Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
3786 results about "Time-division multiplexing" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Time-division multiplexing (TDM) is a method of transmitting and receiving independent signals over a common signal path by means of synchronized switches at each end of the transmission line so that each signal appears on the line only a fraction of time in an alternating pattern. It is used when the bit rate of the transmission medium exceeds that of the signal to be transmitted. This form of signal multiplexing was developed in telecommunications for telegraphy systems in the late 19th century, but found its most common application in digital telephony in the second half of the 20th century.
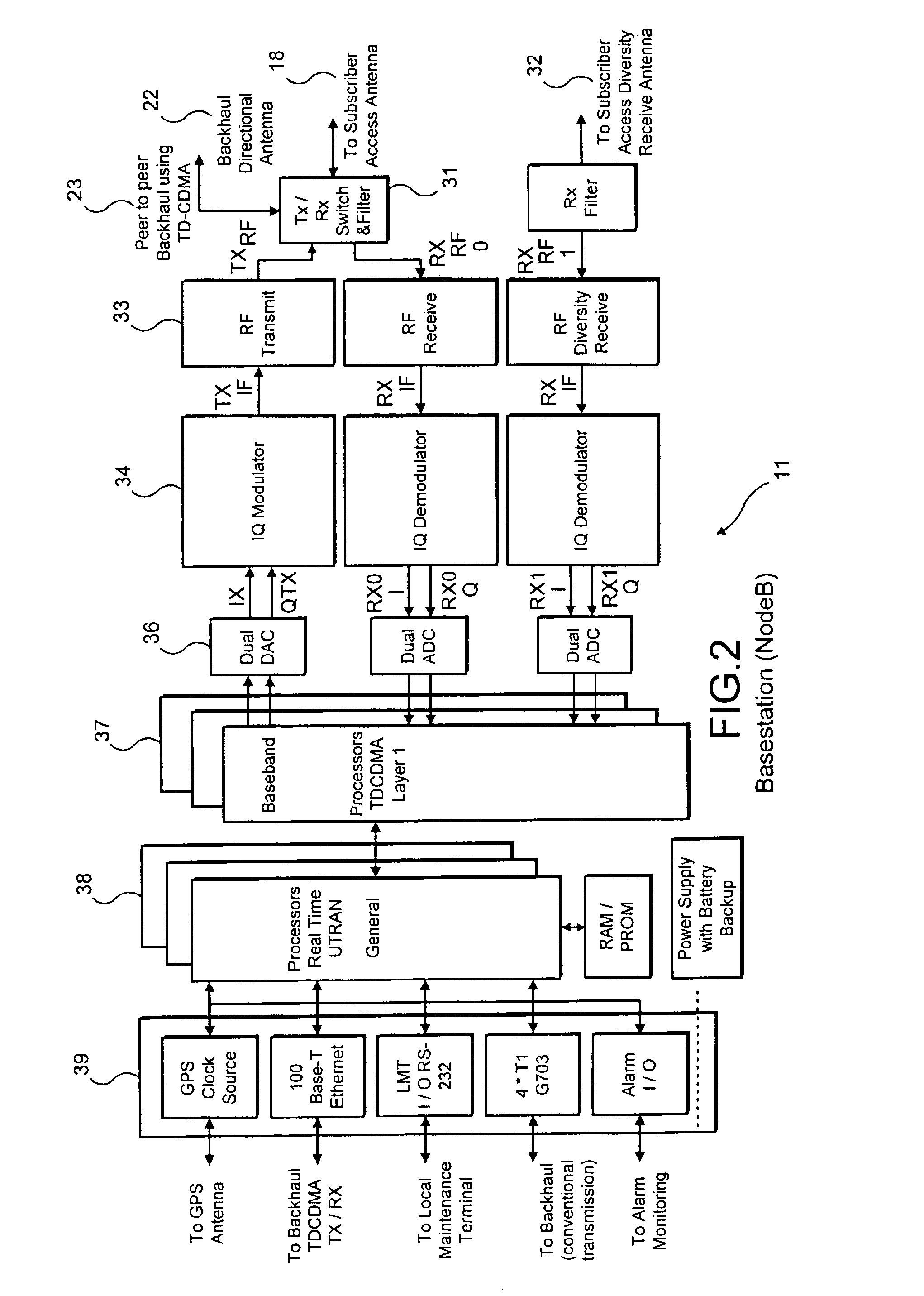
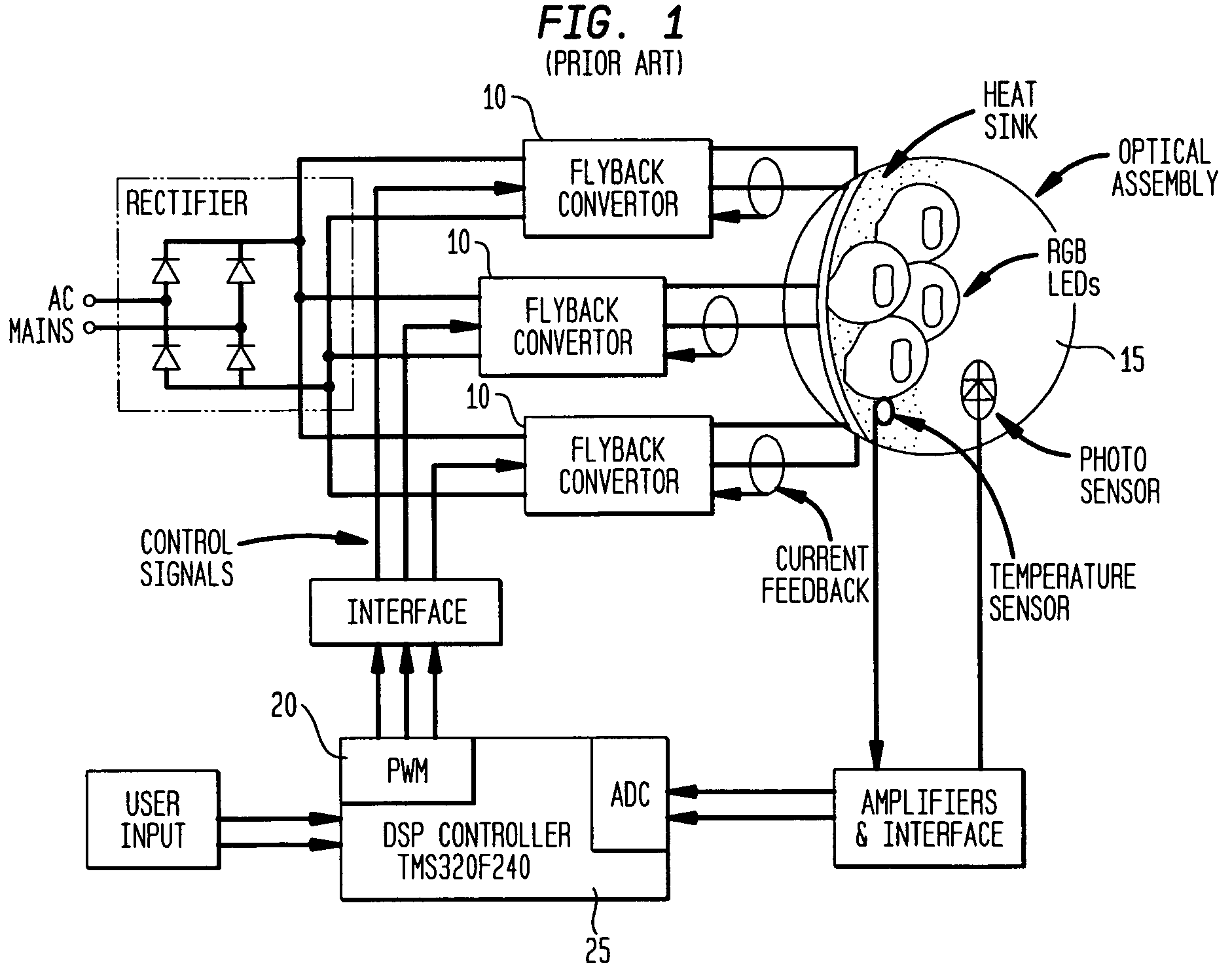
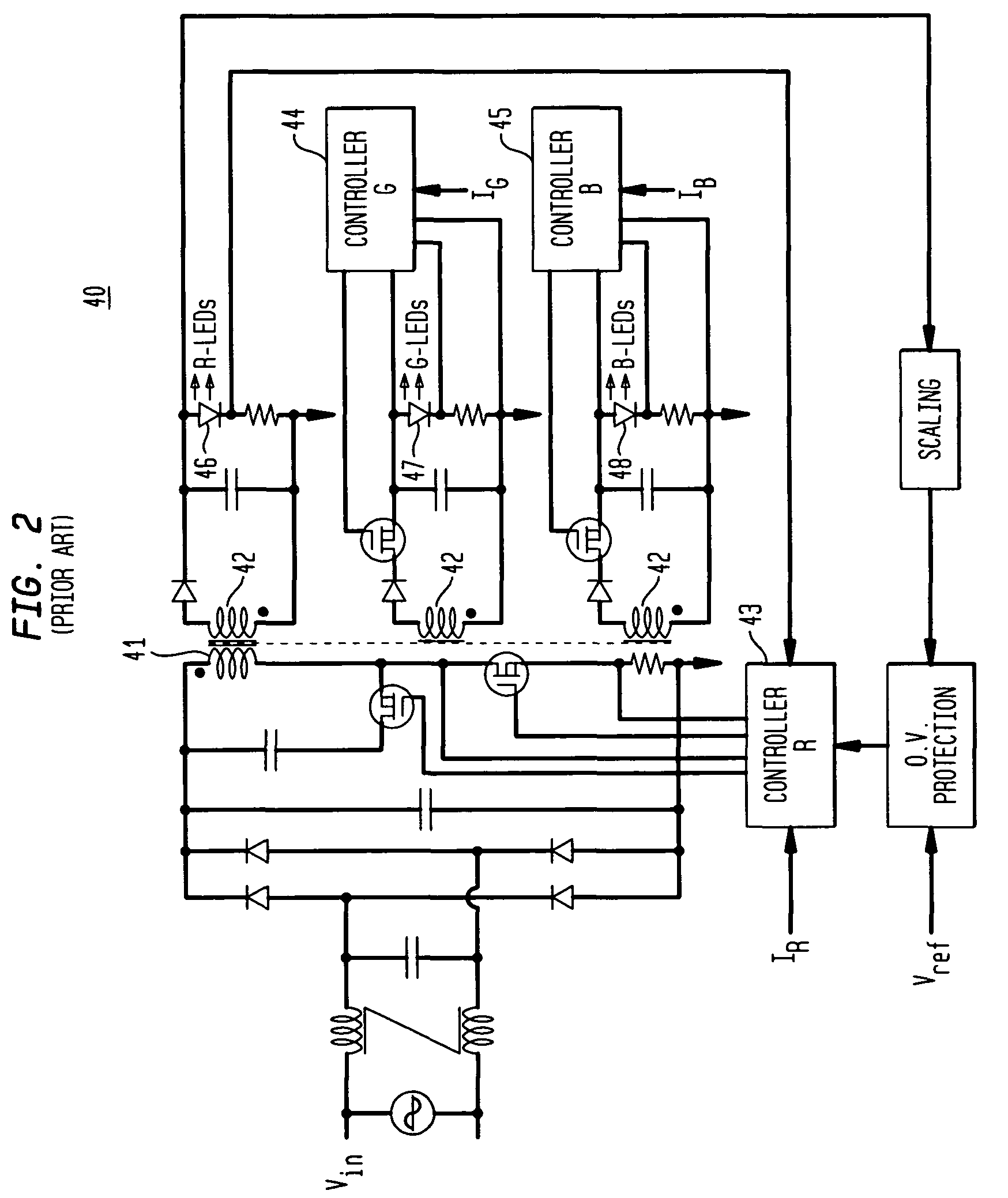
High efficiency high performance communications system employing multi-carrier modulation
InactiveUS20020154705A1Increase diversityImprove performanceSpatial transmit diversityFrequency diversityData streamHigh performance communication
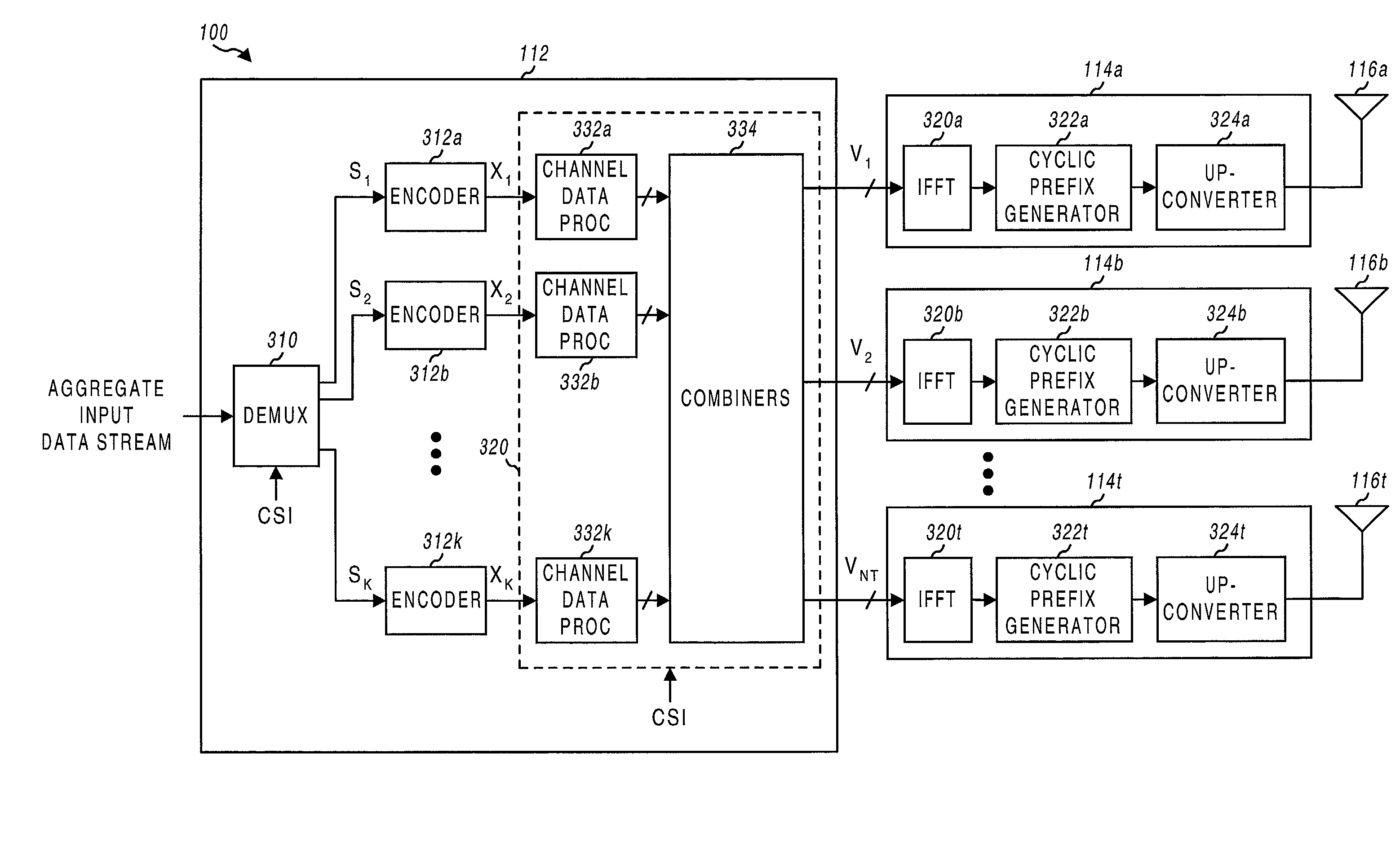
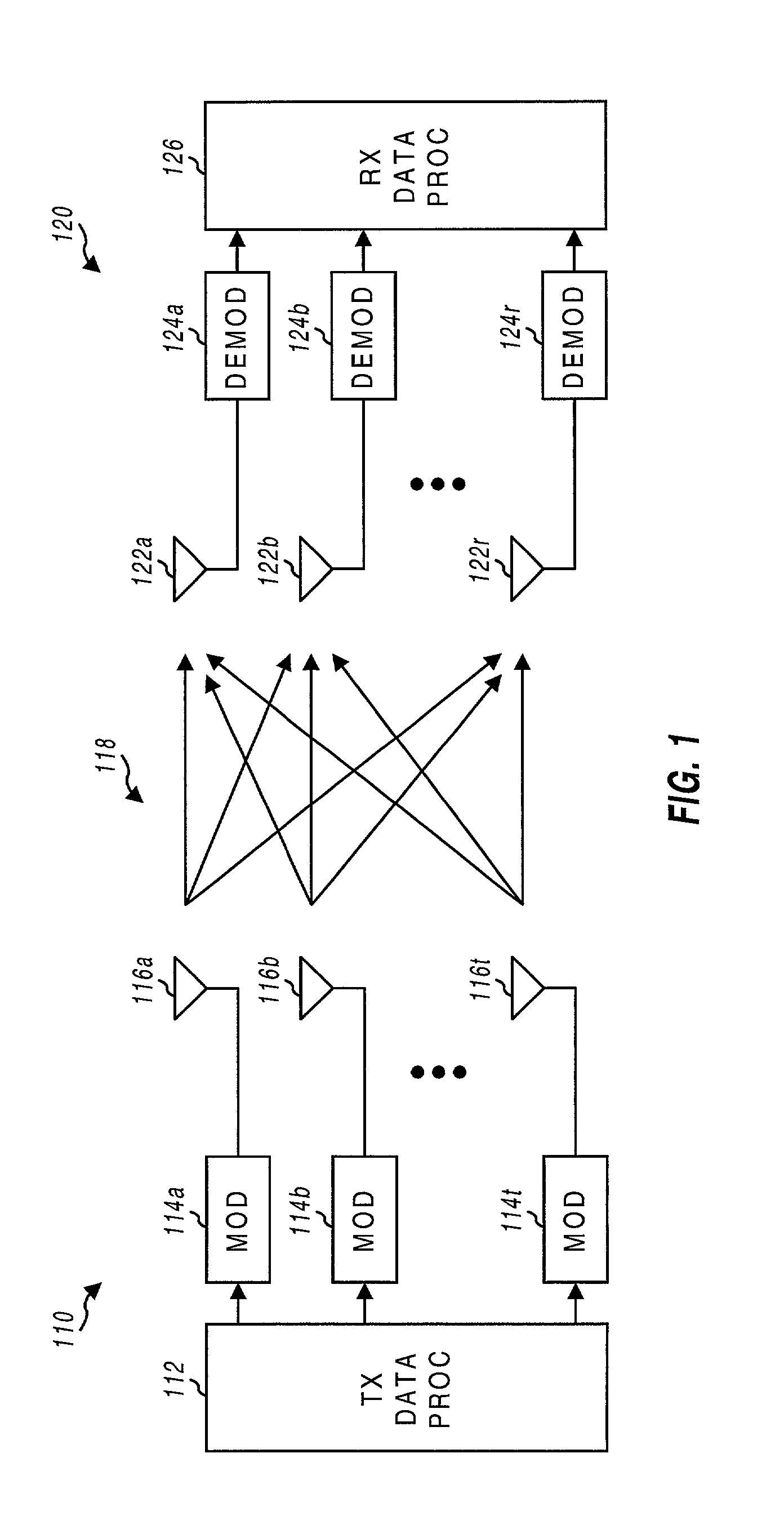
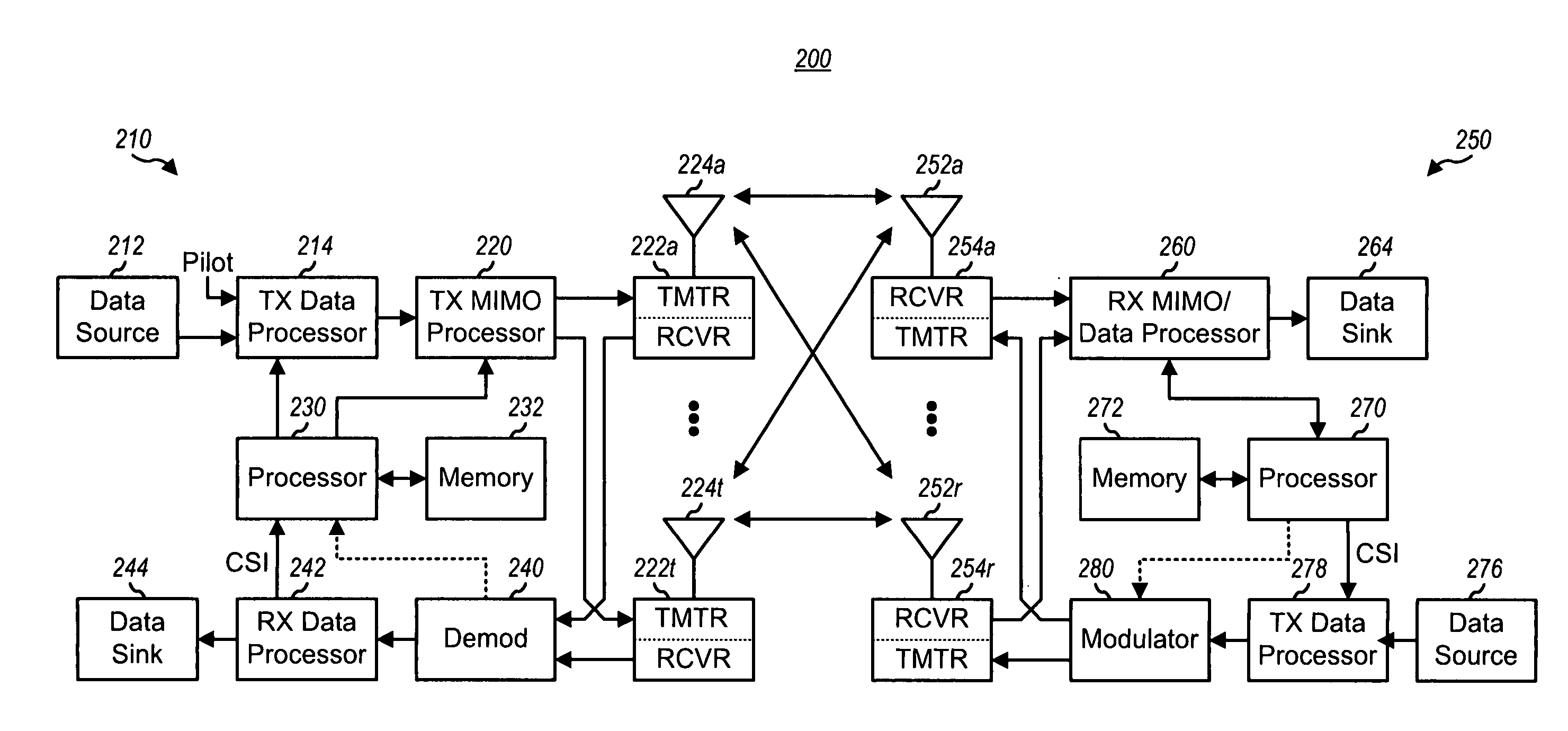
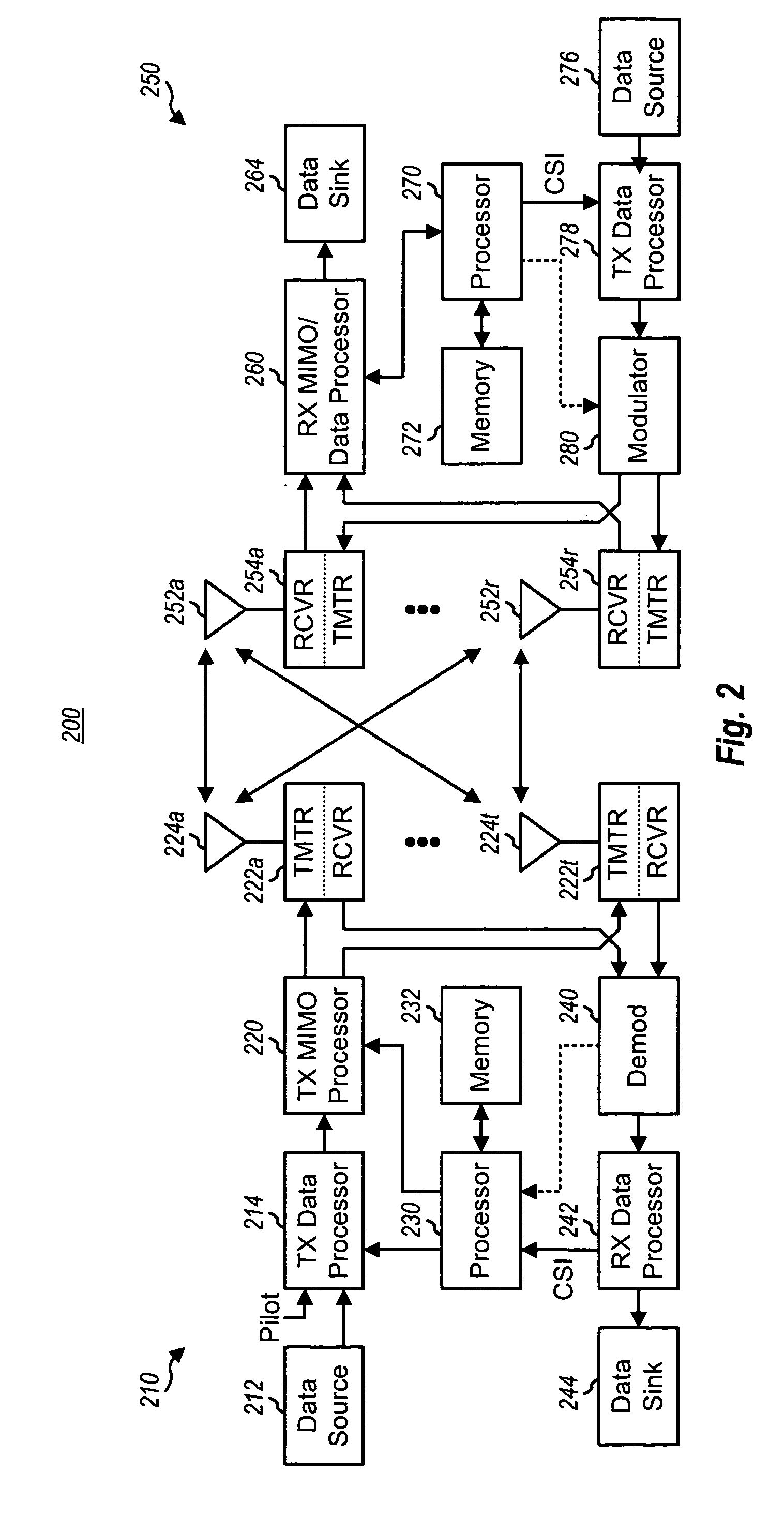
Transmitter and receiver units for use in a communications system and configurable to provide antenna, frequency, or temporal diversity, or a combination thereof, for transmitted signals. The transmitter unit includes a system data processor, one or more modulators, and one or more antennas. The system data processor receives and partitions an input data stream into a number of channel data streams and further processes the channel data streams to generate one or more modulation symbol vector streams. Each modulation symbol vector stream includes a sequence of modulation symbol vectors representative of data in one or more channel data streams. Each modulator receives and modulates a respective modulation symbol vector stream to provide an RF modulated signal, and each antenna receives and transmits a respective RF modulated signal. Each modulator may include an inverse (fast) Fourier transform (IFFT) and a cyclic prefix generator. The IFFT generates time-domain representations of the modulation symbol vectors, and the cyclic prefix generator repeats a portion of the time-domain representation of each modulation symbol vector. The channel data streams are modulated using multi-carrier modulation, e.g., OFDM modulation. Time division multiplexing (TDM) may also be used to increase flexibility.
