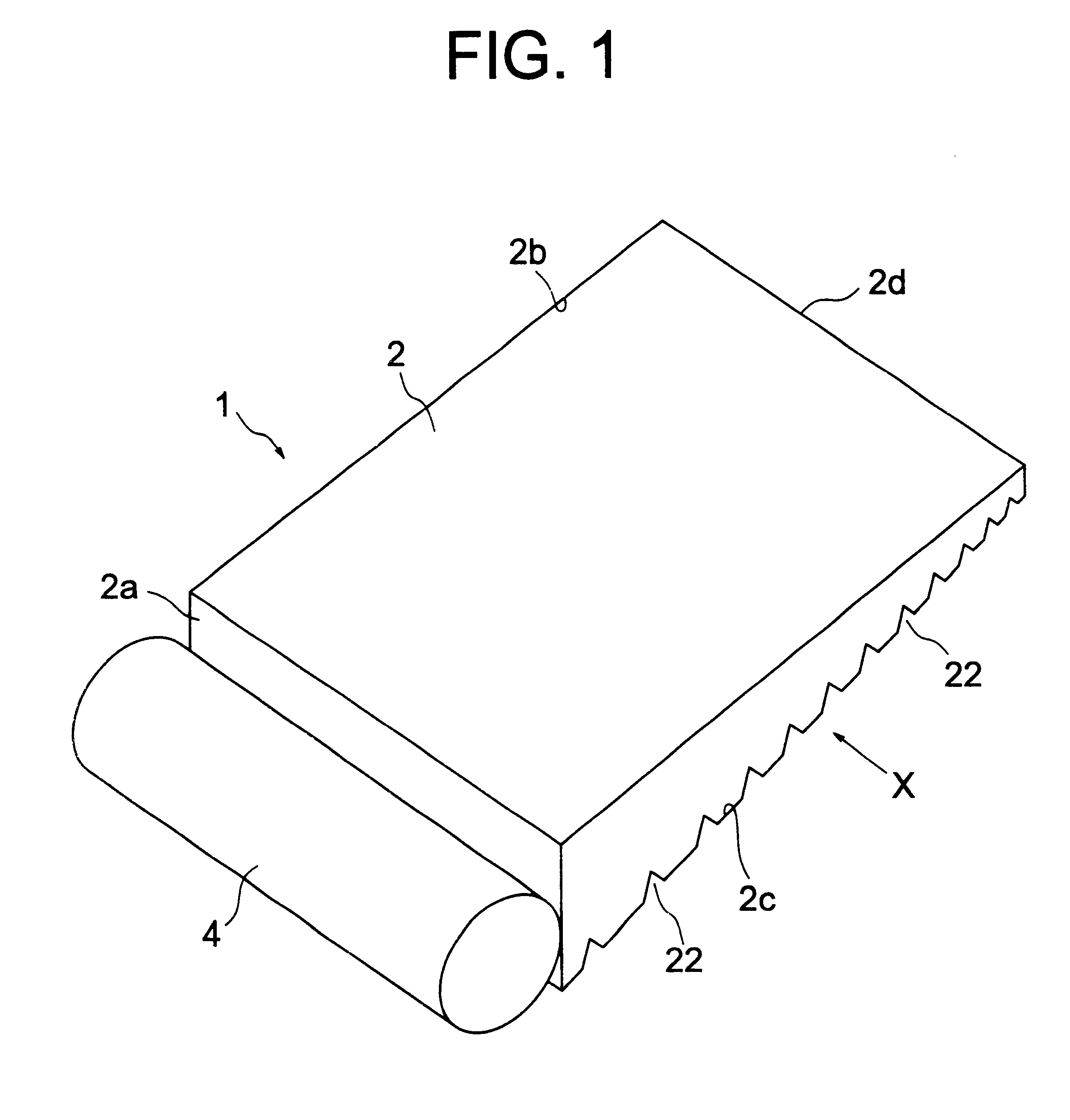
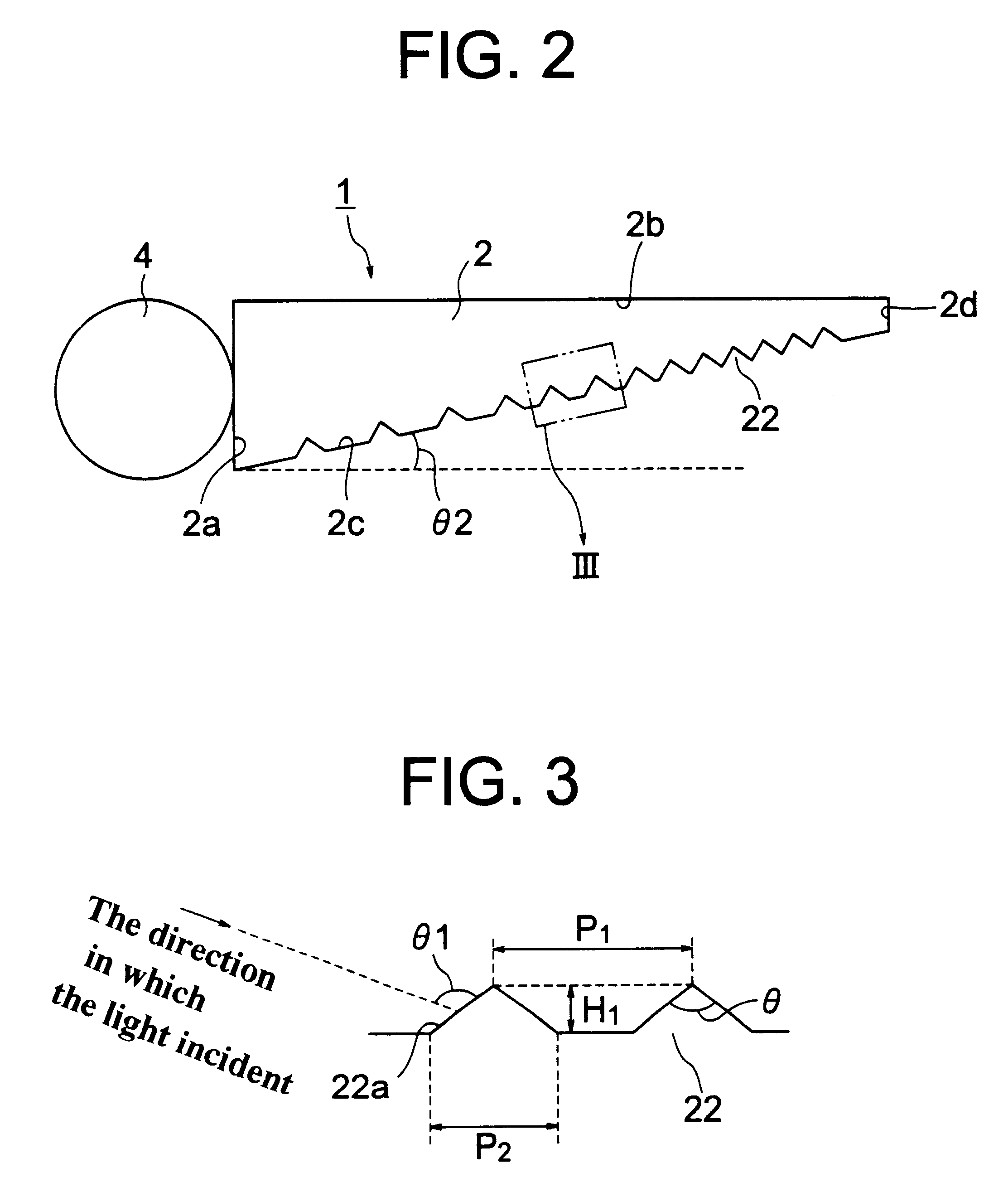
Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
7963 results about "Light reflection" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
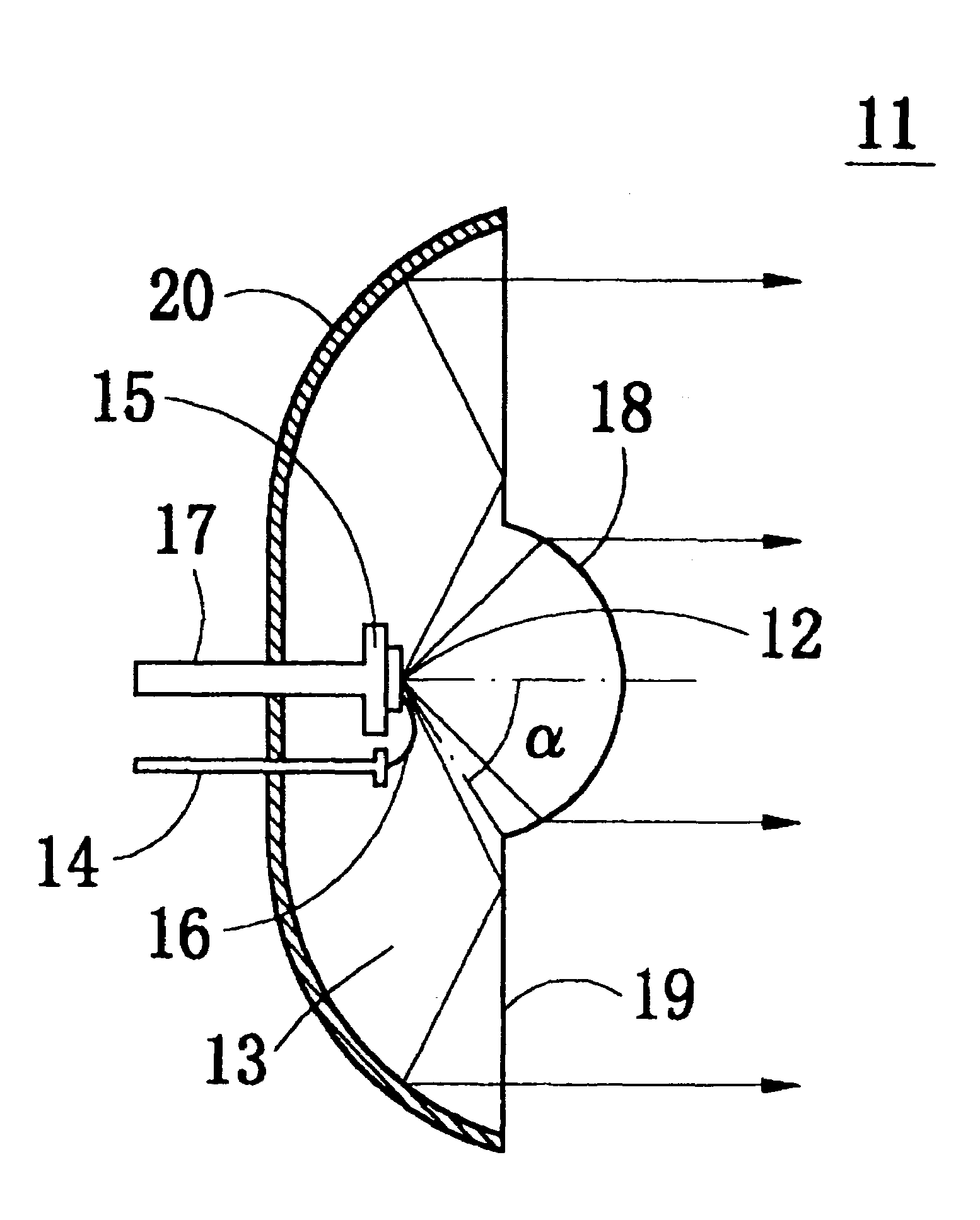
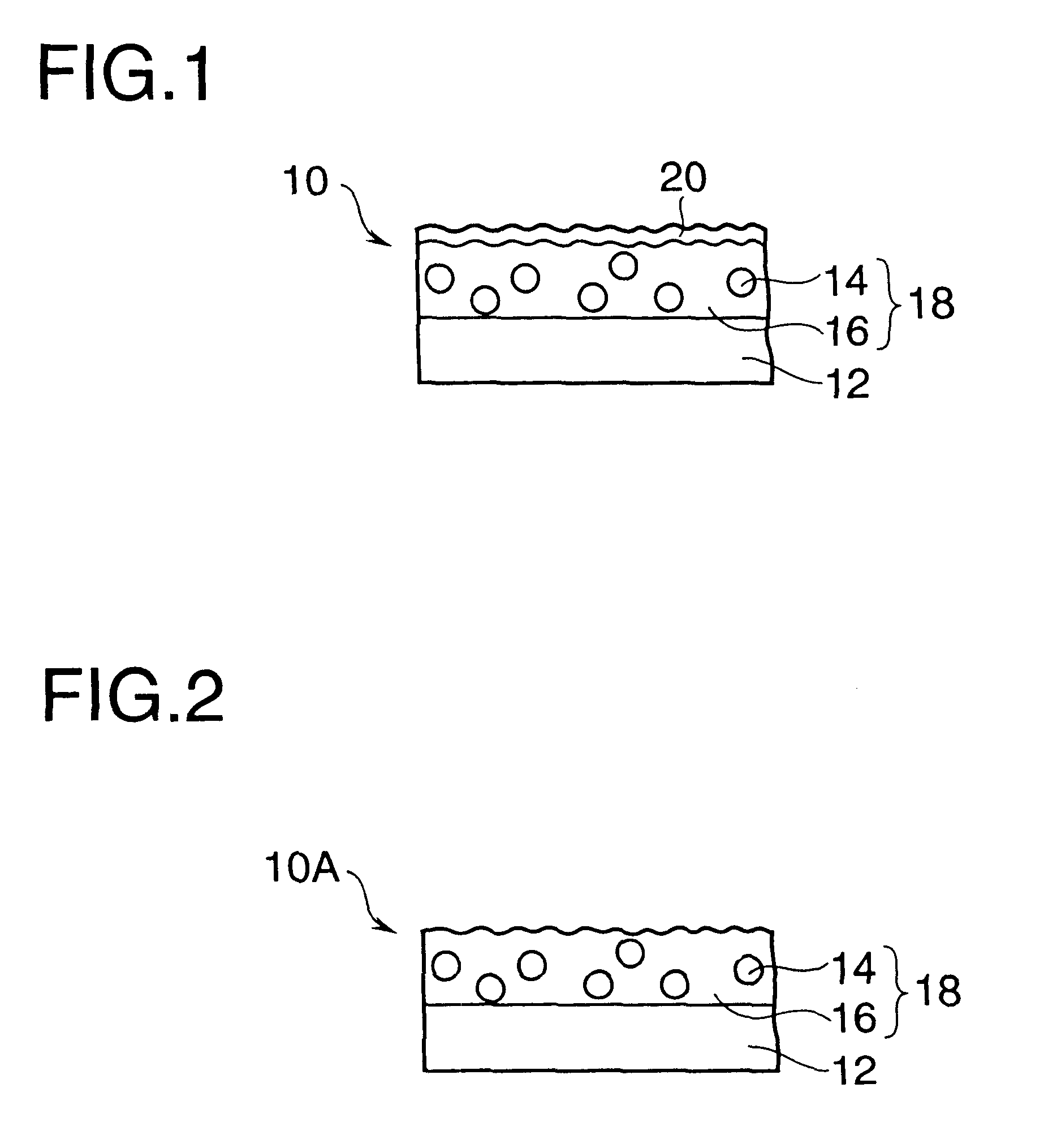
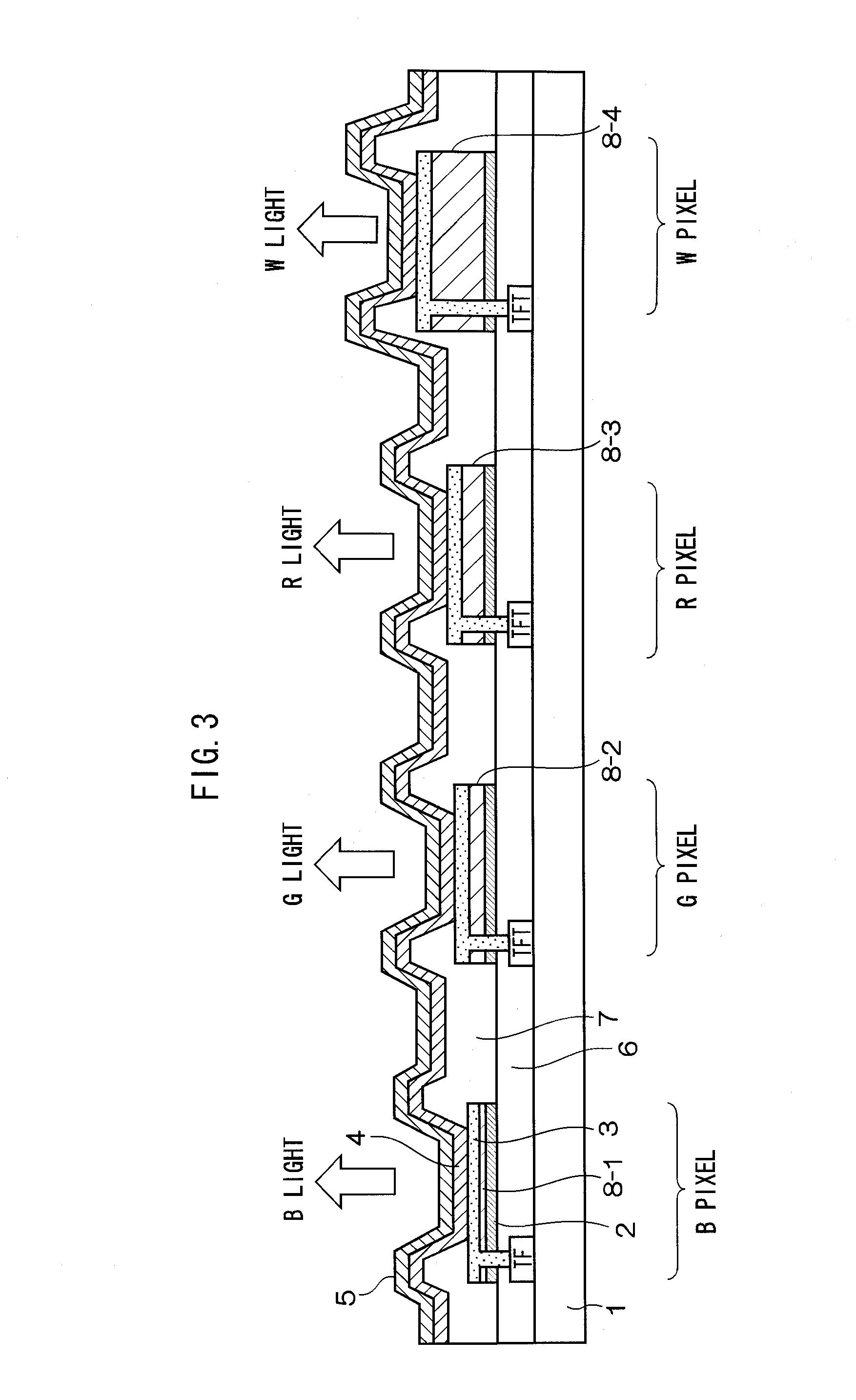
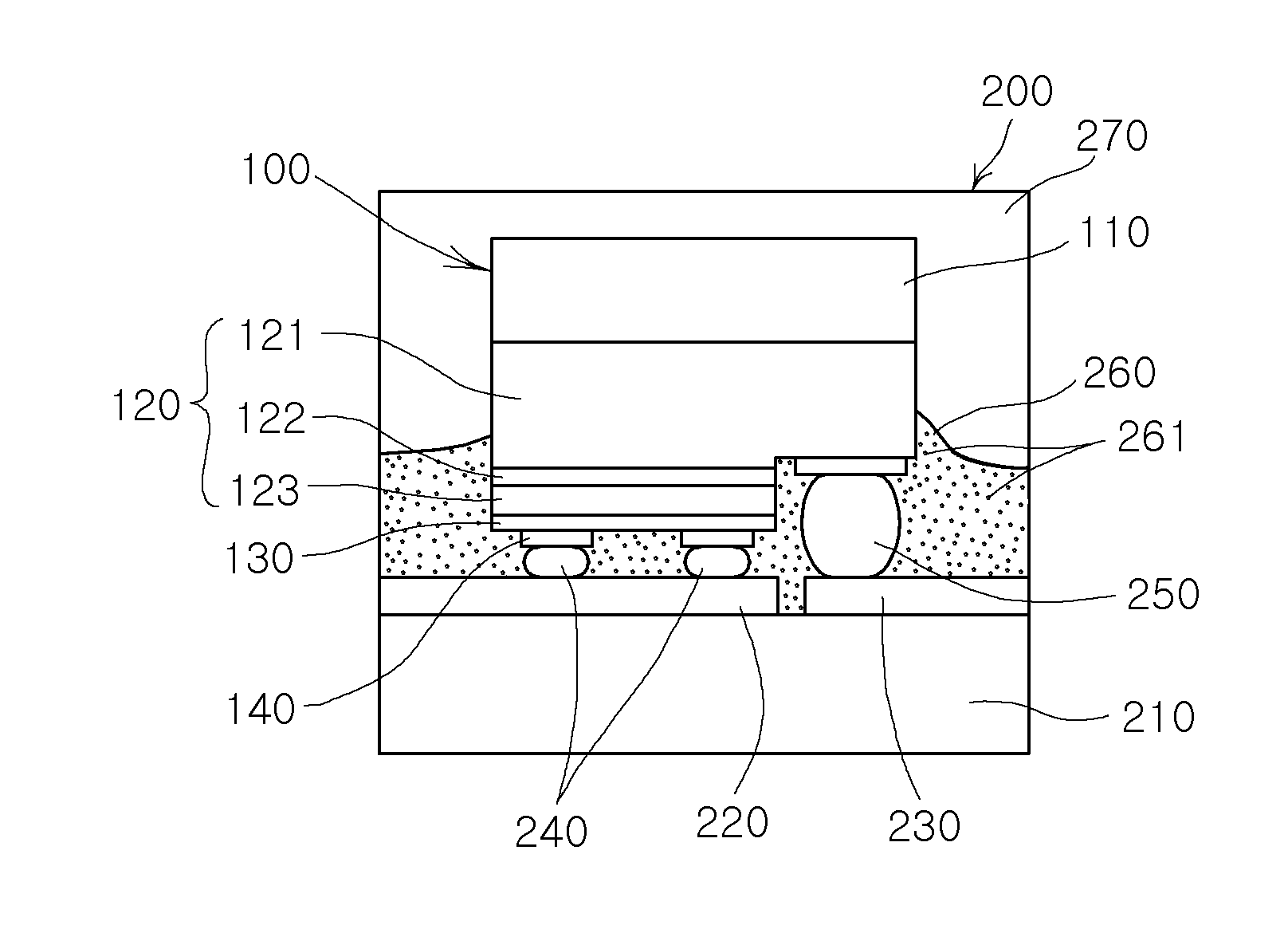
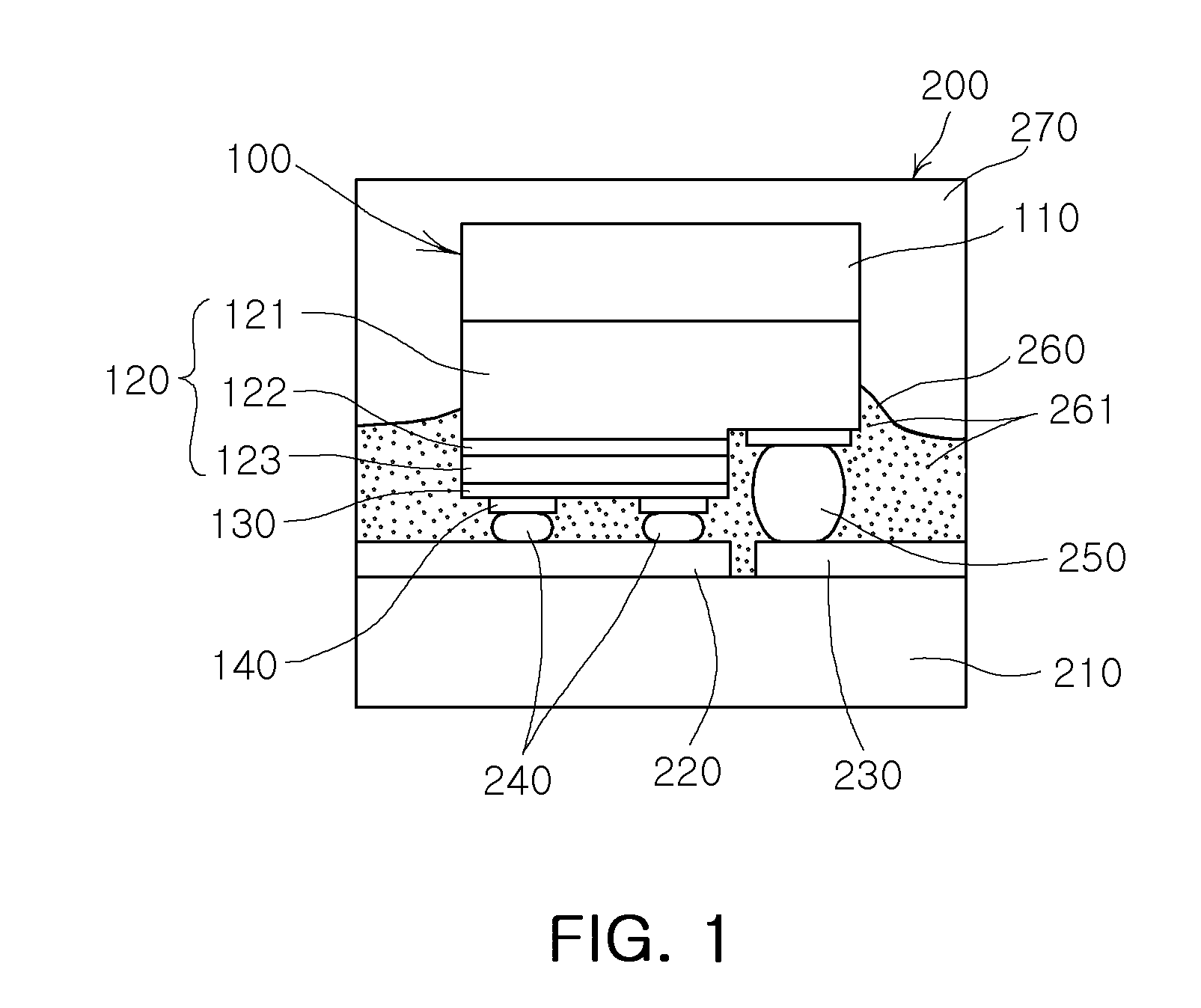
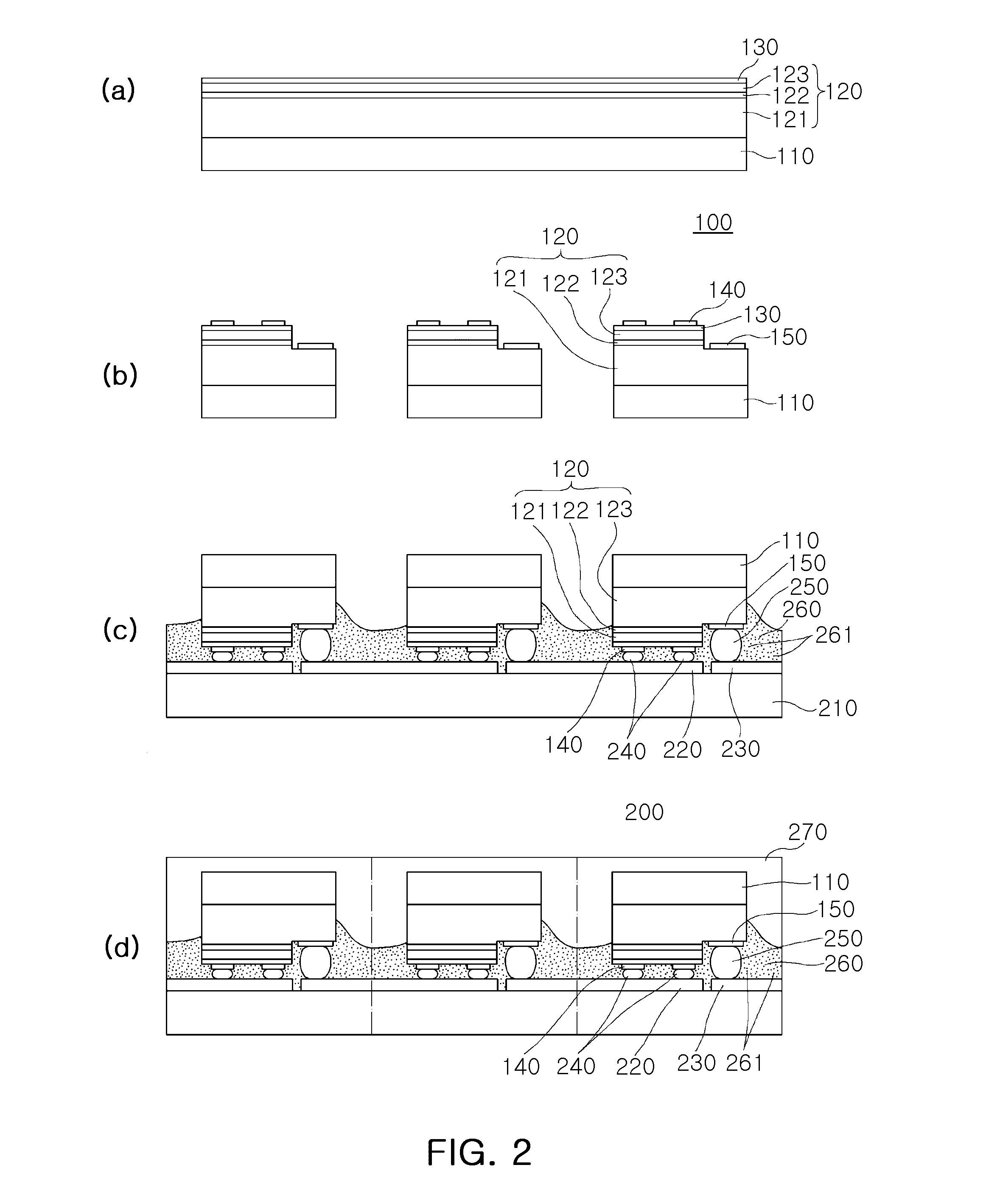
Color-changeable pixels of an optical interference display panel
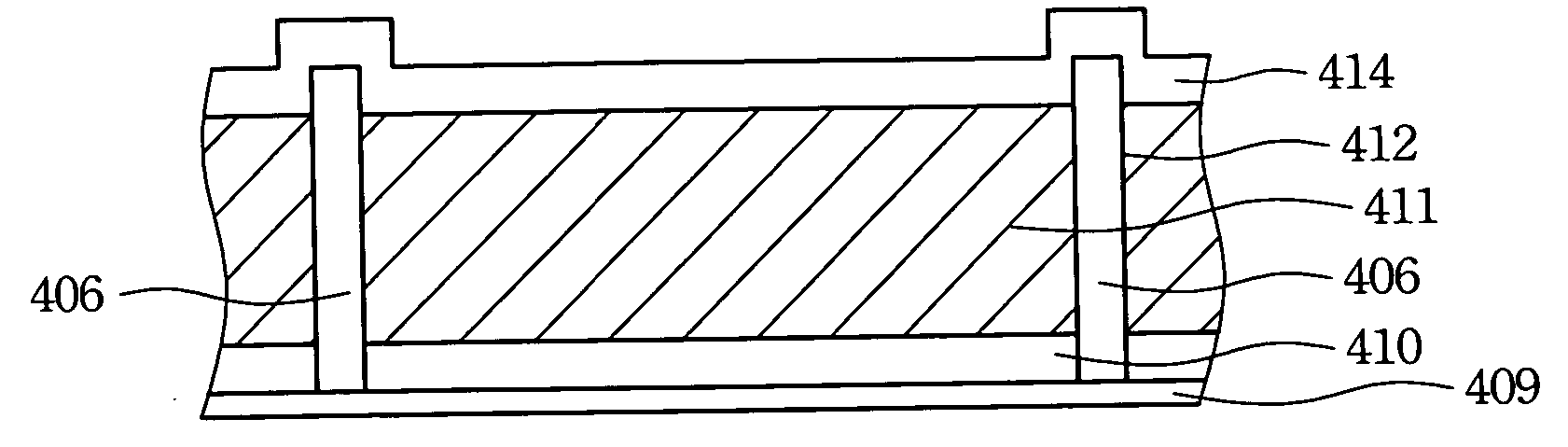
InactiveUS20050036095A1Improve reliabilityReduce delaminationNon-linear opticsOptical elementsLight reflectionEngineering
A distribution density of supports and the spacing therebetween are adjusted to improve a restorability of a light-reflection electrode of a color-changeable pixel. When the spacing between the supports is decreased or the distribution density thereof is increased, a tension per unit area of the light-reflection electrode is raised. If an external force is applied to the light-reflection electrode, the tension caused by the supports will counteract the force and allow the light-reflection electrode to successfully return to the original state after the external force is removed.
