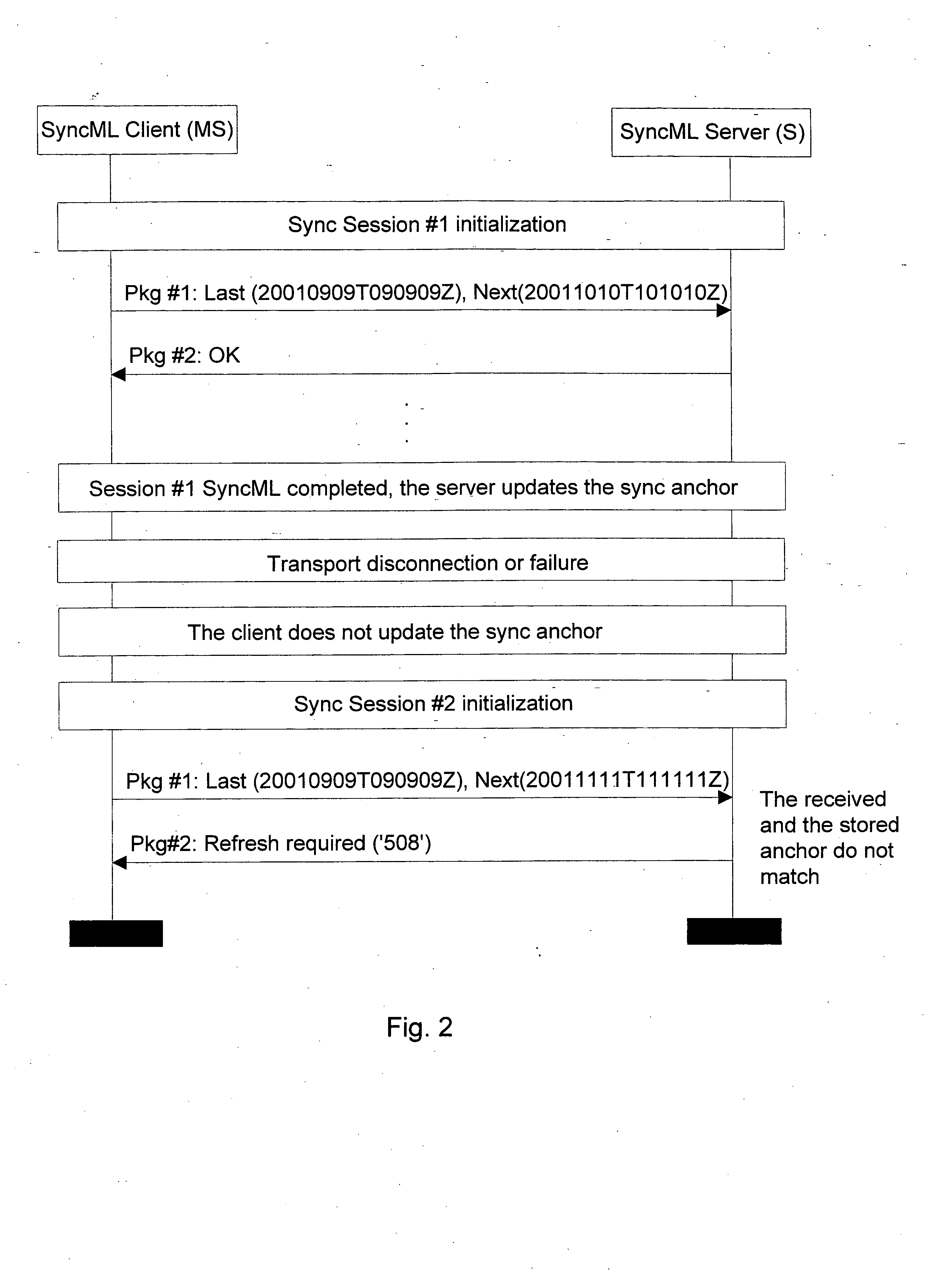
Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
3033 results about "Transport layer" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
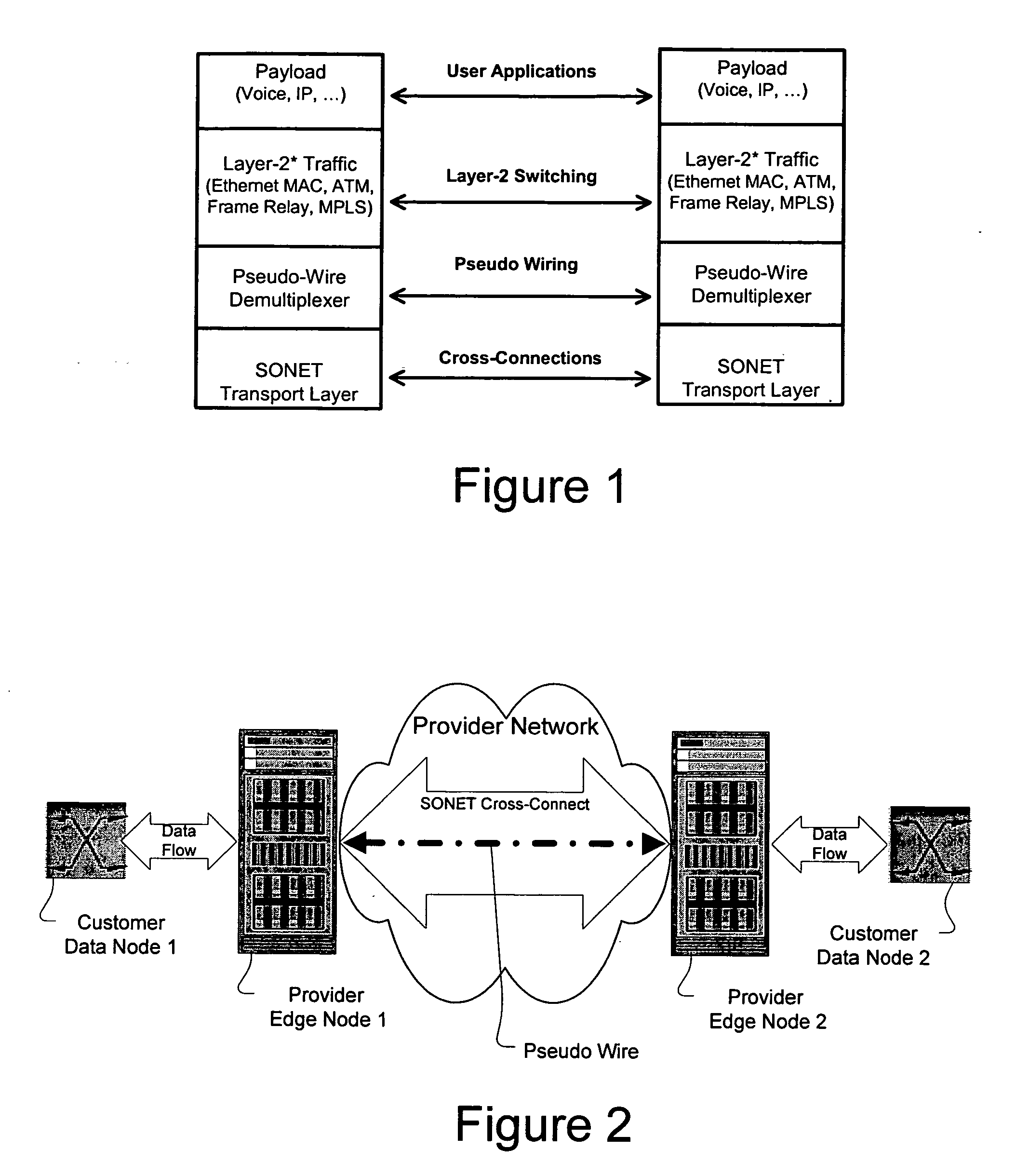
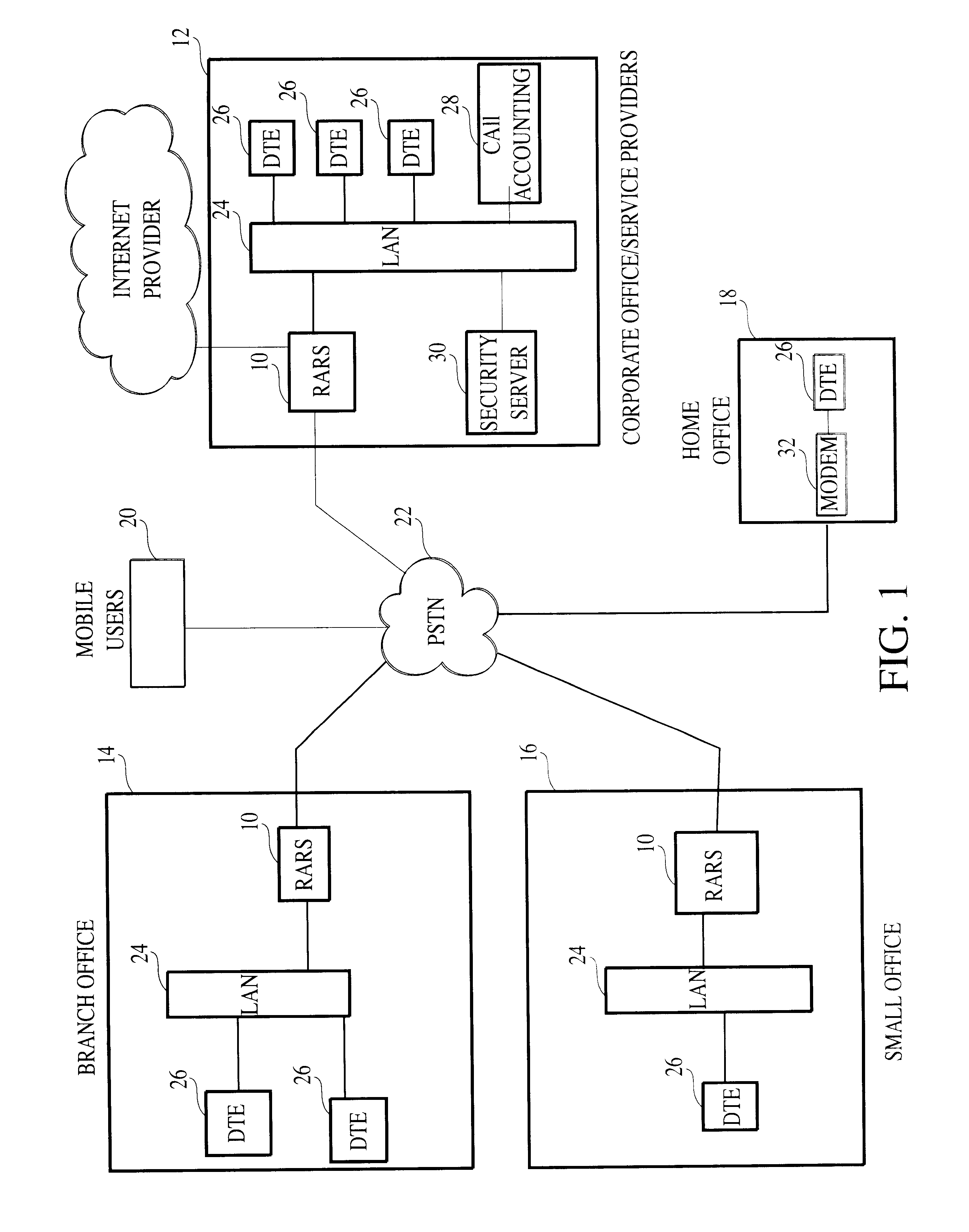
In computer networking, the transport layer is a conceptual division of methods in the layered architecture of protocols in the network stack in the Internet protocol suite and the OSI model. The protocols of this layer provide host-to-host communication services for applications. It provides services such as connection-oriented communication, reliability, flow control, and multiplexing.
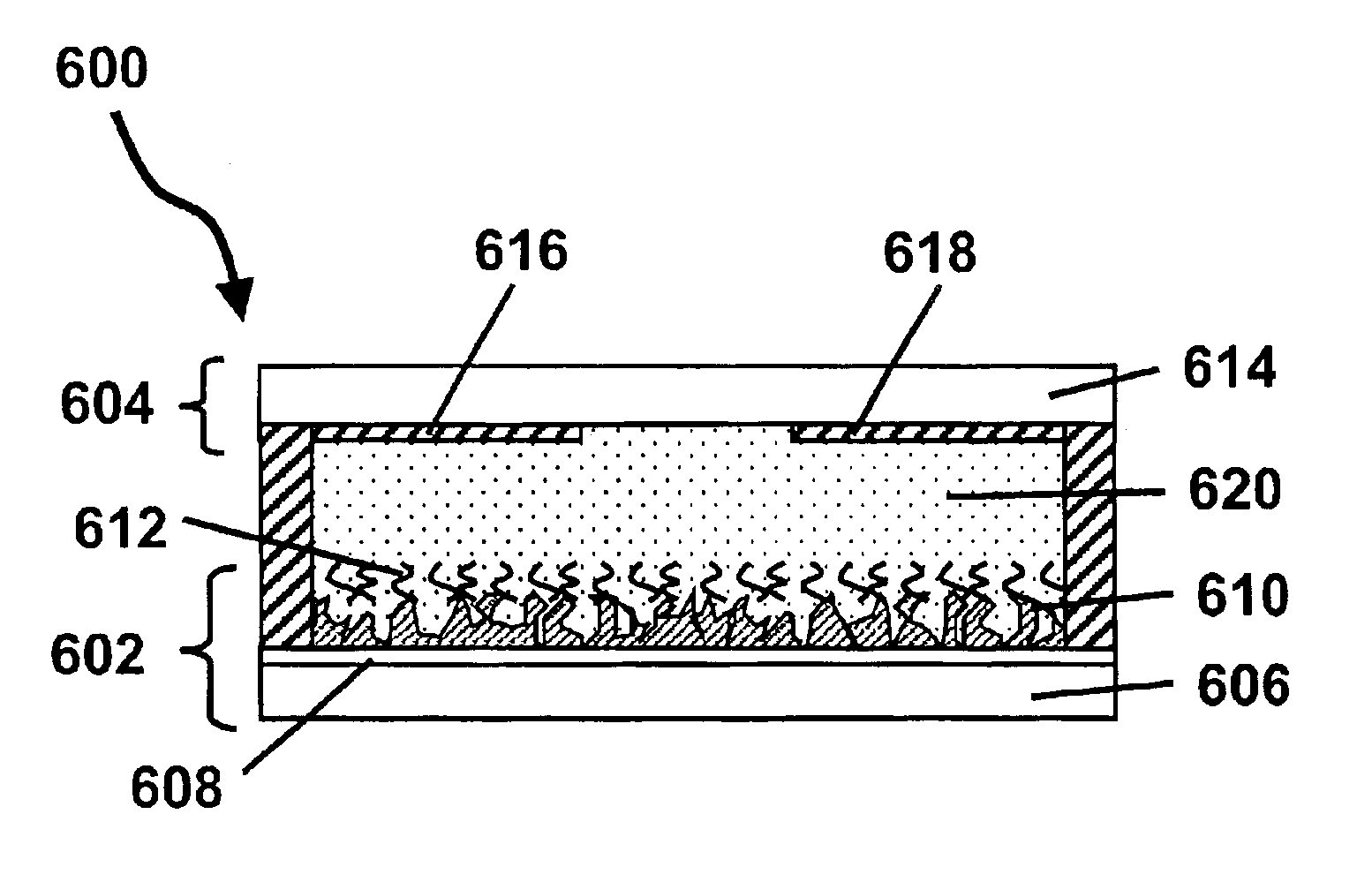
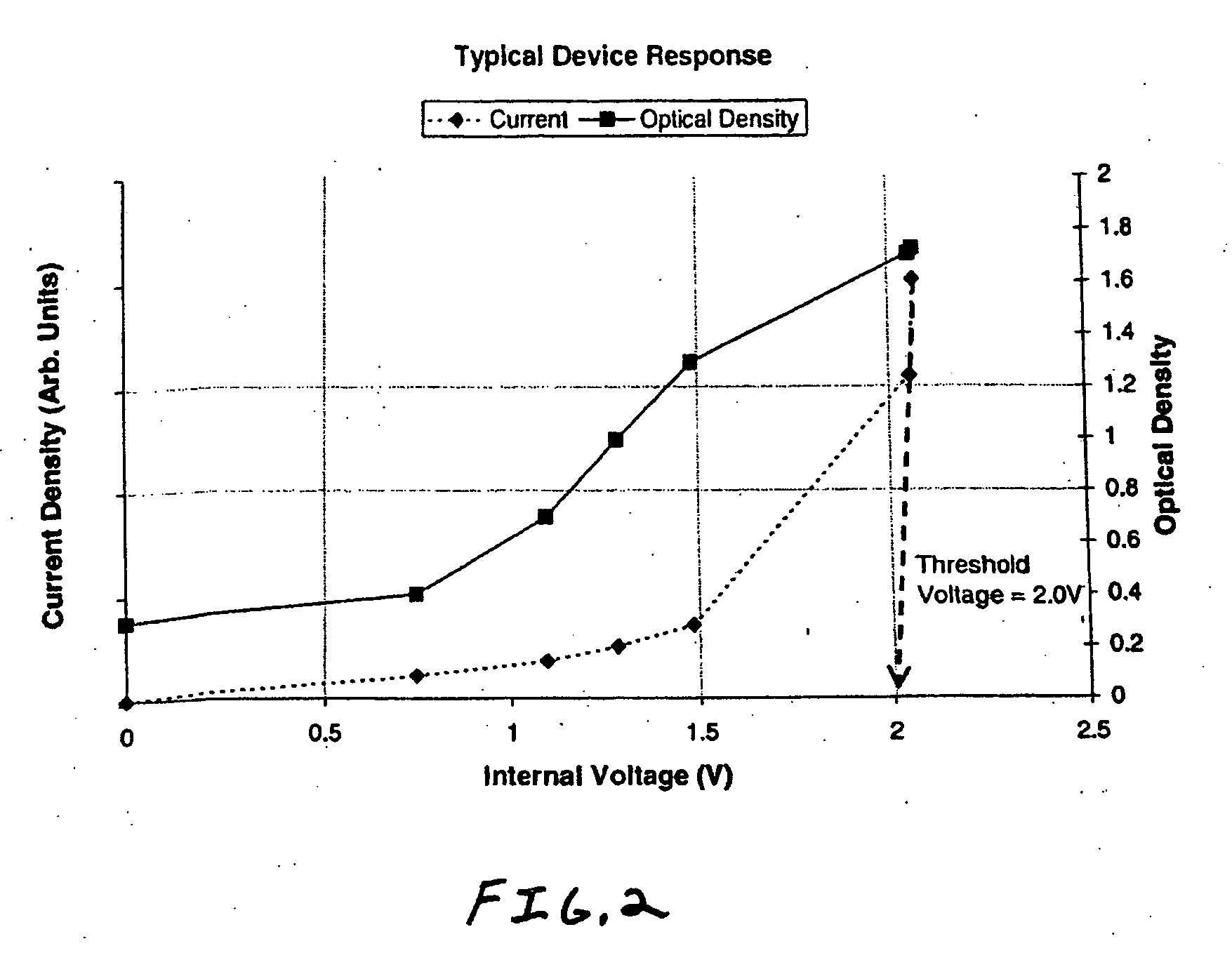
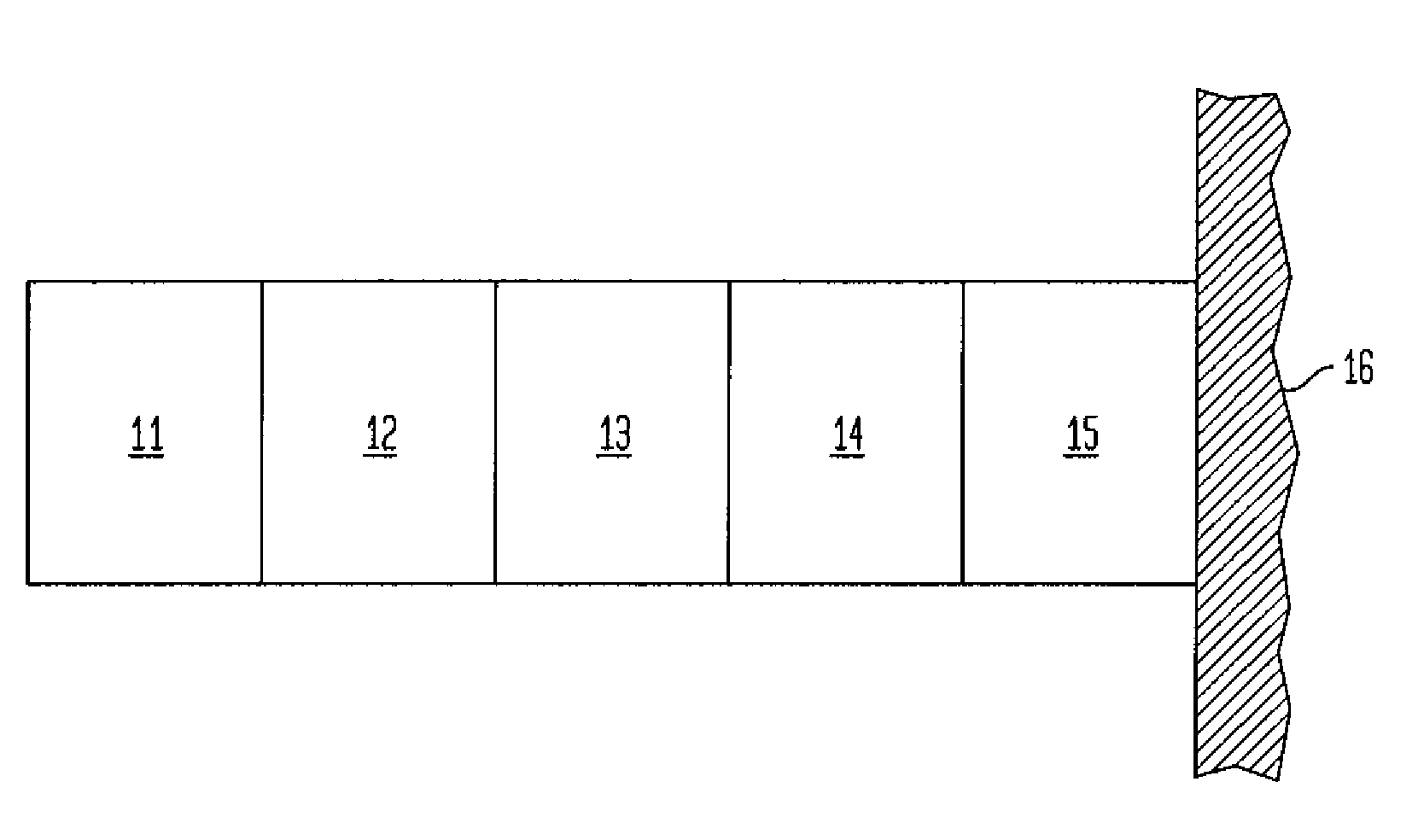
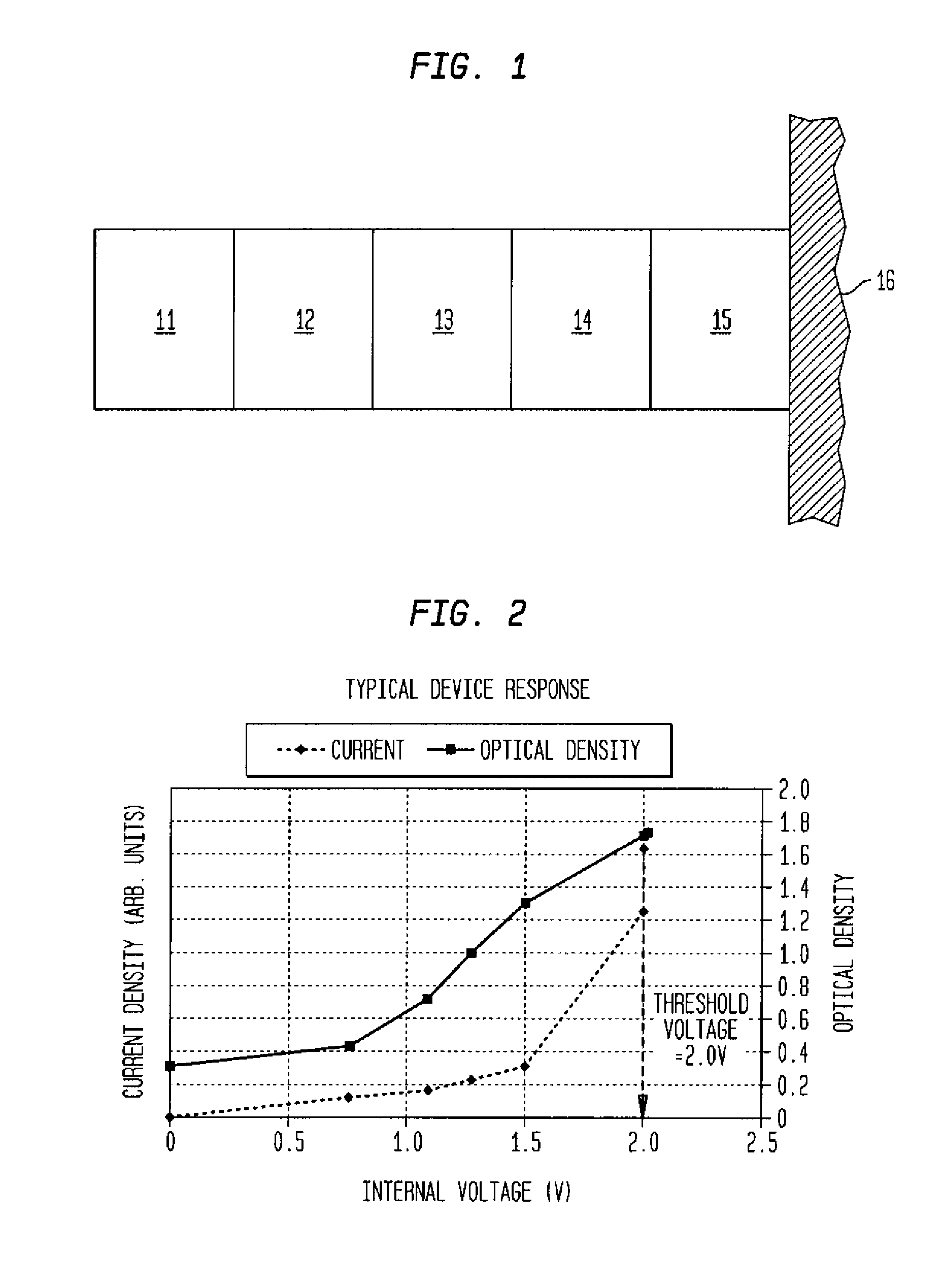
Electro-optic displays, and methods for driving same
InactiveUS6950220B2Reduce and eliminate exposureReducing and eliminating light degradationNon-linear opticsElectricityTransport layer
The invention relates to electro-optic displays and methods for driving such displays. The invention provides (i) electrochromic displays with solid charge transport layers; (ii) apparatus and methods for improving the contrast and reducing the cost of electrochromic displays; (iii) apparatus and methods for sealing electrochromic displays from the outside environment and preventing ingress of contaminants into such a display; and (iv) methods for adjusting the driving of electro-optic displays to allow for environmental and operating parameters.