Owner:QUALCOMM INC
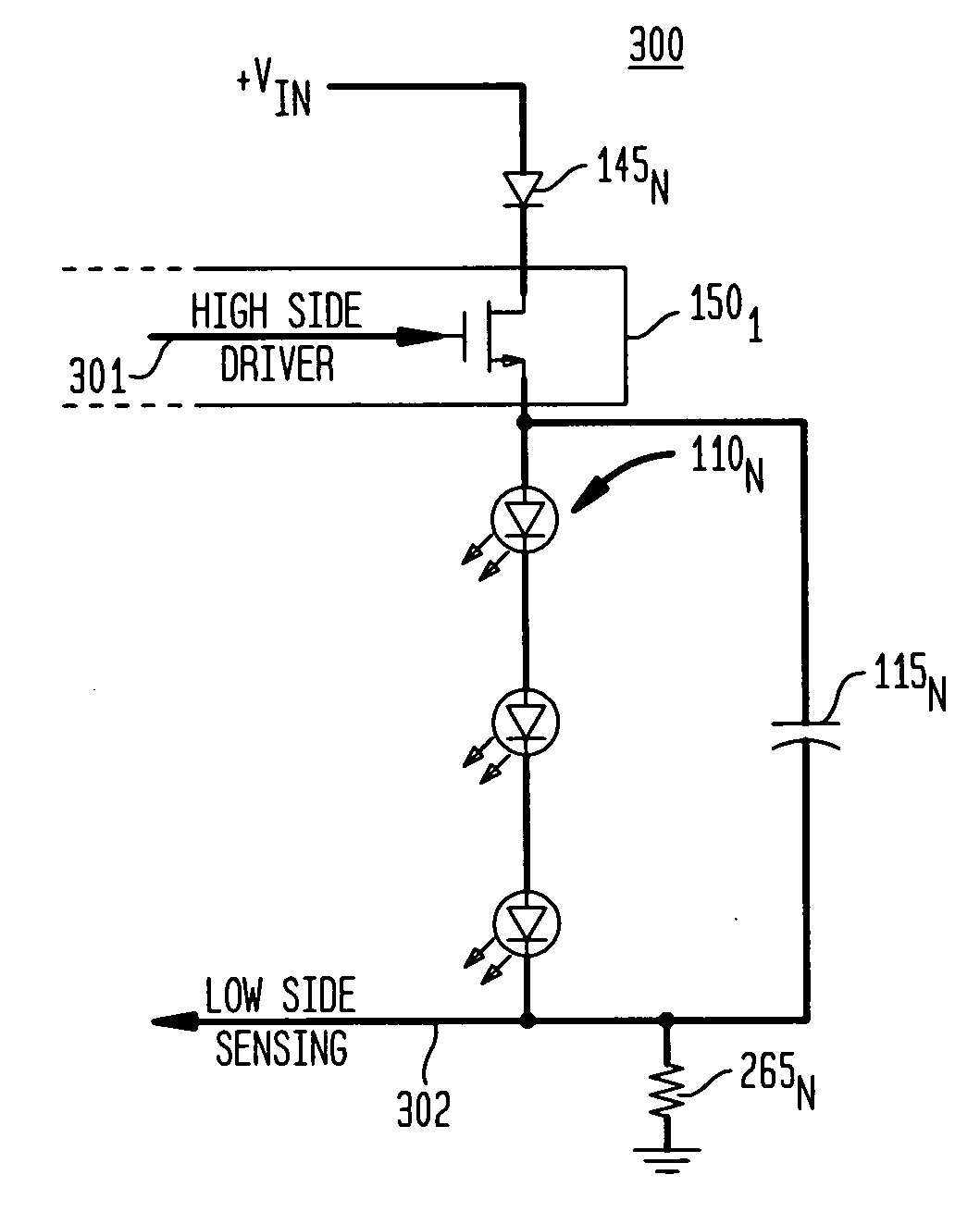
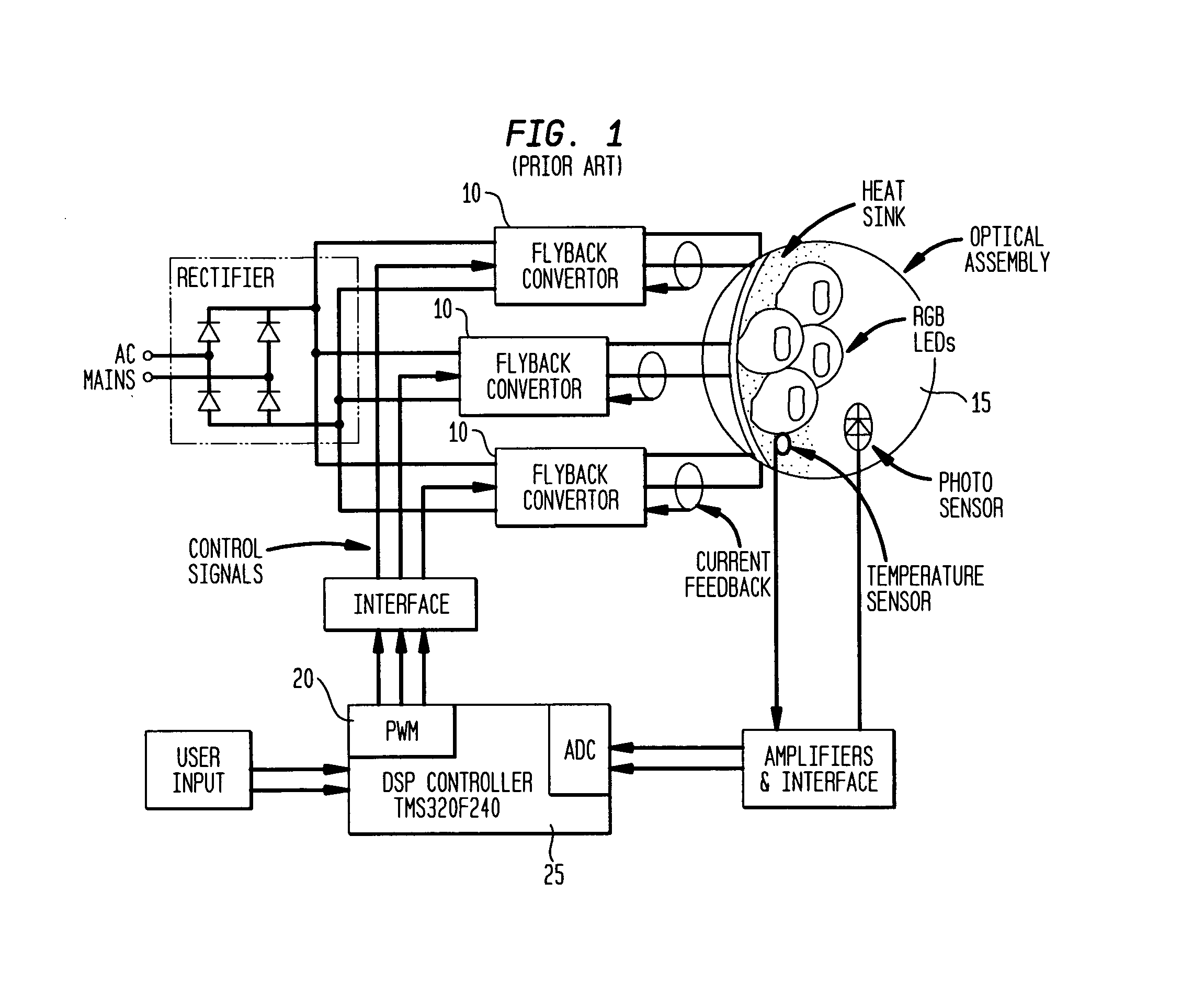
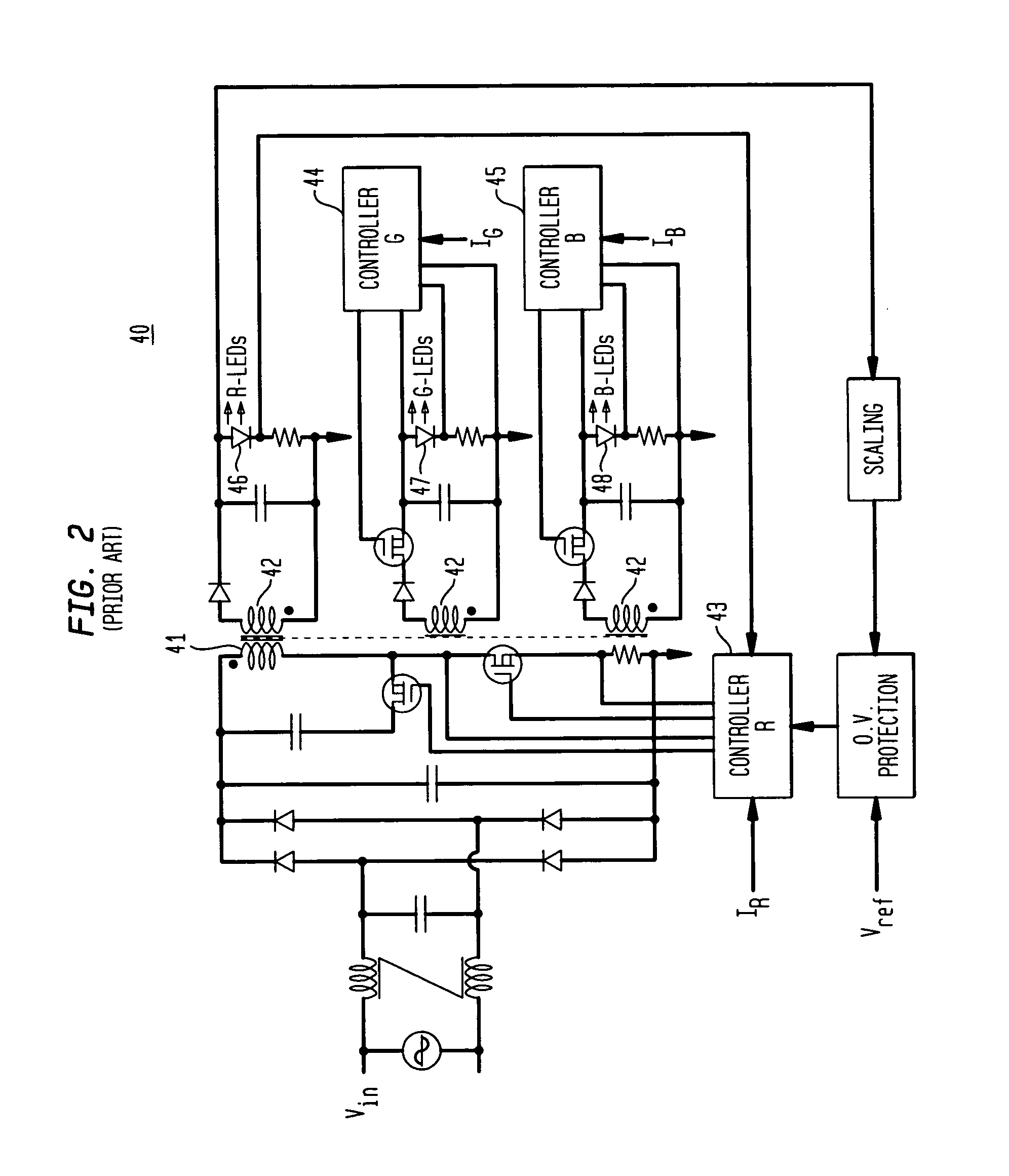
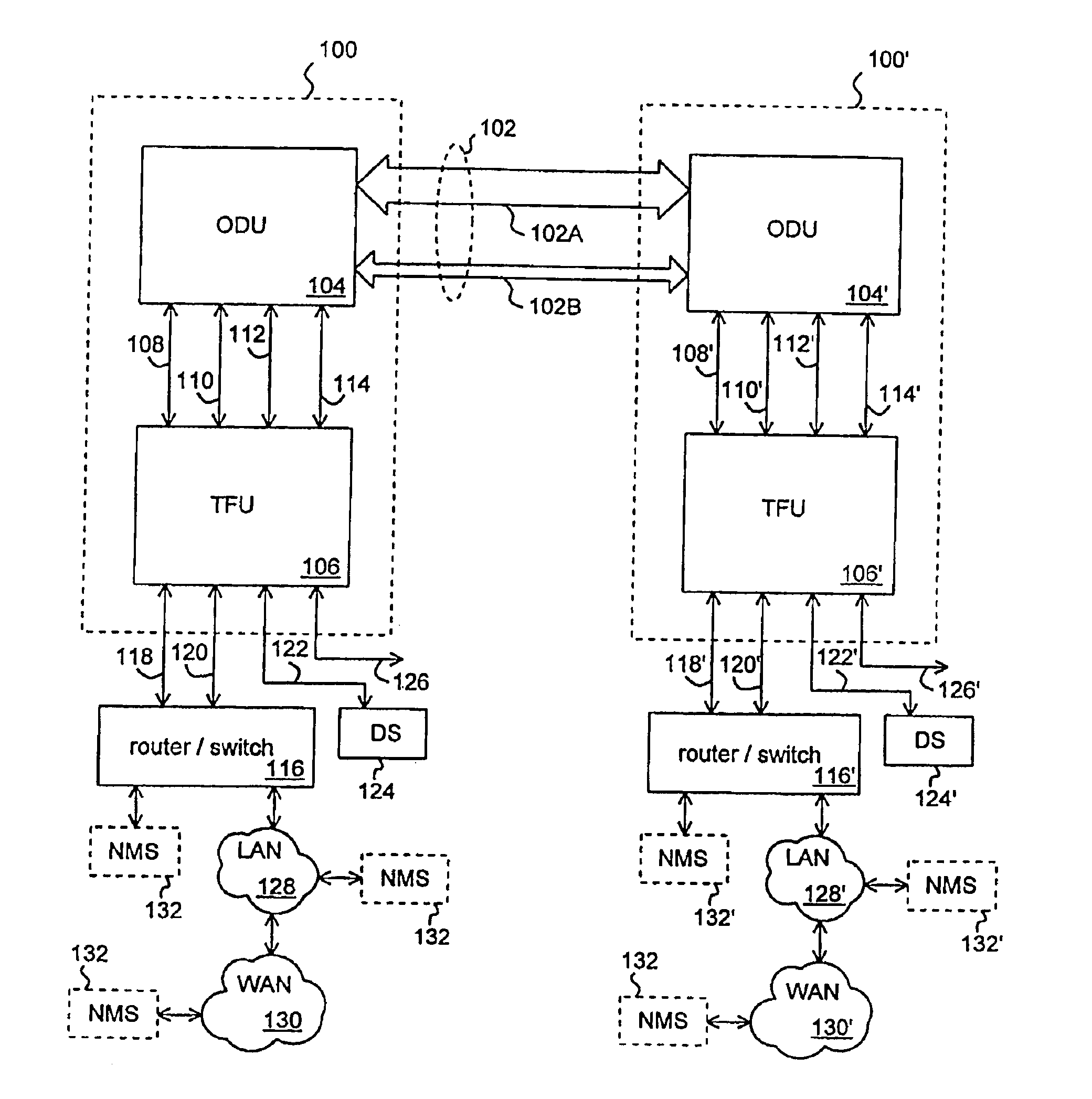
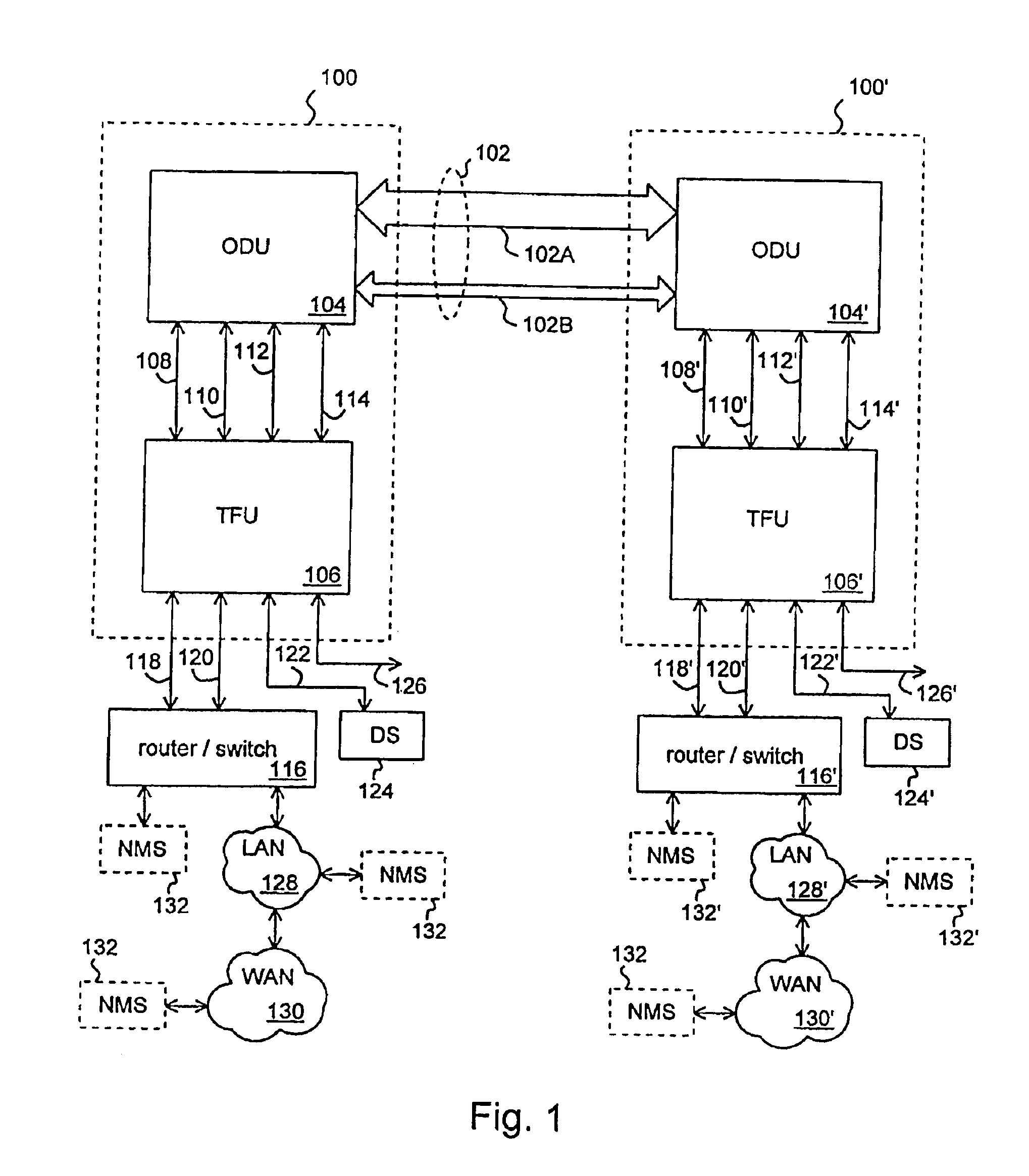
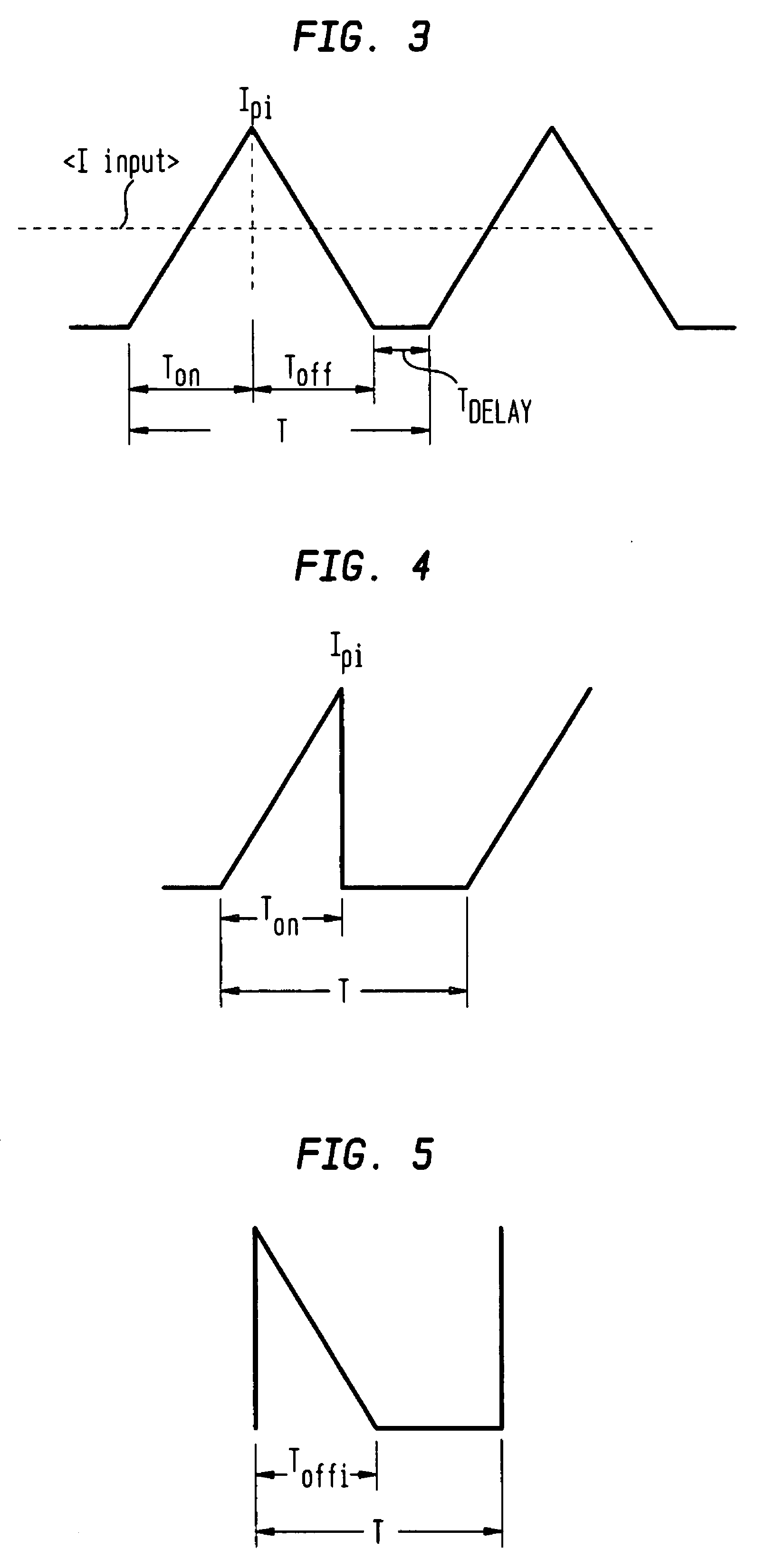
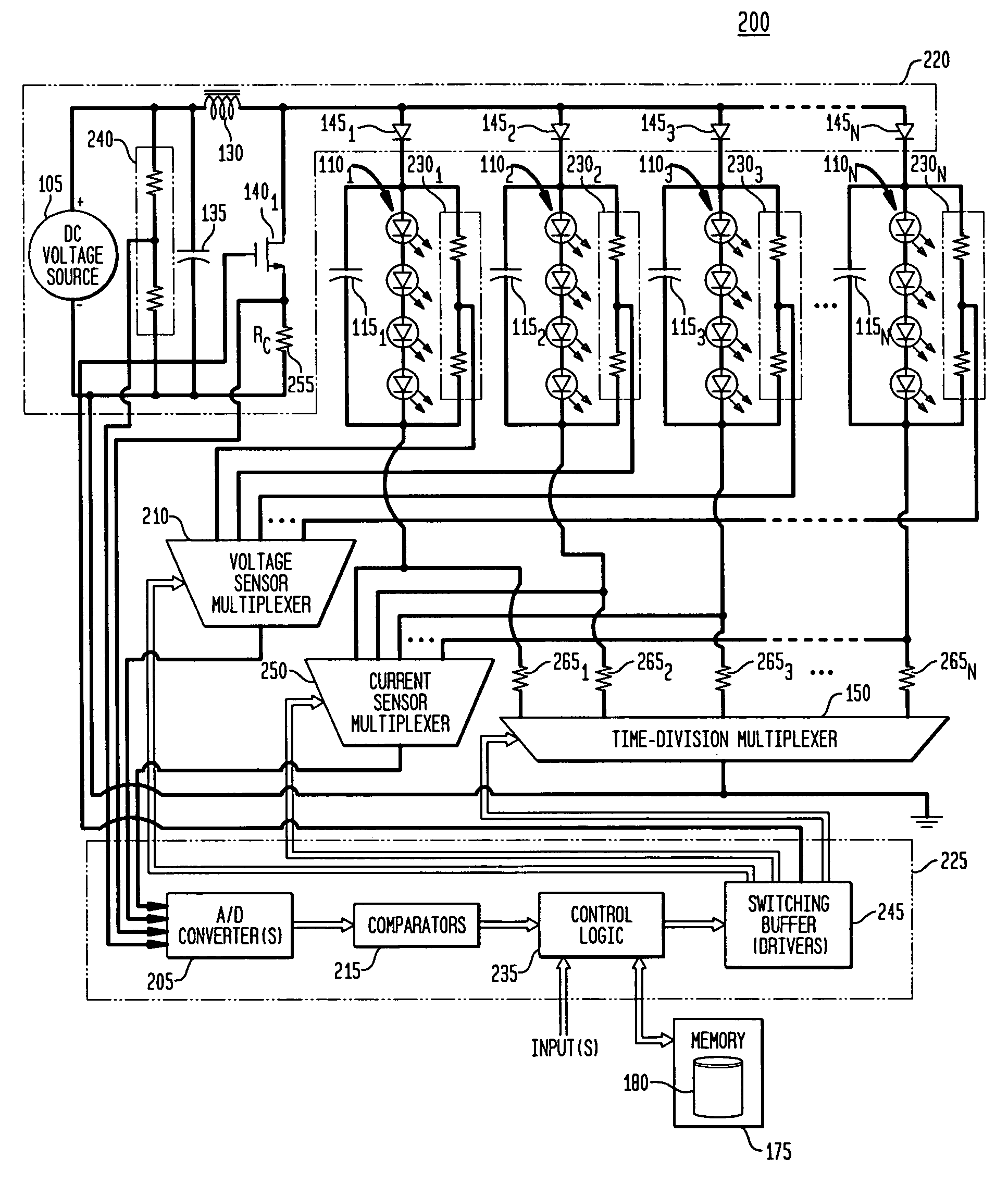
Time division modulation with average current regulation for independent control of arrays of light emitting diodes
ActiveUS20080116818A1Low costFast response timeElectrical apparatusElectroluminescent light sourcesSwitched currentAverage current
Exemplary apparatus, method and system embodiments provide for separately and independently sourcing current to a series of light emitting diodes of a plurality of series of light-emitting diodes. An exemplary apparatus comprises a power converter which generates a current, a first multiplexer, and a controller. The controller provides for sequential and separate switching of the current through the first multiplexer to each of the series of light-emitting diodes for a corresponding period of time. An average current provided by the power converter is determined as substantially equal to a sum of the corresponding currents through the plurality of series of light-emitting diodes. A total period for switching current to all of the series of light-emitting diodes is also determined. A corresponding time period for switching current to a selected corresponding series of light-emitting diodes is substantially equal to a proportion of the total period determined as a ratio of the corresponding current for the selected corresponding series of light-emitting diodes to the average current provided by the power converter.
Owner:CHEMTRON RES
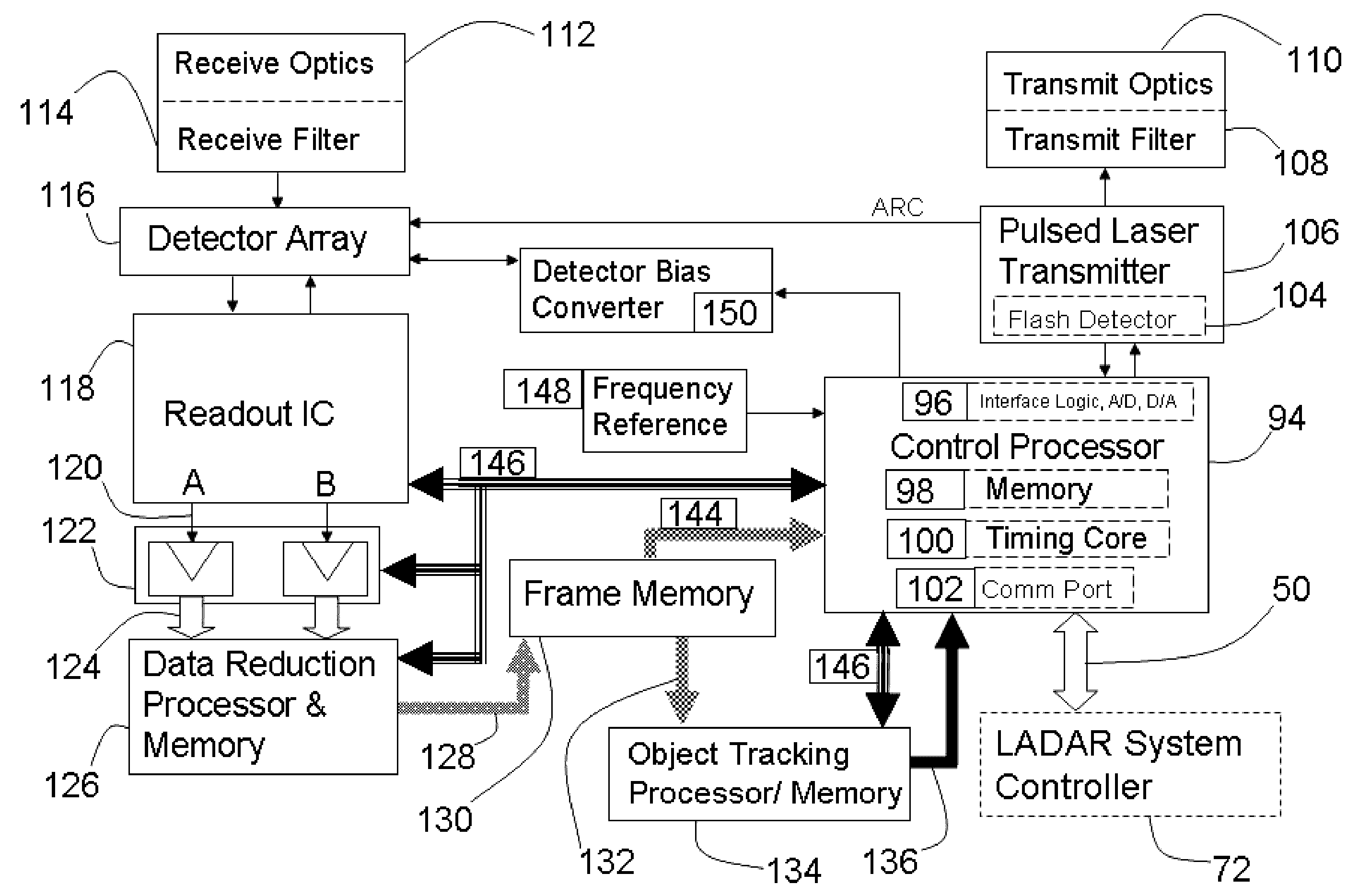
Ladar sensor for a dense environment
ActiveUS20160003946A1Optical rangefindersElectromagnetic wave reradiationDiscriminatorFloating point
A multi-ladar sensor system is proposed for operating in dense environments where many ladar sensors are transmitting and receiving burst mode light in the same space, as may be typical of an automotive application. The system makes use of several techniques to reduce mutual interference between independently operating ladar sensors. In one embodiment, the individual ladar sensors are each assigned a wavelength of operation, and an optical receive filter for blocking the light transmitted at other wavelengths, an example of wavelength division multiplexing (WDM). Each ladar sensor, or platform, may also be assigned a pulse width selected from a list, and may use a pulse width discriminator circuit to separate pulses of interest from the clutter of other transmitters. Higher level coding, involving pulse sequences and code sequence correlation, may be implemented in a system of code division multiplexing, CDM. A digital processor optimized to execute mathematical operations is described which has a hardware implemented floating point divider, allowing for real time processing of received ladar pulses, and sequences of pulses.
