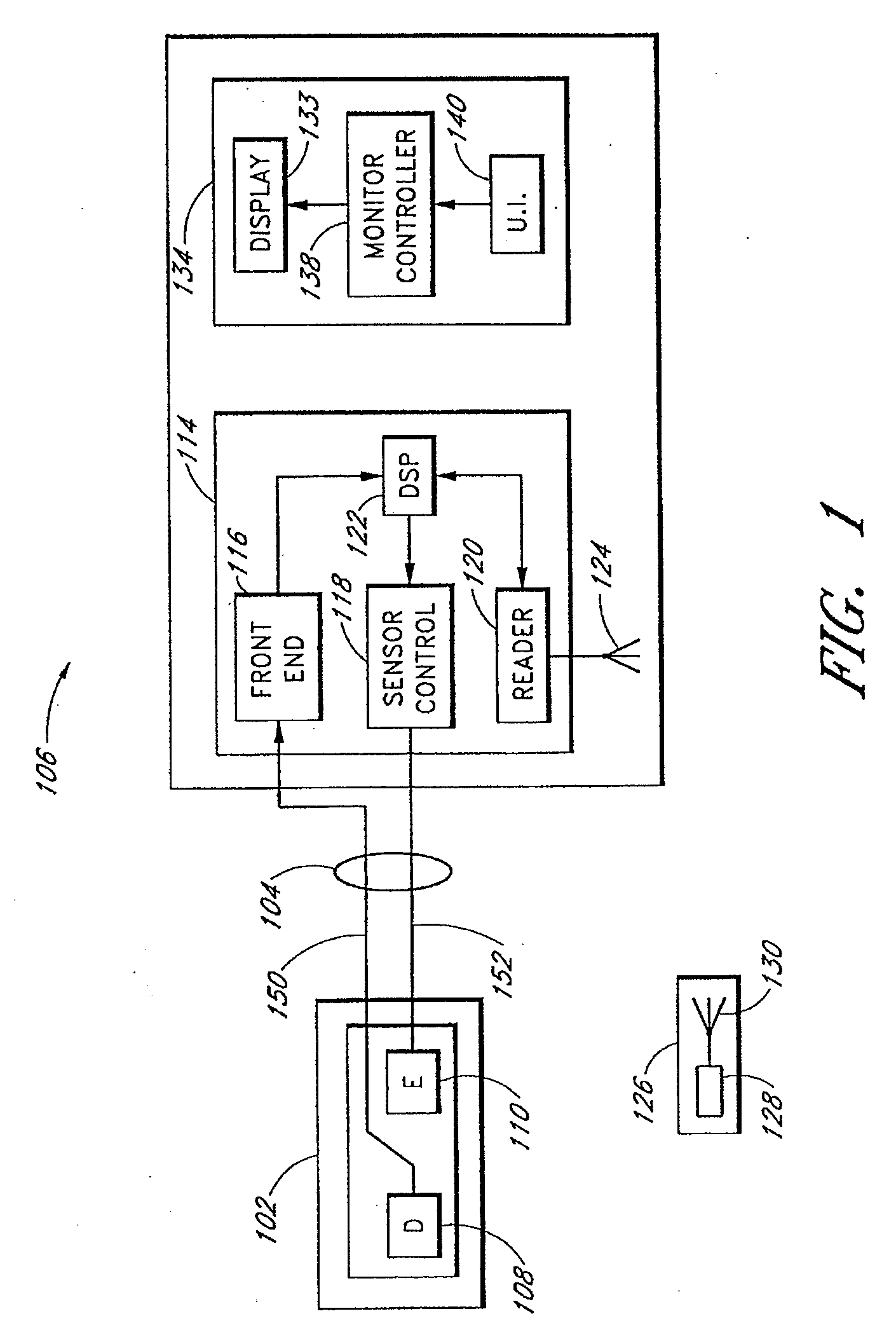
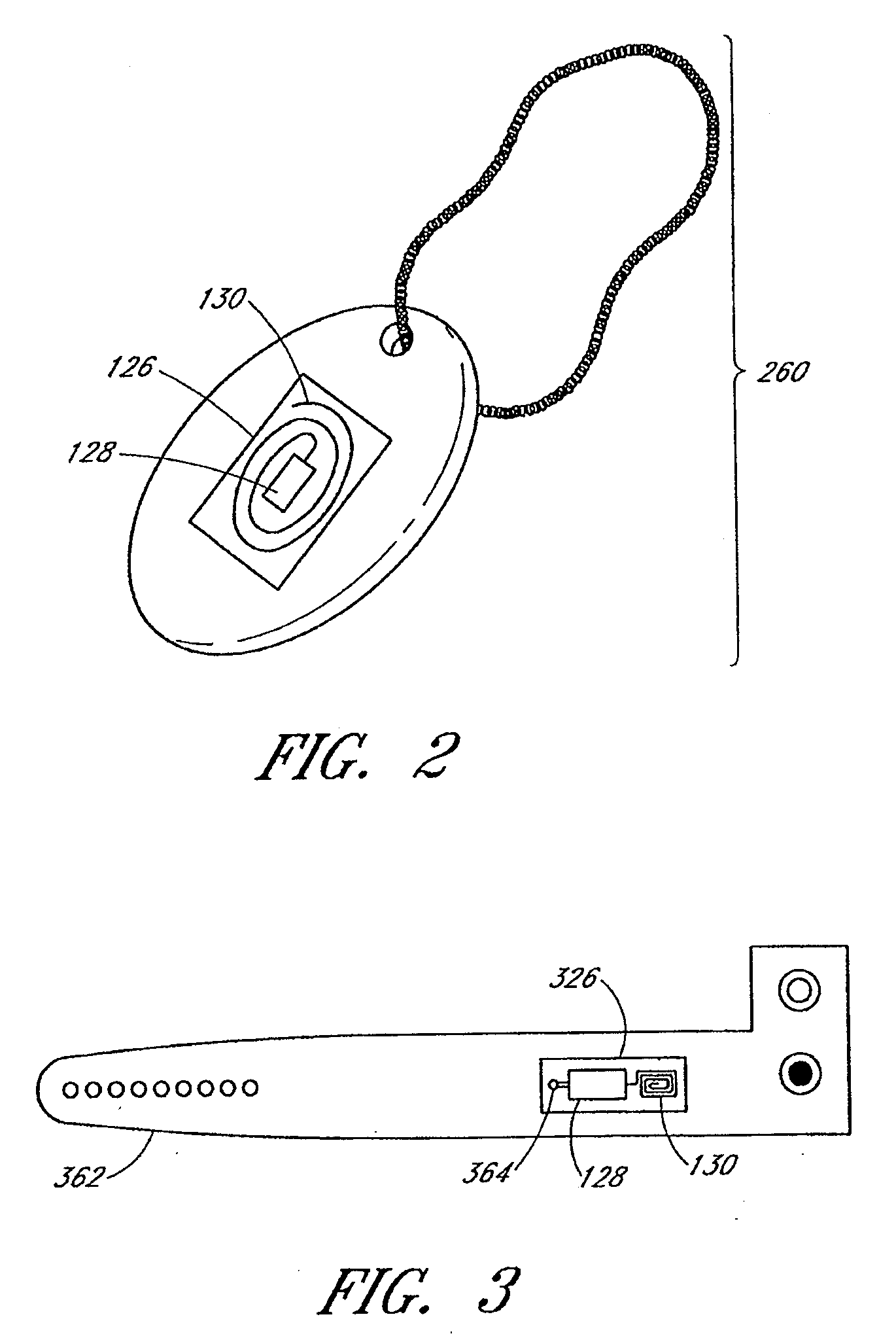
One aspect of the disclosure is to provide a patient monitoring system including a radio frequency identification (RFID) tag. The system comprises a patient monitor capable of communicating with the RFID tag. The RFID tag may advantageously store information useful in hospital environments, triage or disaster environments, home care environments, or the like. In some embodiments, the RFID tags may be provided as parts of wrist bands, dog tags, disposable sensor components, sensors or the like that are left with a patient.
