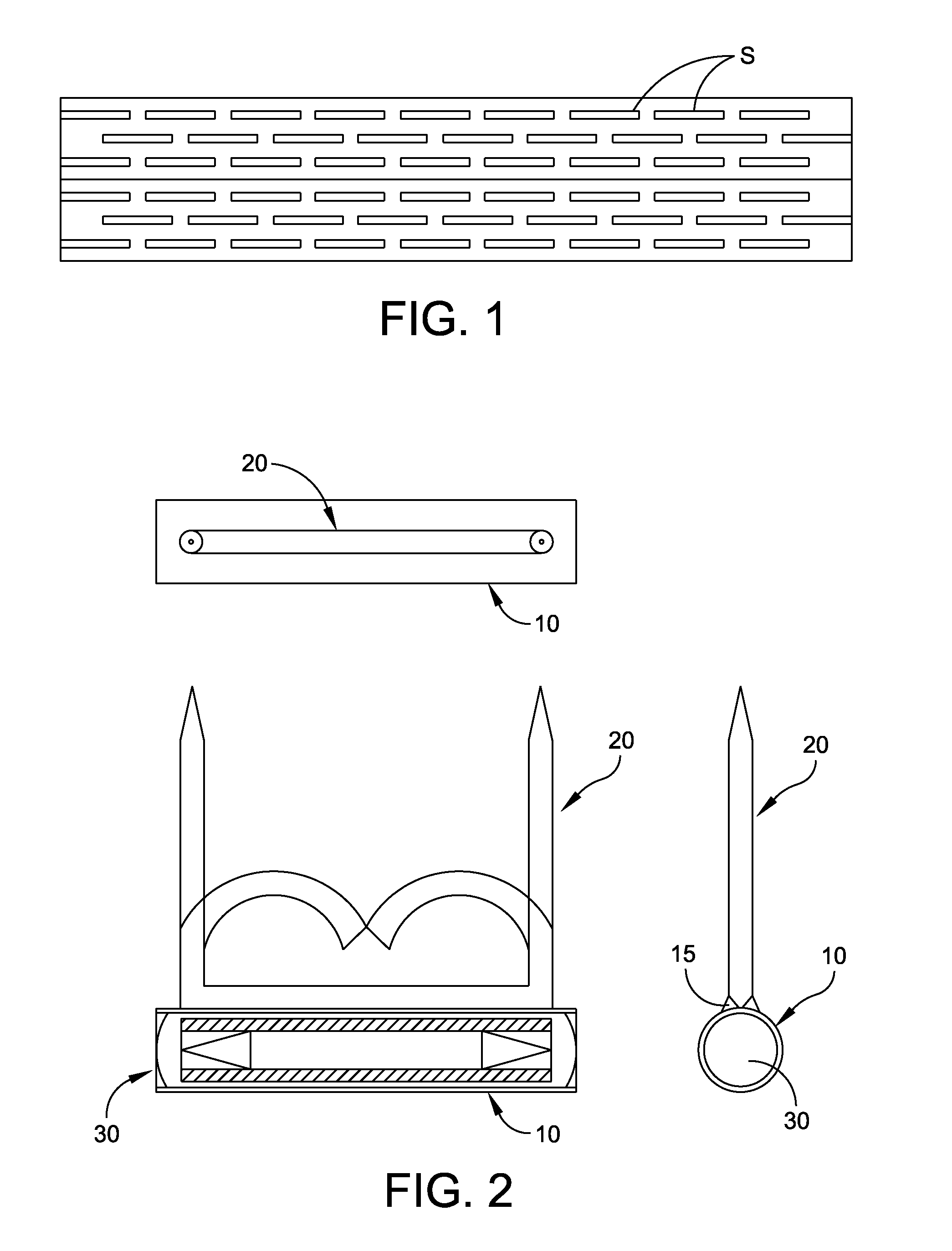
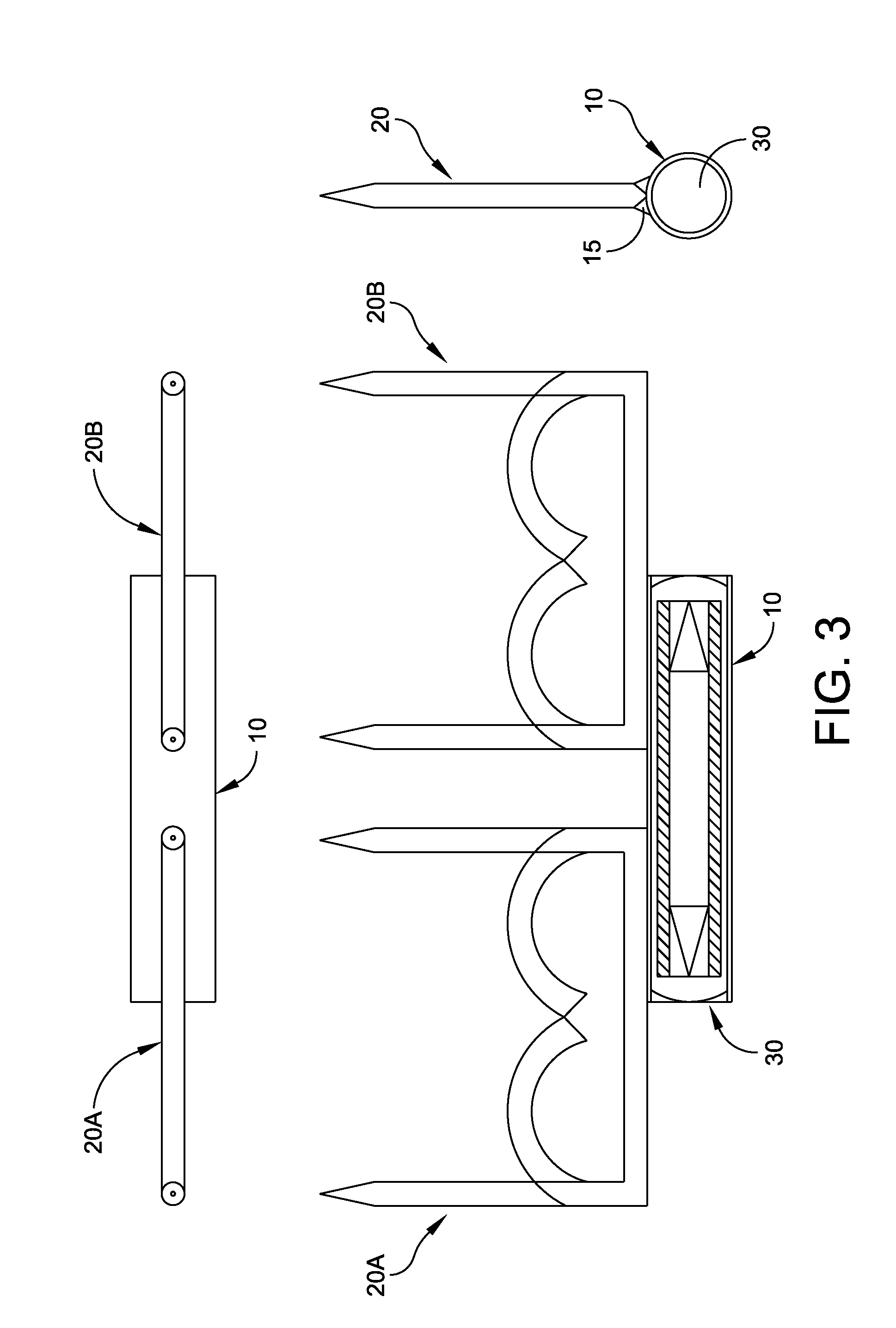
Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
18429 results about "Medical physics" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Medical physics (also called biomedical physics, medical biophysics, applied physics in medicine, physics applications in medical science, radiological physics or hospital radio-physics) is, in general, the application of physics concepts, theories, and methods to medicine or healthcare. Medical physics departments may be found in hospitals or universities.
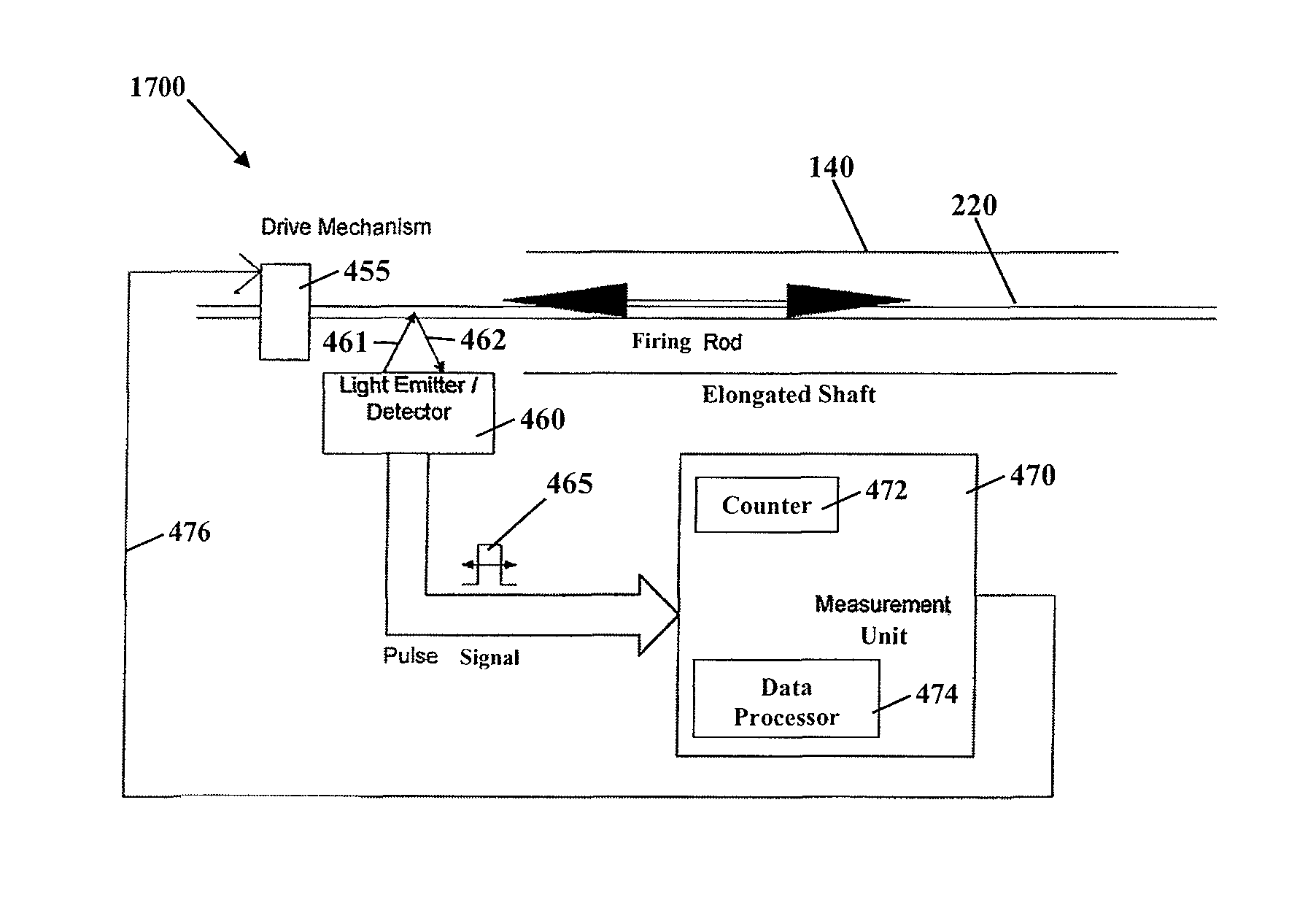
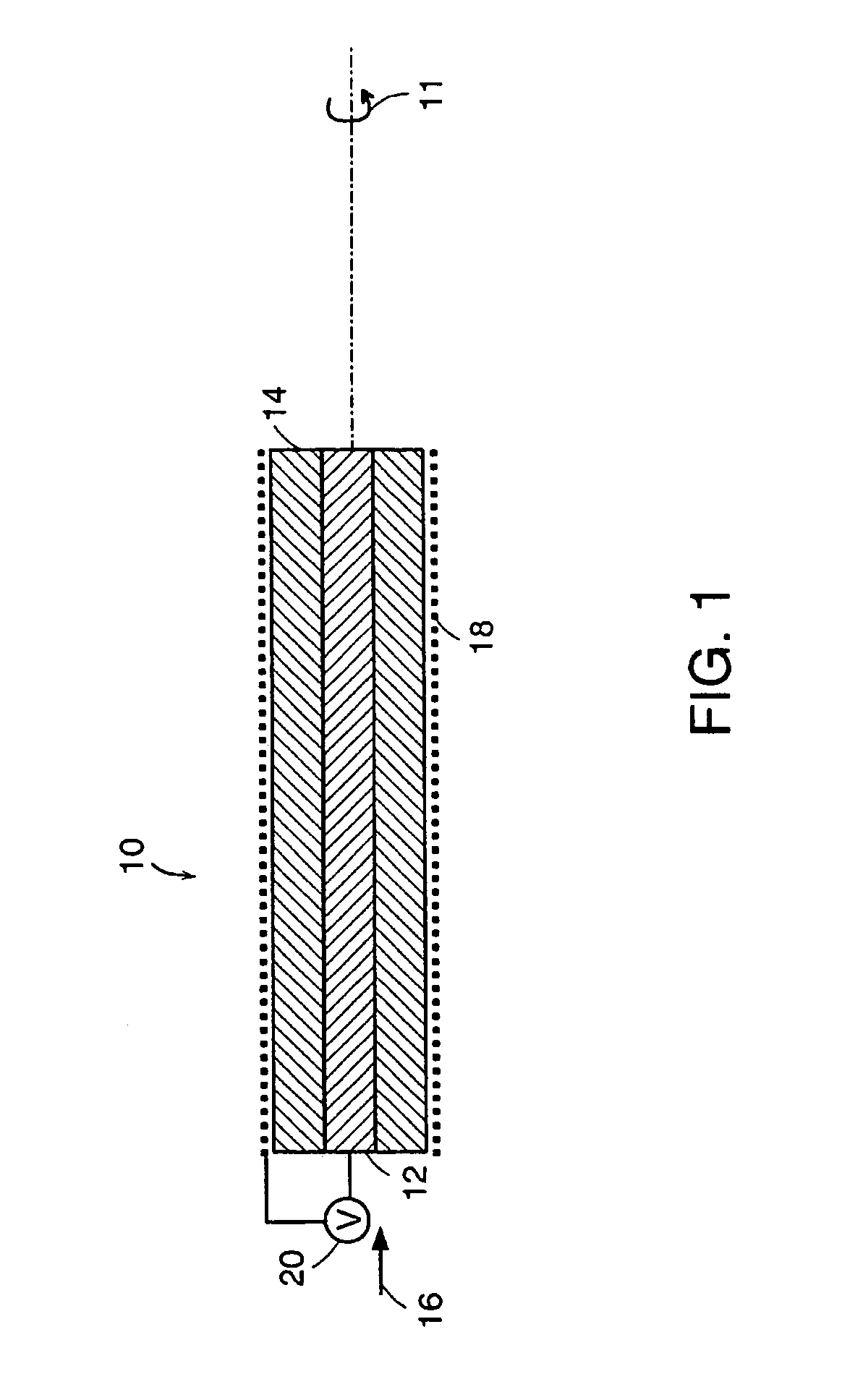
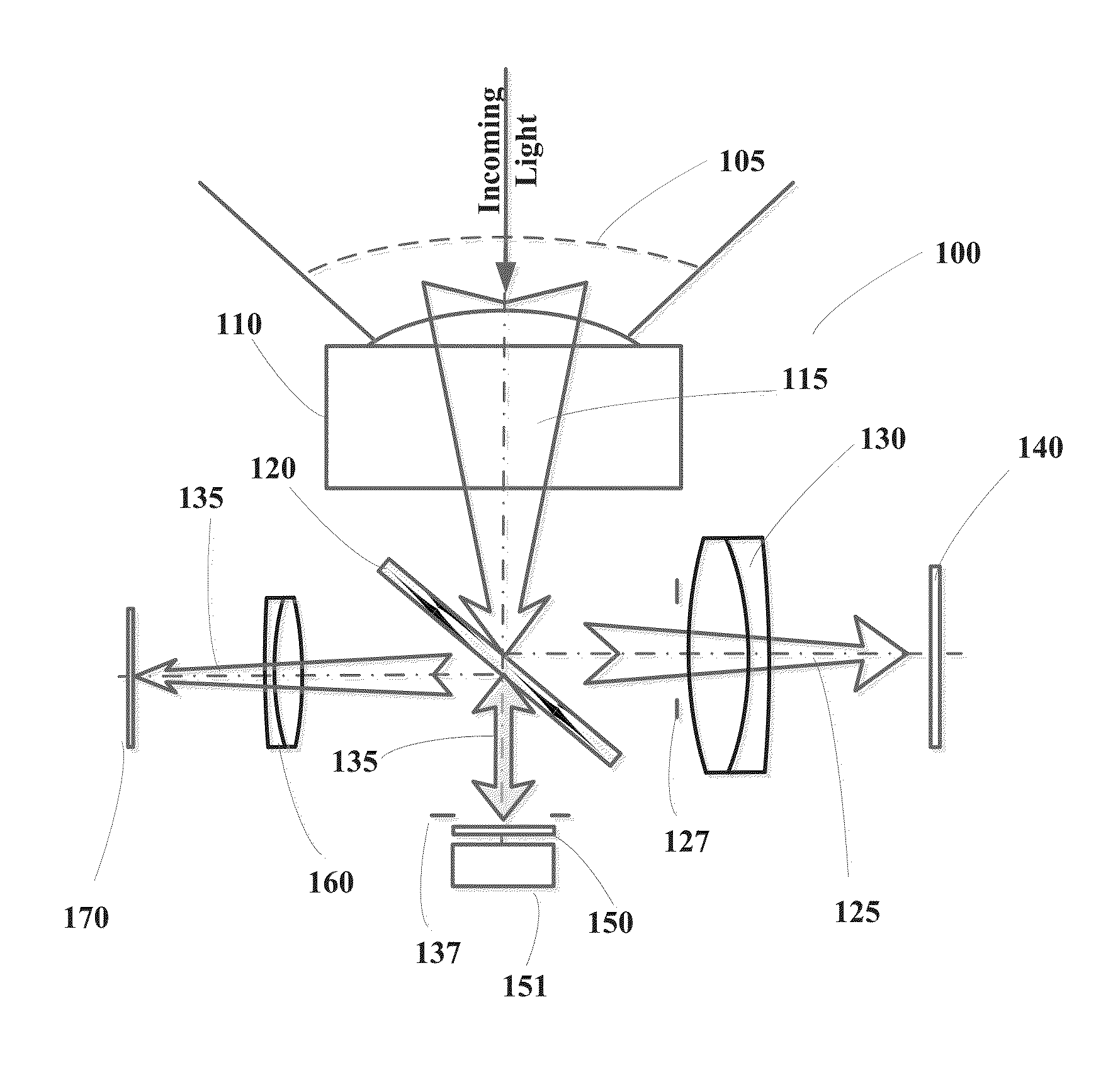
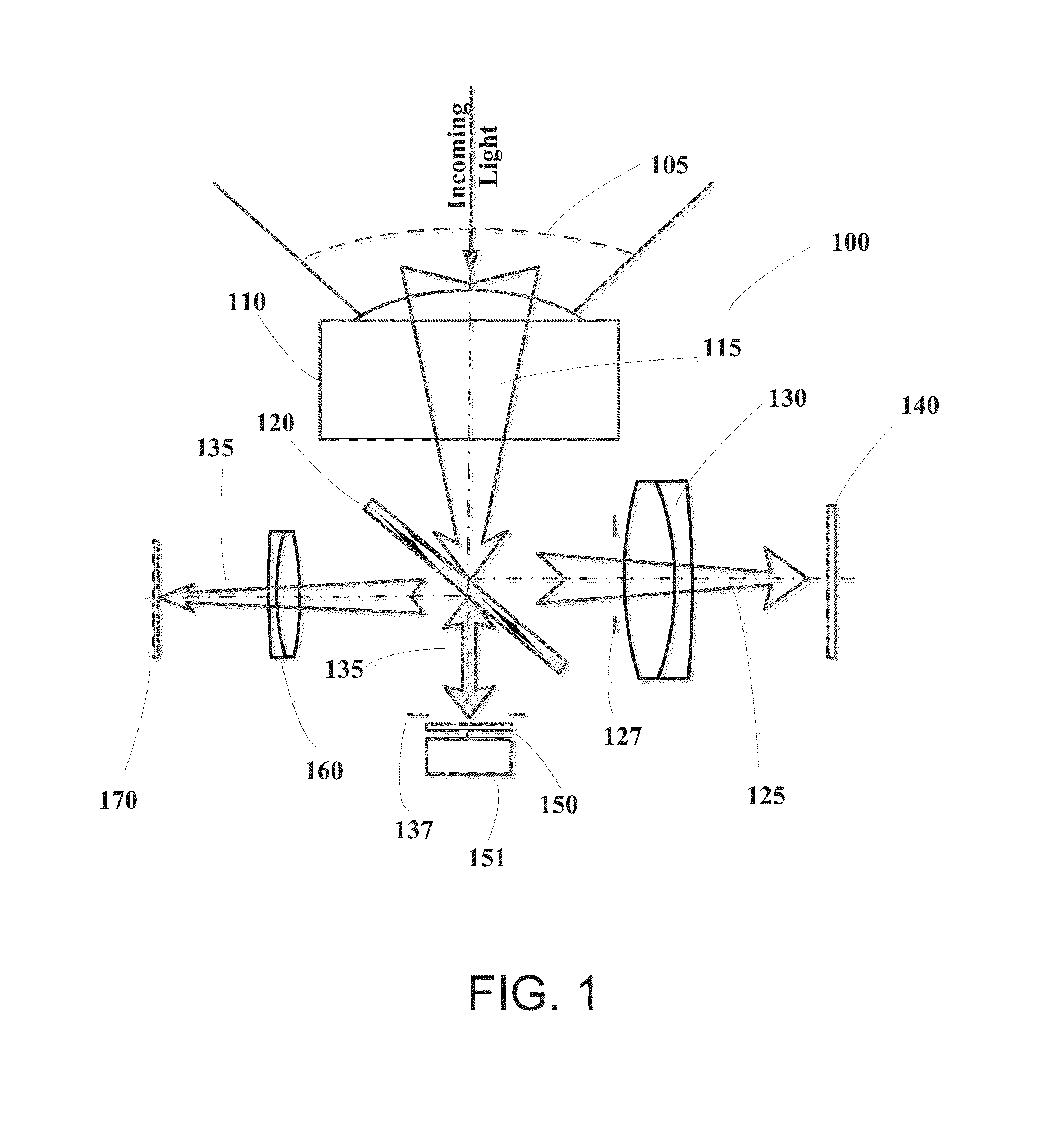
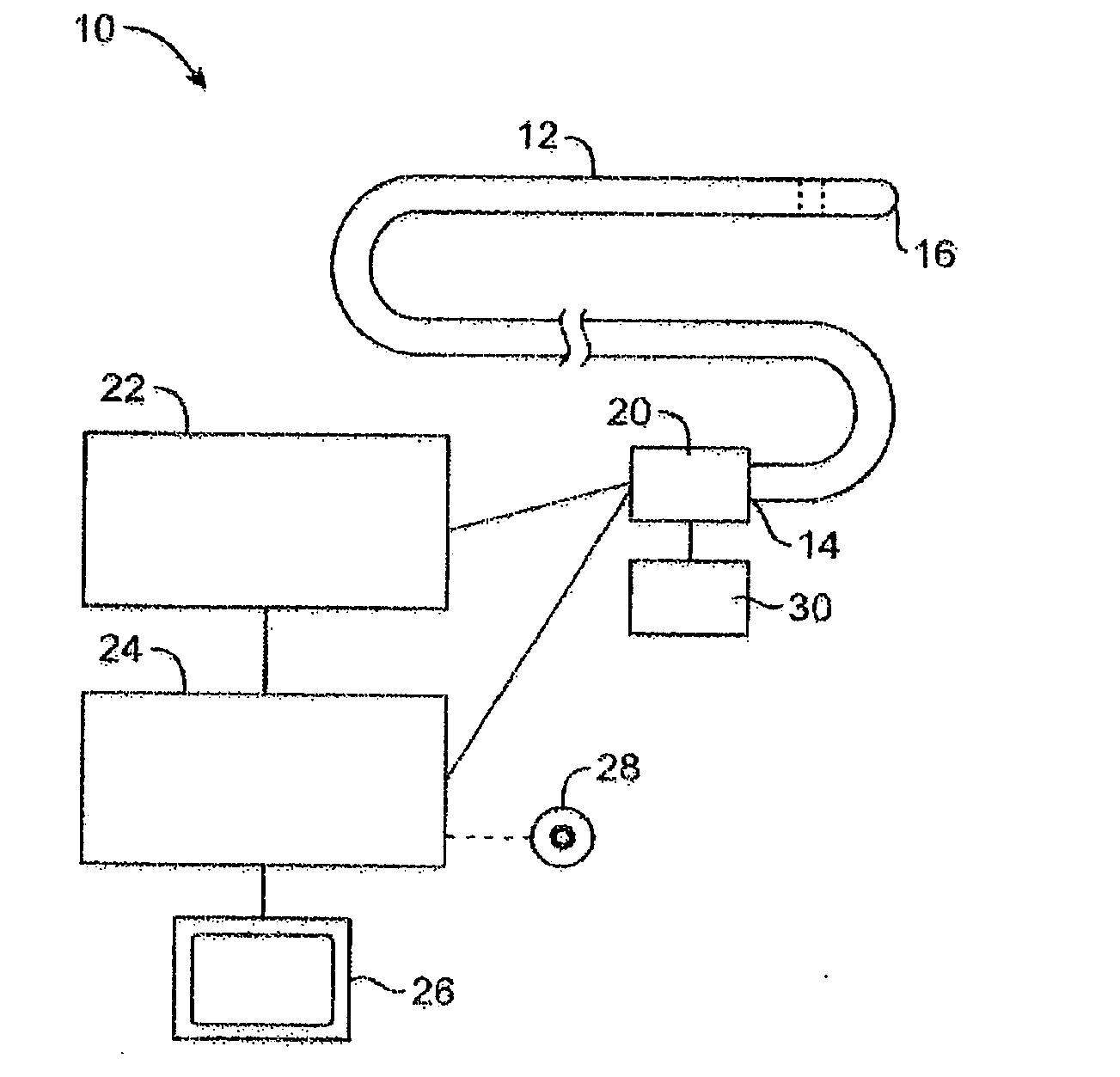
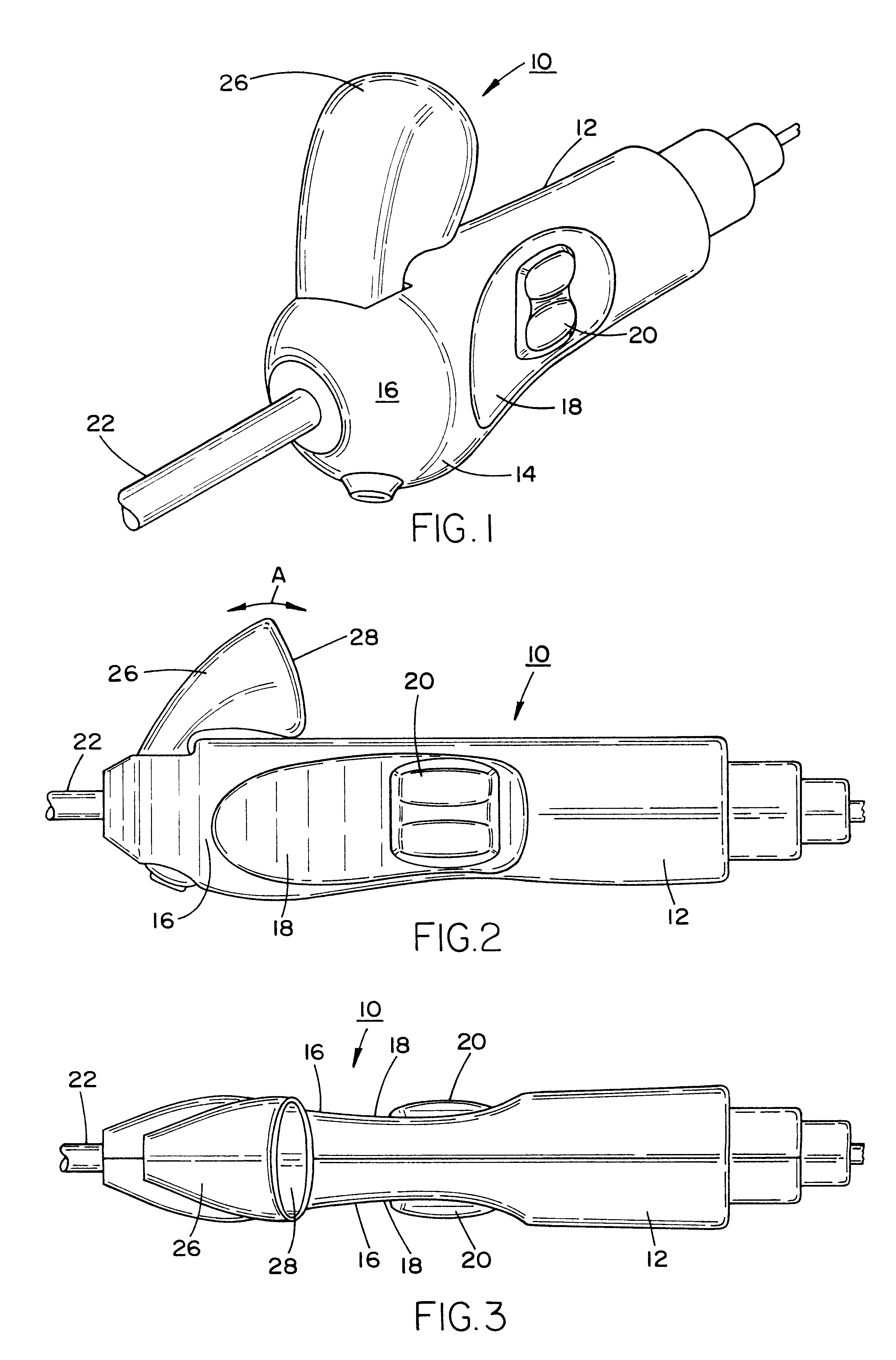
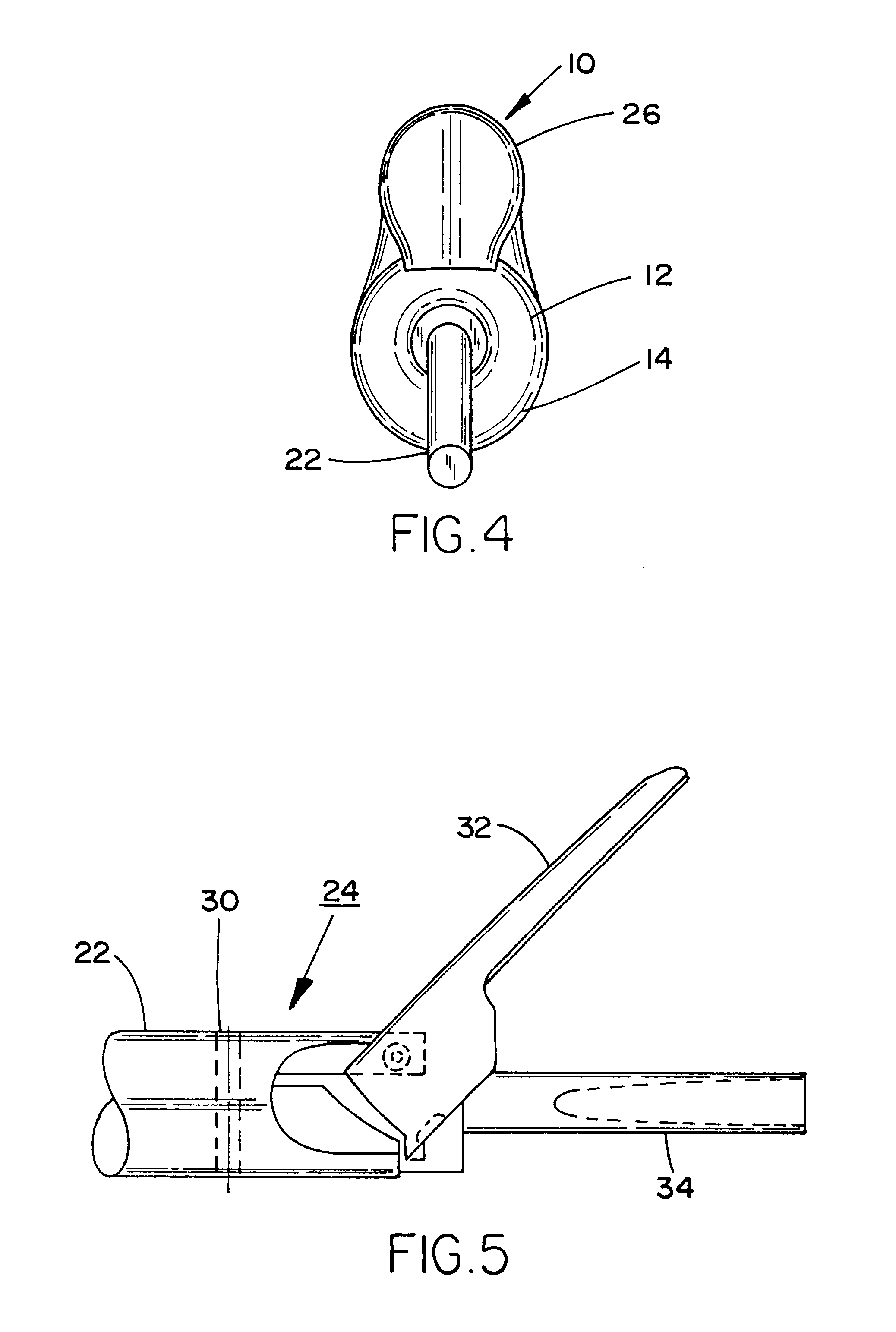
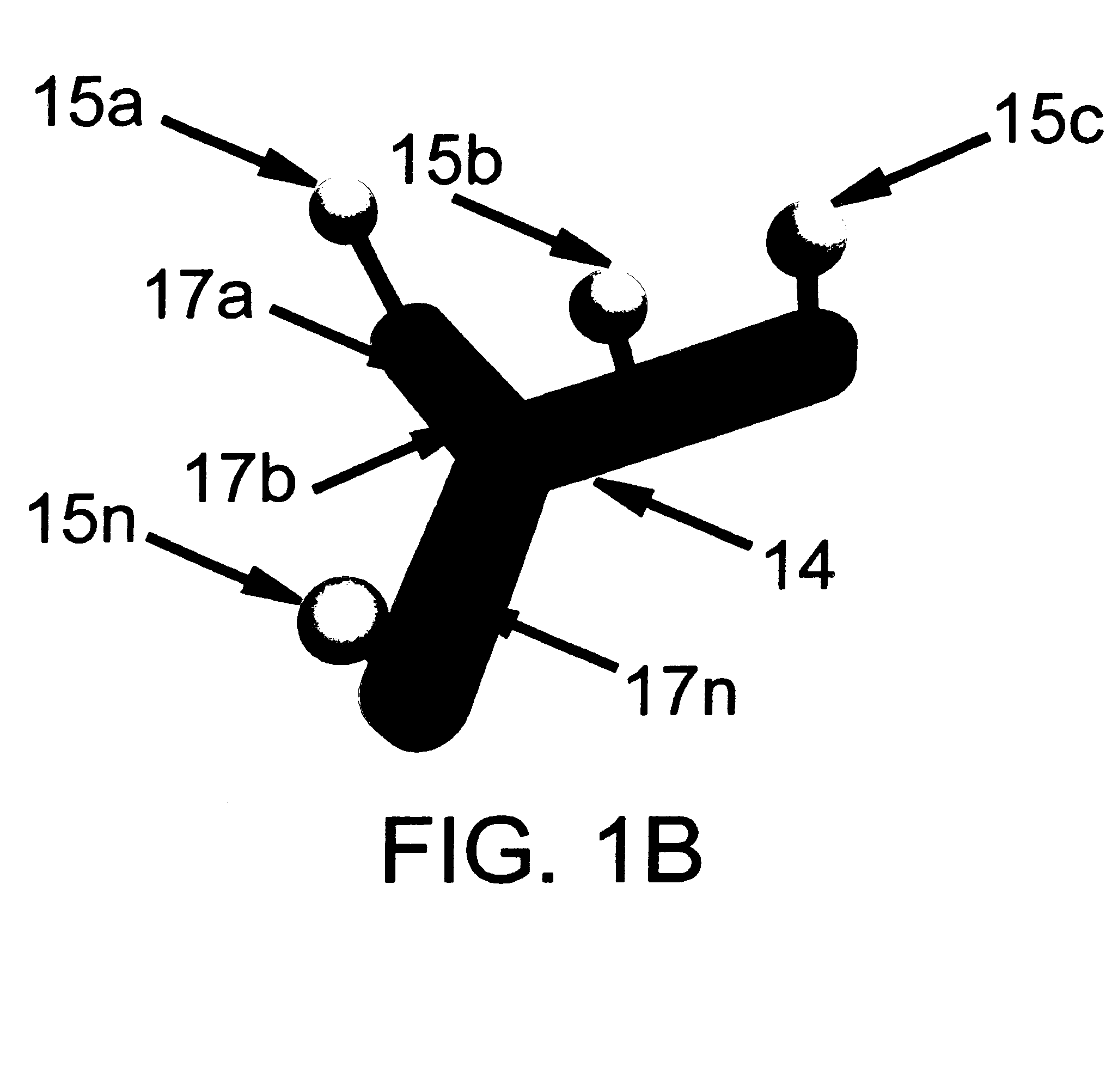
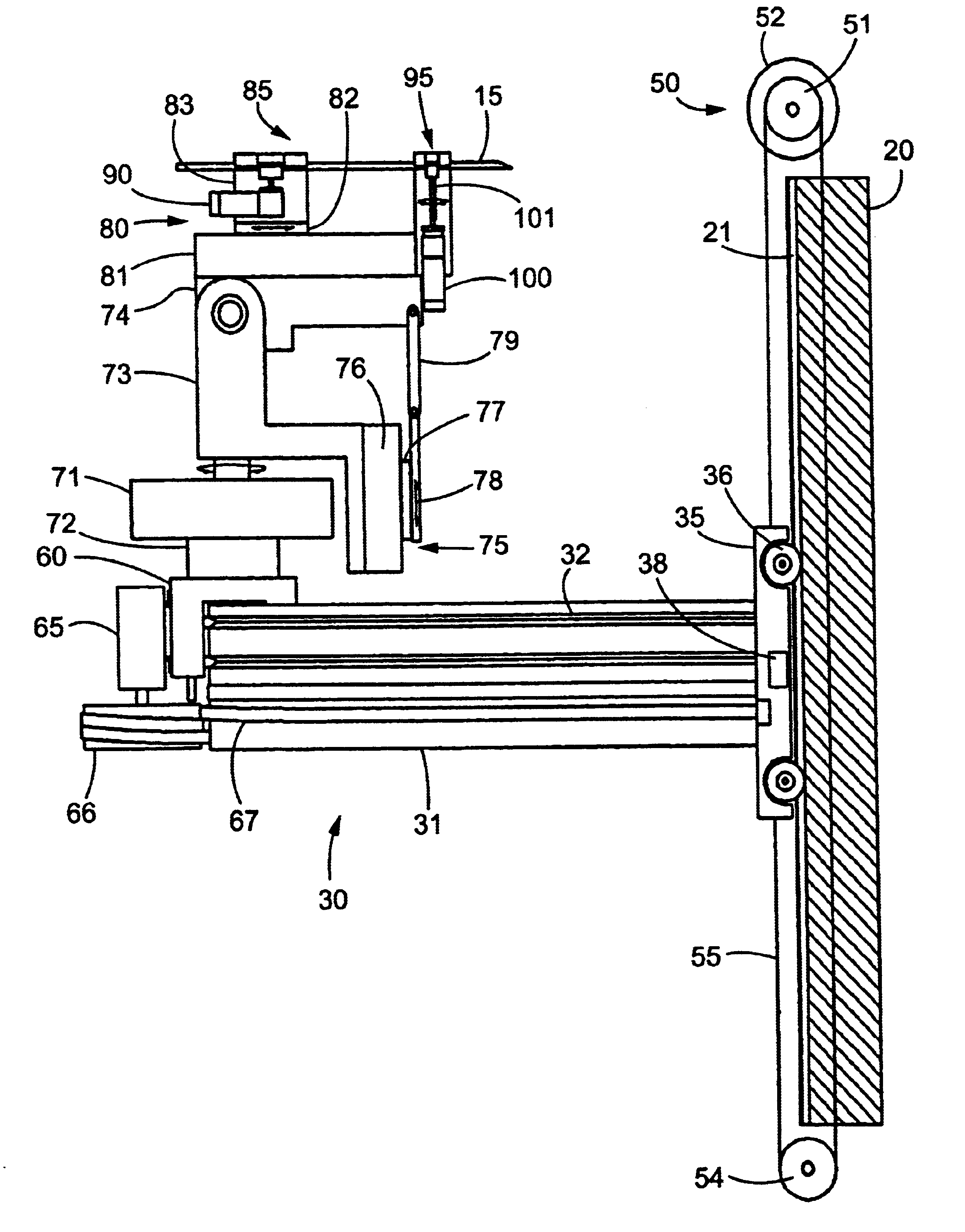
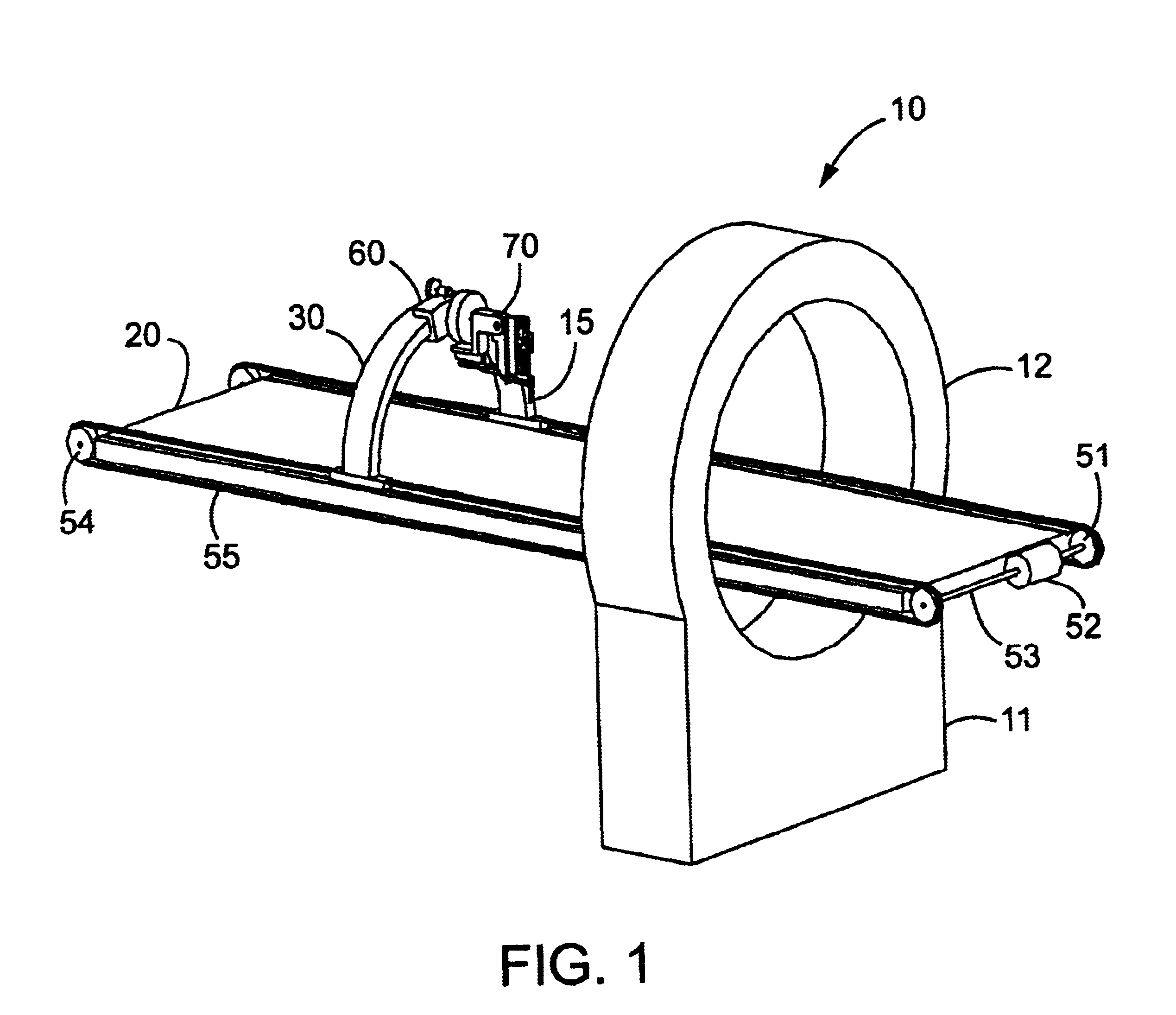
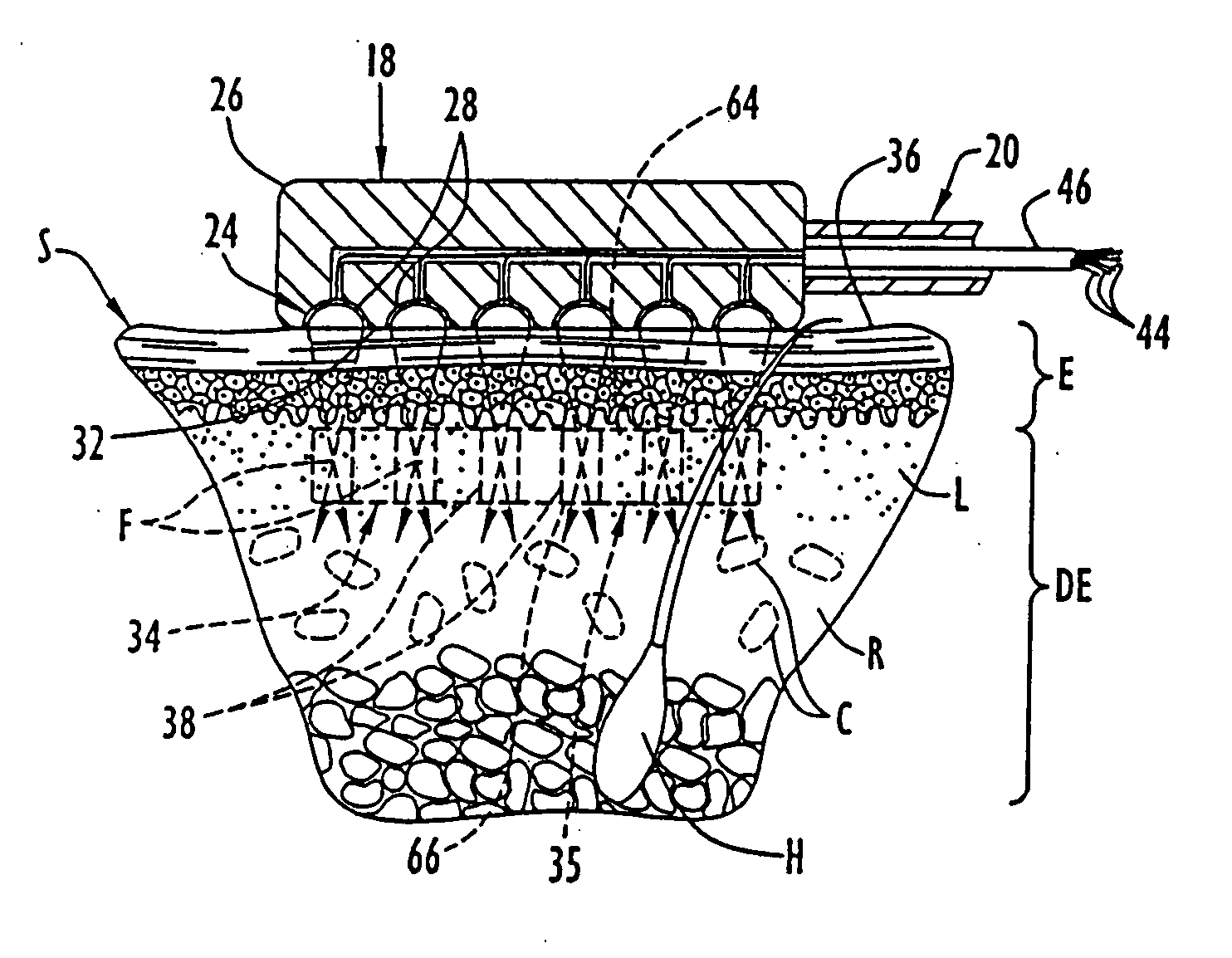
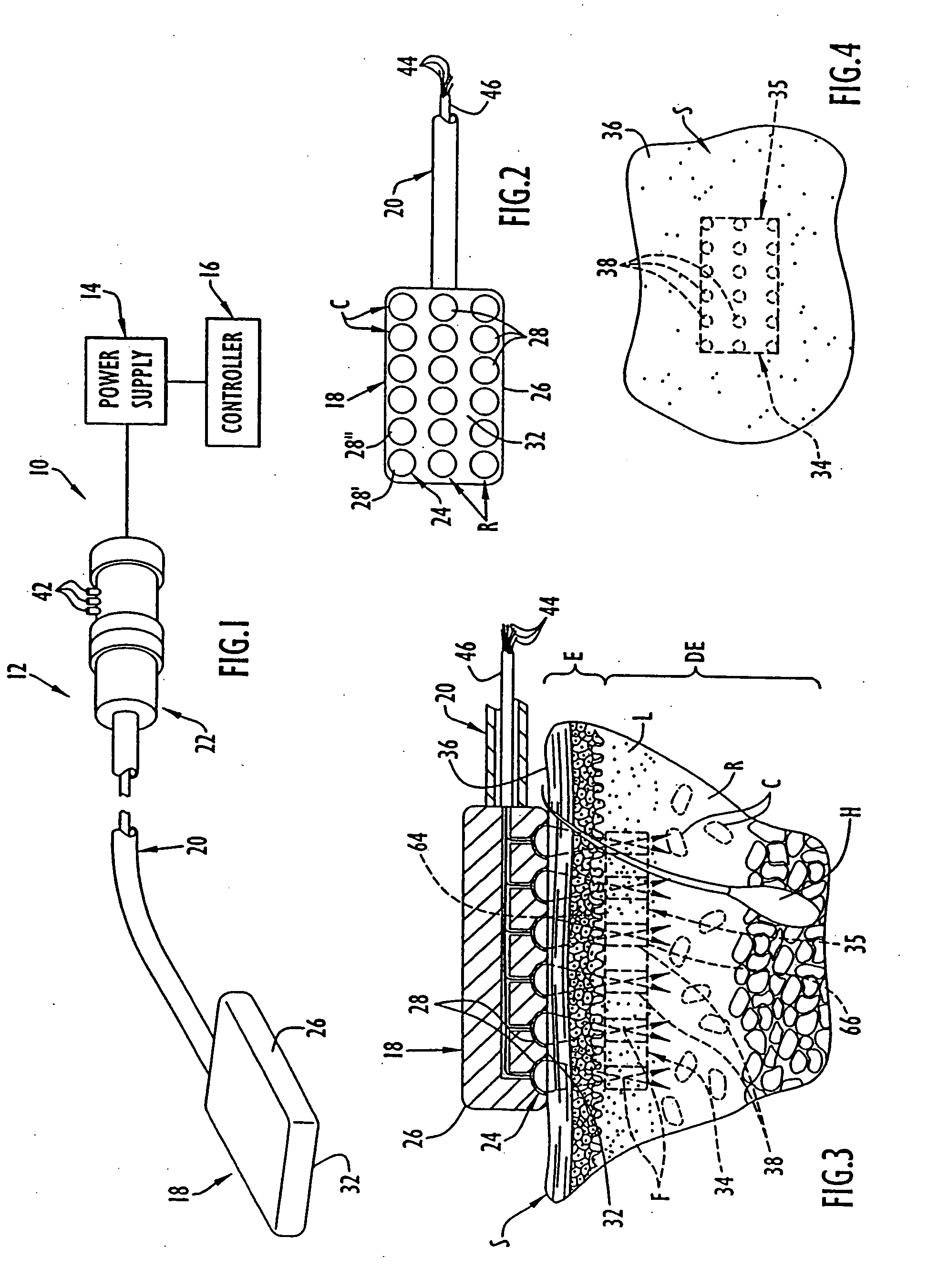
Method and apparatus for determining parameters of linear motion in a surgical instrument
ActiveUS8967443B2Reduce mechanical wearMinimized in sizeSuture equipmentsStapling toolsLinear motionMotion parameter
A surgical instrument and method of controlling the surgical instrument are disclosed. The surgical instrument includes a housing and an elongated shaft that extends distally from the housing and defines a first longitudinal axis. The surgical instrument also includes a firing rod disposed in the elongated shaft and a drive mechanism disposed at least partially within the housing. The drive mechanism mechanically cooperates with the firing rod to move the firing rod. A sensor senses a parameter of light reflected from the surface of the firing rod, which includes markings that change the reflectivity of the firing rod. The measurement unit determines a parameter of the motion of the firing rod, such as the position and speed of the firing rod, based on the sensed parameter of the light reflected from the surface of the firing rod.
