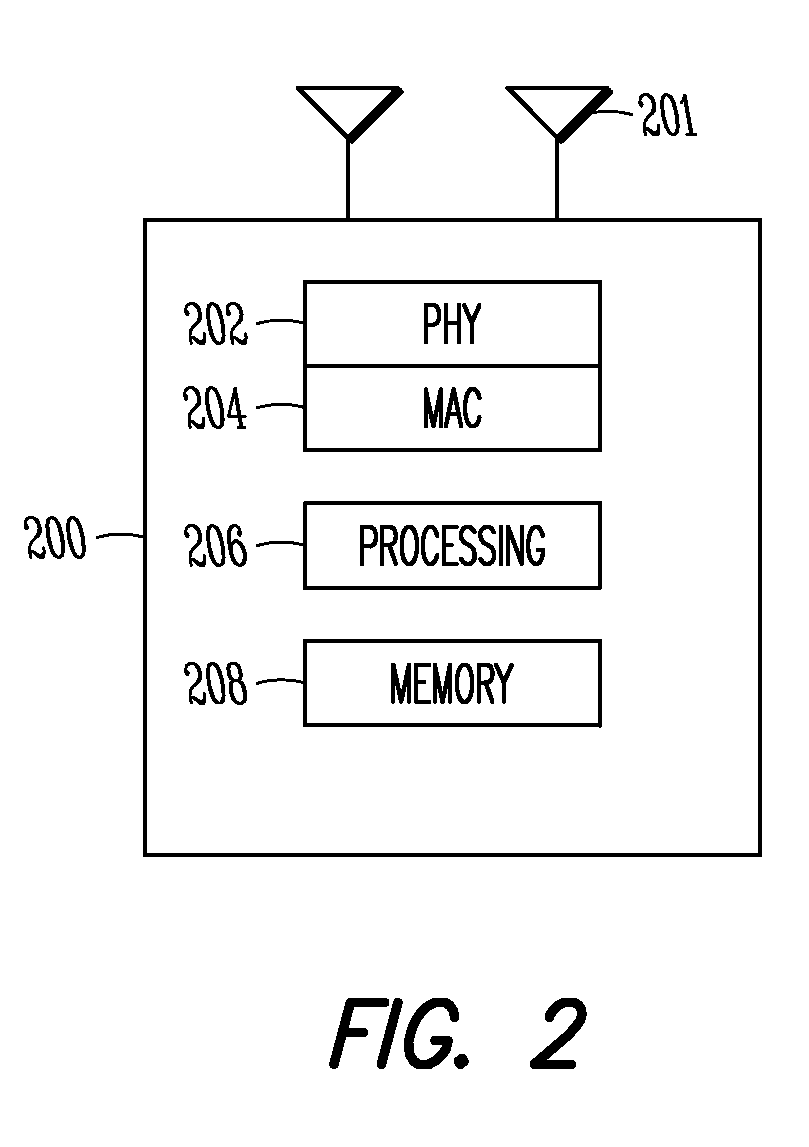
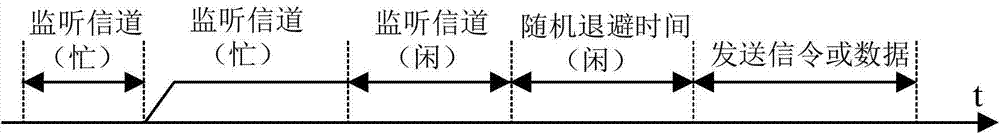
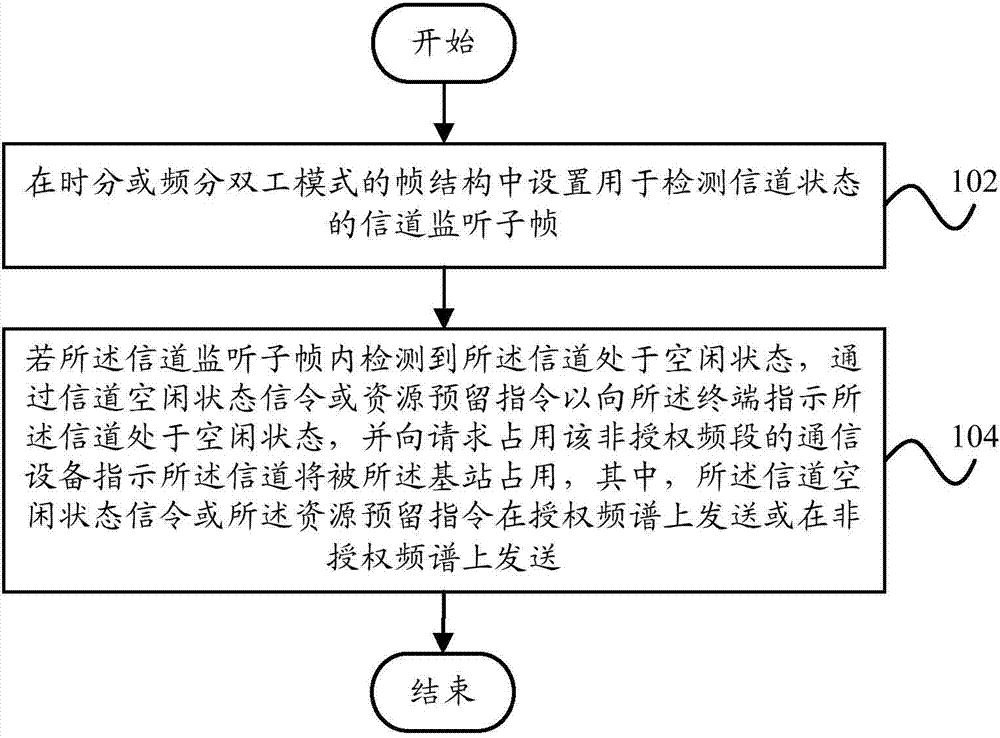
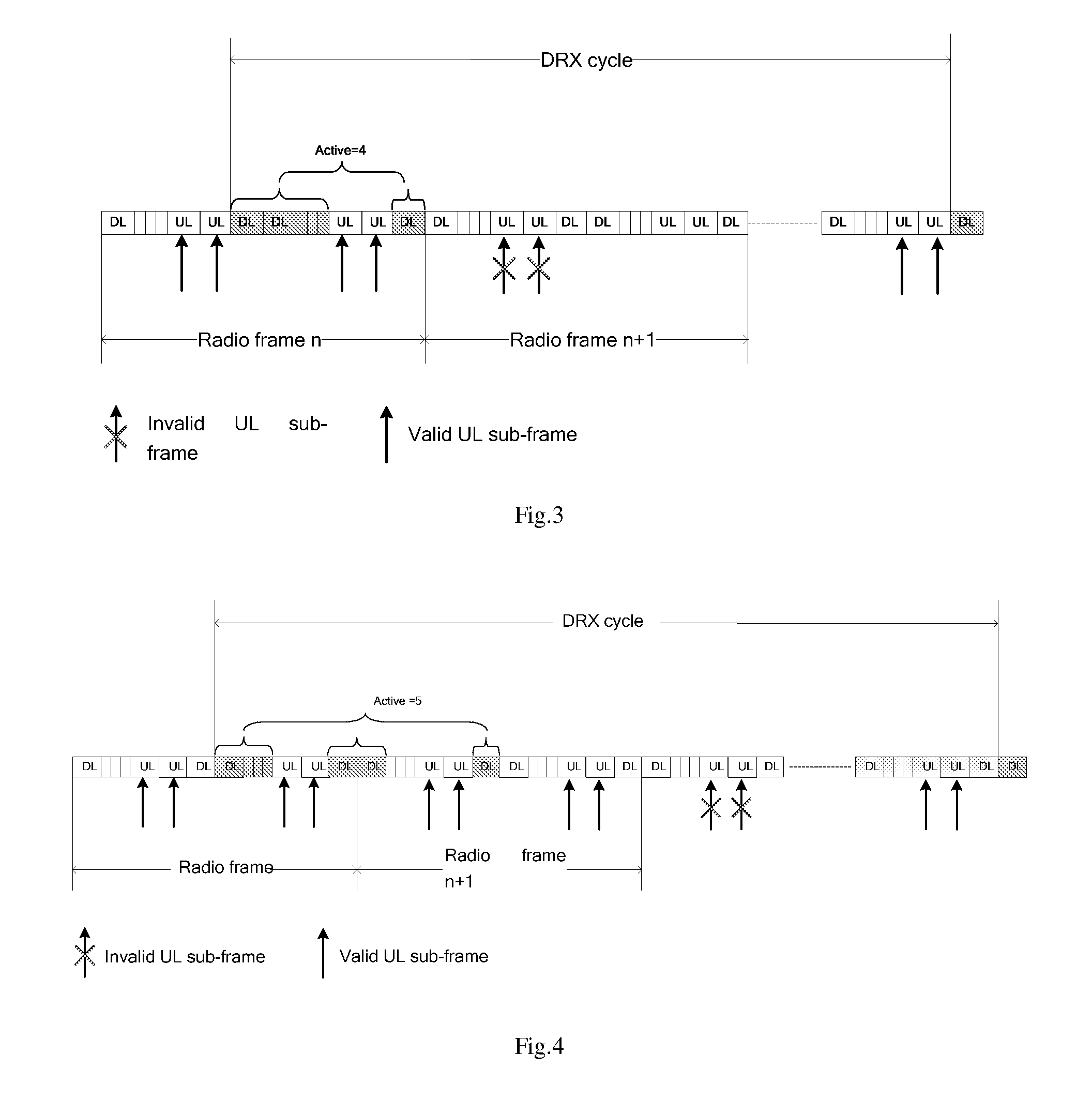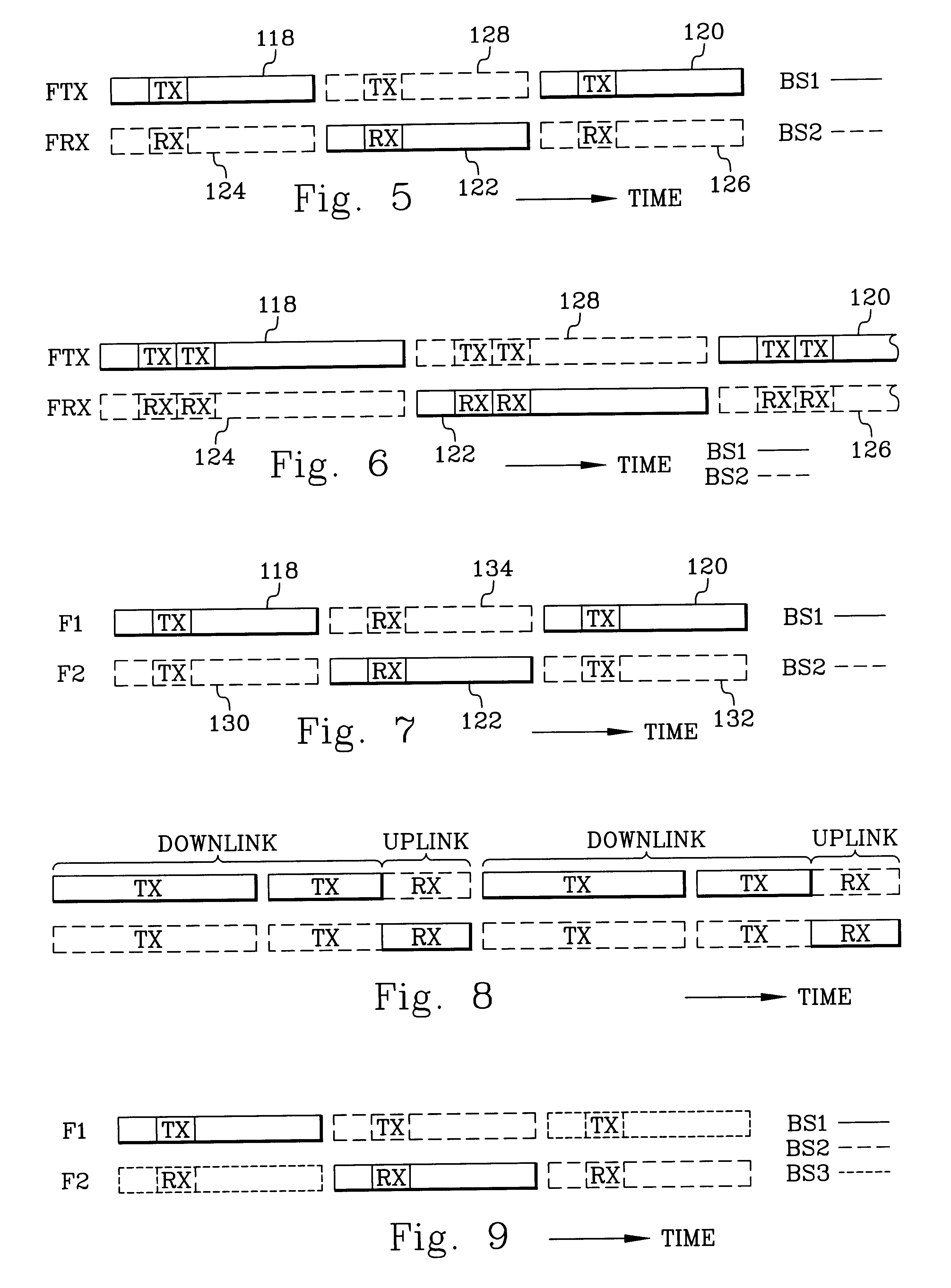Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
822 results about "Frequency division duplex" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
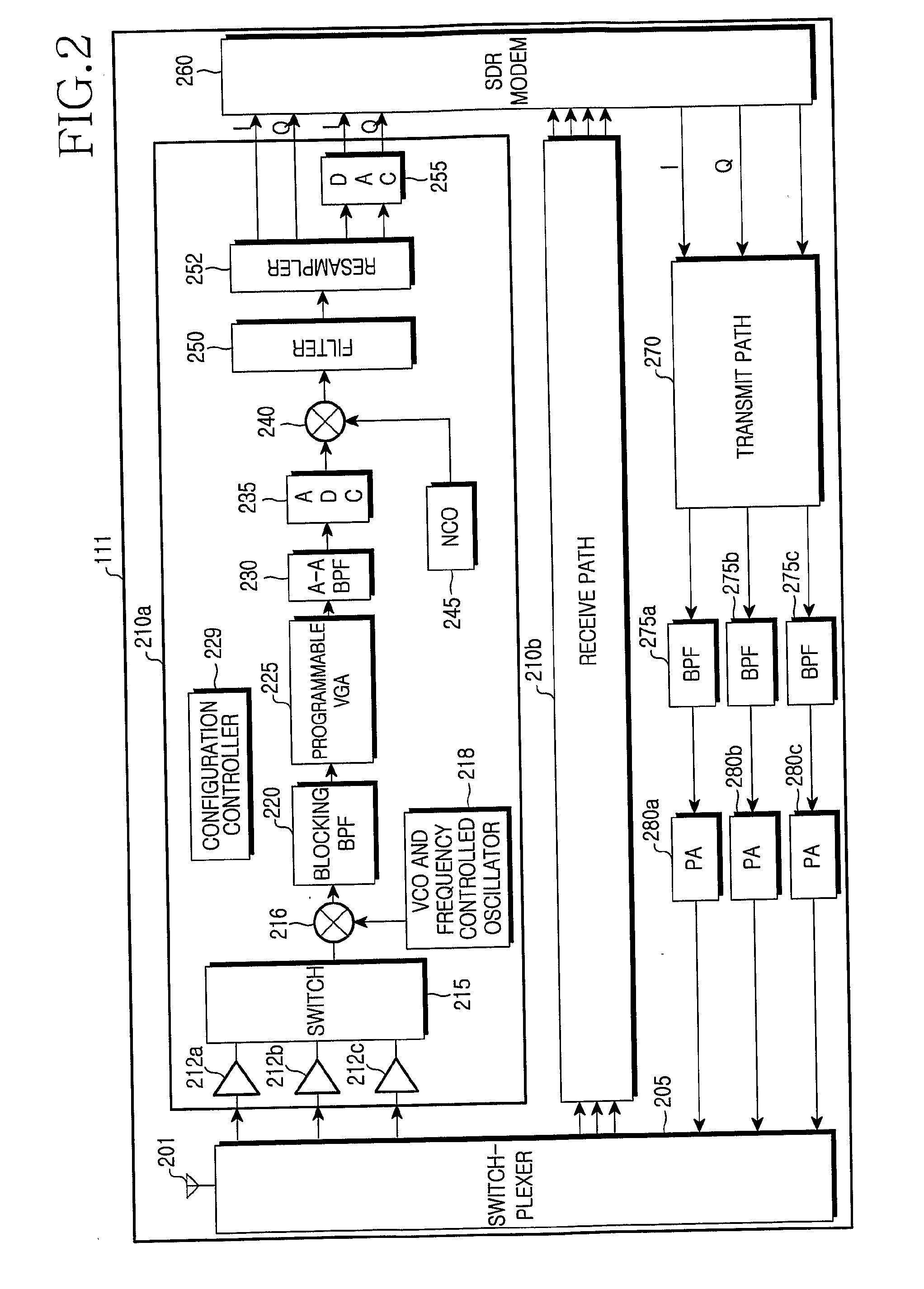
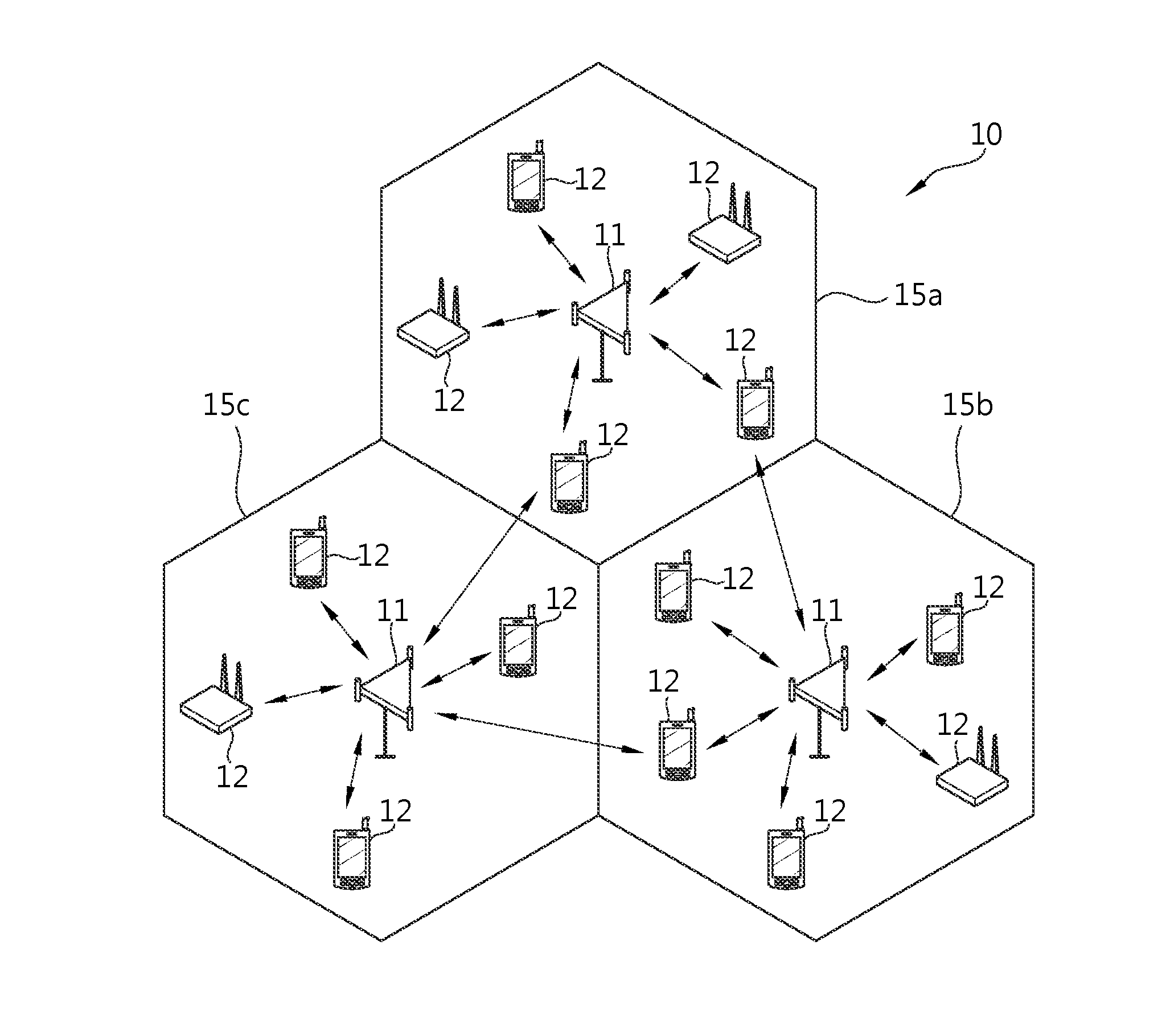
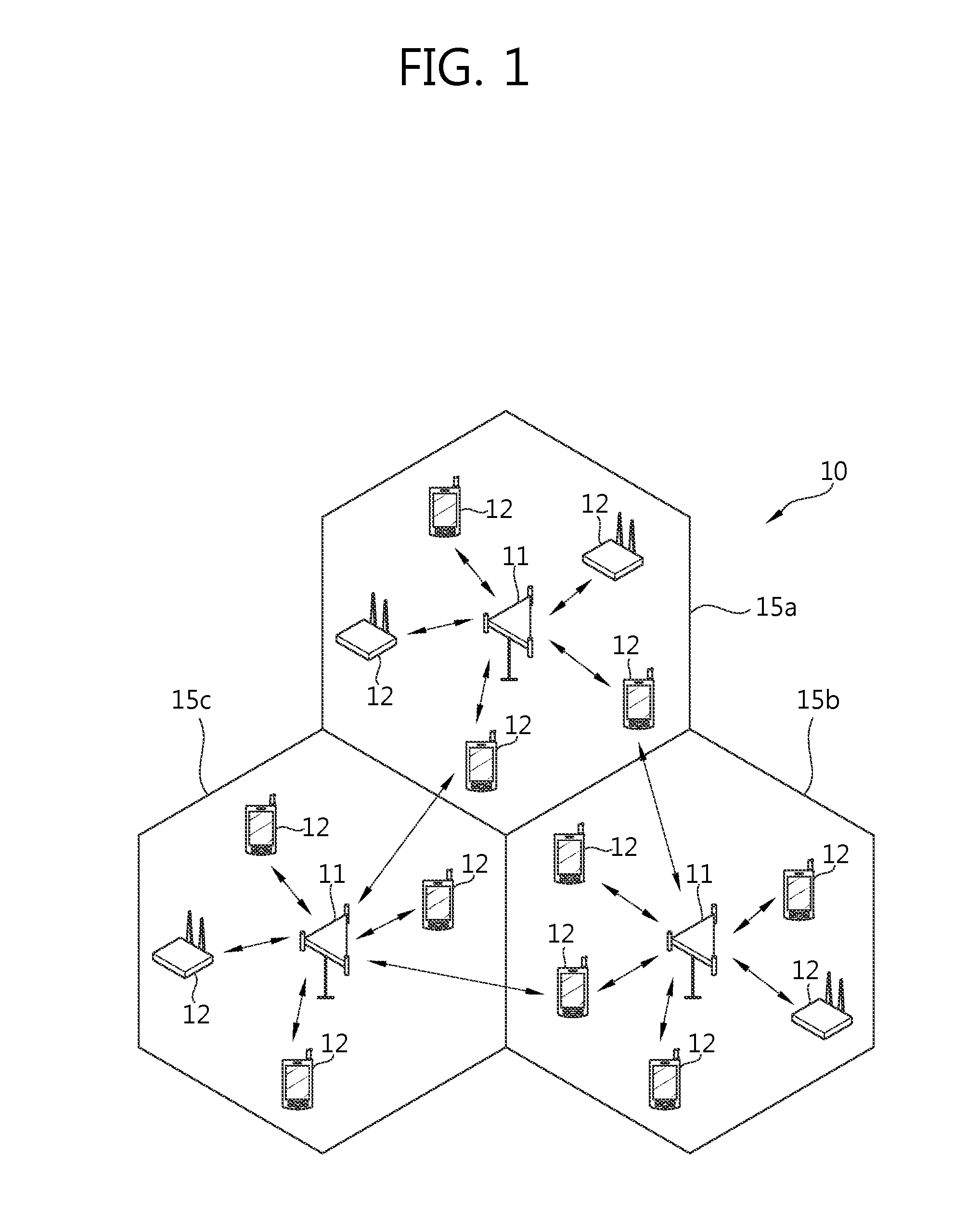
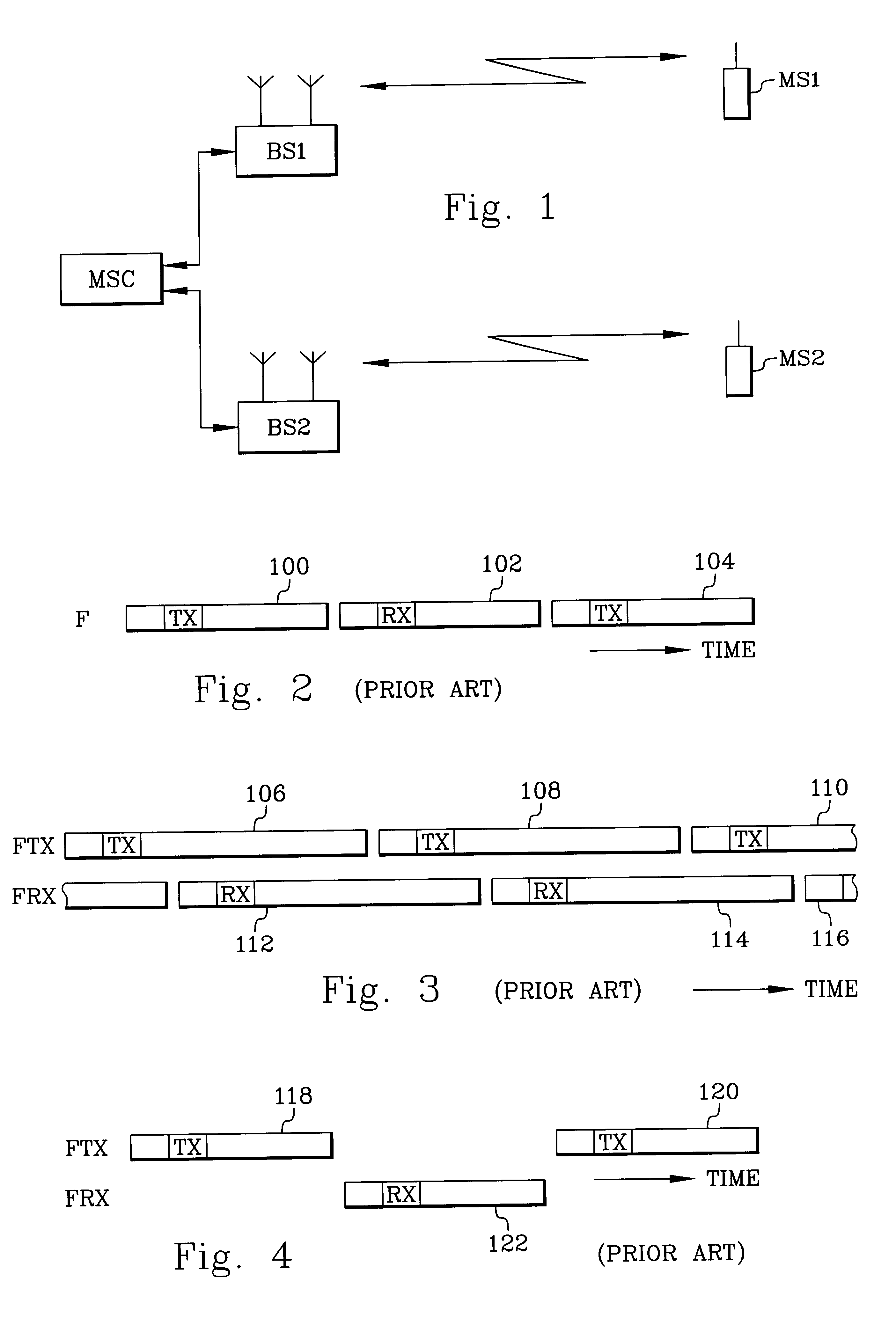
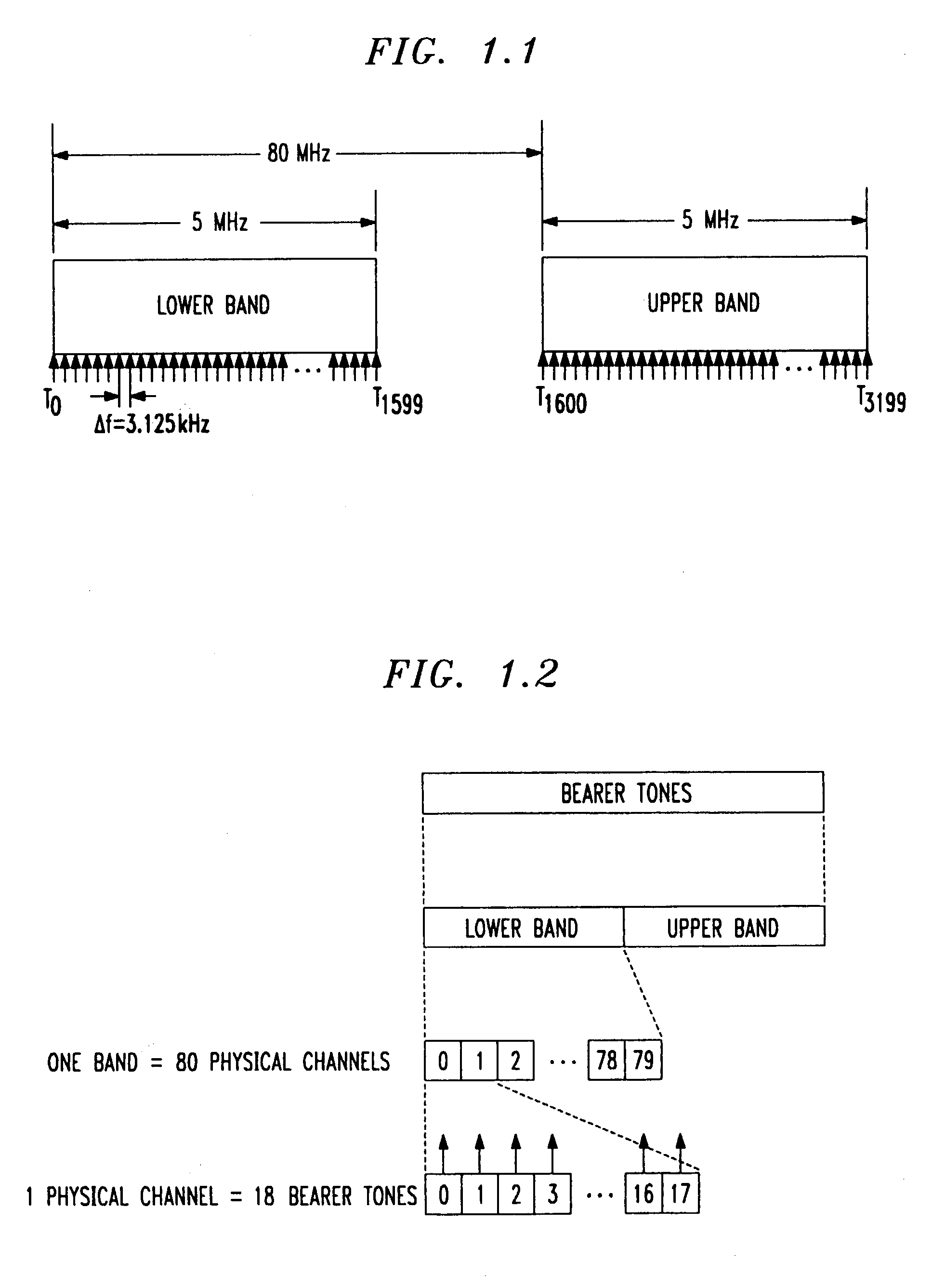
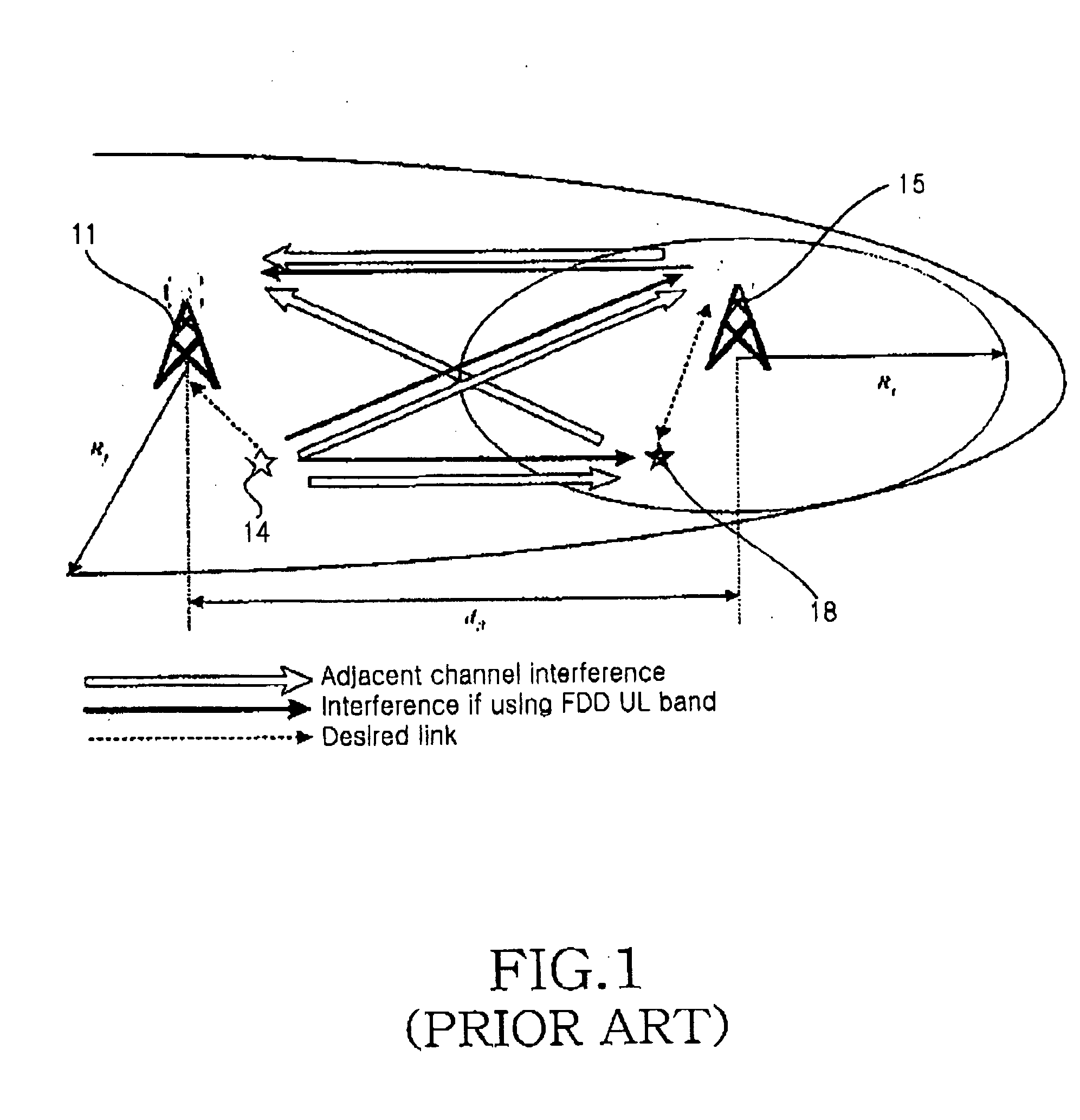
Frequency division duplex (FDD) is a technique where separate frequency bands are used at the transmitter and receiver side. Because the FDD technique uses different frequency bands for send and receive operations, the sending and receiving data signals don't interfere with each other.
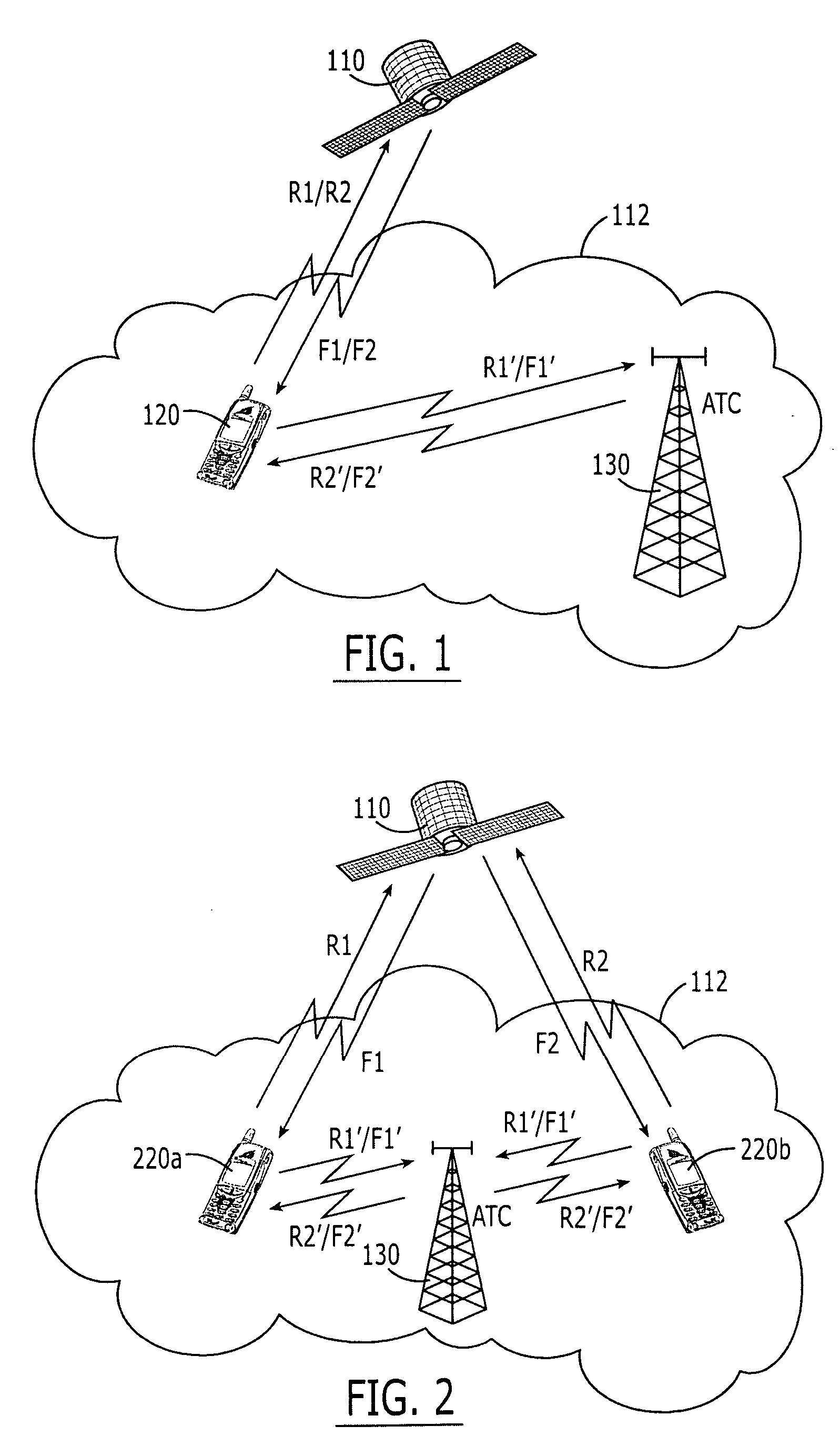
Systems and methods for terrestrial reuse of cellular satellite frequency spectrum in a time-division duplex and/or frequency-division duplex mode
InactiveUS20050118948A1Reduced and minimized useMultiplex system selection arrangementsPower managementFrequency spectrumFrequency division duplex