Owner:MASIMO CORP
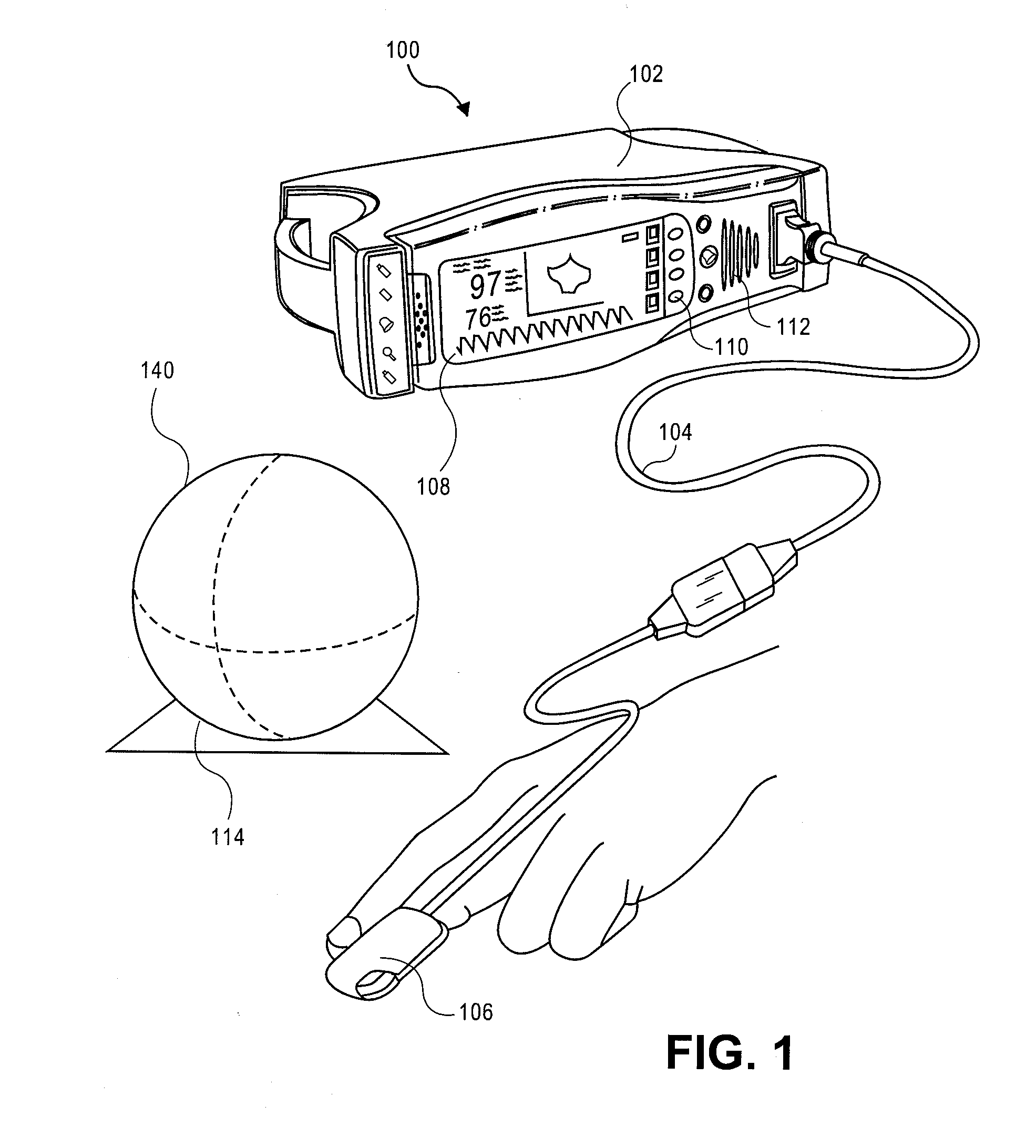
Patient monitor ambient display device
InactiveUS20110028809A1Quick scanScan a hallway, department, or the like more efficientlySensorsBlood characterising devicesPatient monitorIntensive care medicine
Embodiments of the disclosure include an orb or lamp communicating with a noninvasive monitor to provide a readily identifiable point indication of a wellness of a monitored patient. In an embodiment the orb emits a color gradient from a first color through at least two other colors responsive to values of a wellness measurement. Exemplary wellness indications include one or a statistical combination of blood constituent measurements, combinations of other physiological parameters, or the like.