Owner:SNAPTRACK
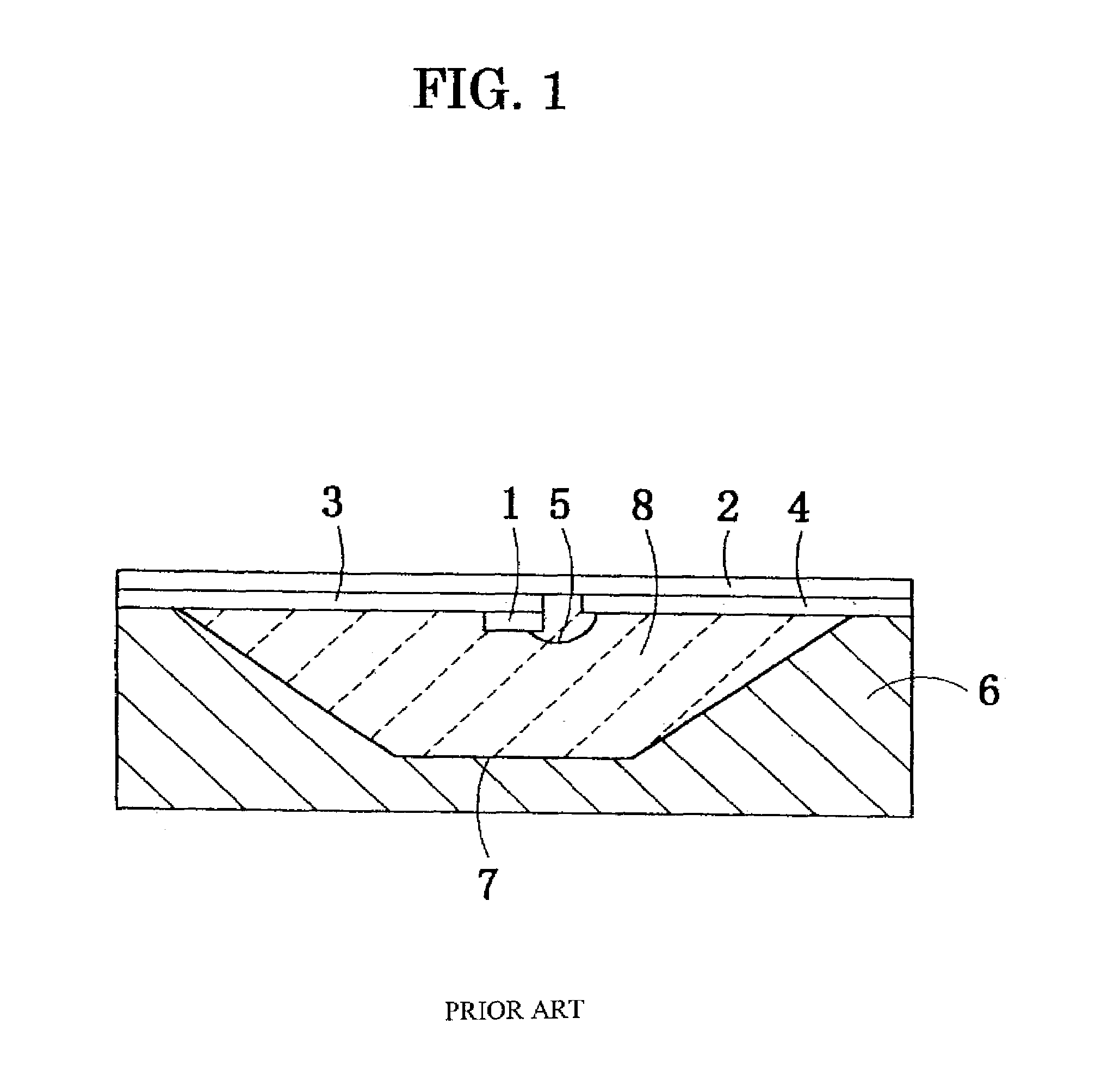
Display unit, method of manufacturing same, organic light emitting unit, and method of manufacturing same
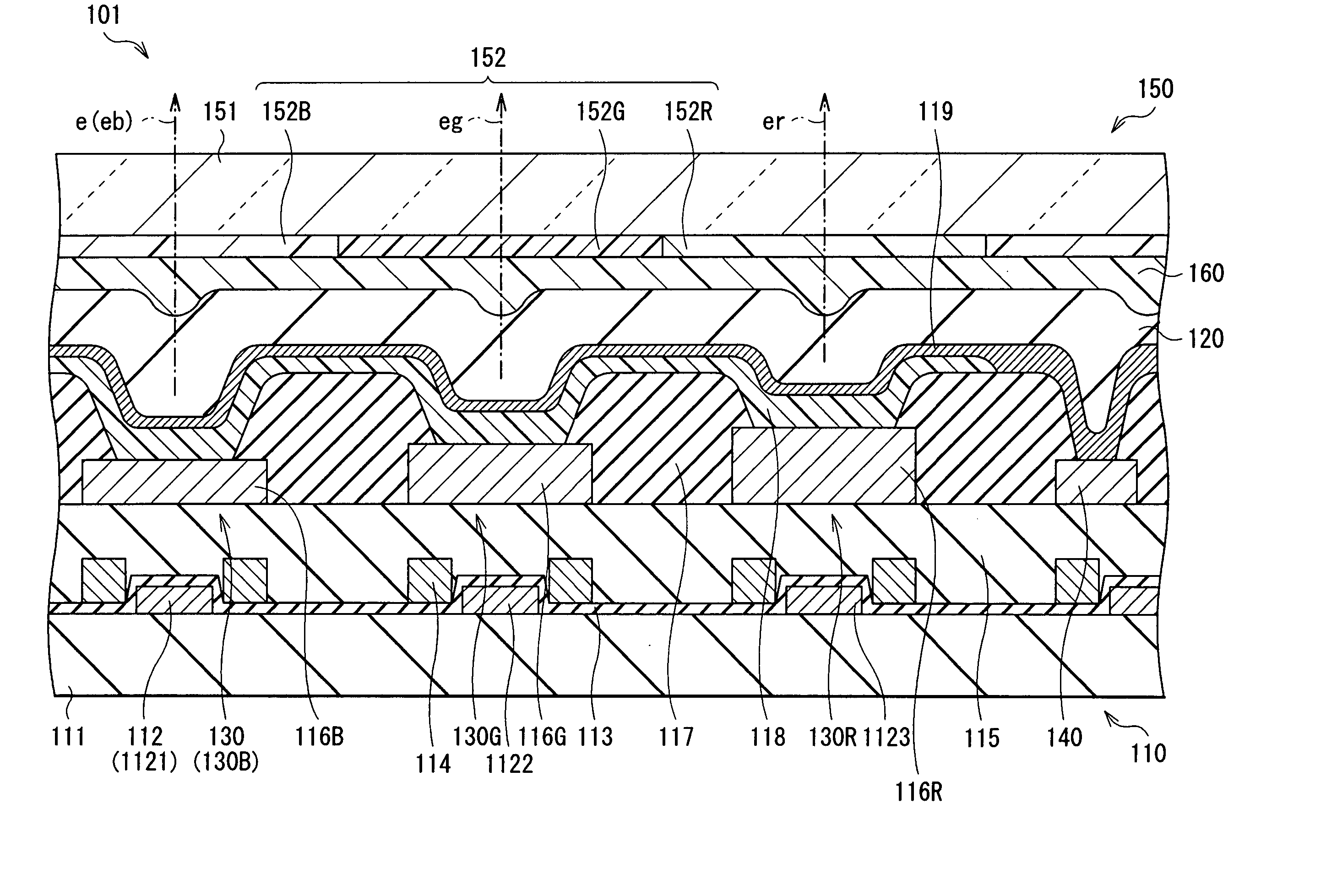
InactiveUS20070102737A1Size for such displayUtilization efficiency of lightElectroluminescent light sourcesSolid-state devicesEngineeringLength wave
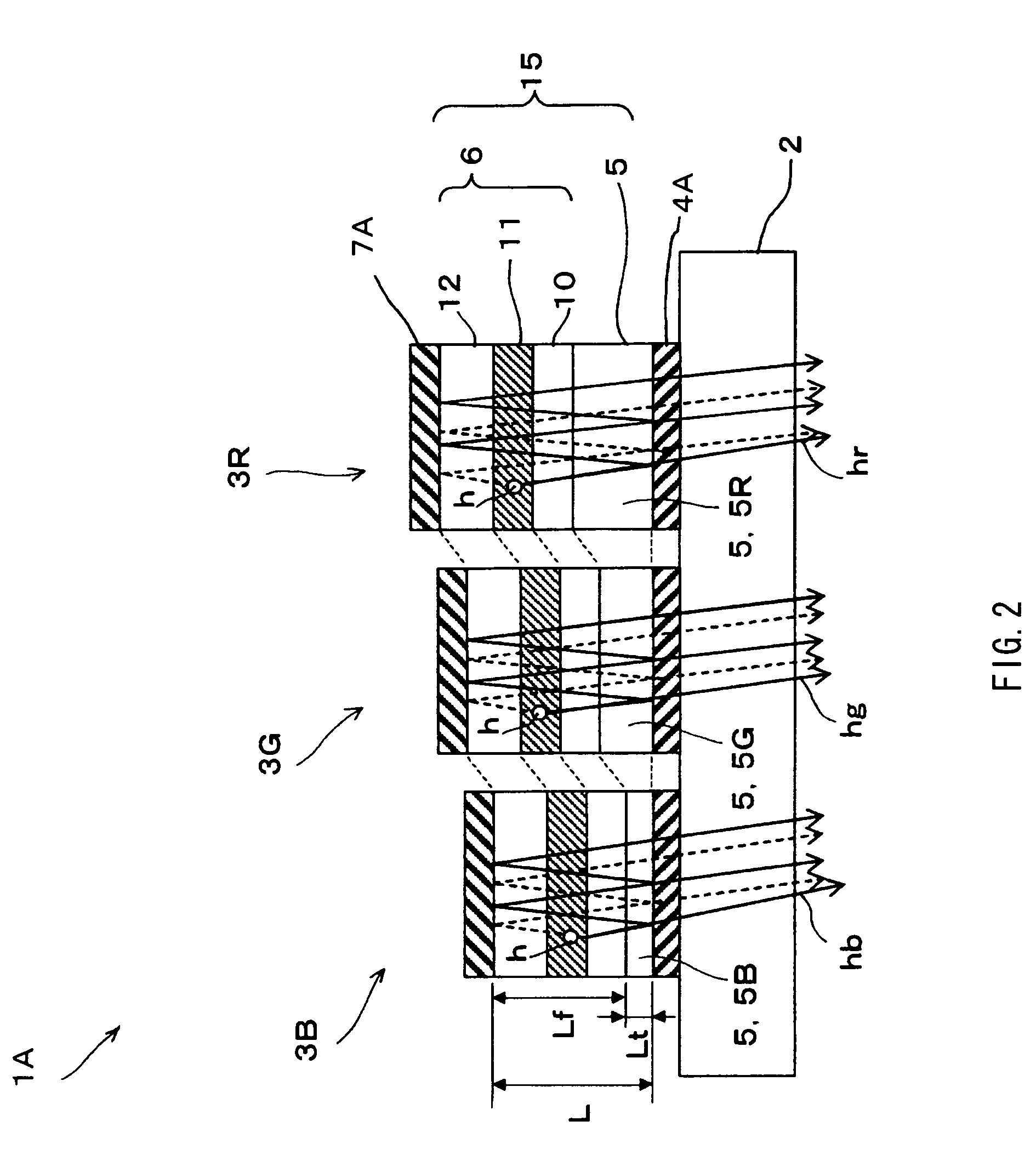
A display unit capable of being simply designed and manufactured by using more simplified light emitting device structure while capable of high definition display and display with superior color reproducibility and a manufacturing method thereof are provided. The display unit is a display unit (1), wherein a plurality of organic EL devices (3B), (3G), and (3R), in which a function layer (6) including a light emitting layer (11) is sandwiched between a lower electrode (4) made of a light reflective material and a semi-transmissive upper electrode (7), and which has a resonator structure in which light h emitted in the light emitting layer (11) is resonated using a space between the lower electrode (4) and the upper electrode (7) as a resonant section (15) and is extracted from the upper electrode (7) side are arranged on a substrate (2). In the respective organic EL devices (3B), (3G), and (3R), the function layer (6) is made of an identical layer, and an optical distance L of the resonant section (15) is set to a value different from each other so that blue, green, or red wavelength region is resonated.
Owner:SONY CORP
Led and led lamp
InactiveUS20050068776A1Great disadvantageIncrease temperatureMechanical apparatusLight source combinationsLight reflectionEngineering
This invention relates to a light emitting diode (LED) and a LED lamp consisted of LEDs. The LED comprises at least one LED chip. The LED is mounted on a high heat conductivity base and is connected to an applied power supply through a circuit board. The LED chip also has a transparent medium layer on it. The base top surface acts as a light reflective surface, or a light reflective surface is provided around the base, the LED comprises a screw extended downwards from the base bottom or a screw hole in the base bottom to connect the LED to a heat sink mechanically. The LED is electrically connected to a driving circuit through its outgoing wires. The driving circuit is in turn electrically connected to an electrical connector through its housing. A LED lamp can be fabricated after the LED is enclosed in a transparent bulb housing. The LED has high efficiency, high power and long lifetime and can be used to fabricate LED traffic lamps, LED plane light sources, etc.
Owner:LOU MANE
Powerhead of a power injection system
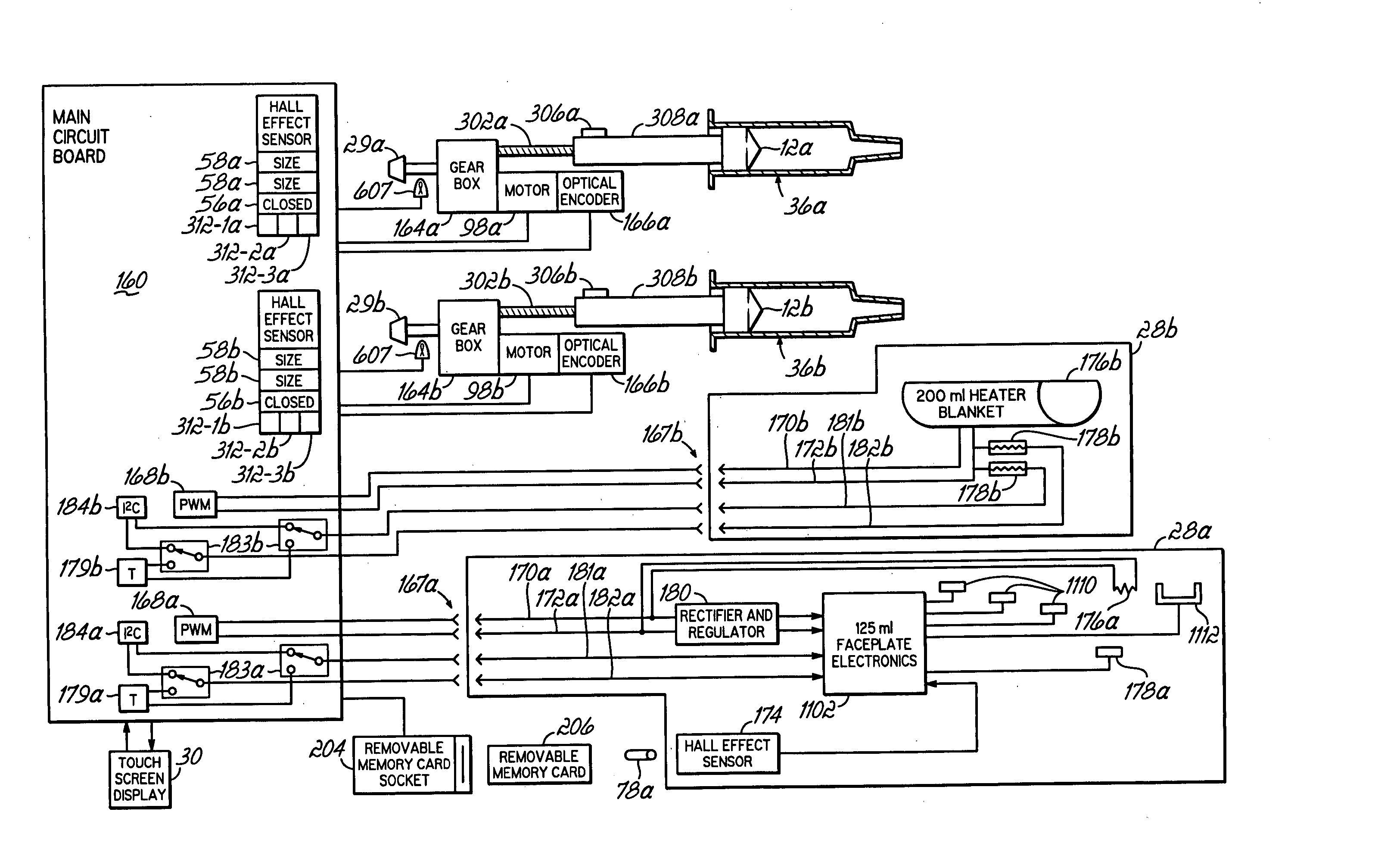
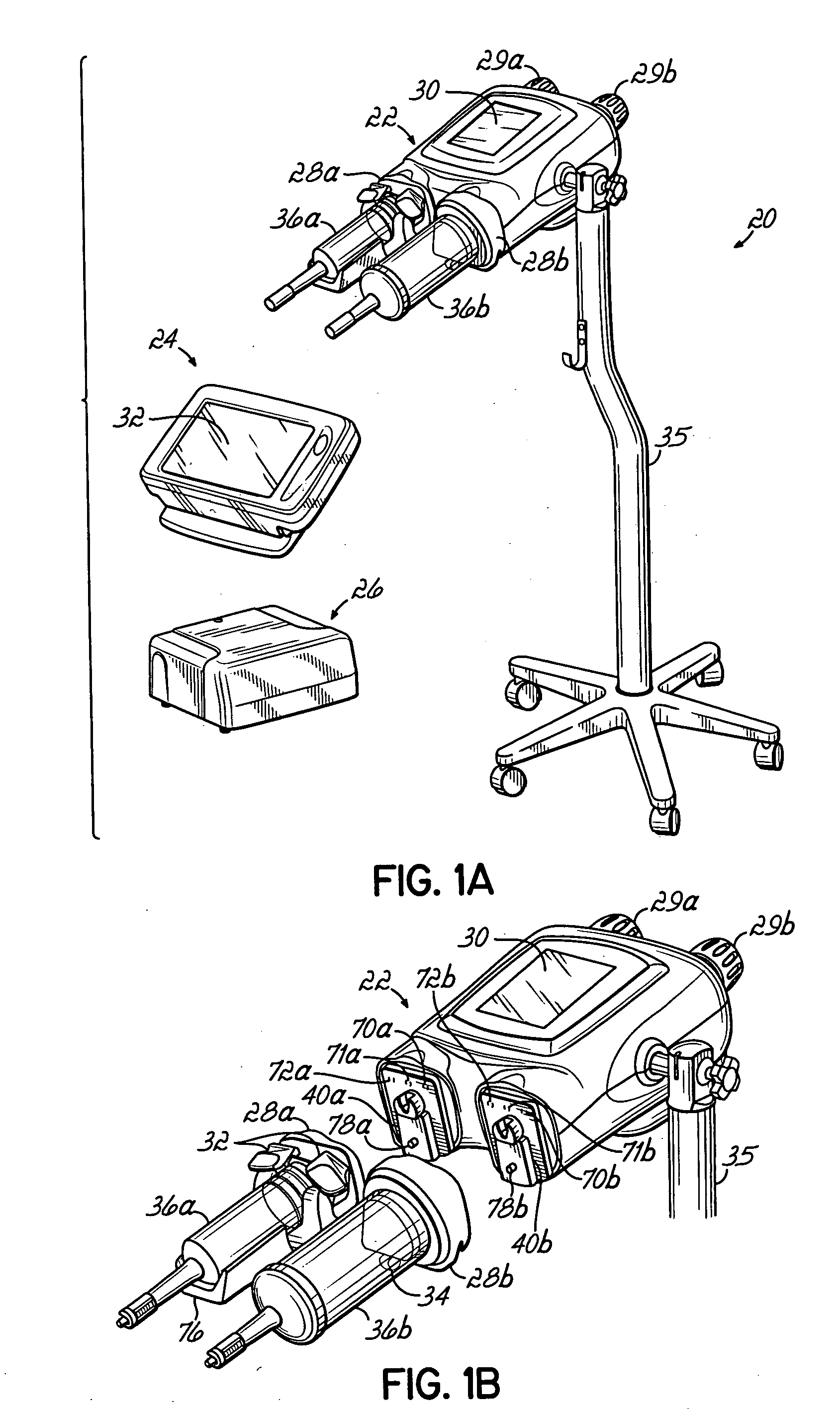
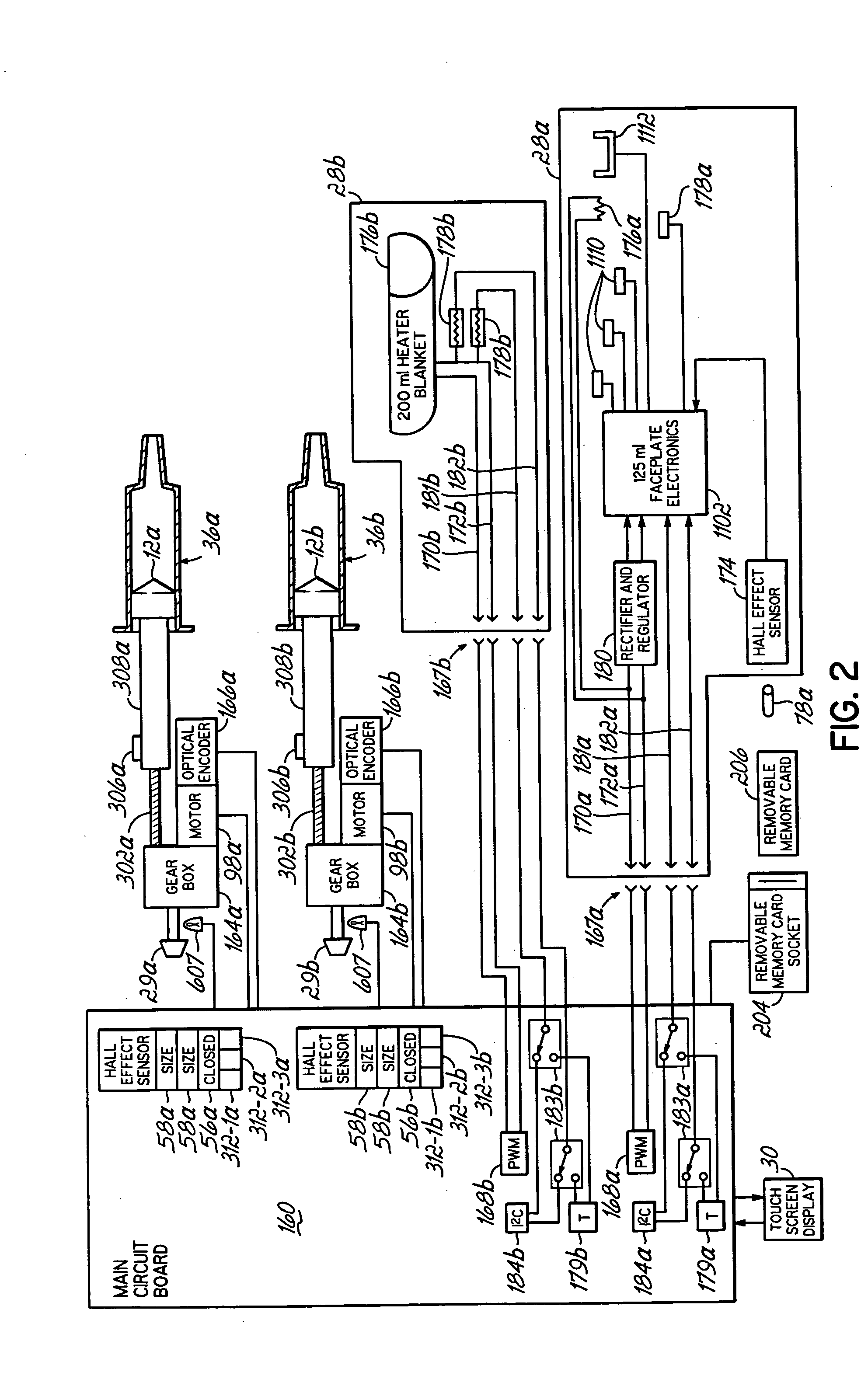
InactiveUS20060079765A1Increase powerImprove accuracyMedical devicesIntravenous devicesEngineeringPassword protection
A contrast media injection system includes detects the absolute position of the syringe ram using a non-contact sensor. A series of magnets and Hall-Effect sensors may be used or an opto-reflective system. Illuminated knobs that are connected to the drive mechanism for the syringe ram rotate with the drive and provide visual feedback on operation through the illumination. Analog Hall-Effect sensors are used to determine the presence or absence of magnets that identify the type of faceplate being used. The faceplates include control electronics, connected to the powerhead through connectors, which may be interchangeably used by the two faceplates. The faceplate electronics include detectors for automatically detecting the capacity of pre-filled syringes. Additional features include using historical data to provide optimum pressure limit values during an injection protocol, a removable memory device for storing and transferring information such as injection protocols and injector statistics, and password protection of such protocols.
Owner:LIEBEL FLARSHEIM CO
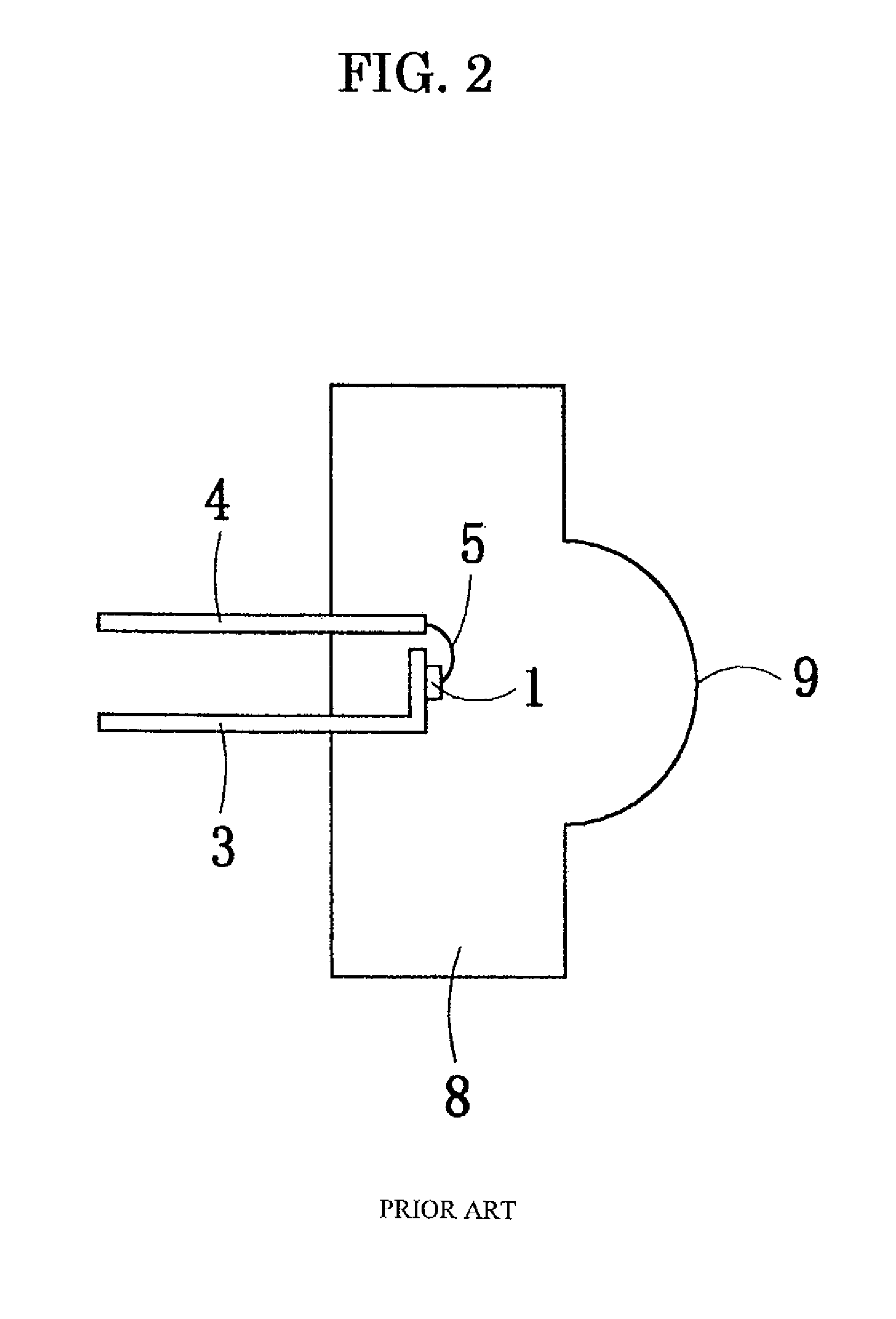
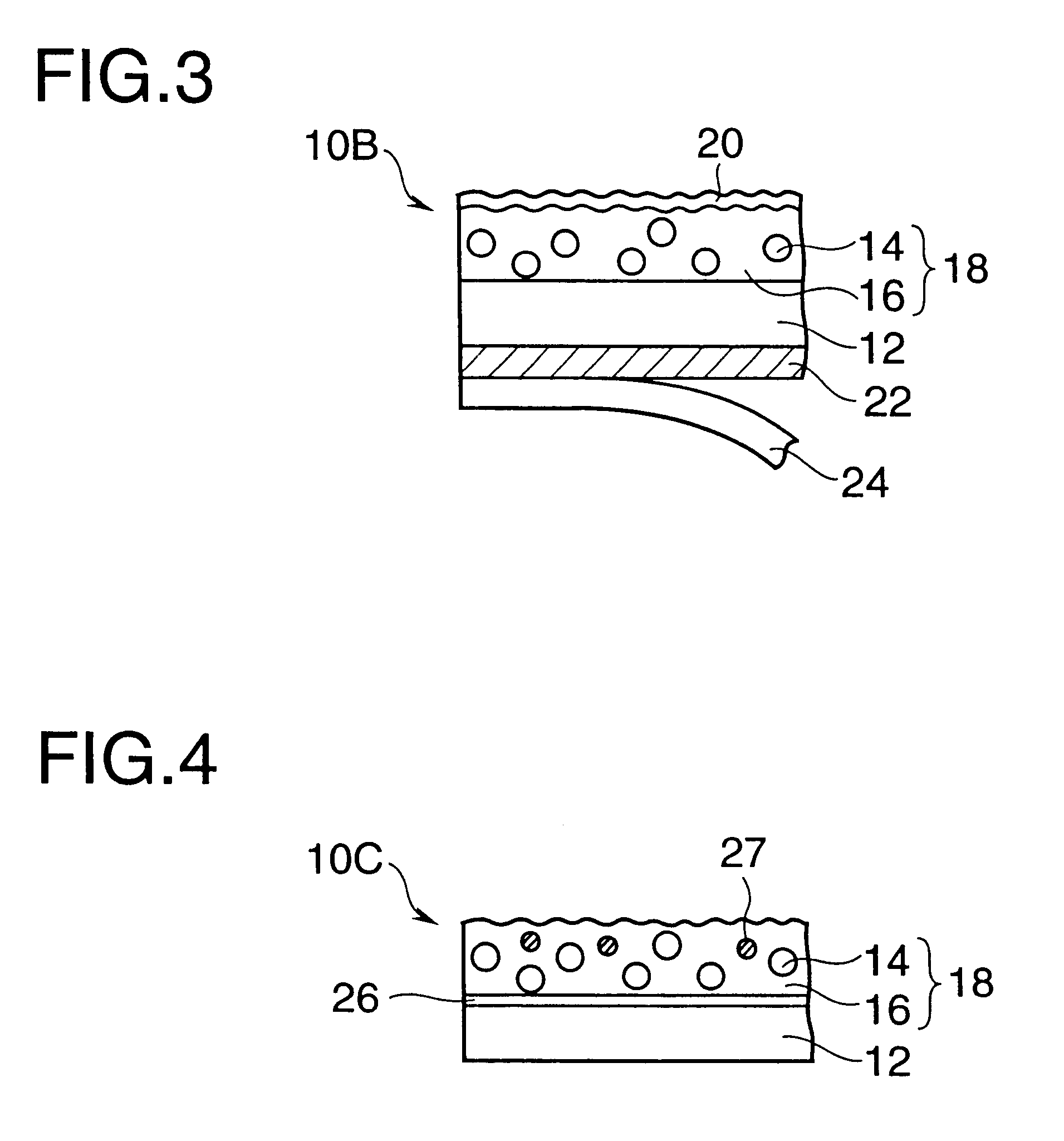
Structure of a light-incidence electrode of an optical interference display plate
InactiveUS20040175577A1Glass/slag layered productsNon-linear opticsLight reflectionMetallic materials
An optical interference display plate at least comprises a light-incidence electrode and a light-reflection electrode. The light-incidence electrode at least comprises an absorption layer and a dielectric layer. A material of the absorption layer does not comprises metallic material.
