Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
1925results about "Receiver specific arrangements" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
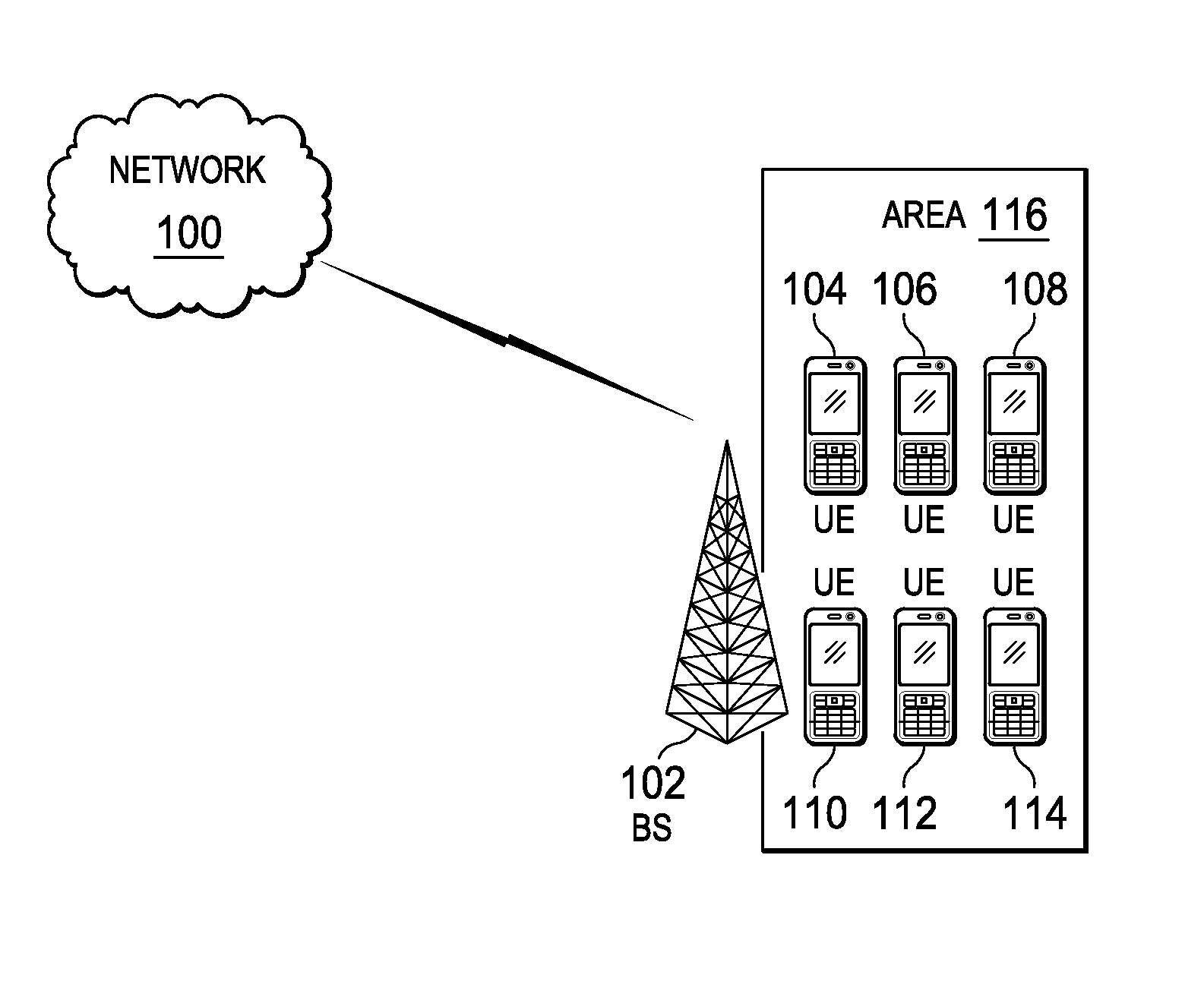
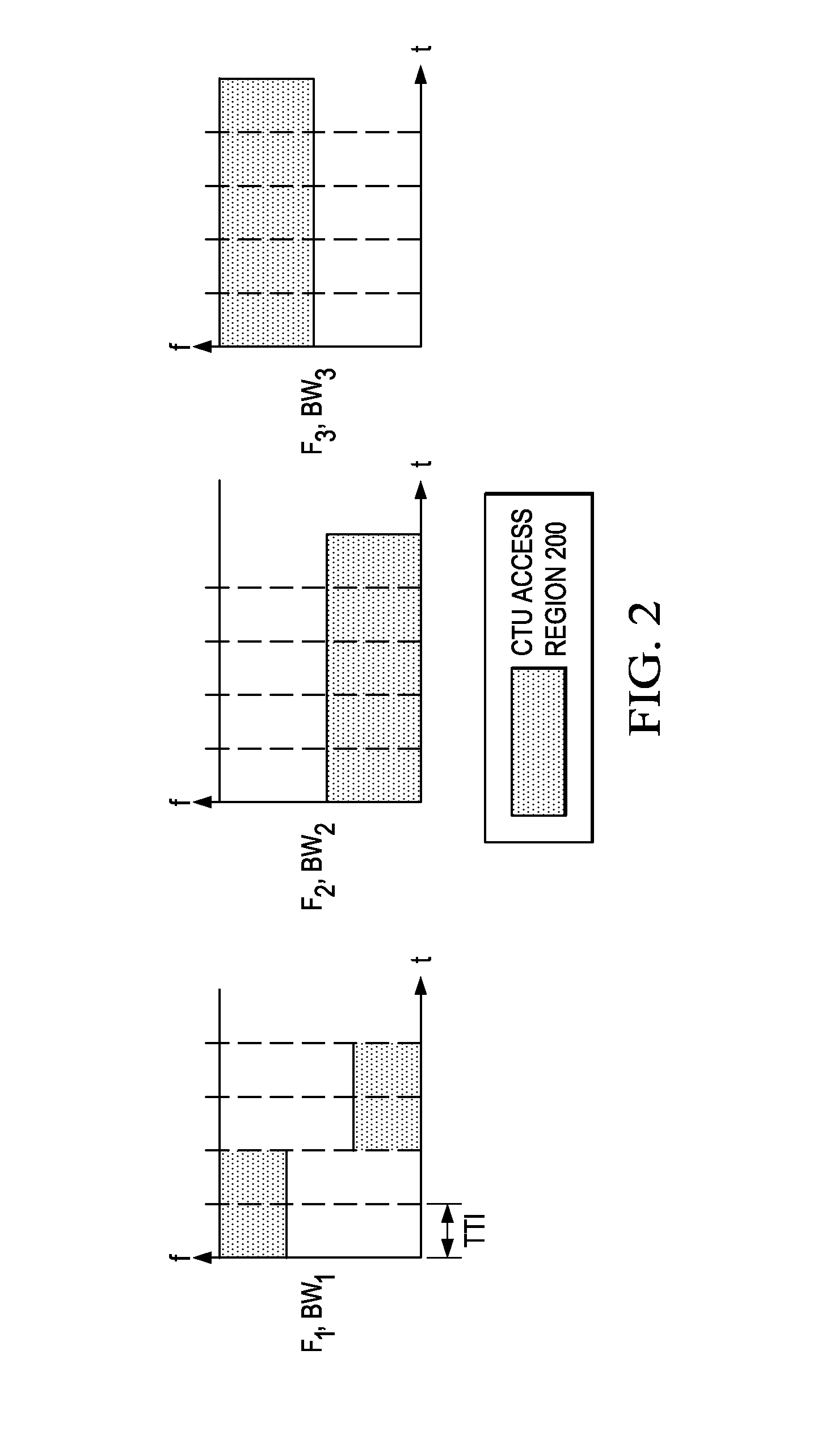
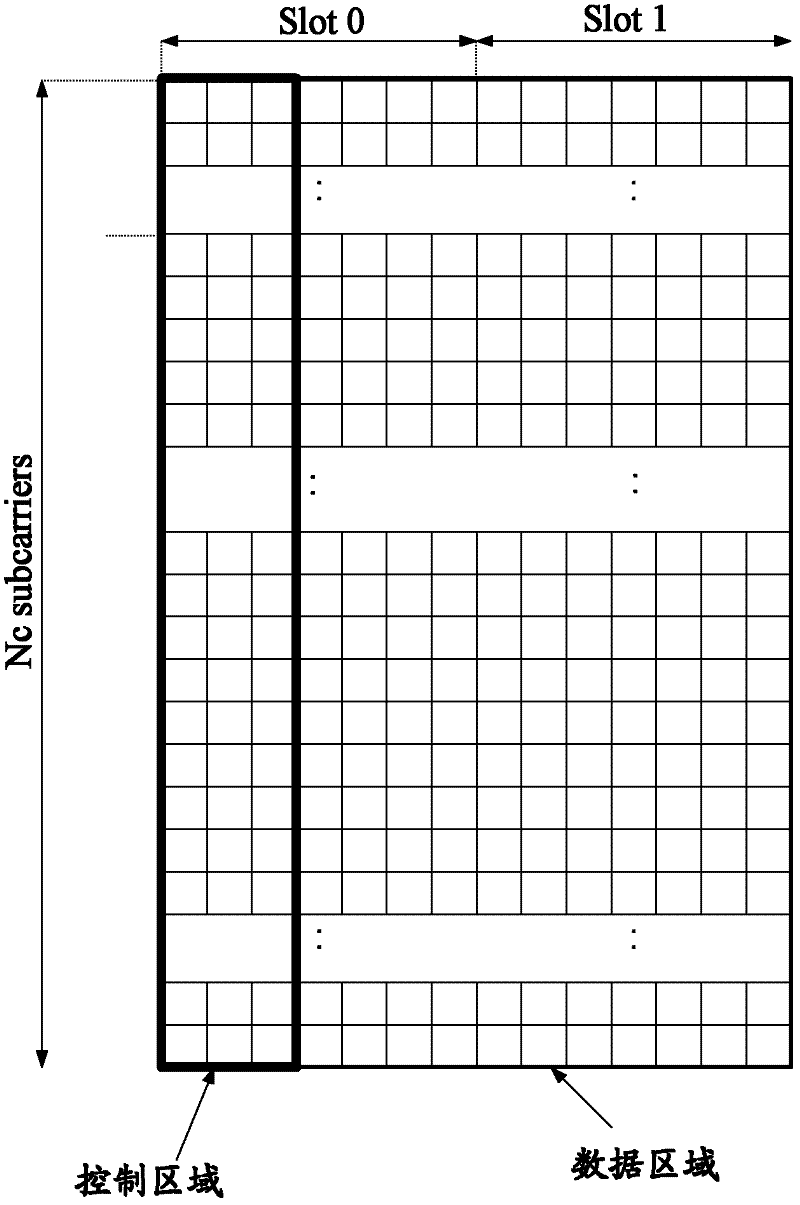
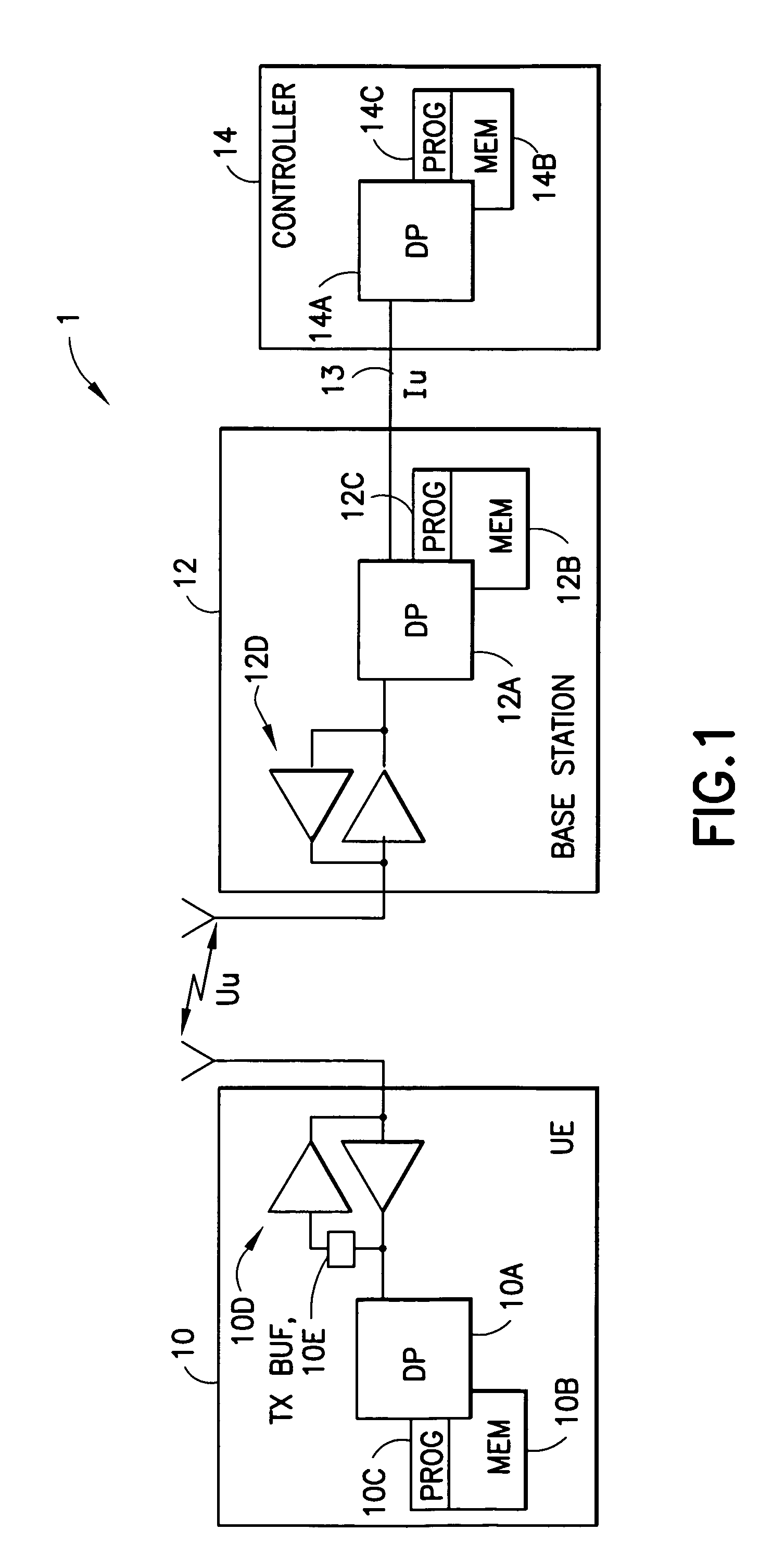
System and Method for Uplink Grant-Free Transmission Scheme
ActiveUS20140254544A1Transmission path divisionReceiver specific arrangementsTime frequency domainUser equipment
