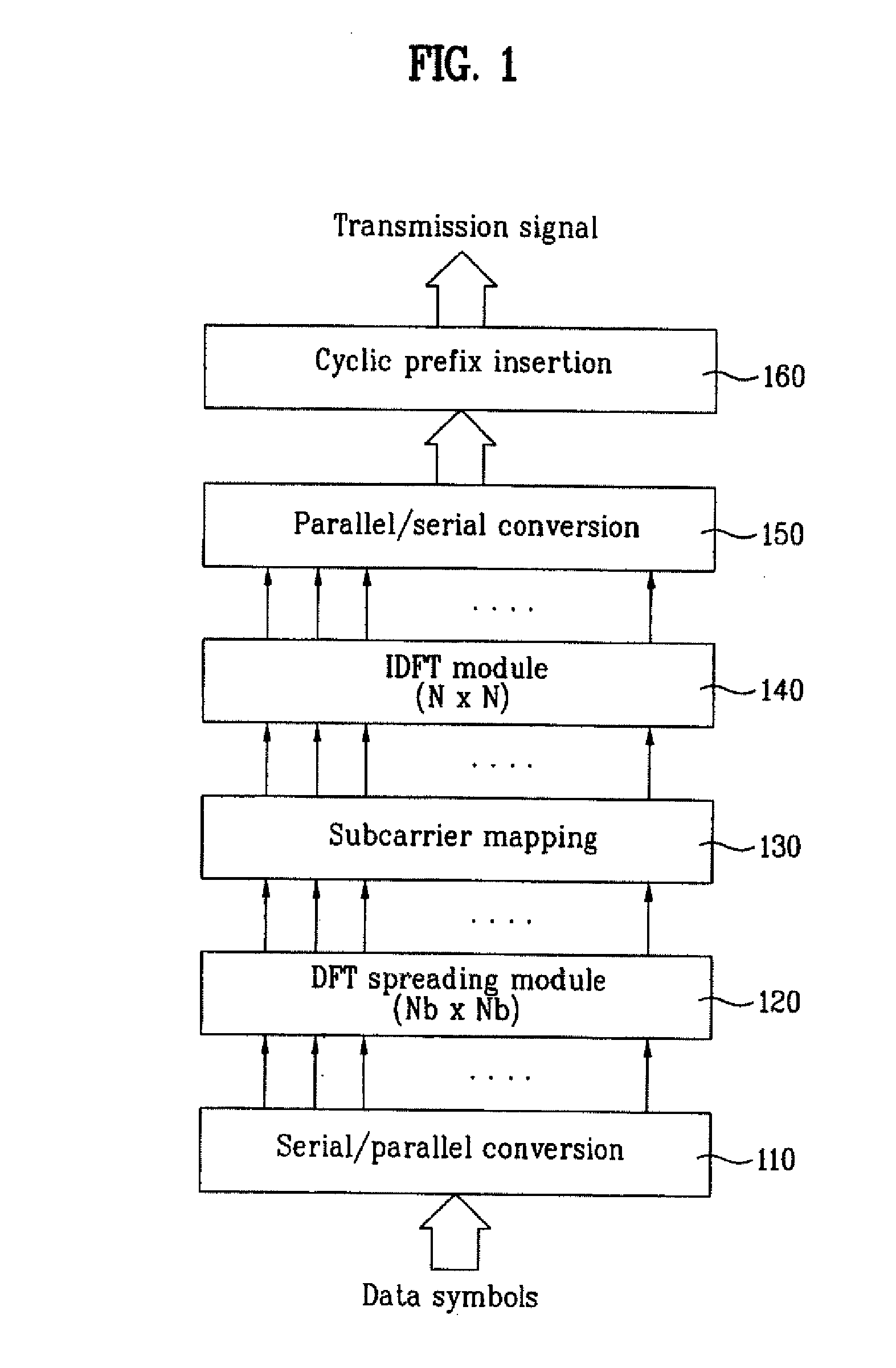
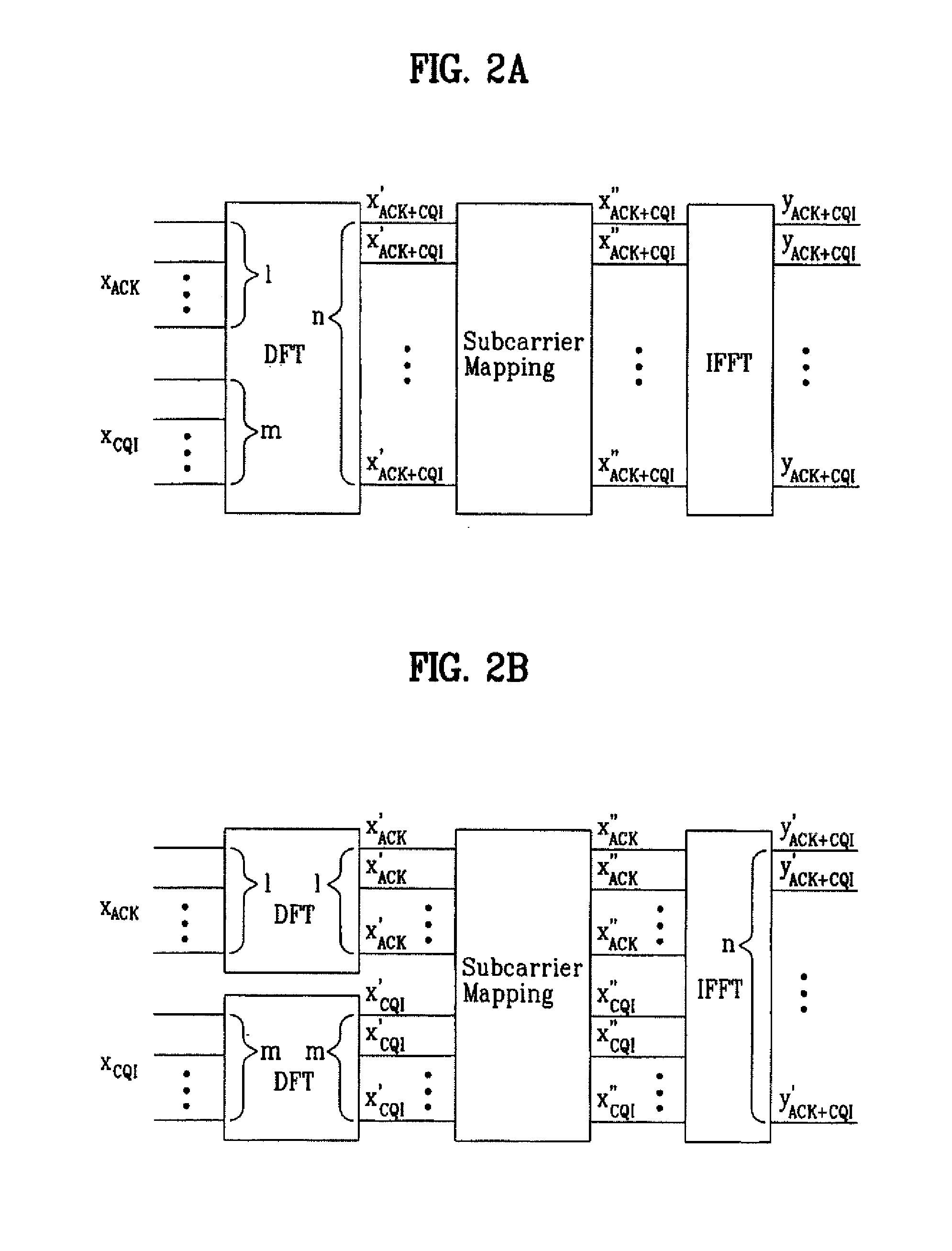
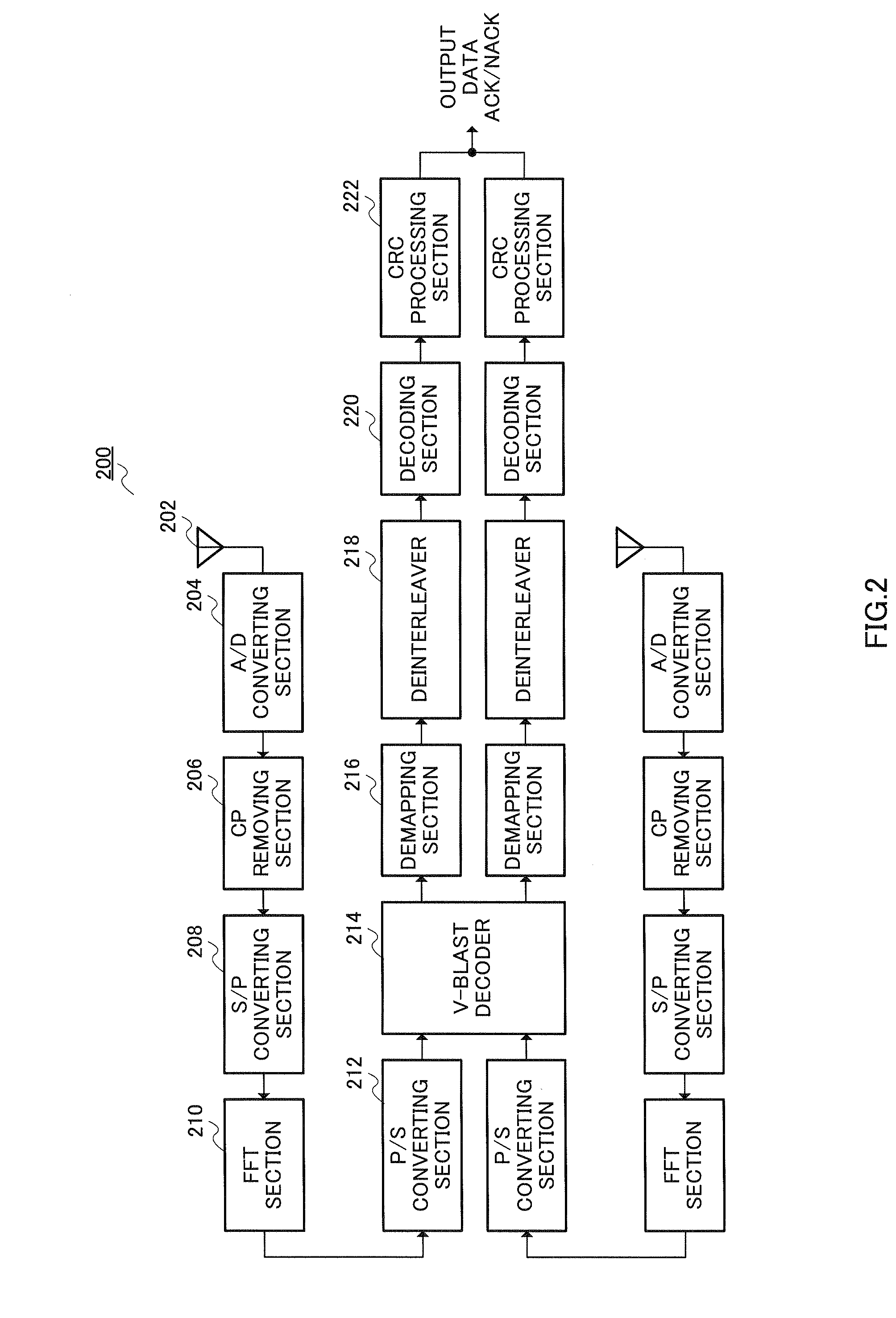
Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
1728 results about "Cyclic redundancy check" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
A cyclic redundancy check (CRC) is an error-detecting code commonly used in digital networks and storage devices to detect accidental changes to raw data. Blocks of data entering these systems get a short check value attached, based on the remainder of a polynomial division of their contents. On retrieval, the calculation is repeated and, in the event the check values do not match, corrective action can be taken against data corruption. CRCs can be used for error correction (see bitfilters).
Interference protection
InactiveUS7239657B1Memory record carrier reading problemsTransmissionInterference resistanceChecksum
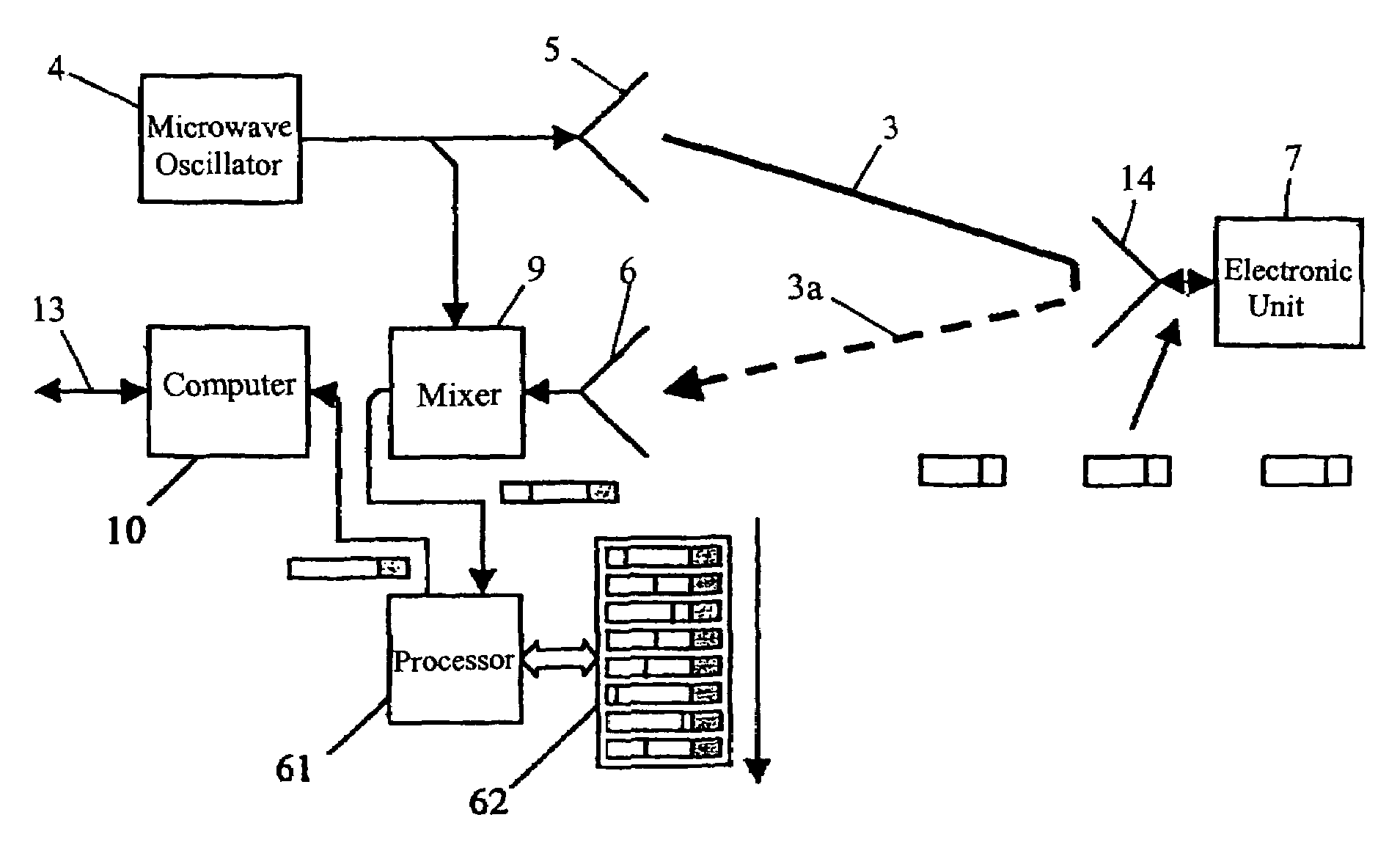
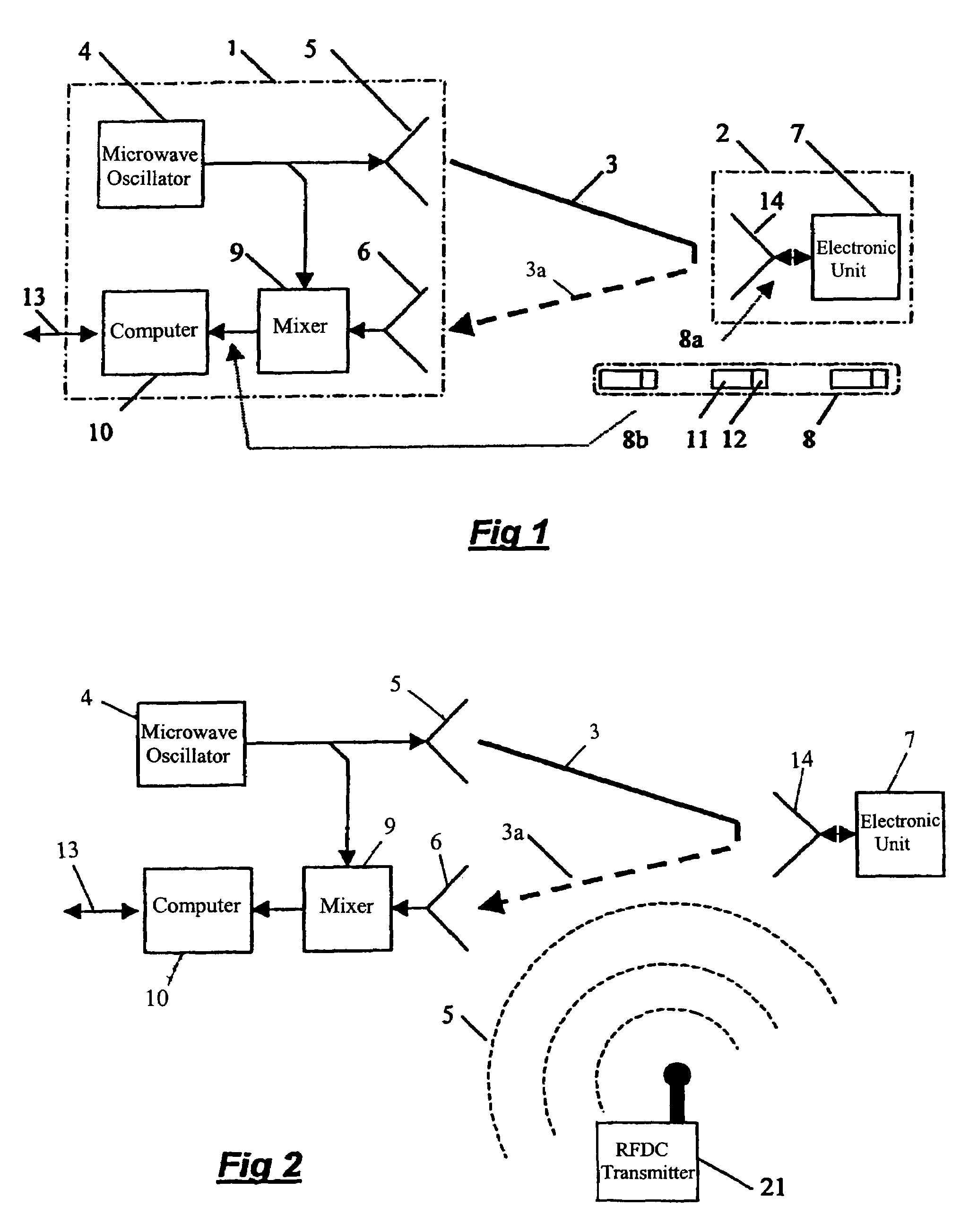
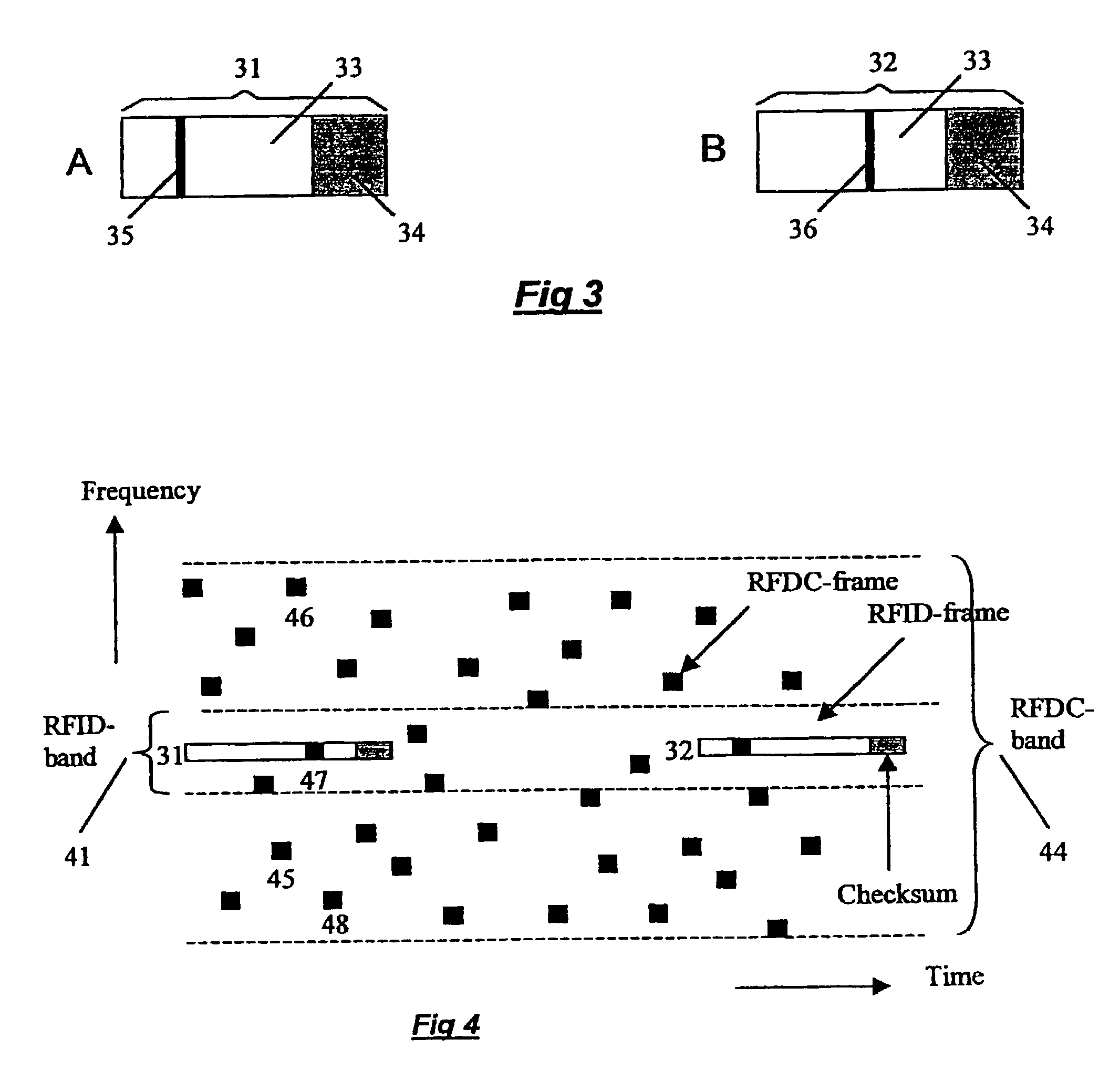
Apparatus and a method for enhancing the interference resistance of so-called RFID systems, wherein identification messages delivered from an identification device are longer than the time for which an anticipated interference or disturbance is calculated to continue, and wherein the messages contain redundancy, such as a checksum. The messages are delivered from the identification device repetitively, and are redundancy checked. In the event of any discrepancy in the redundancy check, such as when the checksum is checked against the data content of the message and is found in disagreement, successive messages are checked bit for bit against each other. Any deviations between otherwise previously rejected messages are assumed to be due to external interference and are thus successively substituted until the redundancy check gives an accepted result, such as through the medium of a checksum check according to the so-called CRC method.
Owner:TAGMASTER AB
Iterative decoder employing multiple external code error checks to lower the error floor
InactiveUS7310768B2Code conversionError correction/detection by combining multiple code structuresError checkDegree of certainty
Owner:ENTROPIC COMM INC
Hybrid automatic repeat request transmission method based on polarization code
ActiveCN103281166AIncrease the probability of correct decodingLow decoding complexityError prevention/detection by using return channelCode conversionHybrid automatic repeat requestComputer engineering
The invention discloses a hybrid automatic repeat request transmission method based on a polarization code. The hybrid automatic repeat request transmission method based on the polarization code comprises the following steps: after a coding bit sequence obtained after polarization coding is carried out to a sent information bit sequence is punched via a sending end, sending into a channel to be transmitted; decoding a received signal by a receiving end for CRC (cyclic redundancy check); if the received signal passes the check, feeding back an ACK (acknowledgement character) signal to the sending end, and otherwise, sending a NACK (negative acknowledgement) signal; if the sending end receives the NACK signal, sending one part of uncoded information bits to a receiving end again; according to the coding bit received for the first time and a newly-received information bit, decoding again by the receiving end; if a decoding result still does not pass the CRC, sending the other part of uncoded information bits to the receiving end again by the sending end; according to the coding bit received for the first time, the information bit received in the previous time and the newly-received information bit, decoding again by the receiving end; continuously executing the process; and finishing one whole transmission process until the sending end receives the ACK signal or the number of sending times reaches a preset maximum value.
