Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
18033 results about "Bonding strength" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
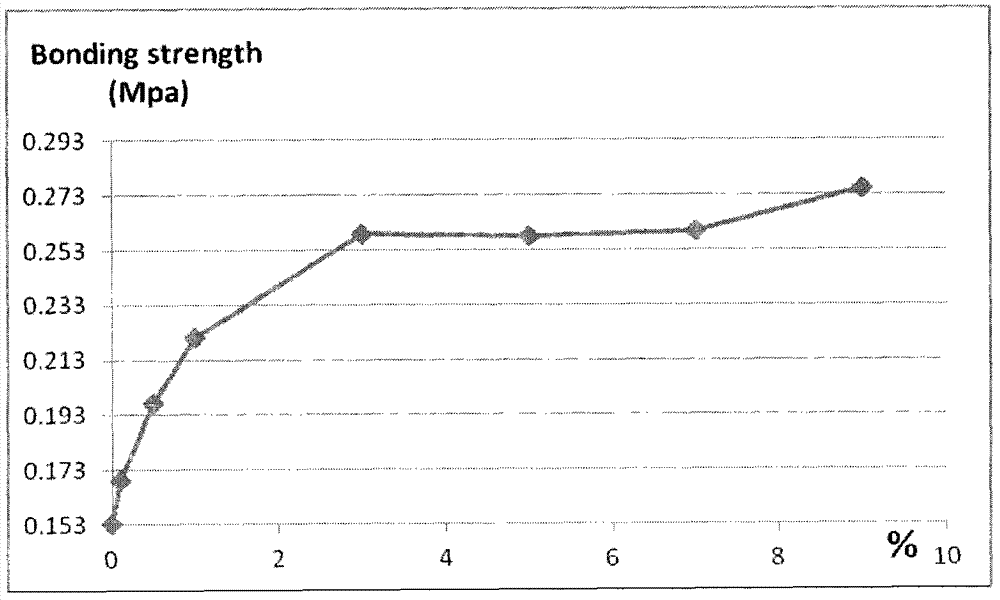
Bonding Strength. Bonding strength is defined as the maximum force born by unit bonding area, which mainly depends on the own strength of adhesives (cohesive power) and the adhesive strength (adhesive power) between adhesives and adherends.
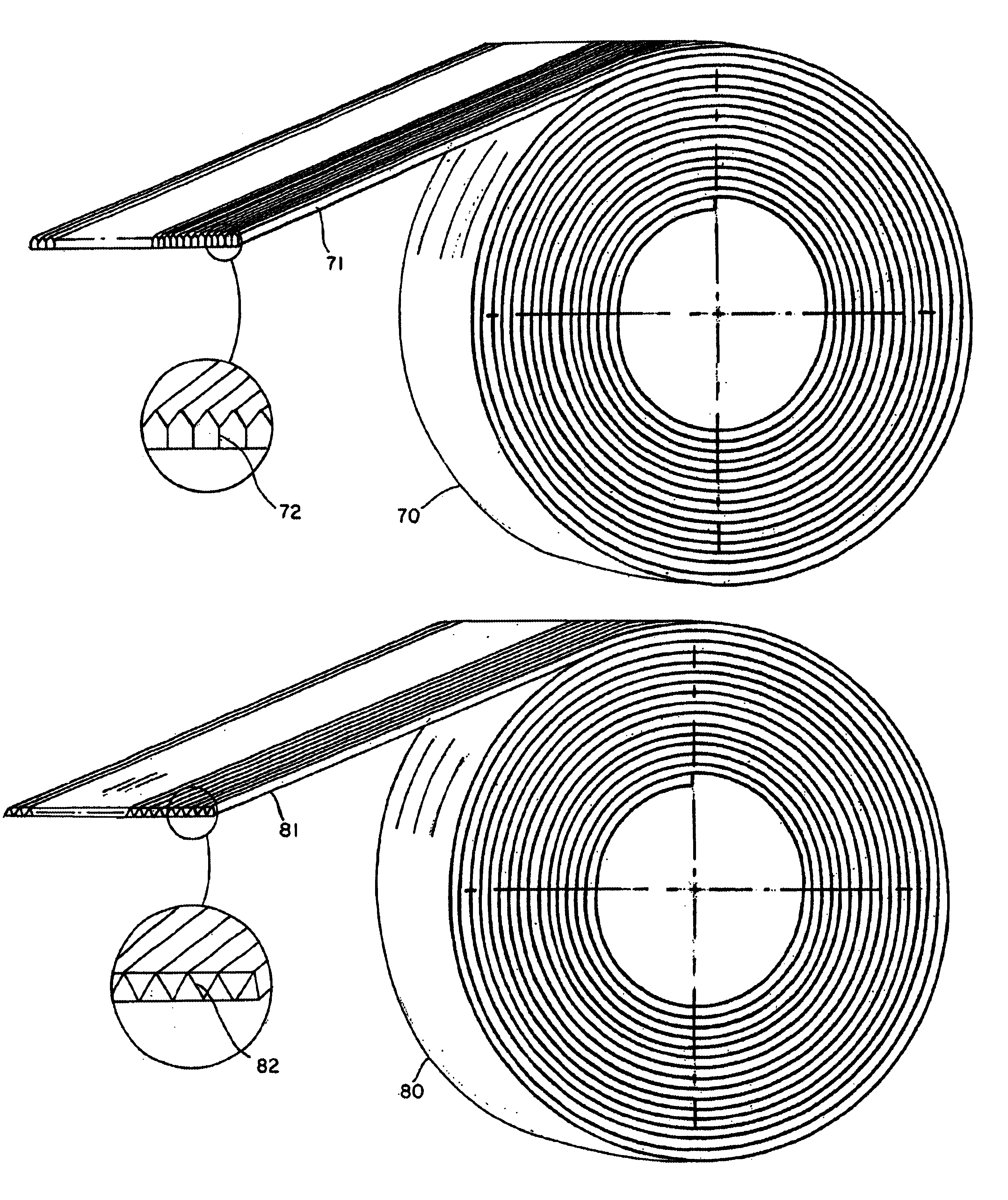
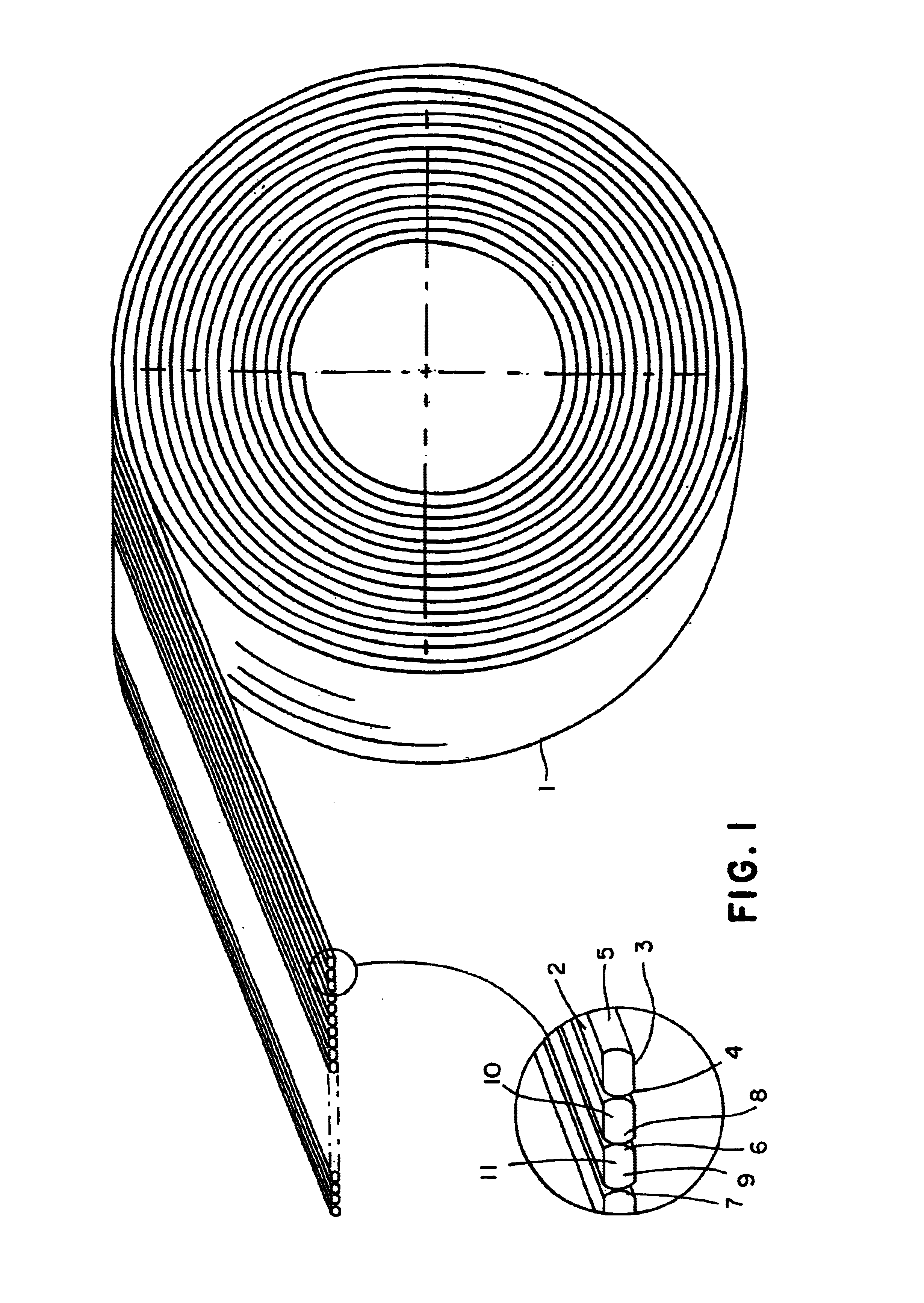
Method of forming a wire package
A method for making a wire package for use as staples or brads is recited as forming a plurality of round wires, forming a plurality of flattened bonding sides on each wire to prepare even bonding surfaces on each wire and bonding each wire to an adjacent wire by adhering the surfaces of each wire. Each staple includes two or more flat surfaces to improve the bonding strength of each staple. A package of diverging staples or brads are formed using the flat bonding surfaces
Owner:LIAO CHASE
Process for producing multilayered gas-barrier film
InactiveUS20120003500A1Satisfactory productivityExcellent gas barrier performanceLiquid surface applicatorsSynthetic resin layered productsPolymer scienceThin membrane
Provided are a method for producing a film, which is satisfactory in productivity, exhibits high gas-barrier property immediately after production, and has excellent adhesive strength between constituent layers while maintaining the excellent gas-barrier property, and a gas-barrier film, which is obtained by the method. The method for producing a gas-barrier film includes the steps of; (1) forming an inorganic thin film by a vacuum deposition method on at least one surface of a base film; (2) forming a thin film by a plasma CVD method on the inorganic thin film formed in the step (1); and (3) forming an inorganic thin film by the vacuum deposition method on the thin film formed in the step (2), in which each of the steps (1) and (3), and the step (2) are sequentially carried out at a pressure of 1×10−7 to 1 Pa, and at a pressure of 1×10−3 to 1×102 Pa, respectively.
