Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
86 results about "Middlebox" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
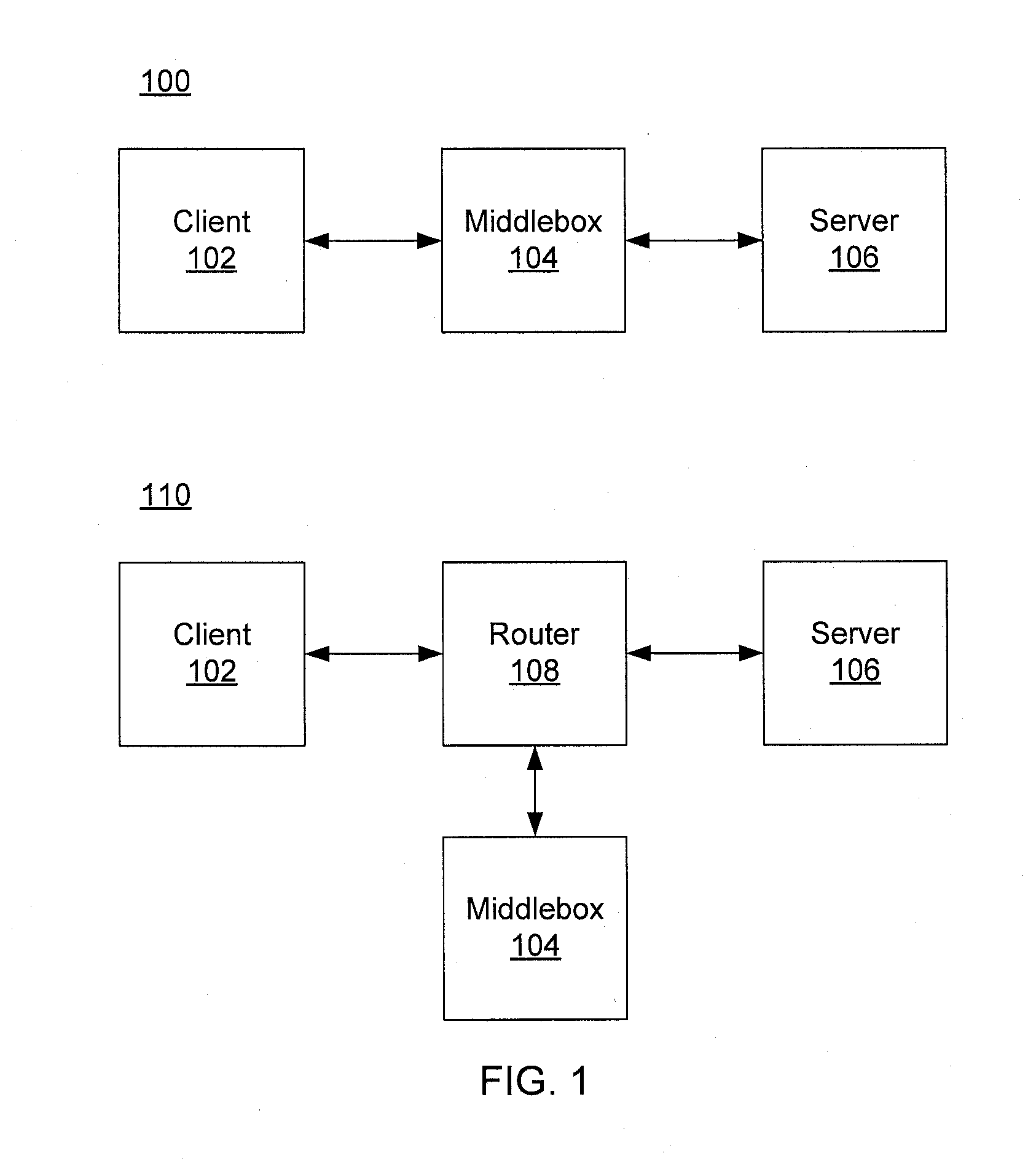
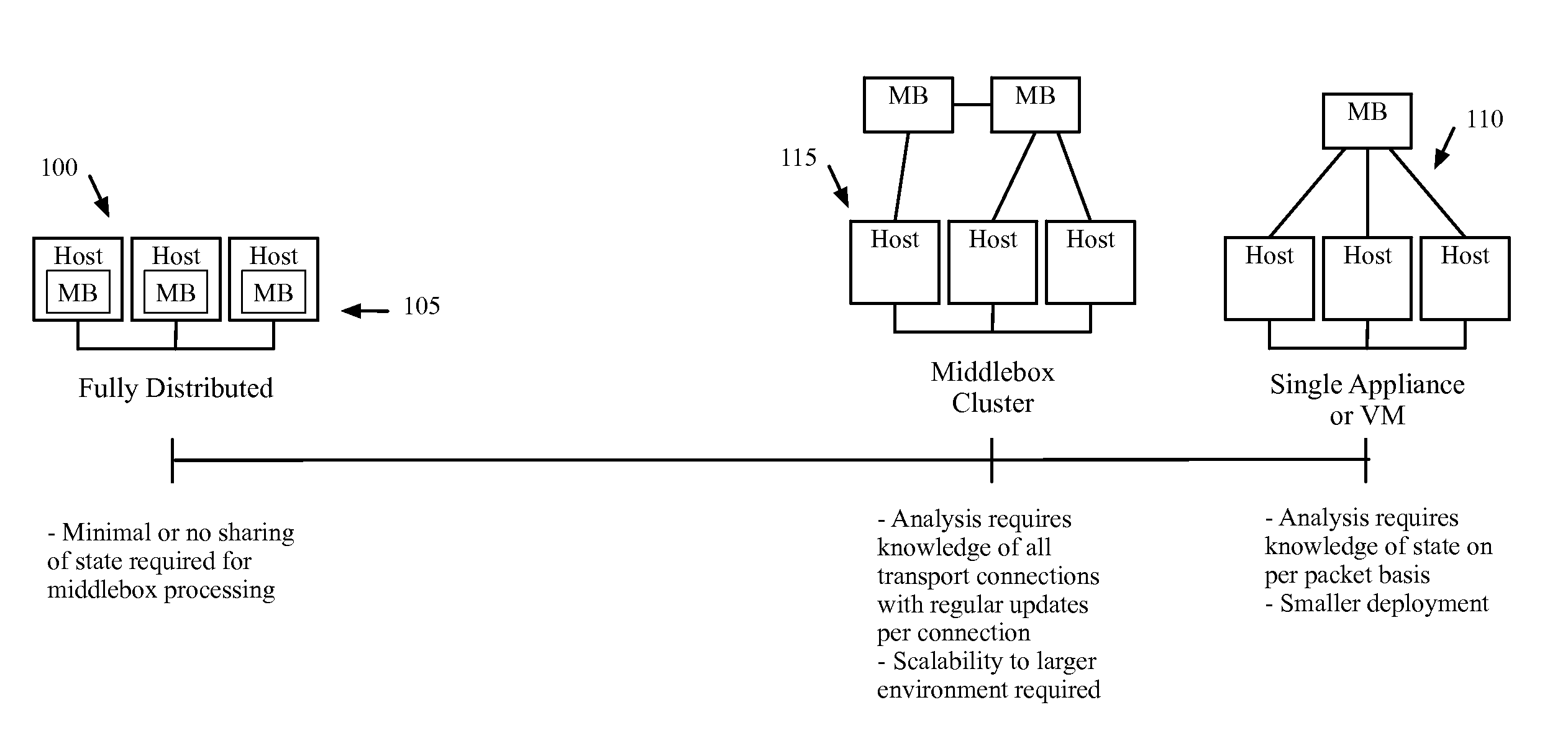
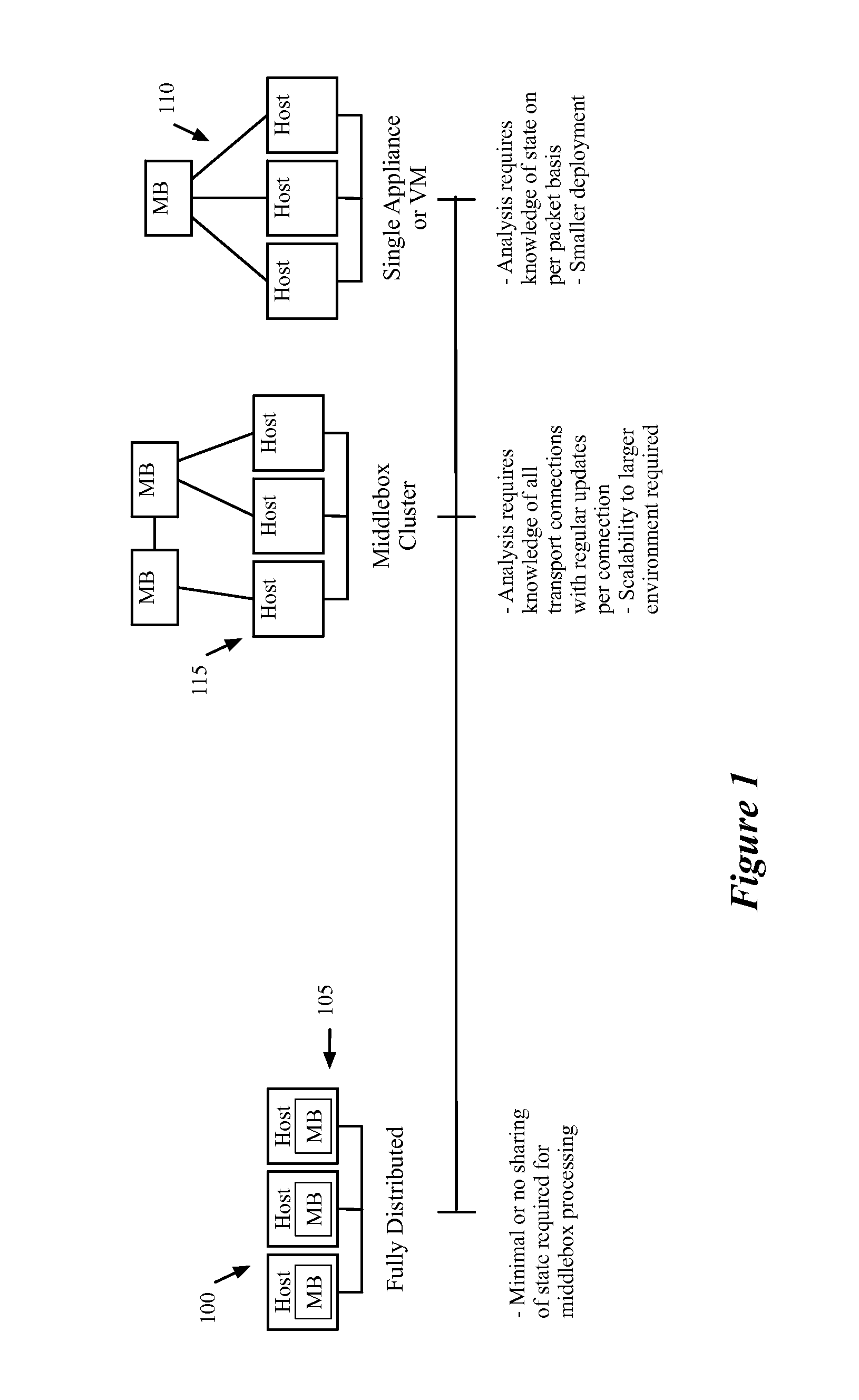
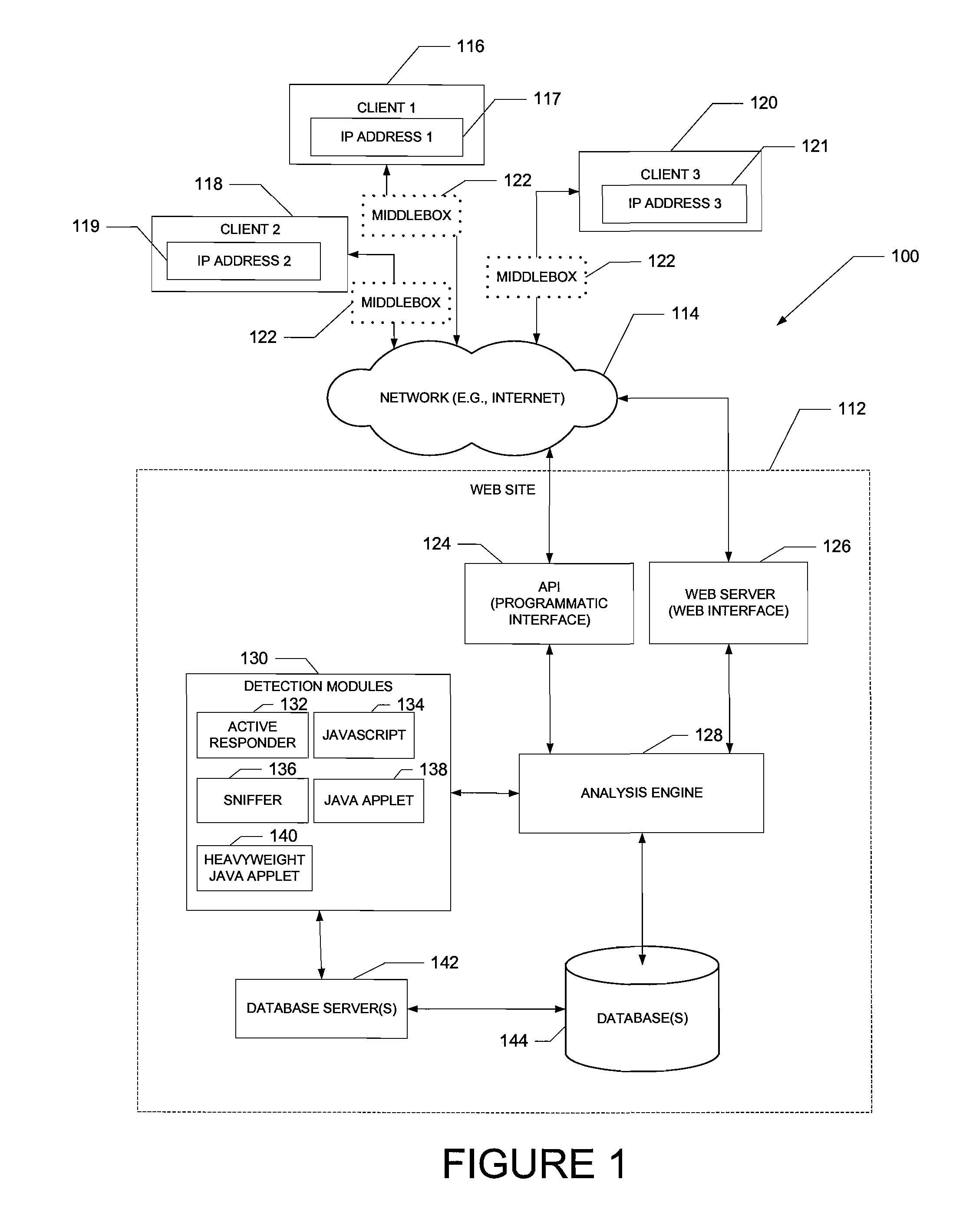
A middlebox or network appliance is a computer networking device that transforms, inspects, filters, or otherwise manipulates traffic for purposes other than packet forwarding. Common examples of middleboxes include firewalls, which filter unwanted or malicious traffic, and network address translators, which modify packets' source and destination addresses. Dedicated middlebox hardware is widely deployed in enterprise networks to improve network security and performance, however, even home network routers often have integrated firewall, NAT, or other middlebox functionality. The widespread deployment of middleboxes and other network appliances has resulted in some challenges and criticism due to poor interaction with higher layer protocols.
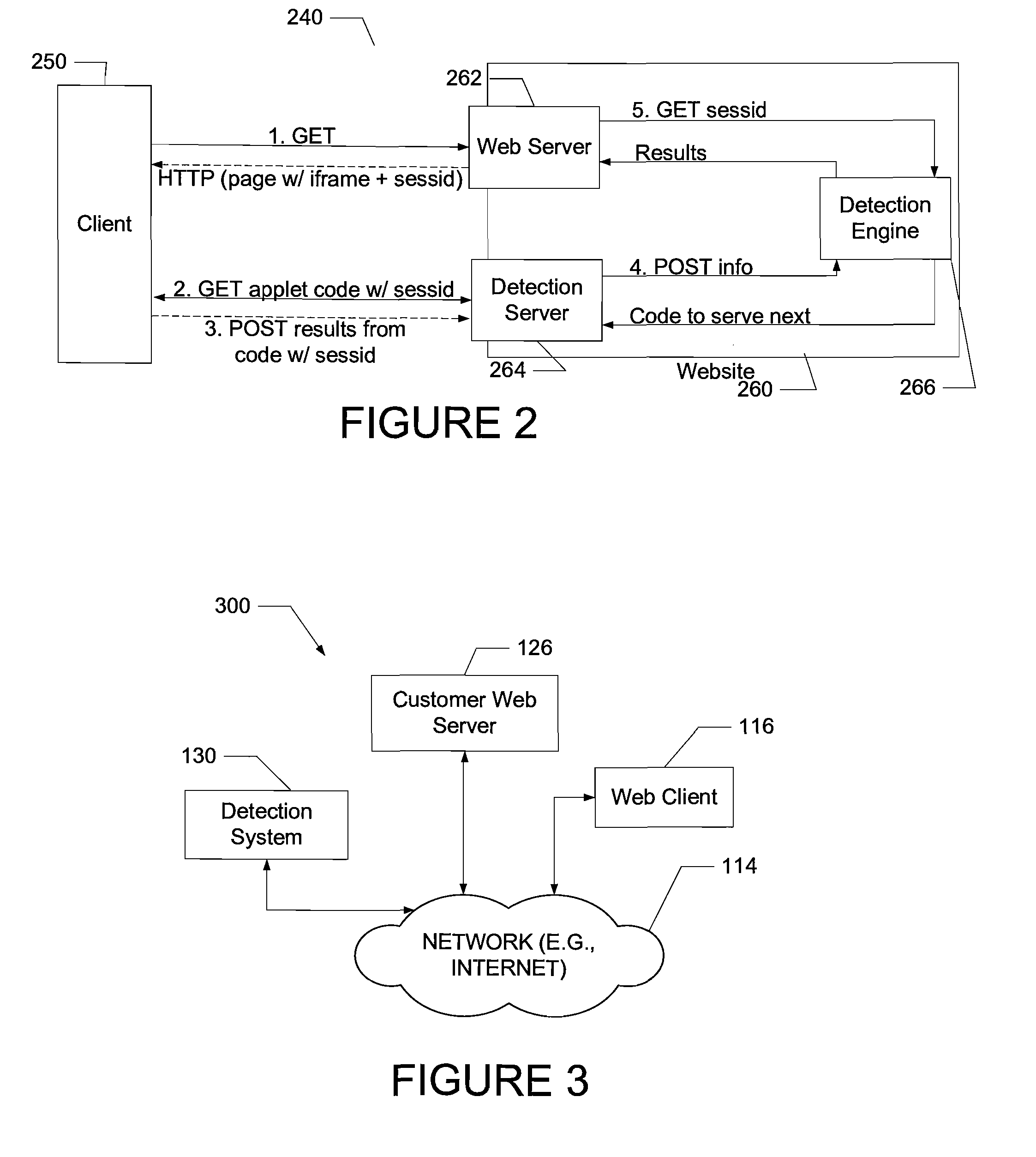
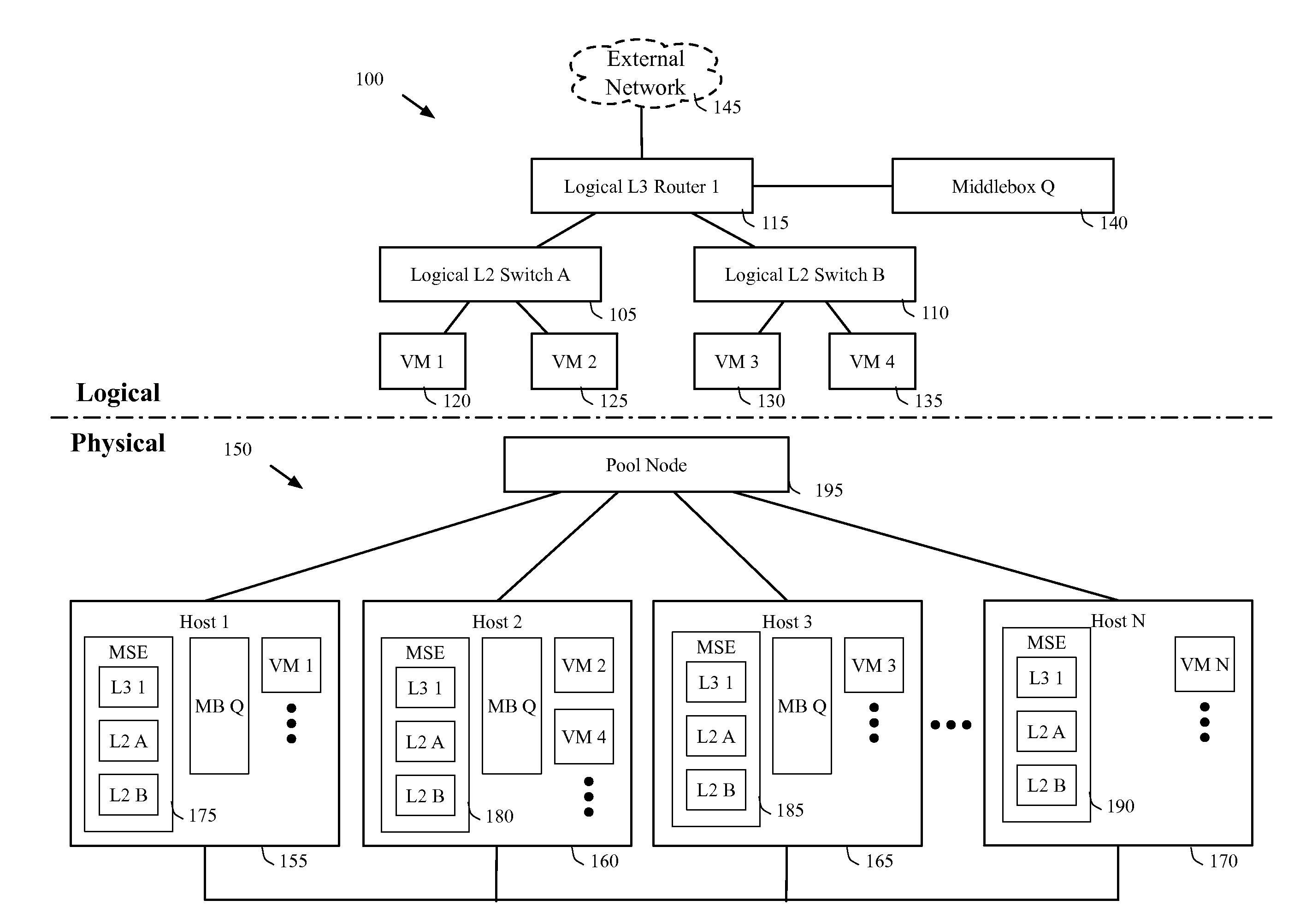
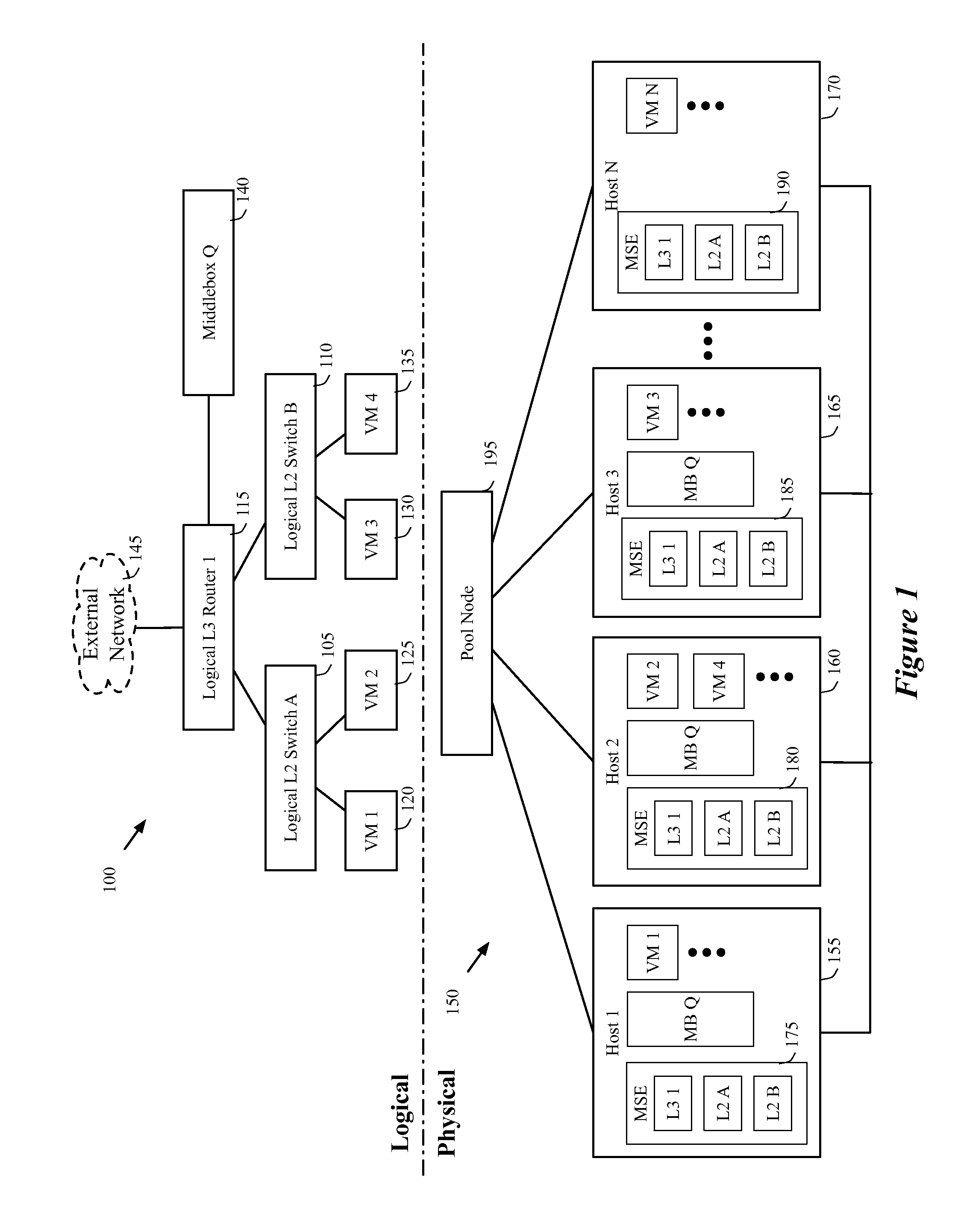
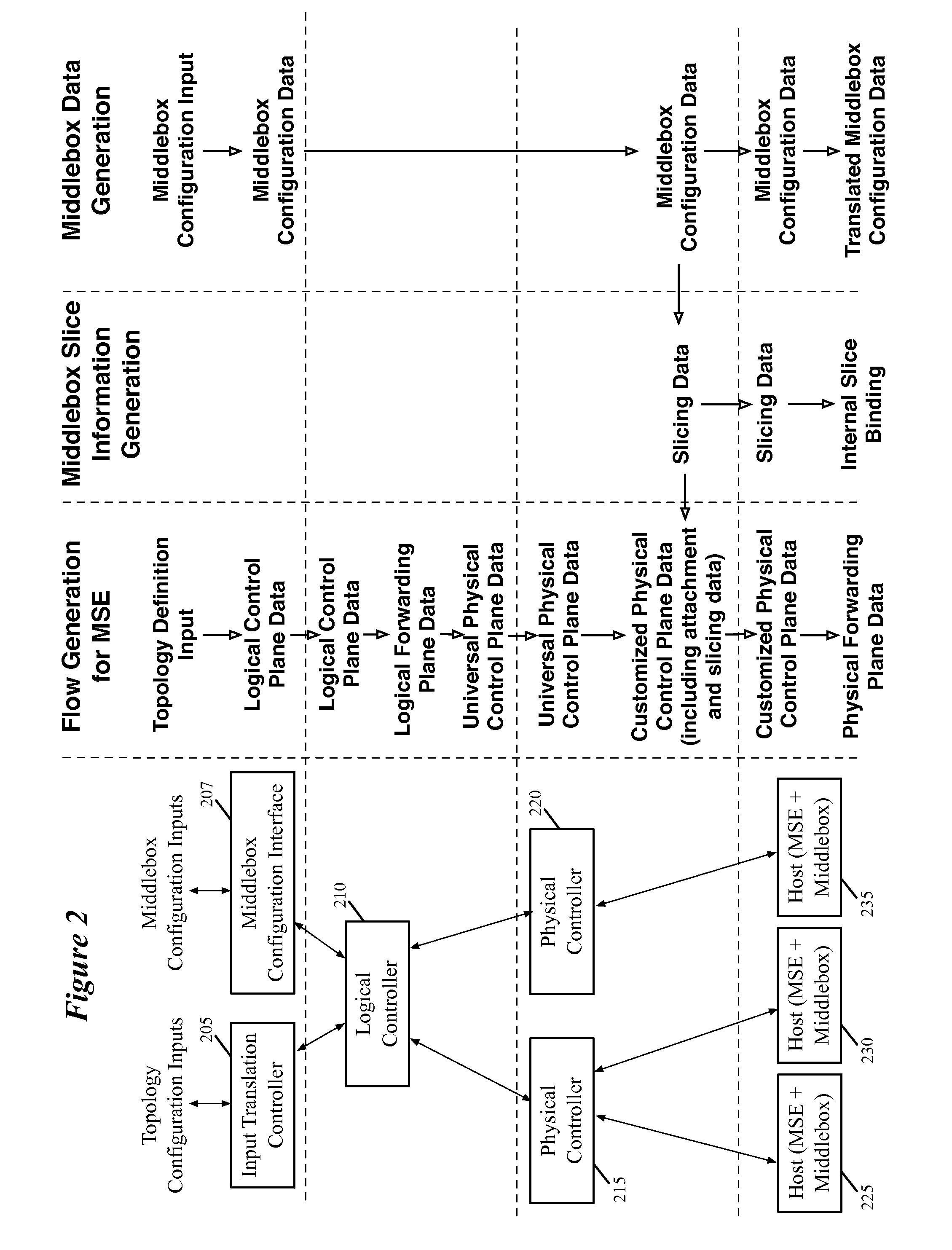
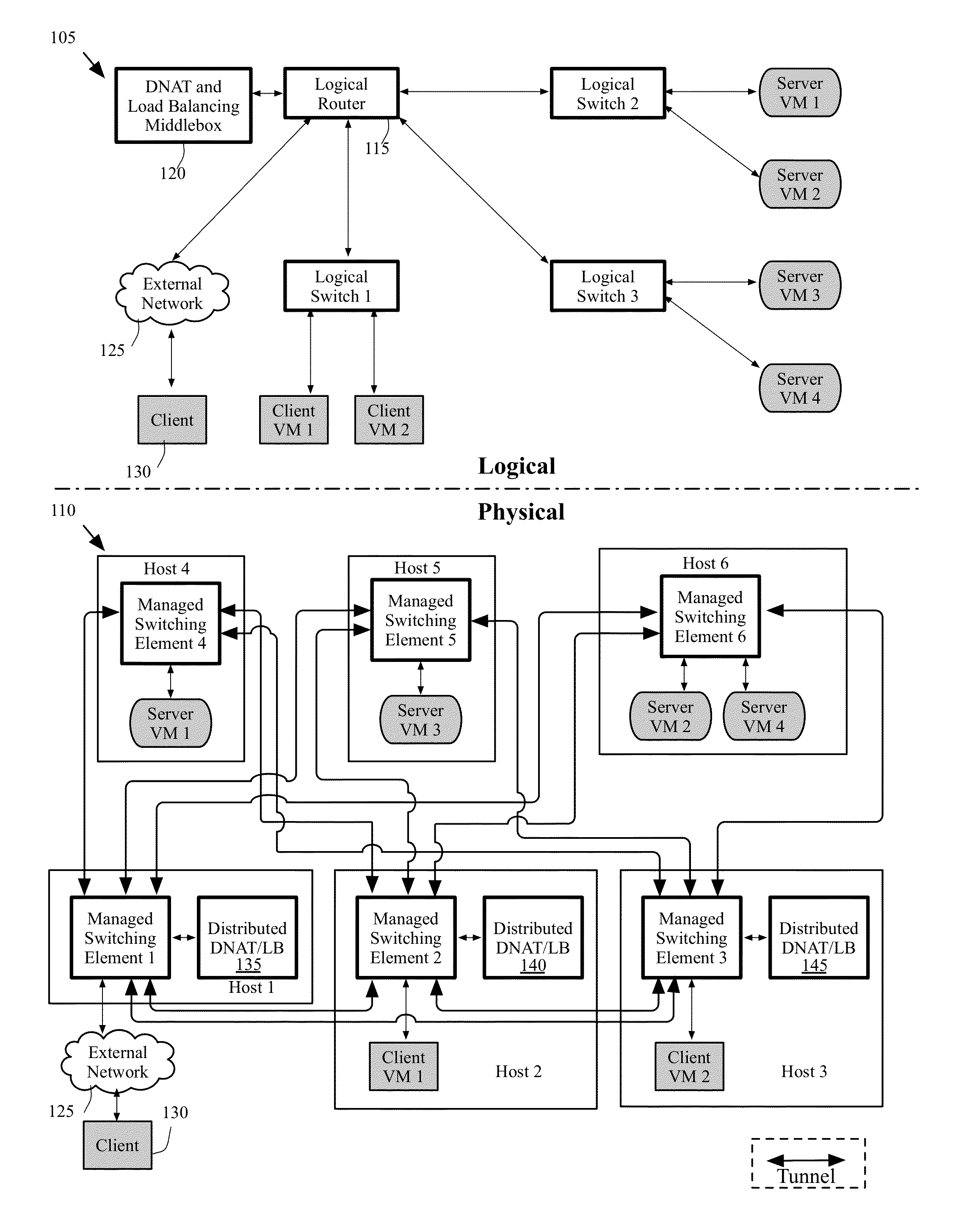
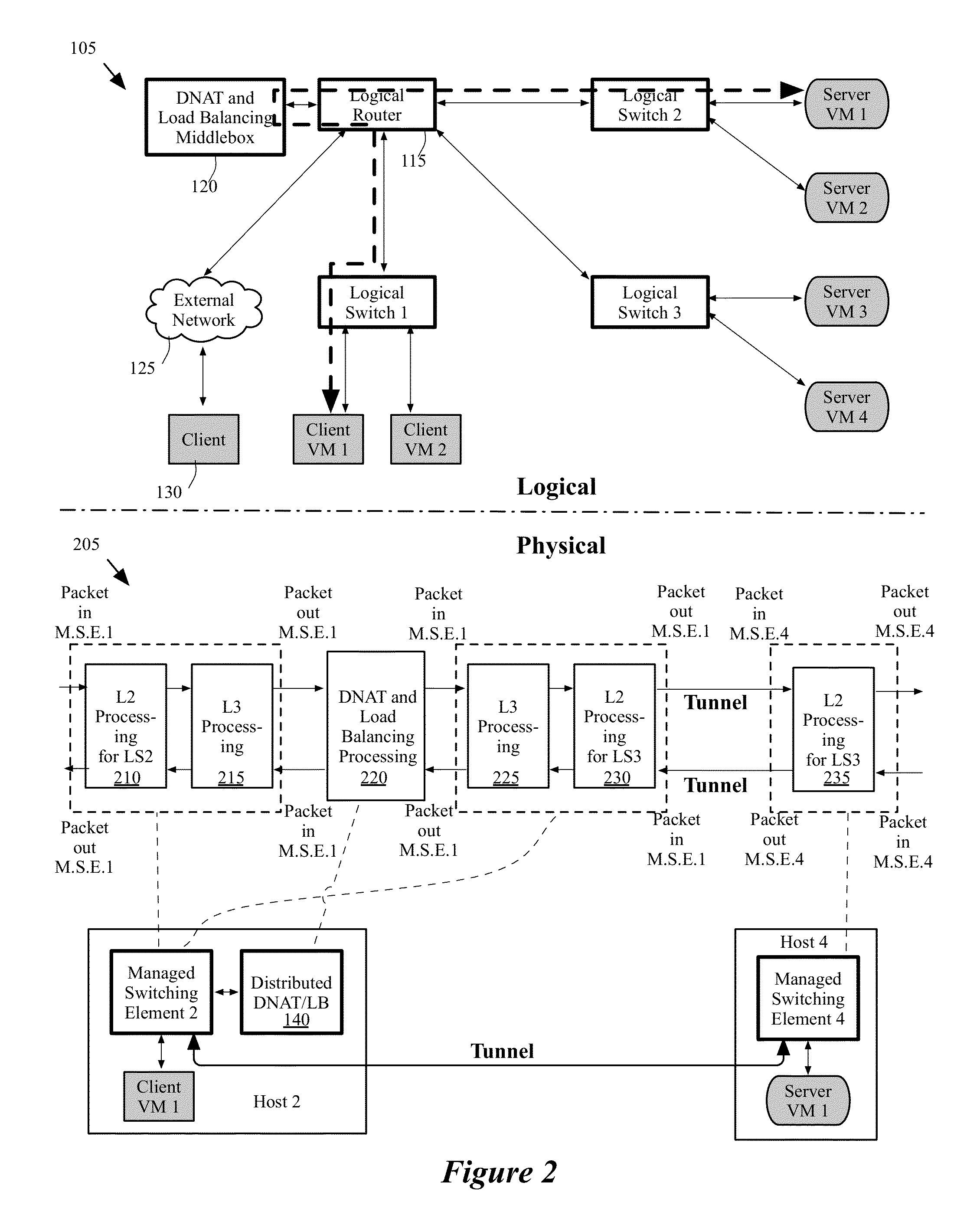
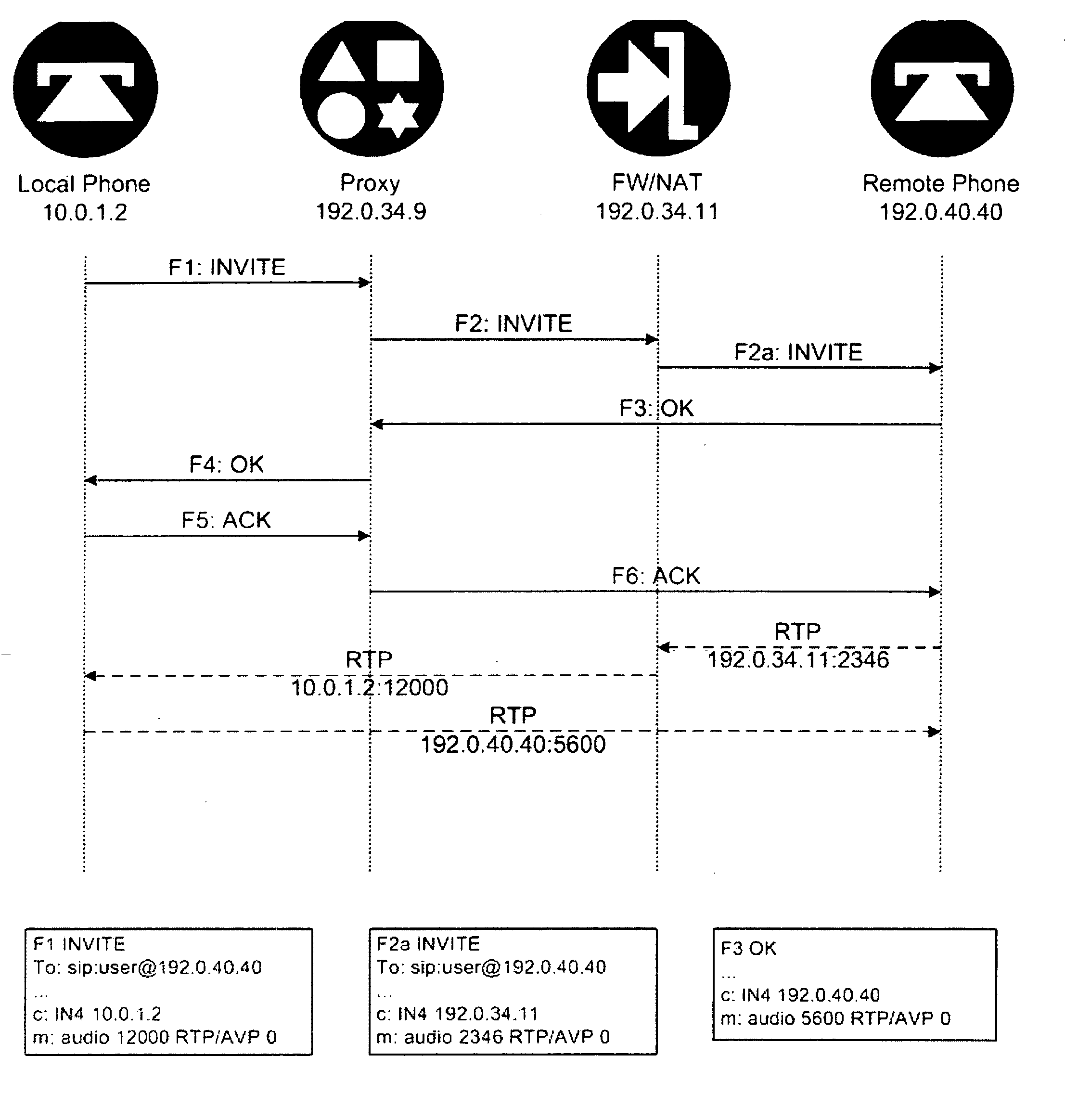
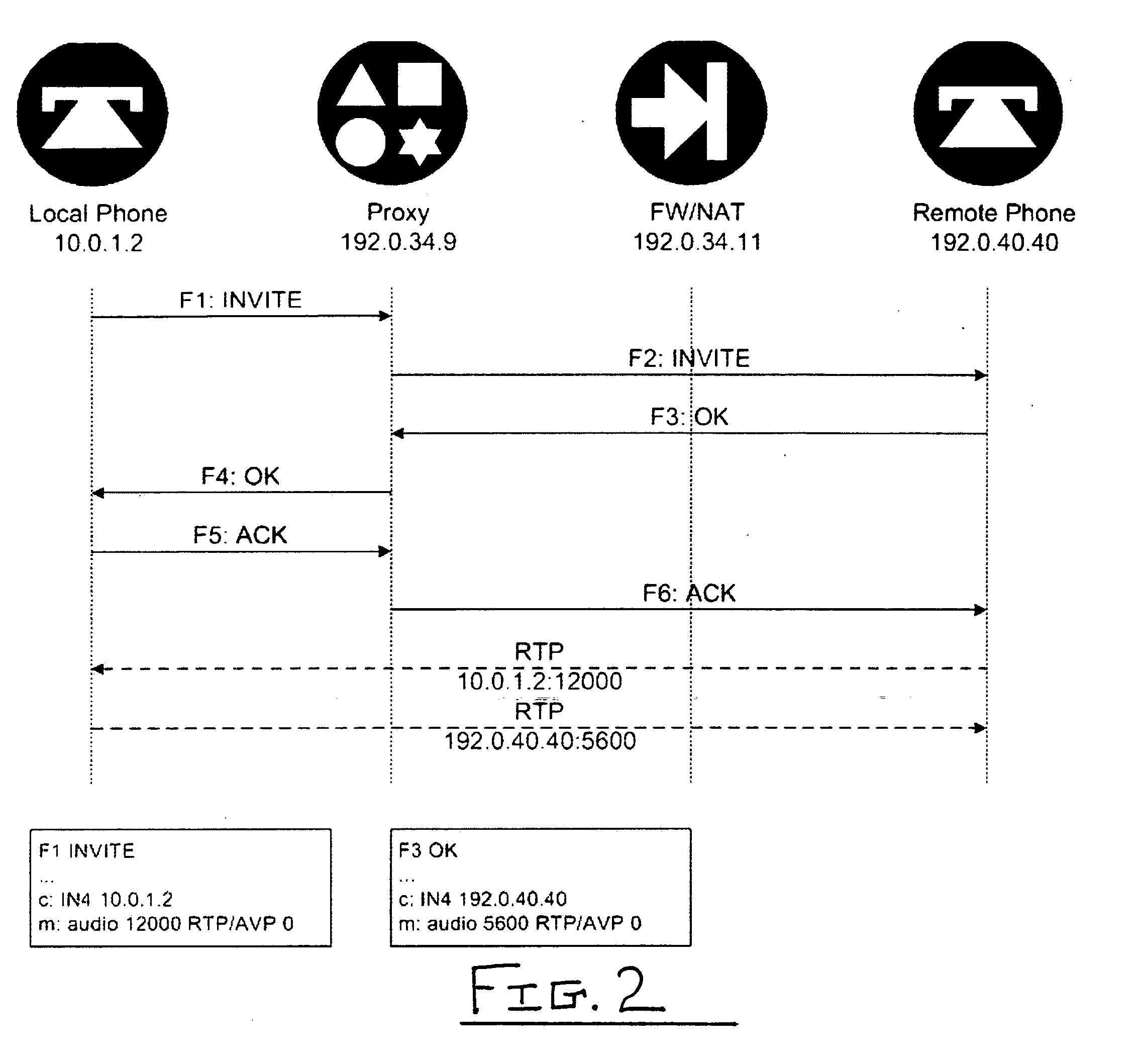
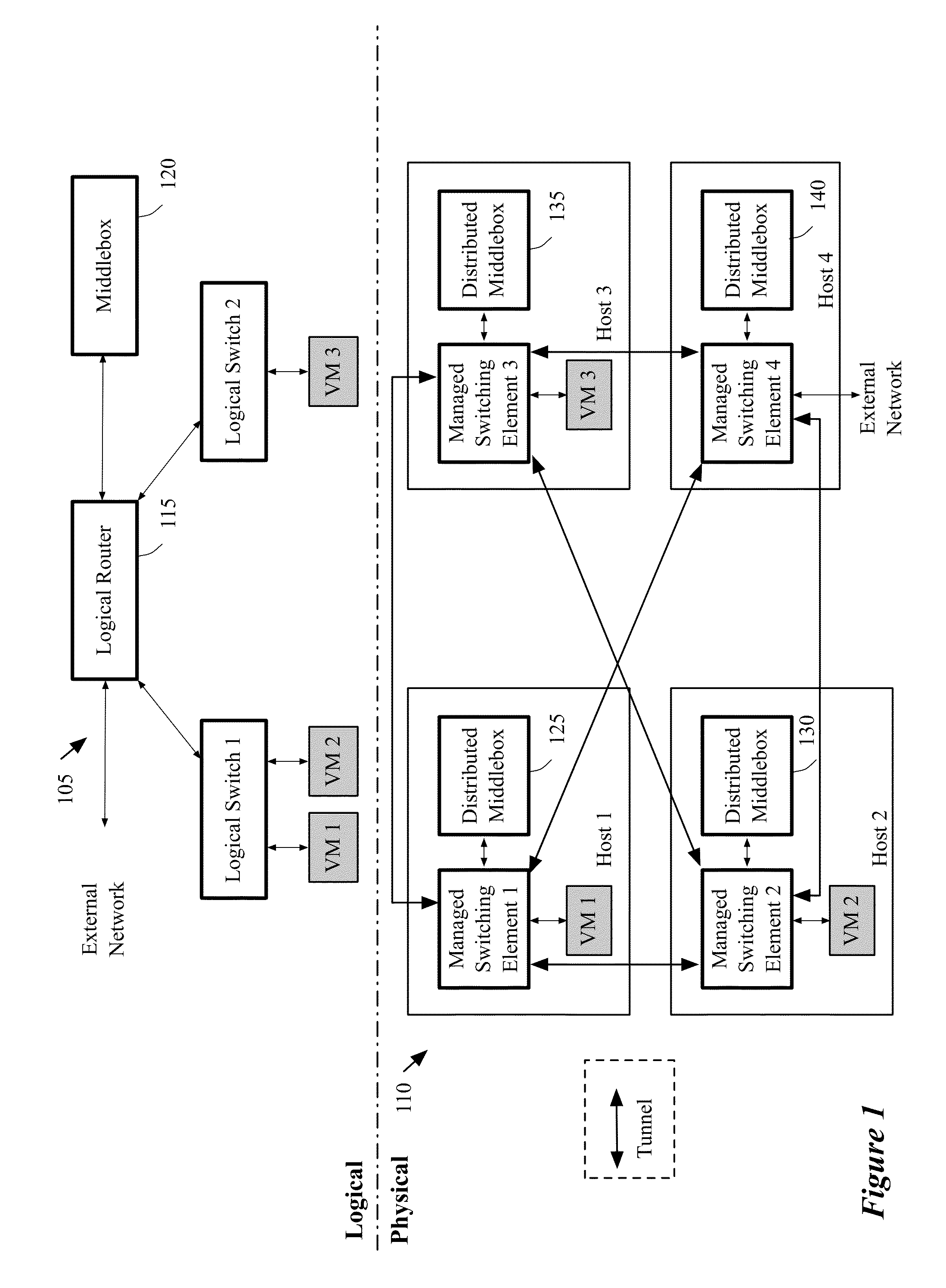
Dynamically provisioning middleboxes
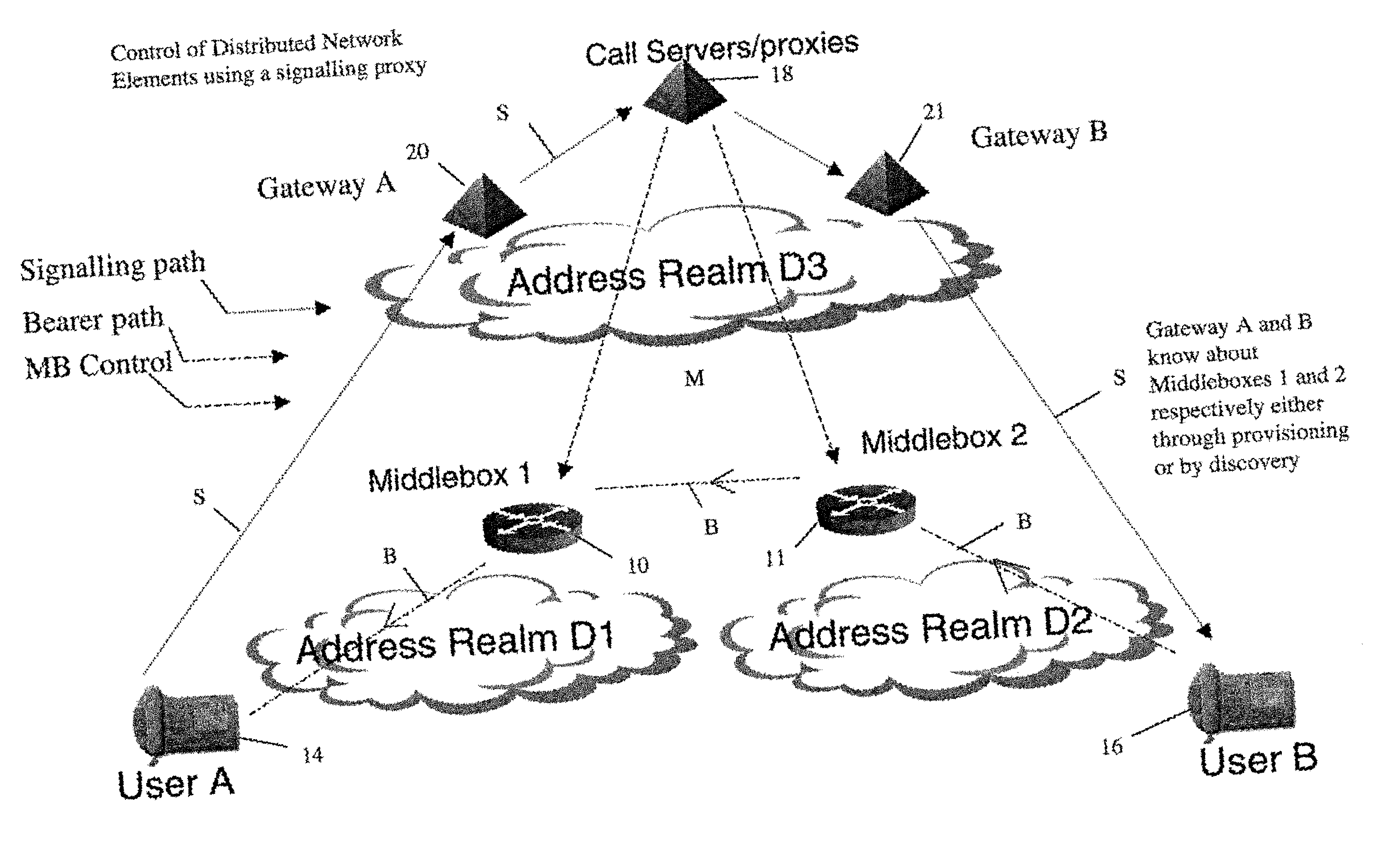
Hybrid security architecture (HSA) provides a platform for middlebox traversal in the network. The HSA decouples the middlebox control from network forwarding. More specifically, such embodiments may receive a data packet having a packet header including an Ethernet header identifying source and destination addresses in the network. A traffic type of the data packet is determined. Then, layer-2 