Owner:BEIJING UNIV OF POSTS & TELECOMM
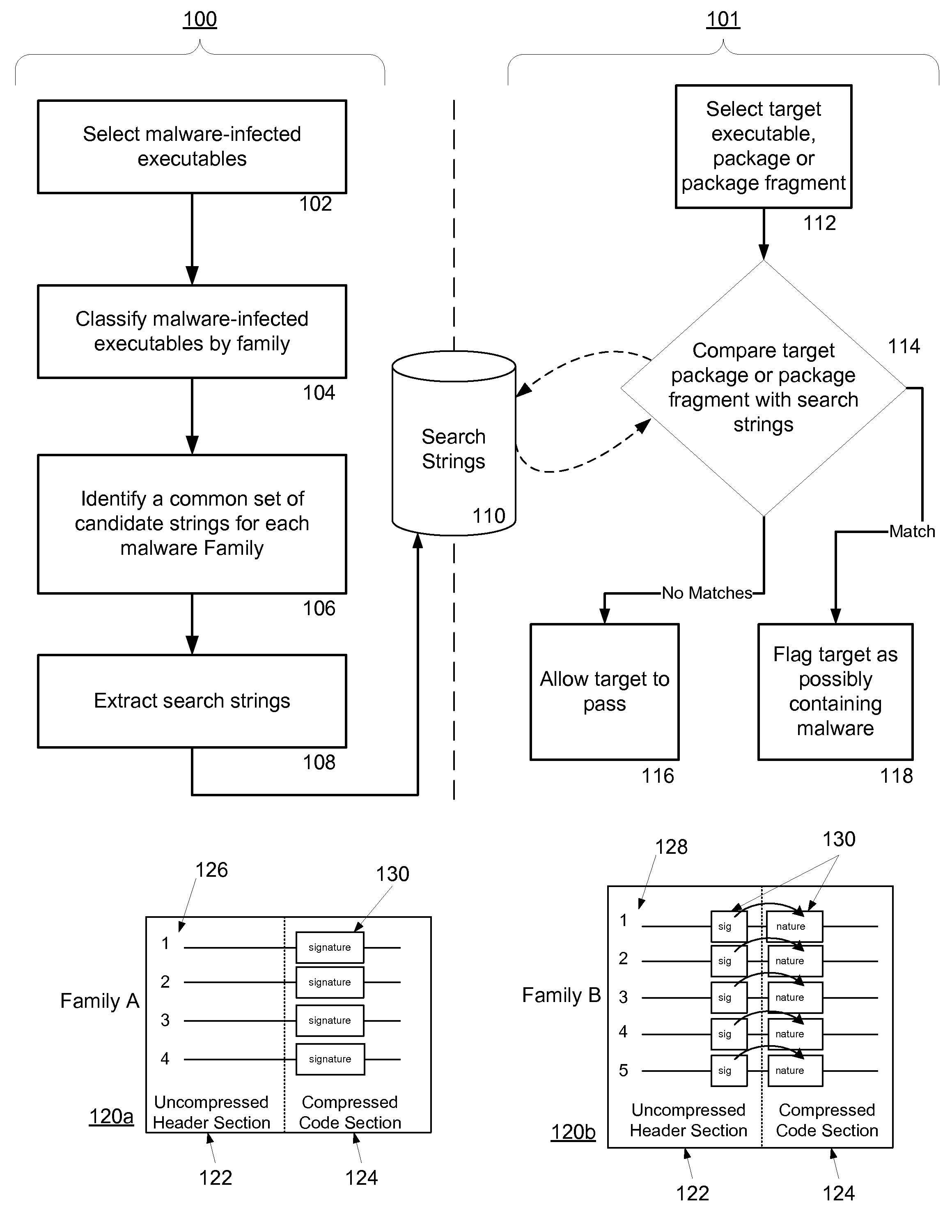
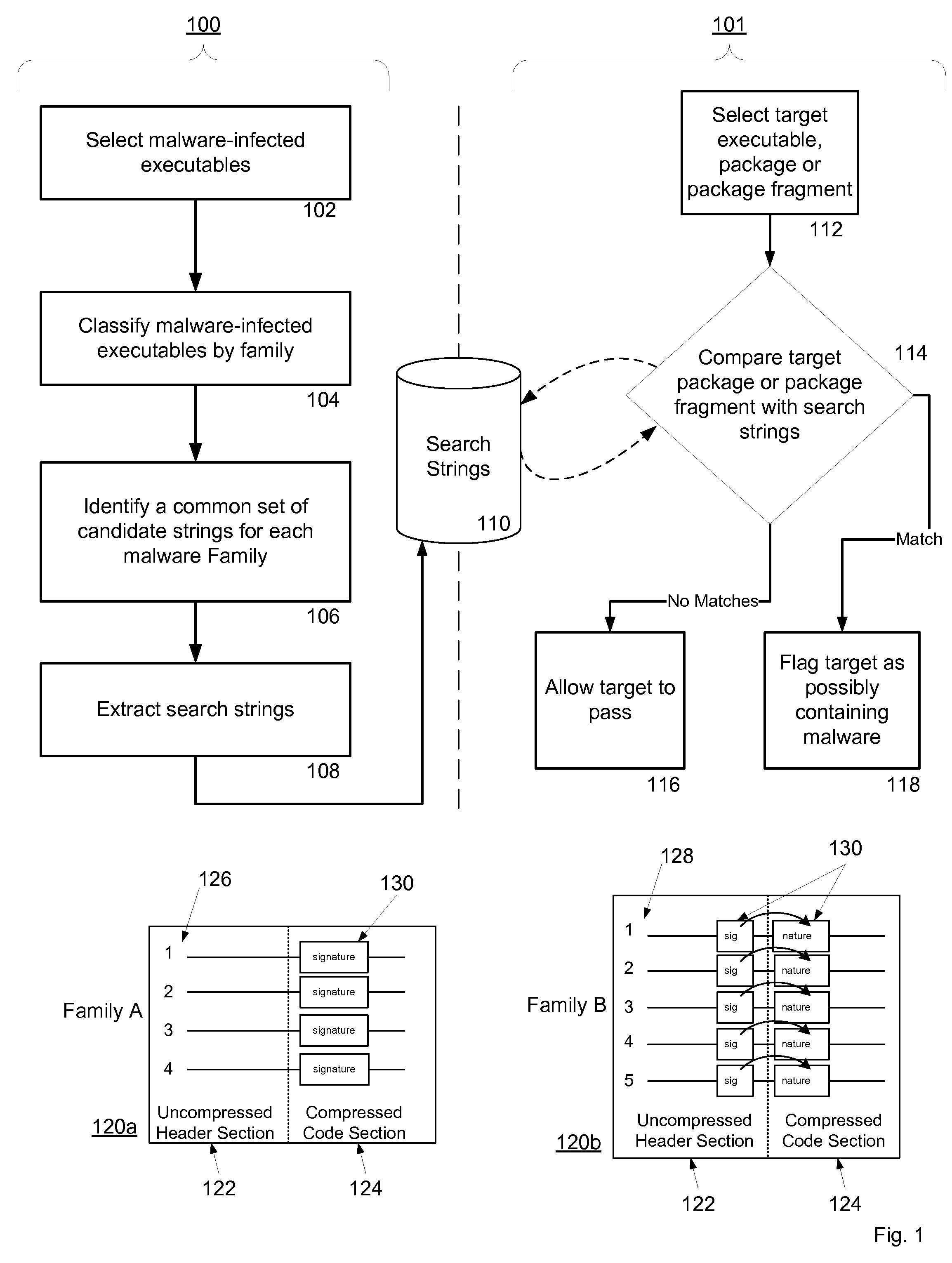
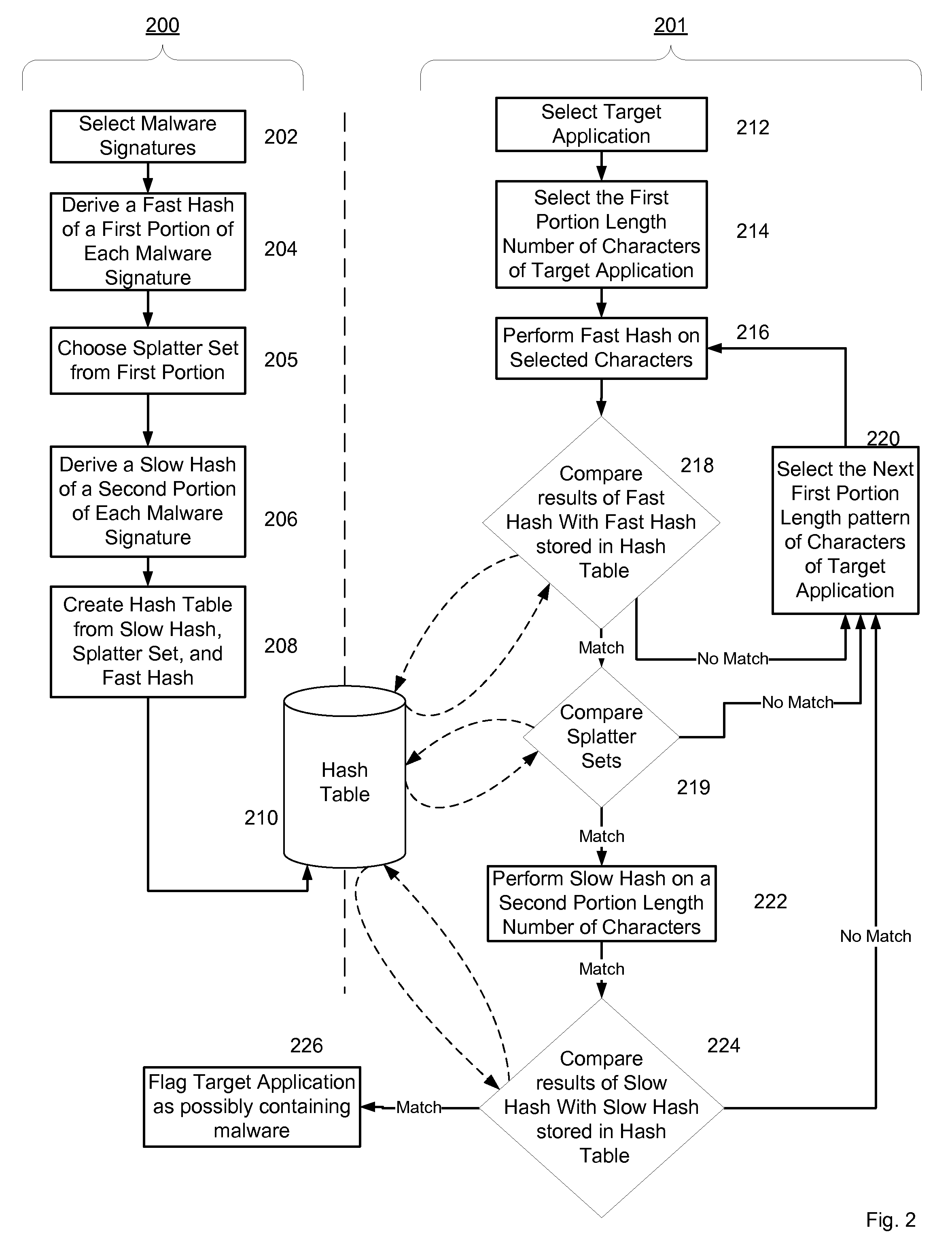
Non-Signature Malware Detection System and Method for Mobile Platforms
ActiveUS20070240221A1Suitable for useReliable detectionMemory loss protectionError detection/correctionEntry pointChecksum
A system and method for detecting malware on a mobile platform in a mobile network. The system and method verifies that an executable is malware-free by computing the checksum of the executable and comparing that checksum with a checksum obtained from a malware-free copy of the executable. The checksum is a sum of all 32-bit values in a code section and an import section of said executable, a byte sequence at an entry point in said executable, a size descriptor of an import table, a size descriptor of said import section, a cyclic redundancy check of said executable, or a combination thereof.
Owner:PULSE SECURE
Segmented CRC assisted polar code encoding and decoding method
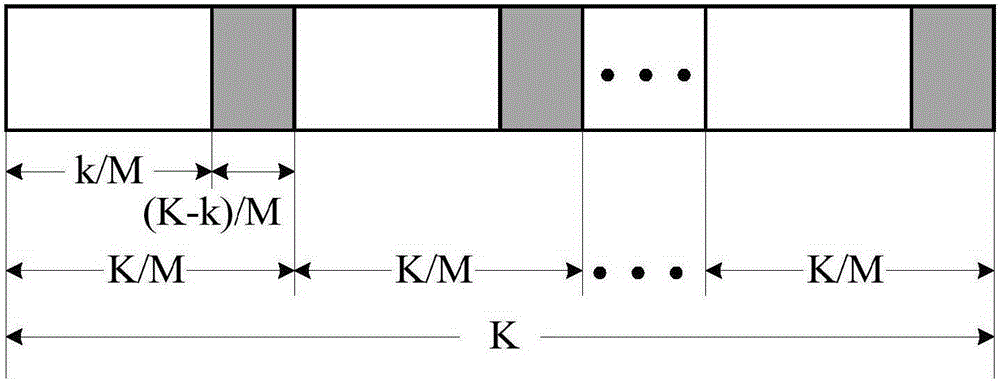
ActiveCN105227189ASave storage spaceFacilitate real-time communicationError preventionError detection onlyComputer architectureProcessor register
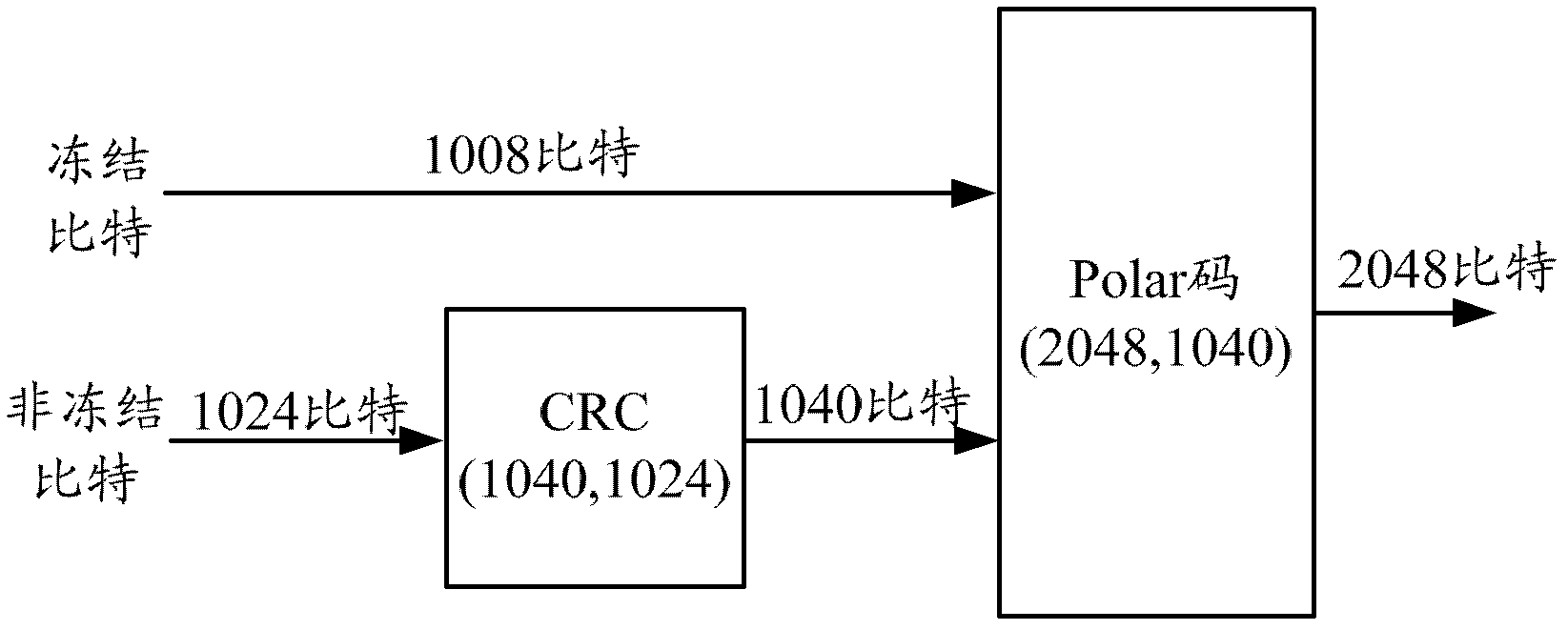
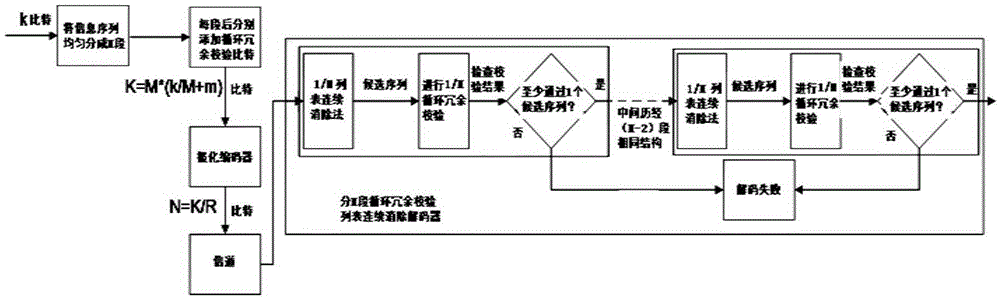
The invention belongs to the field of channel encoding, and particularly relates to a polar code coding and decoding method with segmented cyclic redundancy check (Cyclic Redundancy Check, CRC) auxiliary check. According to the polar code coding and decoding method provided by the invention, certain information bits are sacrificed to check polar codes to improve the decoding performance, and assuming that the length of used CRC is K-k bits, the information is averagely divided into M segments by segmented CRC check, k / M bits of information and (K-k) / M bits of CRC check information constitute an information structure of each segment, as shown in Fig.2. The information bits are encoded and transmitted by a channel, finally, SCL decoding and check are carried out on the information received by a receiving end, and L maximum storage paths are available. The polar code coding and decoding method provided by the invention can be used for shortening the time delay, bringing great convenience for real-time communication, saving the memory space of a register and providing great convenience for hardware realization.
Owner:UNIV OF ELECTRONICS SCI & TECH OF CHINA
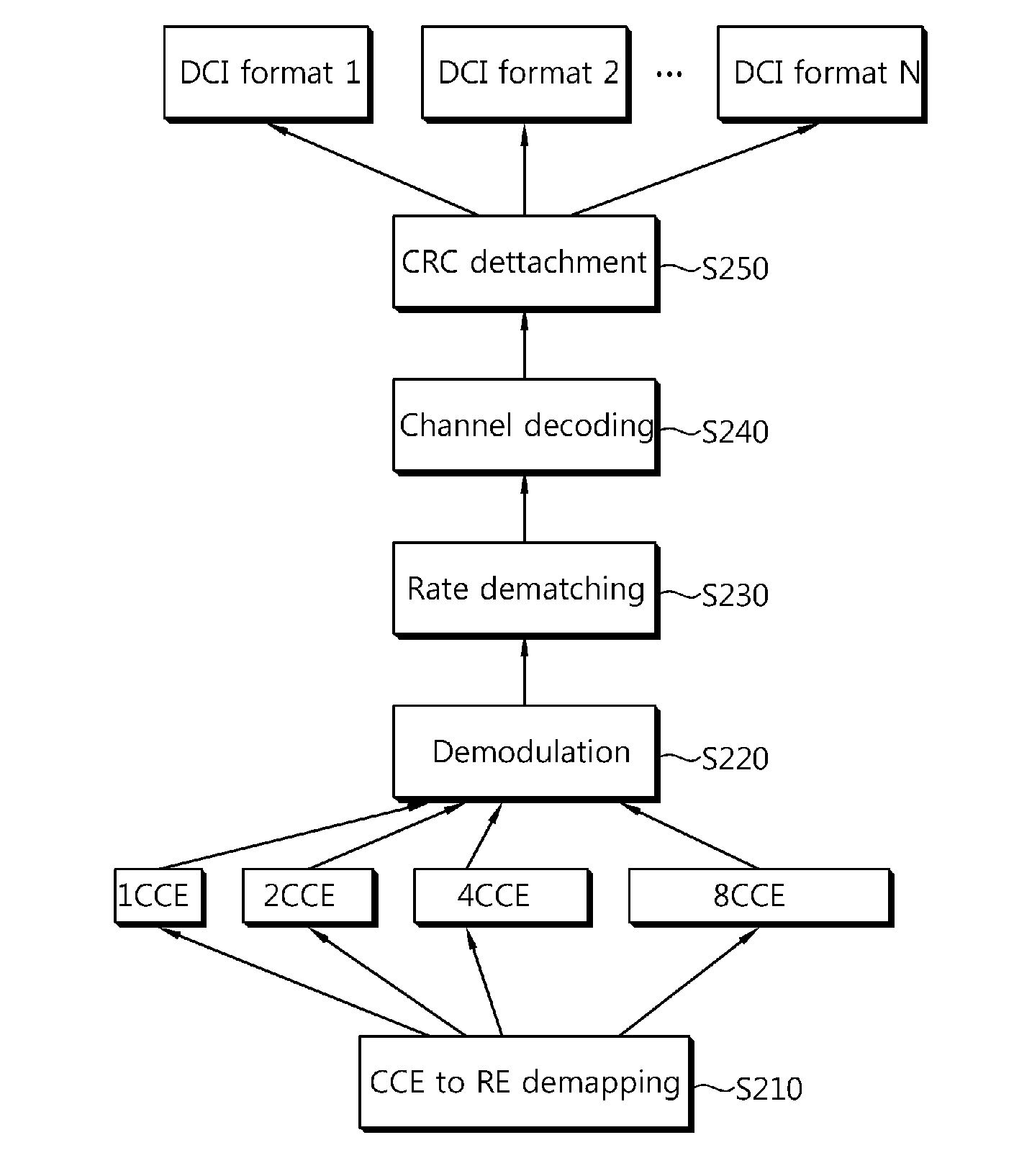
Method for detecting control information in wireless communication system
ActiveUS20110083066A1Improve accuracyAccurate detectionCode conversionSignal allocationError checkCommunications system
A method for detecting control information in a wireless communication system is provided. The method includes checking a cyclic redundancy check (CRC) error by monitoring control channels, determining whether a value of an error check field is equal to a specific value, and, if the value of the error check field is equal to the specific value, detecting the control information on the control channel.
Owner:LG ELECTRONICS INC
Method of controlling transmit power of uplink channel
A method of controlling a transmit power of an uplink channel is provided. Downlink control information of which Cyclic Redundancy Check (CRC) parity bits are masked with a TPC identifier is received on a downlink control channel. The transmit power of the uplink channel is adjusted based on a TPC command in the downlink control information.
Owner:LG ELECTRONICS INC
Encoding uplink acknowledgments to downlink transmissions
ActiveUS20080095252A1Error prevention/detection by using return channelPolarisation/directional diversityUser equipmentTransmitter
A portable device, such as a mobile terminal or user equipment, for encoding uplink acknowledgments to downlink transmissions. The portable device includes a receiver configured to receive a plurality of data blocks, such that each of the data blocks include an associated cyclic redundancy check (CRC), and a processor configured to determine received status for each of the data blocks by checking the CRC of each of the data blocks. The portable device further includes a transmitter for transmitting a response sequence which indicates the received status of all of the data blocks.
Owner:3G LICENSING SA
Wireless communications system that supports multiple modes of operation
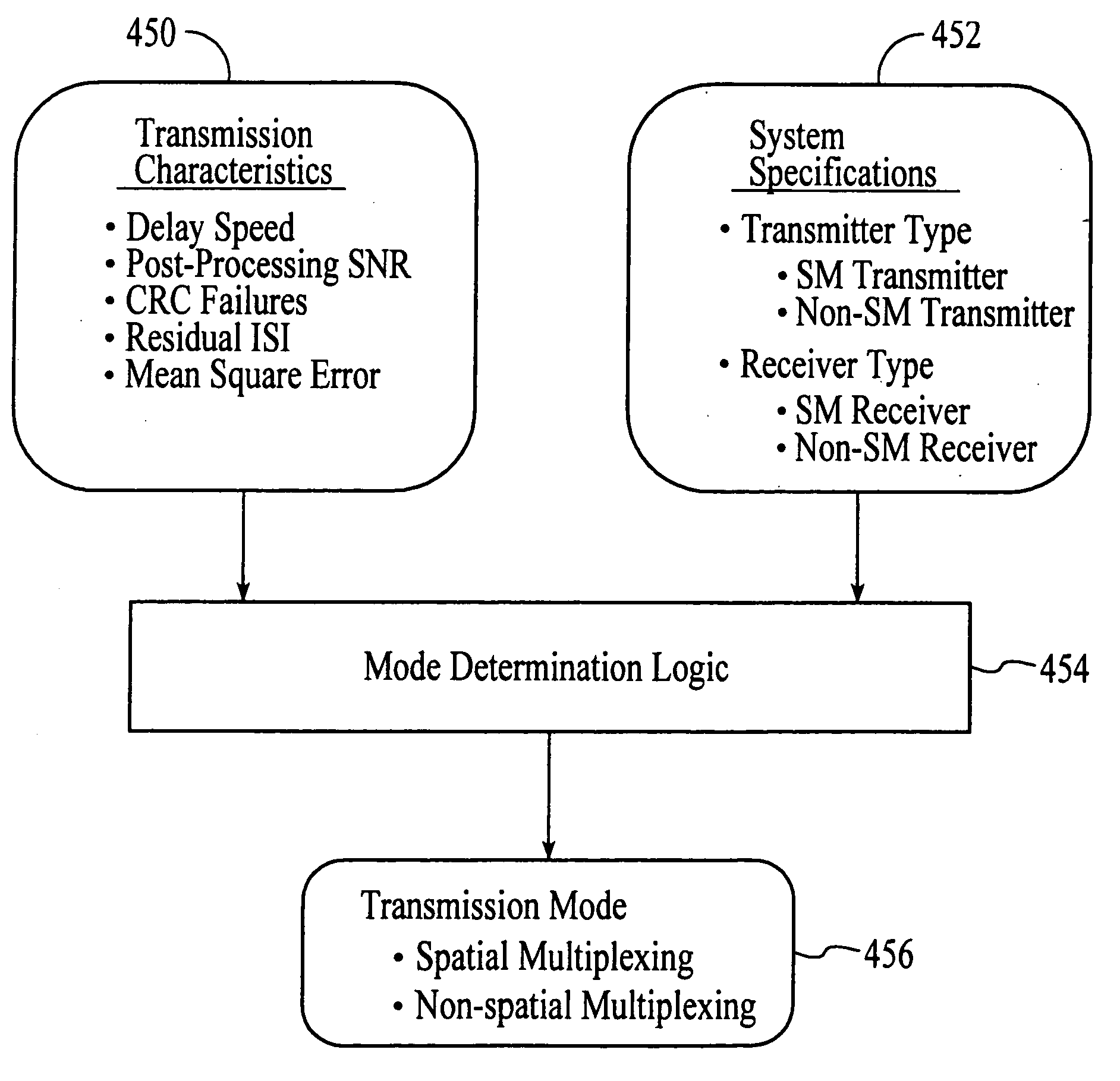
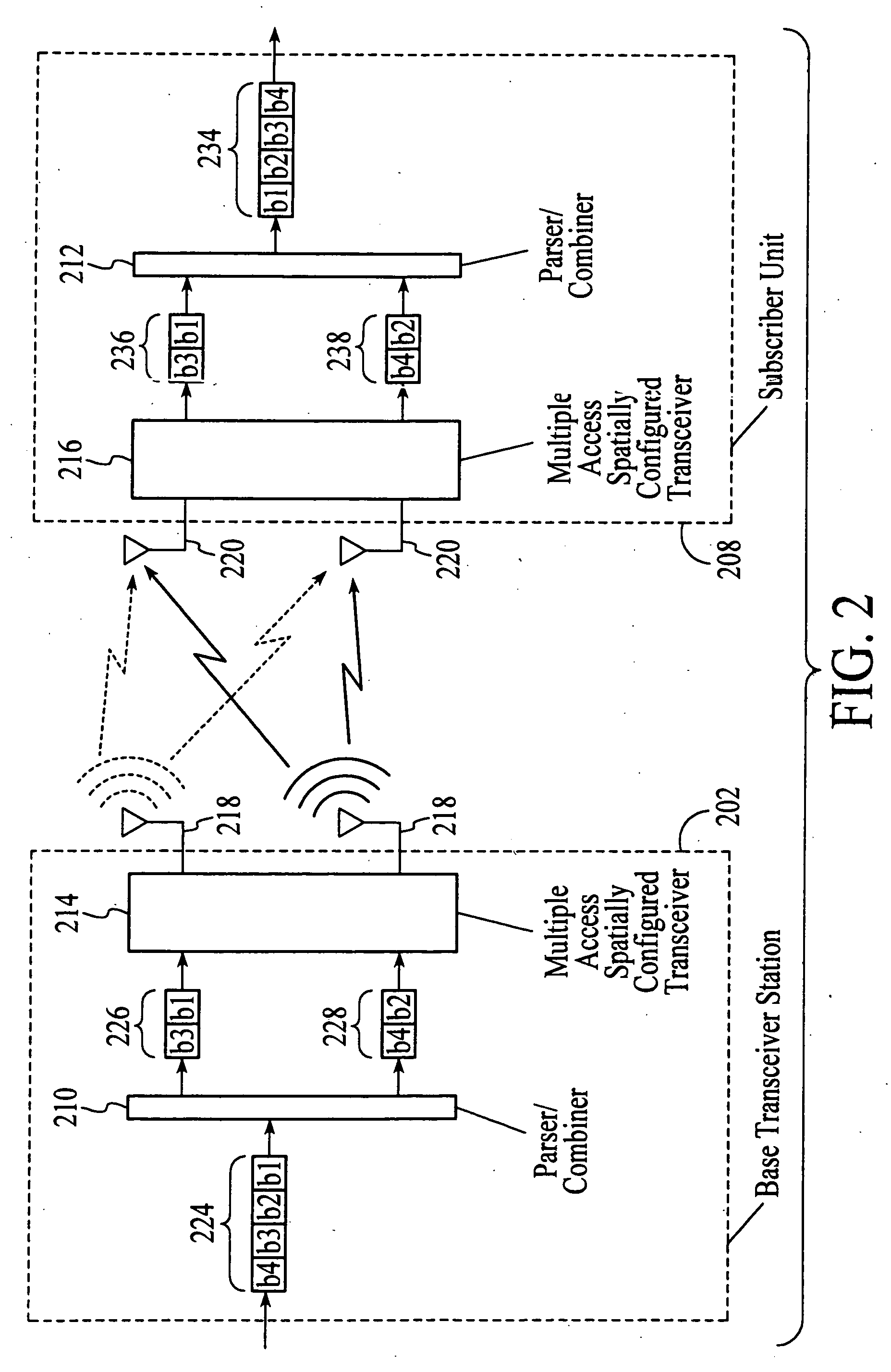
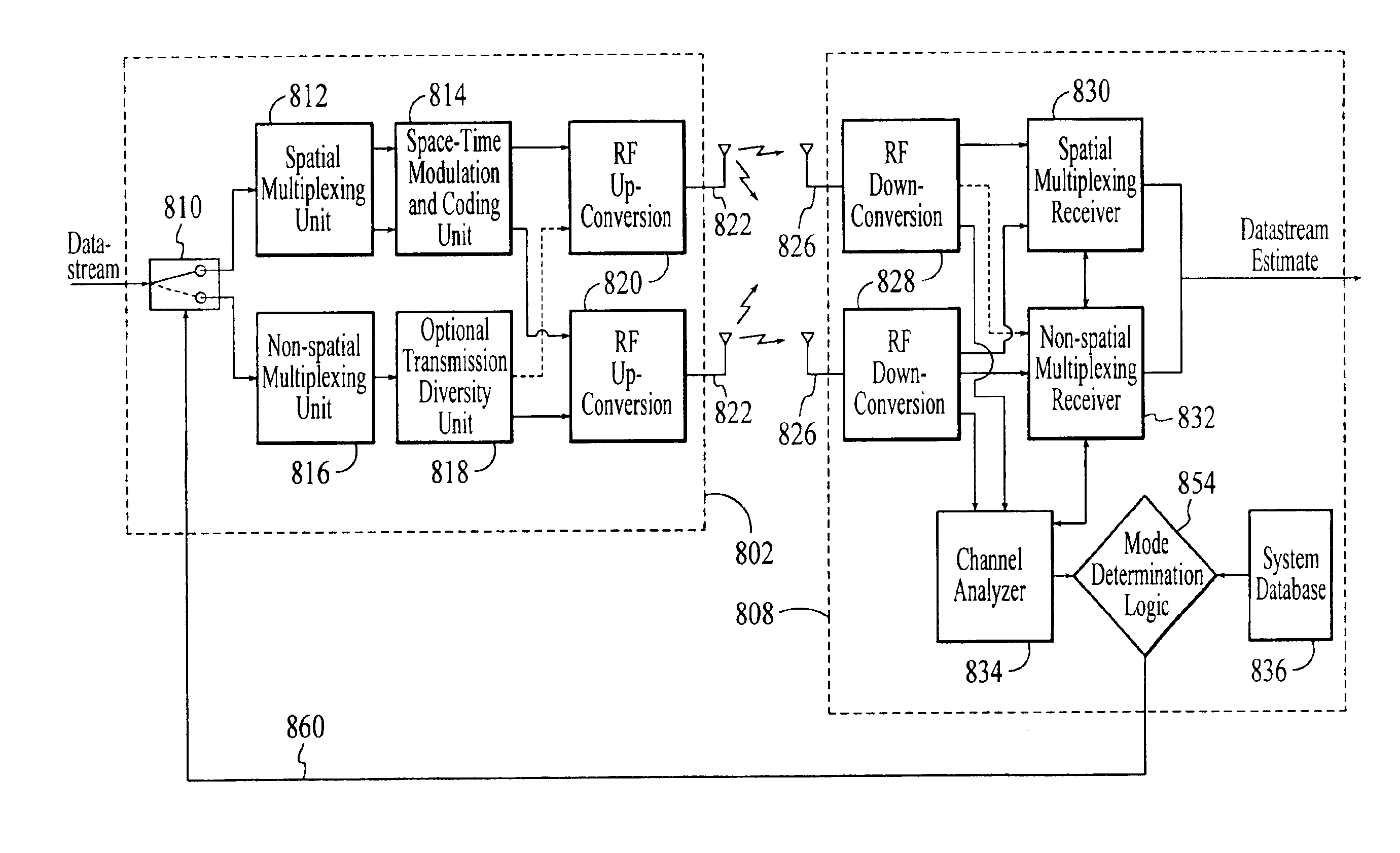
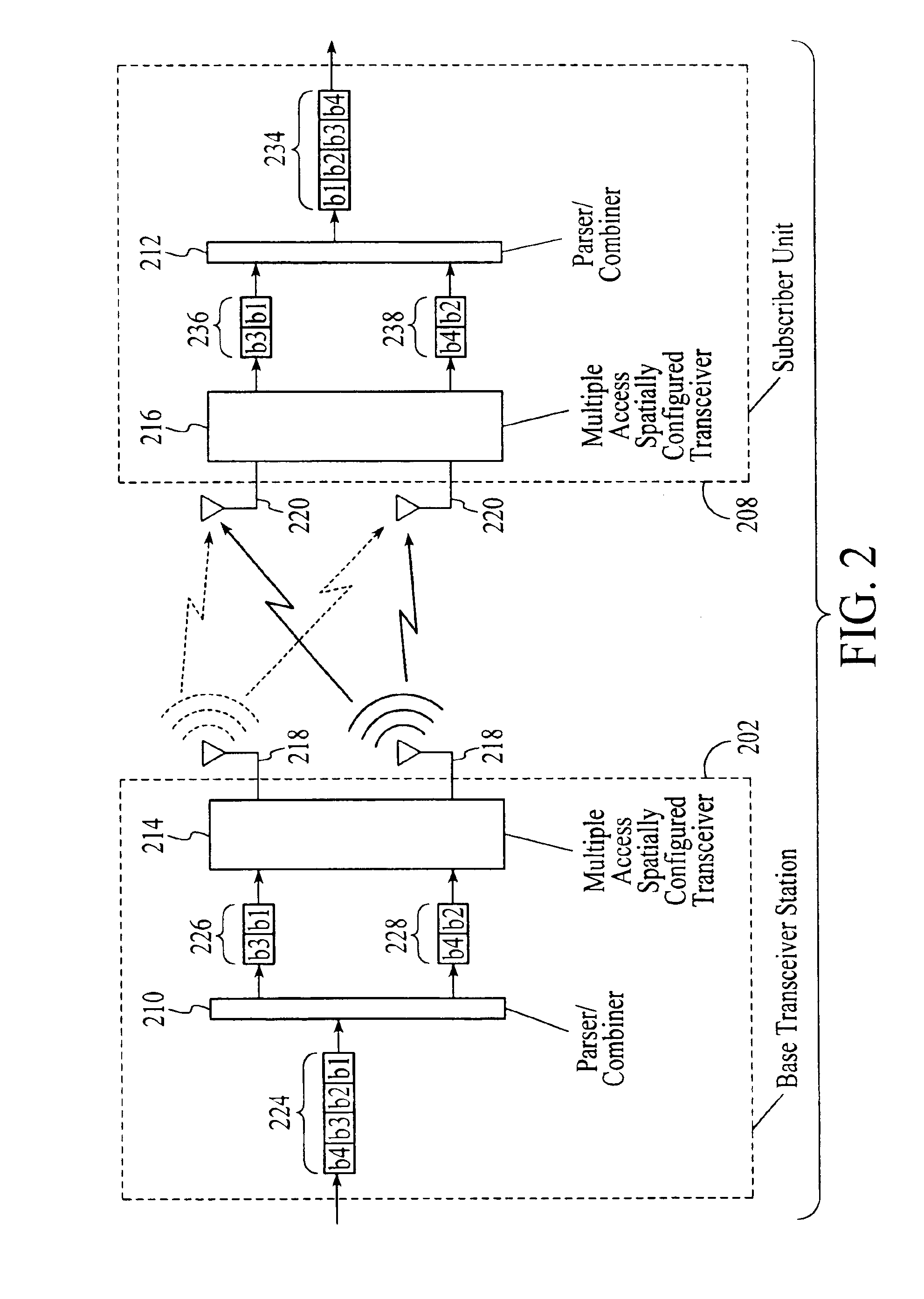
InactiveUS20050174981A1Network traffic/resource managementAssess restrictionTransceiverMultiple modes
A wireless communications adapts its mode of operation between spatial multiplexing and non-spatial multiplexing in response to transmission-specific variables. An embodiment of a wireless communications system for transmitting information between a base transceiver station and a subscriber unit includes mode determination logic. The mode determination logic is in communication with the base transceiver station and the subscriber unit. The mode determination logic determines, in response to a received signal, if a subscriber datastream should be transmitted between the base transceiver station and the subscriber unit utilizing spatial multiplexing or non-spatial multiplexing. In an embodiment, the mode determination logic has an input for receiving a measure of a transmission characteristic related to the received signal. In an embodiment, the mode determination logic includes logic for comparing the measured transmission characteristic to a transmission characteristic threshold and for selecting one of spatial multiplexing and non-spatial multiplexing in response to the comparison of the measured transmission characteristic to the transmission characteristic threshold. In an embodiment, the transmission characteristic includes at least one of delay spread, post-processing signal-to-noise ratio, cyclical redundancy check (CRC) failure, residual inter-symbol interference, mean square error, coherence time, and path loss. By adapting the mode of operation in response to transmission-specific variables, the use of spatial multiplexing can be discontinued in unfavorable conditions. Additionally, because the wireless communications system can adapt its mode of operation between spatial multiplexing and non-spatial multiplexing, the communications system is compatible with both subscriber units that support spatial multiplexing and subscriber units that do not support spatial multiplexing.
