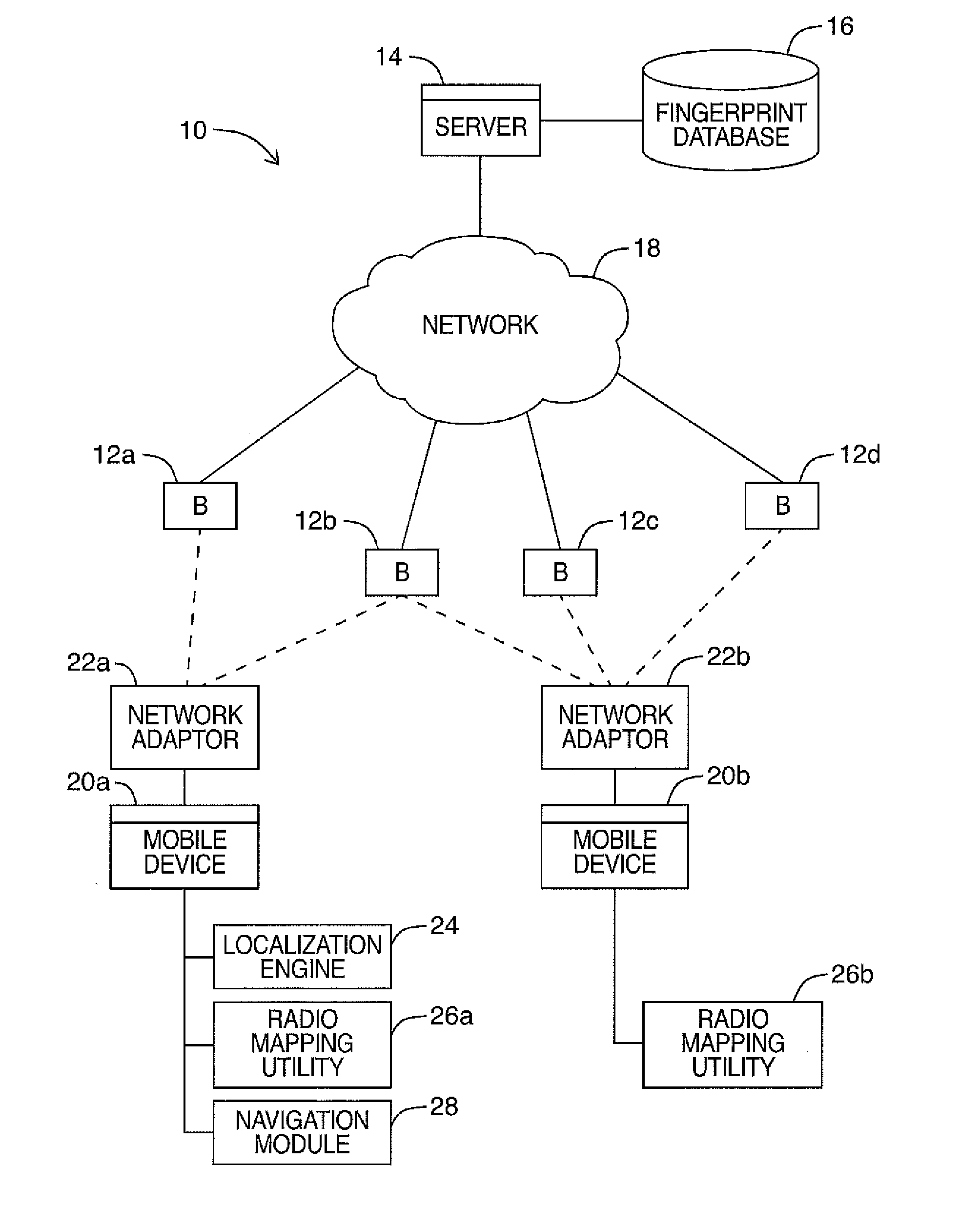
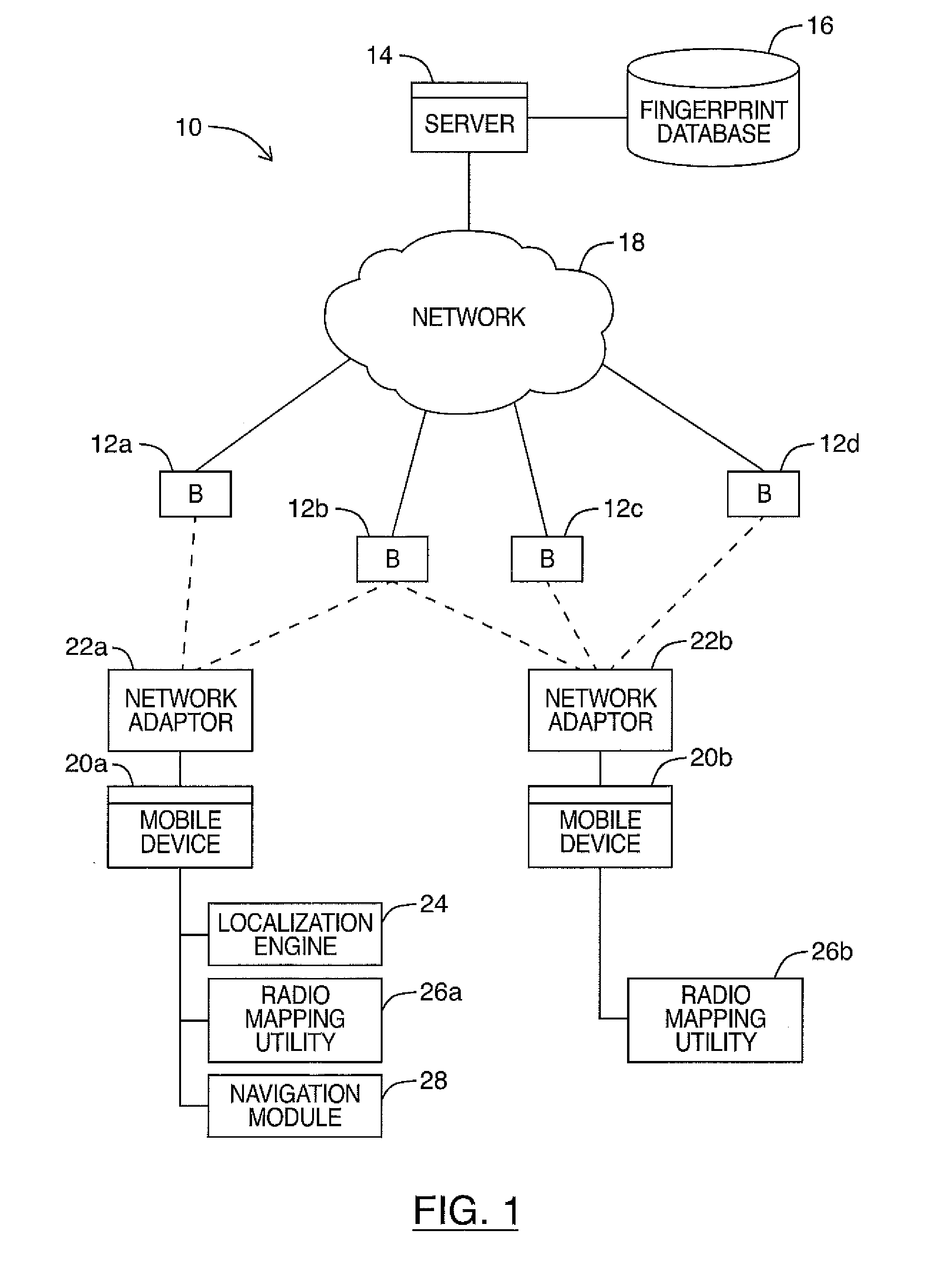
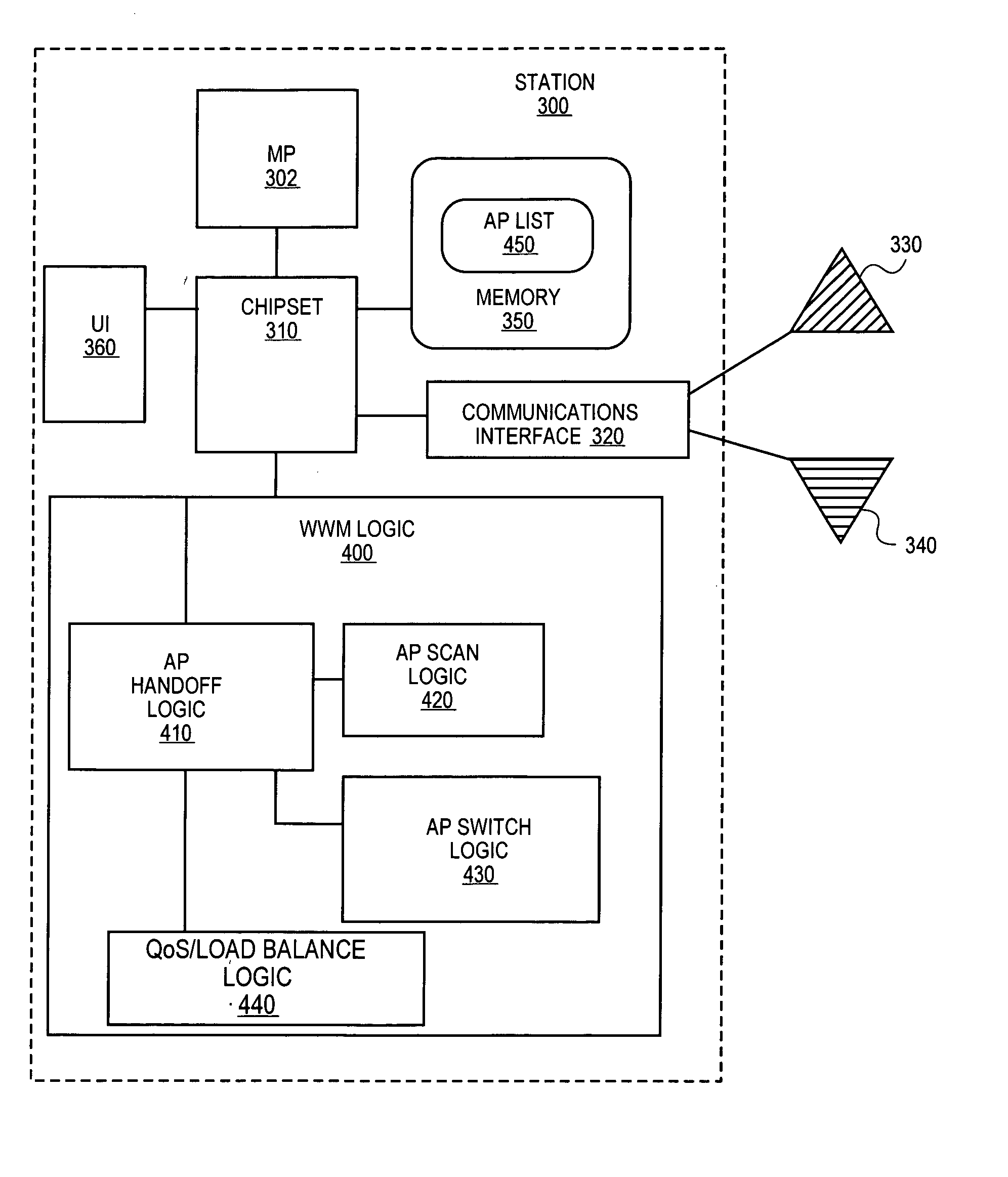
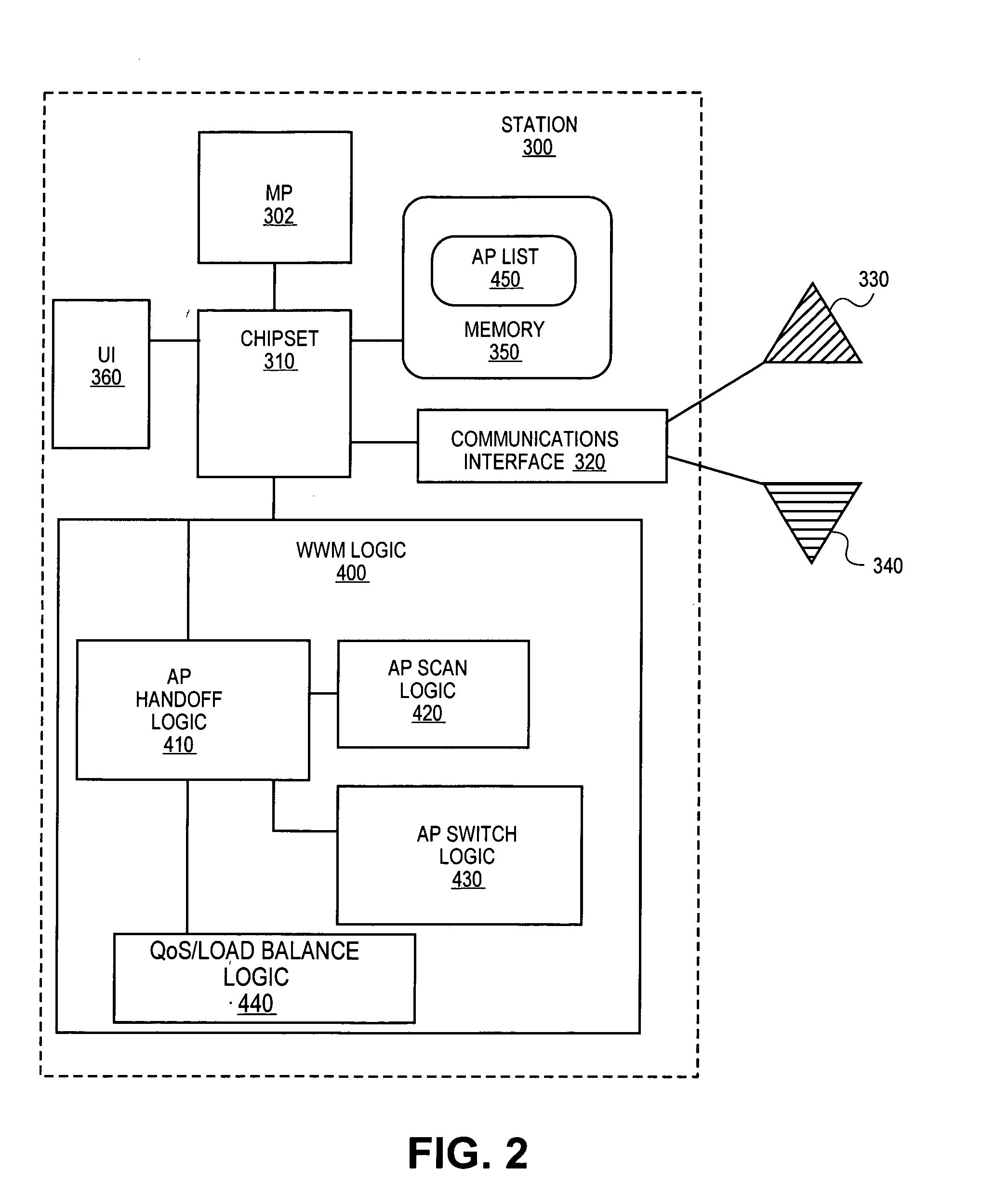
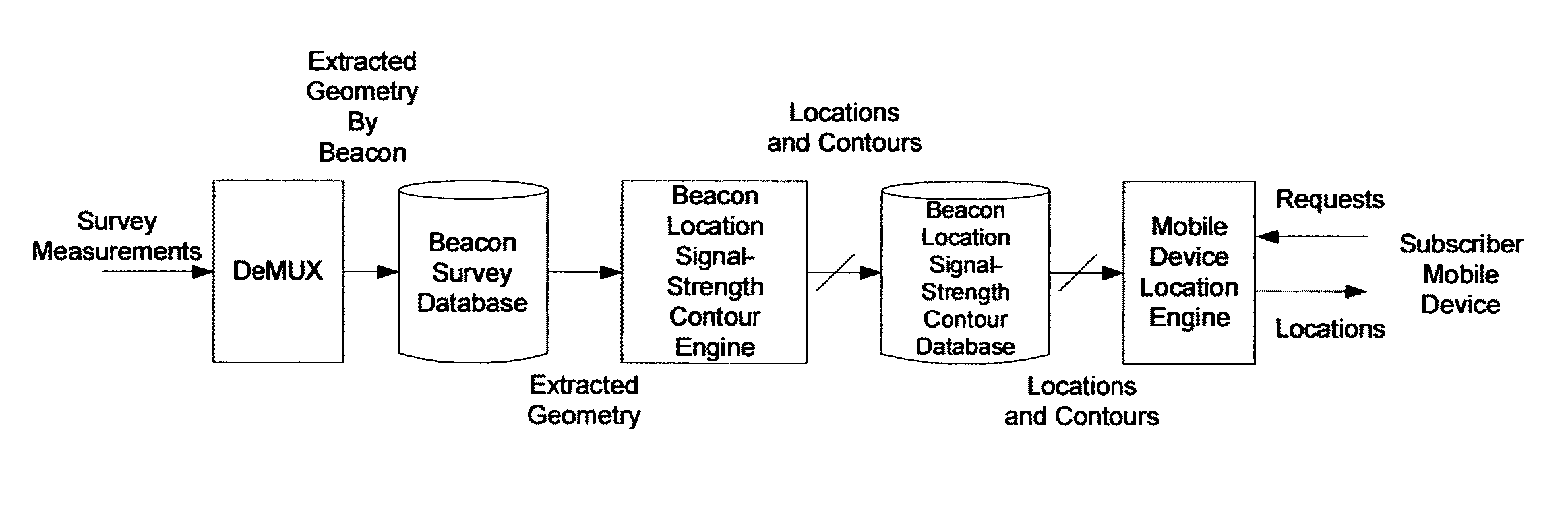
Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
7268 results about "Signal strength" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
In telecommunications, particularly in radio frequency, signal strength (also referred to as field strength) refers to the transmitter power output as received by a reference antenna at a distance from the transmitting antenna. High-powered transmissions, such as those used in broadcasting, are expressed in dB-millivolts per metre (dBmV/m). For very low-power systems, such as mobile phones, signal strength is usually expressed in dB-microvolts per metre (dBμV/m) or in decibels above a reference level of one milliwatt (dBm). In broadcasting terminology, 1 mV/m is 1000 μV/m or 60 dBμ (often written dBu).
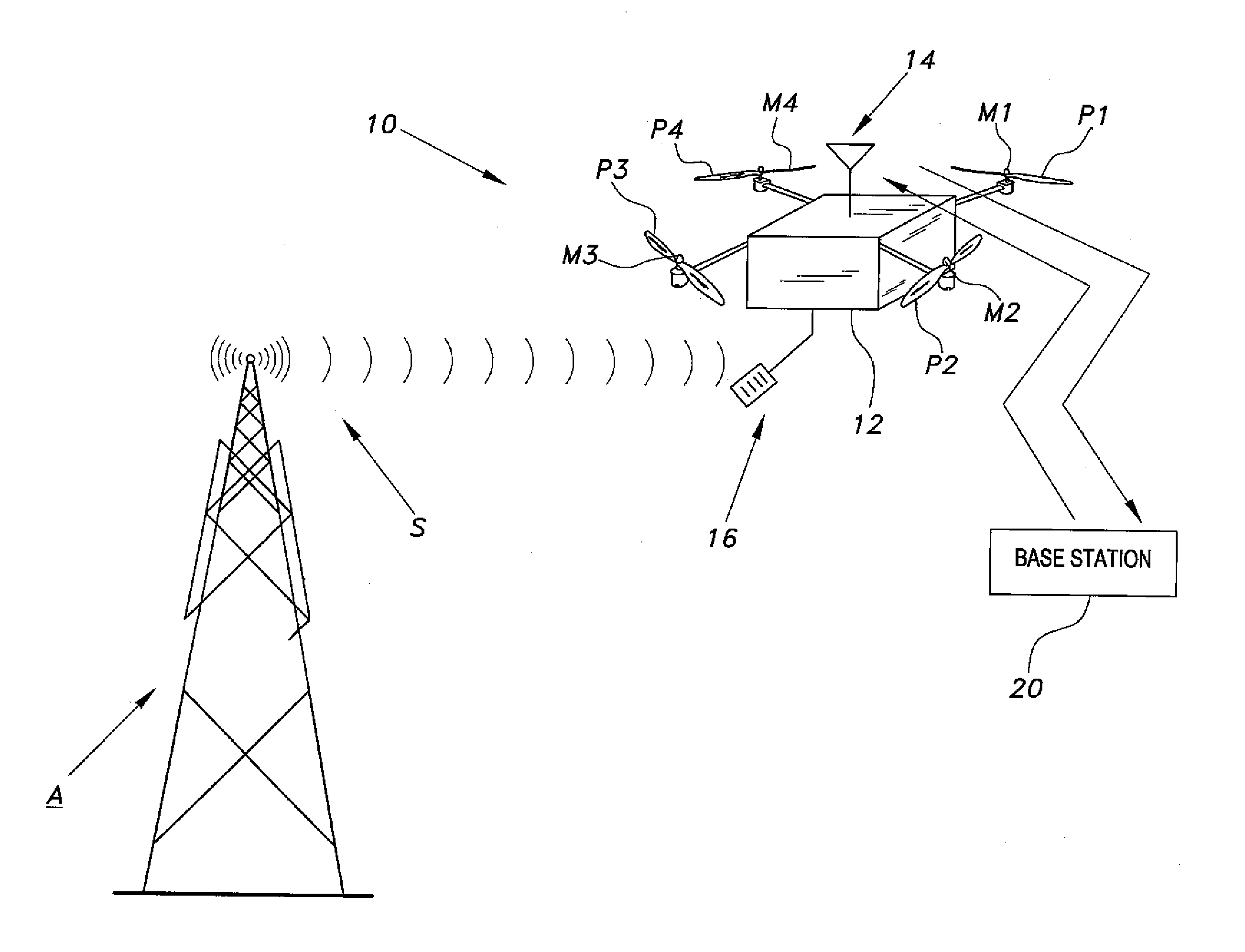
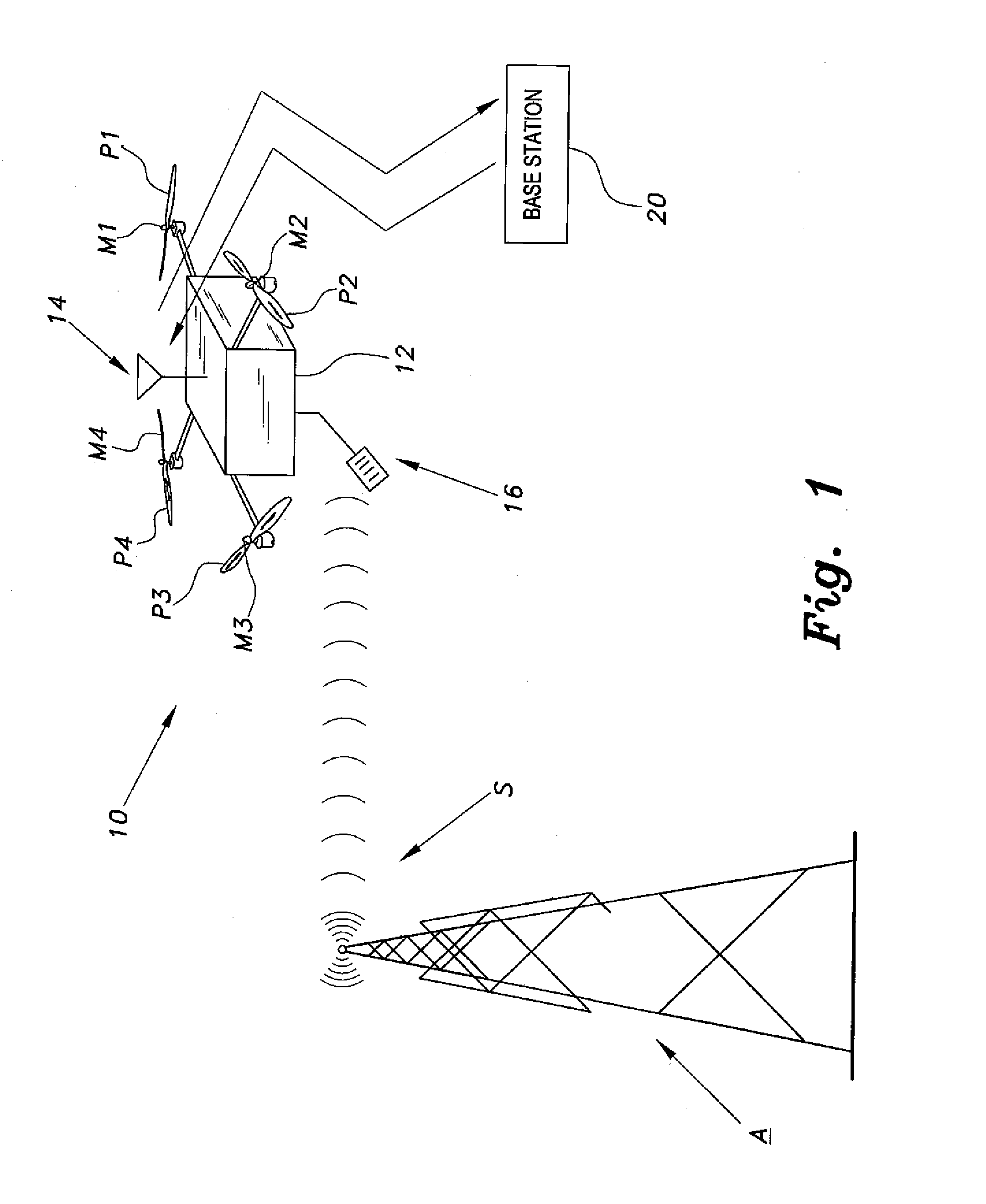
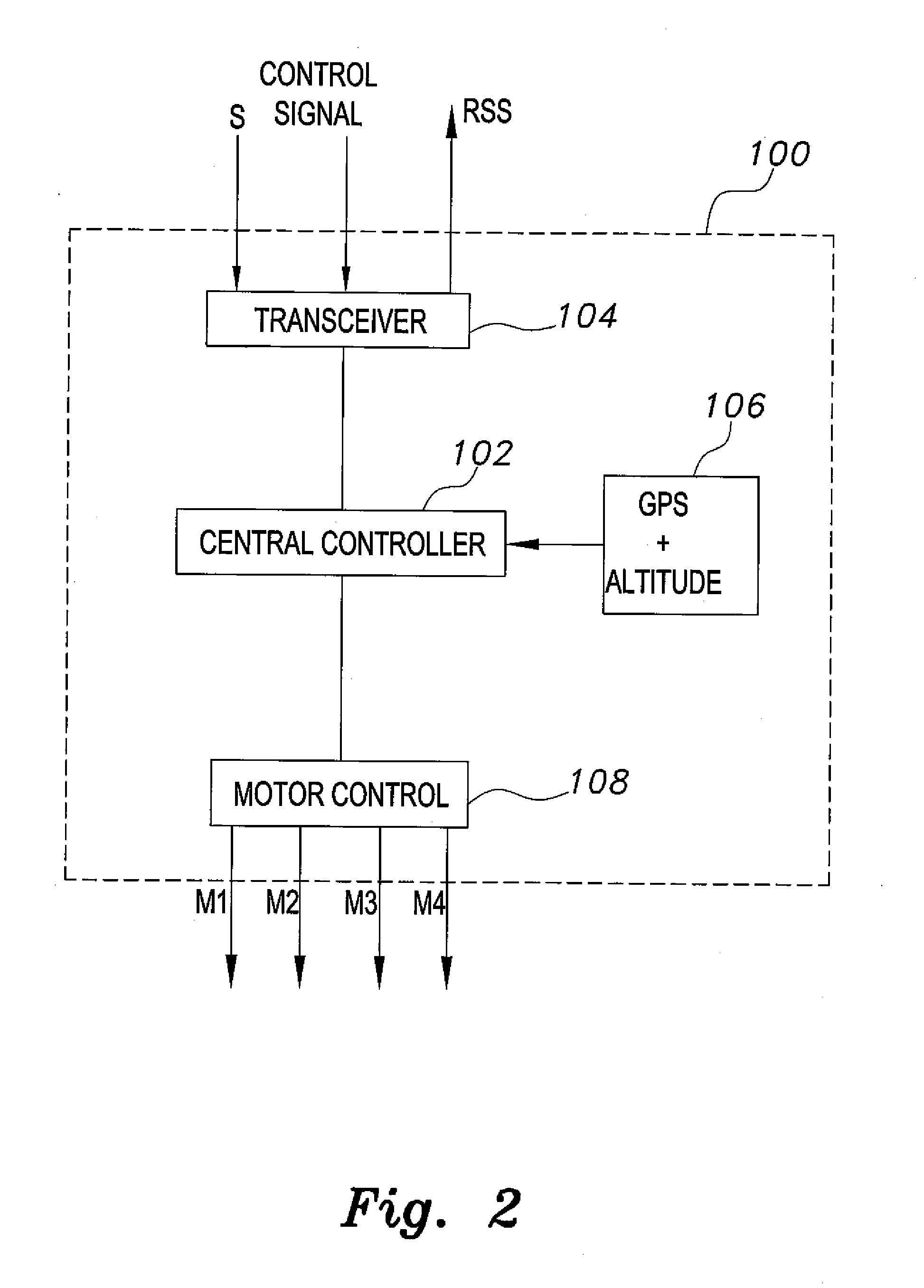
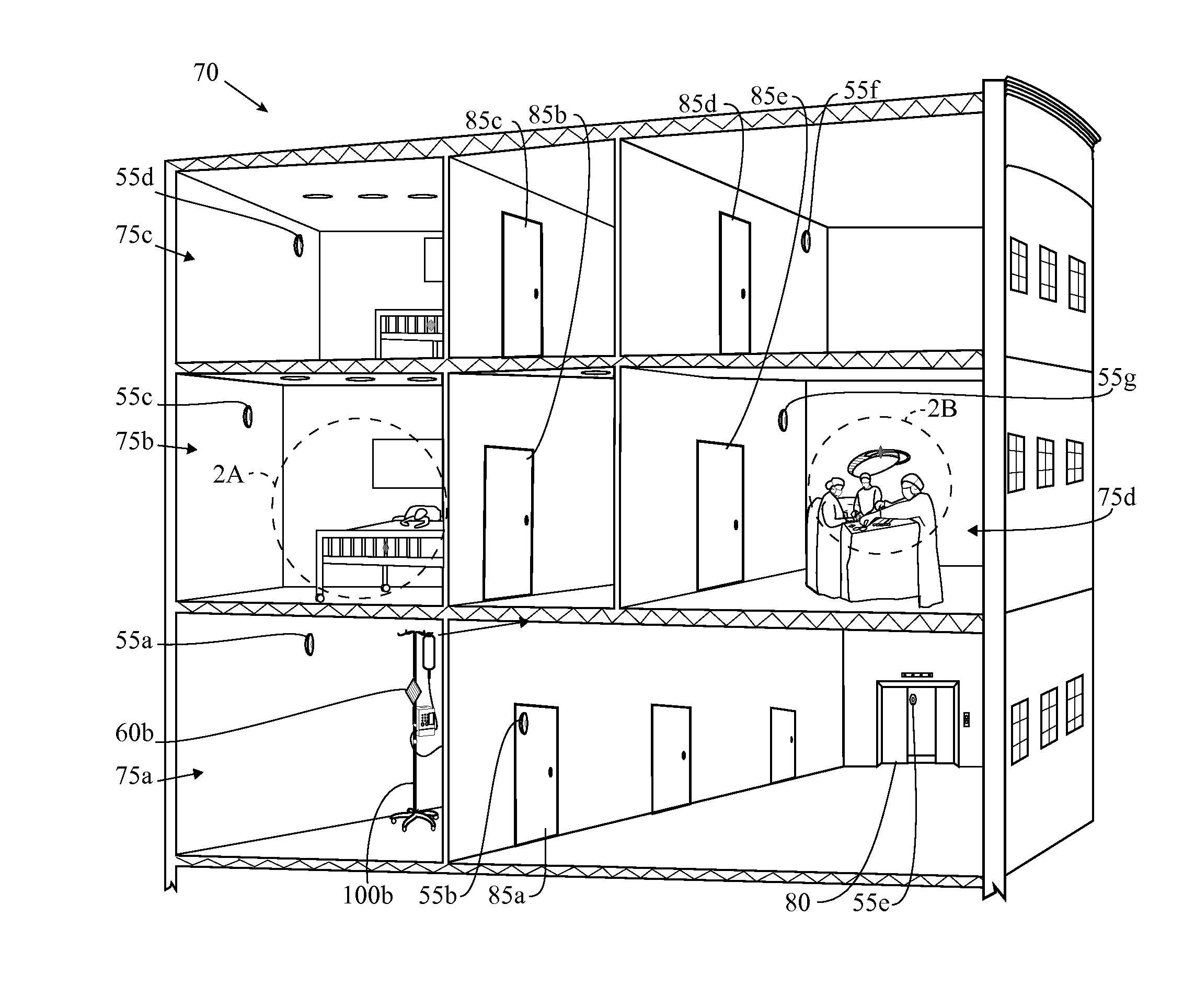
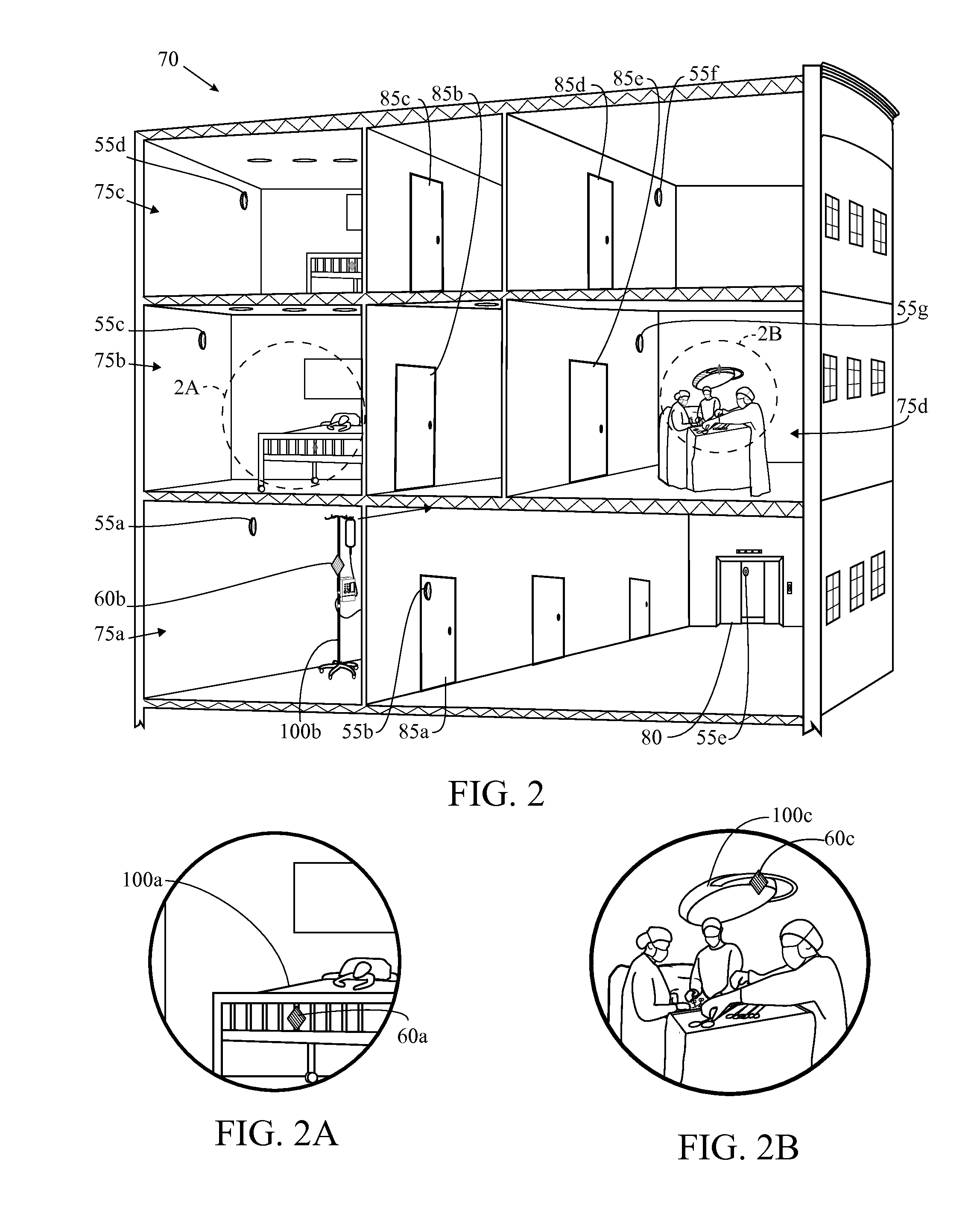
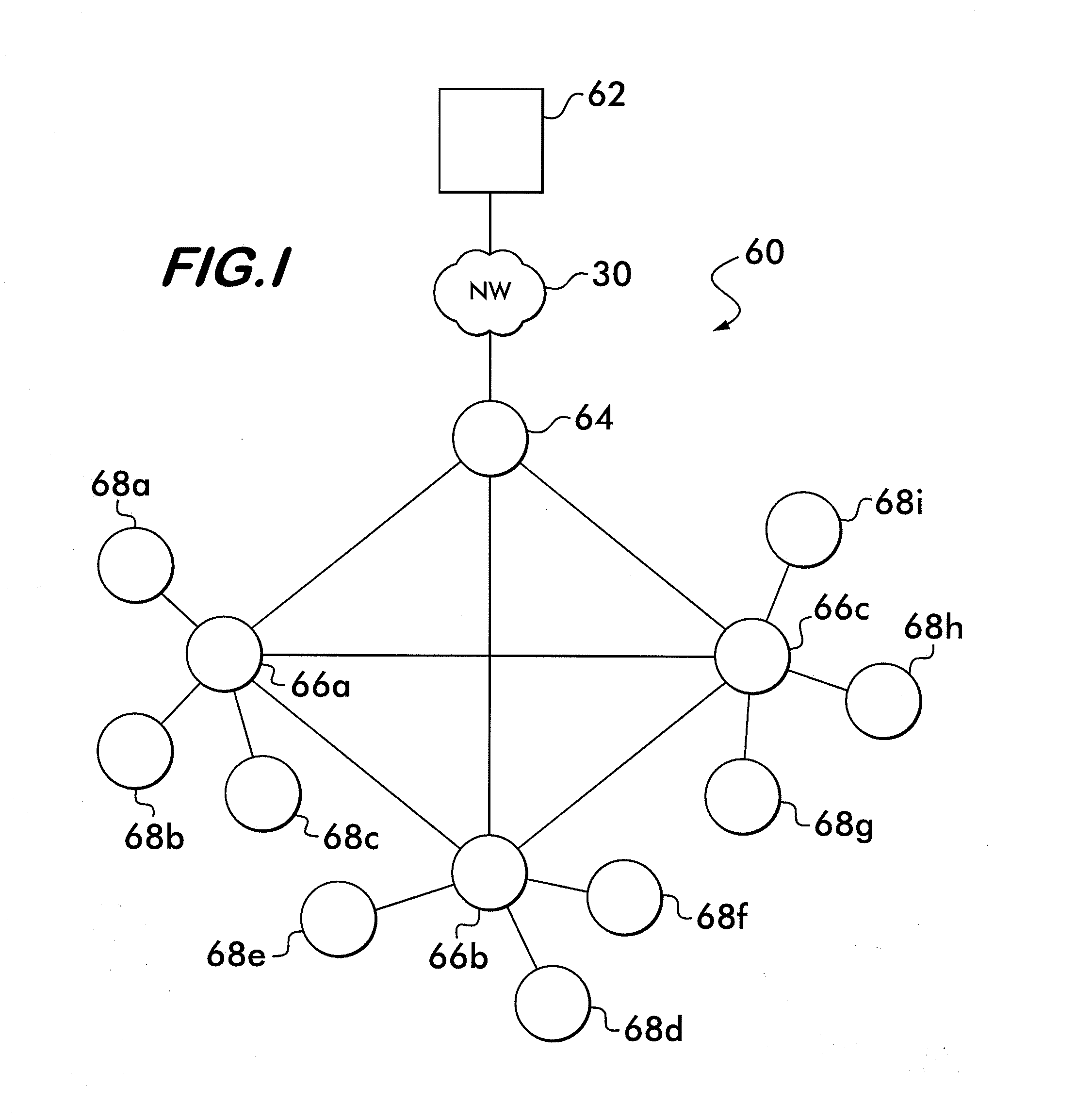
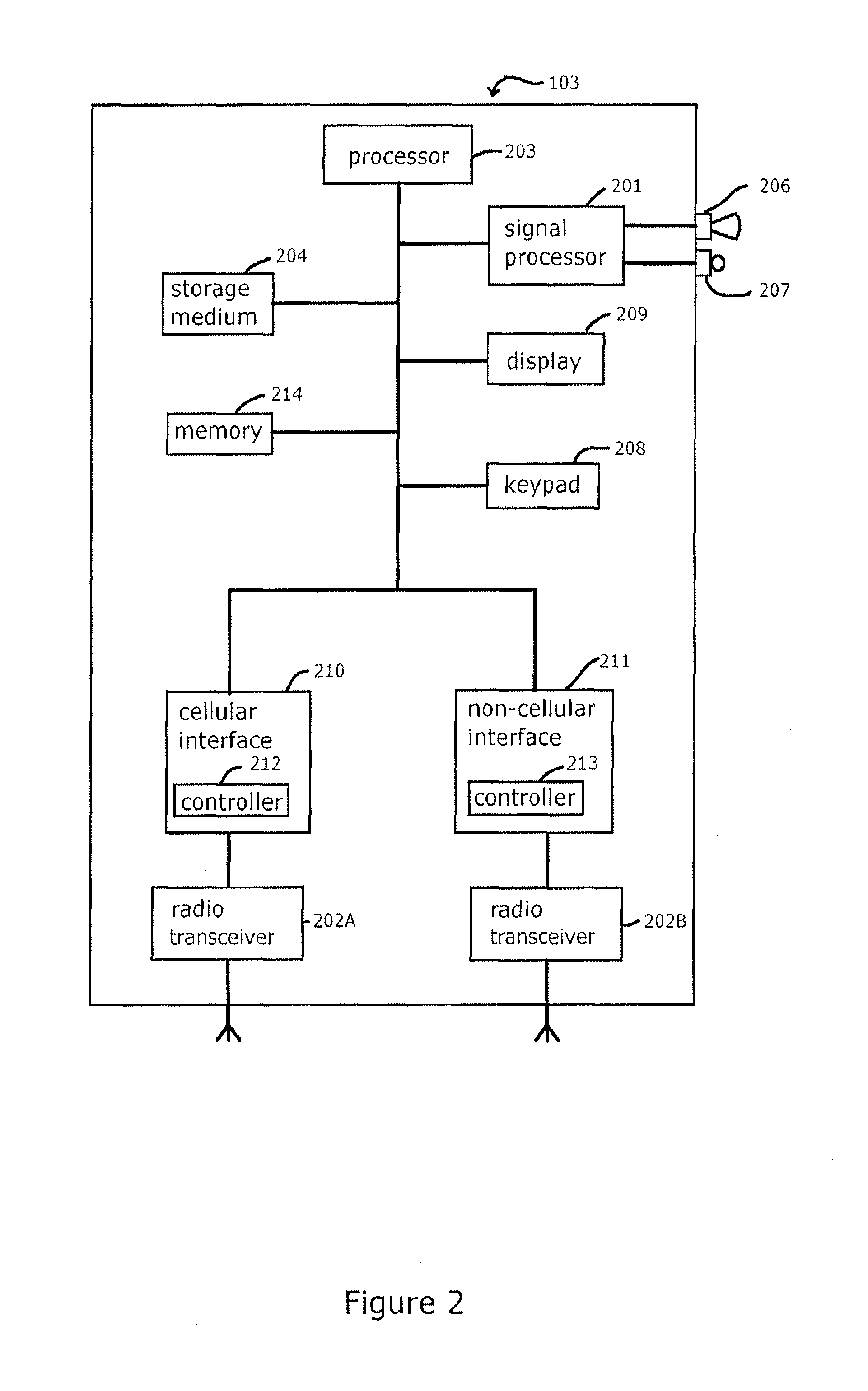
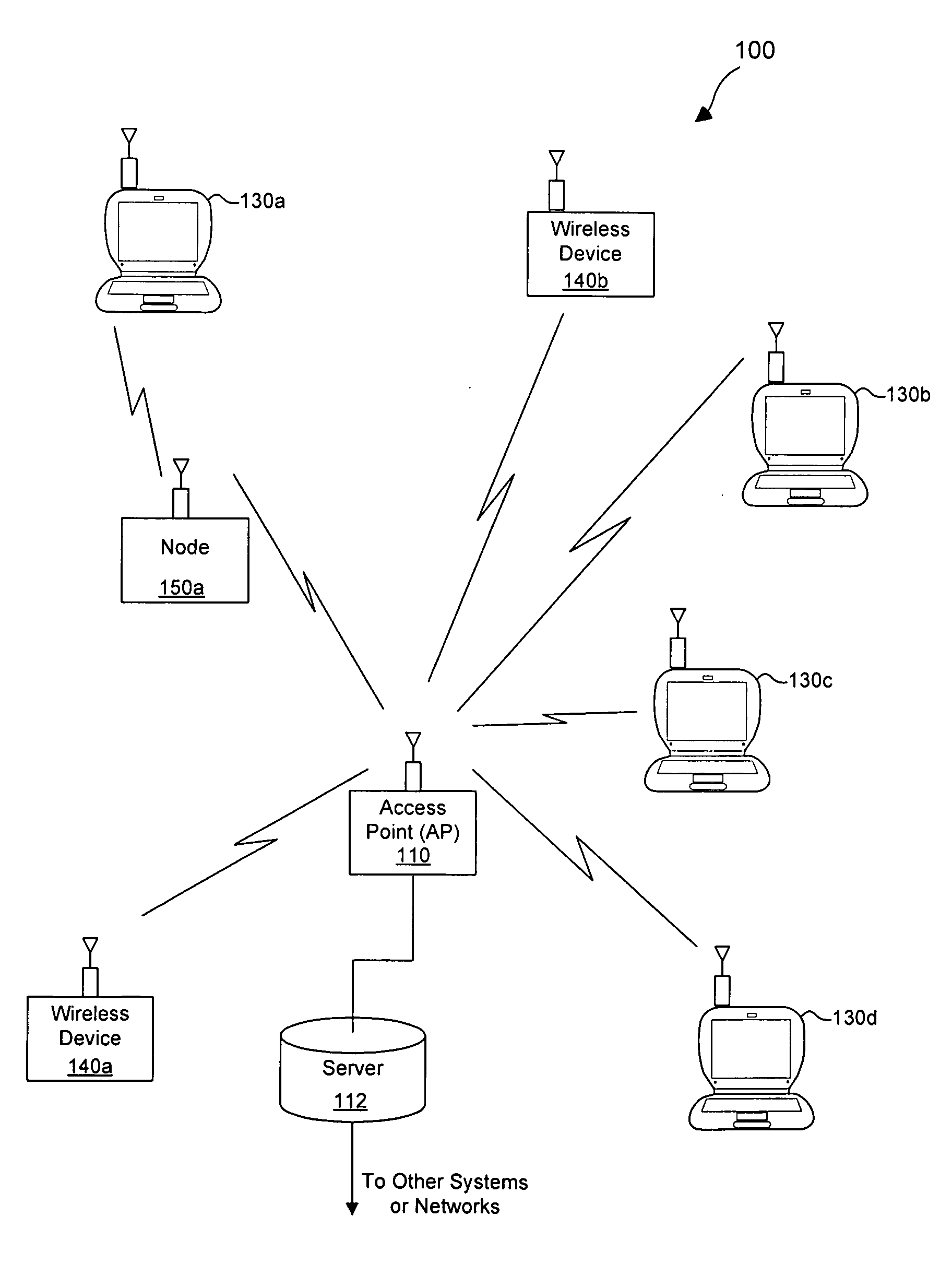
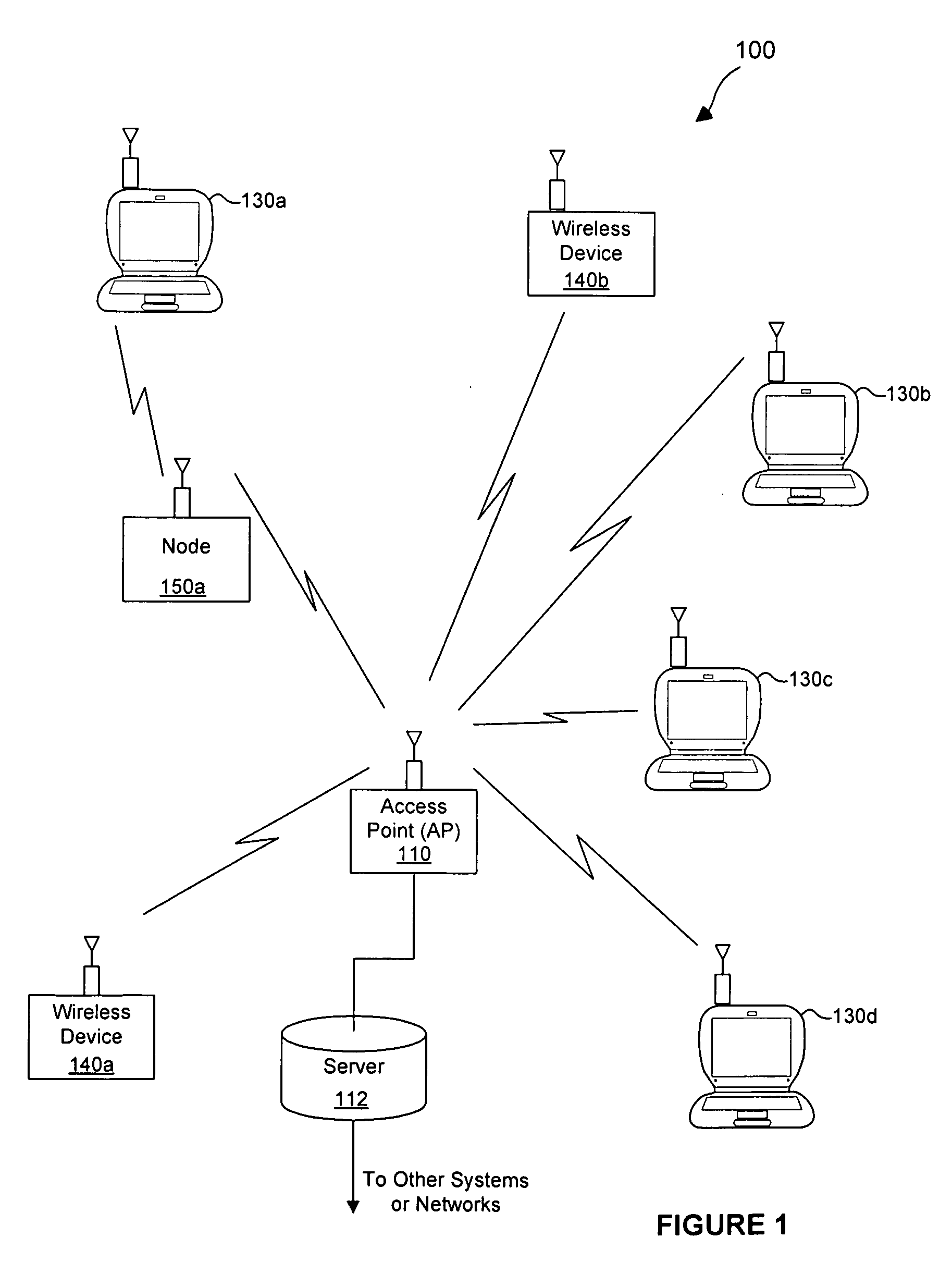
Unmanned aerial vehicle for antenna radiation characterization
InactiveUS20160088498A1Readily apparentError preventionTransmission systemsTransceiverControl signal
The unmanned aerial vehicle for antenna radiation characterization is an unmanned aerial vehicle having a propulsion system and a transceiver. Control signals are transmitted from a base station to position the unmanned aerial vehicle adjacent an antenna of interest. The unmanned aerial vehicle for antenna radiation characterization further includes a signal strength antenna for receiving an antenna signal generated by the antenna of interest for calculating or determining the received signal strength of the antenna signal. A received signal strength signal is then transmitted back to the base station, in real time. The received signal strength signal is representative of a set of received signal strengths of the antenna signal corresponding to a set of three-dimensional measurement coordinates such that the received signal strength signal represents a three-dimensional radiation pattern associated with the antenna of interest.
Owner:KING FAHD UNIVERSITY OF PETROLEUM AND MINERALS
System and method for message redirection between mobile telecommunication networks with different radio access technologies
