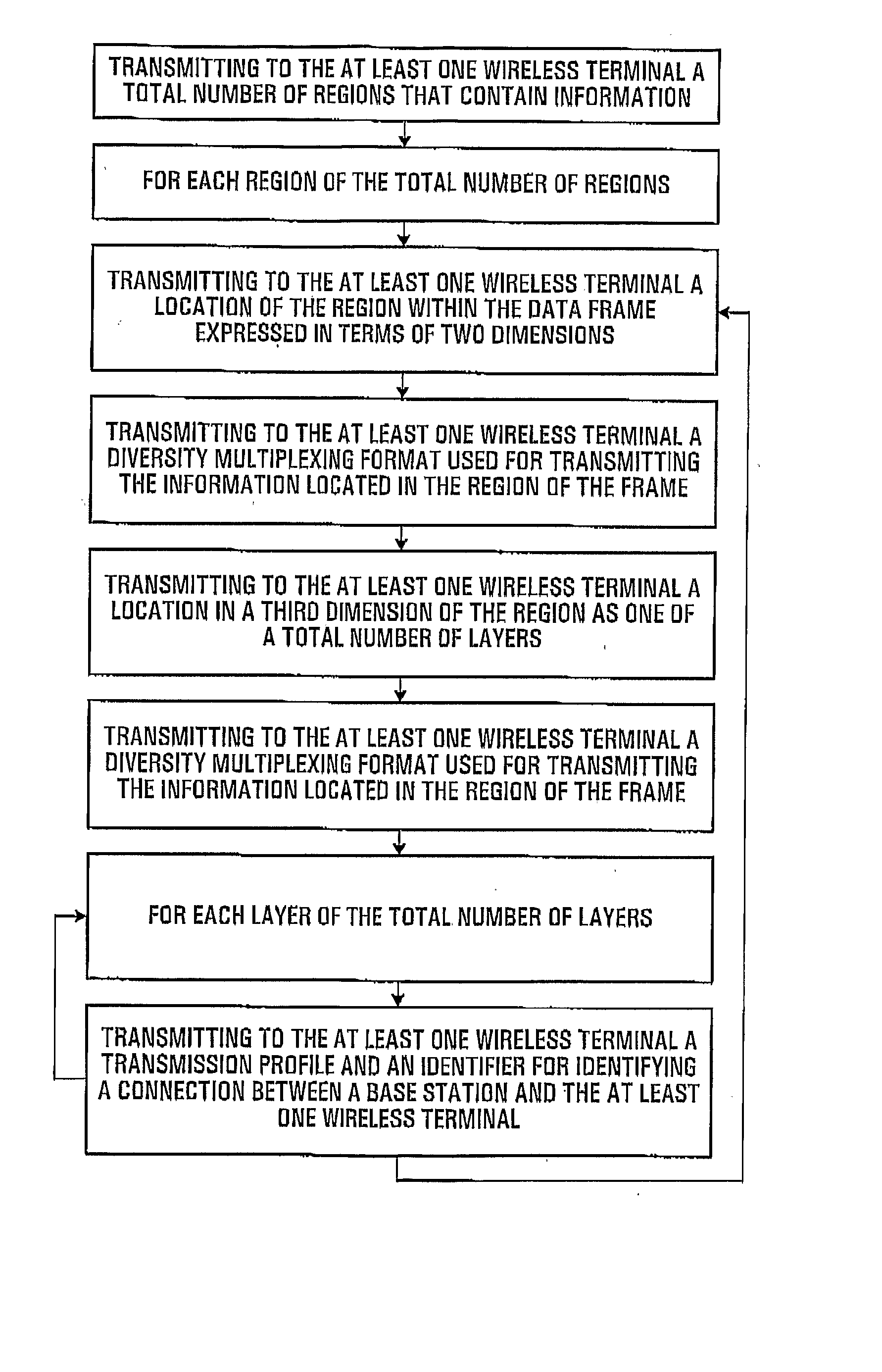
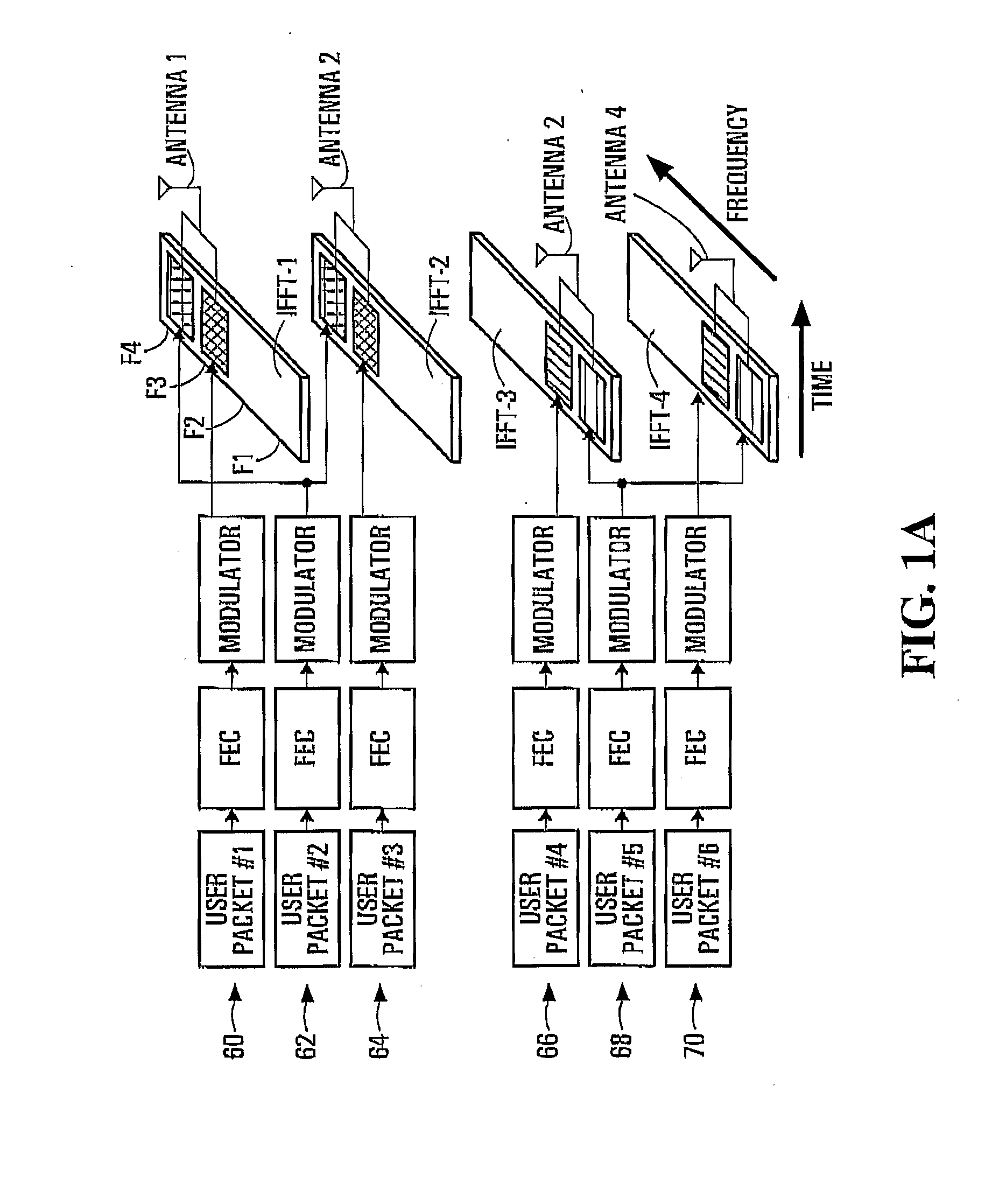
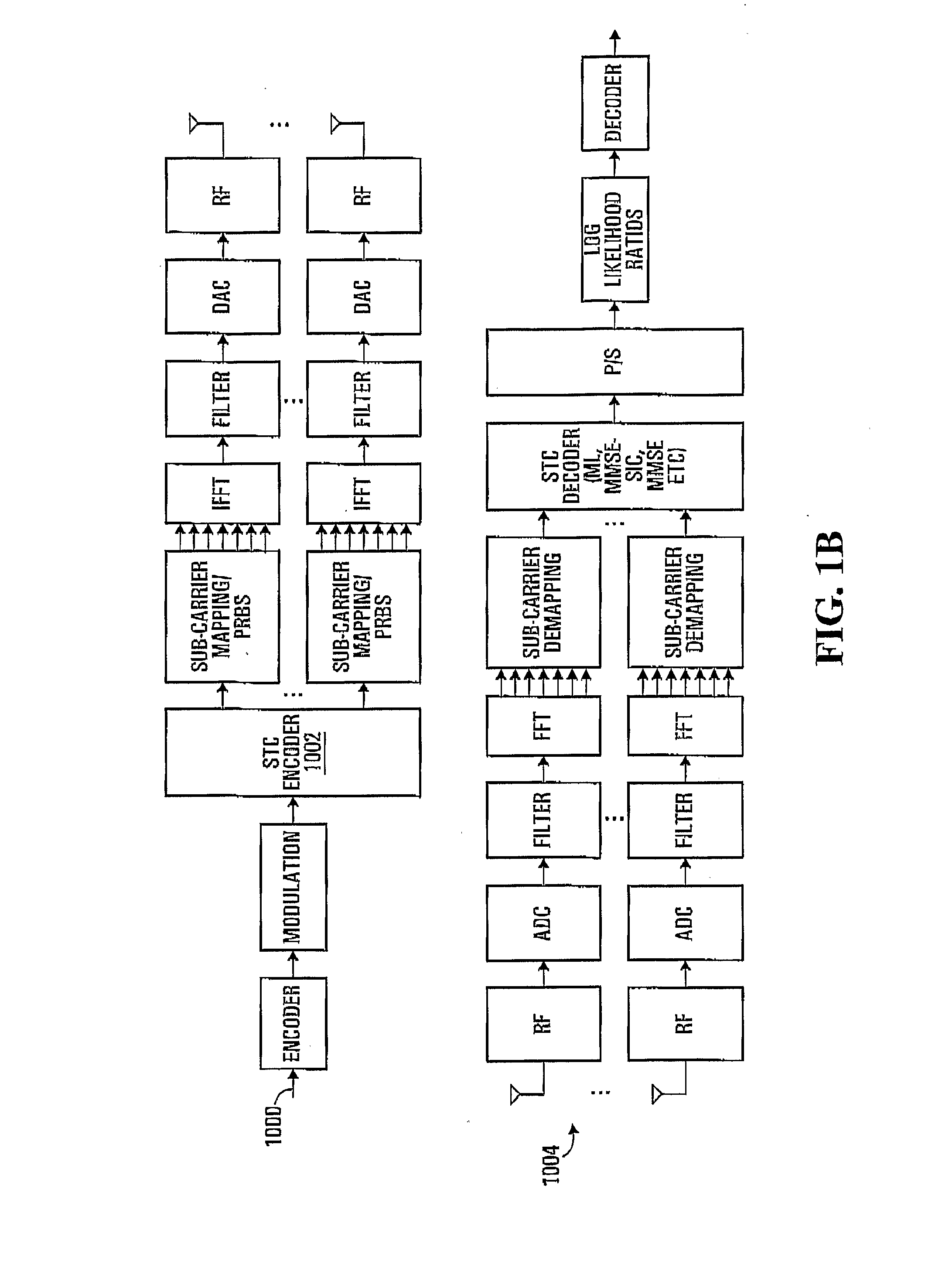
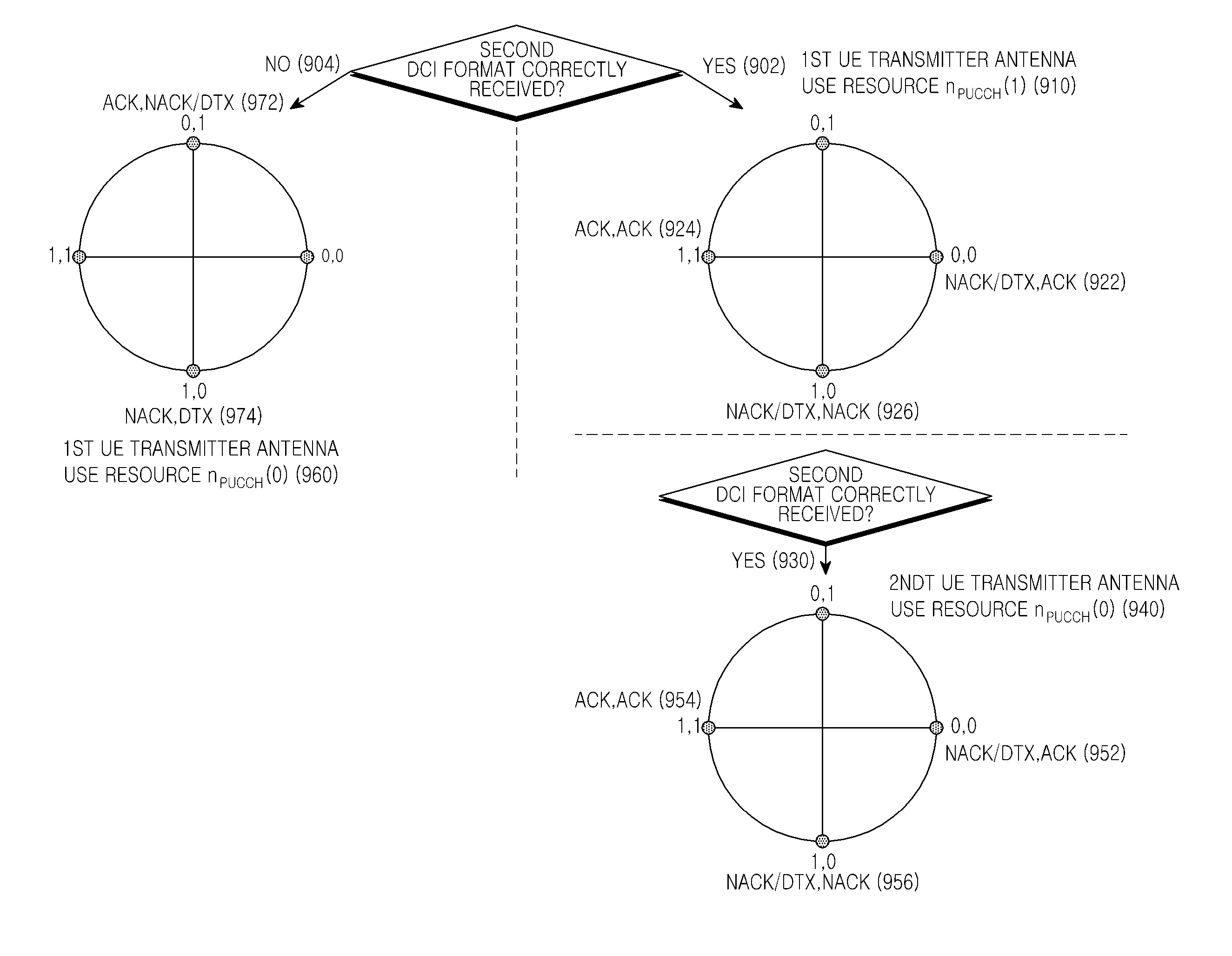
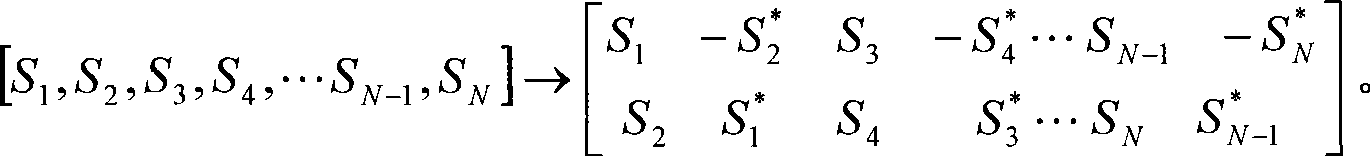Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
344 results about "Transmission diversity" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
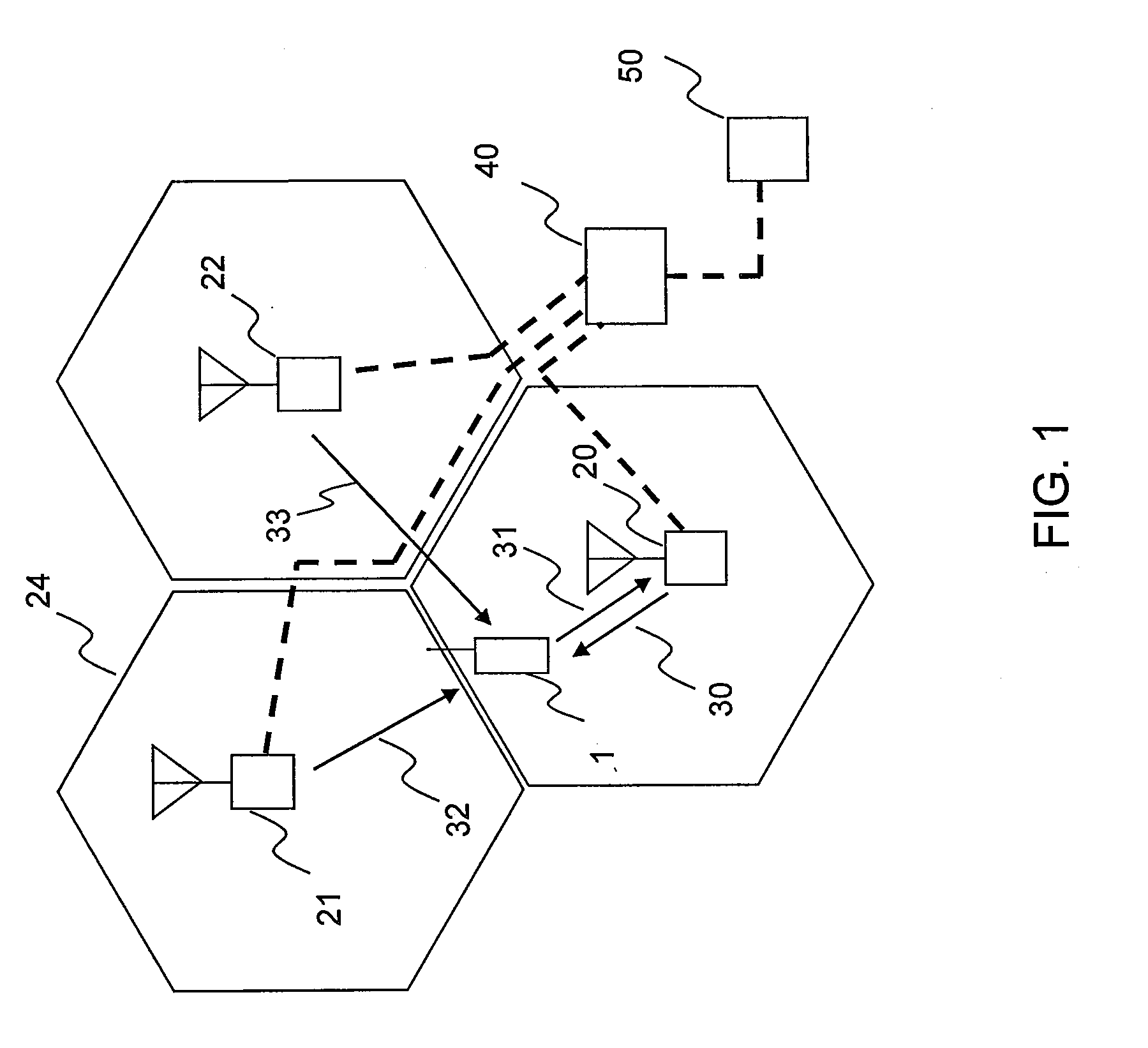
Transmission diversity refers to the possibility of sending a radio signal using several optional methods over one or more paths, such as several antennas/antenna arrays or transmission frequencies or transmission delays.
