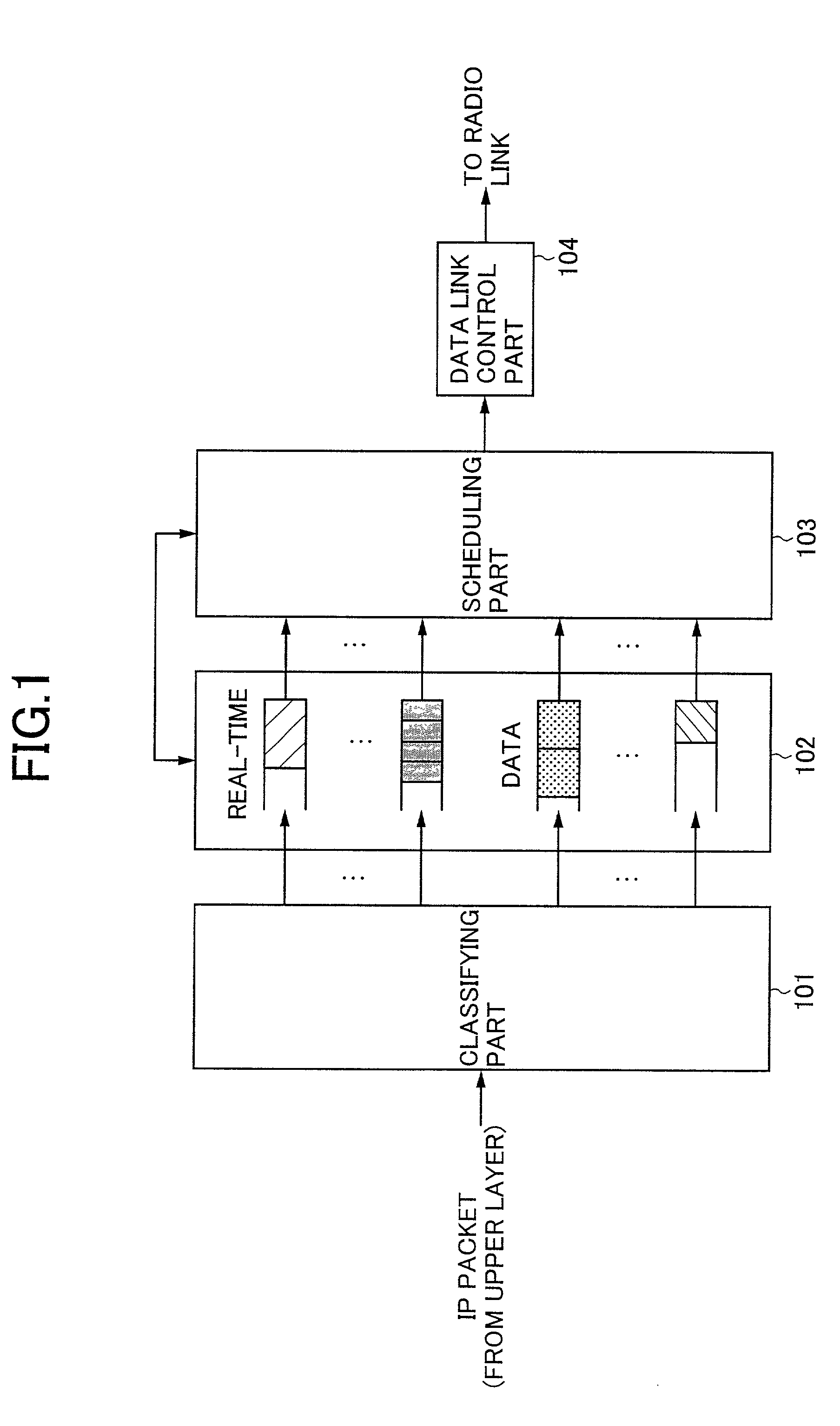
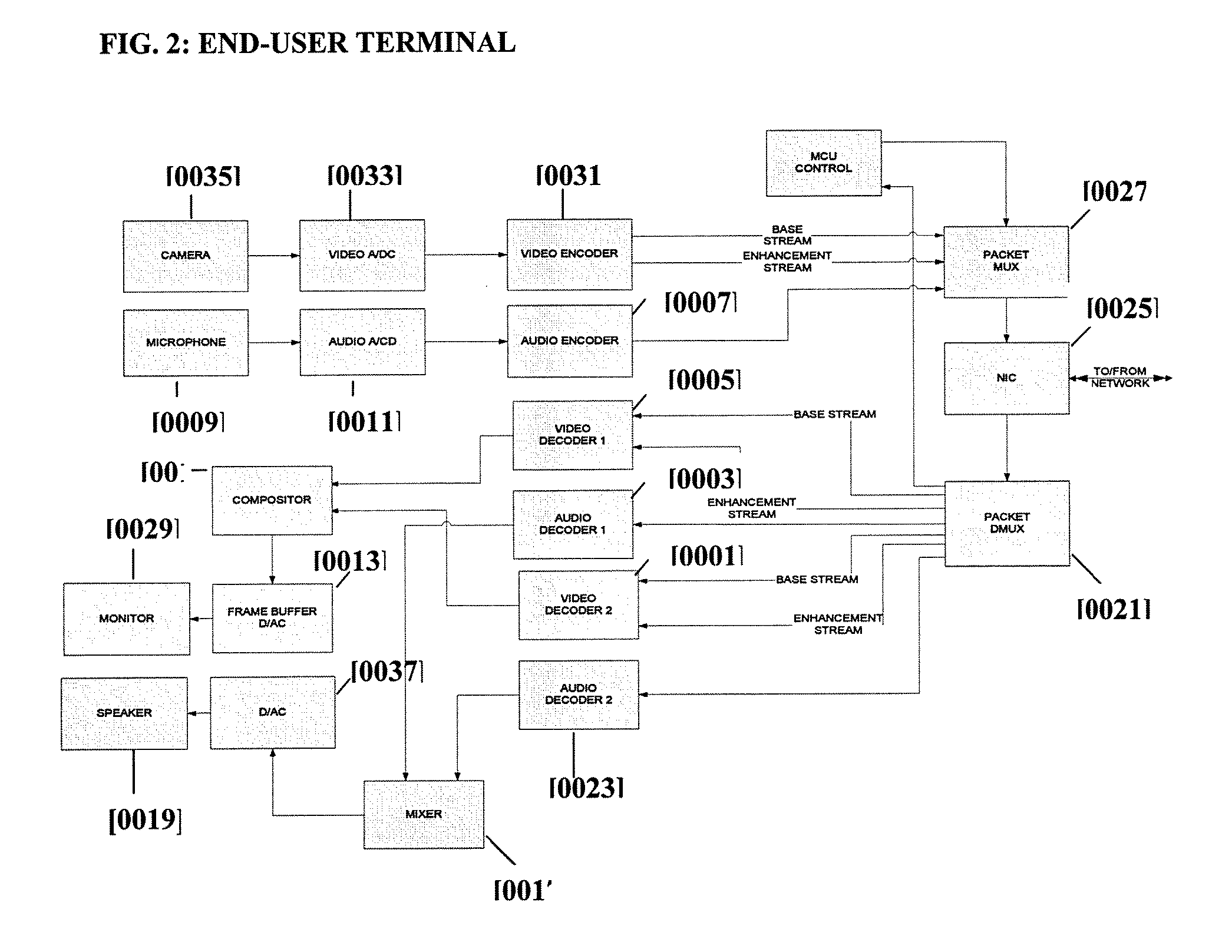
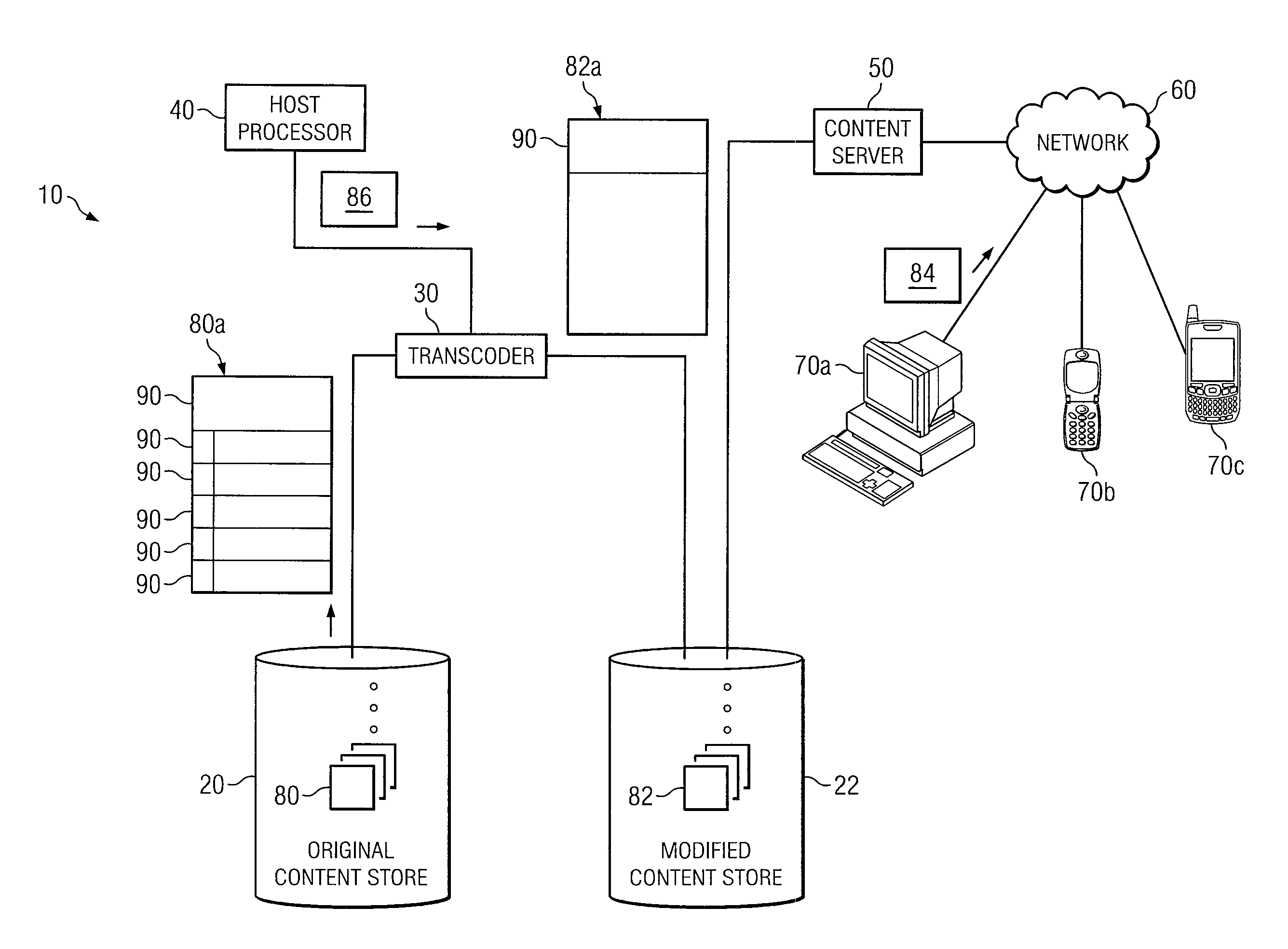
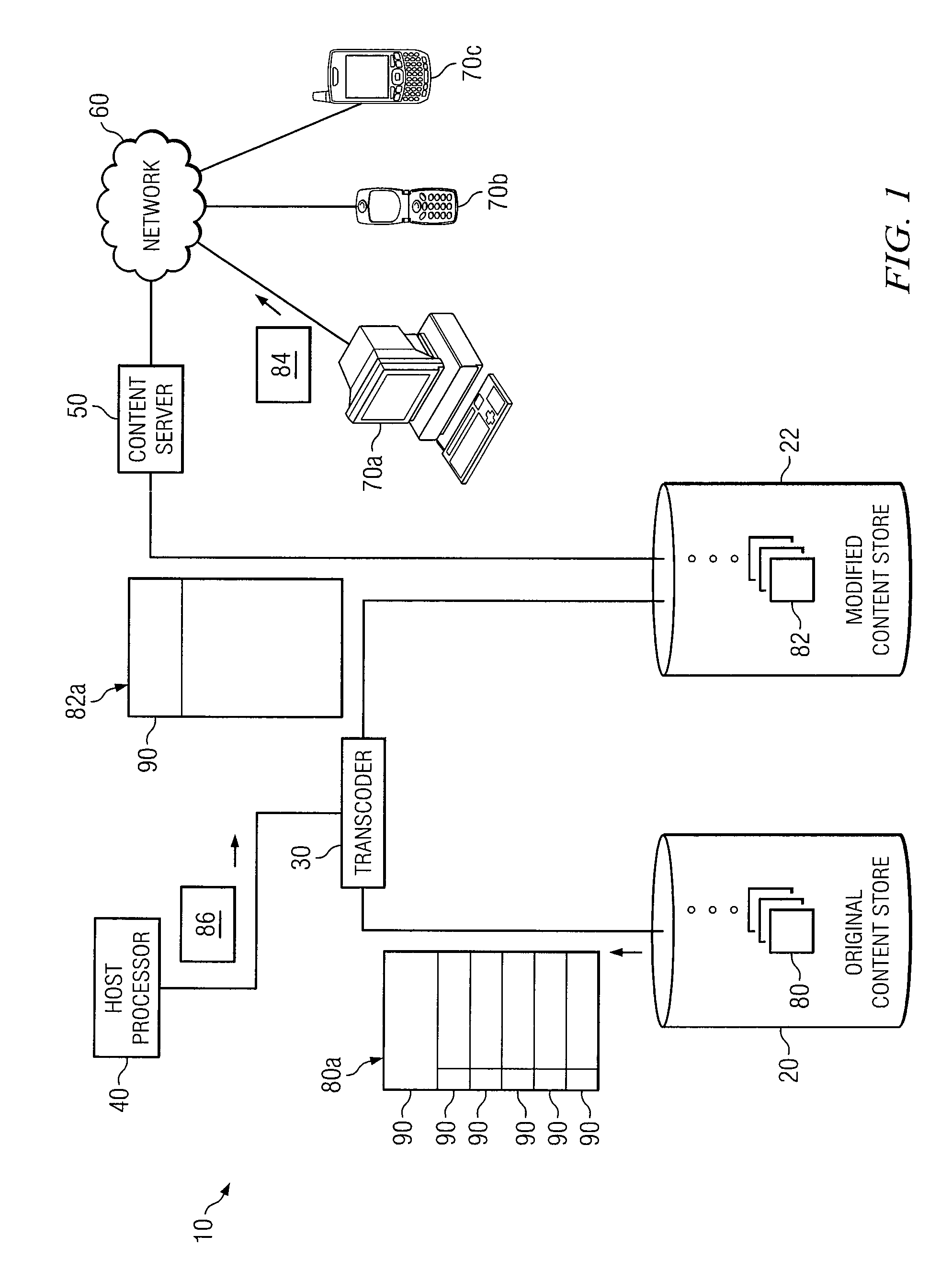
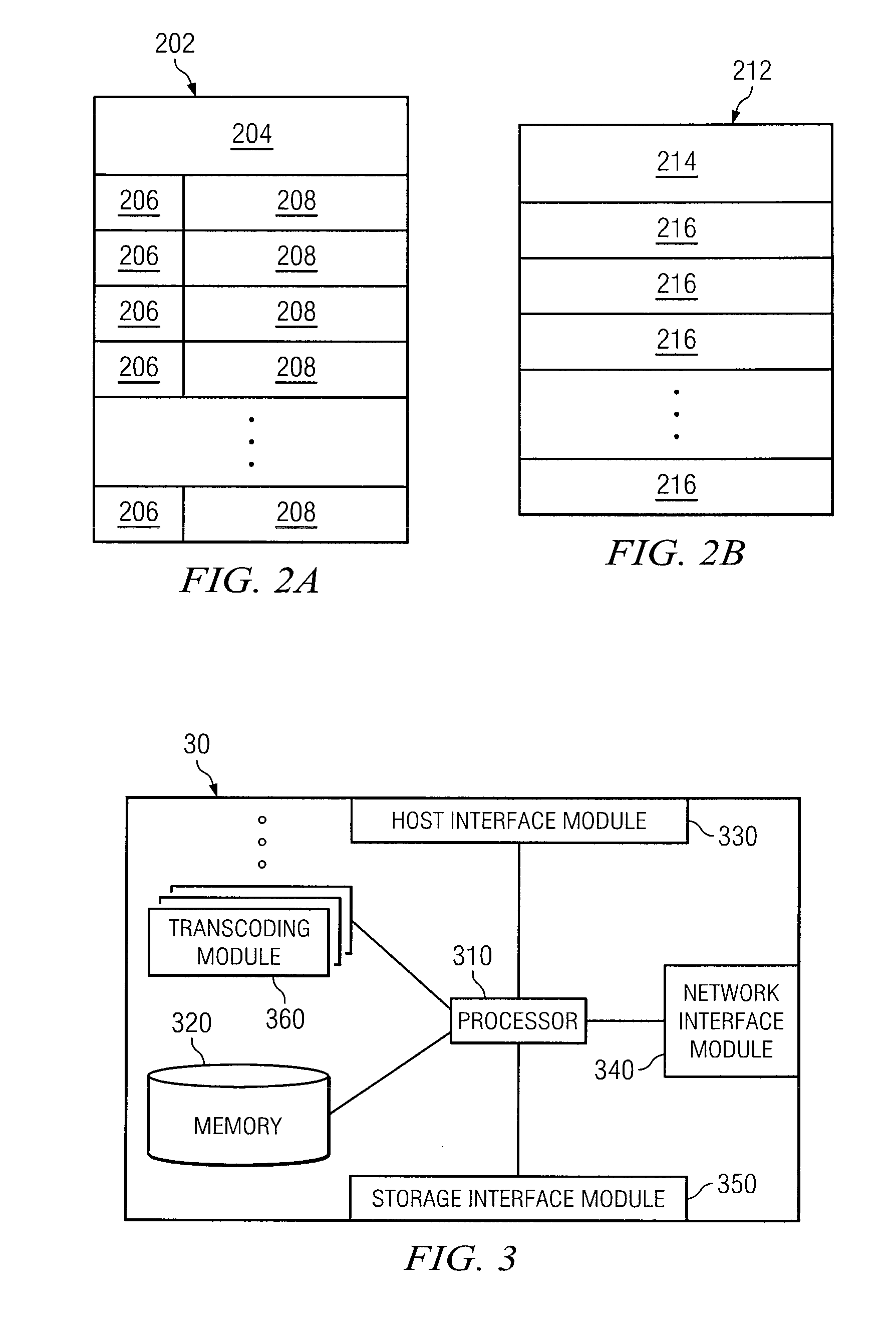
Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
364results about How to "Minimum delay" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
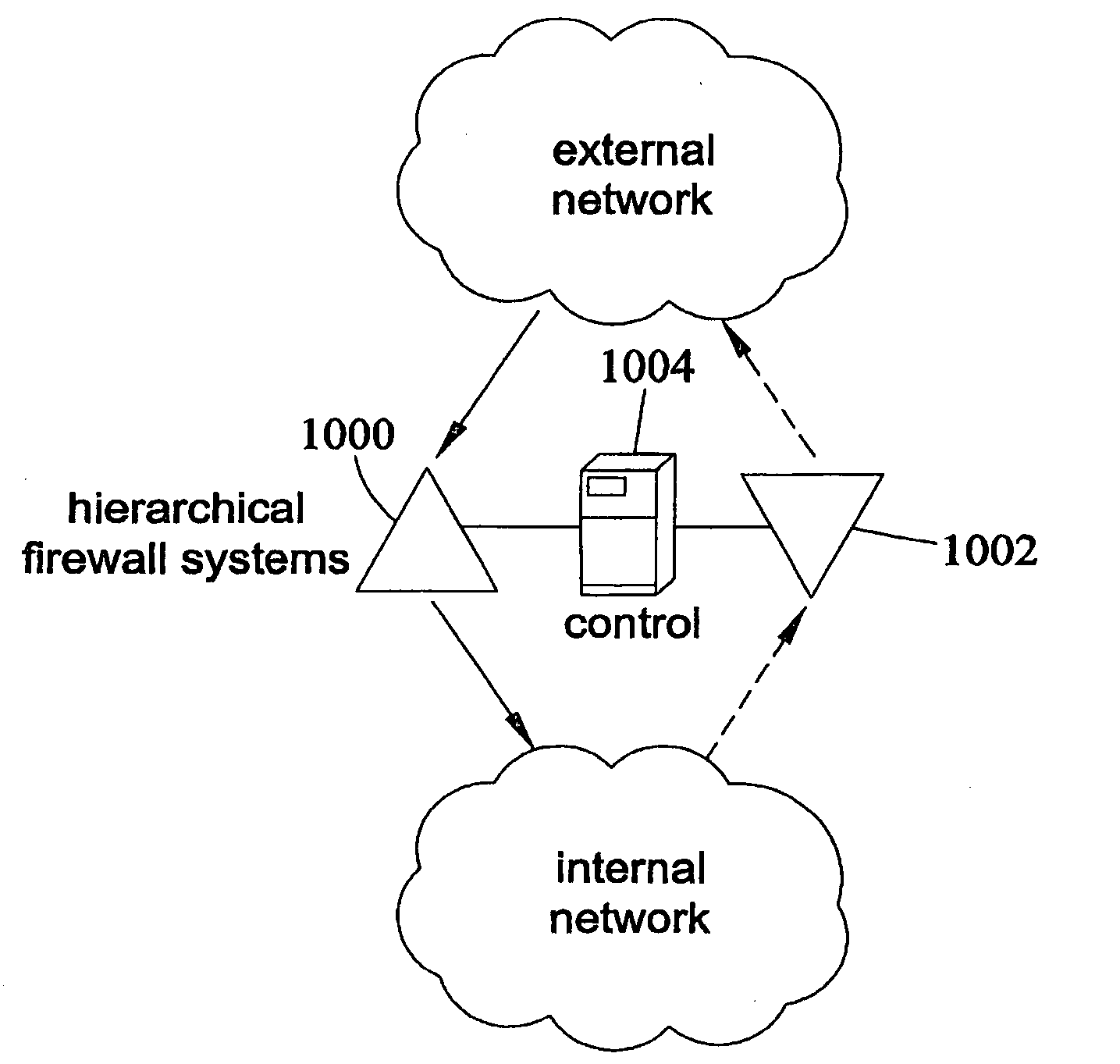
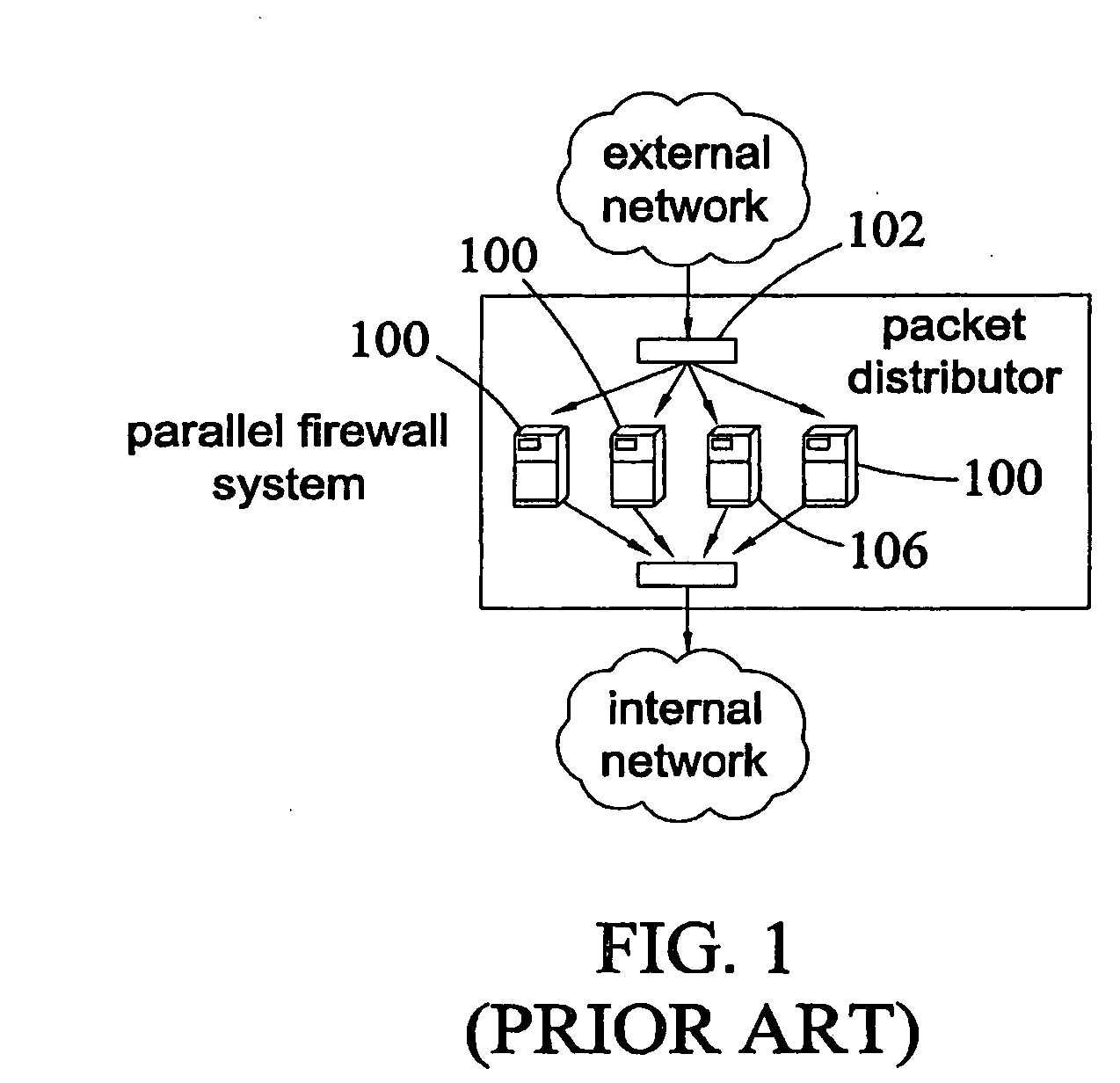
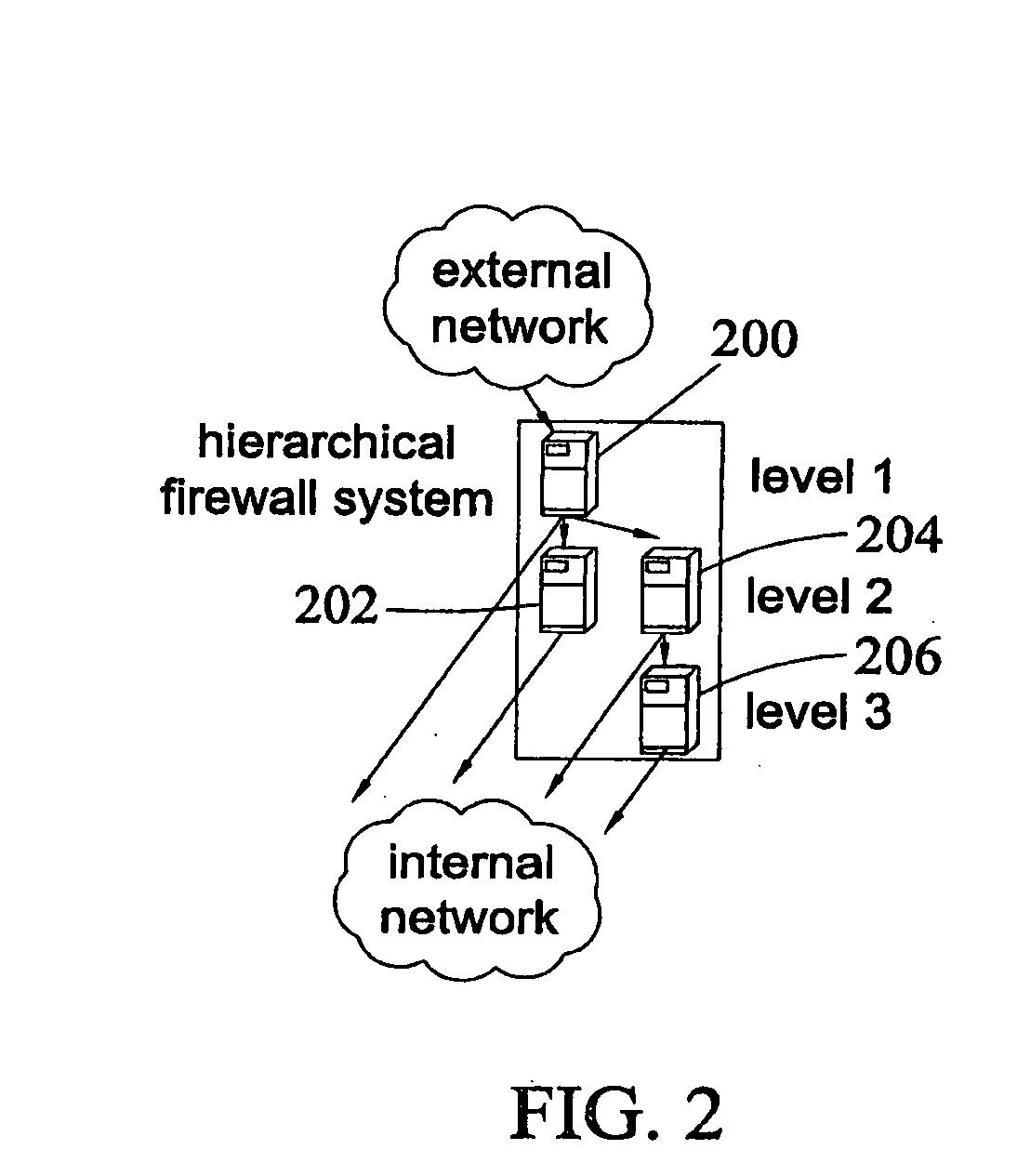
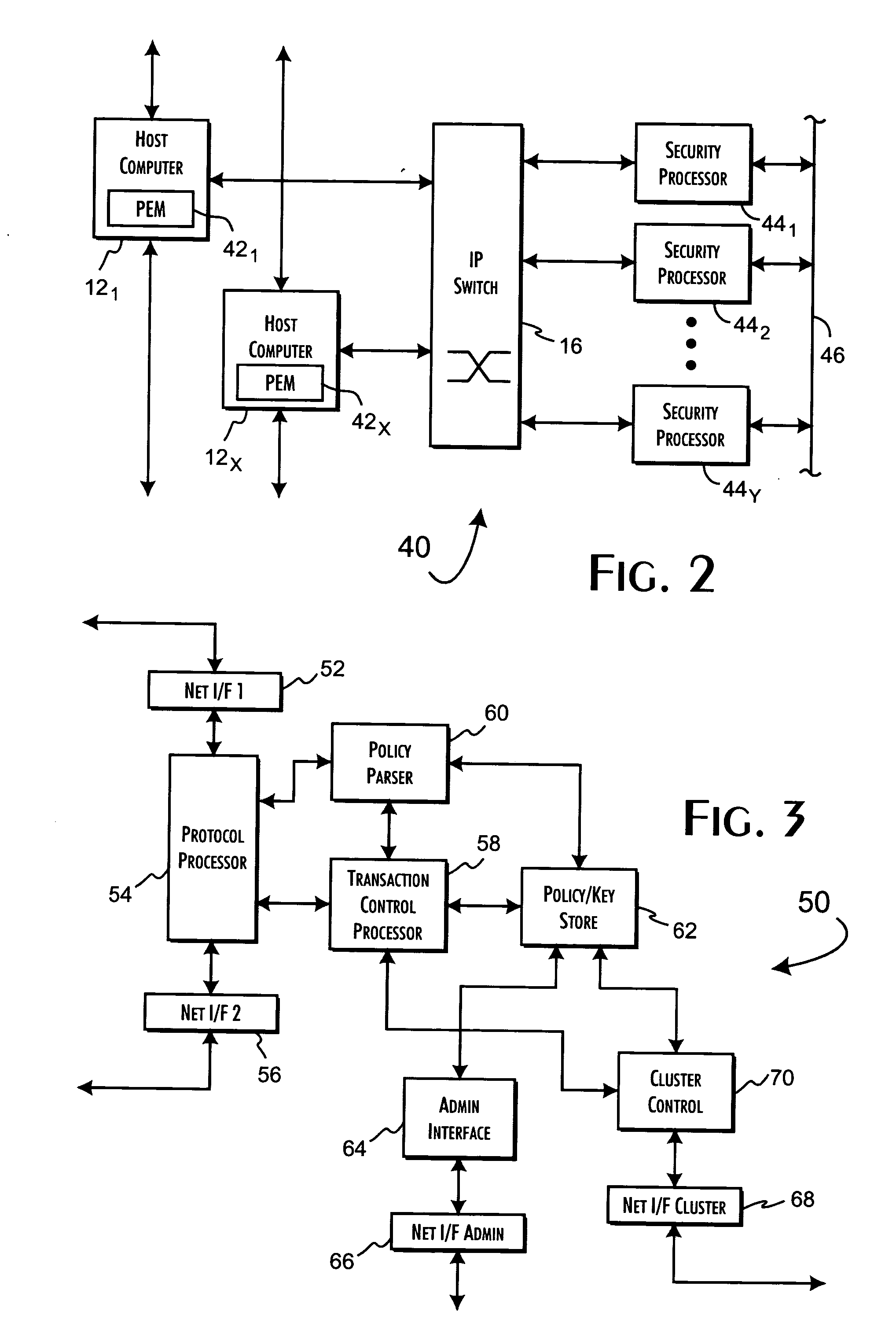
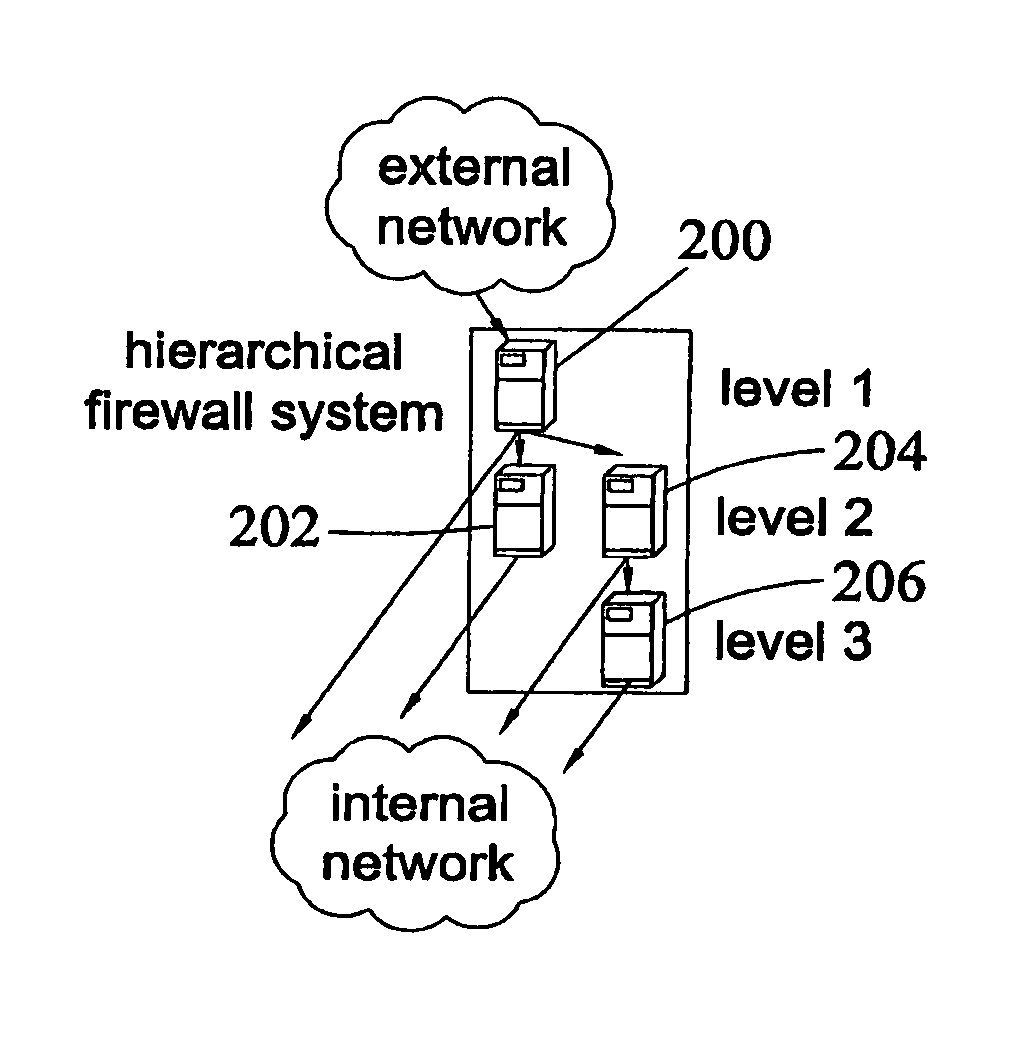
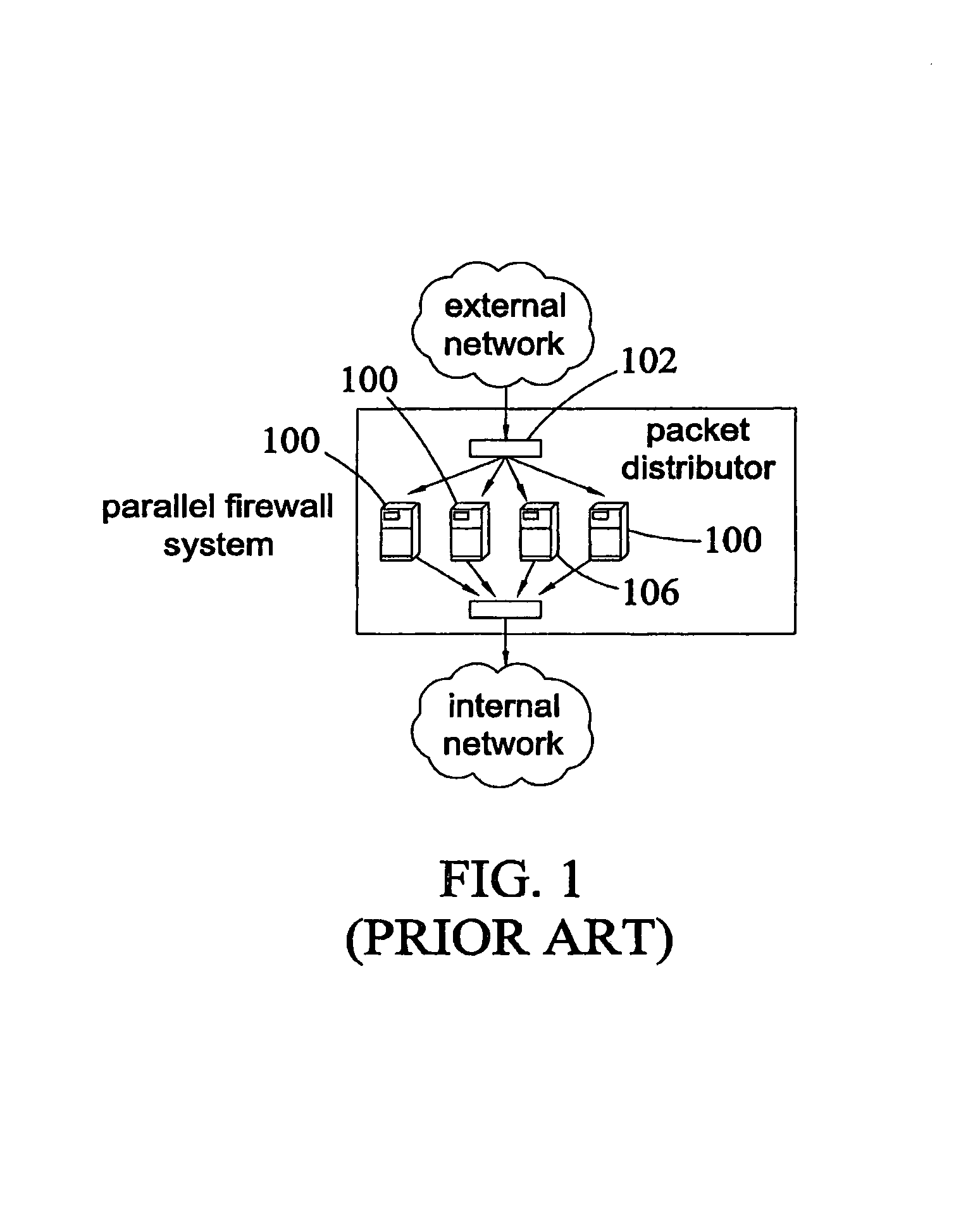
Method, systems, and computer program products for implementing function-parallel network firewall
ActiveUS20060195896A1Reduce impactMinimum delayMemory loss protectionError detection/correctionData packRule sets
Methods, systems, and computer program products for providing function-parallel firewalls are disclosed. According to one aspect, a function-parallel firewall includes a first firewall node for filtering received packets using a first portion of a rule set including a plurality of rules. The first portion includes less than all of the rules in the rule set. At least one second firewall node filters packets using a second portion of the rule set. The second portion includes at least one rule in the rule set that is not present in the first portion. The first and second portions together include all of the rules in the rule set.