Owner:JPMORGAN CHASE BANK NA
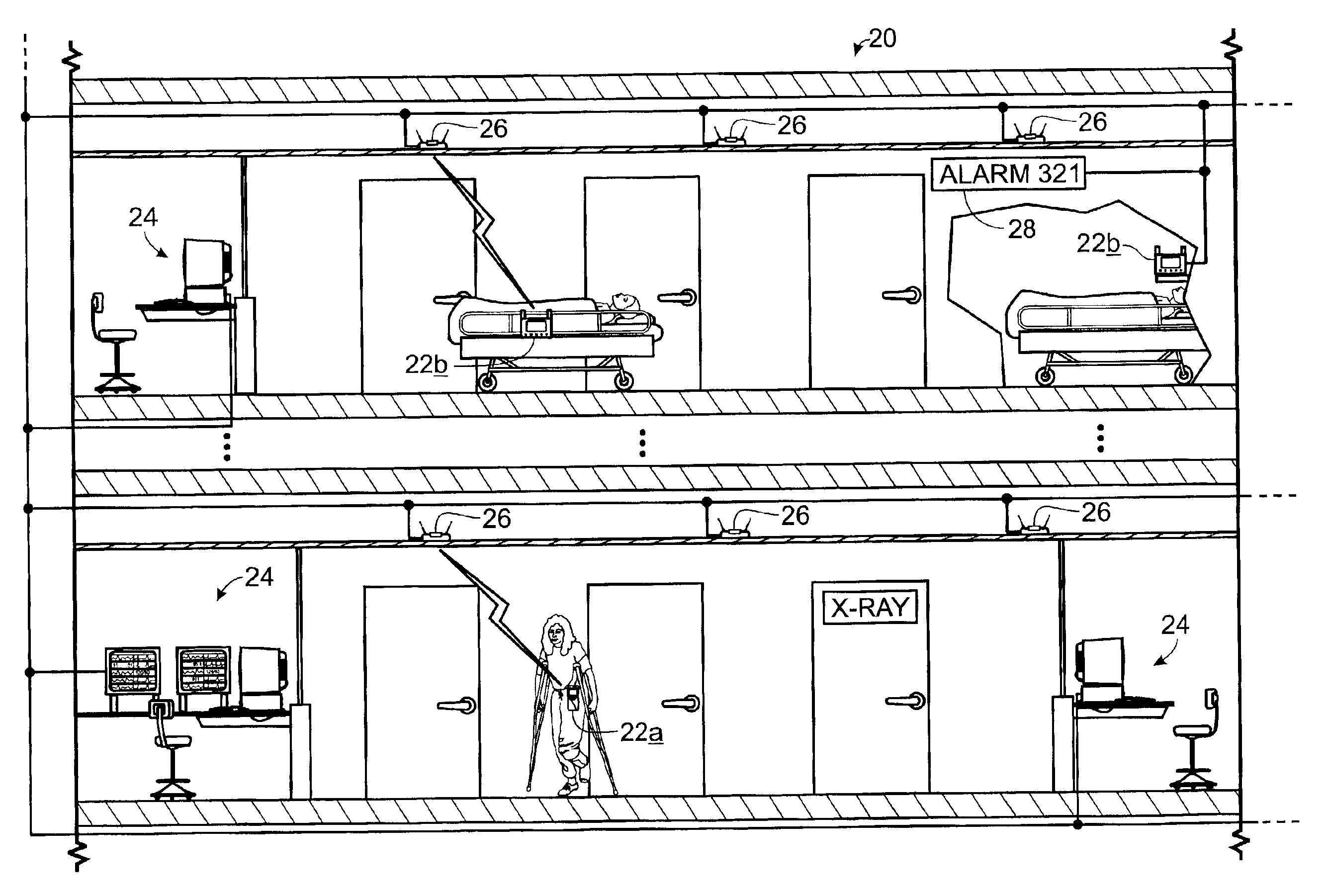
Patient monitoring system
InactiveUS6988989B2Easy to understandBioelectric signal measurementPerson identificationMonitoring systemEmergency medicine
A medical monitoring system includes a central station adapted to receive vital signs data concerning a plurality of patients, and one or more transmitter / receivers associated with the central station. At least one patient monitor is configured to monitor a particular one of the plurality of patients by collecting vital signs data from the particular patient, and configured to establish communications with the central station and communicate the collected vital signs data to the central station via the one or more transmitter / receivers. The at least one patient monitor is operable by a user to identify the particular patient from the plurality of patients, and to inform the central station of the identity of the particular patient. The central station is configured to associate the vital signs data received from the at least one patient monitor with the particular patient. The system, transmitter / receivers and at least one patient monitor may be wireless or wired. There is also a method for monitoring a patient.
Owner:WELCH ALLYN INC
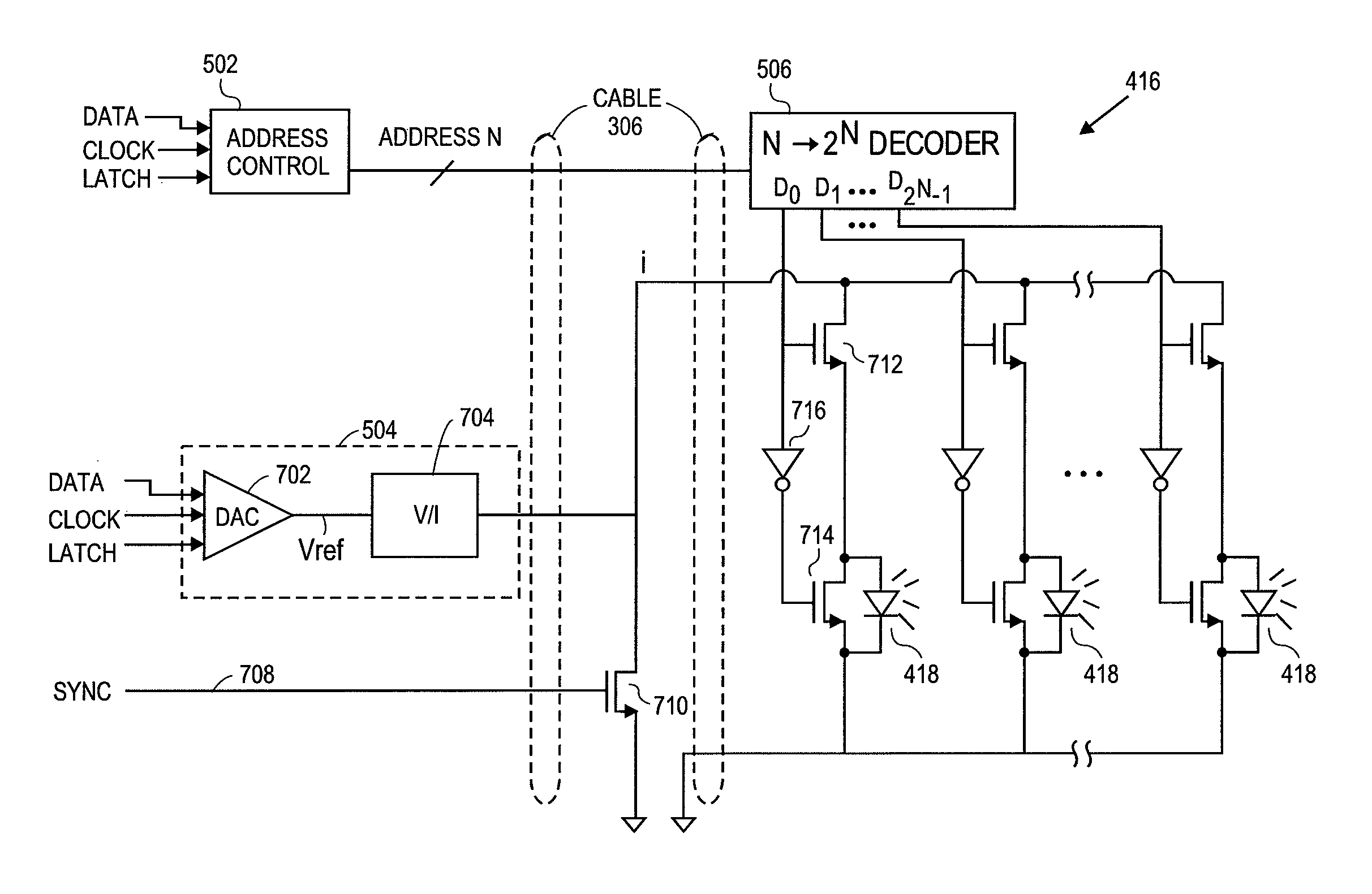
Emitter driver for noninvasive patient monitor
ActiveUS8688183B2Raise the possibilityIncreased complexityDiagnostics using lightOptical sensorsElectrical conductorEngineering
Embodiments of the present disclosure include an emitter driver configured to be capable of addressing substantially 2N nodes with N cable conductors configured to carry activation instructions from a processor. In an embodiment, an address controller outputs an activation instruction to a latch decoder configured to supply switch controls to activate particular LEDs of a light source.