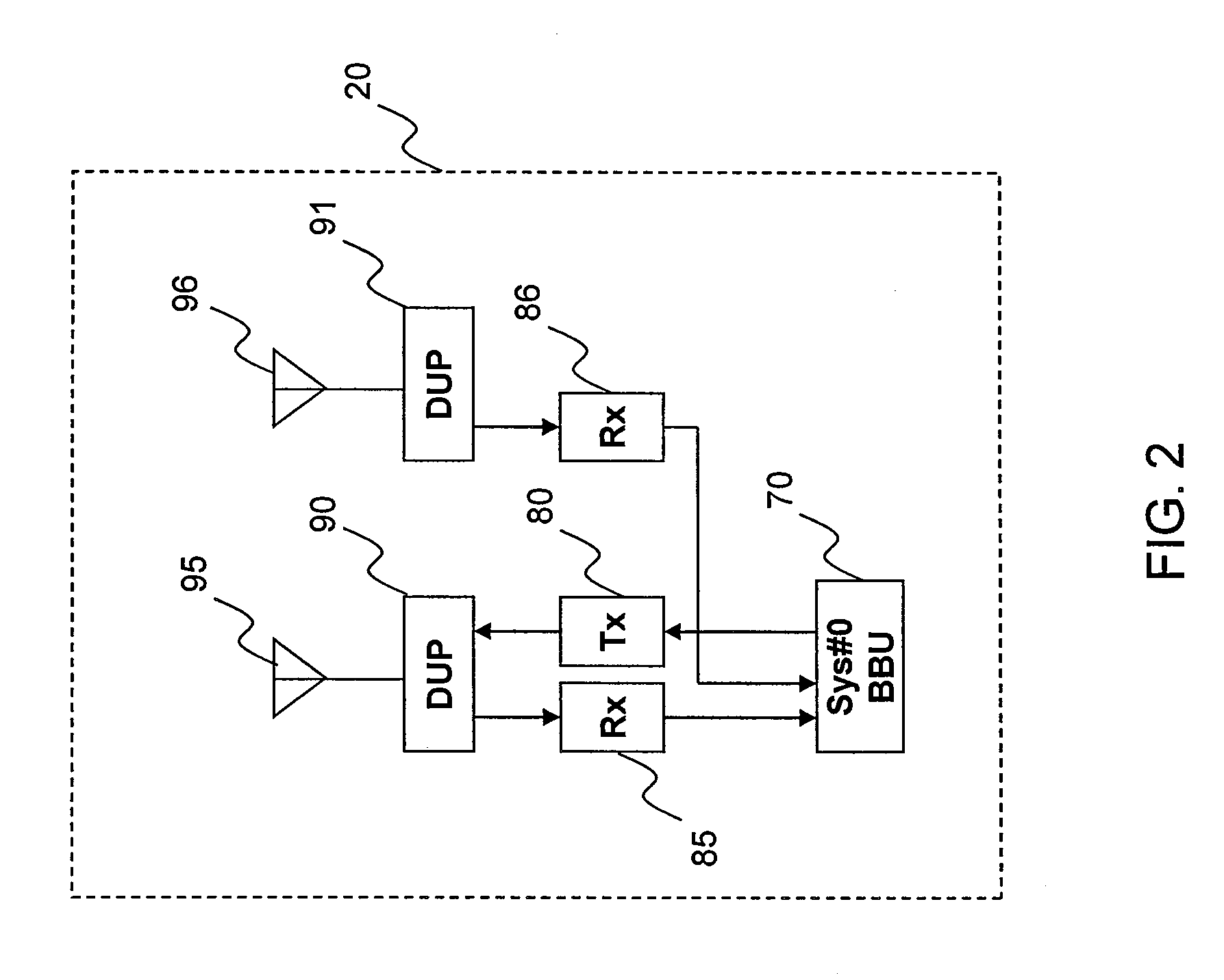
Methods For Supporting Mimo Transmission In Ofdm Applications
ActiveUS20070274253A1Spatial transmit diversityTransmission path divisionSpace time transmit diversityMimo transmission
Aspects of the present invention provide MAC enhancements to support the PHY features of a MIMO-OFDMA framework. The MAC enhancements involve DL burst assignment to support adaptive MIMO transmission, UL burst assignment to support adaptive MIMO transmission, fast feedback channel operation to support wireless terminal dynamic feedback of MIMO mode selection, for example space time transmit diversity (STTD) or spatial multiplexing (SM), and / or permutation mode selection, for example diversity or adjacent subcarrier mode, dynamic CQICH allocation and de-allocation and the use of CQICH_ID for DL burst allocation. One or more of these enhancements is included in a given implementation. Methods are also provided for implementing the MAC enhancements.
Owner:APPLE INC
Transmission diversity and multiplexing for harq-ack signals in communication systems
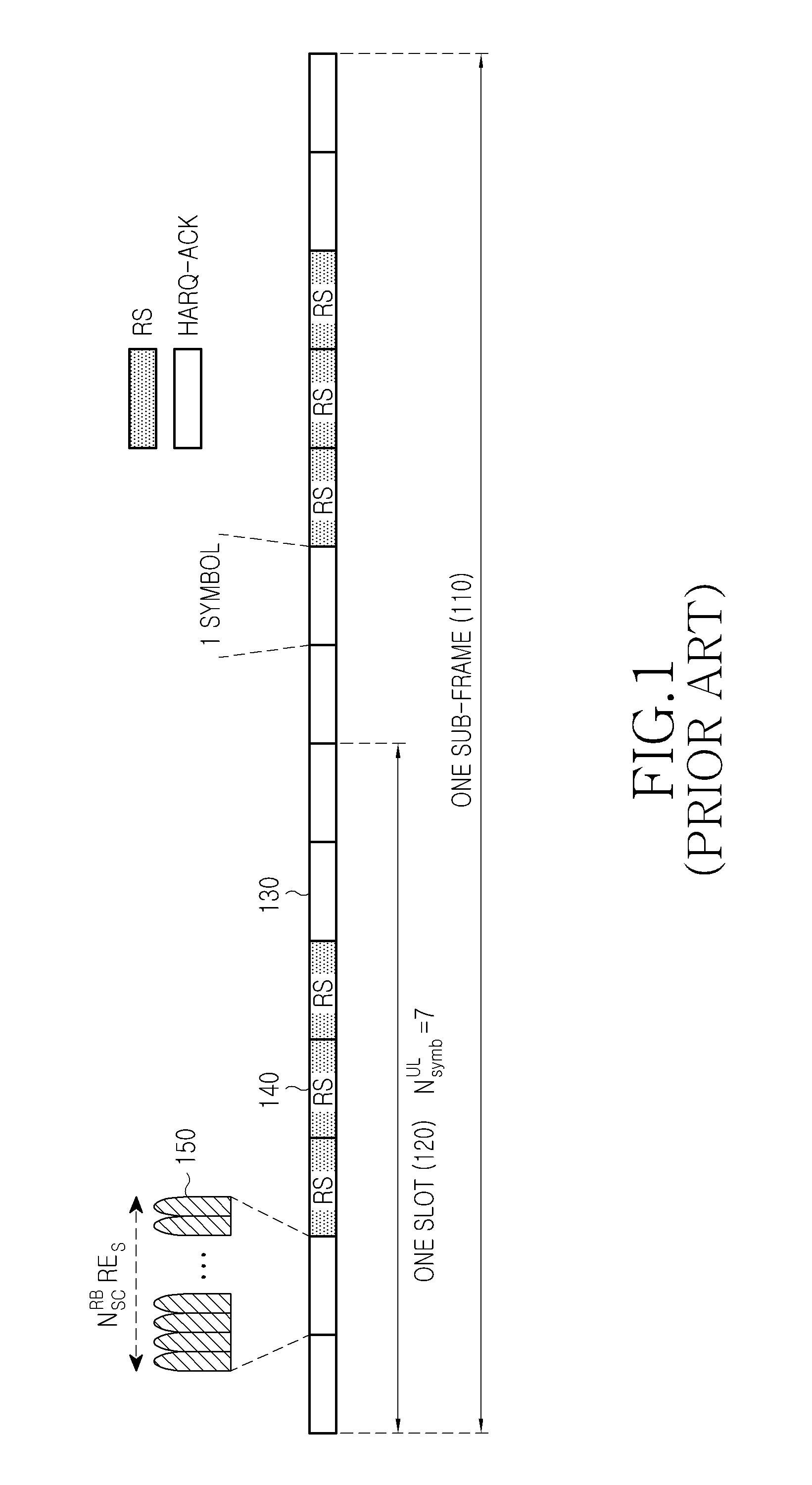
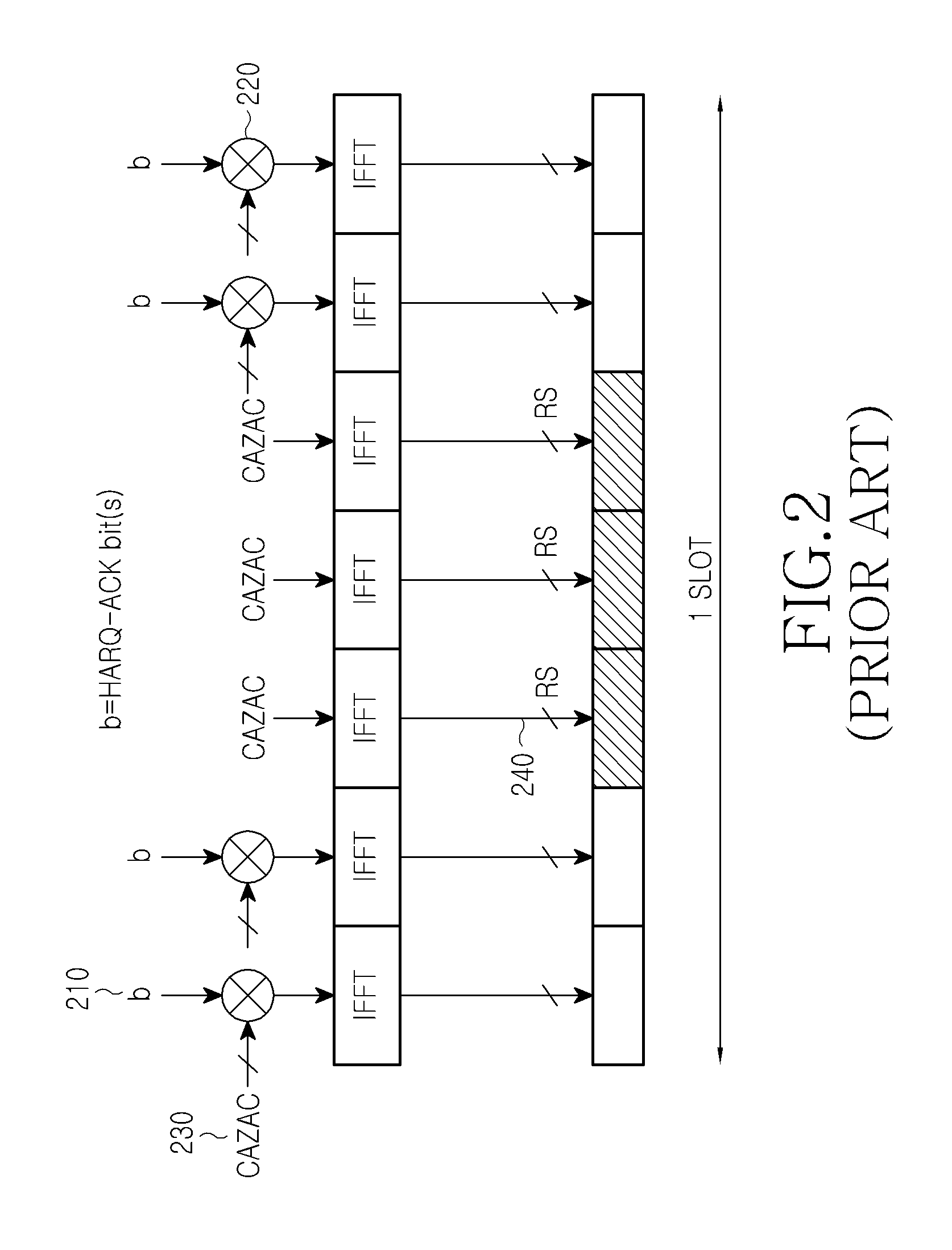
A method and apparatus are described for a User Equipment (UE) to transmit in a control channel ACKnowledgement signals associated with a Hybrid Automatic Repeat reQuest process (HARQ-ACK signals) in response to receiving Transport Blocks (TBs) transmitted from a base station. The UE conveys the HARQ-ACK information by selecting one resource from multiple resources in the control channel and by selecting a constellation point of the modulation scheme for the HARQ-ACK signal. Transmission diversity is supported using different control channel resources that are already available to the UE without configuring additional resources. Design principles are described to optimally map the HARQ-ACK information to control channel resources and modulation constellation points for a Time Division Duplex (TDD) system and for a Frequency Division Duplex (FDD) system.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
Transmission symbols mapping for antenna diversity
InactiveUS20080304593A1Polarisation/directional diversityError detection/correctionTime domainBurst transmission
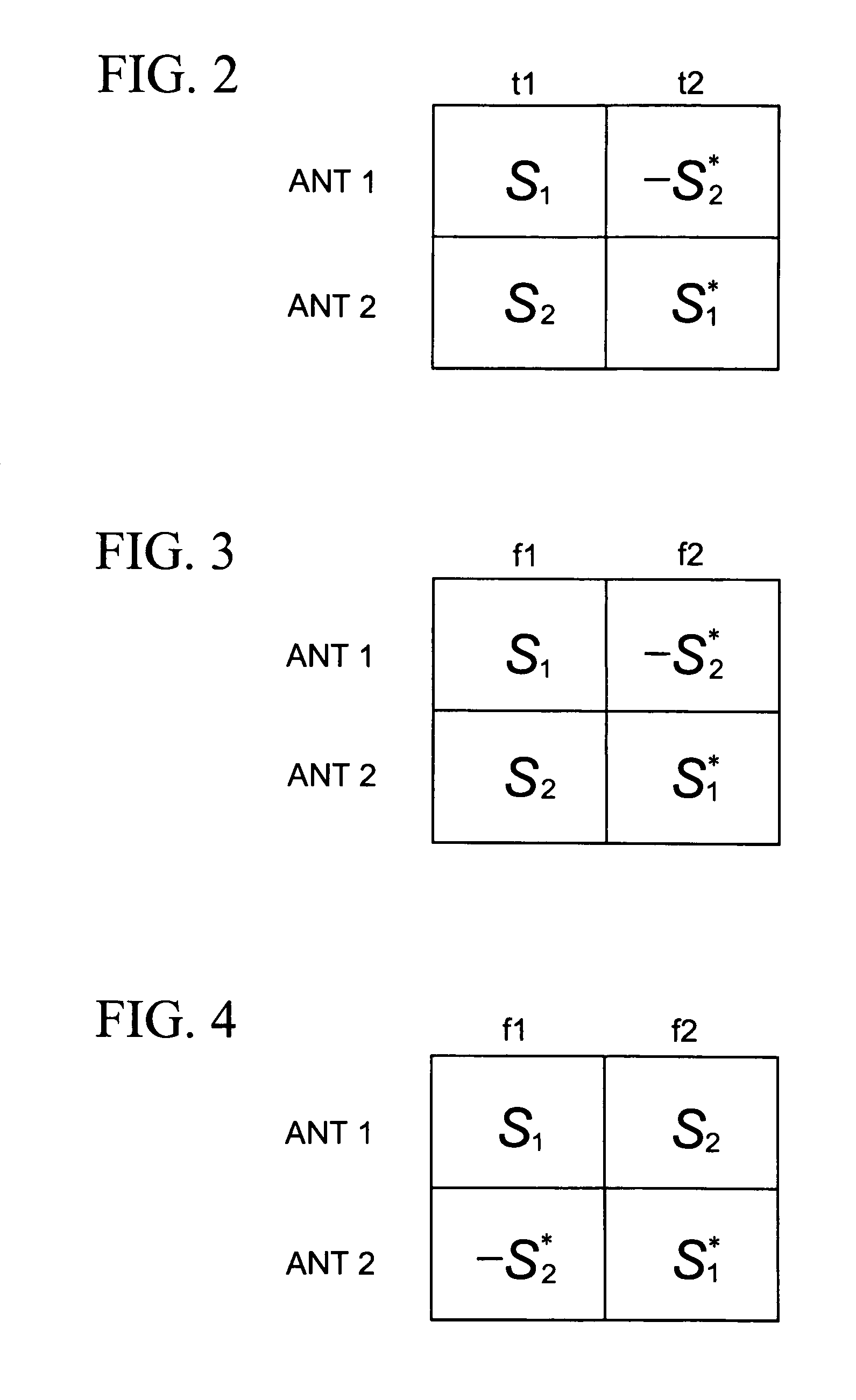
Methods and apparatus for transmitting data via multiple antennas by using antenna diversity. A transmission diversity scheme is established such that two transmission matrices that are in accordance with the space frequency block code combined with Frequency switched transmit diversity (SFBC+FSTD) scheme, are alternatively applied in either the frequency domain, or the time domain, or both of the frequency domain or then time domain. The symbols in the transmission matrices may be transmitted either as one burst in a primary broadcast channel (PBCH), or as discrete bursts in the primary broadcast channel.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
Transmit diversity in a wireless communication system
ActiveUS20080267310A1Spatial transmit diversitySecret communicationCommunications systemDiversity scheme
A method for transmitting data via multiple antennas by modulating data to be transmitted into a plurality of modulated symbols, encoding each pair of modulated symbols from among said plurality of symbols in accordance with a transmission diversity scheme to result in a plurality of N by N matrices, with each N by N matrix corresponding to each pair of modulated symbols, generating a M by M code matrix comprised of the plurality of N by N matrices, orthogonally spreading the M by M code matrix to generate an output matrix, generating a plurality of row-permuted matrices by exchanging at least one pair of rows in the output matrix, and transmitting the symbols in the plurality of row-permuted matrices via a plurality of antennas by using either a space time transmission diversity scheme, a space frequency transmission diversity scheme, or a combination of a space time transmission diversity scheme and a space frequency transmission diversity scheme.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
Method and apparatus for conveying antenna configuration information
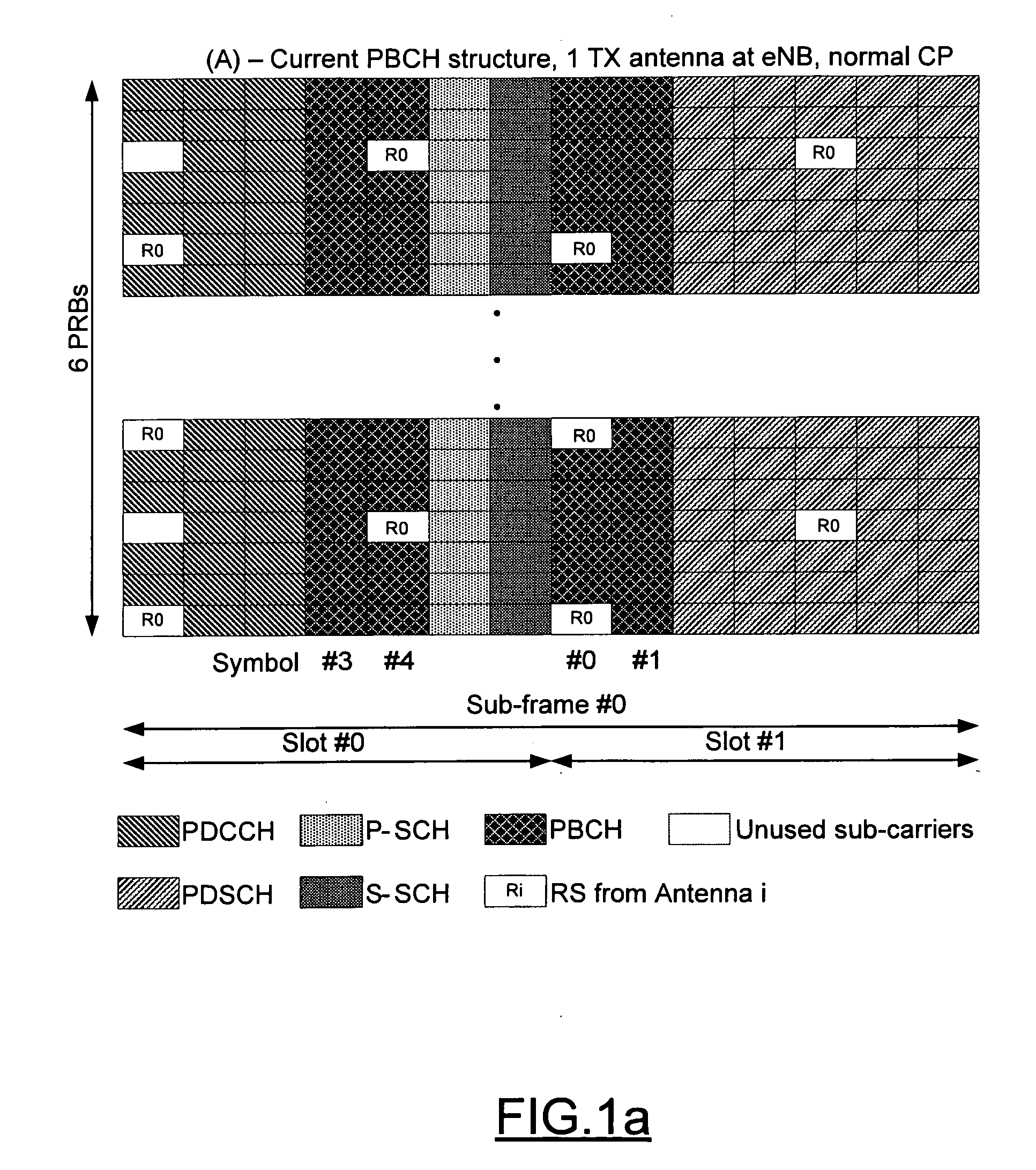
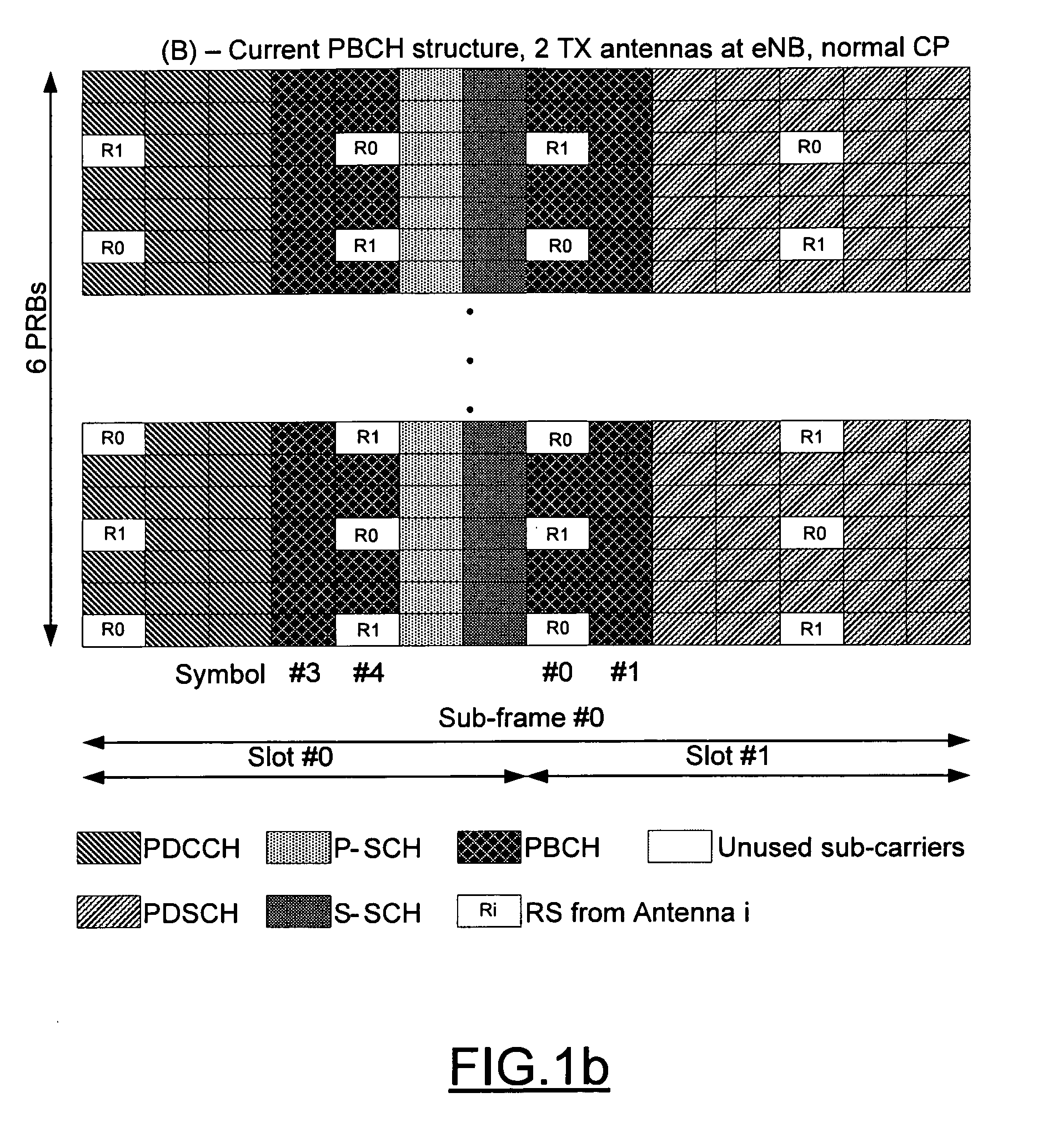
ActiveUS20090176463A1Reliable demodulationReliably interpretedModulated-carrier systemsDiversity/multi-antenna systemsBroadcast channelsEngineering
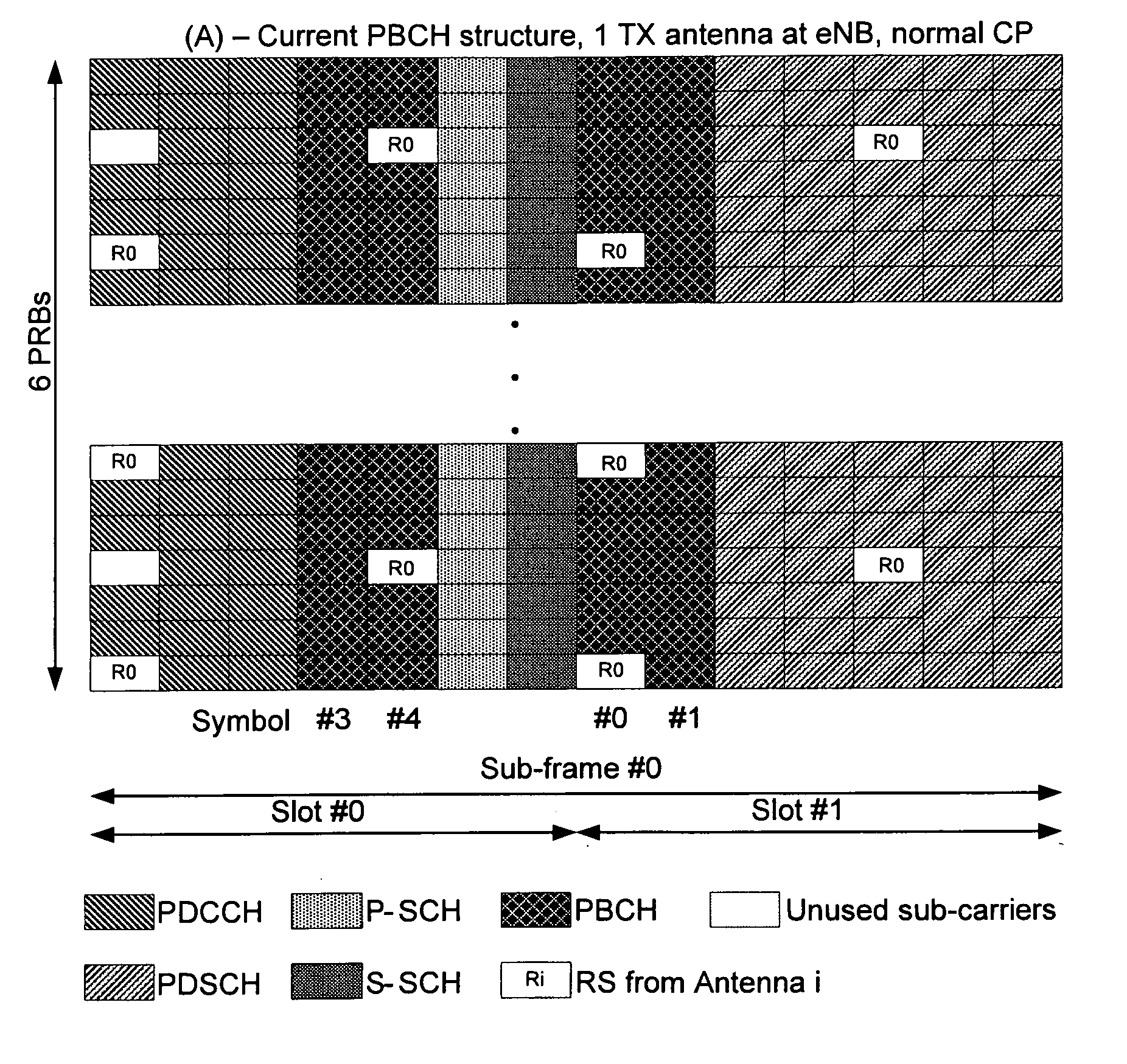
