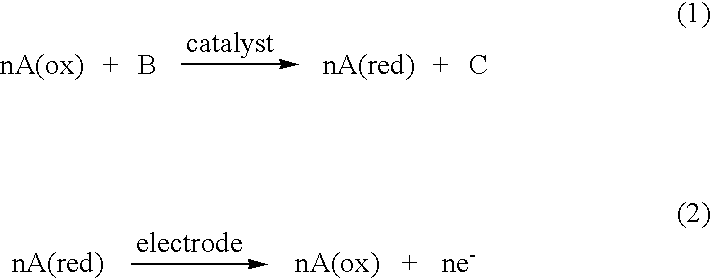Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
27819 results about "Conductive materials" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
'Electrically Conductive' means the ability of any material or object to conduct electricity through it with offering least possible resistance to the flow of electrons. Silver is found to be the most conductive material of all.
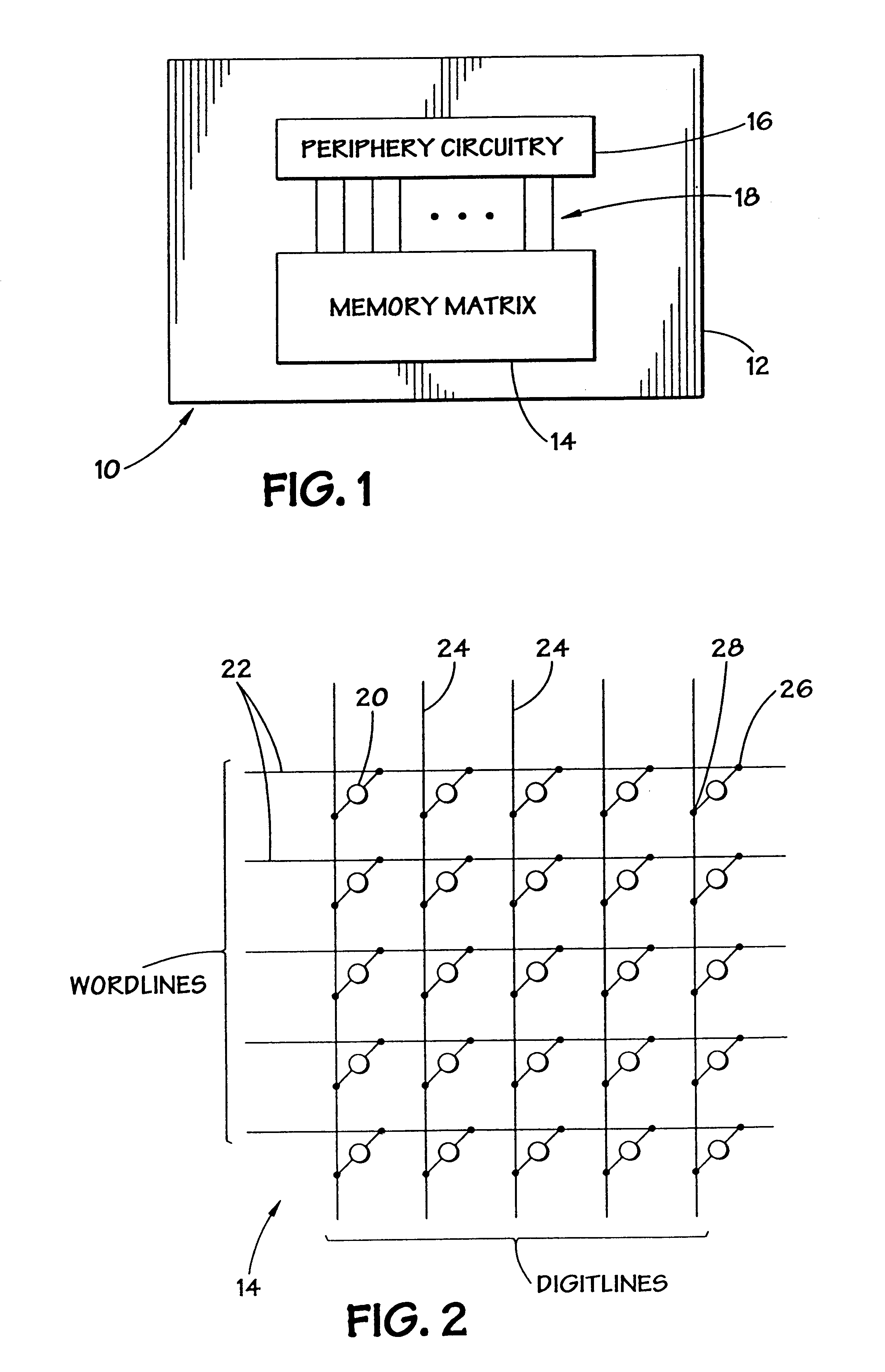
Transistor and semiconductor device
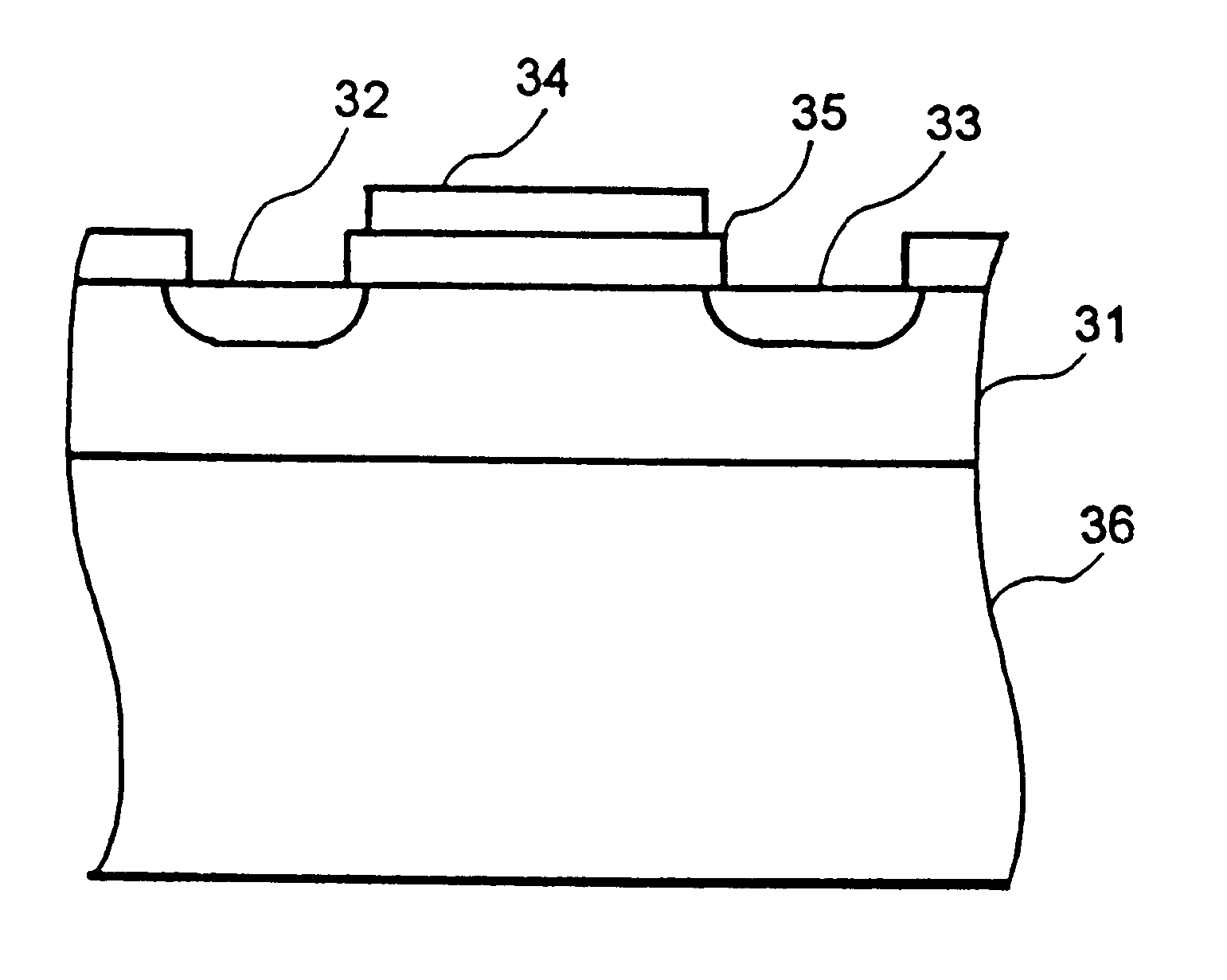
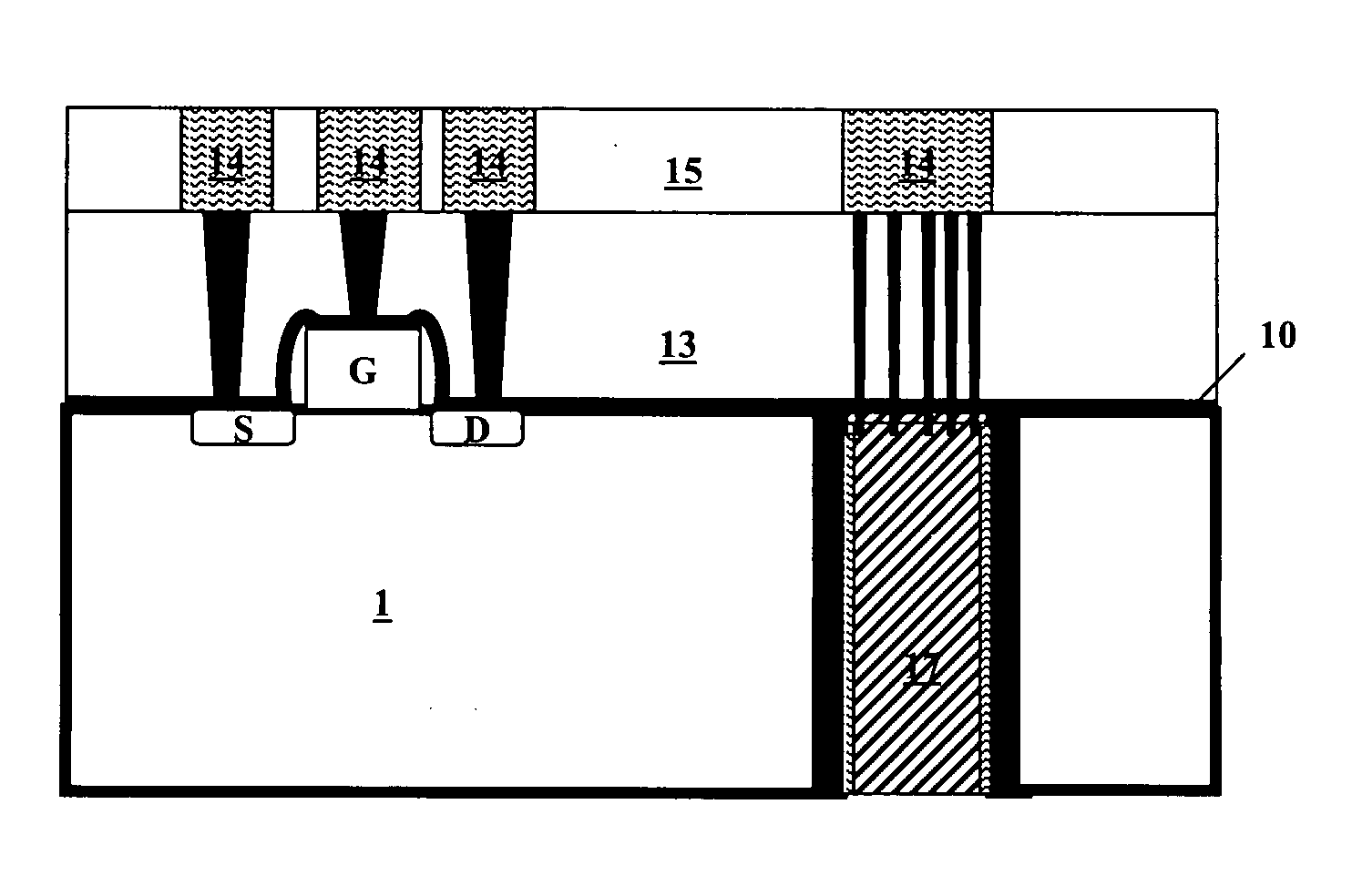
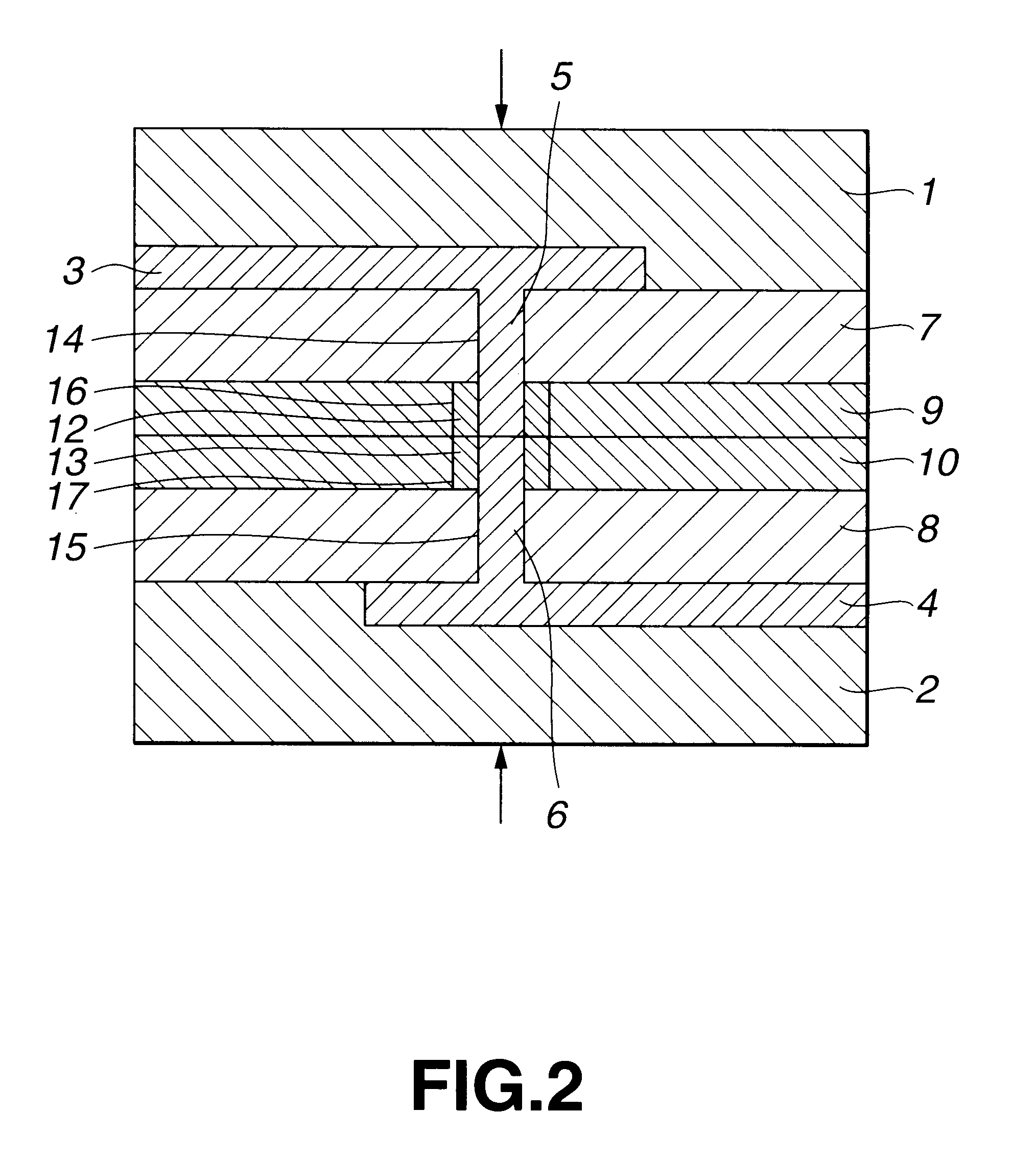
A transistor is provided, which is entirely and partially transparent by the use of a transparent channel layer made of zinc oxide or the like. A channel layer 11 formed of a transparent semiconductor such as zinc oxide ZnO. A transparent electrode is used for all of a source 12, a drain 13 and a gate 14, or a part of them. As the transparent electrode, a transparent conductive material such as conductive ZnO doped with, for example, group III elements is used. As a gate insulating layer 15, a transparent insulative material such as insulative ZnO doped with elements capable of taking a valence of one as a valence number or group V elements is used. If a substrate 16 must be transparent, for example, glass, sapphire, plastic or the like can be used as a transparent material.
Owner:JAPAN SCI & TECH CORP
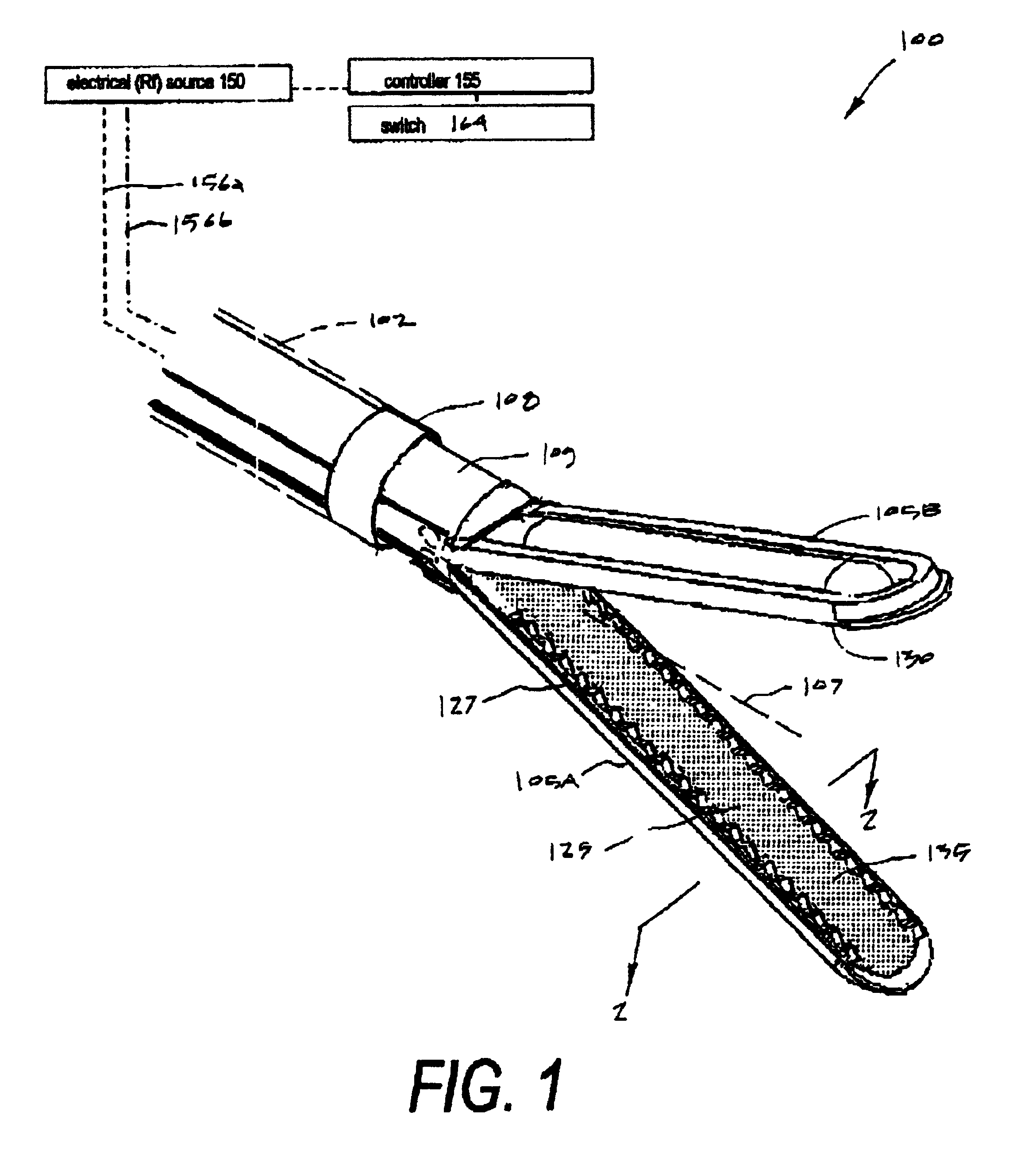
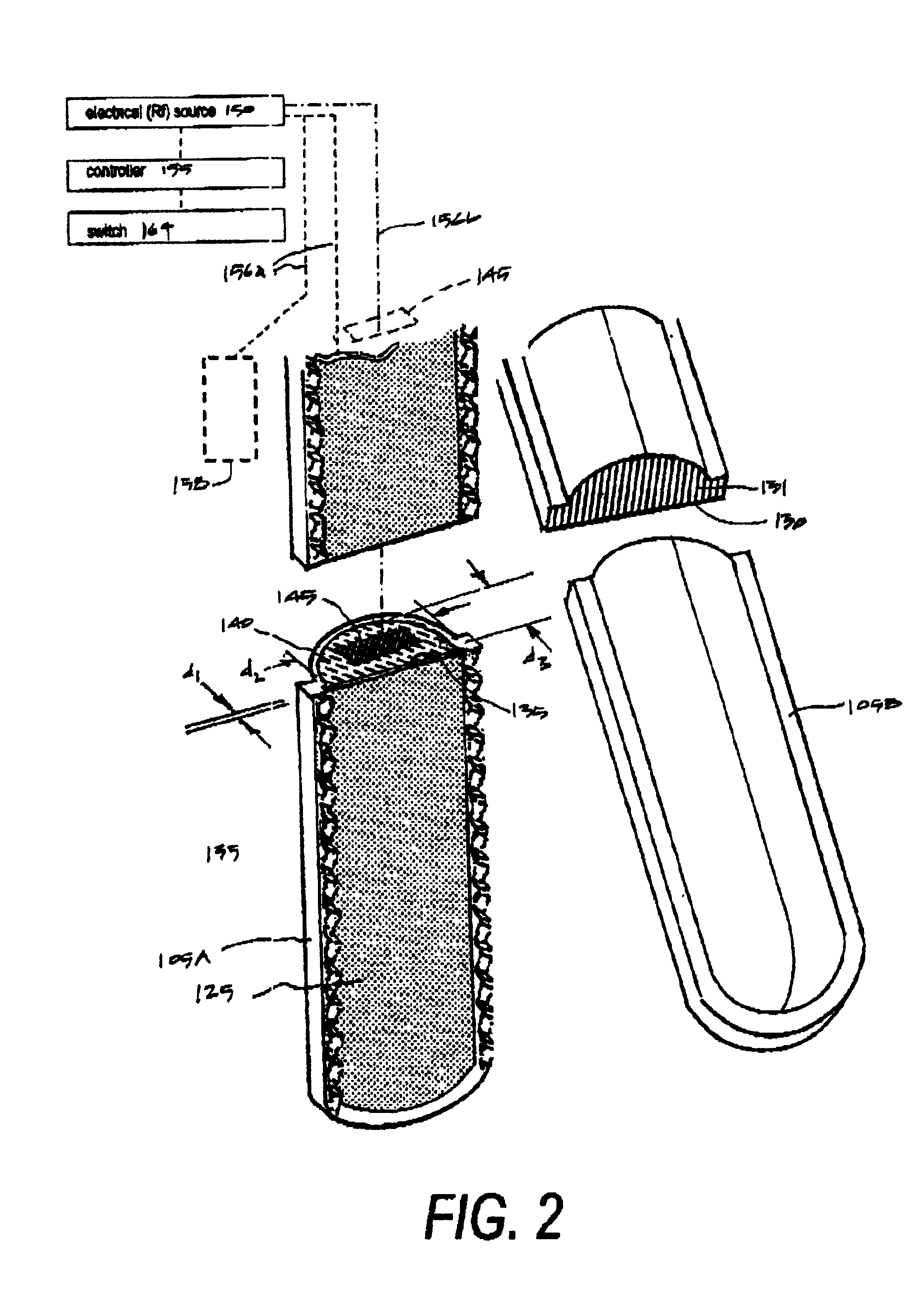
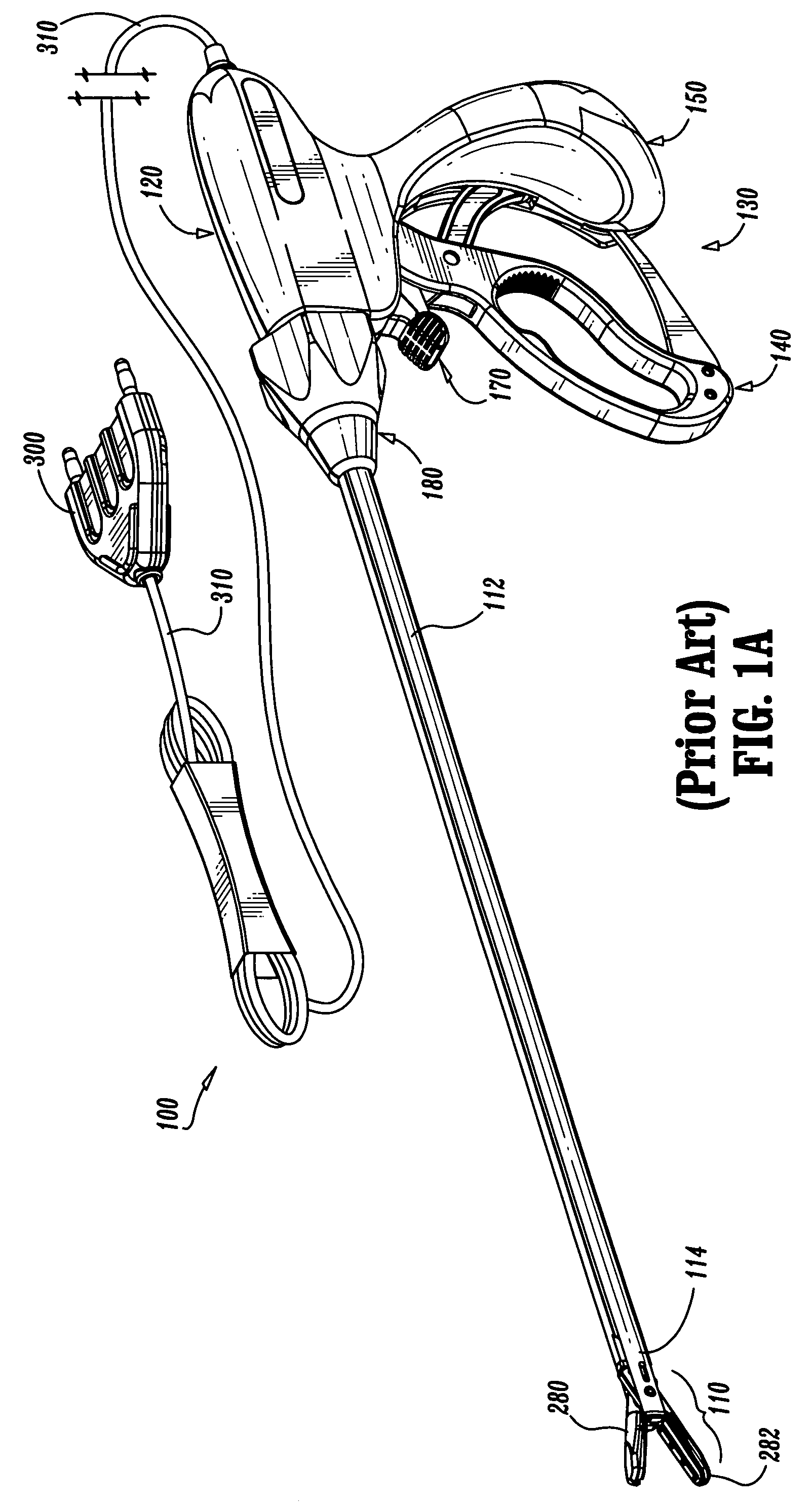
Electrosurgical jaw structure for controlled energy delivery
InactiveUS6929644B2Prevent any substantial dehydrationEnergy efficiencySurgical instruments for heatingCoatingsThermal energyConductive materials
A working end of a surgical instrument that carries first and second jaws for delivering energy to tissue. In a preferred embodiment, at least one jaw of the working end defines a tissue-engagement plane that contacts the targeted tissue. The cross-section of the engagement plane reveals that it defines a surface conductive portion that overlies a variably resistive matrix of a temperature-sensitive resistive material or a pressure-sensitive resistive material. An interior of the jaw carries a conductive material or electrode that is coupled to an Rf source and controller. In an exemplary embodiment, the variably resistive matrix can comprise a positive temperature coefficient (PTC) material, such as a ceramic, that is engineered to exhibit a dramatically increasing resistance (i.e., several orders of magnitude) above a specific temperature of the material. In use, the engagement plane will apply active Rf energy to captured tissue until the point in time that the variably resistive matrix is heated to its selected switching range. Thereafter, current flow from the conductive electrode through the engagement surface will be terminated due to the exponential increase in the resistance of variably resistive matrix to provide instant and automatic reduction of Rf energy application. Further, the variably resistive matrix can effectively function as a resistive electrode to thereafter conduct thermal energy to the engaged tissue volume. Thus, the jaw structure can automatically modulate the application of energy to tissue between active Rf heating and passive conductive heating of captured tissue to maintain a target temperature level.
