Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
1127 results about "Line card" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
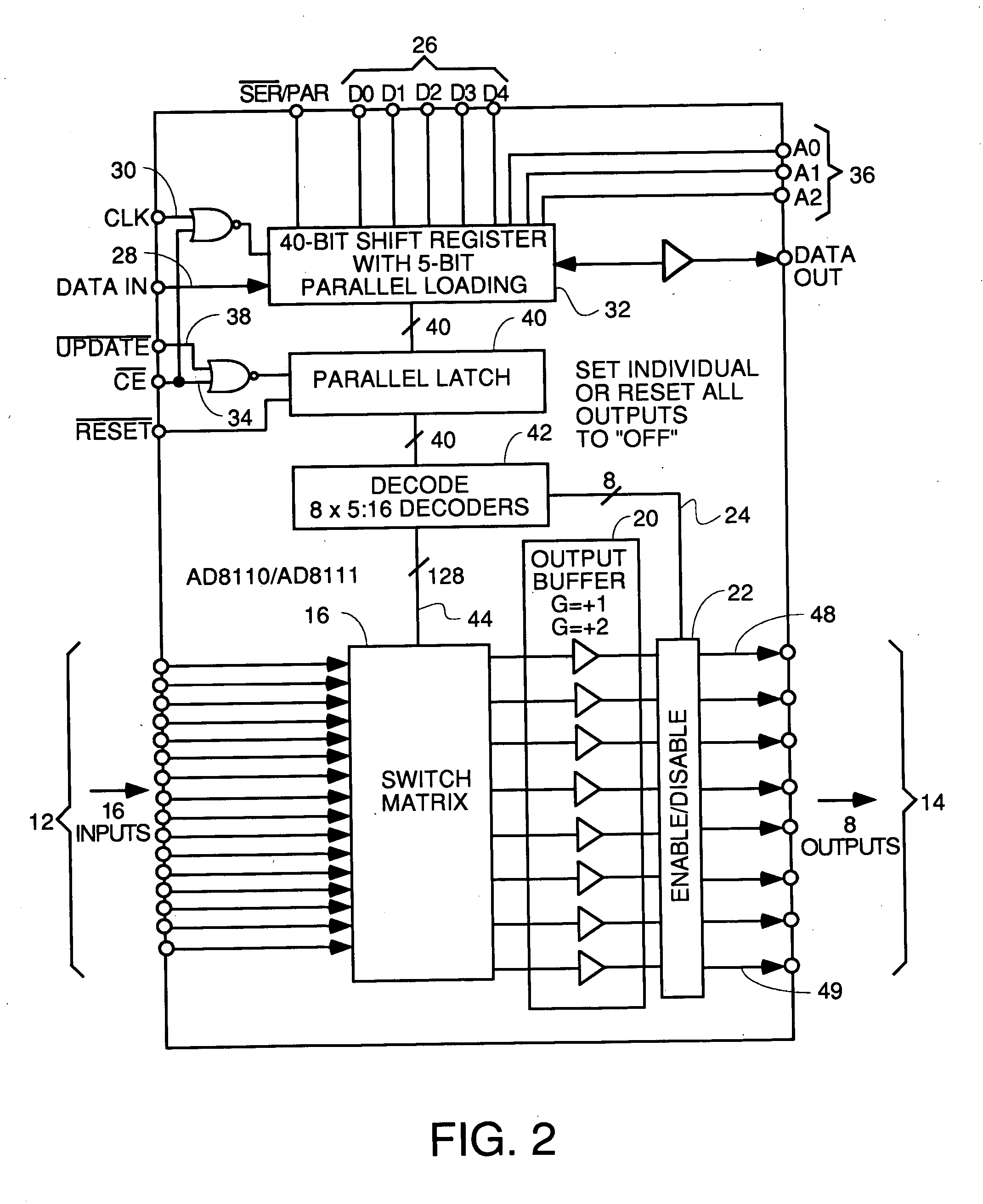
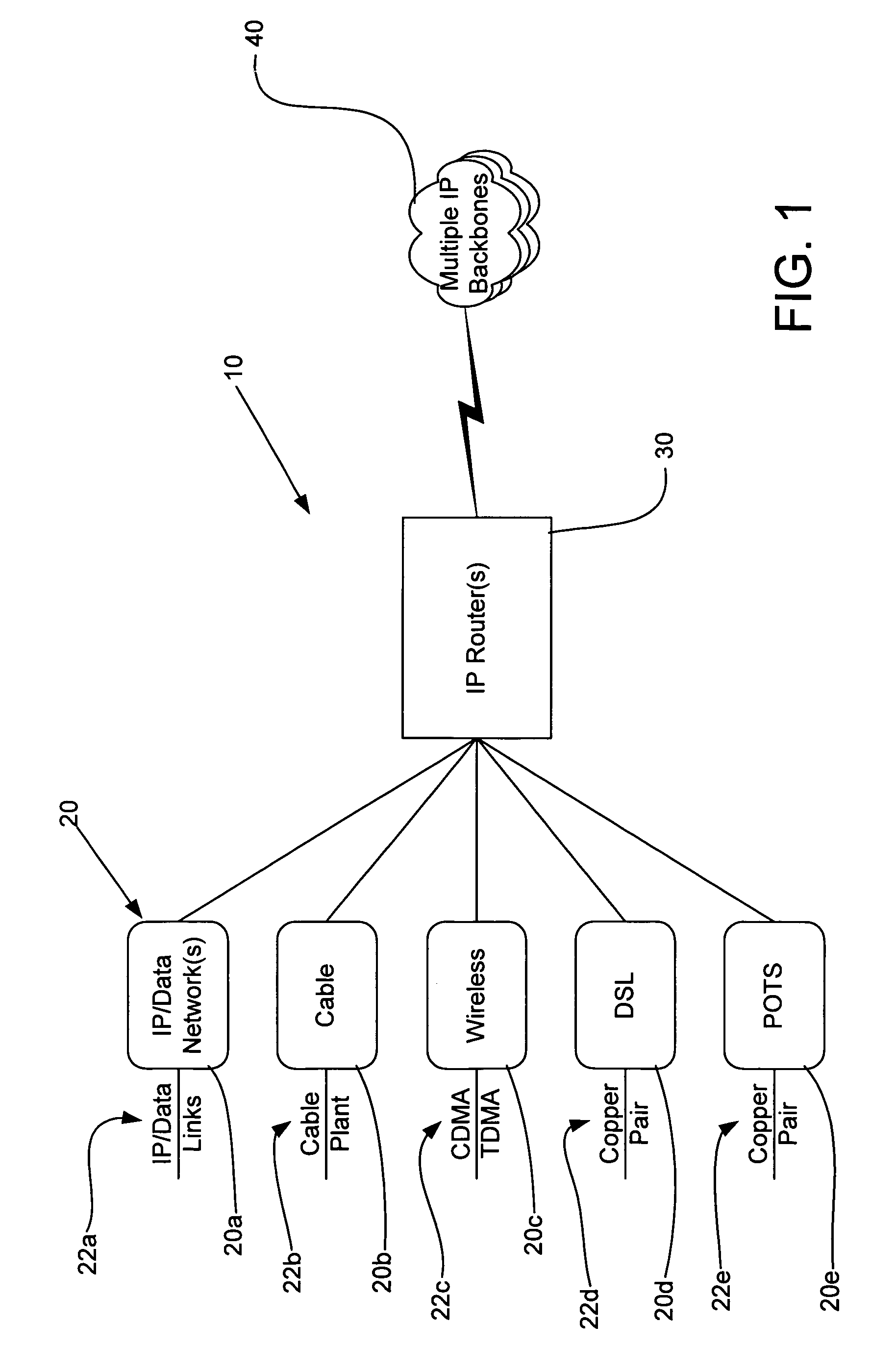
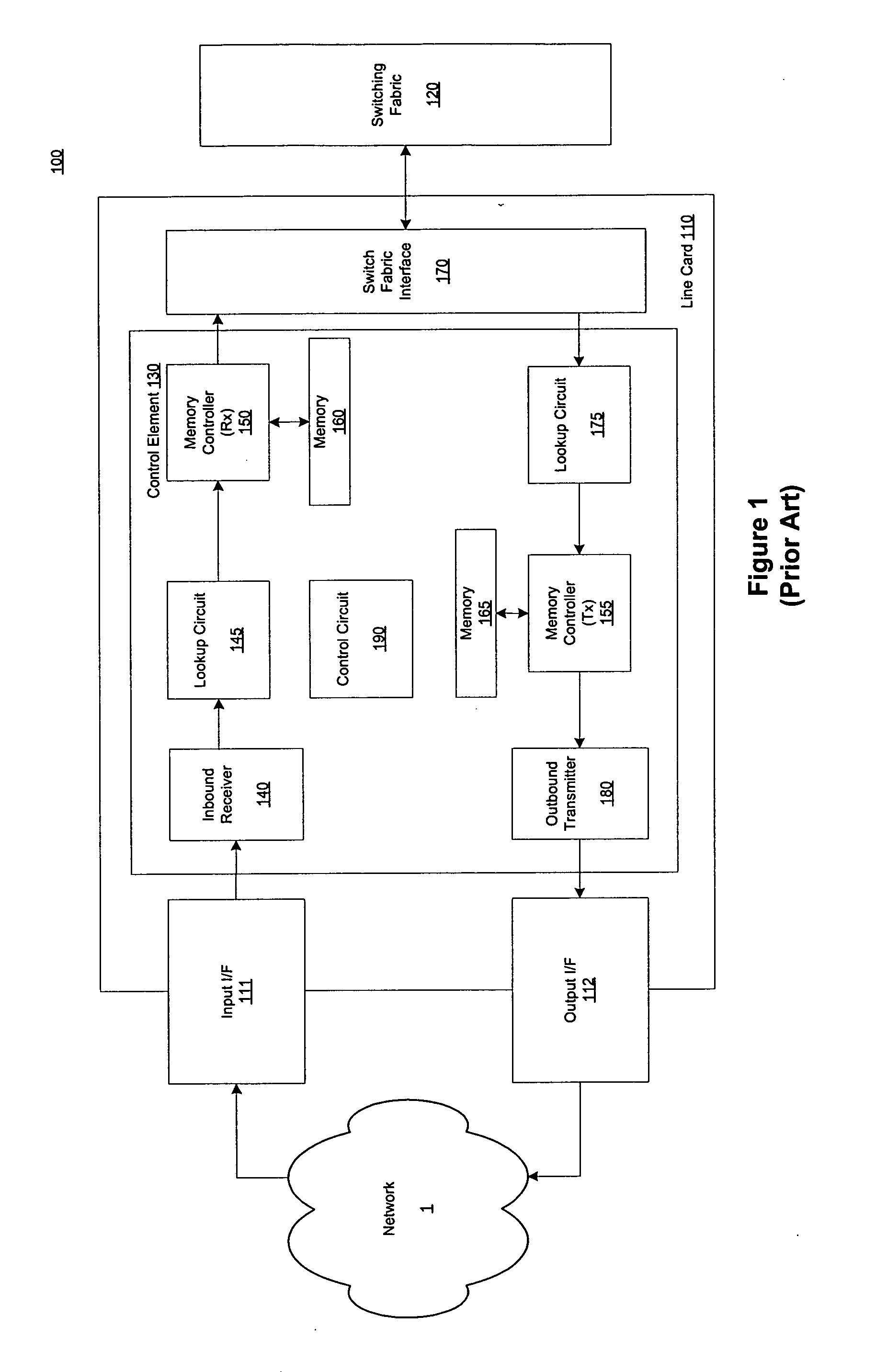
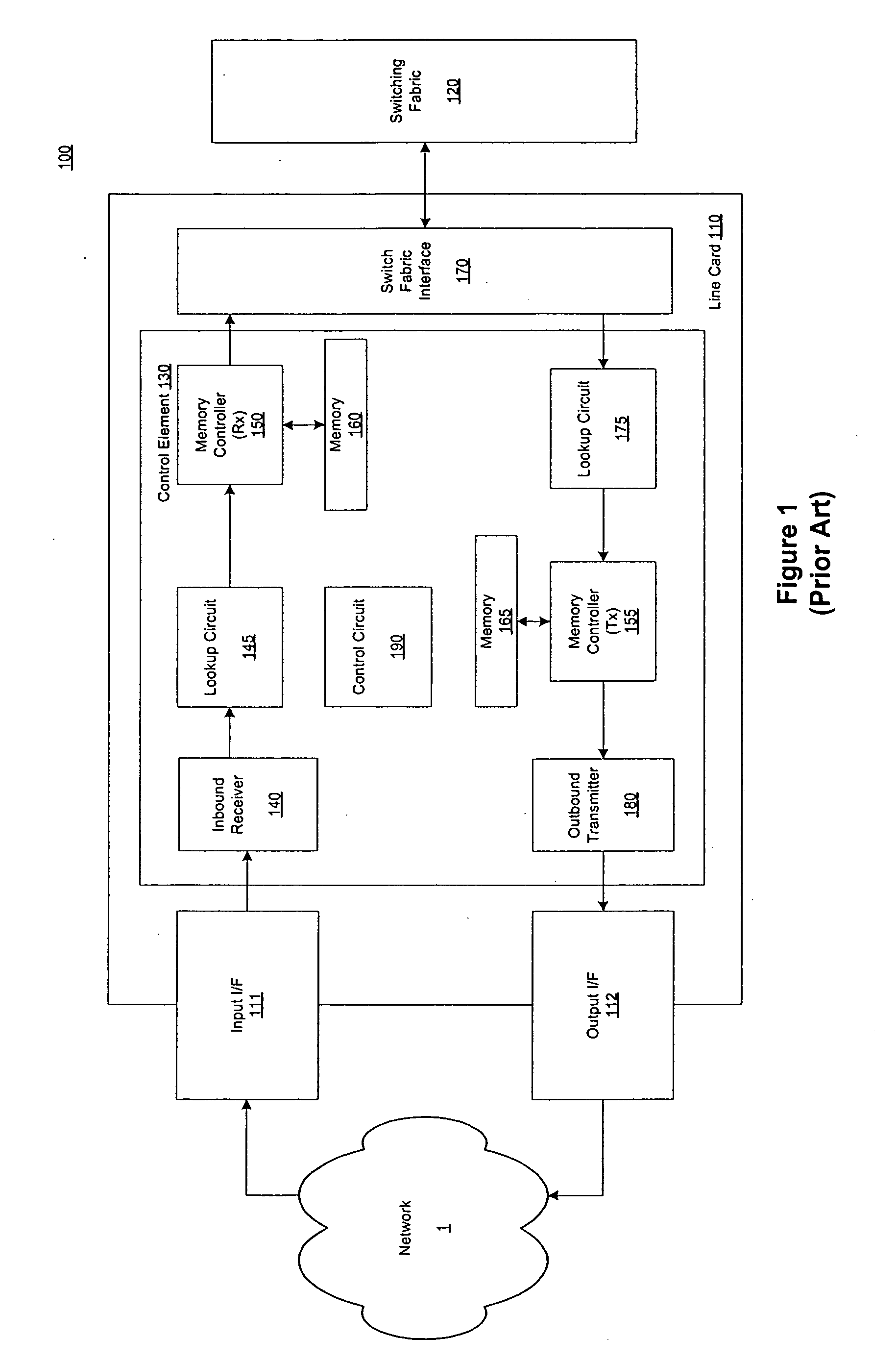
A line card or digital line card is a modular electronic circuit designed to fit on a separate printed circuit board (PCB) and interface with a telecommunications access network. A line card typically interfaces the twisted pair cable of a plain old telephone service (POTS) local loop to the public switched telephone network (PSTN). Telephone line cards perform multiple tasks, such as analog-to-digital and digital-to-analog conversion of voice, off-hook detection, ring supervision, line integrity tests, and other BORSCHT functions. In some telephone exchange designs, the line cards generate ringing current and decode DTMF signals. The line card in a subscriber loop carrier is called a subscriber line interface card (SLIC).
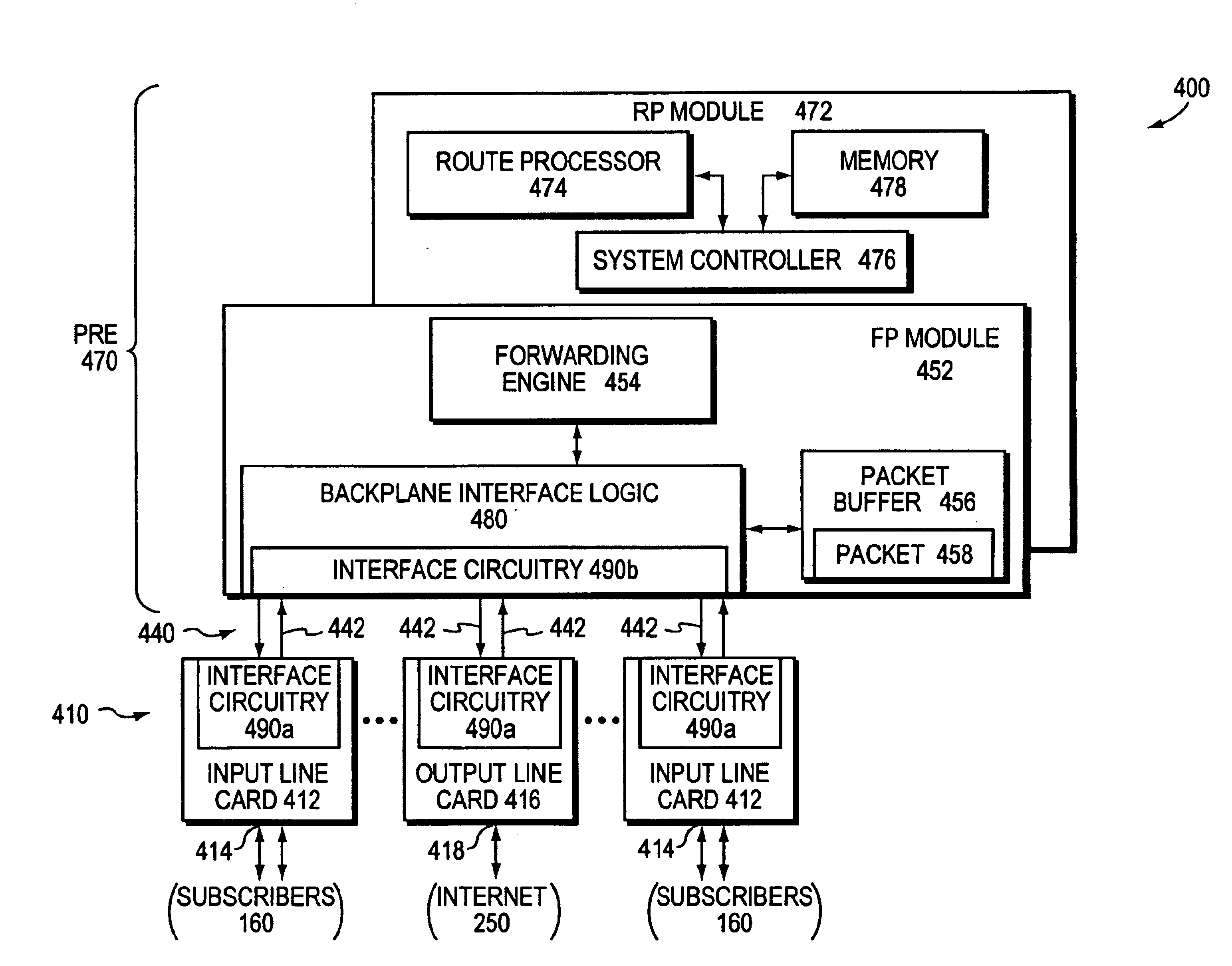
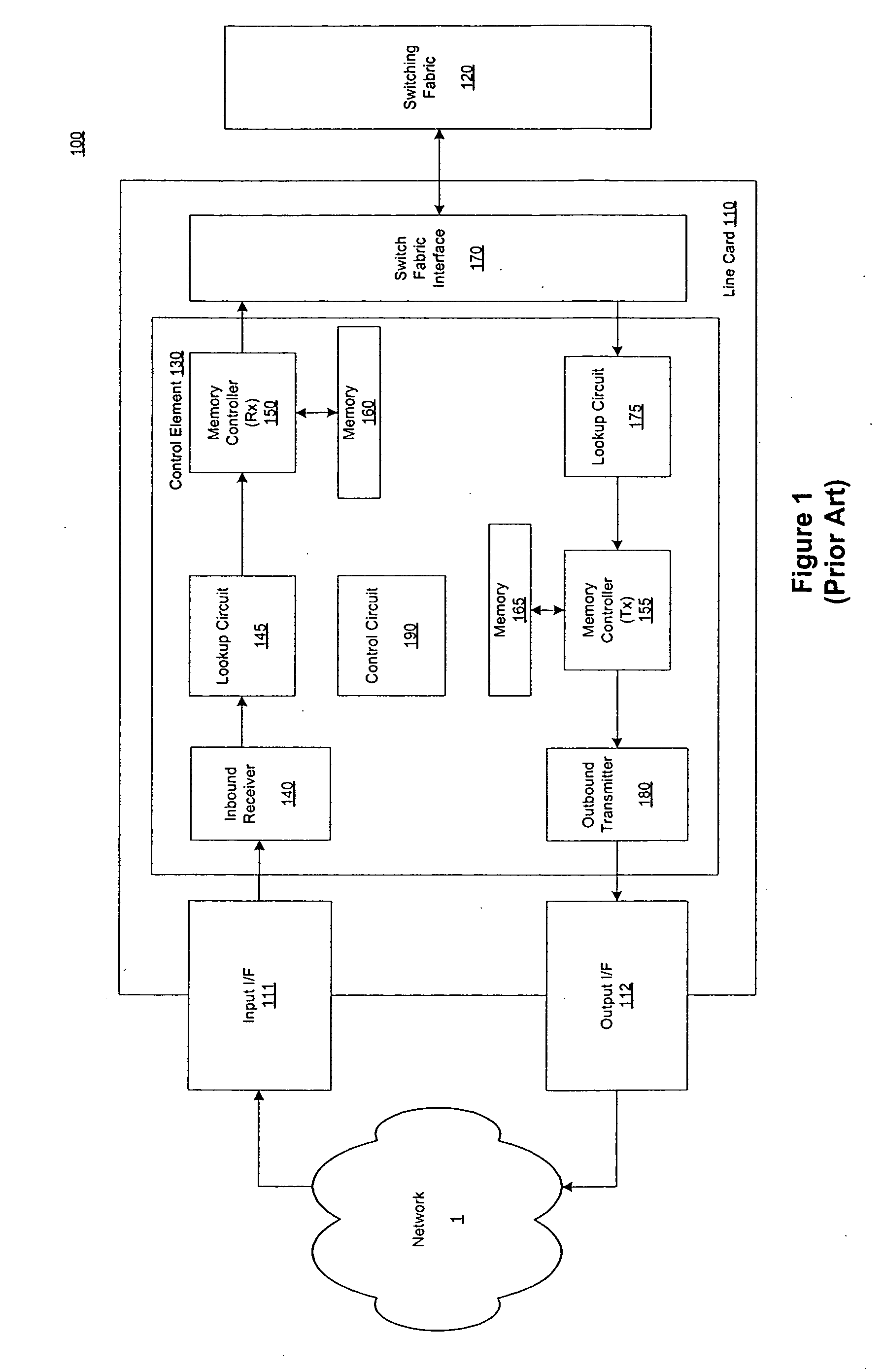
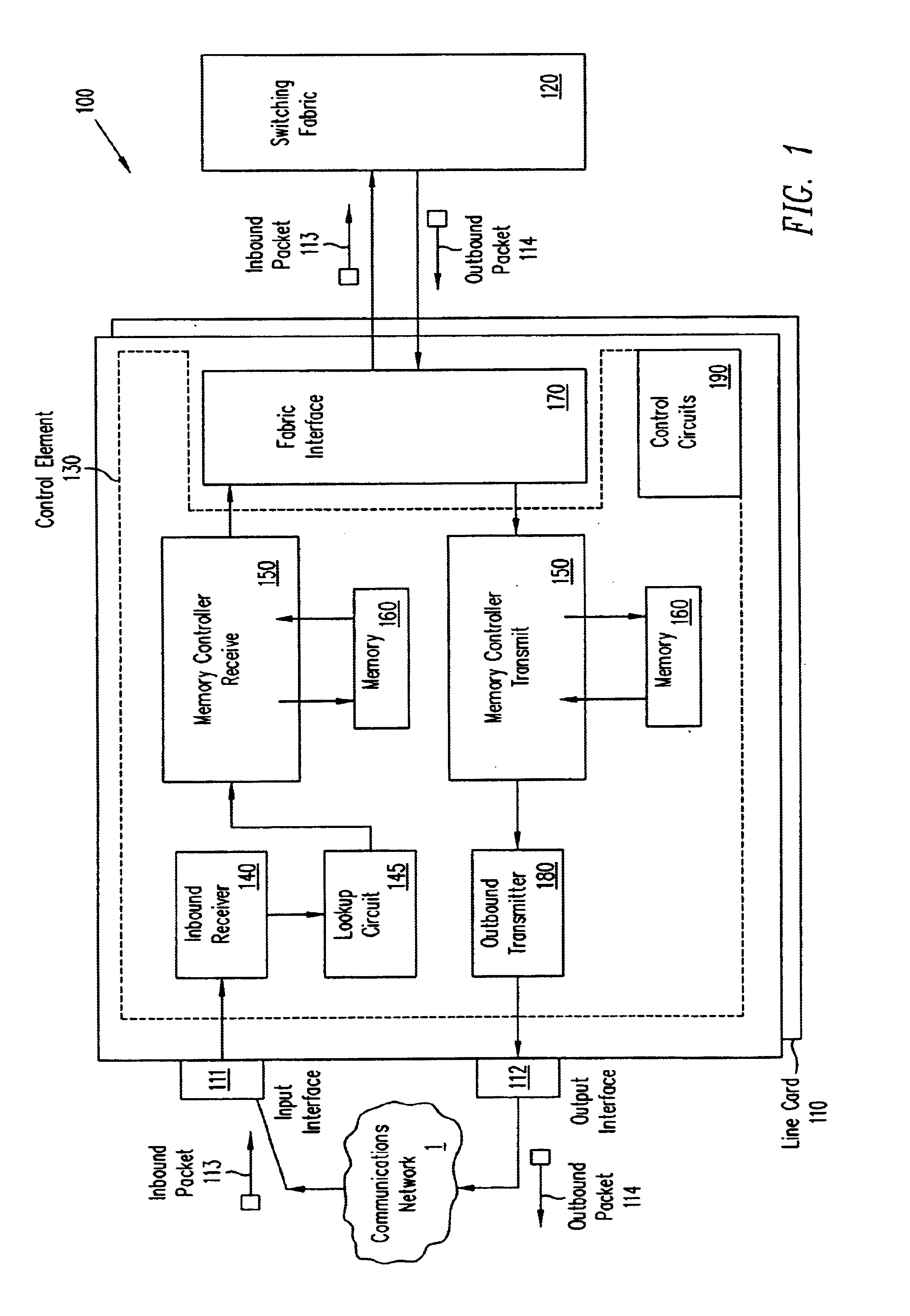
Data plane restart without state change in a control plane of an intermediate network node
A system and technique restarts a data plane of an intermediate node, such as an aggregation router, of a computer network without changing the state of a control plane in the router. The aggregation router comprises a control plane that includes a supervisor processor configured to manage traffic forwarding operations of the node. To that end, the supervisor processor maintains a current state of the control plane pertaining to, e.g., routing protocols and interface states of line cards within the router. The aggregation router further comprises a data plane that includes hardware components, such as a forwarding engine, configured to perform forwarding operations for data forwarded by the router.
Owner:CISCO TECH INC
Space reuse during technology upgrade in a protection area of an outdoor enclosure
An outdoor enclosure for a remote terminal is designed so that a structure supporting protector modules (normally coupled between telephone lines and line cards to prevent damage from a surge in current or voltage) is easily reachable and removable. To upgrade from copper to fiber, the just-described hardware (also called “protect block”) is replaced with other hardware (also called “fiber fanout enclosure”) that supports adapters for receiving connectors of optical fibers. The protect block and the fiber fanout enclosure are designed to have approximately (or even exactly) the same footprint, so that they occupy at least some of the same space (before and after replacement). Reuse of the same space in this manner is advantageous over an outdoor enclosure designed to have additional space dedicated for adapters and fiber fanout enclosures to be added in future, because a more compact arrangement results from reuse of the same space.
Owner:WHITE OAK GLOBAL ADVISORS
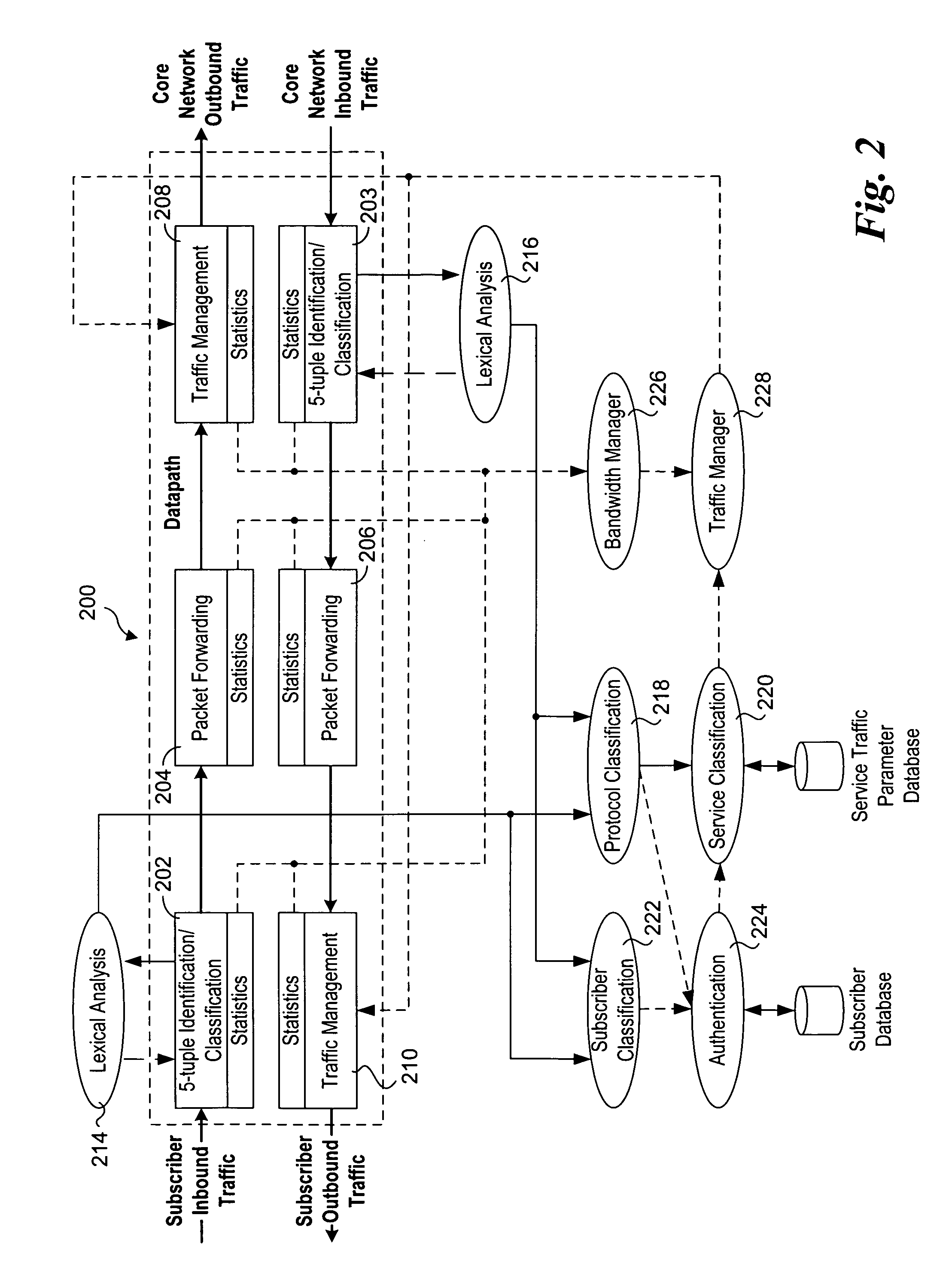
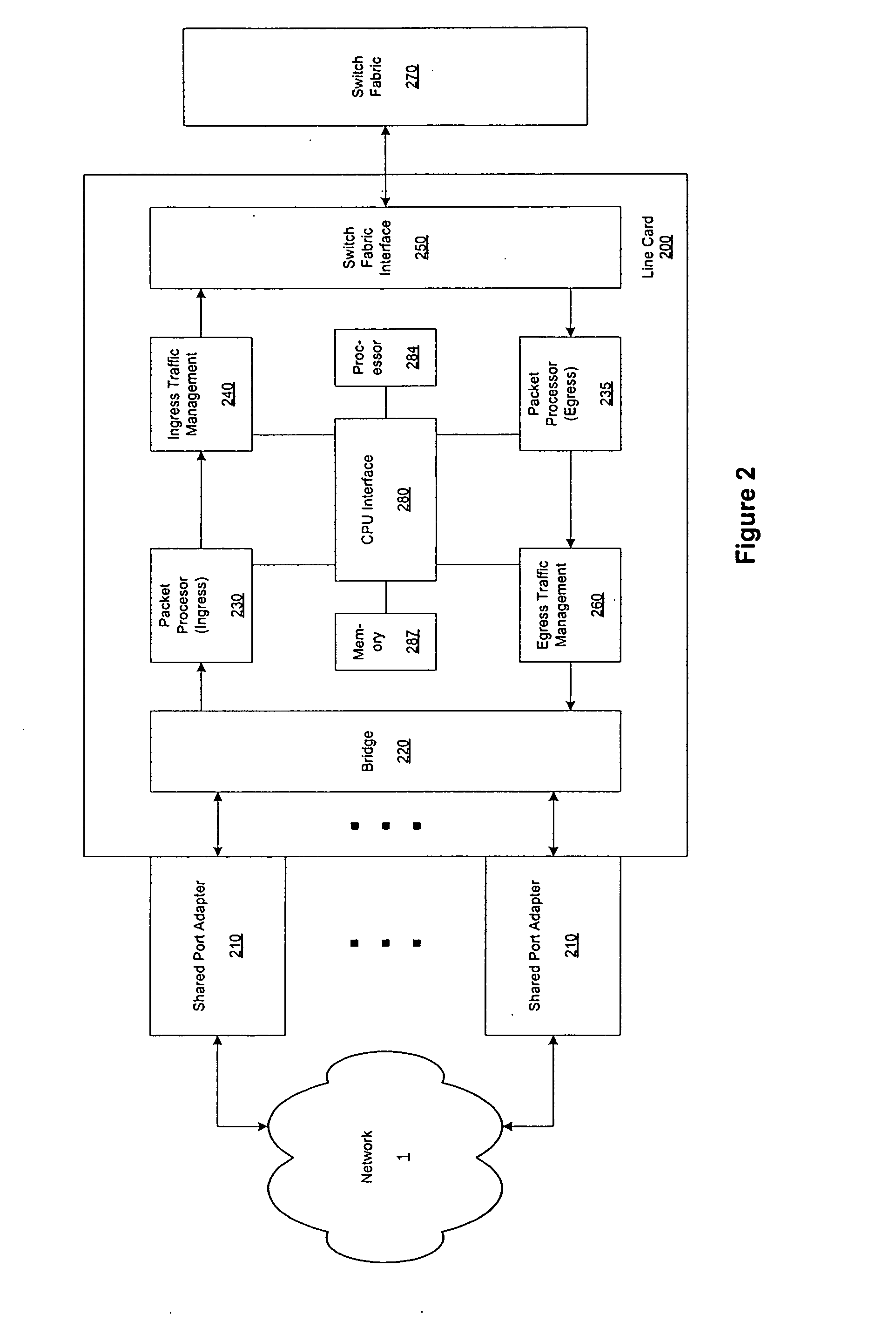
Methods and apparatus to support dynamic allocation of traffic management resources in a network element
Methods and apparatus to support dynamic allocation of traffic management resources in a network element. Shared pools of traffic management resources comprising an aggregation of local line card resources distributed across the line cards or a network element maintained by apparatus software. Incoming packets are classified into subscriber flows using a hierarchical classification scheme. In view of subscriber services and flow application types, traffic management resources are dynamically allocated from the shared pools, and traffic management policies associated with the subscriber services and application types are applied to the subscriber flows via the allocated resources. In response to detecting a subscriber flow has terminated, the allocated resources are release and made available to be dynamically re-allocated to subsequent subscriber flows.