Owner:E INK CORPORATION
Charge transport layers and organic electron devices comprising same
InactiveUS20070181874A1Discharge tube luminescnet screensNanoinformaticsTransport layerHole transport layer
Owner:EI DU PONT DE NEMOURS & CO
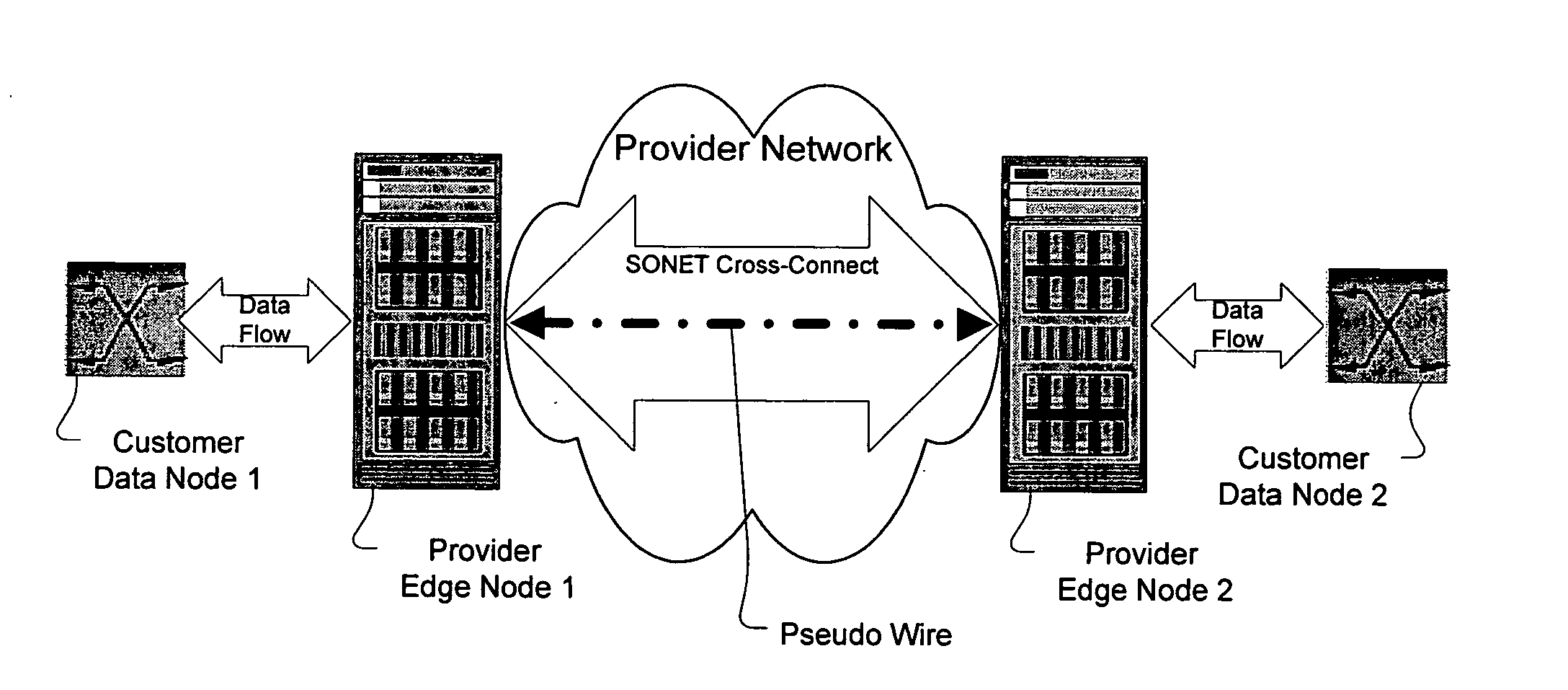
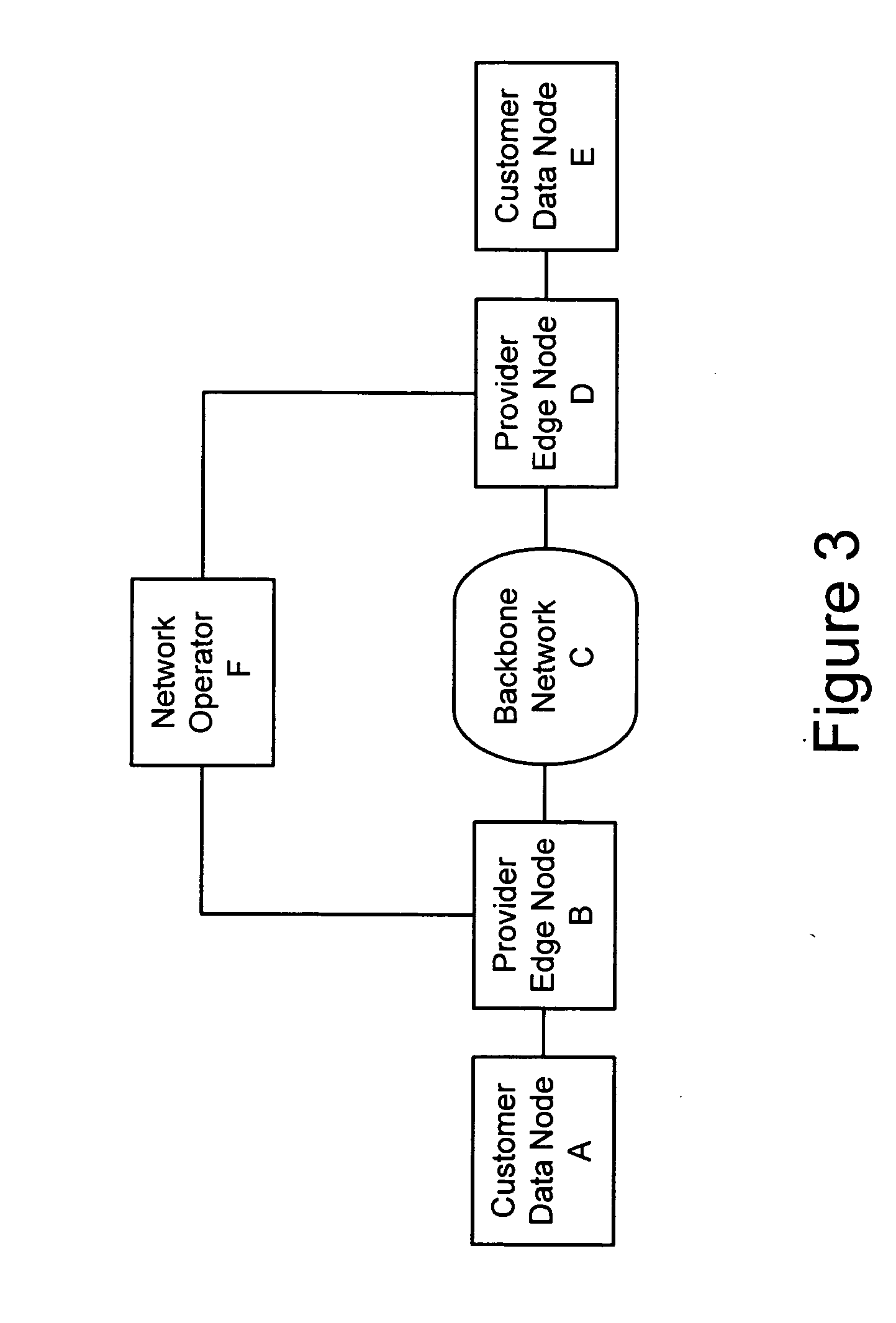
Method and apparatus for performing data flow ingress/egress admission control in a provider network
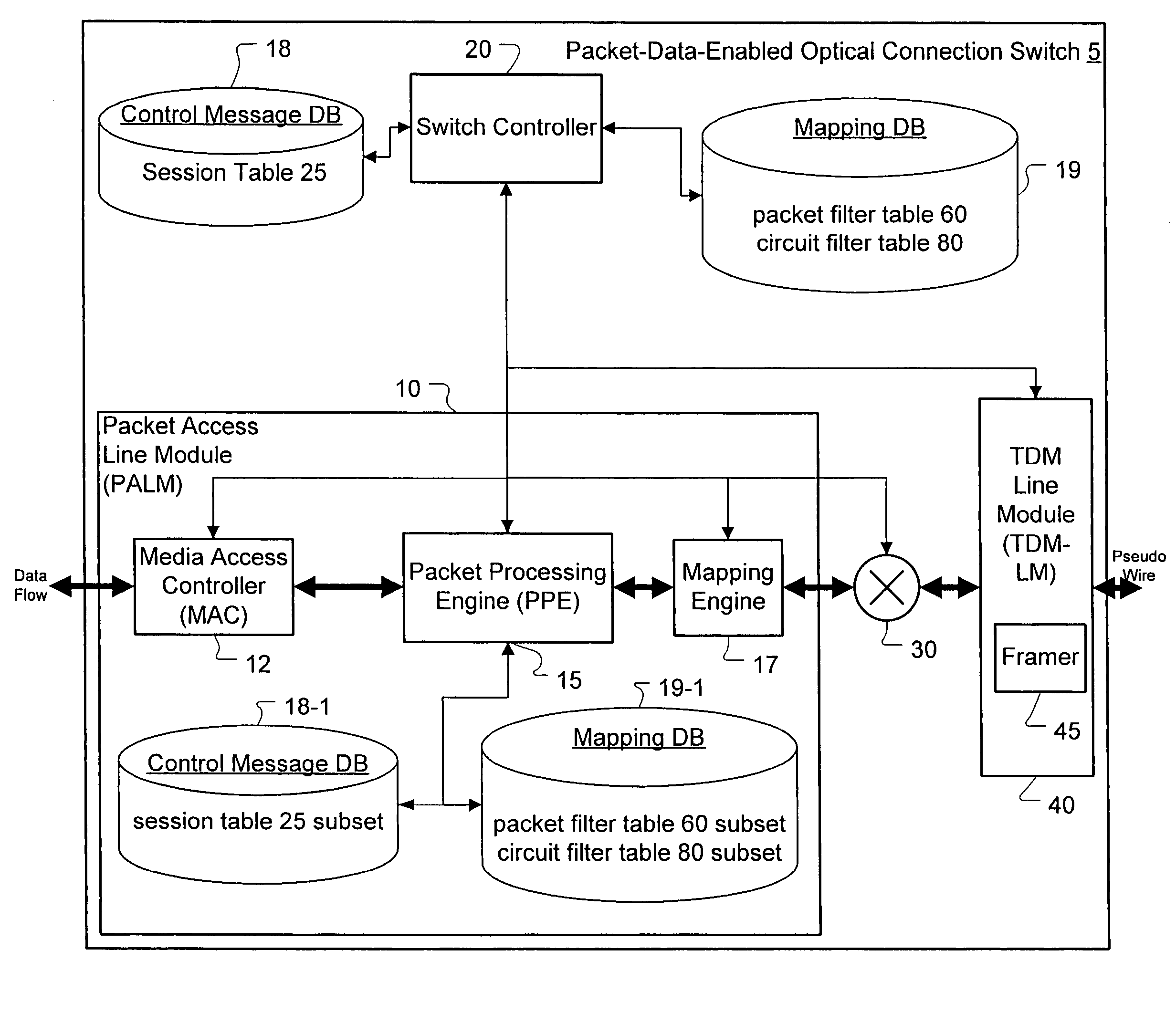
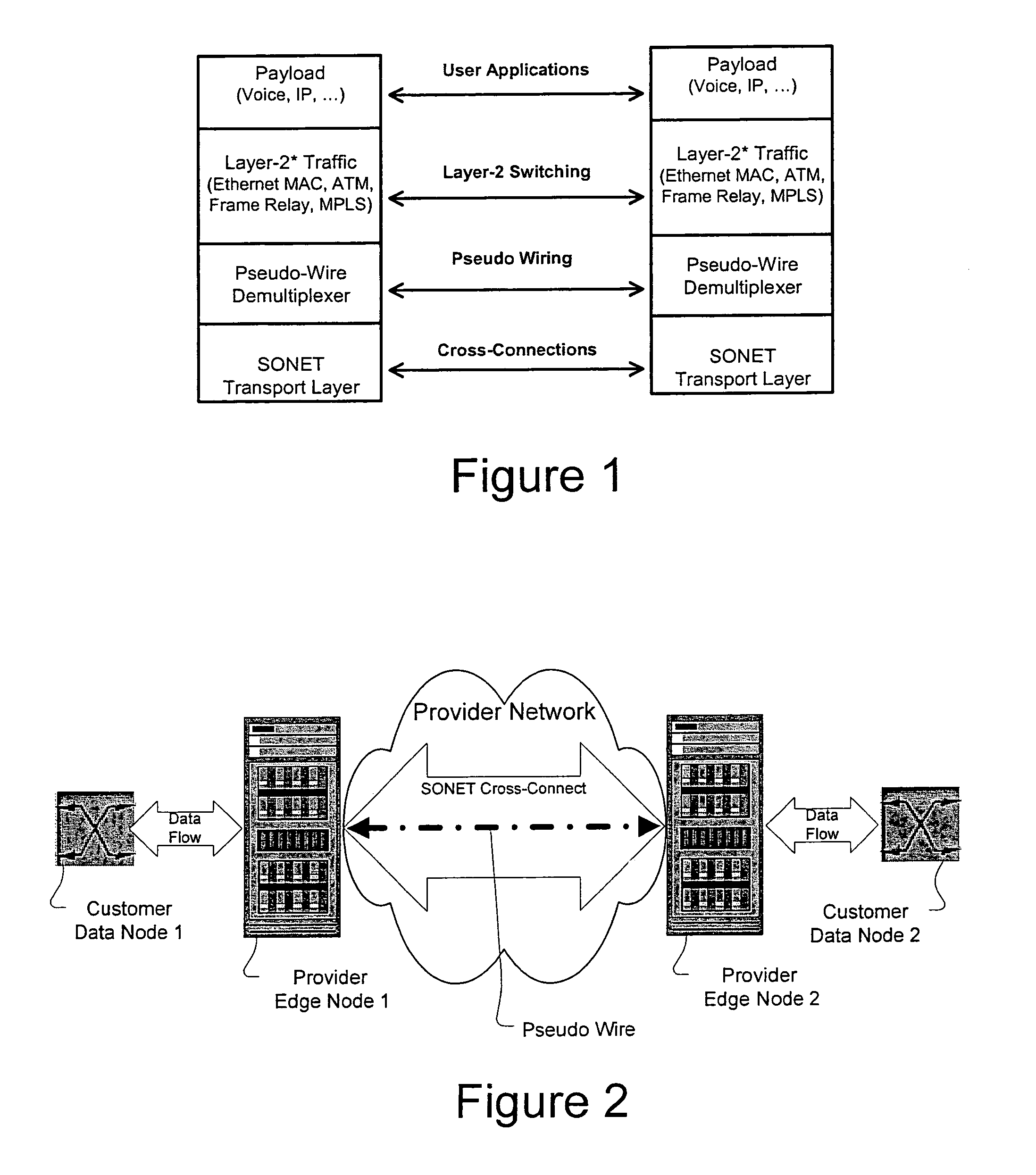
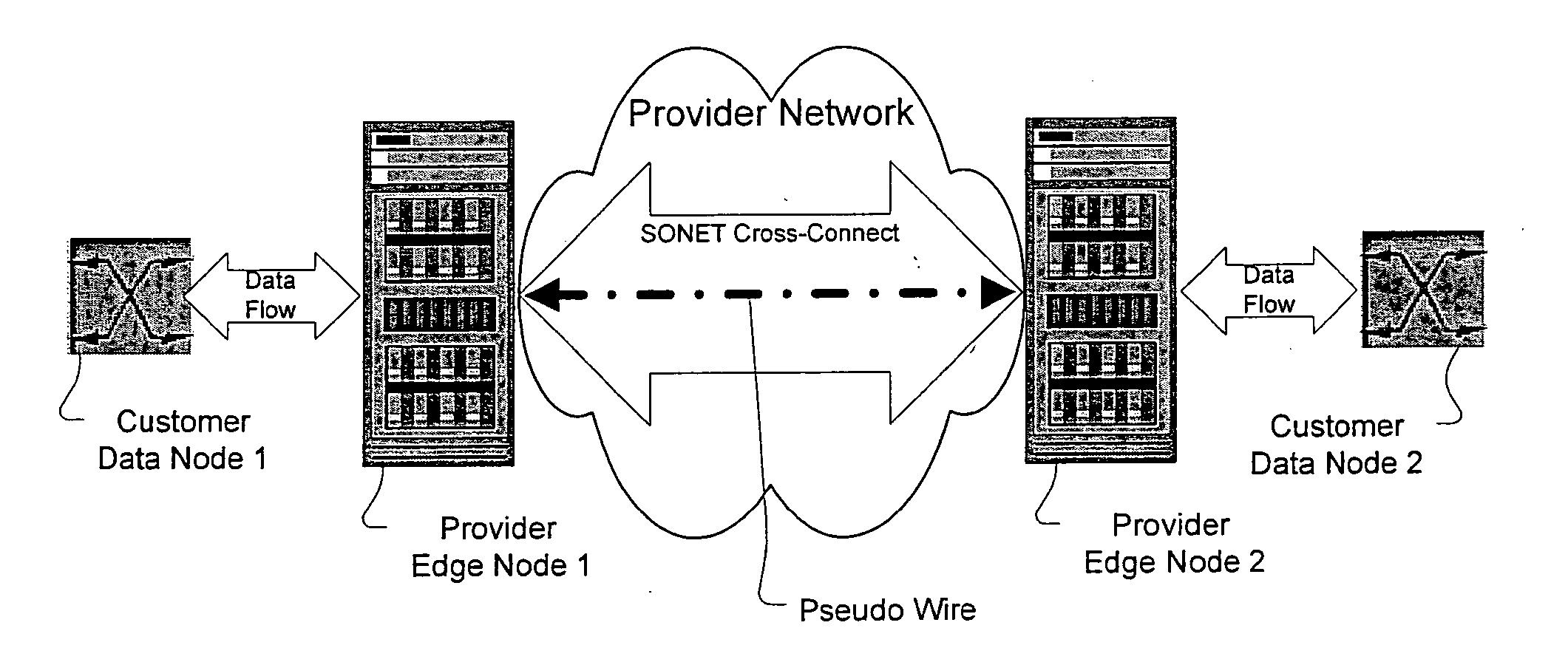
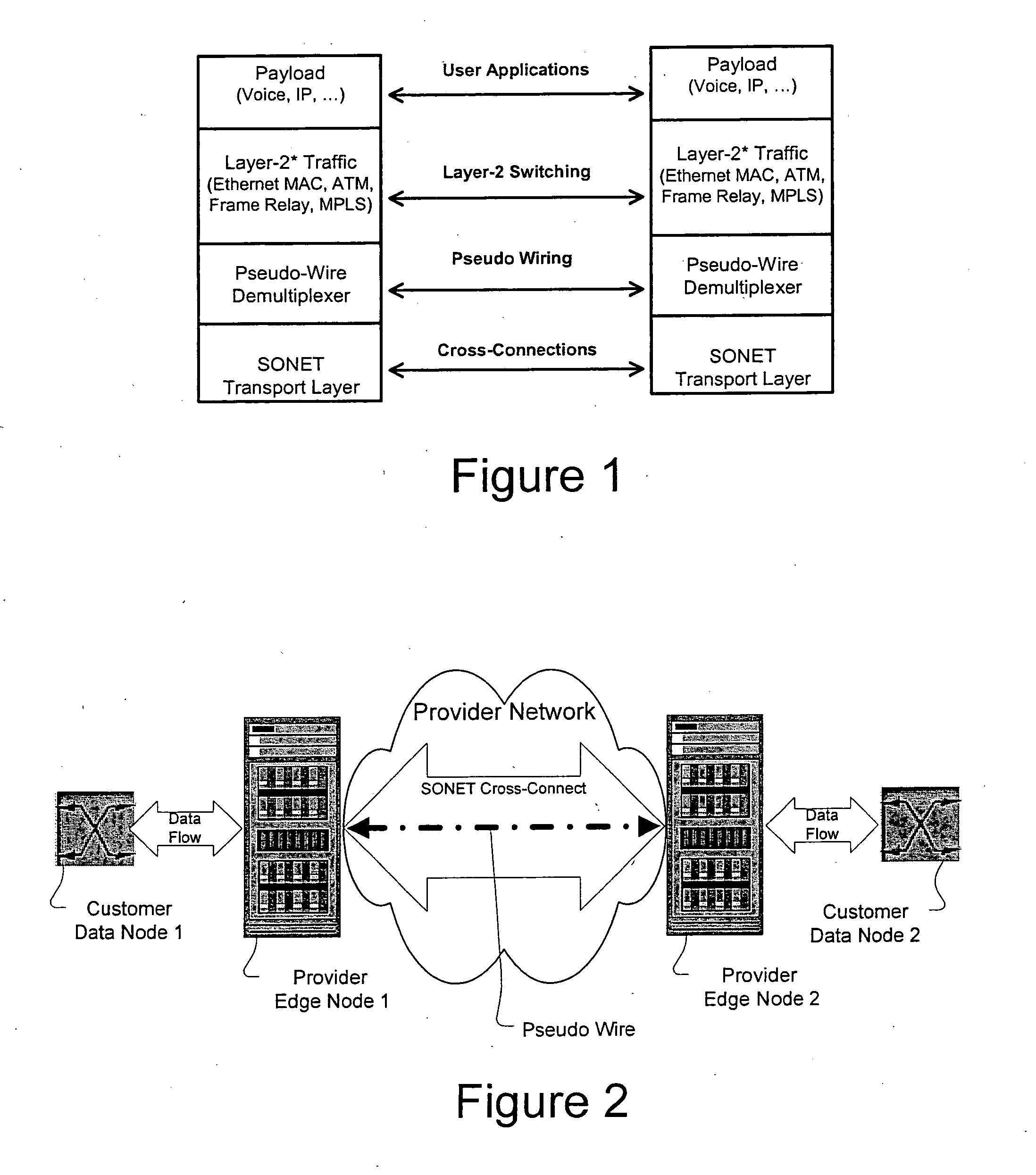
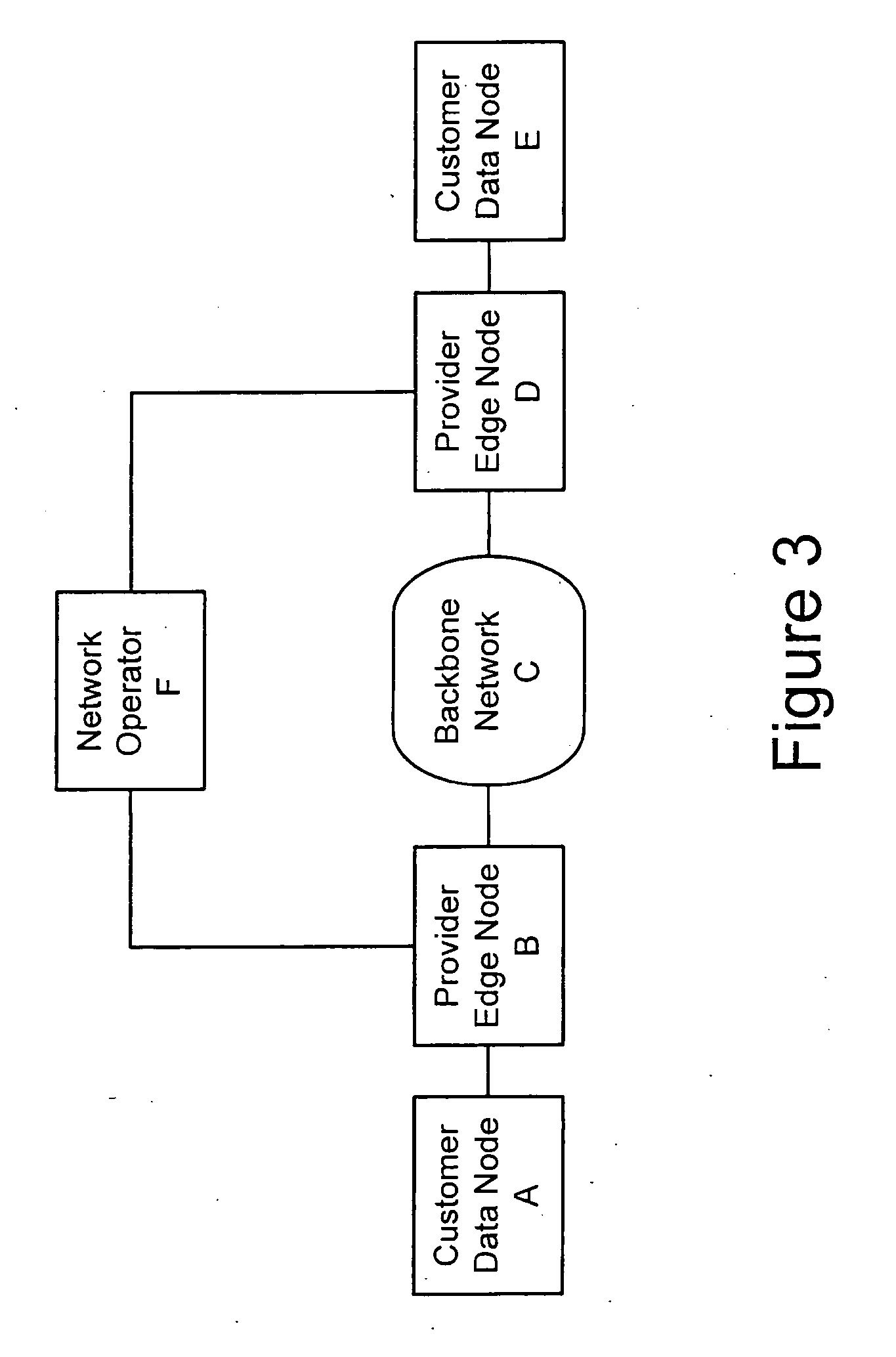
A method, apparatus and network for transporting layer-2 frames, such as Ethernet MAC, ATM AAL5, and Frame Relay, over MPLS, SONET / SDH, or OTN optical transport networks as well as electrical transport networks is disclosed. The method establishes "pseudo-wires" between, for example, routers, Layer-2 packet switches, or SONET / SDH switches. Inter-related ingress and egress resource tables may be used by provider edge nodes to negotiate consistently managed data tunnels across a provider network on behalf of data flowing from / to a diverse base of customer edge nodes. Detailed network resource information particular to each of the data flows is exchanged between provider edge nodes during the creation of pseudo-wires. Admission control algorithms are applied at the ingress and egress points in order to manage the data flows into a provider network and exiting from a provider network to customer equipment. By applying pseudo-wire shuffling and preemption techniques, the providers can make better use of their network resources by admitting more pseudo-wires.
Owner:CIENA
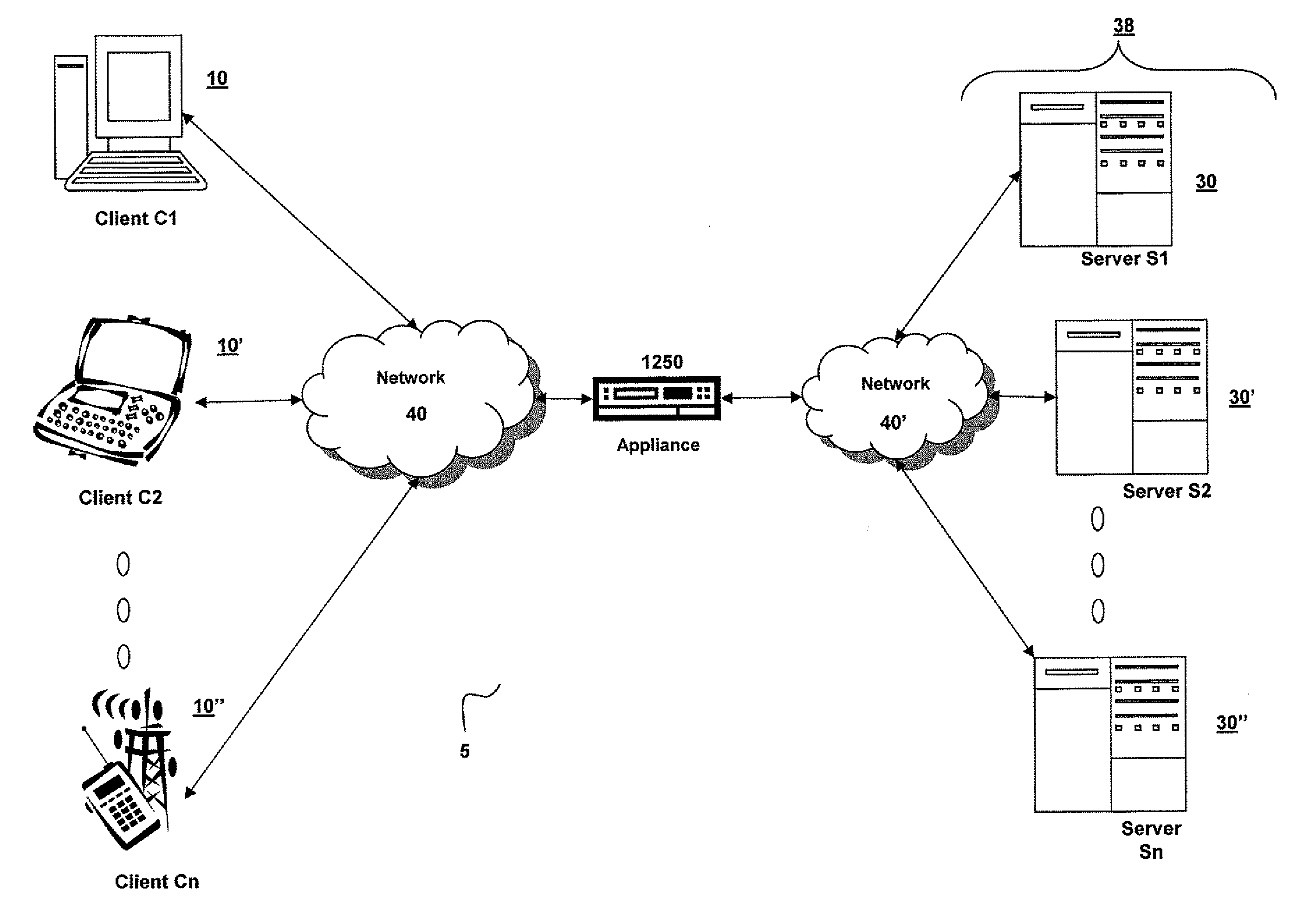
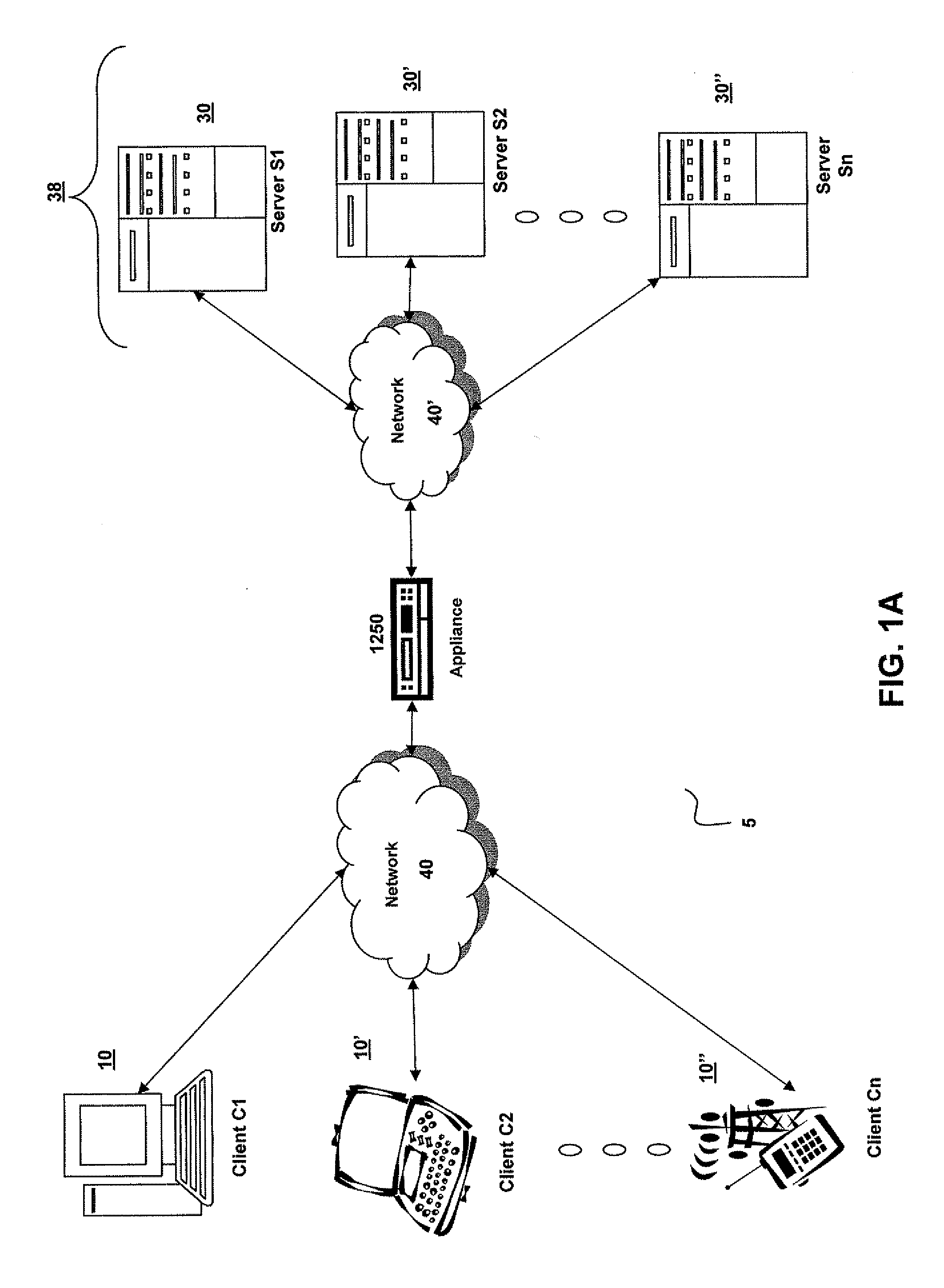
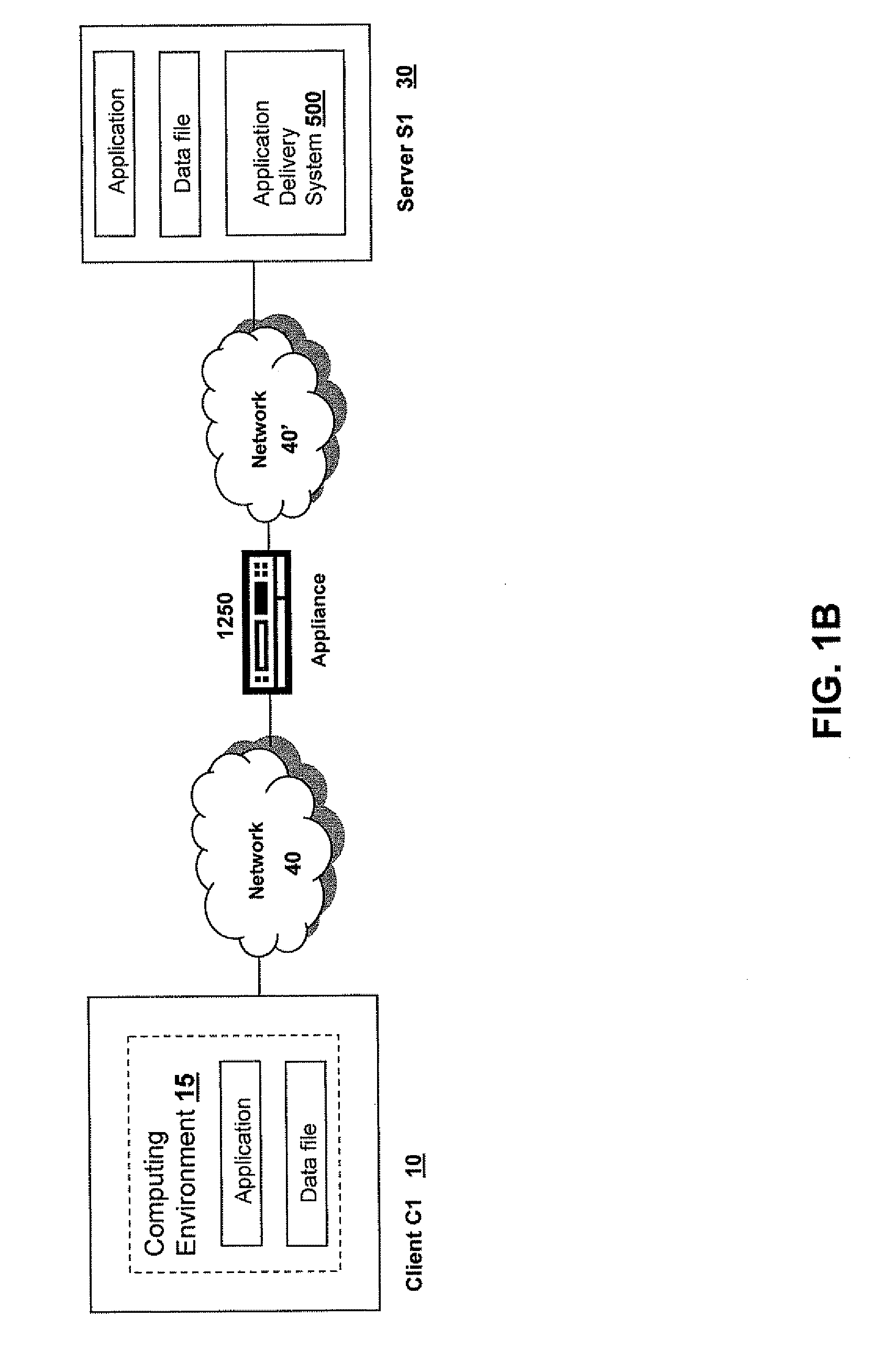
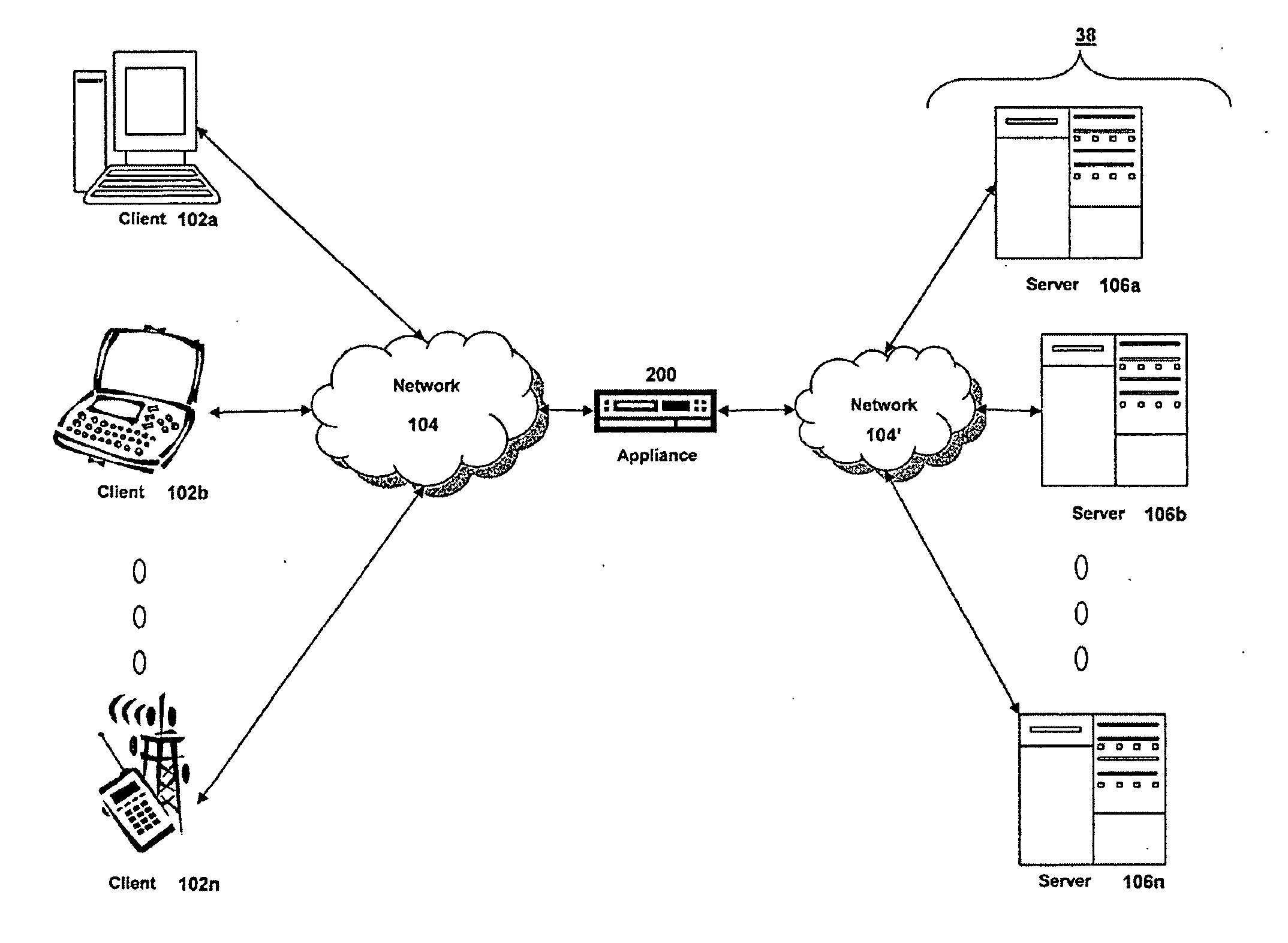
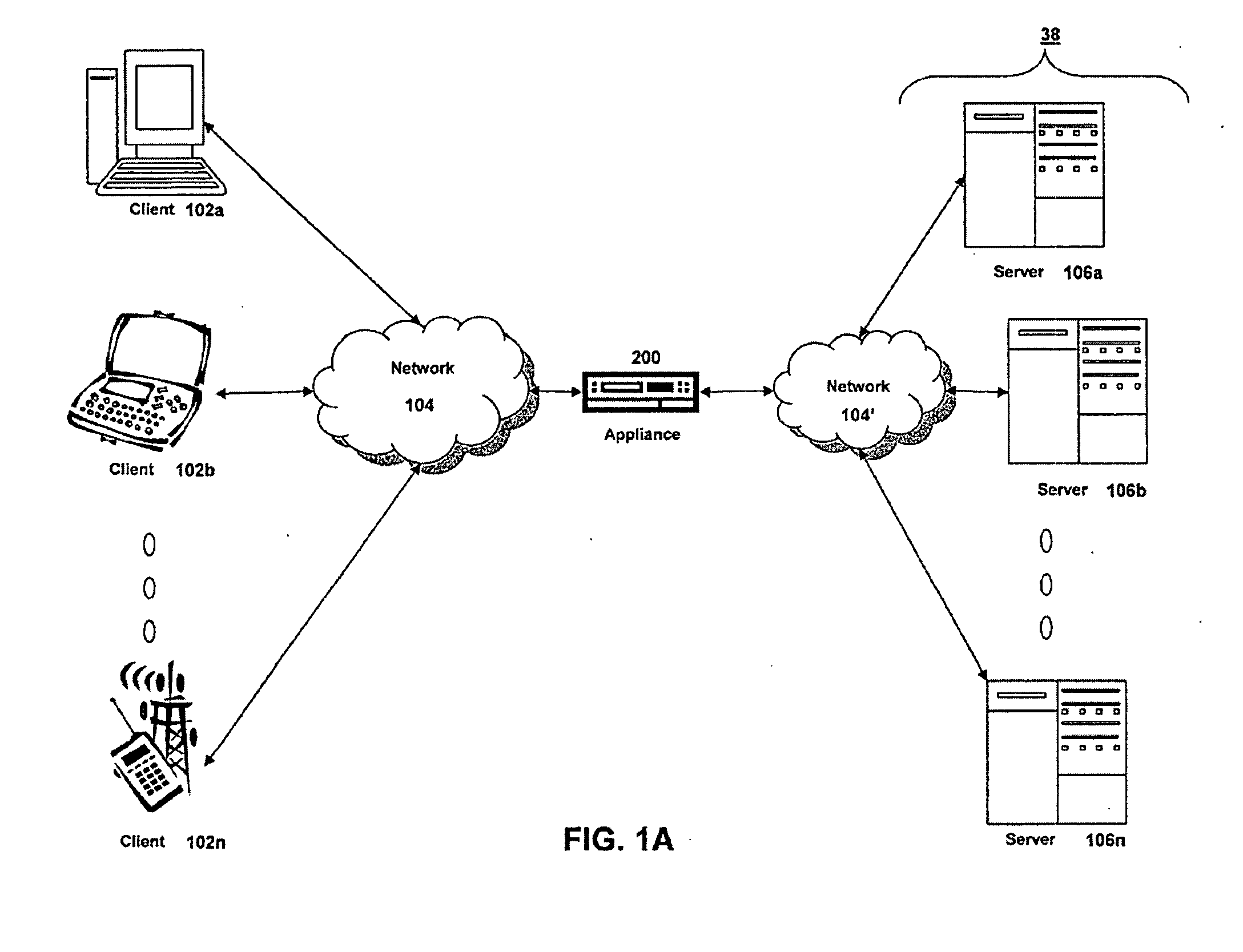
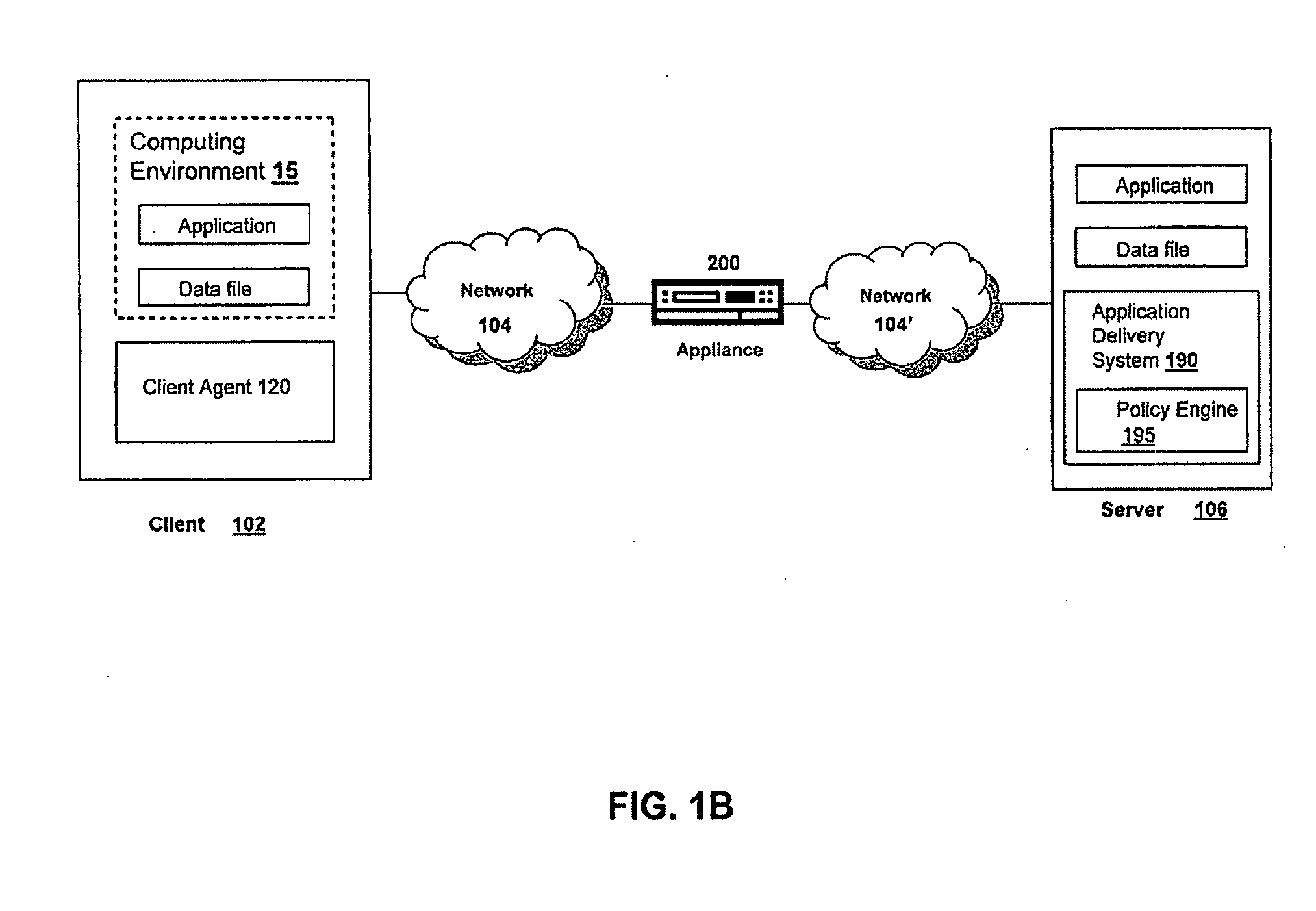
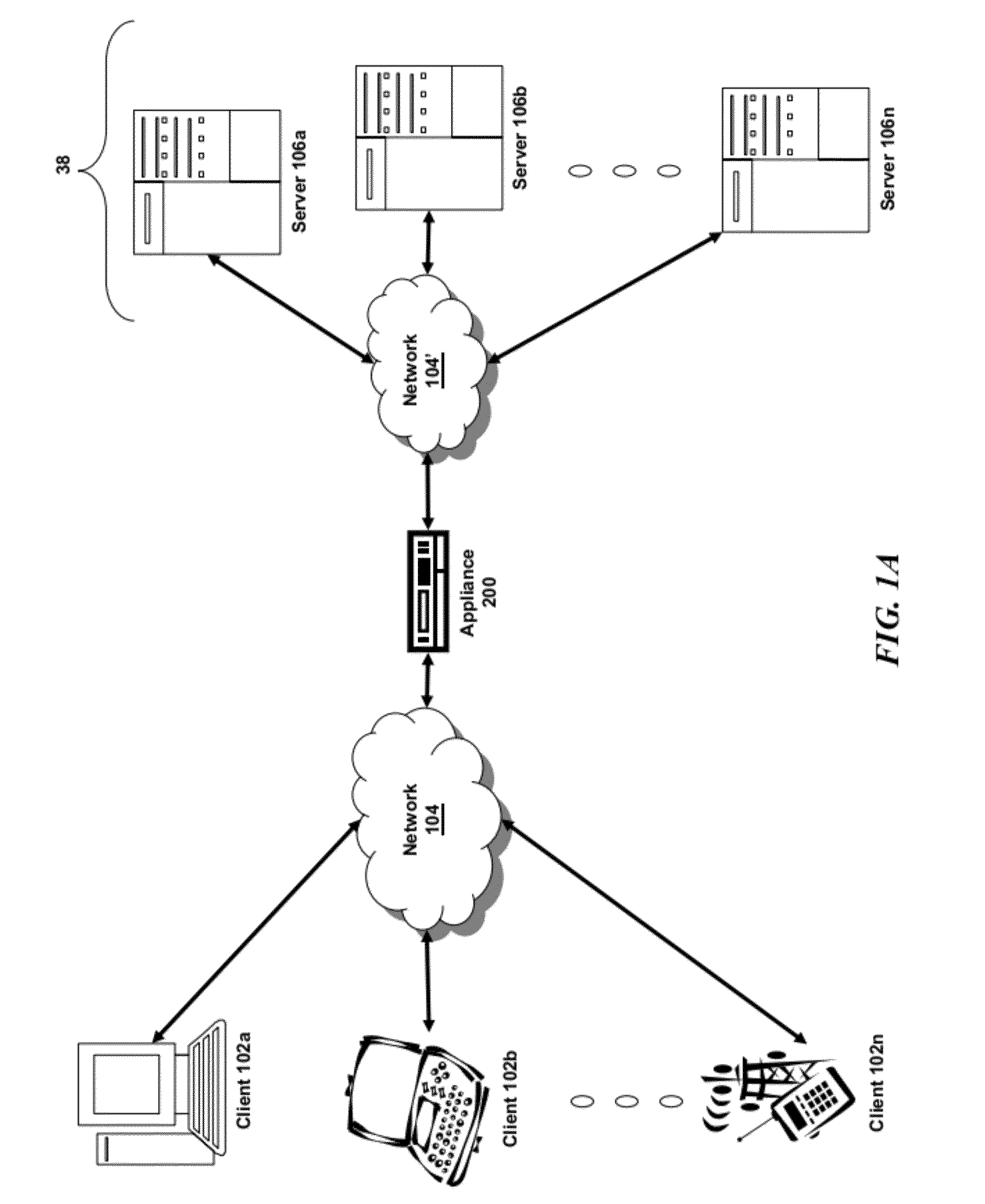
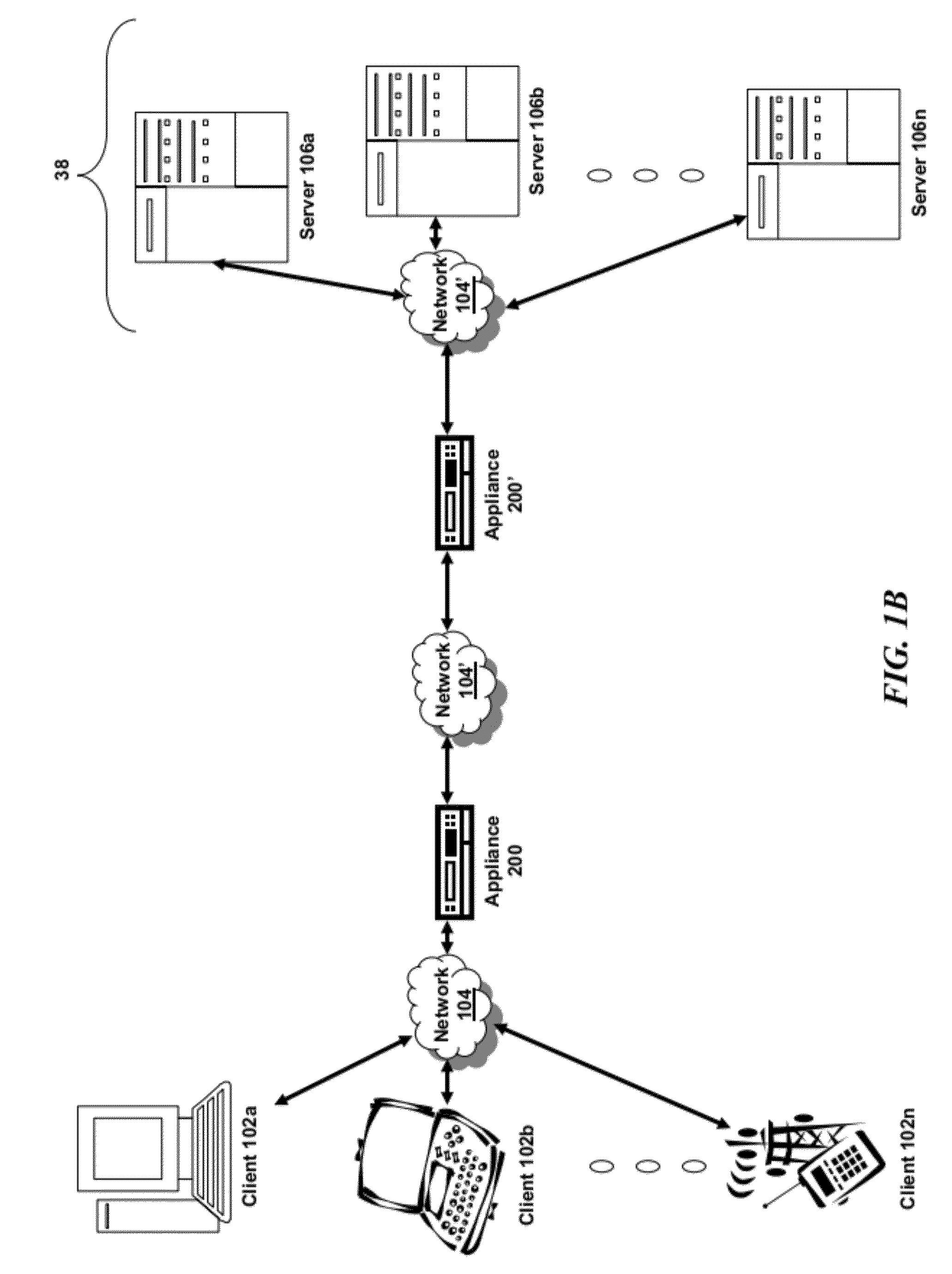
Systems and Methods for Accelerating Delivery of a Computing Environment to a Remote User
ActiveUS20100023582A1Reduce deliveryFacilitate communicationMultiple digital computer combinationsData switching networksTransport layerApplication software