Owner:ETHICON ENDO SURGERY INC
Electrochemical analyte sensor
InactiveUS6484046B1Avoid and reduce corrosionMicrobiological testing/measurementMaterial analysis by electric/magnetic meansAnalyteElectrolysis
An electrochemical analyte sensor having conductive traces on a substrate is used to determine a level of analyte in in vitro or in vivo analyte-containing fluids. The electrochemical analyte sensor includes a substrate and conductive material disposed on the substrate, the conductive material forming a working electrode. In some sensors, the conductive material is disposed in recessed channels formed in a surface of the sensor. An electron transfer agent and / or catalyst may be provided to facilitate the electrolysis of the analyte or of a second compound whose level depends on the level of the analyte. A potential is formed between the working electrode and a reference electrode or counter / reference electrode and the resulting current is a function of the concentration of the analyte in the fluid.
Owner:ABBOTT DIABETES CARE INC
Recognition of interchangeable component of a device
A device and a method are provided for determining a characteristic of an interchangeable component of a surgical instrument. An electrically conductive material having a measurable strength measurable by a hall effect sensor is coupled to the component. In another embodiment, a plurality of conductive materials are arranged to form a binary code representing a corresponding of the interchangeable component. The number and / or strength of the magnets measurable by the sensors may be dynamically altered such that the status of the surgical instrument is determinable.
Owner:COVIDIEN LP
Analyte monitoring device and methods of use
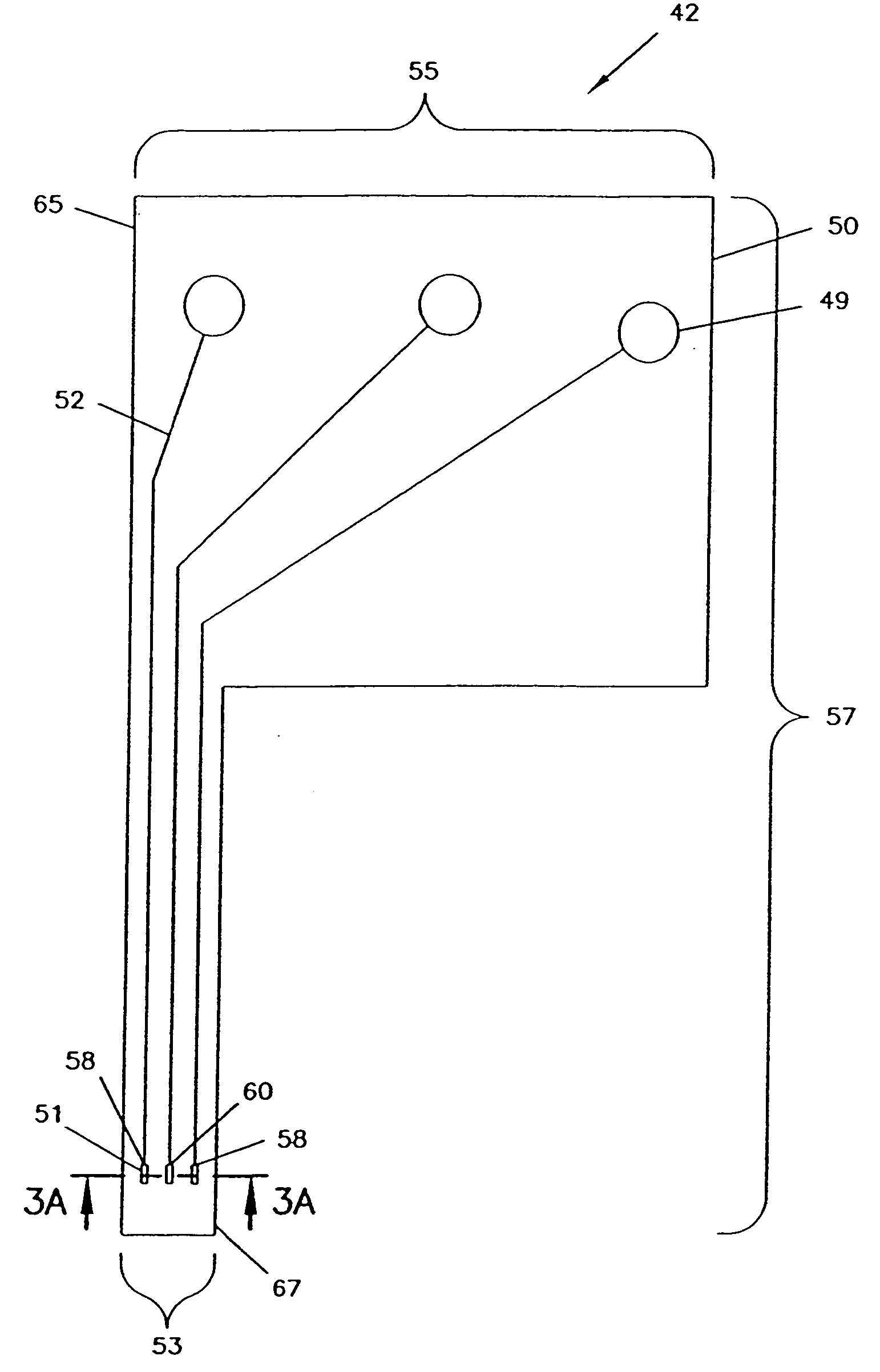
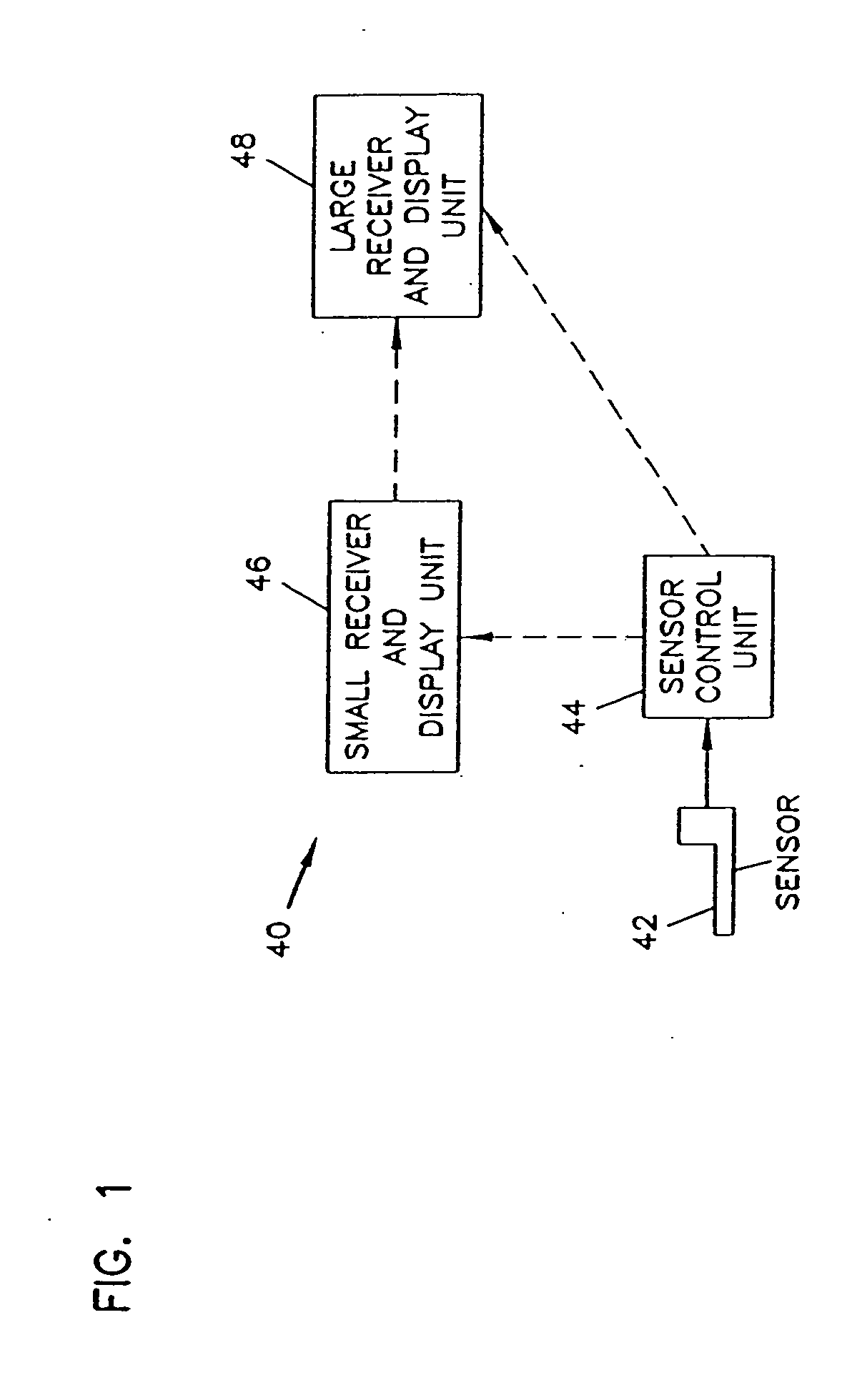
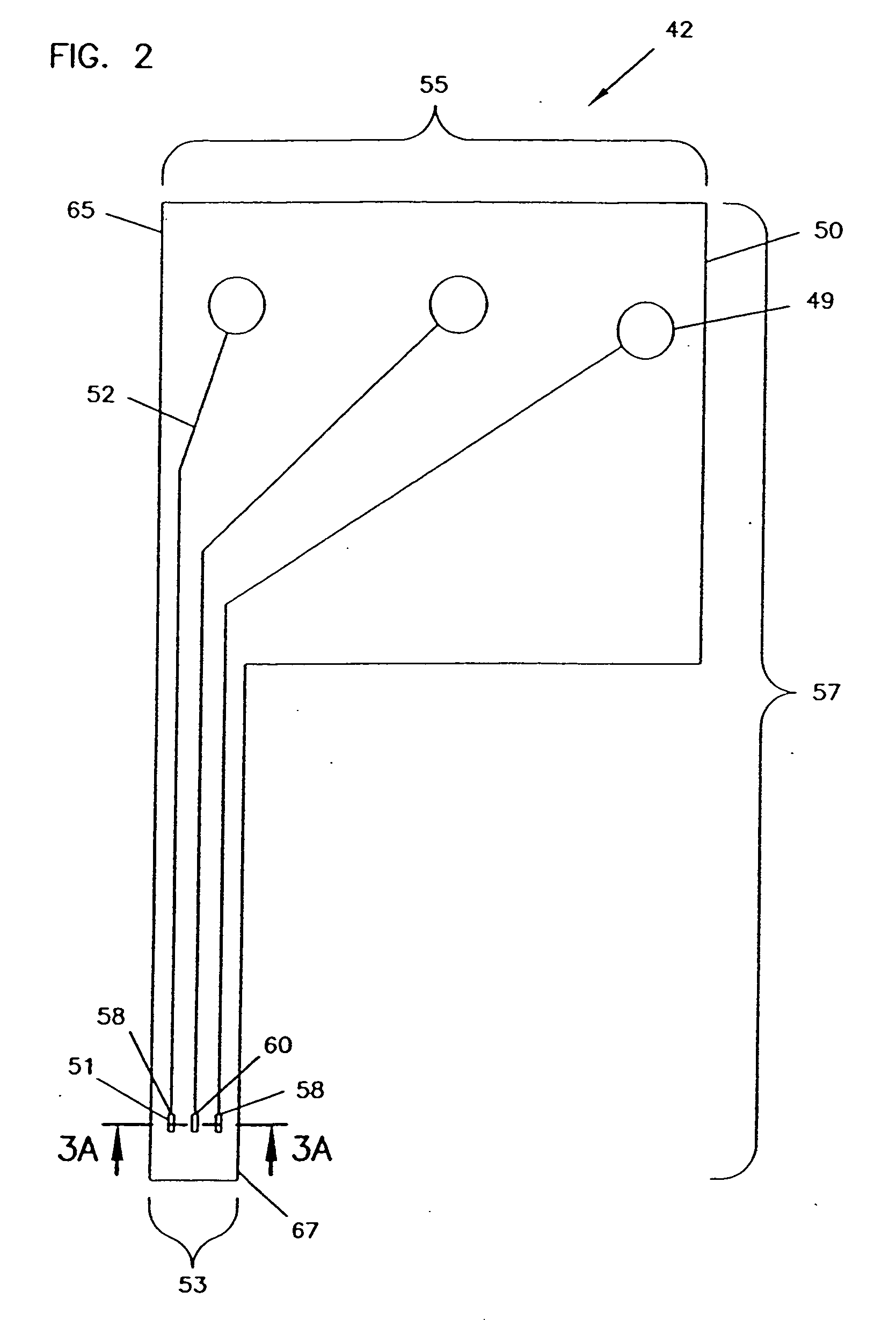
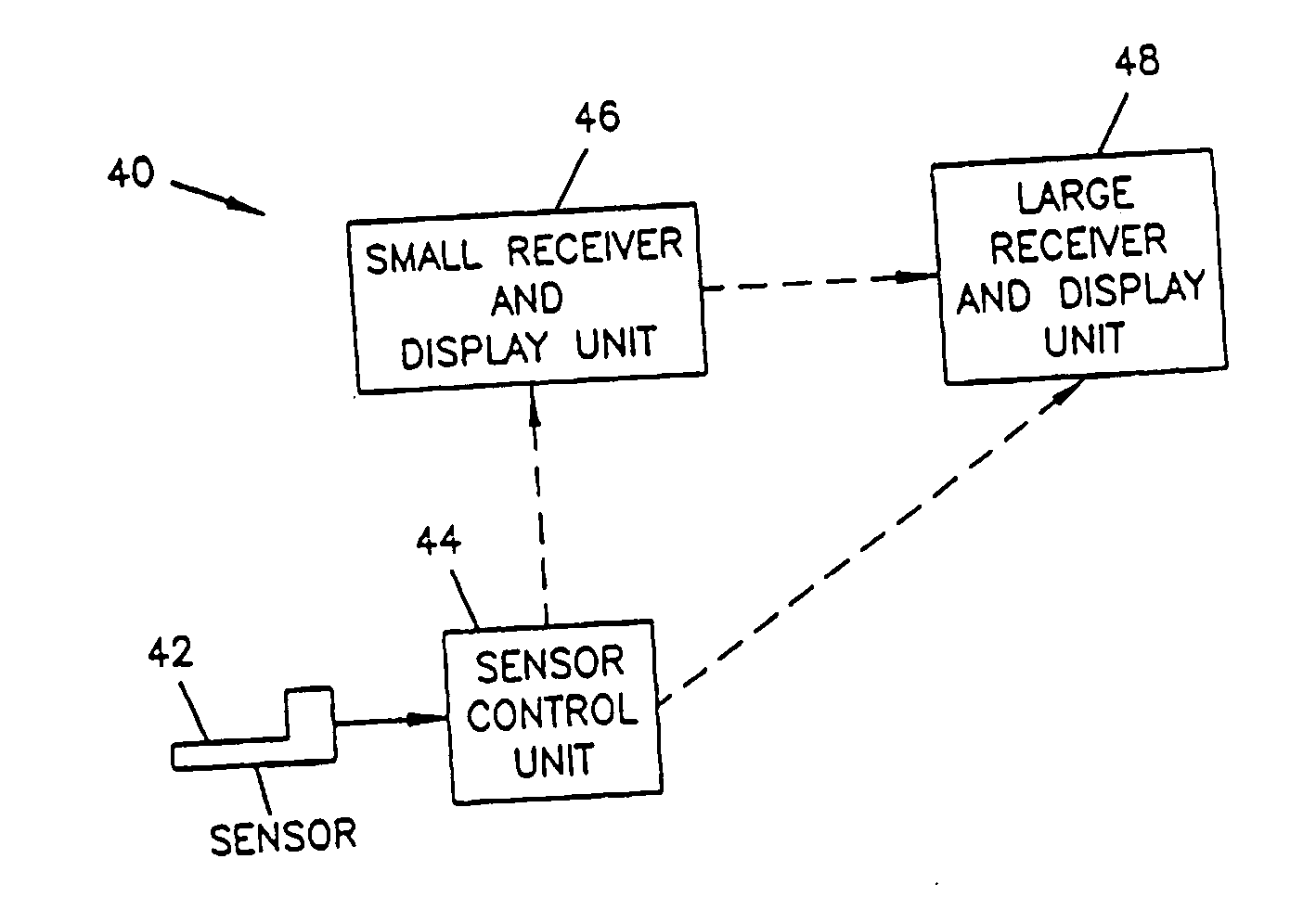
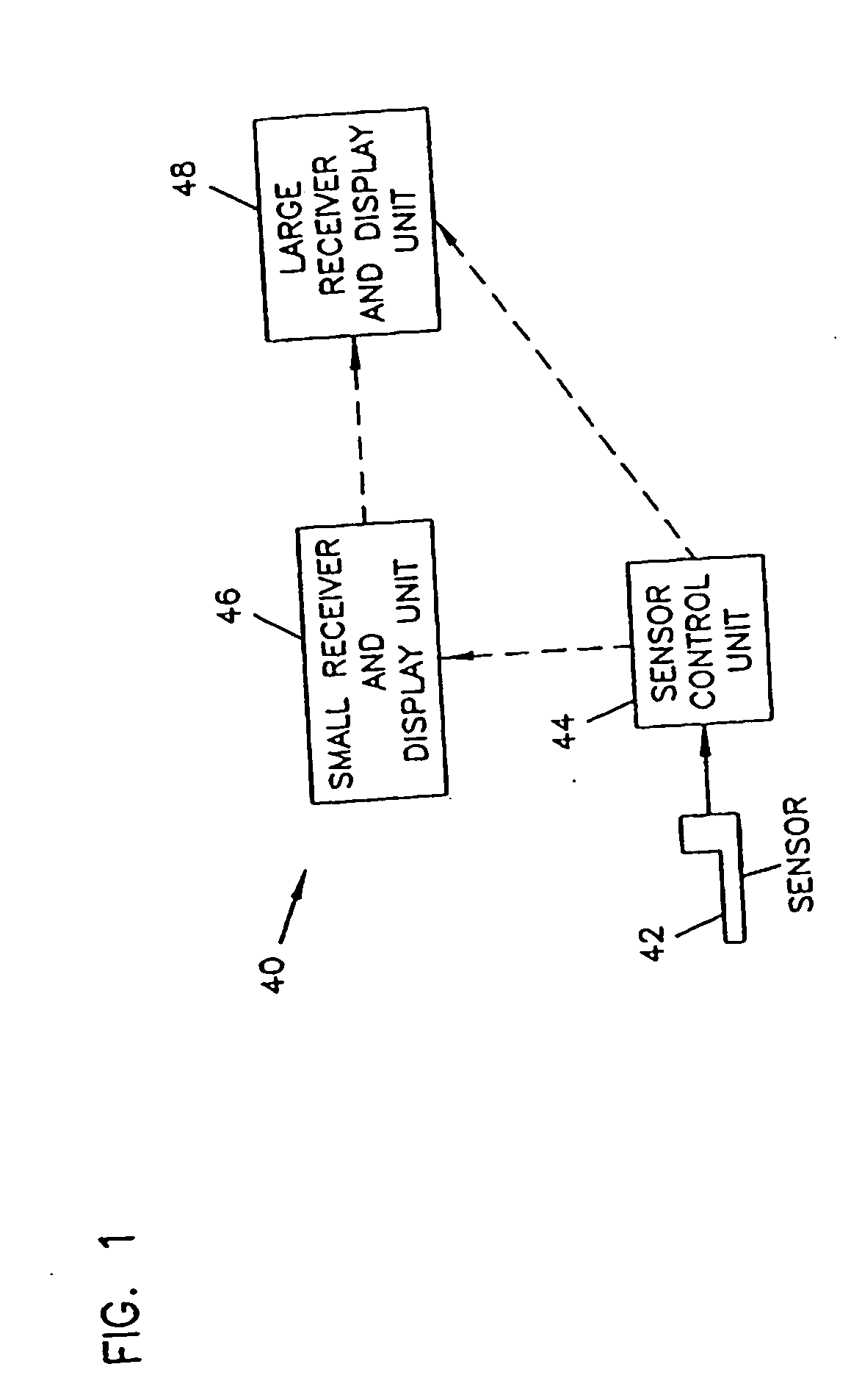
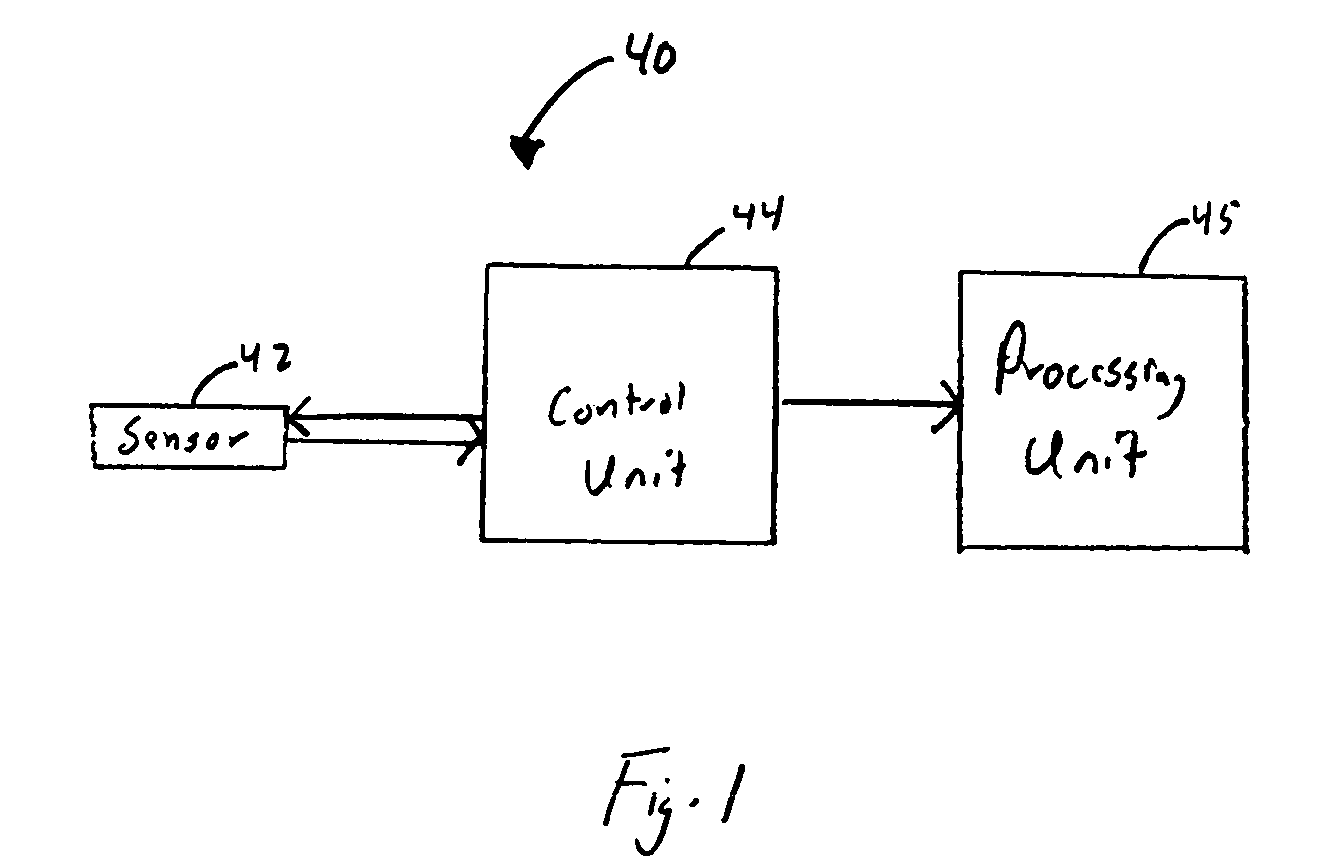
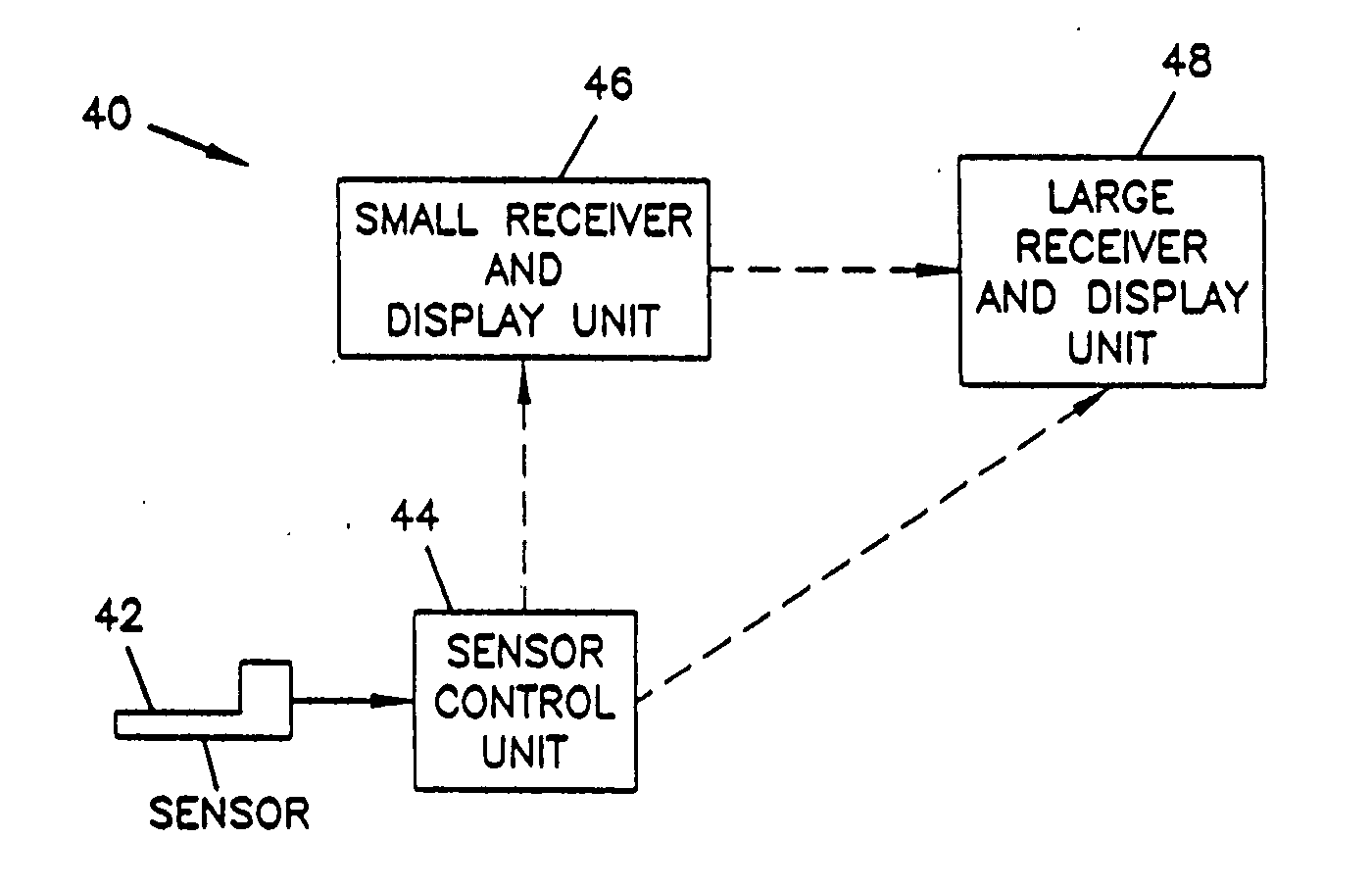
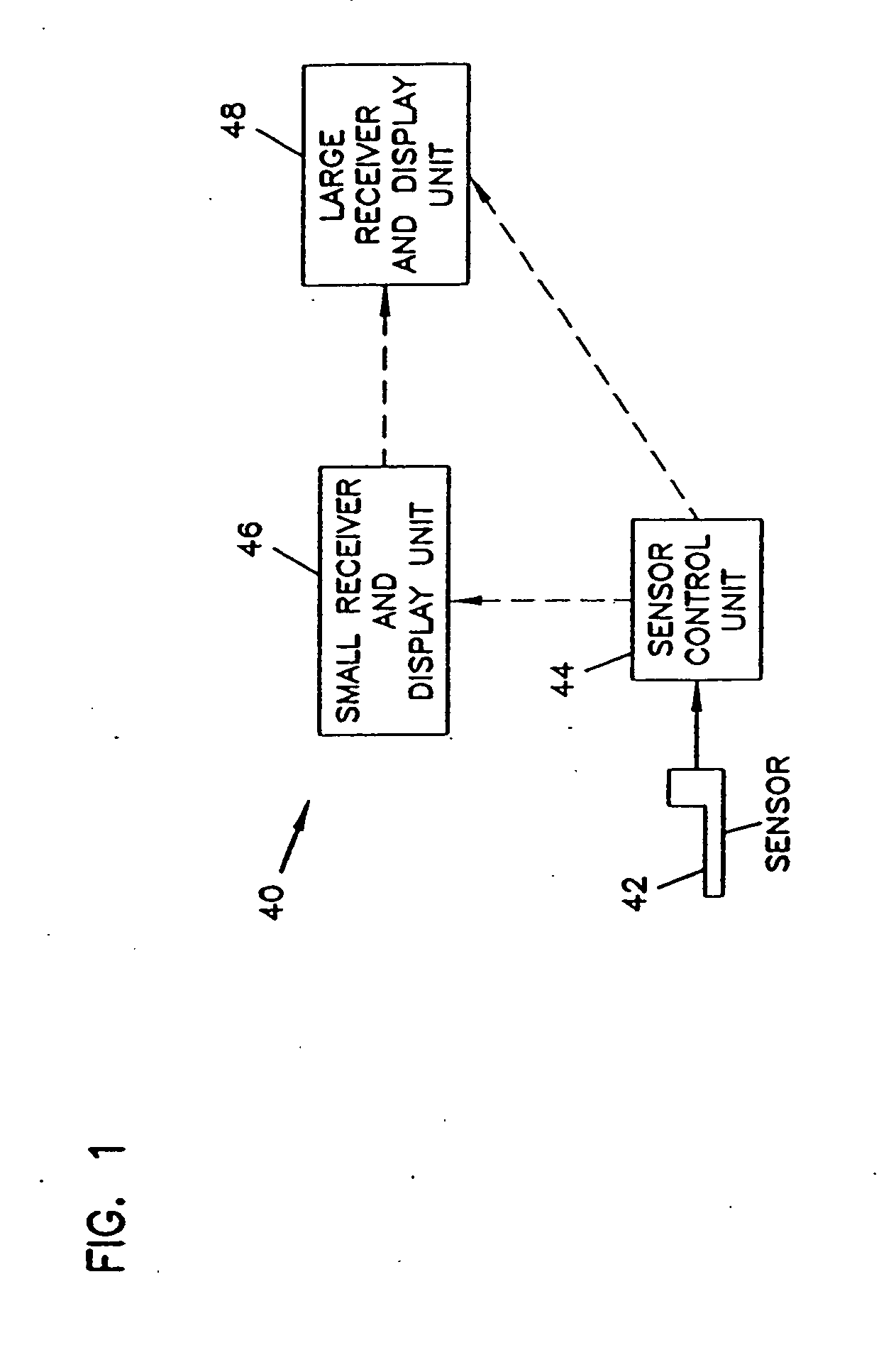
An analyte monitor includes a sensor, a sensor control unit, and a display unit. The sensor has, for example, a substrate, a recessed channel formed in the substrate, and conductive material disposed in the recessed channel to form a working electrode. The sensor control unit typically has a housing adapted for placement on skin and is adapted to receive a portion of an electrochemical sensor. The sensor control unit also includes two or more conductive contacts disposed on the housing and configured for coupling to two or more contact pads on the sensor. A transmitter is disposed in the housing and coupled to the plurality of conductive contacts for transmitting data obtained using the sensor. The display unit has a receiver for receiving data transmitted by the transmitter of the sensor control unit and a display coupled to the receiver for displaying an indication of a level of an analyte. The analyte monitor may also be part of a drug delivery system to alter the level of the analyte based on the data obtained using the sensor.
