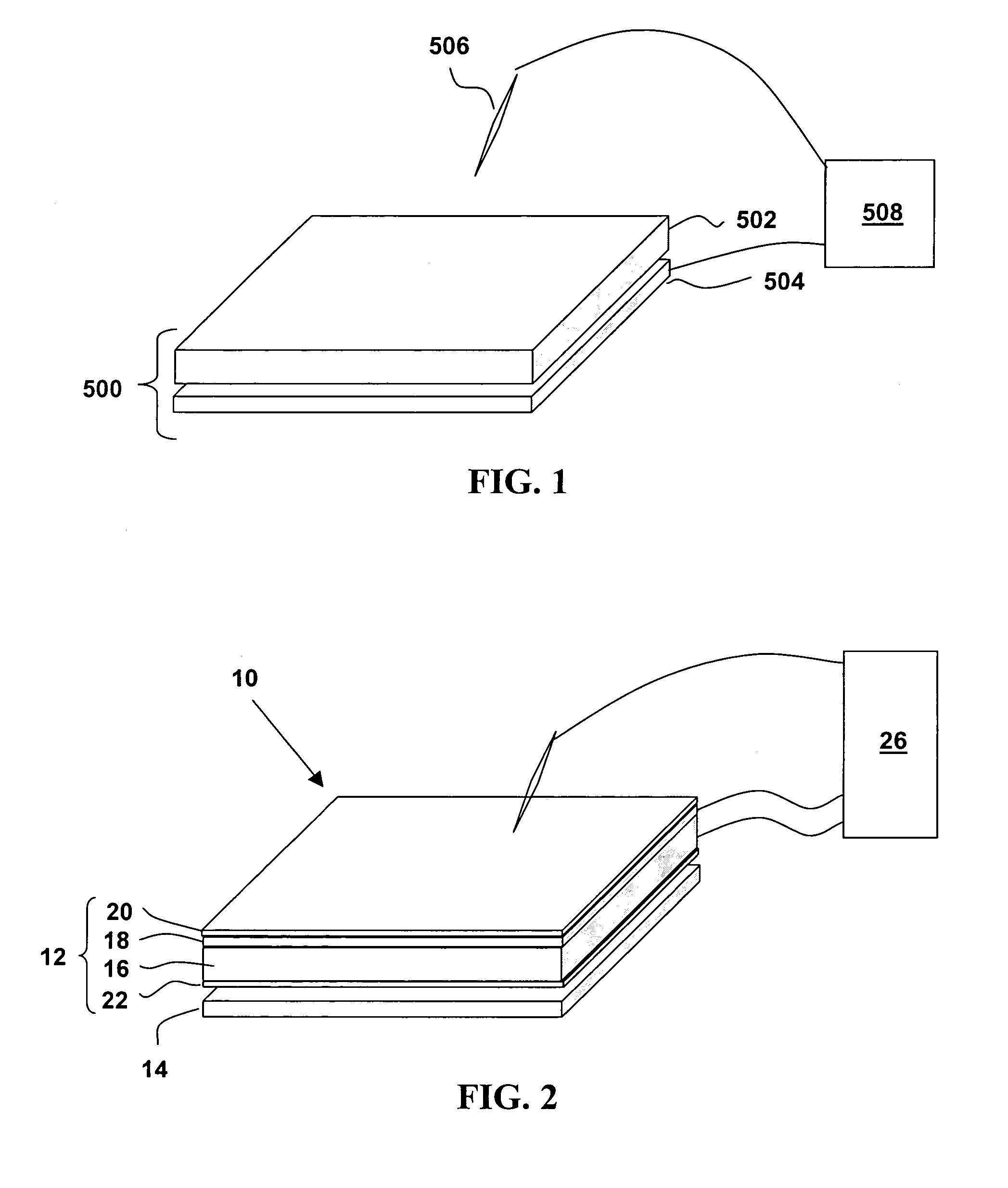
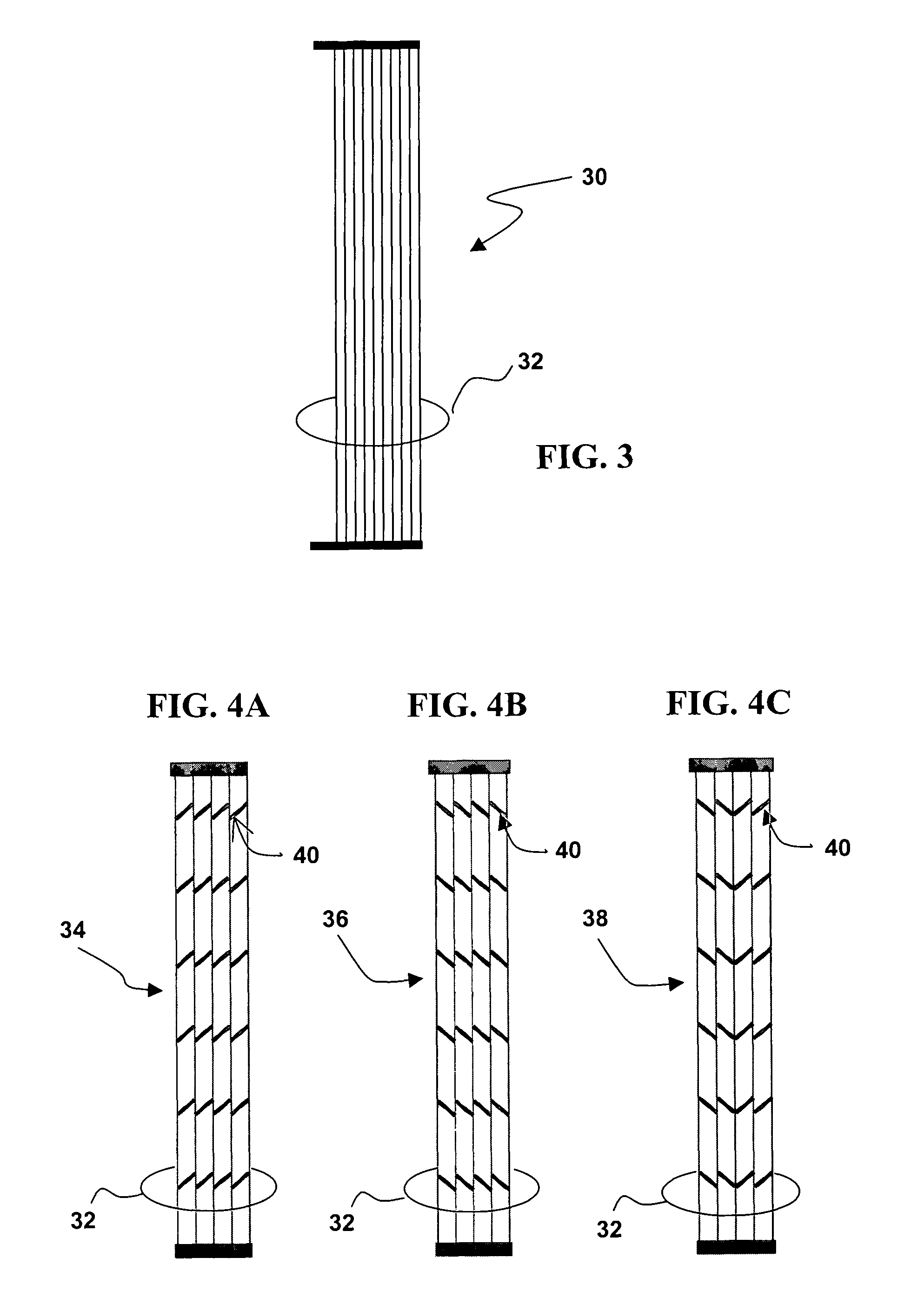
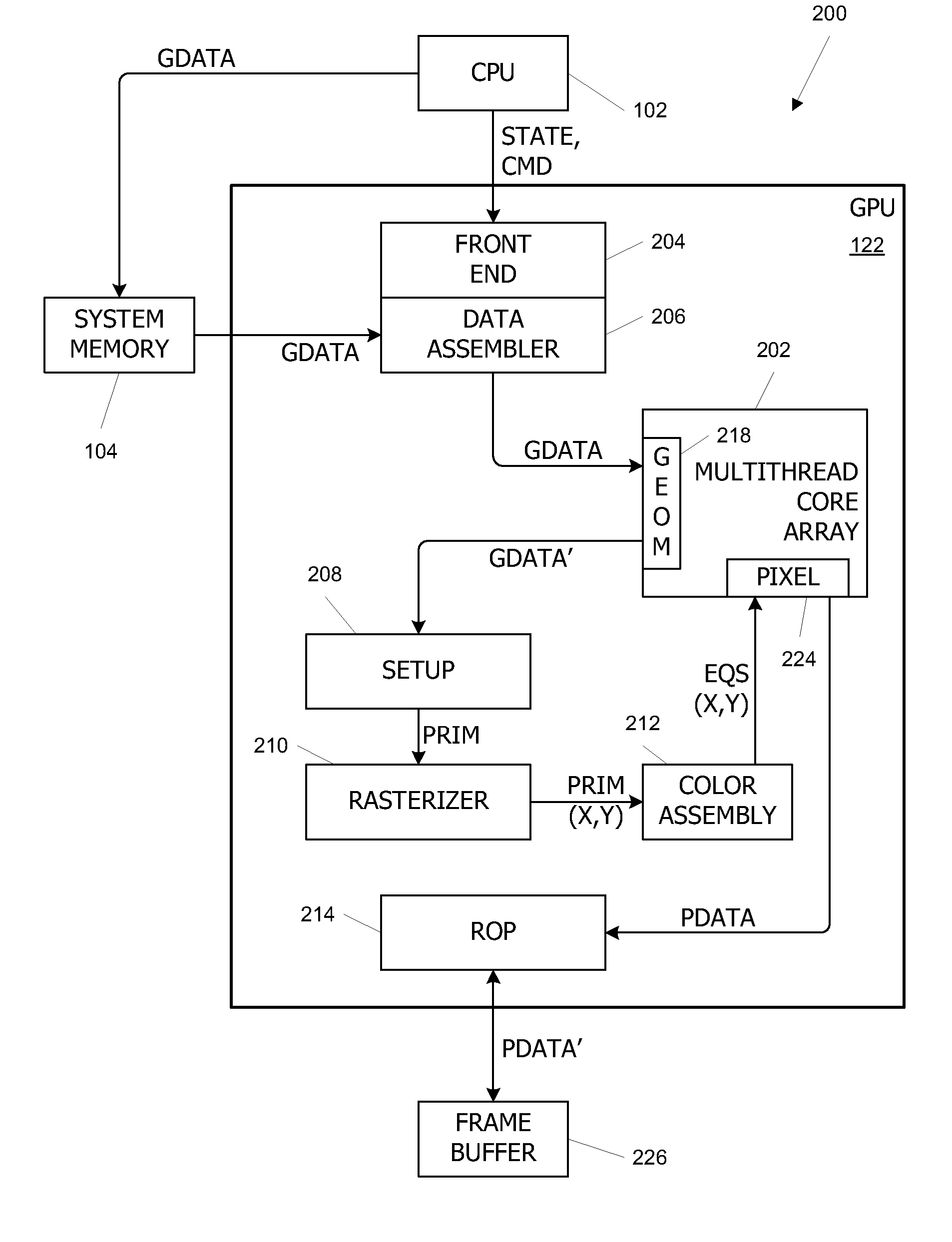
Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
186 results about "Parallel array" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
In computing, a group of parallel arrays (also known as structure of arrays or SoA) is a form of implicit data structure that uses multiple arrays to represent a singular array of records. It keeps a separate, homogeneous data array for each field of the record, each having the same number of elements. Then, objects located at the same index in each array are implicitly the fields of a single record. Pointers from one object to another are replaced by array indices. This contrasts with the normal approach of storing all fields of each record together in memory (also known as array of structures or AoS). For example, one might declare an array of 100 names, each a string, and 100 ages, each an integer, associating each name with the age that has the same index.
Radioactive therapeutic fastening instrument
ActiveUS8267849B2For accurate placementReduce doseSuture equipmentsStapling toolsBrachytherapyEngineering
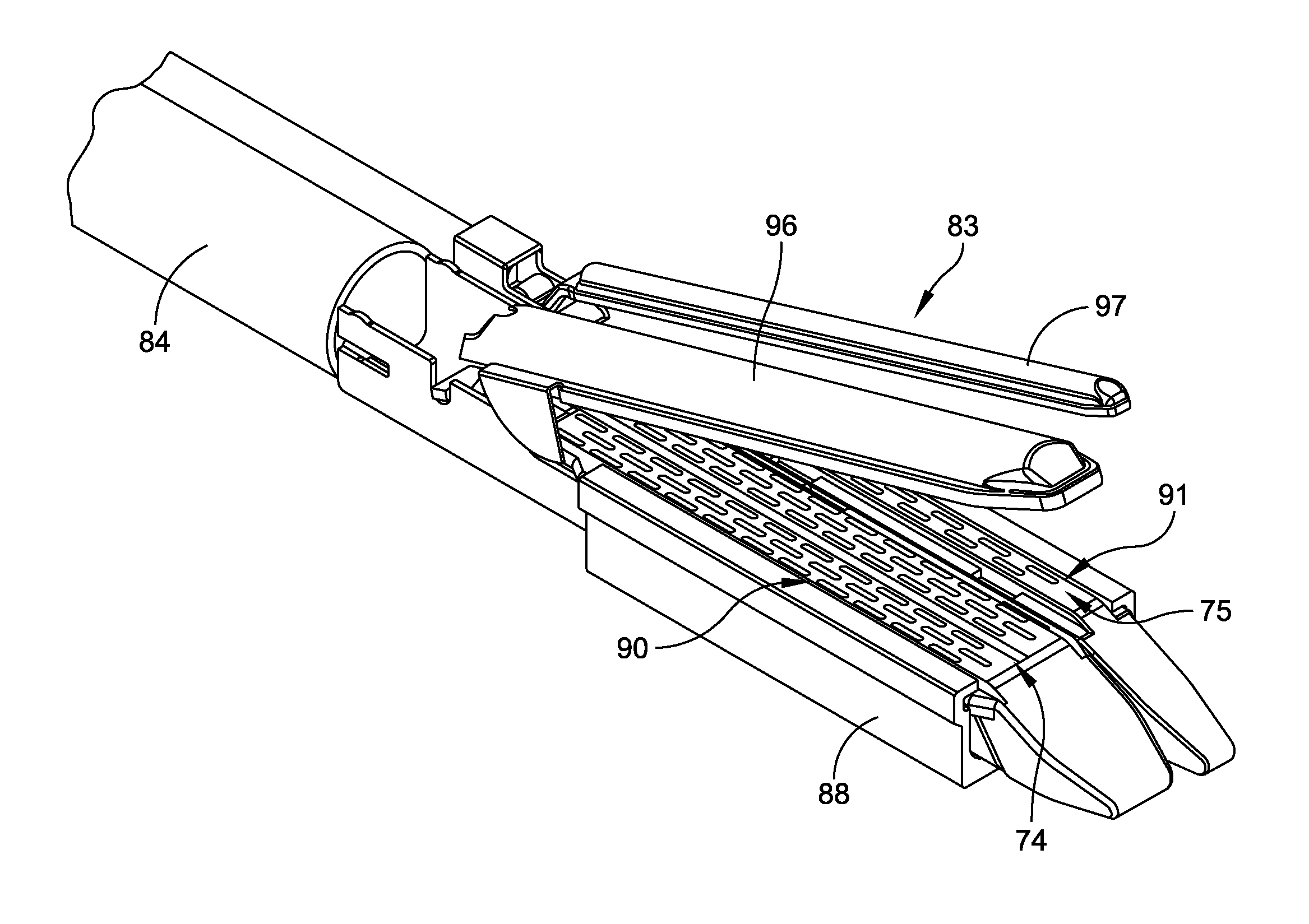
An instrument used for brachytherapy delivery in the treatment of cancer by radiation therapy including a handle having first and second handle actuators; an end effector; and an instrument shaft that connects the handle with the end effector. The end effector has first and second adjacent disposed staple mechanisms that each retain a set of staples. The first mechanism is for holding standard staples in a first array, and dispensing the standard staples under control of the corresponding first handle actuator. The second mechanism is for holding radioactive source staples in a second array, and dispensing said radioactive source staples under control of the corresponding second handle actuator. A holder is for receiving the first and second mechanisms in a substantially parallel array so that the standard staples close the incision at a surgical margin while the source staples are secured adjacent thereto.
Owner:POINT SOURCE TECH
Electromagnetic digitizer sensor array structure
ActiveUS7875814B2Overcomes drawbackHigh sensitivityTransmission systemsGraph readingSensor arrayMiniaturization
Owner:INNOLUX CORP
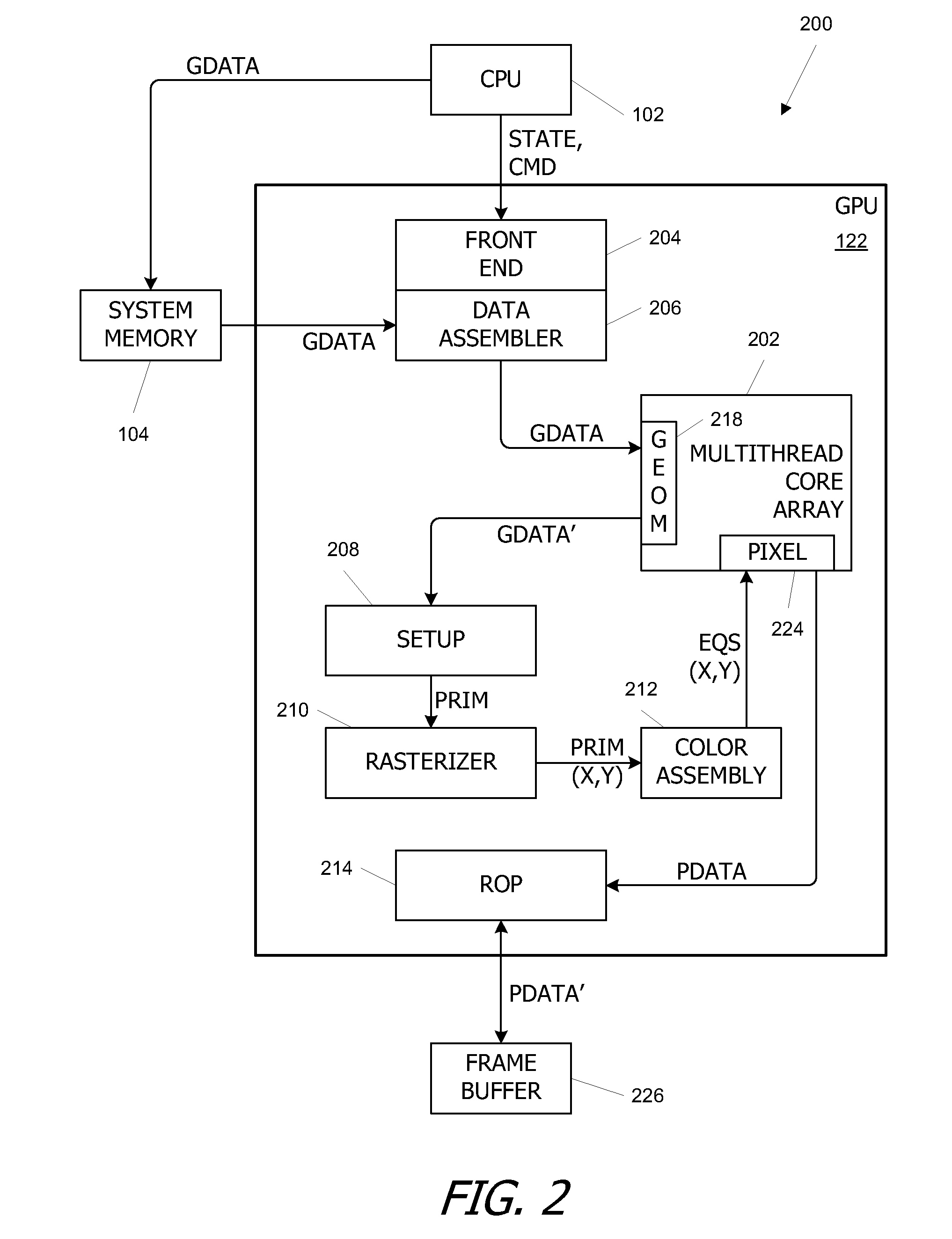
Parallel Array Architecture for a Graphics Processor
InactiveUS20070159488A1Improving memory localityImprove localitySingle instruction multiple data multiprocessorsCathode-ray tube indicatorsProcessing coreParallel computing
A parallel array architecture for a graphics processor includes a multithreaded core array including a plurality of processing clusters, each processing cluster including at least one processing core operable to execute a pixel shader program that generates pixel data from coverage data; a rasterizer configured to generate coverage data for each of a plurality of pixels; and pixel distribution logic configured to deliver the coverage data from the rasterizer to one of the processing clusters in the multithreaded core array. The pixel distribution logic selects one of the processing clusters to which the coverage data for a first pixel is delivered based at least in part on a location of the first pixel within an image area. The processing clusters can be mapped directly to the frame buffers partitions without a crossbar so that pixel data is delivered directly from the processing cluster to the appropriate frame buffer partitions. Alternatively, a crossbar coupled to each of the processing clusters is configured to deliver pixel data from the processing clusters to a frame buffer having a plurality of partitions. The crossbar is configured such that pixel data generated by any one of the processing clusters is deliverable to any one of the frame buffer partitions.