forwarding information, which encodes a set of non-forwarding network service provider middleboxes in the network to be traversed by the data packet, is determined based on the traffic type. The layer-2 forwarding information is inserted into the Ethernet header and the data packet is forwarded into the network. The data packet will then traverse, according to the layer-2 forwarding information, a sequence of the middleboxes in the network, wherein at least one non-forwarding network service will be provided by each of the middleboxes to the data packet in a sequence.
Owner:POLYTECHNIC INSTITUTE OF NEW YORK UNIVERSITY
Middlebox control
InactiveUS20030093481A1Good flexibilityThe process is simple and effectiveData switching by path configurationMultiple digital computer combinationsComputer networkMiddleware
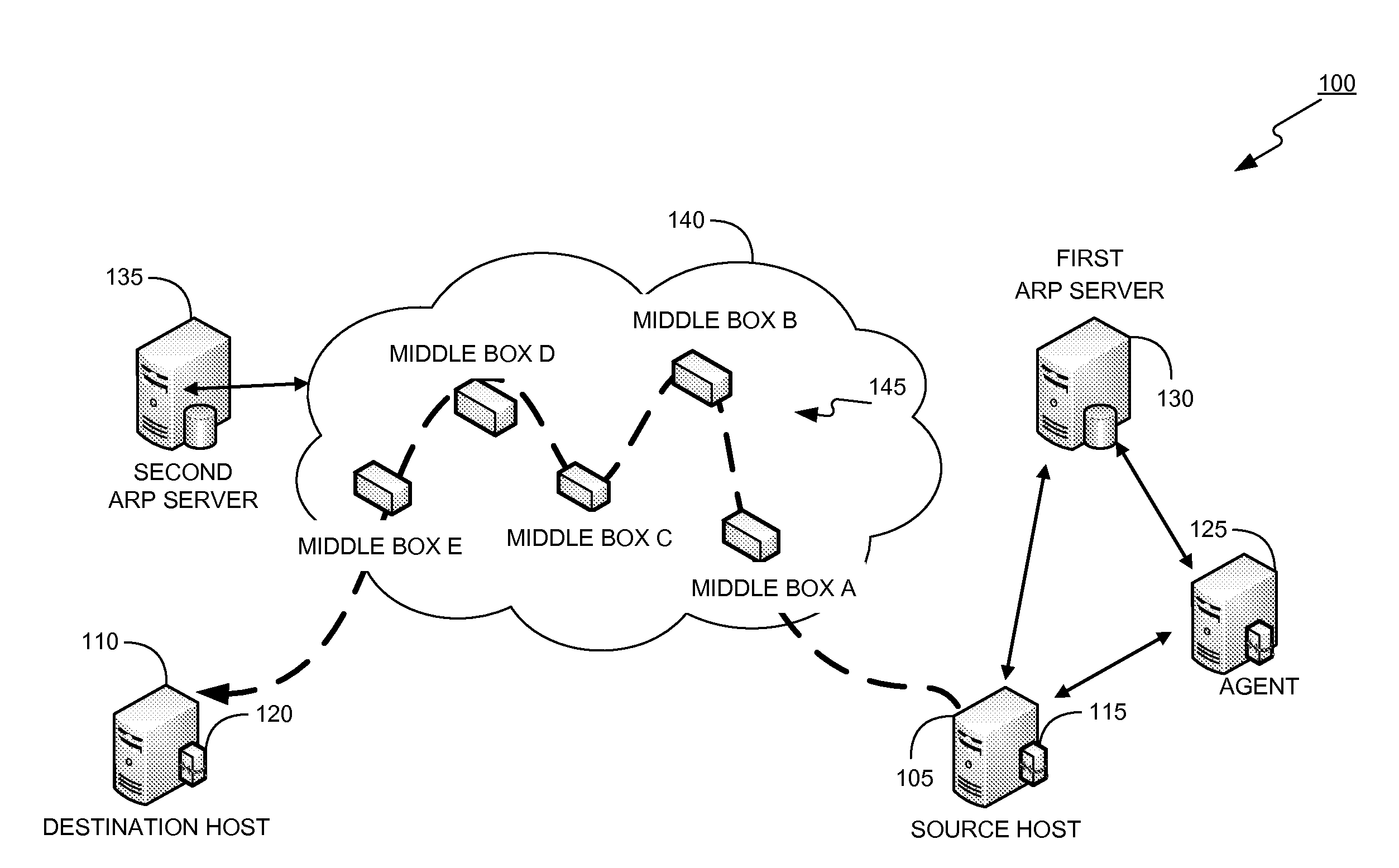
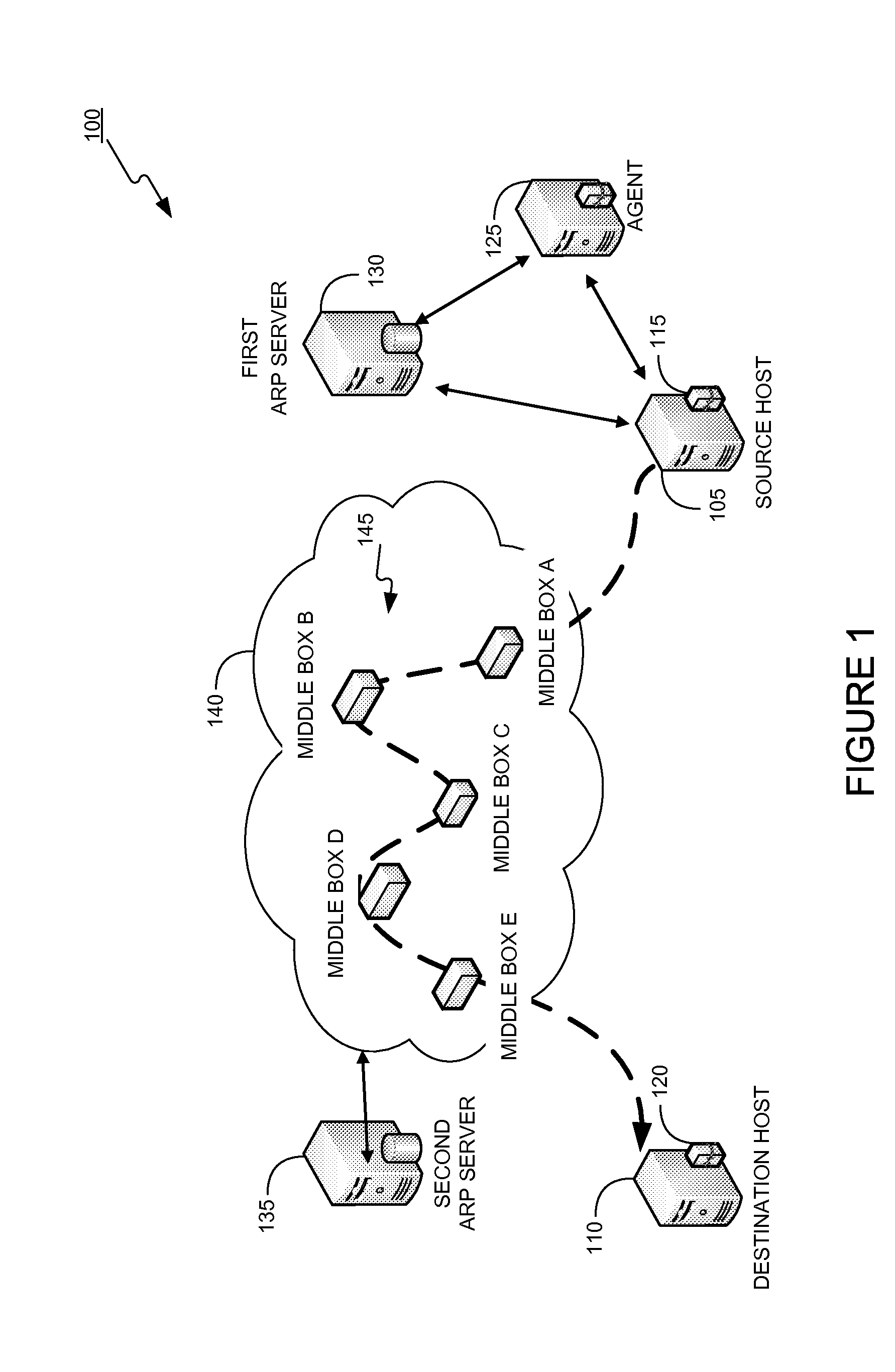
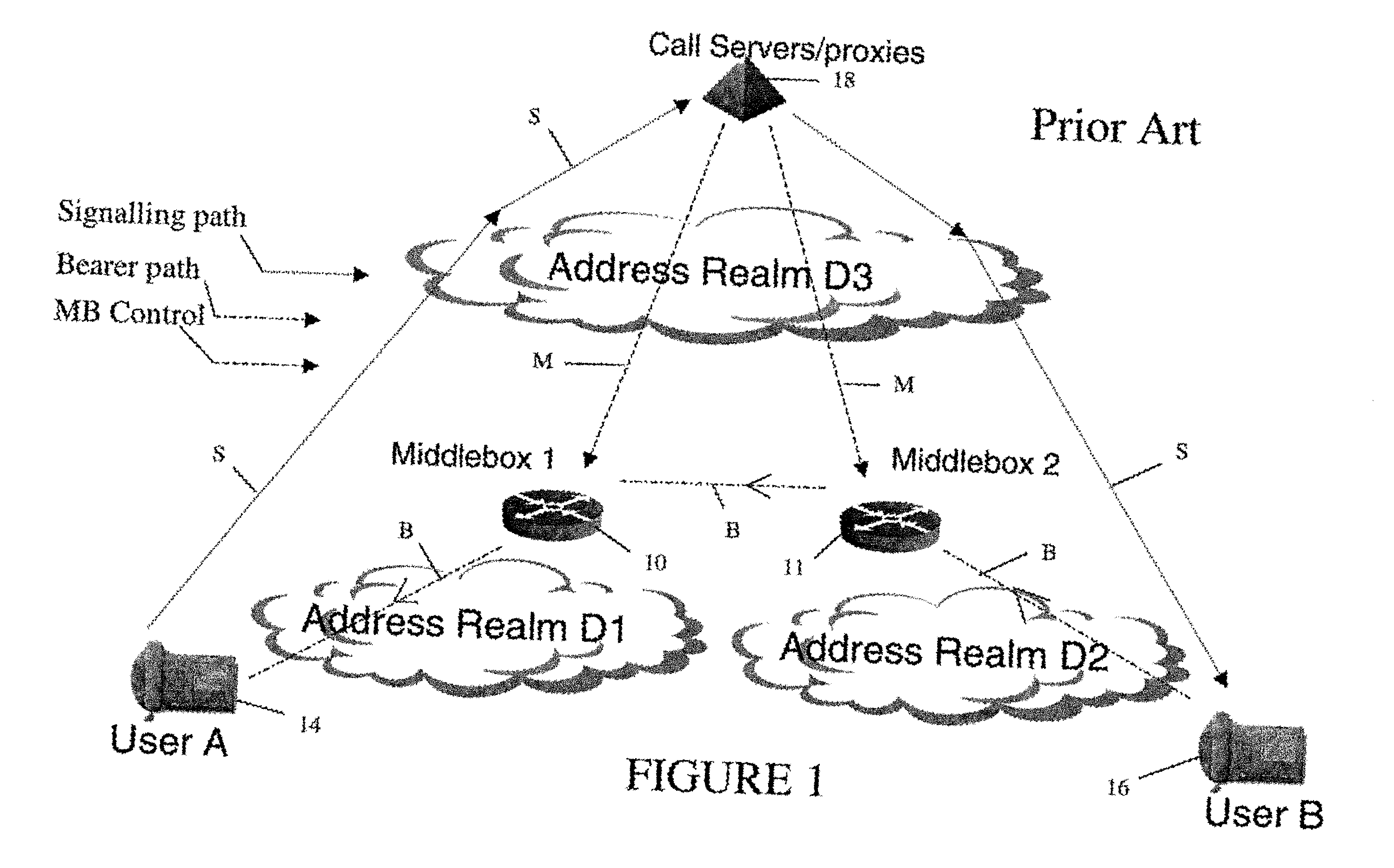
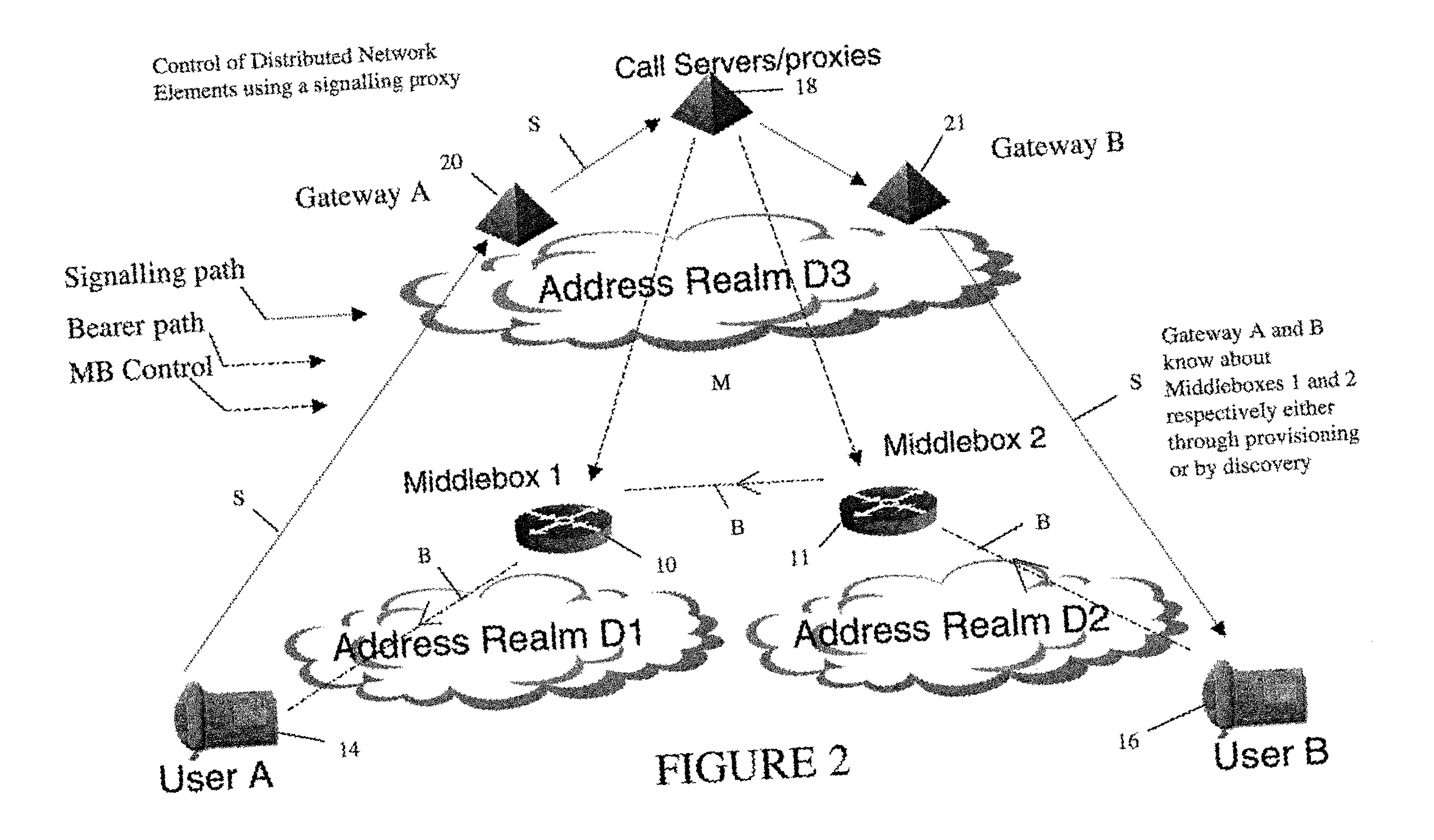
In order to carry out actions such as setting up a call from an entity in the address realm of one middlebox to an entity in the address realm of another middlebox, then a middlebox control node such as a call server is used. Previously, the middlebox control node has needed to have pre-configured information about all the middleboxes and which address realms they are associated with. The present invention provides one or more middlebox-identity-providing nodes which are separate from the middlebox control node, and which are more directly connected to the end users of the service than the middlebox control node. This provides greater flexibility in network design and removes the need for middlebox information to be pre-configured at the middlebox control node. Instead, this information is sent to the middlebox control node, as part of signalling messages, from middlebox-identity-providing nodes.