Owner:MASIMO CORP
Patient monitor for determining microcirculation state
Owner:MASIMO CORP
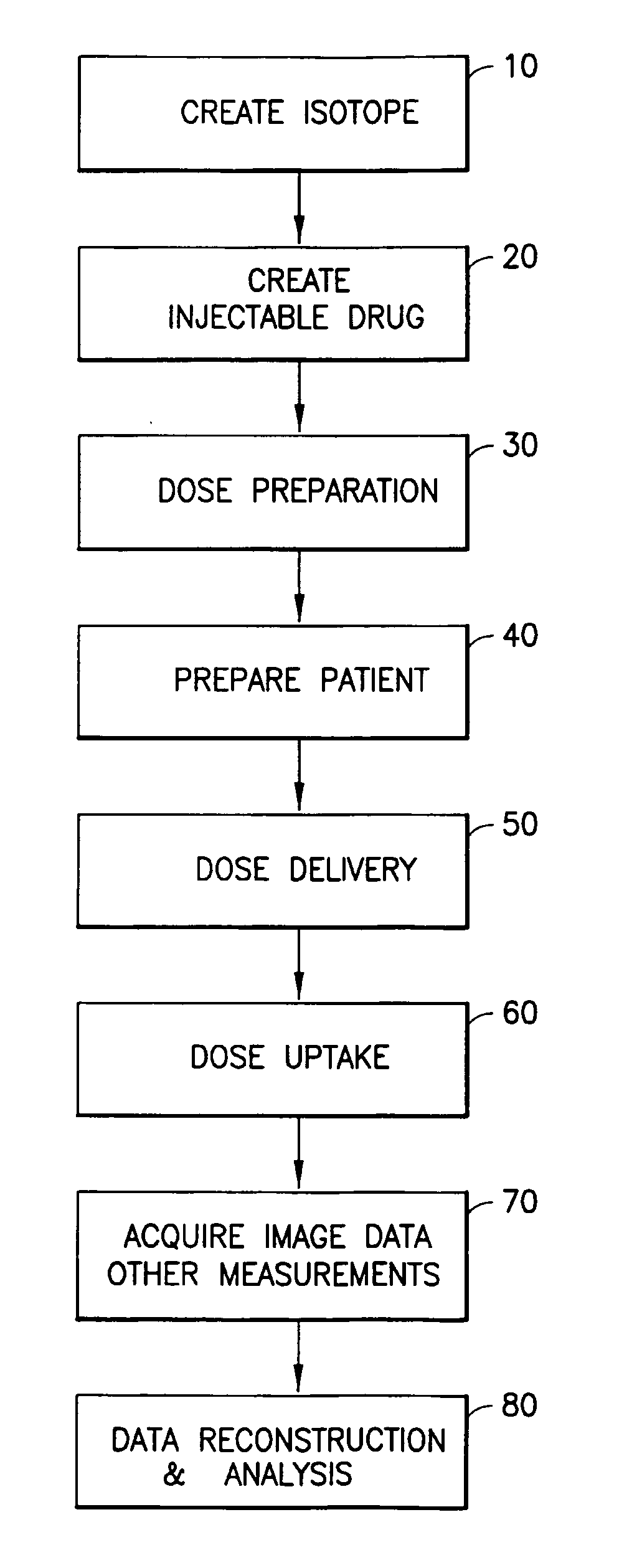
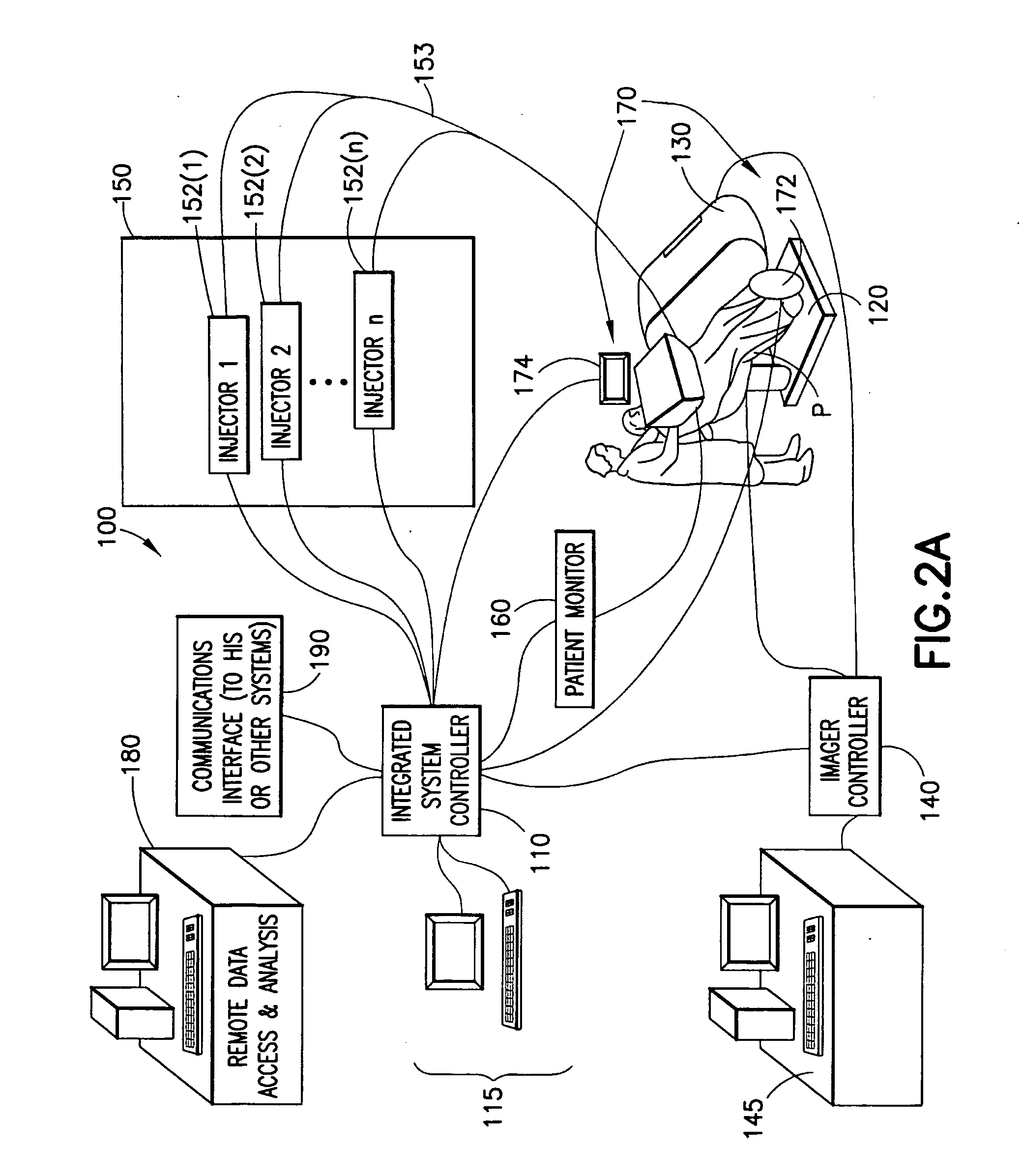
Systems For Integrated Radiopharmaceutical Generation, Preparation, Transportation and Administration
ActiveUS20110178359A1Reduce wasteEliminate needDrug and medicationsMedical devicesDocking stationFluid transport
An integrated radiopharmaceutical patient treatment system is disclosed including a patient support platform with an associated patient stimulus apparatus, an imager proximate the patient support platform, a radiopharmaceutical fluid delivery system for infusing a radiopharmaceutical fluid into a patient, a patient monitor to be associated with a patient, and an integrated system controller operably associated with the patient stimulus apparatus, imager, radiopharmaceutical fluid delivery system, and patient monitor to control and coordinate their operations. Within the patient treatment system the radiopharmaceutical fluid delivery system may be included comprising a radionuclide supply module, a radiopharmaceutical processing module, a quality control module, a patient injection module, and a controller. A hazardous fluid handling system including a docking station and a hazardous fluid transport device adapted to detachably dock with the docking station is further disclosed.
Owner:BAYER HEALTHCARE LLC
Sensing system with auxiliary display