Owner:NVIDIA CORP
Particle separation and concentration system
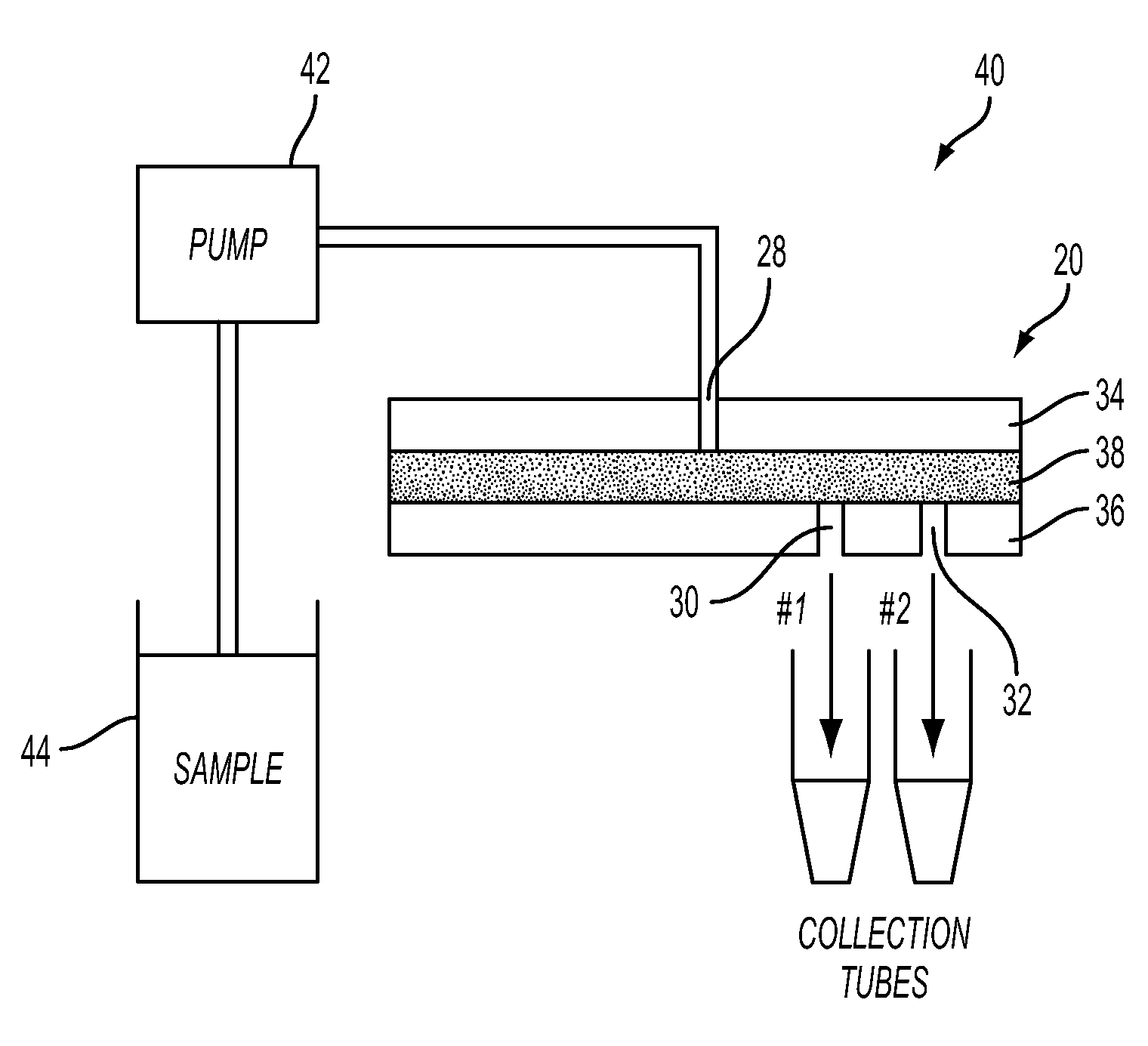
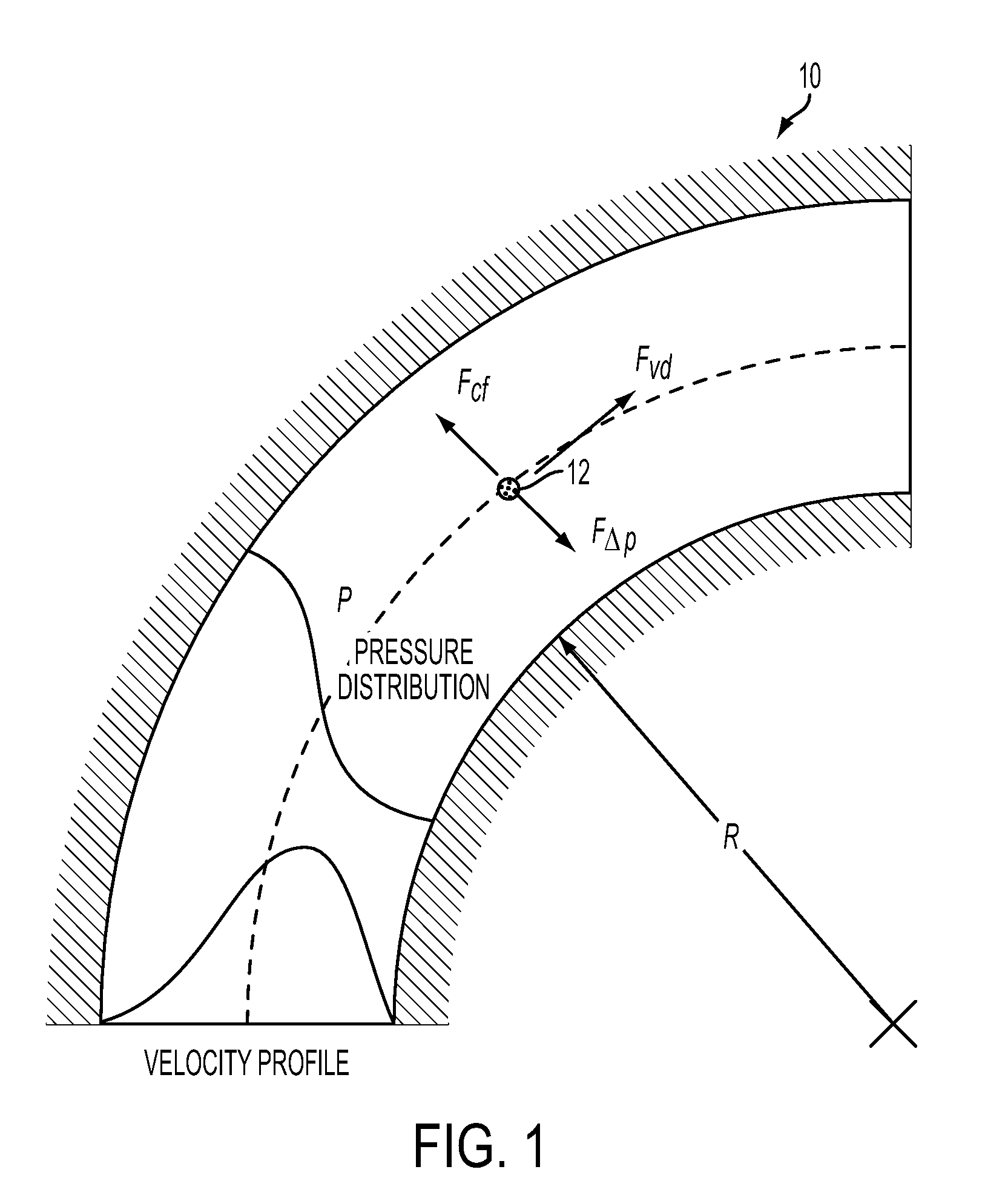
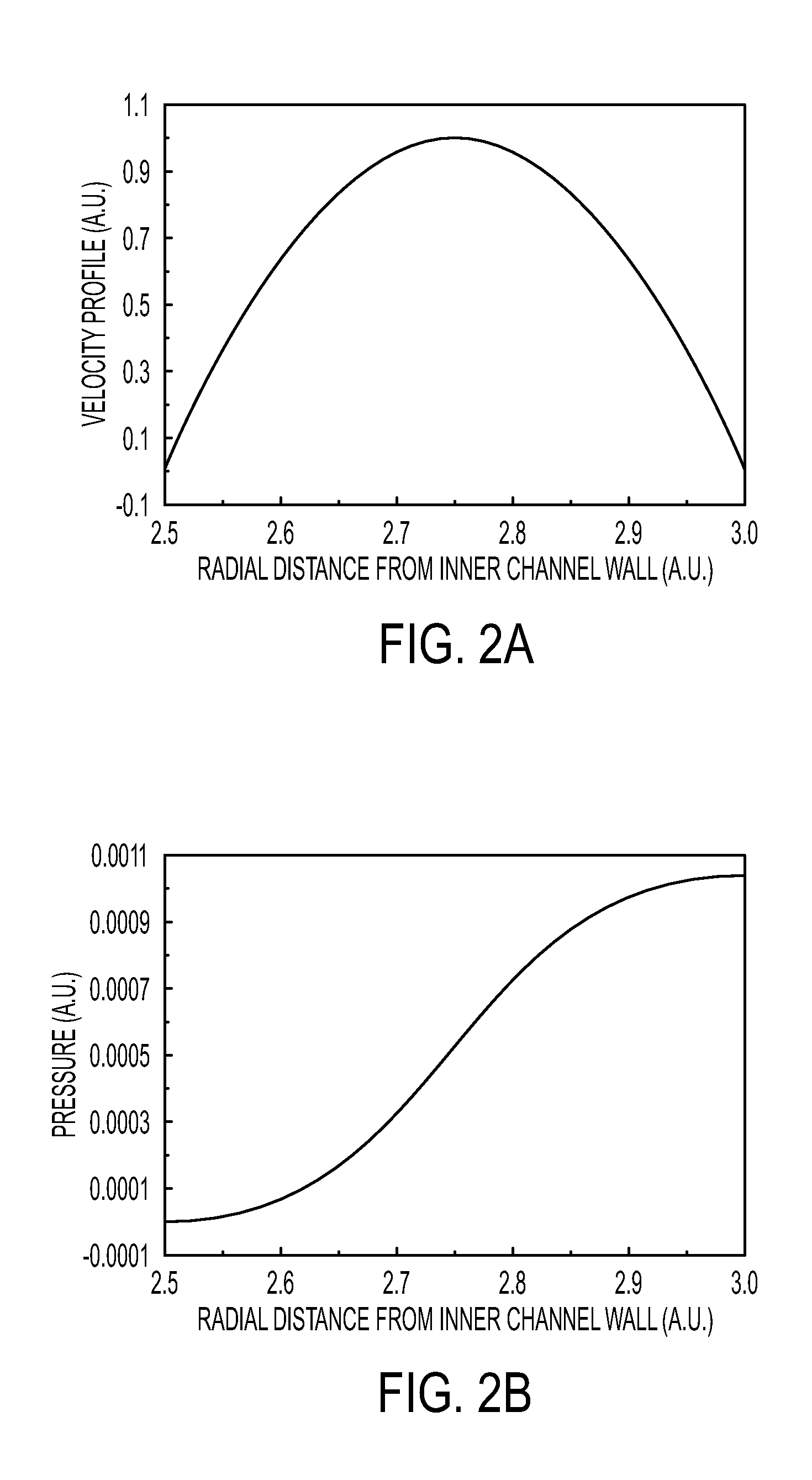
This invention is based on size and mass separation of suspended particles, including biological matter, which are made to flow in a spiral channel. On the spiral sections, the inward directed transverse pressure field from fluid shear competes with the outward directed centrifugal force to allow for separation of particles. At high velocity, centrifugal force dominates and particles move outward. At low velocities, transverse pressure dominates and the particles move inward. The magnitudes of the two opposing forces depend on flow velocity, particle size, radius of curvature of the spiral section, channel dimensions, and viscosity of the fluid. At the end of the spiral channel, a parallel array of outlets collects separated particles. For any particle size, the required channel dimension is determined by estimating the transit time to reach the side-wall. This time is a function of flow velocity, channel width, viscosity, and radius of curvature. Larger particles may reach the channel wall earlier than the smaller particles which need more time to reach the side wall. Thus a spiral channel may be envisioned by placing multiple outlets along the channel. This technique is inherently scalable over a large size range from sub-millimeter down to 1 μm.
Owner:XEROX CORP
Single-mask phase change memory element
A memory device. An array of memory elements is formed on a semiconductor chip. A parallel array of word lines extends in a first direction, connecting each memory element to a data source, and a parallel array of bit lines extends in a second direction, connecting each memory element to a data source, the second direction forming an acute angle to the first direction. The connection between each bit line and each memory element is a phase change element composed of memory material having at least two solid phases.
Owner:MACRONIX INT CO LTD
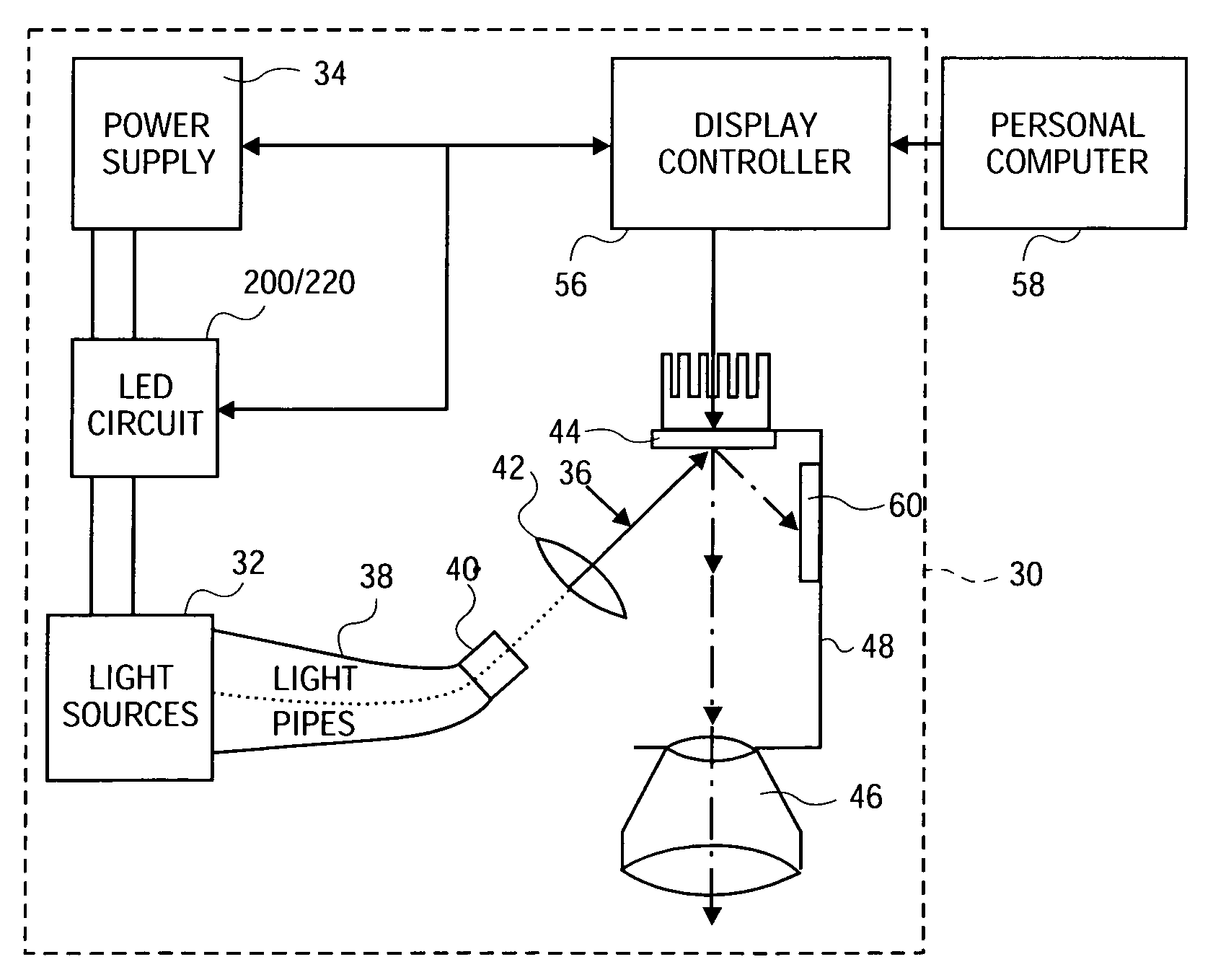
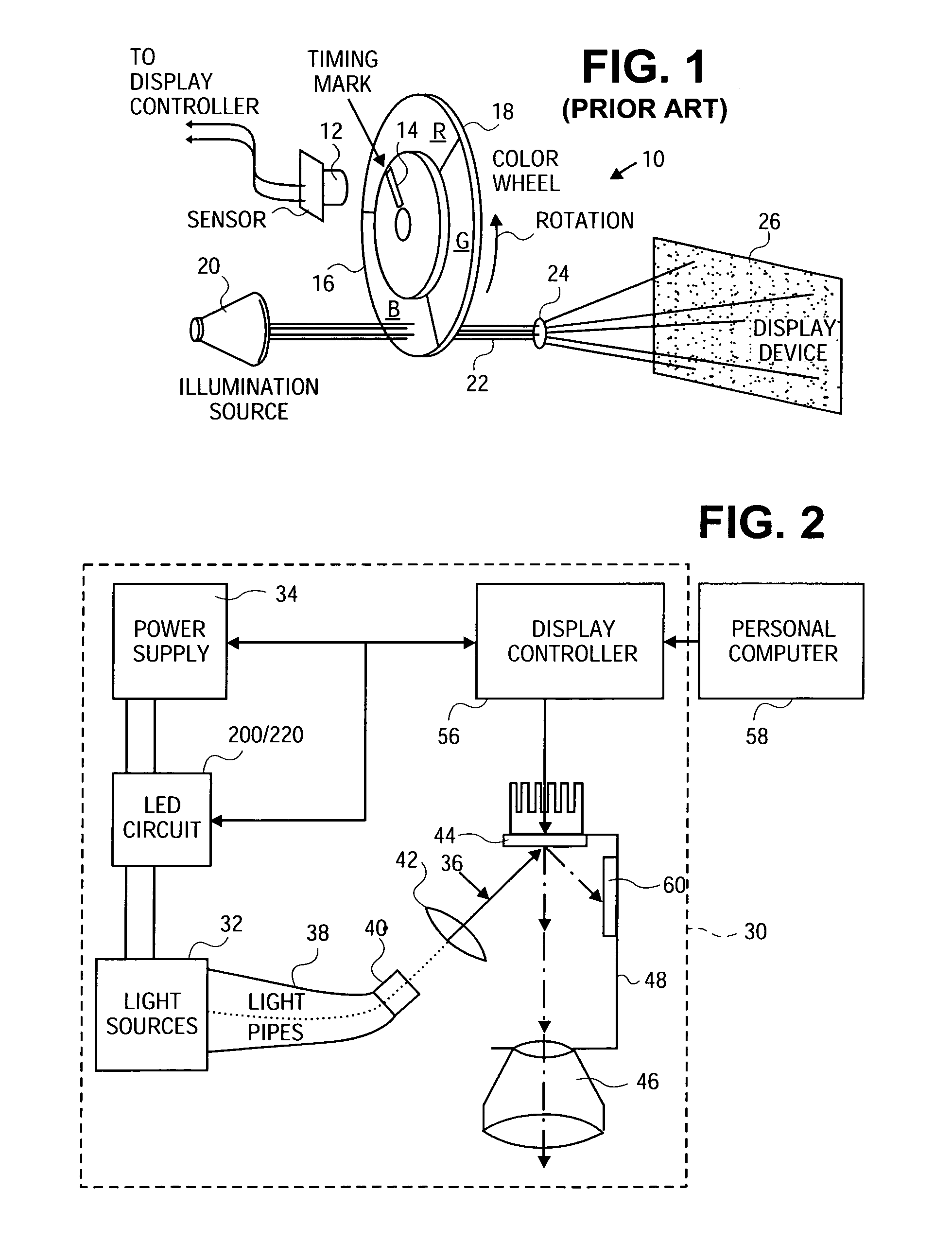
Method and apparatus for driving LED light sources for a projection display
InactiveUS7088321B1Reduce brightnessWithout reducing brightnessLaser detailsProjectorsData synchronizationControl signal
A circuit is provided to drive LEDs or diode lasers that emit light in desired wavelengths, such as the primary colors red, green, and blue, which serve as the light source for a projection display system. A display controller controls one or more series-parallel arrays of each color LED in the LED circuit with control signals to synchronize the color output of the light source with image data received from an image data source such as a personal computer. Synchronization is achieved by sending control signals to the power supply and circuit switches to sequence the color output in a single path system or adjust continuous color output in a triple path system with minimal or no reductions in the brightness of the projected image.
Owner:SEIKO EPSON CORP
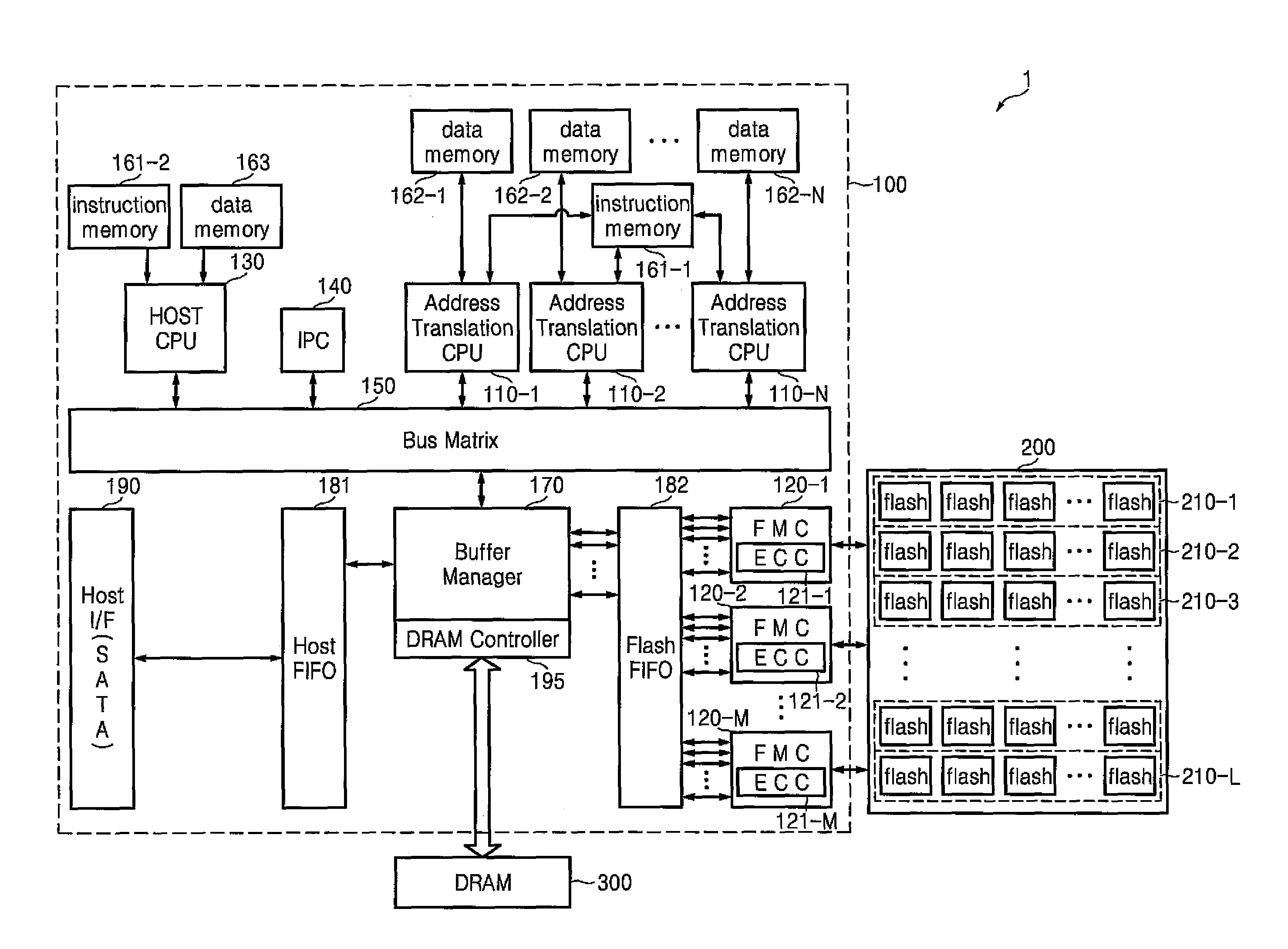