Owner:SNAPTRACK
Structure of an optical interference display unit
InactiveUS6958847B2Avoid pollutionIncreased process complexityTelevision system detailsColor television detailsLight reflectionReflective layer
Owner:SNAPTRACK
Information system and method for providing information using a holographic element
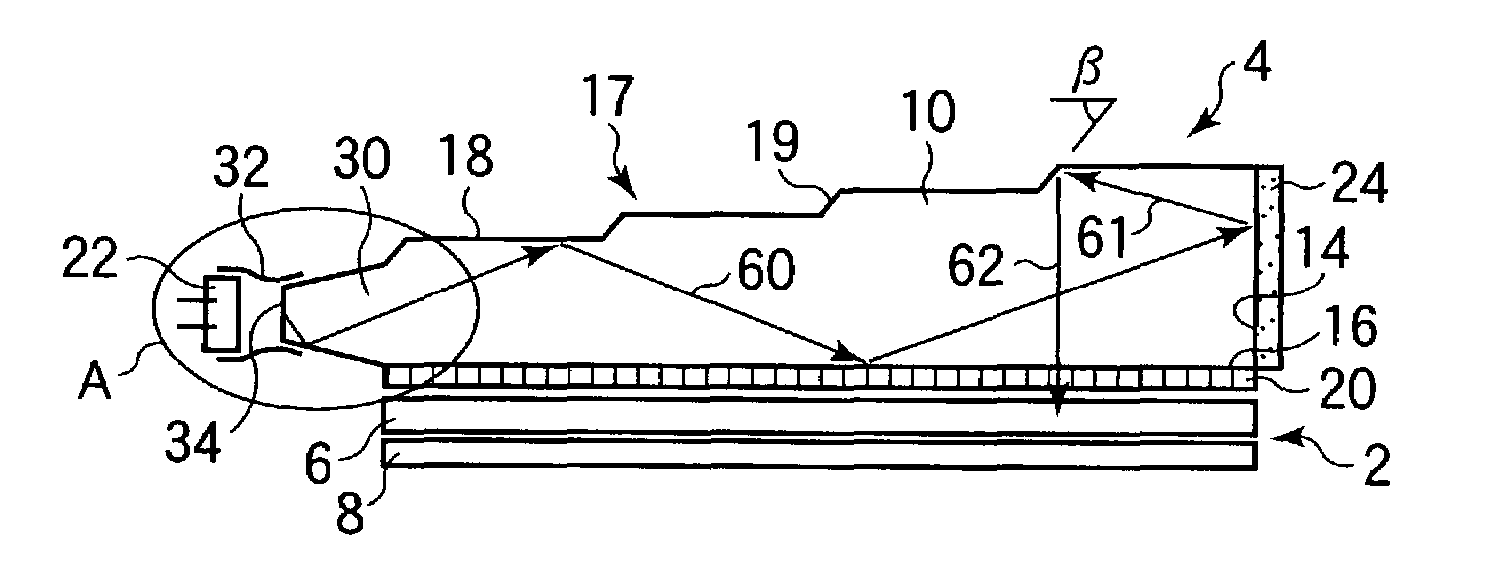
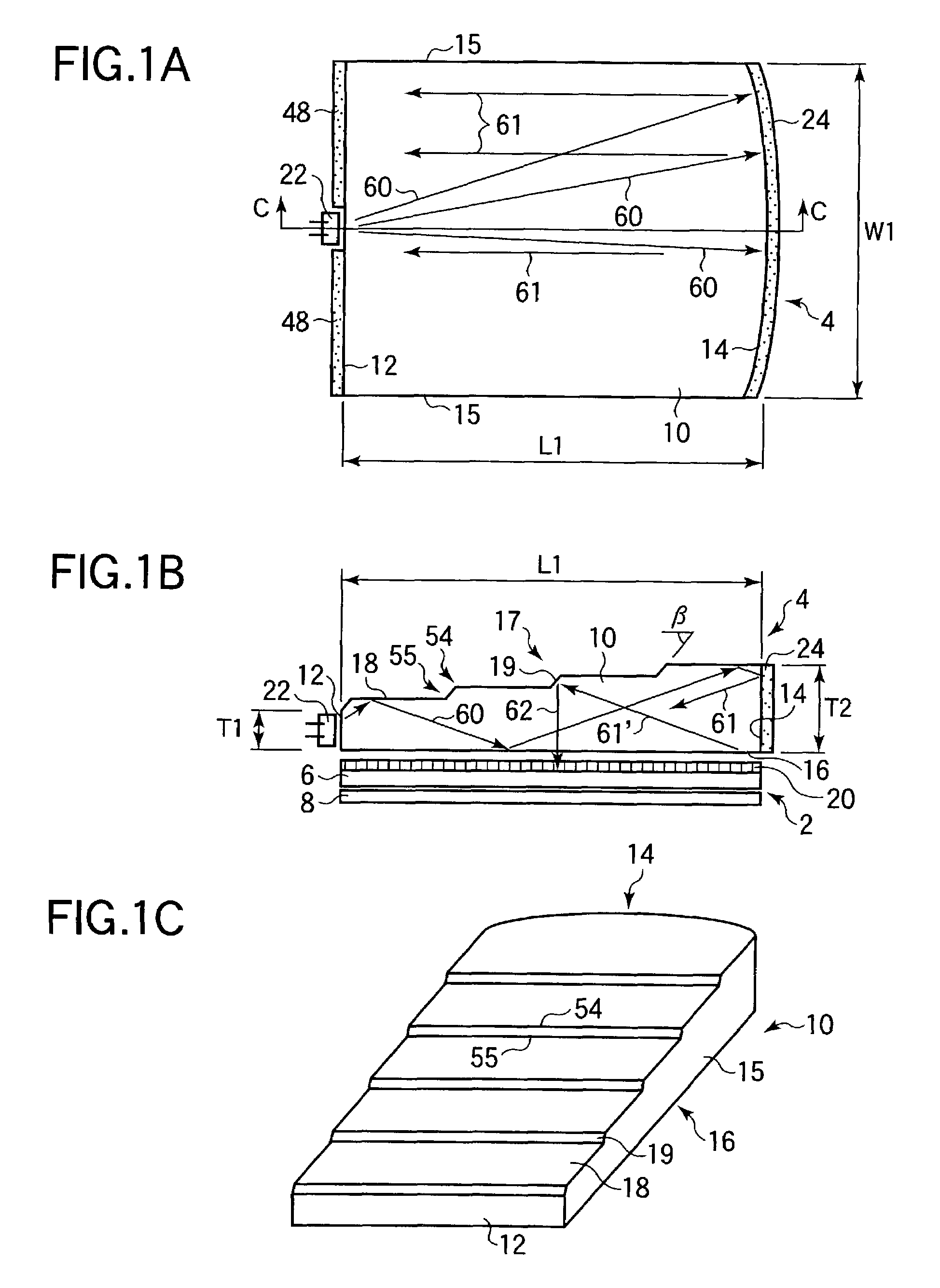
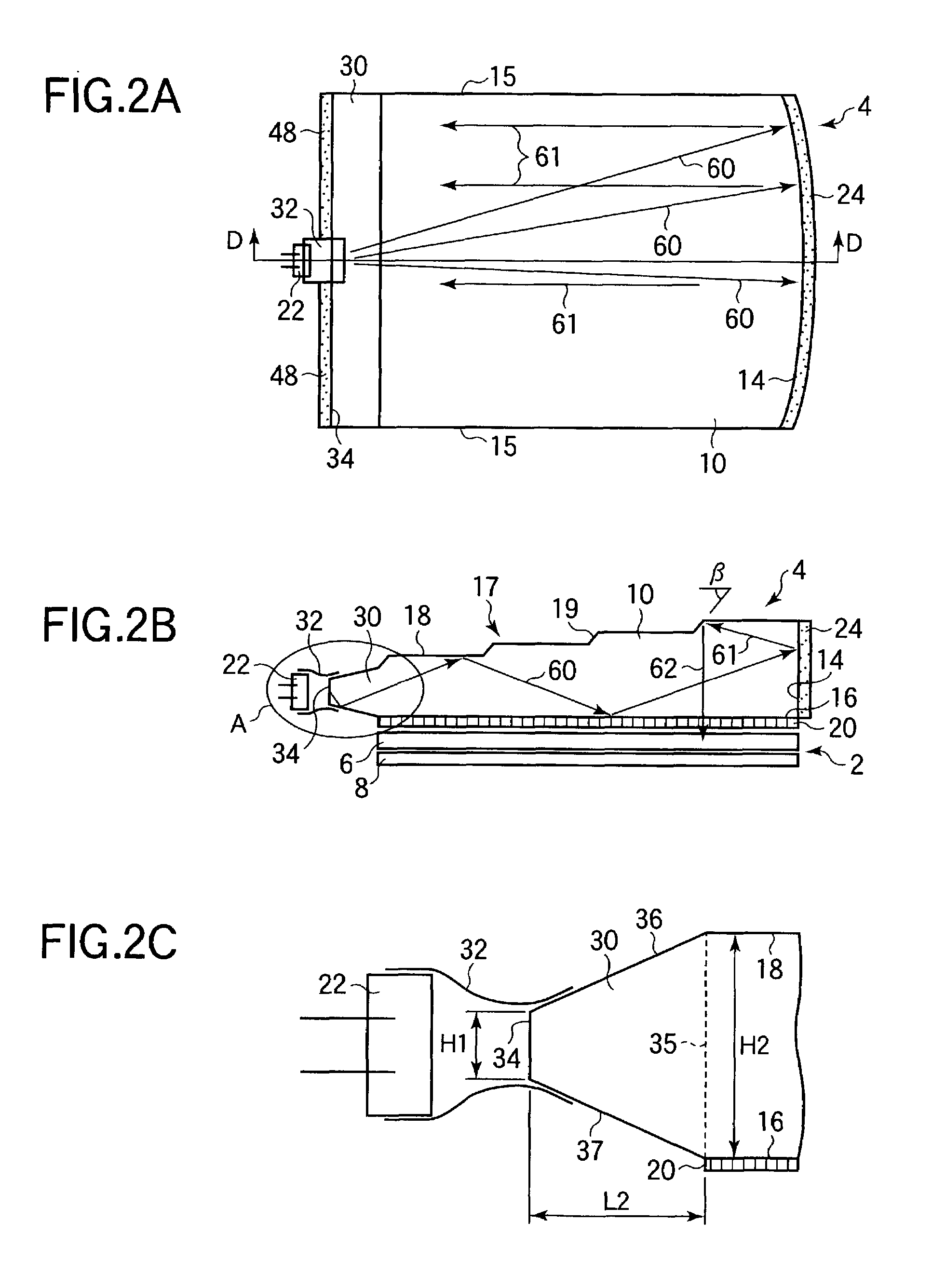
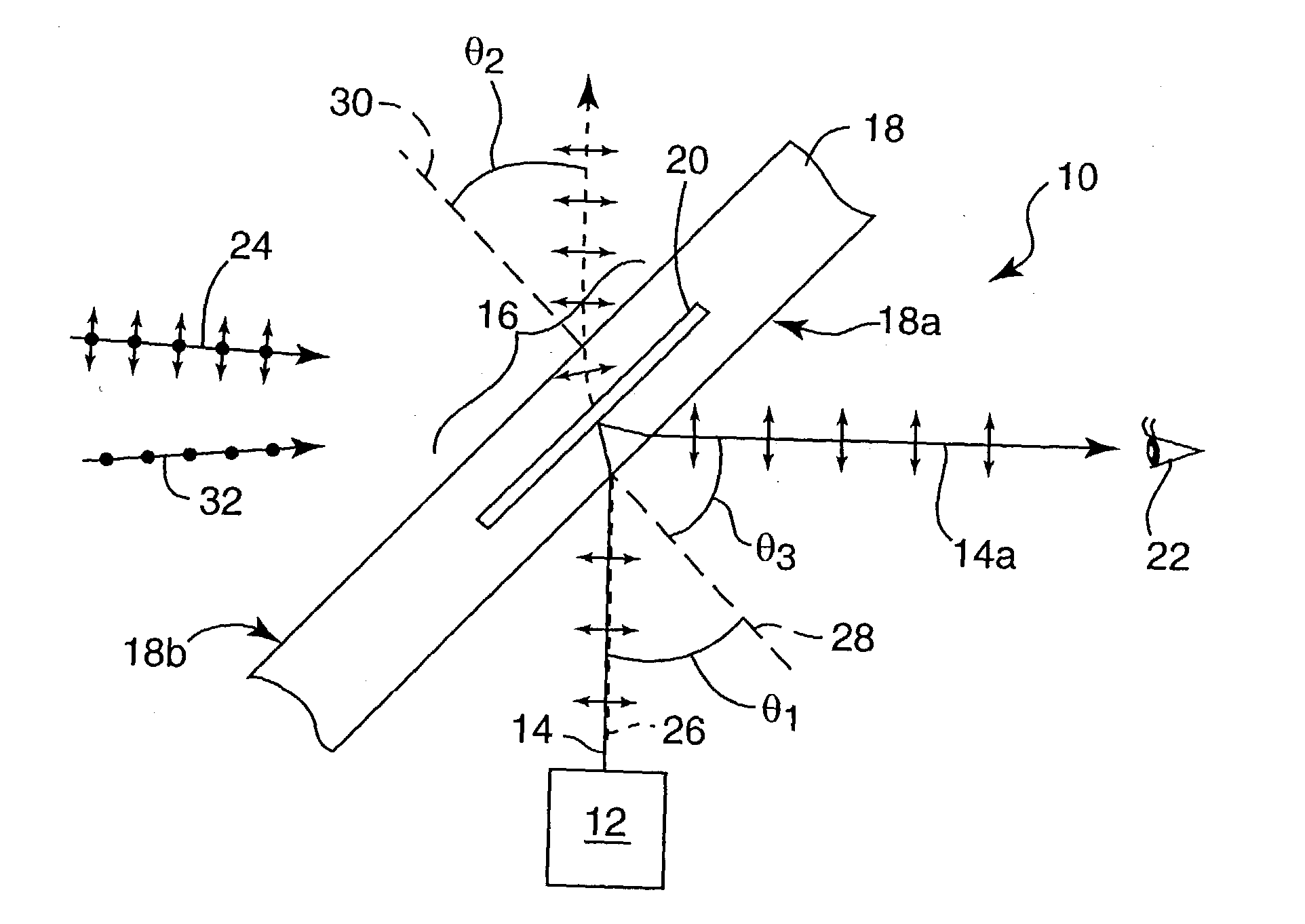
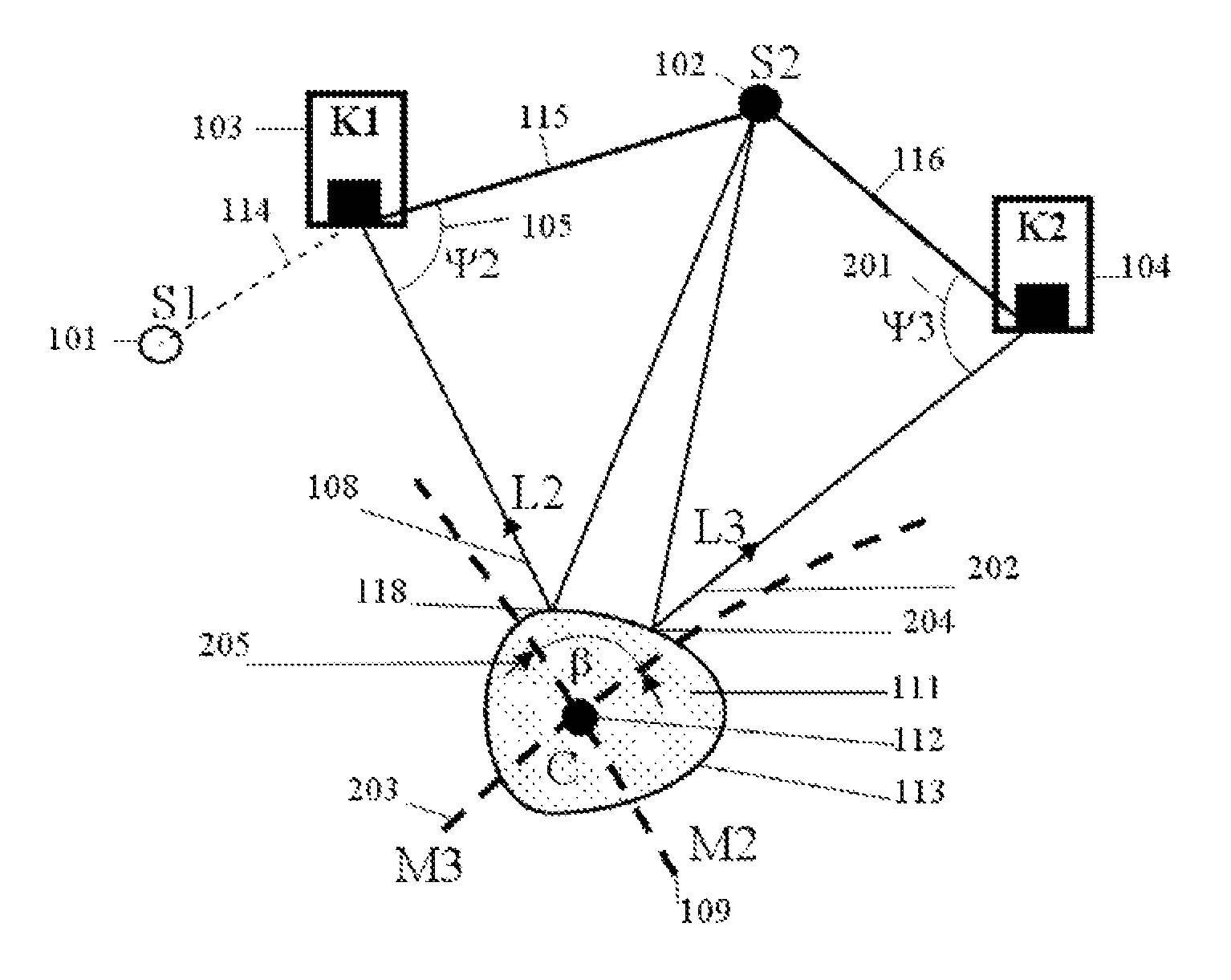
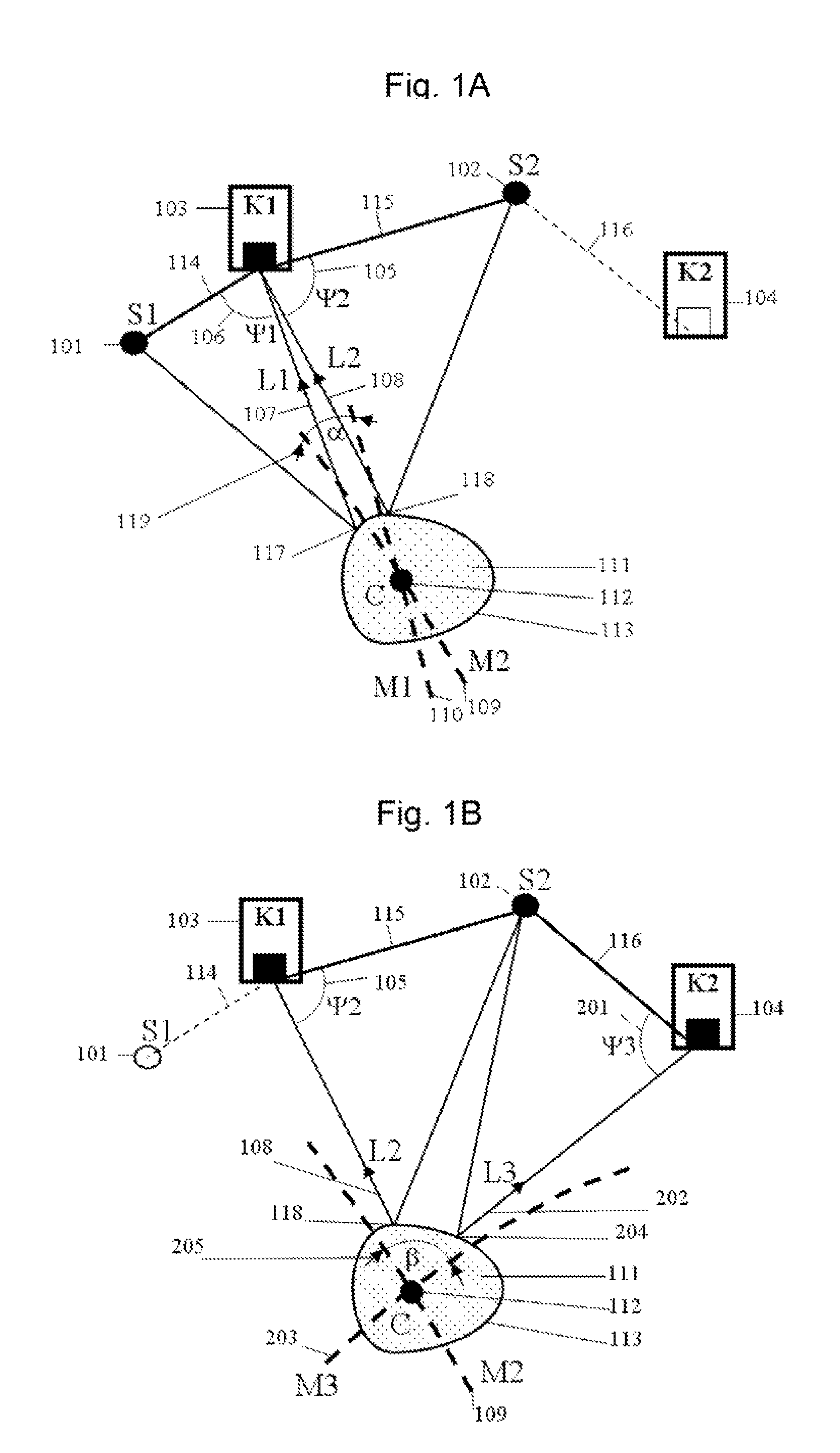
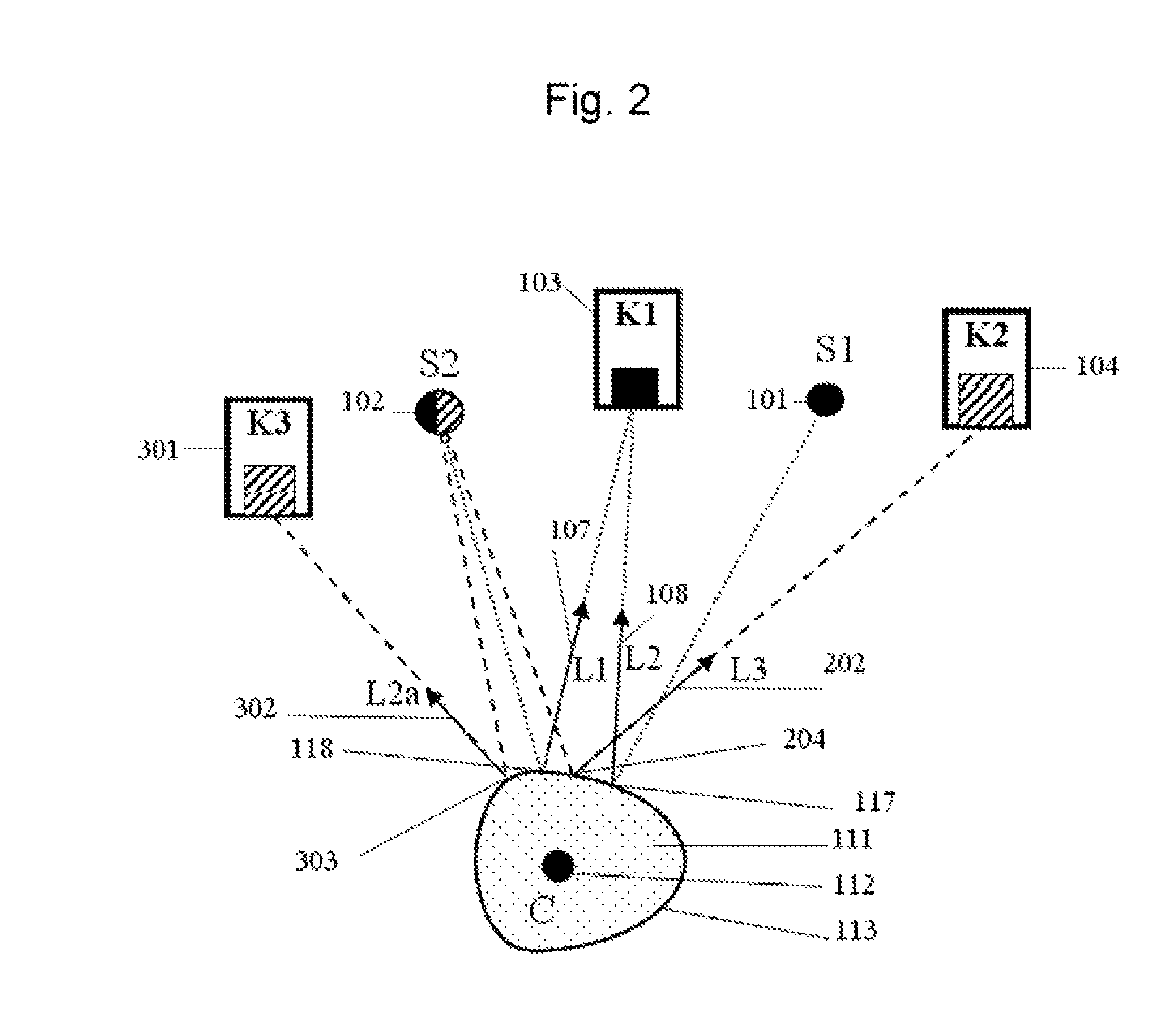
ActiveUS20070109619A1Improve relationshipThe relationship is accurateInput/output for user-computer interactionCathode-ray tube indicatorsAngle of incidencePhotodetector
In the following, the essential points are summarized again by means of groups of characteristics which each individually and in combination with one another characterize the invention specifically: 1. Information system for providing information in correlation with light incident on an eye, having a holographic element disposed in front of the eye, and an optical scanning device which detects light incident on the eye by way of the holographic element. 2. Information system according to Point 1, wherein the optical scanning device is at a fixed predetermined angular ratio with respect to the holographic element. 3. Information system according to Point 1 or 2, wherein the optical scanning device detects light which is refracted by the holographic element before it impinges on the eye and does not enter the eye. 4. Information system according to one of the preceding points, wherein the optical scanning device detects light which was first reflected back from the eye and was then refracted by the holographic element. 5. Information system according to one of the preceding points, wherein the holographic element refracts light originating from the field of vision of the eye only at several discrete wavelengths in the visible range before the light impinges on the eye for the detection by the optical scanning device, and refracts light reflected back from the eye only at one discrete wavelength in the infrared range for the detection by the optical scanning device. 6. Information system according to one of the preceding points, wherein the holographic element refracts light originating from the field of vision of the eye at fewer than 20, fewer than 10 or fewer than 5 discrete wavelengths in the visible range either before the light impinges on the eye or after its backscattering as a result of the eye for the detection by the optical scanning device. 7. Information system according to one of the preceding points, wherein the holographic element refracts light originating from the field of vision of the eye at a discrete wavelength in the infrared range either before the light impinges on the eye or after its backscattering as a result of the eye for the detection by the optical scanning device. 8. Information system according to one of the preceding points, wherein the holographic element refracts light reflected back by the eye only at a discrete wavelength in the infrared range for the detection by the optical scanning device. 9. Information system according to one of the preceding points, wherein the holographic element refracts light of one or several discrete wavelengths, at which the optical scanning device has a high sensitivity. 10. Information system according to one of the preceding points, wherein the holographic element refracts light a several discrete wavelengths such that the refracted light is guided to a common point, and the angle of incidence of the light on this point permits a clear optionally also wavelength-independent conclusion on the angle of incidence of the light upon the holographic element. 11. Information system according to one of the preceding points, having an optical projection device which projects light into the eye by way of the holographic element. 12. Information system according to Point 11, wherein the light detected by the optical detection device and the light projected in front of the optical projection device run in the opposite direction through a common light guiding lens system and can be focused such by the optical scanning device or projection device that their respective beams describe the same path from or into the eye. 13. Information system for providing information in correlation with information obtained from an eye, having a holographic element disposed in front of the eye, and an optical projection device which projects light into the eye by way of the holographic element. 14. Information system according to one of Points 11 to 13, wherein the optical projection device projects light only at one or several discrete wavelengths in the visible range and / or at a wavelength in the infrared range. 15. Information system according to one of Points 11 to 14, wherein the holographic element refracts the wavelengths of the projected light. 16. Information system according to one of Points 11-15, wherein the optical projection device is in a fixed predetermined angular ratio with respect to the holographic element. 17. Information system according to Point 16, wherein the holographic element comprises one or more optical flags, whose light reflection characteristics can be used by the information system by means of a photodetector for calibrating a projection angle of the optical projection device and / or a light guiding device. 18. Information system according to Point 17, including Point 12, wherein the information system uses the light reflection characteristics of the optical flags for calibrating a scanning angle of the optical scanning device and / or a light guiding device. 19. Information system according to Point 17, wherein the optical flags are generated in that reflecting elements are imaged during the creating of the holographic element such in the holographic element that they (something is missing) reflect light of one or several wavelengths which, corresponding to the predetermined angular ratio with respect to the optical projection device is incident on the holographic element, back along the path of incidence. 20. Information system according to Point 19, wherein the photodetector device has a splitter mirror which is arranged such in the light beam of the optical projection device that it guides a portion of the light, which impinges on the splitter mirror against the projection direction, in the direction of a photodetector which detects in at least two areas situated concentrically around one another. 21. Information system according to one of the preceding points, wherein the holographic element has light-refracting characteristics at one or several discrete wavelengths, which correspond to a reflection on the concave side of an area constructed according to the curvature of a rotationally symmetrical ellipsoid. 22. Information system according to one of the preceding points, wherein the holographic element has light refracting characteristics at one or several discrete wavelengths, which correspond to a refraction on the concave side of an area constructed according to the curvature of a rotationally symmetrical ellipsoid, which refraction corresponds to a reflection on a respective conical surface which is rotationally symmetrical about the axis of rotation of the ellipsoid and is perpendicular with respect to the ellipsoid at the site of the refraction. 23. Method of providing information in correlation with light incident on an eye, whereby a holographic element is disposed in front of the eye, and an optical scanning device detects the light incident on the eye by means of the holographic element. 24. Method according to Point 23, whereby the optical scanning device is at a fixed predetermined angular ratio with respect to the holographic element. 25. Method according to Point 23 or 24, whereby the optical scanning device detects light which is refracted by the holographic element before impinging on the eye and does not enter the eye. 26. Method according to one of Points 23 to 25, whereby the optical scanning device detects light which was first reflected back from the eye and was then refracted by the holographic element. 27. Method according to one of Points 23 to 26, whereby the holographic element refracts light originating from the field of vision of the eye only at several discrete wavelengths in the visible range before its impinging on the eye for the detection by the optical scanning device and refracts light reflected back from the eye only at a discrete wavelength in the infrared range for the detection by the optical scanning device. 28. Method according to one of Points 23 to 27, whereby the holographic element refracts light originating from the field of vision of the eye at fewer than 20, fewer than 10 or fewer than 5 discrete wavelengths in the visible range either before its impinging on the eye or after its backscattering as a result of the eye for the detection by the optical scanning device. 29. Method according to one of Points 23 to 28, whereby the holographic element refracts light originating from the visual field of the eye at a discrete wavelength in the infrared range either before its impinging on the eye or after its backscattering as a result of the eye for the detection by the optical scanning device. 30. Method according to one of Points 23 to 29, whereby the holographic element refracts light reflected back from the eye only at a discrete wavelength in the infrared range for the detection by the optical scanning device. 31. Method according to one of Points 23 to 30, whereby the holographic element refracts light of one or several discrete wavelengths, at which the optical scanning device has a high sensitivity. 32. Method according to one of Points 23 to 31, whereby the holographic element refracts light at several discrete wavelengths such that the refracted light is guided to a common point, an the angle of incidence of the light onto this point allows a clear, optionally also wavelength-independent conclusion on the angle of incidence of the light upon the holographic element. 33. Method according to one of Points 23 to 32, whereby an optical projection device projects light by way of the holographic element into the eye. 34. Method according to Point 33, whereby the light detected by the optical scanning device and the light projected in front of the optical projection device run in the opposite direction through a common light guiding lens system and can be focused such by the optical scanning device or projection device that their respective beams describe the same path from or into the eye. 35. Method of providing information in correlation with information obtained from an eye, whereby a holographic element is disposed in front of the eye, and an optical projection device projects light by way of the holographic element into the eye. 36. Method according to points 33 to 35, whereby the optical projection device projects light only at one or several discrete wavelengths in the visible range and / or at a wavelength in the infrared range. 37. Method according to one of Points 33 to 36, whereby the holographic element refracts the wavelengths of the projected light. 38. Method according to one of Points 33 to 37, whereby the optical projection device is in a fixed predetermined angular ratio with respect to the holographic element. 39. Method according to Point 38, whereby the holographic element is equipped with one or more optical flags, whose light reflection characteristics can be used by means of a photodetector device for calibrating a projection angle of the optical projection device and / or a light guiding device. 40. Method according to Point 39, including Point 34, whereby the light reflection characteristics of the optical flags are used for calibrating a scanning angle of the optical scanning device and / or a light guiding device. 41. Method according to Point 39, whereby the optical flags are generated in that reflecting elements are imaged during the creating of the holographic element such in the holographic element that they beam light of one or more wavelengths which, corresponding to the predetermined angular ratio with respect to the optical projection device is incident on the holographic element, back along the incidence path. 42. Method according to Point 41, whereby the photodetector device is equipped with a photodetector detecting in at least two areas situated concentrically around one another, and a splitter mirror which is arranged such in the light beam of the optical projection device that it directs a portion of the light impinging on the splitter mirror against the projecting direction, in the direction of the photodetector. 43. Method according to one of Points 23 to 42, whereby the holographic element has light-refracting characteristics at one or several discrete wavelengths which correspond to a reflection on the concave side of an area constructed according to a curvature of a rotationally symmetrical ellipsoid. 44. Method according to one of Points 23 to 43, whereby the holographic element has light-refracting characteristics at one or several discrete wavelengths, which correspond to a refraction on the concave side of an area constructed according to a curvature of a rotationally symmetrical ellipsoid, which refraction corresponds to a reflection on a respective conical surface rotationally symmetrical about the axis of rotation of the ellipsoid, which conical surface is perpendicular with respect to the ellipsoid at the site of the refraction. While the preceding description with respect to the title is limited to embodiments falling under the initially mentioned generic terms “scanning information system” and “projecting information system”, each individual discussed characteristic of their disclosure can also be used in an embodiment of the systems, devices and methods initially identified by reference to their full content. The applications by the same applicant and / or the same inventors mentioned in the present application should be considered to be a correlated invention complex.
