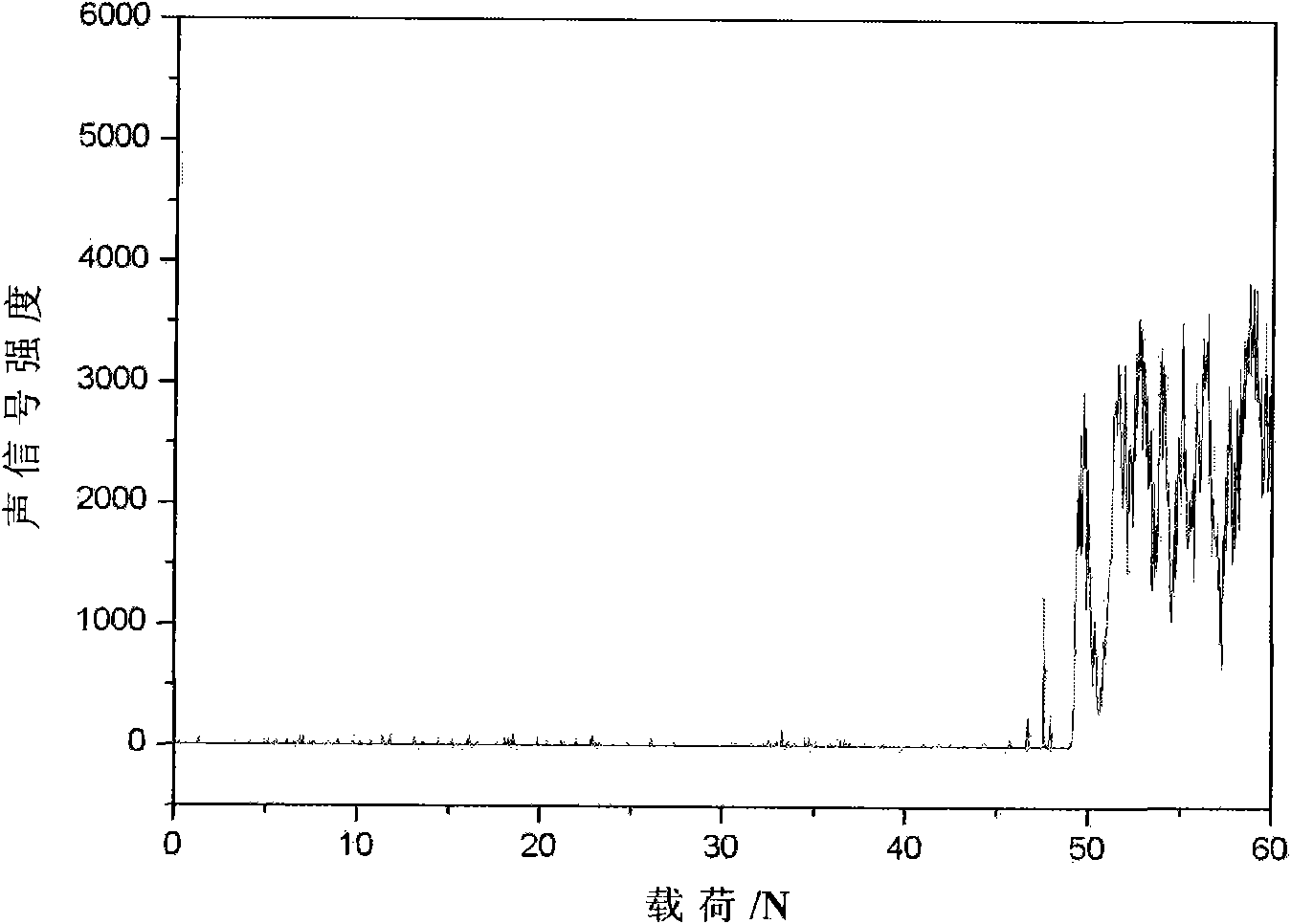
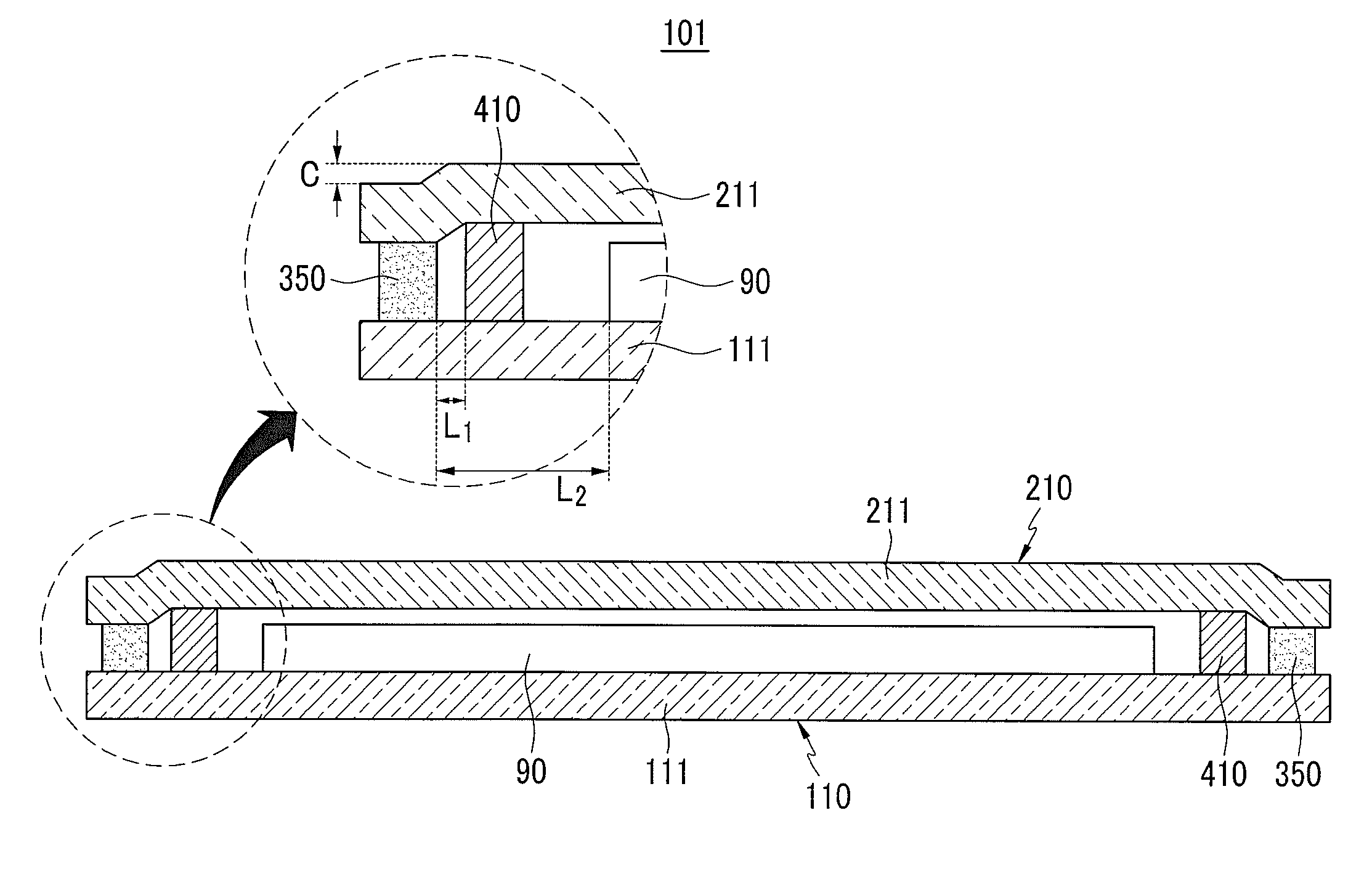
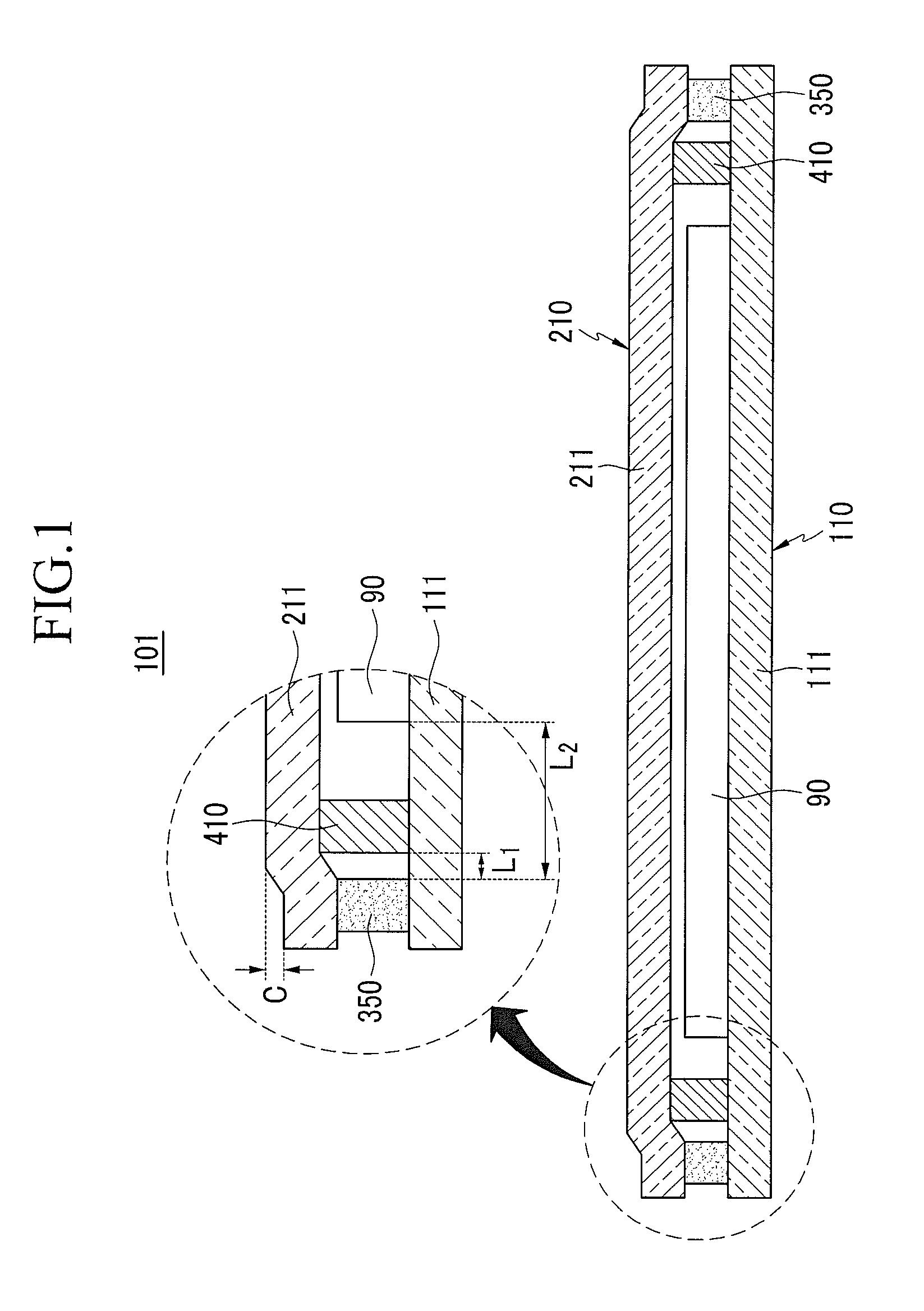
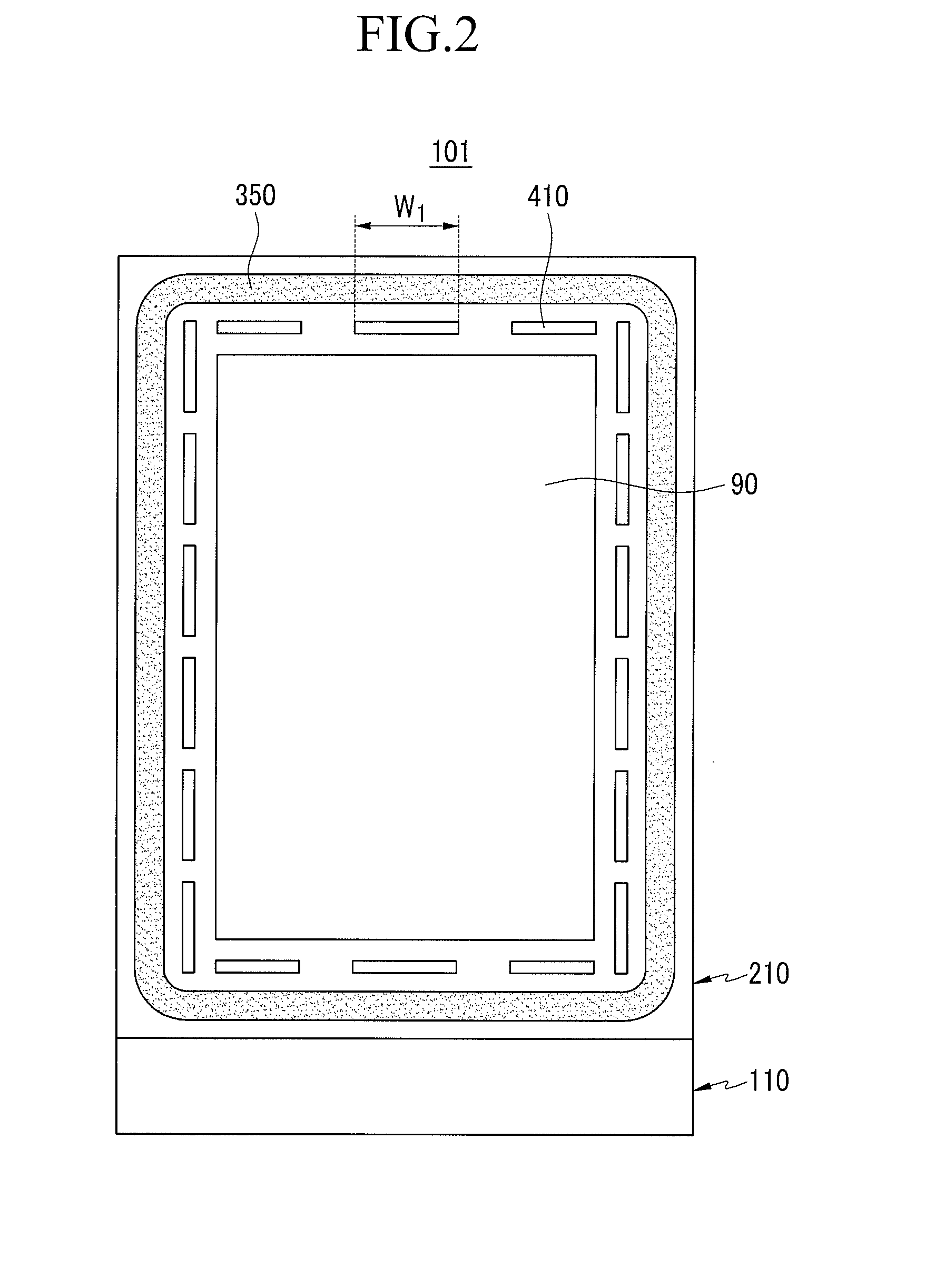
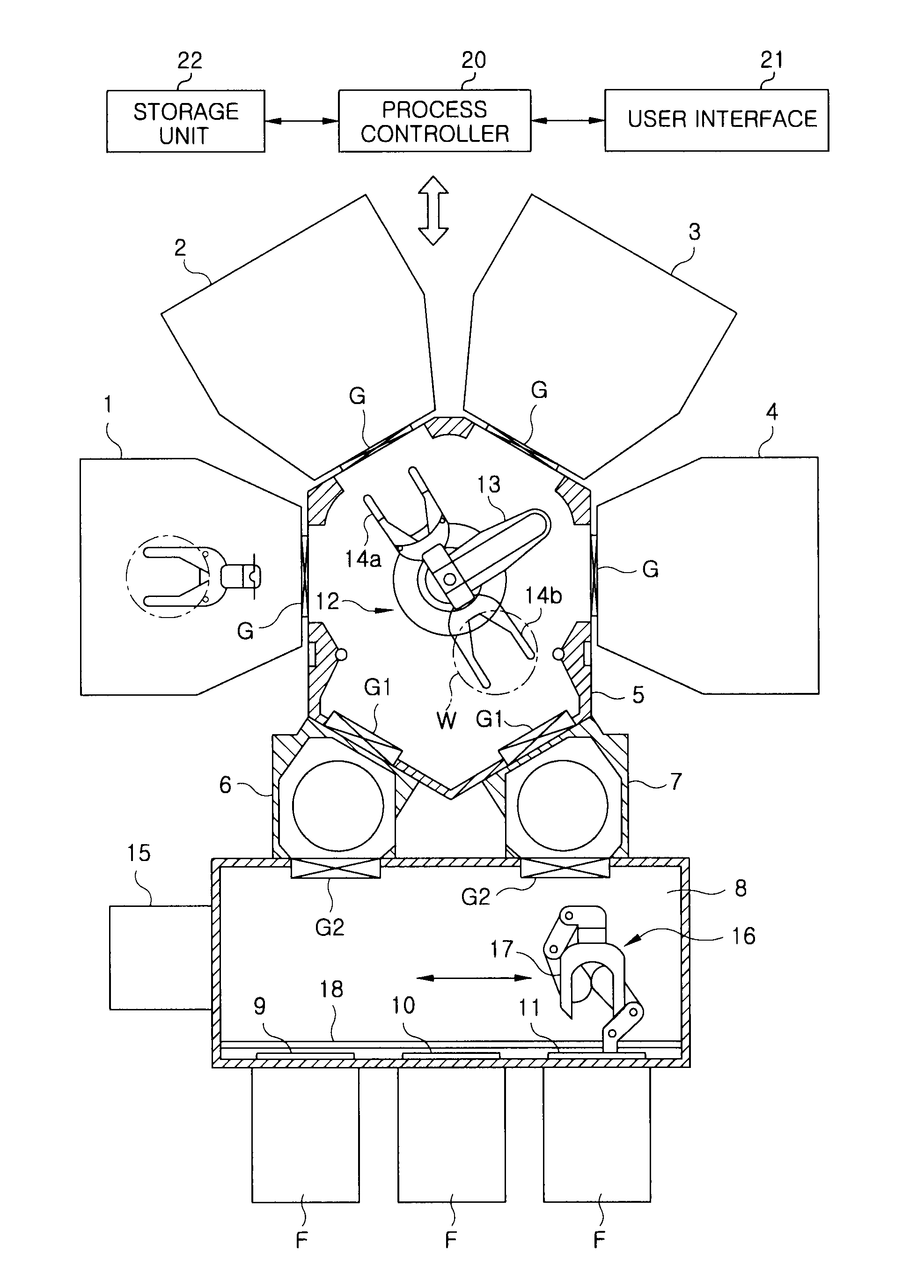
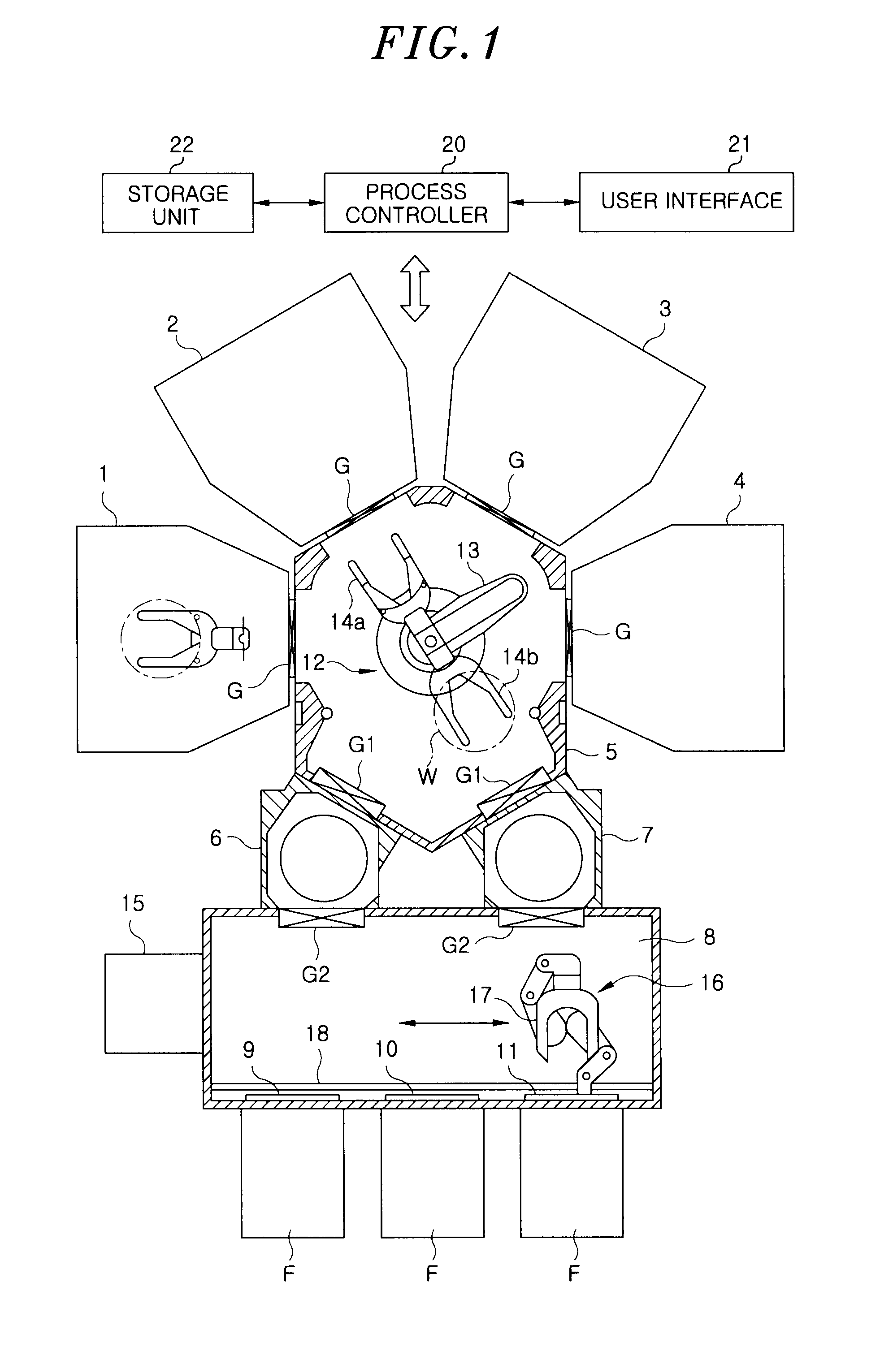
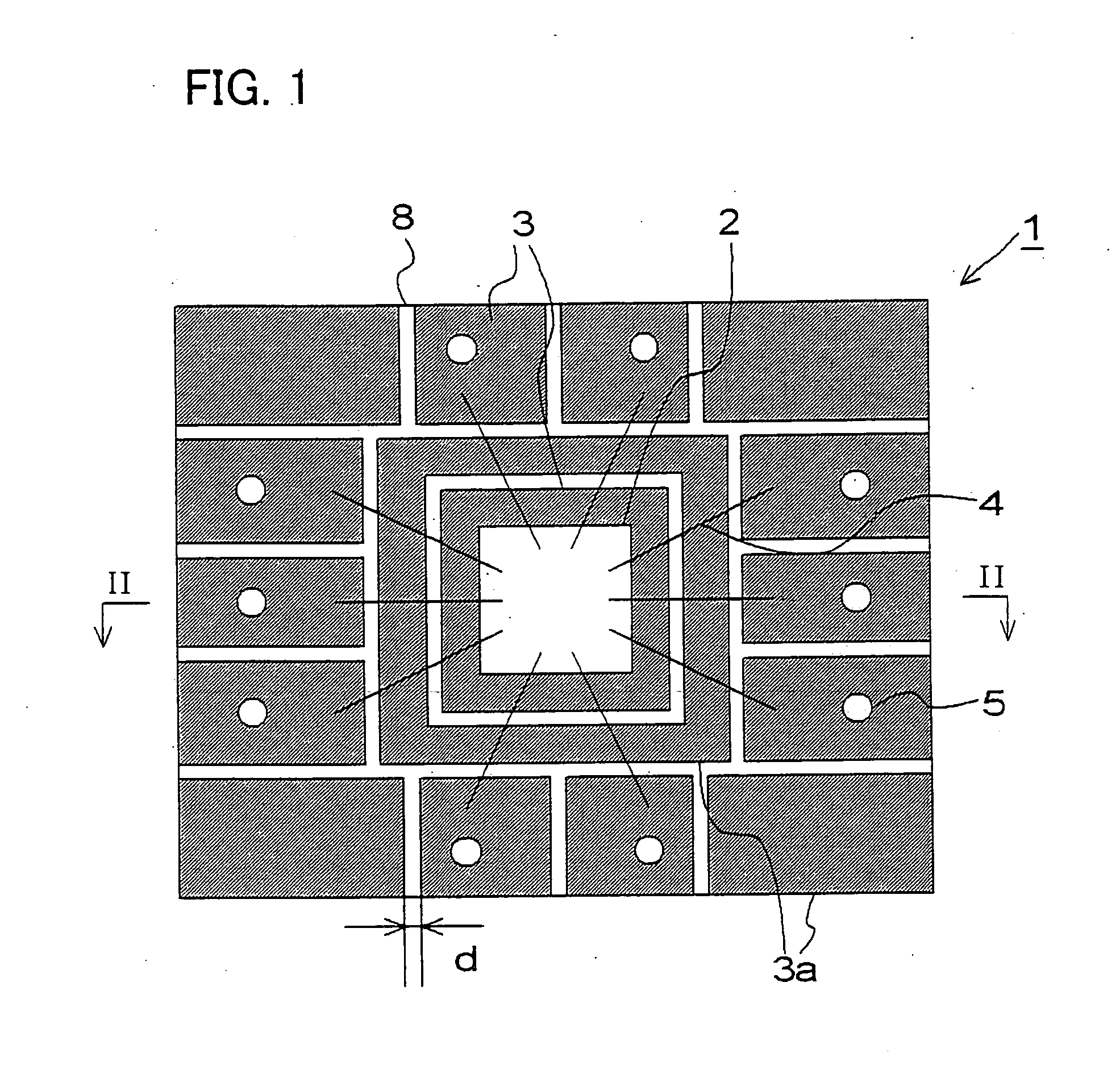
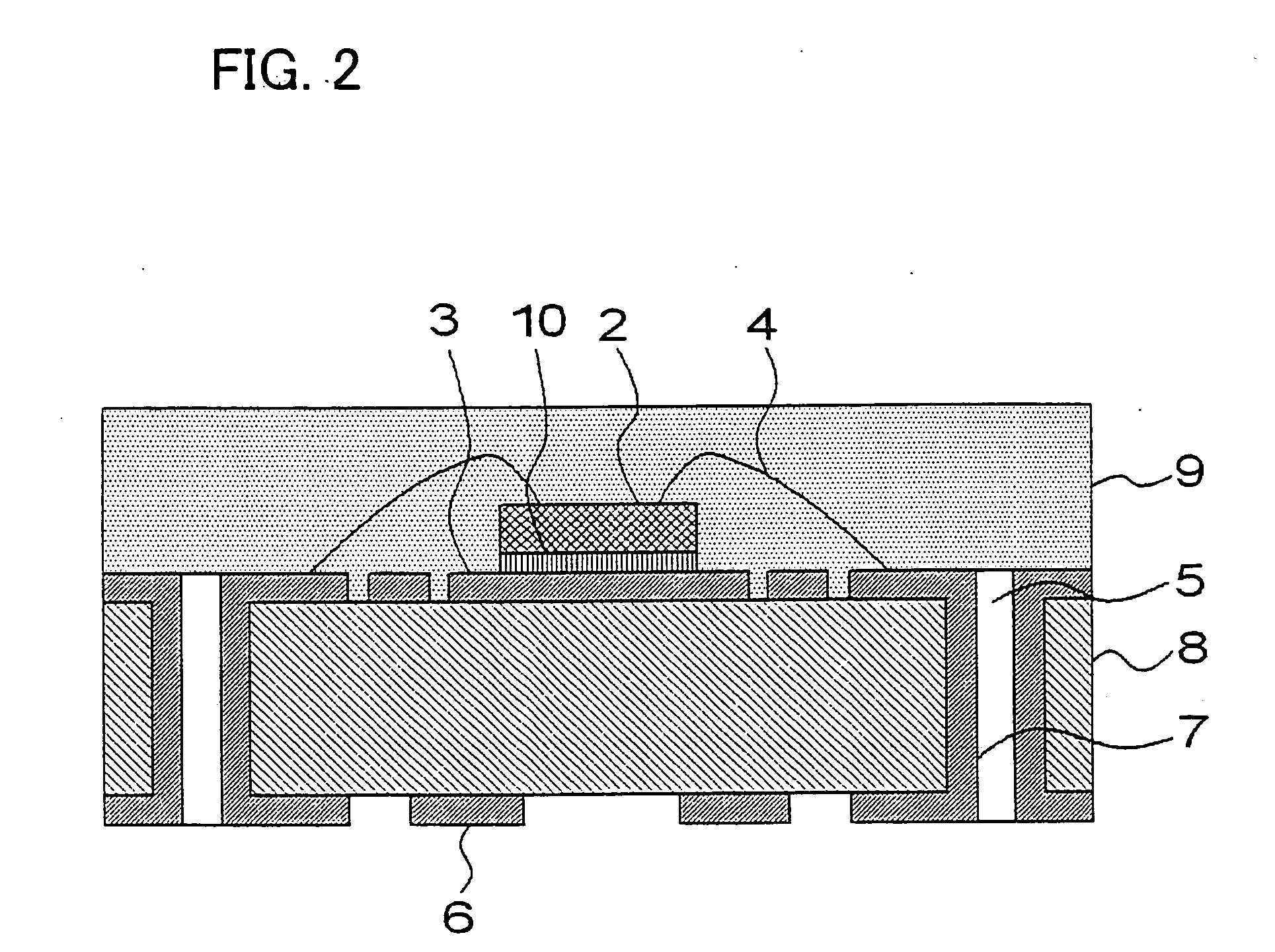
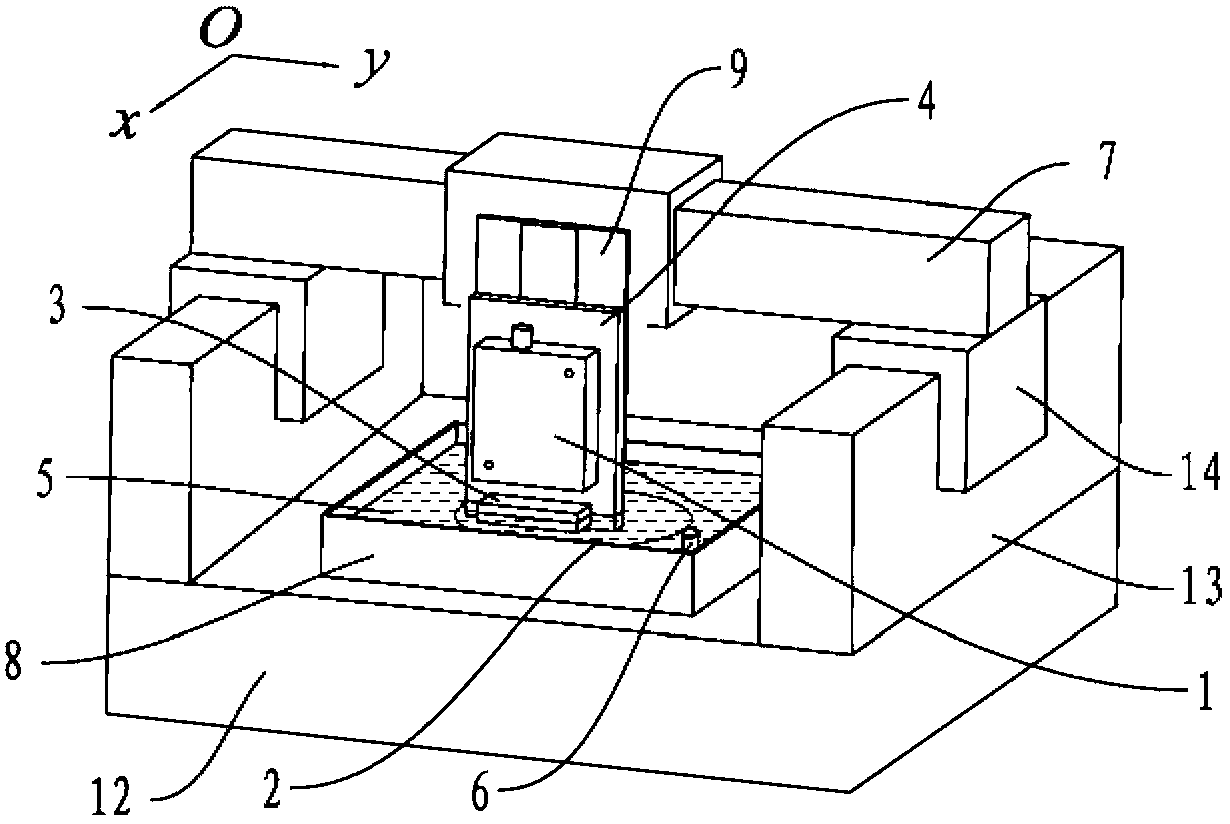
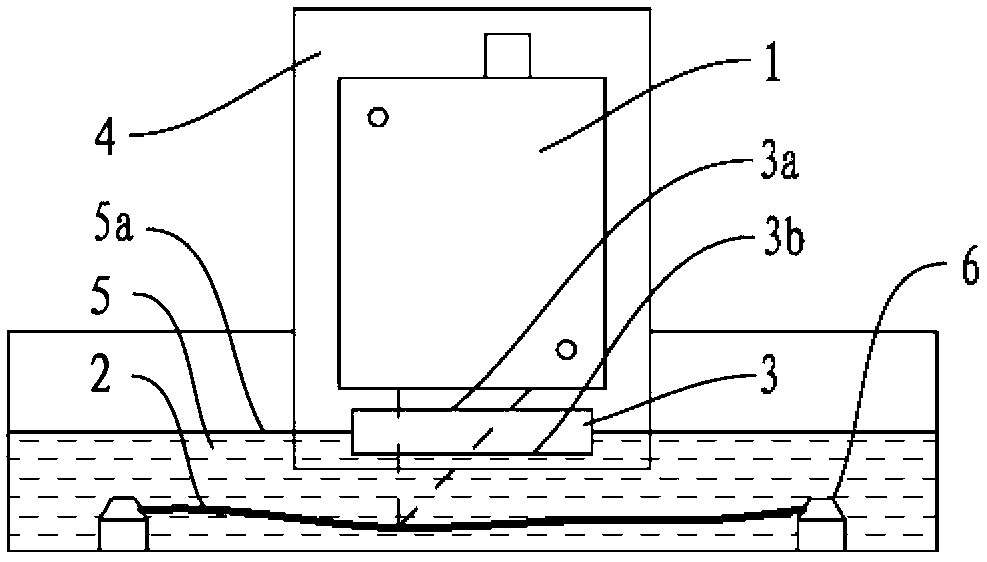
Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
106 results about "Substrate deformation" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
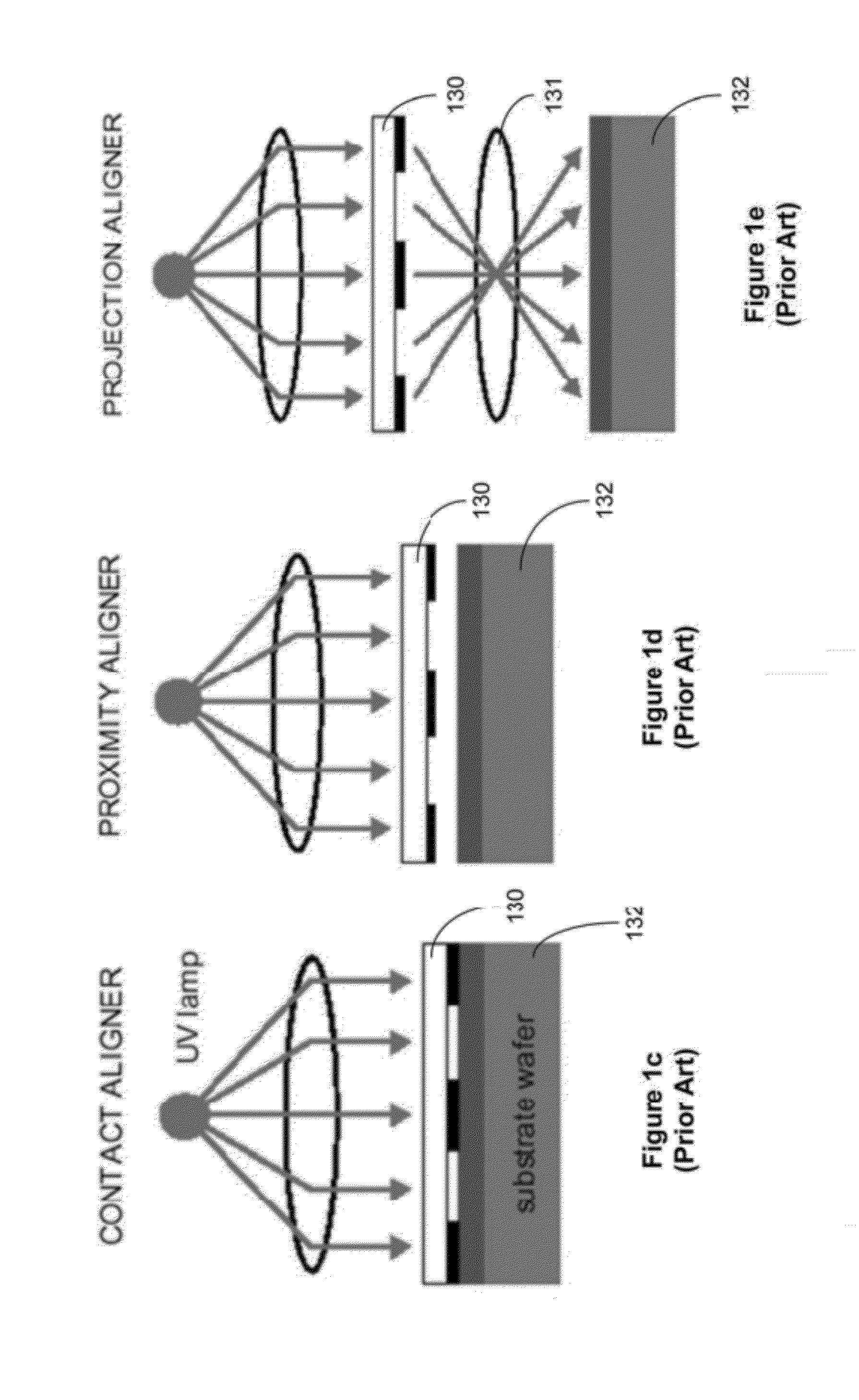
"Such patterns of substrate deformation are revealed by investigating fragmentary and eroded footprints, not by the conventional search for pristine footprints on intact bedding planes. "For that reason it is not known whether similar patterns of substrate deformation might occur at sauropod track-sites elsewhere in the world.".
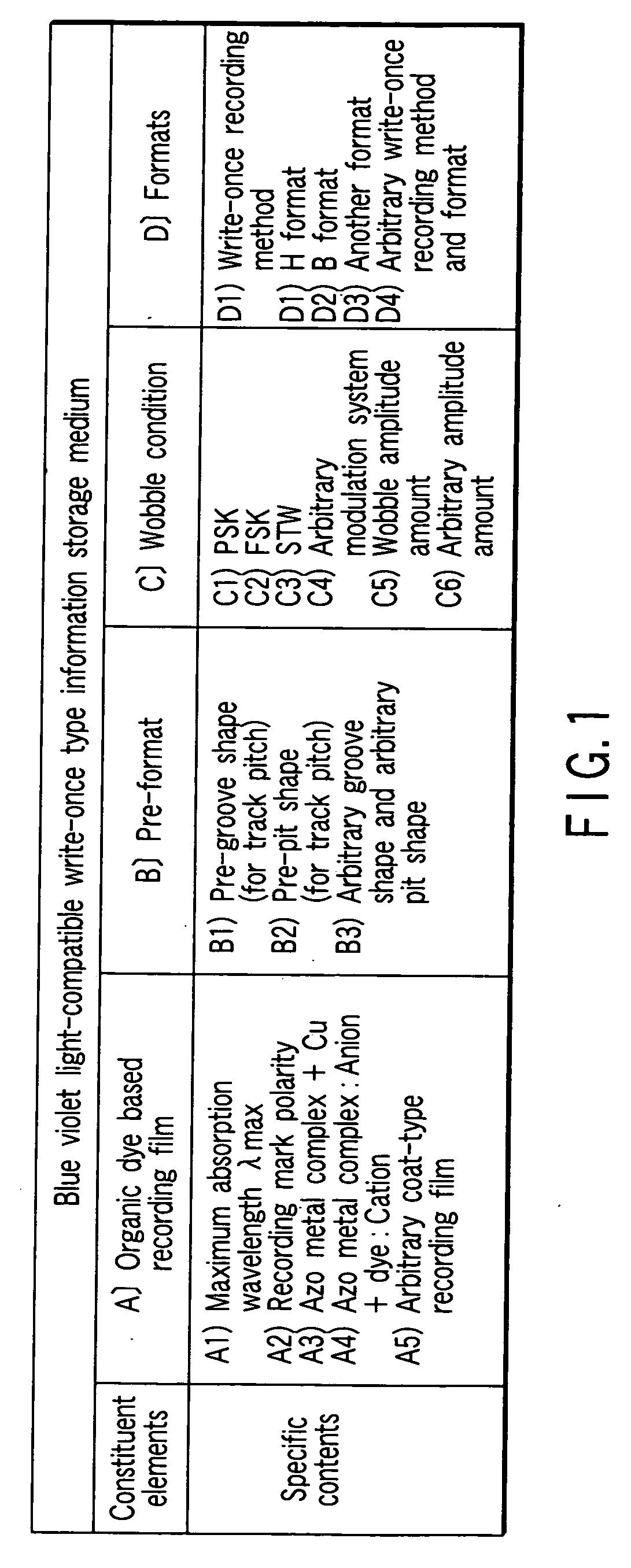
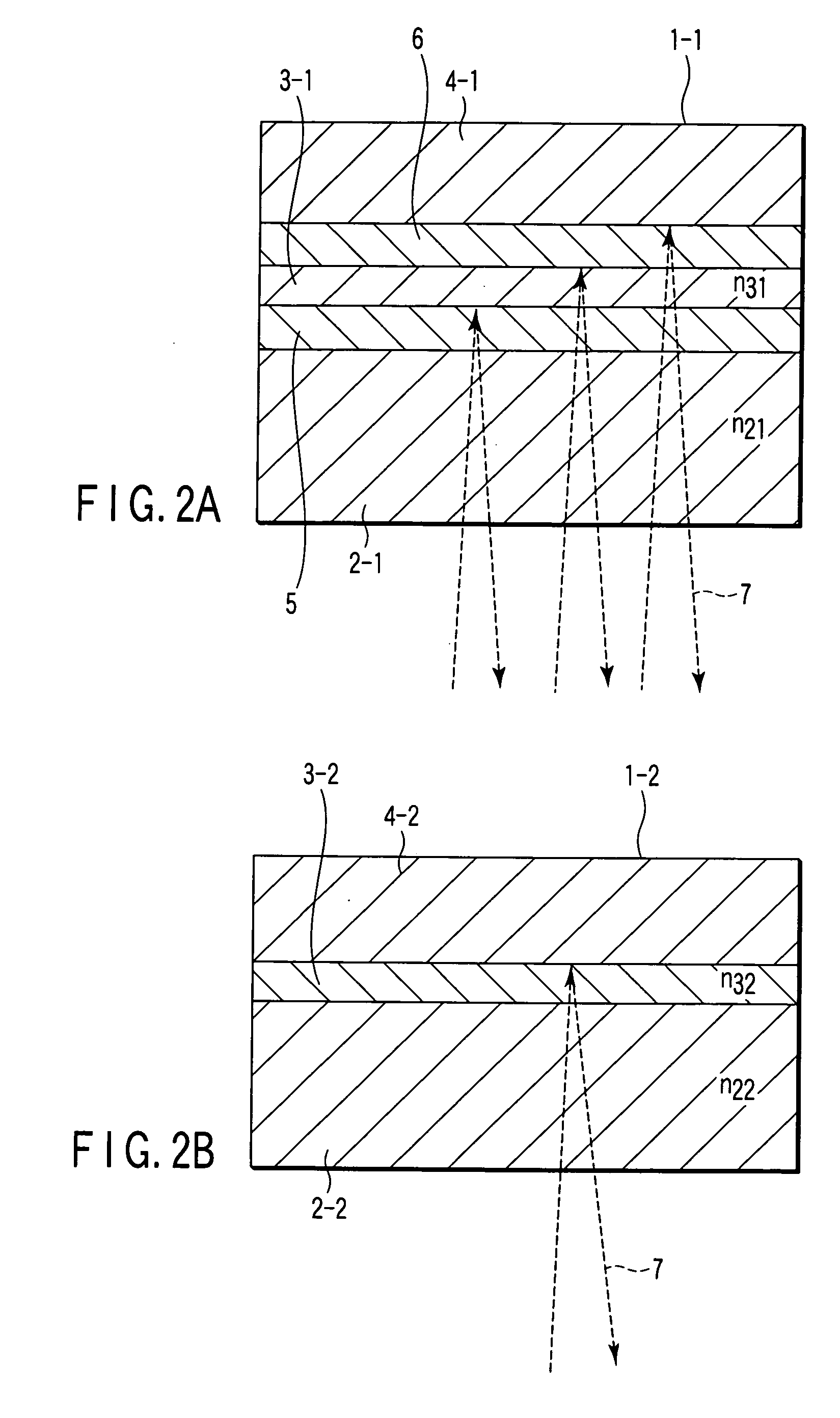
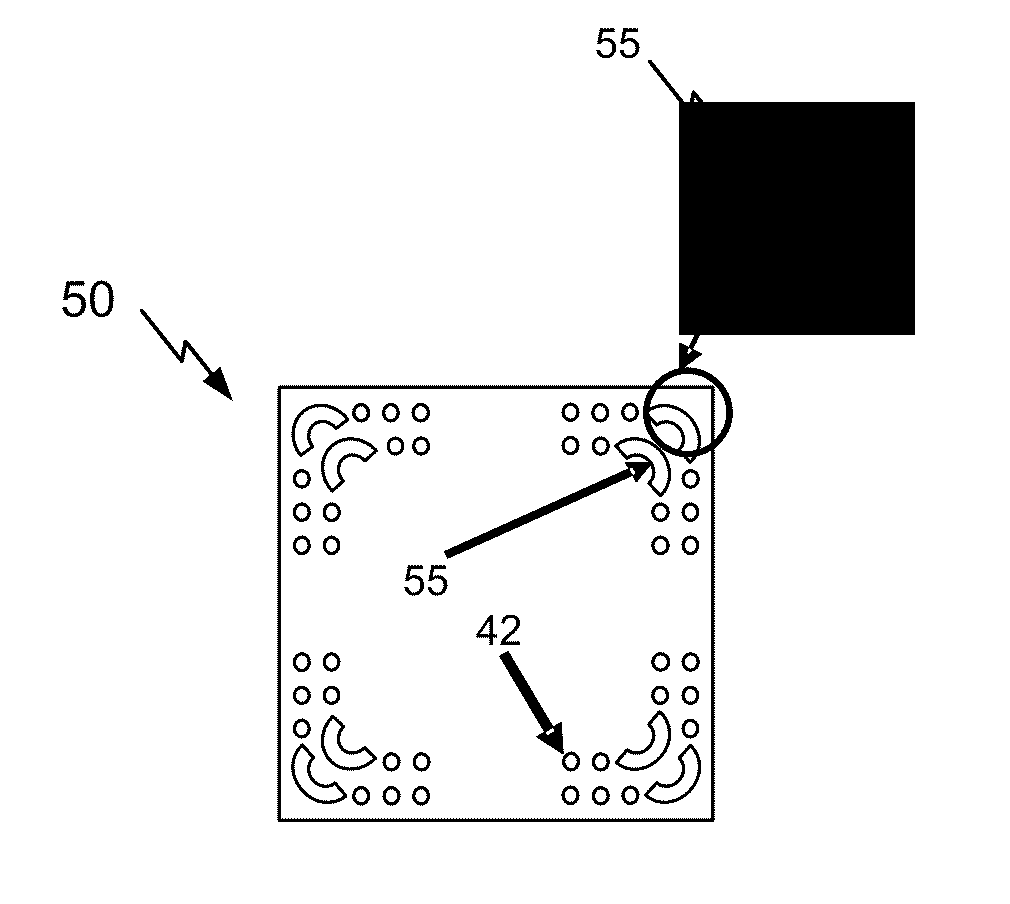
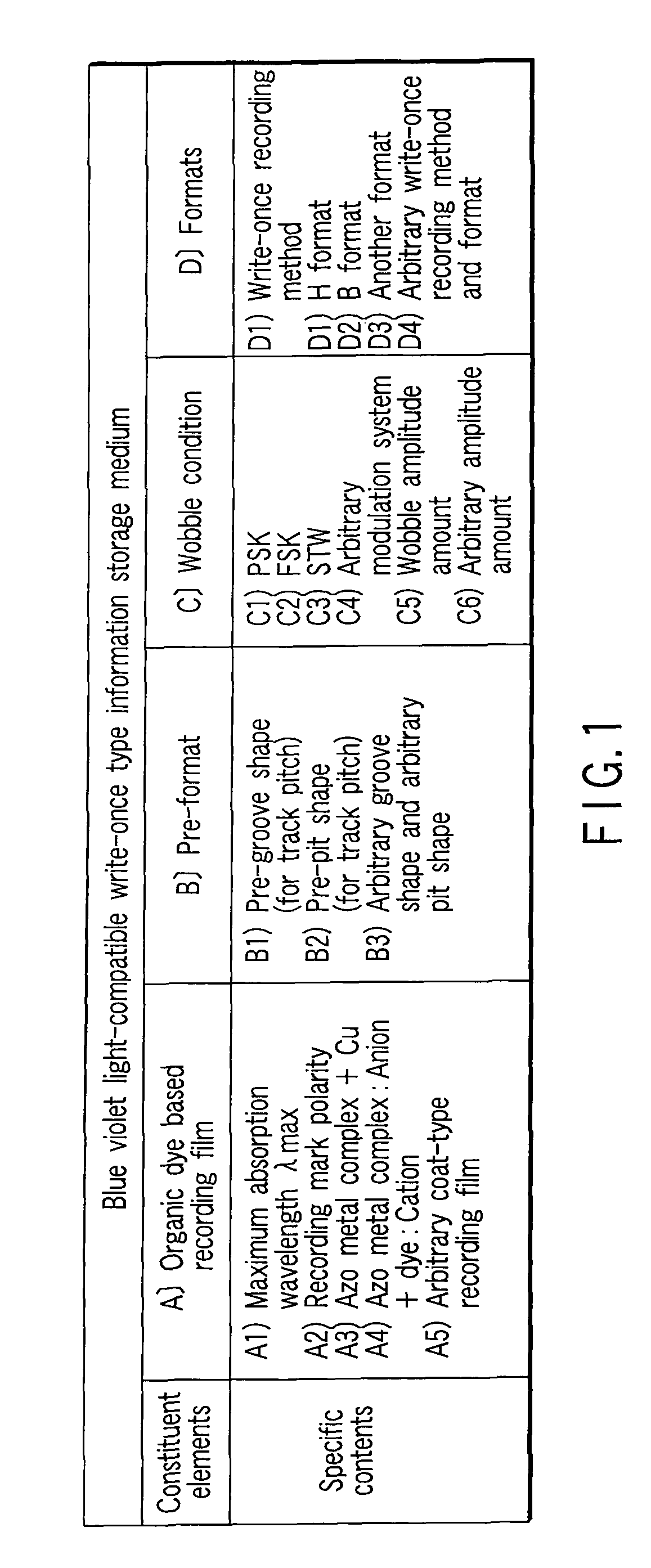
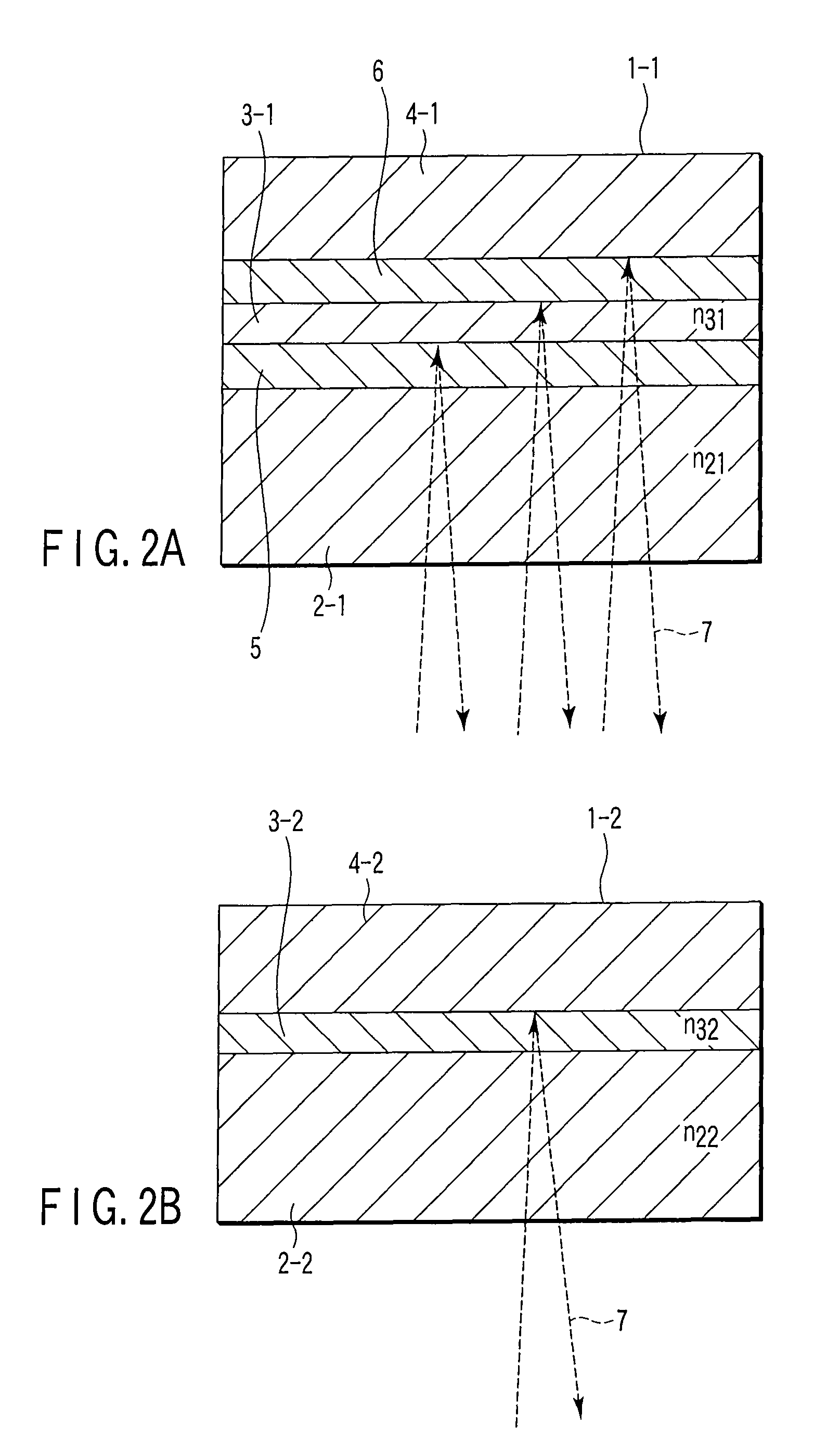
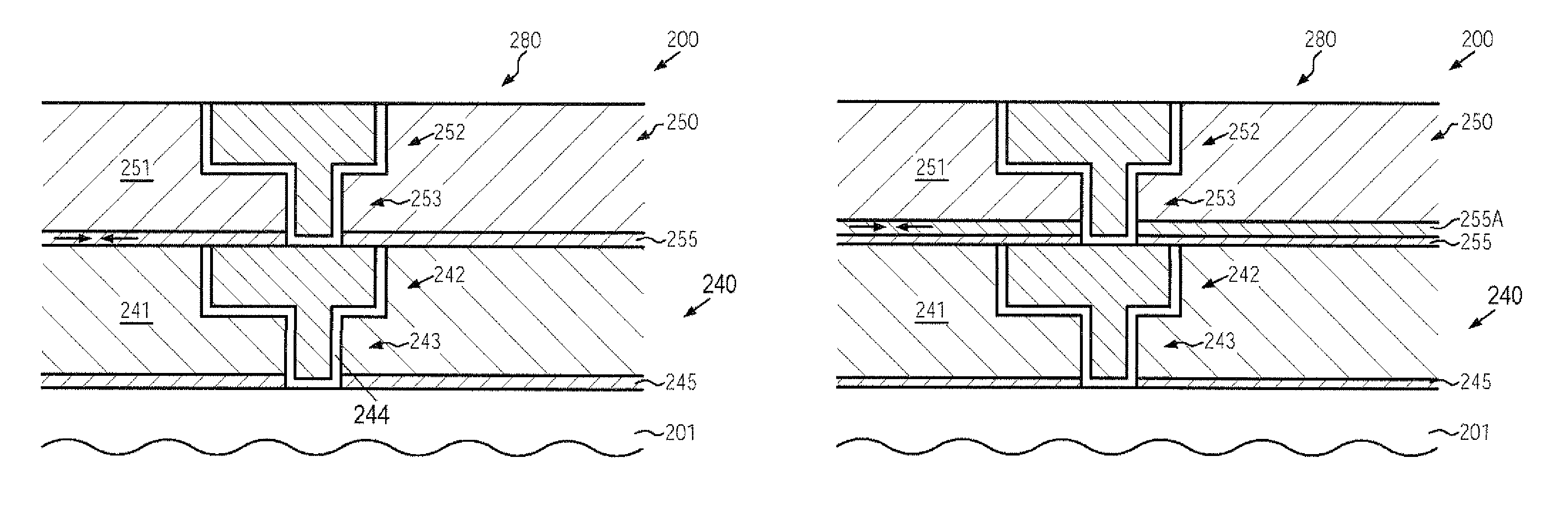
Storage medium, reproducing method, and recording method
InactiveUS20060210925A1High densityHigh speed recordingRecording strategiesRadiation applicationsSubstrate deformationComputer science
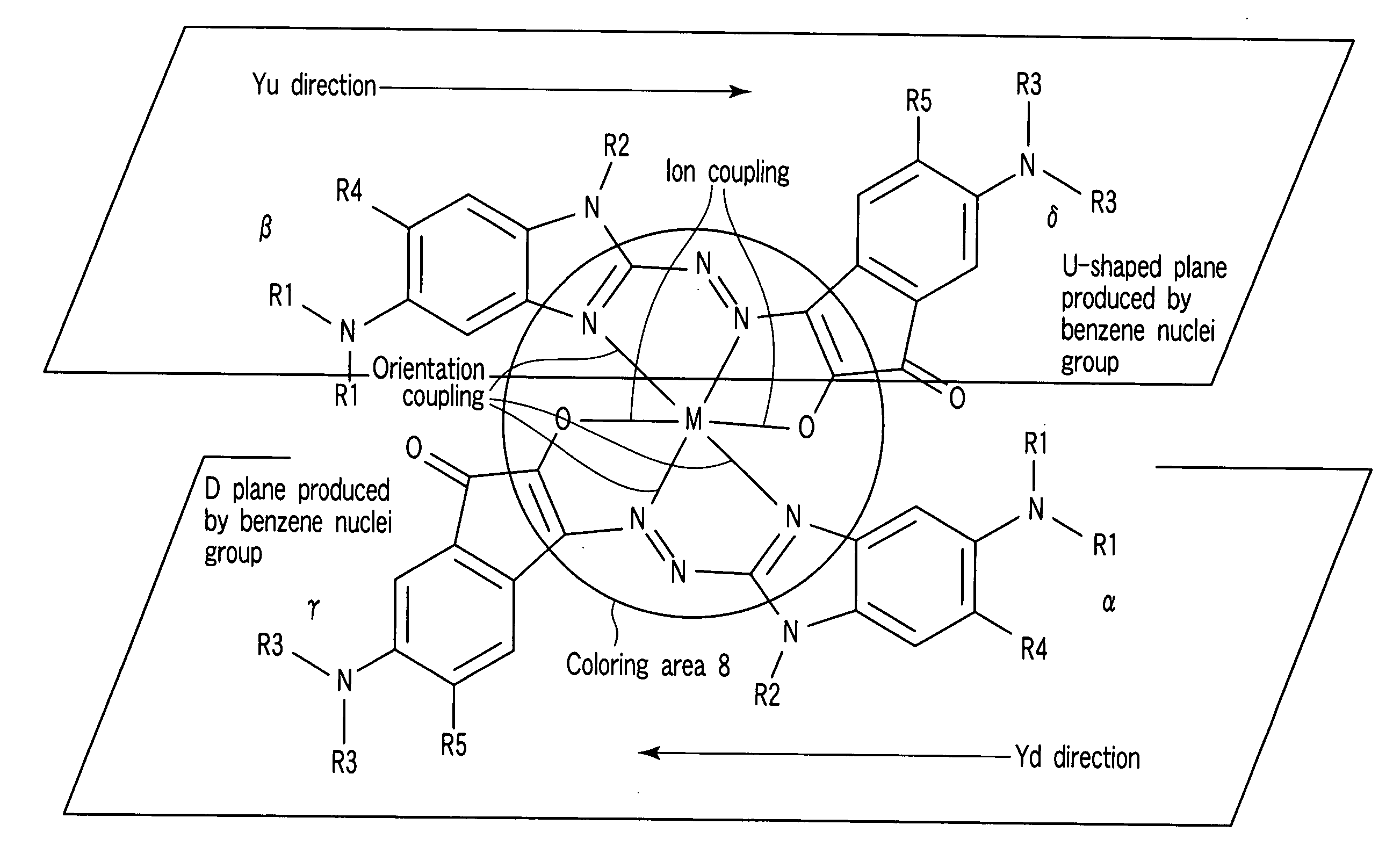
According to one embodiment, a write-once type information storage medium using a recording material which has a low to high characteristic that a light reflectivity in a recording mark increases with respect to a non-recording area and which has a recording characteristic in accordance with a principle of recording without substrate deformation, wherein the recording material includes at least an organic metal complex, and wherein the organic metal complex includes a center metal.
Owner:KK TOSHIBA
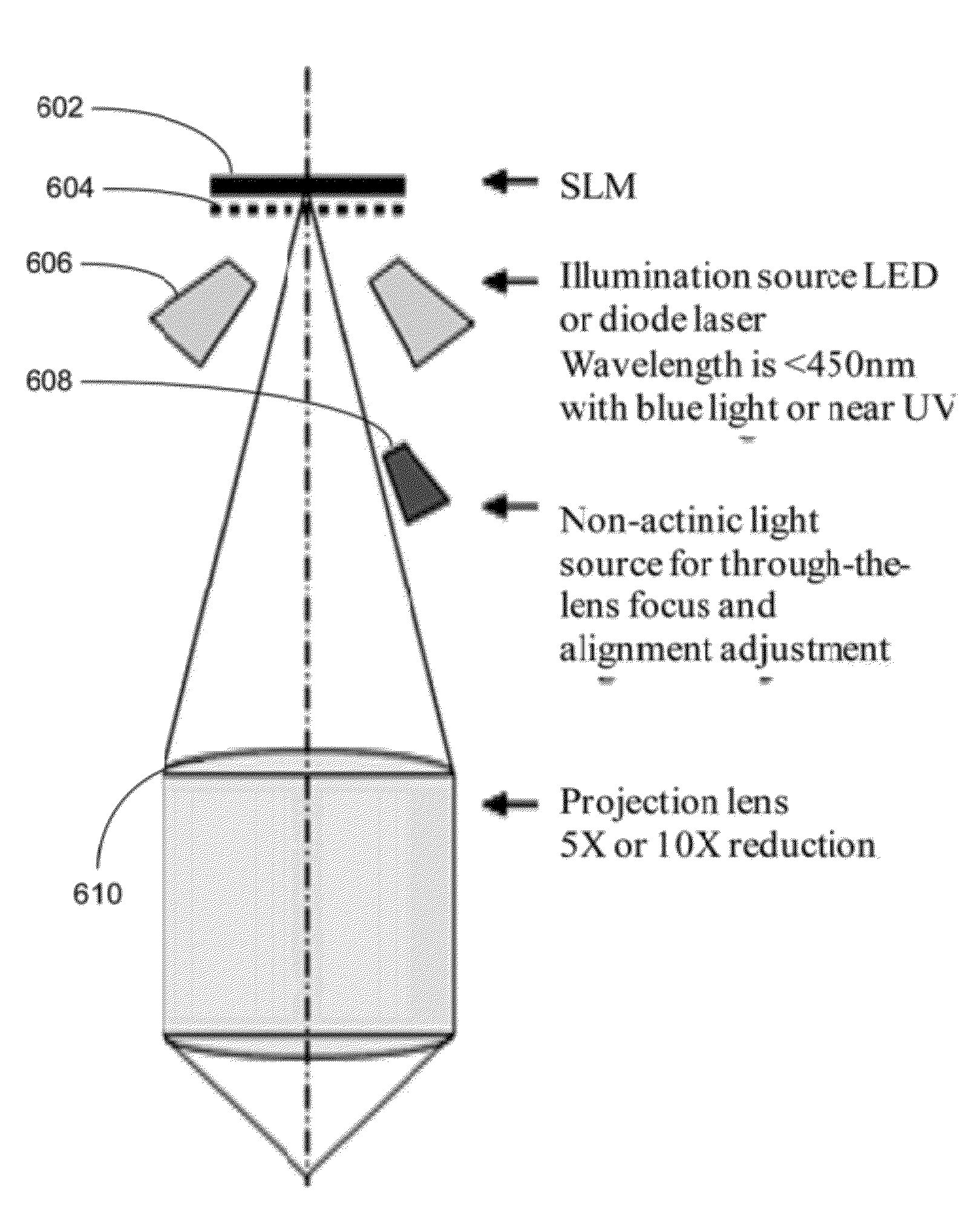
System and Method for Manufacturing Three Dimensional Integrated Circuits
ActiveUS20120026478A1Photomechanical apparatusPhotographic printingSpatial light modulatorEngineering
System and method for manufacturing three-dimensional integrated circuits are disclosed. In one embodiment, the method includes providing an imaging writer system that includes a plurality of spatial light modulator (SLM) imaging units arranged in one or more parallel arrays, receiving mask data to be written to one or more layers of the three-dimensional integrated circuit, processing the mask data to form a plurality of partitioned mask data patterns corresponding to the one or more layers of the three-dimensional integrated circuit, assigning one or more SLM imaging units to handle each of the partitioned mask data pattern, and controlling the plurality of SLM imaging units to write the plurality of partitioned mask data patterns to the one or more layers of the three-dimensional integrated circuits in parallel. The method of assigning performs at least one of scaling, alignment, inter-ocular displacement, rotational factor, or substrate deformation correction.