Owner:TELLABS COMM CANADA
Protection switching for an optical network, and methods and apparatus therefor
InactiveUS20020176131A1Multiplex system selection arrangementsLaser detailsTraffic capacityLine card
An optical communications network having at least one optical switch connected to a network access device. The optical switch includes a first line card disposed along a first communications path over which a first optical signal is transmitted. The first line card is connected to the network access device. A second line card is disposed along a second communications path over which a second optical signal is transmitted. An inter-card communication channel is provided for bridging the second path to the first line card. The system enables the rapid switching of traffic from the first optical path to the second optical path.
Owner:FIRSTWAVE SECURE INTELLIGENT OPTICAL NETWORKS
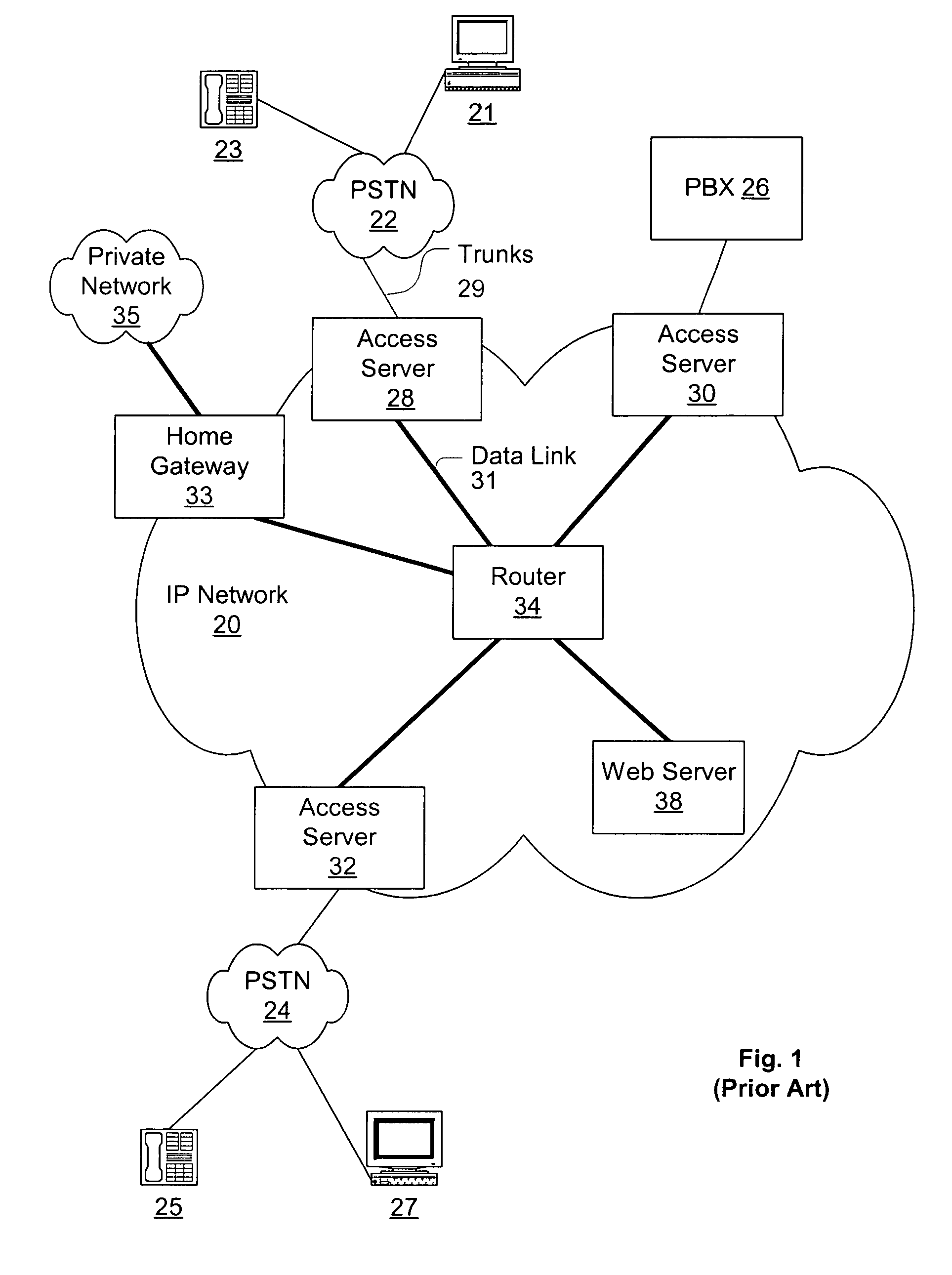
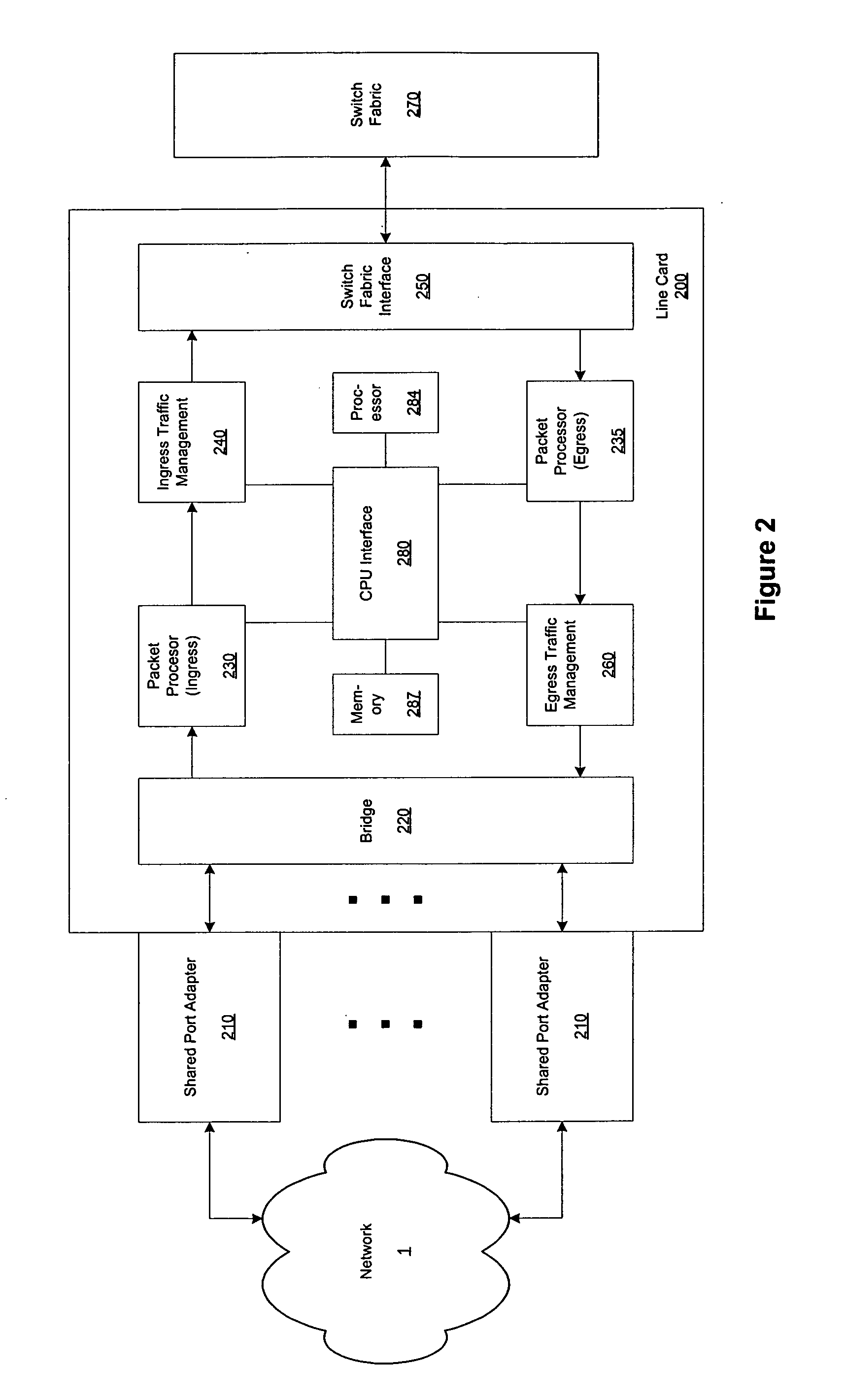
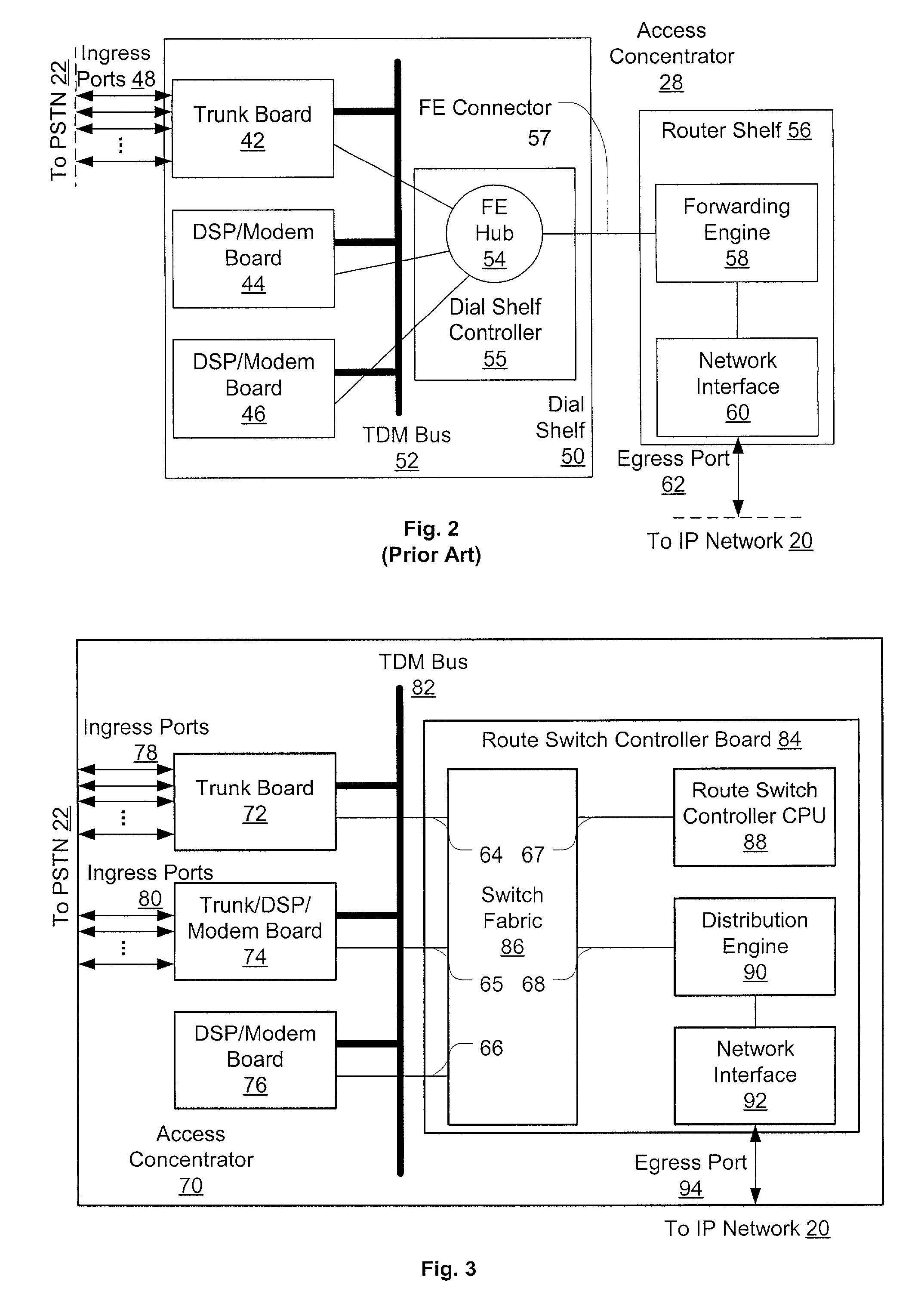
Distributed packet processing architecture for network access servers
InactiveUS6954463B1Increase the number ofRaise countData switching by path configurationNetwork access serverComputer hardware
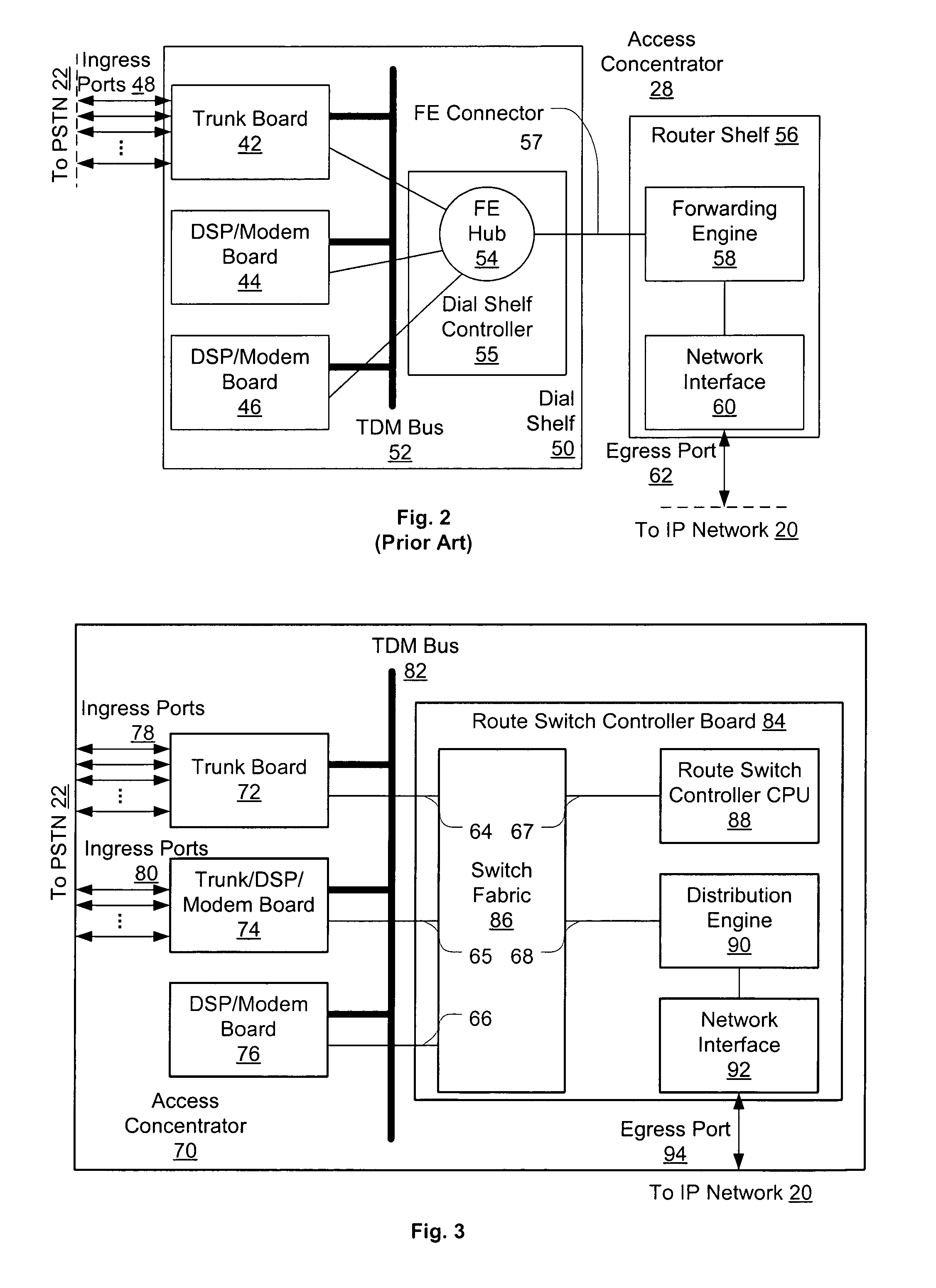
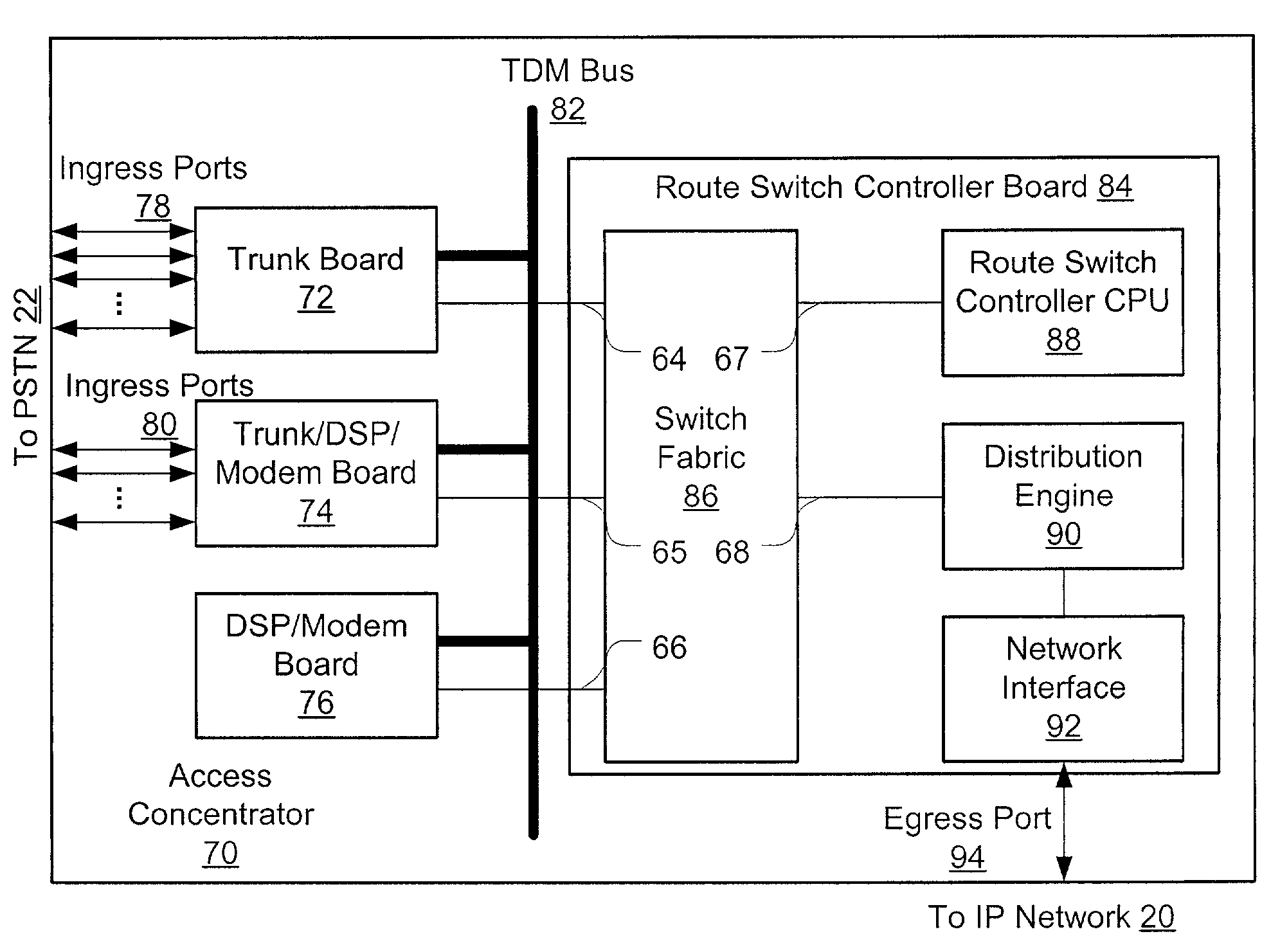
An access server architecture, and methods for use of the architecture, are disclosed. The architecture and methods are designed to increase the scalability of and balance processor load for a network access server. In this architecture, packet forwarding and packet processing are distributed amongst the cards serving the low-speed access lines, such that each line card is responsible for performing forwarding and packet processing for packets associated with the low-speed ports that line card serves. As the number of line cards expands, forwarding resources are expanded in at least rough proportion. The NAS route switch controller, and the high-speed ports, are largely relieved of packet processing tasks because the egress port uses a distribution engine that performs a cursory examination on one or more header fields on packets received—comprehending only enough information to allow each packet to be distributed to the appropriate line card for full processing.
Owner:CISCO TECH INC
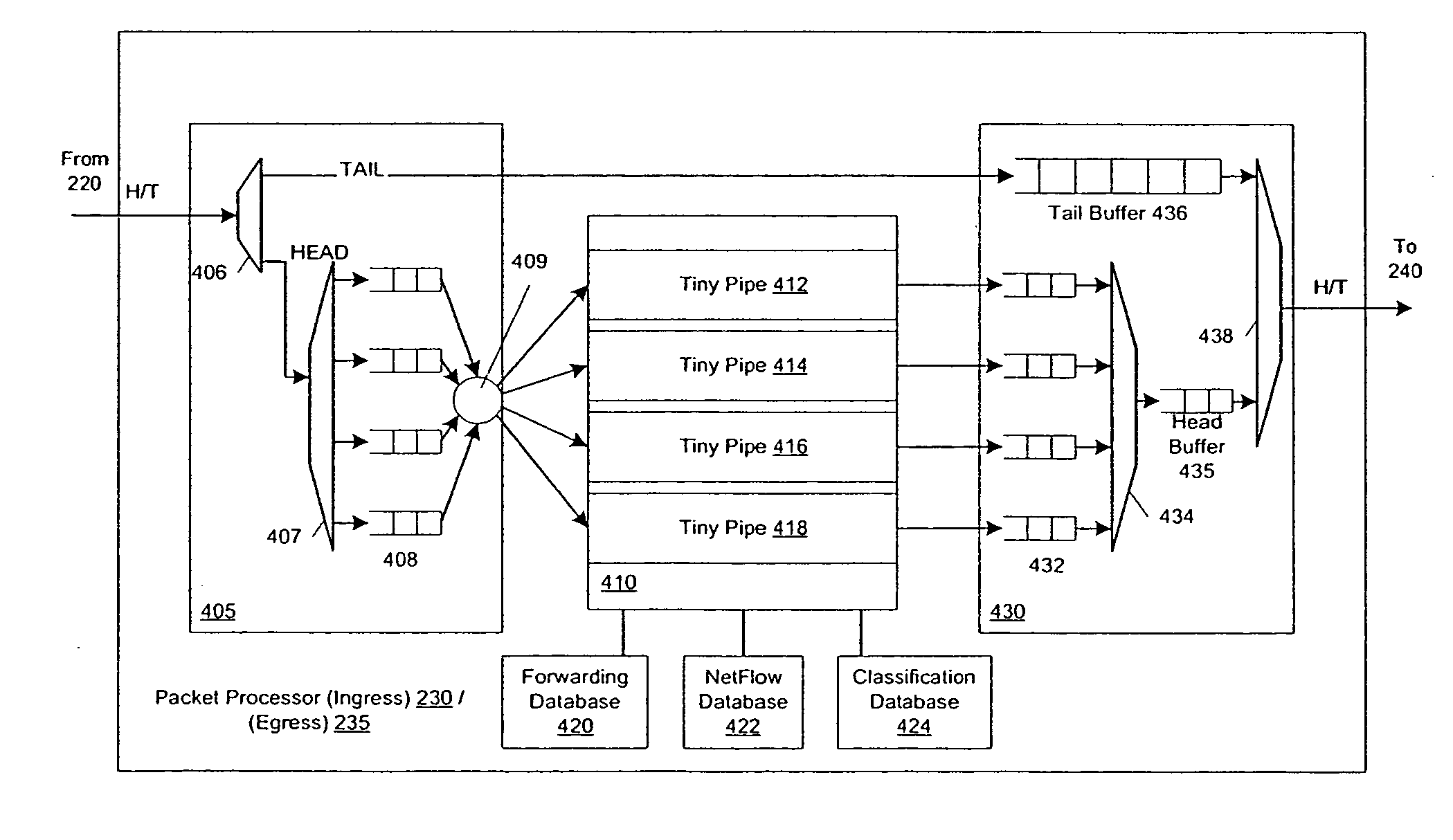
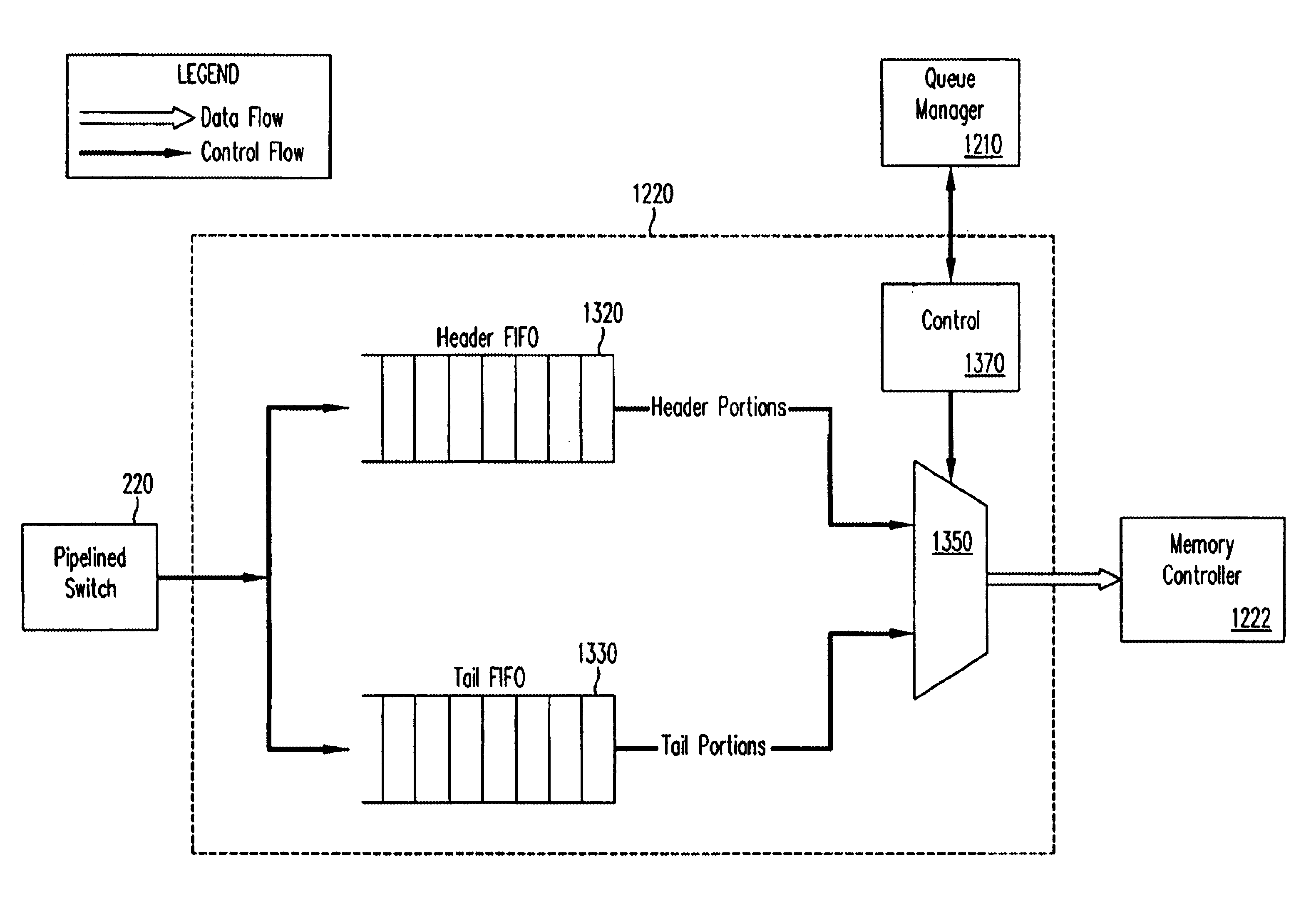
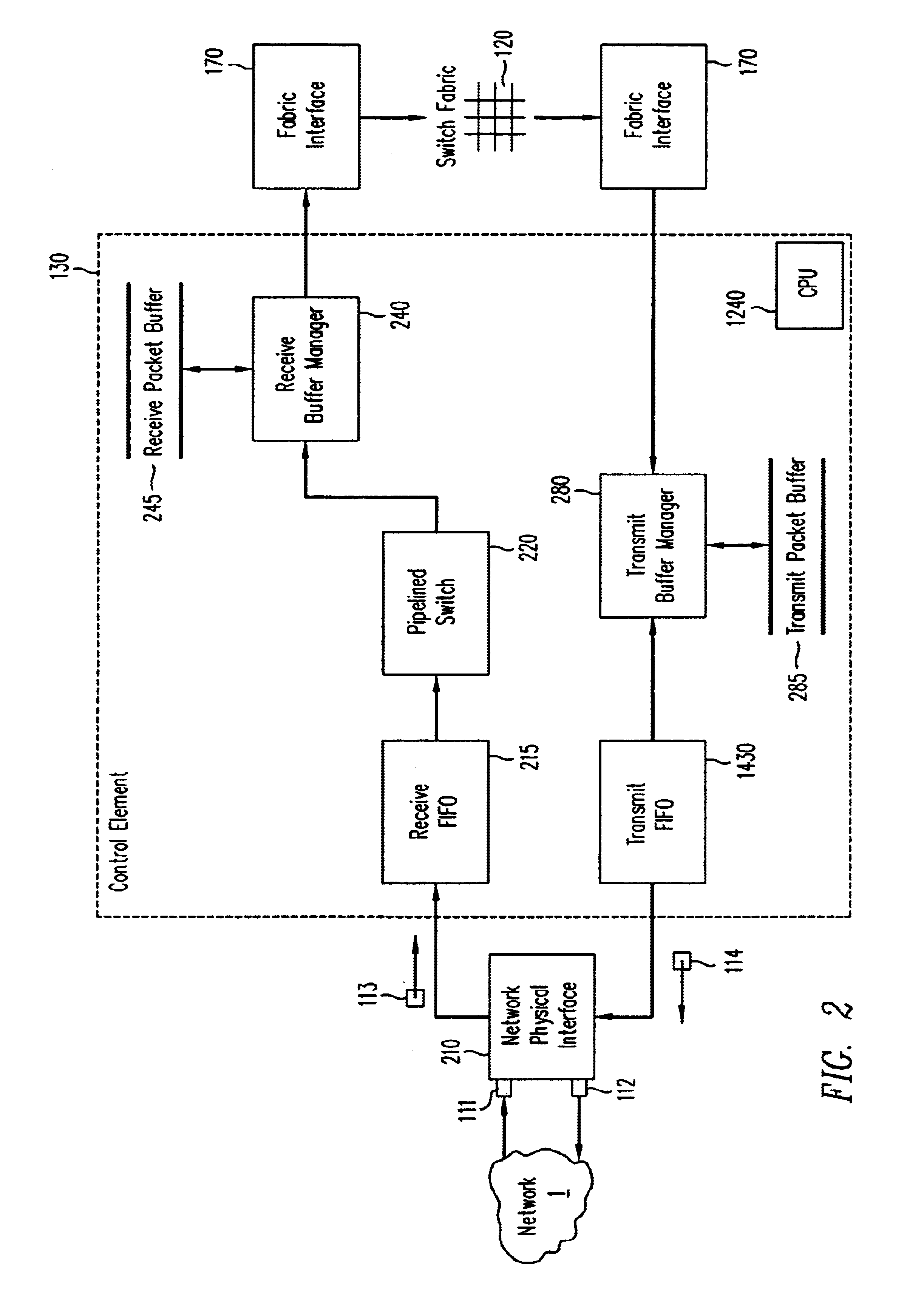
Pipelined packet switching and queuing architecture
An architecture for a line card in a network routing device is provided. The line card architecture provides a bi-directional interface between the routing device and a network, both receiving packets from the network and transmitting the packets to the network through one or more connecting ports. In both the receive and transmit path, packets processing and routing in a multi-stage, parallel pipeline that can operate on several packets at the same time to determine each packet's routing destination is provided. Once a routing destination determination is made, the line card architecture provides for each received packet to be modified to contain new routing information and additional header data to facilitate packet transmission through the switching fabric. The line card architecture further provides for the use of bandwidth management techniques in order to buffer and enqueue each packet for transmission through the switching fabric to a corresponding destination port. The transmit path of the line card architecture further incorporates additional features for treatment and replication of multicast packets.