A system is provided for sensing blood glucose data of a patient. The system includes a sensor, user interface, and an optional auxiliary device. If the connection between the sensor and user interface is by a wire, the sensor remains powered when the wire is disconnected. The communication between the sensor and the user interface may be wireless. The auxiliary device can be a patient monitor or other display or signal device, which displays information about the blood glucose data collected by the sensor. The sensor is connected to sensor electronics, which include a sensor power supply, a voltage regulator, and optionally a memory and processor.
Owner:MEDTRONIC MIMIMED INC
Sensing system with auxiliary display
A system is provided for sensing blood glucose data of a patient. The system includes a sensor, user interface, and an optional auxiliary device. If the connection between the sensor and user interface is by a wire, the sensor remains powered when the wire is disconnected. The communication between the sensor and the user interface may be wireless. The auxiliary device can be a patient monitor or other display or signal device, which displays information about the blood glucose data collected by the sensor. The sensor is connected to sensor electronics, which include a sensor power supply, a voltage regulator, and optionally a memory and processor.
Owner:MEDTRONIC MIMIMED INC
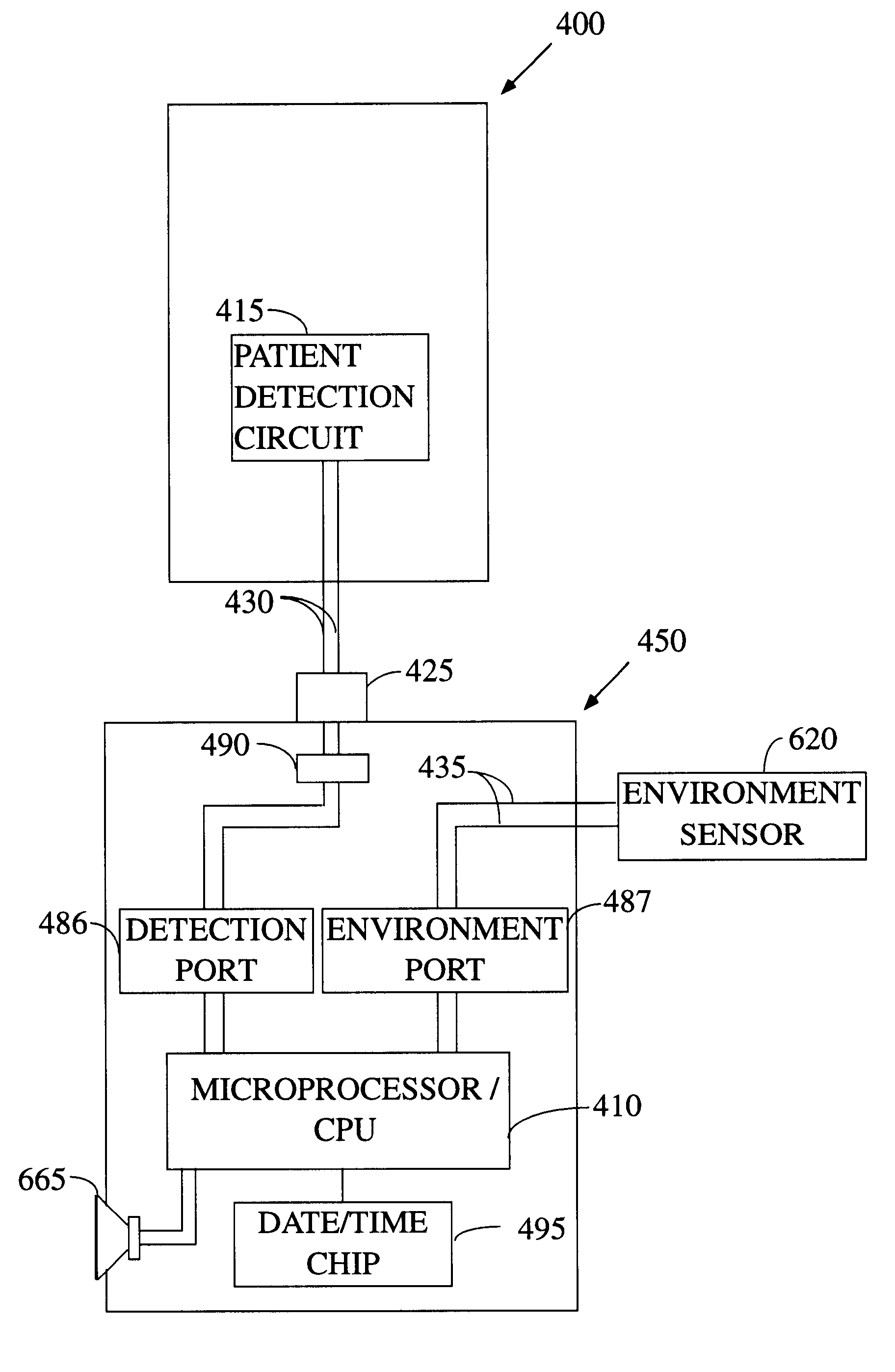