Owner:THERASENSE
Analyte monitoring device and methods of use
An analyte monitor includes a sensor, a sensor control unit, and a display unit. The sensor has, for example, a substrate, a recessed channel formed in the substrate, and conductive material disposed in the recessed channel to form a working electrode. The sensor control unit typically has a housing adapted for placement on skin and is adapted to receive a portion of an electrochemical sensor. The sensor control unit also includes two or more conductive contacts disposed on the housing and configured for coupling to two or more contact pads on the sensor. A transmitter is disposed in the housing and coupled to the plurality of conductive contacts for transmitting data obtained using the sensor. The display unit has a receiver for receiving data transmitted by the transmitter of the sensor control unit and a display coupled to the receiver for displaying an indication of a level of an analyte. The analyte monitor may also be part of a drug delivery system to alter the level of the analyte based on the data obtained using the sensor.
Owner:ABBOTT DIABETES CARE INC
Electrochemical analyte sensor
InactiveUS7003340B2Avoid and reduce corrosionRotary clutchesMicrobiological testing/measurementElectrolysisAnalyte
An electrochemical analyte sensor formed using conductive traces on a substrate can be used for determining and / or monitoring a level of analyte in in vitro or in vivo analyte-containing fluids. For example, an implantable sensor may be used for the continuous or automatic monitoring of a level of an analyte, such as glucose, lactate, or oxygen, in a patient. The electrochemical analyte sensor includes a substrate and conductive material disposed on the substrate, the conductive material forming a working electrode. In some sensors, the conductive material is disposed in recessed channels formed in a surface of the sensor. An electron transfer agent and / or catalyst may be provided to facilitate the electrolysis of the analyte or of a second compound whose level depends on the level of the analyte. A potential is formed between the working electrode and a reference electrode or counter / reference electrode and the resulting current is a function of the concentration of the analyte in the body fluid.
Owner:ABBOTT DIABETES CARE INC
Bendable high flux LED array
ActiveUS6936855B1Easily variableWell formedSolid-state devicesSemiconductor devices for light sourcesLed arrayHigh flux
A bendable light emitting diode (LED) array in accordance with the present invention includes heat spreaders, dielectric material disposed above each heat spreader, and a bendable electrical interconnection layer disposed above these heat spreaders and electrically insulated from these heat spreaders by the dielectric material. At least one via passes through the dielectric material above each heat spreader, and at least one LED die is disposed above each via. The bendable electrical interconnection layer may be a lead frame comprising metal pathways that electrically interconnect some or all LED dice in series, in parallel, in anti-parallel, or in some combination of these configurations. Each via contains a thermally conductive material in thermal contact with the corresponding heat spreader below it and in thermal contact with the corresponding LED die above it. The LED dice may be thermally and electrically coupled to submounts disposed above corresponding heat spreaders in some embodiments.
Owner:EPISTAR CORP
Analyte monitoring device and methods of use
An analyte monitor includes a sensor, a sensor control unit, and a display unit. The sensor has, for example, a substrate, a recessed channel formed in the substrate, and conductive material disposed in the recessed channel to form a working electrode. The sensor control unit typically has a housing adapted for placement on skin and is adapted to receive a portion of an electrochemical sensor. The sensor control unit also includes two or more conductive contacts disposed on the housing and configured for coupling to two or more contact pads on the sensor. A transmitter is disposed in the housing and coupled to the plurality of conductive contacts for transmitting data obtained using the sensor. The display unit has a receiver for receiving data transmitted by the transmitter of the sensor control unit and a display coupled to the receiver for displaying an indication of a level of an analyte. The analyte monitor may also be part of a drug delivery system to alter the level of the analyte based on the data obtained using the sensor.
Owner:ABBOTT DIABETES CARE INC
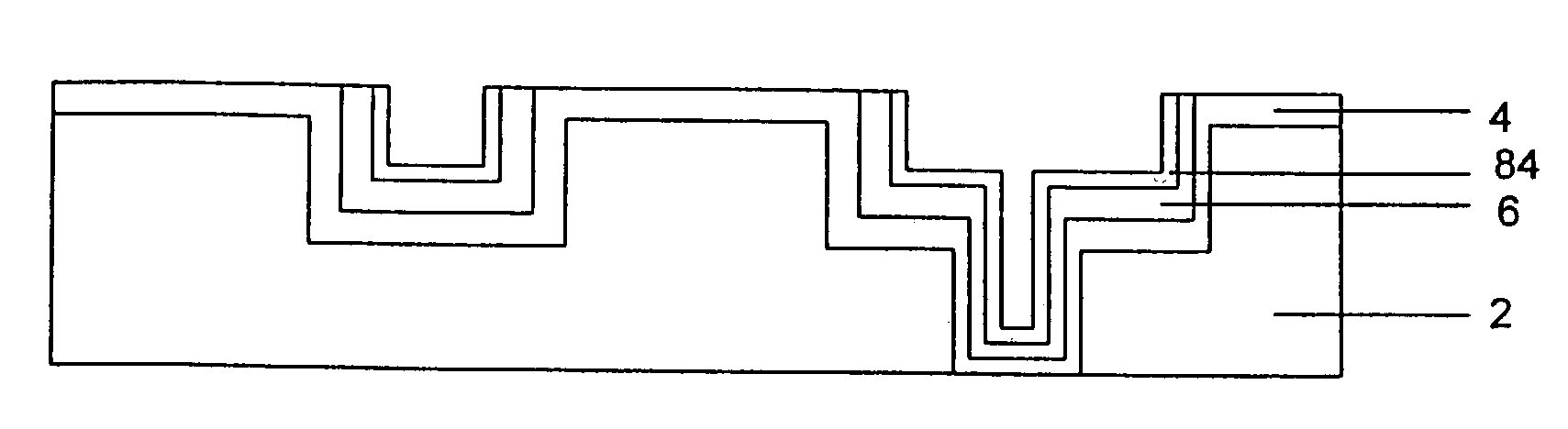
Formation of deep via airgaps for three dimensional wafer to wafer interconnect
InactiveUS20060223301A1Semiconductor/solid-state device detailsSolid-state devicesConductive materialsSemiconductor
Owner:INTERUNIVERSITAIR MICRO ELECTRONICS CENT (IMEC VZW)
Interconnect structure for stacked semiconductor device
InactiveUS6465892B1Shorten the line lengthEasy to produceSemiconductor/solid-state device detailsSolid-state devicesDevice materialInterconnection
In a multi-layer interconnection structure, the wiring length is to be reduced, and the interconnection is to be straightened, at the same time as measures need to be taken against radiation noise. To this end, there is disclosed a semiconductor device in which plural semiconductor substrates, each carrying semiconductor elements, are bonded together. On each semiconductor substrate is deposited an insulating layer through which is formed a connection wiring passed through the insulating layer so as to be connected to the interconnection layer of the semiconductor element. On a junction surface of at least one of the semiconductor substrates is formed an electrically conductive layer of an electrically conductive material in which an opening is bored in association with the connection wiring. The semiconductor substrates are bonded together by the solid state bonding technique to interconnect the connection wirings formed on each semiconductor substrate.
Owner:LAPIS SEMICON CO LTD +9
Electrolytic capacitors with a polymeric outer layer
ActiveUS6987663B2Reduce leakage currentLow ESRHybrid capacitor electrolytesSolid electrolytic capacitorsPolymer scienceElectrolysis
Electrolytic capacitors having low equivalent series resistance and low leakage current are described. The electrolytic capacitors include a solid electrolyte layer of a conductive material in particular a conductive polymer, and an outer layer that includes binders, polymeric anions and conductive polymers (e.g., polythiophenes). Also described is a method of preparing electrolytic capacitors that involves forming the conductive polymer of the solid electrolyte layer in situ by means of chemical oxidative polymerization or electrochemical polymerization. Electronic circuits that include the electrolytic capacitors are also described.
Owner:HERAEUS PRECIOUS METALS GMBH & CO KG
Electrically conductive/insulative over-shoe for tissue fusion
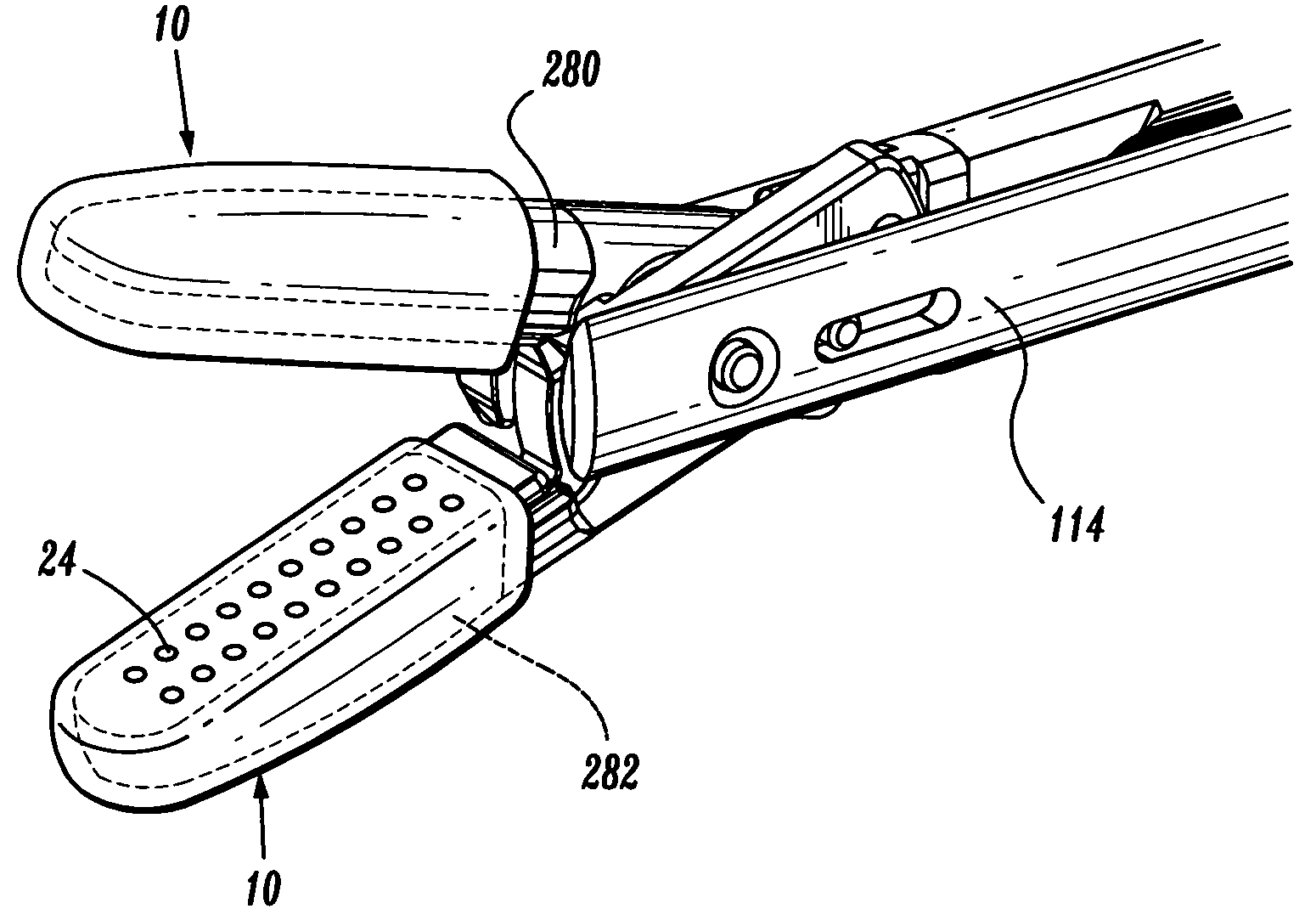
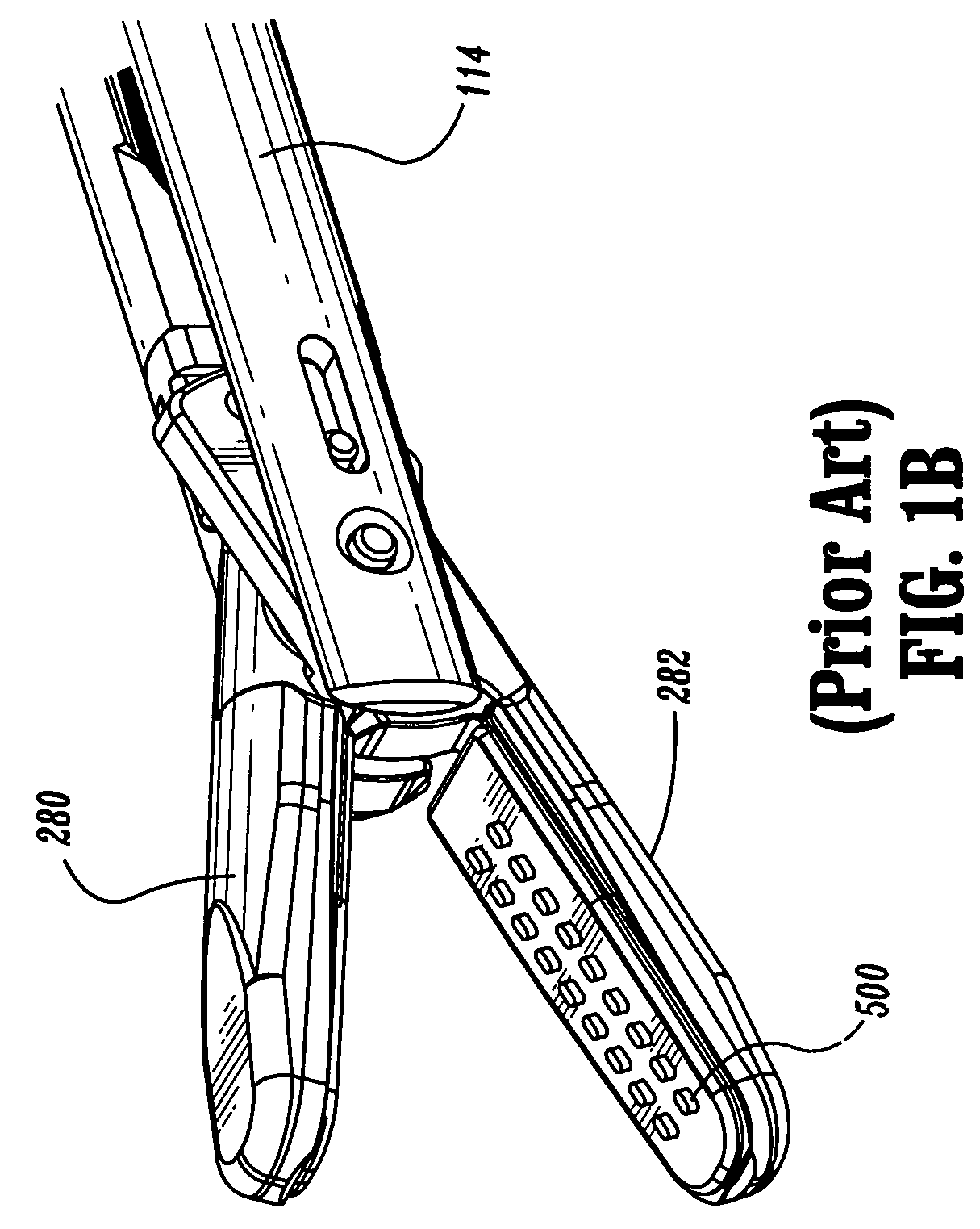
ActiveUS7442193B2Promotes friction fit engagementSurgical instruments for heatingCoatingsConductive materialsAtops
An over shoe for use with electrosurgical instruments having a pair of juxtaposed jaw members pivotably associated with one another, at least one of which includes an electrically conductive surface disposed thereon which is in electrical engagement with an electrosurgical energy source. According to one aspect of the present disclosure, the over shoe includes a tissue contacting wall configured and dimensioned to selectively and substantially overlie the electrically conductive surface of the electrosurgical instrument. The tissue contacting wall is fabricated from a non-conductive material and includes a plurality of apertures formed therethrough. In another embodiment, the tissue contacting wall is electrically conductive and is configured for selective engagement atop on of the jaw members.
Owner:COVIDIEN AG
Chip interconnect and packaging deposition methods and structures
InactiveUS7147766B2Prevent removalMinimizing disparitySolid-state devicesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingEngineeringConductive materials
The present invention relates to a method for fabricating high performance chip interconnects and packages by providing methods for depositing a conductive material in cavities of a substrate in a more efficient and time saving manner. This is accomplished by selectively removing portions of a seed layer from a top surface of a substrate and then depositing a conductive material in the cavities of the substrate, where portions of the seed layer remains in the cavities. Another method includes forming an oxide layer on the top surface of the substrate such that the conductive material can be deposited in the cavities without the material being formed on the top surface of the substrate. The present invention also discloses methods for forming multi-level interconnects and the corresponding structures.