Owner:RPX CLEARINGHOUSE
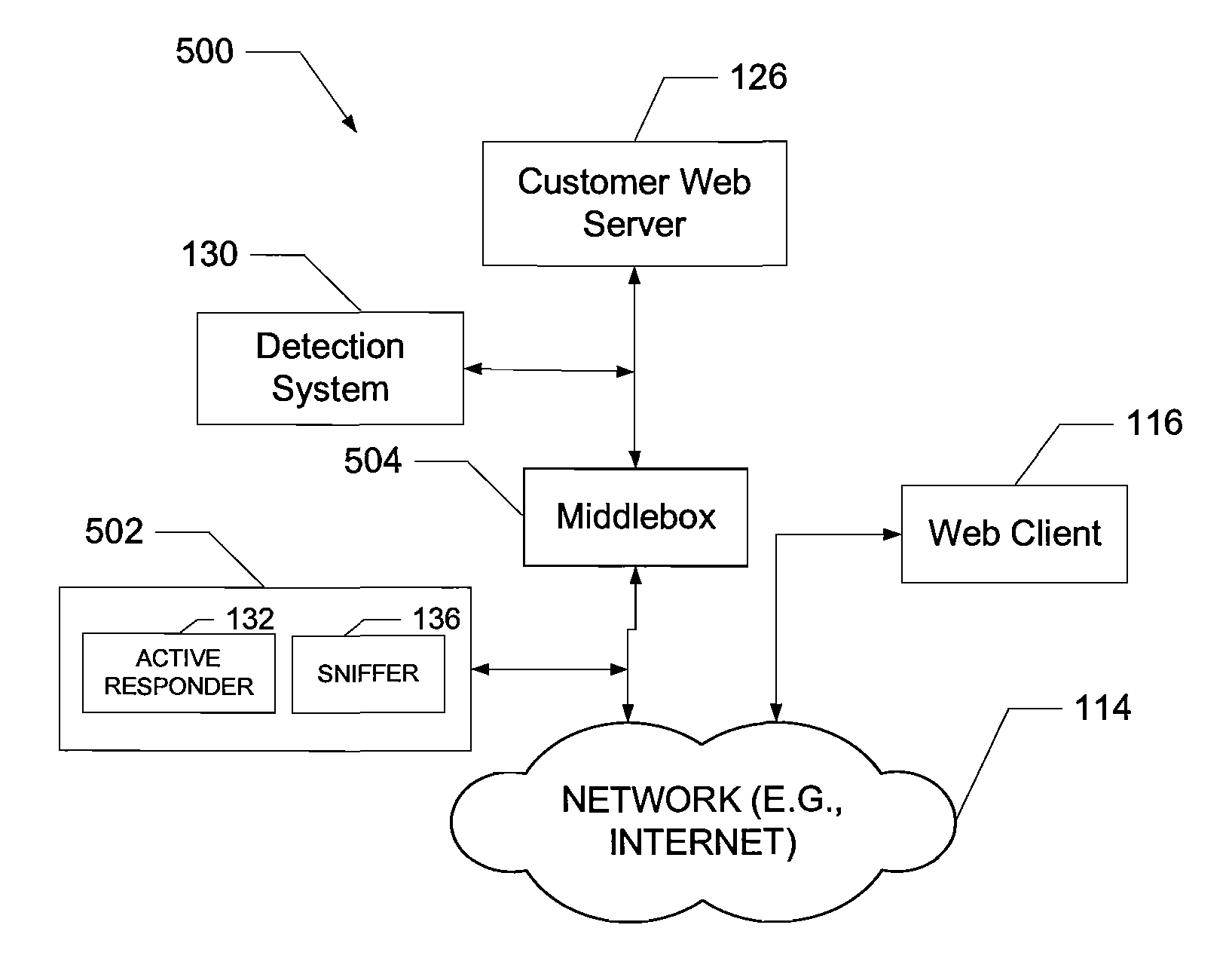
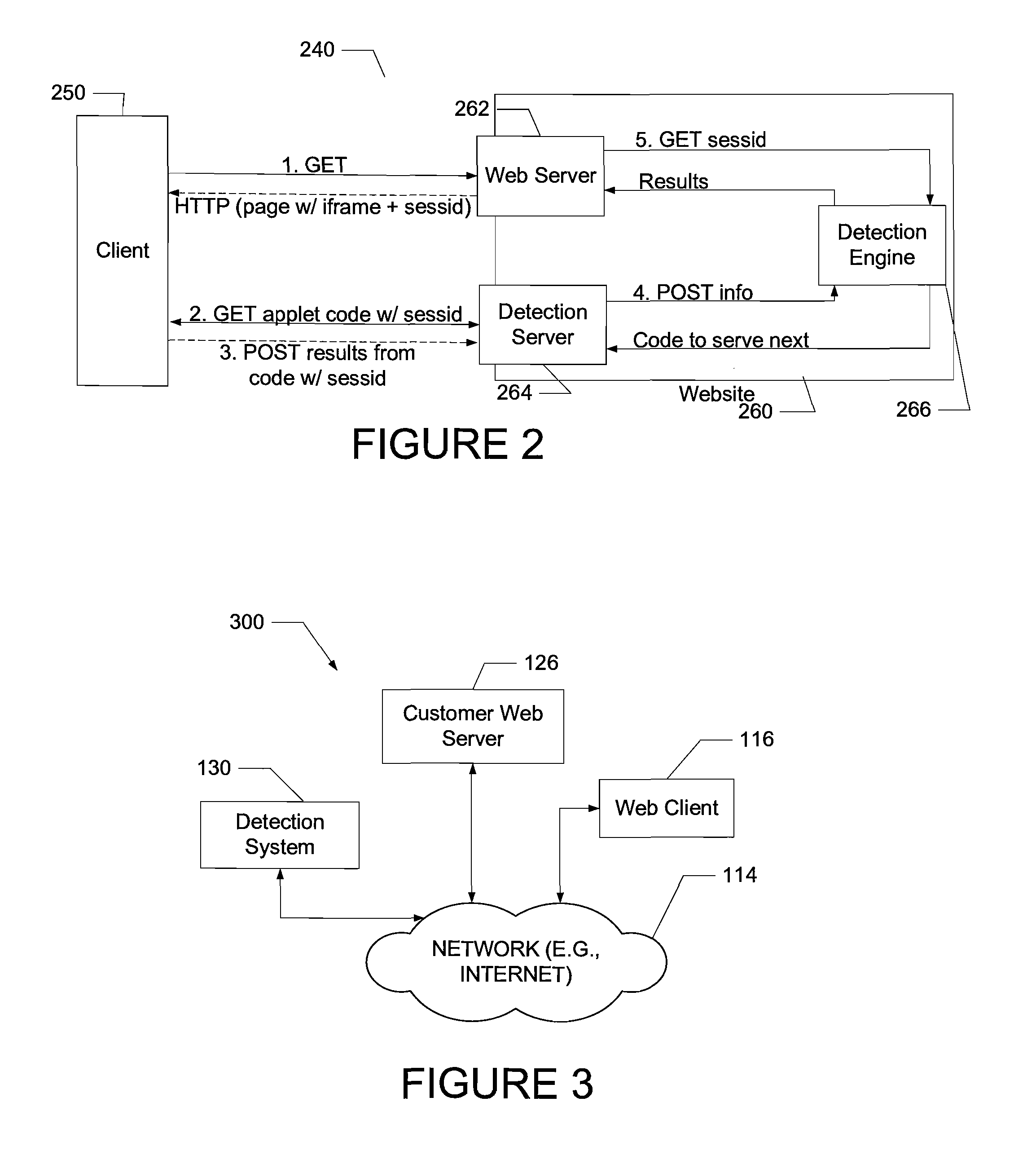
System and method of middlebox detection and characterization
ActiveUS20080072305A1Data switching by path configurationMultiple digital computer combinationsData miningMiddlebox
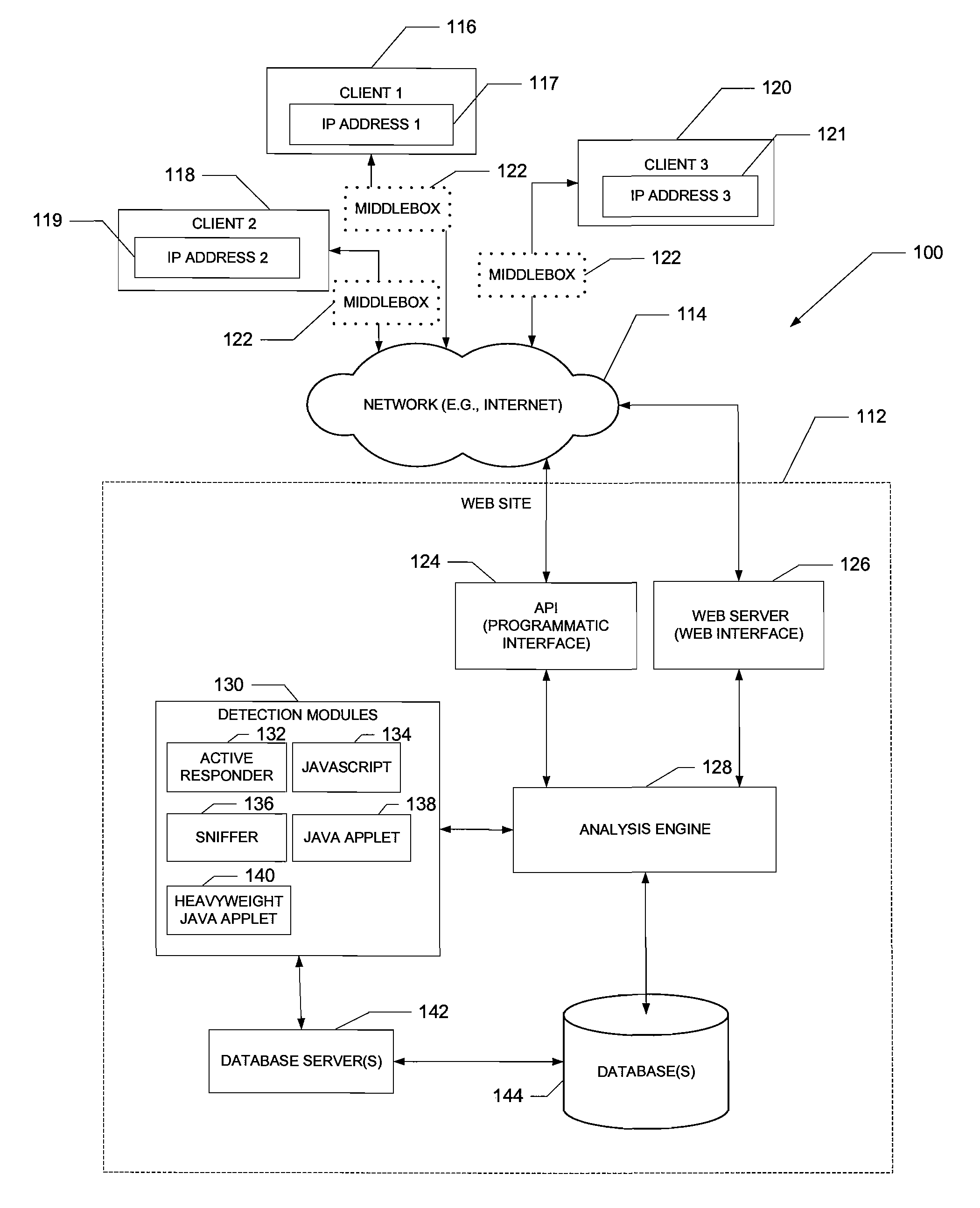
A computer-implemented system and method to detect and characterize middleboxes is disclosed. Embodiments of the system and method include a middlebox detection engine to provide a plurality of middlebox detection modules, and to use at least one middlebox detection module of the plurality of middlebox detection modules to determine if a middlebox exists on a path between a first communicating entity of a network and a second communicating entity of the network
Owner:NEUSTAR IP INTELLIGENCE
Cloud-Based Middlebox Management System
ActiveUS20140068602A1Effectively scaledData switching networksSoftware simulation/interpretation/emulationApplication softwareMiddleware
A virtual network virtual machine may be implemented on a cloud computing facility to control communication among virtual machines executing applications and virtual machines executing middlebox functions. This virtual network virtual machine may provide for automatic scaling of middleboxes according to a heuristic algorithm that monitors the effectiveness of each middlebox on the network performance as application virtual machines are scaled. The virtual machine virtual network may also locate virtual machines in actual hardware to further optimize performance.
Owner:WISCONSIN ALUMNI RES FOUND
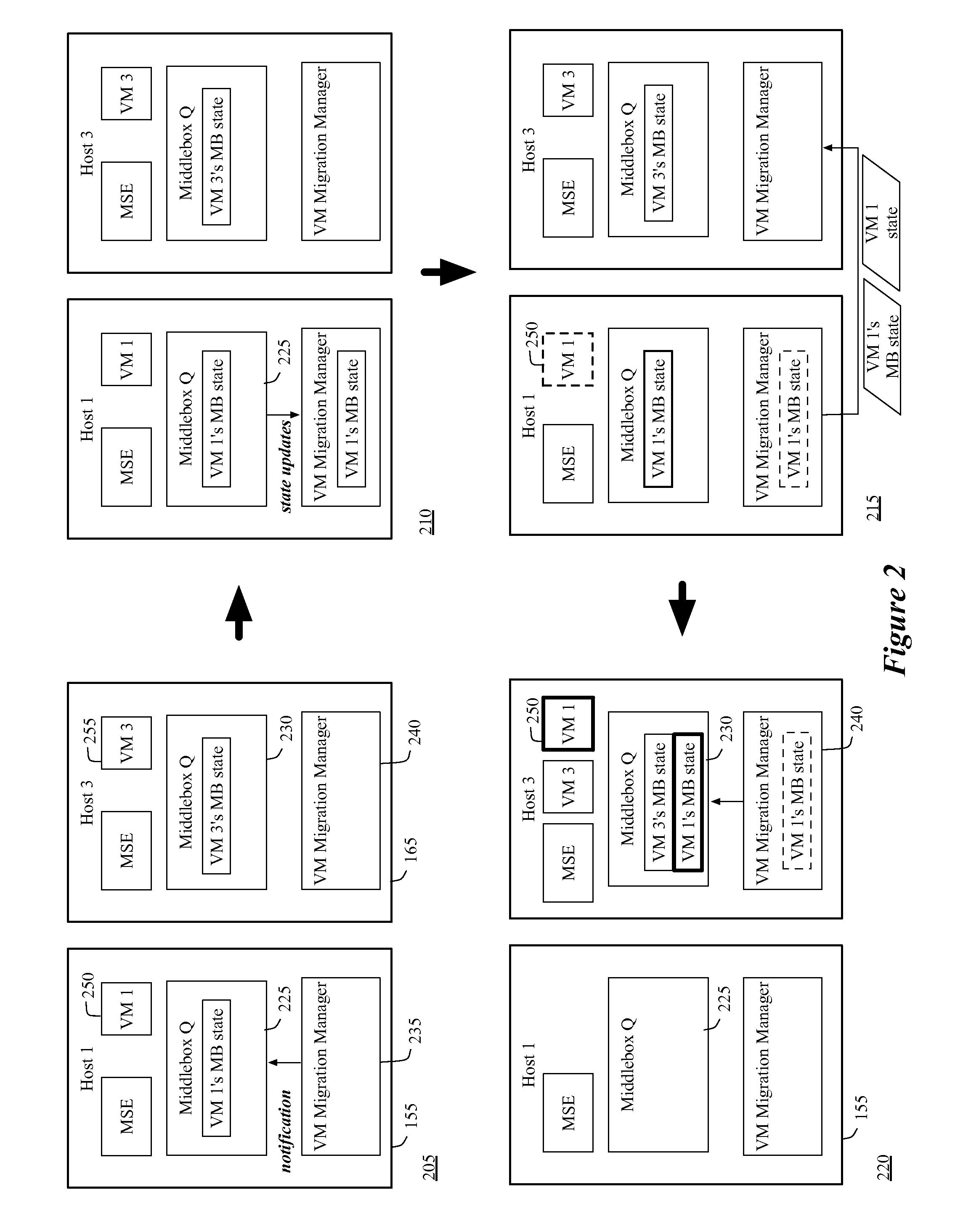
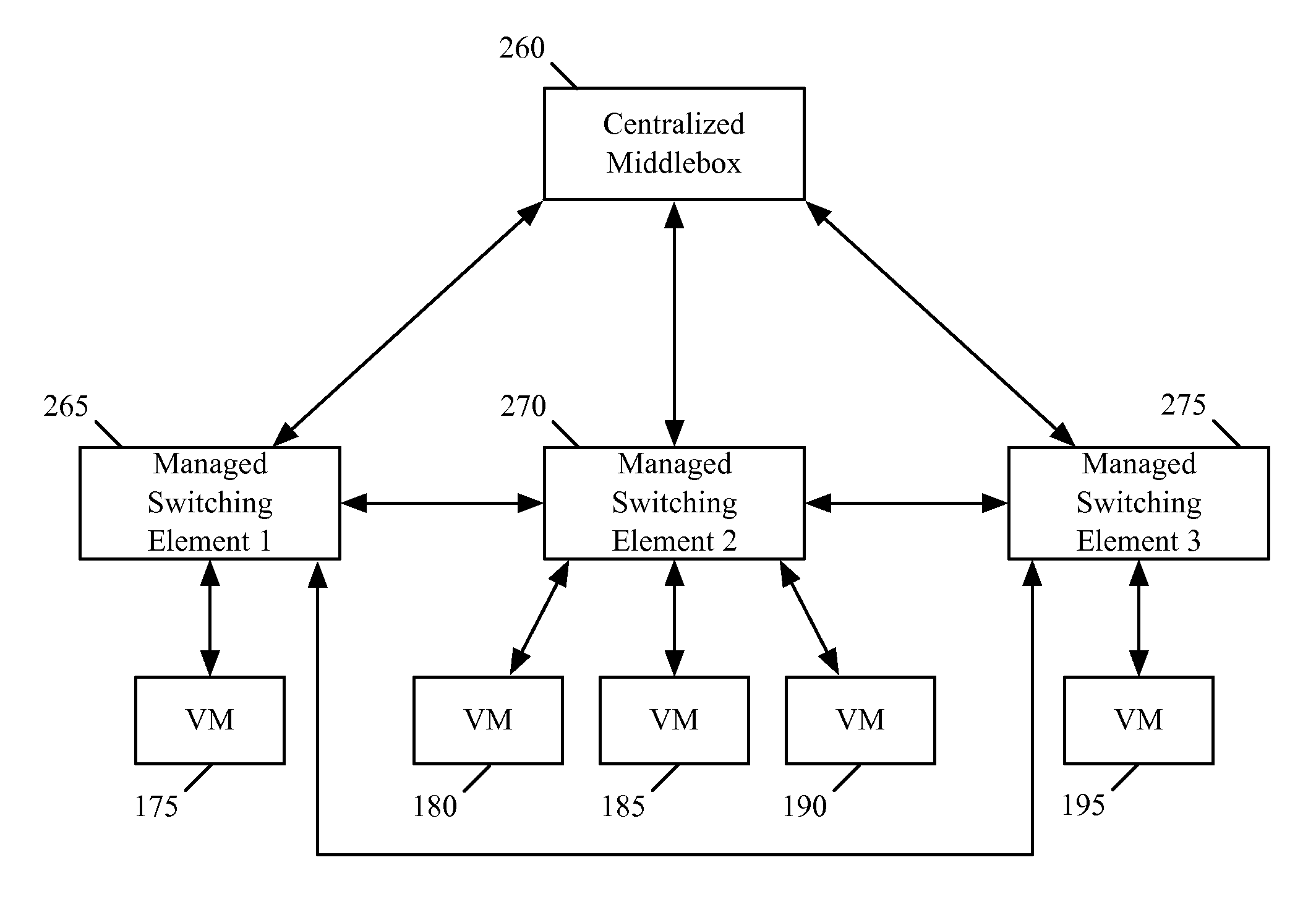
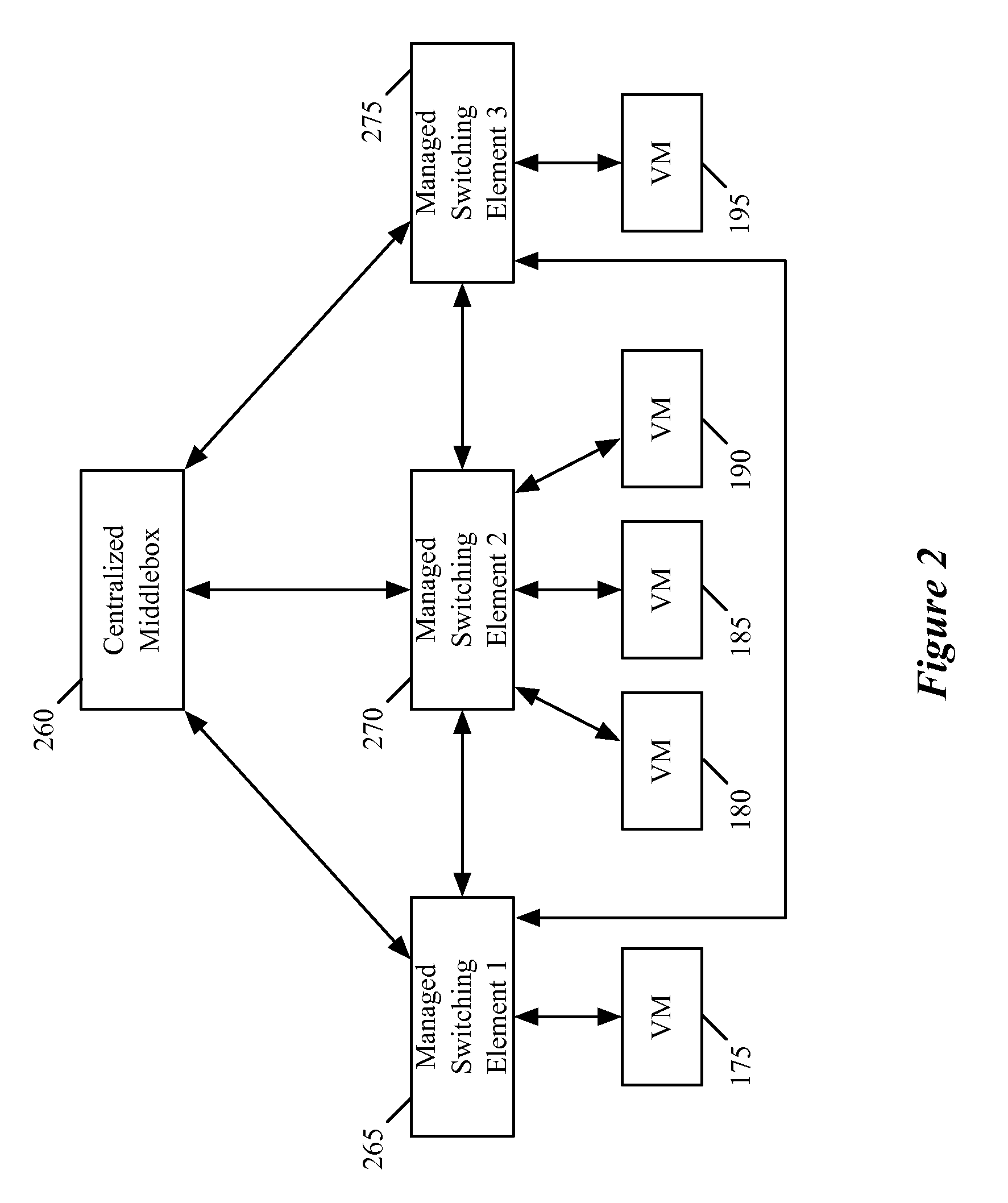
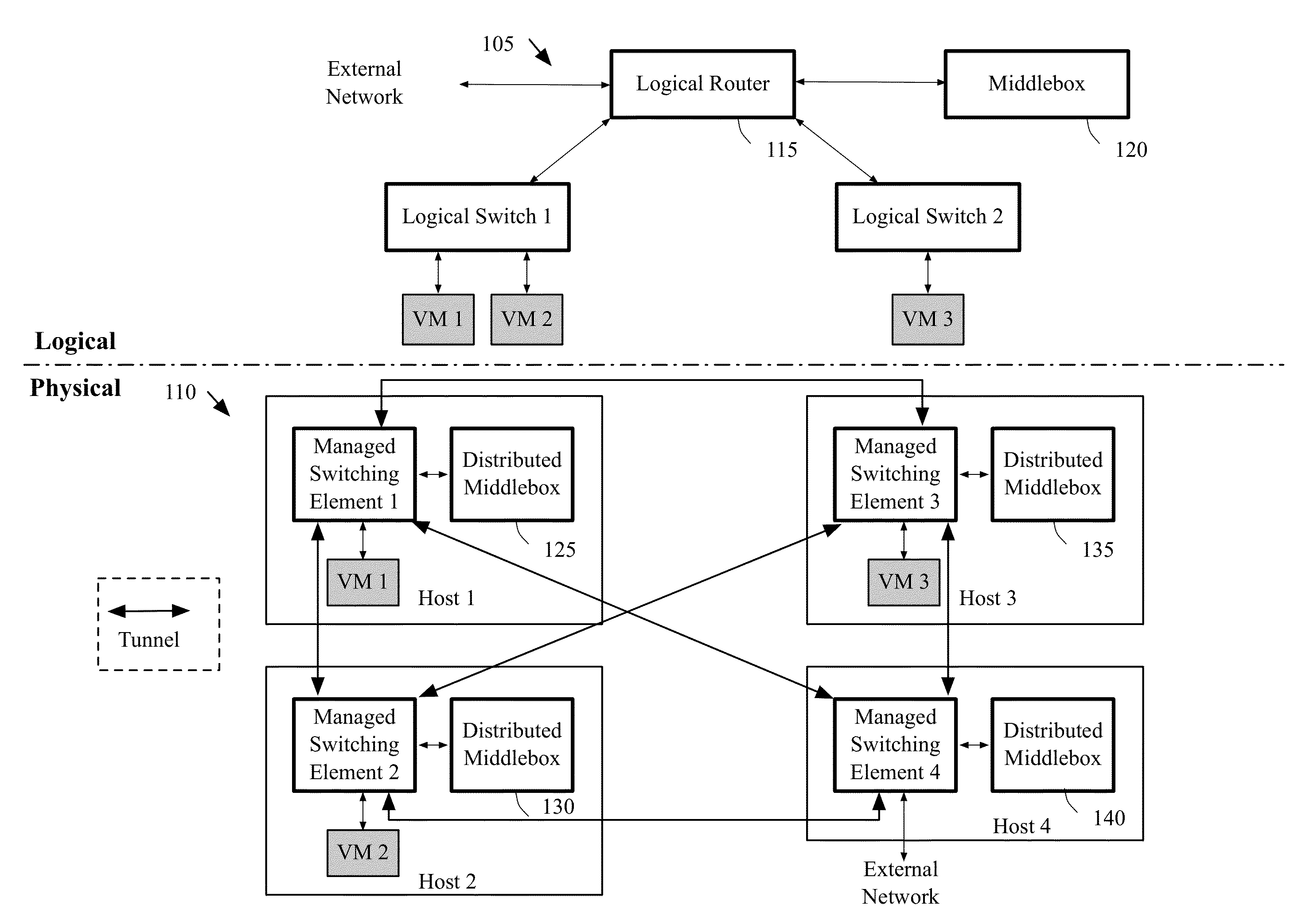
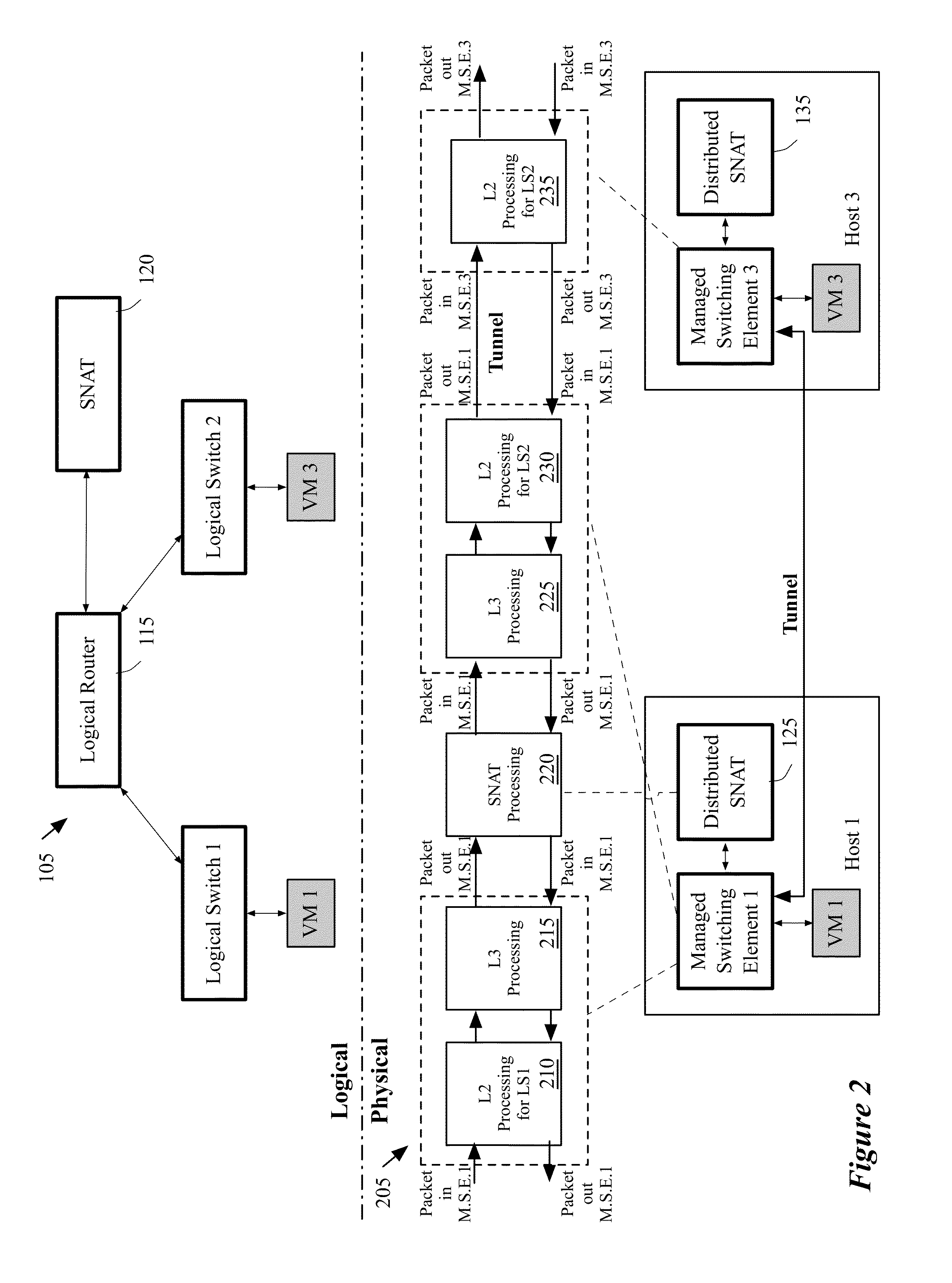
Migrating middlebox state for distributed middleboxes
A controller of a network control system for configuring several middlebox instances is described. The middlebox instances implement a middlebox in a distributed manner in several hosts. The controller configures, in a first host, a first middlebox instance to receive a notification from a migration module before a virtual machine (VM) running in the first host migrates to a second host and to send middlebox state related to the VM to the migration module.