A method embodiment includes implementing, by a base station (BS), a grant-free uplink transmission scheme. The grant-free uplink transmission scheme defines a first contention transmission unit (CTU) access region in a time-frequency domain, defines a plurality of CTUs, defines a default CTU mapping scheme by mapping at least some of the plurality of CTUs to the first CTU access region, and defines a default user equipment (UE) mapping scheme by defining rules for mapping a plurality of UEs to the plurality of CTUs.
Owner:HUAWEI TECH CO LTD
Transmission method and equipment for downside control information
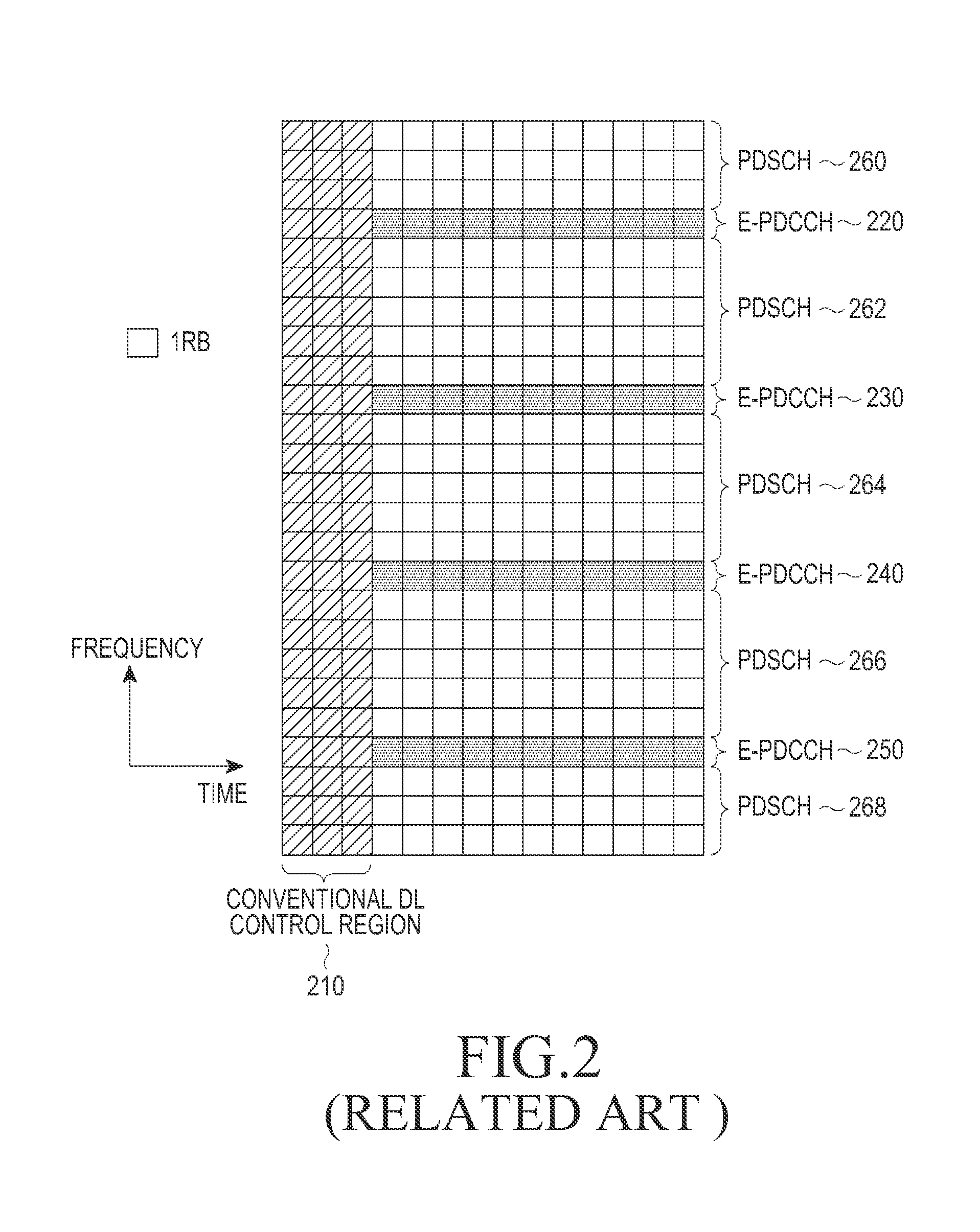
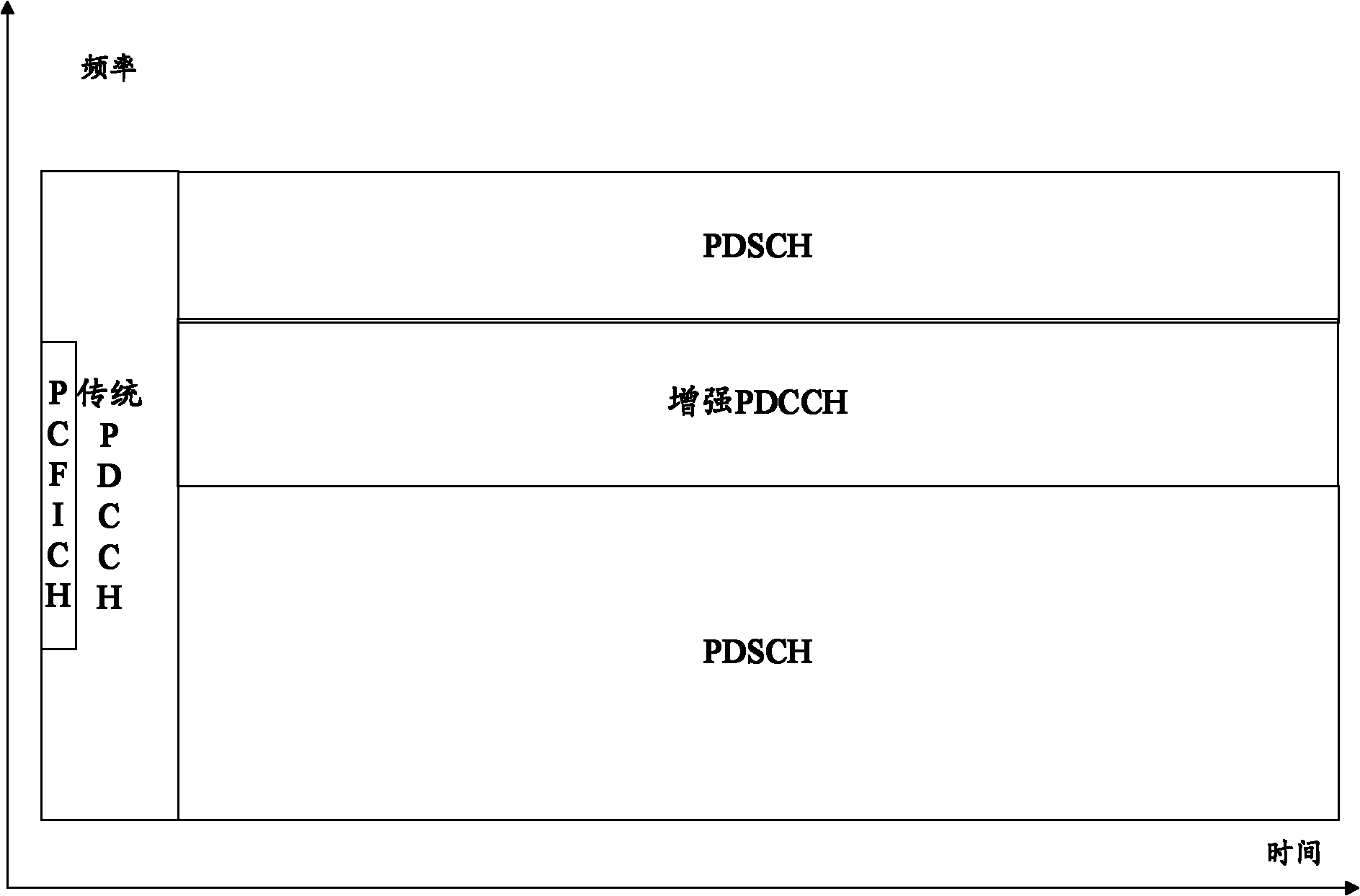
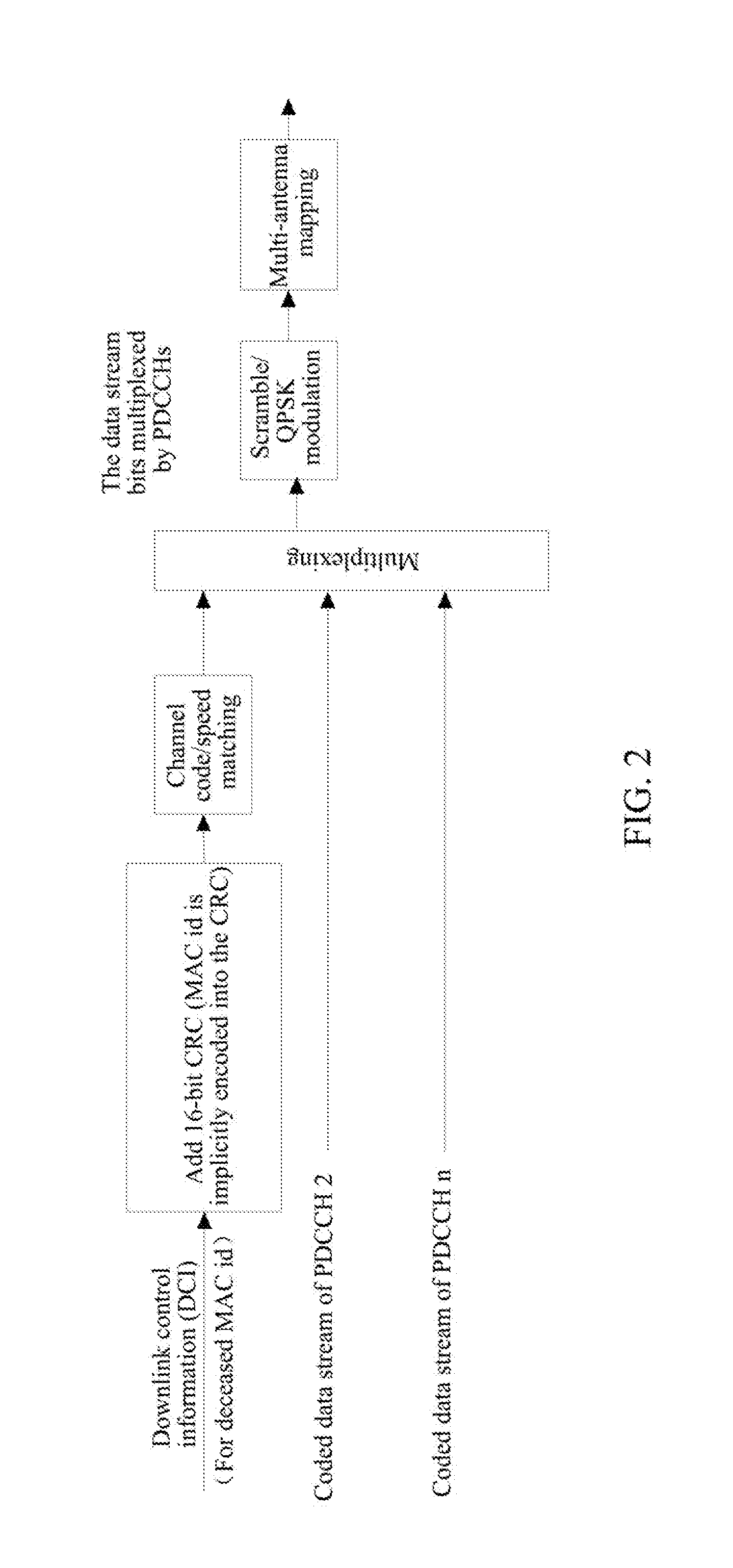
The embodiment of the invention discloses transmission method and equipment for downside control information. By adopting the technical scheme of the embodiment of the invention, the transmission method is capable of supporting two transmission modes of an E-PDCCH (physical downside control information channel) effectively, allocating a localized E-PDCCH resource and a distributed E-PDCCH resource by a base station, detecting DCI formats in search spaces corresponding to the localized E-PDCCH resource and the distributed E-PDCCH resource by terminal equipment, and obtaining the downside control information transmitted by the base station, thereby solving the problem in the existing technical scheme that the specific transmission and allocation schemes for the E-PDCCH in a localized transmission mode and a distributed transmission mode are lacked, so that the E-PDCCH can obtain channel selection gains and diversity transmission gains.