Owner:WAKE FOREST UNIV
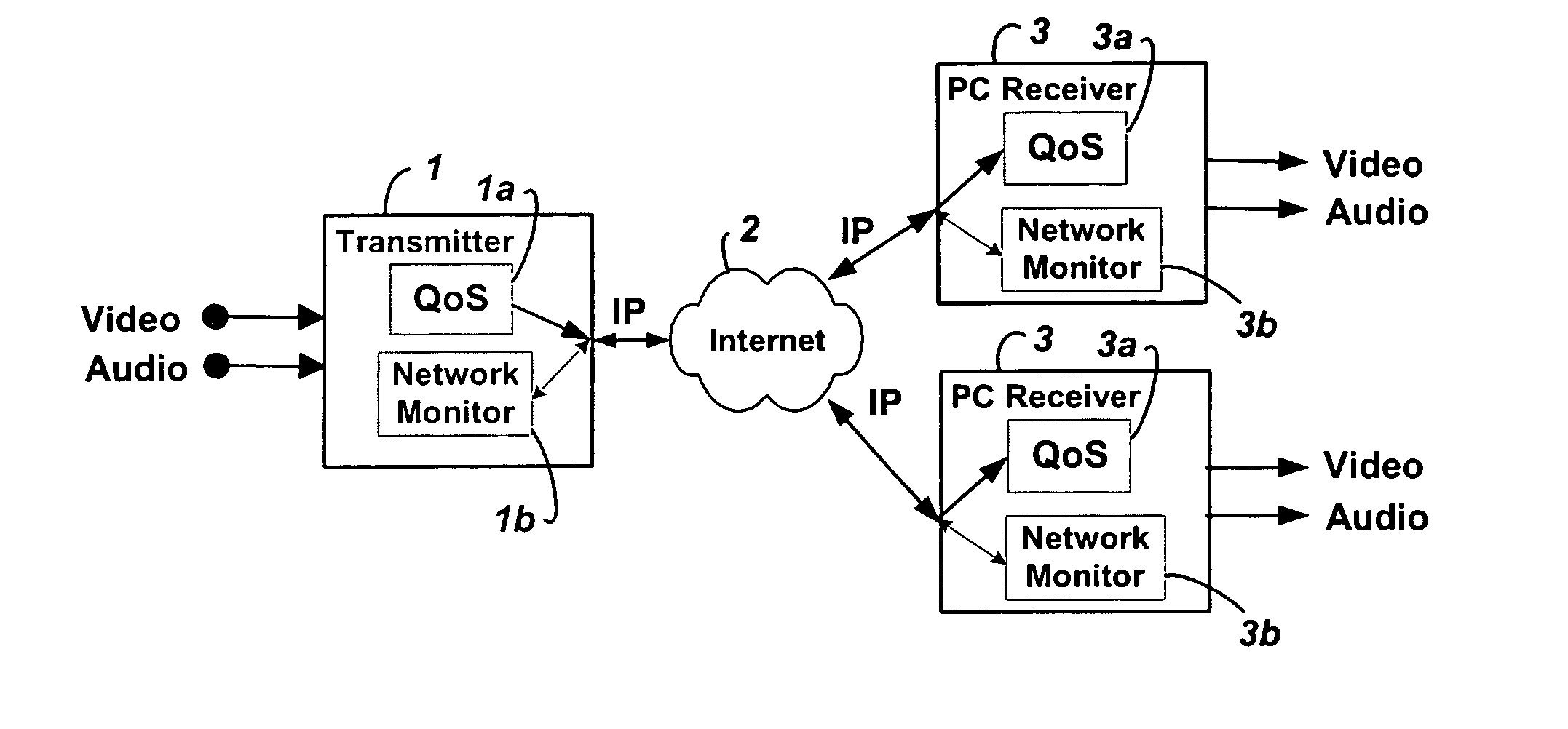
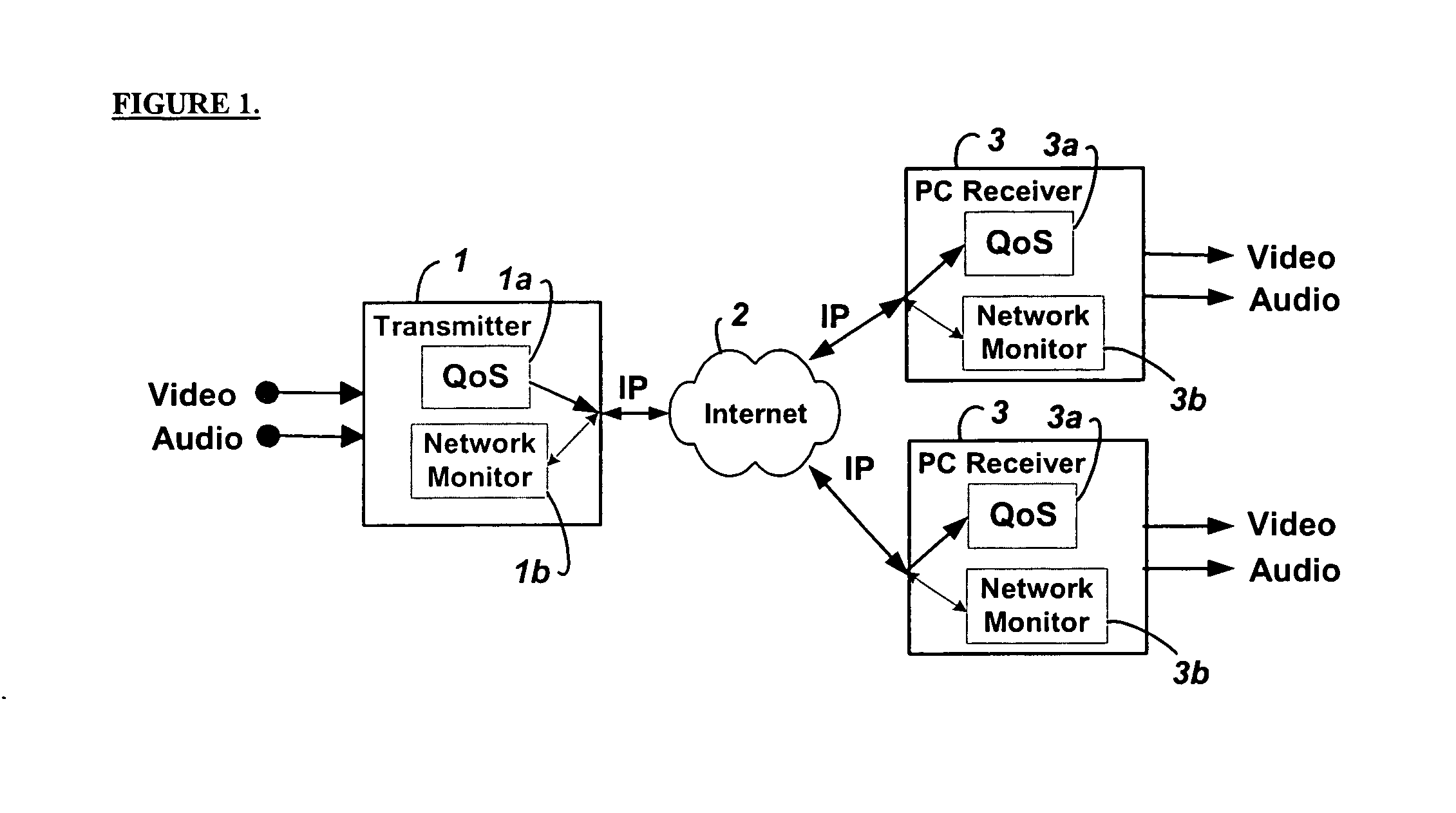
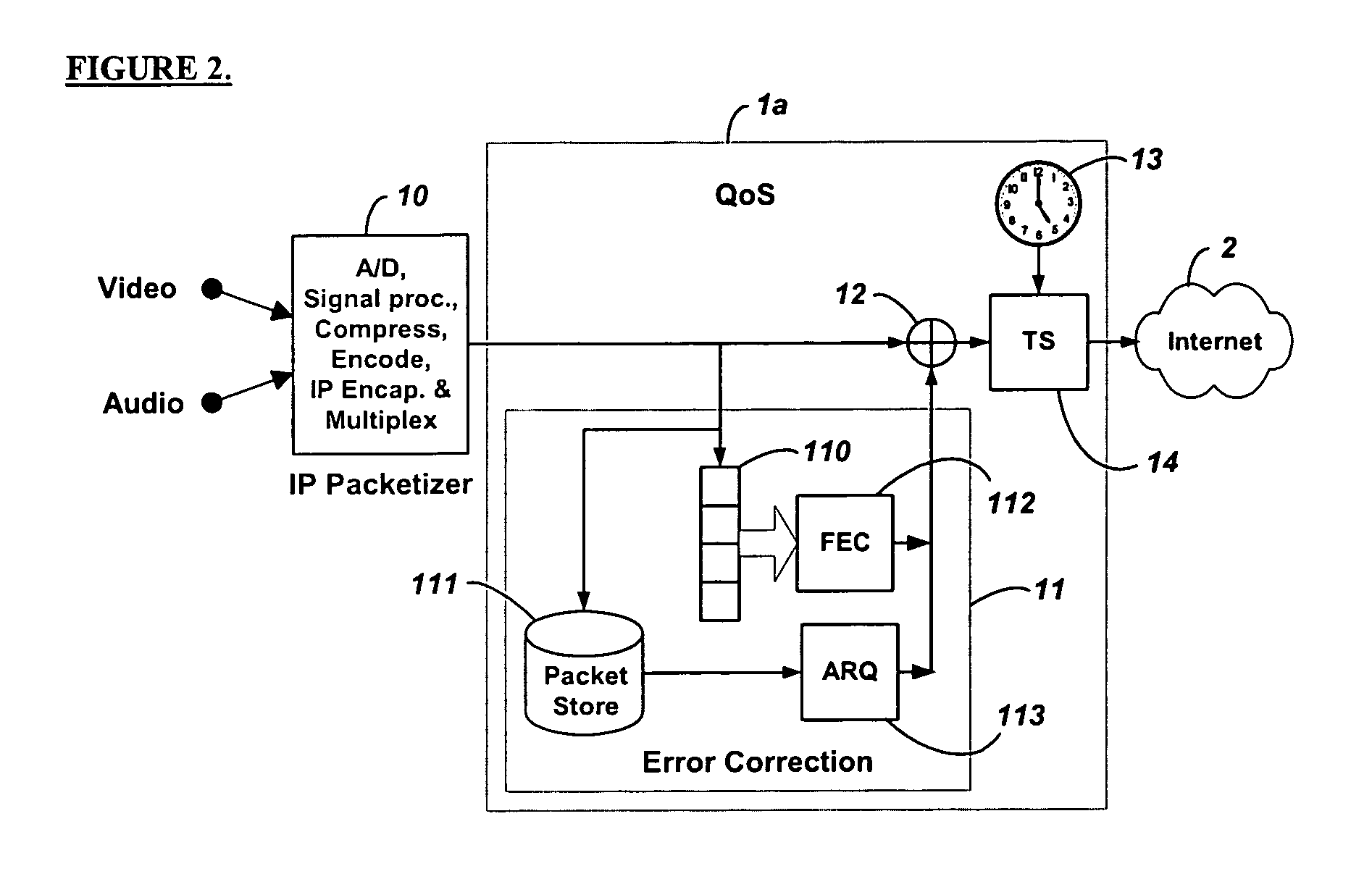
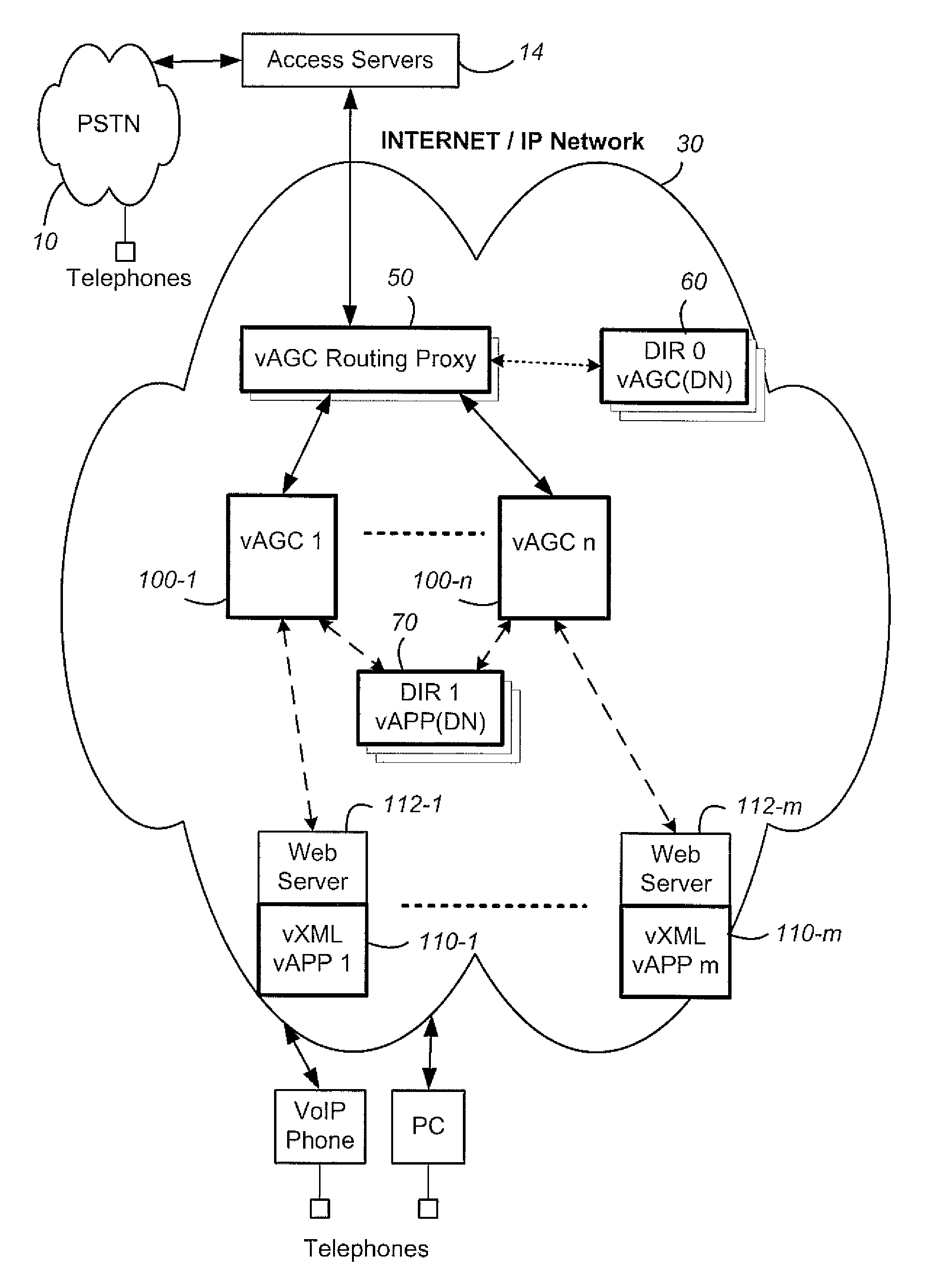
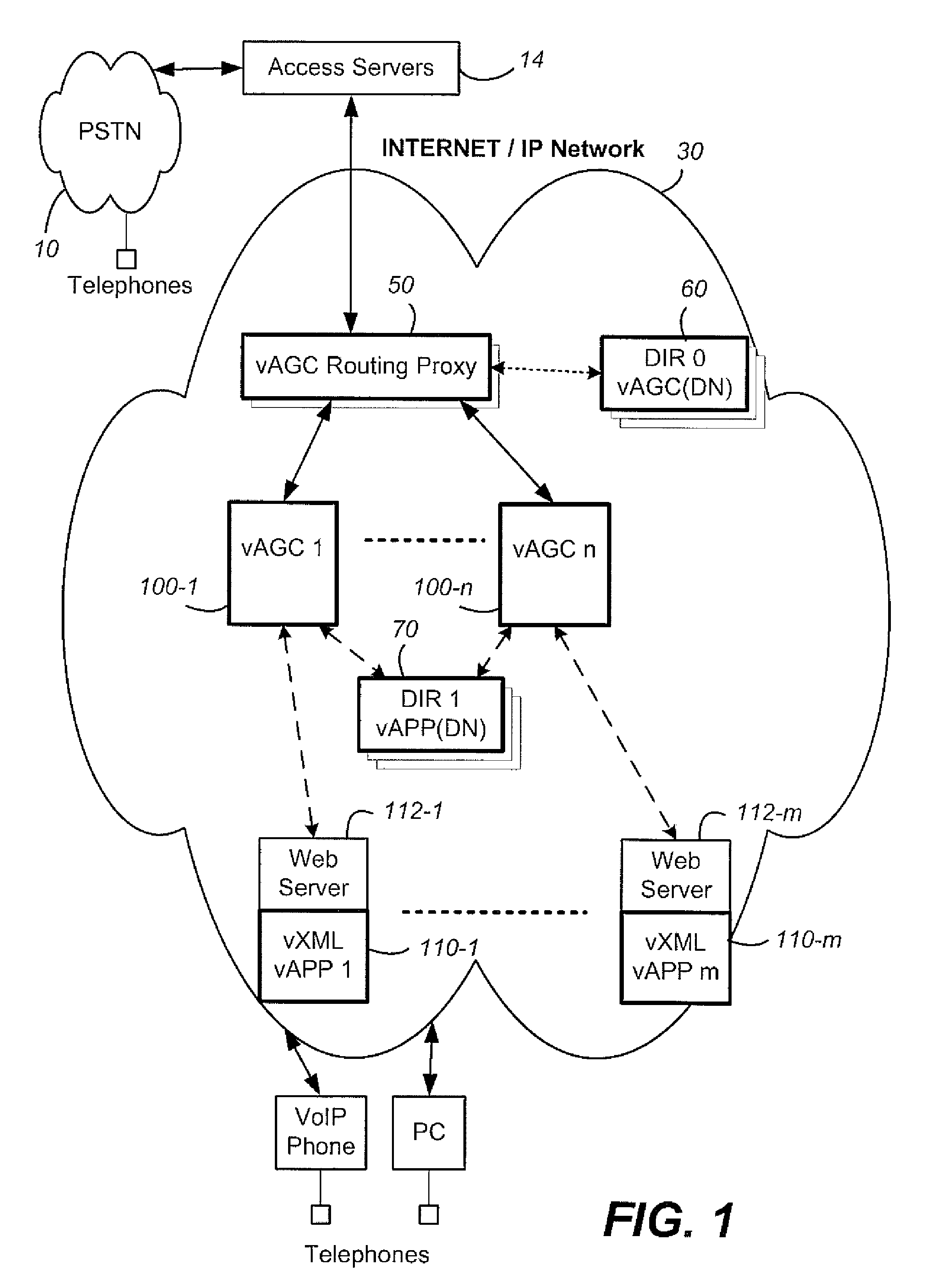
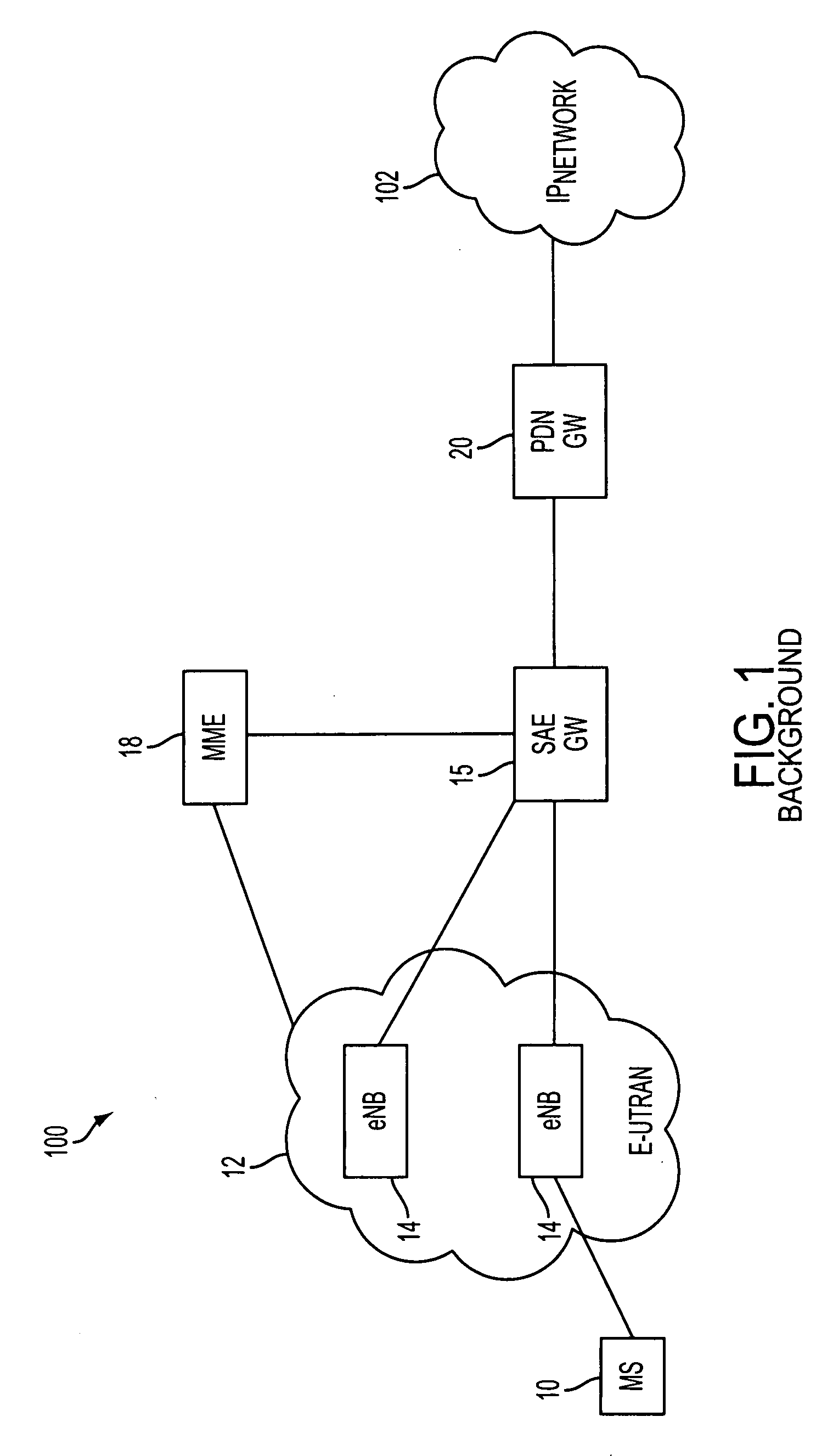
Method and system for providing site independent real-time multimedia transport over packet-switched networks
InactiveUS20060007943A1Minimal latency site-independenceAchieve independenceTime-division multiplexData switching by path configurationData packTimestamp
Embodiments of the invention enable minimum latency site independent real-time video transport over packet switched networks. Some examples of real-time video transport are video conferencing and real-time or live video streaming. In one embodiment of the invention, a network node transmits live or real-tine audio and video signals, encapsulated as Internet Protocol (IP) data packets, to one or more nodes on the Internet or other IP network. One embodiment of the invention enables a user to move to different nodes or move nodes to different locations thereby providing site independence. Site independence is achieved by measuring and accounting for the jitter and delay between a transmitter and receiver based on the particular path between the transmitter and receiver independent of site location. The transmitter inserts timestamps and sequence numbers into packets and then transmits them. A receiver uses these timestamps to recover the transmitter's clock. The receiver stores the packets in a buffer that orders them by sequence number. The packets stay in the buffer for a fixed latency to compensate for possible network jitter and / or packet reordering. The combination of timestamp packet-processing, remote clock recovery and synchronization, fixed-latency receiver buffering, and error correction mechanisms help to preserve the quality of the received video, despite the significant network impairments generally encountered throughout the Internet and wireless networks.
Owner:QVIDIUM TECH
System and methods of cooperatively load-balancing clustered servers
InactiveUS20050027862A1No lost performanceEfficient load balancingDigital computer detailsMultiprogramming arrangementsComputerized systemNetwork service
Host computer systems dynamically engage in independent transactions with servers of a server cluster to request performance of a network service, preferably a policy-based transfer processing of data. The host computer systems operate from an identification of the servers in the cluster to autonomously select servers for transactions qualified on server performance information gathered in prior transactions. Server performance information may include load and weight values that reflect the performance status of the selected server and a server localized policy evaluation of service request attribute information provided in conjunction with the service request. The load selection of specific servers for individual transactions is balanced implicitly through the cooperation of the host computer systems and servers of the server cluster.