Owner:APPLE INC
Polarization code decoding method for cyclic redundancy check assistance
InactiveCN102694625AStrong error correction abilityReduce operational complexityError preventionError correction/detection using linear codesCommunications systemCode division multiple access
The invention relates to a polarization code decoding method for cyclic redundancy check assistance. When a polarization code is decoded, in all the routes with cyclic redundancy check values of corresponding bit estimation sequences of being zero from a root node to leaf nodes on a code tree corresponding to the polarization code, one route with maximum reliability metric value is searched by taking a list or stack as assistance for route search, and the bit estimation sequence corresponding to the route is output as a decoding result. The method comprises the following operation steps of: determining parameters according to a search assistance method, constructing an auxiliary structure of the decoding method, searching a candidate bit estimation sequence and executing cyclic redundancy check. By adopting the method disclosed by the invention, error correcting capability of a communication system which adopts the polarization code as channel coding is greatly improved, operation steps are simpler, and operation complexity is equivalent to or even lower than that of a Turbo code coding and decoding method used in a WCDMA (wideband code division multiple access) system, thus the method disclosed by the invention has a good practical prospect.
Owner:BEIJING UNIV OF POSTS & TELECOMM
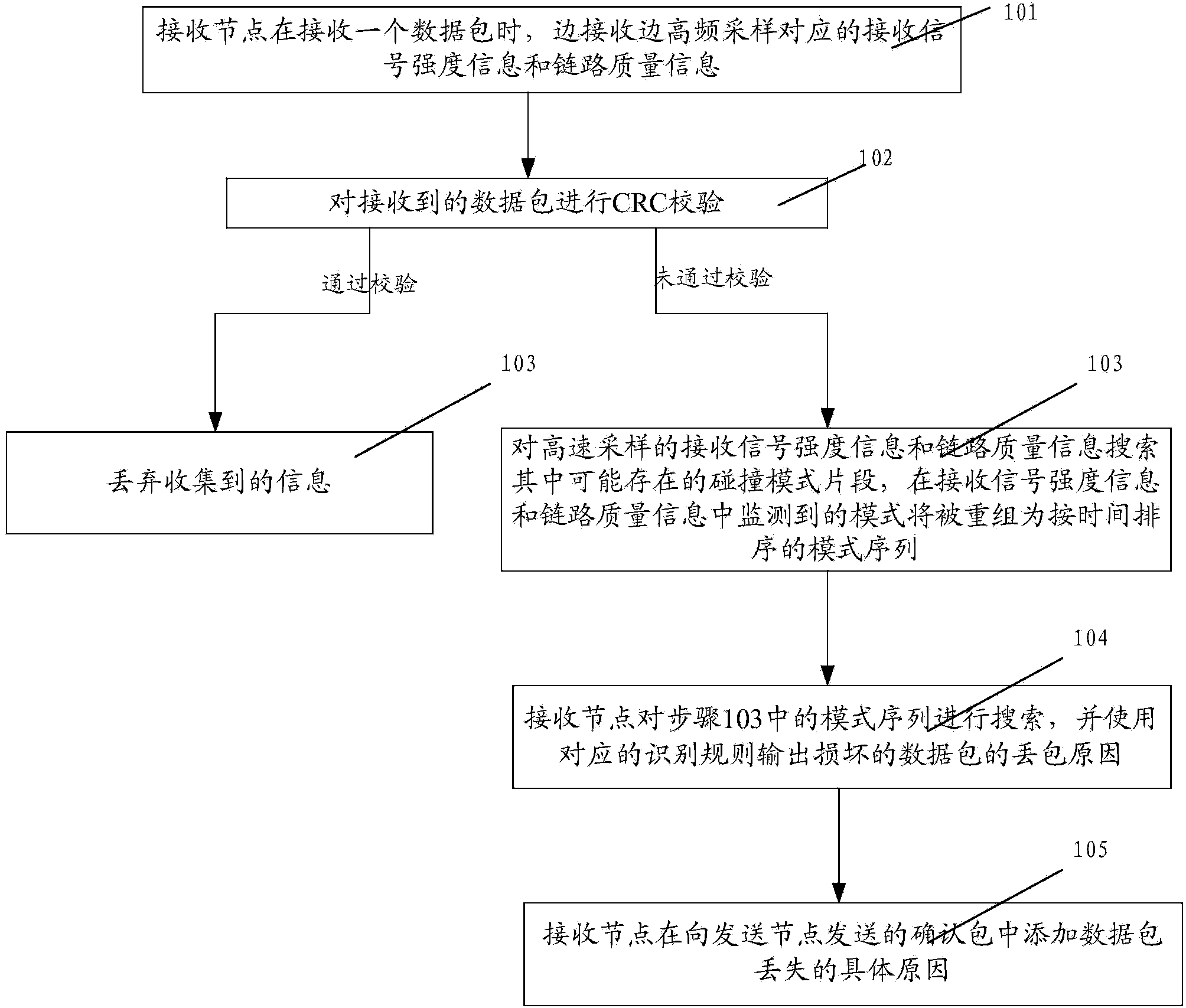
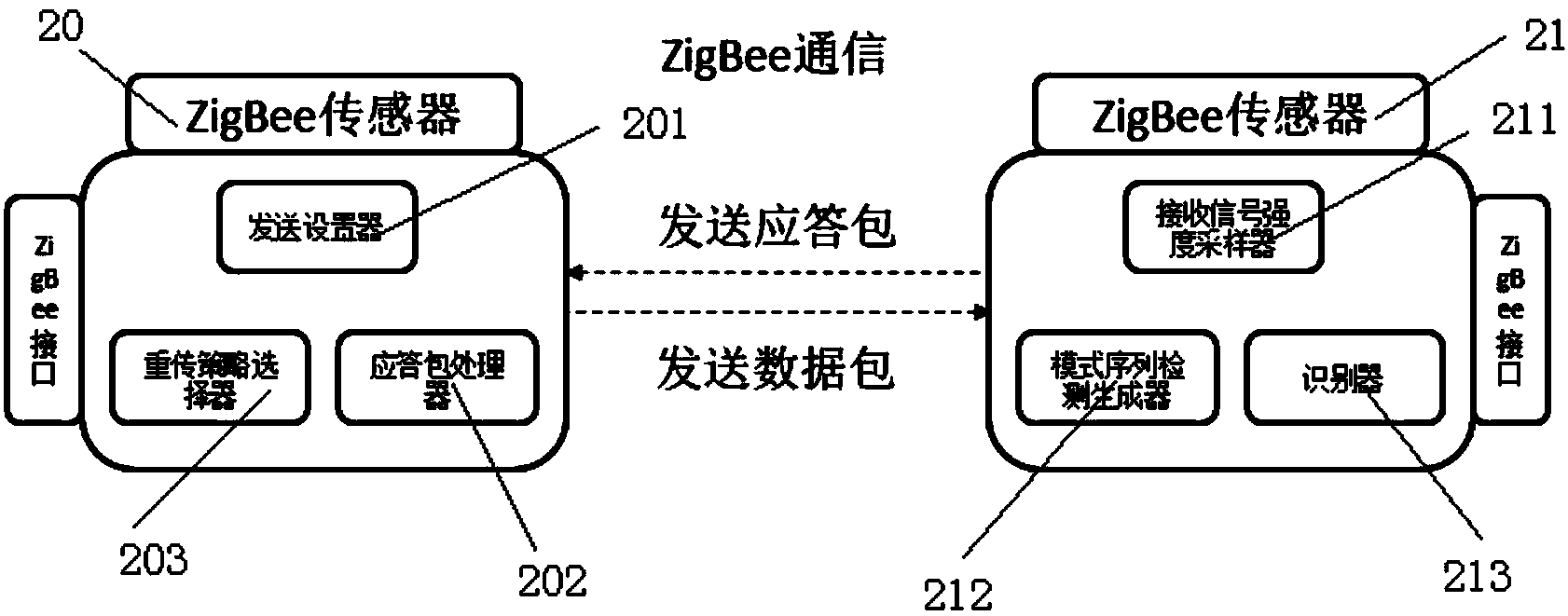
Method and system for identifying reasons of ZigBee sensor network packet loss
ActiveCN103716137AImprove throughputReduce the number of retransmissionsEnergy efficient ICTError prevention/detection by using return channelPacket lossZigbee sensor network
The invention discloses a method and system for identifying reasons of ZigBee sensor network packet loss. The method includes the steps that a receiving node carries out high-frequency sampling on corresponding receiving signal strength information and link quality information while receiving a data package; if the received data package fails to pass the cyclic redundancy check, collision mode fragments possibly existing in the high-frequency sampled receiving signal strength information and the high-frequency sampled link quality information are searched, and the modes monitored in the receiving signal strength information and the link quality information will be regrouped into a time-ordered mode sequence; the receiving node searches for the generated mode sequence and outputs the packet loss reasons of the damaged data package by using corresponding identifying rules; the receiving node adds the specific reasons of data package loss in an acknowledgment packet sent to a sending node. Through the method, network throughput can be improved and retransmission frequency can be reduced, so the purposes of saving energy and prolonging working time can be achieved.
Owner:SHANGHAI JIAO TONG UNIV
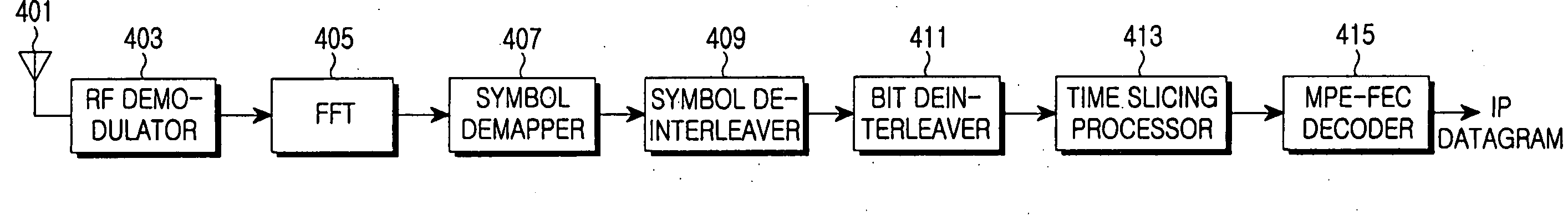
Apparatus and method of multi-cyclic redundancy checking for section detection and reliability information acquisition in a DVB-H system
A method and apparatus of multi-Cyclic Redundancy Checking (CRC) are provided for section detection and reliability information acquisition in a Digital Video Broadcasting-Handheld (DVB-H) system. A Packet Identifier (PID) filtering process is performed for a packet received through a radio network. A transport stream packet including section data is detected. A CRC process is performed for a payload of an associated section using header information of the section data and frame buffering is processed. The method and apparatus can perform CRC in a parallel fashion using multiple CRC checkers without interference between adjacent sections and can perform section detection and reliability verification.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
Method for preventing malicious software installation on an internet-connected computer
ActiveUS20070192854A1Prevents gaining accessAvoid accessMemory loss protectionDigital data processing detailsOperational systemTerm memory
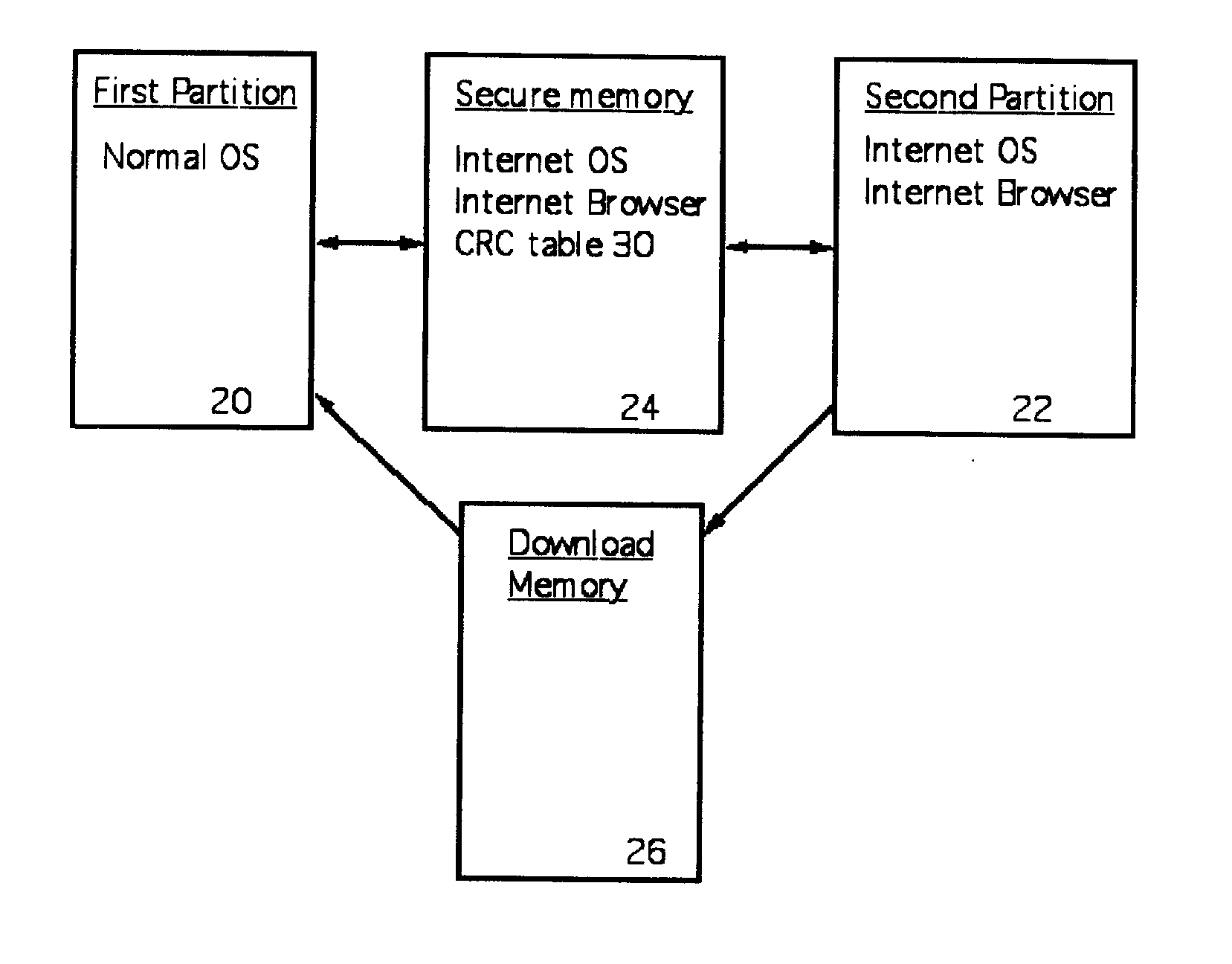
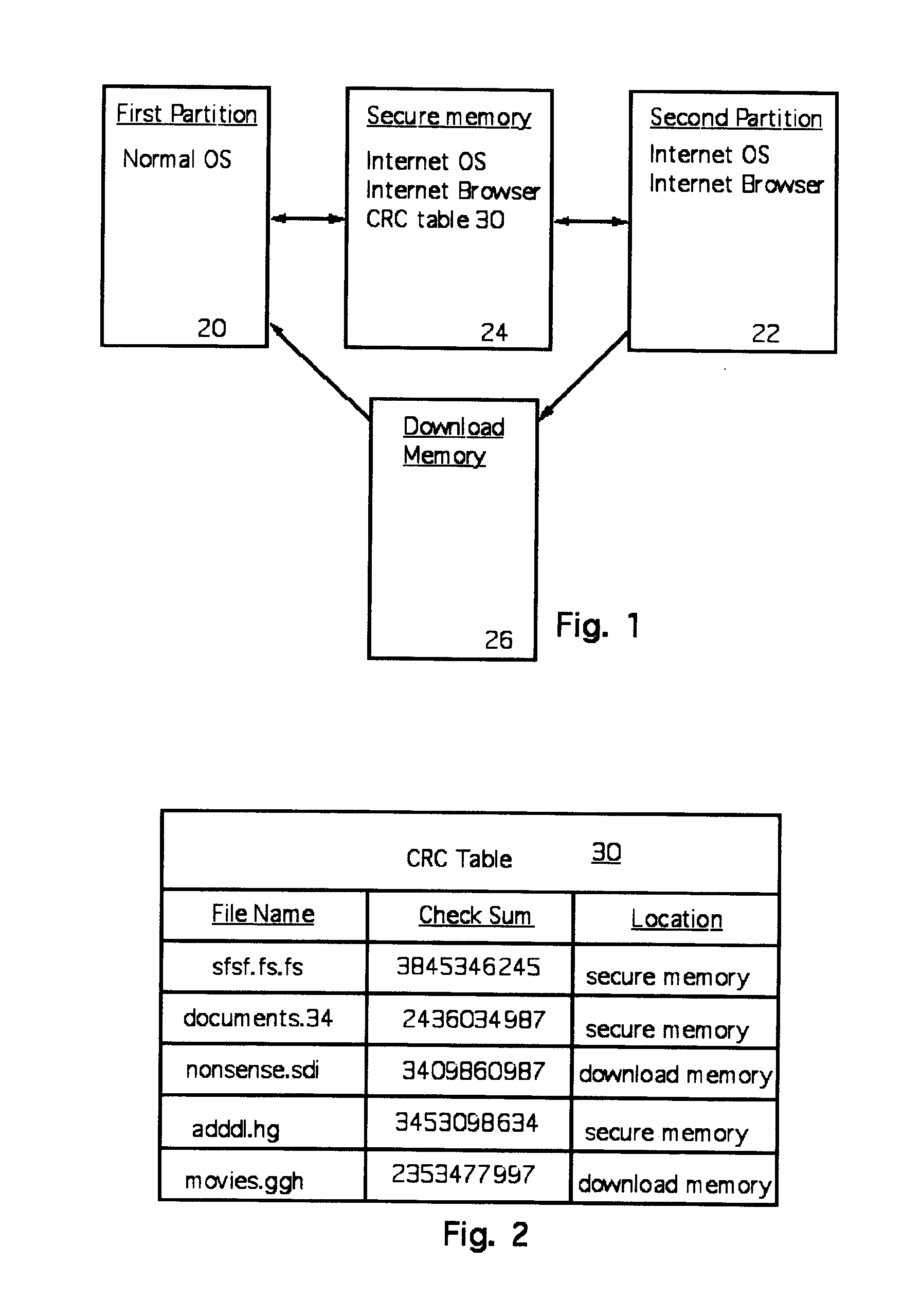
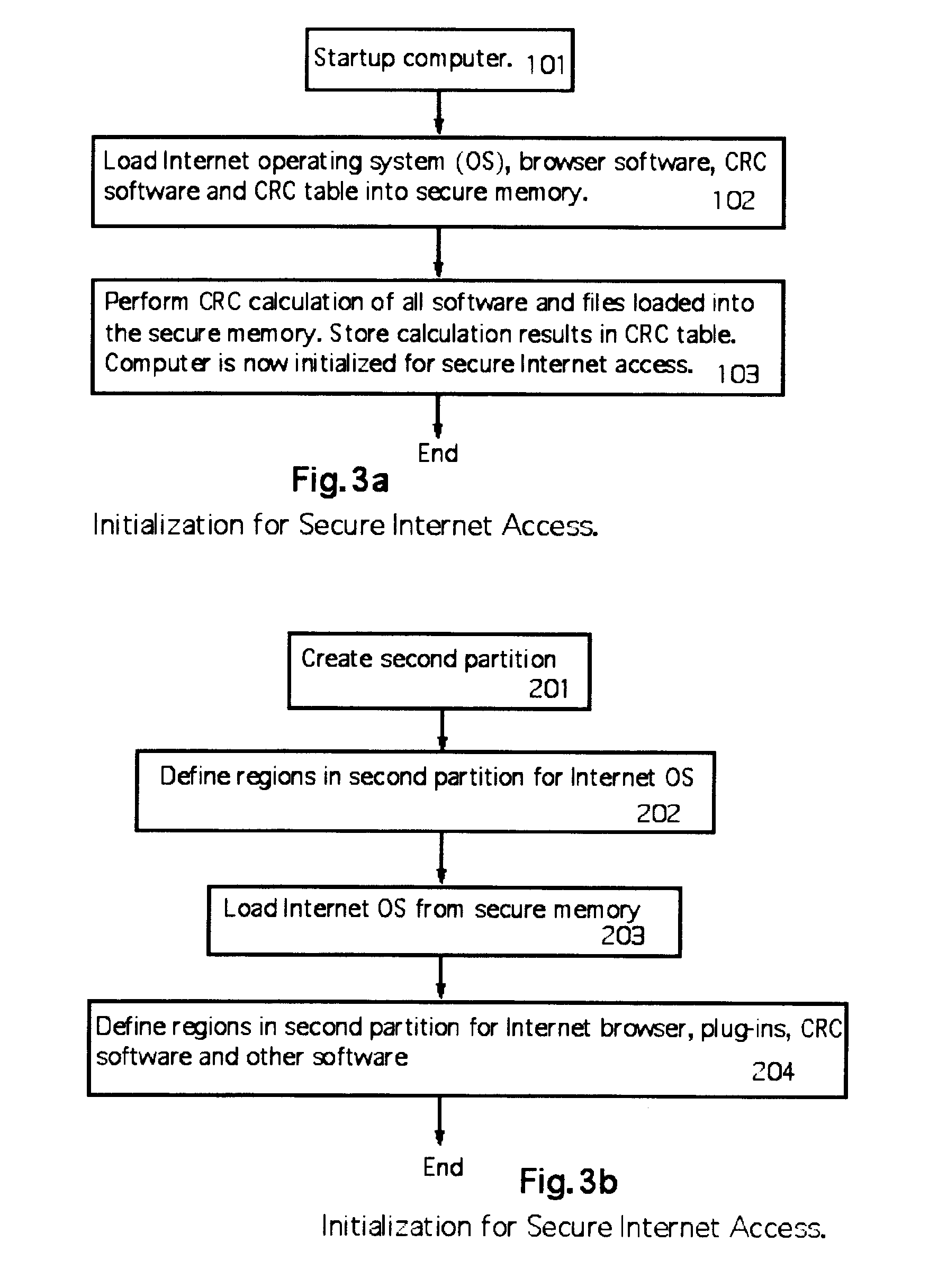
A computer random access memory is divided into first and second partitions. Each partition has its own operating system (OS). The first partition has a conventional OS and is designated for non-Internet use. The second partition is designated for secure Internet access, and has an OS specific for Internet usage. Software in the second partition cannot write or copy files in the second partition. The size of the second partition is fixed and unchangeable while said second partition is open. Each software application in the second partition is allocated a memory region that cannot be changed, thereby preventing memory overflow attacks. A secure memory is designated for temporary storage of software used in the second partition. Cyclic redundancy check (CRC) values are calculated for all files in the secure memory. To detect unauthorized file changes, CRC values are calculated for all files used in the second partition, and checked against values stored in the secure memory. The second partition can write only to a secure memory using a security arrangement such as password protection or a download memory separate from the first partition to allow files stored in the download memory to be examined by scanning and testing from the first partition prior to being stored elsewhere in the computer.