A method, apparatus and computer program product are provided for conveying information regarding the antenna configuration and / or the transmission diversity scheme to a recipient, such as a mobile device. In particular, information regarding the antenna configuration and / or the transmission diversity scheme can be conveyed by appropriately mapping a physical broadcast channel within a sub-frame so as to include reference signals indicative of different antenna configurations or transmission diversity schemes. Alternatively, masking, such as cyclic redundancy check masking, can be used to provide information regarding the antenna configuration and / or the transmission diversity scheme.
Owner:NOKIA CORP
Transmission method and system of downlink control information
InactiveCN101651995AGuaranteed flexibilityImprove compatibilitySpatial transmit diversityNetwork traffic/resource managementTransport systemControl channel
The invention discloses transmission method and system of downlink control information. Aiming at a new transmission mode X corresponding to a double-flow beam forming technology in R9, when a cycliccheck code in a downlink control channel schedules cell wireless network temporary identification scramble by a semi-static way, a downlink control information format 1A for presenting a single-layertransmission mode or a transmission mode with both single-layer transmission and transmission diversity is defined; a base station generates the downlink control information according to the downlinkcontrol information format 1A; user equipment receives the downlink control information and acquires the downlink control information according to the downlink control information format 1A, thereby accurately indicating the adopted transmission mode and an antenna port during single-layer transmission. The invention not only ensures the flexibility of system scheduling, but also adds no any system complexity and signaling cost, and has good compatibility with LTE R8.
Owner:ZTE CORP
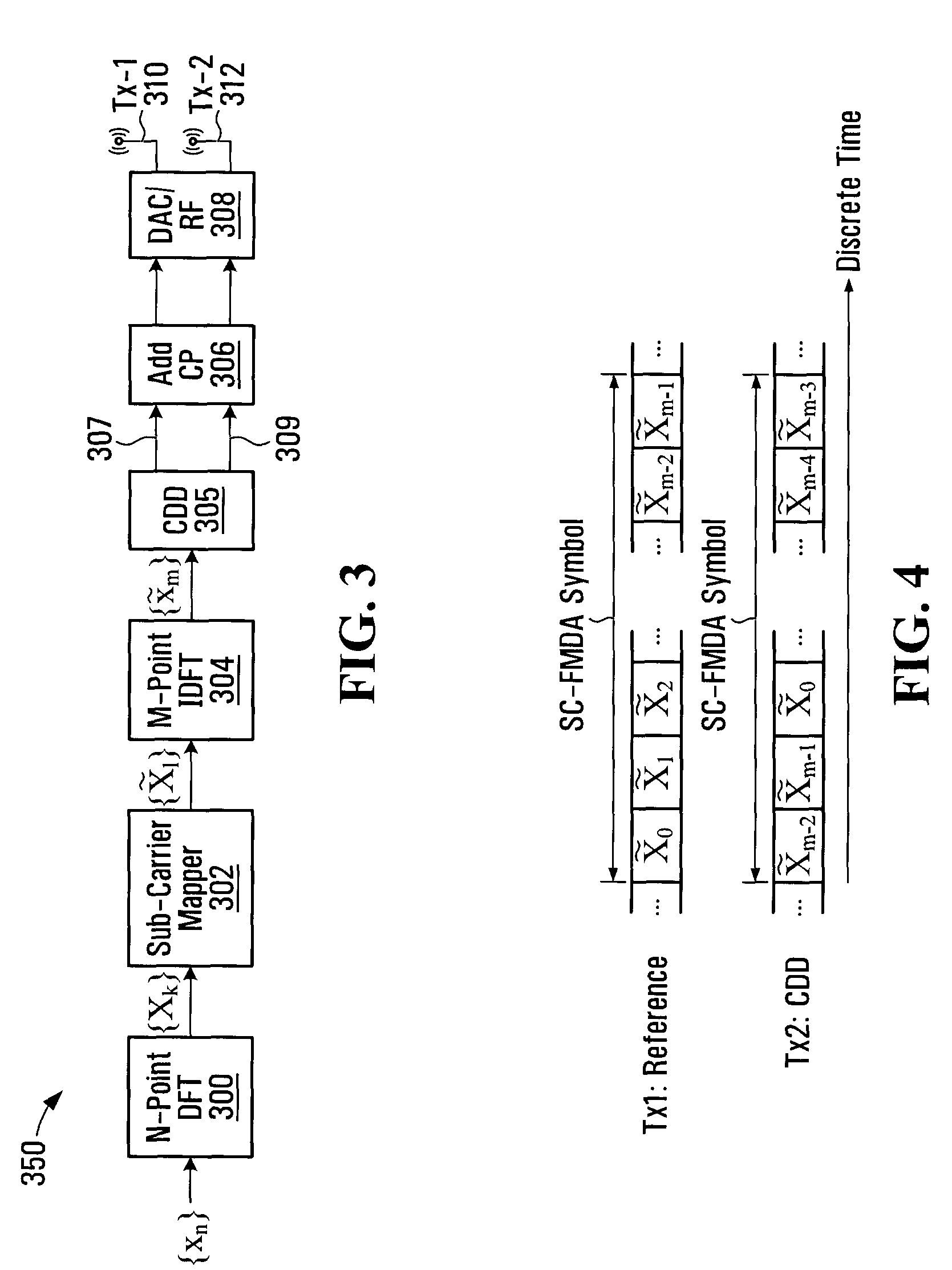
Systems and methods for sc-fdma transmission diversity
The present application provides methods, devices and transmitters that mitigate increases in peak to average power ratio (PAPR) from transmission diversity in a single carrier frequency division multiple access (SC-FDMA) modulated uplink A PAPR preserving precode matrix hopping method that utilizes cyclic shift delays is provided, as well as a sub-band based transmit diversity scheme. The present application also provides methods, devices and transmitters that relax the scheduling restrictions associated with uplink scheduling in the LTE standard.
Owner:APPLE INC
Selective application of frequency hopping for transmission of control signals
A Method and apparatus for selectively applying, by a User Equipment (UE), Frequency Hopping (FH) for a transmission of Uplink Control Information (UCI) signals in a Physical Uplink Control CHannel (PUCCH). The UE applies FH when the UCI is of a first type and does not apply FH when the UCI is of a second type. The UE applies FH when transmission diversity is not applied to the UCI transmission and does not apply FH when transmission diversity is applied to the UCI transmission. UEs operating in a legacy mode do not apply FH to the UCI transmission while UEs operating with additional functionalities may apply FH to the UCI transmission according to the UCI type and the use of transmission diversity.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
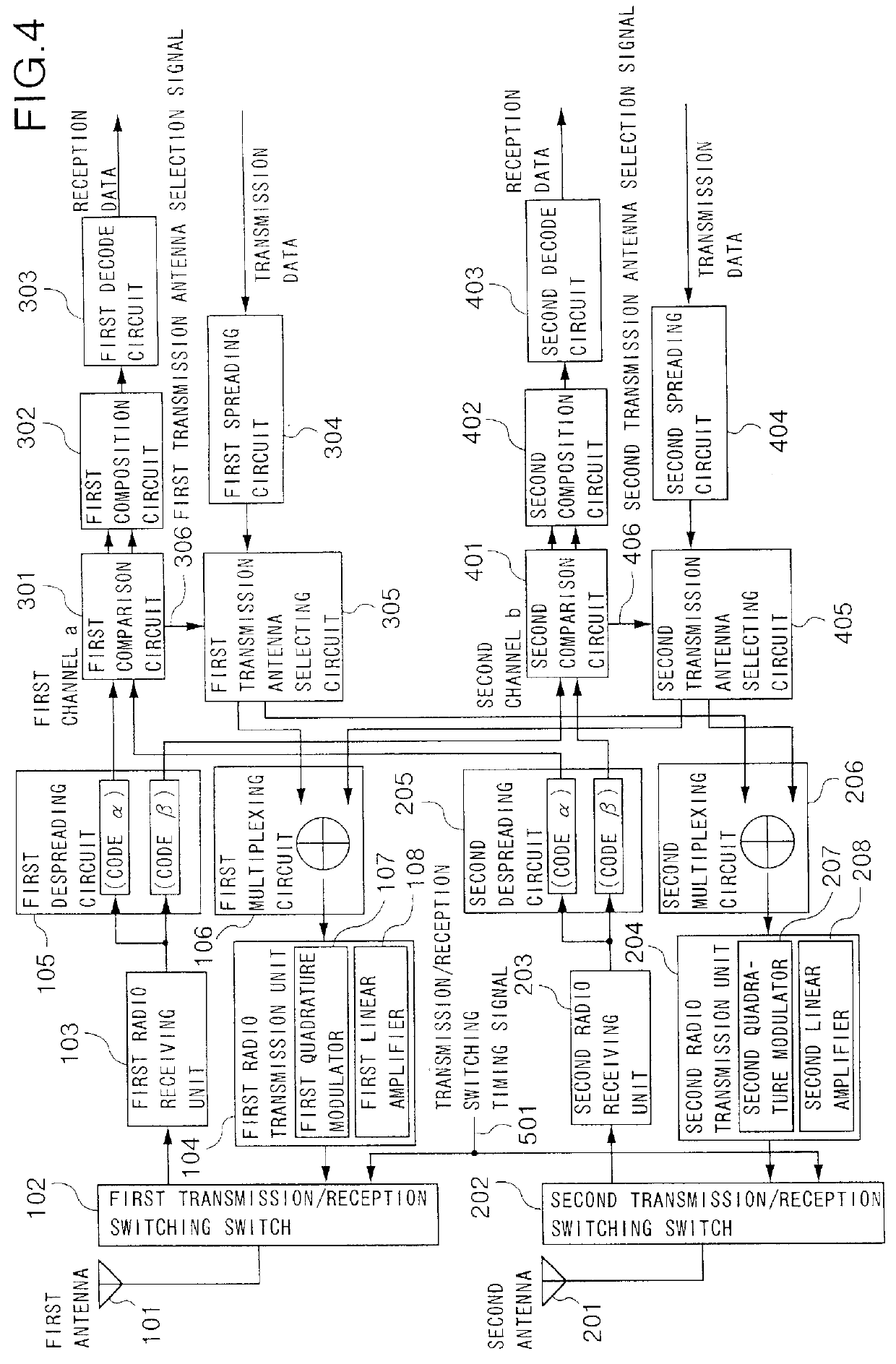
Transmission diversity for a CDMA/TDD mobile telecommunication system
InactiveUSRE36591E1Improve communication qualityExcellent stateSpatial transmit diversityModulated-carrier systemsMultiplexingEngineering
In a base station which has a plurality of antennas, each of a plurality of comparison circuits operates to compare correlation levels, which are obtained by despreading received signals for a plurality of channels, with each other with respect to the antennas. Each of a plurality of transmission antenna selecting circuits operates to determine from which antenna a transmission signal is to be transmitted for every channel. Each of a plurality of multiplexing circuits operates to multiplex the transmission signals of the individual channels, which are spread, for every antenna. As a result, on the basis of the result of the comparison of the correlation levels with respect to the antennas, a transmission antenna is selected for every channel, and the signals of the channels that are to be transmitted by a given antenna are multiplexed, whereby the base station achieves transmission diversity.