Owner:VORMETRIC INC
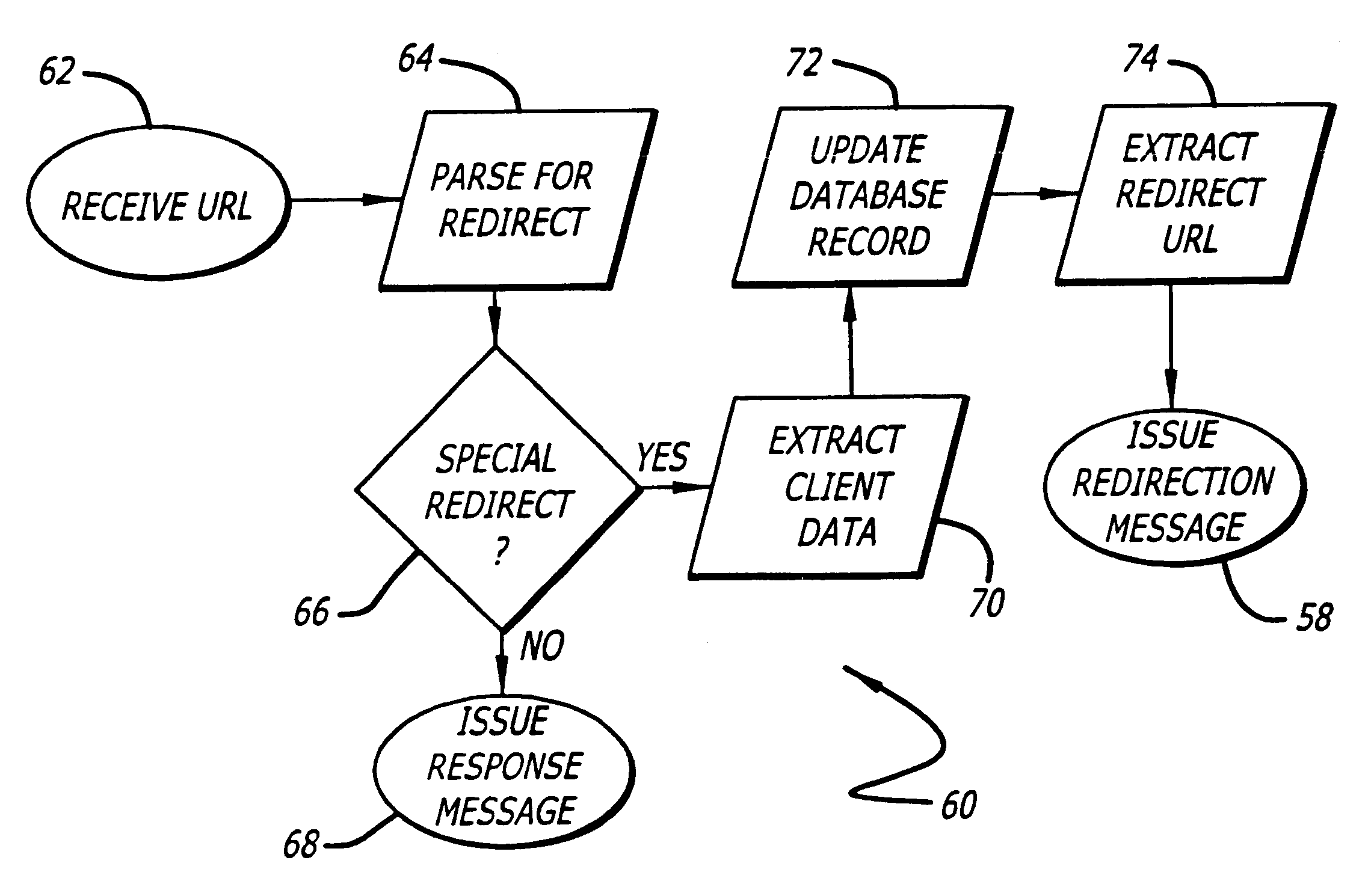
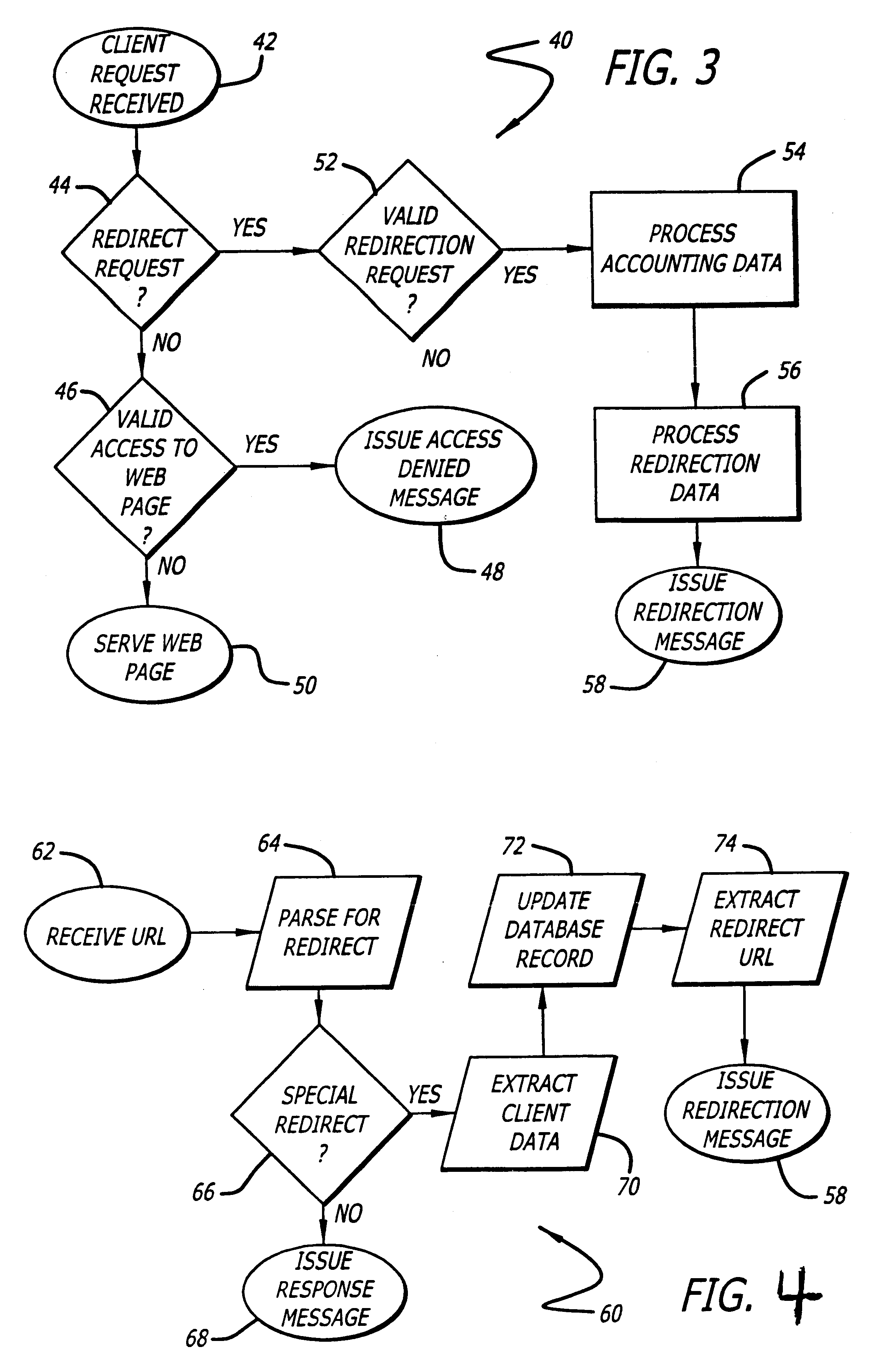
Method and apparatus for redirection of server external hyper-link references
InactiveUS6859833B2Minimum delayMinimum visibility of the redirection protocolMetering/charging/biilling arrangementsAdvertisementsGraphicsHyperlink
A message is provided to a tracking server system in response to a client system referencing a predetermined resource locator that corresponds to a resource external to the tracking server system. The tracking server system indirectly provides for the client system to have an informational element selectable by the client system, where the informational element is graphically identified on the client system with informational content obtainable from a content server system through use of a content resource locator. The informational element includes a tracking resource locator, referencing the tracking server system, and data identifying the informational element. The selection of the informational element causes the client system to use the tracking resource locator to provide the data to the tracking server system and to use the content resource locator to obtain the informational content from the content server system.
Owner:DISNEY ENTERPRISES INC
Control of Mobile Packet Streams
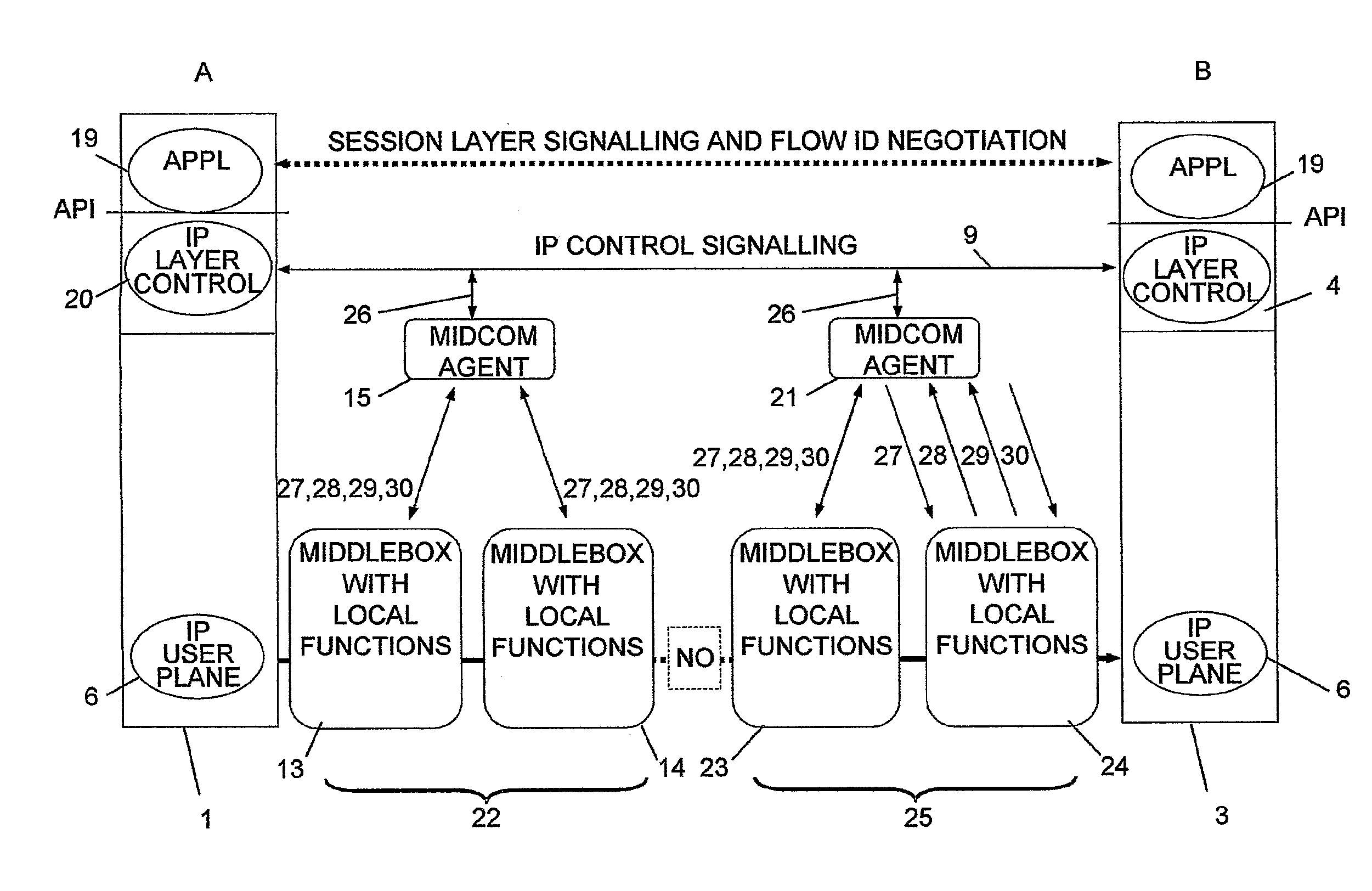
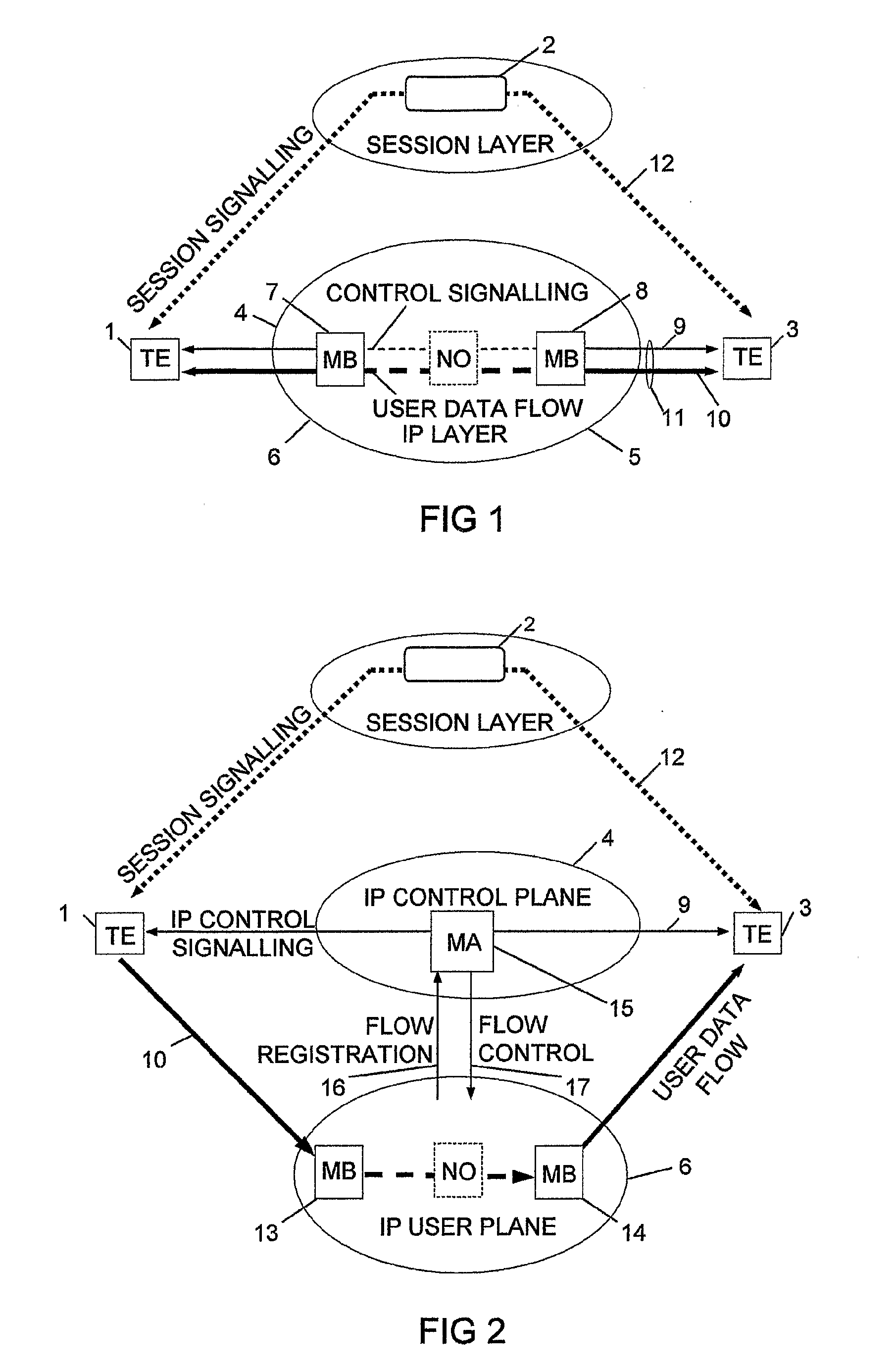
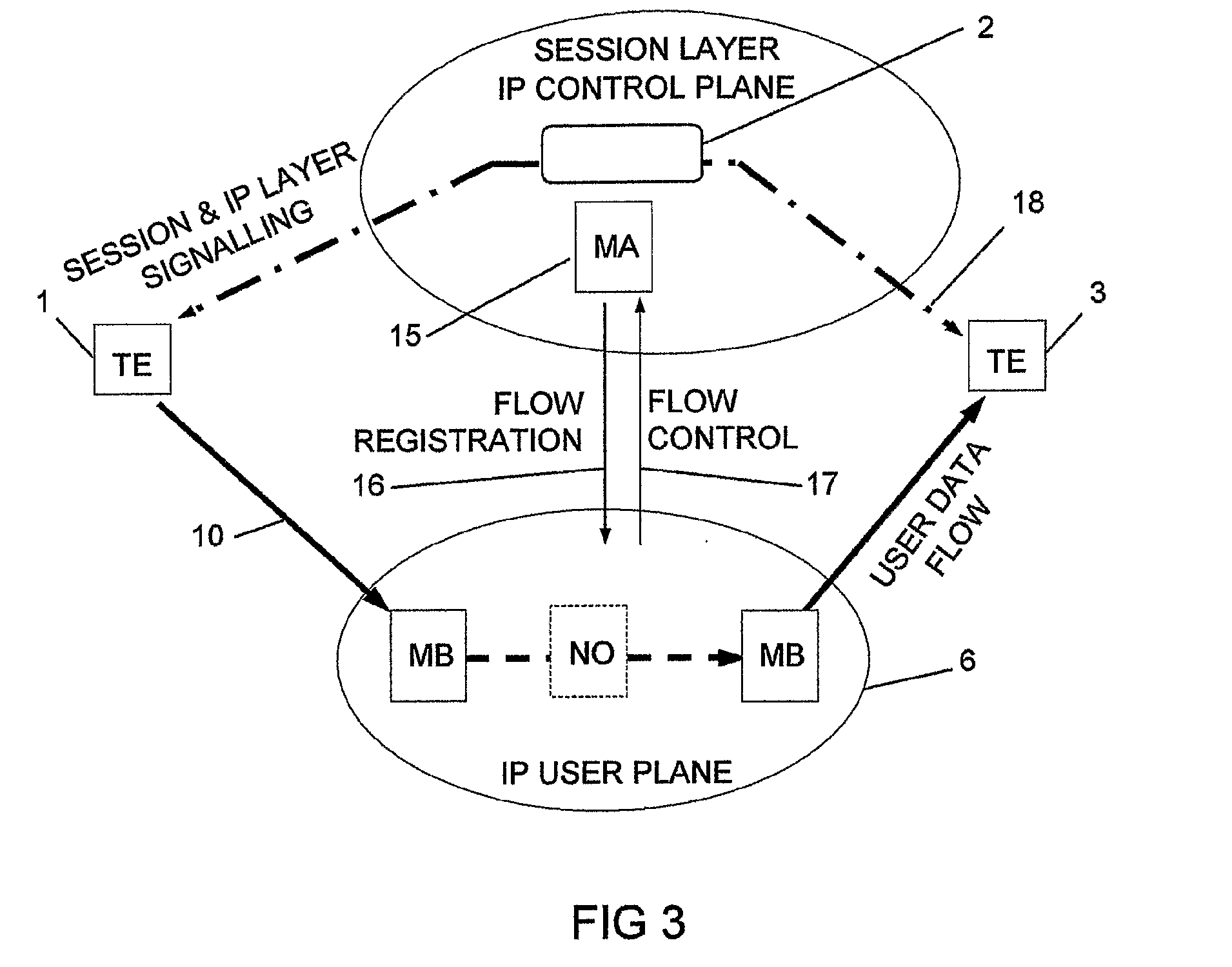
InactiveUS20070286185A1Reduce signaling overheadMinimum delayError preventionTransmission systemsControl signalMiddleware
The invention relates to a method, device and system for control of mobile packet flows forwarded between IP based networks. Individual packet flows on an IP user plane (6) traverse middleboxes (13, 14, 23, 24) that are controlled from a midcom agent (15, 21). Each user flow registers its presence (29) in each middlebox it encounters on its way from its source (A) to its destination (B) at the user plane. In response each middlebox registers itself and the mobile flows it handles at the midcom agent with which they communicate using a midcom signalling protocol. The midcom agent comprises functionalities that its controlled middleboxes have and can provide control messages for how a middlebox shall handle a registered flow. The registration provides the midcom agent (15, 21) with knowledge of registered flows and middleboxes which allows the midcom agent to send control orders to the middleboxes that registered themselves, said orders pertaining to the handling of the flows at the respective middleboxes. A mechanism for control signalling at the IP control plane is described.
Owner:OPTIS WIRELESS TECH LLC
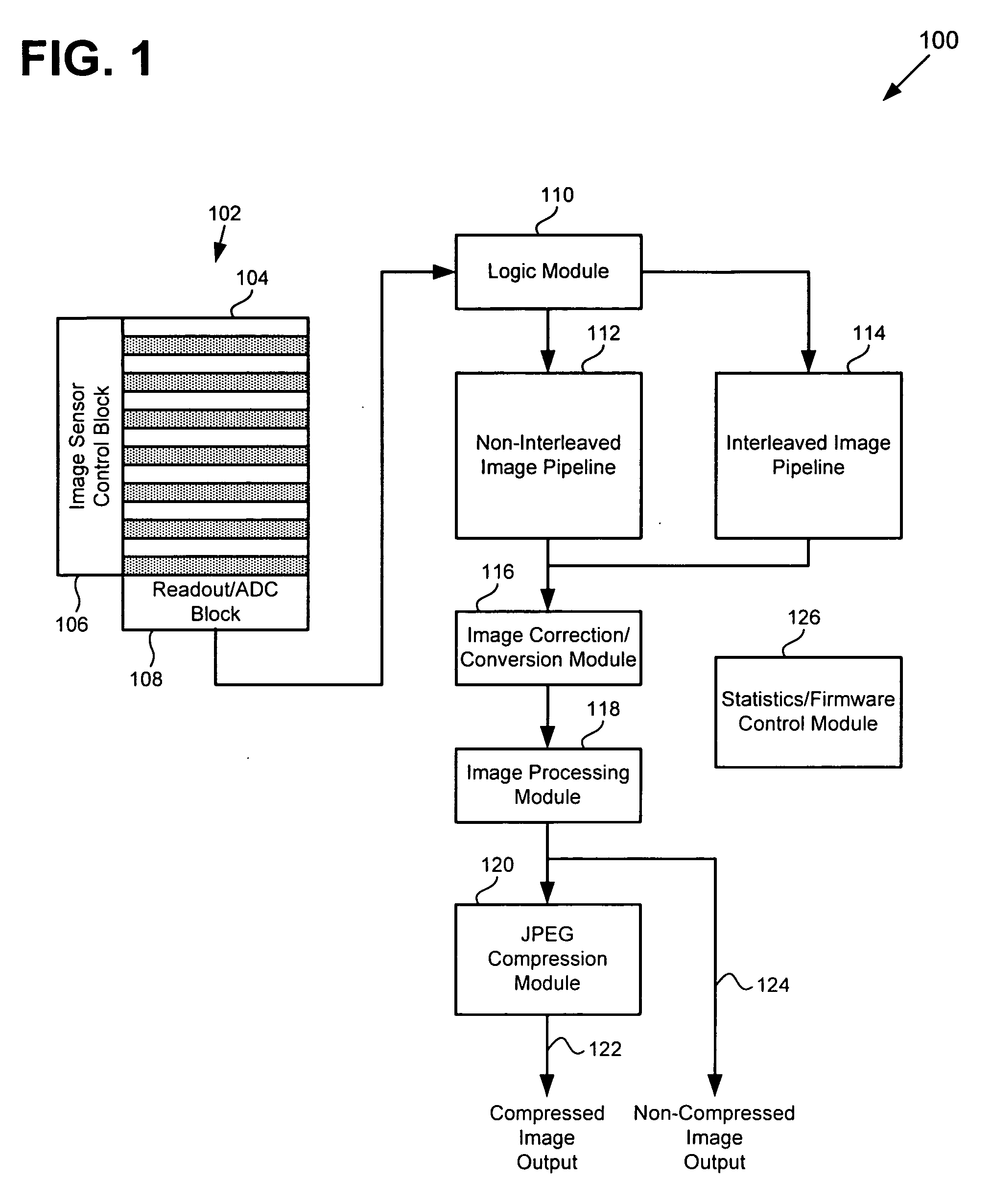
CMOS imager system with interleaved readout for providing an image with increased dynamic range
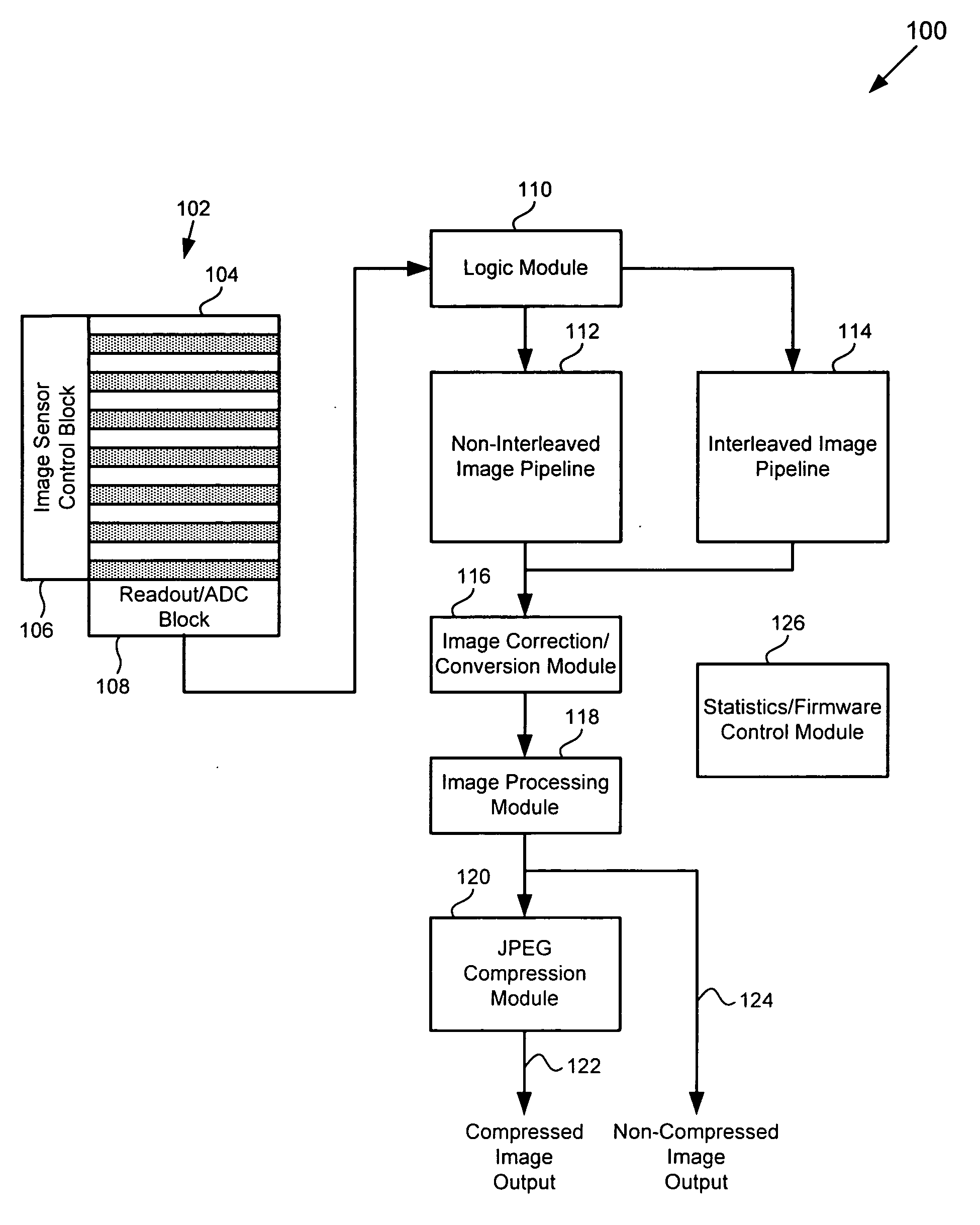
ActiveUS20070285526A1Improve dynamic rangeReduce Motion ArtifactsTelevision system detailsTelevision system scanning detailsCMOSPattern generation
There is provided a CMOS imager system for providing a viewable image having increased dynamic range including an image sensor including a number of sets of pixels. Each set of pixels is configured to receive one of a number of exposures and to generate image data corresponding to the received exposure in the interleaved mode. The image sensor is configured to operate in either an interleaved mode or a non-interleaved mode and to output the image data generated by each set of pixels as a frame of interleaved image data in the interleaved mode. The imager system further includes an interleaved image pipeline in communication with the image sensor, where the interleaved image pipeline is configured to receive the interleaved image data from the image sensor, combine the image data generated by each set of pixels corresponding to one of the exposures to form the viewable image.
Owner:IMPERIUM IP HLDG +1
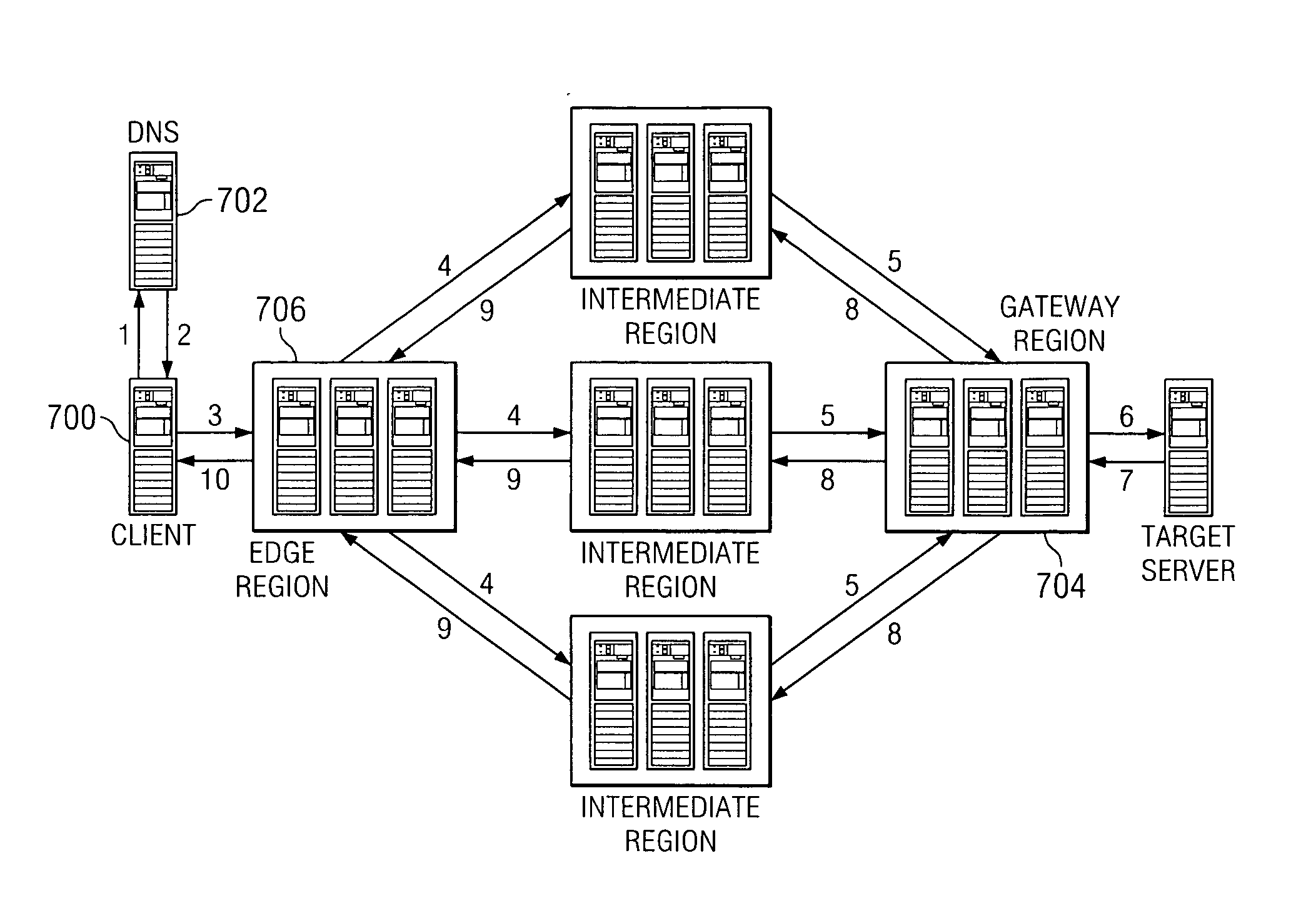
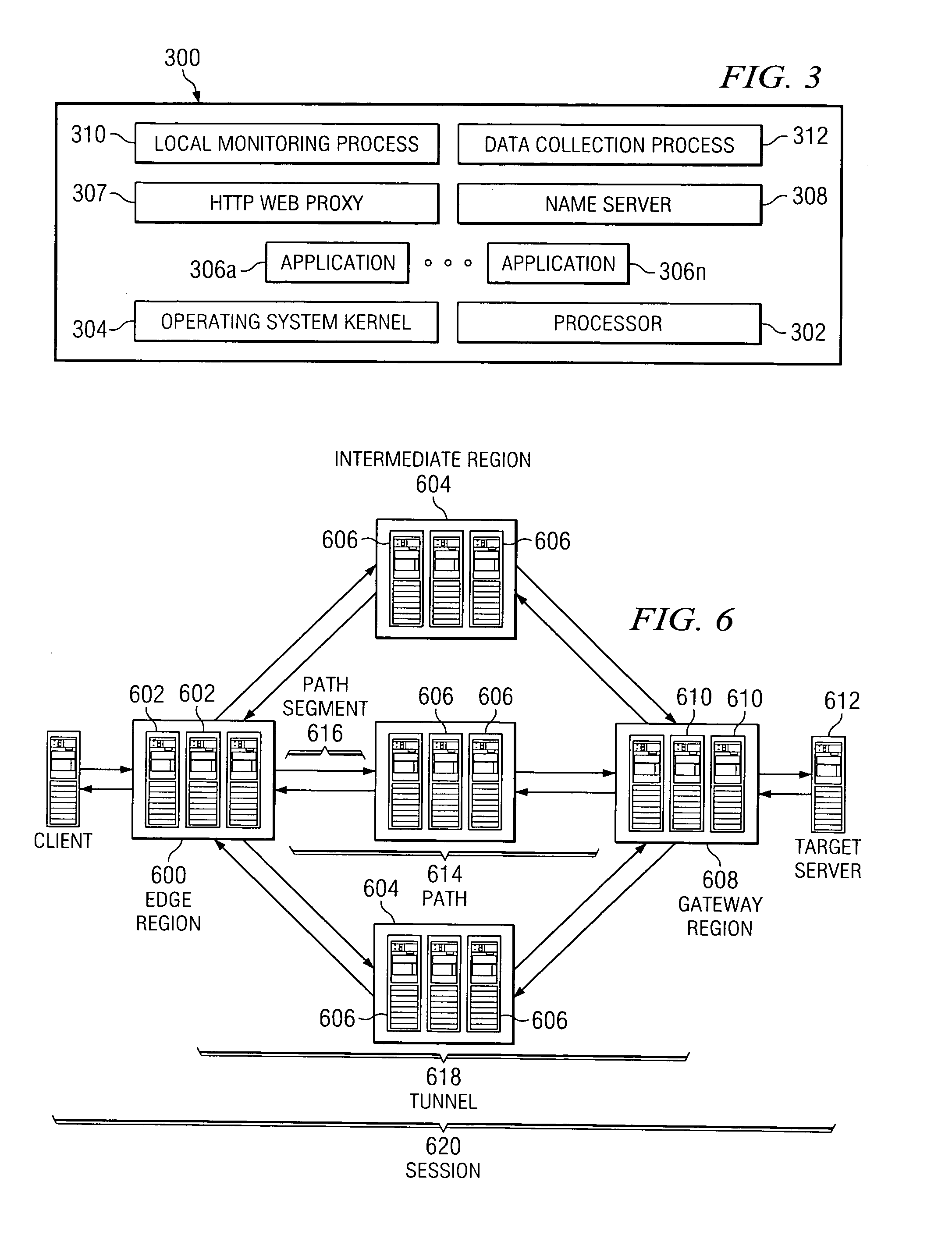
Reliable, high-throughput, high-performance transport and routing mechanism for arbitrary data flows
ActiveUS20070153782A1Minimum delayImprove performanceTime-division multiplexData switching by path configurationData streamEdge node
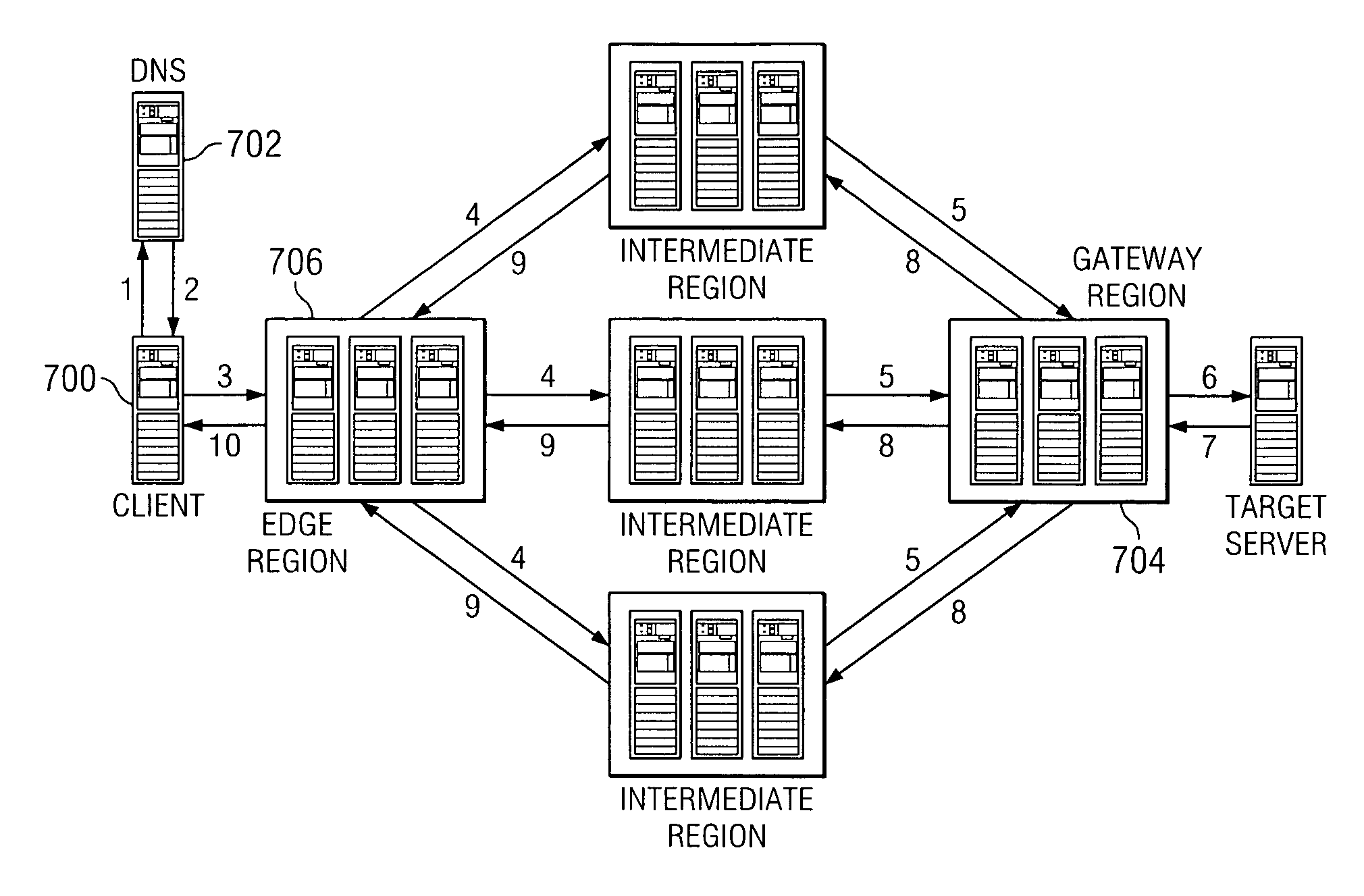
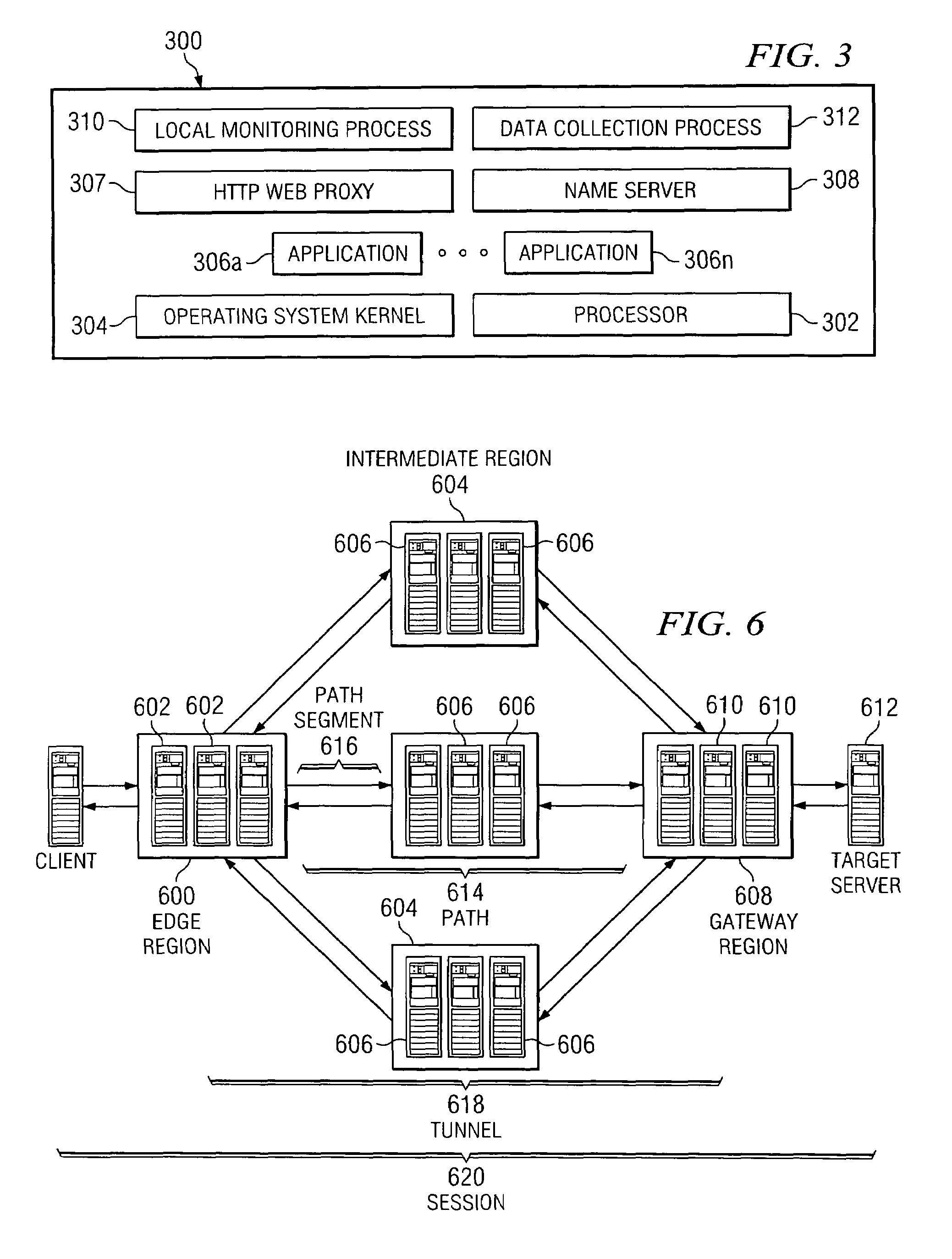
The present invention leverages an existing content delivery network infrastructure to provide a system that enhances performance for any application that uses the Internet Protocol (IP) as its underlying transport mechanism. An overlay network comprises a set of edge nodes, intermediate nodes, and gateway nodes. This network provides optimized routing of IP packets. Internet application users can use the overlay to obtain improved performance during normal network conditions, to obtain or maintain good performance where normal default BGP routing would otherwise force the user over congested or poorly performing paths, or to enable the user to maintain communications to a target server application even during network outages.
