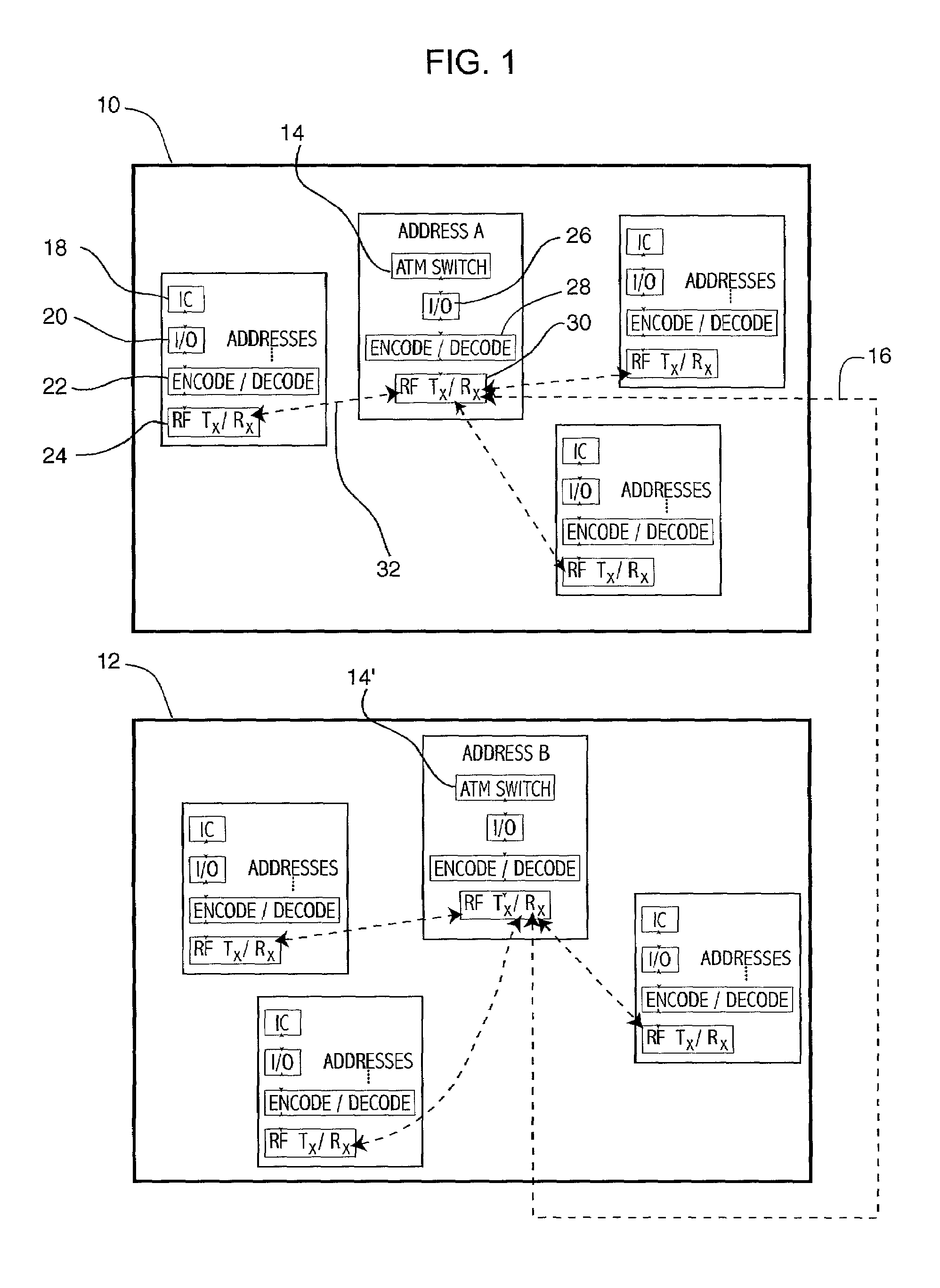
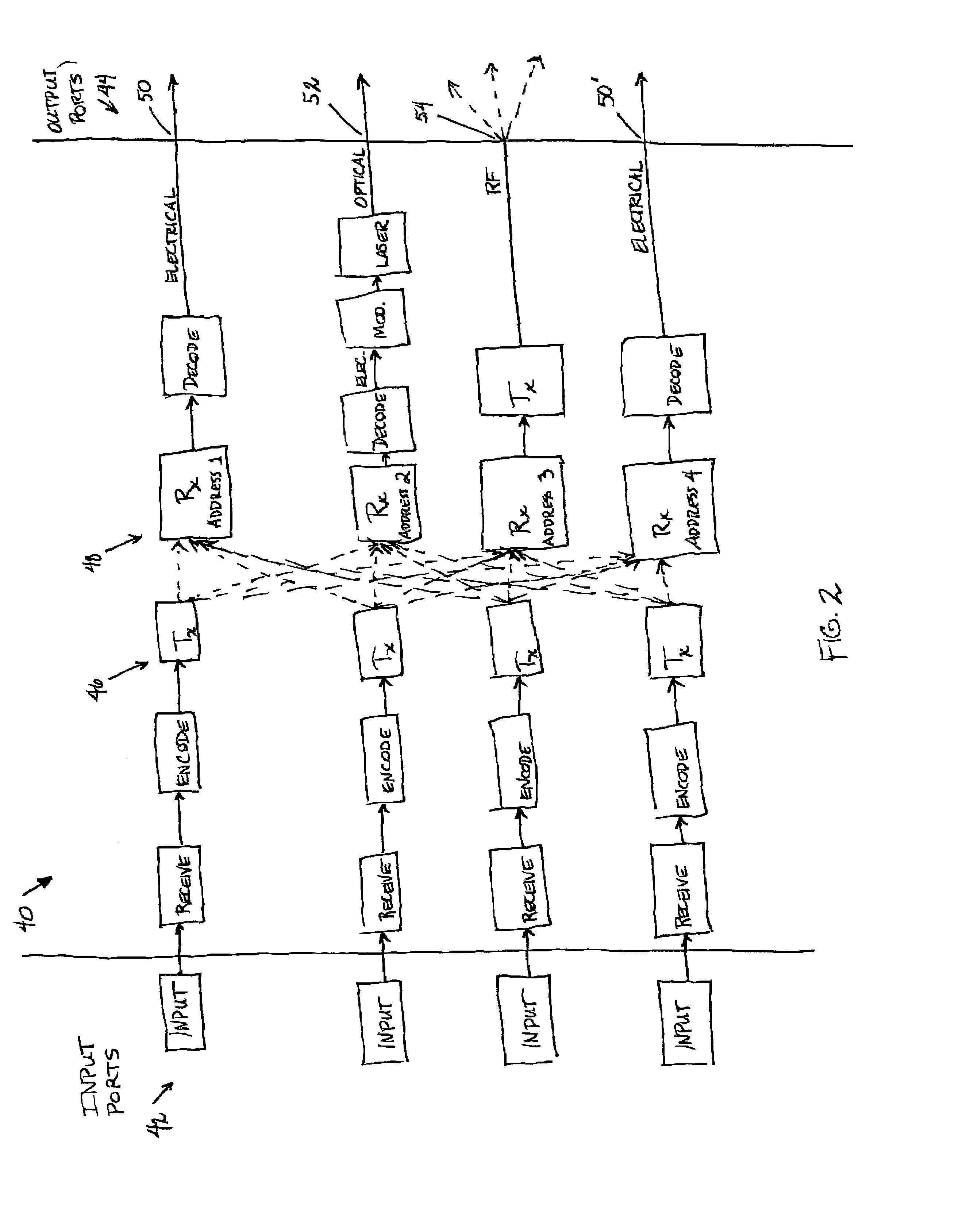
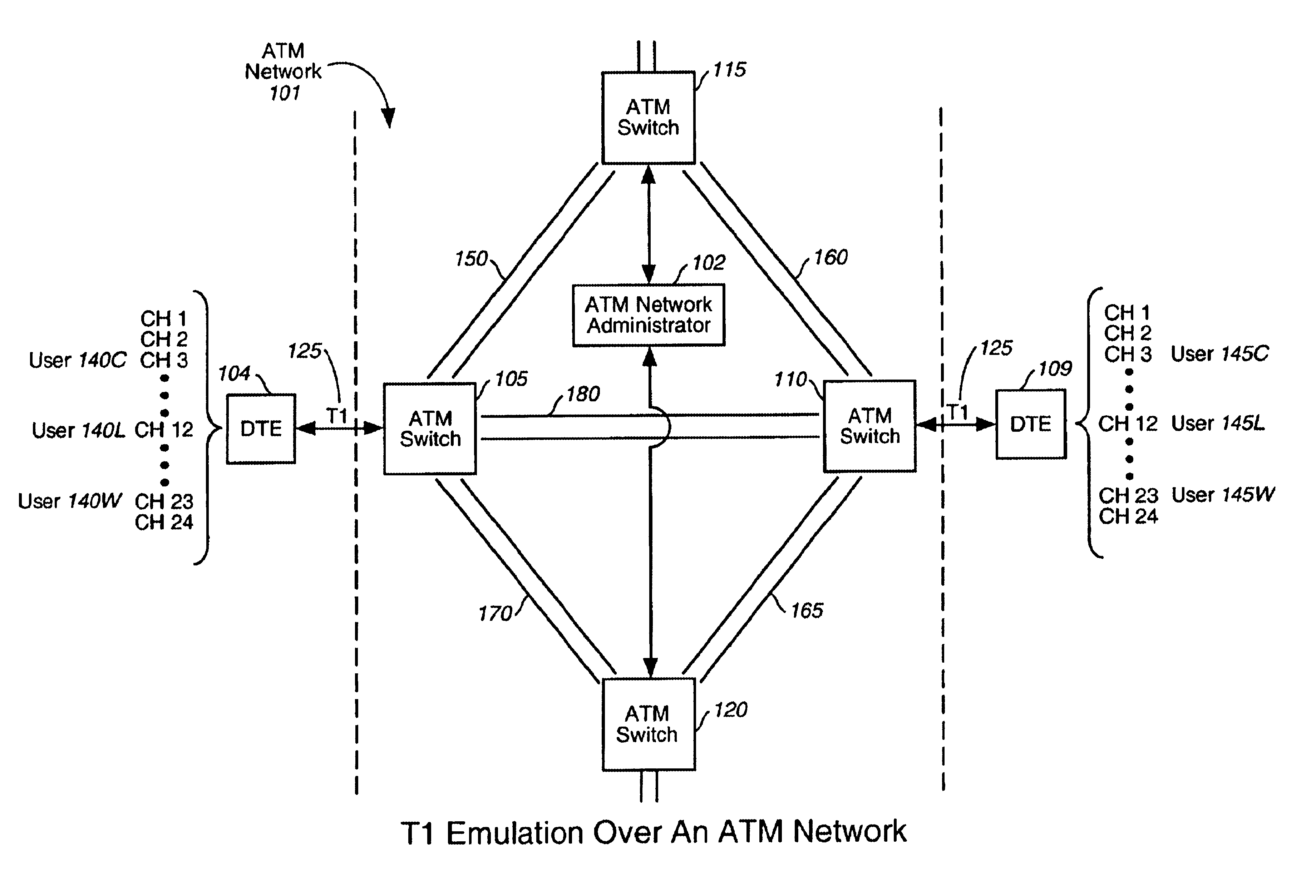
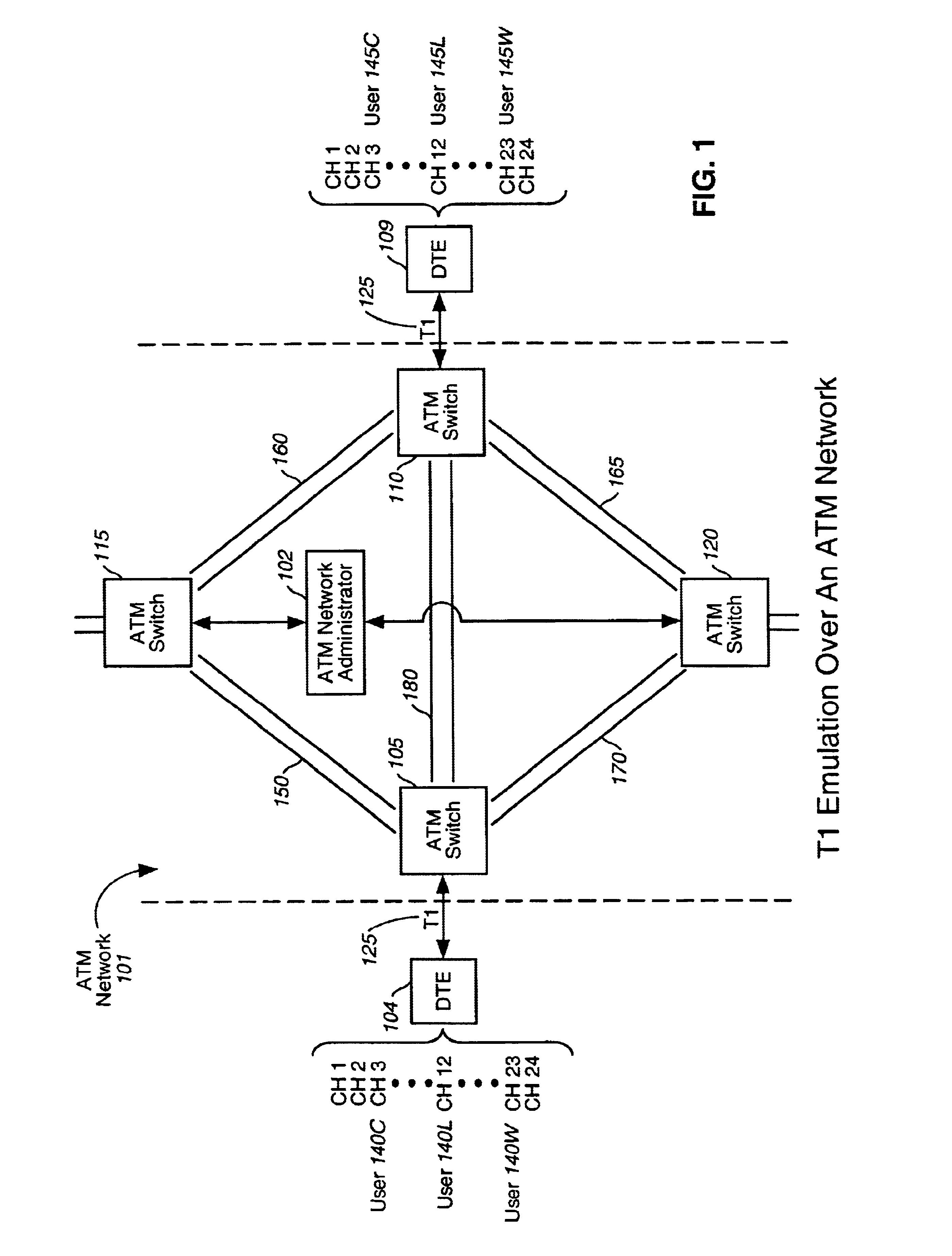
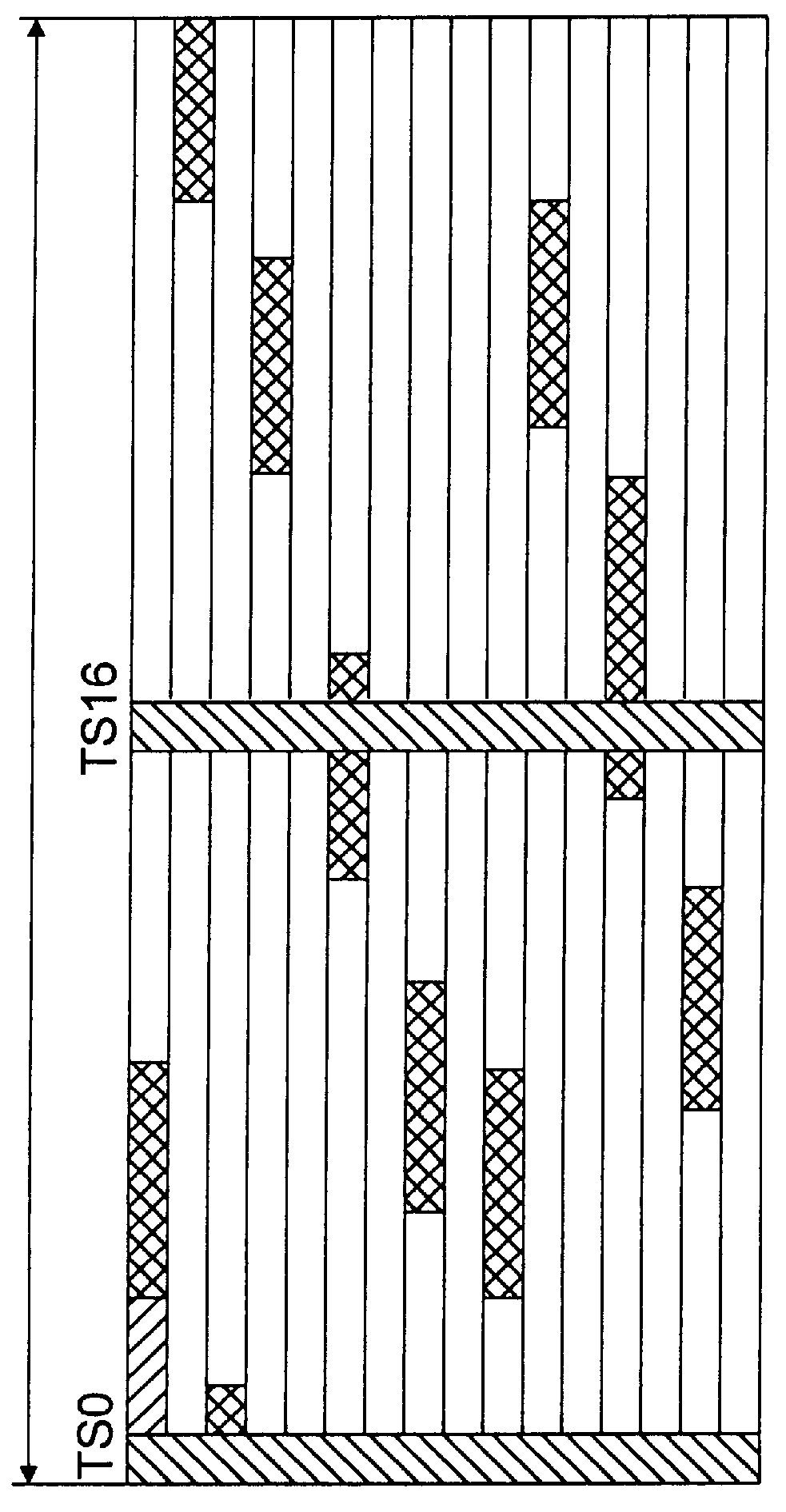
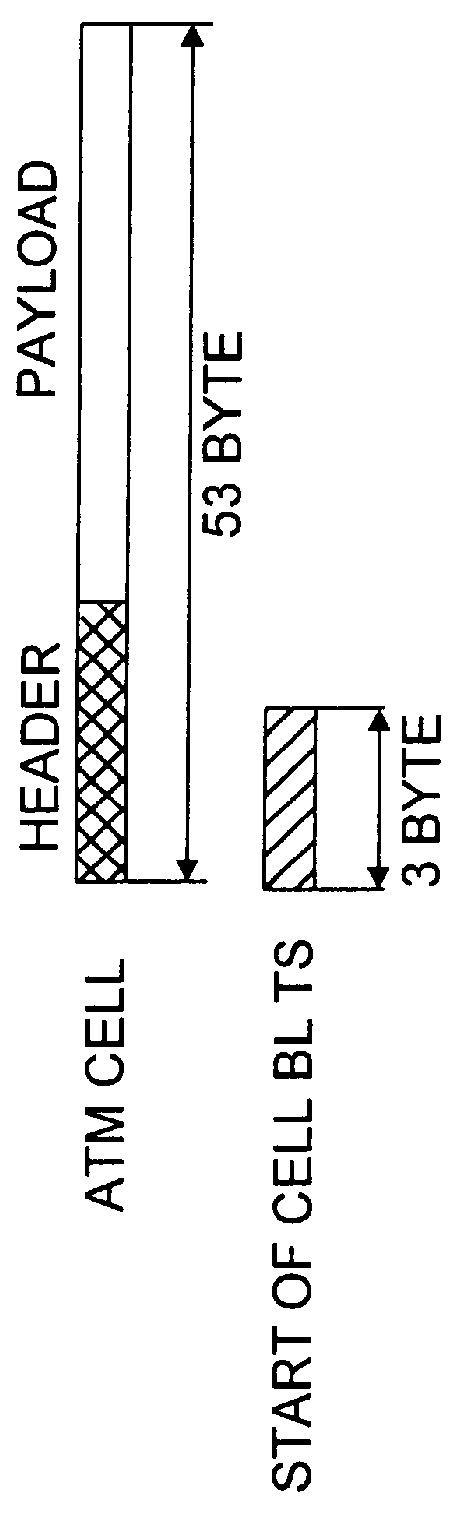
Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
503 results about "Asynchronous Transfer Mode" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
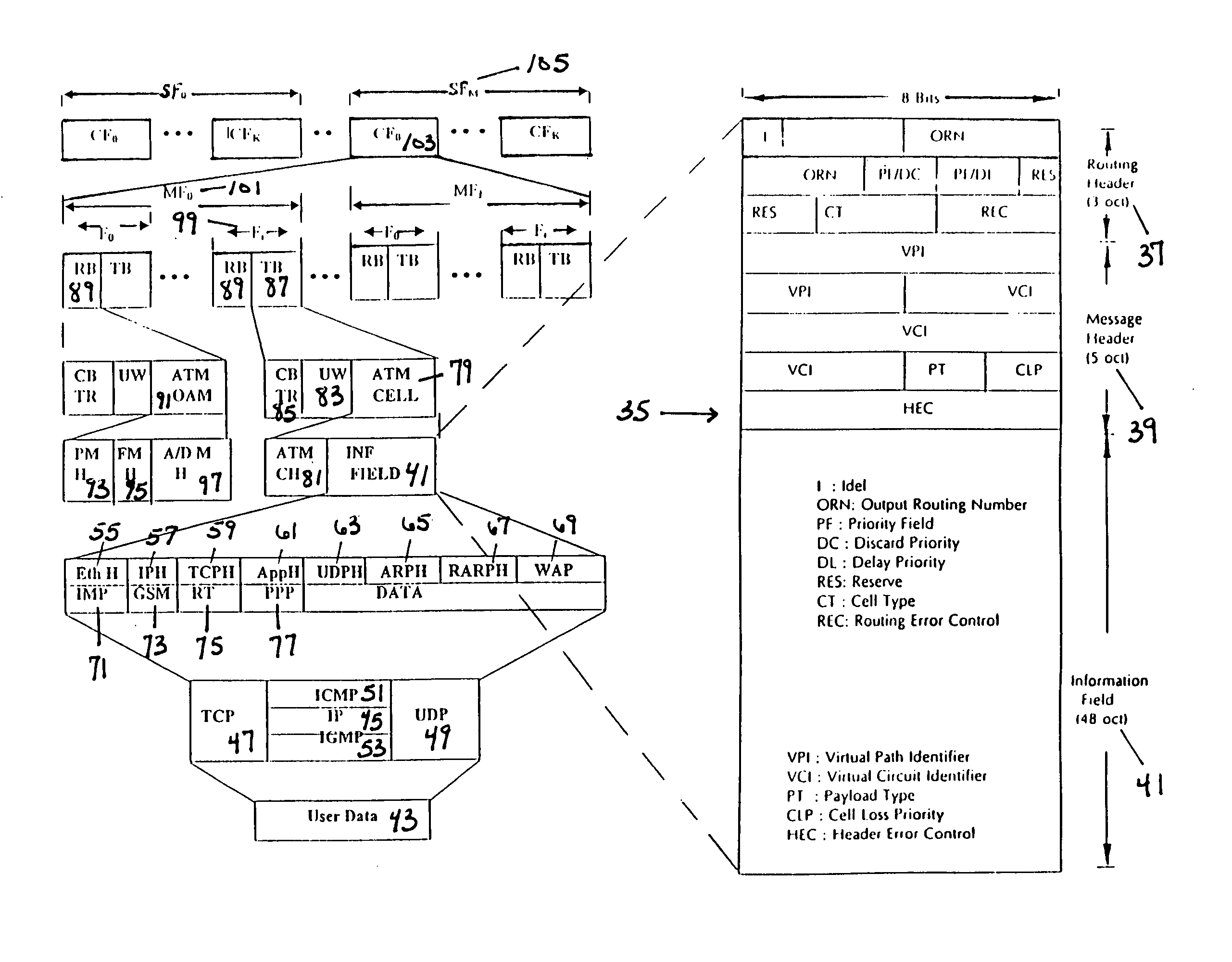
Asynchronous Transfer Mode (ATM) is a telecommunications standard defined by ANSI and ITU (formerly CCITT) standards for carriage of user traffic, including telephony (voice), data, and video signals. ATM was developed to meet the needs of the Broadband Integrated Services Digital Network, as defined in the late 1980s, and designed to integrate telecommunication networks. Additionally, it was designed for networks that must handle both traditional high-throughput data traffic (e.g., file transfers), and real-time, low-latency content such as voice and video. The reference model for ATM approximately maps to the three lowest layers of the ISO-OSI reference model: network layer, data link layer, and physical layer. ATM is a core protocol used over the SONET/SDH backbone of the public switched telephone network (PSTN) and Integrated Services Digital Network (ISDN), but its use is declining in favour of all IP.