InactiveUS20040147262A1Radio/inductive link selection arrangementsWireless commuication servicesRadio access technologyCommunications system
Communication systems and methods are provided allowing a single mode mobile terminal to support mobile assisted signal strength measurement operations in both a fixed frequency reuse based communication network and an adaptive channel allocation based communication network. Candidate base station signal strength measurements are requested by a fixed frequency reuse type network, measured by the mobile terminal and provided to the fixed frequency reuse type network which is seeking to identify a strongest signal for mobile assisted handover operations. In addition, interference signal strength measurements are requested by an adaptive channel allocation type network, measured by the mobile terminal and provided to the adaptive channel allocation type network by the mobile terminal. No redundant circuitry is required in the mobile terminal. Instead, the mobile terminal executes the same operations using the same hardware regardless of whether the requested measurement is of a candidate signal strength or an interference signal.
Owner:APPLE INC
Method for database driven channel quality estimation in a cognitive radio network
ActiveUS20100330919A1Power managementTransmission monitoringCo-channel interferenceGeolocation database
A method of determining operating parameters for a secondary system transmitter is described. The transmitter characteristics, including location and operating frequency band, are provided to a geo-location database. The database determines the maximum allowable transmission power that meets various specifications for different channels and conveys the power and channel(s) to the transmitter. The database estimates channel incumbent signal strengths based on the transmitter location and primary and higher-priority secondary incumbent systems, estimates the splatter levels, determines whether adjacent and co-channel interference protection ratios are met, and adjusts the allowable power level accordingly. The database also estimates aggregate co- and adjacent channel primary and secondary incumbent system interference levels at the transmitter location and predicts channel quality for each allowable channel. The estimated levels are updated using measurements of actual levels at the transmitter location. The database dynamically allocates channels using the secondary system priorities.