Owner:DATANG MOBILE COMM EQUIP CO LTD
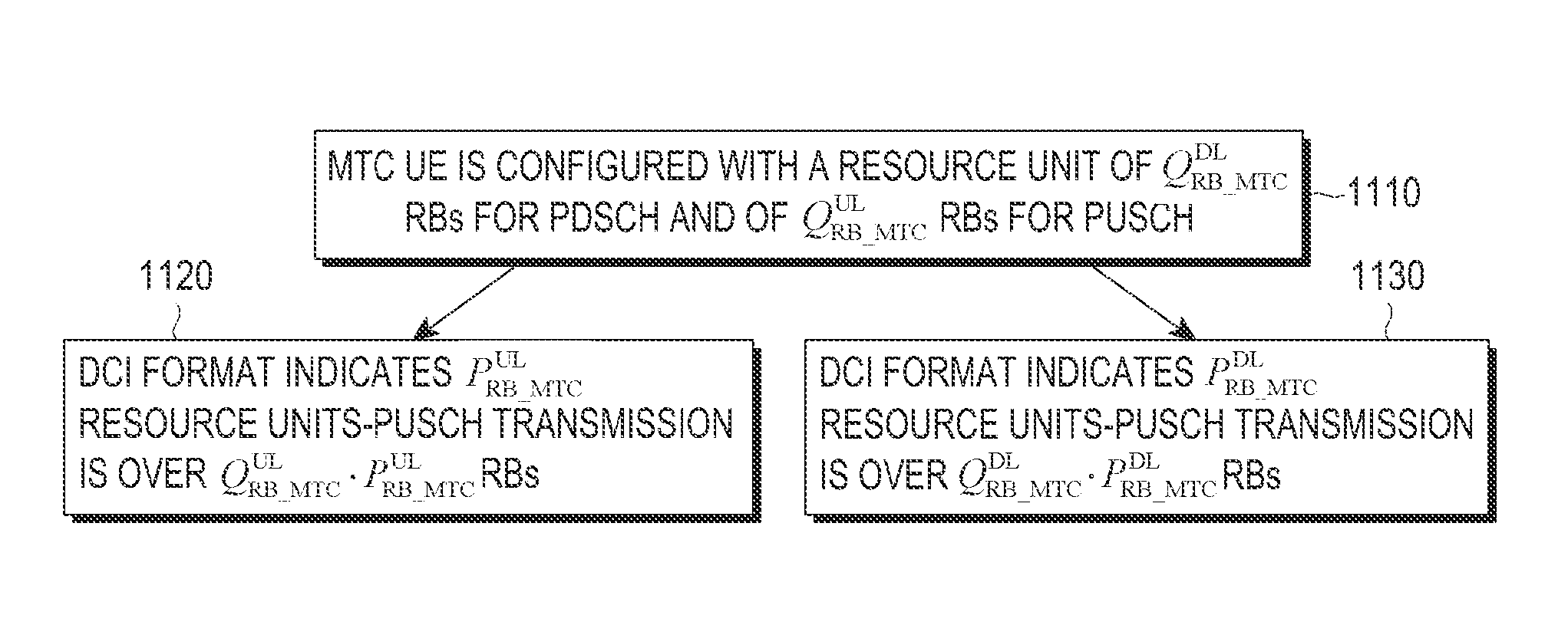
Method and apparatus for scheduling communication for low capability devices
ActiveUS20130195041A1Reduce overheadError prevention/detection by using return channelReceiver specific arrangementsUser equipmentReal-time computing
Methods and apparatus are described for a User Equipment (UE) with reduced processing capabilities (e.g., Machine Type Communication (MTC) UE) to transmit and receive signaling are provided. The Downlink Control Information (DCI) formats scheduling a transmission of a Physical Uplink Shared CHannel (PUSCH) or a reception of a Physical Downlink Shared CHannel (PDSCH) are designed and have a smaller size than respective DCI formats for conventional UEs. DCI formats scheduling PUSCHs to or PDSCHs for a group of MTC UEs are also designed and can have a same size as DCI formats scheduling PUSCH or PDSCH for an individual MTC UE.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
FEC (Forward Error Correction) decoder with dynamic parameters