Owner:MITSUBISHI PLASTICS INC
Method for manufacturing soi substrate
InactiveUS20090142905A1High bonding strengthImprove reliabilitySemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingSemiconductor devicesOptoelectronicsSingle crystal
Owner:SEMICON ENERGY LAB CO LTD
Method for forming dielectric SiOCH film having chemical stability
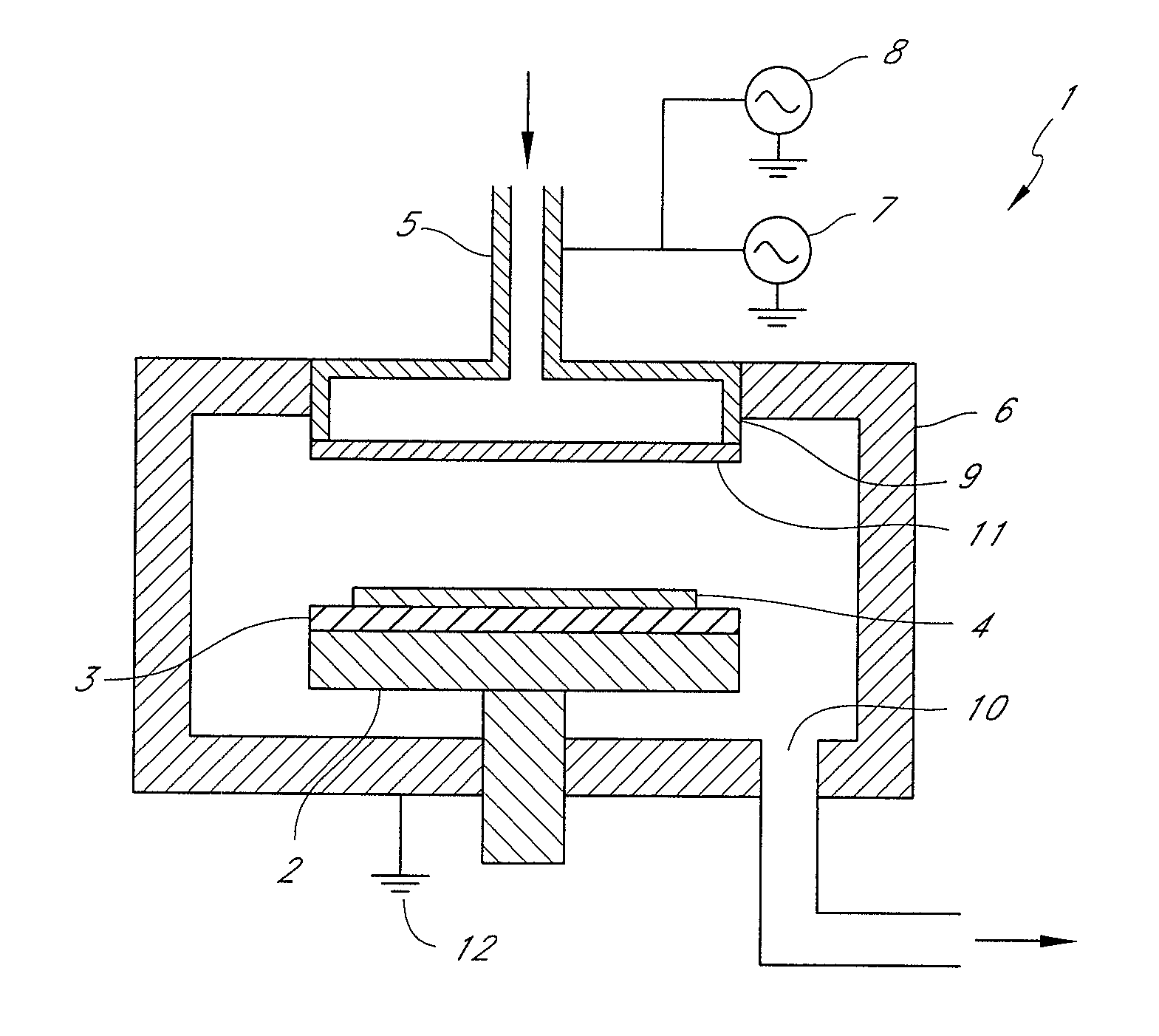
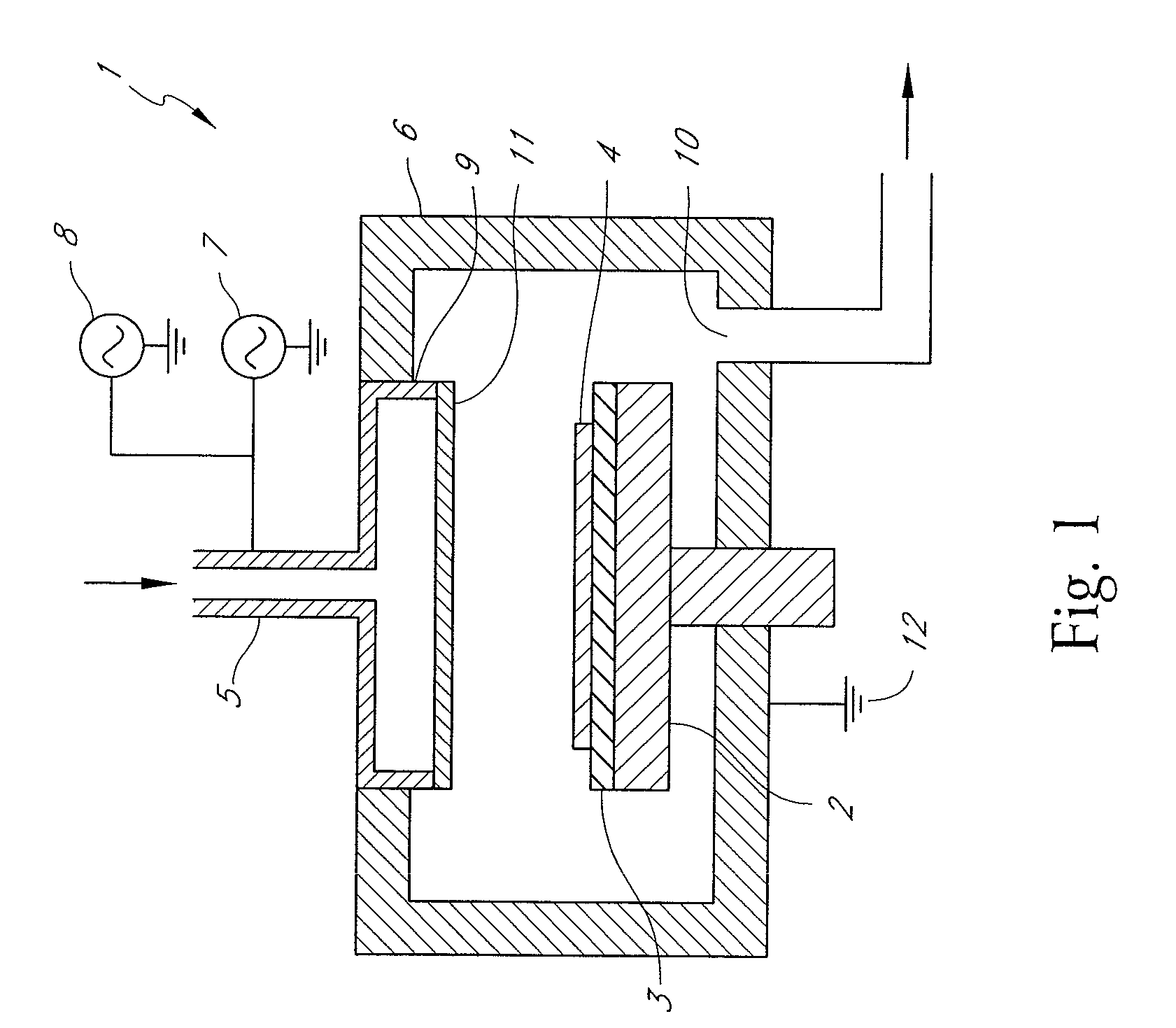
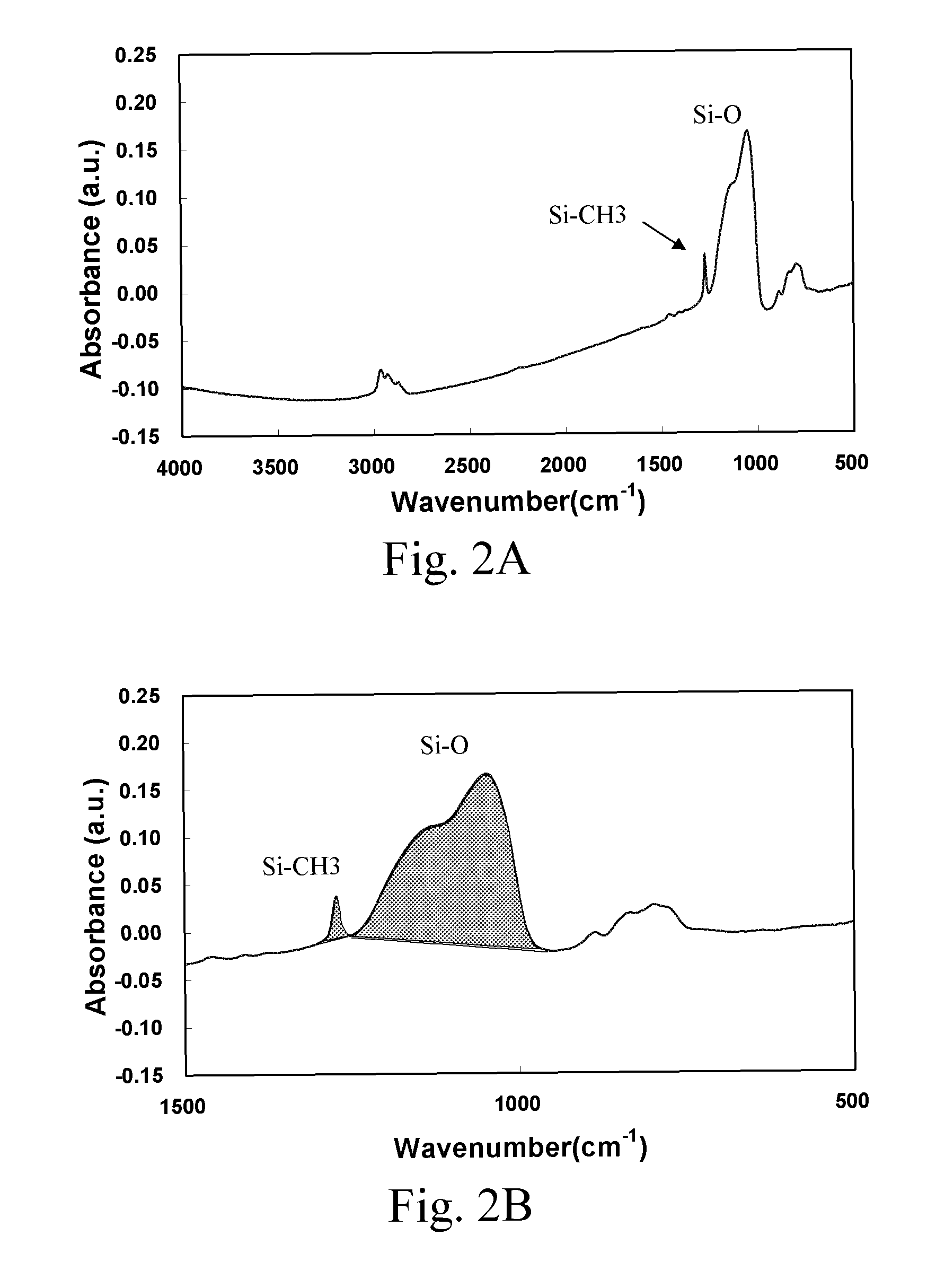
ActiveUS7807566B2Good chemical stabilityLow dielectric constantSemiconductor/solid-state device testing/measurementSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingDielectricSusceptor
A method for determining conditions for forming a dielectric SiOCH film, includes: (i) forming a dielectric SiOCH film on a substrate under conditions; (ii) evaluating the conditions using a ratio of Si—CH3 bonding strength to Si—O bonding strength of the film as formed in step (i); (iii) if the ratio is 2.50 % or higher, confirming the conditions, and if the ratio is less than 2.50 %, changing the conditions by changing at least one of the susceptor temperature, the distance between upper and lower electrodes, the RF power, and the curing time; and (iv) repeating steps (i) to (iii) until the ratio is 2.50 % or higher.
Owner:ASM JAPAN
Thin film device transfer method, thin film device, thin film integrated circuit device, active matrix board, liquid crystal display, and electronic apparatus
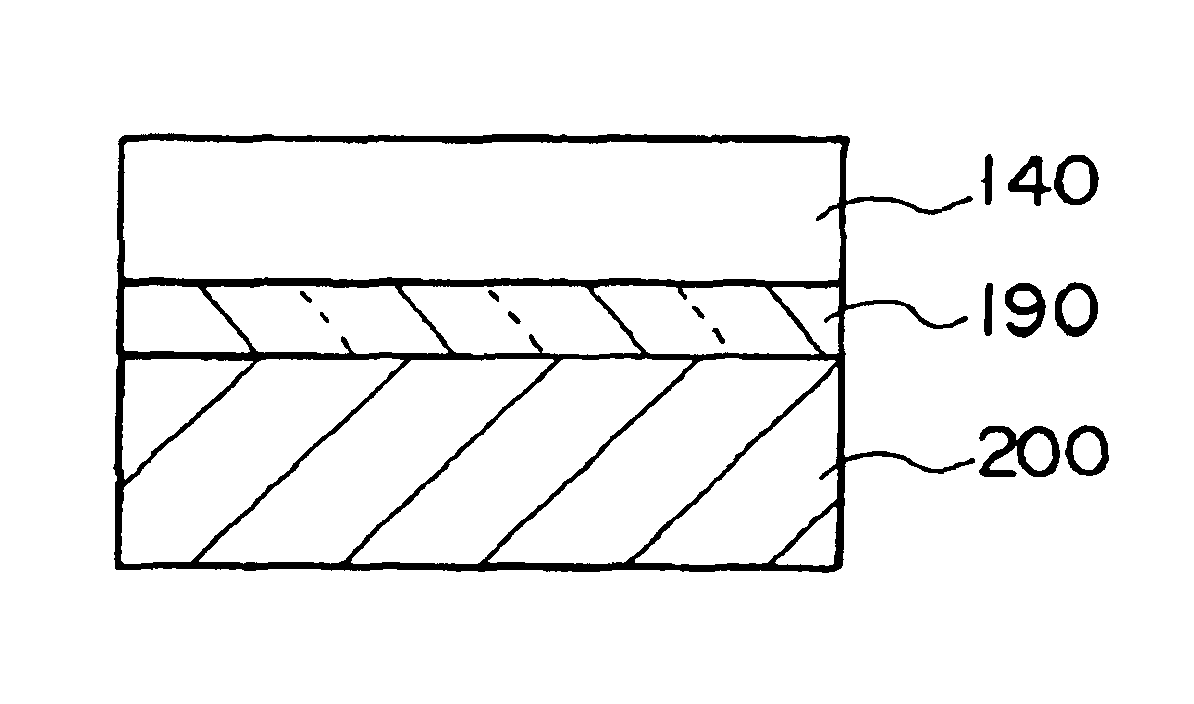
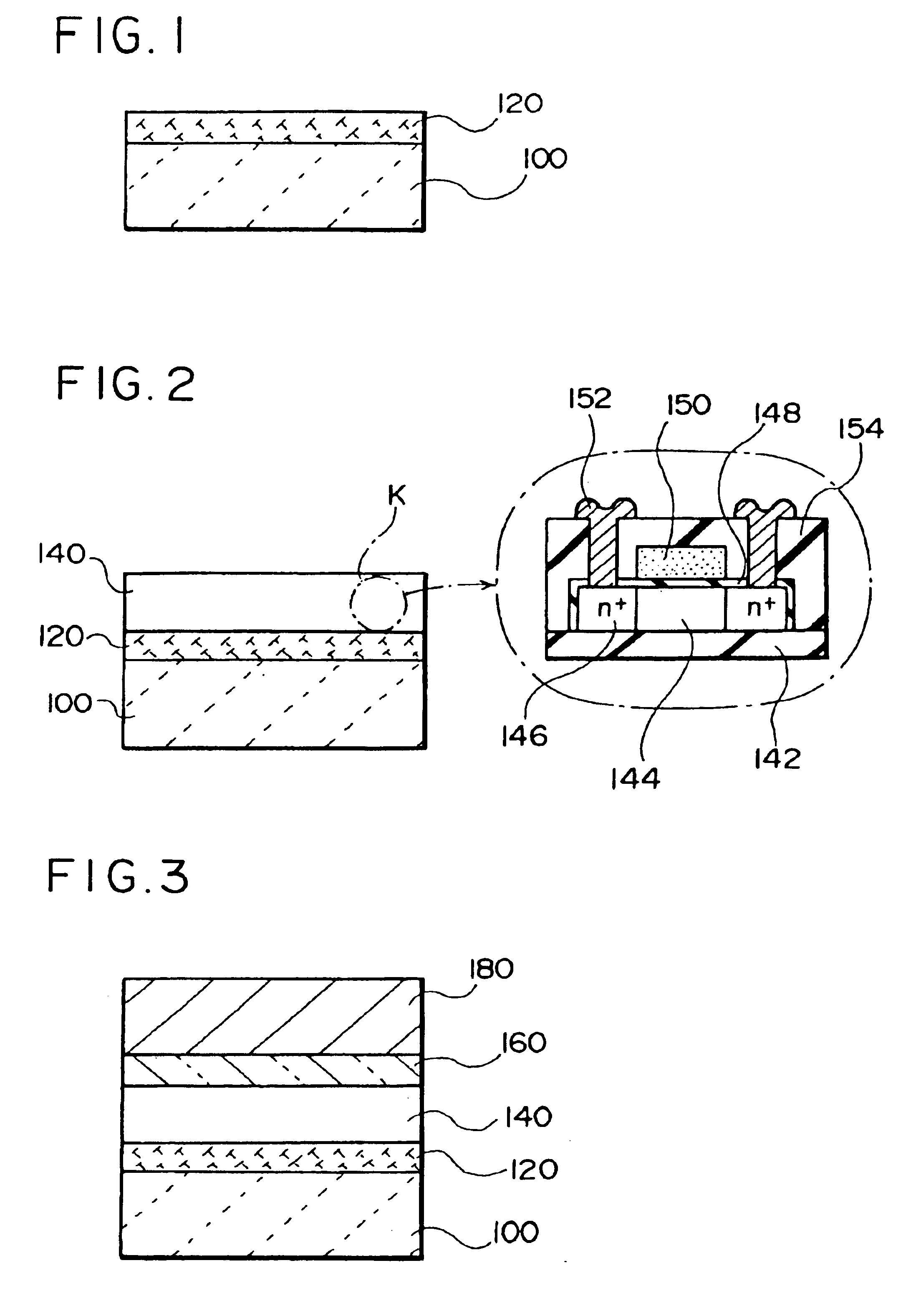
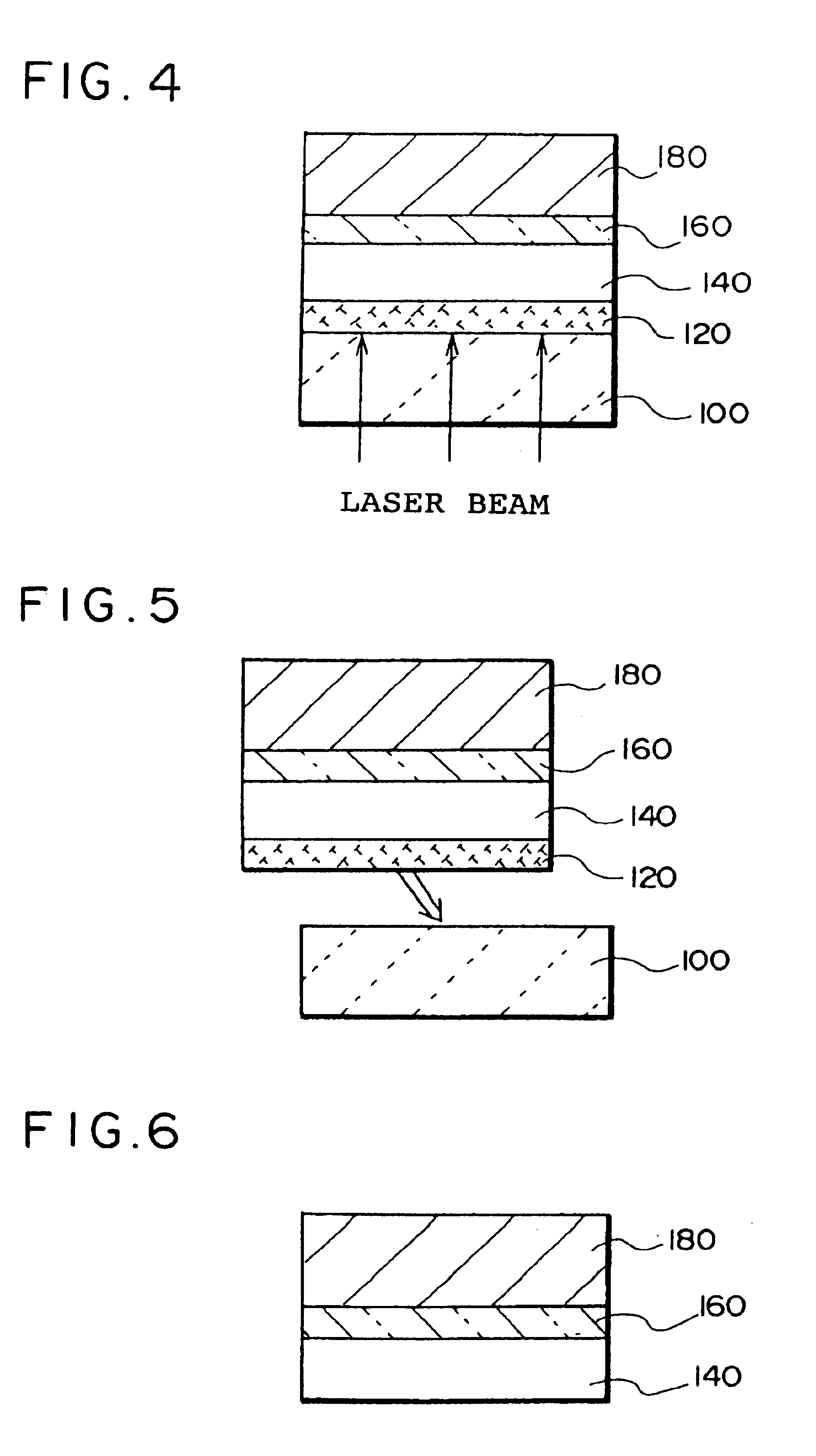
A thin film device fabrication method in which a thin film device formed on a substrate are transferred to a primary destination-of-transfer part and then the thin film device is transferred to a secondary destination-of-transfer part. A first separation layer (120) made of such a material as amorphous silicon is provided on a substrate (100) which allows passage of laser. A thin film device (140) such as TFTs are formed on the substrate (100). Further, a second separation layer (160) such as a hot-melt adhesive layer is formed on the thin film devices (140), and a primary destination-of-transfer part (180) is mounted thereon. The bonding strength of the first separation layer is weakened by irradiation with light, and the substrate (100) is removed. Thus, the thin film device (140) is transferred to the primary destination-of-transfer part. Then, a secondary destination-of-transfer part (200) is attached onto the bottom of an exposed part of the thin film device (140) via an adhesive layer (190). Thereafter, the bonding strength of the second separation layer is weakened by such means as thermal fusion, and the primary destination-of-transfer part is removed. In this manner, the thin film device (140) can be transferred to the secondary destination-of-transfer part (200) while maintaining layering relationship with respect to the substrate (100).