Owner:TYCO HEALTHCARE GRP LP
Electronically activated capture device
InactiveUS7063671B2Great driving forceSurgeryVaccination/ovulation diagnosticsControl signalElectroactive polymer actuators
A novel capture device apparatus comprising: (a) a capture device portion, at least a part of which is adaptable for insertion into a patient and (b) a control unit. The capture device portion comprises one or more apertures and one or more electroactive polymer actuators that open and close the one or more apertures based on control signals sent from the control unit. In another aspect of the present invention, a method of capturing a specimen within a patient's body of provided. The method comprises (a) providing a capture device apparatus like that above, (b) inserting at least a portion of the capture device portion of the apparatus into the patient such that the capture device portion is adjacent the specimen; and (c) closing the one or more apertures using the control unit, thereby capturing the specimen.
Owner:BOSTON SCI SCIMED INC
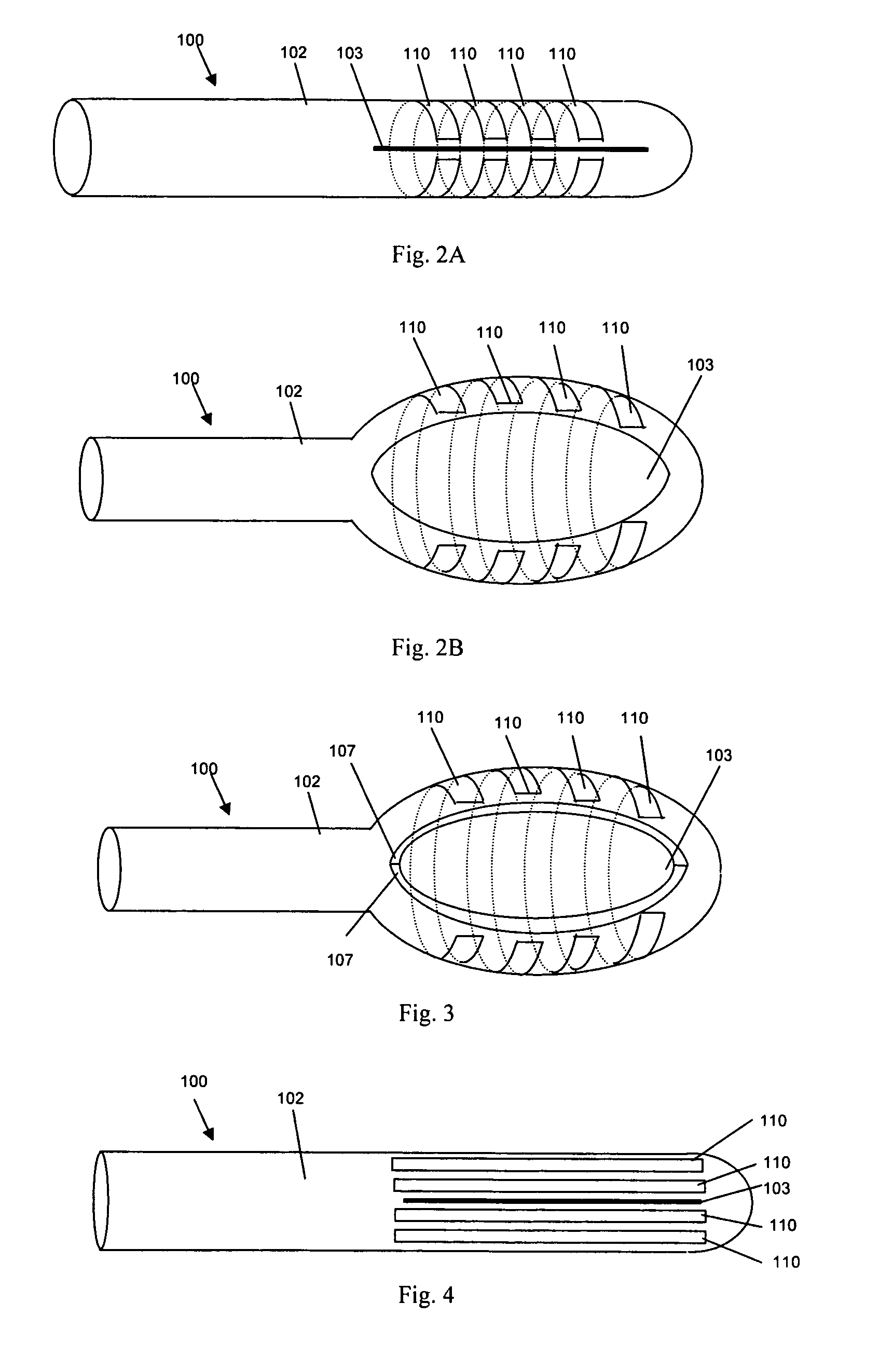
Methods of using high intensity focused ultrasound to form an ablated tissue area containing a plurality of lesions
InactiveUS20080039746A1Easily position and manipulate and stabilize and holdEasily position and manipulate and stabilizeUltrasonic/sonic/infrasonic diagnosticsUltrasound therapyExAblateRadiology
Owner:MEDTRONIC INC
Manual and automatic probe calibration
InactiveUS7526328B2Complicates designIncreased expenseRadiation pyrometrySpectrum investigationFull Term NeonateEngineering
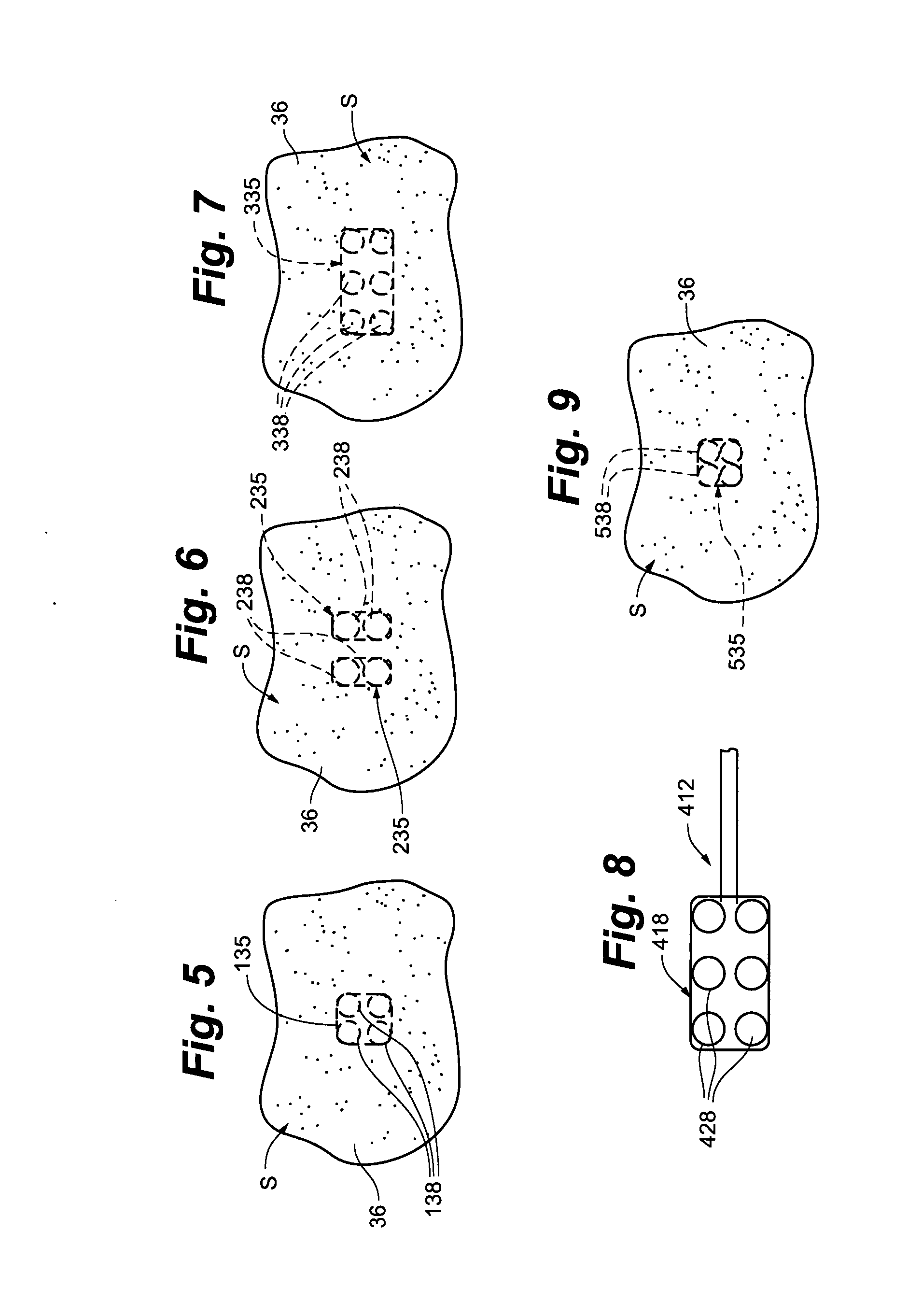
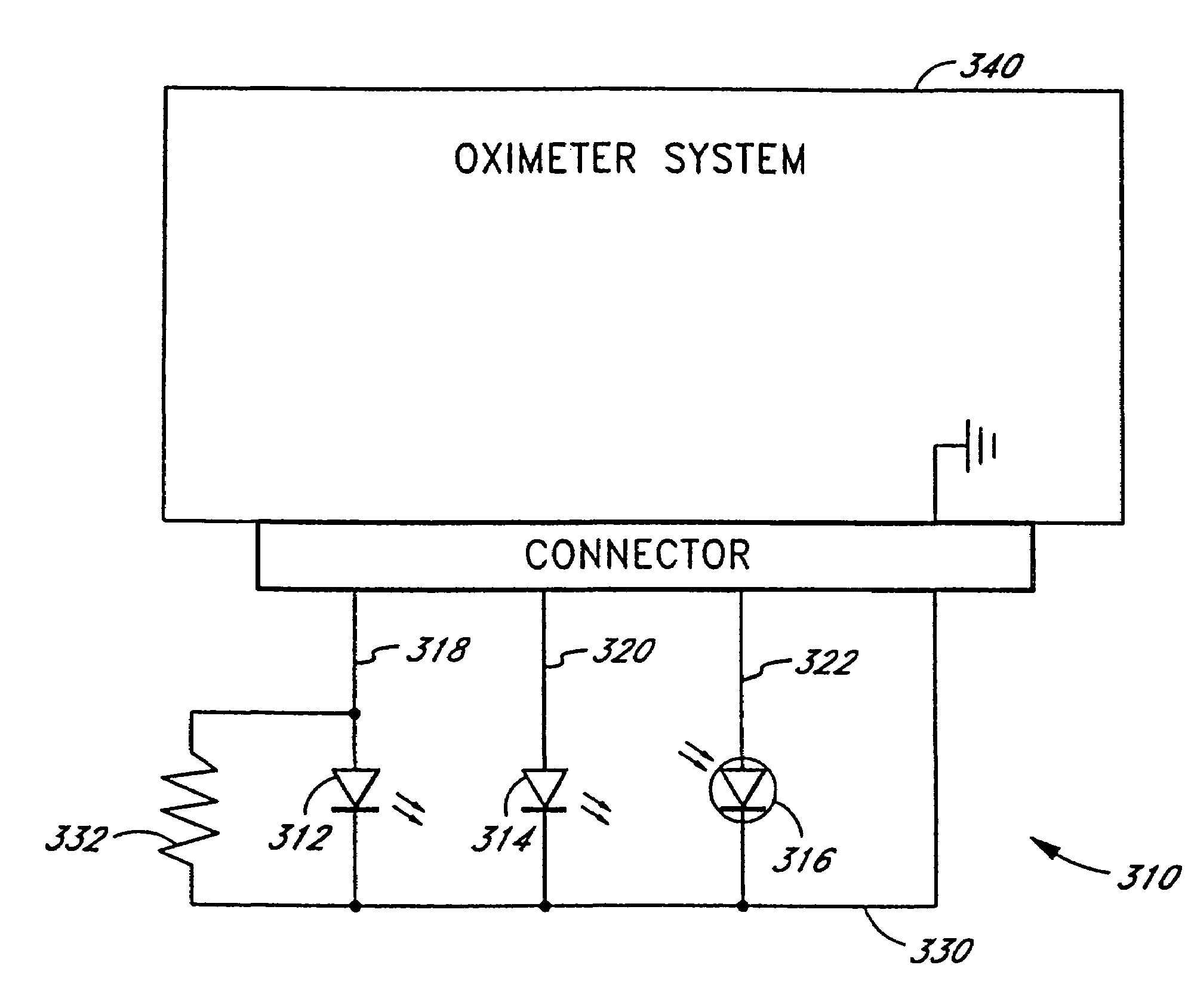
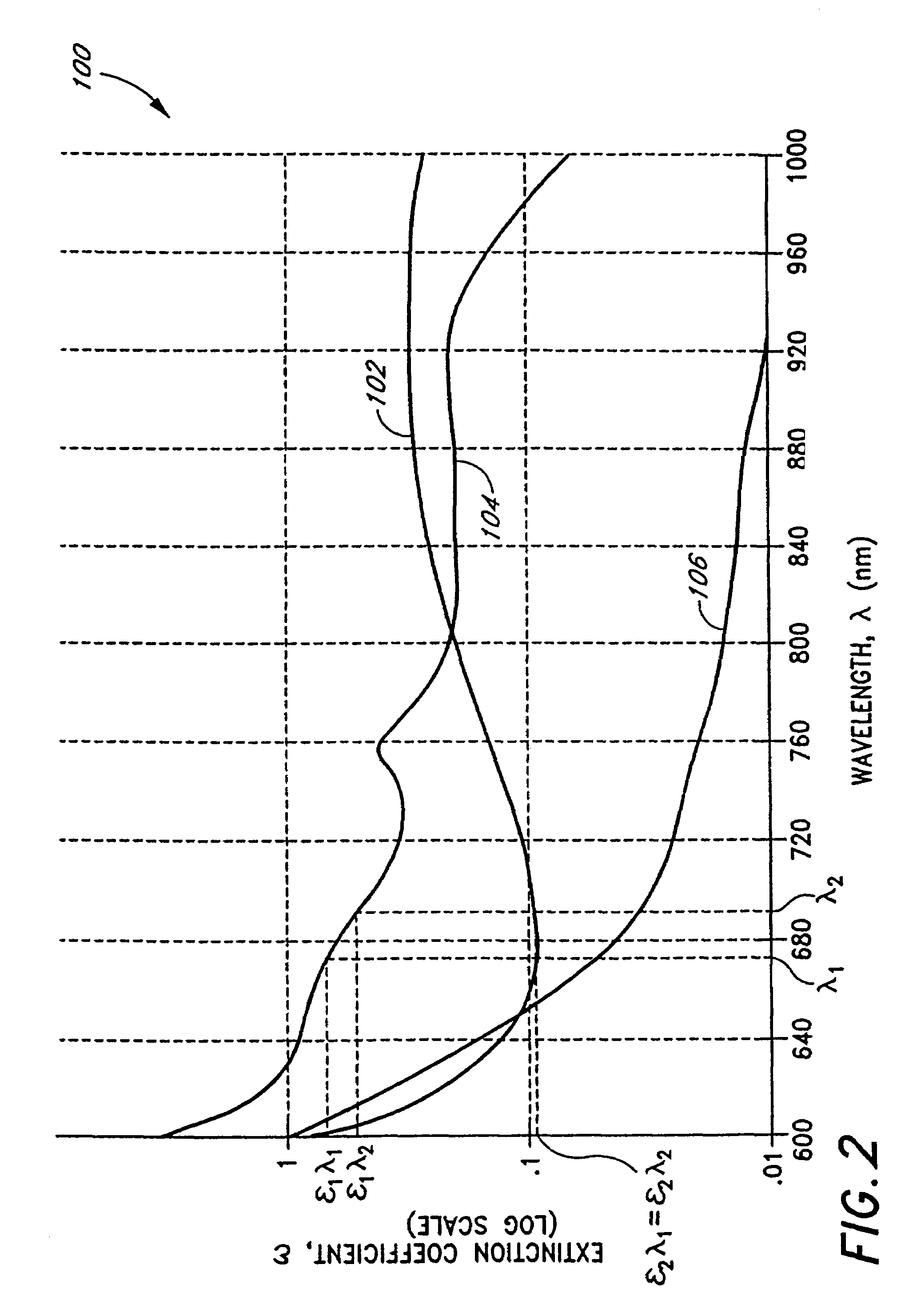
Embodiments of the present disclosure include an optical probe capable of communicating identification information to a patient monitor in addition to signals indicative of intensities of light after attenuation by body tissue. The identification information may indicate operating wavelengths of light sources, indicate a type of probe, such as, for example, that the probe is an adult probe, a pediatric probe, a neonatal probe, a disposable probe, a reusable probe, or the like. The information could also be utilized for security purposes, such as, for example, to ensure that the probe is configured properly for the oximeter, to indicate that the probe is from an authorized supplier, or the like. In one preferred embodiment, coding resistors could be provided across the light sources to allow additional information about the probe to be coded without added leads. However, any device could be used without it being used in parallel.
Owner:JPMORGAN CHASE BANK NA
Universal modular pulse oximeter probe for use with reusable and disposable patient attachment devices
InactiveUSRE41317E1Easy to transportImprove fitDiagnostic recording/measuringSensorsBiomedical engineeringPulse oxymetry
A system and method of standardizing modular probe housings so that the standardized probe housings may be incorporated into probes adapted to work with at least one of a multiplicity of manufacturers' oximeters. The probe housings are adapted to matingly engage at least a disposable bandage apparatus and a reusable finger attachment device.A pulse oximeter system comprises a finger attachment device having first and second probe couplers, the first and second probe couplers are configured to be matingly engageable with probe housings of a pulse oximeter probe.