InactiveUS7257764B2Error prevention/detection by using return channelReceiver specific arrangementsComputer hardwareCommunications system
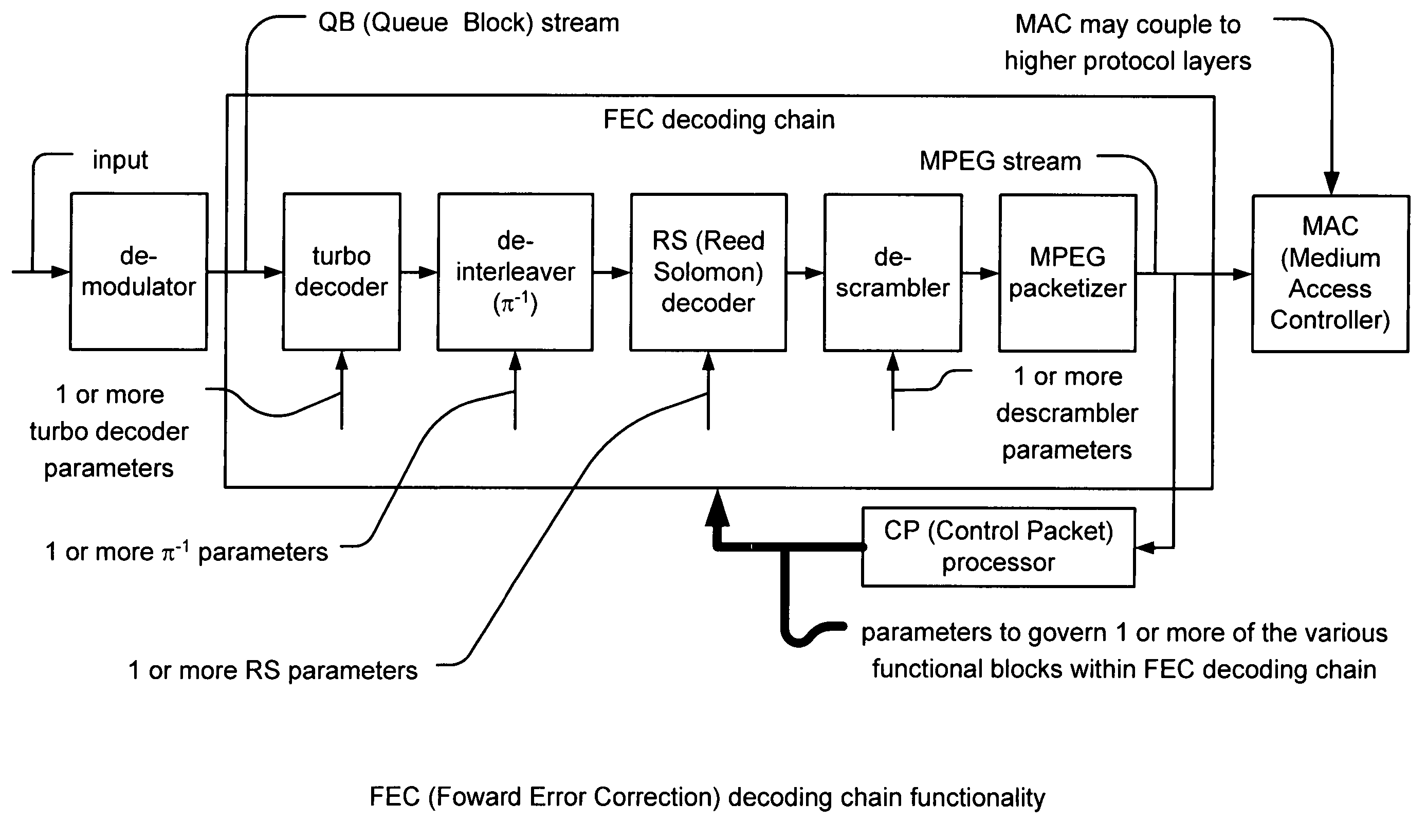
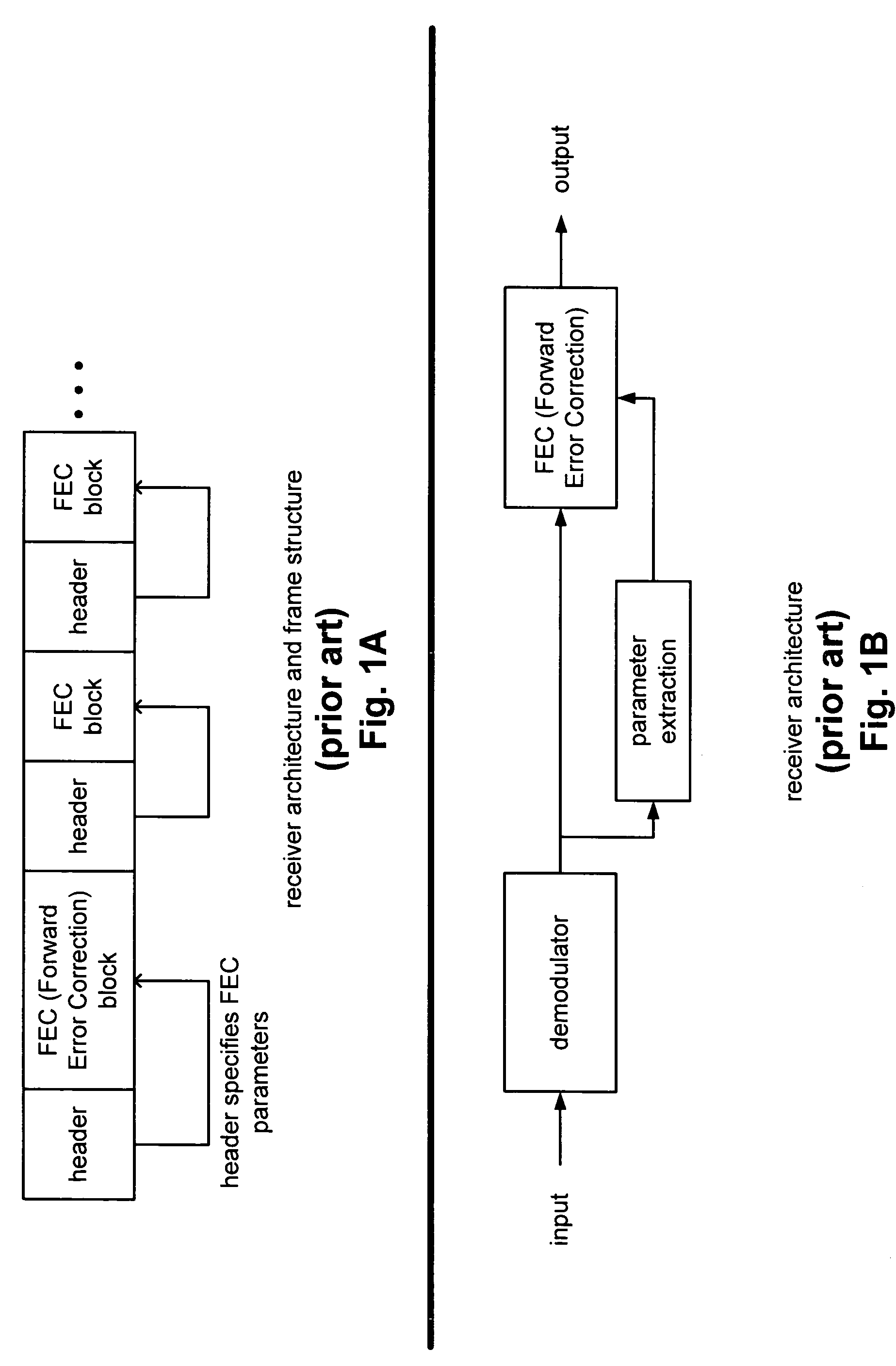
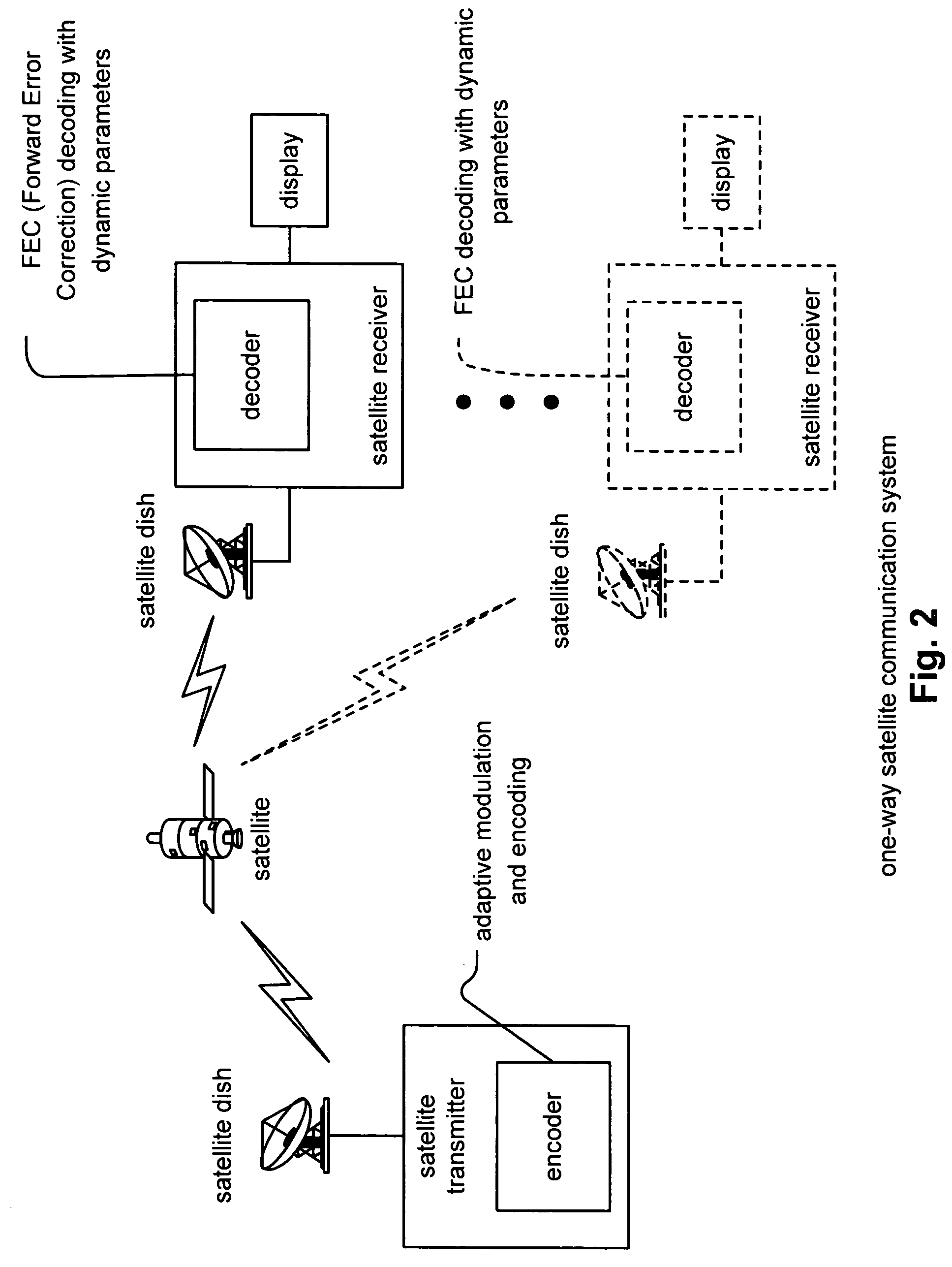
FEC (Forward Error Correction) decoder with dynamic parameters. A novel means by which FEC parameters may be encoded into, and subsequently extracted from, a signal stream to allow for adaptive changing of any 1 or more operational parameters that govern communications across a communication channel. FEC parameters are encoded directly into a data frame such that the data frame is treated identical to all other data frames within the signal stream. When the data frame actually includes FEC parameters, it is characterized as a CP (Control Packet) type. For example, when decoding an MPEG stream, an MPEG block that includes FEC parameters, that MPEG block is characterized as a CP MPEG block. The means by which FEC parameters are encoded and extracted from the signal stream allows for much easier adaptive modification of the manner by which signal are encoded, modulated, and processed within a communication system.