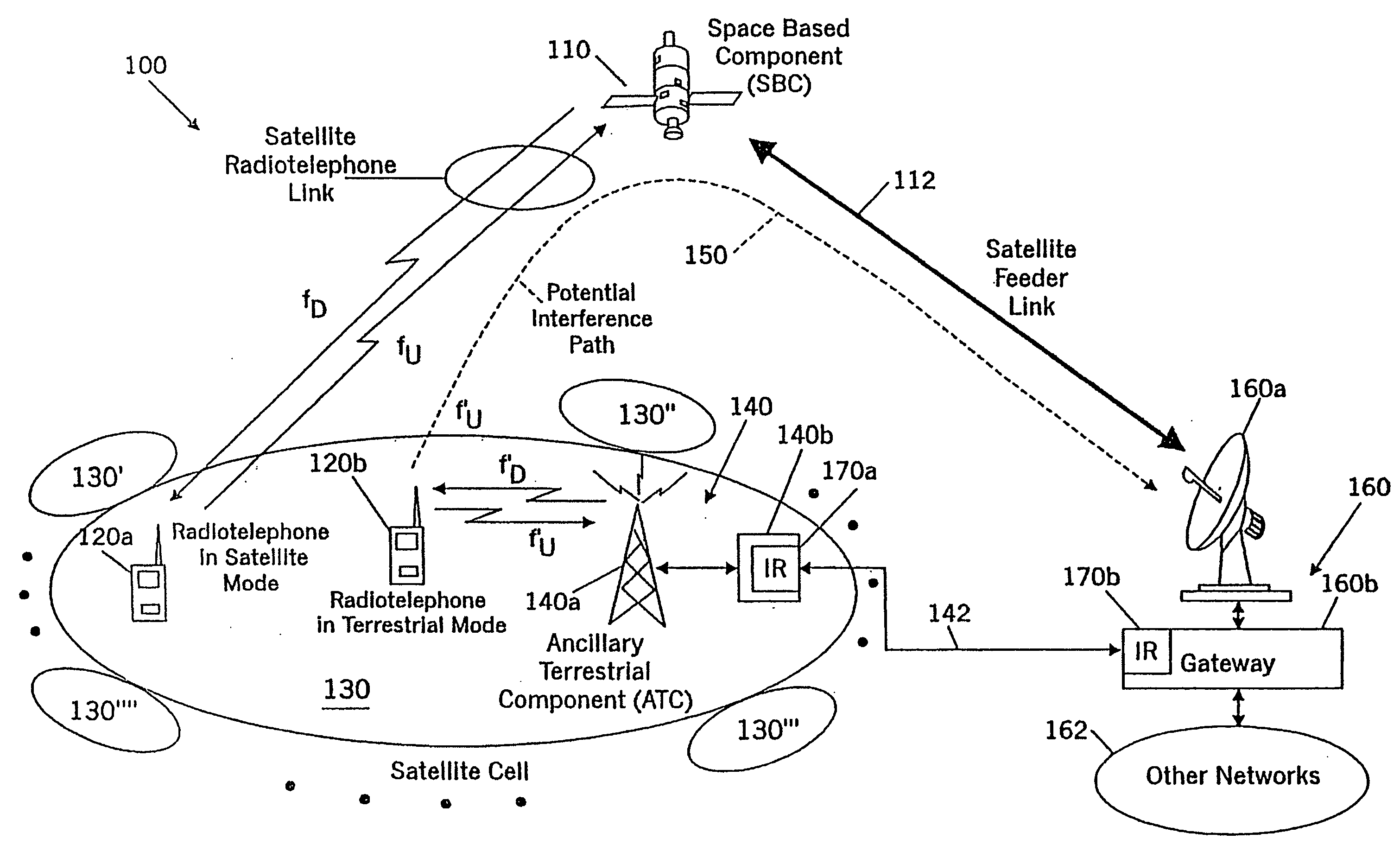
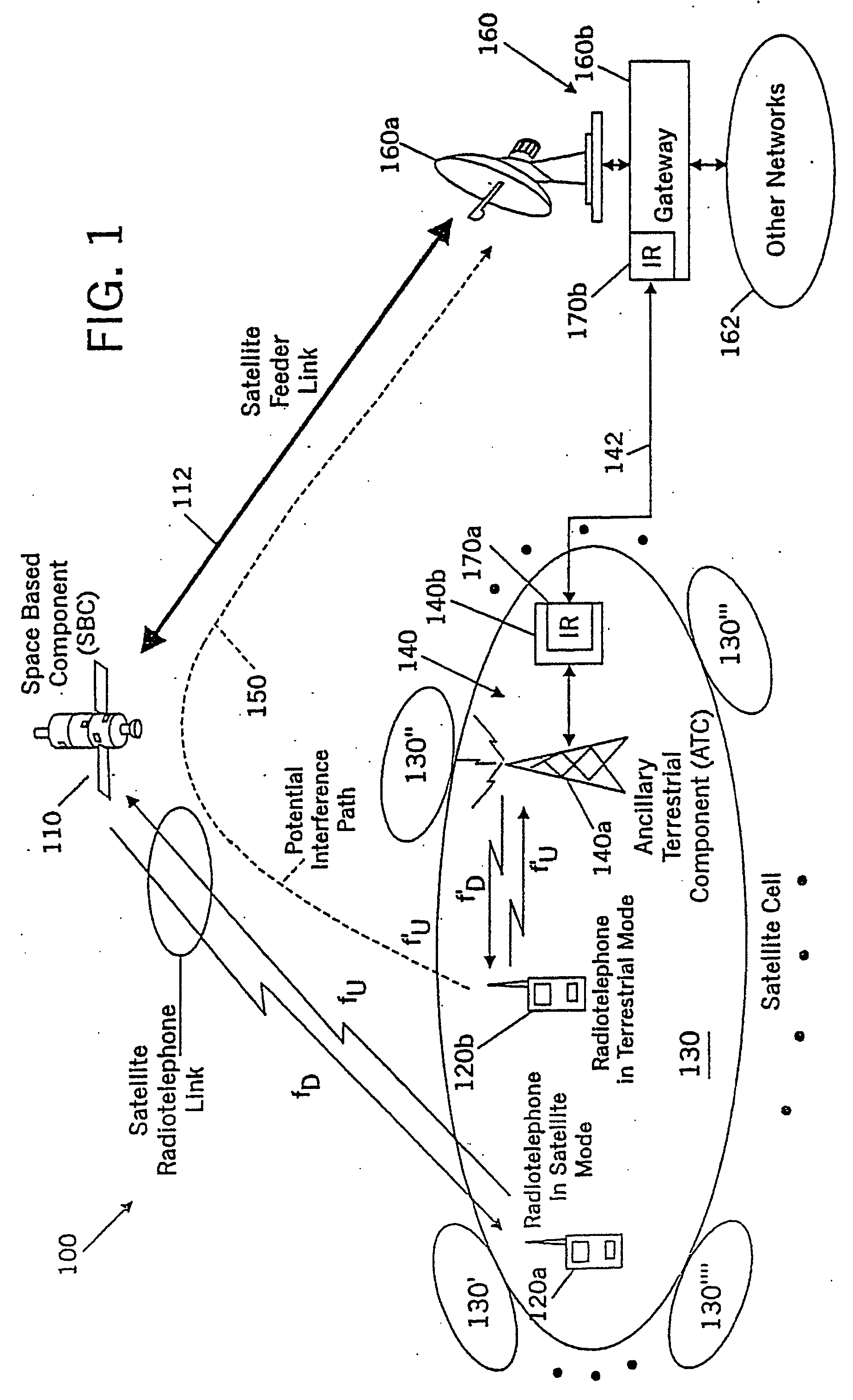
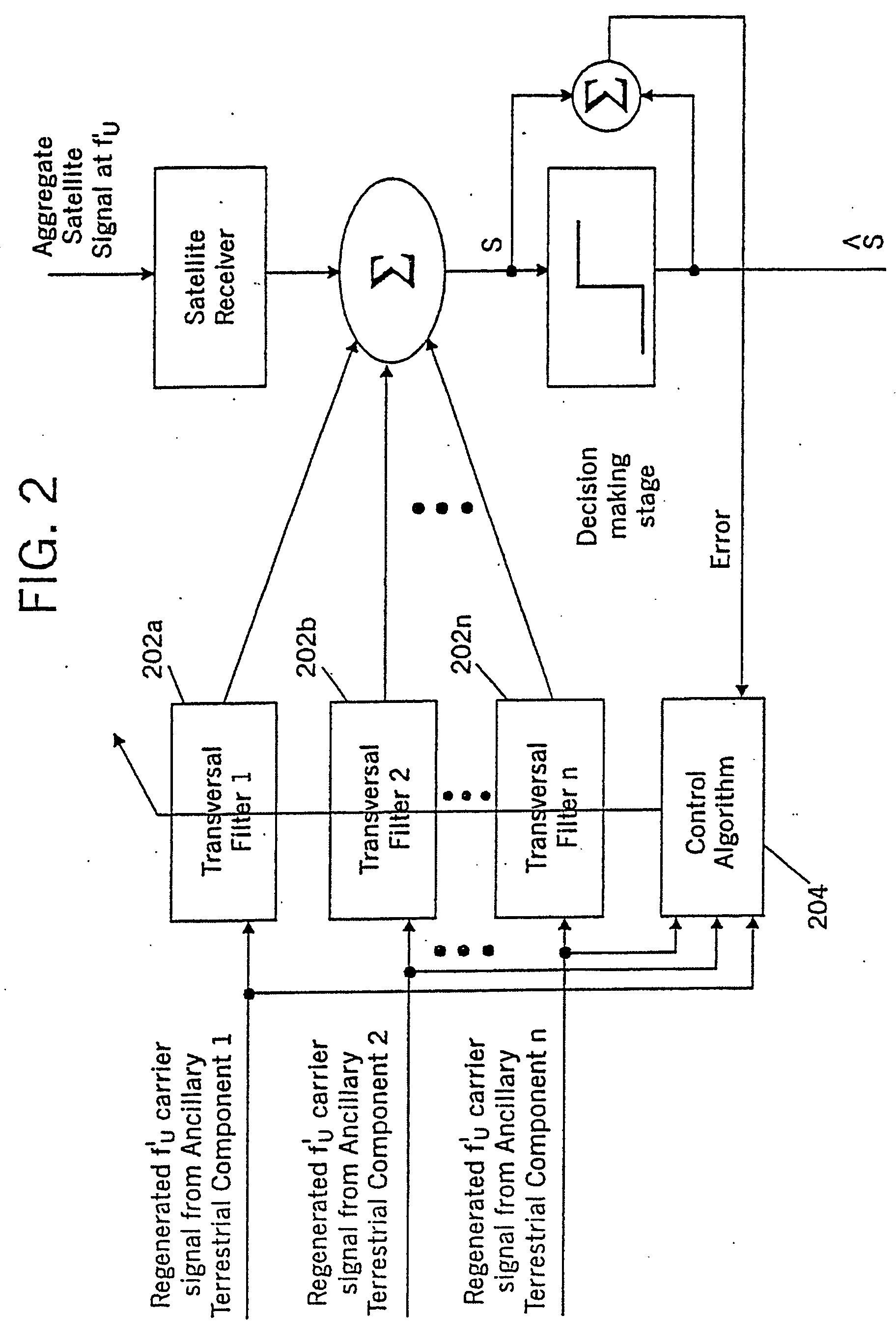
A space-based component, such as a satellite, is configured to receive wireless communications from radiotelephones in a satellite footprint over an uplink satellite radiotelephone frequency, and to transmit wireless communications to the radiotelephones over a downlink radiotelephone frequency. An ancillary terrestrial network, that may include one or more ancillary terrestrial components, is configured to transmit wireless communications to, and receive wireless communications from, the radiotelephones over the uplink satellite radiotelephone frequency in a time-division duplex mode. An interference reducer is configured to reduce interference from the wireless communications that are received by the space-based component from the second radiotelephone and / or from the ancillary terrestrial network over the uplink satellite radiotelephone frequency, using the wireless communications that are transmitted by the ancillary terrestrial to, and / or received by the ancillary terrestrial network from, the second radiotelephone over the uplink satellite radiotelephone frequency.