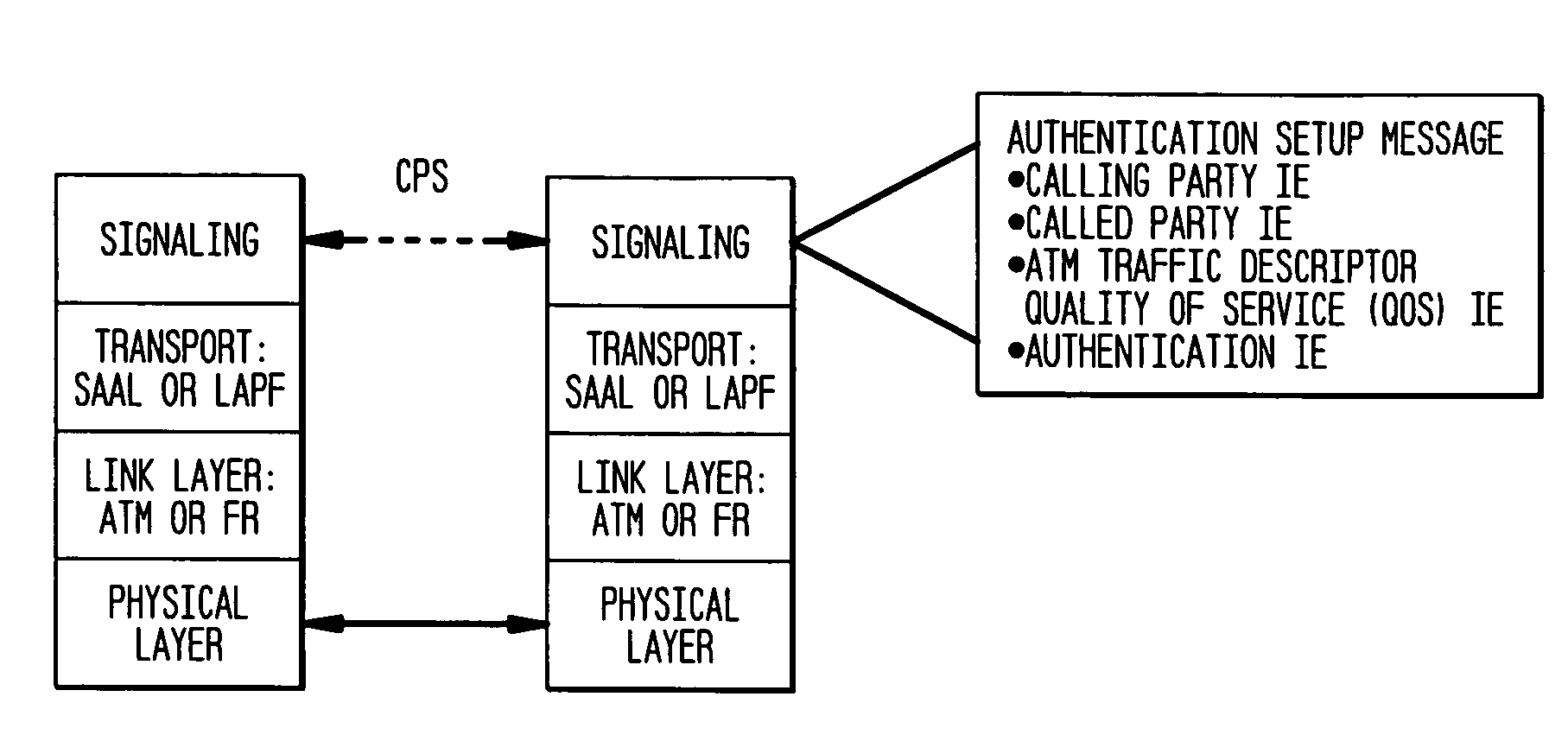
Authentication mechanisms for call control message integrity and origin verification
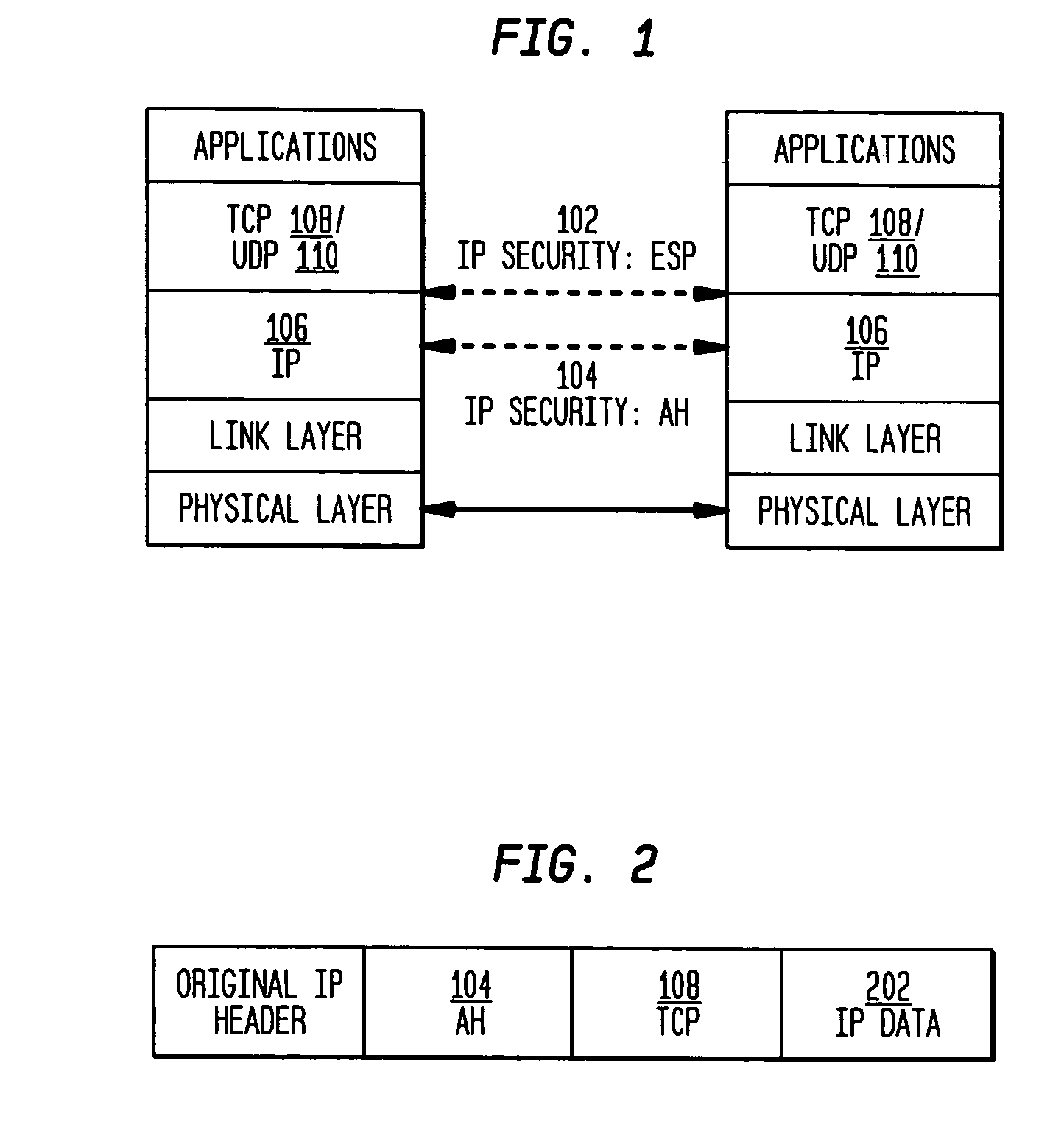
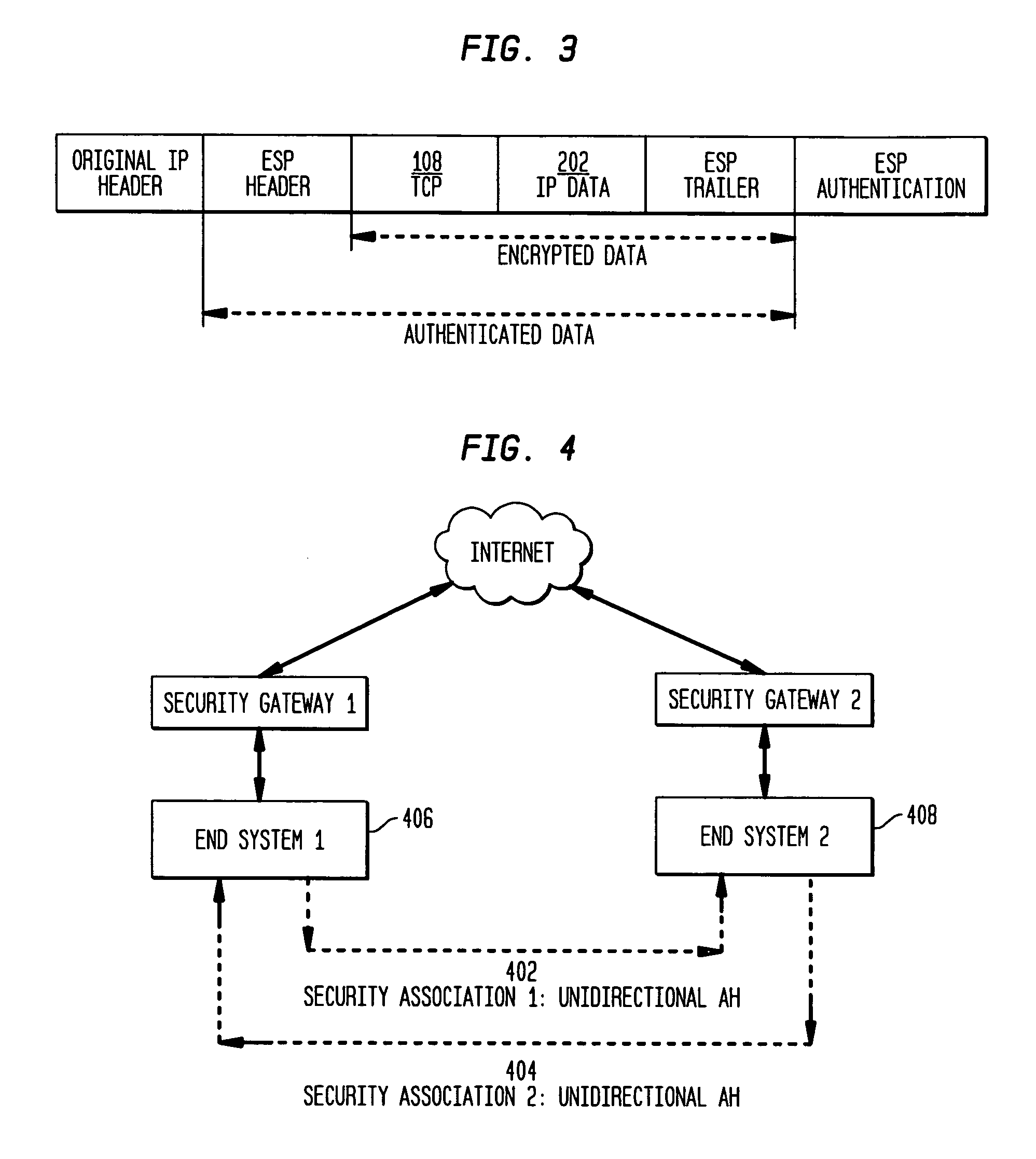
The present invention incorporates methodologies developed in the Internet Engineering Task Force (IETF) Internet Protocol Security (IPSEC) Working Group into asynchronous transfer mode (ATM) and frame relay (FR) signaling to provide message integrity and origin authentication. In one implementation the invention provides a virtual private network (VPN) infrastructure with call control message integrity, origin verification, and transit network filtering. The invention utilizes a set of control plane messages based on the IPSEC authentication header (AH) methodology to provide these security mechanisms for ATM and FR network switching equipment and signaling protocols. This abstract itself is not intended to limit the scope of this patent. The scope of the present invention is pointed out in the appending claims.
Owner:ALCATEL-LUCENT USA INC
Error coding in asynchronous transfer mode, internet and satellites
InactiveUS7190681B1Big impactEasily threshold decodableError detection/correctionTime-division multiplexThree levelSystems design
The transmission of ATM, Internet, and satellite communications is unified through international standardized protocol embedment. Global and Local performance optimization are achieved through the combination of combinatorial, dynamic, and probabilistic programming. A simultaneous domino effect of bandwidth conservation, efficiency enhancement, reliability improvement, traffic congestion prevention, delay minimization, and speed multiplication are realized for any digital communication system, particular in Internet. With three levels of error coding in ATM cells, the loss cell recovery and bit integrity are preserved. From its mathematical roots, new combinatorial sets are systematically generated, and applications of the sets are identified. Among the applications, optimal sequences can be produced for multi-user and multi-function communication system designs. Optimality is in terms of maximum possible number of sequences with given sequence length and sequence characteristics. The results are unique and theoretically proven. By serial and parallel concatenation of error codecs, reliability of multimedia transmission can be satisfied to any desirable level. As a part of the unified transmission scheme, the acquisition and synchronization method of cascading sequences exhibits significant improvement in correlation properties and detection probabilities. A method of using block designs is demonstrated to derive, to generate, and to construct low-density parity check block codes and threshold decodable convolutional codes. An efficiency evaluation method is formulated for the combination operation of ATM, Internet, and satellites.
Owner:WU WILLIAM W
Method and apparatus for transporting ethernet data packets via radio frames in a wireless metropolitan area network
InactiveUS6907048B1Improve efficiencyElectric/magnetic signal storageRadio/inductive link selection arrangementsTransceiverWireless transceiver
Method and apparatus for transporting Ethernet data packets via radio frames in a wireless metropolitan area network. A terminal includes a data packet receiver for receiving data packets for communication over a wireless link wherein not every data packet has a same length; a data packet formatting apparatus for formatting the data packets according to radio frames wherein the radio frames each have a same length and wherein the data packets are formatted into the radio frames such that boundaries for the data packets are not necessarily aligned with boundaries for the radio frames; and a wireless transceiver for communicating the radio frames over the wireless link. The packets can be Fast Ethernet packets. The terminal does not convert the Ethernet data packets into a telephony communication protocol or into an asynchronous transfer mode (ATM) protocol prior to communication of the radio frames over the wireless link. The terminal can include a data packet synchronizer for synchronizing the data packets to a clock signal associated with the radio frames. The data packets can be time-division multiplexed into the radio frames. According to another aspect, a method of transporting Ethernet data packets via radio frames includes steps of receiving Ethernet data packets wherein each data packet includes a preamble and a start-of-frame delimiter, stripping off the preamble and start-of-frame delimiter, formatting the packet data according to radio frames, including appending a synch field to the packet data, and appending a length field to the packet data.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
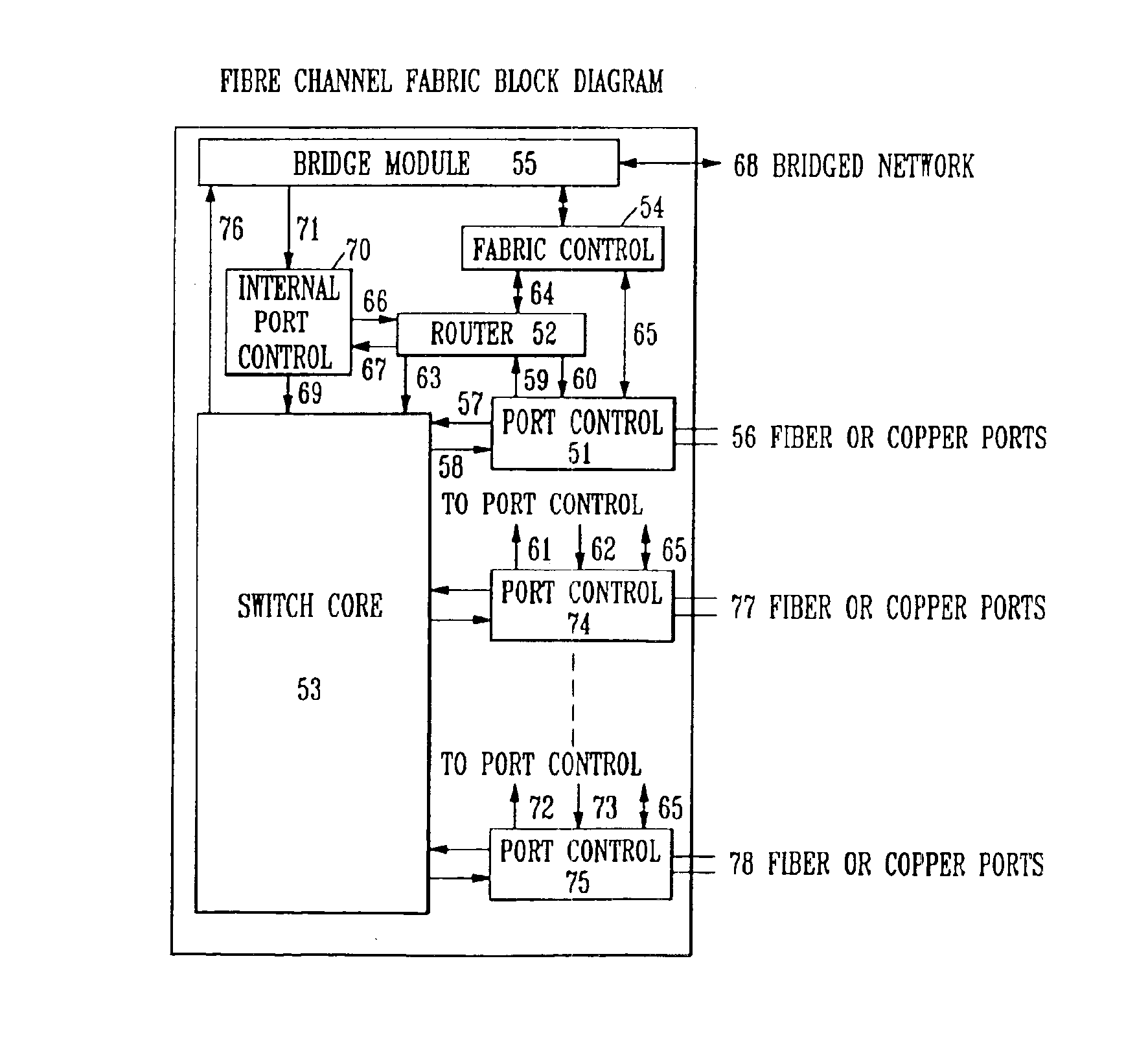
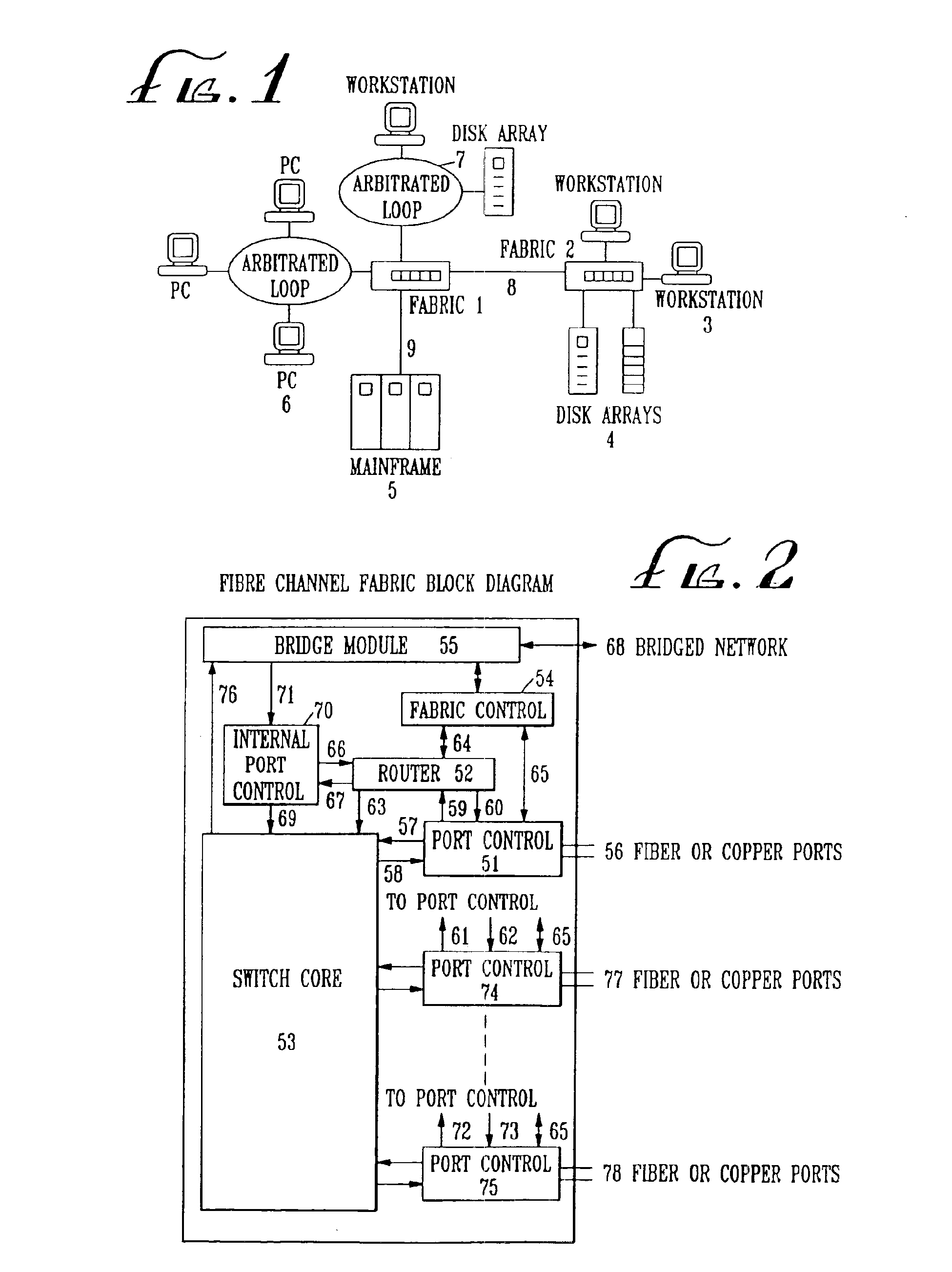
Fibre Channel switching fabric
The Fibre. Channel standard was created by the American National Standard for Information Systems (ANSI) X3T11 task group to define a serial I / O channel for interconnecting a number of heterogeneous peripheral devices to computer systems as well as interconnecting the computer systems themselves through optical fiber and copper media at gigabit speeds (i.e., one billion bits per second). Multiple protocols such as SCSI (Small Computer Serial Interface), IP (Internet Protocol), HIPPI, ATM (Asynchronous Transfer Mode) among others can concurrently utilize the same media when mapped over Fibre Channel. A Fibre Channel Fabric is an entity which transmits Fibre Channel frames between connected Node Ports. The Fibre Channel fabric routes the frames based on the destination address as well as other information embedded in the Fibre Channel frame header. Node Ports are attached to the Fibre Channel Fabric through links.
Owner:AVAGO TECH WIRELESS IP SINGAPORE PTE
Localized radio frequency communication using asynchronous transfer mode protocol
InactiveUS7257093B1High-speed and noise-free connectionImprove cooling effectPrinted circuit aspectsRadio transmissionCommunications systemTransceiver
A localized wireless communication system for communication between a plurality of circuit boards, and between electronic components on the circuit boards. Transceivers are located on each circuit board and electronic component. The transceivers communicate with one another over spread spectrum radio frequencies. An asynchronous transfer mode protocol controls communication flow with asynchronous transfer mode switches located on the circuit boards.
Owner:SANDIA NAT LAB
Method, apparatus and computer program product for interfacing a TDM link with a cell-switched network
InactiveUS6633566B1Efficient use ofAvoid changeMultiplex system selection arrangementsTime-division multiplexTime domainComputer network
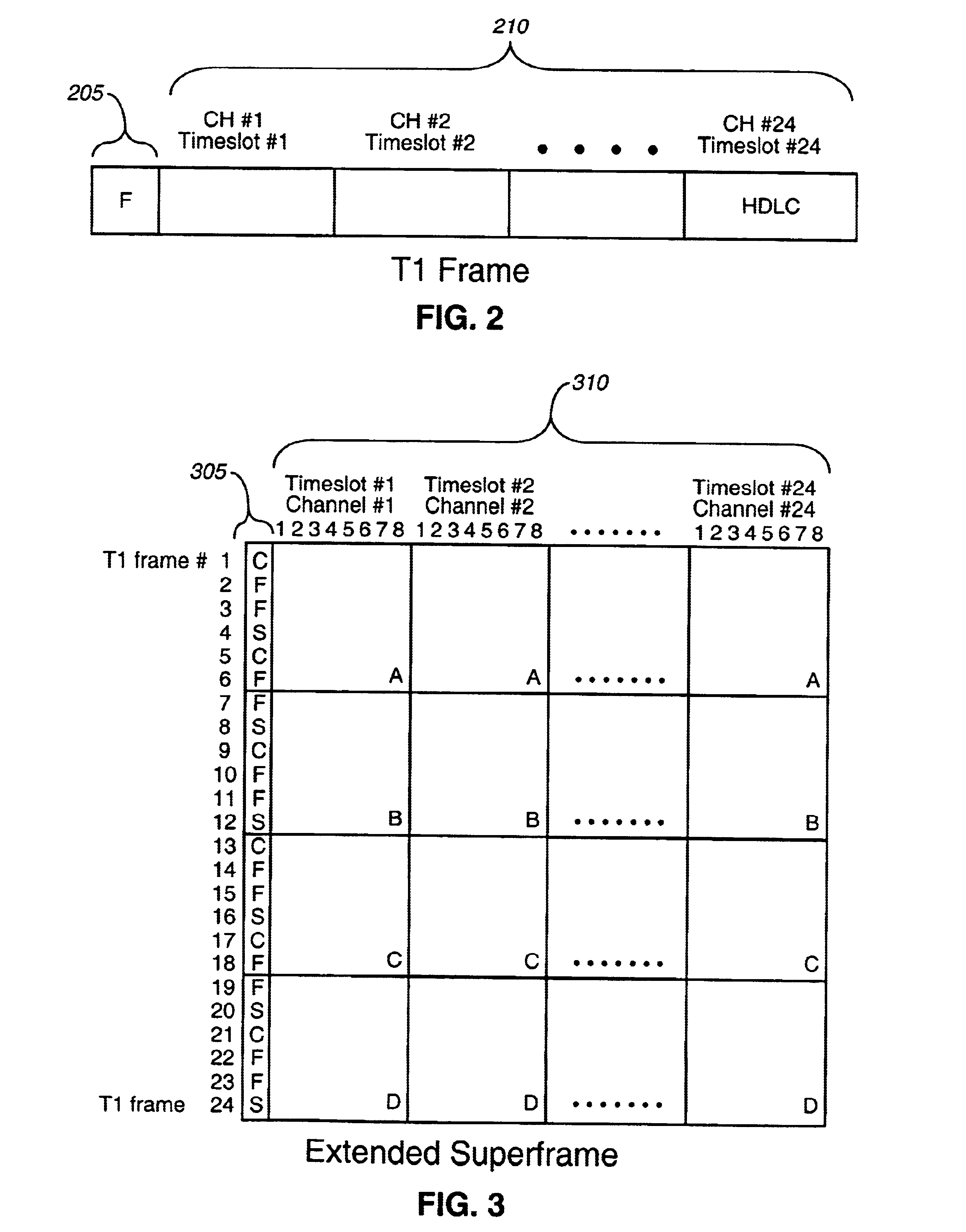
A method, apparatus, and computer program product of interfacing a time-domain multiplexed (TDM) link with a cell-switched network. The TDM link supports one or more active channels and one or more idle channels and supplies TDM frames with a sample of each channel in a dedicated timeslot. The TDM link is terminated at a first network node. One or more idle timeslots are removed from each TDM frame to create a compressed TDM frame, where each idle timeslot carries a sample of an idle channel. One or more compressed TDM frames are loaded in a cell that is sent over the cell-switched network to a second network node. The compressed TDM frames are unloaded from the cell. Idle timeslots are inserted in the compressed TDM frames to restore the compressed TDM frames to complete TDM frames. The bandwidth of the cell switched network is efficiently utilized because idle channel samples are not carried over the cell-switched network. In one embodiment, the TDM link is a T1 link that carries T1 frames, and the cell switched network is an Asynchronous Transfer Mode (ATM) network that carries ATM cells.< / PTEXT>
Owner:VERIZON PATENT & LICENSING INC
Ethernet to ATM interworking with multiple quality of service levels
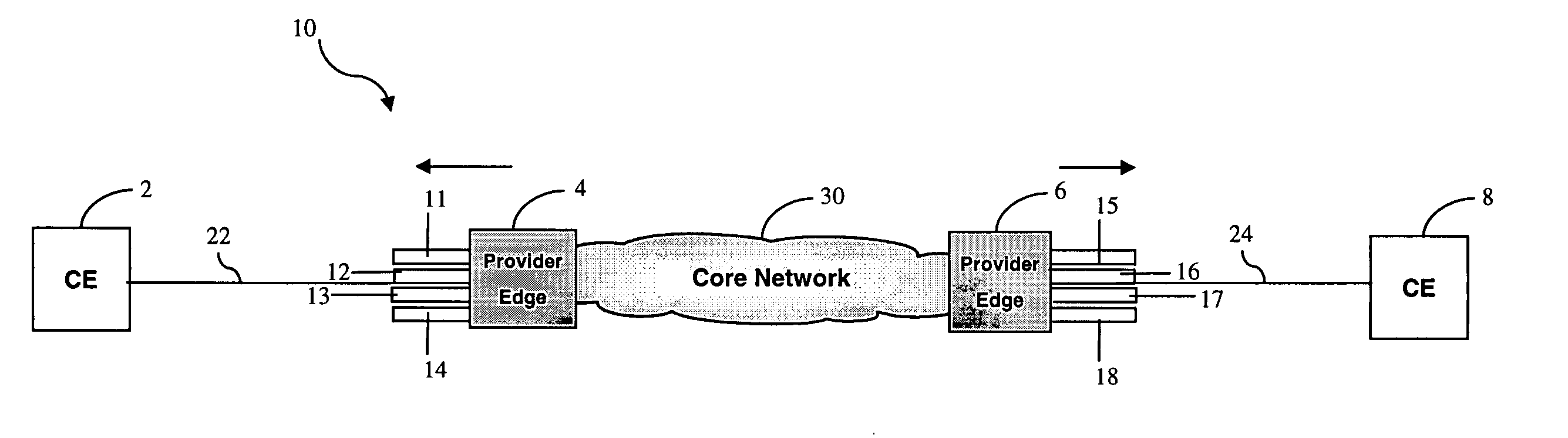
A method of supporting multiple quality of service (QoS) levels for data being transmitted between two networking devices, such as customer equipment (CE), that use Ethernet and Asynchronous Transfer Mode (ATM). The method supports multiple QoS services in a network where a first CE is connected to a first edge device (interworking unit) using the Ethernet protocol and a second CE is connected to a second edge device using the ATM protocol. The edge devices may be directly connected together or they may be connected through a network backbone using any generally accepted network protocol. The first CE may be connected to the first edge device using a single Ethernet port, multiple Ethernet ports, a single virtual local area network (VLAN), or multiple VLAN's. The second CE is connected to an edge device using a single virtual circuit connection (VCC), a single virtual path connection (VPC), or multiple VCC's. The method ensures QoS for data transmitted between the first and the second CE via the Ethernet protocol to the ATM protocol and vice versa.