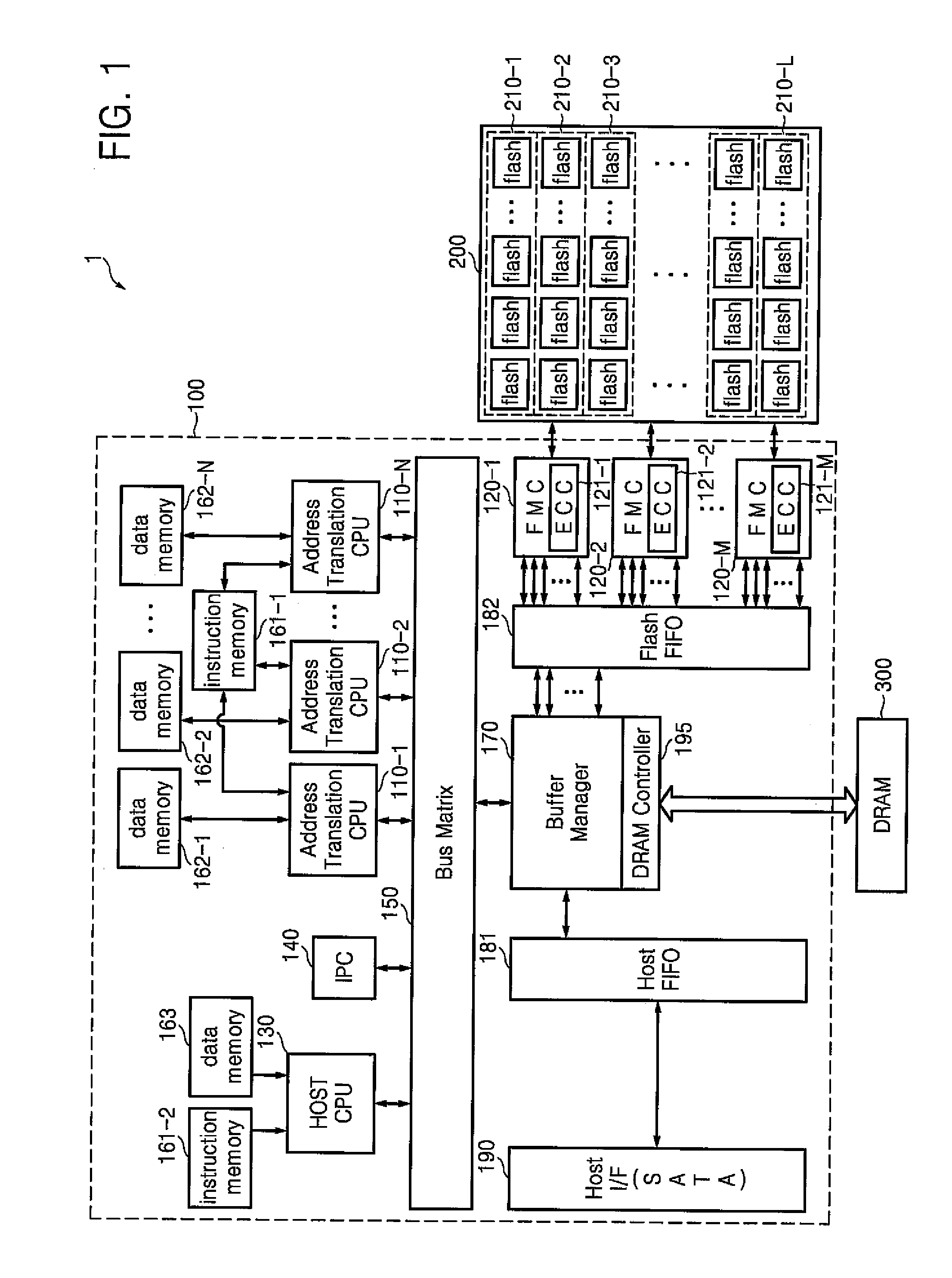
Controller, data storage device and data storage system having the controller, and data processing method
ActiveUS20100274952A1Improve processing speedMemory adressing/allocation/relocationMicro-instruction address formationProcessing elementData treatment
A controller, a data storage device and a data storage system including the controller, and a data processing method are provided. The controller may process a plurality of instructions in parallel by including a plurality of address translation central processing units (CPUs) in a multi-channel parallel array structure, thereby improving the performance of a semiconductor memory system.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
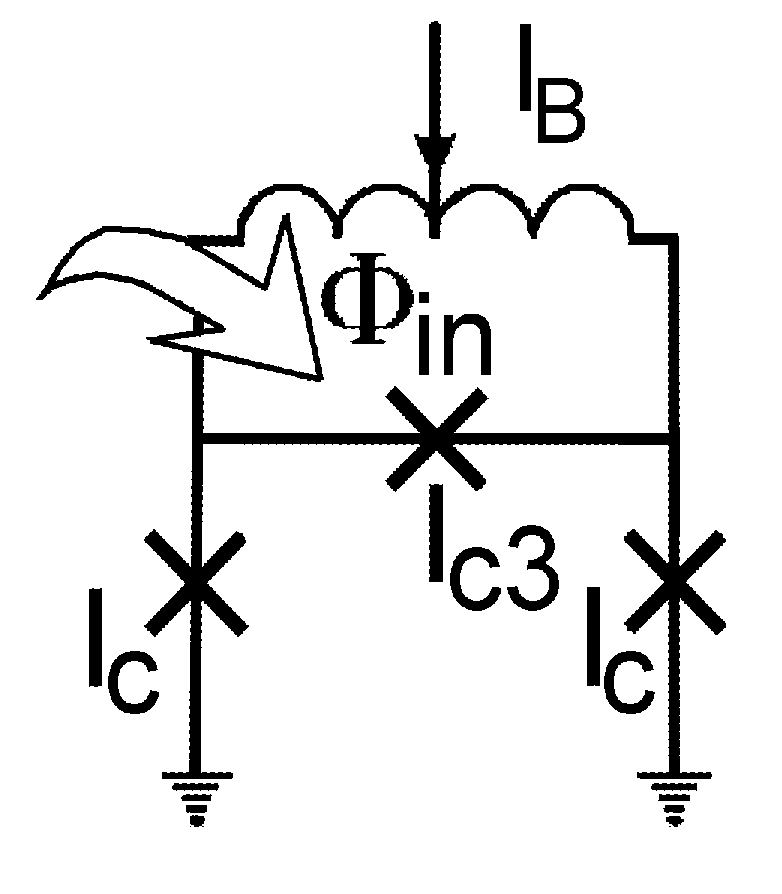
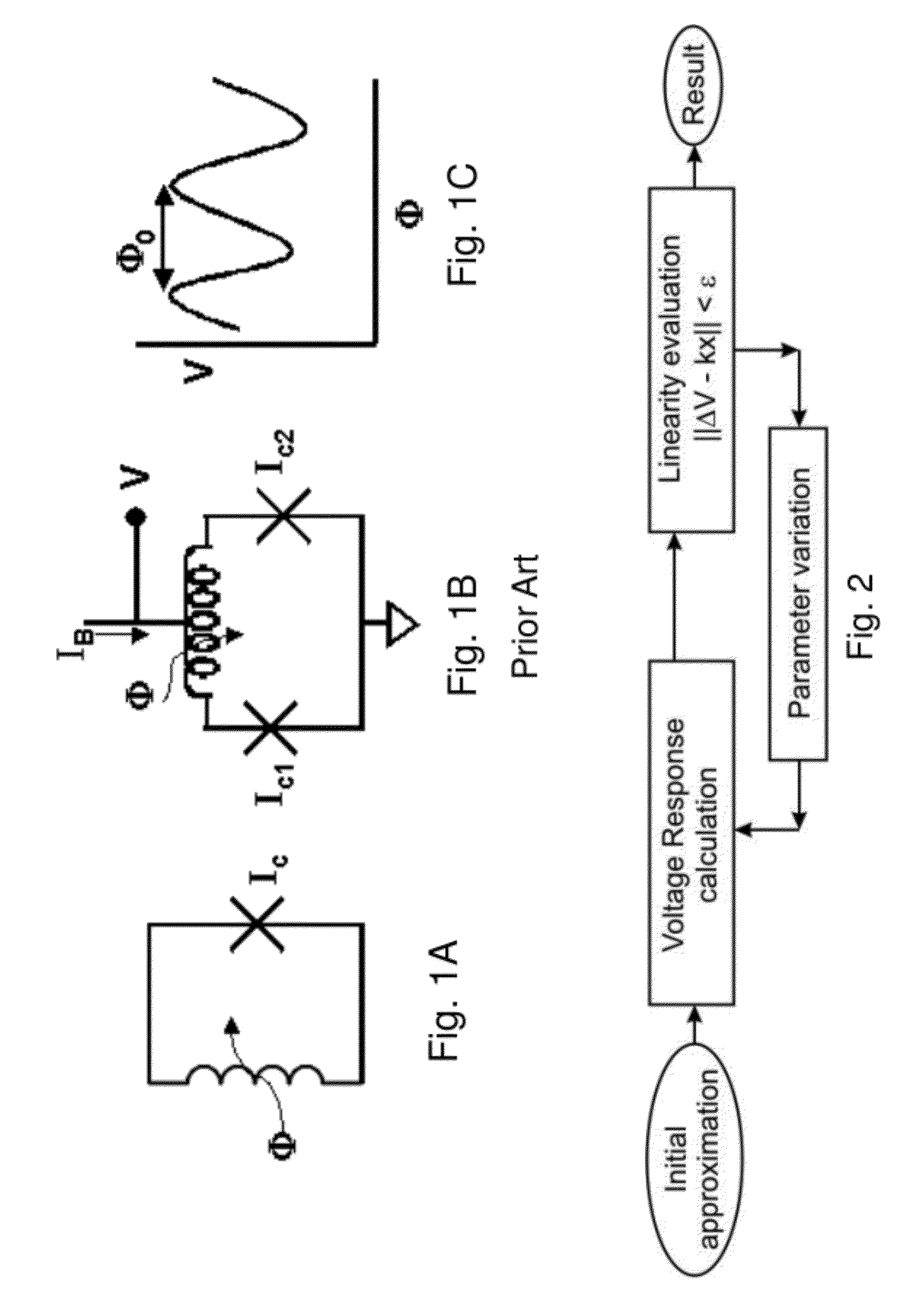
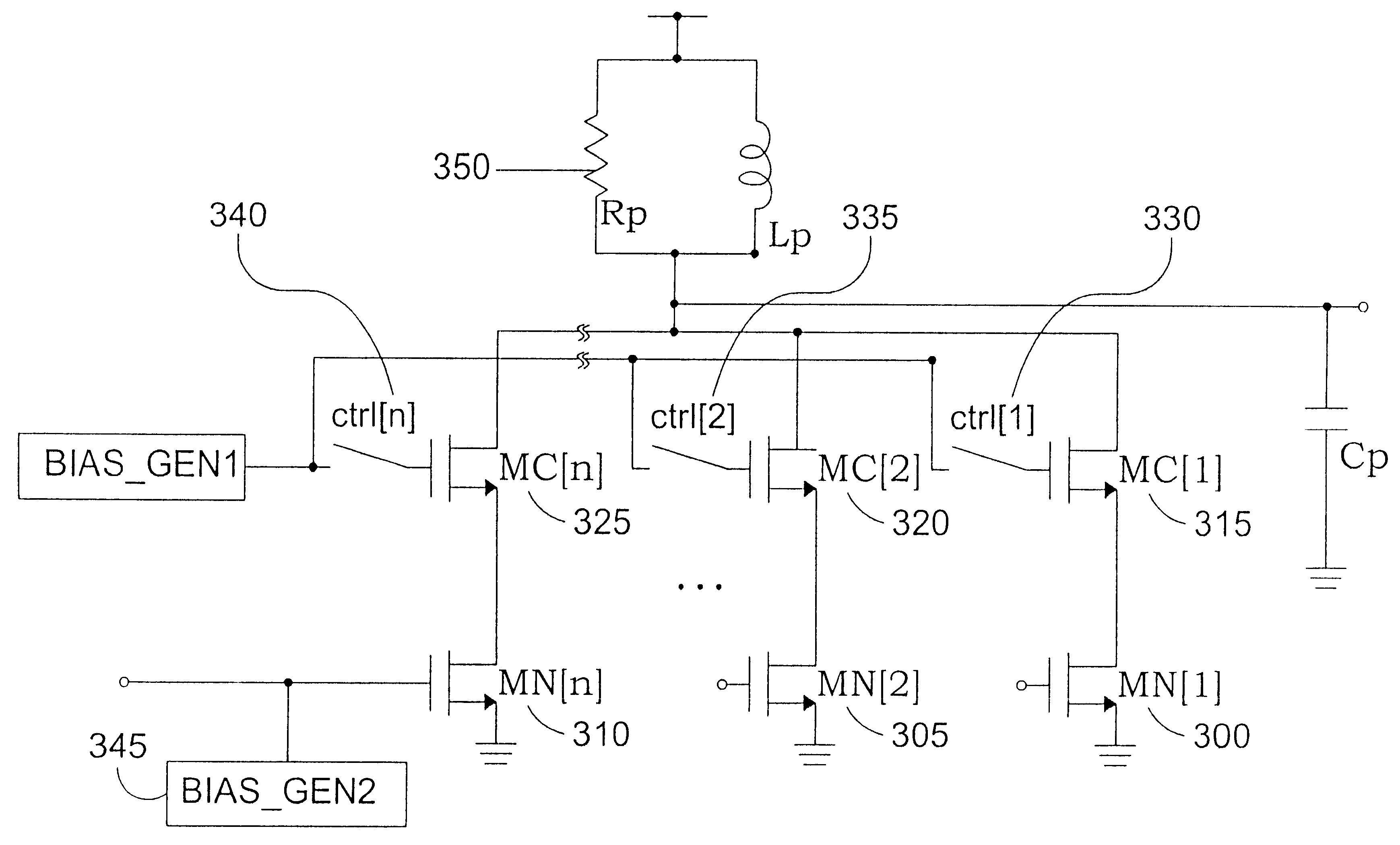
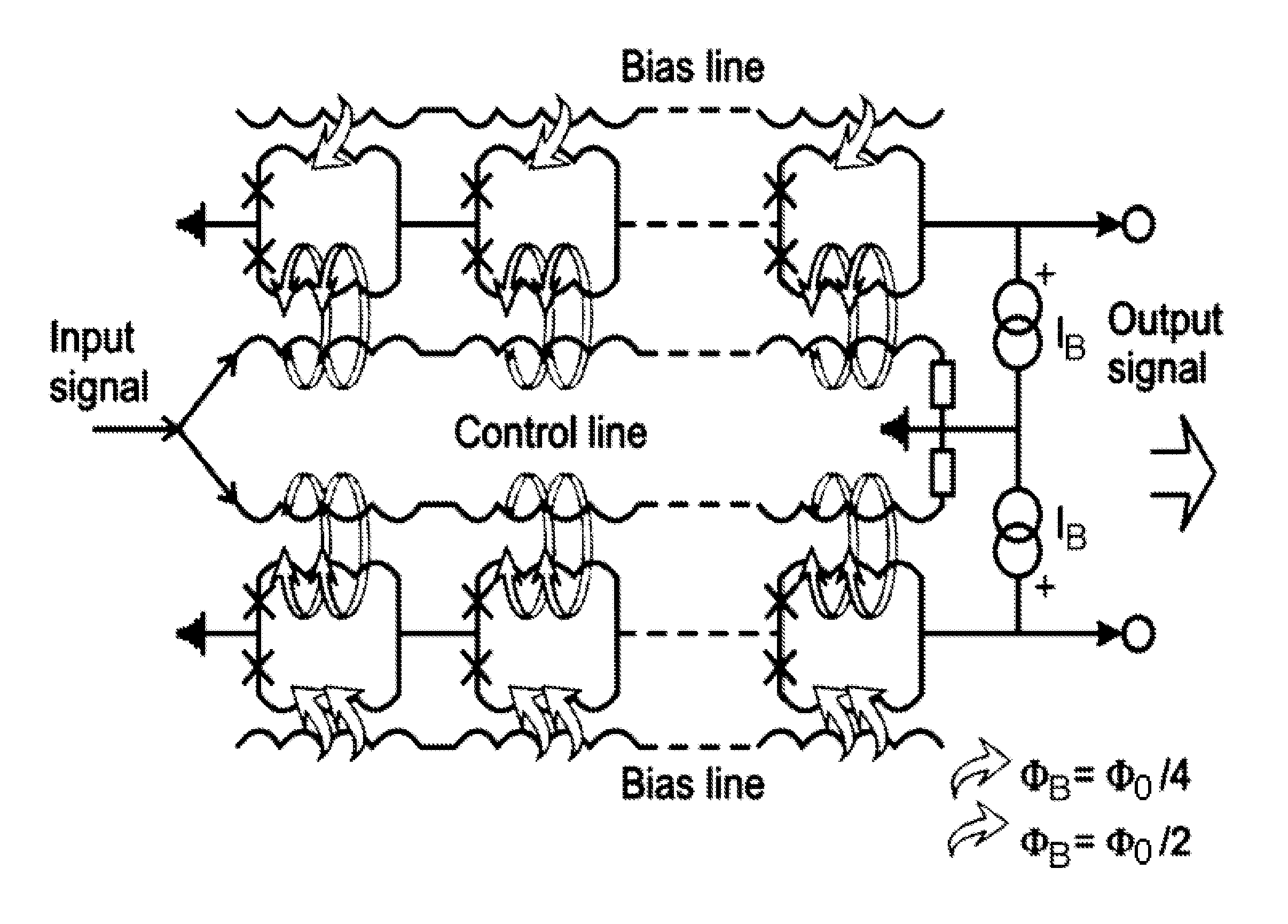
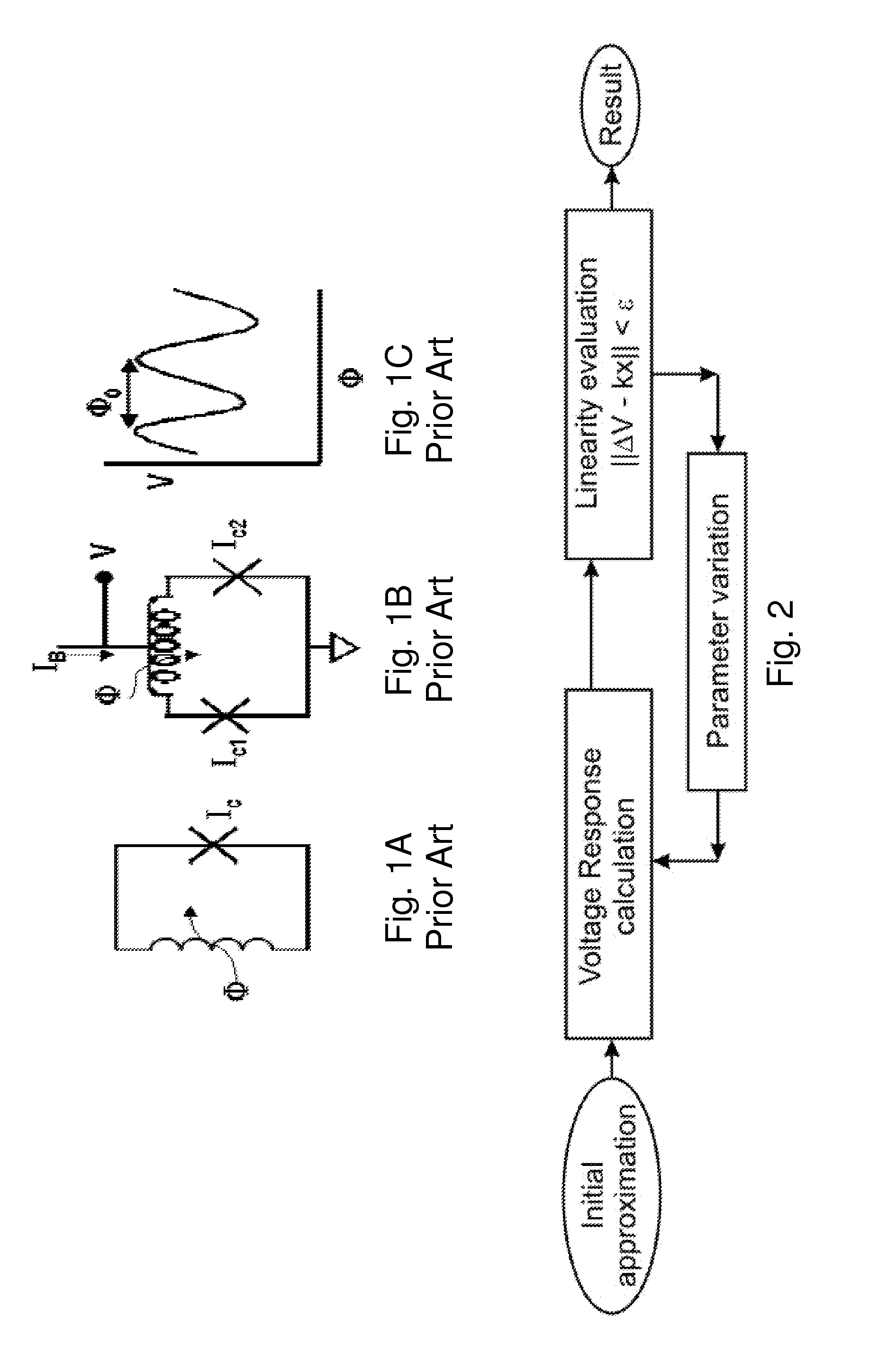
High linearity superconducting radio frequency magnetic field detector
ActiveUS8179133B1Total nonlinearities have been significantly reduced or eliminatedAvoid interferenceSuperconductors/hyperconductorsElectric pulse generatorTotal harmonic distortionRadio frequency
A superconducting quantum interference devices (SQUID) comprises a superconducting inductive loop with at least two Josephson junction, whereby a magnetic flux coupled into the inductive loop produces a modulated response up through radio frequencies. Series and parallel arrays of SQUIDs can increase the dynamic range, output, and linearity, while maintaining bandwidth. Several approaches to achieving a linear triangle-wave transfer function are presented, including harmonic superposition of SQUID cells, differential serial arrays with magnetic frustration, and a novel bi-SQUID cell comprised of a nonlinear Josephson inductance shunting the linear coupling inductance. Total harmonic distortion of less than −120 dB can be achieved in optimum cases.
Owner:SEEQC INC
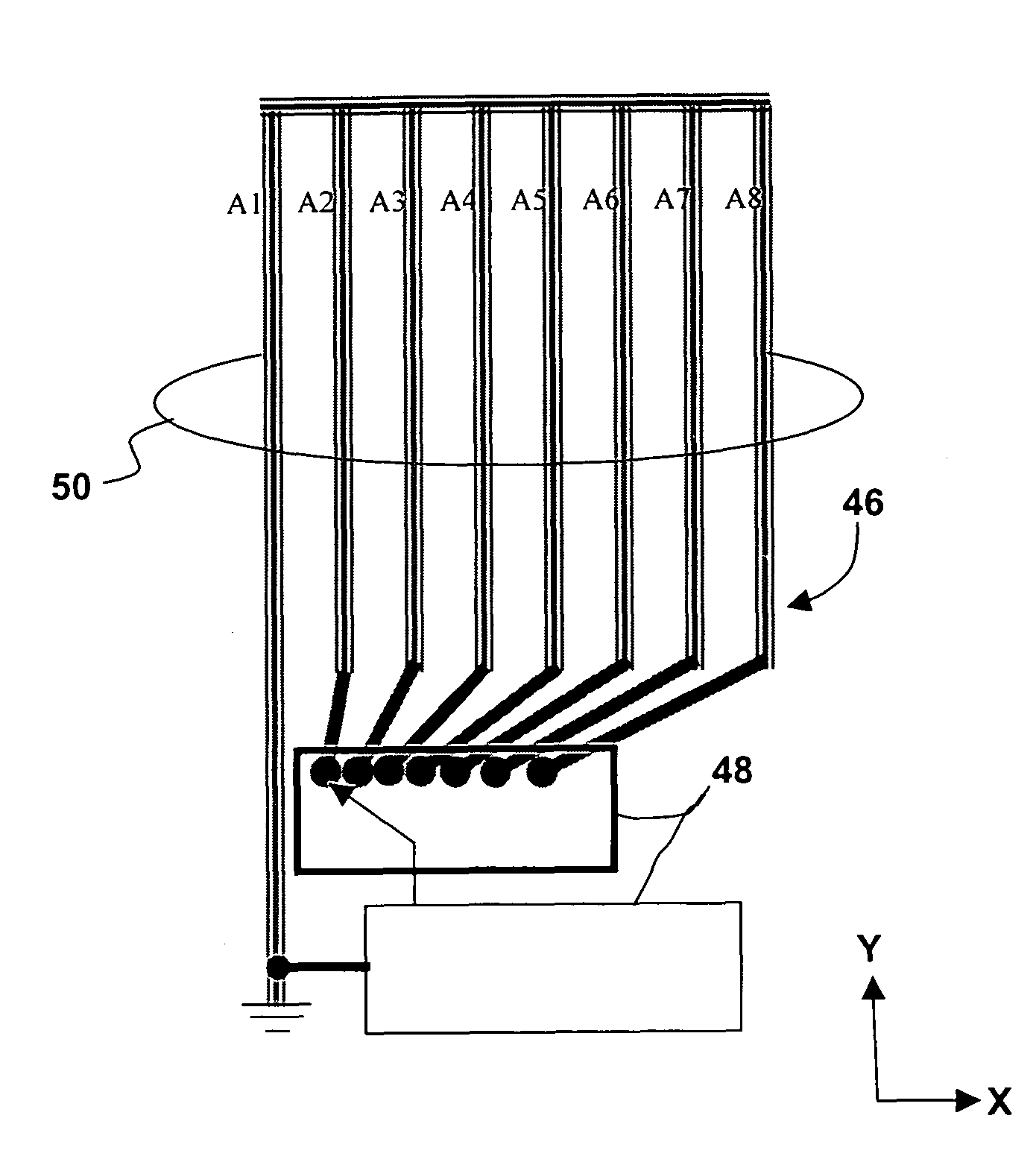
Method and apparatus for high rate data communication utilizing an adaptive antenna array
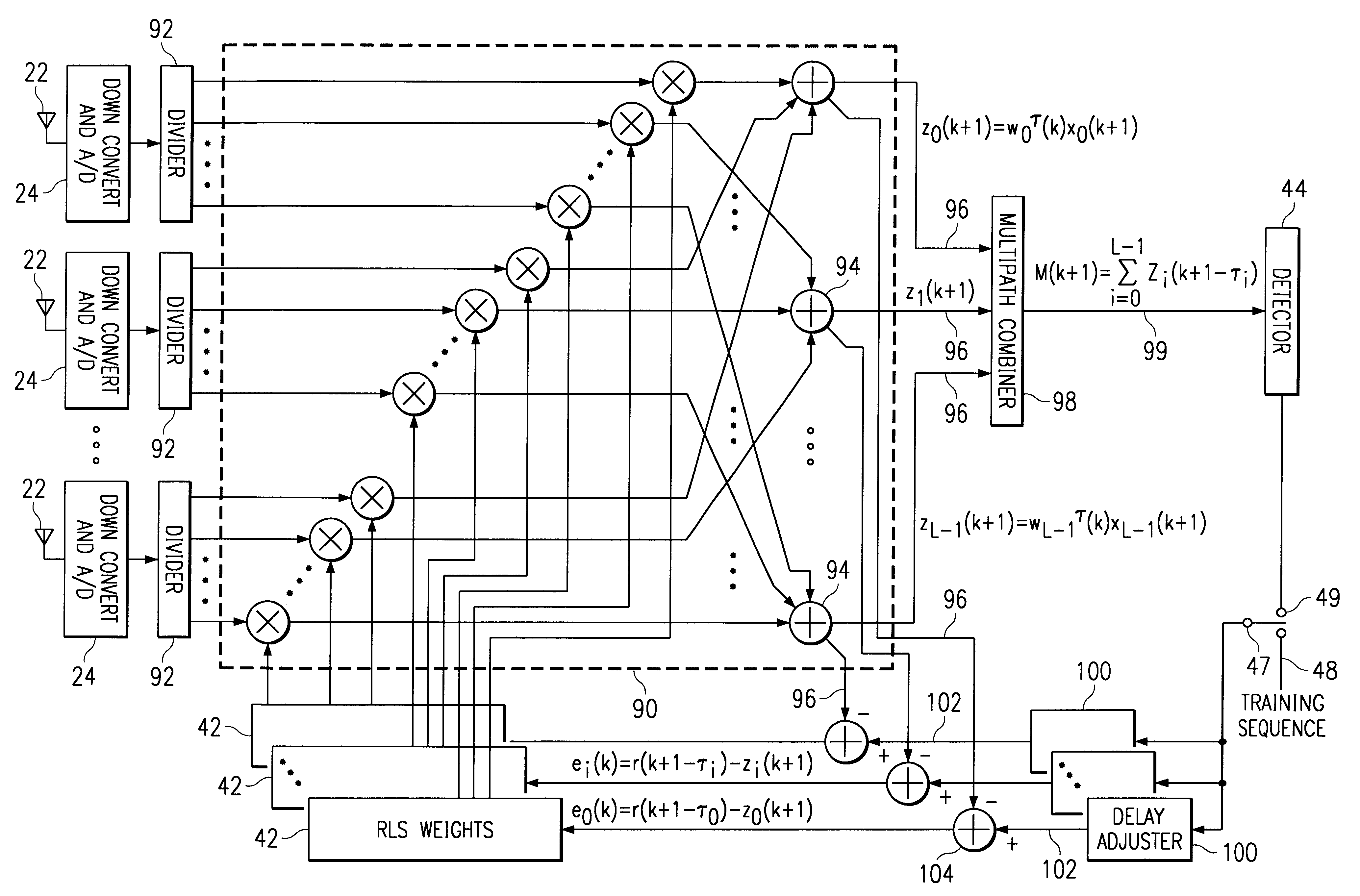
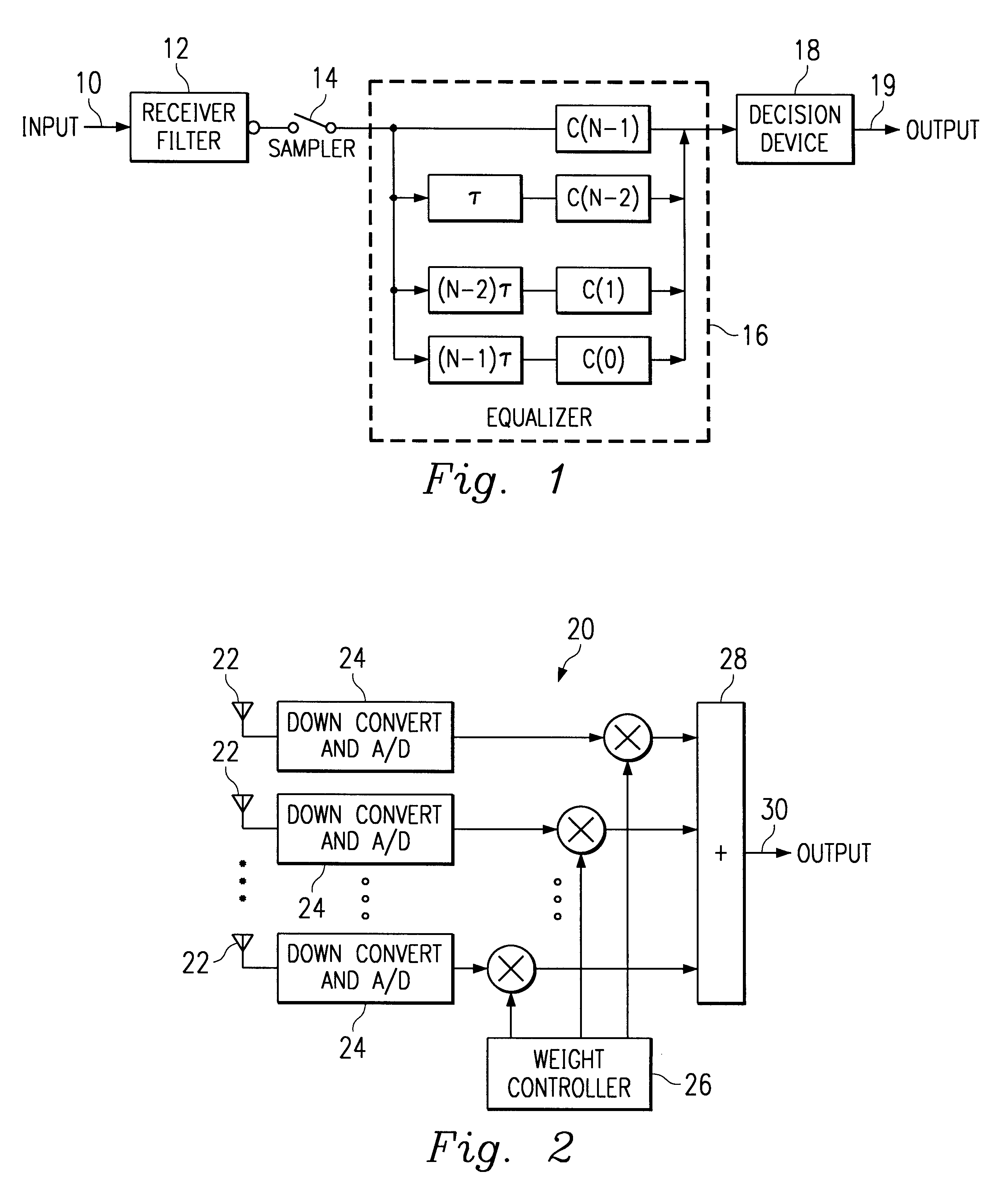
In a wideband Personal Communication Services system, a method and system are proposed for suppressing co-channel interference and reducing inter-symbol interference generated during the transfer of a data packet through a selected radio frequency channel. The system includes a weight controller utilizing recursive least squares algorithm to generate a plurality of appropriate weights to be integrated into received signals in order to maximize signal-to-noise ratio. A detected signal or a training sequence is intelligently switched in as a reference sequence in order to generate a plurality of appropriate weights. To further enhance the adaptive array system and take advantage of the multi-path radio frequency communication environment, two multi-path diversity schemes are included. One embodiment includes an adaptive array system with parallel array processors and another embodiment includes a system with tapped delay line processors.