Owner:NOVELLUS SYSTEMS
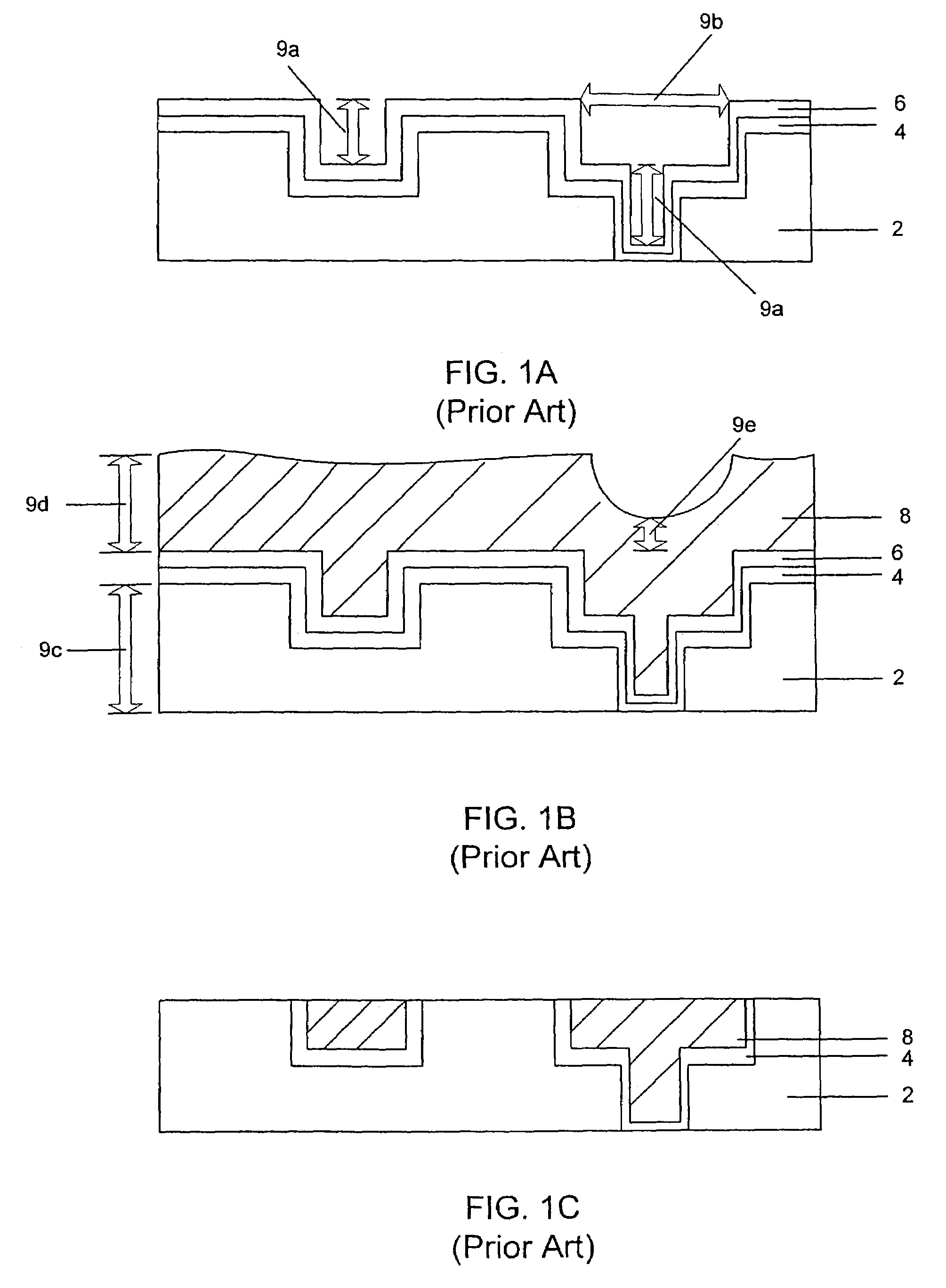
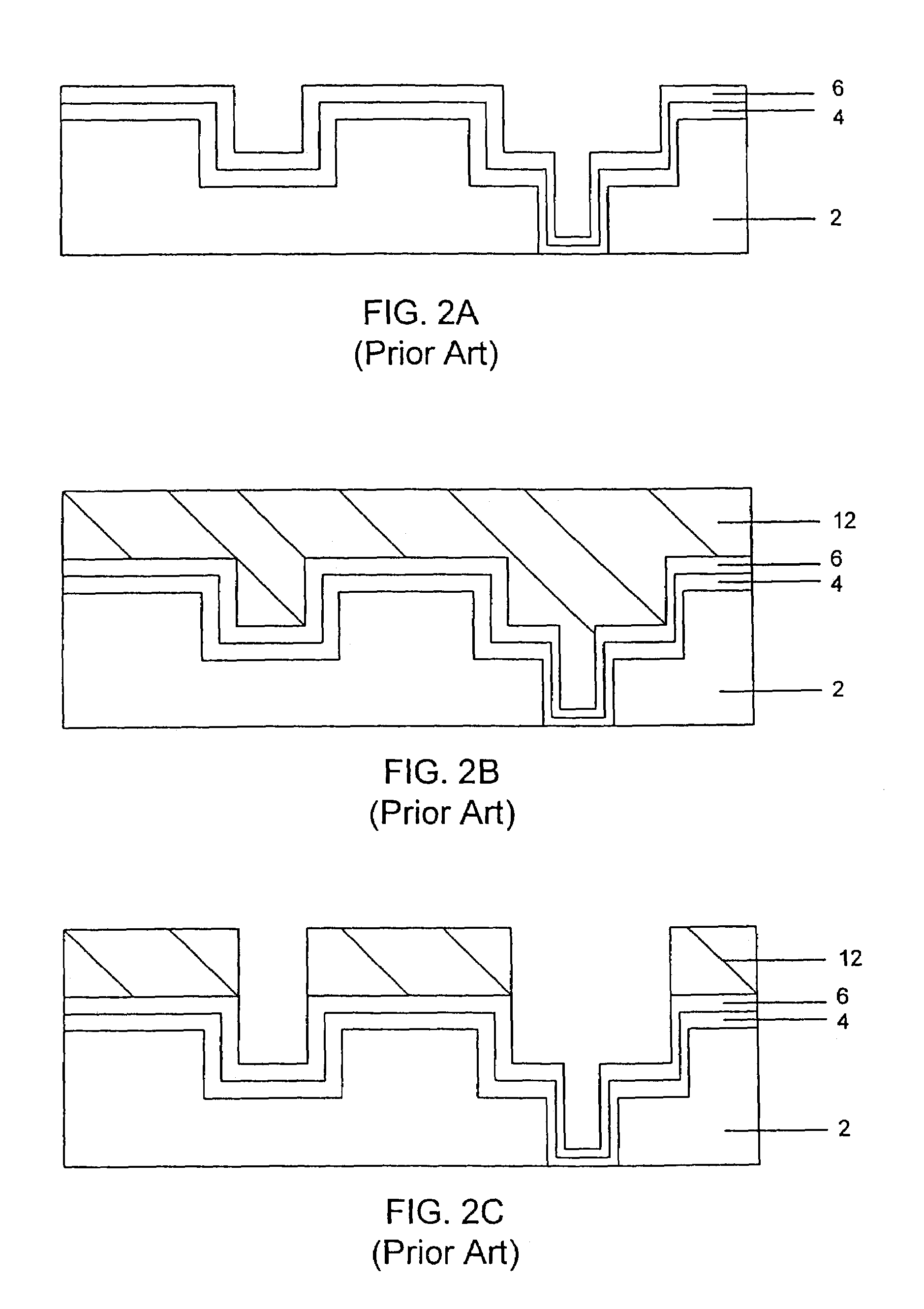
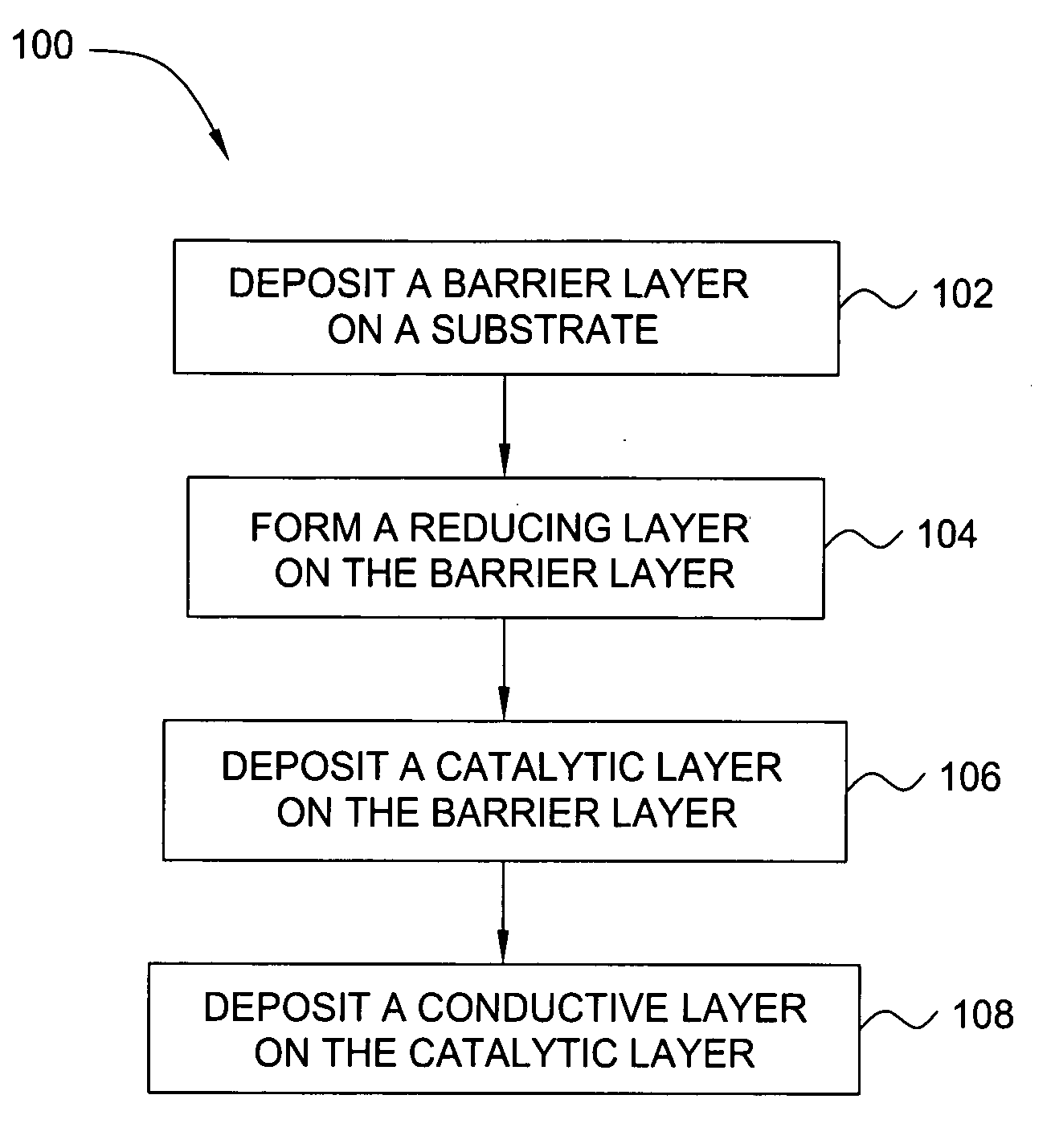
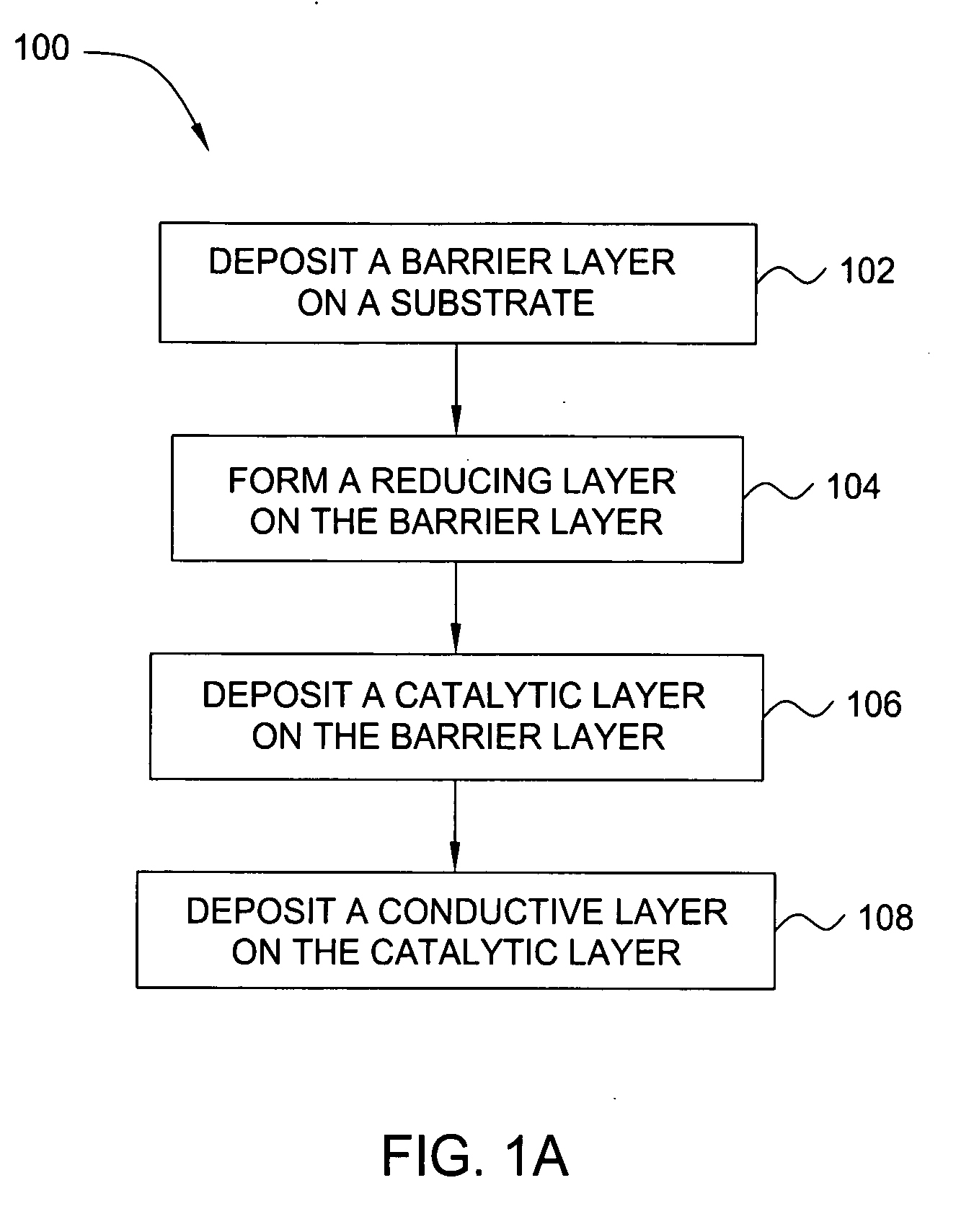
Deposition of an intermediate catalytic layer on a barrier layer for copper metallization
InactiveUS20060240187A1Solid-state devicesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingIridiumSilanes
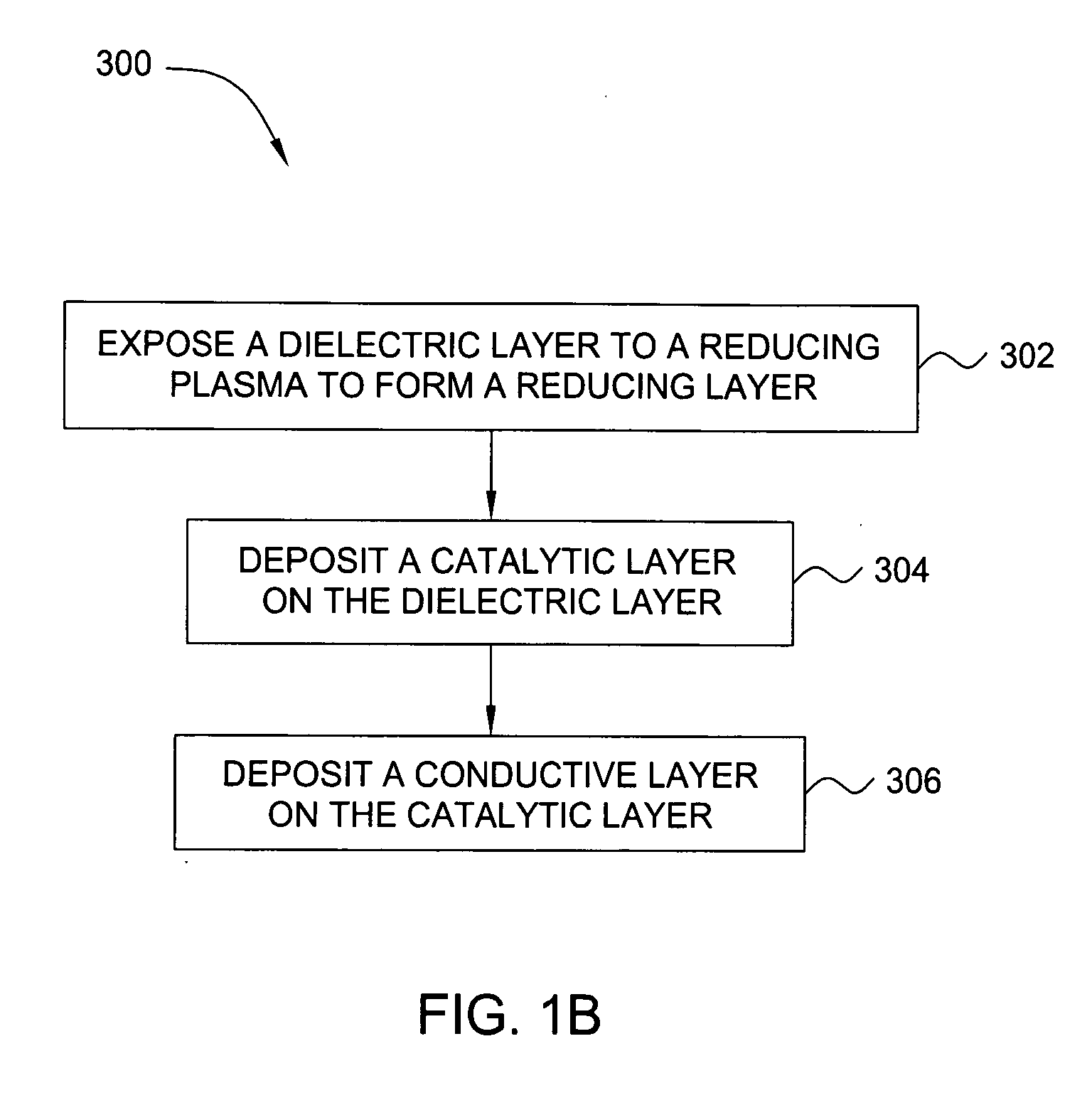
In one embodiment, a method for depositing a conductive material on a substrate is provided which includes exposing a substrate containing a barrier layer to a volatile reducing precursor to form a reducing layer during a soak process, exposing the reducing layer to a catalytic-metal precursor to deposit a catalytic metal-containing layer on the barrier layer, and depositing a conductive layer (e.g., copper) on the catalytic metal-containing layer. The volatile reducing precursor may include phosphine, diborane, silane, a plasma thereof, or a combination thereof and be exposed to the substrate for a time period within a range from about 1 second to about 30 seconds during the soak process. The catalytic metal-containing layer may contain ruthenium, cobalt, rhodium, iridium, nickel, palladium, platinum, silver, or copper. In one example, the catalytic metal-containing layer is deposited by a vapor deposition process utilizing ruthenium tetroxide formed by an in situ process.
Owner:APPLIED MATERIALS INC
Phosphor screen and displays systems
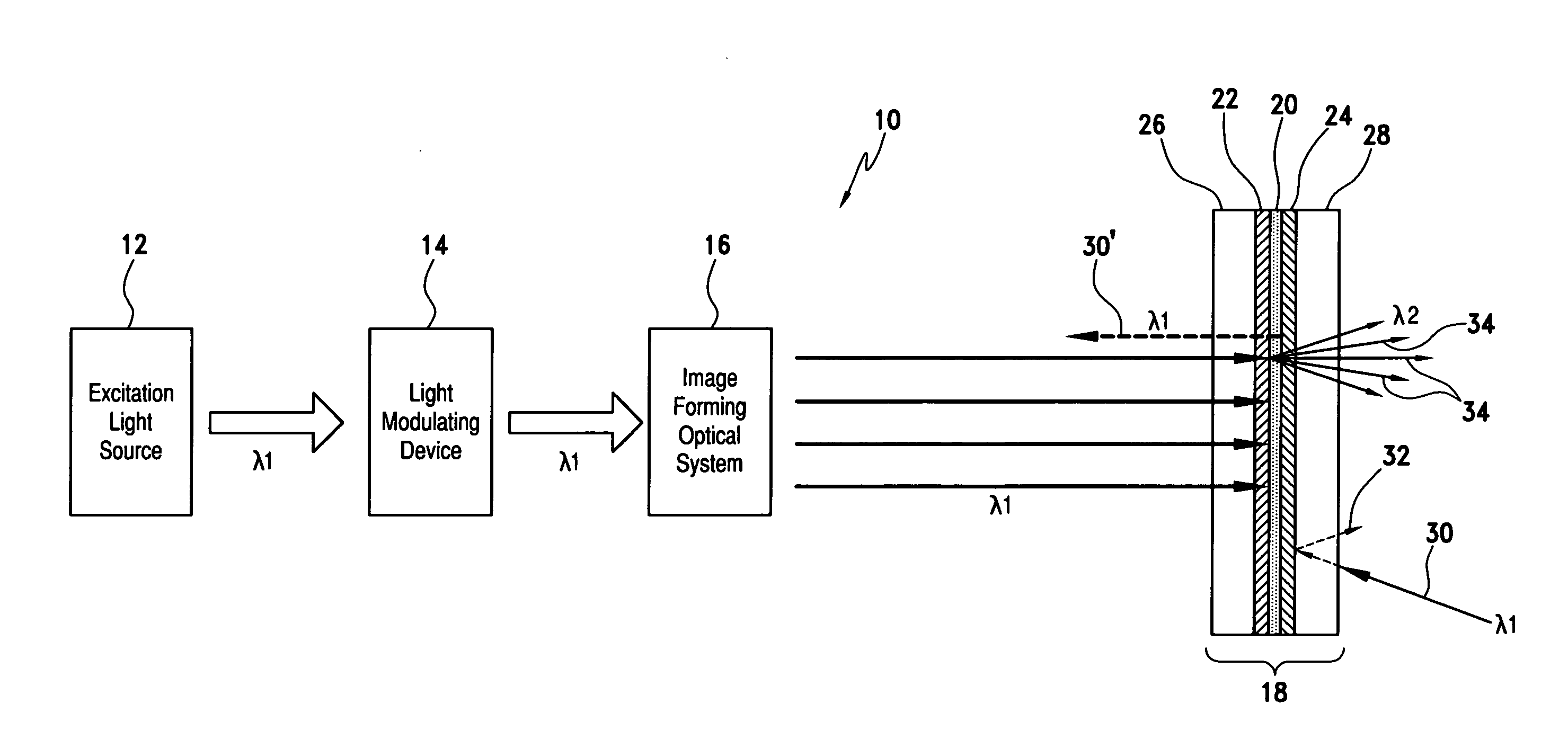
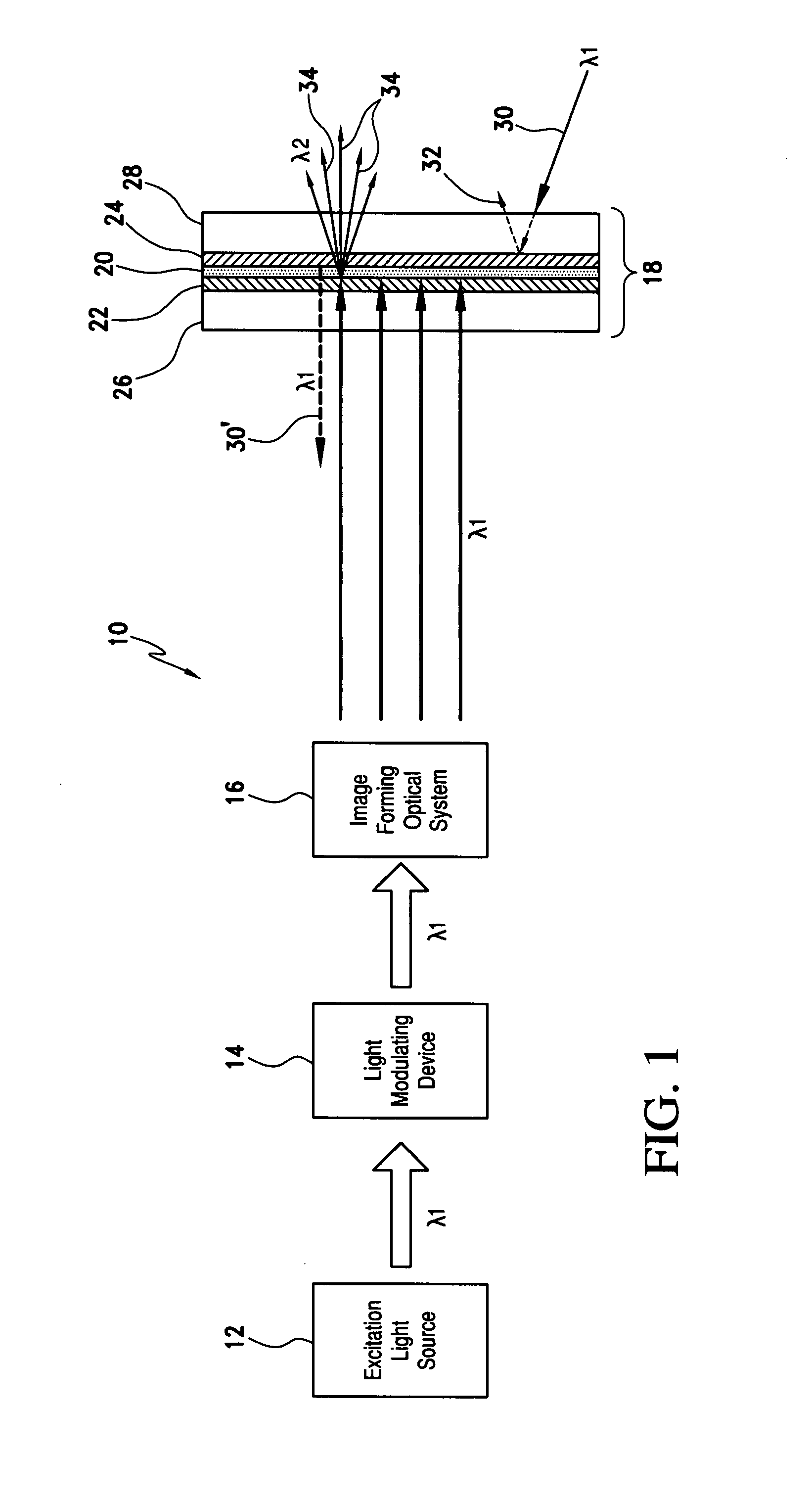
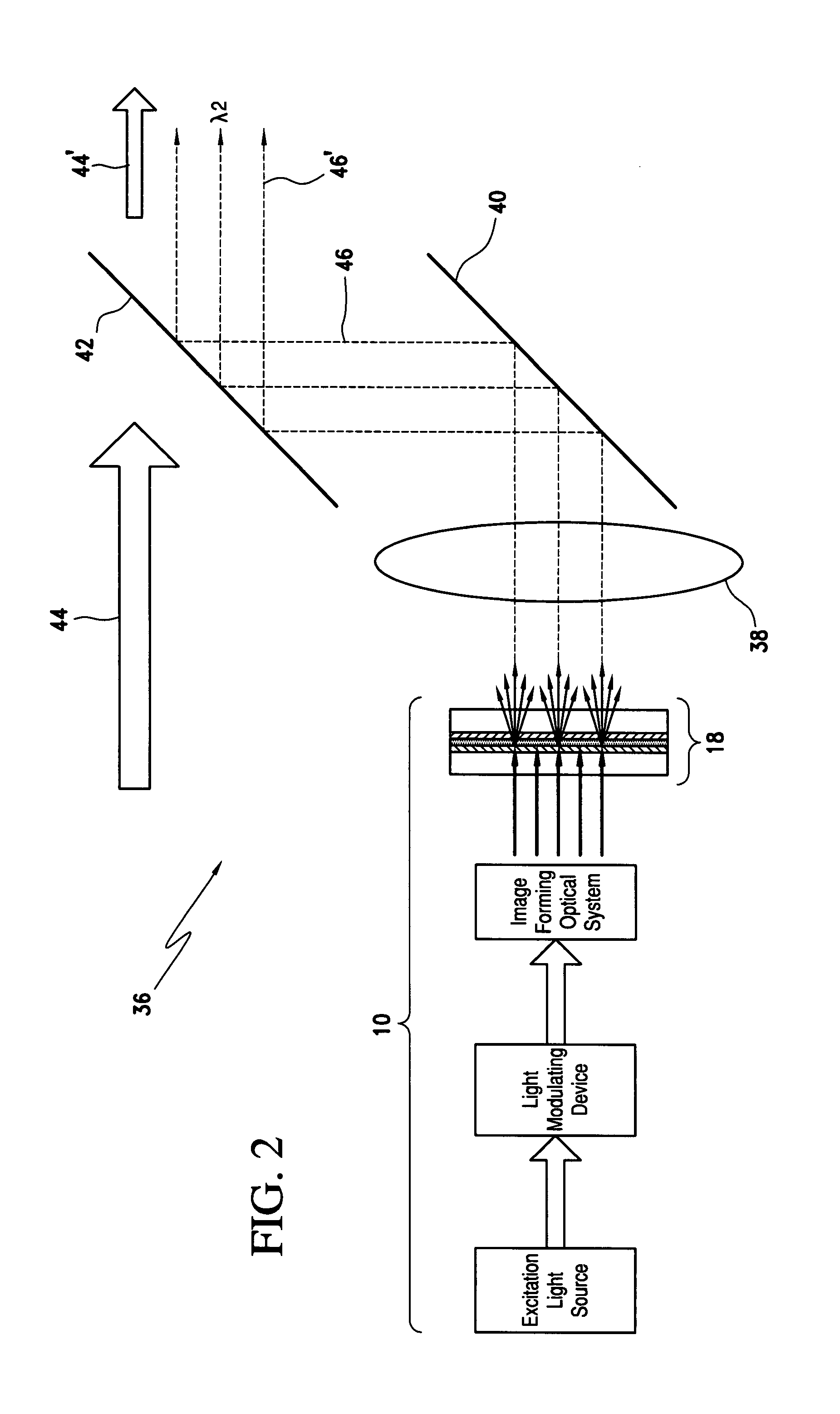
InactiveUS7733571B1Good optical performanceImprove cooling effectOptical filtersNon-linear opticsPhosphorFluorescence
A phosphor screen for image forming including phosphor material being excitable by light in a wavelength λ1. The phosphor screen receives an optical image from an image forming optical system and produces the optical image at a second wavelength λ2. The phosphor screen includes a phosphor layer comprising the phosphor material. A short-pass reflective coating is positioned on a first side of the phosphor layer. The short-pass reflective coating transmits the wavelength λ1 and reflects the wavelength λ2. A long-pass reflective coating is positioned on a second side of the phosphor layer. The long-pass reflective coating transmits the wavelength λ2 and reflects the wavelength λ1. A first substrate is positioned over the short-pass reflective coating. The first substrate is formed of optically clear and thermal conductive material. A second substrate is positioned over the long-pass reflective coating. The second substrate is formed of long-pass absorptive optical filter material that transmits the wavelength λ2 and absorbs wavelength λ1 from ambient light to prevent the phosphor layer from being excited by the ambient light. The phosphor screen may alternatively be used for a direct-view visual display apparatus. These principles can also be utilized for backlighting and general illumination applications.
Owner:ROCKWELL COLLINS INC
Method and apparatus for 3D interconnect
ActiveUS8076237B2Improve adhesionInhibited DiffusionSemiconductor/solid-state device detailsPrinted circuit aspectsConductive materialsEngineering
The present invention discloses methods for depositing a material, particularly a conductive material, in cavities of a substrate and forming bonding contacts or pads thereon. An intracavity structure may be utilized in conjunction with embodiments of the present invention to provide efficient filling of diverse cavities within the substrate. Also provided are embodiments for interconnection structures using filled cavities, along with electrically conductive or reactive structures which may include capacitors fabricated within a substrate.