Electronic patient monitor with automatically configured alarm parameters
There is provided herein an electronic patient monitor that is suitable for use with a variety of different sensors and which automatically configures itself depending on the sensor that is used and / or the environment in which the electronic monitor is placed. In a first preferred embodiment, the electronic monitor determines whether it is being used on a bed or a chair by sensing whether or not a nurse call connector is present. If such a connector is plugged into the monitor, the unit will assume that it is being used with a sensor that has been placed on a bed and will configure its internal parameters appropriately. Such configuration would include changing a delay time to provide for longer delays before sounding an alarm than would be used with a chair monitor.
Owner:BED CHECK
Medical monitoring hub
The present disclosure includes a medical monitoring hub as the center of monitoring for a monitored patient. The hub includes configurable medical ports and serial ports for communicating with other medical devices in the patient's proximity. Moreover, the hub communicates with a portable patient monitor. The monitor, when docked with the hub provides display graphics different from when undocked, the display graphics including anatomical information. The hub assembles the often vast amount of electronic medical data, associates it with the monitored patient, and in some embodiments, communicates the data to the patient's medical records.
Owner:JPMORGAN CHASE BANK NA +1
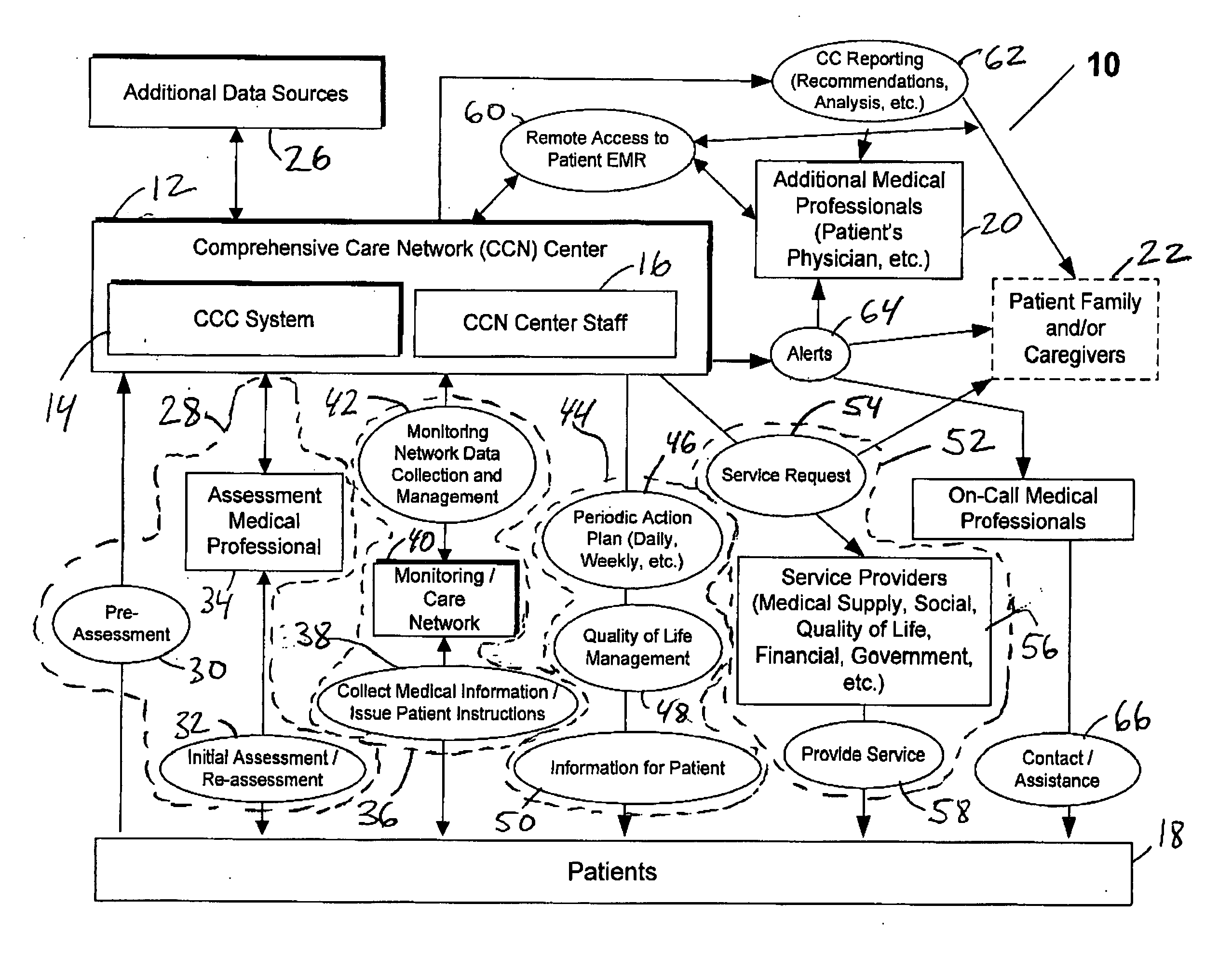
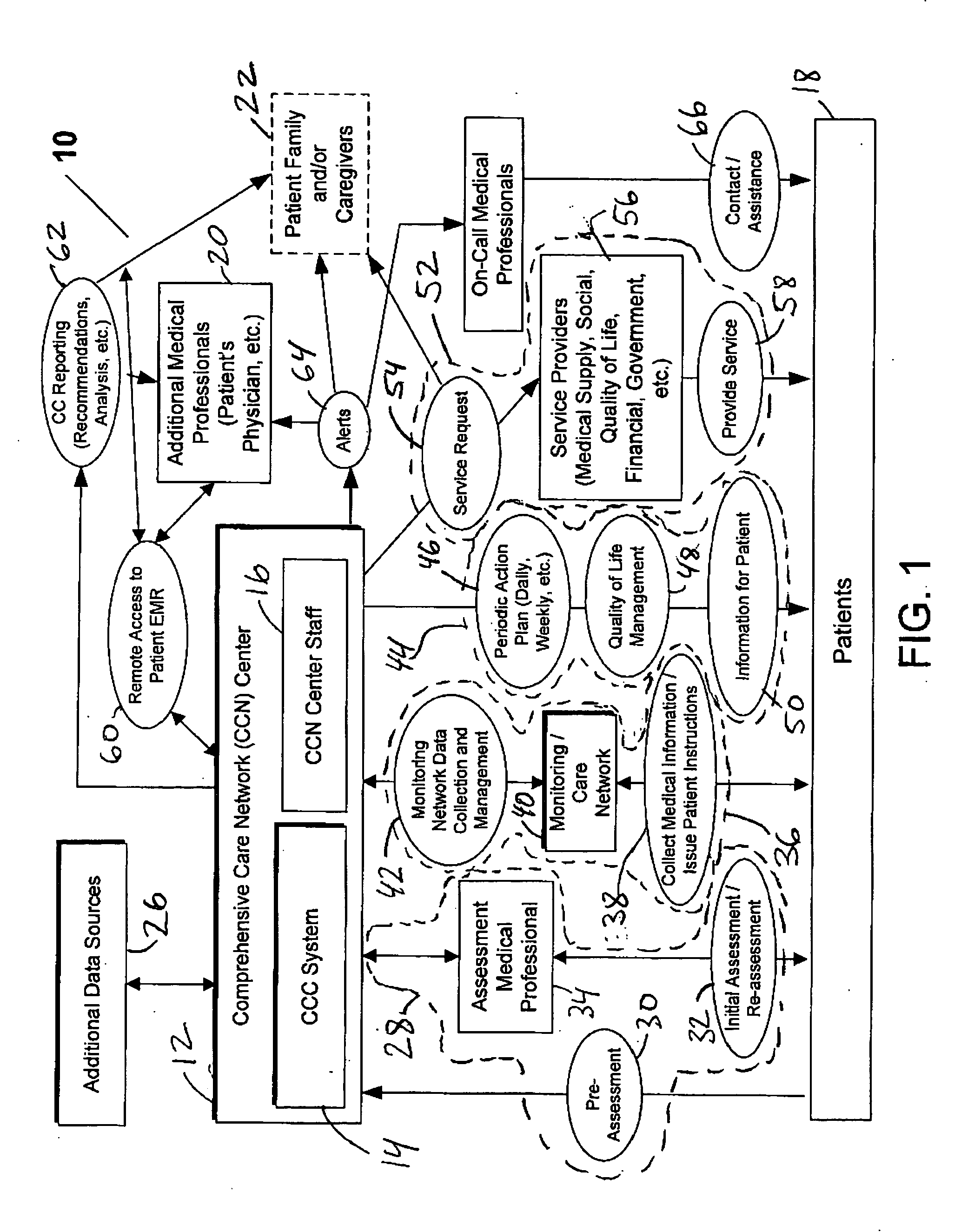
System and method for comprehensive remote patient monitoring and management
InactiveUS20070033072A1Function increaseData processing applicationsTelemedicinePatient needPatient monitor
A system and method are provided for automatically developing and implementing, a comprehensive customized care plan for a patient, to address all of the patient medical and non-medical (e.g., social, quality-of-life, personal) needs, utilizing a wide variety of information: both gathered both personally from a patient by a medical professional and also collected automatically by one or more telemedicine systems. The system and method of the present invention also continually re-assess and dynamically modify the comprehensive care plan, and additionally enable a wide variety of services and benefits to be made available to the patients in a manner automatically customized for their specific needs, with the offered services and benefits being dynamically adjusted as the patient needs change or evolve. In addition, the inventive system provides platform-independent capabilities so that diagnostic systems and devices from various vendors may be freely mixed to provide patients with customized diagnostic monitoring at the lowest possible cost.