Owner:APPLE INC
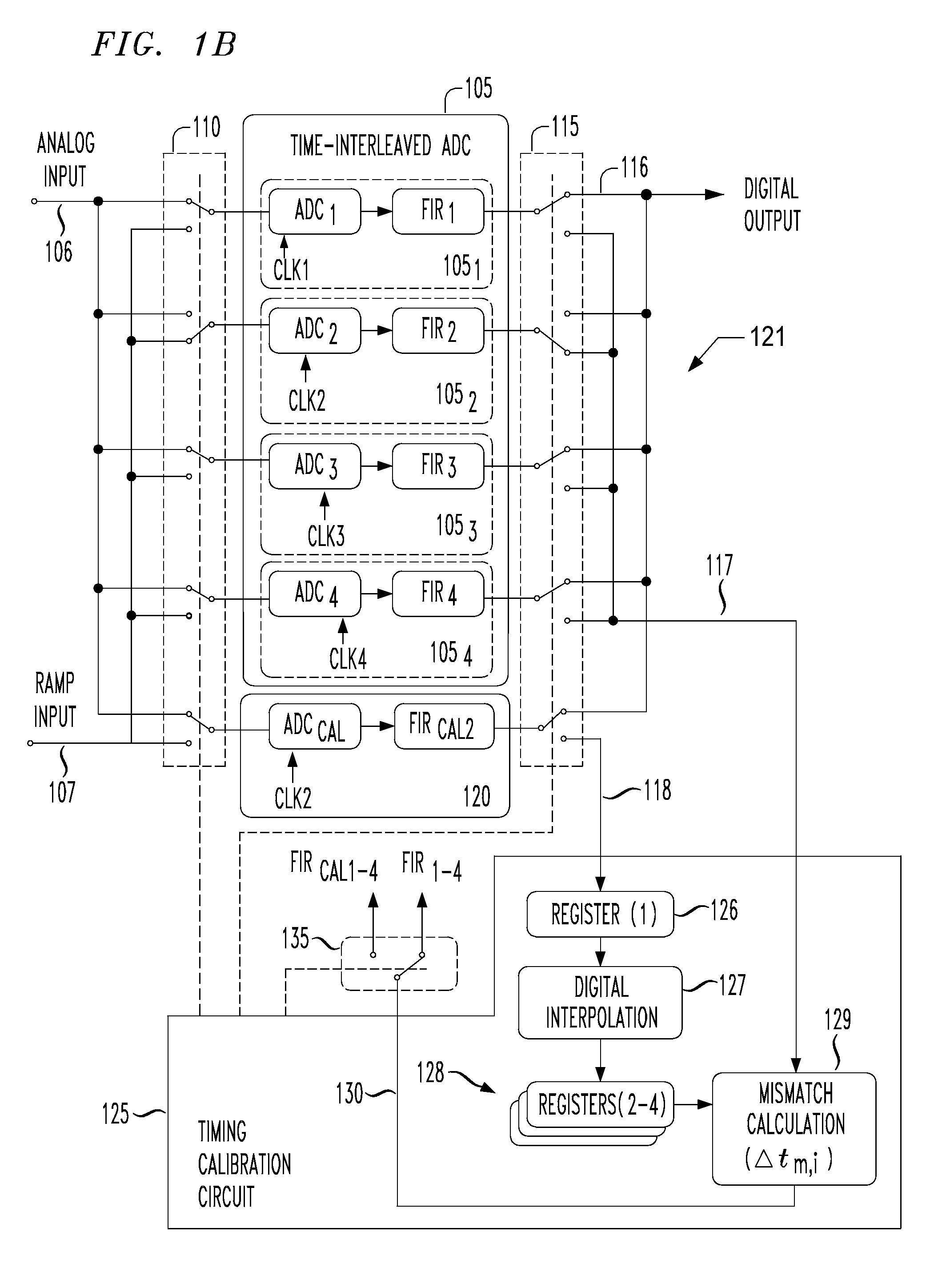
Digital background calibration for time-interlaced analog-to-digital converters
ActiveUS7227479B1Shorten the timeElectric signal transmission systemsAnalogue-digital convertersTime interleavedDigital converter
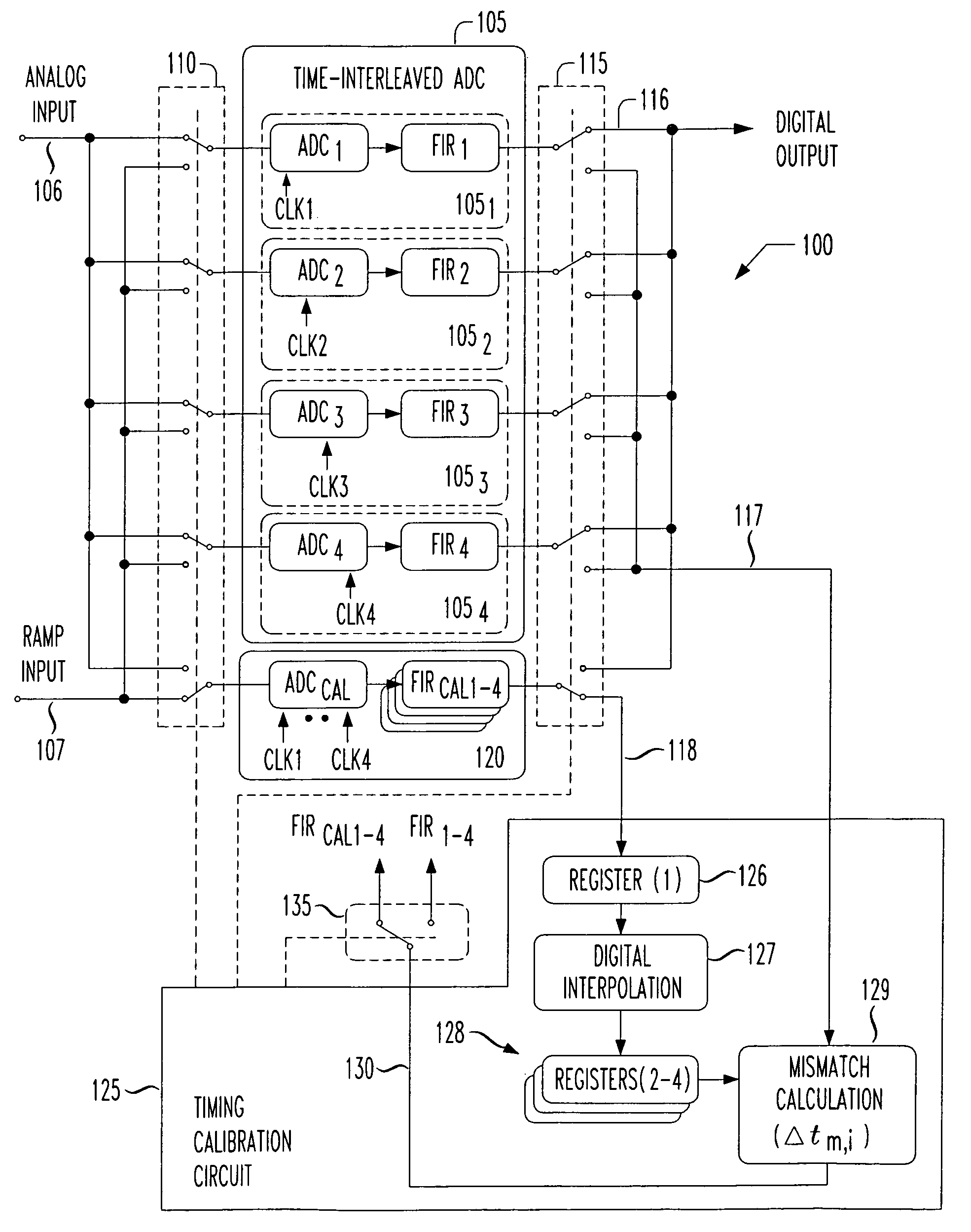
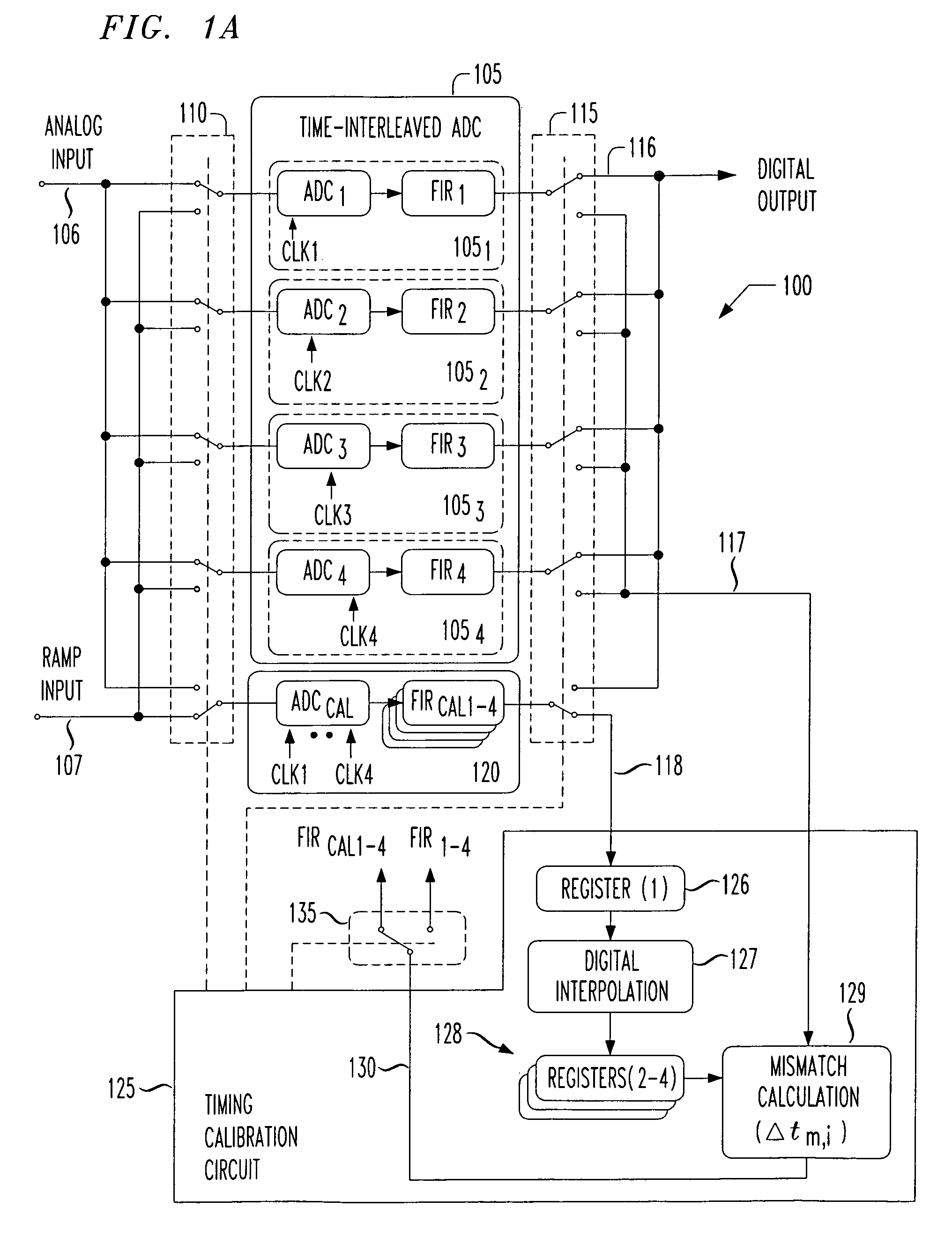
The present invention provides for background calibration of a time-interleaved analog-to-digital converter (TIADC). In one embodiment, a background calibrator includes a TIADC having a parallel array of time-interleaved main signal processors, each main signal processor including an ADC connected to a corresponding output FIR filter. The background calibrator also includes an auxiliary signal processor having an ADC connected to at least one corresponding output FIR filter. Additionally, the background calibrator further includes a timing calibration circuit, wherein the timing calibration circuit is configured to select one of the main signal processors, exchange the auxiliary signal processor with the selected main signal processor in the TIADC and connect the selected main signal processor to the timing calibration circuit. In an alternative embodiment, the timing calibration circuit is further configured to reduce a timing mismatch of the selected main signal processor.
Owner:LUCENT TECH INC
Variable gain low-noise amplifier for a wireless terminal
InactiveUS6657498B2Reduces and avoids clippingNot to wasteGain controlGated amplifiersTuned amplifierEngineering
A variable gain, low noise amplifier is described, which is suitable as the input amplifier for a wireless terminal, or as the pre-amplifier stage of a wireless terminal transmitter. The amplifier may achieve variable gain by deploying a network of transistors in a parallel array, each independently selectable by a PMOS switch, and providing the variable resistance for the resonant circuit. Power dissipation can also be mitigated by using a network of driving transistors, each independently selectable by a PMOS switch. The resonant frequency of the amplifier may be made tunable by providing a selection of optional pull-up capacitors.
Owner:GCT SEMICONDUCTOR INC
Scanning Probe Microscope, Nanomanipulator with Nanospool, Motor, nucleotide cassette and Gaming application
InactiveUS20080149832A1Material analysis using wave/particle radiationNanotechnologyNucleotideScanning probe microscopy
This invention has applications as a scanning probe microscope / nanomanipulator with consumer gaming applications. An integrated compound lever cantilever which can function simultaneously as both a sample substrate actuator and probe tip scanner actuator for modulation of one or more probe tip. In one embodiment a piezoelectric multimorph MEMS structure is fabricated which serves as a Scanning Probe Microscope cantilever probe tip scanner and allows for the substrate to be moved in more than 1 Degree of freedom with subnanometer resolution. Nanomanipulation means such as nanotweezer, nanopore and nanomachine embodiments are possible uses for the device in addition to data storage. Parallel array operation of many sets of cantilevers is a preferred embodiment which can be used as a nanoscale manipulation and fabrication means. In addition an embodiment where the actuation effects of the device are used to propel the scanner can allow for a programmable drivable MEMS / NEMS based autonomous or semi-autonomous robotic scanner, manipulator and assembler. The device has embodiments where it is essentially a planarized MEMS / NEMS derivative version of a Besocke type scanner. The invention also discloses uses for scanning probe microscopes and nanomanipulators as means for gaming systems, erector set and chemistry kit for entertainment and educational applications. Other applications include rotational actuation, linear motion and spooling of material on rotational bodies through coordination of the actuator probe or probes.
Owner:ZORN MIGUEL
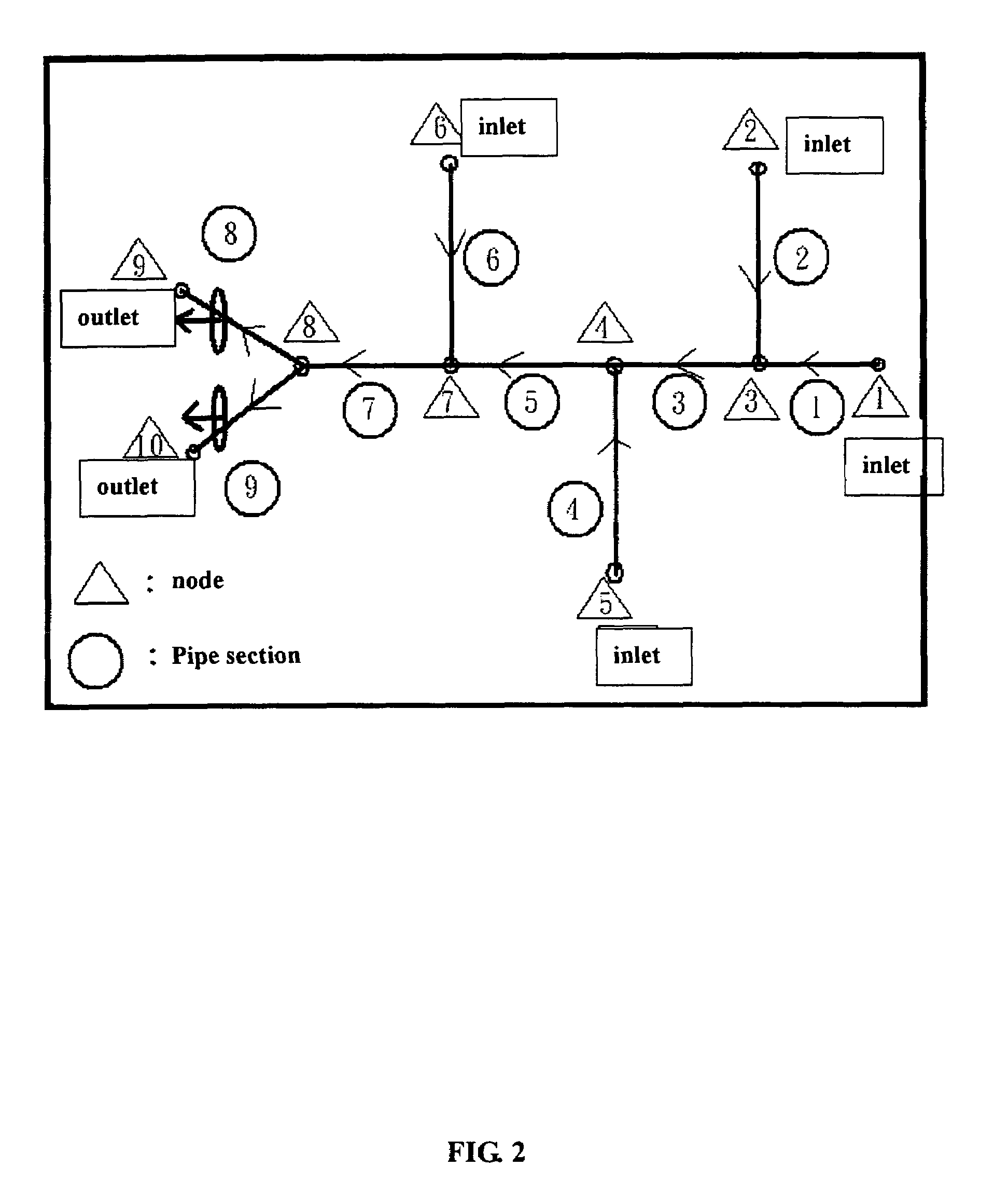
Impinging stream micro-channel reactor and application
ActiveCN101733056AReduced transport kinetic energy requirementsSmall scaleChemical/physical/physico-chemical processesEngineeringRapid response
The invention discloses an impinging stream micro-channel reactor. At least two micro-channels which are coaxial or impinge oppositely with a certain angle and have the equivalent hydraulic diameter of 0.1 to 2 millimeters are engraved on a flat material, and an impinging area with the width (or the opposite impinging distance) of 0.5 to 10 millimeters is formed between the opposite impinging channels. The micro-channels can be distributed in a parallel array and communicated to two inlets with step branch configurations. A plurality of chips can be assembled separately or stacked in order and pressed to form the impinging stream micro-channel reactor with four feeding holes at most. The impinging stream micro-channel reactor of the invention is applicable to an instantaneously finished reaction process or a reactive precipitation process such as gas-liquid and liquid-liquid quick reaction for generating liquid or solid (superfine powder or nano material and the like). The micro-channel form realizes high reaction evenness in the impinging area, and solves the problem that the impinging stream is difficultly provided with a multi-level system (mutual interference among a plurality of pairs of impinging streams) in the past.