Owner:NORTEL NETWORKS LTD
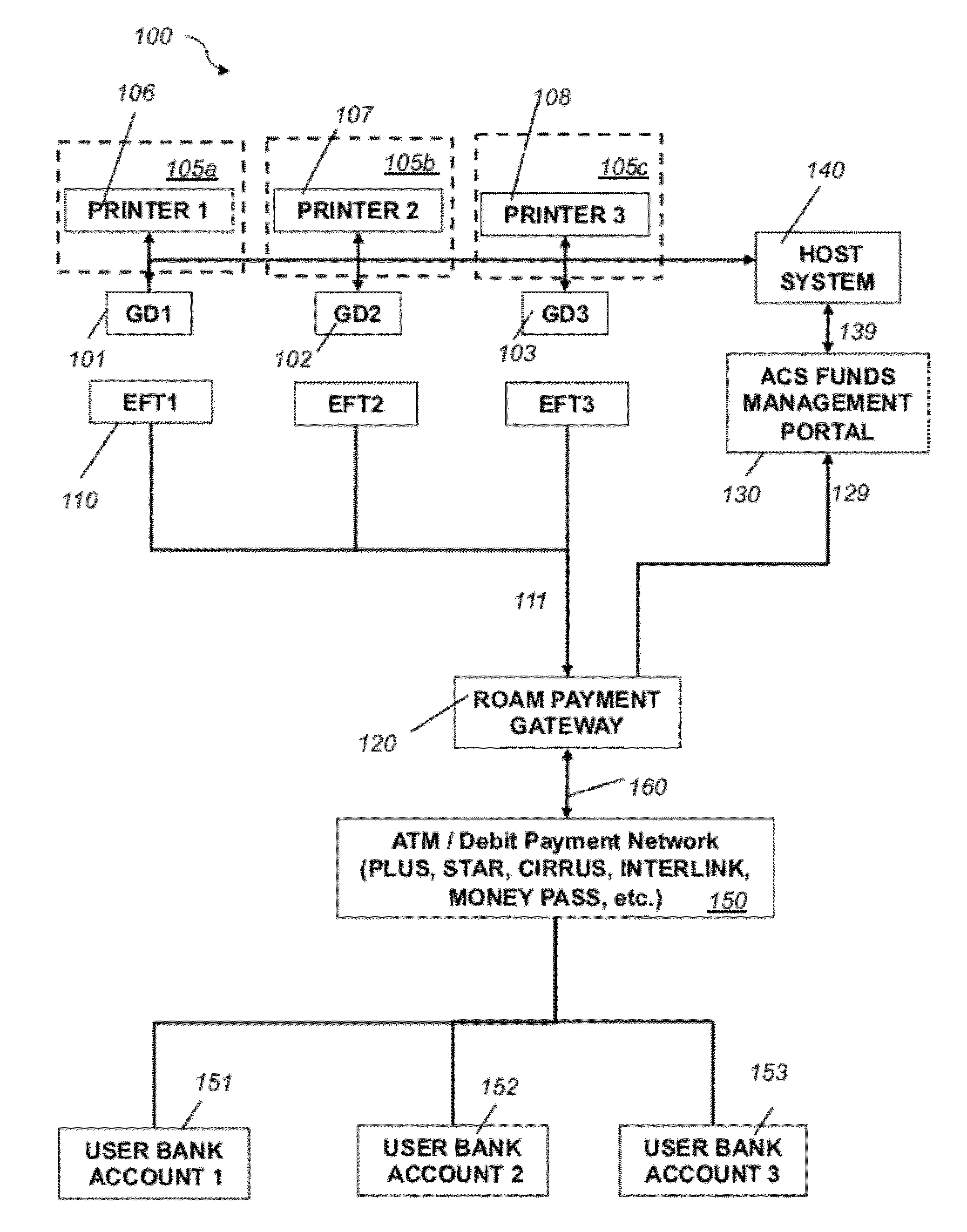
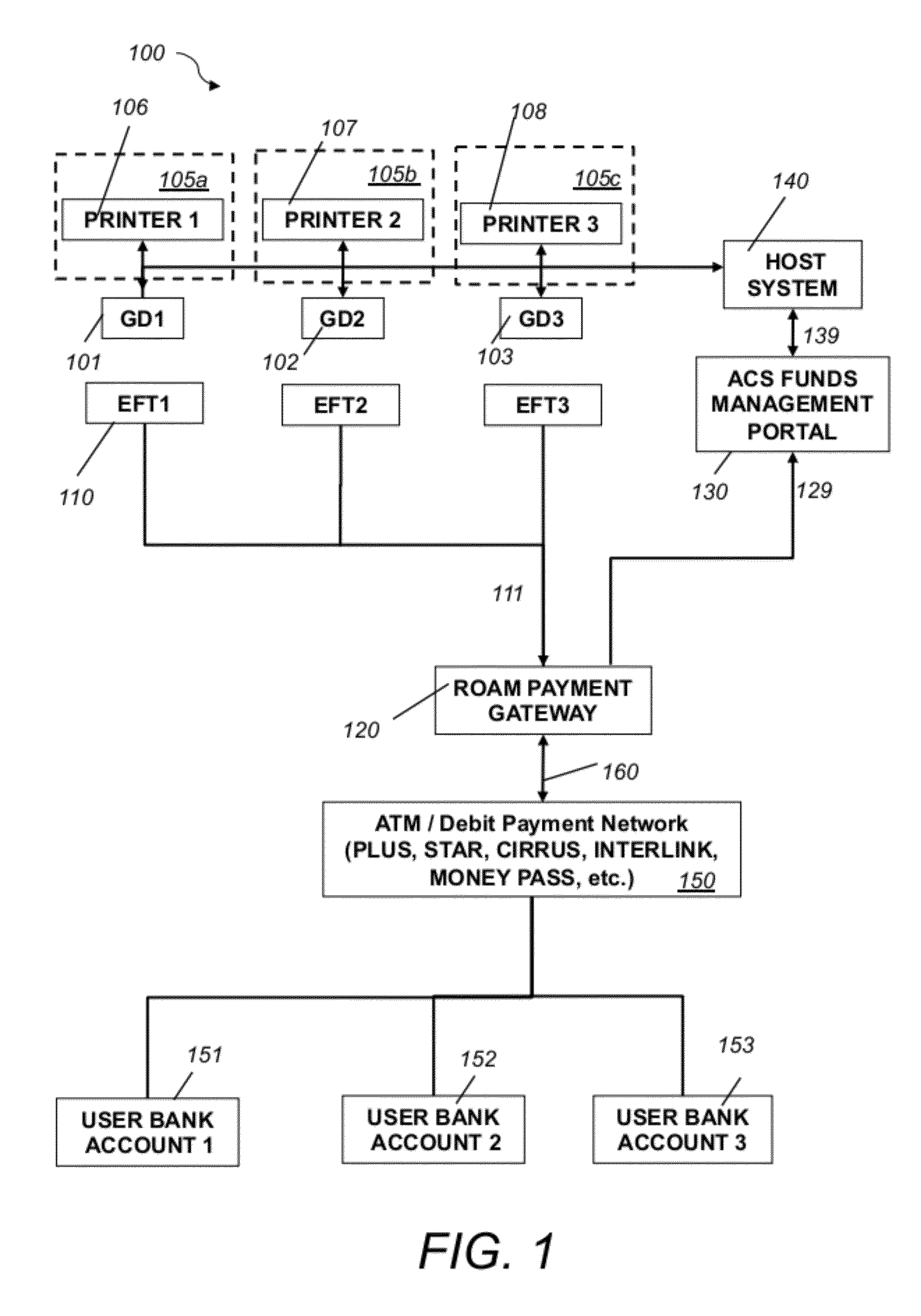
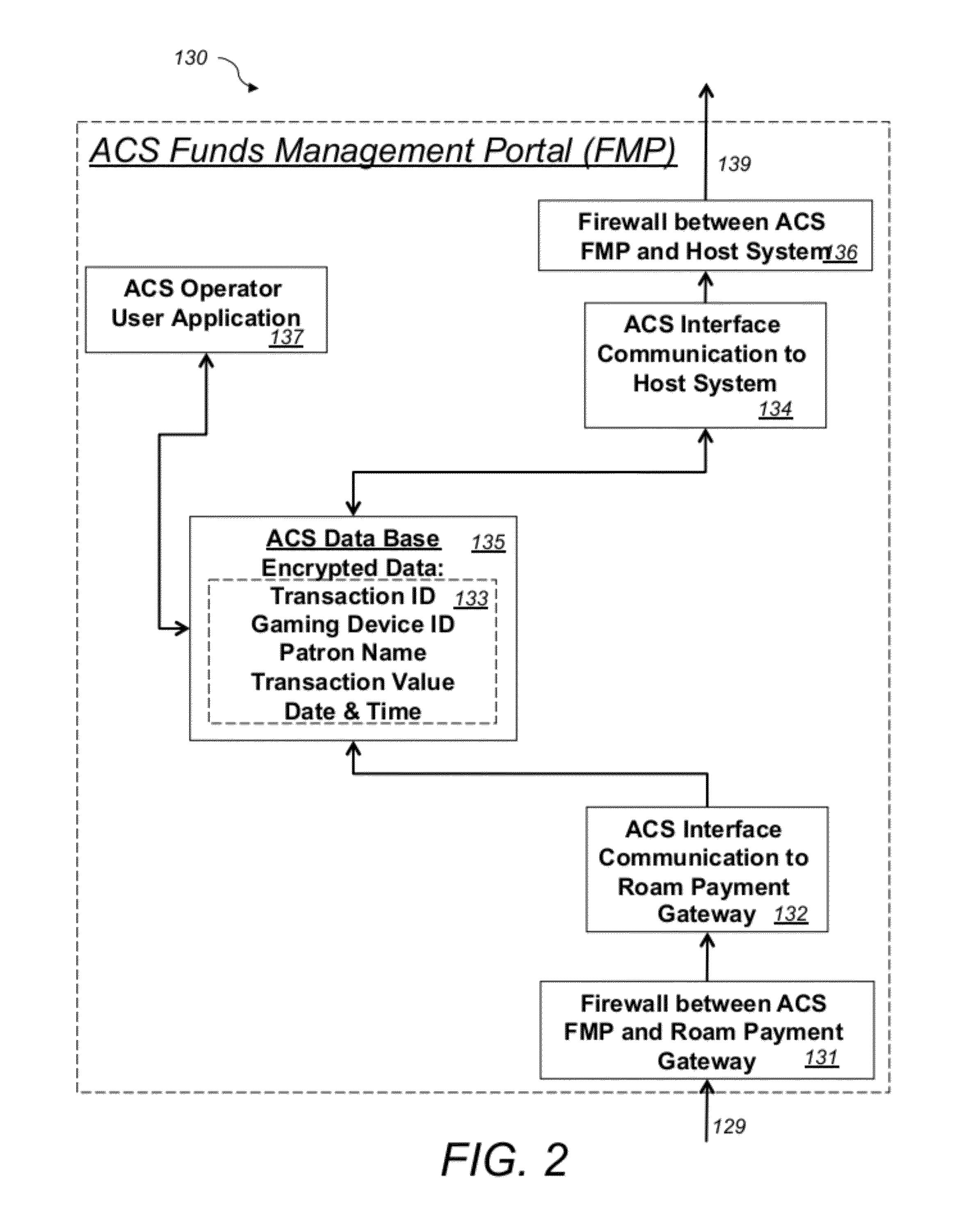
System and method for electronic fund transfers for use with gaming systems
An electronic fund transfer (EFT) system for managing and transferring electronic funds from a user's financial account to a credit system includes a credit system configured to dispense credit to a user via physical or electronic credit means, an electronic fund transfer (EFT) device, a secure payment gateway configured to connect to the user's financial accounts via a financial asynchronous transfer mode (ATM) network, a host system connected to the credit system via a local network, a funds management portal connected to the host system and the secure payment gateway, and means for transferring electronic funds from the user's financial account to the credit system via the secure payment gateway. The funds management portal accounts and reconciles the transferred electronic funds. All communications between the secure payment gateway and the host system pass through the funds management portal. The EFT device includes a secure client-side application for receiving instructions from the user for transferring electronic funds from the user's financial account to the credit system and means for transmitting the fund transfer instructions to the user's financial account. The EFT device is configured to connect to the secure payment gateway and to communicate with the user's financial account and to transmit the instructions for transferring electronic funds from the user's financial account to the credit system via the secure payment gateway.
Owner:AUTOMATED CASHLESS SYST INC
Network protocol for wireless broadband-ISDN using ATM
InactiveUS6151312AInterference minimizationMinimum delaySynchronisation arrangementError preventionNetworking protocolIntegrated Services Digital Network
A network protocol for the delivery of wireless broadband integrated services digital network (ISDN) using asynchronous transfer mode (ATM).
Owner:ALCATEL USA SOURCING
Authentication for use of high speed network resources
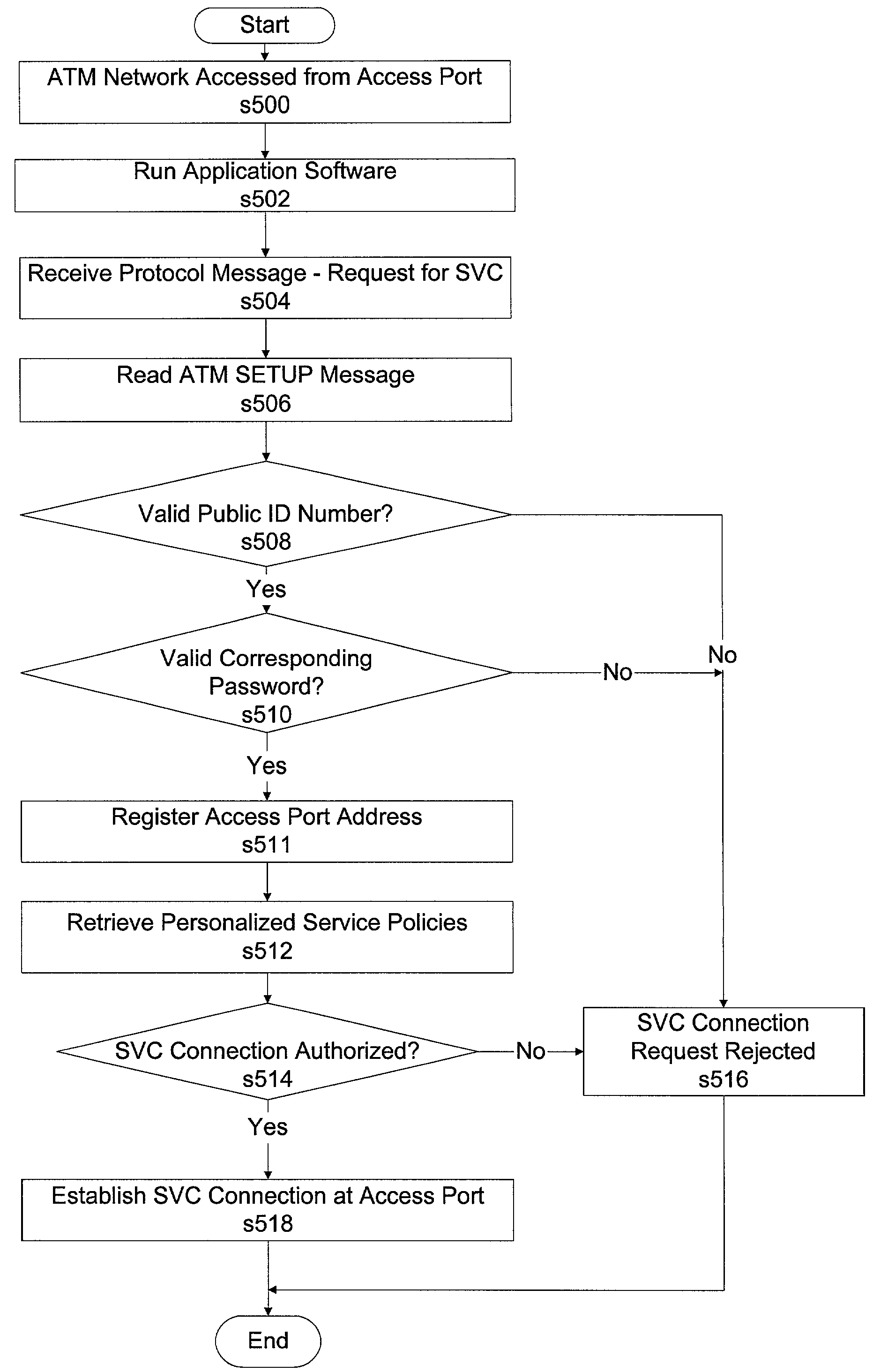
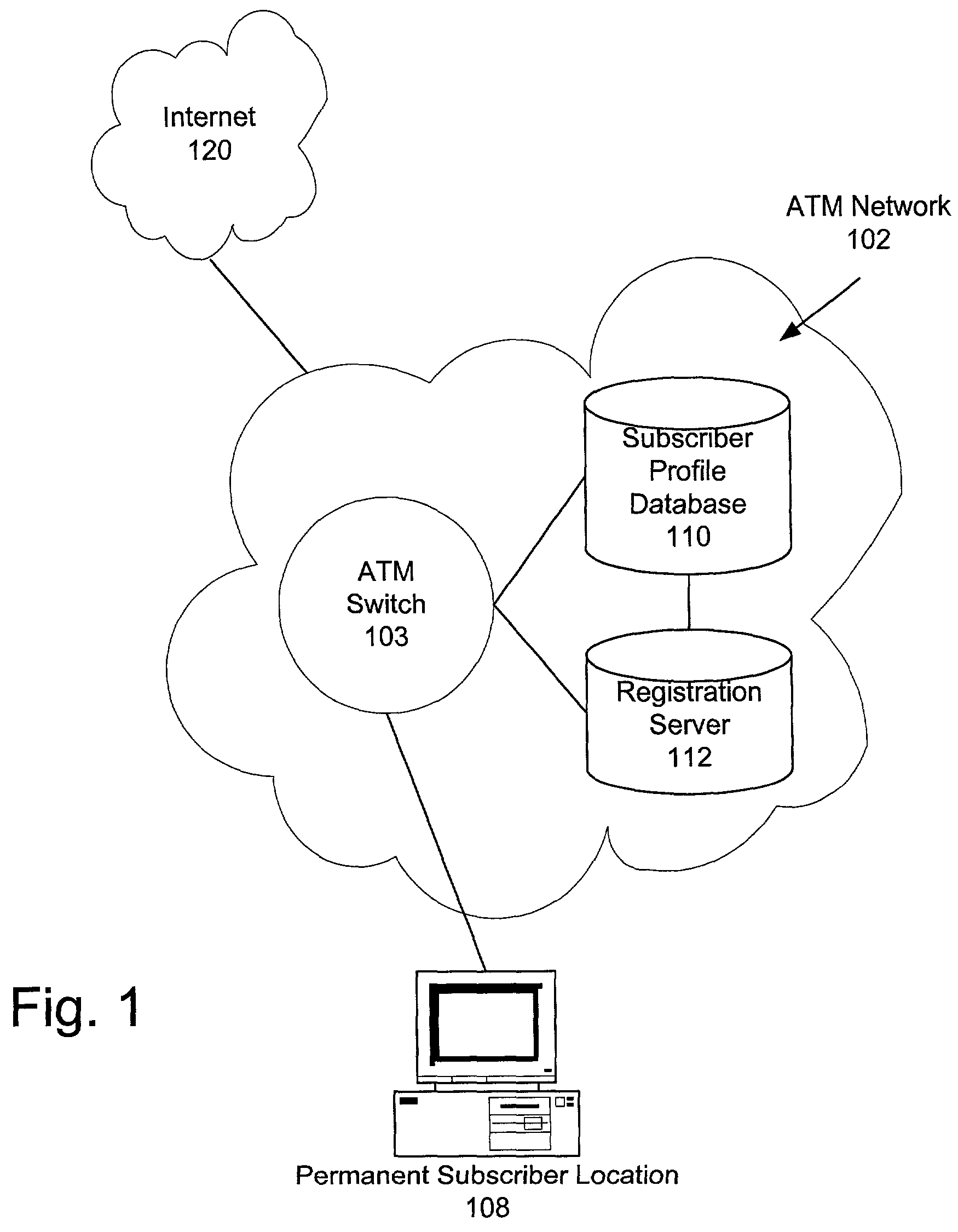
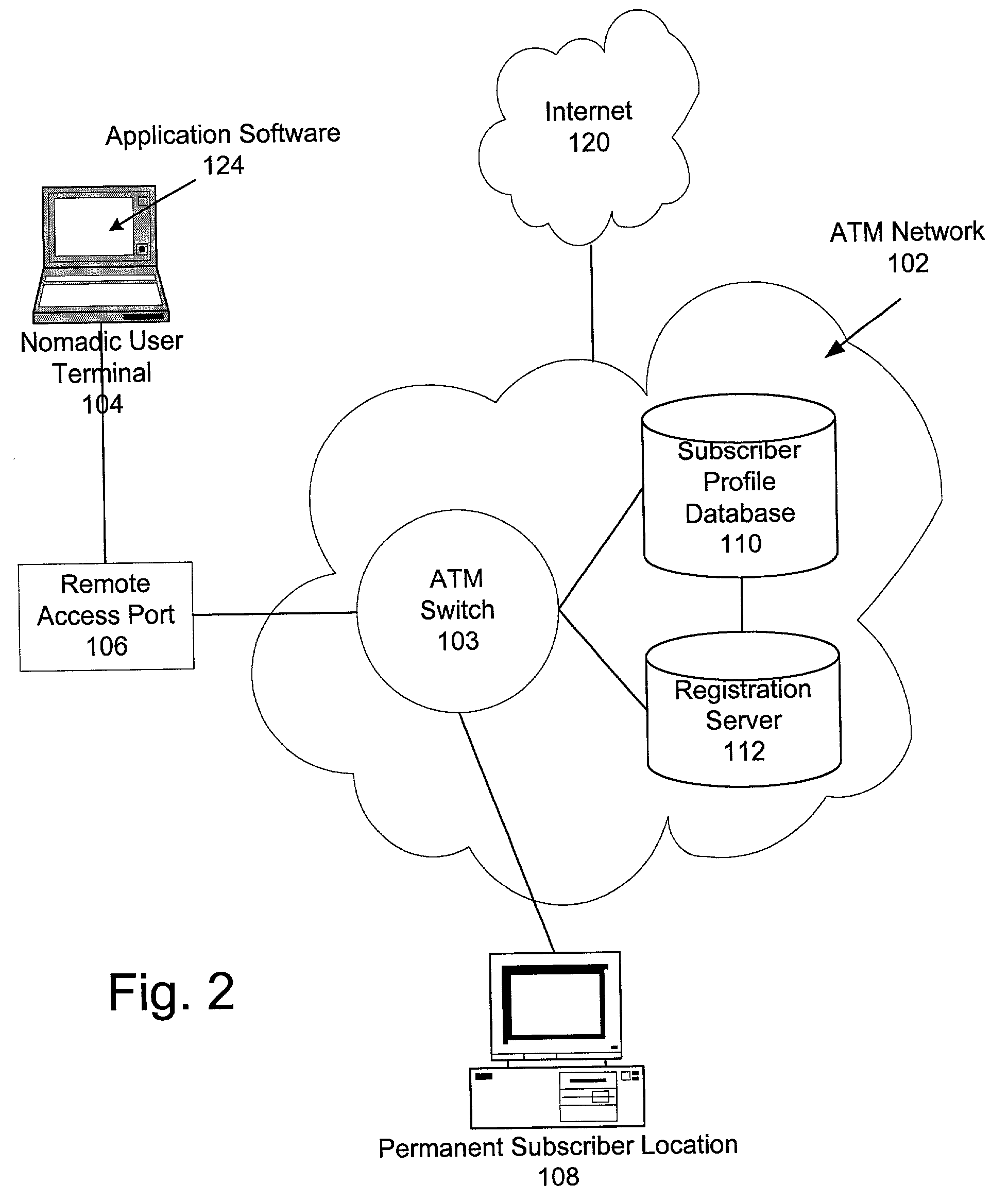
A method and system for associating a switched virtual circuit (SVC) connection request from an access port in an asynchronous transfer mode (ATM) network to a subscriber and optionally registering an address of the access port in relation to the subscriber. The method and system include receiving a signaling protocol message requesting the SVC connection from the access port, determining whether the signaling protocol message contains subscriber authentication data and, when authenticated, establishing the SVC connection. Furthermore, the SVC connection may be established only if service policies corresponding to the subscriber retrieved from a database indicate that the subscriber is entitled to make SVC connections. The method and system further include registering an address of the access port in the ATM network by substituting the address of the access port for an original subscriber address.