Owner:AKAMAI TECH INC
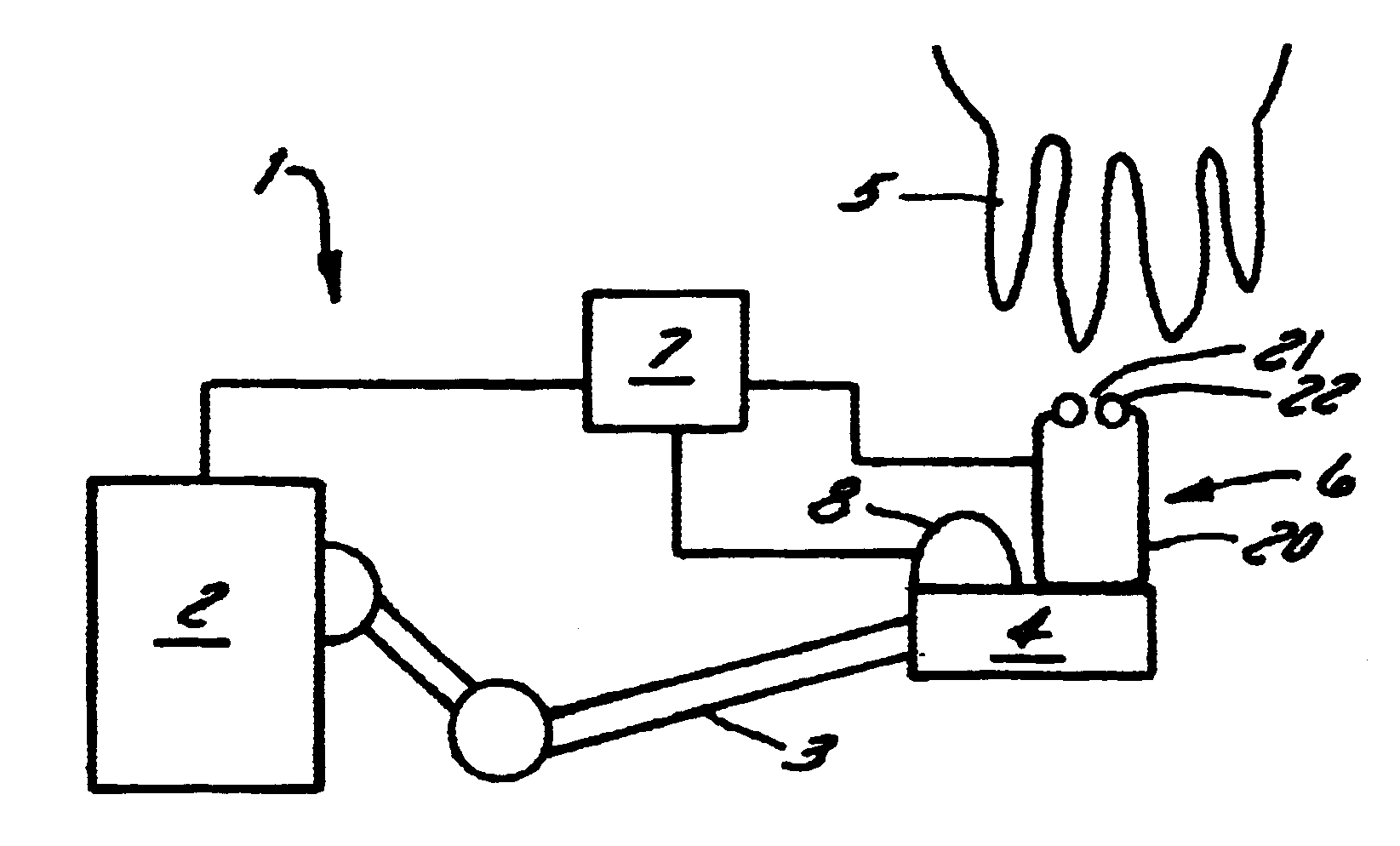
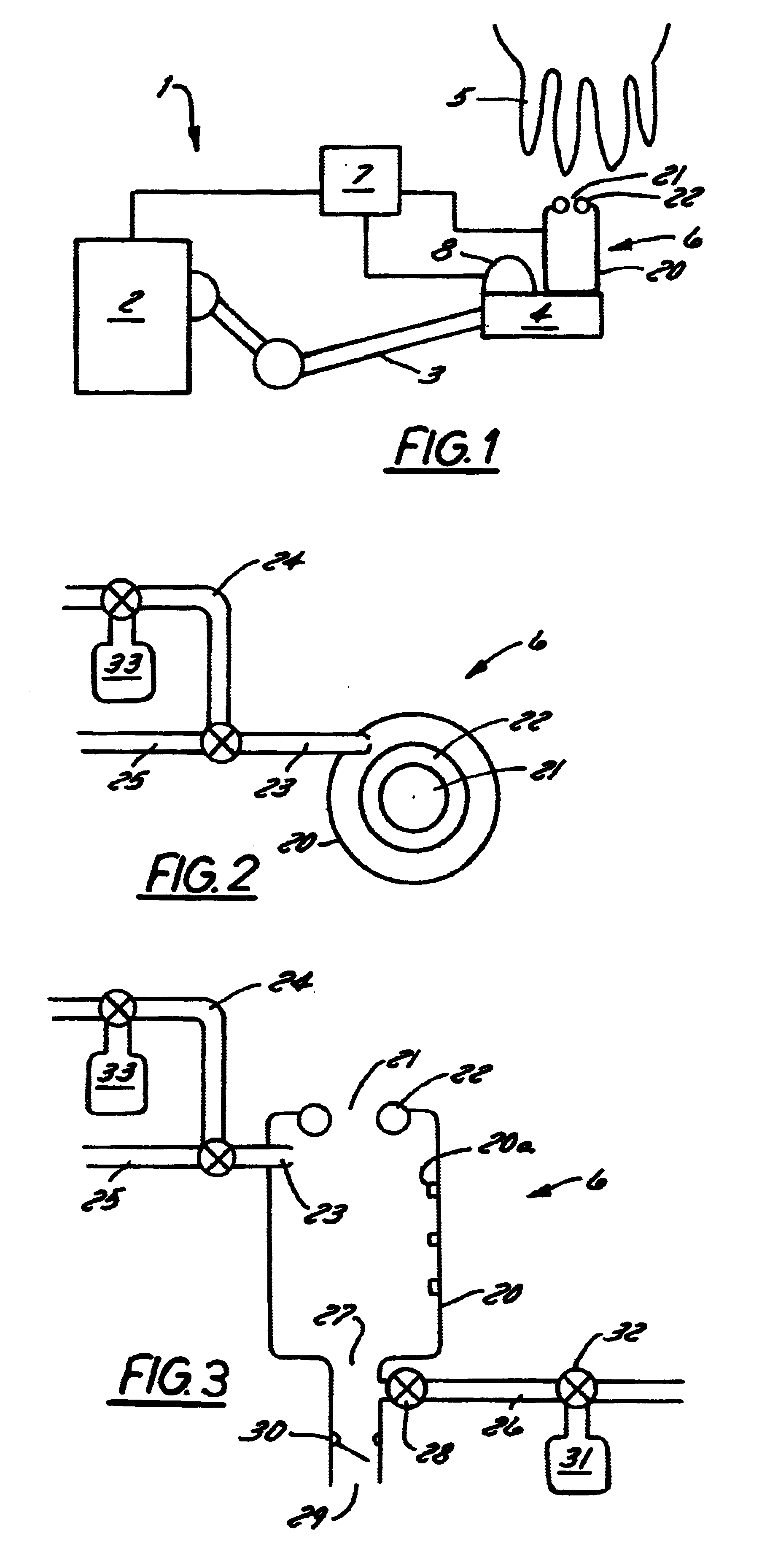
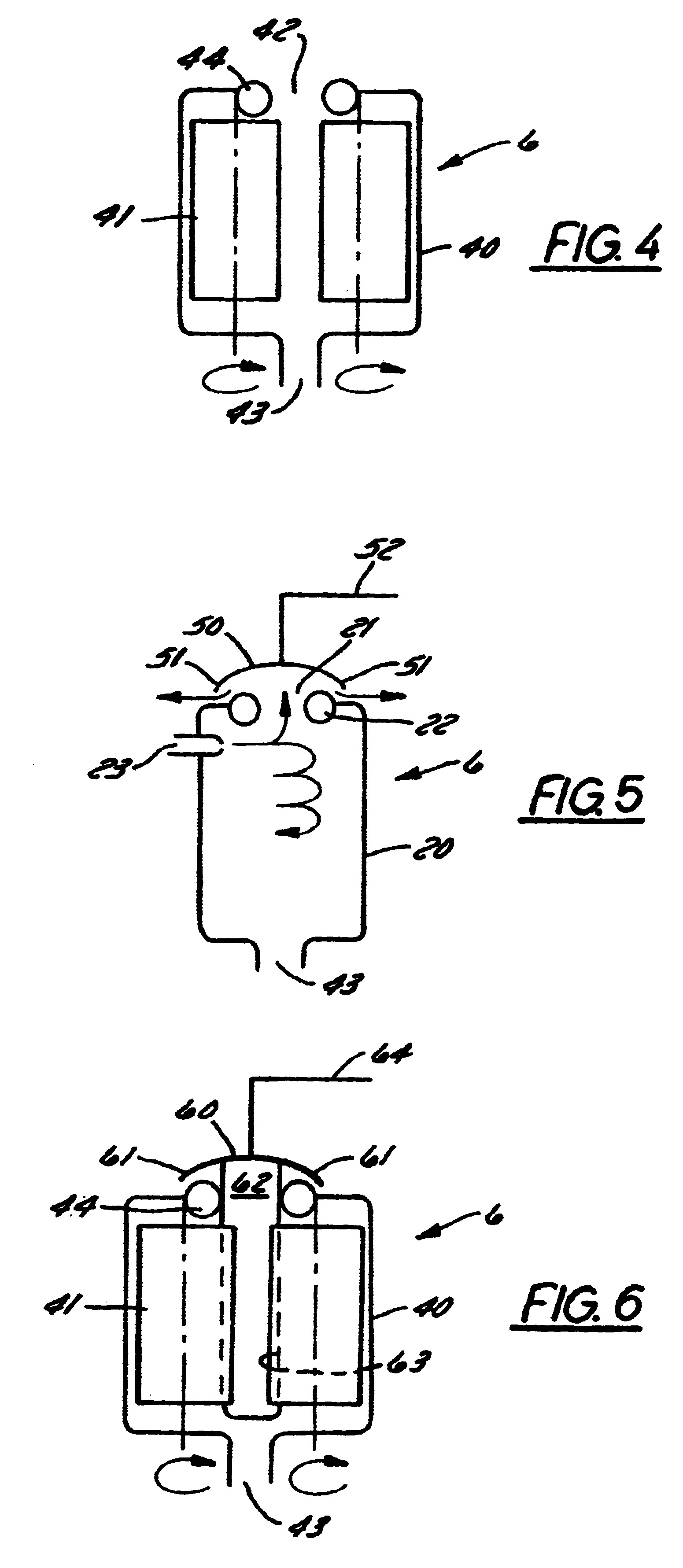
Method and apparatus for cleaning of a teat cleaning device
InactiveUS6626130B1Risk minimizationMinimum delayOther apparatusMilking devicesEngineeringMilking robot
A teat cleaning arrangement (1) for milking equipment, comprising a teat cleaning device (6) with teat cleaning means (23, 41). A milking robot (2) with a robot front end (4) is devised to move the teat cleaning device (6) into engagement with a teat (5), and control means (7) are connectable to the robot (2) for controlling motion thereof. The control means are also connectable to the teat cleaning device (6) for controlling the teat cleaning means (23, 41), and engagement and disengagement with a teat (5). The control means (7) are devised to activate said teat cleaning means (23, 41) to clean said teat cleaning device (6) after each teat disengagement.
Owner:DELAVAL HLDG AB
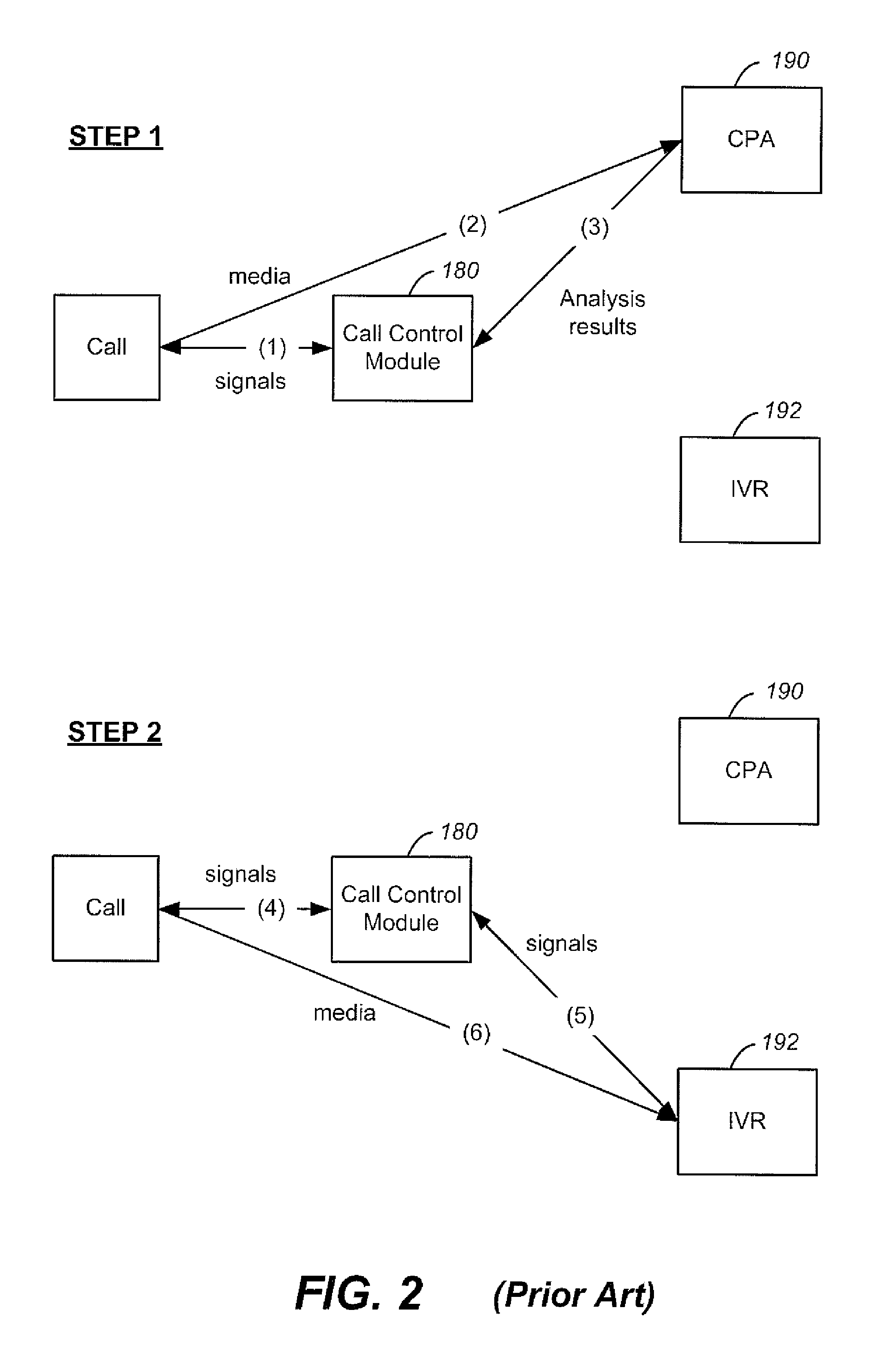
System and method for dynamic call-progress analysis and call processing
ActiveUS8243889B2Minimum delayAutomatic call-answering/message-recording/conversation-recordingAutomatic exchangesSpeech applicationsSpeech sound
A telephony application such as an interactive voice response (“IVR”) needs to identify quickly the nature of the call (e.g., whether it is a person or machine answering a call) in order to initiate an appropriate voice application. Conventionally, the call stream is sent to a call-progress analyzer (“CPA”) for analysis. Once a result is reached, the call stream is redirected to a call processing unit running the IVR according to the analyzed result. The present scheme feeds the call stream simultaneous to both the CPA and the IVR. The CPA is allowed to continue analyzing and outputting a series of analysis results until a predetermined result appears. In the meantime, the IVR can dynamically adapt itself to the latest analysis results and interact with the call with a minimum of delay.
Owner:ALVARIA INC
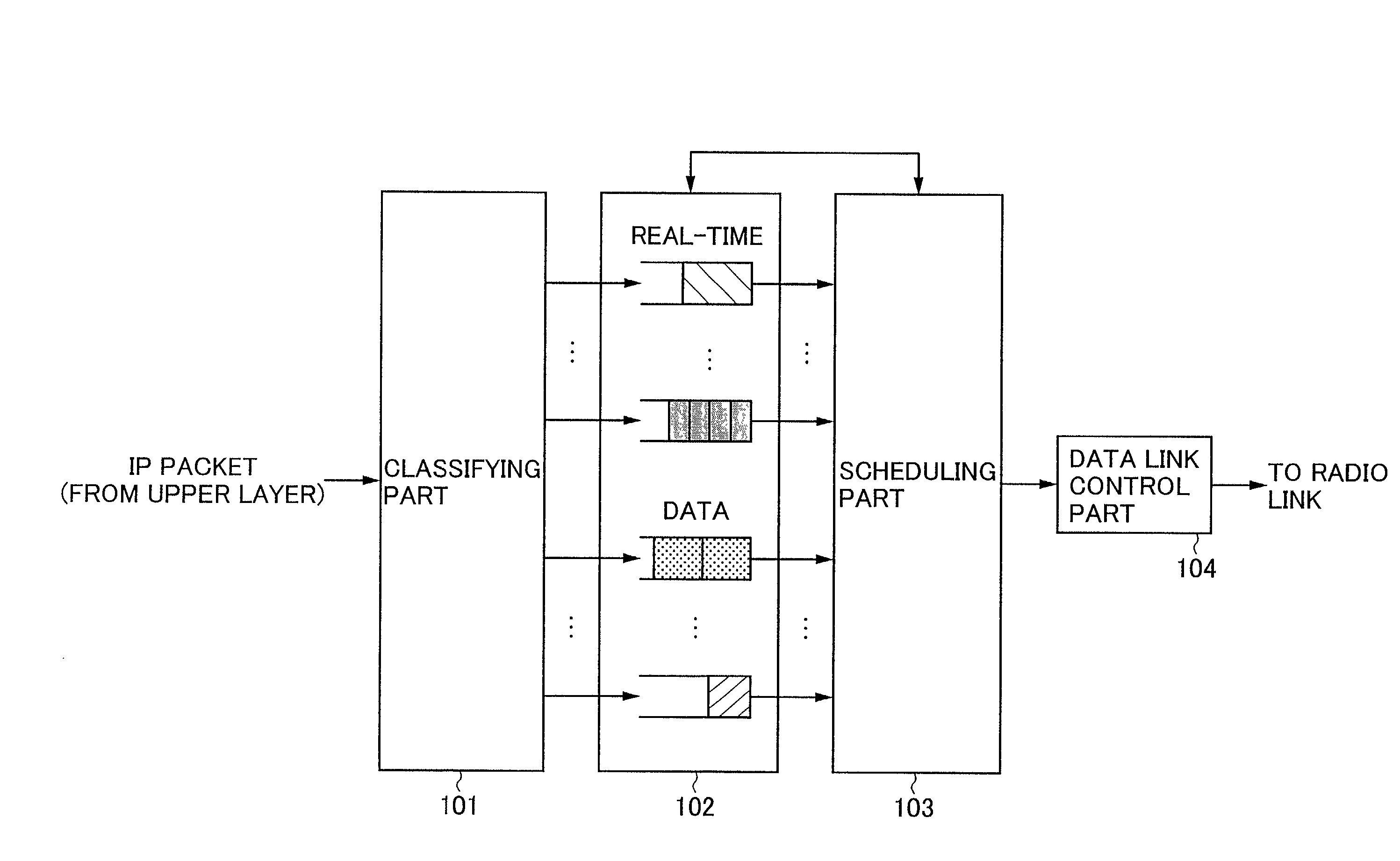
Packet transmission method and system, and packet transmitting apparatus, packet receiving apparatus, and packet transmitting/receiving apparatus
ActiveUS20020126675A1Minimum delayMaintain reliabilityError prevention/detection by using return channelNetwork traffic/resource managementQuality of serviceData type
A packet transmission method for transmitting packets classified according to a quality of service (QoS) requirement from a transmitting node to a receiving node is provided. In the transmitting node, the steps of: selecting sequentially a QoS class; dividing a queued packet to be transmitted belonging to the selected class into a plurality of predetermined data units, and transmitting one of the obtained predetermined data units; and applying a transmitter-side retransmission control process to the data unit to be transmitted when the selected class is a QoS class specified for data type packets are provided. In the receiving node, the steps of: receiving sequentially the data units transmitted from the transmitting node; assembling a plurality of received data units to decompress the original packet for each QoS class; and applying a receiver-side retransmission control process to the received data units to be assembled when the received data unit belongs to one of the QoS classes specified for the data type packets are provided.
Owner:NTT DOCOMO INC
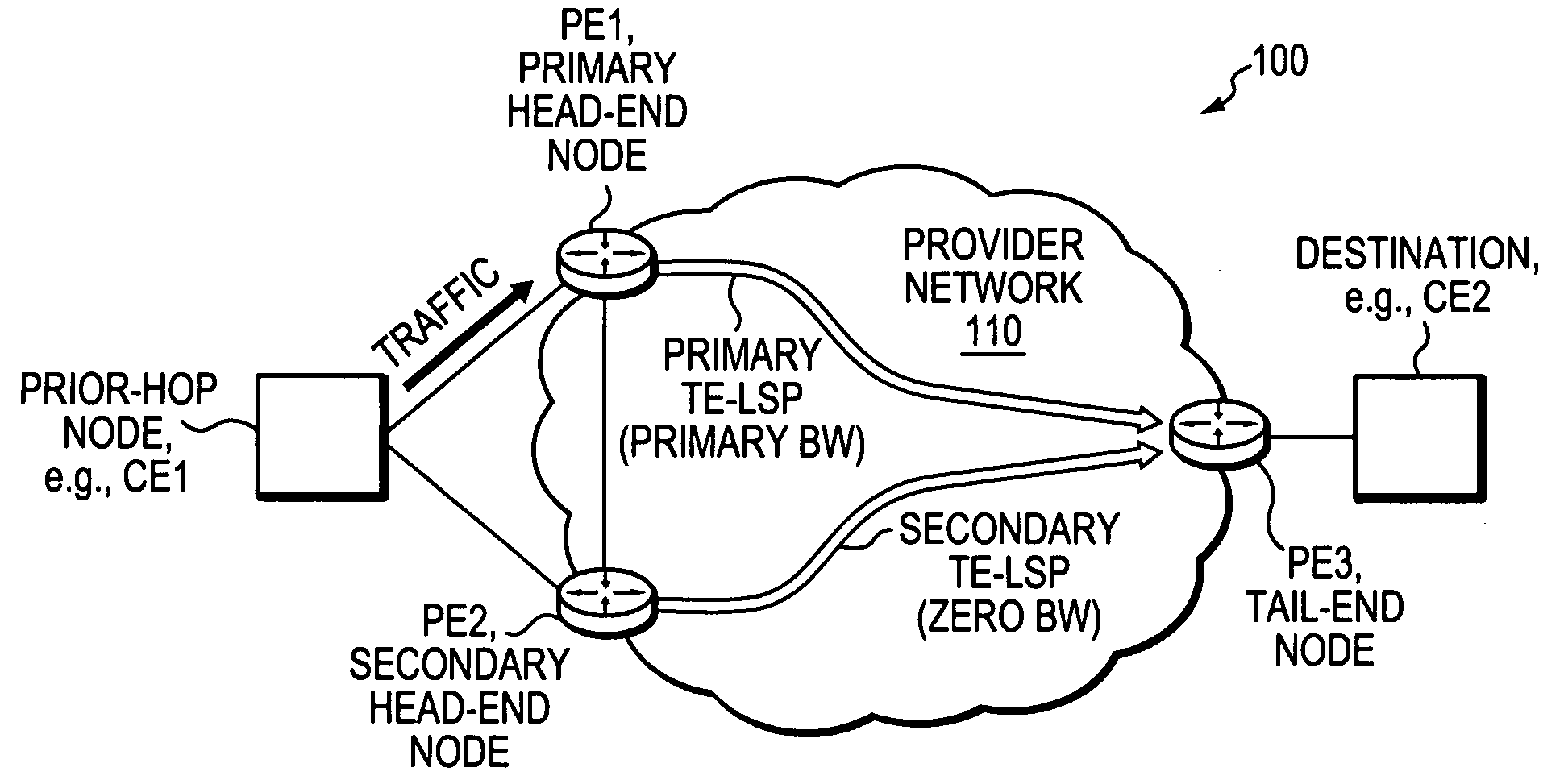
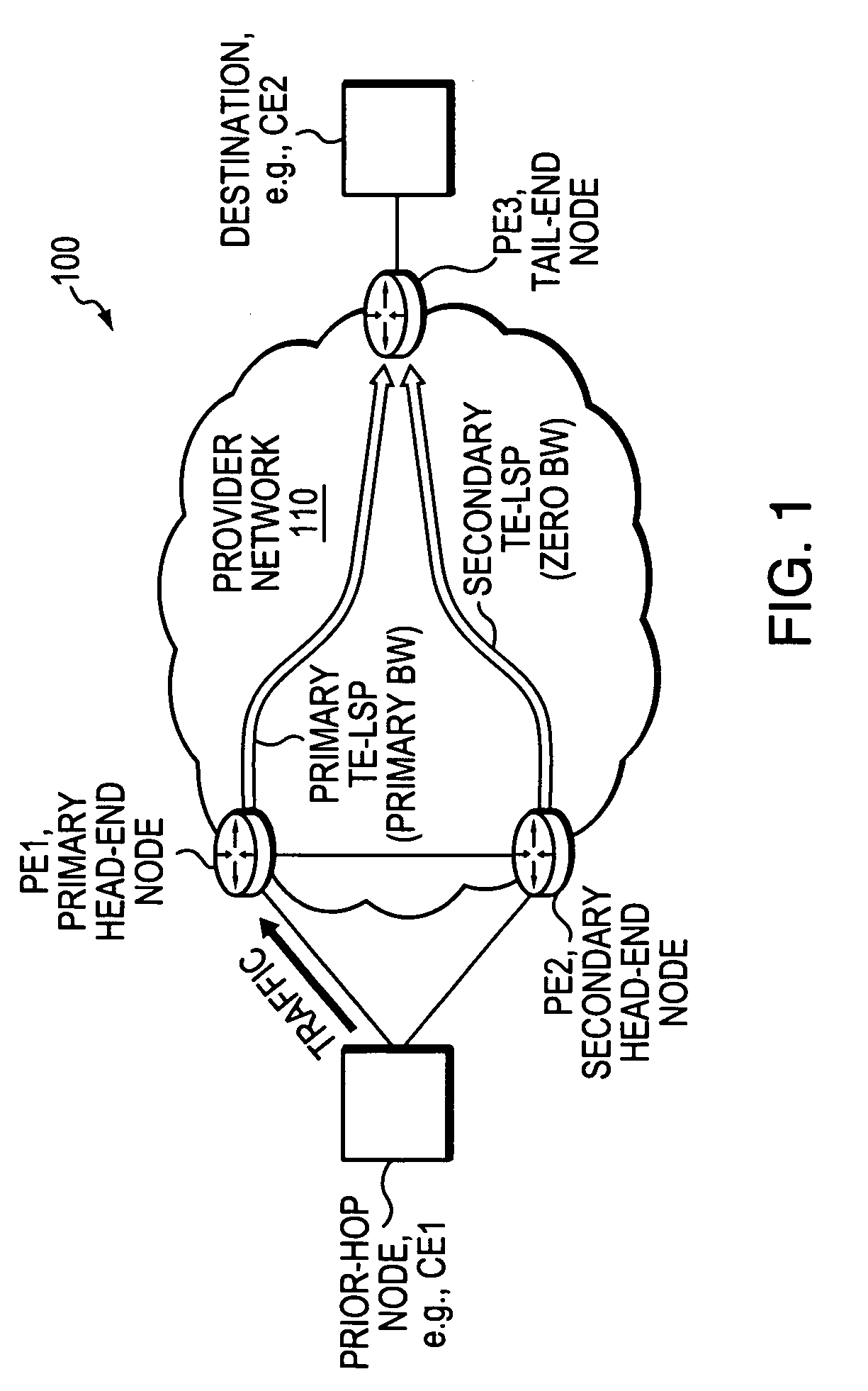
Technique for fast activation of a secondary head-end node TE-LSP upon failure of a primary head-end node TE-LSP
ActiveUS20070280102A1Avoid wastingMinimal delayError preventionTransmission systemsTraffic volumeLabel switching
A technique dynamically activates a secondary Traffic Engineering Label Switched Path (TE-LPs) at a secondary head-end node upon failure of a primary TE-LPs in a computer network. According to the novel technique, a primary head-end node establishes the primary TE-LPs having a primary bandwidth (BW) amount to a primary tail-end node. Also, the secondary head-end node establishes the secondary TE-LPS having zero BW to a secondary tail-end node (e.g., the same as the primary tail-end node). The secondary head-end node monitors the state of the primary TE-LPS, and in response to a failure (e.g., or other state change) substantially immediately adjusts the BW of the secondary TE-LPS to the primary BW amount (“activating” the TE-LPS). A “prior-hop” node to the primary and secondary head-end nodes originally forwarding traffic to the primary head-end node, may then begin forwarding traffic to the secondary head-end node, and thus onto the adjusted secondary TE-LPS.