Owner:APPLIED MATERIALS INC
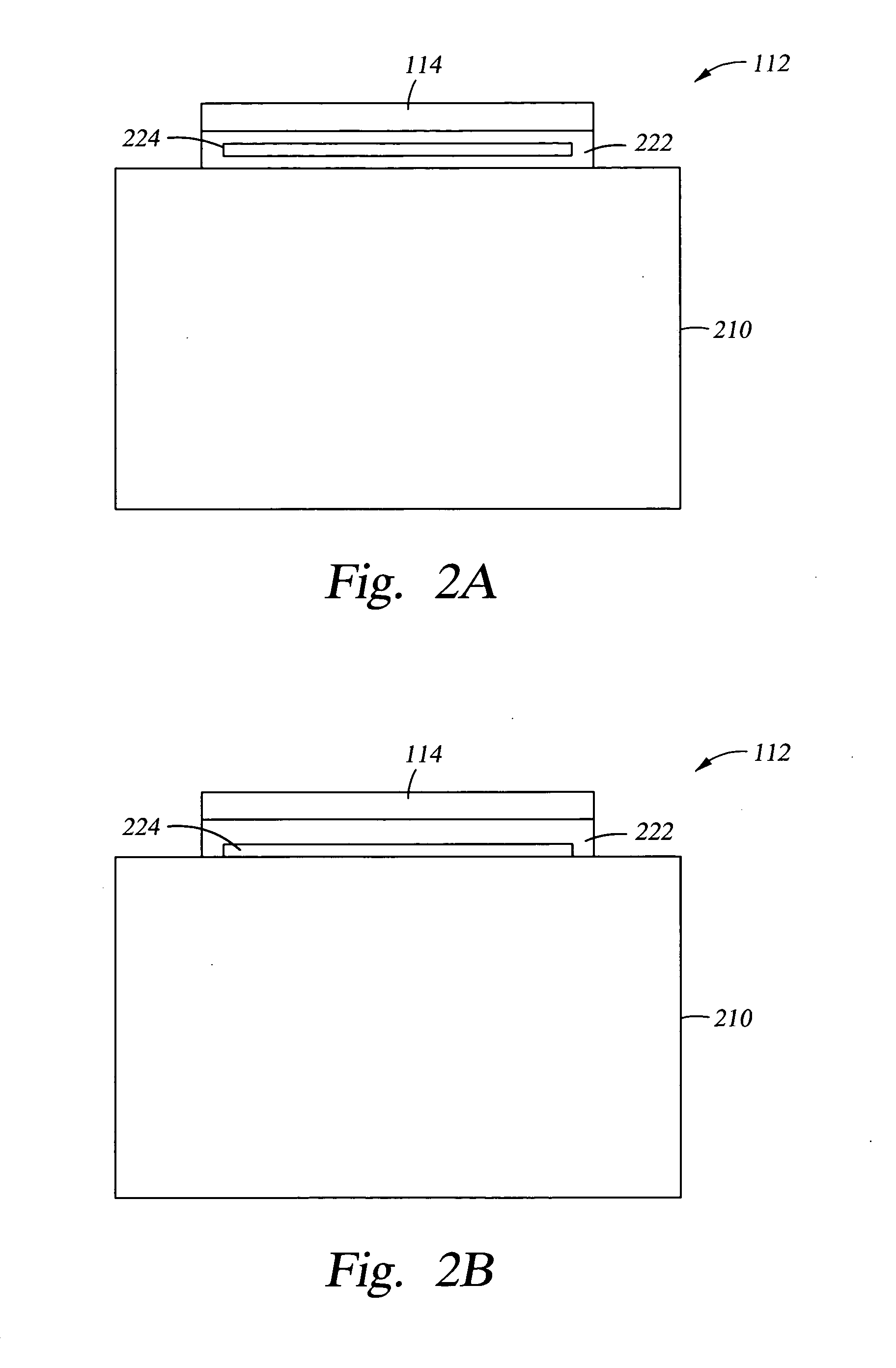
Carrier head with a modified flexible membrane
InactiveUS6855043B1Increasing substrate cleanlinessImprove polishing uniformityPolishing machinesRevolution surface grinding machinesSlurryEngineering
A carrier head for a chemical mechanical polishing apparatus includes a flexible membrane that applies a load to a substrate and a retaining ring. The friction coefficient of the lower surface of the flexible membrane is increased to prevent contact between the substrate and the retaining ring, thereby preventing slurry compaction and buildup and substrate deformation caused by such contact.
Owner:APPLIED MATERIALS INC
Apparatus and Method for Controlling Semiconductor Die Warpage
ActiveUS20110147895A1Reduce warpageGood thermal expansionSemiconductor/solid-state device detailsDetecting faulty computer hardwareSemiconductor chipStress relief
A semiconductor die has through silicon vias arranged to reduce warpage. The through silicon vias adjust the coefficient of thermal expansion of the semiconductor die, permit substrate deformation, and also relieve residual stress. The through silicon vias may be located in the edges and / or corners of the semiconductor die. The through silicon vias are stress relief vias that can be supplemented with round corner vias to reducing warpage of the semiconductor die.
Owner:QUALCOMM INC
Storage medium, reproducing method, and recording method
InactiveUS7960093B2High densityHigh sensitivityRecording strategiesRadiation applicationsSubstrate deformationComputer science
According to one embodiment, a write-once type information storage medium using a recording material which has a low to high characteristic that a light reflectivity in a recording mark increases with respect to a non-recording area and which has a recording characteristic in accordance with a principle of recording without substrate deformation, wherein the recording material includes at least an organic metal complex, and wherein the organic metal complex includes a center metal.
Owner:KK TOSHIBA
Enamel and preparation method thereof
The invention provides enamel, which comprises a substrate and a ceramic glaze layer enamel-fired on the substrate, wherein the ceramic glaze layer is prepared by firing ceramic glaze powder which contains 60 and 90 weight percent of glass frit, 5 to 18 weight percent of crushed sand, 3 to 12 weight percent of clay, 0.3 to 5 weight percent of borax and 0.3 to 5 weight percent of soda ash. The enamel has excellent physiochemical performance such as low sintering temperature, corrosion resistance and the like. The method for preparing the enamel has the advantages of obtaining an enamel coating with high bonding strength and acid and alkali corrosion resistance at lower sintering temperature, solving the problem of substrate deformation, saving energy, and reducing production cost.