Owner:AT&T LABS
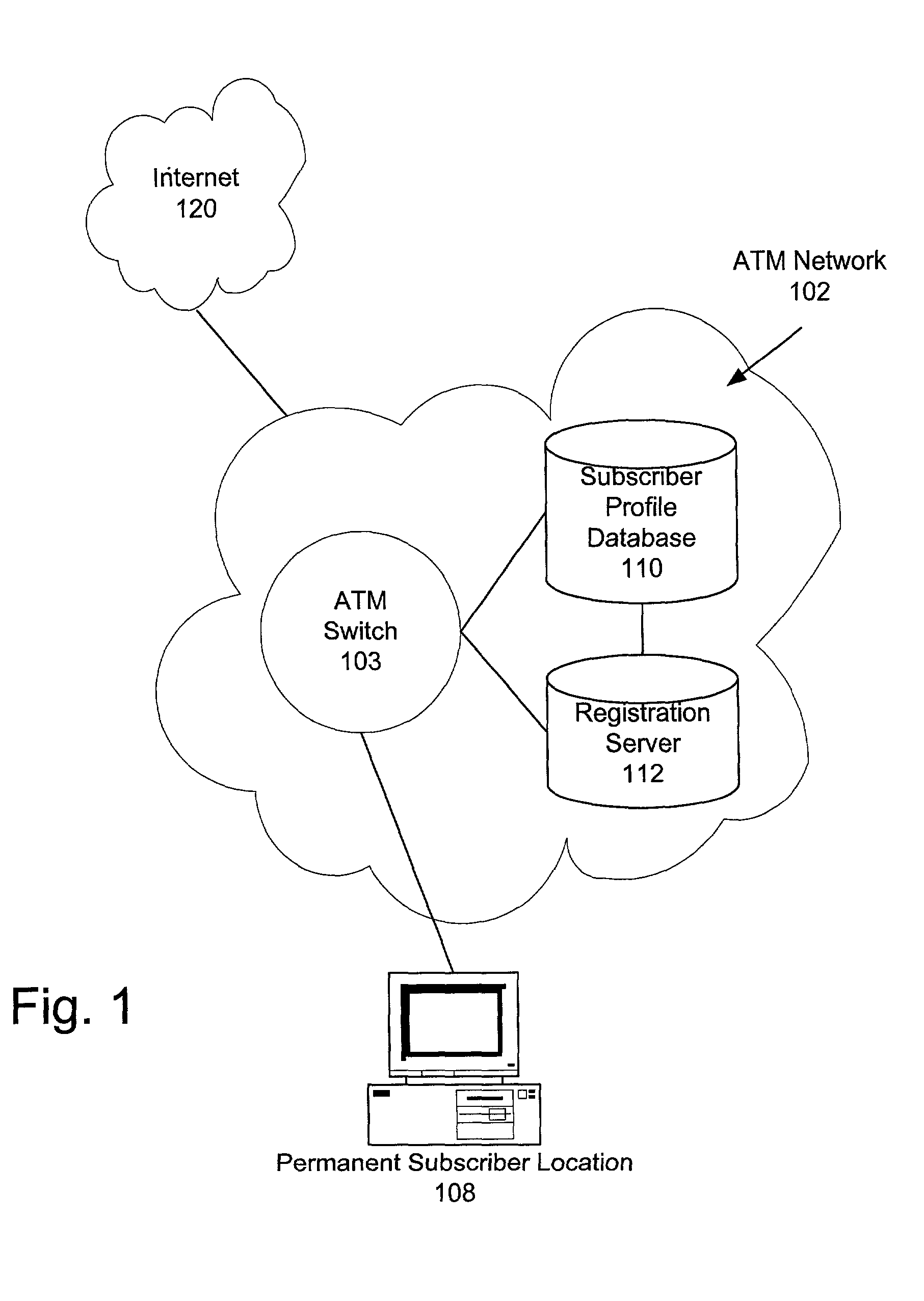
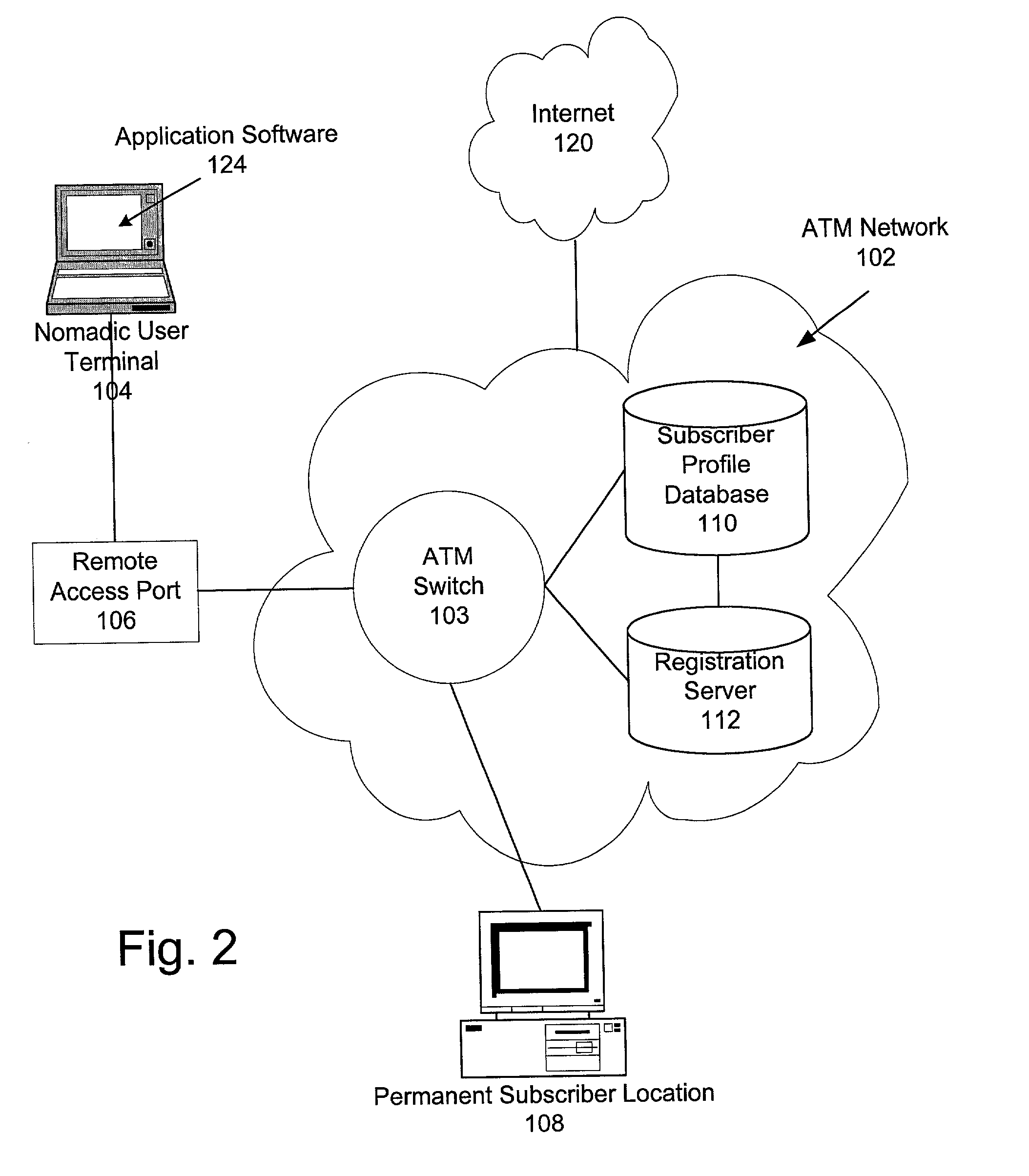
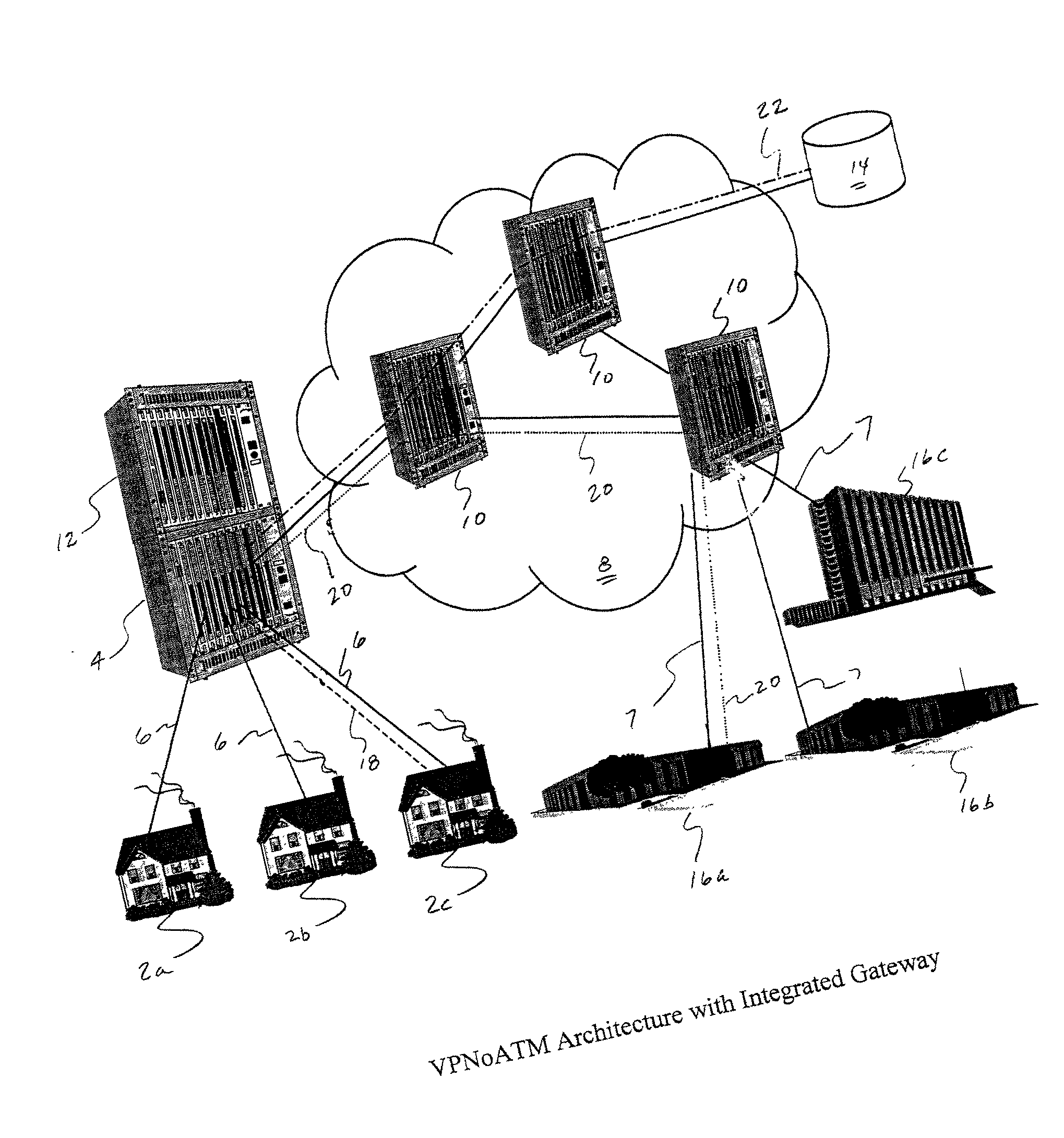
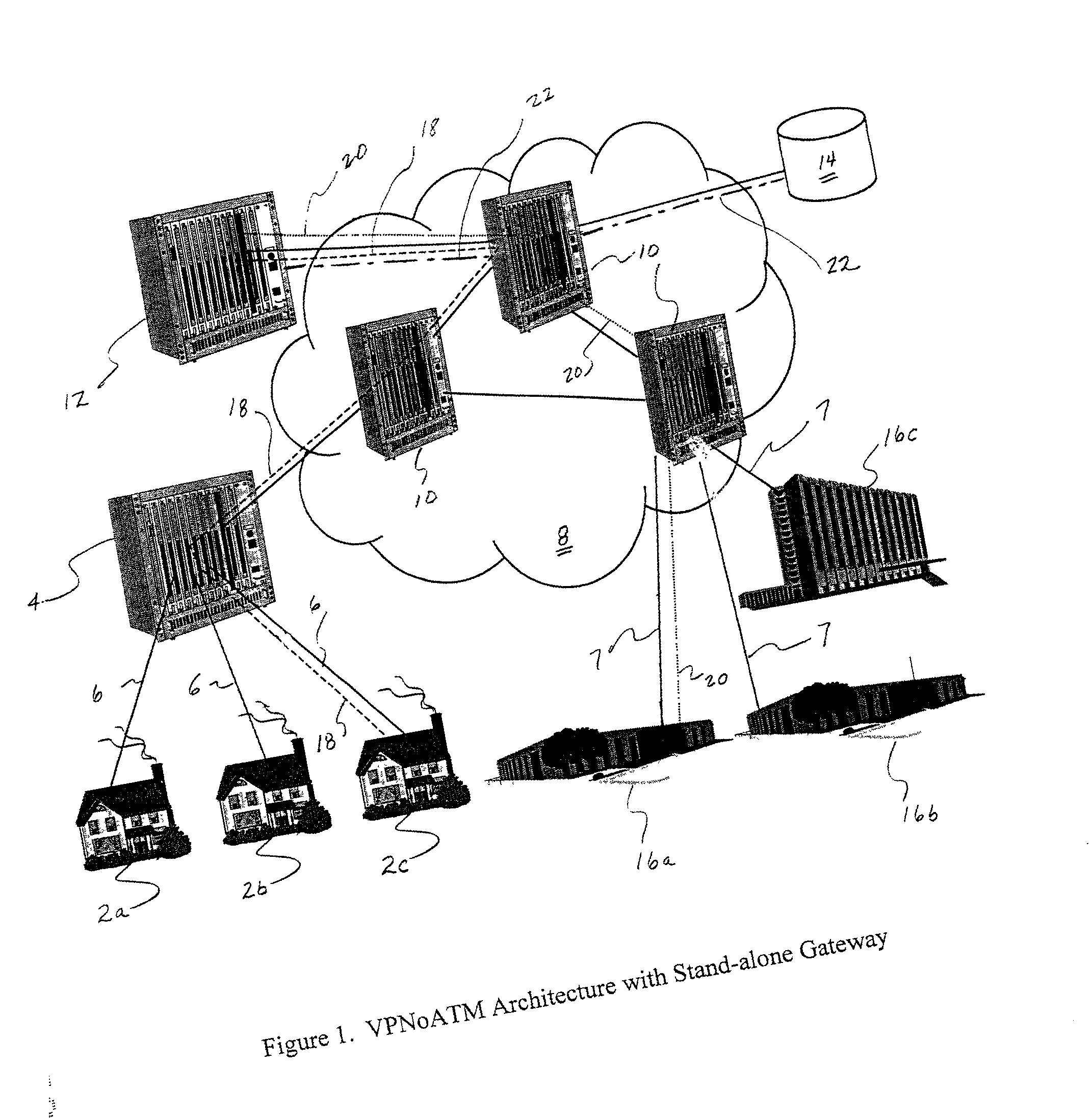
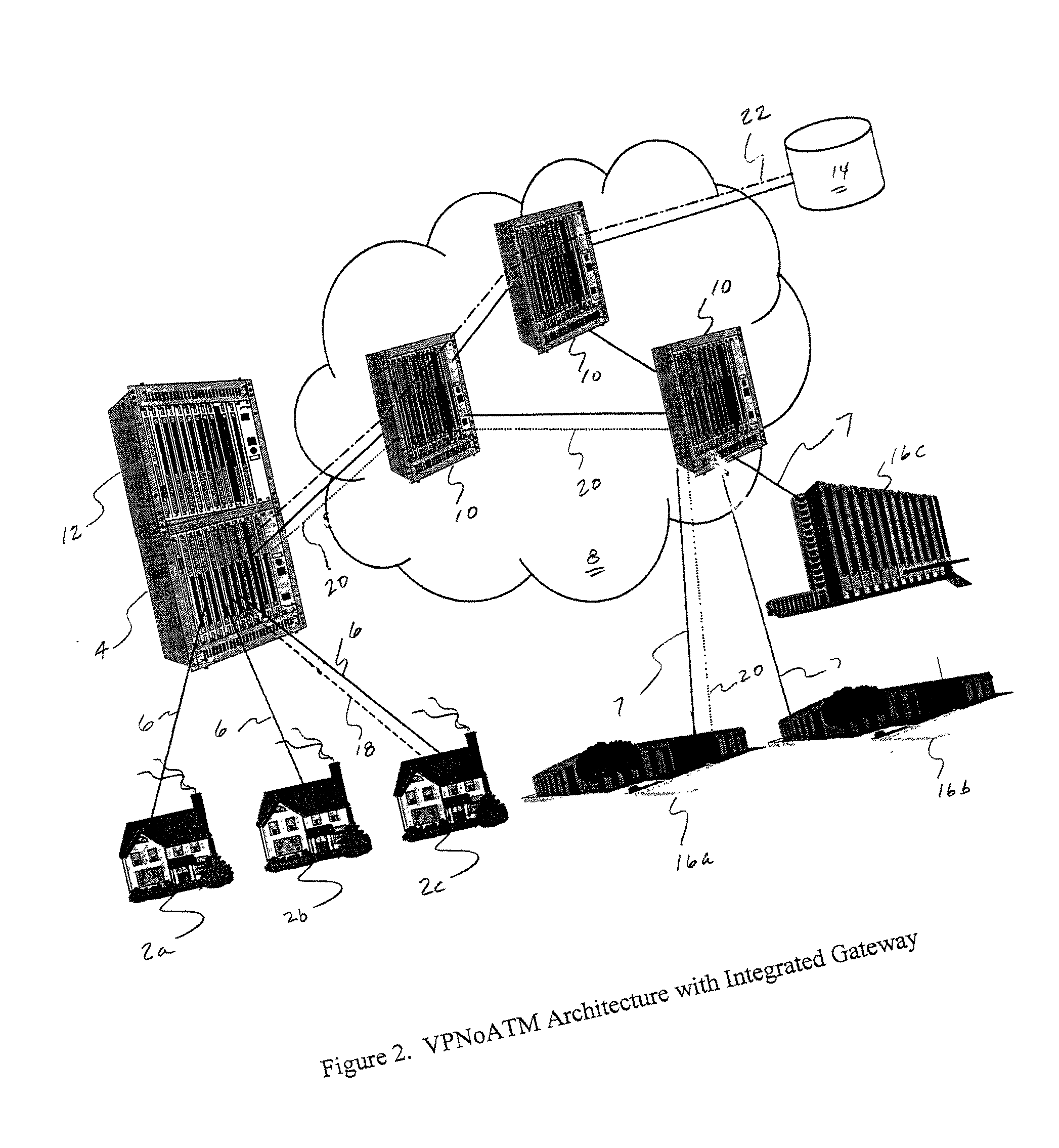
Virtual private network over asynchronous transfer mode
InactiveUS20030016676A1Data switching by path configurationTime-division multiplexing selectionPrivate networkNetwork address
A communications network and method enable broadband service subscribers to dynamically select broadband service destinations they wish to access from subscriber customer premises equipment. The communications network is an ATM network including a plurality of ATM switches. The network also includes at least one directory server connected to the ATM network, at least one fiber terminating device connected to the at least one directory server, and at least one broadband destination connected to the ATM network. Furthermore, the subscribers' customer premise equipment is connected to the at least one fiber terminating device. The method includes receiving a session request, which identifies a destination, in the at least one service gateway, wherein the session request is transmitted over a broadband connection using an Internet protocol. Next, using the at least one service gateway, an ATM network address of the destination from the at least one directory server is retrieved. Then an SVC is launched over the ATM network from the at least one service gateway to connect the subscriber to the ATM network address. Finally, the subsequent packets are forwarded to the destination over the ATM SVC connection.
Owner:SBC TECH RESOURCES
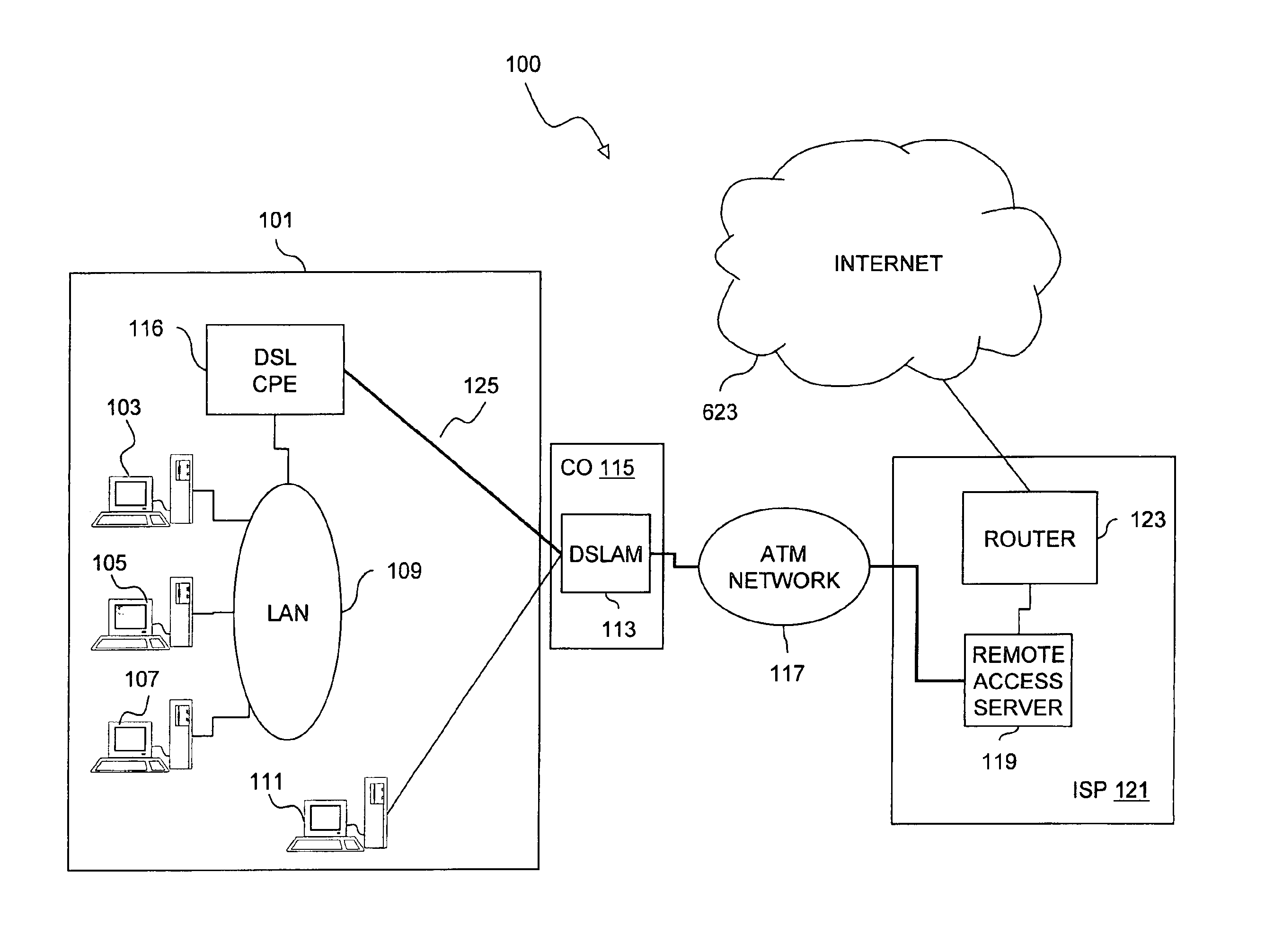
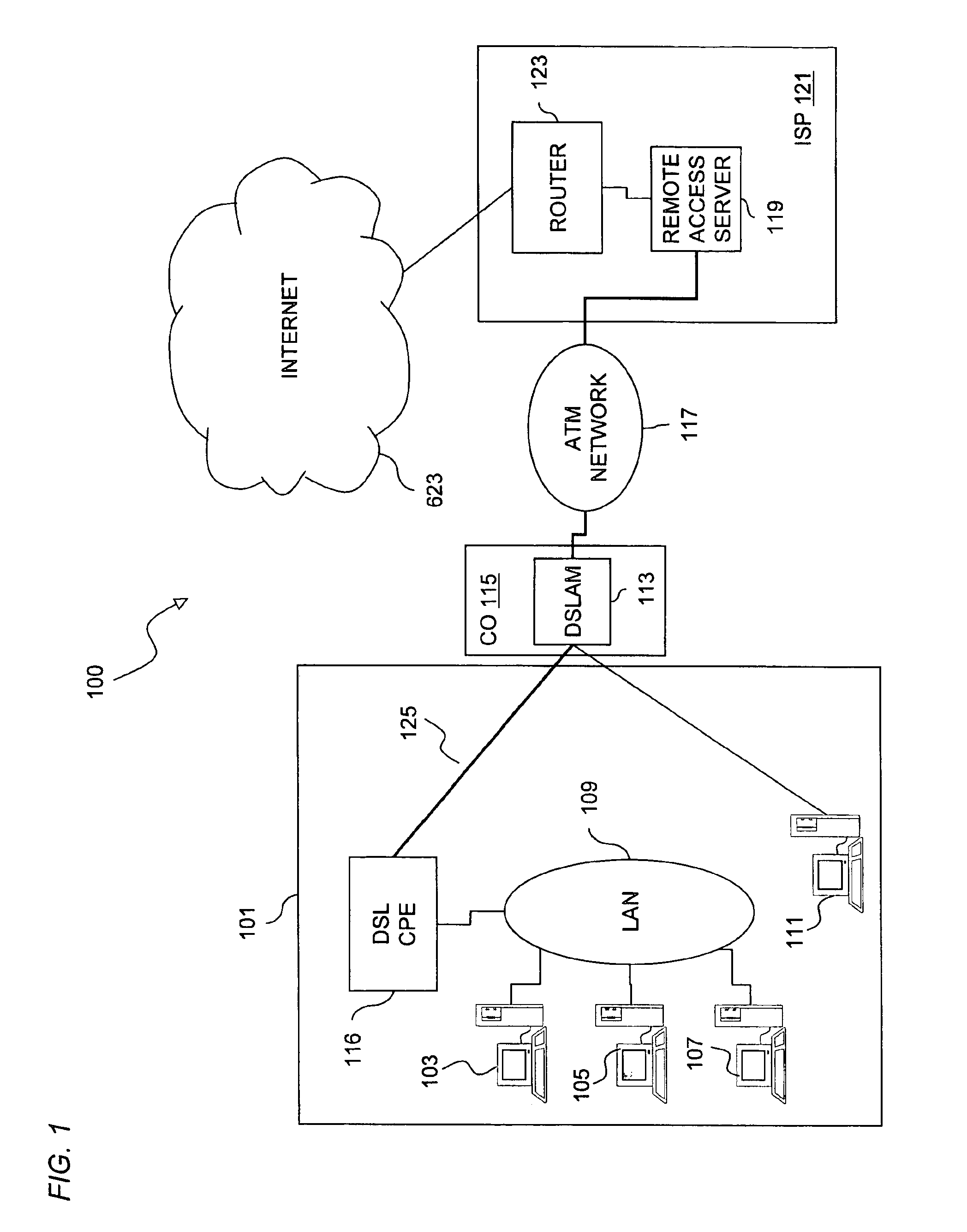
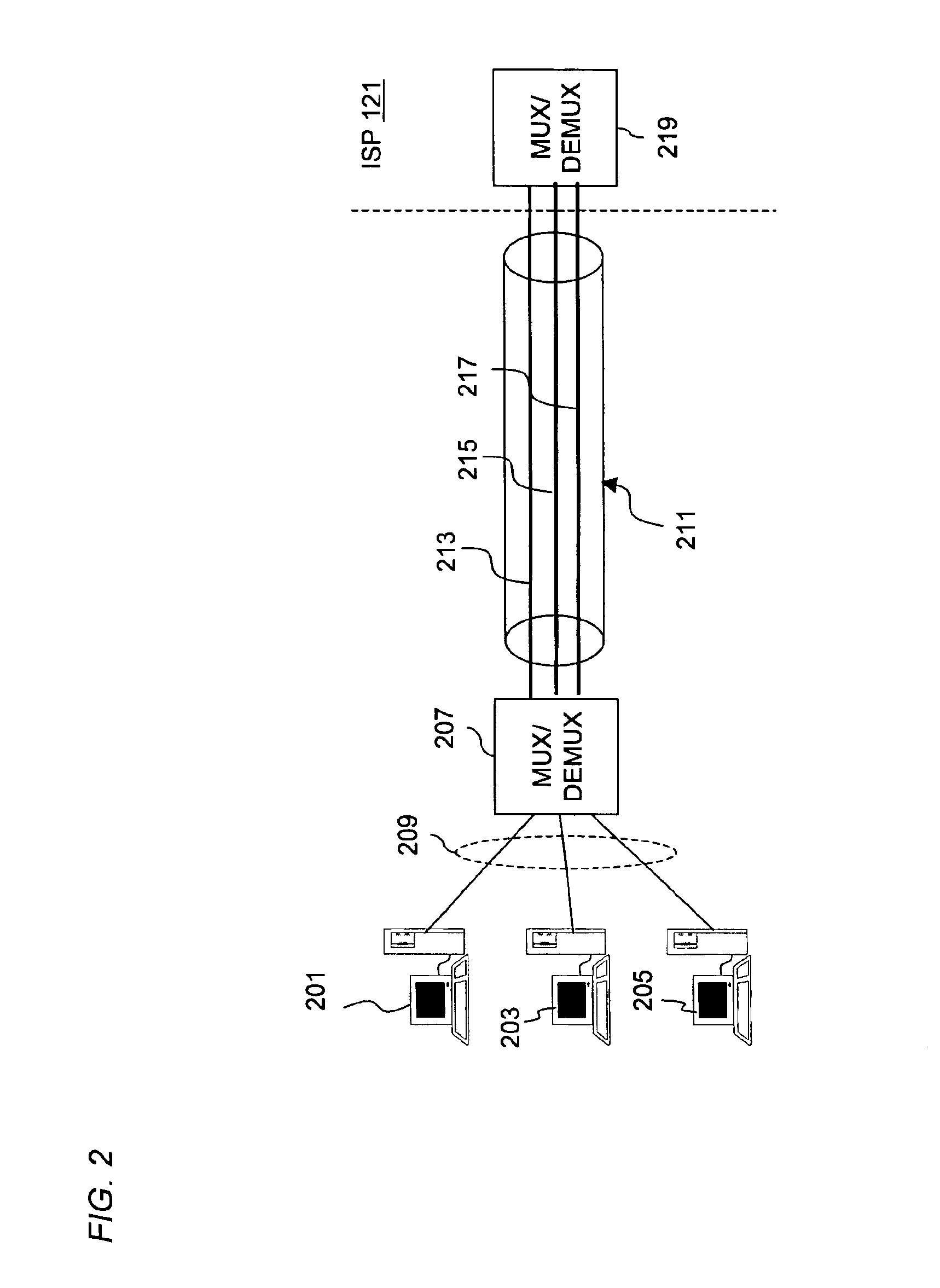
Method and system of providing multi-user access to a packet switched network
InactiveUS6891825B1Low costSimple configurationTelephonic communicationTime-division multiplexCommunications softwareNetwork Communication Protocols
An approach for providing multi-user access to a packet switched network via a shared Ethernet-based local area network (LAN) is disclosed. Multiple end user stations are connected to the LAN, in which each of end user stations executes a communication software. The communication software is based upon a communication protocol (e.g., Point-to-Point Protocol (PPP)) that establishes a point-to-point communication session. The end user stations generate packets based upon the communication protocol. In addition, each of the end user stations selectively encapsulates the communication protocol packets using the Ethernet-based LAN protocol. Further, attached to the LAN is a customer premise equipment (CPE), which transmits the encapsulated packets to a line terminating equipment, which according to one embodiment is a digital subscriber line (DSL) access multiplexer that is located in a central office. The line terminating equipment transports the multiple PPP sessions to a multiplexer / demultiplexer, which is located within a regional carrier's network. In one embodiment, the multiplexer / demultiplexer is an Asynchronous Transfer Mode (ATM) switch, which simultaneously transports the multiple PPP sessions over a single permanent virtual circuit (PVC); VPI / VCIs (Virtual Path Identifier / Virtual Connection Identifier) are mapped to the multiple PPP sessions. The multiple PPP sessions are terminated at a remote access server, which recovers and forwards the packets to a backbone router. Thereafter, the backbone router forwards the packets to the packet switched network.