Owner:KYNDRYL INC
Cyclic redundancy check for partitioned frames
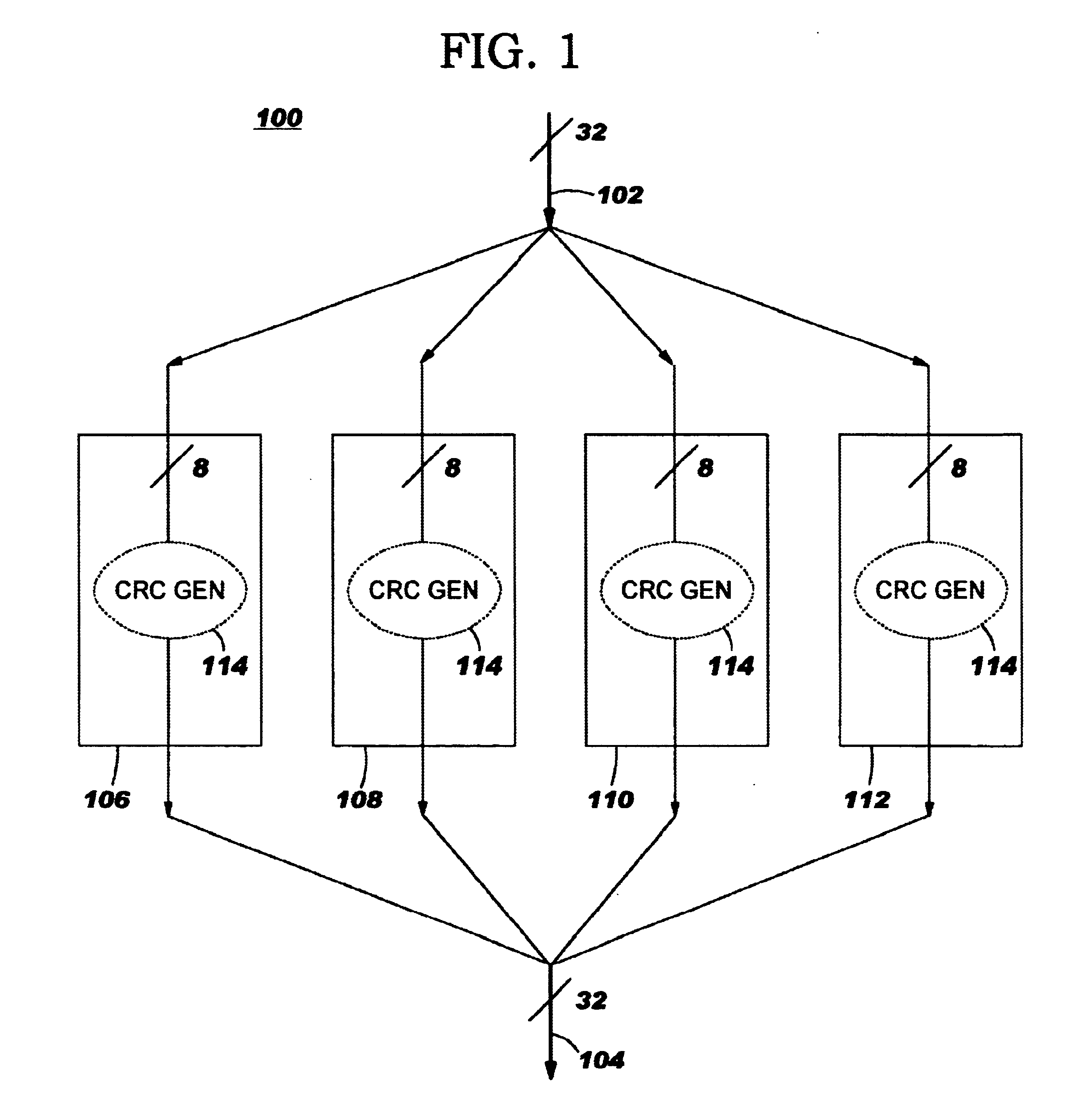
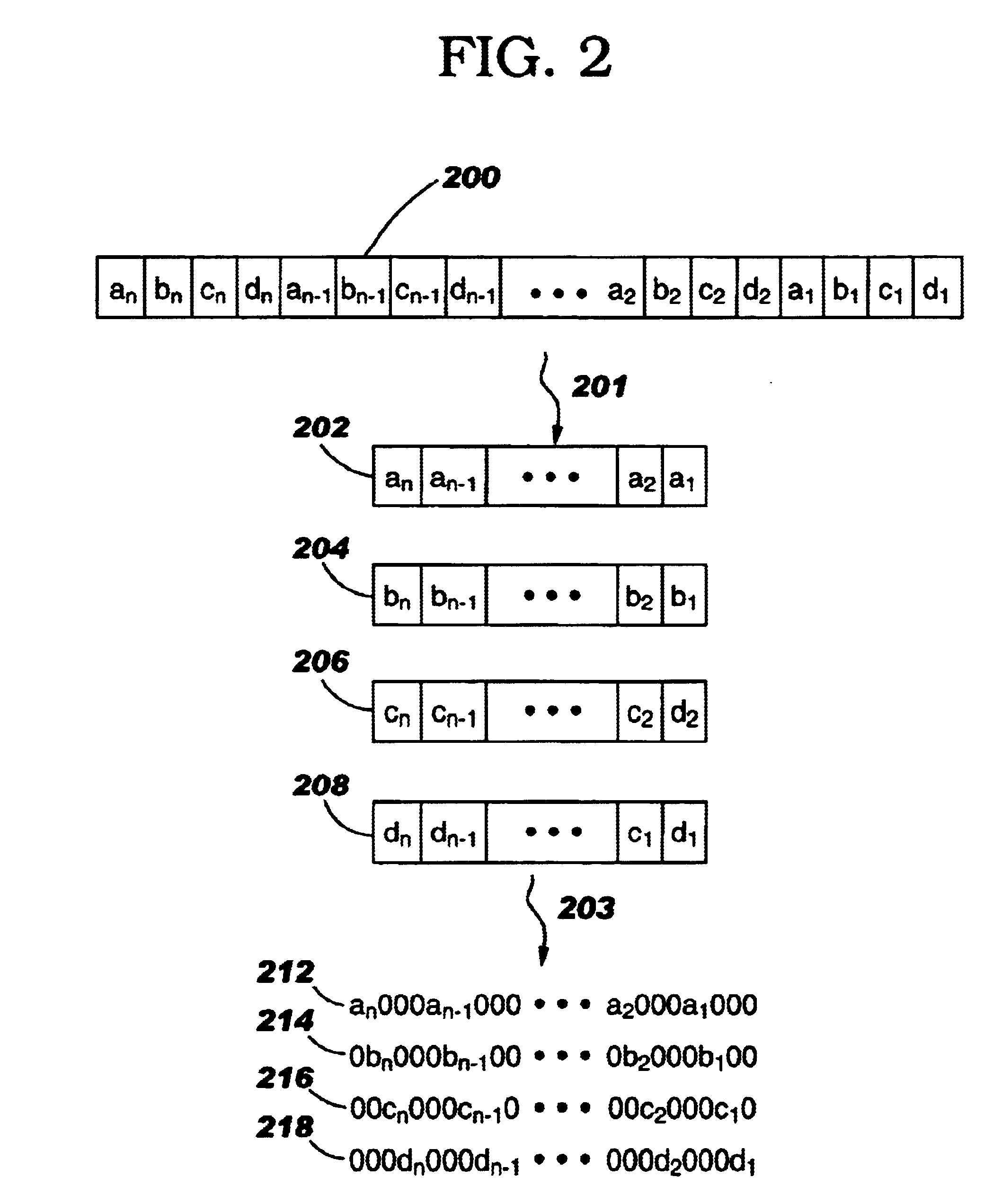
InactiveUS6681364B1Increase flexibilityCode conversionError detection onlyTheoretical computer scienceImproved method
An improved method and system for generating a frame check sequence. A multiple-bit data string, M, is received in which M is of the form:M is thereafter parsed into multiple subframes of the form:andThe subframes are padded with zeros resulting in subframes of the form:andA partial check sum is then generated for each of the multiple subframes. Finally, each of the partial check sums are added together such that a frame check sequence for M is obtained.
Owner:IBM CORP
Wireless communications system that supports multiple modes of operation
InactiveUS6937592B1Network traffic/resource managementAssess restrictionOperation modeMultiple modes
A wireless communications adapts its mode of operation between spatial multiplexing and non-spatial multiplexing in response to transmission-specific variables. An embodiment of a wireless communications system for transmitting information between a base transceiver station and a subscriber unit includes mode determination logic. The mode determination logic is in communication with the base transceiver station and the subscriber unit. The mode determination logic determines, in response to a received signal, if a subscriber datastream should be transmitted between the base transceiver station and the subscriber unit utilizing spatial multiplexing or non-spatial multiplexing. In an embodiment, the mode determination logic has an input for receiving a measure of a transmission characteristic related to the received signal. In an embodiment, the mode determination logic includes logic for comparing the measured transmission characteristic to a transmission characteristic threshold and for selecting one of spatial multiplexing and non-spatial multiplexing in response to the comparison of the measured transmission characteristic to the transmission characteristic threshold. In an embodiment, the transmission characteristic includes at least one of delay spread, post-processing signal-to-noise ratio, cyclical redundancy check (CRC) failure, residual inter-symbol interference, mean square error, coherence time, and path loss. By adapting the mode of operation in response to transmission-specific variables, the use of spatial multiplexing can be discontinued in unfavorable conditions. Additionally, because the wireless communications system can adapt its mode of operation between spatial multiplexing and non-spatial multiplexing, the communications system is compatible with both subscriber units that support spatial multiplexing and subscriber units that do not support spatial multiplexing.
Owner:APPLE INC
Dynamic-content web crawling through traffic monitoring
InactiveUS20040128285A1Avoid custom time-consume integrationEasy to solveData processing applicationsWeb data indexingTraffic capacityUniform resource locator
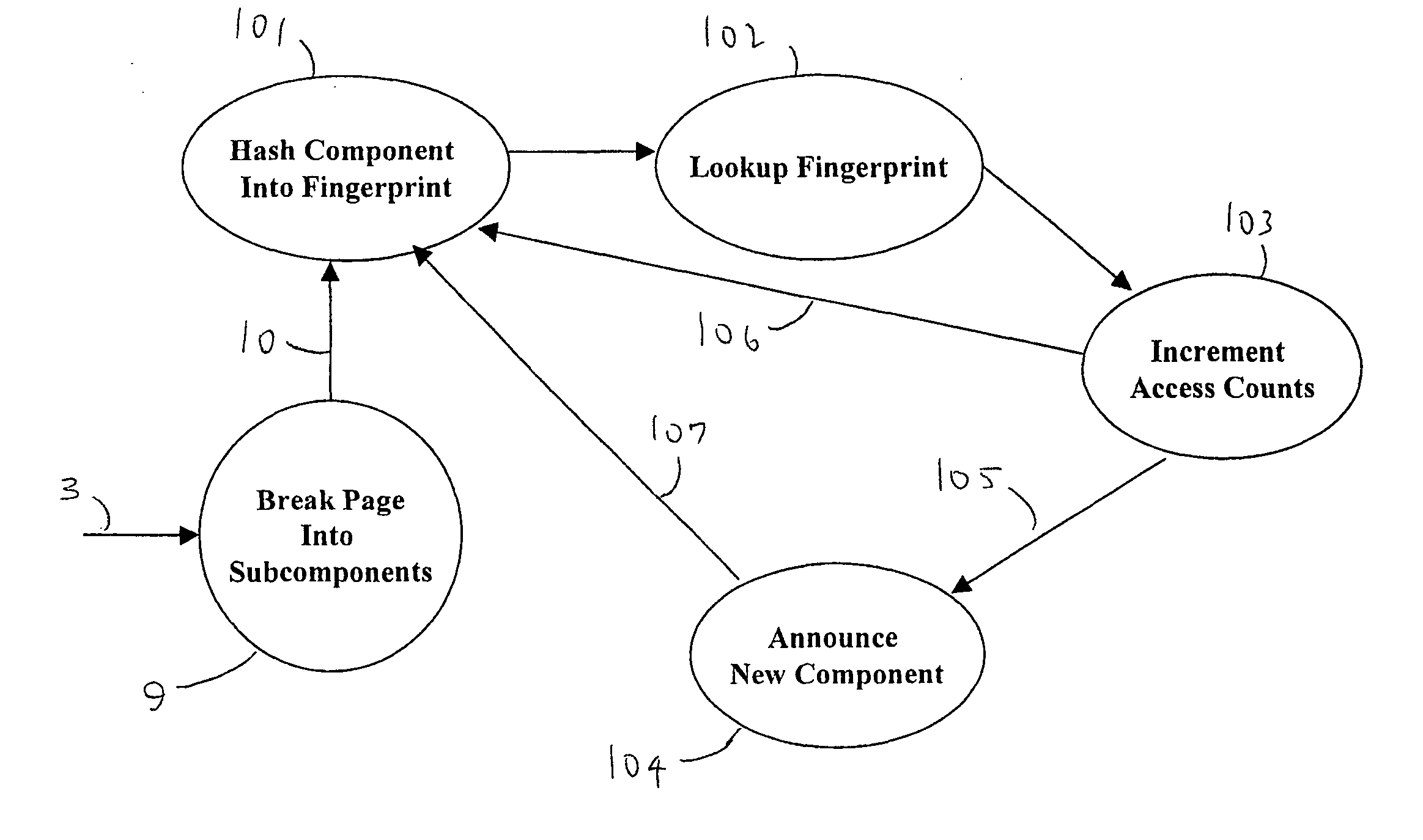
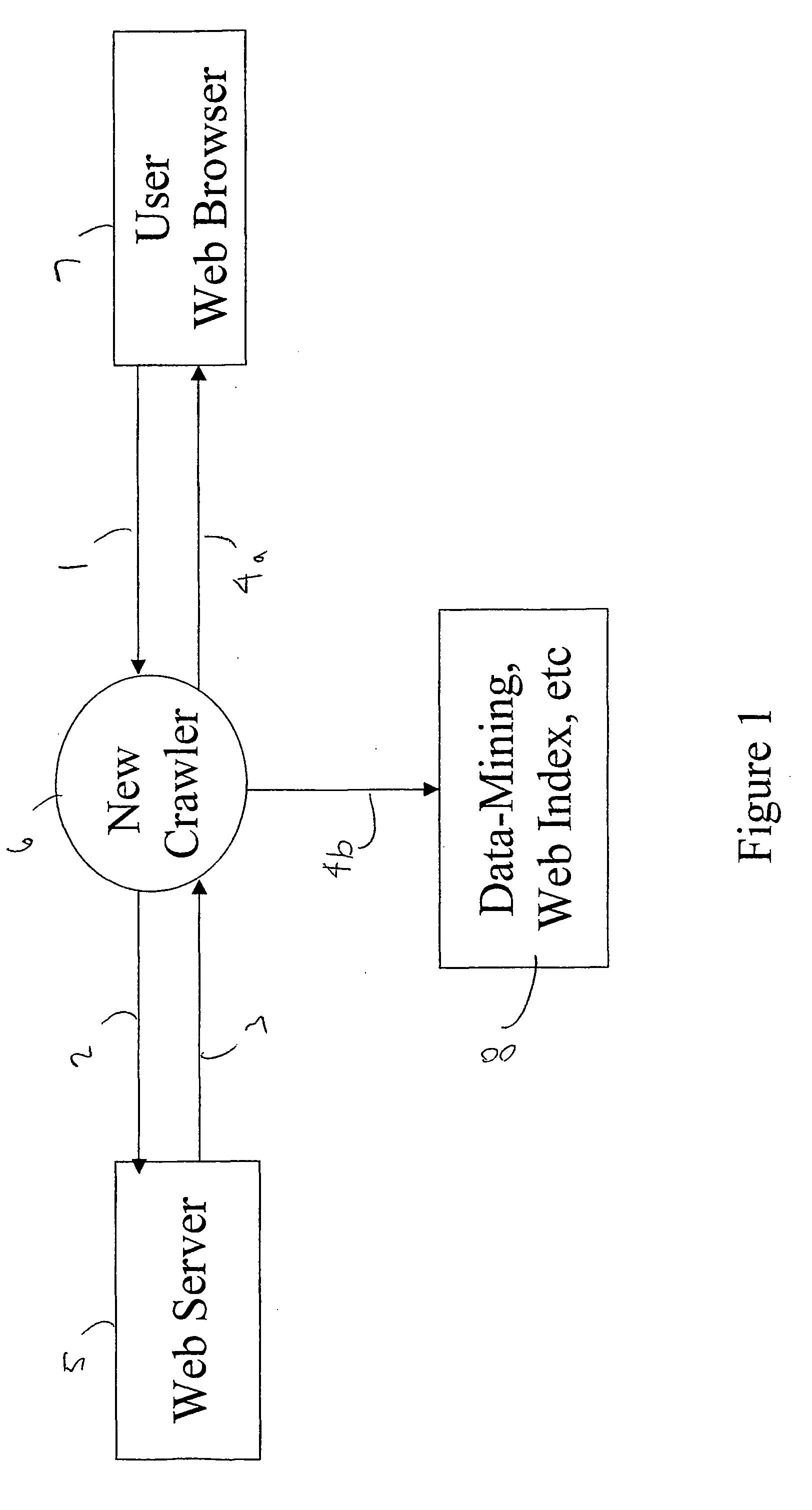
A dynamic-content web crawler is disclosed. These New Crawlers (NCs) are located at points between the server and user, and monitor content from said points, for example by proxying the web traffic or sniffing the traffic as it goes by. Web page content is recursively parsed into subcomponents. Sub-components are fingerpinted with a cyclic redundancy check code or other loss-full compression in order to be able to detect recurrence of the sub-component in subsequent pages. Those sub-components which persist in the web traffic, as measured by the frequency NCs (6) are defined as having substantive content of interest to data-mining applications. Where a substantive content sub-component is added to or removed from a web page, then this change is significant and is sent to a duplication filter (11) so that if multiple NCs (6) detect a change in a web page only one announcement of the changed URL will be broadcast to data-mining applications (8). The NC (6) identifies substantive content sub-components which repeatably are part of a page pointed to by a URL. Provision is also made for limiting monitoring to pages having a flag authorizing discovery of the page by a monitor.
Owner:RESOURCE CONSORTIUM LTD LLC
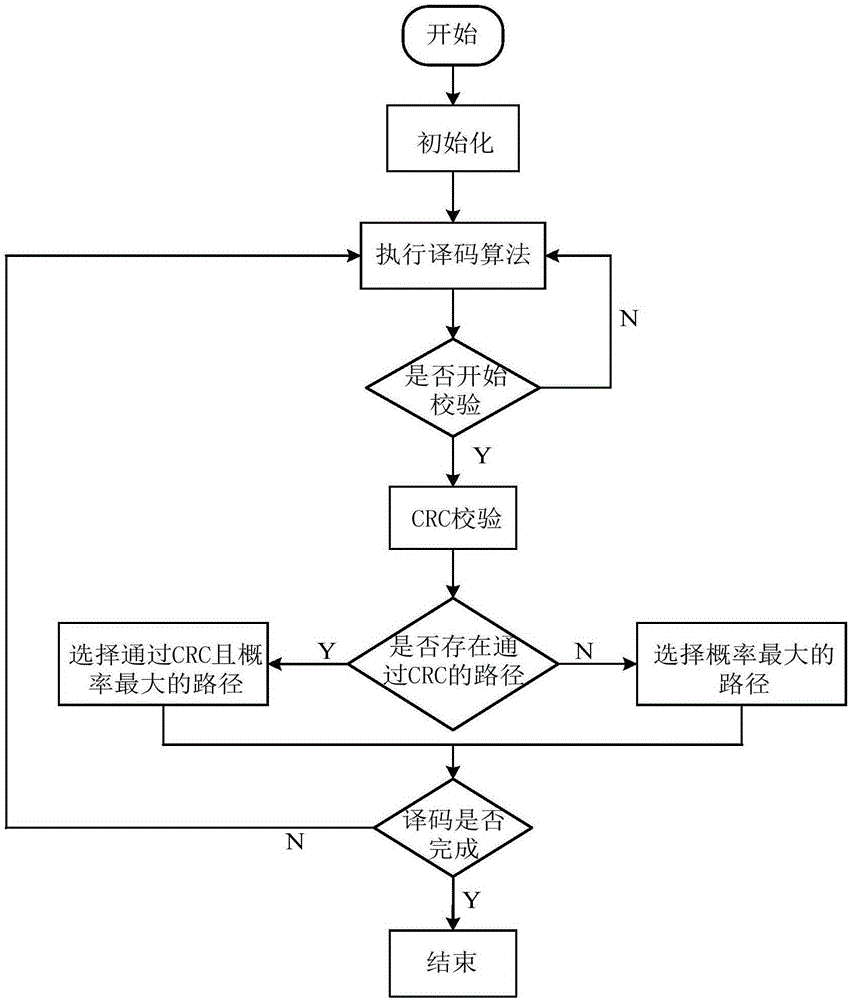
Decoding method and decoding device for polar codes concatenated with cyclic redundancy checks (CRC)
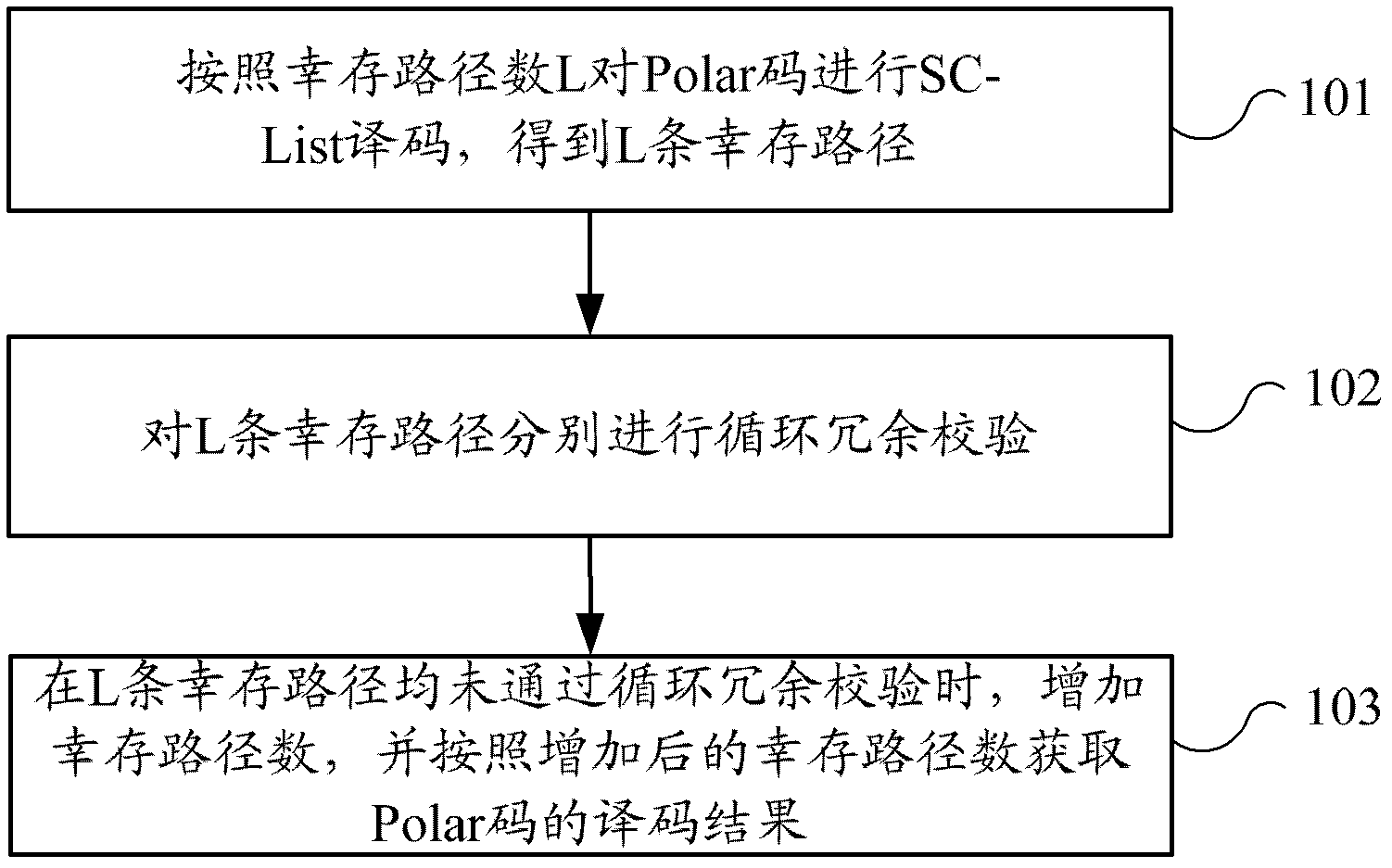
ActiveCN103220001AImprove decoding performanceError preventionCode conversionDecoding methodsPath number
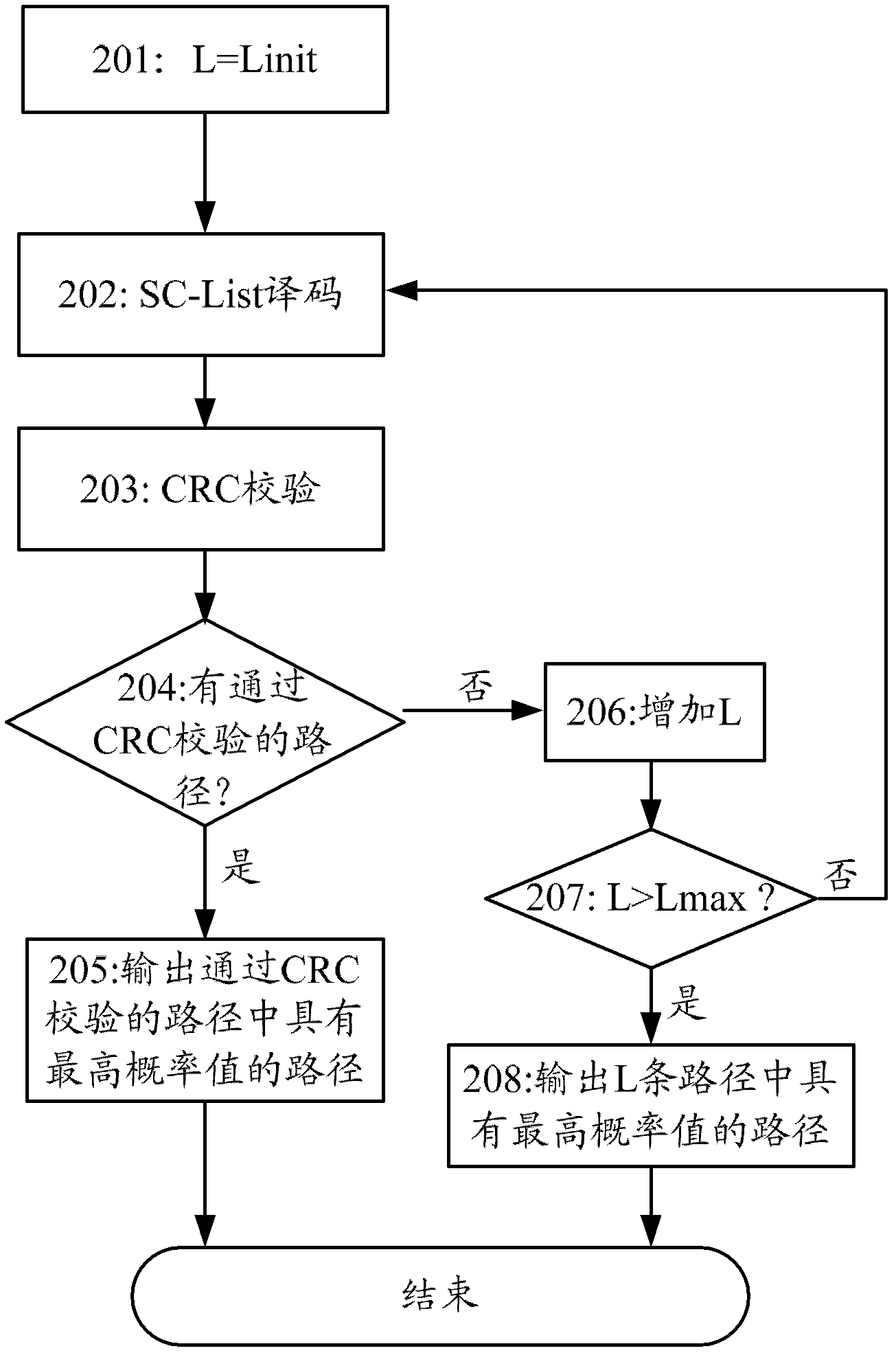
The invention provides a decoding method and a decoding device for polar codes concatenated with a cyclic redundancy check (CRC). The decoding method includes the following steps: SC-list decoding is carried out on the polar codes according to the number, which is L, of survival paths to obtain the L survival paths, wherein the L is a positive integer; each of the L survival paths is subjected to the CRC; and when none of the L survival paths passes the CRC, the number of the survival paths is increased, and decoding results of the polar codes are obtained according to the number, which is increased, of the survival paths. According to the decoding method and the decoding device for the polar codes concatenated with the CRC, the path number of the survival paths is adjusted according to the result of the CRC, and therefore the paths which can pass the CRC can be output as far as possible, and the decoding performance is improved.