Owner:APPLE INC
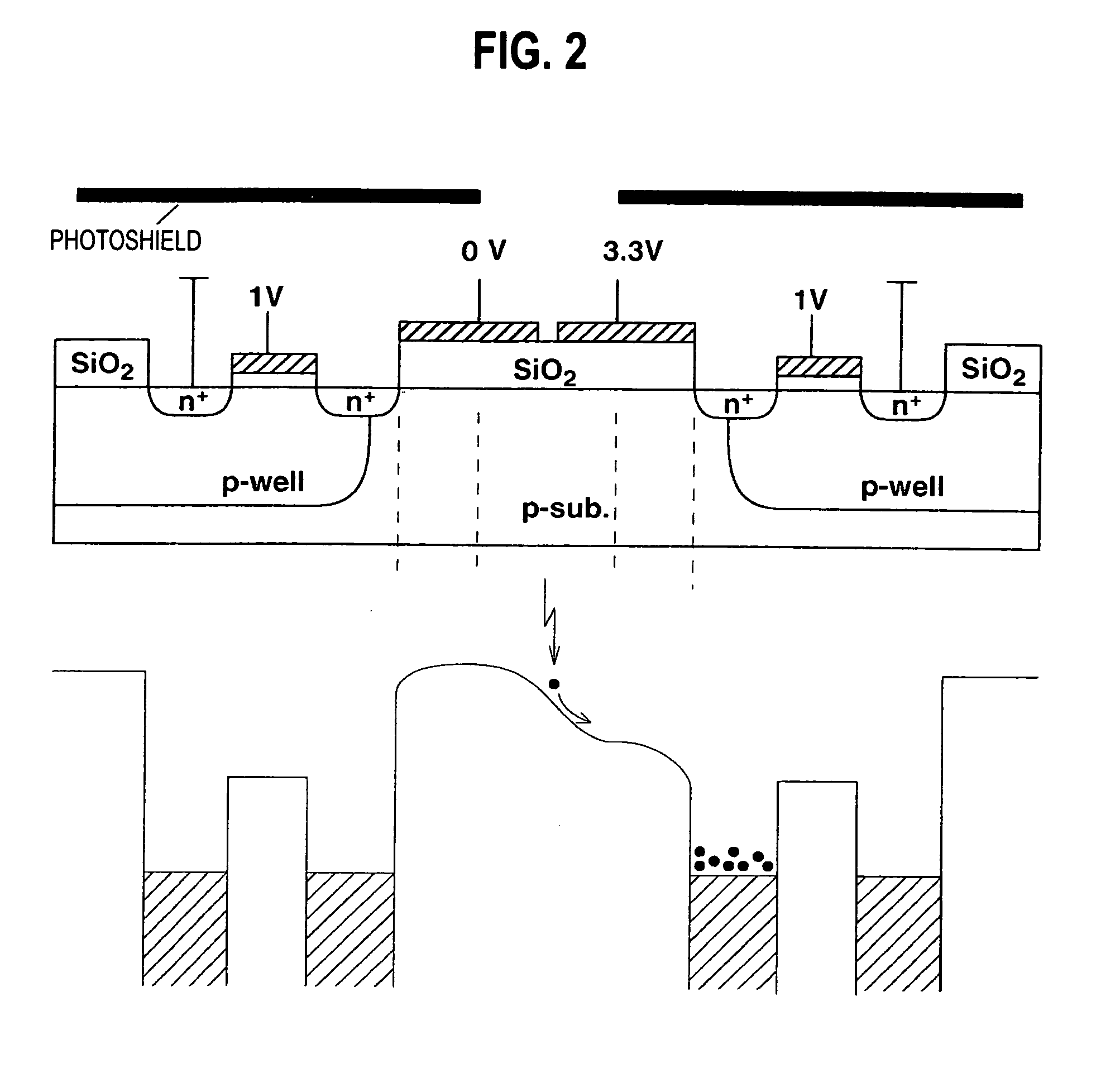
Temperature measuring system, heating device using it and production method for semiconductor wafer, heat ray insulating translucent member, visible light reflection membner, exposure system-use reflection mirror and exposure system, and semiconductor device produced by using them and vetical heat treating device
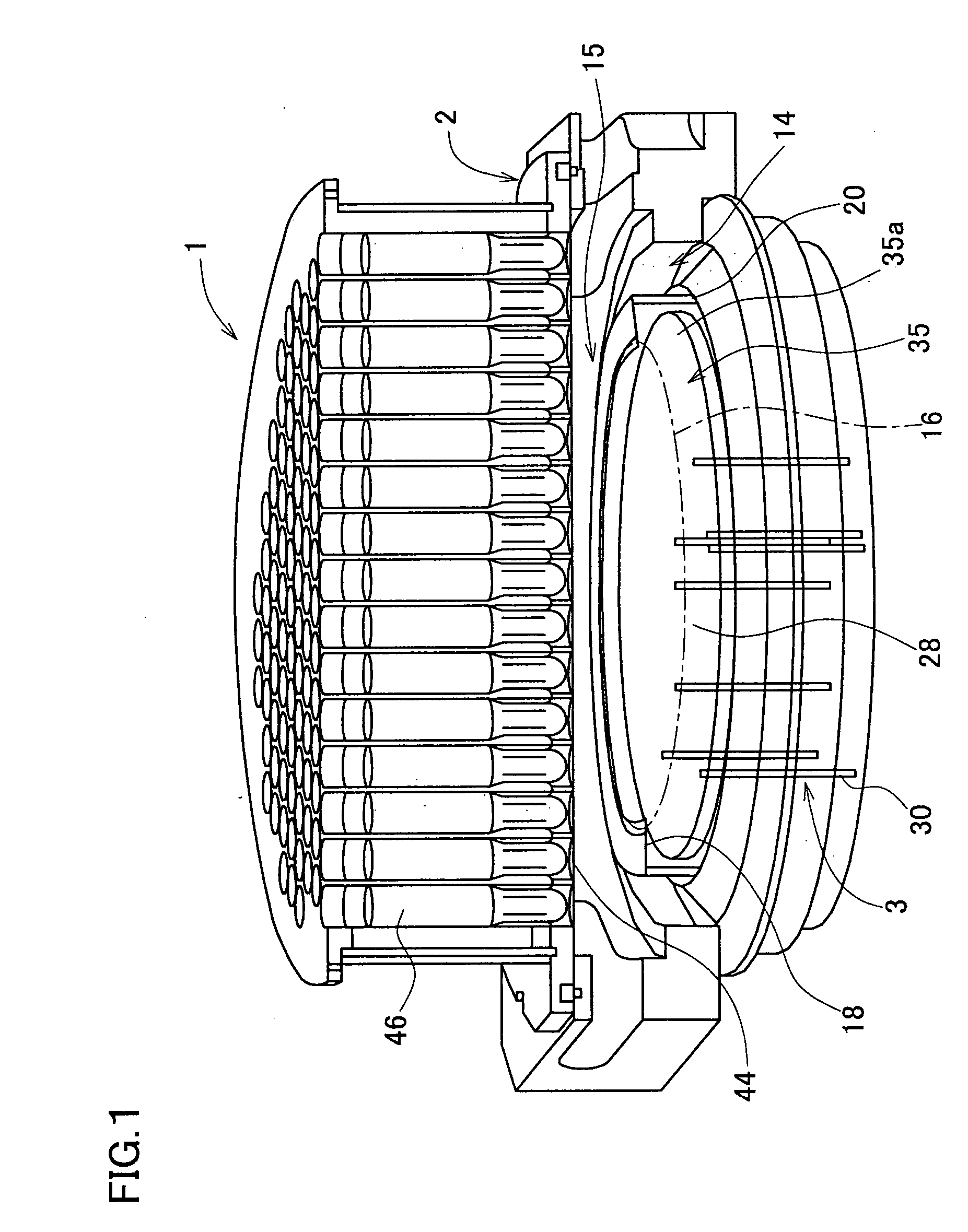
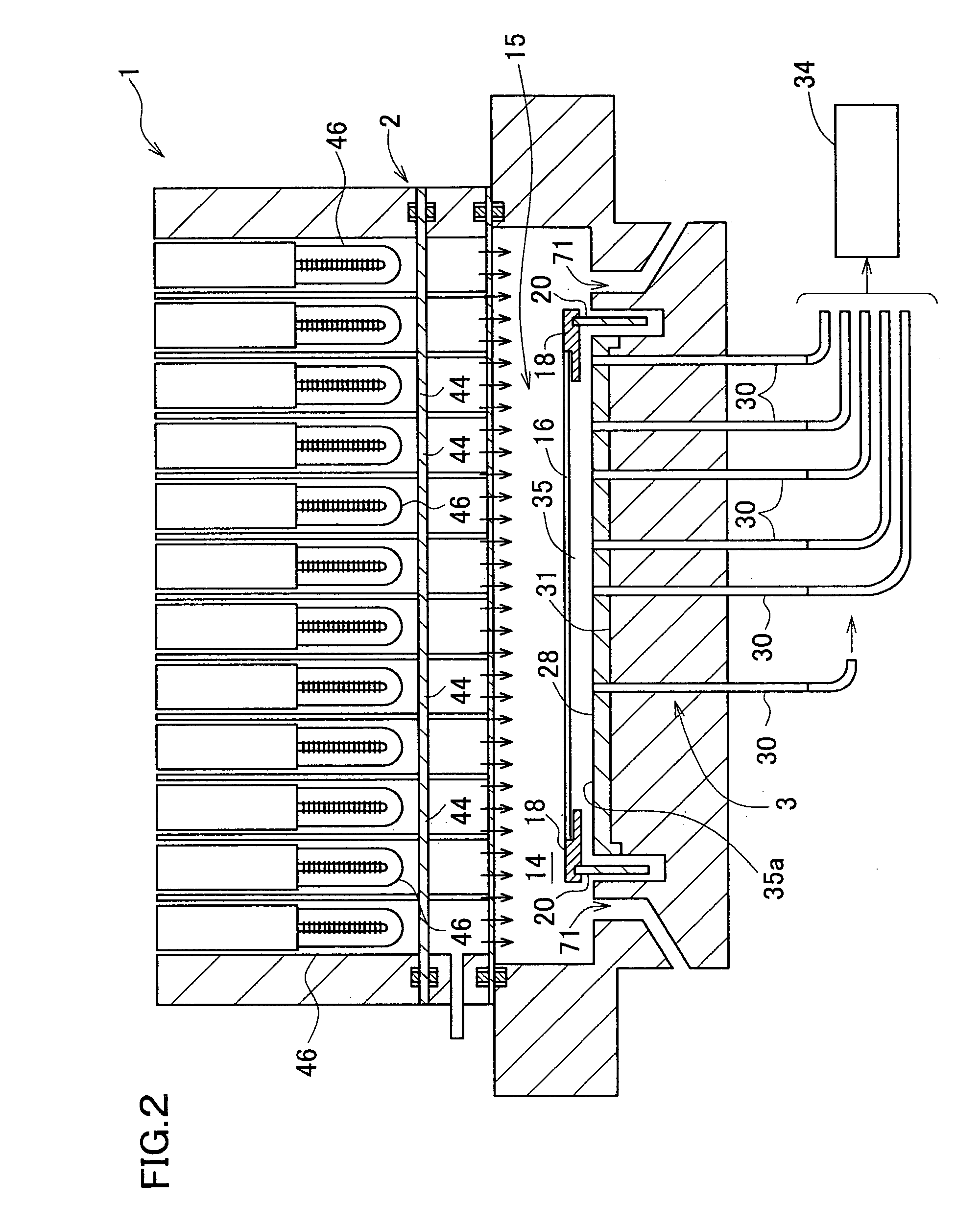
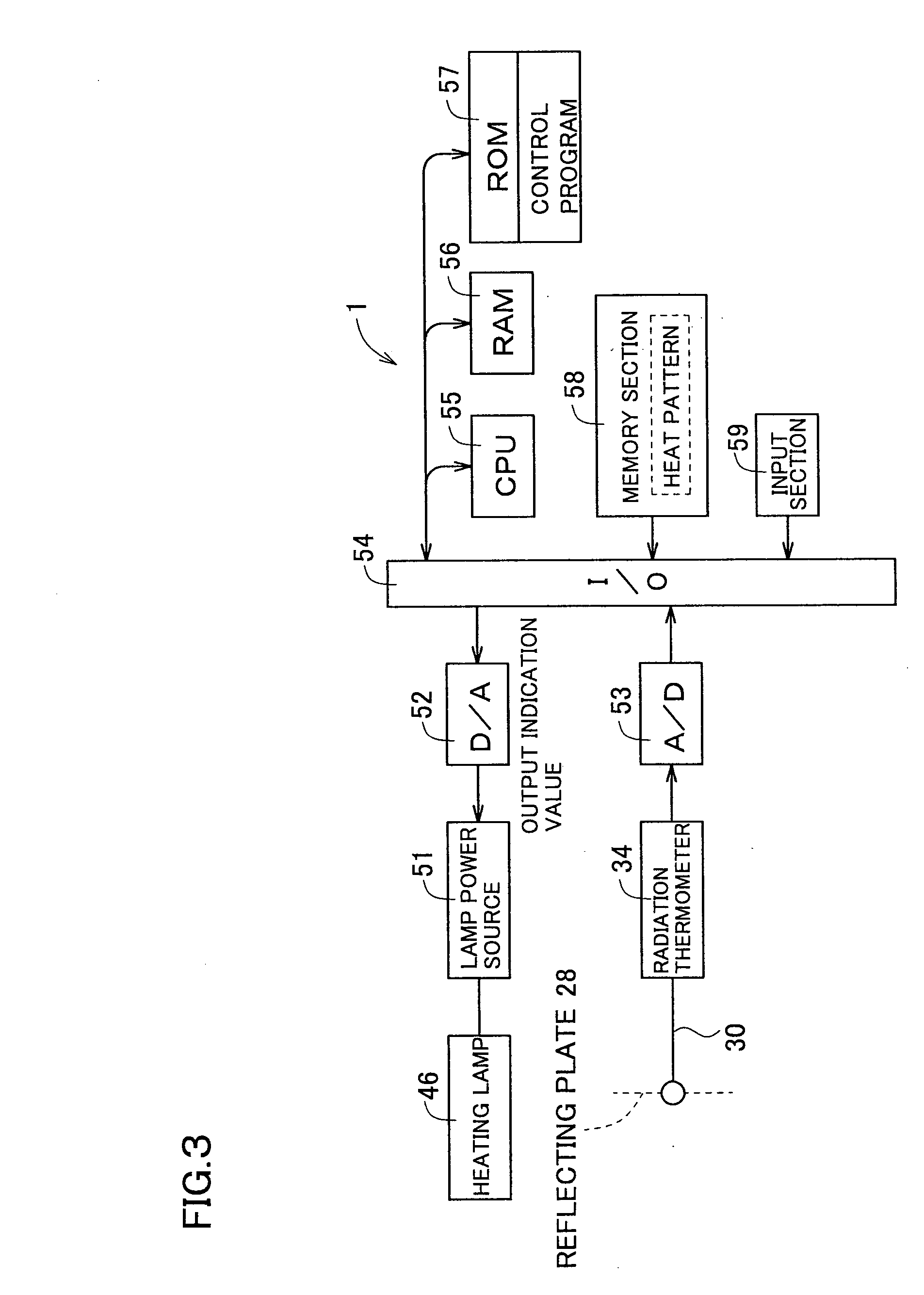
InactiveUS20050063451A1Necessary numberGood choiceRadiation pyrometryDoor/window protective devicesDevice materialRadiation thermometer
Oppositely of a temperature measuring surface of an object-to-be-measured 16, a reflecting member 28 is disposed while being spaced by a reflection gap 35 from the temperature measuring surface. The reflecting member 28 is composed of a heat ray reflecting material capable of reflecting heat ray in a specific wavelength band, in a portion including a reflection surface 35a. A heat ray extraction pathway section 30 is disposed through the reflecting member 28 so that one end thereof faces the temperature measuring surface. Heat ray extracted through the heat ray extraction pathway section from the reflection gap is detected by a temperature detection section 34. The heat ray reflecting material is configured in a form of a stack comprising a plurality of element reflecting layers composed of a material having transparent properties to the heat ray, in which every adjacent two element reflecting layers are composed of a combination of materials having refractive indices which differ from each other by 1.1 or more. This makes the measurement be hardly affected by radiation ratio of the object-to-be-measured when temperature of the object-to-be-measured is measured by a radiation thermometer, enables to measure its temperature more correctly irrespective of the surface state thereof, and can simplify configuration of a measurement system.
Owner:SHIN-ETSU HANDOTAI CO LTD
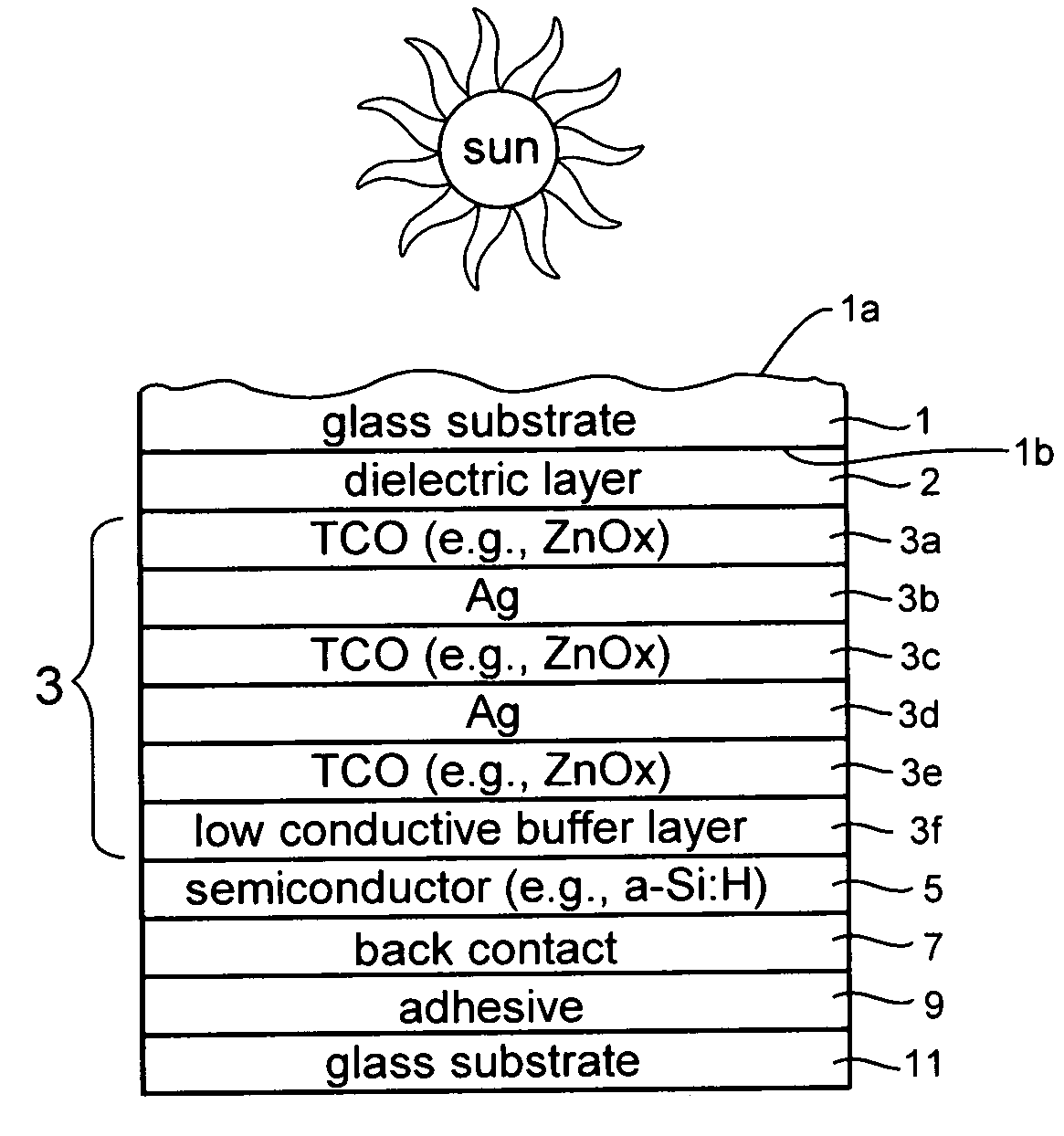
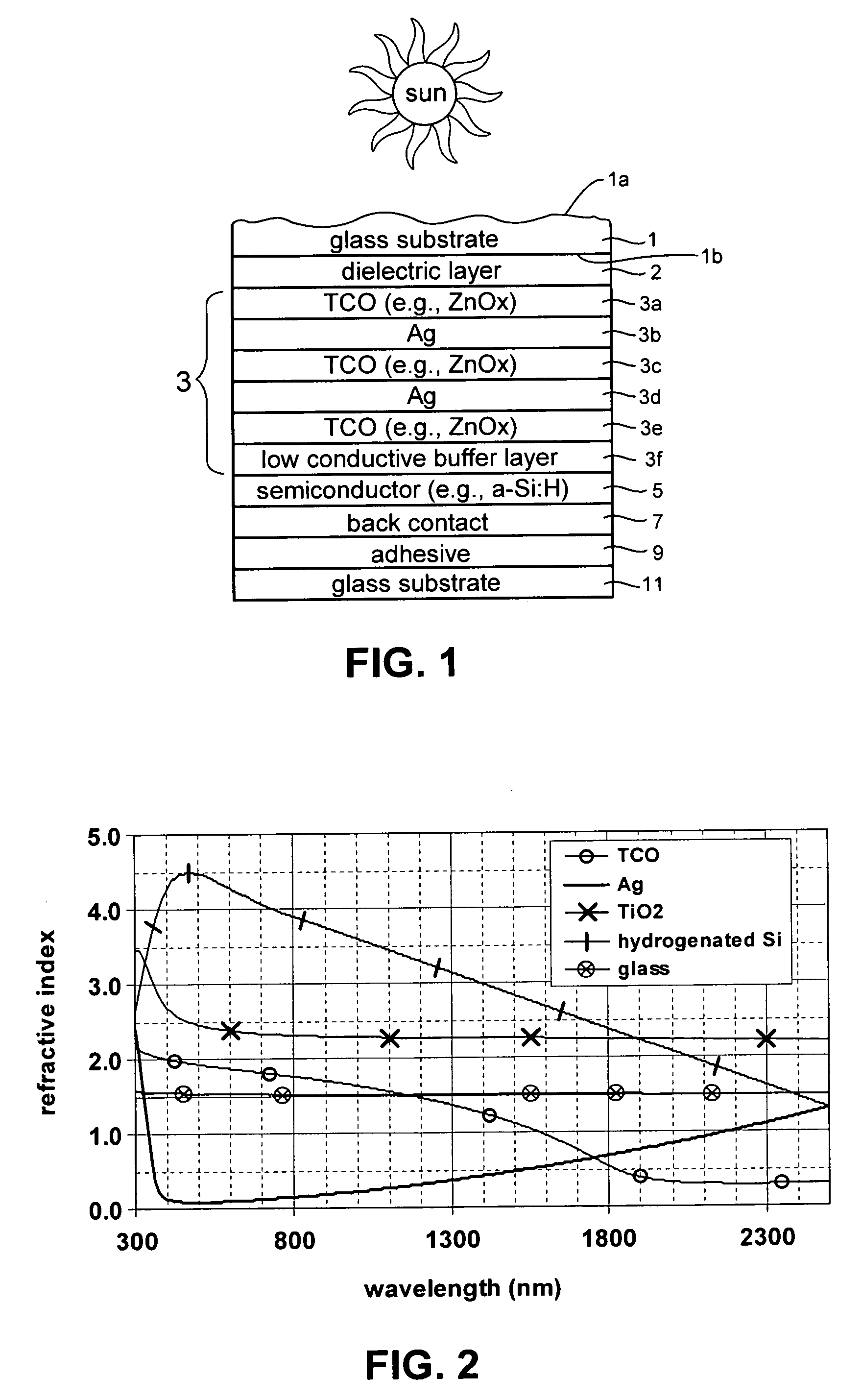
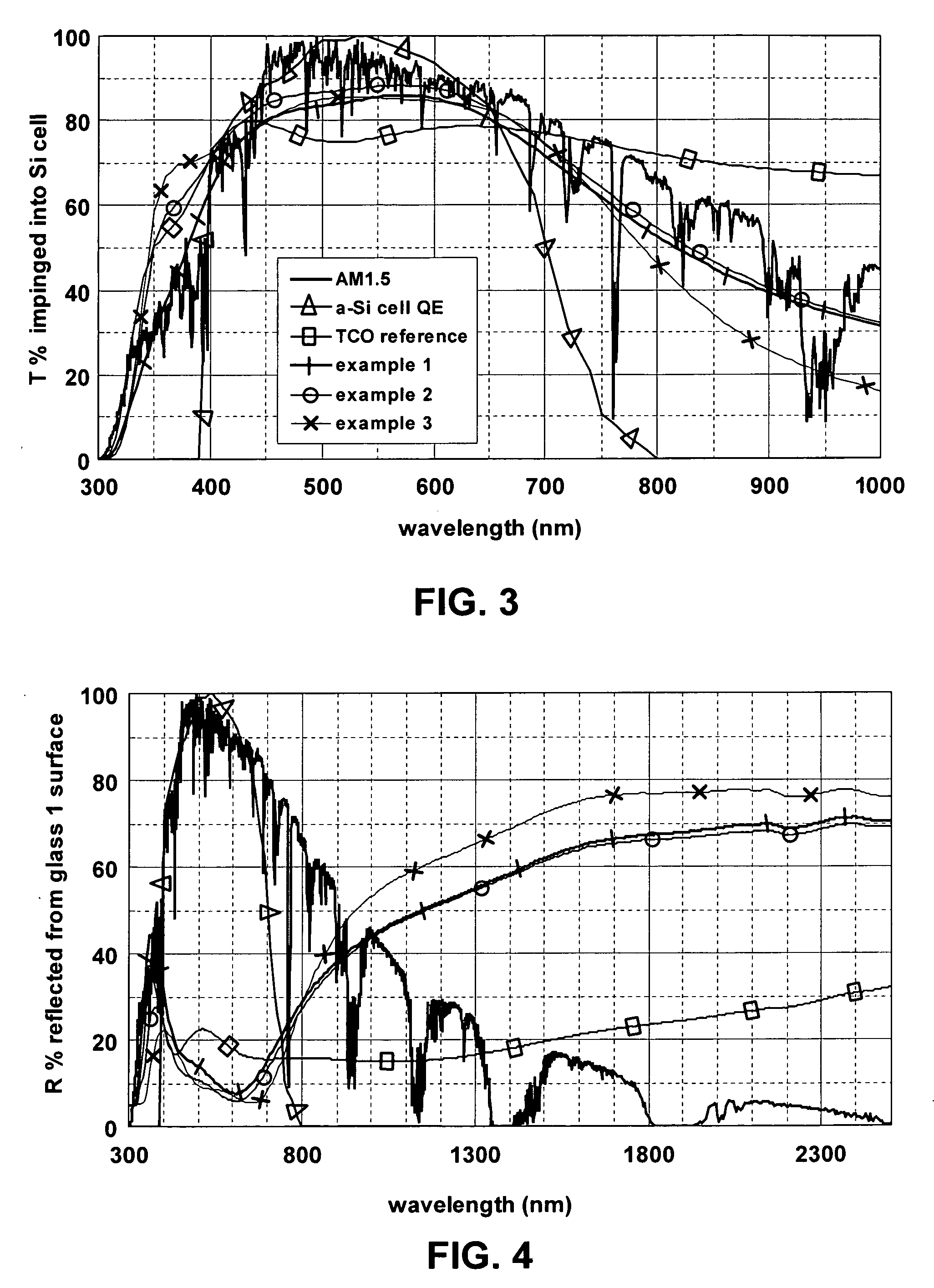
Front electrode for use in photovoltaic device and method of making same
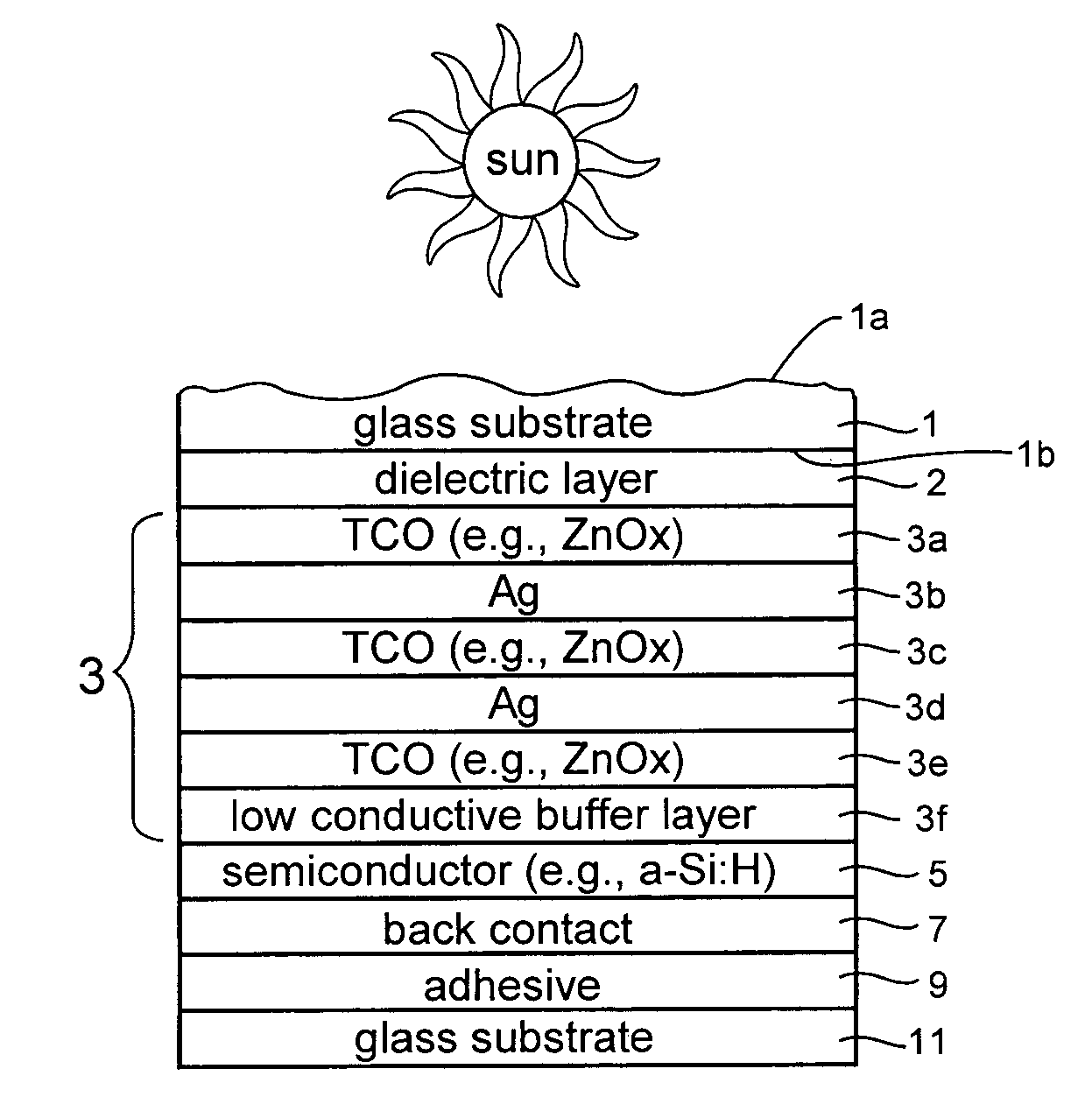
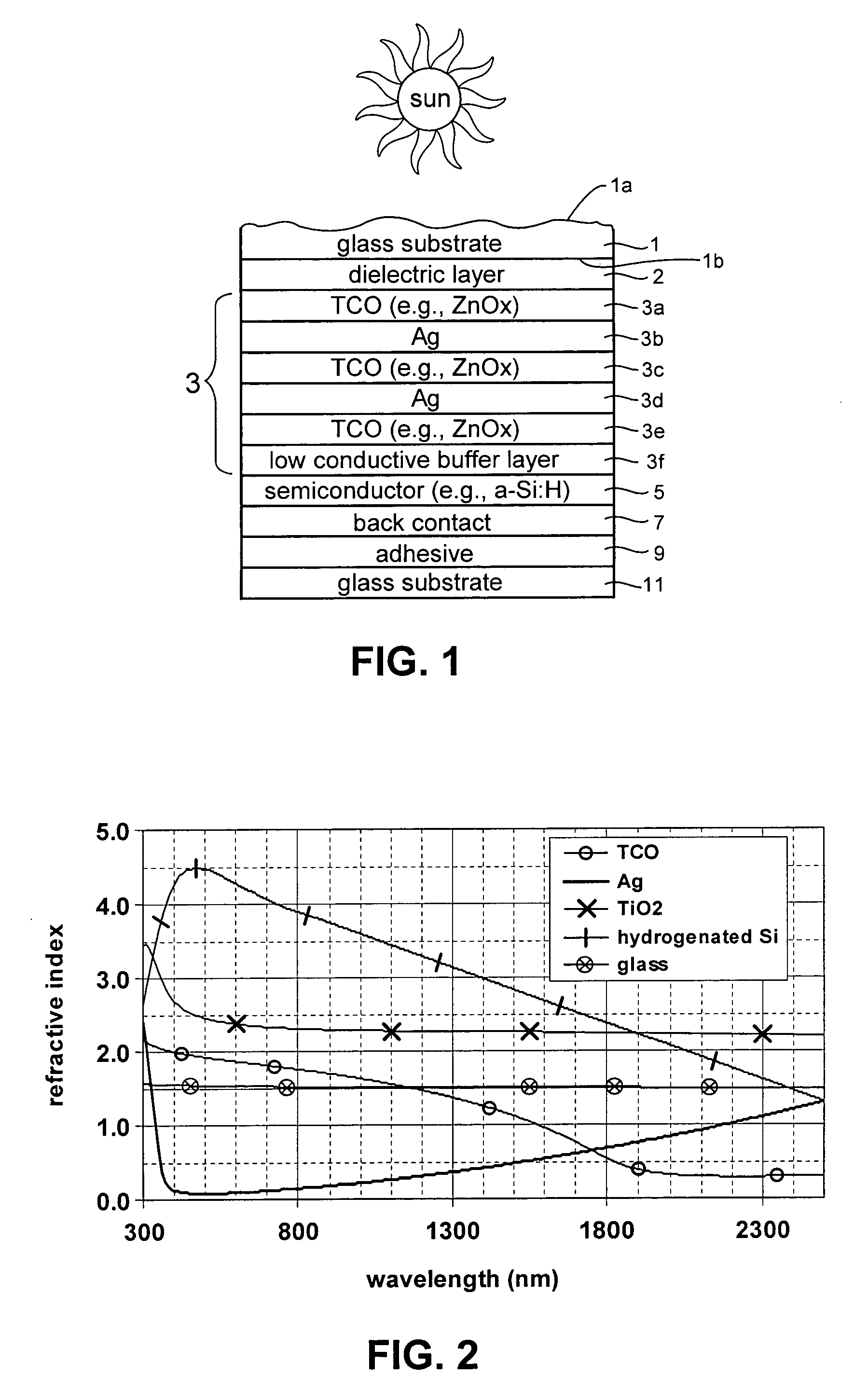
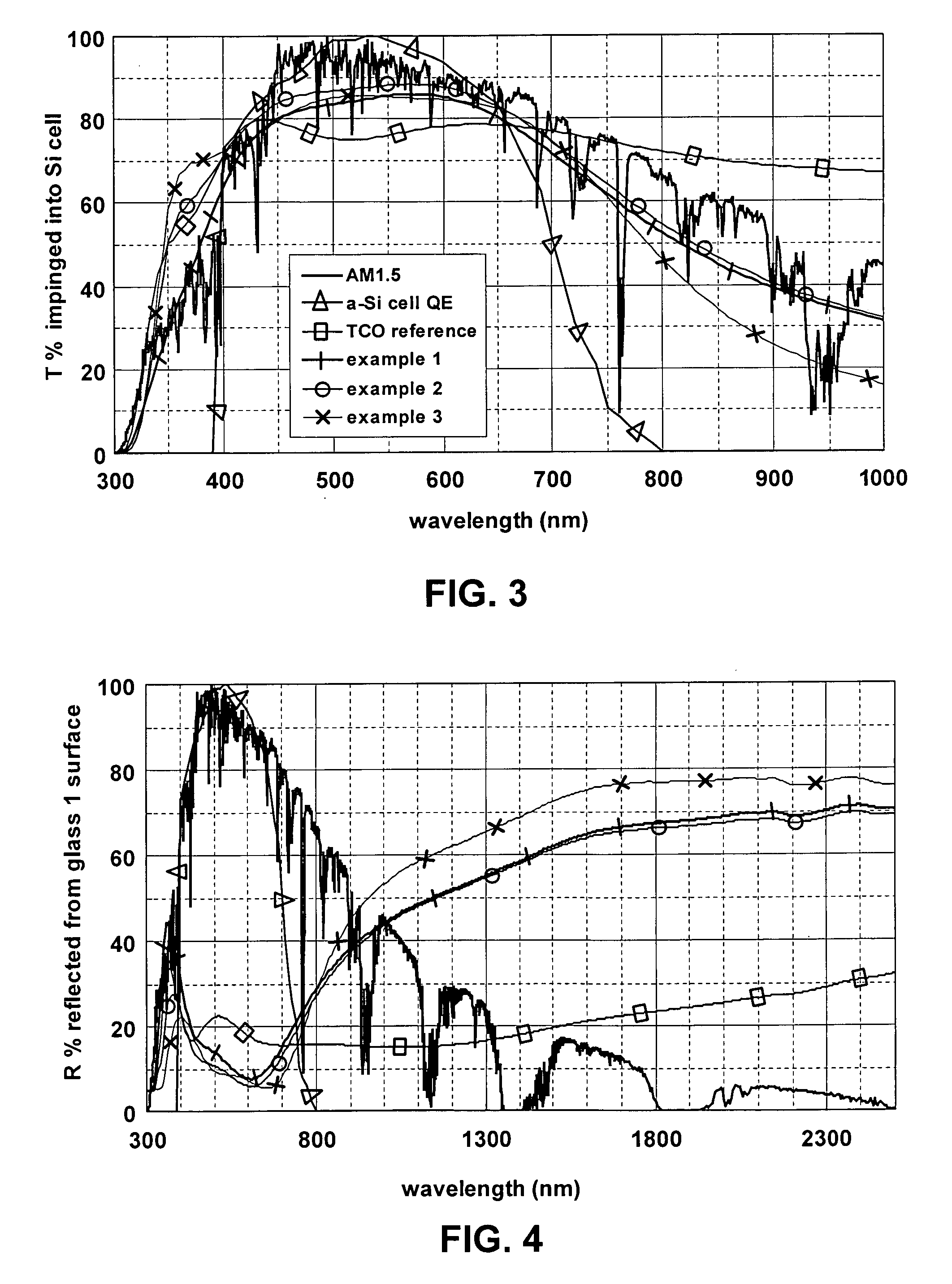
ActiveUS20080210303A1Reduce reflection lossPromote absorptionGlass/slag layered productsCoatingsLight reflectionZinc
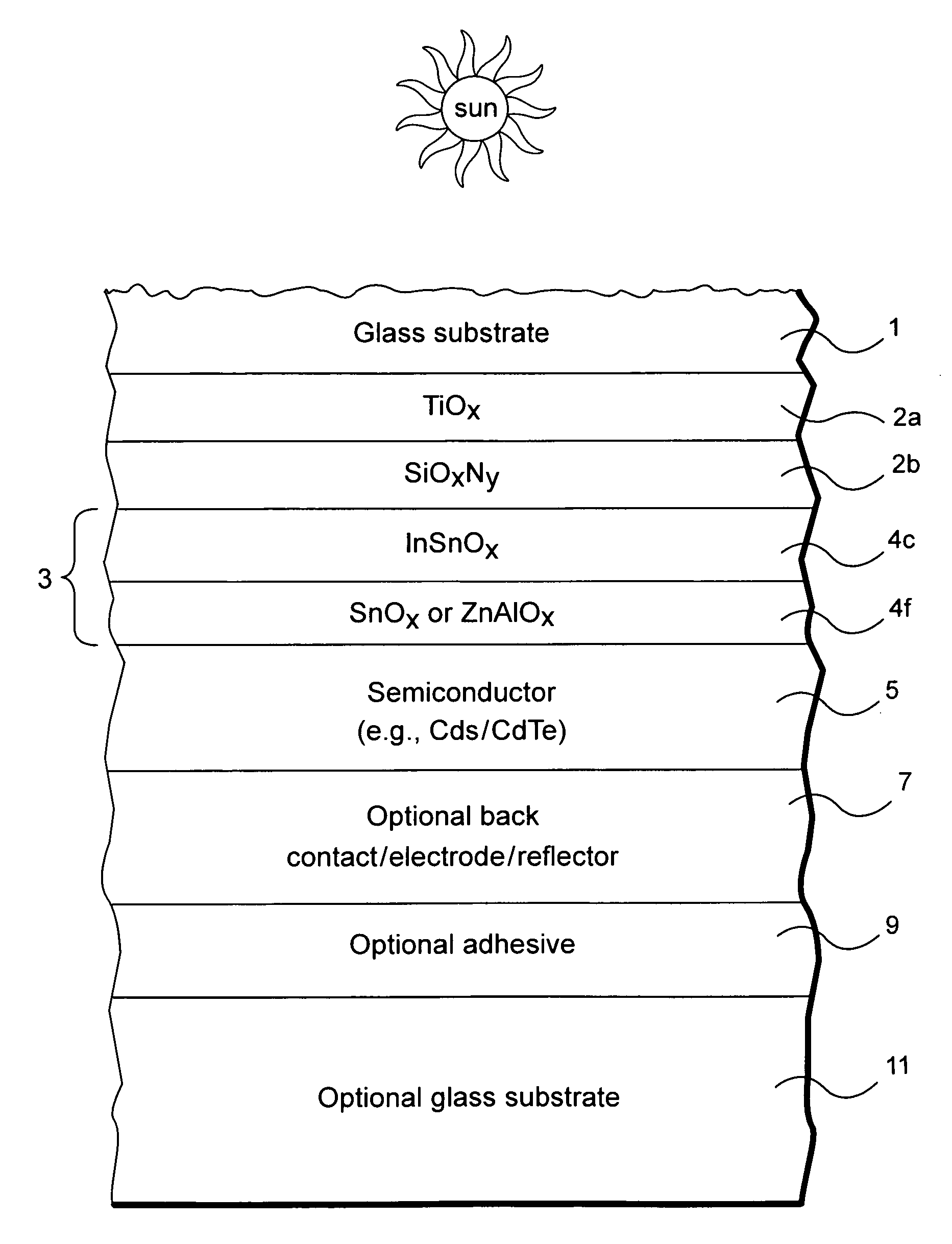
This invention relates to a front electrode / contact for use in an electronic device such as a photovoltaic device. In certain example embodiments, the front electrode of a photovoltaic device or the like includes a multilayer coating including at least one transparent conductive oxide (TCO) layer (e.g., of or including a material such as tin oxide, ITO, zinc oxide, or the like) and / or at least one conductive substantially metallic IR reflecting layer (e.g., based on silver, gold, or the like). In certain example instances, the multilayer front electrode coating may include one or more conductive metal(s) oxide layer(s) and one or more conductive substantially metallic IR reflecting layer(s) in order to provide for reduced visible light reflection, increased conductivity, cheaper manufacturability, and / or increased infrared (IR) reflection capability. At least one of the surfaces of the front glass substrate may be textured in certain example embodiments of this invention.
Owner:GUARDIAN GLASS LLC
Highly efficient gallium nitride based light emitting diodes via surface roughening
ActiveUS20070121690A1Solid-state devicesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingNitrogenLight reflection
A gallium nitride (GaN) based light emitting diode (LED), wherein light is extracted through a nitrogen face (N-face) (42) of the LED and a surface of the N-face (42) is roughened into one or more hexagonal shaped cones. The roughened surface reduces light reflections occurring repeatedly inside the LED, and thus extracts more light out of the LED. The surface of the N-face (42) is roughened by an anisotropic etching, which may comprise a dry etching or a photo-enhanced chemical (PEC) etching.
Owner:JAPAN SCI & TECH CORP