Owner:ATC TECH LLC
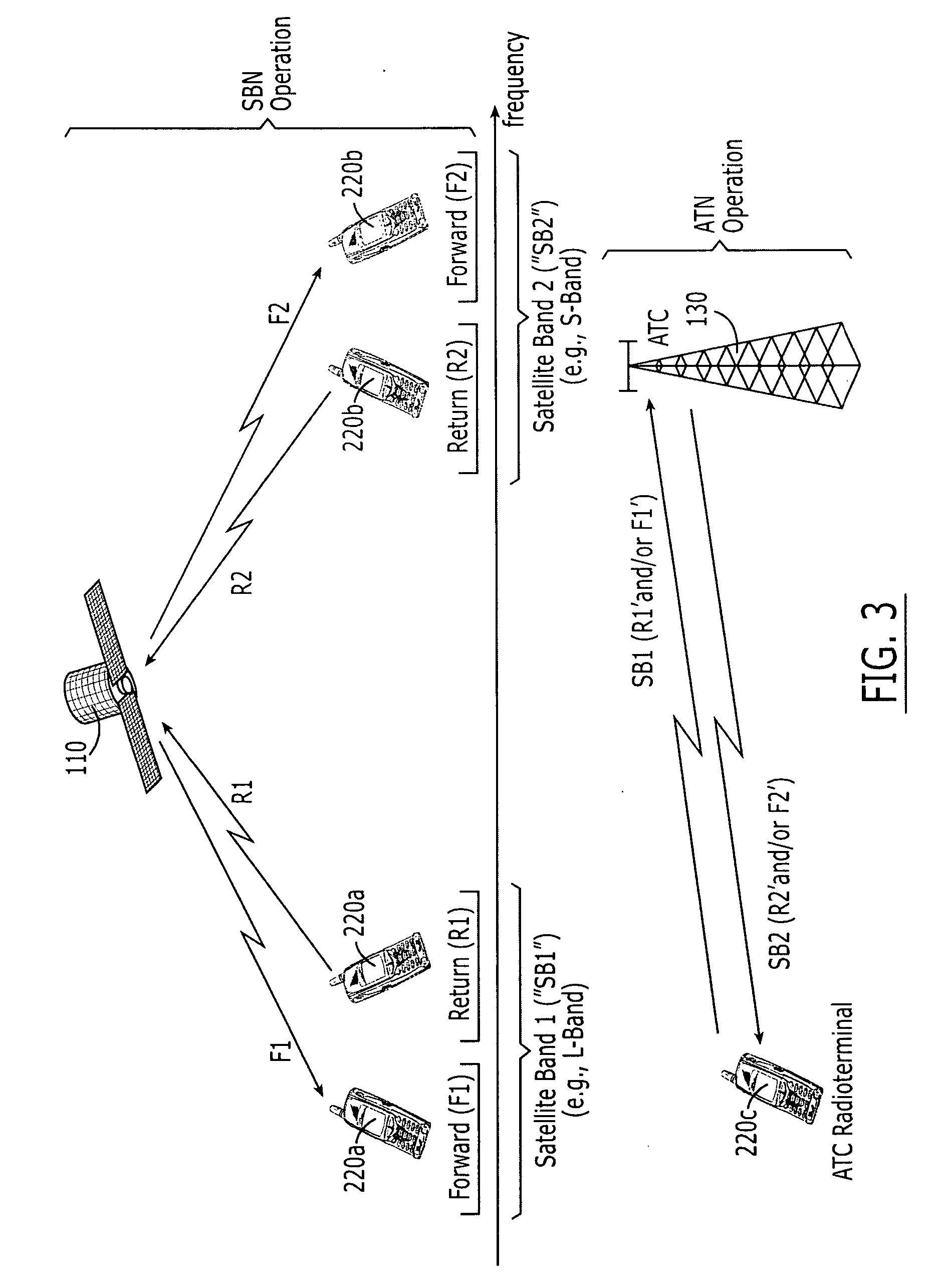
Systems and methods with different utilization of satellite frequency bands by a space-based network and an ancillary terrestrial network
ActiveUS20050239403A1Active radio relay systemsRadio/inductive link selection arrangementsCommunications systemWave band
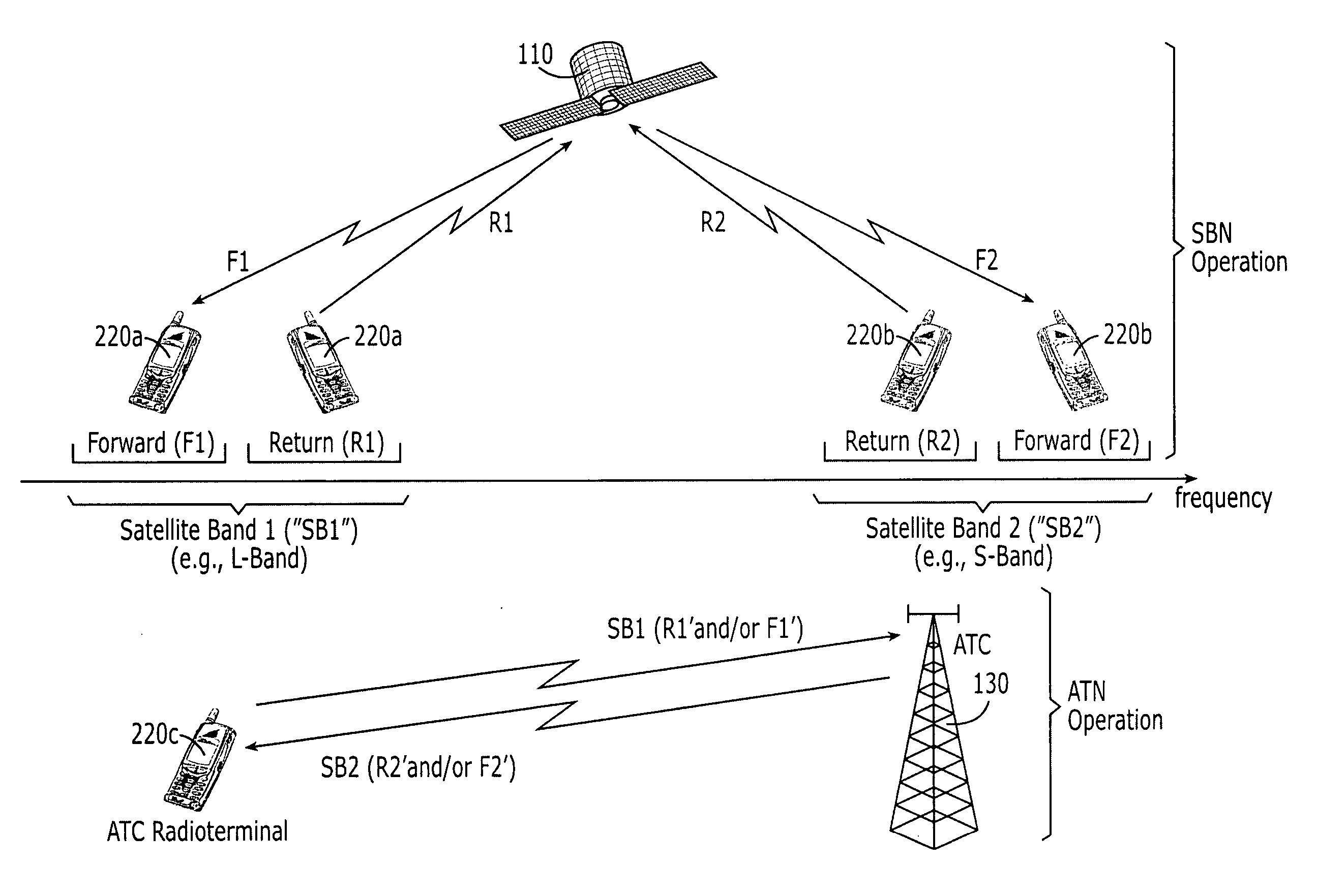
A radioterminal communications system includes an ancillary terrestrial component configured to receive from at least some of a plurality of radioterminals using frequencies from a first satellite frequency band (e.g., an L-band) and to transmit to at least some of the plurality of radioterminals using frequencies from a second satellite frequency band (e.g., an S-band). The system further includes a space-based component configured to communicate with the plurality of radioterminals using at least some of the frequencies from the first satellite frequency band and / or at least some of the frequencies from the second satellite frequency band. In some embodiments the ancillary terrestrial component communicates with radioterminals using a Time Division Duplex (TDD) mode and the space-based component communicates with the same or other radioterminals using a Frequency Division Duplex (FDD) and / or a TDD mode.
Owner:ATC TECH LLC
Multimode/Multiband Mobile Station and Method for Operating the Same
InactiveUS20070243832A1Reduce power consumptionLow sampling rateTransmissionCode division multiple accessMobile station
A multimode / multiband mobile station and a method for operating the same are provided. A transmission module transmits multimode / multiband signals through transmitters. A reception module receives radio signals for different services of the same frequency band among multimode / multiband signals through receivers for the same frequency band, and receives radio signals of different frequency bands among the multimode / multiband signals through receivers for the different frequency bands. As compared with the conventional mobile station, the multimode / multiband mobile station can reduce the number of receivers by making use of one receiver to receive radio signals for different services of the same frequency band. The multimode / multiband mobile station can use a duplexer of the conventional frequency division duplex (FDD) technique (e.g., wideband code division multiple access (WCDMA)) in a time division duplex (TDD) technique (e.g., Global System for Mobile Communication (GSM) 850 or Personal Communication Service (PCS) 1900).
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
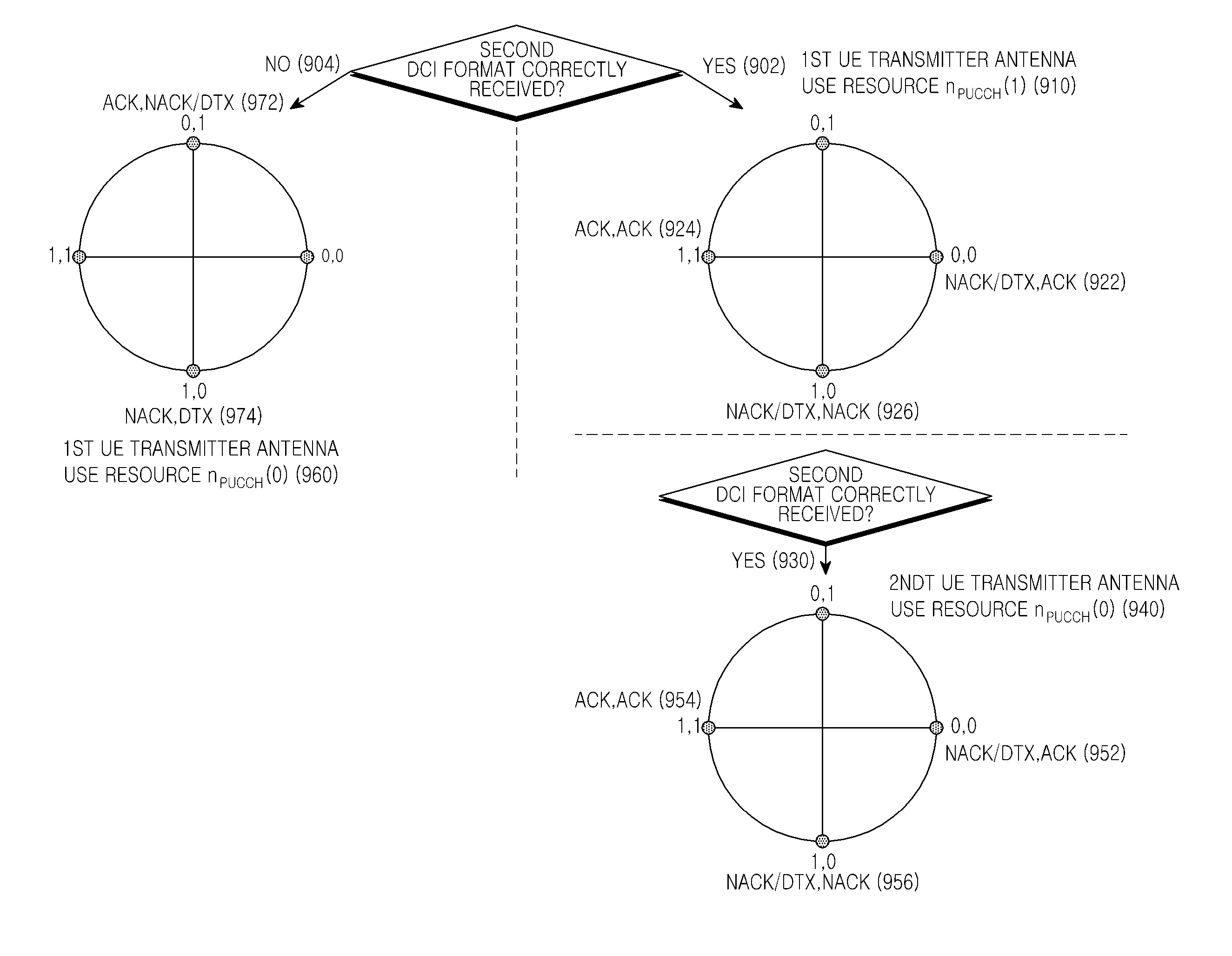
Transmission diversity and multiplexing for harq-ack signals in communication systems
A method and apparatus are described for a User Equipment (UE) to transmit in a control channel ACKnowledgement signals associated with a Hybrid Automatic Repeat reQuest process (HARQ-ACK signals) in response to receiving Transport Blocks (TBs) transmitted from a base station. The UE conveys the HARQ-ACK information by selecting one resource from multiple resources in the control channel and by selecting a constellation point of the modulation scheme for the HARQ-ACK signal. Transmission diversity is supported using different control channel resources that are already available to the UE without configuring additional resources. Design principles are described to optimally map the HARQ-ACK information to control channel resources and modulation constellation points for a Time Division Duplex (TDD) system and for a Frequency Division Duplex (FDD) system.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
Method for frequency division duplex communications
InactiveUS6853629B2Improve bandwidth efficiencyQuality improvementSpatial transmit diversityModulated-carrier systemsTelecommunicationsPolarization diversity
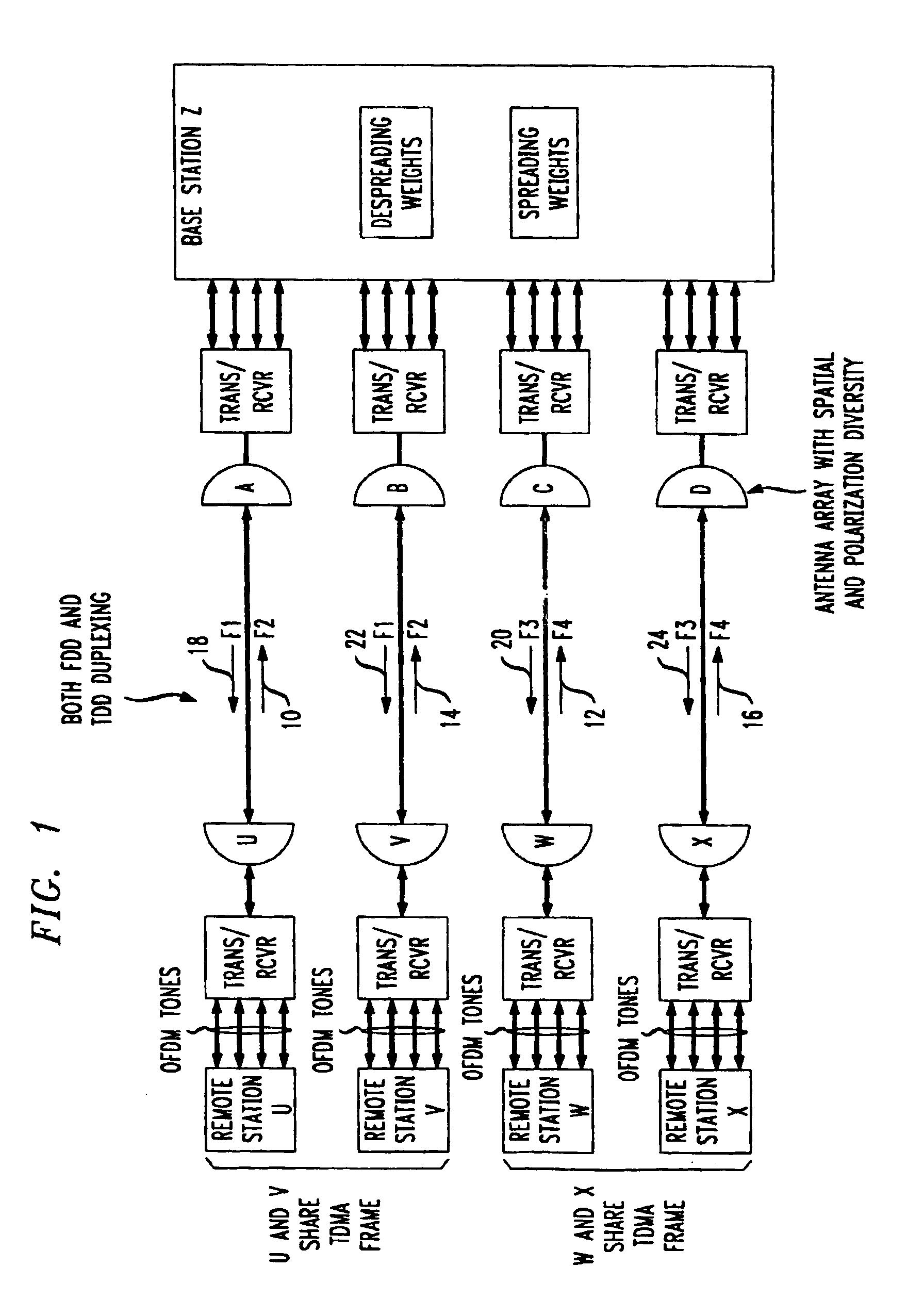
The high quality PCS communications are enabled in environments where adjacent PCS service bands operate with out-of-band harmonics that would otherwise interfere with the system's operation. The highly bandwidth-efficient communications method combines a form of time division duplex (TDD), frequency division duplex (FDD), time division multiple access (TDMA), orthogonal frequency division multiplexing (OFDM), spatial diversity, and polarization diversity in various unique combinations. The method provides excellent fade resistance. The method enables changing a user's available bandwidth on demand by assigning additional TDMA slots during the user's session.