Owner:CISCO TECH INC
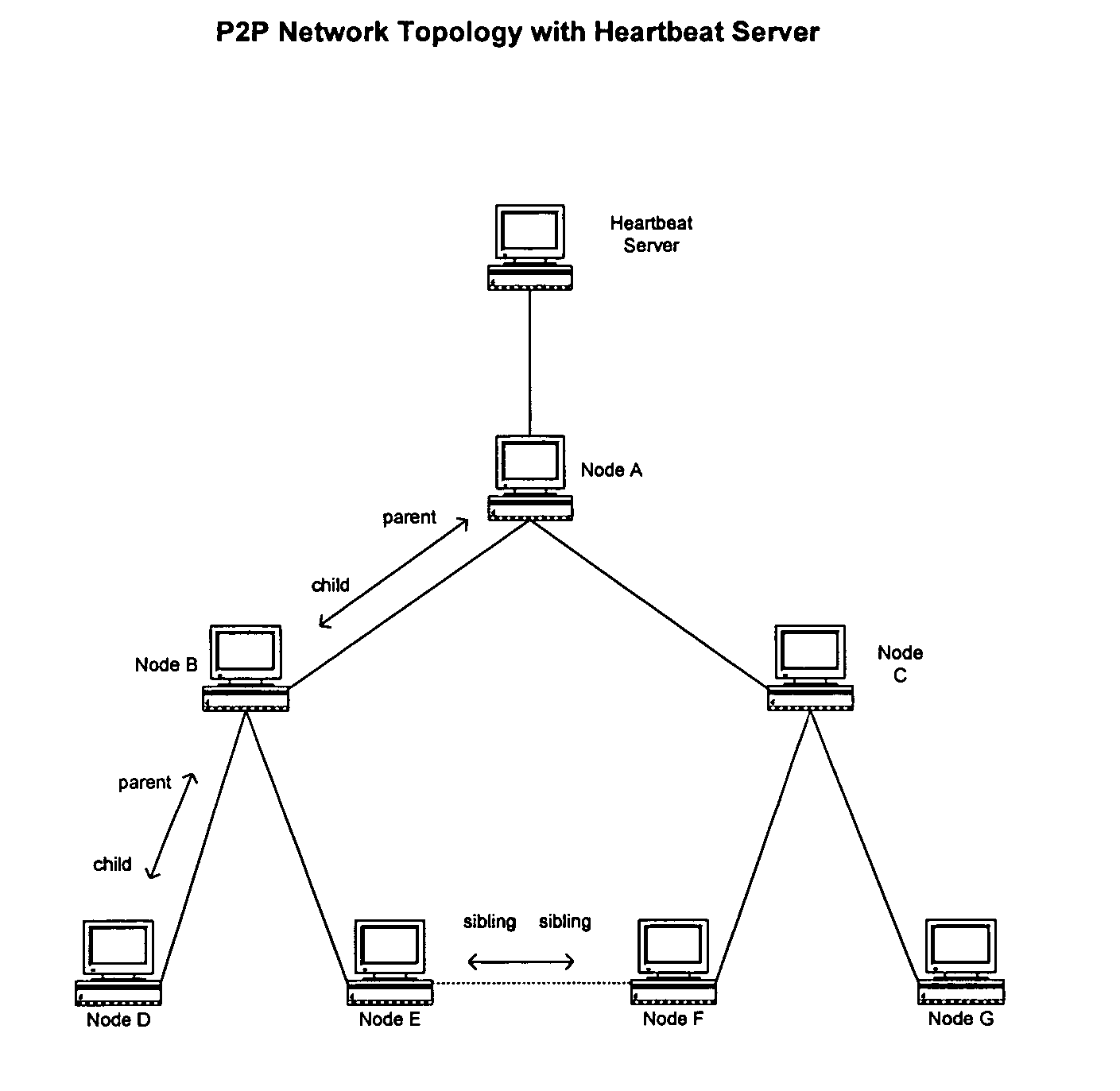
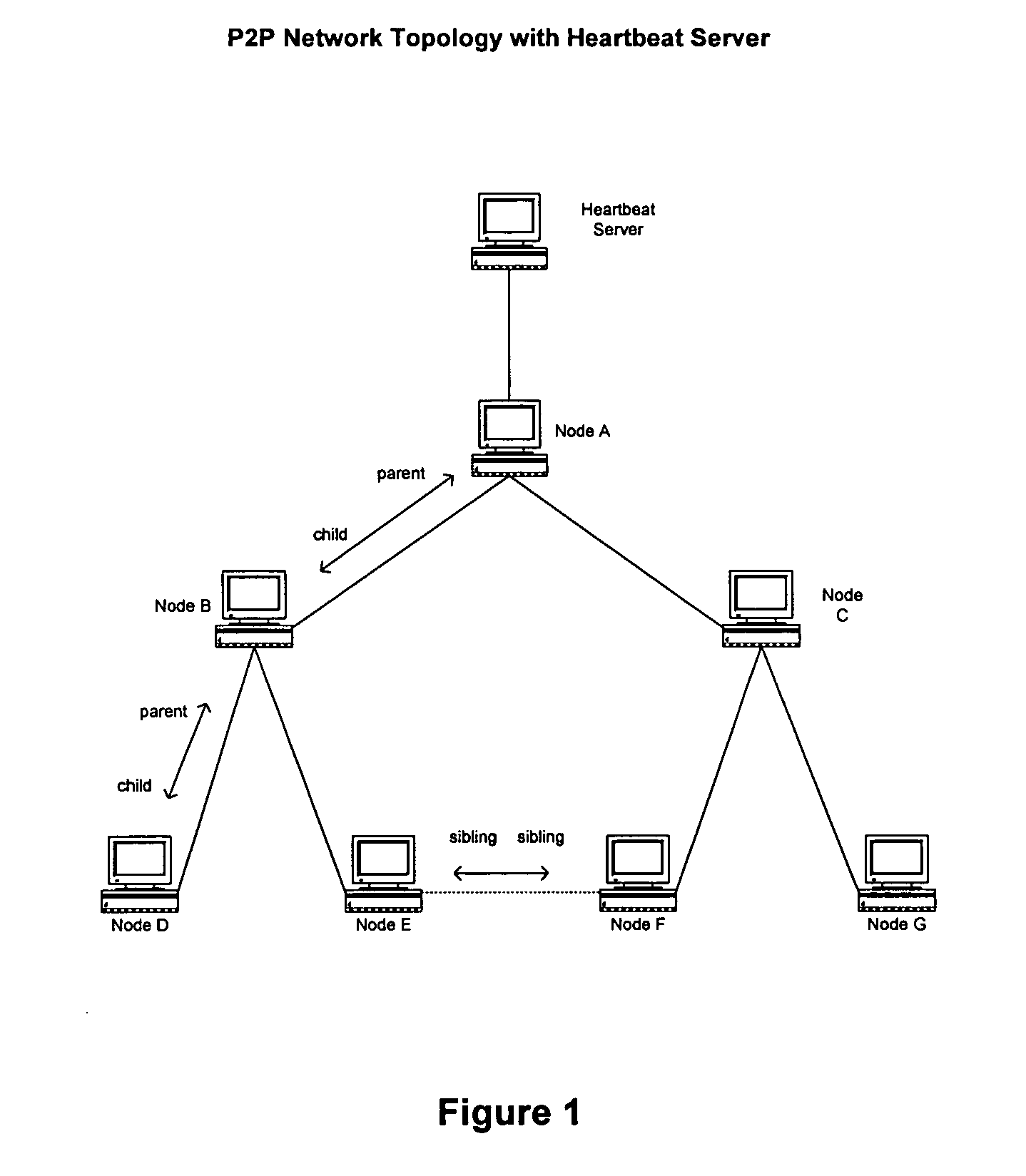
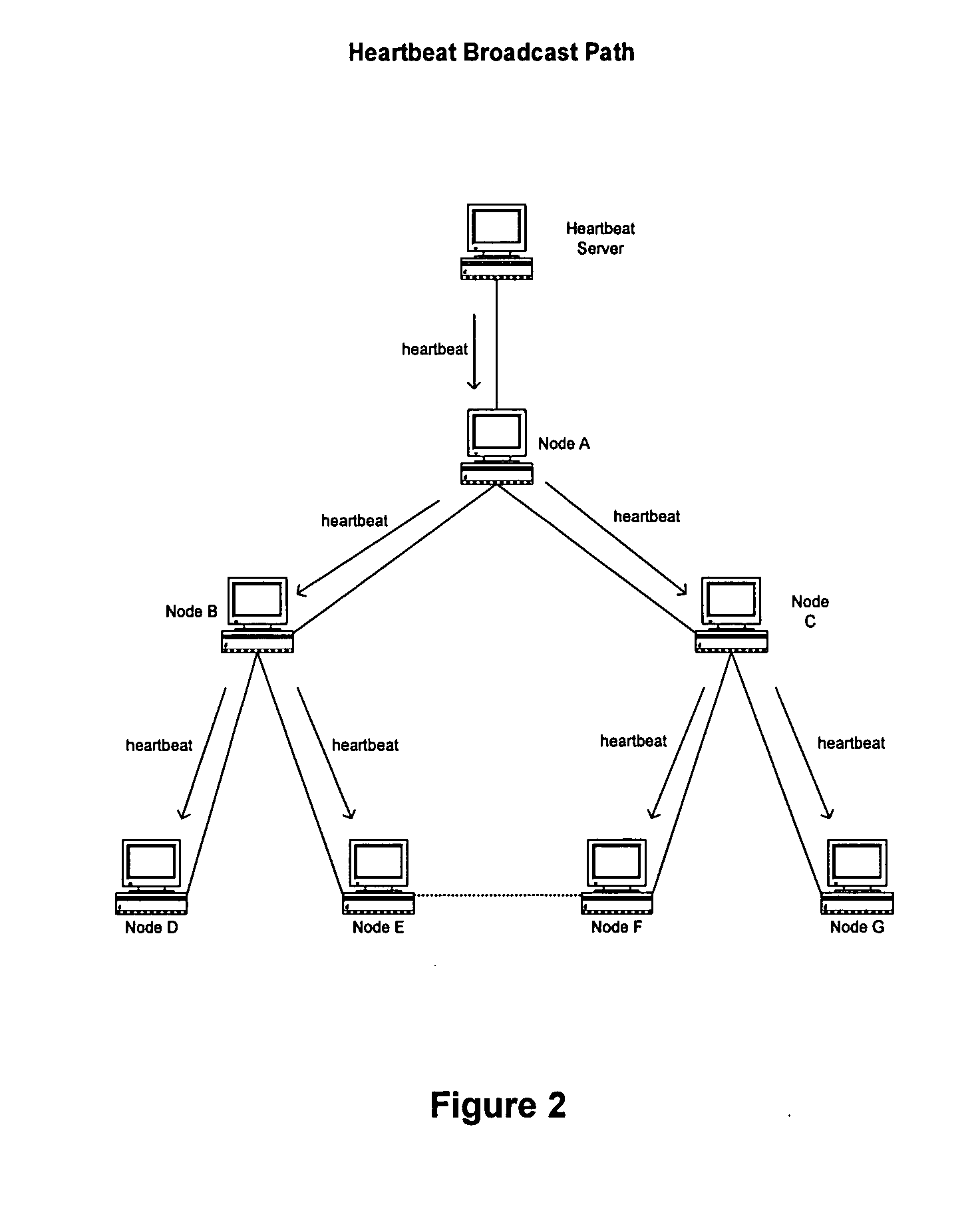
Peer-to-peer network heartbeat server and associated methods
InactiveUS20050007964A1Less bandwidthLess resourcesTime-division multiplexData switching by path configurationAuto-configurationLatency (engineering)
A self-defined, automatically-configured hierarchical peer-to-peer networking method is disclosed. Network hierarchy is determined by the proximity (quantified as lower latency) of nodes in the network to a predetermined heartbeat server node. Nodes in closer proximity to the server node are considered parent of nodes in farther proximity. Nodes in equal proximity to the server node are considered siblings to each other. The disclosed network has a loop-free connectivity topology where a parent node may have multiple child nodes but does not share any child nodes with other parents.
Owner:FREE PEERS
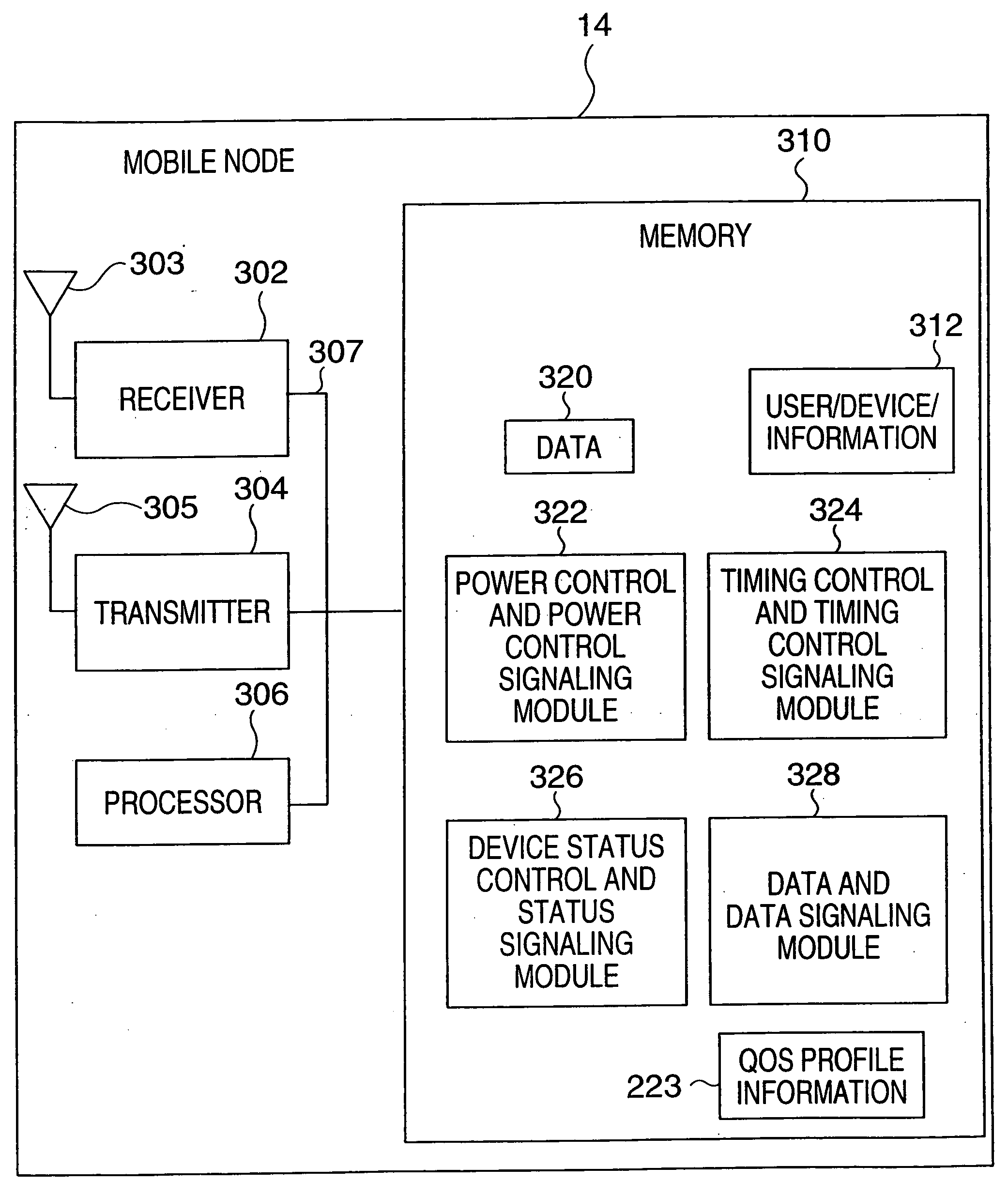
Power and timing control methods and apparatus
InactiveUS20050118981A1Avoid interferenceMinimum delayPower managementResonant long antennasSleep stateControl signal
The use of multiple states of mobile communication device operation to allow a single base station to support a relatively large number of mobile nodes is described. The various states require different amounts of communications resources, e.g., bandwidth. Four supported states of operation are an on-state, a hold-state, a sleep-state, and an access-state. Each mobile node in the on-state is allocated communication resources to perform transmission power control signaling, transmission timing control signaling and to transmit data as part of a data uplink communications operation. Each mobile node in the hold-state is allocated communication resources to perform transmission timing control signaling and is provided a dedicated uplink for requesting a state transition and a shared resource for transmitting acknowledgements. In the sleep state a mobile node is allocated minimal resources and does not conduct power control signaling or timing control signaling. Data may be received in the on and hold states.
Owner:QUALCOMM INC
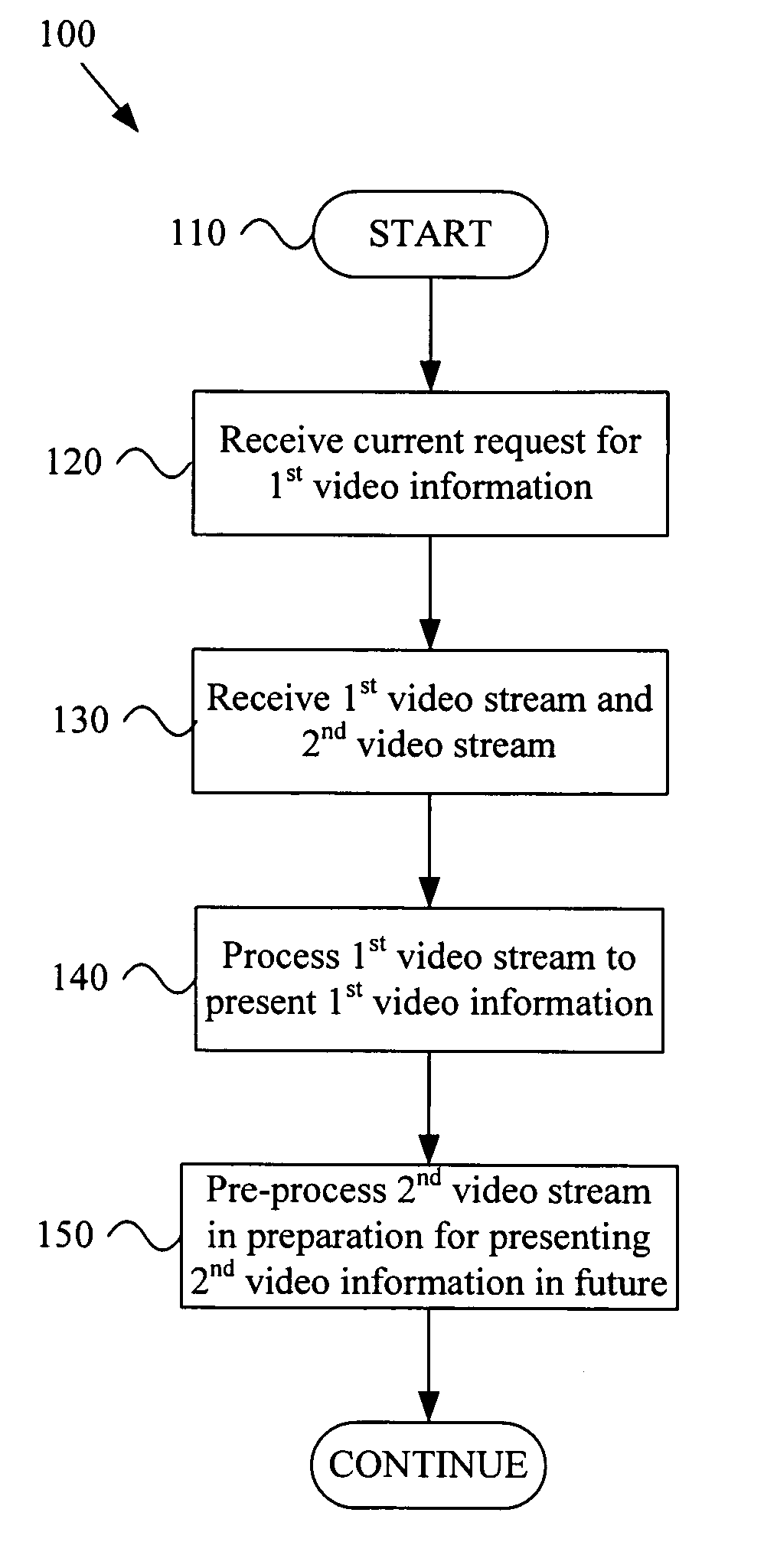
Anticipatory video signal reception and processing
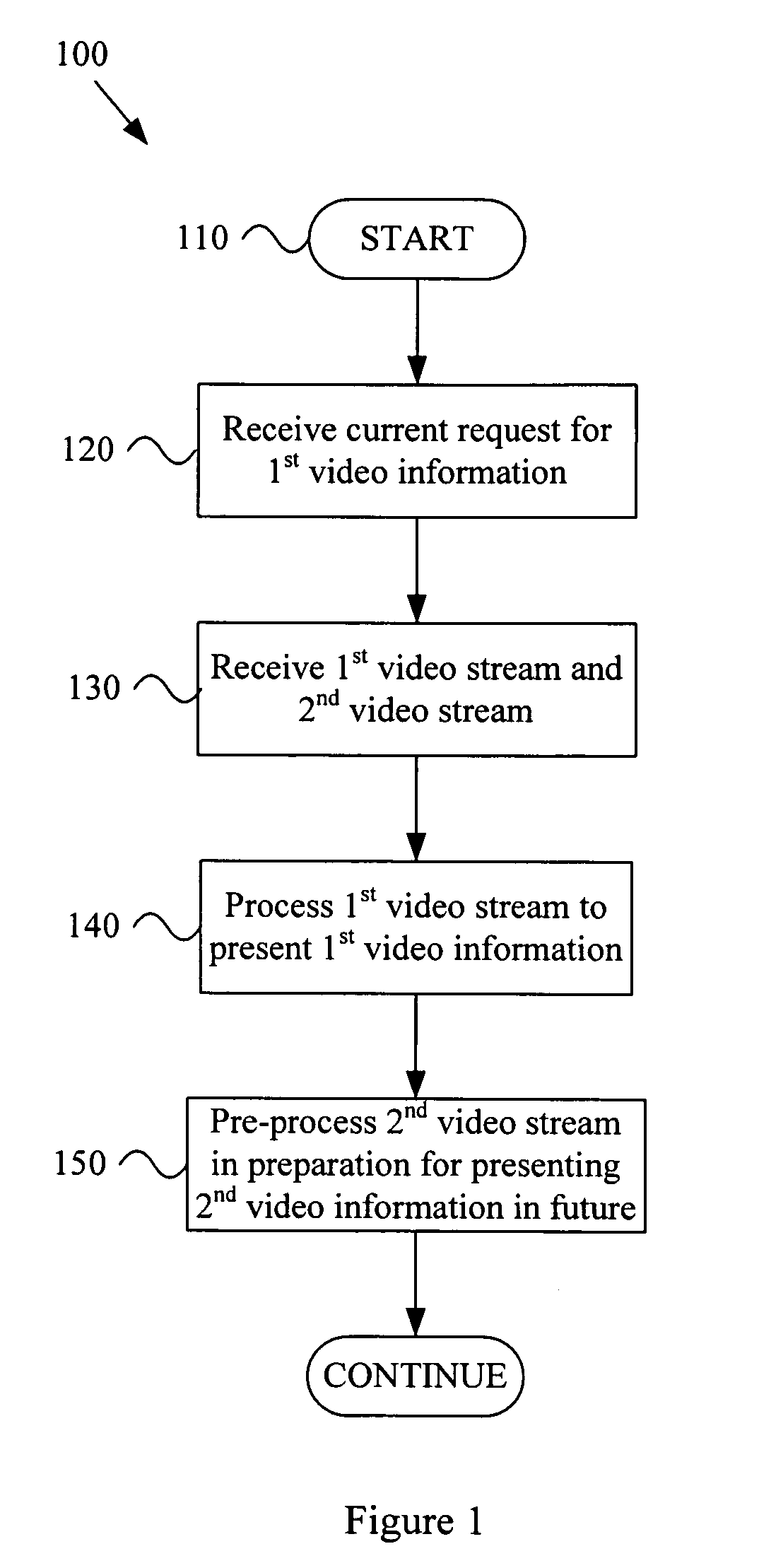
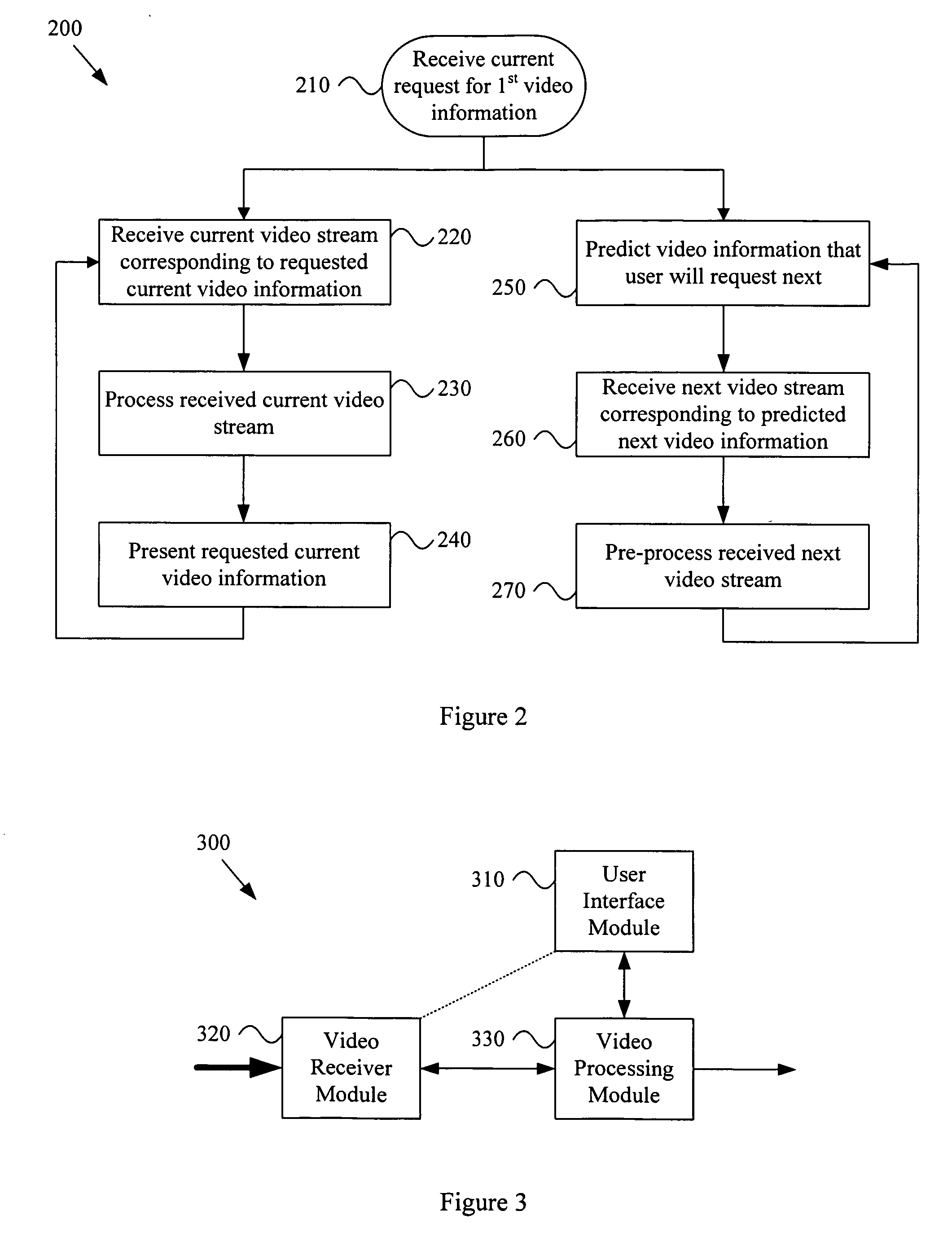
ActiveUS20050216951A1Reduce latencyLower latencyTelevision system detailsAnalogue secracy/subscription systemsCurrent timeComputer graphics (images)
A system and method that provide reduced latency in a video signal processing system. Various aspects of the present invention may comprise receiving a current request from a user for first video information. Such a request may, for example, be received with a user interface module. A first video stream and a second video stream may be received simultaneously, where the first video stream comprises the first video information currently requested by the user, and the second video stream comprises second video information not currently requested by the user. A video receiver module may, for example, perform such receiving. The first video stream may be processed to present the first video information to the user at the current time. Further, the second video stream may be pre-processed in preparation for being presented to the user in the future. A video processing module may, for example, perform such video stream processing.