LED and LED lamp
InactiveUS20060198147A1Great disadvantageIncrease temperatureMechanical apparatusLight source combinationsLight reflectionEngineering
This invention relates to a light emitting diode (LED) and a LED lamp consisted of LEDs. The LED comprises at least one LED chip. The LED is mounted on a high heat conductivity base and is connected to an applied power supply through a circuit board. The LED chip also has a transparent medium layer on it. The base top surface acts as a light reflective surface, or a light reflective surface is provided around the base, the LED comprises a screw extended downwards from the base bottom or a screw hole in the base bottom to connect the LED to a heat sink mechanically. The LED is electrically connected to a driving circuit through its outgoing wires. The driving circuit is in turn electrically connected to an electrical connector through its housing. A LED lamp can be fabricated after the LED is enclosed in a transparent bulb housing. The LED has high efficiency, high power and long lifetime and can be used to fabricate LED traffic lamps, LED plane light sources, etc.
Owner:LOU MANE
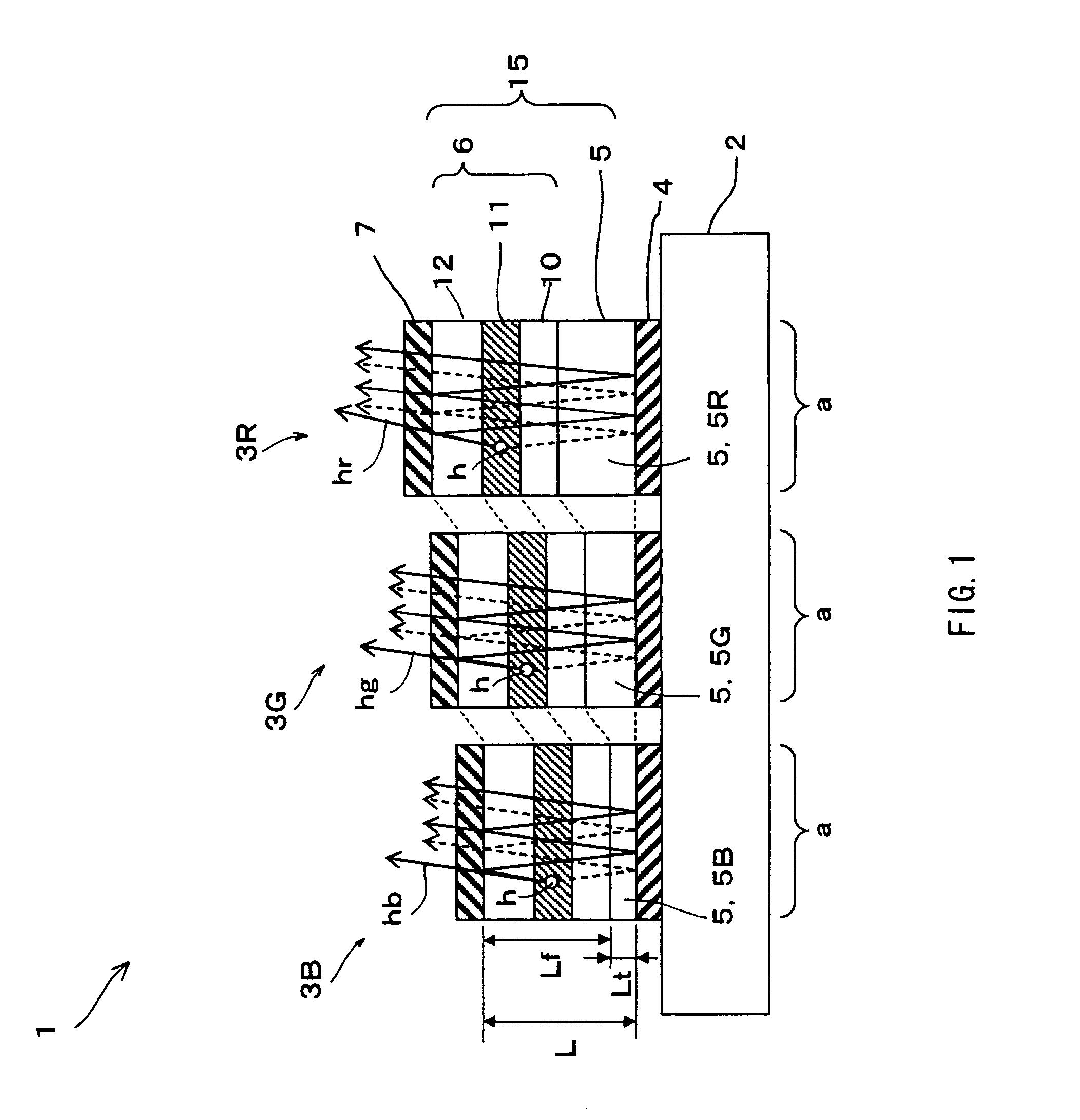
Light guide plate, light source device equipped therewith and display device
InactiveUS7073933B2Dispersion suppressionIncrease contrastPoint-like light sourceMeasurement apparatus componentsForming faceLight guide
A display device used for a display unit of portable electronic equipment, a light source device therefor and a light guide plate, suppressing dispersion in the brightness and featuring a high contrast and a good display quality. The constitution includes a light incidence surface on where light emitted from an LED falls, a light reflection surface formed facing the light incidence surface and reflects light from the light incidence surface, a light outgoing surface arranged between the light incidence surface and the light reflection surface, and has a circularly polarizing plate intimately adhered onto the surface thereof, and an opposing surface formed facing the light outgoing surface and in which there are alternately arranged first opposing surfaces for guiding the incident light to the light outgoing surface as well as to the light reflection surface, and second opposing surfaces for emitting the light reflected by the light reflection surface through the light outgoing surface.
Owner:SHARP KK
Head-up display with polarized light source and wide-angle p-polarization reflective polarizer
InactiveUS20040135742A1Improve reflectivityPolarising elementsCathode-ray tube indicatorsHead-up displayAcute angle
A head-up display includes a projection system and a window having a target area where a reflective polarizer is positioned to reflect light from the projection system to a viewing area. Light from the projection system is p-polarized and strikes exposed window surface(s) at an acute angle to reduce or eliminate multiple or "ghost" images. The acute angle is closely matched to a Brewster angle of the exposed window surface(s). The reflective polarizer includes a multilayer stack with refractive indices of individual layers chosen to reflect p-polarized light substantially more than s-polarized light over a wide angular range that includes the acute angle. The reflective polarizer also can reflect infrared light to reduce cabin heating from solar radiation.
Owner:3M INNOVATIVE PROPERTIES CO
Light guide plate, surface light source using the light guide plate, and liquid crystal display using the surface light source
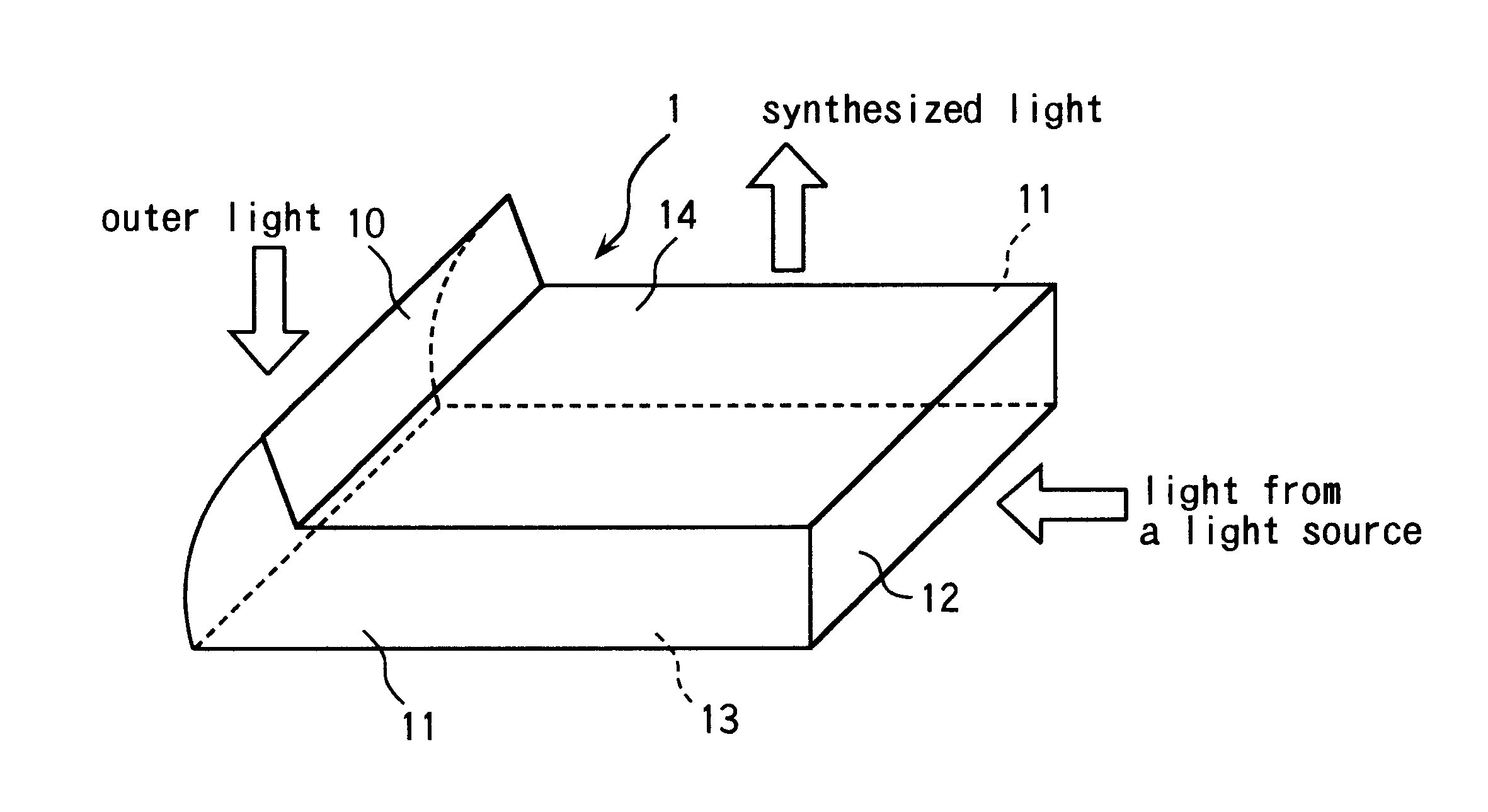
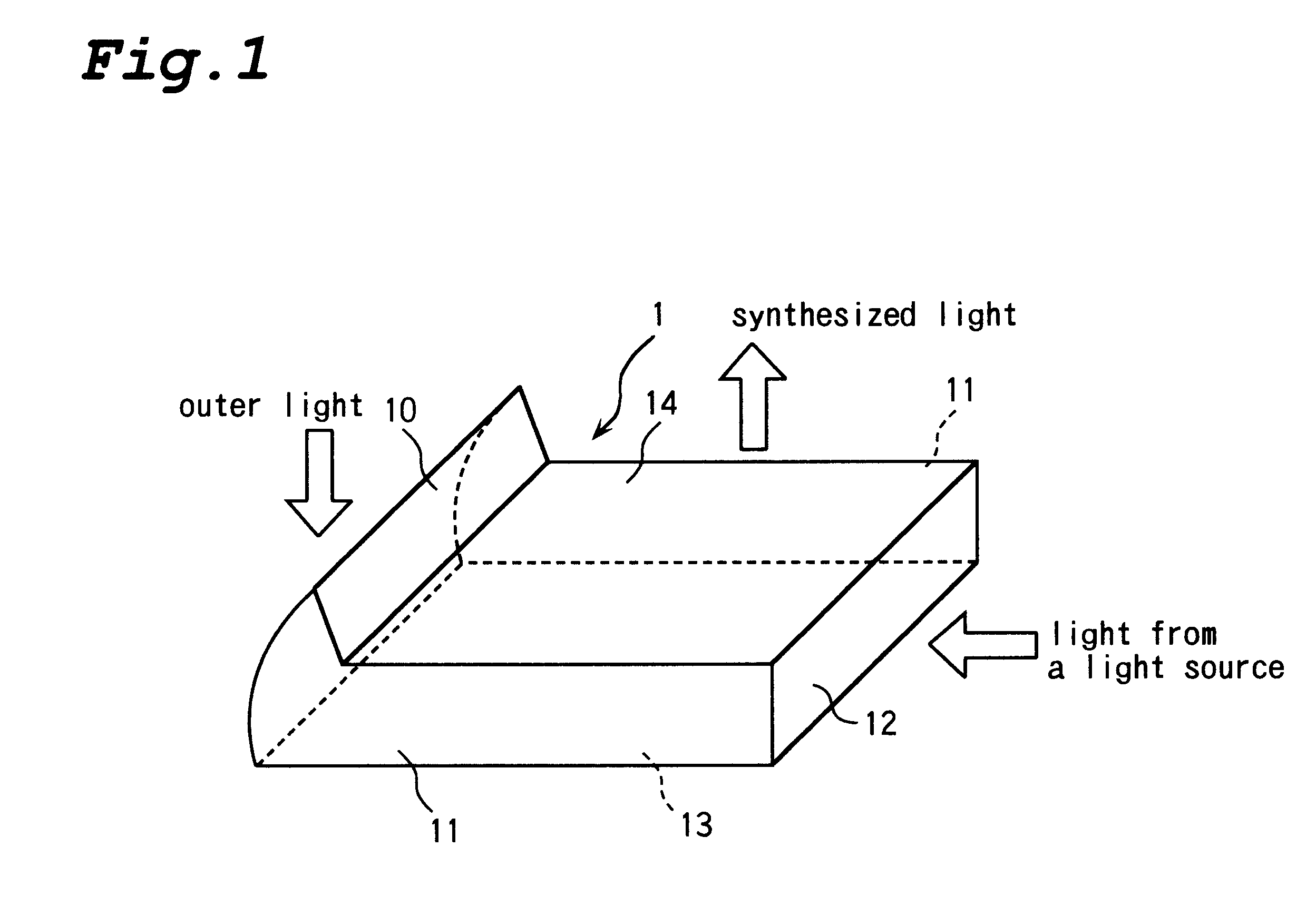
An outer light collecting portion 10 which sticks out of a light emission surface 14 to the light emission direction at the same time when a light guide plate is formed by resin forming with a mold. An area of a surface for collecting outer light is larger than that of a conventional light guide plate so as to collect outer light effectively. Light from a light source which is incidence through a light incident surface 12 reflects from a light reflection surface 13 and two side surface 11 of a light guide plate 1, and is emitted as synthesized light having the even directivity from a light emission surface 14.