Owner:CISCO TECH INC
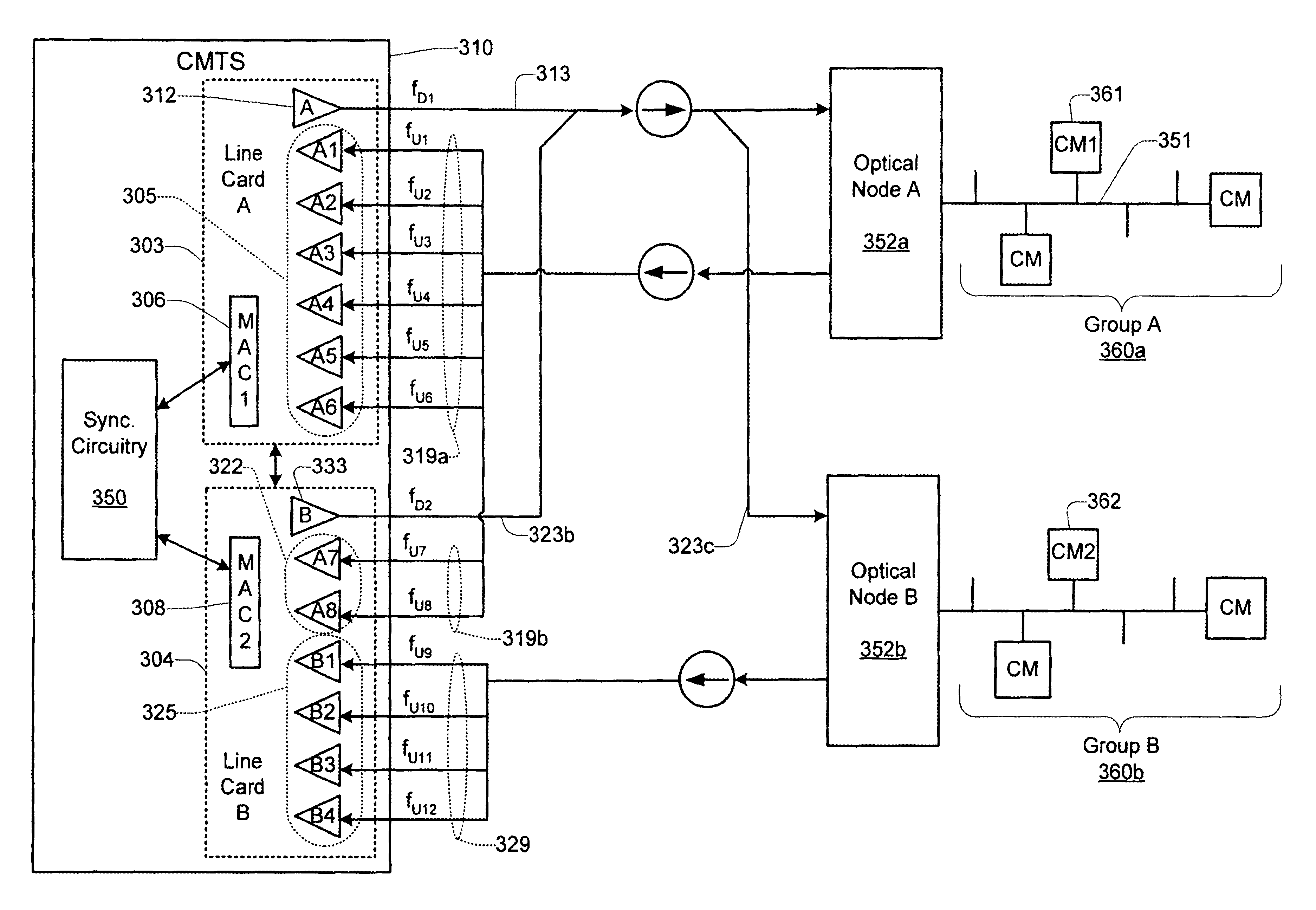
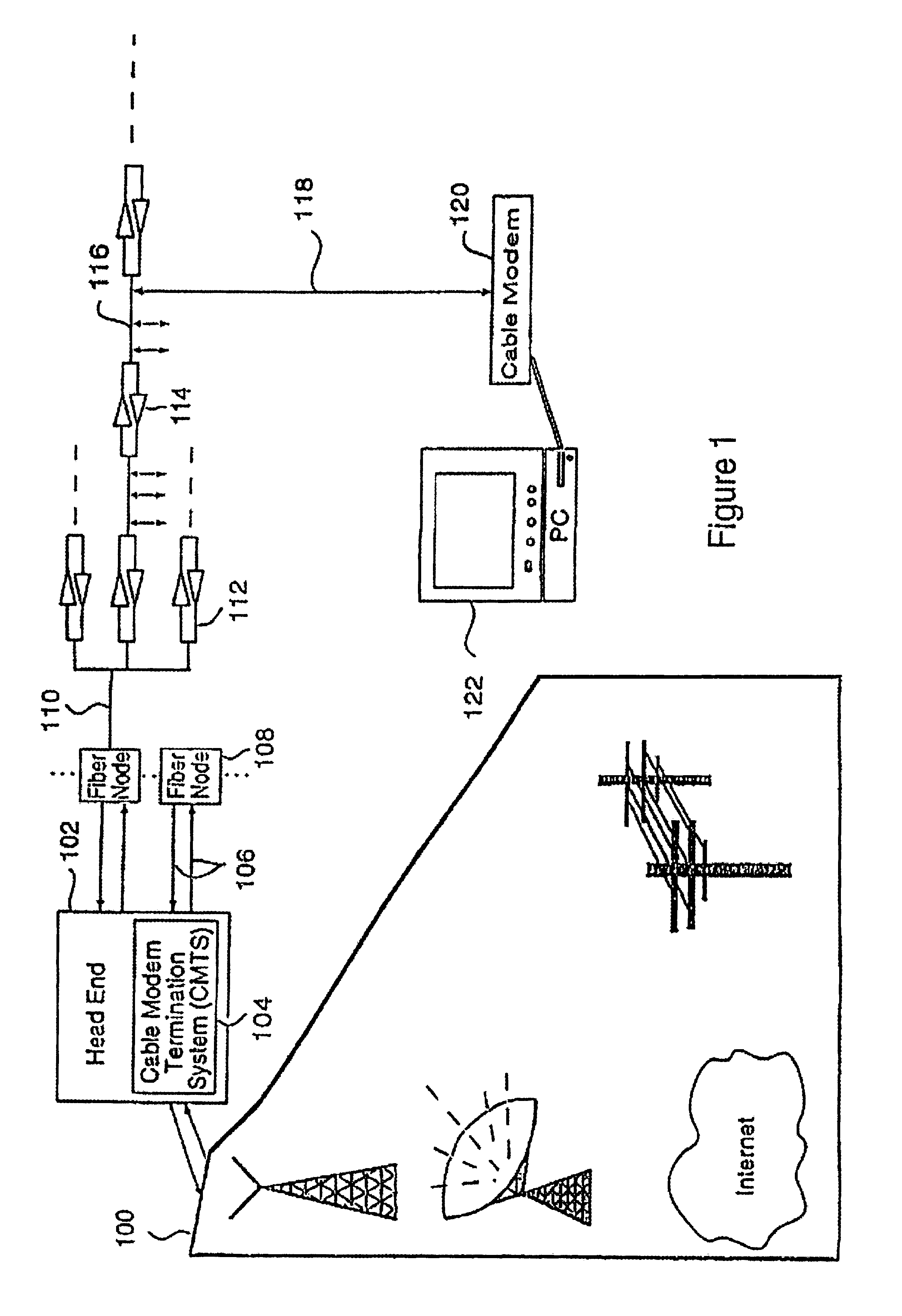
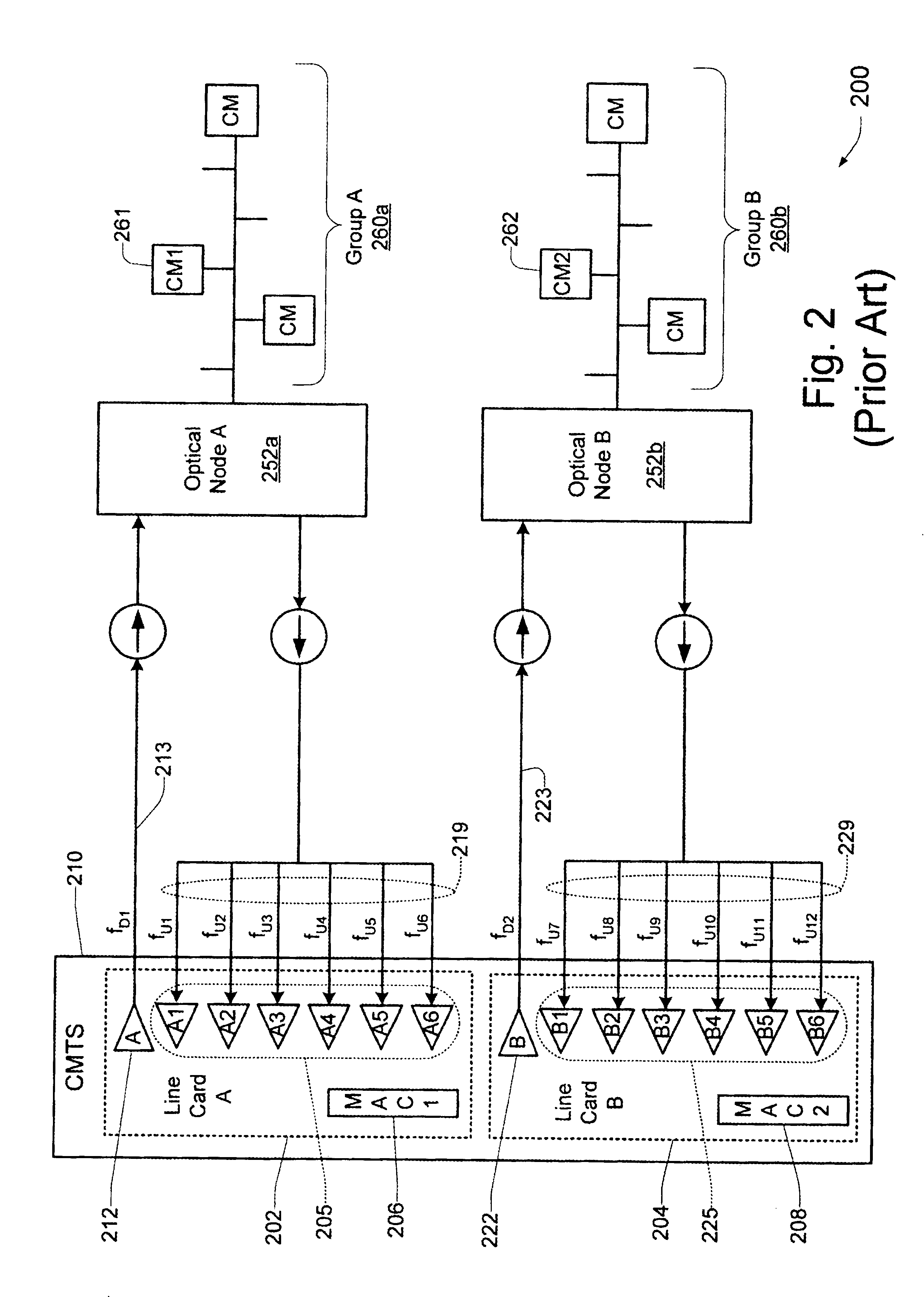
Technique for synchronizing multiple access controllers at the head end of an access network
InactiveUS7065779B1Broadband local area networksAnalogue secracy/subscription systemsAccess networkTimestamp
A technique is described which may be used to synchronize a plurality of different access controllers which control a plurality of distinct ports at the Head End of an access network. In the context of a cable network, the technique of the present invention may be used to synchronize desired upstream and / or downstream channels across different line cards within a Cable Modem Termination System (CMTS). The technique involves utilizing a master time reference device which maintains and updates a current time reference, and periodically distributes synchronization signals to desired line cards in the system in order to synchronize these line cards. In a specific embodiment, the synchronization signals include current timestamp data generated from the master time reference device and distributed to all (or selected) line cards in the system. A slave time reference device on each of the line cards receives the periodic synchronization updates and uses the synchronization data to remain synchronized with the master time reference device. There are also provisions in this protocol to allow for hot insertion and removal of line cards, software reset or loading of the master and / or slave time reference devices, and redundant master time reference devices, including master time reference device fault detection and automatic fail over.
Owner:CISCO TECH INC
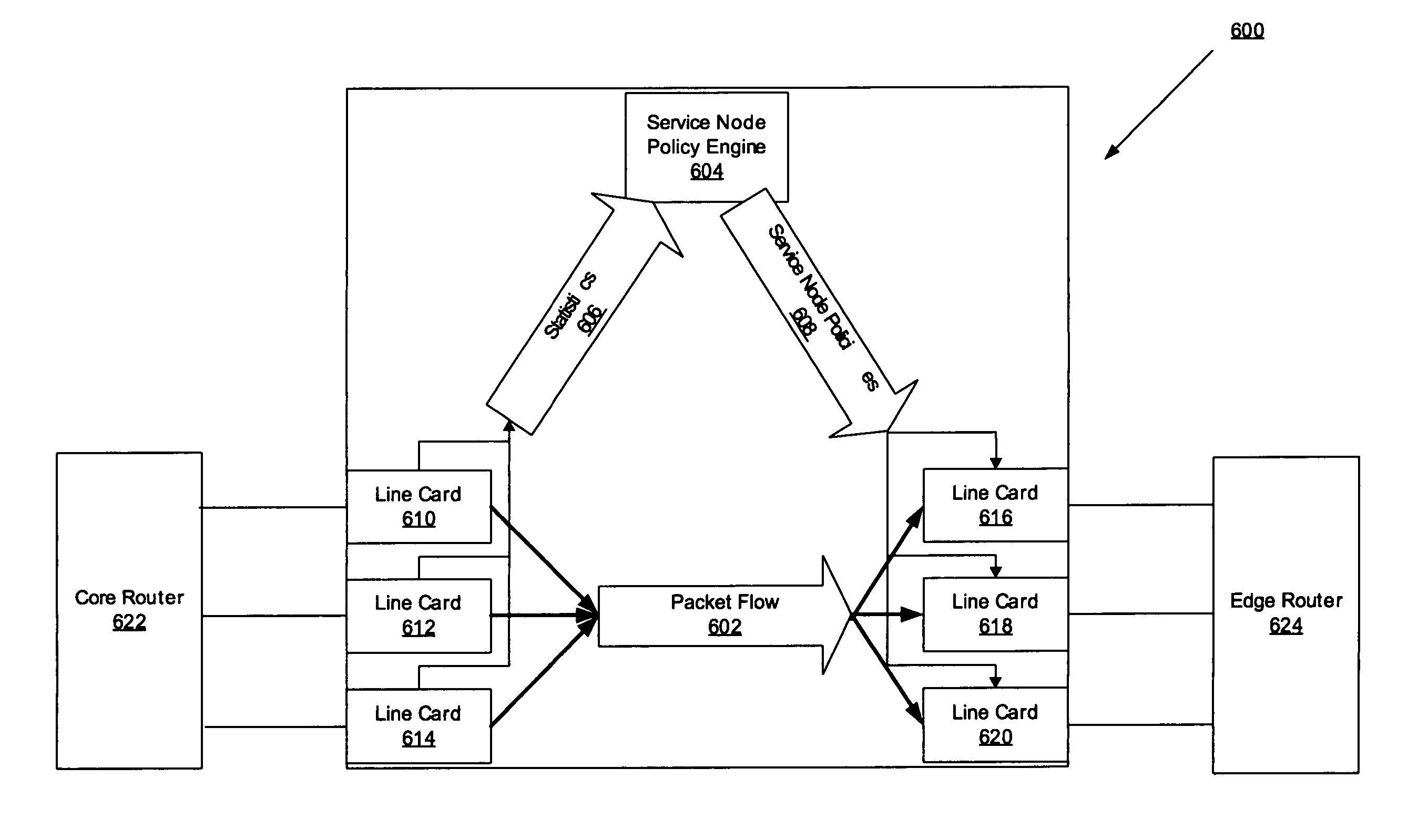
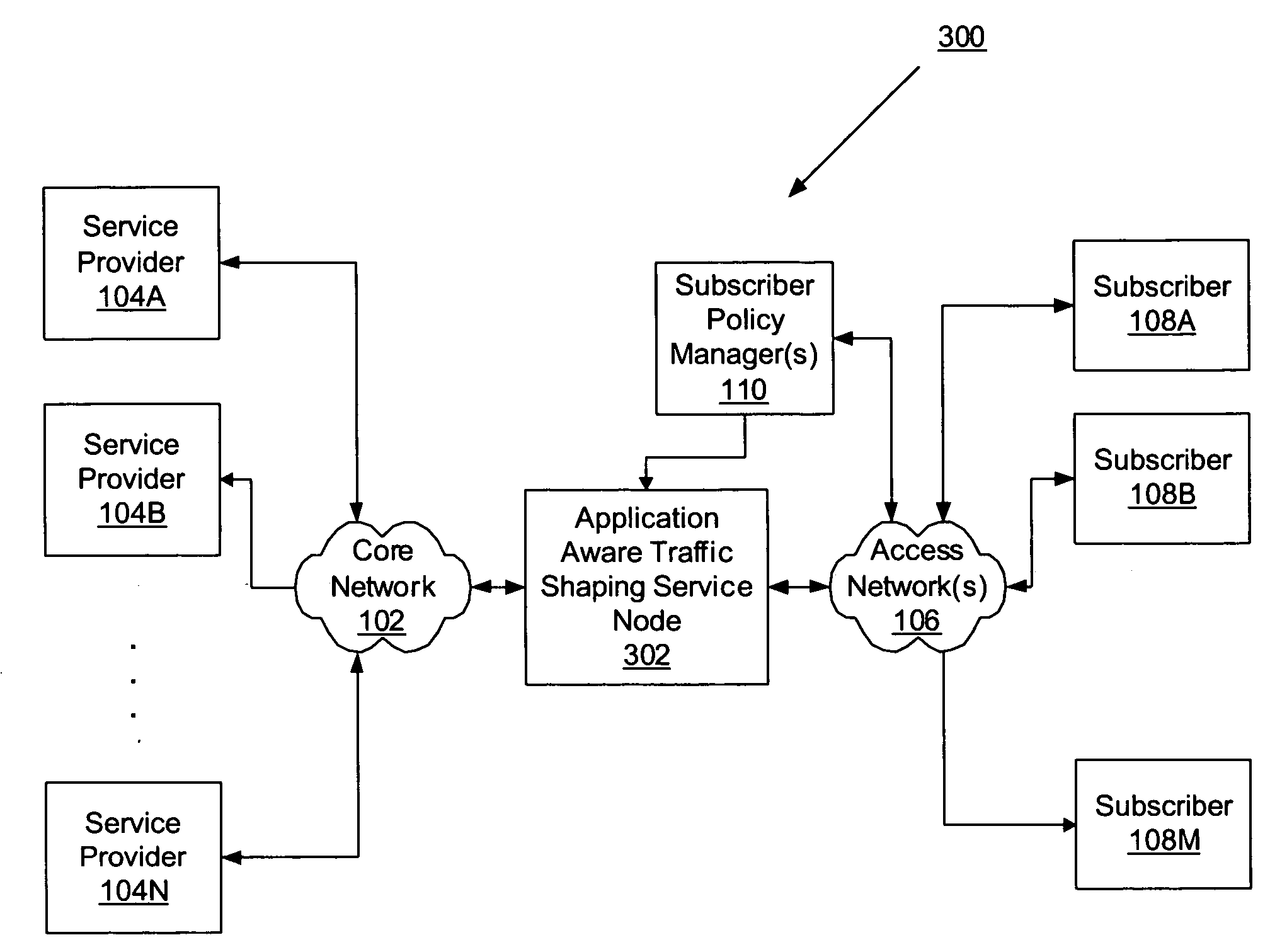
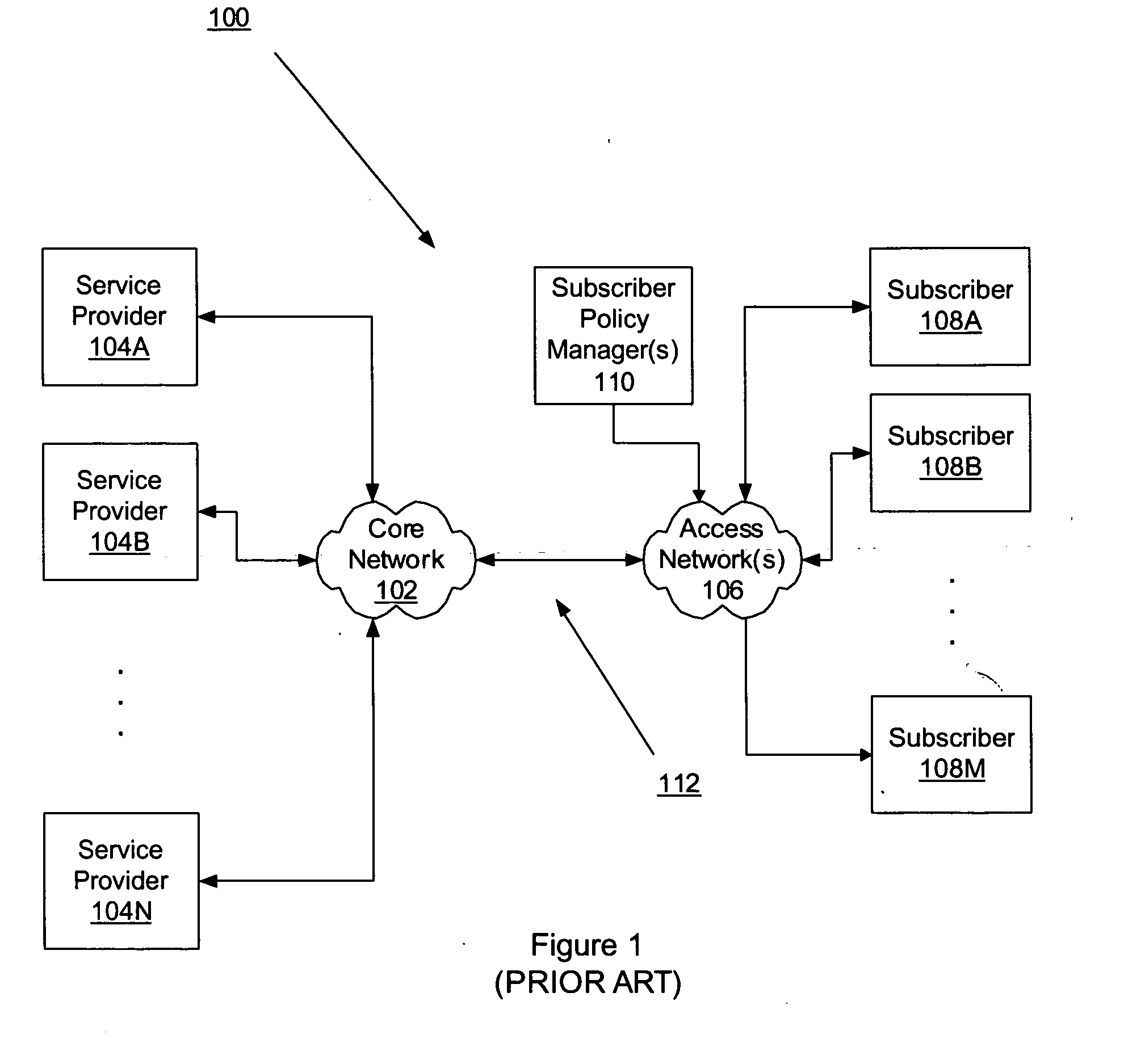
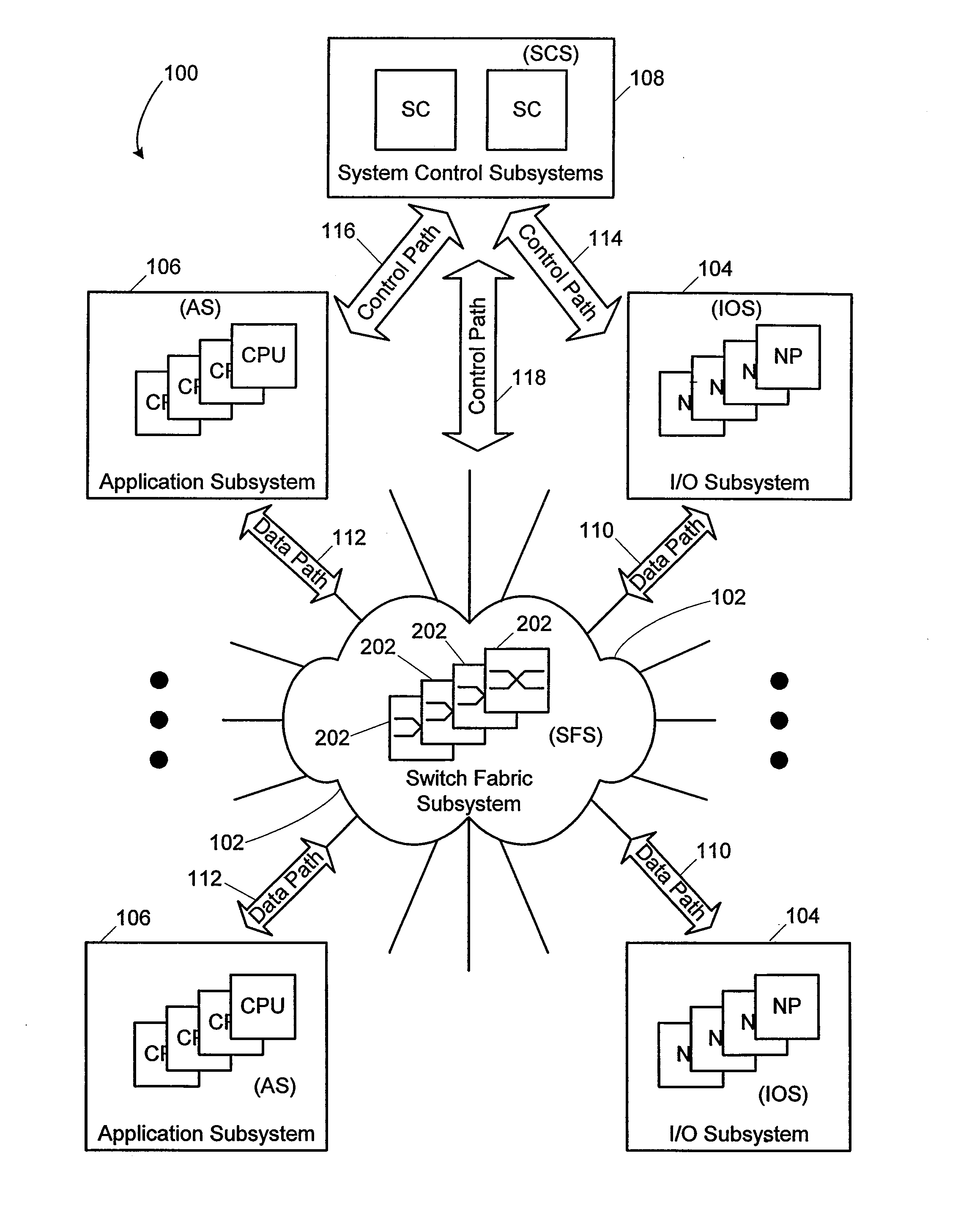
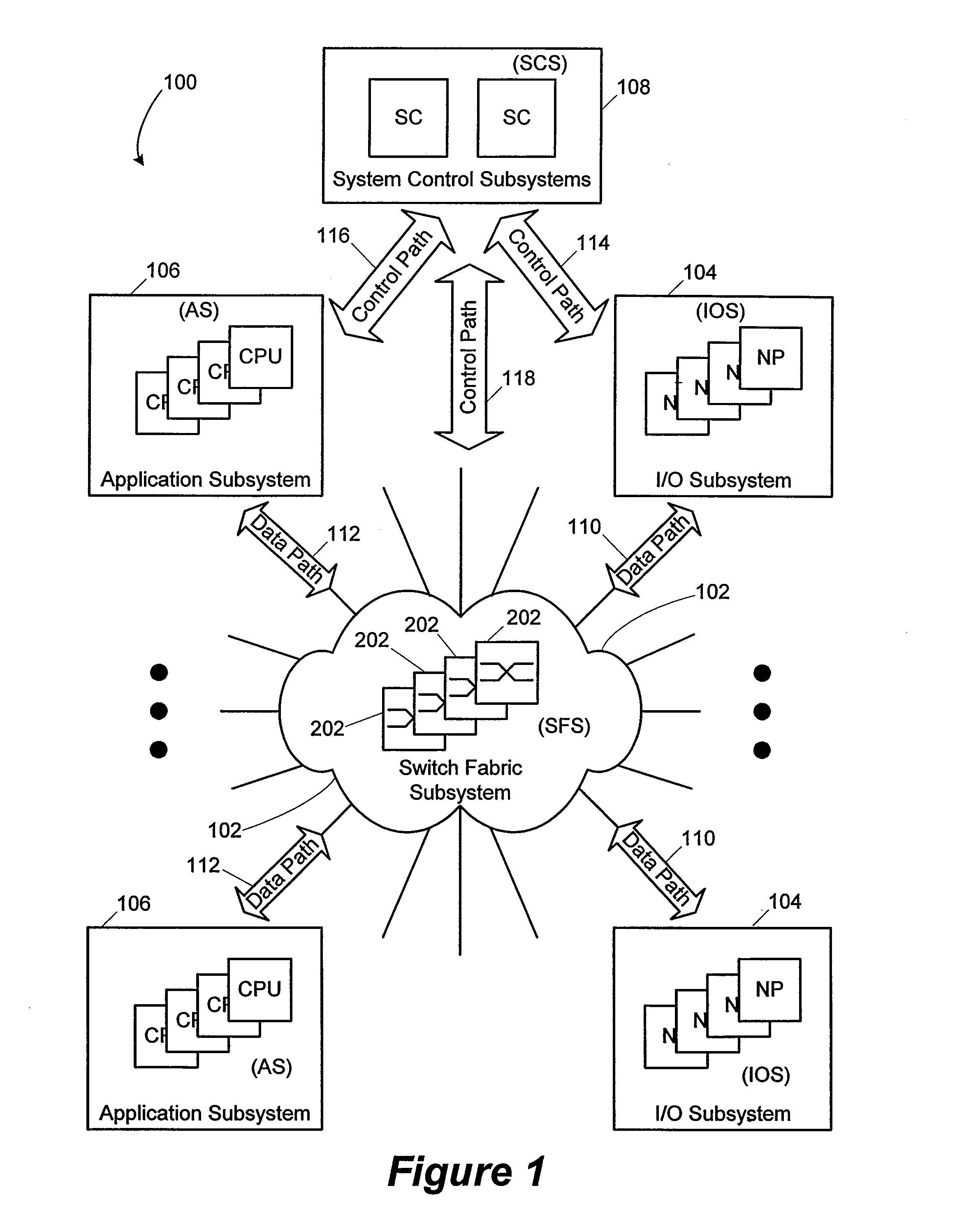
Network element architecture for deep packet inspection
A method and apparatus for an application aware traffic shaping service node architecture is described. One embodiment of the invention, the service node architecture includes a set of one or more line cards, a set of one or more processor cards and a full mesh communication infrastructure coupling the sets of line and processor cards. Each link coupling the sets of line and processor cards is of equal capacity. A line card includes a physical interface and a set of one or policy network processors, with the network processors performing deep packet inspection on incoming traffic and shaping outgoing traffic. Processors cards include a set of one or more policy generating processors. According to another embodiment of the invention, the service node generates a set of statistics based on the incoming traffic and continually updates, in real-time, traffic shaping policies based on the set of statistics.