Owner:DALIAN INST OF CHEM PHYSICS CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
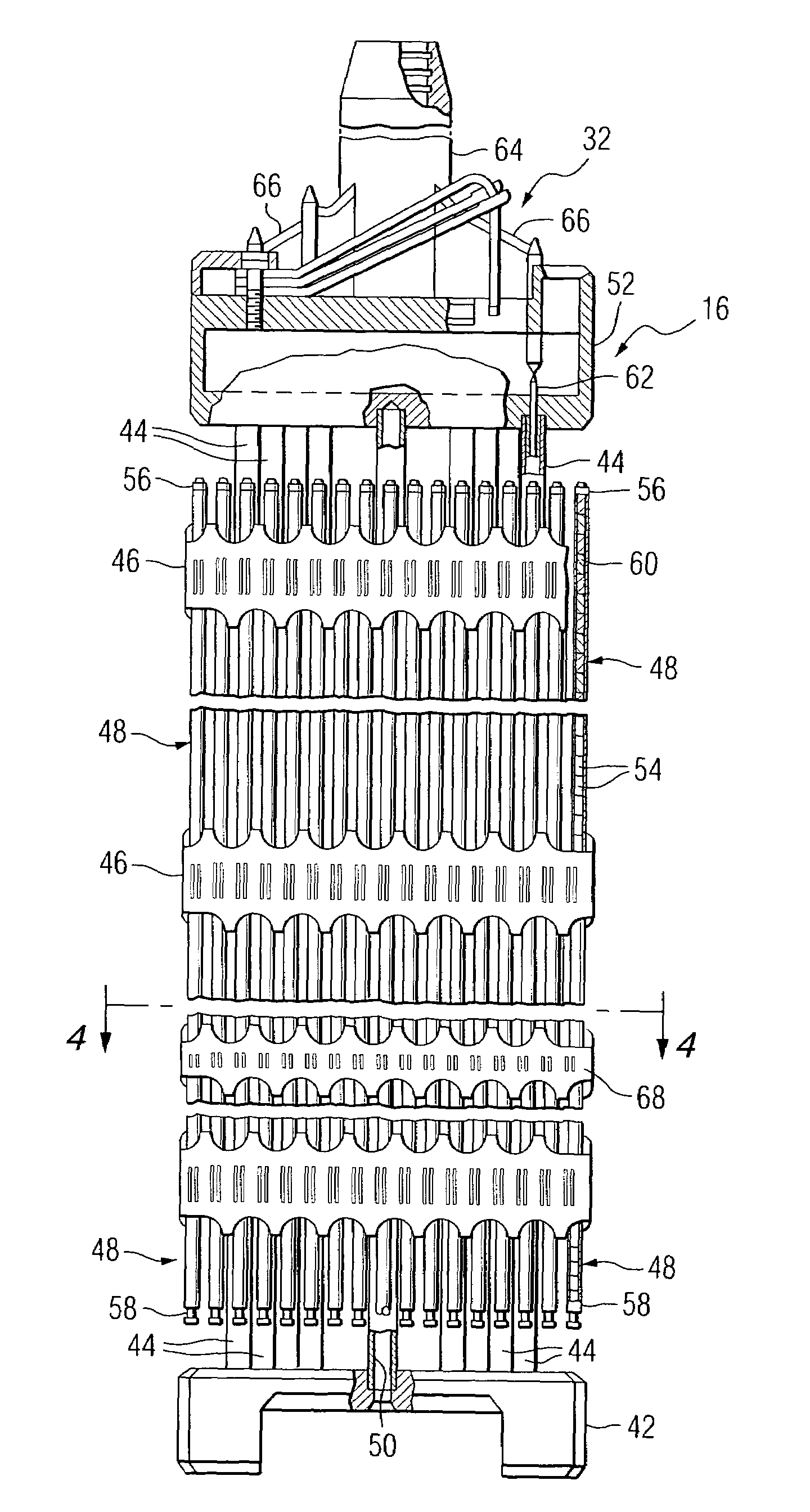
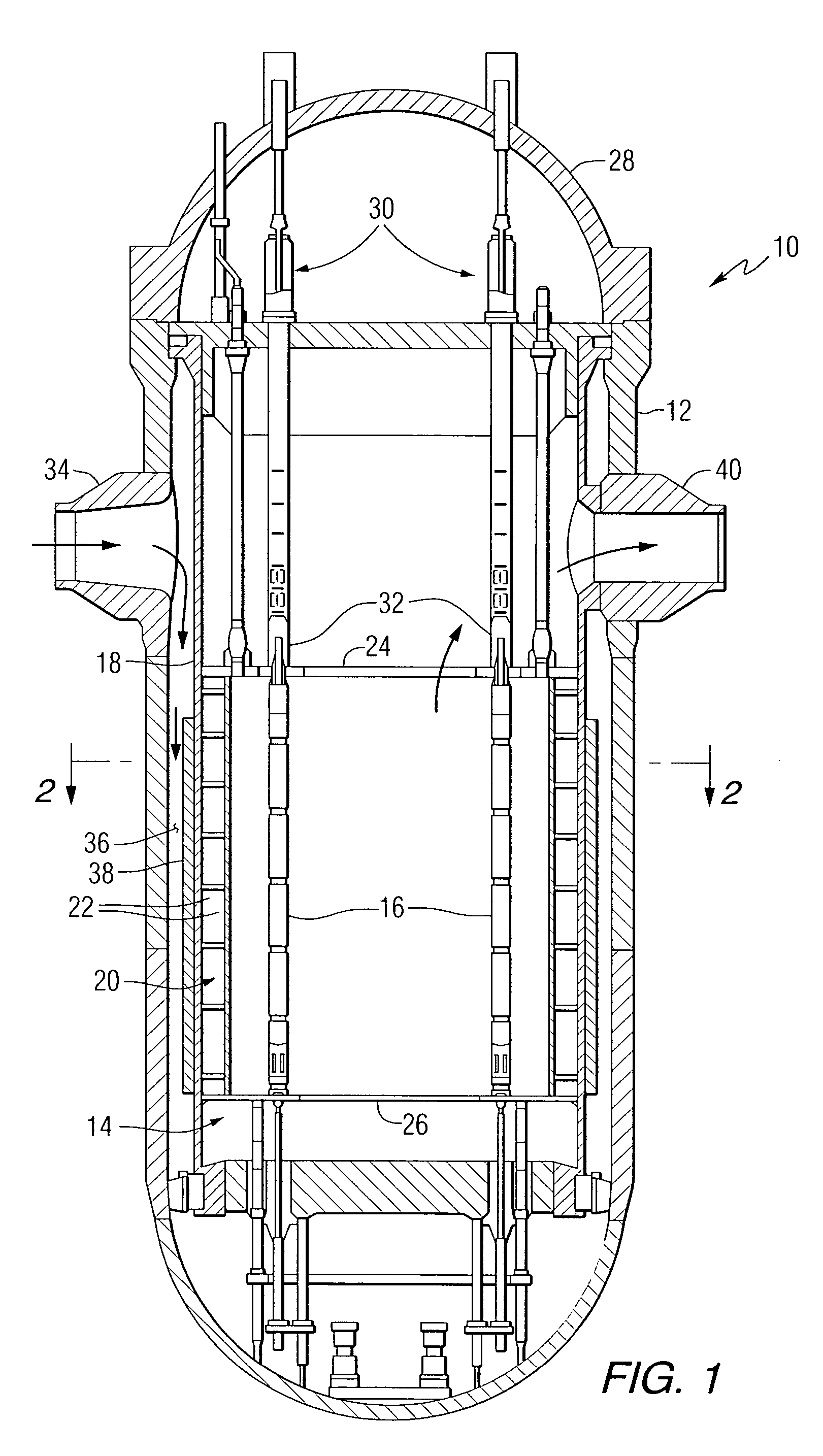
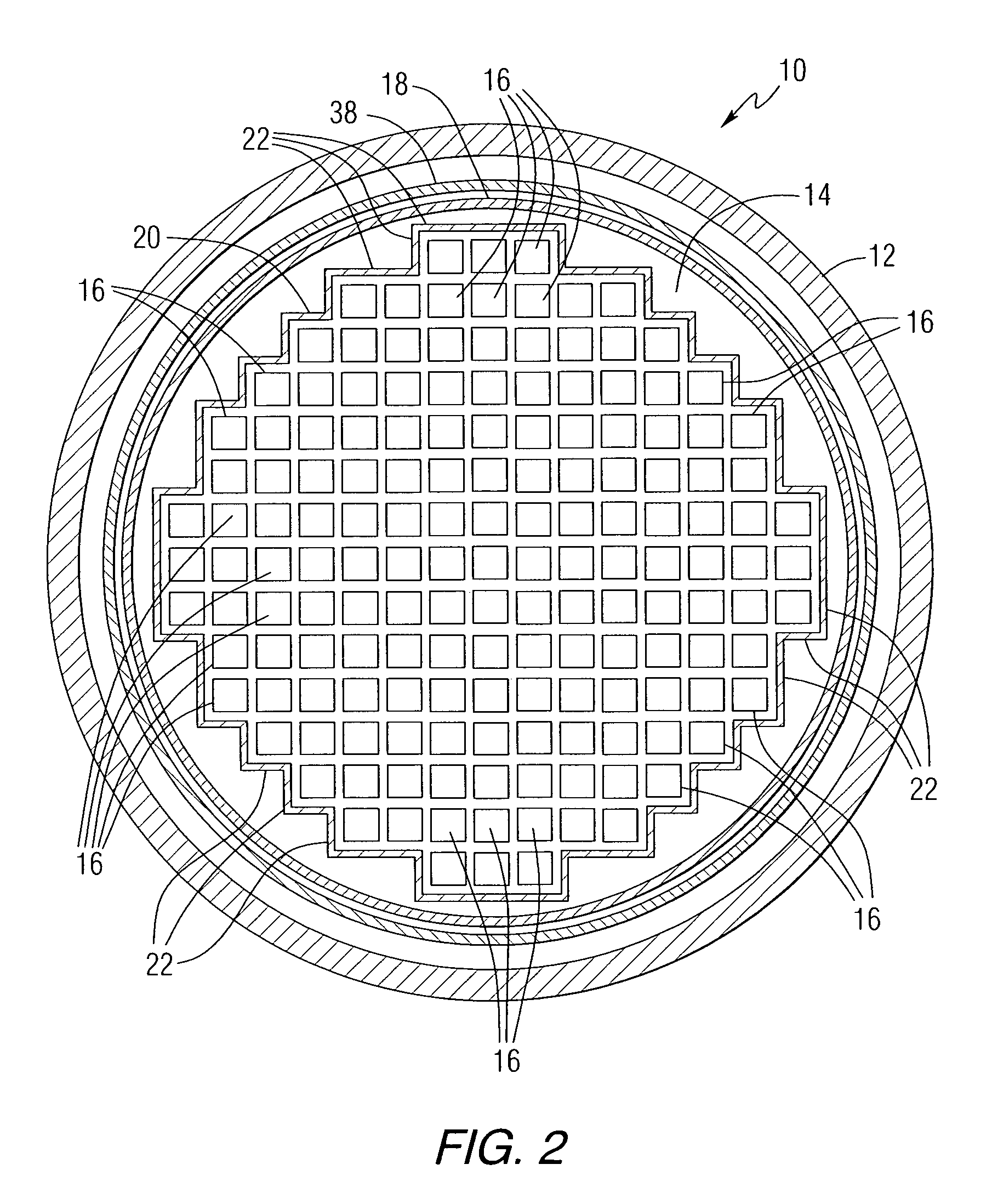
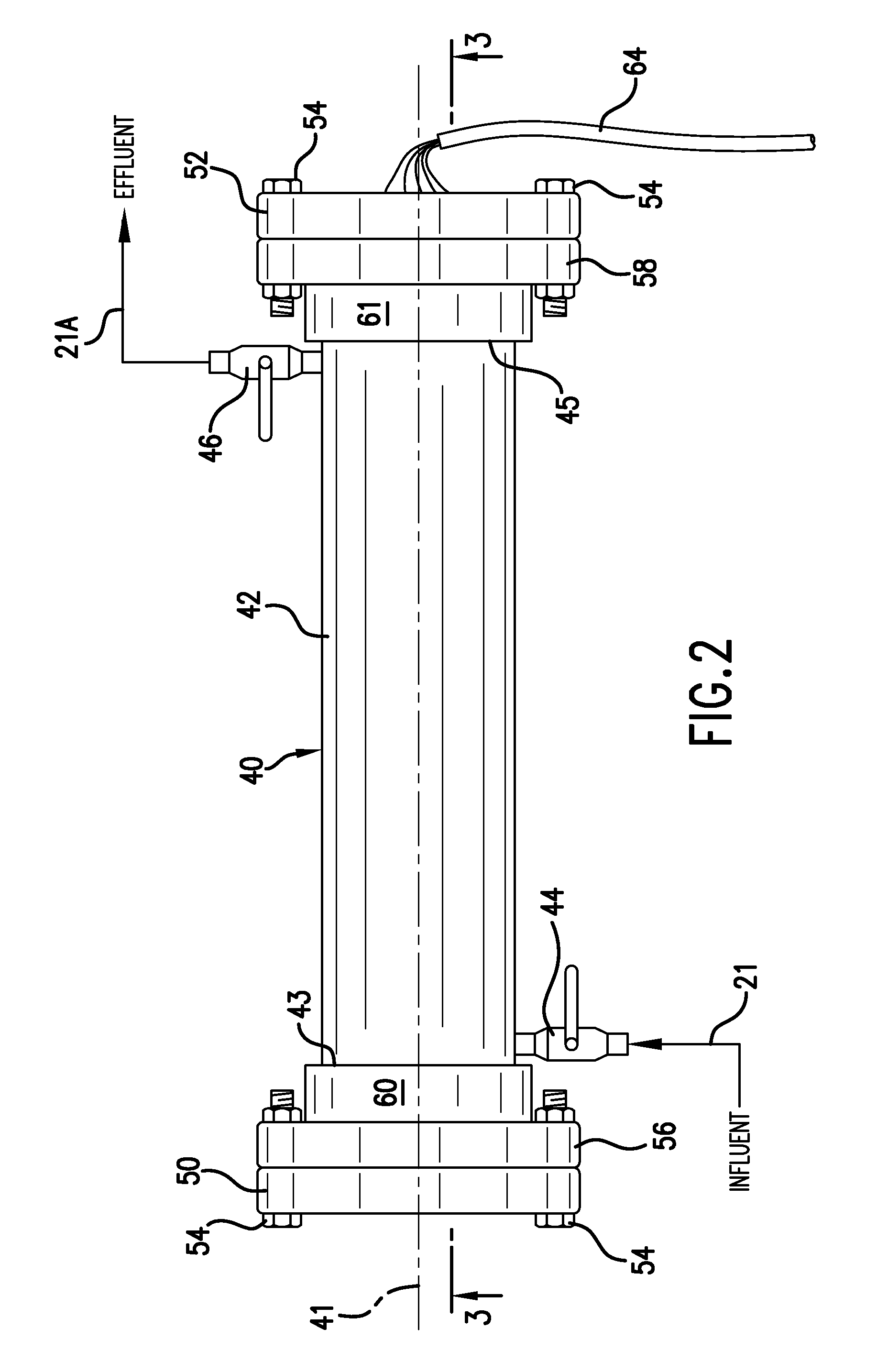
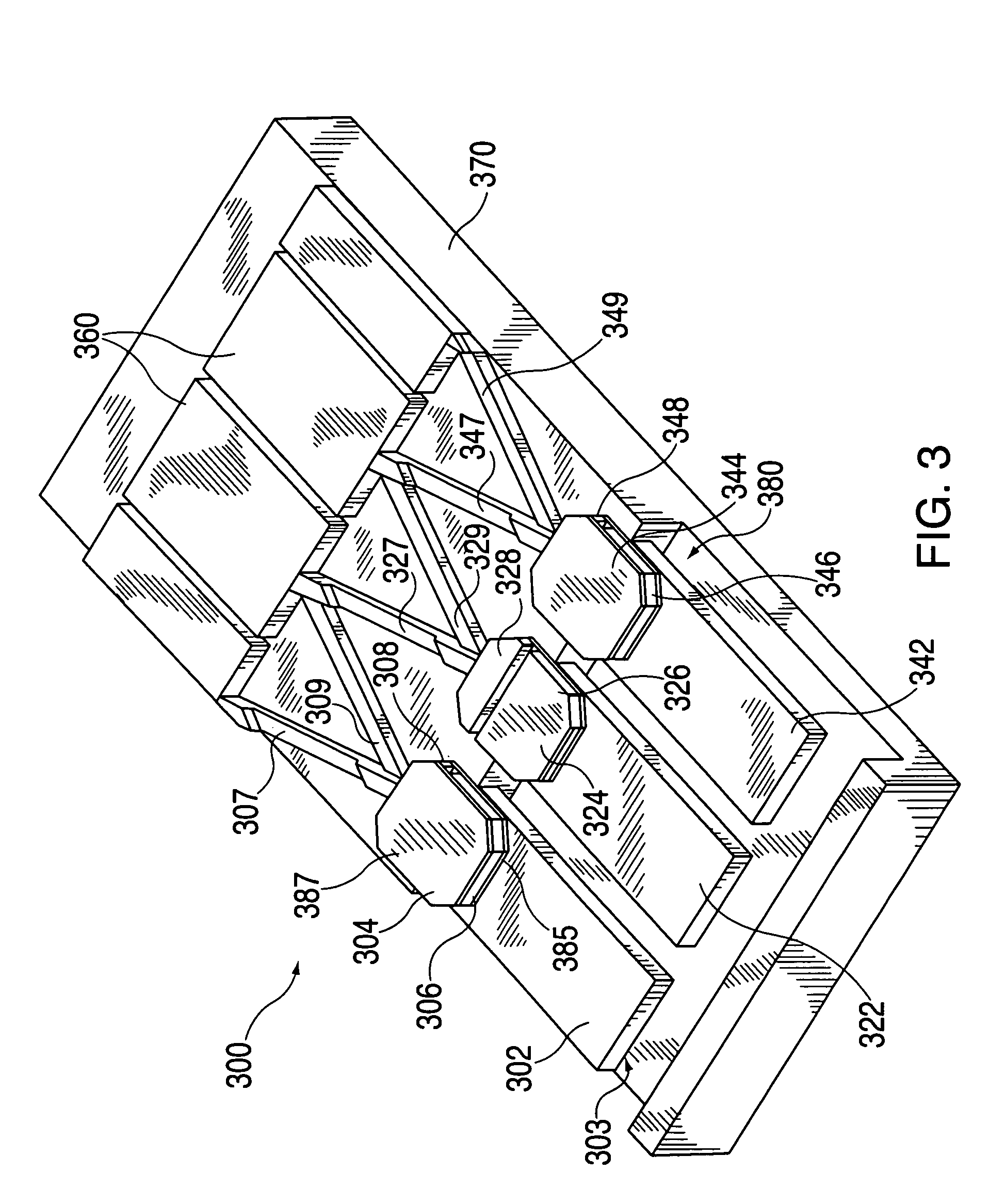
Nuclear reactor fuel assemblies
InactiveUS7085340B2Eliminate wearPrevent “hang-upsNuclear energy generationFuel element assembliesNuclear reactorParallel array
A nuclear fuel assembly having a parallel array of elongated fuel elements supported between an upper and lower nozzle. Main support grids are substantially evenly spaced along the elongated dimension of the assembly to maintain the spacing between fuel elements. A plurality of auxiliary vibration-resistant grids respectively positioned between the main support grids in the middle third elongated dimension of the fuel elements, that are smaller in height and provide a larger fuel element contact area than the main support grids.
Owner:WESTINGHOUSE ELECTRIC CORP
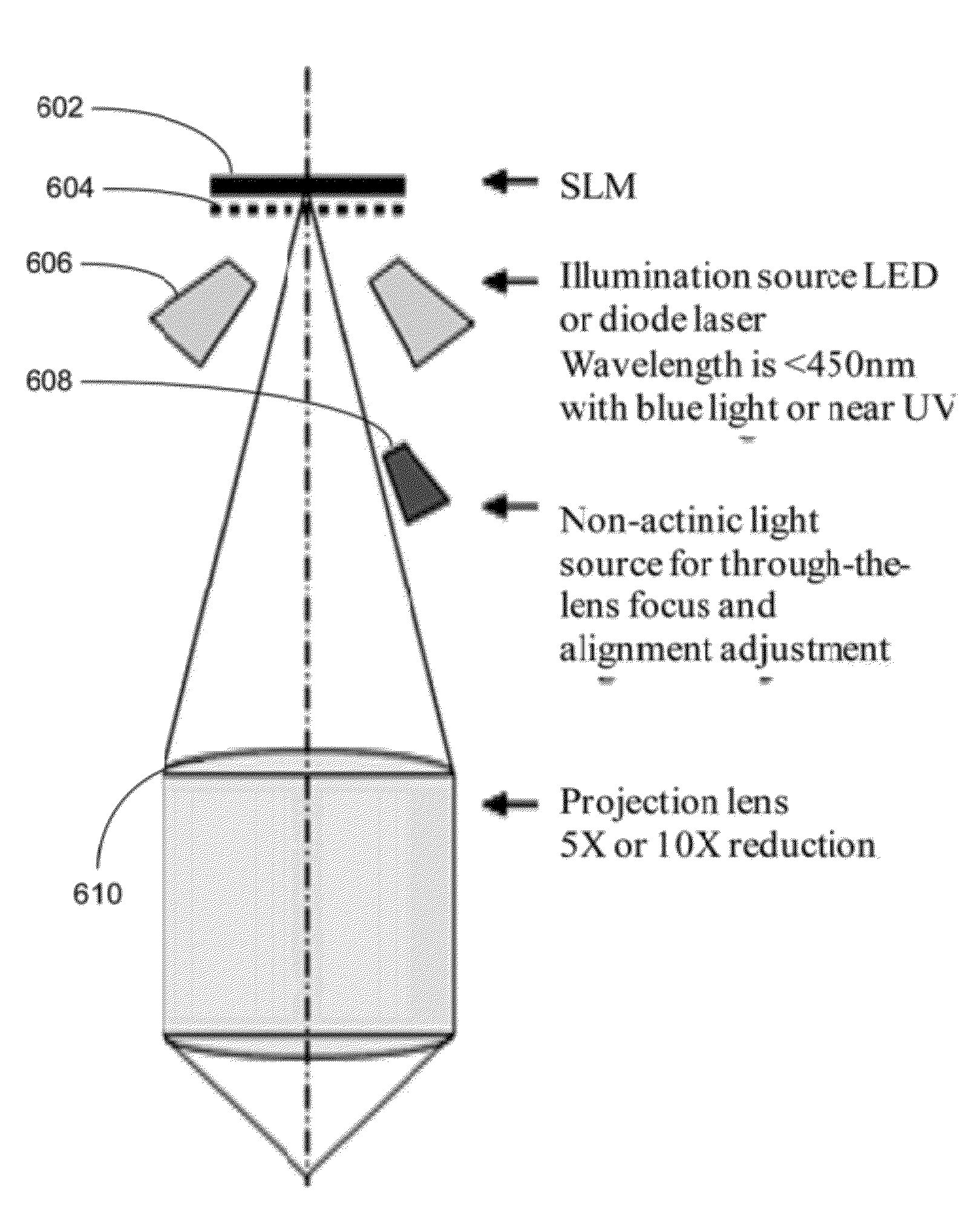
System and Method for Manufacturing Three Dimensional Integrated Circuits
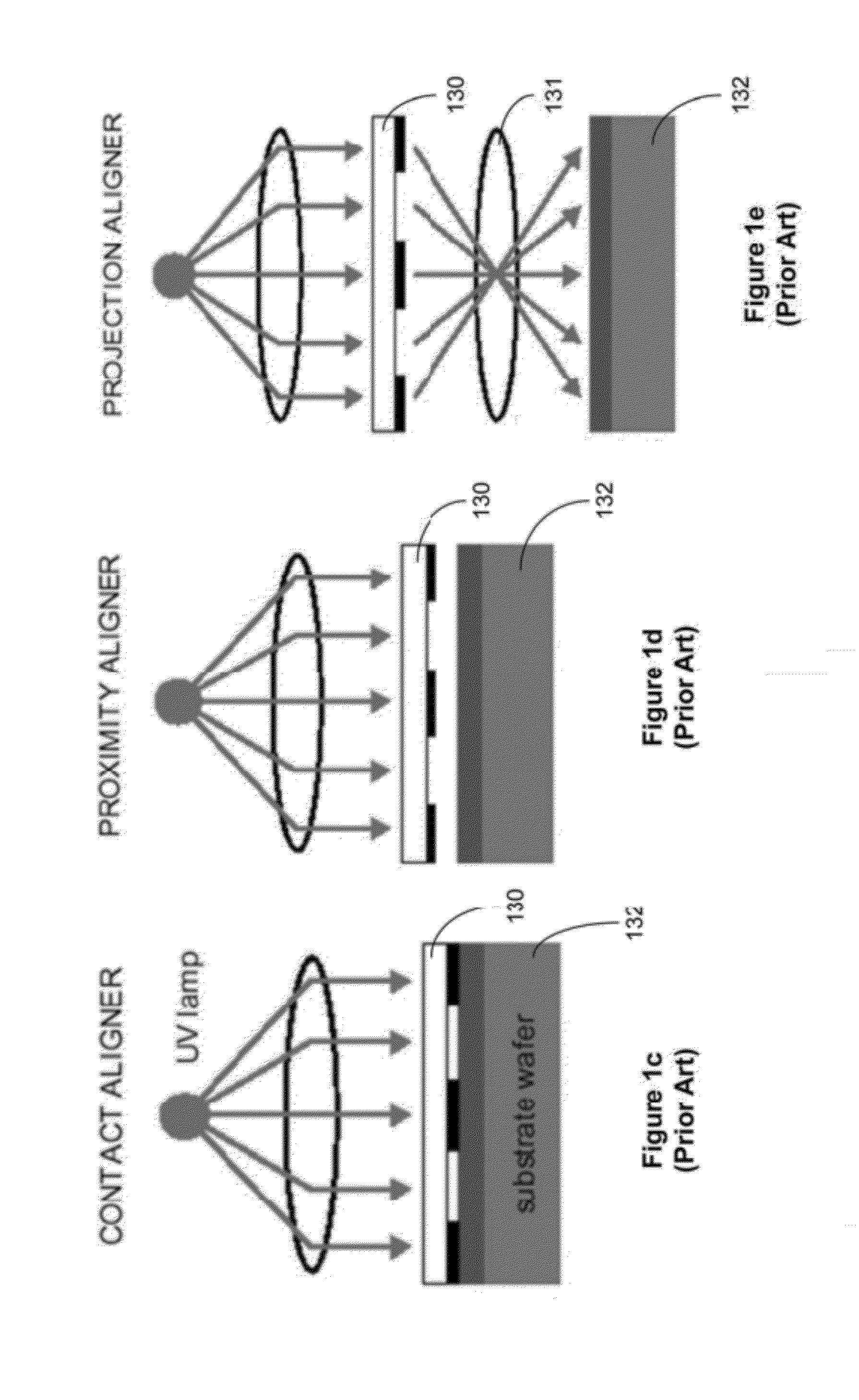
ActiveUS20120026478A1Photomechanical apparatusPhotographic printingSpatial light modulatorEngineering
System and method for manufacturing three-dimensional integrated circuits are disclosed. In one embodiment, the method includes providing an imaging writer system that includes a plurality of spatial light modulator (SLM) imaging units arranged in one or more parallel arrays, receiving mask data to be written to one or more layers of the three-dimensional integrated circuit, processing the mask data to form a plurality of partitioned mask data patterns corresponding to the one or more layers of the three-dimensional integrated circuit, assigning one or more SLM imaging units to handle each of the partitioned mask data pattern, and controlling the plurality of SLM imaging units to write the plurality of partitioned mask data patterns to the one or more layers of the three-dimensional integrated circuits in parallel. The method of assigning performs at least one of scaling, alignment, inter-ocular displacement, rotational factor, or substrate deformation correction.