Owner:CONTINENTAL AUTONOMOUS MOBILITY US LLC
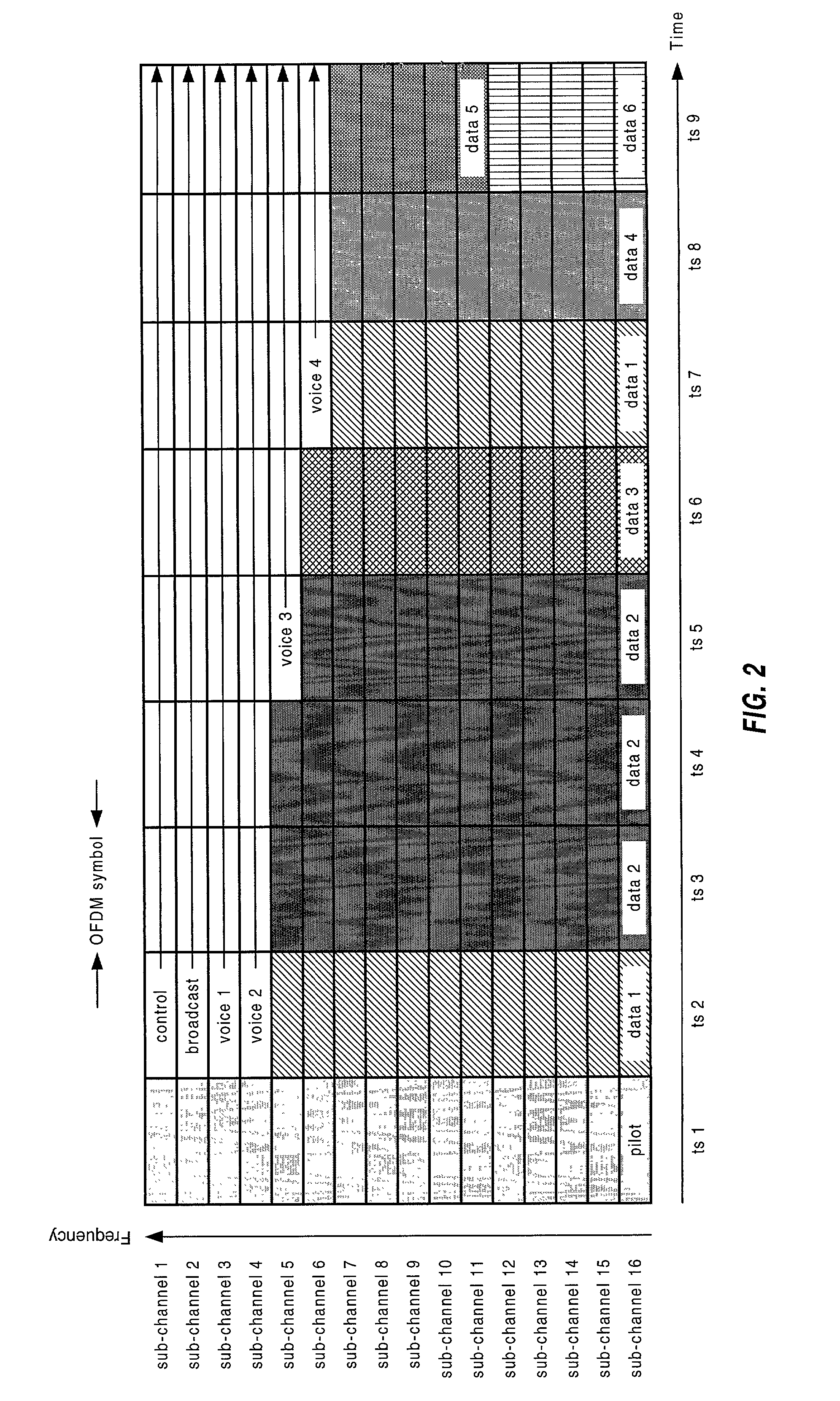
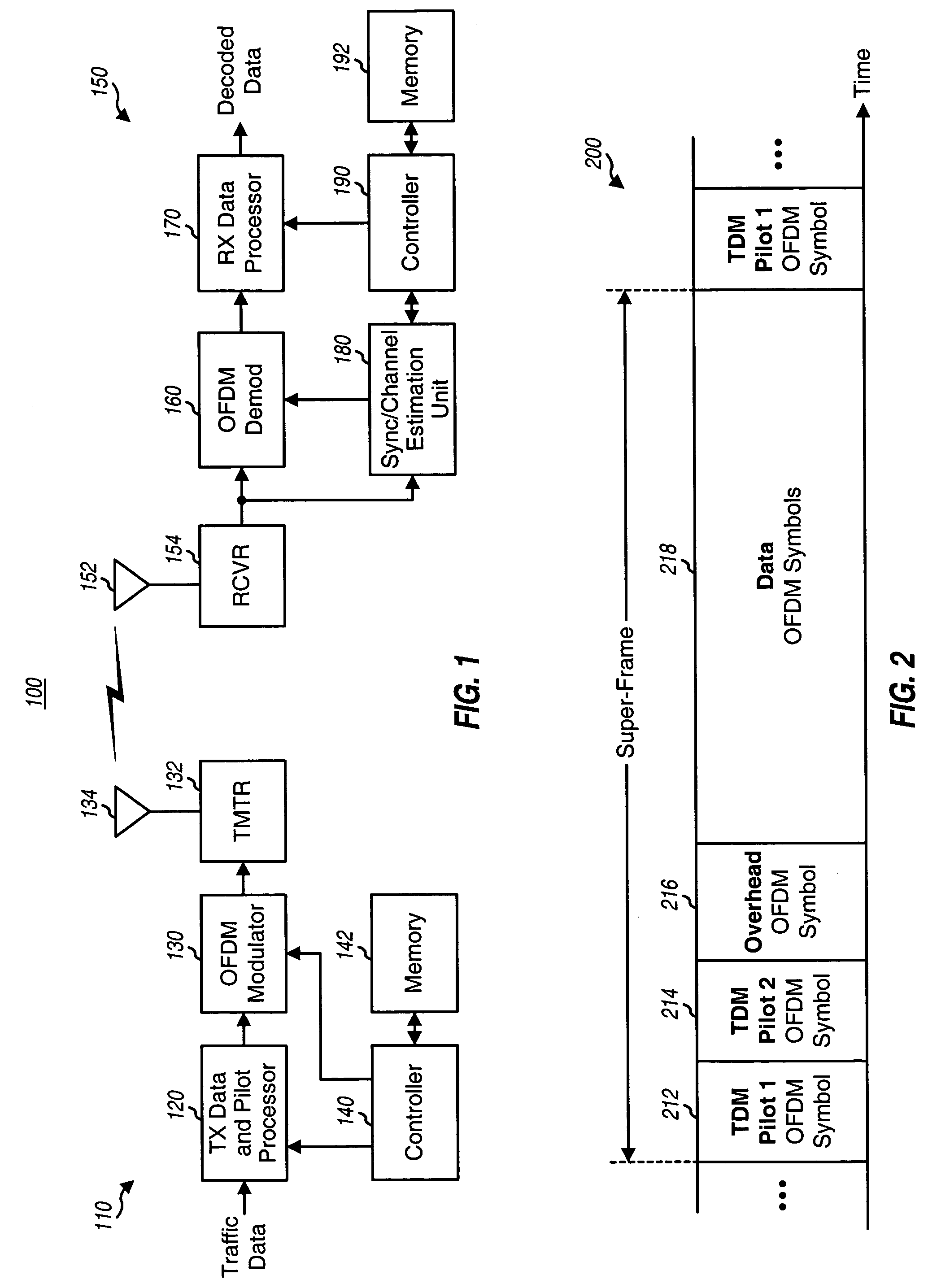
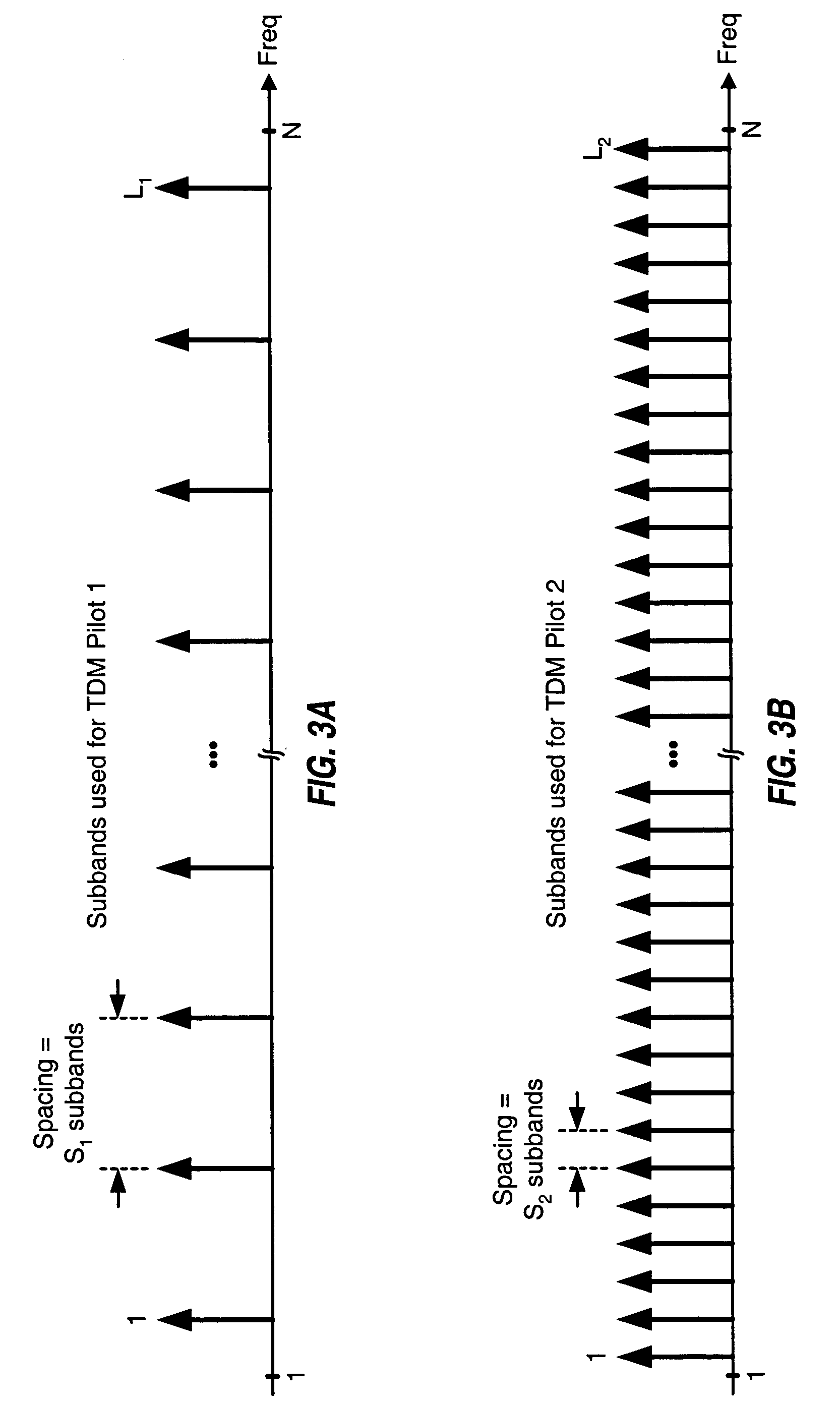
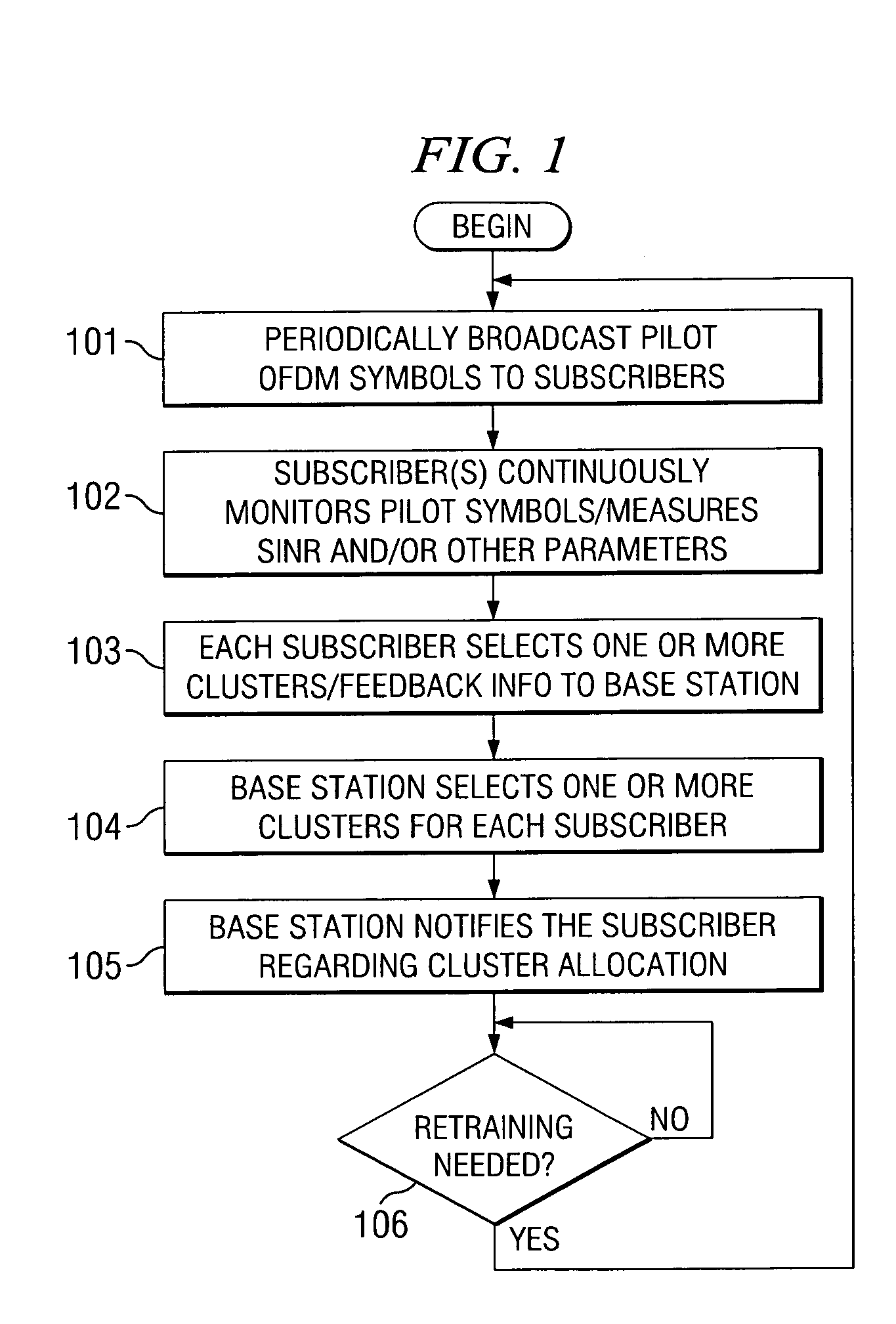
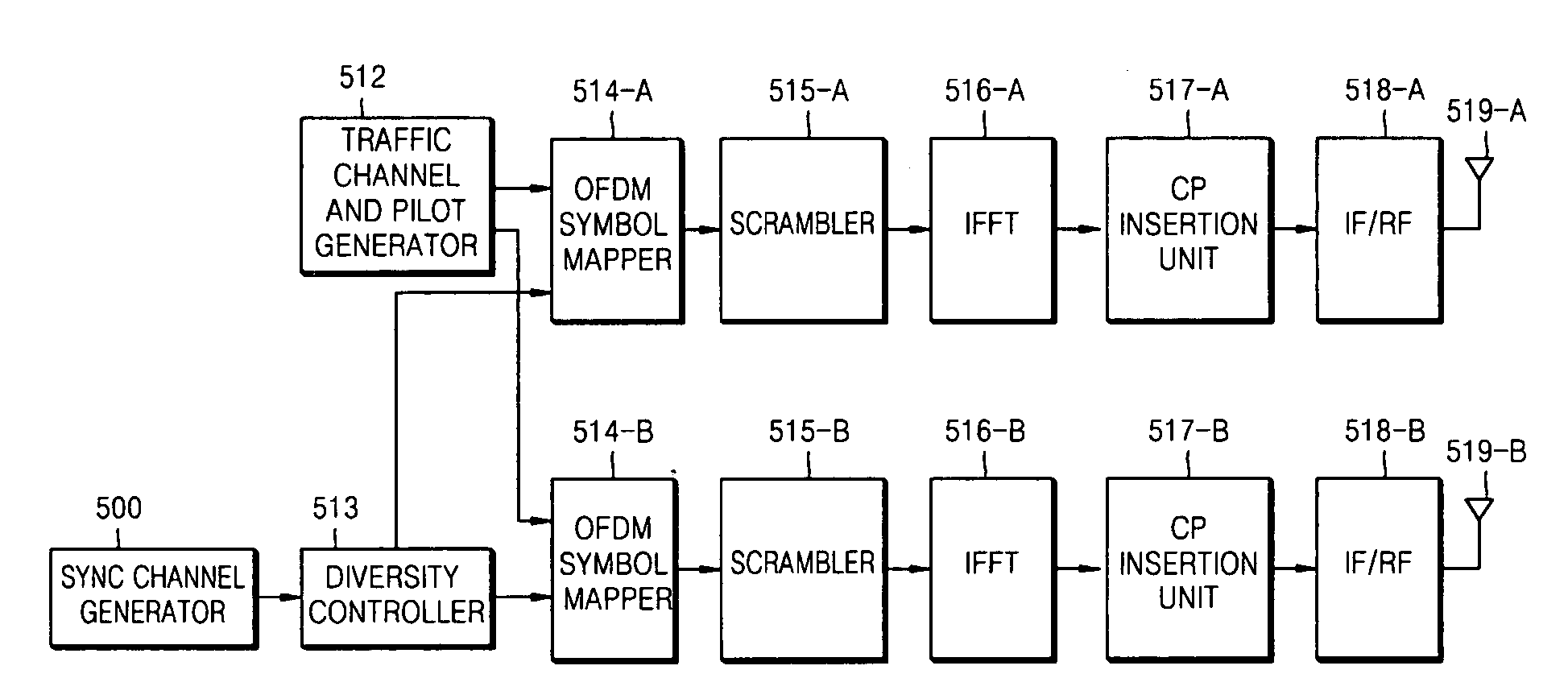
Synchronization in a broadcast OFDM system using time division multiplexed pilots
InactiveUS20050063298A1Accurate channel estimationTransmission control/equlisationFrequency-division multiplex detailsChannel impulse responseTime-division multiplexing
In an OFDM system, a transmitter broadcasts a first TDM pilot on a first set of subbands followed by a second TDM pilot on a second set of subbands in each frame. The subbands in each set are selected from among N total subbands such that (1) an OFDM symbol for the first TDM pilot contains at least S1 identical pilot-1 sequences of length L1 and (2) an OFDM symbol for the second TDM pilot contains at least S2 identical pilot-2 sequences of length L2, where L2>L1, S1·L1=N, and S2·L2=N. The transmitter may also broadcast an FDM pilot. A receiver processes the first TDM pilot to obtain frame timing (e.g., by performing correlation between different pilot-1 sequences) and further processes the second TDM pilot to obtain symbol timing (e.g., by detecting for the start of a channel impulse response estimate derived from the second TDM pilot).
Owner:QUALCOMM INC
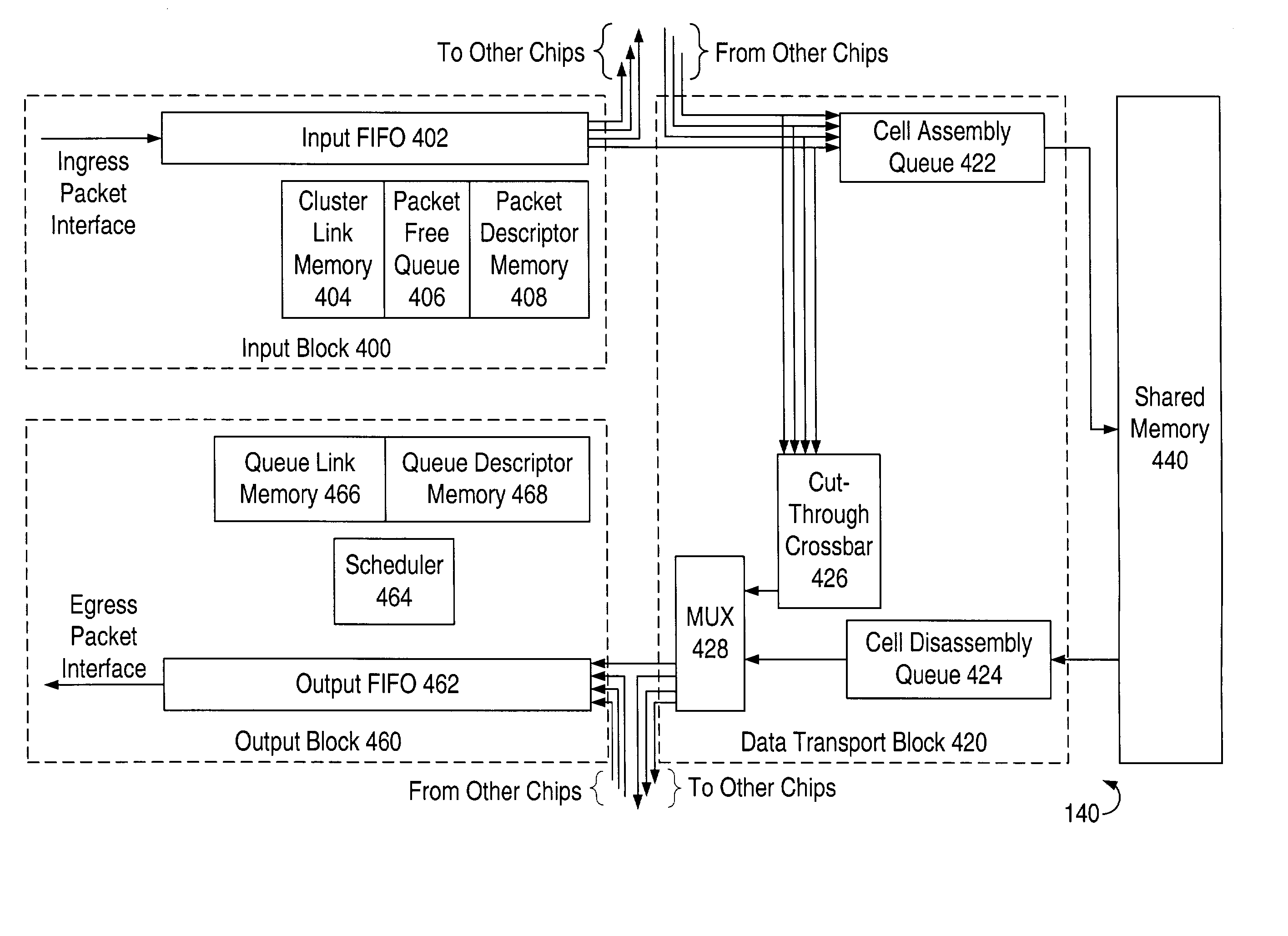
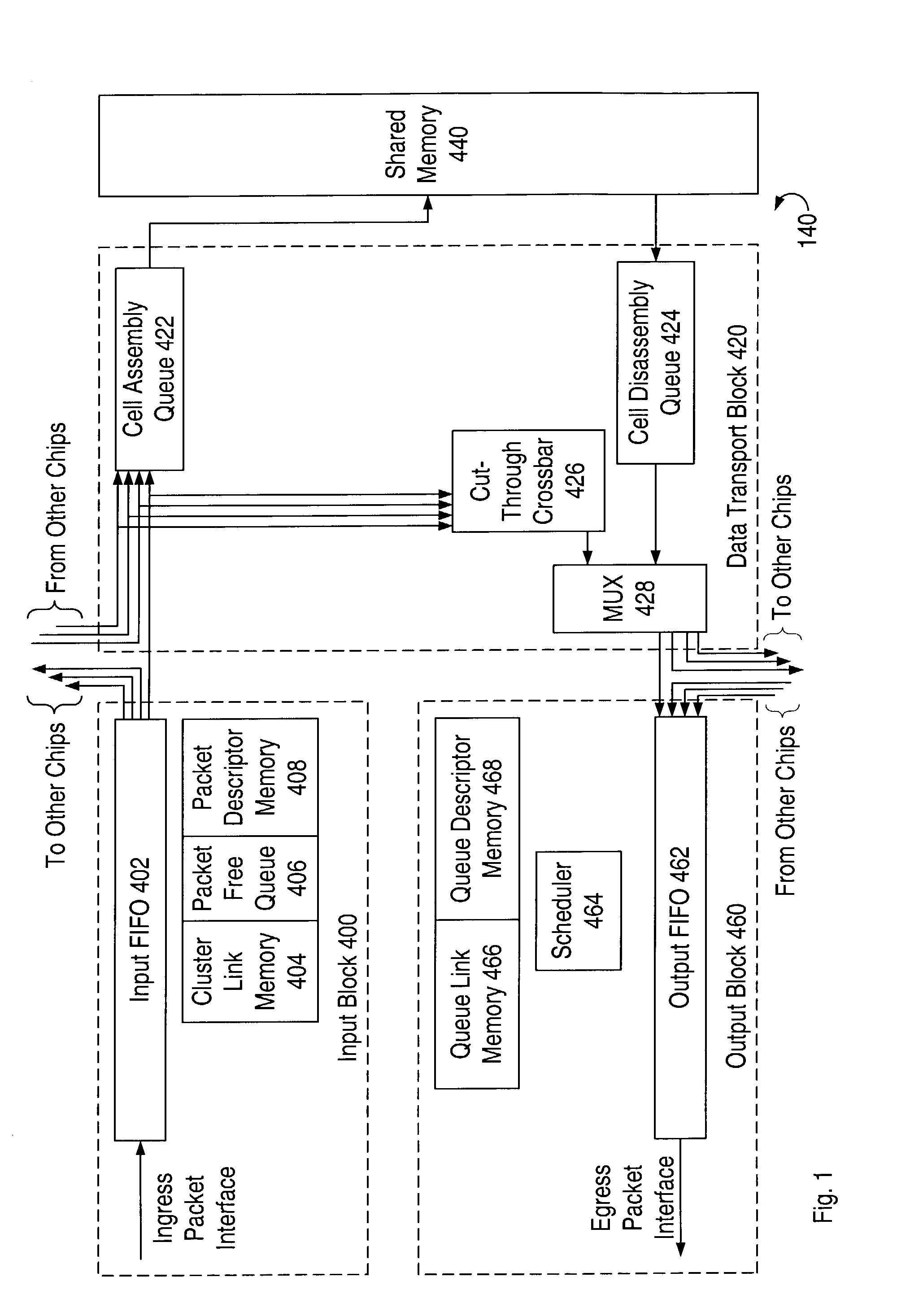
Method and system for managing time division multiplexing (TDM) timeslots in a network switch
InactiveUS20030026287A1Time-division multiplexRadio transmissionStatistical time division multiplexingFibre Channel
A system and method for managing the allocation of Time Division Multiplexing (TDM) timeslots in a network switch. The network switch may use a TDM cycle comprising multiple timeslots to manage shared resources and to schedule data ingress and egress through the ports of the current configuration, wherein each port is assigned one or more timeslots. The network switch may be reprogrammed to support one of multiple timeslot assignment schemes for one of multiple port configurations. The network switch may support configurations with varying numbers of ports, e.g. 8- and 16-port configurations. A network switch may also support configurations where two or more ports are combined to form one port, for example, a 2 Gbs Fibre Channel port. To meet the requirements of the various configurations, the timeslot assignment scheme may be reprogrammed to meet the scheduling requirements of each of the possible port configurations.
Owner:BROCADE COMMUNICATIONS SYSTEMS
System and method for establishing universal real time protocol bridging
InactiveUS20070171898A1Exemption stepsSpecial service for subscribersNetwork connectionsTime-division multiplexingConference call
An apparatus and methods for Real Time Protocol (RTP) based bridging to create calls to and From any communication devices connected to the Public Switched Telephone Network (PSTN) or any public or private Internet Protocol network. The methods are represented in controls residing either in an RTP Bridge apparatus or as middleware on a service creation platform, softswitch, or SIP proxy services incorporating SIP bridging and SIP call relay technologies, with an interface to a TDM (Time Division Multiplexing) switch operated by a Local Exchange Carrier (LEC) or Competitive LEC (CLEC), or hosted by an Internet Telephony Service Provider (ITSP) with connectivity to the PSTN through media gateways. The method permits a party to request an on demand conference call by either dialing into the apparatus from the PSTN or from any type of RTP communication device such as an IP phone; or using a form of signaling from RTP translation device. The moderator initiates the request, enters the participant(s) to be included in the call, and the launch sequence is initiated and the apparatus makes contact with the phone / end point and uses RTP bridging to interlace the packet streams and deliver one stream back to all the devices. The advantage is an on demand conference call to one or many participants, on similar or different communications platforms.