Owner:PANASONIC INTELLECTUAL PROPERTY CORP OF AMERICA
Transmission diversity communication system
InactiveUS20050014474A1SmallReadily and efficiently perform calibrationEnergy efficient ICTSpatial transmit diversityInformation controlCommunications system
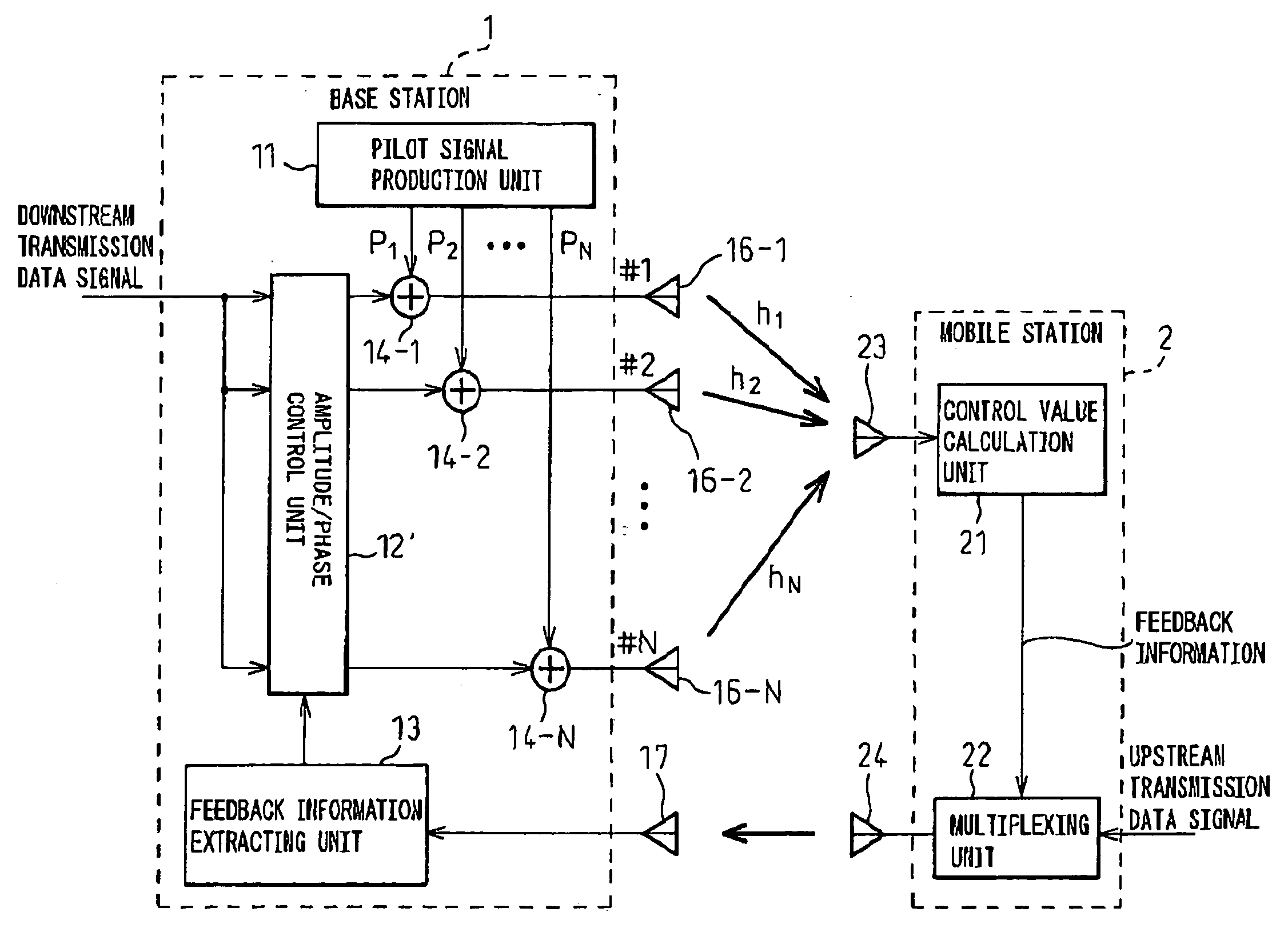
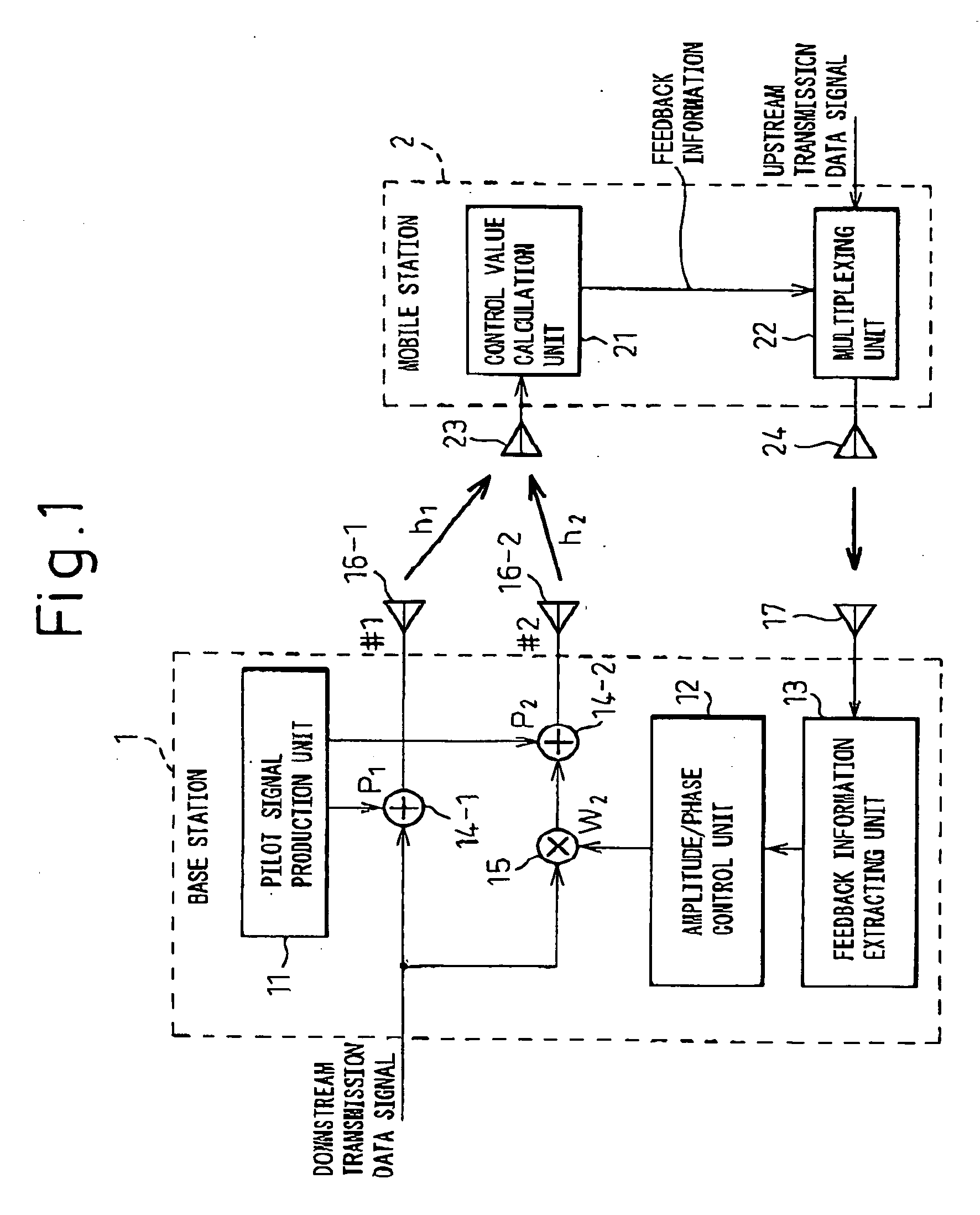
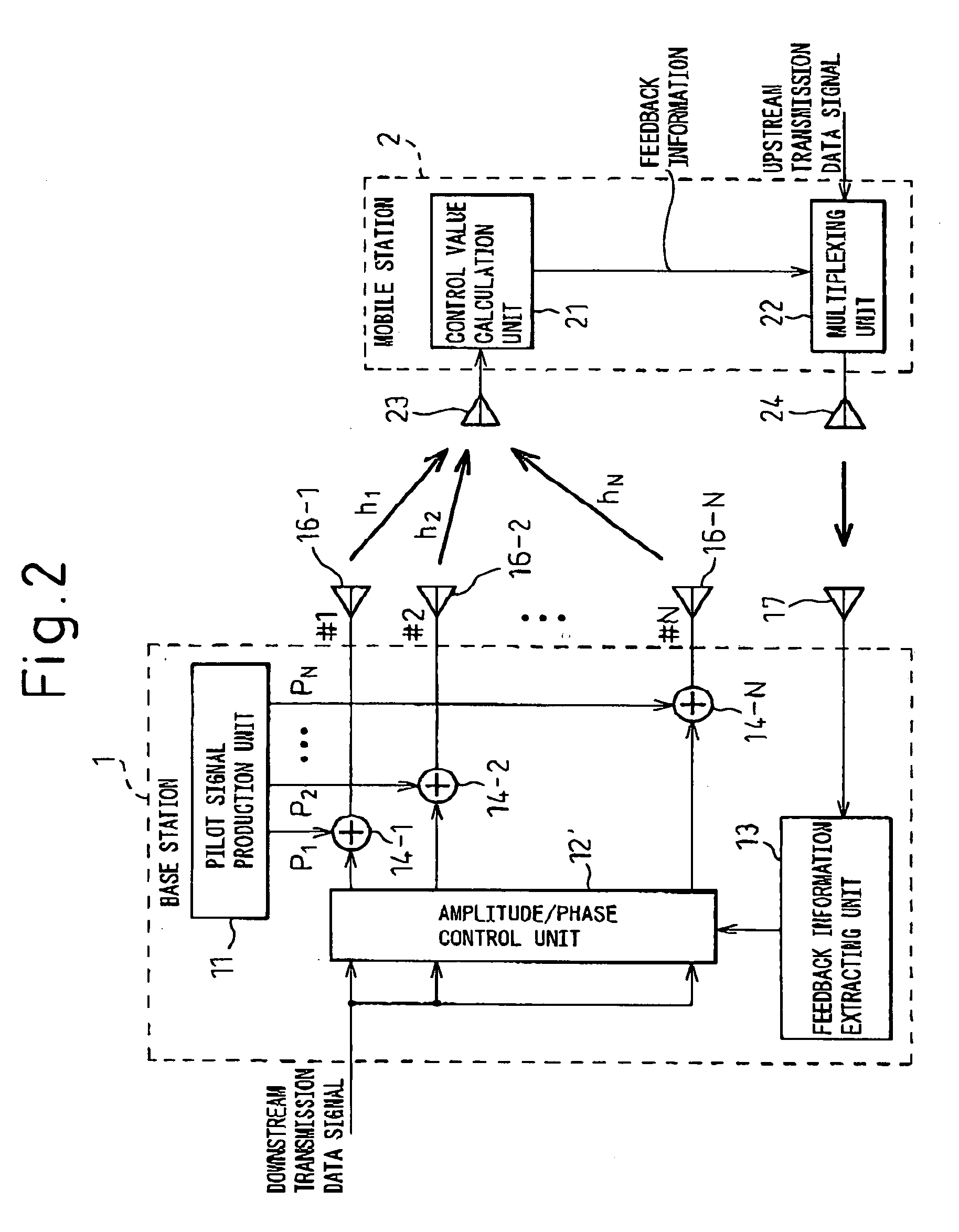
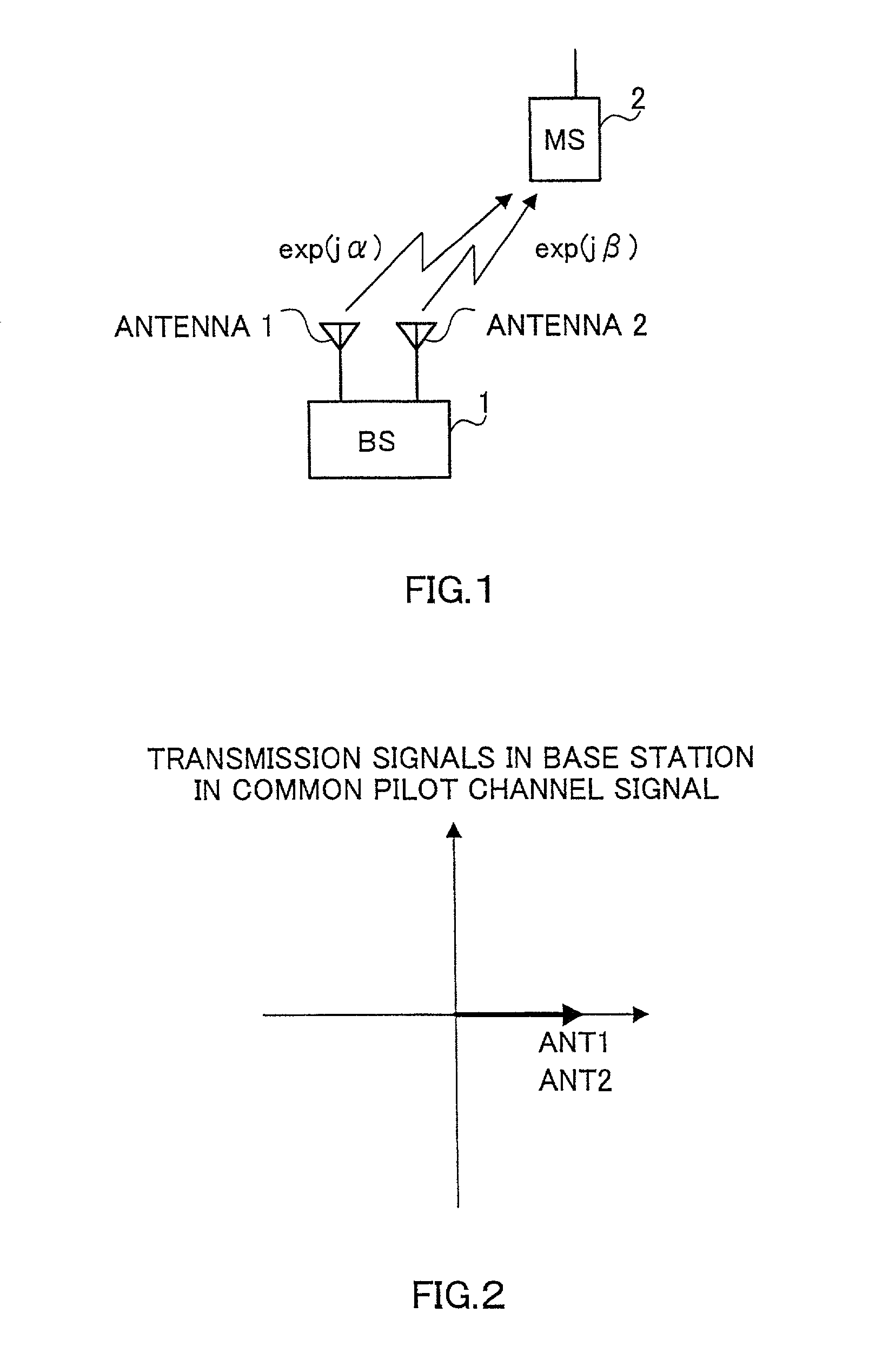
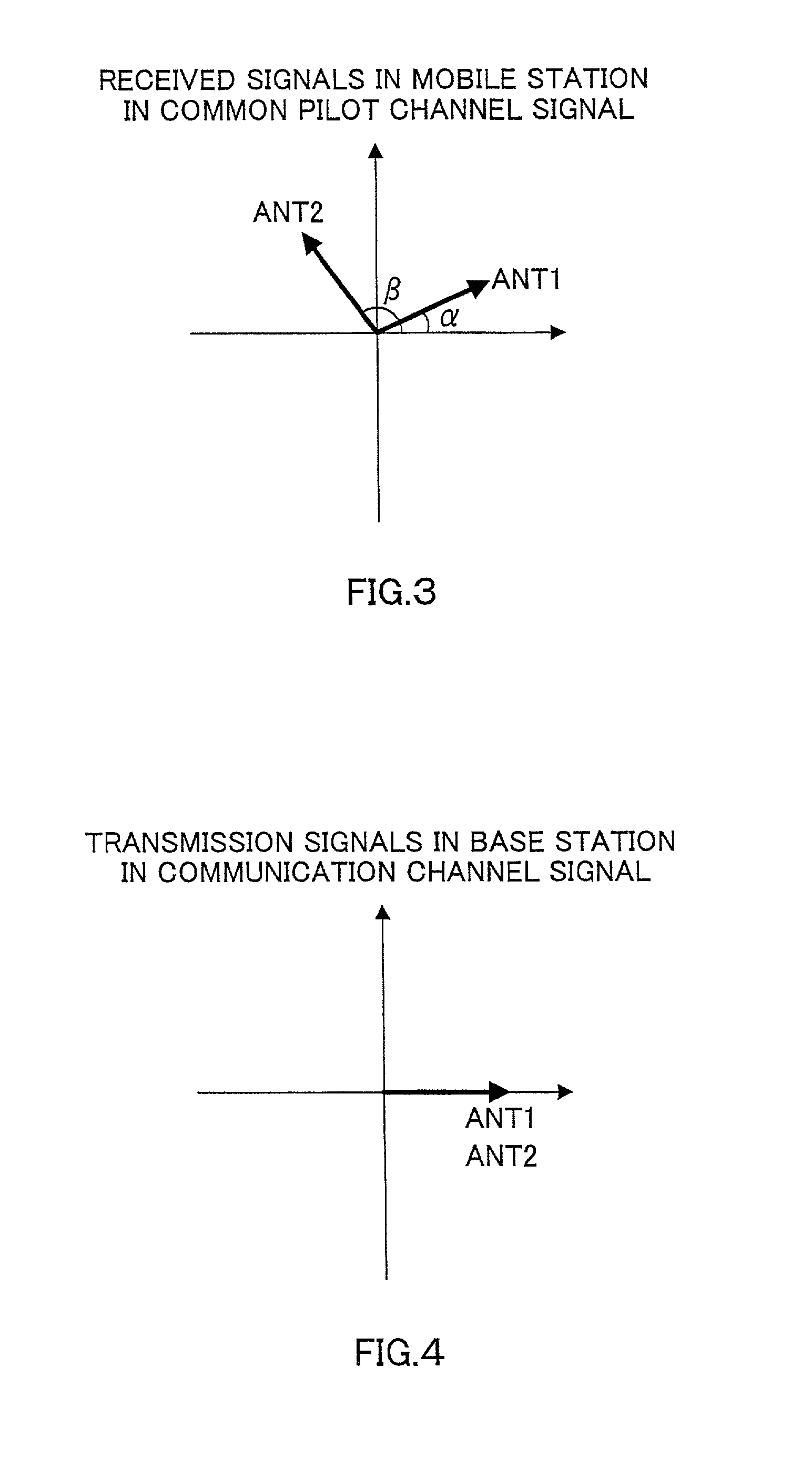
Provided is a mobile cellular communication system or, more particularly, a transmission diversity communication system in which when the number of transmitting antennas is increased, antennas can be calibrated readily and efficiently with power saved without degradation of the characteristic concerning fading. The transmission diversity communication system is a closed-loop transmission diversity communication system. In the transmission diversity communication system, a base station transmits common pilot signals via a plurality of antennas, and a mobile station receives the common pilot signals. The mobile station transmits feedback signals, which are produced through analysis of the common pilot signals, to the base station. The base station controls a downward transmission signal on the basis of the pieces of feedback information. Herein, the plurality of antennas is divided into a plurality of groups. The common pilot signal is transmitted via a reference antenna included in each of the groups. The common pilot signal is alternately transmitted at a low frequency via the other antennas.
Owner:FUJITSU LTD
Beamforming method and apparatus for acquiring transmission beam diversity in a wireless communication system
A data transmission method for a base station to acquire transmission beam diversity in a wireless communication system is provided. The data transmission method includes selecting at least two transmission beams to be used for data transmission from among multiple transmission beams corresponding to transmission beam information, if receiving the transmission beam information regarding the multiple transmission beams from a terminal, and transmitting data encoded with a predetermined orthogonalization code to the terminal via the selected at least two transmission beams.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
Communication terminal apparatus and radio communication method
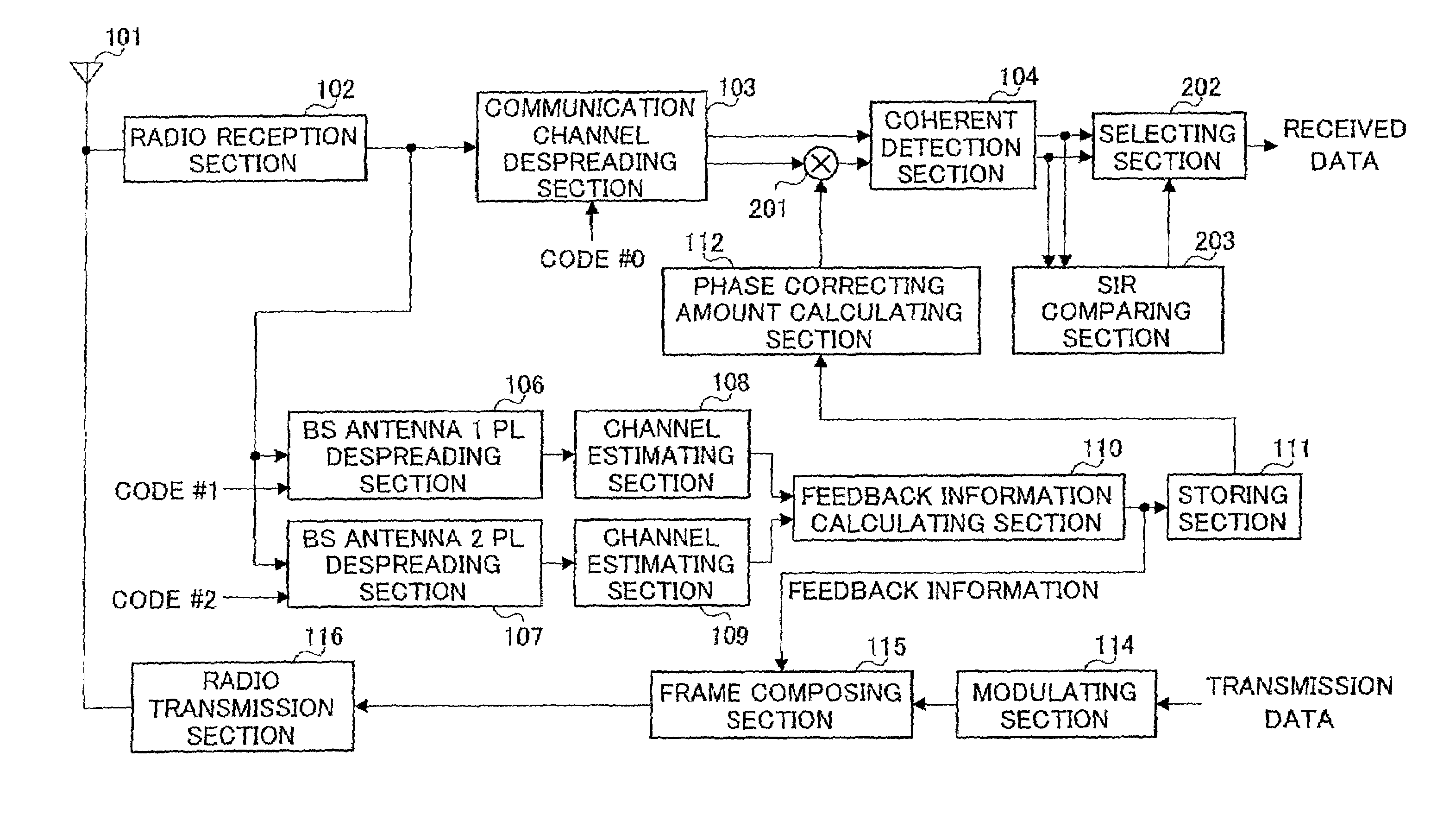
InactiveUS6980612B1Improve reception performanceLower performance requirementsSpatial transmit diversityError preventionPhase correctionSignal on
In closed-loop transmission diversity, a communication terminal apparatus calculates a phase correcting value for compensating for an effect of phase rotation due to the transmission diversity, using known feedback information, and corrects a received signal on a communication channel based on the phase correcting value, or corrects a channel estimation value based on the phase correcting value.