Owner:TELLABS COMM CANADA
Upstream only linecard with front end multiplexer for CMTS
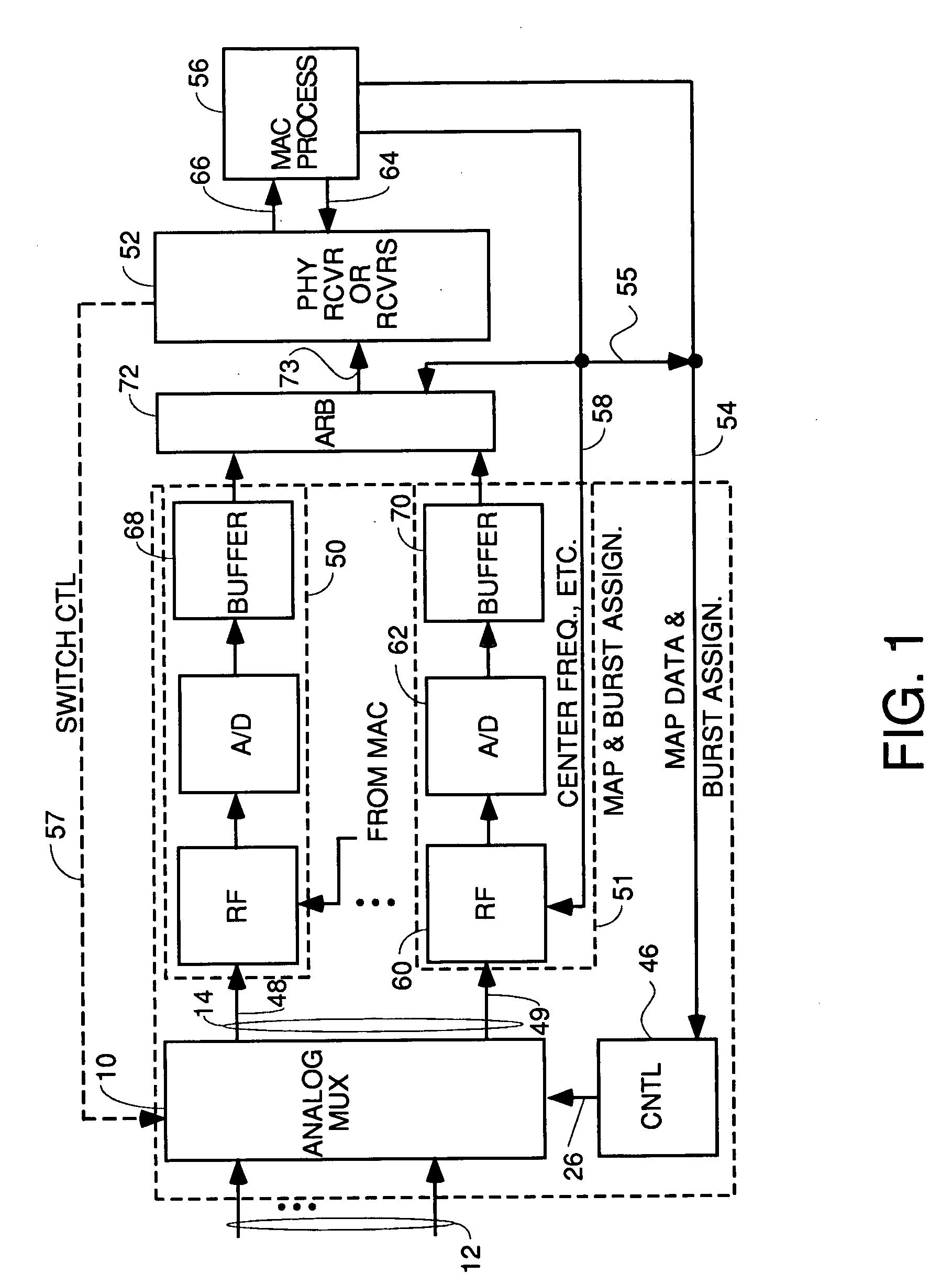
InactiveUS20050010958A1Easy to addMaximize Utilization EfficiencyMultiplex system selection arrangementsBroadband local area networksCrossbar switchMultiplexer
An upstream line card including a digital or analog multiplexer front end circuit for a Cable Modem Termination System. Each upstream line card has only upstream receivers and allows a CMTS to share one or a handful of receiver chips to receive and recover data from a larger number of input cables coupled to the front end multiplexer. A control circuit for the multiplexer uses MAP data and burst assignment data and upstream mini-slot counts for each of the input cables to determine when a burst is about to arrive on a cable and cause appropriate switching by the multiplexer or crossbar switch. In some embodiments, there is only one RF channel circuit coupled to the output of the multiplexer, so the multiplexer is controlled to couple the input cable upon which the burst is expected to the single RF channel. In other embodiments, there are multiple RF channels coupled to the inputs of the multiplexer so the multiplexer is controlled to connect each input cable on which a burst is expected to an available RF channel. In some embodiments, the sample data generated by each RF channel is buffered and an arbiter picks one burst at a time for application to the input of a CMTS receiver or doles out bursts to different receivers. In other embodiments, no buffers or arbiter are used, and each RF channel has its own dedicated CMTS receiver.
Owner:GOOGLE TECH HLDG LLC
Network element architecture for deep packet inspection
ActiveUS20060233101A1Equal capacityError preventionFrequency-division multiplex detailsTraffic capacityNetwork architecture
A method and apparatus for an application aware traffic shaping service node architecture is described. One embodiment of the invention, the service node architecture includes a set of one or more line cards, a set of one or more processor cards and a full mesh communication infrastructure coupling the sets of line and processor cards. Each link coupling the sets of line and processor cards is of equal capacity. A line card includes a physical interface and a set of one or policy network processors, with the network processors performing deep packet inspection on incoming traffic and shaping outgoing traffic. Processors cards include a set of one or more policy generating processors. According to another embodiment of the invention, the service node generates a set of statistics based on the incoming traffic and continually updates, in real-time, traffic shaping policies based on the set of statistics.
Owner:TELLABS COMM CANADA
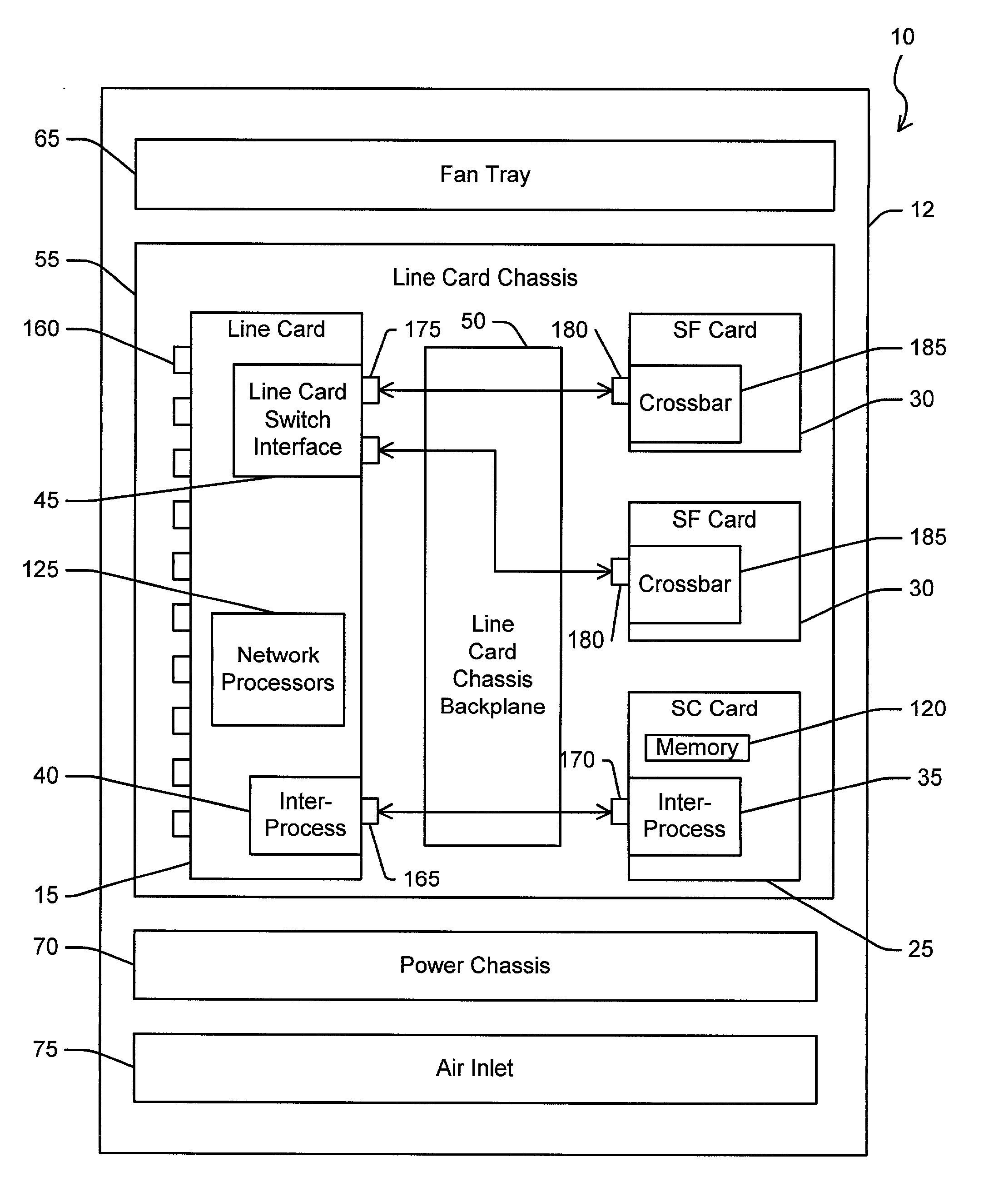
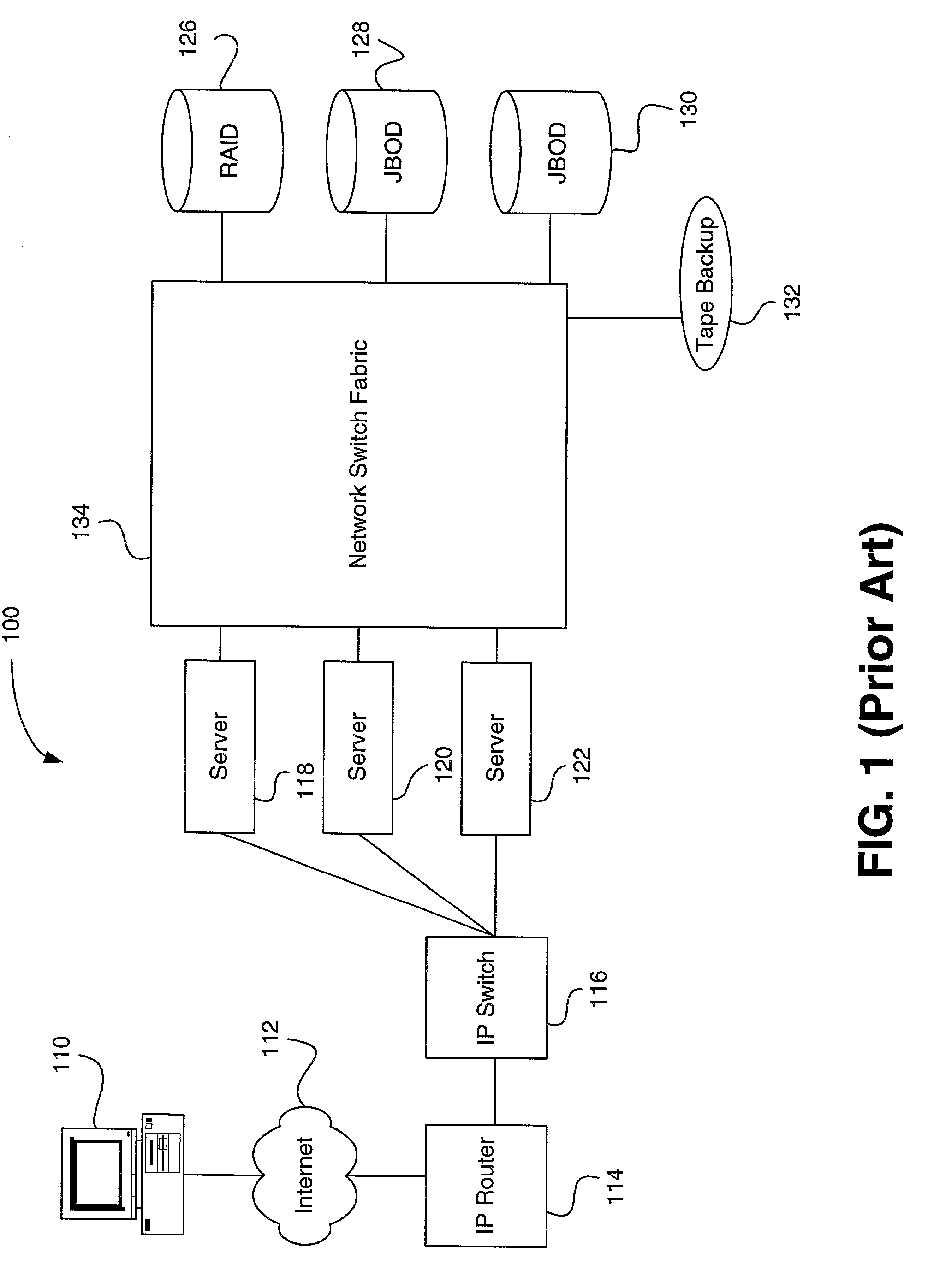
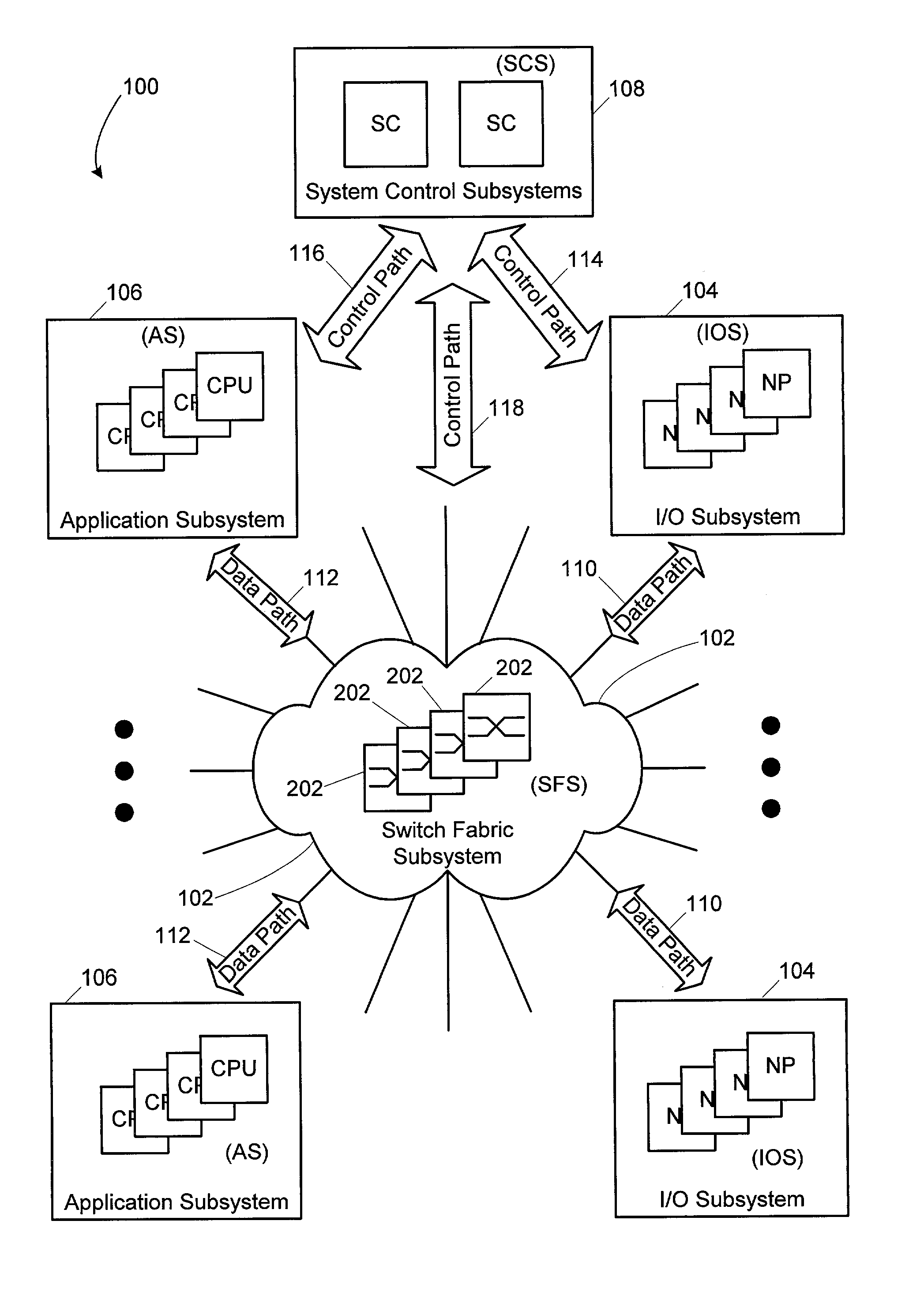
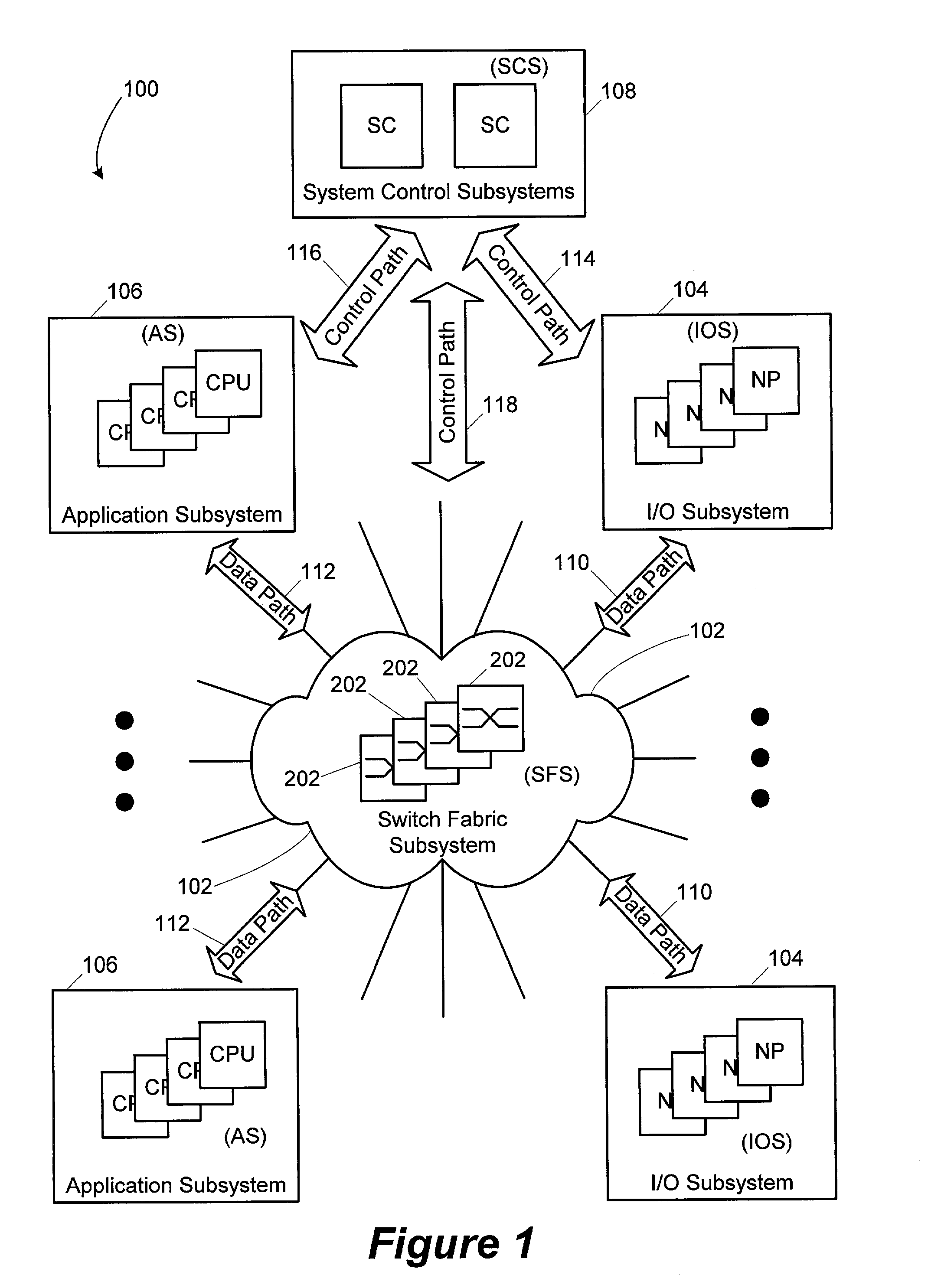
System and method for load-sharing computer network switch
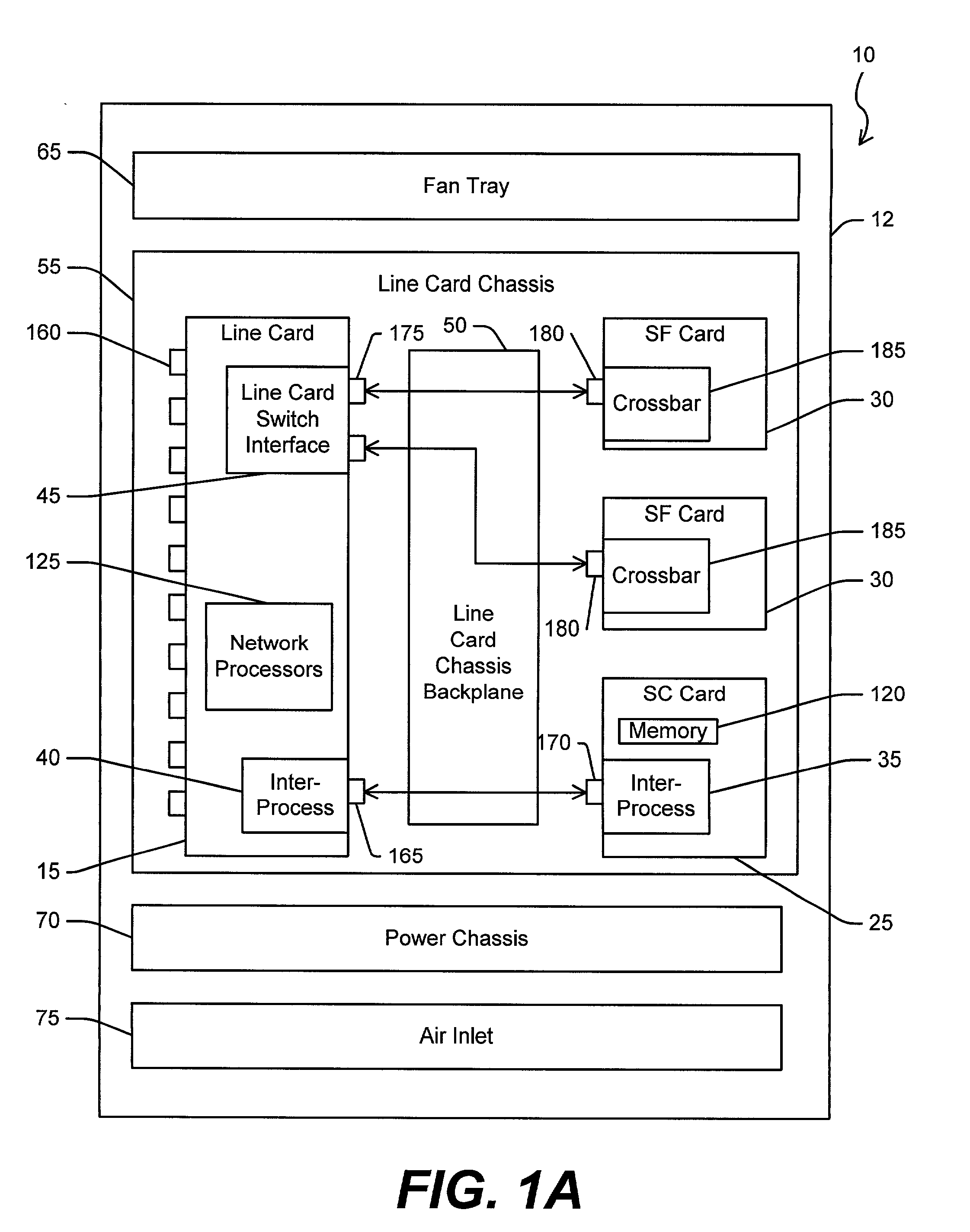
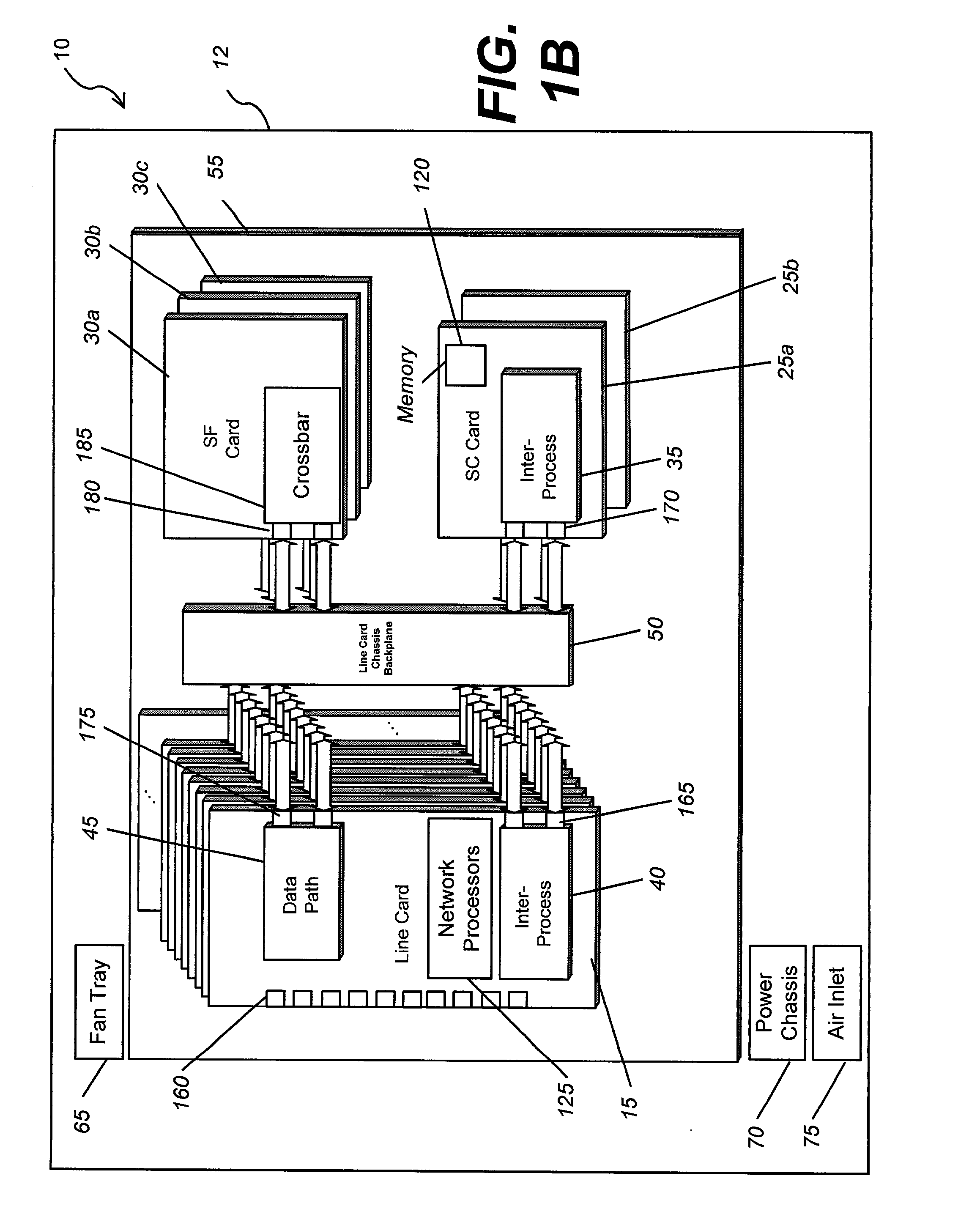
A computer network switch system is disclosed. A switch system may be configured as a single chassis system that has at least one line card, a set of active switch fabric cards to concurrently carry network traffic; and a first system control card to provide control functionality for the line card. The switch system may be configured as a multiple chassis system that has at least one line card chassis containing several line cards, and a switch fabric chassis (or a second line card chassis) that contains several switch fabric cards to provide a switching fabric with multiple ports. Load-sharing is accomplished primarily at the chip level, although card-level load-sharing is possible.
Owner:CIPHERMAX
System and method for scalable switch fabric for computer network
InactiveUS20090080428A1Reduce decreaseImprove performanceData switching by path configurationComputer hardwareLine card
A system and method are provided for processing storage commands between a host and a target. The system includes a first line card, a system card, and a second line card. The storage command that is issued from the host is received by the first line card. The first line card determines whether or not it can process the request by itself and, if so, forwards the storage command to the second line card for forwarding (and eventual processing) by the target. If the first line card cannot process the storage command by itself, it forwards the storage command to the system card for additional processing. The revised storage command is issued from the system card to the first line card. The first line card then issues the revised storage command to the second line card for eventual processing by the target.