Owner:MOTOROLA SOLUTIONS INC +1
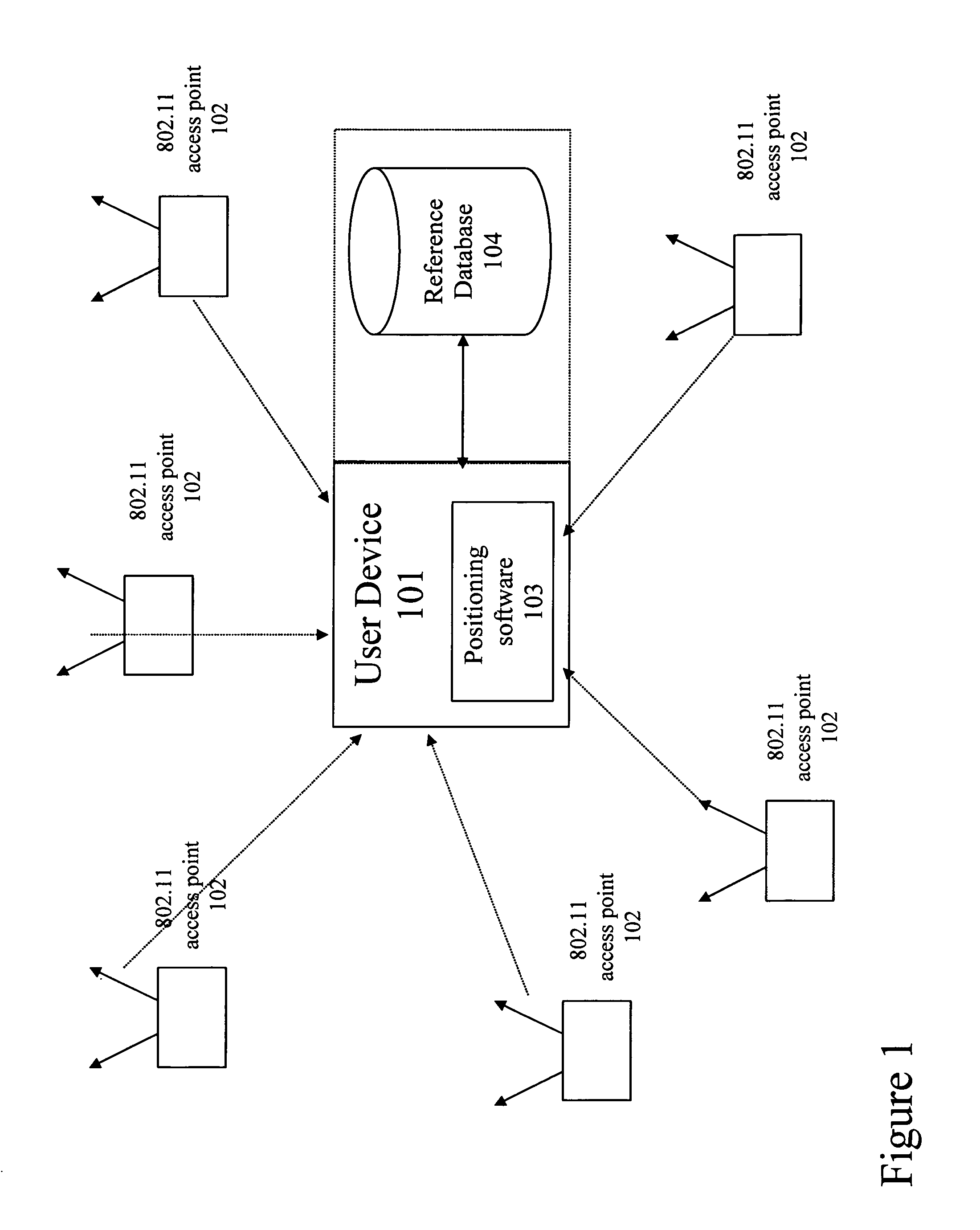
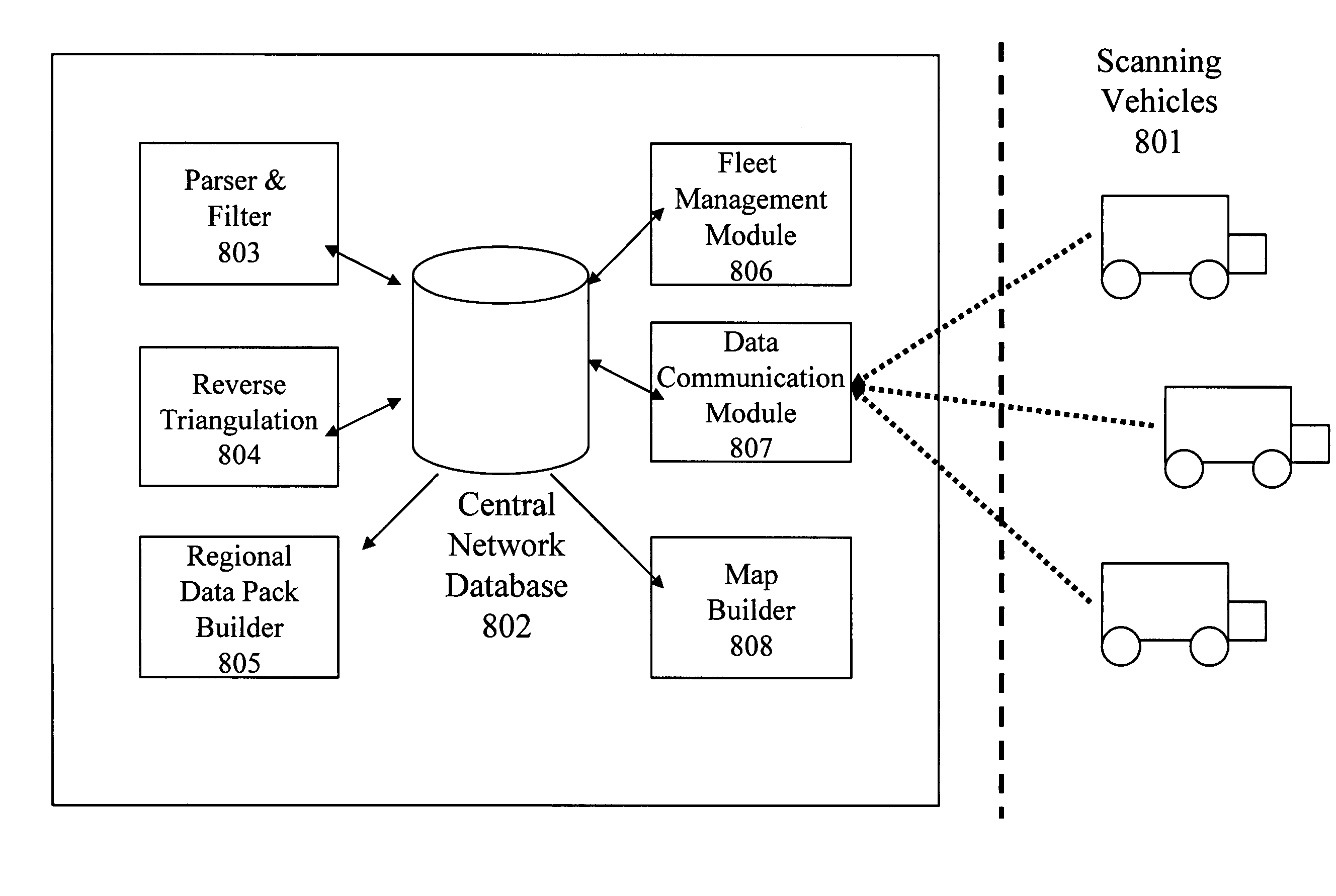
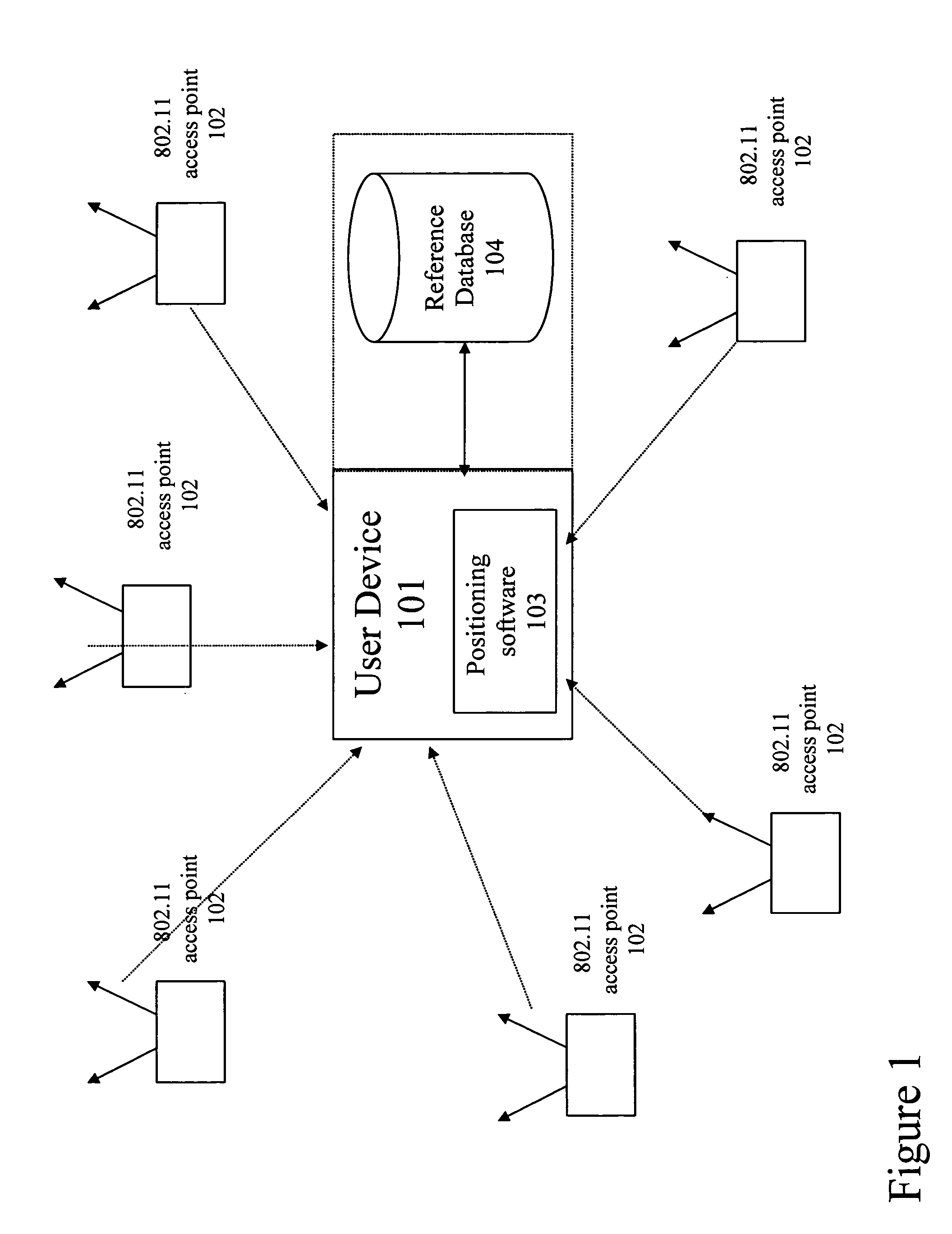
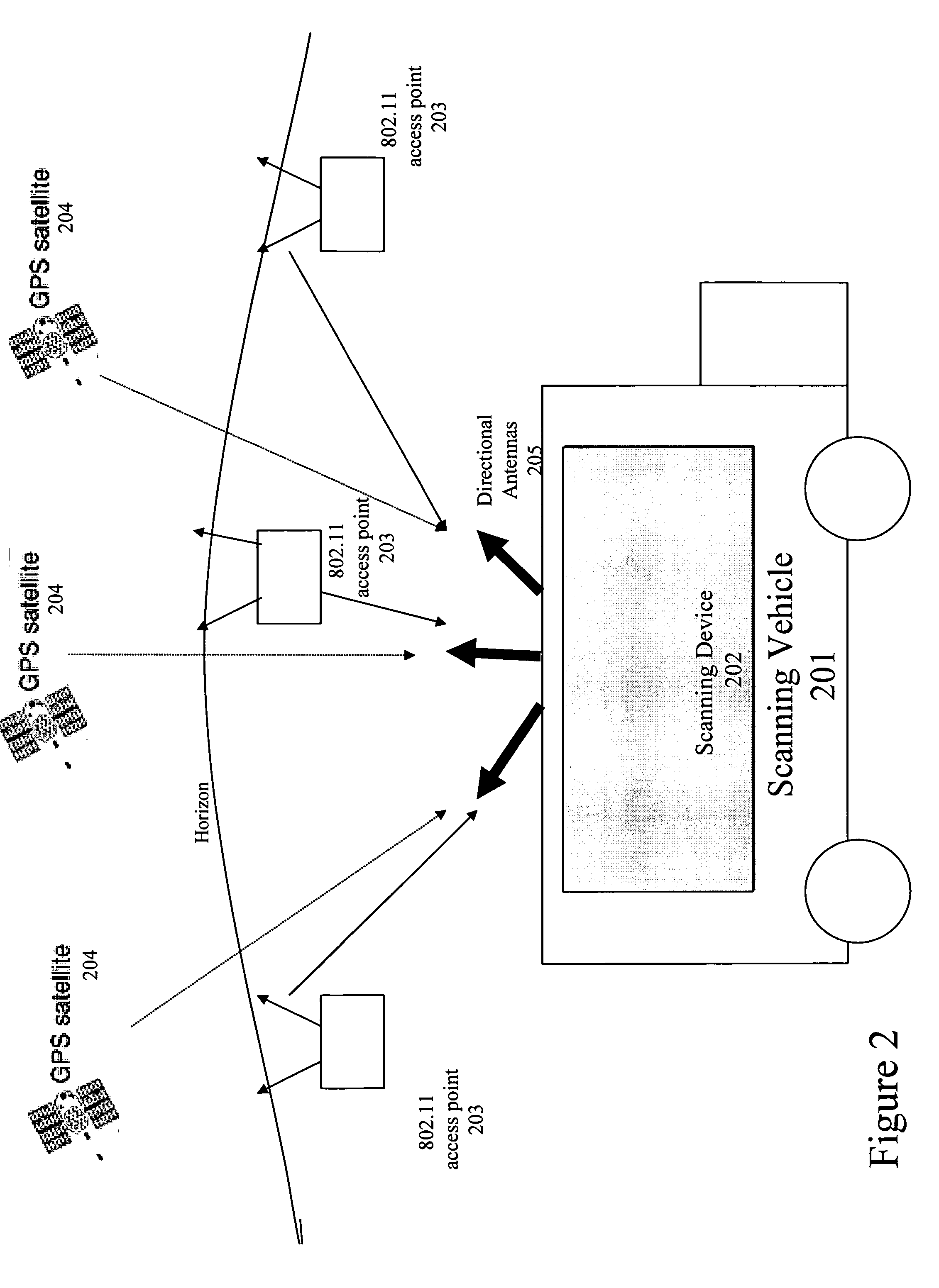
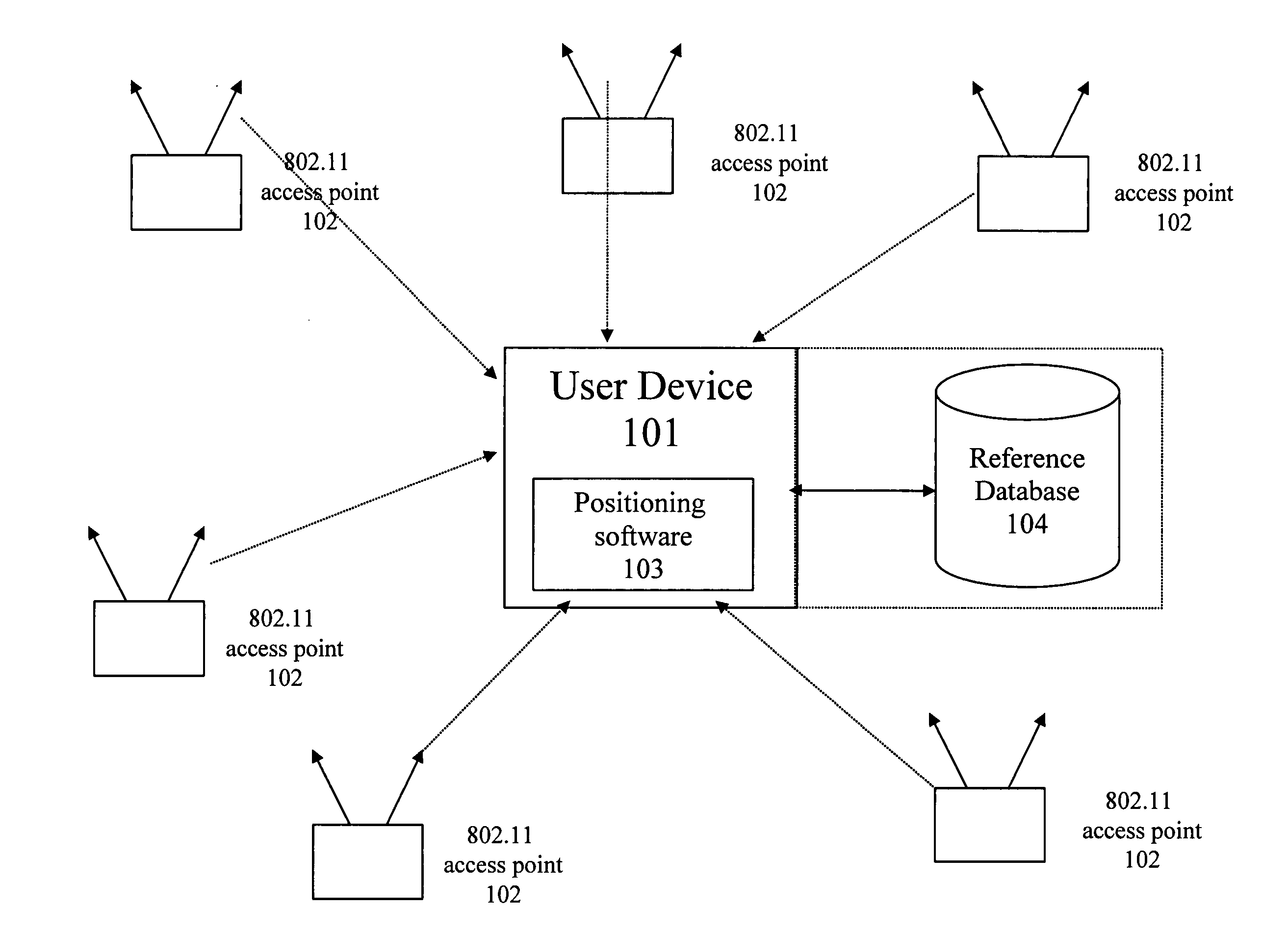
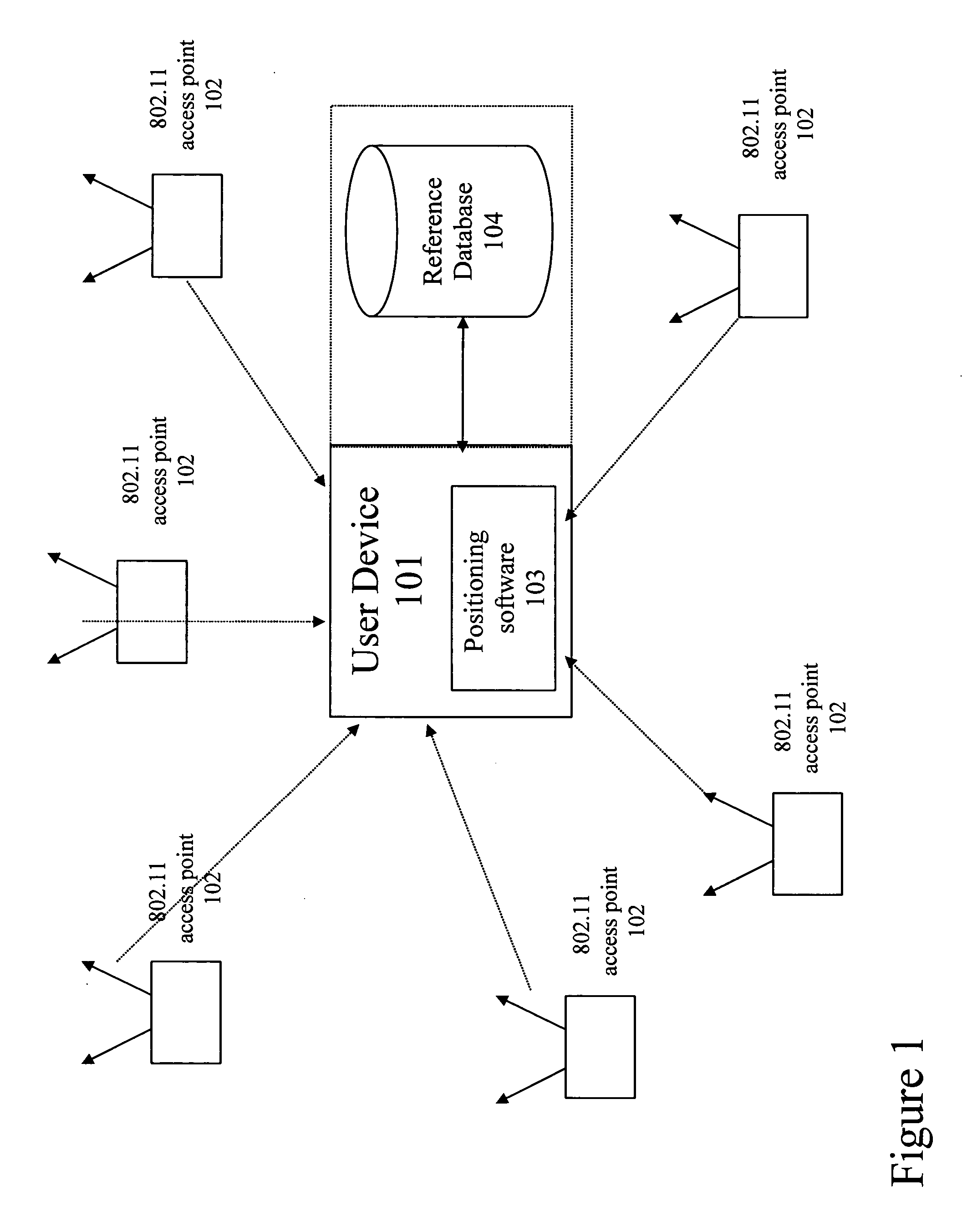
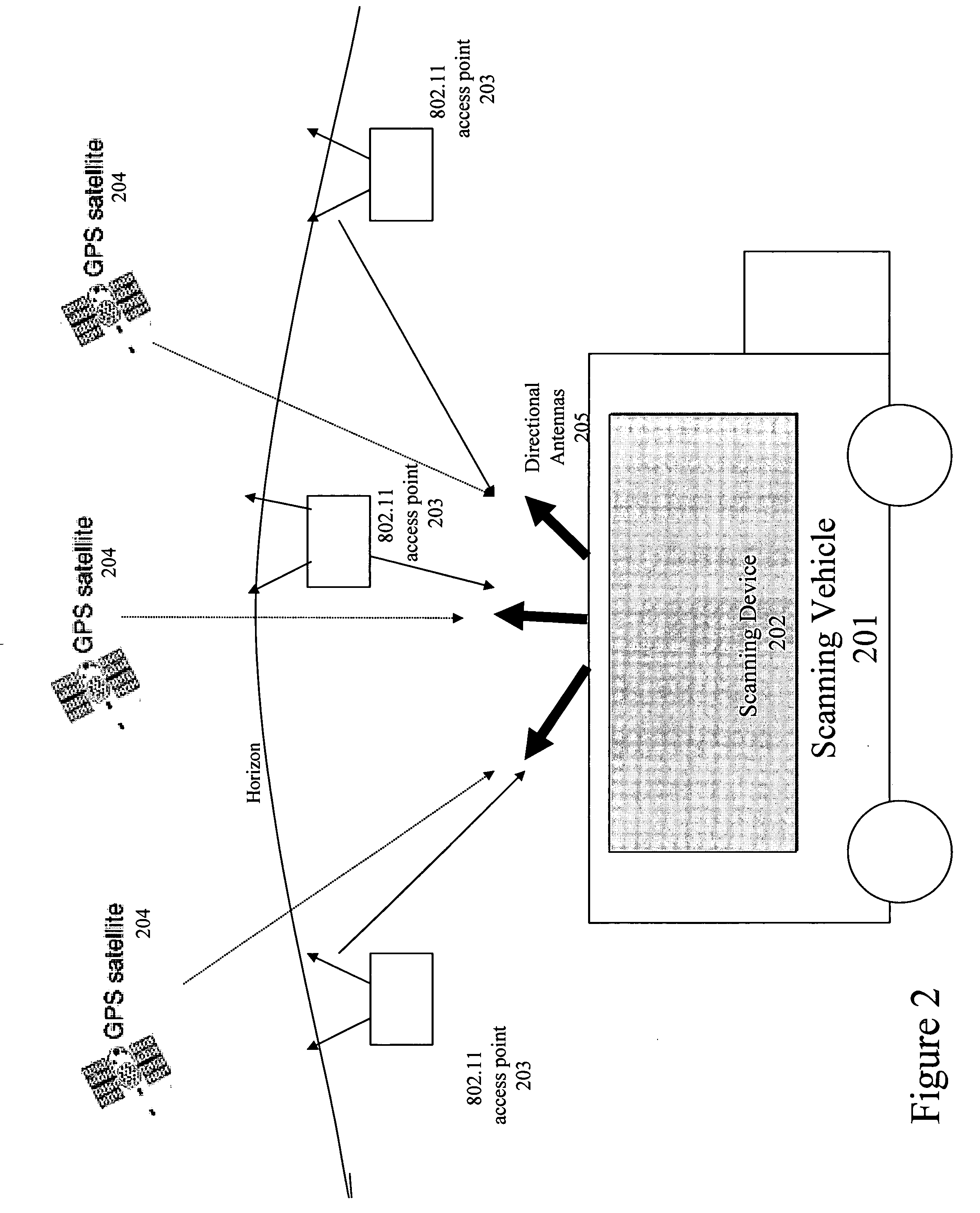
Method and system for building a location beacon database
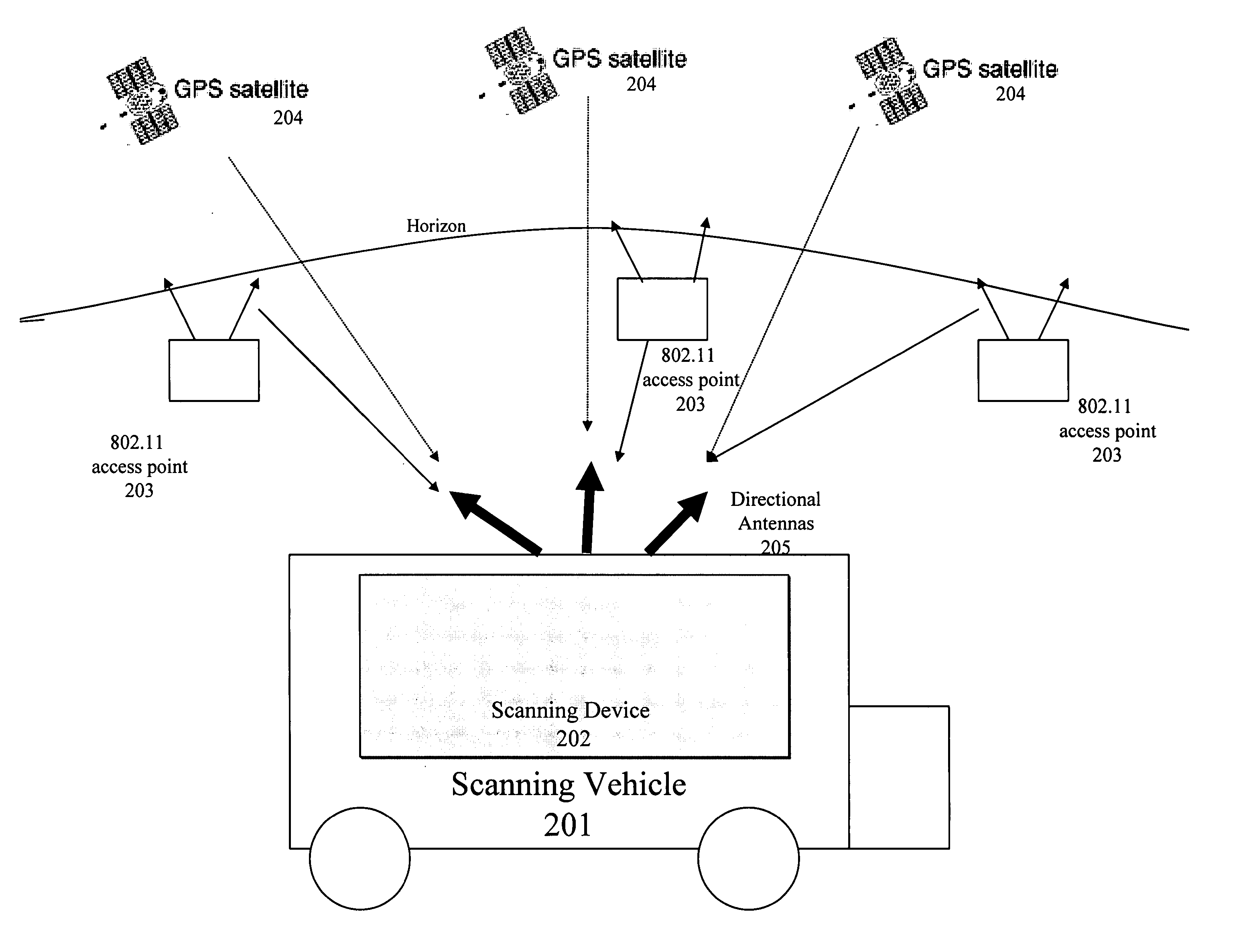
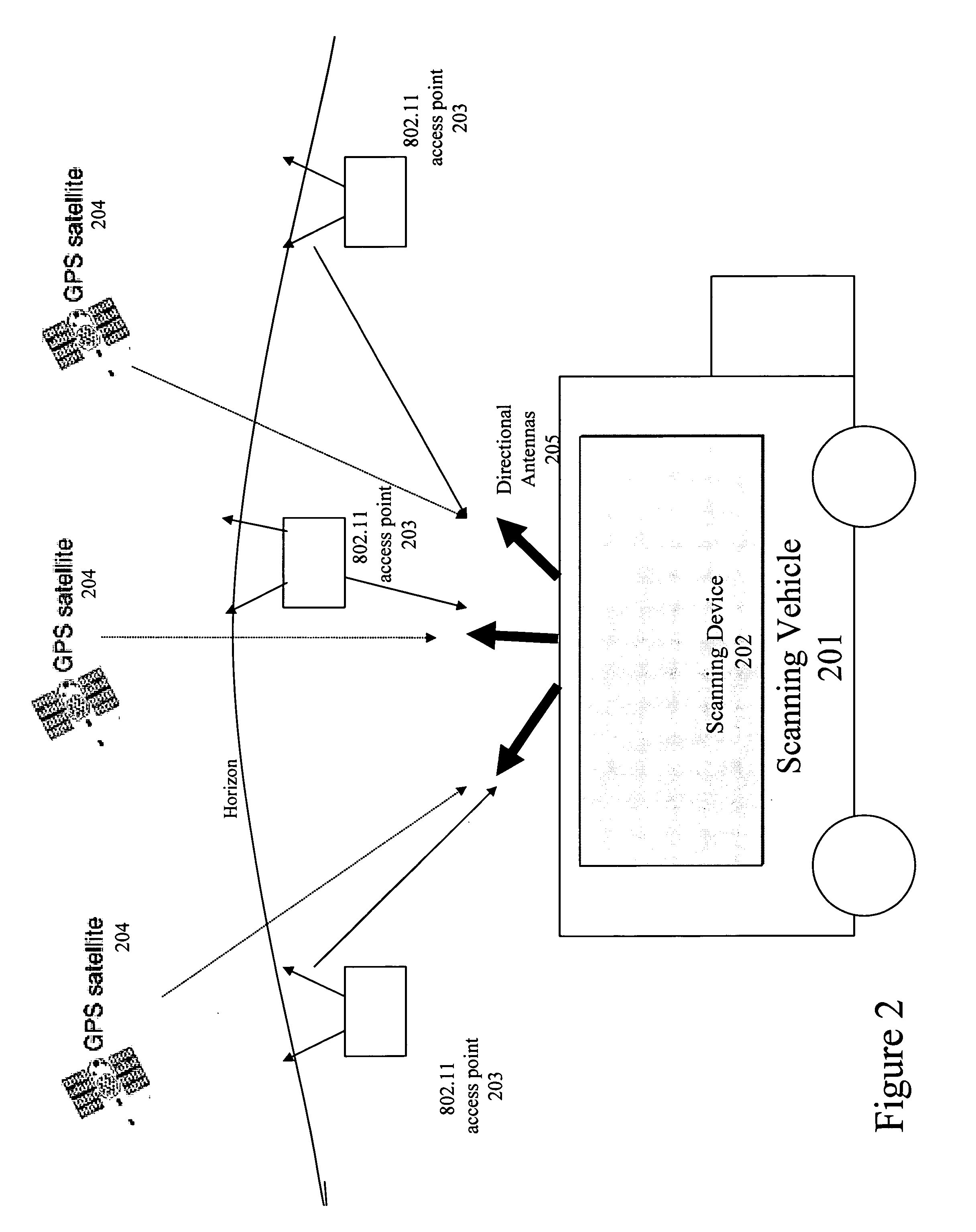
A location beacon database and server, method of building location beacon database, and location based service using same. Wi-Fi access points are located in a target geographical area to build a reference database of locations of Wi-Fi access points. At least one vehicle is deployed including at least one scanning device having a GPS device and a Wi-Fi radio device and including a Wi-Fi antenna system. The target area is traversed in a programmatic route to avoid arterial bias. The programmatic route includes substantially all drivable streets in the target geographical area and solves an Eulerian cycle problem of a graph represented by said drivable streets. While traversing the target area, periodically receive the GPS coordinates of the GPS device. While traversing the target area, detecting Wi-Fi signals from Wi-Fi access points in range of the Wi-Fi device and recording identity information of the detected Wi-Fi access point in conjunction with GPS location information of the vehicle when the detection of the Wi-Fi access point was made. The location information is used to reverse triangulate the position of the detected Wi-Fi access point; and the position of the detected access point is recorded in a reference database. A user-device having a Wi-Fi radio may be located. A reference database of calculated locations of Wi-Fi access points in a target area is provided. In response to a user application request to determine a location of a user-device having a Wi-Fi radio, the Wi-Fi device is triggered to transmit a request to all Wi-Fi access points within range of the Wi-Fi device. Messages are received from the Wi-Fi access points within range of the Wi-Fi device, each message identifying the Wi-Fi access point sending the message. The signal strength of the messages received by the Wi-Fi access points is calculated. The reference database is accessed to obtain the calculated locations for the identified Wi-Fi access points. Based on the number of Wi-Fi access points identified via received messages, choosing a corresponding location-determination algorithm from a plurality of location-determination algorithms, said chosen algorithm being suited for the number of identified Wi-Fi access points. The calculated locations for the identified Wi-Fi access points and the signal strengths of said received messages and the chosen location-determination algorithm are used to determine the location of the user-device. The database may be modified with newly added position information to improve quality of previously determined positions, and error prone information is avoided.
Owner:SKYHOOK WIRELESS
Wireless tracking system and method utilizing multiple location algorithms
The present invention provides a solution to mistaken location calculations based on multipath effects. The present invention determines a real-time location of an object in a facility using a combination of location algorithms, with a signal characteristic for a wireless signal from a communication device attached to the object received at a sensor of a mesh network. The location algorithms preferably include at least two of a proximity algorithm, a radial basis function algorithm, a maximum likelihood algorithm, a genetic algorithm, a minimum mean squared error algorithm, a radiofrequency fingerprinting algorithm, a multilateration algorithm, a time difference of arrival algorithm, a signal strength algorithm, a time of arrival algorithm, an angle of arrival algorithm, a spatial diversity algorithm, and a nearest neighbor algorithm.
Owner:CENTRAK INC
Calibration of Beamforming Nodes in a Configurable Monitoring Device System
InactiveUS20110080267A1Function increaseMultiplex system selection arrangementsTesting sensing arrangementsMonitoring systemEngineering
A system for radio frequency identification of a tag in an interrogation zone, includes a calibration node disposed in the interrogation zone to measure a signal strength of radio frequency identification signals from a beamforming system and provide signal data in accordance with the signal strength. A reader node is configured to receive the signal data and adjust the radio frequency identification signals generated by the beamforming system based upon the signal data. At least one of the calibration node, the reader node and the beamforming system is a configurable monitoring system. The calibration node, the reader node, and the beamforming system are coupled in a feedback control loop. The beamforming system includes a plurality of beamforming nodes. A signal of at least one beamforming node is optimized in accordance with the feedback control loop.
Owner:CHECKPOINT SYST INC
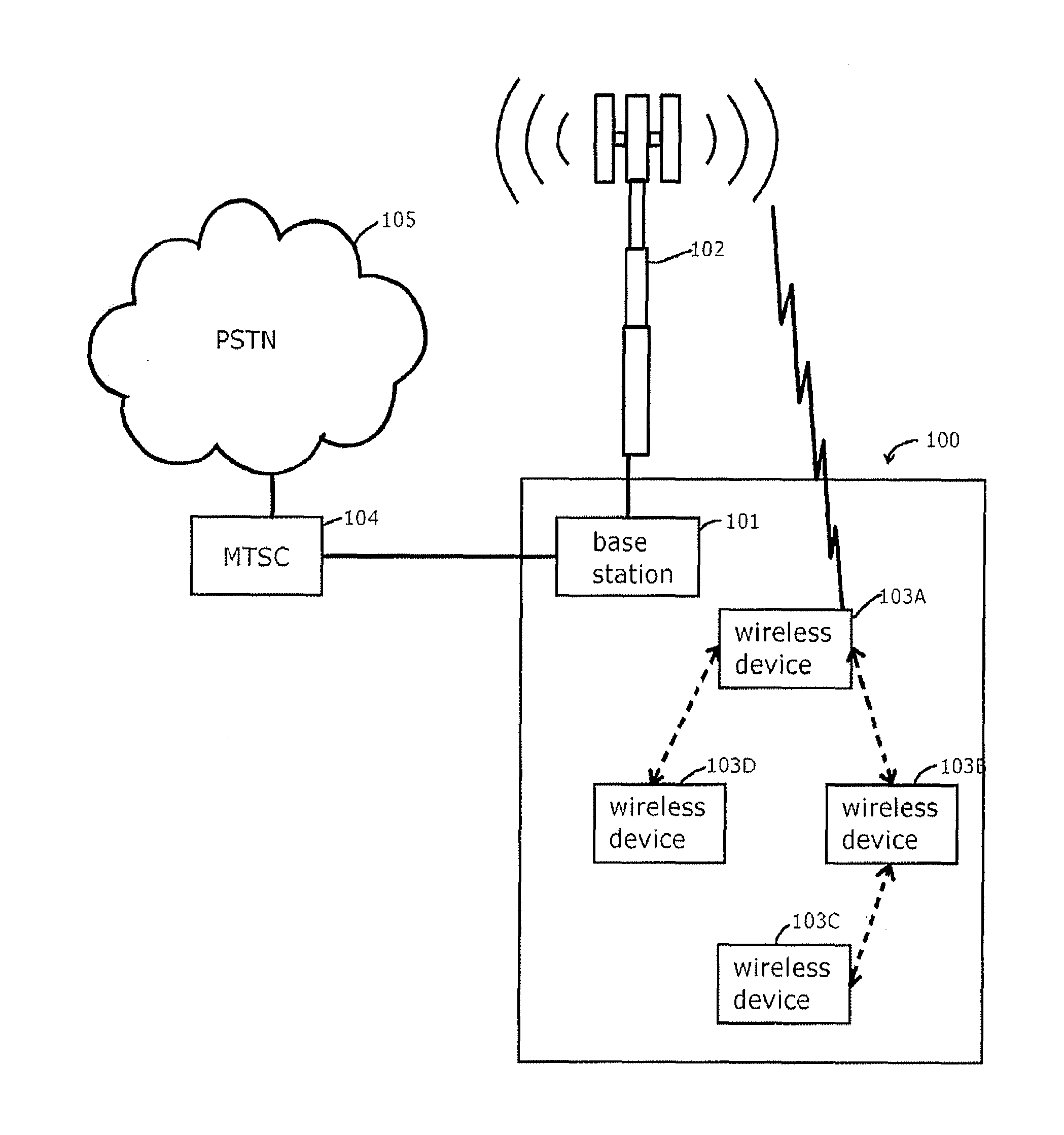
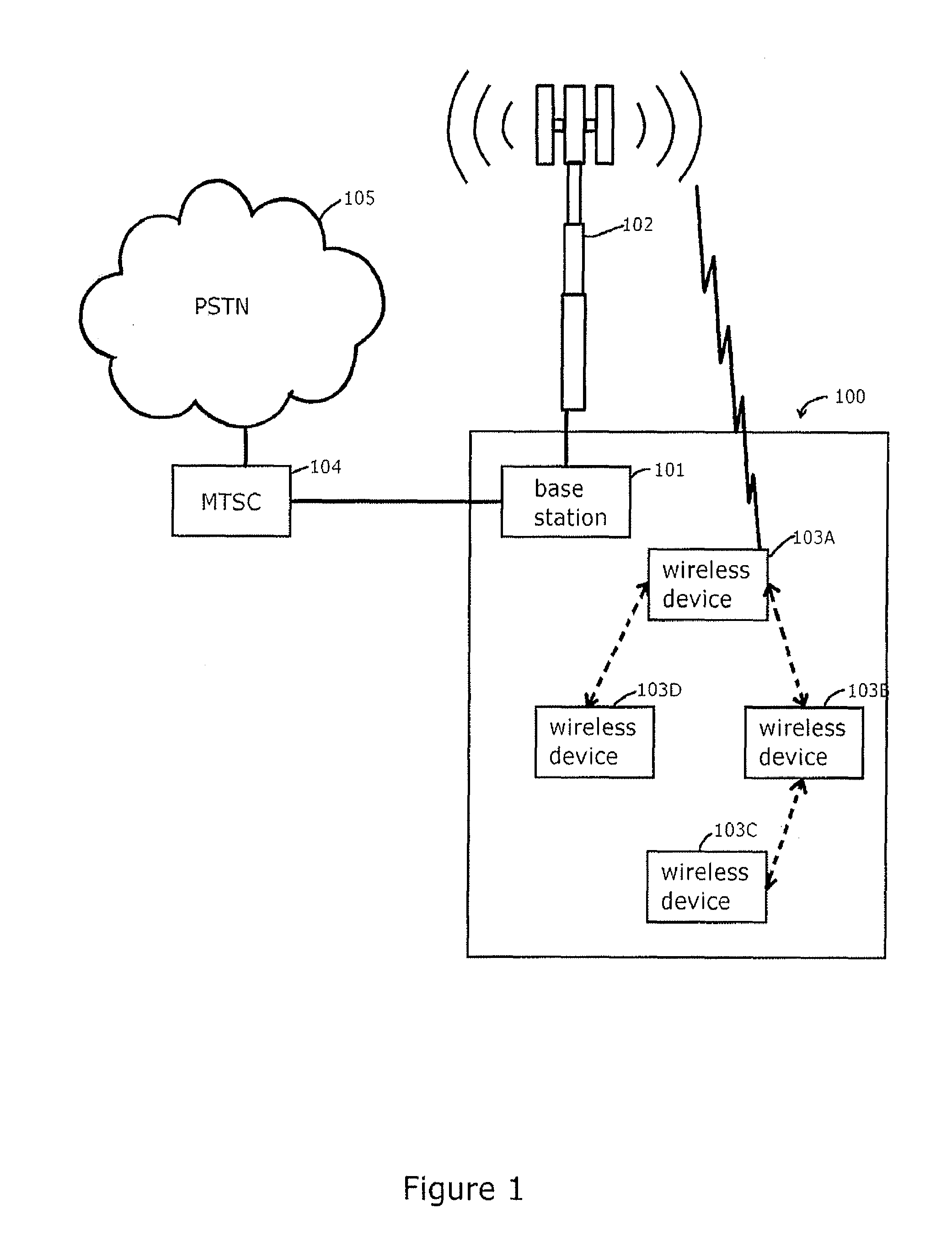
Wireless communication methods, systems, and computer program products
ActiveUS20130083722A1Power managementFrequency-division multiplex detailsSignal strengthCellular telephone
A method, wireless device and computer program product for expanding the coverage of a cellular network. A wireless device (e.g., cellular telephone) is able to communicate with a base station in a cell of the cellular network over a non-cellular interface via another wireless device in the cell through the use of multi-hopping. A wireless device may request permission to communicate with the base station over a non-cellular interface via hopping off another wireless device when its signal strength is below a threshold. Alternatively, a wireless device may receive a request to communicate with the base station over a non-cellular interface via hopping off the wireless device that sent the request when that wireless device has excess capacity in its bandwidth with the base station. By enabling wireless devices to communicate with a base station in such a manner, the effective coverage area of the cellular network is expanded and the effective capacity of the cellular network is improved.