Owner:HUAWEI TECH CO LTD
Data transmission method, device and communication system
InactiveCN101615986AReduce retransmissionsReduce Feedback OverheadError prevention/detection by using return channelCoding blockCommunications system
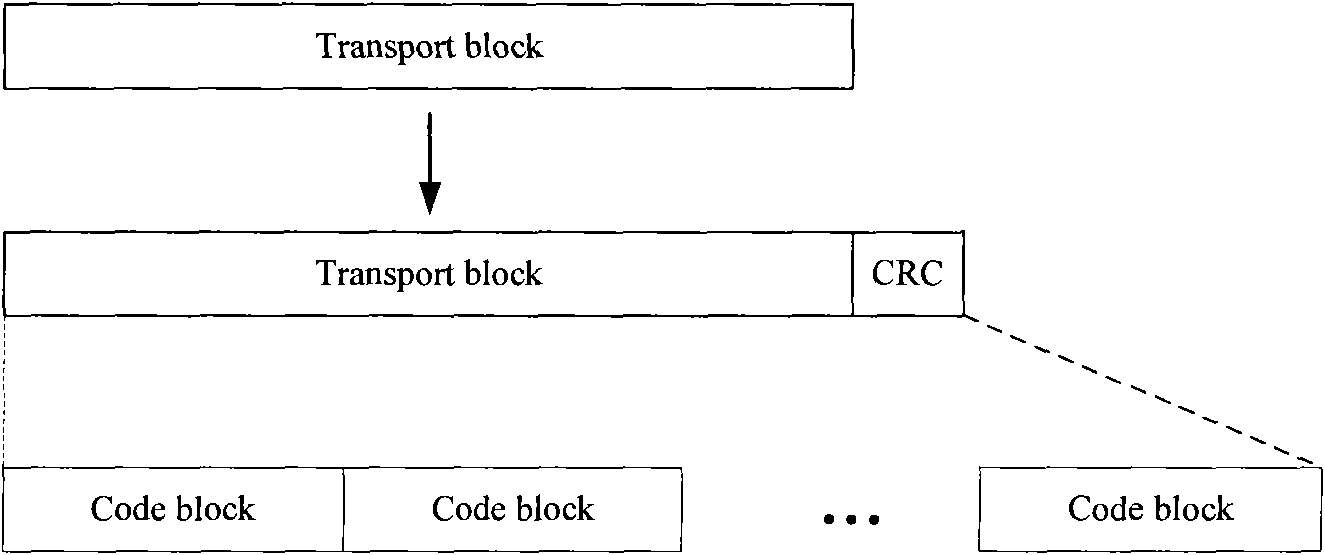
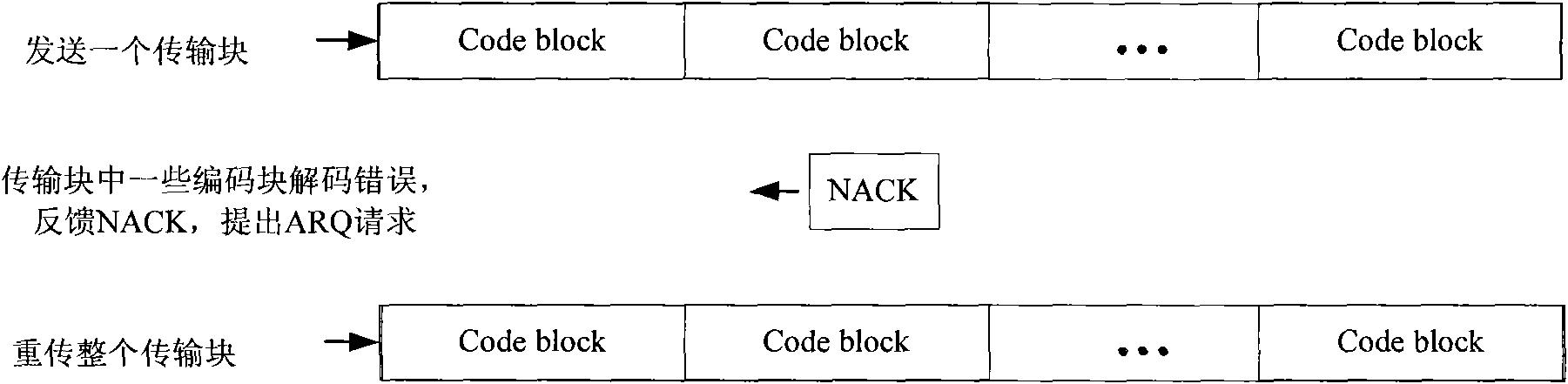
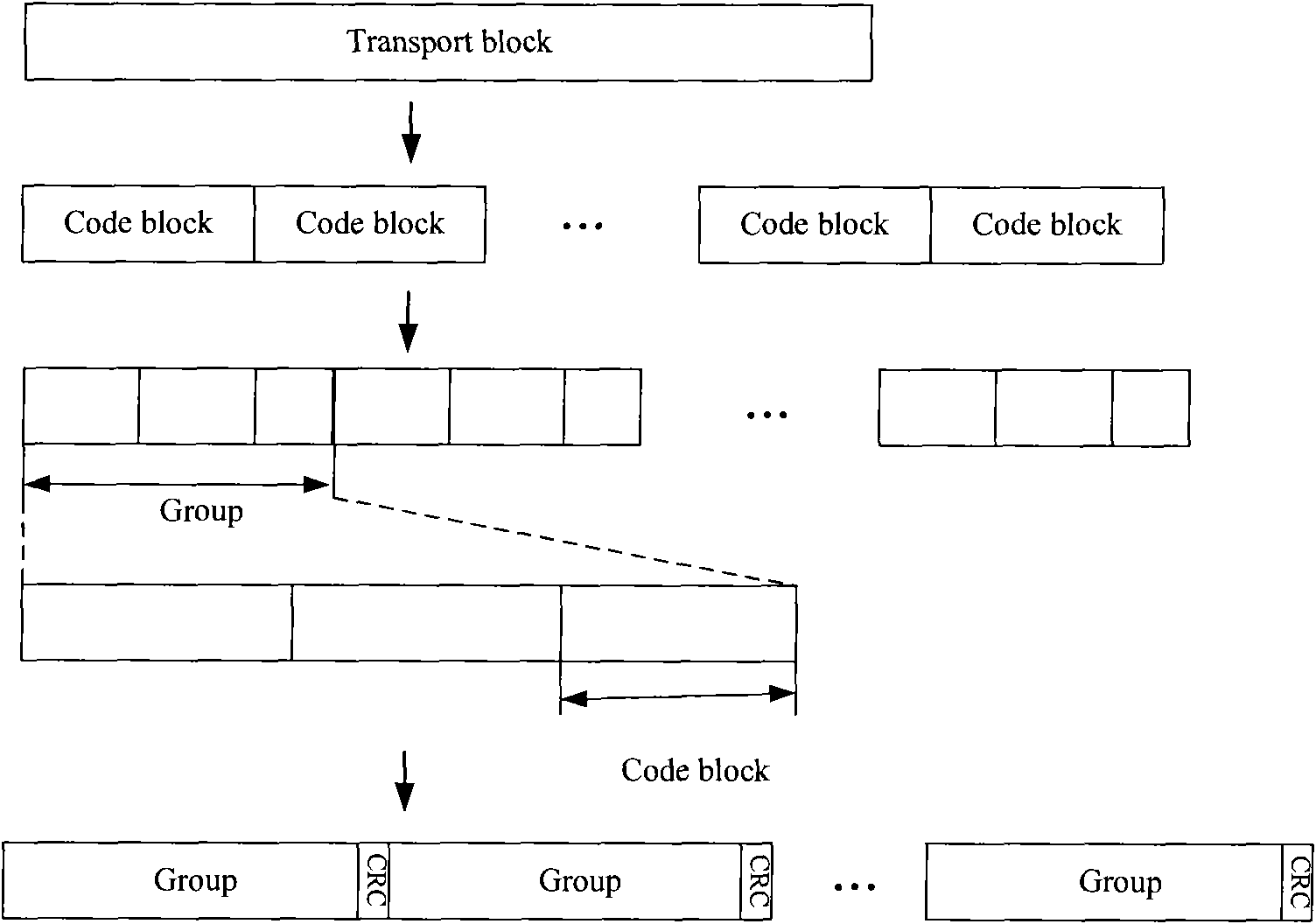
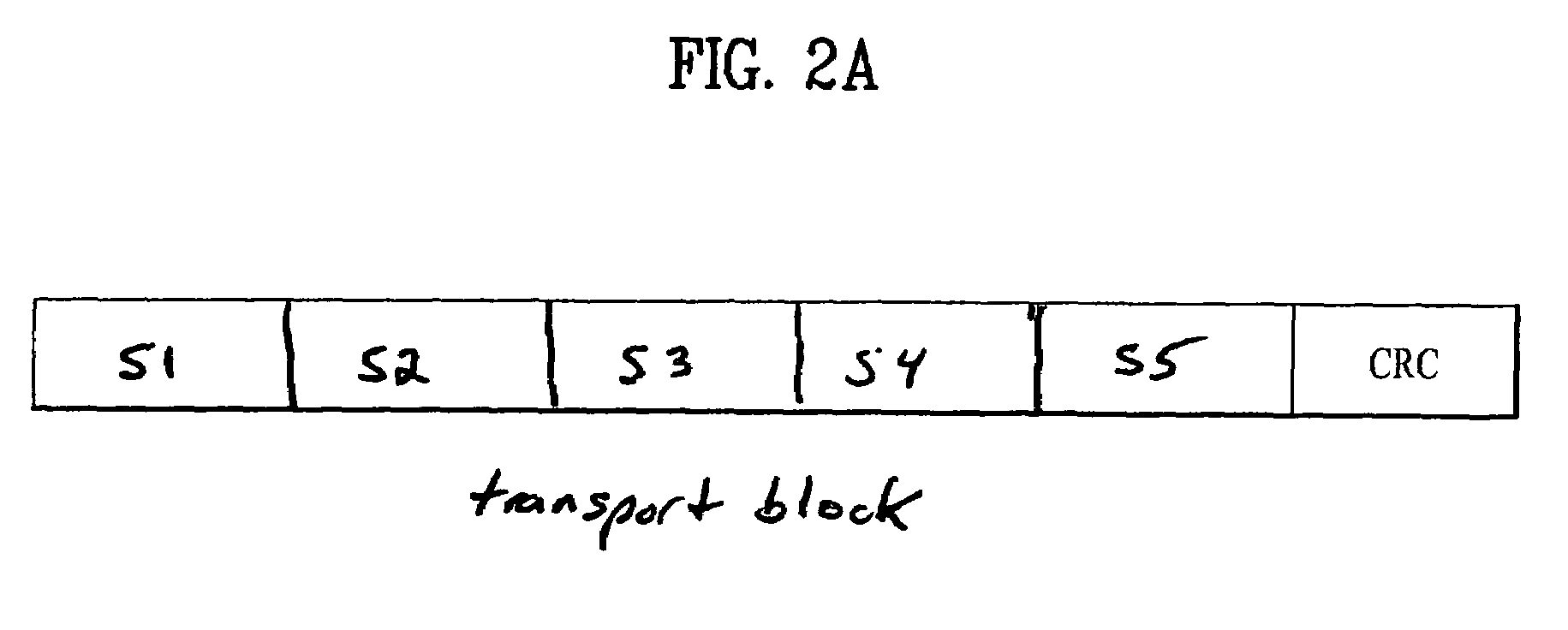
The embodiment of the invention discloses a data transmission method, which comprises the following steps: dividing a transmission block into at least one group, wherein each group comprises at least one coding block; adding cyclic redundancy check CRC bits to each group; and sending the group after addition of the CRC bits. Meanwhile, the embodiment of the invention discloses a data transmission device and a communication system based on grouping concept; and groups corresponding to check errors are retransmitted, so that data retransmission is greatly reduced and simultaneously large throughput gain is acquired.
Owner:HUAWEI TECH CO LTD
Error detection on programmable logic resources
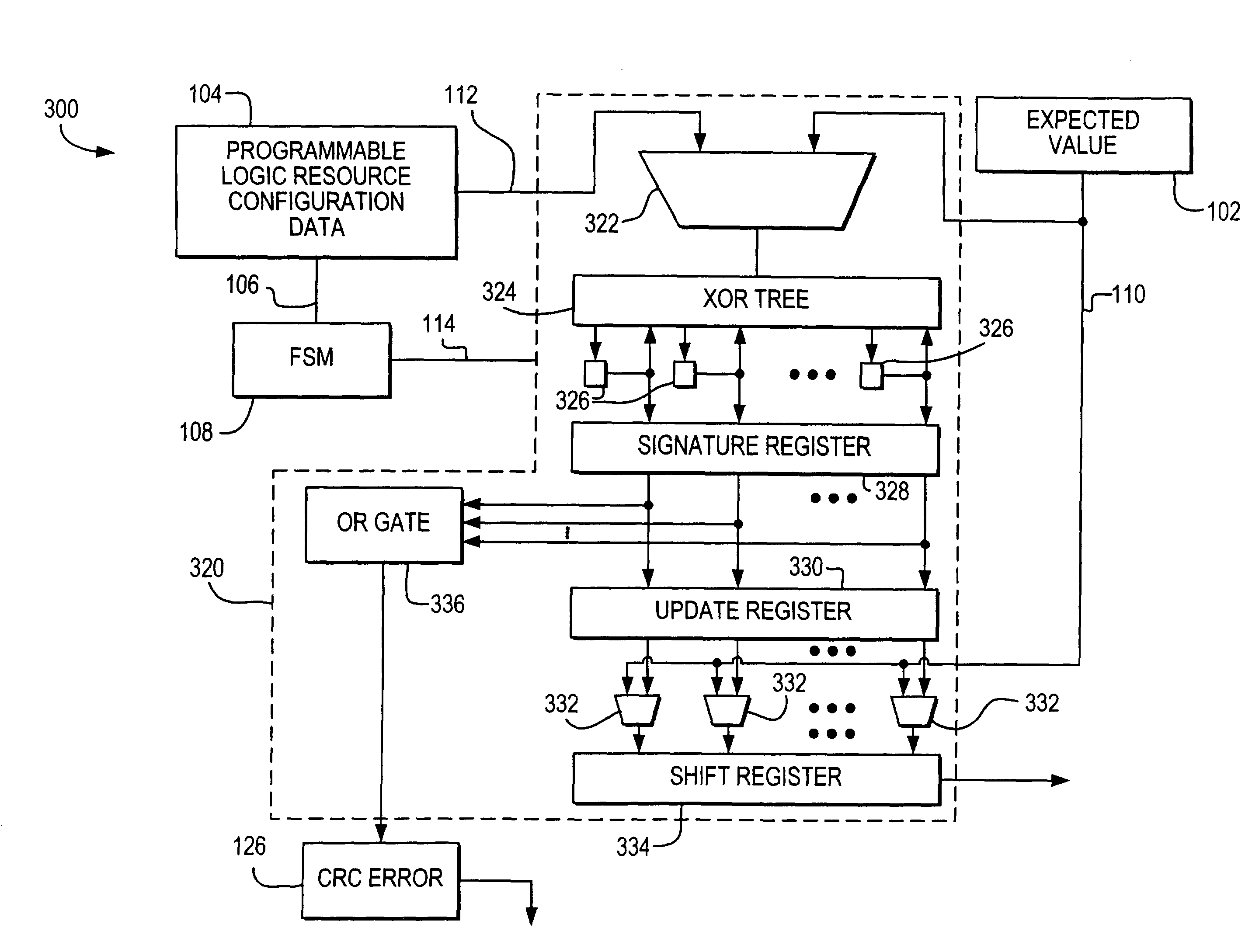
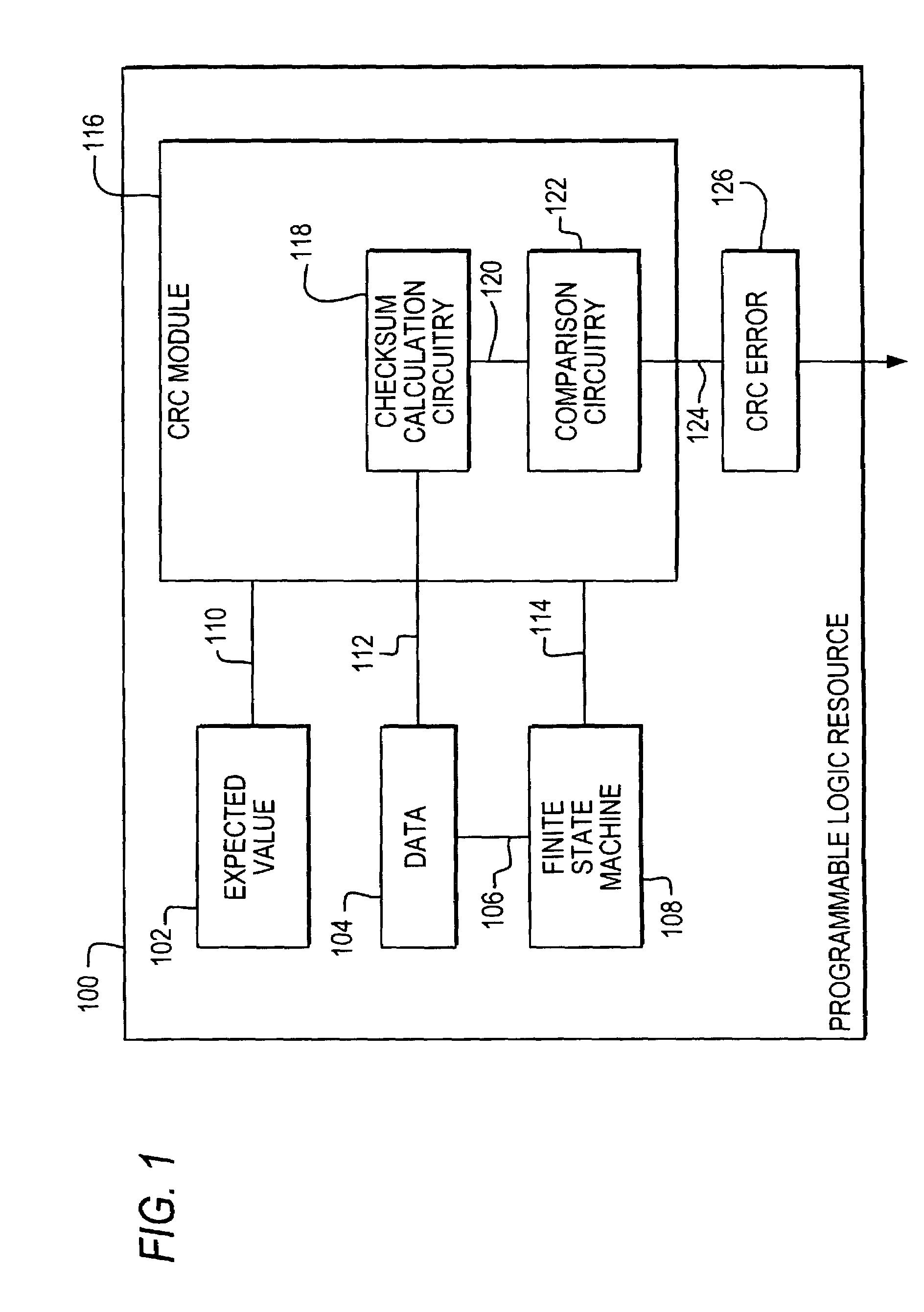
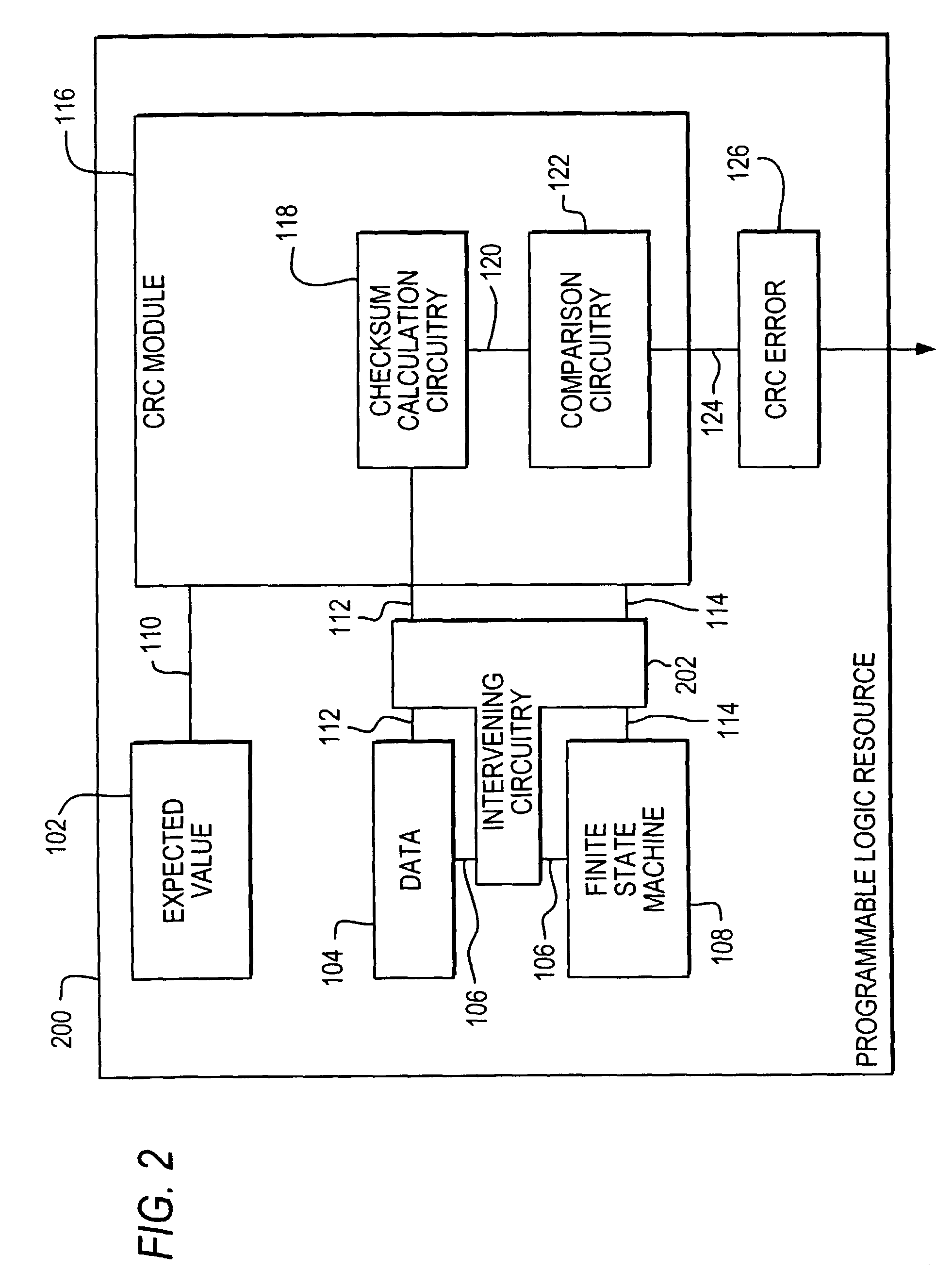
InactiveUS7310757B2Electronic circuit testingDetecting faulty computer hardwareProgrammable logic deviceChecksum
Error detection circuitry is provided on a programmable logic resource. Programmable logic resource configuration data is loaded into a cyclic redundancy check (CRC) module where a checksum calculation may be performed. In one embodiment, the checksum may be compared to an expected value, which is a precomputed checksum on data prior to being programmed into or while data is being programmed into a programmable logic resource. In another embodiment, the expected value may be included in the checksum calculation. An output indicating whether an error is detected may be generated depending on the relationship between the checksum and the expected value, or on the value of the checksum. This output may be sent to an output pin that is accessible by user logic.
Owner:ALTERA CORP
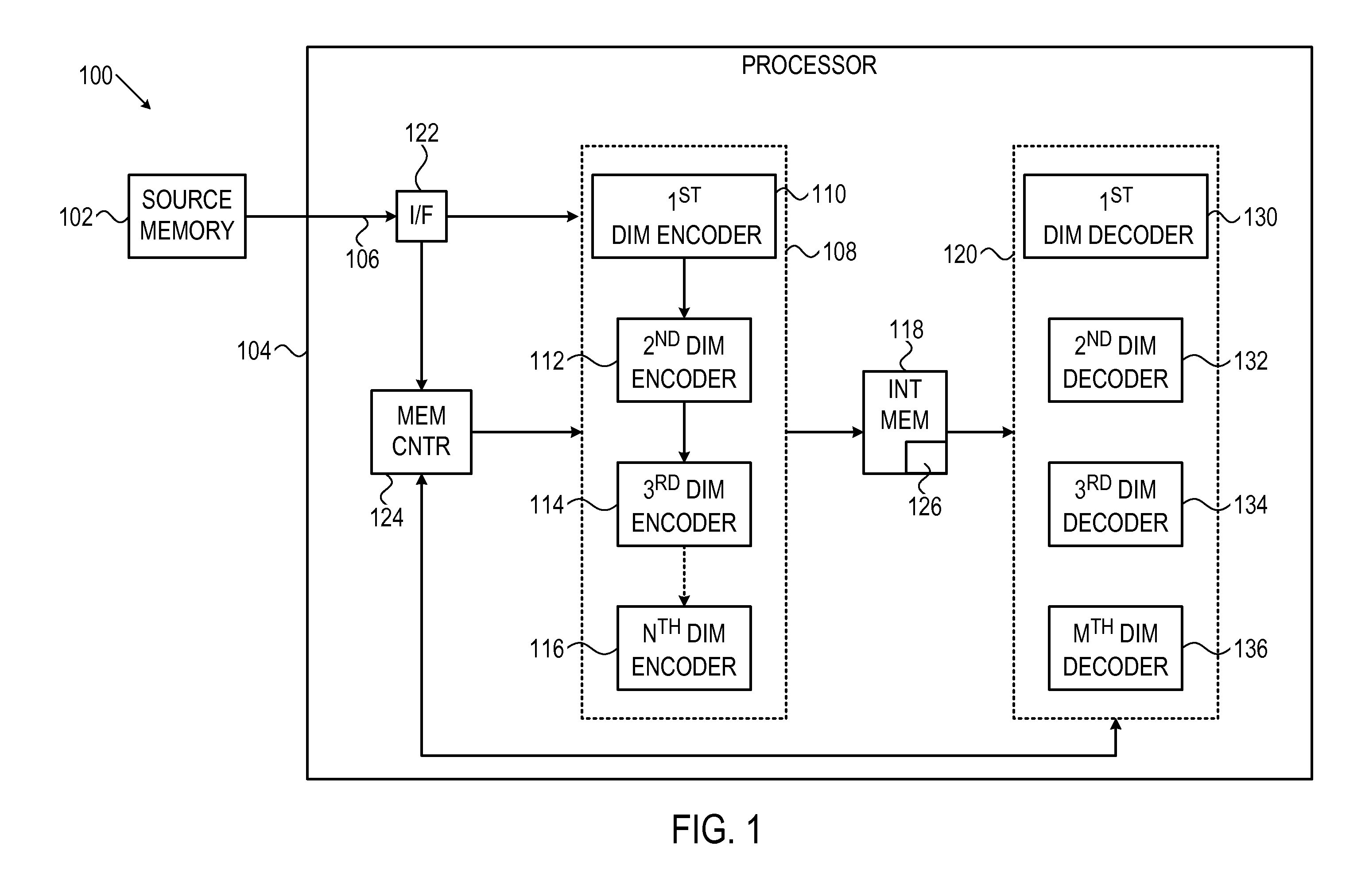
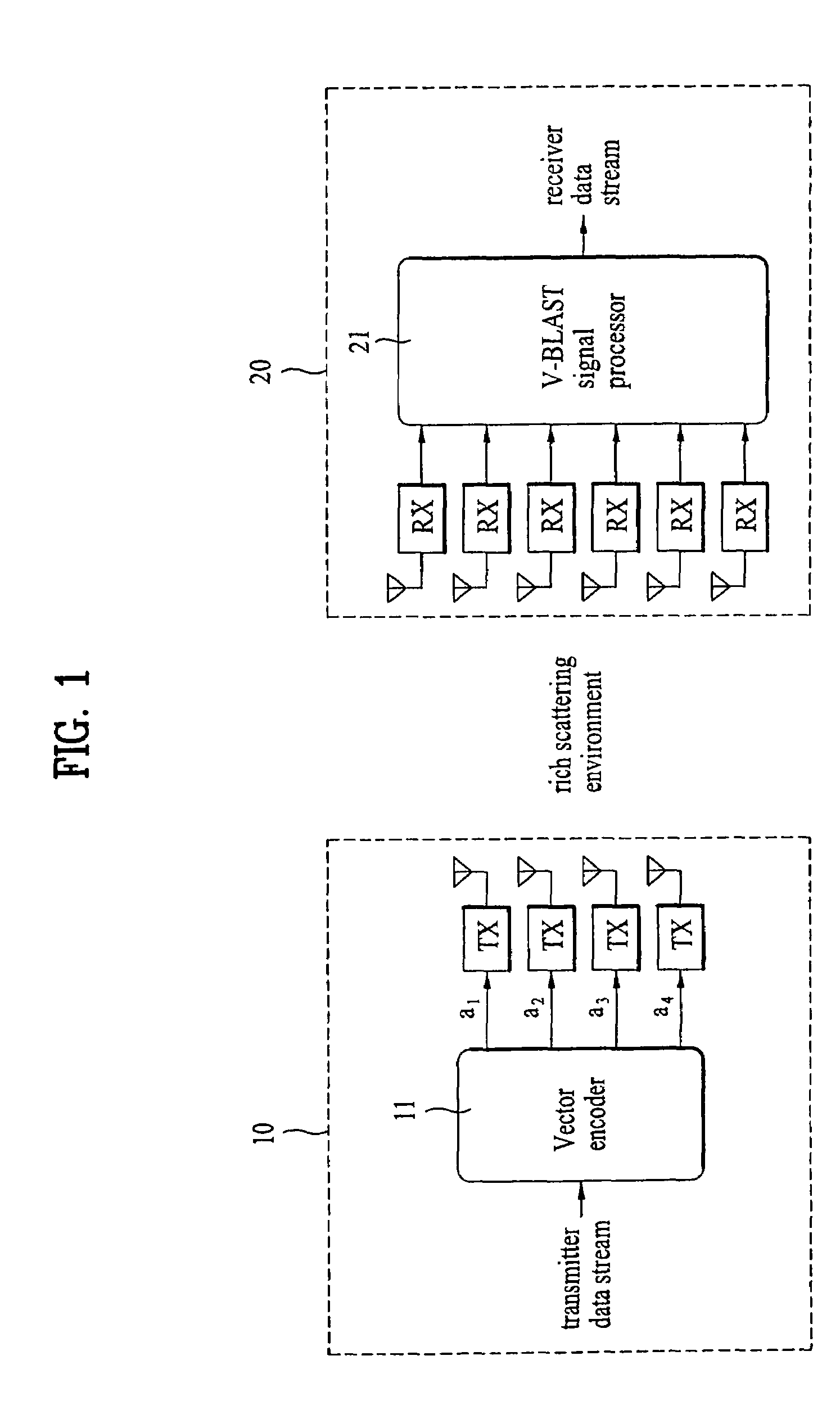
System and method for multi-dimensional encoding and decoding
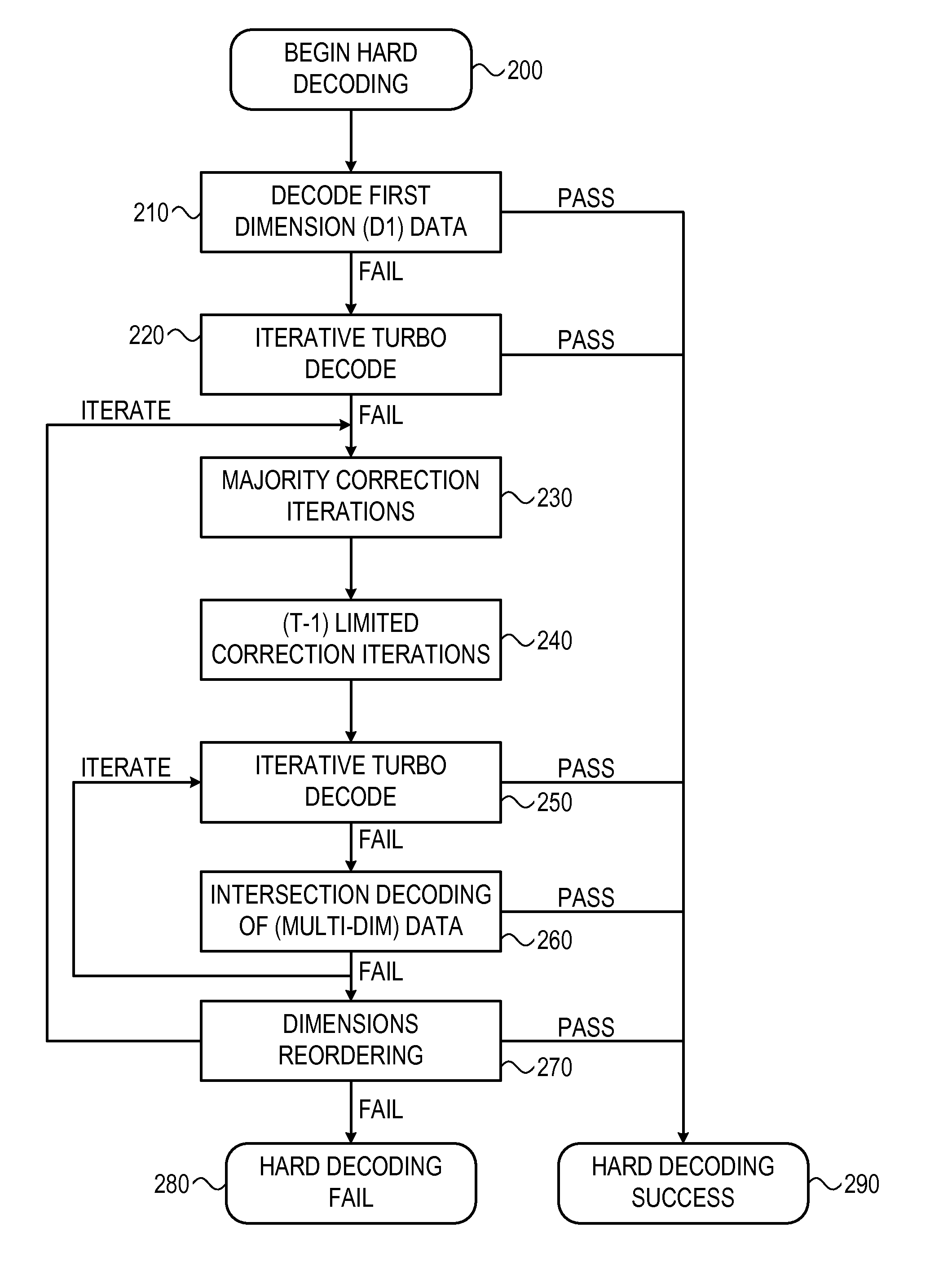
ActiveUS20120005554A1Correction errorError correction/detection using convolutional codesOther decoding techniquesData setMulti dimensional
A system and method for using a cyclic redundancy check (CRC) to evaluate error corrections. A set of data and initial CRC values associated therewith may be received. The set of data by changing a sub-set of the data may be corrected. Intermediate CRC values may be computed for the entire uncorrected set of data in parallel with said correcting. Supplemental CRC values may be computed for only the sub-set of changed data after said correcting. The intermediate and supplemental CRC values may be combined to generate CRC values for the entire corrected set of data. The validity of the corrected set of data may be evaluated by comparing the combined CRC values with the initial CRC values.