Owner:VERIZON PATENT & LICENSING INC
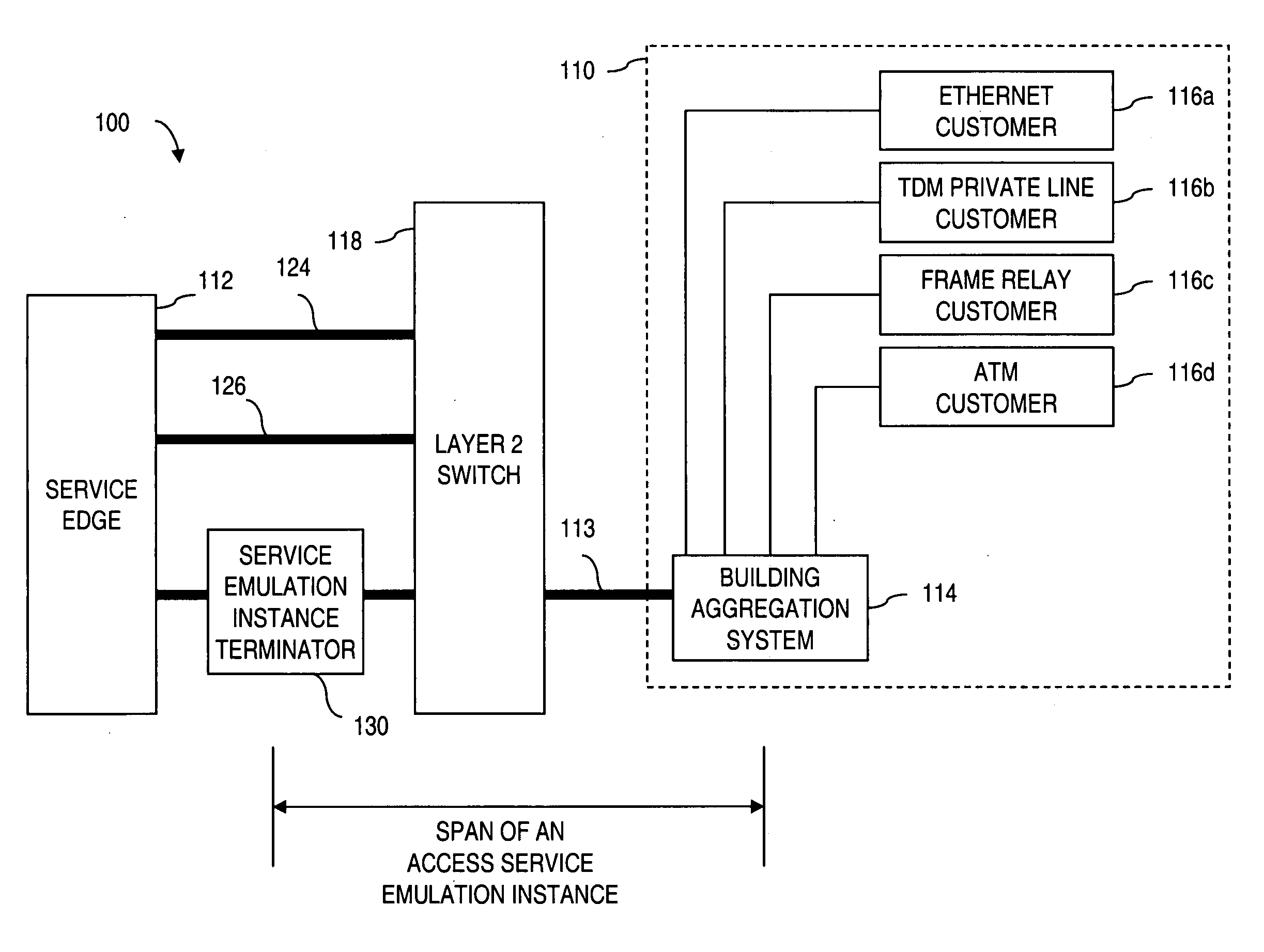
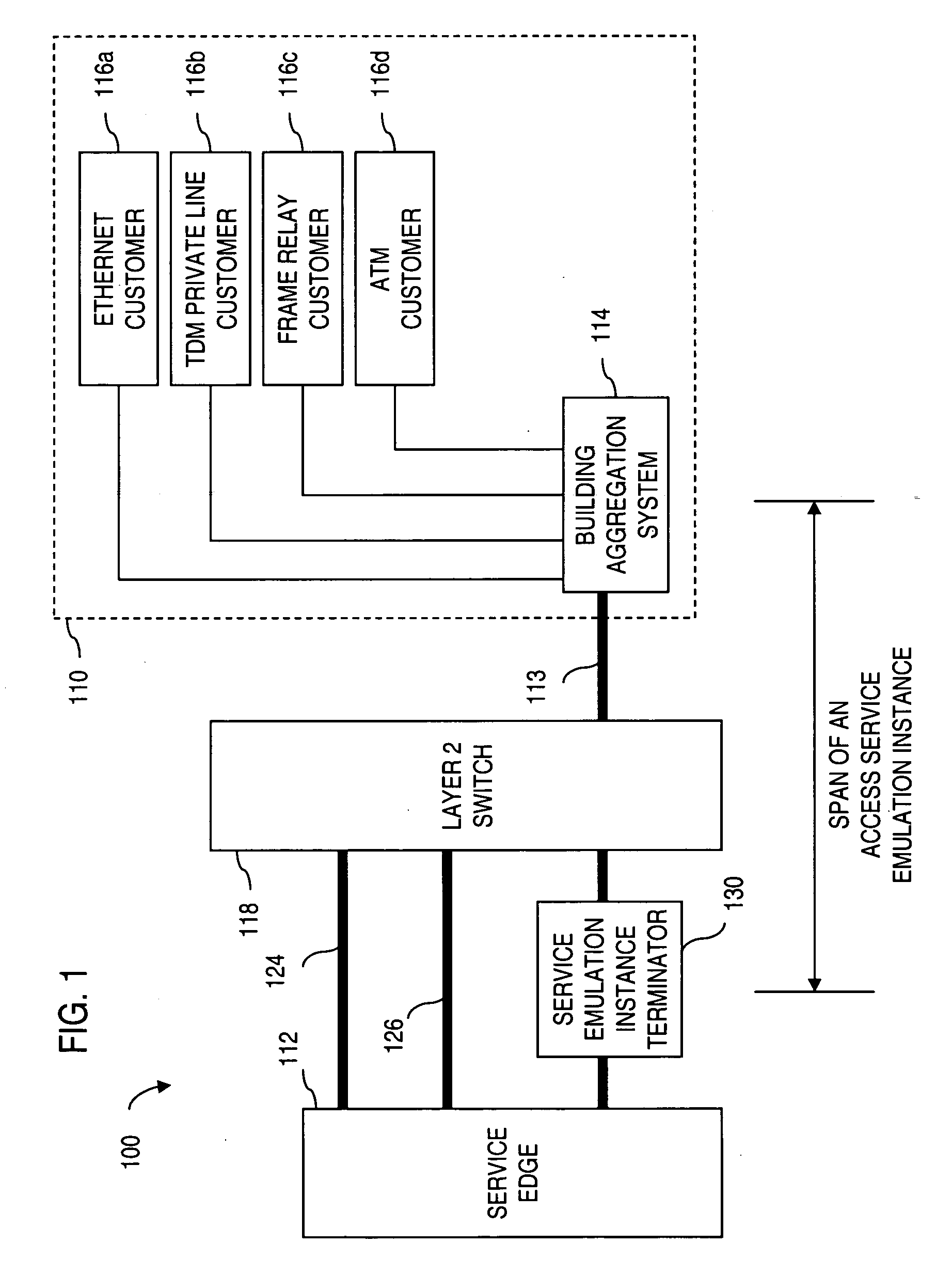
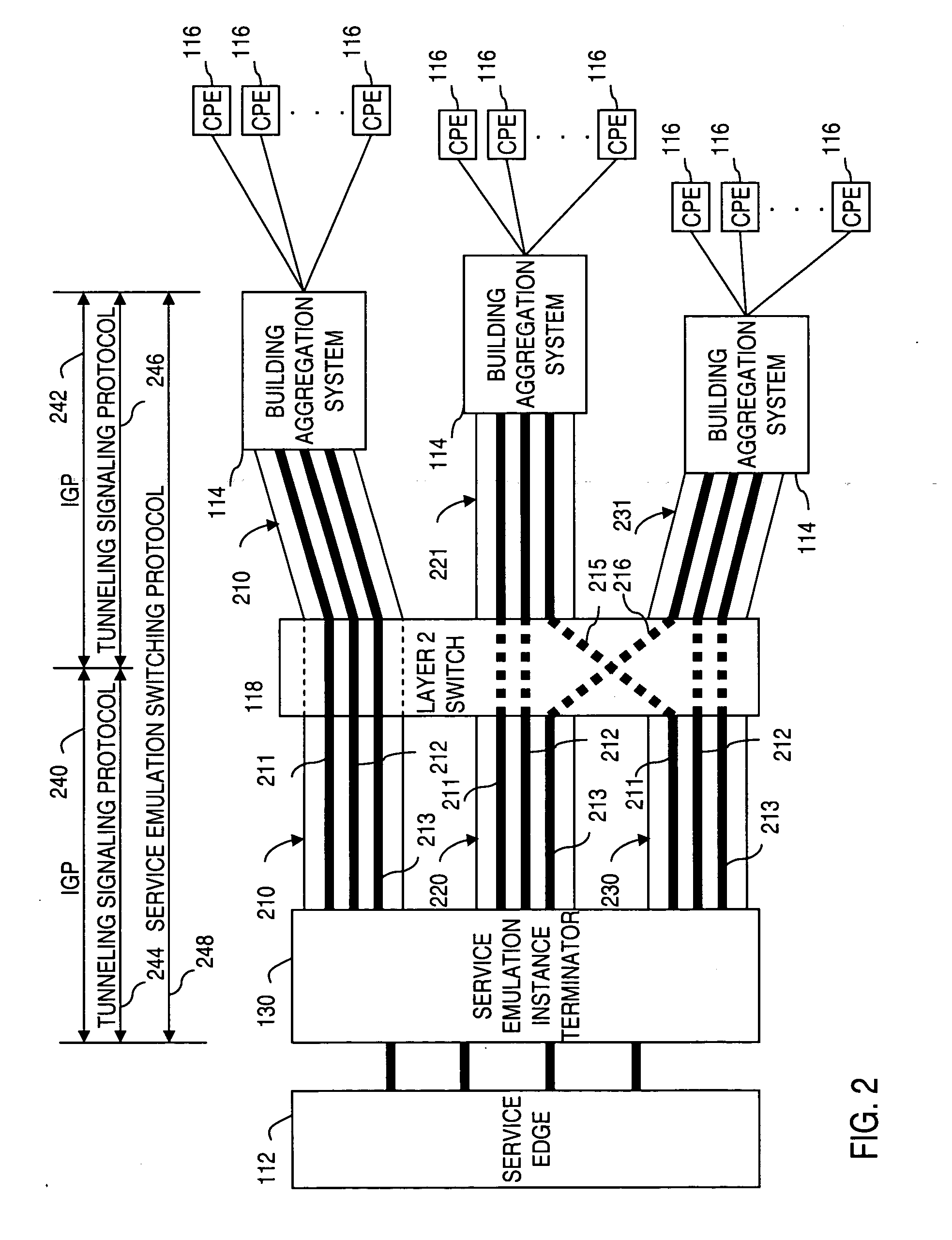
Apparatus and method for providing a network termination point
ActiveUS20050238049A1Efficient executionTime-division multiplexNetworks interconnectionTraffic capacityAccess network
Apparatus and method for providing a termination point for service emulation instances in an access network is provided. In an embodiment, the service emulation instances are implemented utilizing, for example, pseudowires. Communications to and from the access network are aggregated and transmitted via one or more pseudowires to a service emulation instance terminator. The service emulation instance terminator converts the traffic to its native form and, if necessary, converts the traffic to a different type of format or service. The service emulation instance terminator then frames the traffic for the appropriate type of service and transmits the traffic to the service edge. Traffic received from the service is removed prepended with a pseudowire label and aggregated with other traffic. The aggregated traffic is transmitted to the customer via the access network. If necessary, an interworking function may convert the traffic from one type of service to another type of service. Further, functionalities of equipment such as frame relay switching or Asynchronous Transfer Mode (ATM) switching may be realized in the service emulation instance terminator.
Owner:VERIZON PATENT & LICENSING INC
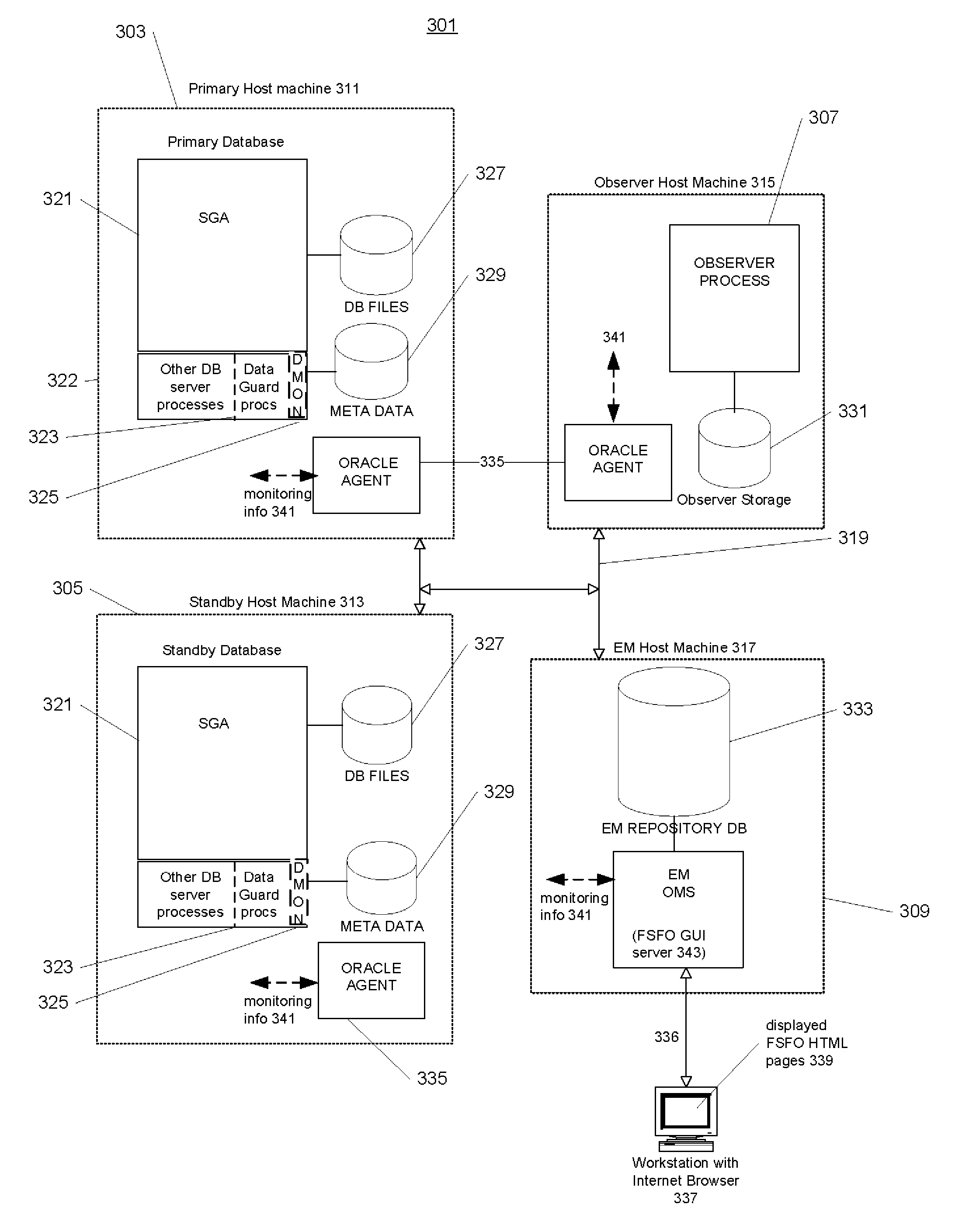
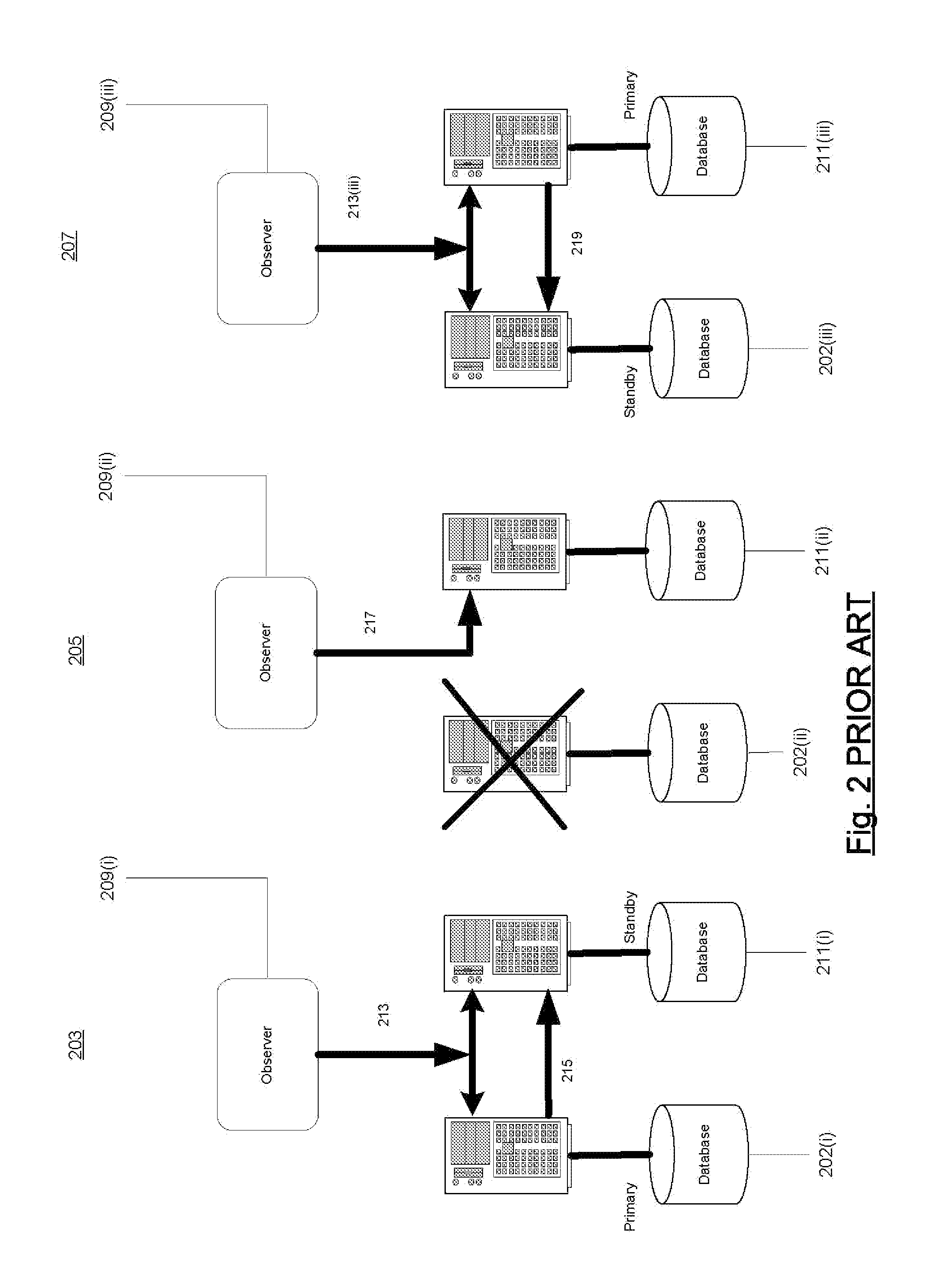
Database system configured for automatic failover with user-limited data loss
ActiveUS20070198700A1Avoid lostDigital data information retrievalDigital data processing detailsFailoverTransfer mode
Techniques used in an automatic failover configuration having a primary database system, a standby database system, and an observer. In the automatic failover configuration, the primary database system remains available even in the absence of both the standby and the observer as long as the standby and the observer become absent sequentially. The failover configuration may use asynchronous transfer modes to transfer redo to the standby and permits automatic failover only when the observer is present and the failover will not result in data loss due to the asynchronous transfer mode beyond a specified maximum. The database systems and the observer have copies of failover configuration state and the techniques include techniques for propagating the most recent version of the state among the databases and the observer and techniques for using carefully-ordered writes to ensure that state changes are propagated in a fashion which prevents divergence.
Owner:ORACLE INT CORP
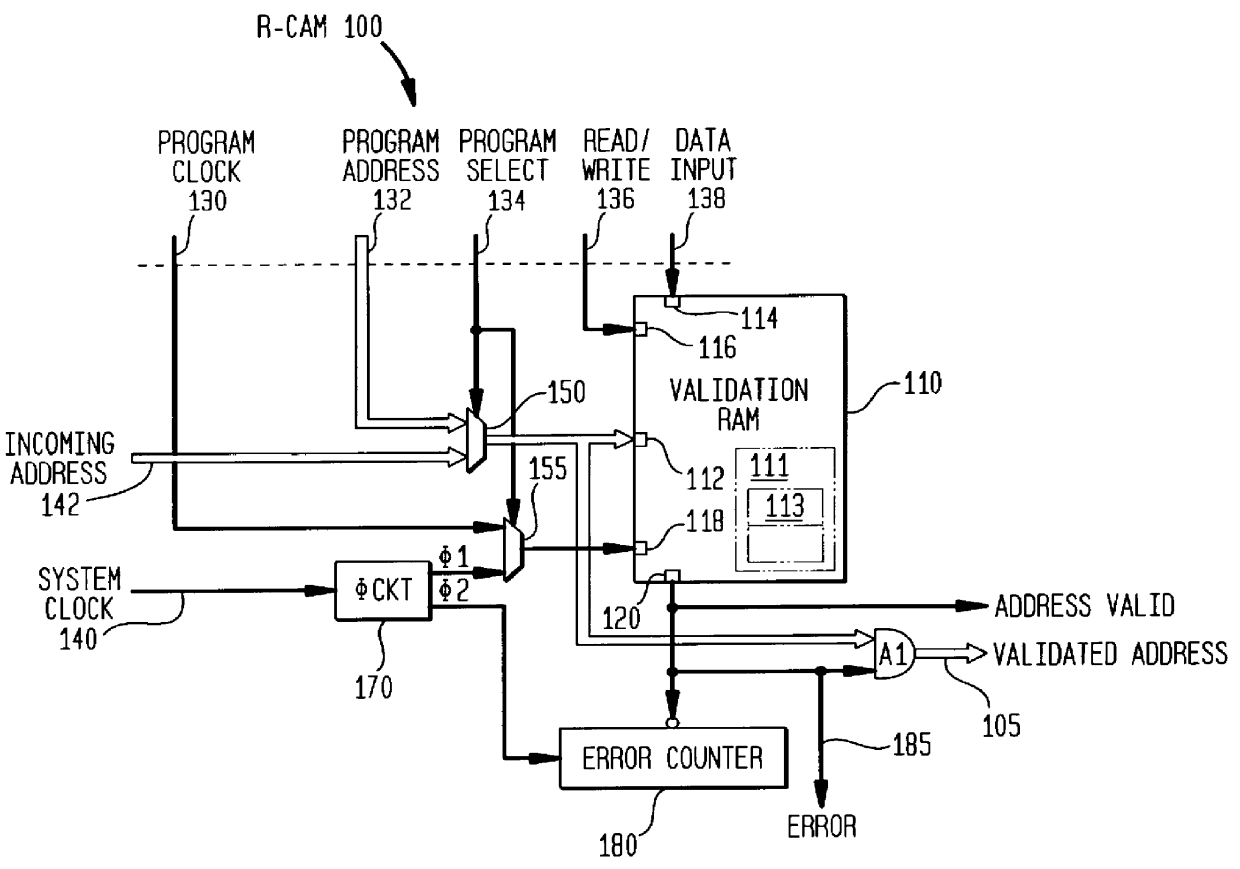
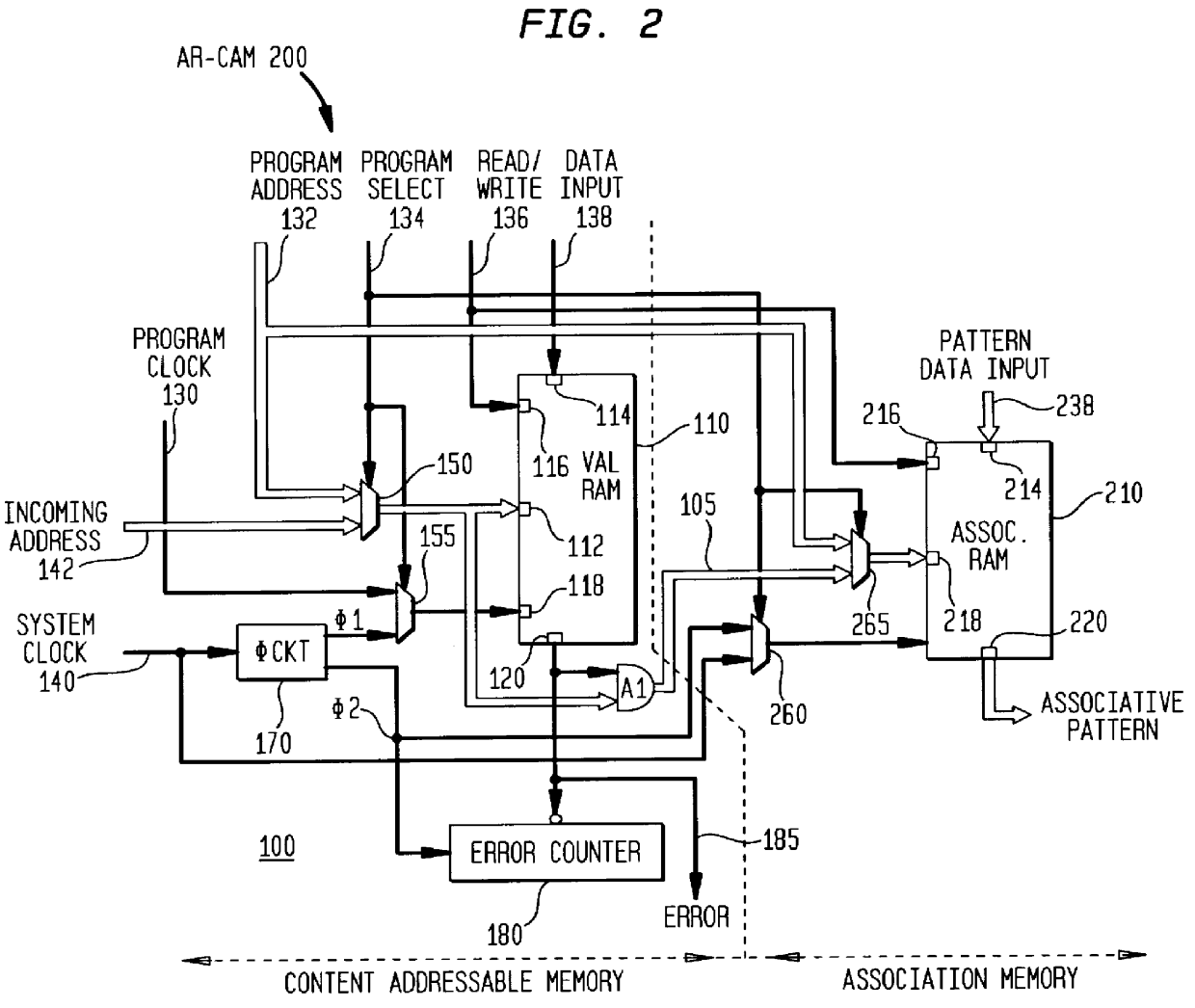
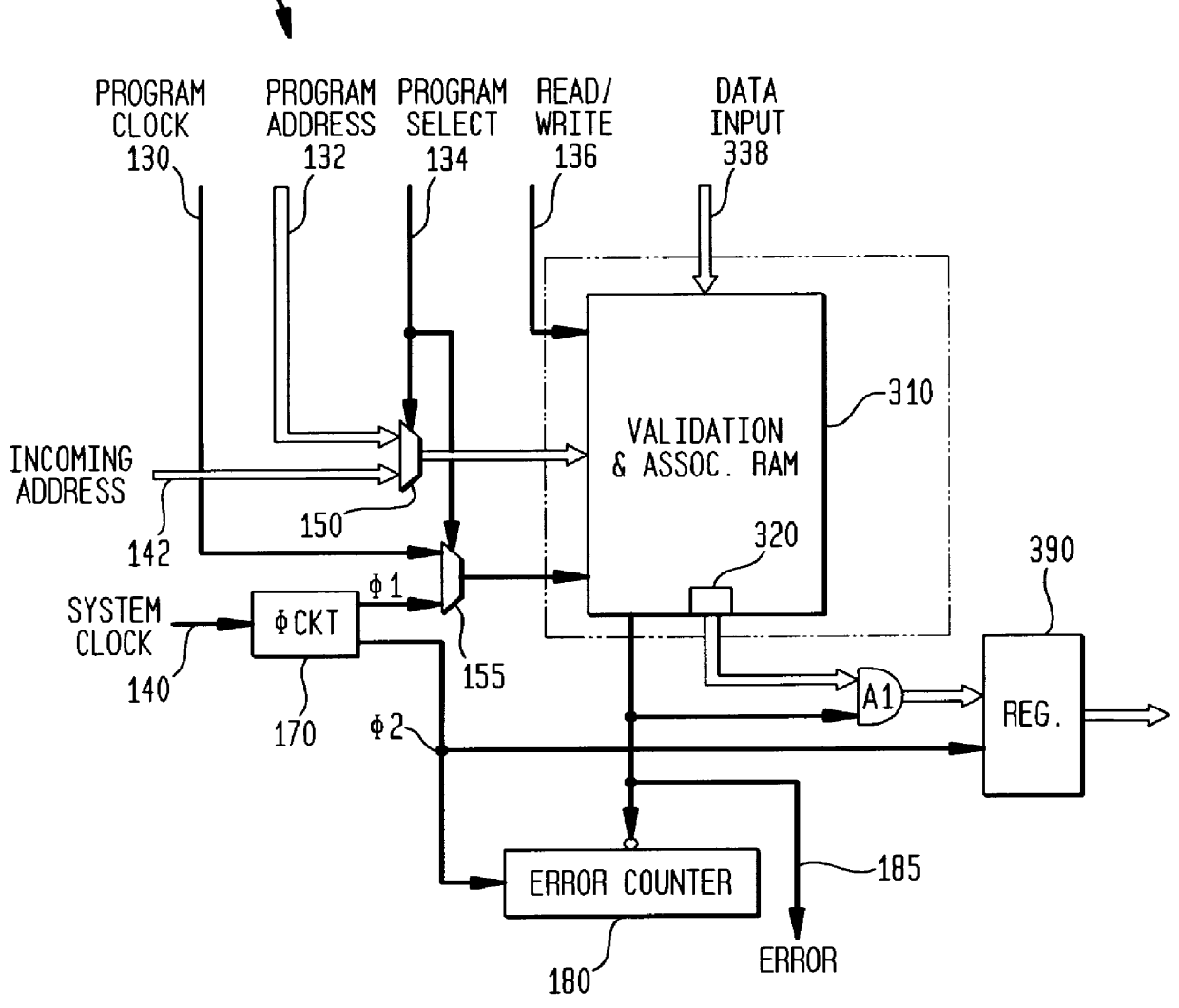
Ram-based associative content-addressable memory device, method of operation thereof and ATM communication switching system employing the same
InactiveUS6097724AIncrease storage capacityLow costData switching by path configurationDigital storageRandom access memoryCam
A memory device, a method of content-addressing a memory device to validate an incoming pattern and an Asynchronous Transfer Mode (ATM) communication switching system incorporating the device or the method. In one embodiment, the device includes: (1) a validation random access memory (RAM) having a plurality of addressable locations therein, the addressable locations containing validation indicators corresponding to patterns that have been programed into the validation RAM and (2) circuitry, coupled to the validation RAM, that provides an incoming pattern to the validation RAM and retrieves a corresponding validation indicator from the validation RAM, the validation indicator indicating whether the incoming pattern had been programed into the validation RAM. The memory device thereby functions as a content-addressable memory (CAM).