Owner:NICIRA
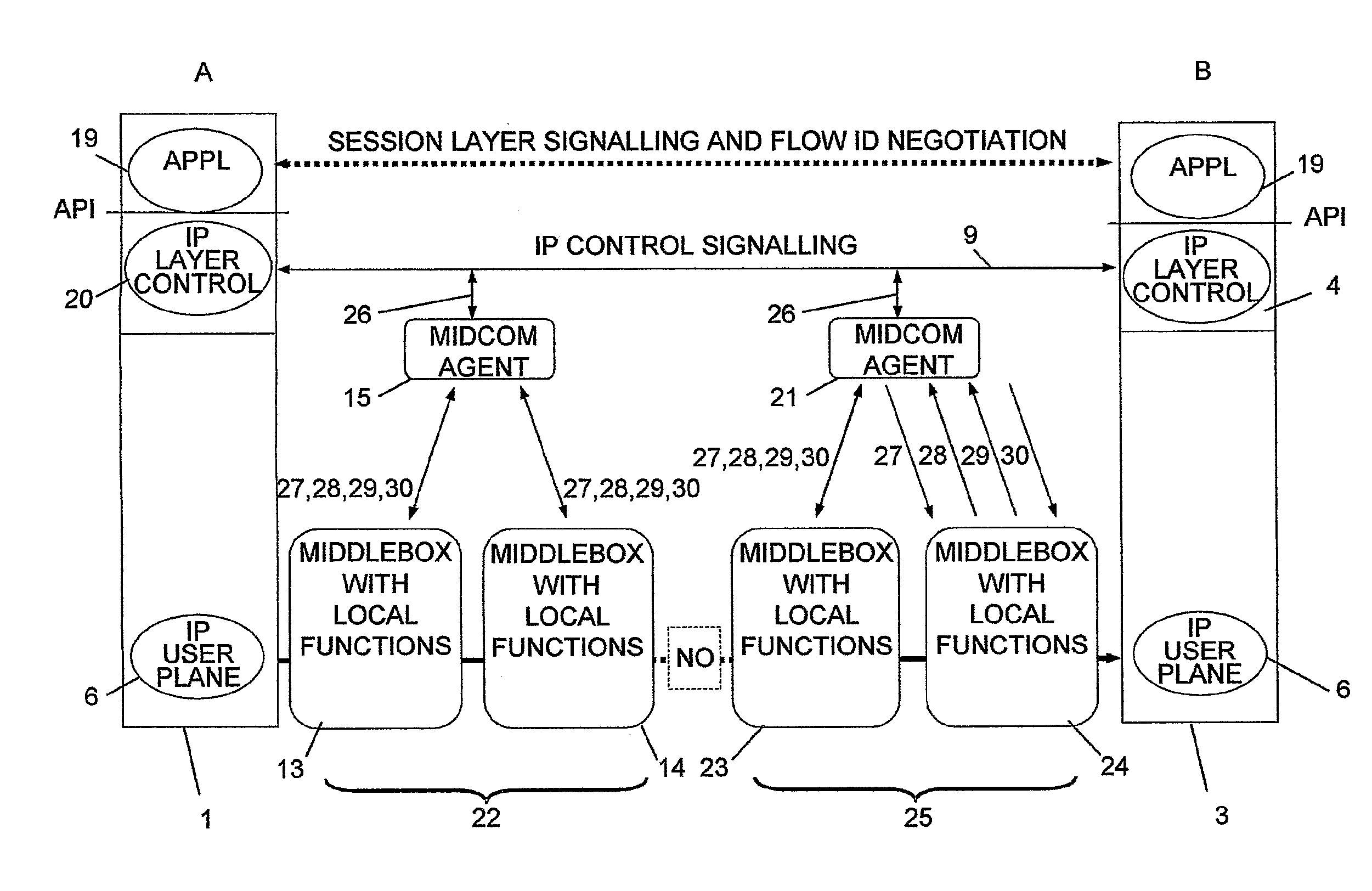
Control of Mobile Packet Streams
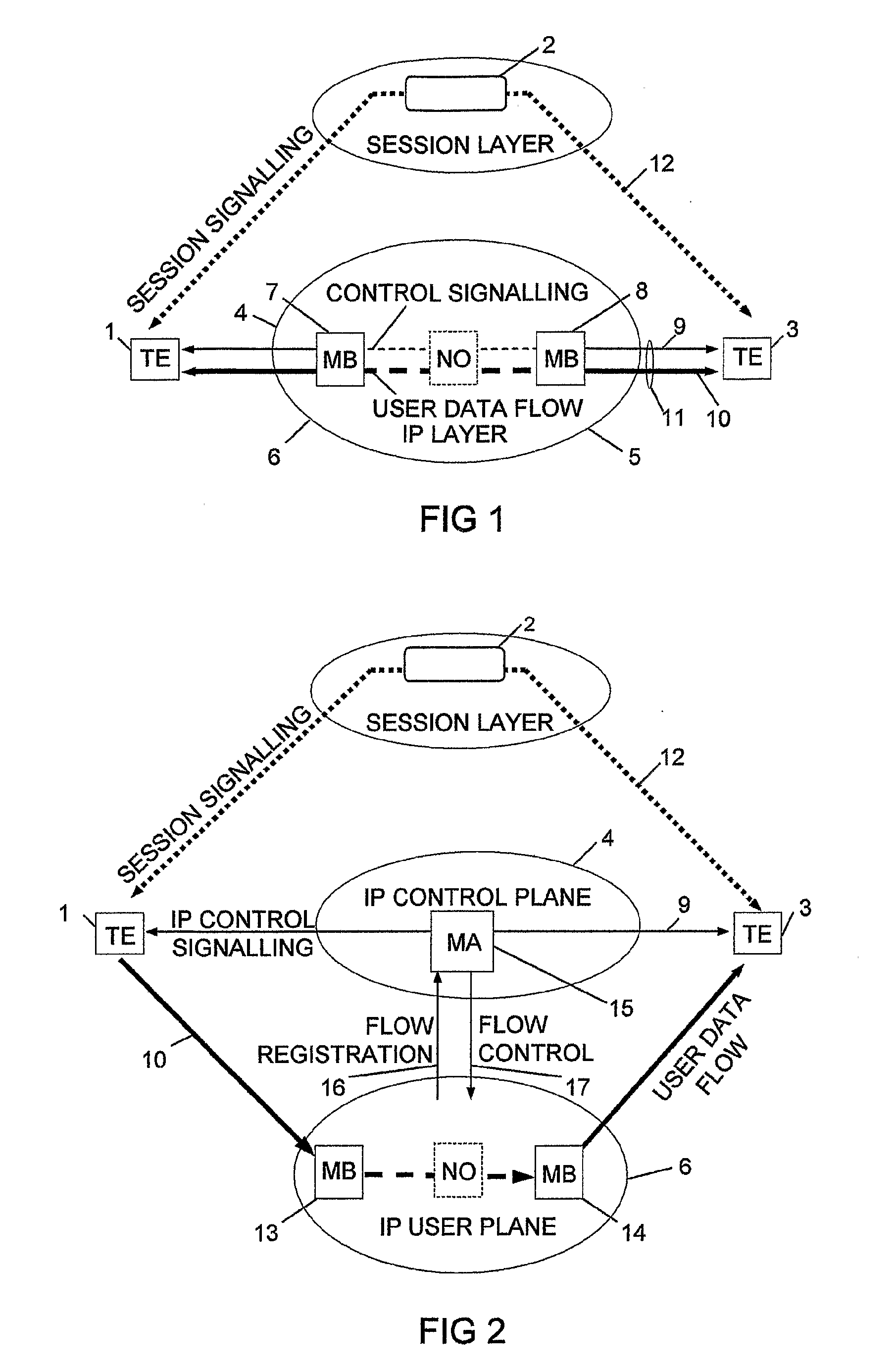
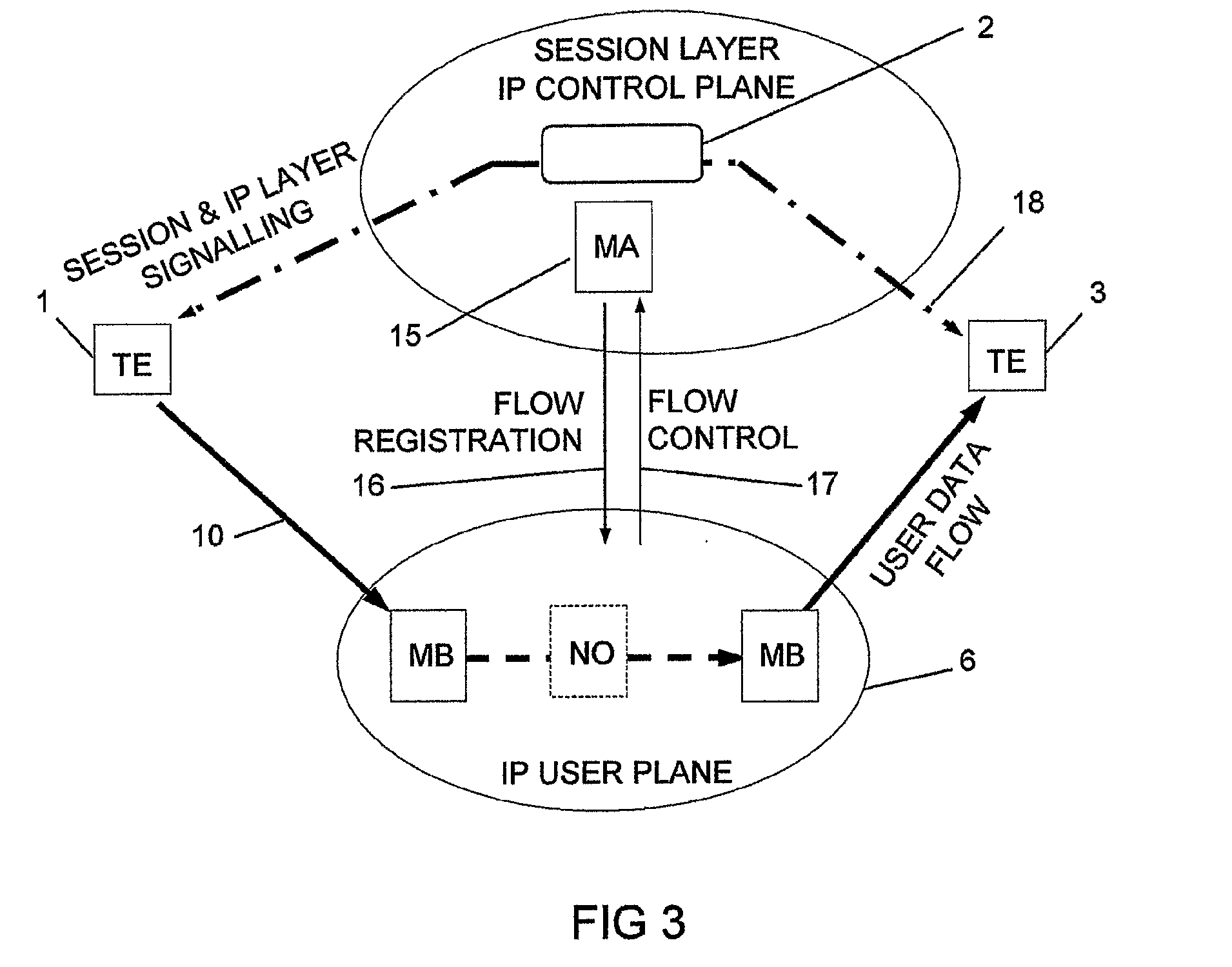
InactiveUS20070286185A1Reduce signaling overheadMinimum delayError preventionTransmission systemsControl signalMiddleware
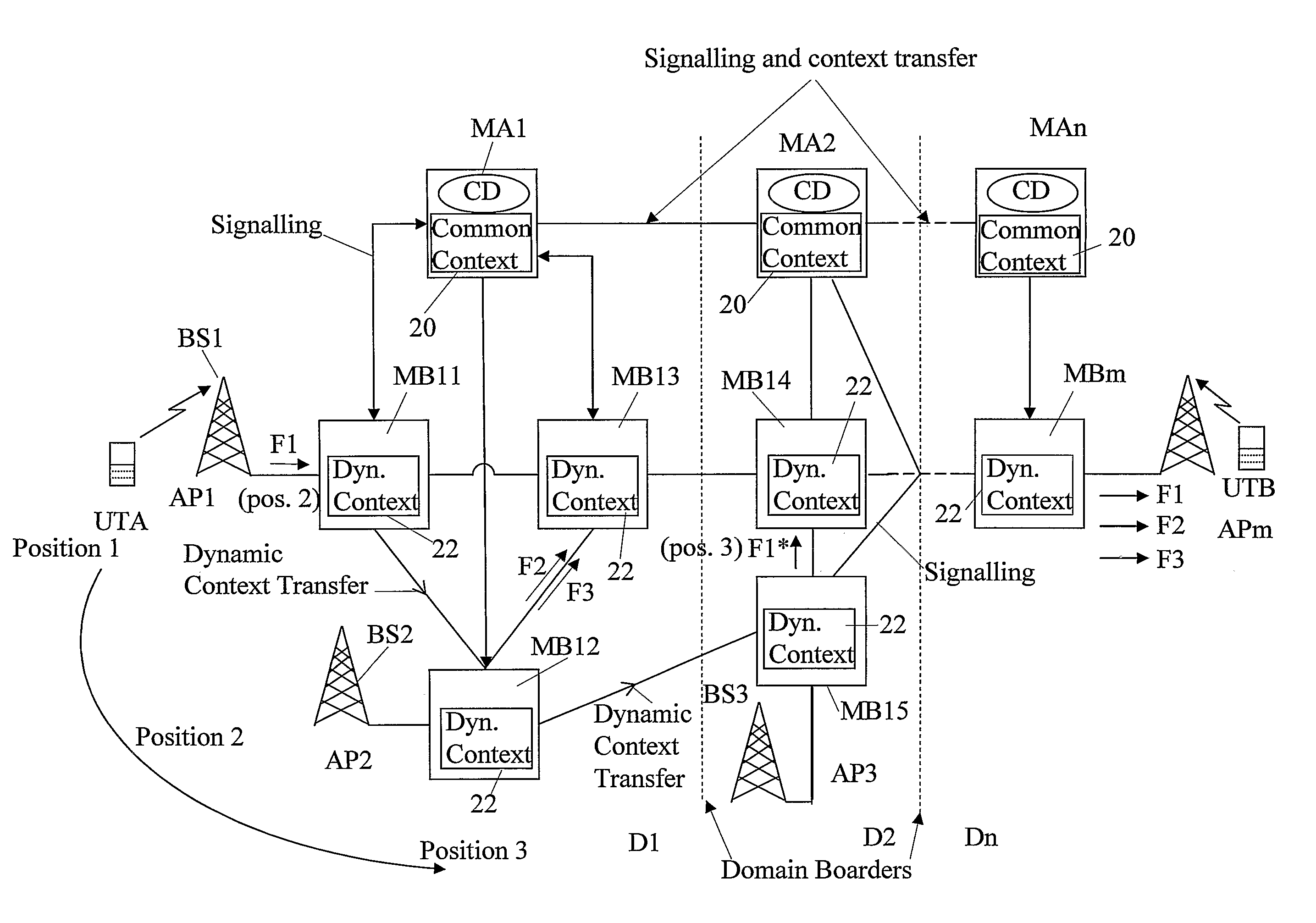
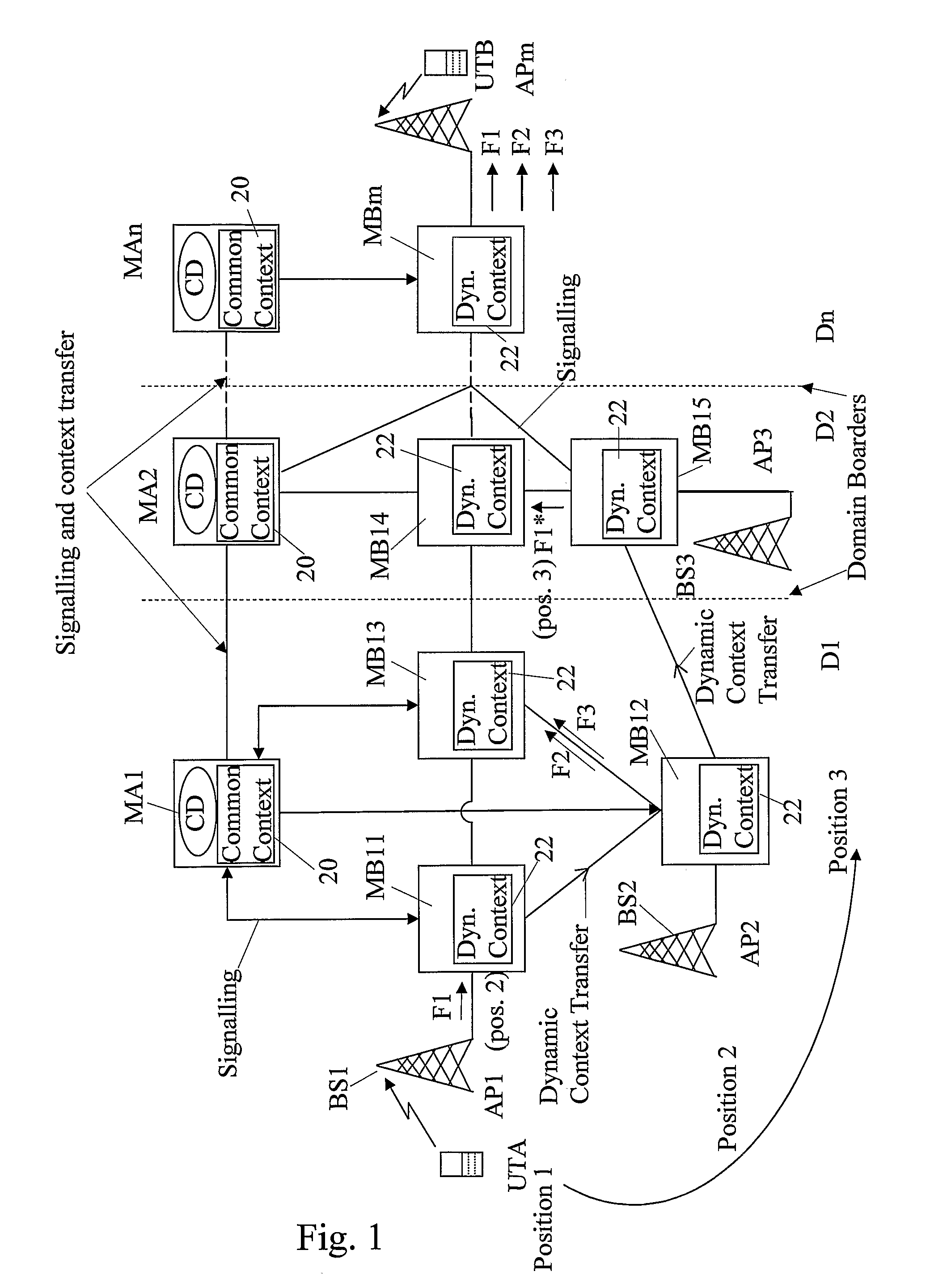
The invention relates to a method, device and system for control of mobile packet flows forwarded between IP based networks. Individual packet flows on an IP user plane (6) traverse middleboxes (13, 14, 23, 24) that are controlled from a midcom agent (15, 21). Each user flow registers its presence (29) in each middlebox it encounters on its way from its source (A) to its destination (B) at the user plane. In response each middlebox registers itself and the mobile flows it handles at the midcom agent with which they communicate using a midcom signalling protocol. The midcom agent comprises functionalities that its controlled middleboxes have and can provide control messages for how a middlebox shall handle a registered flow. The registration provides the midcom agent (15, 21) with knowledge of registered flows and middleboxes which allows the midcom agent to send control orders to the middleboxes that registered themselves, said orders pertaining to the handling of the flows at the respective middleboxes. A mechanism for control signalling at the IP control plane is described.
Owner:OPTIS WIRELESS TECH LLC
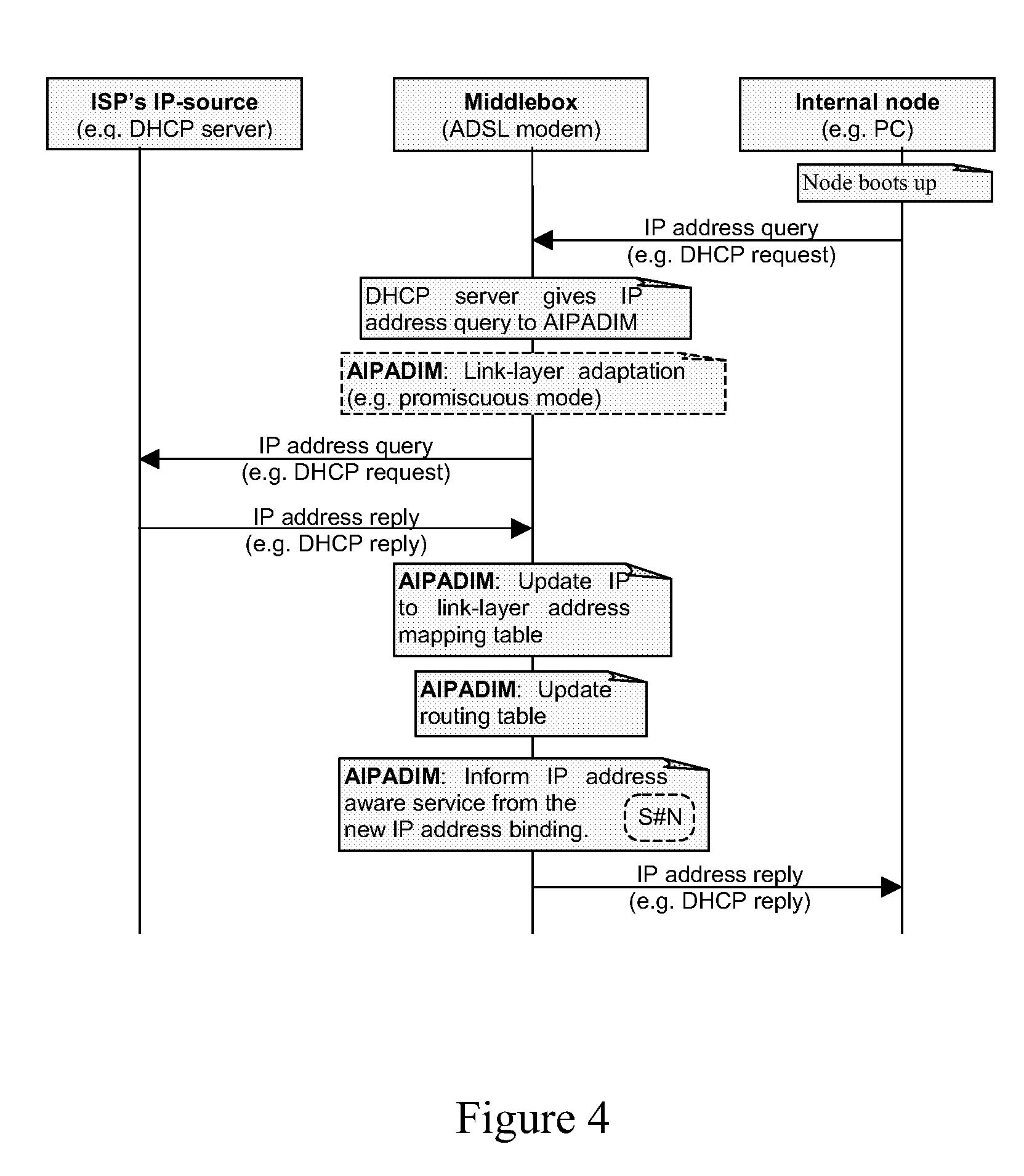
IP Address Distribution in Middleboxes
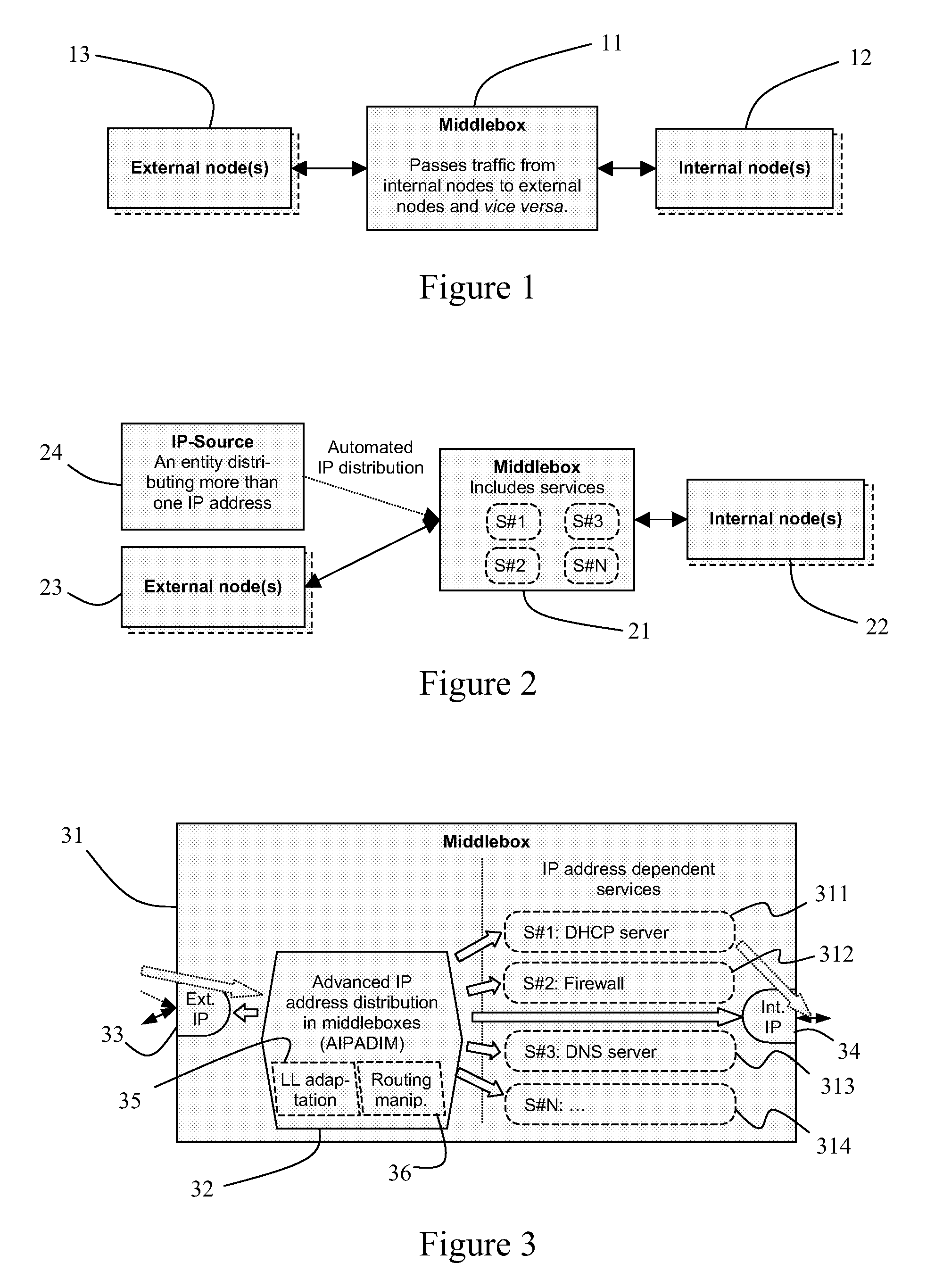
A middlebox and method of operating the middlebox to provide an interface between first and second IP networks. An entity within the first IP network allocates IP addresses to one or more entities in the second IP network. The middlebox routes IP traffic within and between the networks based on the IP addresses, implements at least one IP address dependent service other than routing, and dynamically informs each service of the IP addresses allocated to the network entities and of changes to these addresses.