Owner:AT&T MOBILITY II LLC
Devices and methods for harq-ack feedback scheme on pusch in wireless communication systems
ActiveUS20160212734A1Error prevention/detection by using return channelSignal allocationCommunications systemAutomatic repeat request
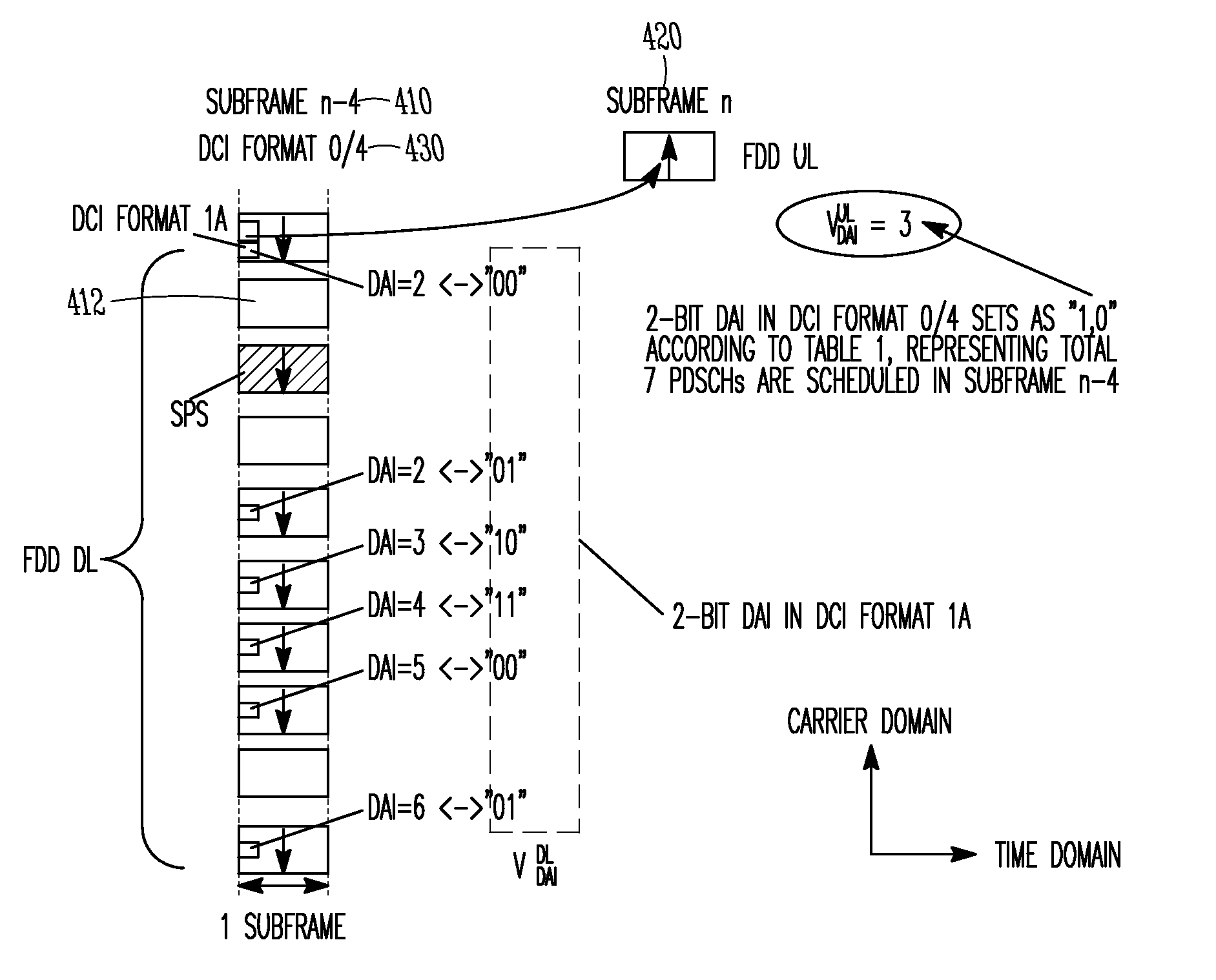
Devices and methods of reducing overall Hybrid Automatic Repeat Request-Acknowledgment (HARQ-ACK) of user equipment (UE) using a large amount of carrier aggregation are generally described. The UE may receive a subframe from an enhanced NodeB (eNB). The subframe may contain a physical downlink control channel (PDCCH) formed in accordance with a Downlink Control information (DCI) format. The DCI format may comprise a Downlink Assignment Index (DAI) for Time Division Duplexed (TDD) and Frequency Division Duplexed (FDD) operation. The UE may determine, dependent on the DAI, a number and ordering of Hybrid Automatic Repeat Request-Acknowledgment (HARQ-ACK) bits to be transmitted on a Physical Uplink Shared Channel (PUSCH) and subsequently transmit the HARQ-ACK bits.
Owner:APPLE INC
Method for indicating idle state of channel or reserving resources, system, terminal and base station
ActiveCN104507108AReduce power lossRealize seamless switchingNetwork traffic/resource managementFrequency division duplexUplink channel
The invention provides a method and a system for indicating an idle state of a channel or reserving resources, a method and a system for indicating an idle state of an uplink channel or reserving the resources, an LTE (Long Term Evolution) terminal, an LTE base station and an LTE system. The method for indicating the idle state of the channel comprises the following steps of setting a channel monitoring sub-frame used for detecting the state of the channel in a frame structure in a time division or frequency division duplex mode; if the channel monitoring sub-frame internally detects that the channel is in the idle state, sending an indication, representing that the channel is in the idle state, to the terminal through a channel idle state signaling or a resource reservation signaling, and sending an indication, representing that the channel is occupied by the base station, to communication equipment requesting to occupy a non-authorized frequency band. According to the technical scheme, the understandings of the idle state of the channel and the reservation state of the resources by the terminal and the base station working in the non-authorized frequency band are consistent, and data based on the same core network can be seamlessly switched and transmitted in an authorized frequency band and the non-authorized frequency band.
Owner:YULONG COMPUTER TELECOMM SCI (SHENZHEN) CO LTD
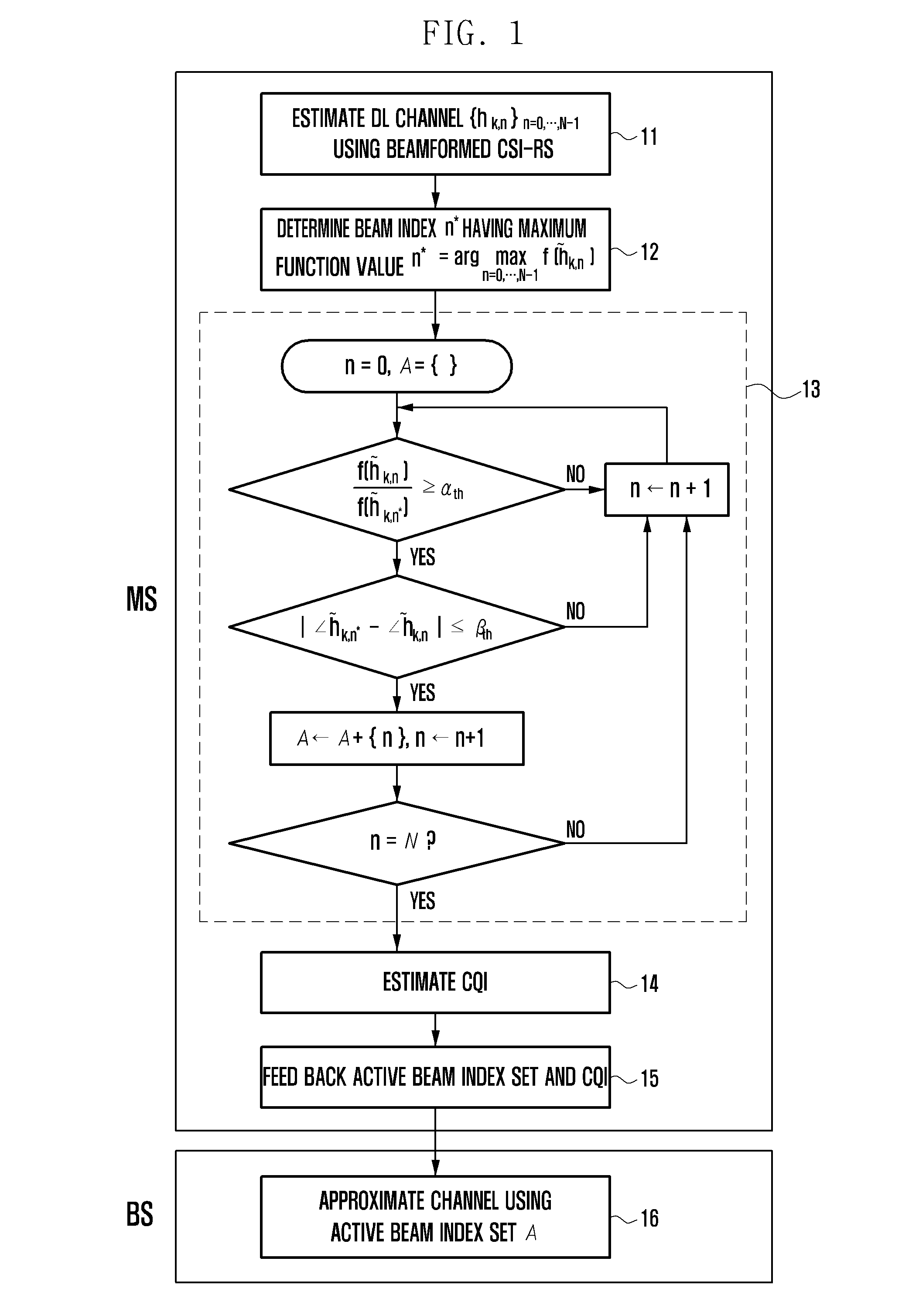
Methods and systems for csi-rs transmission in lte-advance systems
InactiveUS20130094411A1Transmission path divisionFrequency-division multiplexChannel state informationTime domain
A method of allocating resource elements in an orthogonal frequency division multiplexing (OFDM) system for transmission of a channel state information reference signal (CSI-RS) is disclosed. The method includes converting resource elements to a two-dimensional frequency-time domain. The converted resource elements can then be partitioned to units of a physical resource block (PRB), which can be one subframe, for example. It can be determined whether a portion of a PRB is being used by another signal; and if the portion of the PRB is not being used, it can be allocated for transmission of the CSI-RS. The CSI-RS can be transmitted at resource element locations determined by the resource elements available to the CSI-RS in a regular or a frequency-division duplexing (FDD) downlink subframe, for example. The CSI-RS can be transmitted in a downlink subframe configured as a Multi-Media Broadcast over a Single Frequency Network (MBSFN) or a non-MBSFN subframe.
Owner:ZTE (USA) INC
Dual band unidirectional scheme in a cellular mobile radio telecommunications system
InactiveUS20030104816A1Time-division multiplexFrequency-division multiplexCellular radioTelecommunications network
A cellular radio telecommunications system and method of operating the same is described which includes a first cellular radio telecommunications network for providing frequency division duplex radio transmissions over an air interface to one or more fixed or mobile terminals and a second cellular unidirectional radio telecommunications network which at least partly overlaps the first cellular radio telecommunications network for providing unidirectional simplex radio transmissions over an air interface to the one or more fixed or mobile terminals. At least one of access to the unidirectional second cellular network and handover of a communication supported by the unidirectional second cellular network is managed by the first cellular network. A special dedicated uplink channel may be provided in the first network for trasmitting uplink control and / or error messages of the second network.
Owner:RPX CLEARINGHOUSE
Method and apparatus for controlling soft buffer for tdd-fdd carrier aggregation
ActiveUS20150181590A1Error prevention/detection by using return channelTransmission path divisionTelecommunicationsCarrier signal