Owner:PANASONIC CORP
Communication terminal device and channel estimating method
InactiveUS7002939B1Improve reliabilitySpatial transmit diversityModulated-carrier systemsCommunications systemTerminal equipment
A phase rotation amount estimating unit (210) rotates a channel estimation value of a signal in a common pilot channel (B) through a candidate phase rotation amount θ (θ=0, 180) for synthesizing with a channel estimation value of a signal in a common pilot channel (A). A phase rotation is estimated based on the highest one of orthogonalities between this synthesis result and channel estimation values of signals in individual channels. A channel estimation value synthesis unit (211) synthesizes a value obtained by rotating a channel estimation value of a signal in the common pilot channel (B) through a phase rotation amount θ with a channel estimation value of a signal in the common pilot channel (A), whereby the reliability of a channel estimation value can be enhanced in a transmission diversity-introduced radio communication system.
Owner:PANASONIC CORP
Beamforming method and apparatus for acquiring transmission beam diversity in a wireless communication system
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
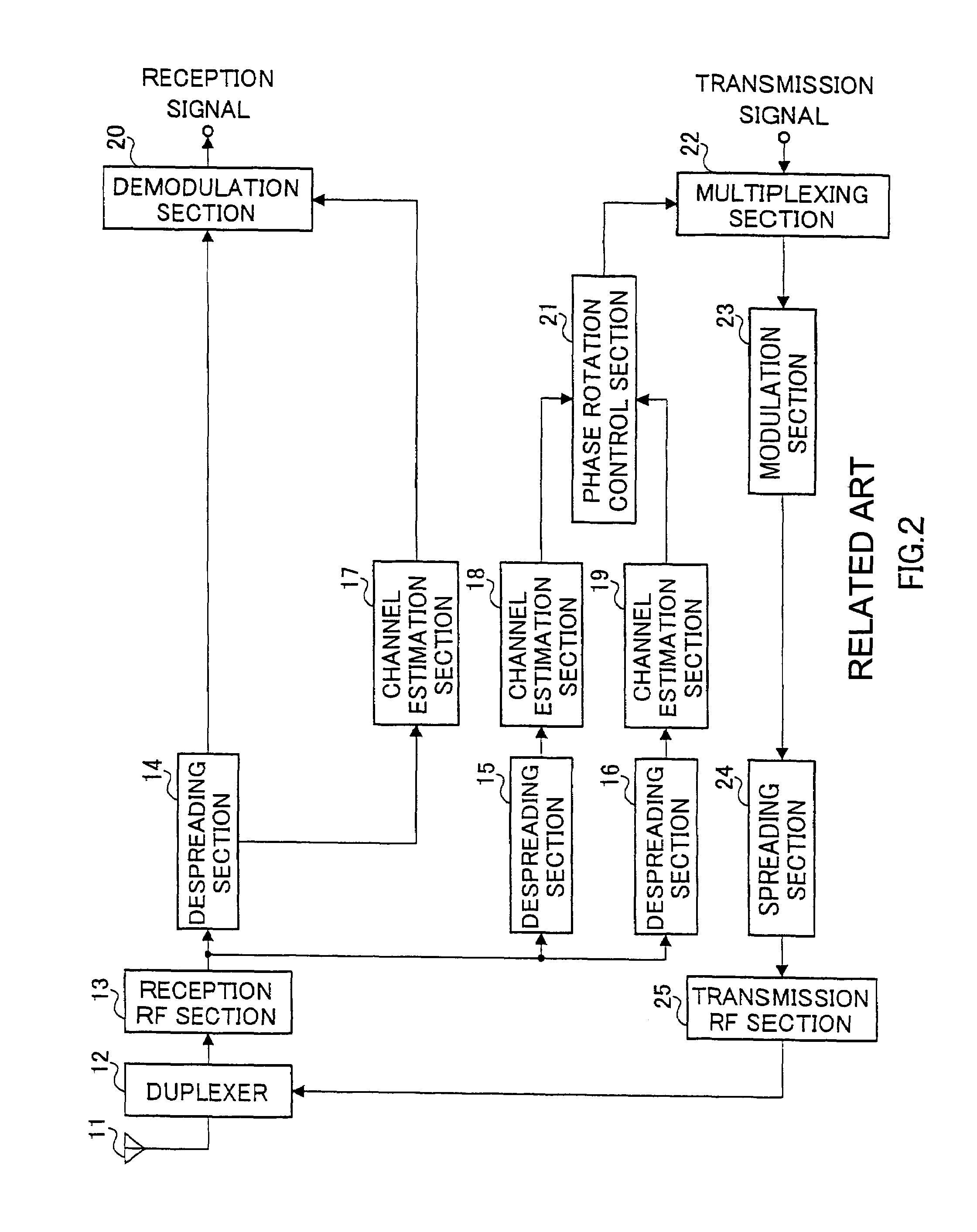
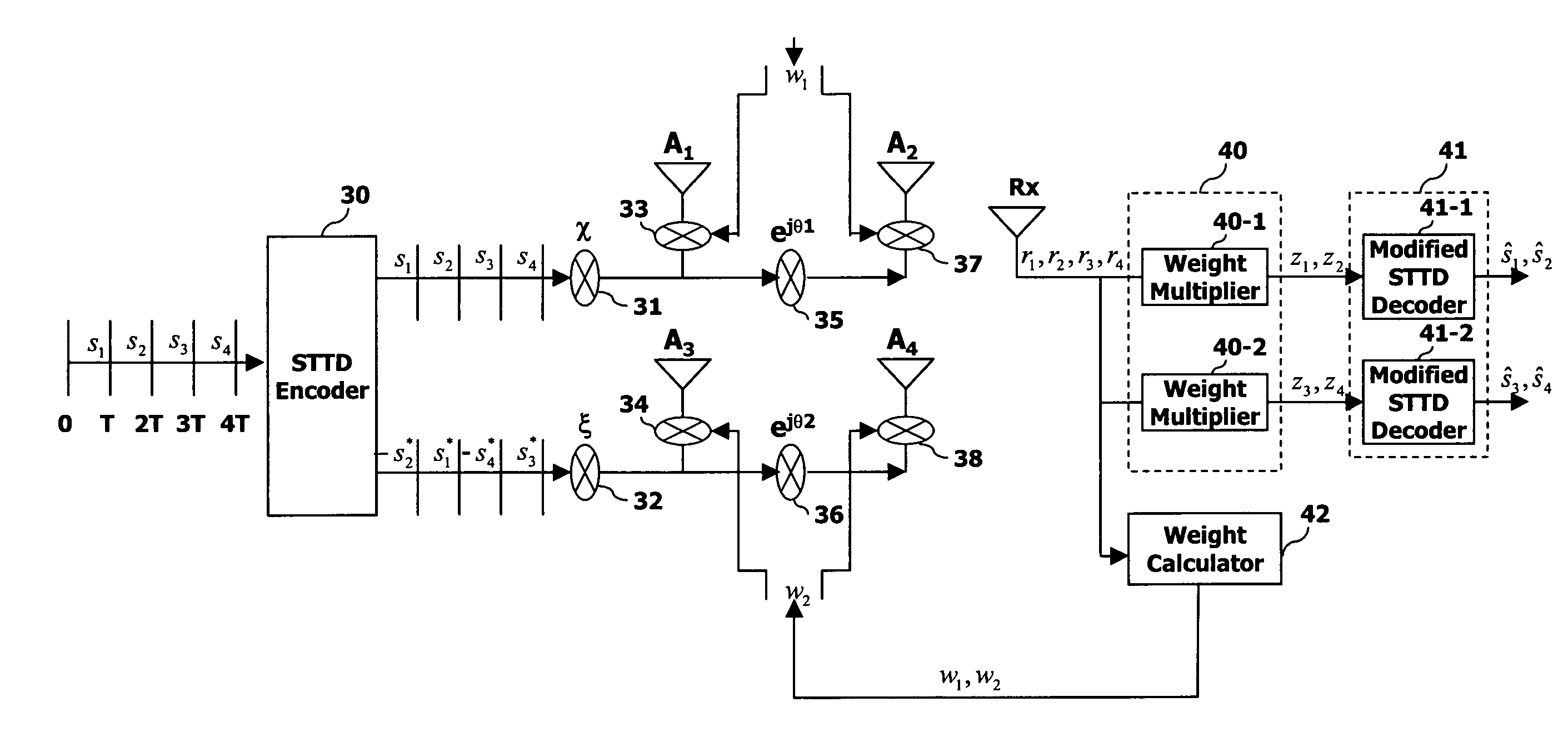
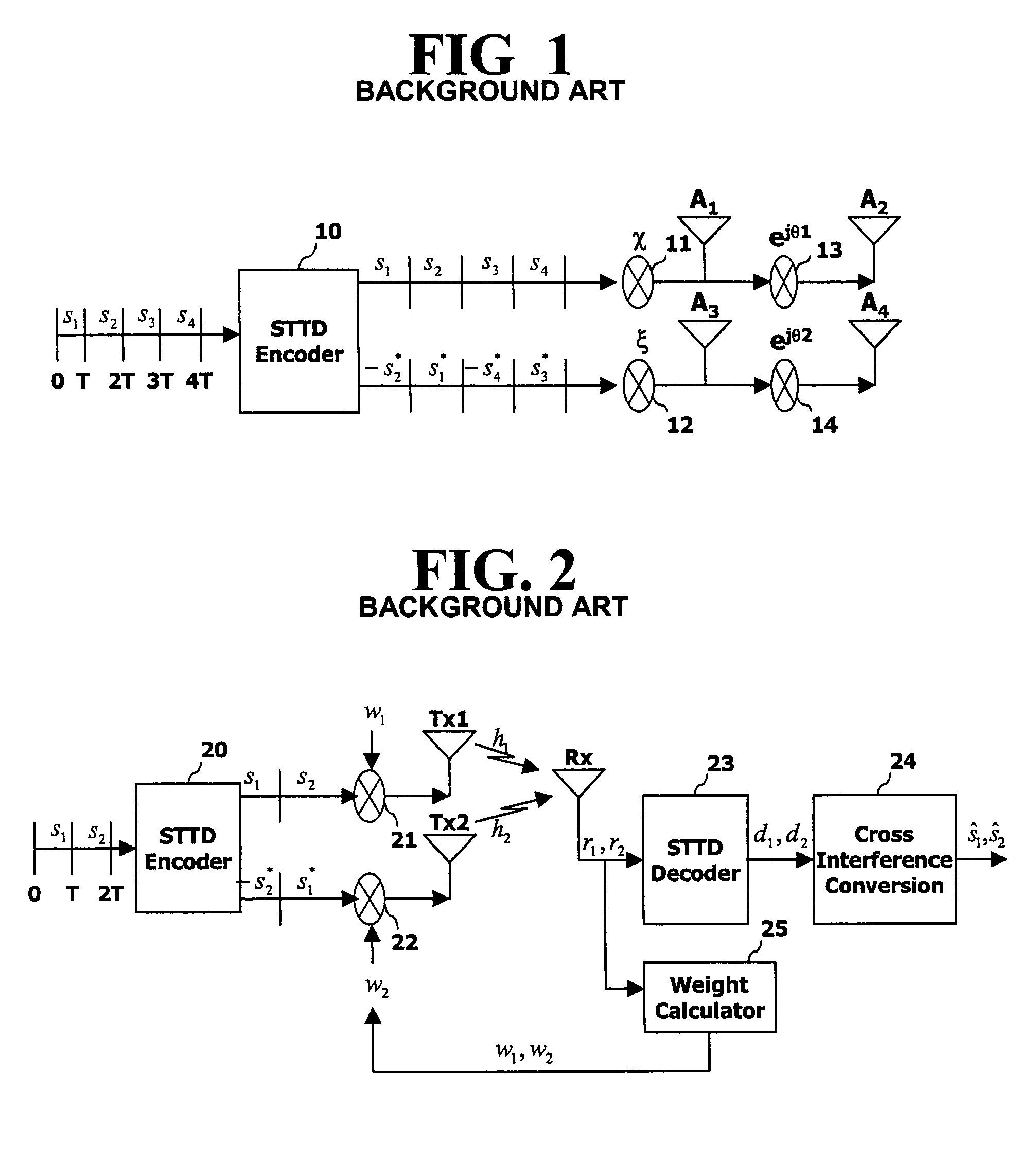
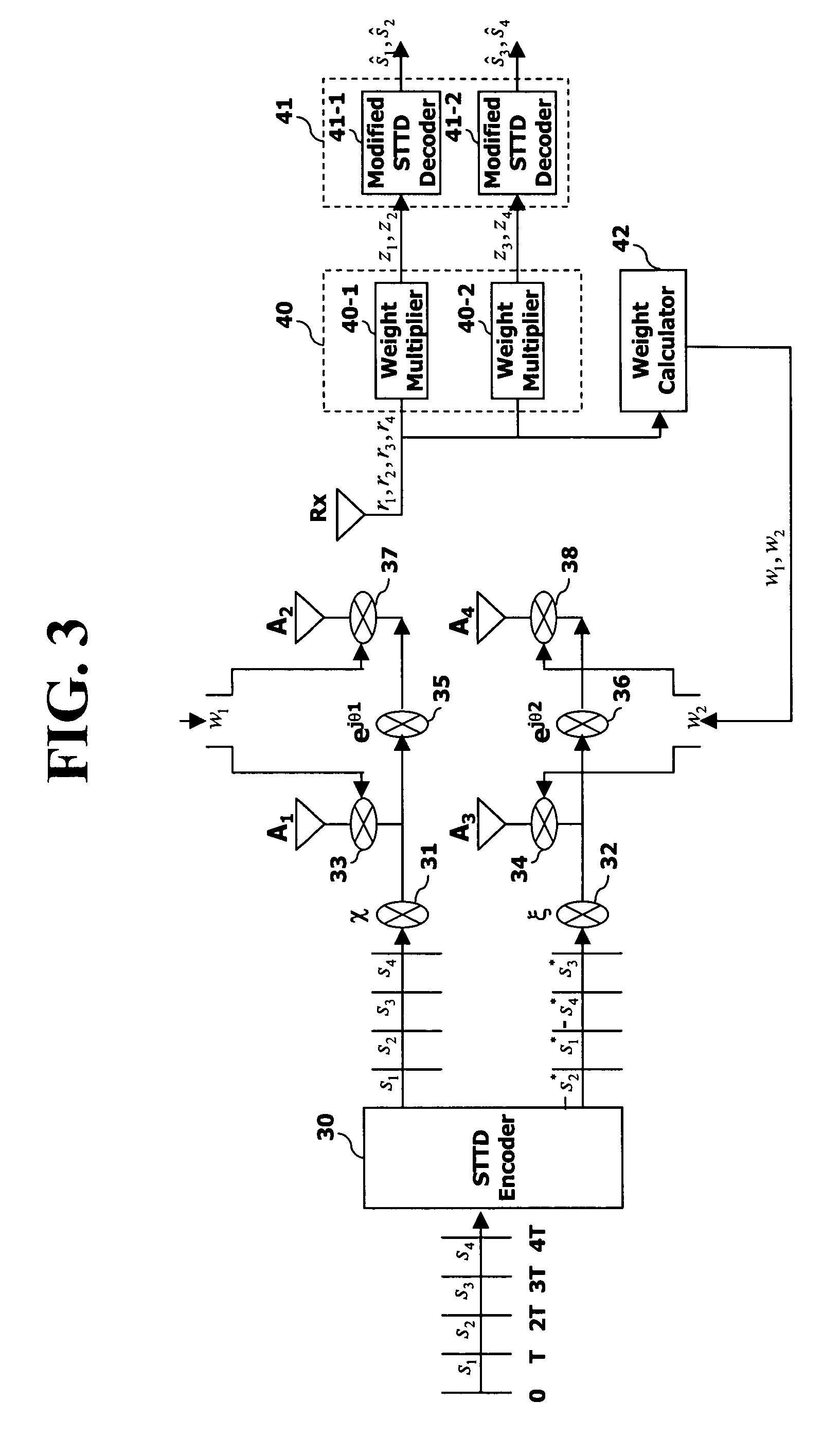
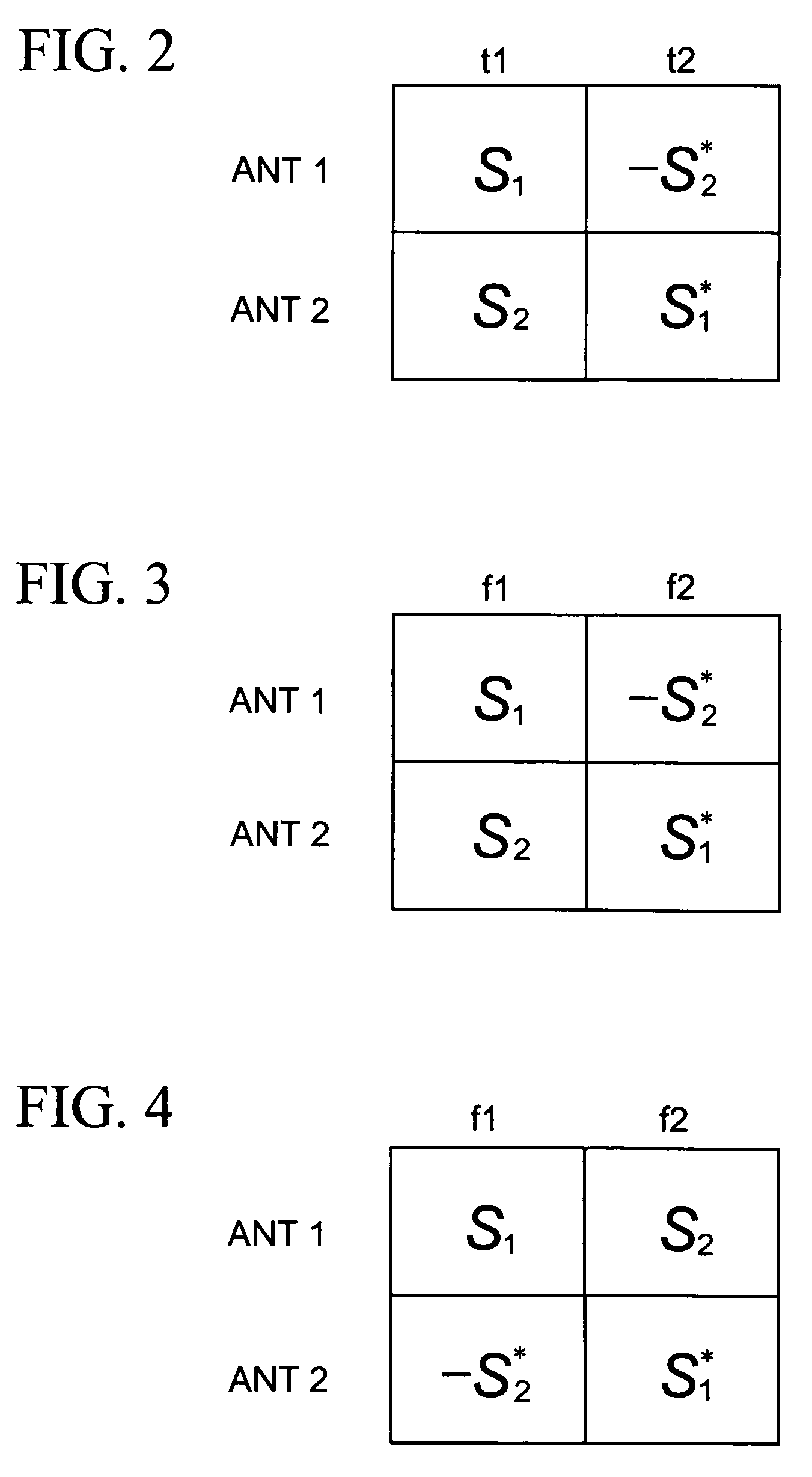
Space-time transmit diversity (STTD) for multiple antennas in radio communications
InactiveUS7266157B2Accurate operationMaximize transmit powerSpatial transmit diversityMultiplex communicationSpace time transmit diversityClosed loop
A closed-loop STTD system extended from an open-loop STTD system adopting four antennas transmission diversity technique and its signal transmitting method are disclosed. The signal transmitting method in a closed-loop space-time transmit diversity (STTD) system having a plurality of transmission antennas, includes: space-time coding symbols to be transmitted; classifying the coded symbols to certain groups; and multiplying different weight values to each transmission symbol group and transmitting them.