Owner:JPMORGAN CHASE BANK NA
Method and apparatus for obtaining blood for diagnostic tests
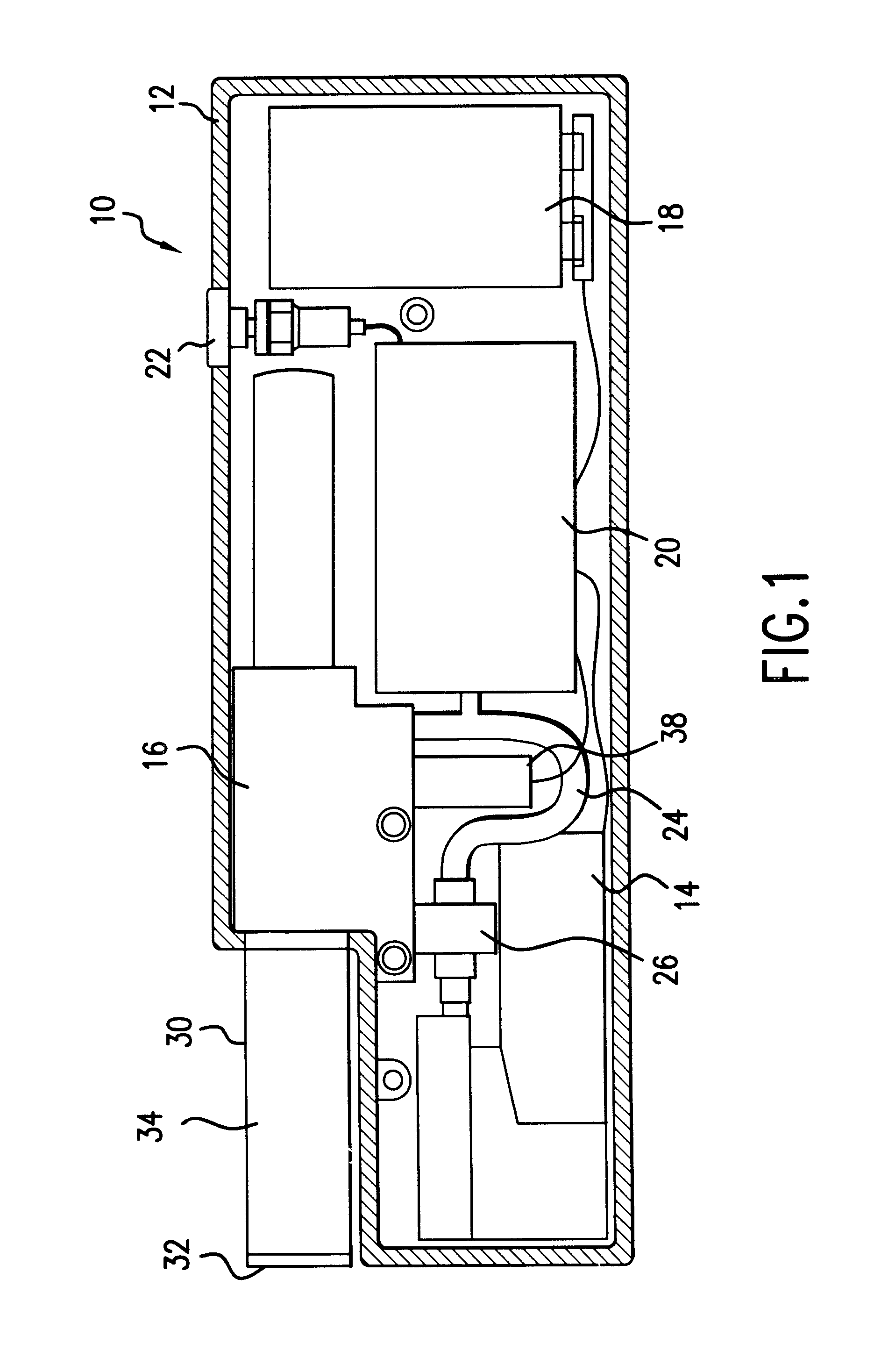
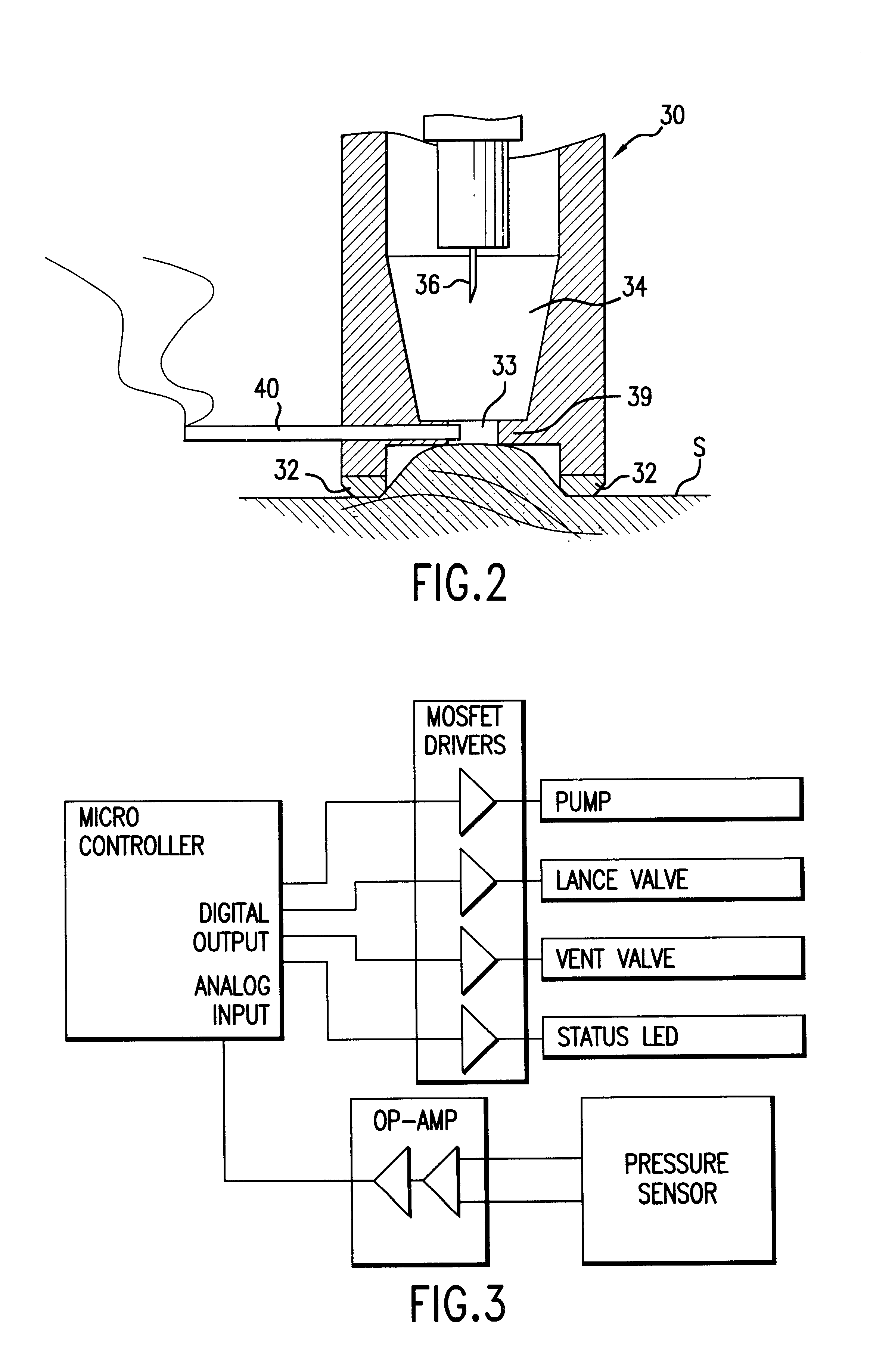
Method and apparatus for obtaining a sample of blood from a patient for subsequent diagnostic tests, e.g., glucose monitoring. In one aspect of the invention, the method comprises the steps of:(a) placing a blood collection device over a region on the surface of the skin from which said sample is to be obtained,(b) forming a seal between said blood collection device and said surface of the skin,(c) creating a vacuum sufficient to result in said surface of the skin becoming stretched and engorged with blood,(d) triggering a lancing assembly and causing a lancet to penetrate said skin,(e) retracting said lancet,(f) withdrawing blood toward and onto a fluid collector, and(g) releasing the vacuum.In another aspect of the invention, an apparatus for carrying out the method described previously is provided. The apparatus comprises:(a) a housing having a sealable chamber located therein and a sealable opening in fluid communication with said sealable chamber,(b) a power source,(c) a vacuum pump operably connected to said power source, said vacuum pump in communication with said sealable chamber,(d) a lancing assembly positioned within said housing, said lancing assembly capable of moving a lancet towards said sealable opening, and(e) a fluid collector positioned in said sealable chamber, said fluid collector in fluid communication with said sealable opening.
Owner:ABBOTT LAB INC
Personal fit medical implants and orthopedic surgical instruments and methods for making
InactiveUS20070118243A1Minimizing Ni toxicityImprove visualizationElectrotherapyMechanical/radiation/invasive therapiesPersonalizationManufacturing technology
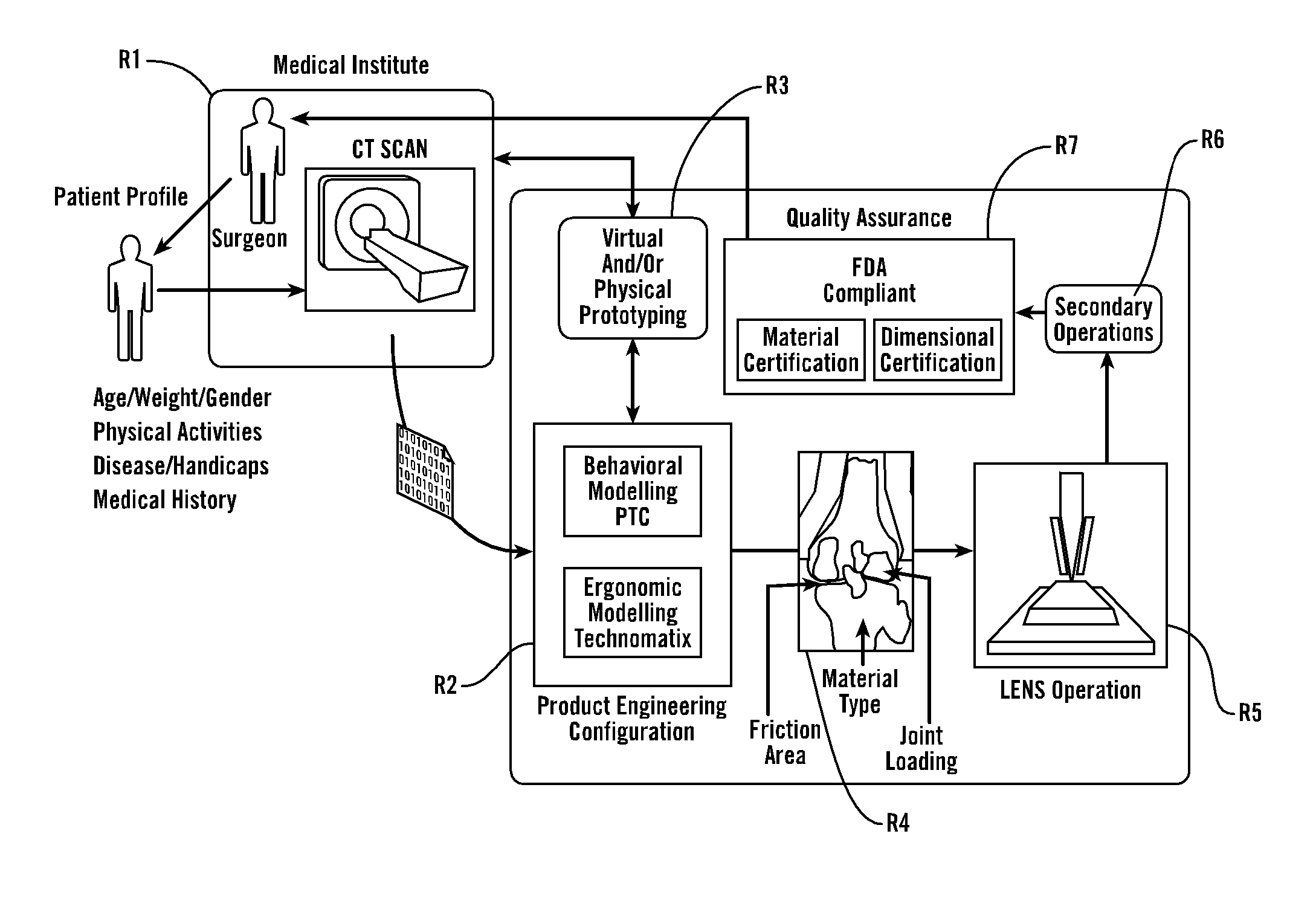
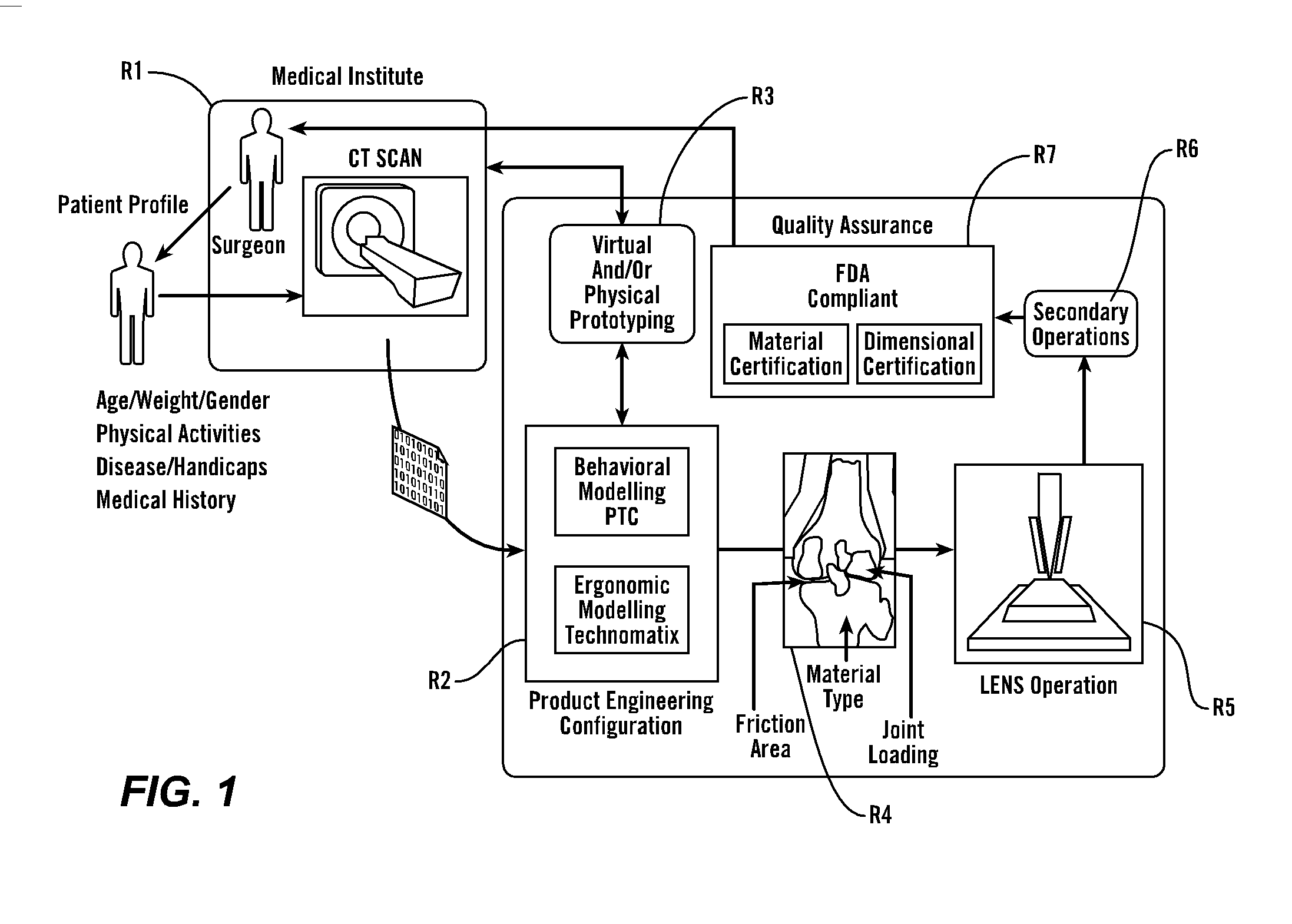
The present invention provides methods, techniques, materials and devices and uses thereof for custom-fitting biocompatible implants, prosthetics and interventional tools for use on medical and veterinary applications. The devices produced according to the invention are created using additive manufacturing techniques based on a computer generated model such that every prosthesis or interventional device is personalized for the user having the appropriate metallic alloy composition and virtual validation of functional design for each use.
Owner:VANTUS TECH CORP
Magnetically guided atherectomy
Atherectomy device are guided by and manipulated by externally applied magnetic fields to treat total or partial occlusions of a patient's vasculature.
Owner:STEREOTAXIS
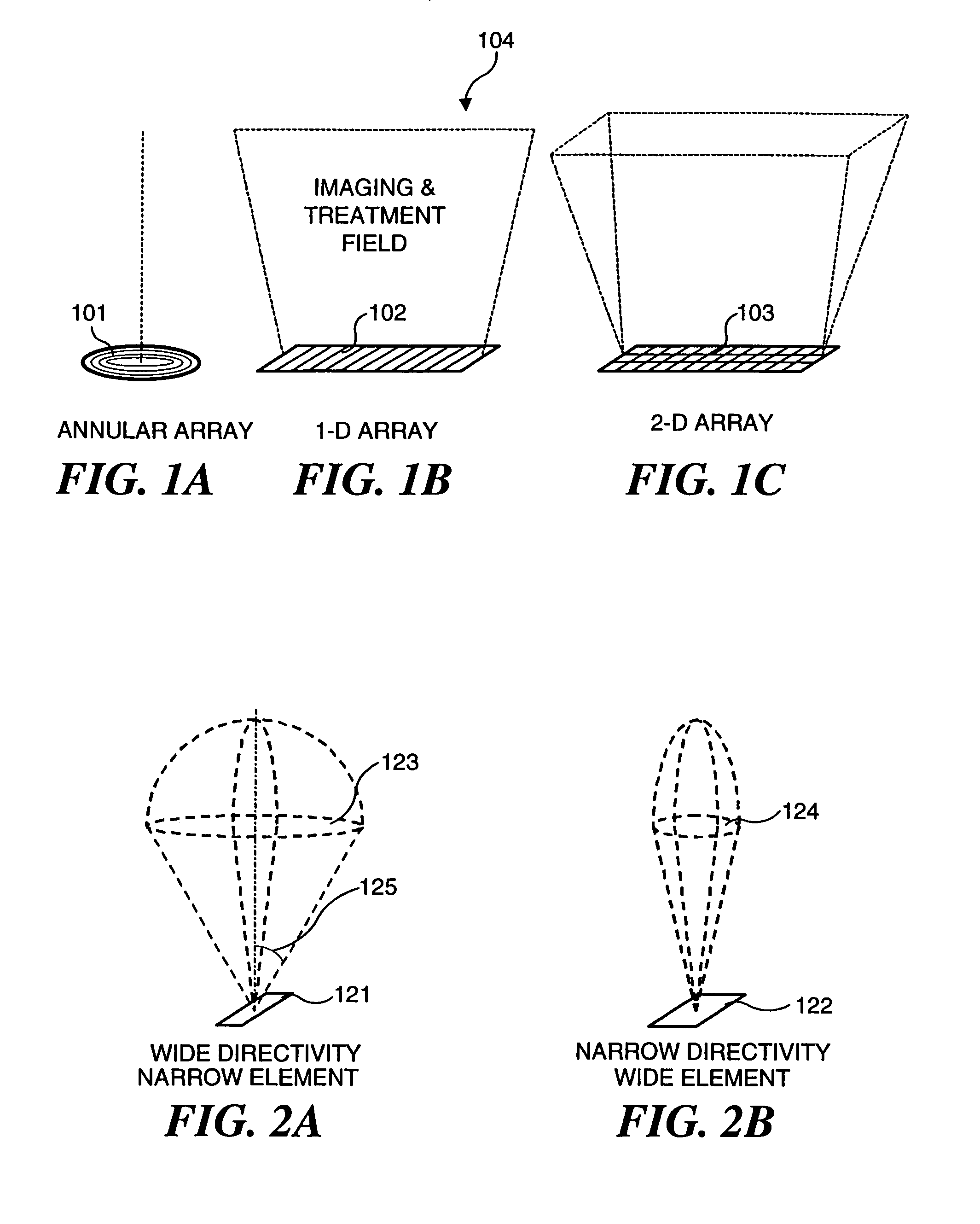
Wide-field of view (FOV) imaging devices with active foveation capability
ActiveUS20140218468A1High resolutionIncrease frame rateTelevision system detailsPrismsWide fieldFoveated imaging
The present invention comprises a foveated imaging system capable of capturing a wide field of view image and a foveated image, where the foveated image is a controllable region of interest of the wide field of view image.
Owner:MAGIC LEAP INC
Radioactive therapeutic fastening instrument
ActiveUS8267849B2For accurate placementReduce doseSuture equipmentsStapling toolsBrachytherapyEngineering
An instrument used for brachytherapy delivery in the treatment of cancer by radiation therapy including a handle having first and second handle actuators; an end effector; and an instrument shaft that connects the handle with the end effector. The end effector has first and second adjacent disposed staple mechanisms that each retain a set of staples. The first mechanism is for holding standard staples in a first array, and dispensing the standard staples under control of the corresponding first handle actuator. The second mechanism is for holding radioactive source staples in a second array, and dispensing said radioactive source staples under control of the corresponding second handle actuator. A holder is for receiving the first and second mechanisms in a substantially parallel array so that the standard staples close the incision at a surgical margin while the source staples are secured adjacent thereto.
Owner:POINT SOURCE TECH
Apparatus and methods for analyte measurement and immuno assay
ActiveUS20030170881A1Avoid disadvantagesBioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsPoint of careOrganism
The present invention relates to an apparatus for conducting a variety of assays for the determination of analytes in liquid samples, and relates to the methods for such assays. In particular, the invention relates to a single-use cartridge designed to be adaptable to a variety of real-time assay protocols, preferably assays for the determination of analytes in biological samples using immunosensors or other ligand / ligand receptor-based biosensor embodiments. The cartridge provides novel features for processing a metered portion of a sample, for precise and flexible control of the movement of a sample or second fluid within the cartridge, for the amending of solutions with additional compounds during an assay, and for the construction of immunosensors capable of adaptation to diverse analyte measurements. The disclosed device and methods of use enjoy substantial benefits over the prior art, including simplicity of use by an operator, rapid in situ determinations of one or more analytes, and single-use methodology that minimizes the risk of contamination of both operator and patient. The disclosed invention is adaptable to the point-of-care clinical diagnostic field, including use in accident sites, emergency rooms, surgery, nursing homes, intensive care units, and non-medical environments.
Owner:ABBOTT POINT CARE
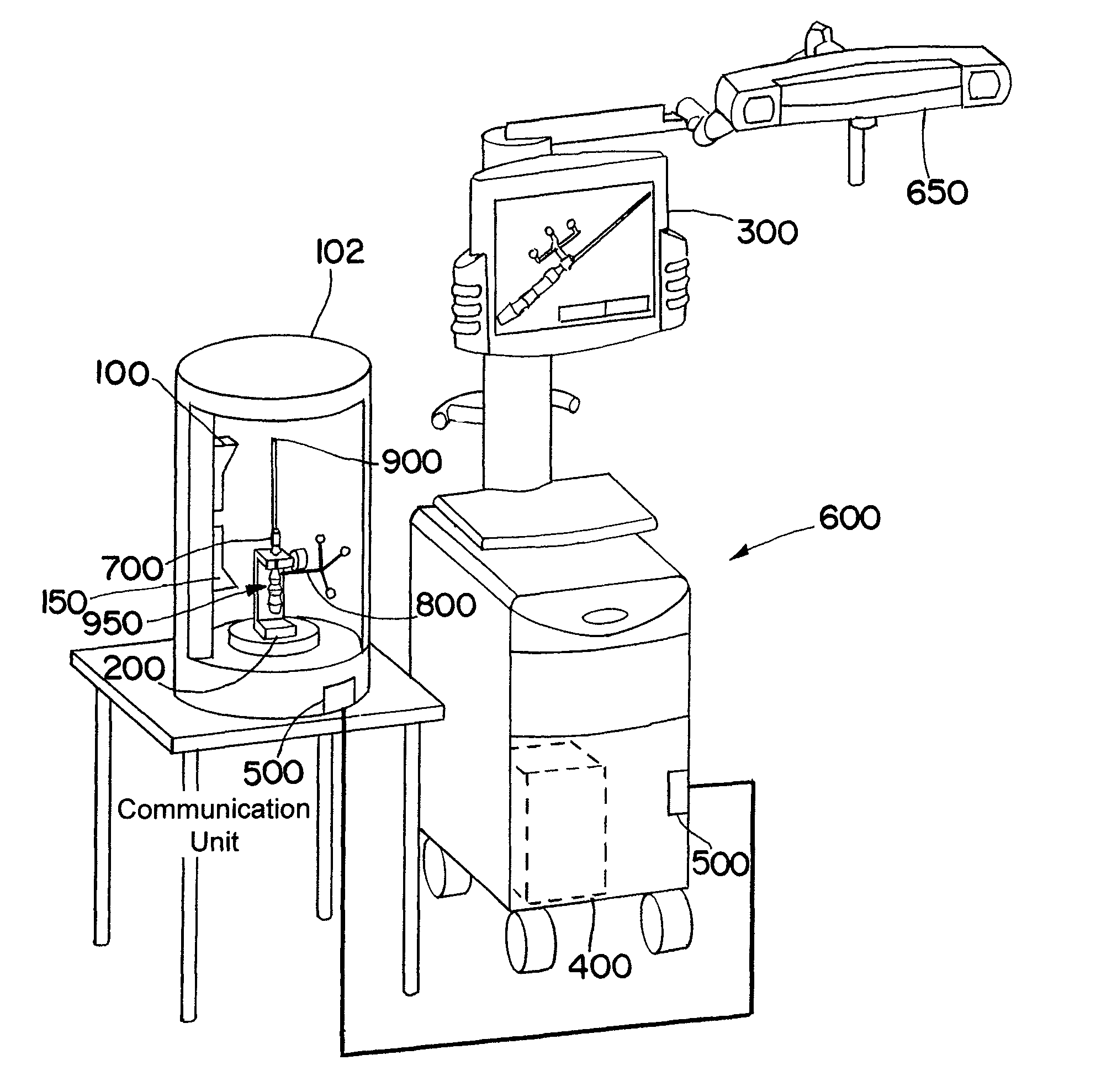
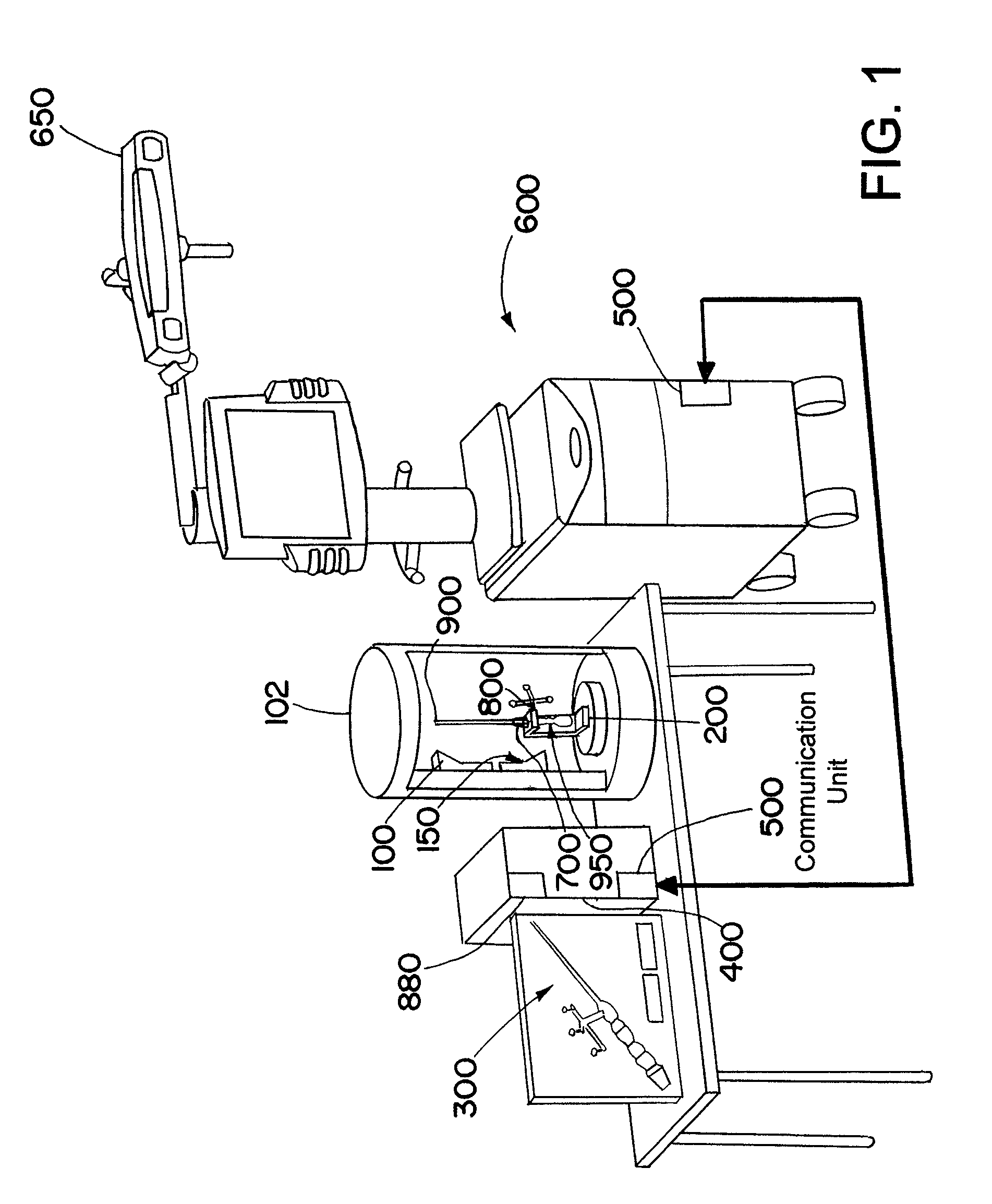
Six degree of freedom alignment display for medical procedures
A display and navigation system for use in guiding a medical device to a target in a patient includes a tracking sensor, a tracking device and display. The tracking sensor is associated with the medical device and is used to track the medical device. The tracking device tracks the medical device with the tracking sensor. The display includes indicia illustrating at least five degree of freedom information and indicia of the medical device in relation to the five degree of freedom information.