Owner:XTELTEK
Time division multiplexing over broadband modulation method and apparatus
InactiveUS6763025B2Low costReduce developmentBroadcast with distributionTime-division optical multiplex systemsFiberData stream
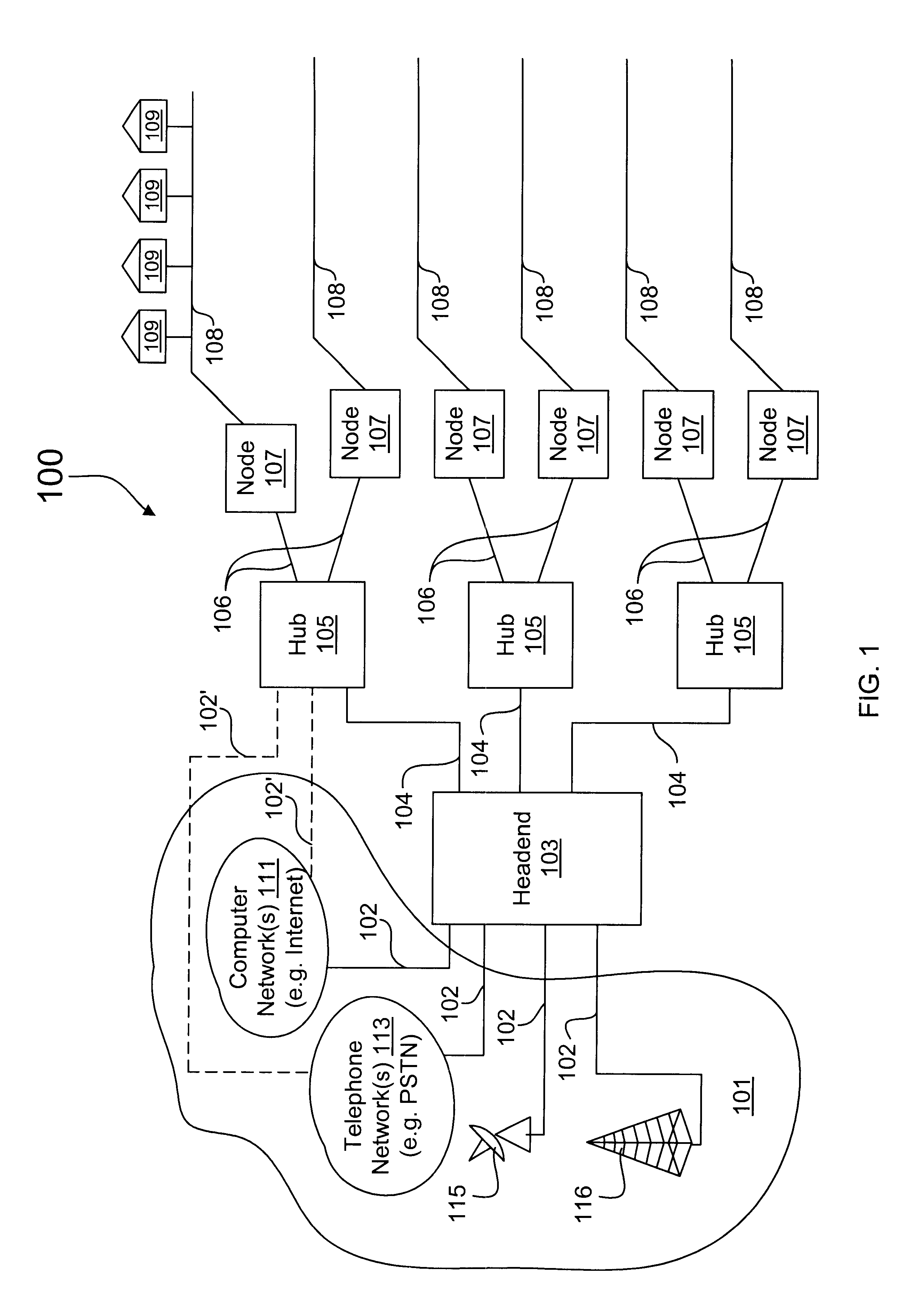
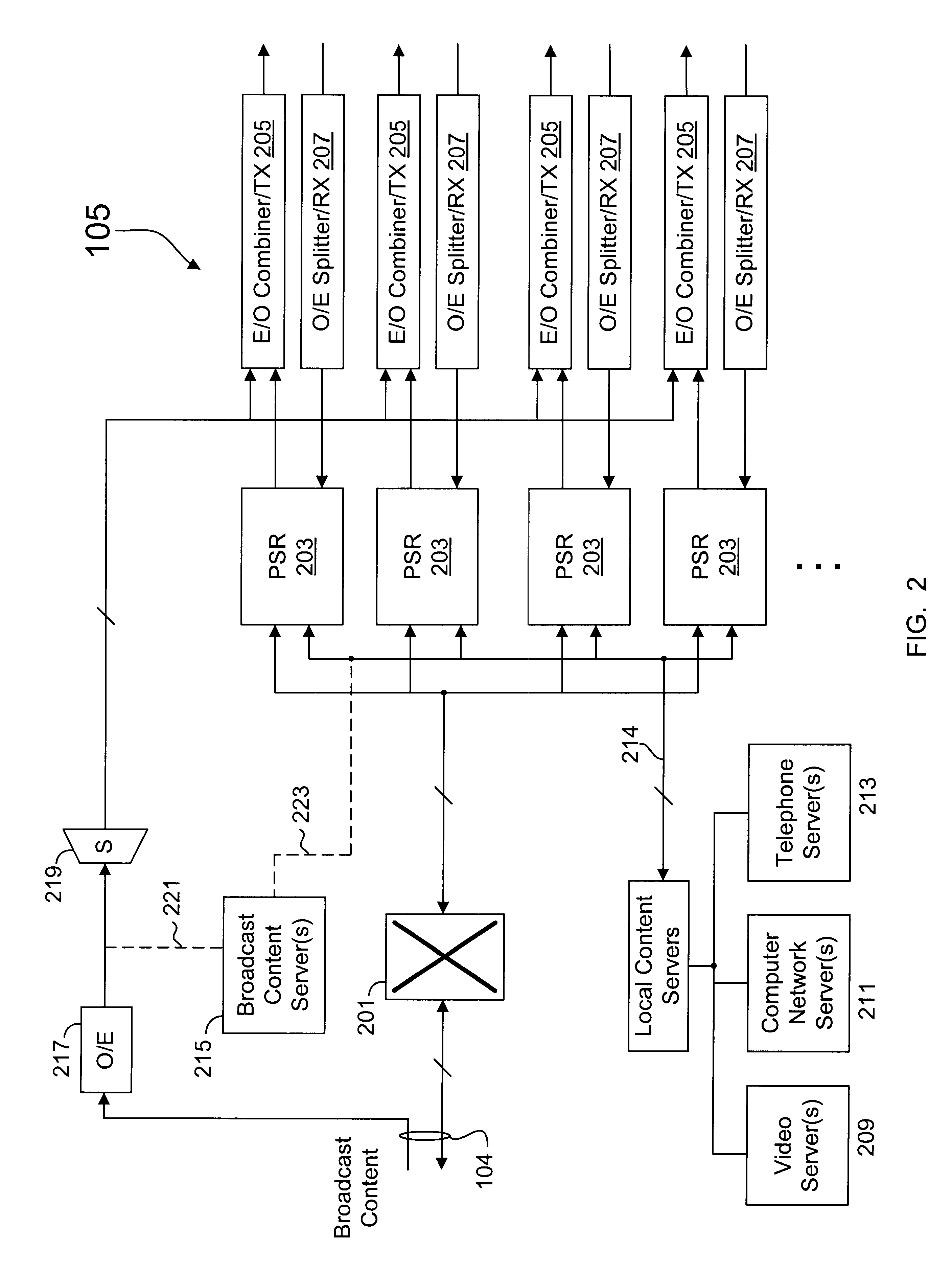
A packet switch router that processes downstream digital information to provide dedicated bandwidth to each subscriber destination in a hybrid fiber coax (HFC) network. The router includes a network module that terminates a network connection, a switch that forwards data from the network module, and a channel module. The channel module includes a switch interface, a cell processing engine, one or more modulators, and a radio frequency (RF) transmitter network. The switch interface forwards packetized data from the switch to the cell processing engine. The cell processing engine organizes the packetized data into multiple data streams, encapsulates data in each data stream into data cells, and multiplexes the data cells into a multiplexed cell stream. Each modulator is configured to modulate a multiplexed cell stream into an analog signal. The RF transmitter network up converts and combines a plurality of analog signals into a combined electrical signal for transmission.
Owner:ADVENT NETWORKS +1
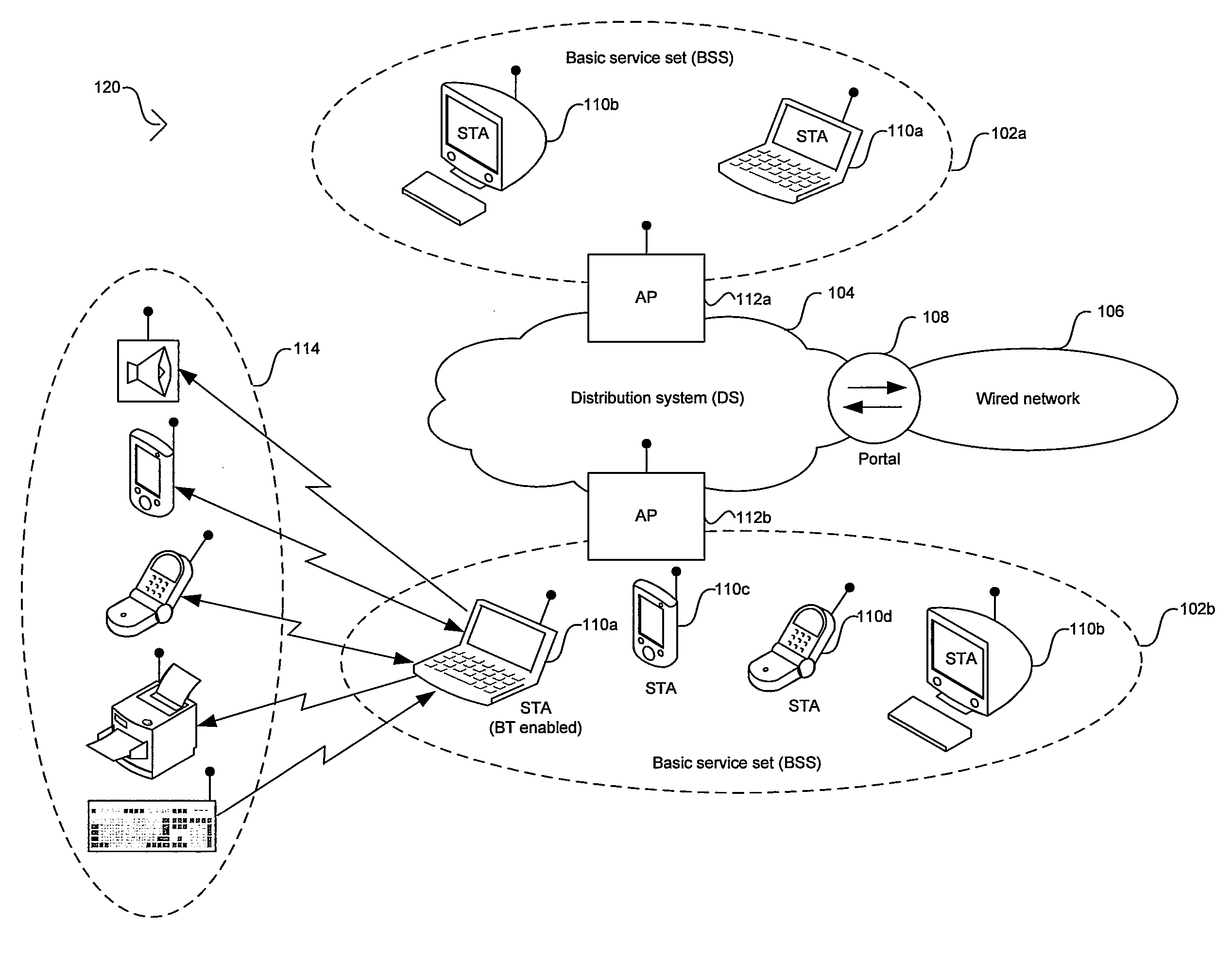
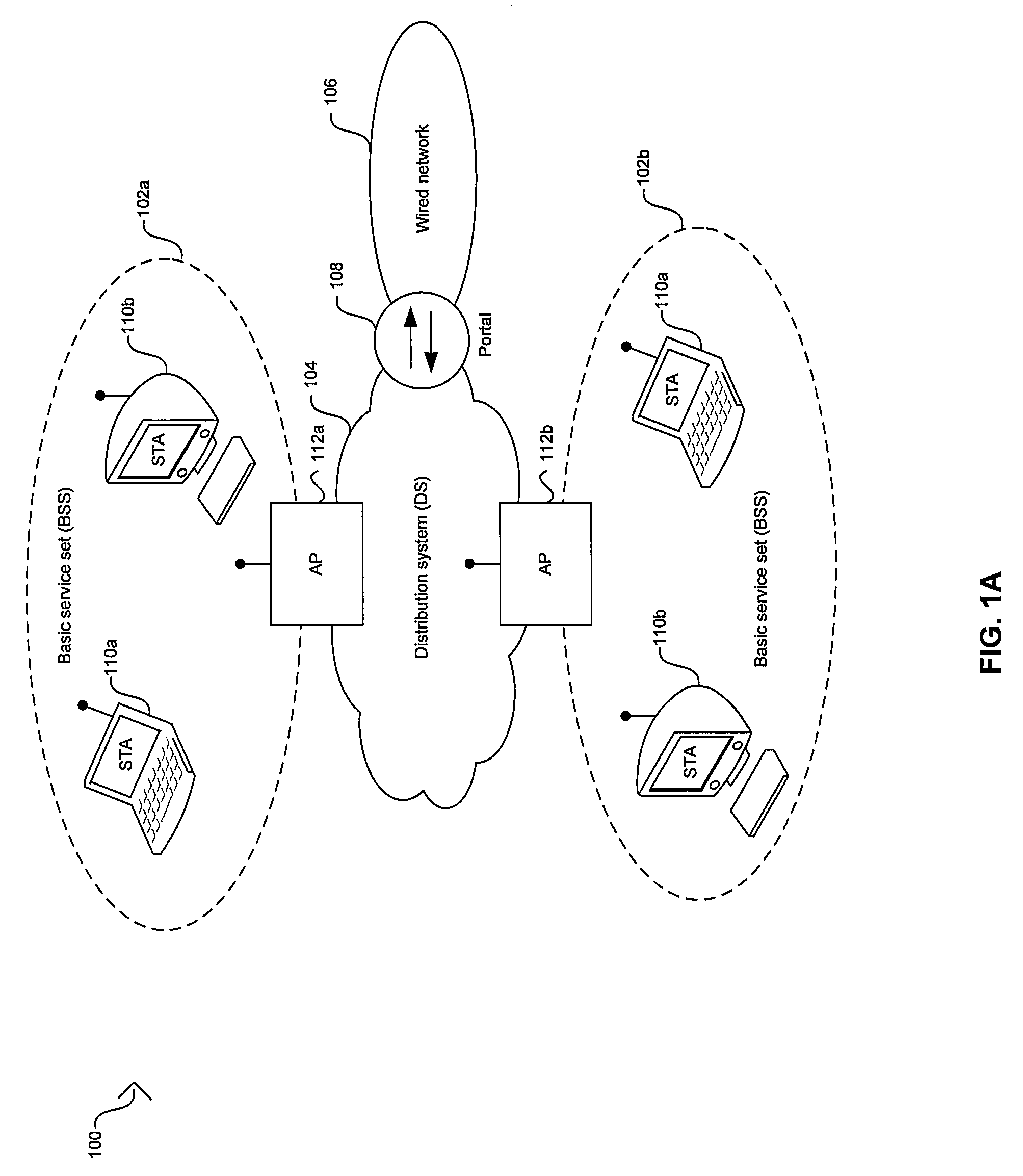
Method of wireless local area network and Bluetooth network coexistence in a collocated device
InactiveUS20060292987A1Power managementDevices with wireless LAN interfaceWireless lanTime-division multiplexing
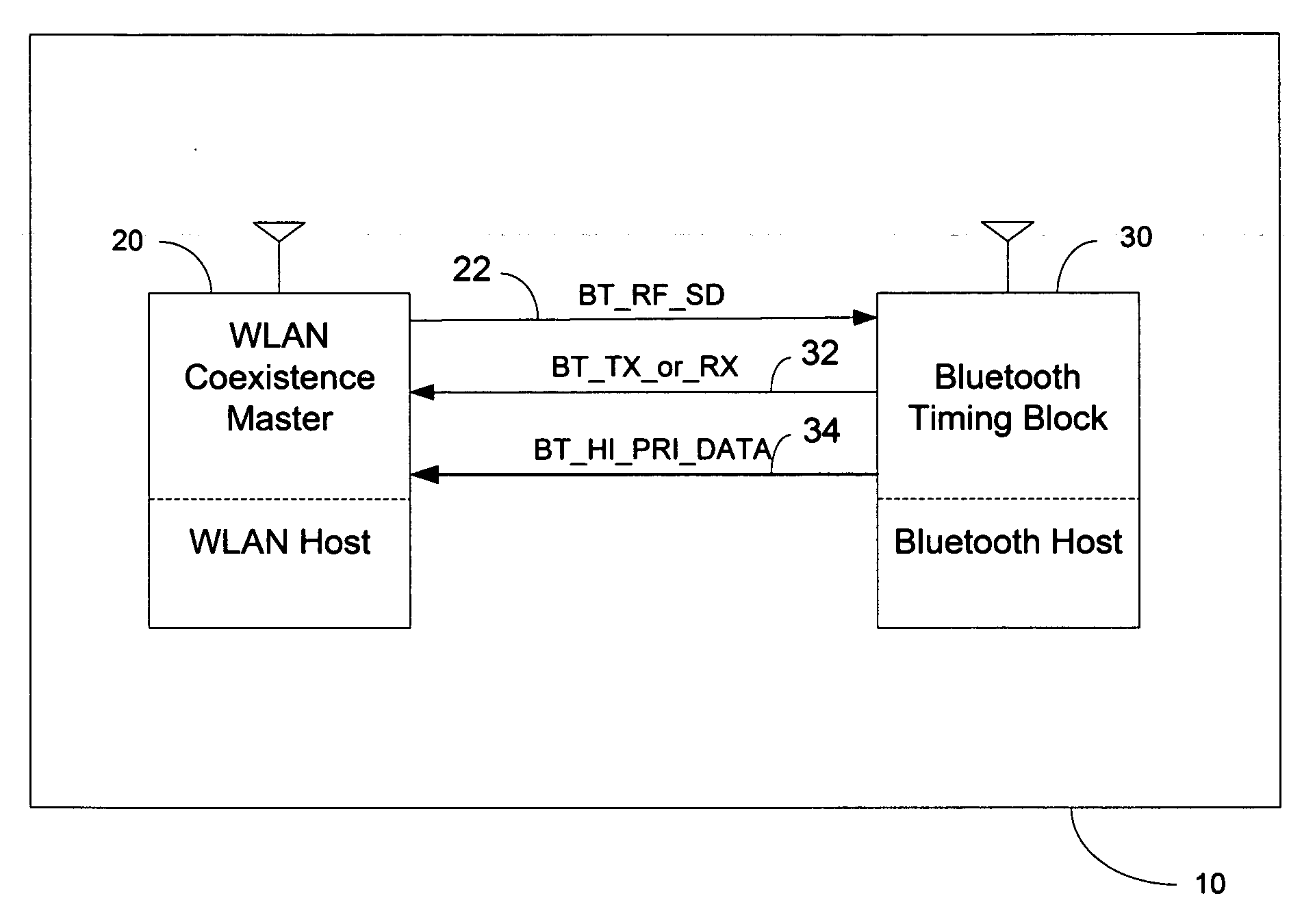
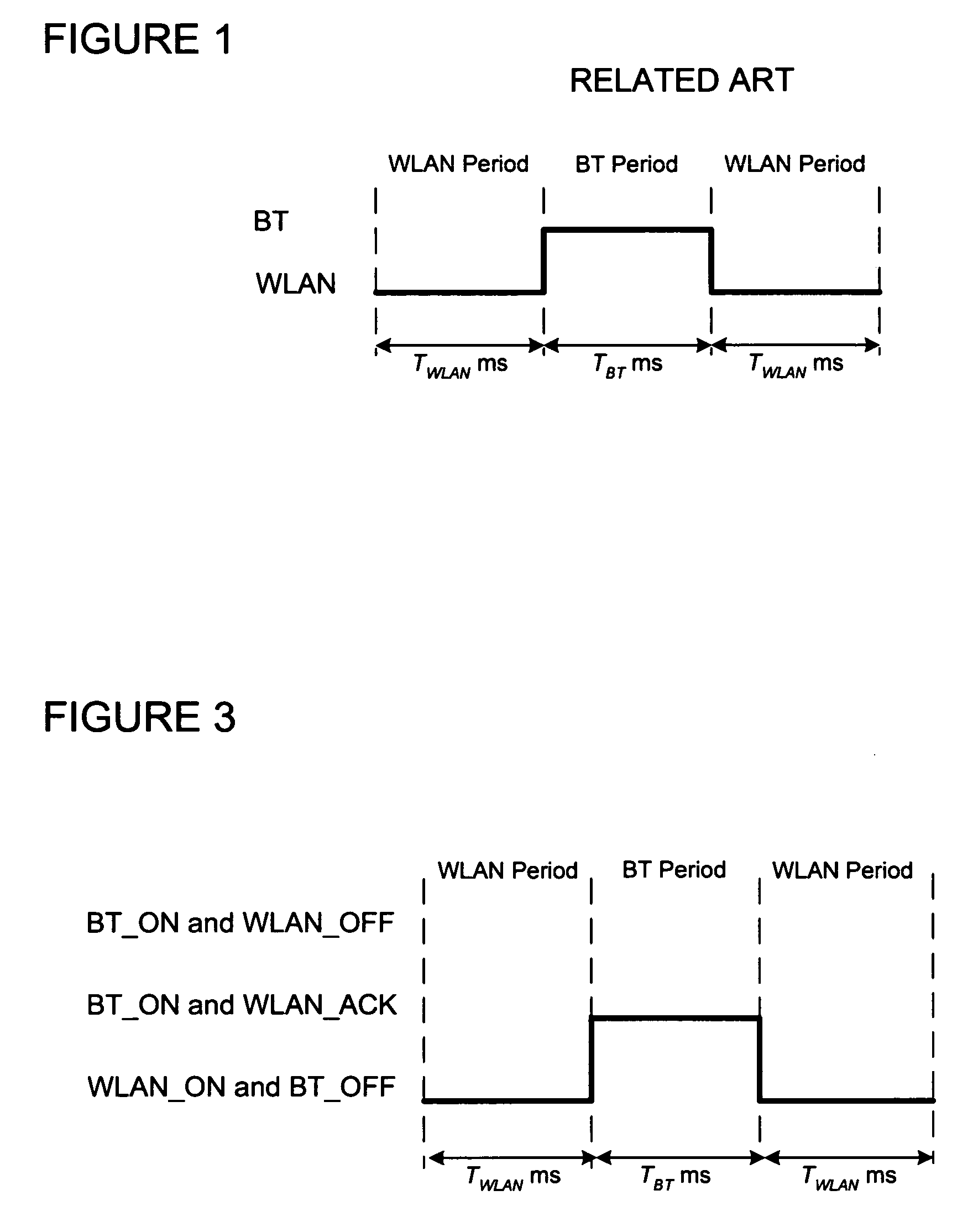
A collated wireless local area network / Bluetooth (WLAN / BT) device avoids radio interference between the two wireless systems by collaborative coexistence mechanisms. The collocated WLAN / BT device and coexistence methods include time division multiplexing based on various operating states of the collocated WLAN and BT systems, respectively. Such operating states include the transmission of low priority WLAN and BT data signals during WLAN and BT periods, the sleep mode of the collocated WLAN system, transmission of high priority data signals from the collocated BT system during time division multiplexed WLAN and BT periods, the transition of the collocated BT system from an active state to an idle state, and the transition of the collocated WLAN system from an active state to an idle state.
Owner:TEXAS INSTR INC
Multi-carrier communication with time division multiplexing and carrier-selective loading
ActiveUS7164669B2Frequency-division multiplex detailsTime-division multiplexStatistical time division multiplexingMultiuser system
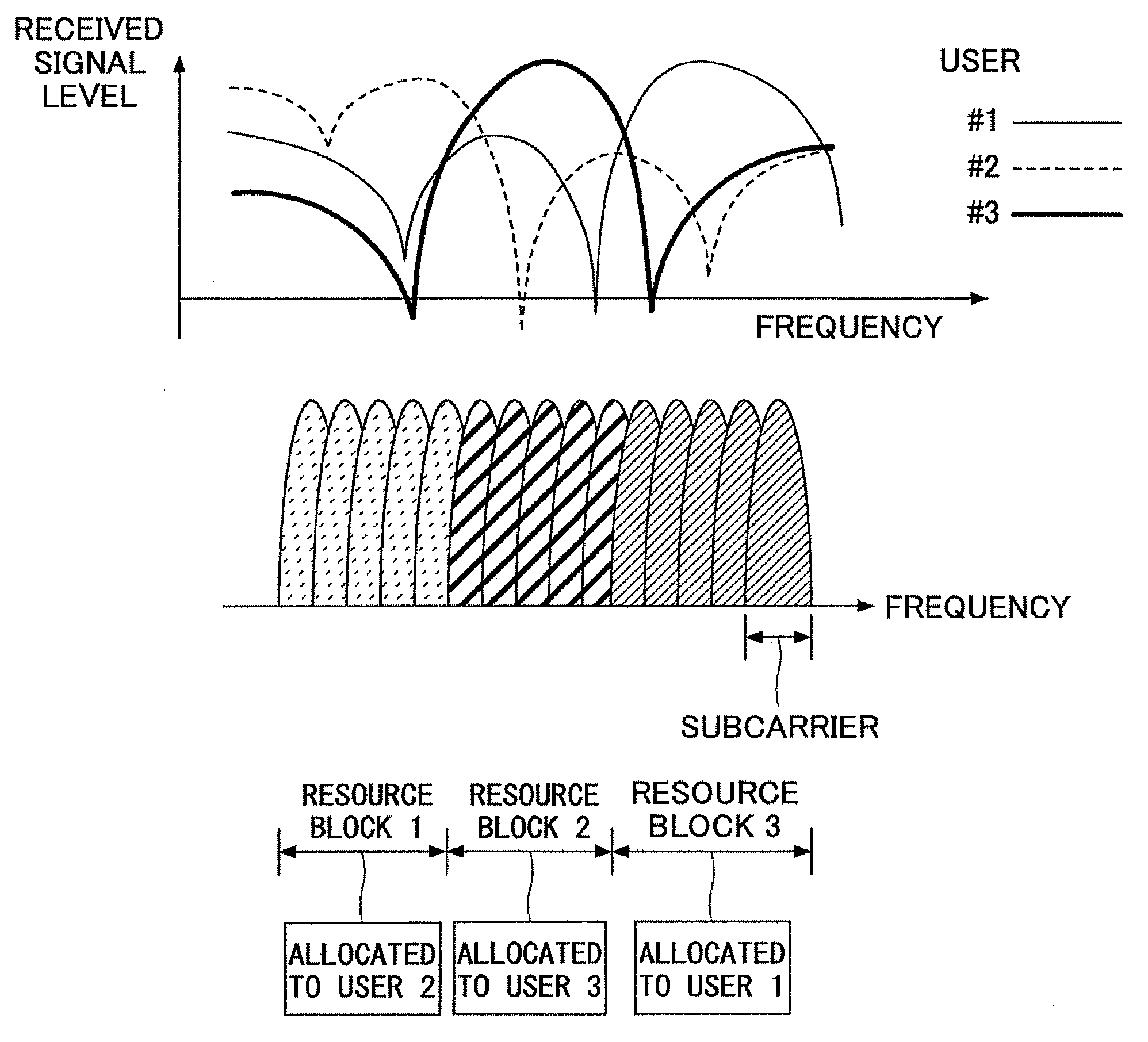
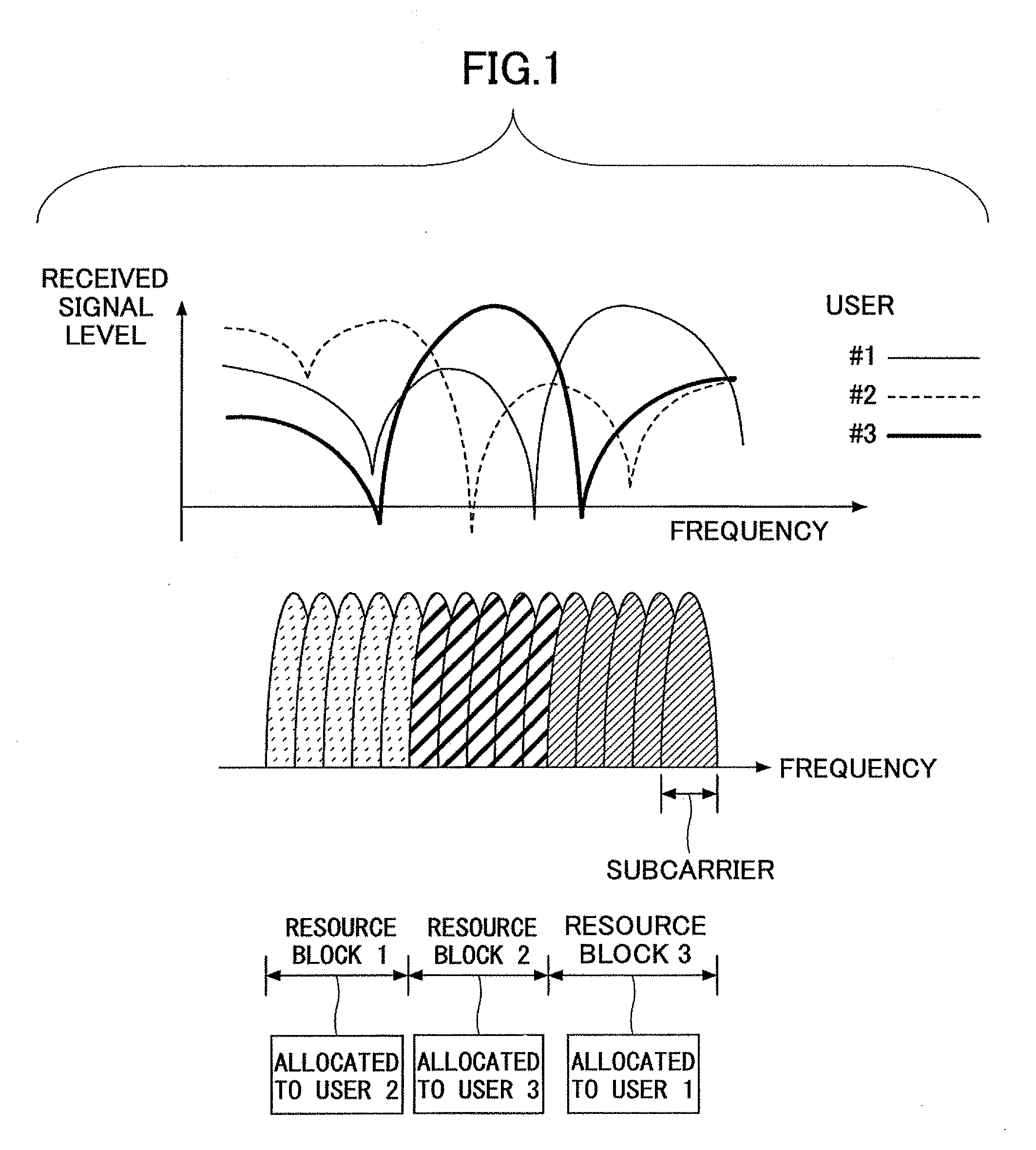
A method for subcarrier allocation and loading for a multi-carrier, multi-subscriber system is described. At least one cluster in a first and second set of clusters of subcarriers is associated for use in communication with a first and second subscriber, respectively. Then, for each cluster associated for use in communication with the first subscriber and the second subscriber, usage of that cluster is multiplexed between the first subscriber during a first time division and the second subscriber during a second time division.