Owner:LG ELECTRONICS INC
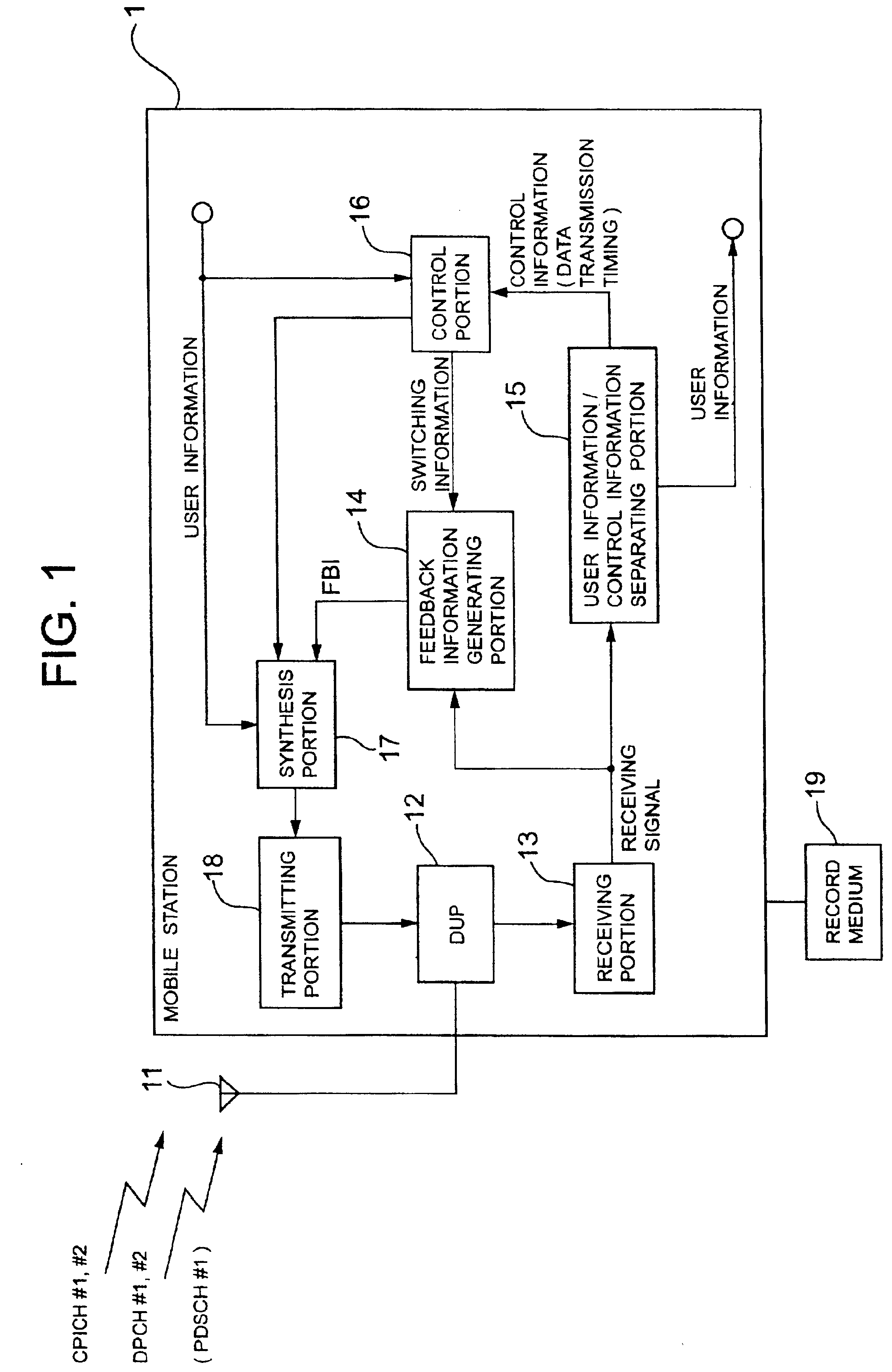
Mobile communication system, mobile terminal, and transmission diversity application method used therefor
InactiveUS6879831B2Efficiently transmission diversityKeep for a long timeSite diversitySpatial transmit diversityMobile communication systemsSoft handover
A mobile terminal is capable of efficiently performing transmission diversity of a PDSCH and a DPCH without increasing the number of bits of control information to be fed back to a base station and rendering a feedback period longer. A feedback information generating portion determines transmission diversity control information on the PDSCH in response to a switching instruction from a control portion, when receiving first PDSCH data during soft handover, based on a receiving state of a signal of a cell for sending the PDSCH data. In addition, when receiving the last PDSCH data during the soft handover, the feedback information generating portion determines the transmission diversity control information on the DPCH in response to the switching instruction from the control portion based on the receiving state after synthesis of the signal of the cell of an active set.
Owner:NEC CORP
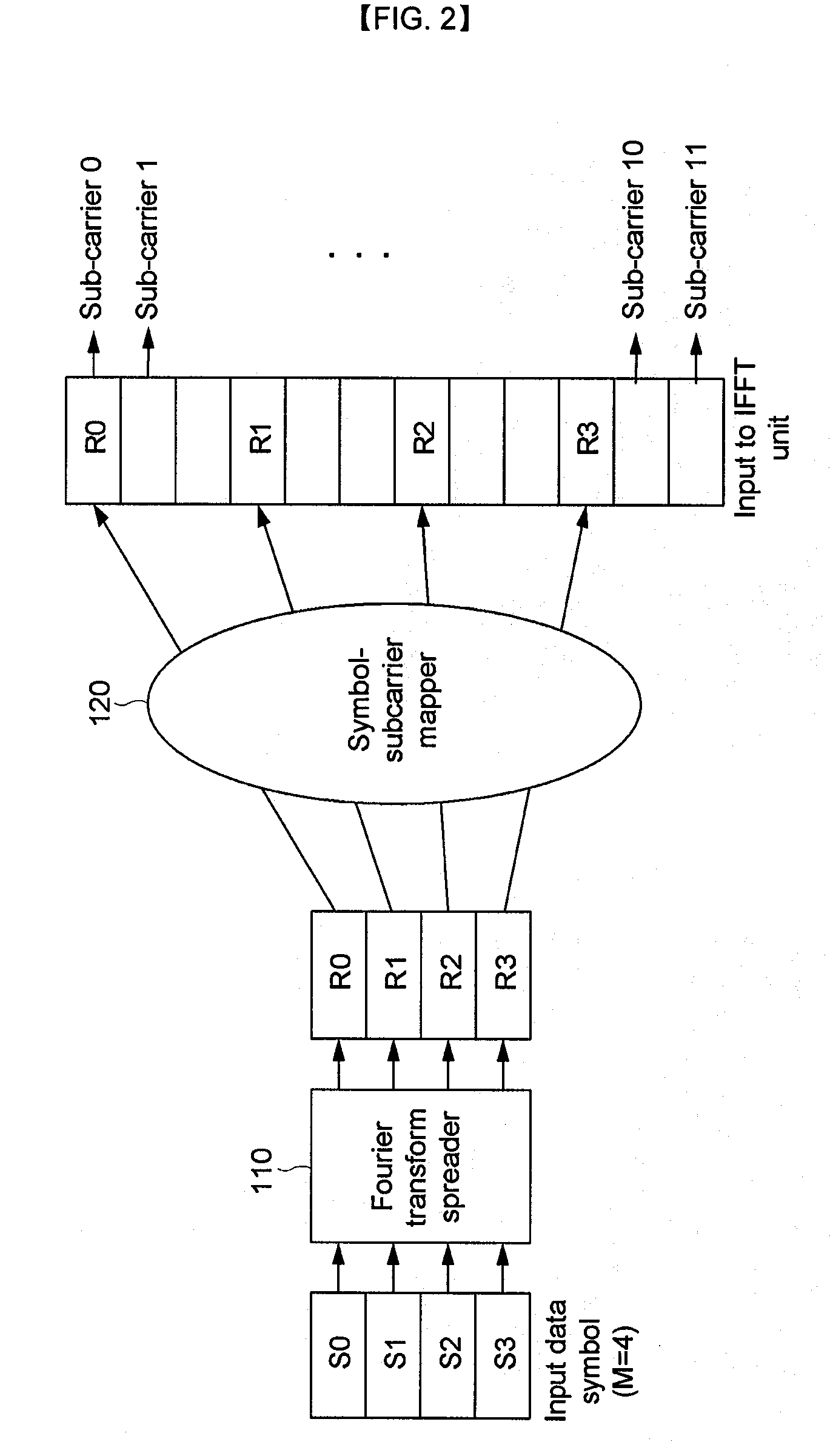
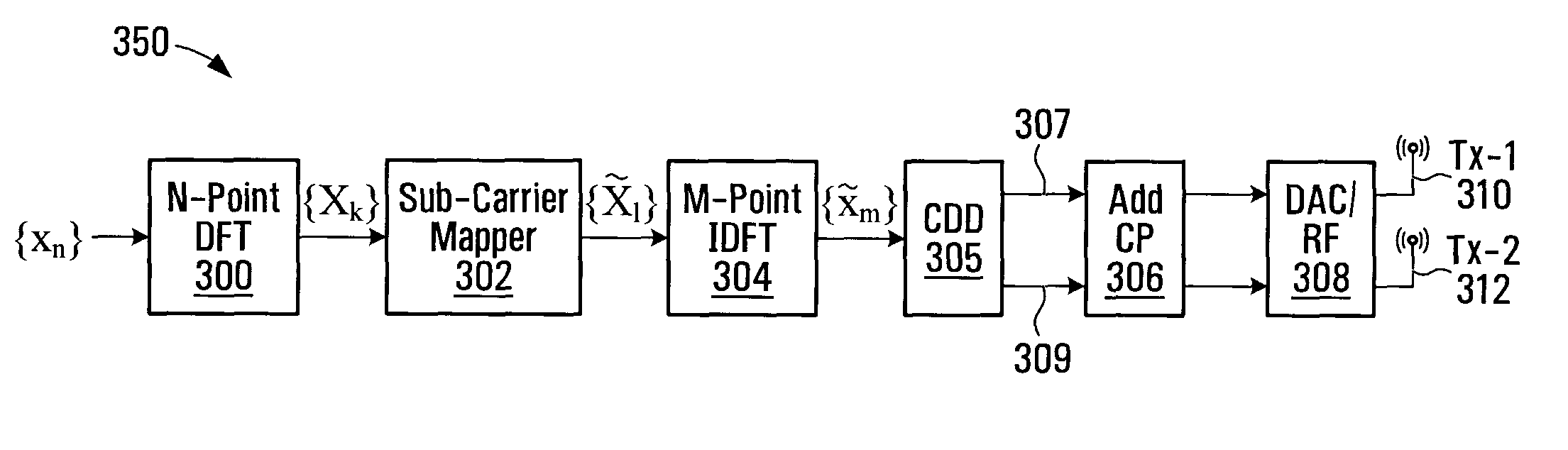
Method and Apparatus for Transmitting by Using Transmit Diversity at Dft Spread Ofdma
ActiveUS20080316913A1Radio transmissionOrthogonal multiplexBurst transmissionPacket data transmission
The present invention relates to a packet data transmission method in an OFDMA system and an apparatus thereof. The present invention provides a user packet data transmission method including generating a RACH burst for channel information estimation, selecting a first antenna among a plurality of antennas, transmitting the RACH burst through the first antenna to a base station, receiving a data transmission acceptance signal from the base station, in response to the RACH burst, transmitting user packet data through the first antenna when receiving a signal indicating that the data transmission is allowed, and selecting a second antenna that is difference from the first antenna and transmitting a RACH burst through the second antenna when receiving a signal indicating that the data transmission is not allowed, and a transmitting apparatus of a mobile station having the plurality of antennas. According to the present invention, the RACH burst and user packet data are transmitted by using a mobile station having a plurality of antennas in an LTE-applied OFDMA system, and therefore data transmission can be performed with a wide bandwidth and high data rate and a deep fading period that may occur during the data transmission can be reduced, thereby preventing call dropping and improving data transmission performance.
Owner:KT CORP +1
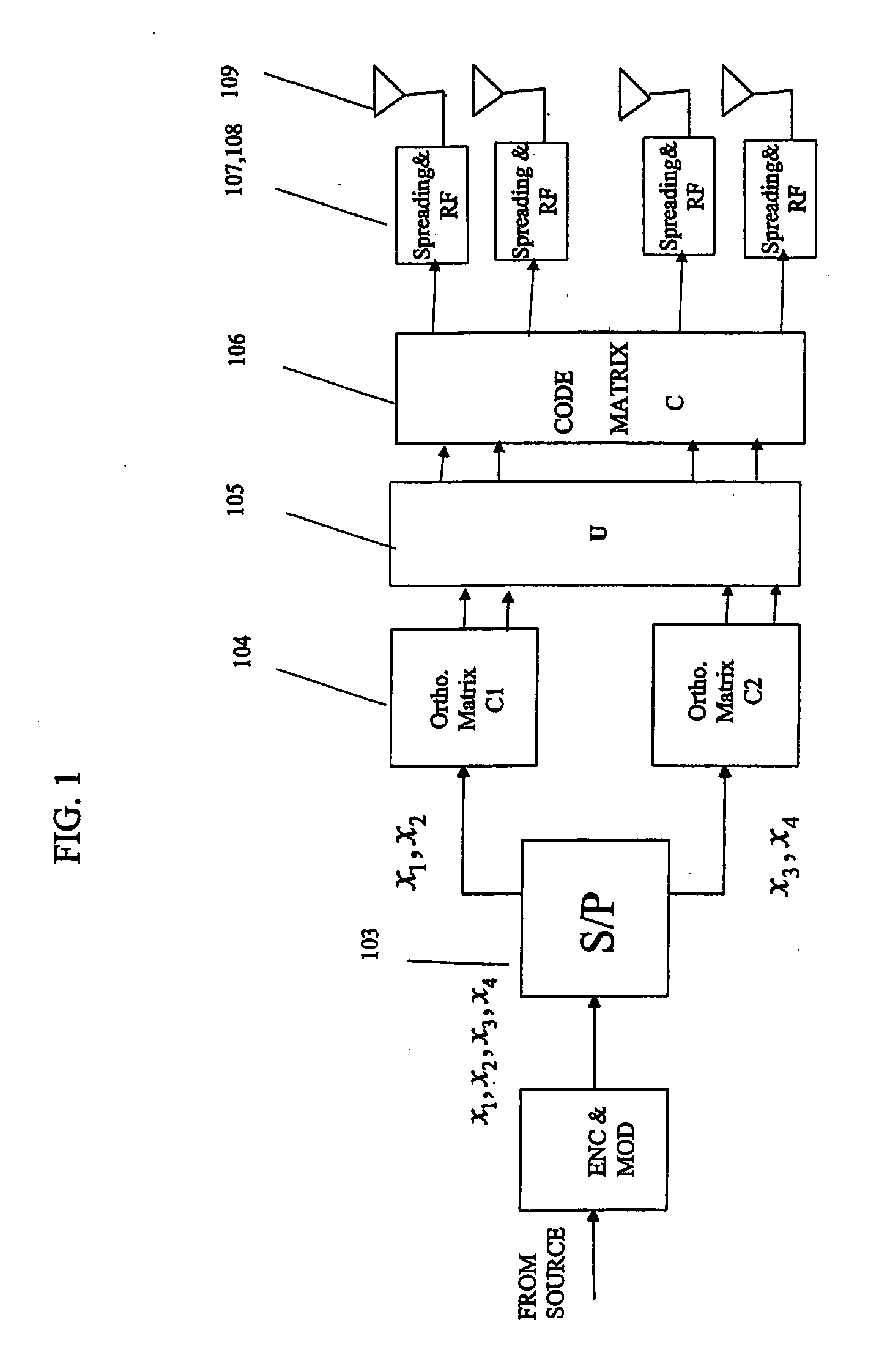
High rate transmission diversity transmission and reception
The performance and symbol rate in a wireless mobile system are increased by forming a transmission code matrix using transformed orthogonal codes, in such a way that the code is robust to channel statistics and operates well in both Ricean and (correlated) Rayleigh channels. Furthermore, the invention enables high symbol rate transmission using multiple transmit antennas, and one or multiple receive antennas, and obtains simultaneously high diversity order and high symbol or data rate.