Owner:LUCENT TECH INC
System and method for communicating asynchronous transfer mode cells in a network environment
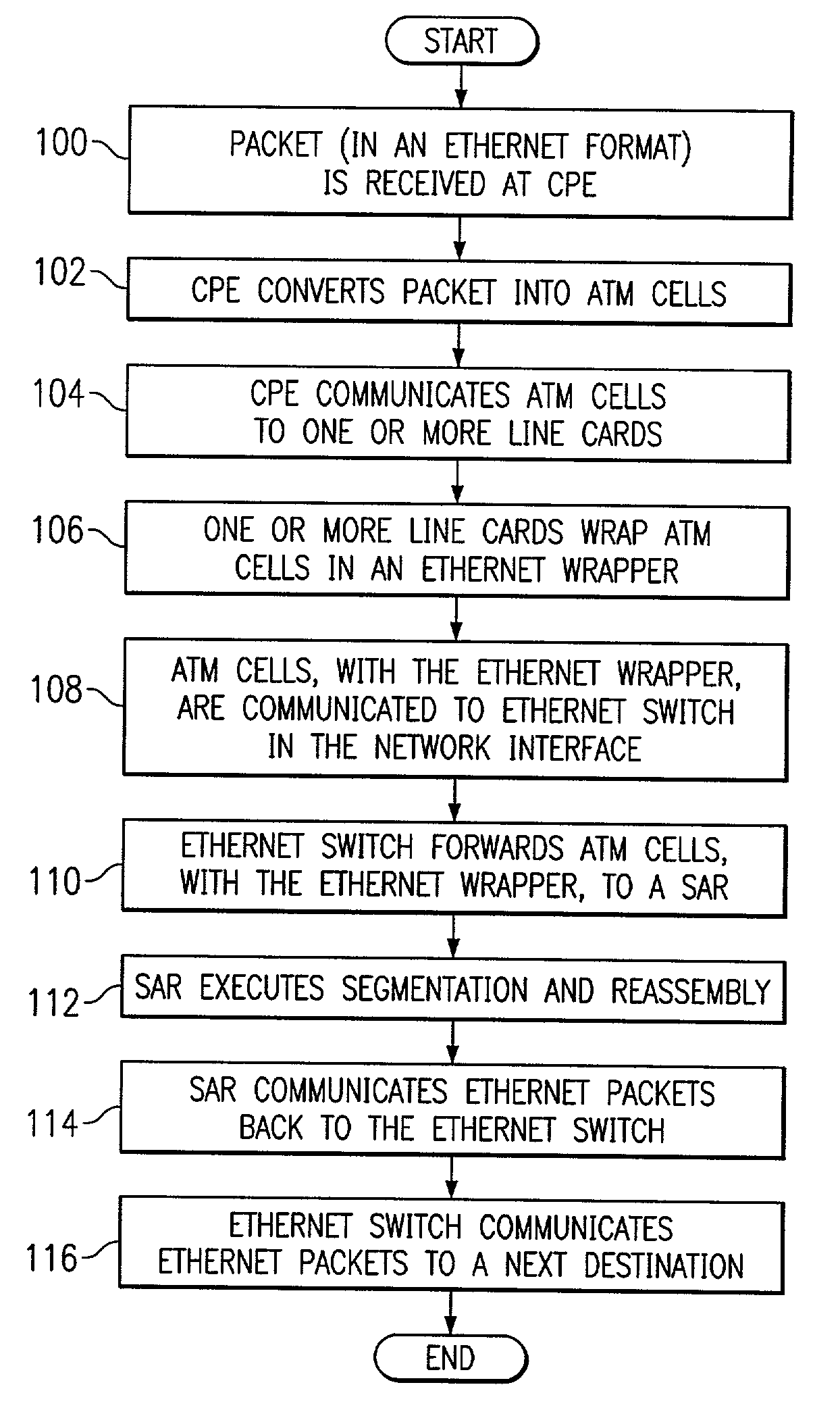
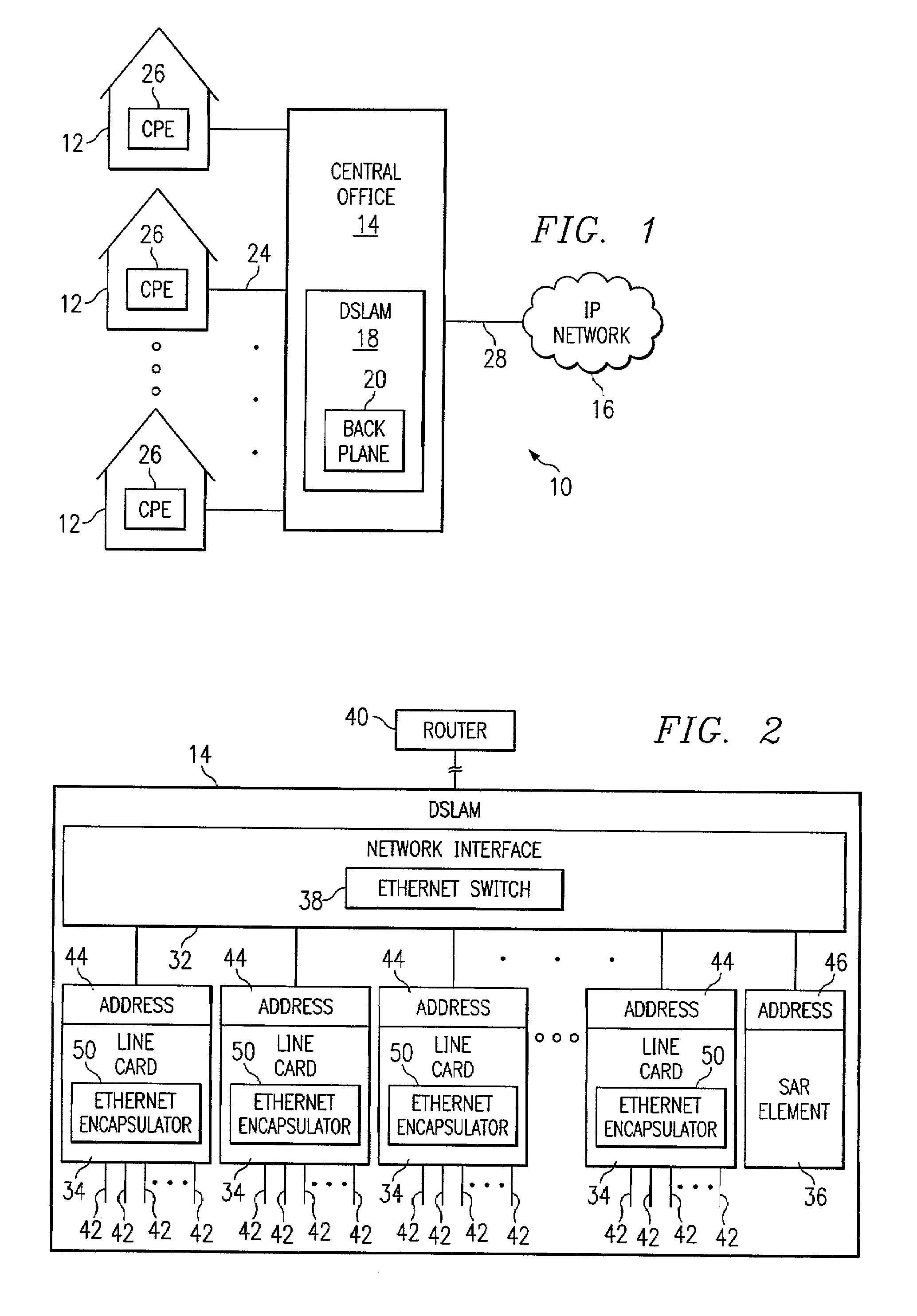
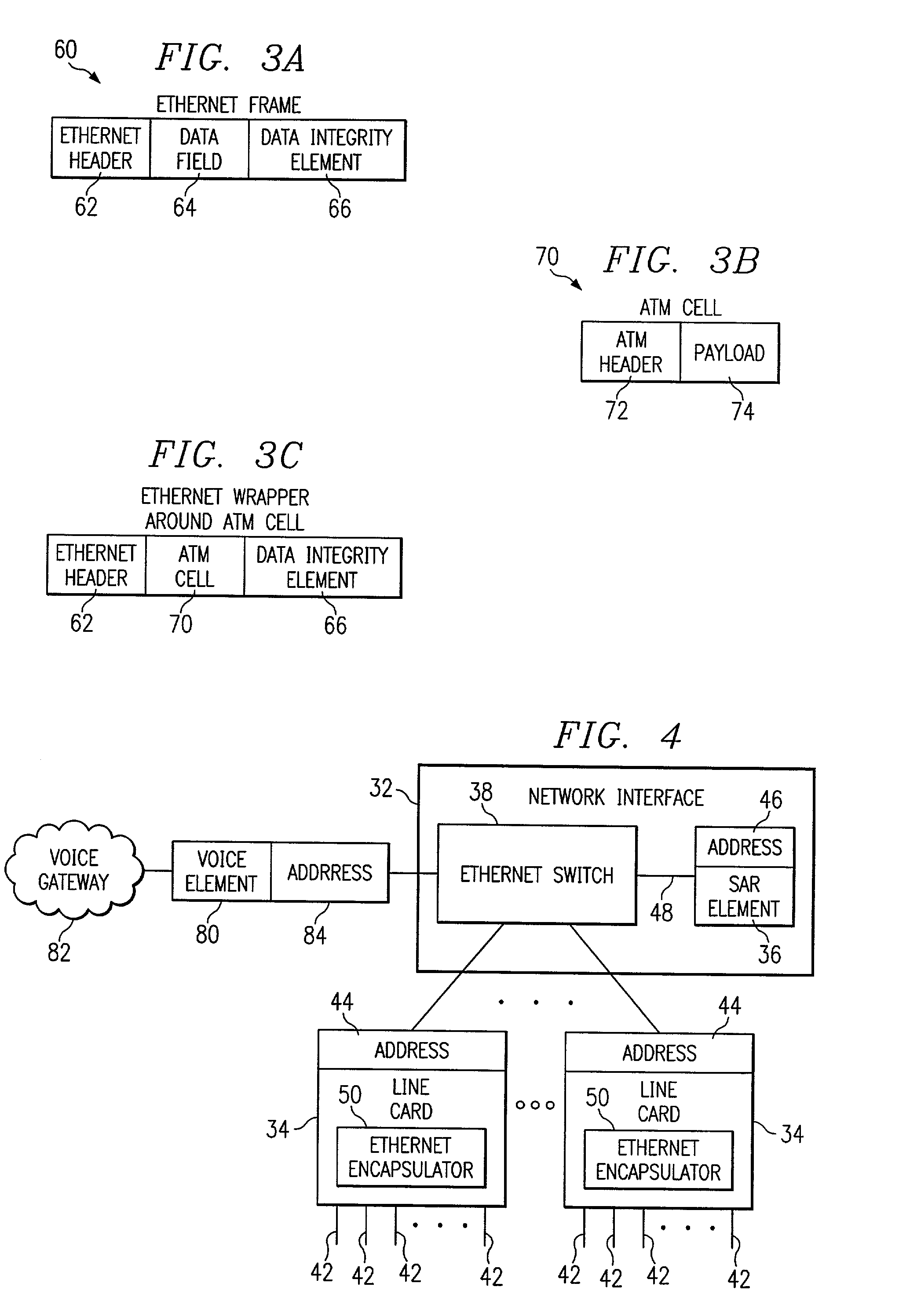
InactiveUS7136384B1Accurate receptionGood flexibilityTime-division multiplexData switching by path configurationData integrityLine card
A method for communicating data is provided that includes receiving an asynchronous transfer mode (ATM) cell at a line card and generating an Ethernet frame that comprises the received ATM cell, an Ethernet-compatible header, and a data integrity element. The Ethernet frame is communicated to a first destination. The Ethernet frame is received at the first destination and directed to a second destination. At the second destination, the Ethernet frame is segmented into portions and reassembled in order to form an Ethernet packet. The Ethernet packet is then communicated to the first destination.
Owner:CISCO TECH INC
Method and system for retrieving link management interface status for a logical port
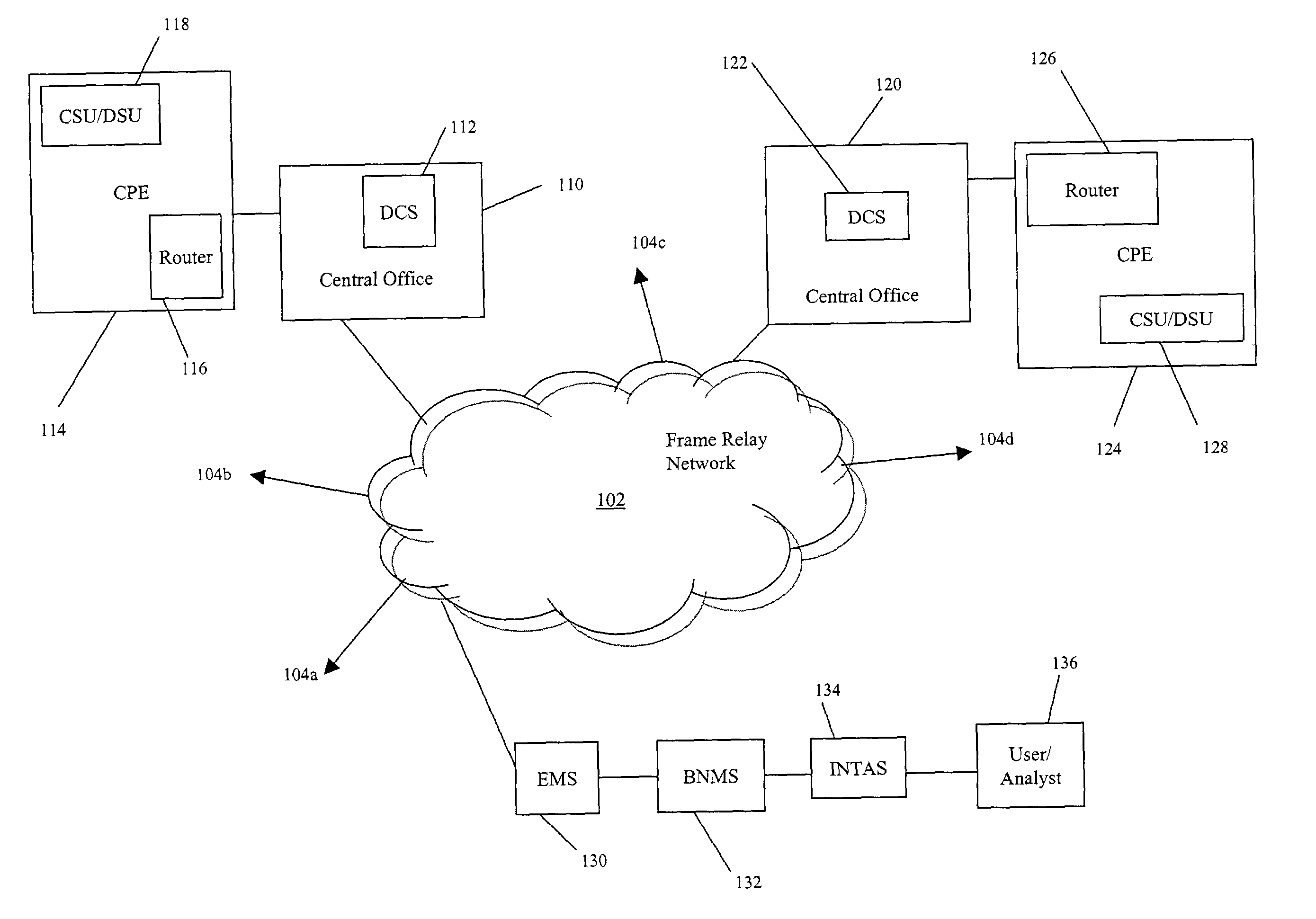
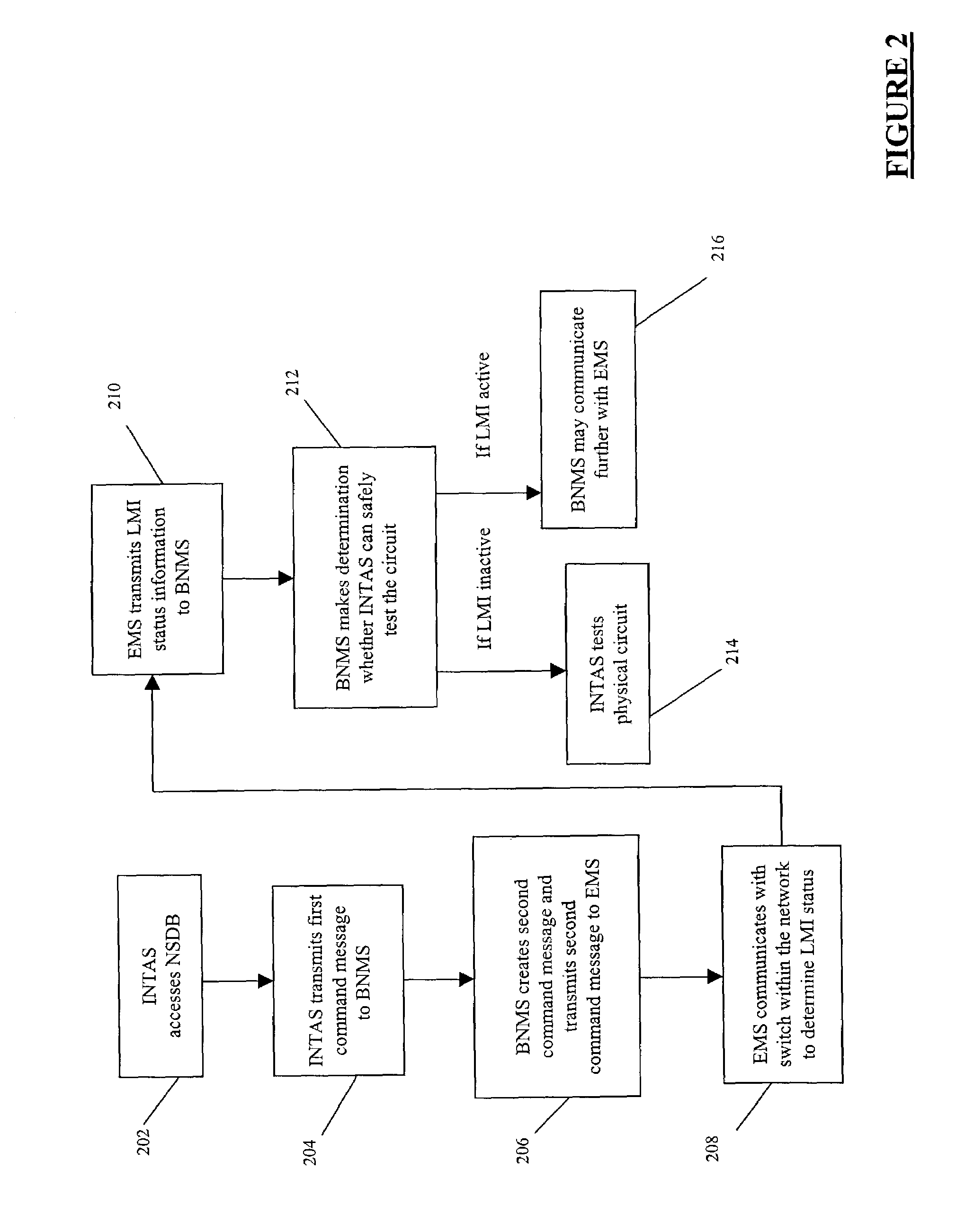
InactiveUS7209452B2Reduce equipment costsReduce personnel costsError preventionTransmission systemsFrame RelayIntegration testing
Systems and methods for obtaining logical layer information in a frame relay and / or asynchronous transfer mode (ATM) network are described. In an exemplary embodiment, a physical layer test system, such as an integrated testing and analysis system, communicates with a broadband network management system, which in turn communicates with an element management system for a frame relay and / or ATM network.
Owner:AT&T INTPROP I L P
ATM system architecture for the convergence of data, voice and video
ActiveUS6990108B2Increase speedData switching by path configurationNetwork connectionsTraffic capacityComputer network
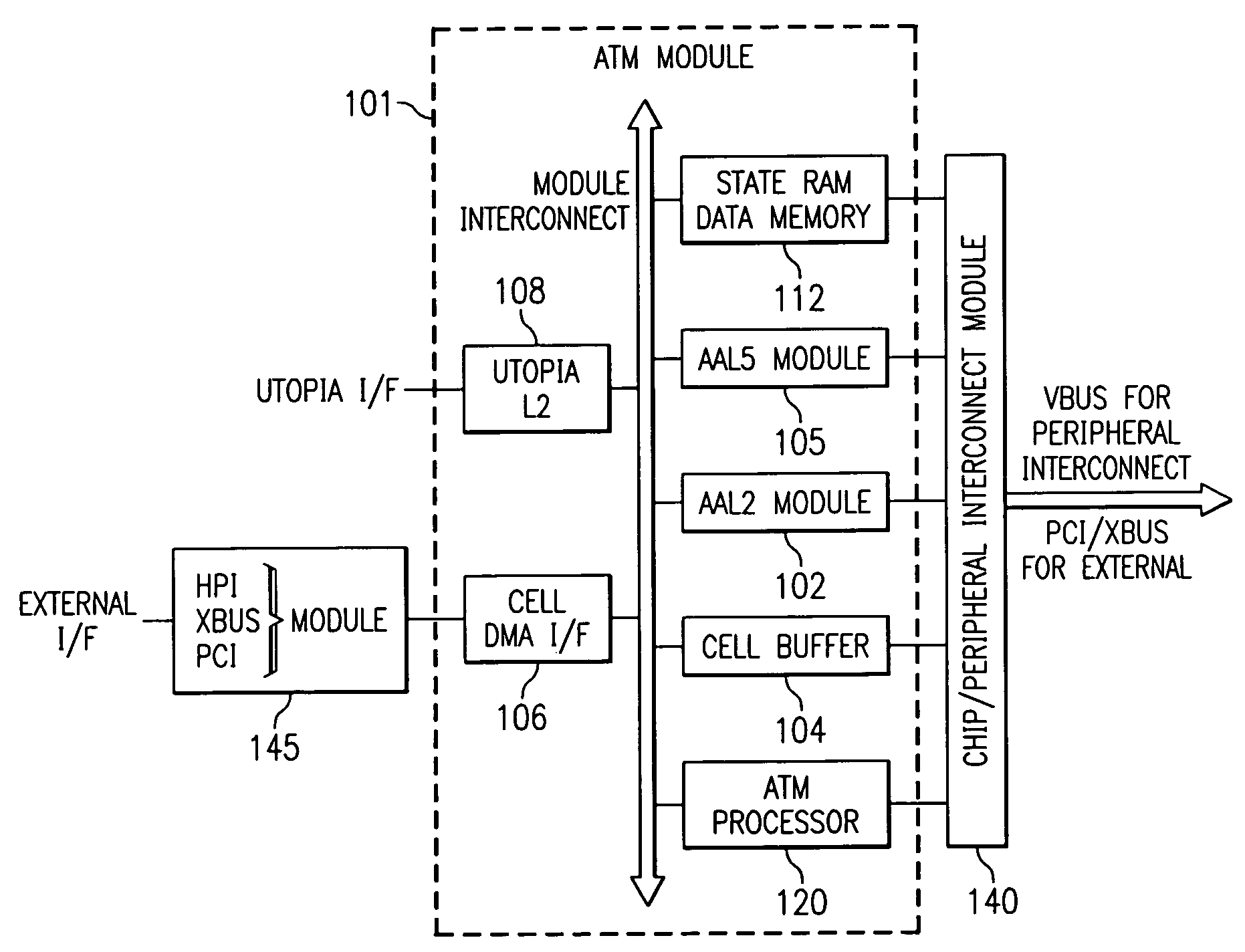
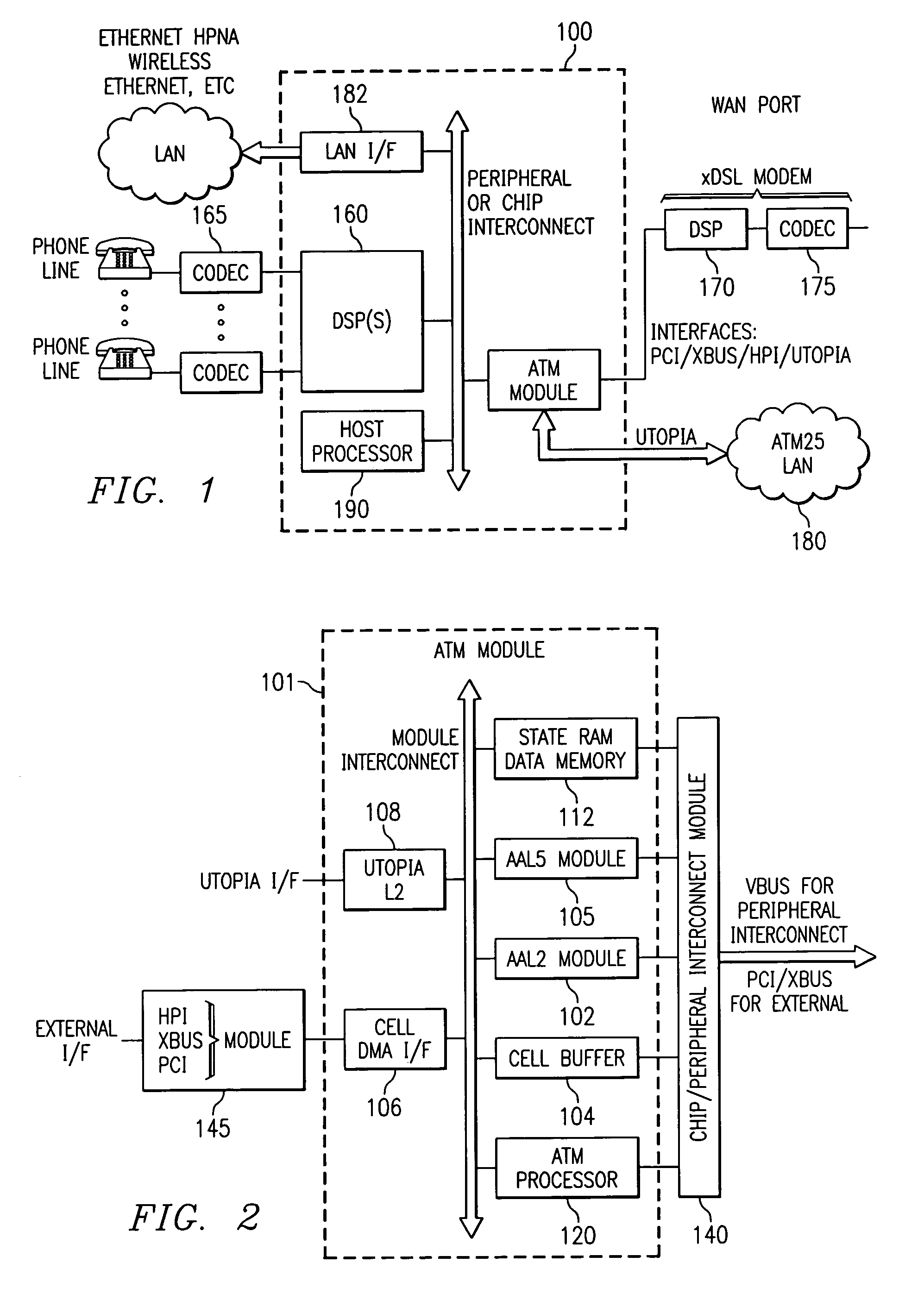
The present invention provides a unitary mechanism for high speed end-to-end telecommunication traffic using an Asynchronous Transfer Mode (ATM) architecture for convergence of video, data and voice in an SOHO application using a DSL router. An ATM module (101) for convergence of the telecommunications traffic includes an ATM processor (120) configured to perform QoS, OAM processing and switching in an ATM system. Function modules (102,104,105) and data ports (106,108) are configurable to transceive data, voice and video traffic in which the traffic is packetized in ATM data cells.