Owner:CIPHERMAX
High availability architecture for network devices
InactiveUS7061858B1Avoiding significant disruptionError preventionFrequency-division multiplex detailsLine cardHigh availability
Owner:CISCO TECH INC
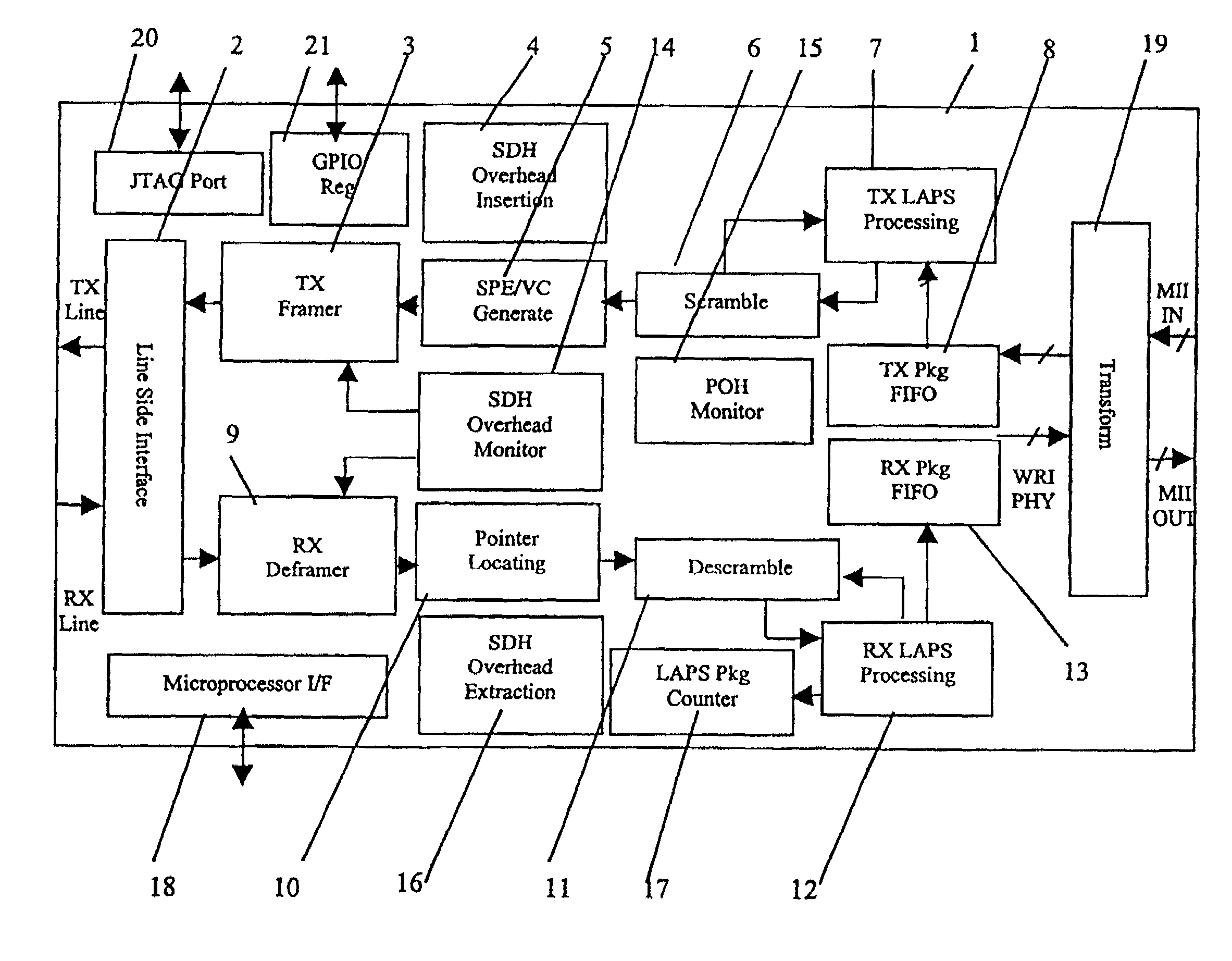
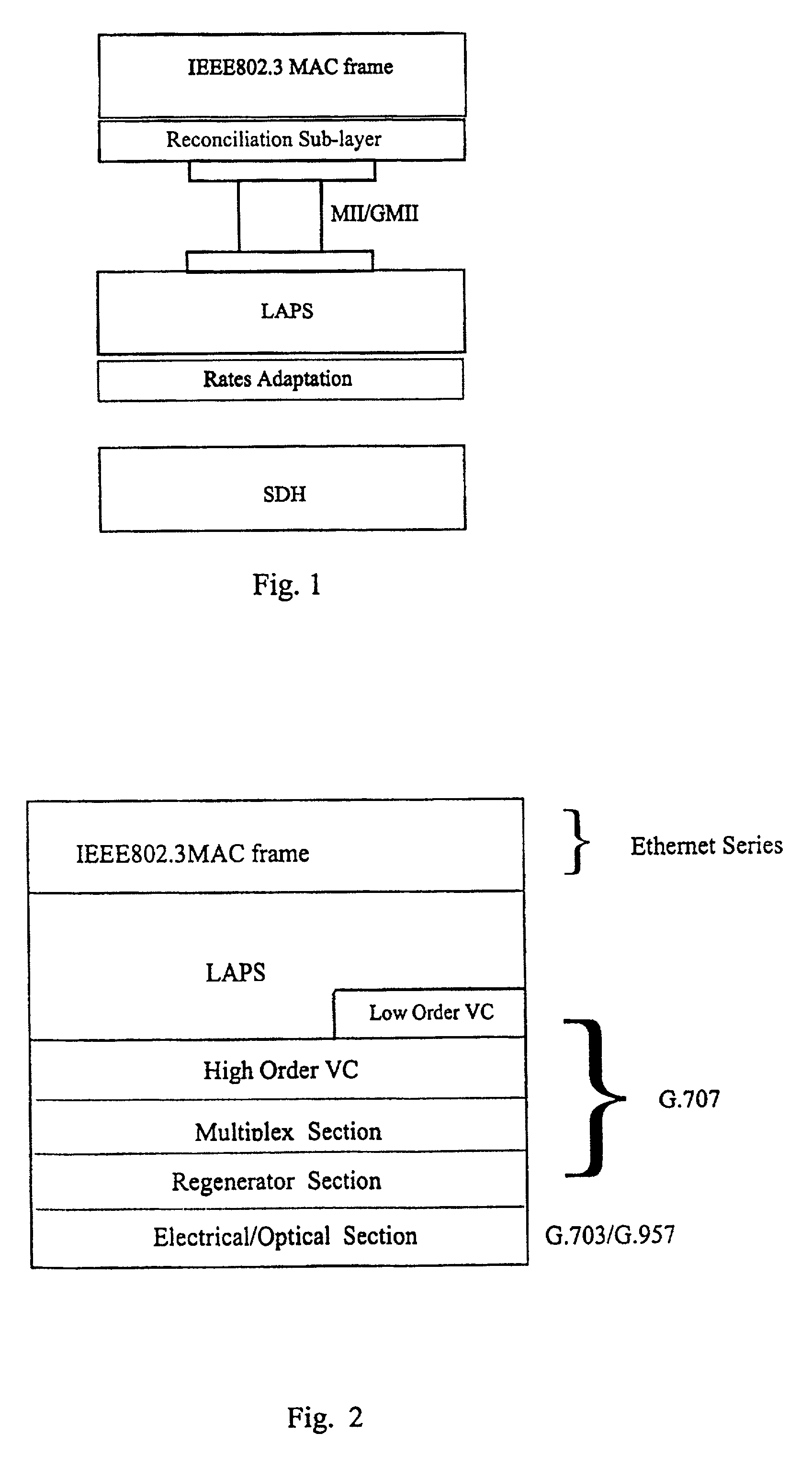
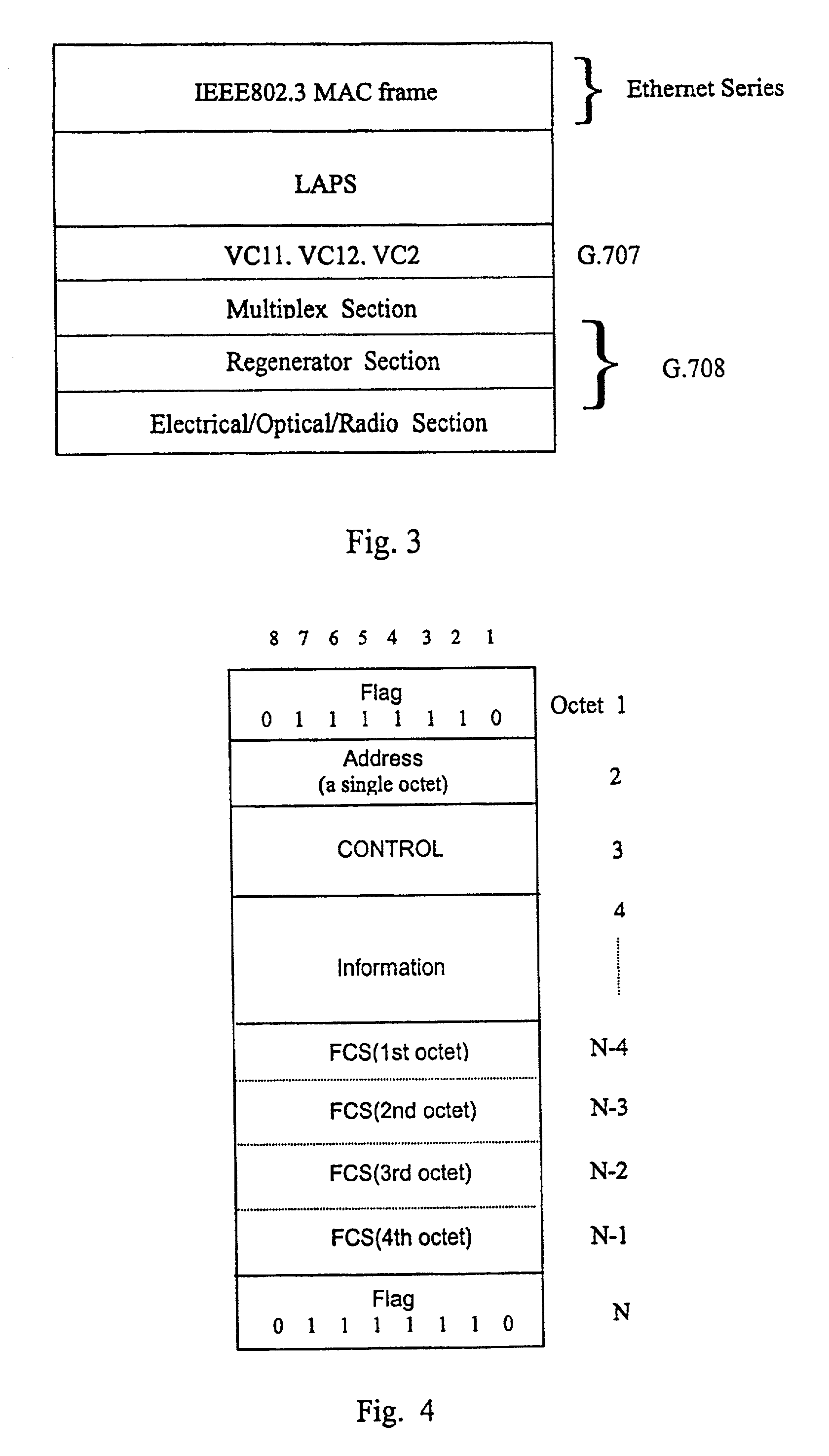
Interfacing apparatus and method for adapting Ethernet directly to physical channel
InactiveUS7031341B2Time-division multiplexTime-division multiplexing selectionLine cardFlag sequence
Owner:WUHAN RES INST OF POSTS & TELECOMM MII
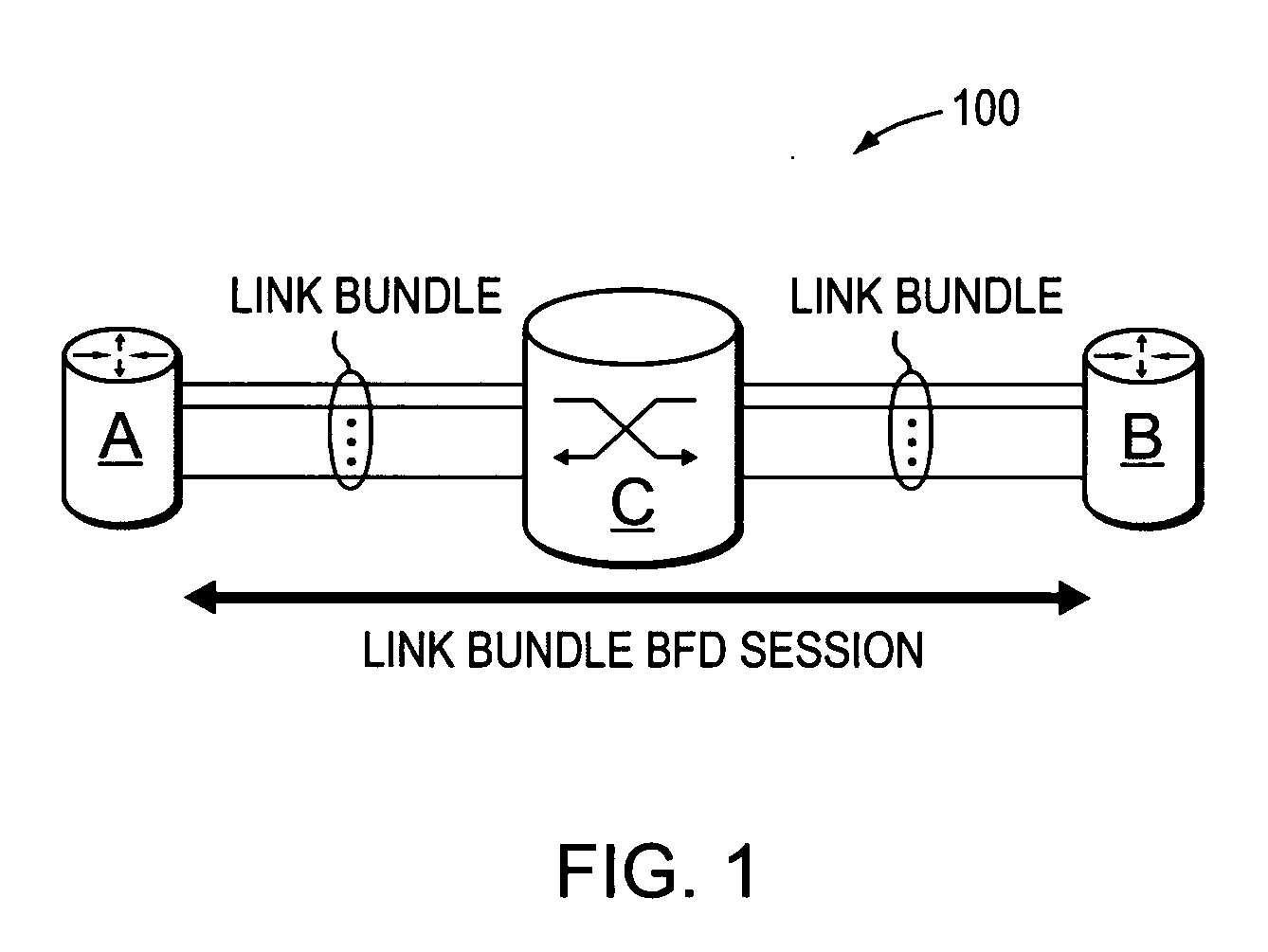
Technique for efficiently and dynamically maintaining bidirectional forwarding detection on a bundle of links
ActiveUS20070207591A1Improve performanceImprove scalabilityMultiplex system selection arrangementsEnergy efficient ICTComputer networkBidirectional Forwarding Detection
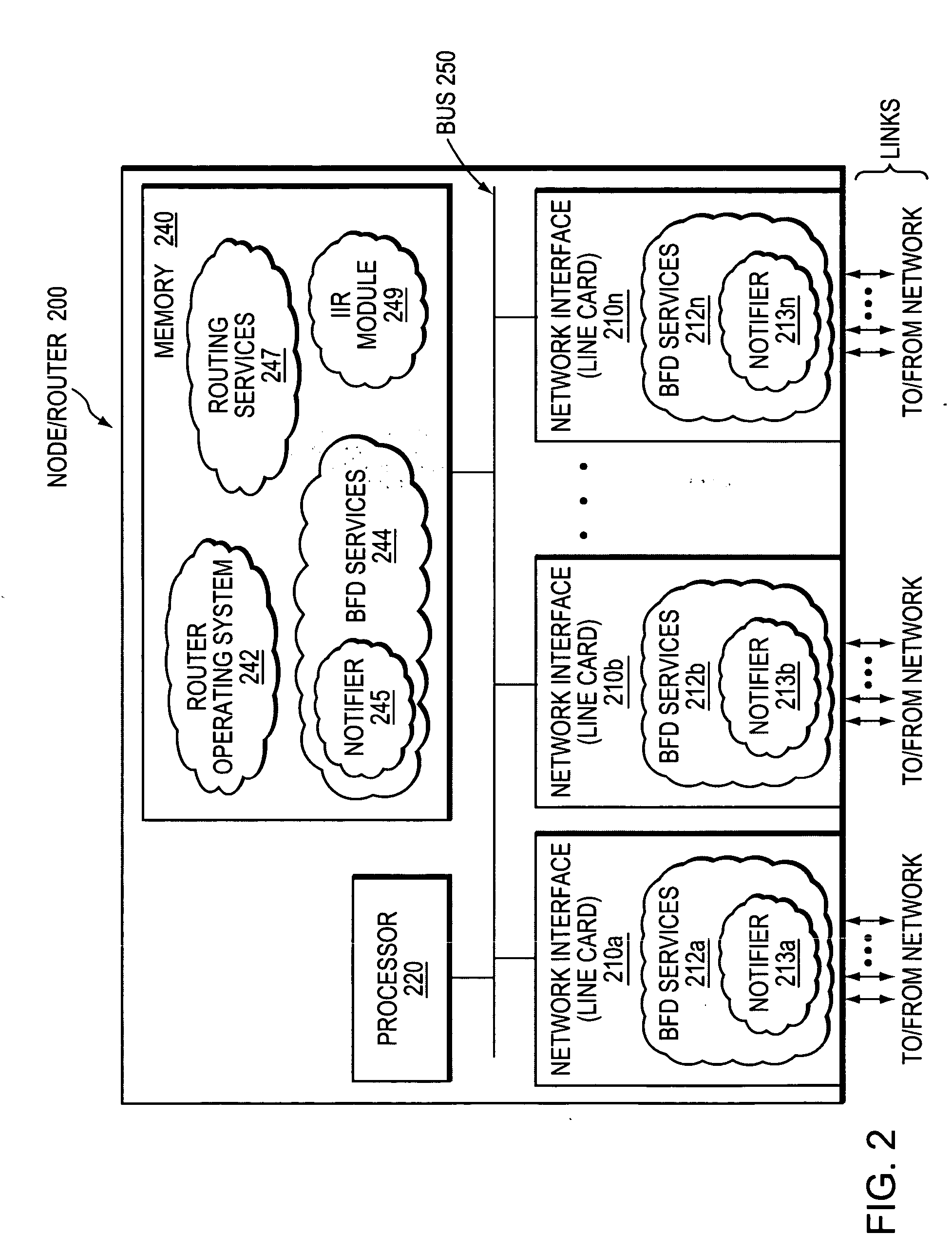
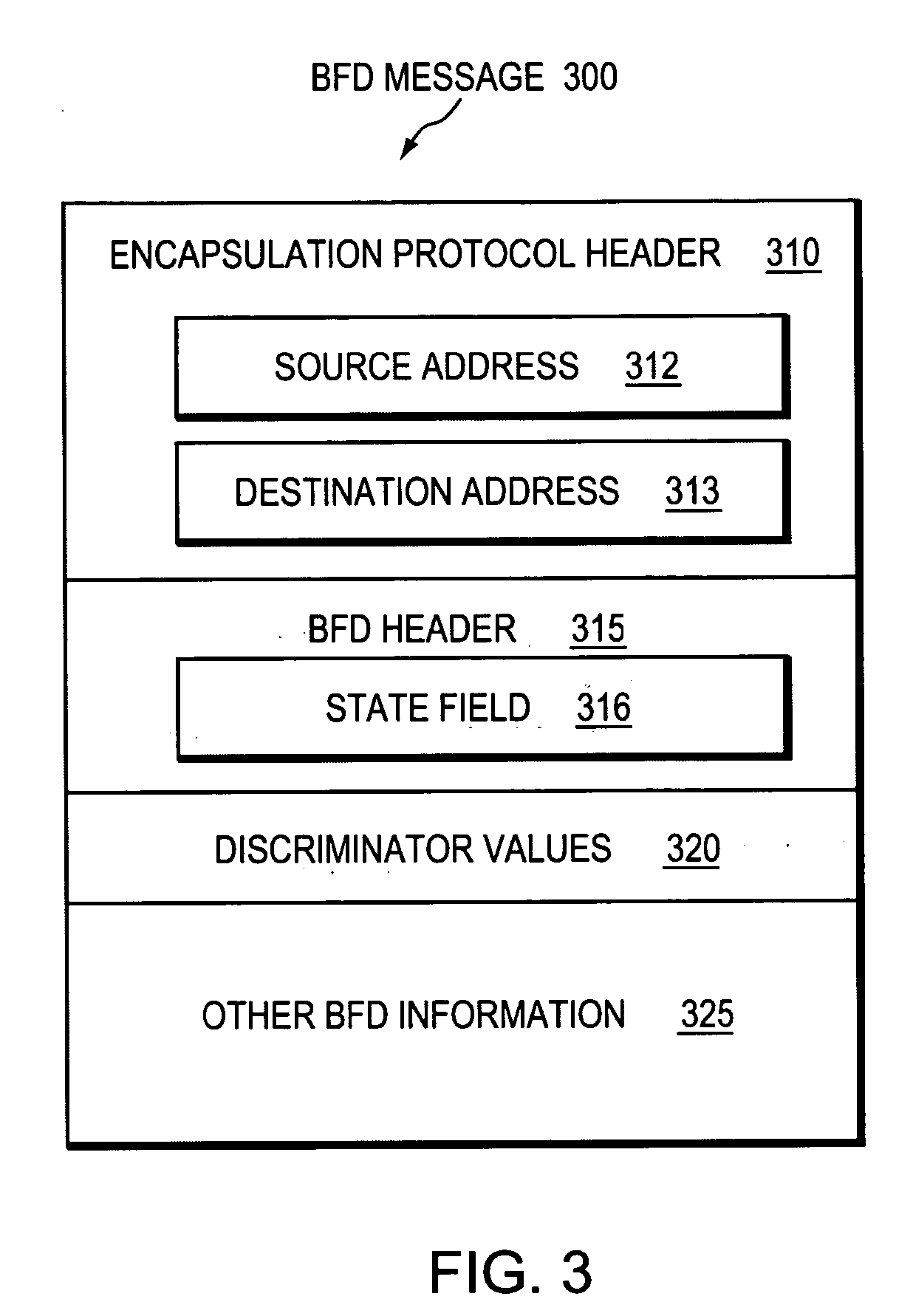
A technique efficiently and dynamically maintains bidirectional forwarding detection (BFD) on a bundle of links in a computer network. According to the novel technique, one or more “standby” BFD sessions may be established on one or more corresponding line cards (LCs), the LCs having one or more links of the bundle (bundle links). Once established, one of the standby BFD sessions may be selected as an “active” BFD session based on activity of one of the bundle links of the corresponding LC. Also, BFD messages may be transmitted from one of the bundle links of the active BFD session, e.g., the link receiving BFD messages. In response to inactivity of the transmitting link (e.g., failure, removal, etc.), the active BFD session may switch to another available active bundle link, and if no other active bundle links are available to the active BFD session, one of the standby BFD sessions is selected as the new active BFD session. In the event no other standby BFD sessions exist, the link bundle is determined to have failed.
Owner:CISCO TECH INC
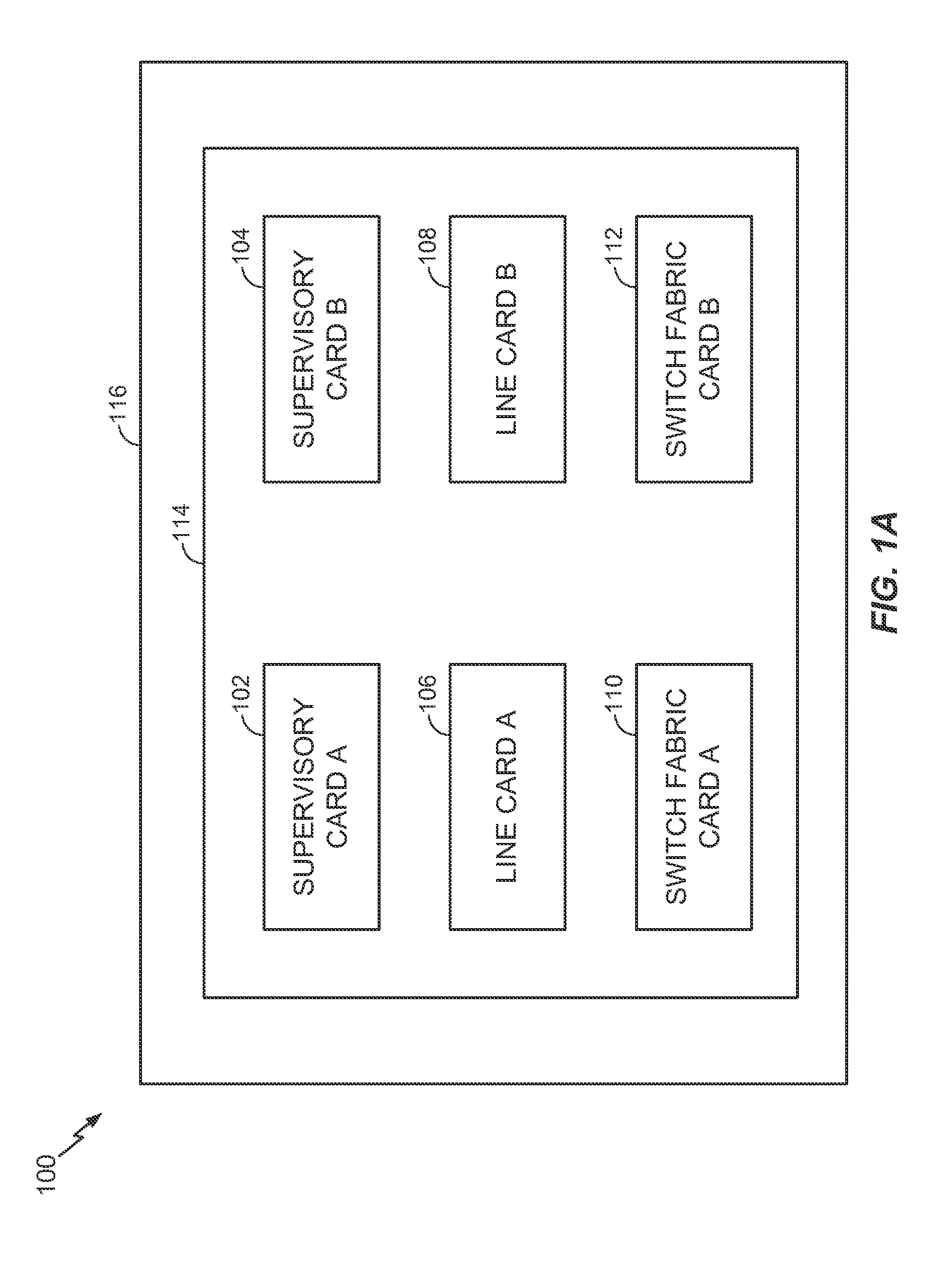
Method and system for intelligent distributed health monitoring in switching system equipment
A method for distributed health monitoring and fault repairing in a switching system. The switching system having one or more supervisory cards, one or more line cards, and one or more switch fabric cards. The method includes transmitting a health status poll request message to the one or more line cards and the one or more switch fabric cards. Thereafter, the method includes receiving health status poll response messages from each of the one or more line cards and the one or more switch fabric cards. Each health status poll response message includes health status summary of the corresponding card. Further, the method involves detecting one or more faults in the switching system based on the health poll response messages. Finally, the method includes triggering at least one action on the detection of the faults in the switching system. These actions are triggered based on a set of predefined rules.
Owner:CIENA
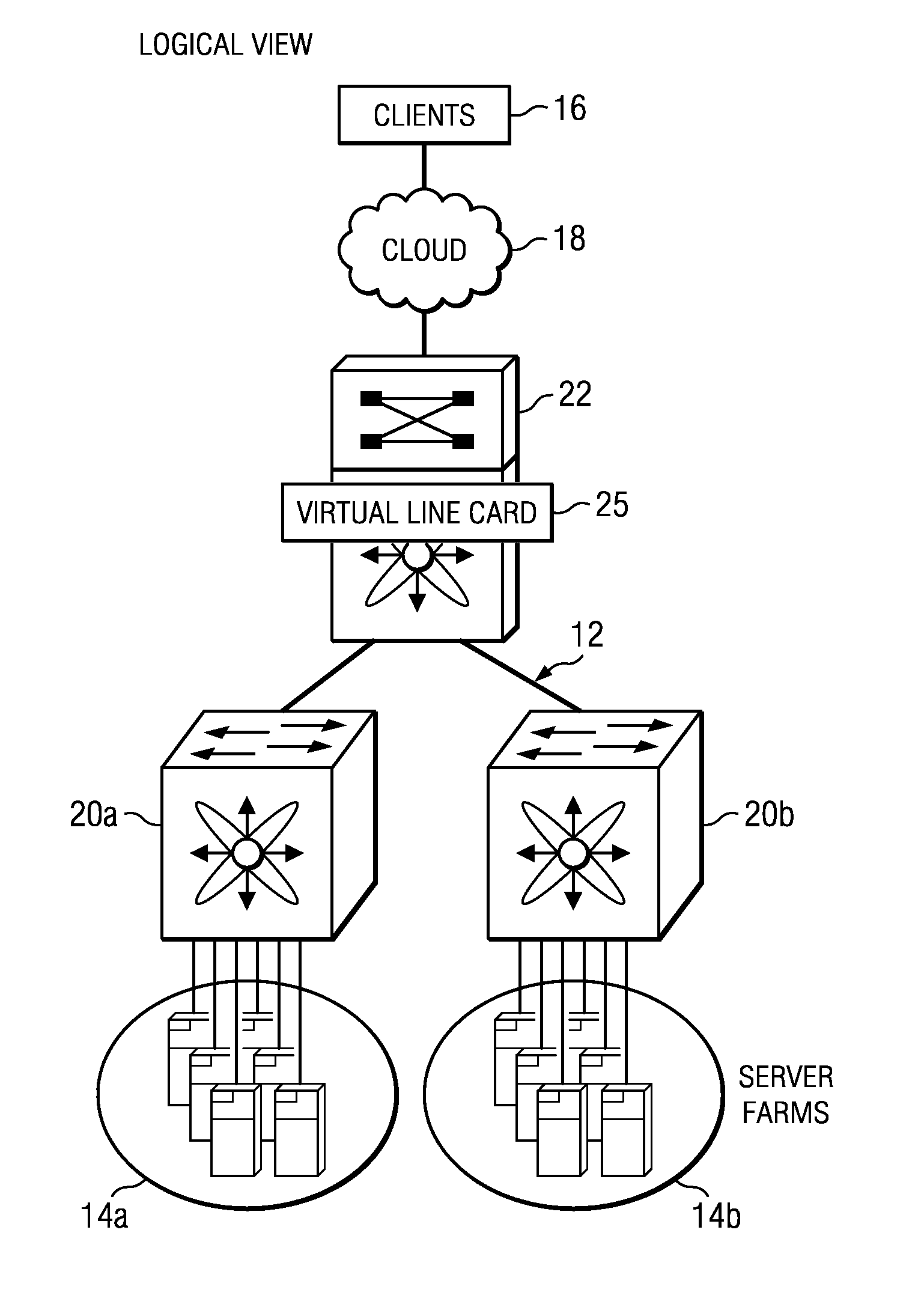
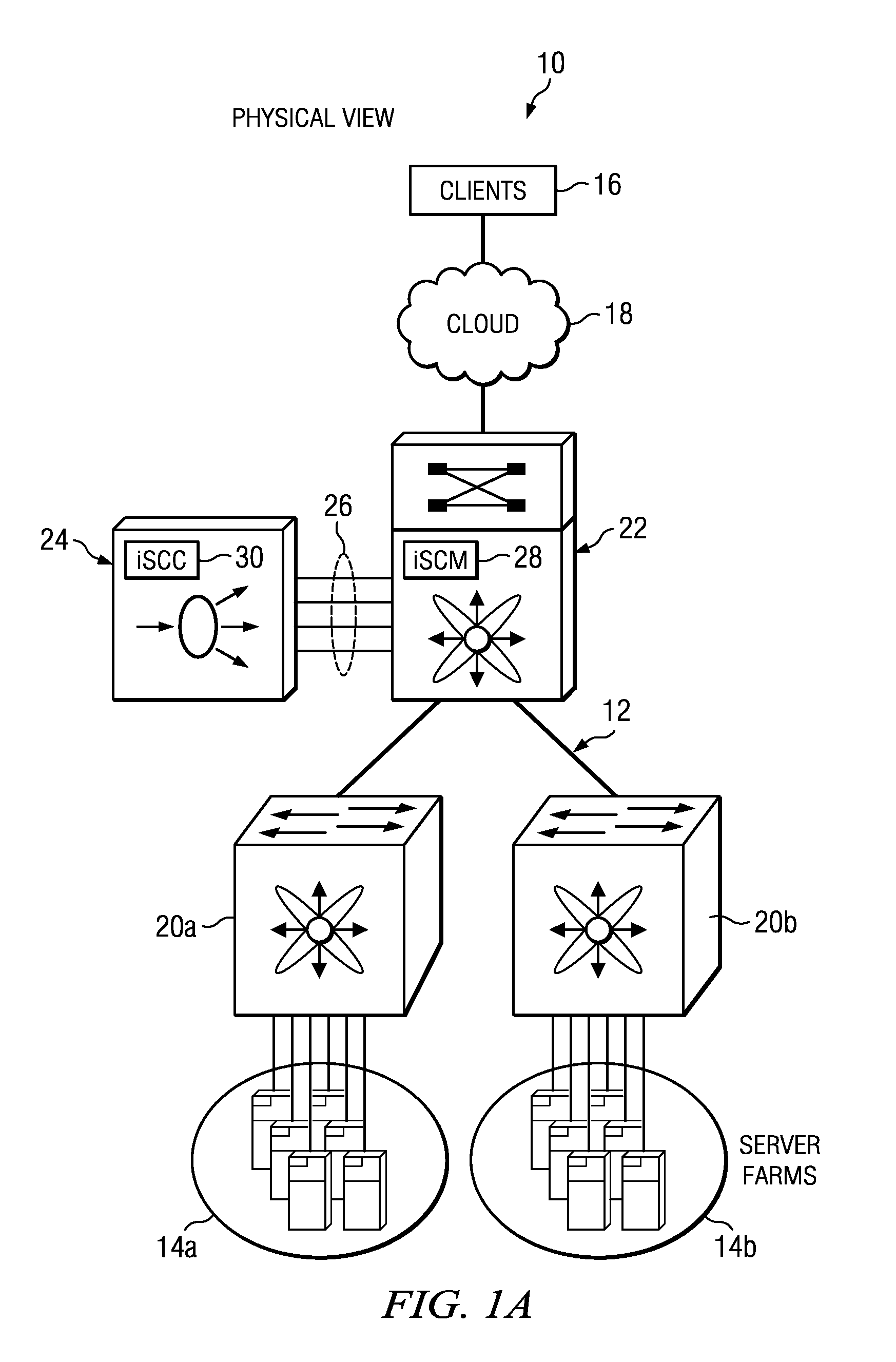
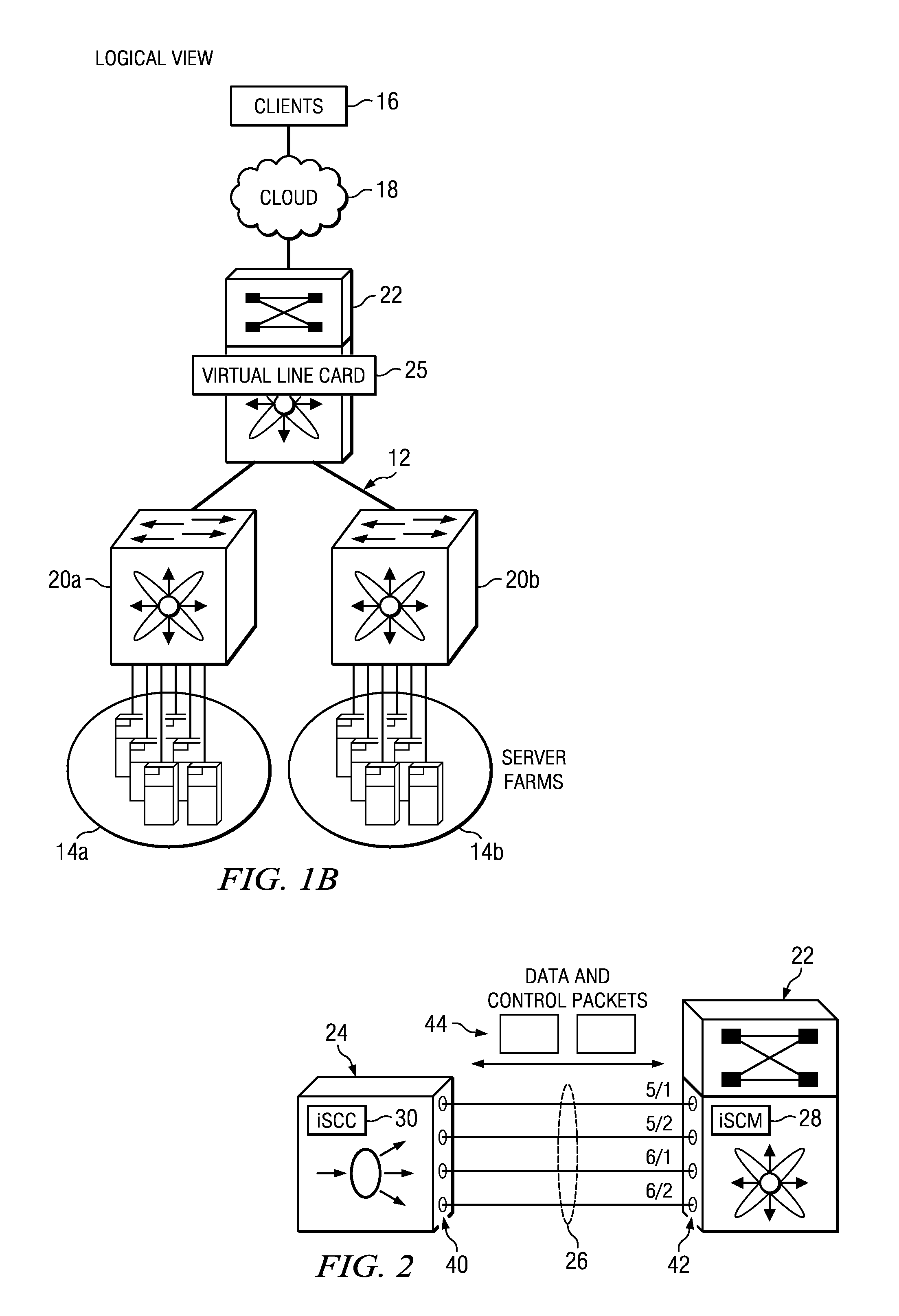
System and method for configuring service appliances as virtual line cards in a network environment
ActiveUS9246702B1Special service provision for substationData switching by path configurationLine cardNetwork control
An example method is provided and includes configuring a service appliance to offload network control plane and network data plane operations to a switch; establishing a communication channel between the service appliance and the switch; and communicating control messages between the service appliance and the switch over the communication channel. In more particular embodiment, the method can include communicating data messages between the service appliance and the switch over the communication channel.