Owner:ASM NUTOOL
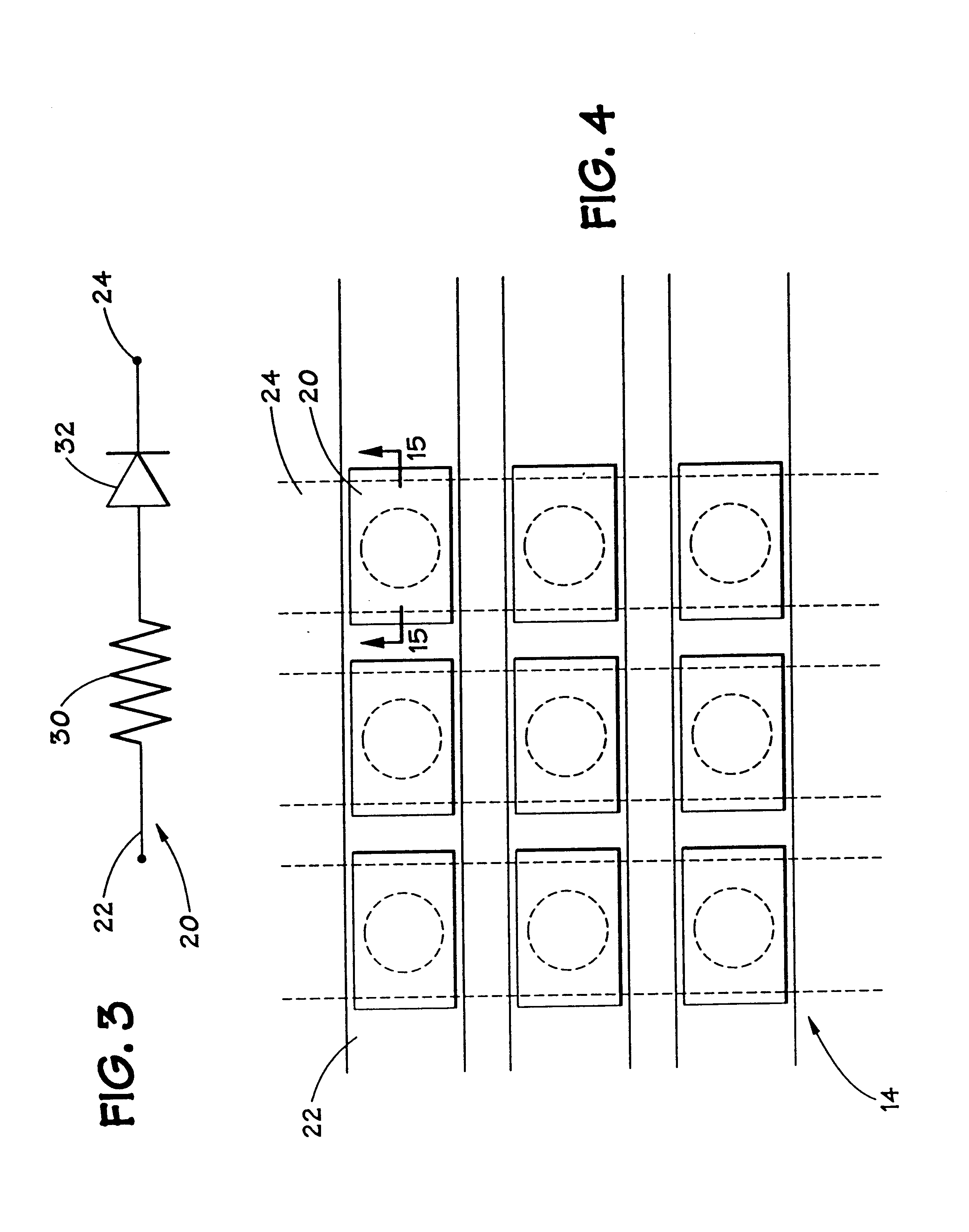
Memory elements and methods for making same
Annular, linear, and point contact structures are described which exhibit a greatly reduced susceptibility to process deviations caused by lithographic and deposition variations than does a conventional circular contact plug. In one embodiment, a standard conductive material such as carbon or titanium nitride is used to form the contact. In an alternative embodiment, a memory material itself is used to form the contact. These contact structures may be made by various processes, including chemical mechanical planarization and facet etching.
Owner:ROUND ROCK RES LLC
Medical instrument with sensor for use in a system and method for electromagnetic navigation
Owner:COVIDIEN LP
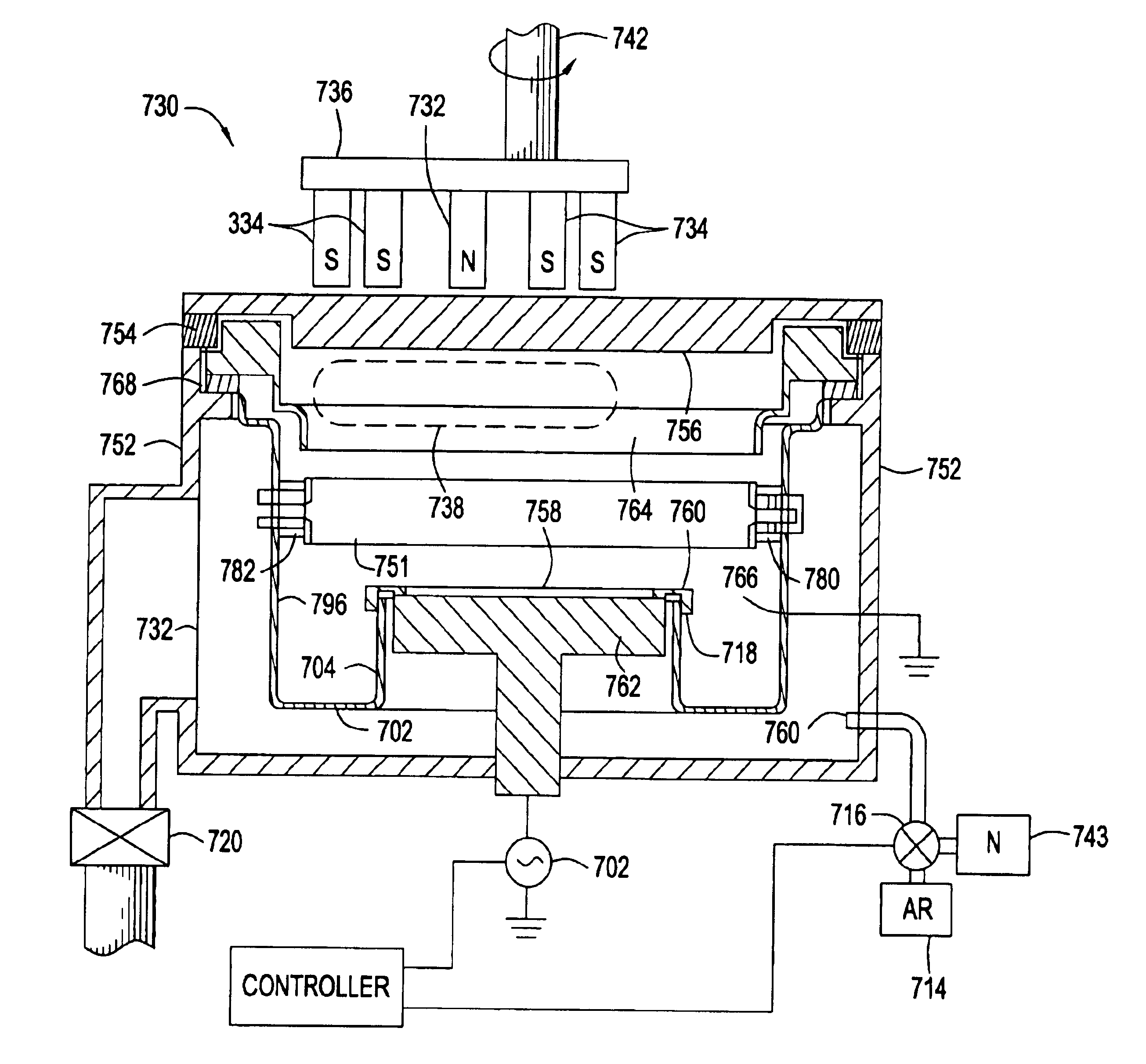
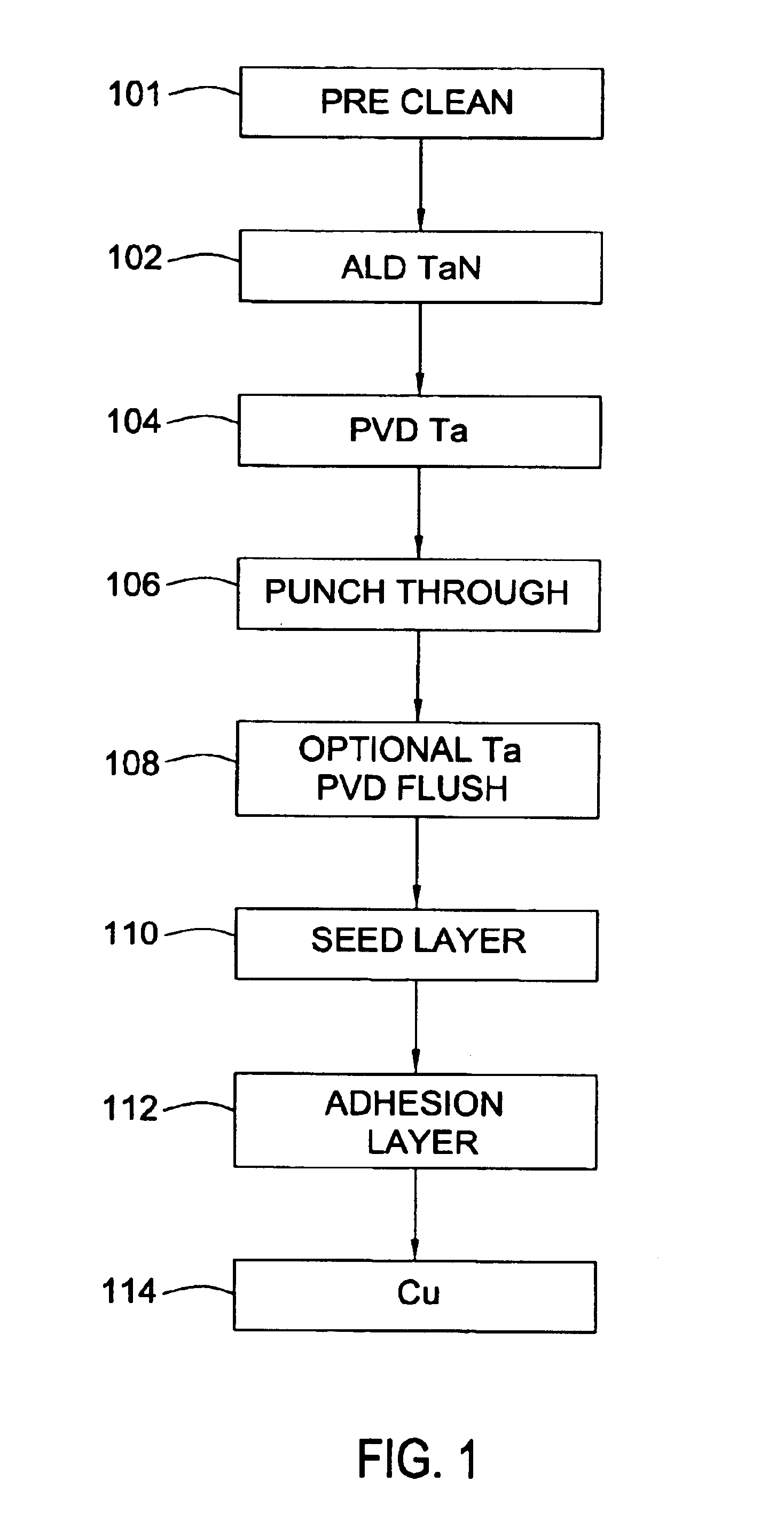
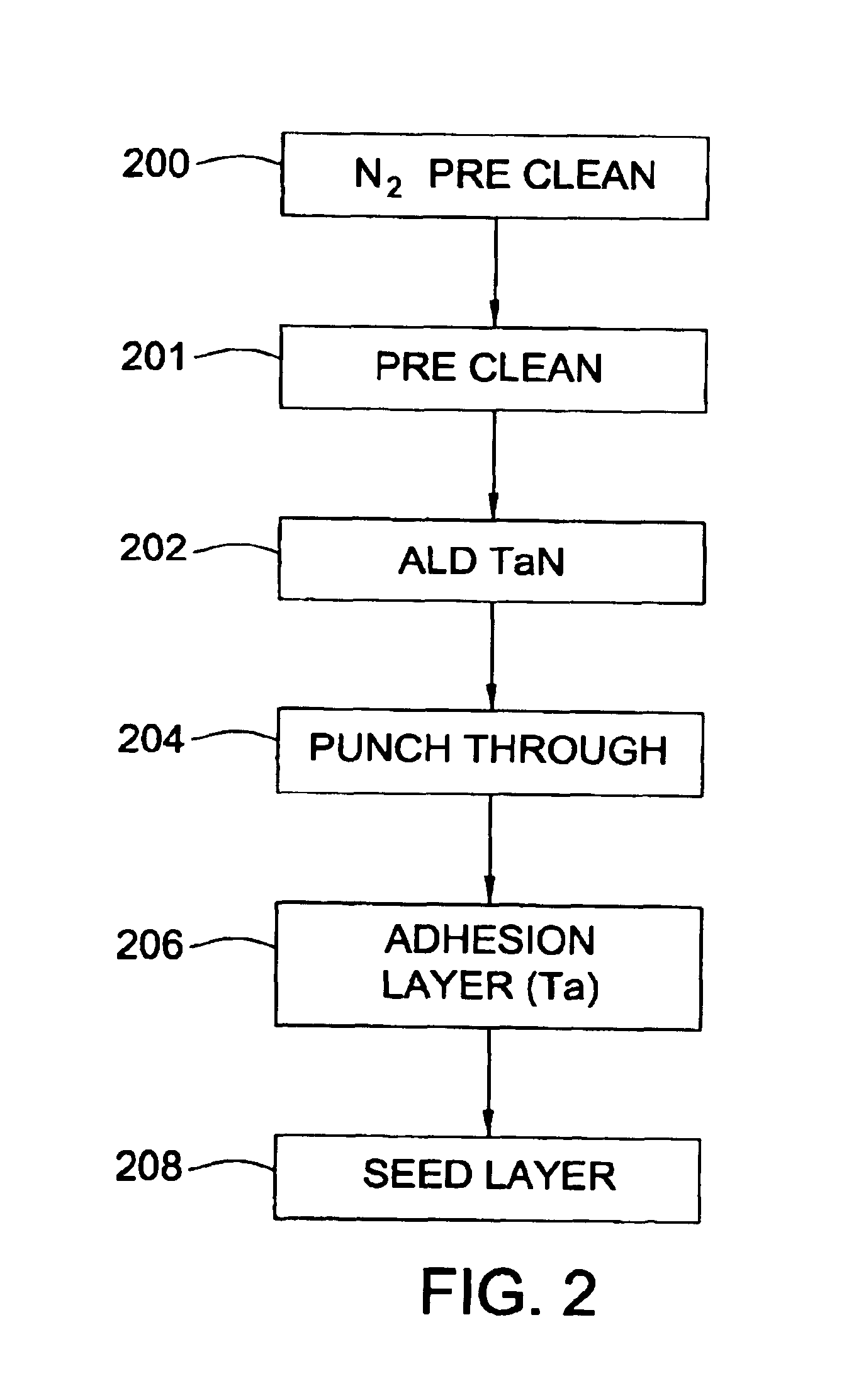
Integration of ALD tantalum nitride for copper metallization
InactiveUS7049226B2Semiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingChemical vapor deposition coatingTantalum nitrideConductive materials
A method and apparatus for depositing a tantalum nitride barrier layer is provided for use in an integrated processing tool. The tantalum nitride is deposited by atomic layer deposition. The tantalum nitride is removed from the bottom of features in dielectric layers to reveal the conductive material under the deposited tantalum nitride. Optionally, a tantalum layer may be deposited by physical vapor deposition after the tantalum nitride deposition. Optionally, the tantalum nitride deposition and the tantalum deposition may occur in the same processing chamber.
Owner:APPLIED MATERIALS INC
Method of forming MEMS device
InactiveUS6861277B1Decorative surface effectsSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingConductive materialsOptoelectronics
A method of forming a MEMS device includes depositing a conductive material on a substructure, forming a first sacrificial layer over the conductive material, including forming a substantially planar surface of the first sacrificial layer, and forming a first element over the substantially planar surface of the first sacrificial layer, including communicating the first element with the conductive material through the first sacrificial layer. In addition, the method includes forming a second sacrificial layer over the first element, including forming a substantially planar surface of the second sacrificial layer, forming a support through the second sacrificial layer to the first element after forming the second sacrificial layer, including filling the support, and forming a second element over the support and the substantially planar surface of the second sacrificial layer. As such, the method further includes substantially removing the first sacrificial layer and the second sacrificial layer, thereby supporting the second element relative to the first element with the support.
Owner:TAIWAN SEMICON MFG CO LTD
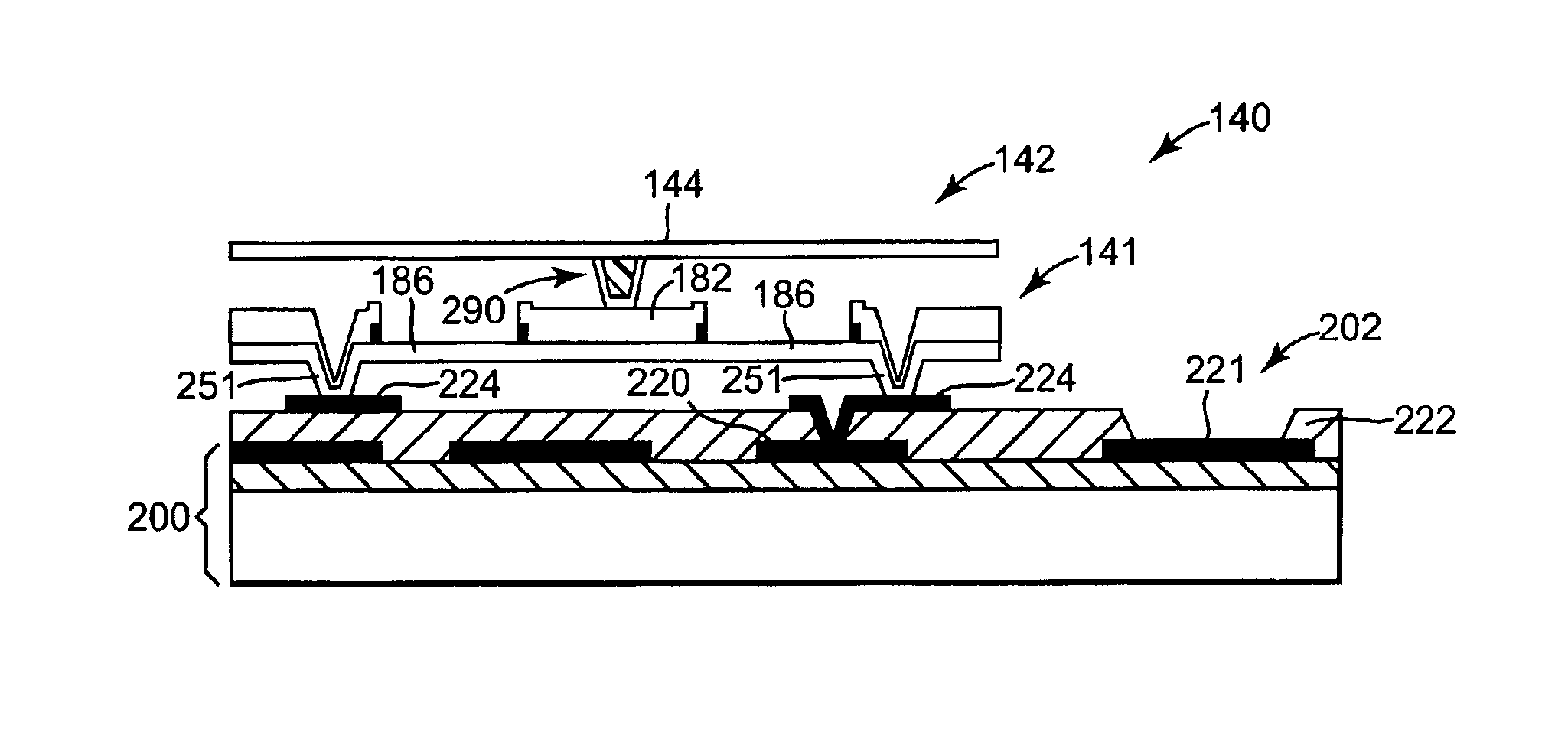
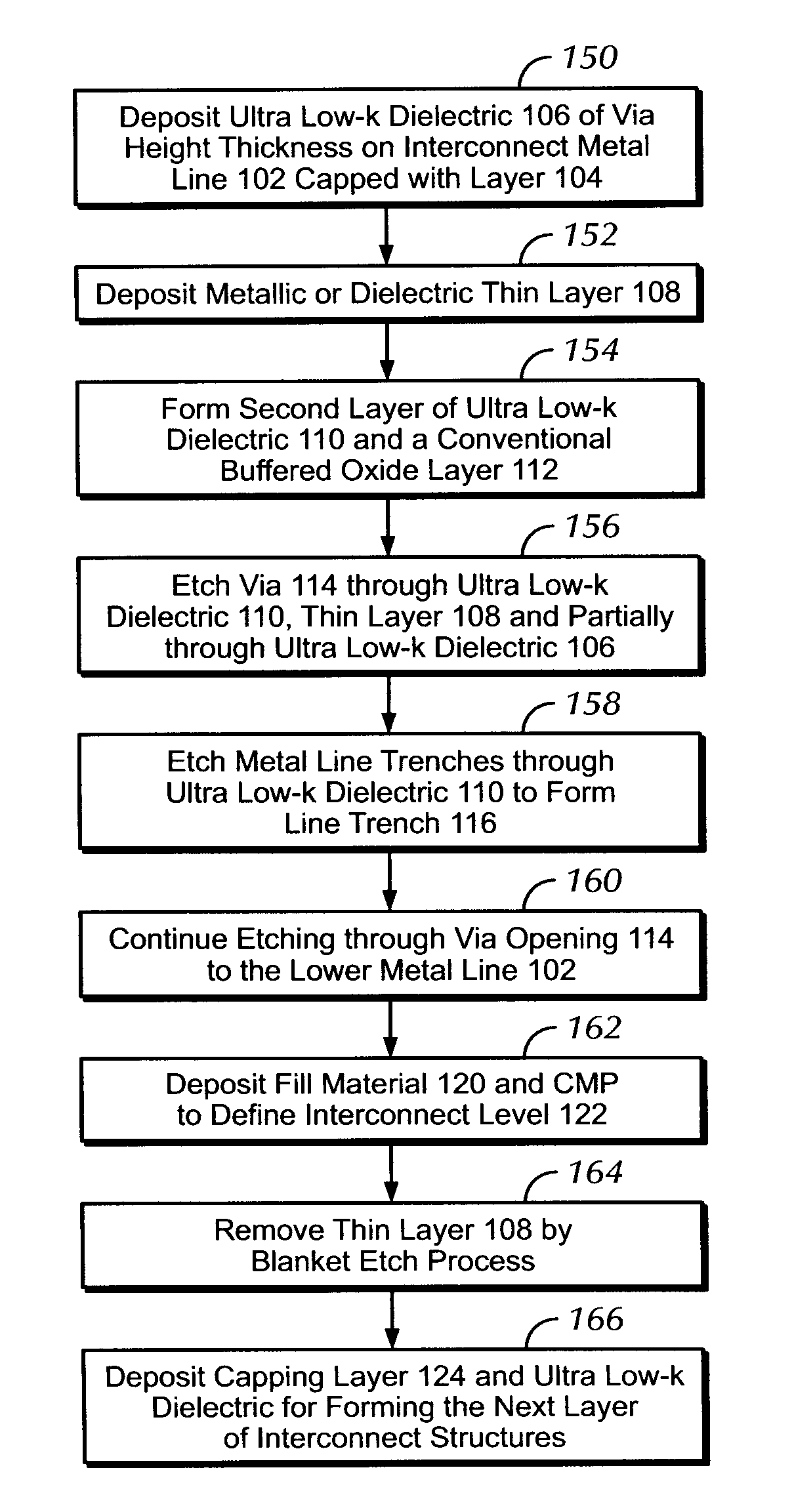
Method of Forming Metal Interconnect Structures in Ultra Low-K Dielectrics
ActiveUS20110117737A1Semiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingMetal interconnectConductive materials
A metal interconnect structure in ultra low-k dielectrics is described having a capped interconnect layer; an interconnect feature with a contact via and a contact line formed in a dielectric layer, where the via is partially embedded into the interconnect layer; and a thin film formed on the dielectric layer and separating the dielectric layer from the contact line. A method of fabricating the interconnect structure is also described and includes forming a first dielectric on a capped interconnect element; forming a thin film over the first dielectric; forming a second dielectric on the thin film; forming a via opening on the second dielectric, the thin film and extending into the first dielectric; forming a line trench on a portion of the second dielectric; and filling the via opening and the line trench with a conductive material for forming a contact via and a contact line, where the contact via is partially embedded in the interconnect element.
Owner:GLOBALFOUNDRIES US INC
Physiological sensor device
InactiveUS6385473B1Improve breathabilityEasy to moveElectrocardiographySensorsEngineeringConductive materials
A physiological sensor device for attachment to a mammalian subject including first and second regions of sensors attachable to a subject in use, which first and second regions of sensors are separated by a flexible web adapted to enable variable separation of the first and second sensor regions from one another in use. The physiological sensor device is manufactured by forming a strip of electrically conductive material on a flexible electrically non-conductive substrate and cutting a slot through both the flexible substrate and conductive strip to define a pair of adjacent edges of conductive material separated by a non-conductive gap thereby also to define adjacent electrode sensors each having one of the pair of adjacent edges formed in the strip of conductive material. The physiological sensor device is attached to the subject for measurement of numerous physiological parameters for a period of time, such as 24 hours, and is then thrown away.
Owner:CLEARPATH PARTNERS
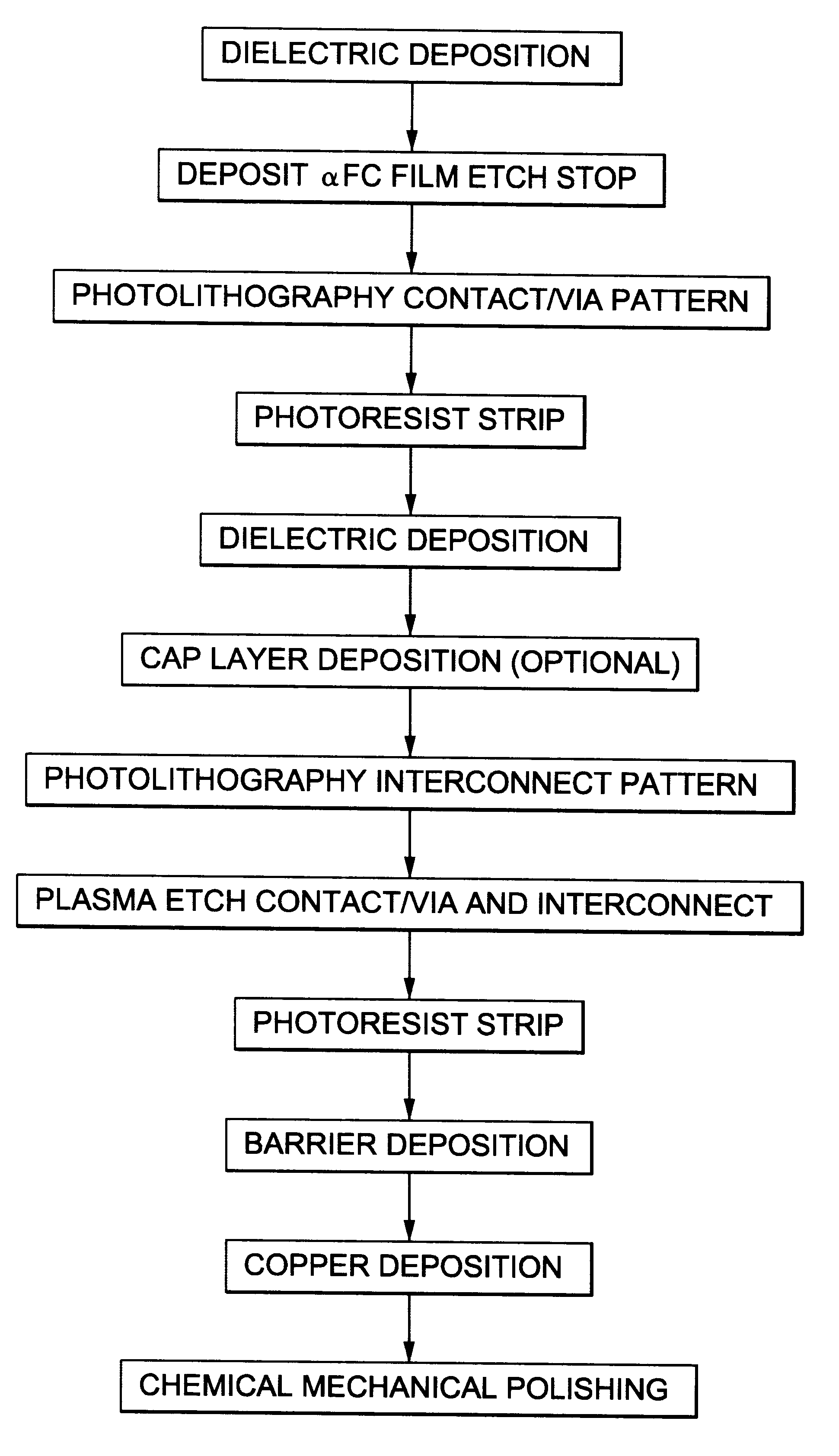
An etch stop layer for dual damascene process
The present invention provides a carbon based etch stop, such as a diamond like amorphous carbon, having a low dielectric constant and a method of forming a dual damascene structure. The low k etch stop is preferably deposited between two dielectric layers and patterned to define the underlying interlevel contacts / vias. The second or upper dielectric layer is formed over the etch stop and patterned to define the intralevel interconnects. The entire dual damascene structure is then etched in a single selective etch process which first etches the patterned interconnects, then etches the contact / vias past the patterned etch stop. The etch stop has a low dielectric constant relative to a conventional SiN etch stop, which minimizes the capacitive coupling between adjacent interconnect lines. The dual damascene structure is then filled with a suitable conductive material such as aluminum or copper and planarized using chemical mechanical polishing.