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
Method of room temperature covalent bonding
InactiveUS7109092B2High densityLow densityLayered productsDecorative surface effectsRoom temperatureFluorine containing
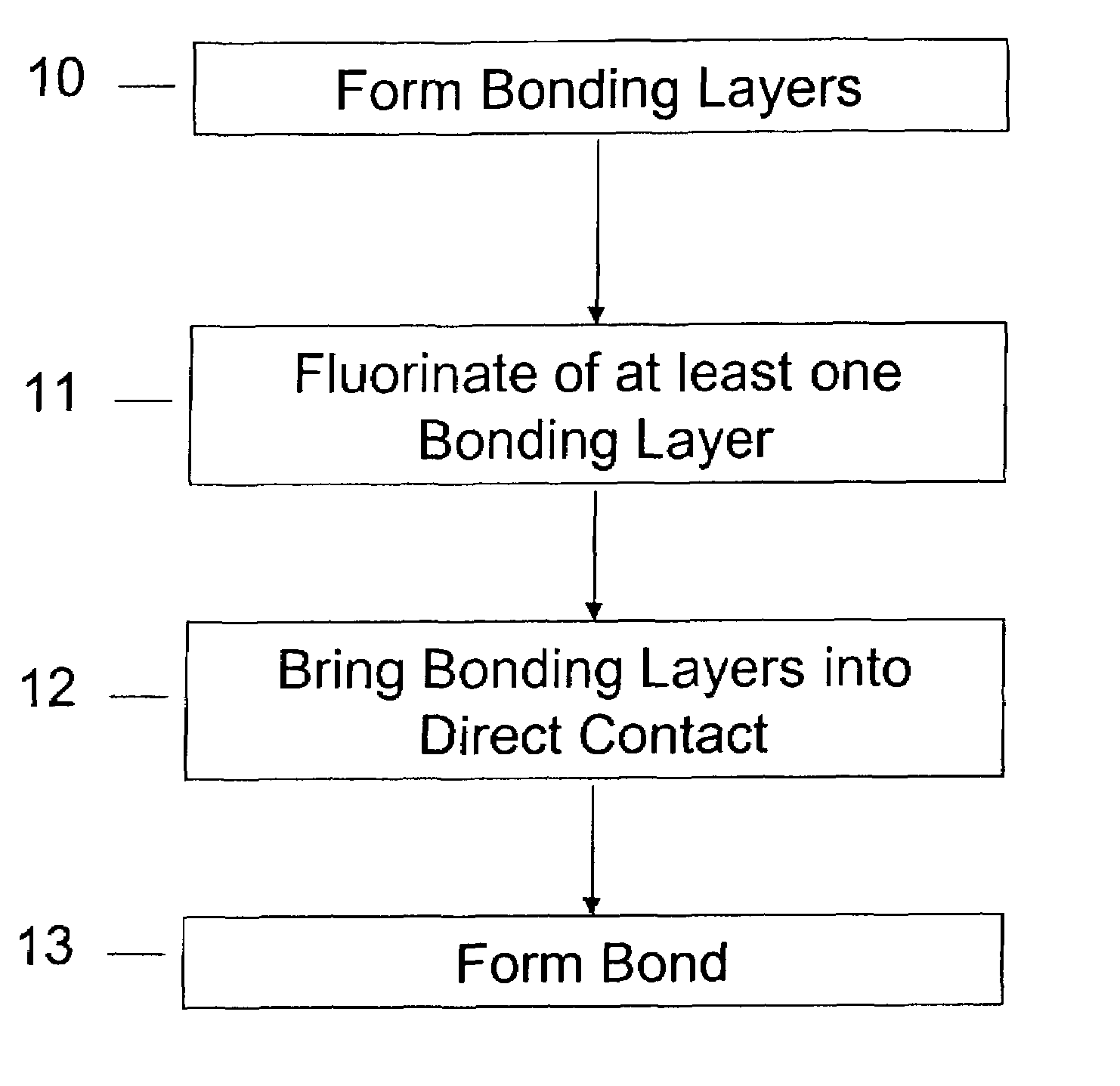
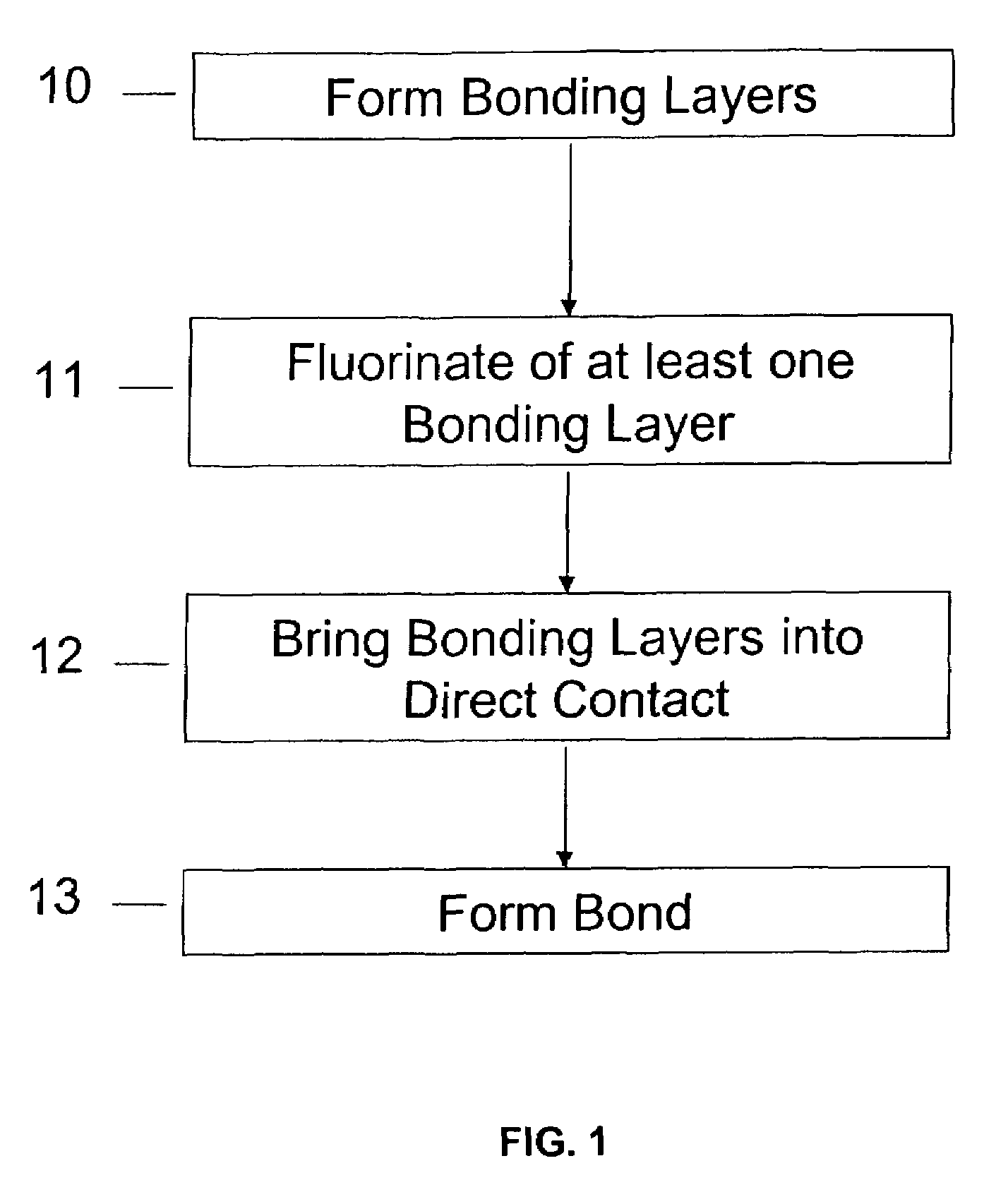
A method of bonding includes using a bonding layer having a fluorinated oxide. Fluorine may be introduced into the bonding layer by exposure to a fluorine-containing solution, vapor or gas or by implantation. The bonding layer may also be formed using a method where fluorine is introduced into the layer during its formation. The surface of the bonding layer is terminated with a desired species, preferably an NH2 species. This may be accomplished by exposing the bonding layer to an NH4OH solution. High bonding strength is obtained at room temperature. The method may also include bonding two bonding layers together and creating a fluorine distribution having a peak in the vicinity of the interface between the bonding layers. One of the bonding layers may include two oxide layers formed on each other. The fluorine concentration may also have a second peak at the interface between the two oxide layers.