Owner:CHERY AUTOMOBILE CO LTD
Method for forming grating for machine tool measurement in two-step solidifying rolling pressing forming manner
ActiveCN102193310ALow costIncrease productivityDiffraction gratingsPhotomechanical exposure apparatusStress concentrationGrating
The invention relates to a method for forming a grating for machine tool measurement in a two-step solidifying rolling pressing forming manner, which comprises the following steps: 1) coating an ultraviolet light solidifying adhesive layer on a grating blank substrate; 2) manufacturing a rolling mould having a prototype grating structure on the surface of a cylindrical mould, making an alignment mark, and polishing and performing low surface energy treatment on the surface of the rolling mould; 3) coating a flexible film on the adhesive layer on the grating blank substrate, carrying out primary exposure and peeling the film; 4) comparing the alignment mark on the grating blank substrate with an acquired alignment mark image on the surface of the rolling mould, adjusting and calibrating; 5) gluing the rolling mould with the grating, applying a pressing force, and compounding the prototype grating structure on the surface of rolling mould on the adhesive layer on the surface of the substrate; 6) carrying out exposure on the compounded ultraviolet light solidifying adhesive layer; and 7) collecting and packaging the grating. According to the method, the required pressing force is small, and thus, the substrate deformation and stress concentration are avoided. The method has high production efficiency and can be used for realizing the mass production of the grating for large-area and altitude machine tool measurement.
Owner:XI AN JIAOTONG UNIV
Organic light emitting diode display
ActiveUS20110037095A1Good strength propertiesInhibition defectElectroluminescent light sourcesSolid-state devicesDisplay deviceSubstrate deformation
An organic light emitting diode (OLED) display includes a display substrate assembly including an organic light emitting structure, an encapsulation substrate assembly disposed facing the display substrate assembly, a sealant disposed between the display substrate assembly and the encapsulation substrate assembly to seal the display substrate assembly and the encapsulation substrate assembly with each other, and a substrate deformation protection body disposed between the sealant and the organic light emitting structure.