Owner:AVAGO TECH INT SALES PTE LTD
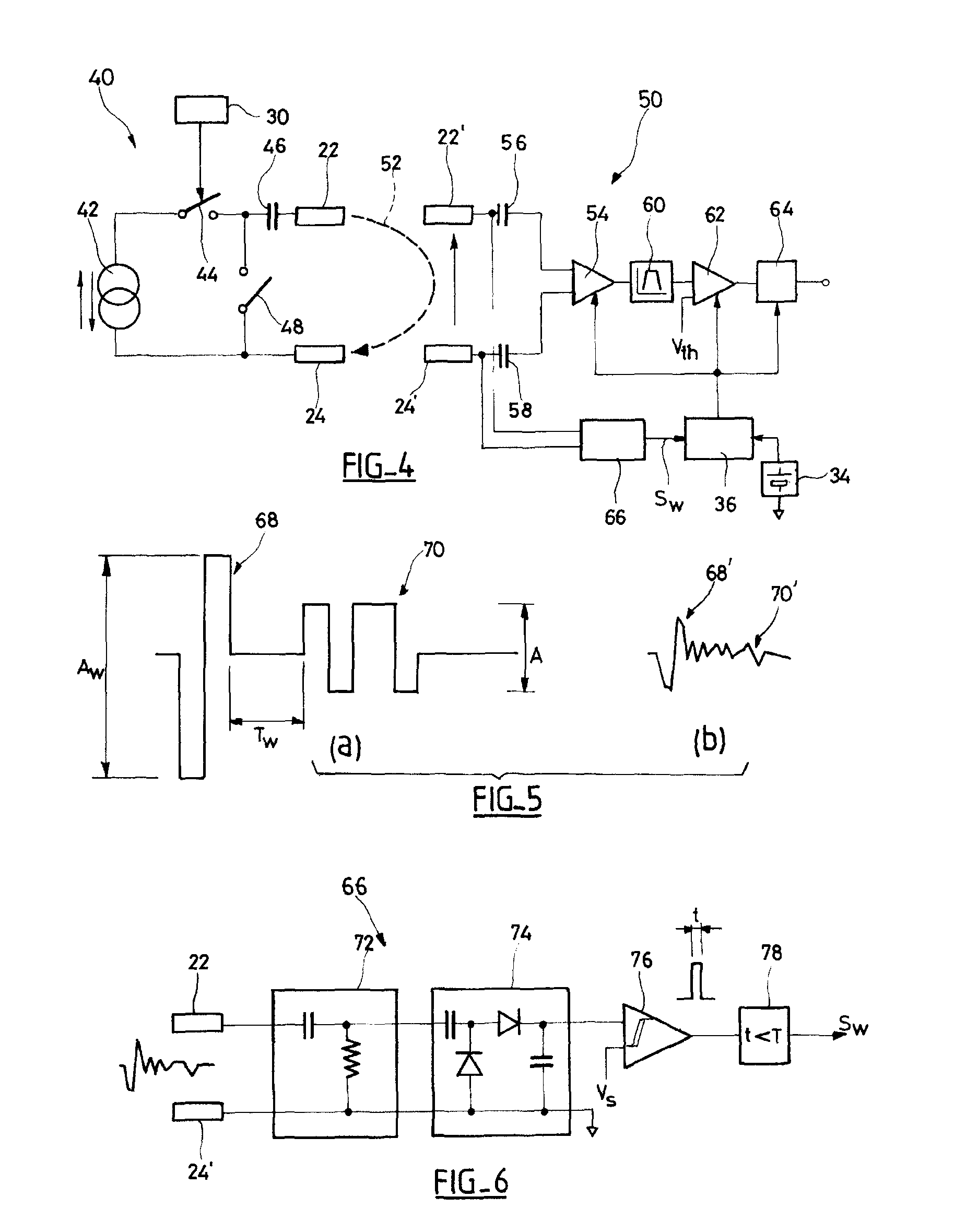
System, methods and apparatus for waking an autonomous active implantable medical device communicating by pulses transmitted through the interstitial tissues of the body
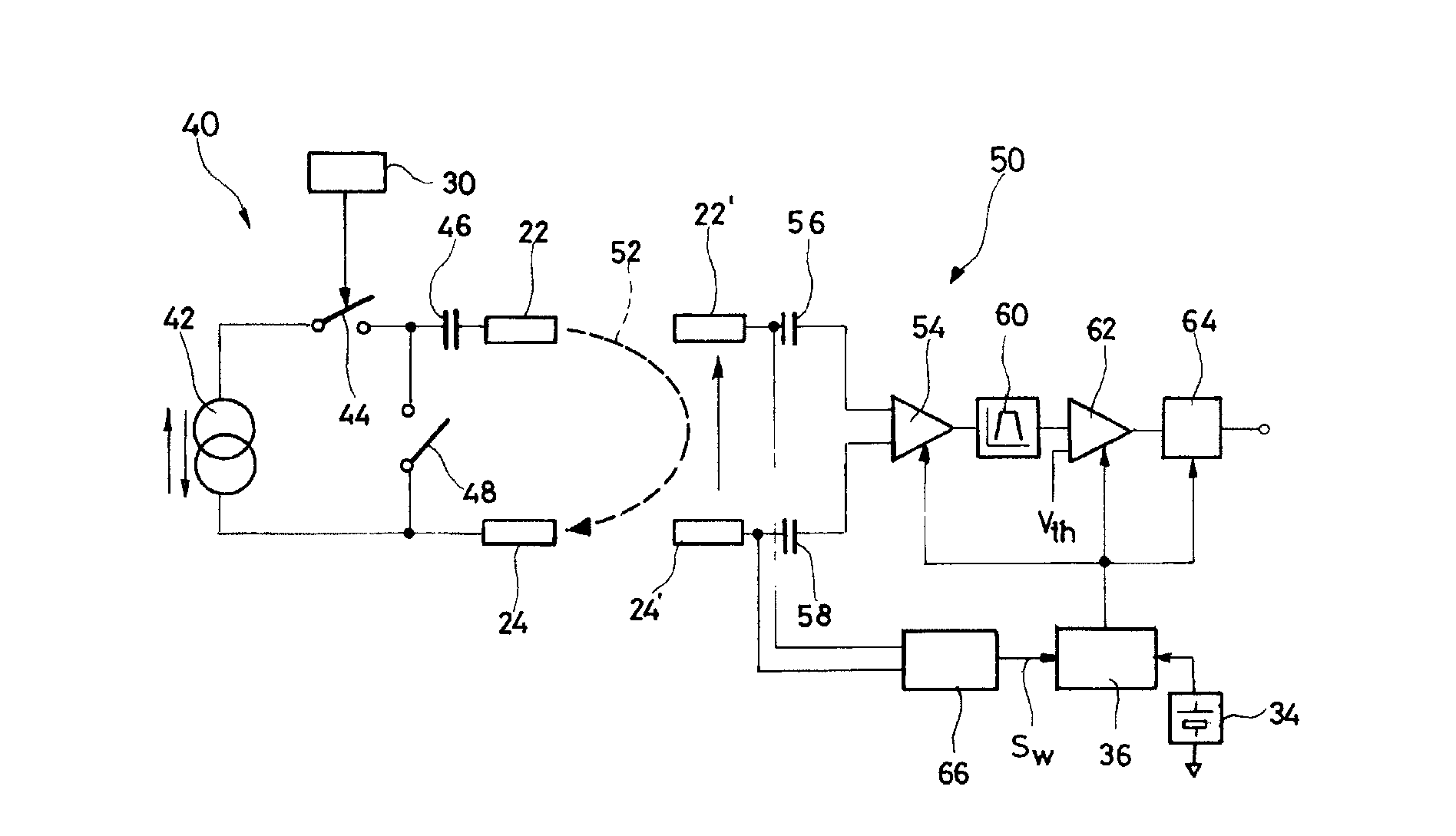
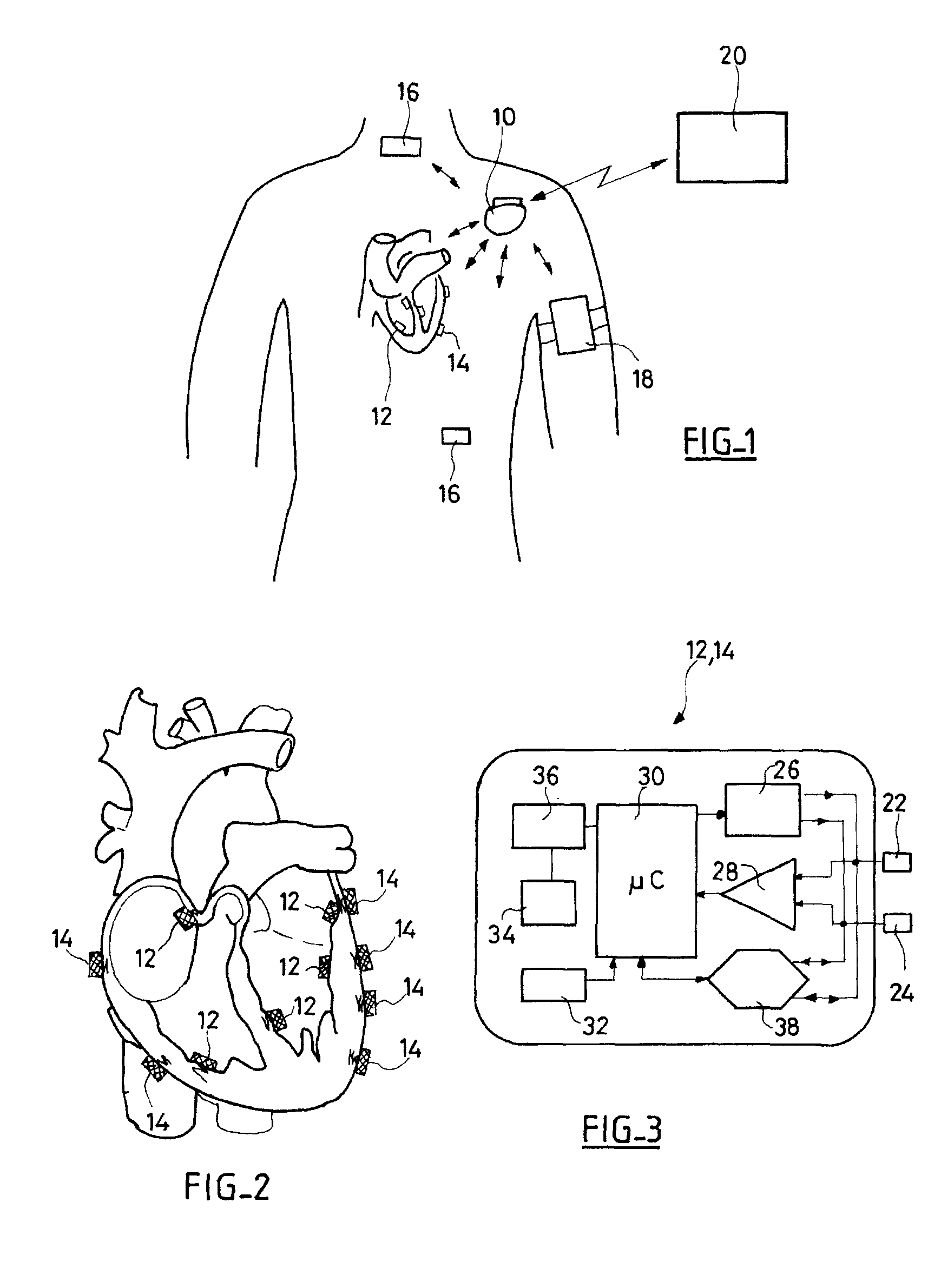
ActiveUS8577327B2Minimum delayImprove responsivenessElectrotherapyModulated-carrier systemsSleep statePulse sequence
An autonomous active medical implantable device, with a power supply and a wake-up circuit that responds to receipt of specific pulses transmitted through the interstitial tissues of the body. A transmitter device (40) generates trains of modulated pulses applied to electrodes (22, 24), and a receiver (50) processes (e.g., filter, amplify and demodulate) pulses collected on electrodes (22′, 24′). The receiver circuits (50) are selectively activated from a dormant (sleep) state in which they are not powered by a power source (34), to an operational (active) state in which they are powered and able to process (e.g., filter, amplify and demodulate) the collected pulses. A specific wake-up pulse train, configured in a predetermined characteristic pulse pattern, triggers passive wake-up circuits (66) in the receiver (50) to switch the receiver circuits from the sleep state to the operational state.
Owner:SORIN CRM
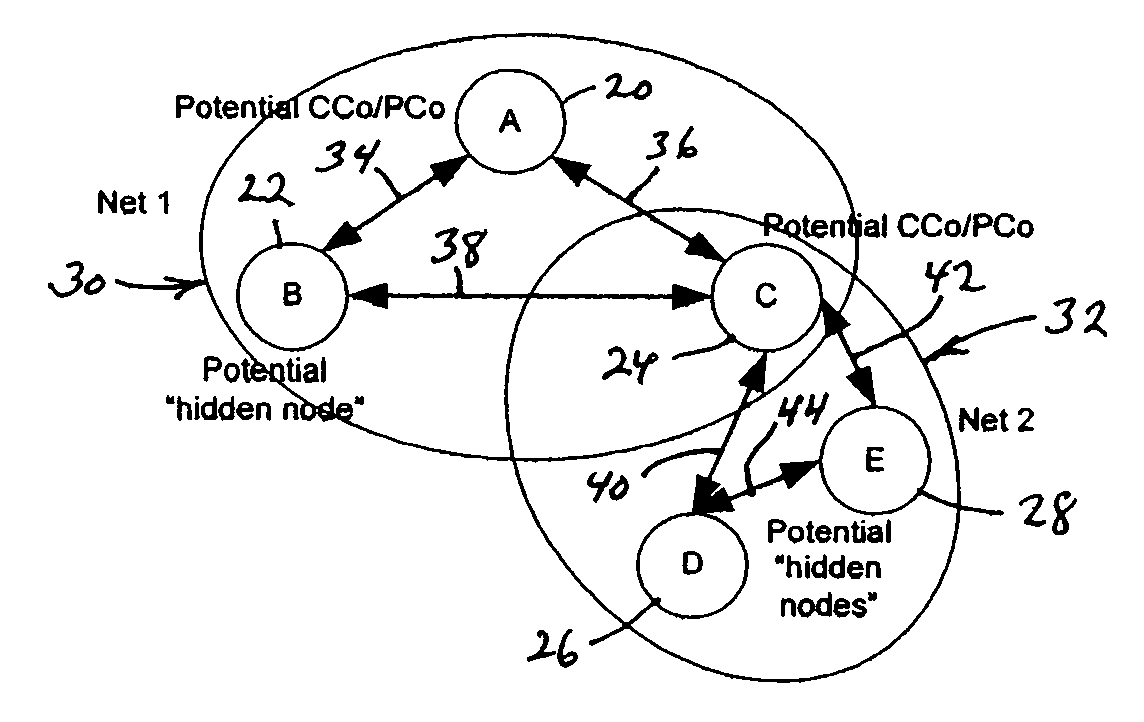
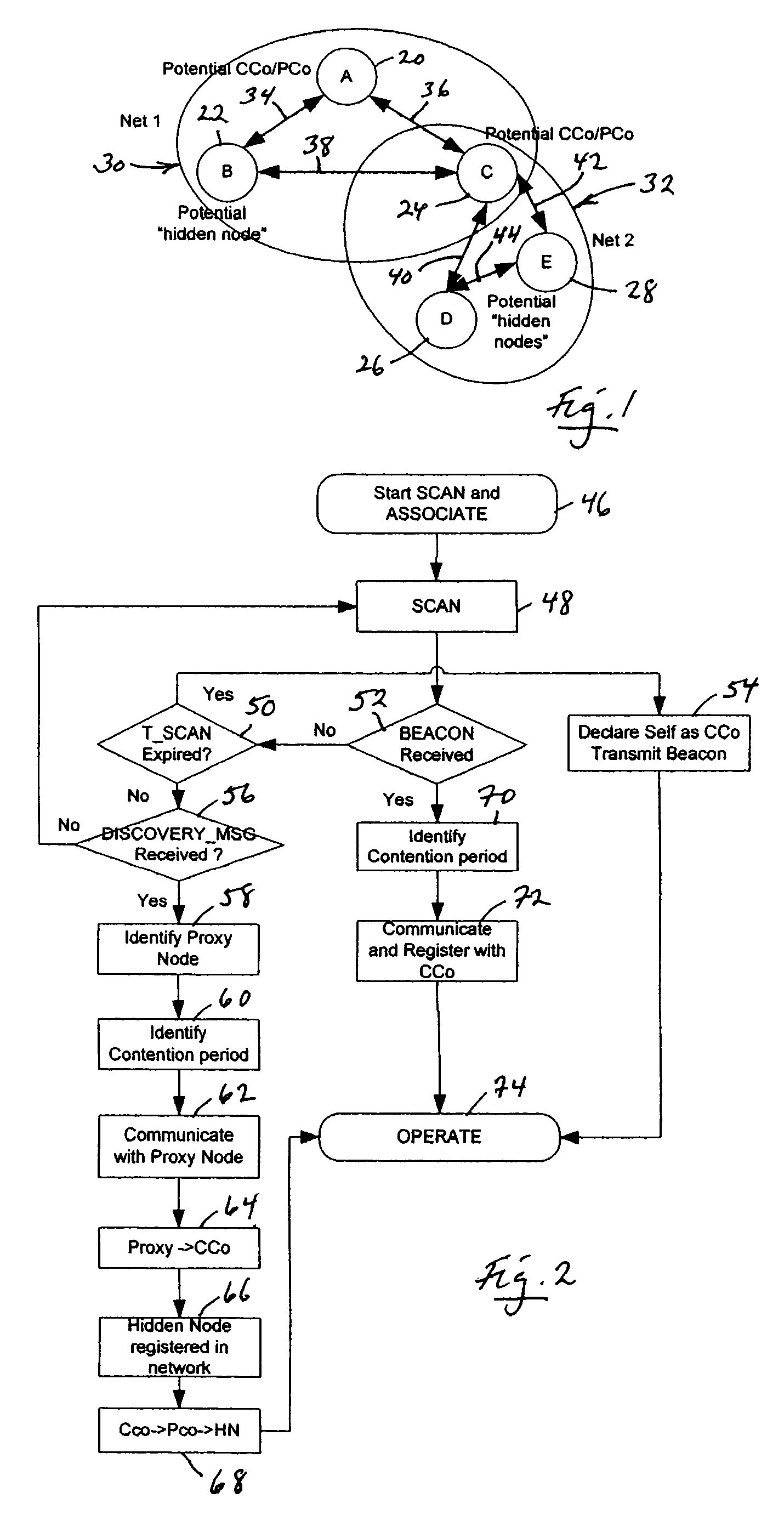
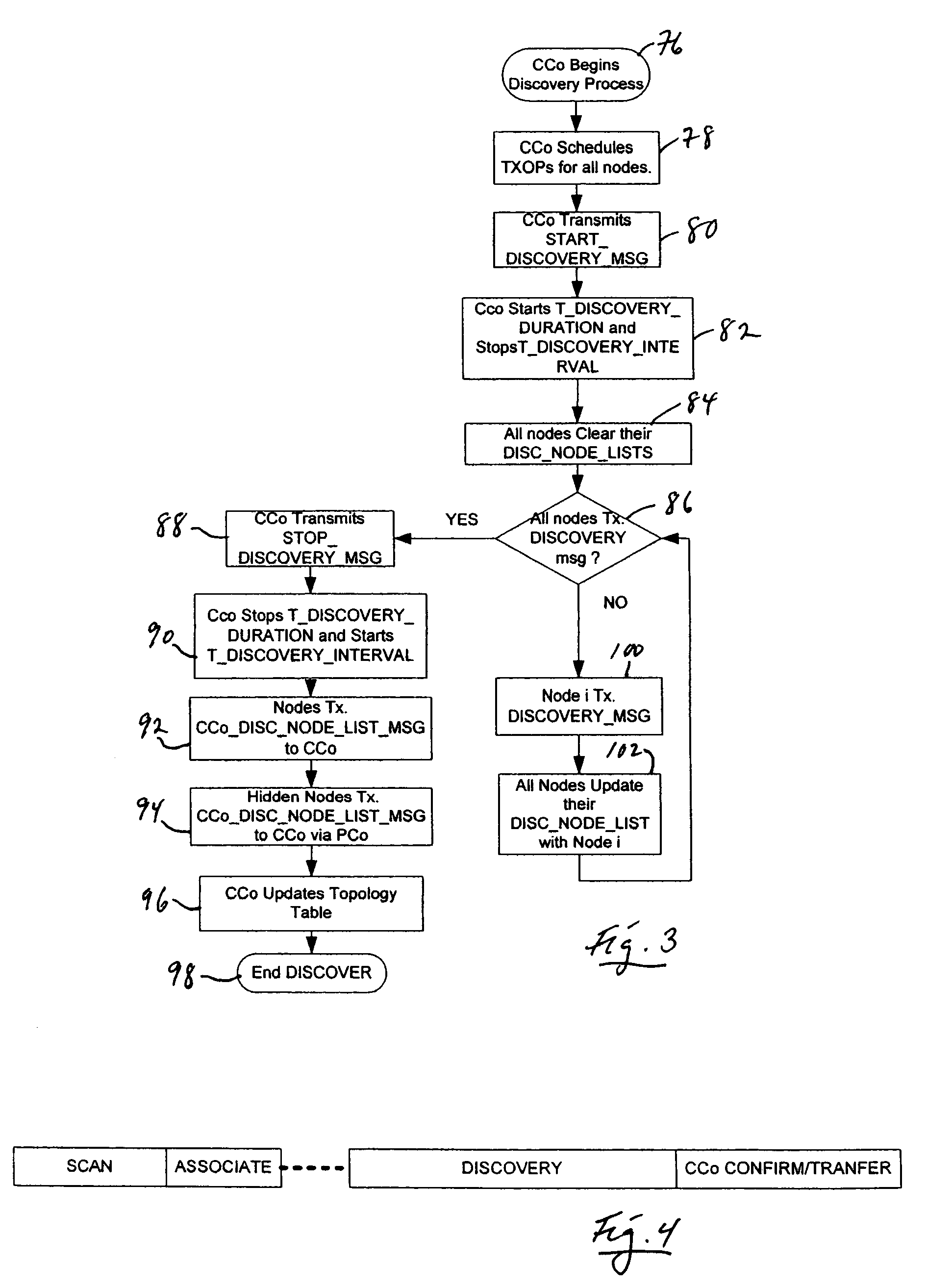
Centralized network organization and topology discover in Ad-Hoc network with central controller
ActiveUS7342896B2Least overheadOptimal configurationData switching by path configurationTopology tableDistributed computing
A method for the self-organization of a plural-node communication network which involves (1) selecting a central coordinator (CCo) node from a collection of nodes initially lacking a CCo, (2) employing the selected CCo to oversee a procedure for discovering, from the mentioned node collection, all nodes which are optimally capable of being organized into a network, in the sense that all such discovered, capable nodes may effectively be organized to communicate bidirectionally with all other nodes, and (3), with respect to such discovered, organizable nodes, creating a network-global connectivity database in the form of a network-organizing communication topology table that describes enablement of bidirectional communication between all nodes. The discovering process includes discovering both non-hidden and hidden nodes, and identifying suitable proxy nodes which are non-hidden nodes, and which may effectively stand as intermediaries for enabling bidirectional communications between these otherwise hidden nodes and all other nodes, including, of course, the CCo.
Owner:SHARP KK
Network protocol for wireless broadband-ISDN using ATM
InactiveUS6151312AInterference minimizationMinimum delaySynchronisation arrangementError preventionNetworking protocolIntegrated Services Digital Network
A network protocol for the delivery of wireless broadband integrated services digital network (ISDN) using asynchronous transfer mode (ATM).
Owner:ALCATEL USA SOURCING
Communications network with wireless gateways for mobile terminal access
InactiveUS7092369B2Noise signalMinimum delayMultimedia data retrievalConnection managementWireless gatewayComputer science
Access to a communications network is provided to a user supporting a mobile unit capable of wireless communication with at least one access node of a local area network that is capable of connecting to the communications network. Initially, wireless communication is established between the mobile unit and the access node by associating the mobile unit with the access node. The user of the mobile unit is authenticated to enable access to the communications network. Communication with a destination on the communications network is then established, and at least some session particulars are recorded of a communications session during which the mobile unit communicates with the destination on a server on the network.
Owner:SYMBOL TECH LLC
Reliable, high-throughput, high-performance transport and routing mechanism for arbitrary data flows
ActiveUS7660296B2Minimum delayImprove performanceTime-division multiplexData switching by path configurationData streamEdge node
The present invention leverages an existing content delivery network infrastructure to provide a system that enhances performance for any application that uses the Internet Protocol (IP) as its underlying transport mechanism. An overlay network comprises a set of edge nodes, intermediate nodes, and gateway nodes. This network provides optimized routing of IP packets. Internet application users can use the overlay to obtain improved performance during normal network conditions, to obtain or maintain good performance where normal default BGP routing would otherwise force the user over congested or poorly performing paths, or to enable the user to maintain communications to a target server application even during network outages.
Owner:AKAMAI TECH INC
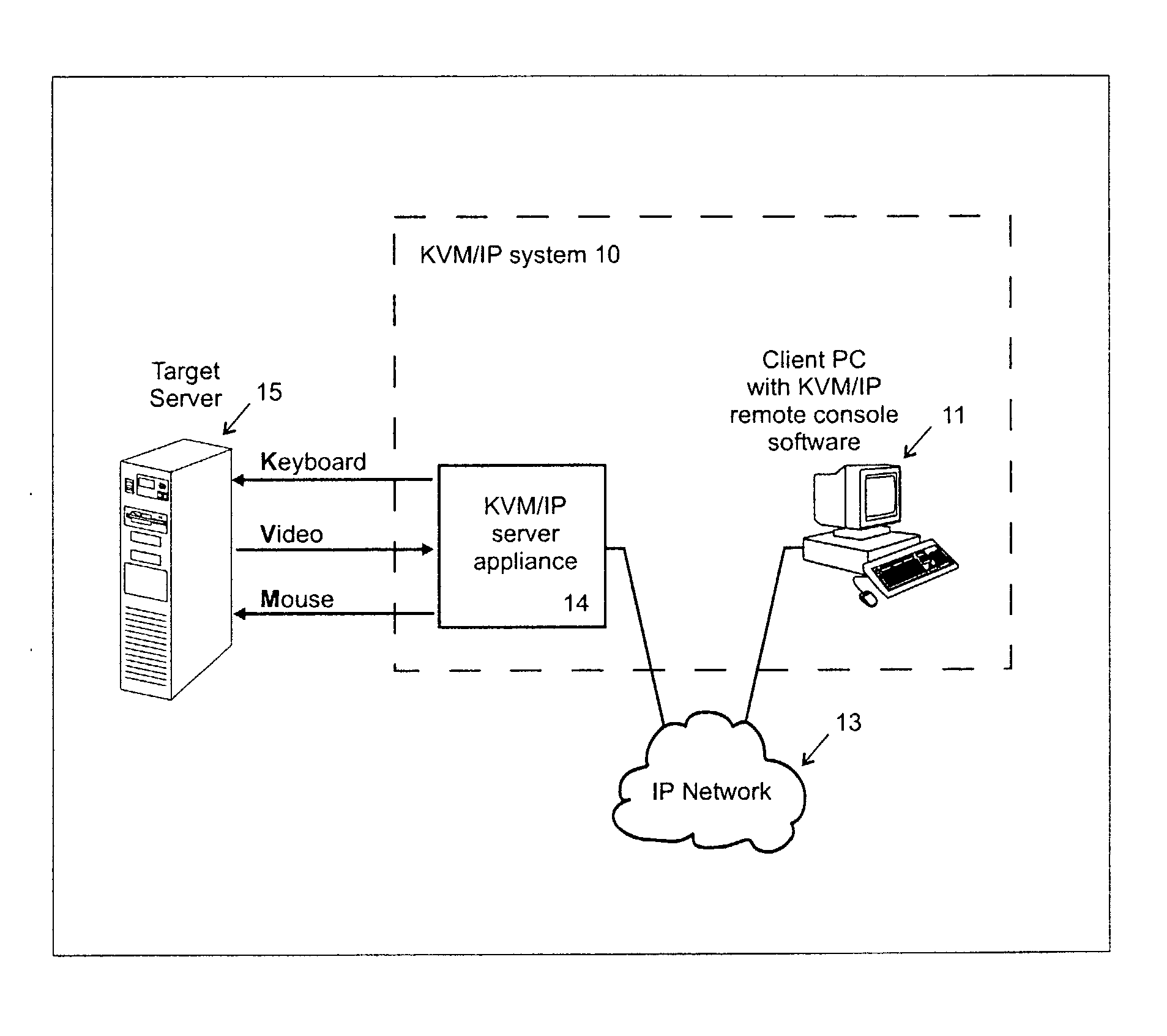
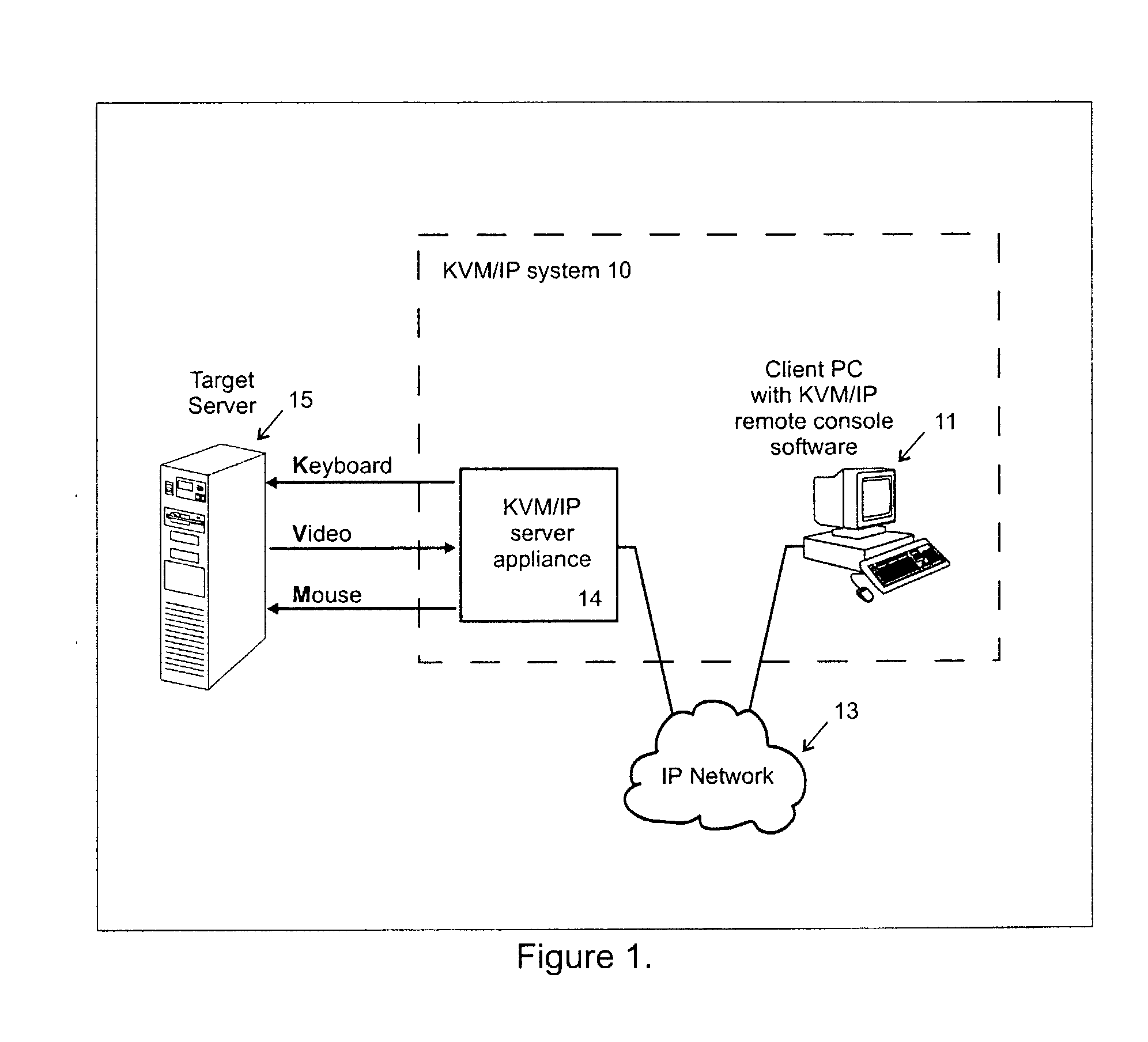
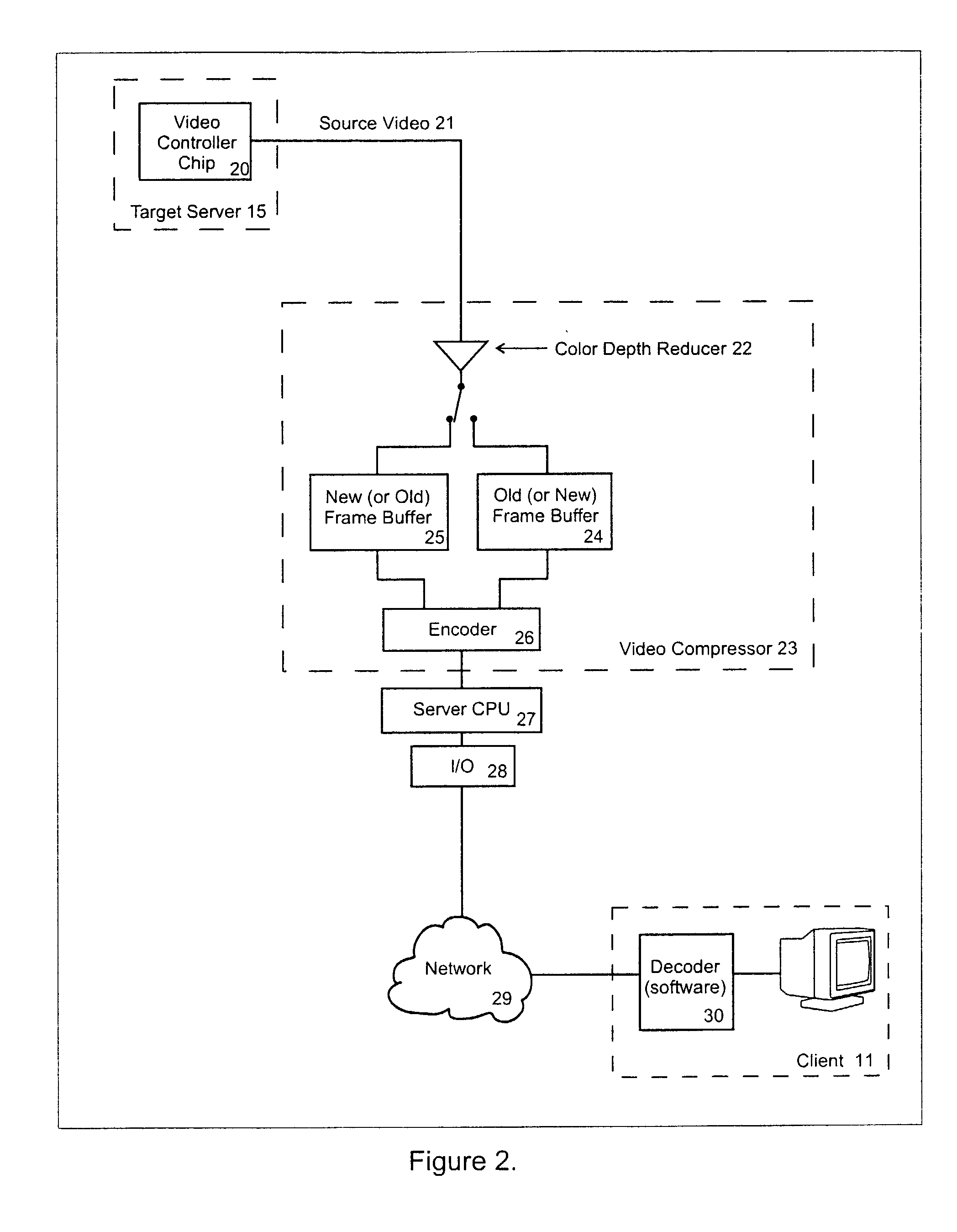
Video compression system
ActiveUS20050069034A1Efficient captureMinimum delayStatic indicating devicesPicture reproducers using cathode ray tubesComputer usersComputer graphics (images)
A video compression system is disclosed that is optimized to take advantage of the types of redundancies typically occurring on computer screens and the types of video loss acceptable to real time interactive computer users. It automatically adapts to a wide variety of changing network bandwidth conditions and can accommodate any video resolution and an unlimited number of colors. The disclosed video compression encoder can be implemented with either hardware or software and it compresses the source video into a series of data packets that are a fixed length of 8 bits or more. Sequences of one or more of these packets create unique encoding “commands” that can be sent over any network and easily decoded (decompressed) with either software or hardware. The commands include 3 dimensional copying (horizontal, vertical and time) and unique efficiencies for screen segments that are comprised of only two colors (such as text). Embodiments are also disclosed that improve the video compression depending on the popularity of pixel colors.