Owner:AVAGO TECH INT SALES PTE LTD
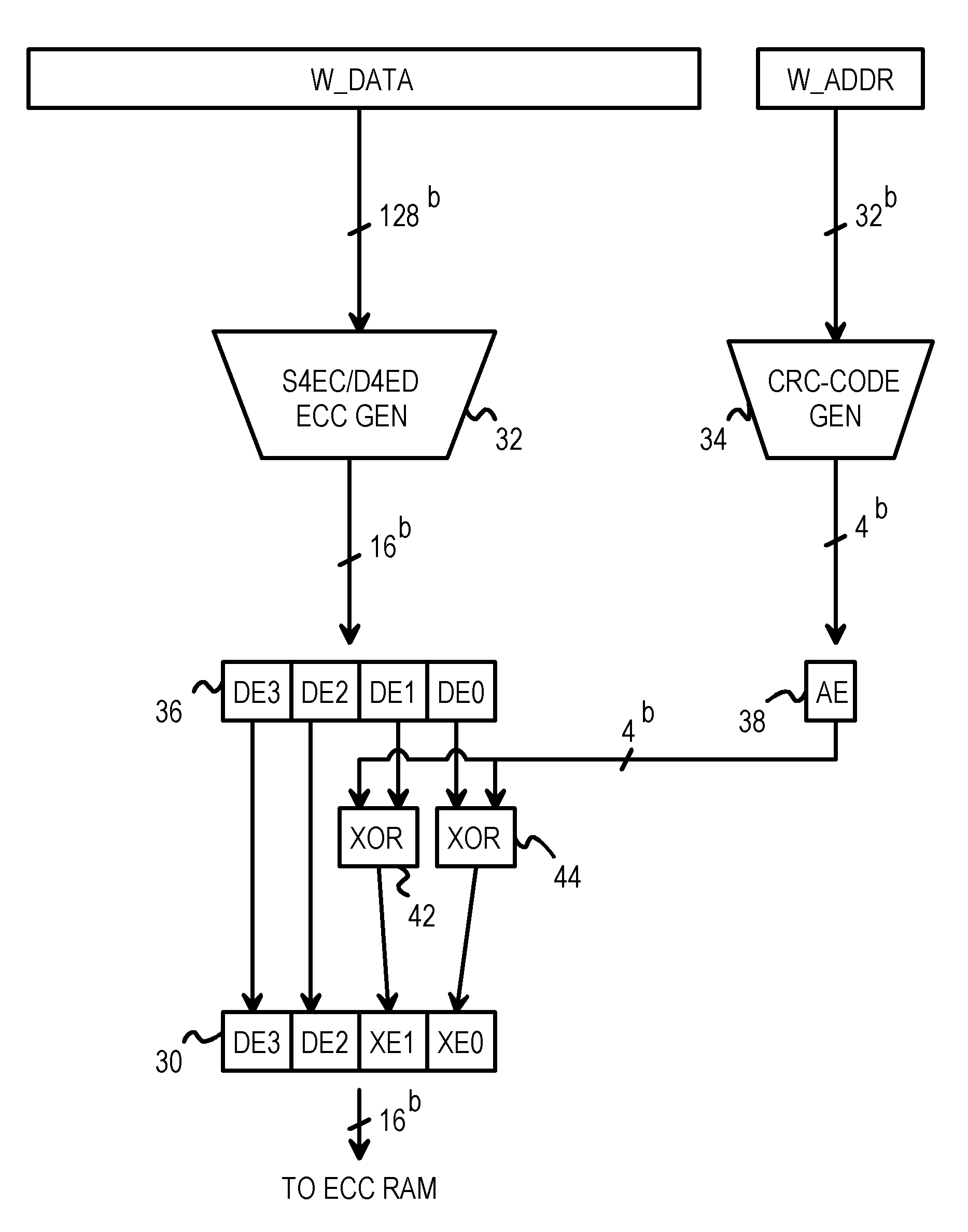
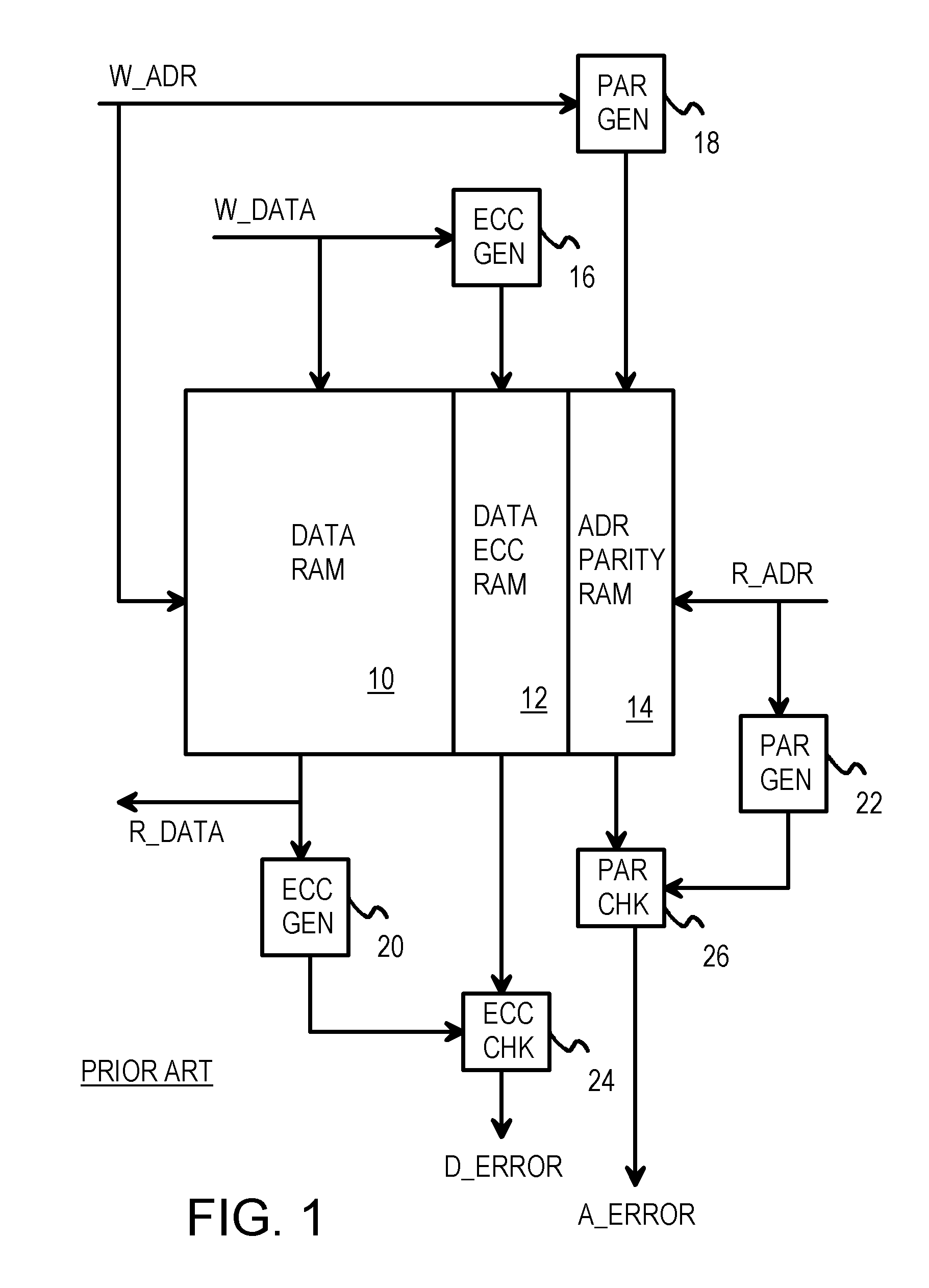
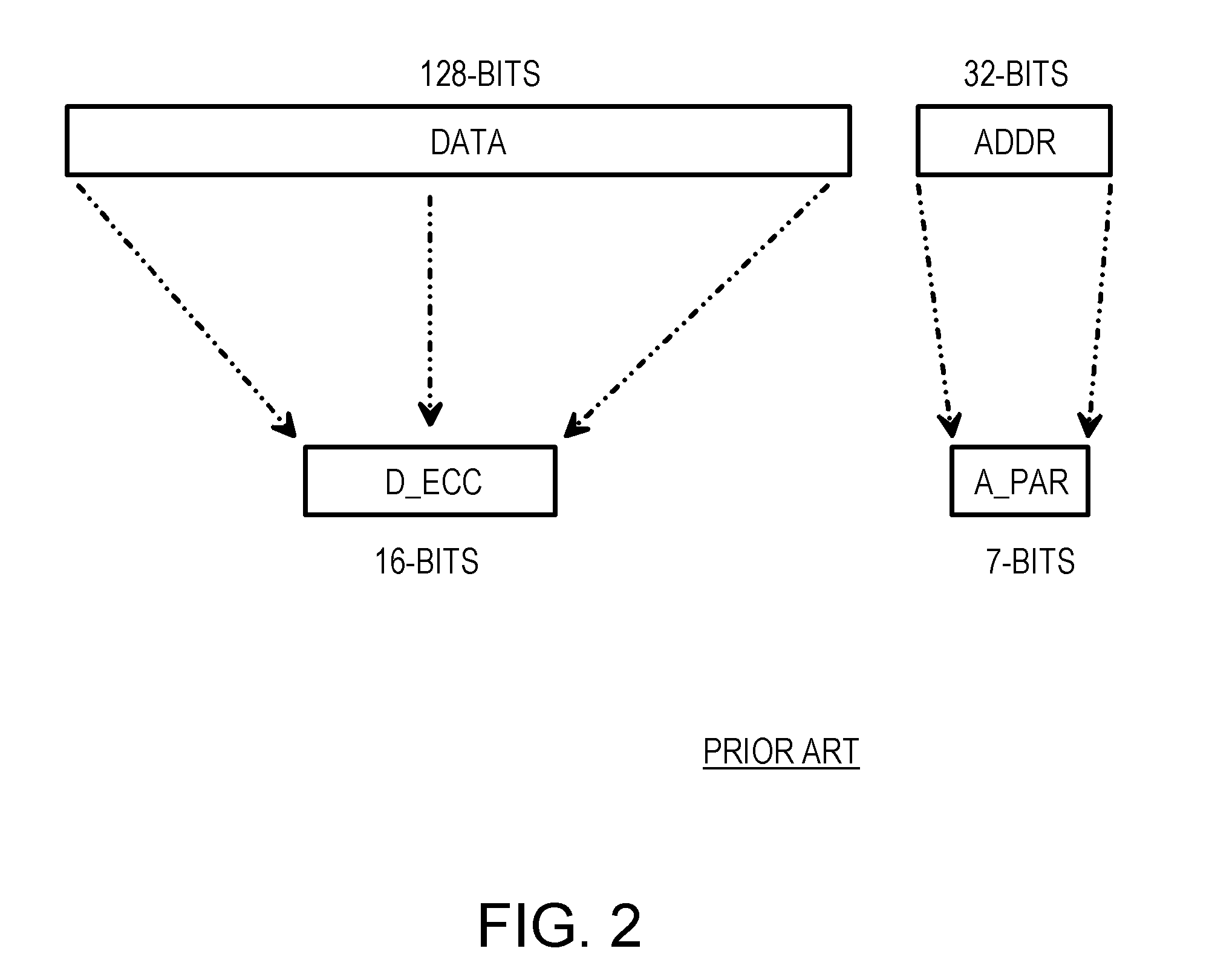
Address error detection by merging a polynomial-based CRC code of address bits with two nibbles of data or data ECC bits
A memory system provides data error detection and correction and address error detection. A Single-byte Error-Correcting / Double-byte Error-Detecting (SbEC / DbED) code with the byte being a 4-bit nibble is used to detect up to 8-bit errors and correct data errors of 4 bits or less. Rather than generating address parity, which is poor at detecting even numbers of errors, a cyclical-redundancy-check (CRC) code generates address check bits. A 32-bit address is compressed to just 4 address check bits using the CRC code. The 4 address check bits are merged (XOR'ed) with two 4-bit nibbles of the data SbEC / DbED code to generate a merged ECC codeword that is stored in memory. An address error causes a 2-nibble mis-match due to the redundant merging of the 4 address check bits with 2 nibbles of data correction code. The CRC code is ideal for detecting even numbers of errors common with multiplexed-address DRAMs.
Owner:AZUL SYSTEMS
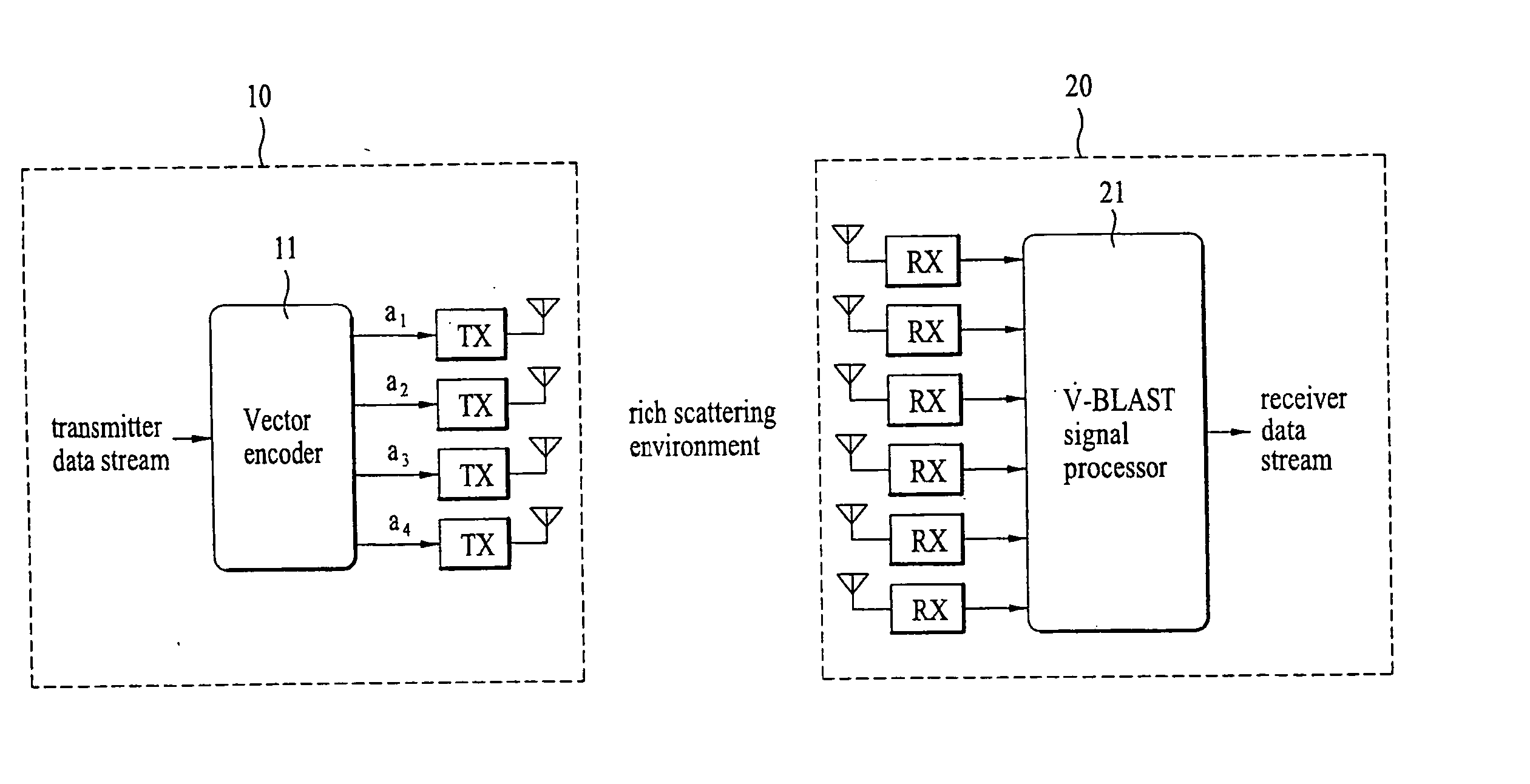
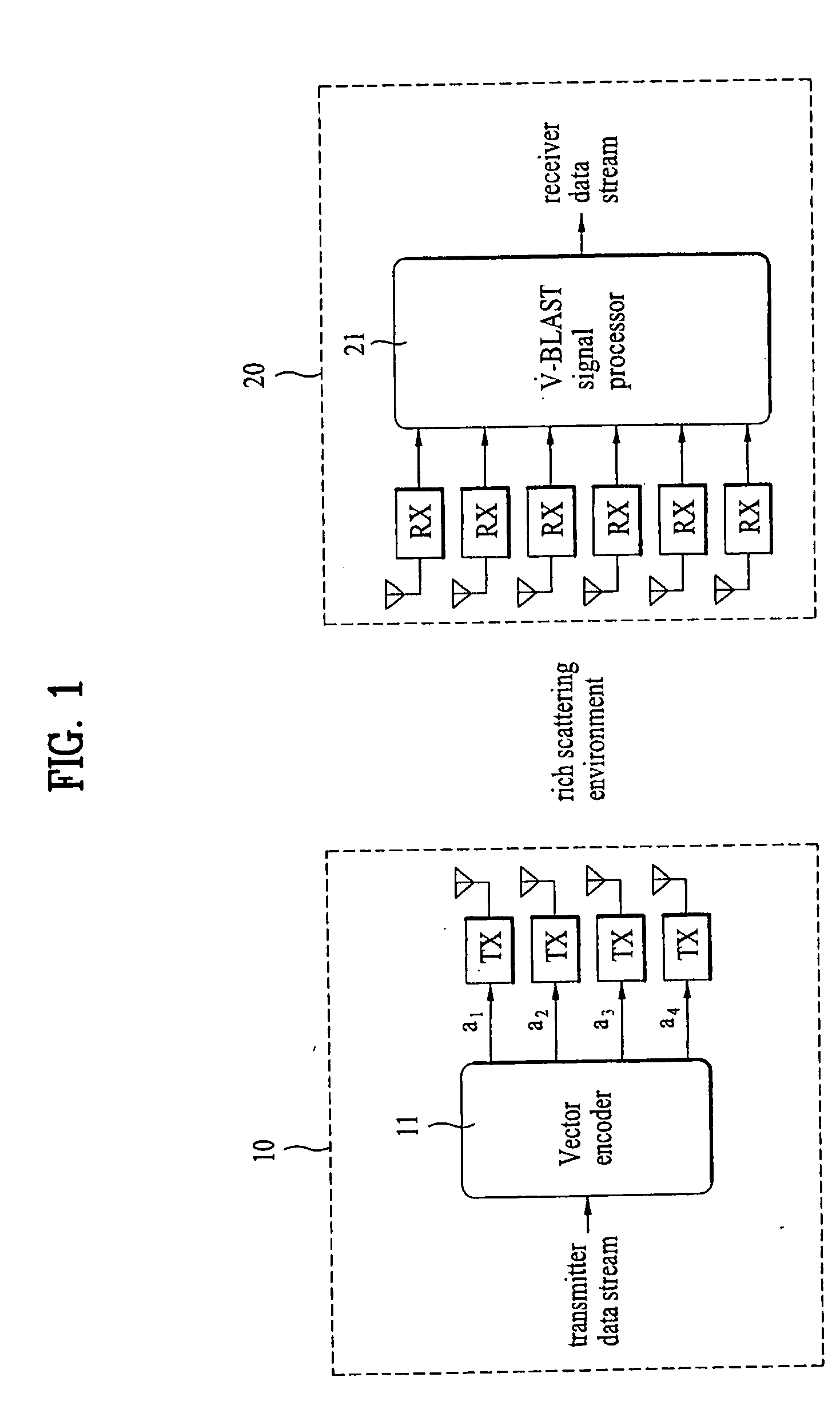
Mobile communication system and signal processing method thereof
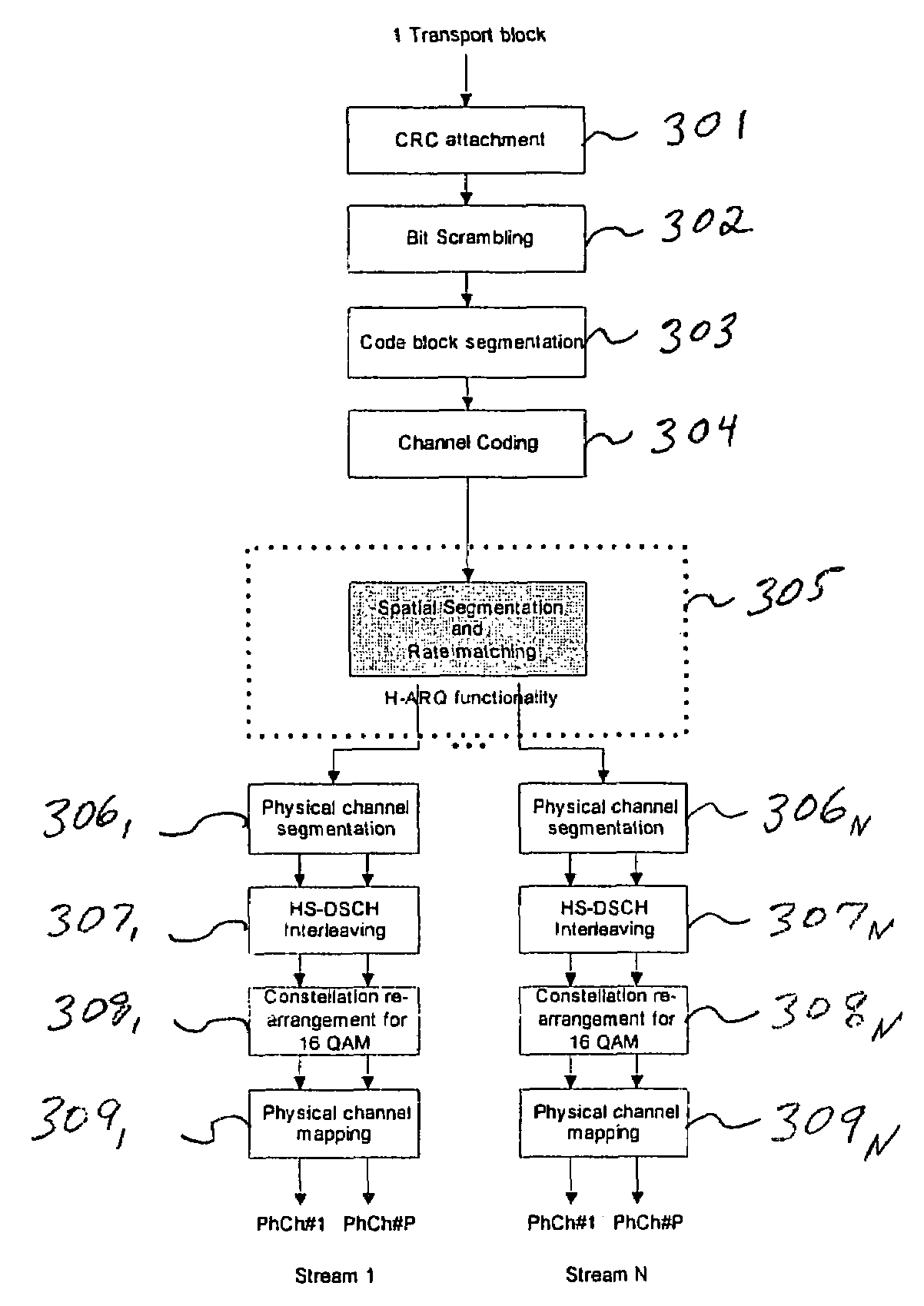
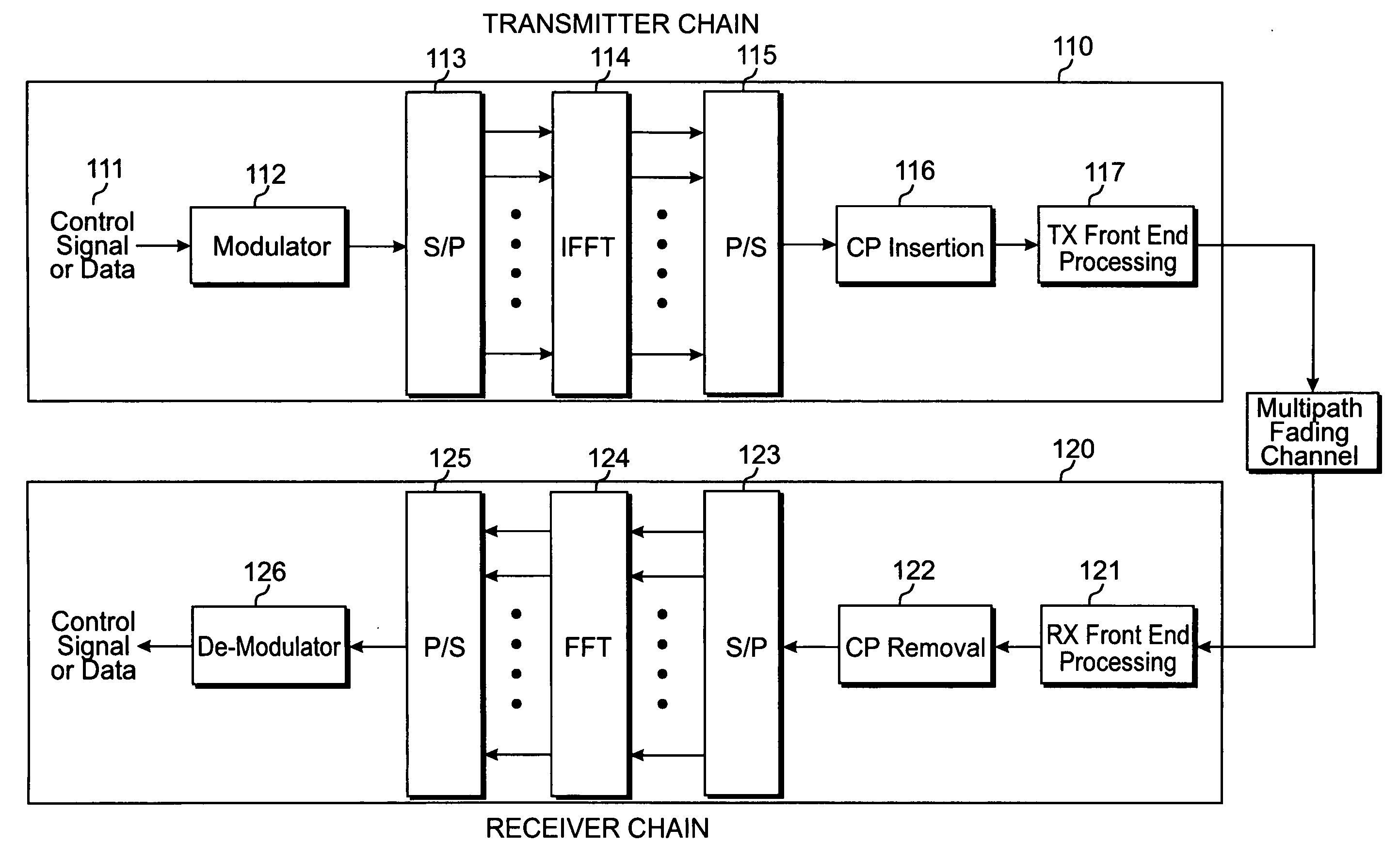
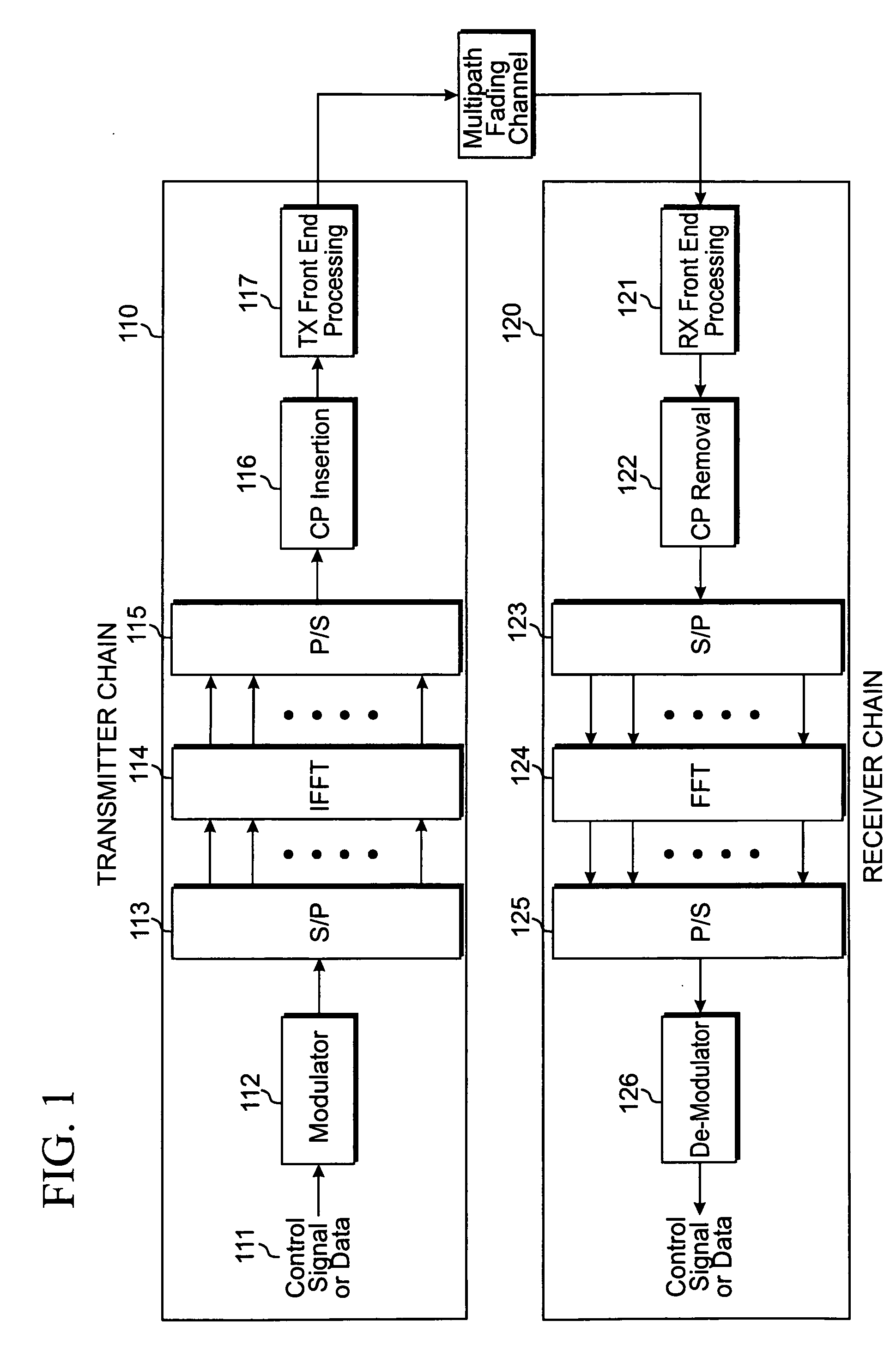
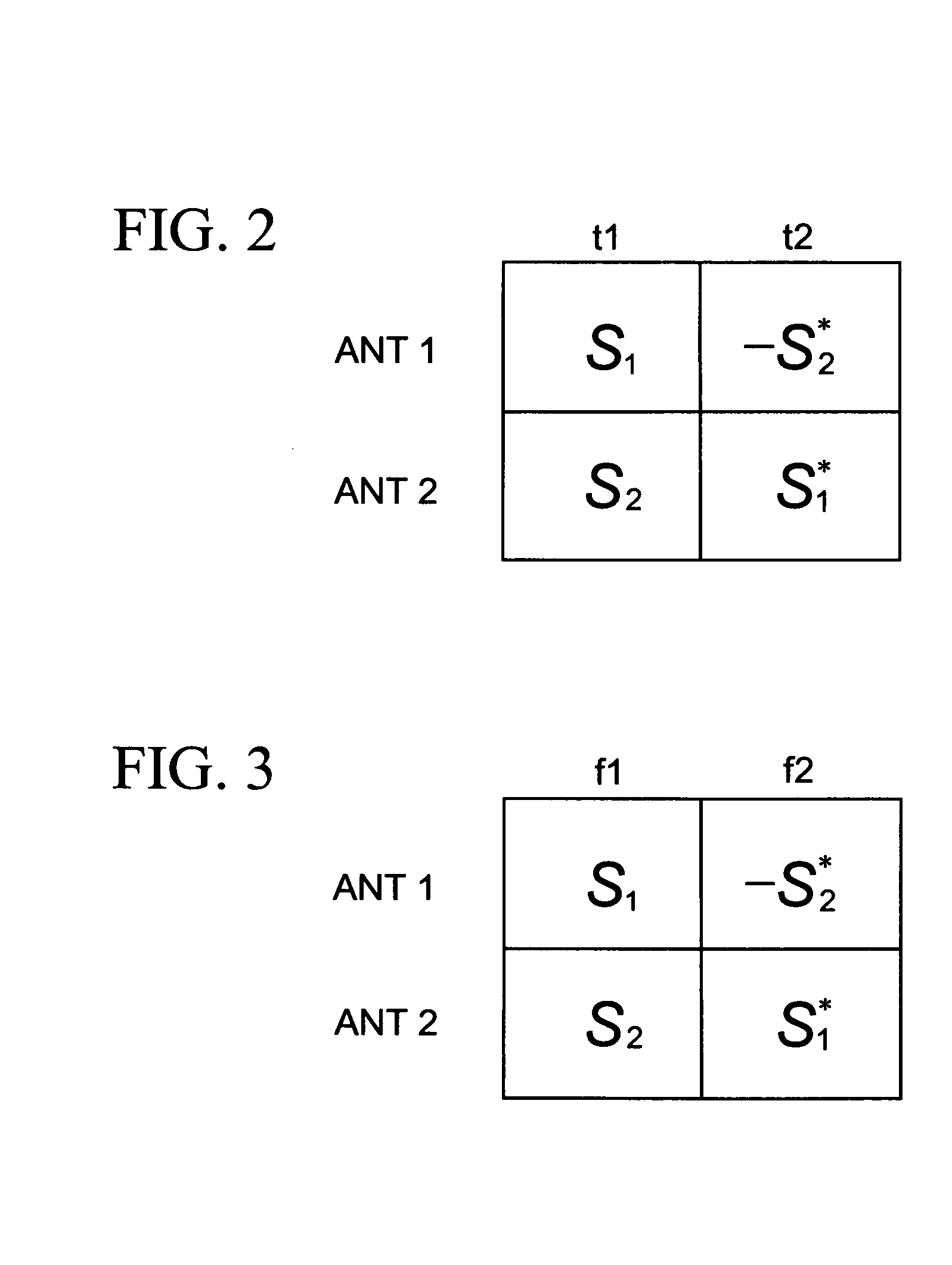
ActiveUS20040268206A1Error prevention/detection by using return channelSpatial transmit diversityMobile communication systemsComputer science
A method of mobile communication including a transmitter having multiple transmitters and a receiver having multiple receivers. The method includes adding a cyclic redundancy check (CRC) code to a data block to be transmitted and spatially segmenting the data block according to a modulation scheme and a coding rate of each respective transmit antenna of the multiple antennas.
Owner:AEGIS 11 SA
Mobile communication system and signal processing method thereof
ActiveUS7392460B2Preserve integrityError prevention/detection by using return channelSpatial transmit diversityMobile communication systemsComputer science
Owner:AEGIS 11 SA
Polarization decoding method based on subsection CRC
ActiveCN105337696AReduce time complexityError preventionError correction/detection using linear codesDecoding methodsSignal-to-noise ratio (imaging)
The invention discloses a polarization decoding method based on subsection CRC and belongs to the technical field of wireless communication channel coding. The subsection CRC (cyclic redundancy check) is utilized to improve an existing list successive elimination polarization decoding algorithm, and subsection polarization code CRC is carried out on an original information sequence at a coding end; and at a decoding end, the whole list successive elimination and decoding process is enabled to be divided into a plurality of subsections, CRC is carried out in each subsection, and unsuccessful decoding is judged according to the CRC check result or screening of ineffective paths is carried out. The subsection CRC and the list successive elimination polarization decoding algorithm are combined, so that time complexity of polarization decoding can be effectively reduced, and especially in the low SNR (signal to noise ratio) region, the time complexity of decoding is reduced obviously.