Owner:NOKIA CORP
Transmission symbols mapping for antenna diversity
InactiveUS7991063B2Polarisation/directional diversityFrequency diversityBroadcast channelsTime domain
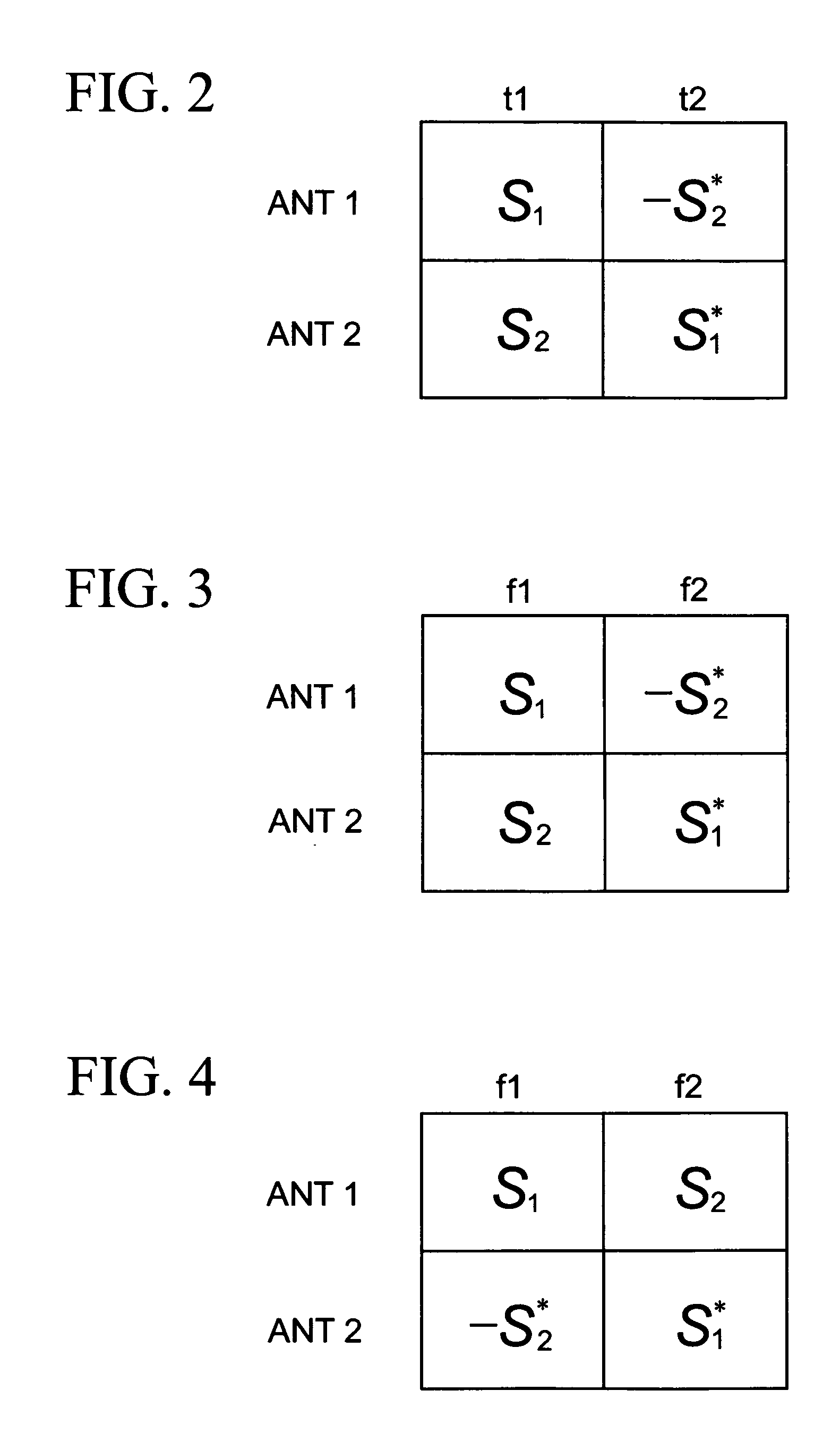
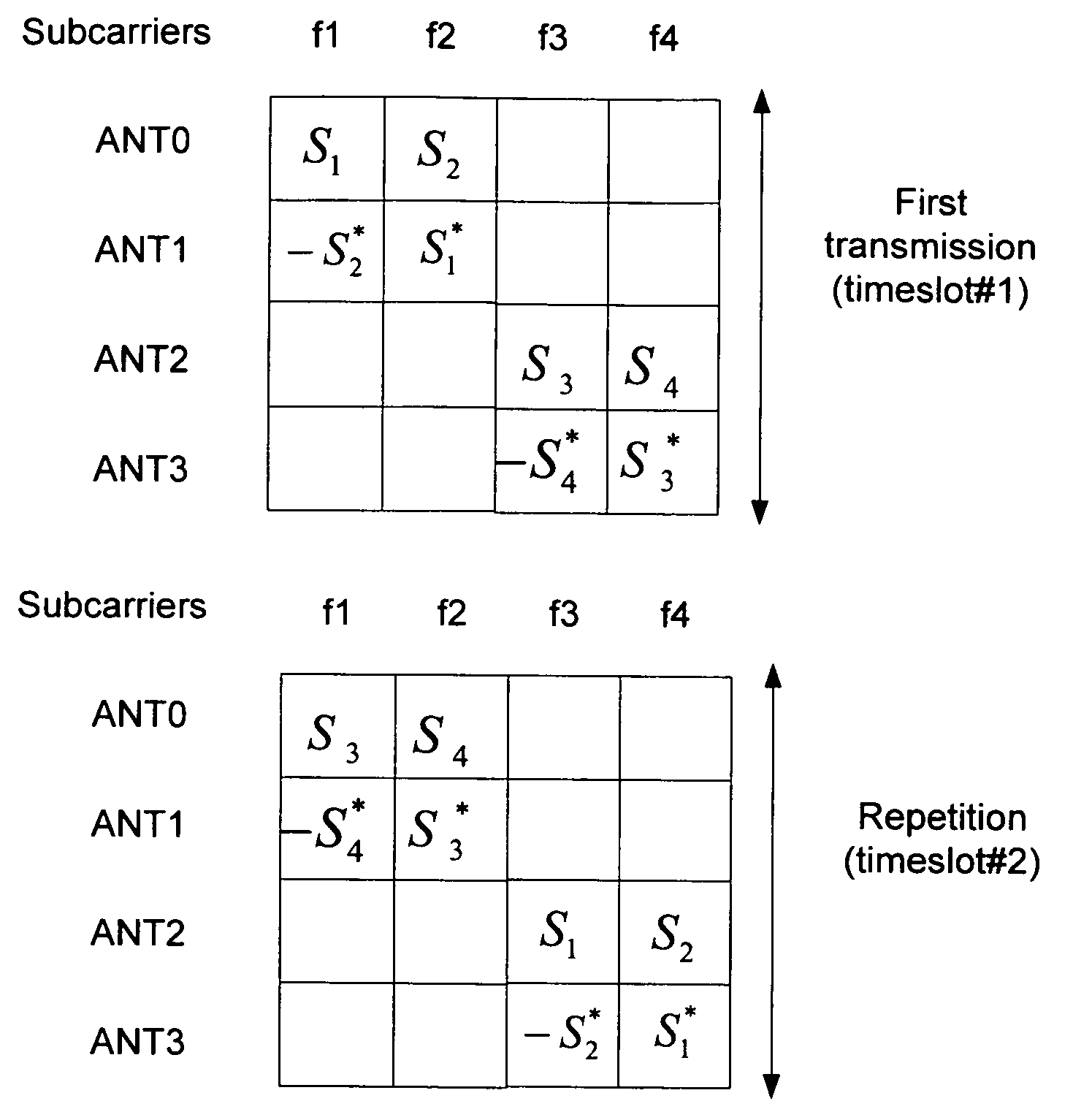
Methods and apparatus for transmitting data via multiple antennas by using antenna diversity. A transmission diversity scheme is established such that two transmission matrices that are in accordance with the space frequency block code combined with Frequency switched transmit diversity (SFBC+FSTD) scheme, are alternatively applied in either the frequency domain, or the time domain, or both of the frequency domain or then time domain. The symbols in the transmission matrices may be transmitted either as one burst in a primary broadcast channel (PBCH), or as discrete bursts in the primary broadcast channel.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
Transmission diversity with two cross-polarised antennas arrays
InactiveUS20050260954A1Simple methodSpatial transmit diversityPolarisation/directional diversityTransmission diversityEngineering
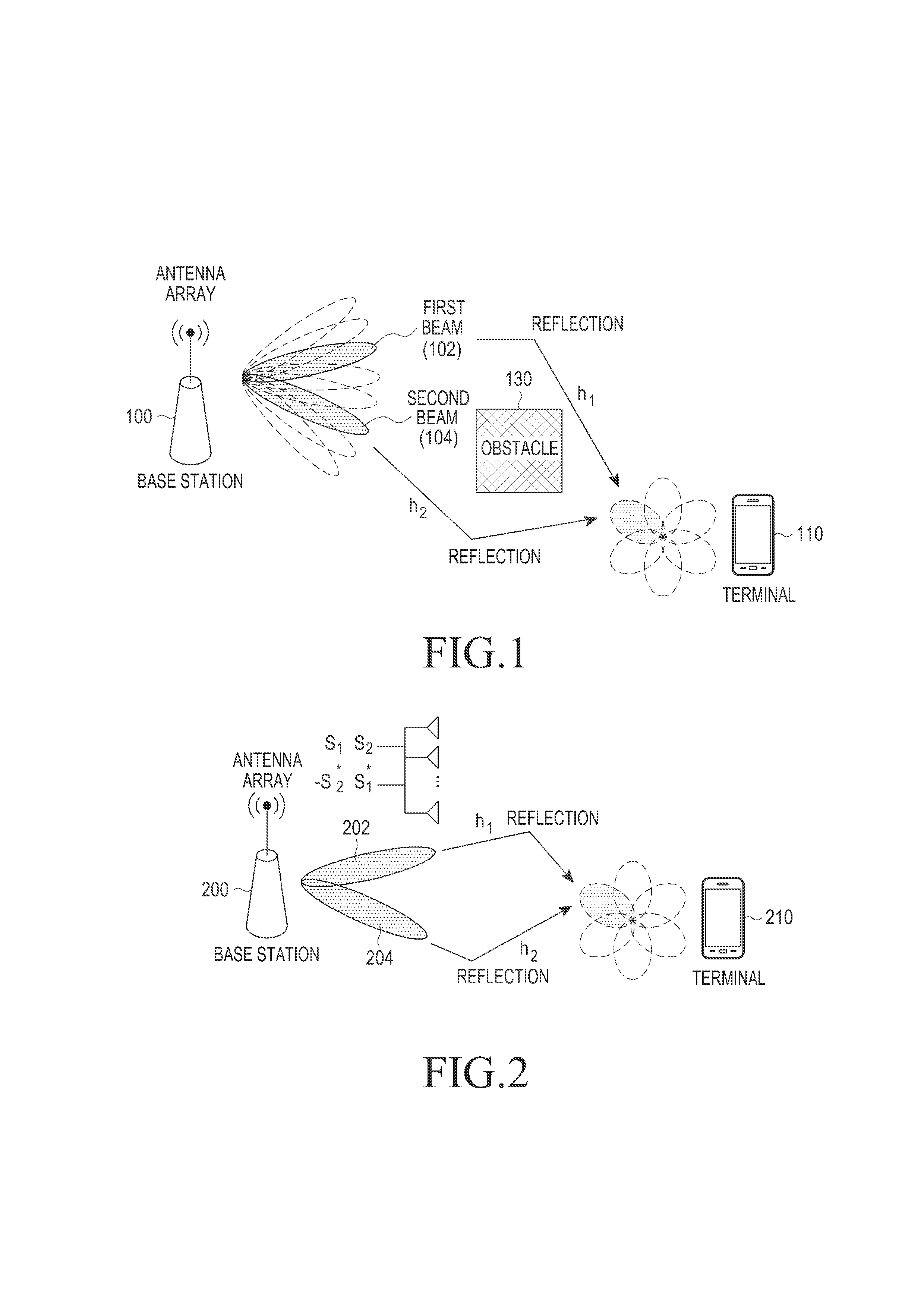
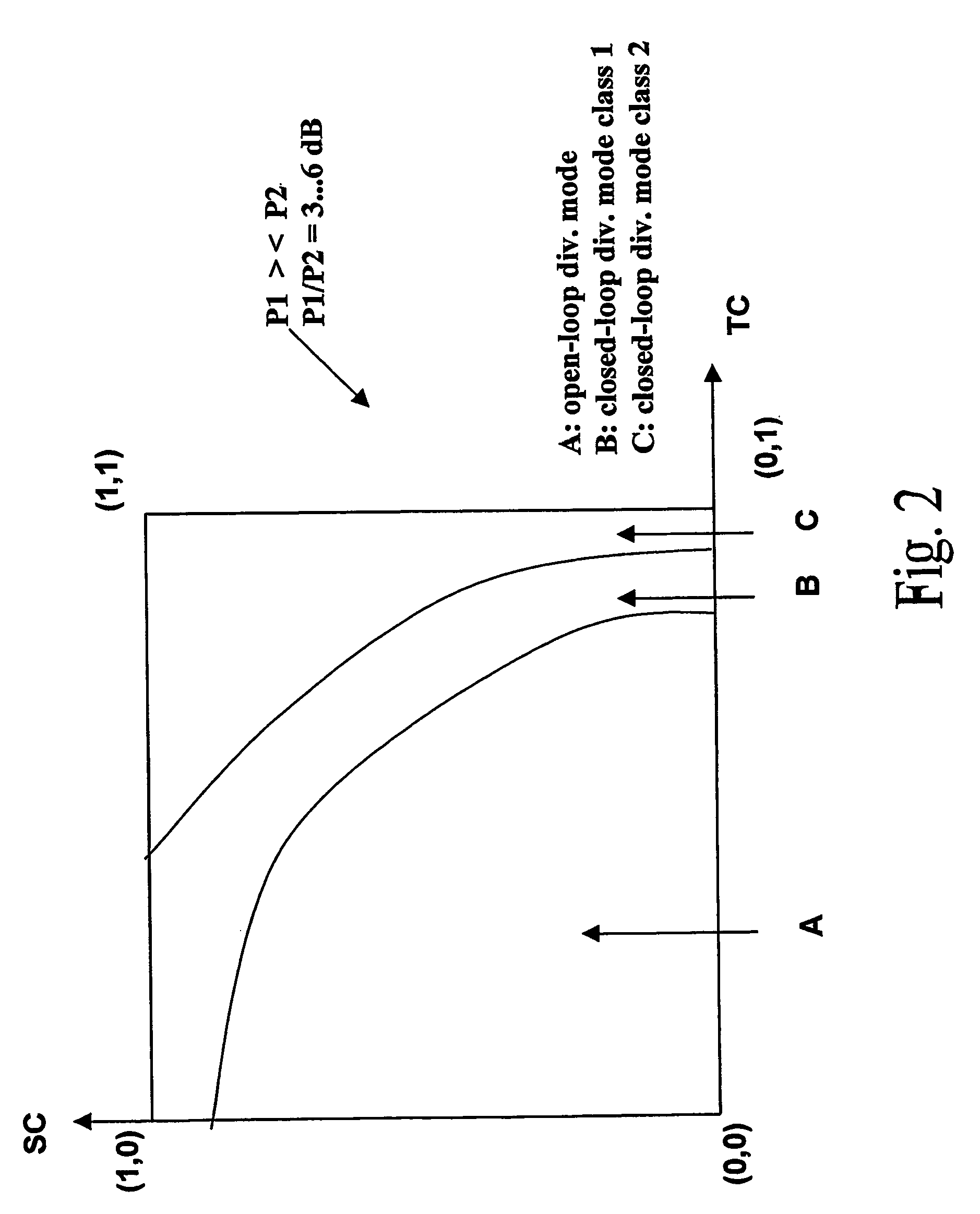
The present invention concerns a method for selecting a diversity mode (A, B, C) to be applied by a transmitter having two cross-polarized antenna arrays (Ant1, Ant 2), each representing a diversity branch, comprising the steps of: providing (S10) a plurality of diversity mode performance chart look-up tables (LUT, LUT1, LUT2, LUT3), mapping a respective individual diversity mode (A, B, C) to a respective pair of time correlation value (TC) and space correlation value (SC) for said two cross-polarized antenna array beams, wherein a respective individual diversity mode is presented by a mapping area, wherein the plurality of performance chart look-up tables is parameterized by an indication of a ratio (P1 / P2) of received powers from said diversity branches, first selecting (S13) one of said performance chart look-up tables dependent on determined ratio (P1 / P2) of received powers from separate beams, and second selecting (S14) one of said individual diversity modes (A, B, C) according to the mapping to the determined actual time 303 relation (TC) and space correlation (SC) values from said first selected performance chart look-up table.
Owner:NOKIA SOLUTIONS & NETWORKS OY
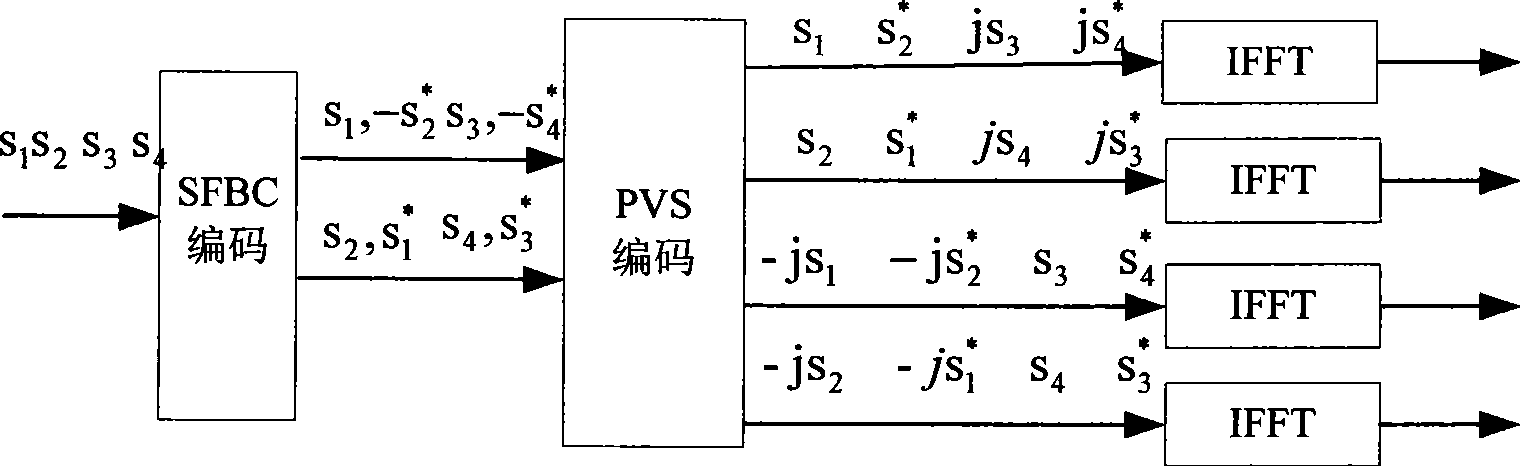
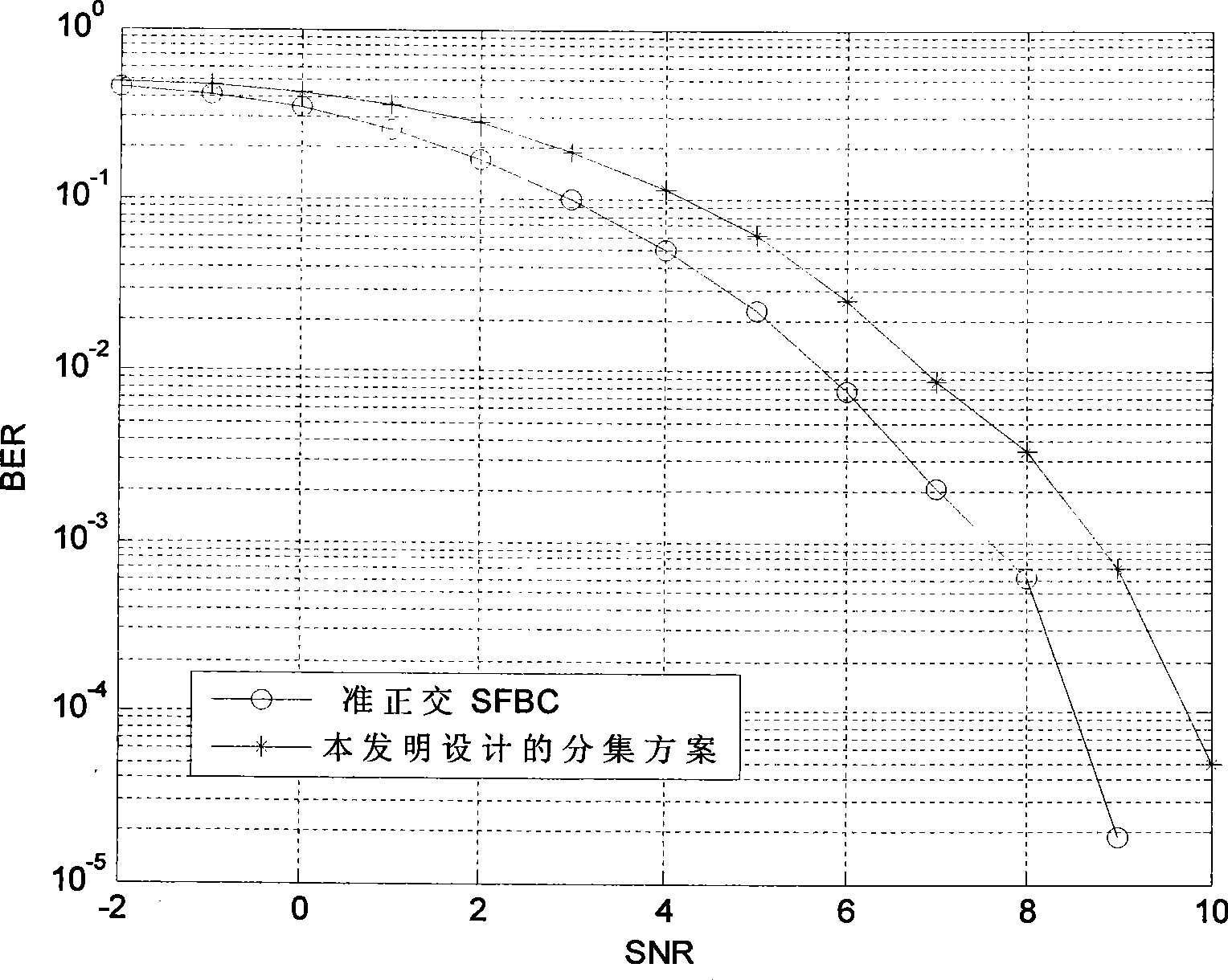
Transmission diversity method base on null-frequency encode
InactiveCN101378299ASimple designEasy to decodeSpatial transmit diversityMulti-frequency code systemsData streamEuclidean vector
The invention discloses a transmission diversity method based on space-frequency coding, which is applicable to an MIMO-OPDM system with a sending antenna which is more than 2. The method takes a combination of the SFBC and pre-coding weighing switching as a diversity mode of SFBC+PVS, taking the objective factor into the account that the stronger the channel correlation is, the weaker the diversity effect is, and uses a weighted vector to remove the effect resulted by the inclination angle between antennae and the channel correlation between different antennae. The method comprises the following steps: step one, two paths of data streams are obtained by carrying out SFBC coding to an input bit stream; step two, two groups of pre-coding weighing vectors are selected; and step three, a coding matrix after pre-coding weighing switching is obtained after the pre-coding weighing vector is adopted to carry out weighing to an SFBC coding data block, and finally an in-time signal obtained by inverse fast Fourier transform is transmitted. By adopting the diversity method, the space diversity effect can be utilized better and the effect on coding gains can be reduced.