Owner:SAMSUNG DISPLAY CO LTD
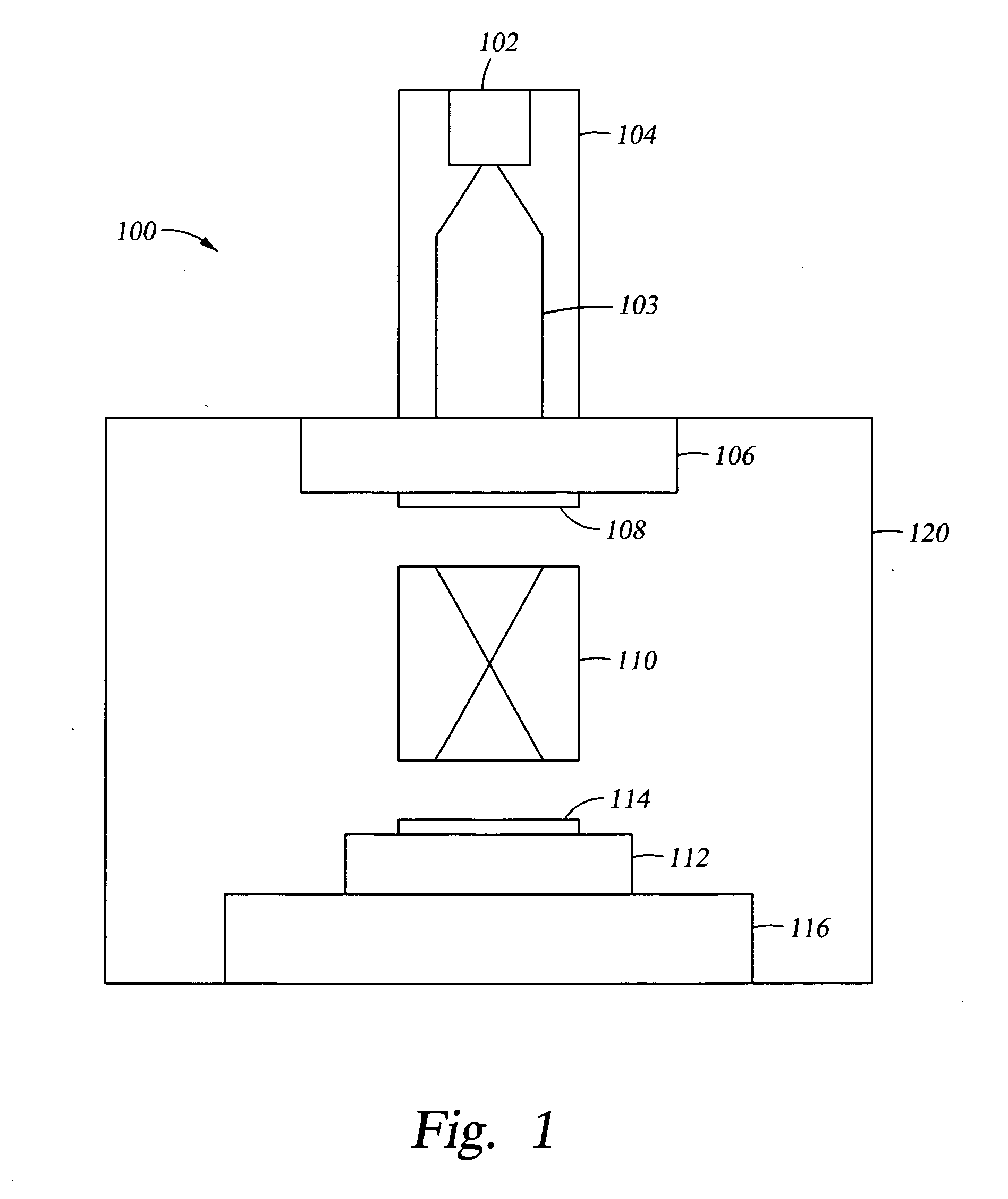
Load-lock apparatus and substrate cooling method
InactiveUS20100326637A1Avoid deformationReduce cooling rateLiquid surface applicatorsVacuum evaporation coatingAtmospheric airEngineering
A load-lock apparatus includes a vessel arranged to change a pressure between a pressure corresponding to the vacuum chamber and the atmospheric pressure, a pressure adjusting mechanism which adjusts a pressure in the vessel to a pressure corresponding to the vacuum chamber and the atmospheric pressure, a cooling member having a cooling mechanism and arranged in the vessel to cool a substrate by having the substrate placed on or in proximity to the cooling member, a substrate deformation detection unit for detecting deformation of the substrate in the vessel, and a controller which reduces a cooling rate of the substrate when the substrate deformation is detected during a substrate cooling period until the vessel is adjusted to have the atmospheric pressure after the vessel is adjusted to have a pressure corresponding to the vacuum chamber and a high temperature substrate is loaded into the vessel from the vacuum chamber.
Owner:TOKYO ELECTRON LTD
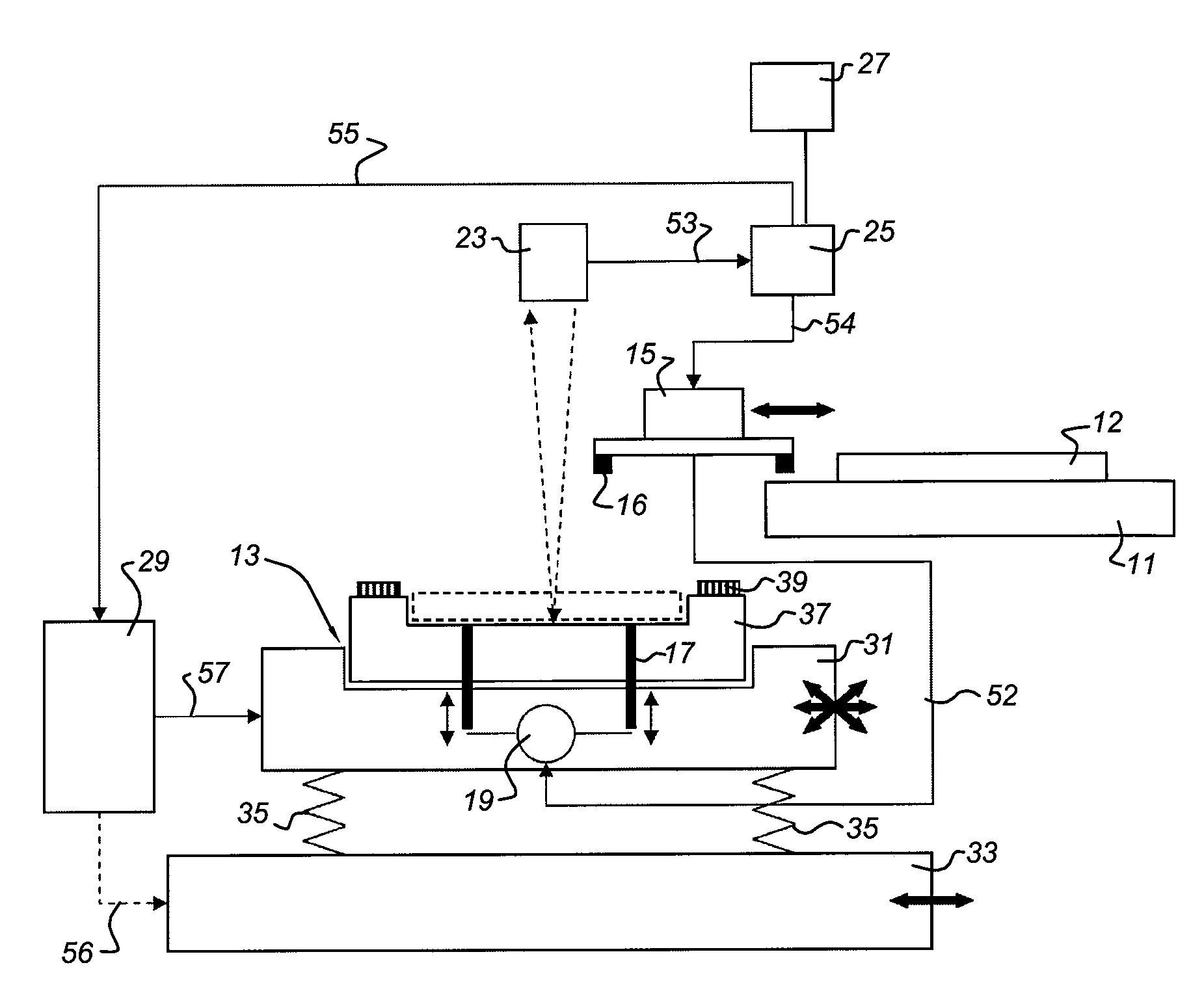
Substrate holder which is self-adjusting for substrate deformation
InactiveUS7372690B2Precise alignmentSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingMachines/enginesLithographic artistLithography process
A wafer chuck is designed to allow the substrate to thermally deform during charged particle beam lithography. The wafer chuck includes a compliant layer disposed over an chuck body. During lithography processing the wafer is electrostatically held in contact with a flexible compliant layer and the wafer is exposed to the charged particle beam resulting in thermal deformation of the wafer. The compliant layer deforms with the substrate and allows the wafer to deform in a predictable manner.
Owner:APPLIED MATERIALS INC
System and method for manufacturing three dimensional integrated circuits
ActiveUS9025136B2Photomechanical exposure apparatusMicrolithography exposure apparatusSpatial light modulatorEngineering
System and method for manufacturing three-dimensional integrated circuits are disclosed. In one embodiment, the method includes providing an imaging writer system that includes a plurality of spatial light modulator (SLM) imaging units arranged in one or more parallel arrays, receiving mask data to be written to one or more layers of the three-dimensional integrated circuit, processing the mask data to form a plurality of partitioned mask data patterns corresponding to the one or more layers of the three-dimensional integrated circuit, assigning one or more SLM imaging units to handle each of the partitioned mask data pattern, and controlling the plurality of SLM imaging units to write the plurality of partitioned mask data patterns to the one or more layers of the three-dimensional integrated circuits in parallel. The method of assigning performs at least one of scaling, alignment, inter-ocular displacement, rotational factor, or substrate deformation correction.
Owner:APPLIED MATERIALS INC
Substrate holder which is self-adjusting for substrate deformation
InactiveUS20050199825A1Precise alignmentSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingMachines/enginesLithographic artistLithography process
A wafer chuck is designed to allow the substrate to thermally deform during charged particle beam lithography. The wafer chuck includes a compliant layer disposed over an chuck body. During lithography processing the wafer is electrostatically held in contact with a flexible compliant layer and the wafer is exposed to the charged particle beam resulting in thermal deformation of the wafer. The compliant layer deforms with the substrate and allows the wafer to deform in a predictable manner.
Owner:APPLIED MATERIALS INC
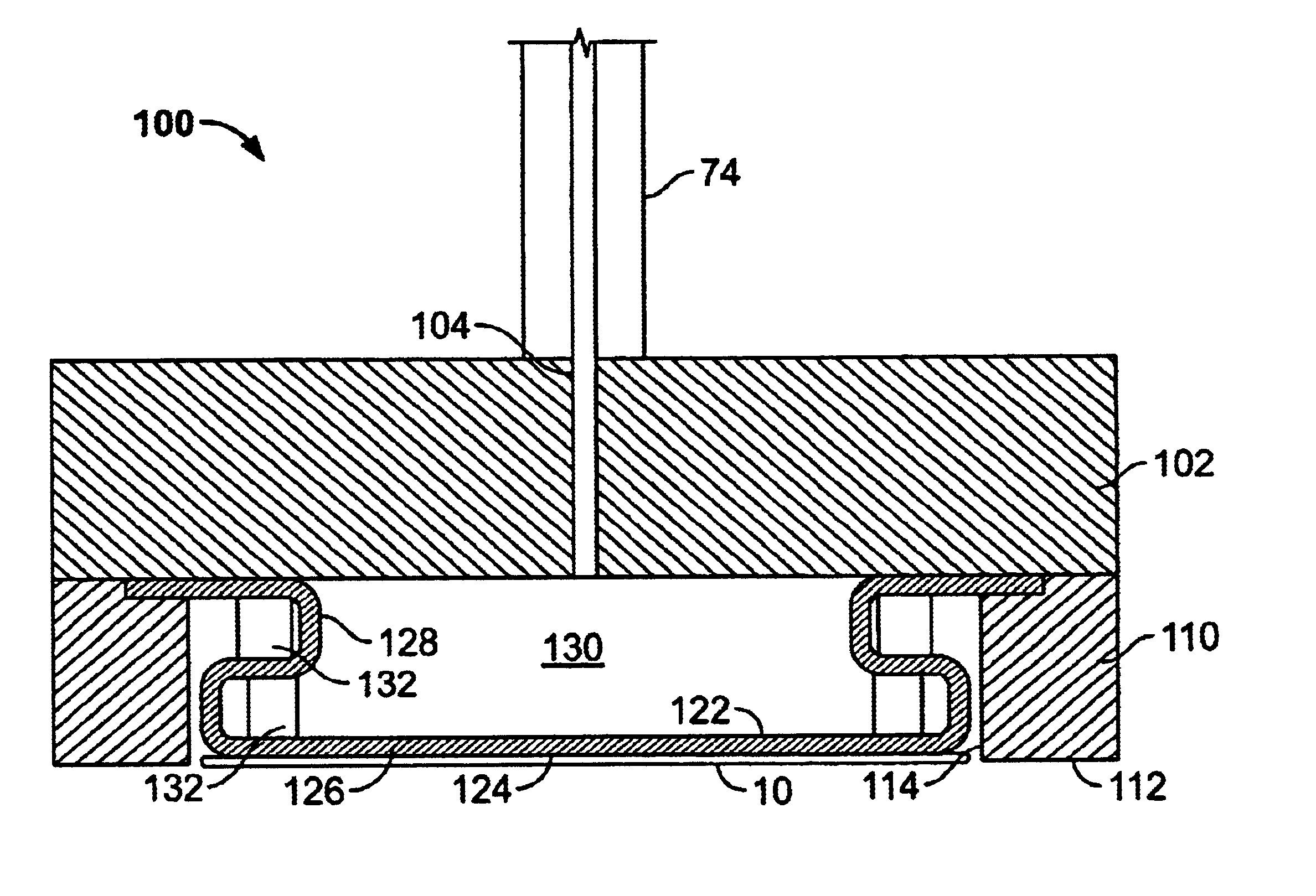
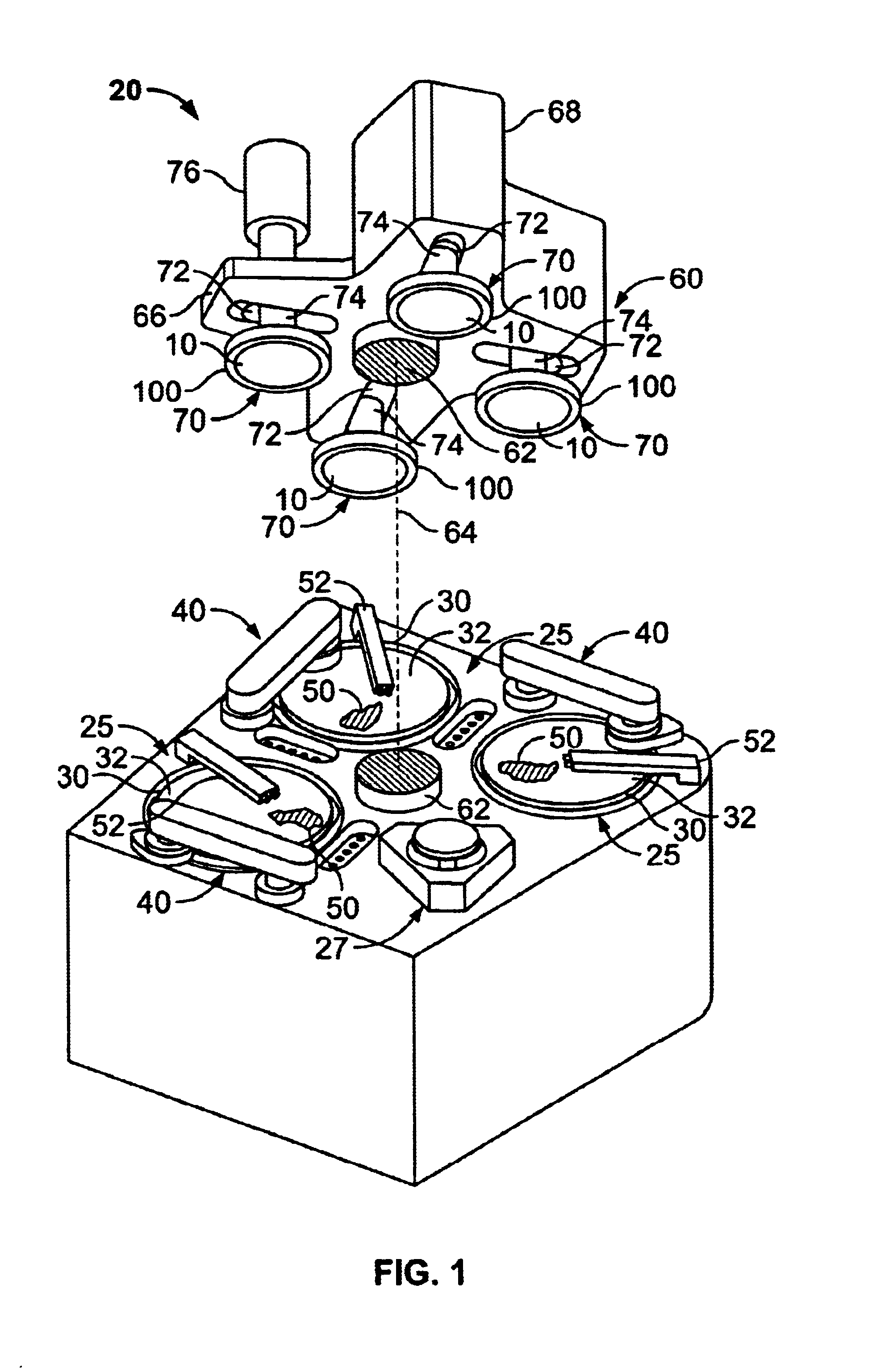
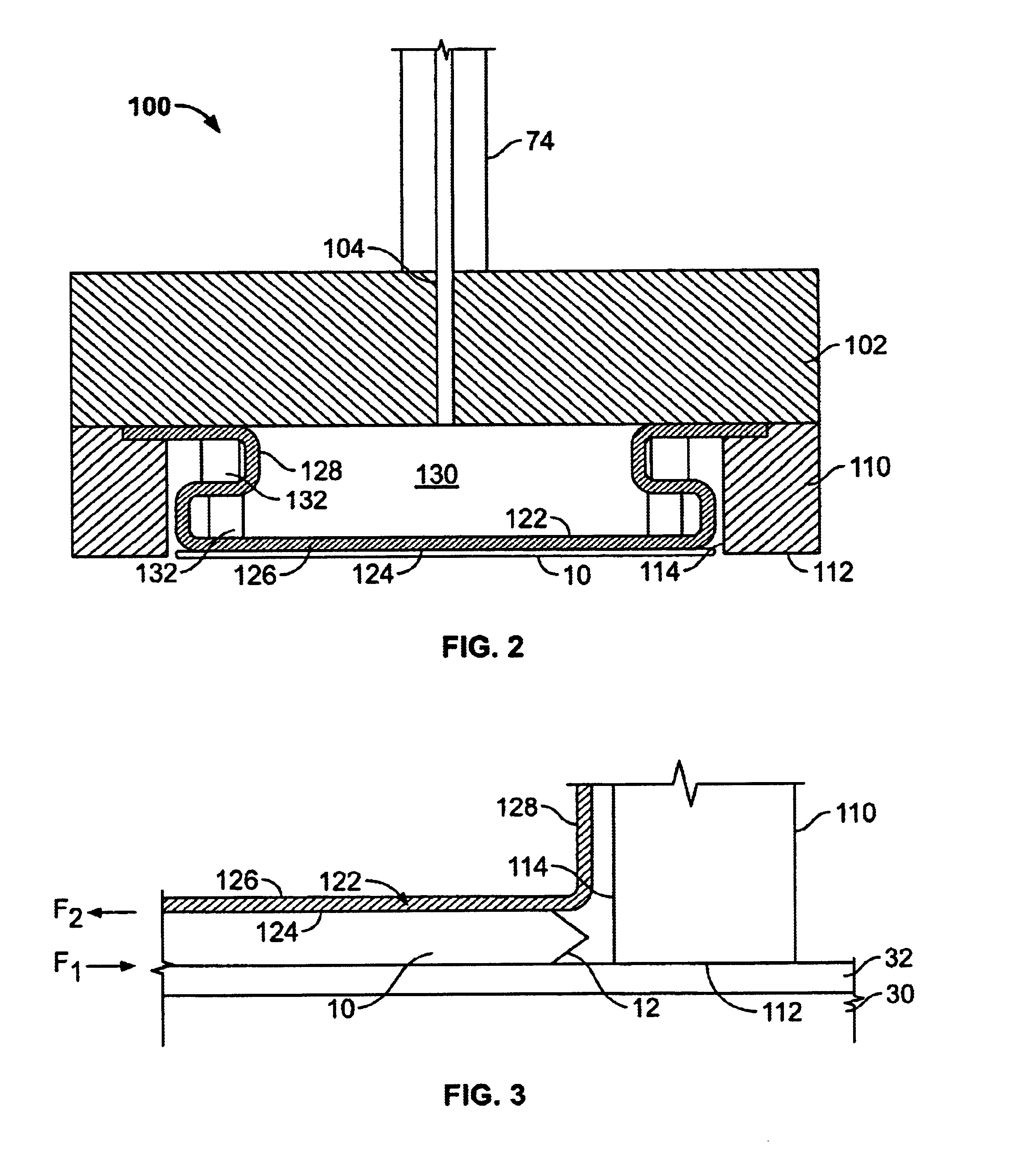
Substrate carrying mechanism, substrate processing apparatus, and semiconductor device manufacturing method
ActiveUS20120064734A1Decrease in substrate holding forceStable high-speed carriageSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingTray containersEngineeringSubstrate deformation
The present invention provides a substrate carrying mechanism, a substrate processing apparatus, and a semiconductor device manufacturing method that, when carrying a substrate, suppress the generation of scratches and particles caused by substrate deformation, suppress a decrease in substrate holding force due to substrate deformation, and realizes stable high-speed carriage. Namely, the substrate carrying mechanism, the substrate processing apparatus, and the semiconductor device manufacturing method of the present invention include: a plate-like body that becomes a support base body of a substrate that is a carrying subject; and substrate support portions in which plural convex portions disposed on a surface of the plate-like body are placed on a circumference of a circle that is smaller than the diameter of the substrate.
Owner:KOKUSA ELECTRIC CO LTD
Apparatus and method for controlling semiconductor die warpage
ActiveUS8710629B2Reduce warpageGood thermal expansionSemiconductor/solid-state device detailsSolid-state devicesStress reliefThermal expansion
A semiconductor die has through silicon vias arranged to reduce warpage. The through silicon vias adjust the coefficient of thermal expansion of the semiconductor die, permit substrate deformation, and also relieve residual stress. The through silicon vias may be located in the edges and / or corners of the semiconductor die. The through silicon vias are stress relief vias that can be supplemented with round corner vias to reducing warpage of the semiconductor die.