Owner:HANGER SOLUTIONS LLC
Front electrode for use in photovoltaic device and method of making same
ActiveUS20090084438A1Reduce reflection lossPromote absorptionPhotovoltaic energy generationSemiconductor devicesIr reflectionLight reflection
This invention relates to a front electrode / contact for use in an electronic device such as a photovoltaic device. In certain example embodiments, the front electrode of a photovoltaic device or the like includes a multilayer coating including at least one transparent conductive oxide (TCO) layer (e.g., of or including a material such as tin oxide, ITO, zinc oxide, or the like) and / or at least one conductive substantially metallic IR reflecting layer (e.g., based on silver, gold, or the like). In certain example instances, the multilayer front electrode coating may include one or more conductive metal(s) oxide layer(s) and / or one or more conductive substantially metallic IR reflecting layer(s) in order to provide for reduced visible light reflection, increased conductivity, cheaper manufacturability, and / or increased infrared (IR) reflection capability.
Owner:GUARDIAN GLASS LLC
Optical device and apparatus comprising the optical device
InactiveUS7300183B2Improve efficiencyBeam/ray focussing/reflecting arrangementsSolid-state devicesLight reflectionLight emitter
On a front wall of a mold resin (13) sealing a light emitter (12), a direct emission region (18), through which the light emitted from the light emitter (12) directly passes to the outside, and a total reflection region (19), by which the light emitted from the light emitter (12) is totally reflected, are formed. The direct emission region (18) is formed into a shape of a convex lens. A light reflection portion (20) which is made of a concave mirror is provided on the rear face of the mold resin (13). When a part of the light emitted from the light emitter (12) passes through the direct emission region (18), it is affected by the lens to be emitted to the front direction. After another part of the light emitted from the light emitter (12) is totally reflected by the total reflection region (19), it is reflected by the light reflection portion (20) to be emitted to the front direction through the total reflection region (19).
Owner:ORMON CORP
Non-glare film, polarizing device and display device
InactiveUS6343865B1Small particle sizeImprove display qualityMirrorsDiffusing elementsRefractive indexDisplay device
A non-glare film 10 is composed of a non-glare layer 18 formed by coating a transparent base film 12 of TAC or the like with a coating material obtained by mixing a light transmissive diffusing material 14 of resin beads and the like in a light transmissive resin 16, and a low refractive index layer 20 composed of a silicon-containing vinylidene fluoride copolymer, said low refractive index layer 20 being laminated onto the surface of the non-glare layer, in which the haze value on the surface of the non-glare layer 18 is 7 to 30 and the haze value inside the non-glare layer 18 is 1 to 15, and when the non-glare film is attached onto the surface of a display panel, it suppresses degradation in contrast and furthermore prevents face-glare, reflecting-in and whitening.
Owner:DAI NIPPON PRINTING CO LTD
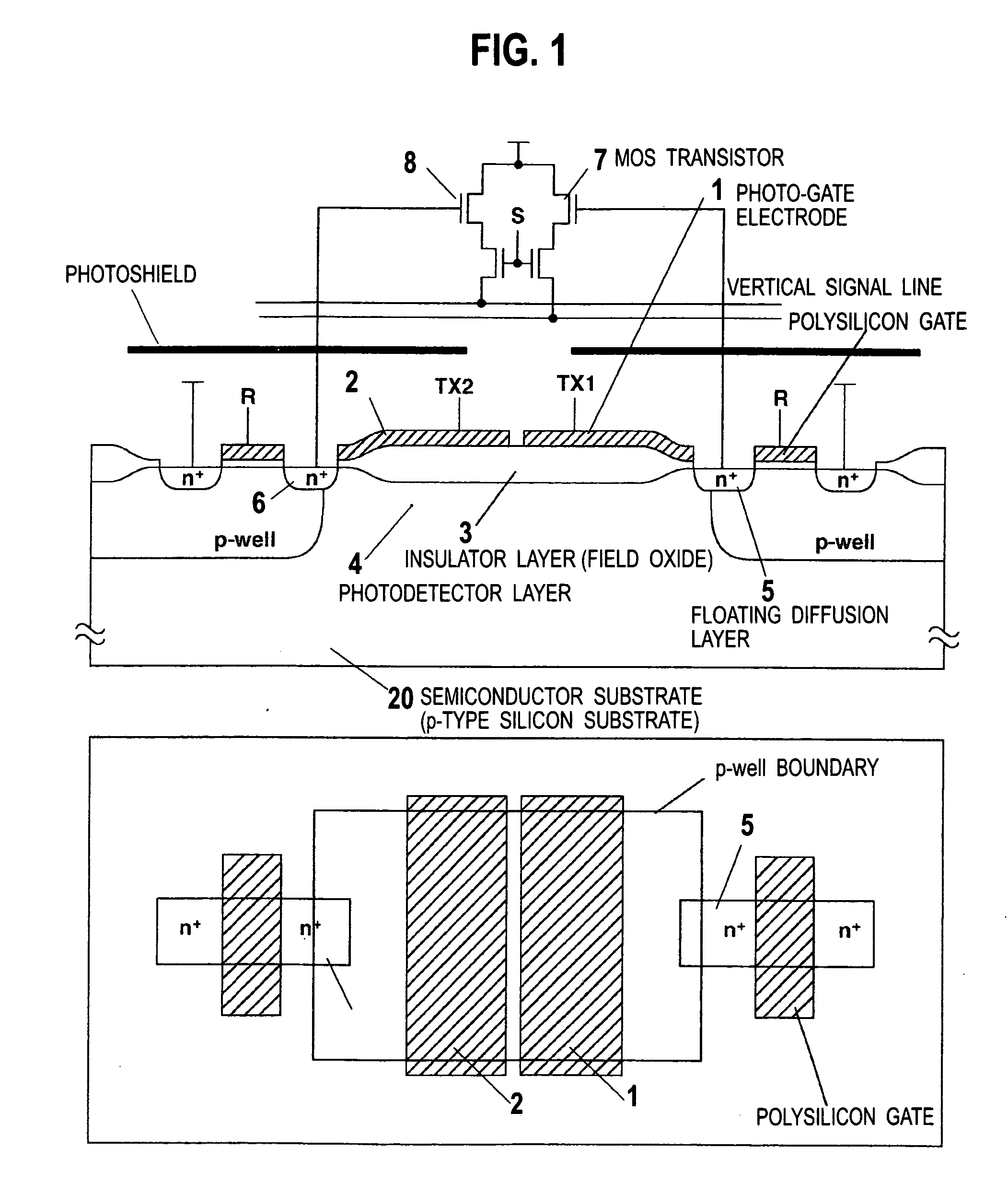
Time-of-light flight type distance sensor
InactiveUS20070158770A1Maximum performanceLow costTelevision system detailsOptical rangefindersManufacturing technologyPhotodetector
A lower cost range-finding image sensor based upon measurement of reflection time of light with reduced fabrication processes compared to standard CMOS manufacturing procedures. An oxide film is formed on a silicon substrate, and two photo-gate electrodes for charge-transfer are provided on the oxide film. Floating diffusion layers for taking charges out from a photodetector layer are provided at the ends of the oxide film, and on the outside thereof are provided a gate electrode for resetting and a diffusion layer for providing a reset voltage.
Owner:NAT UNIV CORP SHIZUOKA UNIV
Projection optical system and projection exposure apparatus
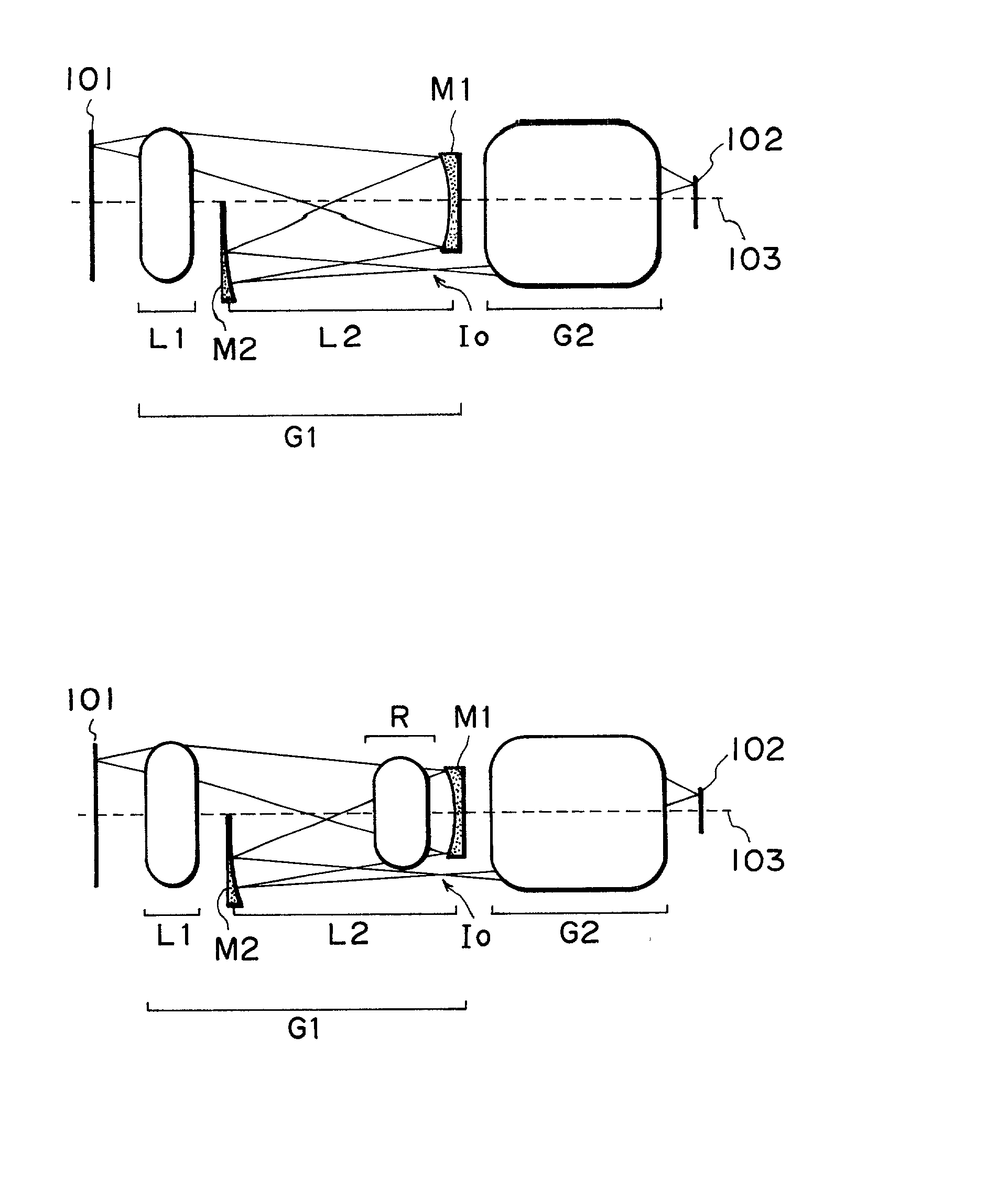
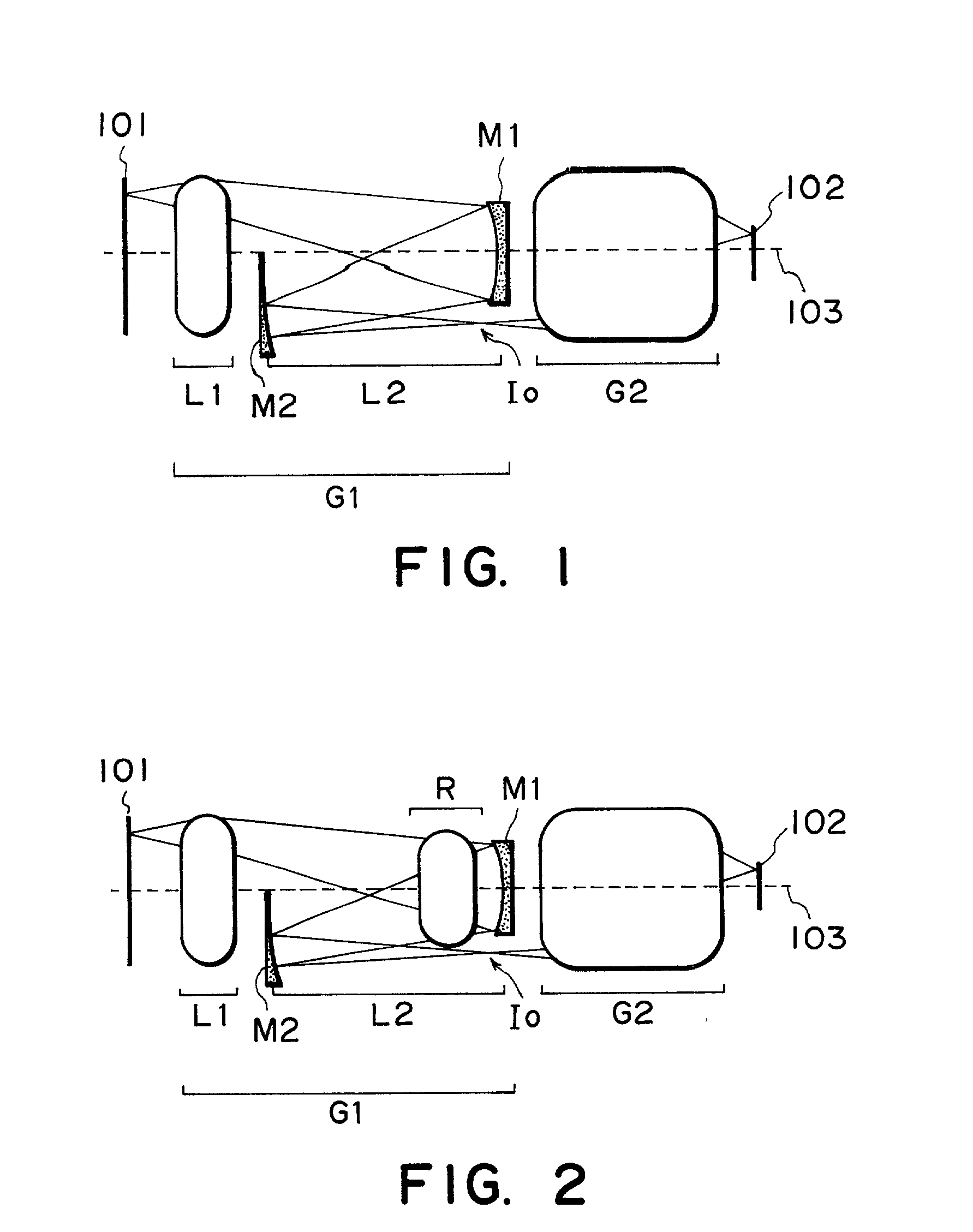
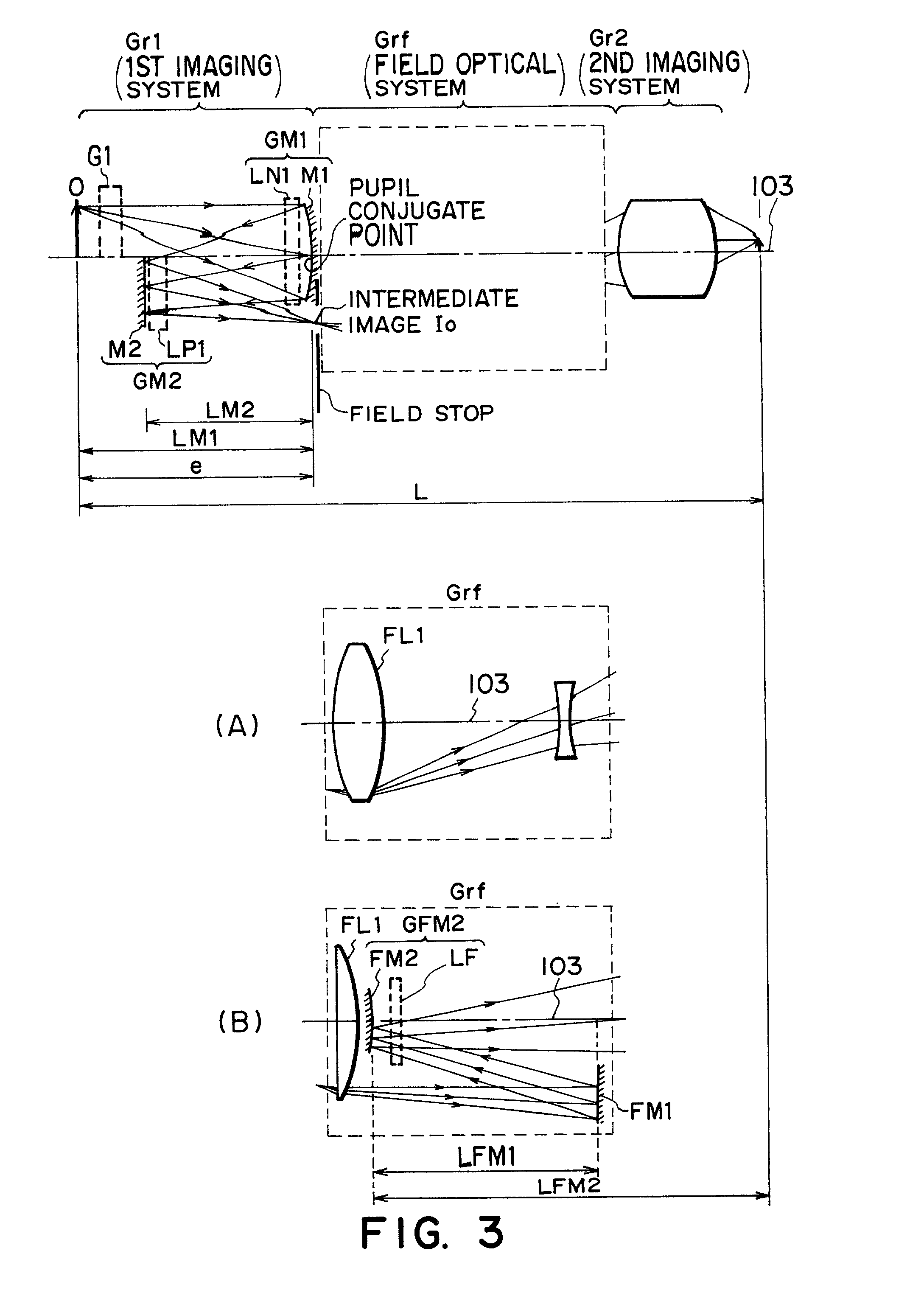
InactiveUS20020024741A1Semiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingPhotomechanical exposure apparatusProjection opticsOptical axis
Disclosed is a projection optical system for projecting an image of an object onto an image plane, which includes a first imaging optical system for forming an image of the object, a second imaging optical system for re-imaging the image upon the image plane, wherein the first and second imaging optical systems are disposed in an order from the object side and are disposed along a common straight optical axis, wherein the first imaging optical system includes a first mirror for reflecting and collecting abaxial light from the object, wherein one of the first and second imaging optical systems includes a second mirror for reflecting light from the first mirror to the image plane side, and wherein, with the second mirror, the abaxial light is caused to pass an outside of an effective diameter of the first mirror.
Owner:CANON KK
Optical tracking apparatus using six degrees of freedom
InactiveUS8077914B1Improve robustnessAccurate trackingAcquiring/recognising eyesEye diagnosticsAngular degreesLight-emitting diode
This invention discloses an optical object tracking method and system with to up to six degrees of freedom: three translational and three angular coordinates. In the preferred embodiment, the system includes two near-infra-red light sources (e.g., light emitting diode), two cameras, and a digital signal processor. The system performs to tasks: object locking and tracking. For object locking and tracking, a single camera and two off-axis light sources are engaged. For more precise object tracking, two spatially-separate cameras and a single diode are used. In another embodiment, a third camera may be used to separate the locking and tracking tasks. The light sources may have different light wavelengths and may operate in a sequential mode. The cameras may be sensitive over different spectral ranges and may also differ in terms of field-of-view and resolution. The invention describes a method based on capturing images of light reflections at the camera focal plane and analyzing them, through mathematical mapping, for known locations of light sources and cameras. Invention can be adopted for the tracking of an eyeball. The related method determines an object location and orientation or a gaze vector and a point-of-regard.
Owner:KAPLAN ARKADY
Light guide plate with alicyclic resin
InactiveUS6633722B1Superior in optical characteristicIncrease brightnessMechanical apparatusLight guides for lighting systemsLight guideLight reflection
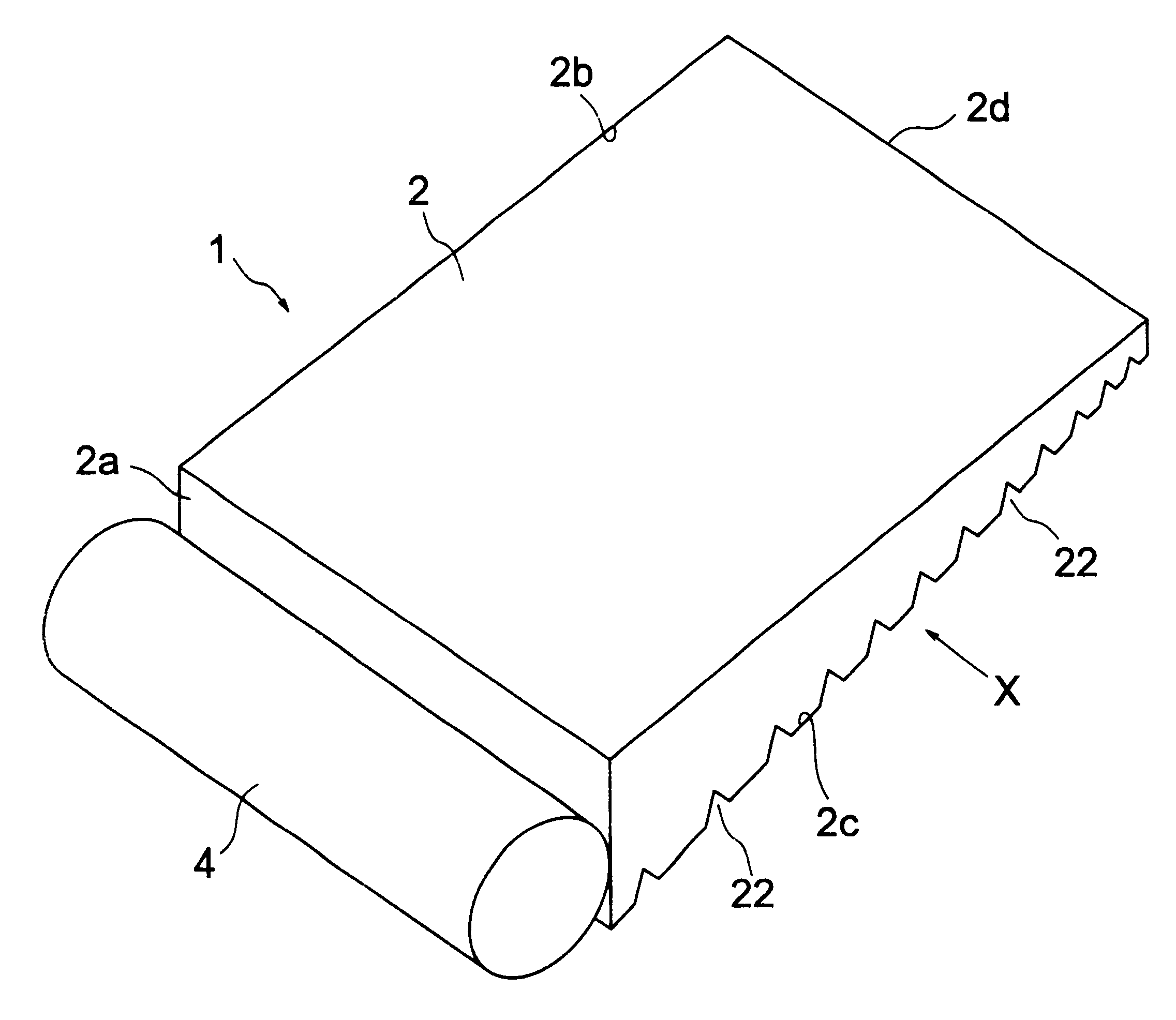
A light guide plate which is made of a polymeric resin having an alicyclic structure and has recesses for reflection formed on a light reflecting surface, the recesses being so arranged that the density of the recesses increases with the distance from a light source. Each recess is preferably a V-shaped groove each having an angle of 70° to 150° and a depth of 1 mum to 1000 mum or a groove which is long and approximately perpendicular to the direction in which light is incident at any position on the light reflection surface.< / PTEXT>
Owner:ZEON CORP
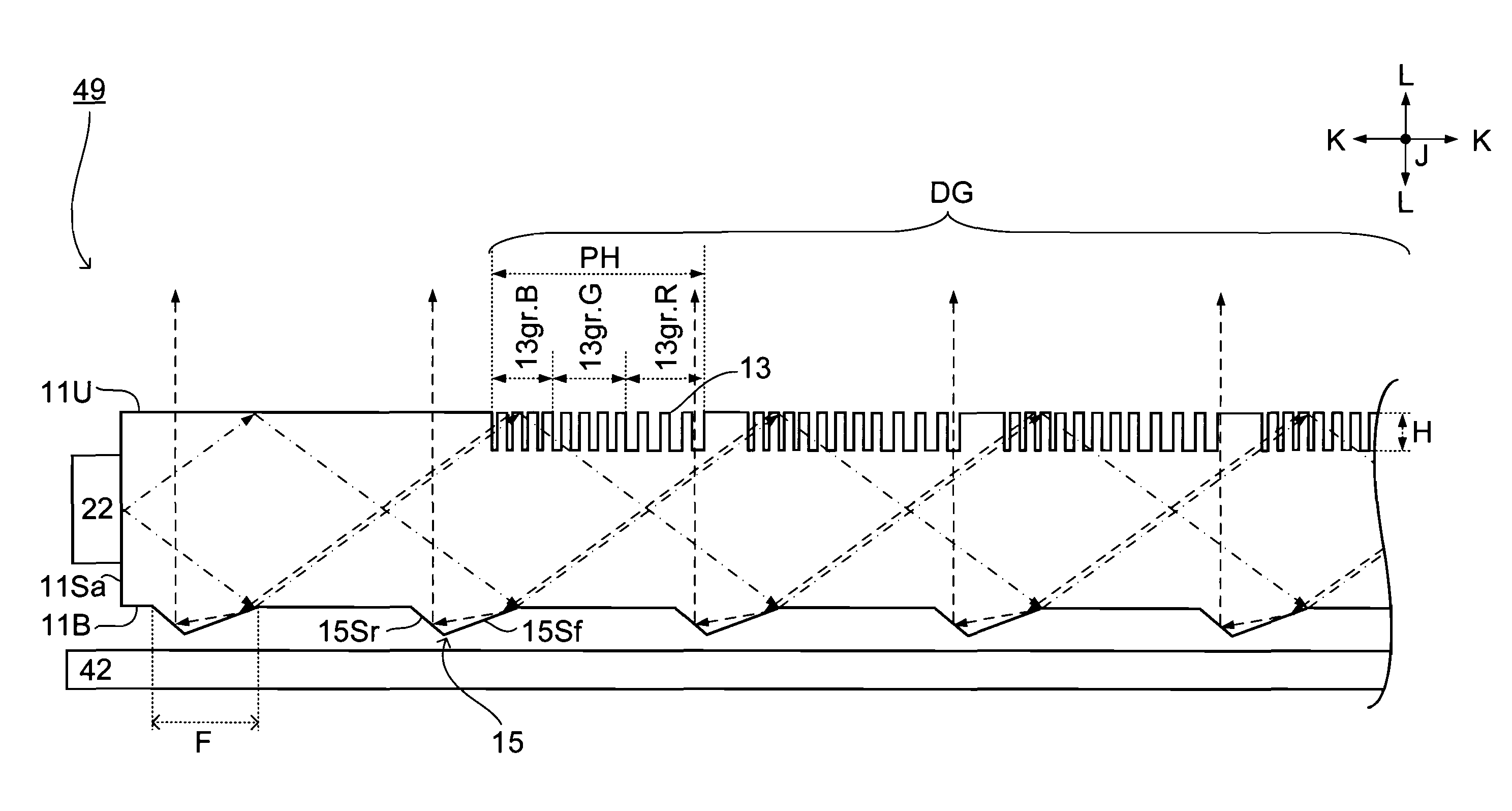
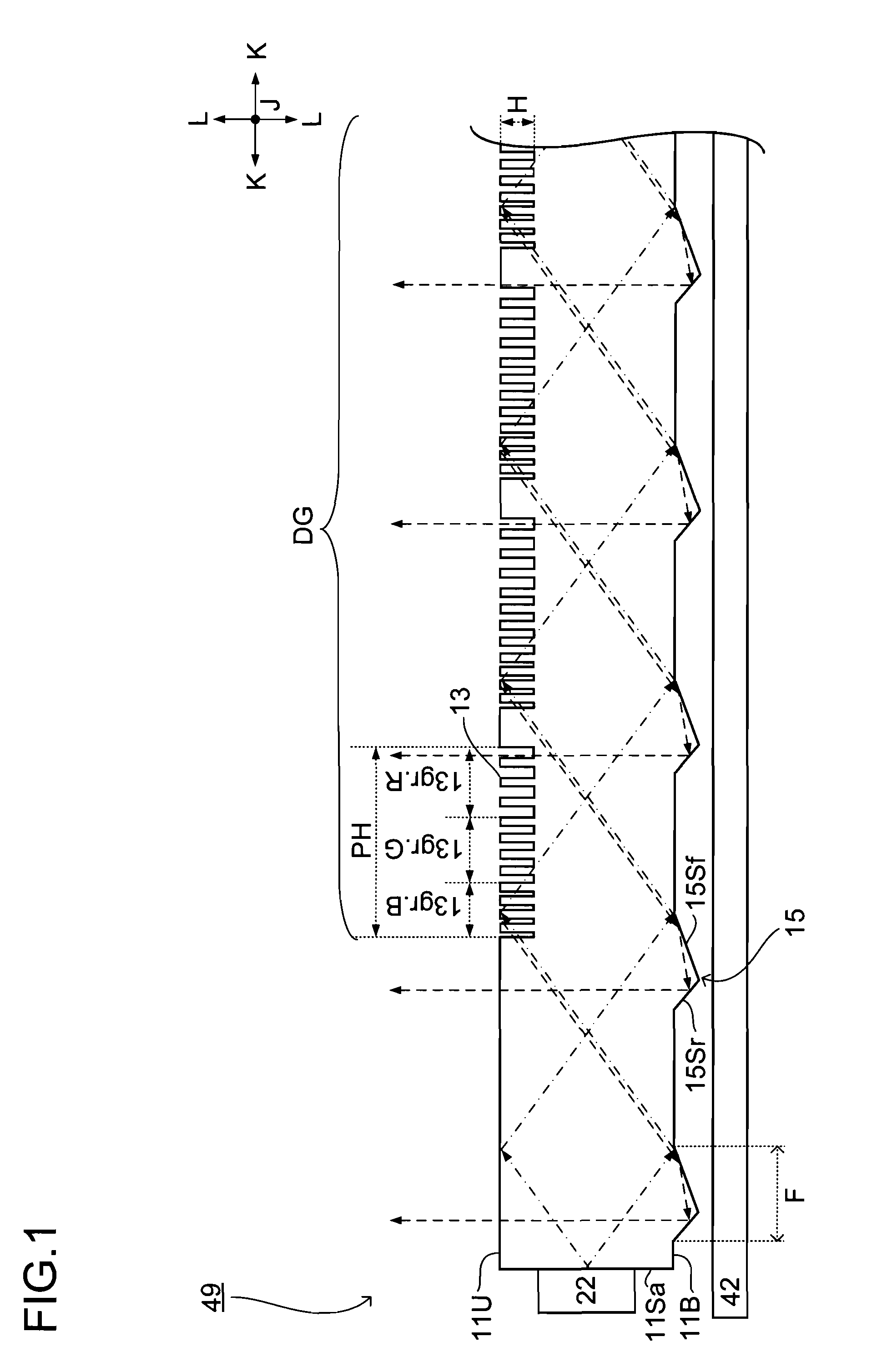
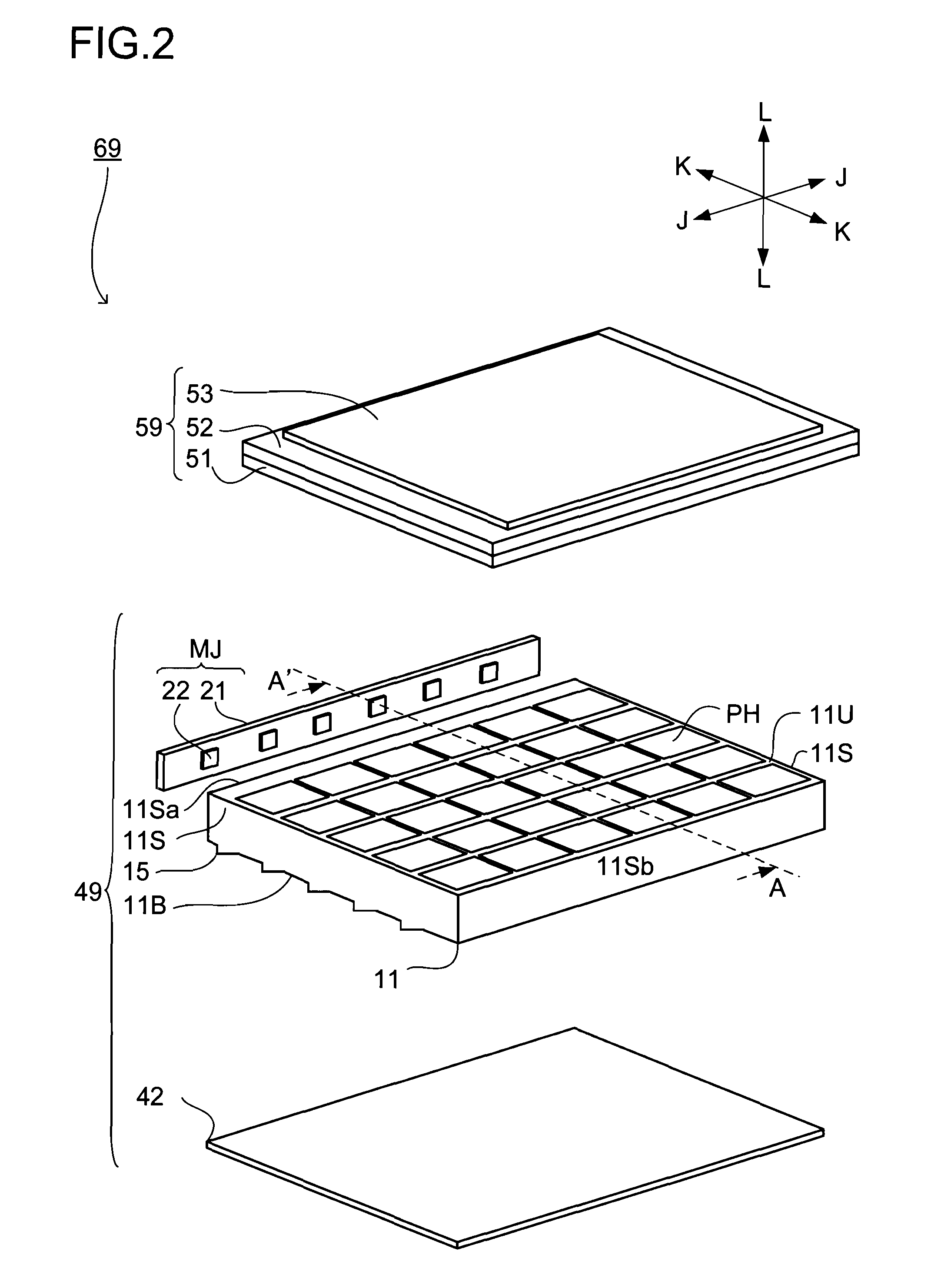
Backlight unit and liquid crystal display device
Three grating piece groups (13gr.Gr.B, 13G, 13R) on the top surface (11U) of a light guide plate correspond to light of different wavelength regions, and respectively diffract and reflect light of the corresponding wavelength region, which is incident thereon at an incident angle within a specific range, back to the incoming direction of the light. The bottom surface (11B) of the light guide plate (11) is provided with a prism (15) for reflecting the backwardly diffracted and reflected light toward the top surface (11U).