Owner:TEXAS INSTR INC
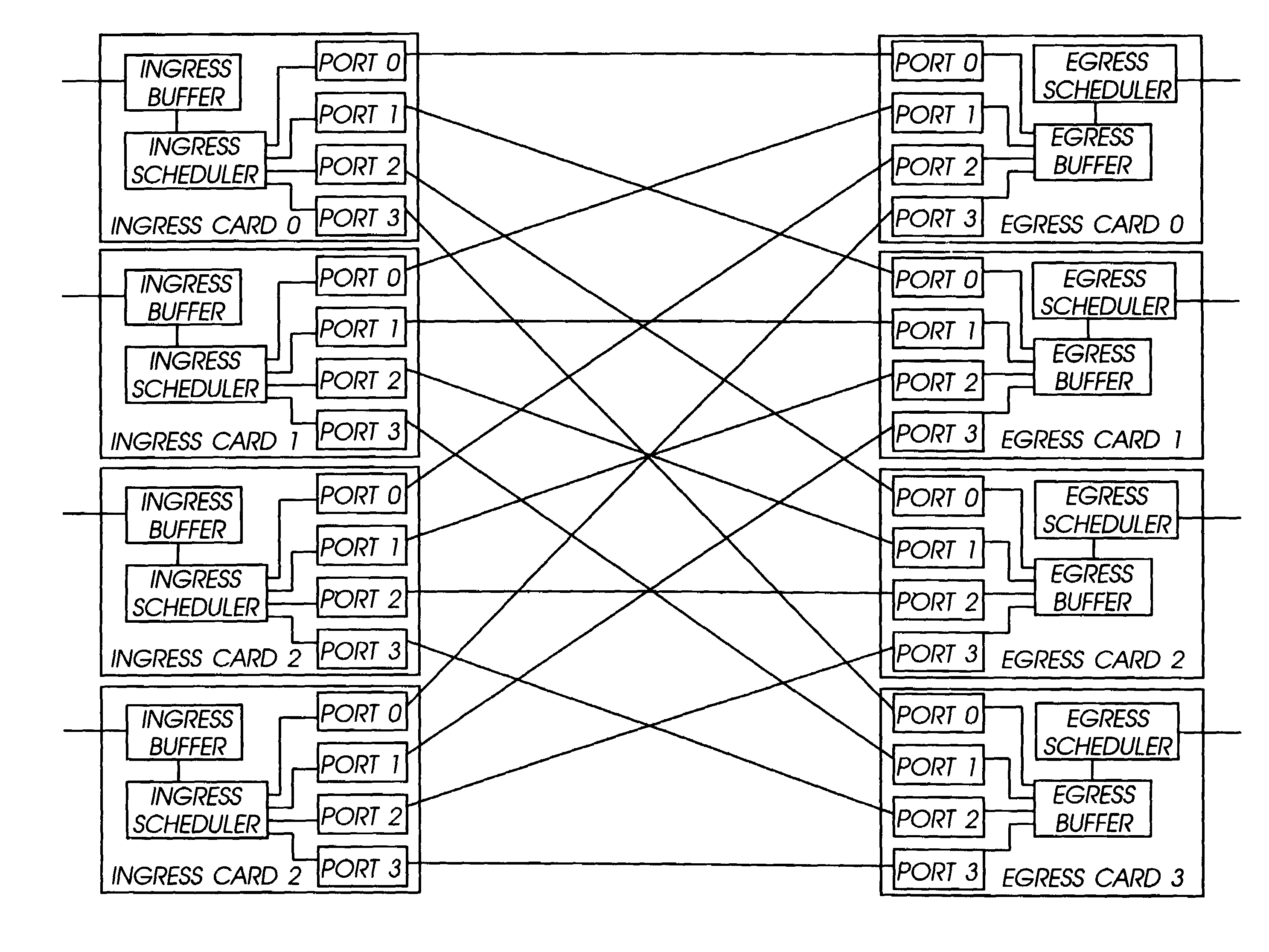
Distributed control of data flow in a network switch
The network switch described herein provides a cell / packet switching architecture that switches between line interface cards across a meshed backplane. In one embodiment, the switching can be accomplished at, or near, line speed in a protocol independent manner. The protocol independent switching provides support for various applications including Asynchronous Transfer Mode (ATM) switching, Internet Protocol (IP) switching, Multiprotocol Label Switching (MPLS) switching, Ethernet switching and frame relay switching. The architecture allows the network switch to provision service on a per port basis. In one embodiment, the network switch provides a non-blocking topology with both input and output queuing and per flow queuing at both ingress and egress. Per flow flow-control can be provided between ingress and egress scheduling. Strict priority, round robin, weighted round robin and earliest deadline first scheduling can be provided.
Owner:FORCE10
Antenna system for communicating with mobile devices
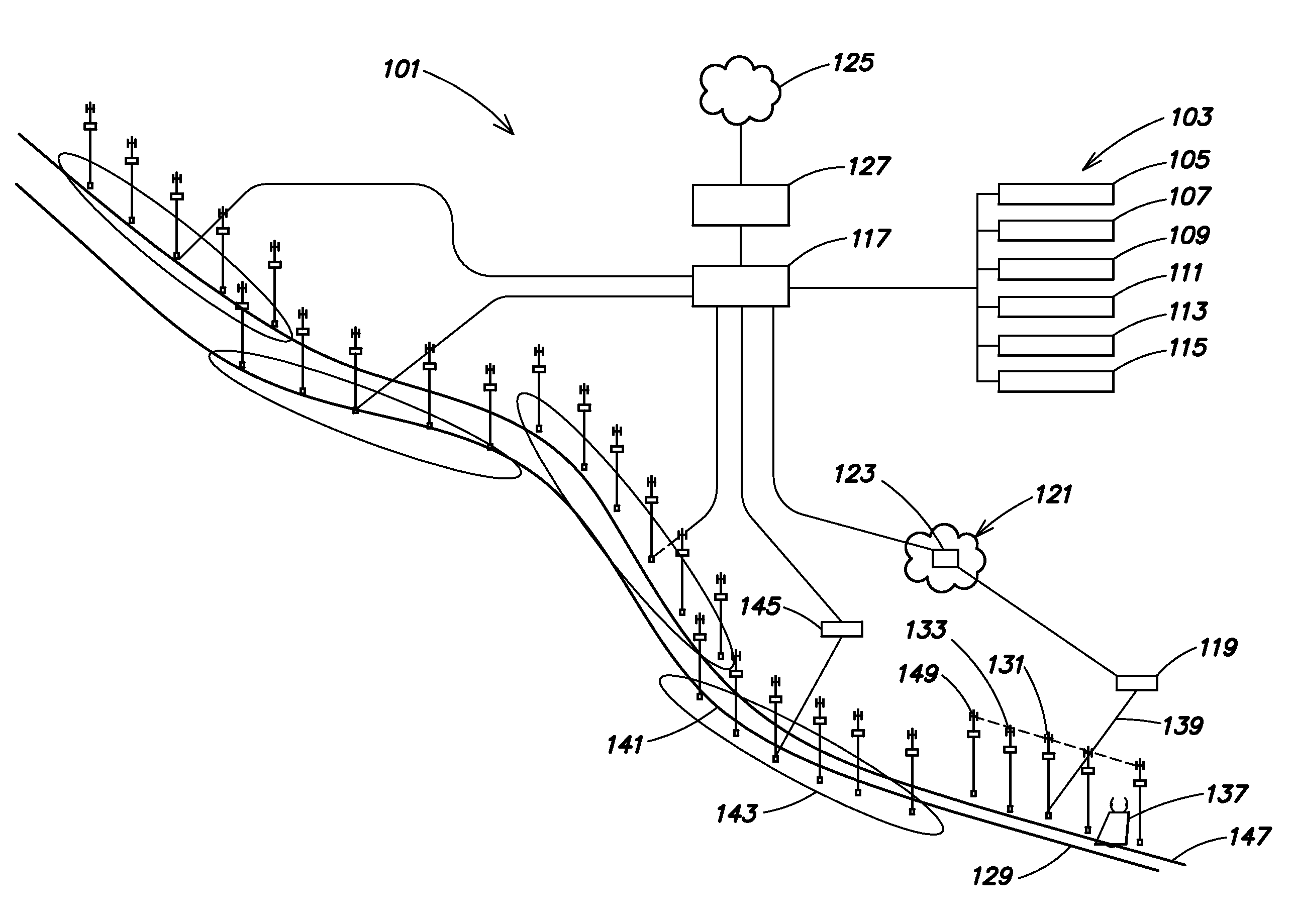
ActiveUS20080042912A1Minimize time neededShorten the timeAntenna arraysAntenna adaptation in movable bodiesTelecommunicationsMobile device
Systems and methods for providing network access to mobile devices that travel with a vehicle, such as a train, a bus, a boat, etc. along or adjacent to a relatively fixed path that may extend over a large geographic area. Mobile devices access the network through stationary access points arranged along or adjacent to the path and communicate with a communication network. The communication network may be arranged as an asynchronous transfer mode (ATM) local area network emulation (LANE) network. One of the mobile devices may be a mobile access point which can couple other mobile devices to the network and record authentication information of other mobile devices so that fast transitions can be made from one stationary access point to another as the vehicle moves along the path.
Owner:WIFI RAIL
Authentication for use of high speed network resources
A method and system for associating a switched virtual circuit (SVC) connection request from an access port in an asynchronous transfer mode (ATM) network to a subscriber and optionally registering an address of the access port in relation to the subscriber. The method and system include receiving a signaling protocol message requesting the SVC connection from the access port, determining whether the signaling protocol message contains subscriber authentication data and, when authenticated, establishing the SVC connection. Furthermore, the SVC connection may be established only if service policies corresponding to the subscriber retrieved from a database indicate that the subscriber is entitled to make SVC connections. The method and system further include registering an address of the access port in the ATM network by substituting the address of the access port for an original subscriber address.
Owner:AT&T LABS
System for providing redundant communication with mobile devices
ActiveUS20080125129A1Minimization needsShorten the timeNetwork topologiesRadio/inductive link selection arrangementsMobile deviceAsynchronous Transfer Mode
Systems and methods for providing network access to mobile devices that travel with a vehicle, such as a train, a bus, a boat, etc. along or adjacent to a relatively fixed path that may extend over a large geographic area. Mobile devices access the network through stationary access points arranged along or adjacent to the path and communicate with a communication network. The communication network may be arranged as an asynchronous transfer mode (ATM) local area network emulation (LANE) network. One of the mobile devices may be a mobile access point which can couple other mobile devices to the network and record authentication information of other mobile devices so that fast transitions can be made from one stationary access point to another as the vehicle moves along the path.
Owner:WIFI RAIL
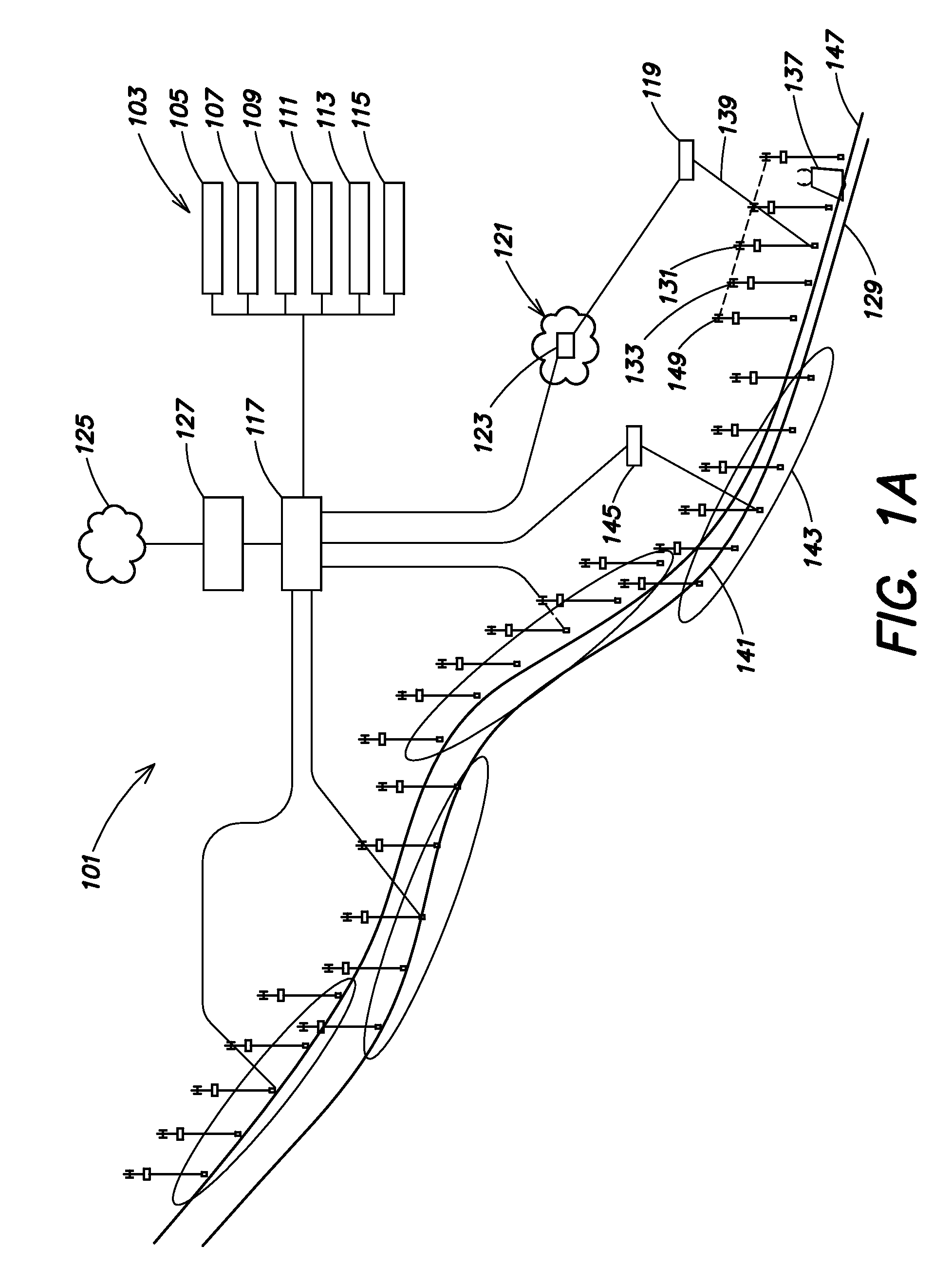
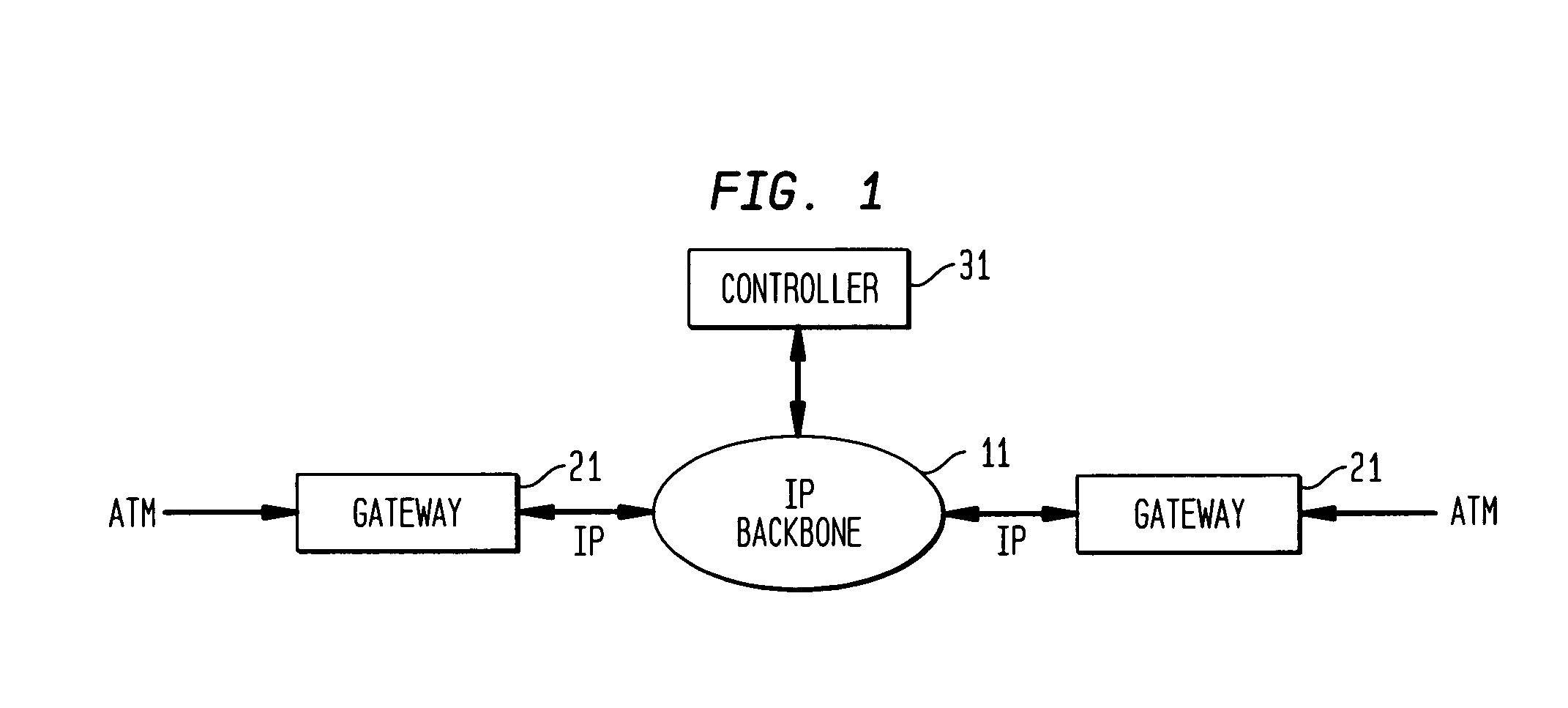
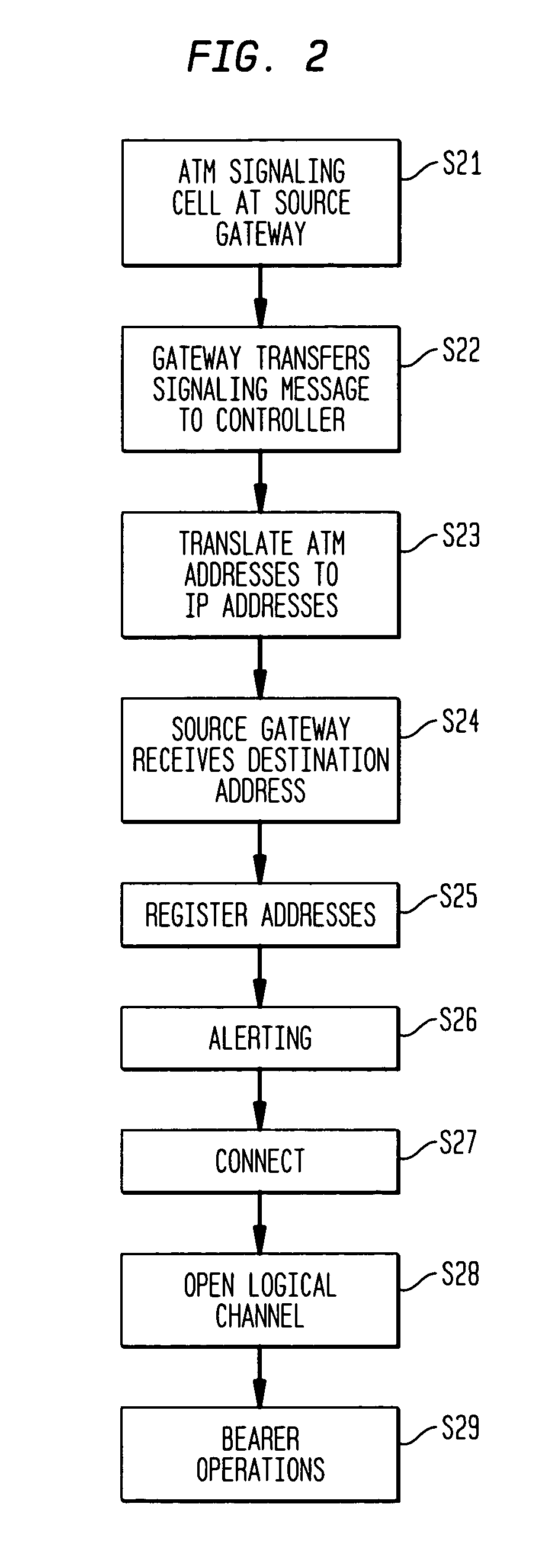
Method and apparatus for transporting ATM cell traffic over IP networks
A method and apparatus for transporting Asynchronous Transfer Mode protocol cells over an Internet Protocol backbone network is disclosed herein. ATM signaling cells are initially received at a source gateway interconnected to the IP backbone. The signaling message is converted to an H.323 message and transmitted to a controller which provides ATM to IP address translation. The corresponding IP address is received at the source gateway and ATM bearer cells of the same call as the original ATM signaling cell are encapsulated with IP headers which include the IP address to form an IP packet which keeps the ATM cells intact within the packet. The IP packet is transferred onto the IP backbone network and routed to the appropriate destination gateway where the IP packets are decapsulated to retrieve the original ATM bearer cell.
Owner:SOUND VIEW INNOVATIONS
Method and system for mediating traffic between an asynchronous transfer mode (ATM) network and an adjacent network
InactiveUS20030123449A1Reduce congestionLower latencyData switching by path configurationStore-and-forward switching systemsComputer networkClass of service
The present invention provides a system and method of mediating cell traffic between an asynchronous transmission mode (ATM) network and an adjacent network, each cell in said cell traffic having a set of transmission parameters related to the ATM network and a respective ATM connection for the cell. In an embodiment the method comprises: (i) identifying for the cell an egress queue family by utilizing a first set of parameters from said set of transmission parameters; (ii) associating with the cell one of a predefined number of egress class of service (COS) levels by mapping a second set of parameters from the set of transmission parameters into one of the egress COS levels; (iii) utilizing the egress COS level associated with the cell to select an egress queue member of the egress queue family identified in step (i), the selected egress queue member being associated with the egress COS level associated with the cell in step (ii); and (iv) providing said cell to said identified queue member for forwarding to said another network.
Owner:ALCATEL CANADA
Queue management with support for multicasts in an asynchronous transfer mode (ATM) switch
InactiveUS6219352B1Quantity minimizationImprove throughput performanceSpecial service provision for substationTime-division multiplexQueue management systemAsynchronous Transfer Mode
An ATM switch supporting multicast transmissions and efficient transmission of frames. A cell is received on a multicast connection and transmitted on several branches / ports. Instead of copying a multicast cell several times for each output branch, only one copy of each multicast cell is maintained. The cell order and the stored cell data form a physical queue. Several logical queues are maintained, one for each output branch. In one embodiment, linked lists are used to maintain the queues. A cell in the physical queue is deleted after all logical queues traverse that cell. A shared tail pointer is used for all the logical queues to minimize additional processing and memory requirements due to the usage of logical queues. The queues enable cells forming a frame to be buffered until the end of frame cell is received, which provides for efficient handling of frames.
Owner:RIVERSTONE NETWORKS
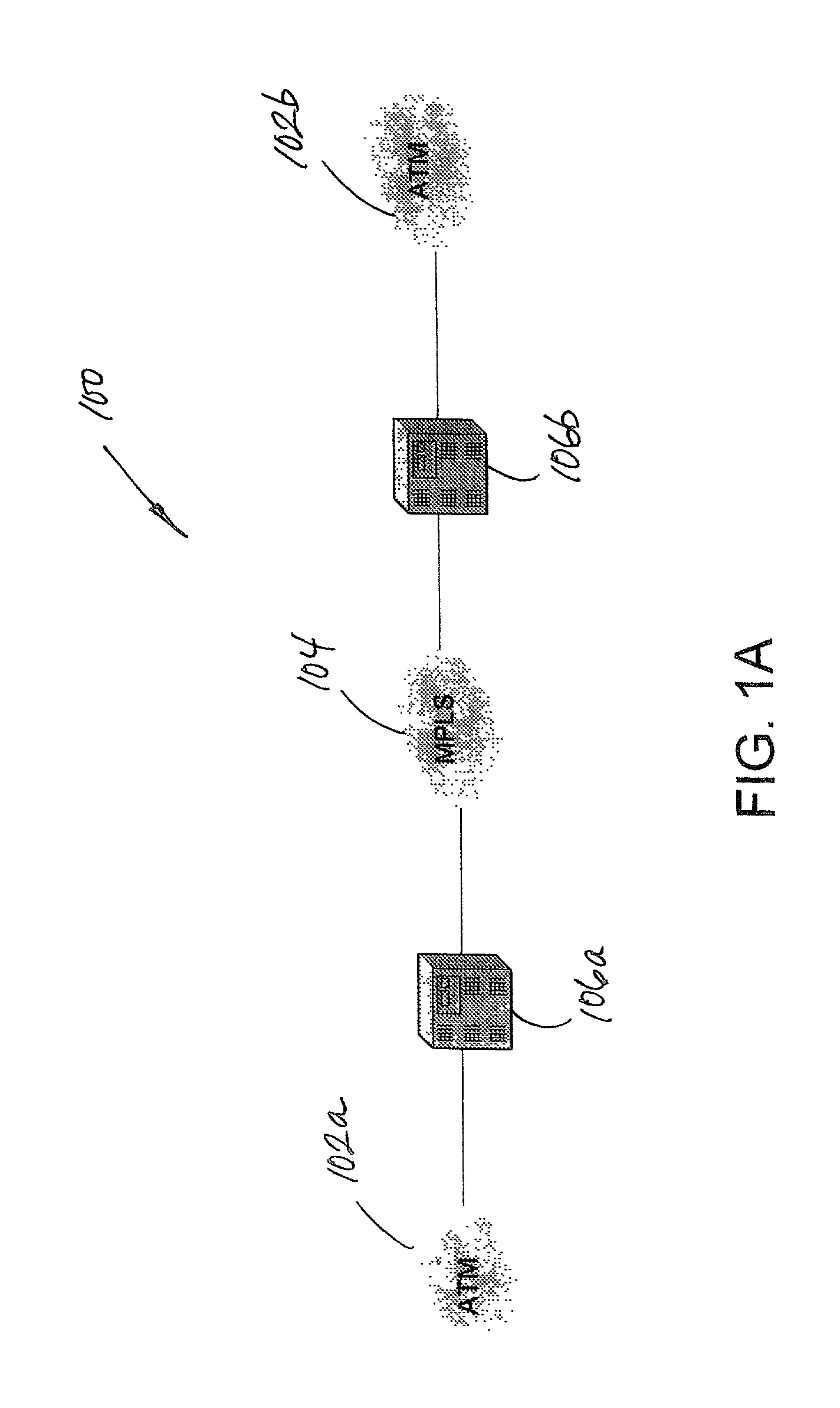
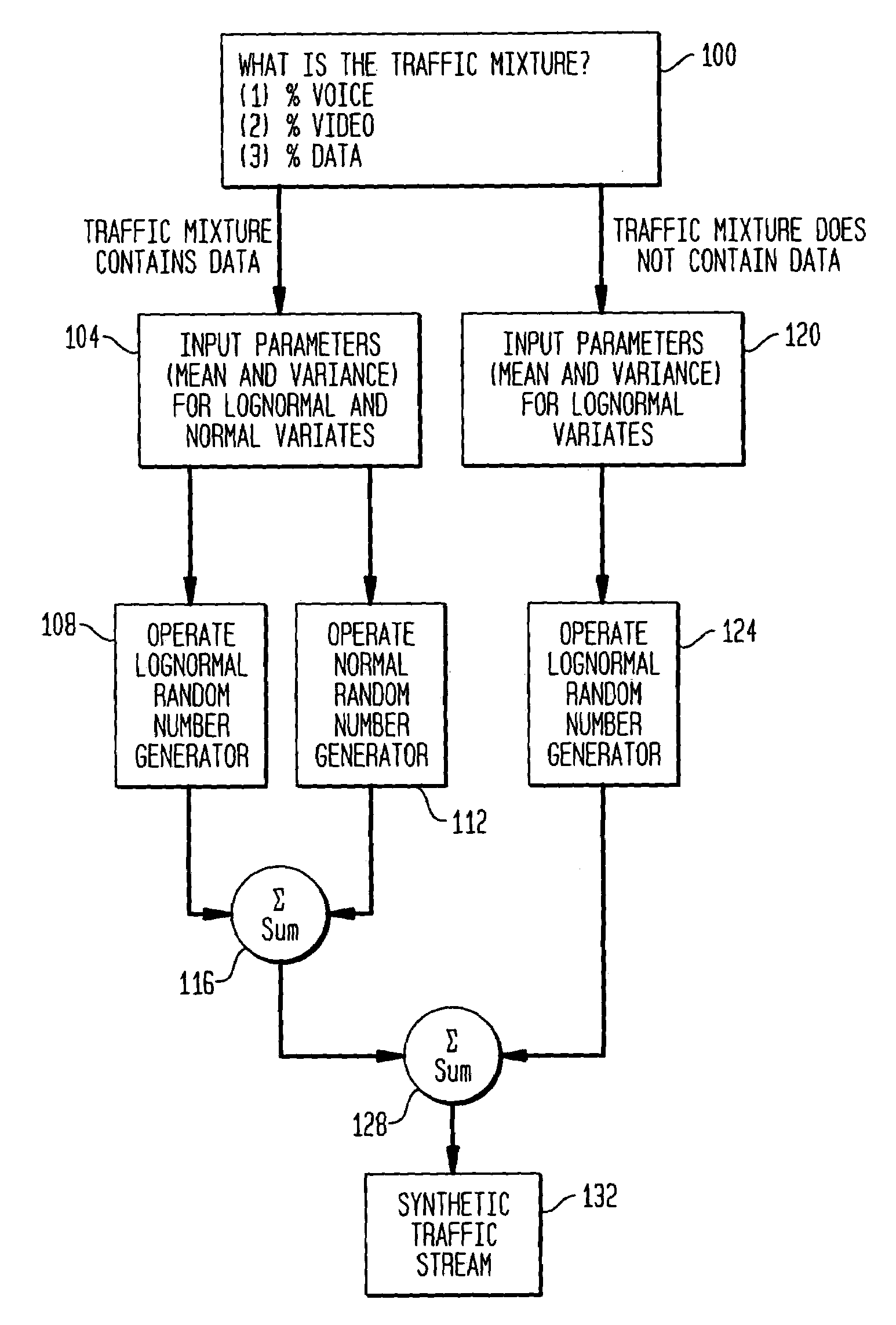
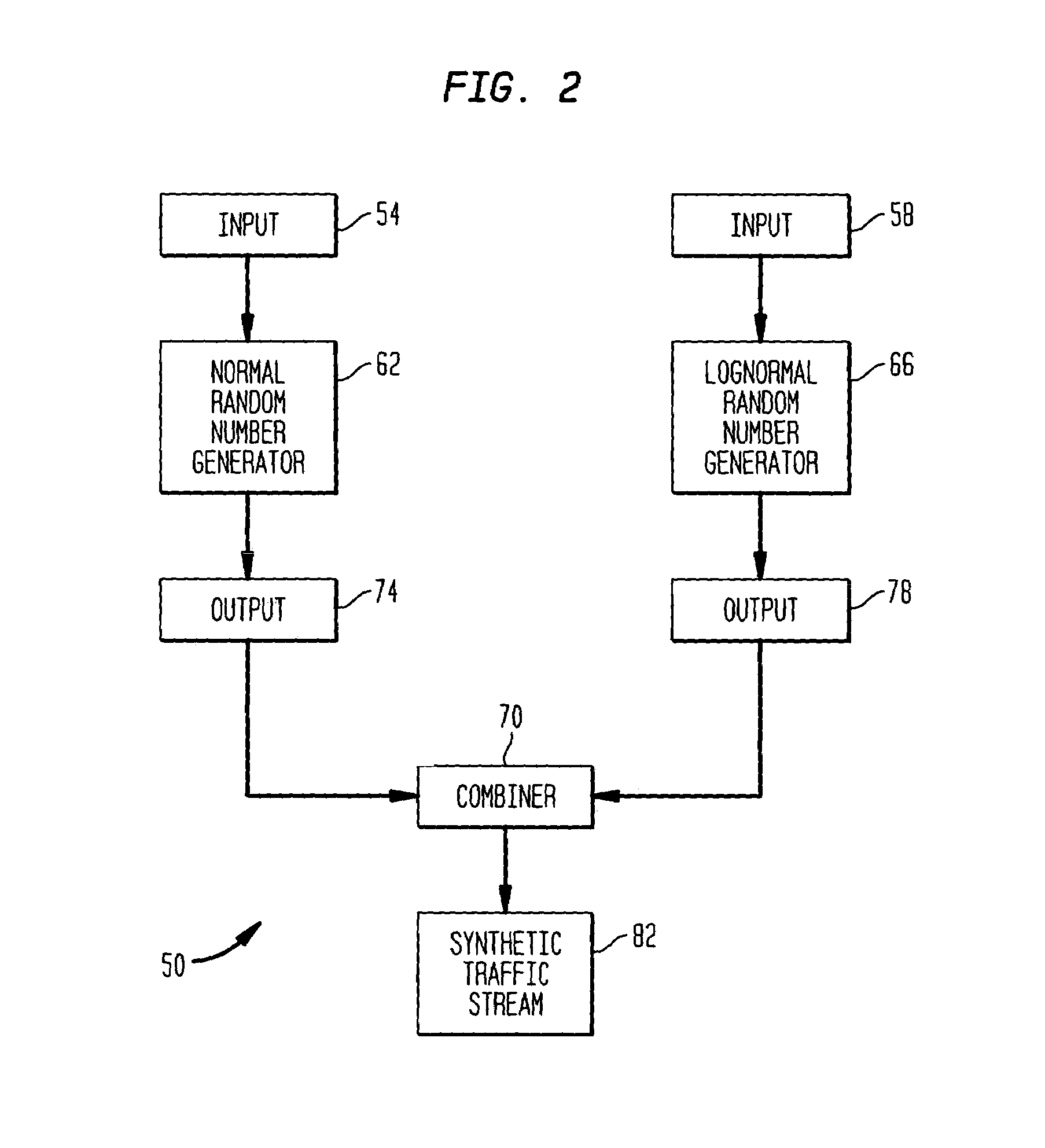
Traffic simulation algorithm for asynchronous transfer mode networks
InactiveUS7013255B1The effect is accurateAnalogue computers for electric apparatusDigital computer detailsTraffic capacityNetwork packet
The present invention is directed to a traffic simulation algorithm for an asynchronous transfer mode communications (ATM) network. The algorithm recognizes that packets in ATM networks can have interarrival times that are lognormally distributed or lognormally and normally distributed. Lognormal and, in some cases, normal random number generators are used to generate packet interarrival times of a synthetic traffic stream.