Owner:VERTIV IT SYST INC
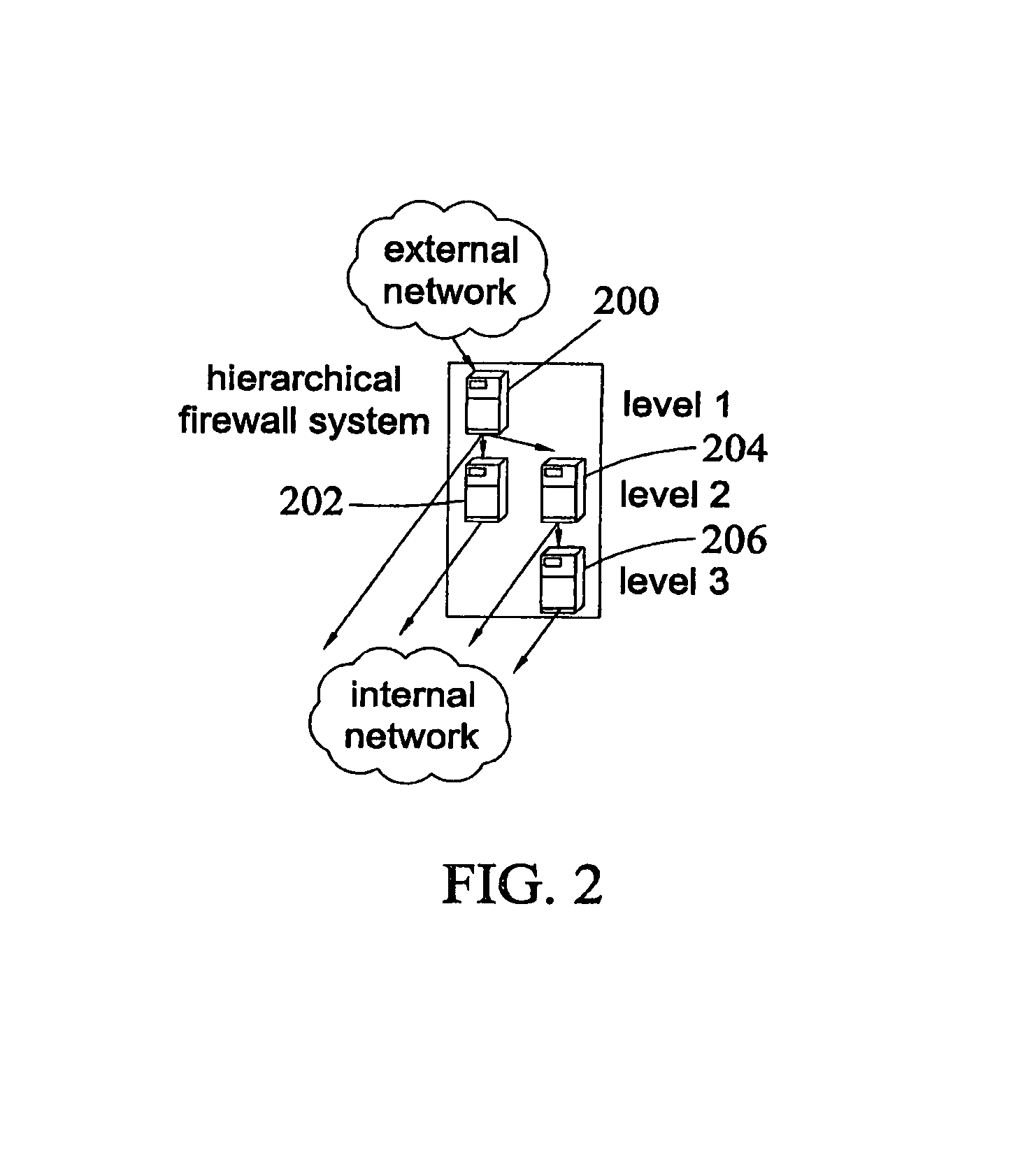
Method, systems, and computer program products for implementing function-parallel network firewall
ActiveUS8037517B2Reduce impactMinimum delayMemory loss protectionDigital data processing detailsRule setsComputer program
Methods, systems, and computer program products for providing function-parallel firewalls are disclosed. According to one aspect, a function-parallel firewall includes a first firewall node for filtering received packets using a first portion of a rule set including a plurality of rules. The first portion includes less than all of the rules in the rule set. At least one second firewall node filters packets using a second portion of the rule set. The second portion includes at least one rule in the rule set that is not present in the first portion. The first and second portions together include all of the rules in the rule set.
Owner:WAKE FOREST UNIV
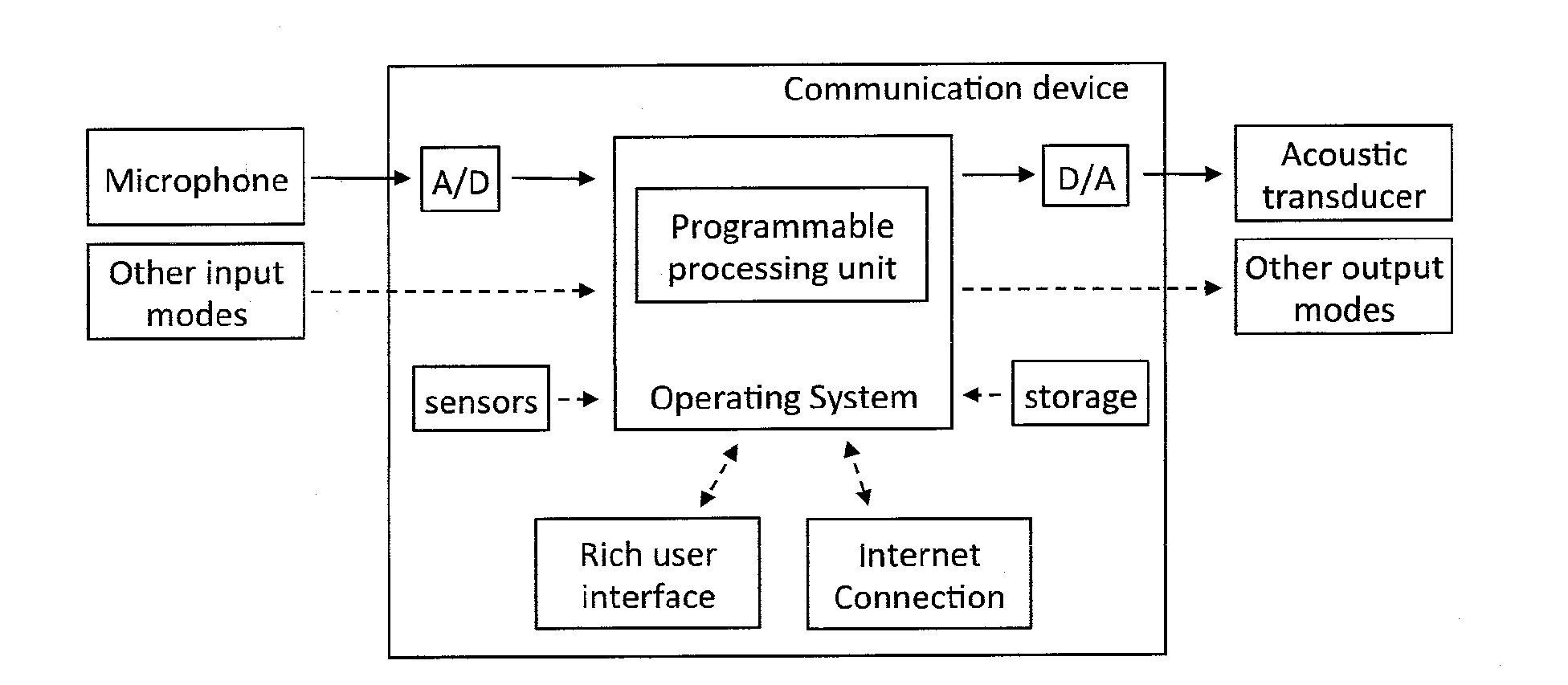
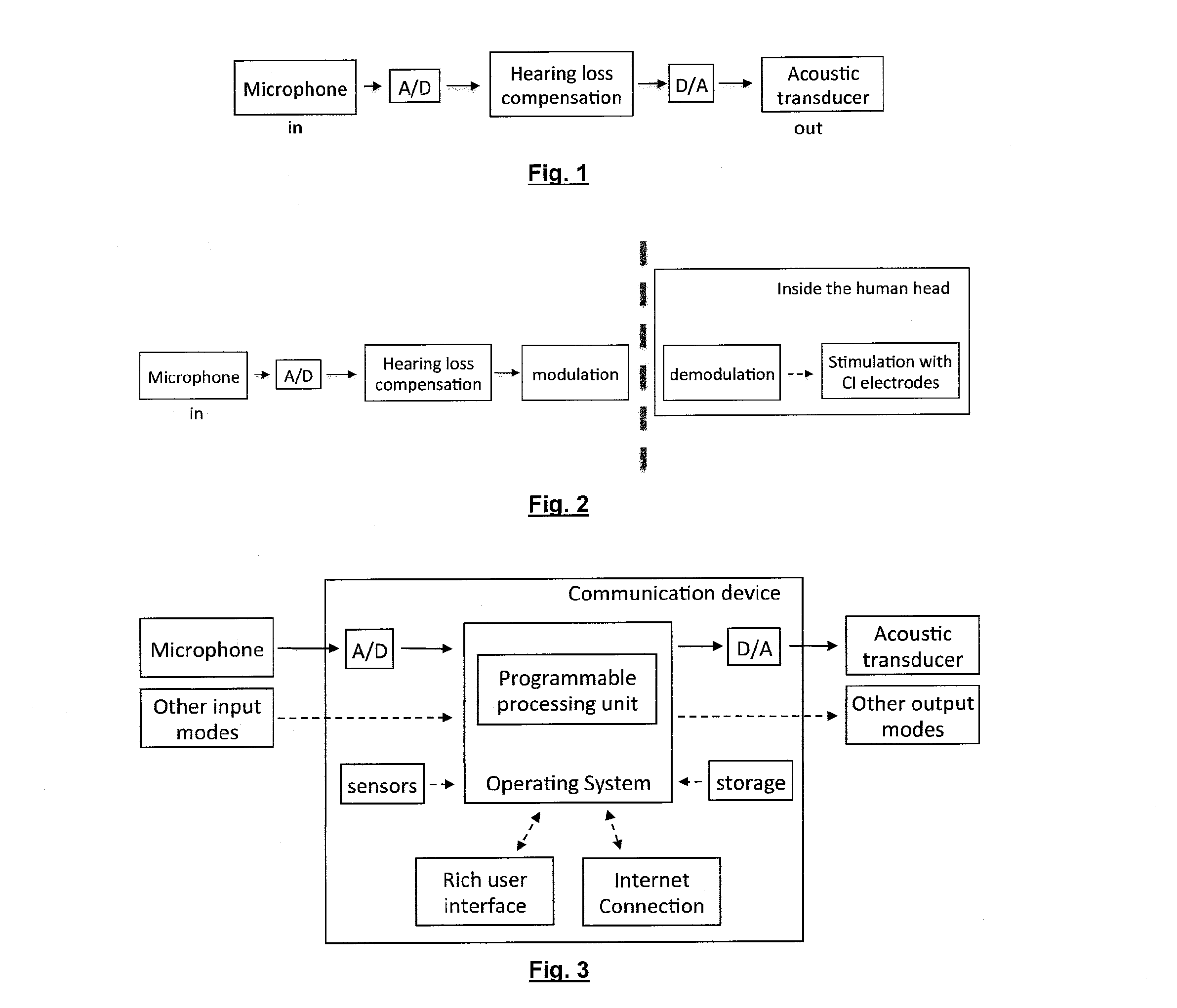
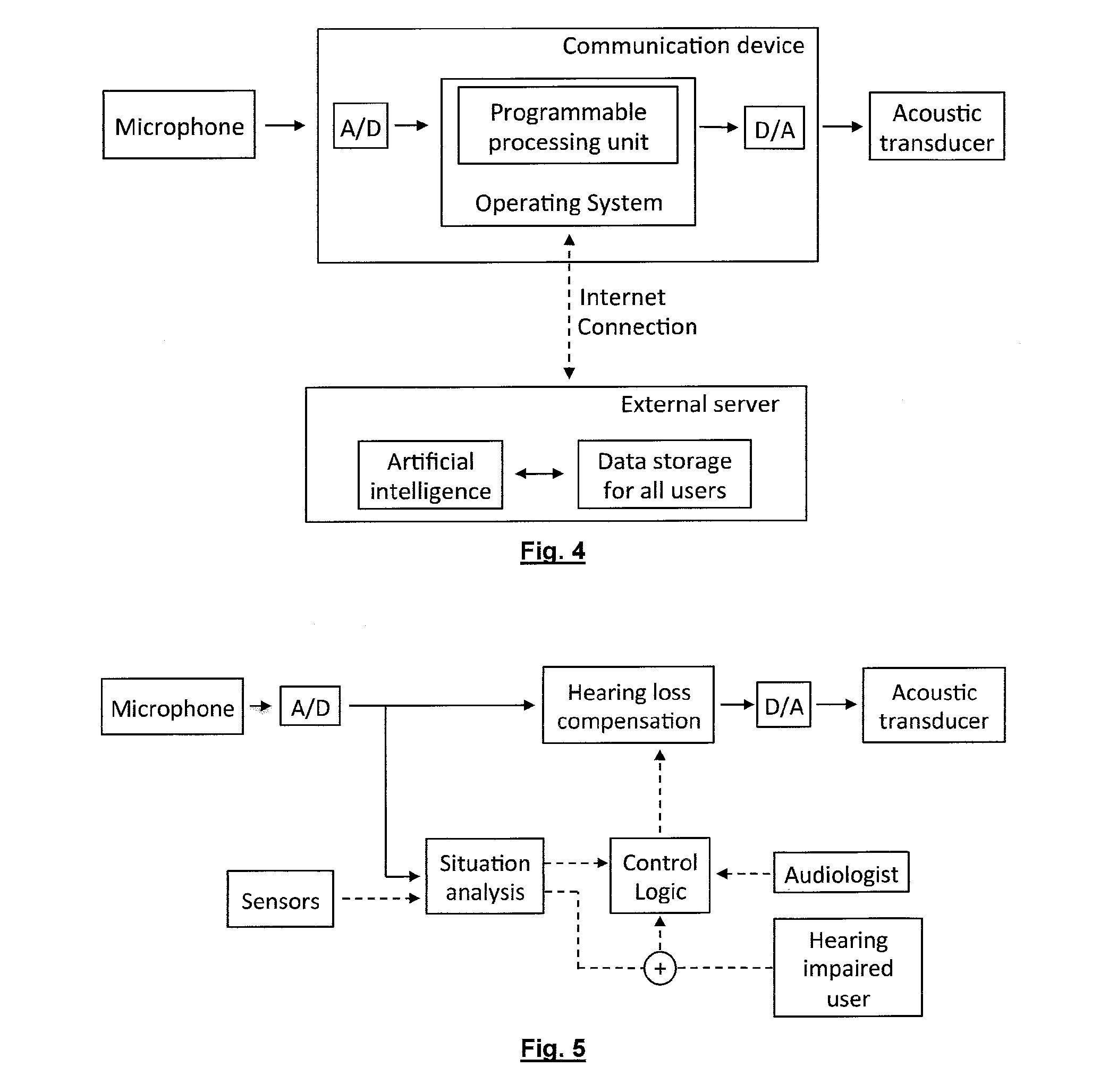
Personal communication device with hearing support and method for providing the same
ActiveUS20130243227A1Minimal signal delaySufficient flexibilityPublic address systemsSubstation equipmentComputer scienceAudio frequency
A personal communication device provides hearing support, and includes an input receiving an audio signal, a programmable processor, and an output outputting the processed signal. The programmable processor performs a filtering operation on a digital version of the audio signal in a first signal path based on parameter settings and provides control logic that determines the parameter settings based on information on user preferences, on audiological information and on information on the listening situation to provide hearing loss compensation. The programmable processor has a second signal path in parallel with the first signal path that receives the digital version of the audio signal and parameter settings and determining the filter coefficients of the filtering operation based on the parameter settings and the digital version of the audio signal.
Owner:JACOTI
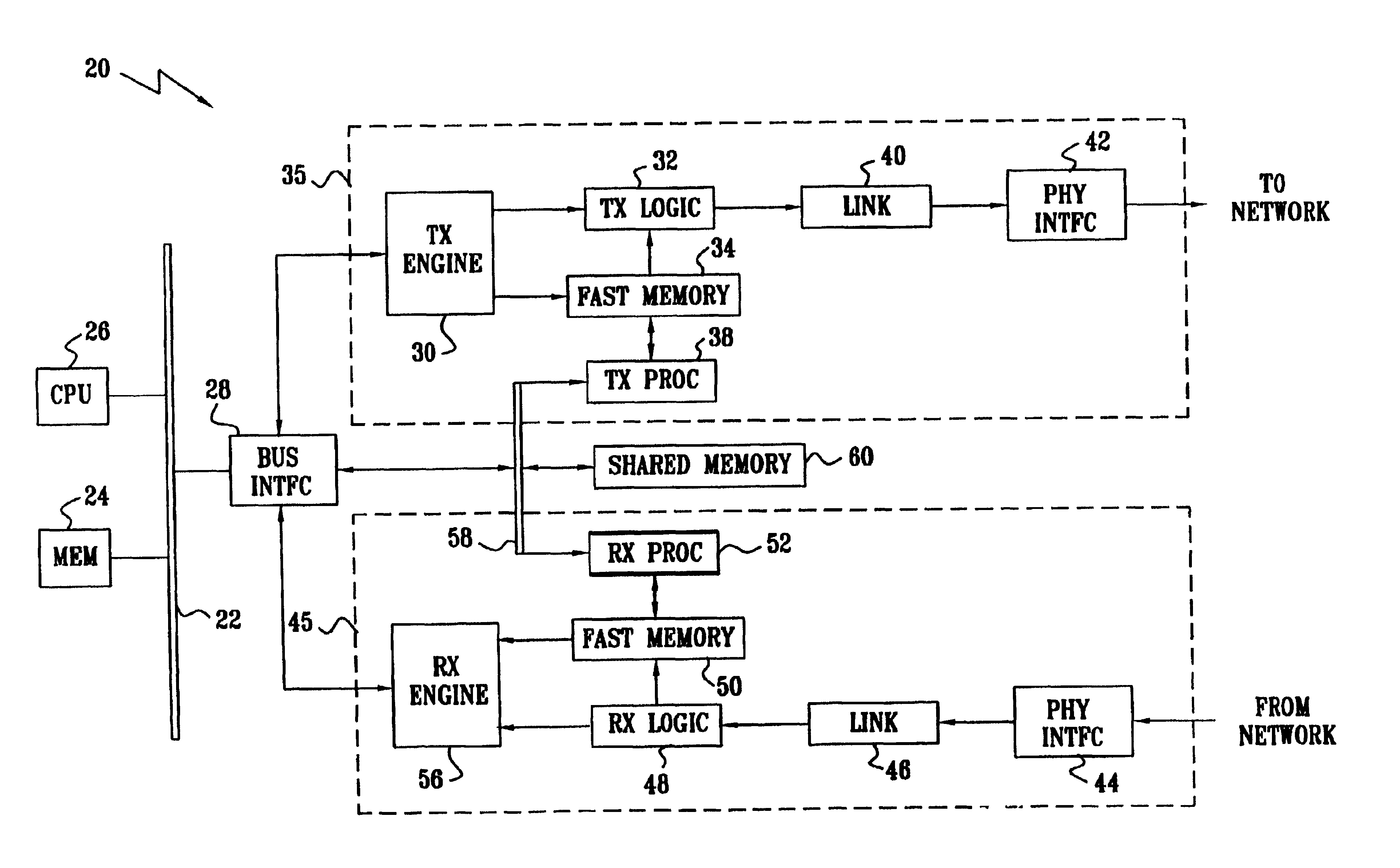
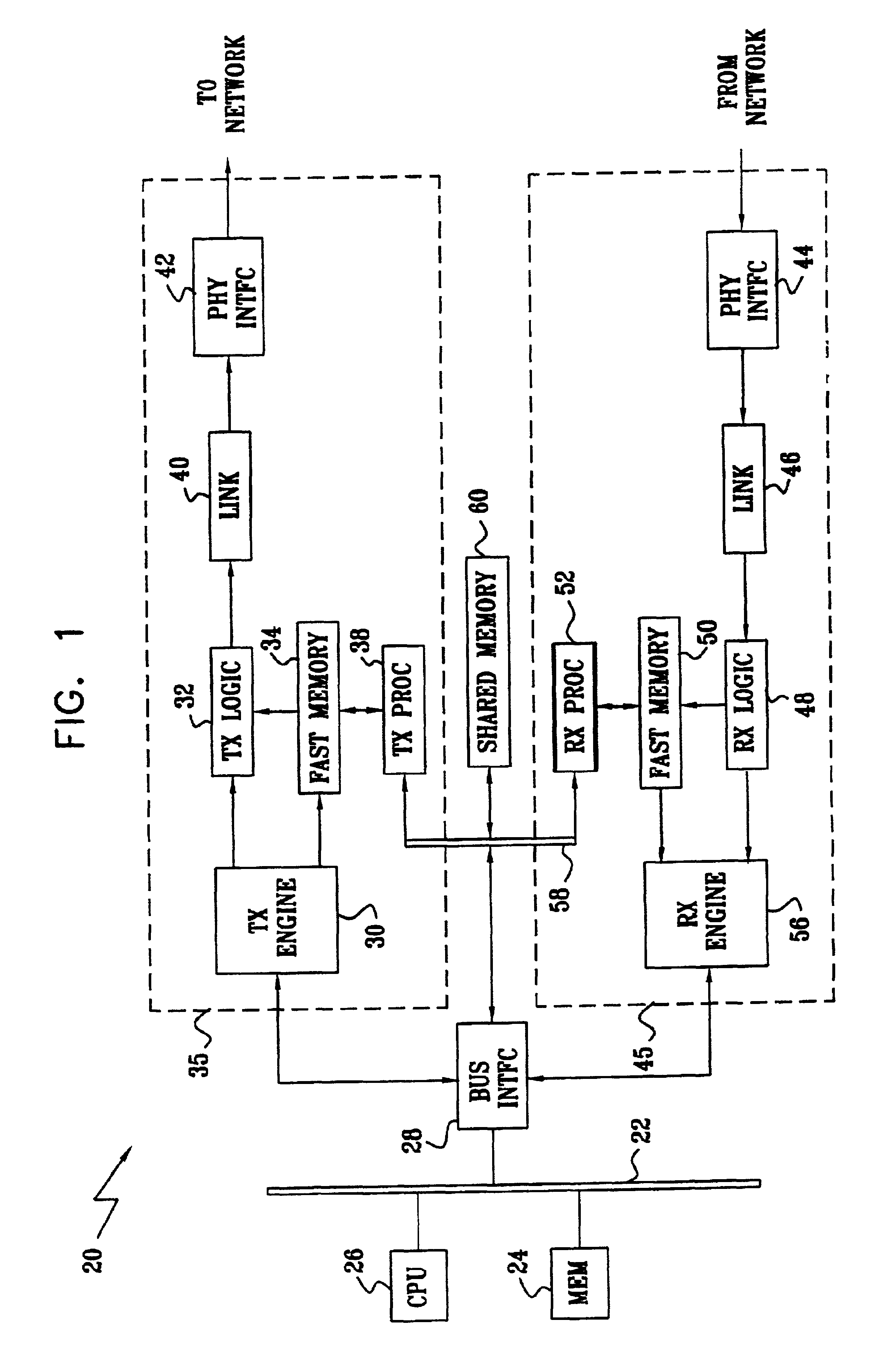
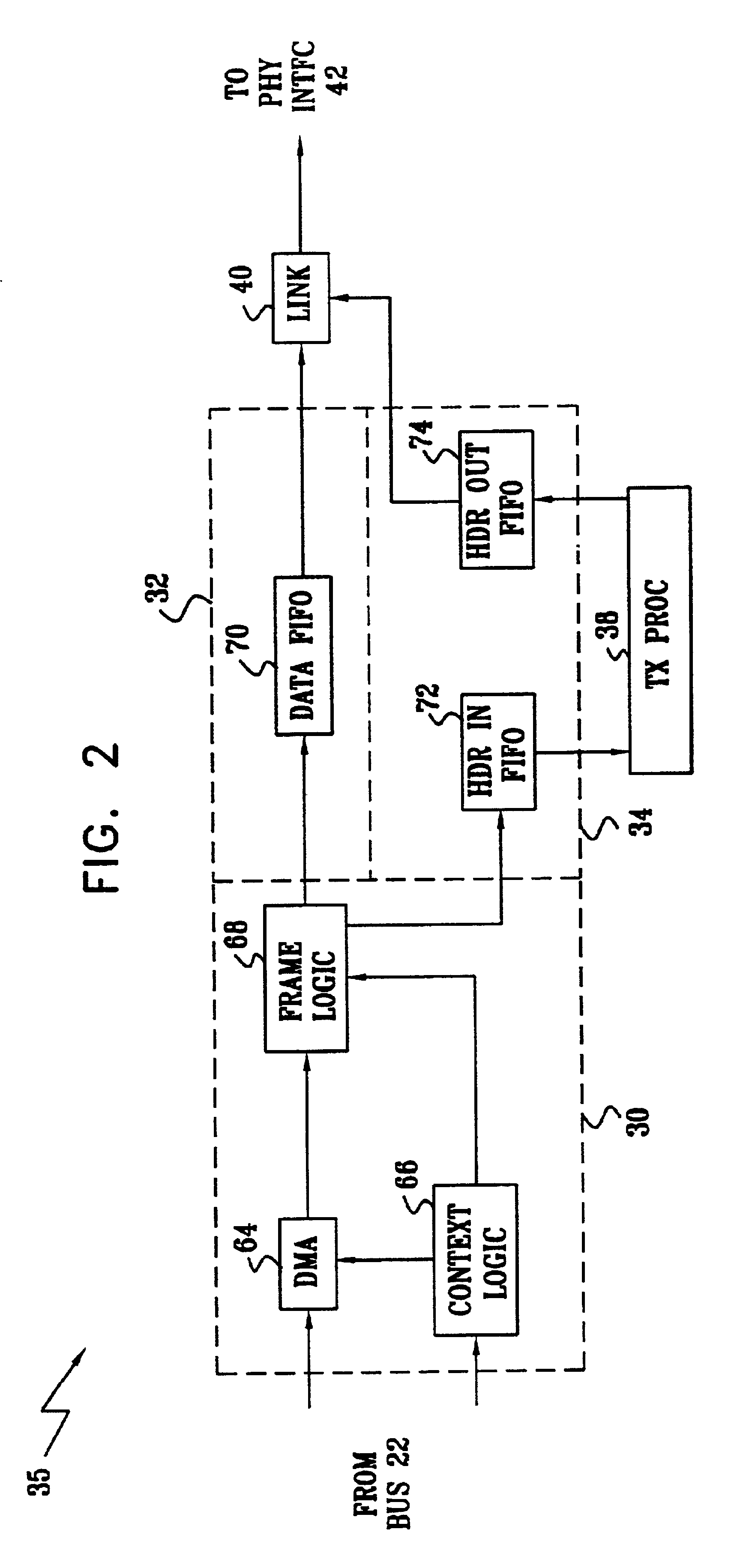
Network adapter with embedded deep packet processing
InactiveUS6947430B2Raise transfer toIncrease speedTime-division multiplexData switching by path configurationProtocol processingNetwork interface device
A network interface device includes host interface logic, arranged to receive from a host processor a frame of outgoing data that includes outgoing header information and outgoing payload data, and to separate the header information from the payload data. A transmit protocol processor is coupled to read and process the outgoing header information from the outgoing header memory so as to generate at least one outgoing packet header in accordance with a predetermined network protocol. Transmit logic is coupled to receive and associate the at least one outgoing packet header with the outgoing payload data from the outgoing data memory, so as to generate at least one outgoing data packet for transmission over a network in accordance with the protocol.
Owner:IBM CORP
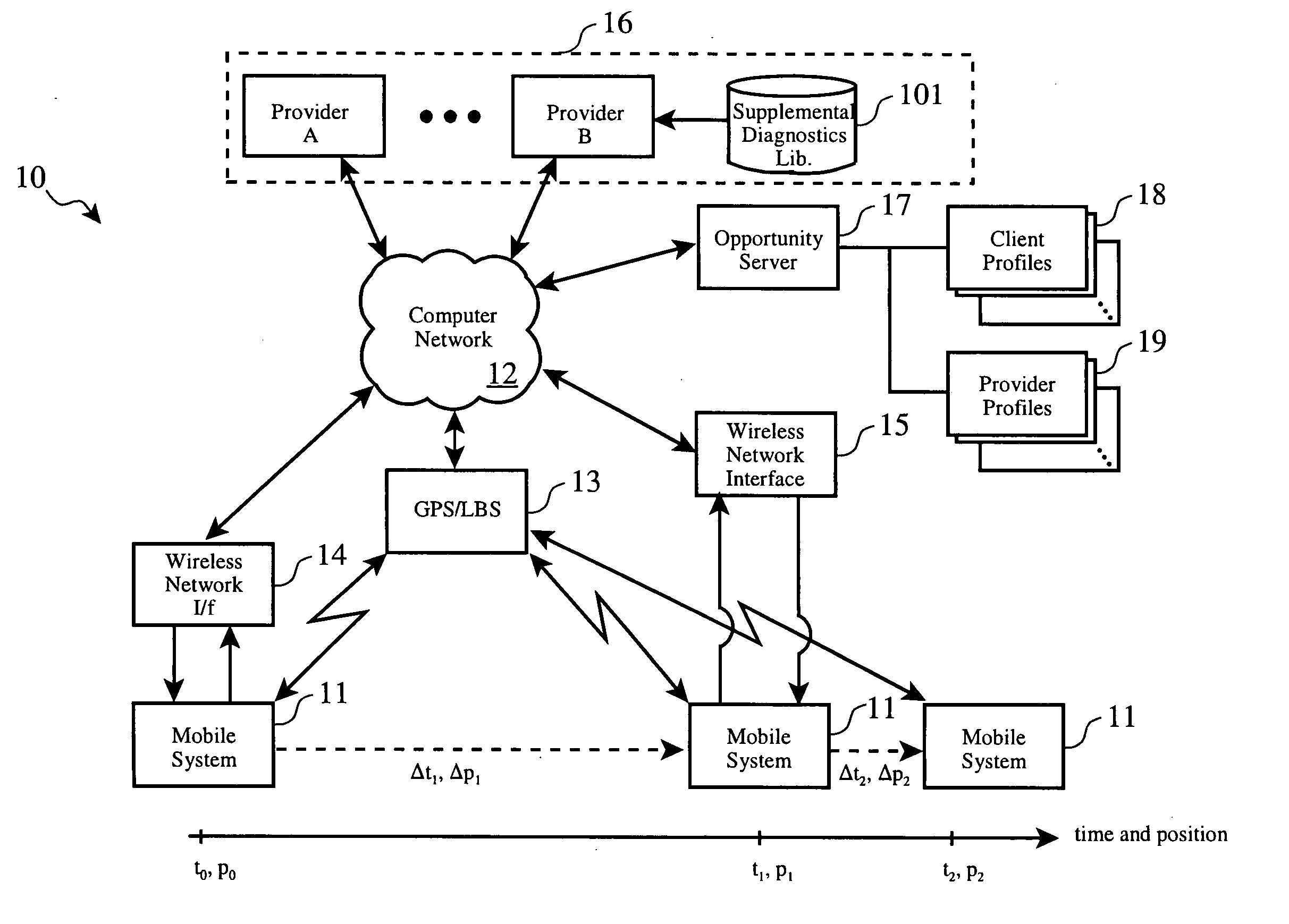
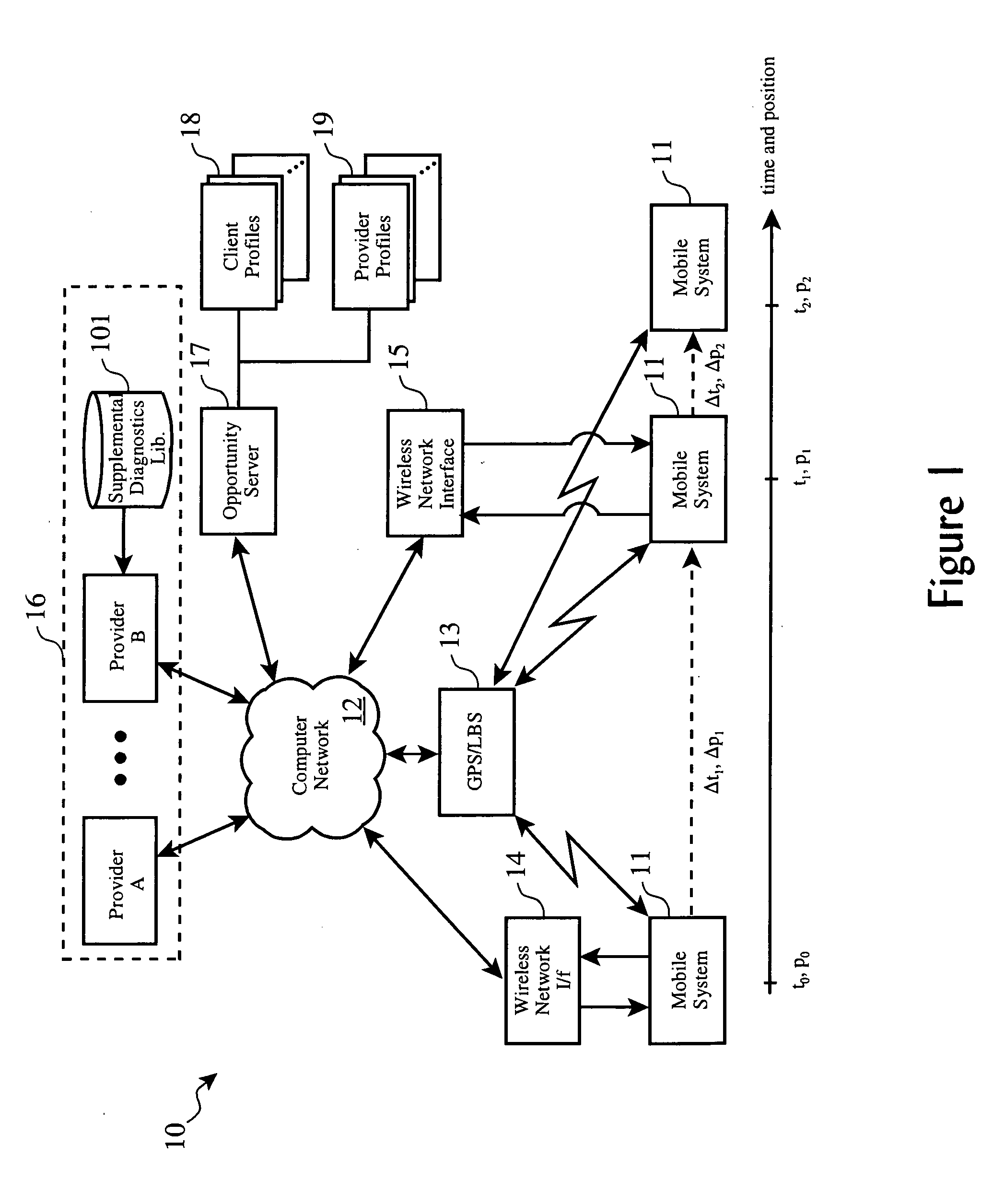
On-demand system for supplemental diagnostic and service resource planning for mobile systems
InactiveUS20060052921A1Minimum delayVehicle testingComplete banking machinesTransport systemService provision
In an on-demand computing environment, diagnostic codes from a vehicle or other system in transit are transmitted to an opportunity server, which forwards the codes to a supplemental diagnostic service provider. The diagnostic service provider determines if supplemental diagnostics software functions are available, and if so, downloads them to the vehicle. After executing the supplemental diagnostics, the vehicle reports updated codes to the opportunity server. Multiple cycles of selection, downloading and execution of supplemental diagnostics may be performed until fault isolation is achieved, following which the opportunity server issues requests for bids to potential repair service provides. Responding offers are received, coalesced and presented to the operator. The operator of the vehicle is presented with one or more coalesced offers, upon selection of which, a service is scheduled.