Owner:SURGICAL NAVIGATION TECH
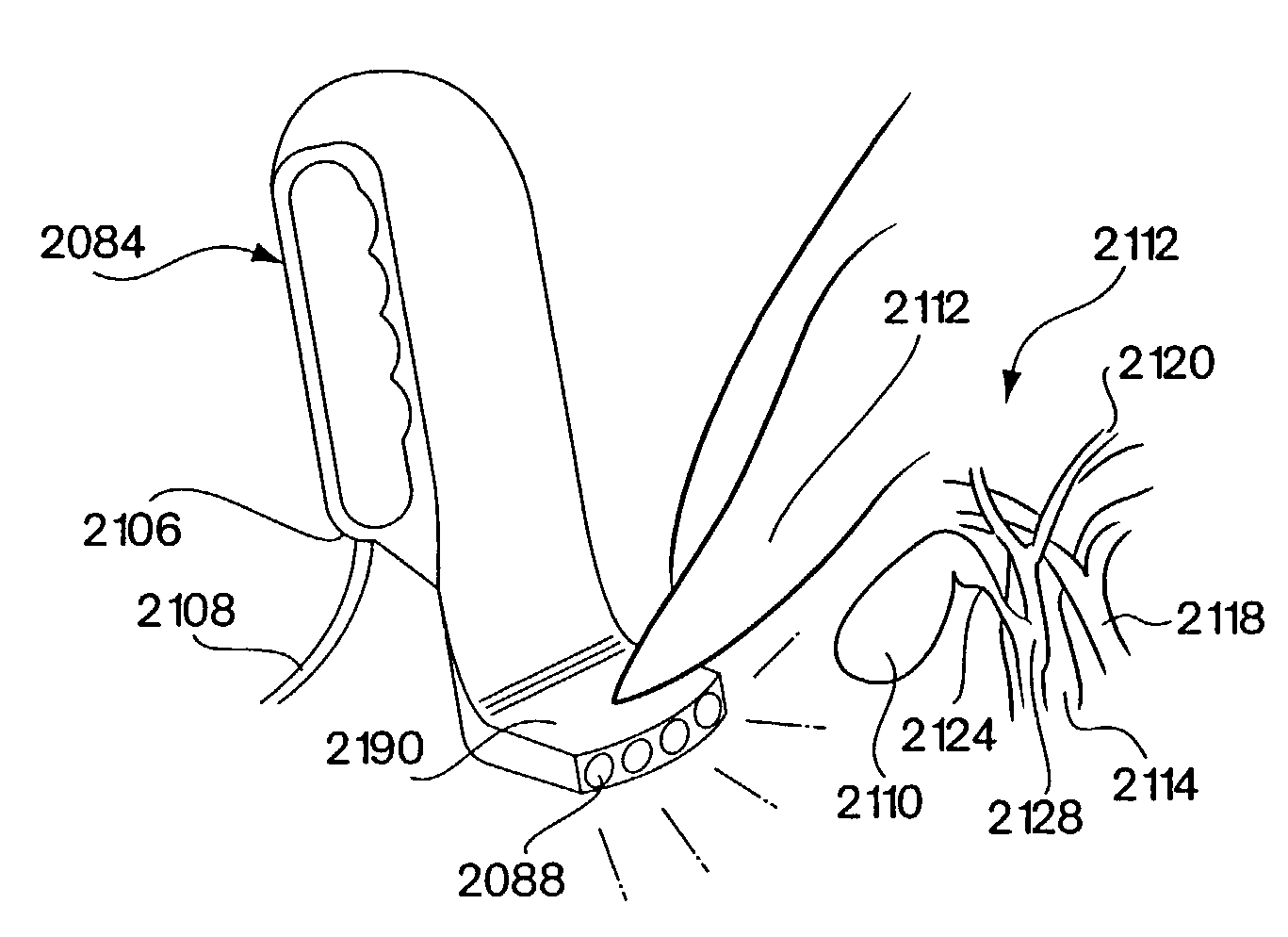
Imaging and eccentric atherosclerotic material laser remodeling and/or ablation catheter
Devices, systems, and methods for treating atherosclerotic lesions and other disease states, particularly for treatment of vulnerable plaques, can incorporate optical coherence tomography or other imaging techniques which allow a structure and location of an eccentric plaque to be characterized. Remodeling and / or ablative laser energy can then be selectively and automatically directed to the appropriate plaque structures, often without imposing mechanical trauma to the entire circumference of the lumen wall.
Owner:VESSIX VASCULAR
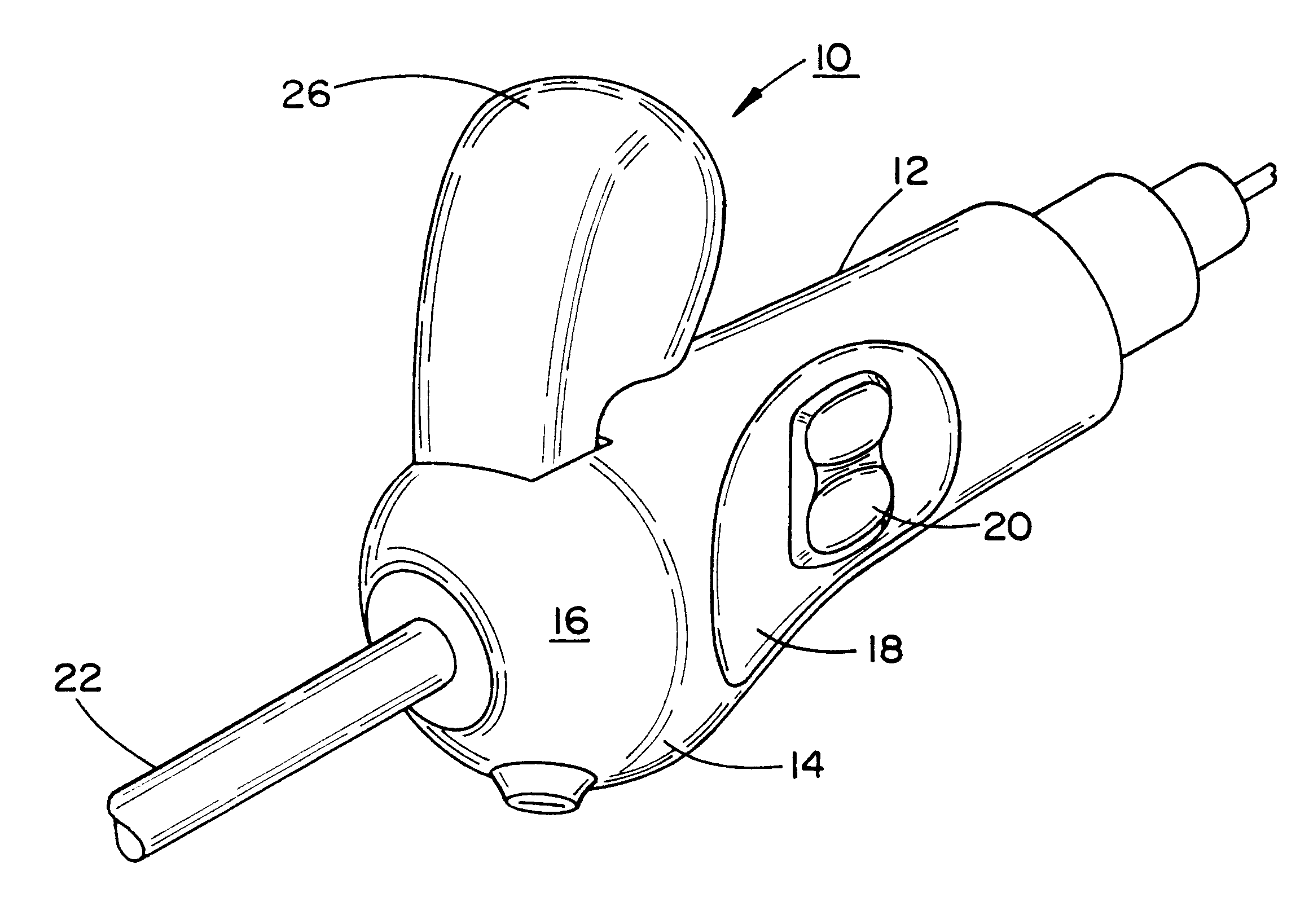
Ultrasonic surgical instrument with finger actuator
Owner:ET HICON ENDO SURGERY
Geometrical properties measuring device for a medical treatment device including an RFID transponder
ActiveUS8207863B2Improve reliabilityProvide goodDiagnosticsSurgical navigation systemsGeometric propertyMedical device
Owner:BRAINLAB
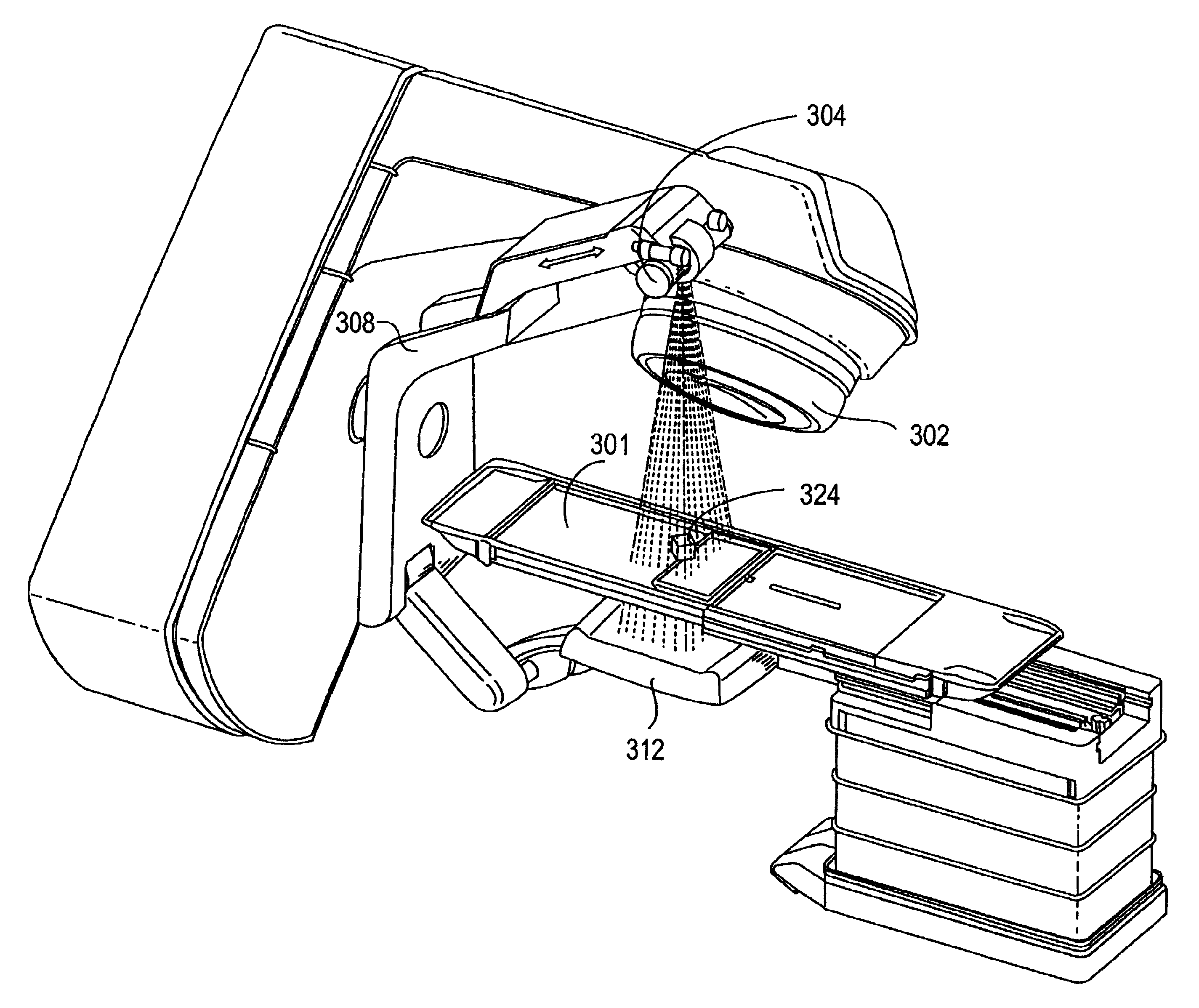
Cone beam computed tomography with a flat panel imager
InactiveUS6842502B2Adequate visualizationReduce errorsMaterial analysis using wave/particle radiationRadiation/particle handlingX-rayAmorphous silicon
A radiation therapy system that includes a radiation source that moves about a path and directs a beam of radiation towards an object and a cone-beam computer tomography system. The cone-beam computer tomography system includes an x-ray source that emits an x-ray beam in a cone-beam form towards an object to be imaged and an amorphous silicon flat-panel imager receiving x-rays after they pass through the object, the imager providing an image of the object. A computer is connected to the radiation source and the cone beam computerized tomography system, wherein the computer receives the image of the object and based on the image sends a signal to the radiation source that controls the path of the radiation source.
Owner:WILLIAM BEAUMONT HOSPITAL
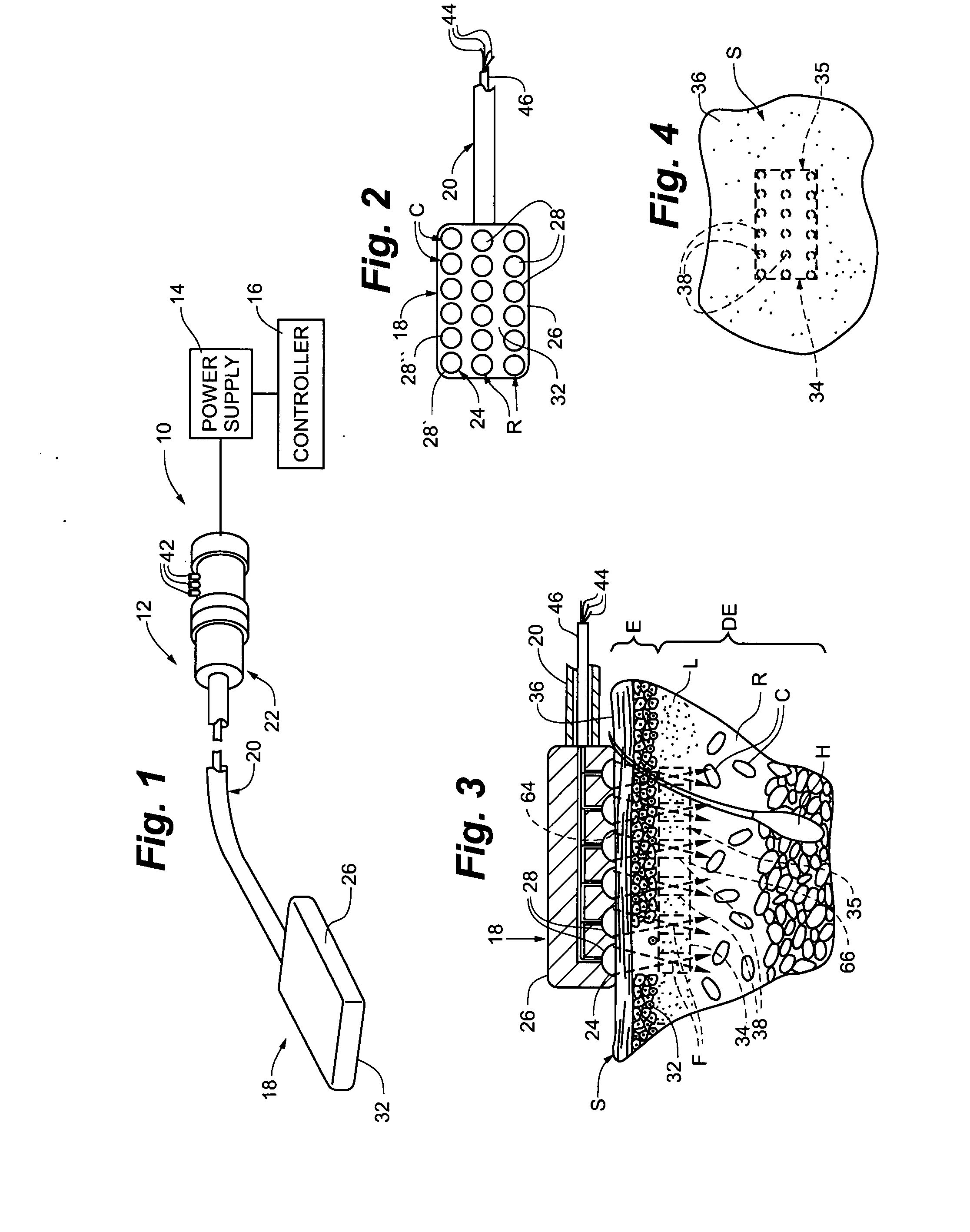
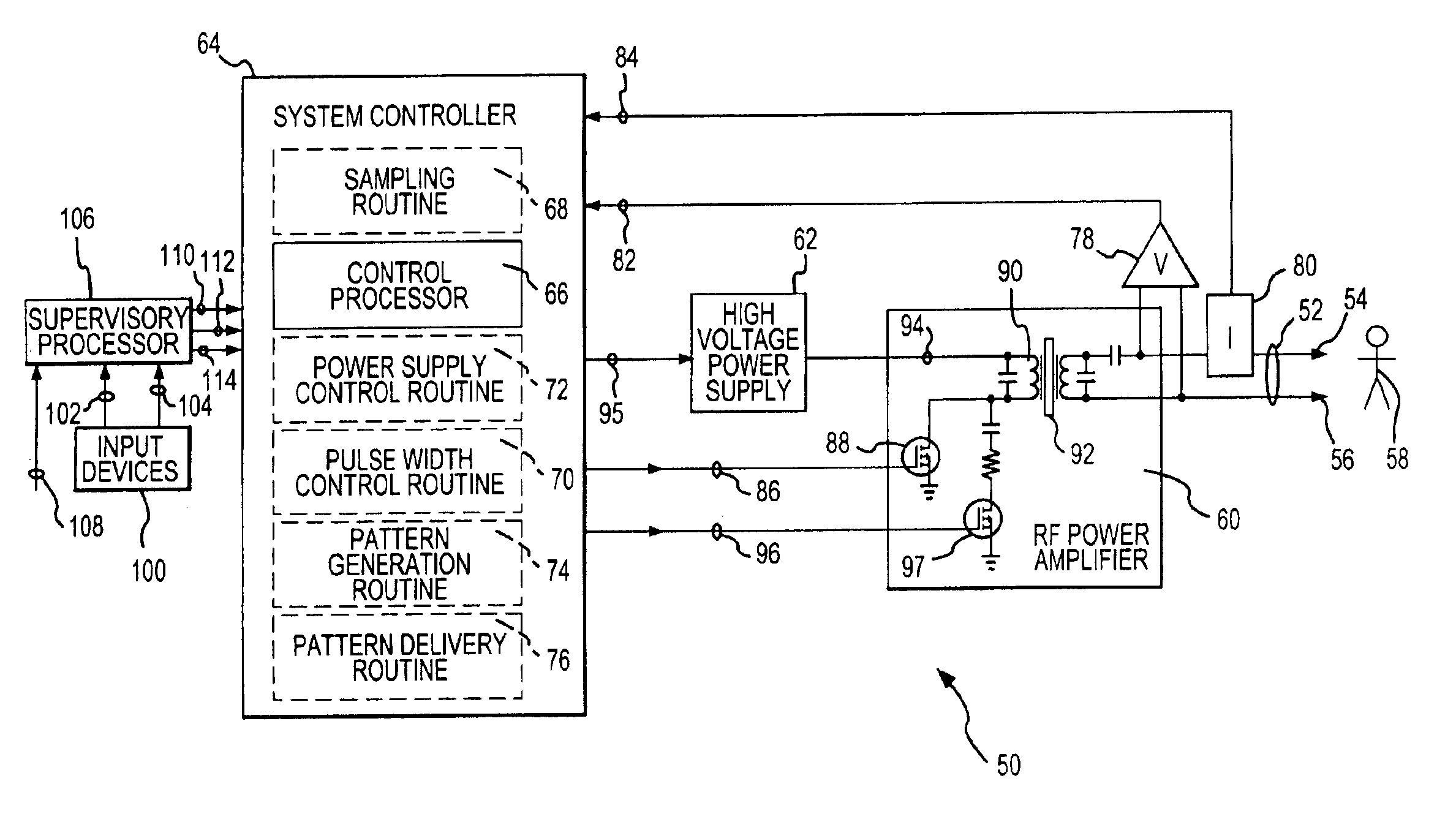
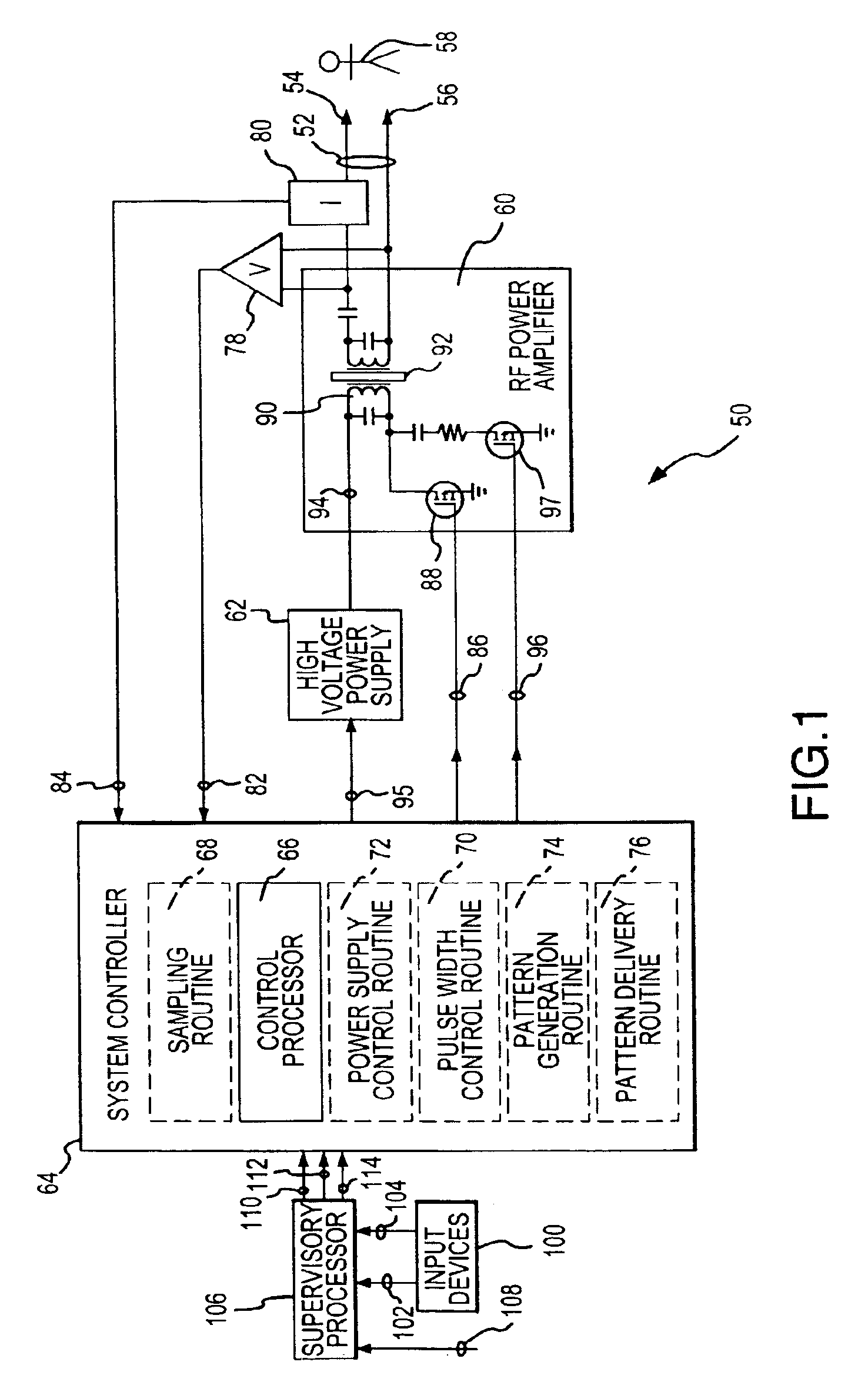
Electrosurgical generator and method with multiple semi-autonomously executable functions
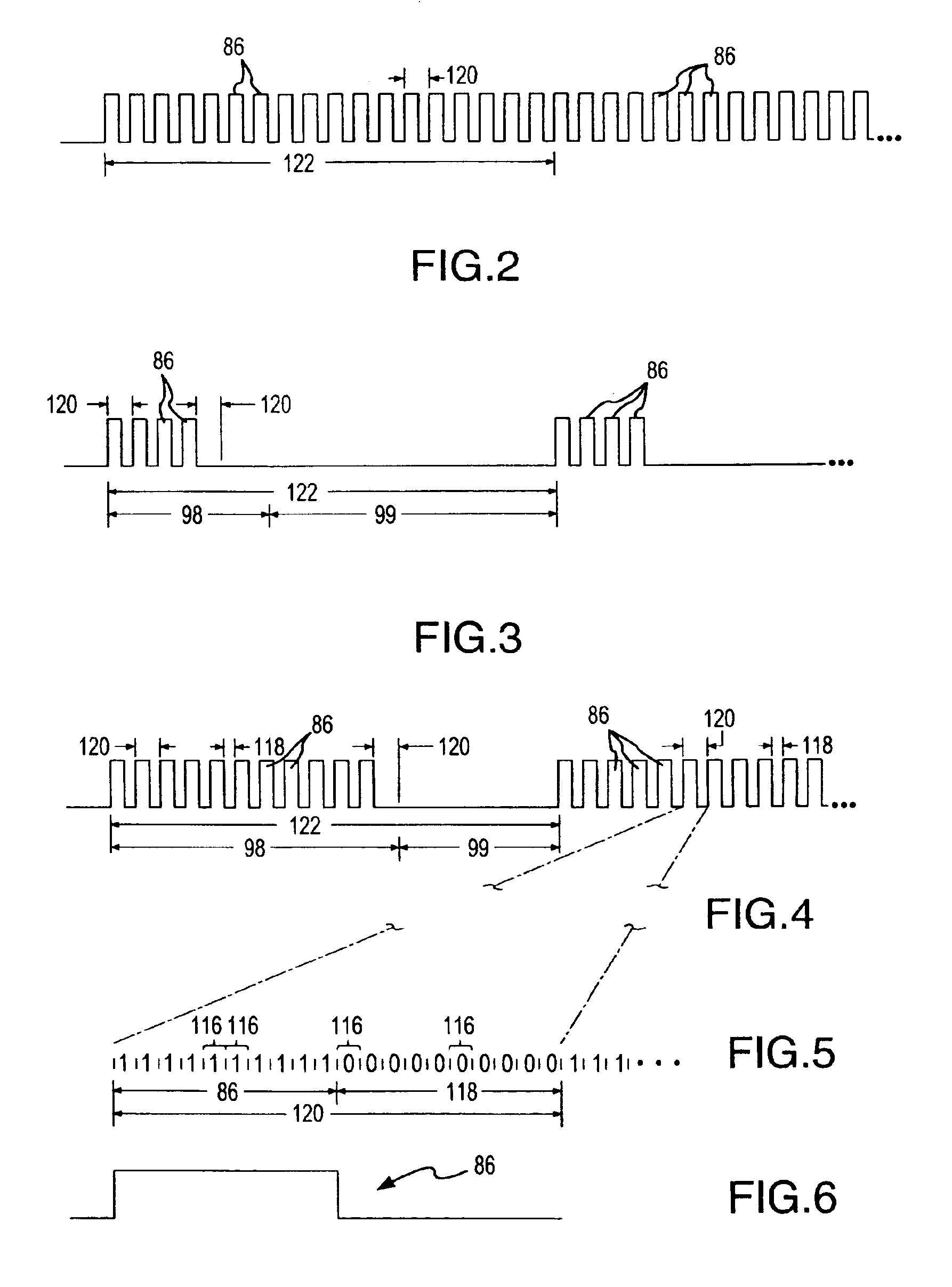
InactiveUS6942660B2Compromising performanceCompromising safetySurgical instruments for heatingPattern generationOperation mode
Semi-autonomously executed routines accomplish the primary functions of electrosurgical energy delivery on a responsive basis for power control purposes and to adapt the delivered output waveform to perform new and better surgical procedures. The routines include and output voltage and output current sampling routine, a control routine for establishing the width of drive pulses used to create the output waveform, a pattern generation routine for establishing the pattern of drive pulses to be delivered in one mode cycle established by a selected mode of operation, a pattern delivery routine for repeatedly delivering sequences of the mode cycle pattern of drive pulses, and a power supply control routine for varying the voltage of the drive pulses in coordination with varying the width of the drive pulses.