Owner:AVAYA INC
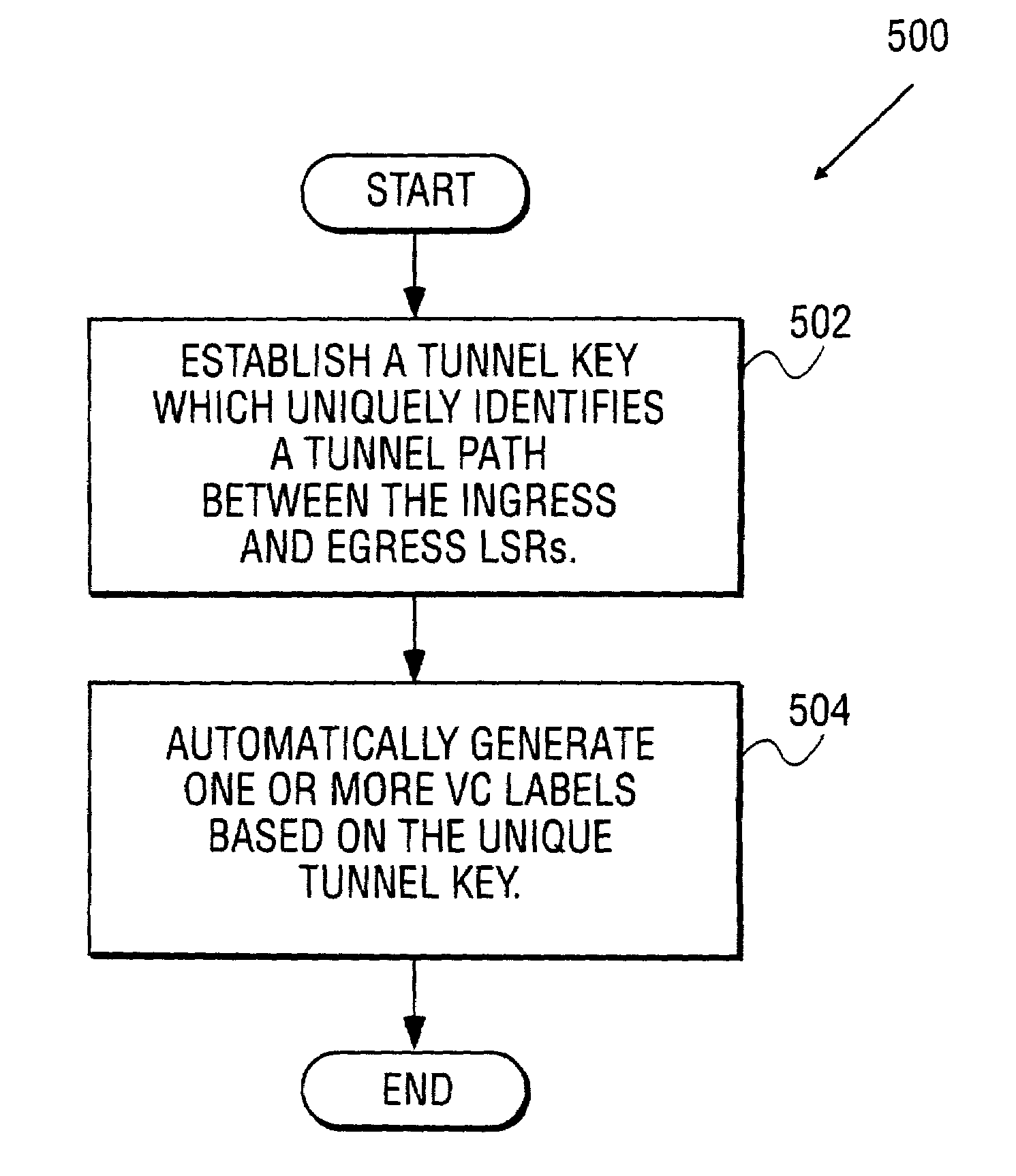
Method and system for assigning multiprotocol label switching (MPLS) VC (VC) labels when transporting asynchronous transfer mode (ATM) data over MPLS network
A first and a second switching node establish a tunnel to transport a packet through a multiprotocol label-switching (MPLS) network. The tunnel is associated with a unique tunnel key. One or more virtual ciruit (VC) labels are automatically generated using the tunnel key.
Owner:CISCO TECH INC
Apparatus and method for identifying boundary of asynchronous transfer mode cell
InactiveUS6151320AData switching by path configurationNetwork connectionsIdentification deviceComputer science
An ATM cell boundary identification apparatus and method. The apparatus comprises an idle cell inserting unit for inserting an idle cell into a cell transmitted from an ATM layer to be matched therewith in its speed; a header error cell generating unit for generating a header error cell by means of header information of the cell transmitted from the idle cell inserting unit; a cell scrambling unit for scrambling payload of the cell received from the header error cell generating unit; a transmission framer for converting the cell obtained in the cell scrambling unit to be suitable to a frame E1; a line interfacing unit for transmitting a transmission frame obtained in the transmission framer to a transmission line after converting it into a bipolar transmission signal, and for transmitting the cell received from the transmission line to a reception framer; a reception framer for identifying a boundary of the cell according to each time slot of the cell transmitted from the line interfacing unit to thereby extract a header error cell; and a header error cell detecting unit for detecting the header error cell extracted from the reception framer, and checking whether the extracted cell is effective or not.
Owner:FENNER INVESTMENTS
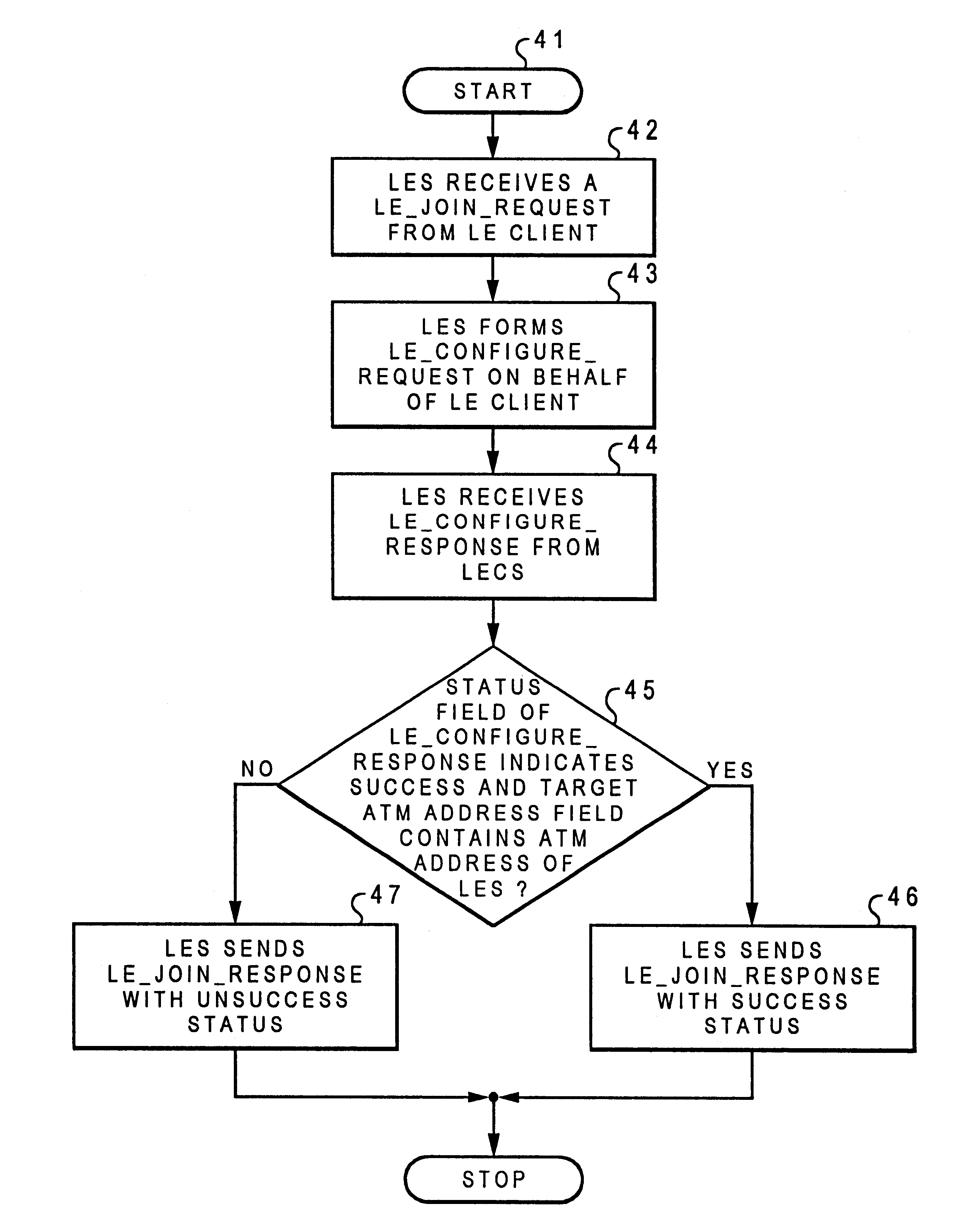
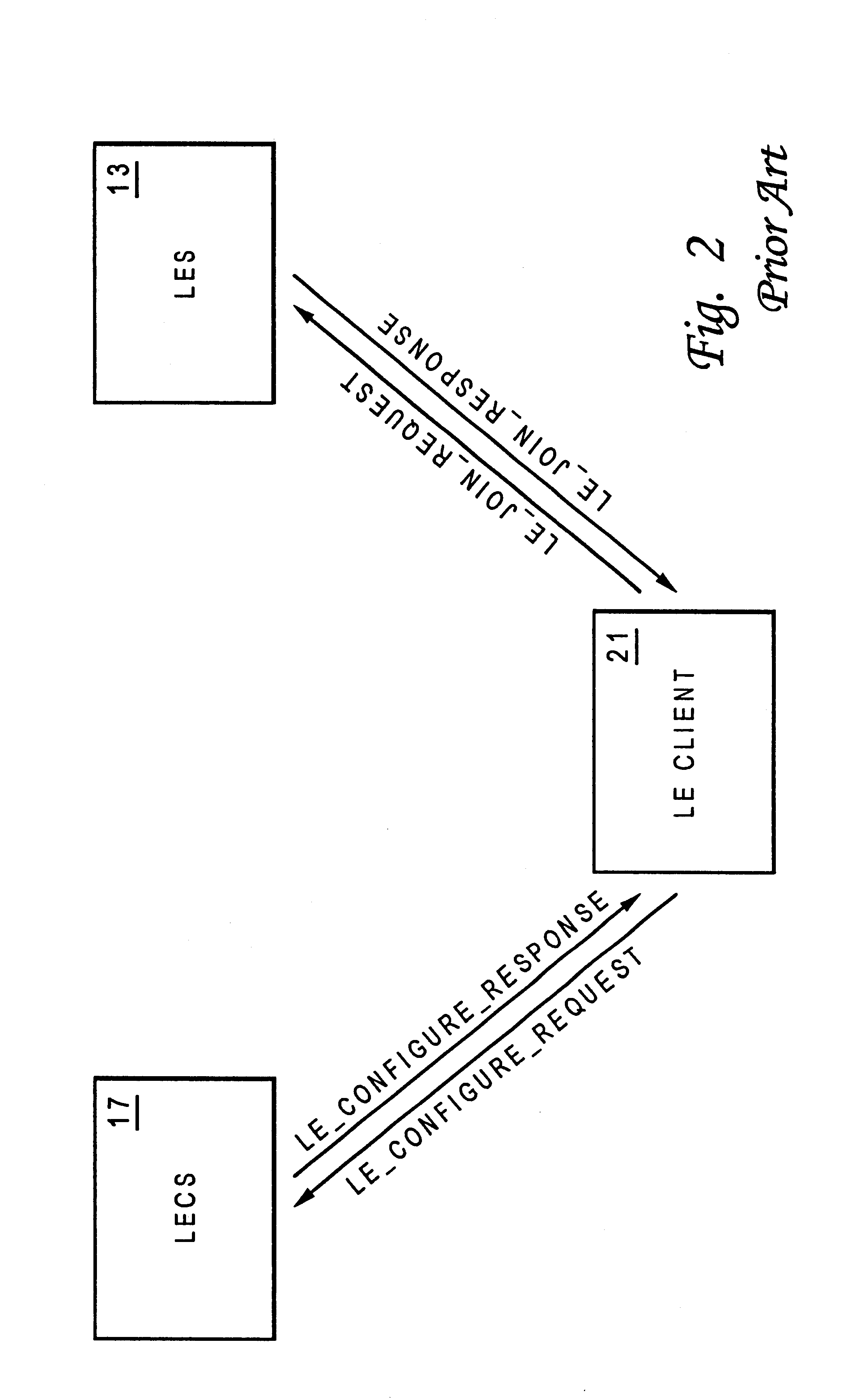
Method and system for providing security to asynchronous transfer mode emulated local-area networks
A method for providing a security mechanism to an Asynchronous Transfer Mode (ATM) emulated local-area network (LAN) is disclosed. The ATM emulated LAN is served by a LAN Emulation Server (LES), a Broadcast and Unknown Server (BUS), and a LAN Emulation Configuration Server (LECS). After receiving a LE_JOIN_REQUEST from an LE client within the emulated LAN, the LES forms a LE_CONFIGURE_REQUEST on behalf of the LE client, by utilizing the information from the LE_JOIN_REQUEST. The LES then sends the LE_CONFIGURE_REQUEST to the LECS. In turn, the LECS sends back a LE_CONFIGURE_RESPONSE to the LES. After receiving the LE_CONFIGURE_RESPONSE from the LECS, a determination is made as to whether or not a status field within the LE_CONFIGURE_RESPONSE indicates a success and a target ATM address field within the LE_CONFIGURE_RESPONSE contains an ATM address of the LES. If both of the above-mentioned conditions are met, the LES then sends a LE_JOIN_RESPONSE with a success status back to the requesting LE client such that the requesting LE client is allowed to join the emulated LAN.
Owner:IBM CORP
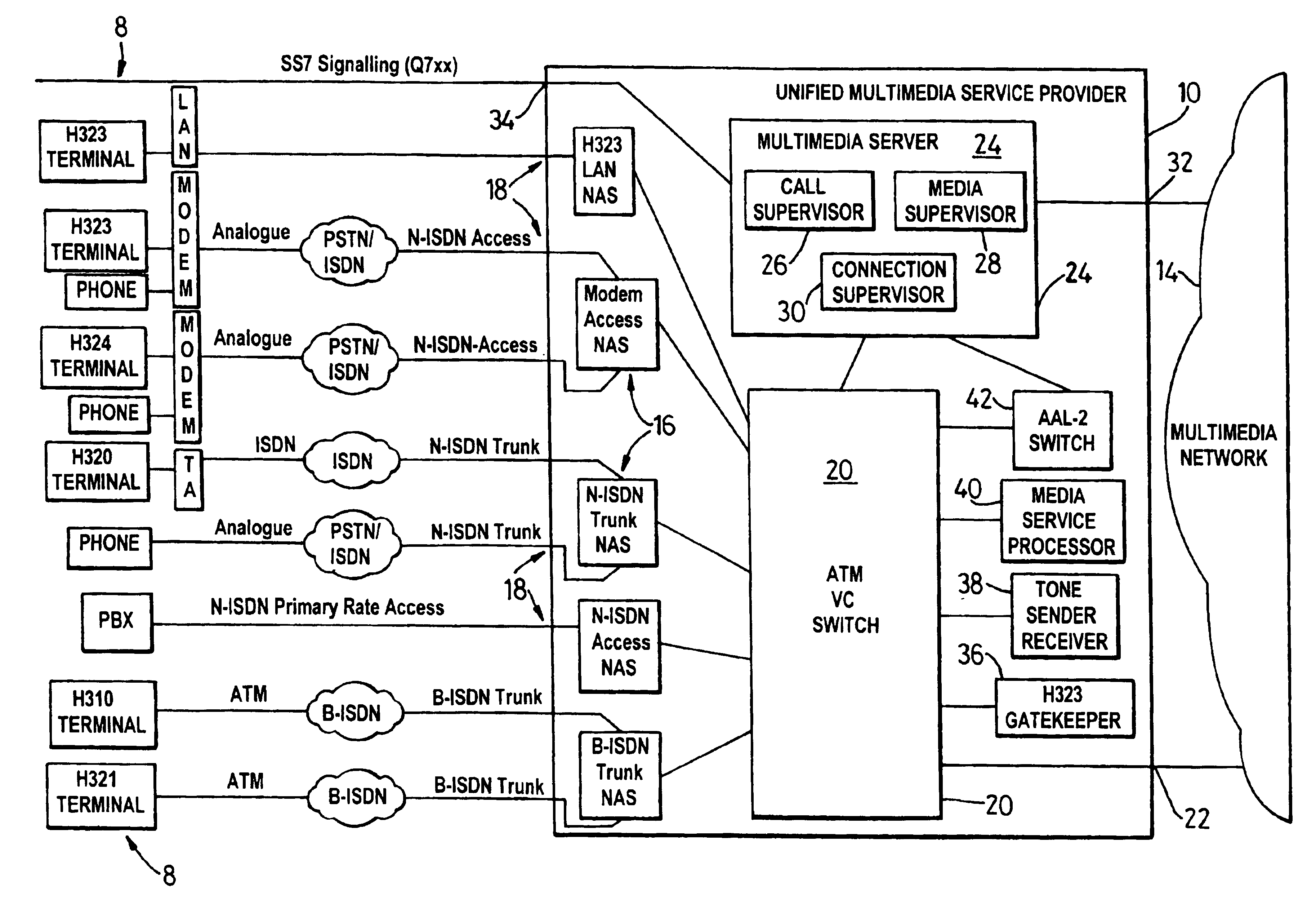
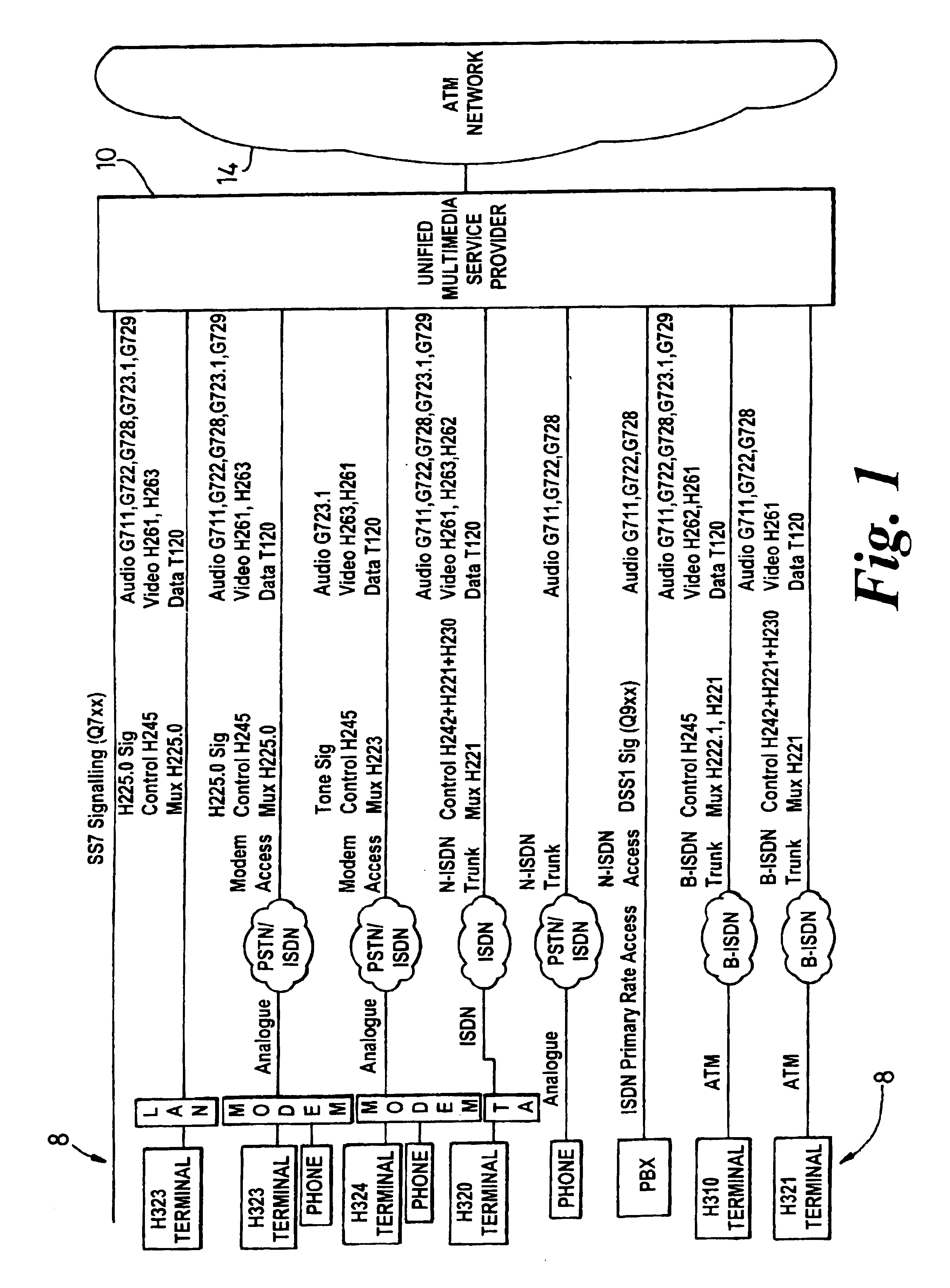
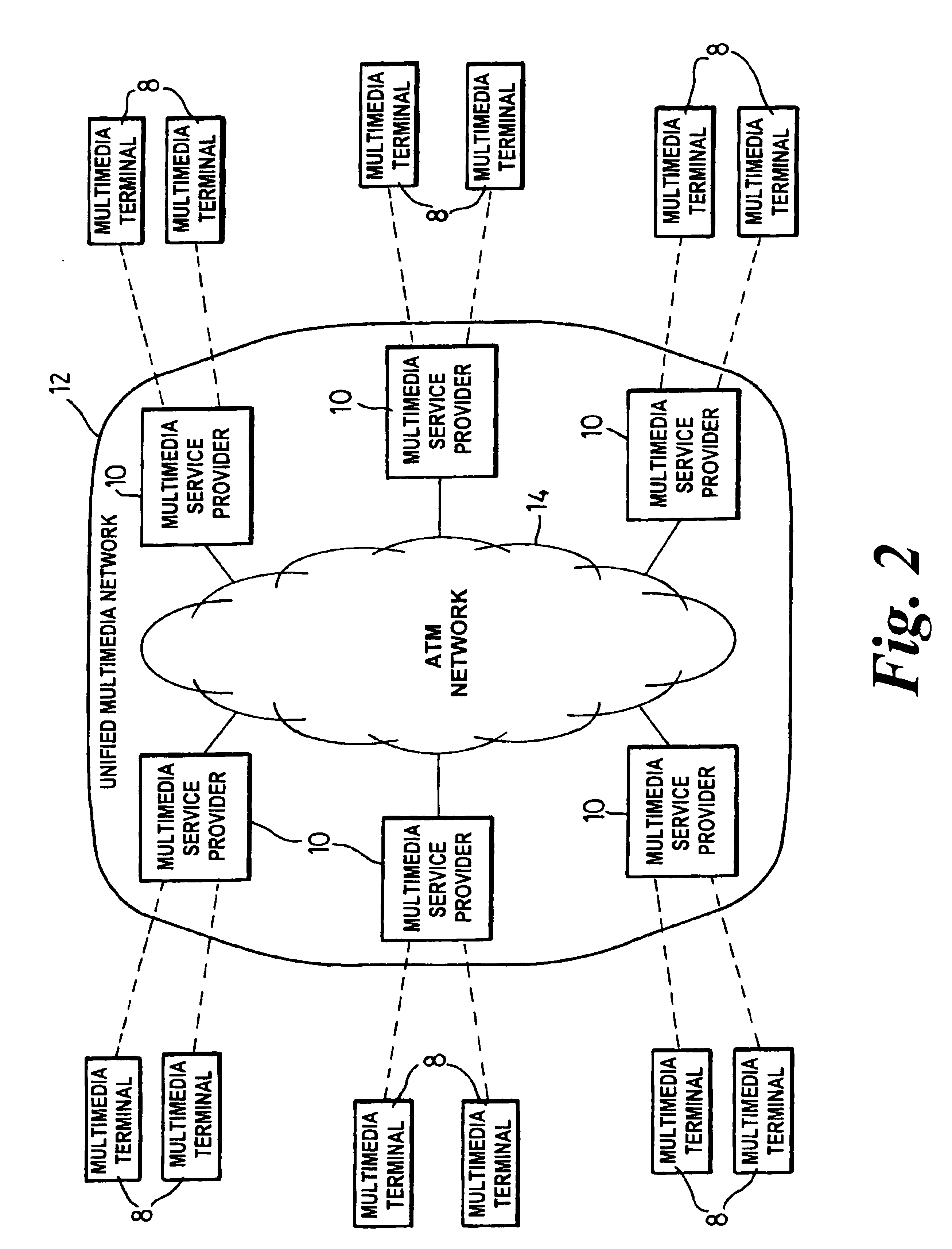
Communications method and apparatus
InactiveUS6937612B1Improve transmission efficiencyQuantity minimizationInterconnection arrangementsTime-division multiplexNetwork access serverTraffic capacity
A method for enabling traffic to be carried between devices which may use different communications protocols employs a multimedia service provide, which provides an interface between two devices or between a device and a multimedia network. The service provider enables conversion between the communications protocols used by the two devices by comparing the protocols used by each device and, preferably, carrying out a conversion which minimises the amount of traffic conversion required. If two devices are interfaced to an intermediate network via respective service providers, the service providers preferably negotiate before communication between the devices begins to ensure, if possible, that traffic conversion is only performed by one of the service providers. Each device is connected to the service provider at a network access server of a type matched to the device type and traffic conversion is carried out as required using an Asynchronous Transfer Mode Virtual Channel switch controlled by a multimedia server.
Owner:RPX CLEARINGHOUSE
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com