Owner:QUALCOMM INC
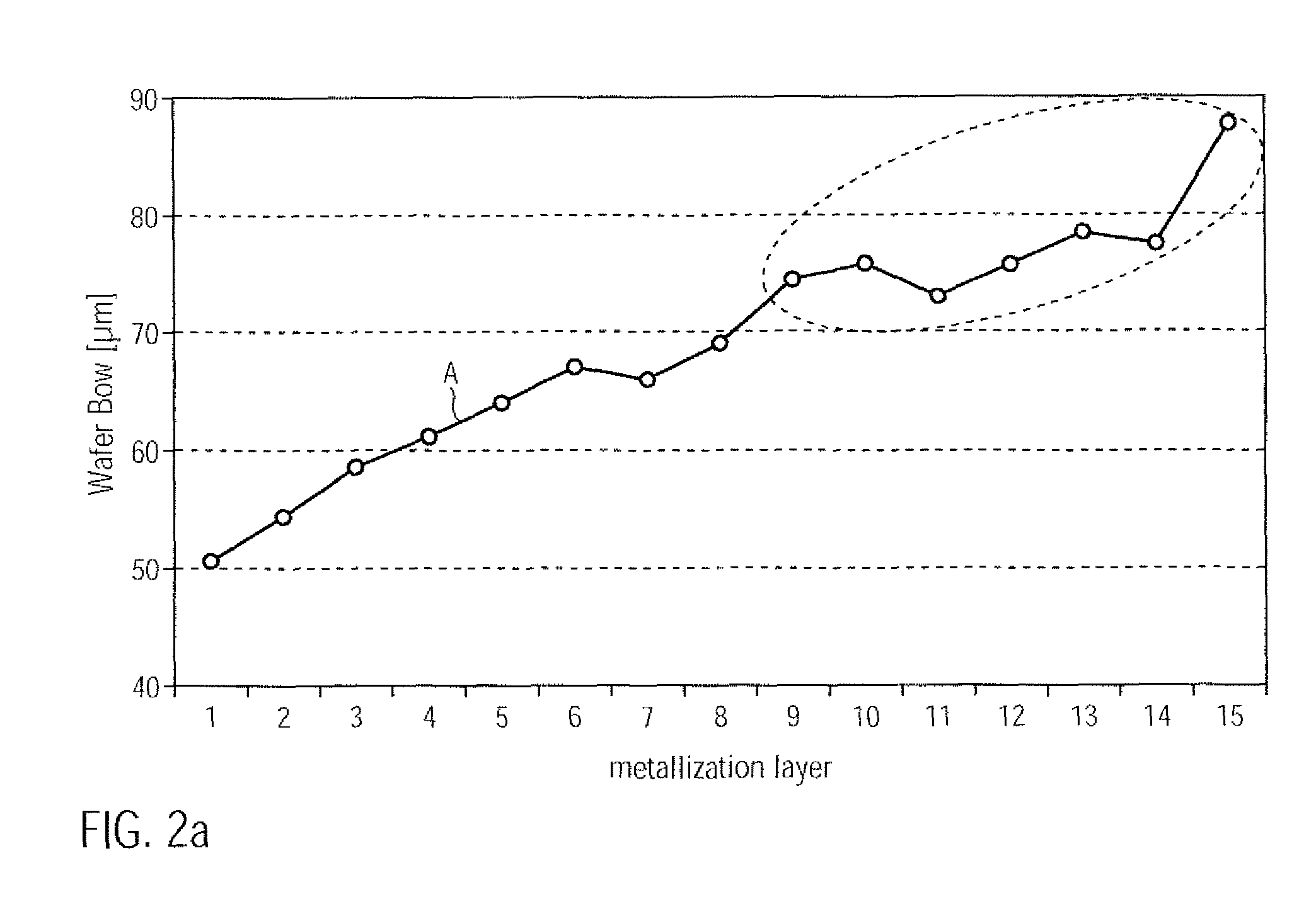
Reduced wafer warpage in semiconductors by stress engineering in the metallization system
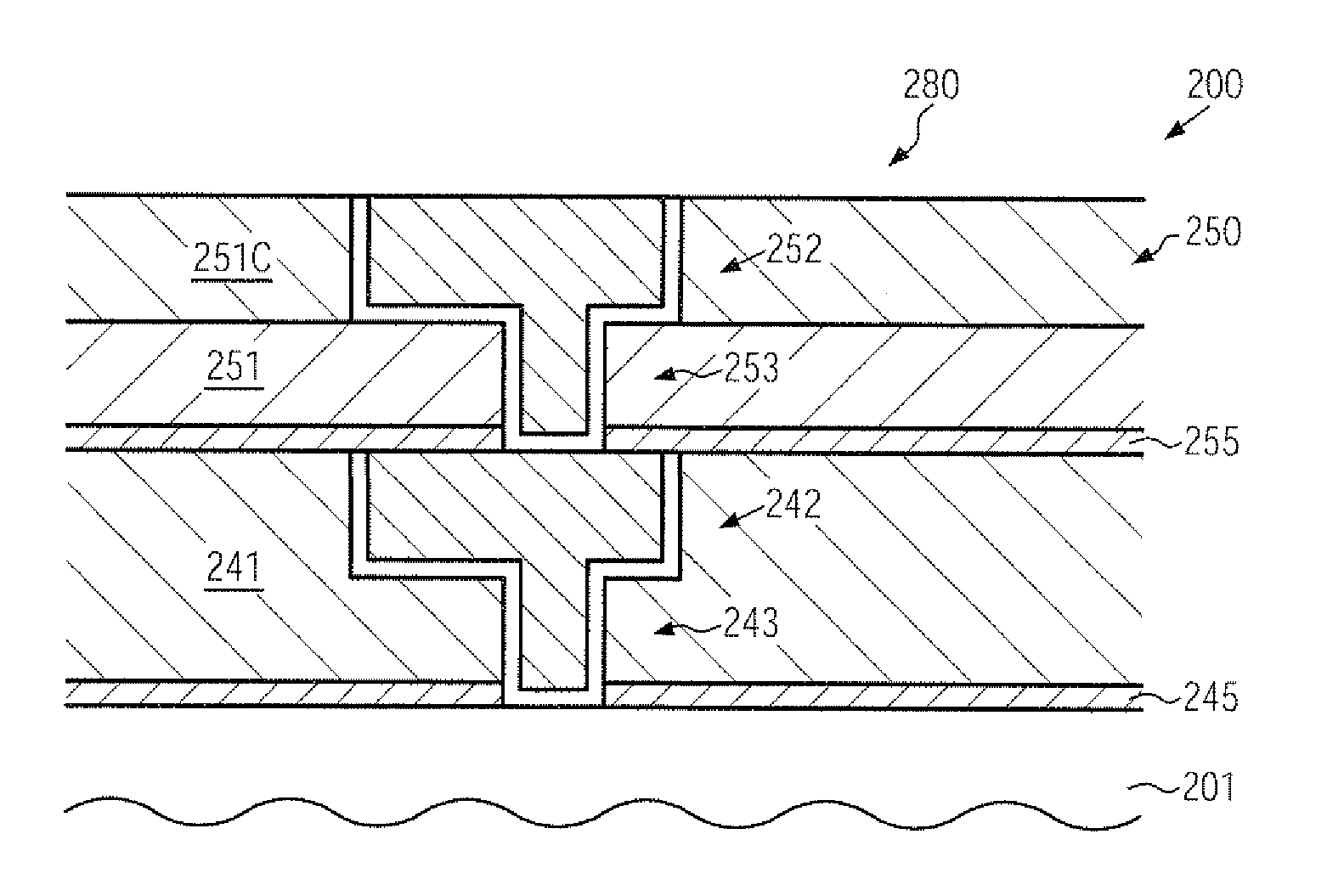
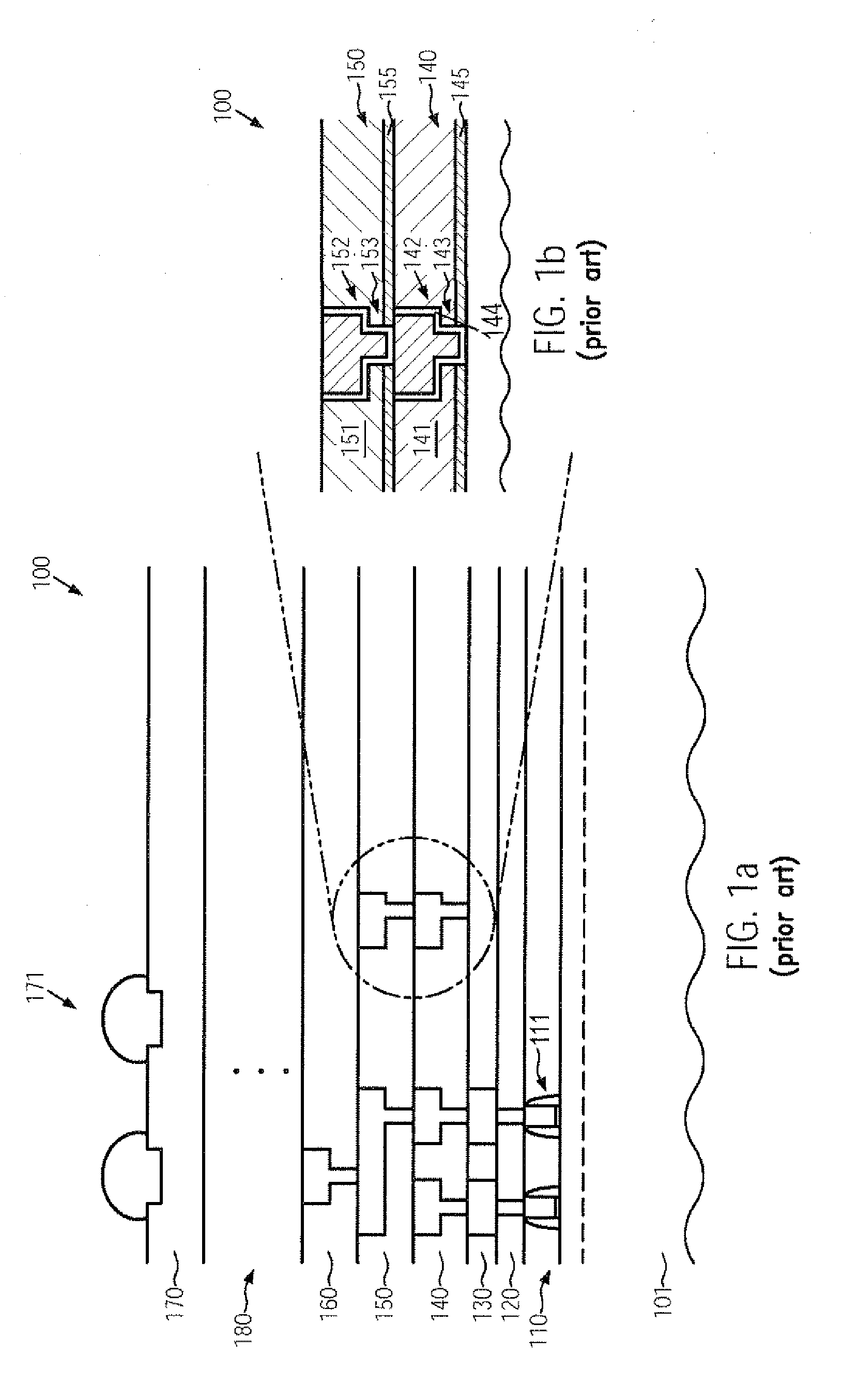
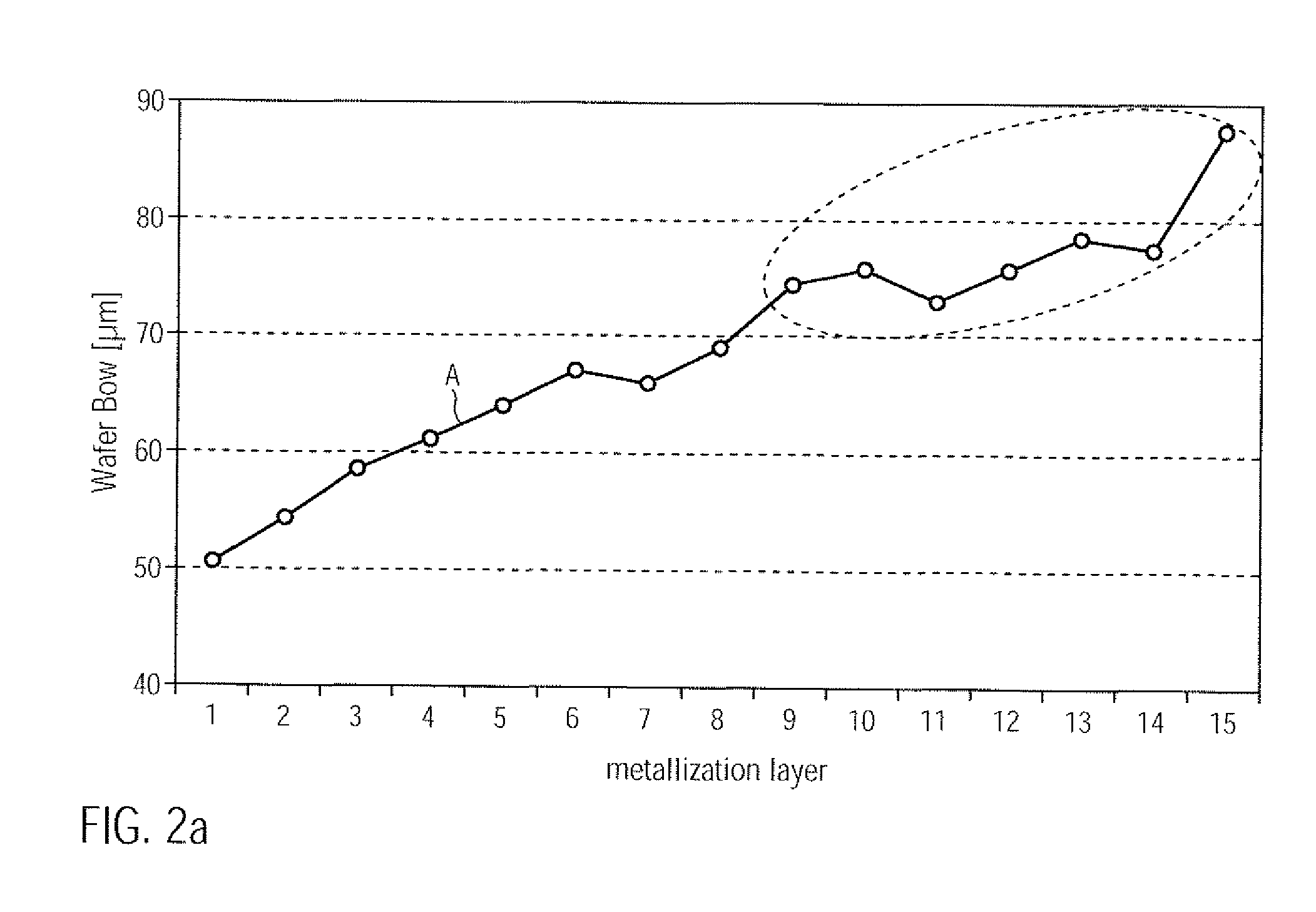
InactiveUS20100109131A1Improve compatibilityReduce probabilitySemiconductor/solid-state device testing/measurementSemiconductor/solid-state device detailsEngineeringSubstrate deformation
In complex metallization systems of sophisticated semiconductor devices, appropriate stress compensation mechanisms may be implemented in order to reduce undue substrate deformation during the overall manufacturing process. For example, additional dielectric material and / or functional layers of one or more metallization layers may be provided with appropriate internal stress levels so as to maintain substrate warpage at a non-critical level, thereby substantially reducing yield losses in the manufacturing process caused by non-reliable attachment of substrates to substrate holders in process and transport tools.
Owner:GLOBALFOUNDRIES INC
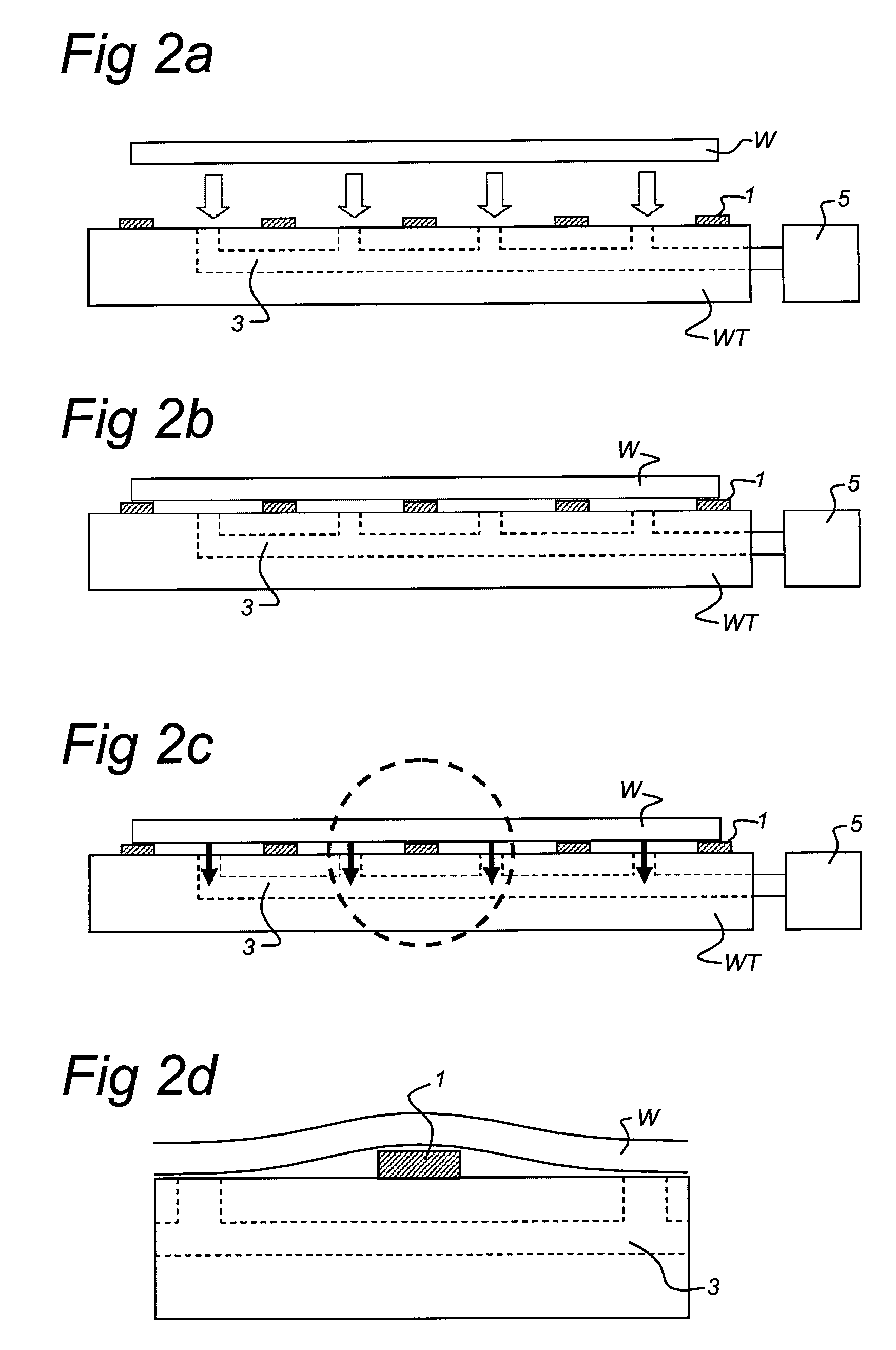
Contact lithography apparatus and method employing substrate deformation
InactiveUS20070164476A1Reduce retentionNanoinformaticsConfectionerySubstrate deformationMechanical engineering
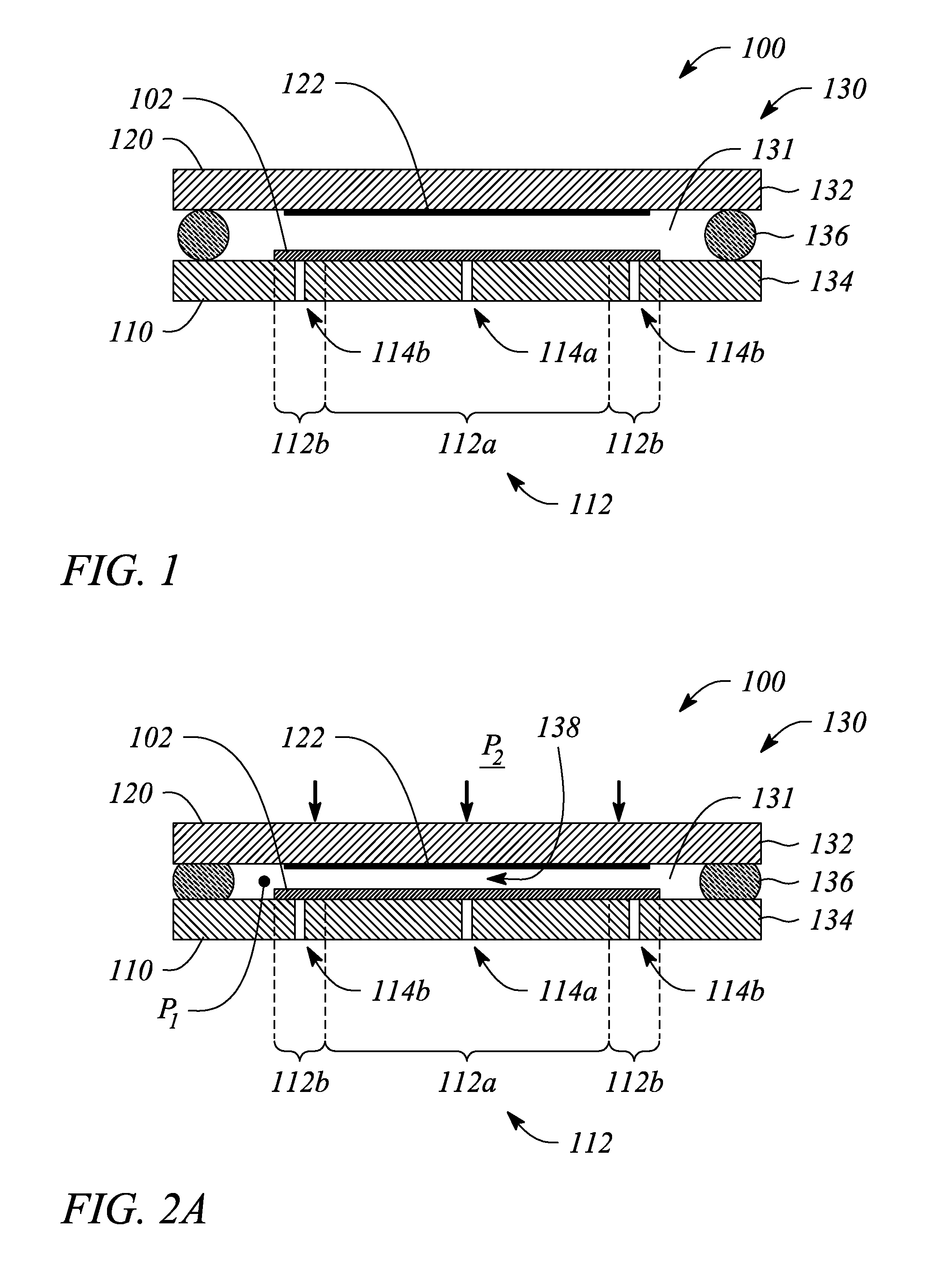
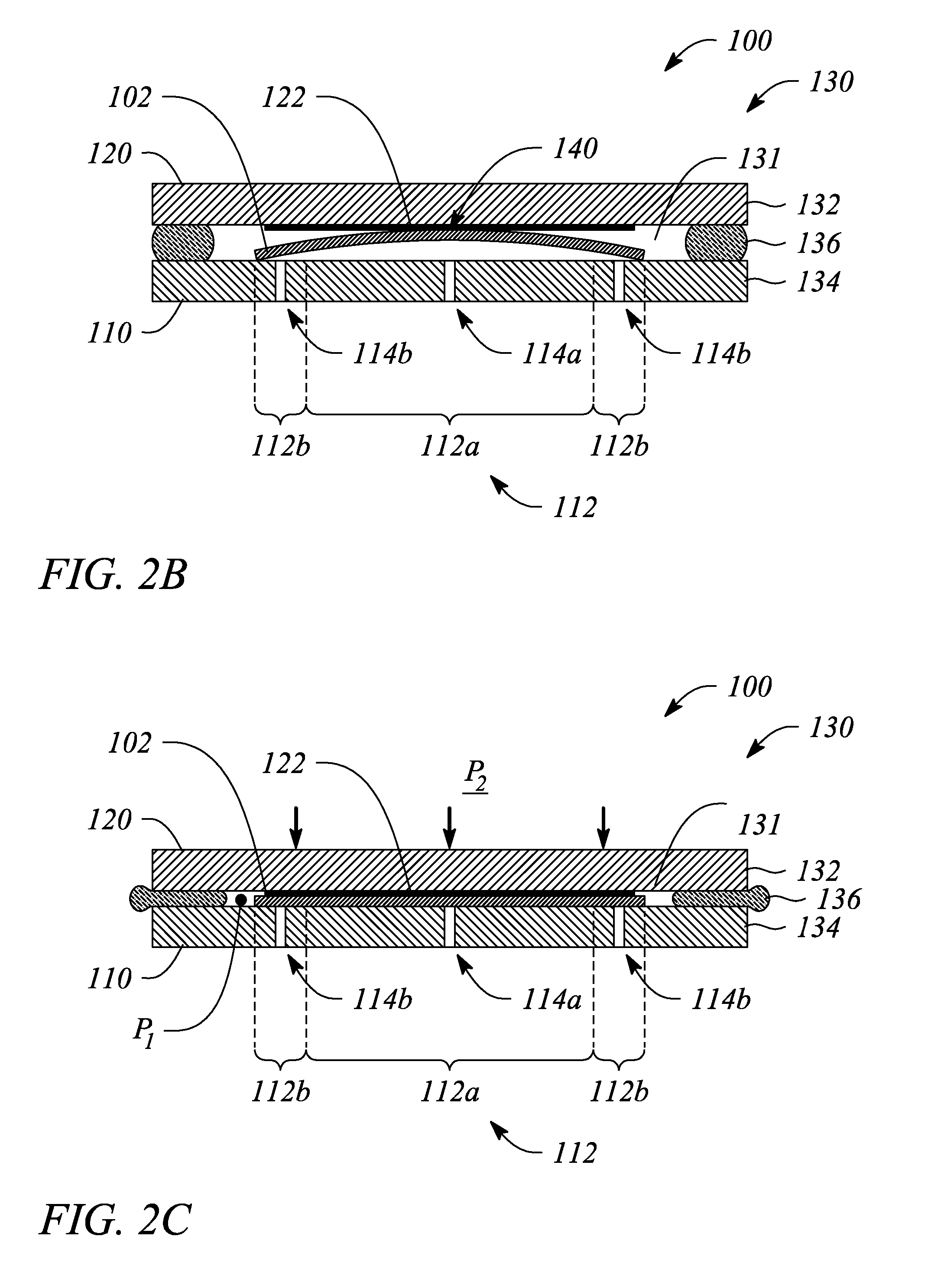
A contact lithography apparatus and a method of transferring a pattern to a surface employ deformation of a substrate for pattern transfer. The contact lithography apparatus includes a patterning tool and a substrate holder that variably retains a substrate. The substrate holder includes a plurality of retention zones. Each retention zone imparts a zone-specific retention force to the substrate that induces a deformation of the substrate toward the patterning tool. The method includes deforming the substrate. The deformation forms both an initial point of contact and a propagating contact front between the patterning tool and the substrate during pattern transfer.