Owner:SOUTHEAST UNIV
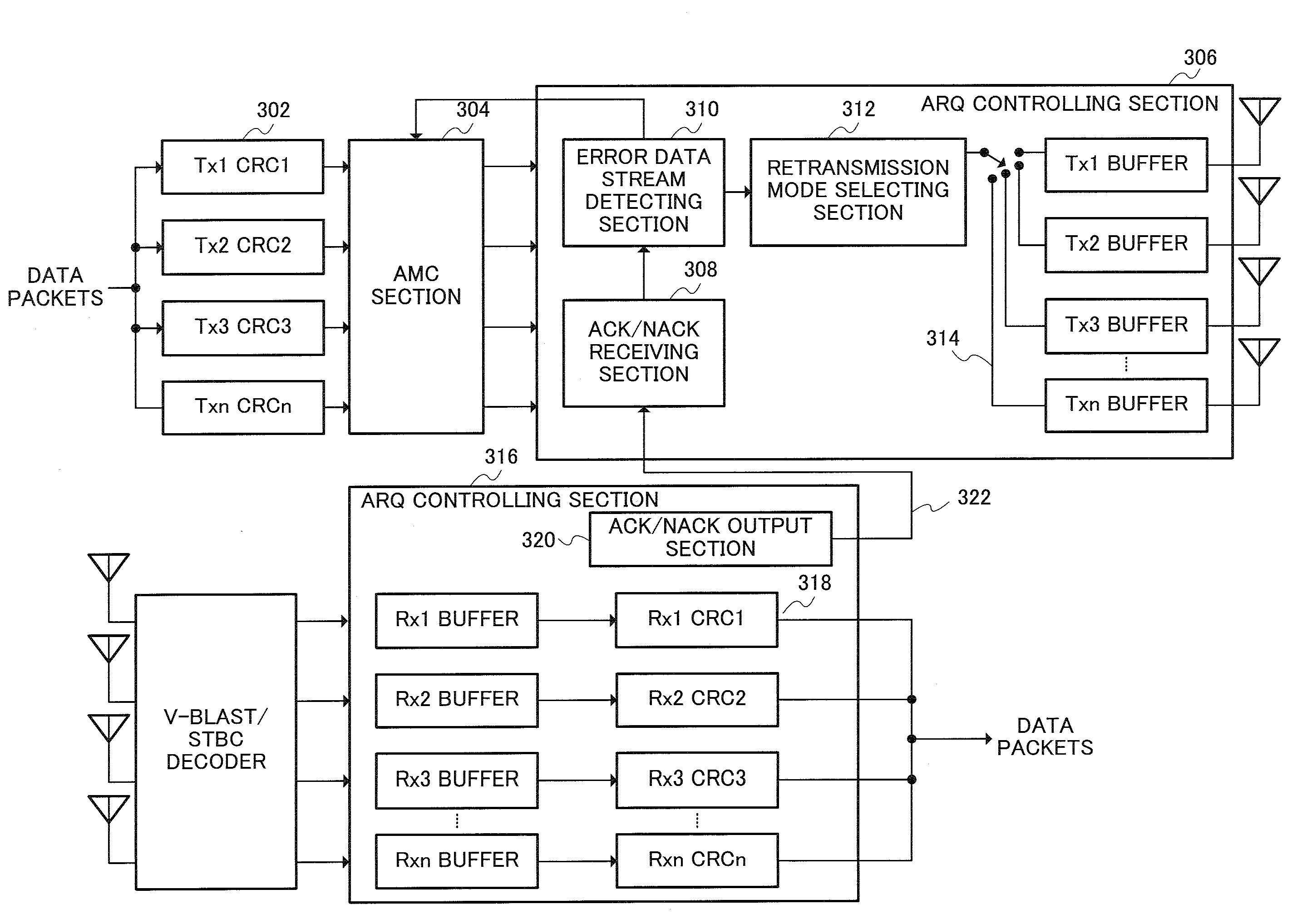
Automatic Retransmission Request Control System and Retransmission Method in Memo-Ofdm System
ActiveUS20070255993A1Improvement of data throughput performanceReduce in quantityError prevention/detection by using return channelError correction/detection using convolutional codesData streamAutomatic repeat request
An automatic retransmission request control system in OFDM-MIMO communication system. In this system, an ACK / NACK output part (320) of a receiver transmits, to a transmitter, a feedback information of positive or negative response based on the result of a cyclic redundancy check. An error data stream decision part (310) of the transmitter determines, based on the feedback information, a data stream that need be retransmitted, and a retransmission mode selection part (312) selects a retransmission mode from among (a) a mode in which to transmit the data, which are to be retransmitted, via the same antenna as in the previous transmission, while transmitting, at the same time, new data by use of an antenna via which no data retransmission is requested; (b) a mode in which to transmit the data, which are to be retransmitted, via an antenna via which no retransmission is requested, while transmitting new data via another antenna at the same time; (c) a mode in which to use STBC to retransmit the data via an antenna via which no retransmission is requested; and (d) a mode in which to use STBC to retransmit the data via all the available antennas.
Owner:INVT SPE LLC
Data transmission using arithmetic coding based continuous error detection
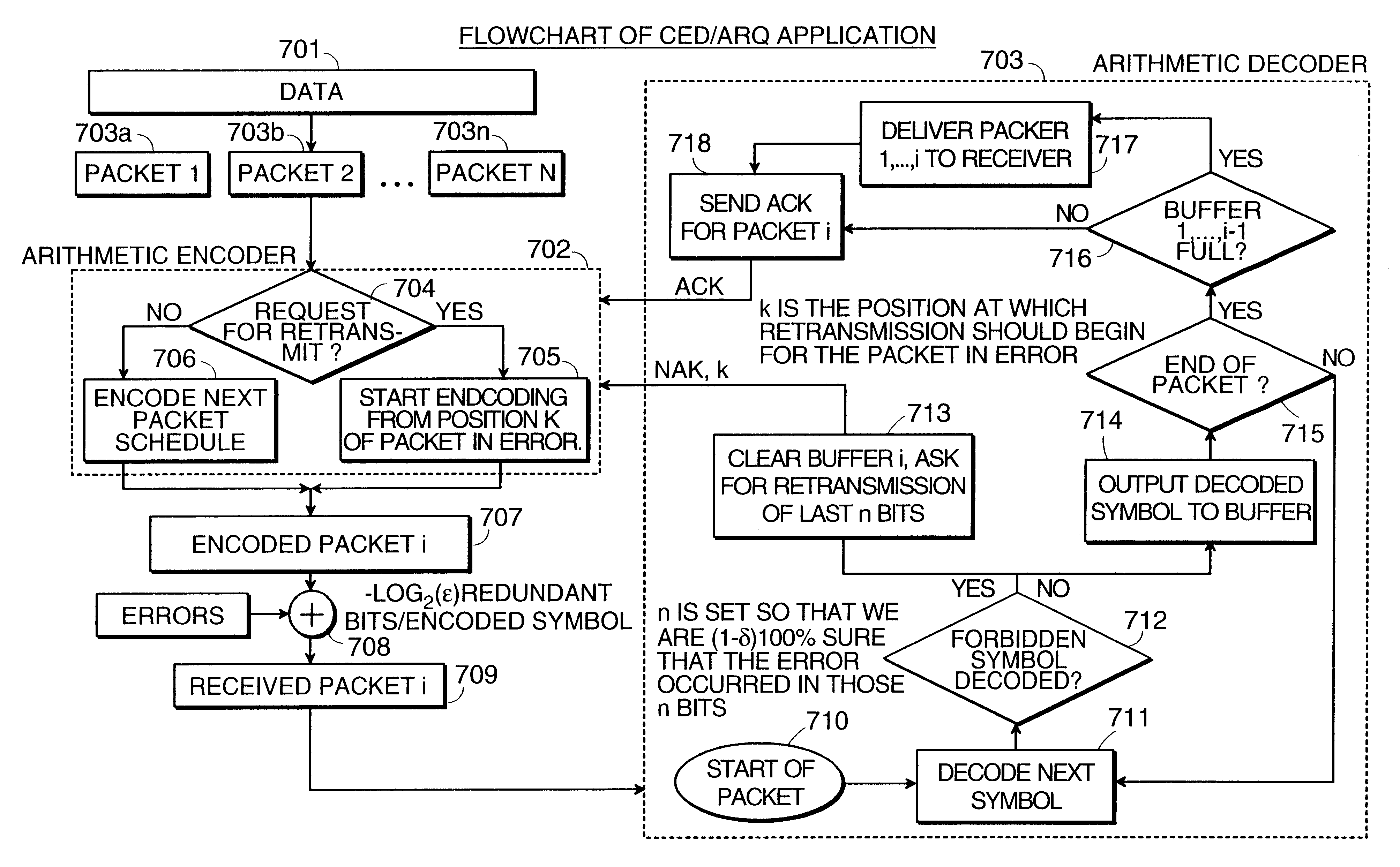
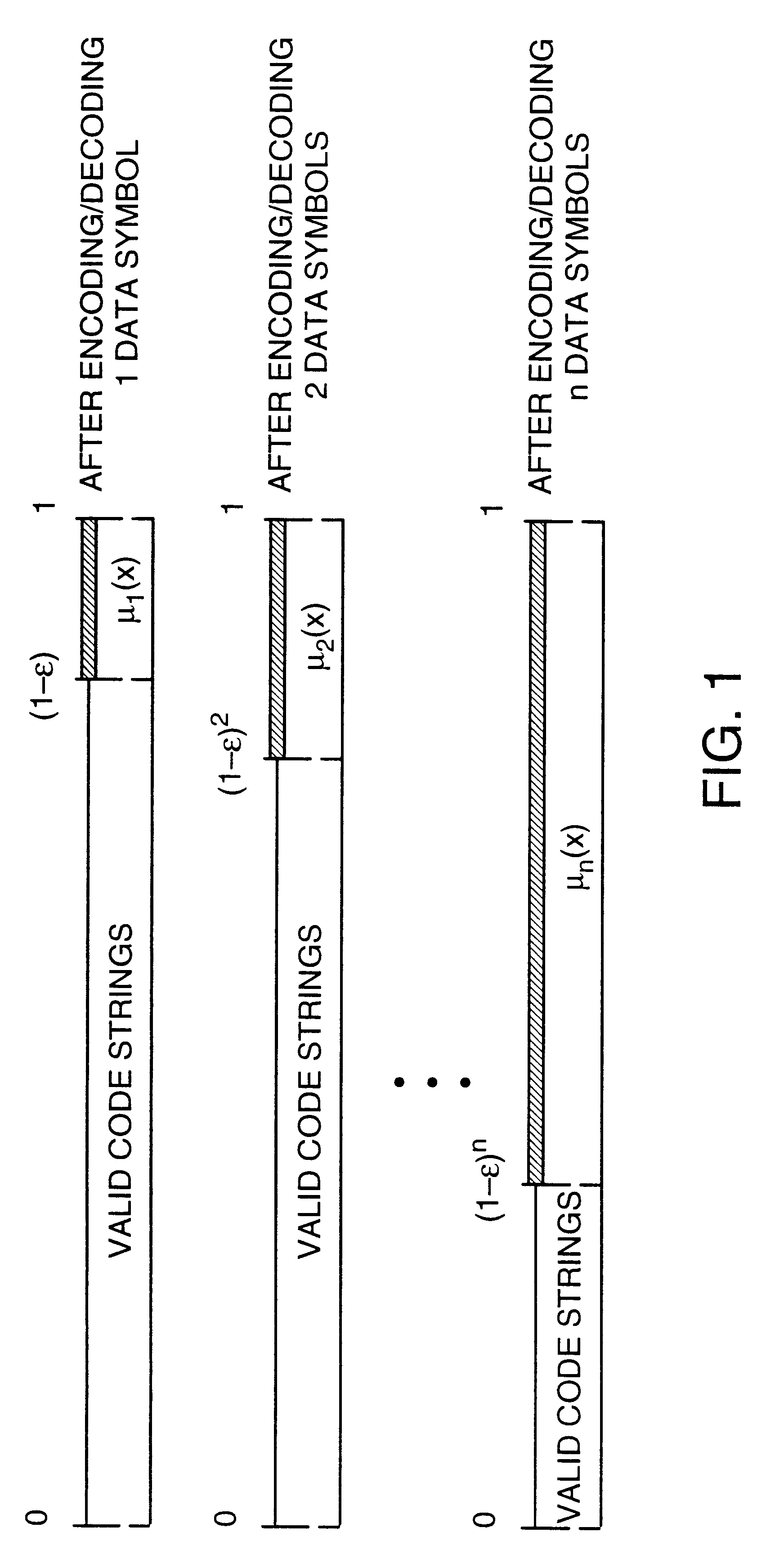
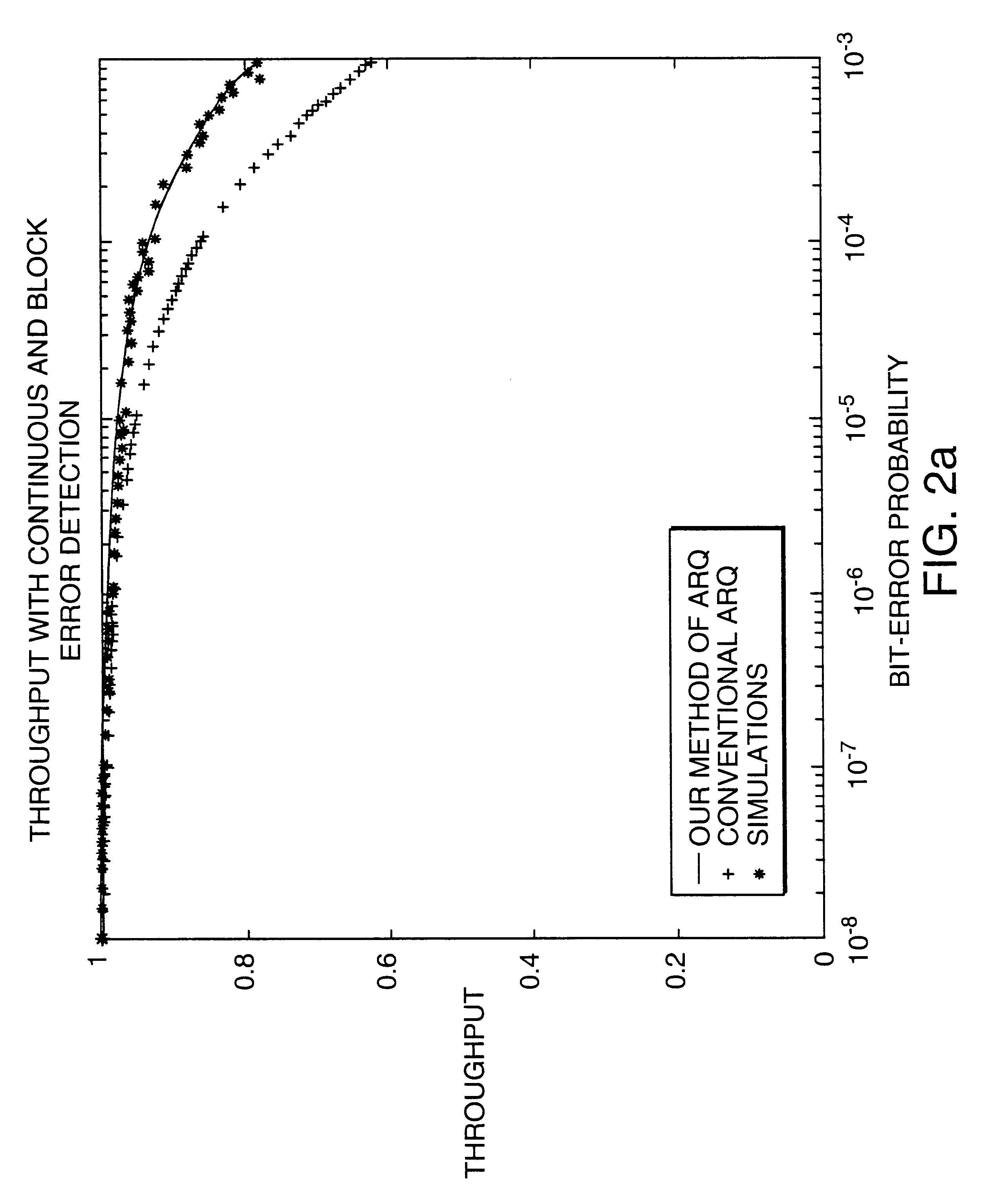
InactiveUS6418549B1Error prevention/detection by using return channelTransmission systemsAutomatic repeat requestTrade offs
Method and apparatus for image transmission using arithmetic coding, based on continuous error detection uses a controlled amount of added redundancy. A continuous error detection scheme is provided, wherein there is a trade-off between the amount of added redundancy and the time needed to detect an error once it occurs. Herein, there is no need for the cyclic redundancy check (CRC) to wait until an entire block of data has been received and processed before an error can be detected. The invention can be used to great advantage both in the automatic repeat request (ARQ) and other concatenated coding schemes. Errors in the received bit stream are detected by introducing added redundancy, e.g., a forbidden symbol, in the arithmetic coding operation. The forbidden symbol is never intended to be encoded. The redundancy error causes loss of synchronization, which is used to detect errors. If a forbidden symbol gets decoded, it means that an error has occurred. In this invention, there is direct control over the amount of redundancy added vs. the amount of time it takes to detect an error. For image compression systems, by using the invention and ARQ, only one device would suffice both for source compression and channel coding.