Owner:TELEFON AB LM ERICSSON (PUBL)
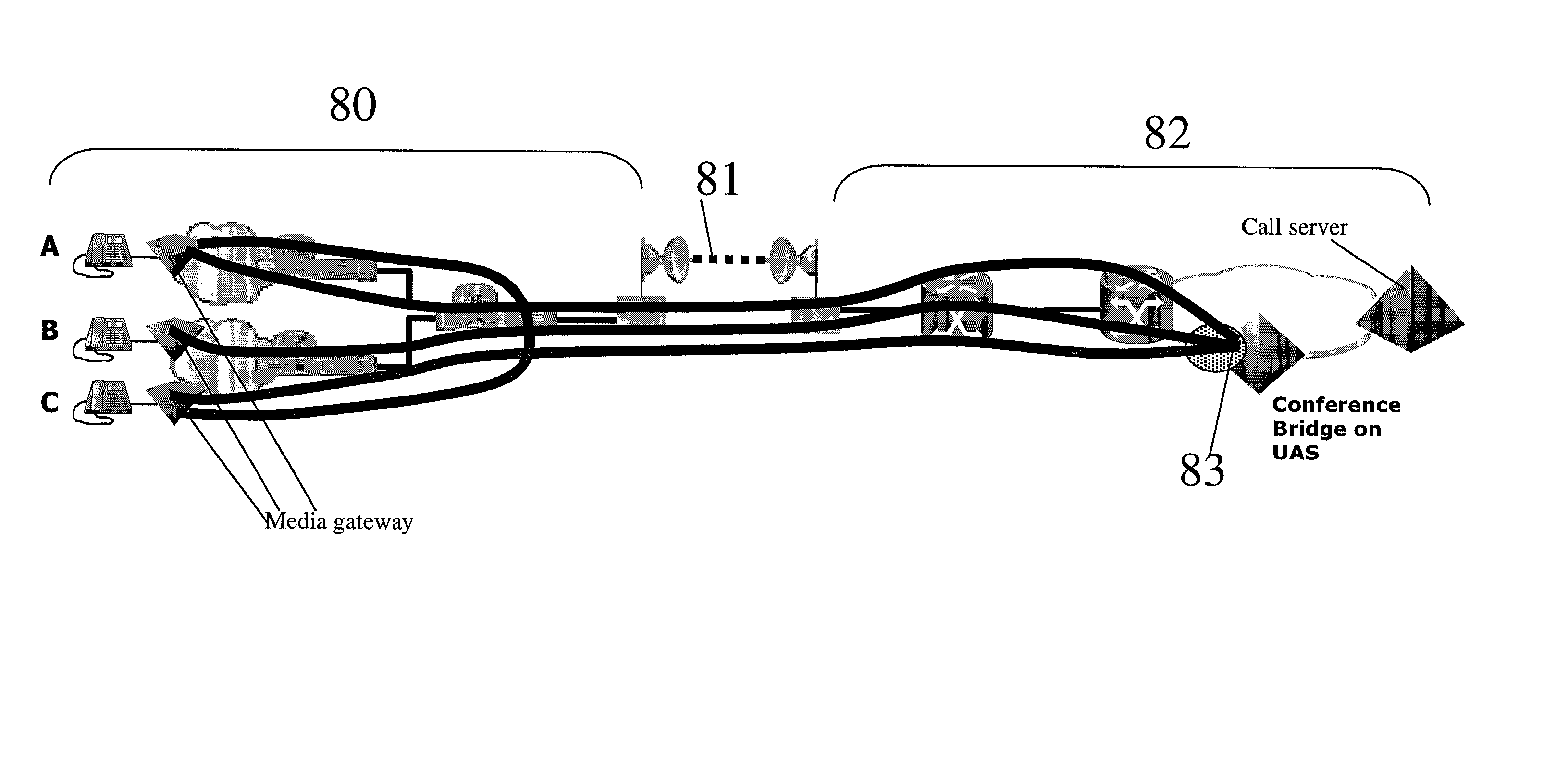
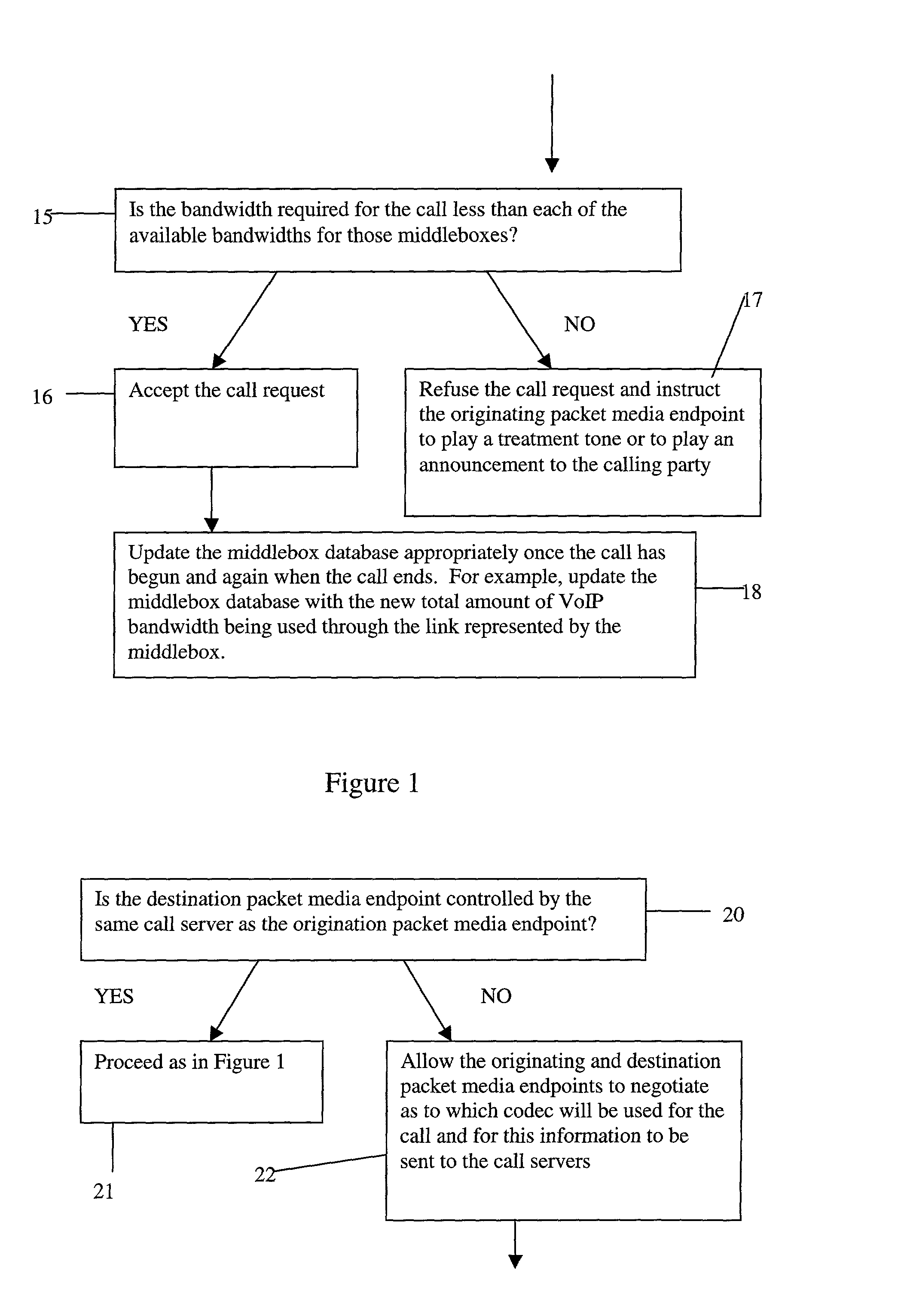
Admissions control in a connectionless communications network
InactiveUS20030123388A1Easy to implementCost-effectiveInterconnection arrangementsError preventionConnectionless communicationTeleconference
A method of providing call admission control which does not require using MIDCOM protocol methods, Packetcable protocols or COPS-RSVP approaches is described which is simple to implement, cost-effective and which is able to deal with particular situations such as conference calls. Each link in a communications network over which it is required to perform call admissions control is provided with a middlebox connected at each end of that link such that admissions control can be carried out at one end of the link. Call services are provided by Call Servers, each of which has access to a database containing pre-specified information about all middleboxes in that call server's realm. The database also has information about maximum bandwidths for the link associated with each middlebox. The call servers are used to keep a running tally of the amount of VolP call bandwidth associated with each middlebox on the edge of a low-bandwidth link, and to accept or refuse calls on the basis of the bandwidth information on a per-call basis.
Owner:NORTEL NETWORKS LTD
Network control system for configuring middleboxes
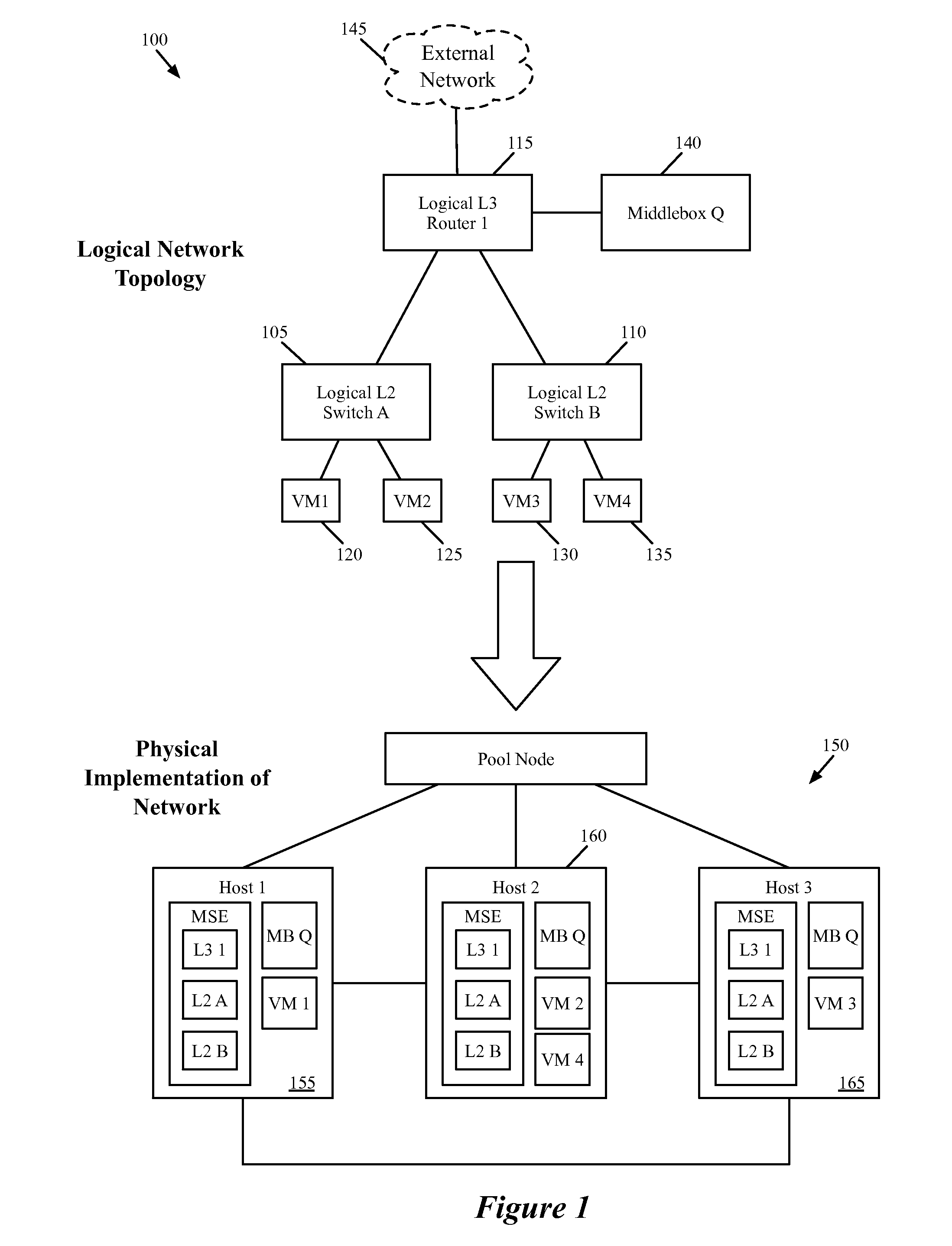
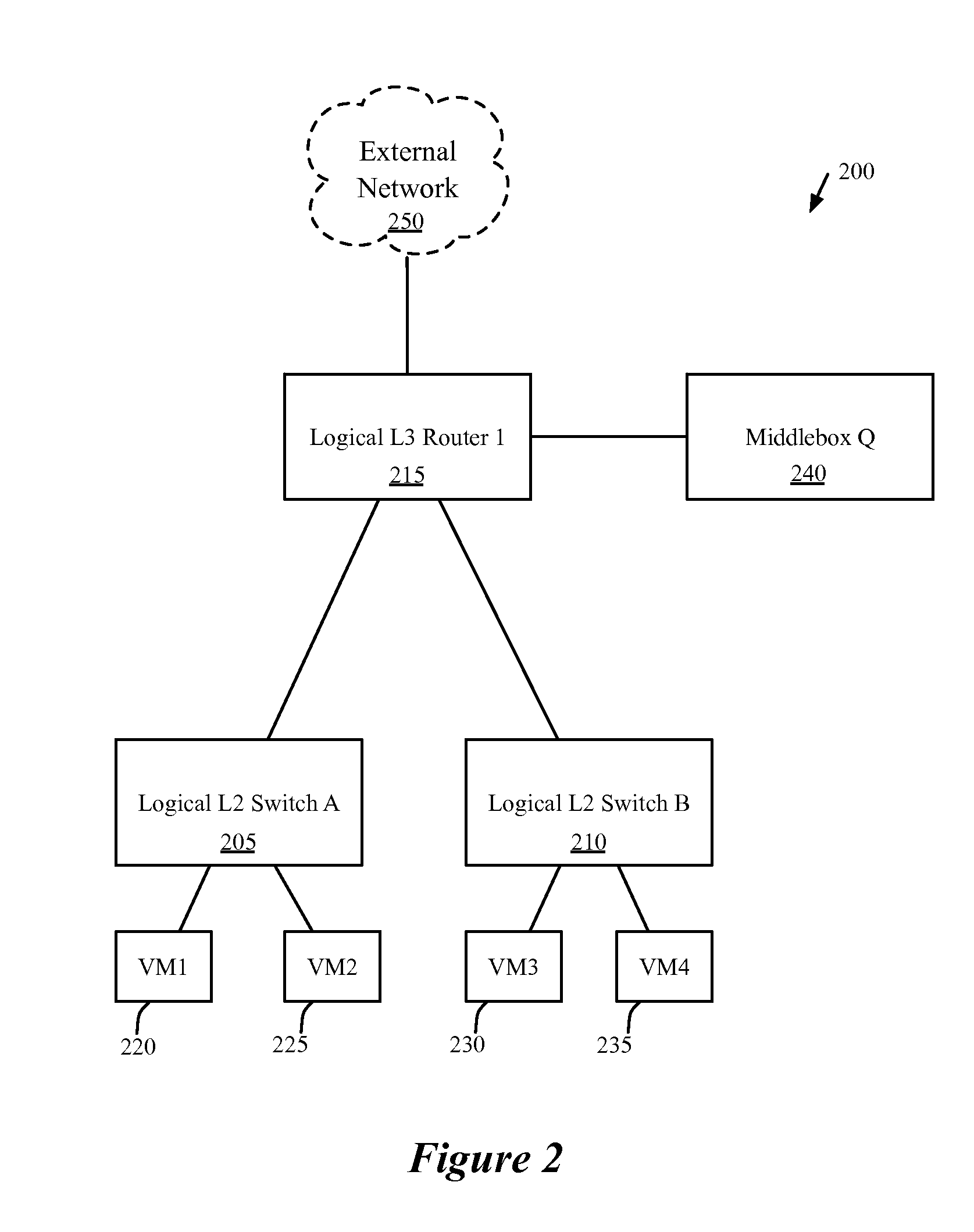
Some embodiments provide a method for configuring a logical middlebox in a hosting system that includes a set of nodes. The logical middlebox is part of a logical network that includes a set of logical forwarding elements that connect a set of end machines. The method receives a set of configuration data for the logical middlebox. The method uses a stored set of tables describing physical locations of the end machines to identify a set of nodes at which to implement the logical middlebox. The method provides the logical middlebox configuration for distribution to the identified nodes.
Owner:NICIRA
Control plane interface for logical middlebox services
ActiveUS20130132533A1Digital computer detailsData switching networksInternal identifierLogical network
Owner:NICIRA
Load balancing and destination network address translation middleboxes
A controller of a network control system for configuring several middlebox instances is described. The middlebox instances implement a middlebox in a distributed manner in several hosts. The controller configures a first middlebox instance to obtain status of a set of servers and disseminate the obtained status to a second middlebox instance. The controller configures the second middlebox instance to use the status to select a server from the set of servers.
Owner:NICIRA
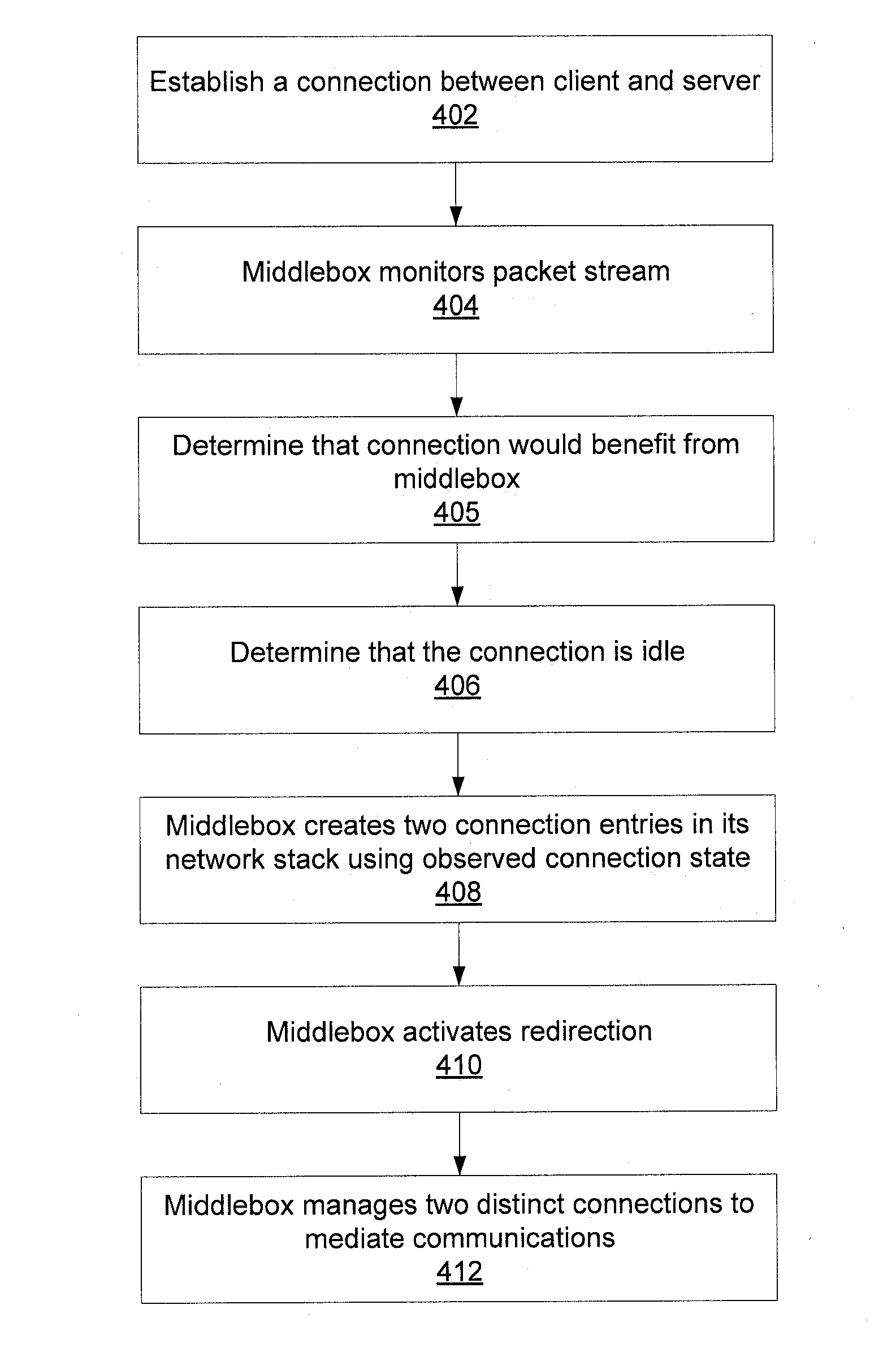
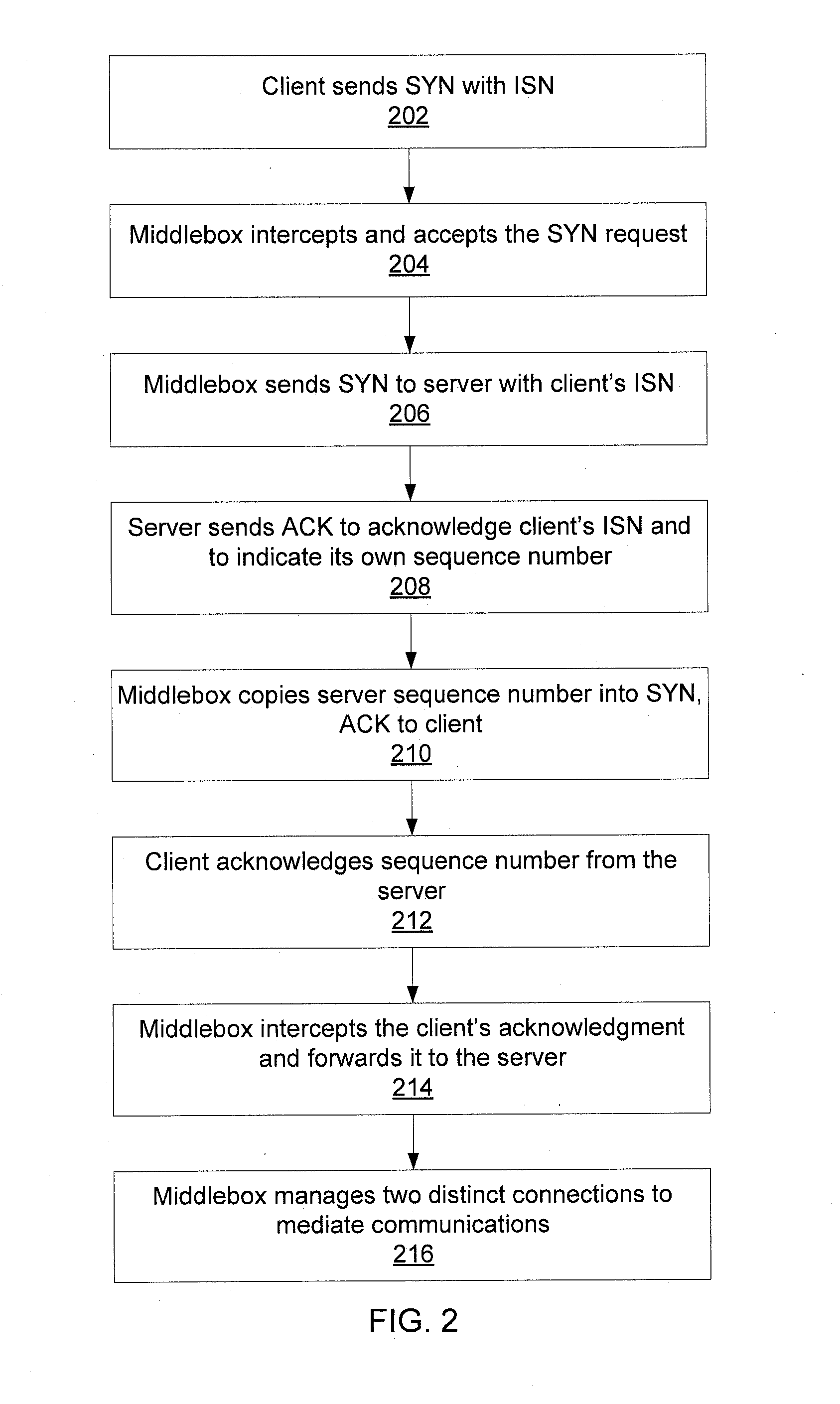
Transparent middlebox with graceful connection entry and exit
ActiveUS20140040451A1Reduce the degree of mismatchDigital computer detailsTransmissionChannel state informationNetwork connection
Methods for inserting a middlebox into a network connection include monitoring network state information in a connection between a client and a server. When the connection is idle, a connection entry is created for each device and is initialized using state information gathered by monitoring the network connection. Redirection of the network connection is activated between the client and the server such that the middlebox mediates the connection. Methods for removing a middlebox from a network connection include determining a degree of mismatch between a sequence number in a first connection between the middlebox and a client and a sequence number in a second connection between the middlebox and a server, delaying acknowledgment signals from the middlebox on a connection to decrease the degree of mismatch, and establishing a direct connection between the client and the server without mediation by the middlebox when the degree of mismatch is zero.
Owner:IBM CORP
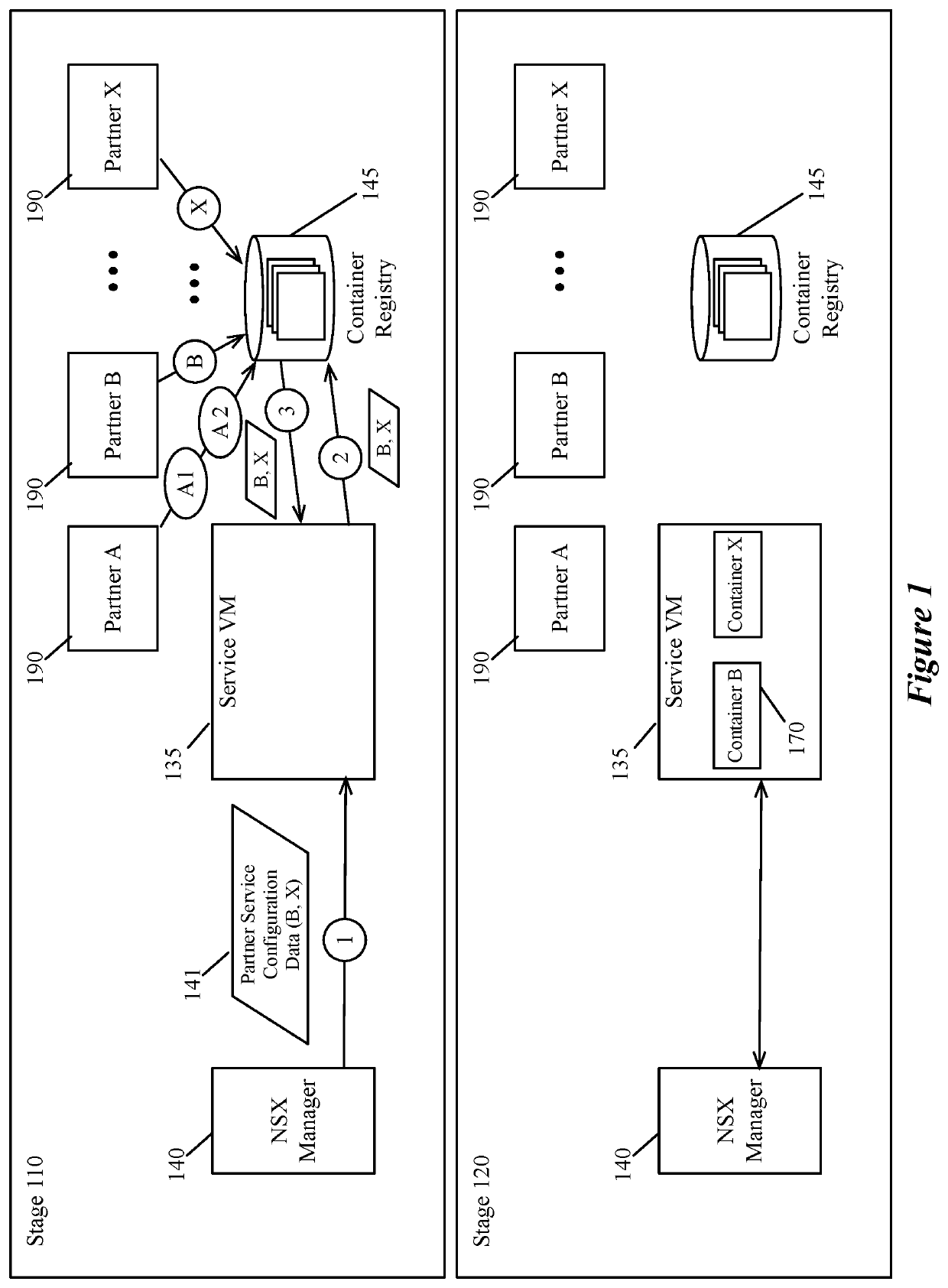
Configuring a compute node to perform services on a host
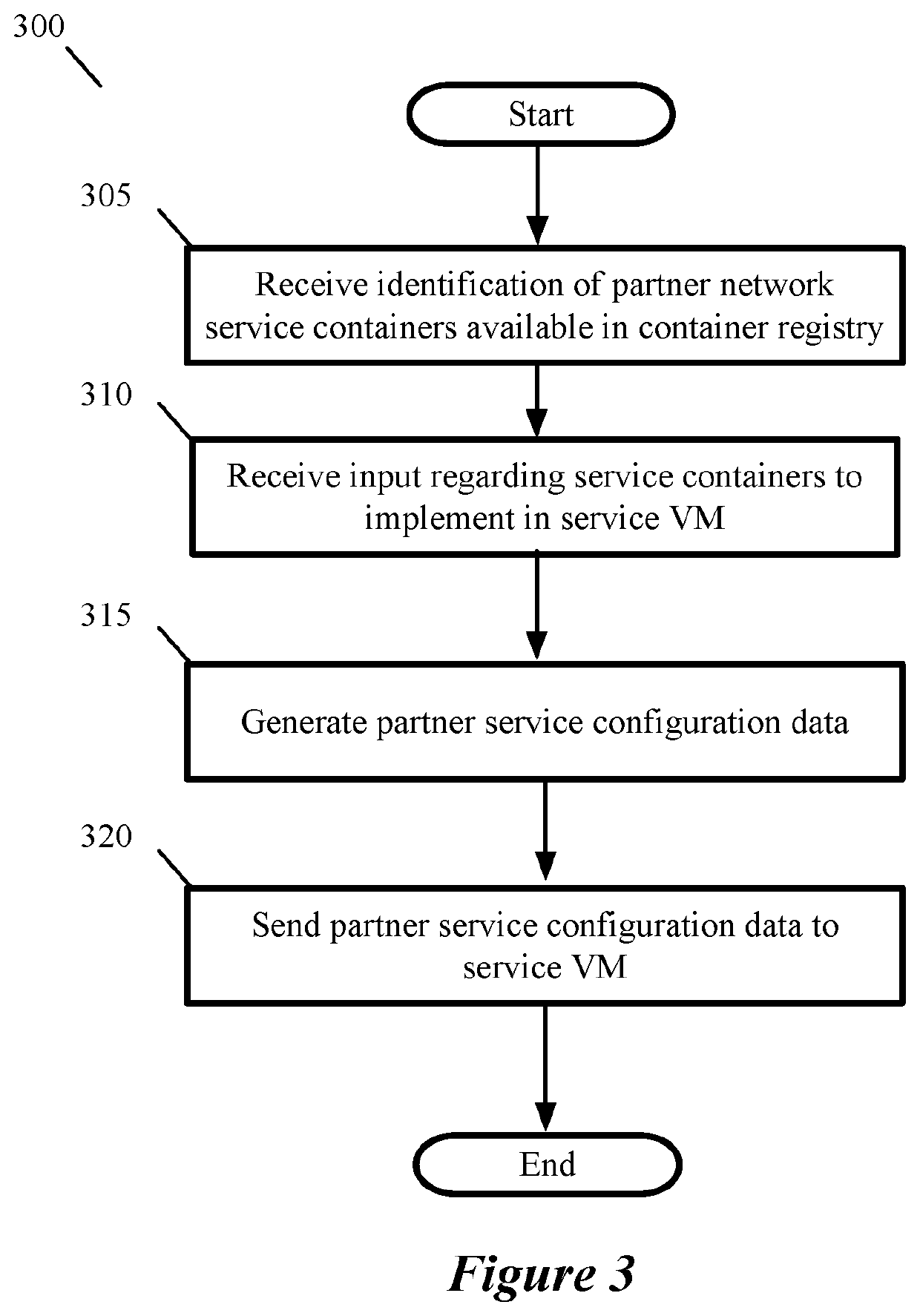
Some embodiments provide a novel method for configuring a service data compute node (DCN) executing on a host computer to perform network services (e.g., firewall, load balancing, intrusion detection, network address translation (NAT), other middlebox services, etc.) for several DCNs executing on the host computer. The method receives, at the service DCN, an identification of a set of container specifications that will be implemented (e.g., will be executed by) the service DCN. The method then retrieves the identified set of container specifications (e.g., container images) from a container repository storing multiple received container specifications. In some embodiments, the container specifications include container images generated by a third party service partner for providing a particular service or set of services and stored in a container repository. The method then instantiates the retrieved containers to provide the identified network services to data messages received at the service DCN.