Owner:KAON SYST +1
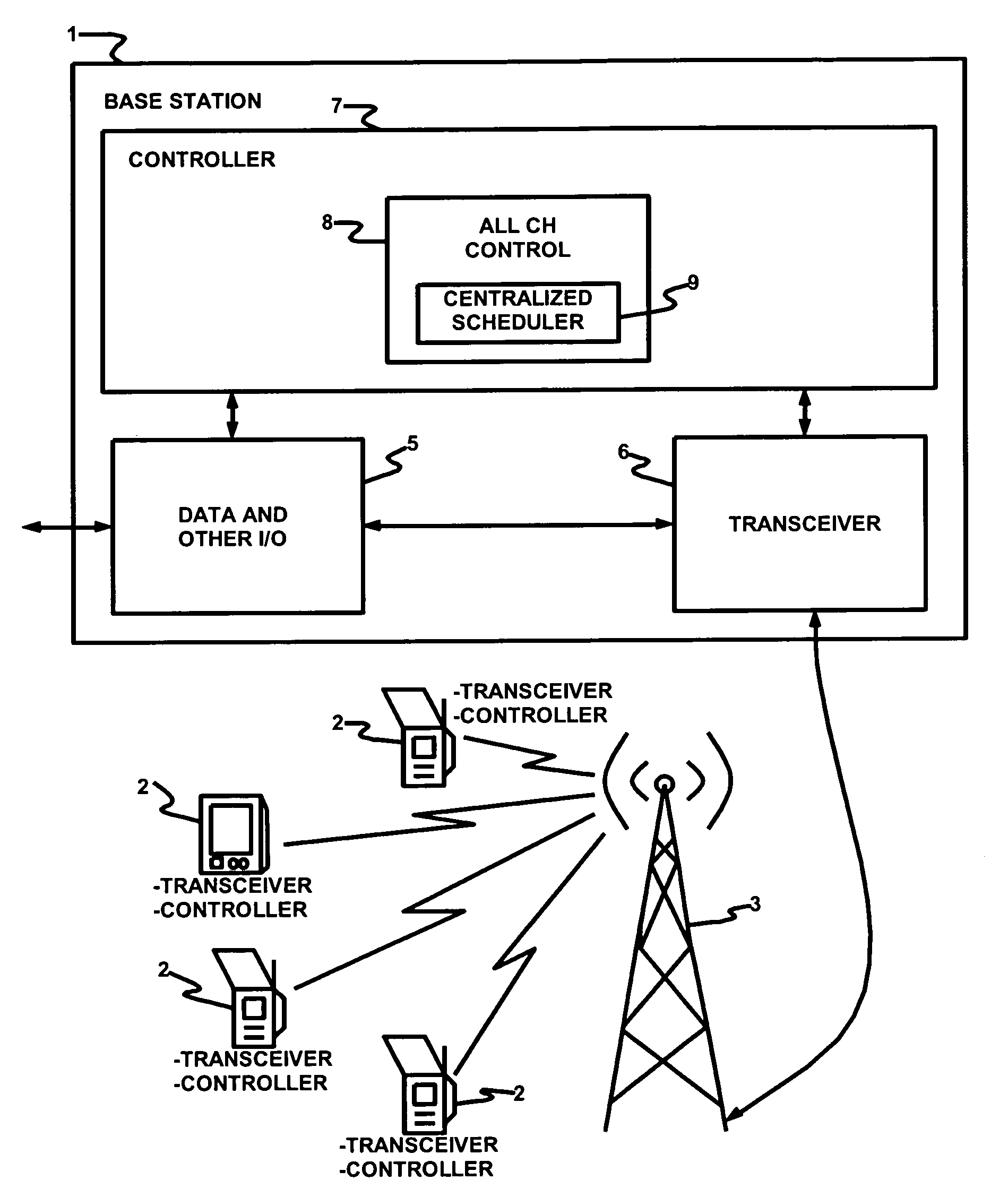
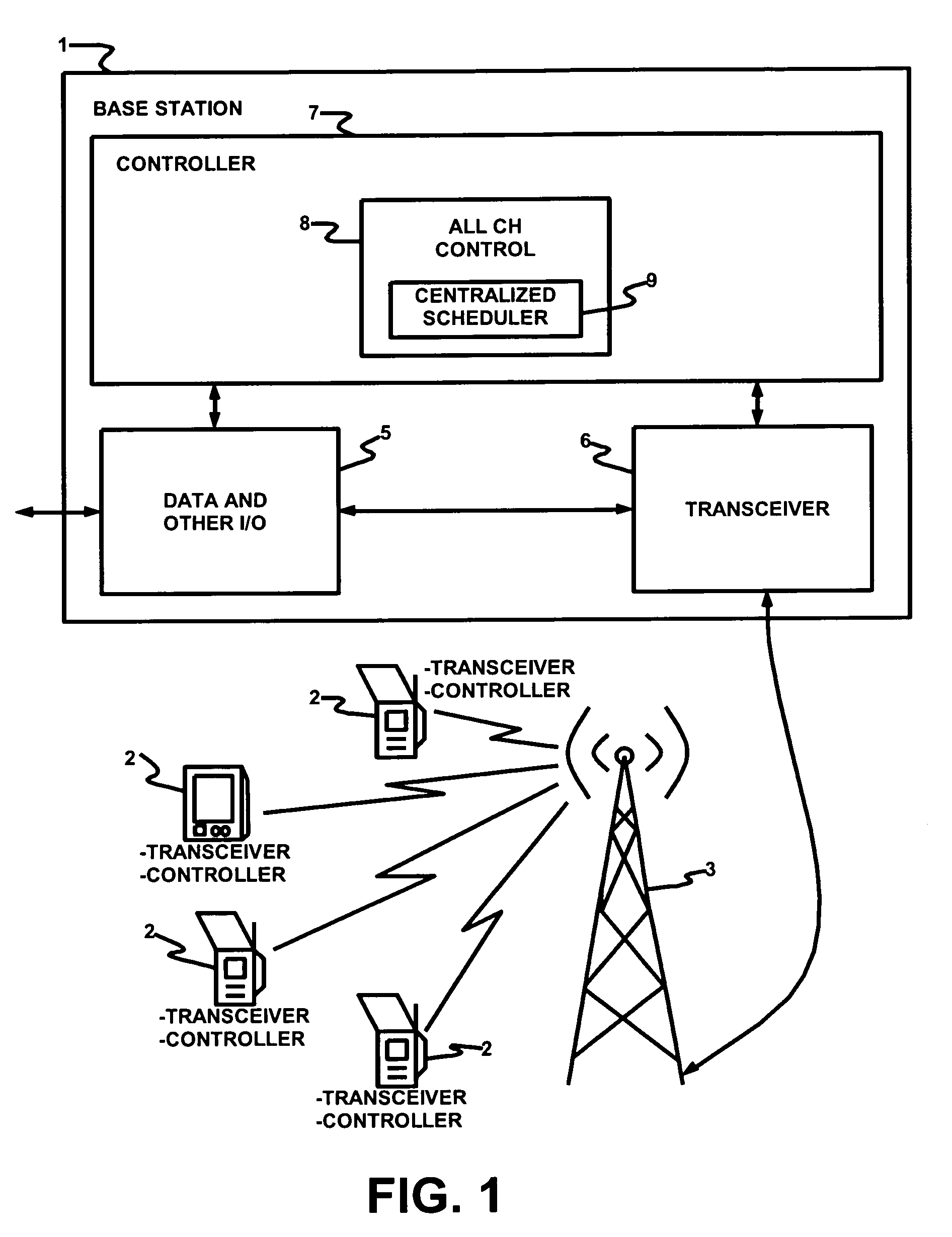
Synchronized plural channels for time division duplexing
InactiveUS7068639B1Efficient use ofEasy to useTime-division multiplexRadio transmissionTime-division multiplexingMedia access
A method of managing TDD across plural channels. In the method, frames are synchronized across the plural channels so that upstream frames and downstream frames coincide across the plural channels. Preferable, one channel is assigned to each of plural CPEs. Each CPE receives MAP messages on its assigned channel. A base station controller preferably generates the MAP messages. The MAP messages instruct the CPEs to switch channels so as to receive data bursts. The base station controller preferably includes a centralized scheduler that allocates channels and slots in those channels to the CPEs for receipt of the data bursts. Also, a method of receiving TDD messages. According to the method, CPEs switch channels based on received media access protocol messages so as to receive data bursts on plural channels. The channel to which a CPE switches need not be the same channel as the one on which the CPE receives its MAP messages. Additionally, systems, base stations, CPEs, and / or software that utilizes and / or implements these methods.
Owner:MONUMENT BANK OF INTPROP LLC
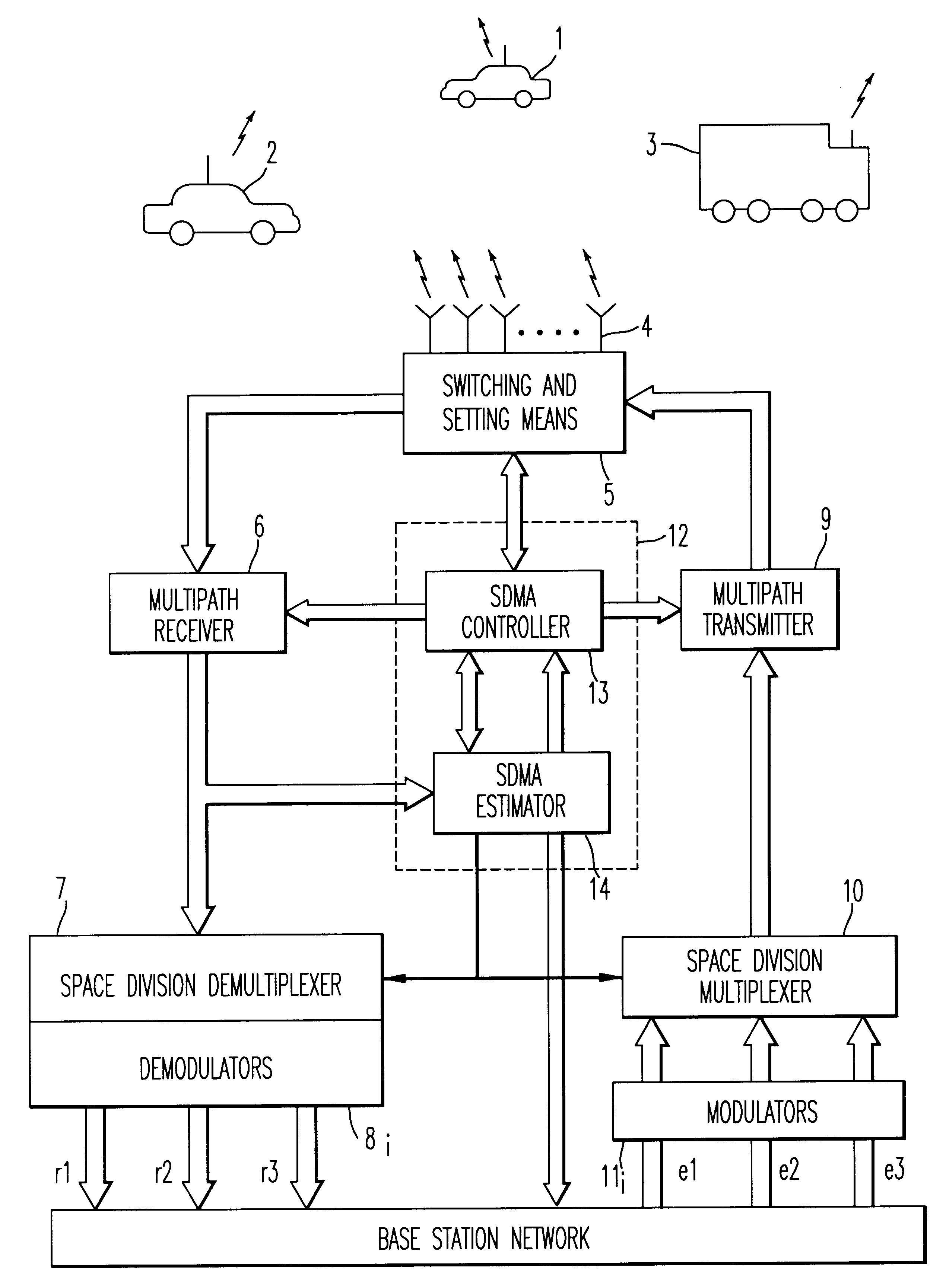
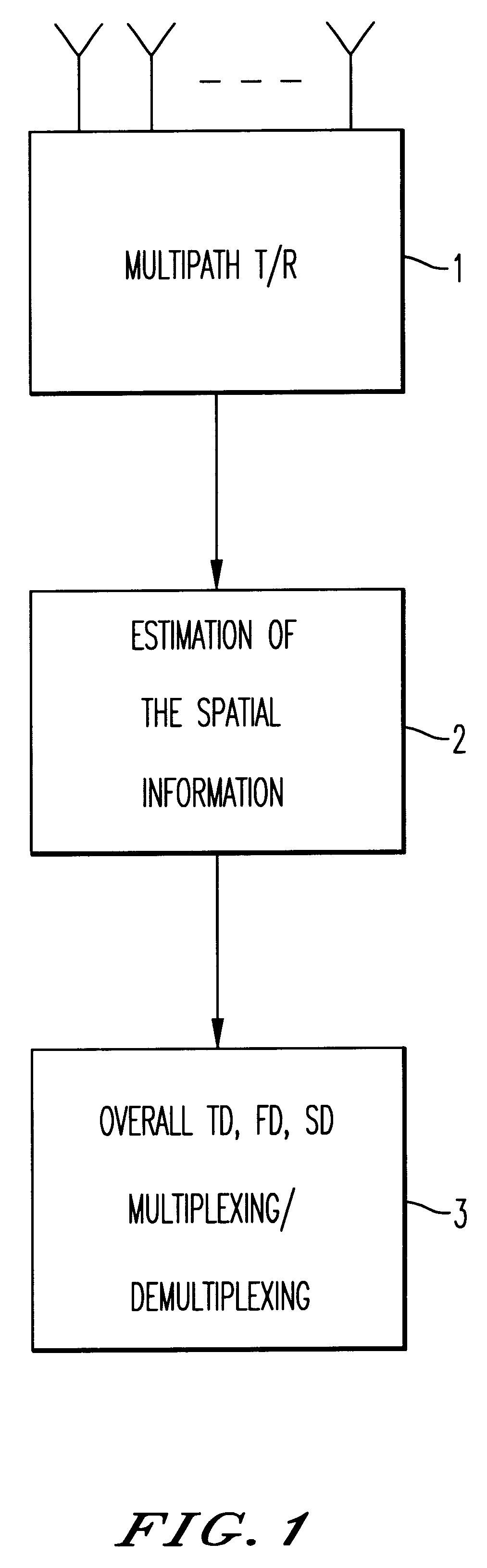
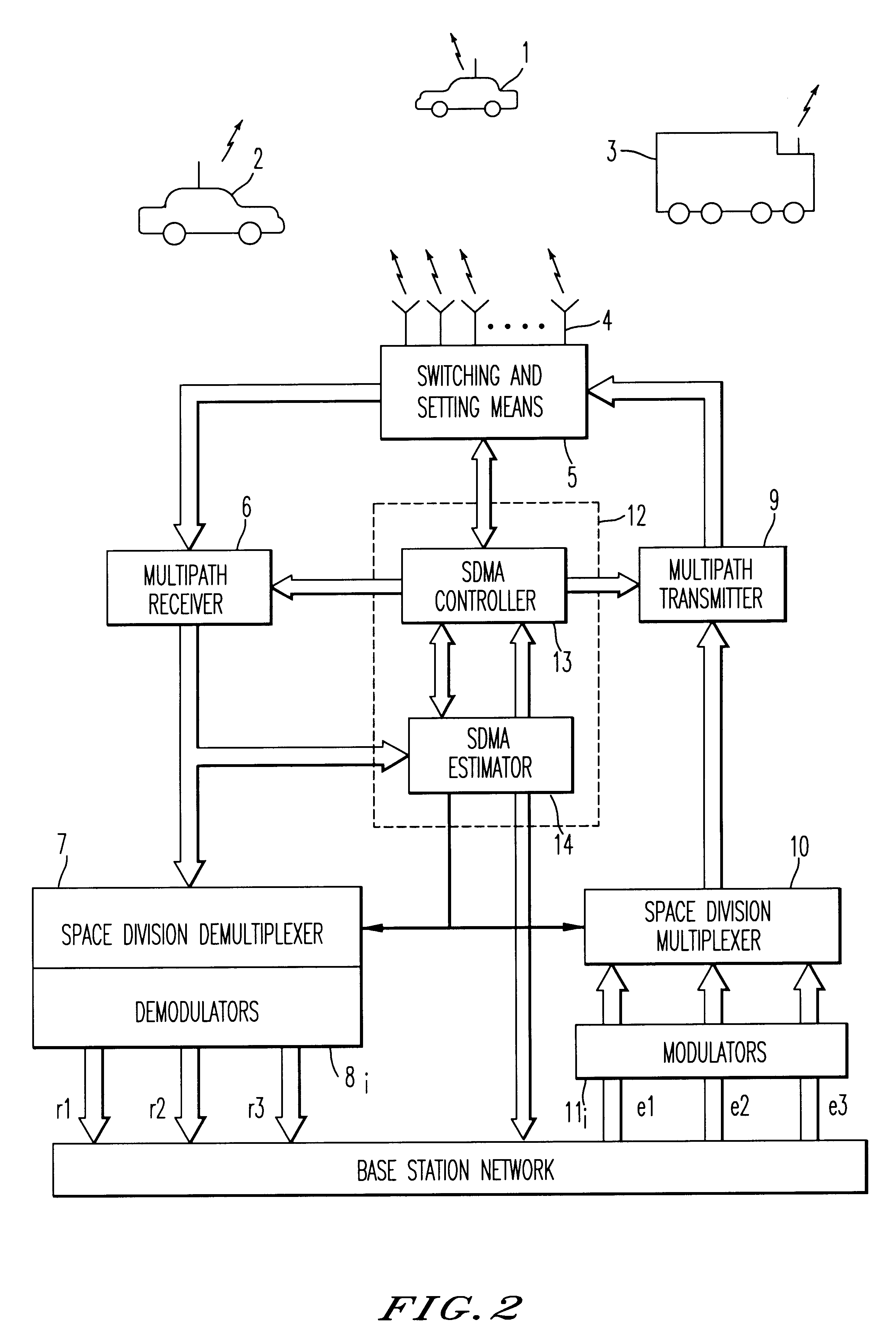
Method and device for space division multiplexing of radio signals transmitted in cellular radio communications
InactiveUS6240098B1Space can be allowedImprove performanceRadio wave direction/deviation determination systemsSpatial transmit diversityEngineeringTime-division multiplexing
A method and apparatus for spatial multiplexing and demultiplexing of radio signals. A multichannel transmitter and receiver is integrated in a base station and coupled to an antenna array. Using digital radio signals containing previously known or non-Gaussian sequences and arranged in frames, the spatial information about each mobile unit is estimated on the basis of the signal received by the receiver for the reception and transmission frequencies. This is done by known sequences or by blind source separation methods. The respective paths of each mobile unit with the power above a predetermined threshold is isolated by spatial filtering in the presence of multiple channel paths in order to provide spatial demultiplexing. Simultaneously, the intended signal is transmitted in the direction of the main path of each mobile unit while protecting each mobile unit from signals transmitted in the direction of other mobile units by spatial filtering with cancelling constraints in order to provide spatial multiplexing.
Owner:THOMSON CSF SA
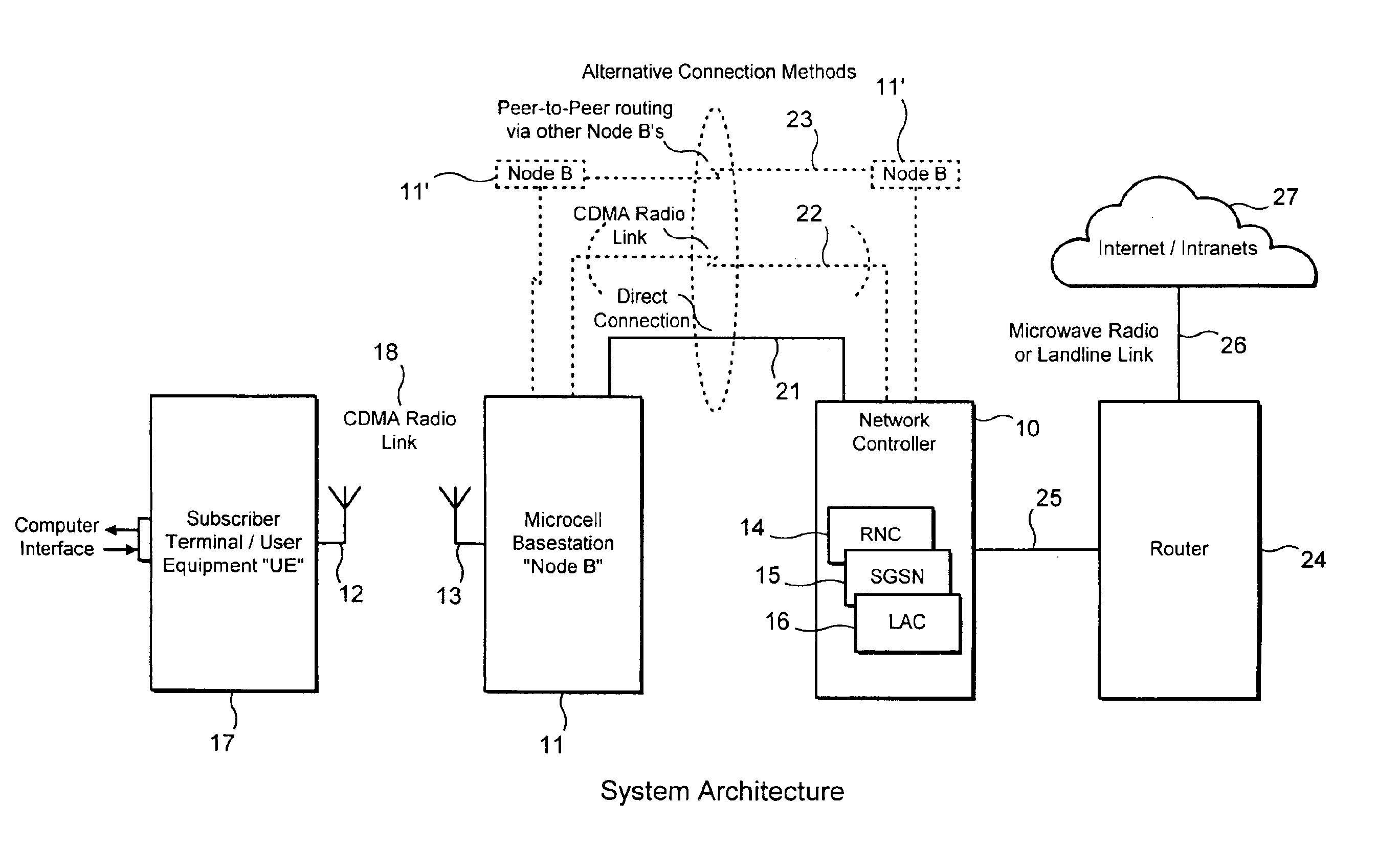
Cellular wireless internet access system using spread spectrum and internet protocol
InactiveUS6865169B1Reduce environmental impactOvercome lossMultiplex communicationNetwork topologiesTime-division multiplexingUser equipment
A cellular wireless internet access system which operates in the 2.5 to 2.68 GHz band and which must comply with complex government regulations on power levels, subscriber equipment and interference levels yet which provides high data rates to users and cell sizes of 1½ miles radius or more from base stations with subscriber equipment and antennas mounted indoors. Such base stations are mounted low and use spread-spectrum transmission to comply with interference rules with respect to adjacent license areas. An unidirectional tear-drop coverage pattern is used at multiple cells to further reduce interference when required. Time division duplex is used to allow the system to operate on any single channel of varying bandwidth within the 2.5 to 2.68 GHz band. Backhaul transmission from base stations to the Internet is provided using base station radio equipment, operating either on a different frequency in the band or on the same frequency using a time-division peer-to-peer technique. Different effective data-rates are provided by a prioritization tiering technique.