The present invention is directed towards a method and system for accelerating delivery of a computing environment to a remote client. The computing environment may include a plurality of files comprising an application program and may be streamed to a remote client from a server. Responsive to a determination of whether transmission of the application may be accelerated, an appliance, intercepting the plurality of files, may accelerate transmission of the application program by applying one or more transport layer transmission acceleration techniques to the plurality of files.
Owner:CITRIX SYST INC
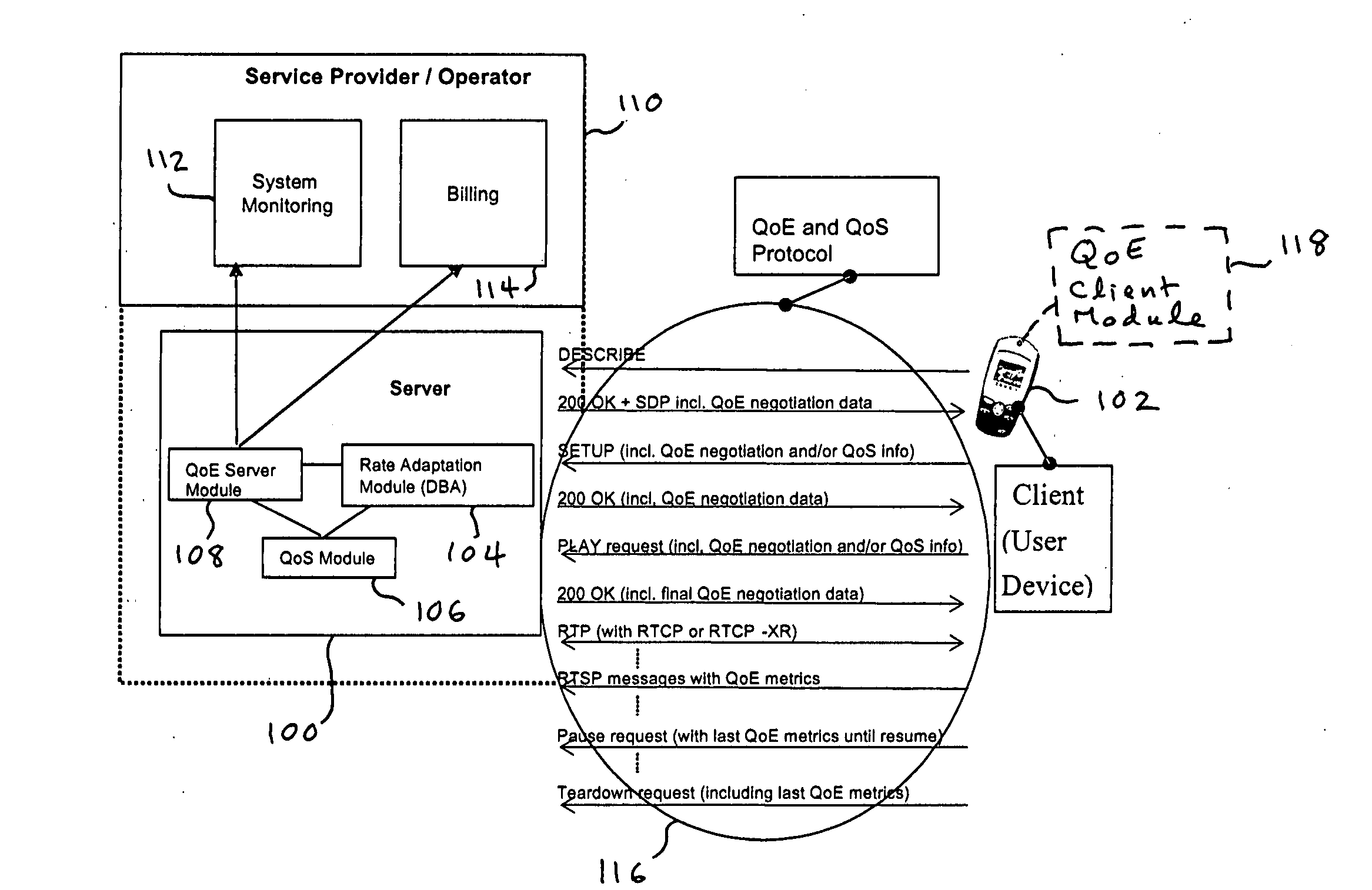
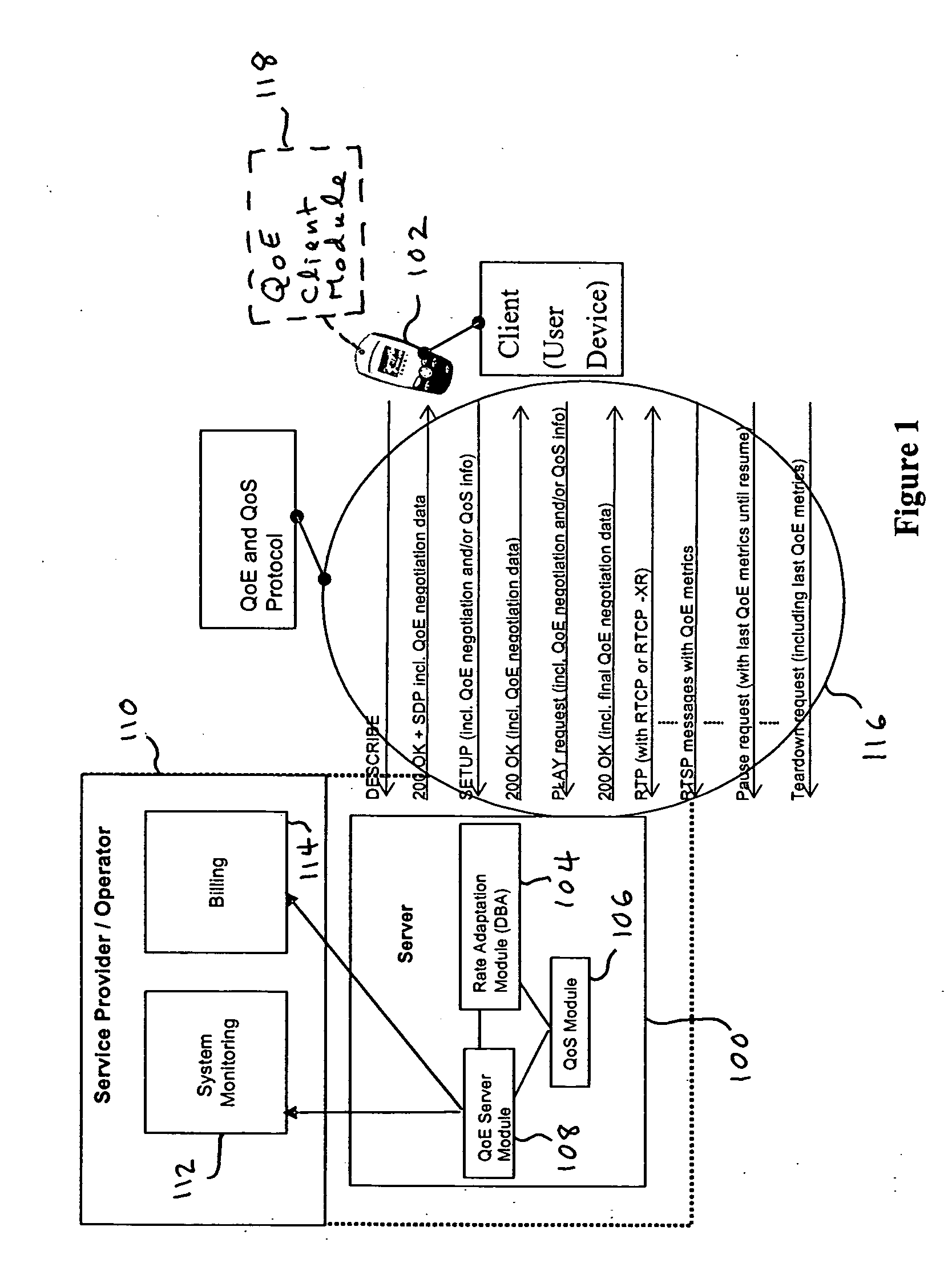
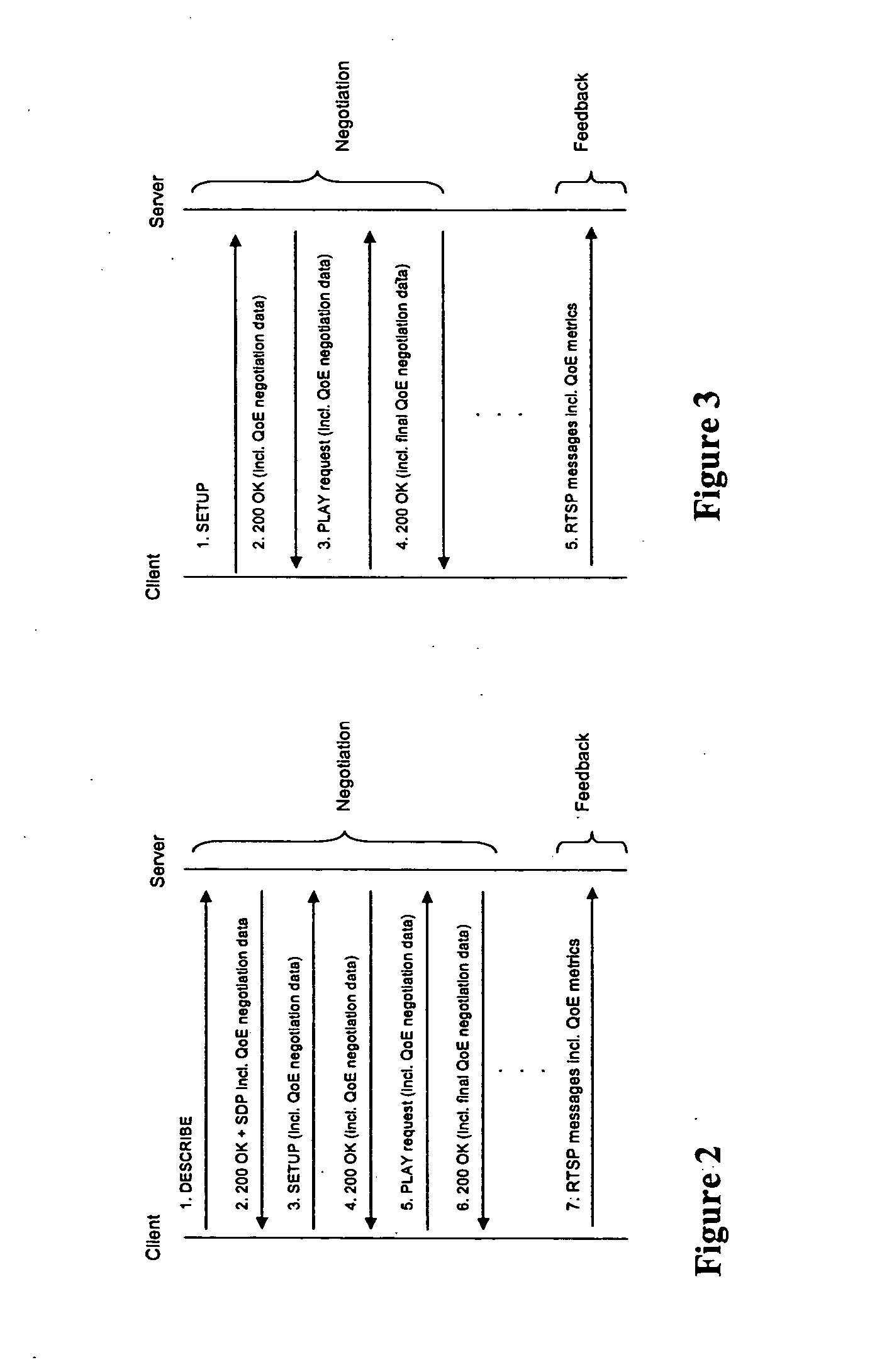
Quality of experience (QOE) method and apparatus for wireless communication networks
A Quality of Experience (QoE) framework provides a technique to assess the end user experience in a mobile wireless communication environment, such as 2.5G or 3G networks, or in any other wireless or hardwired communication environment. The framework is usable in conjunction with media streaming applications and enables a combination of network layer, transport layer, codec layer, and application layer measurements in extracting results. The extracted results can be used to monitor and improve, if necessary, the end user experience over severely variable network conditions.
Owner:VIDIATOR ENTERPRISES INC
Method and apparatus for operating the internet protocol over a high-speed serial bus
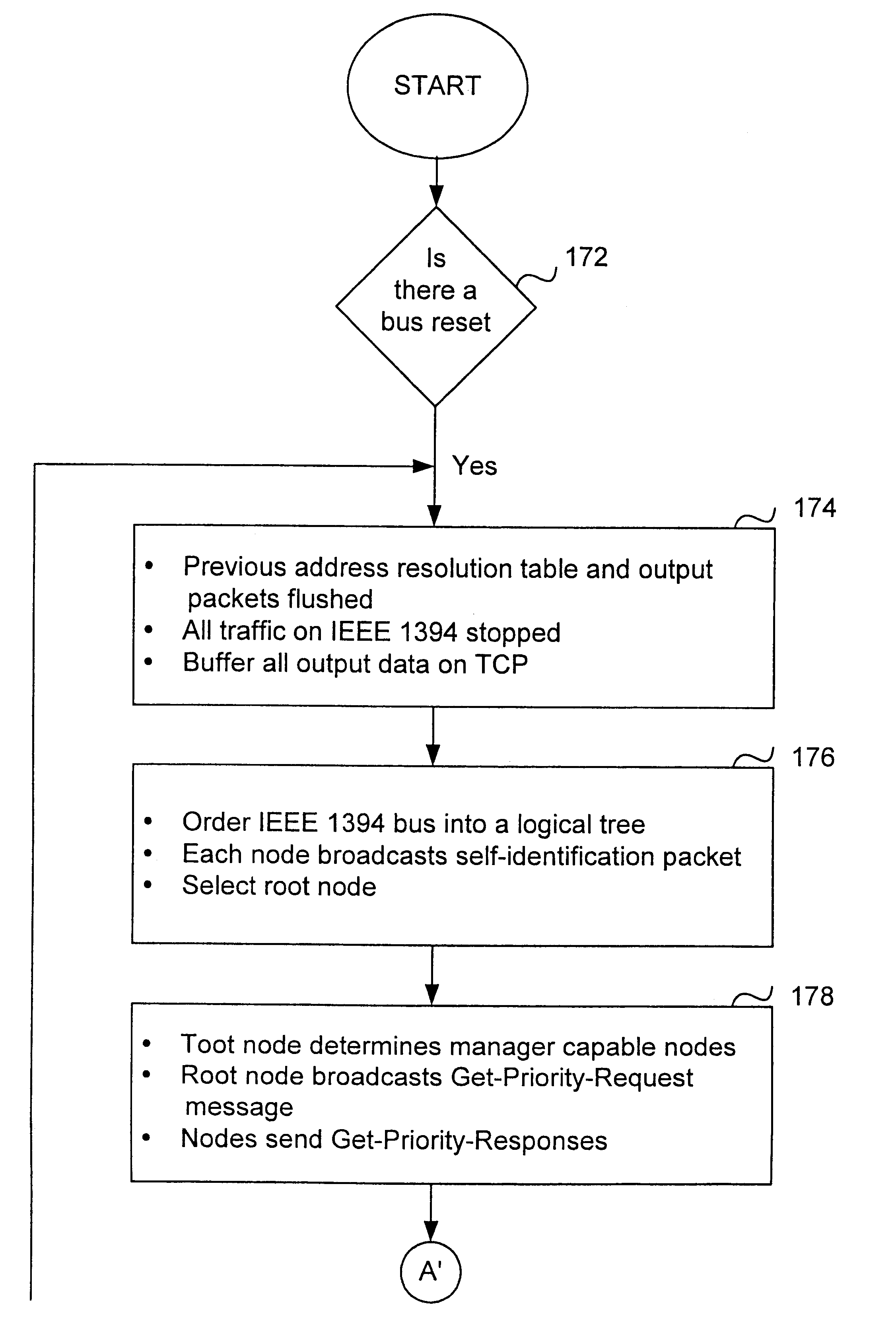
InactiveUS6219697B1Efficiently and correctly determineDigital computer detailsTransmissionInternet protocol suiteTransport layer
A method and apparatus of integrating the IEEE 1394 protocol with the IP protocol in which the IEEE 1394 high speed serial bus operates as the physical and link layer medium and the IP operates as the transport layer. There are differences in the protocols which require special consideration when integrating the two protocols. The IEEE 1394 configures packets with memory information and the IP operates under channel based I / O thereby necessitating a modification of the data transfer scheme to accomplish IP transfers over the IEEE 1394. Further, due to differences in packet headers, the IEEE 1394 packet header is modified to encapsulate IP packets. Moreover, in order to determine network packets quickly and efficiently, an identifier is inserted in each network packet header indicating that the packet should be processed by the network. Finally, in order to support the ability to insert or remove nodes on the network without a loss of data, the IP interface must not be disturbed. This is accomplished by maintaining constant IP addresses across bus resets which are caused by insertion or removal of nodes from the network.