Owner:SHARP KK
Light emitting assembly with heat dissipating support
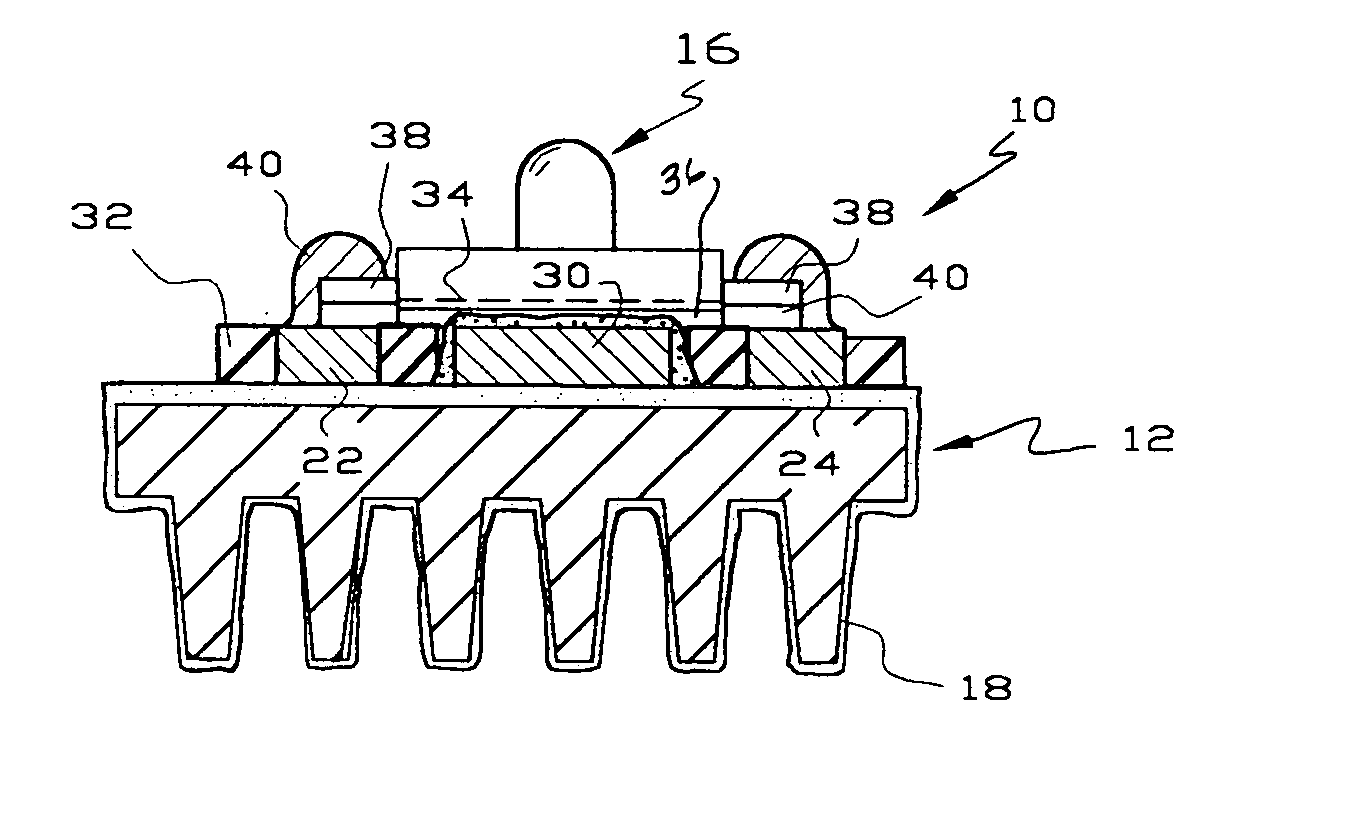
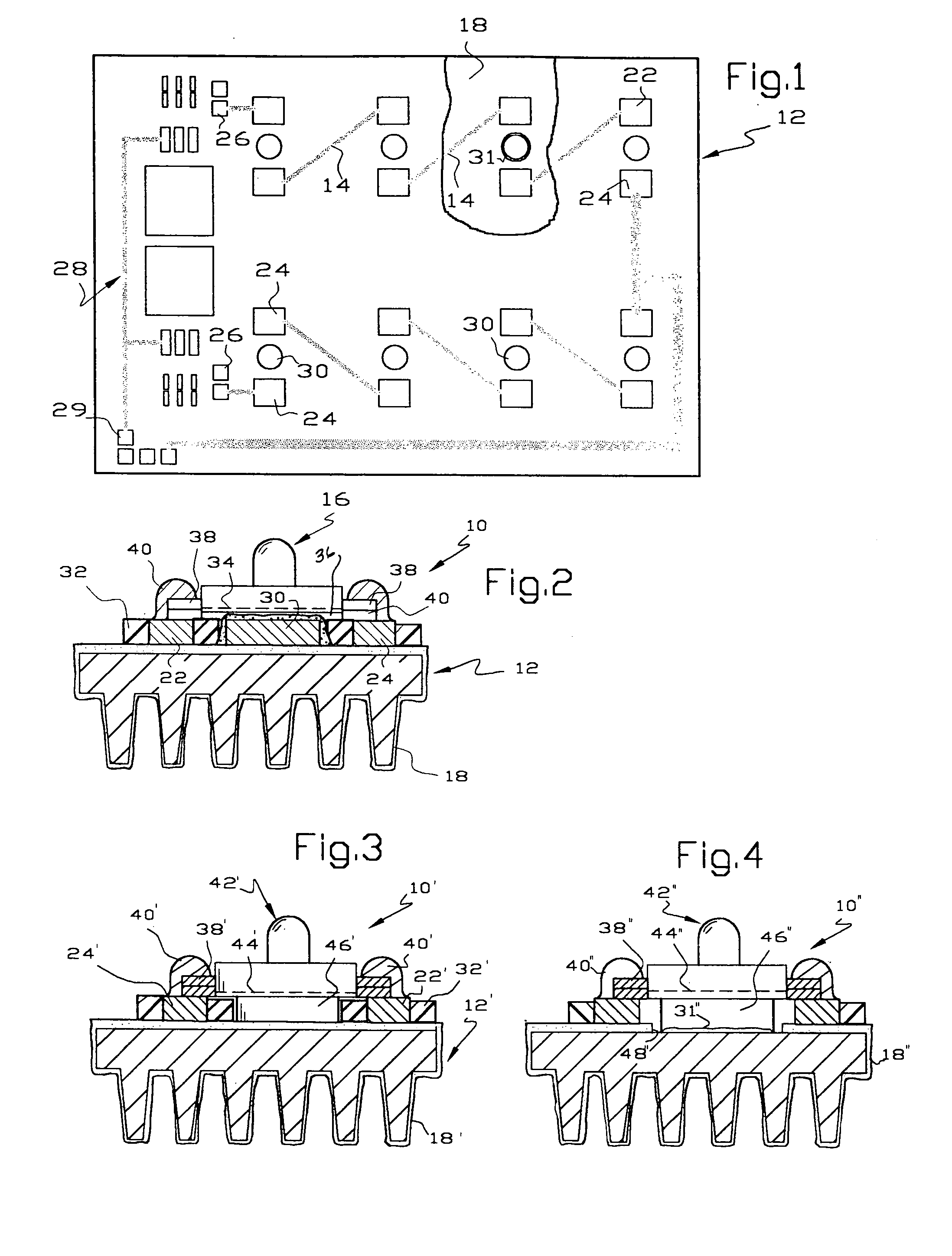
InactiveUS20050122018A1Low costImprove cooling effectPoint-like light sourceDischarge tube main electrodesLight reflectionEngineering
A light emitting assembly includes a metal substrate for dissipating heat from the assembly. The metal substrate includes an electrically insulating layer or coating on at least one side. Circuit traces are applied to the electrically insulating layer using either thick or thin film techniques. At least the ends of the circuit traces include a metallic section to which leads of light emitting elements are soldered or wire-bonded. A metallic section is provided adjacent the light emitting element to transfer heat to the underlying substrate and / or to reflect light from the element away from the substrate. A clear finish retards tarnishing of the reflecting metallic section.
Owner:INT RESISTIVE OF TEXAS
Front electrode for use in photovoltaic device and method of making same
InactiveUS20080105298A1Reduced visible light reflectionImprove conductivityPhotovoltaic energy generationSemiconductor devicesLight reflectionZinc
This invention relates to a front electrode / contact for use in an electronic device such as a photovoltaic device. In certain example embodiments, the front electrode of a photovoltaic device or the like includes a multilayer coating including at least one transparent conductive oxide (TCO) layer (e.g., of or including a material such as tin oxide, zinc oxide, or the like) and at least one conductive substantially metallic IR reflecting layer (e.g., based on silver, gold, or the like). In certain example instances, the multilayer front electrode coating may include a plurality of TCO layers and / or a plurality of conductive substantially metallic IR reflecting layers arranged in an alternating manner in order to provide for reduced visible light reflection, increased conductivity, and / or increased infrared (IR) reflection capability.
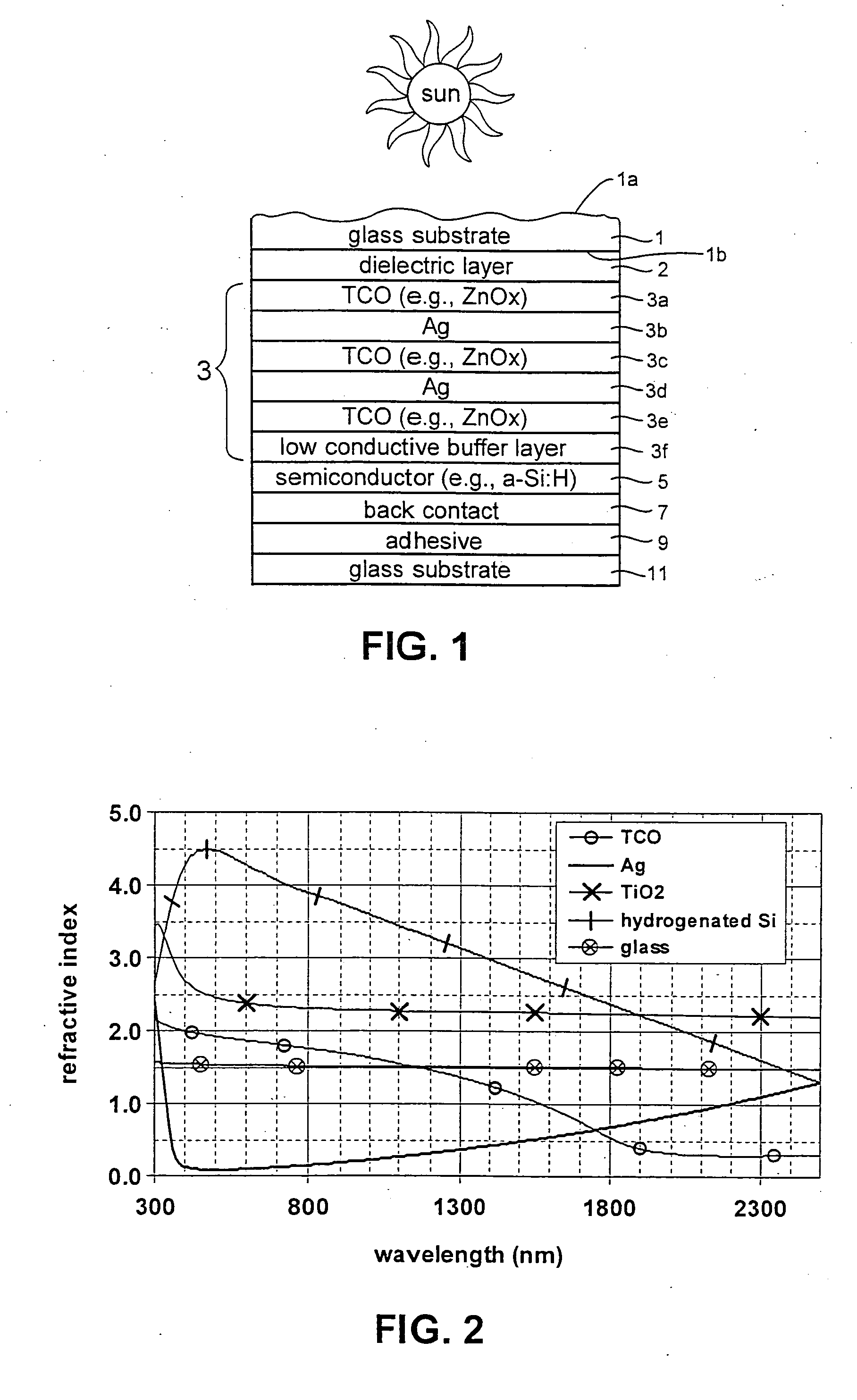
Owner:GUARDIAN GLASS LLC
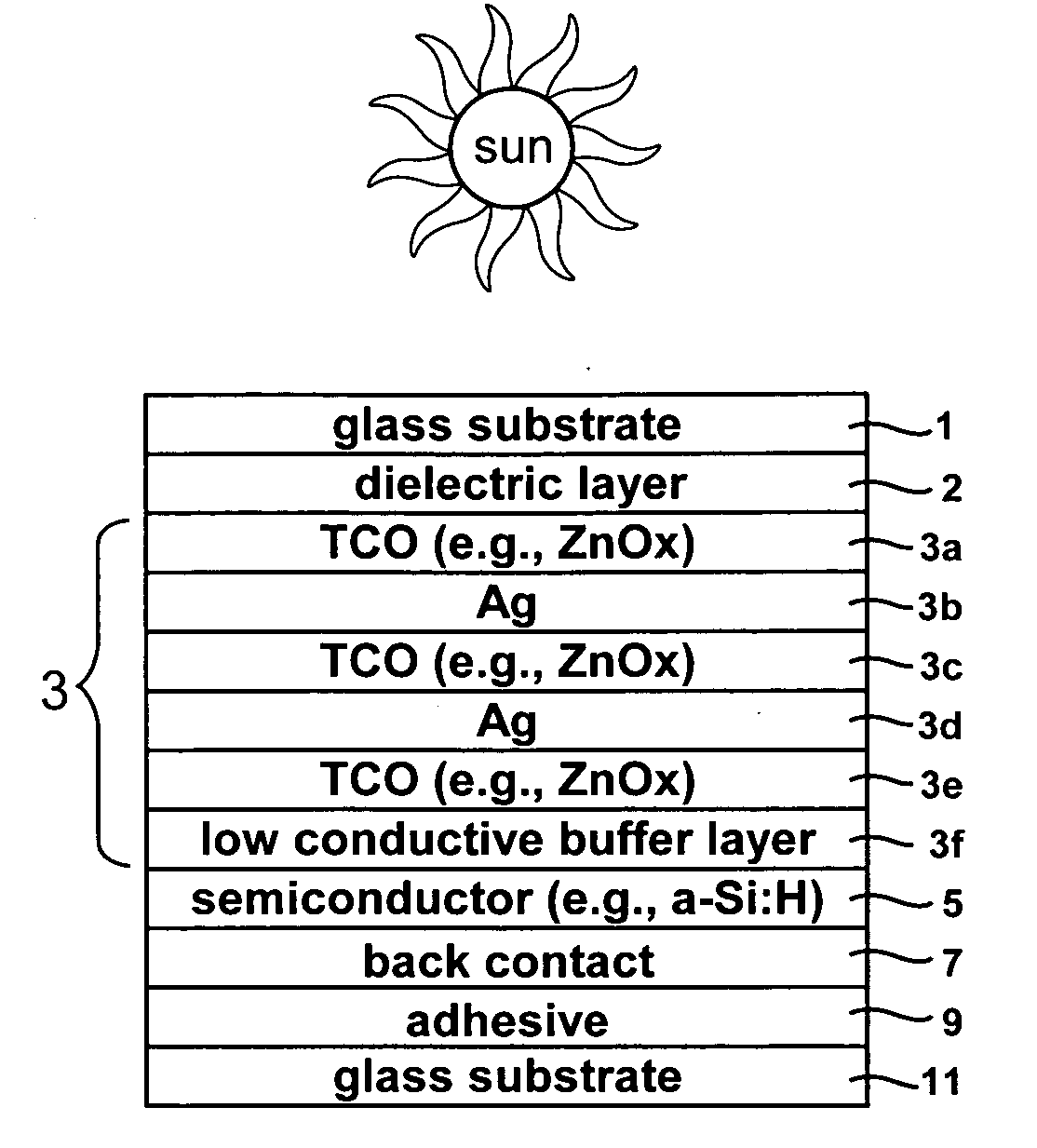
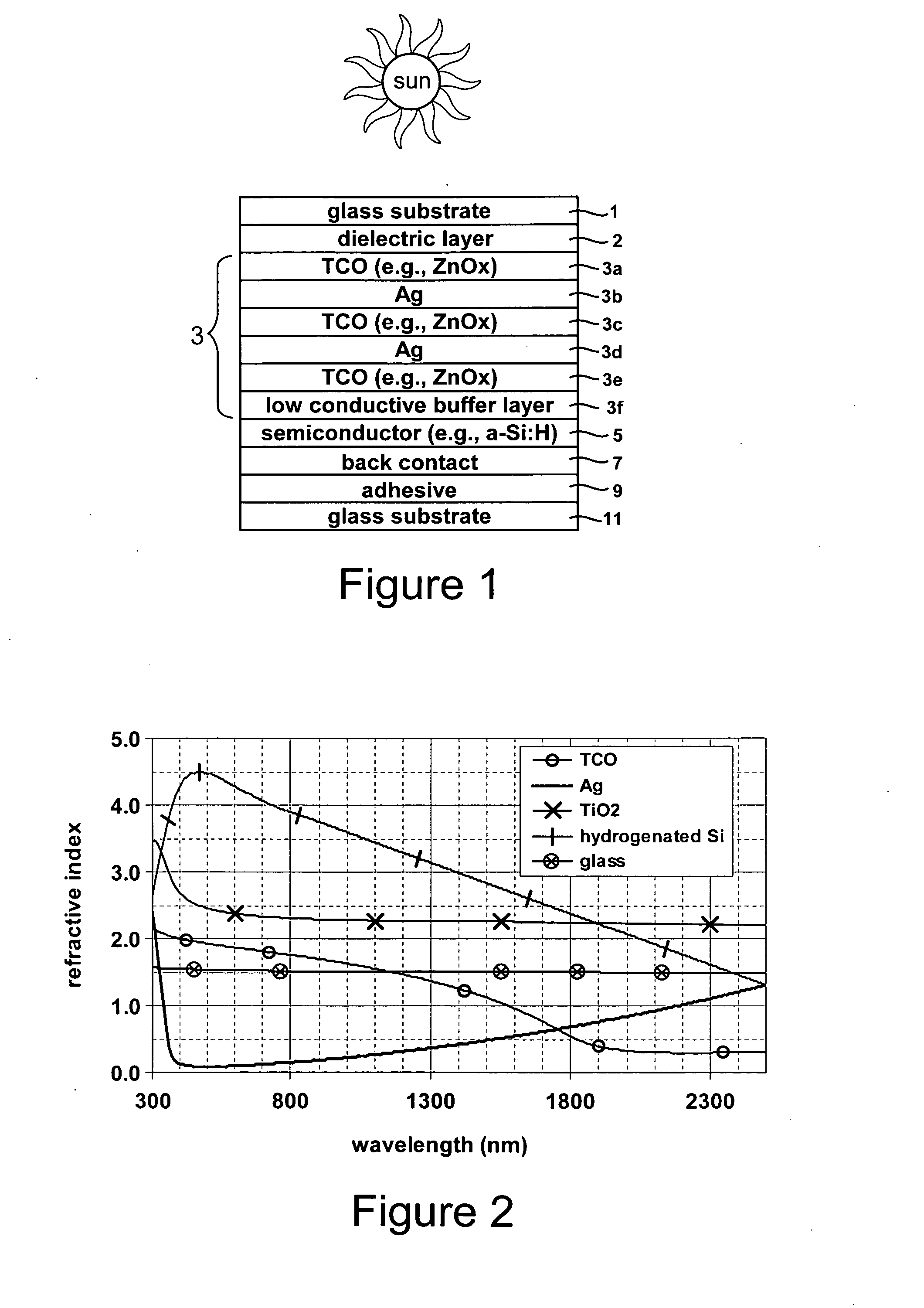
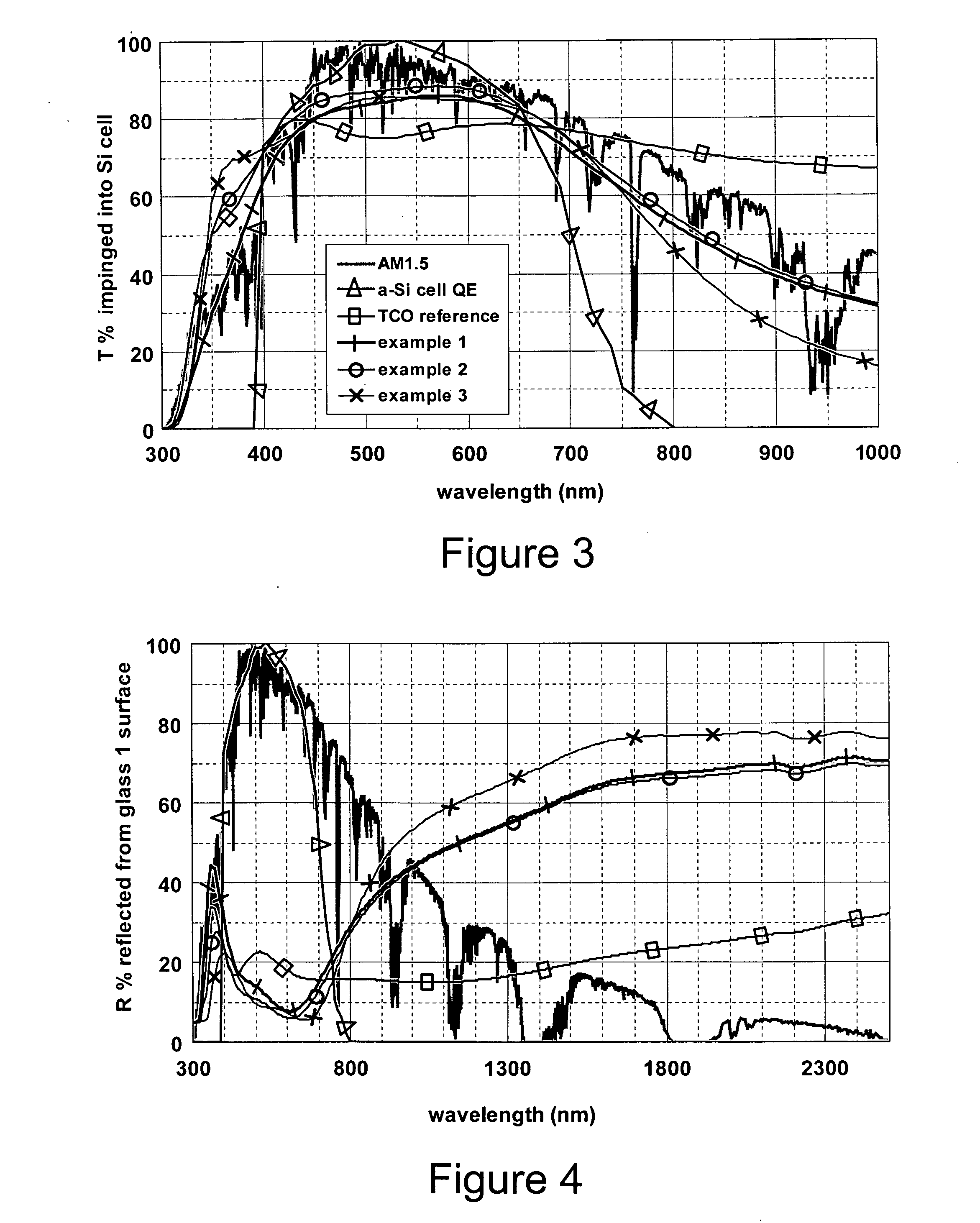
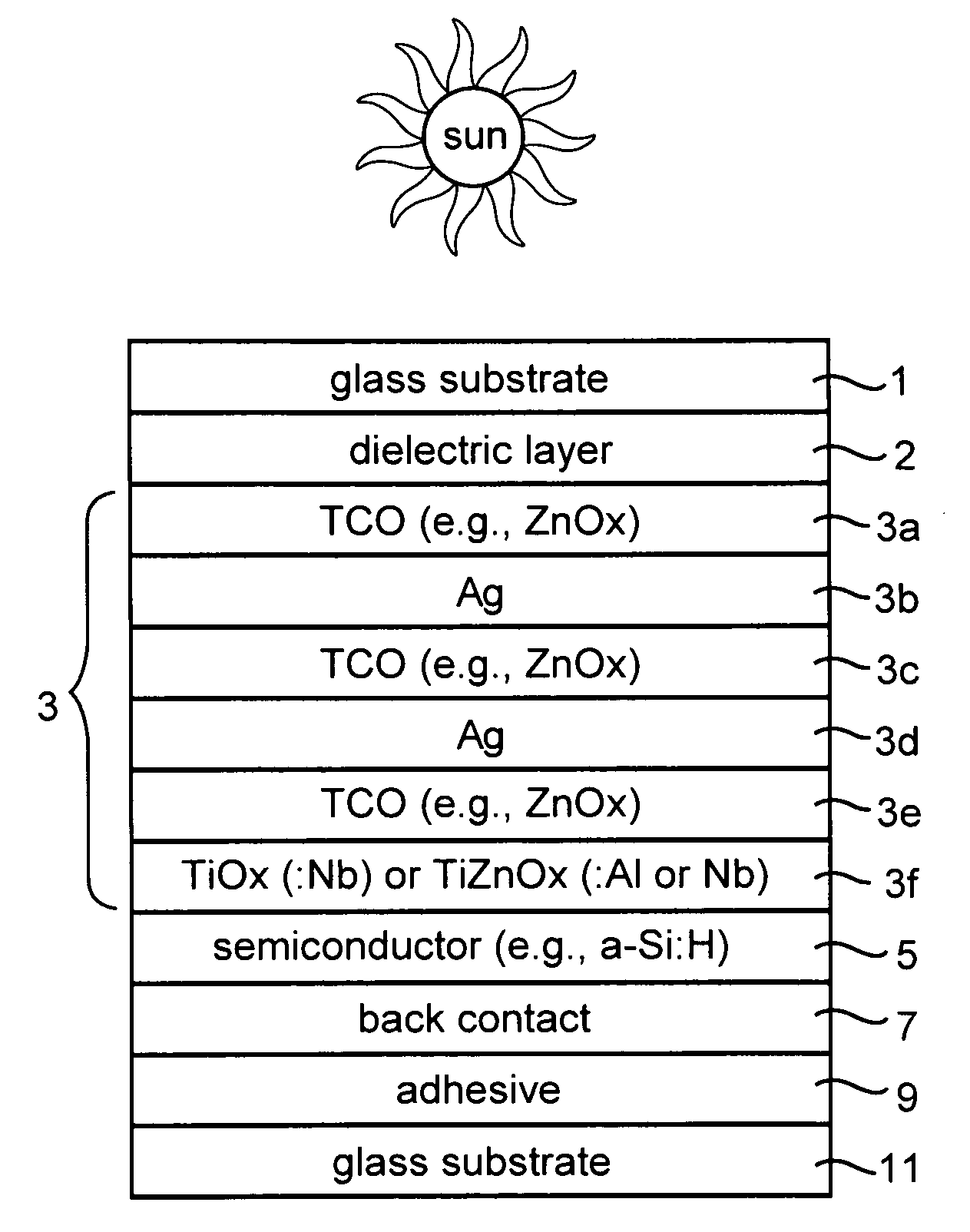
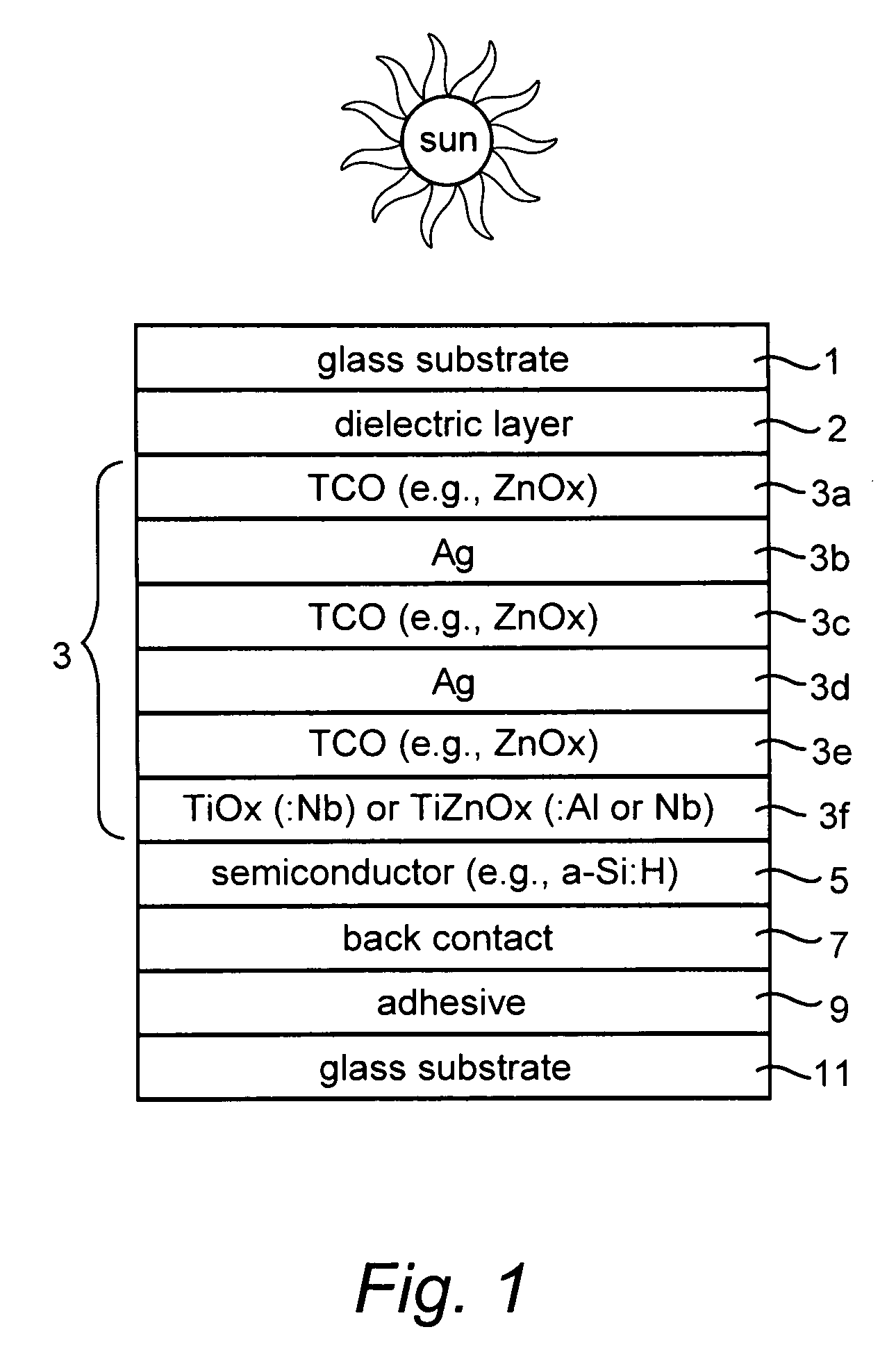
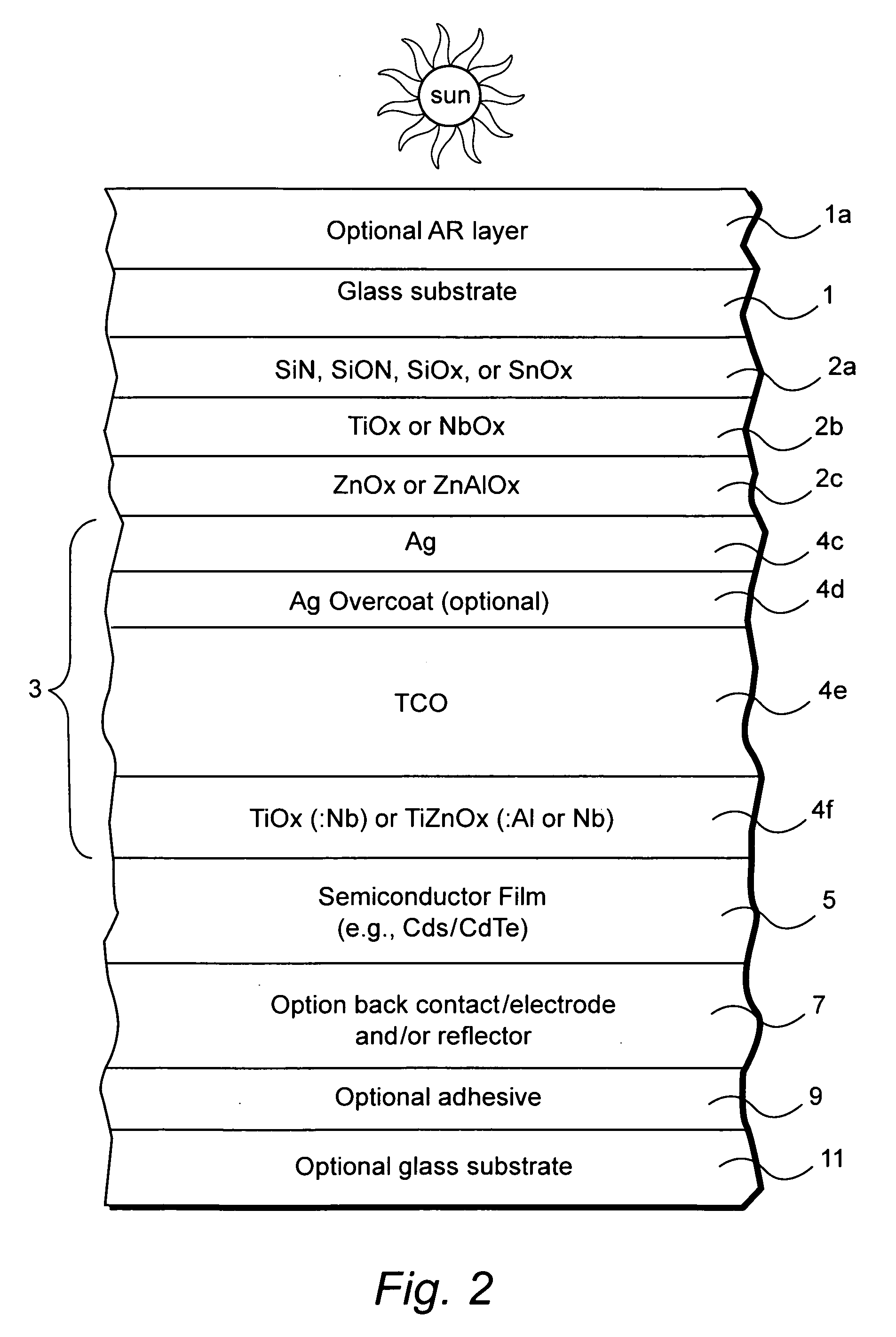
Photovoltaic device including front electrode having titanium oxide inclusive layer with high refractive index
InactiveUS20090126791A1Low efficiencyLow refractive indexGlass/slag layered productsCoatingsRefractive indexLight reflection
Certain example embodiments of this invention relate to an electrode (e.g., front electrode) for use in a photovoltaic device or the like. In certain example embodiments, a transparent conductive oxide (TCO) of the front electrode for use in a photovoltaic device is of or includes titanium oxide doped with one or more of Nb, Zn and / or Al. Additional layers may also be provided in the front electrode in certain example embodiments. It has been found that the use of transparent conductive TiOx(:Nb) or TiZnOx(:Al and / or Nb), in a front electrode of a photovoltaic device, is advantageous in that such materials have a high refractive index (n) and have a higher transparency than conventional titanium suboxide (TiOx). Thus, the use of such materials in the context of a front electrode of a photovoltaic device reduces light reflection due to the high refractive index, and increases transmission into the active semiconductor film due to the higher transmission characteristics thereof, thereby improving the efficiency of the device.