Owner:CISCO TECH INC
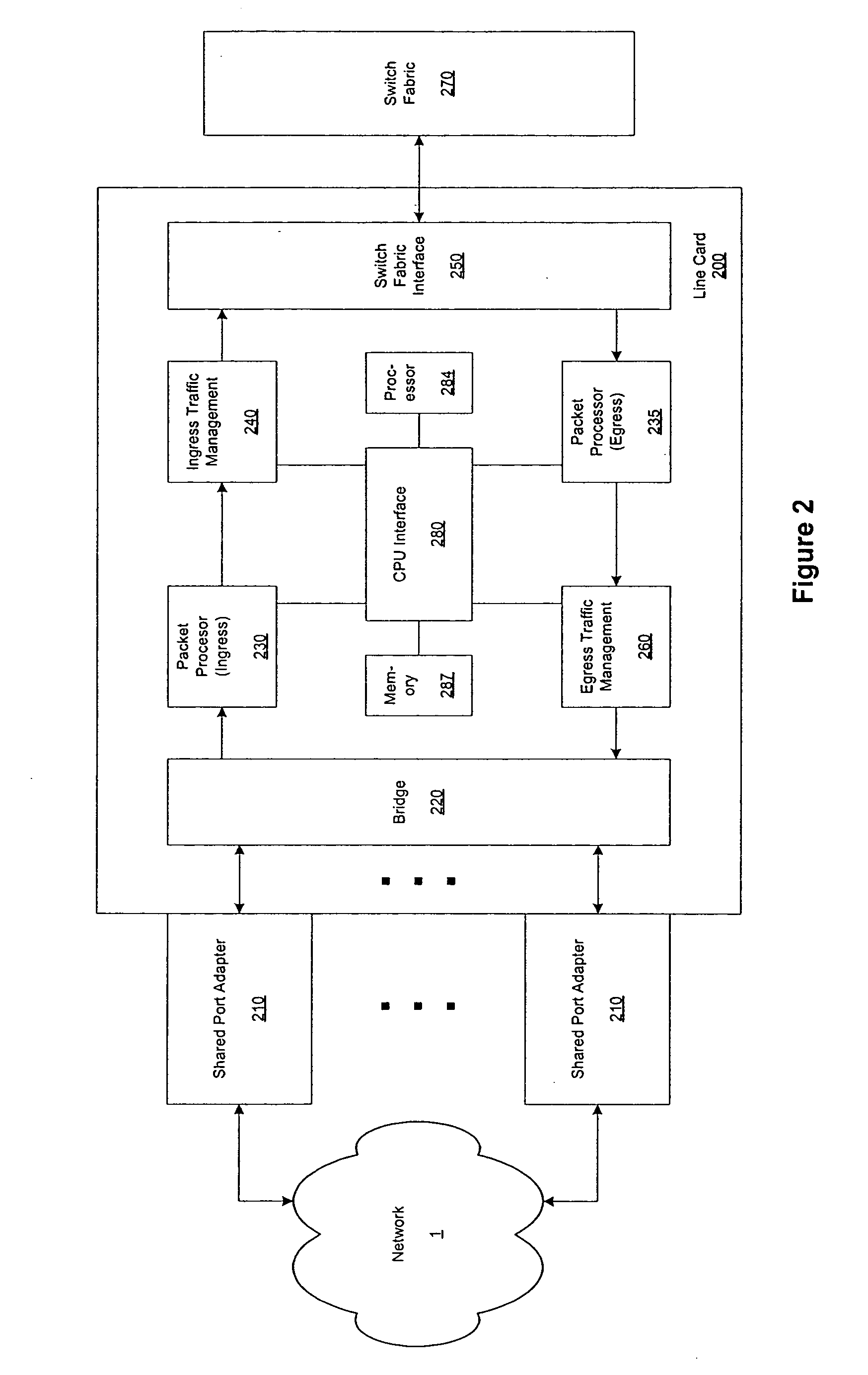
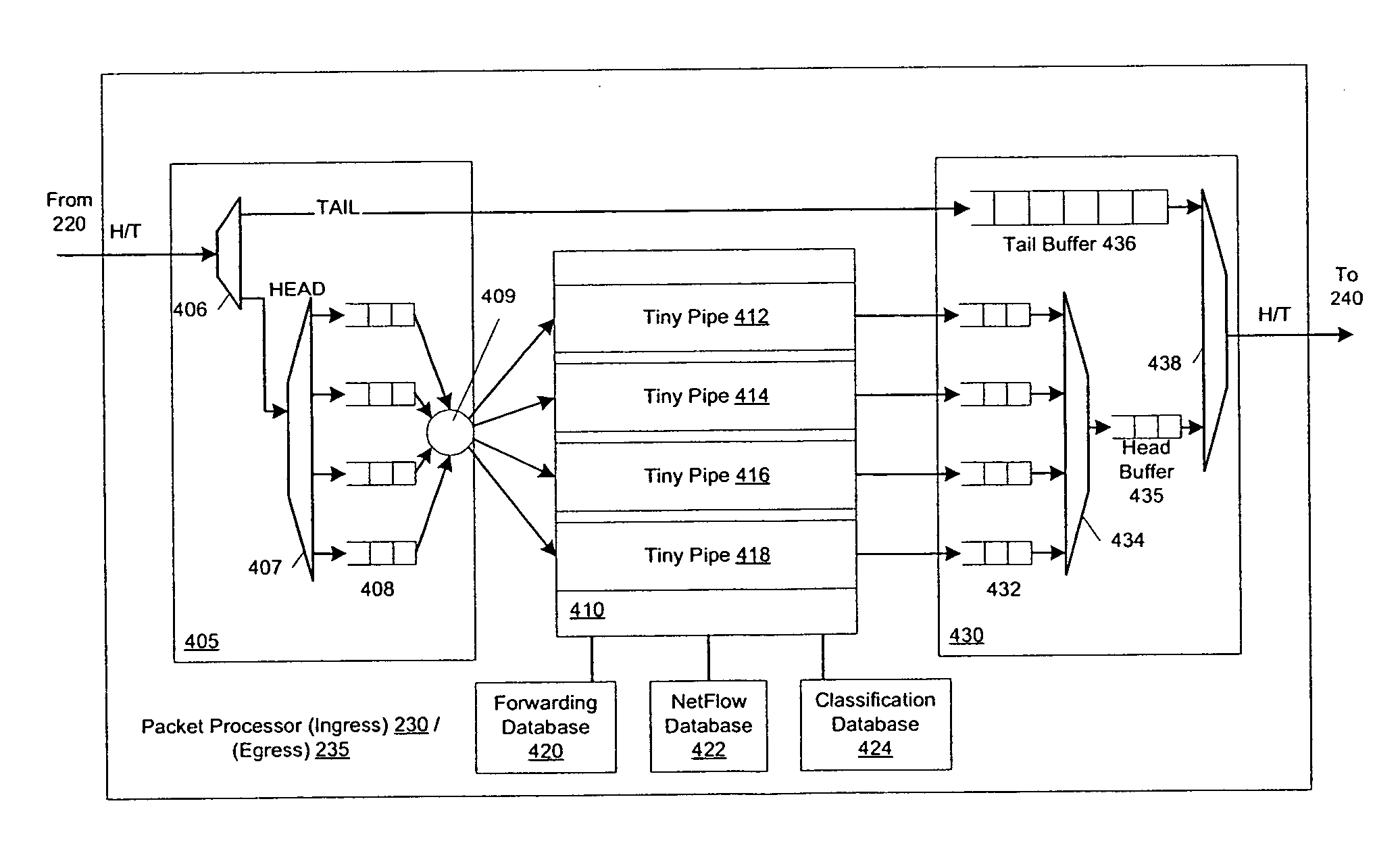
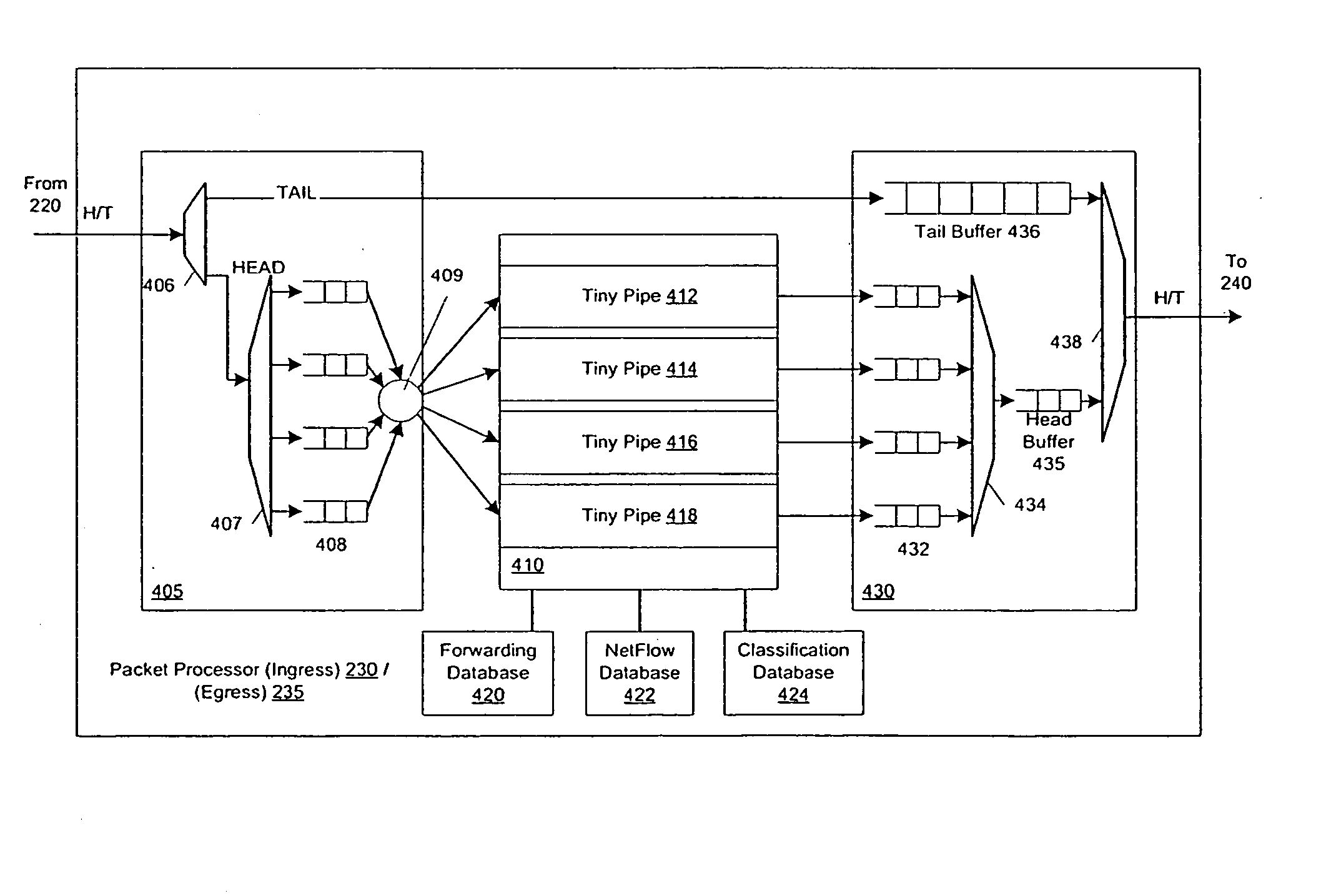
Flexible DMA engine for packet header modification
A pipelined linecard architecture for receiving, modifying, switching, buffering, queuing and dequeuing packets for transmission in a communications network. The linecard has two paths: the receive path, which carries packets into the switch device from the network, and the transmit path, which carries packets from the switch to the network. In the receive path, received packets are processed and switched in an asynchronous, multi-stage pipeline utilizing programmable data structures for fast table lookup and linked list traversal. The pipelined switch operates on several packets in parallel while determining each packet's routing destination. Once that determination is made, each packet is modified to contain new routing information as well as additional header data to help speed it through the switch. Each packet is then buffered and enqueued for transmission over the switching fabric to the linecard attached to the proper destination port. The destination linecard may be the same physical linecard as that receiving the inbound packet or a different physical linecard. The transmit path consists of a buffer / queuing circuit similar to that used in the receive path. Both enqueuing and dequeuing of packets is accomplished using CoS-based decision making apparatus and congestion avoidance and dequeue management hardware. The architecture of the present invention has the advantages of high throughput and the ability to rapidly implement new features and capabilities.
Owner:CISCO TECH INC
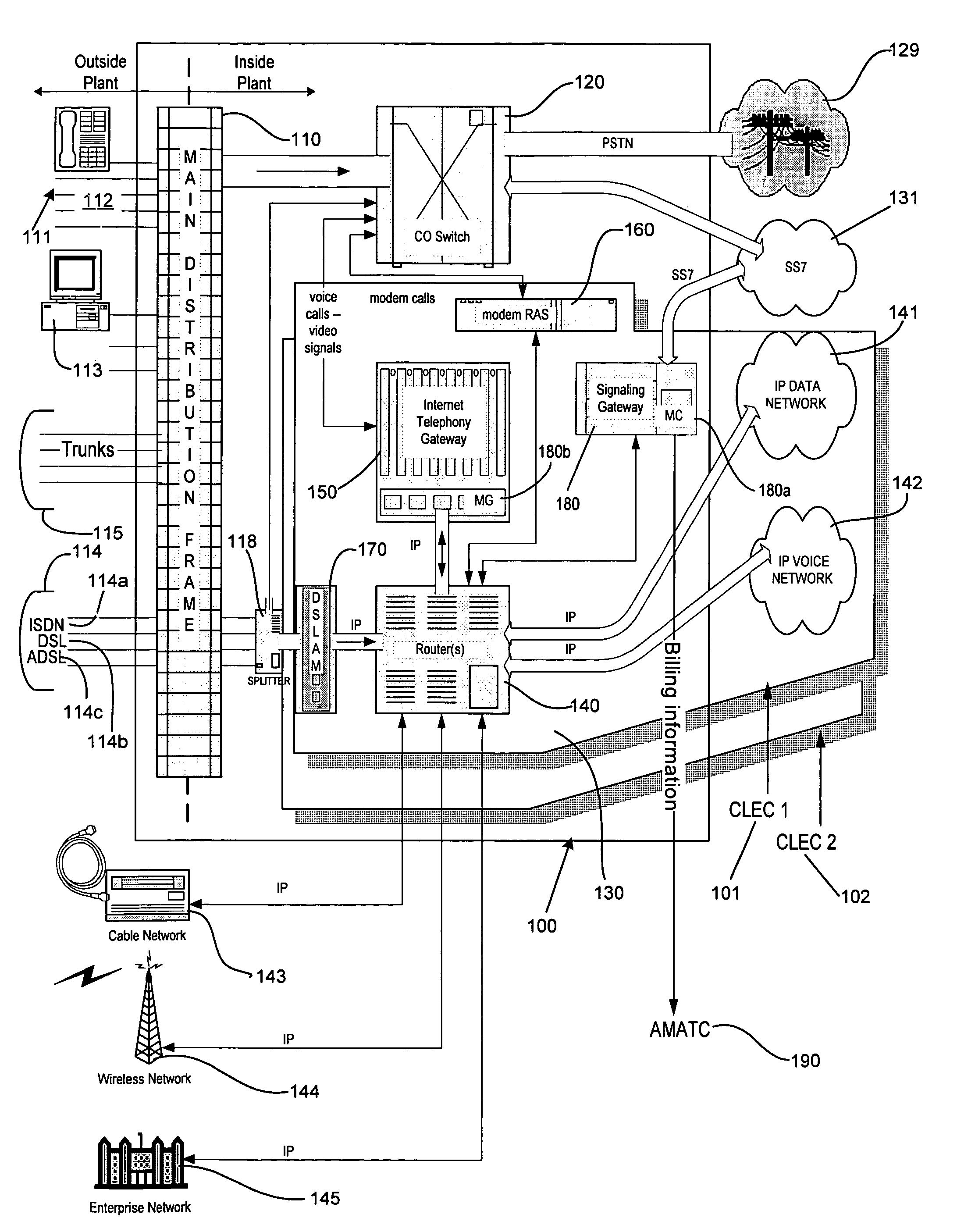
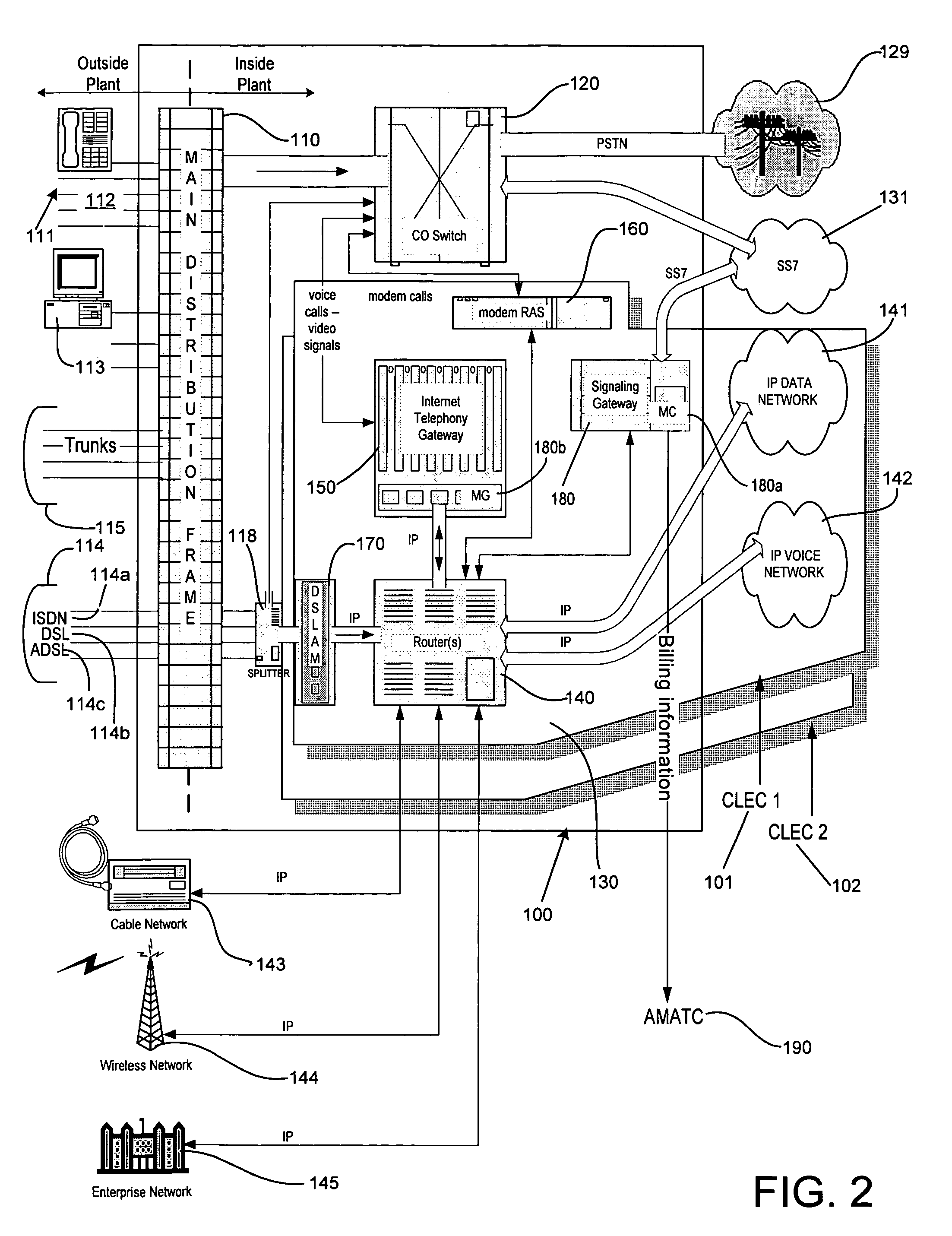
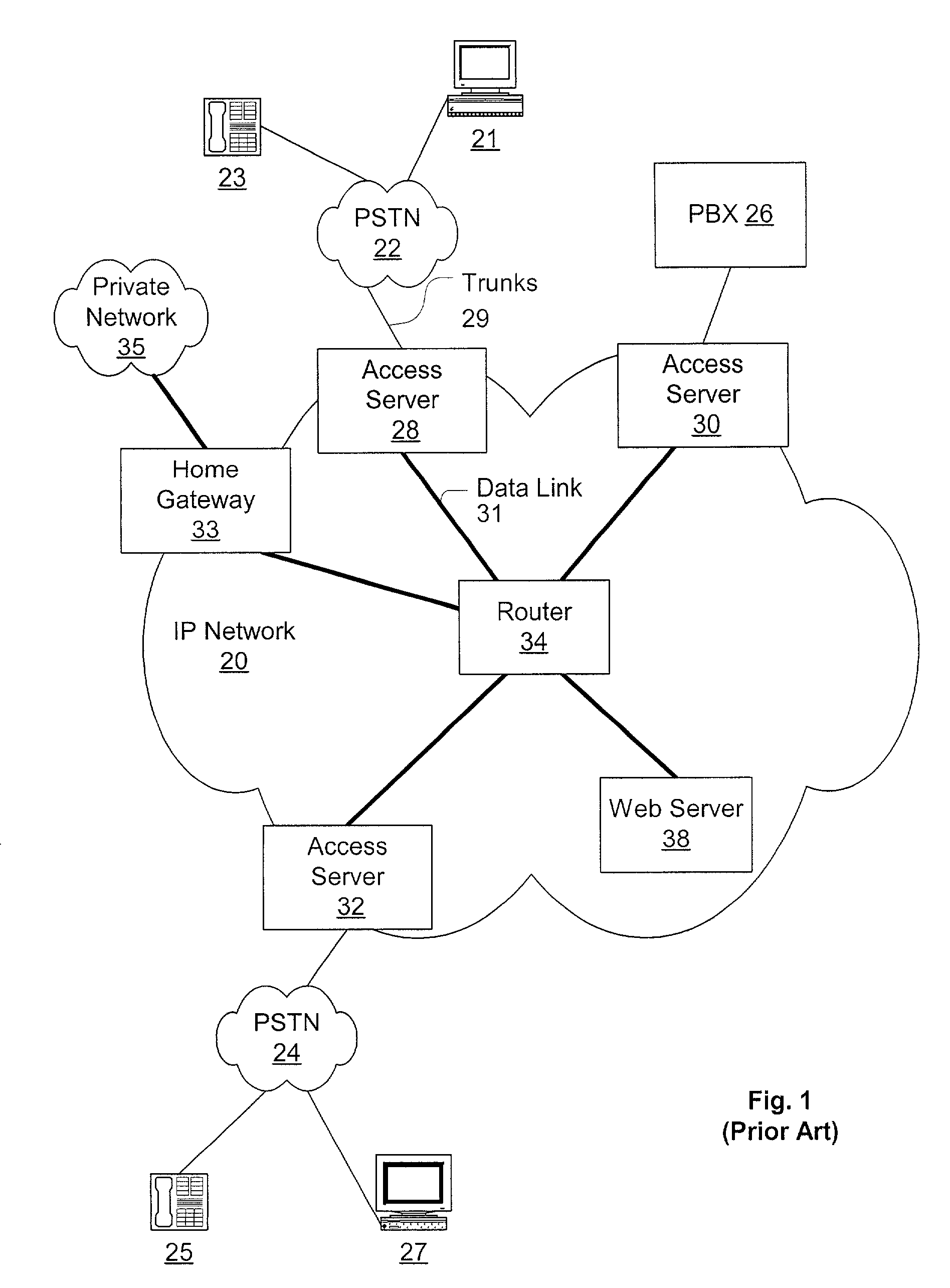
Architecture for a central office using IP technology
A telephony system and method having a switch for analog voice and data signals that is connected to a first network, and a router for routing Internet Protocol packets that is connected to a second network using Internet Protocol addressing. The telephony system and method also includes a telephony gateway that is connected to both the switch and the router for converting analog voice signals into Internet Protocol packets and for converting Internet Protocol packets into analog voice signals, the telephony gateway being connected, and a remote access server that is connected to both the switch and the router for converting analog data signals into Internet Protocol packets and for converting Internet Protocol packets into analog data signals. The switch may have a switch matrix capable of being connected to the Public Switched Telephone Network, a line rack with a plurality of line cards connected to the switch matrix, and a trunk rack with a plurality of trunk cards connected to the switch matrix. The switch matrix may also be connected to the telephony gateway and the remote access server.
Owner:UTSTARCOM INC
Packet switching apparatus including cascade ports and method for switching packets
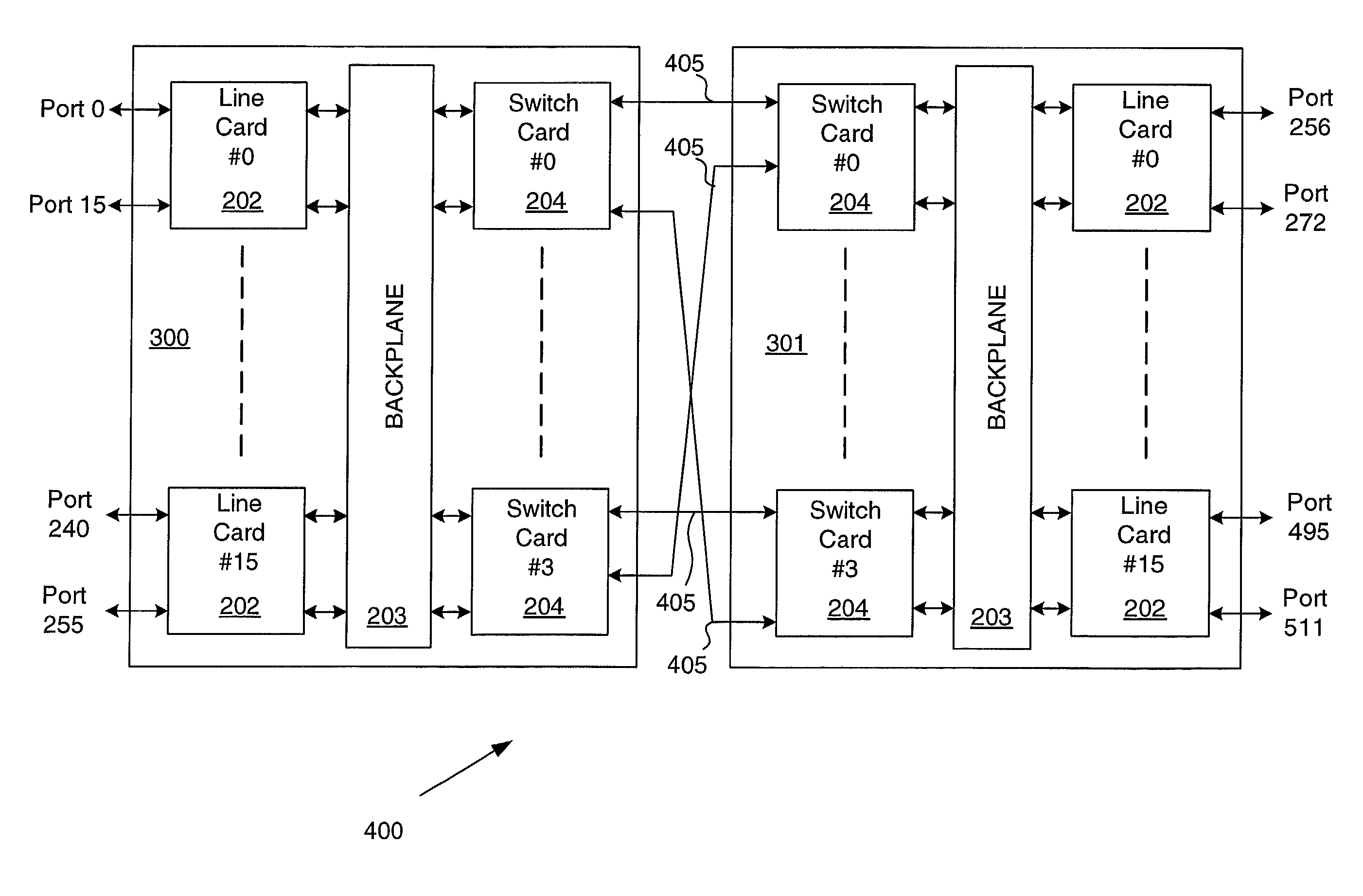
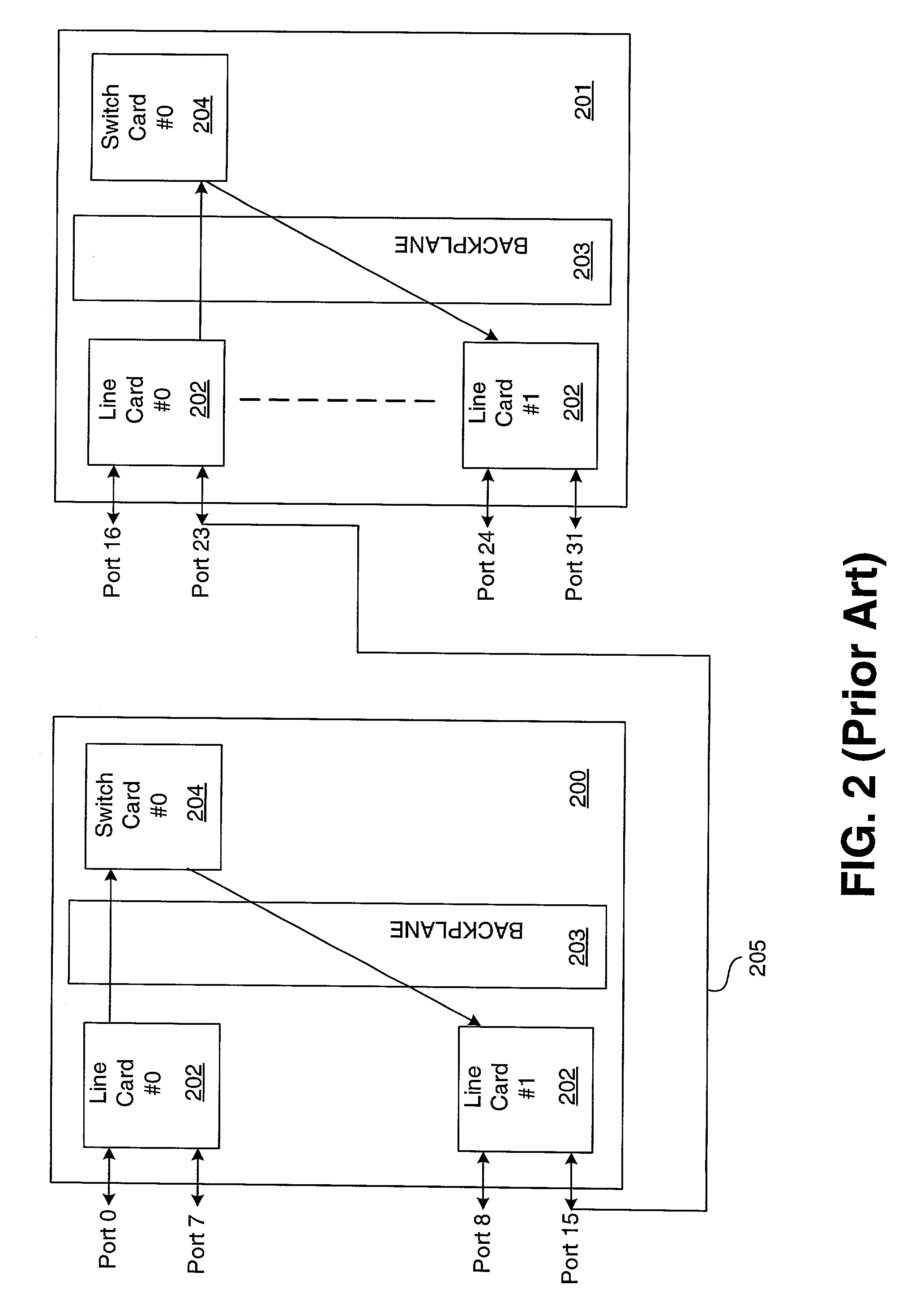
InactiveUS7110394B1Shorten the pathPath is shortenedMultiplex system selection arrangementsTime-division multiplexLine cardBackplane
A switching device comprises at least two base racks, each base rack including a switch card in communication with a line card across a backplane, the line card having at least an external port. The at least two base racks are coupled such that the switch cards of each are linked. A method for switching a packet comprises introducing the packet into an external port on a first base rack, transmitting the packet from a first cascade port on the first base rack to a second cascade port on a second base rack, and sending the packet out of the second base rack through a second external port.
Owner:AVAGO TECH INT SALES PTE LTD
Pipelined packet switching and queuing architecture
An architecture for a line card in a network routing device is provided. The line card architecture provides a bi-directional interface between the routing device and a network, both receiving packets from the network and transmitting the packets to the network through one or more connecting ports. In both the receive and transmit path, packets processing and routing in a multi-stage, parallel pipeline that can operate on several packets at the same time to determine each packet's routing destination is provided. Once a routing destination determination is made, the line card architecture provides for each received packet to be modified to contain new routing information and additional header data to facilitate packet transmission through the switching fabric. The line card architecture further provides for the use of bandwidth management techniques in order to buffer and enqueue each packet for transmission through the switching fabric to a corresponding destination port. The transmit path of the line card architecture further incorporates additional features for treatment and replication of multicast packets.