Owner:CONMED CORP
Architecture tool and methods of use
InactiveUS6986739B2Liquid surface applicatorsAdditive manufacturing apparatusTemperature controlIn vitro
The invention provides an apparatus and methods for depositing materials on a substrate, and for performing other selected functions, such as material destruction and removal, temperature control, imaging, detection, therapy and positional and locational control. In various embodiments, the apparatus and methods are suitable for use in a tabletop setting, in vitro or in vivo.
Owner:SCIPERIO
Optical image-based position tracking for magnetic resonance imaging applications
InactiveUS20050054910A1Improve data qualityImprove stress conditionImage analysisMagnetic measurementsThermal energyIonizing radiation
An optical image-based tracking system determines the position and orientation of objects such as biological materials or medical devices within or on the surface of a human body undergoing Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI). Three-dimensional coordinates of the object to be tracked are obtained initially using a plurality of MR-compatible cameras. A calibration procedure converts the motion information obtained with the optical tracking system coordinates into coordinates of an MR system. A motion information file is acquired for each MRI scan, and each file is then converted into coordinates of the MRI system using a registration transformation. Each converted motion information file can be used to realign, correct, or otherwise augment its corresponding single MR image or a time series of such MR images. In a preferred embodiment, the invention provides real-time computer control to track the position of an interventional treatment system, including surgical tools and tissue manipulators, devices for in vivo delivery of drugs, angioplasty devices, biopsy and sampling devices, devices for delivery of RF, thermal energy, microwaves, laser energy or ionizing radiation, and internal illumination and imaging devices, such as catheters, endoscopes, laparoscopes, and like instruments. In other embodiments, the invention is also useful for conventional clinical MRI events, functional MRI studies, and registration of image data acquired using multiple modalities.
Owner:SUNNYBROOK & WOMENS COLLEGE HEALTH SCI CENT
Medical manipulator for use with an imaging device
InactiveUS6665554B1Easy to insertLess stressSurgical needlesVaccination/ovulation diagnosticsDegrees of freedomEngineering
A manipulator for use in medical procedures can manipulate a medical tool with one or more degrees of freedom with respect to a patient. The manipulator is particularly useful for positioning a medical tool with respect to a patient disposed inside an imaging device such as a computer tomography machine.
Owner:MICRODEXTERITY SYST
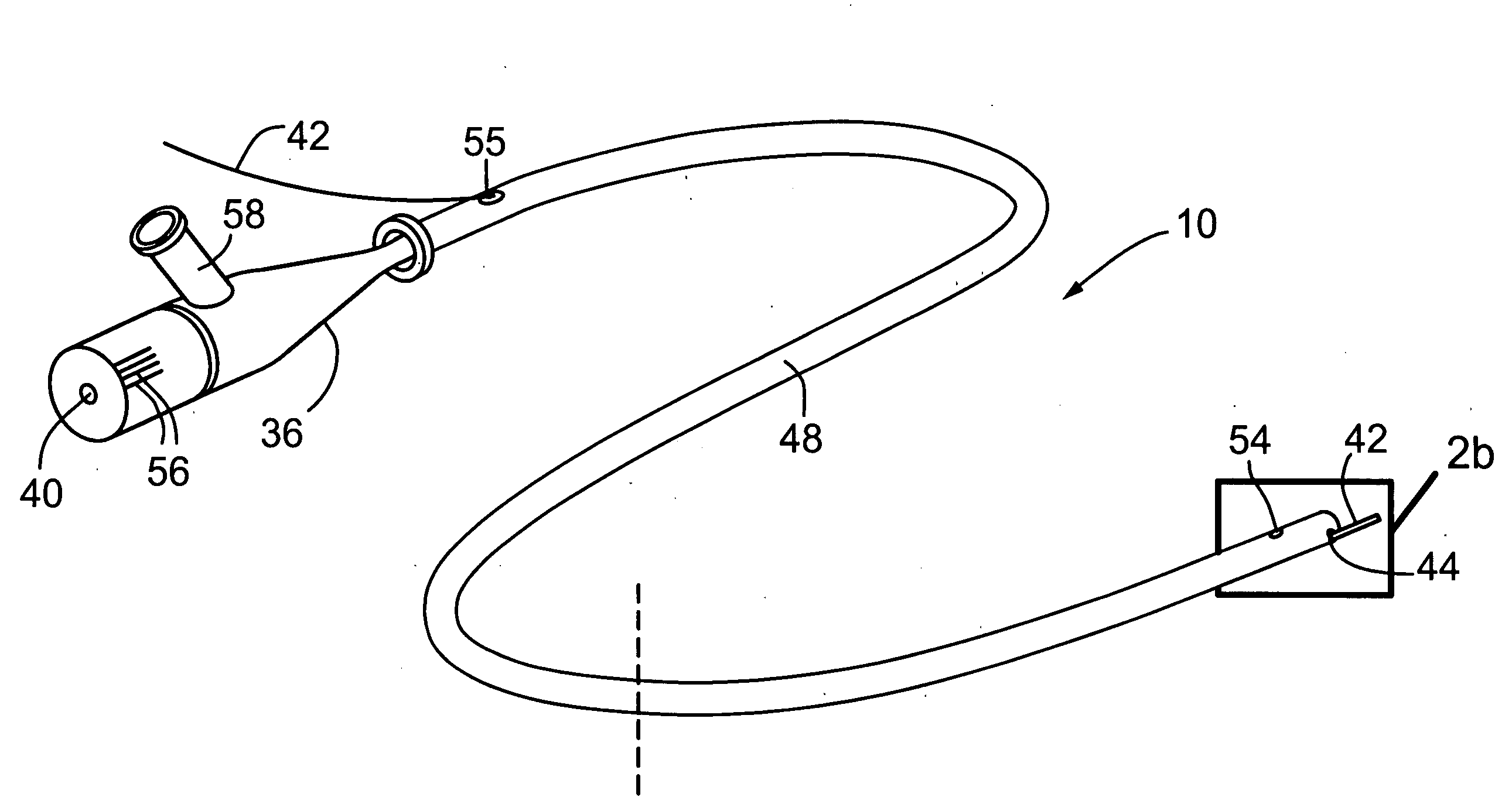
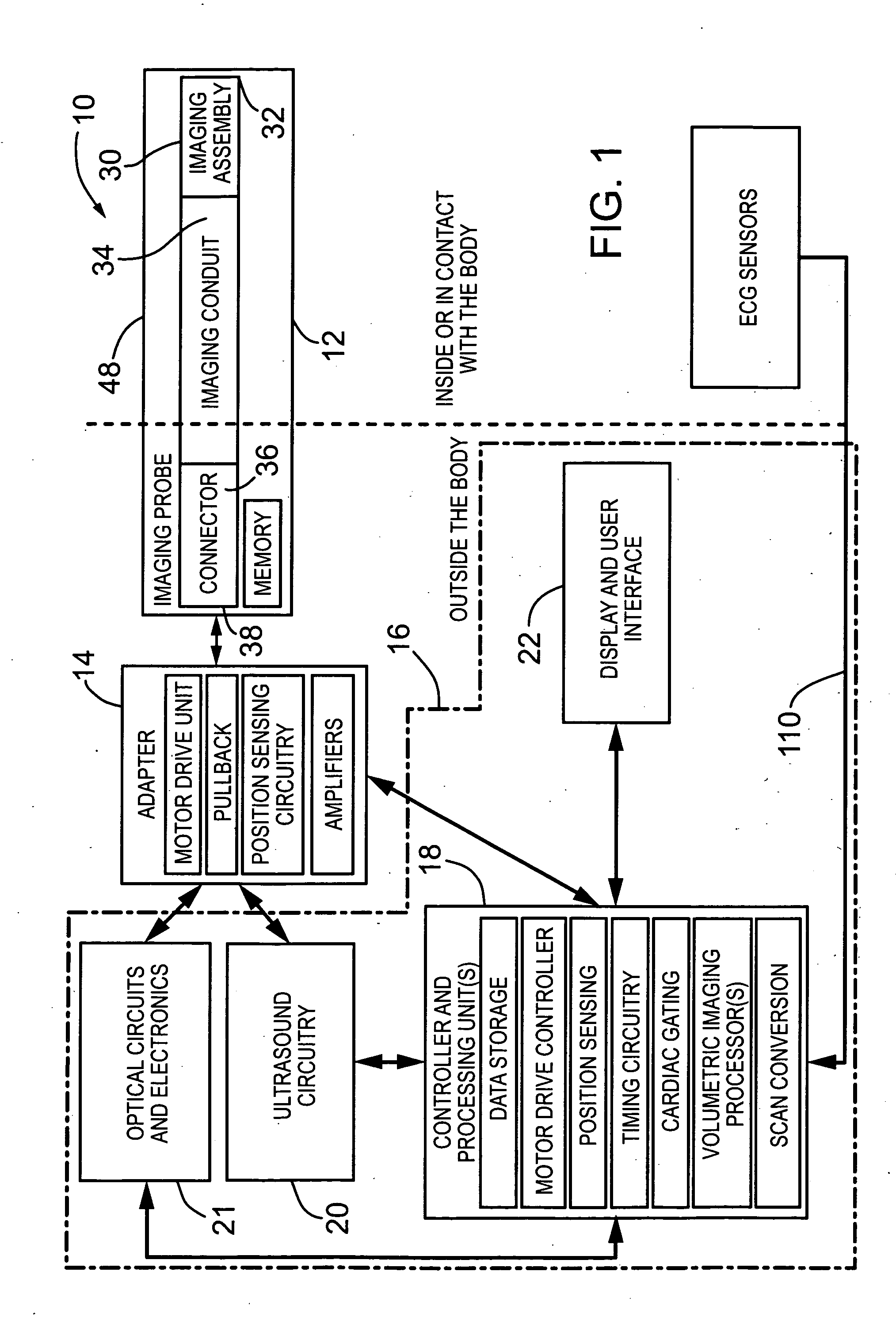
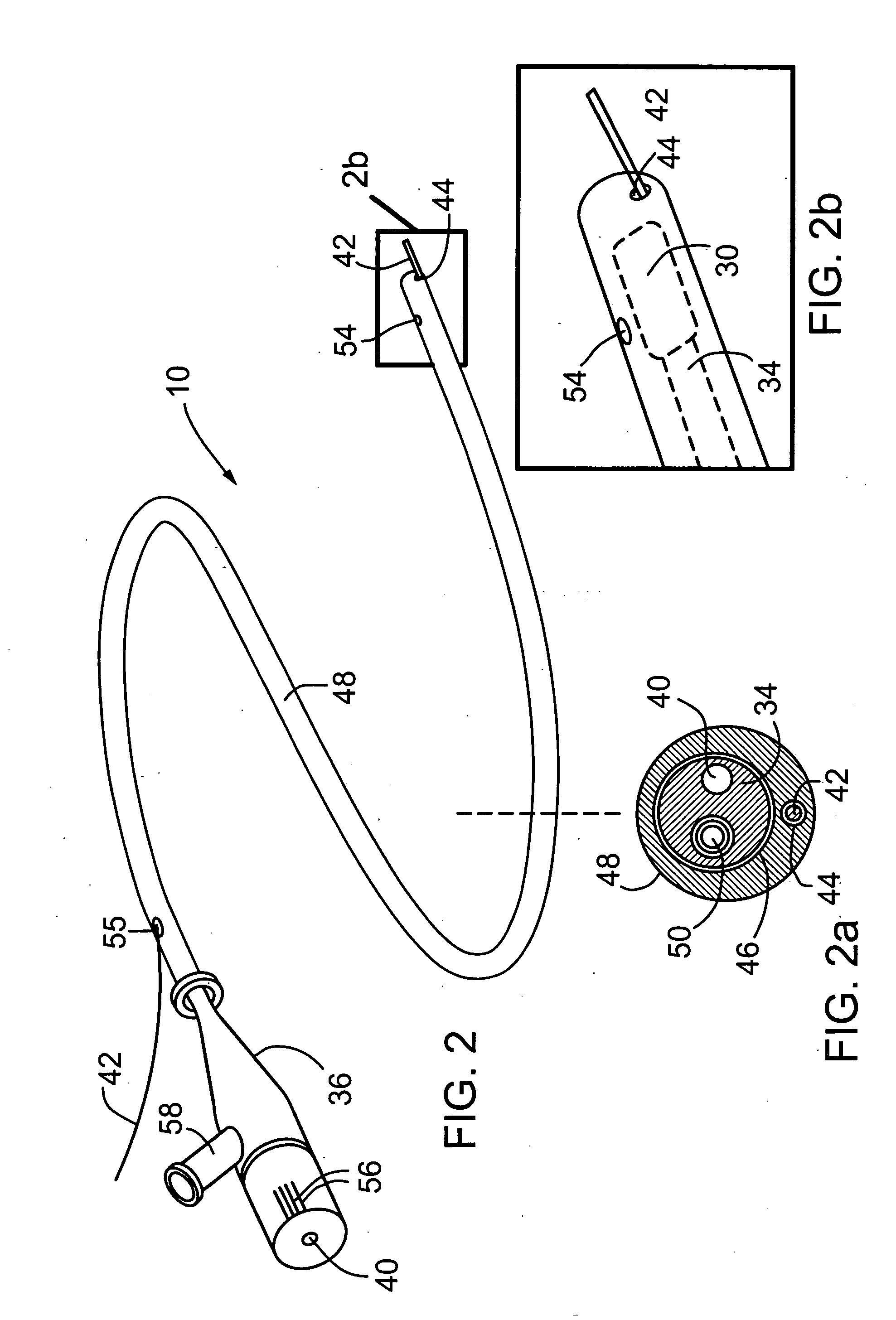
Medical imaging probe with rotary encoder
ActiveUS20080177139A1High resolutionAccurately measuring and estimating rotational velocityUltrasonic/sonic/infrasonic diagnosticsSurgeryRotary encoderMedical imaging
The present invention provides minimally invasive imaging probe having an optical encoder integrated therewith for accurately measuring or estimating the rotational velocity near the distal end of the medical device, such as an imaging probe which undergoes rotational movement during scanning of surrounding tissue in bodily lumens and cavities.
Owner:SUNNYBROOK HEALTH SCI CENT
Precision illumination methods and systems
Owner:PHILIPS LIGHTING NORTH AMERICA CORPORATION
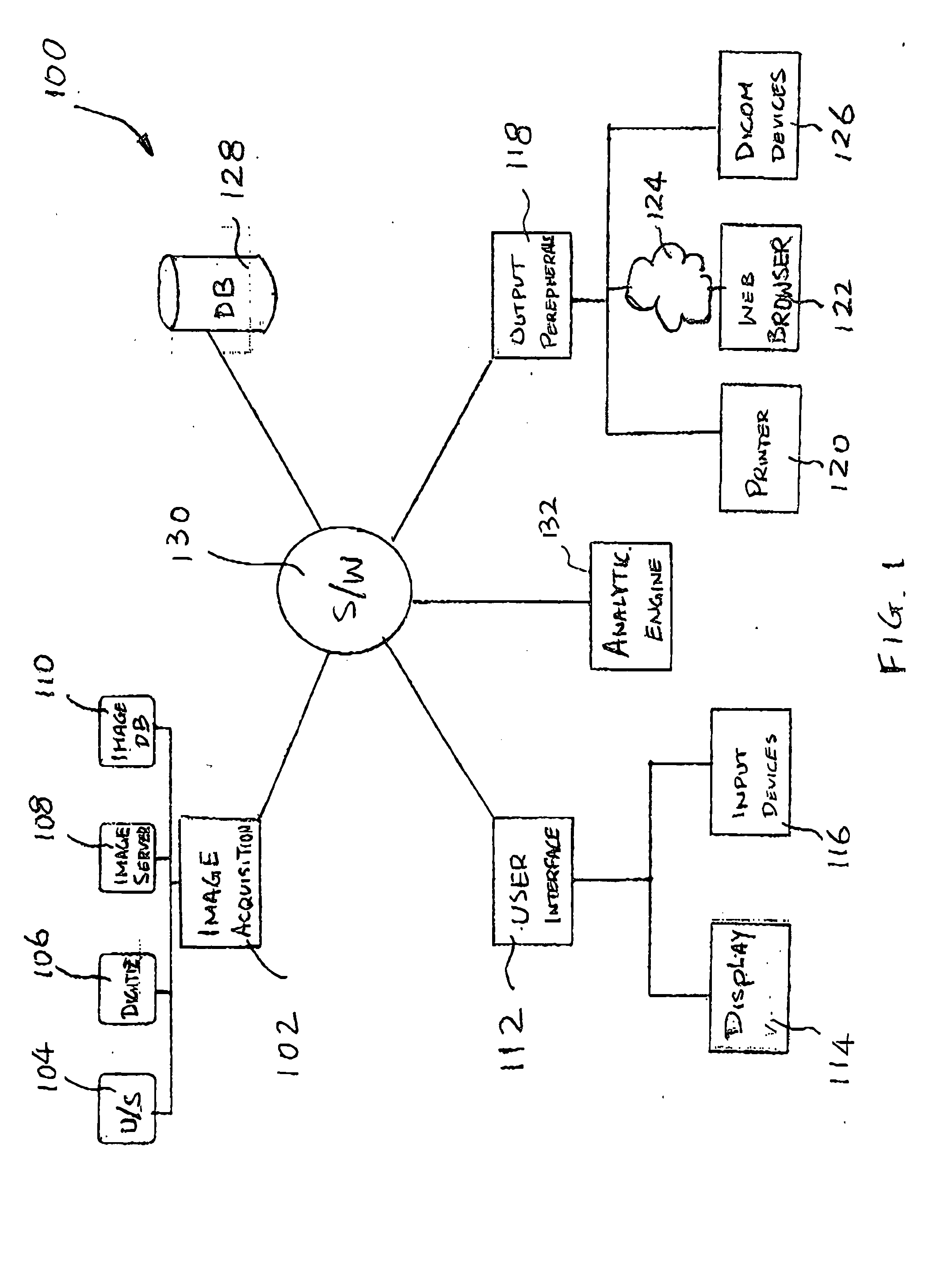
System and method for enabling a software developer to introduce informational attributes for selective inclusion within image headers for medical imaging apparatus applications
InactiveUS20050063575A1Character and pattern recognitionMedical imagesSoftware engineeringSoftware development
A system and method for enabling a developer to introduce informational attributes suitable for selective inclusion within image headers is disclosed herein. The image headers, along with their selectively included informational attributes, are displayable on a monitor screen together with associated digital images produced by an imaging apparatus. The image headers are also selectively storable in a database together with the pixel data of the associated digital images. The system includes an interactive workstation computer system having memory-stored software applications for operating the imaging apparatus, a memory-stored updatable table of defined informational attributes suited for selective inclusion within image headers, an interactive computer for generating software files of image header definitions from the table of defined informational attributes, and a means to transport the software files of image header definitions to the interactive workstation computer system.