Provided is a method and apparatus for controlling soft buffer for TDD-FDD carrier aggregation. The method includes: establishing a Radio Resource Control (RRC) connection with a base station through a first serving cell, the first serving cell supporting a Time Division Duplex (TDD) mode; receiving an RRC message from the base station through the first serving cell, the RRC message comprising carrier aggregation (CA) configuration information, the CA configuration information comprising information of a second serving cell supporting a Frequency Division Duplex (FDD) mode; determining a maximum number of DL HARQ processes for the second serving cell, the maximum number of DL HARQ processes for the second serving cell being differently determined according to a DL reference timing; and storing soft channel bits for a received transport block (TB) based on the determined maximum number of DL HARQ processes for the second serving cell.
Owner:SK TELECOM CO LTD +1
Multiple Data Services Over a Distributed Antenna System
InactiveUS20100093391A1Avoid spendingReduce energy costsSite diversityNetwork traffic/resource managementDistributed antenna systemGps receiver
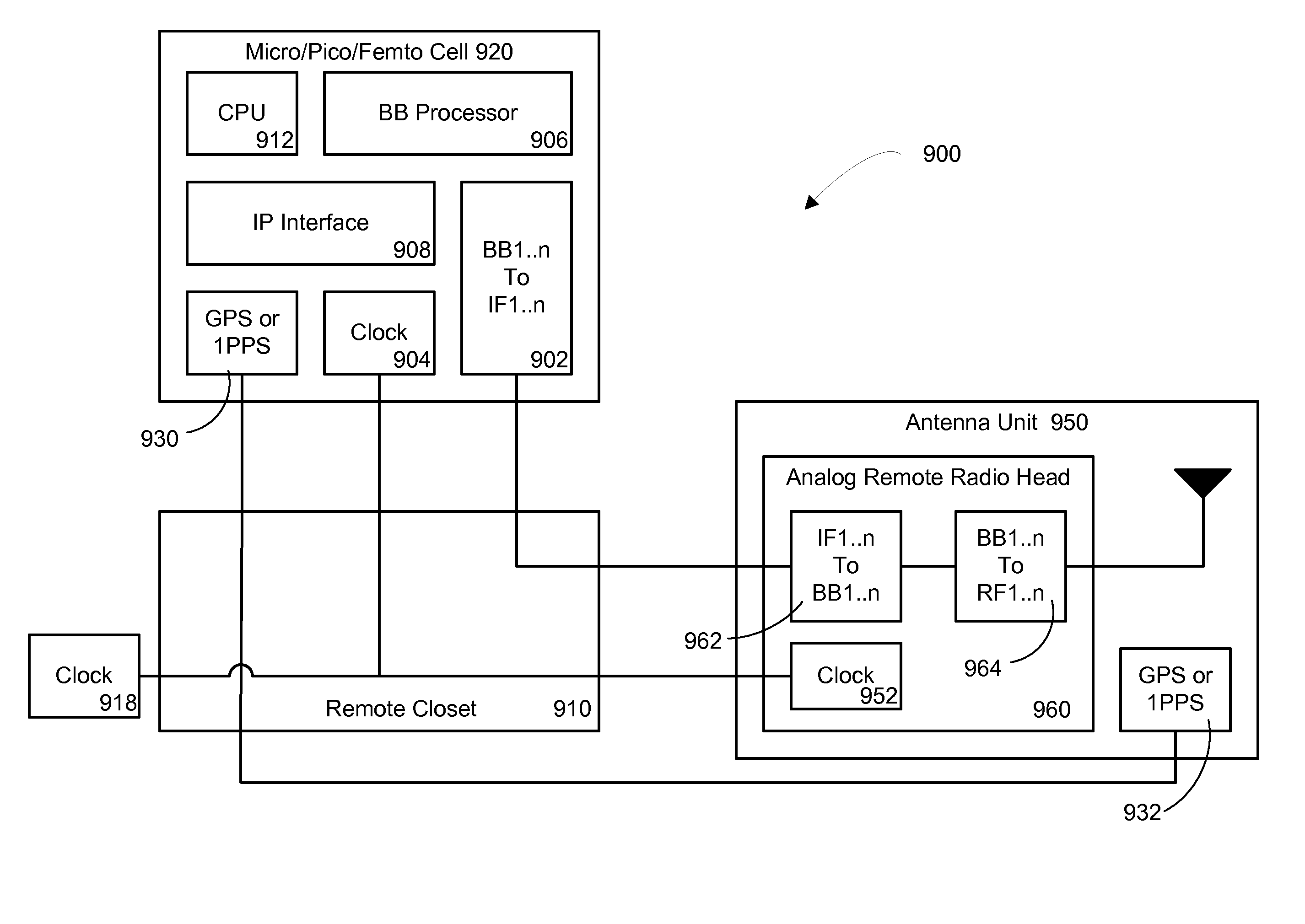
The invention is directed to a method and system for supporting multiple time division duplexed (TDD) based wireless services or frequency division duplexed (FDD) wireless services on a Distributed Antenna System (DAS). A DAS can support a many wireless services, including voice and data services using the same physical equipment. TDD based services use a common clock signal to synchronize the components of the DAS for transmission and reception of TDD signals. In accordance with the invention, the DAS can include a GPS receiver which can extract a timing signal (such as a 1 pps signal) from a GPS signal and distribute the timing signal to any and all components of the DAS to enable synchronization of the components for transmitting and receiving TDD signals. The GPS receiver can be part of the interface that connects a TDD based service to the DAS or separate component of the DAS. In accordance with the invention, the DAS can distribute a reference clock signal to all of the components of the DAS in order to maintain zero frequency shift while manipulating with the carrier frequencies of the various wireless services carried by the DAS. In addition, and in accordance with the invention, two analog architectures for better integration between the services sources (BTS) and the DAS are disclosed.
Owner:CORNING OPTICAL COMM WIRELESS
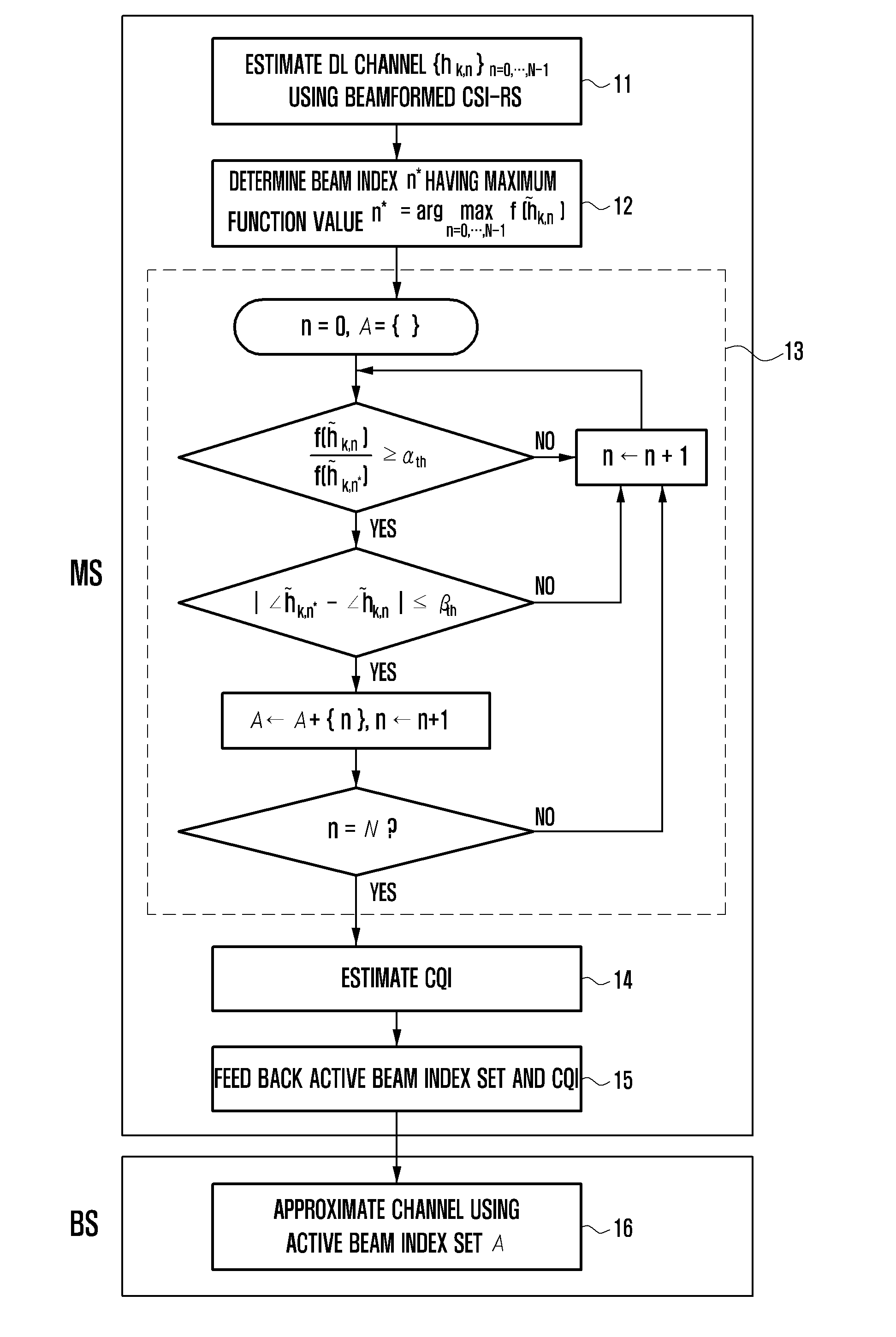
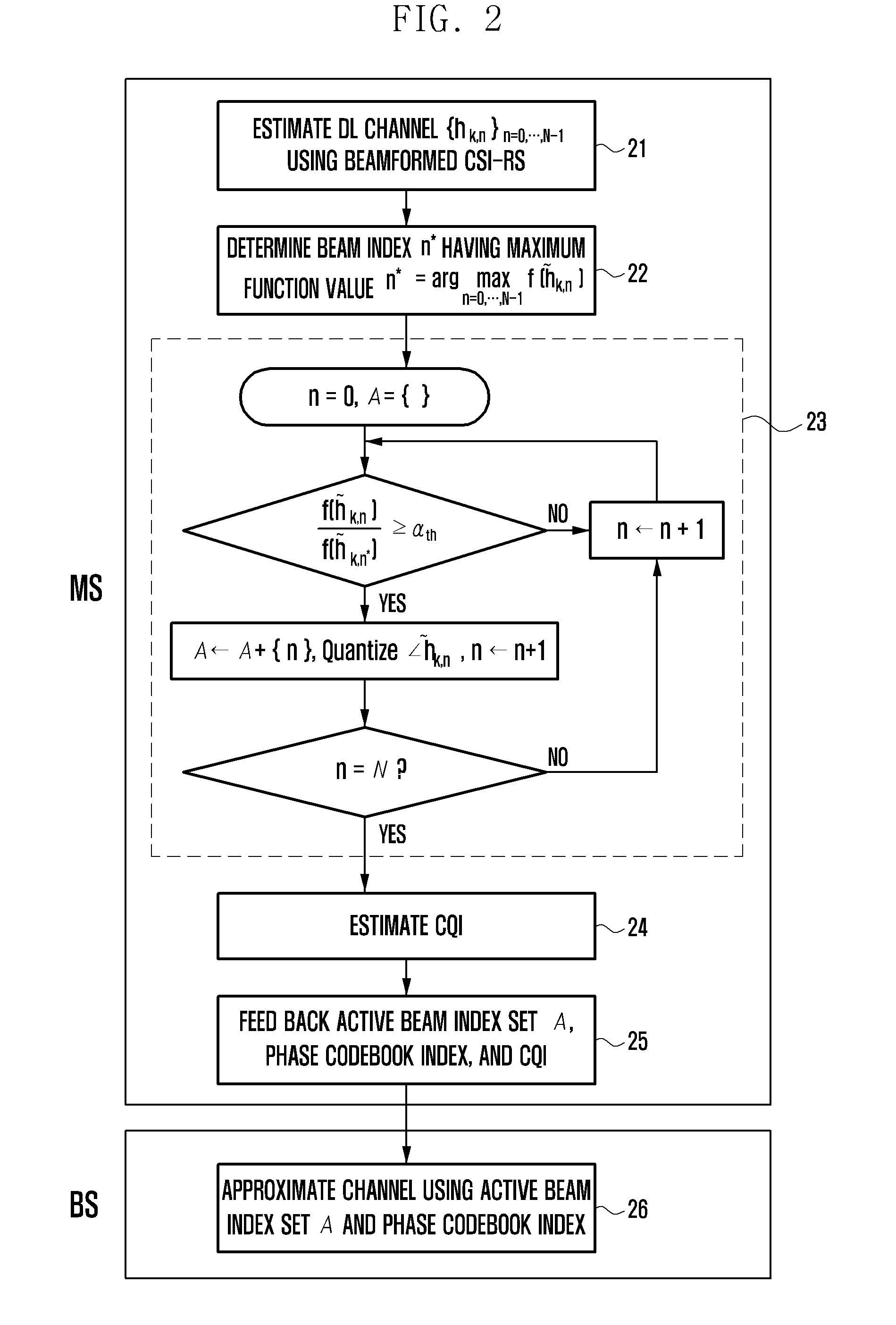
Channel state information feedback apparatus and method in wireless communication system operating in fdd mode
ActiveUS20130163457A1Efficient receptionFeedback information efficientlyError preventionTransmission systemsCommunications systemMobile station
A Channel State Information (CSI) feedback method and apparatus is provided for transmitting, at a base station, the CSIs for plural transmit antennas with a limited amount resource and receiving, at a mobile station, the CSIs efficiently in a massive Multiple Input Multiple Output (MIMO) system operating in the Frequency Division Duplex (FDD) mode.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD +1
Method and equipment for determining the transmission resource of channel quality indicator
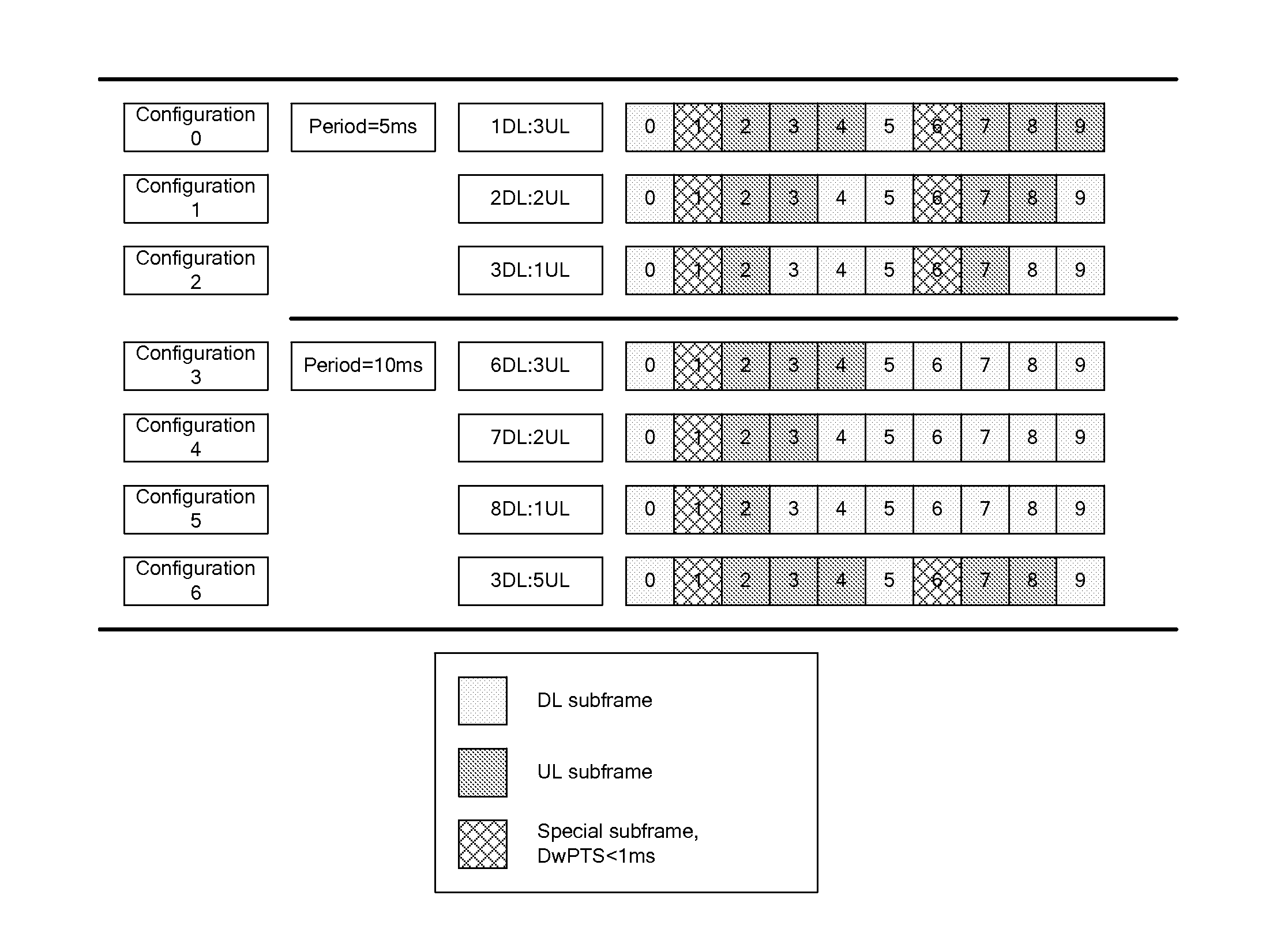
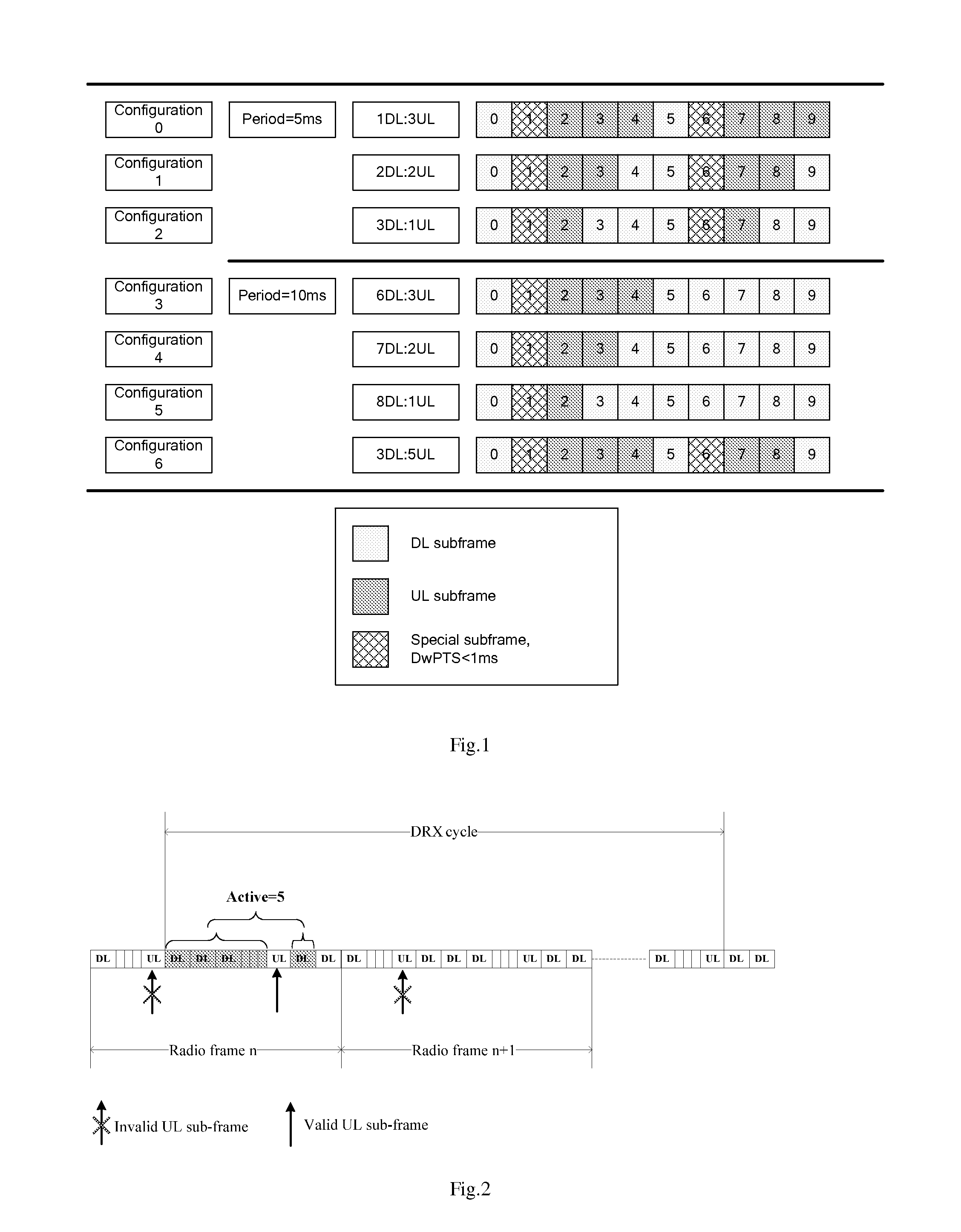
ActiveUS20110038277A1Effective supportSave resourcesFrequency-division multiplex detailsTransmission systemsTelecommunicationsControl channel
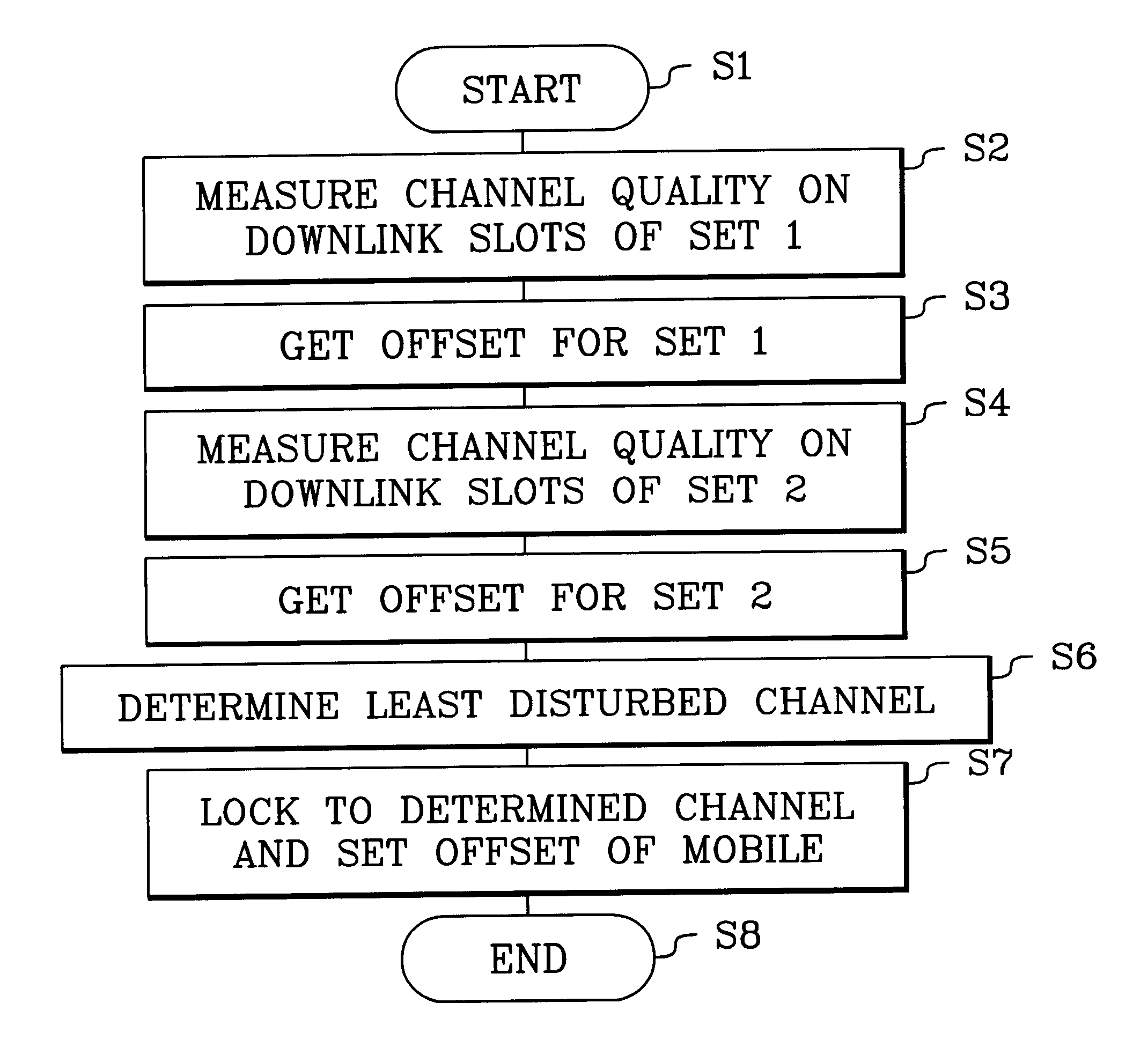
A method and equipment for determining the transmission resource of channel quality indicator are disclosed. They are applied in Time Division Duplex TDD system and Half Duplex-Frequency Division Duplex HD-FDD system when Discontinuous Reception DRX operation is adopted. The method includes the following steps: determining the location of the downlink subframe where the start point of monitoring Physical Downlink Control Channel PDCCH in DRX cycle is located; determining whether the transmission resource used for transmitting the Channel Quality Indicator CQI is an uplink subframe previous to the determined location or one or more uplink subframes after the determined location. Availability of the CQI information when performing downlink schedule is guaranteed, and the transmission resource used for transmitting CQI can be effectively saved.
Owner:CHINA MOBILE COMM GRP CO LTD
Framing for an adaptive modulation communication system
ActiveUS7197022B2Synchronisation arrangementTime-division multiplexTime division multiple accessCommunications system
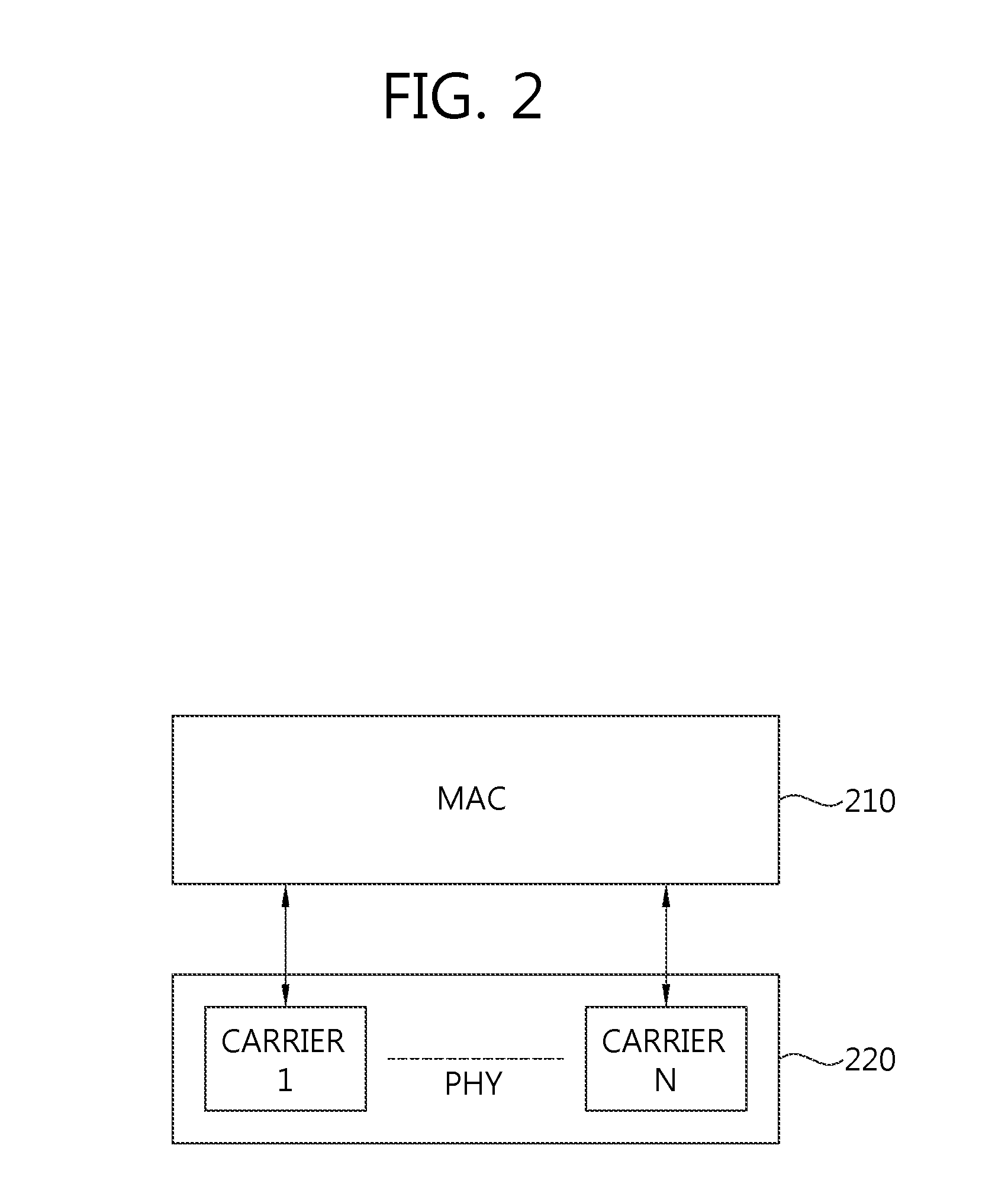
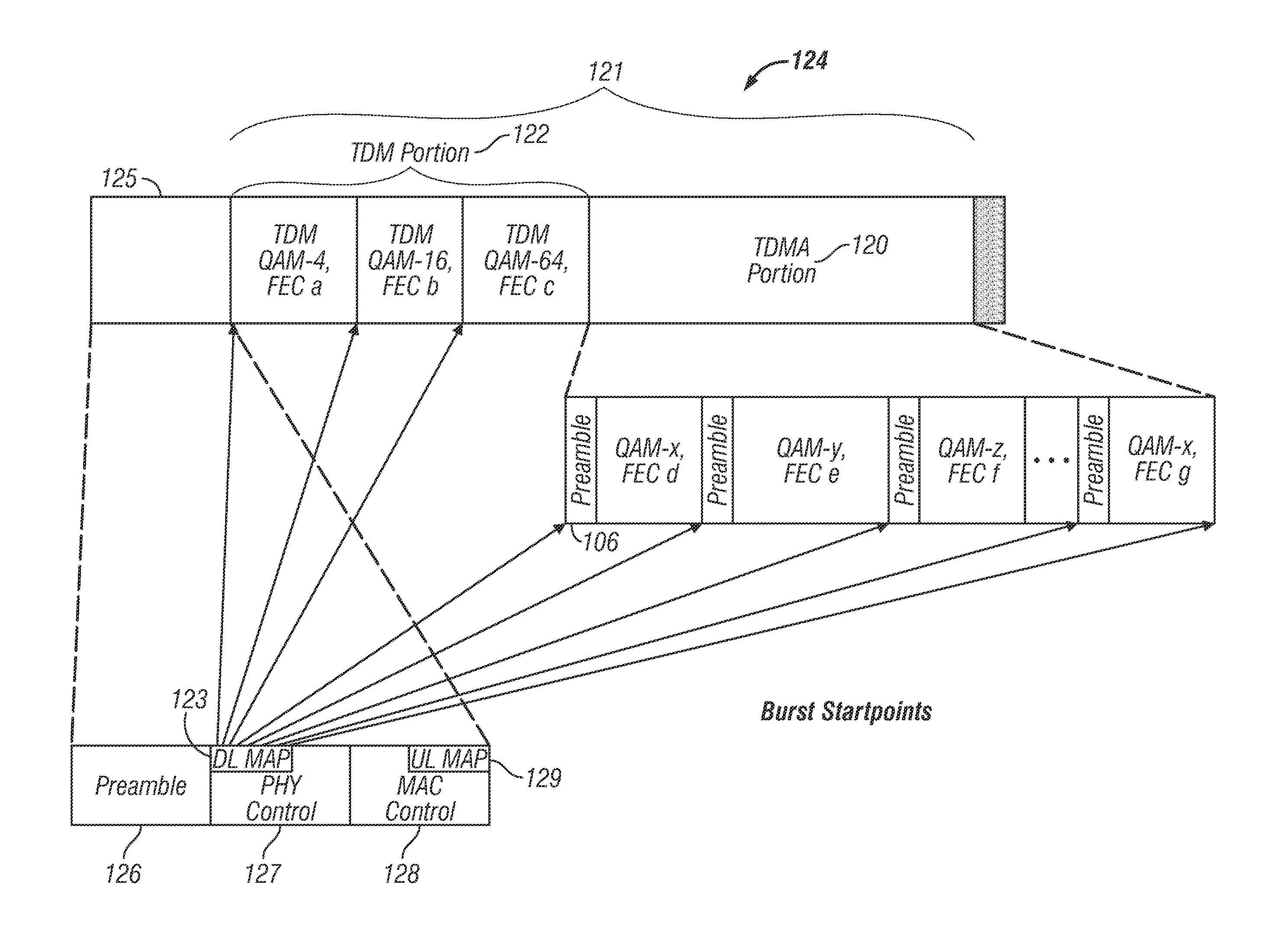
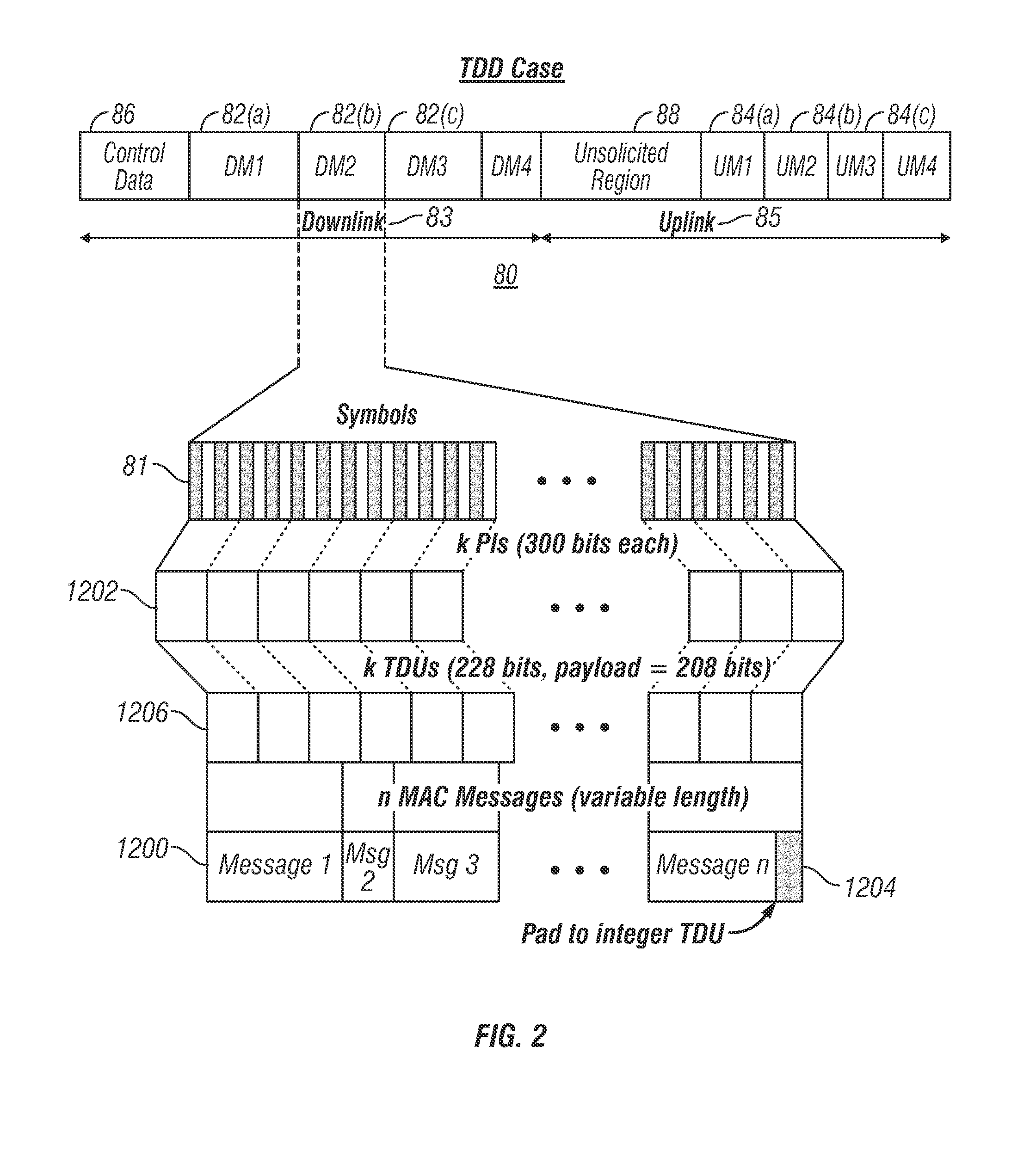
A system and method for mapping a combined frequency division duplexing (FDD) Time Division Multiplexing (TDM) / Time Division Multiple Access (TDMA) downlink subframe for use with half-duplex and full-duplex terminals in a communication system. Embodiments of the downlink subframe vary Forward Error Correction (FEC) types for a given modulation scheme as well as support the implementation of a smart antennae at a base station in the communication system. Embodiments of the system are also used in a TDD communication system to support the implementation of smart antennae. A scheduling algorithm allows TDM and TDMA portions of a downlink to efficiently co-exist in the same downlink subframe and simultaneously support full and half-duplex terminals. The algorithm further allows the TDM of multiple terminals in a TDMA burst to minimize the number of map entries in a downlink map. The algorithm limits the number of downlink map entries to not exceed 2n+1, where n is the number of DL PHY modes (modulation / FEC combinations) employed by the communication system.