Owner:BOARD OF RGT THE UNIV OF TEXAS SYST
Server for updating location beacon database
A location beacon database and server, method of building location beacon database, and location based service using same. Wi-Fi access points are located in a target geographical area to build a reference database of locations of Wi-Fi access points. At least one vehicle is deployed including at least one scanning device having a GPS device and a Wi-Fi radio device and including a Wi-Fi antenna system. The target area is traversed in a programmatic route to avoid arterial bias. The programmatic route includes substantially all drivable streets in the target geographical area and solves an Eulerian cycle problem of a graph represented by said drivable streets. While traversing the target area, periodically receive the GPS coordinates of the GPS device. While traversing the target area, detecting Wi-Fi signals from Wi-Fi access points in range of the Wi-Fi device and recording identity information of the detected Wi-Fi access point in conjunction with GPS location information of the vehicle when the detection of the Wi-Fi access point was made. The location information is used to reverse triangulate the position of the detected Wi-Fi access point; and the position of the detected access point is recorded in a reference database. A user-device having a Wi-Fi radio may be located. A reference database of calculated locations of Wi-Fi access points in a target area is provided. In response to a user application request to determine a location of a user-device having a Wi-Fi radio, the Wi-Fi device is triggered to transmit a request to all Wi-Fi access points within range of the Wi-Fi device. Messages are received from the Wi-Fi access points within range of the Wi-Fi device, each message identifying the Wi-Fi access point sending the message. The signal strength of the messages received by the Wi-Fi access points is calculated. The reference database is accessed to obtain the calculated locations for the identified Wi-Fi access points. Based on the number of Wi-Fi access points identified via received messages, choosing a corresponding location-determination algorithm from a plurality of location-determination algorithms, said chosen algorithm being suited for the number of identified Wi-Fi access points. The calculated locations for the identified Wi-Fi access points and the signal strengths of said received messages and the chosen location-determination algorithm are used to determine the location of the user-device. The database may be modified with newly added position information to improve quality of previously determined positions, and error prone information is avoided.
Owner:SKYHOOK WIRELESS
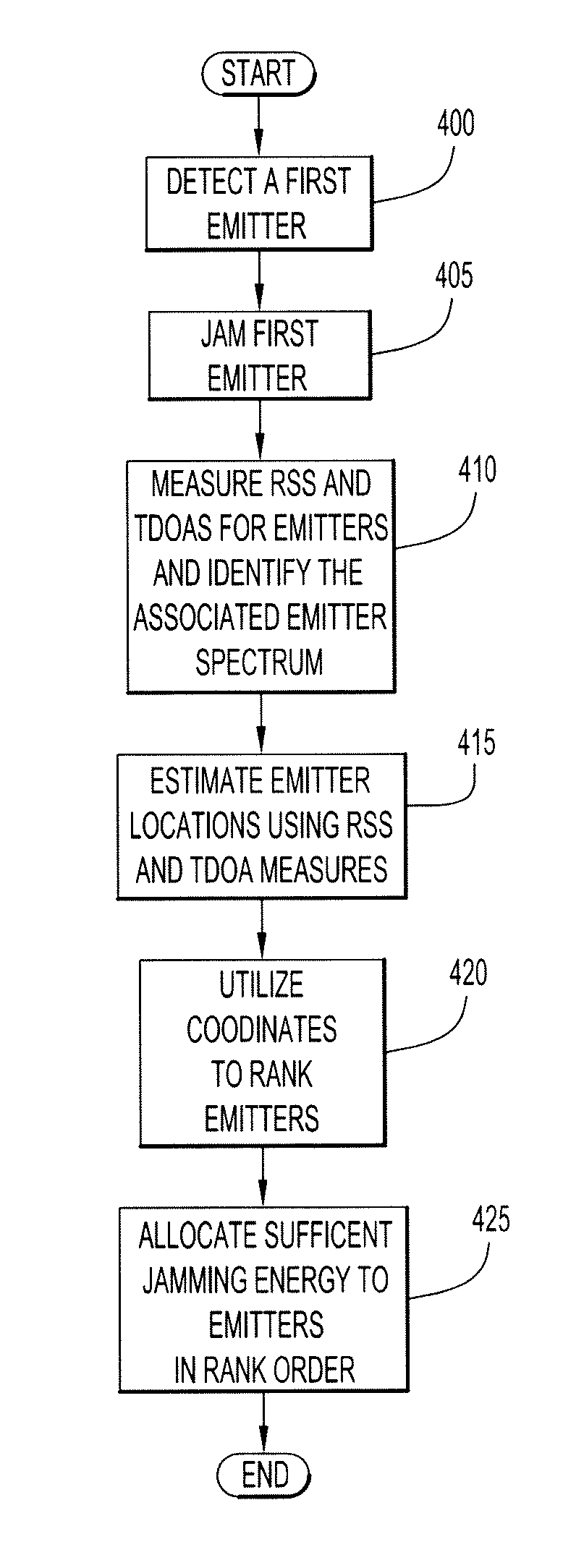
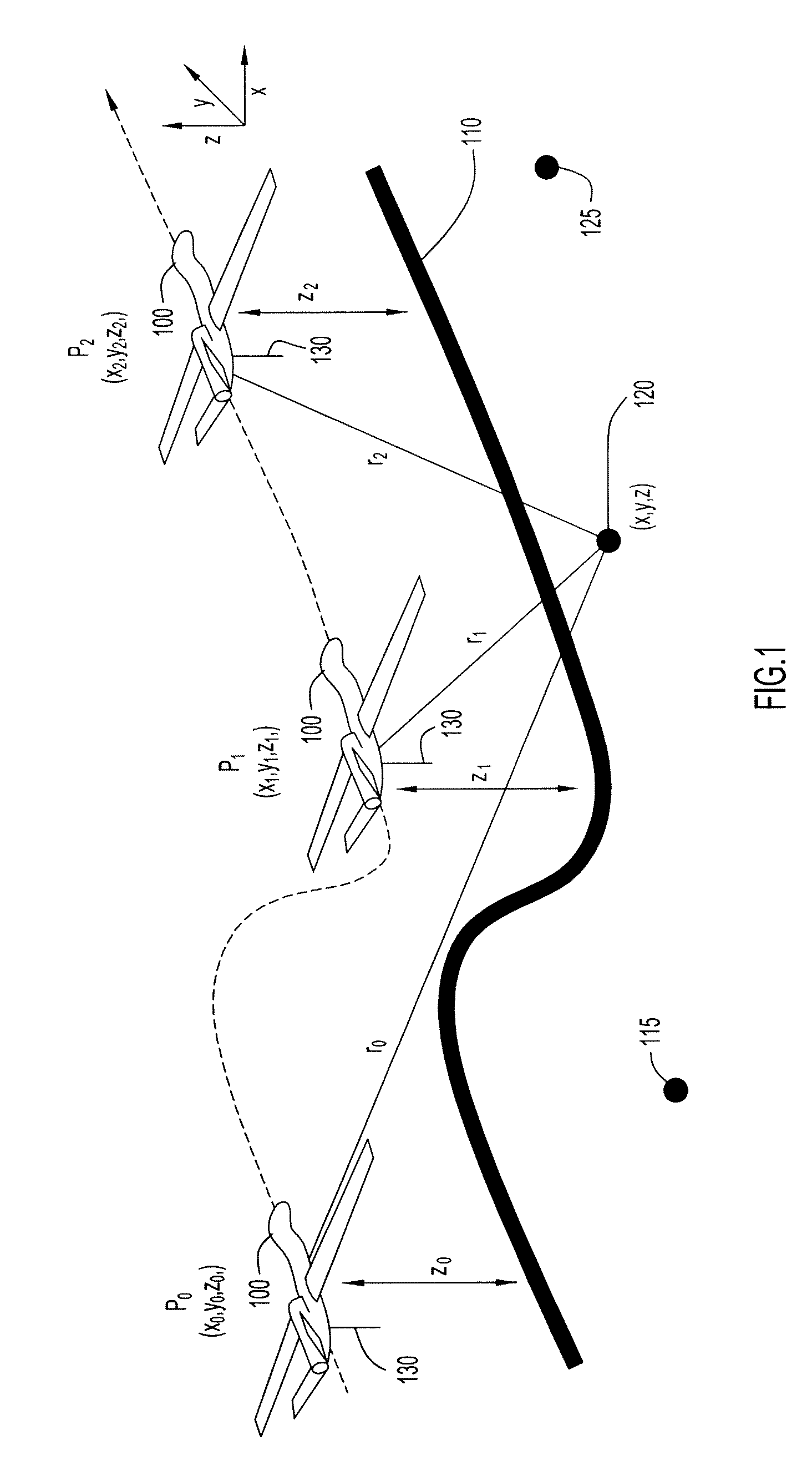
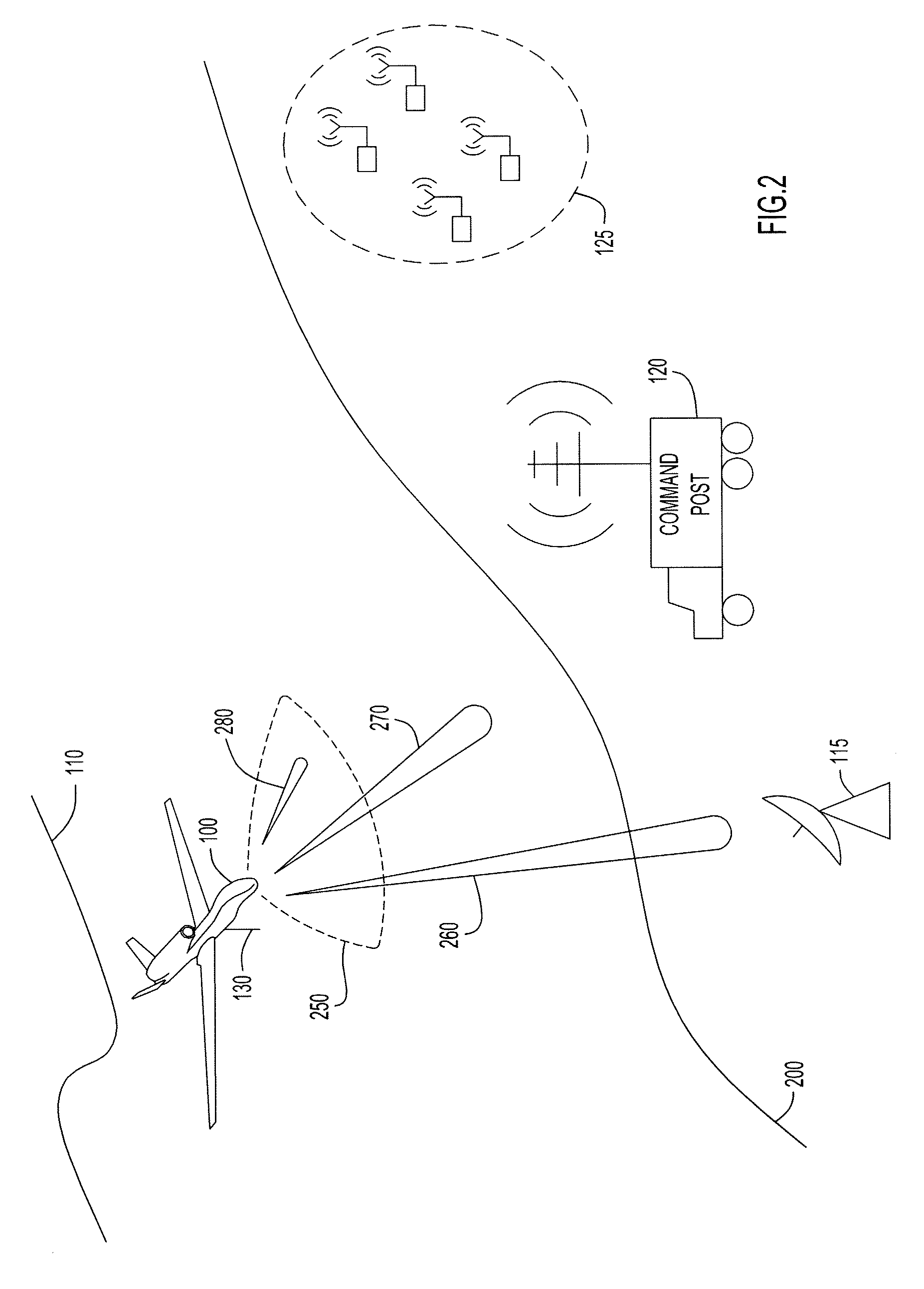
System and method for allocating jamming energy based on three-dimensional geolocation of emitters
ActiveUS8615190B2Cost-effectiveSmallWave based measurement systemsTelephonic communicationGeolocationEnergy based
According to an embodiment of the present invention jamming energy is allocated to a plurality of emitters based on a three-dimensional (3-D) emitter geolocation technique that determines the geolocation of radio frequency (RF) emitters based on energy or received signal strength (RSS) and / or time differences of arrival (TDOAs) of transmitted signals. The three-dimensional (3-D) emitter geolocations are used to rank emitters of interest according to distance and available radio frequency (RF) jamming energy is allocated to the emitters in rank order. The techniques may be employed with small unmanned air vehicles (UAV), and obtains efficient use of jamming energy when applied to radio frequency (RF) emitters of interest.
Owner:HARRIS CORP
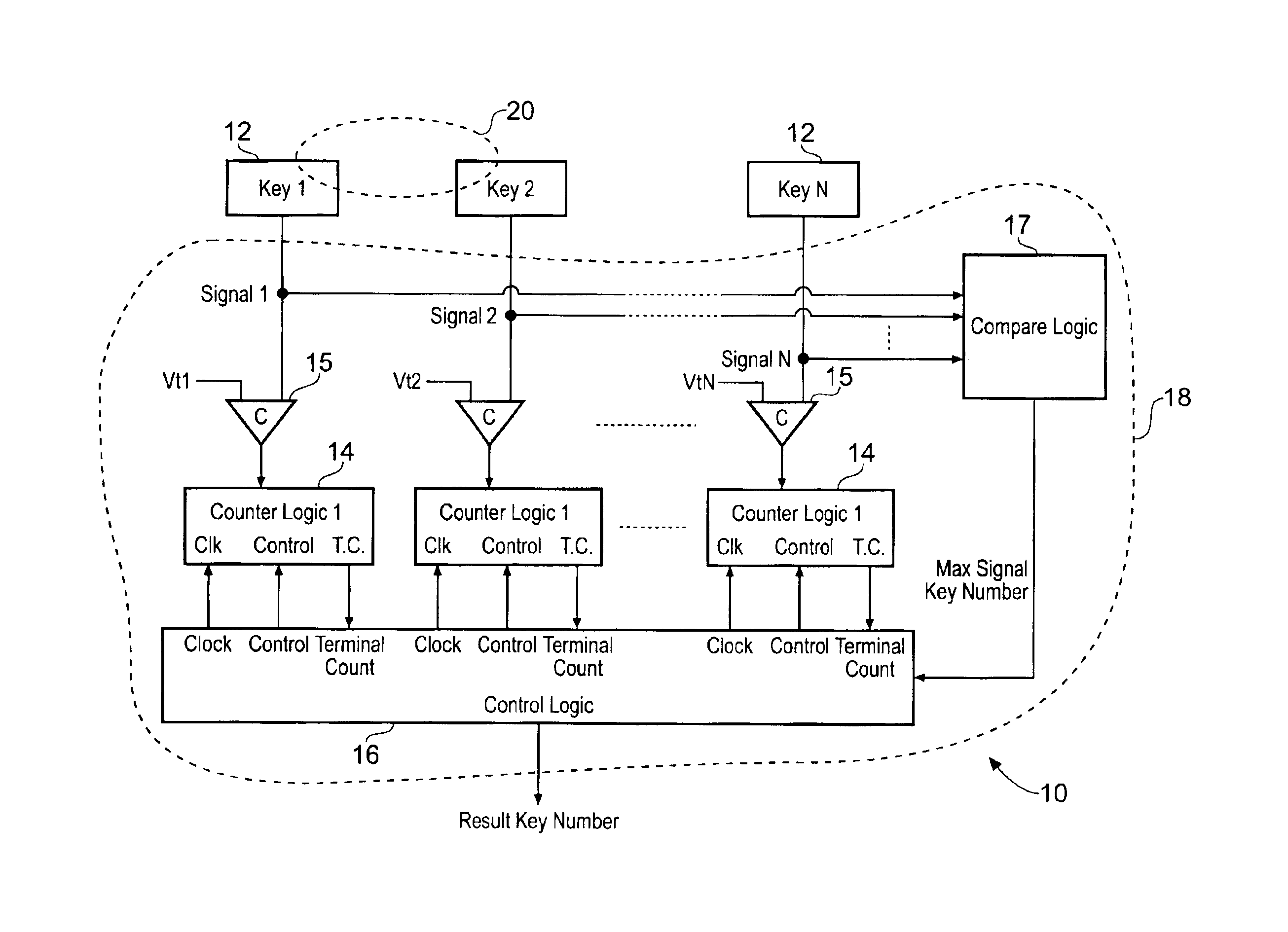
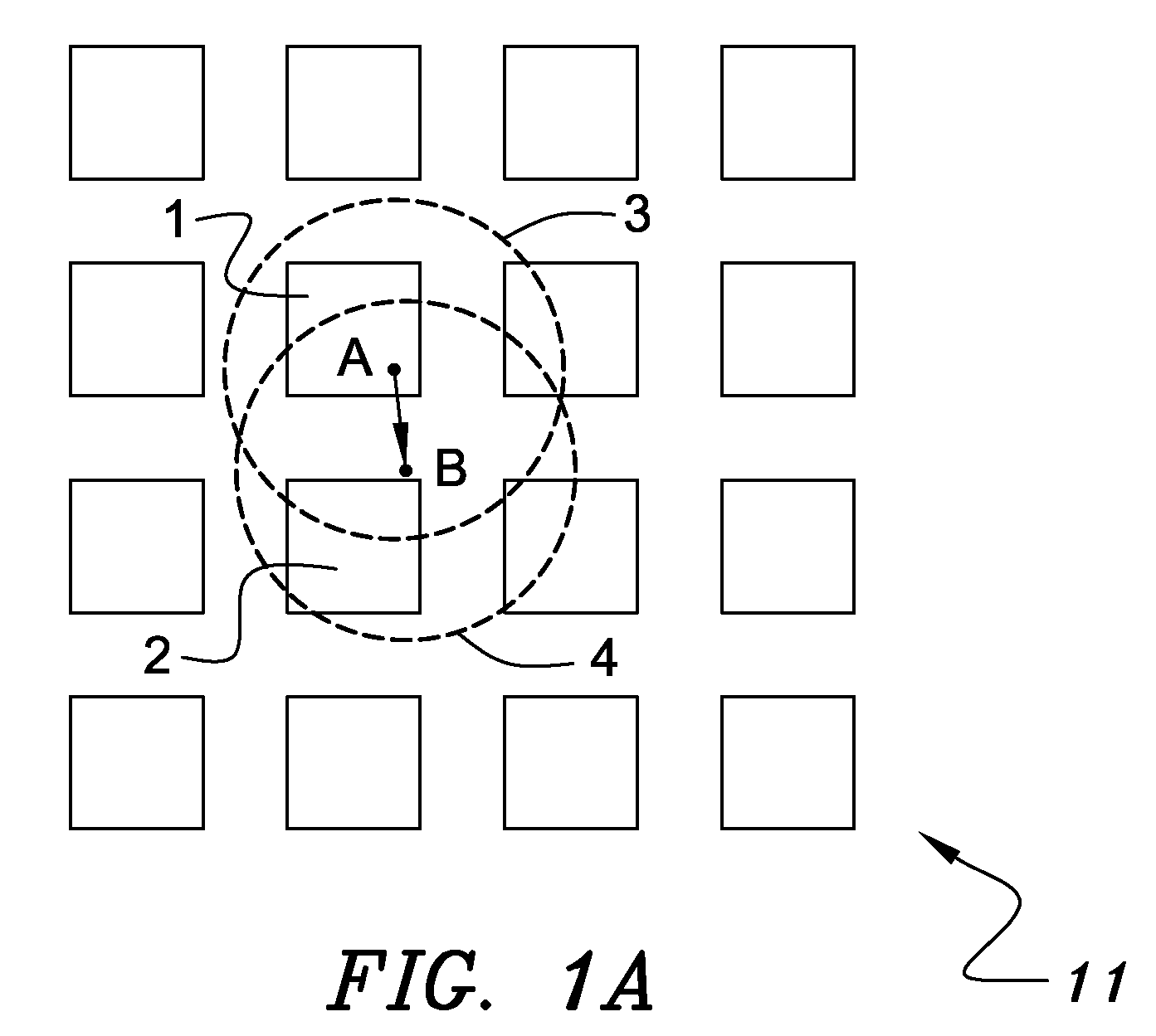
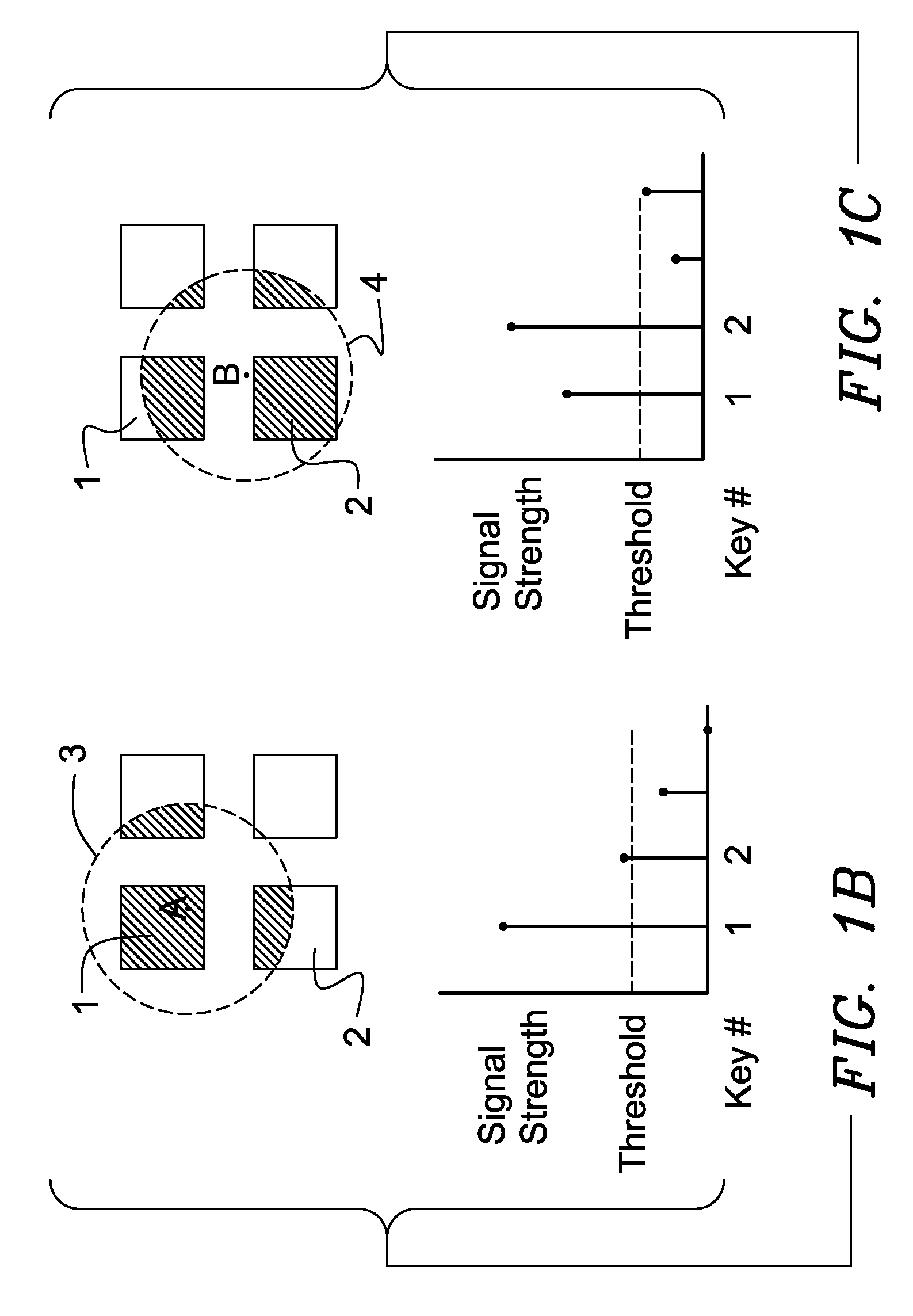
Keyboard with reduced keying ambiguity
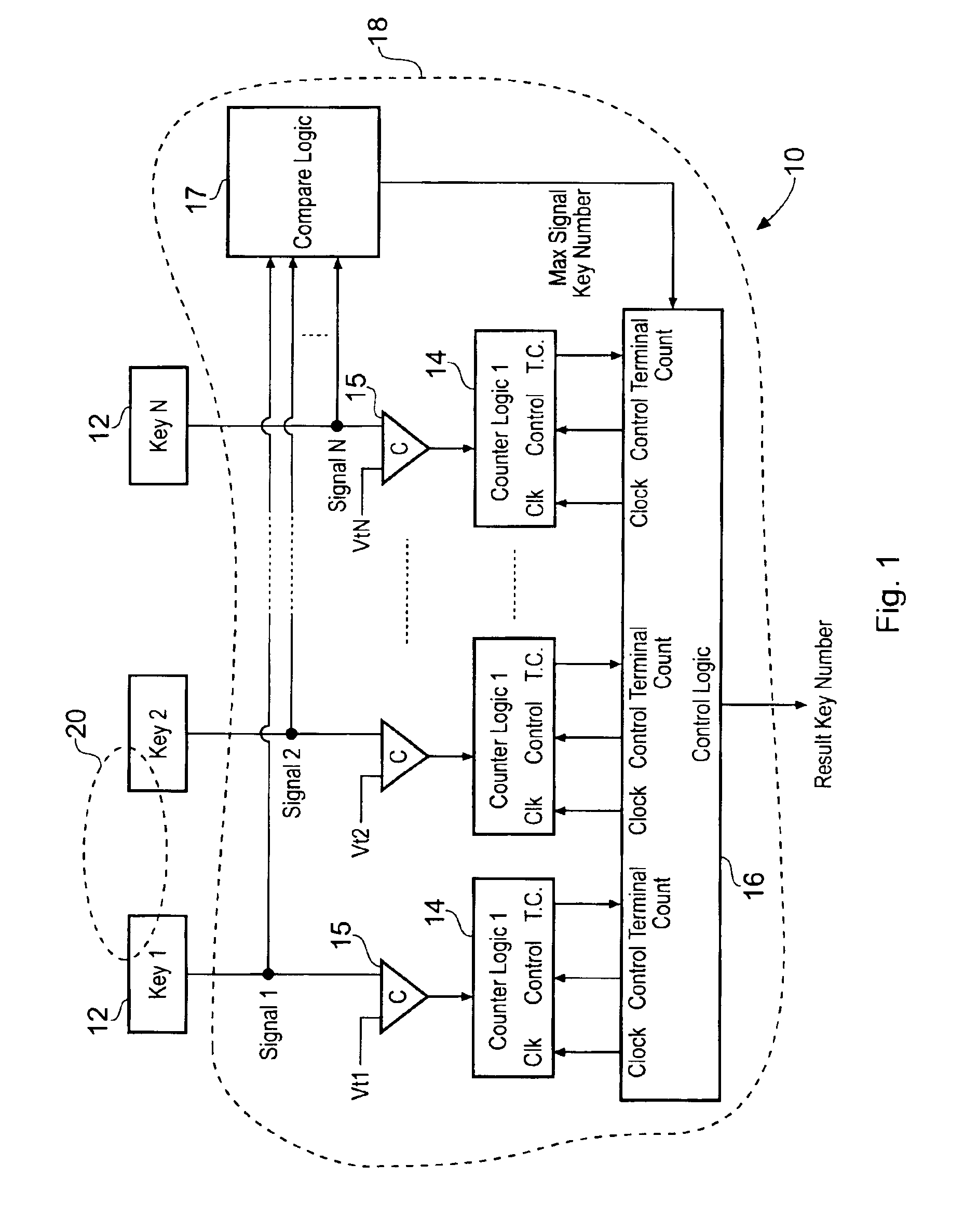
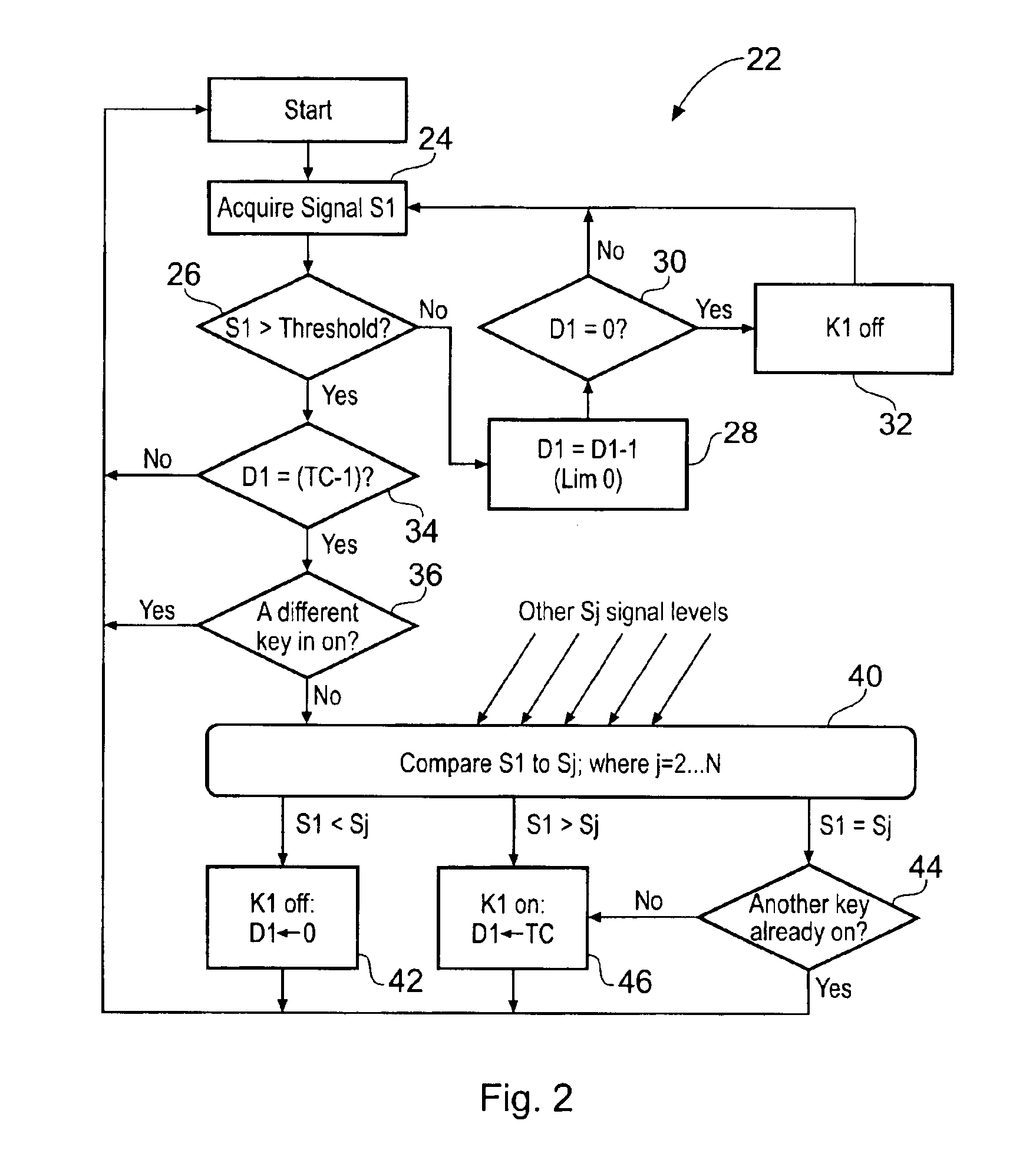
When an array of proximity sensors is used as a keyboard, it can provide an ambiguous output if a user's finger overlaps several keys or if liquid is spilled on the keyboard. This ambiguity is reduced by an iterative method that repeatedly measures a detected signal strength associated with each key, compares all the measured signal strengths to find a maximum, determines that the key having the maximum signal strength is the unique user-selected key and then suppresses or ignores signals from all other keys as long as the signal from the selected key remains above some nominal threshold value.