Owner:CISCO TECH INC
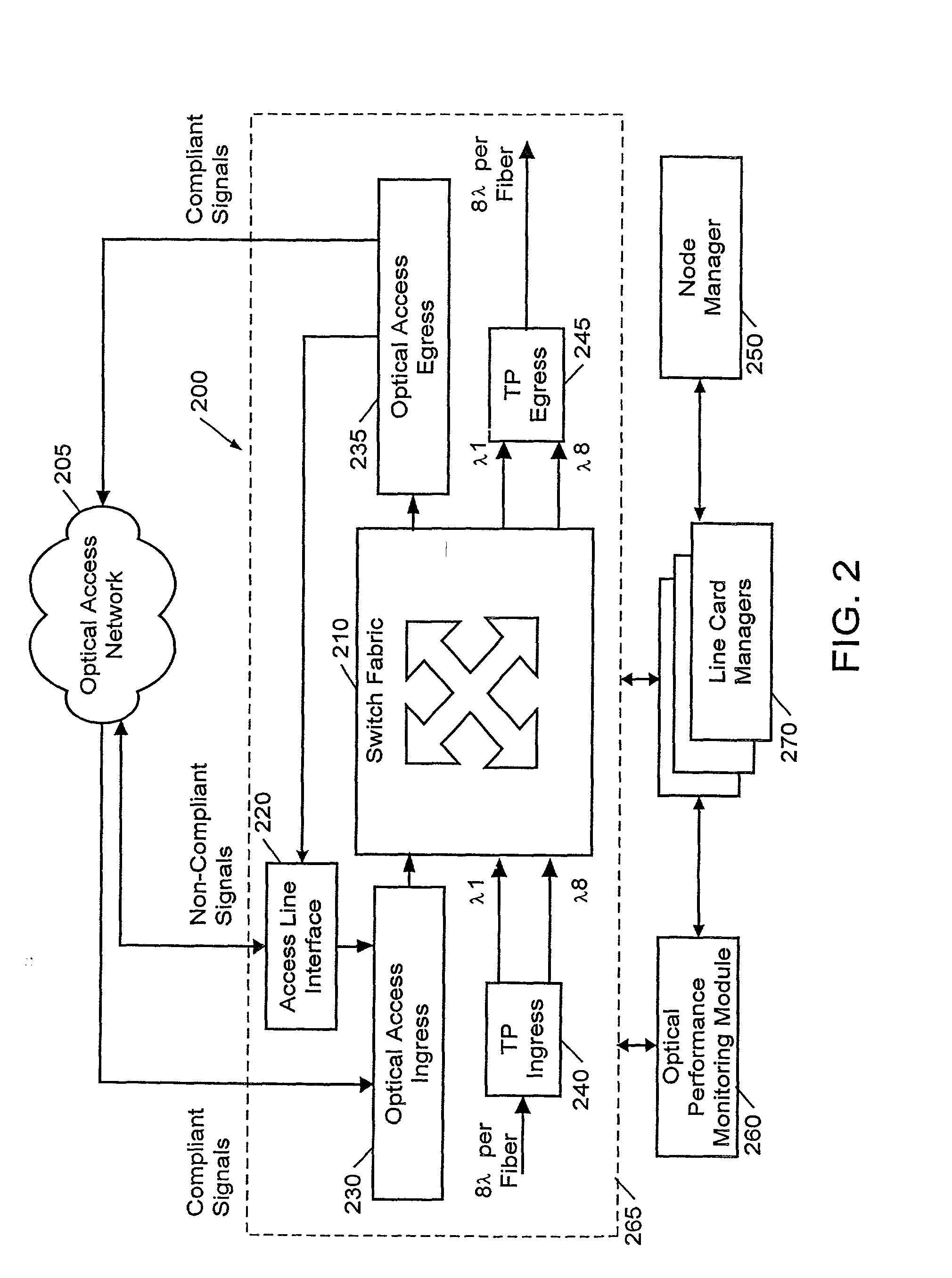
Apparatus, method and system having reduced power consumption in a multi-carrier wireline environment
InactiveUS6353628B1Reduce impactSelectively ignoring noise-effected sub-channel carriersModulated-carrier systemsTransmission systemsDigital signal processingAudio power amplifier
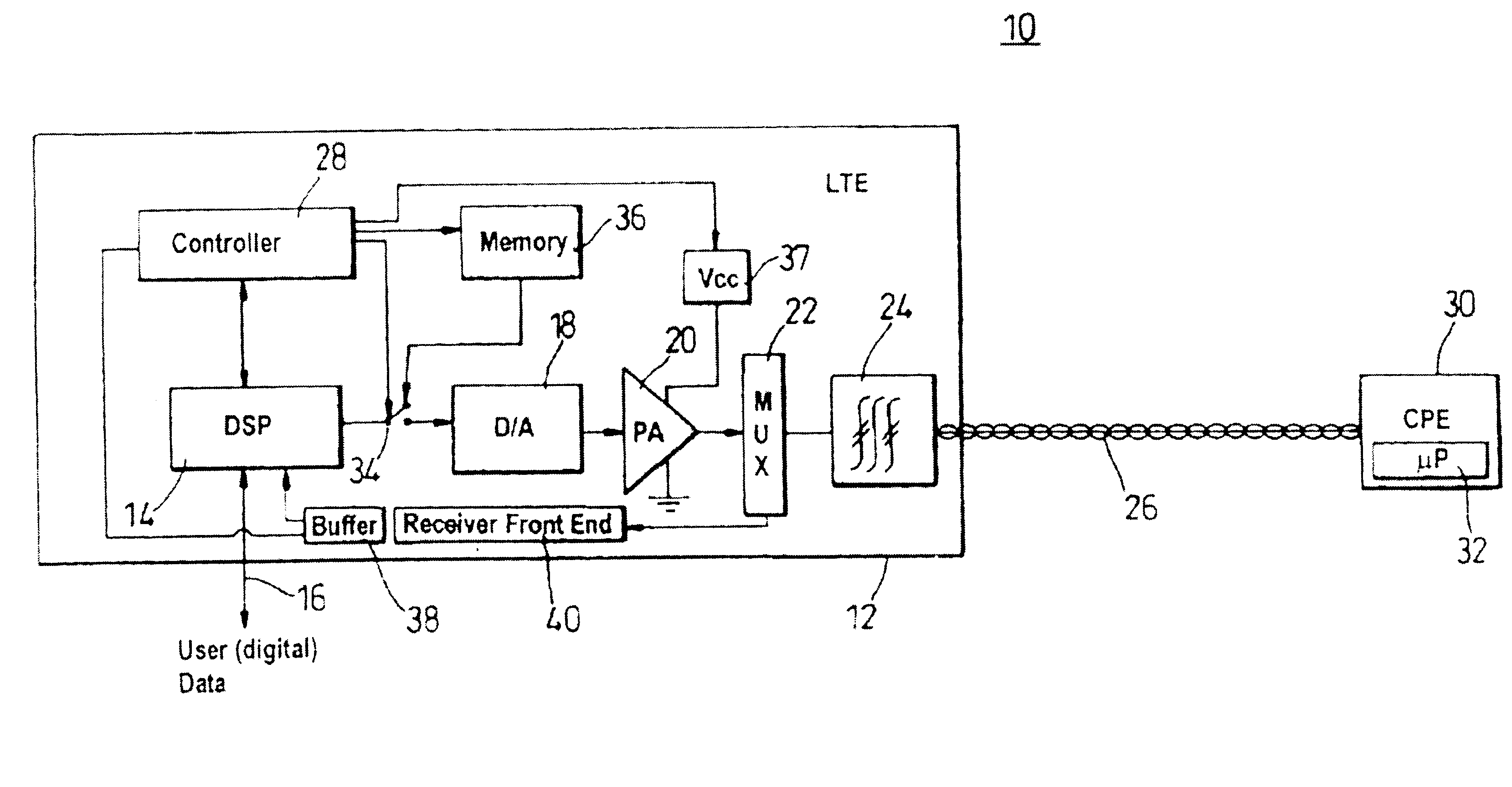
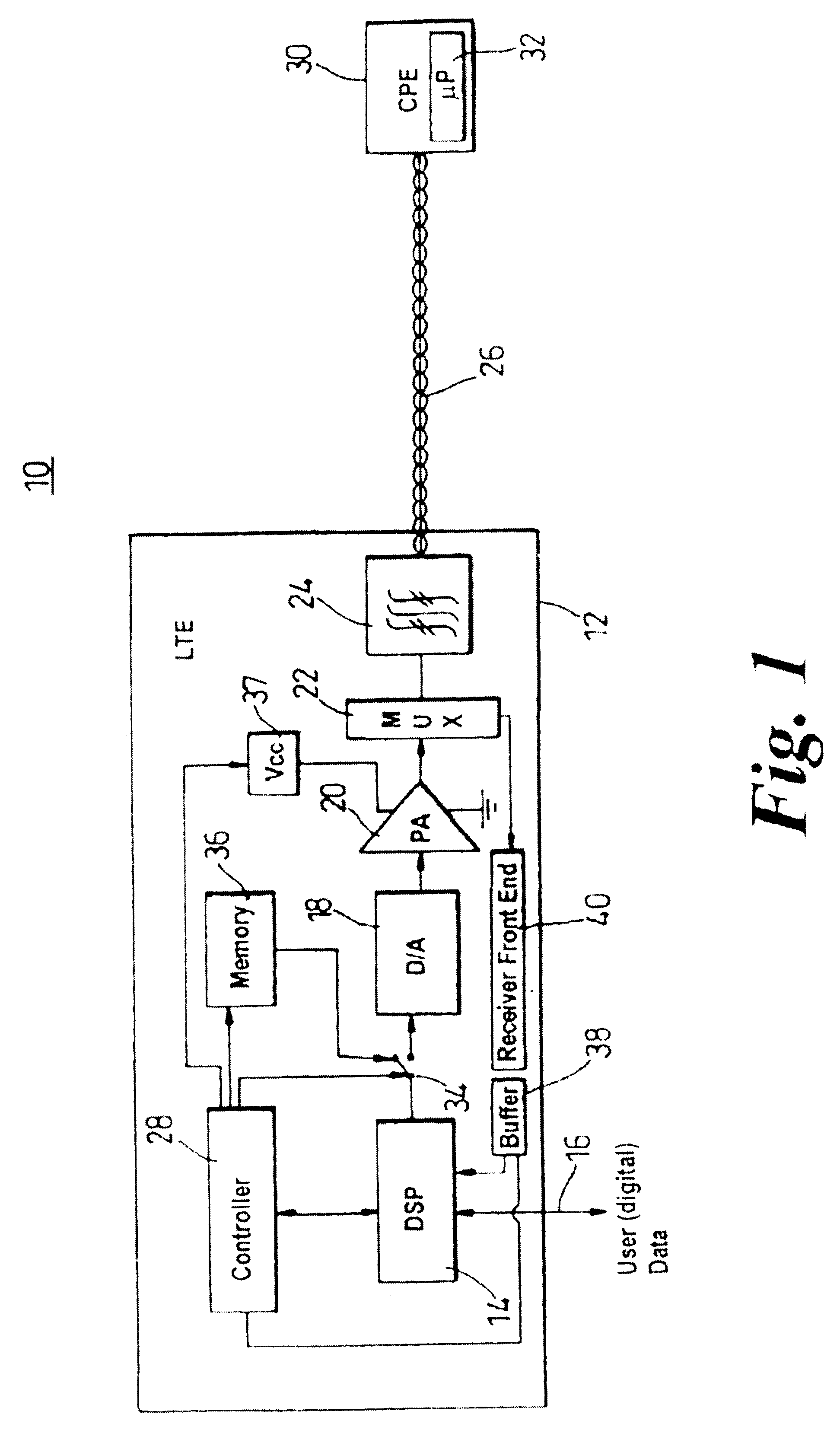
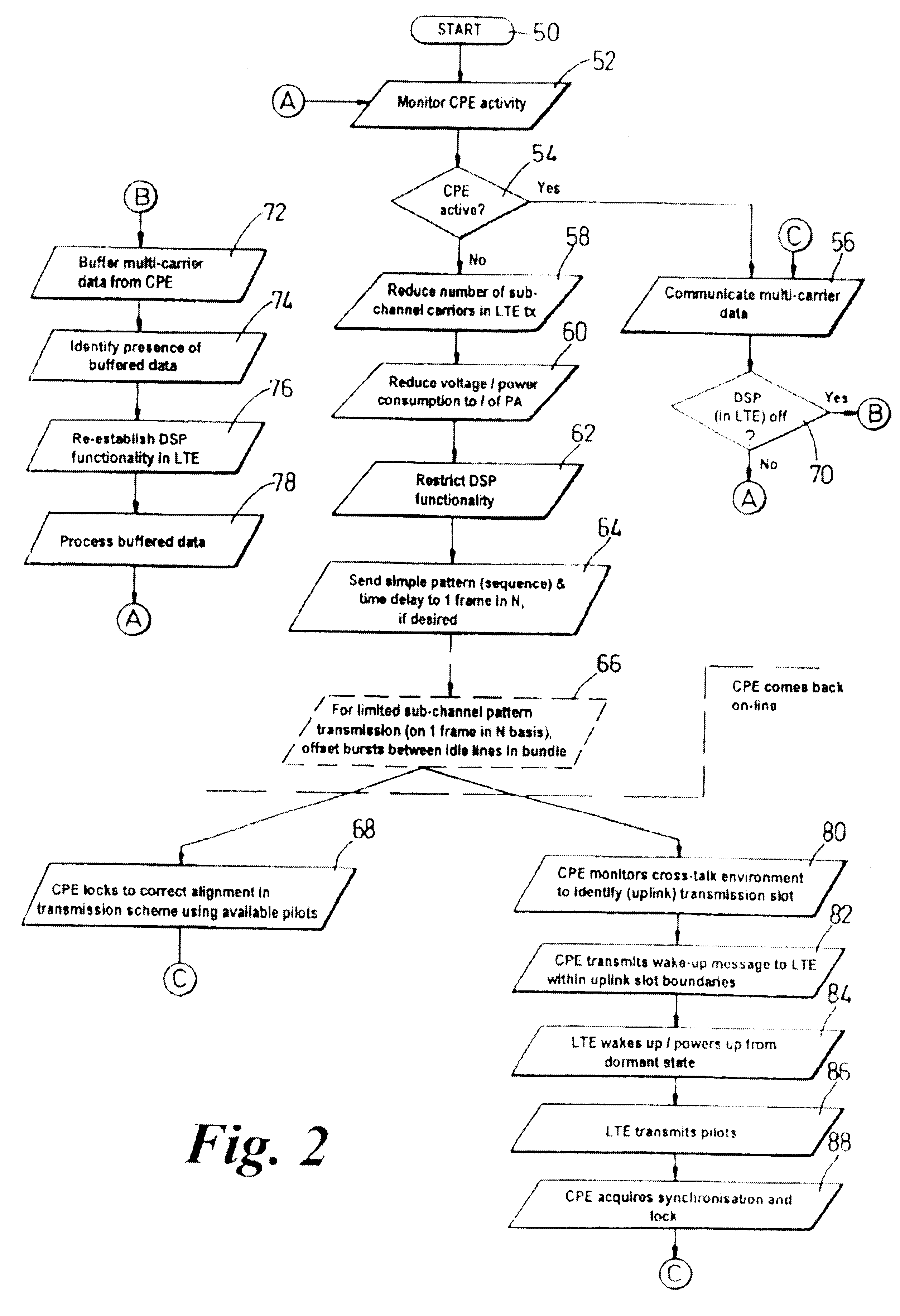
To reduce power consumption and associated heating in a line card of line termination equipment (LTE, 12) employing multiple cub-channel carriers to communicate broadband information to customer premise equipment (CPE, 30) down a wireline communication resource (26, sub-channel carrier transmissions are restricted (58) during periods of CPE inactivity. Power supplies to a power amplifier (30) associated with the line card and wireline resource (26) are reduced, with digital signal processing capabilities of the LTE (12) further restricted (64). When the CPE wishes to re-start communication, the CPE (30) locks (68) to a correct alignment in a transmission scheme using a pilot tone that is transmitted within a simple pattern sent during reduced sub-channel carrier transmissions. Alternatively, should all transmission from the LTE cease during CPE inactivity, then the CPE monitors (80) the transmission environment and sends (82) a wake-up call to the LTE between boundaries of an uplink slot. The LTE (12) re-establishes pilot tone transmissions (86), with synchronization and lock (88) subsequently achievable by the CPE (30): this is illustrated in FIG. 2.
Owner:RPX CLEARINGHOUSE
Intraserver tag-switched distributed packet processing for network access servers
Owner:CISCO TECH INC
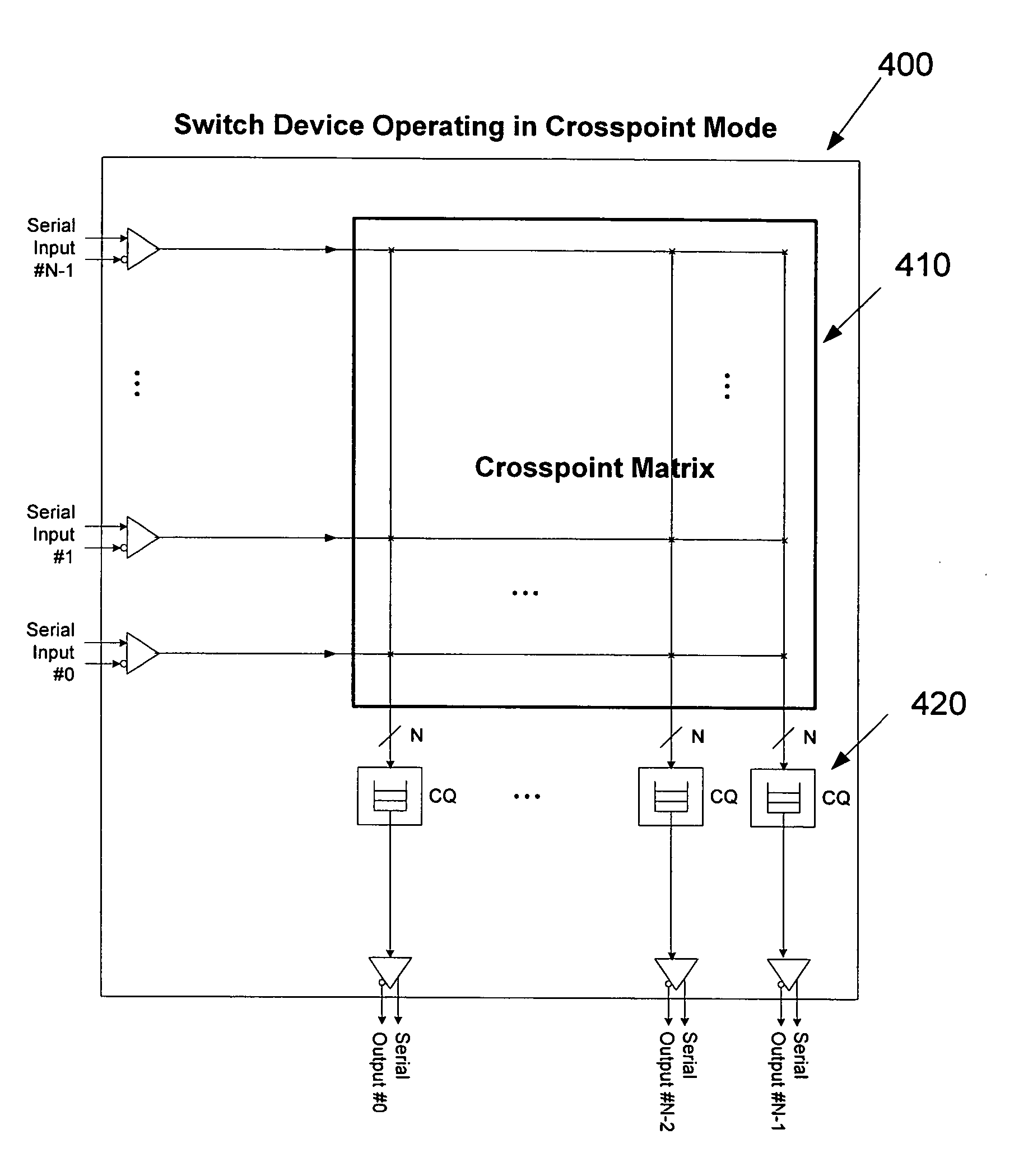
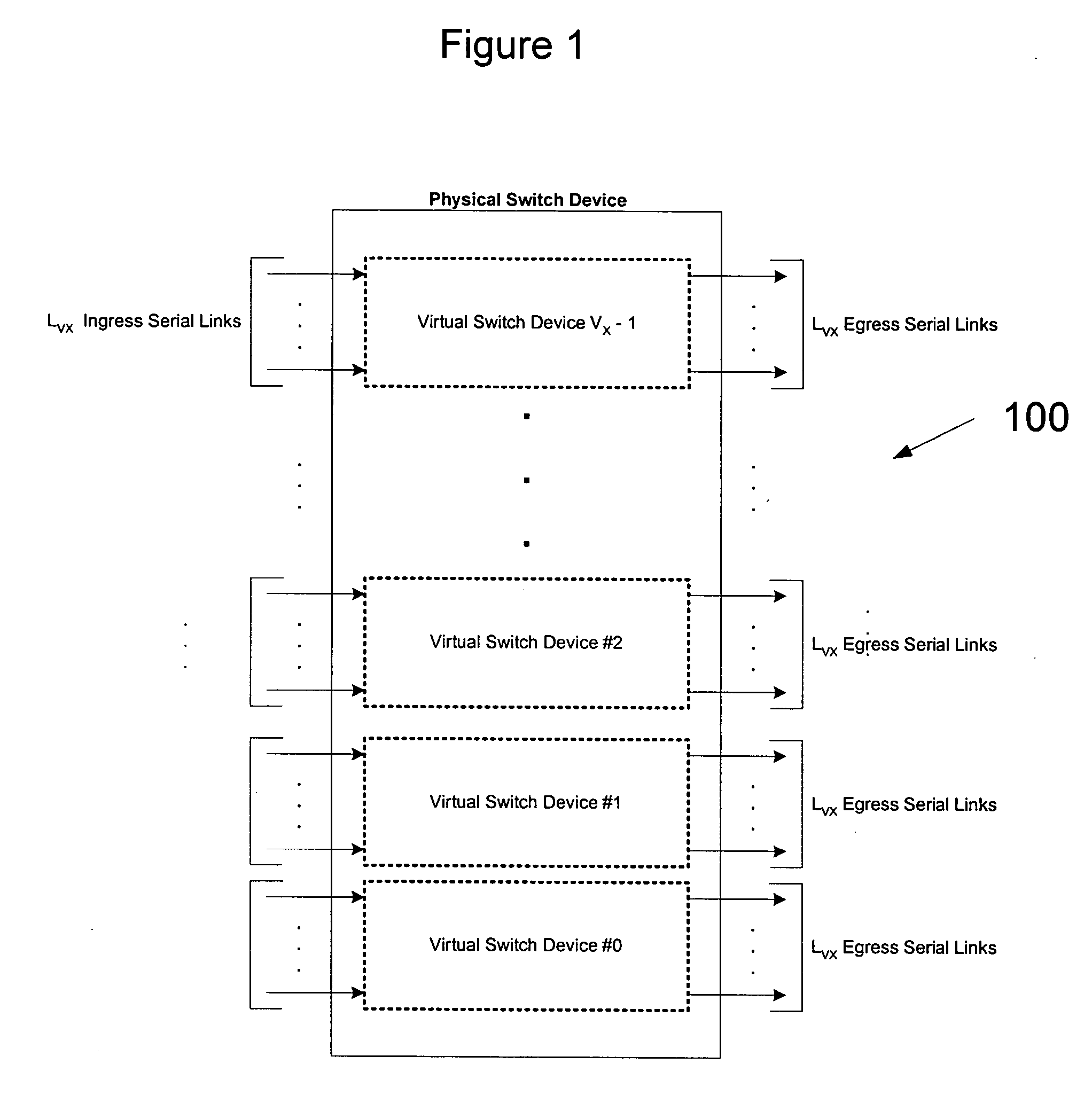
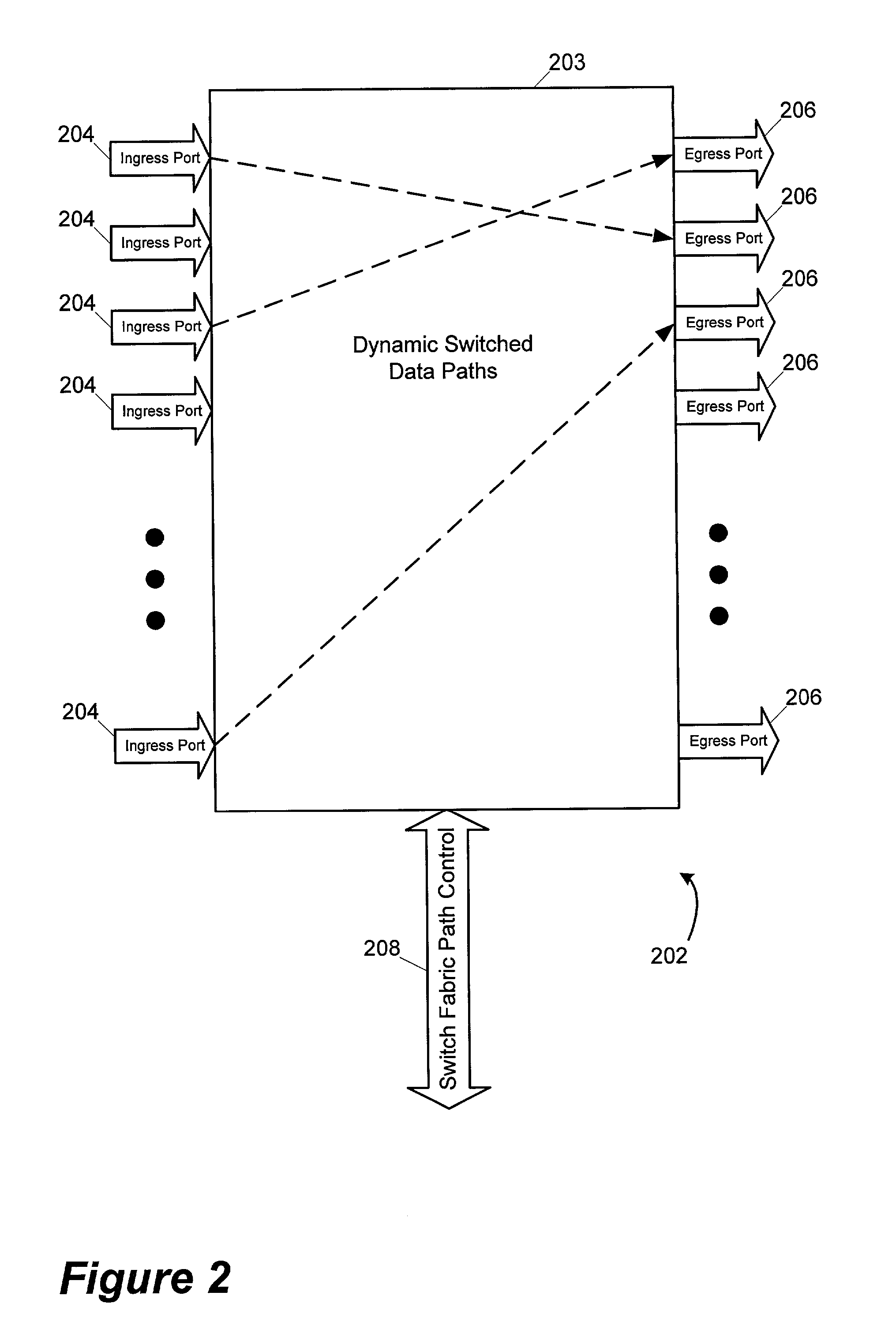
Network interconnect crosspoint switching architecture and method
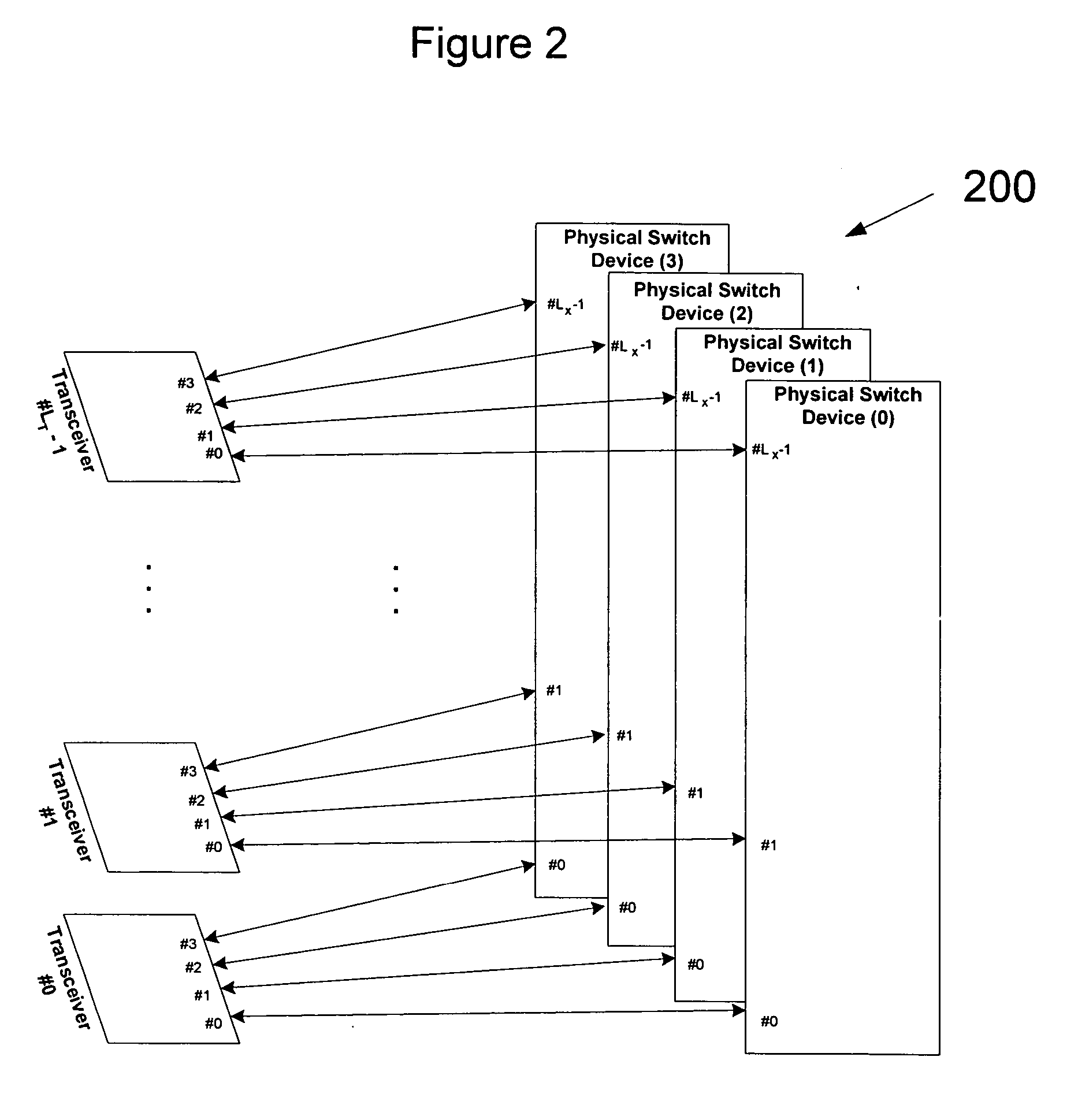
A network switching system includes transceiver devices respectively provided for a plurality of input line cards. The switching system also includes transceiver devices respective provided for a plurality of output line cards. The switching system further includes a switch device communicatively coupled to each of the plurality of input line cards and the plurality of output line cards. The switch device includes a crosspoint matrix for communicatively connecting one of the input line cards to one of the output line cards. The switch device is capable of operating in either a crosspoint mode for routing cells or packets from one of the input line cards to one of the output line cards, or a scheduler mode for controlling flow of cells and / or packets through at least one other switch device.
Owner:MARVELL ASIA PTE LTD
Mac address learning in a distributed bridge
ActiveUS20070268915A1Facilitate MAC learningSimple methodNetworks interconnectionSecuring communicationComputer hardwareLine card
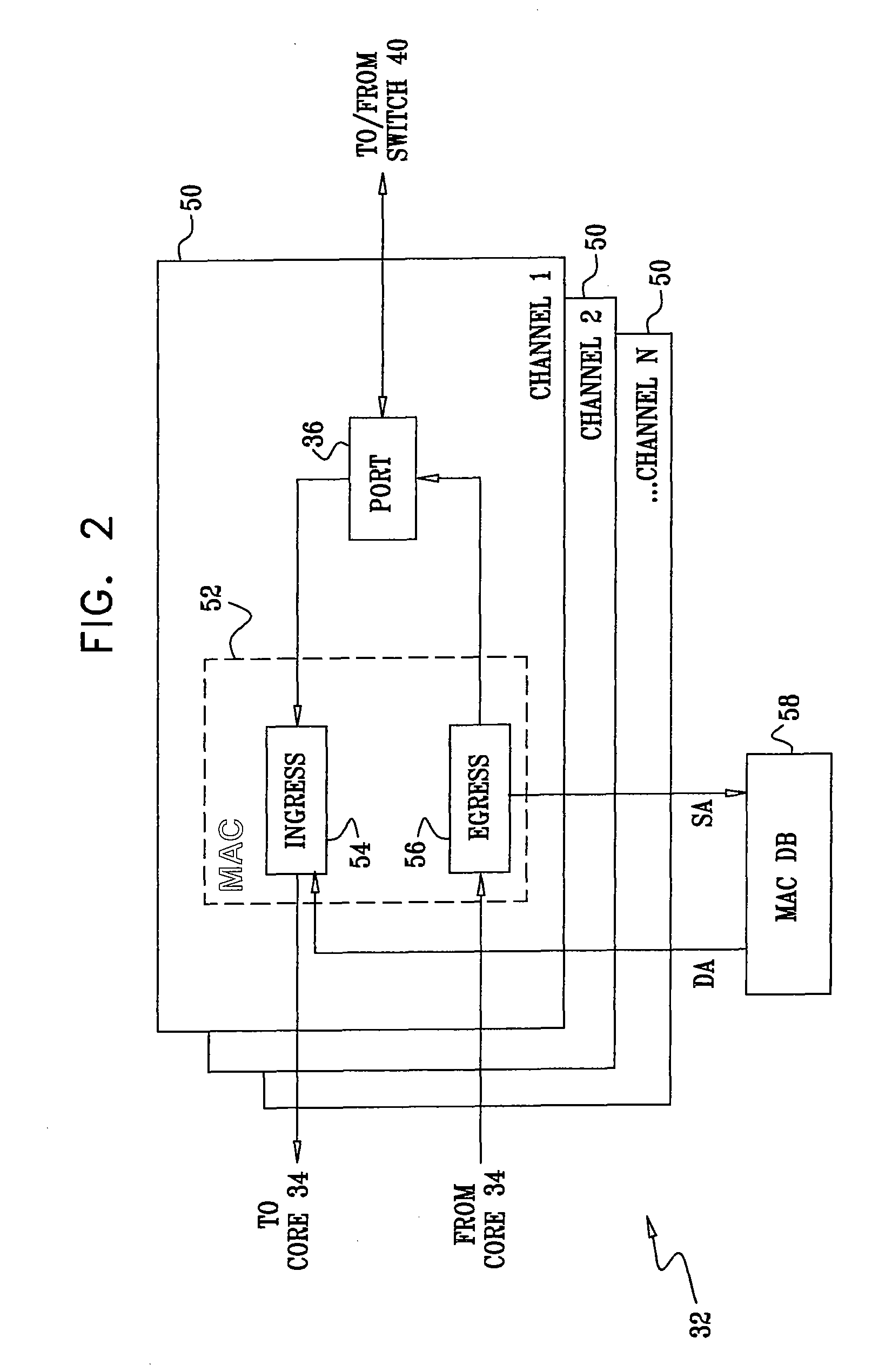
A method for communication includes configuring a network node having at least first and second line cards, the line cards having respective ports, to operate as a distributed media access control (MAC) bridge in a Layer 2 network. Each of the line cards has a respective forwarding database (FDB). Upon receiving a data packet on a port of the network node from a MAC source address, the data packet is conveyed to at least the first line card for transmission to the MAC destination address. The MAC source address of the data packet is checked against the records in the FDB of the first line card. If the FDB does not contain a record of an association of the MAC source address with the port on which the data packet was received, the record is added to the FDB of the first line card, which sends a message to at least the second line card informing the second line card of the association.