Owner:APPLIED MATERIALS INC
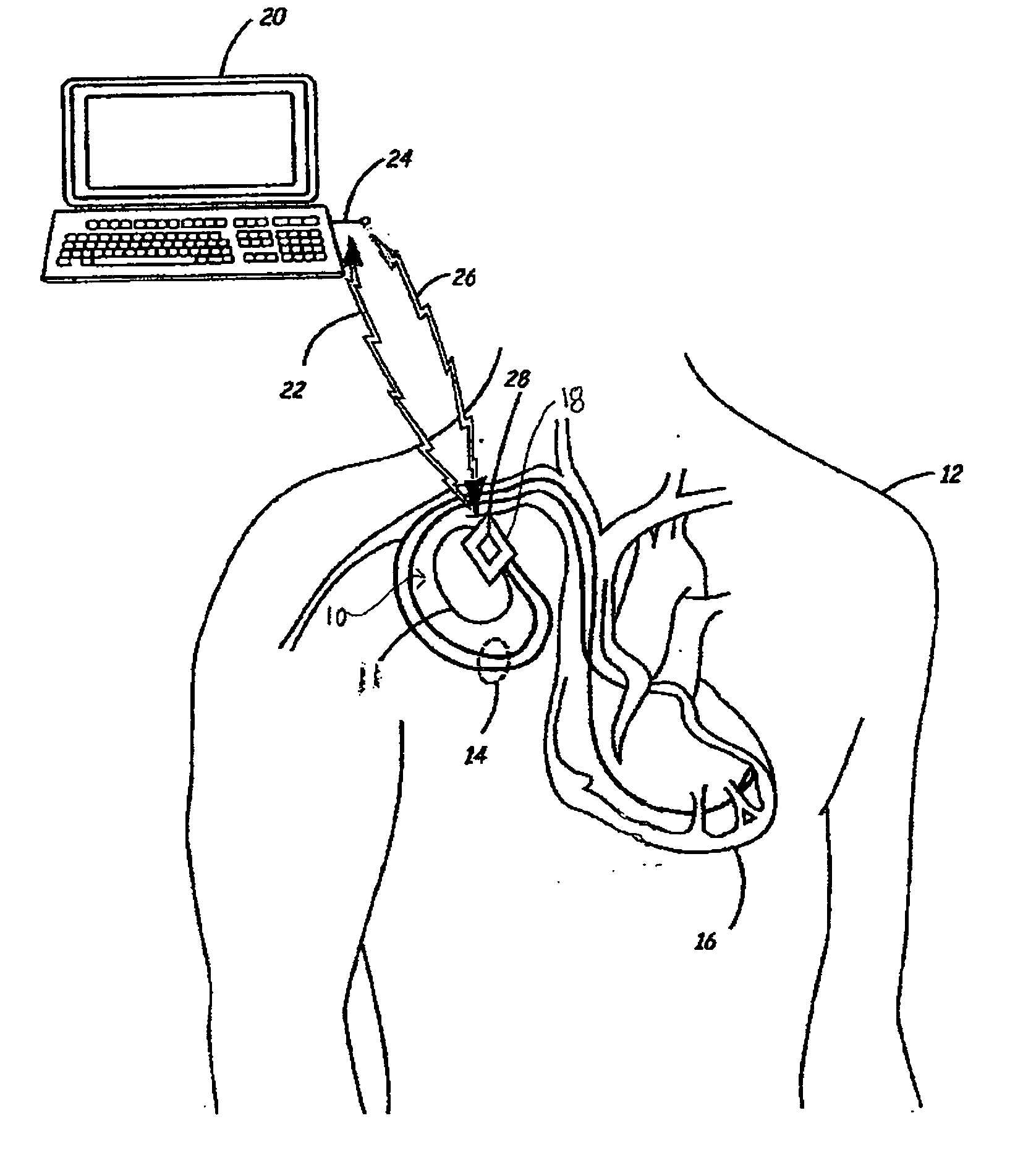
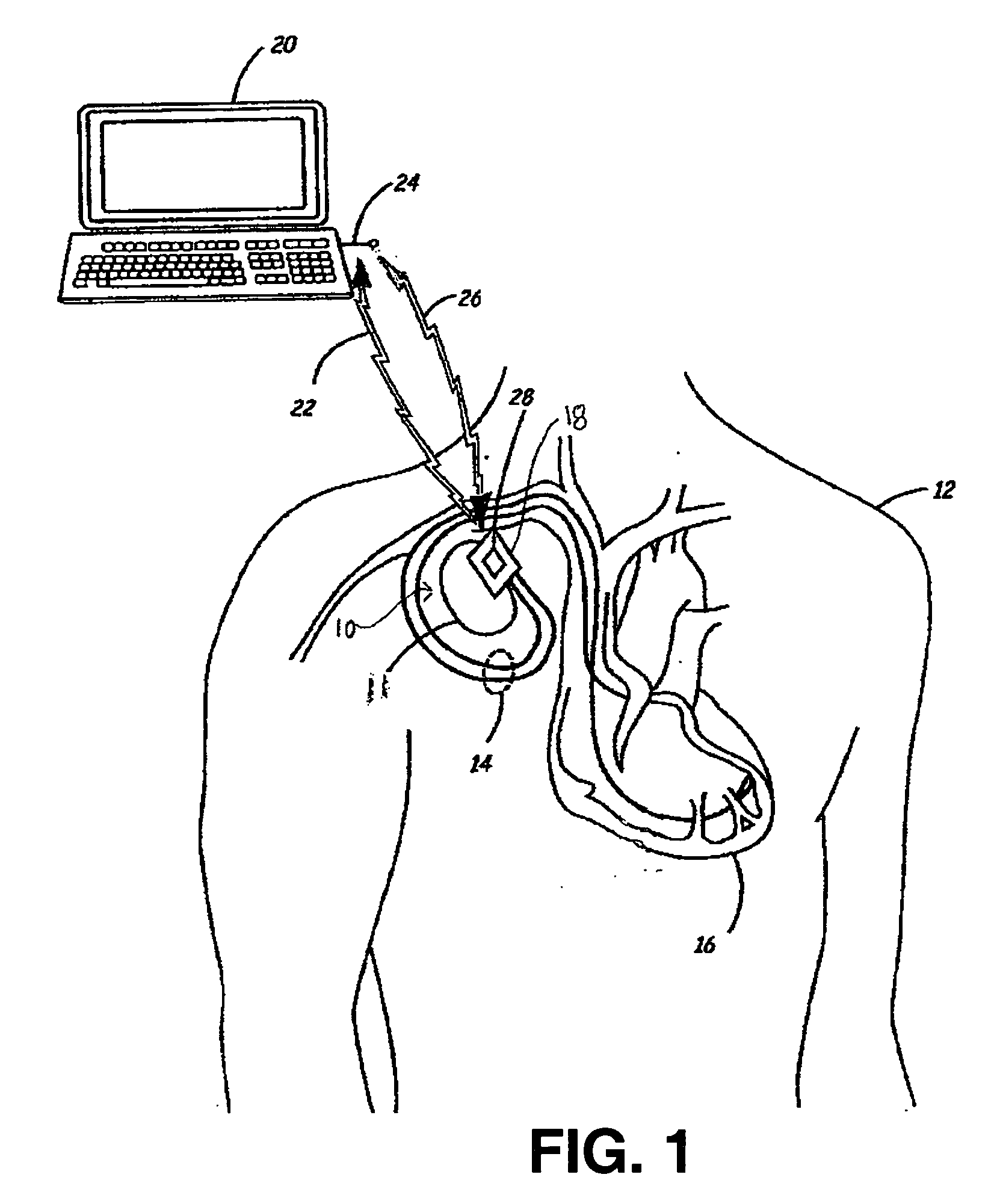
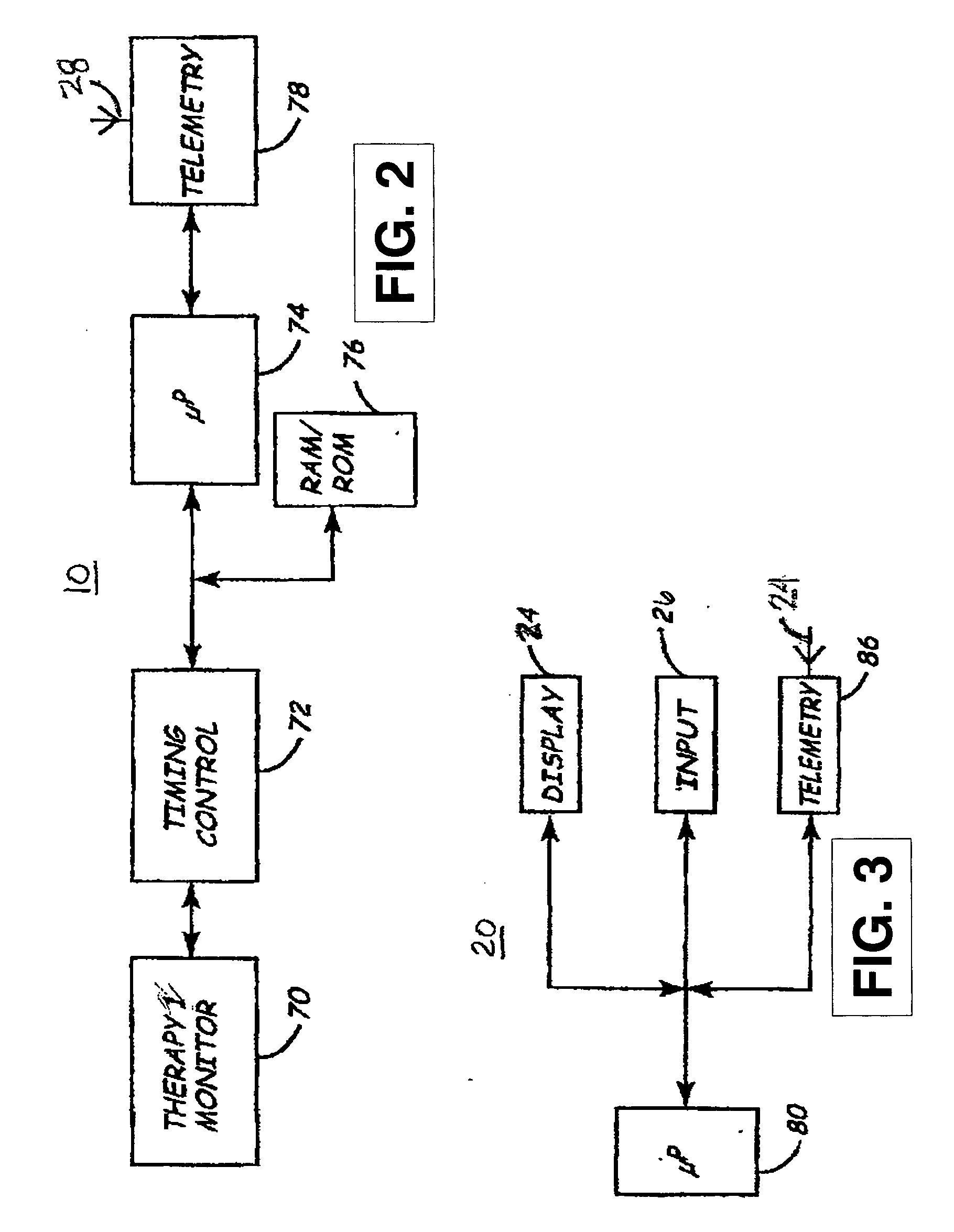
Implantable medical device package antenna
InactiveUS20060020300A1Improve efficiencyImprove reliabilityElectrotherapySurgical furnitureTelecommunications linkCommunications system
A wireless communication system is provided that includes an antenna structure adapted for coupling to a medical device antenna when the medical device is not implanted in a patient's body. The antenna structure effectively extends the medical device antenna length, thereby improving the efficiency and reliability of a communication link between the medical device and a programmer or monitor outside the implanted environment. The antenna structure is fabricated from any conductive material, which may be in the form of conductive wire, tape, ink, foil, film, adhesive or the like, and is attached to a portion of a medical device packaging assembly or another accessory device or substrate such as a pouch or overlay. The antenna structure may be a monopole, dipole, slot antenna, microstrip patch, or loop antenna, and may be fixed or movable relative to the substrate on which it is implemented.
Owner:MEDTRONIC INC
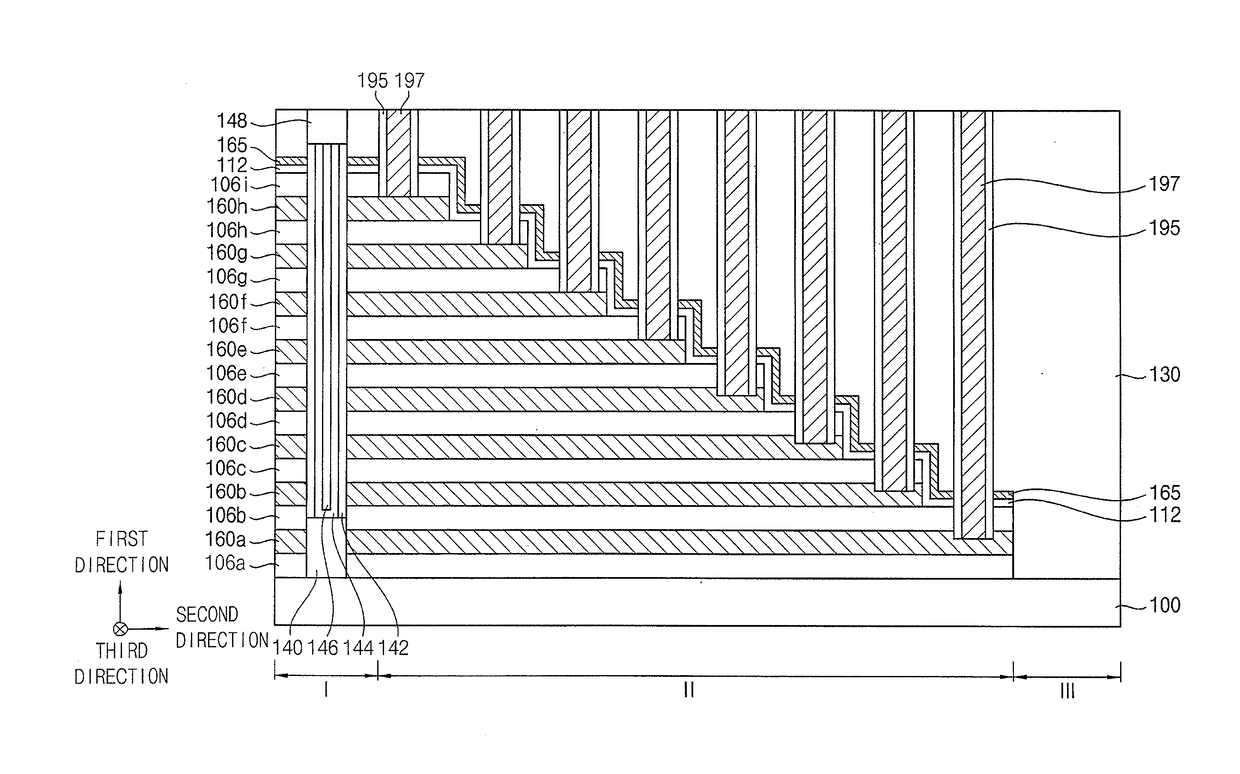
Vertical memory devices and methods of manufacturing the same
ActiveUS20170117222A1Semiconductor/solid-state device detailsSolid-state devicesConductive materialsElectrical and Electronics engineering
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
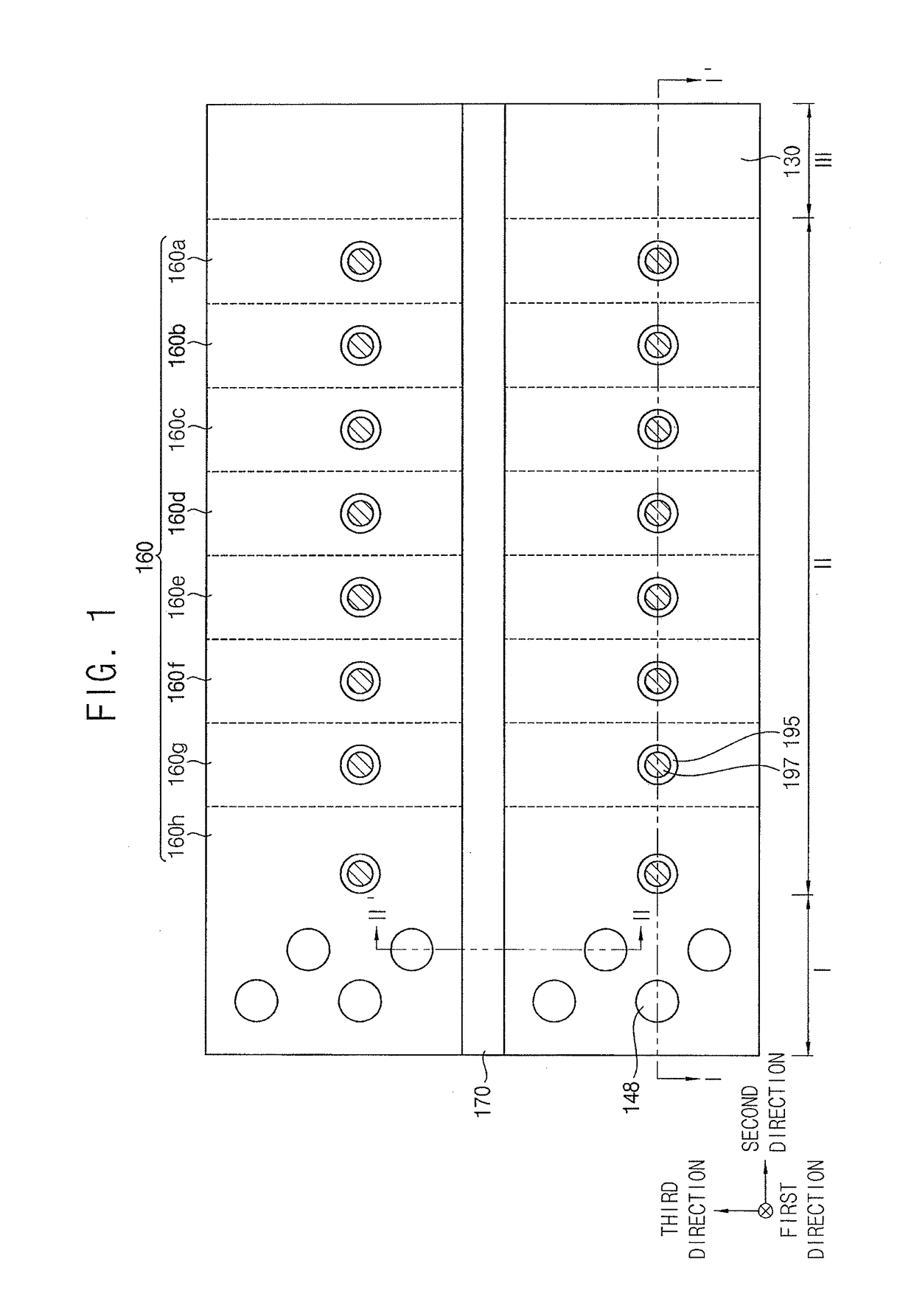
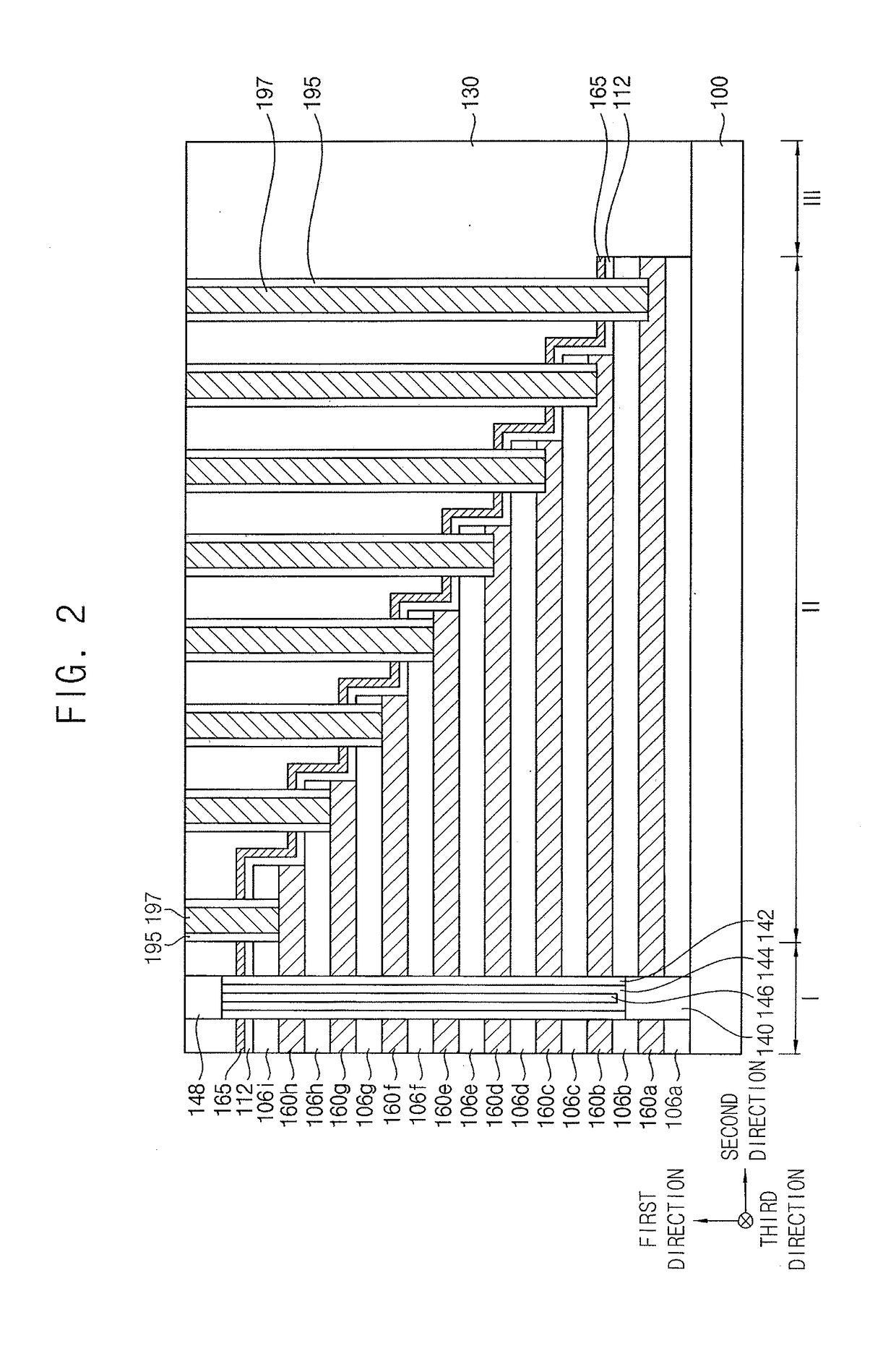
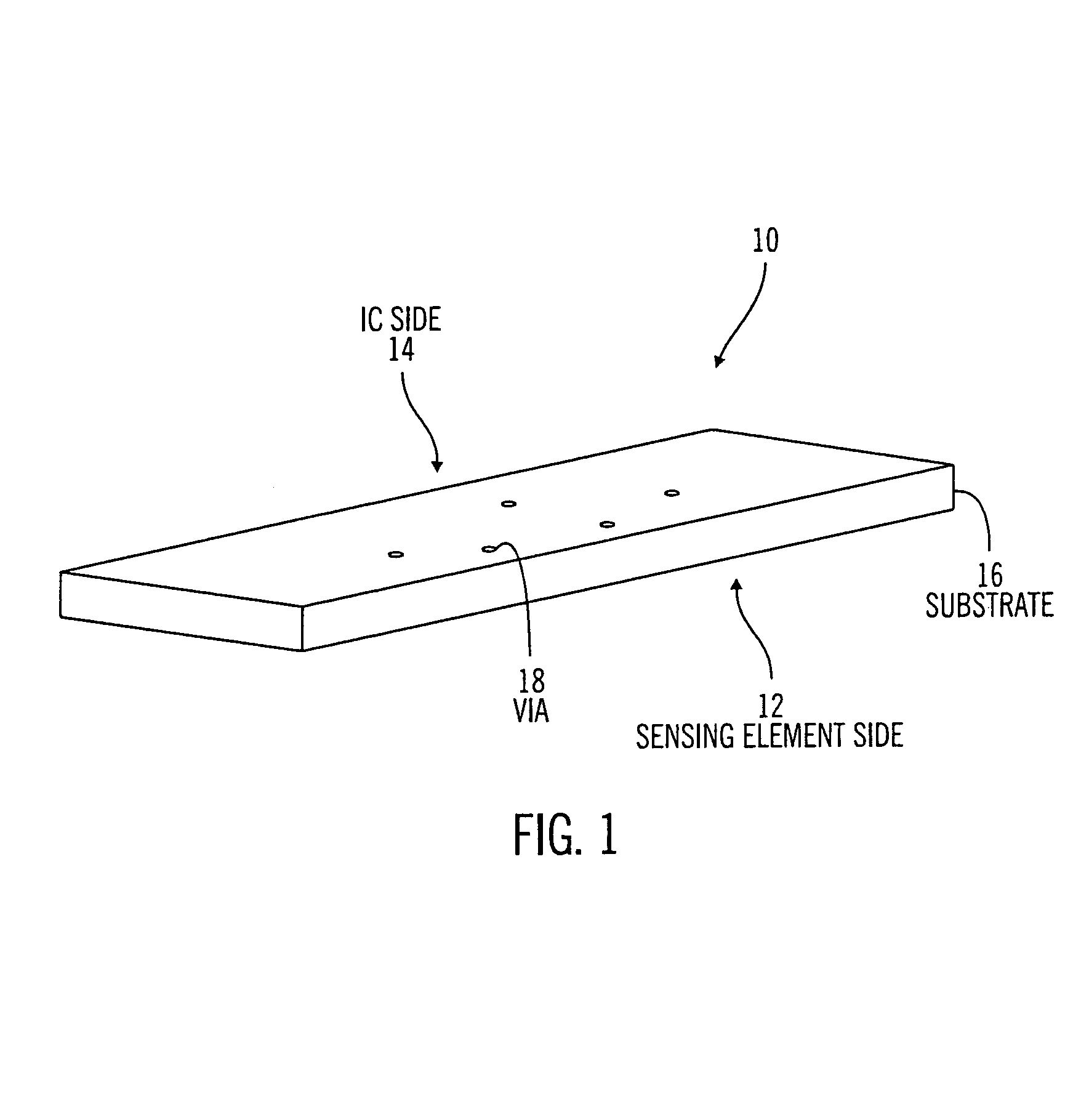
Sensor substrate and method of fabricating same
A substrate with hermetically sealed vias extending from one side of the substrate to another and a method for fabricating same. The vias may be filled with a conductive material such as, for example, a fritless ink. The conductive path formed by the conductive material aids in sealing one side of the substrate from another. One side of the substrate may include a sensing element and another side of the substrate may include sensing electronics.