Owner:MERU NETWORKS
Method and apparatus for conveying antenna configuration information
ActiveUS20090176463A1Reliable demodulationReliably interpretedModulated-carrier systemsDiversity/multi-antenna systemsBroadcast channelsEngineering
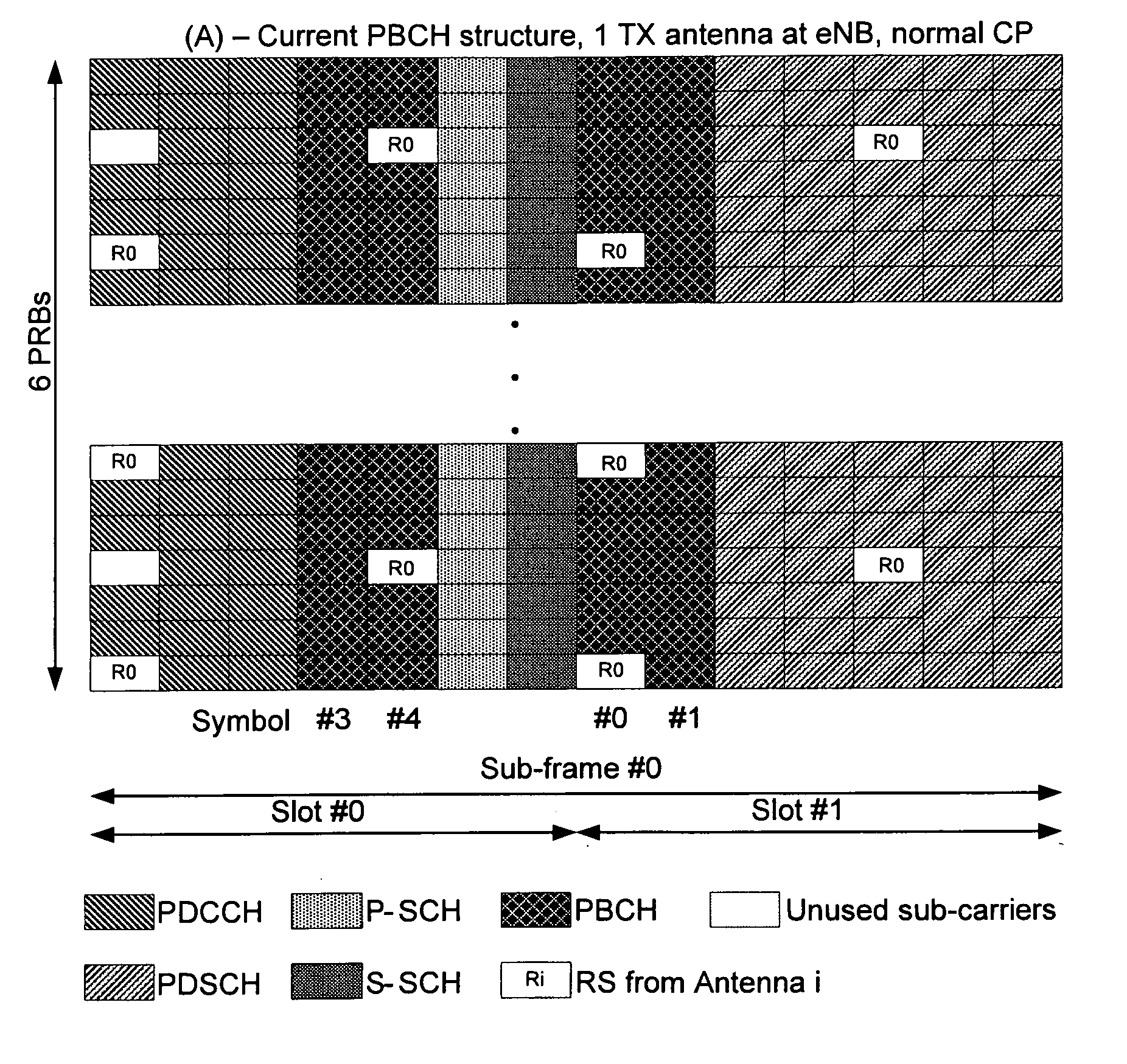
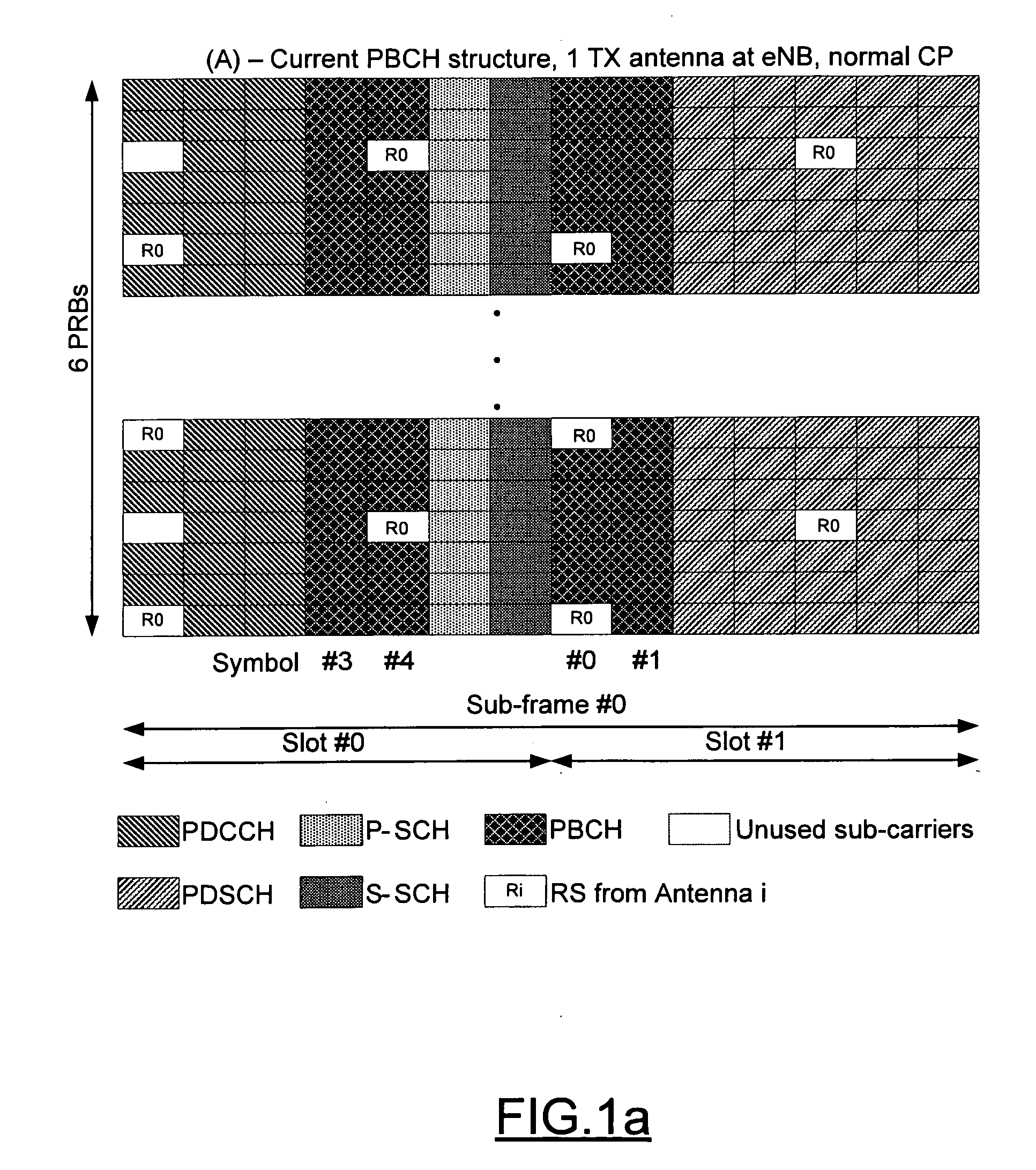
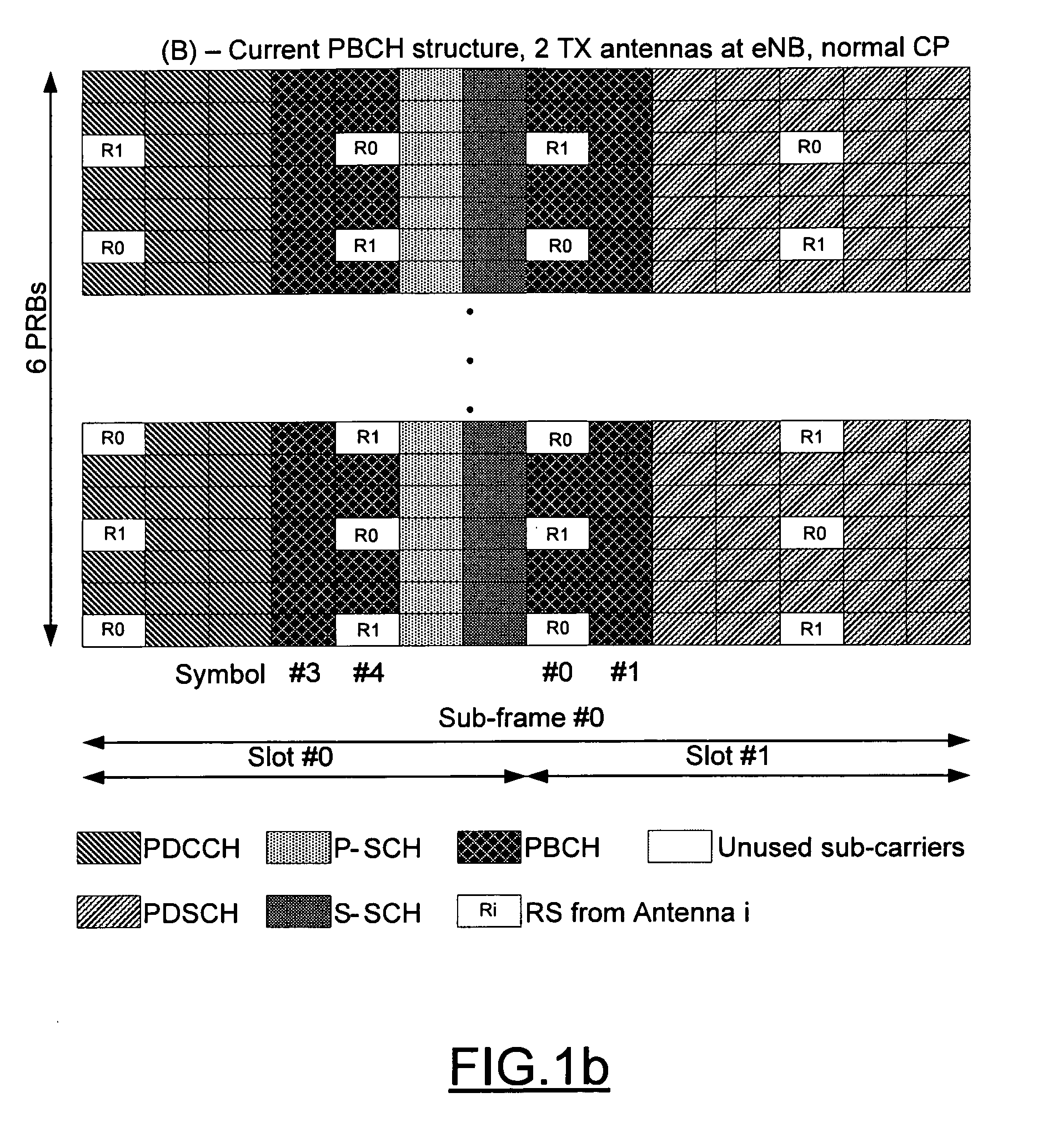
A method, apparatus and computer program product are provided for conveying information regarding the antenna configuration and / or the transmission diversity scheme to a recipient, such as a mobile device. In particular, information regarding the antenna configuration and / or the transmission diversity scheme can be conveyed by appropriately mapping a physical broadcast channel within a sub-frame so as to include reference signals indicative of different antenna configurations or transmission diversity schemes. Alternatively, masking, such as cyclic redundancy check masking, can be used to provide information regarding the antenna configuration and / or the transmission diversity scheme.
Owner:NOKIA CORP
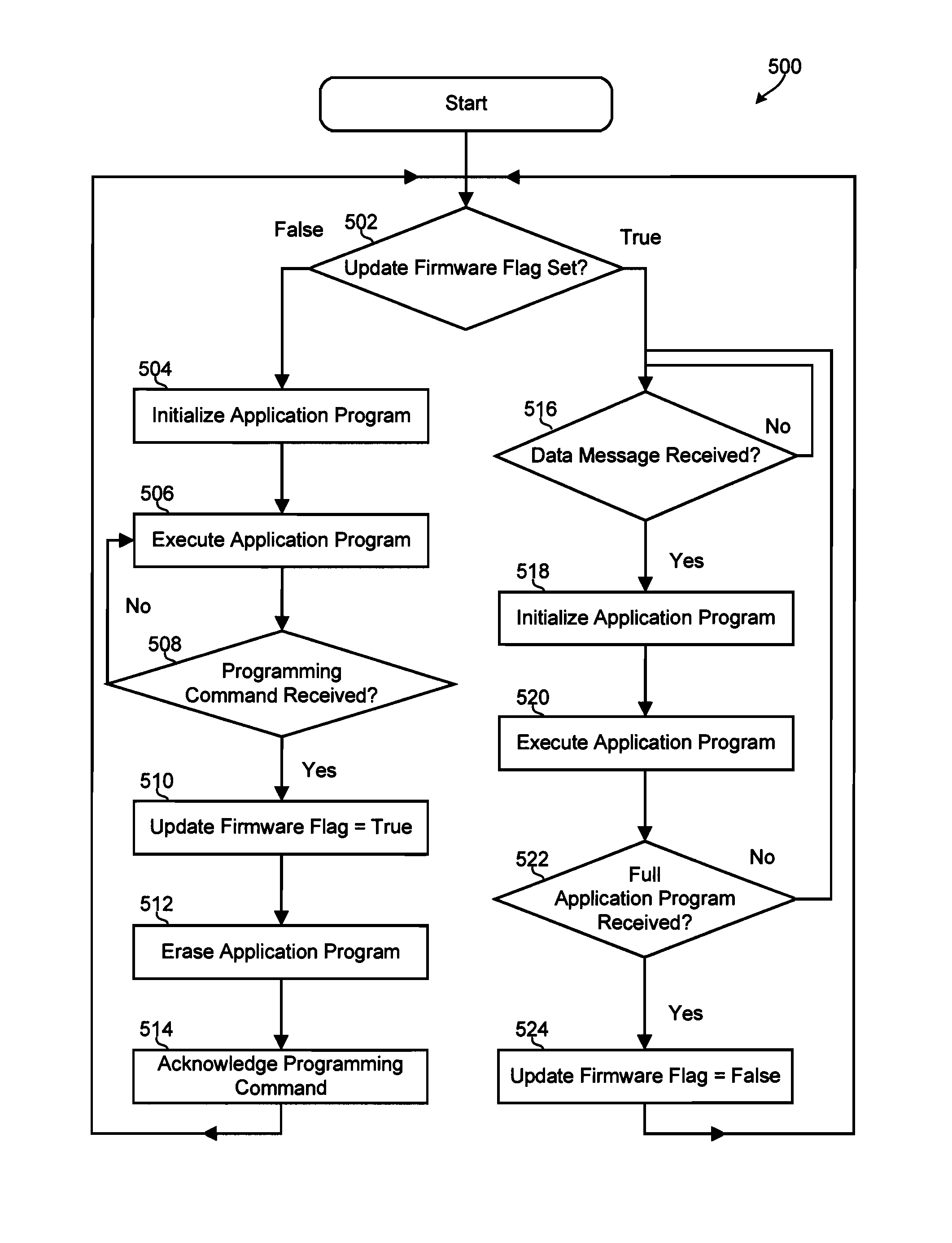
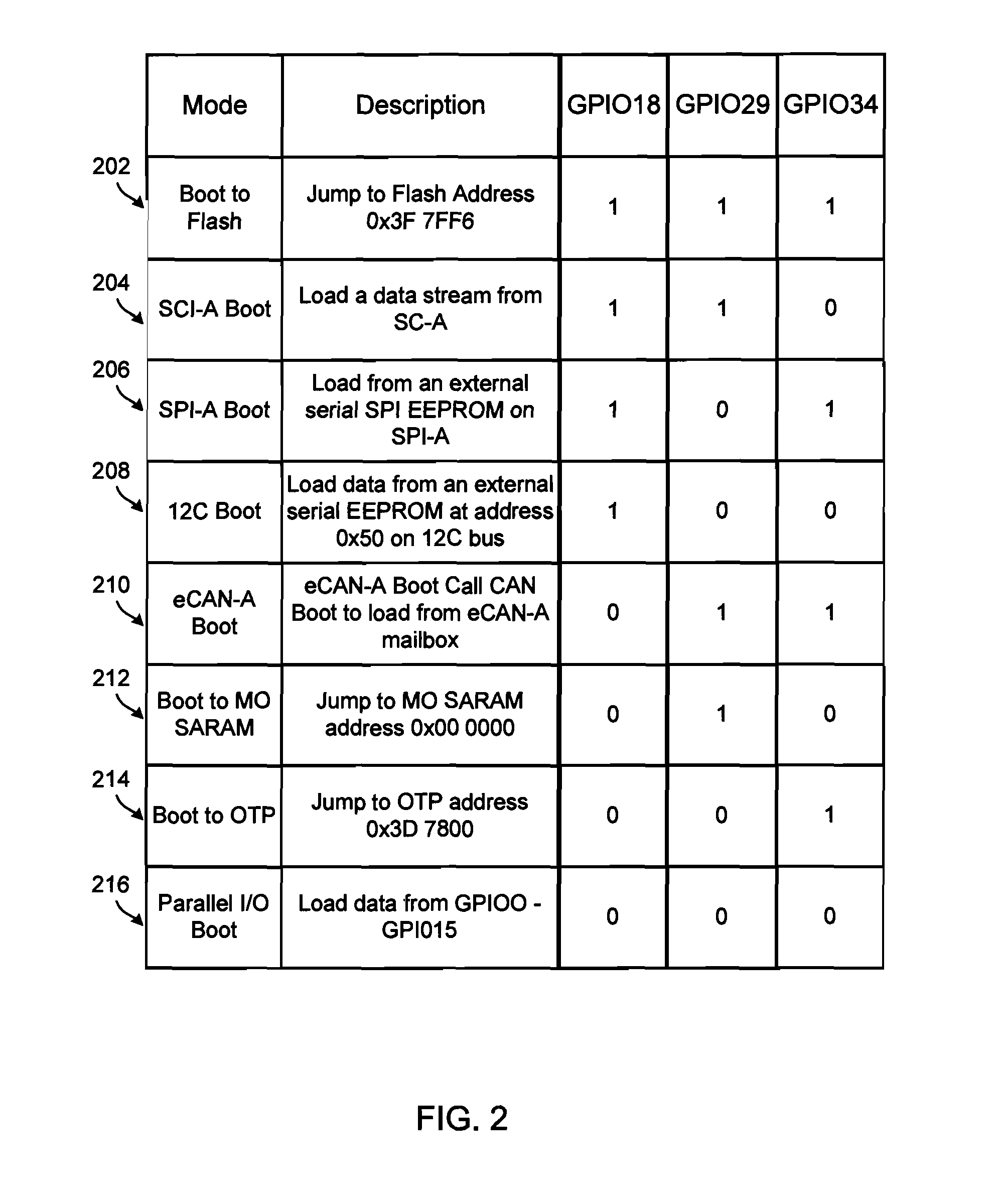
Programming processors through CAN interface without changing the boot mode select pins
Methods, systems and devices for remotely updating software installed on a digital signal processor (DSP) without setting the mode select pins on the DSP control card. Firmware configured to suspend operations upon receiving a programming signal is installed on the processor. A controlling computing device send the programming signal, causing the processor to halt execution, erase portions of the firmware, set an update firmware flag, and send control signals to the controlling computing device. The remote computing device sends updated firmware and an application program cyclic redundancy check to the processor. The processor compares a cyclic redundancy check of an on-chip flash memory with the received application program cyclic redundancy check. If the two match, the processor installs the received firmware, unsets the update firmware flag, and restarts itself.
Owner:BLOOM ENERGY CORP
Antenna mapping in a MIMO wireless communication system
InactiveUS20080273452A1Improve transmission performanceImprove system throughputModulated-carrier systemsCode conversionCommunications systemSymbol mapping
A method for transmission is provided to generate a plurality of reference signals for a plurality of antenna ports, with each reference signal corresponding to an antenna port; to map the plurality of reference signals to a plurality of physical antennas in accordance with a selected antenna port mapping scheme, with each reference signal corresponding to a physical antenna, and the plurality of physical antennas being aligned sequentially with equal spacing between two immediately adjacent physical antennas; to demultiplex information to be transmitted into a plurality of stream blocks; to insert a respective cyclic redundancy check to each of the stream blocks; to encode each of the stream blocks according to a corresponding coding scheme; to modulate each of the stream blocks according to a corresponding modulation scheme; to demultiplex the stream blocks to generate a plurality of sets of symbols, with each stream block being demultiplexed into a set of symbols; to map the plurality of sets of symbols into the plurality of antenna ports in accordance with a selected symbol mapping scheme; and to transmit the plurality of sets of symbols via the corresponding antenna ports, with each set of symbols being transmitted via a subset of antenna ports, with, within each subset of antenna ports, the distance between the physical antennas of the corresponding antenna ports being larger than the average distance among the plurality of physical antennas.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
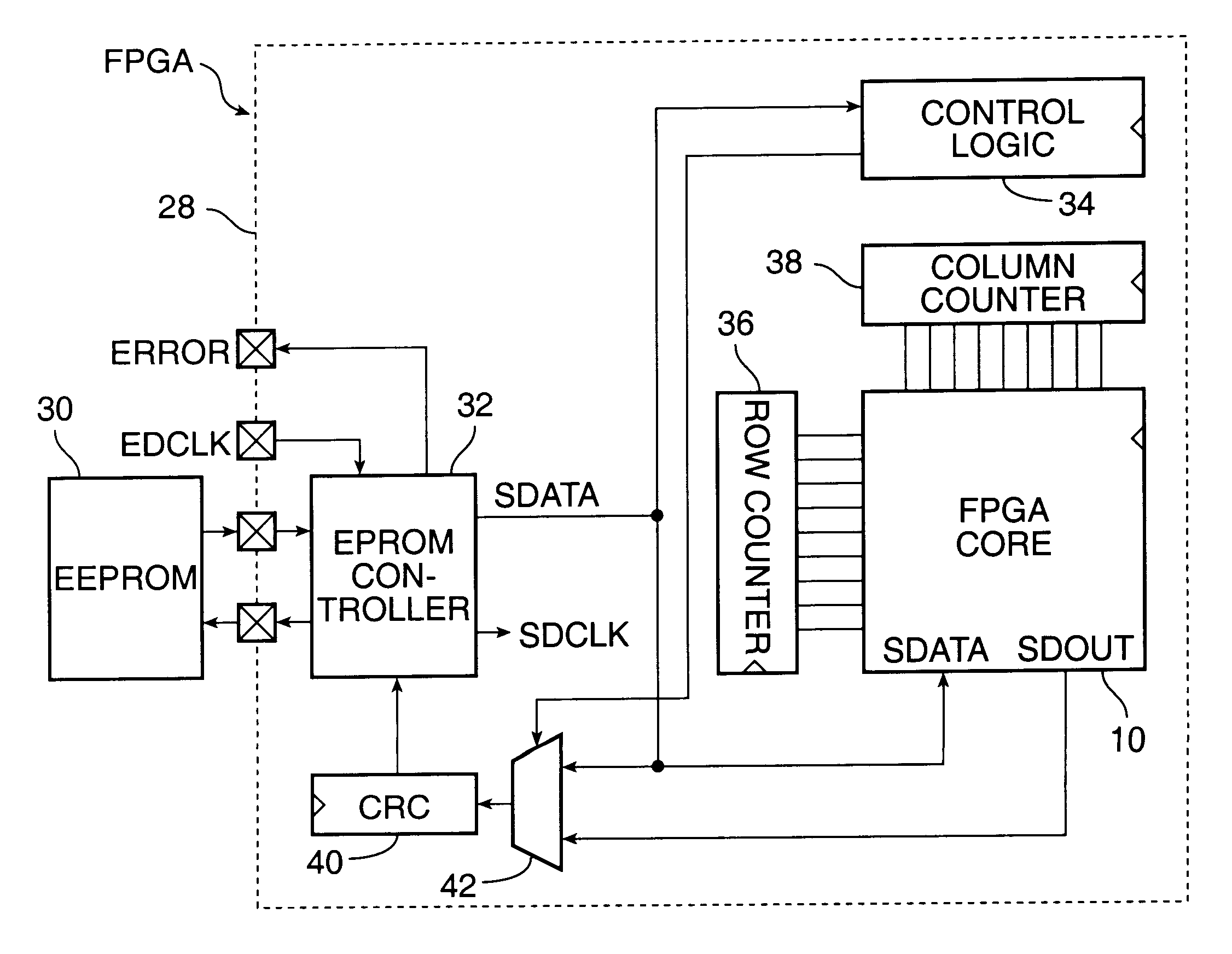
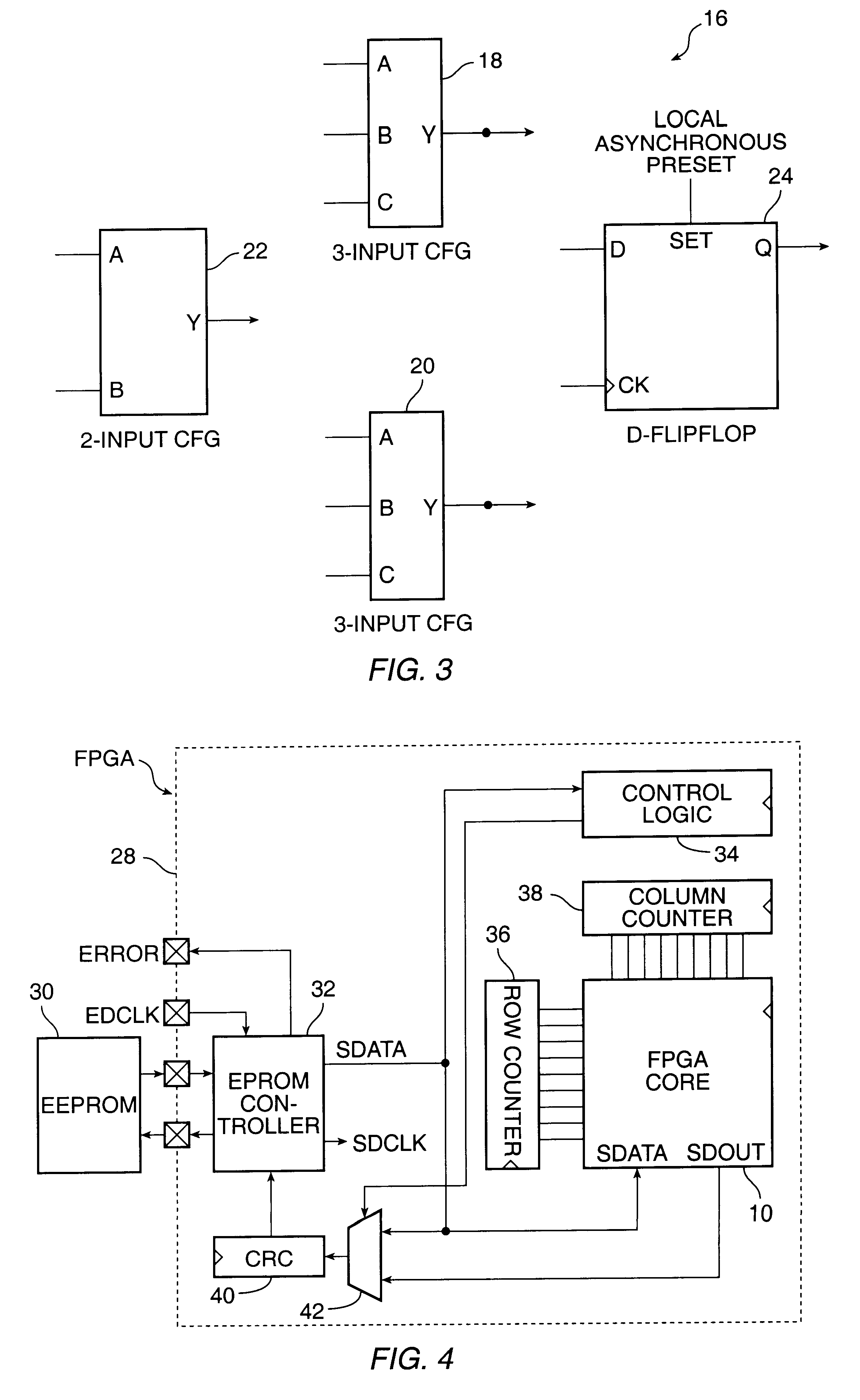
Methods for errors checking the configuration SRAM and user assignable SRAM data in a field programmable gate array
A method for detecting an error in data stored in configuration SRAM and user assignable SRAM in a FPGA comprises the steps of providing a serial data stream into the FPGA from an external source, loading data from the serial data stream into the configuration SRAM in response to address signals generated by row column counters, loading data from the serial data stream into the user assignable SRAM in response to address signals generated by row and column counters, loading a seed and signature from the serial data stream into a cyclic redundancy checking circuit, cycling data out of the configuration SRAM and the user assignable SRAM by the row and column counters; performing error checking on the data that has been cycled out of the configuration SRAM and out of the user assignable SRAM by the cyclic redundancy checking circuit, and generating an error signal when an error is detected by the error checking circuit.
Owner:MICROSEMI SOC
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com