Owner:NVIDIA CORP
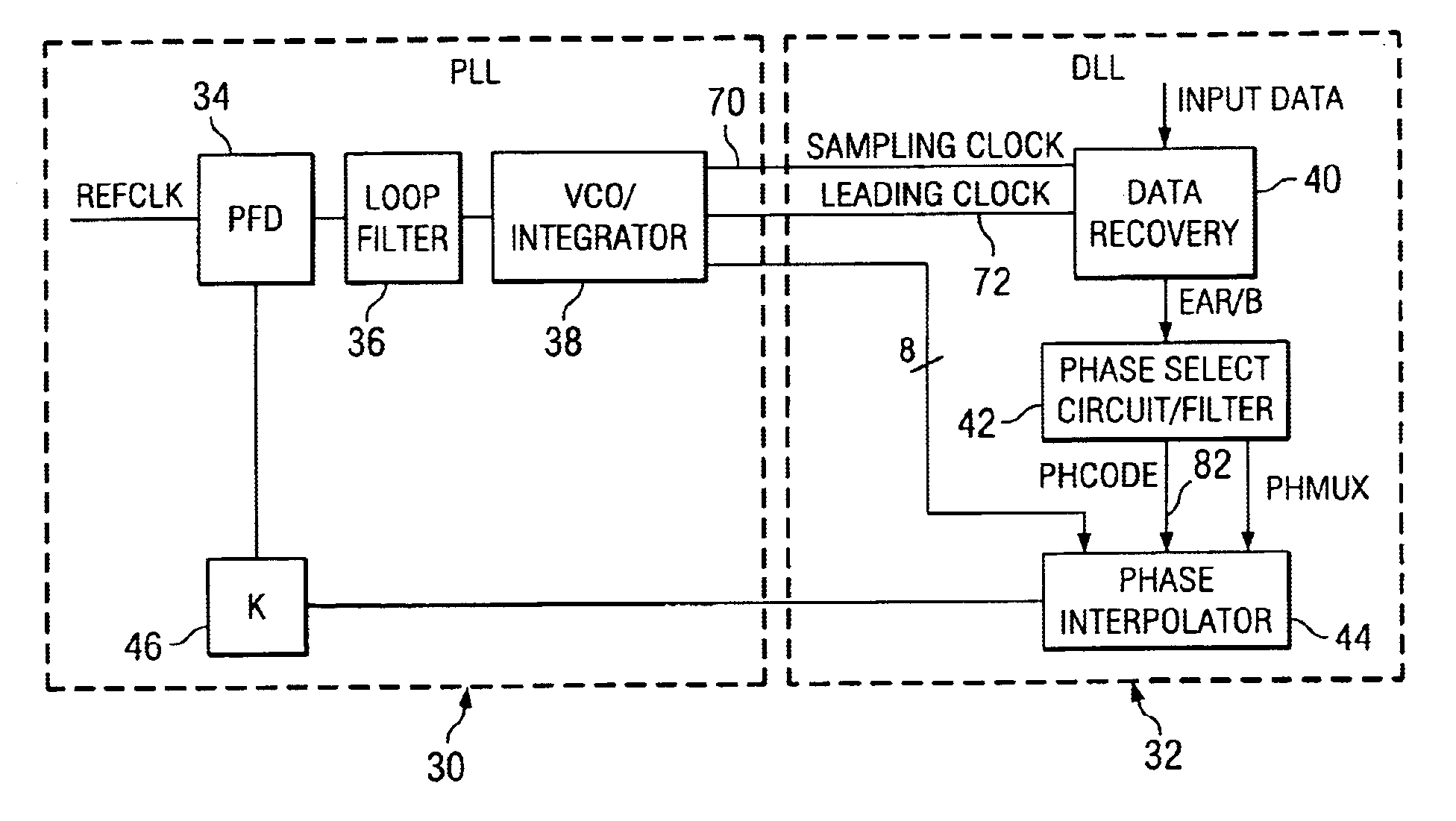
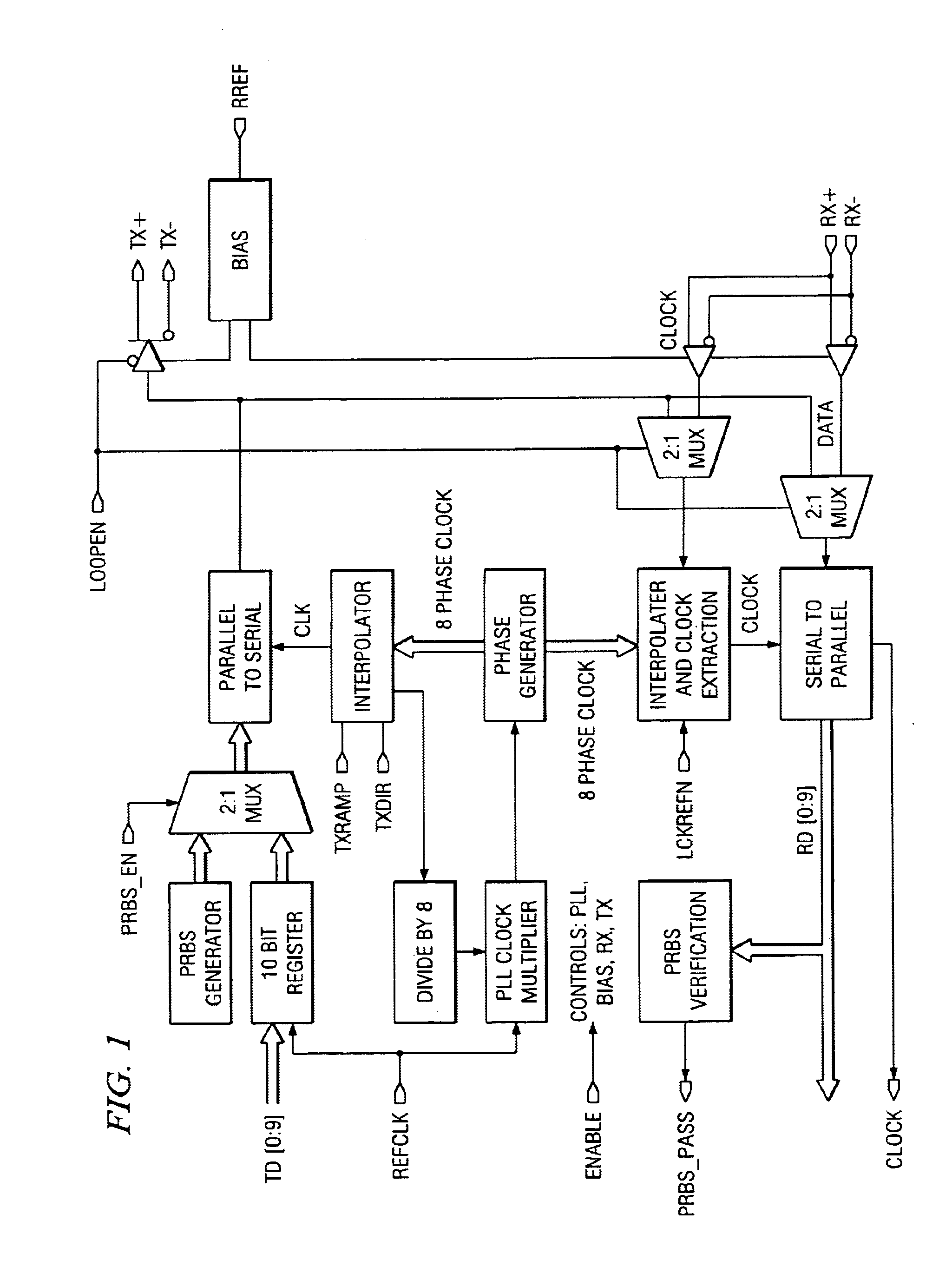
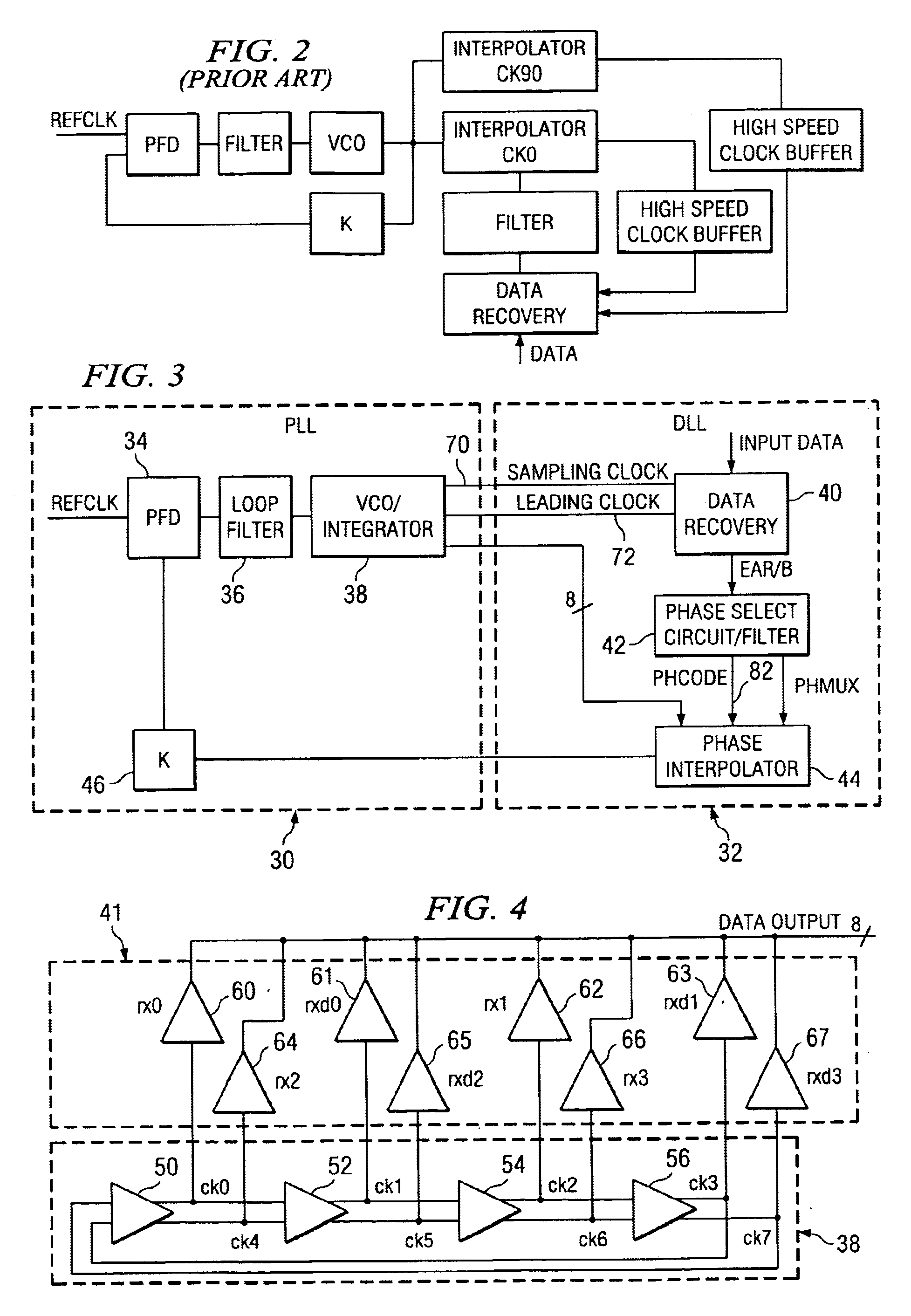
Time division multiplex data recovery system using close loop phase and delay locked loop
InactiveUS6901126B1Alleviate duty cycle issuesHigh bandwidthPulse automatic controlAngle demodulation by phase difference detectionDelay-locked loopClosed loop
A time division multiplex data recovery system using a closed-loop phase lock loop (PLL) and delay locked loop (DLL) is disclosed. In other words, one closed loop comprises both a phase locked loop (PLL) and a delay locked loop (DLL) in a novel time division multiplex data recovery system. This new architecture comprises a 4 stage Voltage Controlled Oscillator (VCO) used to generate 8 clock signals, 45 degrees phase shifted from one another, for 8 receivers to do the oversampling. An interpolator tracks the received data signal and feeds it back to the Phase / Frequency Detector (PFD). The PFD has a second input of the reference clock which the PFD uses along with the interpolator input to correct the frequency of the PLL. The PLL operates at a high bandwidth. The DLL's bandwidth is several orders lower than the PLL. The DLL activates only a multiplexer and an interpolator continuously, thereby drawing a minimum amount of power.
Owner:TEXAS INSTR INC
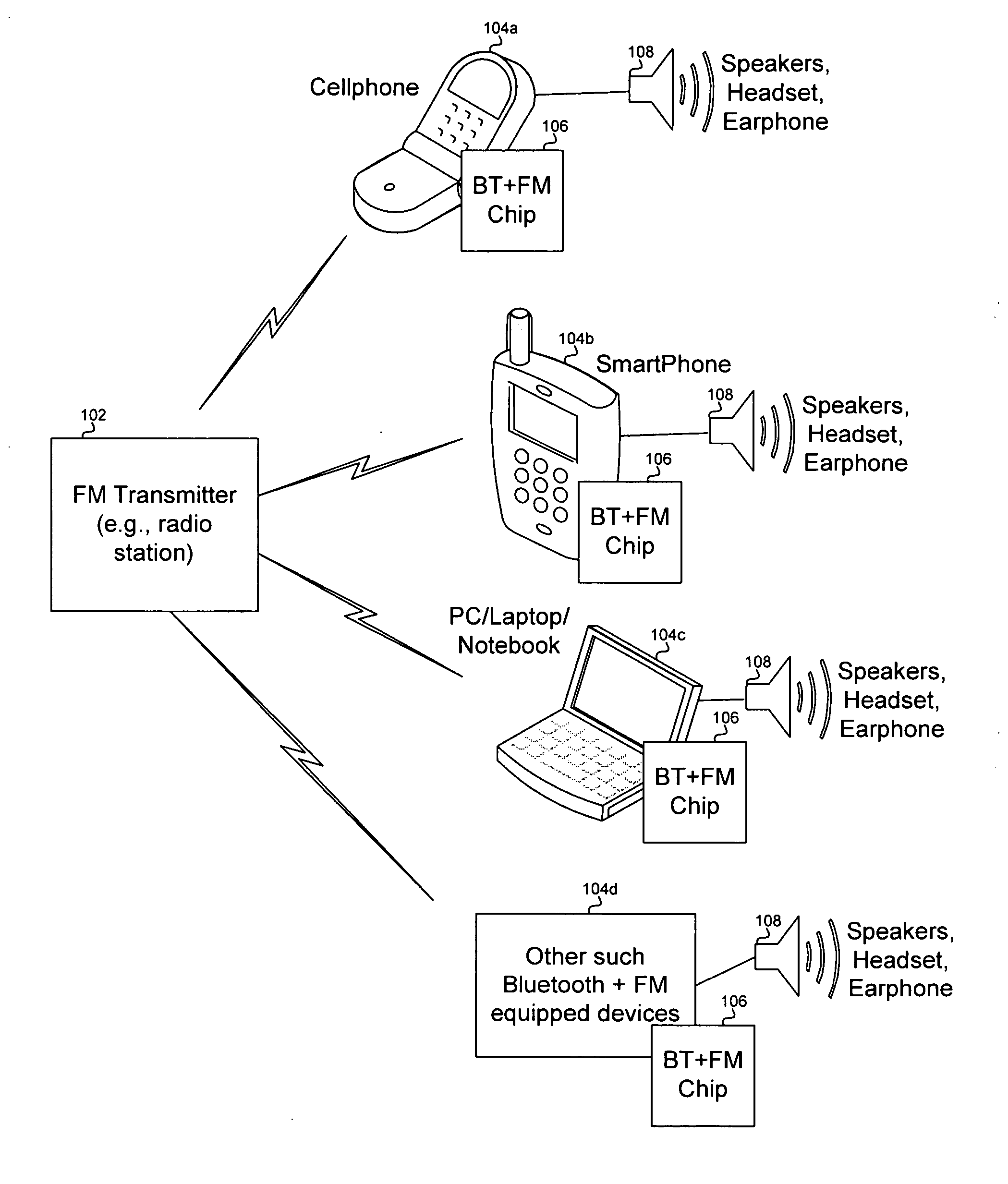
Method and system for a single chip integrated Bluetooth and FM transceiver and baseband processor
A method and system for a single chip integrated Bluetooth and FM transceiver and baseband processor are provided. The single chip may comprise a Bluetooth radio, an FM radio, a processor system, and a peripheral transport unit (PTU). FM data may be received and / or transmitted via the FM radio and Bluetooth data may be received and / or transmitted via the Bluetooth radio. The FM radio may receive radio data system (RDS) data. The PTU may support digital and analog interfaces. A processor in the processor system may time-multiplex processing of FM data and processing of Bluetooth data. The single chip may operate in an FM-only, a Bluetooth-only, and an FM-Bluetooth mode. The single chip may reduce power consumption by disabling portions of the Bluetooth radio during FM-only mode and / or disabling analog circuitry when performing digital processing. Communication between Bluetooth and FM channels may be enabled via the single chip.
Owner:NXP USA INC
Digital television signals using linear block coding
InactiveUS20060245505A1Color television with pulse code modulationColor television with bandwidth reductionData segmentBlock code
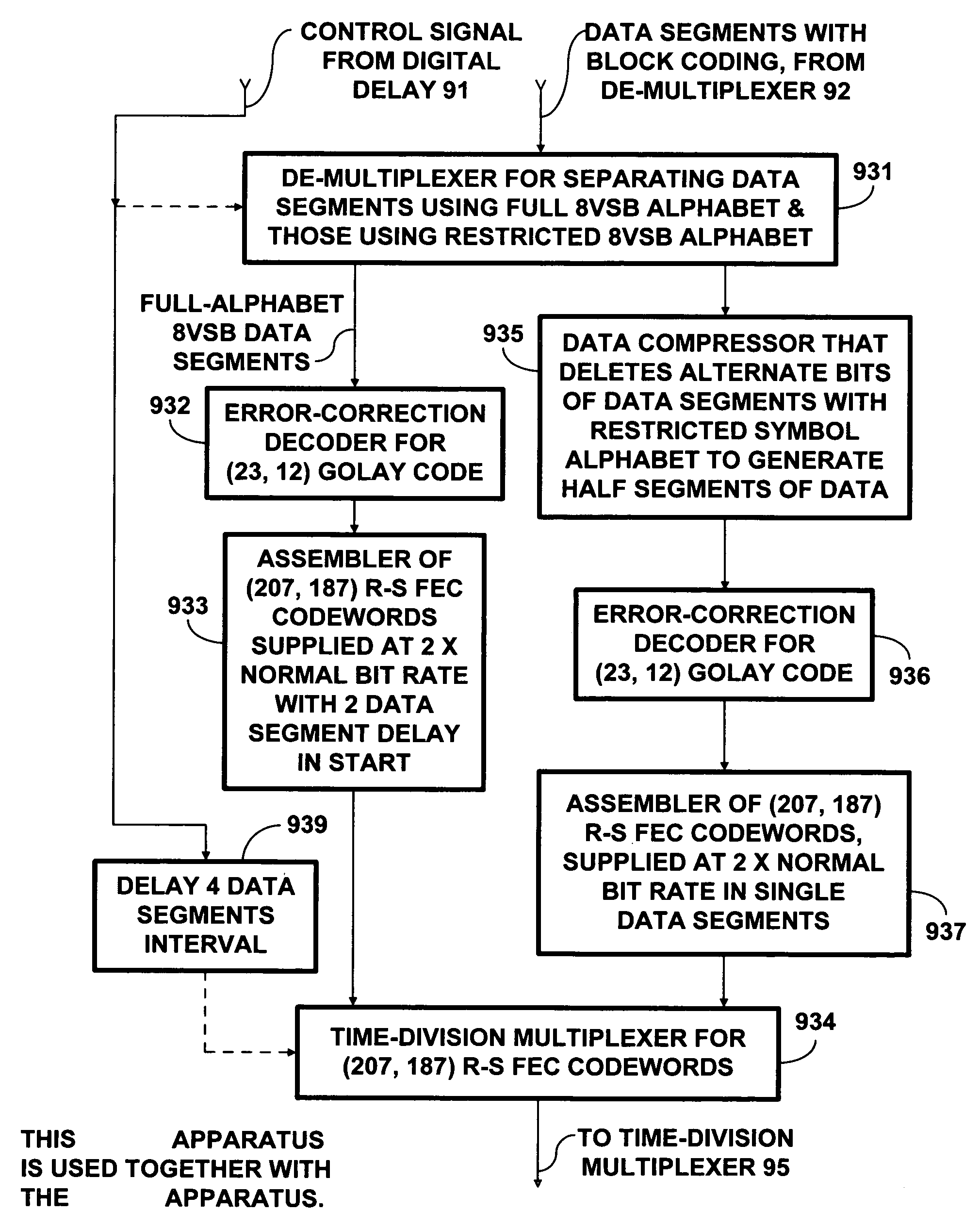
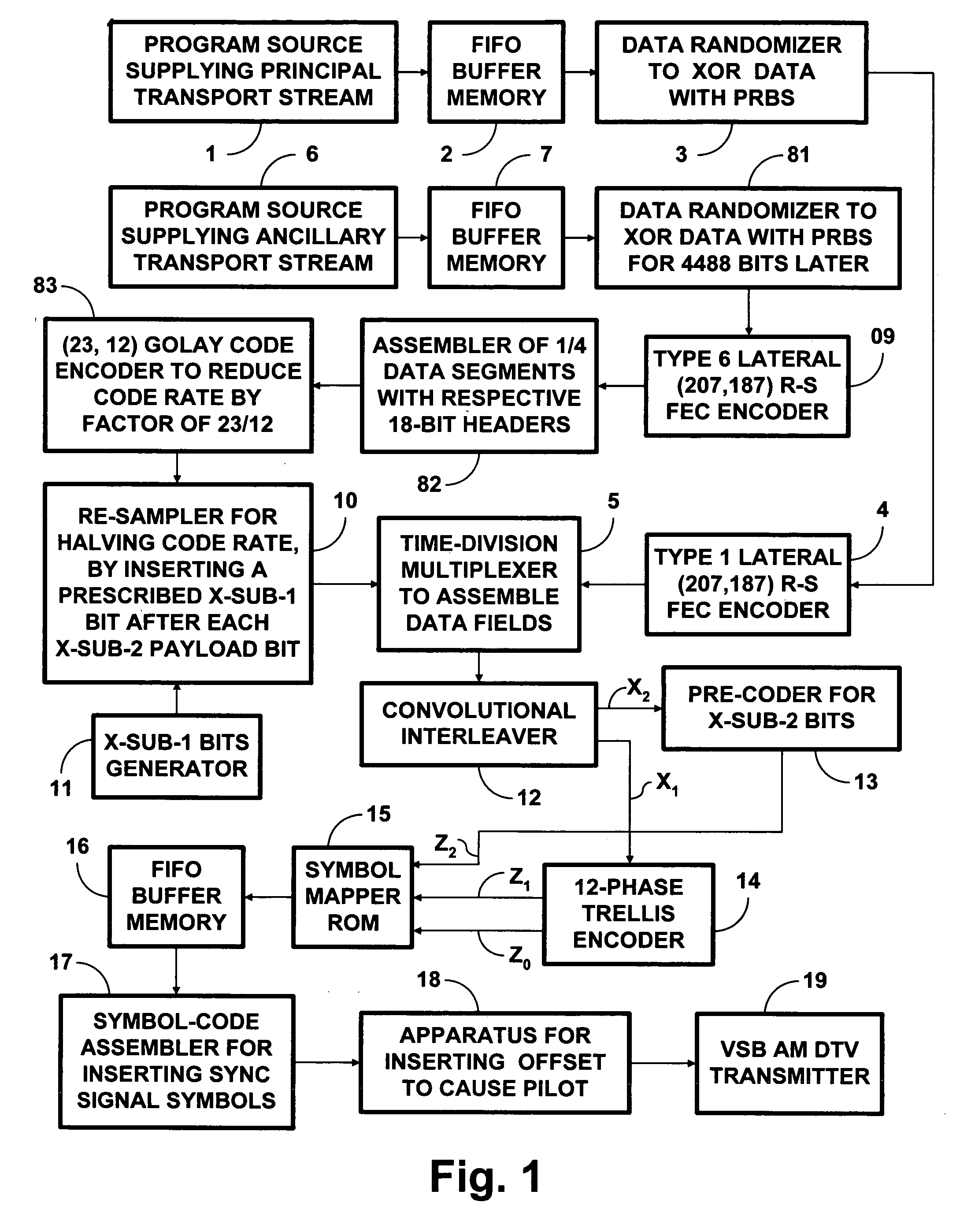
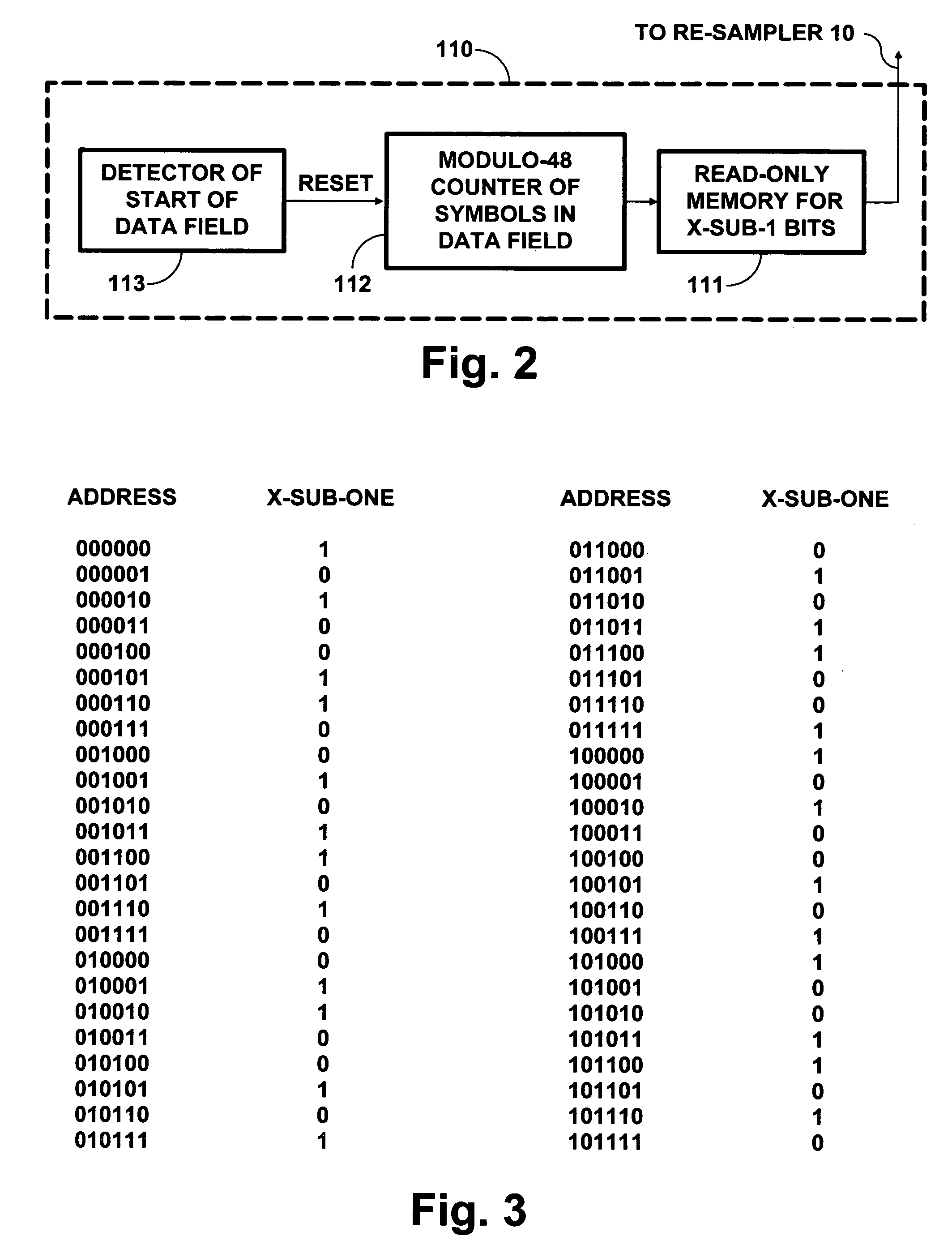
To increase the robustness of a broadcast DTV signal, complete (207, 187) Reed-Solomon forward-error-correction codewords are coded using binary linear block codes that reduce code rate by two or slightly less, enabling a DTV receiver to correct bit errors. Also, a DTV receiver can use a (15, 8), (16, 8) or (8, 4) block code to locate erroneous bytes for decoding (207, 187) Reed-Solomon code, so twice as many erroneous bytes can be corrected in a 187-byte data packet. The reduced code rate permits robust transmission of a 187-byte data packet in only two data segments and its super-robust transmission using a restricted symbol alphabet in only four data segments. This simplifies time-division multiplexing of data segments used for ordinary 8VSB transmissions with those used for robust and super-robust transmissions. Procedures to make legacy DTV receivers disregard data segments used for robust and super-robust transmission are disclosed.
Owner:LIMBERG ALLEN LEROY
LADAR sensor for a dense environment
A multi-ladar sensor system is proposed for operating in dense environments where many ladar sensors are transmitting and receiving burst mode light in the same space, as may be typical of an automotive application. The system makes use of several techniques to reduce mutual interference between independently operating ladar sensors. In one embodiment, the individual ladar sensors are each assigned a wavelength of operation, and an optical receive filter for blocking the light transmitted at other wavelengths, an example of wavelength division multiplexing (WDM). Each ladar sensor, or platform, may also be assigned a pulse width selected from a list, and may use a pulse width discriminator circuit to separate pulses of interest from the clutter of other transmitters. Higher level coding, involving pulse sequences and code sequence correlation, may be implemented in a system of code division multiplexing, CDM. A digital processor optimized to execute mathematical operations is described which has a hardware implemented floating point divider, allowing for real time processing of received ladar pulses, and sequences of pulses.