Owner:INVENSAS BONDING TECH INC
Ferromagnetic powder for dust core
InactiveUS7498080B2Increase resistanceTotal current dropLiquid surface applicatorsInductances/transformers/magnets manufactureElectrical resistance and conductanceEddy current
Owner:HON HAI PRECISION IND CO LTD
Coil component
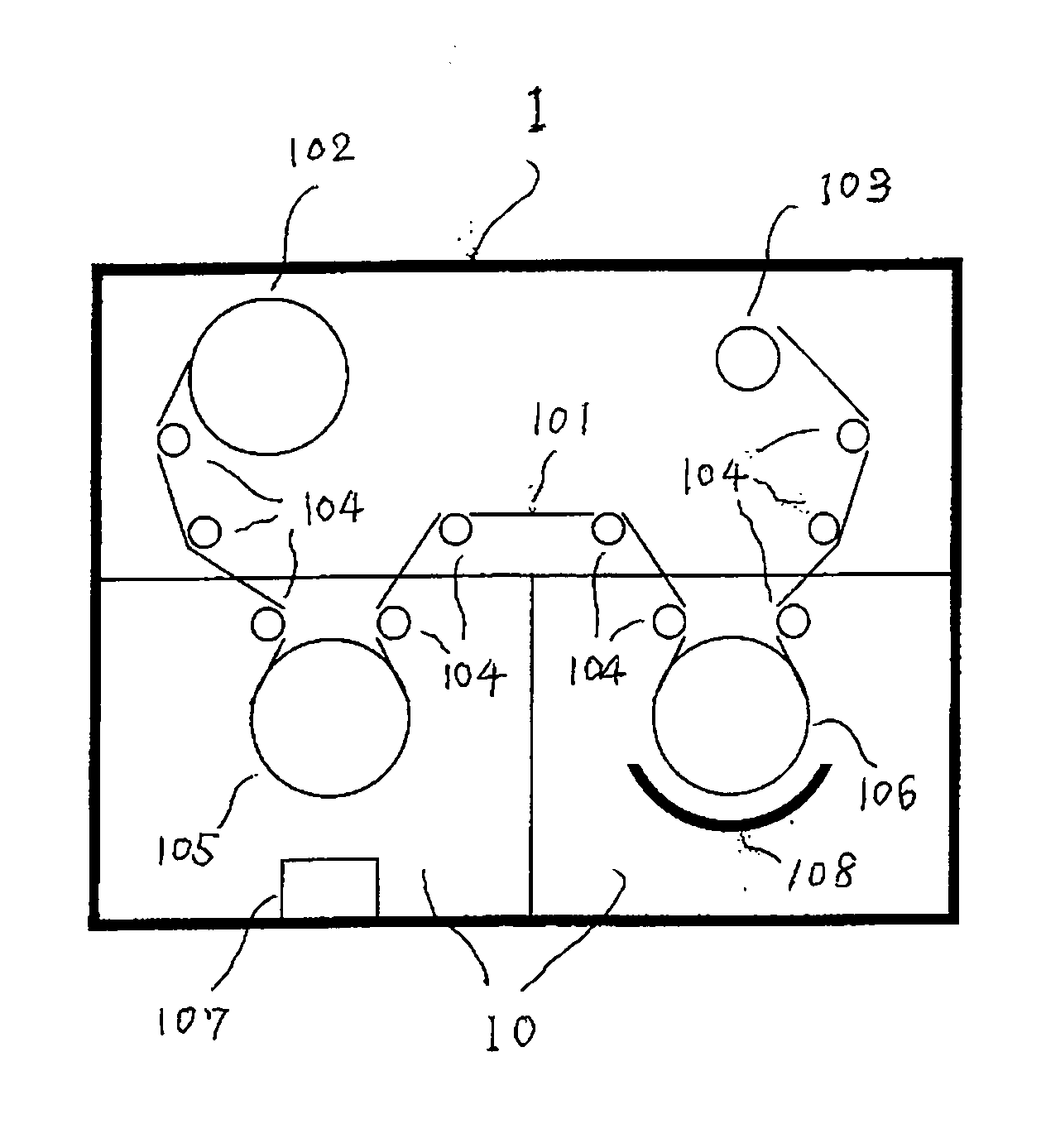
ActiveUS20140009254A1Prevent thickening of outermost turnImprove installation strengthTransformers/inductances coils/windings/connectionsCoils manufactureElectrical connectionEngineering
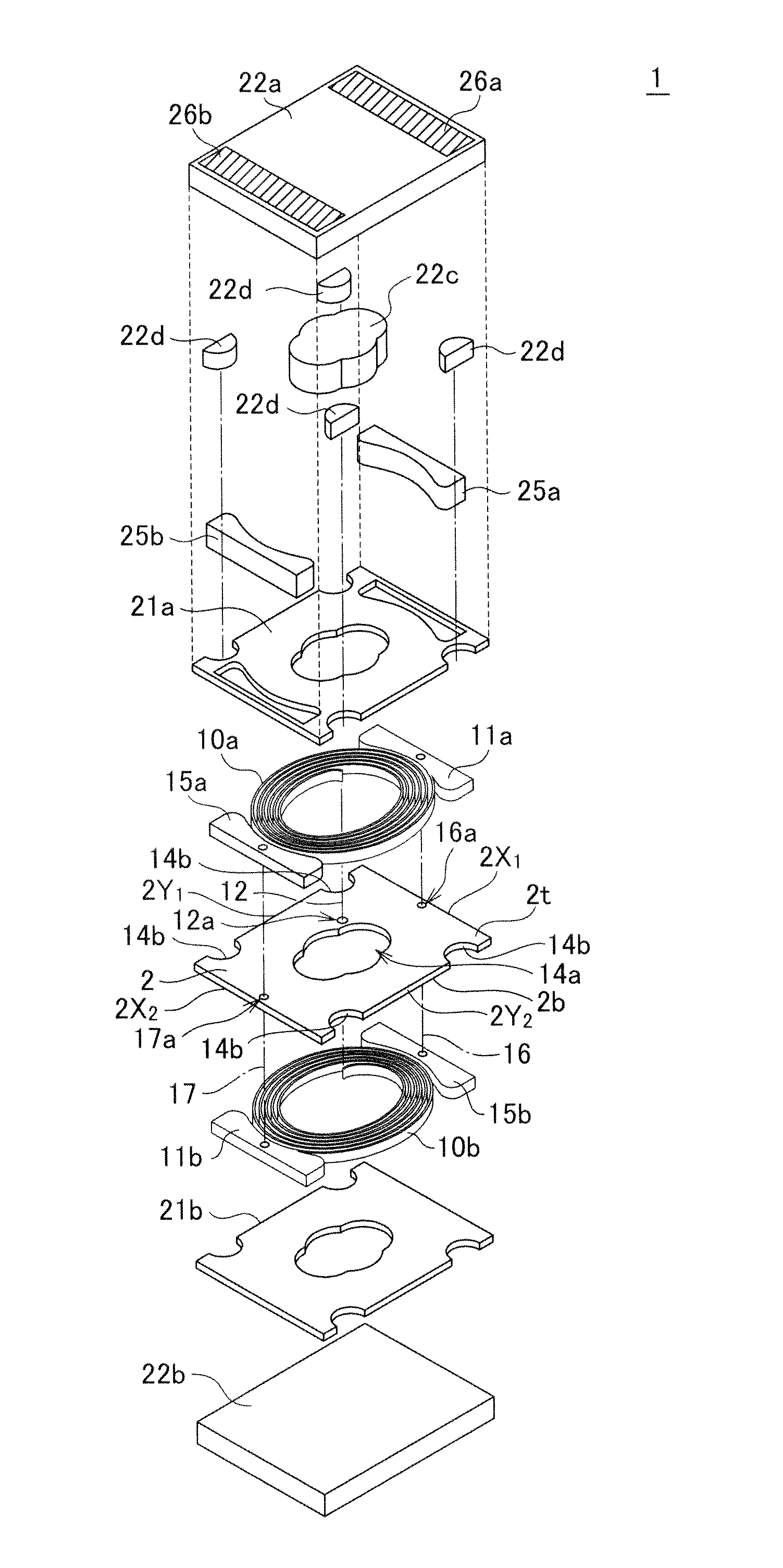
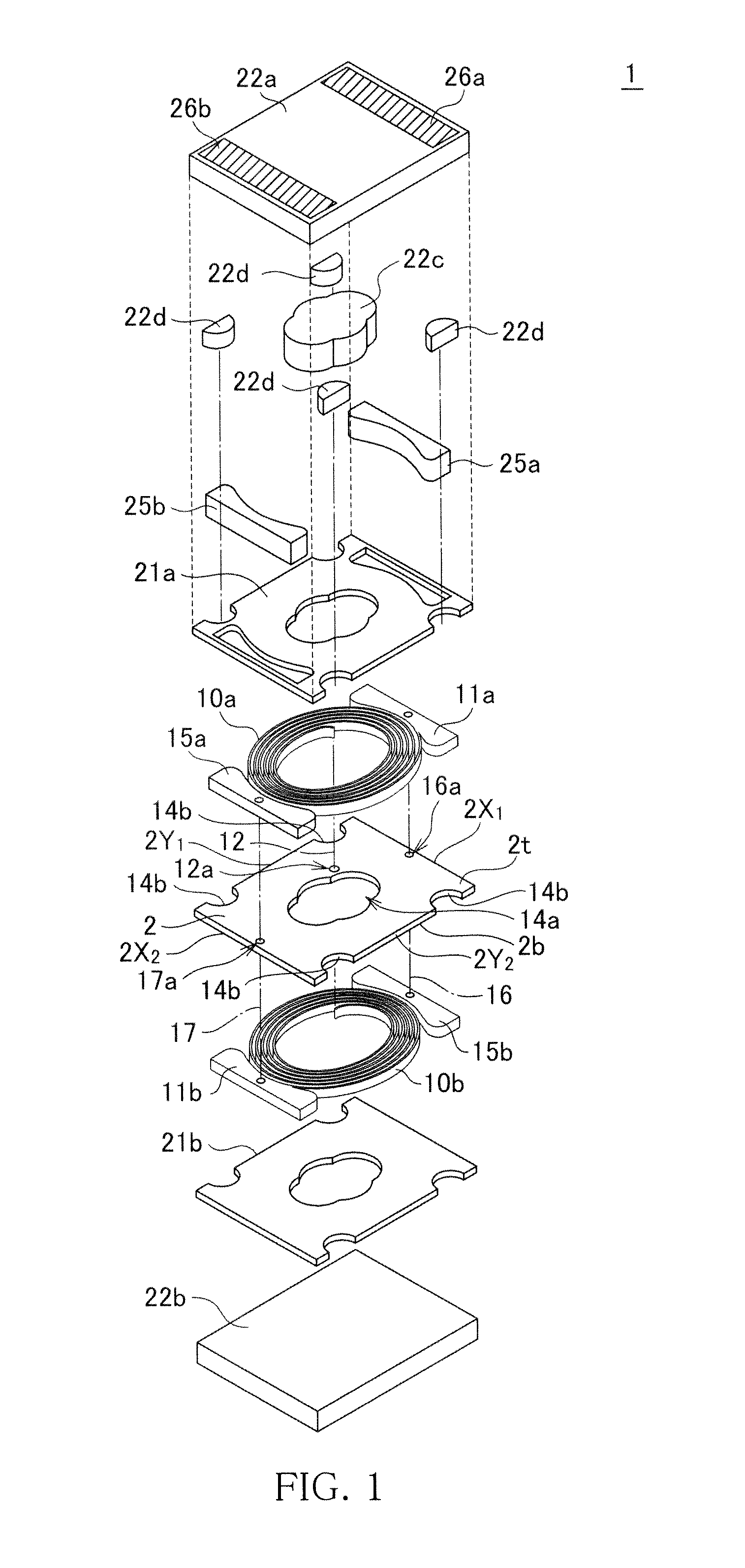
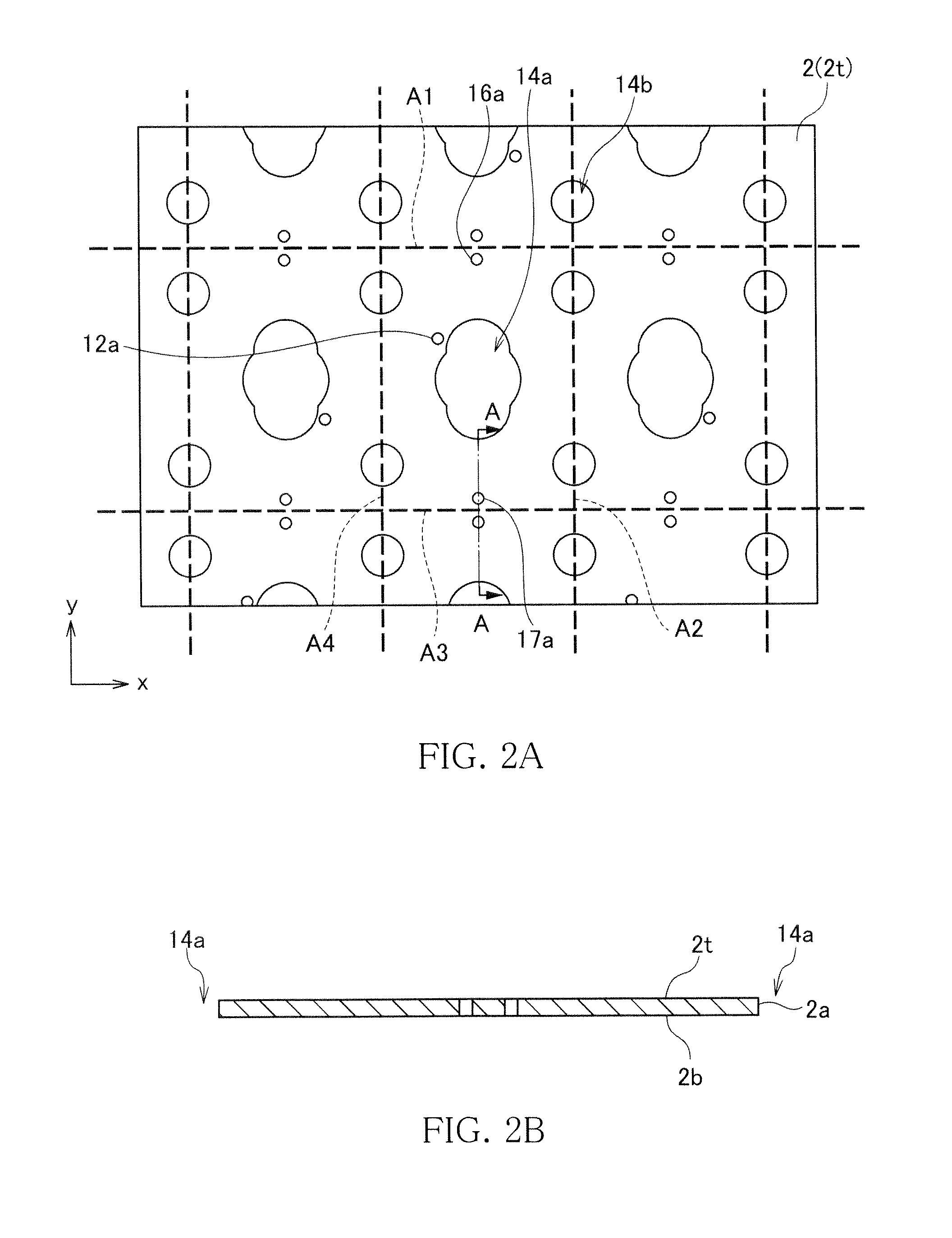
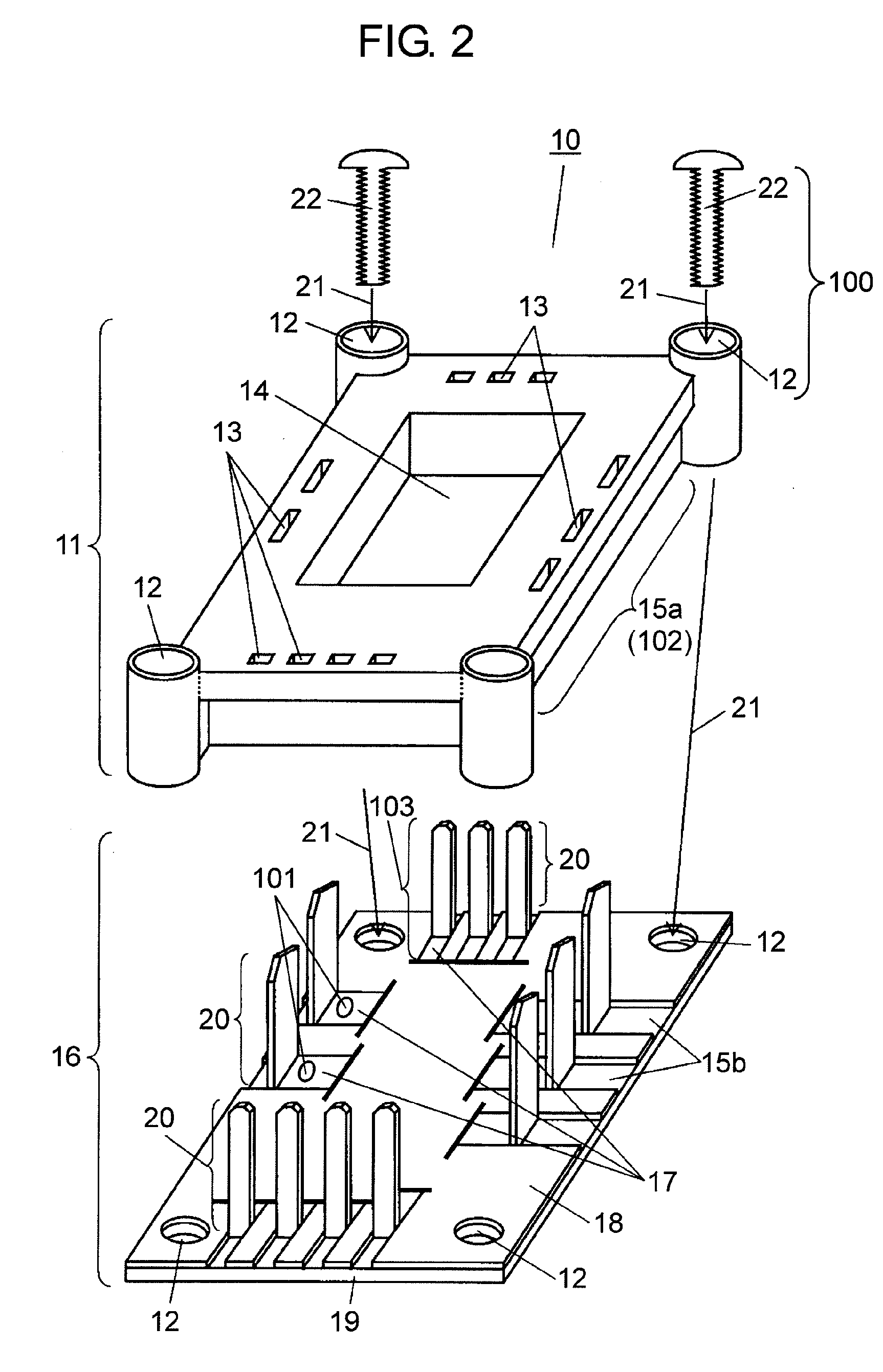
A coil component 1 includes a substrate 2, a planar spiral conductor 10a formed on a top surface 2t of the substrate 2, a lead conductor 11a connected to an outer peripheral end of the planar spiral conductor 10a, a dummy lead conductor 15a formed on the top surface of the substrate 2 and between an outermost turn of the planar spiral conductor 10a and an end 2X2 of the substrate 2 and free from an electrical connection with another conductor within the same plane, external electrodes 26a and 26b arranged in parallel with the top surface of the substrate 2, and a bump electrode 25a formed on a surface of the lead conductor 11a and connects the lead conductor 11a with the external electrode 26a. The external terminals 26a and 26b have a larger area than the bump electrodes 15a and 15b for securing a bonding strength.