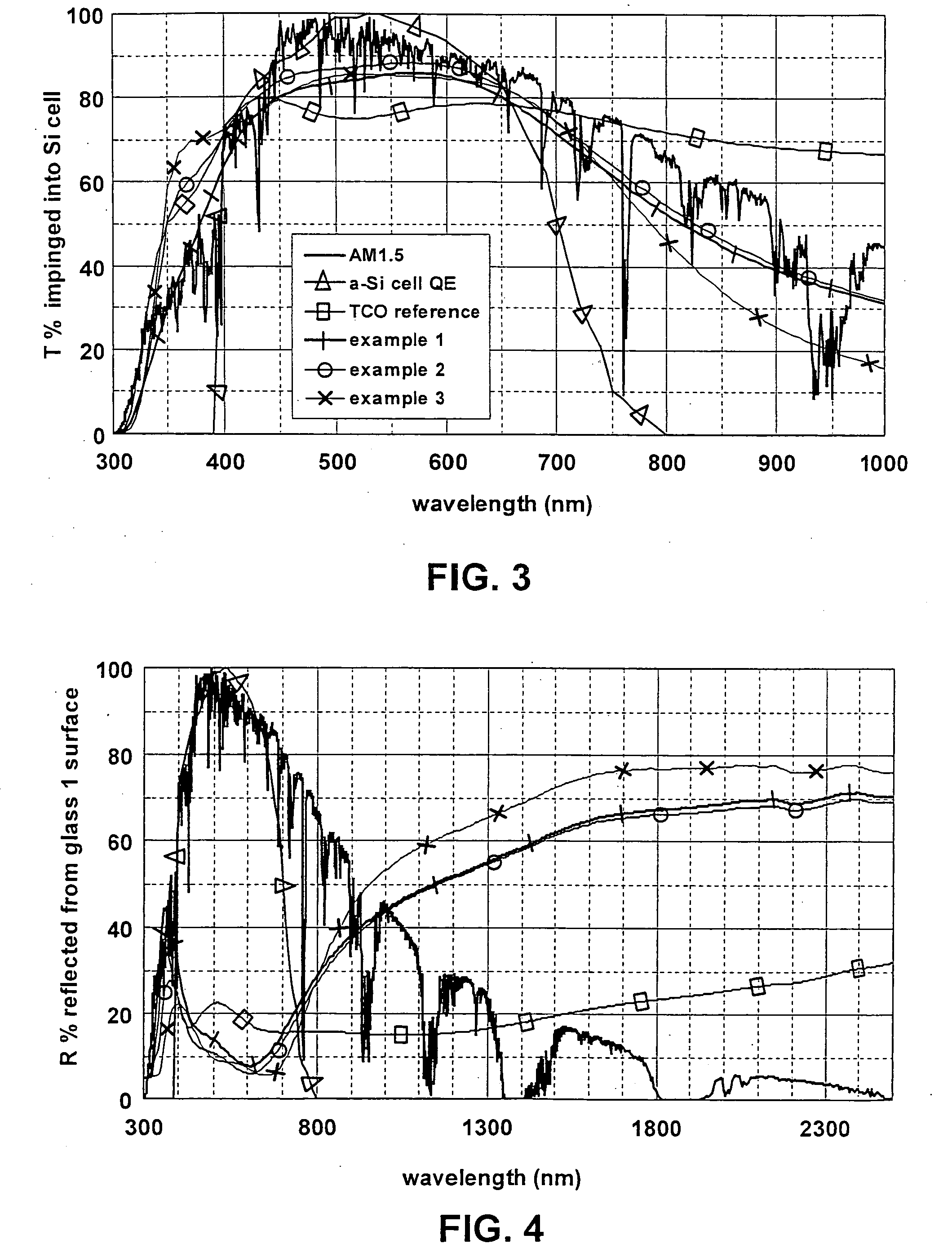
Owner:GUARDIAN GLASS LLC
Color display device and method for manufacturing the same
Disclosed is a color display device containing plural pixels on a substrate, each pixel is composed of plural sub-pixels which emit lights different in wavelength in the visible range and a white sub-pixel, the plural sub-pixels and the white sub-pixel each have a white organic electroluminescence layer interposed between an optically semitransparent reflection layer and a light reflection layer, the optical distance between the optically semitransparent reflection layer and the light reflection layer in each of the plural sub-pixels forms a resonator having a distance for resonating emitted light, and the optical distance between the optically semitransparent reflection layer and the light reflection layer in the white sub-pixel is longer than the maximum optical distance between the optically semitransparent reflection layer and the light reflection layer in each of the plural sub-pixels.
Owner:UDC IRELAND
Front electrode for use in photovoltaic device and method of making same
InactiveUS20080308151A1Reduce reflection lossPromote absorptionFinal product manufacturePhotovoltaic energy generationHigh energyLight reflection
This invention relates to a front electrode / contact for use in an electronic device such as a photovoltaic device. In certain example embodiments, the front electrode of a photovoltaic device or the like includes a multilayer coating including at least one transparent conductive oxide (TCO) layer (e.g., of or including a material such as tin oxide, ITO, zinc oxide, or the like) and / or at least one conductive substantially metallic IR reflecting layer (e.g., based on silver, gold, or the like). In certain example instances, the multilayer front electrode coating may include one or more conductive metal(s) oxide layer(s) and one or more conductive substantially metallic IR reflecting layer(s) in order to provide for reduced visible light reflection, increased conductivity, cheaper manufacturability, and / or increased infrared (IR) reflection capability. In certain example embodiments, the front electrode acts as not only a transparent conductive front contact / electrode but also a short pass filter that allows an increased amount of photons having high energy (such as in visible and near infra-red regions of the spectrum) into the active region or absorber of the photovoltaic device.
Owner:GUARDIAN GLASS LLC
Light-emitting-device package and a method for producing the same
ActiveUS20110291143A1Reduce light absorptionImprove responseSolid-state devicesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingLight reflectionLight emitting device
A light emitting device package includes: a substrate with a mounting surface; a light emitting device bonded to the mounting surface of the substrate; a light reflecting resin part containing a high reflective material, filled on the substrate around the light emitting device so as to extend in a space between the light emitting device and the substrate; and a packing resin part hermetically sealed to cover the light emitting device and the light reflection resin part.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
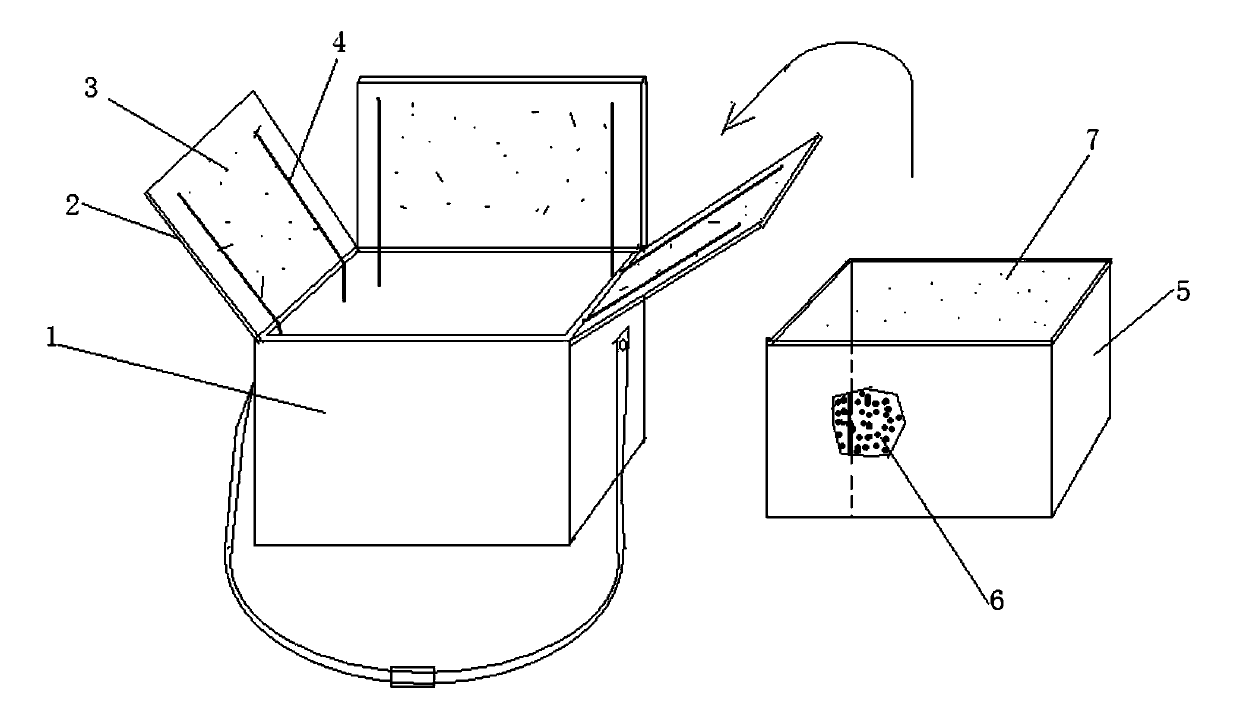
Convenient heat-insulation and cooking method for outdoor picnic food and device thereof
The invention discloses a convenient heat-insulation and cooking method for outdoor picnic food and a device thereof. According to the convenient heat-insulation and cooking method disclosed by the invention, a soft heat-insulation bag with a cover, which can be folded and can also be molded by supporting, is firstly machined; a light reflection film is arranged on the inner surface of a cover body; then, a liner which is tightly adhered to the inner surface of the heat-insulation bag is also machined; a transparent film is arranged on the bottom face of the liner; and the periphery of the liner is provided with a heat-absorption shell fabric. When people prepare to travel outdoors, the food is put into the liner of the soft heat-insulation bag. and the cover body of the heat-insulation bag is closed to keep fresh; when the people have a meal, the liner is turned over, and the bottom face is upwards buckled on the food in the soft heat-insulation bag; the cover body of the heat-insulation bag is wholly opened and is bent and molded, and the rear side faces the sun to heat and cook the food. According to the convenient heat-insulation and cooking method for the outdoor picnic food and the device thereof disclosed by the invention, heating equipment and fuel do not need to be carried when the people have an outdoor picnic, the applicant is convenient, and energy sources are saved; and particularly, open fire is not used so that the method and the device are not limited by prohibitive regulations.
Owner:QINGDAO LINGDING TECH
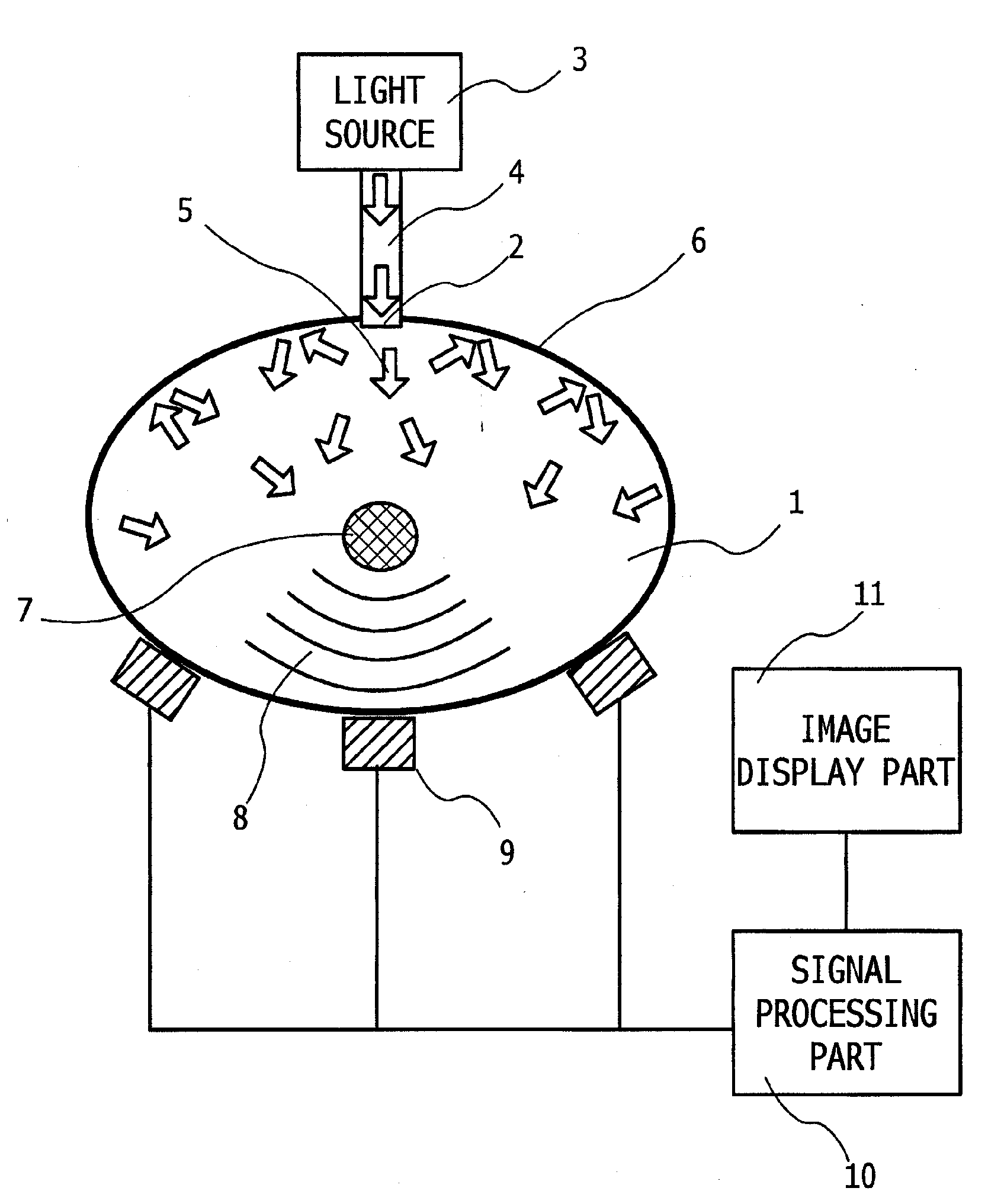
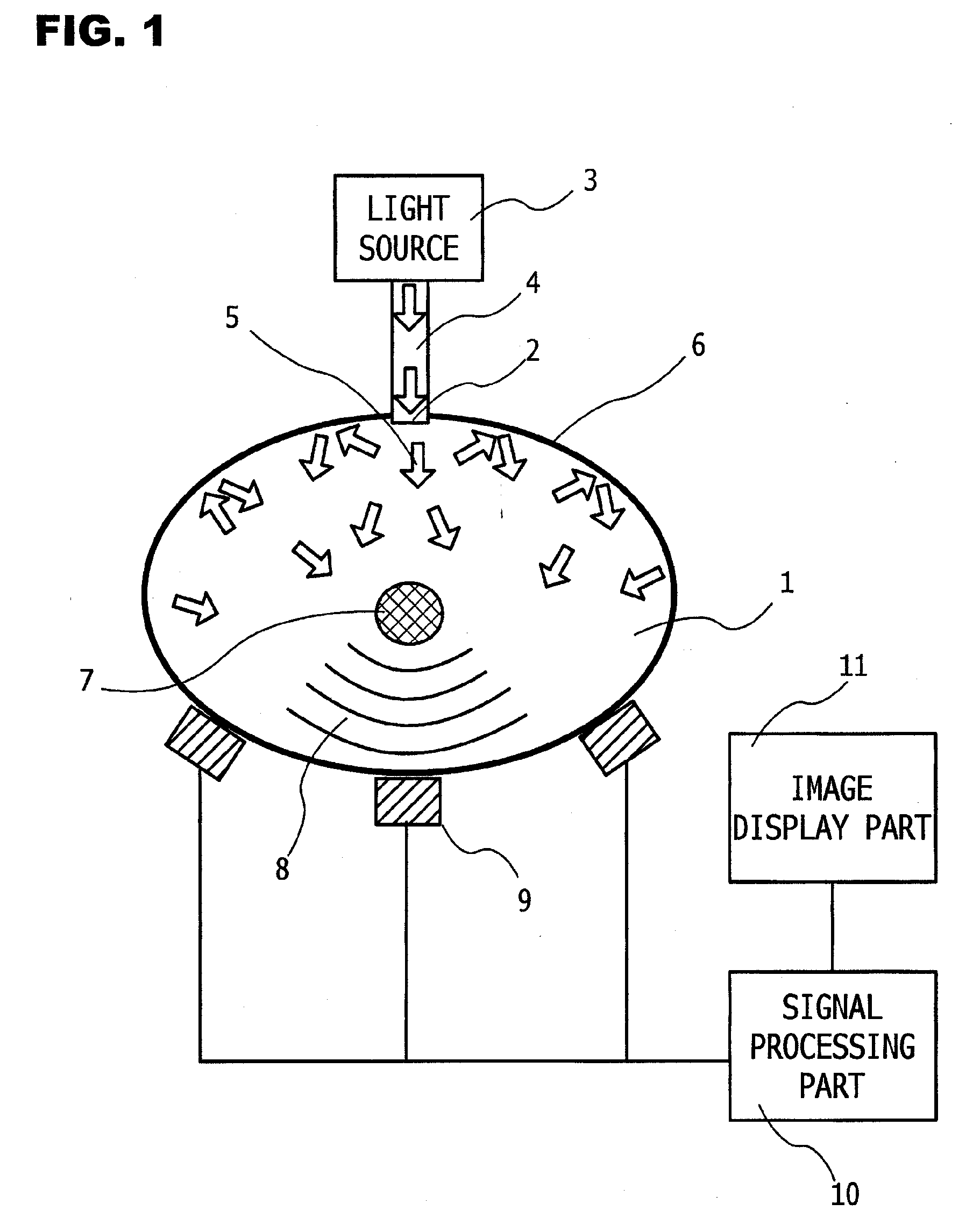
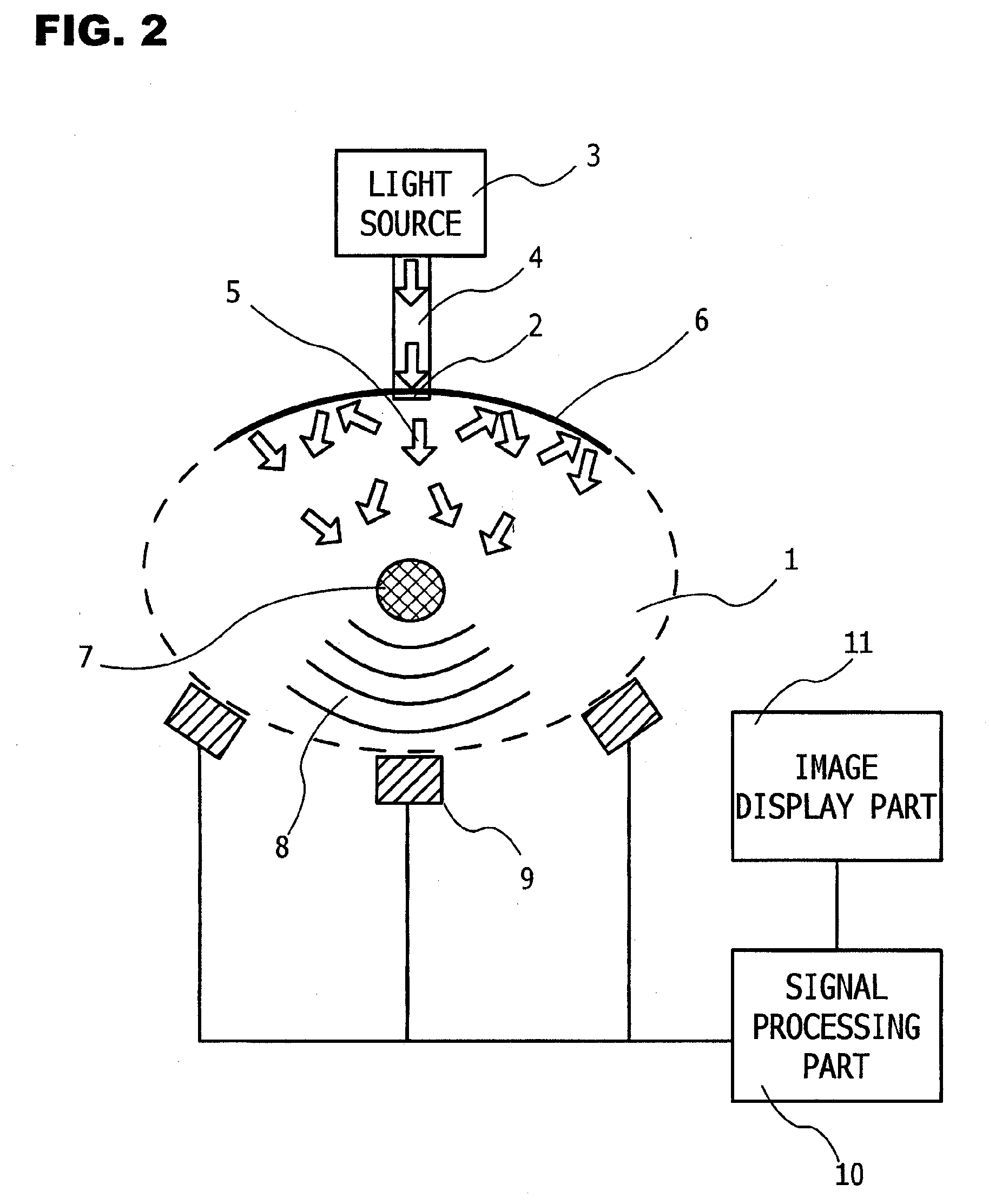
Photoacoustic Apparatus, and Probe for Receiving Photoacoustic Waves
ActiveUS20100053618A1Light utilization efficiencyImprove efficiencyMaterial analysis using sonic/ultrasonic/infrasonic wavesDiagnostics using lightDiffusionLight reflection
A photoacoustic apparatus obtains information on a specimen by receiving photoacoustic waves which are generated from the specimen resulting from light irradiated to the specimen. The apparatus includes a light source for irradiating light to the specimen, an acoustic wave receiver for receiving the photoacoustic waves, and a light reflection member for causing the light, which is radiated out of the specimen by optical diffusion thereof after having entered an interior of the specimen from the light source, to reenter the interior of the specimen, wherein the light reflection member allows elastic waves to pass therethrough. As a result, a photoacoustic apparatus and a probe are provided which can confine scattered light from the specimen into the specimen, and which can reliably prevent photoacoustic waves from being generated from a receiving element region of the probe by the scattered light.
Owner:CANON KK
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com