Owner:HEWLETT-PACKARD ENTERPRISE DEV LP
Light emitting component comprising organic layers
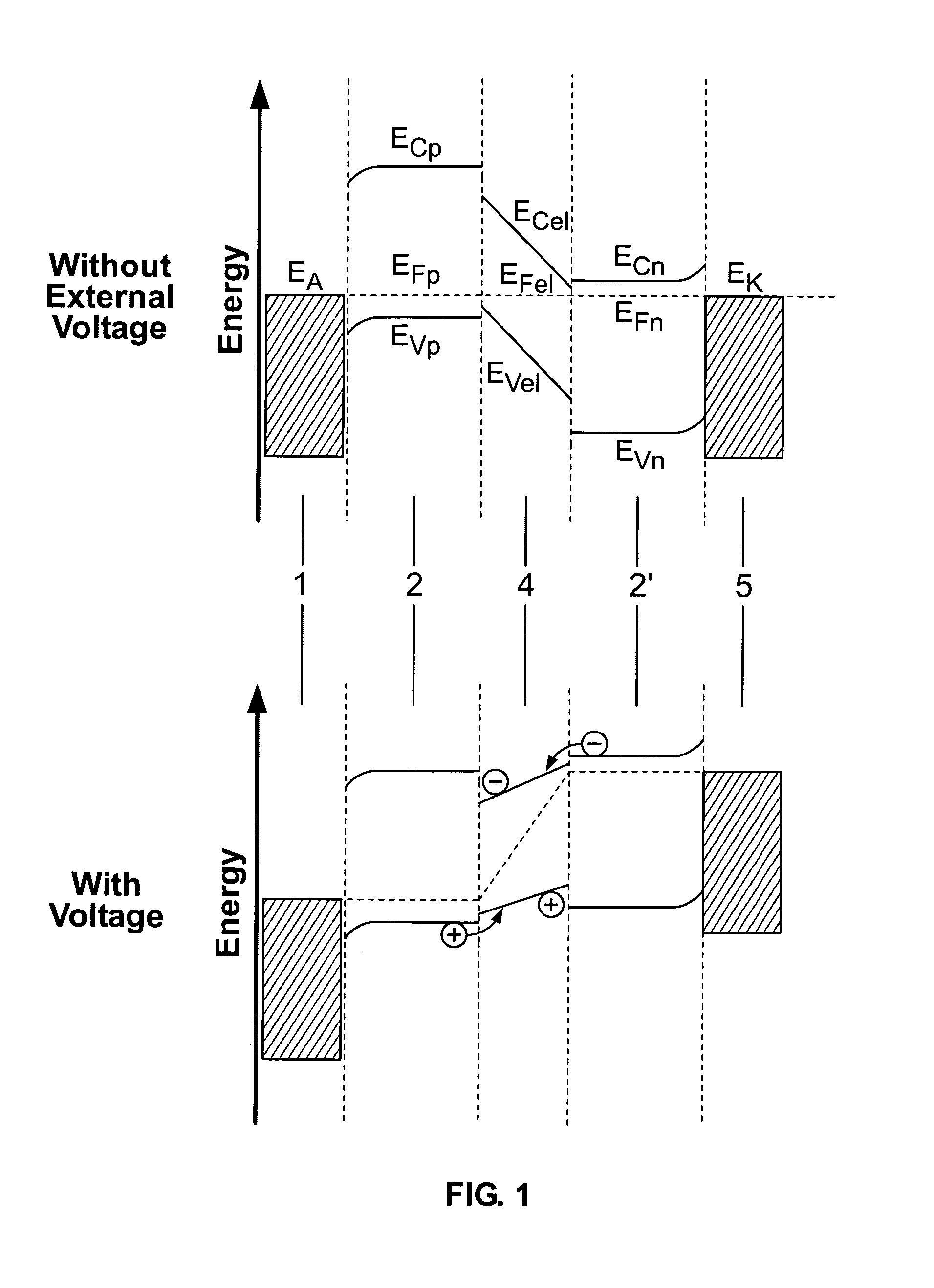
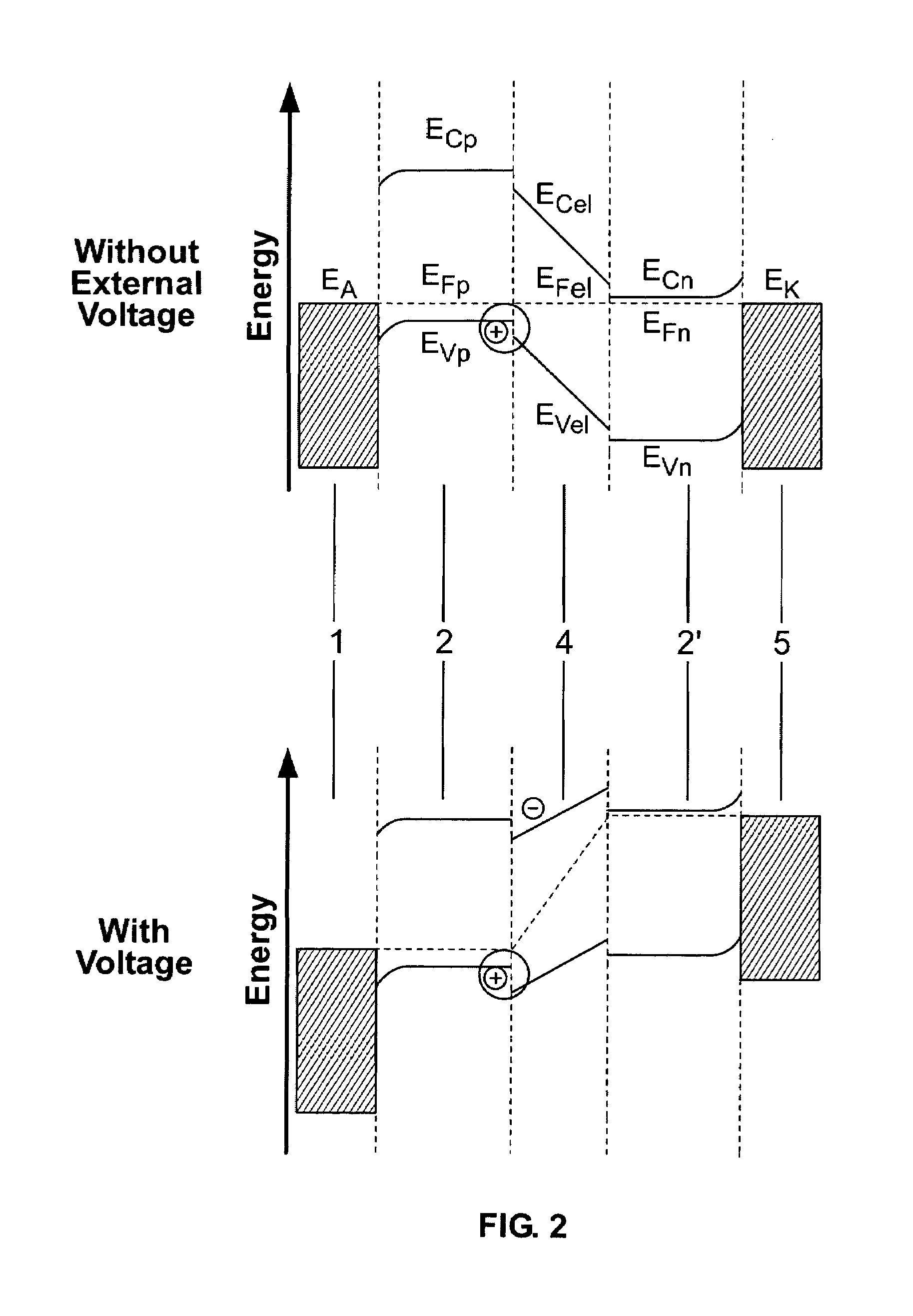
InactiveUS7074500B2Inhibit injectionDischarge tube luminescnet screensElectroluminescent light sourcesTransport layerCharge carrier
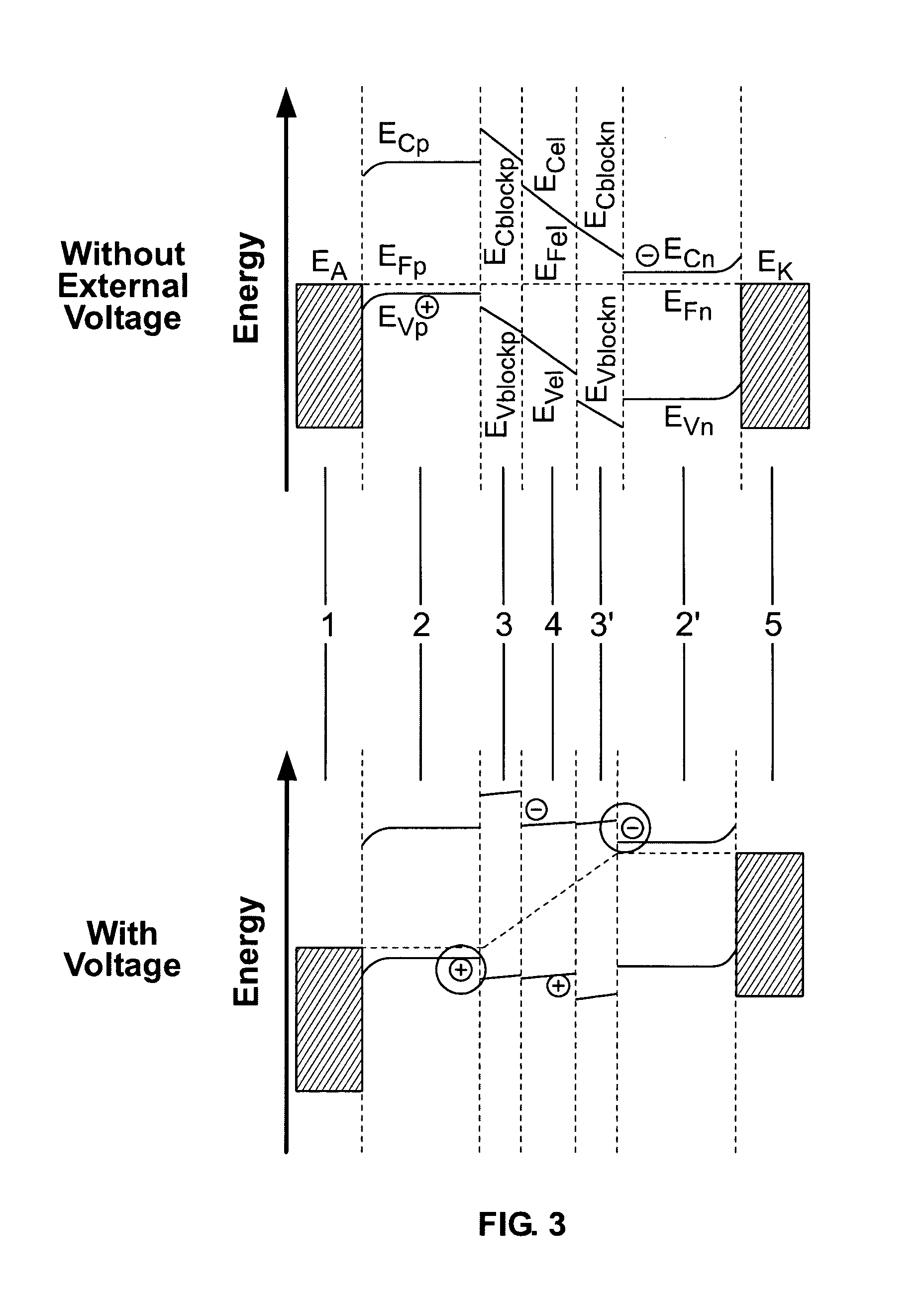
The invention relates to a light-emmiting component having organic layers, in particular to an organic light-emmiting diode. The component has at least one doped charge carrier transport layer (2), a light-emmiting layer (4) and contact layers (1, 5) and also has a blocking layer (3; 3′) wherein an organic material is provided between the charge carrier transport layer (2, 2′) and the light-emmiting layer (4). The energy levels of the charge carried transport layer are chosen in such a way that efficient doping is possible and the blocking layer nevertheless ensures that non-radiating recombination processes on the interface with the emitting layer are prevented.
Owner:NOVALED GMBH
Electro-optic displays, and methods for driving same
InactiveUS7787169B2Reduce and eliminate exposureReducing and eliminating light degradationNon-linear opticsOptical elementsElectricityTransport layer
The invention relates to electro-optic displays and methods for driving such displays. The invention provides (i) electrochromic displays with solid charge transport layers; (ii) apparatus and methods for improving the contrast and reducing the cost of electrochromic displays; (iii) apparatus and methods for sealing electrochromic displays from the outside environment and preventing ingress of contaminants into such a display; and (iv) methods for adjusting the driving of electro-optic displays to allow for environmental and operating parameters.
Owner:E INK CORP
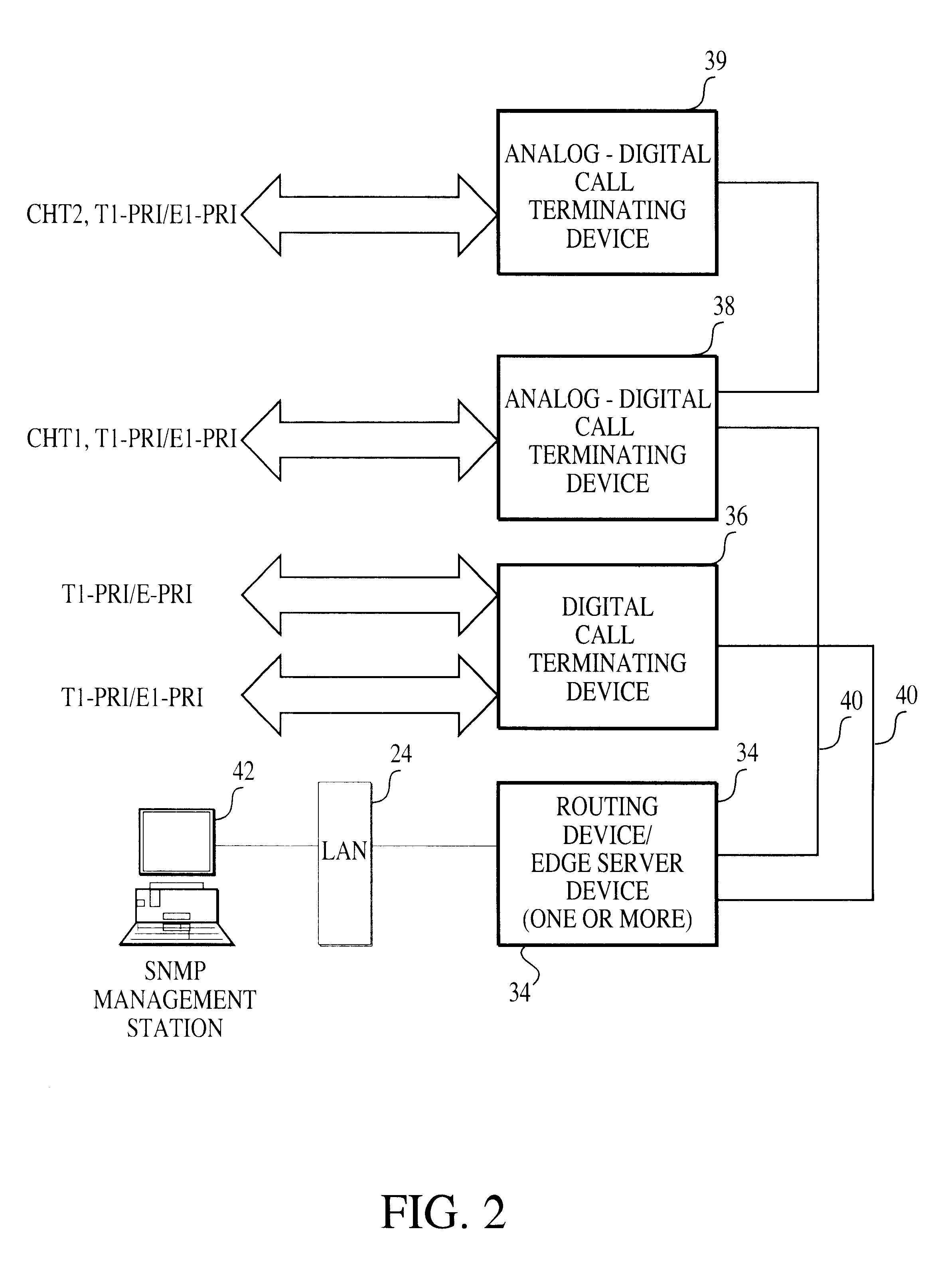
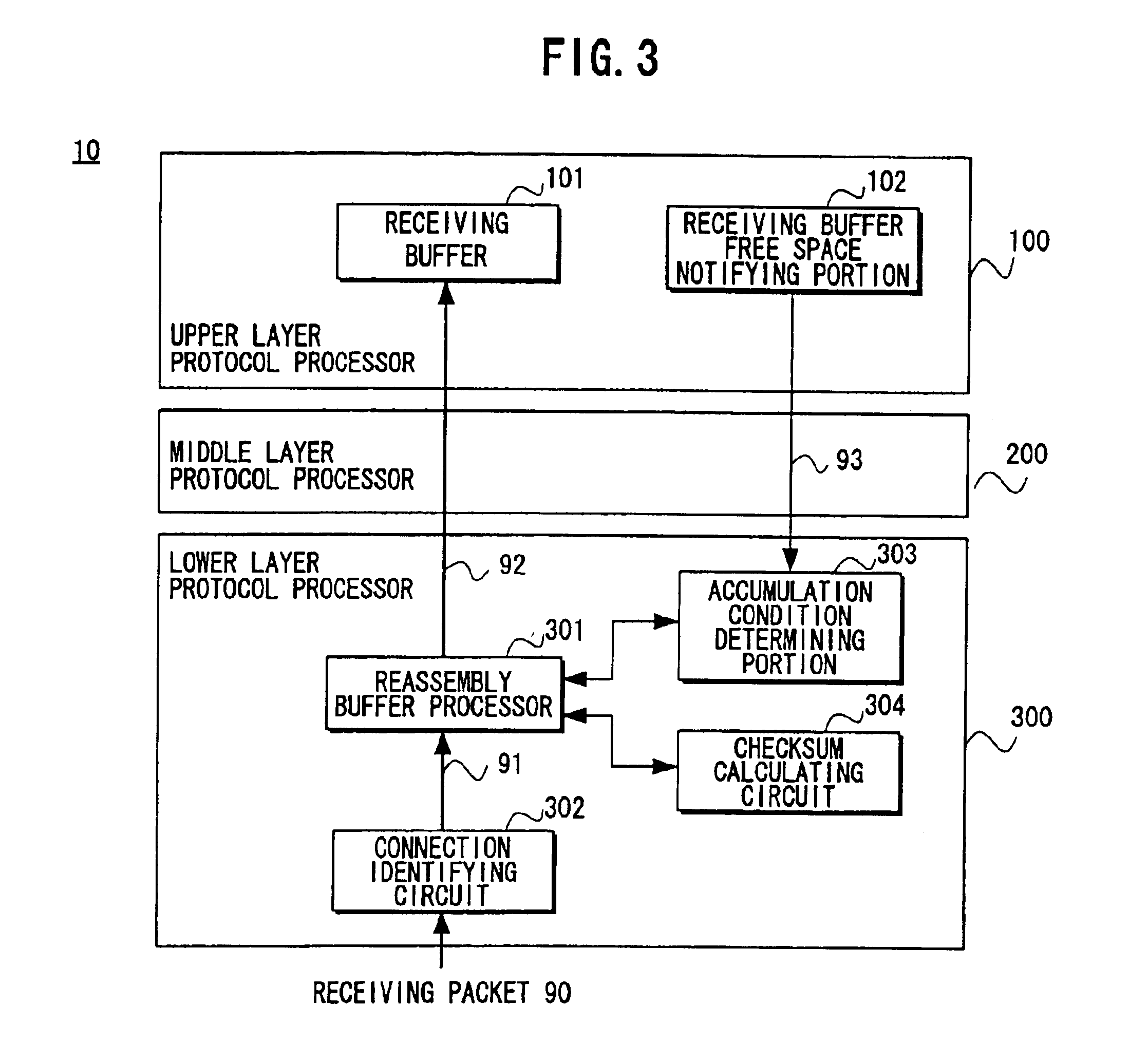
Packet processing device
InactiveUS6907042B1Reduce the number of processesEliminate overheadError preventionFrequency-division multiplex detailsTransport layerProtocol Application
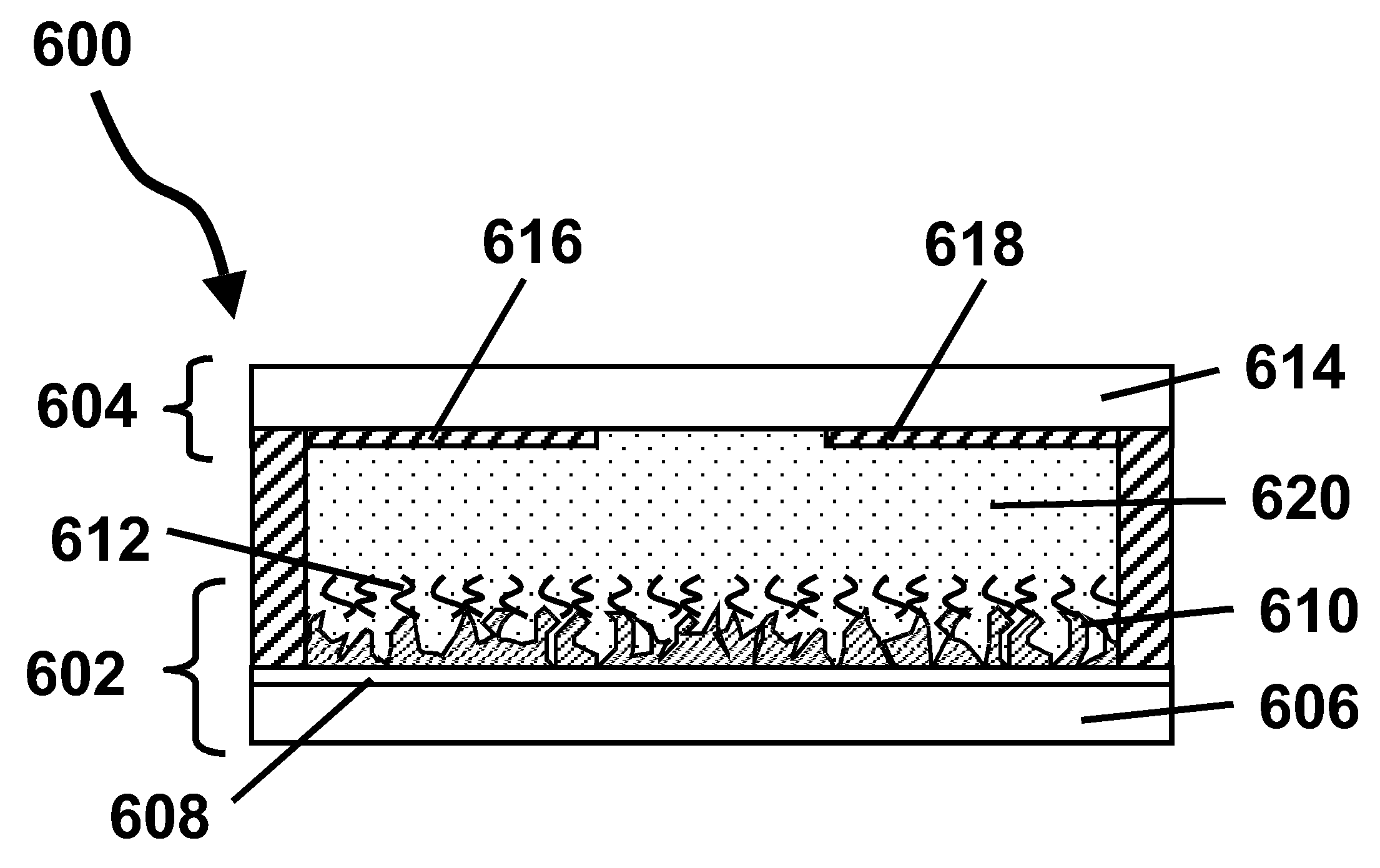
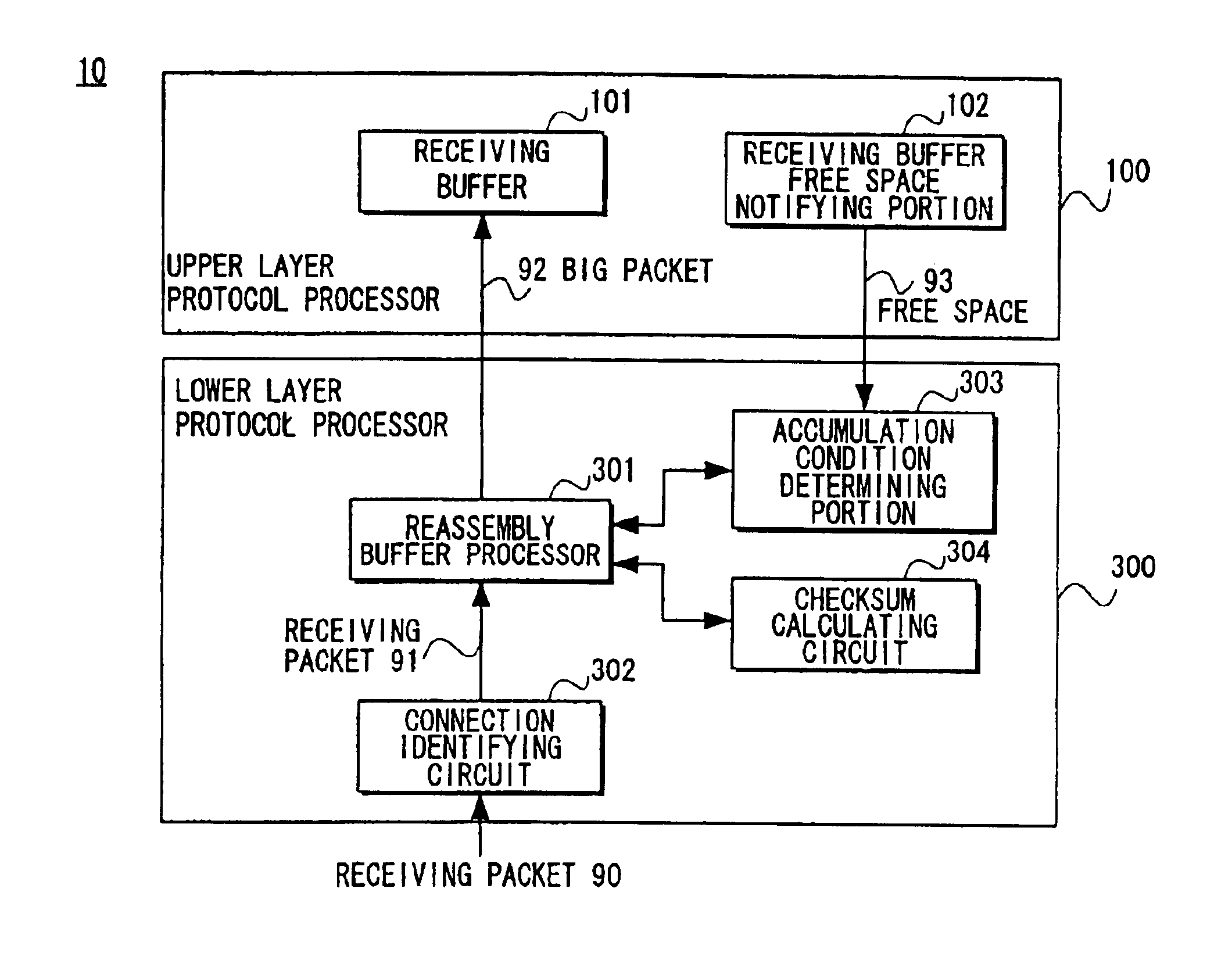
A packet processing device in which a receiving buffer free space notifying portion notifies a free space of a receiving buffer, an accumulation condition determining portion determines a size of a big packet based on the free space, and a reassembly buffer processor reassembles a plurality of receiving packets into a single big packet to be transmitted to the receiving buffer. A backward packet inclusive information reading circuit for detecting the free space based on information within a backward packet from the upper layer may be used as the receiving buffer free space notifying portion. Also, an application layer may be used as the upper layer so that the big packet is transmitted not through a buffer of a transport layer but directly to the receiving buffer.
Owner:FUJITSU LTD
Systems and methods for gslb mep connection management across multiple core appliances
ActiveUS20110153840A1Improve performanceAvoid any of the servers being overburdened or crashingMultiple digital computer combinationsTransmissionInformation dispersalTransport layer
The present disclosure presents systems and methods for obtaining metric information by a multi-core GSLB intermediary device and providing global server load balancing services using the obtained information. A first core of a multi-core GSLB appliance establishes a transport layer connection to a remote load balancer at a site of a plurality of sites. The first core transmits a message to each of the other cores of the multi-core GSLB appliance that that the first core is a master core for receiving metric information from the load balancer. The first core receives metric information of the remote site from the load balancer. The first core propagates the metric information to each of the other cores of the GSLB appliance. A GSLB virtual server on a slave core receives a DNS request. The GSLB virtual server determines a DNS resolution for the DNS request based on the metric information.