Owner:HEWLETT PACKARD DEV CO LP
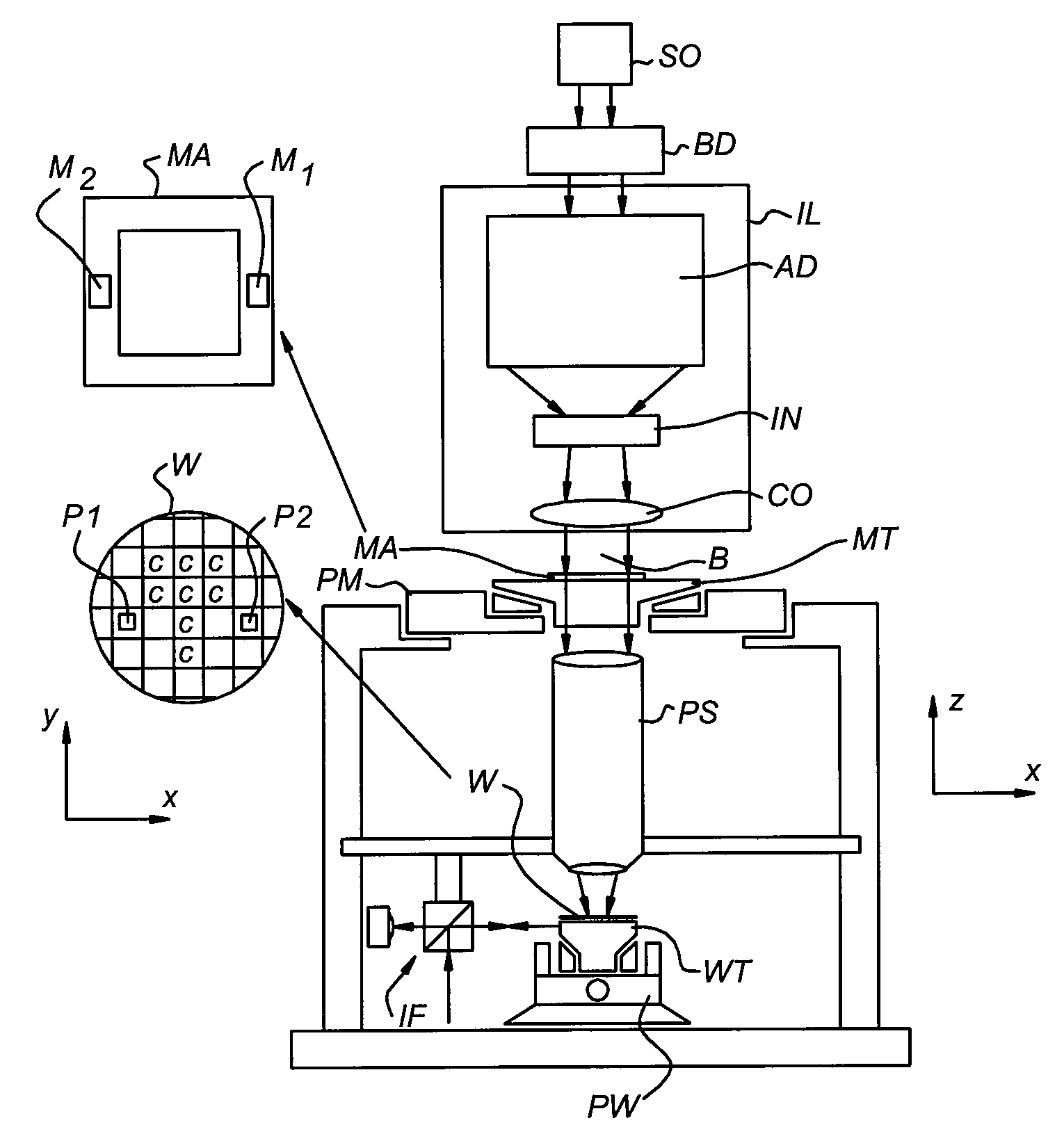
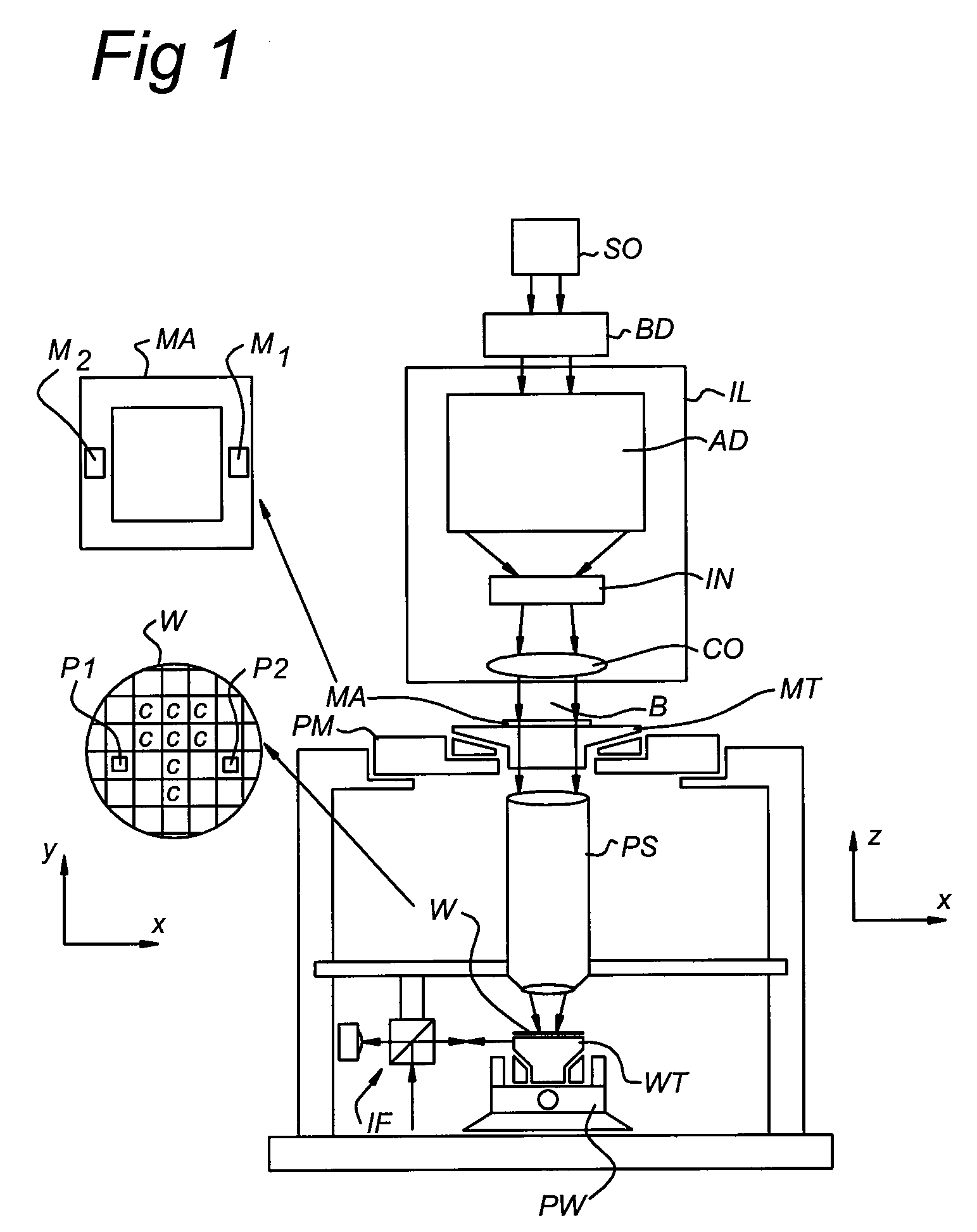
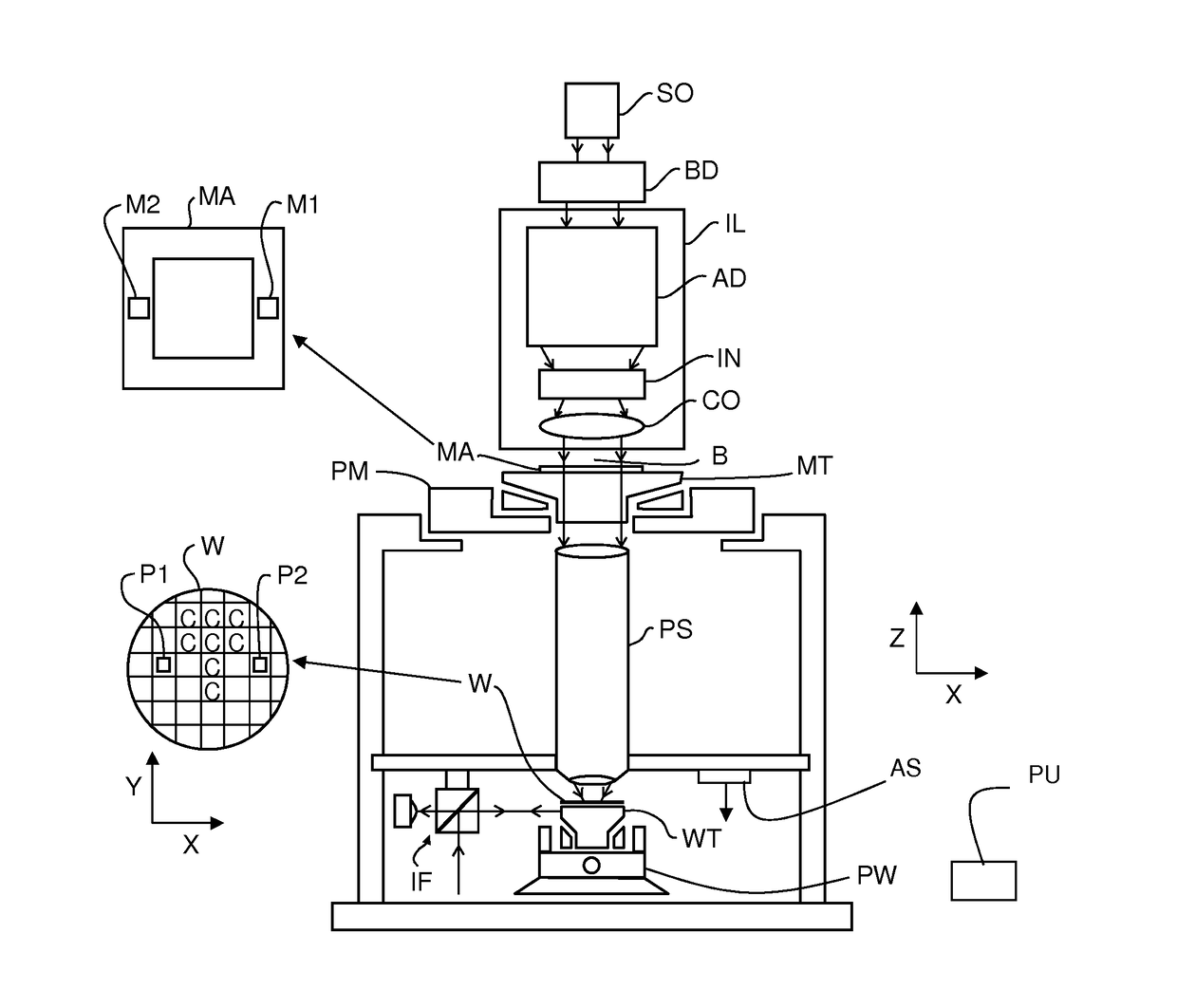
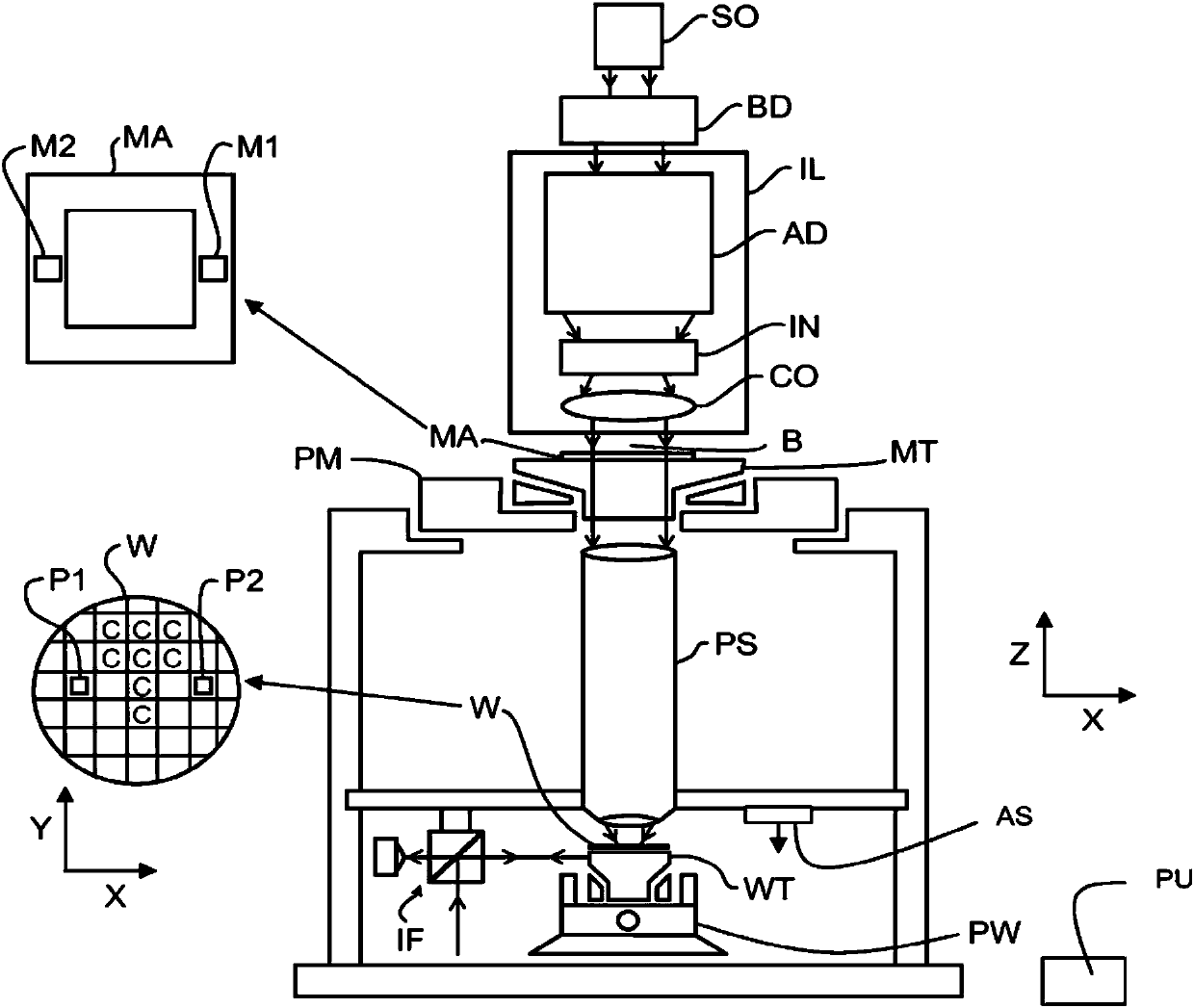
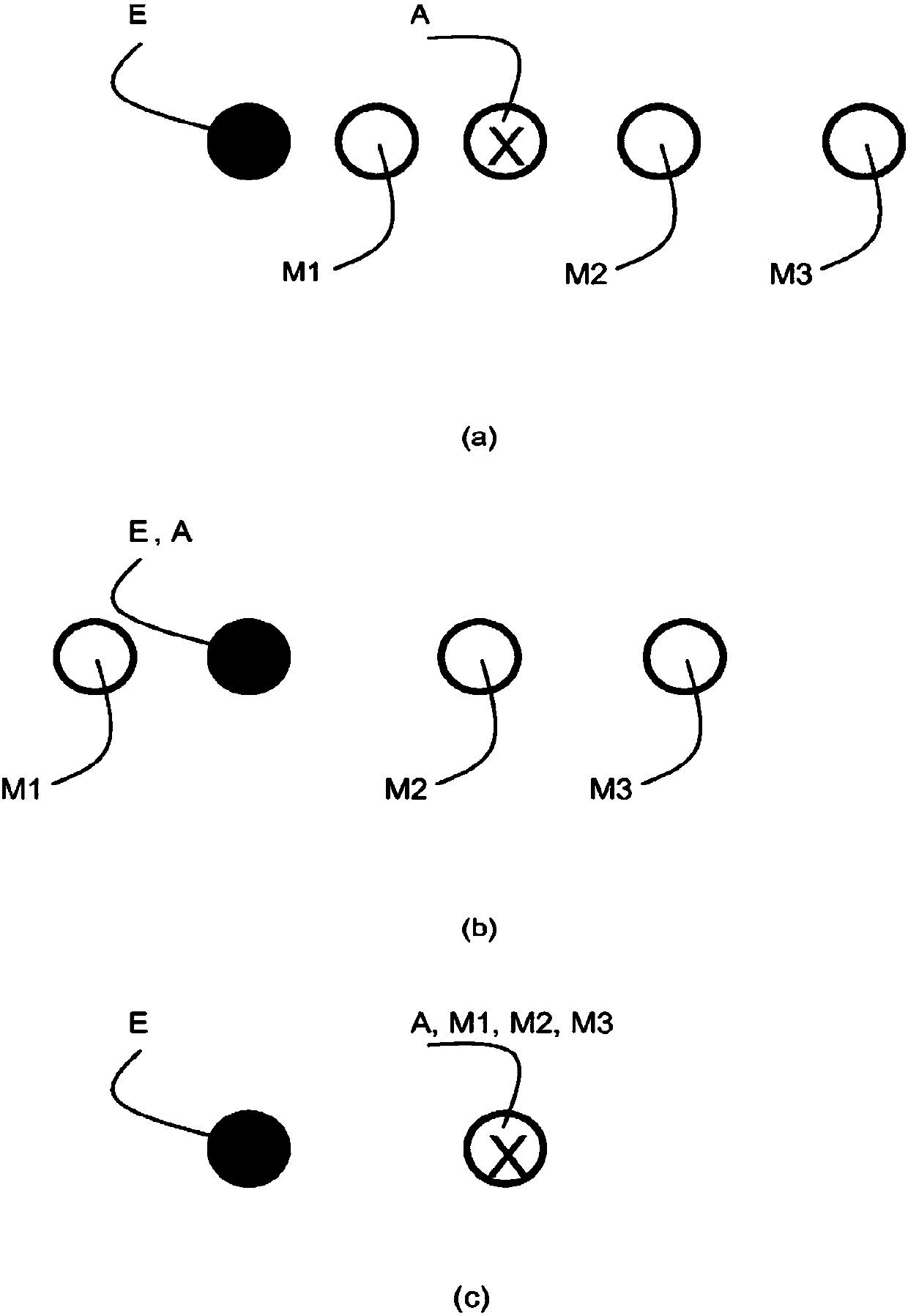
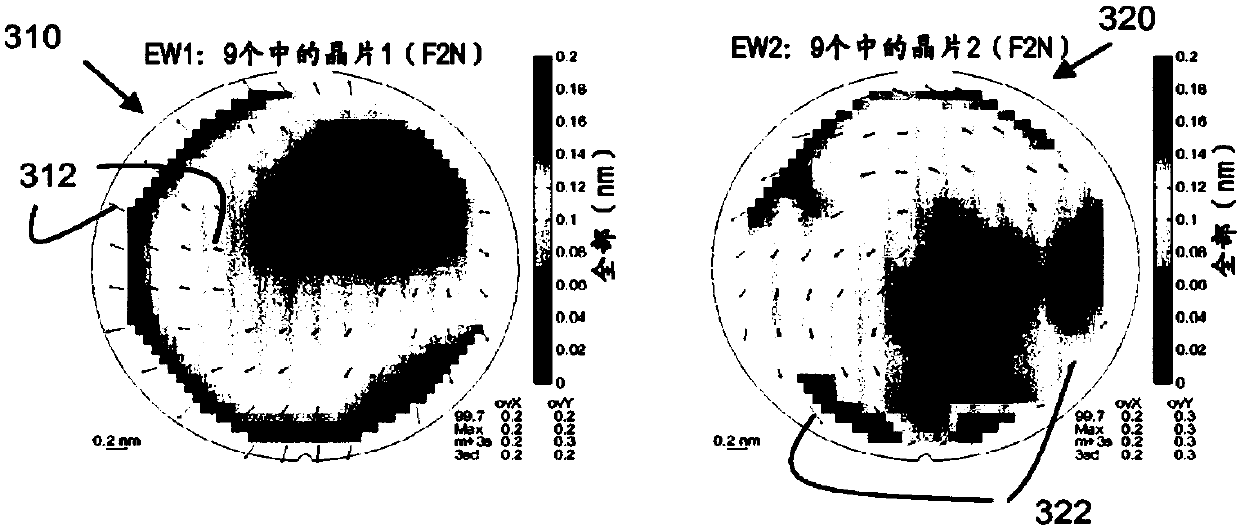
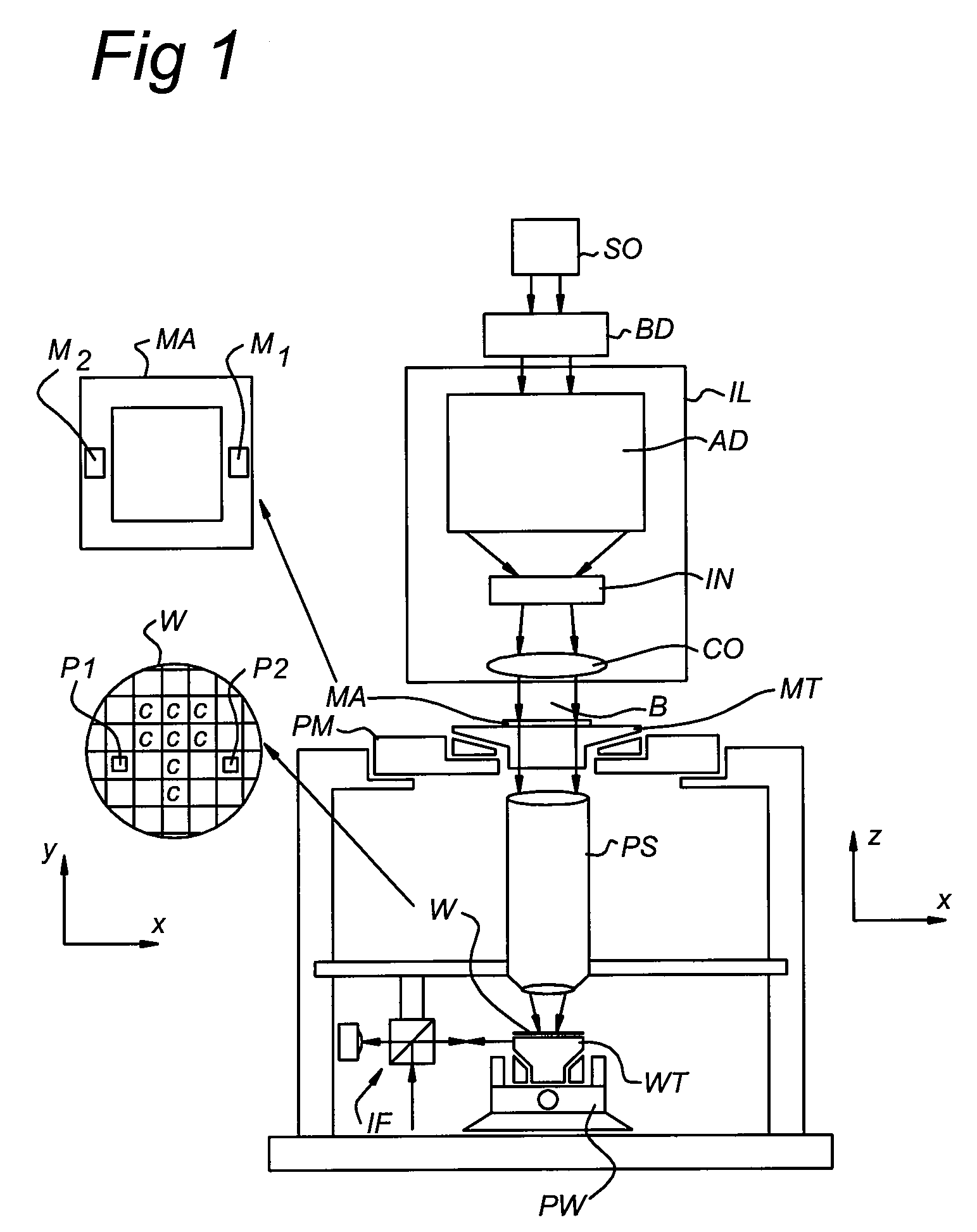
Lithographic apparatus and device manufacturing method
ActiveUS20180348654A1Precise alignmentAccurate assessmentPhotomechanical exposure apparatusMicrolithography exposure apparatusSubstrate deformationComputer science
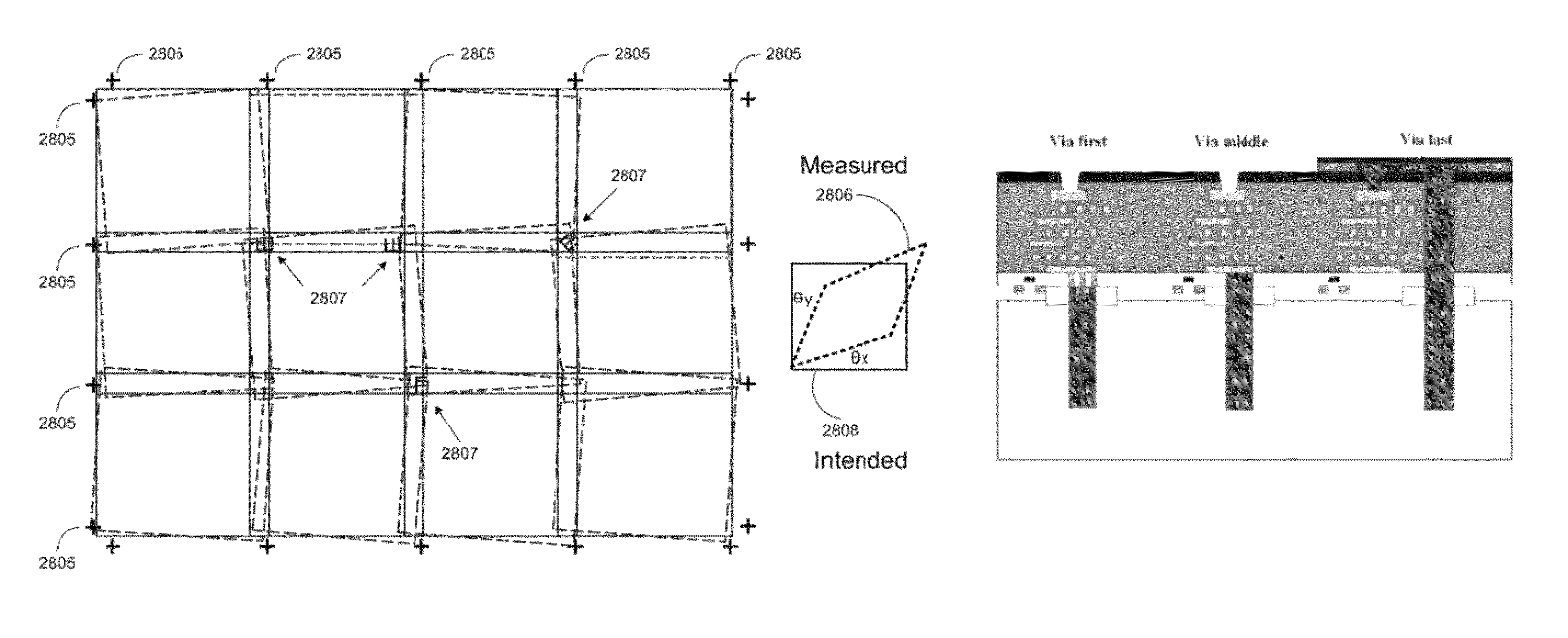
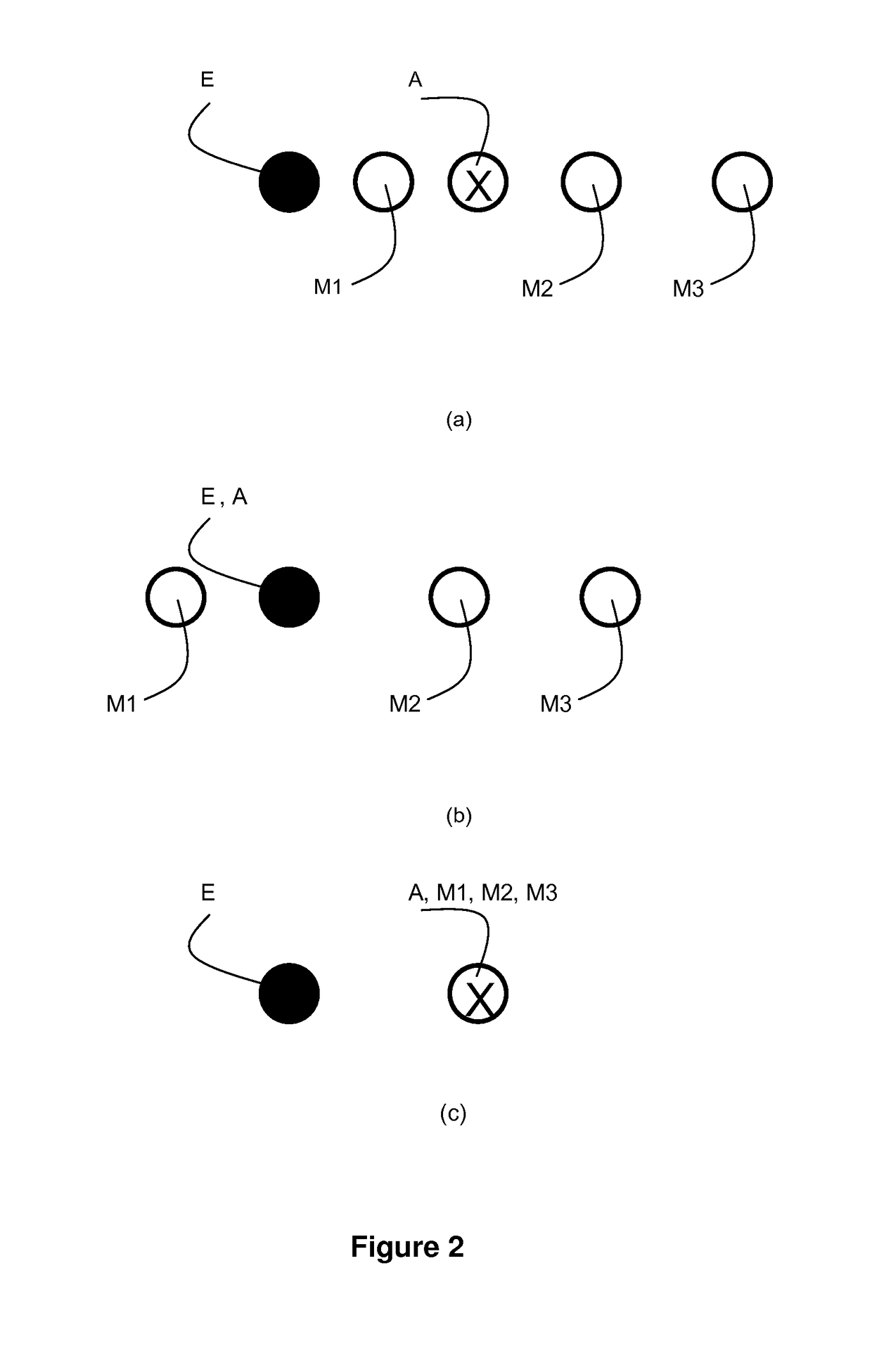
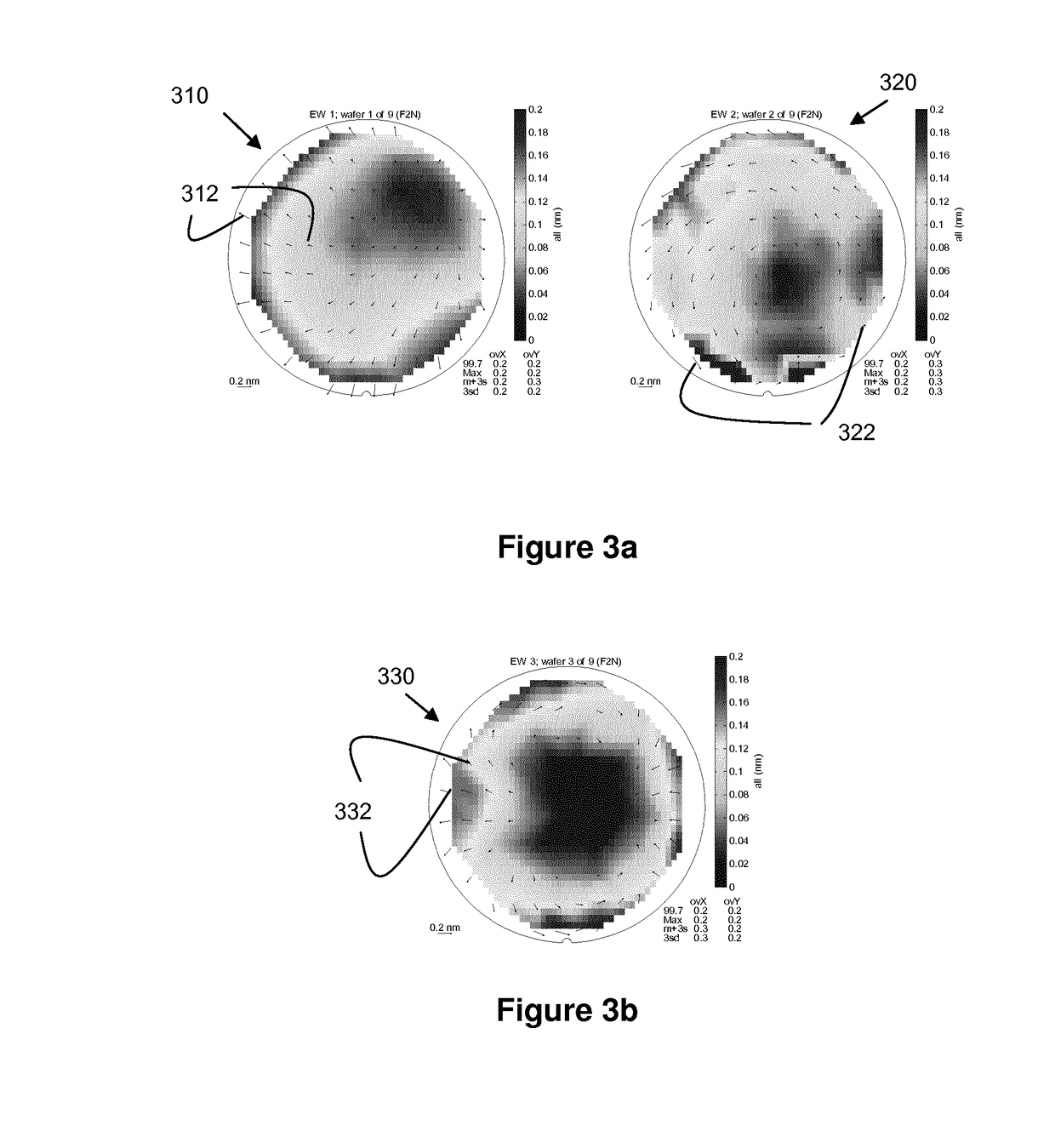
A method of characterizing a deformation of a plurality of substrates is described. The method comprising the steps of: —measuring, for a plurality of n different alignment measurement parameters λ and for a plurality of substrates, a position of the alignment marks; —determining a positional deviation as the difference between the n alignment mark position measurements and a nominal alignment mark position; —grouping the positional deviations into data sets; —determining an average data set; —subtracting the average data set from the data sets to obtain a plurality of variable data sets; —performing a blind source separation method on the variable data sets, thereby decomposing the variable data sets into a set of eigenwafers representing principal components of the variable data sets; —subdividing the set of eigenwafers into a set of mark deformation eigenwafers and a set of substrate deformation eigenwafers.