Owner:NEODRON LTD
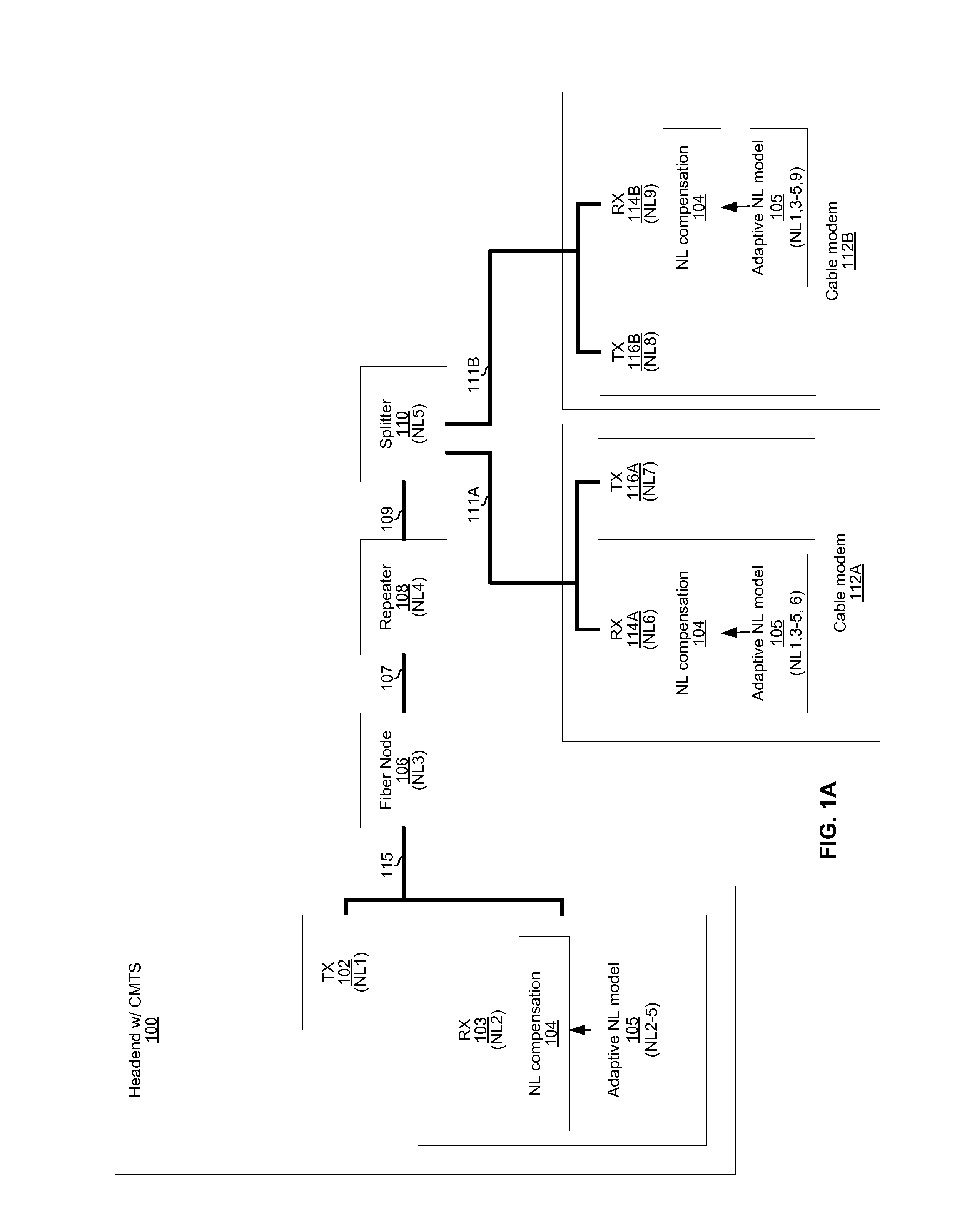
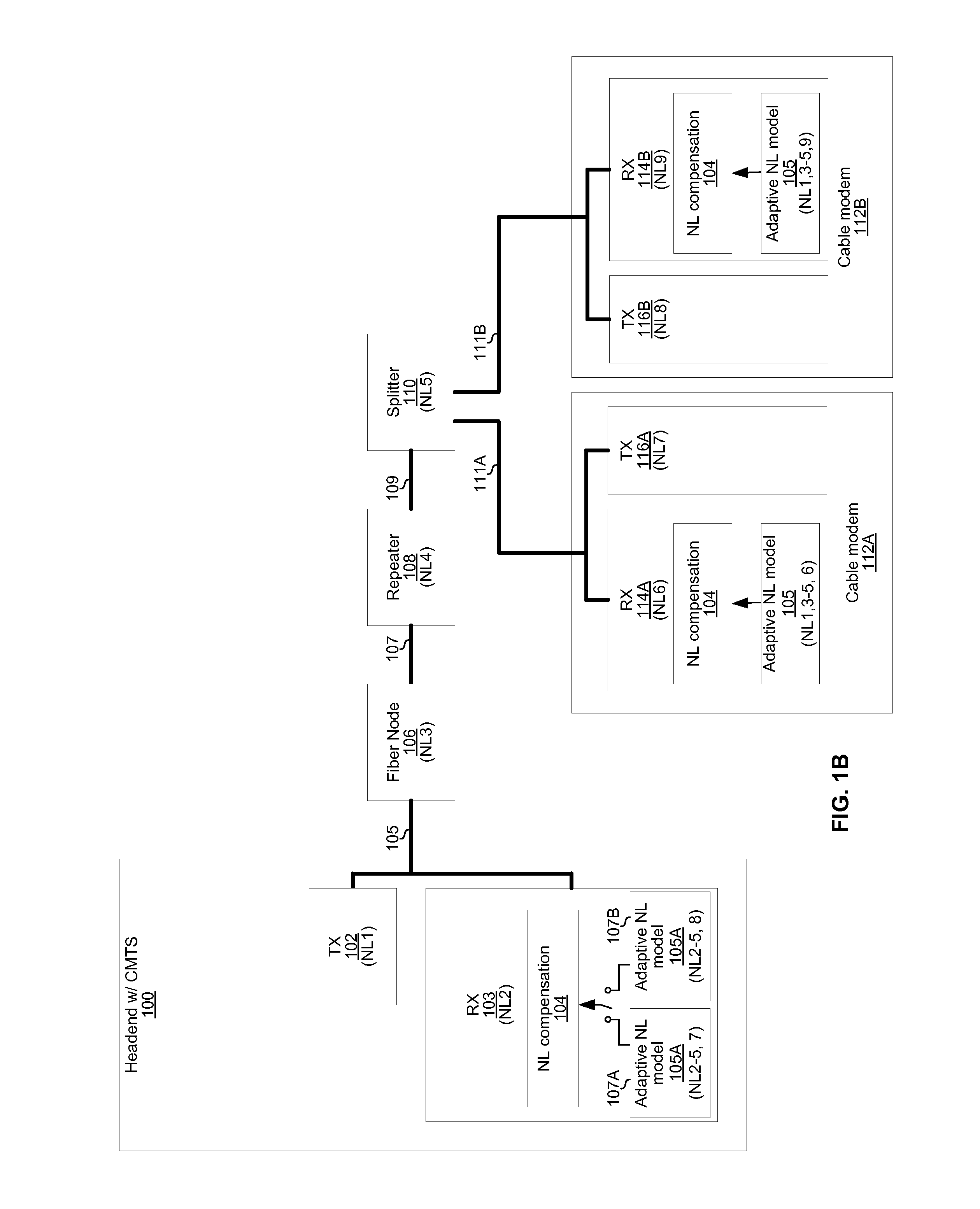
Communication methods and systems for nonlinear multi-user environments
InactiveUS20150207527A1Error preventionModulated-carrier systemsNonlinear distortionMulti user environment
An electronic receiver comprises a nonlinear distortion modeling circuit and a nonlinear distortion compensation circuit. The nonlinear distortion modeling circuit is operable to determine a plurality of sets of nonlinear distortion model parameter values, where each of the sets of nonlinear distortion model parameter values representing nonlinear distortion experienced by signals received by the electronic receiver from a respective one a plurality of communication partners. The nonlinear distortion compensation circuit is operable to use the sets of nonlinear distortion model parameter values for processing of signals from the plurality of communication partners. Each of the sets of nonlinear distortion model parameter values may comprises a plurality of values corresponding to a plurality of signal powers. The sets of nonlinear distortion model parameters may be stored in a lookup table indexed by a signal strength parameter.
Owner:AVAGO TECH INT SALES PTE LTD
Method and system for adaptive location determination for mobile device
ActiveUS20140106782A1Particular environment based servicesSubstation equipmentSelf adaptiveMobile device
An example method includes connecting to a call center by a user equipment (UE) device via a voice call and receiving a request for a current location. The device is determined to be in an outdoor environment if the signal strength of satellite signals used by a global positioning system (GPS) is greater than a threshold. The device is determined to be in an indoor environment if a beacon signal strength is greater than a further threshold. If the device is in an outdoor environment, the current location is determined using a standalone or assisted GPS method. If the device is in an indoor environment, the current location is the known location of the beacon or an assisted GPS method. If neither the signal strength of the satellite signals nor the signal strength of the beacon exceeds its respective threshold, the current location is determined as a last stored location.
Owner:CELLCO PARTNERSHIP INC
Soft handoff in Ofdma system
ActiveUS20090129334A1Increase frequency diversityBroaden the use of channelsSite diversitySpatial transmit diversityCarrier signalSoft handover
The soft handoff in an OFDMA system. If the pilot signal strength for a base station exceeds the defined threshold, the base station is added to an active set list. Subcarriers in a plurality of orthogonal frequency division multiplexing (OFDM) symbols are divided and allocated into subchannels. The OFDM symbols are divided and multiplexed. A soft handoff zone with a first dimension of the subchannels and a second dimension of the divided and multiplexed OFDM symbols is defined. The soft handoff zone have subcarriers with a subchannel definition, for example, an identical permutation.
Owner:APPLE INC
Uplink control method and apparatus in wireless communication system
An UpLink (UL) control method and apparatus for in a wireless communication system supporting beamforming are provided. A method of a Mobile Station (MS) for UL control in the wireless communication system supporting the beamforming includes receiving a plurality of DownLink (DL) reference signals from a plurality of Base Station (BS) transmission beams using a plurality of MS reception beams having different directivity, measuring a path loss based on a reception signal strength of each of the plurality of DL reference signals received through different transmission / reception beams, selecting an MS transmission beam for uplink based on the path loss value measured for each of the plurality of DL reference signals, and transmitting a UL signal to a BS using the selected MS transmission beam.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
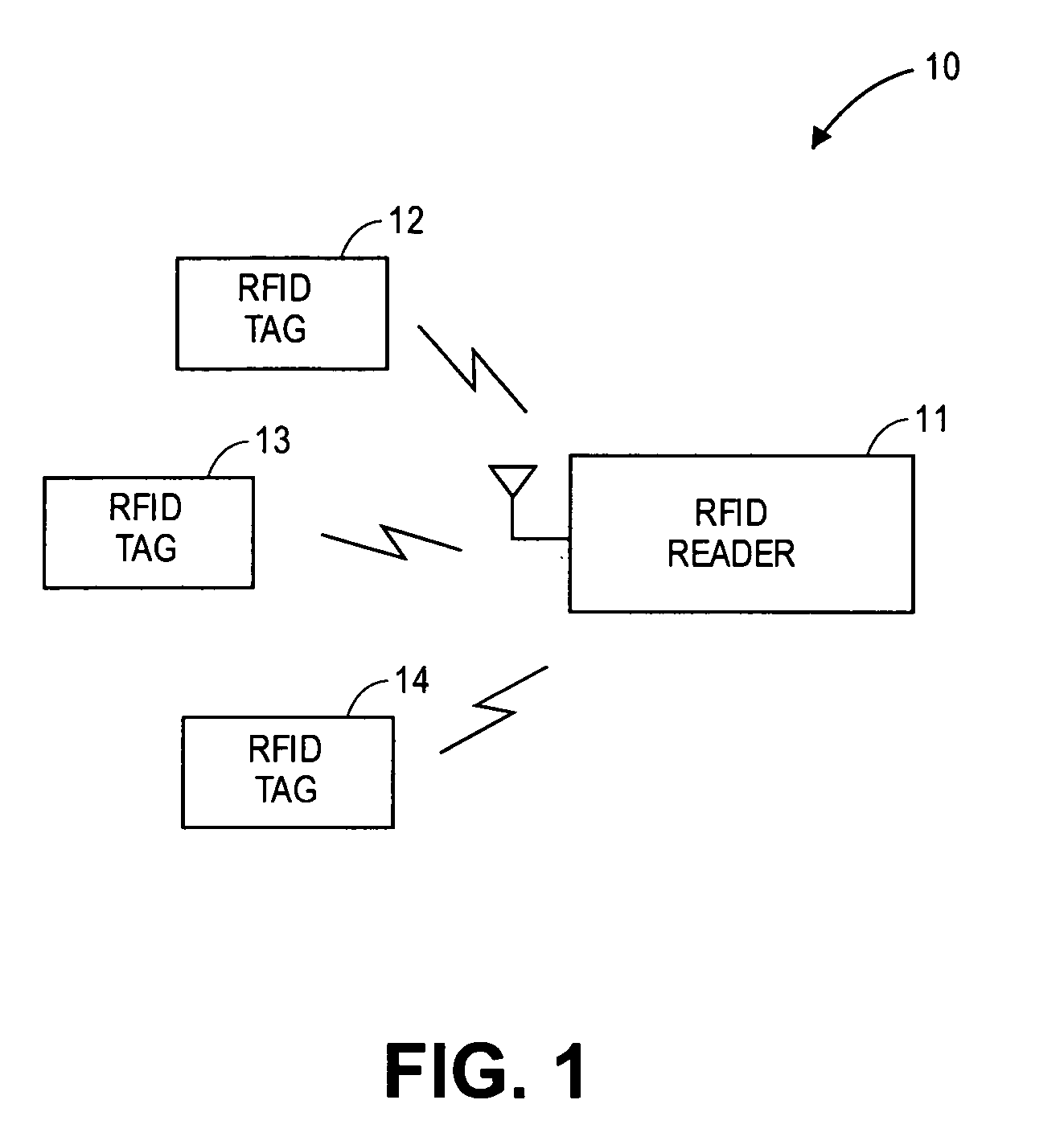
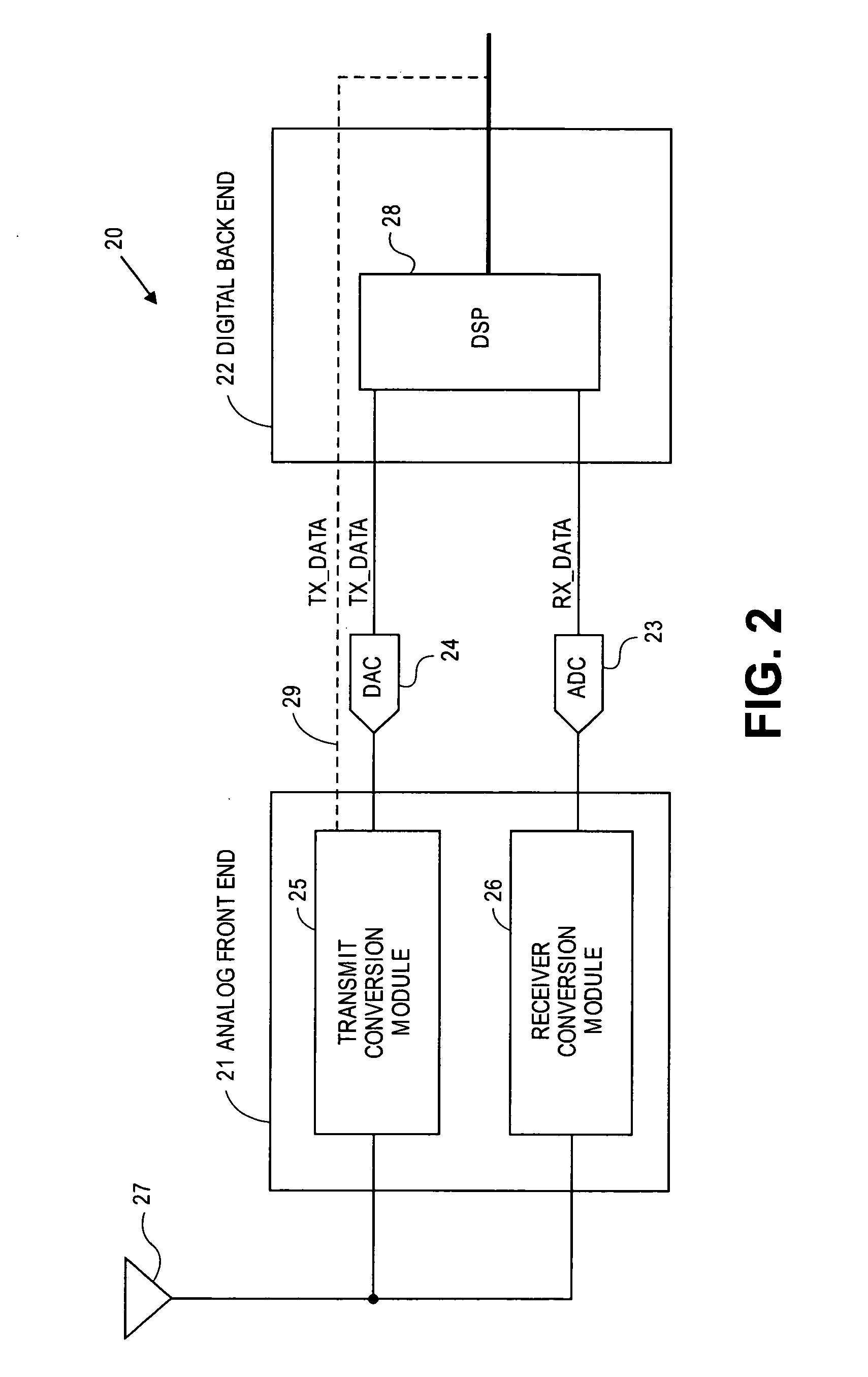
Multi-protocol radio frequency identification transponder transceiver
ActiveUS20060238301A1Memory record carrier reading problemsNear-field in RFIDTransceiverIn-phase and quadrature components
A transceiver for a RFID reader and a transceiver for a RFID transponder (tag) allow communication between the two devices. The RFID reader utilizes an analog front end and a digital backend. In the receiver portion of the transceiver, the front end of the RFID reader uses a pair of down-conversion mixers to demodulate a received signal into in-phase (I) and quadrature (Q) components and analog-to-digital converters (ADC) digitize the signal. A digital signal processor (DSP) in the back end processes the digital signal and uses a matched filter for data detection. The RFID tag receives an inductively coupled signal from the reader and the receiver portion of the tag uses a pulse / level detector that employs an analog comparator and a sample and hold circuit to detect the received signal. A digital decoder / controller is used to decode the incoming data and to establish a sampling clock for the pulse / level detector. An automatic gain control (AGC) circuit adjusts a receiver gain according to the received signal strength and controls tuning of magnetic coupling circuitry.
Owner:NXP USA INC
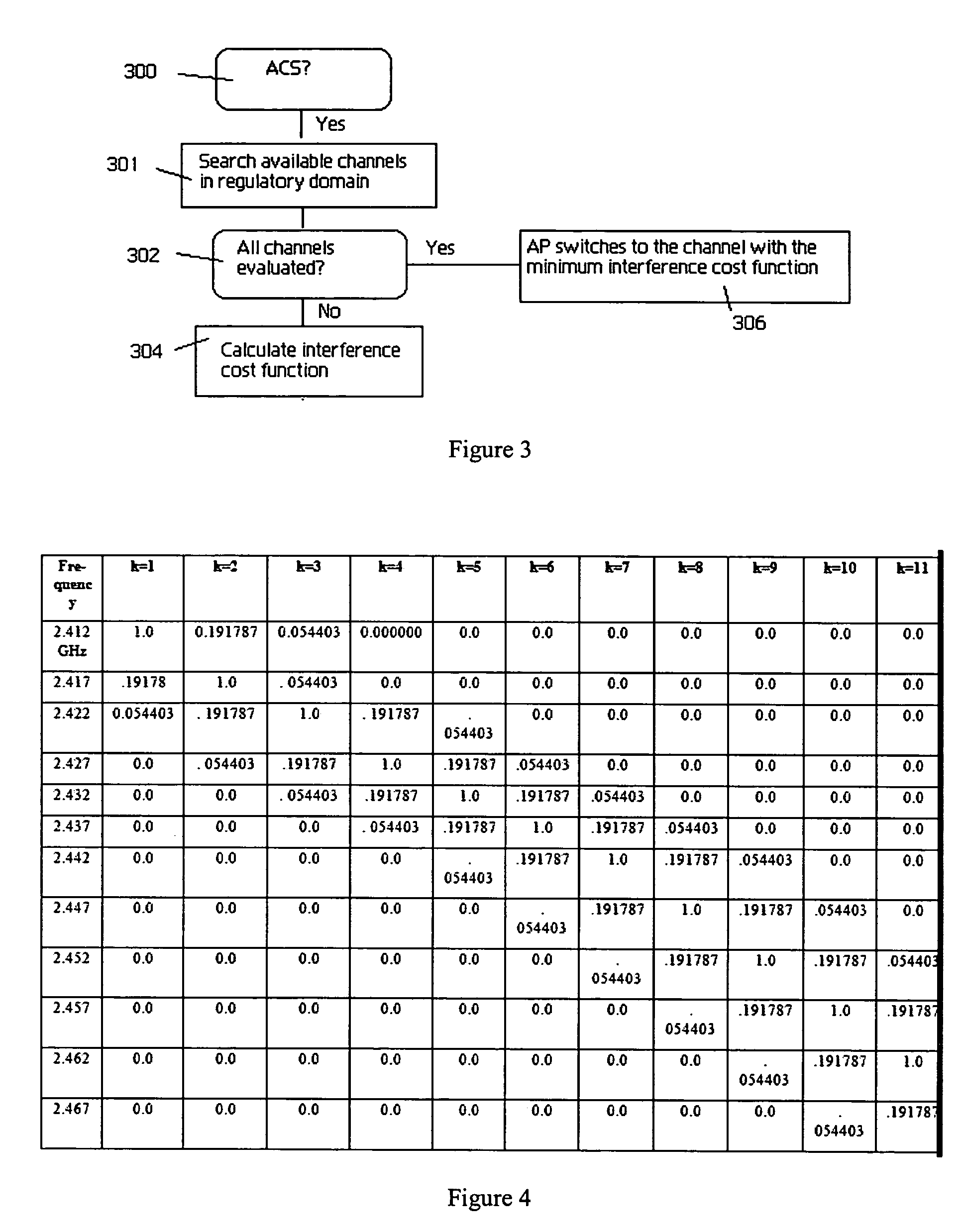
Wireless access point (AP) automatic channel selection
An automatic channel selection (ACS) process enables an access point to determine a best channel available, i.e., the channel with a least amount of interference, for it operation. When ACS is enabled, the access point scans frequencies for all neighboring access points and their signal strengths. Based on this data, the access point then determines which frequency is least likely to be interfered with by these other access points. The access point switches itself to this frequency and begins operation. During normal operation, the access point may periodically rescan the air space and reevaluate its current operating channel. Preferably, every neighboring access point has its own channel, and the co-channel interference levels should be low enough so that there is a maximum coverage and high throughput for the network. If these characteristics cannot be achieved, the access point may then adjust its power automatically to reduce the interference level in the network. This automatic power adjustment (APA) feature preferably operates across a set of access points, each of which has the function. In this manner, the transmitting power of the neighboring access points in the wireless network is “cooperatively” adjusted to minimize the channel interference and maximize the coverage and throughput for the network. A method of determining optimal access point locations for access points that perform the ACS and APA functions is also described.