Owner:SLINGSHOT IOT LLC
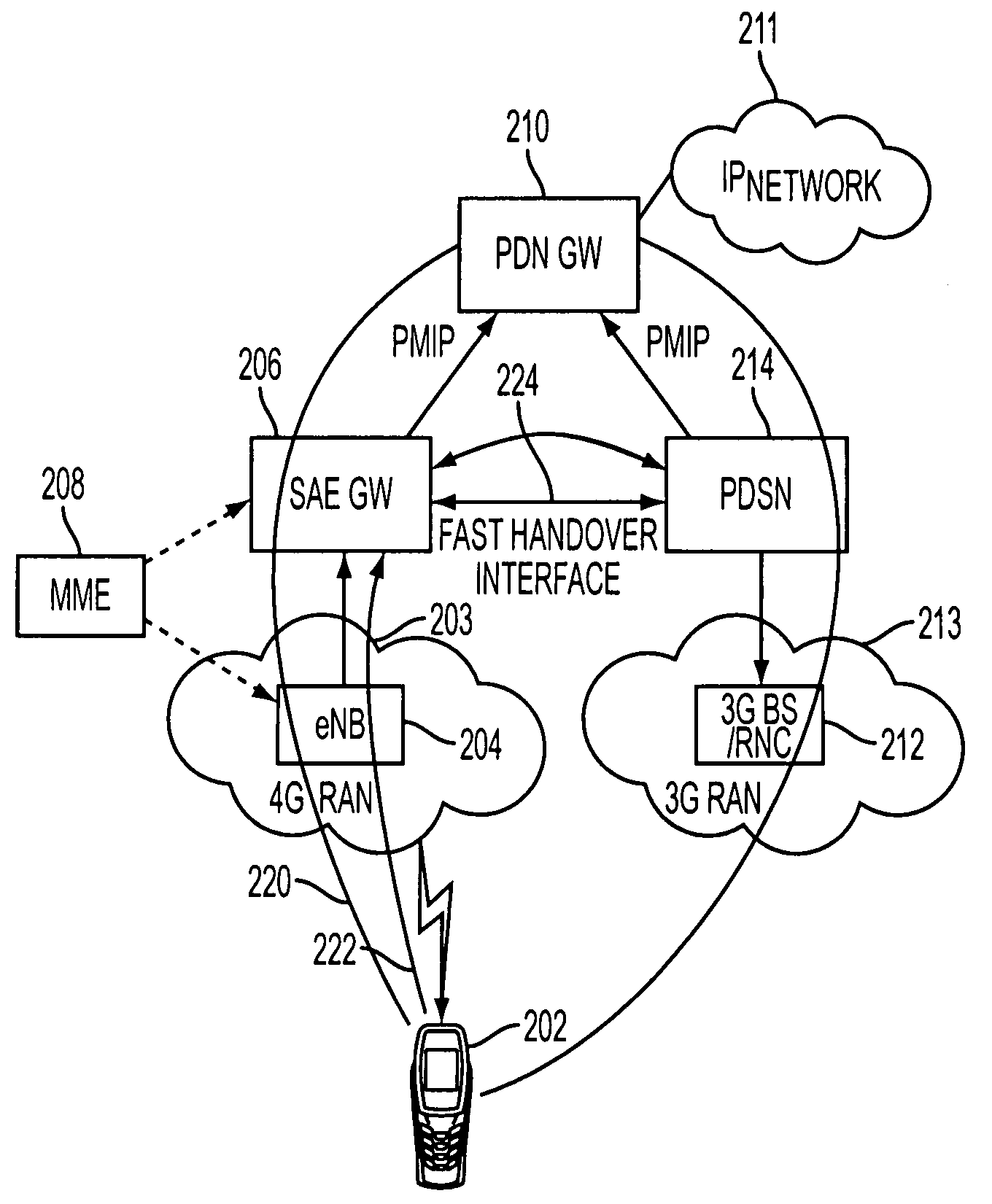
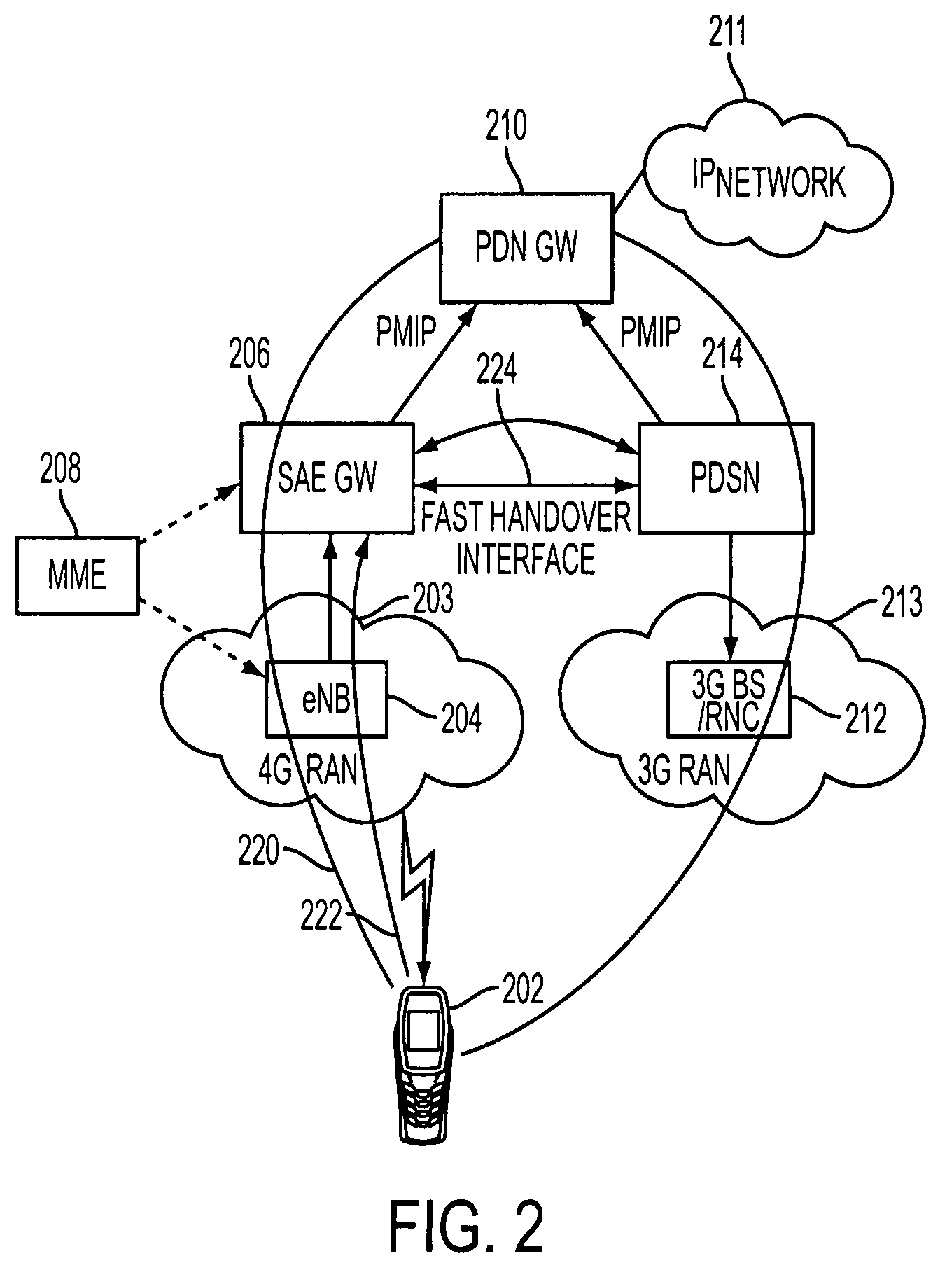
Low latency handover between wireless communication networks using different radio access technologies
ActiveUS20090201878A1Minimum delayRadio/inductive link selection arrangementsWireless commuication servicesRadio access technologyAccess network
A communications system for providing a user's mobile station (MS) with an Internet Protocol (IP) connectivity, has an IP network gateway for allocating an IP address to the MS to enable it to access an IP network. First and second base stations are respectively configured to support communications of the MS over first and second radio access networks using different radio access technologies. A first access gateway provides an interface between the IP network gateway and the first radio access network, whereas a second access gateway provides an interface between the IP network gateway and the second radio access network. A handover interface is provided between the first access gateway and the second access gateway for enabling the MS to switch between the first and second radio access networks with minimum latency.
Owner:CELLO PARTNERSHIP DBA VERIZON WIRELESS
System And Method For Thinning Of Scalable Video Coding Bit-Streams
InactiveUS20070263087A1Flexibility in processingImprove coding efficiencyColor television with pulse code modulationColor television with bandwidth reductionExtensibilityComputer architecture
A system for videoconferencing that offers, among other features, extremely low end-to-end delay as well as very high scalability. The system accommodates heterogeneous receivers and networks, as well as the best-effort nature of networks such as those based on the Internet Protocol. The system relies on scalable video coding to provide a coded representation of a source video signal at multiple temporal, quality, and spatial resolutions. These resolutions are represented by distinct bitstream components that are created at each end-user encoder. System architecture and processes called SVC Thinning allow the separation of data into data used for prediction in other pictures and data not used for prediction in other pictures. SVC Thinning processes, which can be performed at video conferencing endpoints or at MCUs, can selectively remove or replace with fewer bits the data not used for prediction in other pictures from transmitted bit streams. This separation and selective removal or replacement of data for transmission allows a trade-off between scalability support (i.e. number of decodable video resolutions), error resiliency and coding efficiency.
Owner:VIDYO
System and method for progressive delivery of media content
ActiveUS20100094931A1Minimum delayReadily apparentMultiple digital computer combinationsTelevision systemsClient-sideMedia content
A method for delivering media content includes receiving a request for media content from a client and identifying a first media file containing media content associated with the request. The first file has a first media format. The method further includes initiating creation of a second media file associated with the request and estimating one or more characteristic of the second media file. The second media file has a second media format. Additionally, the method includes generating media information for the second media file based on the estimated characteristics of the second media file and transmitting the media information to the client before creation of the second media file has been completed.
Owner:IMAGINE COMM
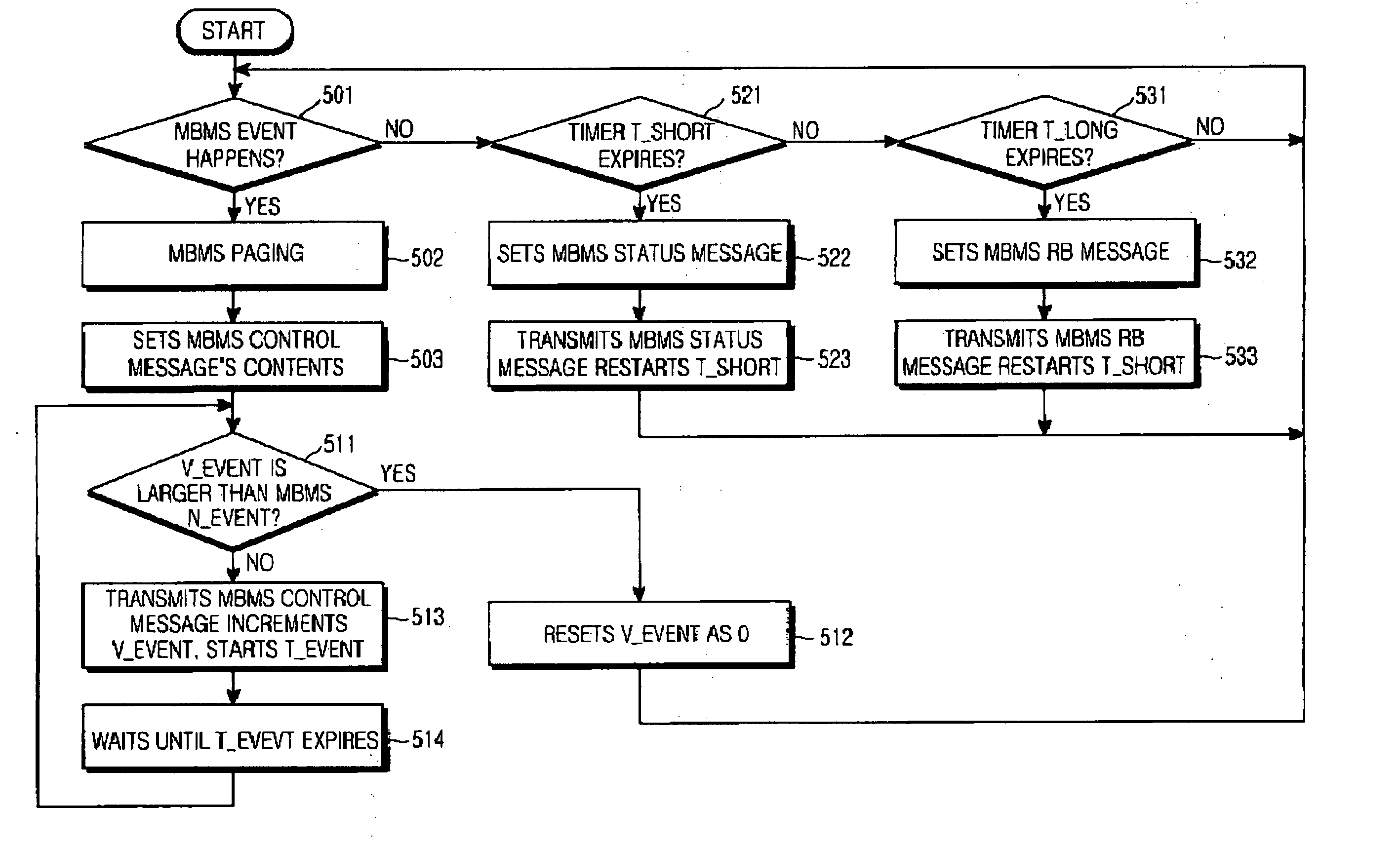
Method for transmitting an MBMS control message in a mobile communication system
InactiveUS20050007971A1Guaranteed normal transmissionEffective mobilitySpecial service provision for substationBroadcast transmission systemsTelecommunicationsMobile communication systems
A method for dividing MBMS control information provided to UEs for an MBMS service into three types and separately transmitting the divided MBMS control information according to their types. The MBMS control information is divided into first MBMS control information that is periodically transmitted, and second MBMS control information that is aperiodically transmitted due to occurrence of an event. The periodically transmitted first MBMS control information is divided into MBMS control information that is transmitted at a first periodic interval and MBMS control information that is transmitted at a second periodic interval. The first periodic interval is shorter than the second periodic interval to enable a UE desiring to receive a particular MBMS service to preferentially receive MBMS status information in advance of MBMS RB information.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
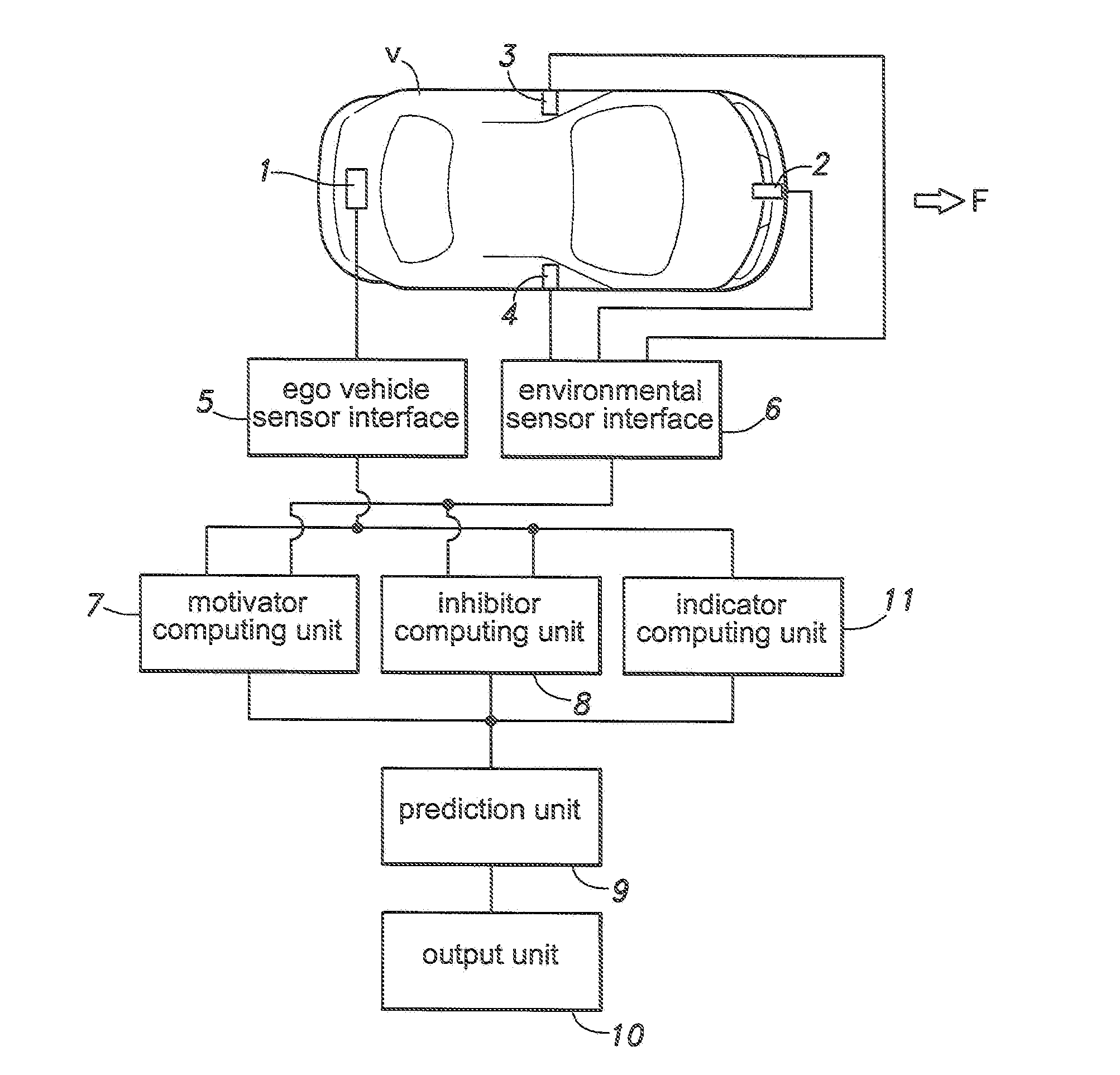
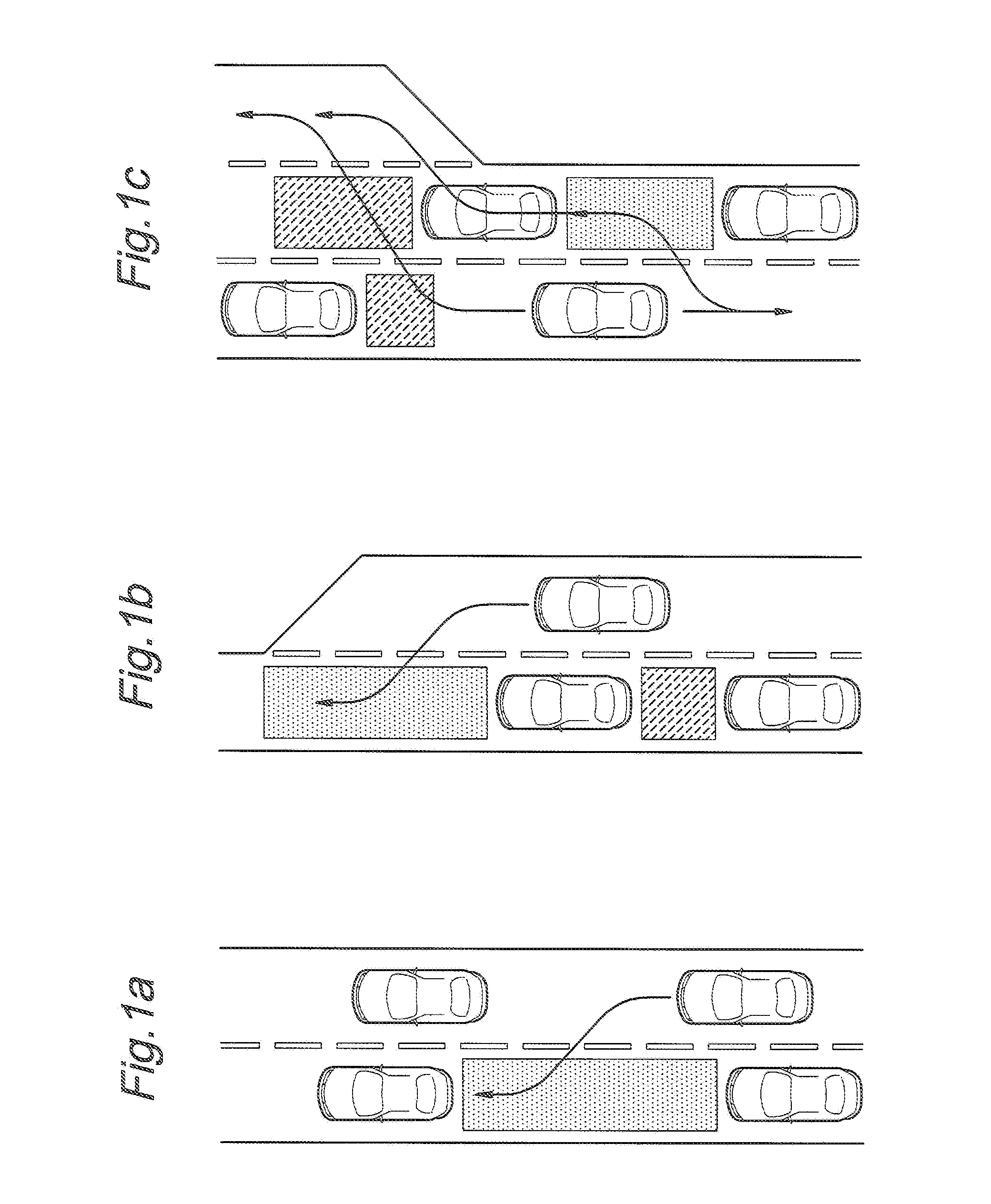
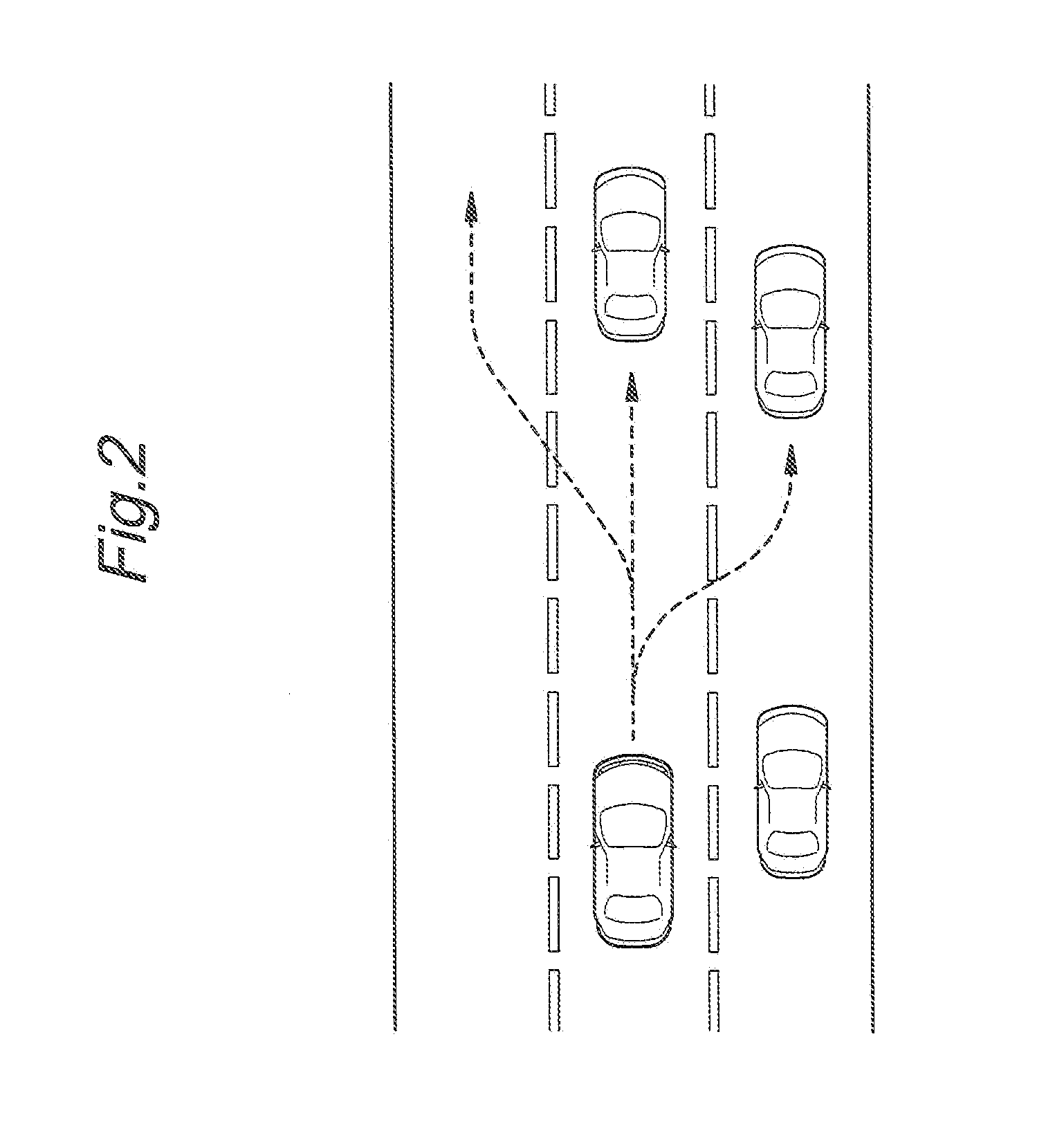
System for predicting a driver's intention to change lanes
ActiveUS20130085976A1Minimum delayImprove accuracyRoad vehicles traffic controlExternal condition input parametersDriver/operatorRadar
Provided is a system for predicting a driver's intention to change lanes at a high accuracy involving a minimum amount of time delay. A driver's intention to change lanes is predicted by a prediction unit (9) by comparing motivators and inhibitors (7, 8) which may be determined from the speed of the traffic in particular the vehicle traveling ahead of the vehicle and the traffic in the adjacent lanes in relation to the traveling speed of the ego vehicle by using an ego vehicle sensor (1) and an environmental sensor (3, 4, 5) that may comprise a radio wave, optical or acoustic radar. The criteria for the motivators and inhibitors may be empirically or statistically determined, preferably by conducting a large number of tests on roads. As they can be determined before the vehicle operator starts a lane changing maneuver, the prediction made by the prediction unit may be used on a real time basis in a warning system or steering / acceleration assist system.
Owner:HONDA MOTOR CO LTD
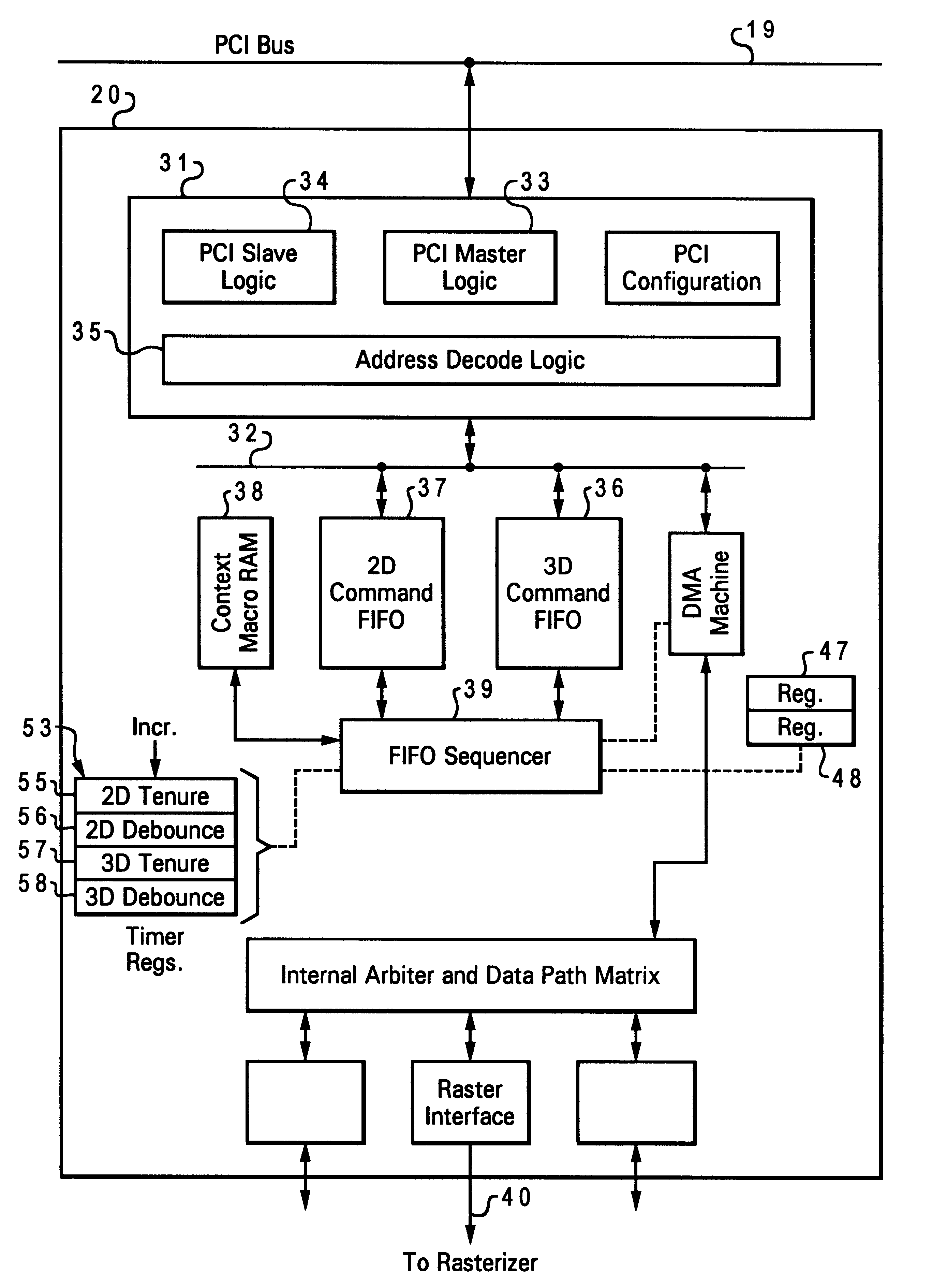
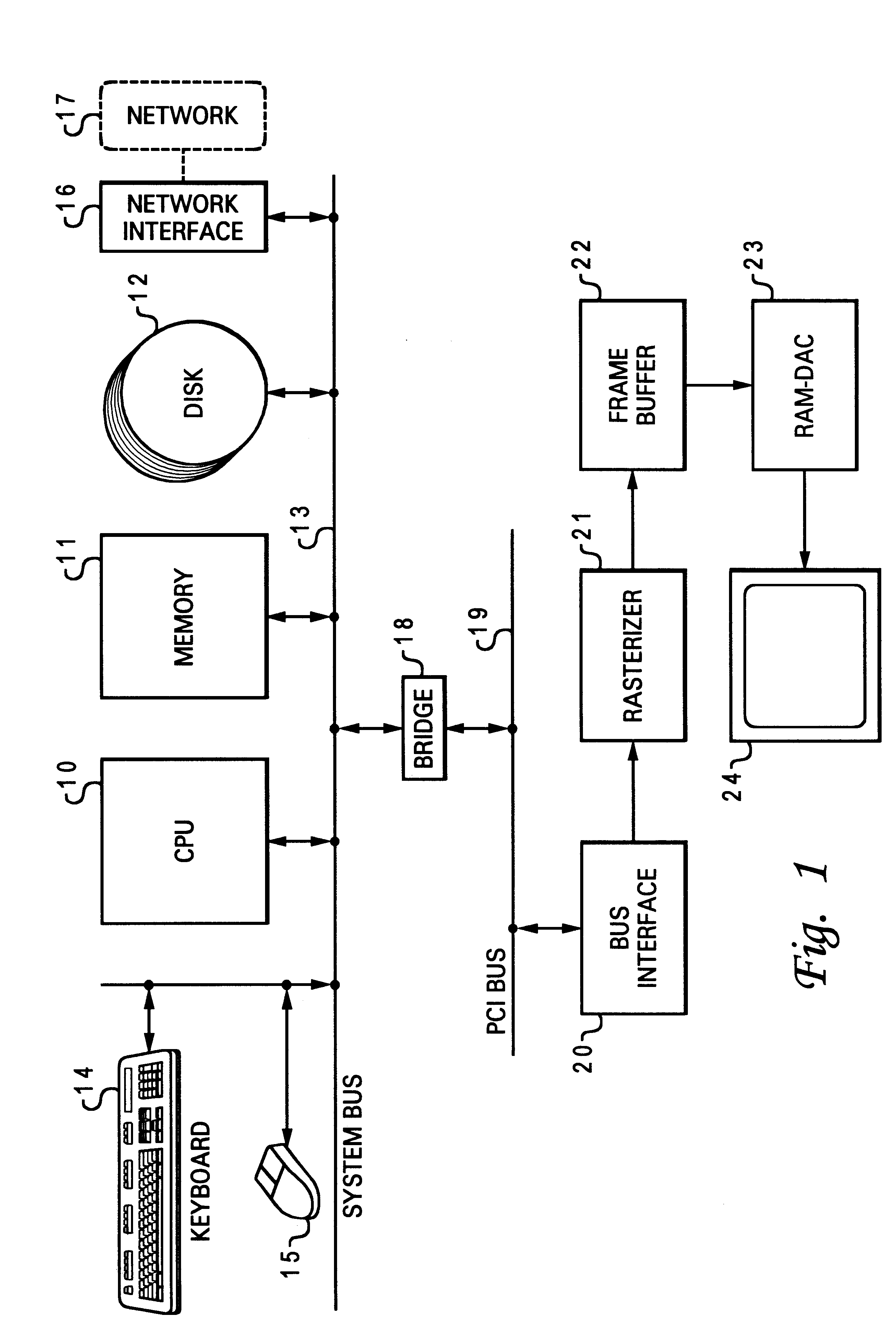
Computer graphics system with dual FIFO interface
InactiveUS6252600B1Minimum delayEasy to useImage memory managementCathode-ray tube indicatorsGraphic systemComputerized system
A computer system has a graphics subsystem employing a rasterizer and a frame buffer, with a digital-to-analog converter for producing drive signals to a video display. A bus interface acts as a gateway between a PCI bus and the graphics subsystem; this interface manages commands and DMAs passing between the host processor and various parts of the graphics subsystem. Within the interface, two command FIFOs are employed, one for storing commands / data sent from the host for 2D display (window management) and another for 3D applications. Using two command FIFOs eliminates the need for host semaphore, FIFO draining, and the latency associated with these operations. Timers are provided in the interface, associated with the two command FIFOs, to manage and regulate the frequency with which the system automatically switches between 2D and 3D FIFO processing. Host intervention is minimized by use of a context macro store for holding locally the sequences for context save and context restore which are used repeatedly.
Owner:IBM CORP
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com