Owner:APPLIED MATERIALS INC
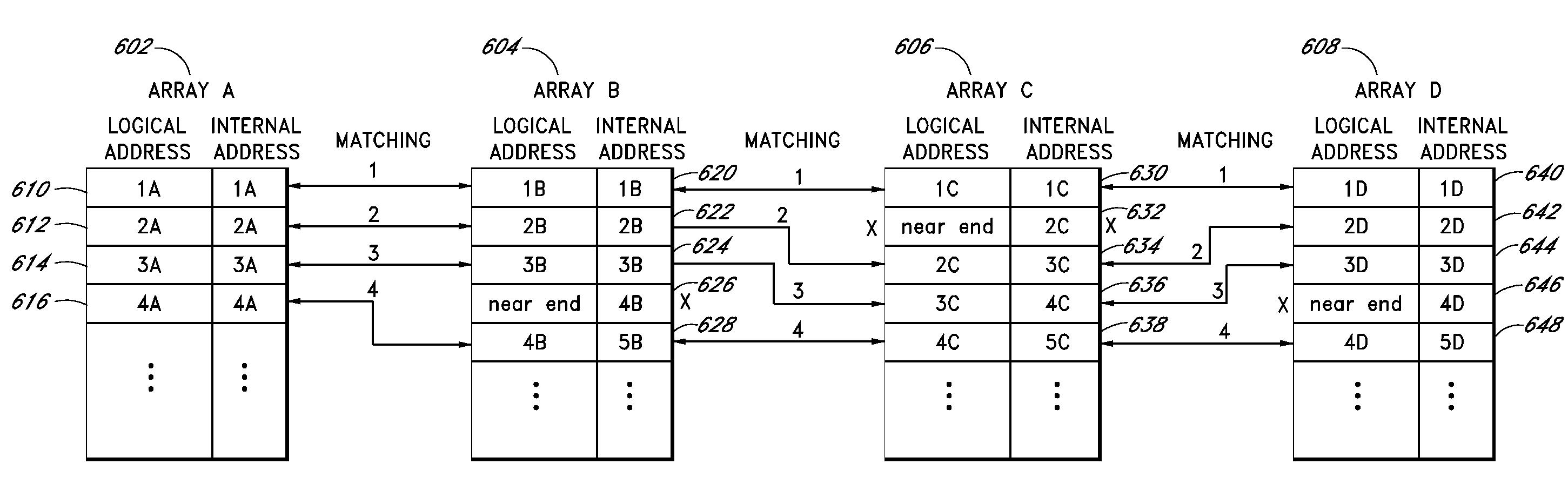
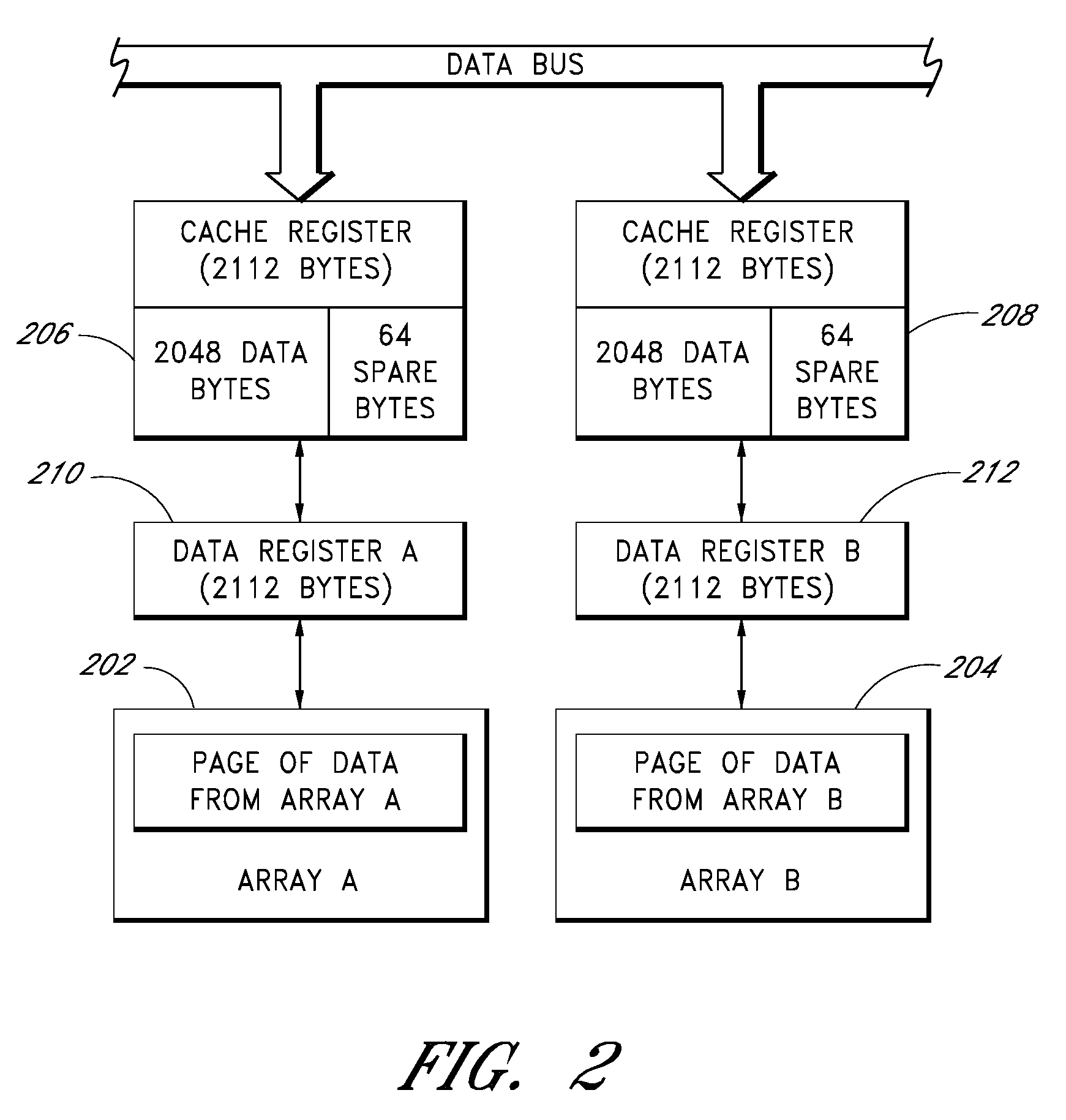
Block addressing for parallel memory arrays
InactiveUS20090013148A1Memory architecture accessing/allocationMemory adressing/allocation/relocationParallel arrayThroughput
Apparatus and methods provide associative mapping of the blocks of two or more memory arrays such that data, such as pages of data, from the good blocks of the two or more memory arrays can be read in an alternating manner for speed or can be read in parallel for providing data to relatively wide data channels. This obviates the need for processor intervention to access data and can increase the throughput of data by providing, where configured, the ability to alternate reading of data from two or more arrays. For example, while one array is loading data to a cache, the memory device can be providing data that has already been loaded to the cache.
Owner:MICRON TECH INC
High linearity superconducting radio frequency magnetic field detector
ActiveUS8933695B1Total nonlinearities have been significantly reduced or eliminatedAvoid interferenceSuperconductors/hyperconductorsElectric pulse generatorTotal harmonic distortionRadio frequency
A superconducting quantum interference devices (SQUID) comprises a superconducting inductive loop with at least two Josephson junction, whereby a magnetic flux coupled into the inductive loop produces a modulated response up through radio frequencies. Series and parallel arrays of SQUIDs can increase the dynamic range, output, and linearity, while maintaining bandwidth. Several approaches to achieving a linear triangle-wave transfer function are presented, including harmonic superposition of SQUID cells, differential serial arrays with magnetic frustration, and a novel bi-SQUID cell comprised of a nonlinear Josephson inductance shunting the linear coupling inductance. Total harmonic distortion of less than −120 dB can be achieved in optimum cases.
Owner:SEEQC INC
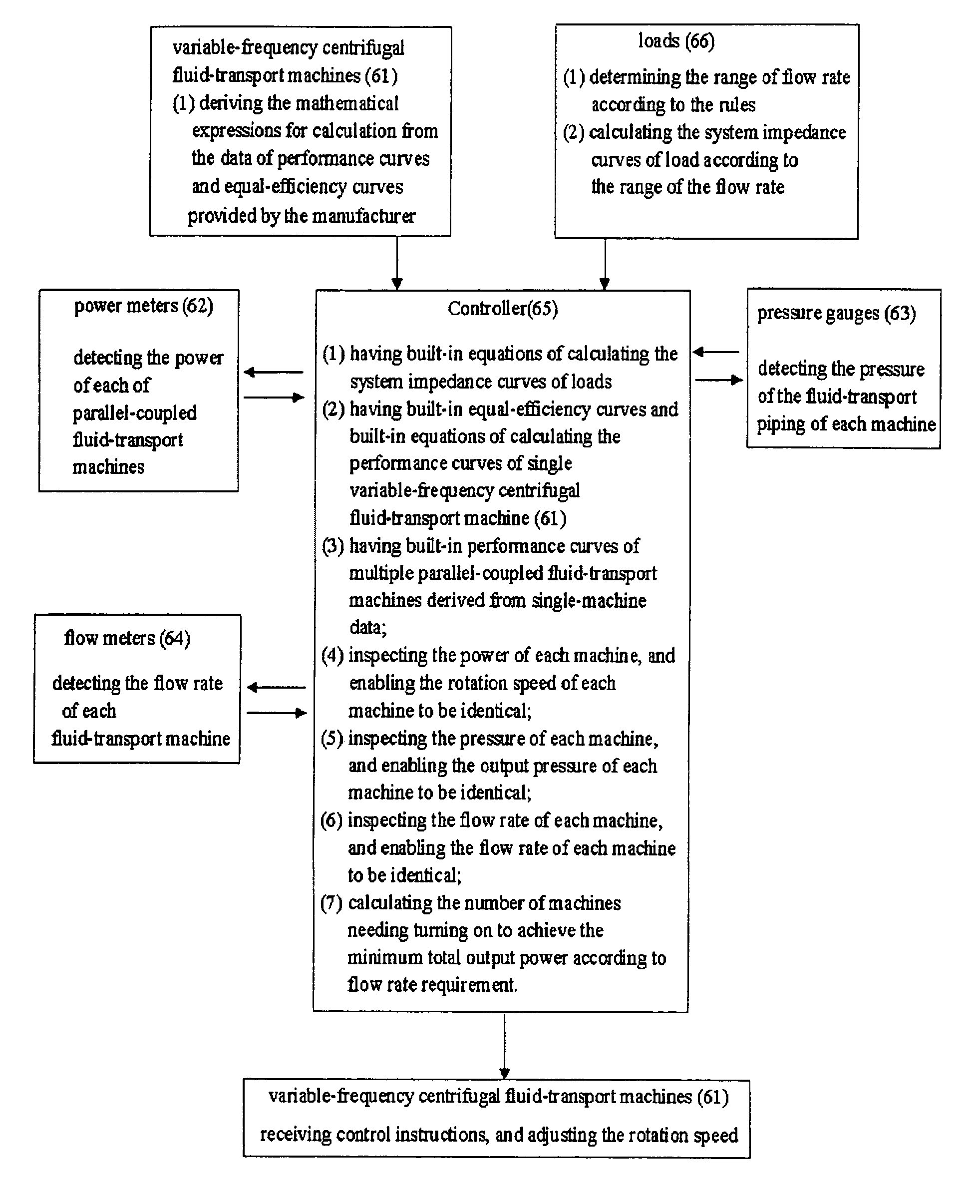
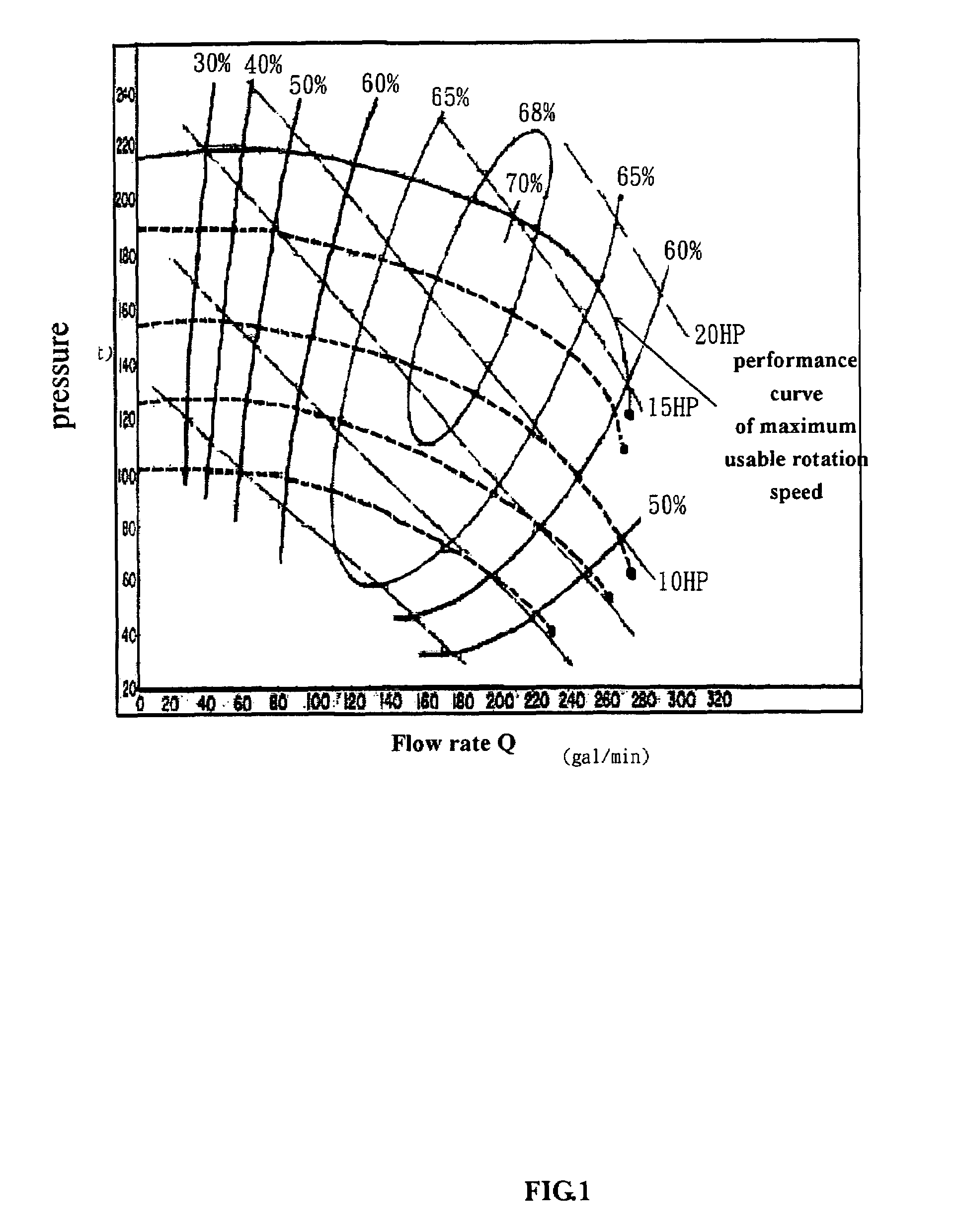
Operation method of energy-saving fluid transporting machineries in parallel array with constant pressure
The present invention discloses a system of energy-efficient and constant-pressure fluid-transport machines coupled in parallel, which can flexibly and massively provide gas and water to every fabrication unit. The system of the present invention comprises: variable-frequency centrifugal fluid-transport machines, pressure gauges, power meters, flow meters, and controllers. The performance curves of the abovementioned system of fluid-transport machines coupled in parallel and the system impedance curves of the loads are analyzed theoretically and built in the controllers together with the equal-efficiency curves provided by the manufacturer. When the system is operating, the data detected by the pressure gauges, power meters, and flow meters are compared with the built-in data to obtain the optimal energy-efficient conditions as the operational criteria of the system of the present invention.
Owner:HUANG WEN CHENG
Electrochemical system and method for the treatment of water and wastewater
ActiveUS20090321251A1Improves of drinking water and sanitary conditionEffective treatmentFrom normal temperature solutionsLiquid separation by electricityElectrical polarityWastewater
Contaminants are removed from raw water or discharge water from plants, such as sewerage and industrial plants, by applying direct current through an array of spaced, alternately charged electrodes to eliminate or minimize clogging of the electrodes with precipitated contaminants. Polarity may be switched periodically to assist in eliminating or minimizing clogging. In illustrated embodiments, electrode arrays are contained in housings of dielectric material to form modules, To increase processing capacity, the modules are arranged in parallel arrays. Alternatively, a single module is scaled up for large or industrial applications or scaled down for personal use. Instead of housing the electrode arrays in modules through which liquid passes, the electrode arrays for some batch applications are dipped in the water or aqueous solutions.
Owner:ELECTRO CHEM CORP
Polarization detection
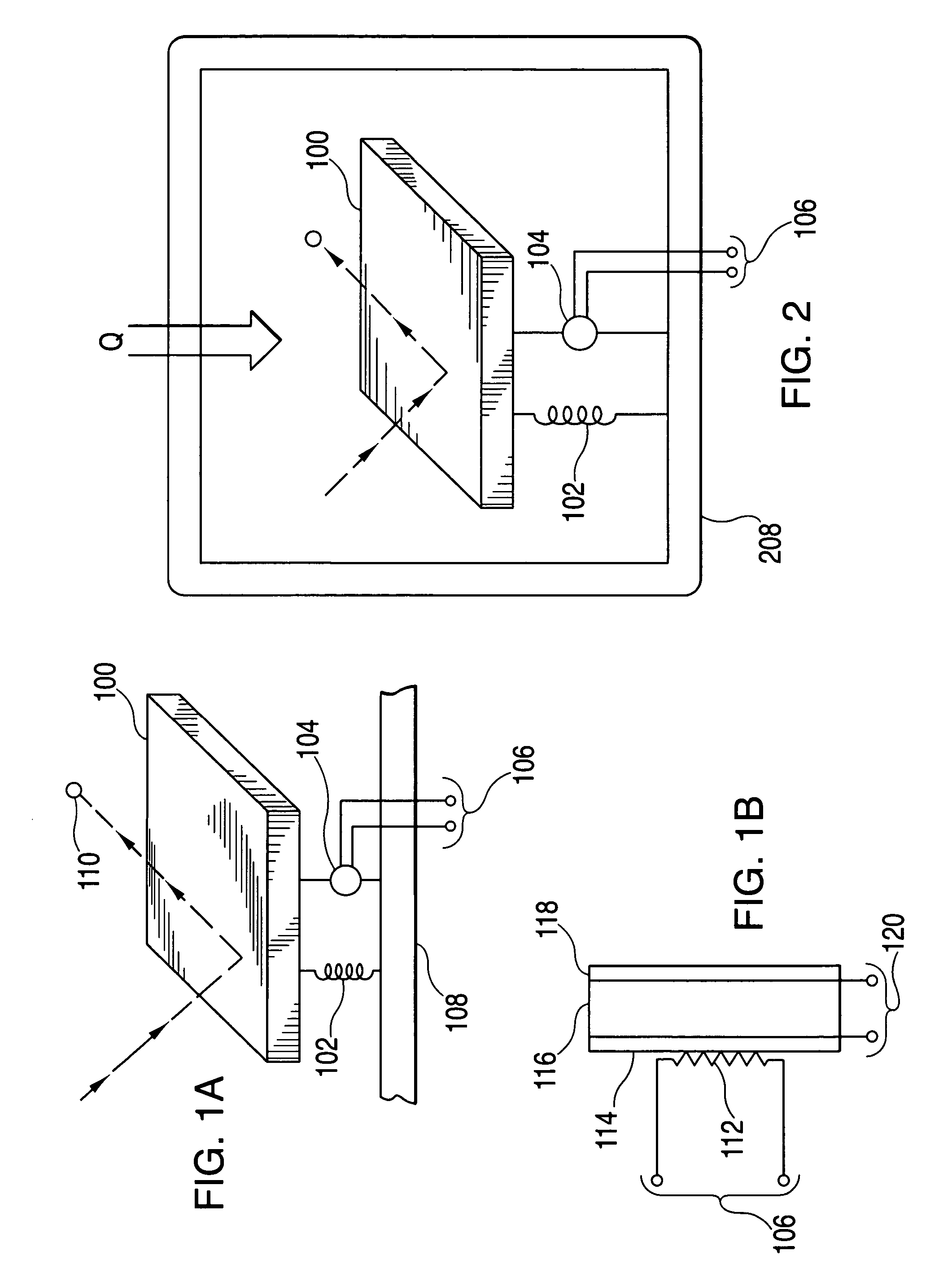
InactiveUS20060192960A1Raman/scattering spectroscopyMicrobiological testing/measurementBeam splitterFluorescence
Disclosed is an optical device for receiving light having a wavelength between 400 nm and 680 nm. The device has a polarizing beam splitter (PBS) that comprises a substrate having a first and second surface, at least one of which being coated with a substantially parallel array of elongated conducting elements, wherein the PBS reflects light of a first polarity and transmits light of the opposite polarity; and a reflector positioned to reflect the opposite polarity light back through the PBS to the front surface, wherein the reflector does not substantially alter the polarity of light at any position. The device can be used to detect fluorescence polarization of a sample.