Owner:WI LAN INC +1
Control system and multiple access method in wireless communication system
InactiveUS7313126B2Effectively utilizing frequencyHigh-speed multimediaTransmission path divisionTime-division multiplexCommunications systemAccess method
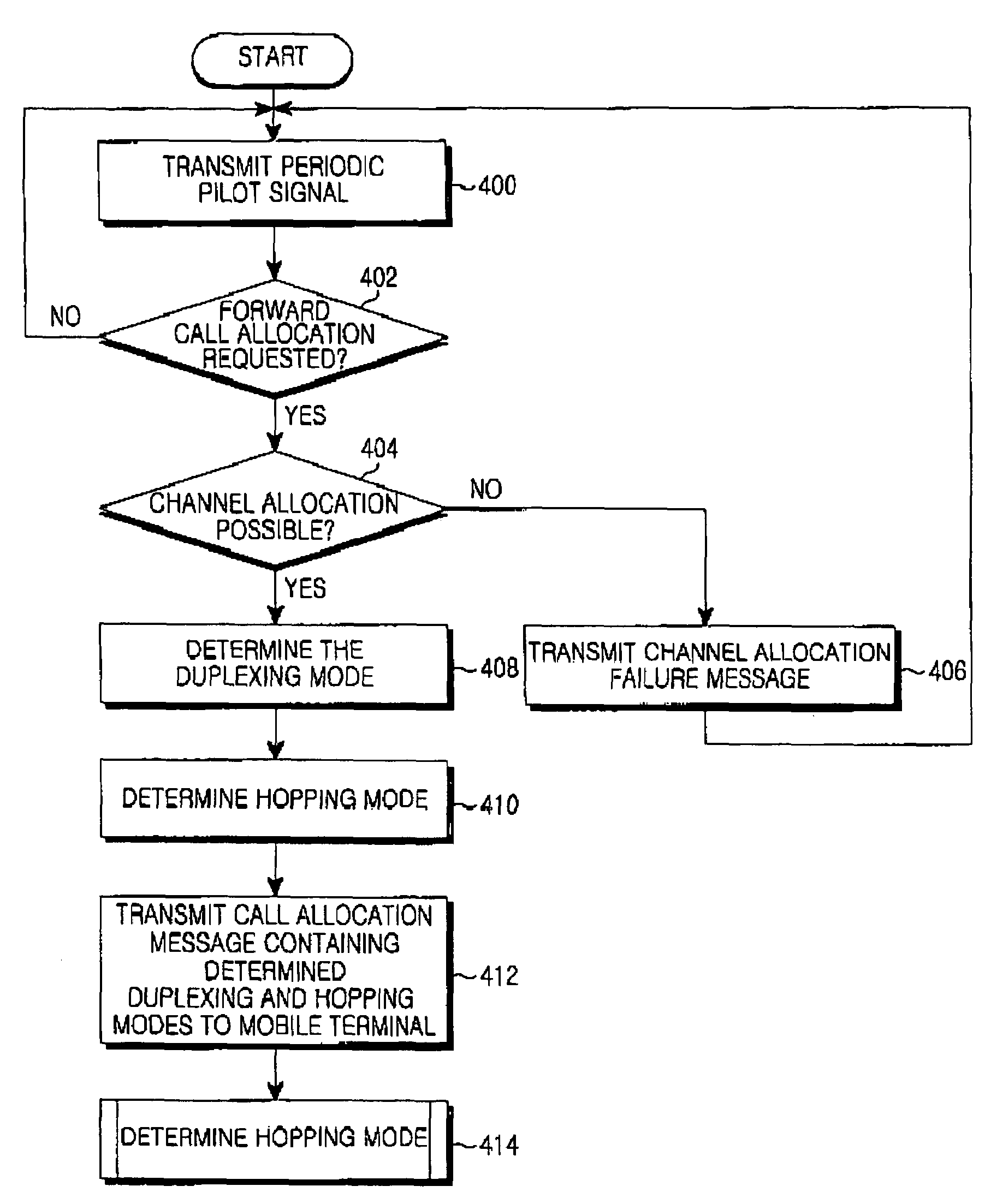
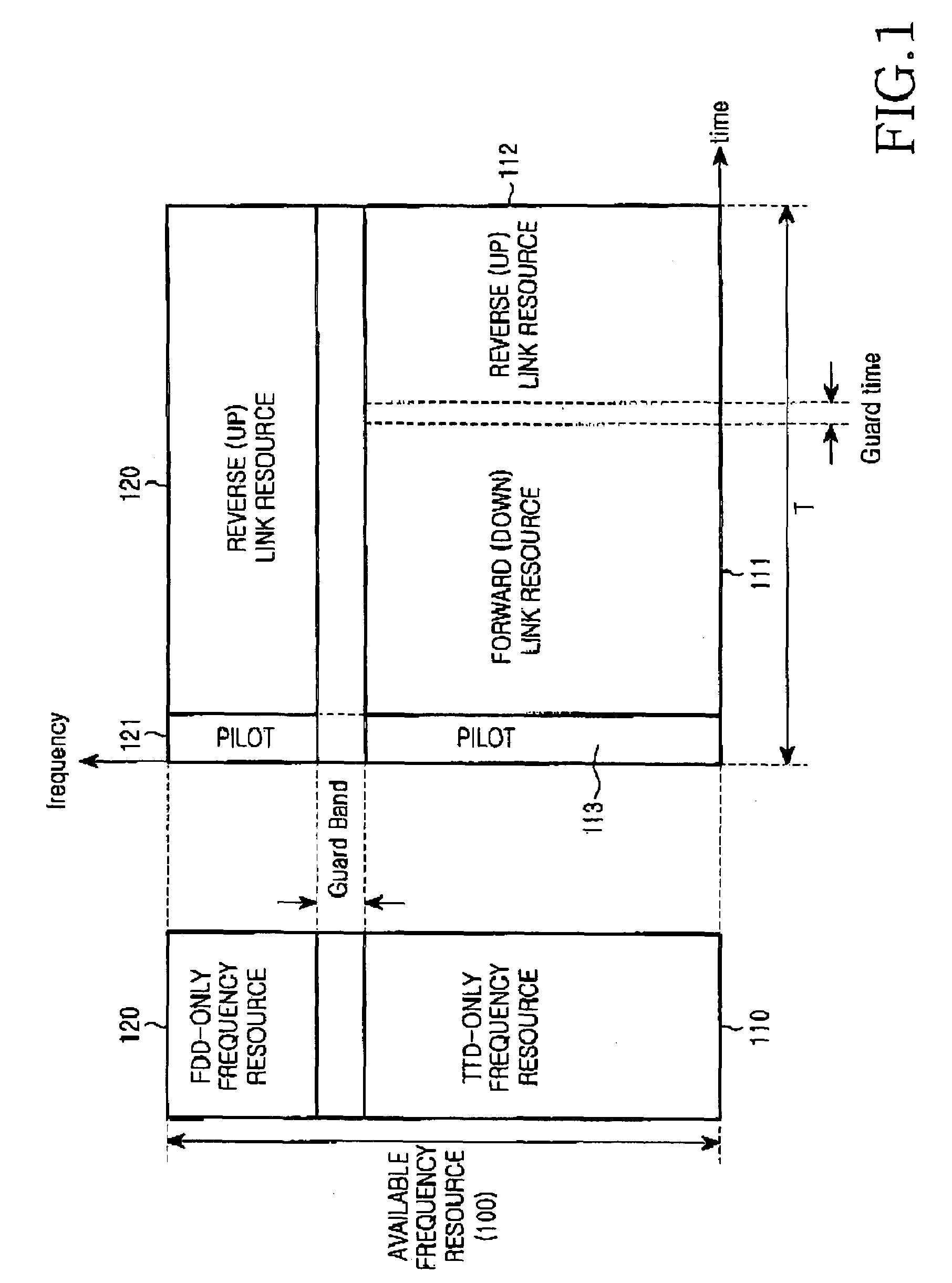
A multiple access method in a wireless communication system using a plurality of multiple access techniques is provided. When a call is established with a wireless terminal, the terminal transmits a duplexing mode determination factor to the base station to set a time or frequency division duplexing mode for reverse transmission and determine access and hopping modes according to each of the division duplexing modes, and establishes forward and reverse channels according to the set time or frequency division duplexing mode for reverse transmission to communicate with the base station. The base station receives the duplexing mode determination factor from the terminal, sets a time or frequency division duplexing mode for reverse transmission and sets a time division duplexing mode for forward transmission based on the received factor, and determines frequency hopping and multiple access modes to communicate with the terminal according to the determined frequency and multiple access modes.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
TDMA-TDD/FDD radio communication system and channel selection method and apparatus for such a system
InactiveUS6839333B1Provides spectrum efficiencySatisfies requirementSynchronisation arrangementNetwork topologiesRadio coverageCommunications system
A TDMA radio communication system combines time and frequency division duplex. It includes a first base station transmitting in first downlink frames on a first carrier frequency in a first frequency band and receiving in first uplink frames, which have no time overlap with the first downlink frames, on a second carrier frequency in a second frequency band, which has no frequency overlap with the first frequency band. The system also includes a second base station, which has partially overlapping radio coverage area with the first base station, but is geographically separated from the first base station in order to avoid transmission from one base station disturbing reception from radio terminals on the other base station. The second base station transmits in second downlink frames on the first carrier frequency and receives in second uplink frames, which have no time overlap with the second downlink frames, on the second carrier frequency. The first and second downlink frames are offset to have no time overlap. A network controller synchronizes transmission from the first and second base stations.
Owner:TELEFON AB LM ERICSSON (PUBL) +1
Method for frequency division duplex communications
InactiveUS20030156570A1Efficient communicationEasy to separateSpatial transmit diversityModulated-carrier systemsTelecommunicationsTime division multiple access
The high quality PCS communications are enabled in environments where adjacent PCS service bands operate with out-of-band harmonics that would otherwise interfere with the system's operation. The highly bandwidth-efficient communications method combines a form of time division duplex (TDD), frequency division duplex (FDD), time division multiple access (TDMA), orthogonal frequency division multiplexing (OFDM), spatial diversity, and polarization diversity in various unique combinations. The method provides excellent fade resistance. The method enables changing a user's available bandwidth on demand by assigning additional TDMA slots during the user's session.
Owner:AT&T MOBILITY II LLC
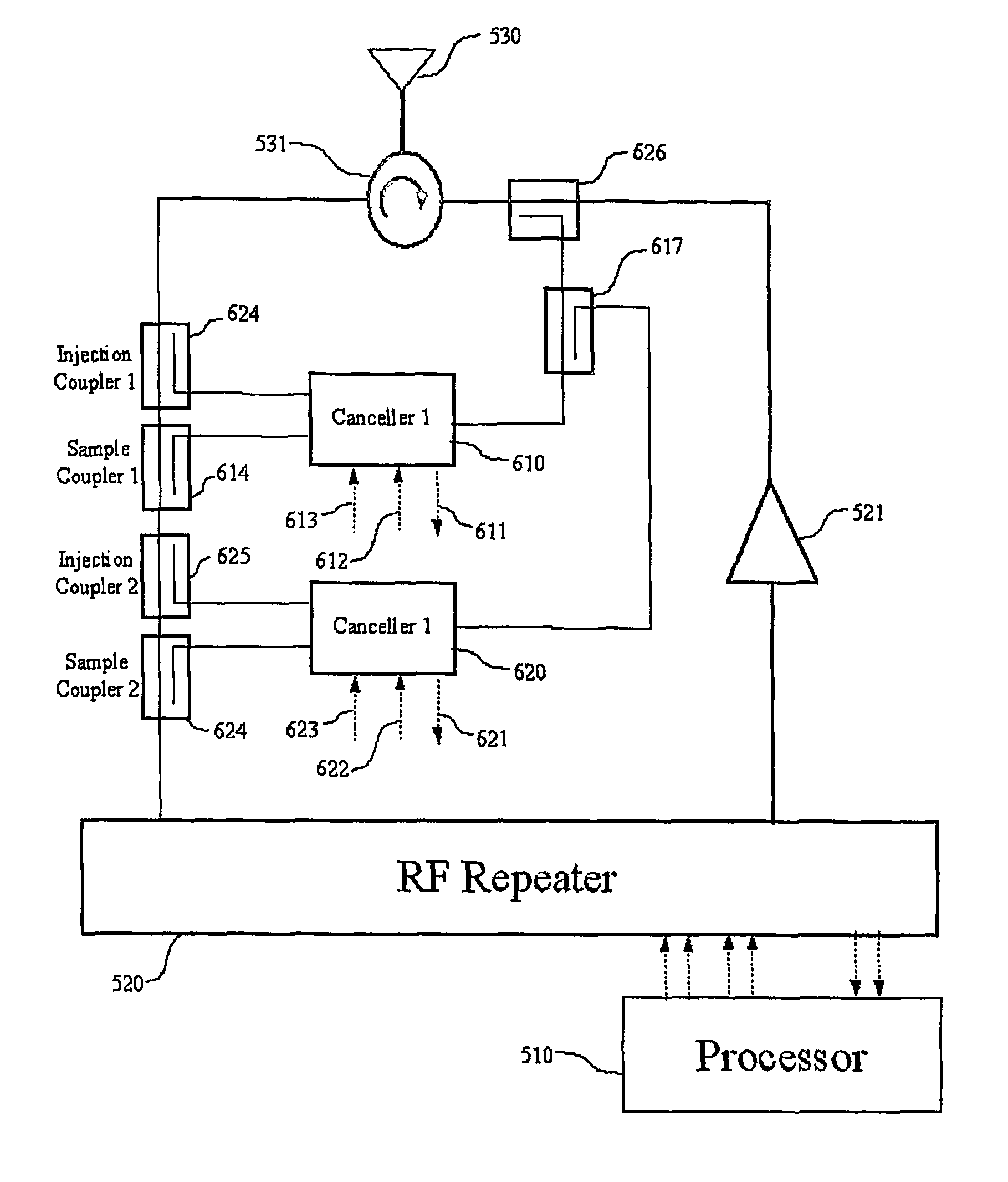
Transmission canceller for wireless local area network
InactiveUS8027642B2Improve performanceIncrease the areaPulse transformerFrequency-division multiplex detailsTransceiverEngineering
A frequency translating repeater (200) for use in a wireless local area network includes a cancellation unit. Canceller (402) is controlled by control (401) to provide an injection signal for canceling leakage in a receive signal path. Reference coupler (403) provides a reference signal from the transmit signal, injection coupler (404) injects a correction signal, and sample coupler (405) provides a sample for feedback. A processor (510) receives the sample signal through a detector (415). Although the present invention is intended for a frequency translating repeater, it has broad applications in radio transceivers in general. One specific application is with frequency division duplex (FDD) handsets or base stations utilizing CDMA technologies such as W-CDMA and IS-2000 or 1XEV-DV / DO.
Owner:QUALCOMM INC
Method and system for an improved user group selection scheme with finite-rate channel state information feedback for FDD multiuser MIMO downlink transmission
InactiveUS7630337B2Frequency-division multiplex detailsSubstation equipmentCommunications systemEngineering
Certain embodiments of the invention may be found in a method and system for an improved user group selection scheme with finite-rate channel state information feedback for frequency division duplex (FDD) multiuser multiple-input-multiple-output (MIMO) downlink transmission. Aspects of the method may include selecting, from a plurality of users in a FDD multiuser communication system, a first user having a channel gain that is greater than a channel gain corresponding to a remaining portion of the plurality of users. A second user may be selected from the remaining portion of the plurality of users, based on a channel gain of the second user and orthogonality of the second user's channel direction with respect to the first user. The selected second user may have a channel gain that is greater than a channel gain corresponding to the remaining portion of the plurality of users.
Owner:AVAGO TECH INT SALES PTE LTD
Method for configuring and allocating forward channel in orthogonal frequency division multiple access frequency division duplex system
ActiveUS20050048979A1Minimize inter-cell interferenceLess inter-cell interferenceNetwork traffic/resource managementAssess restrictionMobile stationOrthogonal frequency-division multiple access
Disclosed is a forward channel configuring method in an OFDMA FDD system. The method comprises: classifying the cells into a specific number of patterns based on location relations of the respective cells; allowing the respective base stations of the cells having different classified patterns to transmit control information to the mobile station at different times within a period of the forward channel, and allowing the respective base stations of the cells having the same classified patterns to transmit control information to the mobile station at the same time; and allowing the respective base stations to transmit traffic data to the mobile station irrespective of the classified patterns when the control information is transmitted.
Owner:PANTECH CORP
Method and apparatus for transmitting/receiving downlink synchronization channels in a cellular communication system supporting scalable bandwidth
ActiveUS20080080476A1Scalability of systemModulated-carrier systemsTransmission path divisionCommunications systemCell search
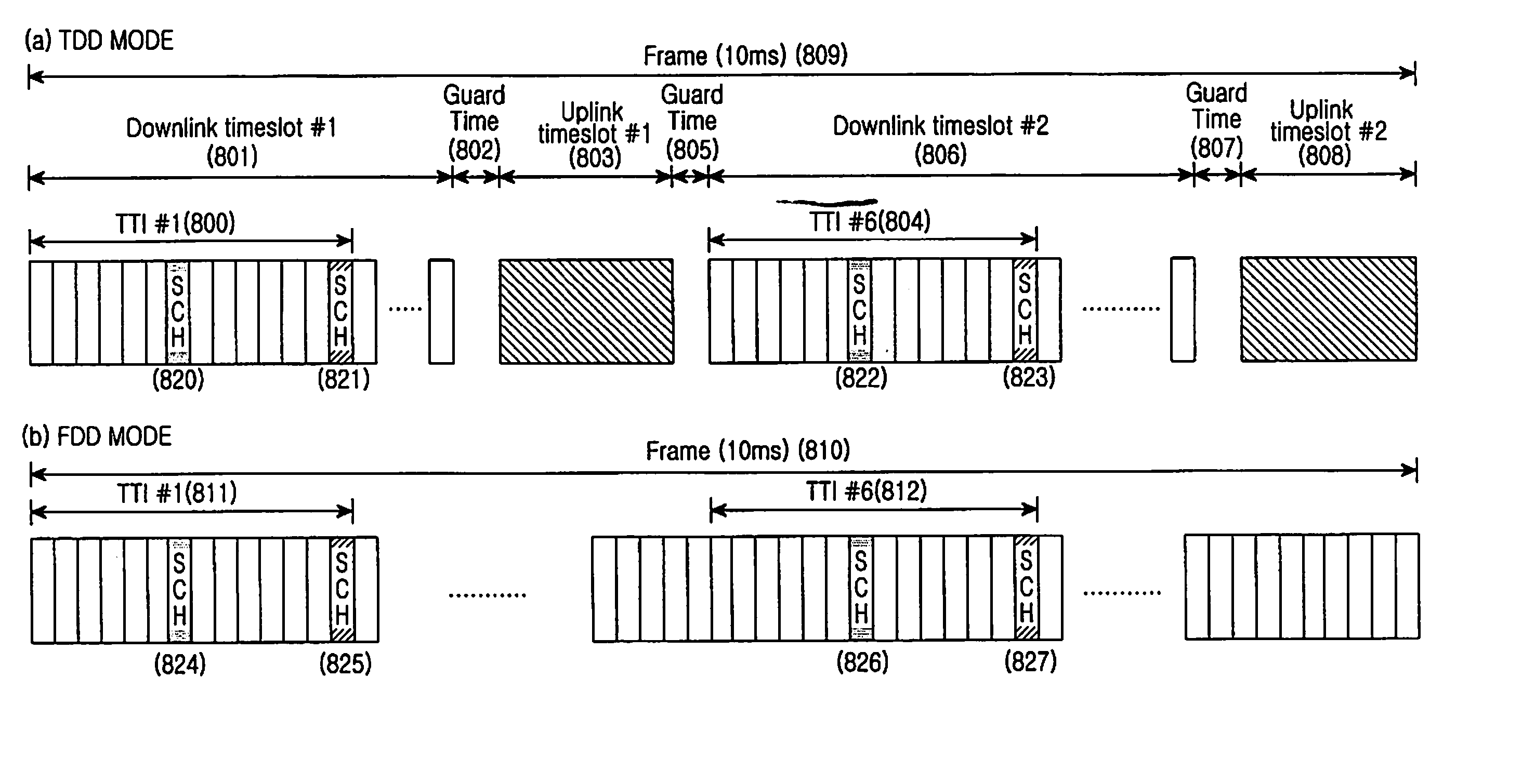
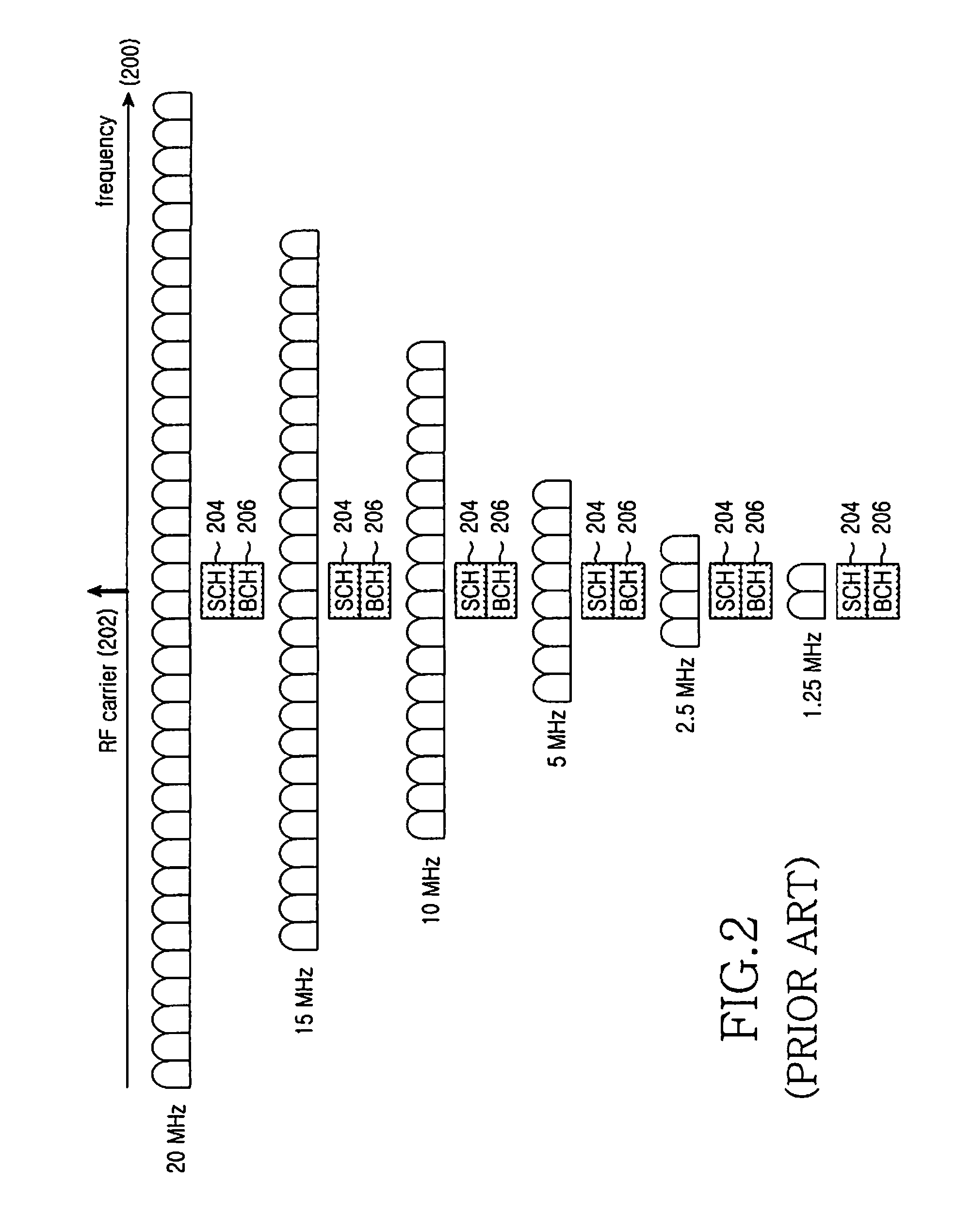
Disclosed is a method and an apparatus for transmitting a downlink Synchronization CHannel (SCH) in an Orthogonal Frequency Division Multiplexing (OFDM)-based cellular wireless communication system supporting a scalable bandwidth. Herein, initial cell search and neighbor cell search are seamlessly performed. The disclosed method and apparatus disclose a synchronization channel structure applicable to both a Frequency Division Duplex (FDD) system and a Time Division Duplex (TDD) system.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
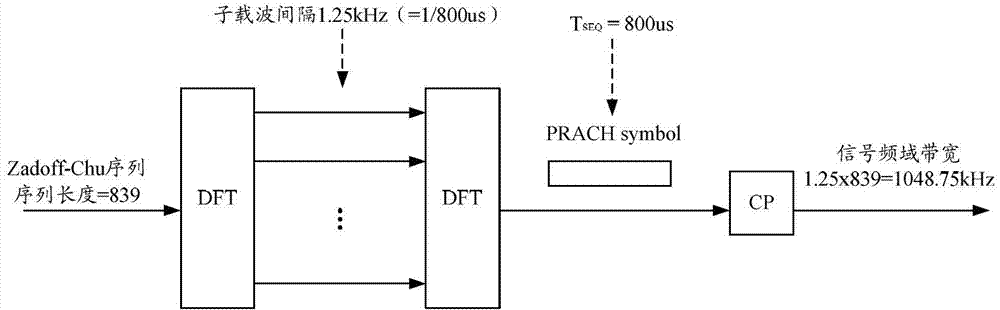
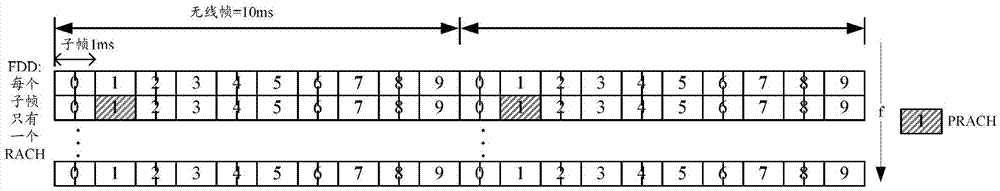
Resource determining method and device for physical random access channel
ActiveCN103716895AImprove resource reuse capacityImprove access efficiencyWireless communicationTime domainTelecommunications
The invention discloses a resource determining method for a physical random access channel. The method comprises the step of configuring a plurality of physical random access channel resources for each piece of user equipment (UE), and the physical random access channel resources include at least one of the following resources: time domain resource, frequency domain resource, code domain resource and space domain resource, wherein the time domain resource is emission sub-frame configuration of a physical random access channel, the frequency domain resource is emission band configuration of the physical random access channel, the code domain resource emission sequence or orthogonal mask configuration of the random access channel, and the space domain resource is space access location configuration of the random access channel. The invention further discloses a resource determining device for a physic al random access channel. The PRACH resource reusing capability in a frequency division duplex system is improved, the PRACH collision probability is reduced, and the terminal access efficiency and the system throughput are improved.