Owner:GE MEDICAL SYST GLOBAL TECH CO LLC
Methods of using high intensity focused ultrasound to form an ablated tissue area
InactiveUS20060025756A1Easy positioningEasily manipulateUltrasonic/sonic/infrasonic diagnosticsUltrasound therapyHigh intensityHigh-intensity focused ultrasound
A method of thermal ablation using high intensity focused ultrasound energy includes the steps of positioning one or more ultrasound emitting members within a patient, emitting ultrasound energy from the one or more ultrasound emitting members, focusing the ultrasound energy, ablating with the focused ultrasound energy to form an ablated tissue area and removing the ultrasound emitting member.
Owner:MEDTRONIC INC
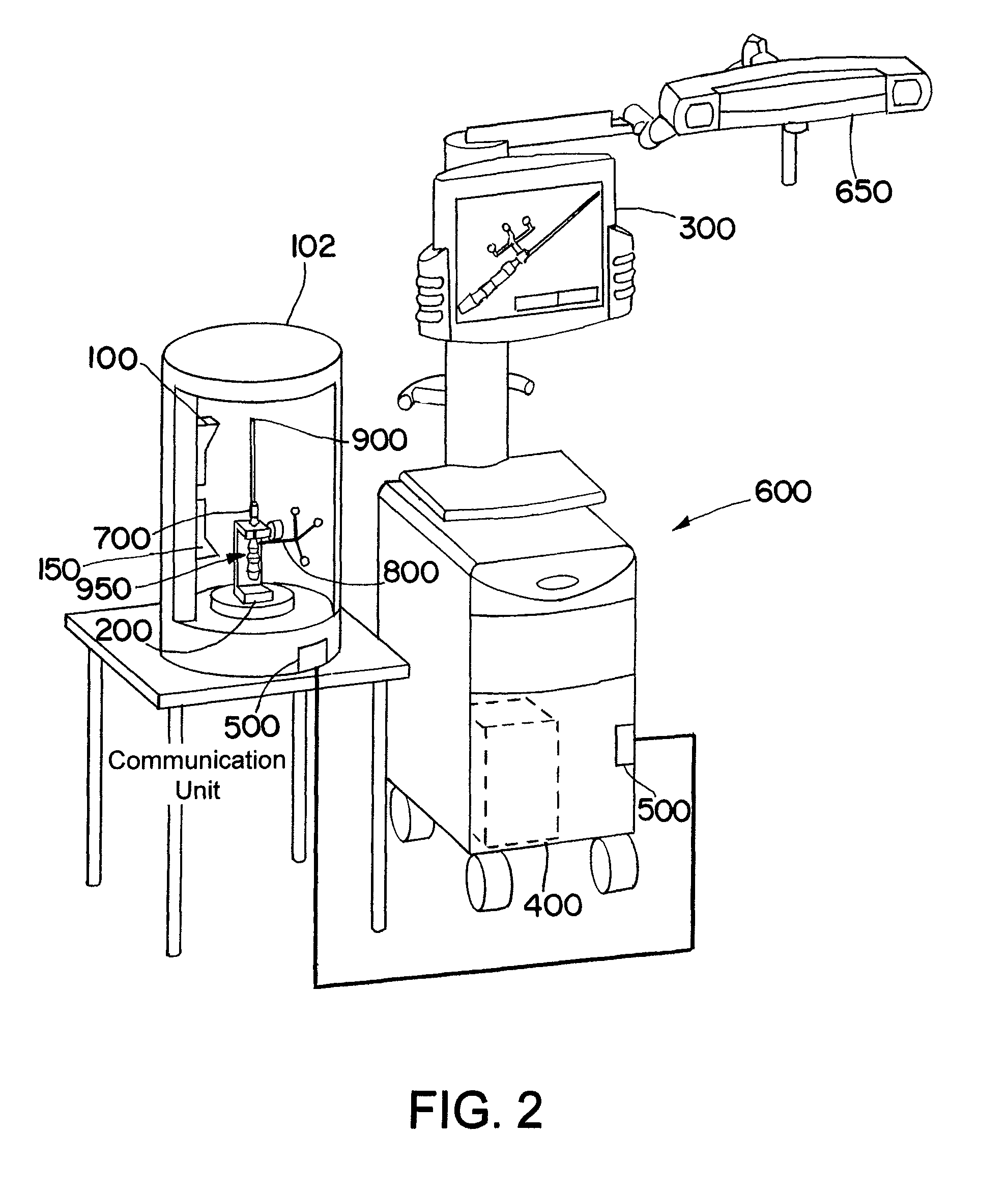
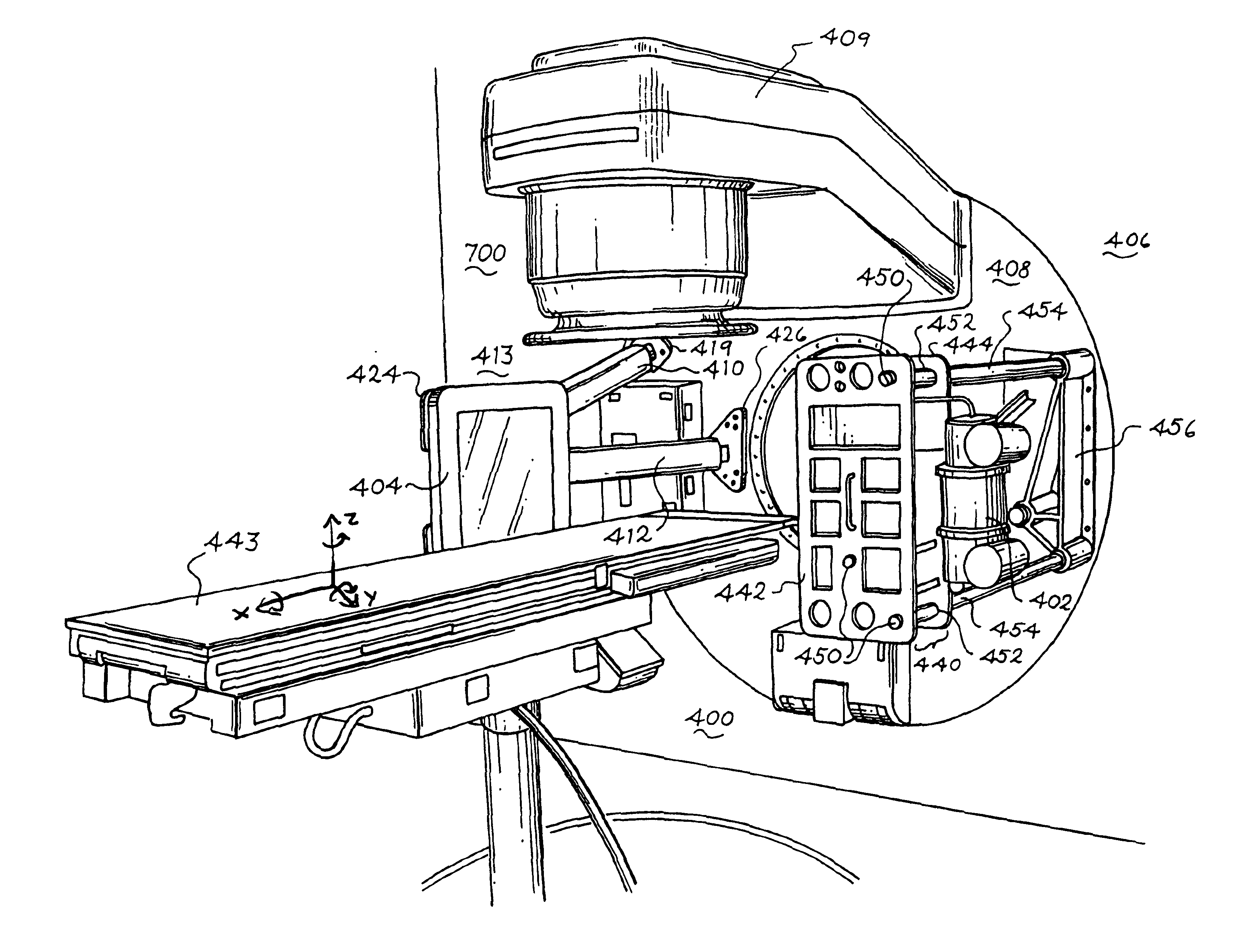
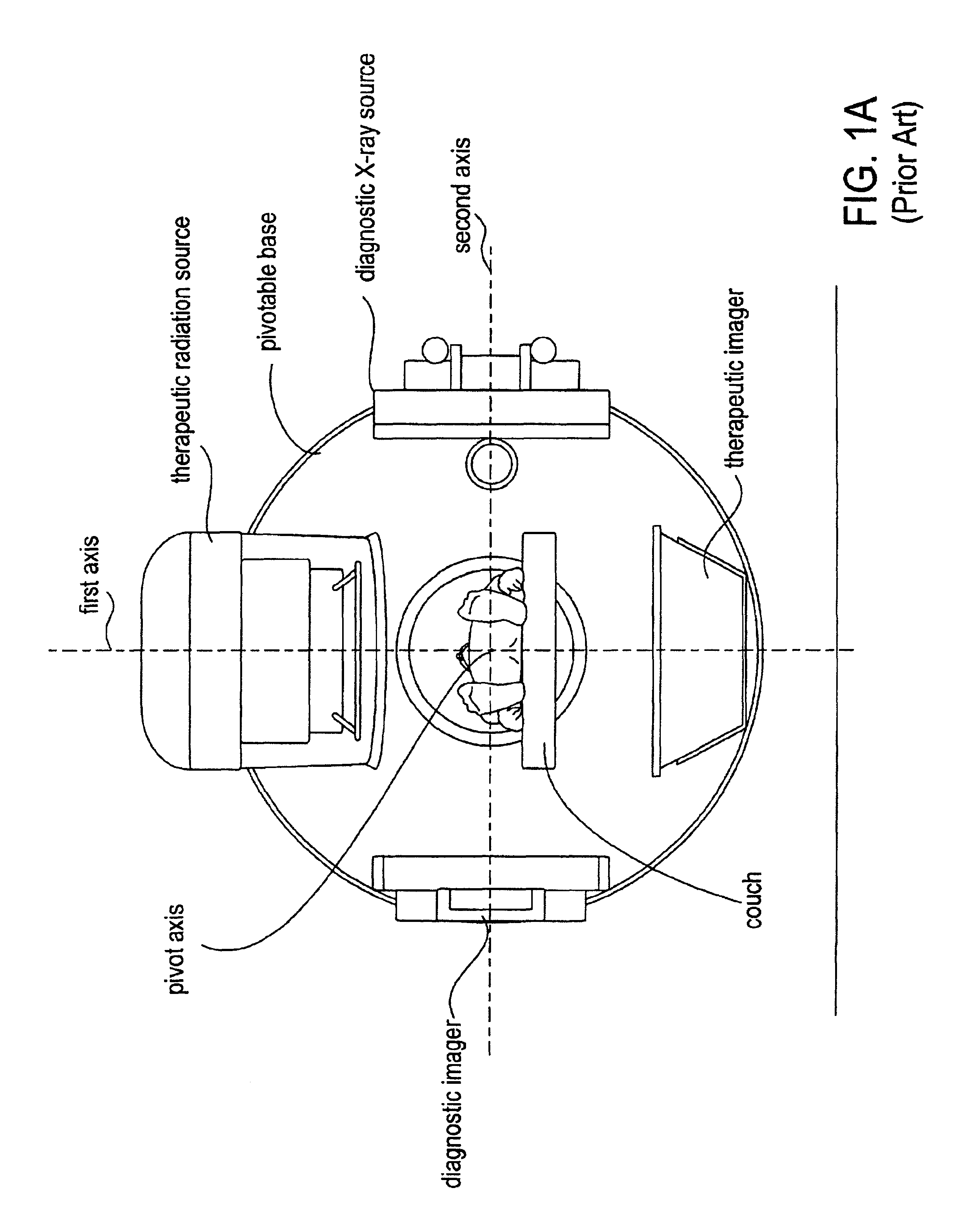
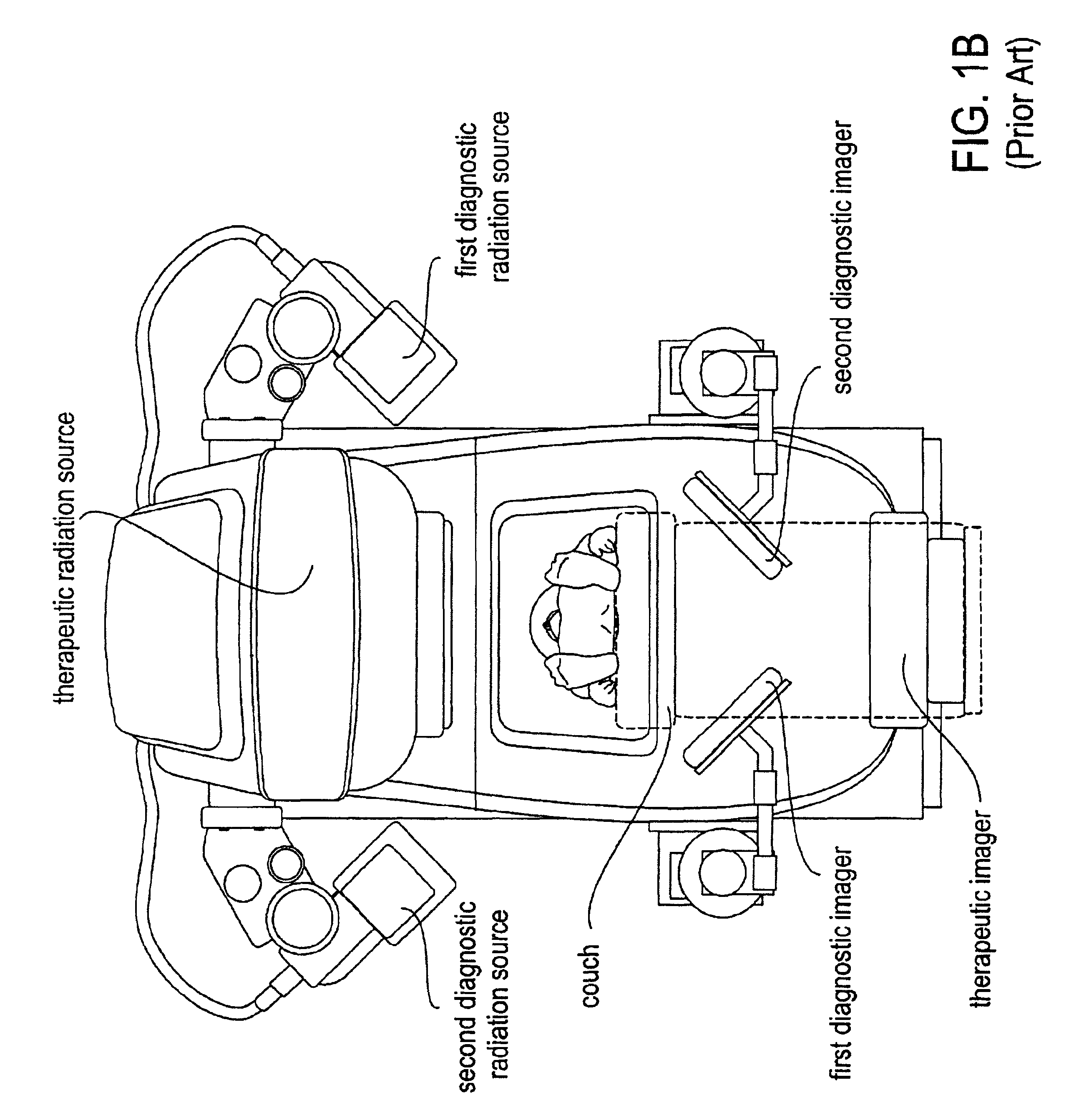
Radiotherapy apparatus equipped with an articulable gantry for positioning an imaging unit
Owner:VARIAN MEDICAL SYSTEMS
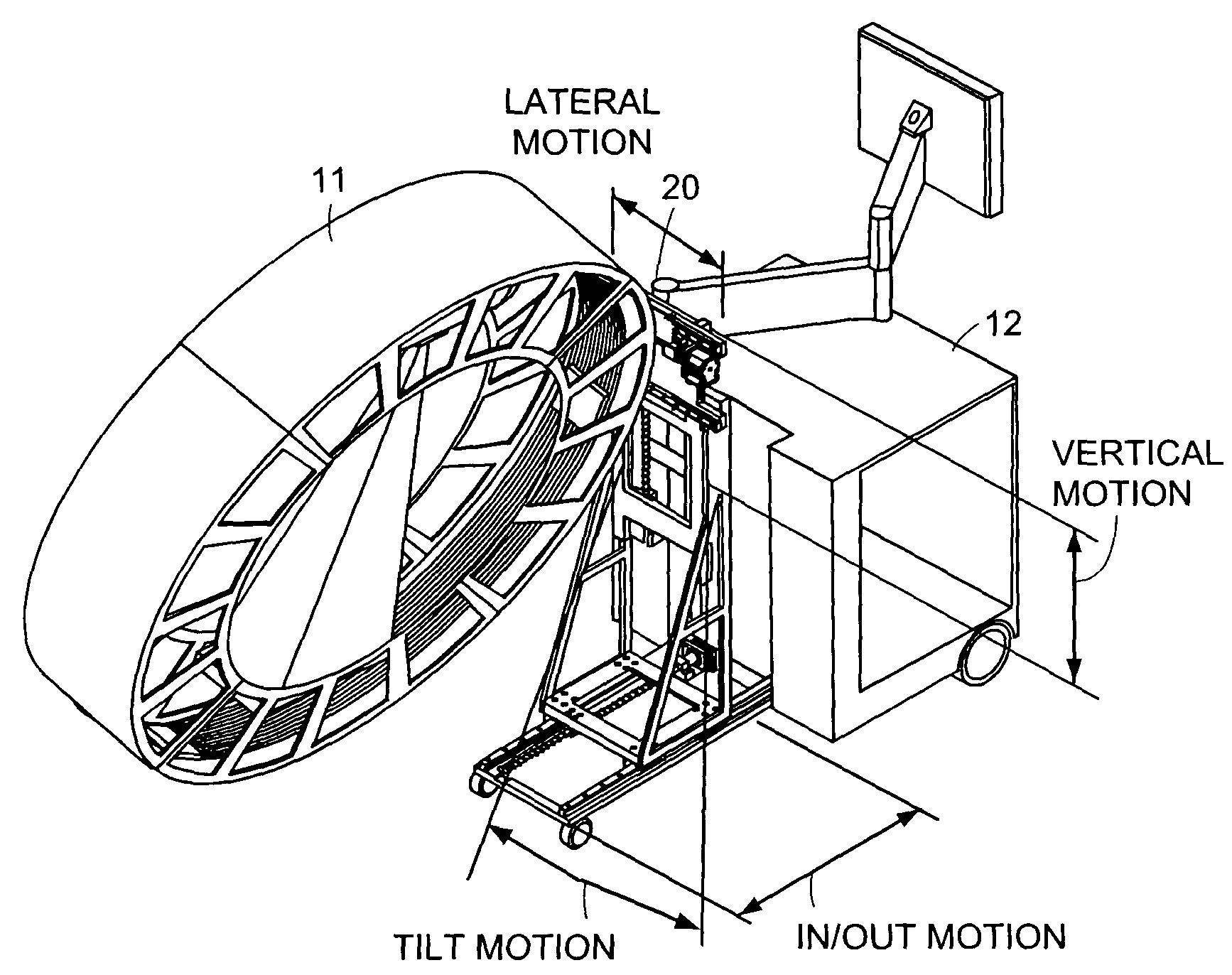
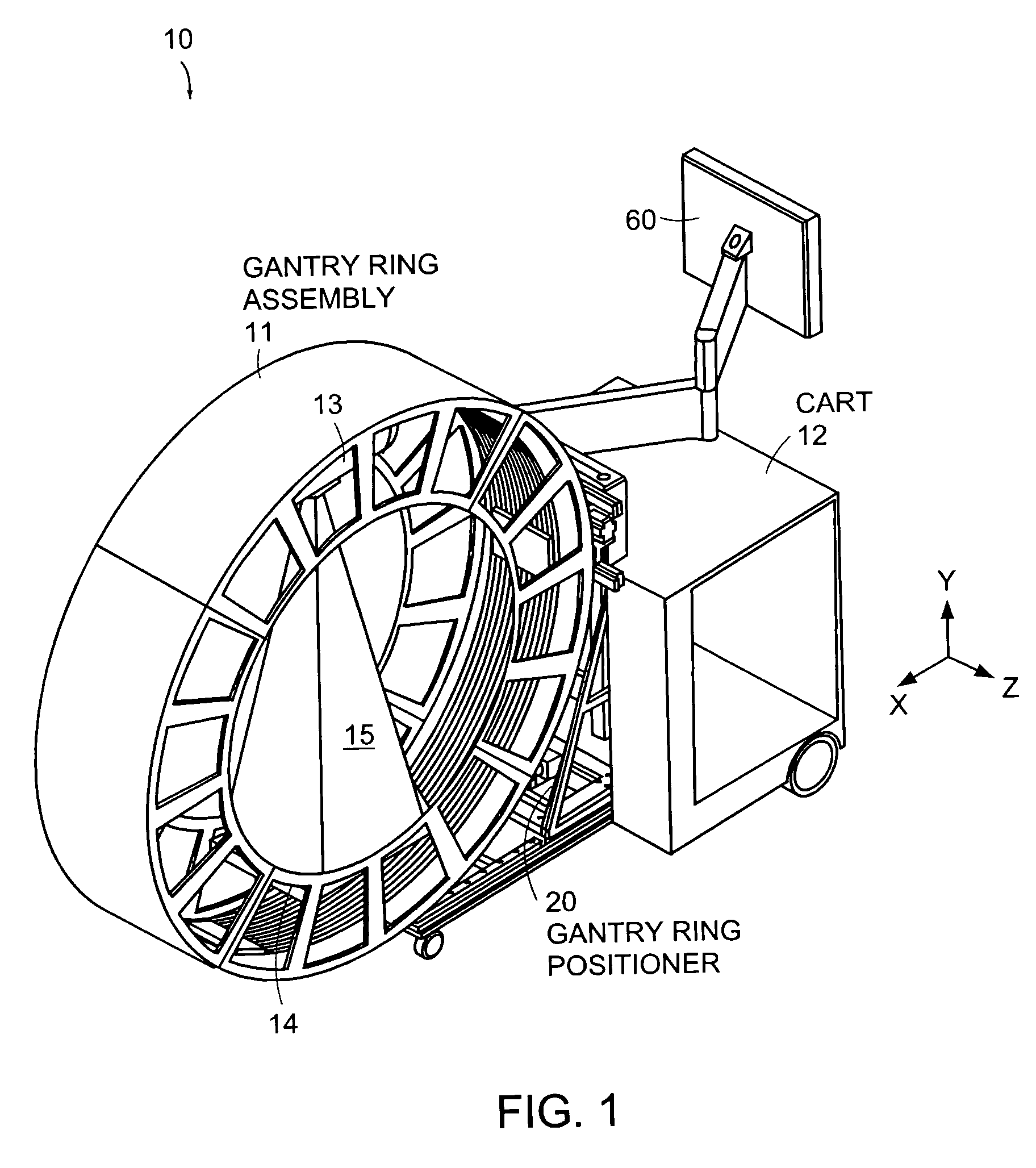
Cantilevered gantry apparatus for x-ray imaging
An x-ray scanning imaging apparatus with a rotatably fixed generally O-shaped gantry ring, which is connected on one end of the ring to support structure, such as a mobile cart, ceiling, floor, wall, or patient table, in a cantilevered fashion. The circular gantry housing remains rotatably fixed and carries an x-ray image-scanning device that can be rotated inside the gantry around the object being imaged either continuously or in a step-wise fashion. The ring can be connected rigidly to the support, or can be connected to the support via a ring positioning unit that is able to translate or tilt the gantry relative to the support on one or more axes. Multiple other embodiments exist in which the gantry housing is connected on one end only to the floor, wall, or ceiling. The x-ray device is particularly useful for two-dimensional multi-planar x-ray imaging and / or three-dimensional computed tomography (CT) imaging applications
Owner:MEDTRONIC NAVIGATION INC
Modular point-of-care devices, systems, and uses thereof
ActiveUS20090088336A1Sequential/parallel process reactionsHeating or cooling apparatusAnalytePoint of care device
The present invention provides devices and systems for use at the point of care. The methods devices of the invention are directed toward automatic detection of analytes in a bodily fluid. The components of the device are modular to allow for flexibility and robustness of use with the disclosed methods for a variety of medical applications.