Owner:CITRIX SYST INC
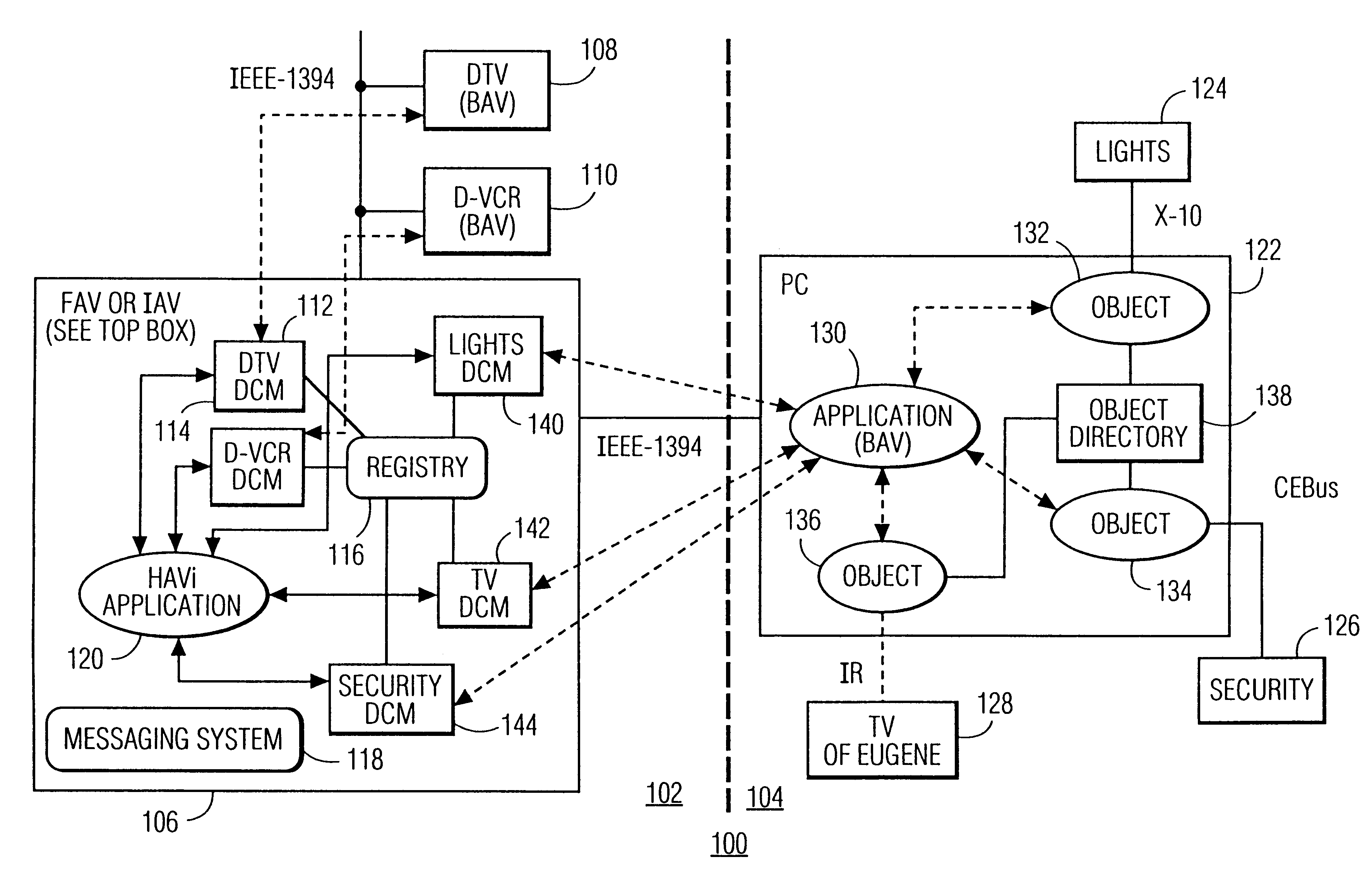
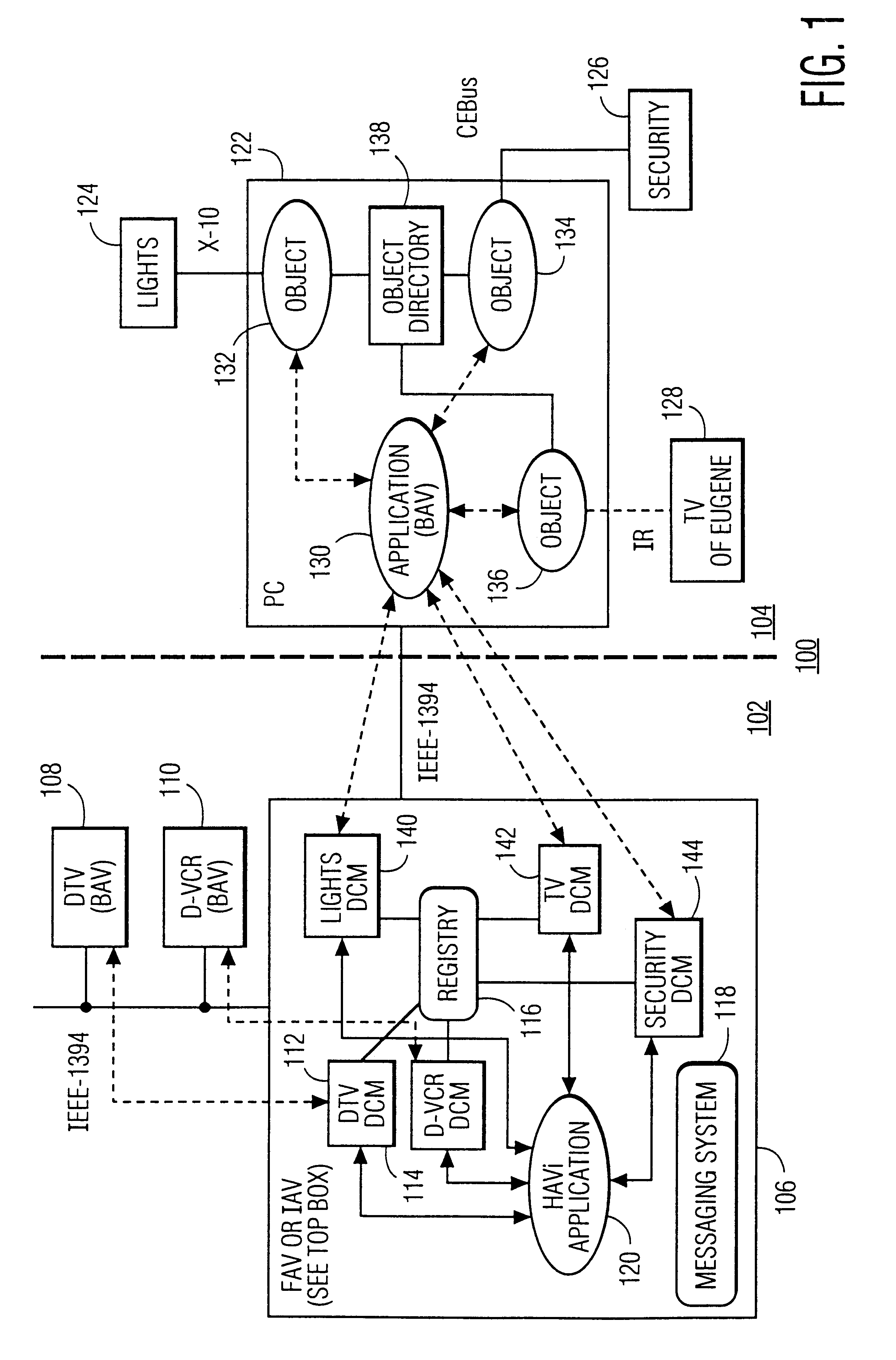
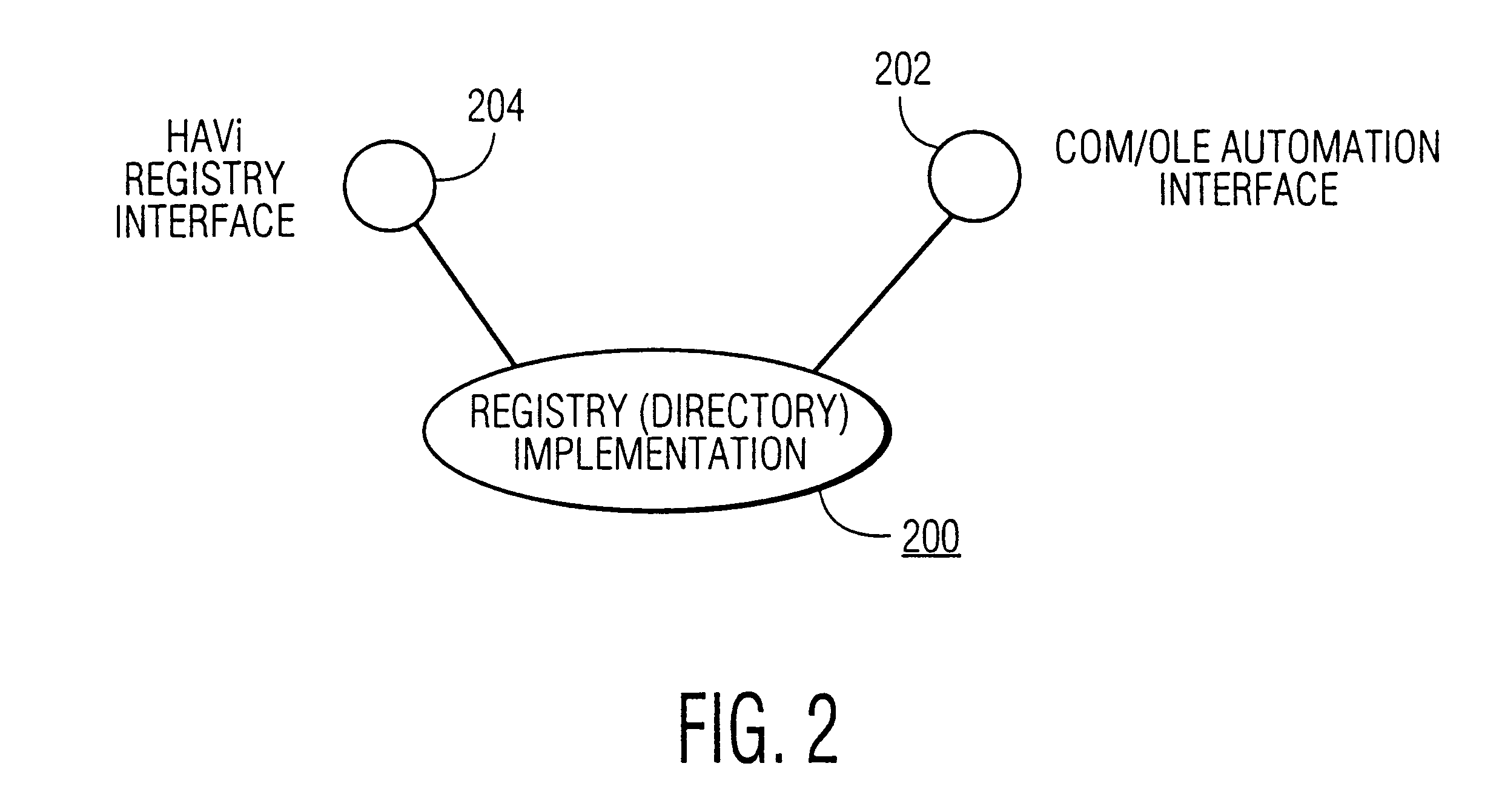
Method and apparatus for a low data-rate network to be represented on and controllable by high data-rate home audio/video interoperability (HAVi) network
InactiveUS6199136B1Function increaseMultiplex system selection arrangementsSpecial service provision for substationVideo equipmentEmbedded system
A PC-based home automation system uses a low data-rate transport layer and COM-based software components for control of devices in a home automation network. The home automation system is merged with a messaging-based HAVi-network that uses IEEE 1394 as a high data-rate transport layer. The HAVi-network controls audio / video equipment in a home entertainment system. The home automation services and devices are registered as a HAVi-compliant elements with the HAVi network's FAV or IAV device. The home automation resources (devices and services) have both COM OLE Automation Interfaces and HAVI-compliant interfaces to permit control of the home automation system from the HAVi-network.
Owner:U S PHILIPS CORP
Dynamically integrating disparate systems and providing secure data sharing
InactiveUS20050203892A1Digital data information retrievalDigital data processing detailsTime informationScripting language
Owner:FATPOT TECH
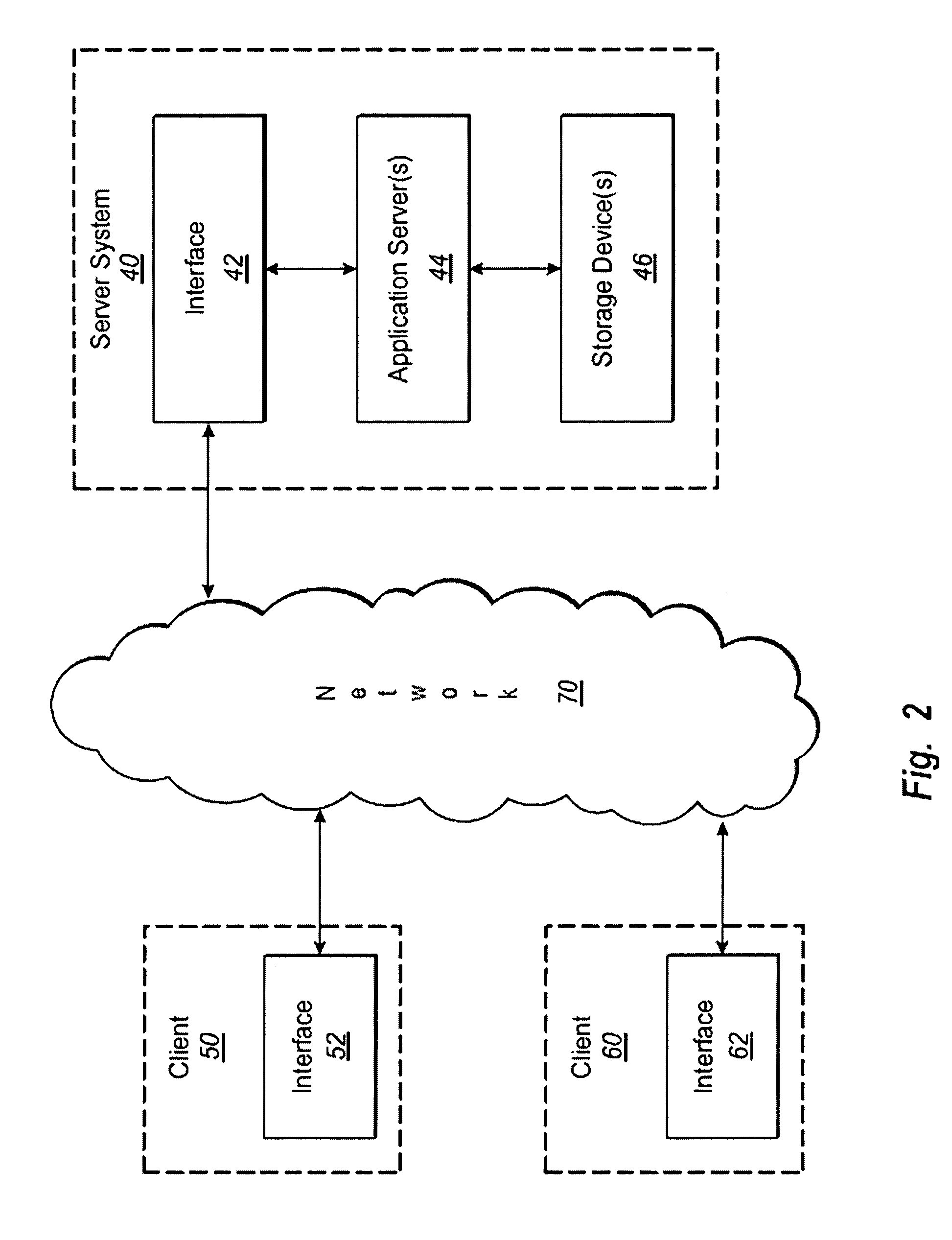
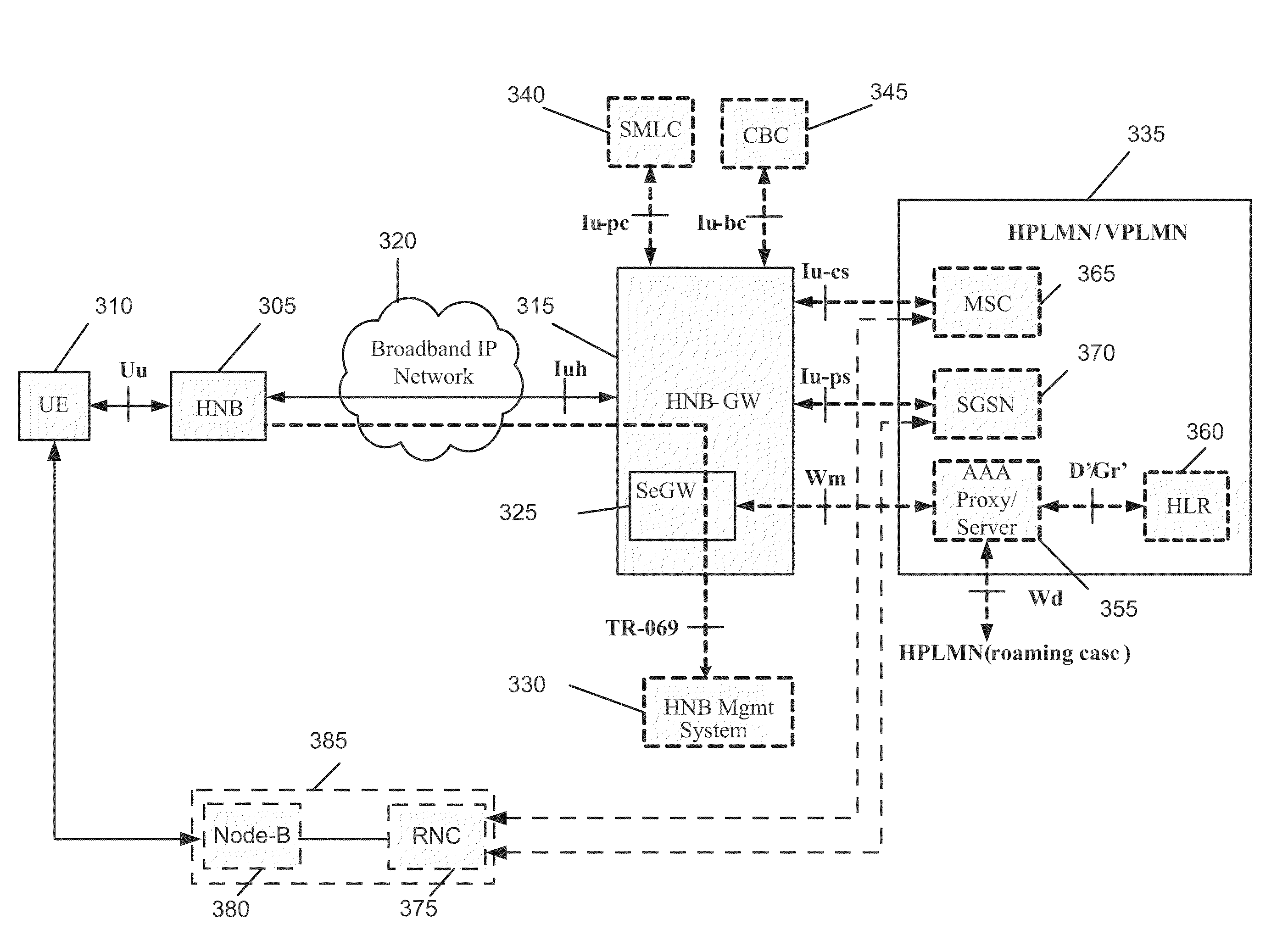
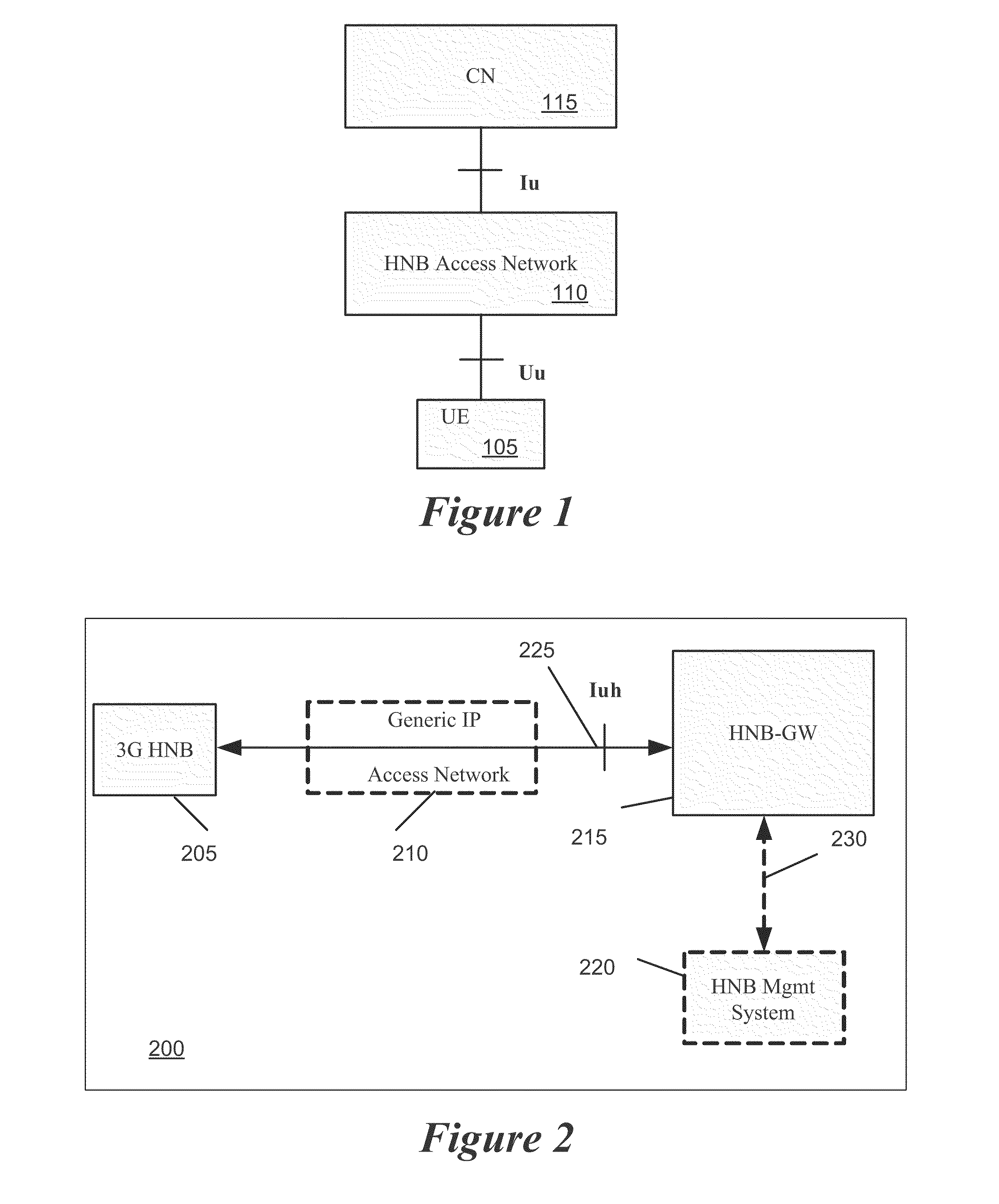
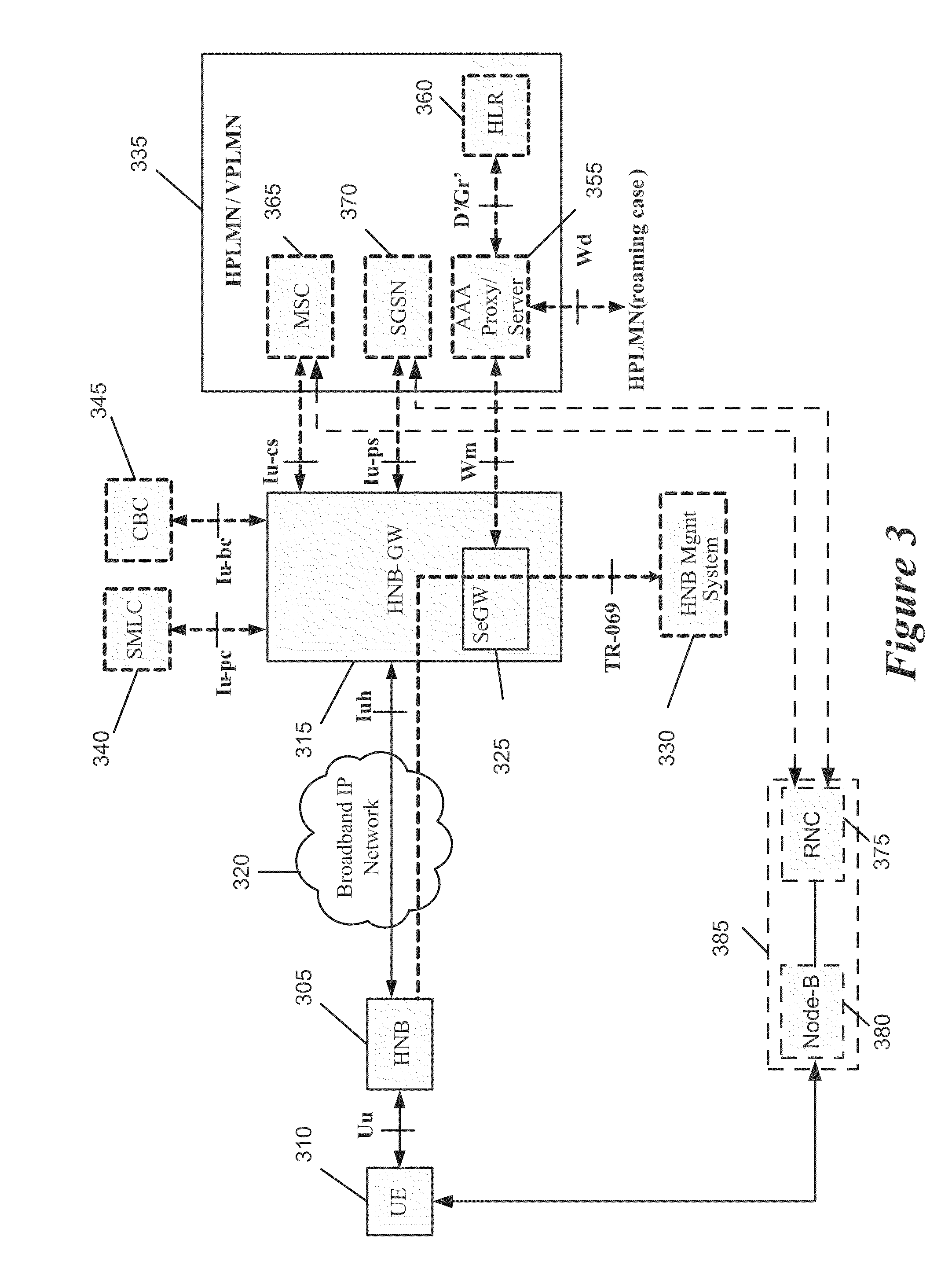
Home Node B System Architecture with Support for RANAP User Adaptation Protocol
InactiveUS20090265543A1Lower deployment costsSpeed andAssess restrictionNetwork topologiesHome Node BTransport layer
Some embodiments are implemented in a communication system that includes a first communication system comprised of a licensed wireless radio access network and a core network, and a second communication system comprising a plurality of user hosted access points and a network controller. In some embodiments, each access point operates using short range licensed wireless frequencies to establish a service region. In some embodiments, the network controller communicatively couples the core network to the plurality of access points. The method uses three sets of protocol layers: a security layer, a transport layer, and a layer for transferring Radio Access Network Application Part (RANAP) messages, to communicate between the network controller and one of the access points. The method also uses the Iuh interface for the transport of messages across the three sets of protocol layers.
Owner:KINETO WIRELESS
Systems and Methods of Symmetric Transport Control Protocol Compression
ActiveUS20080046616A1Reduce network latencyImprove experienceNetwork traffic/resource managementWireless network protocolsTraffic capacityData compression
A method for compressing a stream of application layer network traffic communicated over a transport layer connection of a virtual private network connection between a client and a server using an appliance. The appliance intercepts one or more transport layer packets of a stream of application network traffic communicated via a transport layer connection of a virtual private network connection between a client and a server. The appliance accumulates data from a payload of the intercepted transport layer packets, determines data accumulated for transmission should be compressed based on one or more compression trigger, and compresses the accumulated data into a self-contained compression block for transmission.