Owner:HEWLETT-PACKARD ENTERPRISE DEV LP
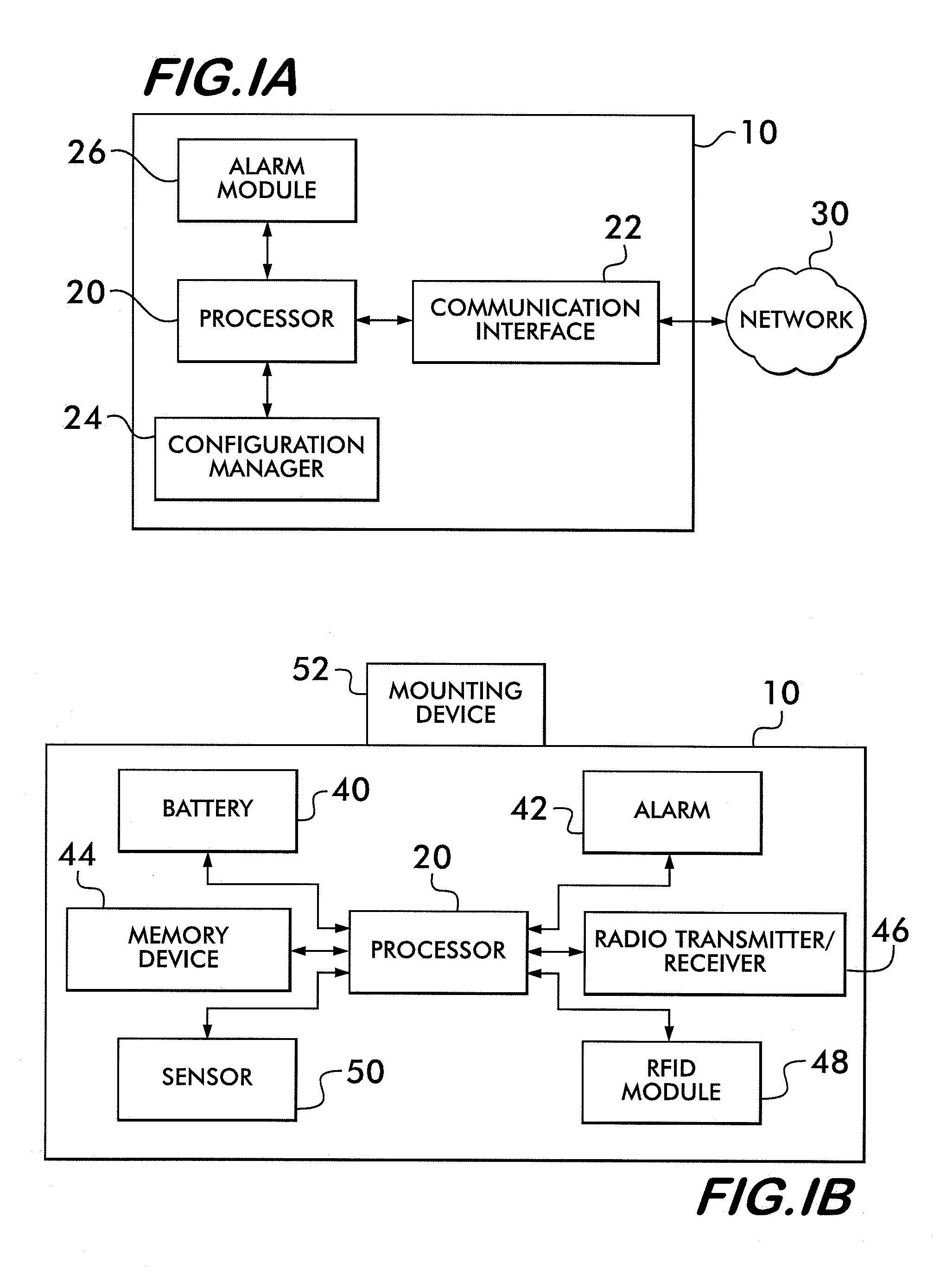
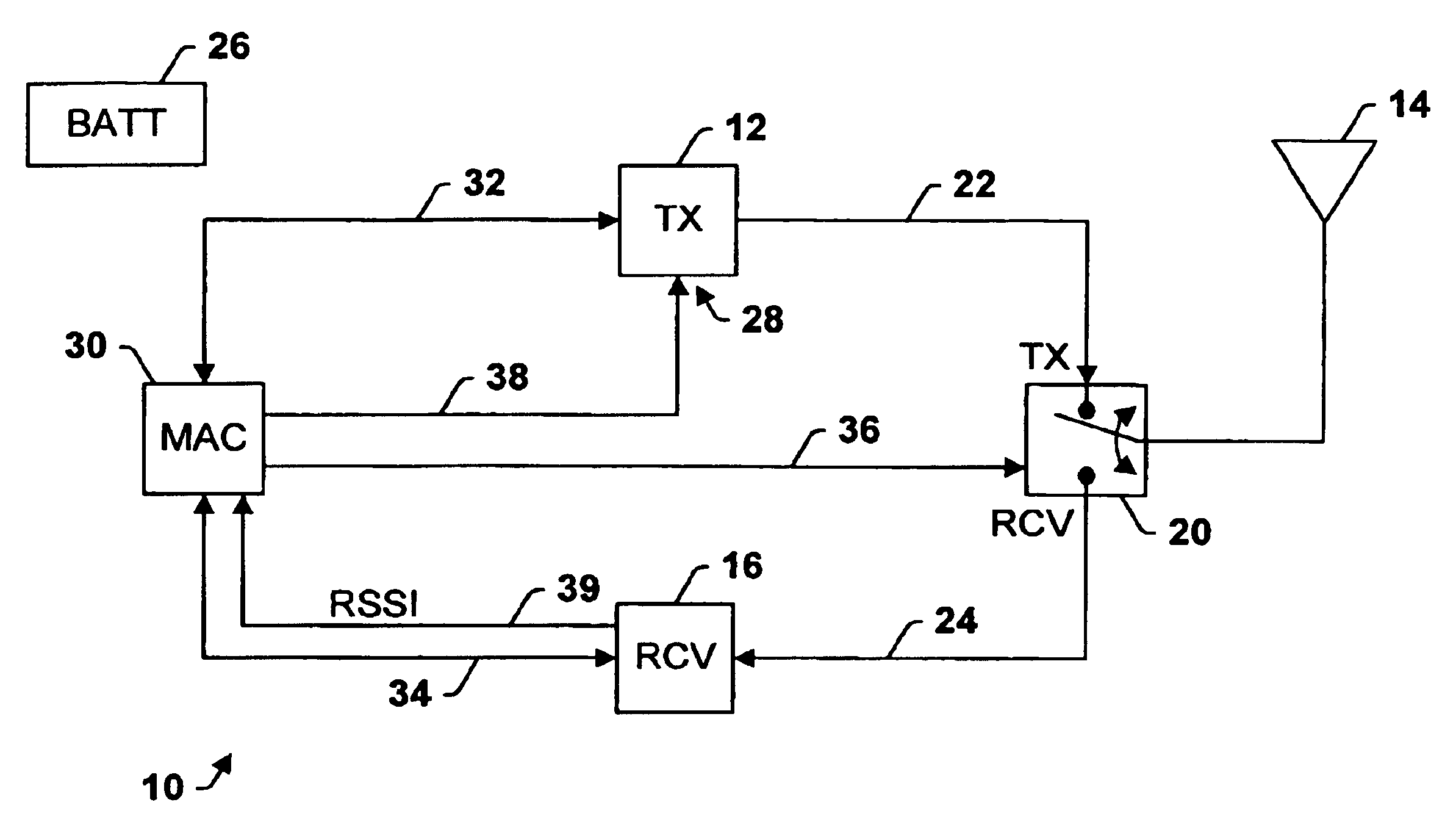
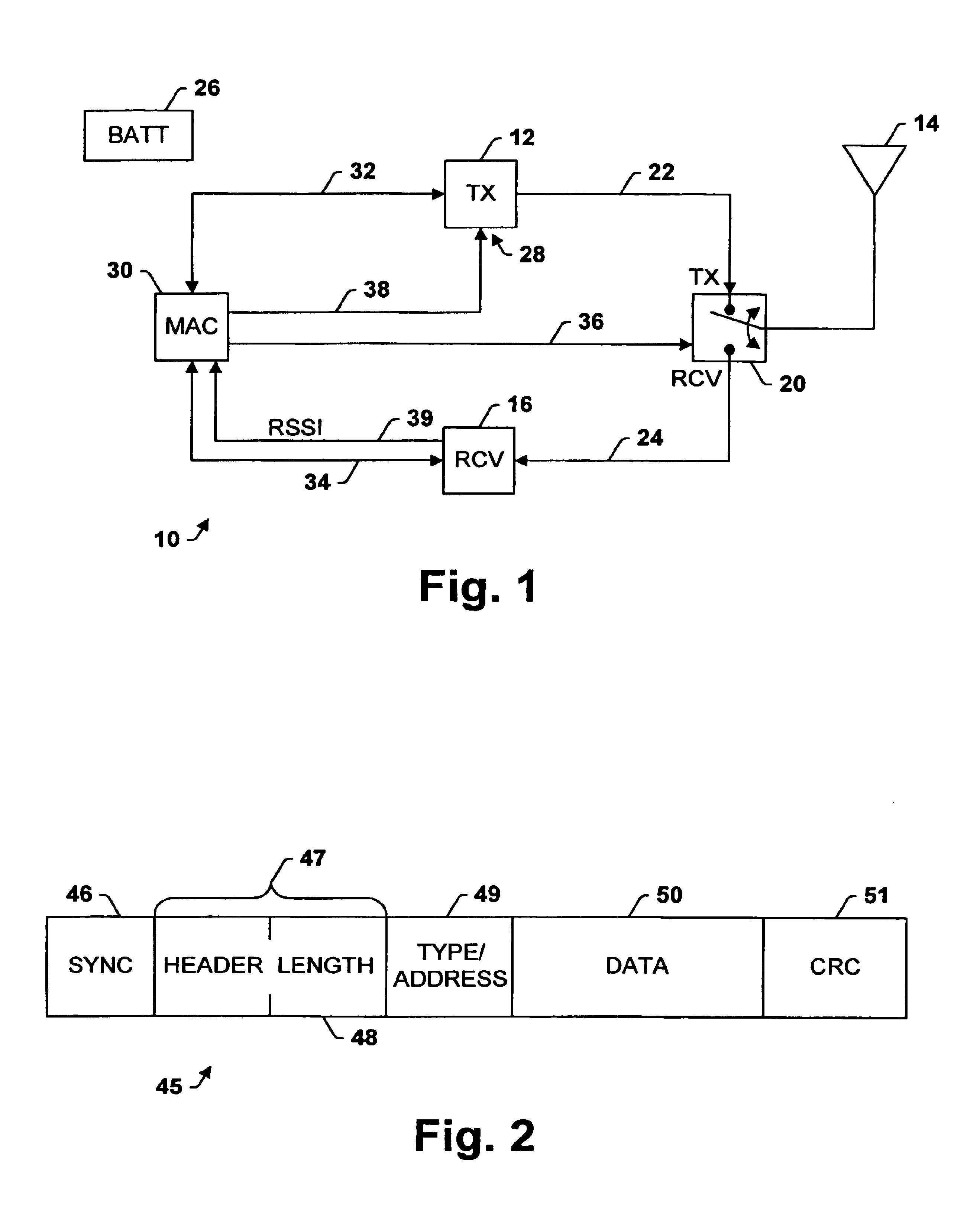
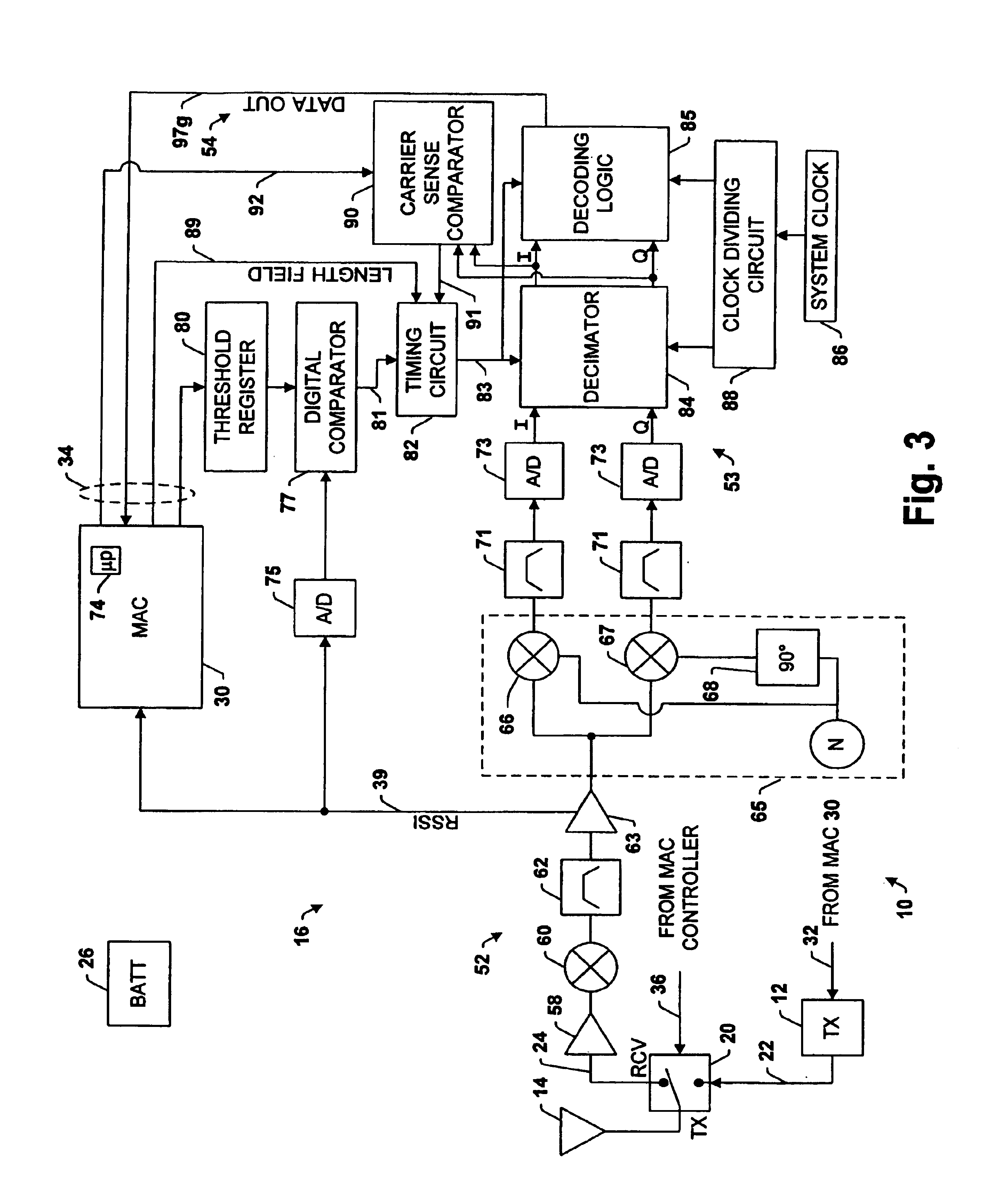
Transceiver control with sleep mode operation
InactiveUS6978149B1No delay exchangeHigh strengthEnergy efficient ICTPower managementTransceiverControl signal
A transceiver which keeps circuitry associated with a receiver in a powered down state during periods when a Received Signal Strength Indicator (RSSI) indicates that a signal being received is below a pre-determined threshold level, and which begins to power up the transmitter as soon as it is determined that a packet being received requires a response. The RSSI signal represents the strength of any signal current being received, and if the RSSI signal falls below a given threshold level, digital circuitry associated with the back-end circuitry of the receiver system is disabled. If the RSSI signal rises above the threshold level, the digital circuitry of the receiver is enabled. A control circuit within the transceiver processes the packet as it is received to determine whether the packet requires a response. If it is determined that a response is necessary, the control circuit provides a control signal to the transmitter to power up the transmitter from a sleep mode even before the entire packet has been received and processed. The control circuit then continues to process the remainder of the packet as it is received while the transmitter powers up from the sleep mode. In this manner, the transmitter will become stabilized much earlier. Accordingly, the transceiver is able to respond more quickly than conventional devices and is thus able to increase response times and overall data exchange rates. Moreover, battery power of the transceiver is utilized more efficiently compared to devices which must continuously maintain the receiver and transmitter in fully powered modes.
Owner:TELXON INC
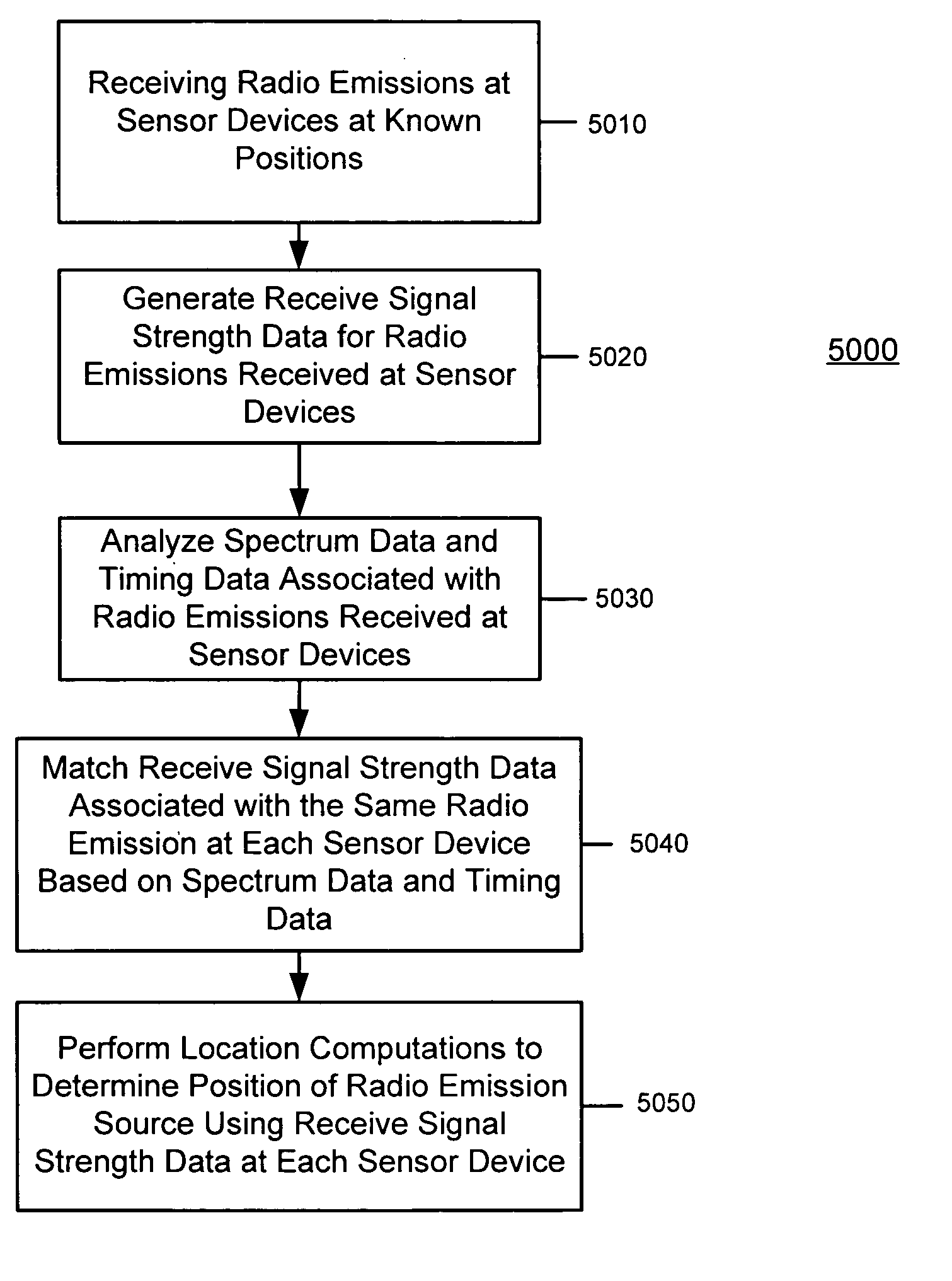
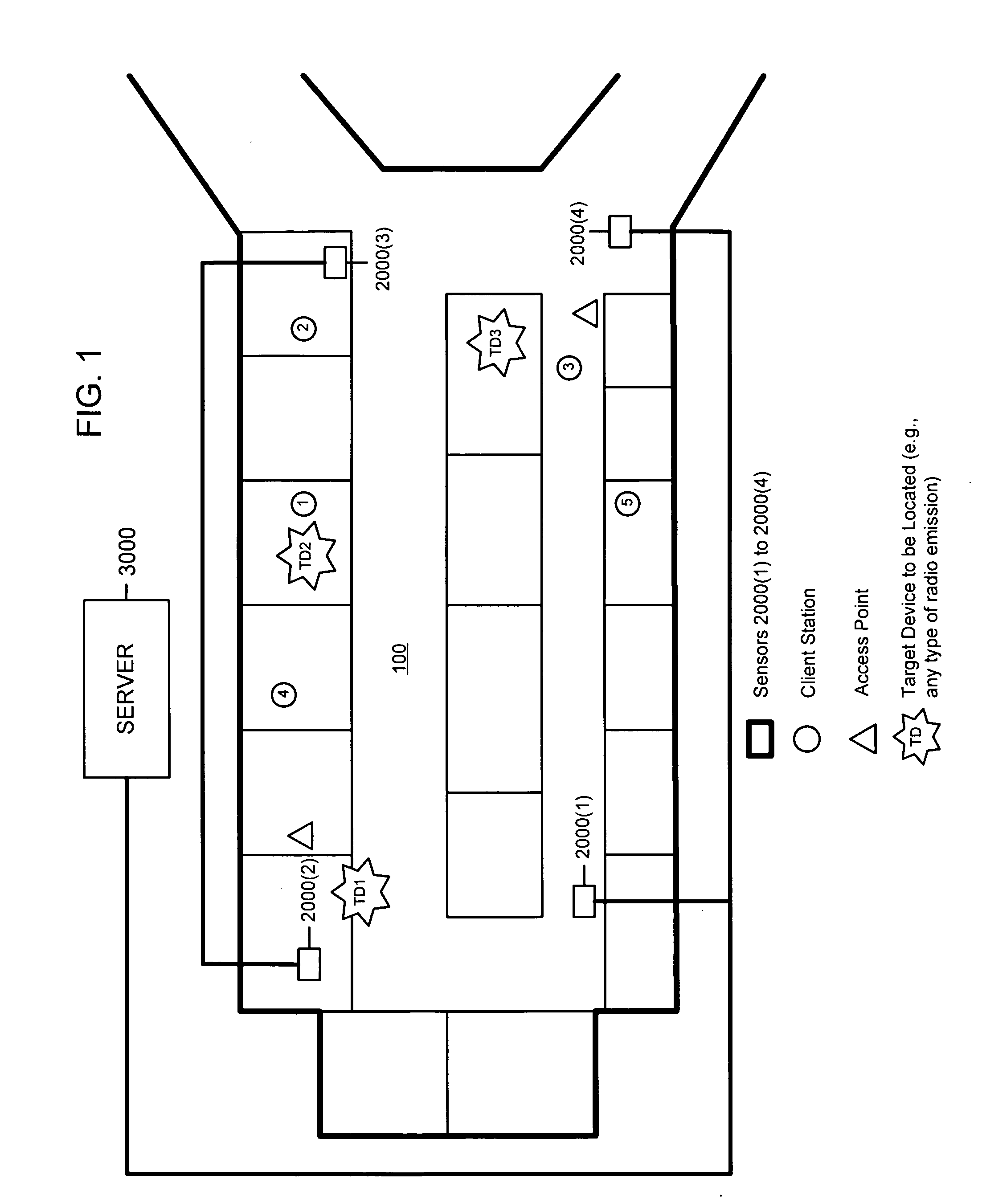
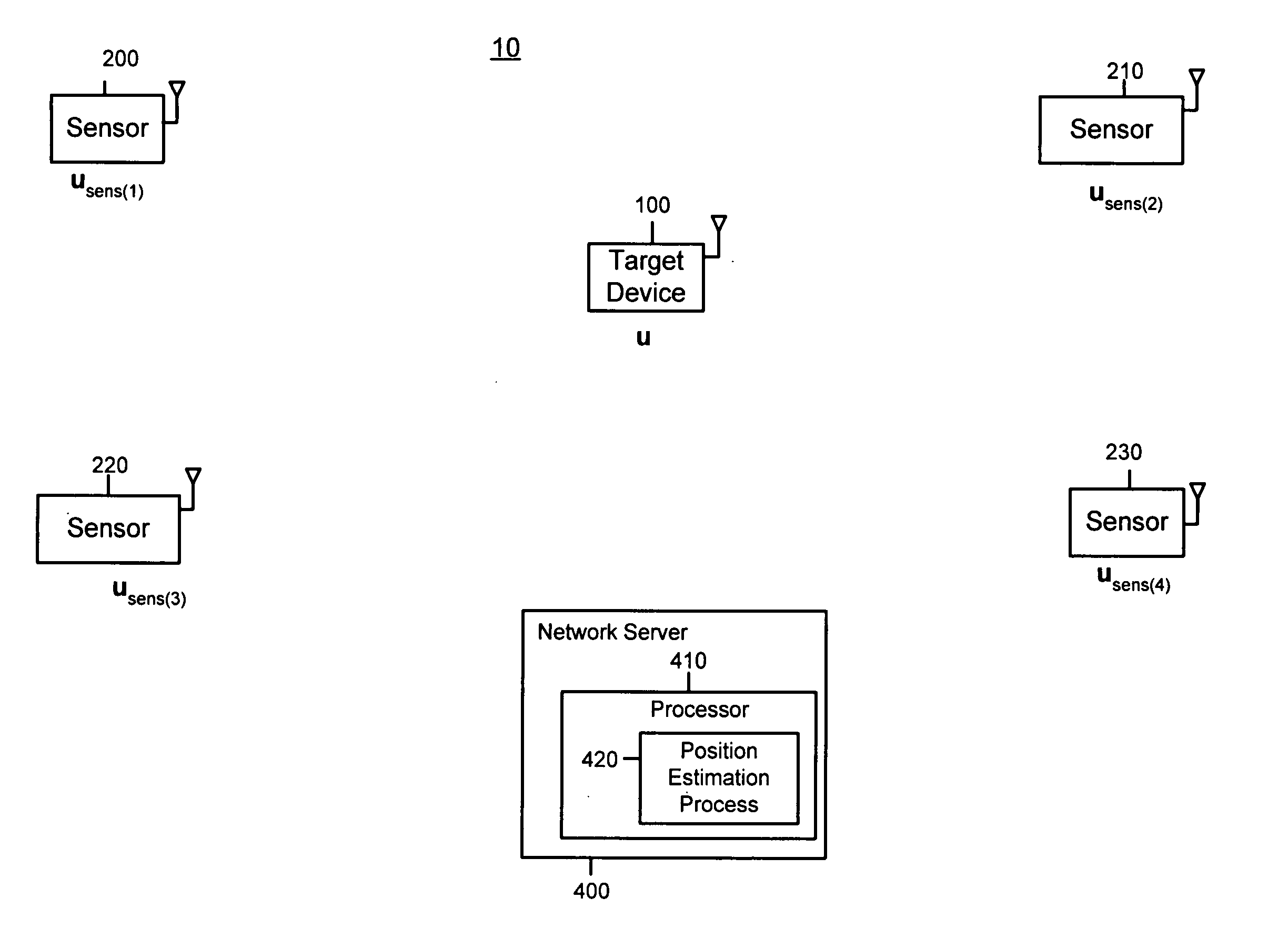
Matching receive signal strenth data associated with radio emission sources for positioning applications
A system, method and software for determining a position of a source of a radio emission. Receive signal strength data associated with reception of radio emissions is generated at each of a plurality of radio sensor devices that are at corresponding known positions in an area where the radio emissions are occurring. Using characteristics associated with reception of the radio emissions at each of the sensor devices, the receive signal strength data generated by each of the sensors is matched as corresponding to a radio emission from the same source. The characteristics used to match receive signal strength data may include spectrum analysis data and / or timing analysis data. Once the receive signal strength data is matched, position computations may be performed on the appropriate set of receive signal strength data to compute the position of the source of the radio emission.
Owner:CISCO TECH INC
Self-optimizing networks for fixed wireless access
ActiveUS20110136478A1Network traffic/resource managementTime-division multiplexTelecommunicationsSignal strength
An embodiment of the invention relates to a method of modifying communication parameters of a wireless network, the wireless network having at least two antennas, and each of the antennas providing coverage to at least one sector. The method including obtaining measurement data for at least two sectors of the wireless network, determining, from the obtained measurement data, if a signal strength indicator of one or more sectors of the at least two sectors is at or below a target value, determining, if the one or more sectors is at or below the target value, a communication parameter to be applied to the wireless network such that the signal strength indicator of the one or more sectors is above the target value, and modifying the communication parameters of the wireless network such that the determined communication parameter is applied to the wireless network.