Owner:LABRADOR DIAGNOSTICS LLC
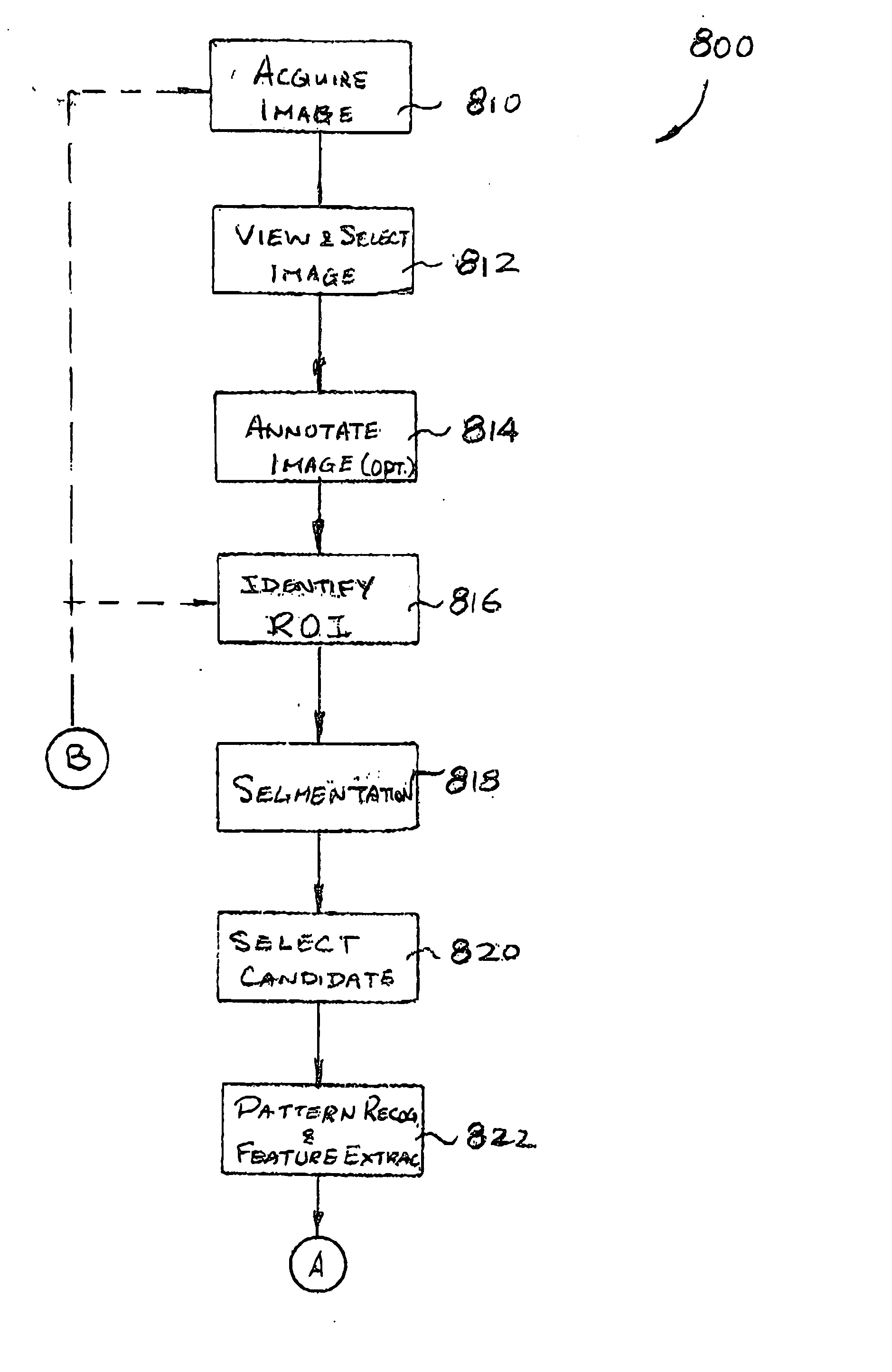
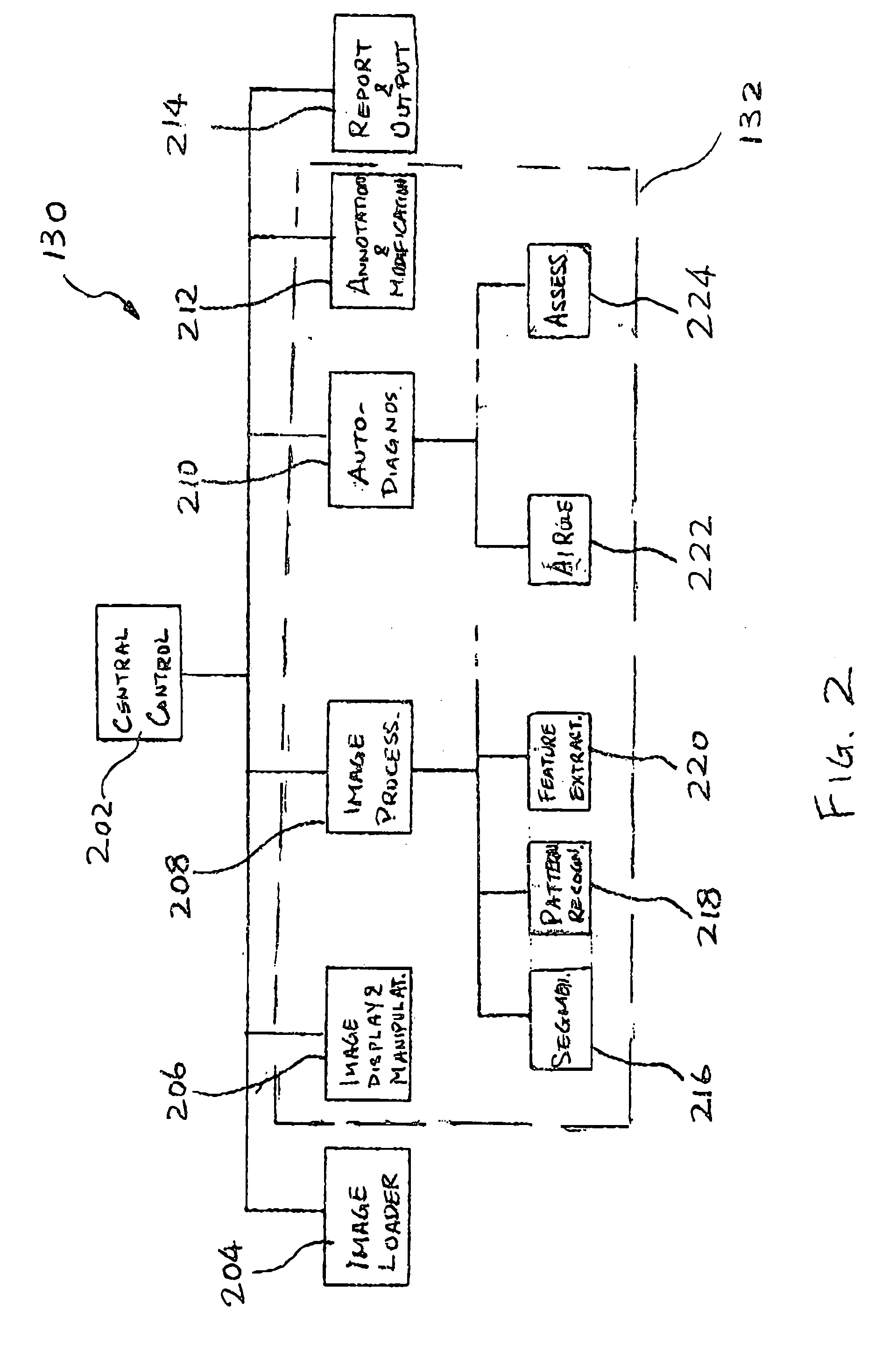
System and method of computer-aided detection
ActiveUS20060274928A1Ultrasonic/sonic/infrasonic diagnosticsImage enhancementPattern recognitionComputer-aided
The invention provides a system and method for computer-aided detection (“CAD”). The invention relates to computer-aided automatic detection of abnormalities in and analysis of medical images. Medical images are analyzed, to extract and identify a set of features in the image relevant to a diagnosis. The system computes an initial diagnosis based on the set of identified features and a diagnosis model, which are provided to a user for review and modification. A computed diagnosis is dynamically re-computed upon user modification of the set of identified features. Upon a user selecting a diagnosis based on system recommendation, a diagnosis report is generated reflecting features present in the medical image as validated by the user and the user selected diagnosis.
Owner:THE MEDIPATTERN CORP +1
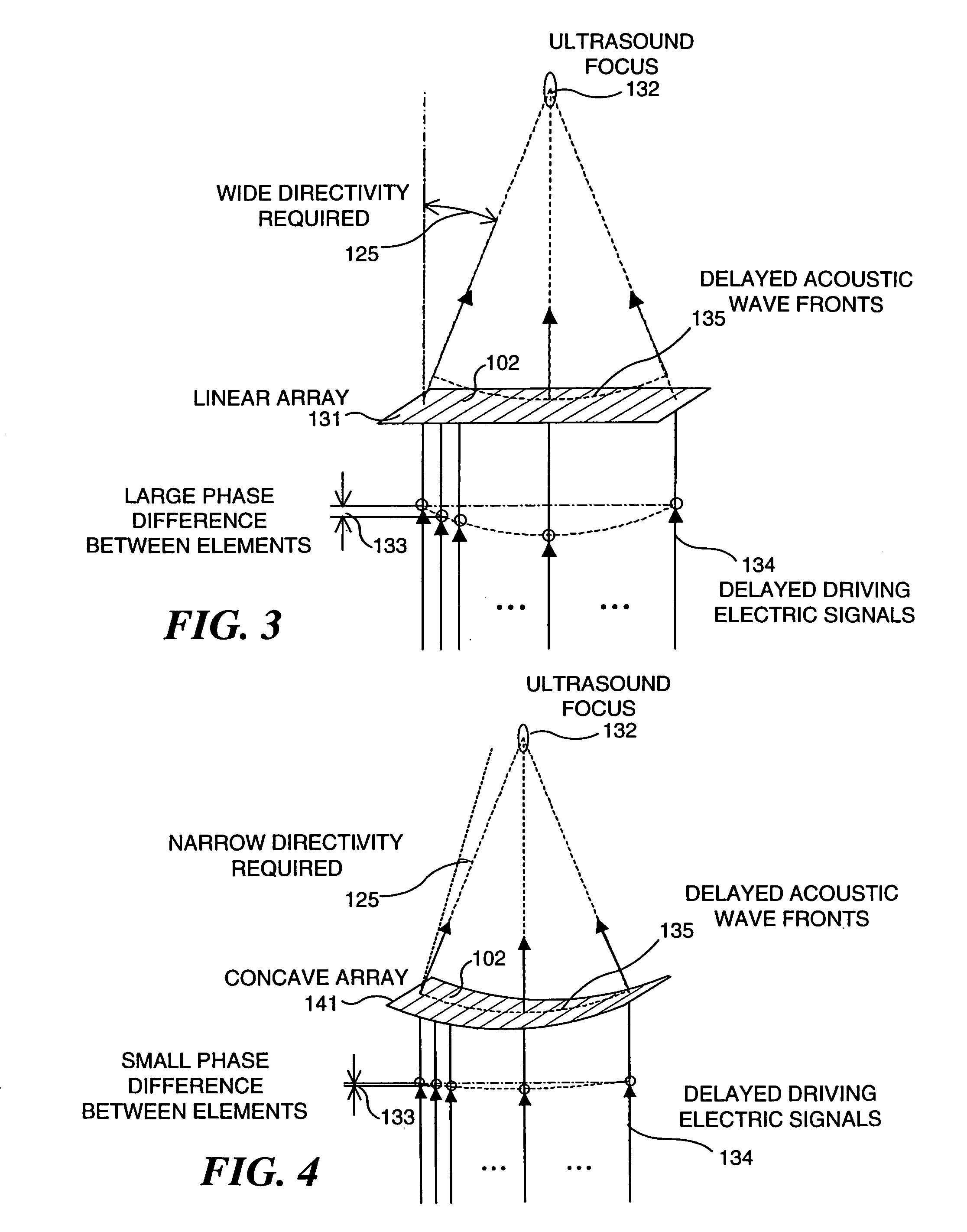
Ultrasound transducers for imaging and therapy
InactiveUS7063666B2Reduce in quantityReducing cross-talk and heatingUltrasonic/sonic/infrasonic diagnosticsUltrasound therapyElectrical resistance and conductanceSonification
Owner:OTSUKA MEDICAL DEVICES
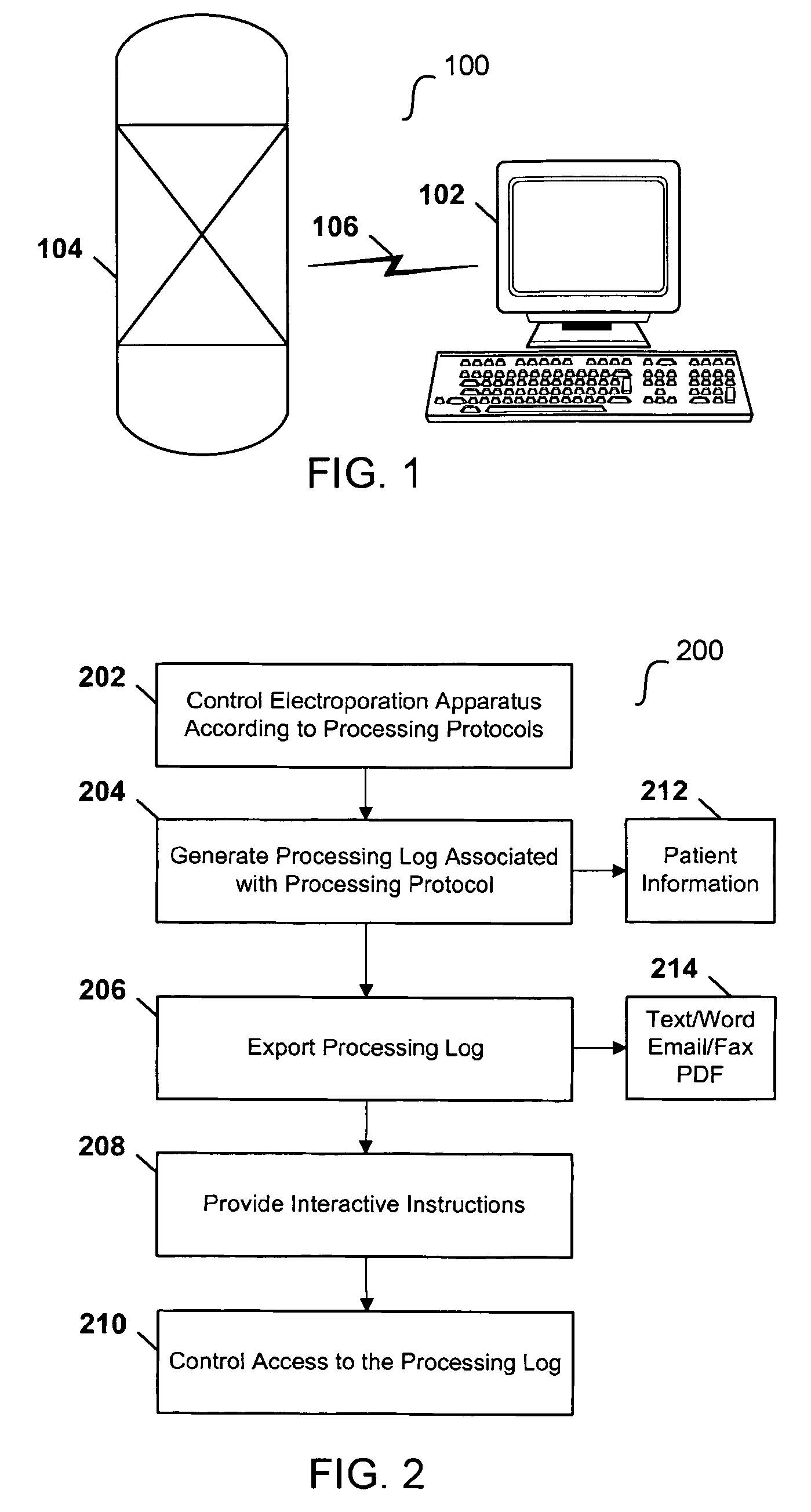
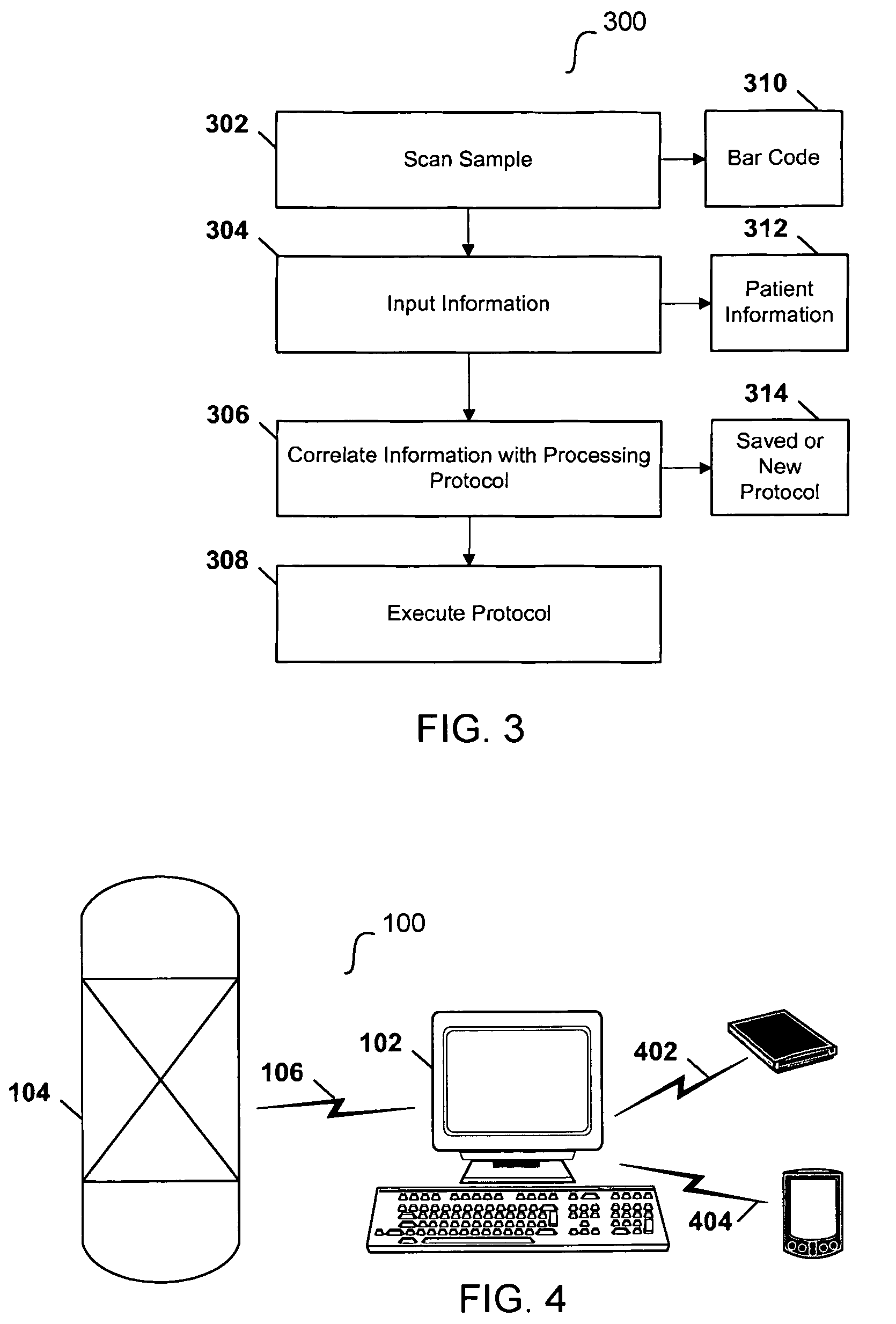
Computerized electroporation
ActiveUS7991559B2General purpose stored program computerOther foreign material introduction processesInformation processingProcessing
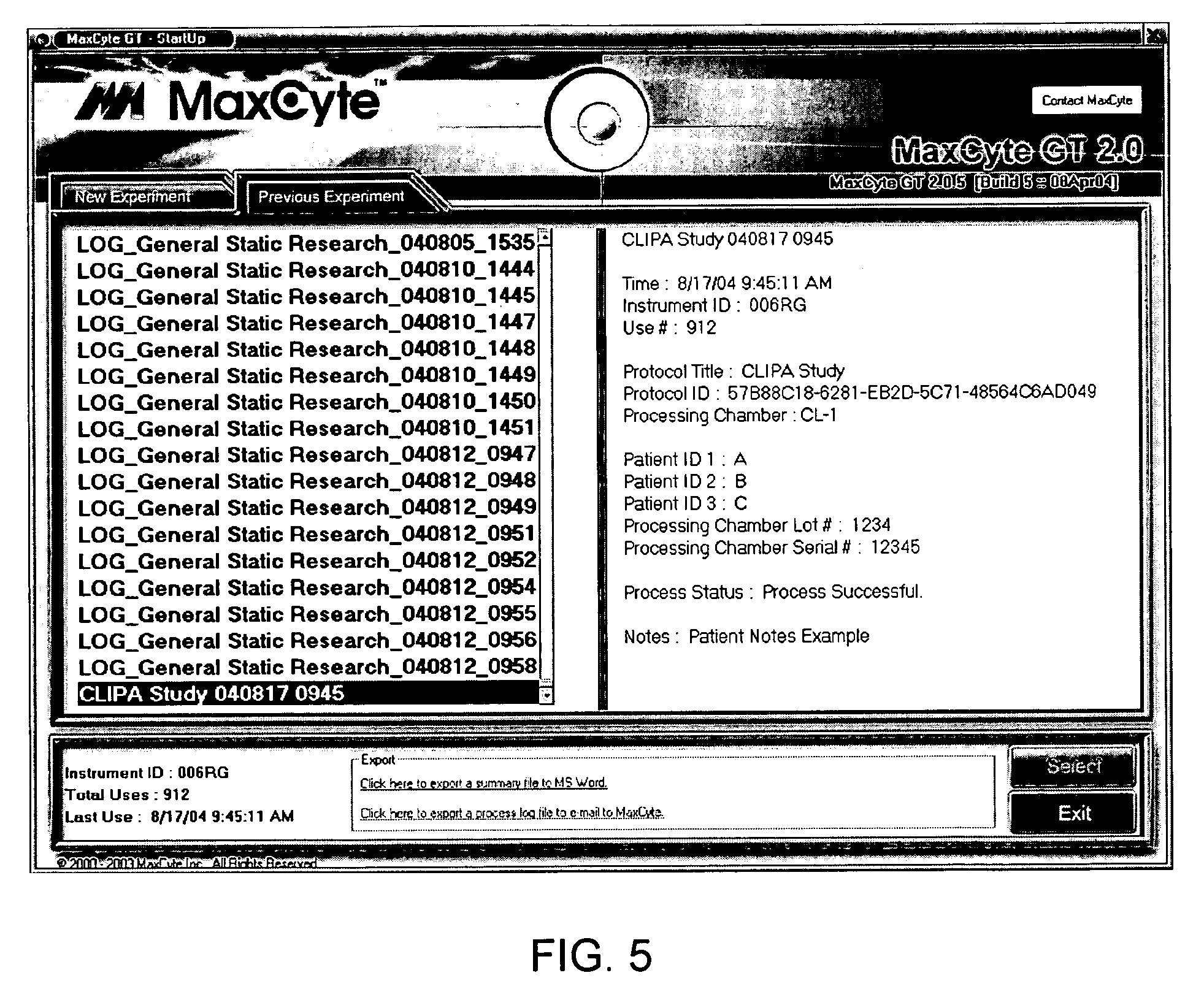
Techniques for computerized electroporation. An electroporation apparatus may be controlled according to one of a plurality of previously-saved, user-defined processing protocols. A processing log associated with a processing protocol may be generated, and the processing log may include patient or sample specific information. The processing log or a summary of the processing log may be exported to a user. Interactive instructions may be provided to a user. Those instructions may correspond to one or more steps of a processing protocol.
Owner:MAXCYTE INC
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com