Owner:CONTINENTAL AUTONOMOUS MOBILITY US LLC
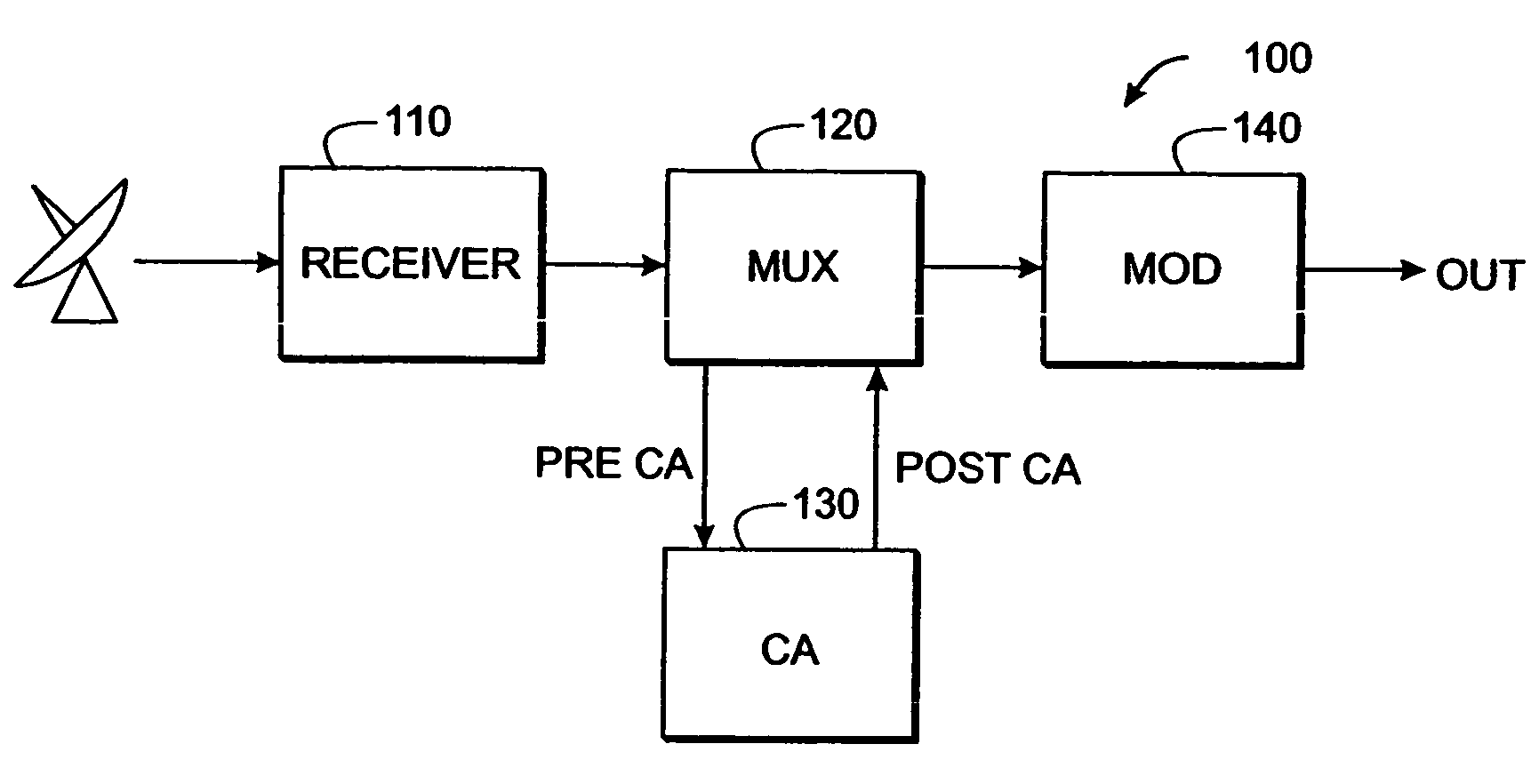
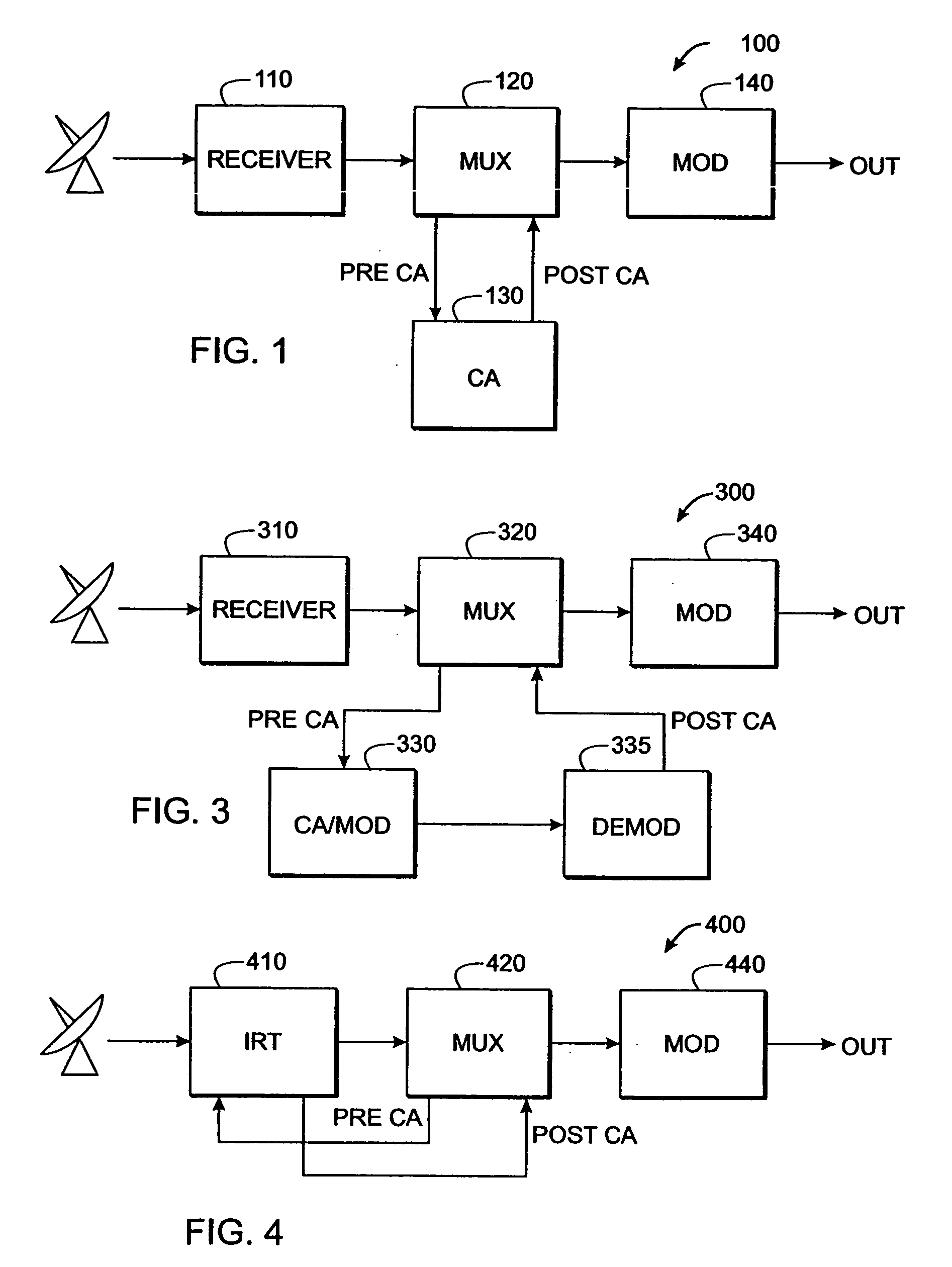
Time-multiplexed multi-program encryption system
ActiveUS20050180568A1Increase the number ofImprove throughputPulse modulation television signal transmissionSecret communicationComputer hardwareRe sequencing
A system and method are described for greatly increasing the number of services that can be encrypted with existing conditional access equipment. The method is most useful when many digitally compressed programs are encrypted at the same time. Only the most critical components of each compressed video, audio, or data stream are selected and then sequenced into a single stream. Additional formatting causes this sequence of segments from multiple sources to appear as a single continuous stream to the conditional access system. Once this stream has been encrypted, it is demultiplexed and the components are restored and re-sequenced into their respective programs. Messages such as the Entitlement Control Messages that are inserted into the stream by the encryption system, are also adjusted and included with each of the reconstructed programs. The technique not only allows encryption systems to be designed using less encryption hardware, but also simplifies the management of encryption sessions, particularly in on-demand programming applications.
Owner:IMAGINE COMM
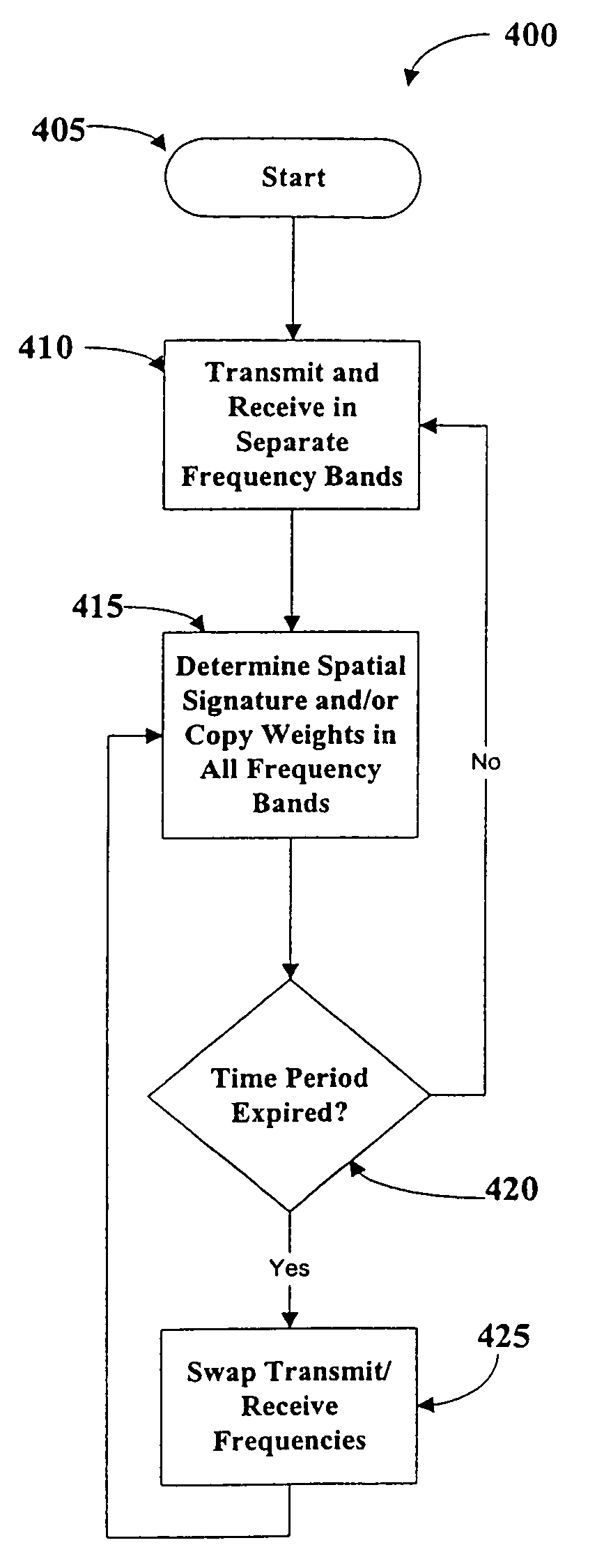
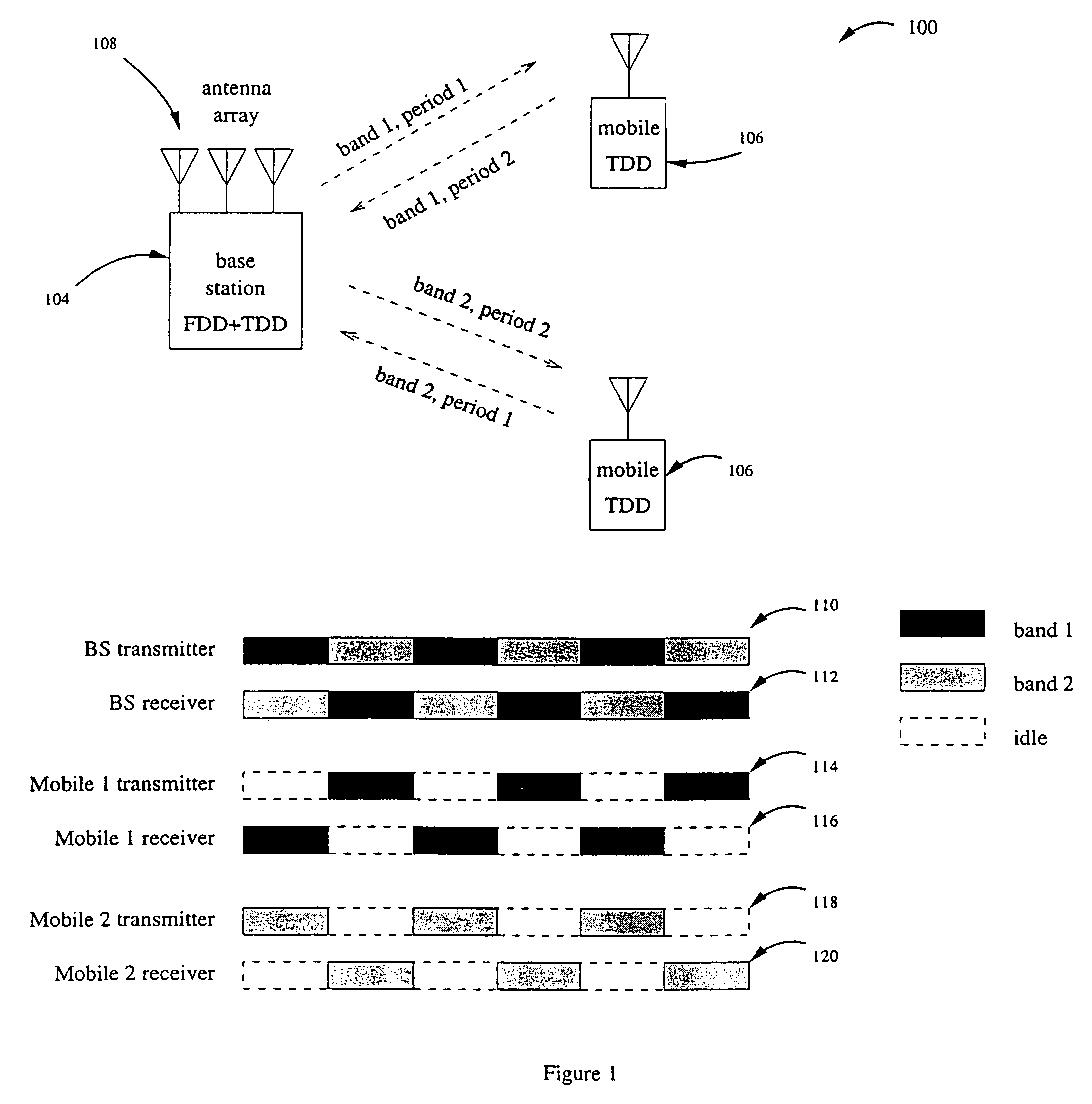
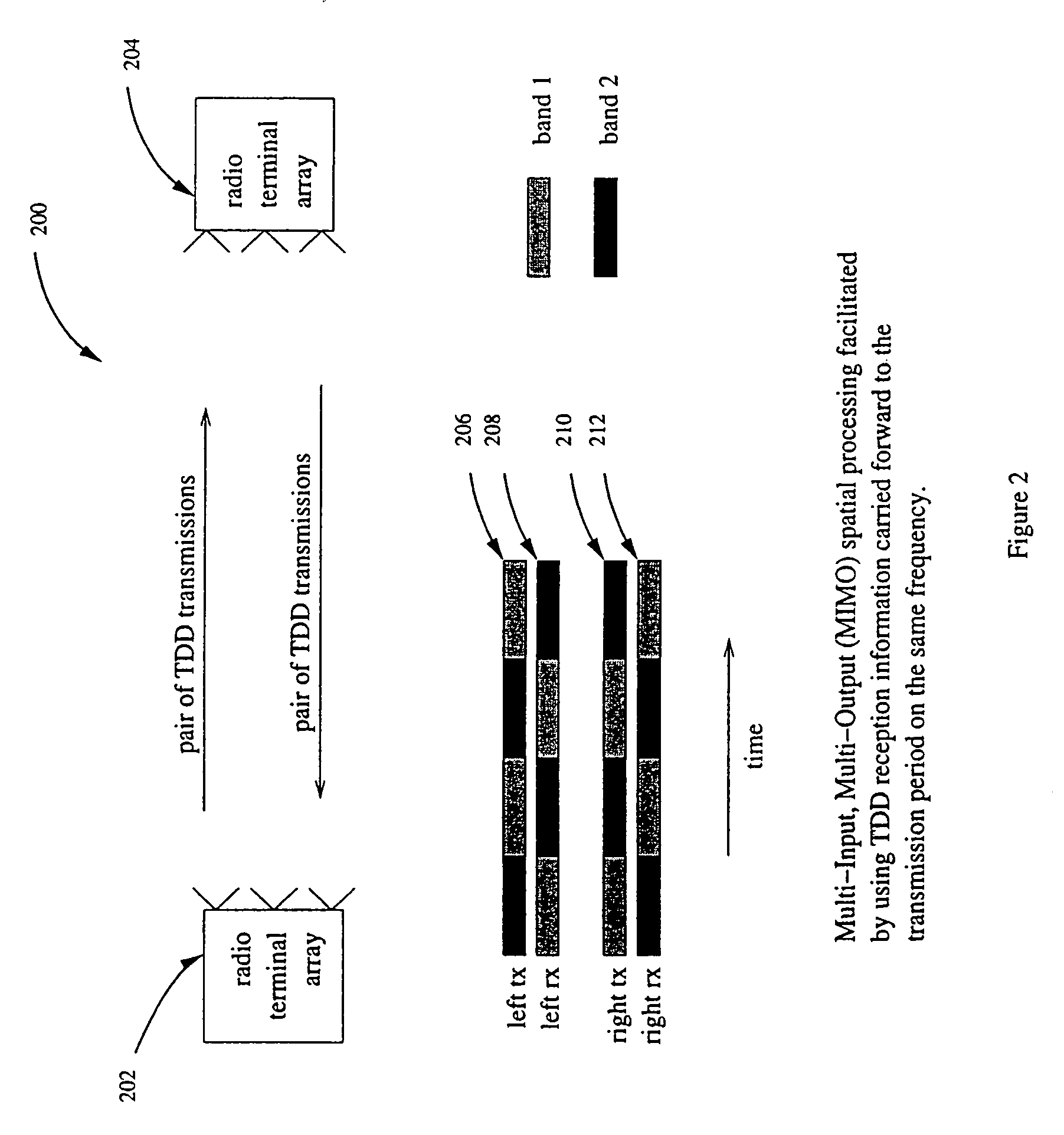
Operating time division duplex (TDD) wireless systems in paired spectrum (FDD) allocations
ActiveUS7336626B1Easy to copyIncrease profitFrequency-division multiplex detailsFrequency diversityCommunications systemTime segment
A wireless communication system operates in a combined FDD and TDD mode. During a first time period, data may be transmitted at a first frequency band and received at a second frequency band. During a second time period, data is transmitted at the second frequency band and received at the first frequency band. The first and second time periods may be of identical durations, thereby creating a 50% duty cycle. When the base station operates with multiple frequency bands, spatial processing parameters such as the spatial signature or copy weights of the mobile stations may be collected in all frequency bands, thereby allowing the full processing advantage of adaptive antenna.
Owner:TAHOE RES LTD
Method and System for Bluetooth and Wireless LAN Coexistence
A method and system for Bluetooth® and Wireless LAN coexistence may include controlling wireless local area network (WLAN) communication and Bluetooth® communication in a coexistence system that handles at least a WLAN communication protocol and a Bluetooth® communication protocol based on time division multiplexing (TDM) and adaptive frequency hopping (AFH). Switching may occur between the WLAN communication and the Bluetooth® communication based on the TDM and the AFH. In one embodiment of the invention, the switching may occur adaptively. Notwithstanding, in instances where it may be determined that AFH is disabled, switching to TDM may occur. WLAN communication and / or Bluetooth® communication may be disabled or enabled based on a state of at the WLAN communication and / or the Bluetooth® communication. Use of the AFH may be enabled or disabled based on a link status of the WLAN communication and / or the Bluetooth® communication.
Owner:AVAGO TECH INT SALES PTE LTD
Tdm based cell search method for OFDM system
ActiveUS20090196279A1Shorten the timeReduce complexityEnergy efficient ICTSynchronisation arrangementComputer hardwareCell search
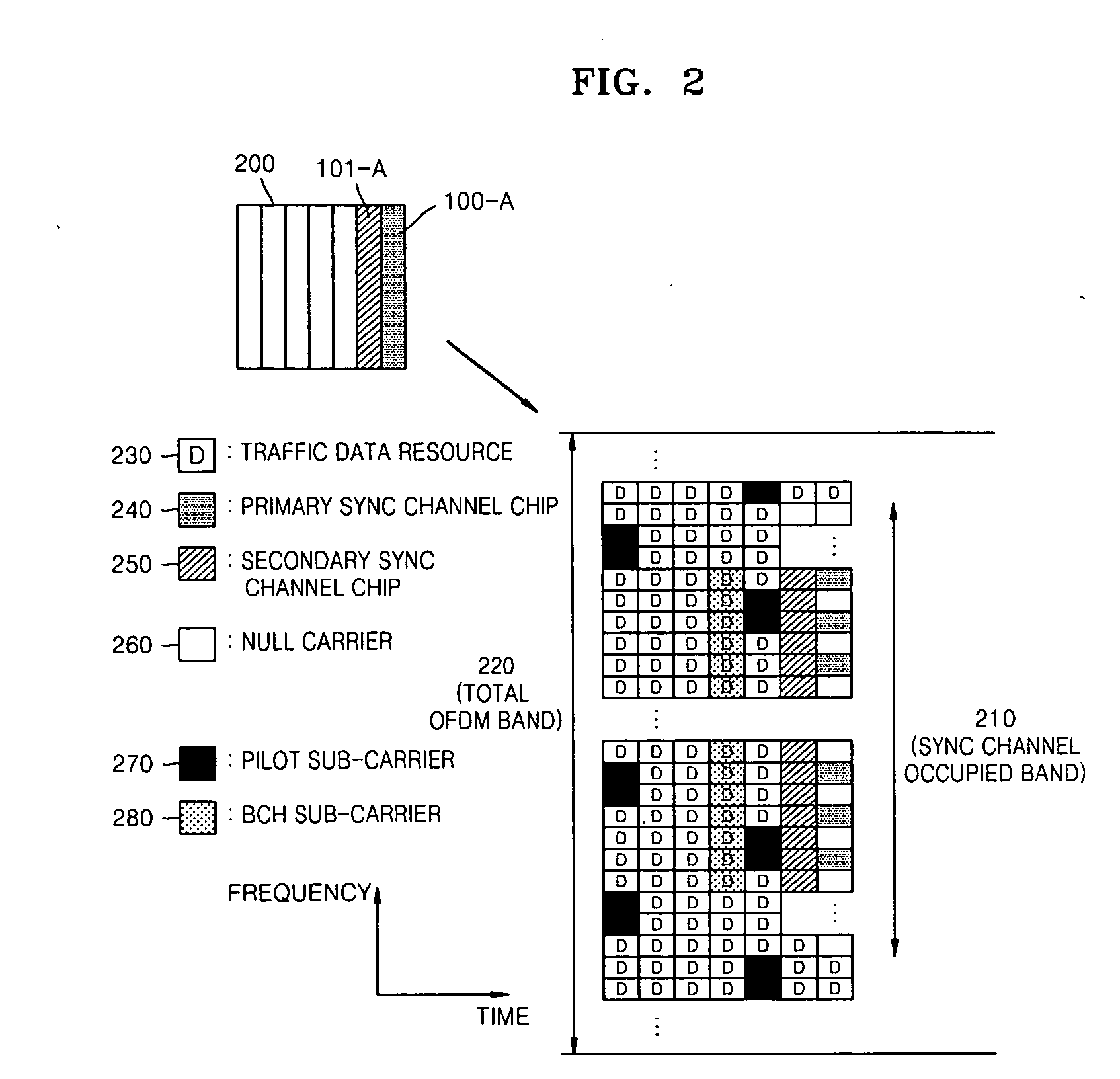
Provided are a sync channel of a forward link, a common pilot channel structure, and an initial cell search method and an adjacent cell search method for handover in a cellular system using orthogonal frequency division multiplexing (OFDM). A cell search method in an OFDM cellular system in which a primary sync channel and a secondary sync channel are configured based on time division multiplexing (TDM) includes acquiring sync block synchronization and a primary sync channel sequence number using a primary sync channel symbol included in a frame received by a terminal, detecting a boundary of the frame and a scrambling code group using the sync block and a secondary sync channel symbol included in the frame received by the terminal, and acquiring a scrambling code using the primary sync channel sequence number and the scrambling code group, thereby reducing cell search time with low complexity.
Owner:ELECTRONICS & TELECOMM RES INST +1
Base station, communication terminal, transmission method, and reception method
ActiveUS20100103901A1Guaranteed normal transmissionTransmission path divisionMultiplex communicationUser deviceBroadcast domain
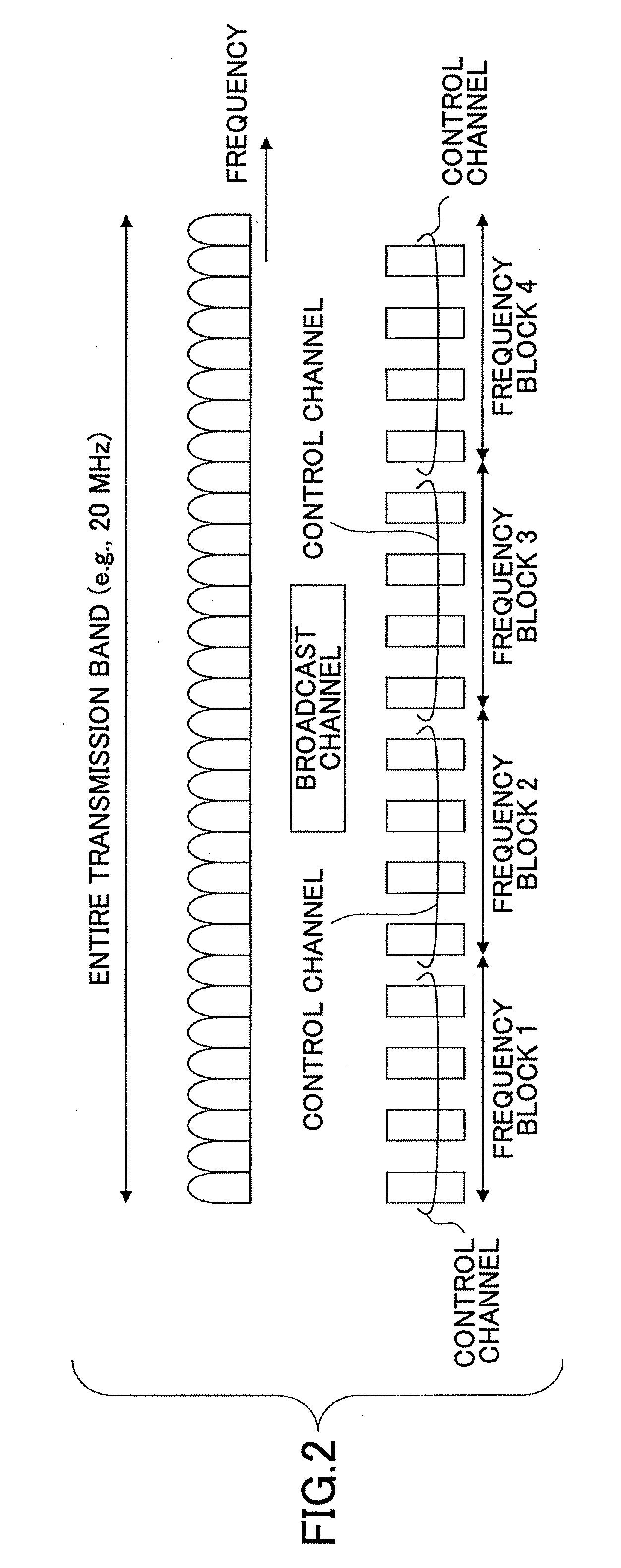
A base station includes a scheduler configured to perform frequency scheduling for each subframe; a control channel generating unit configured to generate a control channel including common control information to be mapped to radio resources distributed across a system frequency band and specific control information to be mapped to one or more resource blocks allocated to each selected user device; and a transmission signal generating unit configured to generate a transmission signal by time-division-multiplexing the common control information and the specific control information according to scheduling information from the scheduler. The common control information includes a format indicator representing one of preset options that indicates the number of symbols occupied by the common control information in one subframe. The common control information includes information units with a predetermined data size. The number of the information units is less than or equal to a specified multiplicity included in broadcast information.