Owner:VIAVI SOLUTIONS INC
Method and system for providing physical security in an area of interest
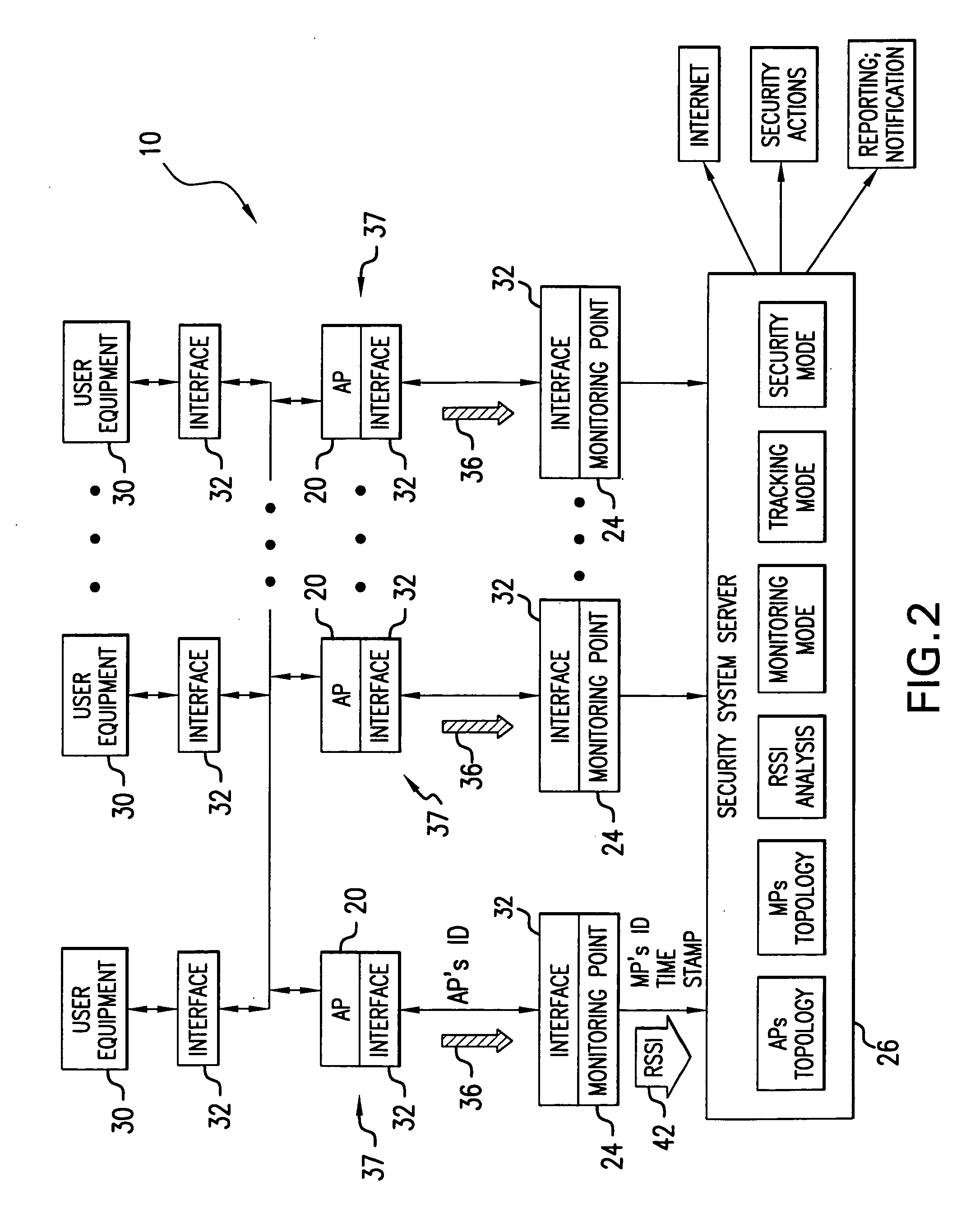
InactiveUS20050055568A1Keep trackDigital data processing detailsHardware monitoringWi-FiPhysical security
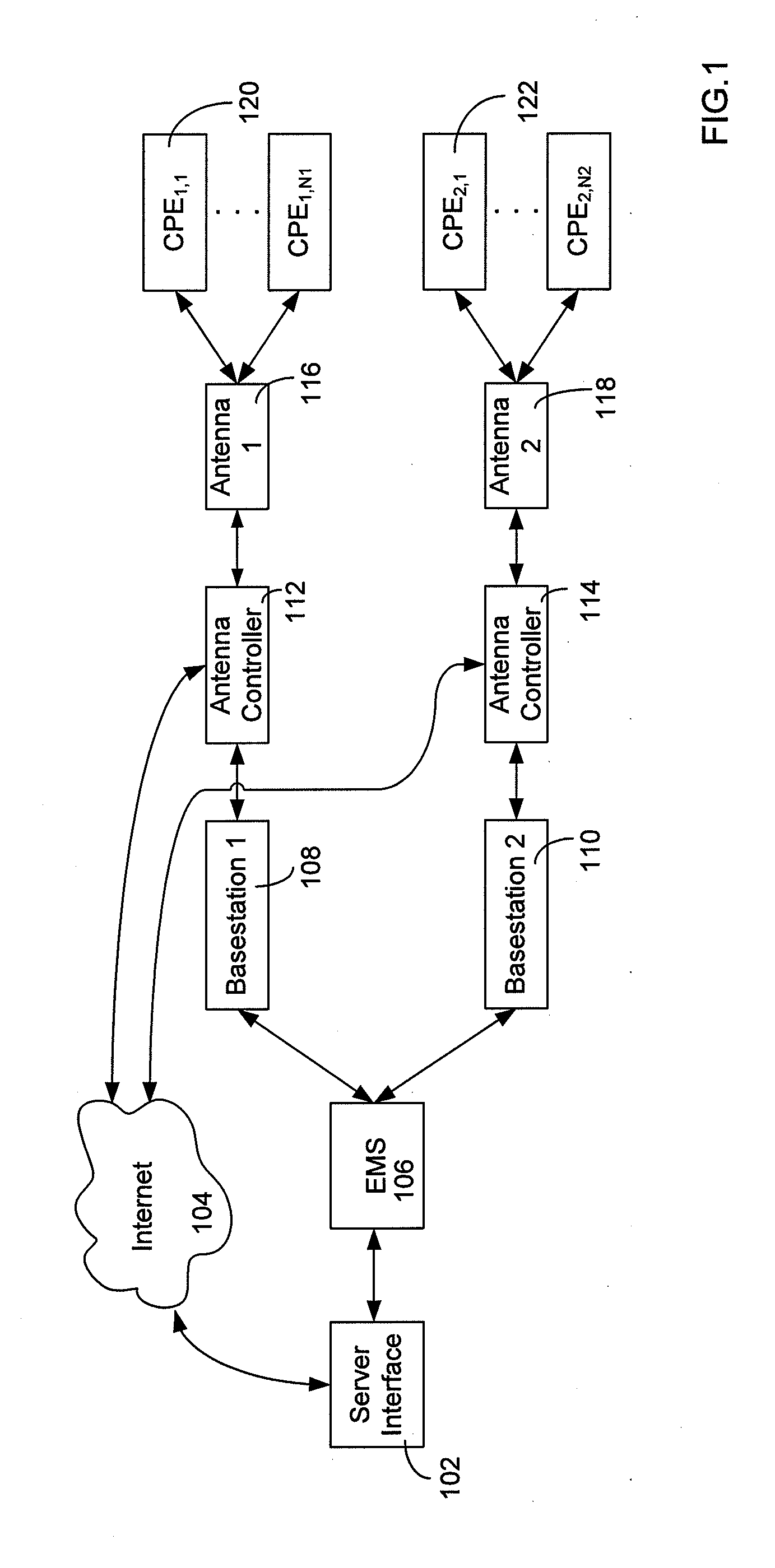
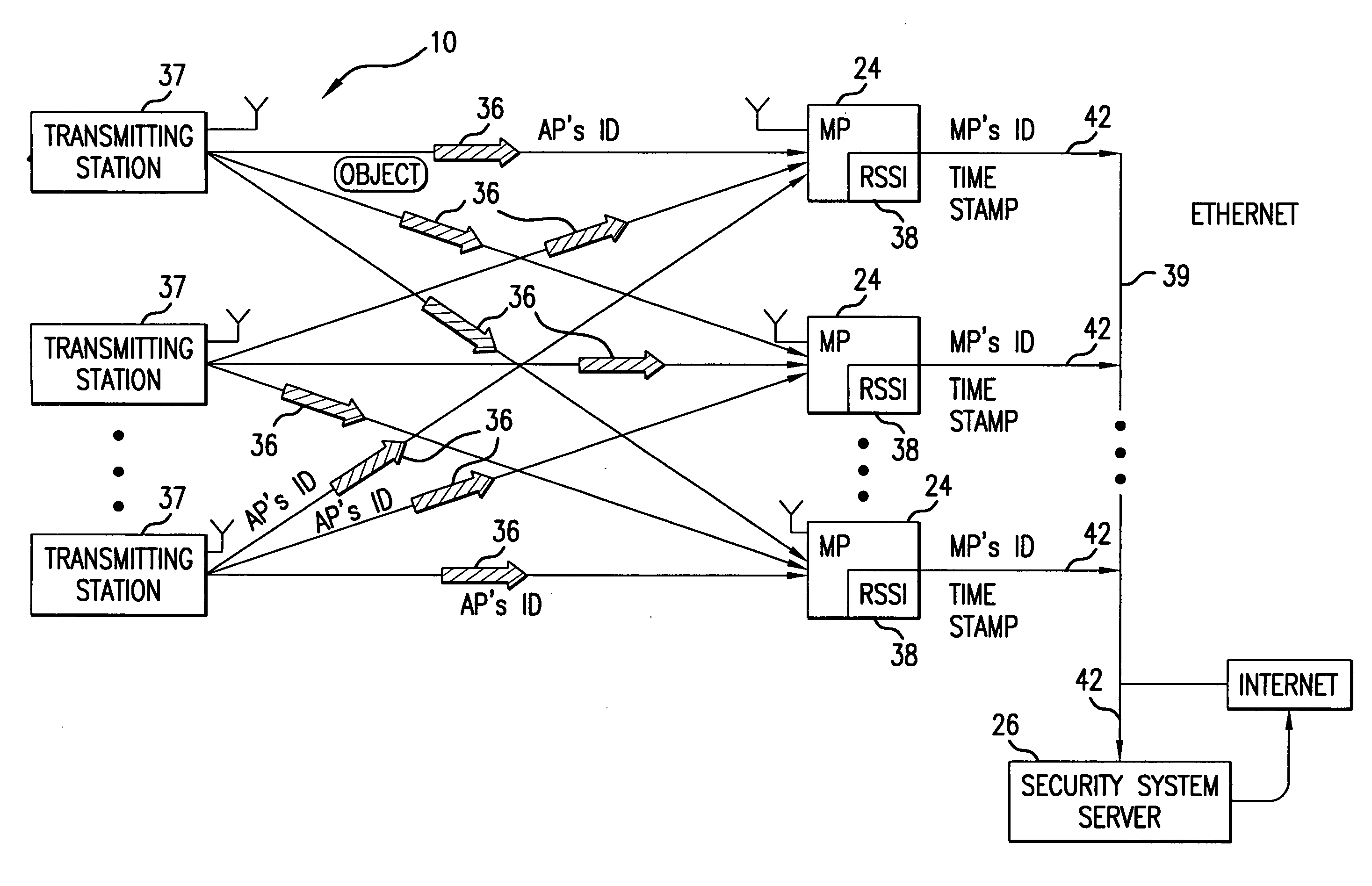
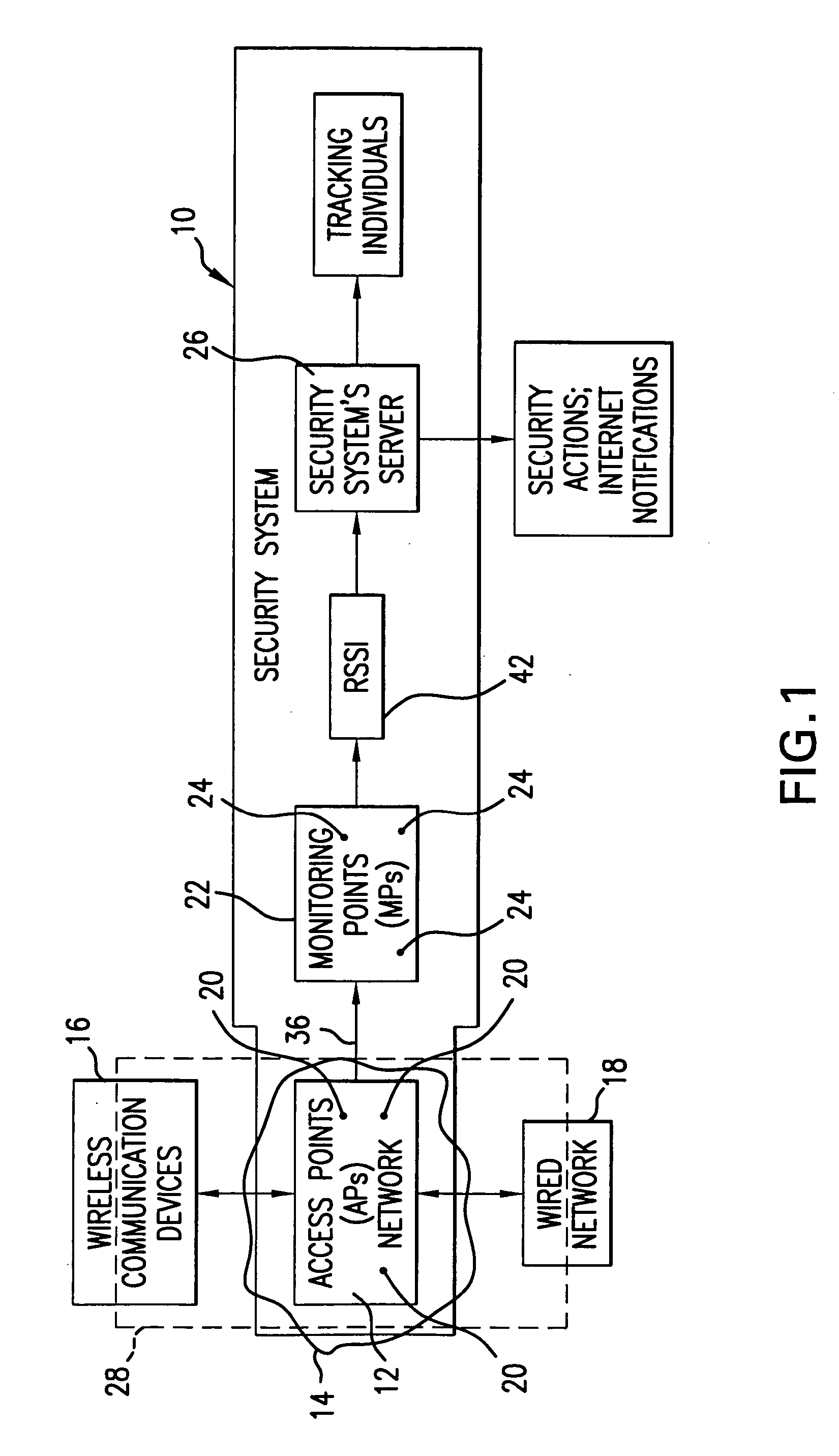
A system for detecting the presence of an intruder in a protected area utilizes a received signal strength indicator (RSSI) value of signals broadcast from transmitting stations deployed in the protected area. The system includes monitoring points for receiving broadcast signals, measuring the RSSI values of the received signals, and transmitting the measured RSSI values to a security system server. The security system server analyzes the RSSI values, and initiates security measures when the physical security of the protected area is violated which is detected when the measured RSSI values deviate from a predetermined strength of the broadcast signals. The security system also has the ability to track objects in the protected area and keep track of their movement in real time and report such movement. The system may be based on a Wi-Fi infrastructure in the protected area.
Owner:UNIV OF MARYLAND
Location beacon database
ActiveUS20060106850A1Avoid arterial biasData processing applicationsDigital data processing detailsWi-FiUser device
A location beacon database and server, method of building location beacon database, and location based service using same. Wi-Fi access points are located in a target geographical area to build a reference database of locations of Wi-Fi access points. At least one vehicle is deployed including at least one scanning device having a GPS device and a Wi-Fi radio device and including a Wi-Fi antenna system. The target area is traversed in a programmatic route to avoid arterial bias. The programmatic route includes substantially all drivable streets in the target geographical area and solves an Eulerian cycle problem of a graph represented by said drivable streets. While traversing the target area, periodically receive the GPS coordinates of the GPS device. While traversing the target area, detecting Wi-Fi signals from Wi-Fi access points in range of the Wi-Fi device and recording identity information of the detected Wi-Fi access point in conjunction with GPS location information of the vehicle when the detection of the Wi-Fi access point was made. The location information is used to reverse triangulate the position of the detected Wi-Fi access point; and the position of the detected access point is recorded in a reference database. A user-device having a Wi-Fi radio may be located. A reference database of calculated locations of Wi-Fi access points in a target area is provided. In response to a user application request to determine a location of a user-device having a Wi-Fi radio, the Wi-Fi device is triggered to transmit a request to all Wi-Fi access points within range of the Wi-Fi device. Messages are received from the Wi-Fi access points within range of the Wi-Fi device, each message identifying the Wi-Fi access point sending the message. The signal strength of the messages received by the Wi-Fi access points is calculated. The reference database is accessed to obtain the calculated locations for the identified Wi-Fi access points. Based on the number of Wi-Fi access points identified via received messages, choosing a corresponding location-determination algorithm from a plurality of location-determination algorithms, said chosen algorithm being suited for the number of identified Wi-Fi access points. The calculated locations for the identified Wi-Fi access points and the signal strengths of said received messages and the chosen location-determination algorithm are used to determine the location of the user-device. The database may be modified with newly added position information to improve quality of previously determined positions, and error prone information is avoided.
Owner:SKYHOOK WIRELESS
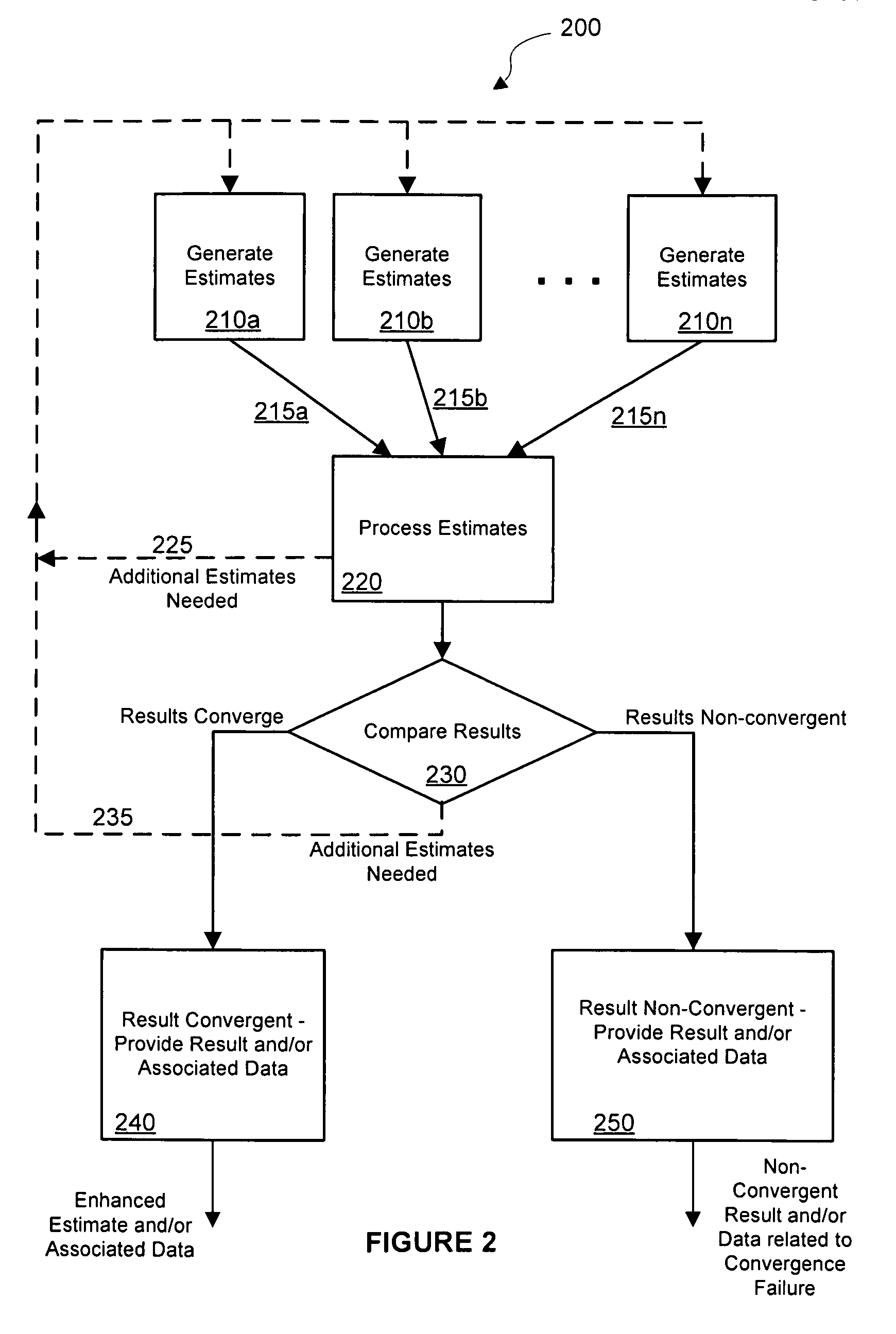
Systems and methods for distance measurement in wireless networks
InactiveUS20090011713A1Distance can be measured is lengthenEnhanced distance estimateSatellite radio beaconingTransmission monitoringEstimation methodsSignal strength
Systems and methods for distance measurement in wireless networks are disclosed. A method for measuring distance between nodes or devices in a wireless network comprises estimating a distance between network devices based on a first distance measurement method, estimating the distance based on a second distance measurement method, and processing the first and second distance estimates to determine convergence and to generate an enhanced distance measurement. Additional distance estimates may be combined to further improve accuracy. Convergence information may be provided indicating whether two or more distance estimates converge. In some implementations, the first distance estimate may be generated by a transmission time estimation method, the second distance estimate may be generated by a received signal strength distance estimate, the two estimates may be combined by averaging to generate an enhanced distance estimate, and the difference between the estimates may be compared to a threshold to determine whether the estimates have sufficiently converged to within a desired convergence range.
Owner:PROXIMETRY
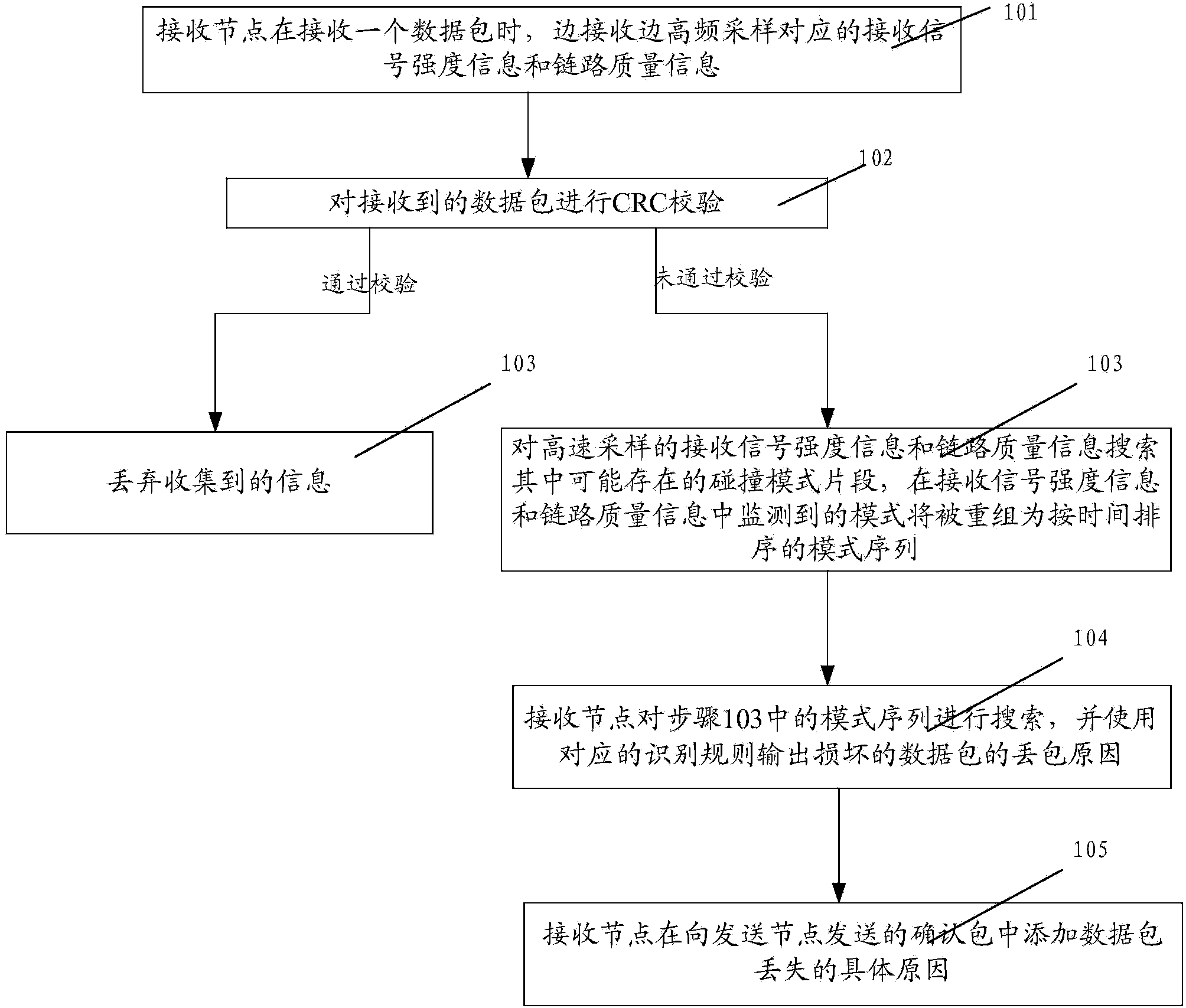
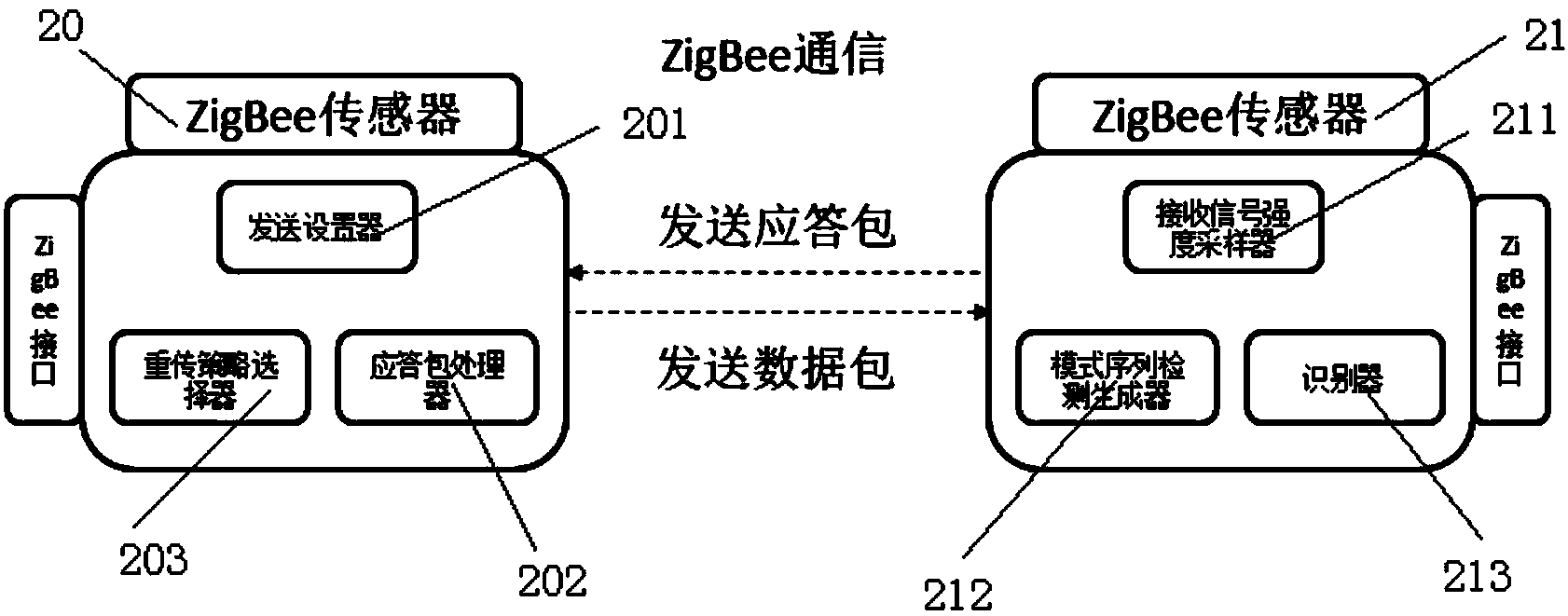
Method and system for identifying reasons of ZigBee sensor network packet loss
ActiveCN103716137AImprove throughputReduce the number of retransmissionsEnergy efficient ICTError prevention/detection by using return channelPacket lossZigbee sensor network
The invention discloses a method and system for identifying reasons of ZigBee sensor network packet loss. The method includes the steps that a receiving node carries out high-frequency sampling on corresponding receiving signal strength information and link quality information while receiving a data package; if the received data package fails to pass the cyclic redundancy check, collision mode fragments possibly existing in the high-frequency sampled receiving signal strength information and the high-frequency sampled link quality information are searched, and the modes monitored in the receiving signal strength information and the link quality information will be regrouped into a time-ordered mode sequence; the receiving node searches for the generated mode sequence and outputs the packet loss reasons of the damaged data package by using corresponding identifying rules; the receiving node adds the specific reasons of data package loss in an acknowledgment packet sent to a sending node. Through the method, network throughput can be improved and retransmission frequency can be reduced, so the purposes of saving energy and prolonging working time can be achieved.
Owner:SHANGHAI JIAO TONG UNIV
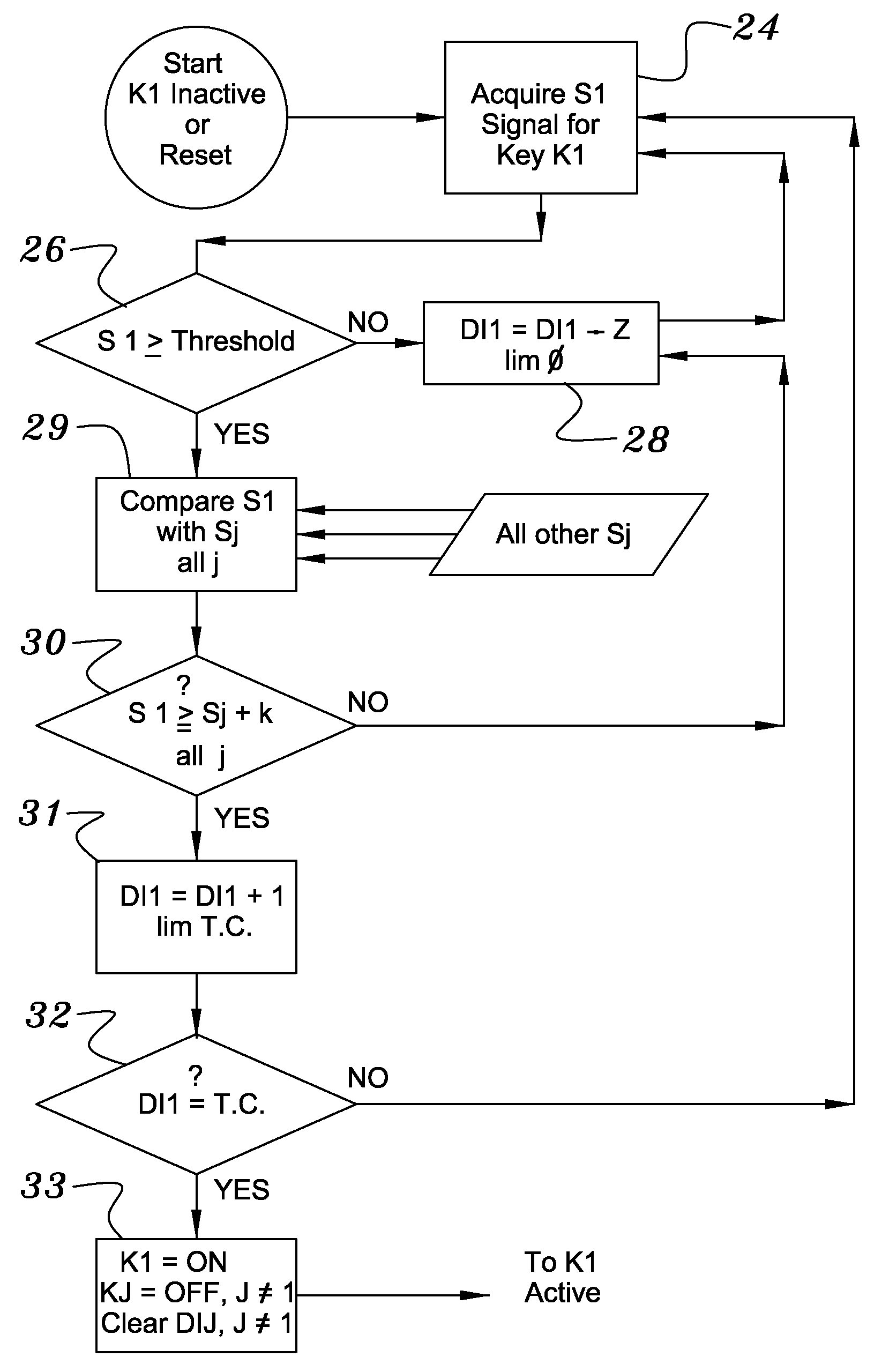
Capacitive Keyboard with Non-Locking Reduced Keying Ambiguity
ActiveUS20060192690A1Reduce ambiguitySignal strength valueElectronic switchingDevice coding detailsEngineeringIterative method
Keyboards, keypads and other data entry devices can suffer from a keying ambiguity problem. In a small keyboard, for example, a user's finger is likely to overlap from a desired key to onto adjacent ones. An iterative method of removing keying ambiguity from a keyboard comprising an array of capacitive keys involves measuring a signal strength associated with each key in the array, comparing the measured signal strengths to find a maximum, determining that the key having the maximum signal strength is the unique user-selected key, and maintaining that selection until either the initially selected key's signal strength drops below some threshold level or a second key's signal strength exceeds the first key's signal strength.
Owner:NEODRON LTD
System, method and computer program for dynamic generation of a radio map
ActiveUS20140011518A1Reduce labor costsSatisfactory level of localization accuracyParticular environment based servicesPosition fixationGraphicsRadio map
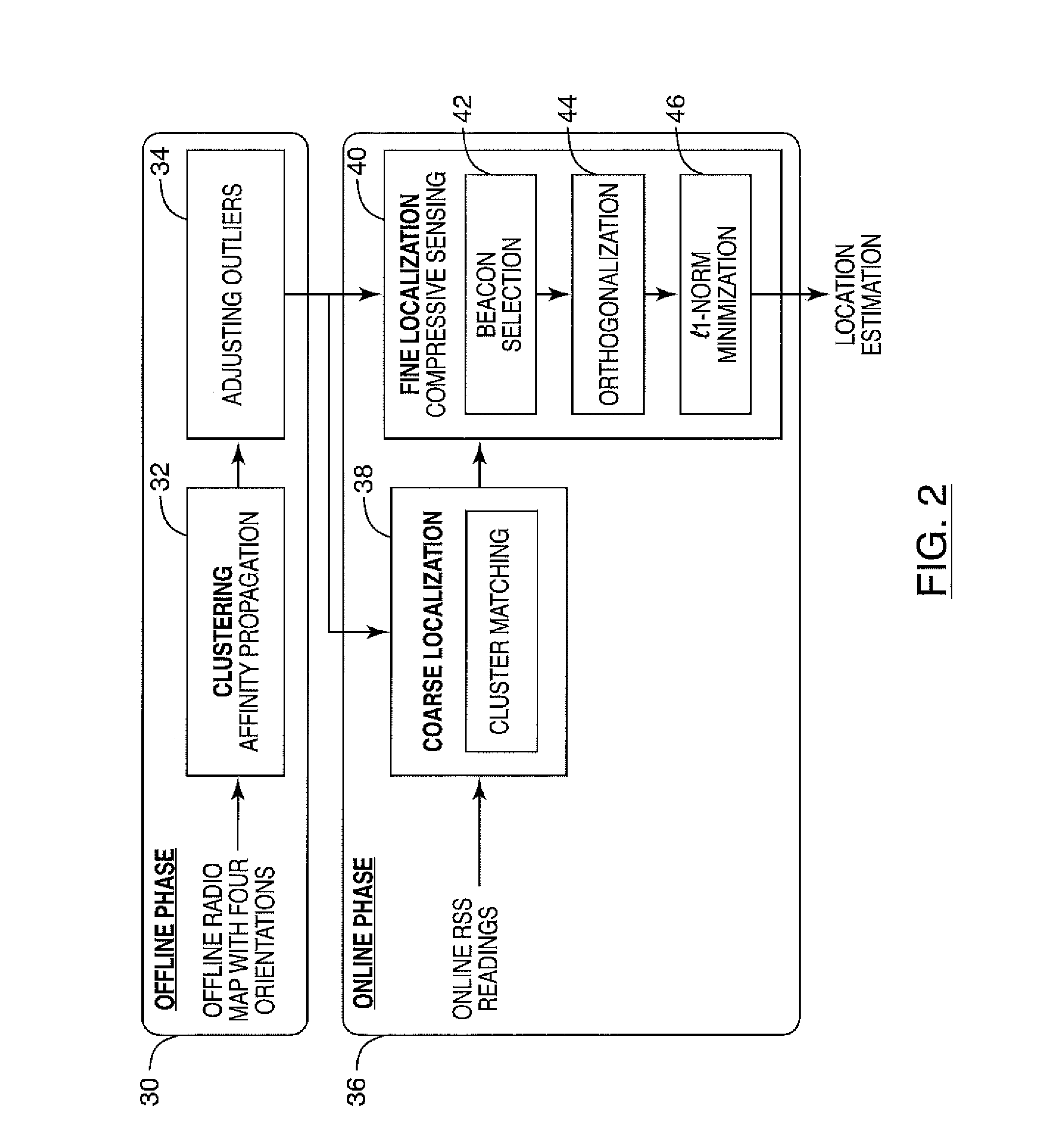
Embodiments described herein provide a system, method and computer program for dynamic radio map generation, which may be used for indoor positioning of one or more mobile devices based on received signal strength (RSS) in some examples. In an aspect, a dynamic scheme may be used to learn the RSS radio map from only a small number of fingerprint samples. Compressive sensing may be applied to build the graph structure and calculate the graph weight in some embodiments. Once the RSS radio map is learned, a mobile device may be located and location based services can be provided to the user in some example embodiments. An indoor learning and positioning system on a mobile device may be used to evaluate the performance. Embodiments described herein may not require a large amount of offline calibrations, which may reduce the labor cost of collecting fingerprints significantly while maintaining a satisfactory level of localization accuracy.