Owner:CORRIGENT CORP
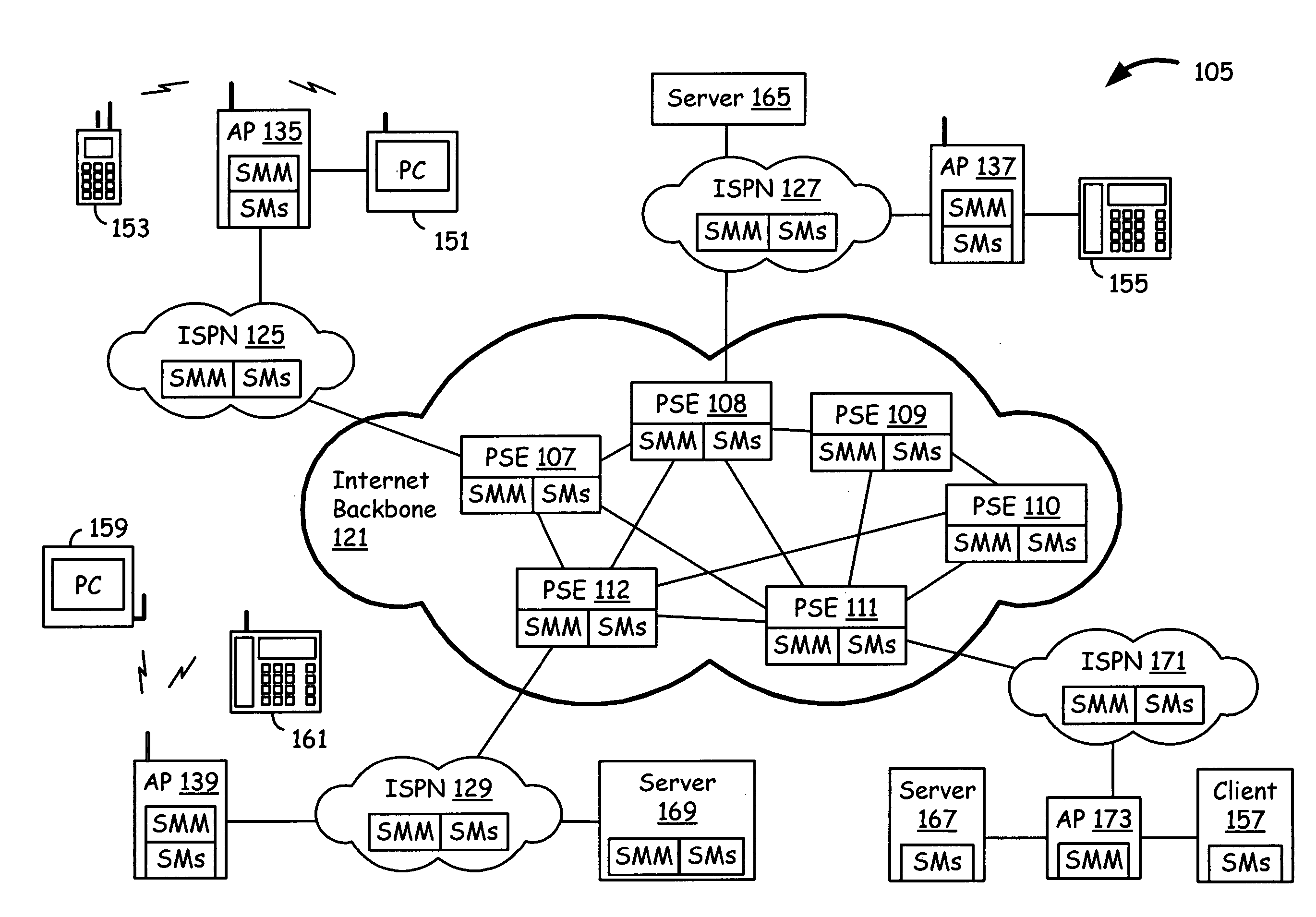
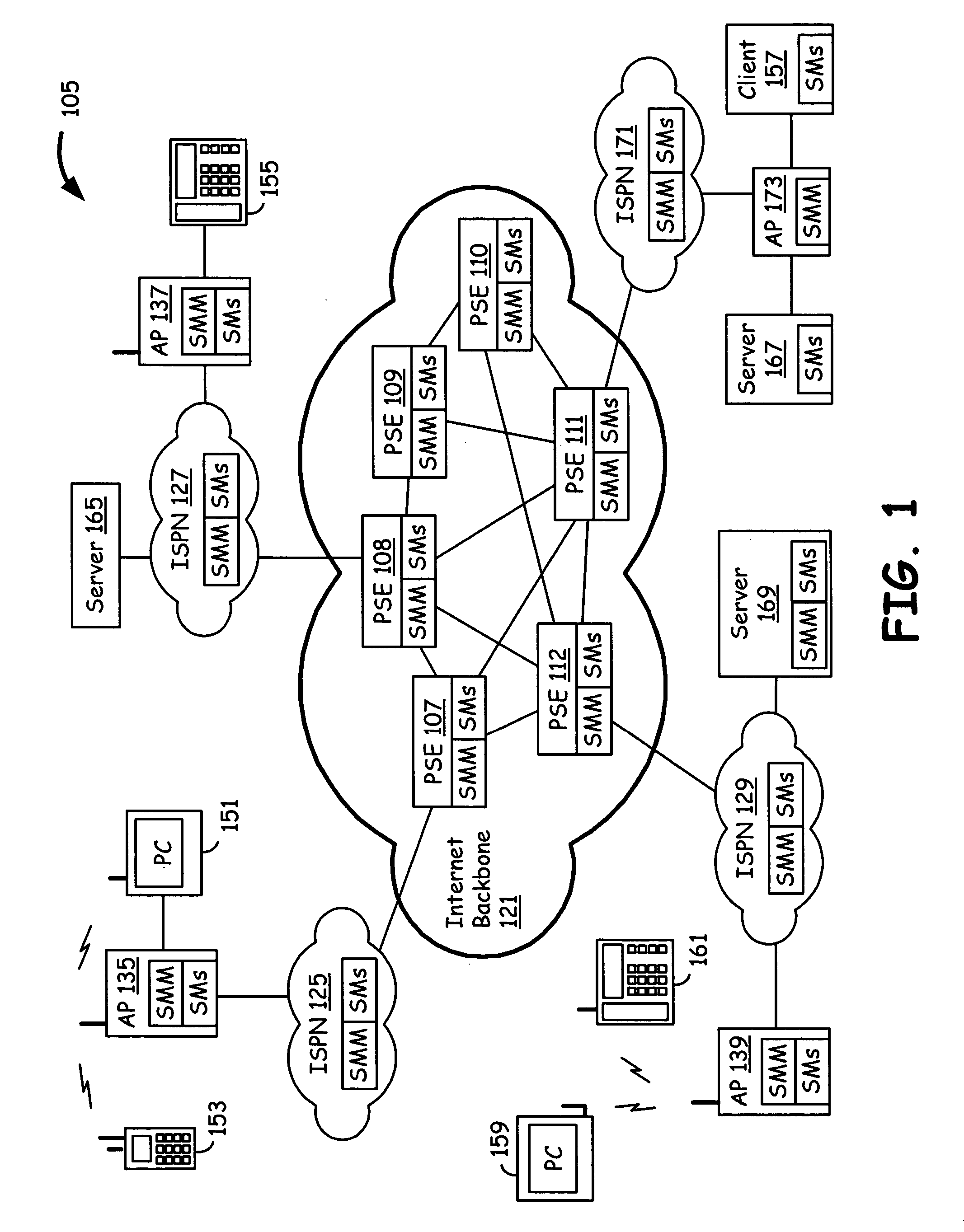
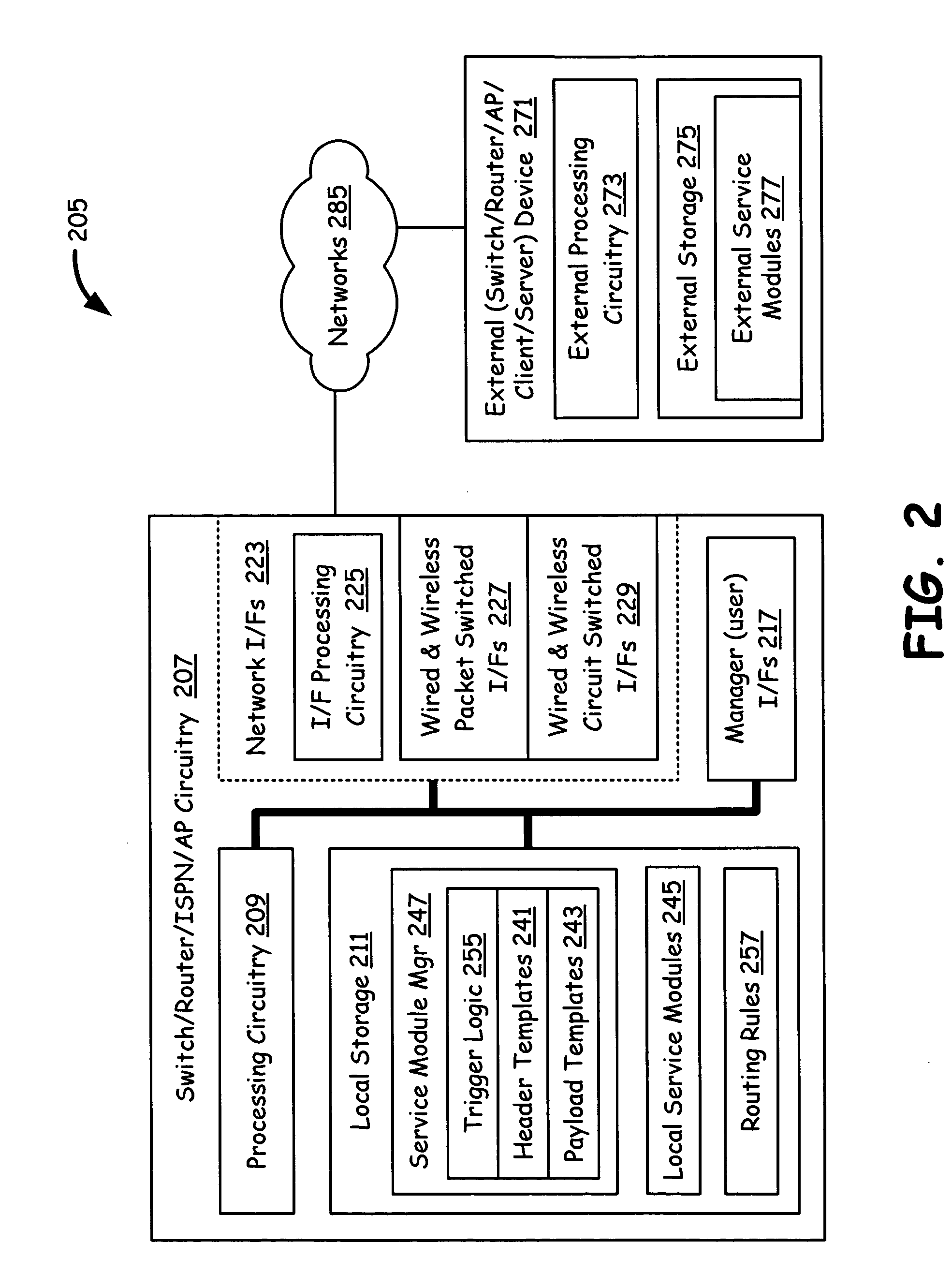
Packet routing with payload analysis, encapsulation and service module vectoring
An Internet infrastructure with network devices and end point devices containing service module manager and service modules, that supports packet analysis, encapsulation and vectoring, and interleaving applications. The network device that supports packet content analysis on arriving packet, consists of a plurality of packet switched interface circuitries, user interface circuitry, local storage comprising the service module manager software and a plurality of local service modules, and processing circuitry communicatively coupled to each of the packet switched interfaces, local storage and user interface circuit. The processing circuitry executes service module manager and thus analyzes the packet content and applies one or more selected local service module processing using the packet. The processing circuitry thus takes one or more actions on the packet. A packet switching exchange that supports packet content analysis, encapsulation and vectoring on arriving packet, consisting a plurality of interconnecting switches, a plurality of line cards, general primary processing card. A client device that supports packet content analysis on arriving packet containing a plurality of network interfaces, user interface circuitry, local storage and processing circuitry communicatively coupled to each of the network interfaces, local storage and user interface circuitry.
Owner:AVAGO TECH INT SALES PTE LTD
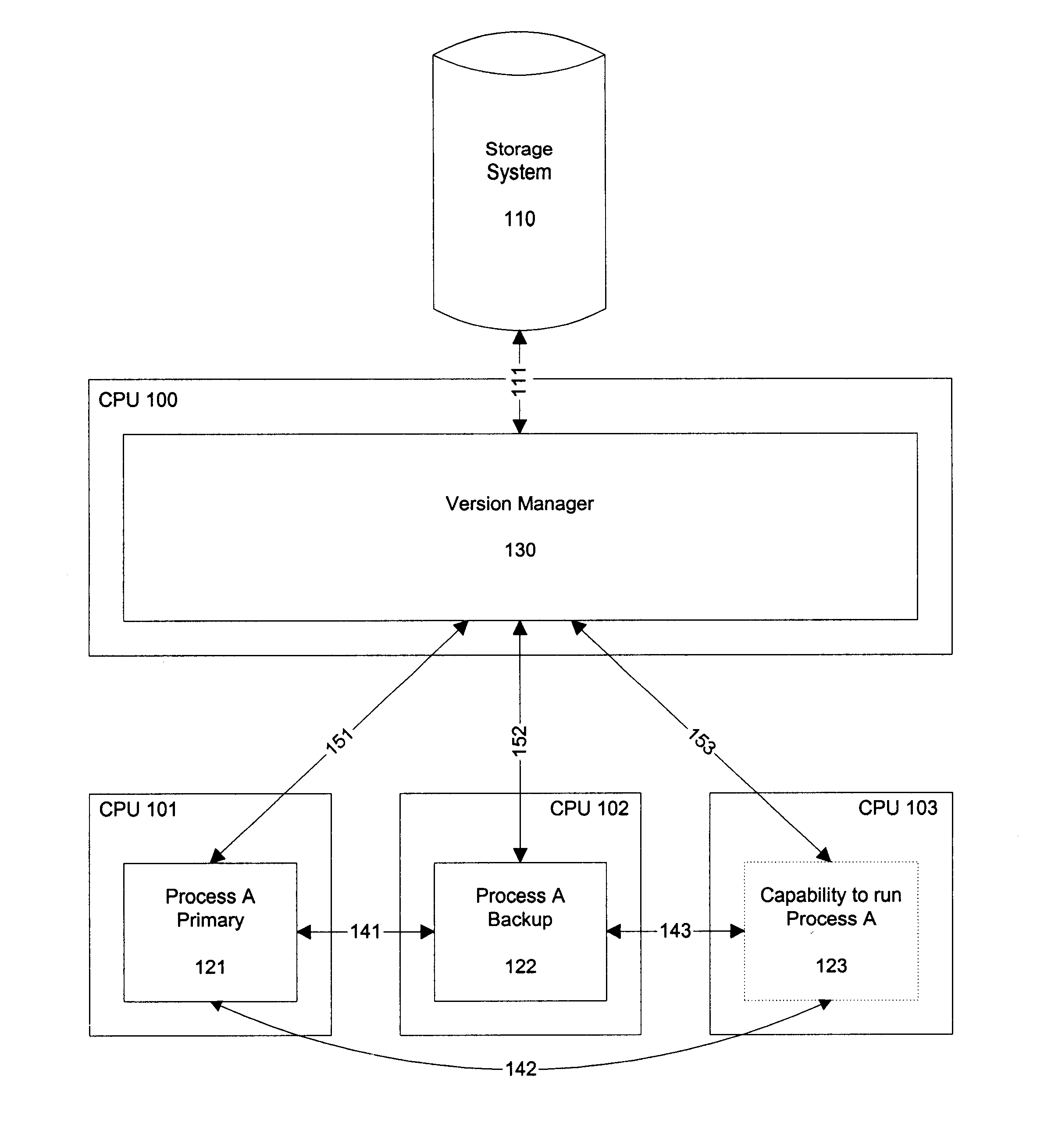
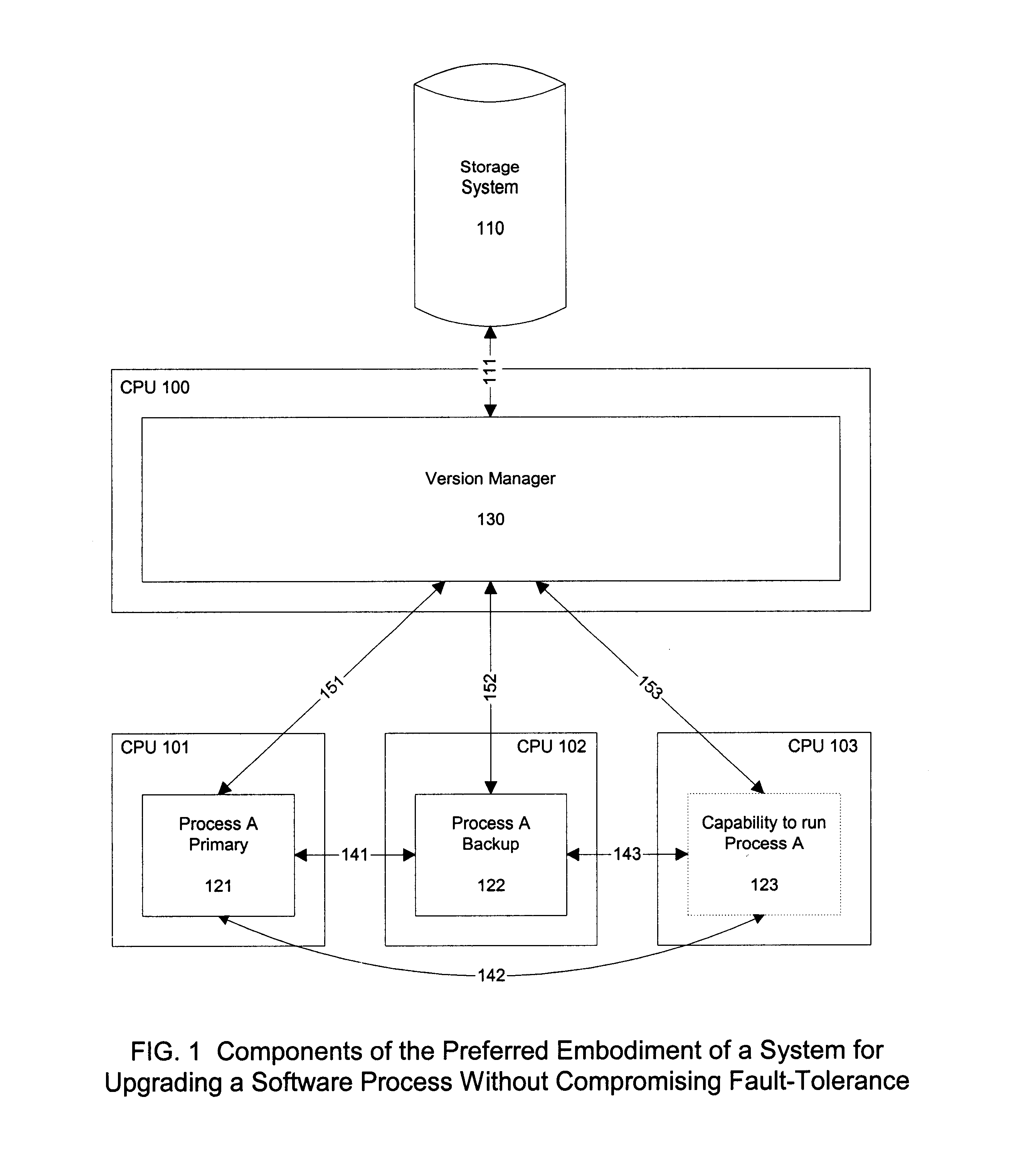
Method for upgrading running software processes without compromising fault-tolerance
When updating a running program in a system that uses a one-to-one backup program, fault-tolerance is lost while the backup program is itself being updated. To overcome this temporary loss of an available backup program, the number of backup copies of a software process is temporarily and dynamically increased during the software upgrade. The extra backup software processes may run on an unused processing unit or may run as an extra software process on a processing unit which is already performing a task. The technique may be applied to communication line cards.
Owner:METASWITCH NETWORKS LTD
System and method for scalable switch fabric for computer network
InactiveUS20030202510A1Reduce decreaseImprove performanceMultiplex system selection arrangementsDigital computer detailsComputer hardwareLine card
A system and method are provided for processing storage commands between a host and a target. The system includes a first line card, a system card, and a second line card. The storage command that is issued from the host is received by the first line card. The first line card determines whether or not it can process the request by itself and, if so, forwards the storage command to the second line card for forwarding (and eventual processing) by the target. If the first line card cannot process the storage command by itself, it forwards the storage command to the system card for additional processing. The revised storage command is issued from the system card to the first line card. The first line card then issues the revised storage command to the second line card for eventual processing by the target.
Owner:MAXXAN SYST
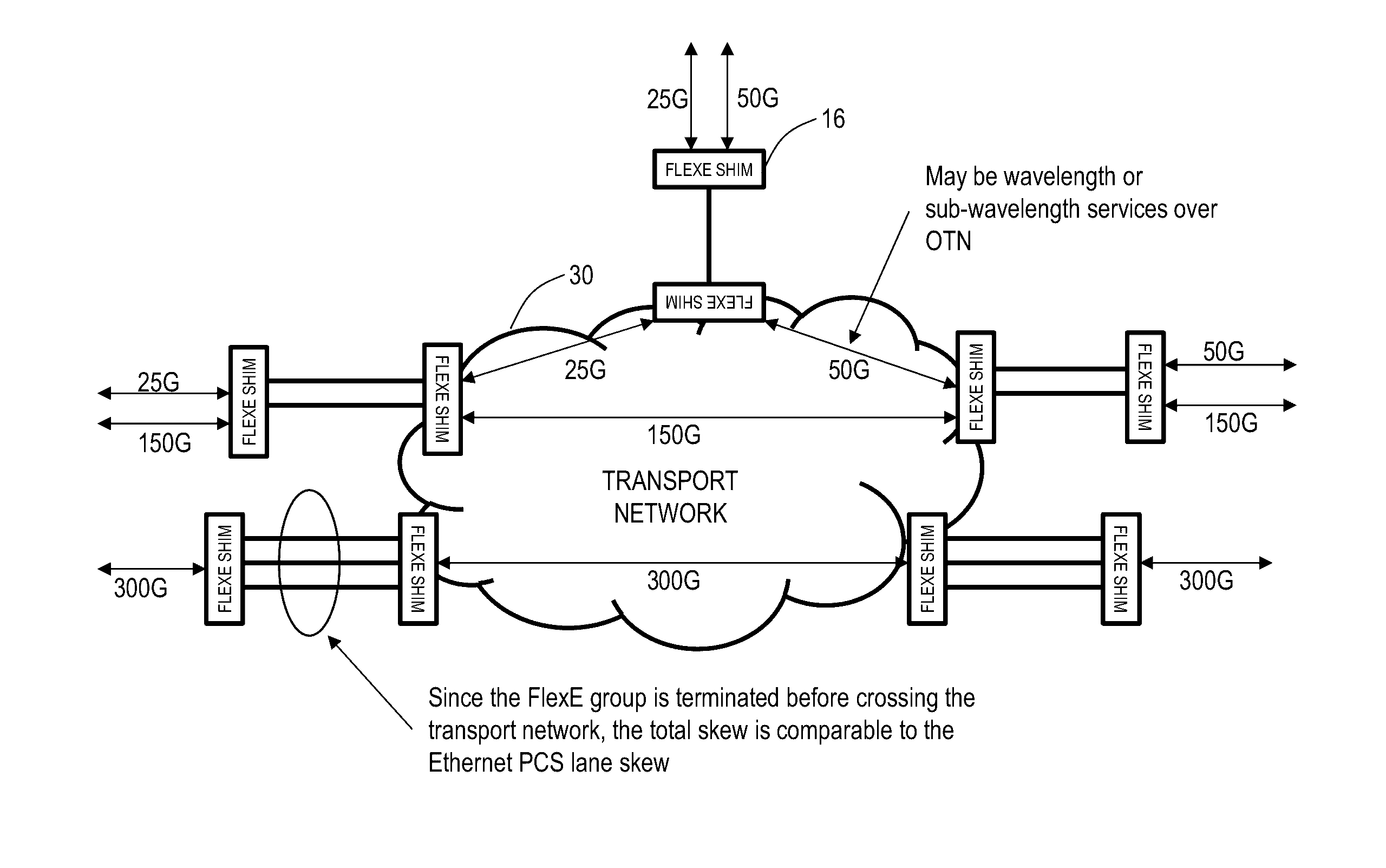
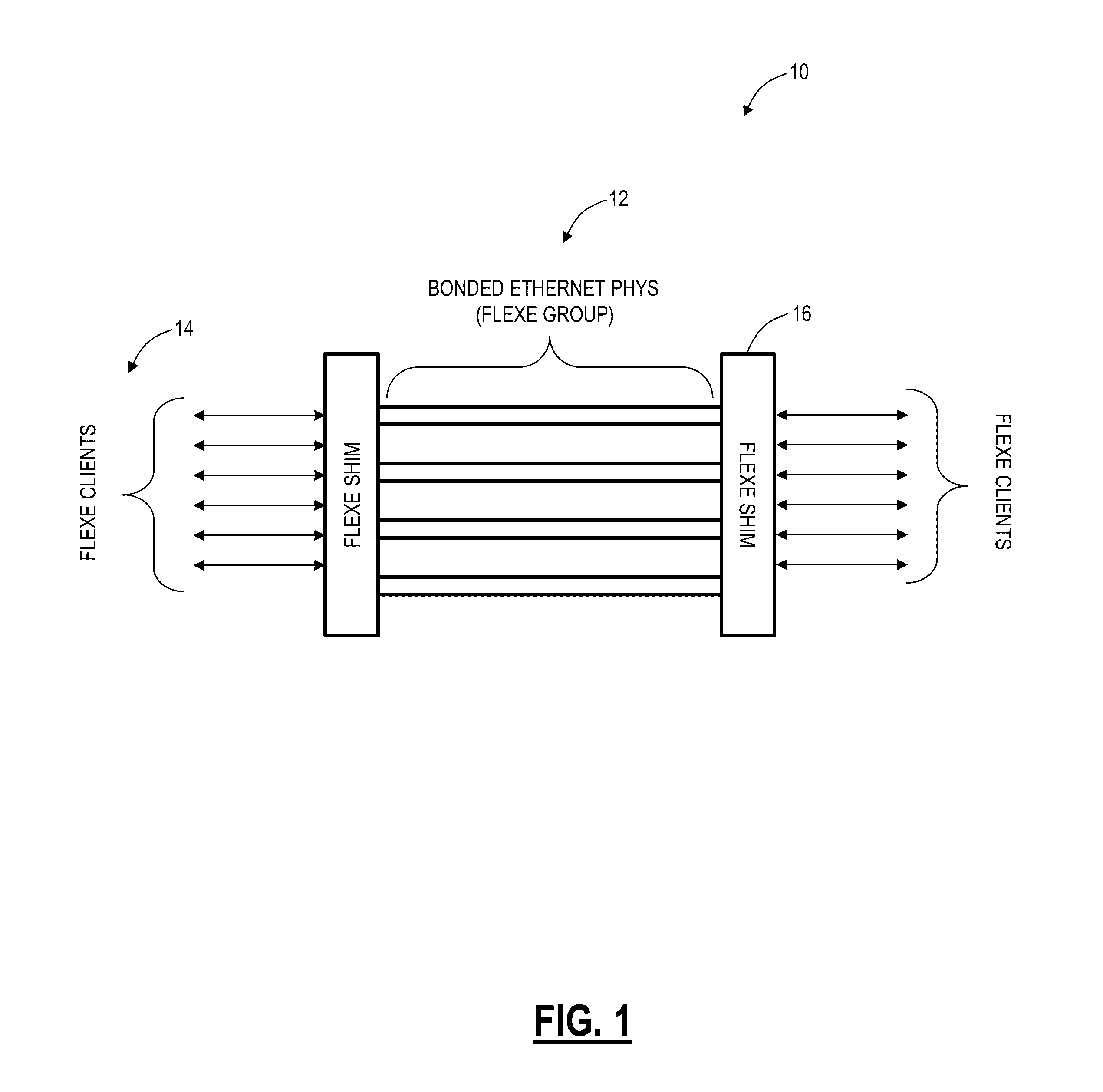
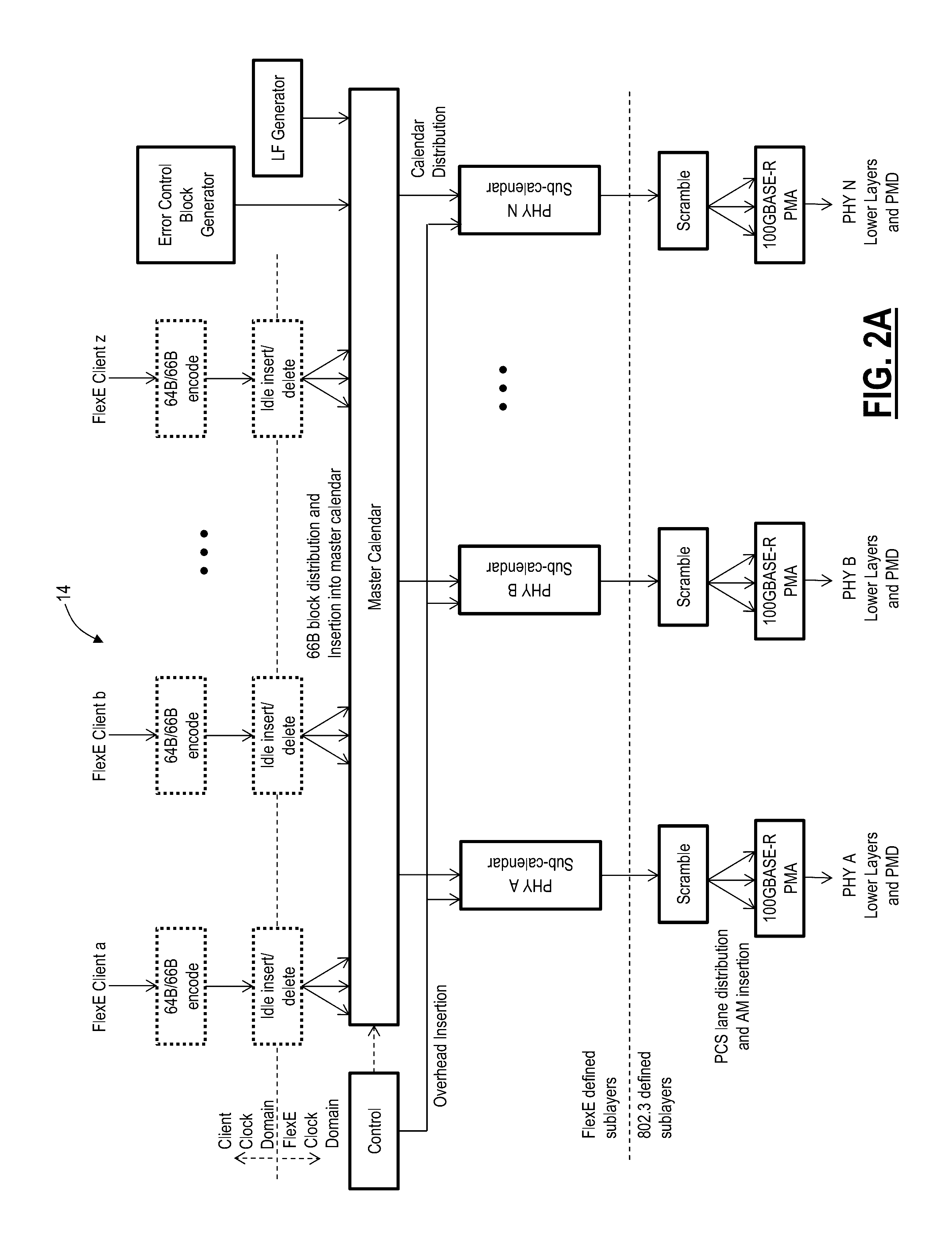
Flexible ethernet switching systems and methods
A Flexible Ethernet (FlexE) switch system configured to switch a FlexE client service includes interface circuitry configured to ingress and egress a plurality of FlexE clients; and switch circuitry configured to switch portions of the FlexE clients based on 64b / 66b block boundaries between the interface circuitry. A node configured to switch a Flexible Ethernet (FlexE) client service in a network includes one or more line cards configured to ingress and egress a plurality of FlexE clients; and one or more switch fabrics configured to switch portions of the FlexE clients based on 64b / 66b block boundaries between the one or more line cards.
Owner:CIENA
Pipelined packet switching and queuing architecture
An architecture for a line card in a network routing device is provided. The line card architecture provides a bi-directional interface between the routing device and a network, both receiving packets from the network and transmitting the packets to the network through one or more connecting ports. In both the receive and transmit path, packets processing and routing in a multi-stage, parallel pipeline that can operate on several packets at the same time to determine each packet's routing destination is provided. Once a routing destination determination is made, the line card architecture provides for each received packet to be modified to contain new routing information and additional header data to facilitate packet transmission through the switching fabric. The line card architecture further provides for the use of bandwidth management techniques in order to buffer and enqueue each packet for transmission through the switching fabric to a corresponding destination port. The transmit path of the line card architecture further incorporates additional features for treatment and replication of multicast packets.
Owner:CISCO TECH INC
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com