Owner:TDK CORPARATION
Touch panel and electronic device using the same
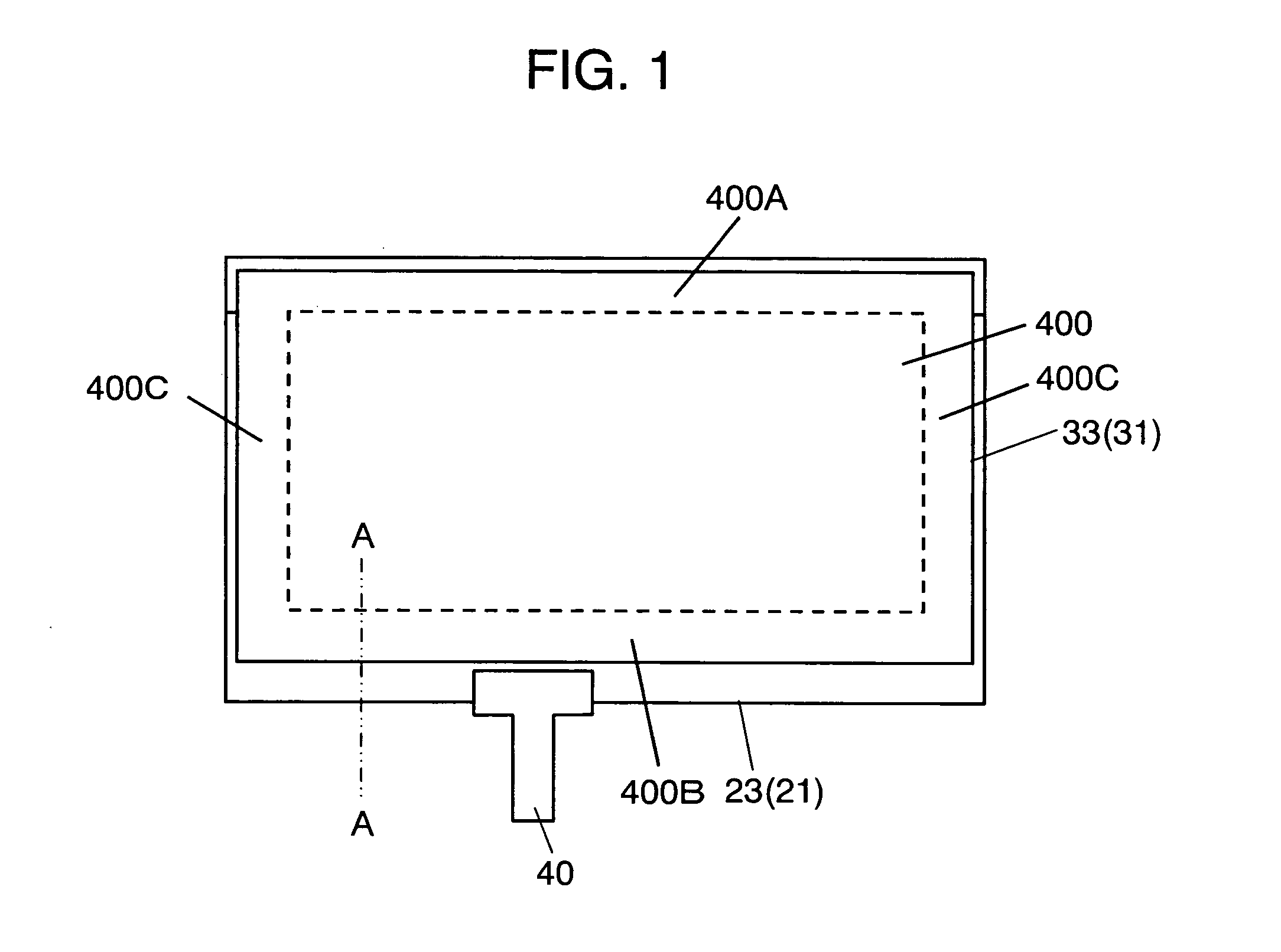
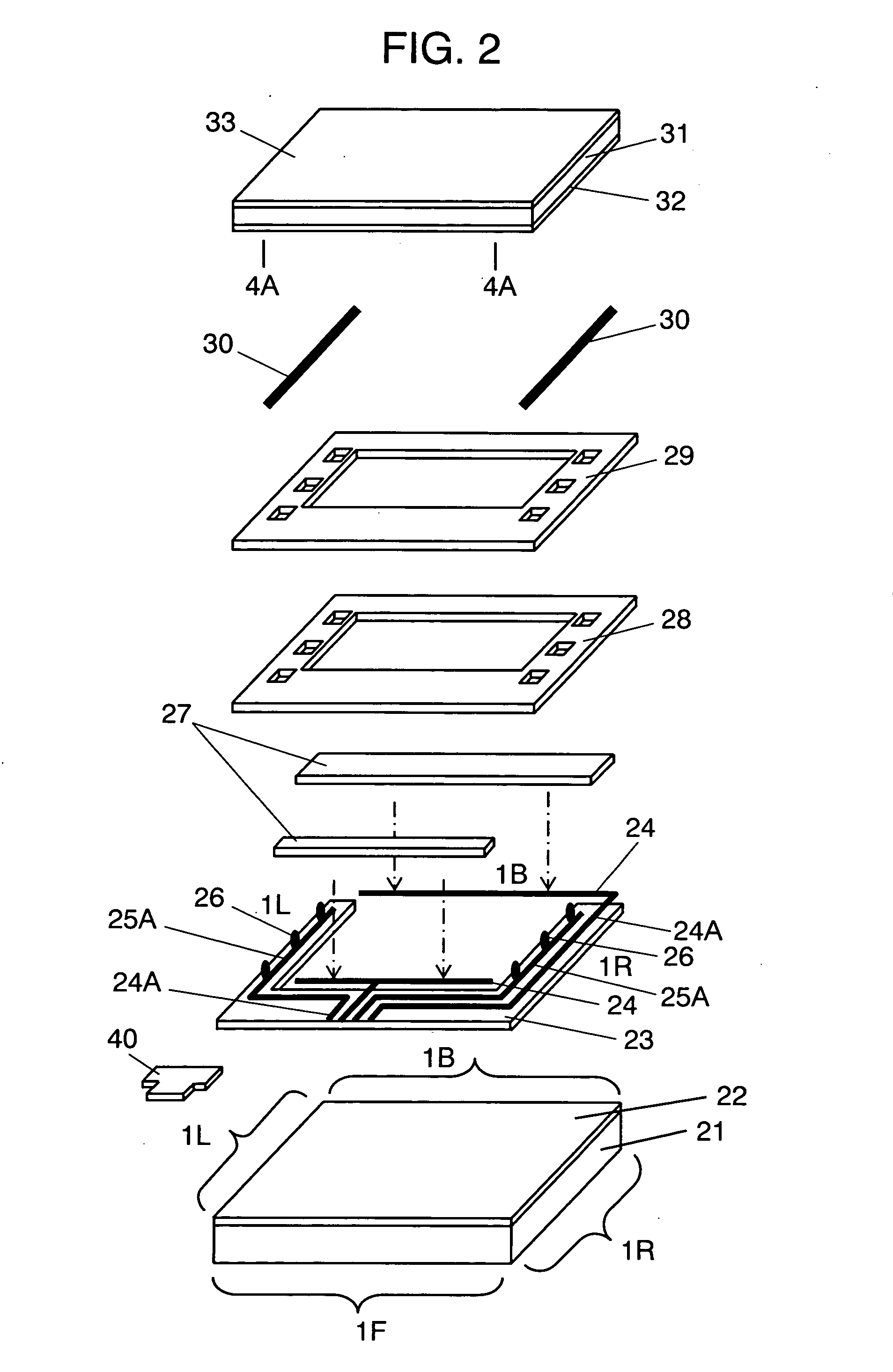
InactiveUS20050046622A1Avoid contactWell formedCathode-ray tube indicatorsInput/output processes for data processingEnvironmental resistanceLiquid-crystal display
The invention presents a touch panel disposed at the display screen side of a liquid crystal display device or the like, and excellent in surface smoothness and environmental resistance. In marginal outer circumferential part 400B for adhering and fixing first transparent substrate 21 and second transparent substrate 31 face to face, insulating layer 27 for correction of step difference is disposed in order to make uniform the film thickness. Adhesive layer 29 is disposed on insulating layer 27, and first transparent substrate 21 and second transparent substrate 31 are adhered to each other. As a result, the adhesion fixing state if stabilized, and the adhesion strength is enhanced, and a touch panel suitable for car-mount unit excellent in surface smoothness and environmental resistance can be presented.
Owner:PANASONIC CORP
High-efficiency light extraction structures and methods for solid-state lighting
InactiveUS20060237735A1Improve performanceImprove lighting effectsSolid-state devicesSemiconductor devicesPhotonicsLight emitting device
A soft solder flowing into the recesses of a semiconductor thin film LED provides: (a) increased bonding strength and better mechanical durability, (b) improved heat dissipation, (c) enhanced light extraction when the LED film is bonded to a new carrier. Annealing localized islands of absorbing metal creates an ohmic contact. Those isolated islands are inter-connected by a layer of a highly reflective metal. This design enables a significant absorption reduction within the LED device and leads to a significant improvement of light extraction. Additionally, the light extraction efficiency of an isotropic light emitting device is improved via surface shaping of the device by a 2D-array of micro-lenses and photonic band gap structure. For manufacturability purpose the making of micron-size lenses of the surface of the chip may preferably be performed as a final step, preferably with optical lithography.
Owner:DICON FIBEROPTICS
Self-leveling polymer cement base repair mortar and preparation method thereof
The invention provides a self-leveling polymer cement base repair mortar which is used for repairing cracks of a concrete building. The self-leveling polymer cement base repair mortar comprises the following components in part by weight: 25 to 60 parts of cement, 40 to 70 parts of sand, 1 to 5 parts of redispersible rubber powder, 0.2 to 1.0 part of interface reinforcing agent, 0.1 to 0.5 part of water-retaining agent, and 0.1 to 1 part of water reducing agent; the self-leveling polymer cement base repair mortar has high self-leveling performance; after the building is repaired by the mortar, the whole flatness is high, surface finishment is uniform, and the decoration performance is high; the mortar has high crack infiltration capacity, can infiltrate the crack with the length of less than 1mm, has high bonding strength between the mortar and the original concrete, and does not fall off after being dried and hardened; and after being hardened, the mortar has micro expansion performance, and can compensate the partial shrinkage of concrete, improve the impermeability of the concrete, and is suitable for crack repairing of the concrete.
Owner:BEIJING ORIENTAL YUHONG WATERPROOF TECH CO LTD +2
Controllable drug releasing gradient coatings for medical devices
InactiveUS20070078513A1Prevent vessel occlusionSlow and more prolonged releaseOrganic active ingredientsSurgerySolubilityMedicine
Implantable medical devices having a polymer gradient coating capable of controllably releasing at least one pharmaceutical compound to a localized area are disclosed. More specifically, the gradient coatings comprise at least two layers where at least one of these layers incorporates at least one pharmaceutical compound. Each of the layers of the gradient coating has at least one physical property affecting the releasability of the pharmaceutical compound incorporated therein that differs from that of at least one other layer. These physical properties include, but are not limited to, solubility constants, molecular weights, elution profiles, and bonding strengths.
Owner:MEDTRONIC VASCULAR INC
Bond pad structure with stress-buffering layer capping interconnection metal layer
InactiveUS20060091536A1Prevent stress-induced damageSimple structureSemiconductor/solid-state device detailsSolid-state devicesYoung's modulusHardness
A bond pad structure for an integrated circuit chip has a stress-buffering layer between a top interconnection level metal layer and a bond pad layer to prevent damages to the bond pad structure from wafer probing and packaging impacts. The stress-buffering layer is a conductive material having a property selected from the group consisting of Young's modulus, hardness, strength and toughness greater than the top interconnection level metal layer or the bond pad layer. For improving adhesion and bonding strength, the lower portion of the stress-buffering layer may be modified as various forms of a ring, a mesh or interlocking-grid structures embedded in a passivation layer, alternatively, the stress-buffering layer may has openings filled with the bond pad layer.