Owner:MEDTRONIC MIMIMED INC
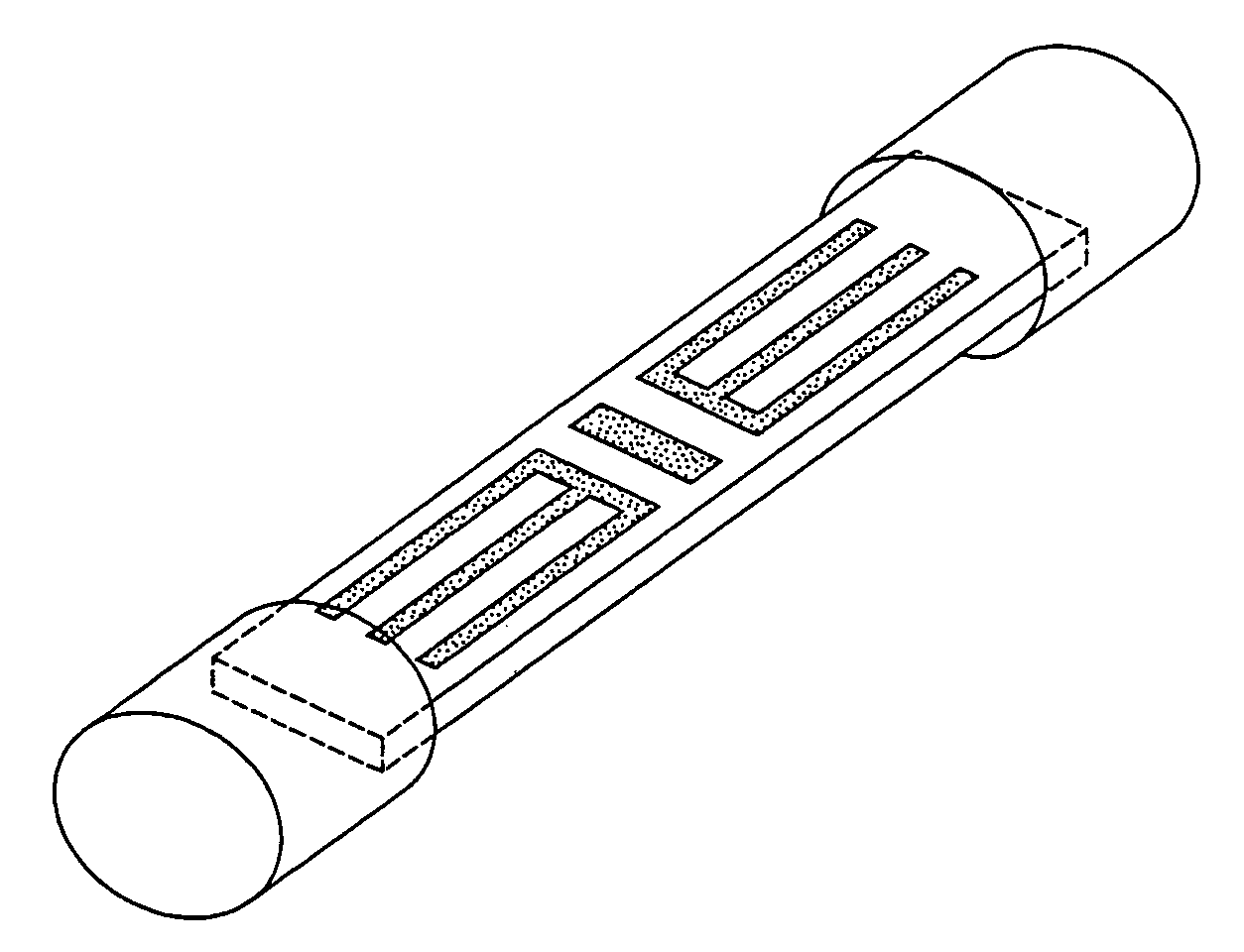
Method of making a transcutaneous electrochemical sensor
InactiveUS6973706B2Efficient productionWave amplification devicesDecorative surface effectsEngineeringConductive materials
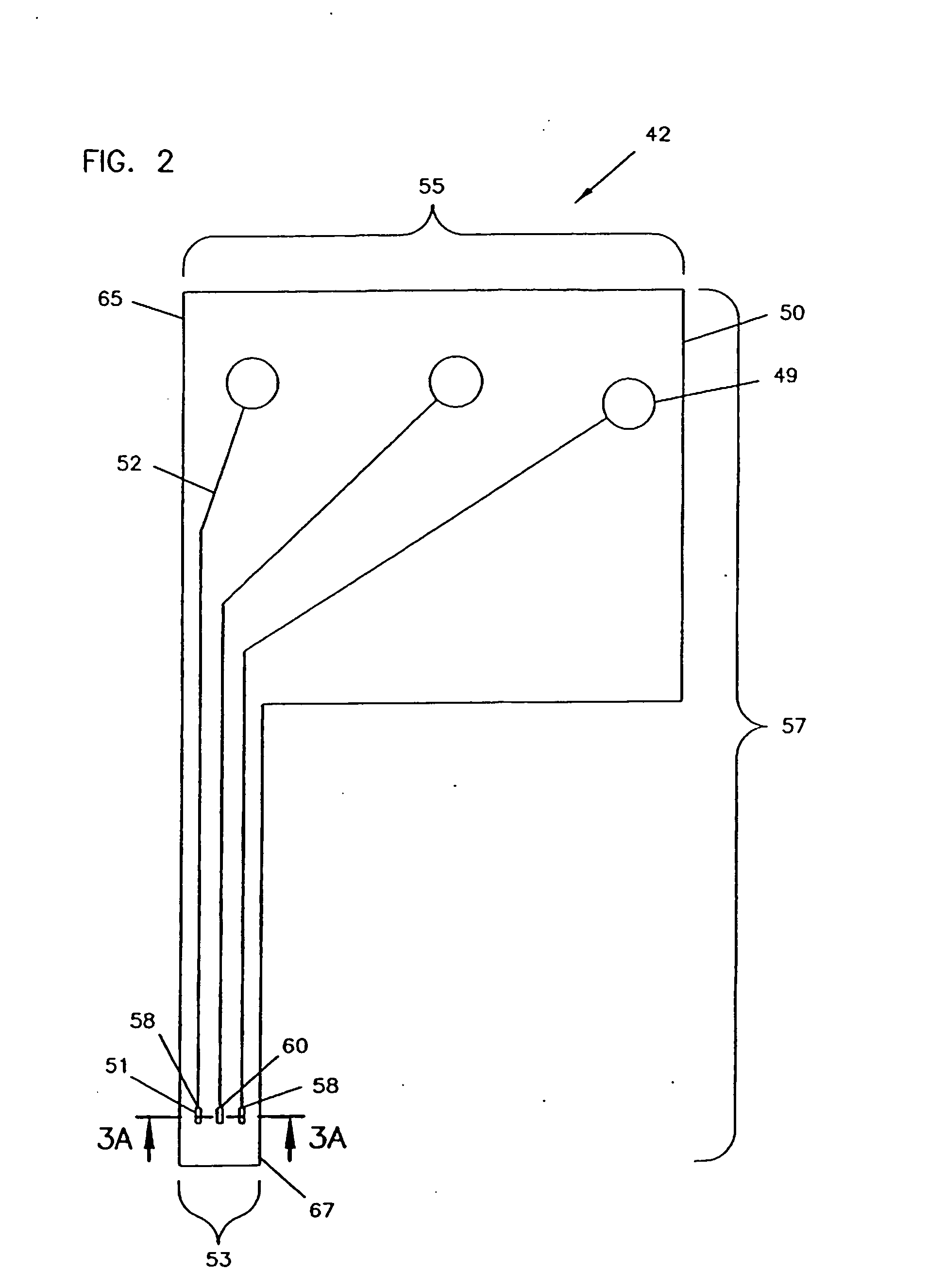
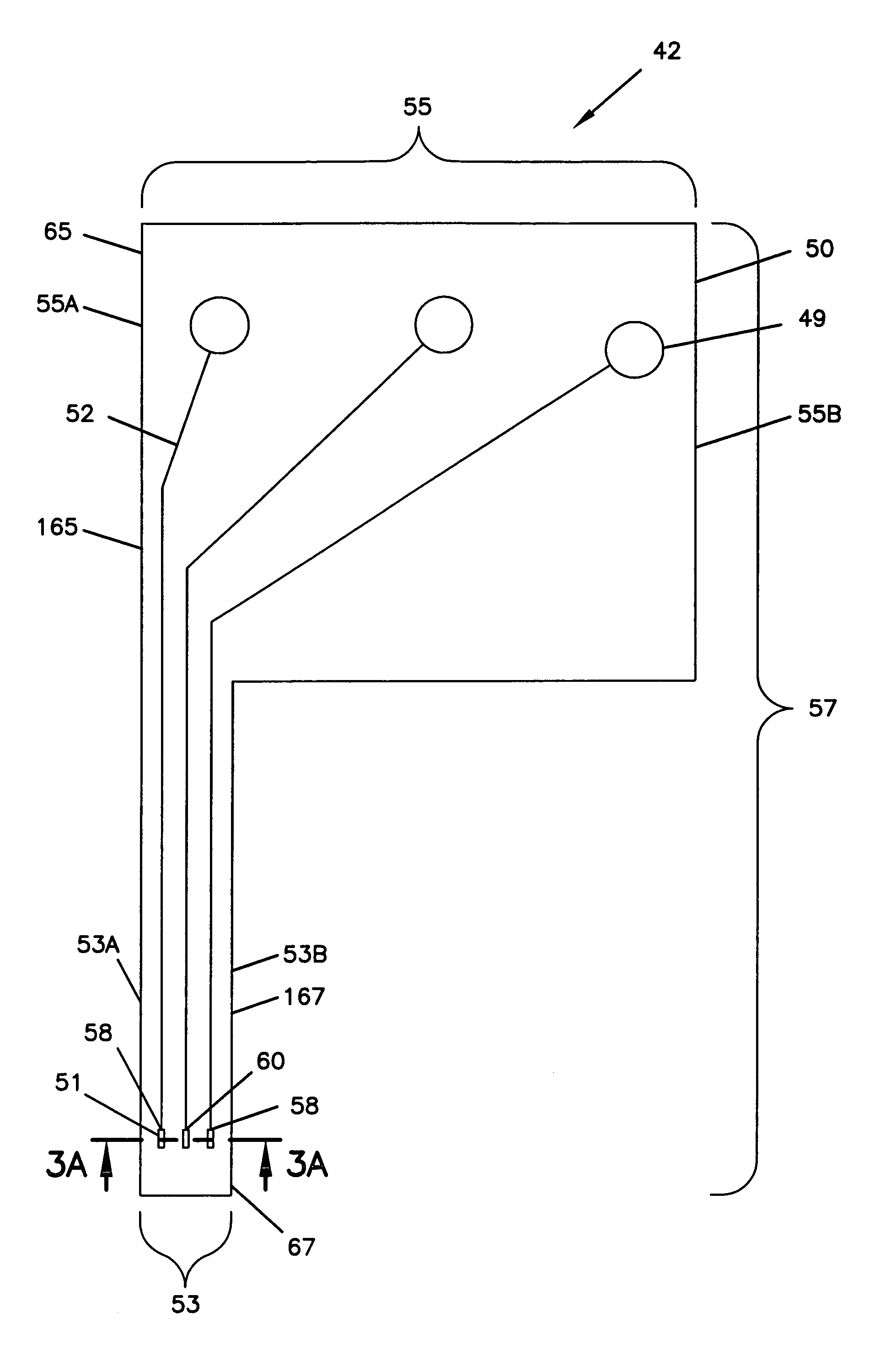
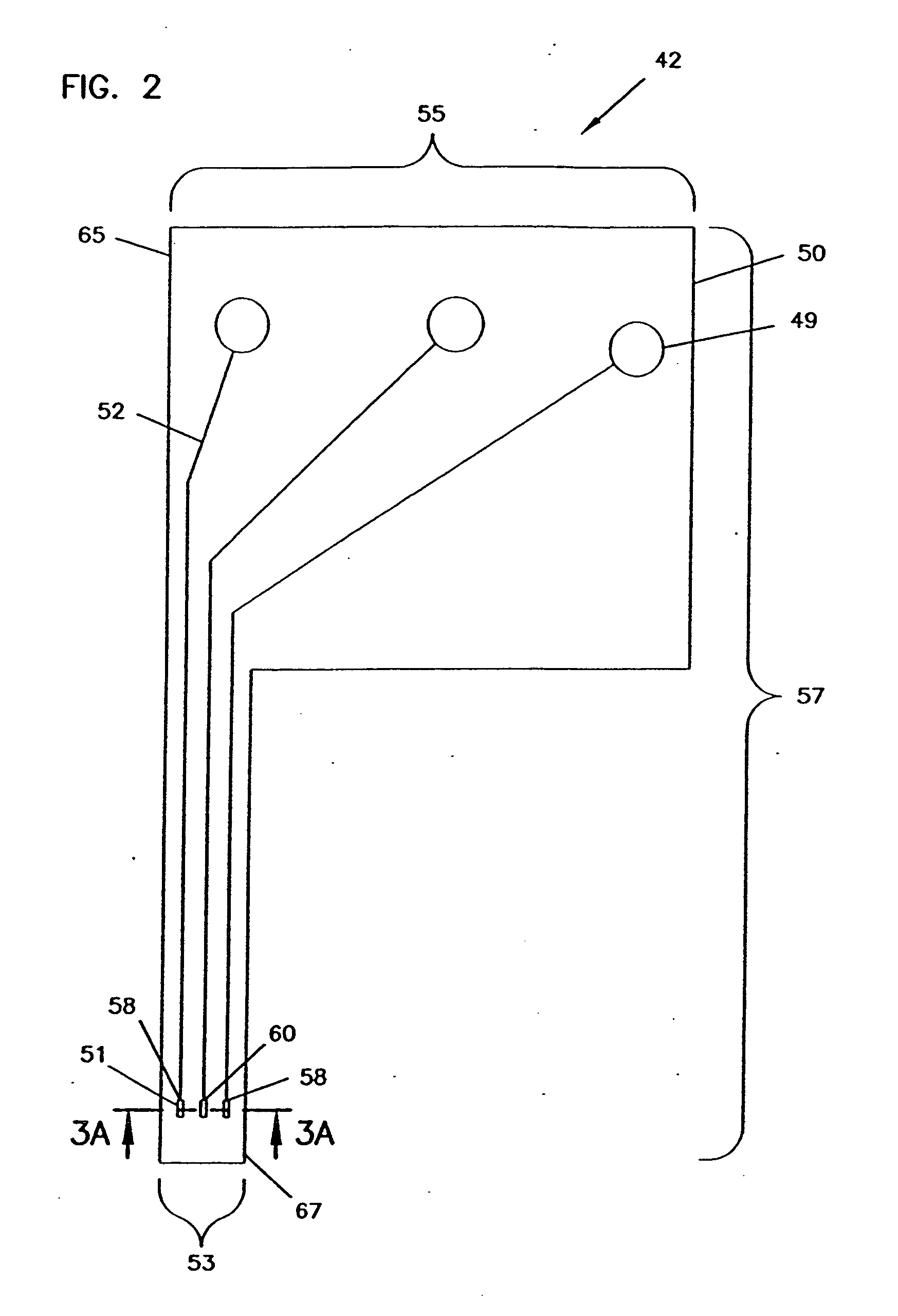
A process for the manufacture of small sensors with reproducible surfaces, including electrochemical sensors. One process includes fanning channels in the surface of a substrate and disposing a conductive material in the channels to form an electrode. The conductive material can also be formed on the substrate by other impact and non-impact methods. In a preferred embodiment, the method includes cutting the substrate to form a sensor having a connector portion and a transcutaneous portion, the two portions having edges that define one continuous straight line.
Owner:THERASENSE
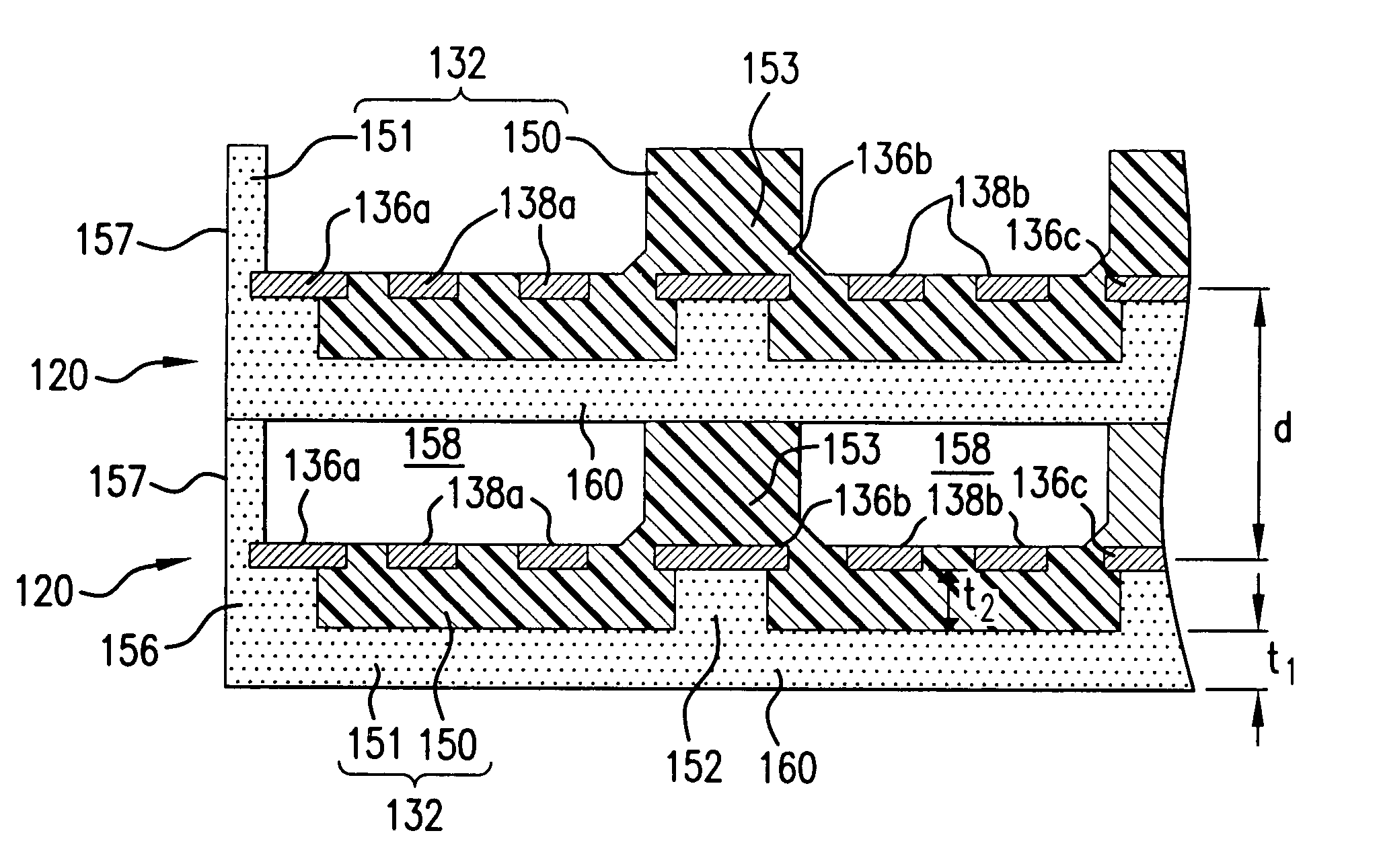
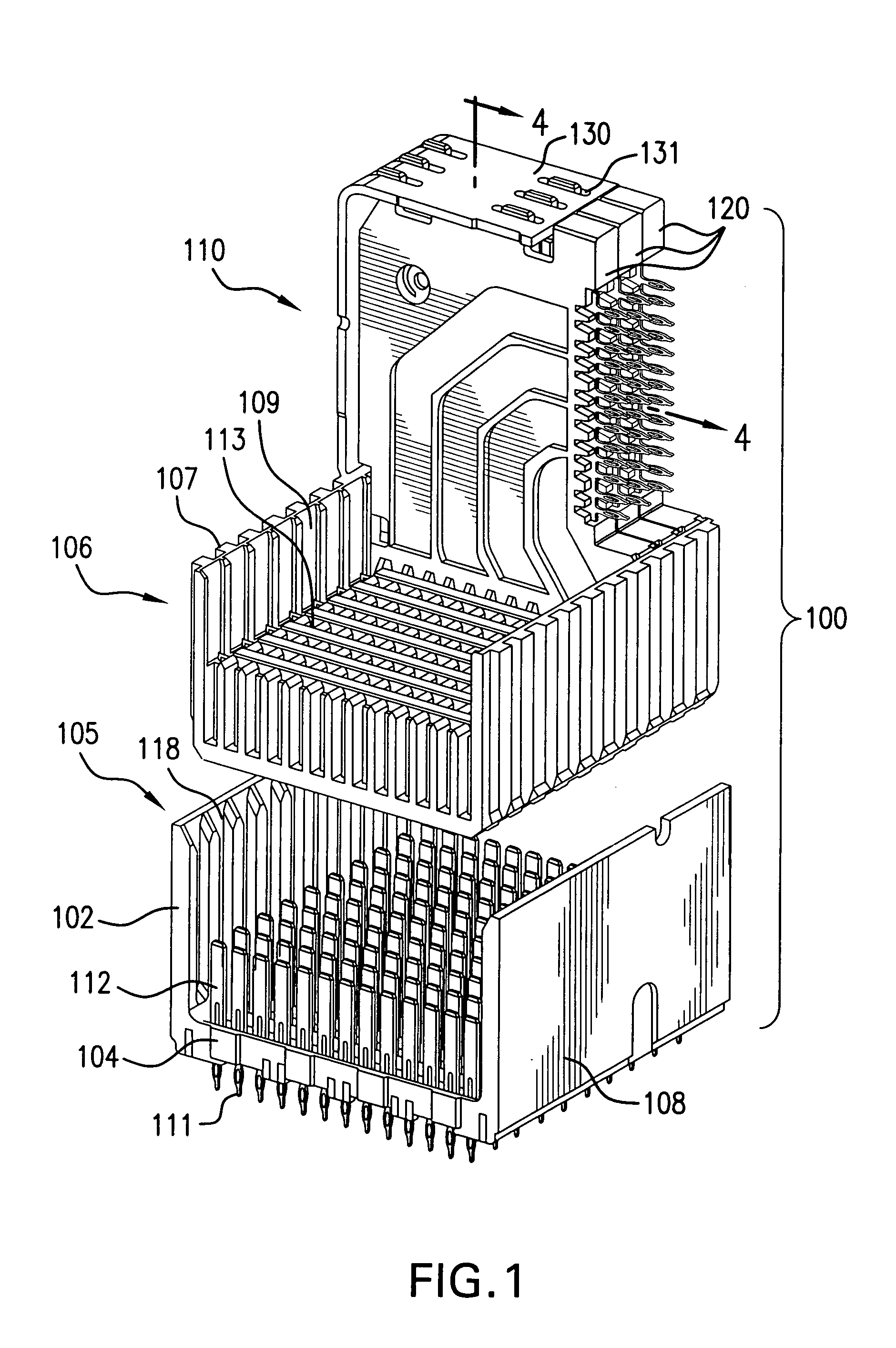
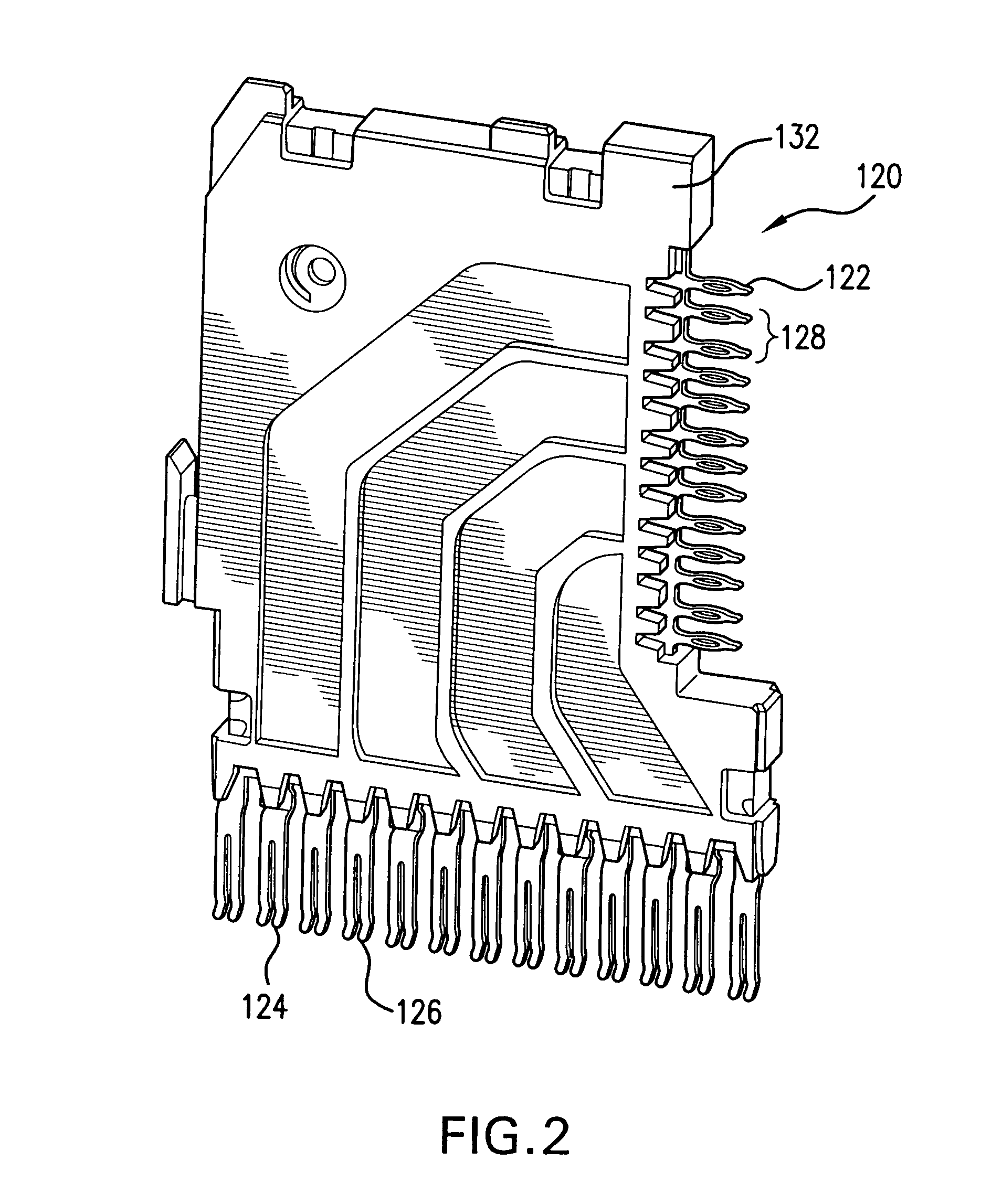
High speed high density electrical connector
ActiveUS7163421B1Reduce noiseContact member manufacturingContact member assembly/disassemblyState of artHigh density
An electrical connector includes a wafer formed with a ground shield made from a non-conductive material made conductive with conductive particles disposed therein, thereby eliminating the necessity of the metal ground shield plate found in prior art connectors while maintaining sufficient performance characteristics and minimizing electrical noise generated in the wafer. The wafer housing is formed with a first, insulative housing at least partially surrounding a pair of signal strips and a second, conductive housing at least partially surrounding the first, insulative housing and the signal strips. The housings provide the wafer with sufficient structural integrity, obviating the need for additional support structures or components for a wafer. Ground strips may be employed in the wafer and may be formed in the same plane as the signal strips. The second, conductive housing may be connected (e.g., molded) to the ground strips and spaced appropriately from the signal strips. The wafer may also include air gaps between the signal strips of one wafer and the conductive housing of an adjacent wafer further reducing electrical noise or other losses (e.g., cross-talk) without sacrificing significant signal strength.