Owner:NICIRA
Content compression in networks
ActiveUS7975071B2Well formedTime-division multiplexMultiple digital computer combinationsData packRecipient side
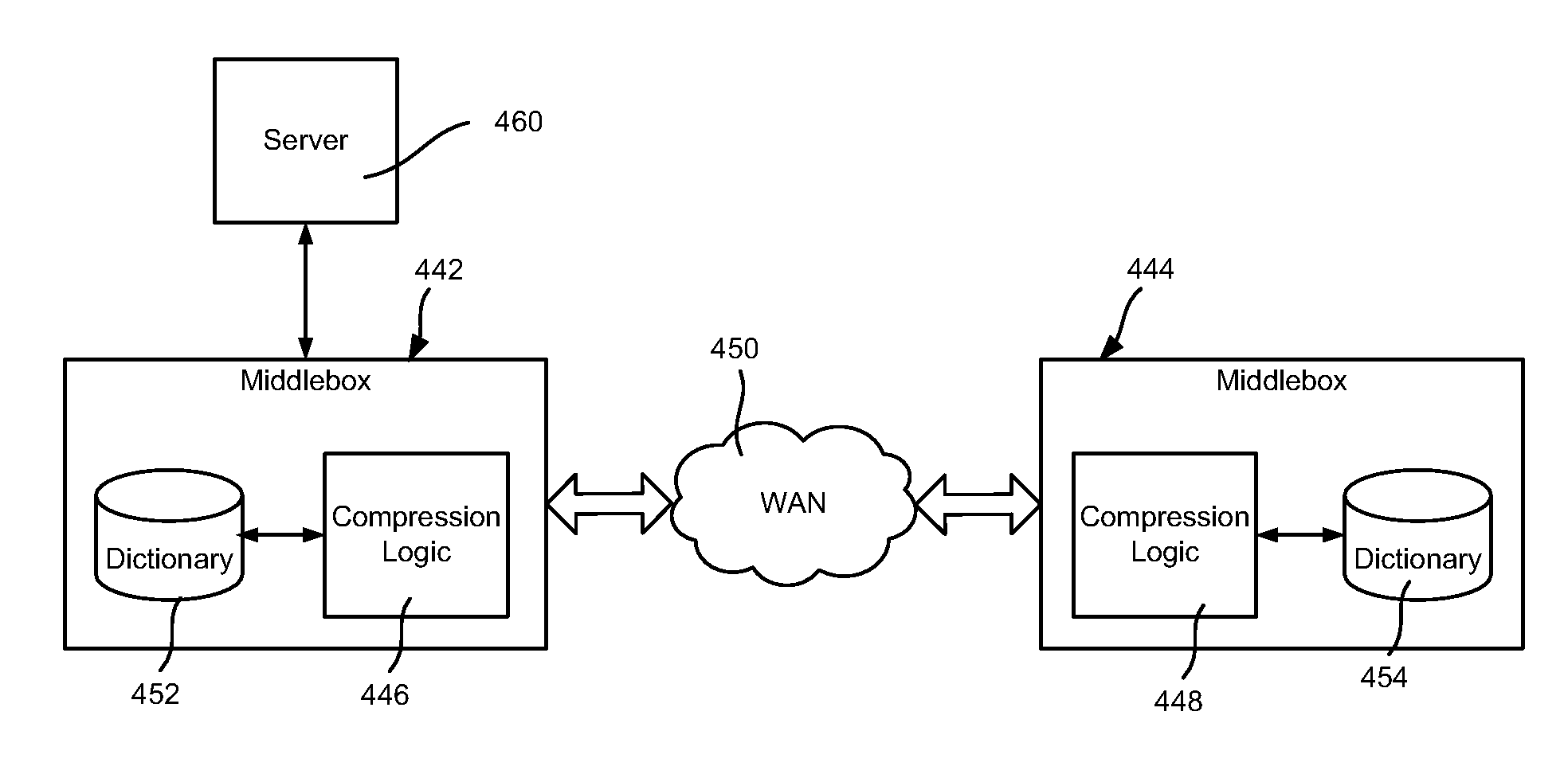
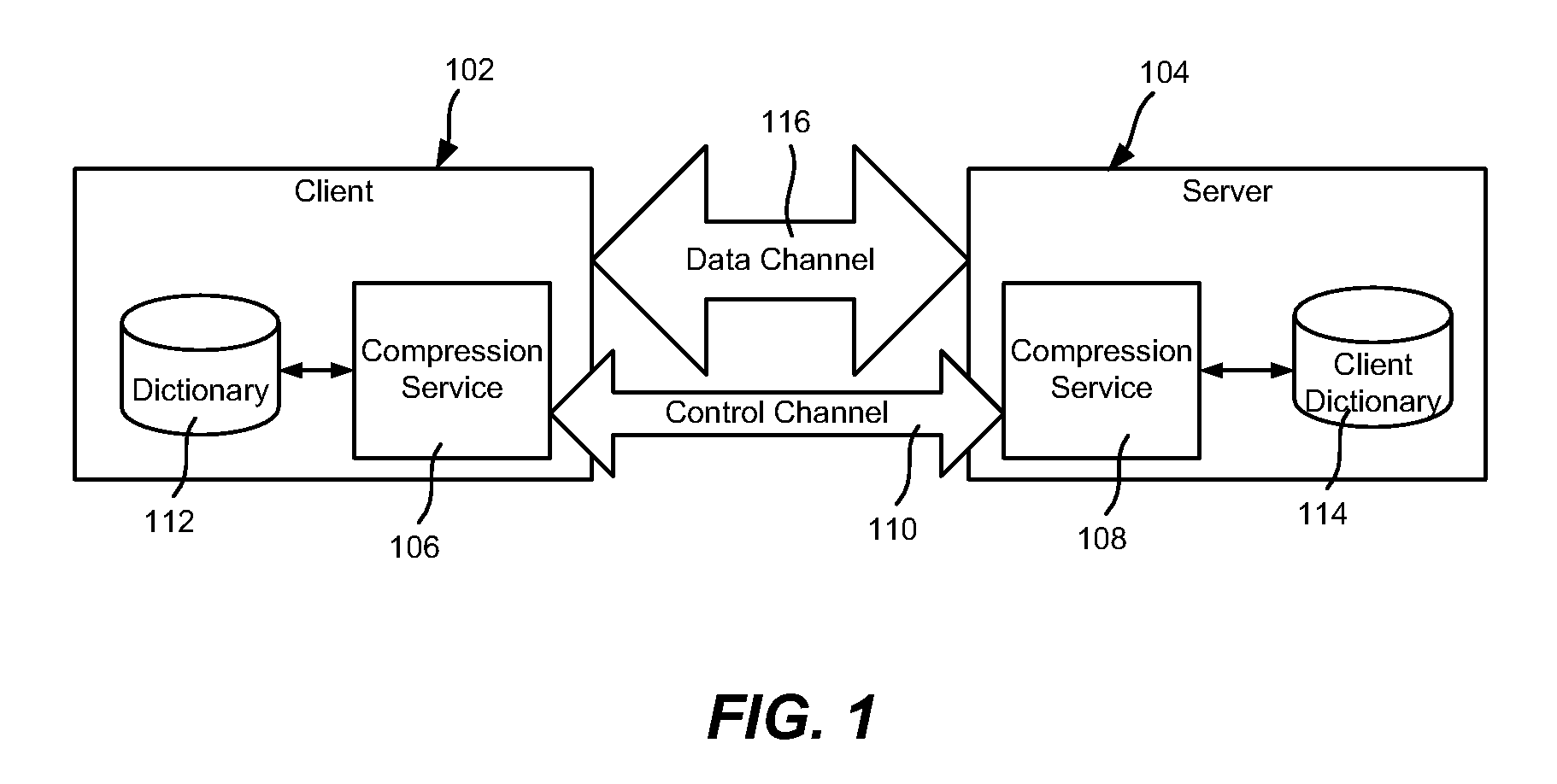
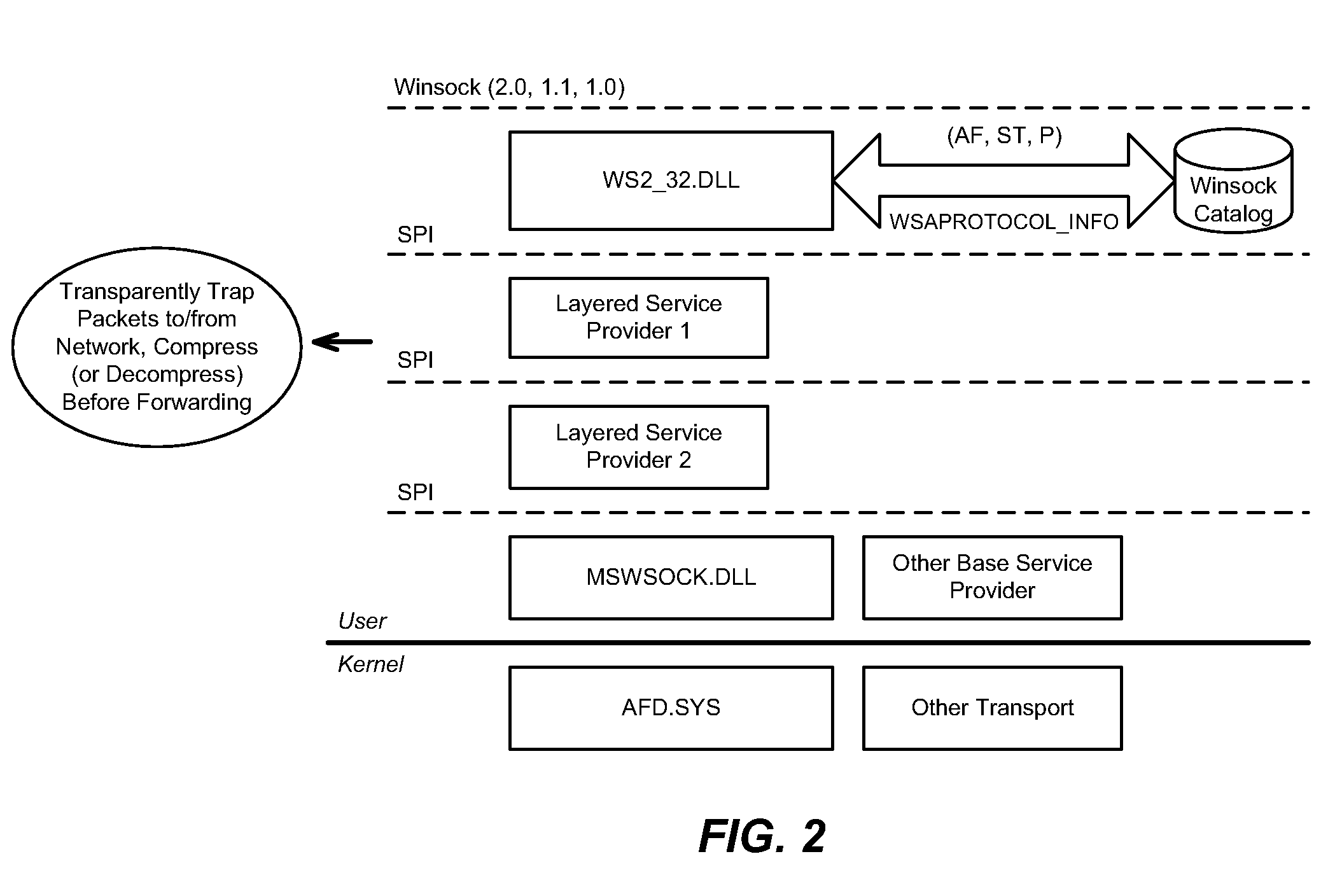
Described is transparently compressing content for network transmission, including end-to-end compression. An end host or middlebox device sender sends compressed packets to an end host or middlebox device receiver, which decompresses the packets to recover the original packet. The sender constructs compressed packets including references to information maintained at the receiver, which the receiver uses to access the information to recreate actual original packet content. The receiver may include a dictionary corresponding to the sender, e.g., synchronized with the sender's dictionary. Alternatively, in speculative compression, the sender does not maintain a dictionary, and instead sends a fingerprint (hash value) by which the receiver looks up corresponding content in its dictionary; if not found, the receiver requests actual content. Scheduling to maintain fairness and smoothing bursts to coexist with TCP congestion control are also described, as are techniques for routing compressed data over networked end hosts and / or compression-enabled middlebox devices.
Owner:MICROSOFT TECH LICENSING LLC
Method for securing RTS communications across middleboxes
ActiveUS20060272009A1Digital data processing detailsUser identity/authority verificationReal time servicesSignaling protocol
A new method is provided for establishing real-time services that can coexist with NAT and firewalls, even when the signaling protocol uses cryptography. A communication channel between the call server and the middlebox passes information between them about the bearer channels associated with each signaling session.
Owner:LGS INNOVATIONS
Connection identifier assignment and source network address translation
ActiveUS20130128891A1Digital computer detailsData switching by path configurationControl systemNetwork control
A controller of a network control system for configuring several middlebox instances is described. The middlebox instances implement a middlebox in a distributed manner in several hosts. The controller assigns a first set of identifiers to a first middlebox instance that associates an identifier in the first set with a first packet. The controller assigns a second set of identifiers to a second middlebox instance that associates an identifier in the second set with a second packet.
Owner:NICIRA
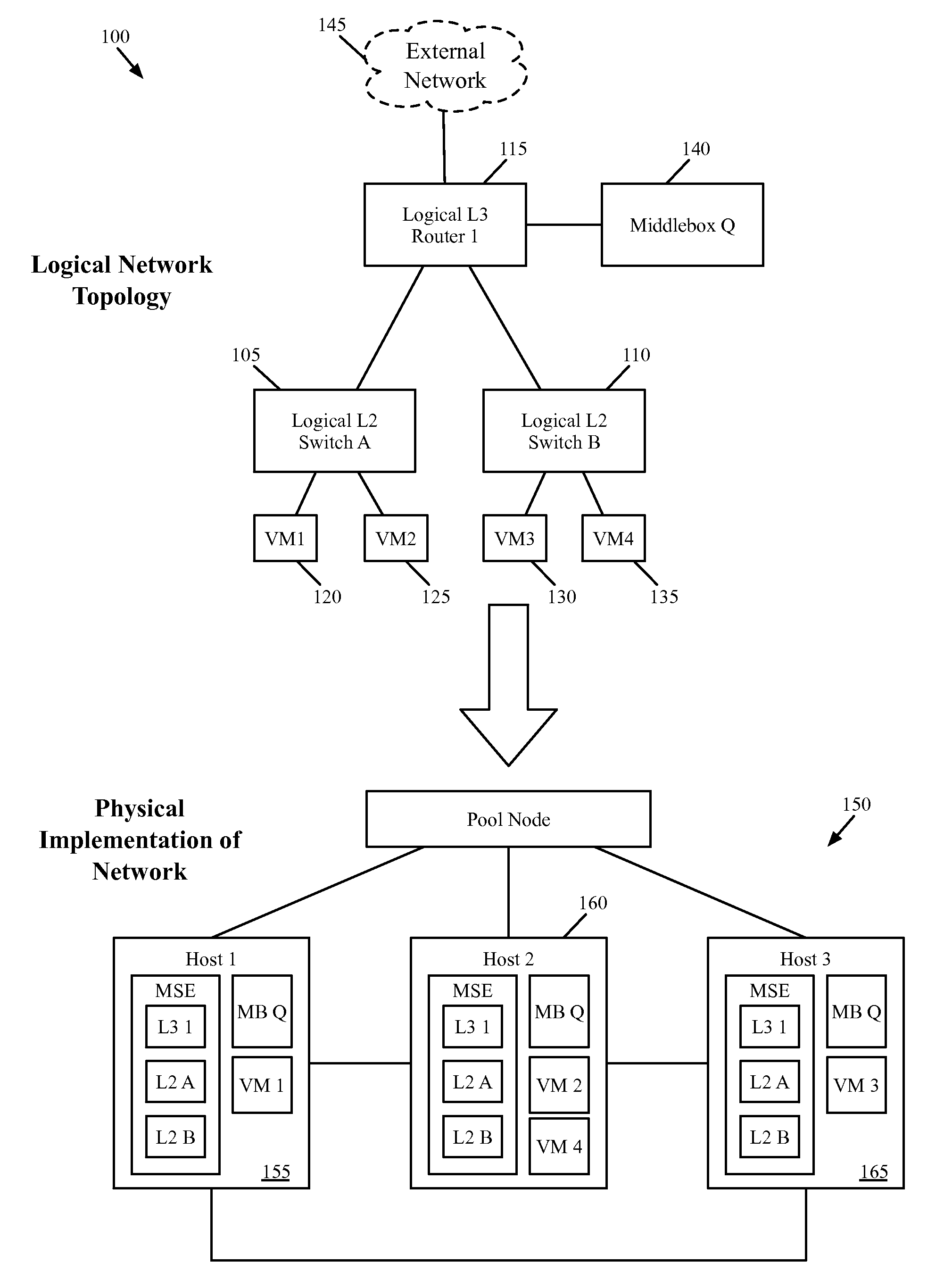
Architecture of networks with middleboxes
Some embodiments provide a system for implementing a logical network that includes a set of end machines, a first logical middlebox, and a second logical middlebox connected by a set of logical forwarding elements. The system includes a set of nodes. Each of several nodes includes (i) a virtual machine for implementing an end machine of the logical network, (ii) a managed switching element for implementing the set of logical forwarding elements of the logical network, and (iii) a middlebox element for implementing the first logical middlebox of the logical network. The system includes a physical middlebox appliance for implementing the second logical middlebox.
Owner:NICIRA
Solutions for dynamic NAT and firewall traversal
InactiveUS20110299554A1Communication securityError preventionTime-division multiplexNetwork addressingNetwork address translation
Solution methods for ensuring control and data packets to traverse network address translators (NATs) and firewalls, when a mobile terminal acquires a new (Internet Protocol) address and may move behind a new NAT / firewall are provided. These solutions form an integral part of seamless mobility and multipath packet delivery in IP networks. The solution approach decomposes the problem into downstream control-plane, downstream data-plane, and upstream data-plane sub-problems. The solution is scalable as it does not require a new routing infrastructure, except in the case of traversing a symmetric NAT, a middle box is used as a relay
Owner:ROS GIRALT JORDI +1
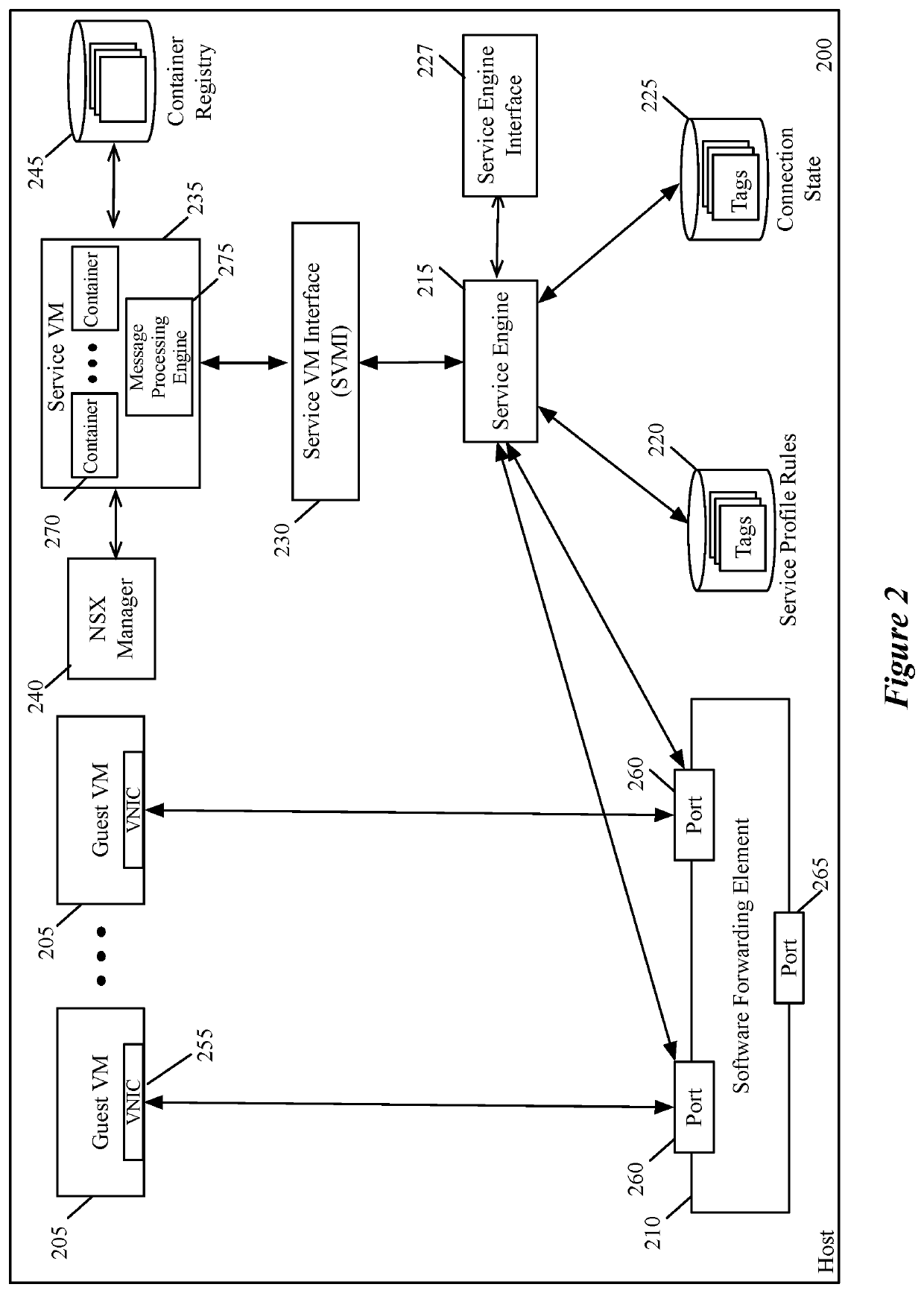
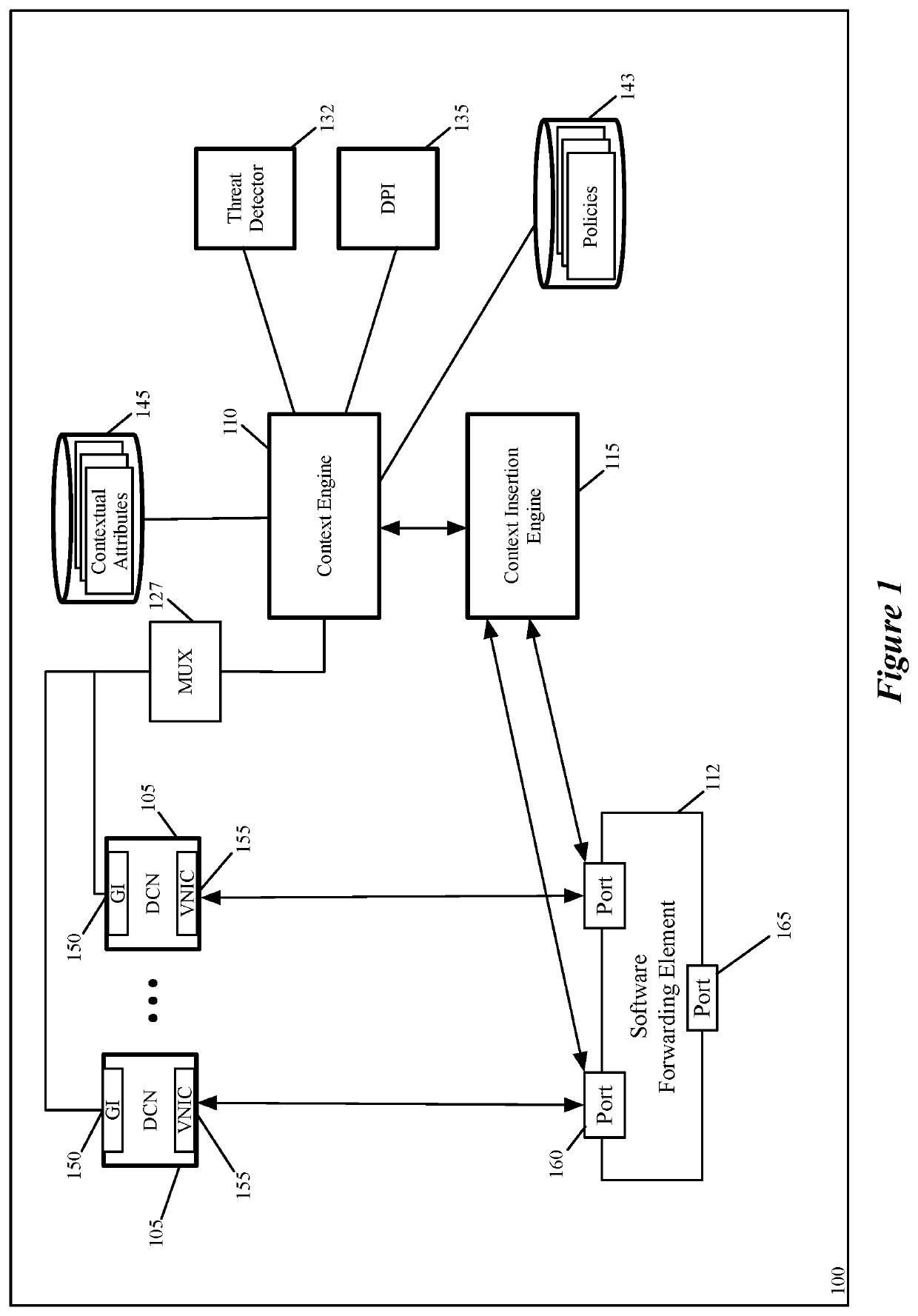
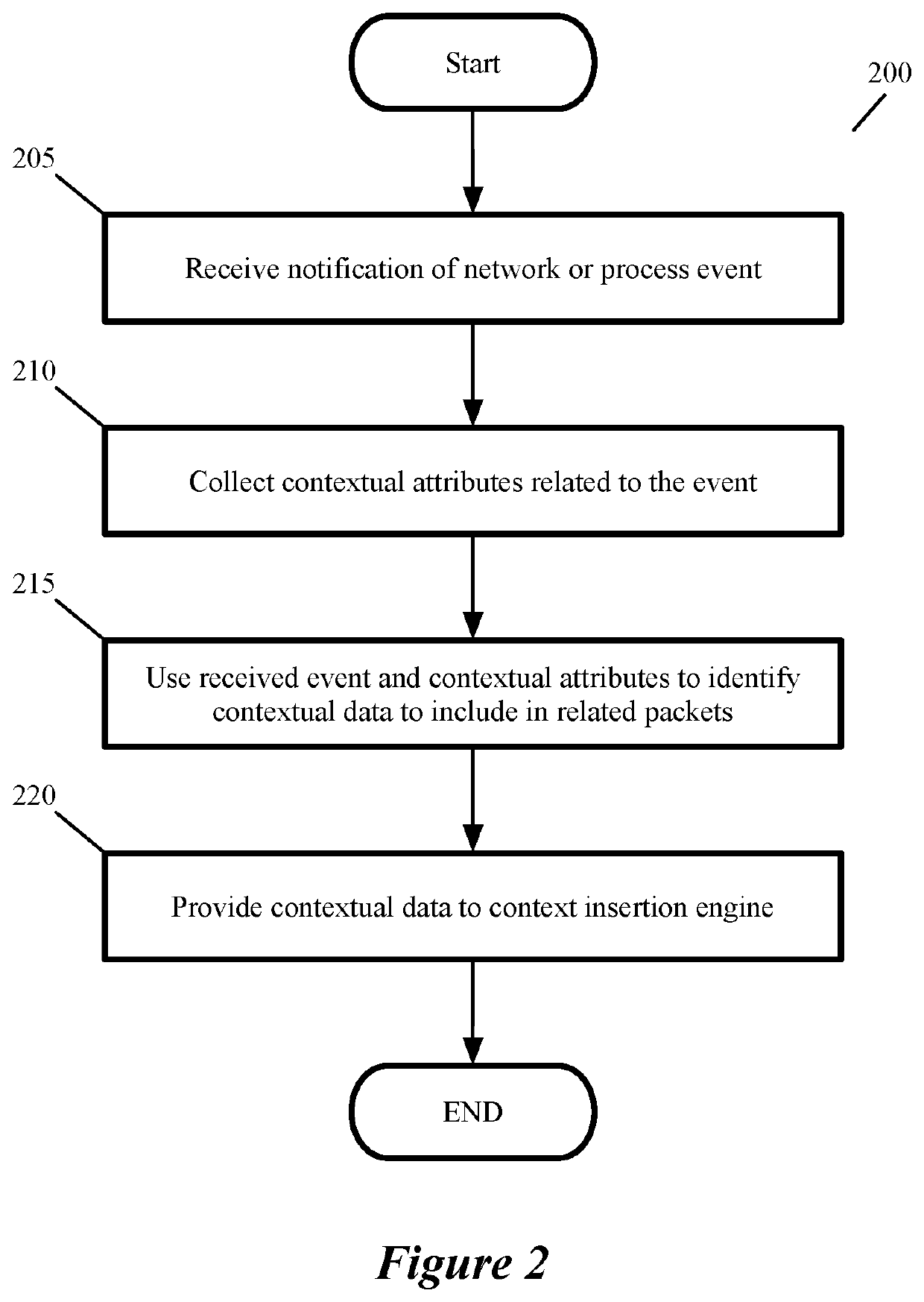
Context aware middlebox services at datacenter edges
ActiveUS20200014663A1TransmissionSoftware simulation/interpretation/emulationEngineeringWorld Wide Web
Some embodiments of the invention provide a novel architecture for providing context-aware middlebox services at the edge of a physical datacenter. In some embodiments, the middlebox service engines run in an edge host (e.g., an NSX Edge) that provides routing services and connectivity to external networks (e.g., networks external to an NSX-T deployment). Some embodiments use a novel architecture for capturing contextual attributes on host computers that execute one or more machines and providing the captured contextual attributes to context-aware middlebox service engines providing the context-aware middlebox services. In some embodiments, a context header insertion processor uses contextual attributes to generate a header including data regarding the contextual attributes (a “context header”) that is used to encapsulate a data message that is processed by the SFE and sent to the context-aware middlebox service engine.