Owner:ADVANCED MONITORED CAREGIVING
Process and system for setting a patient monitor
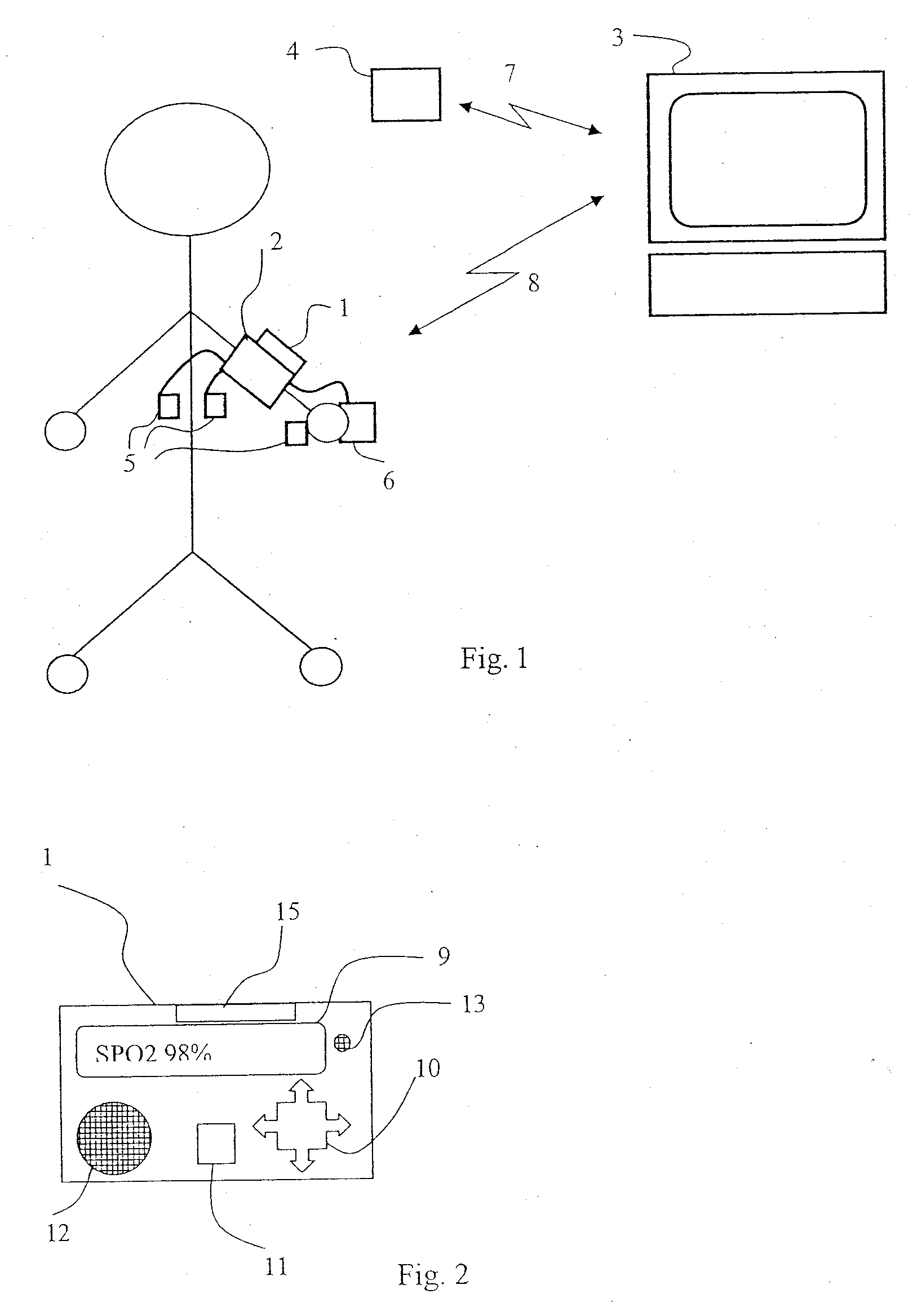
InactiveUS20070232867A1Reduce data volumeReduce energy consumptionLocal control/monitoringTelemedicineStatistical analysisPatient monitor
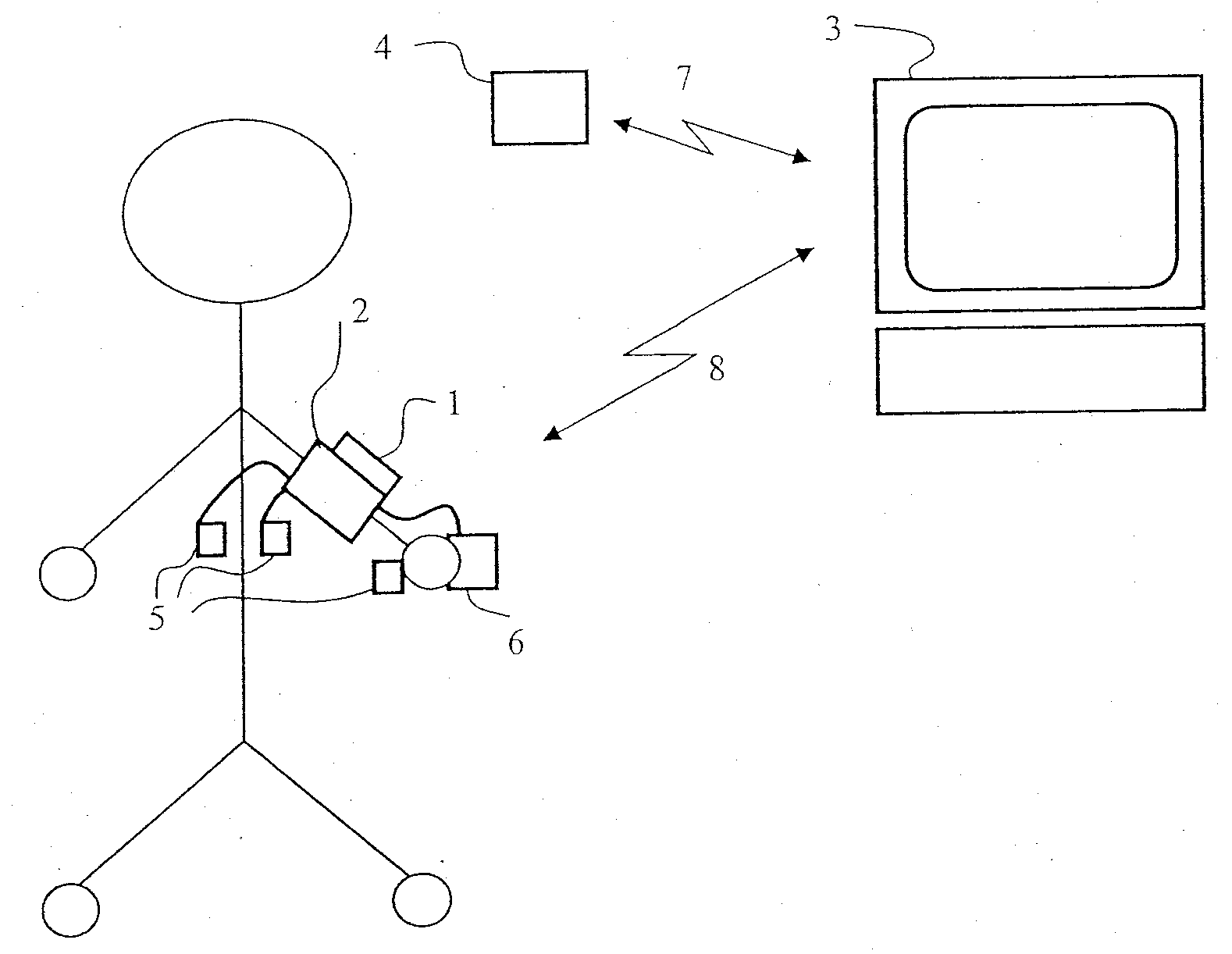
An automated process for setting a patient monitor (1) for detecting vital parameters of the patient measured by patient sensors as a function of the patient's current situation is provided. The process includes performing a statistical analysis from the measured values of the vital parameters in a computing unit for a plurality or all measured data of at least one of the measured vital parameters. The settings of the patient monitor (1) are adapted as a function of the statistical analysis performed, the adaptation of the settings pertaining at least to the vital parameters to be measured themselves, the frequency of measurements, the data quality and / or properties of the data transmission.
Owner:DRAGERWERK AG
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com