Owner:TAIWAN SEMICON MFG CO LTD
Weight member for a golf club head
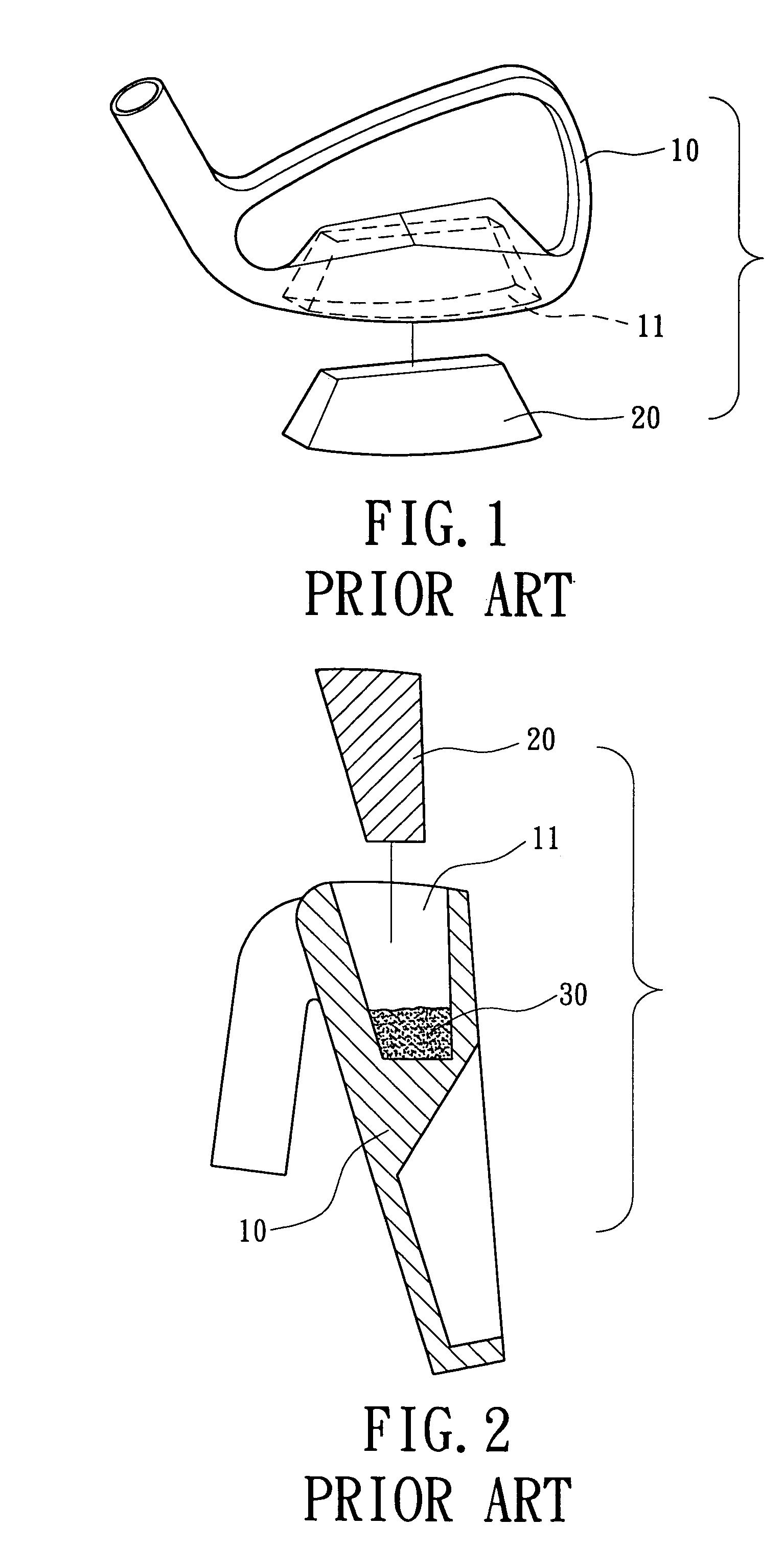
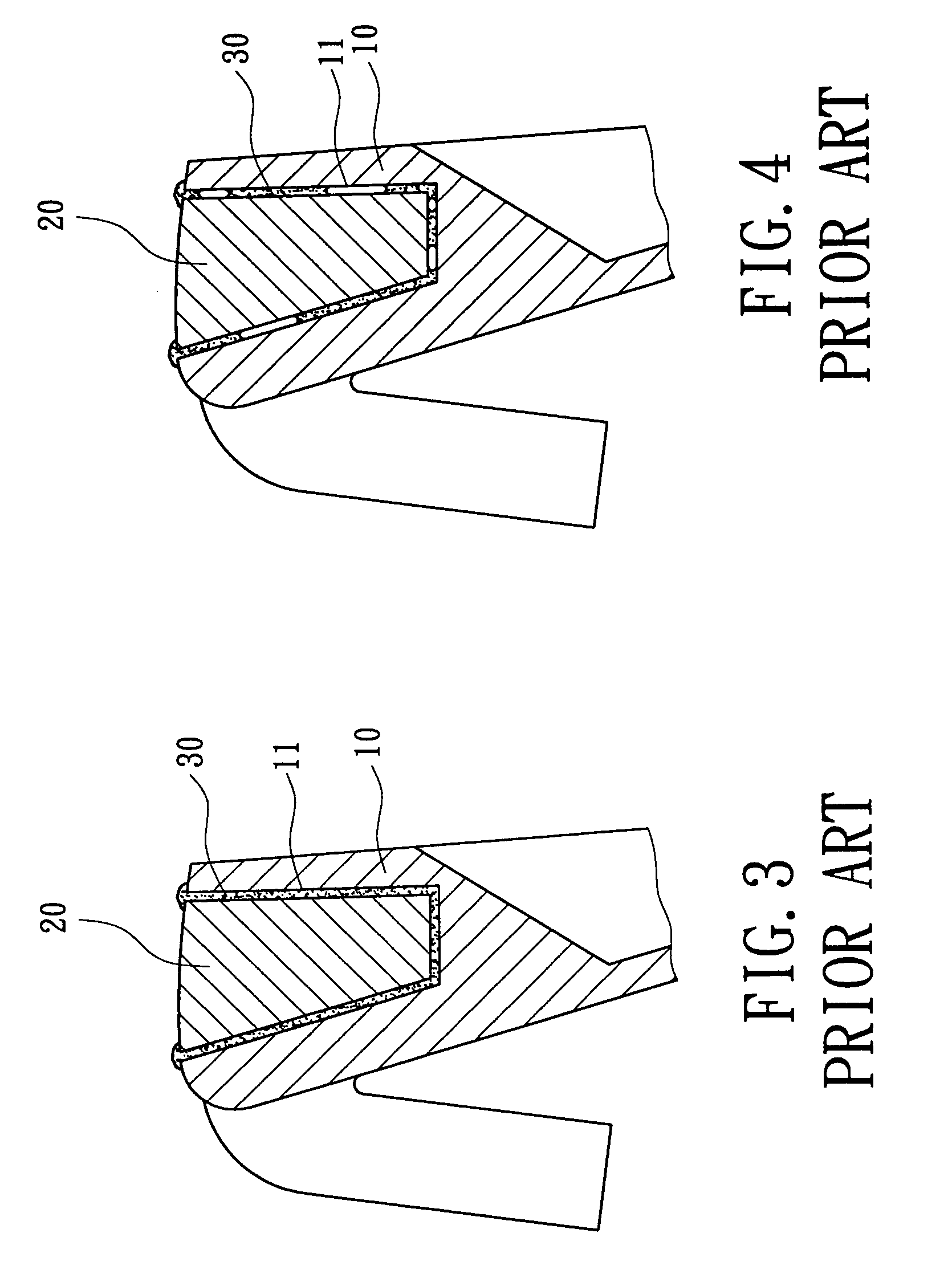
InactiveUS7086964B2Improve reliabilityRaise the ratioSoldering apparatusGolf clubsFilling materialsEngineering
A golf club head includes a golf club head body and a weight member mounted in a recession of the golf club head body. The weight member includes at least one compartment for receiving a filling material. The weight member is mounted in the recession of the golf club head body before a brazing process for bonding the weight member with the golf club head body. During the brazing process, the filling material is melted and fills a gap between the weight member and walls delimiting the recession of the golf club head body to thereby increasing bonding strength between the weight member and the walls delimiting the recession of the golf club head body.
Owner:FUSHENG IND CO LTD
Heat dissipating structure base board, module using heat dissipating structure base board, and method for manufacturing heat dissipating structure base board
ActiveUS20100091464A1Improve the fixing strengthMechanical strengthSemiconductor/solid-state device detailsSolid-state devicesEngineeringLead frame
The present invention relates to a heat dissipation structure board and a module using this heat dissipation structure used for purpose required of high reliability such as a hybrid vehicle or an electric vehicle and to a method of manufacturing the heat dissipation structure. A resin structure is disposed on a lead frame constituting a heat dissipation board and an odd-shaped electronic component or the like mounted on this lead frame or the like to cover up the lead frame and the odd-shaped electronic component or the like, and this resin structure is fixed to a metal plate, a chassis of a device and the like to constitute the heat dissipation structure board as a whole, whereby fixing strengths of fixing the lead frame and the odd-shaped electronic component or the like, a bonding strength at an interface between the lead frame and the heat transfer layer and the like can be reinforced.
Owner:PANASONIC CORP
Flux-cored wire for different-material bonding and method of bonding different materials
InactiveUS20090017328A1High bonding strengthRaise checkHot-dipping/immersion processesArc welding apparatusHigh intensityChloride
There are provided a flux cored wire for joining dissimilar materials with each other, capable of enhancing a bonding strength upon joining an aluminum-base material with a steel-base material, and excellent in bonding efficiency, a method for joining the dissimilar materials with each other, and a bonded joint obtained by the method. In particular, there is provided a method for joining dissimilar materials with each other, in the case of melt weld-bonding of high-strength dissimilar materials with each other, that is, the high-strength steel member with the high-strength 6000 series aluminum alloy member and in the case of the steel member being a galvanized steel member. In one mode, use is made of a flux cored wire wherein the interior of an aluminum alloy envelope is filled up with a flux, the flux has fluoride composition containing a given amount of AlF3 without containing chloride, and the aluminum alloy of the envelope contains Si in a range of 1 to 13 mass %. If such a flux cored wire is use, it is possible to obtain a high bonding strength in the case of melt weld-bonding of high-strength dissimilar materials with each other, that is, the high-strength steel member with the high-strength 6000 series aluminum alloy member.
Owner:KOBE STEEL LTD
Bonding wire for semiconductor device
ActiveUS20090188696A1Economical in material costSuperior in ball bondability bondabilityNon-insulated conductorsSolid-state devicesConcentration gradientControllability
The present invention provides a bonding wire improved in formability of a ball part, improved in bondability, good in loop controllability, improved in bonding strength of a wedge connection, securing industrial production ability as well, and mainly comprised of copper which is more inexpensive than gold wire, that is, provides a bonding wire for a semiconductor device comprised of a bonding wire having a core material having copper as its main ingredient and a surface covering layer over the core material and of a conductive metal of a composition different from the core material, characterized in that the surface covering layer has as its main ingredients two or more types of metals selected from gold, palladium, platinum, rhodium, silver, and nickel and the surface covering layer has a concentration gradient of one or both of a main ingredient metal or copper in the wire radial direction.
Owner:NIPPON STEEL CHEMICAL CO LTD
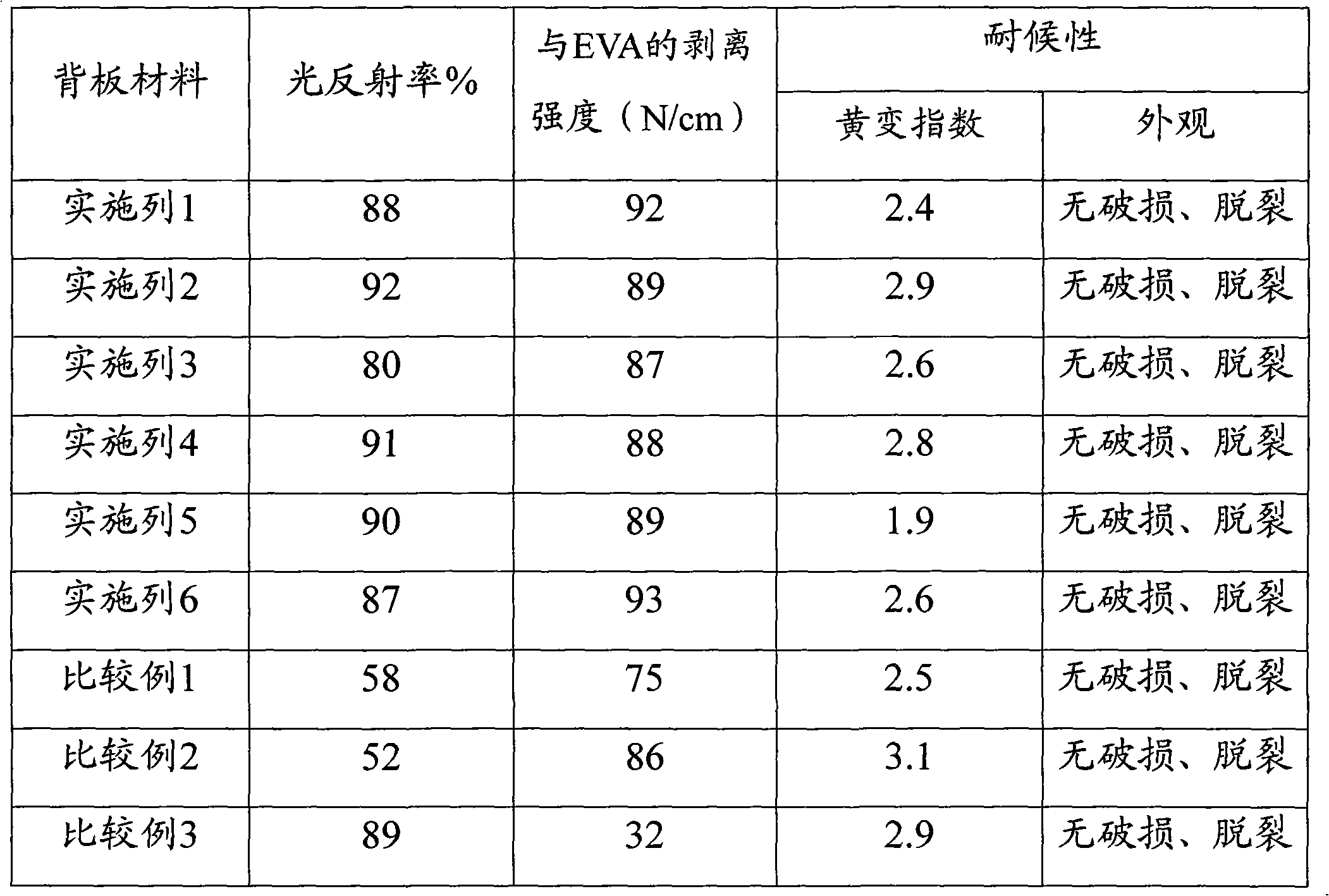
Solar cell module back veneer material
InactiveCN101645465AGood weather resistanceGood adhesionSynthetic resin layered productsPhotovoltaic energy generationSolar cellSolvent
A solar cell module back veneer material comprises a base coat layer having high adhesive strength with EVA, two layers of fluororesin-containing weather resistance coating films and an intermediate polymer basilemma between the two layers of fluororesin-containing resin weather resistance coating films, wherein at least one layer of fluororesin-containing resin weather resistance coating film hashigh light reflection performance, the base coat layer having high adhesive strength with EVA and the weather resistance coating film having high light reflection performance in the coating film arearranged at the side close to a cell sheet in an encapsulated cell module, the fluororesin-containing resin masking liquid has good coating uniformity and good adhesive force with the polymer basilemma, and contains high reflection filler component with the constituents as the follows according to parts by weight: 100 parts of fluororesin-containing resin, 3-20 parts of curing agent, 10-30 parts of high reflection filler, 0.0003-0.0001 part of catalyst, and 50-200 parts of solvent.
Owner:SUZHOU FIRST PV MATERIAL CO LTD
Hollow golf club head
InactiveUS20030134693A1High bonding strengthImprove performanceGolf clubsRacket sportsFiberGolf Ball
A hollow golf club head enables to increase the bonding strength of an outer shell member made of metal and an outer shell member made of fiber reinforced plastic. The hollow golf club head comprises a hollow golf club having a head body of a hollow structure formed by bonding the metallic outer shell member and the fiber reinforced plastic outer shell member, wherein the fiber reinforced plastic outer shell member is bonded to both faces of the bonding portion of the metallic outer shell member.
Owner:YOKOHAMA RUBBER CO LTD
Preparation of graft modification protein-based adhesive
InactiveCN101302410ASolve application problemsIncrease added valueGraft polymer adhesivesAdhesiveRedox
The invention relates to a method for preparing graft modification protein adhesives, belonging to the adhesive technical field. The method obtains the graft modification protein adhesives by adopting redox system initiator to react for a period of time at a certain temperature and linking vinyl monomer branched chains on a protein trunk chain. During the production and use processes, substances such as formaldehydes and so on are not released, thereby the method is favorable for environmental protection; and simultaneously the method can increase the added value of protein products and has important economic value. Because more hydrophobic groups are linked on the protein trunk chain, the interaction between the graft modification protein adhesives obtained and molecular groups on the wood surface is stronger and the adhesives are difficult to damage by water molecules, thereby the graft modification protein adhesives have good bonding strength and superior water resistance. The method widens the application environment and solves the problem which disturbs actual application of the protein adhesives for a long time, consequently having obvious technical advance.
Owner:JIANGNAN UNIV
Nano-material-containing high-strength high-heat insulation exterior wall inorganic heat-retaining face brick
The invention belongs to the field of building materials, relates to a use of a nano-material in a building exterior wall heat-retaining system and provides a nano-material-containing high-strength high-heat insulation exterior wall inorganic heat-retaining face brick. The nano-material-containing high-strength high-heat insulation exterior wall inorganic heat-retaining face brick is characterized in that nano-particles are used so that compressive strength, tensile strength and bonding strength are improved. The nano-material-containing high-strength high-heat insulation exterior wall inorganic heat-retaining face brick is prepared by adding a nano-material having a nanoscale particle size into a mixed system of cement, an auxiliary gel material, a polymer binder, an inorganic light heat-retaining material, fibers and water, uniformly mixing, carrying out pressing molding of the mixture, carrying out organic polymer crosslinking and cement hydration drying, and carrying out waterproof layer coating. The nano-material-containing high-strength high-heat insulation exterior wall inorganic heat-retaining face brick has the advantages of excellent flame resistance, high compressive strength, high tensile strength, high bonding strength and good insulation effects.