Owner:VMWARE INC
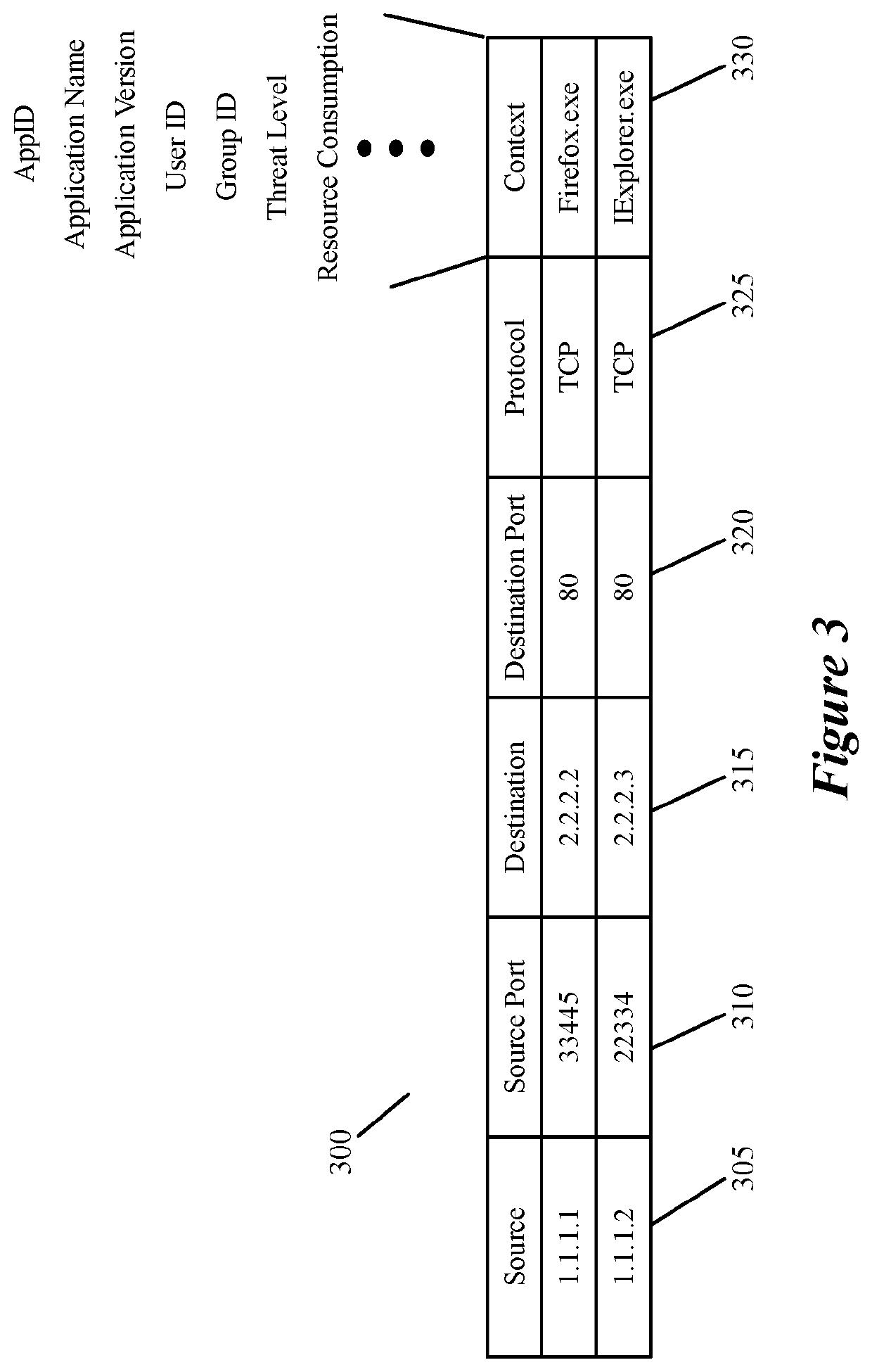
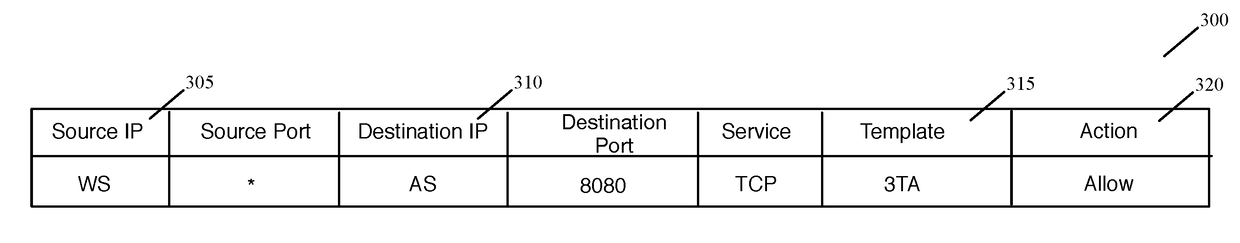
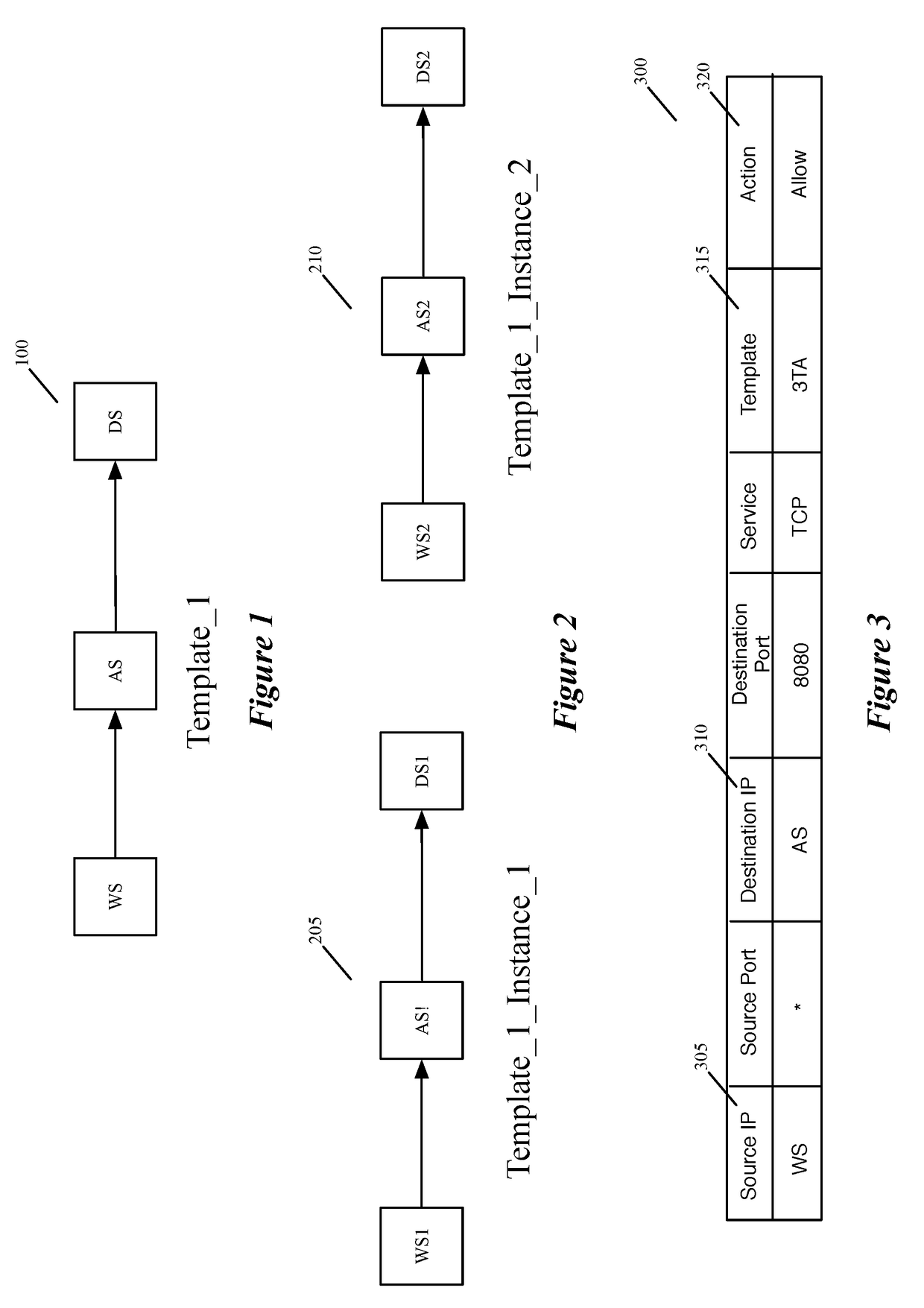
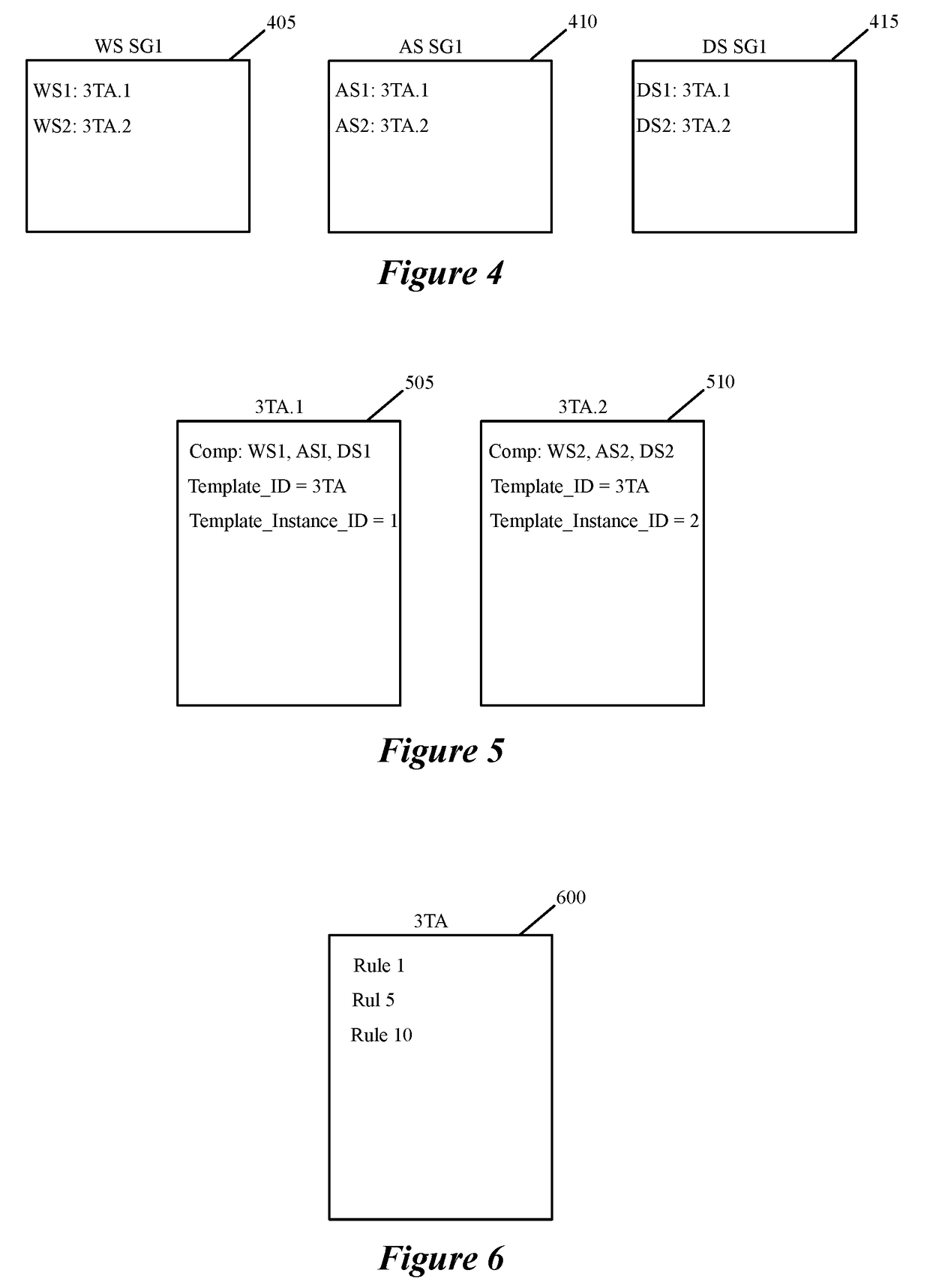
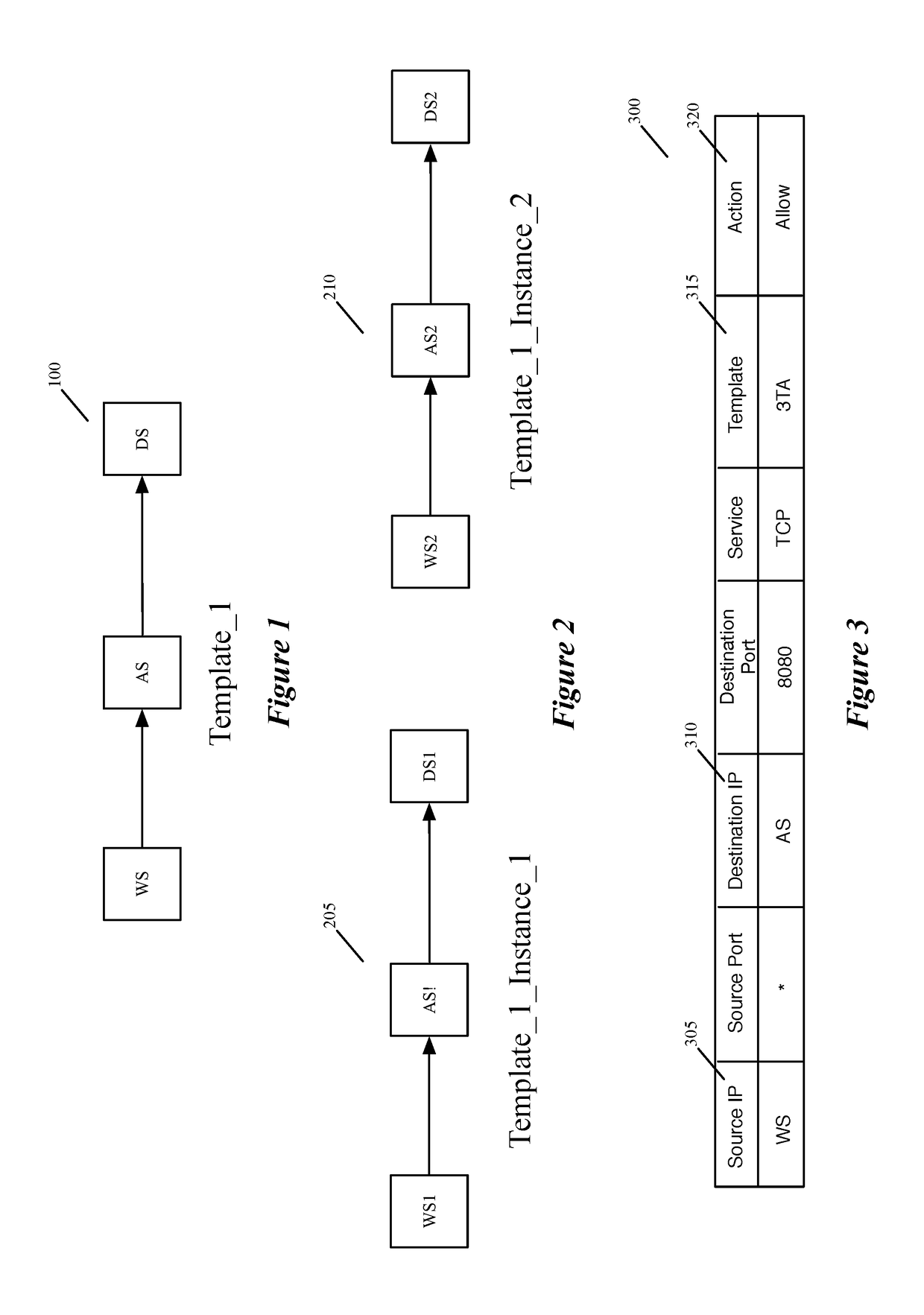
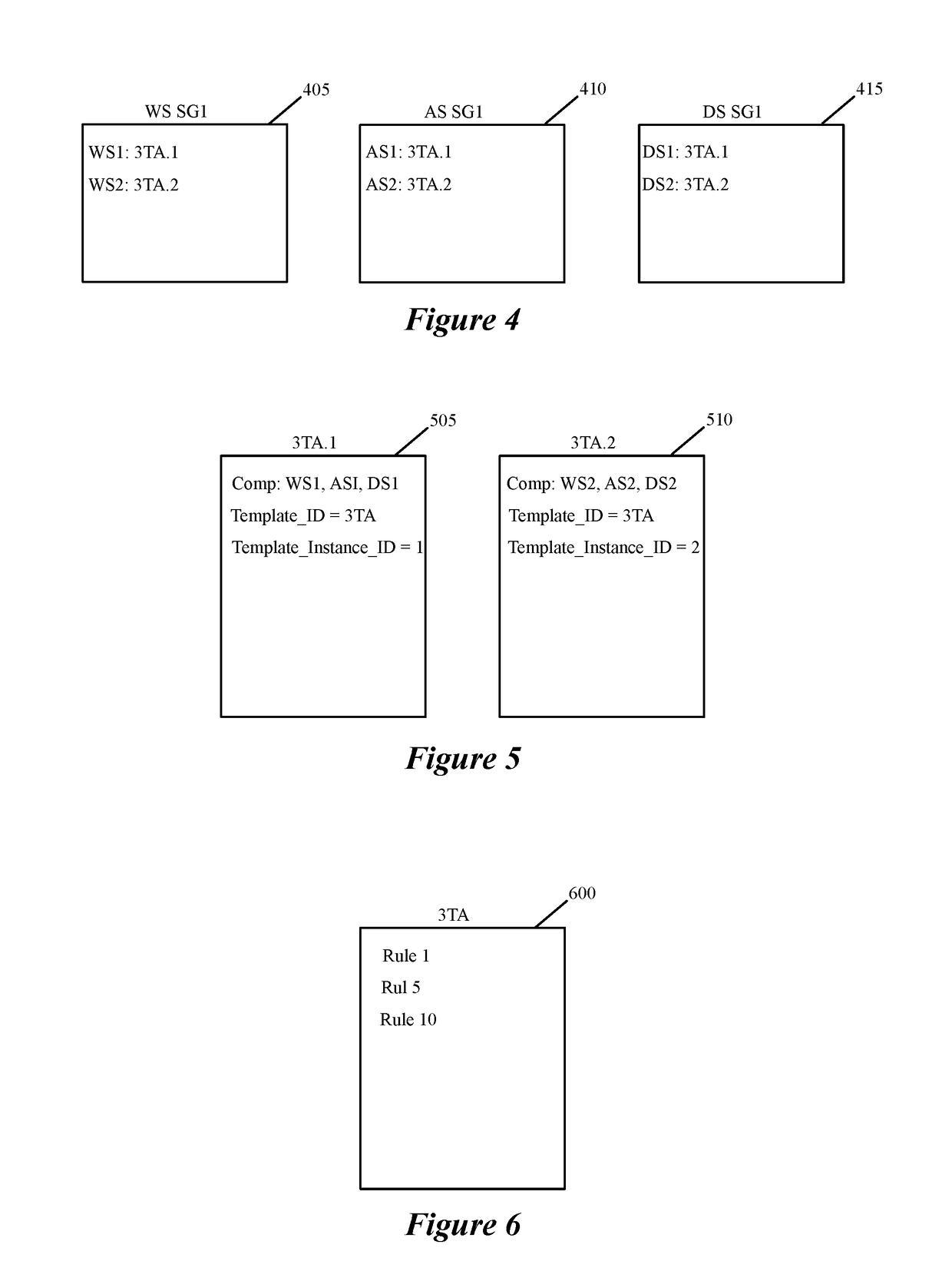
Datapath processing of service rules with qualifiers defined in terms of template identifiers and/or template matching criteria
Some embodiments of the invention introduce cloud template awareness in the service policy framework. Some embodiments provide one or more service rule processing engines that natively support (1) template-specific dynamic groups and template-specific rules, and (2) dynamic security tag concepts. A service rule processing engine of some embodiments natively supports template-specific dynamic groups and rules as it can directly process service rules that are defined in terms of dynamic component groups, template identifiers, template instance identifiers, and / or template match criteria. Examples of such services can include any kind of middlebox services, such as firewalls, load balancers, network address translators, intrusion detection systems, intrusion prevention systems, etc.
Owner:NICIRA
Multipath data communication
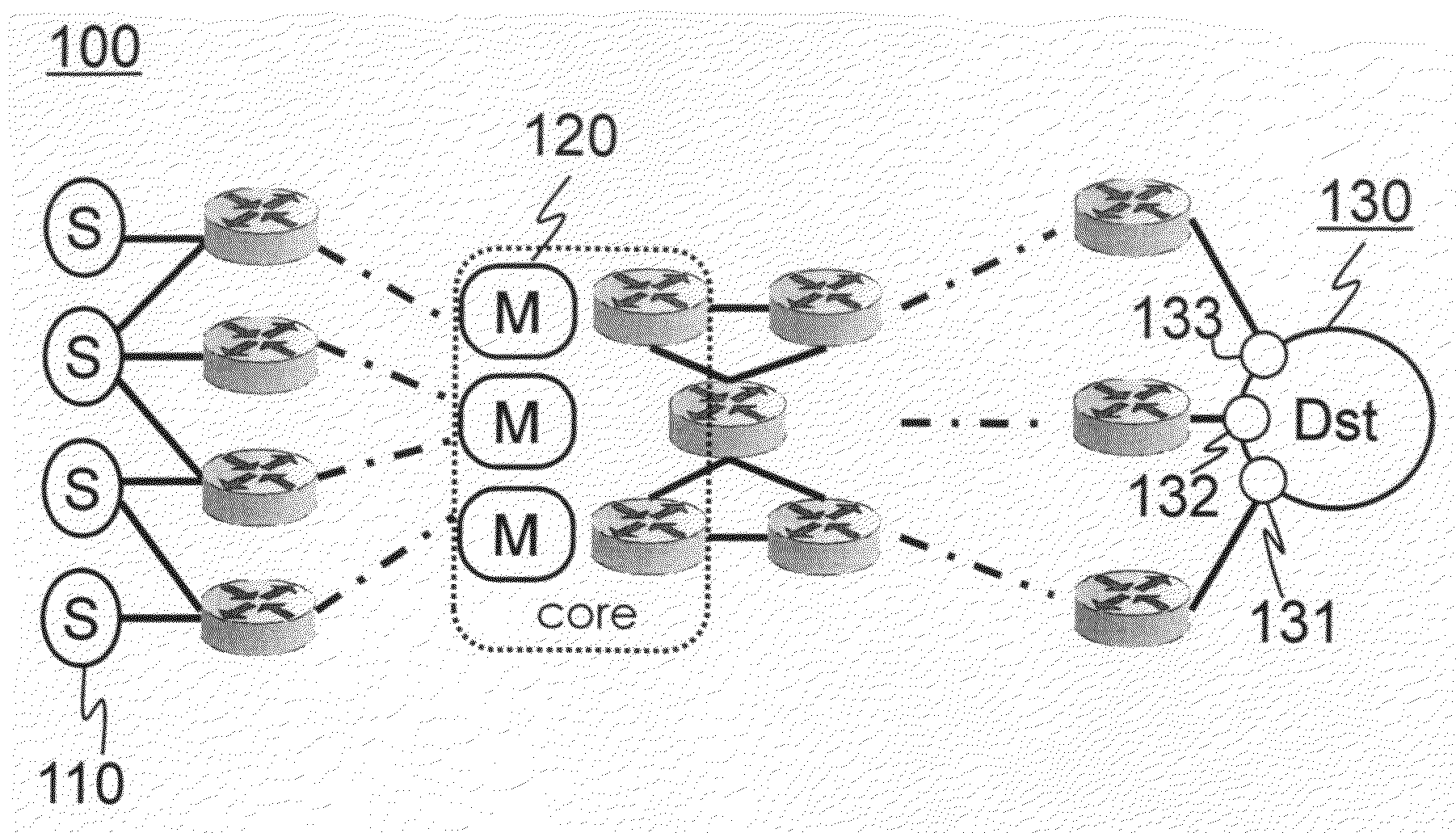
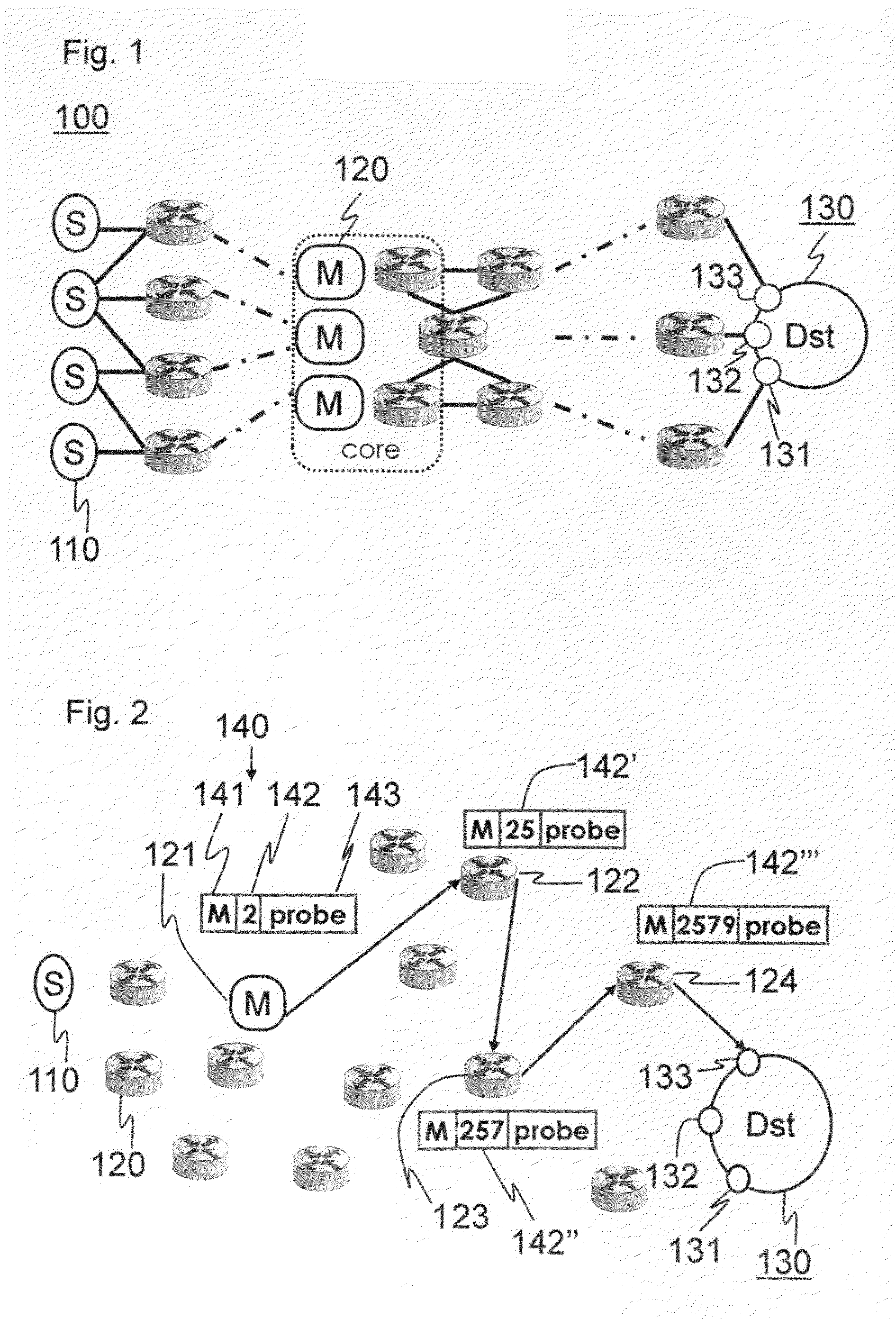
A multipath data communication network structure in which probing middle-boxes send periodical probe messages through their different interfaces and subsequent routers map the probe messages through their randomly selected interfaces until each probe message arrives at a destination, engages to a loop or meets a time-to-live limit. The probing middle boxes select a random interface for each probe message and furnish their routable identification and a temporary random number correlated to the selected interface to each probe messages. Subsequent multipath routers select a random outgoing interface and random forwarding state descriptor (FSD) and temporarily correlate the selected random outgoing interface with the FSD and add the FSD to the probe message. The probe messages provide different destinations with various hidden paths. Each hidden path enables forwarding of packets from probing middle-boxes to the destination without identifying any routable address en-route to the destination. The destination then provides a data source with the hidden path. Each multipath network element only store their mappings related to the paths for limited term so that each path expires and vanishes after the term. Attackers are not issued a new path and thus denial of service attacks are shortly stopped.
Owner:RPX CORP
Method, system & computer program product for discovering characteristics of middleboxes
InactiveUS20070011731A1Multiple digital computer combinationsProgram controlState dependentMiddleware
A method, computer program product, communications device and system for enabling an end node or terminal to discover one or more characteristics of a firewall on the communications path between the end node and a data network are provided. In particular, middlebox configuration protocols have been extended to allow a user to run additional tests in order to determine, for example, whether a discovered firewall blocks unsolicited incoming requests, as well as what the length of time associated with a particular state created by the discovered firewall is.
Owner:NOKIA CORP
Datapath processing of service rules with qualifiers defined in terms of dynamic groups
Some embodiments of the invention introduce cloud template awareness in the service policy framework. Some embodiments provide one or more service rule processing engines that natively support (1) template-specific dynamic groups and template-specific rules, and (2) dynamic security tag concepts. A service rule processing engine of some embodiments natively supports template-specific dynamic groups and rules as it can directly process service rules that are defined in terms of dynamic component groups, template identifiers, template instance identifiers, and / or template match criteria. Examples of such services can include any kind of middlebox services, such as firewalls, load balancers, network address translators, intrusion detection systems, intrusion prevention systems, etc.
Owner:NICIRA
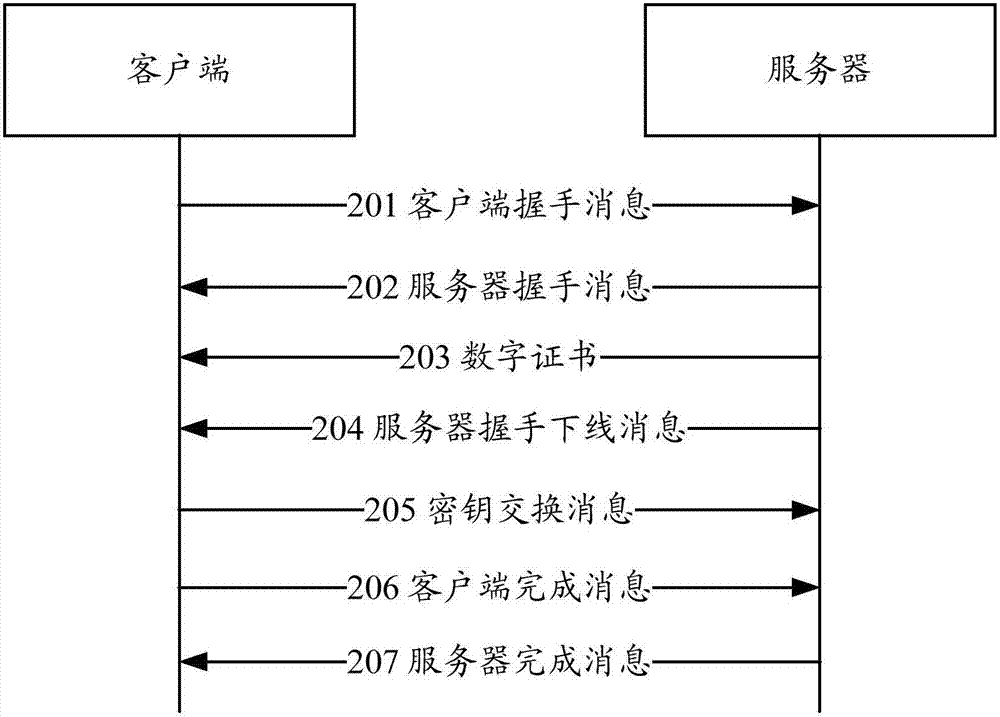
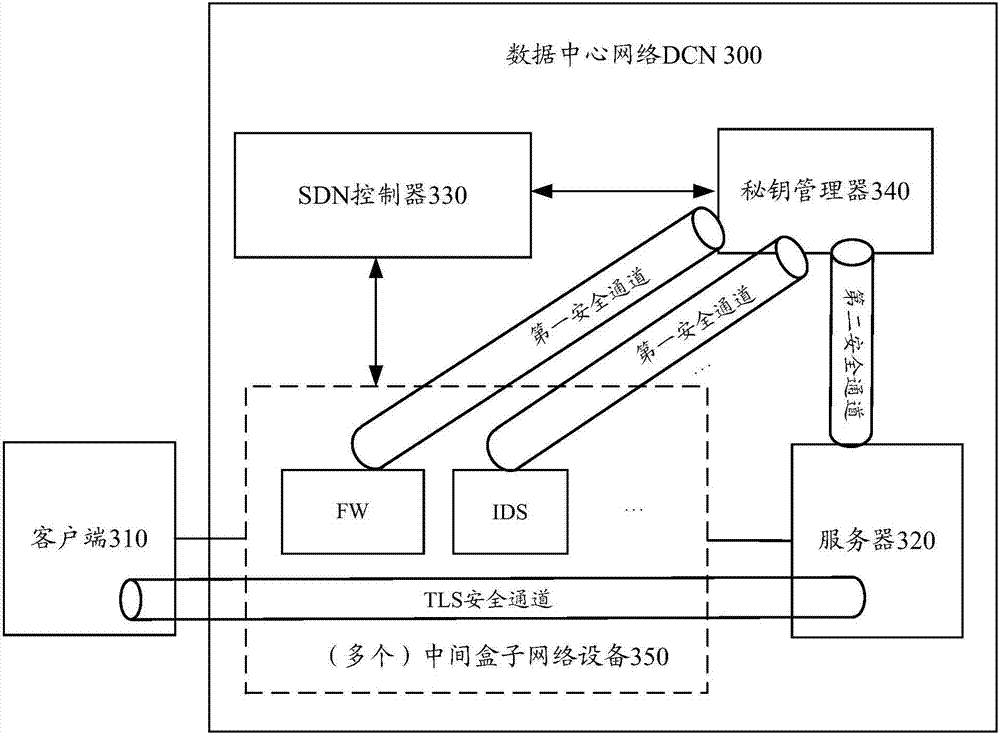
Encrypted content detection method and device
ActiveCN107517183AReduce Detection ComplexityReduce testing costsSecuring communicationProxy serverTransport Layer Security
The embodiment of the invention provides an encrypted content detection method and device. The method comprises the steps that a middle box network device receives key information of a TLS (Transport Layer Security) channel through a first security channel, wherein the key information is sent by a key manager; the middle box network device obtain encrypted application data according to quintuple information of the TLS channel, wherein the encrypted application data is transmitted through the TLS channel; and the middle box network device decrypts the encrypted application through adoption of a session key and detects decrypted content. According to the encrypted content detection method provided by the invention, the encrypted application data is decrypted through the middle box network device and the decrypted application data is detected through the middle box network device, so the detection of the encrypted content no longer depends on a TLS proxy server, the detection complexity can be reduced, and the detection cost can be reduced.
Owner:HUAWEI TECH CO LTD
System and method of middlebox detection and characterization
ActiveUS20120079104A1Digital computer detailsData switching by path configurationData miningMiddlebox
A computer-implemented system and method to detect and characterize middleboxes is disclosed. Embodiments of the system and method include a middlebox detection engine to provide a plurality of middlebox detection modules, and to use at least one middlebox detection module of the plurality of middlebox detection modules to determine if a middlebox exists on a path between a first communicating entity of a network and a second communicating entity of the network.