Owner:RENCS ERIK V +1
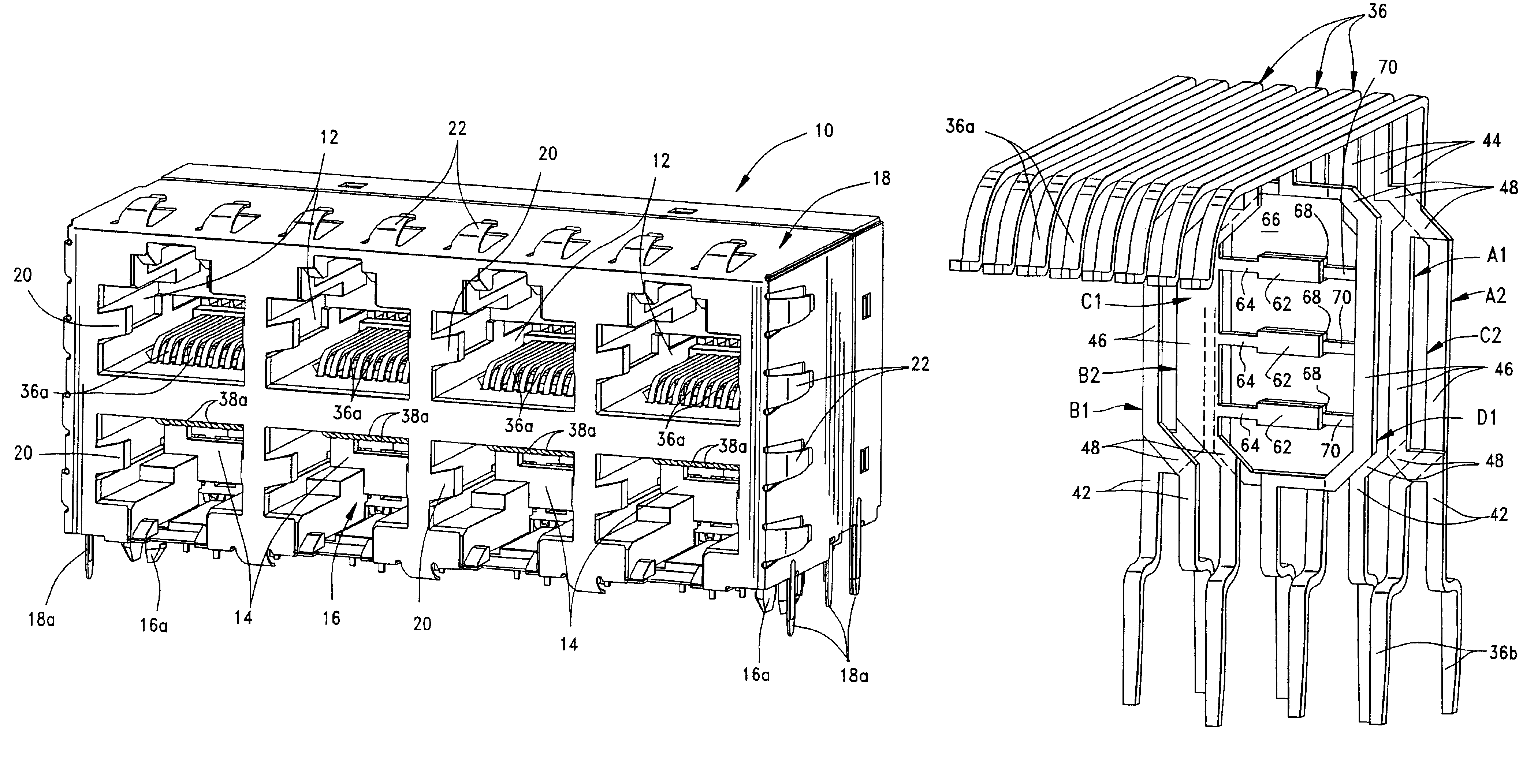
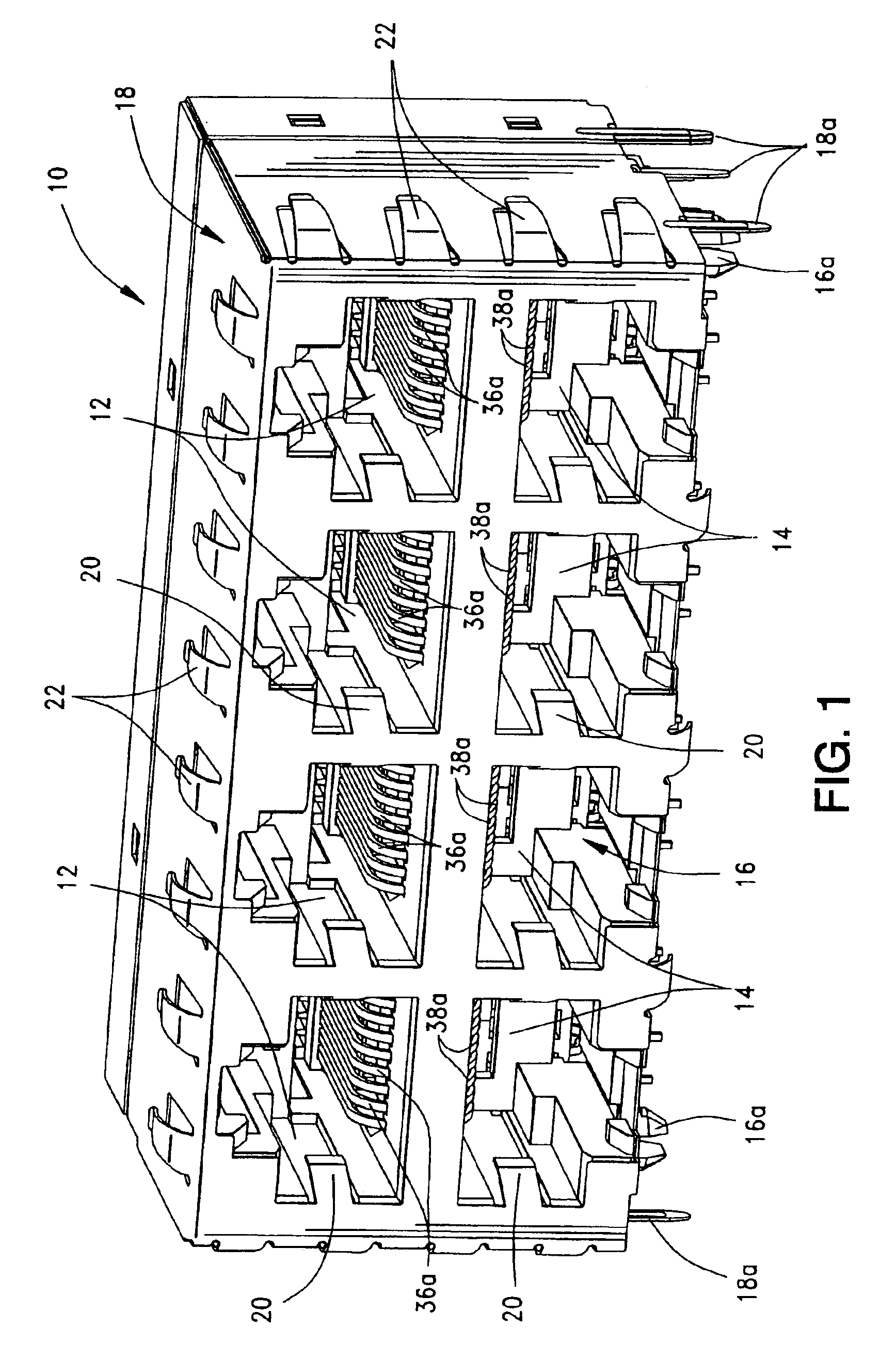
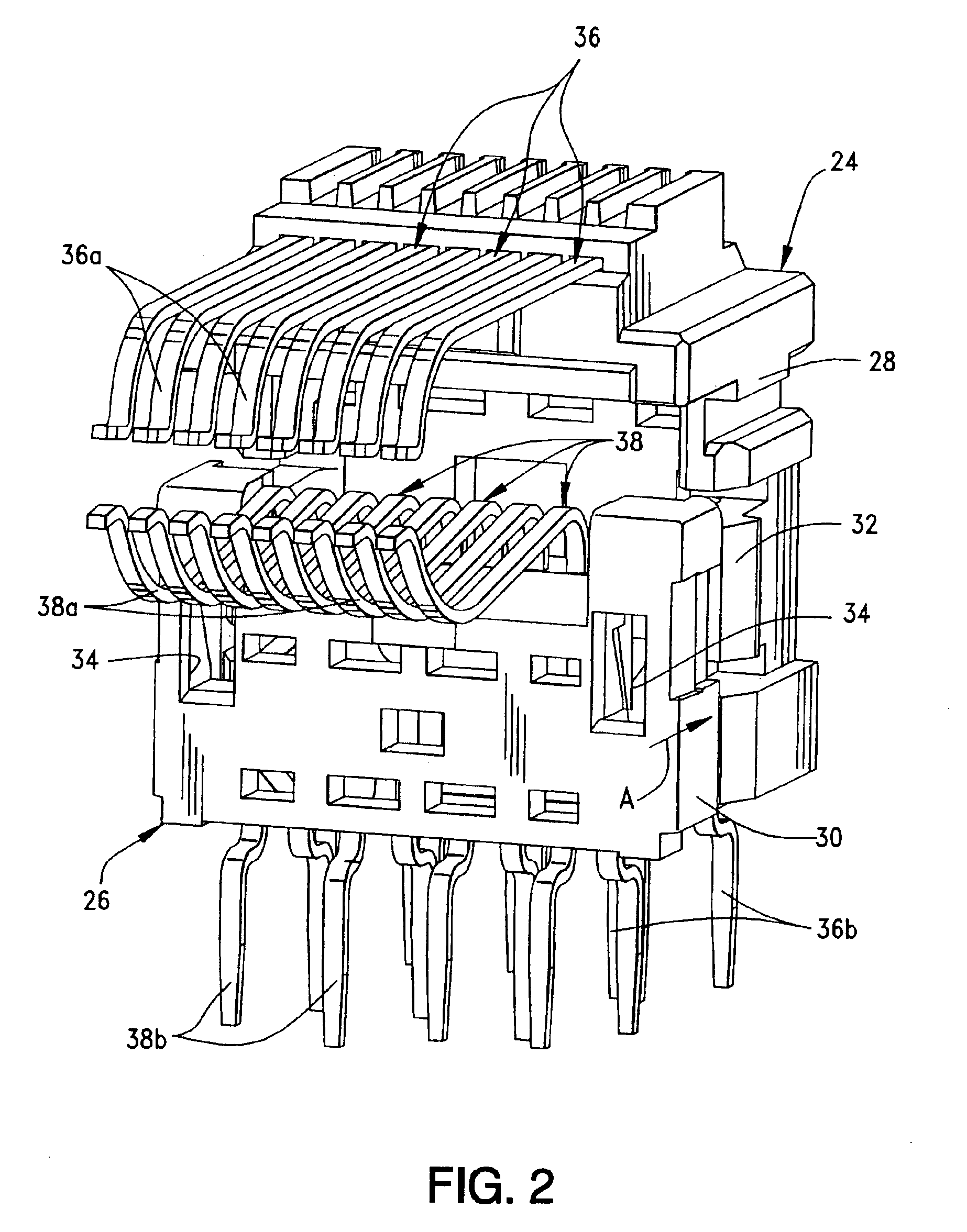
Electrical signal transmission system
An electrical signal transmission system includes a plurality of elongated conductors extending in a generally parallel array. The conductors have input ends at one end of the array and output ends at an opposite end of the array. Each conductor includes an elongated intermediate section and transition sections at opposite ends of the intermediate section joining the intermediate section to the input and output ends of the conductor. The array of conductors define two outside pairs of conductors and at least one inside pair of conductors. The elongated intermediate sections of the conductors in the inside pair thereof being spaced apart wider than the elongated intermediate sections of the conductors in each outside pair thereof.
Owner:MOLEX INC
Energy conversion systems utilizing parallel array of automatic switches and generators
InactiveUS7148579B2Shorten speedReduce thermal energyNanotechInternal combustion piston enginesThermal energyForms of energy
Nanoelectromechanical systems utilizing nanometer-scale assemblies are provided that convert thermal energy into another form of energy that can be used to perform useful work at a macroscopic level. These systems may be used to, for example, produce useful quantities of electric or mechanical energy, heat or cool an external substance or propel an object in a controllable direction. In particular, the present invention includes nanometer-scale beams that reduce the velocity of working substance molecules that collide with this nanometer-scale beam by converting some of the kinetic energy of a colliding molecule into kinetic energy of the nanometer-scale beam. In embodiments that operate without a working substance, the thermal vibrations of the beam itself create the necessary beam motion. In some embodiments, an automatic switch is added to realize a regulator such that the nanometer-scale beams only deliver voltages that exceed a particular amount. Various devices including, piezoelectric, electromagnetic and electromotive force generators, are used to convert the kinetic energy of the nanometer-scale beam into electromagnetic, electric or thermal energy. Systems in which the output energy of millions of these devices is efficiently summed together are also disclosed as well as systems that include nanometer-scale transistors.
Owner:CJP IP HLDG
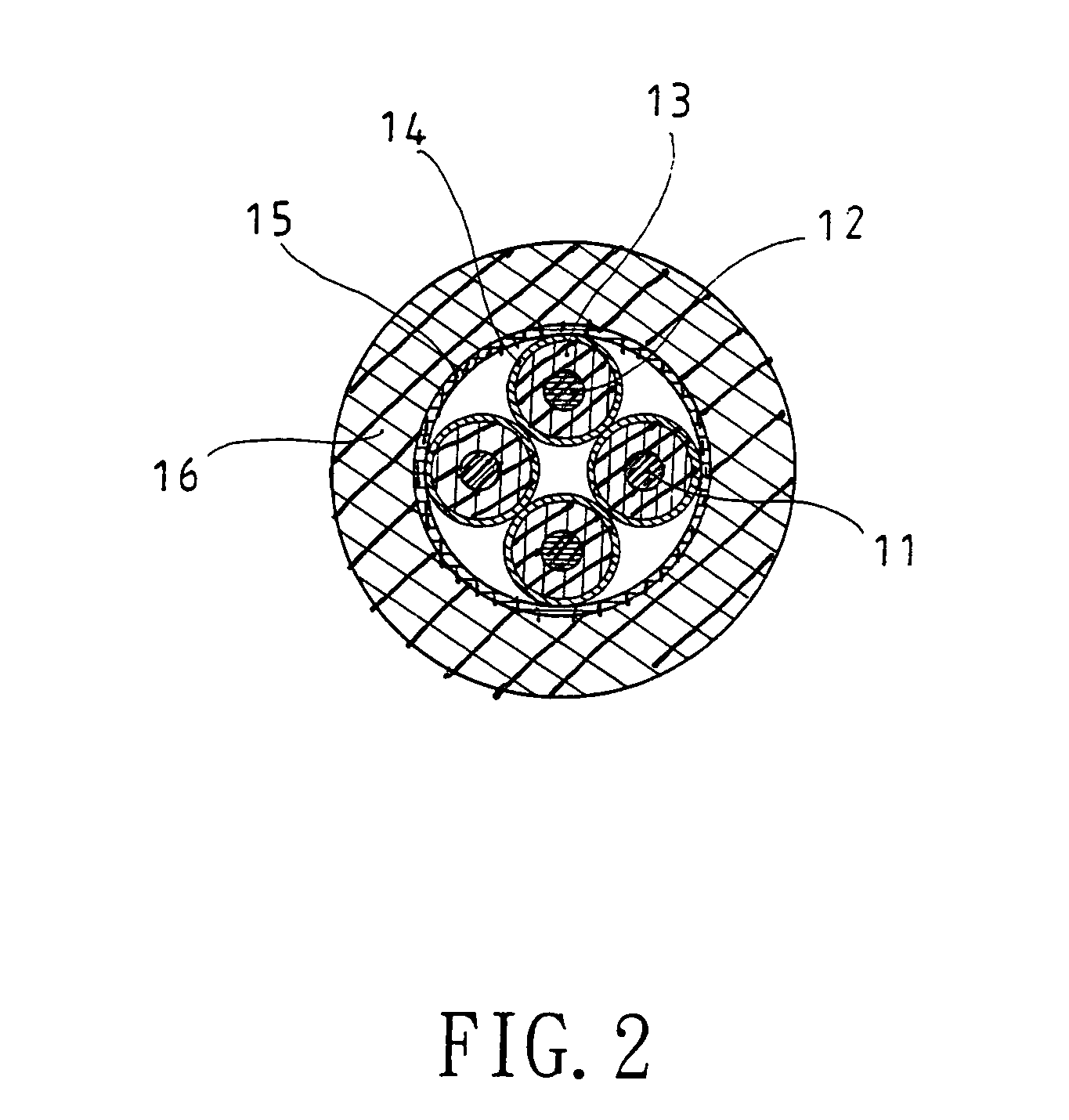
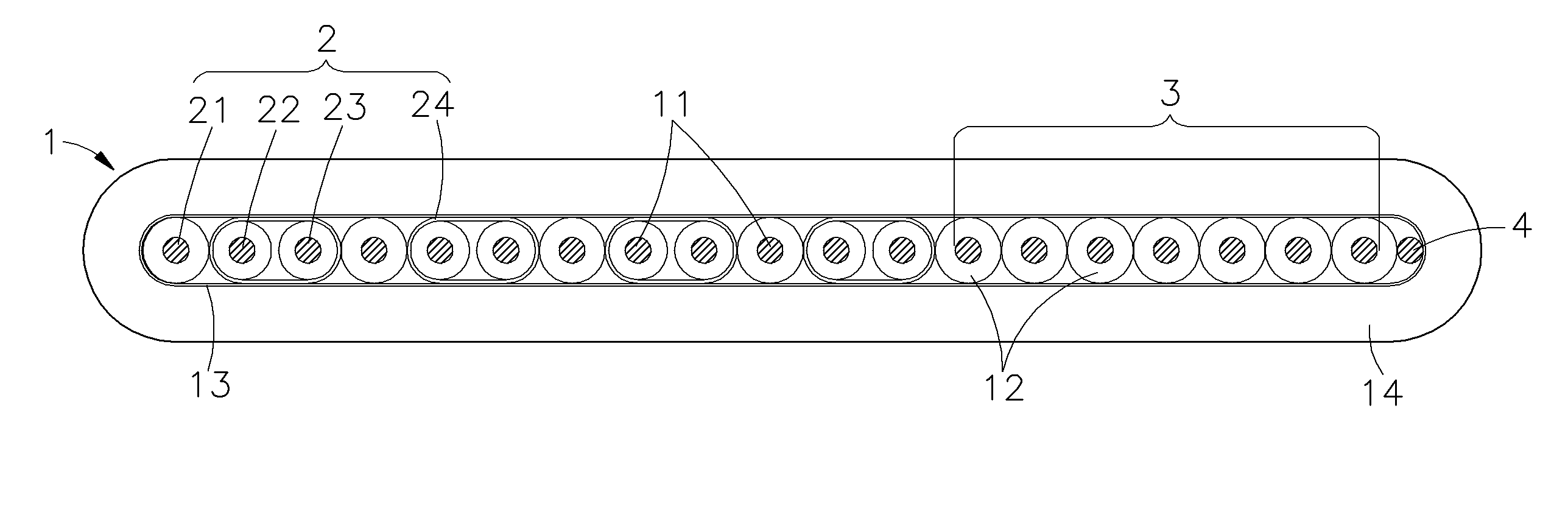
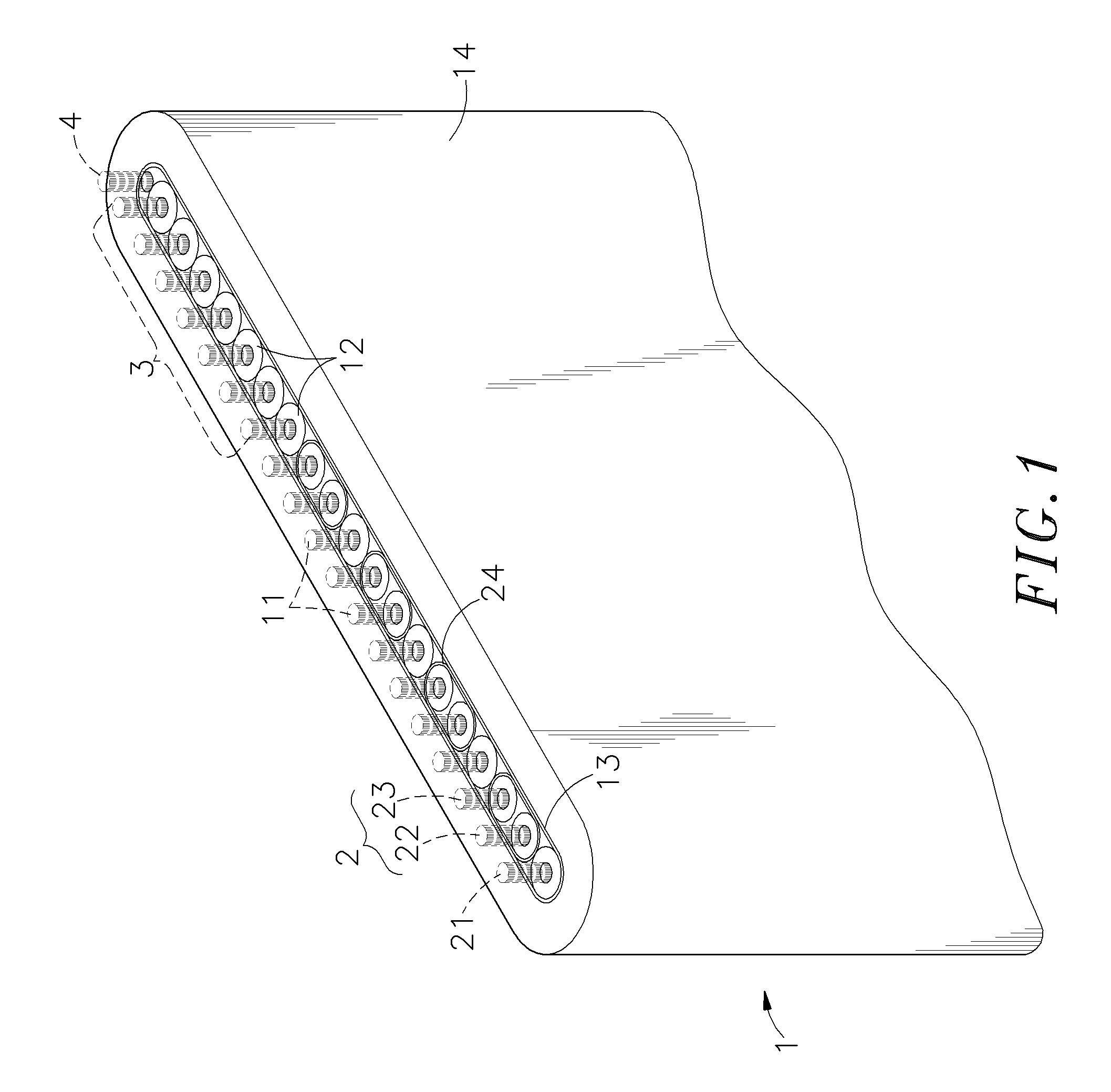
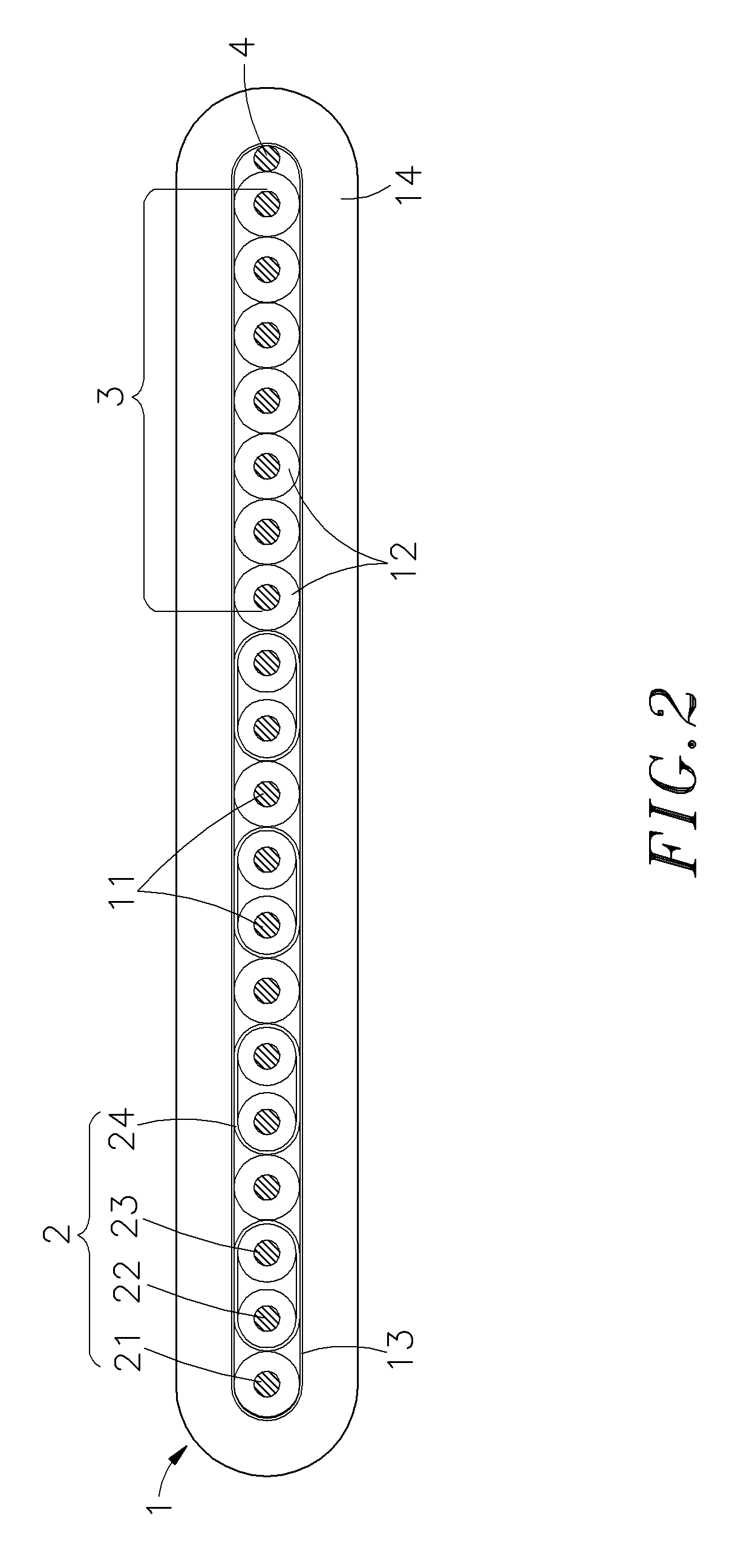
Audio and video signal cable
InactiveUS20050121222A1Avoid it happening againImprove high-frequency phase characteristicInsulated cablesDetails of conductive coresFiberElectrical conductor
An audio and video signal cable consisting of solid conductors of different cross-sectional areas that are parallel arrayed, and after each conductor is insulated, all are surrounded in an insulation, wherein the conductor structure is composed of numerous wires of unequal cross-sectional areas that are furthermore individually insulated. Tinsel, enamel covered wire, or 100% fiber covered copper are utilized for conductors of smaller cross-sectional area, which not only reduces cable outer diameter and increases tensile strength, but also effectively benefits skin effect and enhances high frequency transmission, while larger cross-sectional area conductors facilitate rapid low frequency passage. As such, the present invention is capable of high- and low-frequency band phase synchronicity as well as optimal balance across all frequencies.