Owner:CITRIX SYST INC
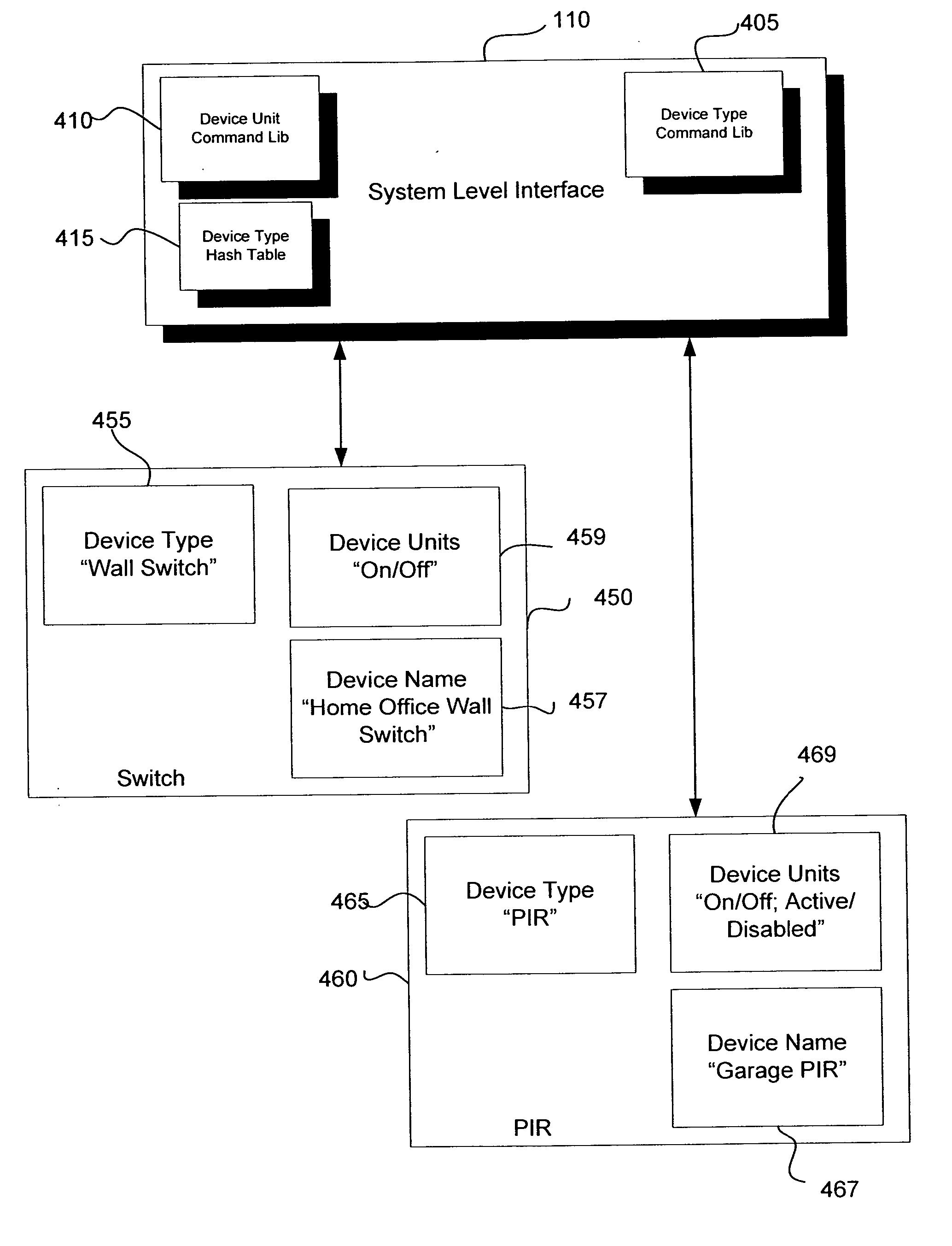
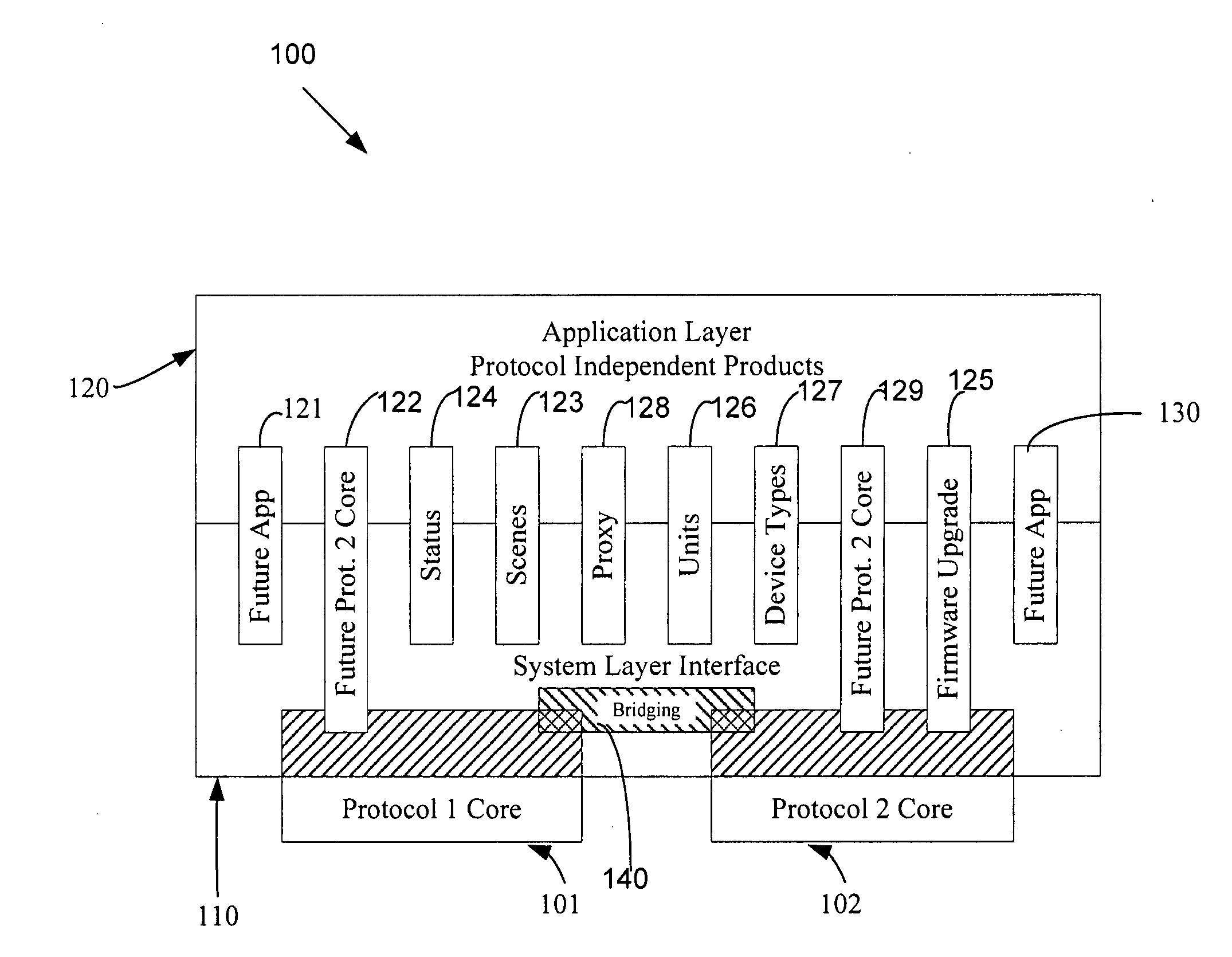
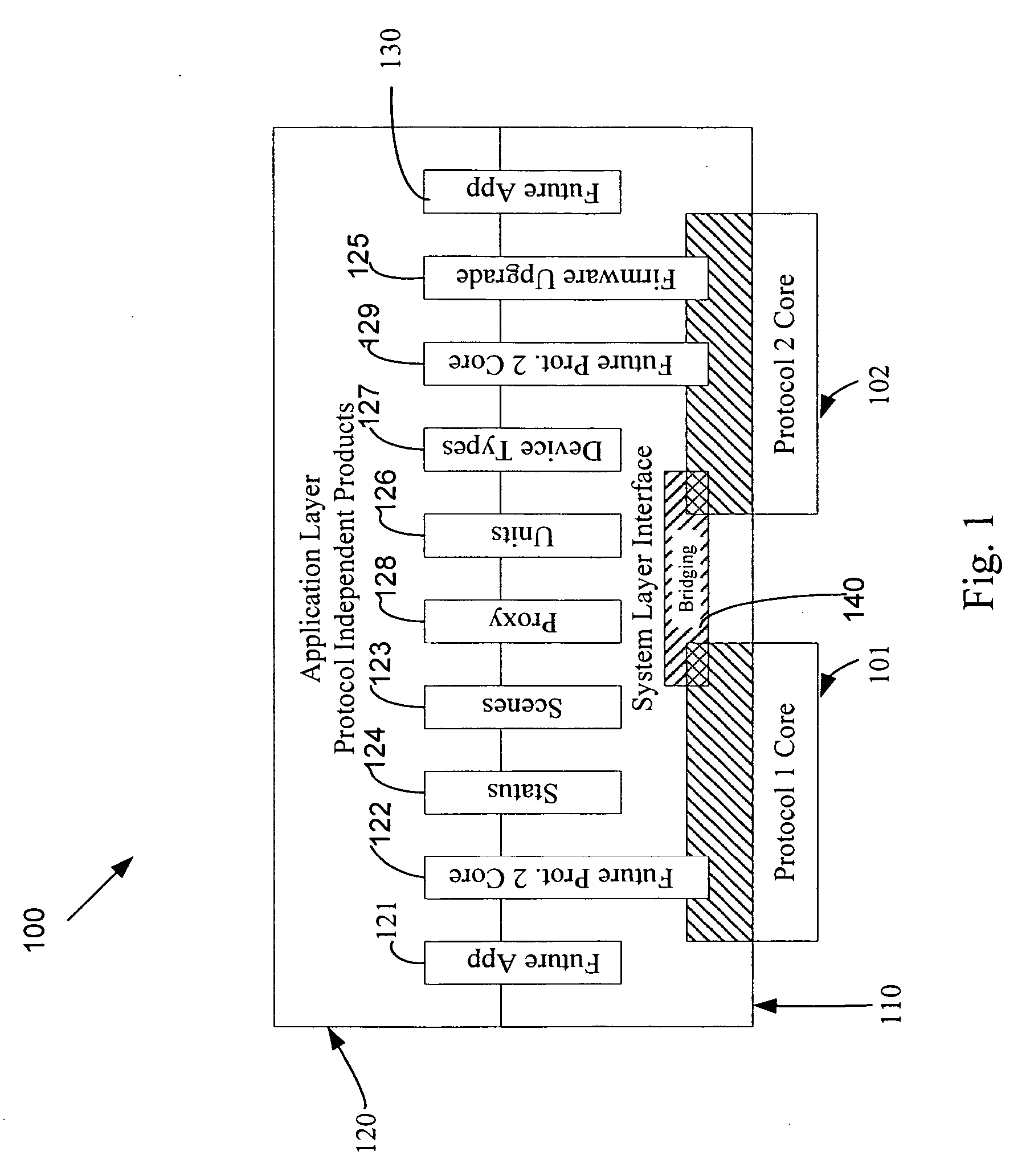
Application updating in a home automation data transfer system
InactiveUS20070143440A1Simple interfaceEfficient upgradeMultiple digital computer combinationsData switching networksData packTransport layer
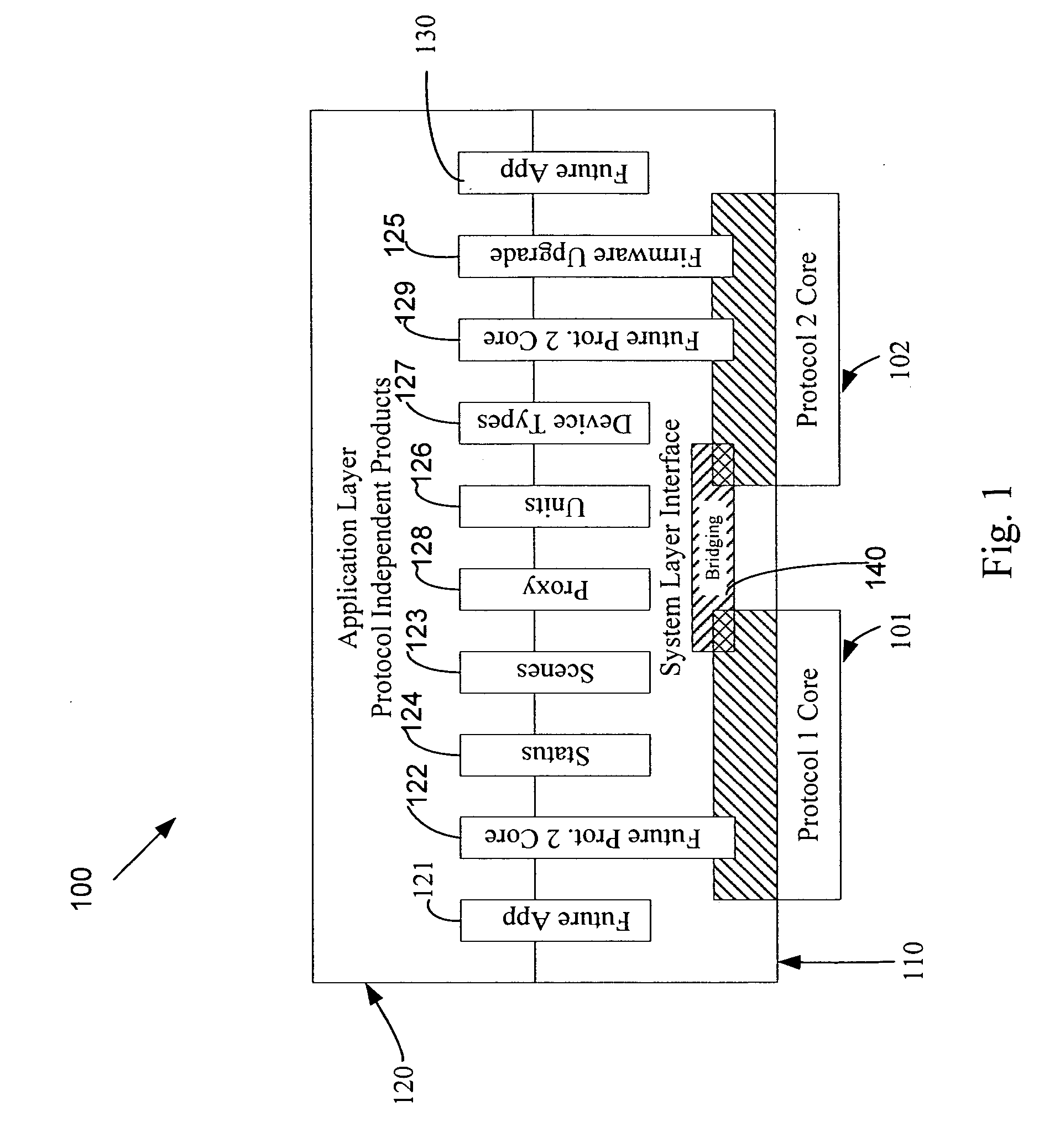
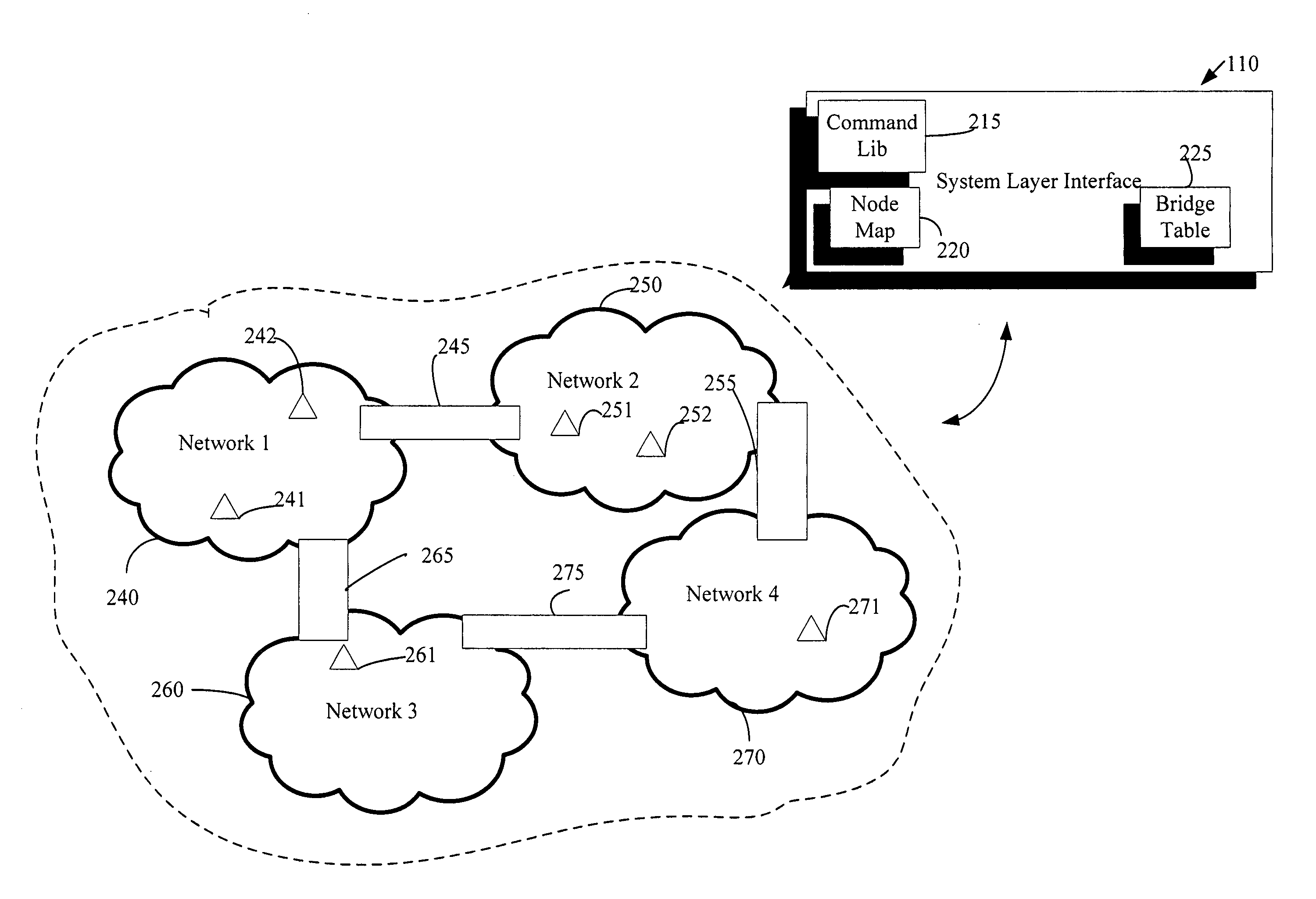
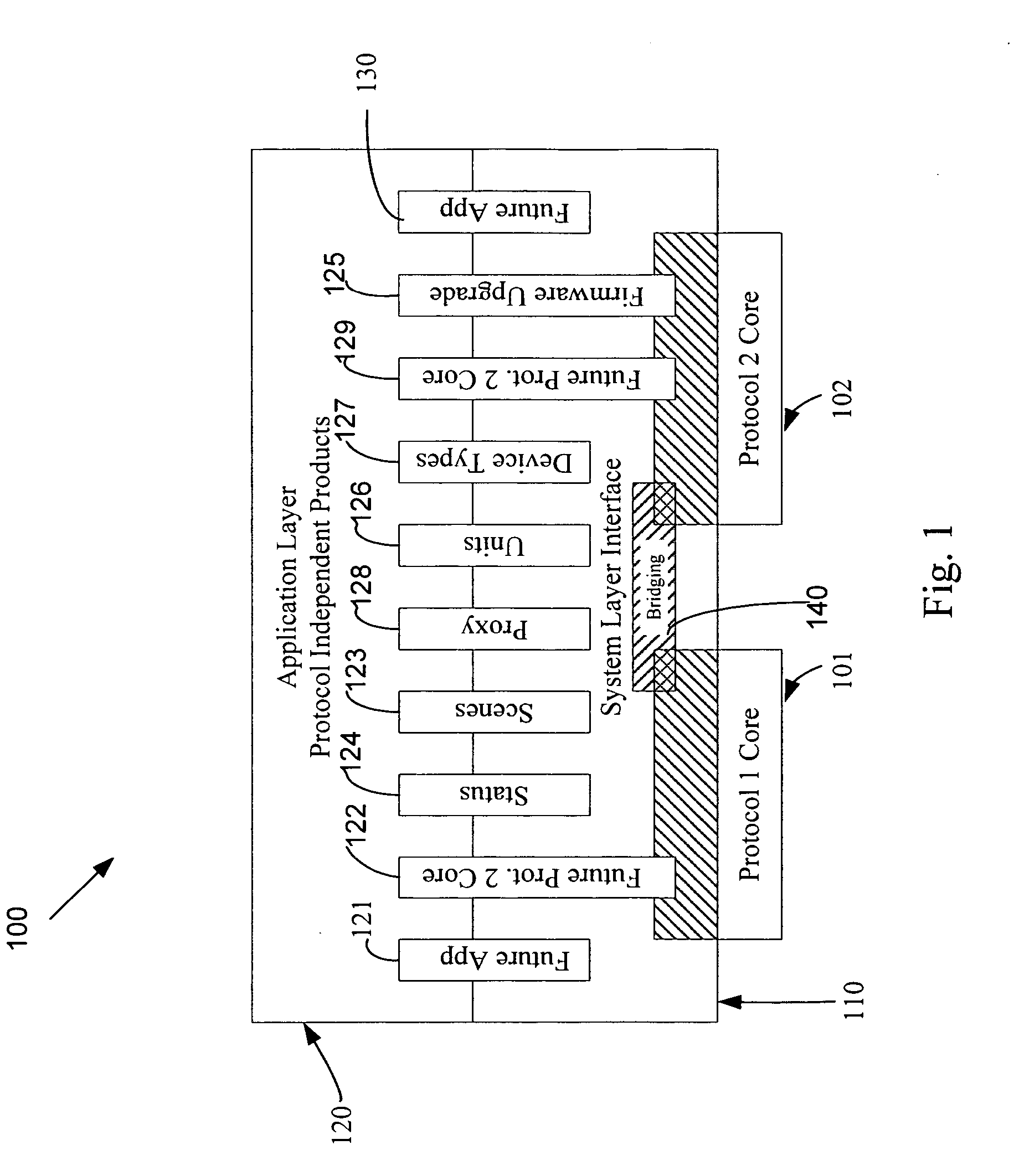
An automation network includes automation network devices connected to the network and a system level interface that interfaces with a transport layer and an application layer of the automation network. A method is disclosed that programs an automation network device in communication with an automation network, where the automation network includes an access point coupled with an external network. The method includes receiving application upgrade data at the access point, where the application upgrade data includes upgrade data associated with a target automation network device in communication with the automation network. Application upgrade data is transmitted through the home to the target automation network device. A next application upgrade data packet to be transmitted across the automation network is requested from the target automation network device. An application stored in the target automation network device is programmed, using an application upgrade data command transmitted to the target home automation network device.
Owner:INTERMATIC
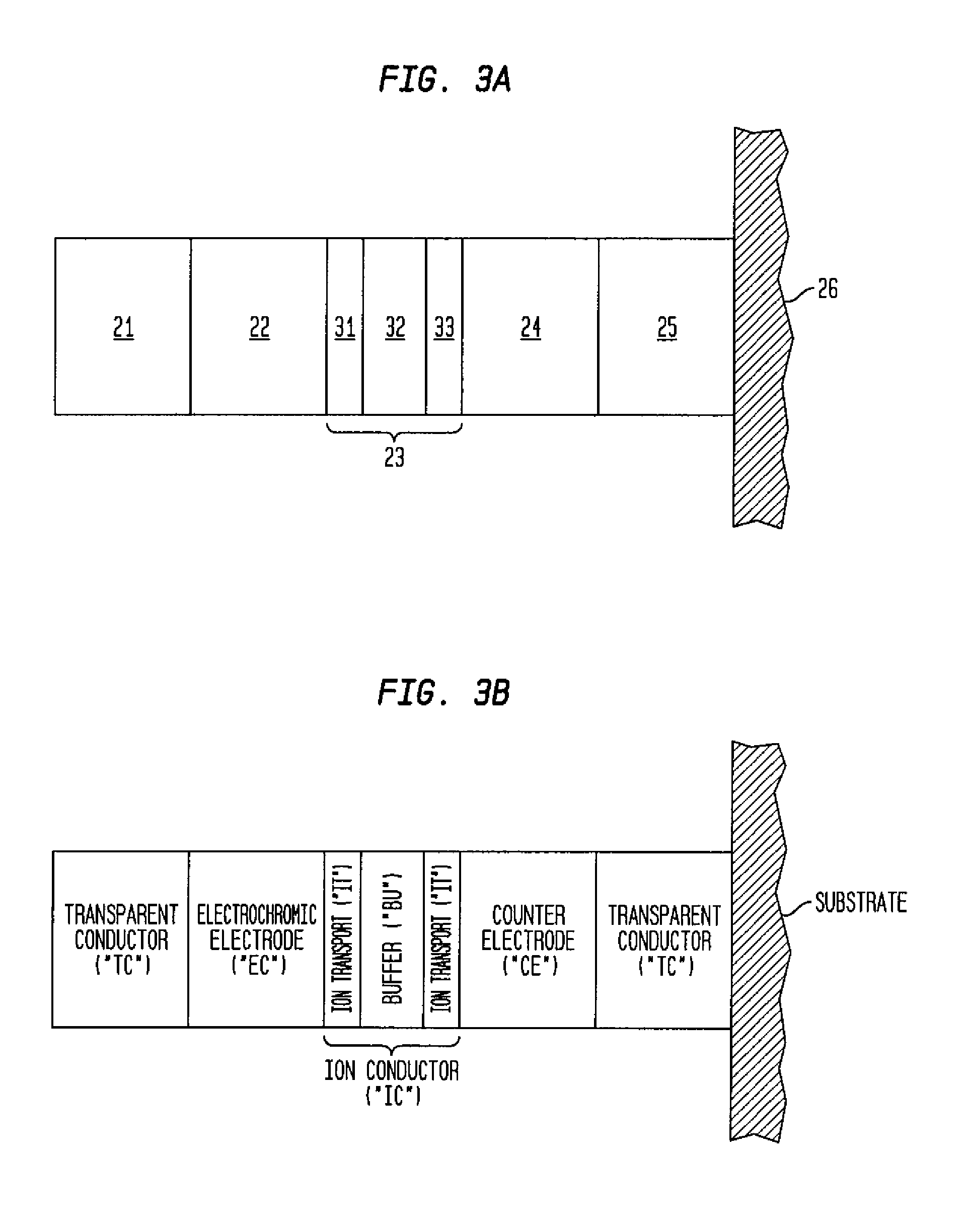
Electrochromic devices having improved ion conducting layers
InactiveUS20070097481A1Less susceptible to electronic leakageHigh voltageNon-linear opticsElectricityElectrical conductor
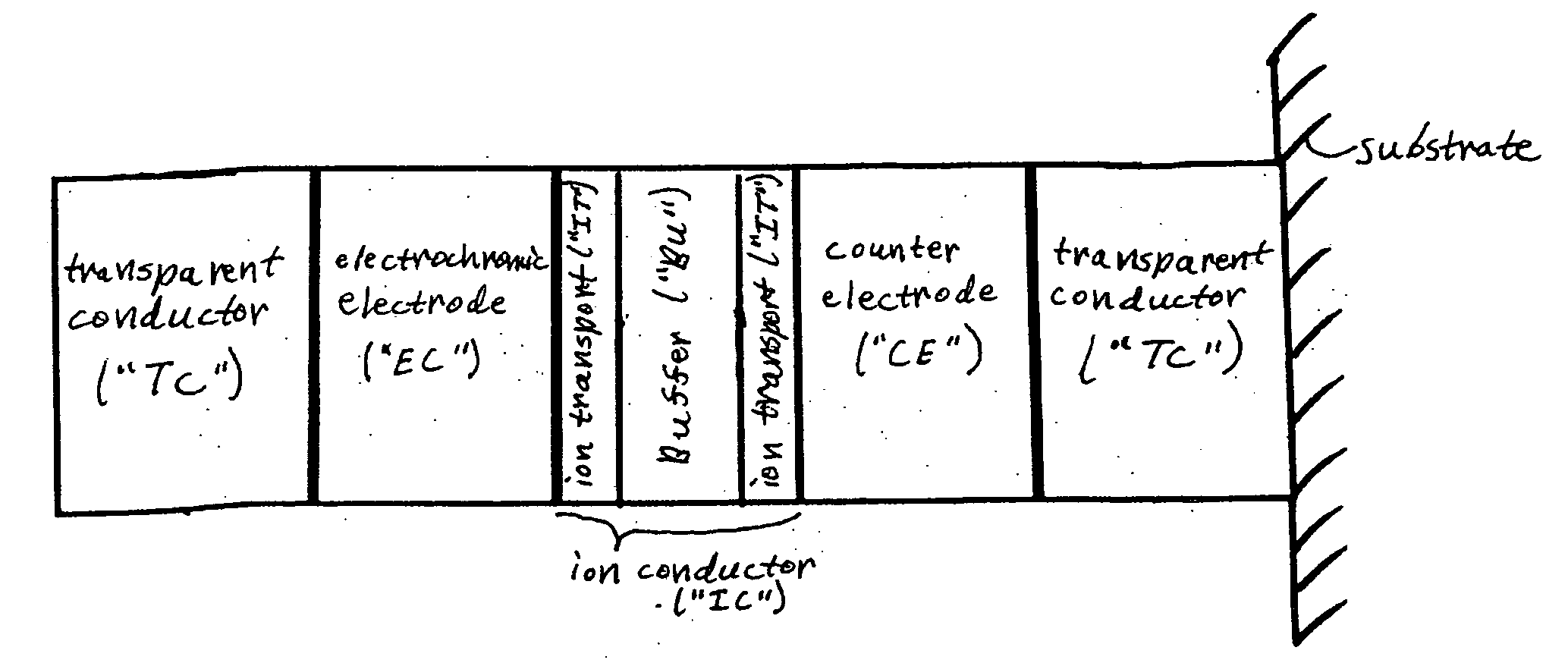
An improved ion conductor layer for use in electrochromic devices and other applications is disclosed. The improved ion-conductor layer is comprised of at least two ion transport layers and a buffer layer, wherein the at least two ion transport layers and the buffer layer alternate within the ion conductor layer such that the ion transport layers are in communication with a first and a second electrode. Electrochromic devices utilizing such an improved ion conductor layer color more deeply by virtue of the increased voltage developed across the ion conductor layer prior to electronic breakdown while reducing the amount of electronic leakage. Also disclosed are methods of making electrochromic devices incorporating the improved ion conductor layer disclosed herein and methods of making ion conductors for use in other applications.
Owner:SAGE ELECTROCHROMICS
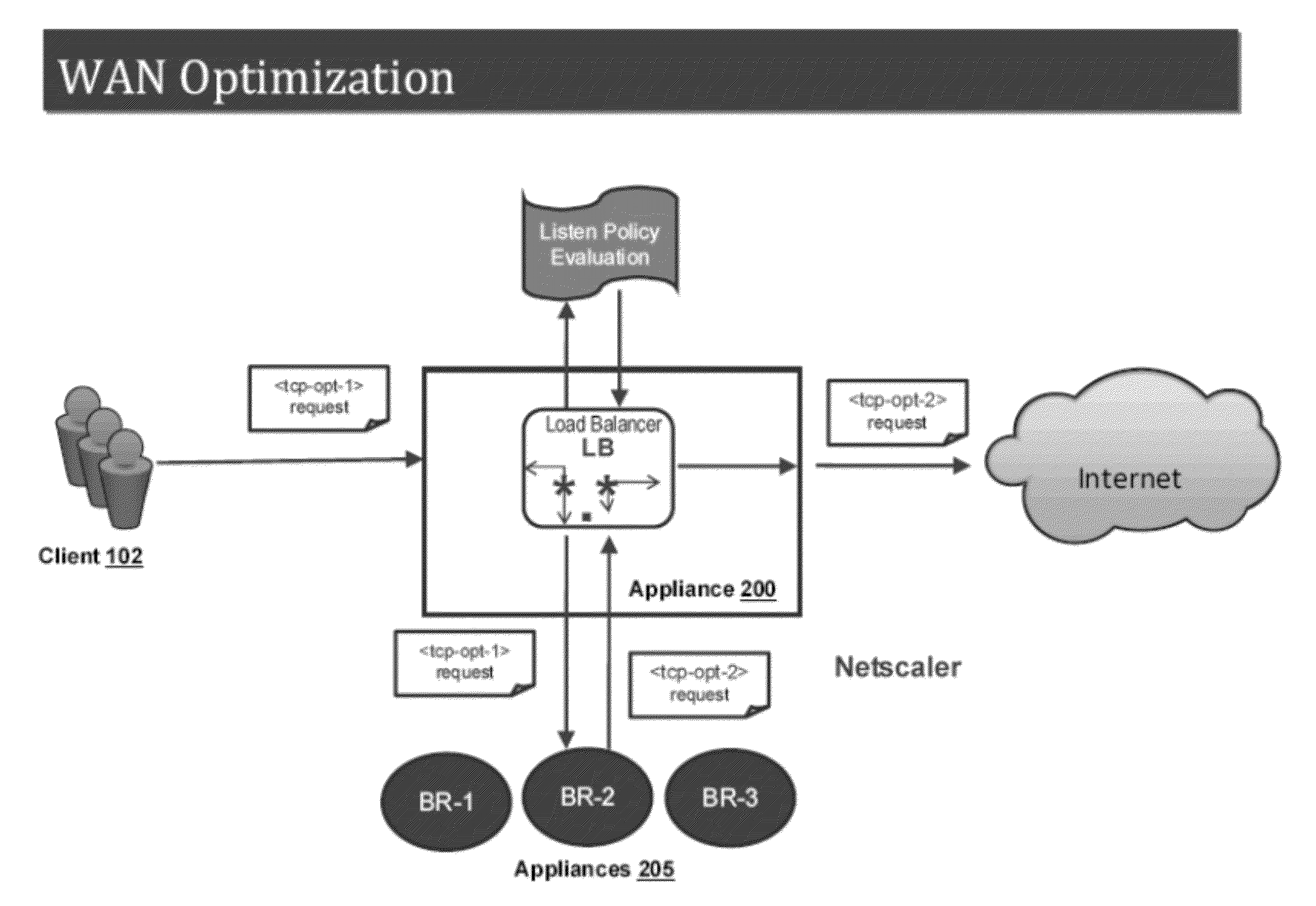
Systems and Methods for Policy Based Integration to Horizontally Deployed WAN Optimization Appliances
The present disclosure presents systems and methods for policy-based redirection of network traffic, by an intermediary device, to a horizontally deployed WAN device. An intermediary receives a request from a client to access a server. The request was previously modified by a first WAN device to include information in an option field of a transport layer. The intermediary may determine, responsive to a redirection policy, to send the request to a second WAN device deployed horizontally from the intermediary, instead of the server. The intermediary transmits the request to the second WAN device, while maintaining the information from the option field. The intermediary device receives the request including the information identifying the first WAN optimization device to the second WAN device. The intermediary receives a modified request from the second WAN device, the modified request determined by the intermediary to be sent to the destination server.
Owner:CITRIX SYST INC
Organic electroluminescent element
InactiveUS20070090756A1Reduce the driving voltageImprove luminous efficiencyDischarge tube luminescnet screensLamp detailsTransport layerOrganic layer
The invention provides an organic electroluminescent element comprising an organic layer containing at least one luminescent layer and at least one charge transporting layer being interposed between a pair of electrodes, wherein the organic electroluminescent element comprises: (1) two or more kinds of host materials and at least one luminescent material contained in the luminescent layer; (2) at least one layer adjacent to the luminescent layer, the layer containing a host material and substantially no luminescent material; and (3) at least one charge transporting layer being doped with at least one of an electron-accepting compound and an electron-donating compound.