Owner:NEUSTAR IP INTELLIGENCE
Service chain realization method and device
InactiveCN105099960ADoes not affect forwardingEase of deployment and flexibilityHybrid transportMedia access controlSoftware define network
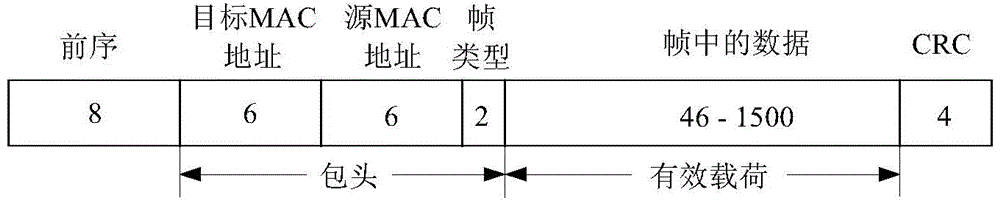
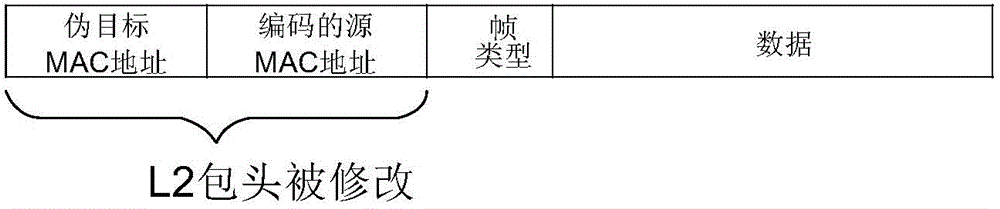
Techniques for realizing service chaining, a corresponding apparatus and an SDN (Software Defined Network) controller are disclosed. The method includes temporarily modifying an original destination MAC (media access control) address of a packet and an original source MAC address the packet during the time the packet makes a hop from one middlebox to another. A restore operation is used to restore the original source and destination MAC addresses after the hop is made.
Owner:IBM CORP
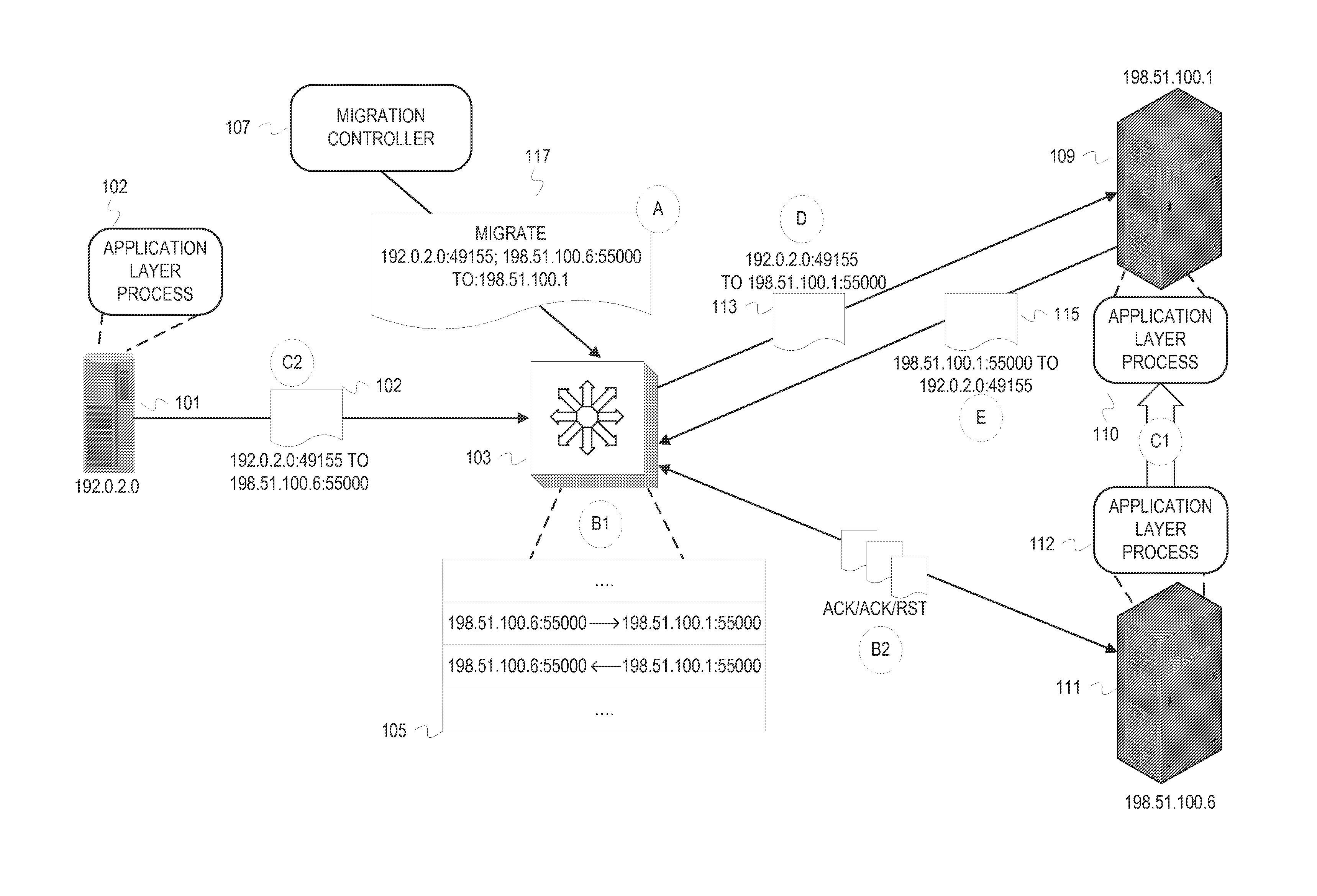
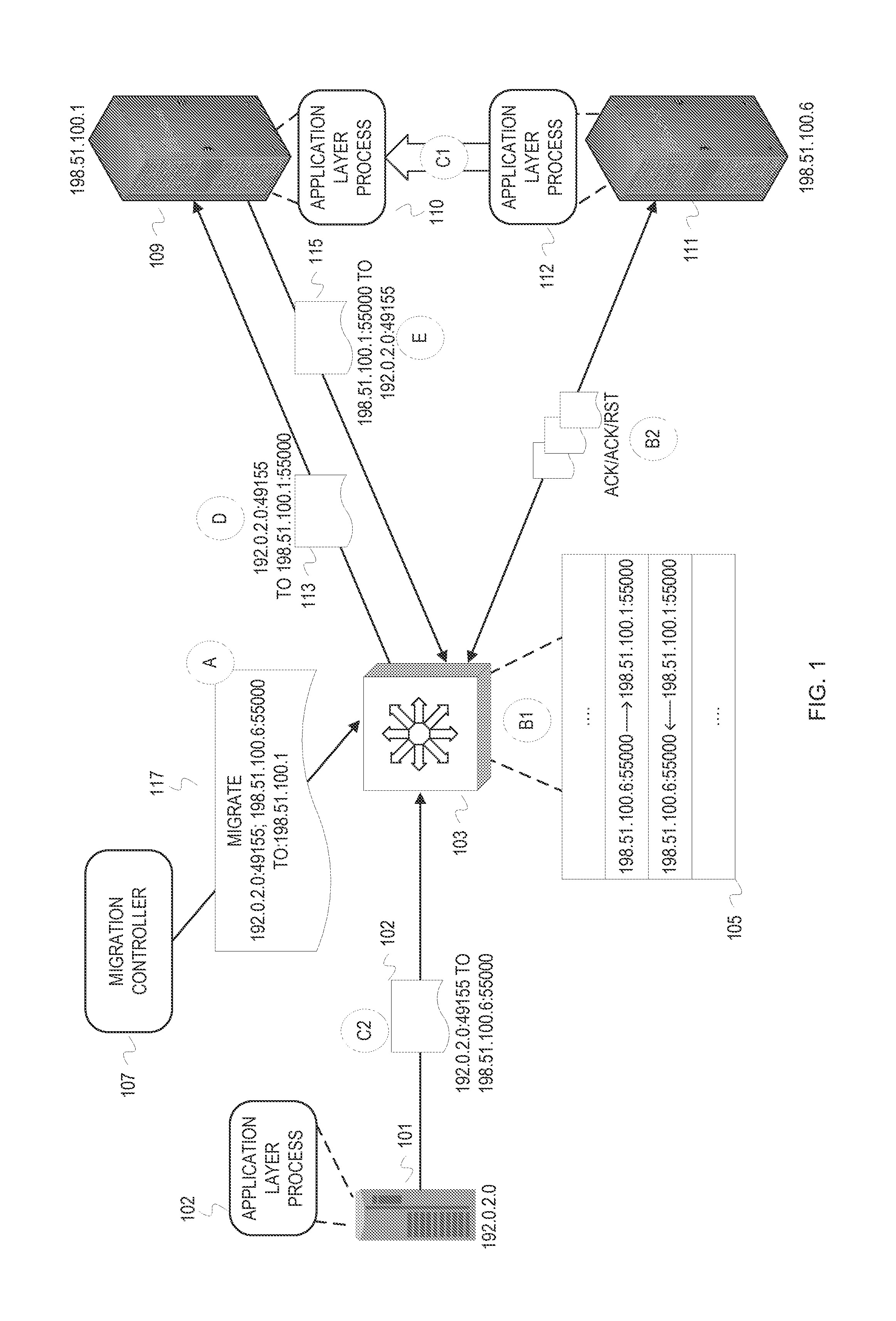
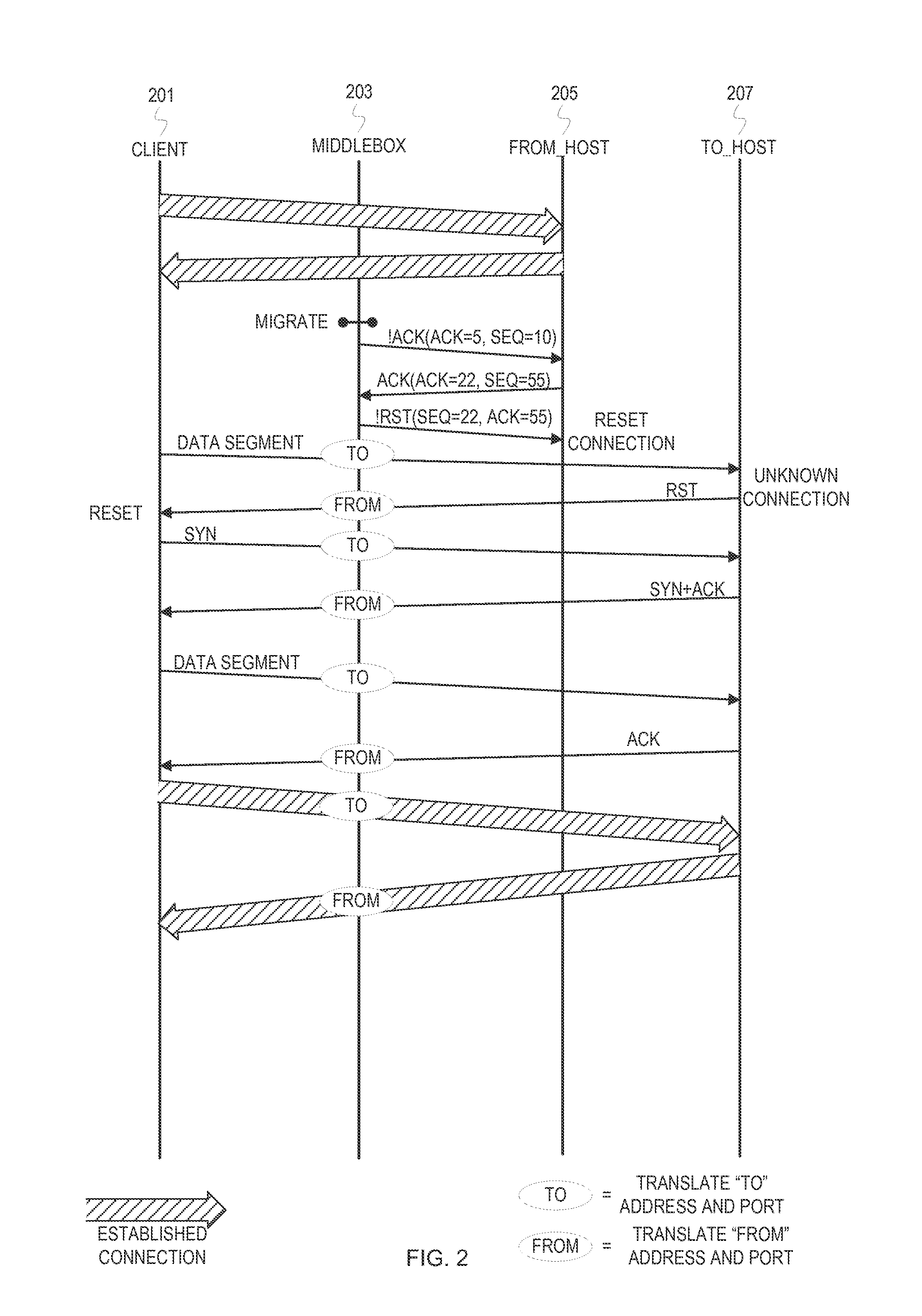
Externally initiated application session endpoint migration
ActiveUS20150215406A1Multiple digital computer combinationsTransmissionTransport layerNetwork address translation
In storage networks (e.g., SAN and NAS), various reasons can arise for migrating an application layer communication session endpoint to a different host. To achieve scalability and robustness, the migration can be enacted externally and carried out at a middlebox at the transport layer. When a migration is triggered to migrate an application layer communication session endpoint from a host A to a host B, the middlebox coordinates network address translation with a transport protocol reset mechanism to switch the connection to host B and close the connection on host A with minimal disruption to the non-migrating application layer communication session endpoint using the connection. At the application layer, the non-migrating application layer communication session endpoint will initiate a new connection in response to detecting the reset, and retry any operation that was aborted as a result of the connection switch.
Owner:NETWORK APPLIANCE INC
Method and system for handling context of data packet flows
InactiveUS7706325B2Facilitates session management and chargingOrganized and controlledConnection managementWireless network protocolsSession controlMiddlebox
Owner:UNWIRED PLANET
Method of facilitating IP connections to hosts behind middleboxes
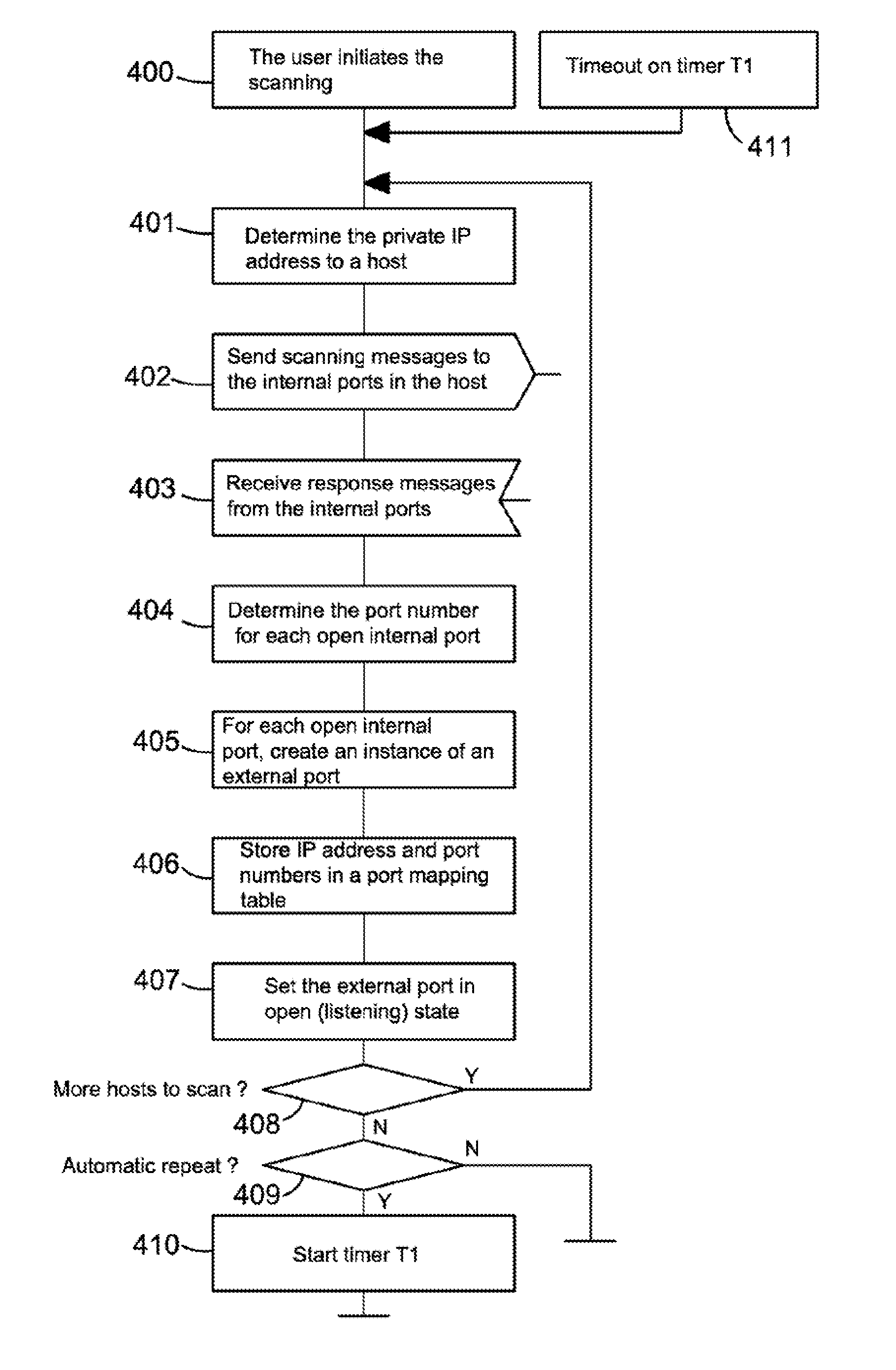
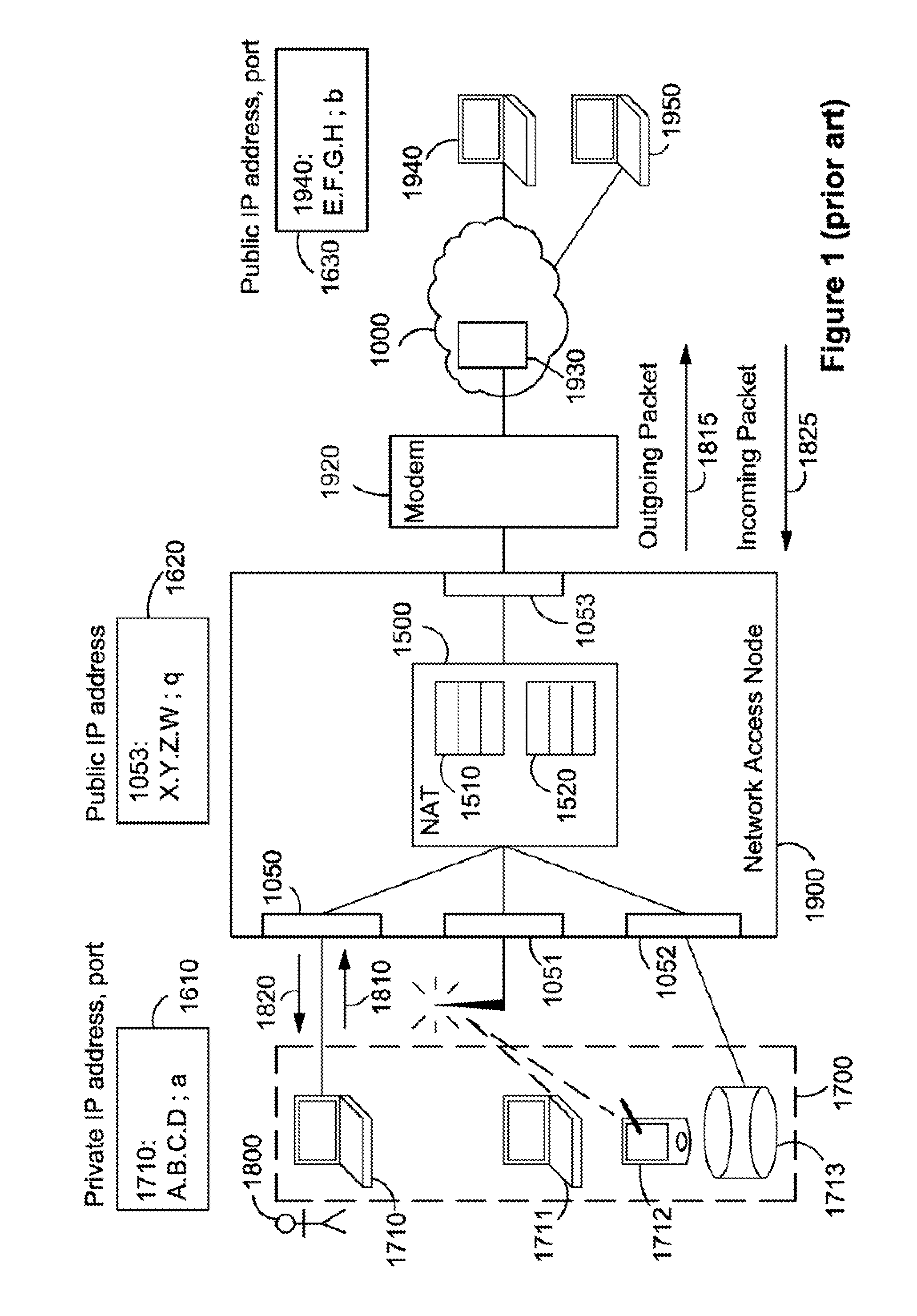
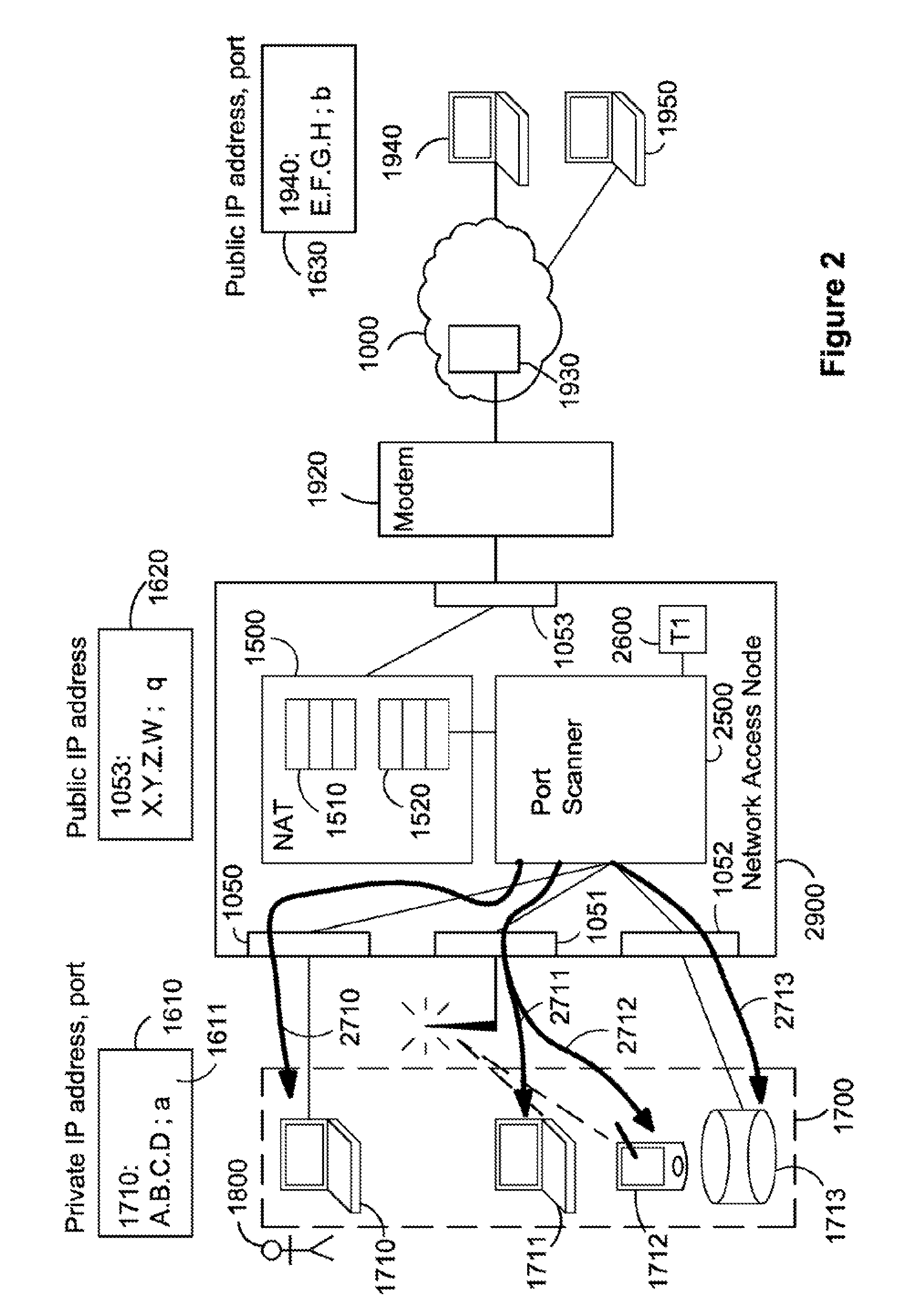
ActiveUS8874757B2Good for forwardingMultiple digital computer combinationsTransmissionPrivate IPAuto-configuration
The present invention relates to a method and arrangement of facilitating the establishment of peer-to-peer IP connections between a public network and hosts in a private or home network. The method uses a port mapping table residing in a NAT that maps external public IP addresses and external port numbers to private IP addresses and internal port numbers. This table has so far been configured manually by a user of the private or home network. Apart from being cumbersome, it demands skills in router and network technology, skills an ordinary user of a home network often does not have. The present invention solves this problem by automatically configuring the table comprising the steps of scanning the hosts using a port scanner and detecting the internal ports in the hosts that are in an open state.
Owner:SAGO STRATEGIC SOLUTIONS LLC
Service chain optimization method for low transmission time delay
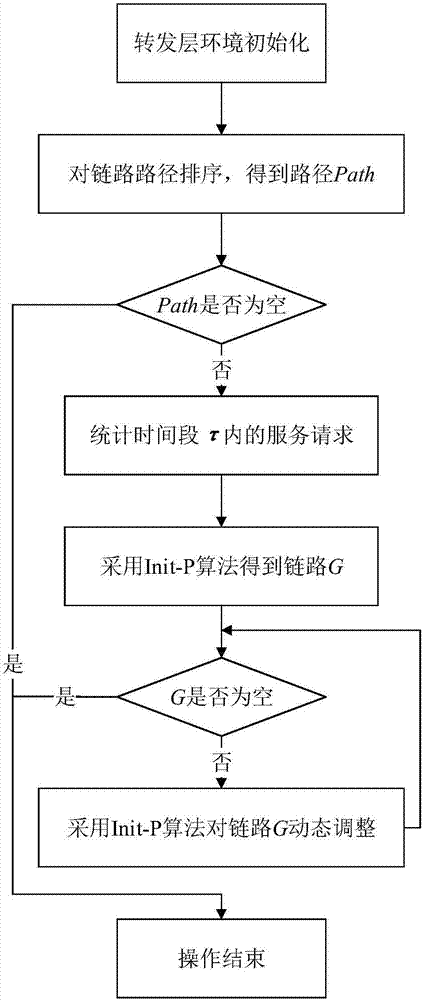
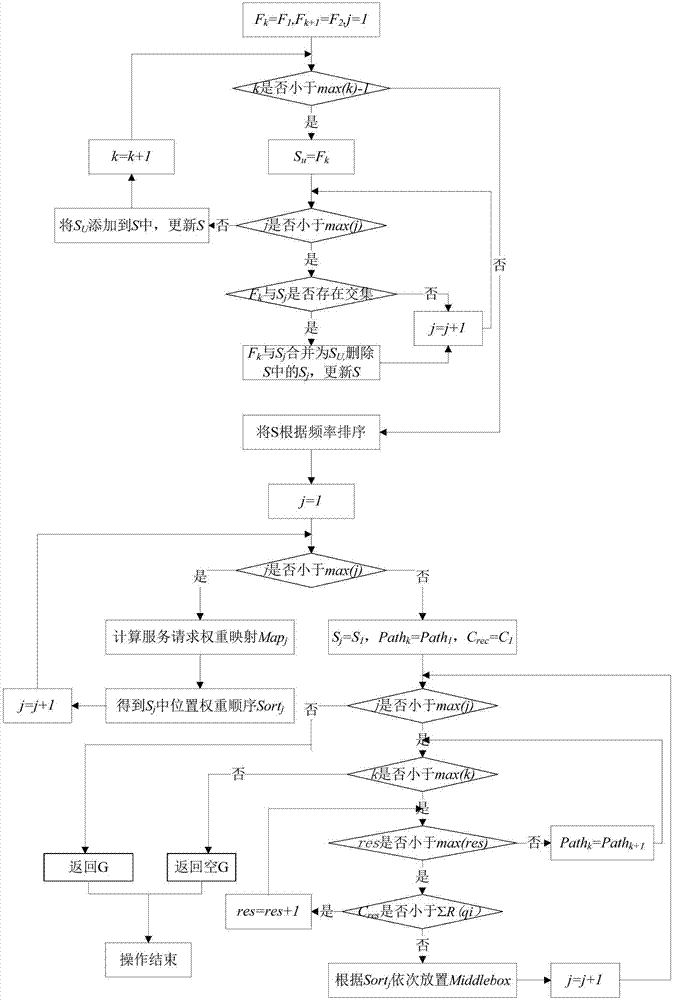
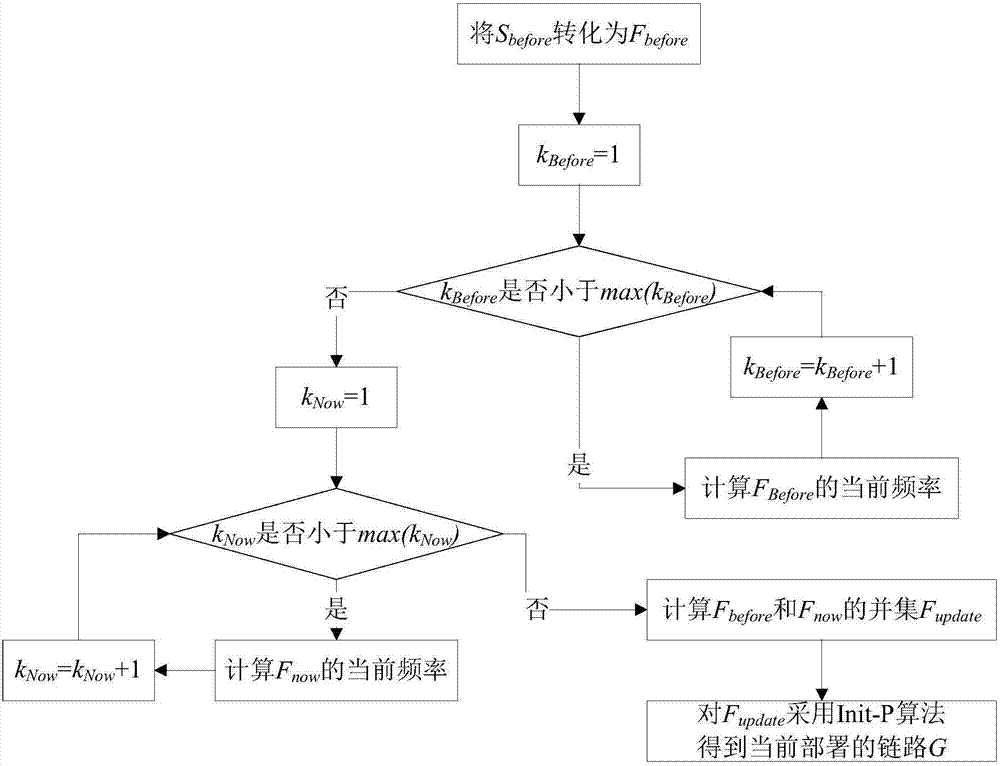
ActiveCN107124303AAchieve optimized deploymentOptimizing Deployment ScalingData switching networksTime delaysTime segment
The invention discloses a service chain optimization method for a low transmission time delay. The method comprises the following steps: initializing the environment of a forwarding layer by use of an Init-OL algorithm, ordering paths from starting points to terminal points of links, performing classification ordering on service requests by use of an Init-P algorithm, successively matching a host providing service with switches, respectively endowing service requests before a time period tau and service requests in the time period tau with different weights by use of an Update-P algorithm so as to dynamically adjust a link G. According to the invention, links are dynamically adjusted by performing statistical processing on service requests in historical messages and analyzing precedence relations between the service requests, optimized deployment of Middlebox in service chains is realized, the transmission time delay from the time when the messages enter the service chains for various processing to the time when the messages leave the service chains is enabled to be the smallest, and the method can be expanded to application in service chain deployment optimization for low transmission time delays in various networks.
Owner:UNIV OF ELECTRONICS SCI & TECH OF CHINA
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com