Owner:RICH ELECTRIC WIRE & CABLE
Method of forming micro-tubular polymeric materials
The present invention discloses the design and fabrication of highly porous (up to 97%) scaffolds from biodegradable polymers with a novel phase-separation technique to generate controllable parallel array of micro-tubular architecture. The porosity, diameter of the micro-tubes, the tubular morphology and their orientation may be controlled by the polymer concentration, solvent system and temperature gradient. The mechanical properties of these scaffolds are anisotropic. Osteoblastic cells are seeded in these 3-D scaffolds and cultured in vitro. The cell distribution and the neo-tissue organization are guided by the micro-tubular architecture. The method has general applicability to a variety of polymers, therefore the degradation rate, cell-matrix interactions may be controlled by the chemical composition of the polymers and the incorporation of bioactive moieties. These micro-tubular scaffolds may be used to regenerate a variety of tissues with anisotropic architecture and properties.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF MICHIGAN
Four-degree-of-freedom parallel manipulator for producing schonflies motions
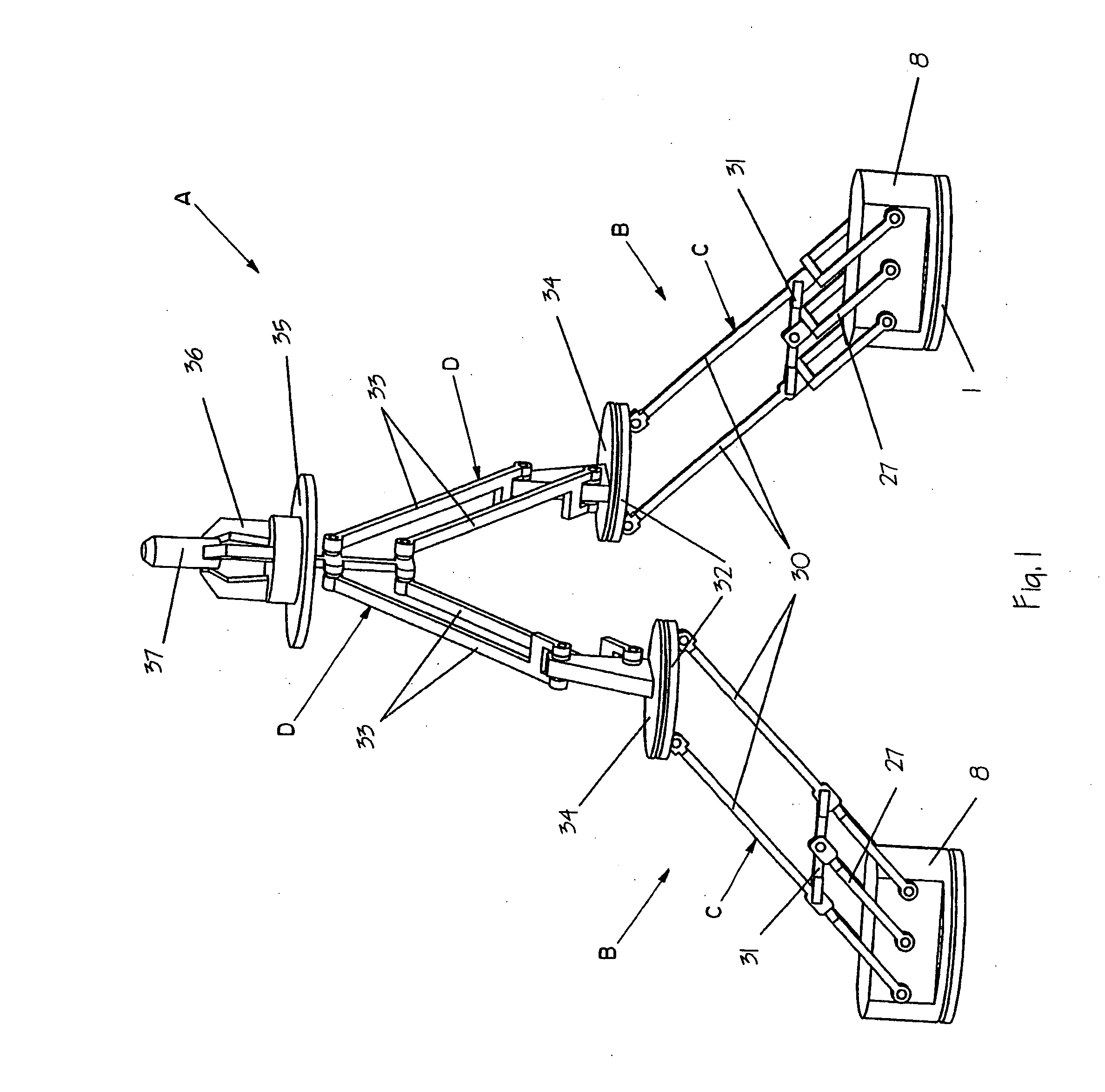
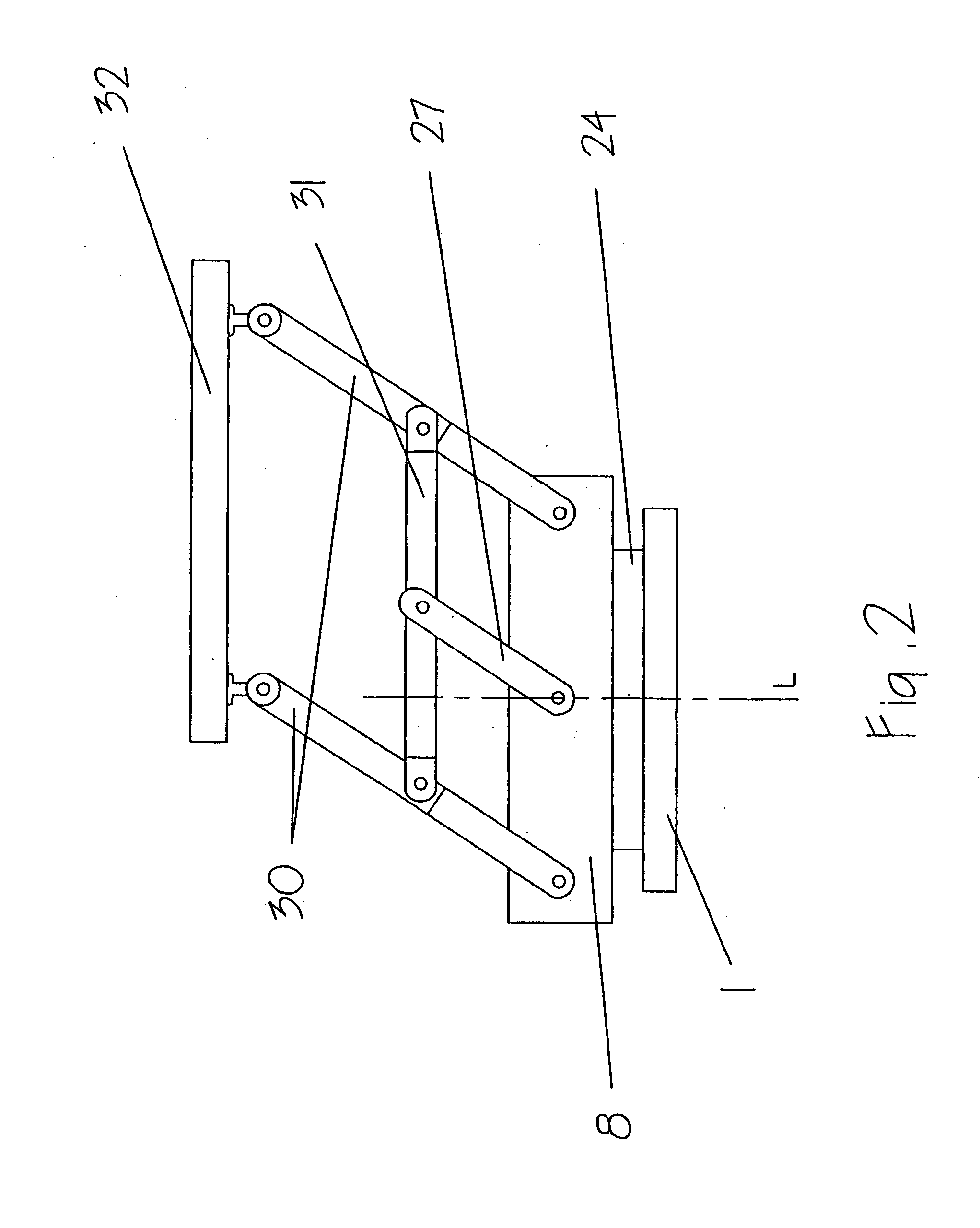
InactiveUS20050262959A1Increase computing speedMaximize production throughputProgramme-controlled manipulatorMechanical apparatusDegrees of freedomActuator
The present invention relates to a manipulating device (A) for producing Schönflies motions comprising a parallel array of at least two legs (B), each leg (B) including an actuator unit (C) having first and second ends and producing a pan-tilt motion, each leg (B) also including a passive unit (D) having first and second ends, the first end of the passive unit (D) being coupled to the first end of the actuator unit (C) such that the passive unit (D) reacts to the pan-tilt motion, a base (1) connected to the second end of each actuator unit (C), all second ends having a constant relative position with respect to one another; and a common end-effector (36) connected to the second end of all passive units (D) such that the common end-effector (36) is provided with a Schönflies motion by the legs (B).
Owner:MCGILL UNIV
Electronic system with non-parallel arrays of circuit card assemblies
InactiveUS20060067069A1Clamping/extracting meansRack/frame constructionElectronic systemsShortest distance
An electronic assembly for housing circuit cards of different types, which communicate with one another at high speed. Circuit cards of a first type plug into a backplane side-by-side. Circuit cards of a second type are arranged perpendicularly to the circuit cards of the first type. The arrangement allows cards of the first type to communicate with cards of the second type over short distances, thus improving system throughput. It also allows cards of different types to be cooled differently, thus promoting efficient cooling.
Owner:AMPHENOL CORP
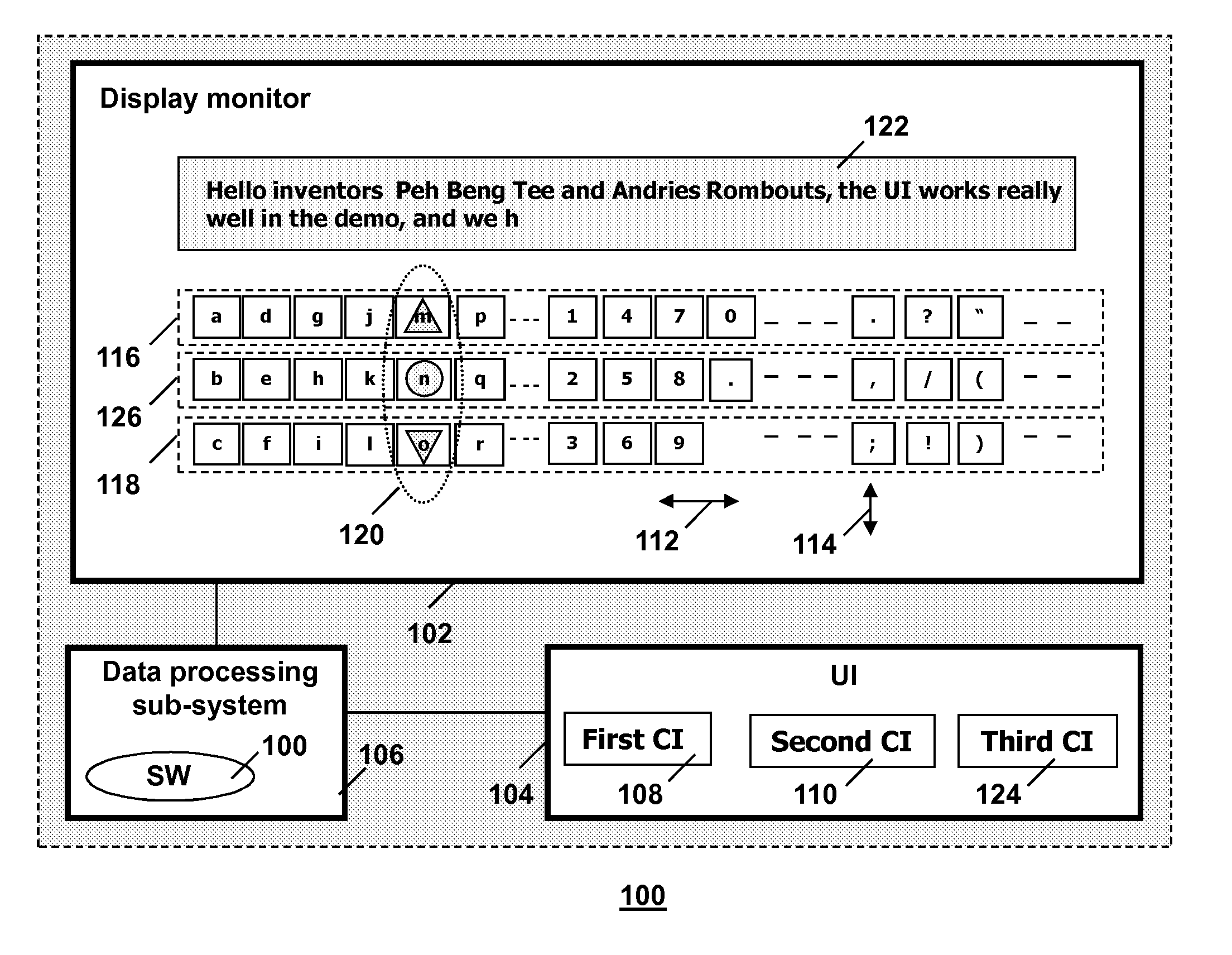
User-interface for entering alphanumerical characters
An information processing system has a display monitor and a user-interface for text entry. The display monitor presents the set of alphanumerical characters in a spatial configuration of three parallel horizontal rows or three parallel vertical columns. The “left”-button and the “right” button of the directional buttons of the user-interface control the selection of a group of alphanumerical characters, one of each of the three parallel arrays and positioned in the same column. The “up”-button and the “down”-button of the directional buttons and the “OK”-button, sitting in between, are used to select a specific one of the alphanumerical characters from the selected group.
Owner:HOME CONTROL SINGAPORE
High-frequency digital A/V cable
InactiveUS7956290B2Improve protectionFlat/ribbon cablesInsulated conductorsIsolation layerParallel array
In high-frequency digital A / V cable having high-frequency signal line sets and low-frequency signal lines arranged in a parallel array, a metal shielding layer is set within an isolation layer inside the outer plastic sheath to surround the two high-frequency signal lines of each high-frequency signal line set for EMI protection, and a metal ground wire is arranged within the outer plastic sheath at one lateral side of the parallel array of the high-frequency signal line sets and low-frequency signal lines in a parallel manner.
Owner:SURE FIRE ELECTRICAL
Energy conversion systems utilizing parallel array of automatic switches and generators
InactiveUS20070018537A1Shorten speedValid conversionNanotechInternal combustion piston enginesThermal energyForms of energy
Owner:CJP IP HLDG
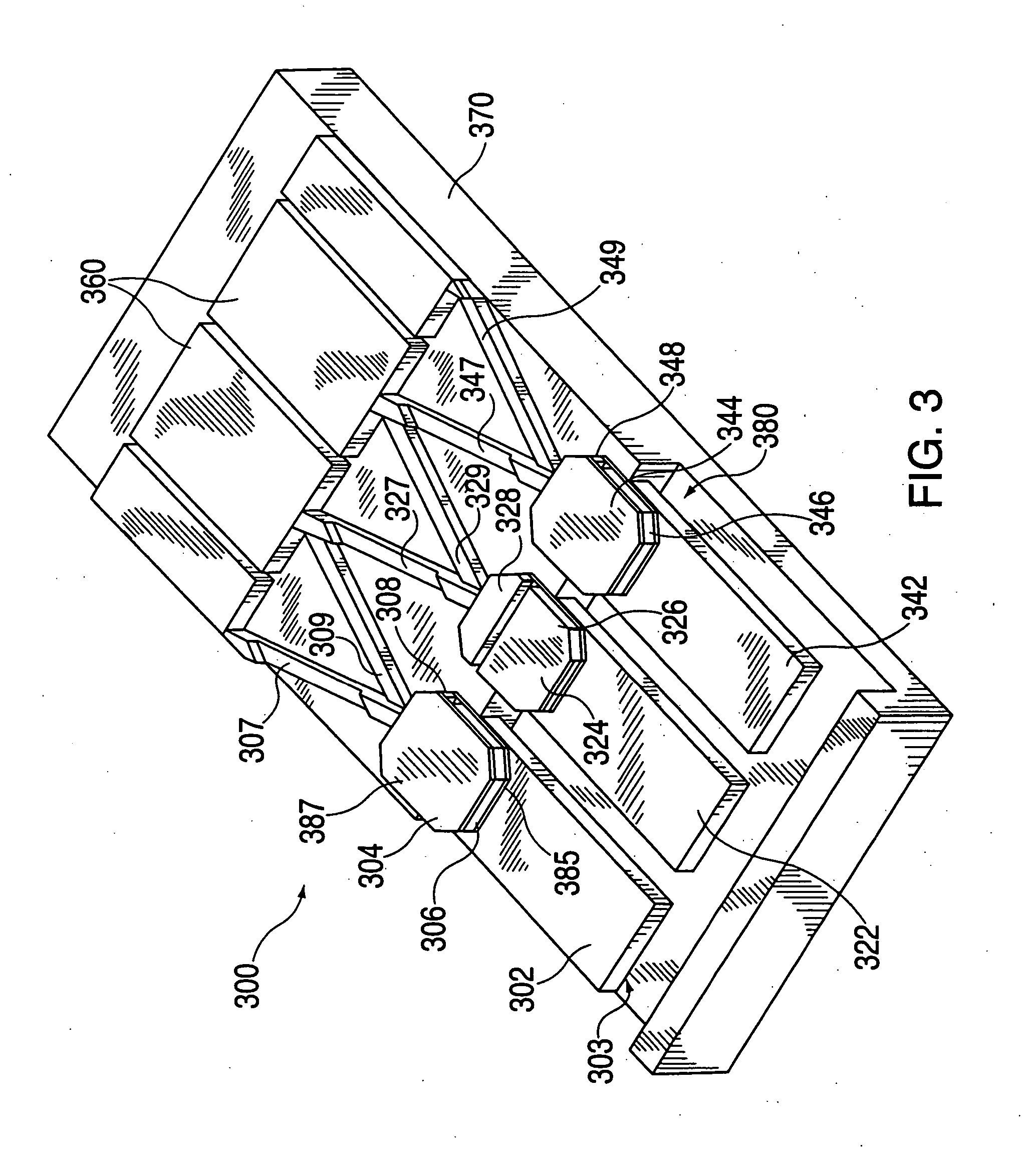
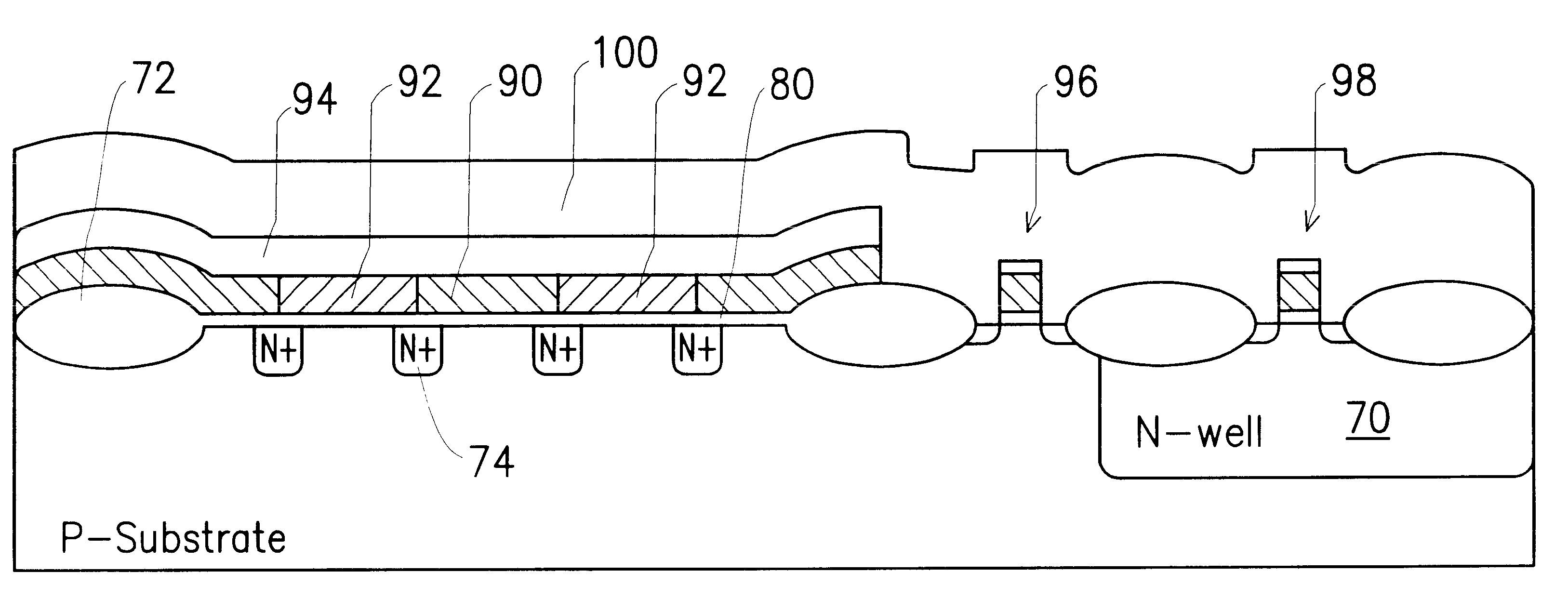
Variable work function transistor high density mask ROM
InactiveUS6417548B1Solid-state devicesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingBit lineMask ROM
A mask ROM stores information by selecting the work function of the gates of each FET in an array of FETs. The polysilicon gates of some of the FETs are doped N-type and the gates of the other FETs are doped P-type to form gates having different work functions, thereby forming FETs having different threshold voltages. The ROM consists of a parallel array of buried N+ bit lines formed in the substrate, a gate oxide layer deposited over the bit lines and a layer of polysilicon deposited on the gate oxide. The polysilicon is blanket doped P-type and then an encoding mask is formed, with openings in the encoding mask exposing regions of the polysilicon to be formed into gates of FETs with low threshold voltages. Either arsenic or phosphorus is doped into the polysilicon through the mask openings. The mask is removed, a layer of conductive material such as tungsten silicide is deposited and the polysilicon and the conductive material are formed into word lines for the ROM. The word lines of the ROM serve as gates for the FETs and the bit lines serve as sources and drains for the FETs.
Owner:UNITED MICROELECTRONICS CORP
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com