Owner:NTT DOCOMO INC
Method and apparatus for transporting ethernet data packets via radio frames in a wireless metropolitan area network
InactiveUS6907048B1Improve efficiencyElectric/magnetic signal storageRadio/inductive link selection arrangementsTransceiverWireless transceiver
Method and apparatus for transporting Ethernet data packets via radio frames in a wireless metropolitan area network. A terminal includes a data packet receiver for receiving data packets for communication over a wireless link wherein not every data packet has a same length; a data packet formatting apparatus for formatting the data packets according to radio frames wherein the radio frames each have a same length and wherein the data packets are formatted into the radio frames such that boundaries for the data packets are not necessarily aligned with boundaries for the radio frames; and a wireless transceiver for communicating the radio frames over the wireless link. The packets can be Fast Ethernet packets. The terminal does not convert the Ethernet data packets into a telephony communication protocol or into an asynchronous transfer mode (ATM) protocol prior to communication of the radio frames over the wireless link. The terminal can include a data packet synchronizer for synchronizing the data packets to a clock signal associated with the radio frames. The data packets can be time-division multiplexed into the radio frames. According to another aspect, a method of transporting Ethernet data packets via radio frames includes steps of receiving Ethernet data packets wherein each data packet includes a preamble and a start-of-frame delimiter, stripping off the preamble and start-of-frame delimiter, formatting the packet data according to radio frames, including appending a synch field to the packet data, and appending a length field to the packet data.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
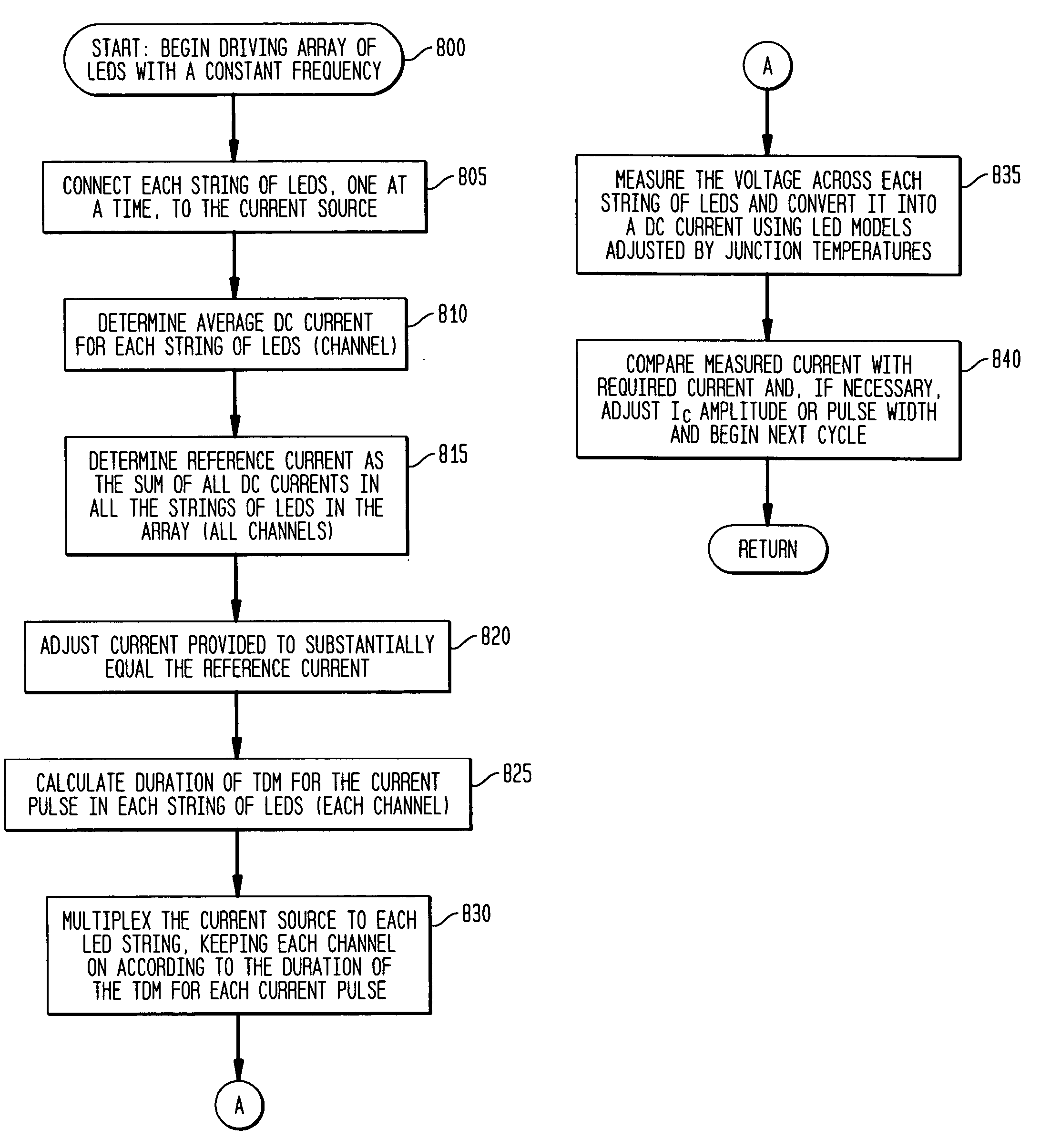
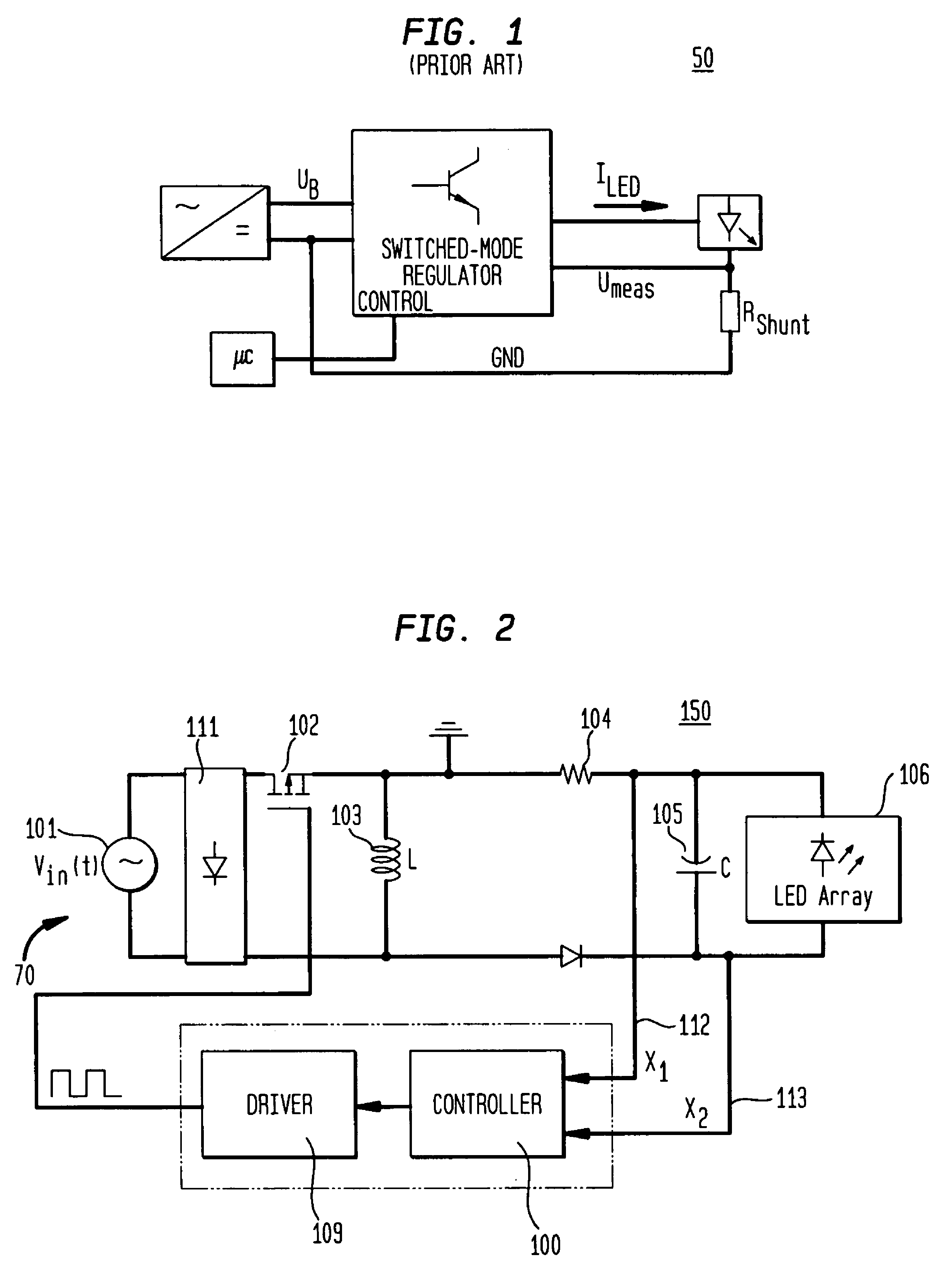
Pulsed current averaging controller with amplitude modulation and time division multiplexing for arrays of independent pluralities of light emitting diodes
ActiveUS7888881B2Improve efficiencySmall sizeElectrical apparatusElectroluminescent light sourcesSwitched currentAverage current
Exemplary embodiments provide a system, method and apparatus for regulating current in loads, such as in an array of independent pluralities of light emitting diodes (“LEDs”). An exemplary system comprises a multiplexer adapted to switch current to each independent string of LEDs; a first controller to maintain a substantially constant average current level to the plurality of LEDs; and a second controller to modulate a current amplitude and duration of time division multiplexing for each independent string of LEDs. Another aspect of the system provides for modulating the on time for switching current to maintain a substantially constant average current level and to respond and converge quickly to changing current reference levels.
Owner:CHEMTRON RES
Time division modulation with average current regulation for independent control of arrays of light emitting diodes
ActiveUS7902771B2Low costFast response timeElectrical apparatusElectroluminescent light sourcesSwitched currentAverage current
Exemplary apparatus, method and system embodiments provide for separately and independently sourcing current to a series of light emitting diodes of a plurality of series of light-emitting diodes. An exemplary apparatus comprises a power converter which generates a current, a first multiplexer, and a controller. The controller provides for sequential and separate switching of the current through the first multiplexer to each of the series of light-emitting diodes for a corresponding period of time. An average current provided by the power converter is determined as substantially equal to a sum of the corresponding currents through the plurality of series of light-emitting diodes. A total period for switching current to all of the series of light-emitting diodes is also determined. A corresponding time period for switching current to a selected corresponding series of light-emitting diodes is substantially equal to a proportion of the total period determined as a ratio of the corresponding current for the selected corresponding series of light-emitting diodes to the average current provided by the power converter.
Owner:CHEMTRON RES
Quick paging channel with reduced probability of missed page
ActiveUS20060285485A1Secret communicationMulti-frequency code systemsCommunications systemForward error correction
A quick paging channel in a random access wireless communication system includes at least one bit in a quick paging frame identifying the presence of a paging message for an access terminal or group of access terminals. The quick paging bits identifying the presence of a paging message for a first access terminal is encoded with one or more quick paging bits corresponding to one or more additional access terminals to produce one or more forward error correction bits. The jointly encoded quick paging bits are broadcast to the access terminals by time division multiplexing the quick paging frame with additional frames of information.
Owner:QUALCOMM INC
Portable programming device for supervisory remote control system
InactiveUS6546435B1Readily and efficiently correctedAvoid it happening againTelemetry/telecontrol selection arrangementsComputer controlDisplay deviceHand held
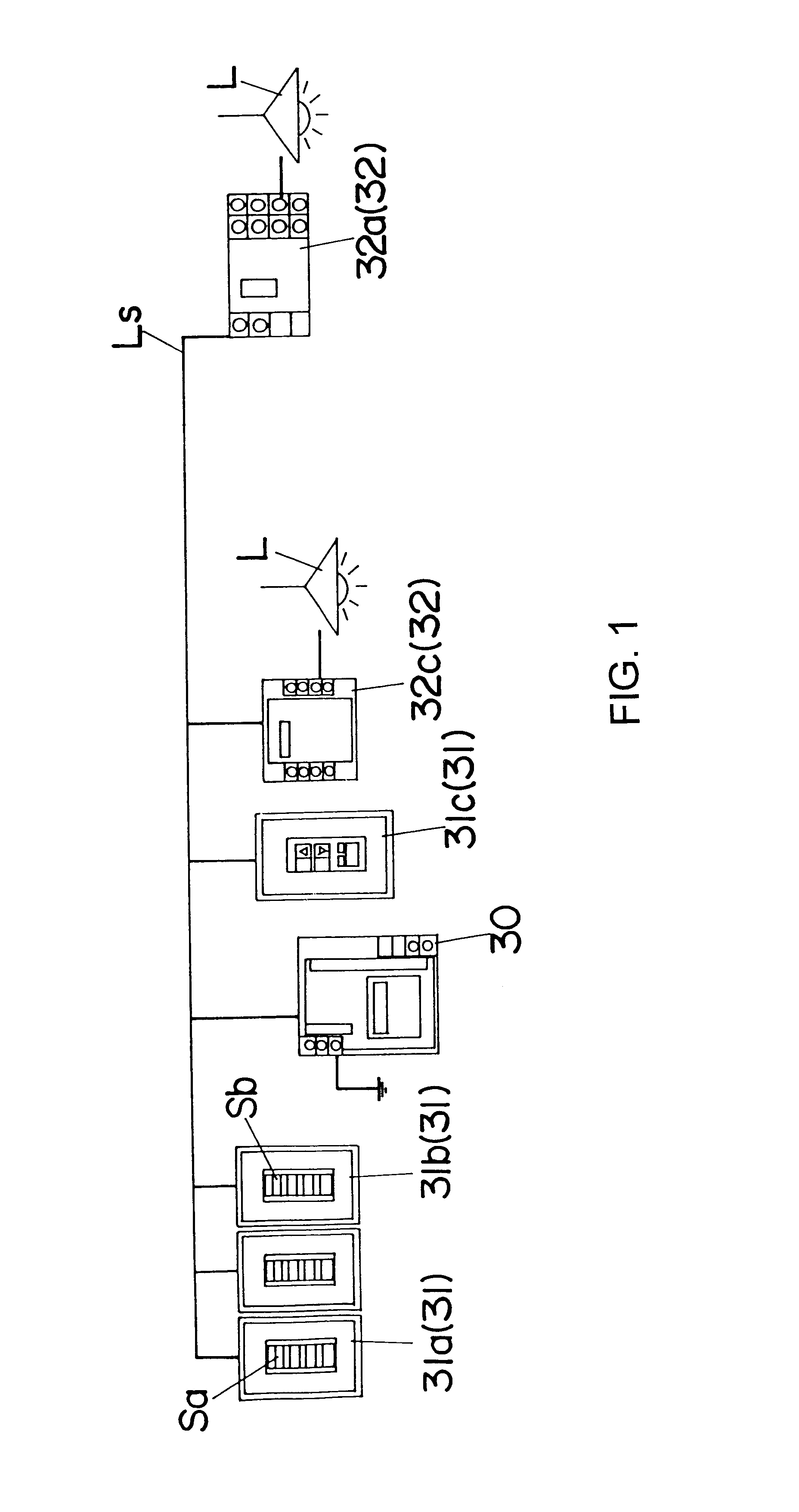
A portable programming device is used in a supervisory remote control system comprising a signal transmission unit for supplying a signal according to a TDM (Time Division Multiplexing) manner, first and second terminals having individual addresses, and a signal line connecting therebetween. According to a set of relation data including an address correspondence between one of the second terminals and one of the first terminals and control data including control parameters of a load, the load connected to the one of the second terminals can be controlled according to a supervisory input provided to the one of the first terminals. The programming device has a hand-held type housing for accommodating a display, operation unit for programming an address, the relation data and the control data, data memory, and a signal processor for transferring the address to a required one of the first and second terminals, and transferring the relation data and the control data stored in the data memory to the transmission unit. The signal processor further comprises a data retrieving unit for retrieving at least one set of the relation data and the control data corresponding to an address designated by the operation unit from the transmission unit, and listing a name given to the set on the display.
Owner:MATSUSHITA ELECTRIC WORKS LTD
Method and an apparatus for determining the radio frame structure of time division duplex system
ActiveUS20100246456A1Improve interferenceFlexible supportSynchronisation arrangementTime-division multiplexEngineeringTime-division multiplexing
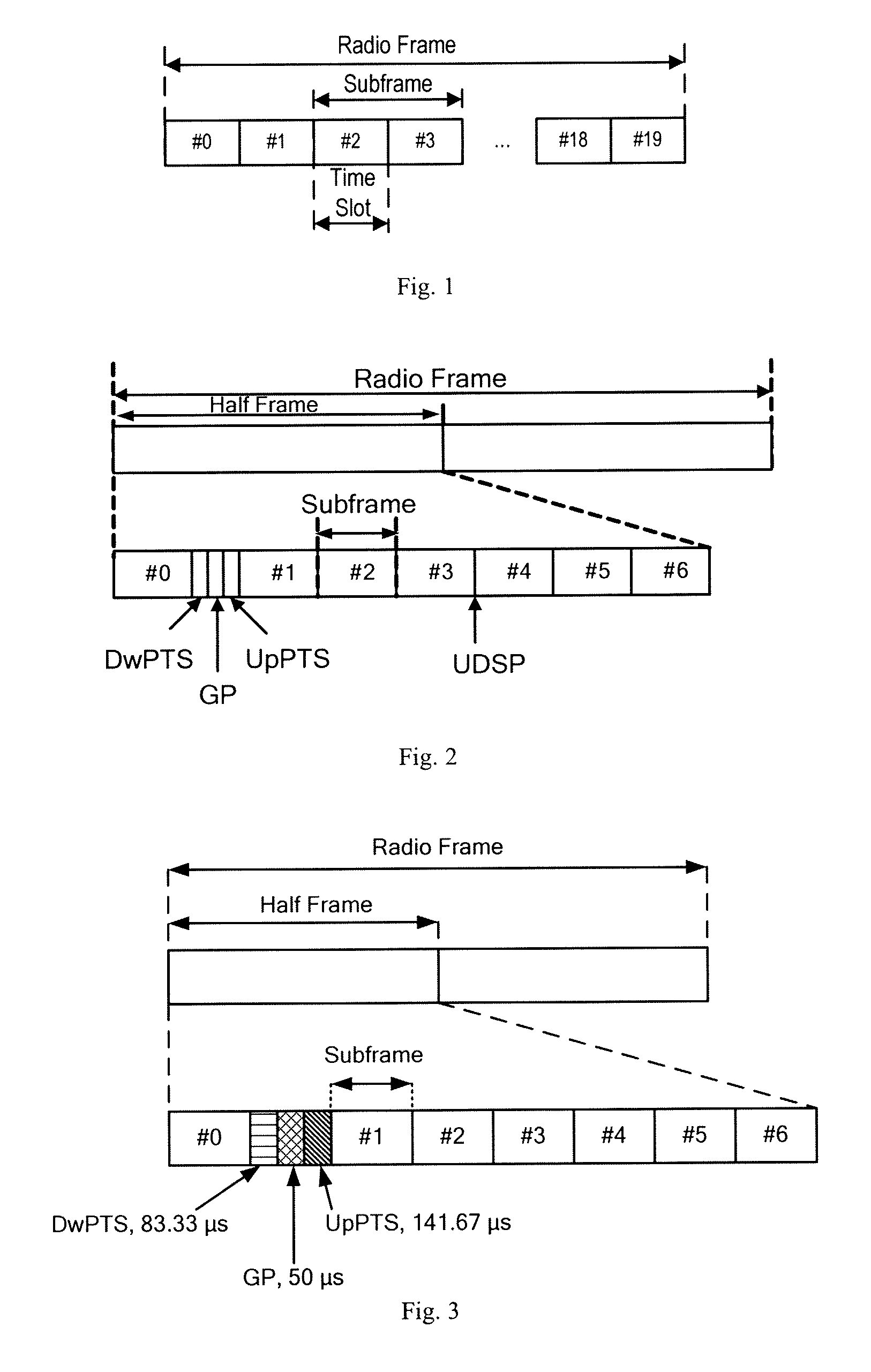
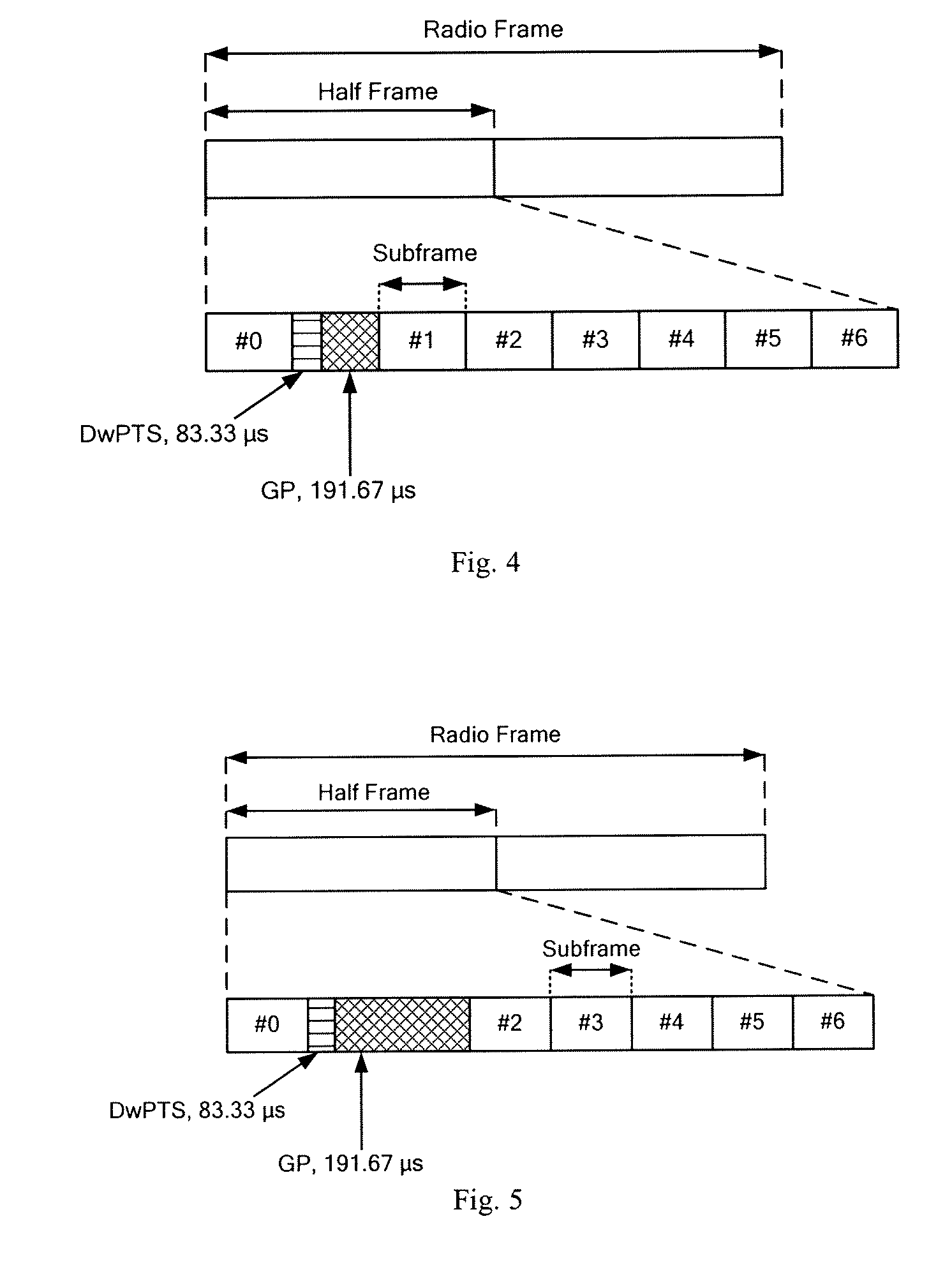
A method for determining the radio frame structure of a Time Division Duplex system is disclosed, which comprises: configuring, by the network side, the radio frame structure used for service transmission as containing two half-frames each of 5 ms, wherein each half-frame consists of eight service time slots of 0.5 ms and one special time slot field of 1 ms, two consecutive service time slots form a subframe of which the length is 1 ms, and the special time slot field contains a DwPTS, a GP and an UpPTS; determining the lengths of the DwPTS, the GP and the UpPTS in the special time slot field according to the requirements of the coverage range, and determining the radio frame structure used for service transmission. By reconfiguring the radio frame structure, the invention can flexibly support different coverage ranges, enhance the flexibility of satisfying different service requirements, and implement the coexistence of two types of TDD systems.
Owner:DATANG MOBILE COMM EQUIP CO LTD
Point-to-multipoint passive optical network that utilizes variable-length packets
InactiveUS7031343B1Reduce transmission overheadRemoves distance limitationMultiplex system selection arrangementsTime-division multiplexVariable lengthTime-division multiplexing
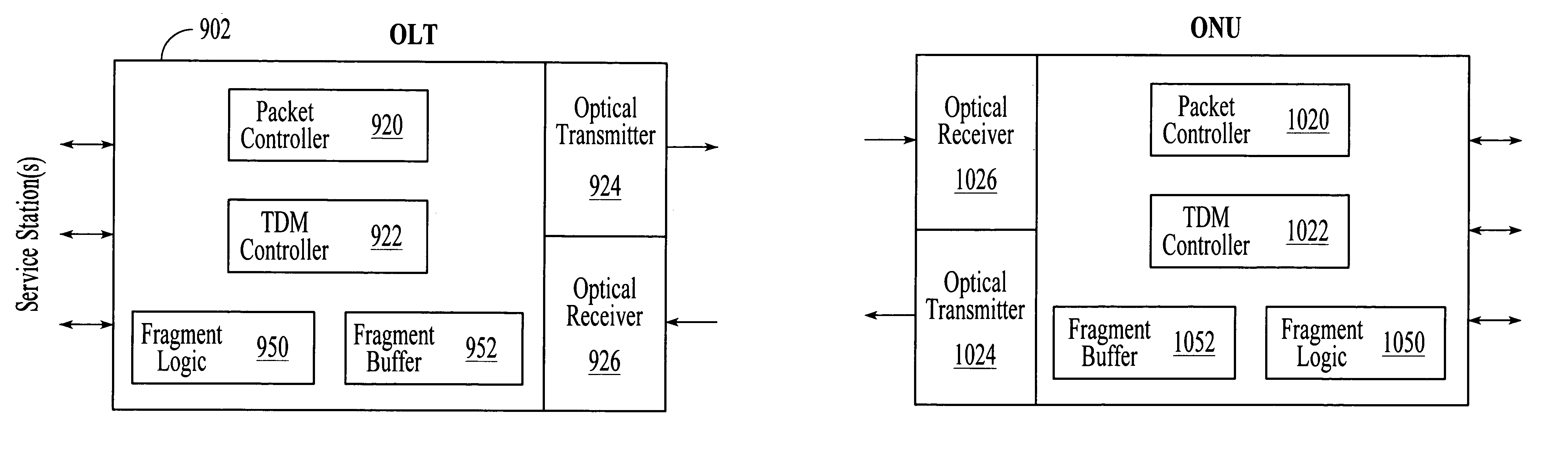
A point-to-multipoint passive optical network transmits downstream data from an optical line terminal (OLT) to multiple optical network units (ONUs) in variable-length packets and upstream data from the ONUs to the OLT in variable-length packets utilizing time division multiplexing to avoid transmission collisions. In an embodiment, the variable-length downstream packets and the variable-length upstream packets are formatted according to IEEE 802.3. In an embodiment, the length of the variable-length downstream and upstream packets is related to the length of Internet protocol (IP) datagrams carried within the packets.
Owner:FUTUREWEI TECH INC
Method and apparatus for multiplexing audio program channels from one or more received broadcast streams to provide a playlist style listening experience to users
ActiveUS20100268361A1Metadata audio data retrievalReceiver side switchingPersonalizationRadio channel
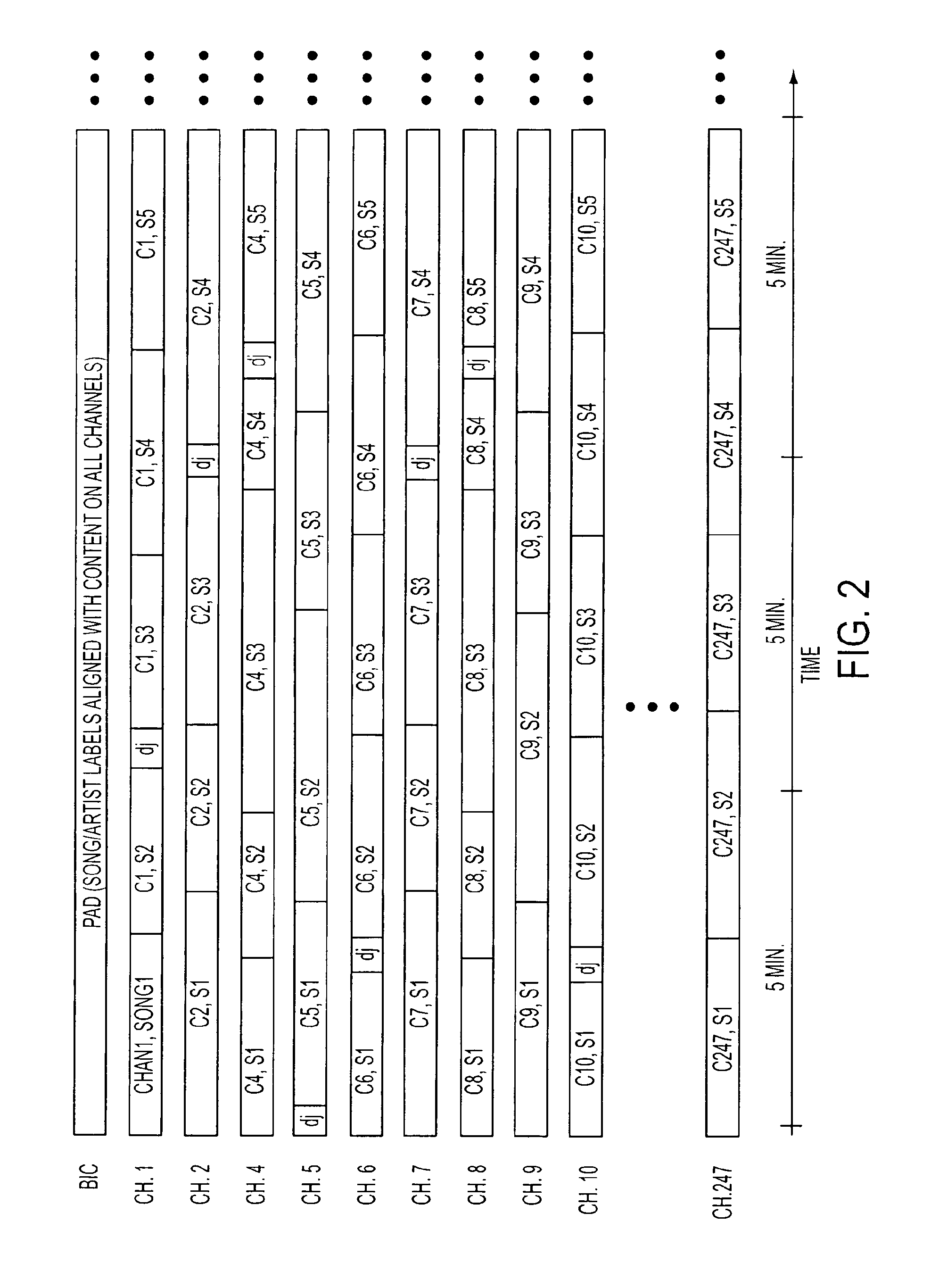
A method and apparatus for generating a personalized radio channel playlist by time division multiplexing songs from multiple received channels from one or more broadcast source streams in a queue. Users can specify favorite channels for building their personal playlists, or multiple default playlist channels can be provided by genre. If matches are found, the channel carrying the favorite is extracted and added to the playlist. Channel searching for matches involves monitoring real-time song and artist labels for all channels carried in a separate data channel. Preview times can vary depending on the size of the playlist or number of channels used. During a preview of a segment, users can, opt to listen to the full song or back up in the playlist to listen to a previous song. Connectivity options and web interfaces are provided to facilitate transfer and sharing of customization parameters for personalized radio configuration.
Owner:SIRIUS XM RADIO INC
Time-division multiplexed link for use in a service area network
ActiveUS6985502B2Multiplex system selection arrangementsWavelength-division multiplex systemsArea networkStorage area network
A data transmission system uses a method of aligning a plurality of transmission lanes with a plurality of reception lanes in a time-division multiplexing arrangement. The method utilizes a plurality of control symbols and lane identifiers that are transmitted on each of the transmission lanes during link initialization and training. The control symbols and lane identifiers are time-division multiplexed onto a data link and subsequently demultiplexed onto the plurality of reception lanes. One of the reception lanes is monitored for receipt of a control symbol followed by a lane identifier. Upon receipt, a lane identifier is compared to the identity of the reception lane being monitored. If the received lane identifier does not match the identity of the reception lane being monitored, the assignment of the reception lanes is rotated.
Owner:HEWLETT-PACKARD ENTERPRISE DEV LP
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com