Owner:平湖市法而特建筑保温科技有限公司
Wire-bonding method for chips with copper interconnects by introducing a thin layer
InactiveUS20050266672A1Prevent oxidationGood adhesionSemiconductor/solid-state device detailsSolid-state devicesCopper interconnectLead bonding
A wire-bonding method for chips with copper interconnects by introducing a thin layer is provided for solving the problem of oxidizing a copper bonding-pad during bonding processing in order not to deteriorate the bonding strength and yield rate thereof. The wire-bonding method of the present invention comprises: a step for providing a chip with a copper bonding-pad; another step for providing an aqueous solution to form a Cuprous oxide thin layer on the copper bonding-pad; and yet another step for setting a plurality of copper interconnects on the copper bonding-pad and providing an ultrasonic power for removing the Cuprous oxide layer to have the interconnects bonded on the copper bonding-pad.
Owner:NATIONAL CHUNG CHENG UNIV
Ceramic and polymer composite coated lithium ion diaphragm and preparation method thereof
ActiveCN107275550AImprove ionic conductivityHigh bonding strengthCell component detailsSecondary cells servicing/maintenanceLithiumPolyolefin
The invention discloses a ceramic and polymer composite coated lithium ion diaphragm and a preparation method thereof. The ceramic and polymer composite coated lithium ion diaphragm comprises a polyolefin porous diaphragm, a ceramic coating coated on one side or the two sides of the diaphragm surface and a polymer coating coated on the ceramic surface or the diaphragm surface. The composite diaphragm prepared by the preparation method disclosed by the invention has the advantages that the heat resistance of the diaphragm is greatly improved, and the infiltration of an electrolyte is improved; the bonding strength of the diaphragm and a positive and negative pole piece is improved, so that the internal short-circuit caused by staggering between the diaphragm and an electrode is prevented; meanwhile, the hardness of a battery is improved, so that the safety performance of the battery is greatly improved. In the production process, the ceramic coating and the polymer coating are uniform in thickness and good in uniformity and facilitate continuous and large-scale production.
Owner:SHENZHEN SENIOR TECH MATERIAL
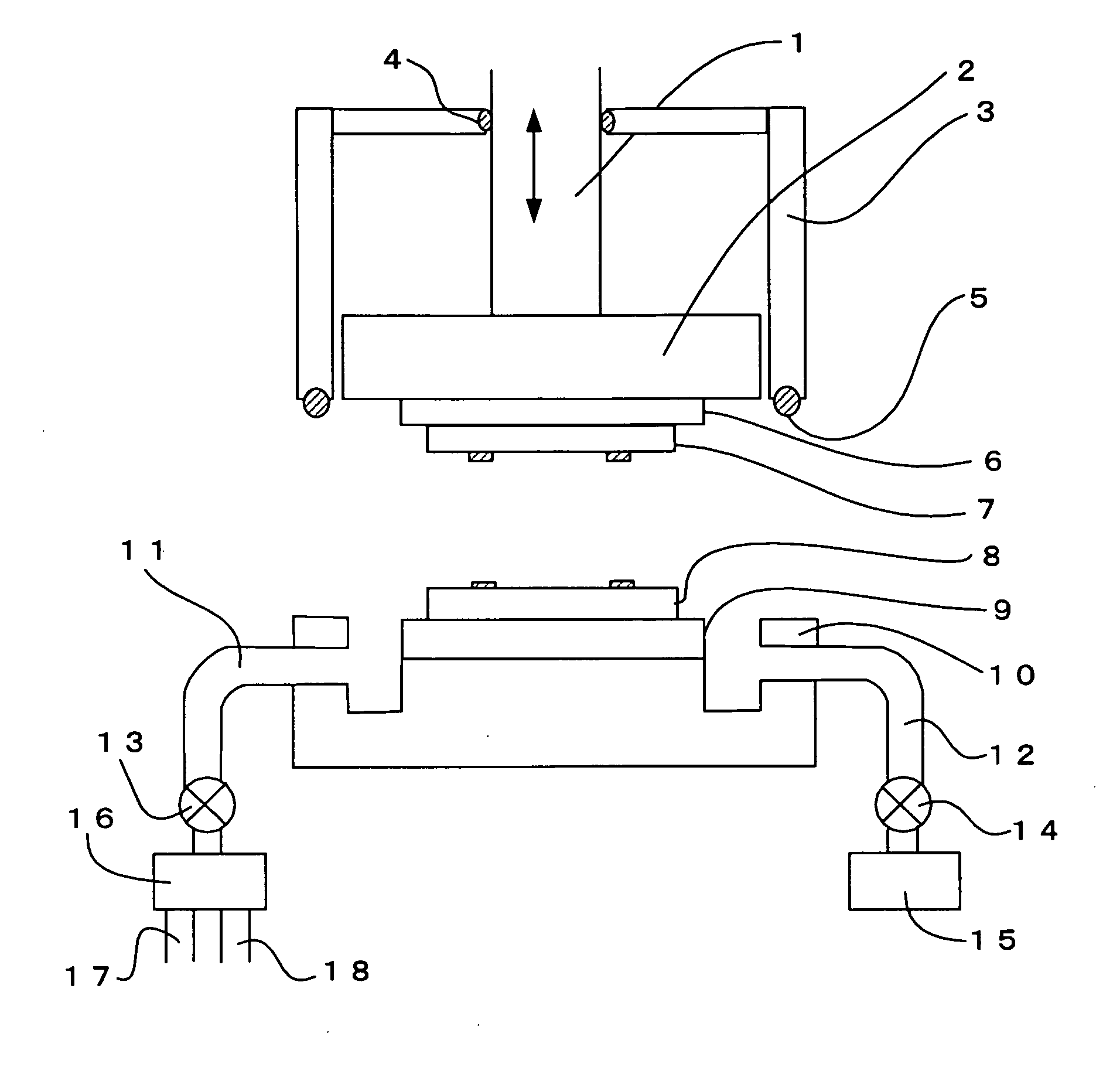
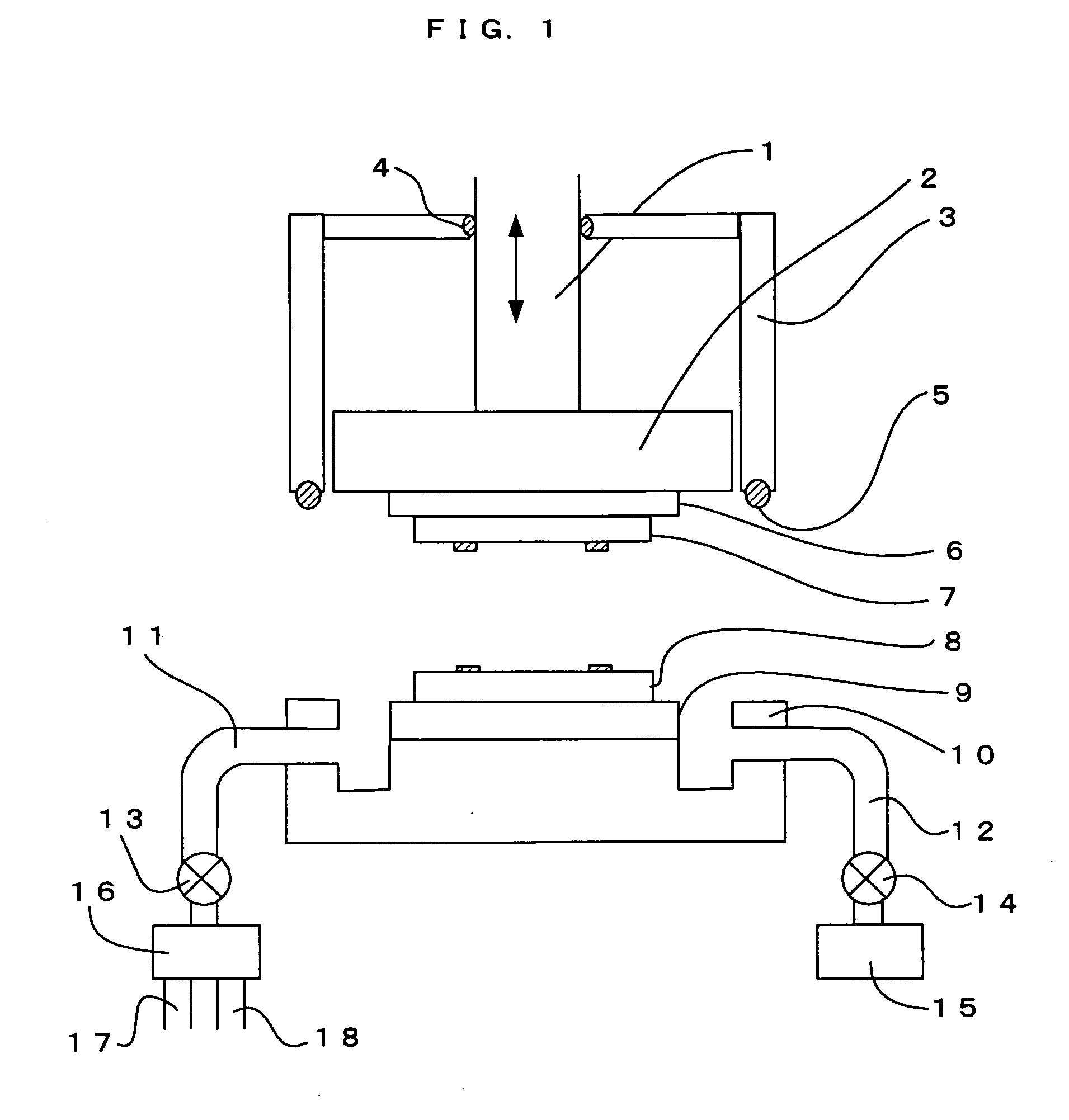
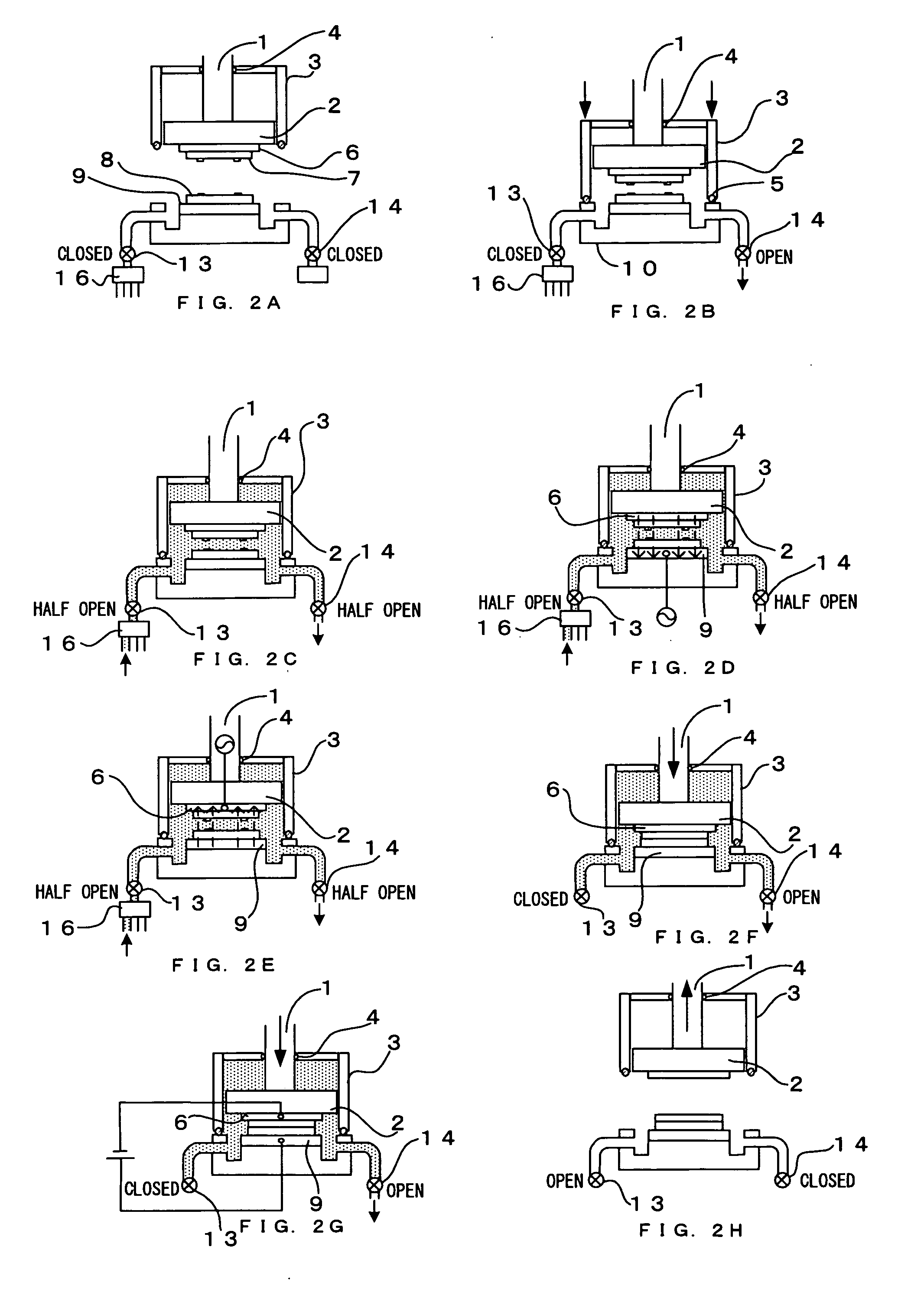
Bonding method, device produced by this method, and bonding device
ActiveUS20070111471A1High bonding strengthIncrease productivitySemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingMicrostructural device assemblyThermal expansionEngineering
Conventional heat bonding and anodic bonding require heating at high temperature and for a long time, leading to poor production efficiency and occurrence of a warp due to a difference in thermal expansion, resulting in a defective device. Such a problem is solved. An upper wafer 7 made of glass and a lower wafer 8 made of Si are surface-activated using an energy wave before performing anodic bonding, thereby performing bonding at low temperature and increasing a bonding strength. In addition, preliminary bonding due to surface activation is performed before main bonding due to anodic bonding is performed in a separate step or device, thereby increasing production efficiency, and enabling bonding of a three-layer structure without occurrence of a warp.
Owner:BONDTECH
Bonding pad with high bonding strength to solder ball and bump
InactiveUS20070108619A1High bonding strengthBonding strengthSemiconductor/solid-state device detailsPrinted circuit aspectsSolder maskSolder ball
A bonding pad with high bonding strength to a solder ball and a bump includes a carrier, a wiring layer formed on the carrier, a protection layer formed on top of the wiring layer and a solder mask layer surrounded around the protection layer and the wiring layer to form a bonding pad opening. The protection layer is extended outside the bonding pad opening such that when solder are extended into the bonding pad opening, the solder balls engage with side faces defining the bump pad opening as well as the protection layer outside the bump pad opening and a bonding strength between the bonding pad and the solder performance is increased.
Owner:KINSUS INTERCONNECT TECH
Robotic apparatus and method for treatment of conduits
InactiveUS6887014B2Novel methodMeasurement devicesRailway tunnelsElectrical conductorTeleoperated robot
A robotic apparatus and method for treatment of system of conduits and lateral sub-conduits comprising a remotely controlled robotic vehicle which navigates main conduits which delivers a series of tools to locations within the conduit. The mule's tools comprise a variety of devices including a tape head and a transport housing for a second remotely controlled robotic vehicle, or mouse which can be deployed for traversing and treating sub-conduits. Further, a method to install one or more small diameter flexible elongate members, such as conductors or sheathes to the inside of the system of conduits comprises advancing an elongate member through the conduit system with the mule or mouse, anchoring the elongate member and then taping the elongate member with the taping head while retreating out of the conduit. Preferably the tape is pre-shaped to minimize wrinkling upon application and more preferably, greater security and tape bonding strength is achieved by spraying over the tape and elongate member.
Owner:GEOLYN CONSULTANTS INC
Weight member for a golf club head
InactiveUS20050049075A1Improve reliabilityRaise the ratioSoldering apparatusGolf clubsFilling materialsEngineering
A golf club head includes a golf club head body and a weight member mounted in a recession of the golf club head body. The weight member includes at least one compartment for receiving a filling material. The weight member is mounted in the recession of the golf club head body before a brazing process for bonding the weight member with the golf club head body. During the brazing process, the filling material is melted and fills a gap between the weight member and walls delimiting the recession of the golf club head body to thereby increasing bonding strength between the weight member and the walls delimiting the recession of the golf club head body.