Owner:FUJIFILM CORP
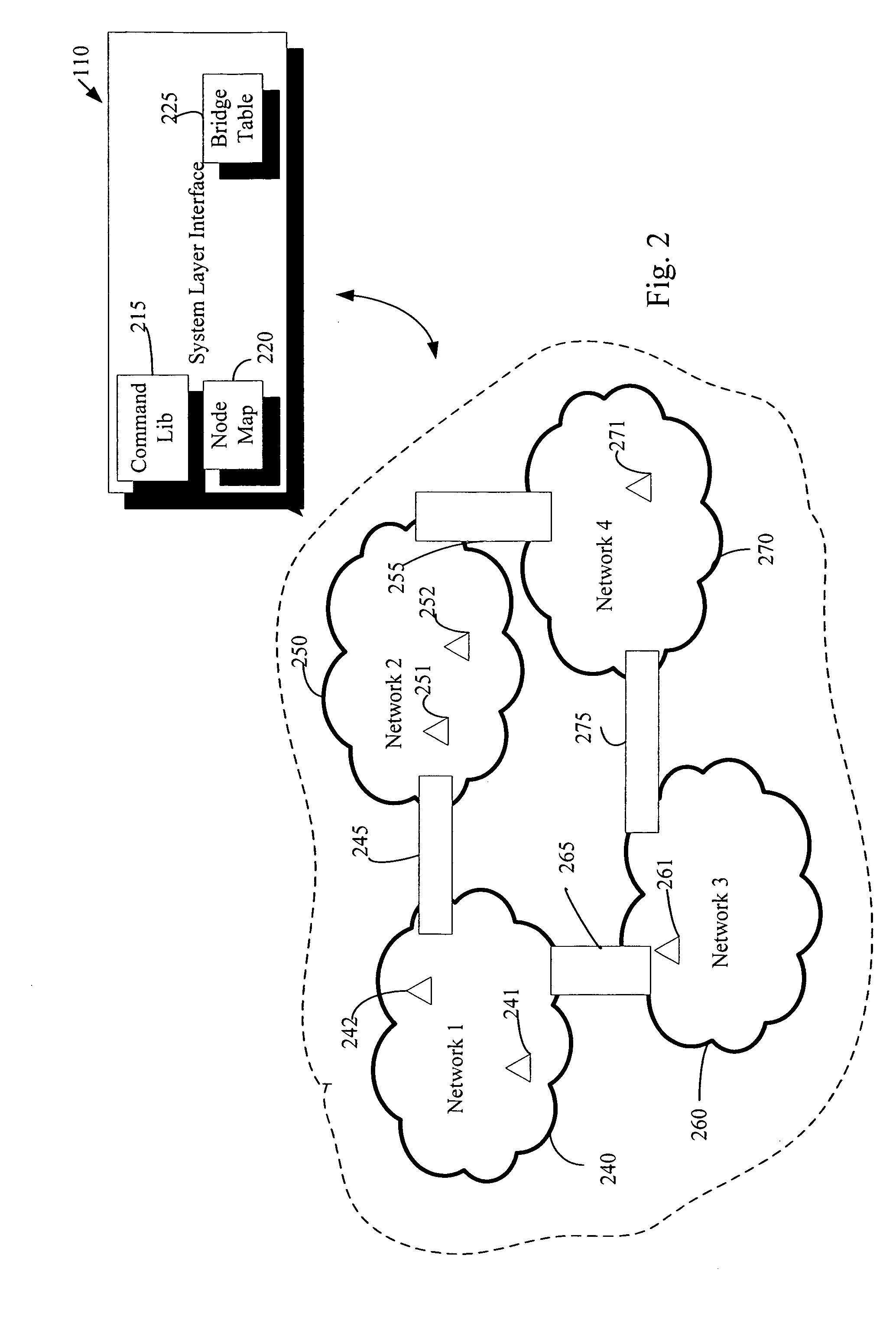
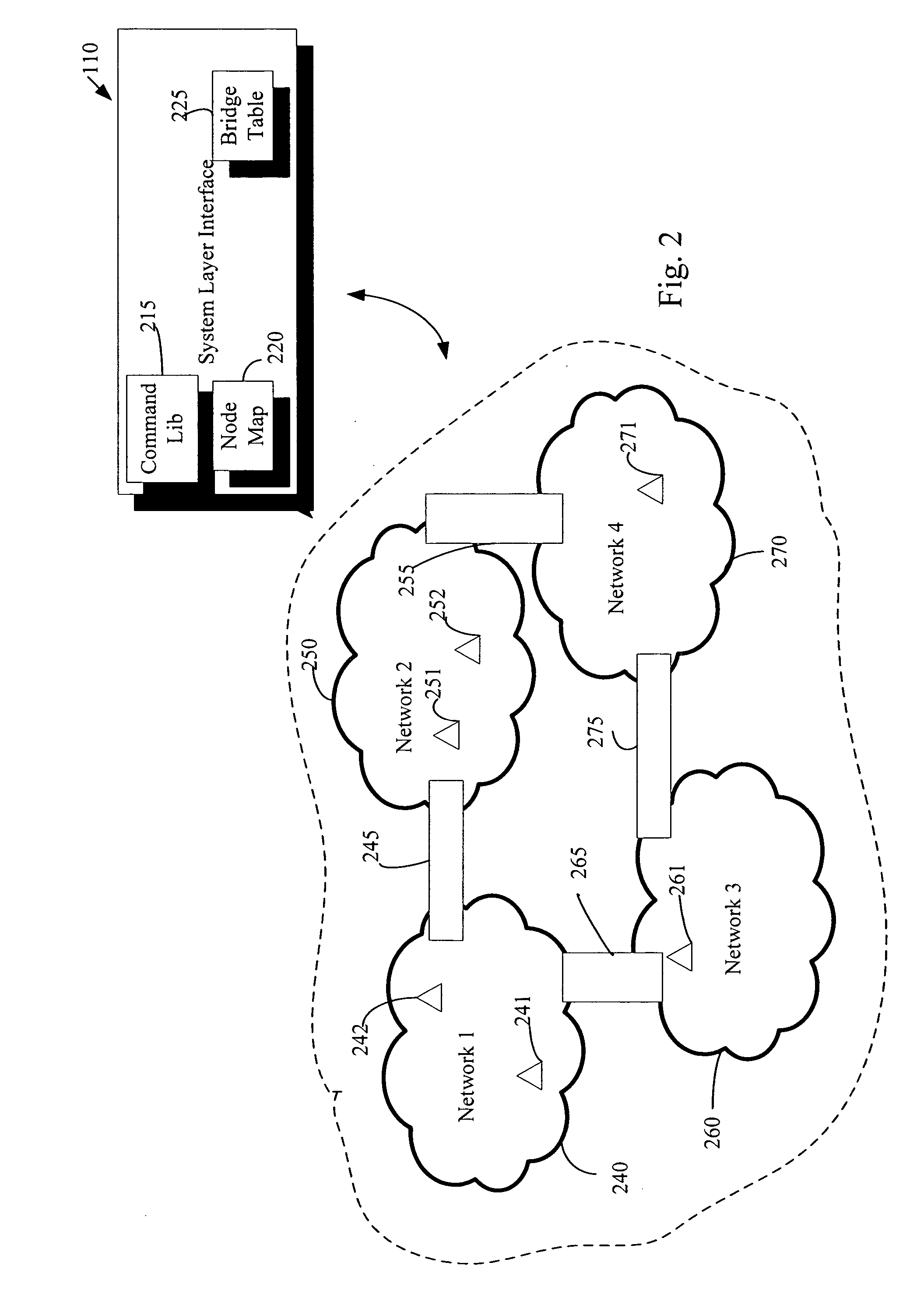
Remote device management in a home automation data transfer system
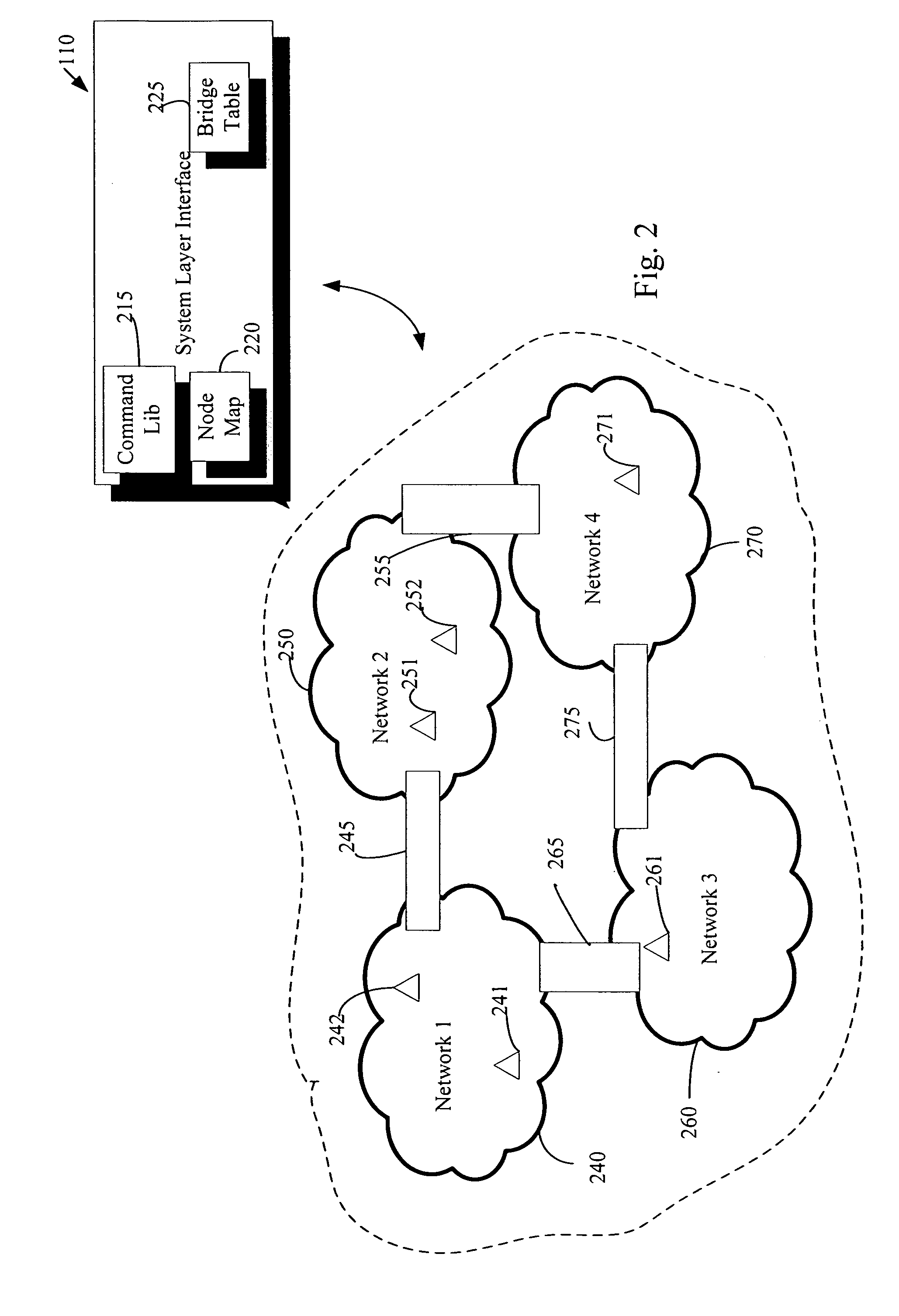
An automation network includes automation network devices connected to the network and a system layer interface that interfaces with a transport layer and an application layer of the home automation network. The system layer interface includes command libraries configured to upgrade a remote network device. The automation network queries the network devices to determine if there are lost network devices or newly added network devices. The automation network may update a new remote device with scene information related to any lost network devices.
Owner:INTERMATIC
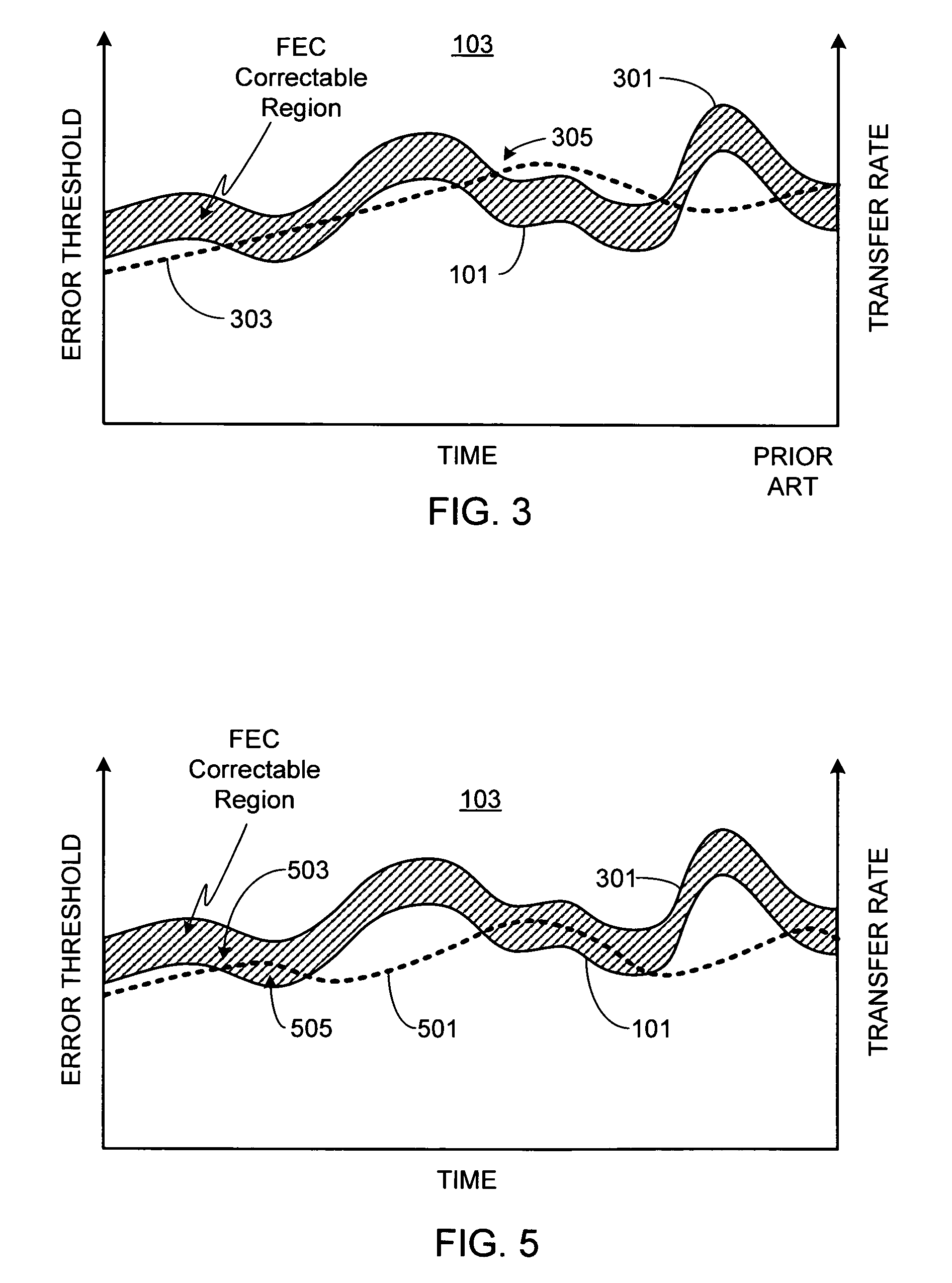
Adaptive information delivery system using FEC feedback
InactiveUS20060150055A1Useful resultError detection/prevention using signal quality detectorReceiver specific arrangementsTelecommunications linkThe Internet
A method and apparatus for optimizing the data transfer rate over a transport layer (i.e., communication link) such as the Internet is provided. Initially the data is prepared for transmission by a transfer rate controller, then the data is encoded by a Forward Error Correction (FEC) encoder. After the data has been transferred over the transport layer, the quality of the data transfer link is assessed by an FEC decoder that determines if any errors occurred during data transfer and if errors are detected, the magnitude of the errors (i.e., FEC-correctable packets, FEC-uncorrectable packets). This information is used to generate a feedback message which is used by the transfer rate controller to adjust and optimize the data transfer rate for the link quality as determined at that point in time. By continually monitoring and assessing link quality and providing feedback to the transfer rate controller, the transfer rate can be continually adapted to the varying link quality. In addition to generating feedback used by the transfer rate controller to optimize data transfer rate, the FEC decoder can generate feedback that is used by the FEC encoder to optimize the FEC algorithm. If desired, feedback from the FEC decoders within the link layer demodulator and / or feedback from the receiver can be used to augment the feedback generated by the FEC decoder.
Owner:TERAYON COMM SYST
Proxy commands and devices for a home automation data transfer system
InactiveUS20070255856A1Simple interfaceMultiple digital computer combinationsData switching networksTransport layerTransfer system
An automation network includes automation network devices connected to the network and a system level interface that interfaces with a transport layer and an application layer of the automation network. The system level interface includes proxy command libraries configured to designate a proxy device from the automation network devices. The proxy device accepts commands or messages to be transmitted to another automation network device.
Owner:INTERMATIC
Electrochromic devices having improved ion conducting layers
InactiveUS7593154B2Less susceptible to electronic leakageHigh voltageNon-linear opticsElectricityElectrical conductor
An improved ion conductor layer for use in electrochromic devices and other applications is disclosed. The improved ion-conductor layer is comprised of at least two ion transport layers and a buffer layer, wherein the at least two ion transport layers and the buffer layer alternate within the ion conductor layer such that the ion transport layers are in communication with a first and a second electrode. Electrochromic devices utilizing such an improved ion conductor layer color more deeply by virtue of the increased voltage developed across the ion conductor layer prior to electronic breakdown while reducing the amount of electronic leakage. Also disclosed are methods of making electrochromic devices incorporating the improved ion conductor layer disclosed herein and methods of making ion conductors for use in other applications.
Owner:SAGE ELECTROCHROMICS
Method and system for fast setup of group voice over IP communications
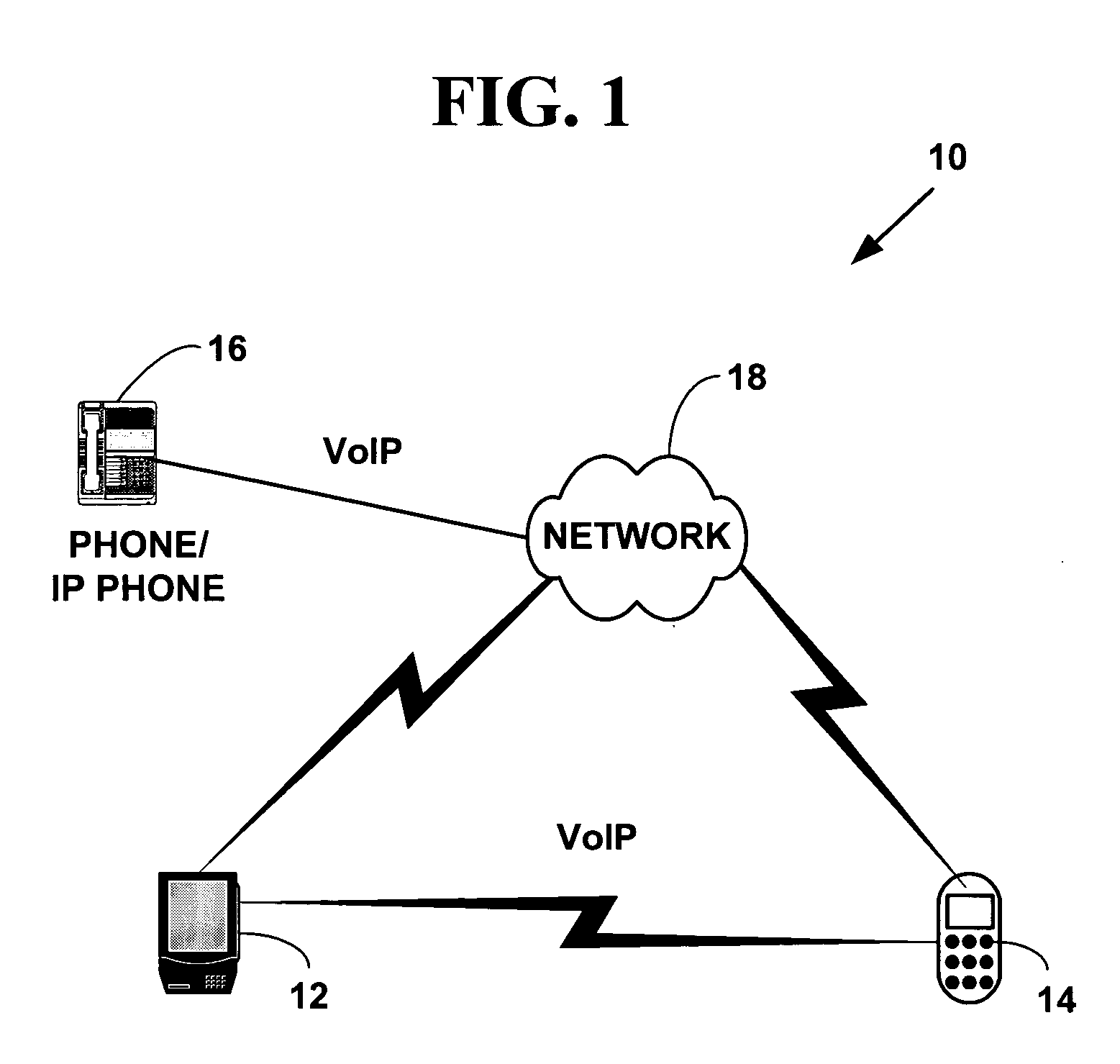
ActiveUS20050073964A1Faster setup-timeReduce signaling overheadSpecial service provision for substationMultiplex system selection arrangementsTransport layerVoice over internet protocol voip
A method and system for fast setup of group Voice over Internet Protocol (VoIP) communications. The method and system provide a lower VoIP signaling overhead and a faster setup-time of group calls such as N-way audio and / or audio-video conference calls. Multi-party VoIP connections are quickly set-up over one or more virtual communications channels established between plural network devices using a session layer application, one or more group transport layer ports and a broadcast destination network address.
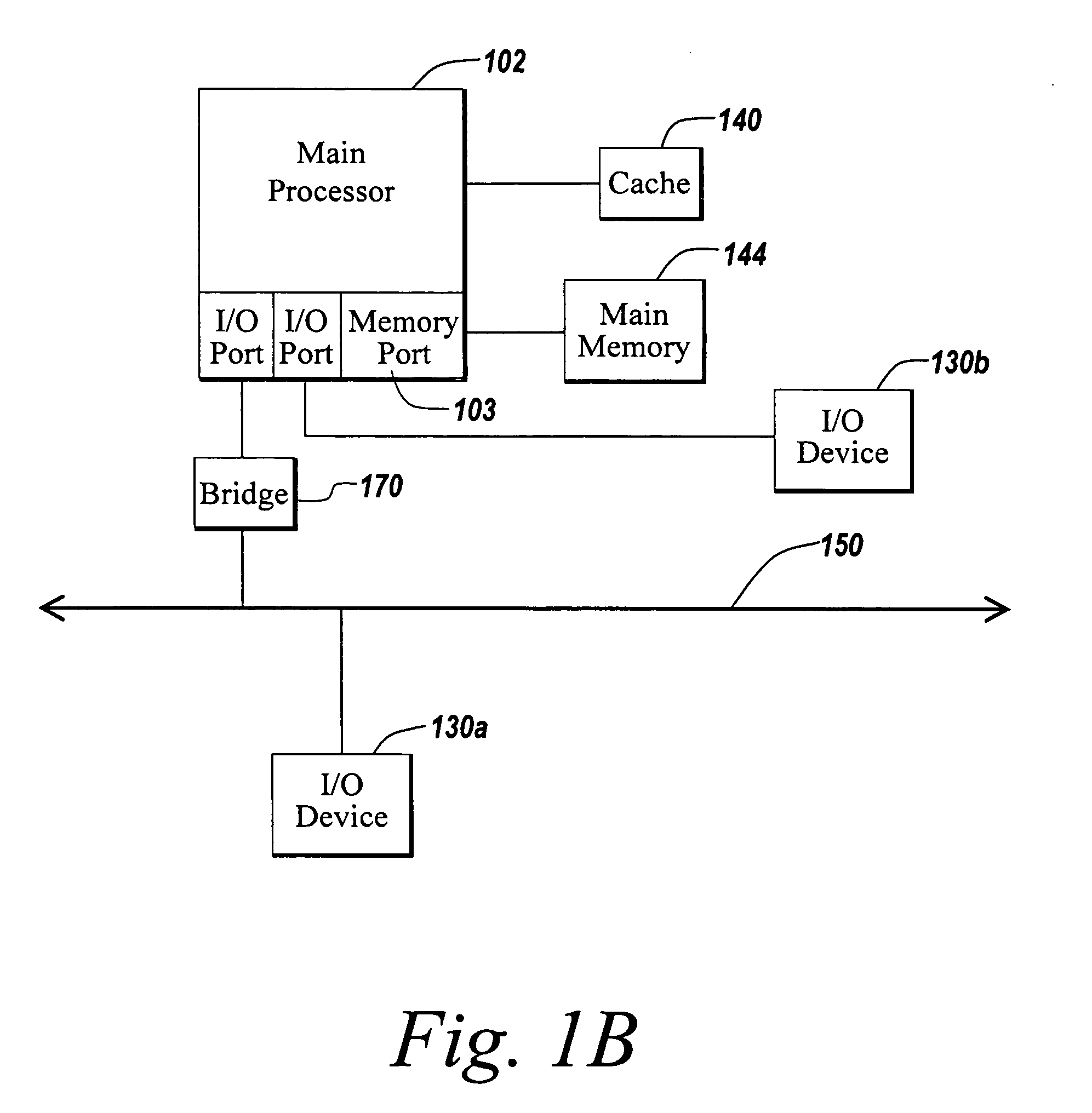
Owner:ZHIGU HLDG
Method and apparatus for developing web services using standard logical interfaces to support multiple markup languages
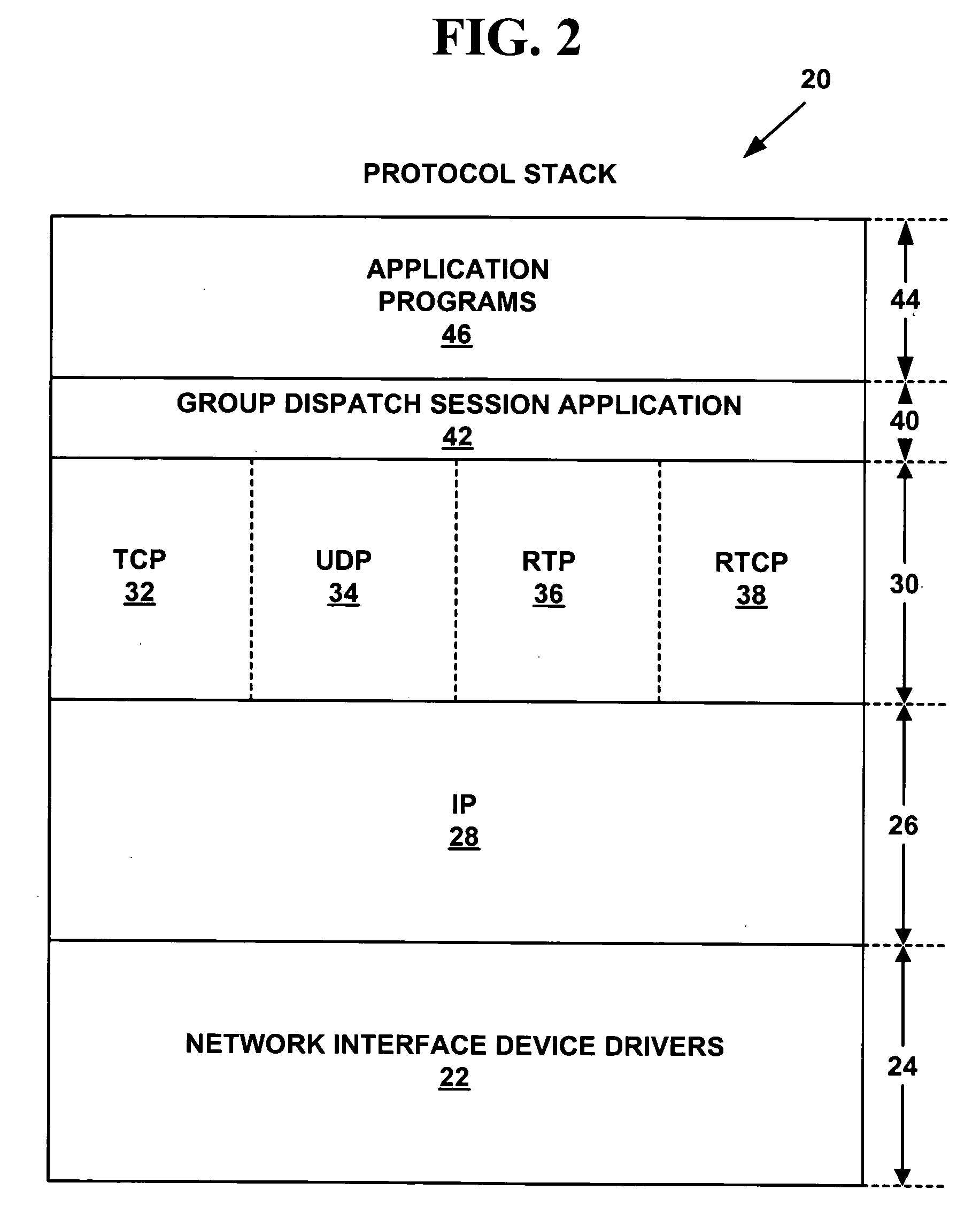
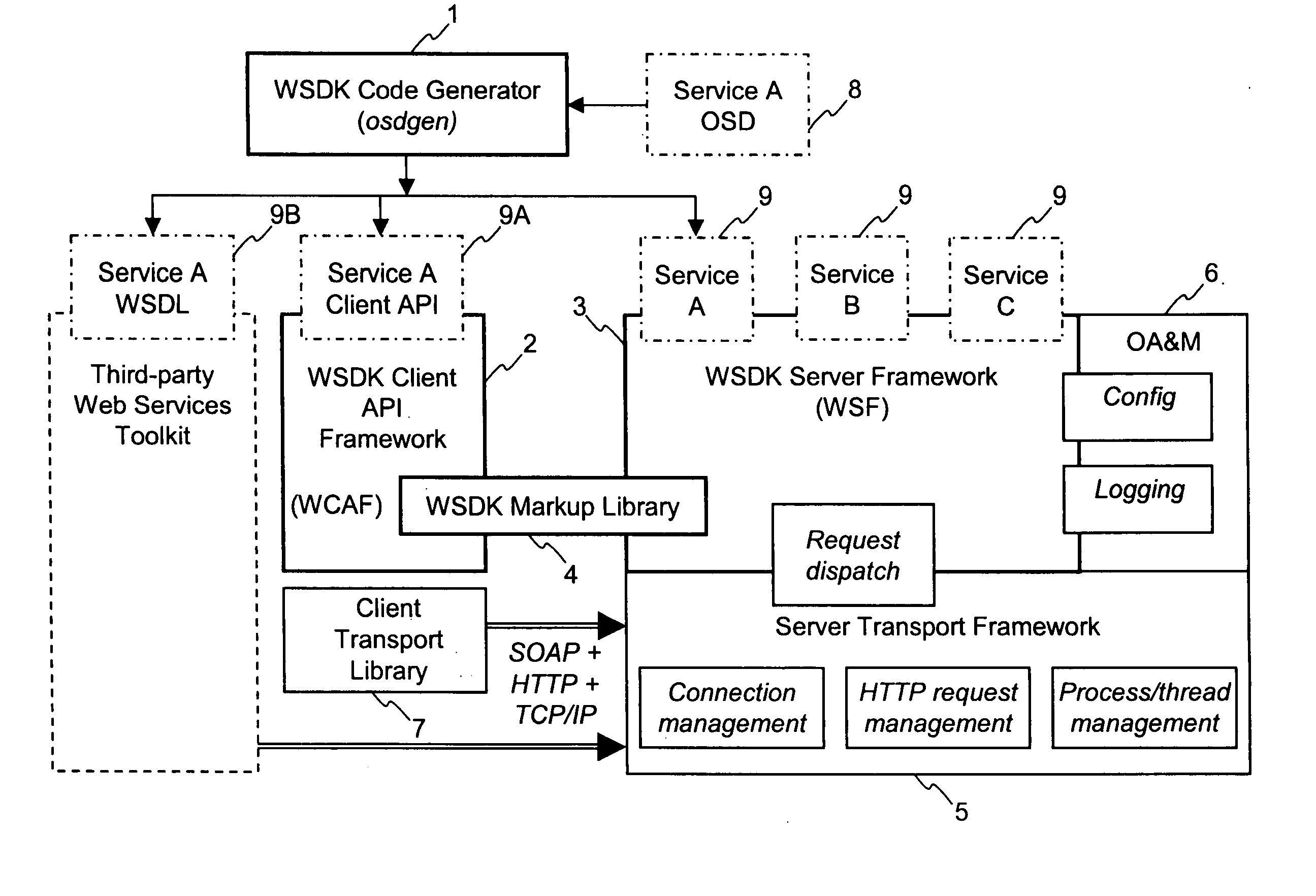
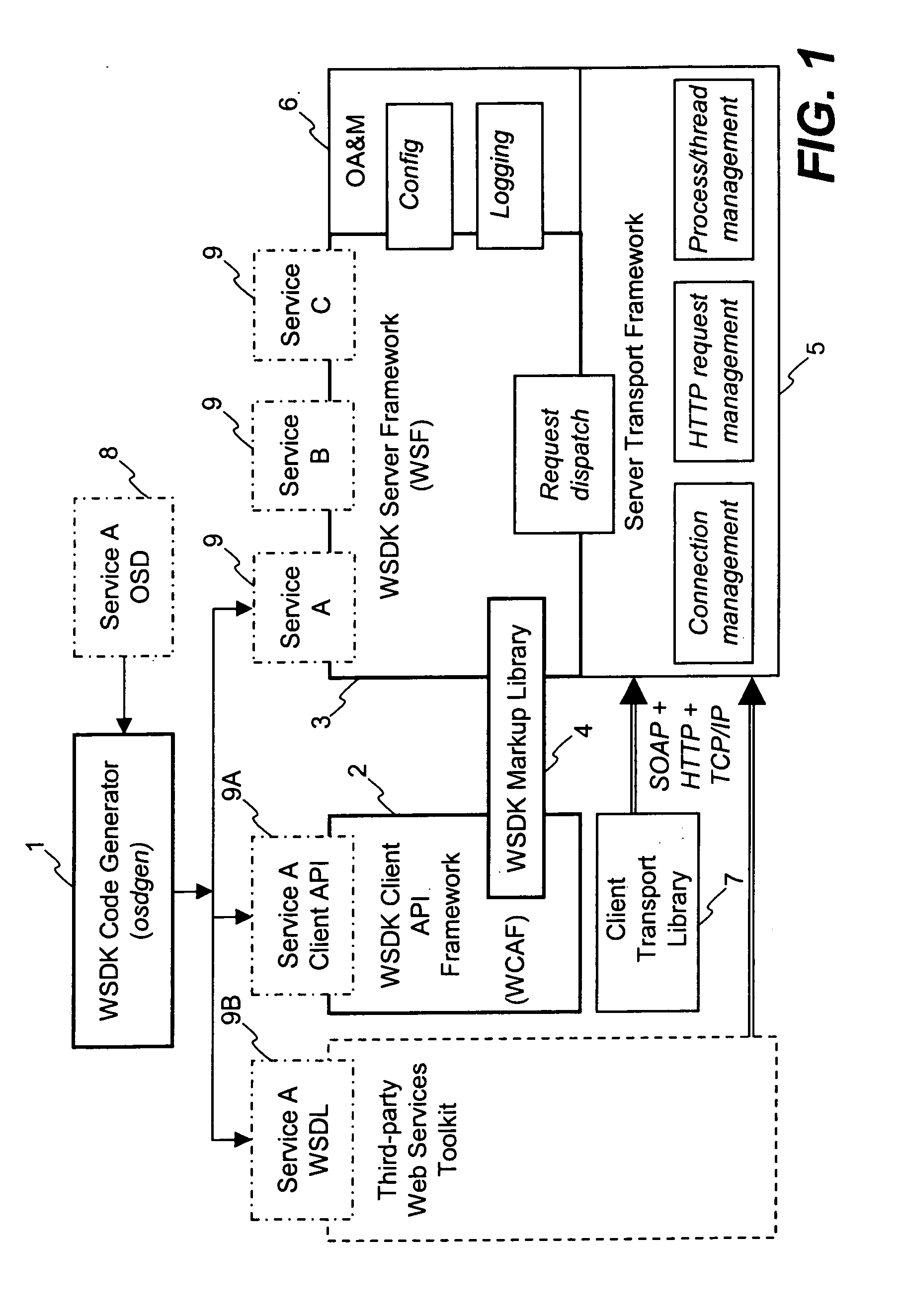
InactiveUS7127700B2Website content managementSpecific program execution arrangementsTransport layerService development
The Web Services Development Kit (WSDK) comprises a set of build-time tools and run-time components designed to support the development of web services and the interface to those services. WSDK provides a framework for the development of web services that isolates developers from the implementation details of the markup and transport layers, by separating the logical aspects of the service development from the physical aspects. A “call” generated by a client contains a batch of operations to be executed in the context of a single request / reply message exchange. A markup library translates logical structure to a specific markup language. Additional markup languages are supported by adding additional modules to the markup library.