Owner:ZTE CORP
Method and system for an improved user group selection scheme with finite-rate channel state information feedback for FDD multiuser MIMO downlink transmission
InactiveUS20070064632A1Frequency-division multiplex detailsSubstation equipmentEngineeringChannel state information feedback
Certain embodiments of the invention may be found in a method and system for an improved user group selection scheme with finite-rate channel state information feedback for frequency division duplex (FDD) multiuser multiple-input-multiple-output (MIMO) downlink transmission. Aspects of the method may include selecting, from a plurality of users in a FDD multiuser communication system, a first user having a channel gain that is greater than a channel gain corresponding to a remaining portion of the plurality of users. A second user may be selected from the remaining portion of the plurality of users, based on a channel gain of the second user and orthogonality of the second user's channel direction with respect to the first user. The selected second user may have a channel gain that is greater than a channel gain corresponding to the remaining portion of the plurality of users.
Owner:AVAGO TECH INT SALES PTE LTD
Method and apparatus for operating supplementary cells in licensed exempt spectrum
InactiveCN103460740AError preventionNetwork traffic/resource managementFrequency spectrumTelecommunications
A method and an apparatus for operating supplementary cells in licensed exempt (LE) spectrum are disclosed. An aggregating cell operating in a frequency division duplex (FDD) licensed spectrum is aggregated with a LE supplementary cell operating in a time sharing mode for uplink (UL) and downlink (DL) operations. The LE supplementary cell may be an FDD supplementary cell dynamically configurable between an UL only mode, a DL only mode, and a shared mode, to match requested UL and DL traffic ratios. The LE supplementary cell may be a time division duplex (TDD) supplementary cell. The TDD supplementary cell may be dynamically configurable between multiple TDD configurations. A coexistence capability for coordinating operations between the LE supplementary cell with other systems operating in the same channel is provided. Coexistence gaps are provided to measure primary / secondary user usage and permit other systems operating in the LE supplementary cell channel to access the channel.
Owner:INTERDIGITAL PATENT HLDG INC
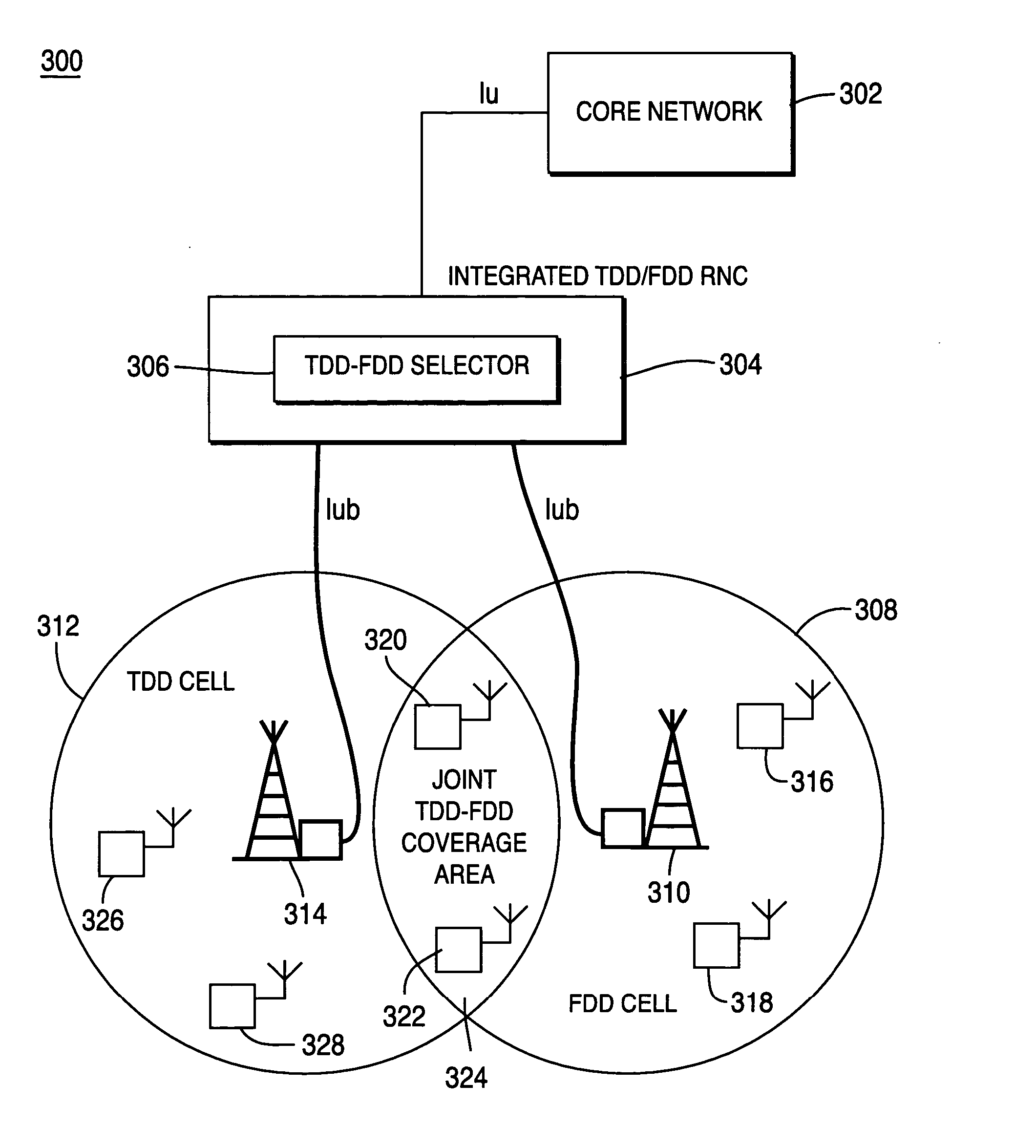
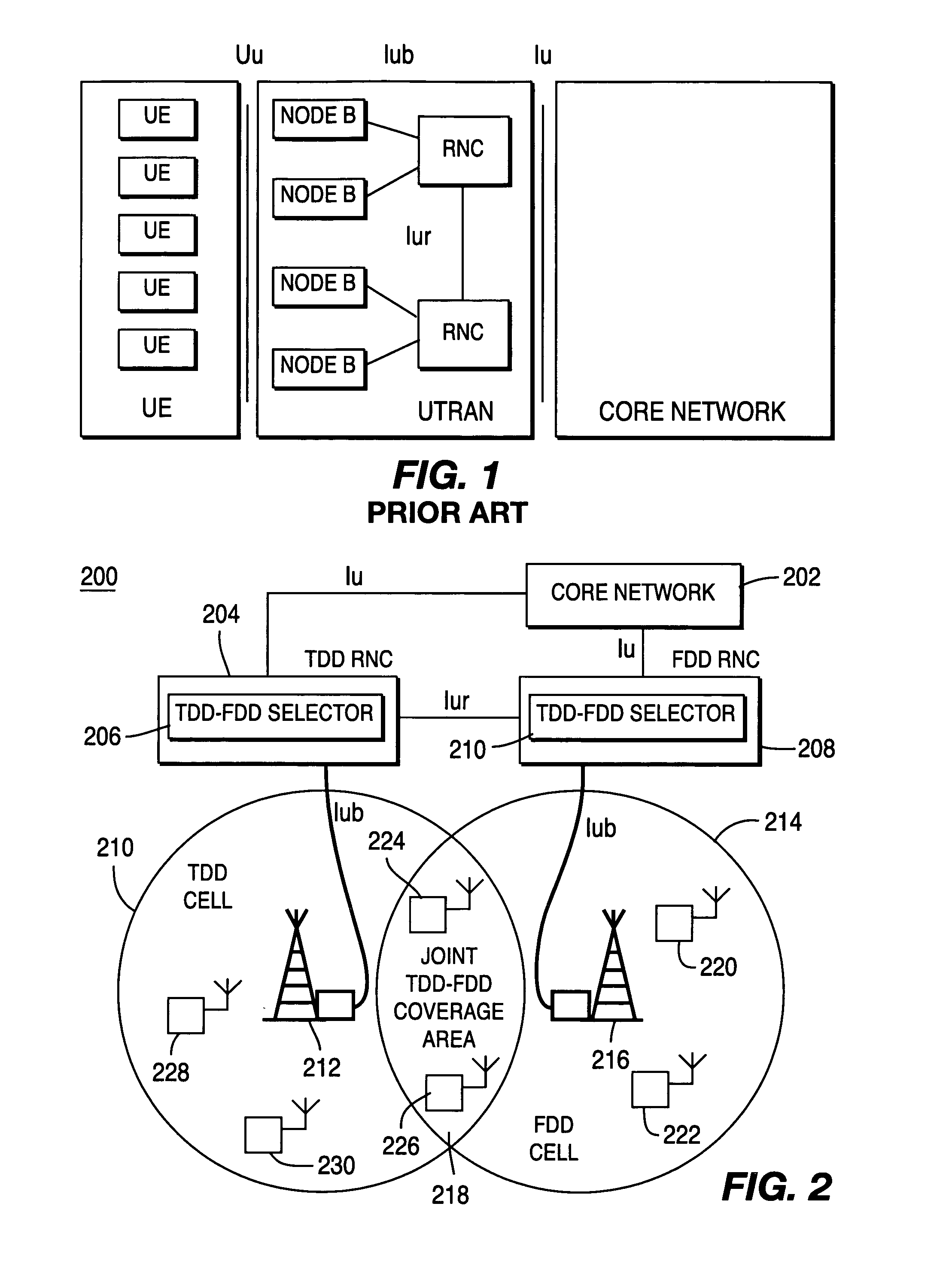
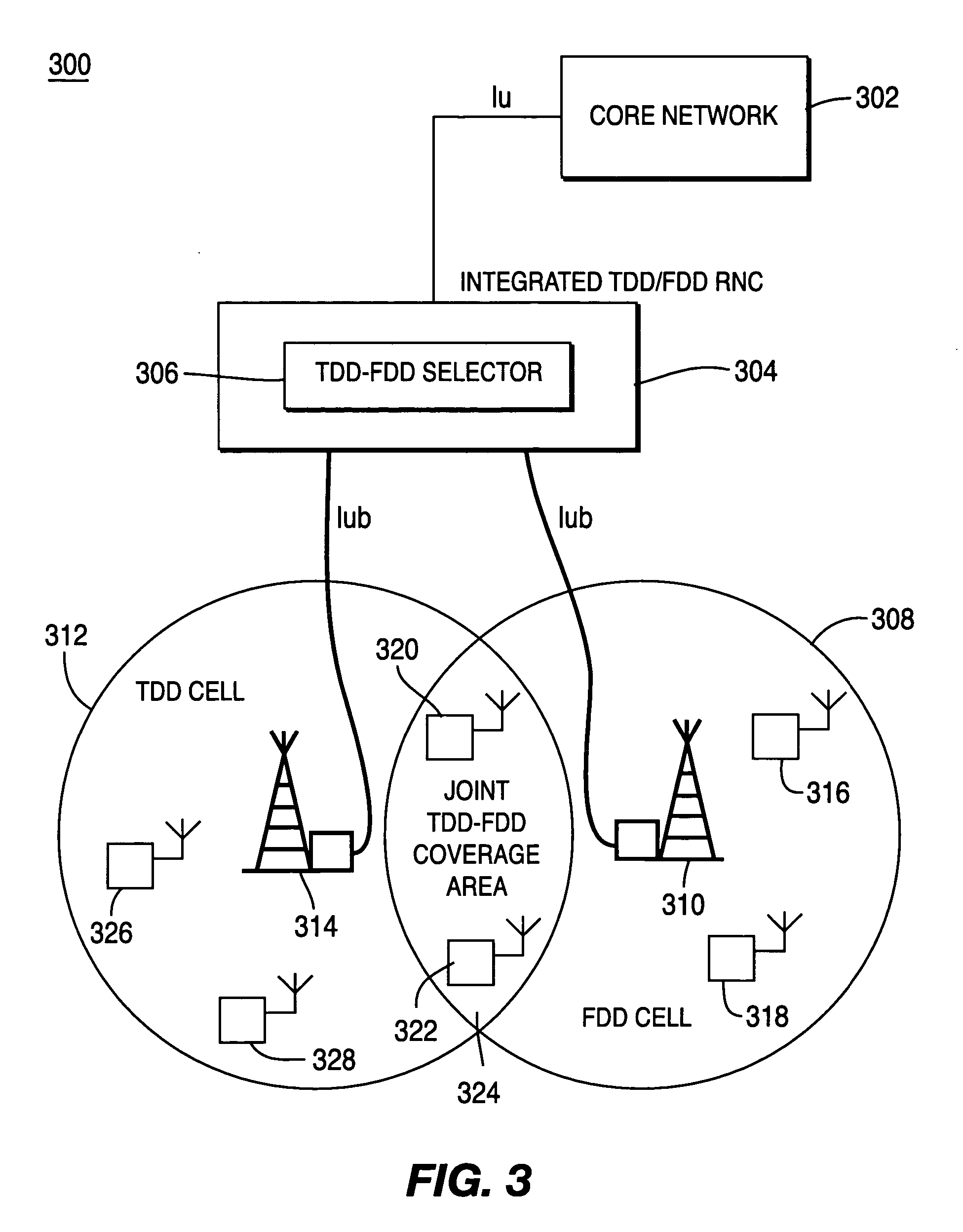
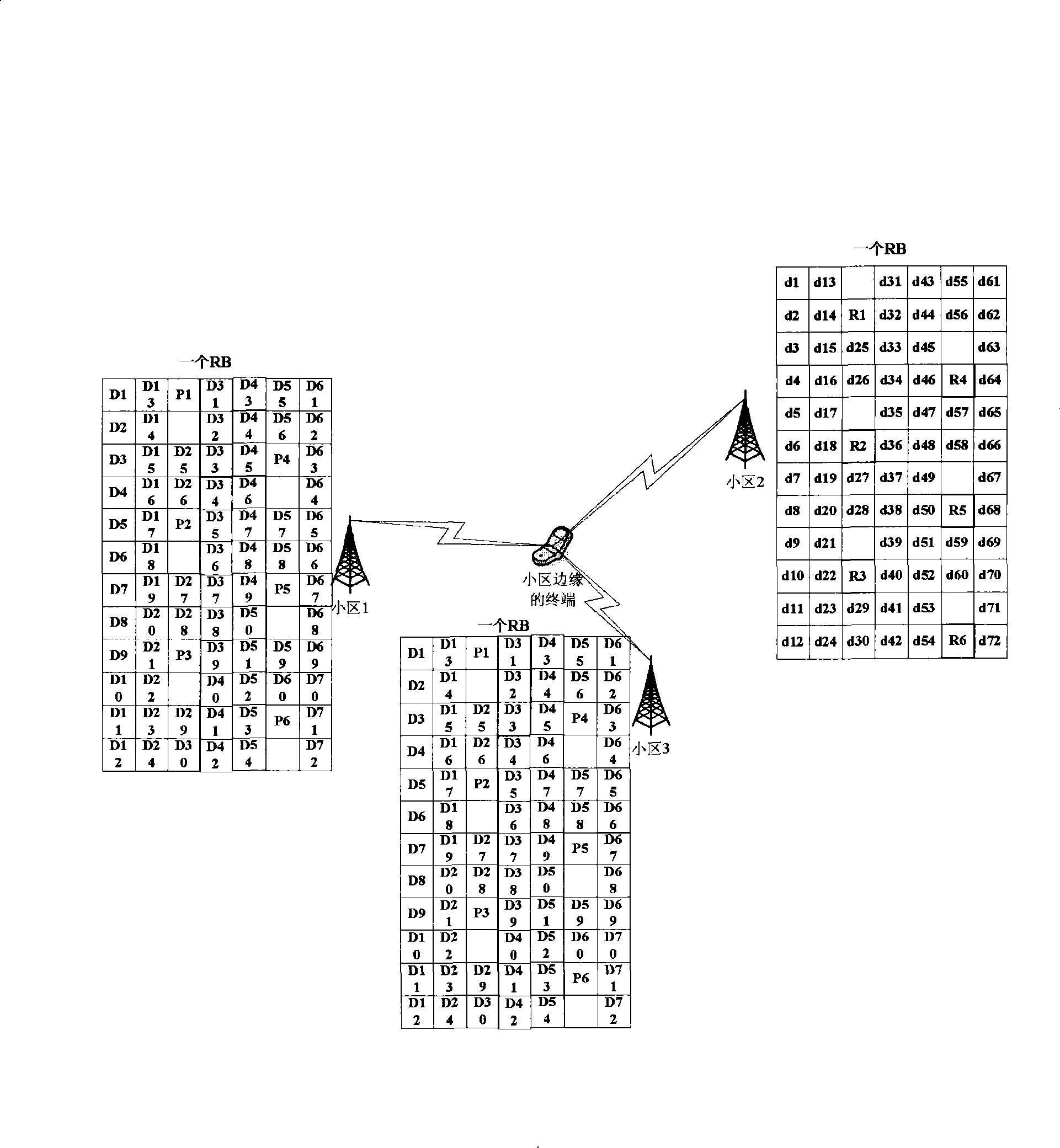
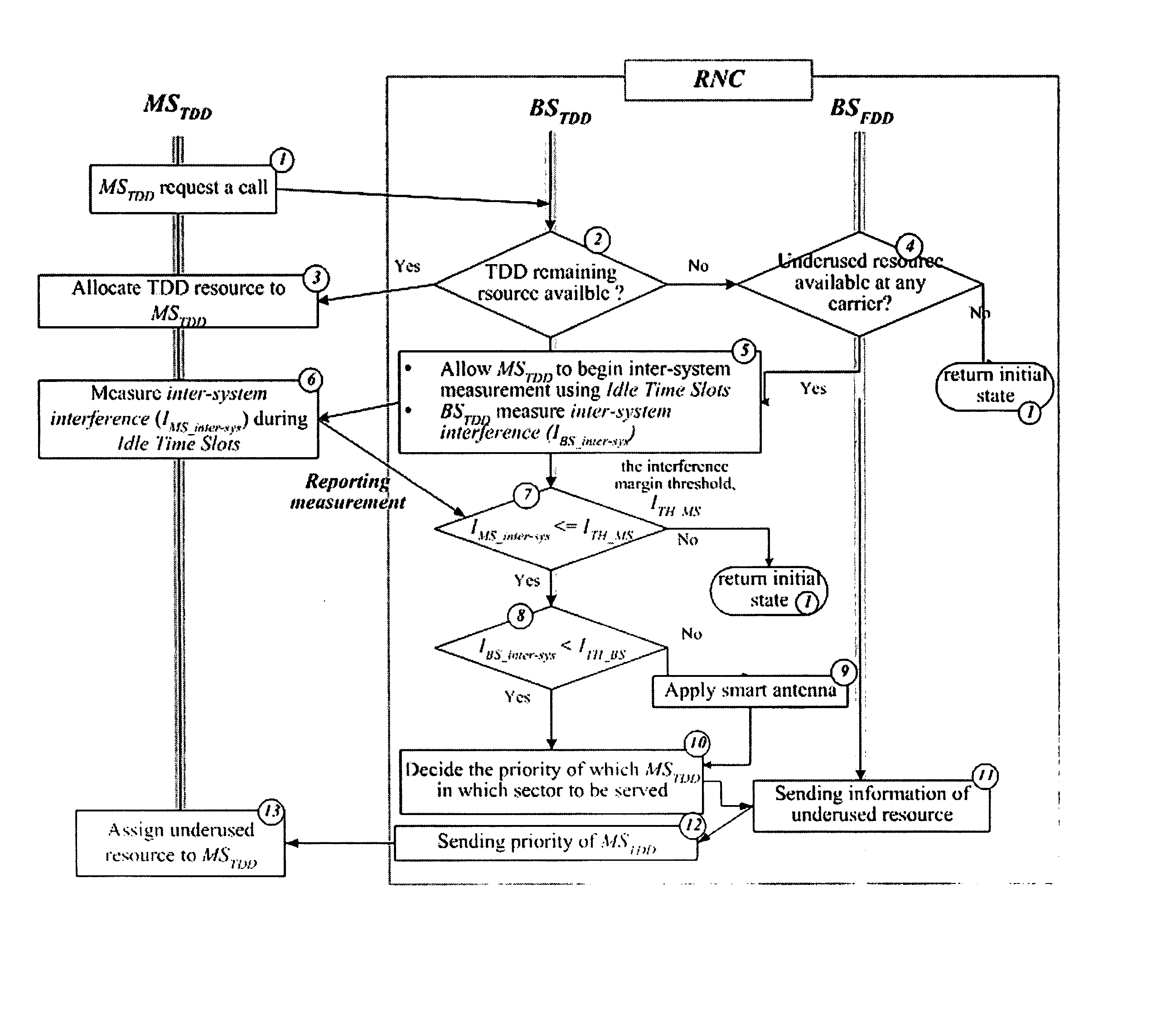
Method and system for integrating resource allocation between time division duplex and frequency division duplex in wireless communication systems
InactiveUS20050141450A1Network traffic/resource managementRadio/inductive link selection arrangementsCommunications systemRadio Network Controller
The present invention integrates resource allocation between time division duplex (TDD) and frequency division duplex (FDD) in wireless communication systems. A radio network controller (RNC) receives a radio access bearer (RAB) request from a core network or a wireless receive / transmit unit. The RNC utilizes a TDD-FDD selector to assign radio resources in response to the request. The TDD-FDD selector evaluates various parameters regarding the received RAB request and determines whether it is preferable to assign TDD resources or FDD resources and whether such resources are currently available. Once resources are assigned, system conditions are evaluated to determine whether optimizations may be made to a current resource allocation.