Owner:ASML NETHERLANDS BV
Liquid crystal display device and manufacturing method thereof
InactiveUSRE37945E1Prevent substrate deformationAvoid deformationNon-linear opticsIdentification meansLiquid-crystal displayEngineering
In a liquid crystal display device, support columns are formed on the outside of a seal area in an edge area of opposing substrates, thus reducing substrate deformation and preventing the occurrence of air bubbles inside the liquid crystal layer, undesirable coloring of the display area, and color irregularity. Support columns 9 formed using a conductive ink are provided on the outside of seal material 6 used for sealing liquid crystal layer 5 contained between top substrate 1 and bottom substrate 2. The support columns 9 prevent the warping of substrates 1 and 2 caused by the shrinkage of mold material 8 during hardening, reducing the changes in the liquid crystal layer thickness. Support columns 9 are print-formed simultaneously with the conductive connection area of the liquid crystal panel, and are hardened simultaneously with the seal material.
Owner:SEIKO EPSON CORP
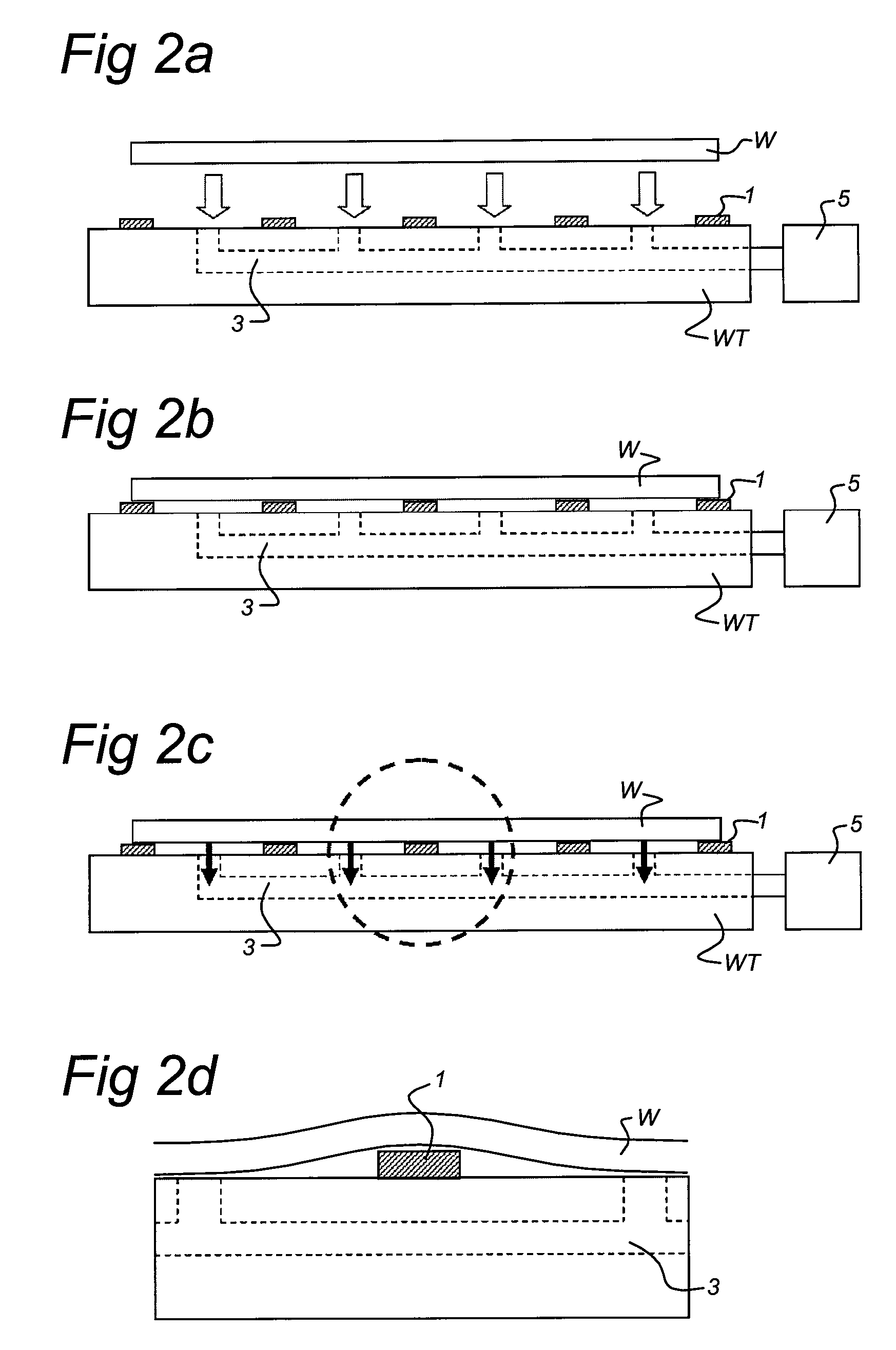
Method of Placing a Substrate, Method of Transferring a Substrate, Support System and Lithographic Projection Apparatus
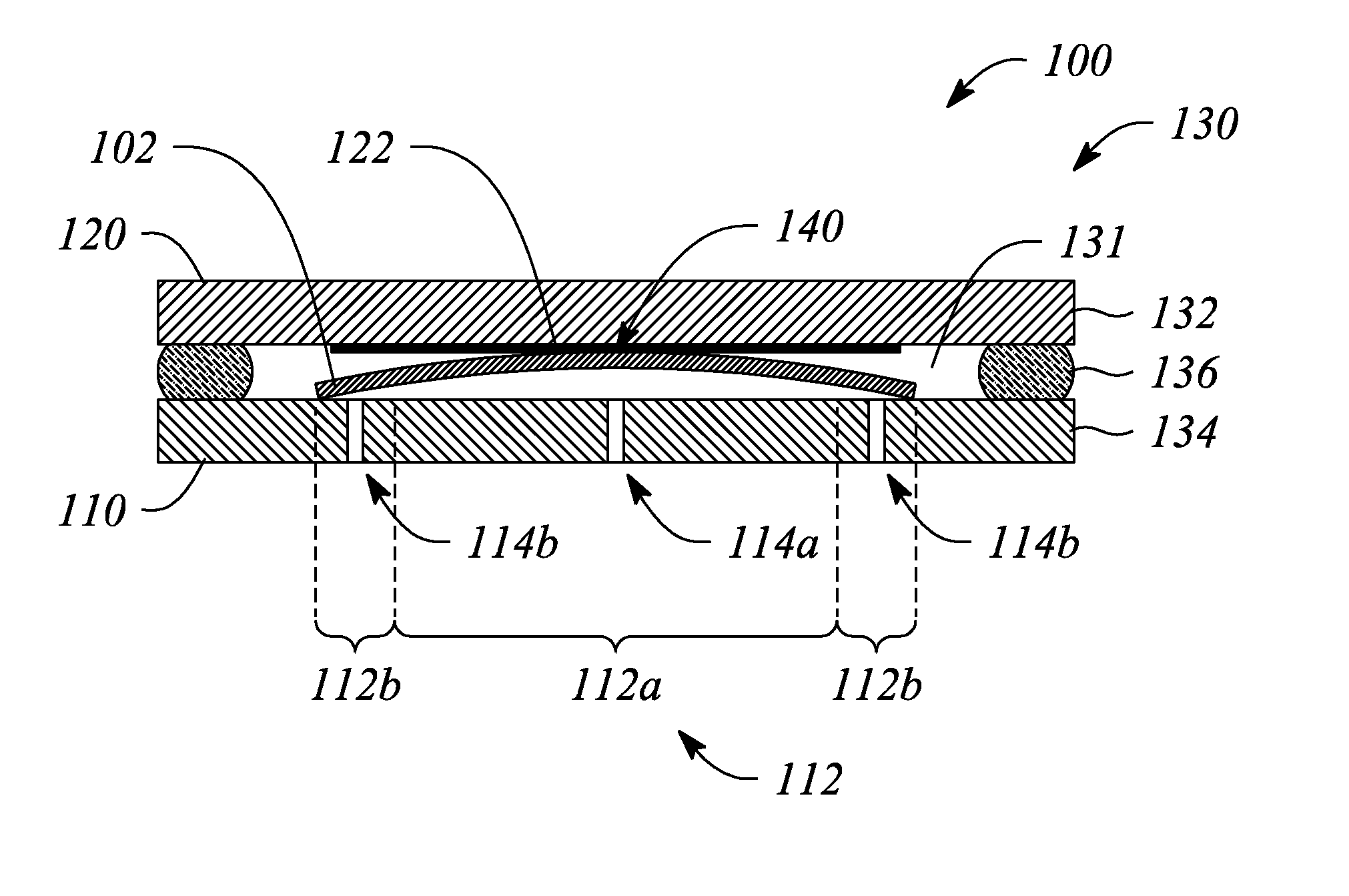
A method is provided for placing a substrate onto a surface of a substrate holder, the surface having a plurality of burls. First substrate placement data is calculated. This data enables placement of the substrate at a certain position with respect to a position of the plurality of burls on the surface of the substrate holder. Then, the substrate is placed at the certain position in accordance with the substrate placement data. The certain position may be based on the position at which placement would result in a minimized overlay error or may be based on the position at which placement would result in minimized substrate deformation.
Owner:ASML NETHERLANDS BV
PCBA (printed circuit board assembly) test bench and application method thereof
InactiveCN103472383AReduce the probability of false positivesPrecise positioningElectronic circuit testingMeasurement instrument housingEngineeringSubstrate deformation
The invention relates to a PCBA (printed circuit board assembly) test bench. The PCBA test bench comprises a control cabinet, a needle bed, a supporting plate and a supporting plate compressing assembly, wherein the needle bed is encapsulated at an open part of the upper end of the control cabinet, the supporting plate compressing assembly is vertically arranged at the rear part of the upper end of the needle bed, the supporting plate is vertically slidably arranged on the needle bed corresponding to the lower end of the supporting plate compressing assembly, multiple probe holes are formed in the supporting plate, probes are vertically fixedly arranged on the needle bed corresponding to each probe hole, the supporting plate compressing assembly pushes down the supporting plate, and the end part of each probe is arranged in one probe hole formed in the supporting plate. The PCBA test bench has the advantages that the supporting plate is pushed down by virtue of the supporting plate compressing assembly, so that a point TEST of a PCBA can be contacted with the probes, and the aim of rapidly and accurately detecting performances of the PCBA can be realized. The supporting plate is made from agglomerated stone, so that substrate deformation and static breakdown can be prevented; meanwhile, various specially-shaped substrates with irregular outlines or flexible plates can be detected, and the probes and a tested point TEST can be accurately positioned.
Owner:TIANJIN KEYI ELECTRONICS TECH
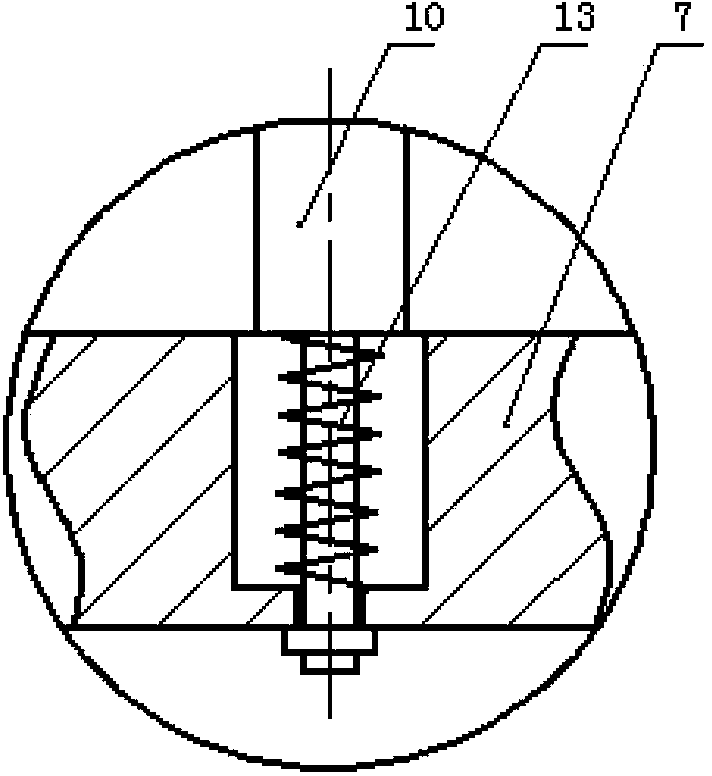
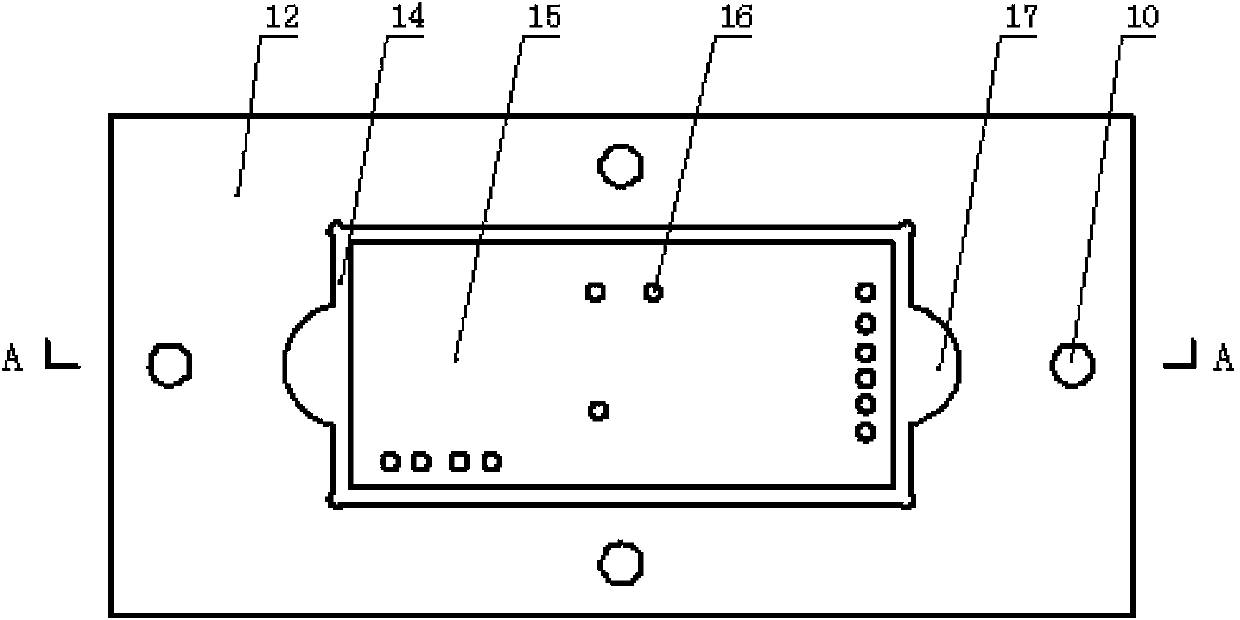
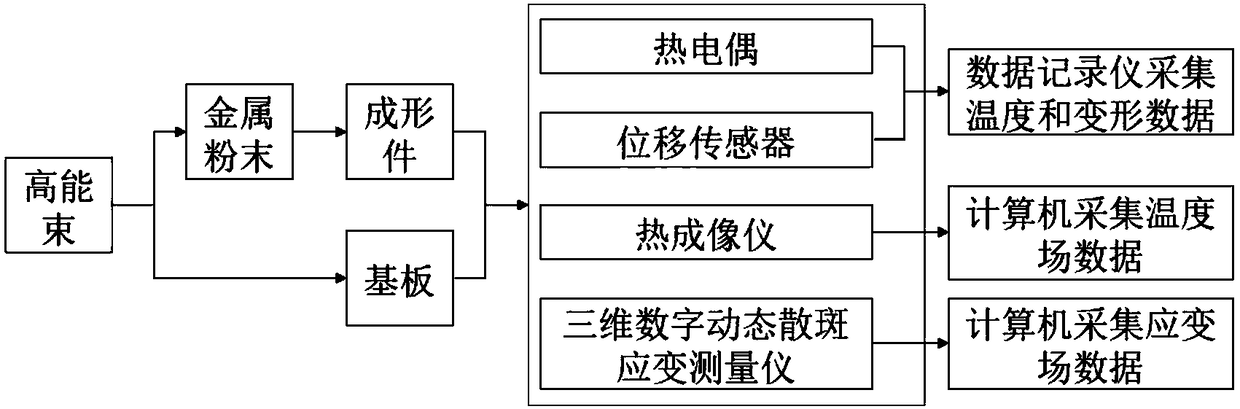
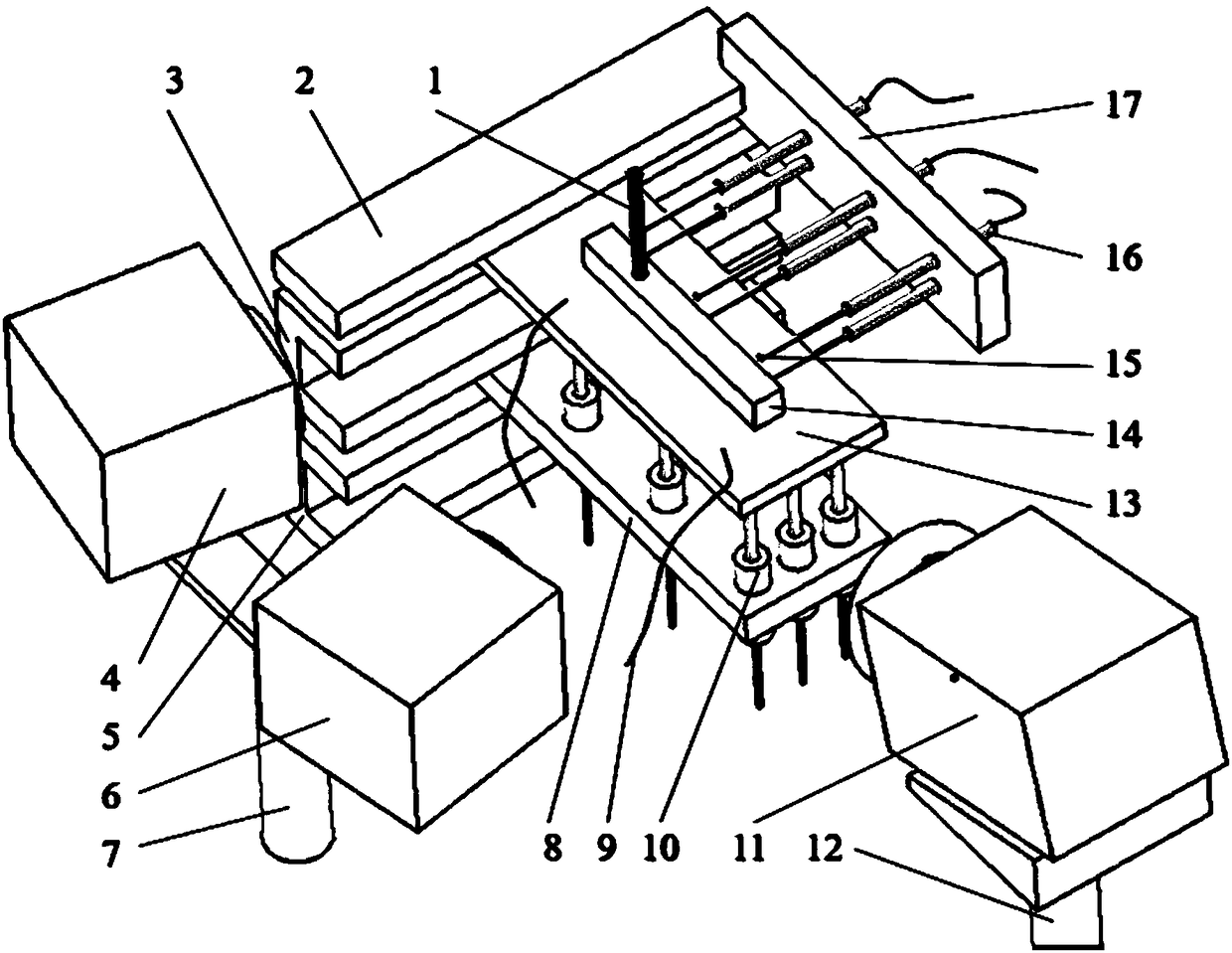
Checking method and checking data measurement apparatus of high-energy-beam additive-manufacturing finite-element thermal coupling model
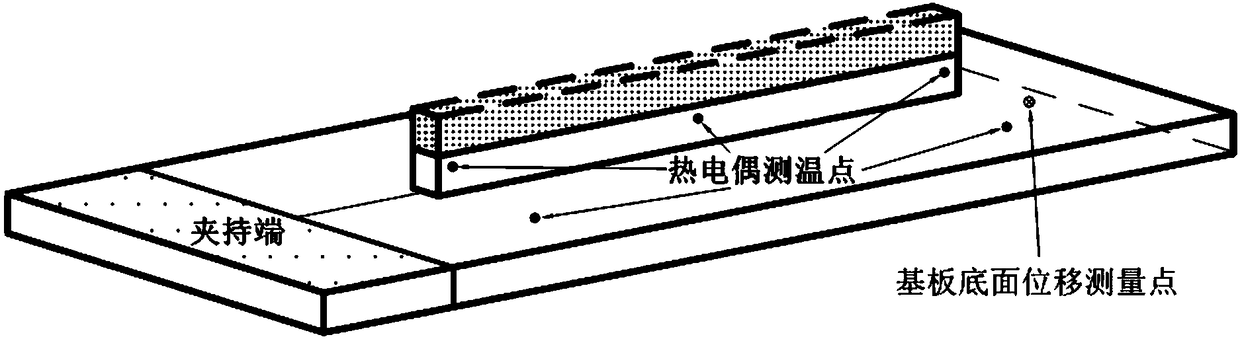
ActiveCN108132075AReal-time synchronous temperature monitoringReal-time and synchronous monitoring of strain in the whole fieldMeasurement devicesSpecial data processing applicationsMeasurement deviceManufacturing technology
The invention shows a checking method and checking data measurement apparatus of a high-energy-beam additive-manufacturing finite-element thermal coupling model. The apparatus comprises a workbench, afixture system and a data acquisition system, wherein the fixture system and the data acquisition system are installed on the workbench. In addition, the checking method includes: step one, carryingout real-time experiment measurement on a fusion covering process and heat-deformation-strain during high-energy-beam additive-manufacturing processing; step two, establishing a model framework, inputting a material property, and dividing a grid, and completing calibration of a finite-element temperature field; and step three, setting a force field boundary condition and using a calibrated temperature field results as an initial condition, obtaining a substrate deformation and strain field results, completing calibration of a finite-element force field, and thus completing calibration of a high-energy-beam additive-manufacturing finite-element thermal coupling model. According to the invention, reliable experiment data are provided for simulation of the high-energy-beam additive manufacturing; the scientific guidance is provided for establishing a process method for controlling deformation of the substrate and finished elements effectively; and thus application of the additive-manufacturing technology is prompted.