Owner:UNWIRED PLANET
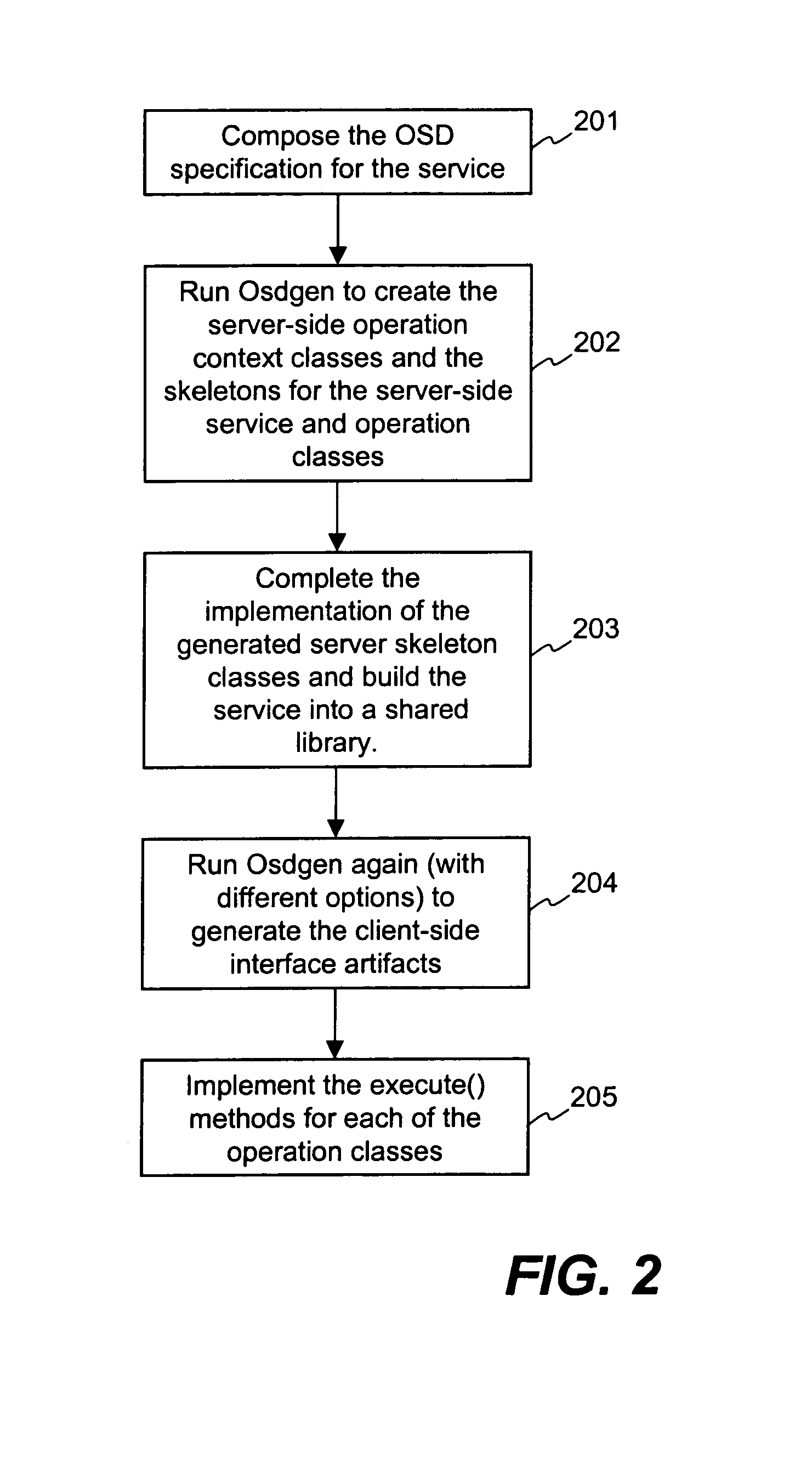
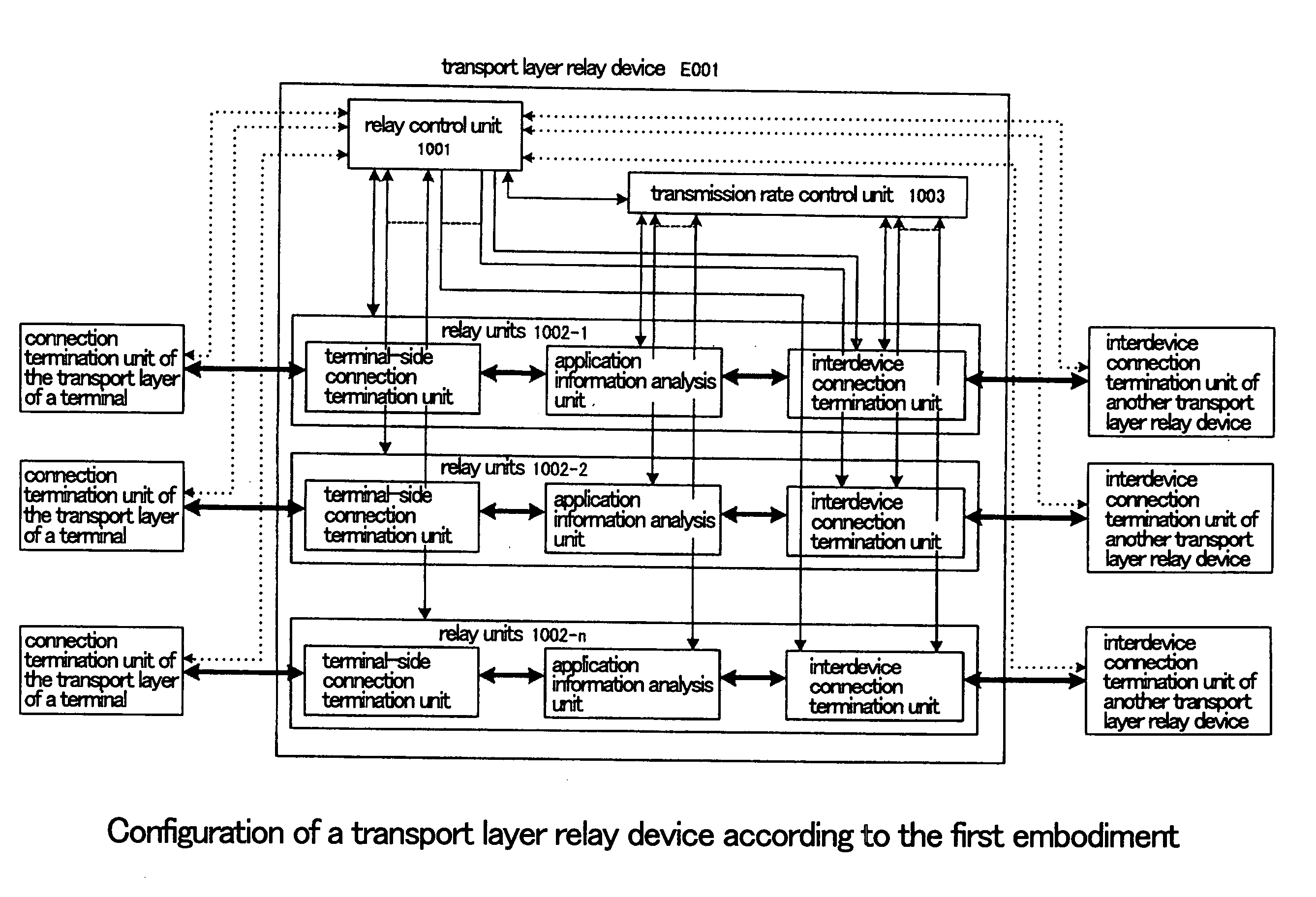
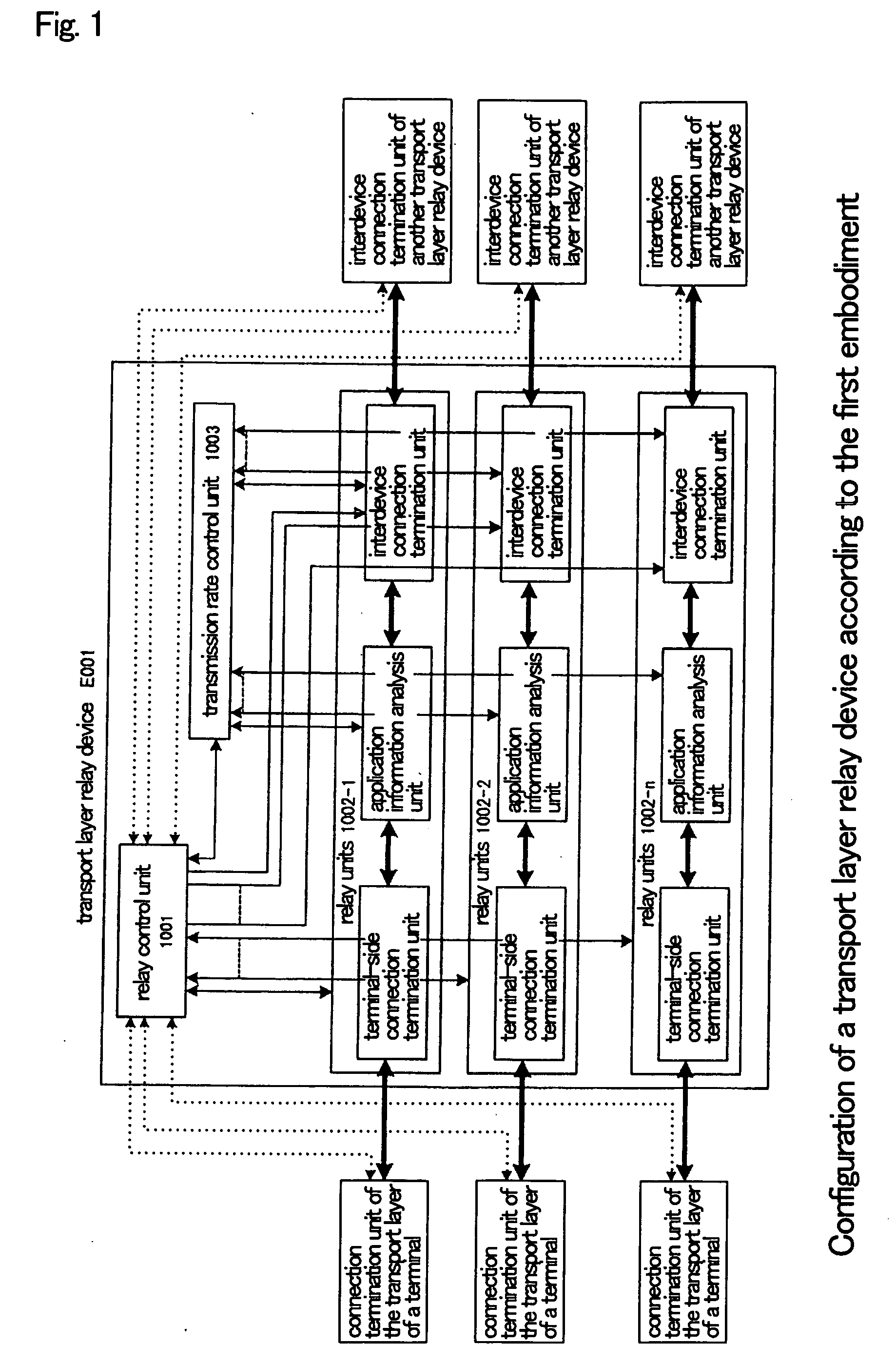
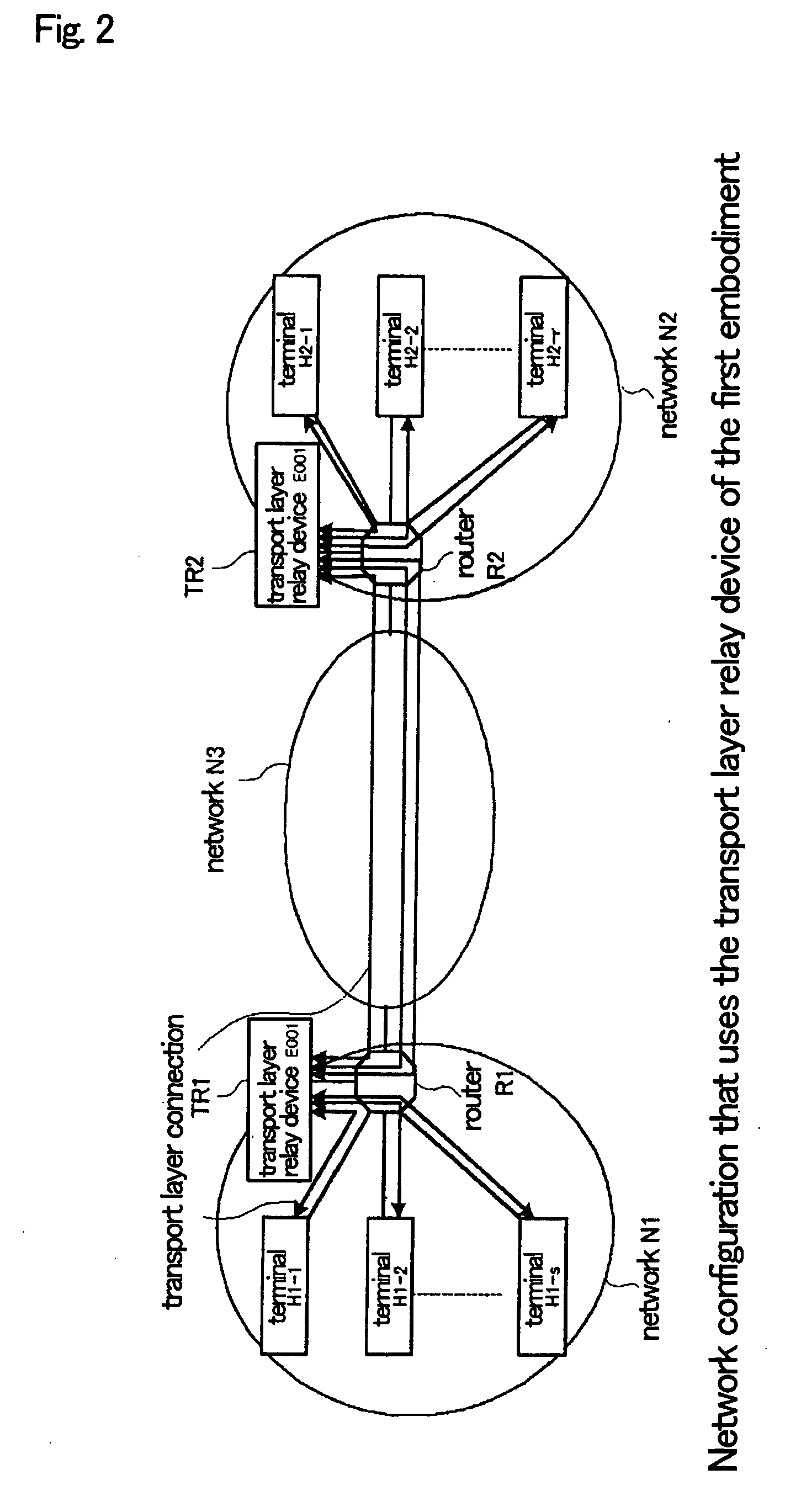
Transport layer relay method, transport layer relay device, and program
ActiveUS20070008883A1Low costRedistribute bandwidthError preventionTransmission systemsTransport layerEngineering
Relay units (1002-1-1002-n) terminate a plurality of transport layer connections from terminals in a transport layer and relay each of these connections to other transport layer connections (relay connections). A transmission rate control unit (1003) determines the total transmission rate of the relay connections according to the number of connections that are being relayed and network congestion conditions such that a desired effective rate is obtained, and moreover, allots the total transmission rate as transmission rates to each of relay units (1002-1-1002-n) in accordance with the results of the analysis of information of the applications being carried on the transport layer connections during relay.
Owner:NEC CORP
Method and apparatus for transporting packet data over an optical network
ActiveUS6985488B2Time-division multiplexStore-and-forward switching systemsFrame RelayTransport layer
A method, apparatus and network for transporting layer-2 frames, such as Ethernet MAC, ATM AAL5, and Frame Relay, over SONET, SDH, or OTN transport networks is disclosed. The method establishes “pseudo-wires” between, for example, SONET switches and directly on top of the SONET layer. The method may implement MPLS signaling protocols on traditional SONET switches for the purpose of aggregating layer-2 frames from the transport network edges, while the transport network itself is independent from IP and MPLS routing. This approach provides a number of advantages to the network carriers in terms of operation and equipment expense reduction. To enable the transport network to be independent from IP and MPLS, and avoid subsequent IP control message processing inside the networks, an edge-to-edge “tunneling” mechanism is designed to transmit control messages as a part of the SONET (or SDH or OTN) frame payload.
Owner:CIENA
Synchronization of database data
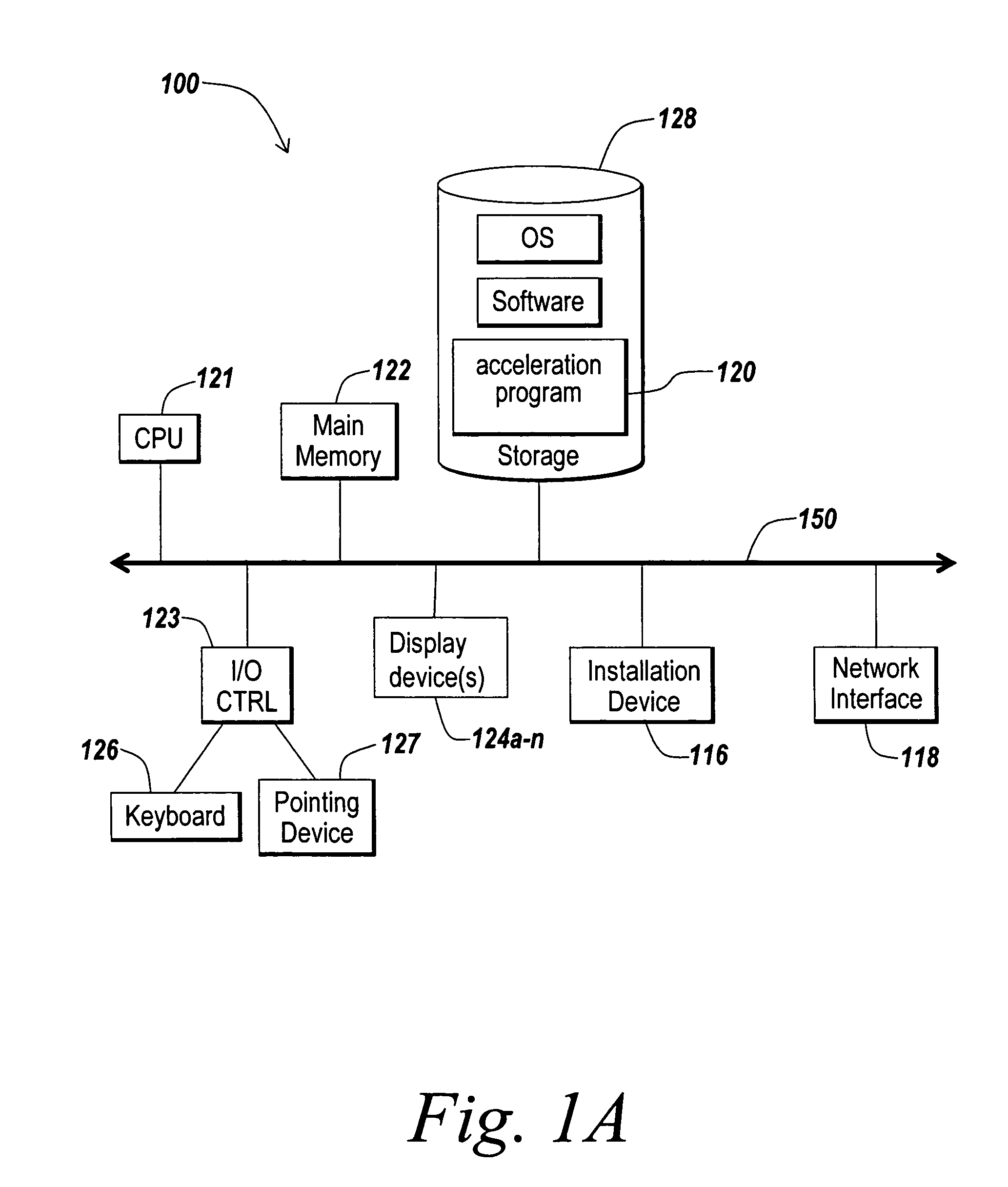
InactiveUS20050125459A1Good synchronizationData processing applicationsNetwork traffic/resource managementTransport layerDistributed computing
A method of arranging synchronization of databases, the method comprising the steps of establishing a transport layer connection for synchronization between a first and a second device which synchronize databases. During initialization of synchronization a first update identifier, which is stored at least in the first device and describes the latest synchronization event the devices have performed in the databases, and a second update identifier, which is defined by the first device and describes the present synchronization, are transmitted from the first device to the second device. The second update identifier is stored in the first and the second device. The contents of the first update identifiers stored in the devices are updated in the first and the second device if synchronization has been performed and after this said transport layer connection has been ended substantially properly.
Owner:NOKIA TECH OY
Method and apparatus for transporting packet data over an optical network
A method, apparatus and network for transporting layer-2 frames, such as Ethernet MAC, ATM AAL5, and Frame Relay, over SONET, SDH, or OTN transport networks is disclosed. The method establishes "pseudo-wires" between, for example, SONET switches and directly on top of the SONET layer. The method may implement MPLS signaling protocols on traditional SONET switches for the purpose of aggregating layer-2 frames from the transport network edges, while the transport network itself is independent from IP and MPLS routing. This approach provides a number of advantages to the network carriers in terms of operation and equipment expense reduction. To enable the transport network to be independent from IP and MPLS, and avoid subsequent IP control message processing inside the networks, an edge-to-edge "tunneling" mechanism is designed to transmit control messages as a part of the SONET (or SDH or OTN) frame payload.
Owner:CIENA
Organic electroluminescence device
ActiveUS20050140275A1High color purityDischarge tube luminescnet screensElectroluminescent light sourcesTransport layerArray element
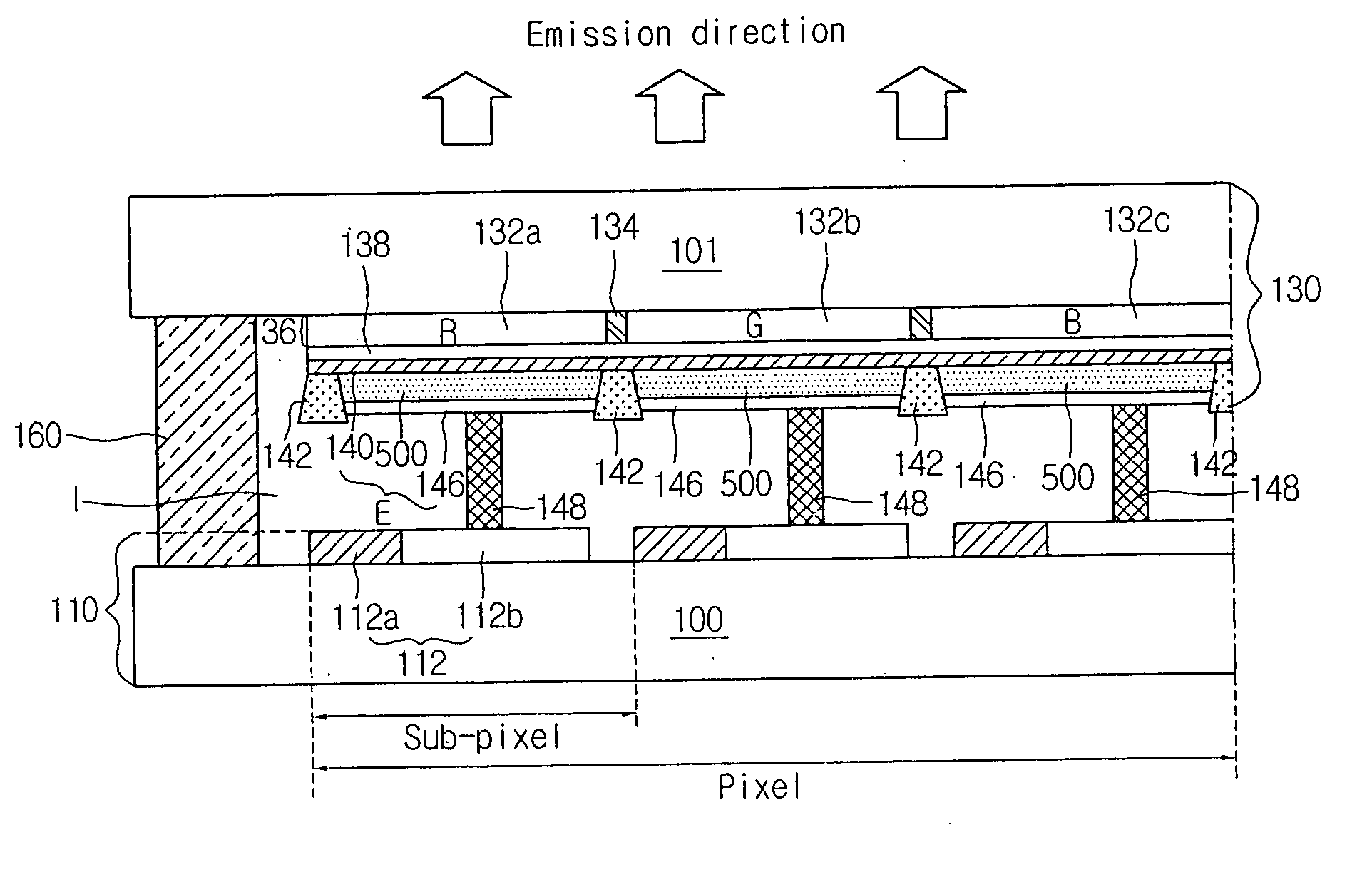
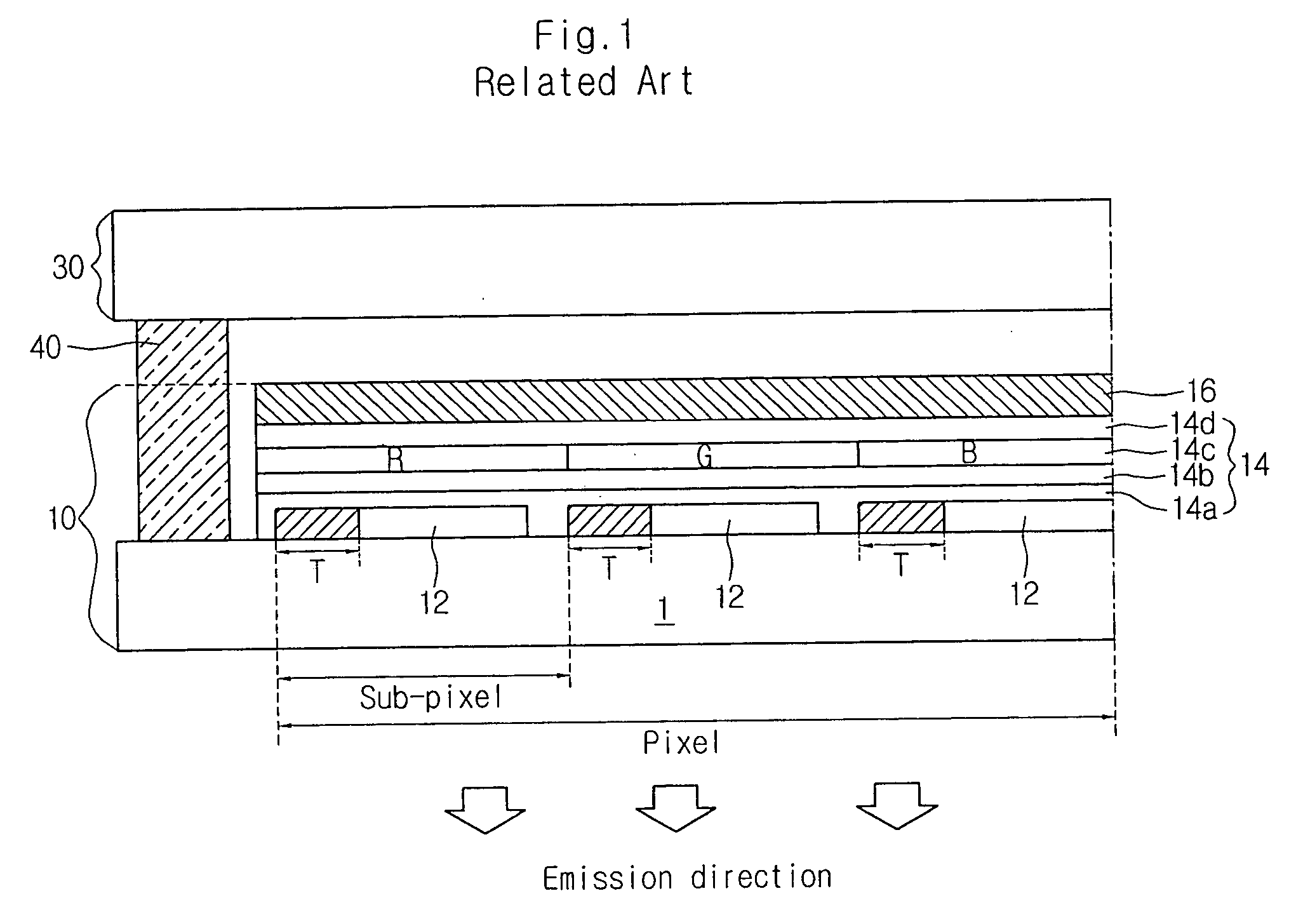
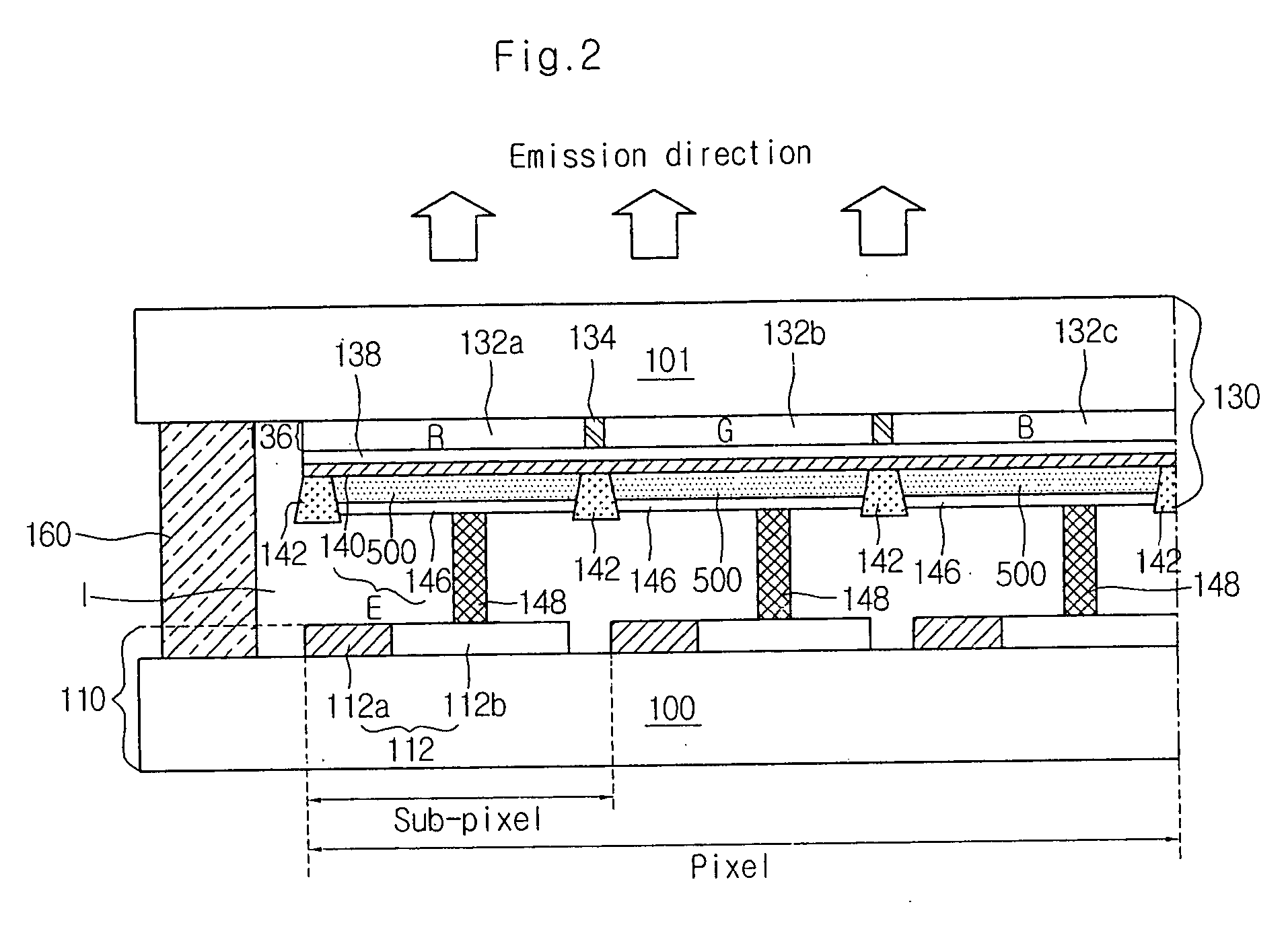
An organic electronluminescence device includes an array element divided into sub-pixels and including thin film transistors formed in the sub-pixels; a color conversion portion disposed below a second substrate and including a red (R), green (G) and blue (B) conversion layer for converting white light into three primary colors of red (R), green (G) and blue (B); a first electrode disposed below the color conversion portion and including a transparent conductive material; an organic EL layer disposed below the first electrode in the sub-pixels and including a plurality of stack units each including a charge generation layer, an electrode transporting layer, a hole transporting layer and an emission layer; a second electrode patterned below the organic EL layer in the sub-pixels; and a conductive spacer electrically connecting the thin film transistors with the second electrode.
Owner:LG DISPLAY CO LTD
Systems and methods for providing integrated client-side acceleration techniques to access remote applications
InactiveUS20060253605A1Improve performanceReduce deliveryDigital computer detailsTransmissionTransport control protocolInterface point
The present invention is directed towards systems and methods for dynamically deploying and executing acceleration functionality on a client to improve the performance and delivery of remotely accessed applications. In one embodiment. The client-side acceleration functionality is provided by an acceleration program that performs a plurality of the following acceleration techniques in an integrated and efficient manner: 1) multi-protocol compression 2) transport control protocol pooling, 3) transport control protocol multiplexing 4) transport control protocol buffering, and 5) caching. The acceleration program establishes a transport layer connection between the client and server, and intercepts network packets at the transport layer. The acceleration program uses a kernel-level data structure to access the network packet intercepted at the transport layer, and performs subsequently one or more of the acceleration techniques on the intercepted network packet at one interface point or point of execution of the acceleration program.
Owner:CITRIX SYST INC
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com