Owner:FUSHENG IND CO LTD
Individual package of absorbent article
InactiveUS20030065302A1Stay softMaintain forceContainers for flexible articlesCatheterEngineeringUltimate tensile strength
An individual package of an absorbent article permits a base end of a tape to be bonded with sufficiently large bonding strength without complicating packaging process and increasing manufacturing cost. The absorbent article is wrapped by a package sheet having side edge portions and end edges, and one end edge is overlapped over the other end edge. The package sheet is sealed along the side edge portions, a base end of a tape is fixed on the surface of the package sheet located outside in an overlapping portion, and a free end of the tape extends across one end edge and is releasably adhered on the outer surface of the package sheet adjacent one end edge. The package sheet has a surface, on which the base end of the tape is fixed, the surface being smoothed by a smoothing process.
Owner:UNI CHARM CORP
Method and apparatus to apply surface release coating for imprint mold
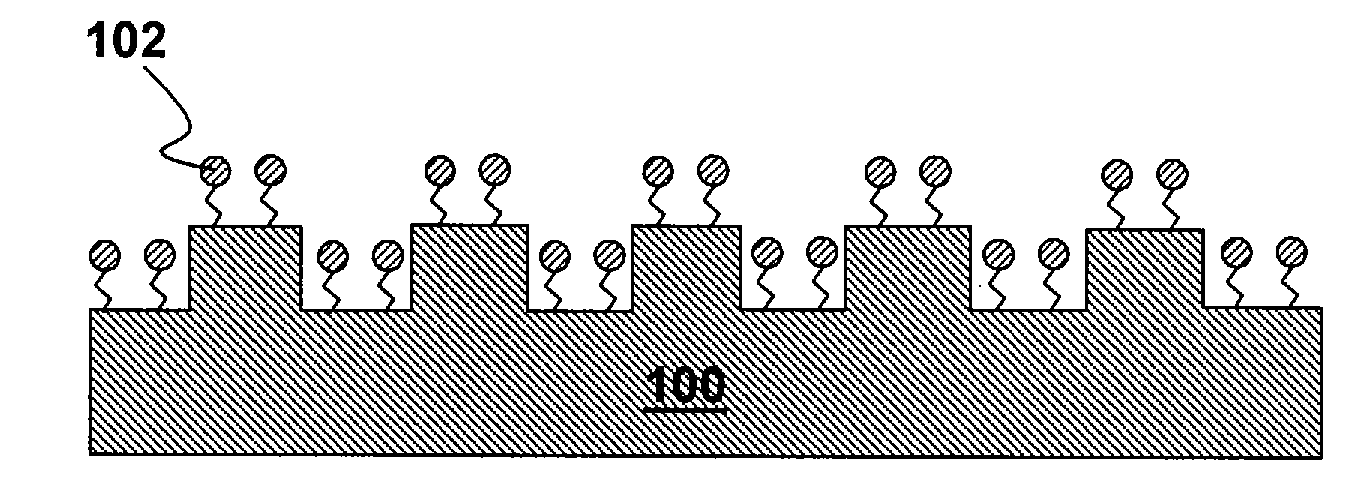
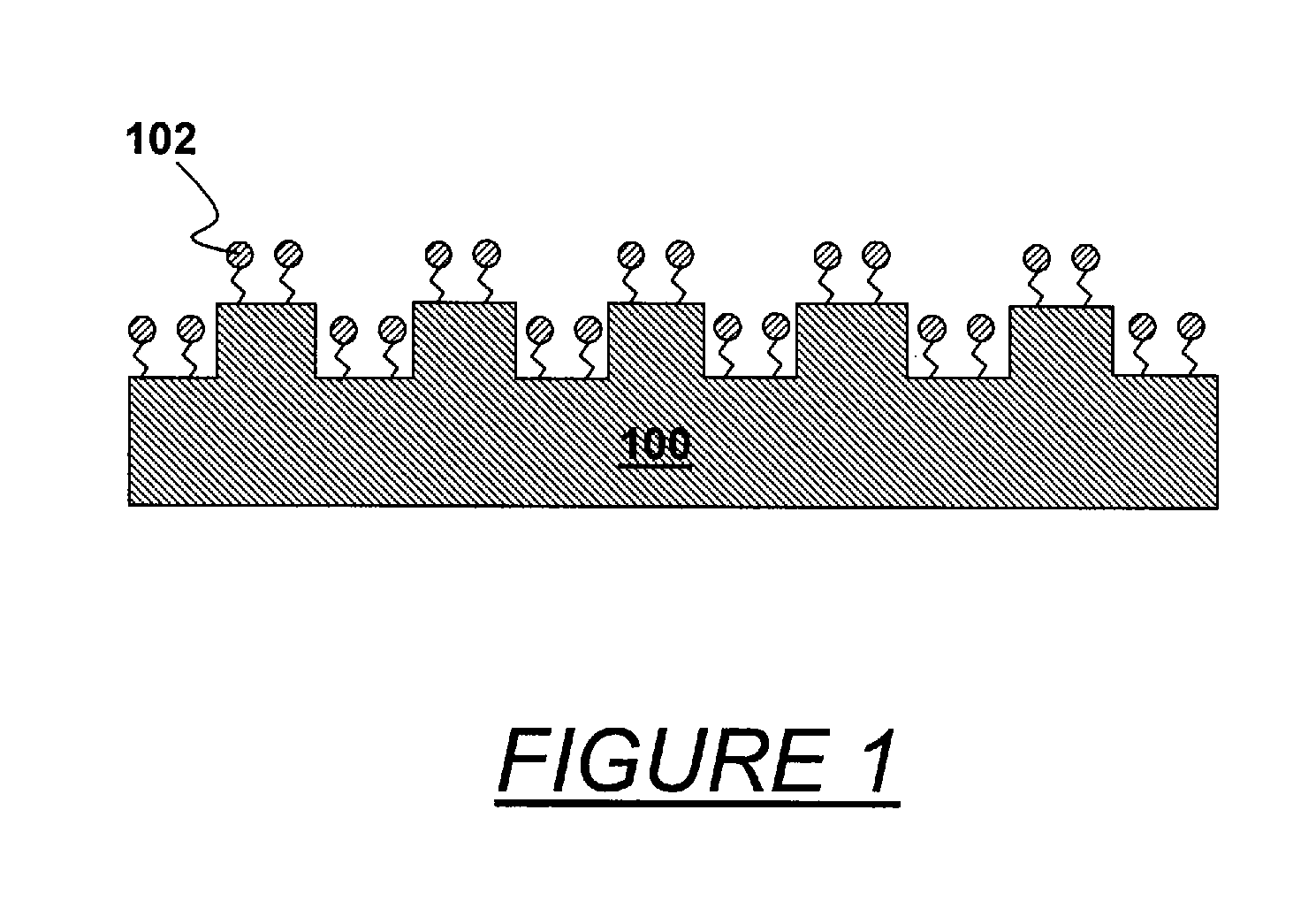
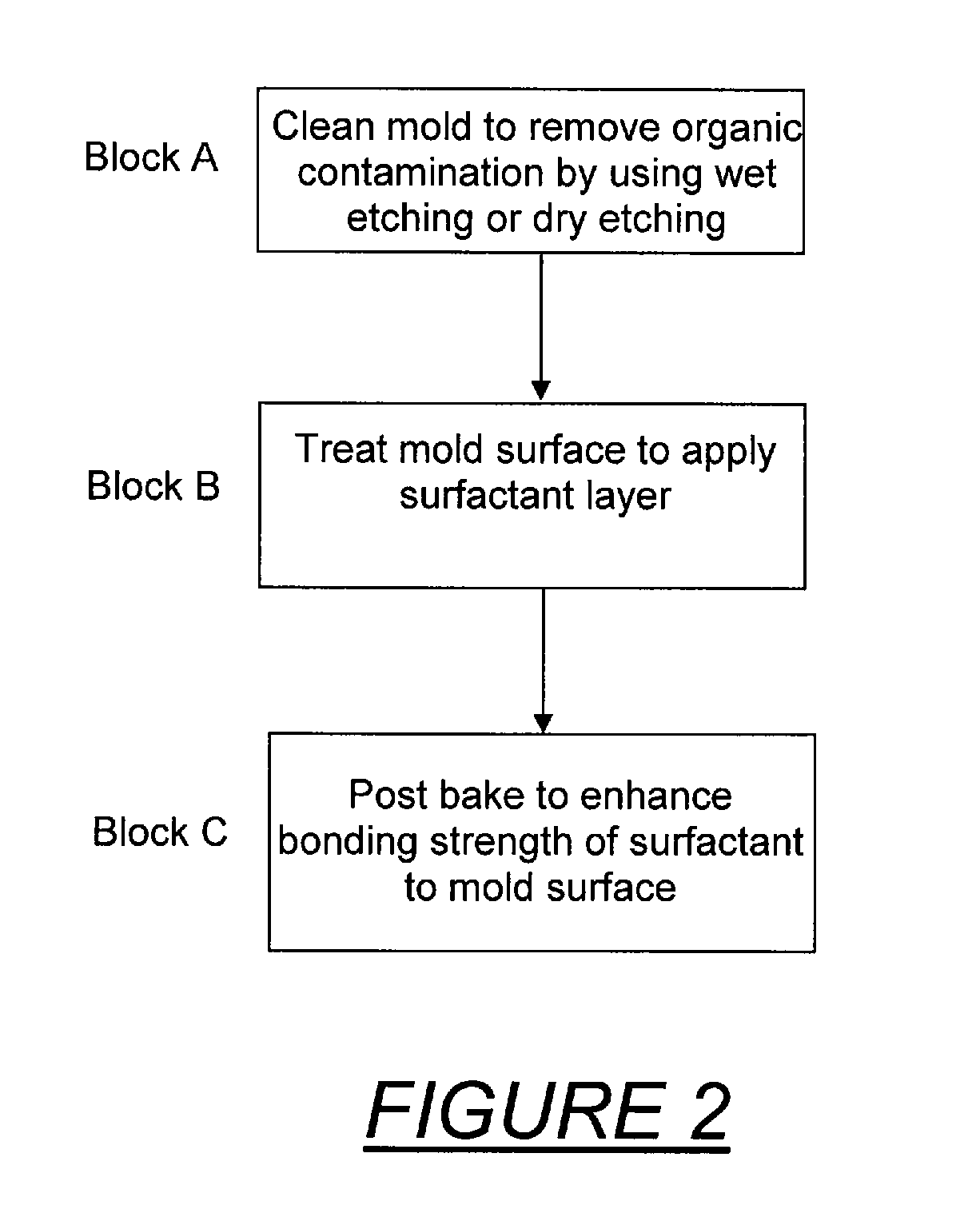
In imprint lithography, the mold is coated with a surface release layer for a non-sticking separation. Bonding strength of the release layer to the mold depends on the cleanness of the surface and the process of release layer deposition. In accordance with the invention, the mold is disposed in an evacuable chamber, cleaned to remove surface organic contamination and coated with the surface release layer in a chamber, all without relocation or undesired time delay. The chamber encloses a support chuck for the mold or substrate, a surface cleaner unit adjacent the support, a heating source adjacent the support, and advantageously, sensors of measuring chamber pressure, vapor partial pressure and moisture concentration. A vapor source connected to the chamber supplies release surfactant vapor. The mold is cleaned, and the cleaning is followed by vapor phase deposition of the surfactant. The mold is advantageously heated. Typical ways of cleaning include exposure to ozone or plasma ion etch. Surfactant vapor may be generated by liquid surface vaporization, liquid injection or spray vaporization. A surface adhesion promoter can be coated on the substrate by a similar method with the same apparatus.
Owner:NANONEX
Integrated permeate channel membrane
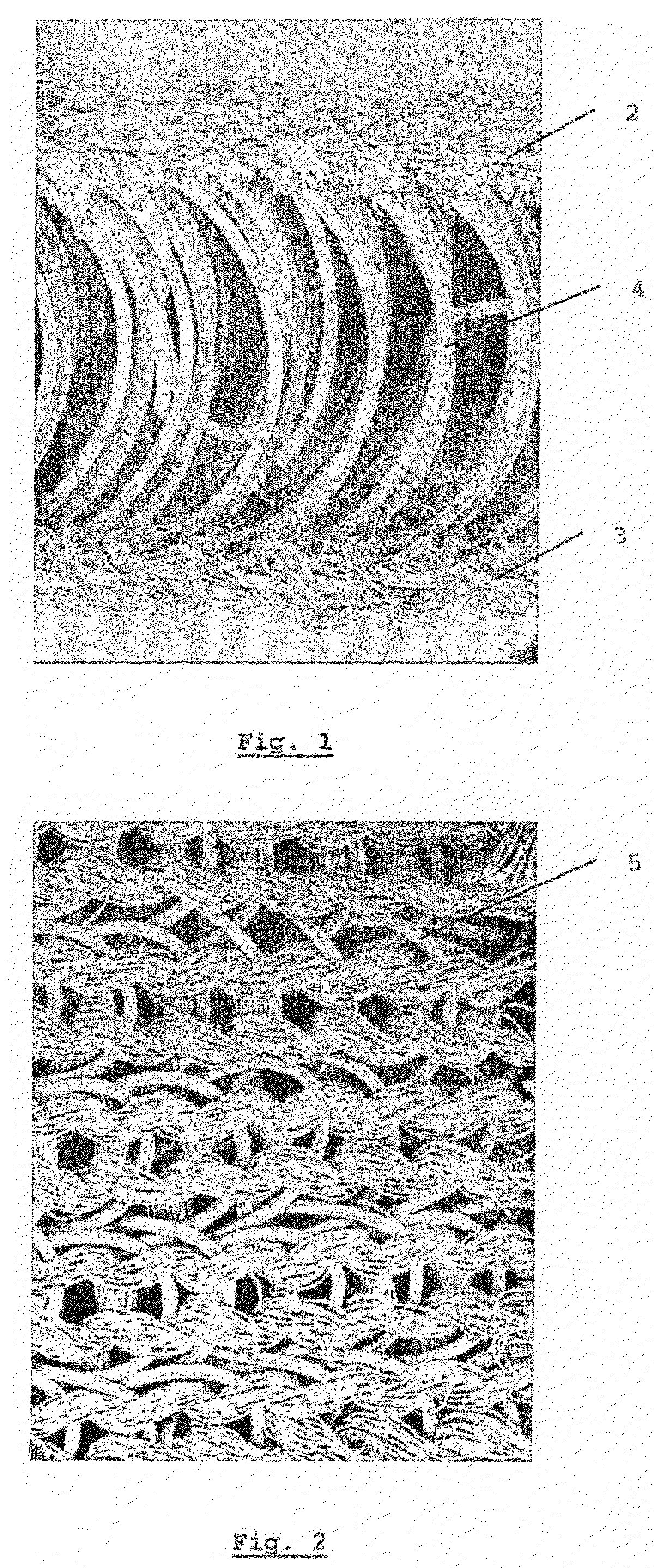
A membrane has a permeate channel including a 3D spacer fabric having an upper and a lower fabric surface (2,3) spaced apart by monofilament thread (4) at a predefined distance, the permeate channel being interposed between two membrane layers (12, 13), wherein the membrane layers are linked at a multitude of points with the upper and lower fabric surfaces to form an integral structure with a high bonding strength suitable for backflush operations. A method provides an integrated permeate channel membrane, including the steps of: —Providing a 3D spacer fabric having an upper and lower surface fabric (2,3) spaced apart by monofilament thread (4) at a predefined distance; and—Applying a membrane layer to both the upper and the lower surface fabric.
Owner:BLUE FOOT MEMBRANES NV
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com