Owner:AMPHENOL CORP
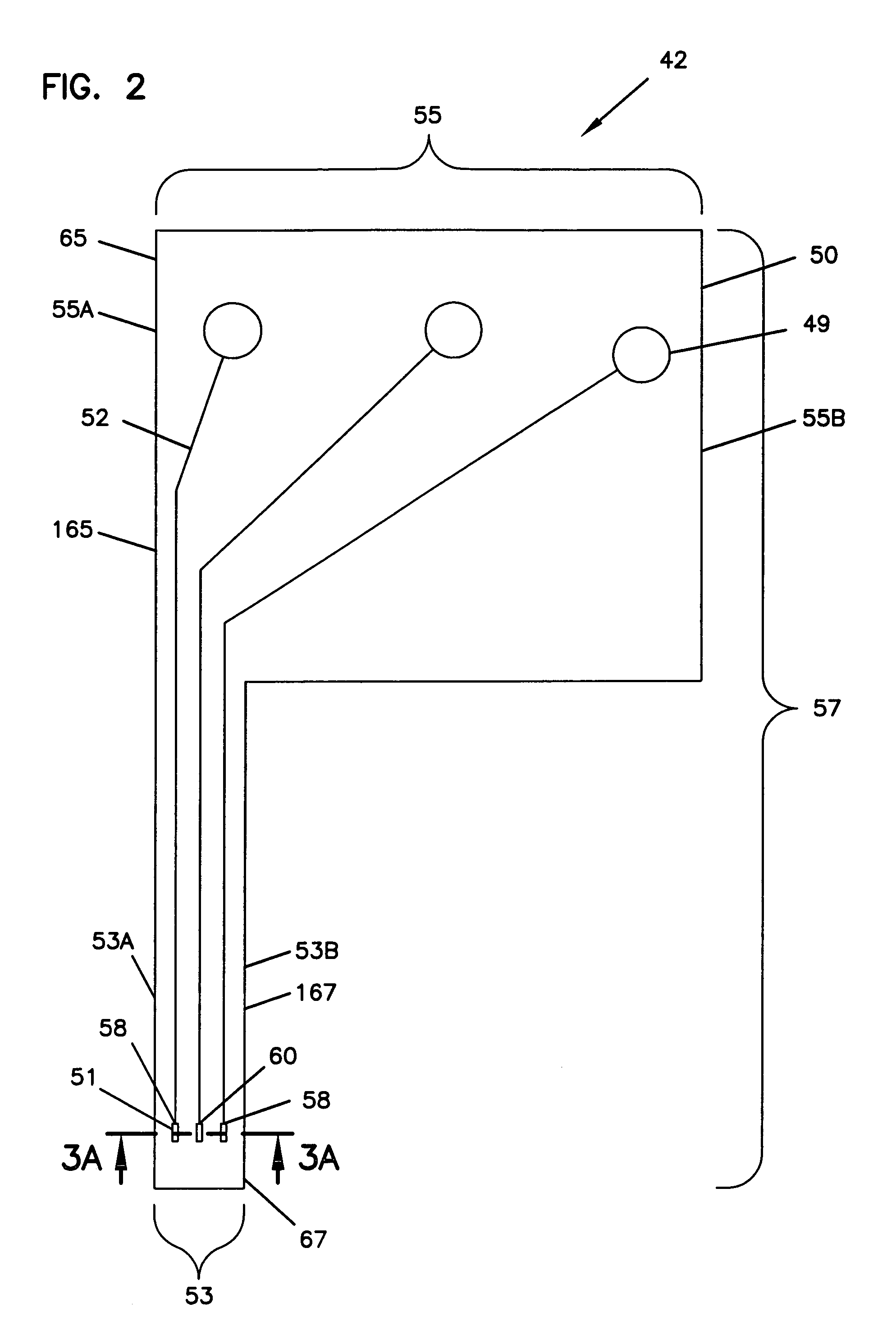
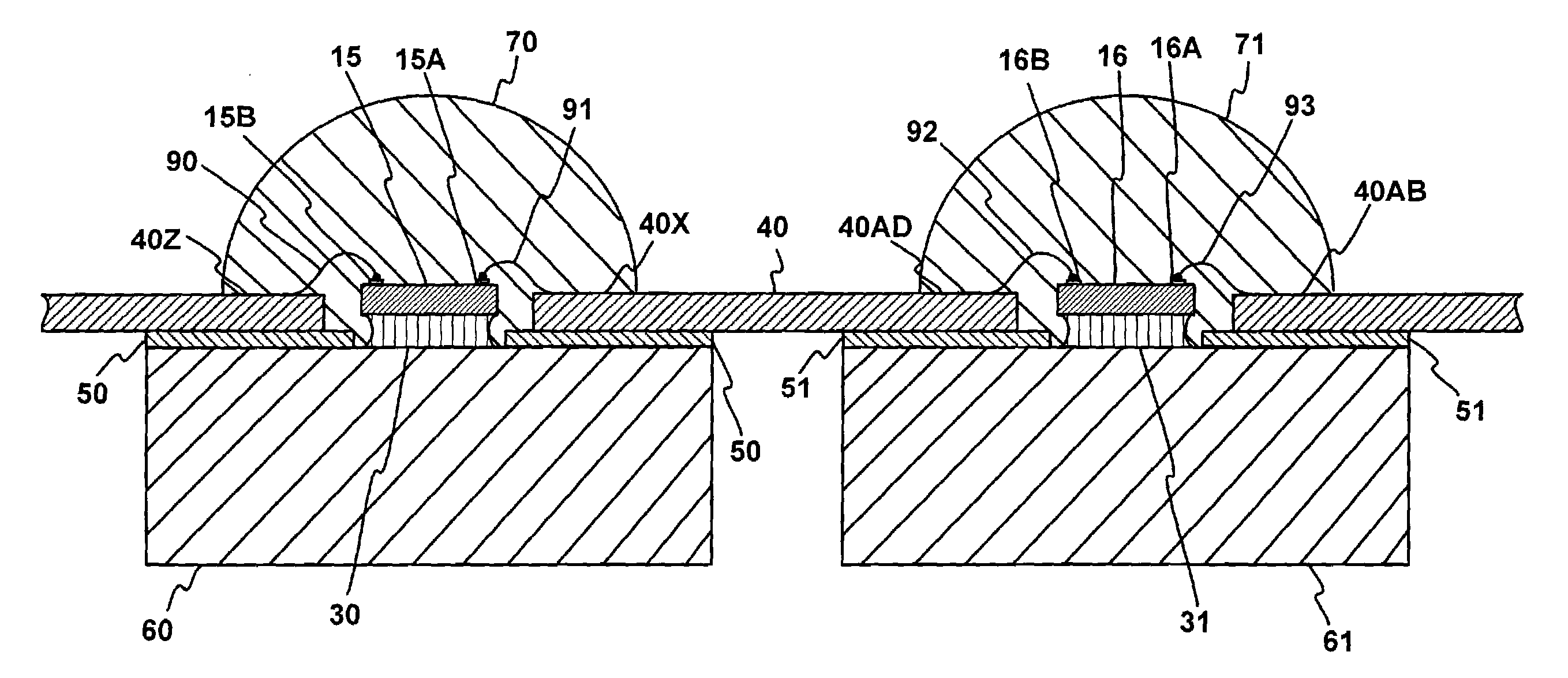
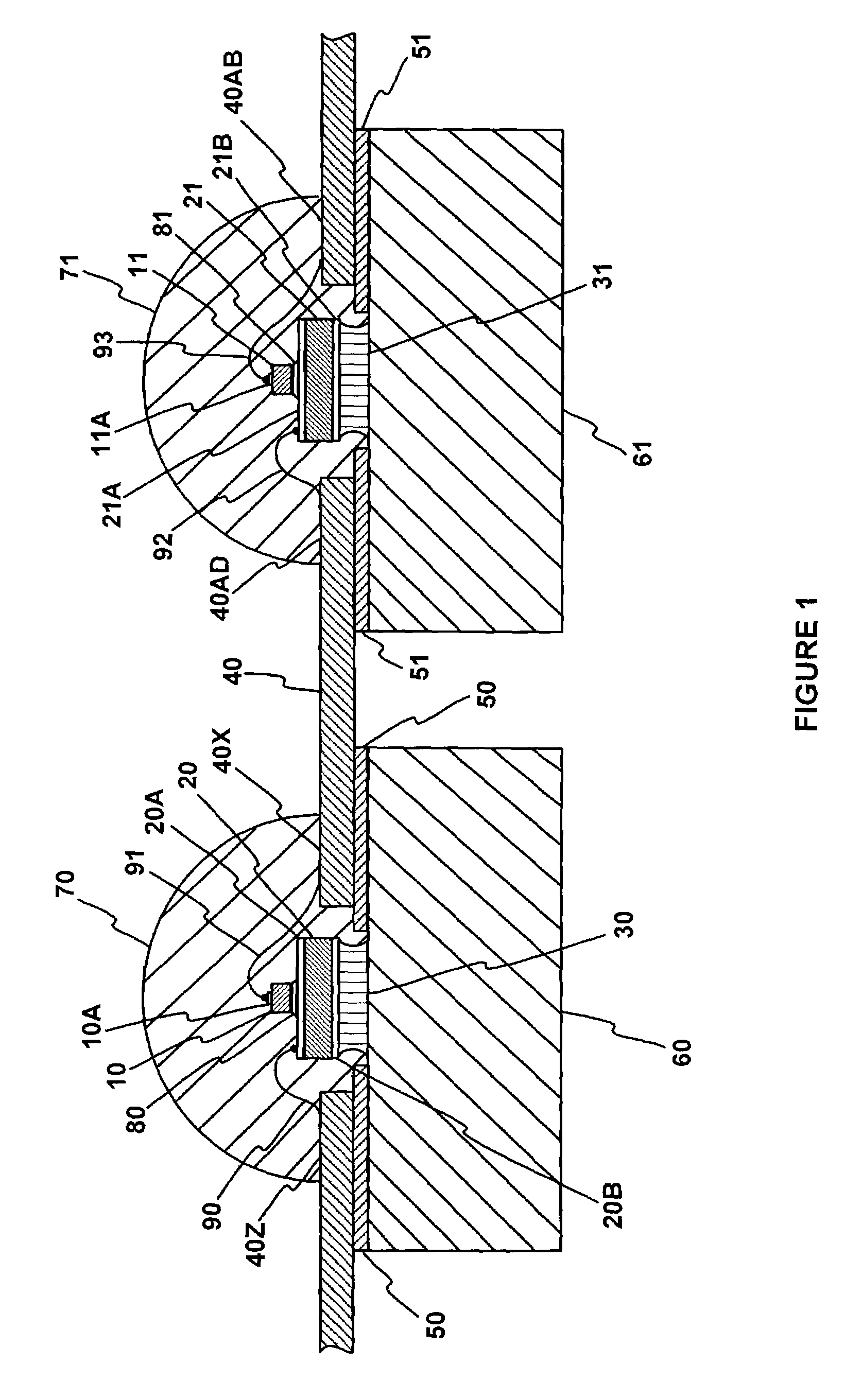
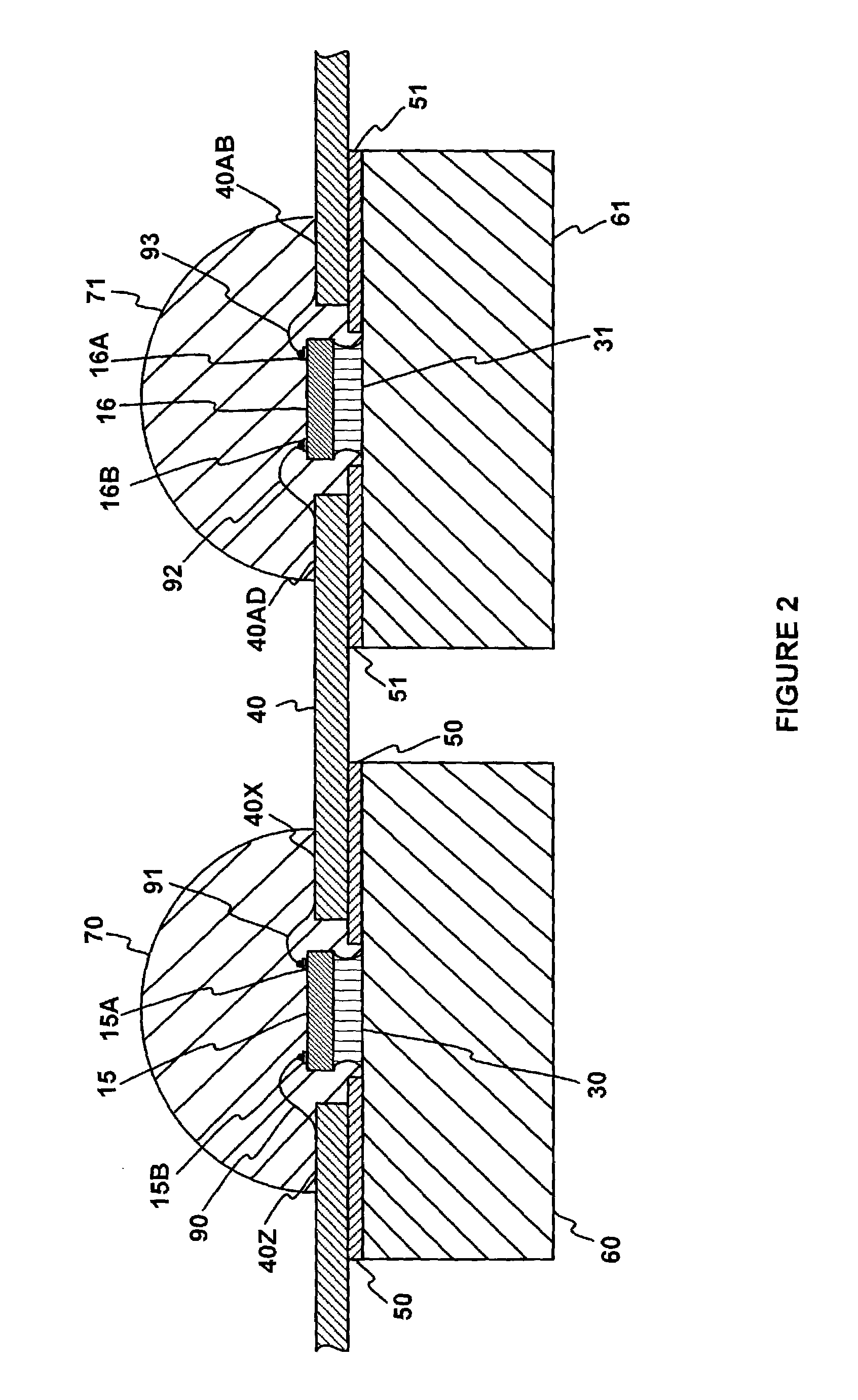
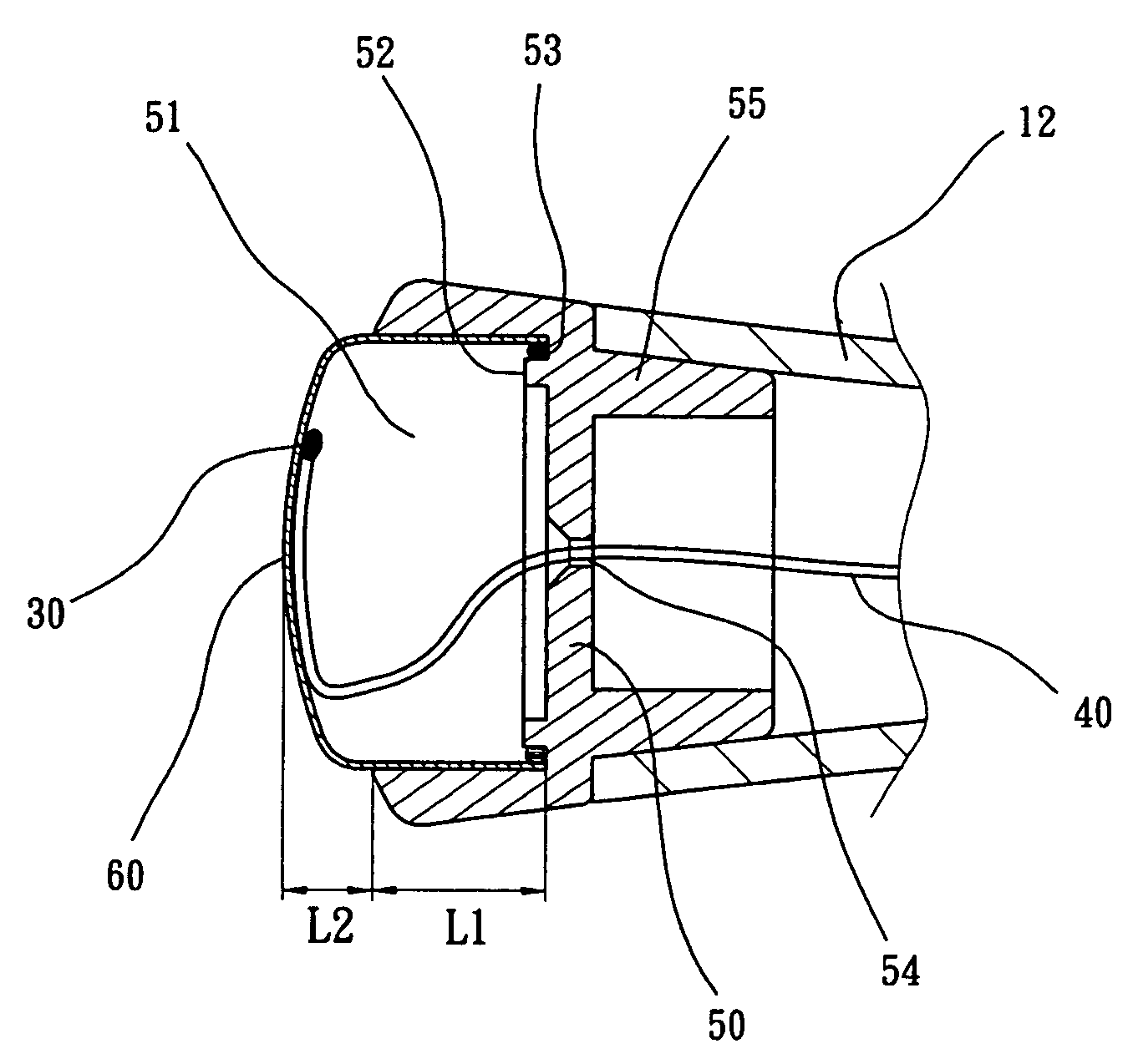
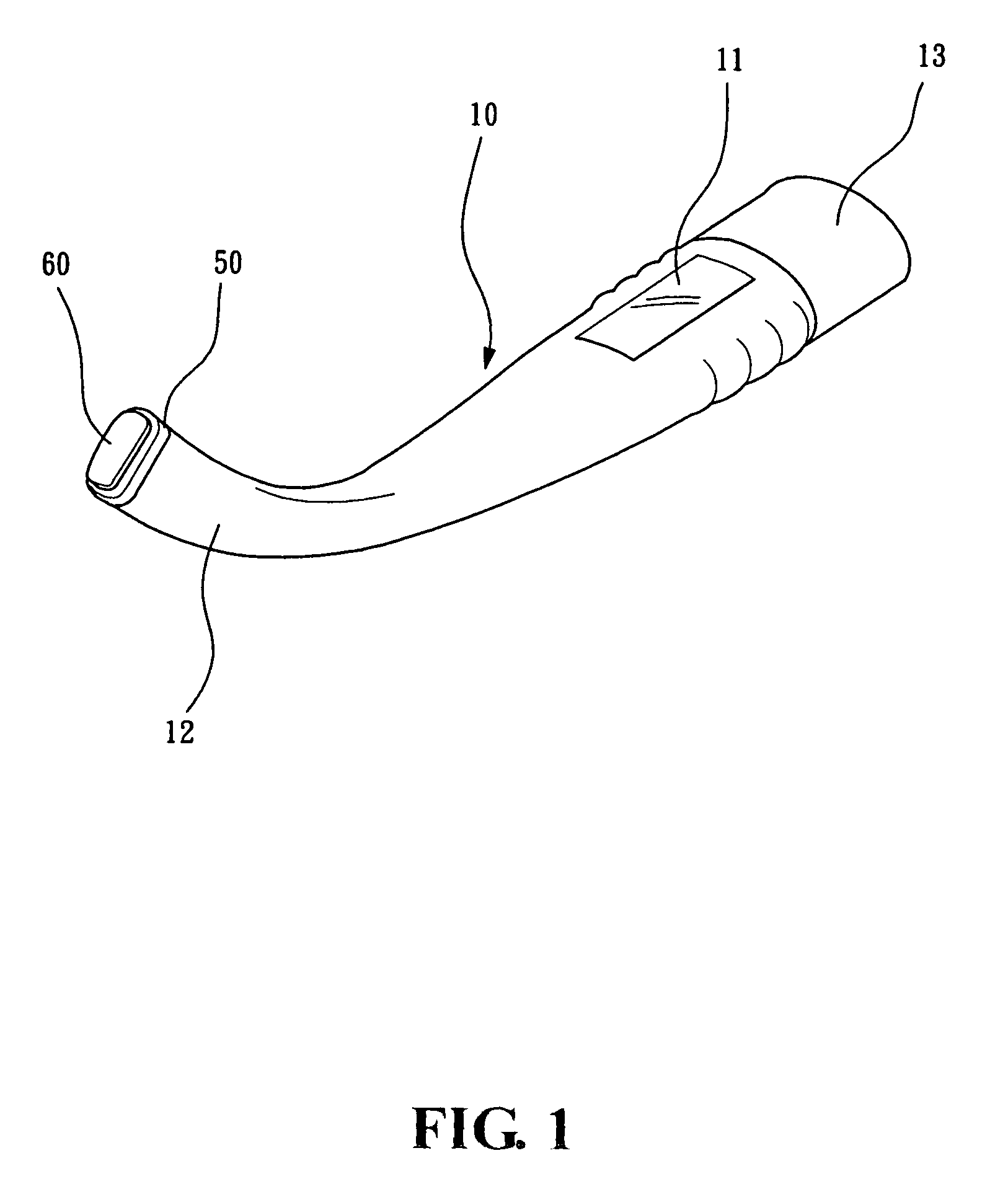
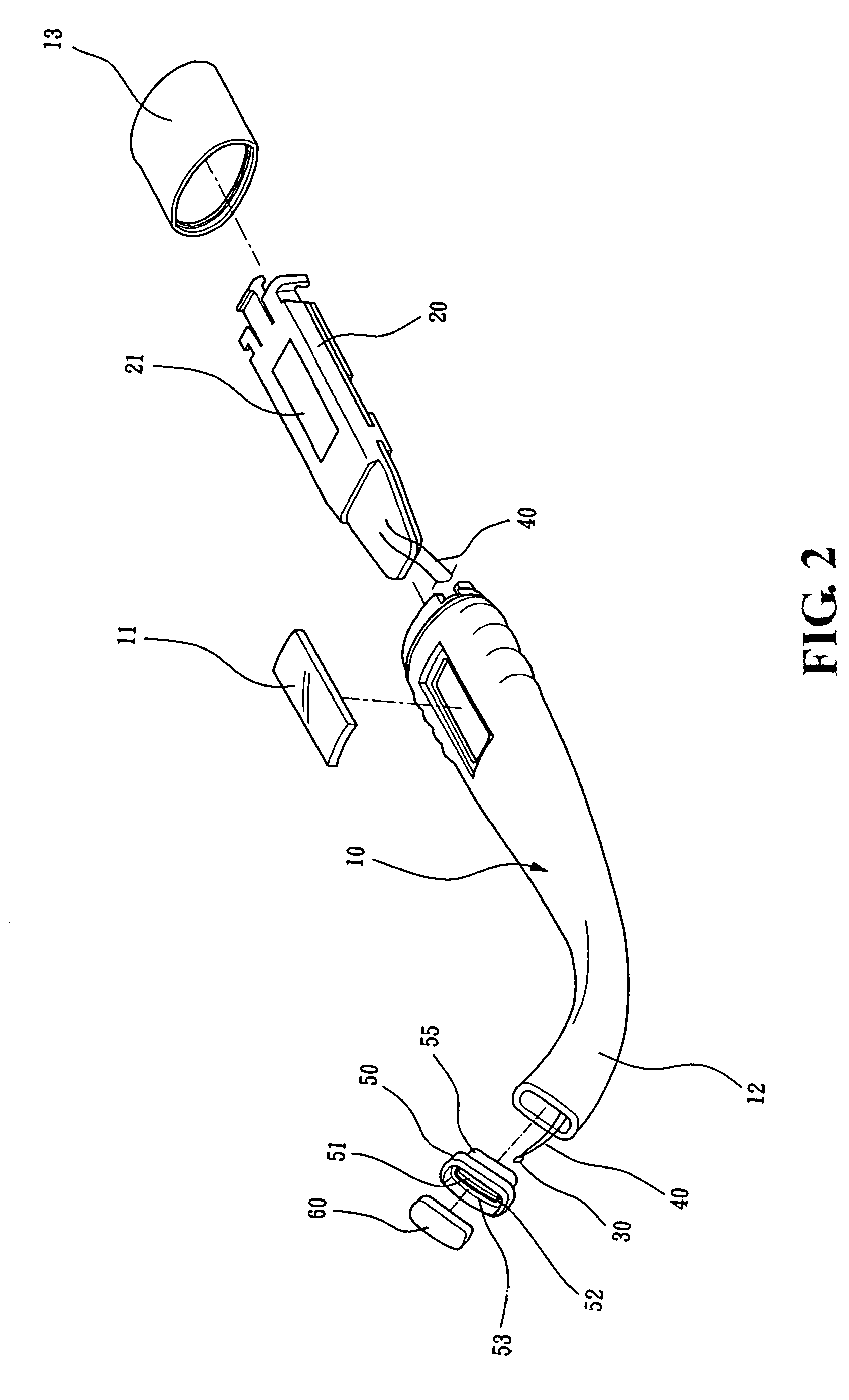
Conducting structure and electronic clinical thermometer embodying the structure
InactiveUS7320544B2Fully contactedHeld easily and comfortablyThermometer detailsThermometers using electric/magnetic elementsHeat balanceEngineering
A conducting structure and an electronic clinical thermometer, wherein the conducting structure is provided on the measuring end of the clinical thermometer, and the measuring end has a recess, a temperature sensor and conducting wires fitted in the recess, and a contact member having a curved top and made of metallic conductive material and having a predetermined length embedded in the recess thereby providing the contact member with a large temperature sensing contact area but only with a small portion protruded out of the measuring end, and therefore enabling the thermometer to be fully in contact with a certain portion of the human body such as the armpit, preventing the thermometer from being broken, and achieving heat balance rapidly. The measuring end of the thermometer may be bent at a predetermined angle or the contact member may be arranged at either side of the measuring end as required.
Owner:ACTHERM INC
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com