Owner:ZTE CORP
Space-frequency coding-based multi-antenna transmitter diversity method and system thereof
ActiveCN101039136AMeet the needs of encoding timeImprove reception performanceSpatial transmit diversityError preventionCarrier signalEngineering
The invention relates to the mobile communication field, disclosing a space frequency coding based multi-antenna transmission diversity method and the system thereof. When the number of transmission antenna is over 2, a coding can be accomplished within an OFDM symbol period and meanwhile a diversity gain similar to STTD+CSD can be obtained. The invention uses space frequency coding to obtain the diversity gain and at the same time introduces phase offset in the frequency-domain to obtain extra frequency diversity similar to CSD through the channel of the frequency-domain data. The phase offset satisfies: the frequency-domain data loaded in the sub-carrier wave set used in SFTD on the same antenna possesses the same phase offset and the frequency-domain data loaded between the sub-carrier wave sets possesses different phase offsets. Moreover, the frequency-domain data loaded on the same sub-carrier wave on different antenna in the same antenna stack possesses different phase offsets.
Owner:HUAWEI TECH CO LTD
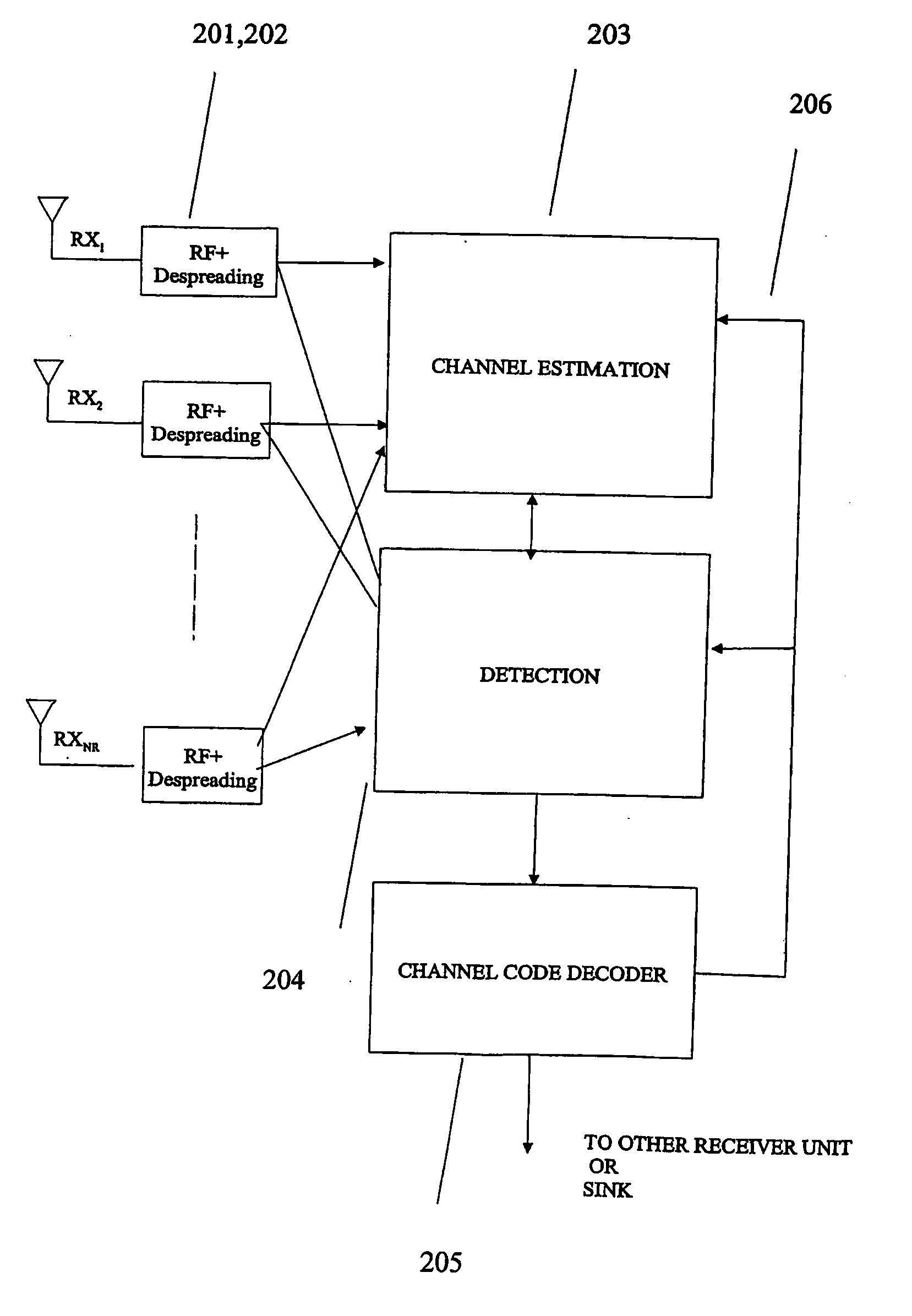
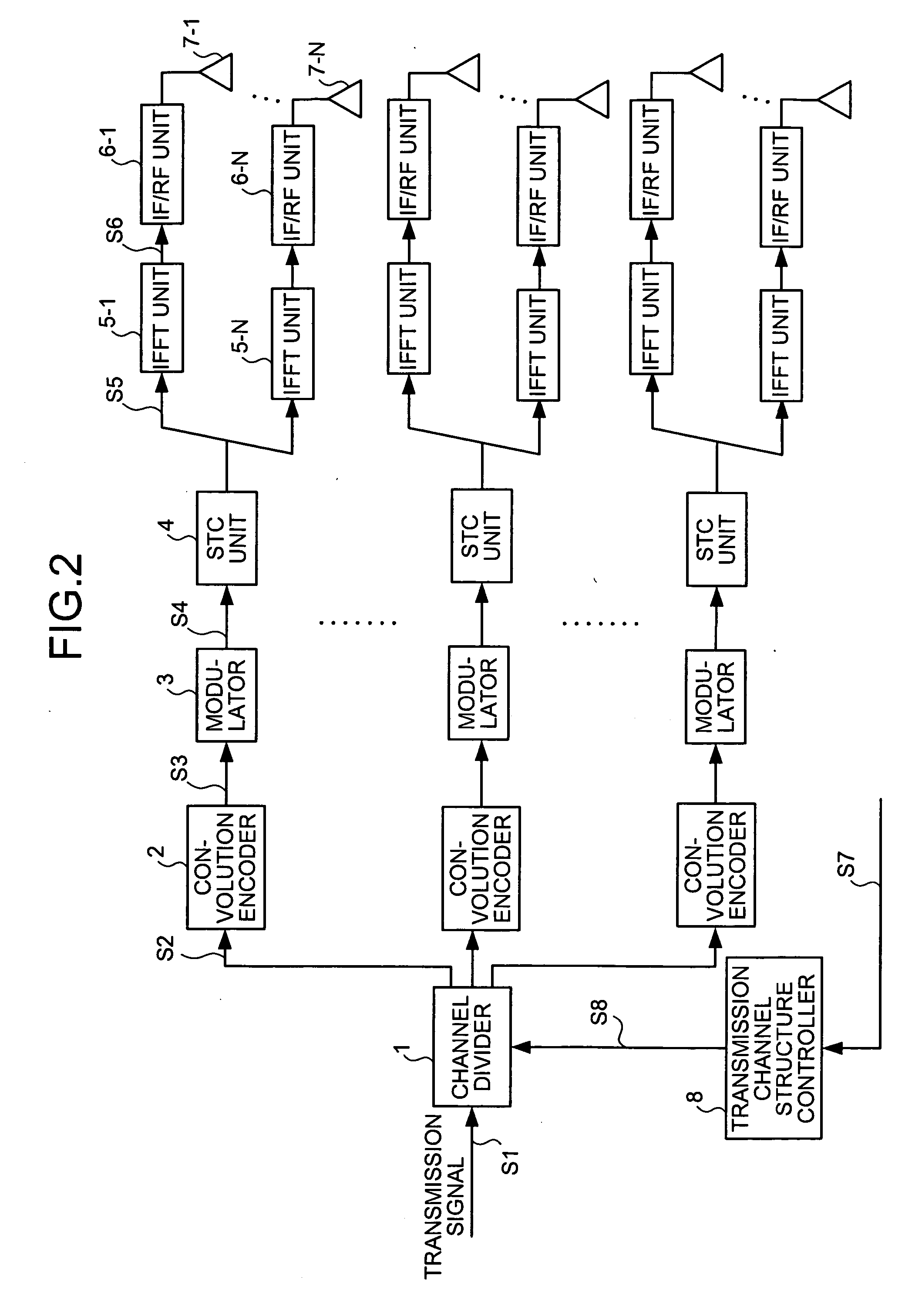
Radio communication apparatus, transmitter apparatus, receiver apparatus and radio communication system
InactiveUS20060258303A1Efficient communicationImprove communication qualitySpatial transmit diversityModulated-carrier systemsCommunications systemDiversity scheme
A channel dividing unit of a transmitter divides a transmission signal into a plurality of channels based on channel structure information indicating a method of structuring an MIMO informed from a receiver. An STC unit realizes transmission diversity according to STC processing for each of the channels divided. A channel estimating unit of the receiver estimates a channel gain for transmission and reception of a signal. Based on a result of estimation of the channel gain, a physical configuration of the transmitter, and a physical configuration of the receiver, a transmission-side channel-structure determining unit of the receiver determines a structure of an MIMO channel, and informs channel structure information to the transmitter.
Owner:MITSUBISHI ELECTRIC CORP
Systems and methods for SC-FDMA transmission diversity
Owner:APPLE INC
Transmission diversity
The present invention is based on the idea that the base transceiver station can make a decision as to changing transmission diversity in response to the power control message sent by the mobile station. The decision to change transmission diversity is made, for instance, on the basis of the result obtained from filtering the power control requests. For example, filtering can be carried out using a sliding window that contains power control information on the basis of which the decision is made. It is not necessary for the mobile station to transmit a special request to change transmission diversity; instead, the decision on changing transmission diversity is made by the base transceiver station in response to the power control information that the mobile station would, in any case, send to the base transceiver station.
Owner:NOKIA NETWORKS OY
Transmit diversity and spatial spreading for an ofdm-based multi-antenna communication system
InactiveUS20120213181A1Spatial transmit diversityMulti-frequency code systemsCommunications systemDiversity scheme
A multi-antenna transmitting entity transmits data to a single- or multi-antenna receiving entity using (1) a steered mode to direct the data transmission toward the receiving entity or (2) a pseudo-random transmit steering (PRTS) mode to randomize the effective channels observed by the data transmission across the subbands. For transmit diversity, the transmitting entity uses different pseudo-random steering vectors across the subbands but the same steering vector across a packet for each subband. The receiving entity does not need to have knowledge of the pseudo-random steering vectors or perform any special processing. For spatial spreading, the transmitting entity uses different pseudo-random steering vectors across the subbands and different steering vectors across the packet for each subband. Only the transmitting and receiving entities know the steering vectors used for data transmission. Other aspects, embodiments, and features are also claimed and disclosed.
Owner:QUALCOMM INC
Method for transmitting harq-ack information based on transmission diversity
ActiveUS20130176918A1Improve throughputAvoid spatial bundlingTransmission path divisionSignal allocationCarrier signalDiversity scheme
A method for transmitting HARQ-ACK information based on transmission diversity is provided. The method includes configuring two component carriers, referred to as Cells, for a User Equipment (UE); when a base station configures the UE to transmit HARQ-ACK information adopting the transmission diversity technique, the base station indicates dynamically whether an other Cell is scheduled in the same subframe via a PDCCH scheduling a PDSCH of one Cell, so as to enable the UE to know the number of Cells scheduled in the same downlink subframe by the base station, and to generate HARQ-ACK information based on the number of Cells. Unnecessary spatial bundling of the HARQ-ACK information may be avoided, unnecessary downlink data retransmission is reduced and throughput of downlink data is improved.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
Self-adapting switching method and device of transmission mode of LTE (Long Term Evolution) multi-antenna system
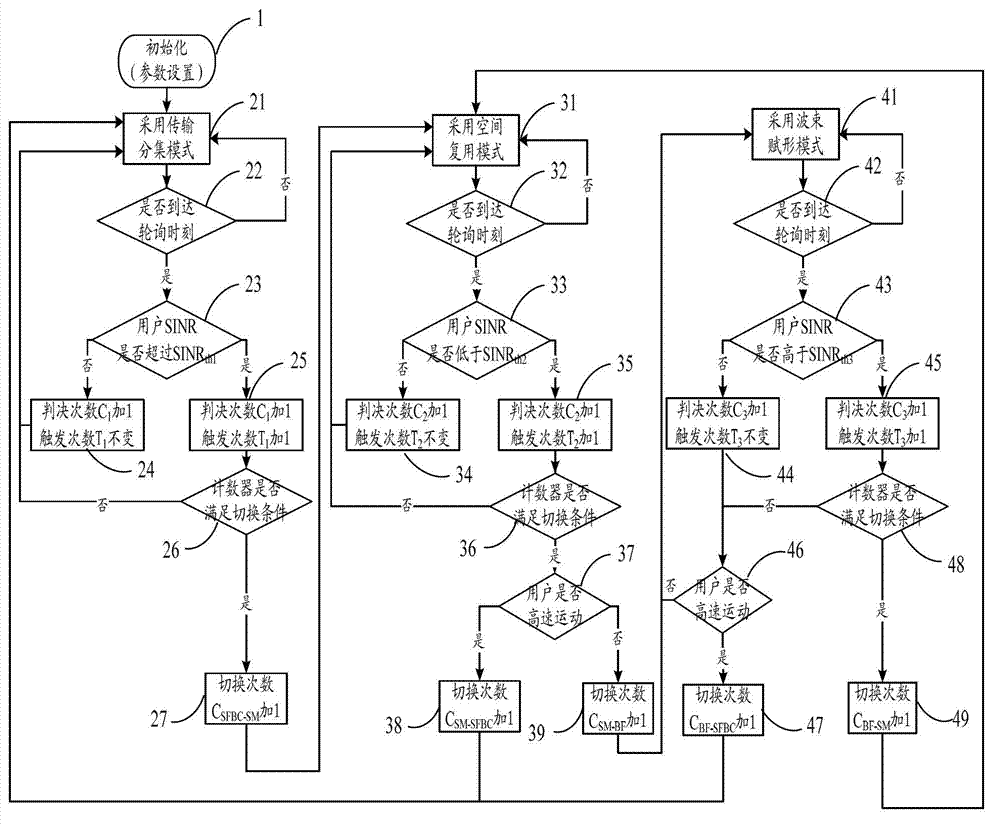
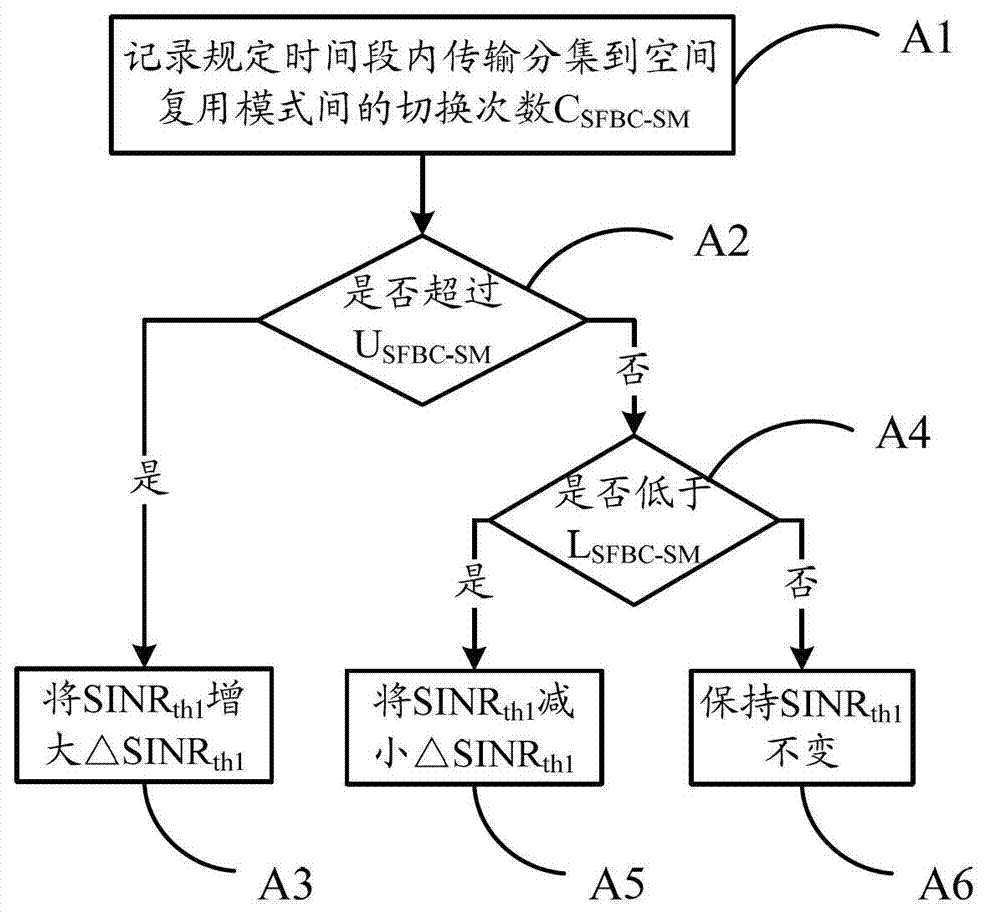
InactiveCN103179619ASimple structureReduce complexityWireless communicationSignal-to-interference-plus-noise ratioGeolocation
The invention relates to a self-adapting switching method of a transmission mode of an LTE (Long Term Evolution) multi-antenna system, and the self-adapting switching method comprises the following steps that: a base station sets an appropriate transmission mode in a self-adapting way for a user by taking the SINR (Signal to Interference plus Noise Ratio), the movement speed and the geographic position of the user as judgment conditions. The self-adapting switching method comprises the following operation steps of: firstly initially determining multiple parameters, namely a polling period needed by transmission mode switching, a mode switching threshold value, a counter threshold value and a user movement speed threshold value; then determining transmitting data of an acquiescent transmission diversity mode; then calculating an SINR value according to CQI (Channel Quality Indicator) fed back by the user, and comparing the SINR value with a predetermined switching threshold; updating corresponding judgment time and triggering time counters; judging whether a mode switching condition is met or not; and switching a current mode into an ideal target mode, or continuously keeping the current mode to carry out data transmission. The self-adapting switching method disclosed by the invention can be used for regulating the mode switching threshold value and the user movement speed threshold value in real time by counting switching times within set time, thereby realizing the effective balance of network transmission efficiency and timeliness in the switching process.
Owner:BEIJING UNIV OF POSTS & TELECOMM
Base station apparatus and interference reducing method
InactiveUS20100317292A1Reduce distractionsImprove throughputSubstation equipmentRadio transmissionDiversity schemeTransmission diversity
A base station has a first antenna for emitting radio waves at a first tilt angle and a second antenna for emitting radio waves at a second tilt angle different from the first tilt angle. If the antennas have different propagation lengths, a transmission diversity gain is not obtained and interference occurs in an adjacent area. In such a case, when one antenna having a shorter propagation length, which means less interference in the adjacent area, is used for transmission, the throughput of each terminal is increased at the area. For example, a controller changes two antenna transmission to one antenna transmission when the difference between the reception qualities of signals sent from the base station and an adjacent base station adjacent to the base station is smaller than a predetermined reference, the reception qualities being measured at the terminal.
Owner:HITACHI LTD
Apparatus and Method for Transmitting Data Using Transmission Diversity in Wireless Communication System
InactiveUS20110222588A1Reduce PAPRModulated-carrier systemsPolarisation/directional diversityCommunications systemData treatment
An apparatus for transmitting data in a wireless communication system is provided. The apparatus includes a data processor for generating modulation symbols by coding information bits and by constellation-mapping the coded information bits, a transmission (TX) processor for generating transmission symbols by applying any one of first and second transmission diversity schemes to the modulation symbols and for configuring a subframe including the transmission symbols, and a plurality of antennas for transmitting the subframe. The subframe comprises a plurality of slots and has a varying frequency band every slot by frequency hopping.
Owner:LG ELECTRONICS INC
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com