Owner:THE GOVERNINIG COUNCIL OF THE UNIV OF TORANTO
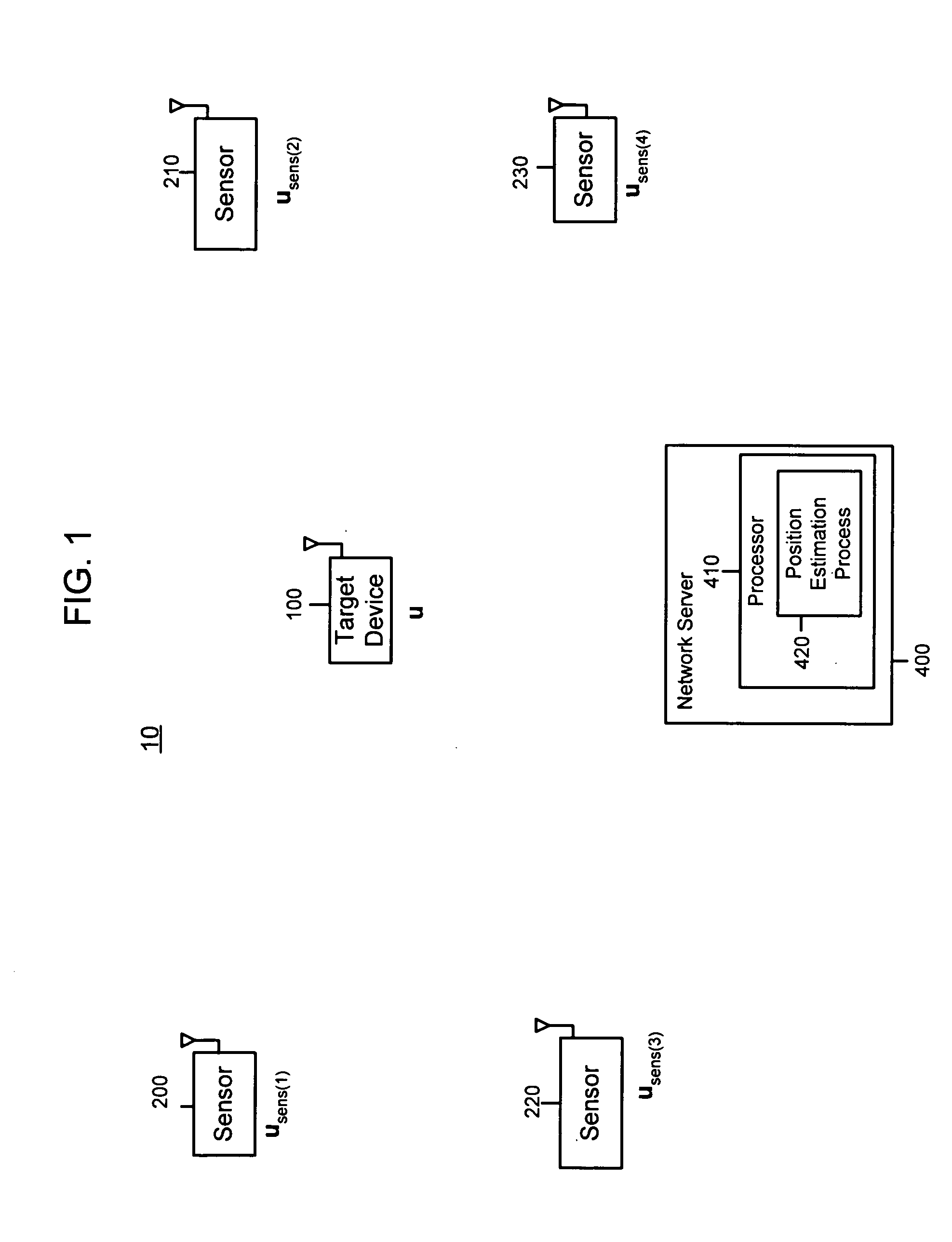
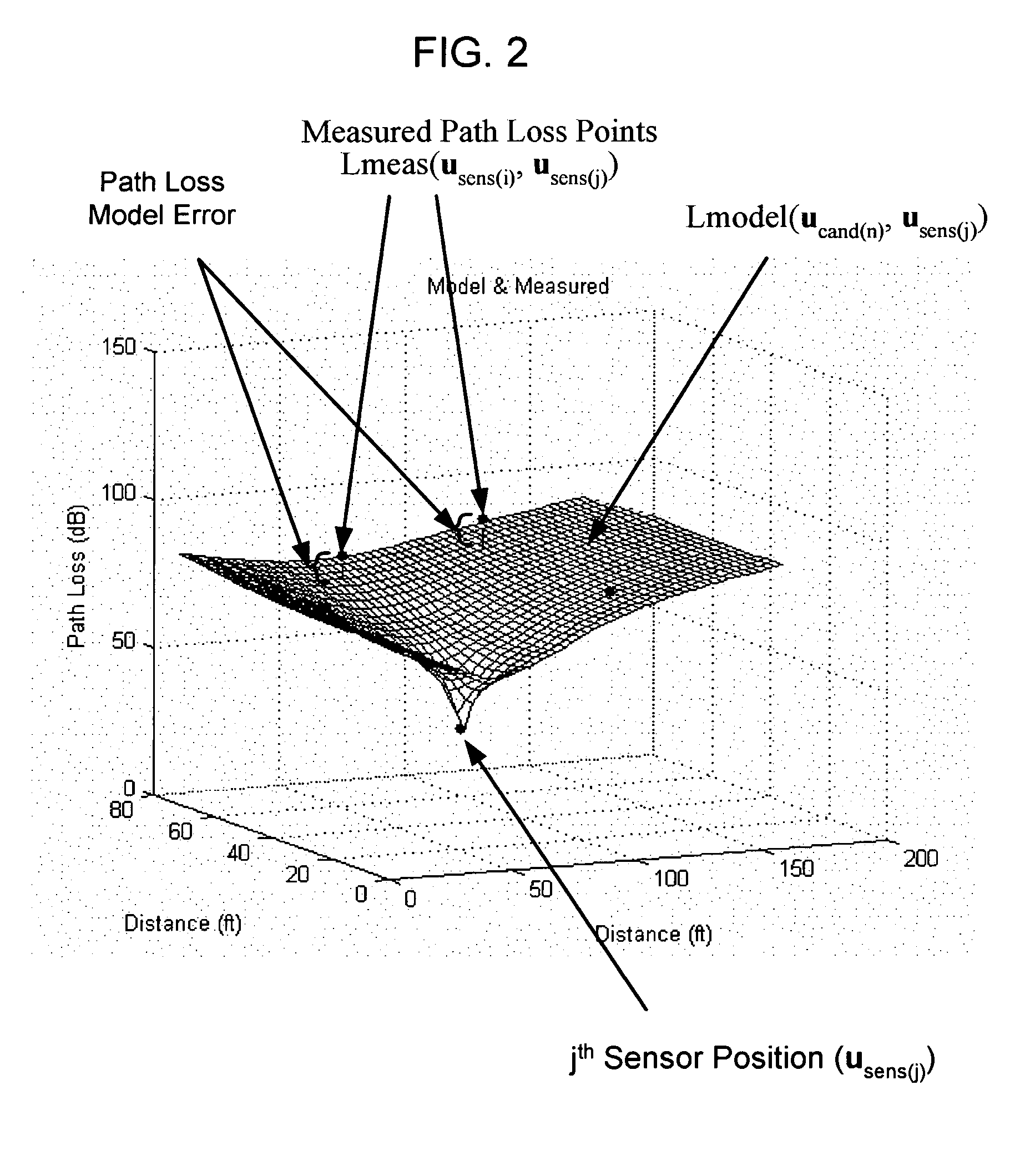
System and method for locating radio emitters using self-calibrated path loss computation
ActiveUS20050285792A1Reduce complexityImprove accuracyDirection finders using radio wavesPosition fixationRadiotransmitterDevice placement
Techniques for reducing the complexity and improving the accuracy of receive signal strength based location systems. The system comprises a plurality of radio sensor devices placed at known positions within a space in which devices are to be located. According to one technique, the path loss is measured between all combinations of pairs of radio sensor devices based on a test signal transmitted by each radio sensor device. A path loss model is evaluated to compute modeled path loss data between all combinations of pairs of radio sensor devices. For each measured path loss, a path loss error relative to each radio sensor device is computed by taking the difference between the measured path loss and the modeled path loss. The path loss error relative to each radio sensor device at any candidate position is interpolated from the computed path loss errors. A path loss estimate between a candidate position and each radio sensor device is computed by adding the interpolated path loss error relative to that radio sensor device at the candidate position and path loss data obtained by evaluating the path loss model based on the distance between at each candidate position and the corresponding radio sensor device. When determining the position of a device emitting radio signals (called a target device), the improved path loss estimate is used. According to another technique, for each radio sensor device, parameters are derived for a path loss model function from the measured path loss between that radio sensor device and each of the other radio sensor devices using a minimization computation. Then, a path loss estimate between a position and each radio sensor device is computed by evaluating the path loss model function using the parameters derived for each radio sensor device.
Owner:CISCO TECH INC
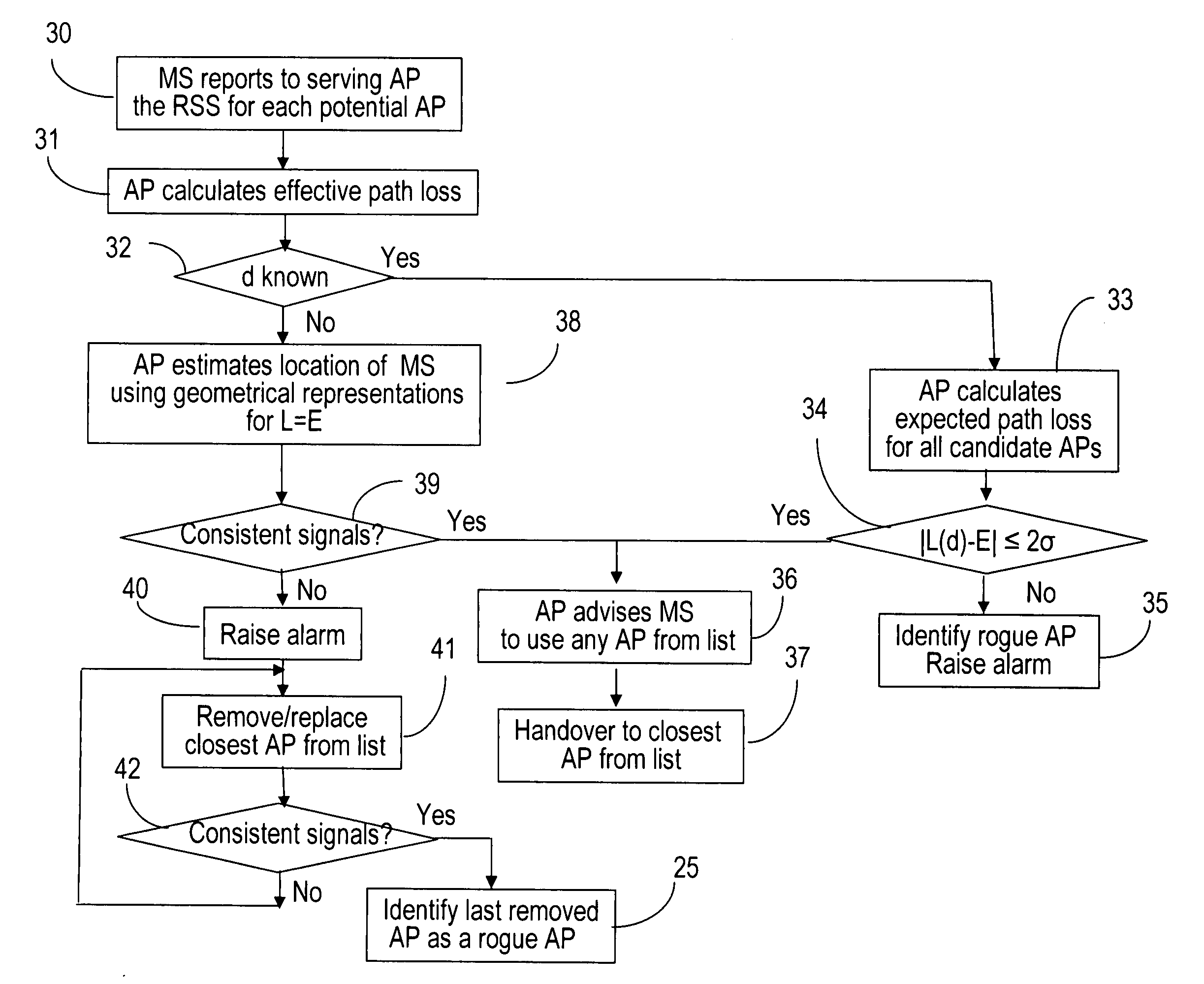
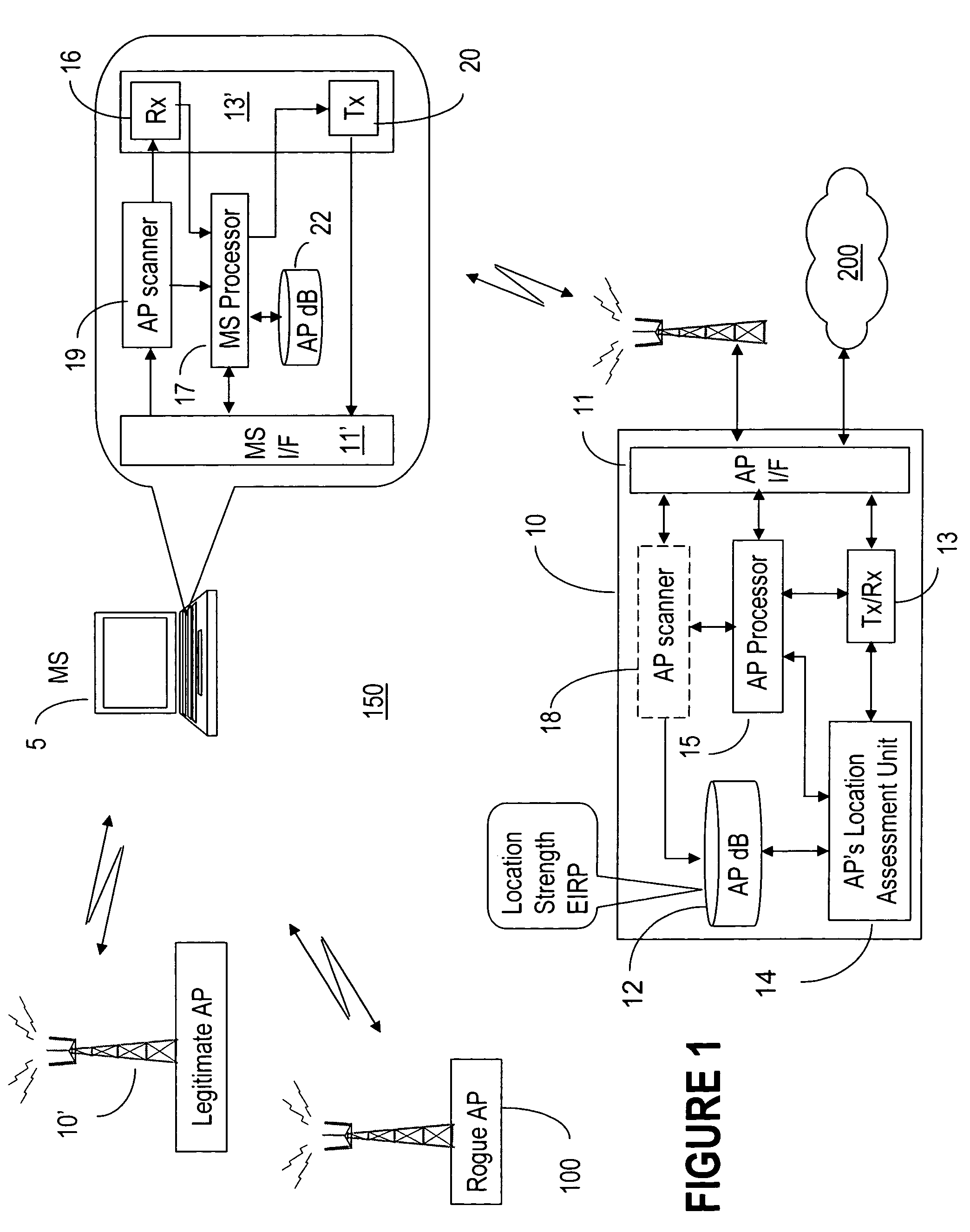
Rogue access point detection in wireless networks
InactiveUS20070079376A1Unauthorised/fraudulent call preventionDigital data processing detailsWireless mesh networkRogue access point
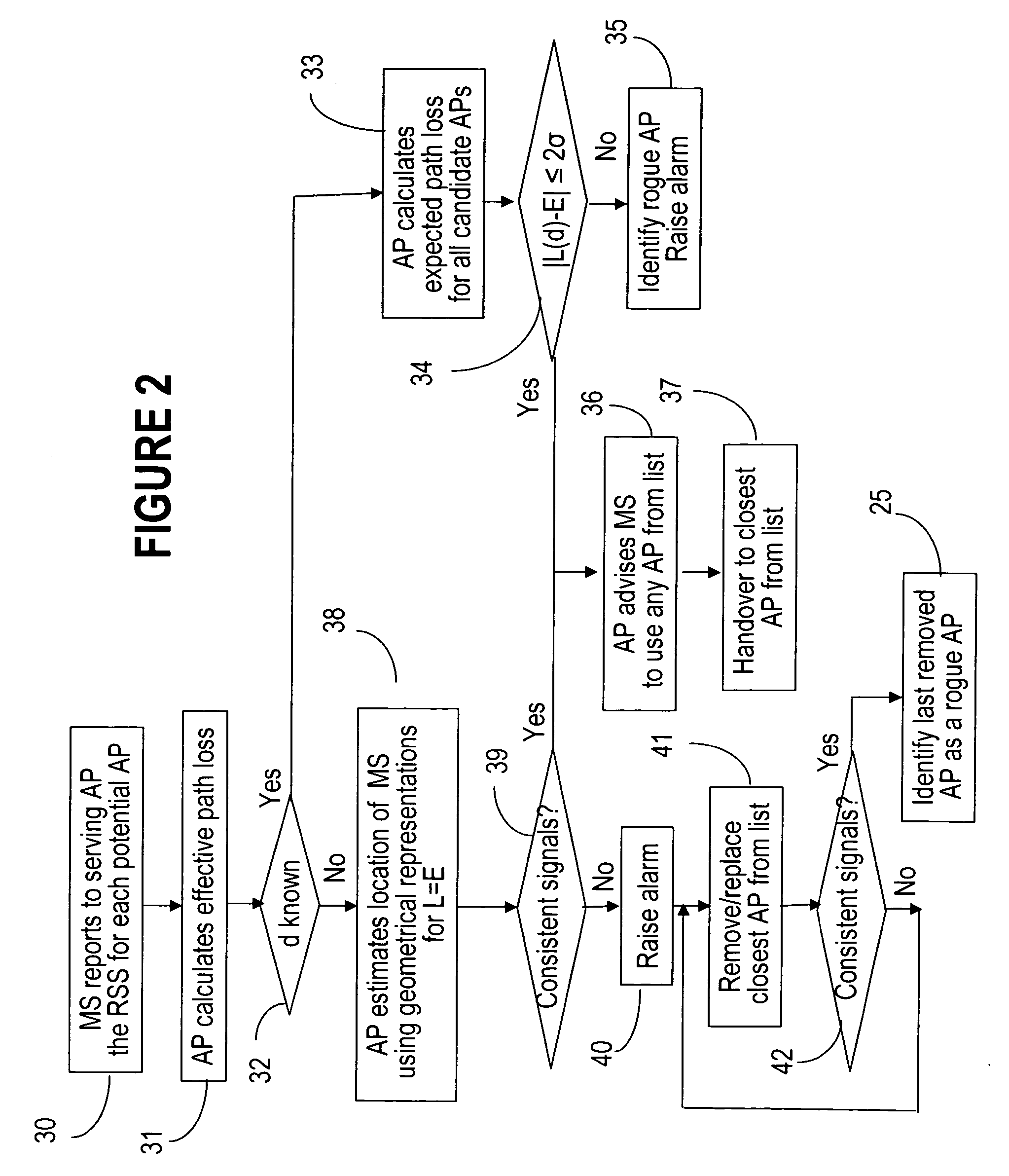
Methods to detect rogue access points (APs) and prevent unauthorized wireless access to services provided by a communication network are provided. A mobile station (MS) reports to a serving AP the received signal strength (RSS) for all APs in the area it travels. The serving AP detect a rogue AP based on inconsistencies perceived in the RSS reports, assessed during the handover phase or whilst the communication is active.
Owner:WSOU INVESTMENTS LLC
Method and Apparatus for Dynamically Creating and Updating Base Station Neighbor Lists
The invention includes a method and apparatus for creating a base station neighbor list for a target base station in a network comprising a plurality of base stations. A method includes obtaining signal strength measurement information associated with a set of candidate base stations, creating the base station neighbor list by selecting ones of the candidate base stations for inclusion in the base station neighbor list in a manner for substantially maximizing a number of locations in the coverage area of the target base station receiving signal coverage from at least a threshold number of selected ones of the candidate base stations, and storing the base station neighbor list. The base station neighbor list may be updated periodically, or in response to changes to signal strength measurement information. The base station neighbor list is distributed from the base station to wireless user devices served by the base station for use by the wireless user devices in making handoff decisions.
Owner:LUCENT TECH INC
Wireless mobility manager
InactiveUS20050138178A1Connection managementData switching by path configurationQuality of serviceMobility management
Embodiments of a wireless mobility manager and its method of operation are described. In one embodiment, the method includes a wireless station that automatically scans a current communication range to identify a first group of wireless access points. In one embodiment, scanning is performed if a signal strength of a current wireless connection to a wireless access point falls below a user selected scan threshold. Subsequently, the wireless device automatically establishes a wireless connection with a selected wireless access point from the first group of wireless access points. In one embodiment, the wireless connection is established once the current signal strength of the current wireless connection falls below a user selected switch threshold. Alternatively, the wireless station may determine quality of service (QoS) characteristics of the first group of wireless access points to select an access point.
System framework for mobile device location
ActiveUS7994981B1Rapid and inexpensive compilationRapid and inexpensive and maintenanceBeacon systems using radio wavesPosition fixationMobile deviceUltimate tensile strength
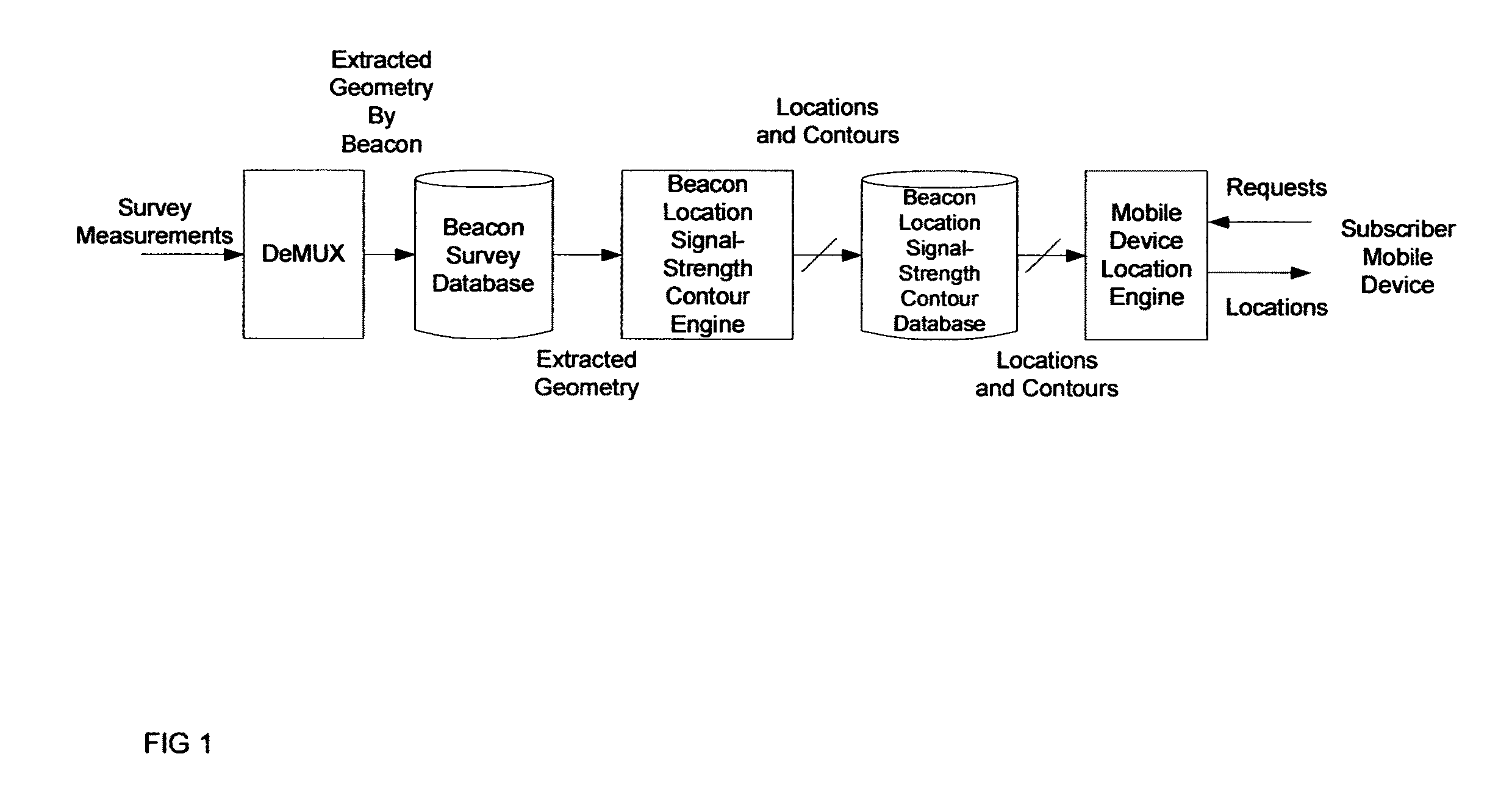
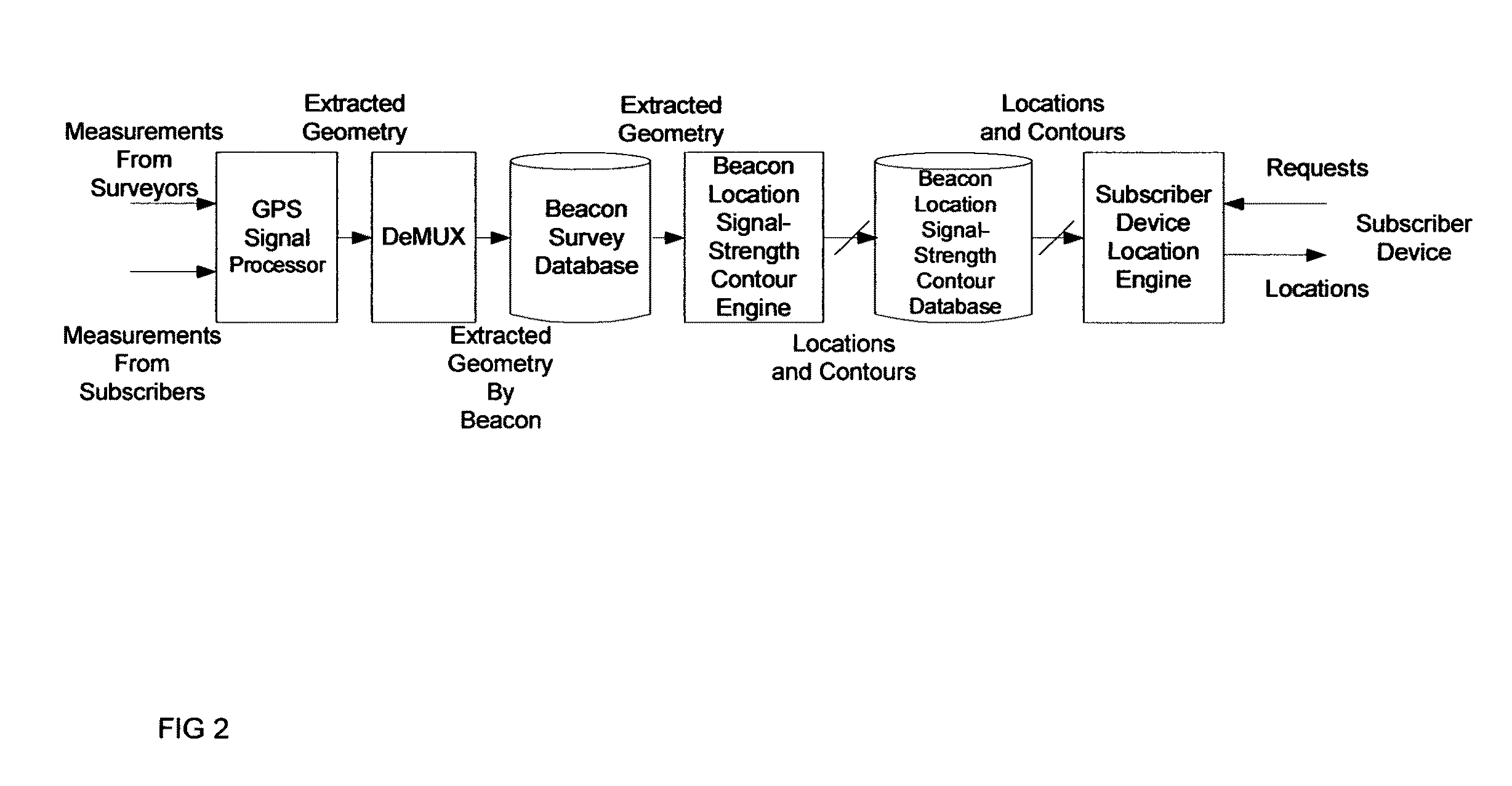
A method for estimating the location of a beacon from an ensemble of measurements associated with said beacon, where, contained in each measurement, are GPS data from which surfaces of location may be extracted, together with the ID's of beacons detectable at the point of measurement, is disclosed. The method comprises extracting the canonical set of surfaces of location implicit in each of the associated measurements, and determining the estimate of the location of the beacon as the point for which the sum of the squares of the distances to each of the surfaces so extracted is minimized. A system for the compilation of a database of beacon locations from measurements containing a time-stamped recording of the composite GPS signal (which recording is referred to as a datagram), together with the ID's and associated signal strengths of beacons detectable at the point of measurement, is also disclosed. The system comprises GPS signal processing means for extracting, from each time-stamped datagram, the canonic set of surfaces of location, and beacon location estimation means for estimating the location of a beacon from an ensemble of surfaces of location associated with said beacon.
Owner:ETHERWHERE CORP
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com