Owner:INTERDIGITAL TECH CORP
Pilot transmission method for down collaboration multi-point transmission
ActiveCN101373999AReduce overheadEasy to receiveDiversity/multi-antenna systemsMulti-frequency code systemsMultiplexingResource block
The invention discloses a pilot frequency transmission method for downlink shared multicast transmission, which is used in a long term evolution advance (LTE-A) system. The system is allocated with a plurality of sets of pilot frequencies for downlink multicast transmission and multiplexing modes thereof; and each transmission point involved in downlink share transmits one of the pilot frequencies in a resource block carrying user data, the same set of pilot frequency occupies the same time and frequency sites in the resource block, and the different sets of pilot frequencies are discriminated via frequency division, time division or code division in the resource block. The inventive method needs not a receiving terminal to discriminate channels corresponding to the transmission points which are involved in the share and only needs to allocate one set or a plurality of sets of logic pilot frequencies for multicast transmission, thereby resulting in low cost of pilot frequencies, simple terminal reception and less downlink control signaling.
Owner:ZTE CORP
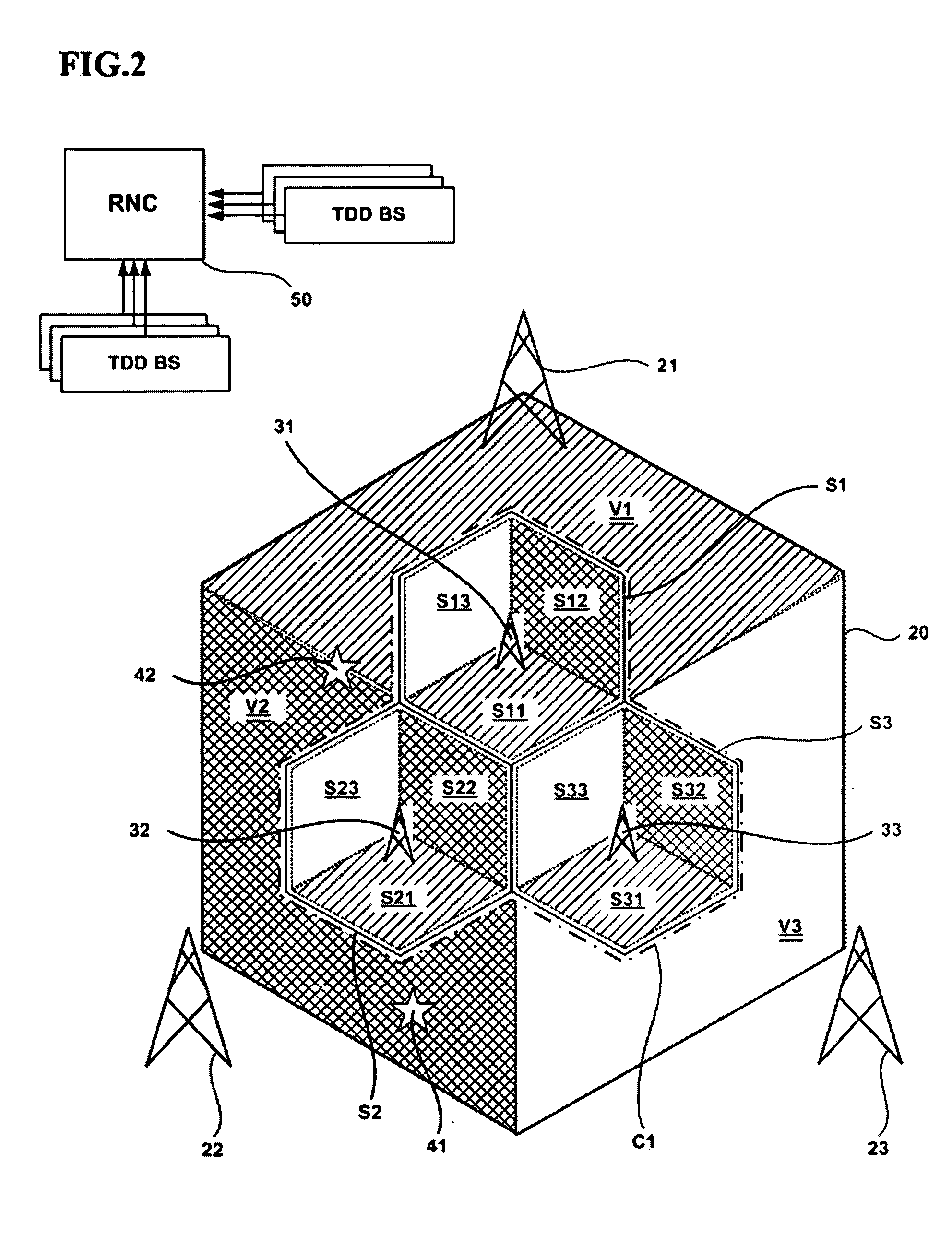
Method of operating a TDD/virtual FDD hierarchical cellular telecommunication system
ActiveUS20050174954A1Suppress interferenceFlexible and easy resource borrowing mechanismTime-division multiplexSubstation equipmentTelecommunicationsVirtual cell
A cellular communication system and method supporting both a time division duplexing (TDD) scheme and a frequency division duplexing (FDD) scheme. The apparatus includes a plurality of mobile stations, at least three first fixed stations communicate with the mobile station based on the FDD scheme, the first fixed station defining respective macro cells that are contiguous and form a virtual cell, and a cluster including at least one second fixed station communicating with the mobile stations based on the TDD scheme, the second fixed station defining a micro cell in the virtual cell.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD +1
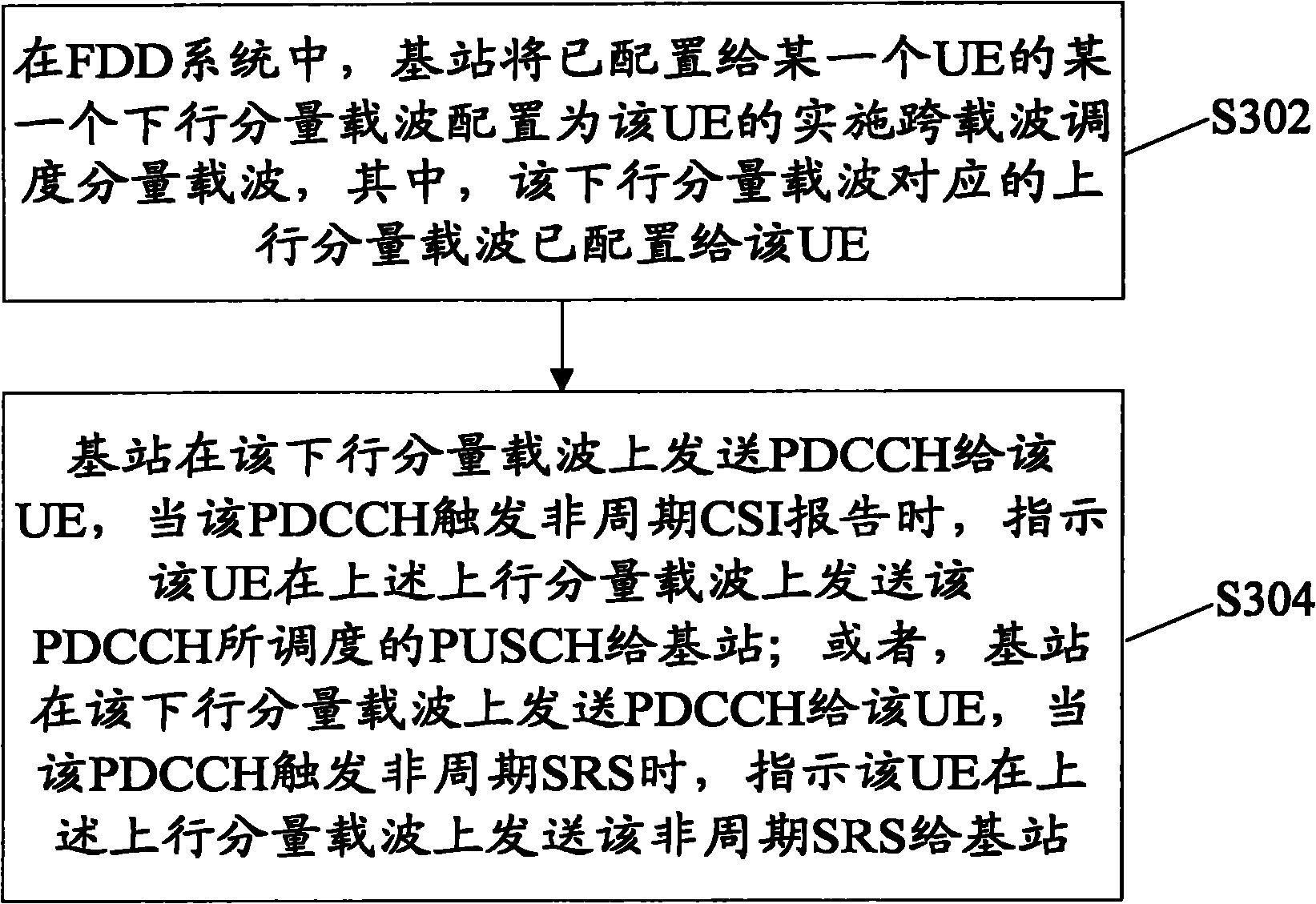
Physical downlink control channel sending method and base station for cross-carrier scheduling
ActiveCN101958772ATransmission path divisionPilot signal allocationChannel state informationSounding reference signal
The invention discloses a PDCCH (Physical Downlink Control Channel) sending method and a base station for cross-carrier scheduling. The method comprises the following steps that: in FDD (Frequency Division Duplex) system, the base station configures a downlink component carrier configured to UE (User Equipment) as a component carrier of the UE for implementing cross-carrier scheduling, wherein the uplink component carrier corresponding to the downlink component carrier is configured to the UE; the base station sends PDCCH to the UE on the downlink component carrier; the UE sends PUSCH (Physical Uplink Shared Channel) scheduled by the PDCCH to the base station on the uplink component carrier when the PDCCH triggers an aperiodic CSI (Channel State Information) report; or, the base station sends PDCCH to the UE on the downlink component carrier; and the UE sends SRS (Sounding Reference Signal) triggered by the PDCCH to the base station on the uplink component carrier when the PDCCH triggers an aperiodic SRS report.
Owner:ZTE CORP
Wireless communication apparatus and frequency hopping method
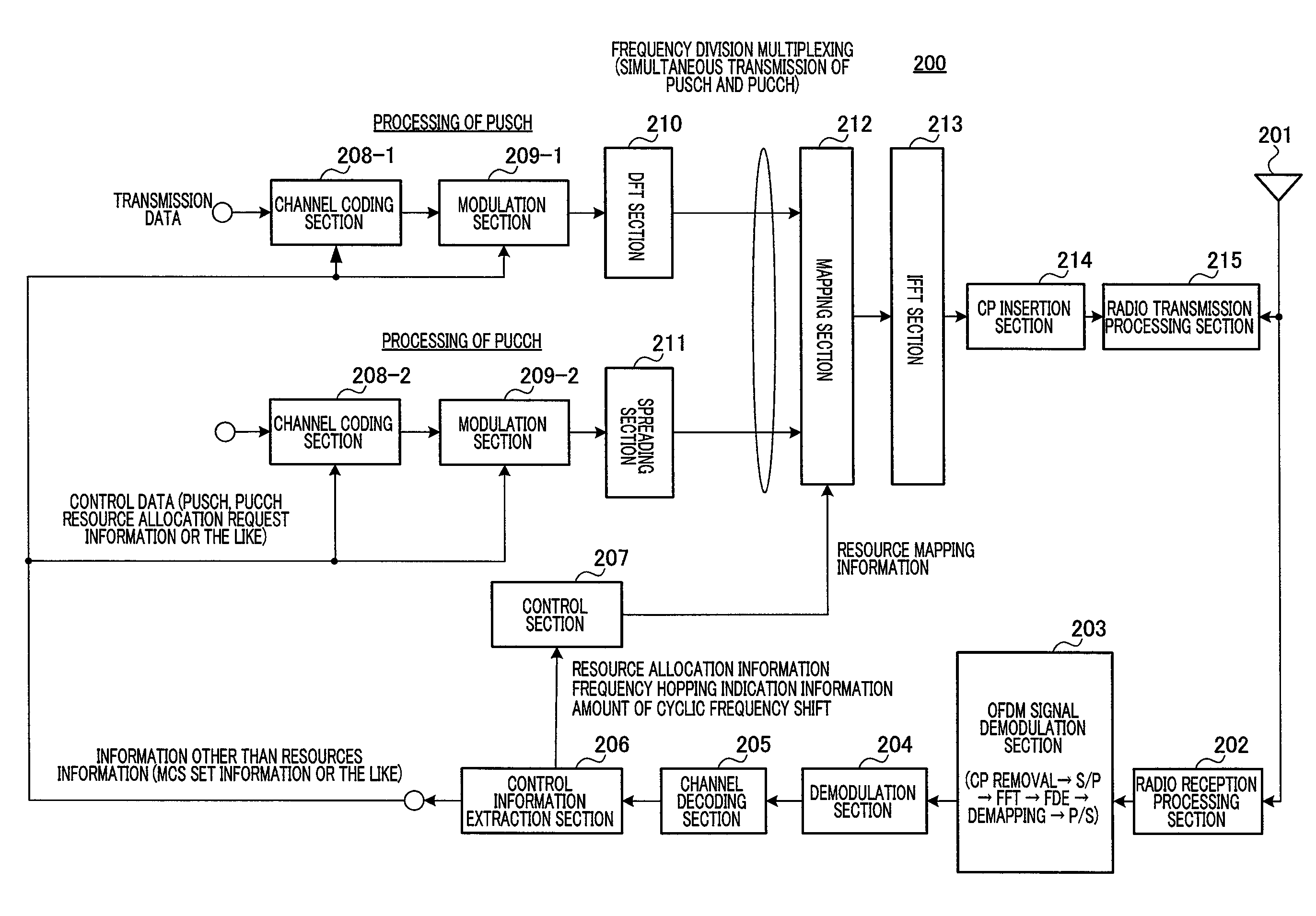
ActiveUS20120057449A1Inhibit deteriorationFrequency-division multiplex detailsModulated-carrier systemsMultiplexingDistribution characteristic
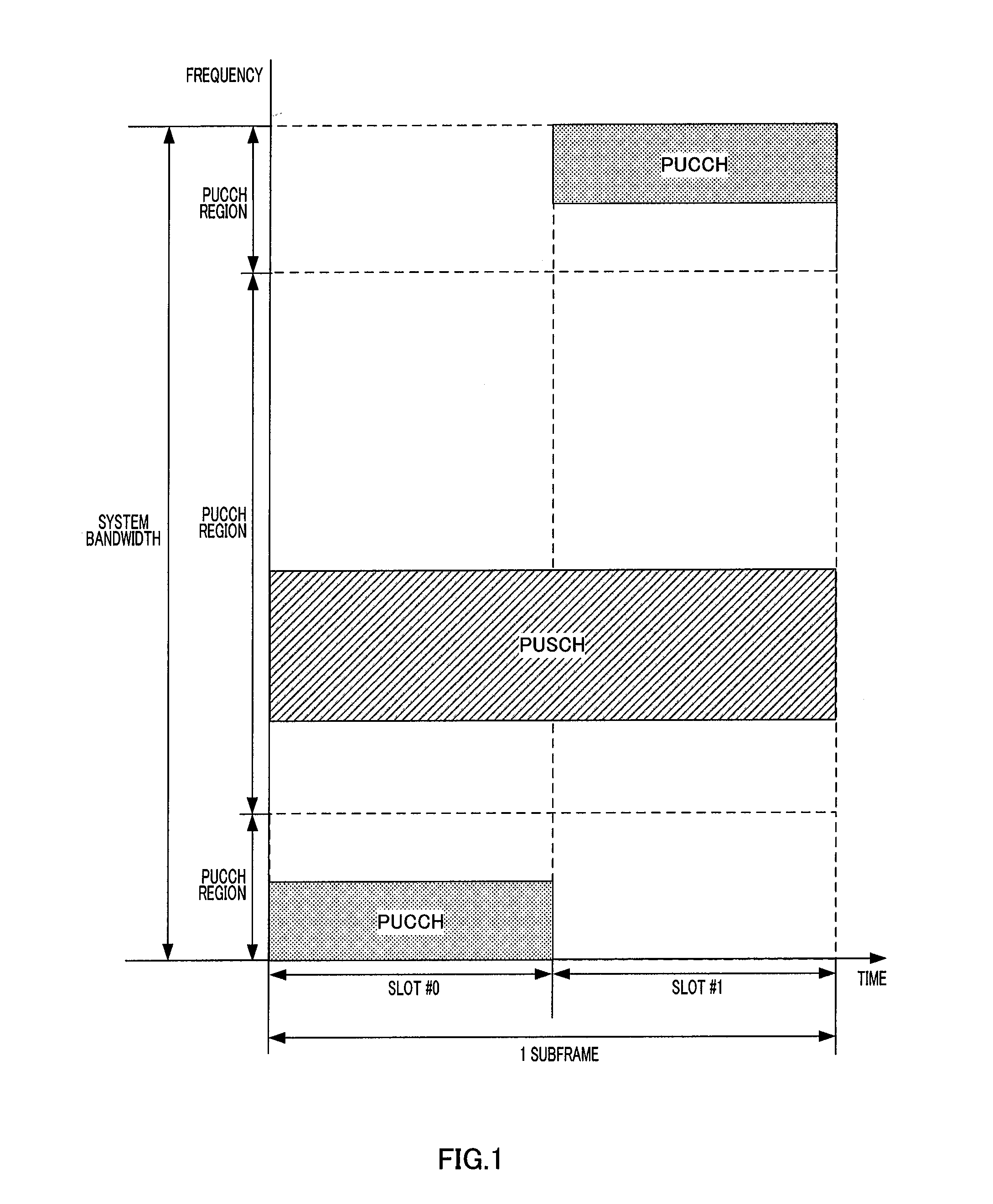
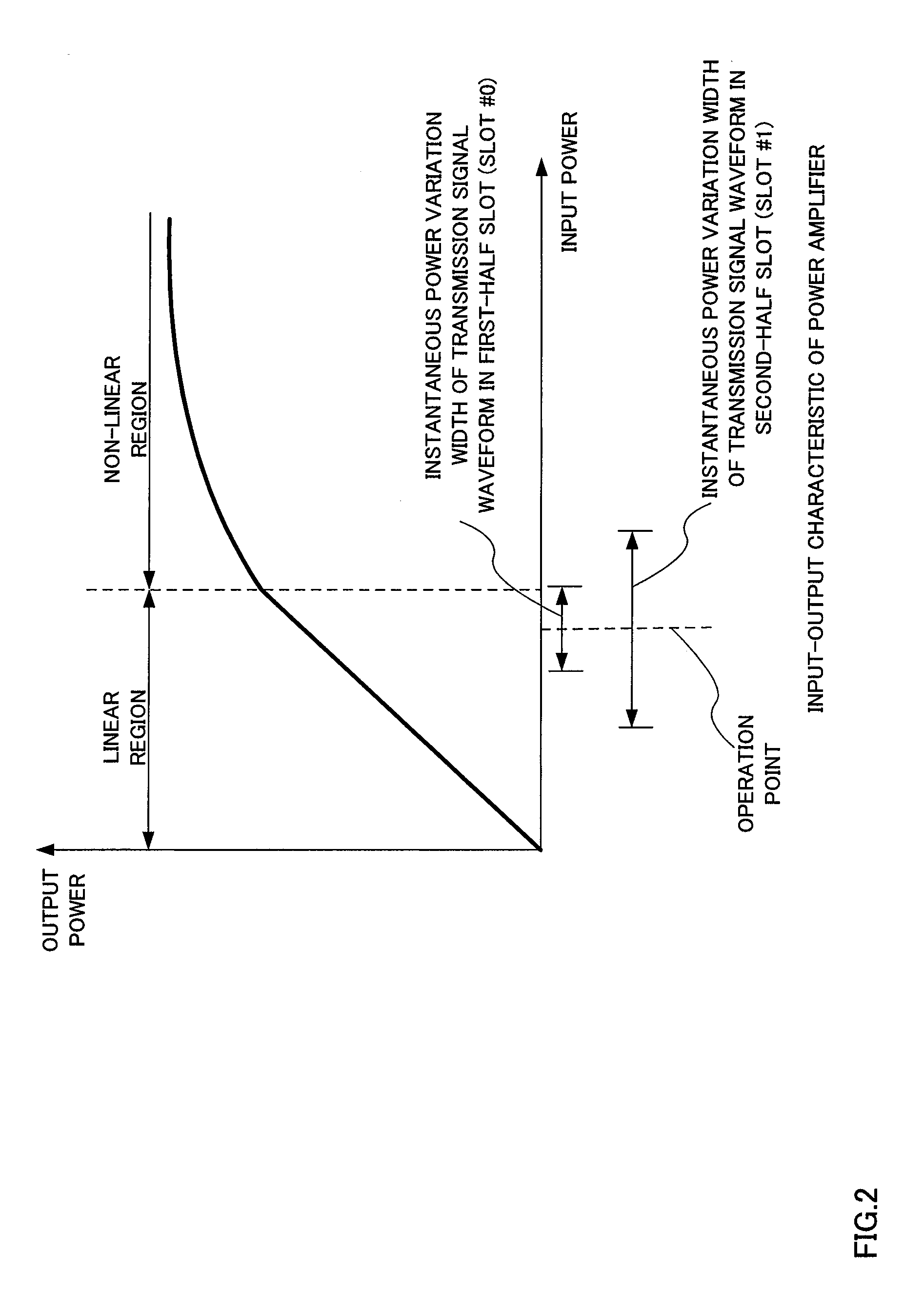
Disclosed are a wireless communication apparatus and frequency hopping method which minimize the change in the instantaneous power distribution characteristics of the time waveform of transmission signals when a plurality of channels are multiplexed by frequency division. At a terminal (200), a mapping unit (212) maps the PUCCH to frequency resources of a first slot, maps the PUSCH to frequency resources, among the frequency resources of the first slot, separated exactly by predetermined frequency spacing (B) from the frequency resources to which the PUCCH is mapped, and cyclically shifts the frequencies so as to map the PUCCH and PUSCH to frequency resources, within an IDFT or IFFT bandwidth, of a second slot while maintaining the predetermined frequency spacing (B), thereby allowing frequency hopping of the PUCCH and PUSCH between the first slot and the second slot.
Owner:SUN PATENT TRUST
Method and device for transmitting response message
InactiveCN101989898ASolve the problem that the sending of reply message cannot be completedImprove performanceError prevention/detection by using return channelControl channelCorrect response
The invention provides method and device for transmitting a response message. The method comprises the steps that: the type of a current system is determined when a terminal needs to transmit a response message, wherein the response message can be a correct response message ACK or a wrong response message NACK; the type of the system comprises a frequency division duplex FDD system and a time division duplex TDD system; the terminal determines the feedback mode of the response message, wherein the feedback mode consists of a channel selection mode and a physical uplink control channel PUCCH format 3; and the terminal can determine the PUCCH resource of the response message according to the type of the system and the feedback mode, and then transmits the response message by using the determined PUCCH resource. By the method and the device, the problem that a UE (user equipment) can not transmit the response message in some cases is overcome, and the performance of the system is improved.
Owner:ZTE CORP
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com