Owner:NORTHWESTERN POLYTECHNICAL UNIV
Transistor Device Formed on a Flexible Substrate Including Anodized Gate Dielectric
InactiveUS20080135891A1Enable productionStress minimizationSolid-state devicesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingGate dielectricDevice form
A transistor device is formed on a flexible substrate such that device processing remains at a low temperature. A first gate dielectric layer is formed over gate metal by annodization, eliminating relatively high-temperature dielectric deposition processes and difficulties with in-process substrate deformation. A second gate dielectric layer may optionally be provided over the first in order to provide an improved dielectric / semiconductor interface. A high performance pixel, and process for producing same, may thus be provided on a flexible substrate.
Owner:PALO ALTO RES CENT INC
Lithographic apparatus and device manufacturing method
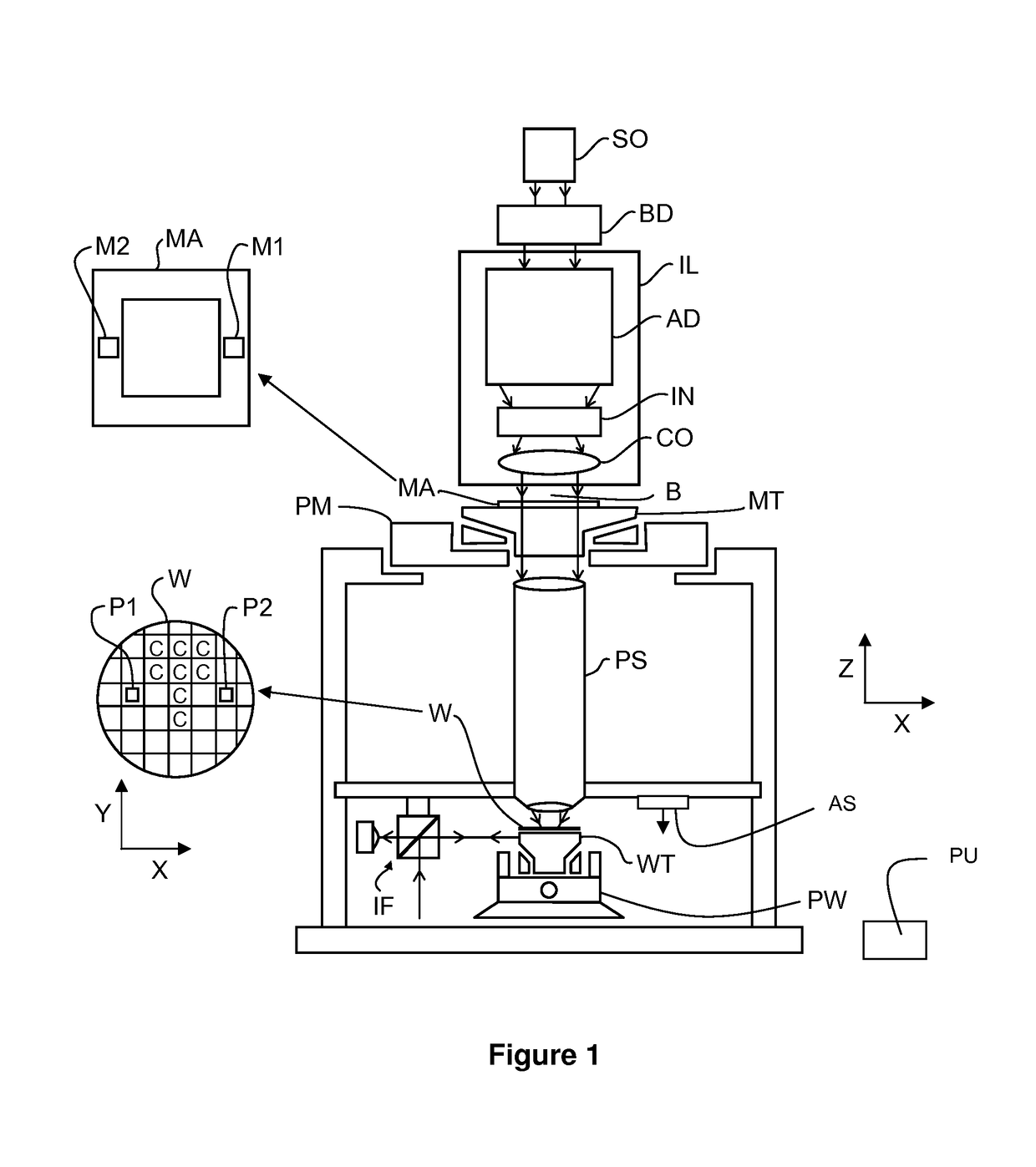
ActiveUS20180196363A1Accurate measurementPhotomechanical exposure apparatusMicrolithography exposure apparatusProcessing elementProjection system
A lithographic apparatus is described, the apparatus comprising: an illumination system configured to condition a radiation beam; a support constructed to support a patterning device, the patterning device being capable of imparting the radiation beam with a pattern in its cross-section to form a patterned radiation beam; a substrate table constructed to hold a substrate; and a projection system configured to project the patterned radiation beam onto a target portion of the substrate, wherein the apparatus further comprises an alignment system configured to perform, for one or more alignment marks that are present on the substrate: —a plurality of alignment mark position measurements for the alignment mark by applying a respective plurality of different alignment measurement parameters, thereby obtaining a plurality of measured alignment mark positions for the alignment mark; the apparatus further comprising a processing unit, the processing unit being configured to: —determine, for each of the plurality of alignment mark position measurements, a positional deviation as a difference between an expected alignment mark position and a measured alignment mark position, the measured alignment mark position being determined based on the respective alignment mark position measurement; —define a set of functions as possible causes for the positional deviations, the set of functions including a substrate deformation function representing a deformation of the substrate, and at least one mark deformation function representing a deformation of the one or more alignment marks; —generating a matrix equation PD=M*F whereby a vector PD comprising the positional deviations is set equal to a weighted combination, represented by a weight coefficient matrix M, of a vector F comprising the substrate deformation function and the at least one mark deformation function, whereby weight coefficients associated with the at least one mark deformation function vary depending on applied alignment measurement; —determining a value for the weight coefficients of the matrix M; —determining an inverse or pseudo-inverse matrix of the matrix M, thereby obtaining a value for the substrate deformation function as a weighted combination of the positional deviations. —applying the value of the substrate deformation function to perform an alignment of the target portion with the patterned radiation beam.
Owner:ASML NETHERLANDS BV
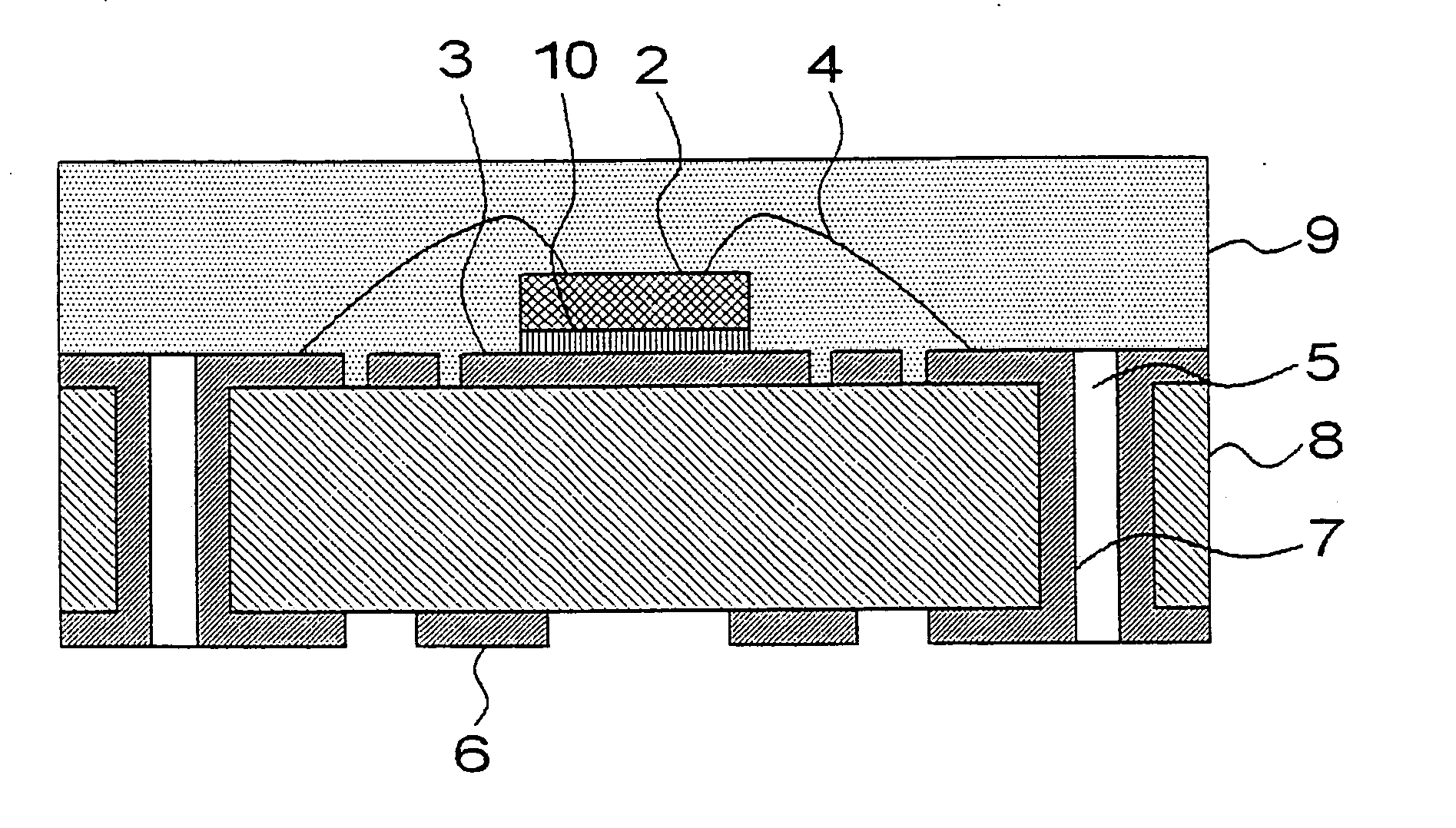
Semiconductor device
InactiveUS20070096307A1Improve toughnessFor active controlSemiconductor/solid-state device detailsSolid-state devicesElectrical conductorDevice material
In a semiconductor device, a occupation ratio of the surface of a resin substrate encapsulated with resin by conductor patterns provided on the same surface is set so as to be 70% or higher in order to raise the toughness of the resin substrate during heating and pressurization. Preferably, the distance between conductor patterns is set so as to be 0.15 mm or less. The resin substrate may be prevented from becoming deformed, that is, a semiconductor device in which cracking in a resin substrate, at the time of resin encapsulation, may be prohibited in a simplified manner from occurrence.
Owner:NEC ELECTRONICS CORP
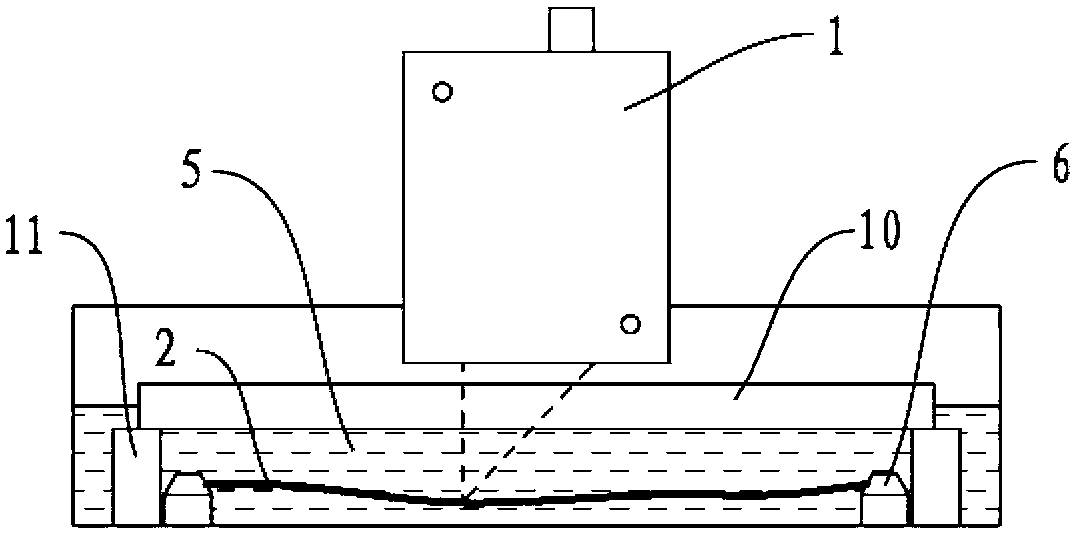
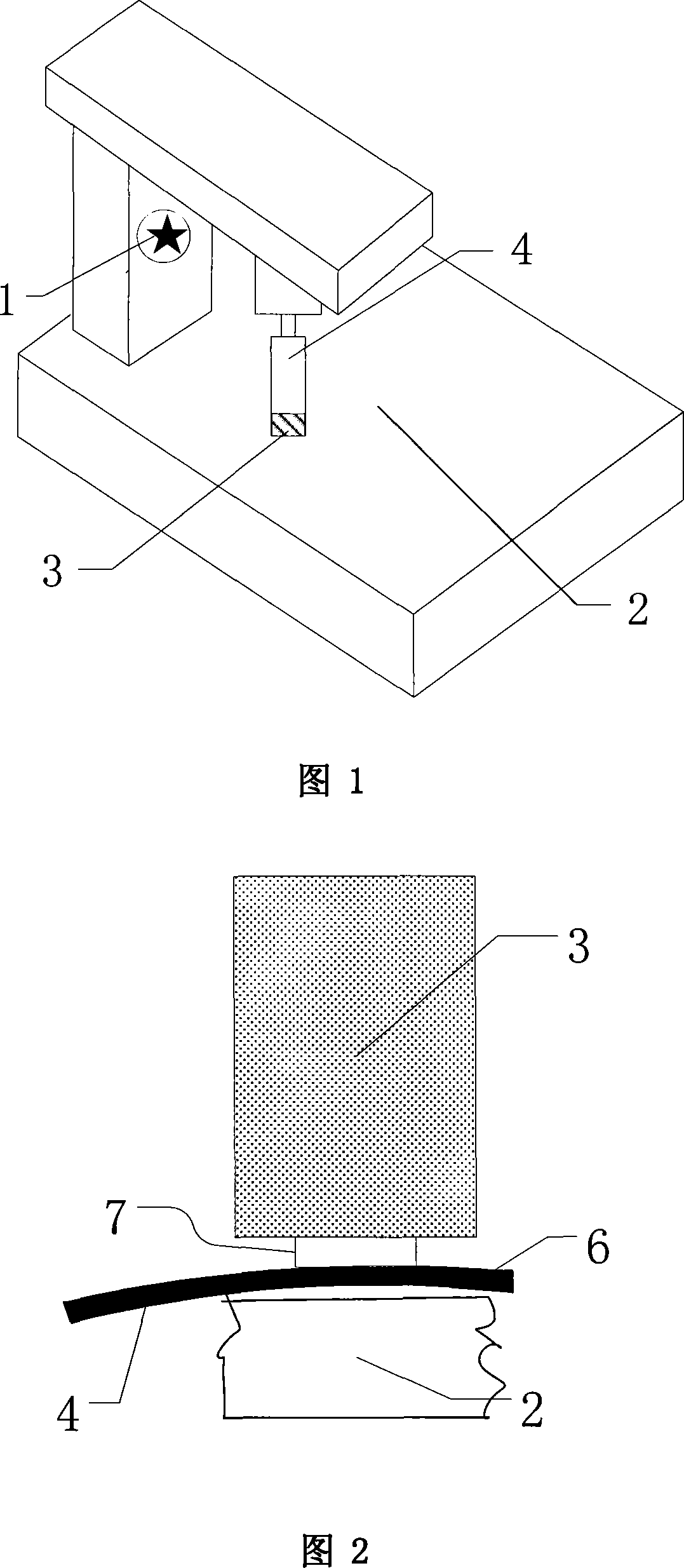
Method and device for measuring thin substrate deformation
ActiveCN103278103AReduce the effect of gravity additional deformationAccurate measurementUsing optical meansOptoelectronicsSubstrate deformation
The invention relates to a method and a device for measuring thin substrate deformation, belonging to the field of the method and the device for measuring object deformation. The measuring method comprises the following steps of submerging a measured thin substrate into liquid of which the density is close to that of the thin substrate; limiting the thin substrate at a horizontal position in the liquid by adopting a fixing pin; placing a transparent flat plate with high planeness and high parallelism at the junction of the air and the liquid, wherein the upper surface of the transparent flat plate is positioned above the surface of the liquid, and the lower surface of the transparent flat plate is positioned below the surface of the liquid; and scanning and measuring the surface displacement of the thin substrate by adopting an optical displacement sensor. In the measuring device, the optical displacement sensor is fixedly arranged on a vertical translation table through a mounting plate, the thin substrate is supported and limited through three conical pins, and the entire thin substrate is fixed in a solution. Due to the adoption of the method and the device, the influences of the additional deformation of gravity in a thin substrate measuring process are lowered effectively, the deformation of the thin substrate which is small in thickness and is large in planar size can be measured accurately, and the measuring result is accurate and reliable.
Owner:DALIAN UNIV OF TECH
Lithographic apparatus and device manufacturing method
ActiveCN107850862APhotomechanical exposure apparatusMicrolithography exposure apparatusData setSubstrate deformation
A method of characterizing a deformation of a plurality of substrates is described. The method comprising the steps of: - measuring, for a plurality of n different alignment measurement parameters lambda and for a plurality of substrates, a position of the alignment marks; - determining a positional deviation as the difference between the n alignment mark position measurements and a nominal alignment mark position; - grouping the positional deviations into data sets; - determining an average data set; - subtracting the average data set from the data sets to obtain a plurality of variable datasets; - performing a blind source separation method on the variable data sets, thereby decomposing the variable data sets into a set of eigenwafers representing principal components of the variable data sets; - subdividing the set of eigenwafers into a set of mark deformation eigenwafers and a set of substrate deformation eigenwafers.
Owner:ASML NETHERLANDS BV
Method of placing a substrate, method of transferring a substrate, support system and lithographic projection apparatus
A method is provided for placing a substrate onto a surface of a substrate holder, the surface having a plurality of burls. First substrate placement data is calculated. This data enables placement of the substrate at a certain position with respect to a position of the plurality of burls on the surface of the substrate holder. Then, the substrate is placed at the certain position in accordance with the substrate placement data. The certain position may be based on the position at which placement would result in a minimized overlay error or may be based on the position at which placement would result in minimized substrate deformation.
Owner:ASML NETHERLANDS BV
Method for sticking module group substrates with driver circuit and equipment thereof
InactiveCN101140362AAvoid adhesive misalignment and other defectsReduced wiggle roomStatic indicating devicesNon-linear opticsDriver circuitThermal compression
The present invention discloses a method of gluing a liquid crystal module substrate with a drive circuit and a device. Wherein, the method includes steps below: Fixing a liquid crystal module substrate onto a supporting table to absorb the liquid crystal module substrate through vacuum; driving a thermal compression head to move horizontally to press the drive circuit with the substrate one by one. In addition, the gluing device comprises a digital program control unit, a supporting table, a thermal compression head and a drive mechanism, of which the thermal compression head is driven by the drive mechanism to shift horizontally. Vacuum intakes are arranged on the supporting table. The gluing method and the device of the present invention can not only avoid aberration resulting from the substrate deformation due to larger liquid crystal module substrate during pressing and improve rate of quality products but also reduce revolving space of the liquid crystal module substrate in the device and shrink overall device size.
Owner:AU OPTRONICS (SUZHOU) CORP LTD
Method for depositing nano-grade TiO2 film on textile material
InactiveCN102899623ASmall particle sizeReduce surface roughnessVacuum evaporation coatingSputtering coatingFiberOptoelectronics
The invention provides a method for depositing a nano-grade TiO2 film on a textile material. The method comprises the steps that: high-purity metal Ti target is adopted as a target material; a pretreated textile material is adopted as a substrate; and the textile-material-based nano-grade TiO2 film is prepared under room temperature by using a DC reactive magnetron sputtering device. All samples adopt a structure that the substrate is on the upper side and the target is on the lower side, such that the nano-grade TiO2 film is prepared by sputtering from bottom to top, and impurity particles are prevented from falling onto the surface of the substrate. Also, the substrate is cooled with a water cooling device, such that substrate temperature during film deposition is controlled, and substrate deformation caused by high temperature is avoided. For ensuring the purity of the nano-grade TiO2 film, a reaction chamber is first pumped to base vacuum; high-purity argon is delivered as a sputtering gas; and high-purity oxygen is adopted as a reaction gas. With the method provided by the invention, a relatively uniform and compact TiO2 film can be deposited on the non-woven fabric fiber surface. The average particle size of the film is relatively small, and the surface roughness of the film is relatively low.
Owner:KUNSHAN TIENIU SHIRT FACTORY
Reduced wafer warpage in semiconductors by stress engineering in the metallization system
InactiveUS8053354B2Reduce probabilityImprove compatibilitySemiconductor/solid-state device detailsSolid-state devicesEngineeringConductive materials
In complex metallization systems of sophisticated semiconductor devices, appropriate stress compensation mechanisms may be implemented in order to reduce undue substrate deformation during the overall manufacturing process. For example, additional dielectric material and / or functional layers of one or more metallization layers may be provided with appropriate internal stress levels so as to maintain substrate warpage at a non-critical level, thereby substantially reducing yield losses in the manufacturing process caused by non-reliable attachment of substrates to substrate holders in process and transport tools.
Owner:GLOBALFOUNDRIES INC
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com