Owner:AVAGO TECH WIRELESS IP SINGAPORE PTE
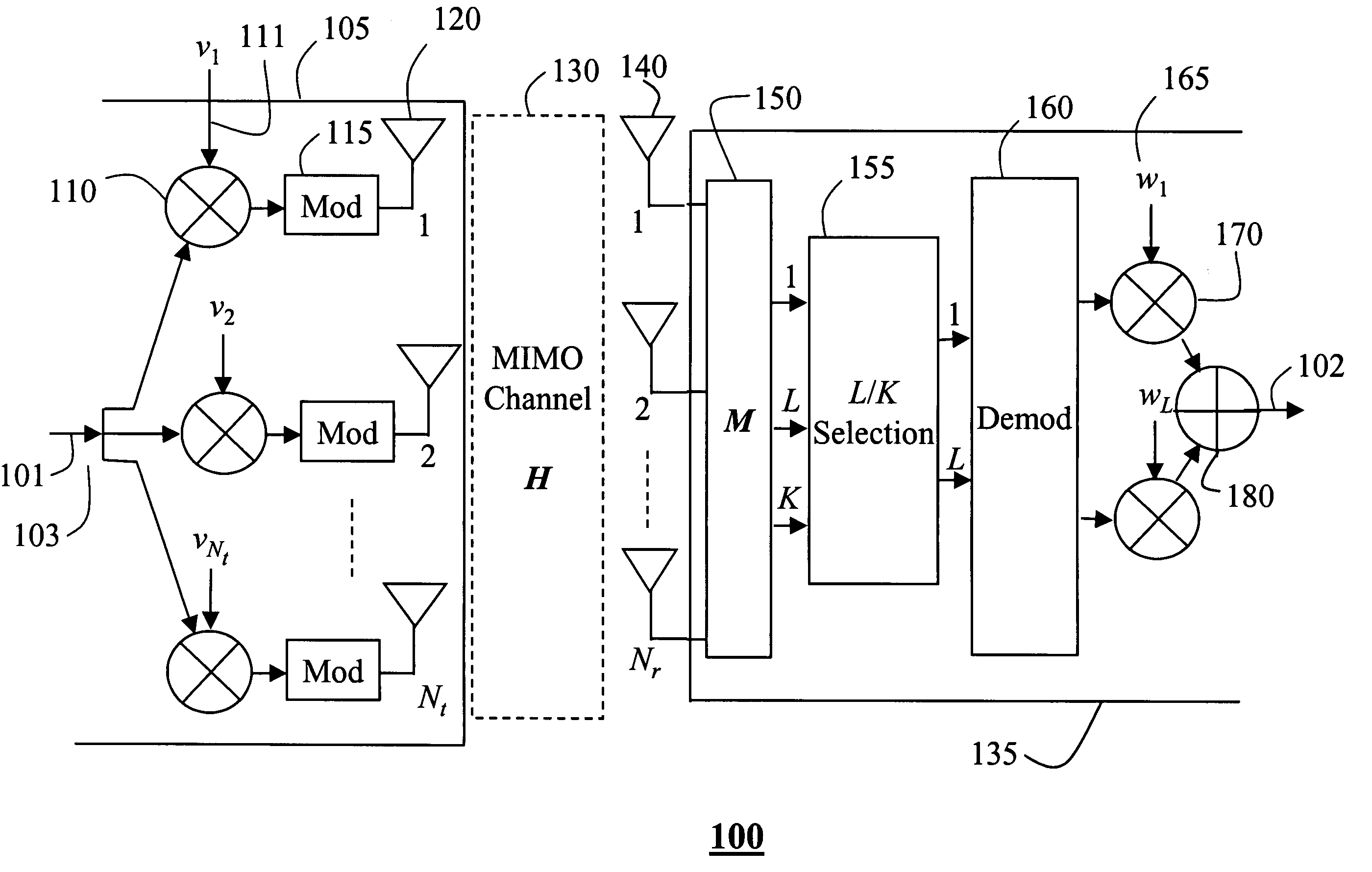
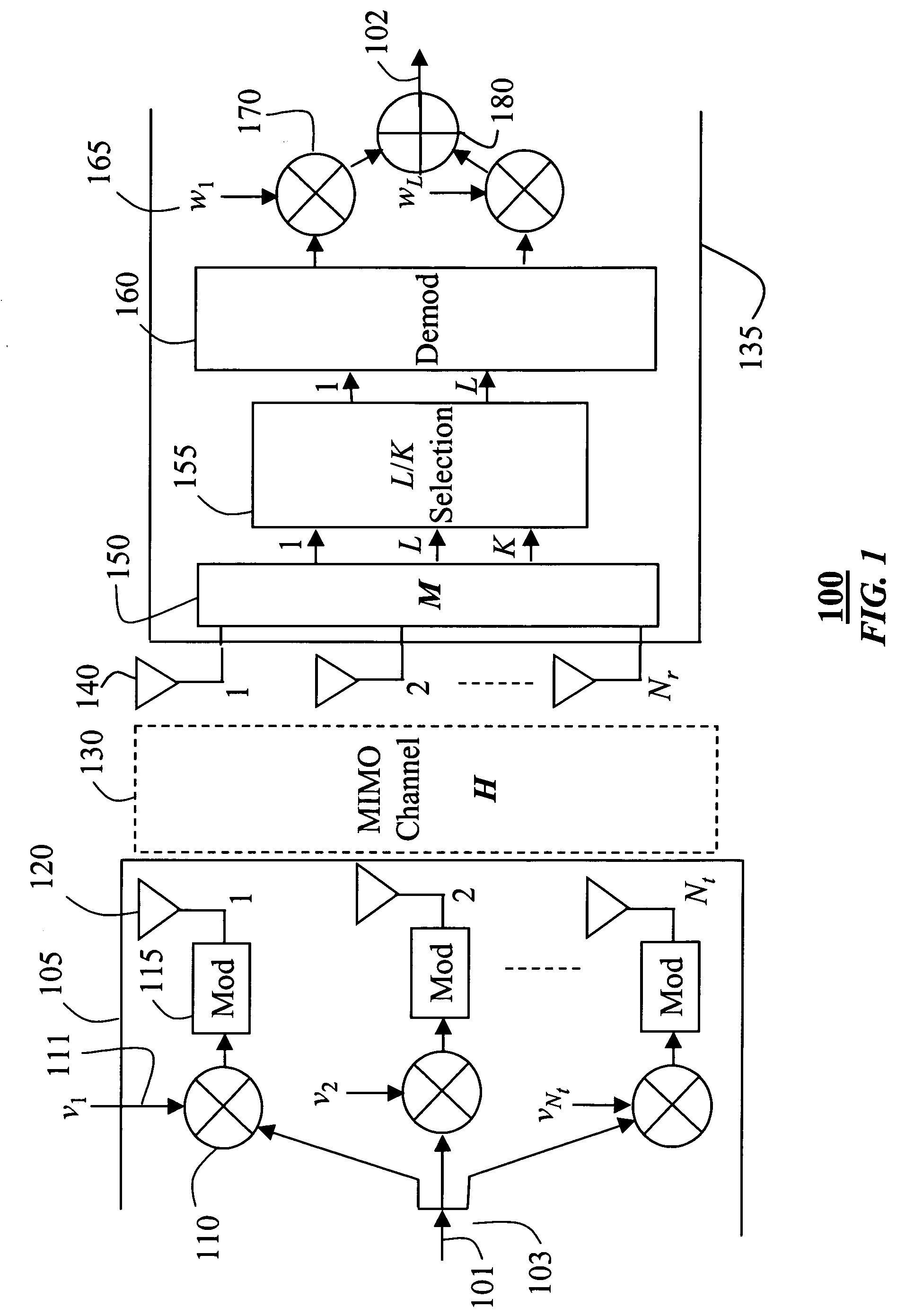
RF-based antenna selection in MIMO systems
InactiveUS20050287962A1Additional wireless bandwidthReduce system complexitySpatial transmit diversityMultiplex communicationCommunications systemEngineering
A method is presented for processing signals of a multiple-input, multiple-output communications system in the RF domain. The system includes multiple transmit antennas and multiple receive antennas connected by a wireless channel. A matrix M is generated based on long-term characteristics of the wireless channel. The matrix M is multiplied times input RF signals to obtain output RF signals. The matrix can be generated in a transmitter, a receiver, or both.
Owner:MITSUBISHI ELECTRIC RES LAB INC
Two-stage pdcch with dci flag and dci format size indicator
ActiveUS20160128028A1Well formedError prevention/detection by using return channelReceiver specific arrangementsTelecommunicationsControl channel
Methods, systems, and devices are described for wireless communication employing two-stage control channel messaging. Systems, methods, and apparatuses for two stage two-stage physical downlink control channel (PDCCH) with a downlink control information (DCI) flag and DCI format size indicator are described. For instance, the present disclosure presents an example method of wireless communication at a wireless device, which may include receiving, at a first bandwidth and during a transmission time interval (TTI), a first control channel message. In addition, the example method may include determining, based on a flag in the first control channel message, whether a second control channel message is present in the TTI. Furthermore, the example method may include receiving, at a second bandwidth, the second control channel message where the flag indicates that the second control channel message is present for the TTI.
Owner:QUALCOMM INC
Adaptive information delivery system using FEC feedback
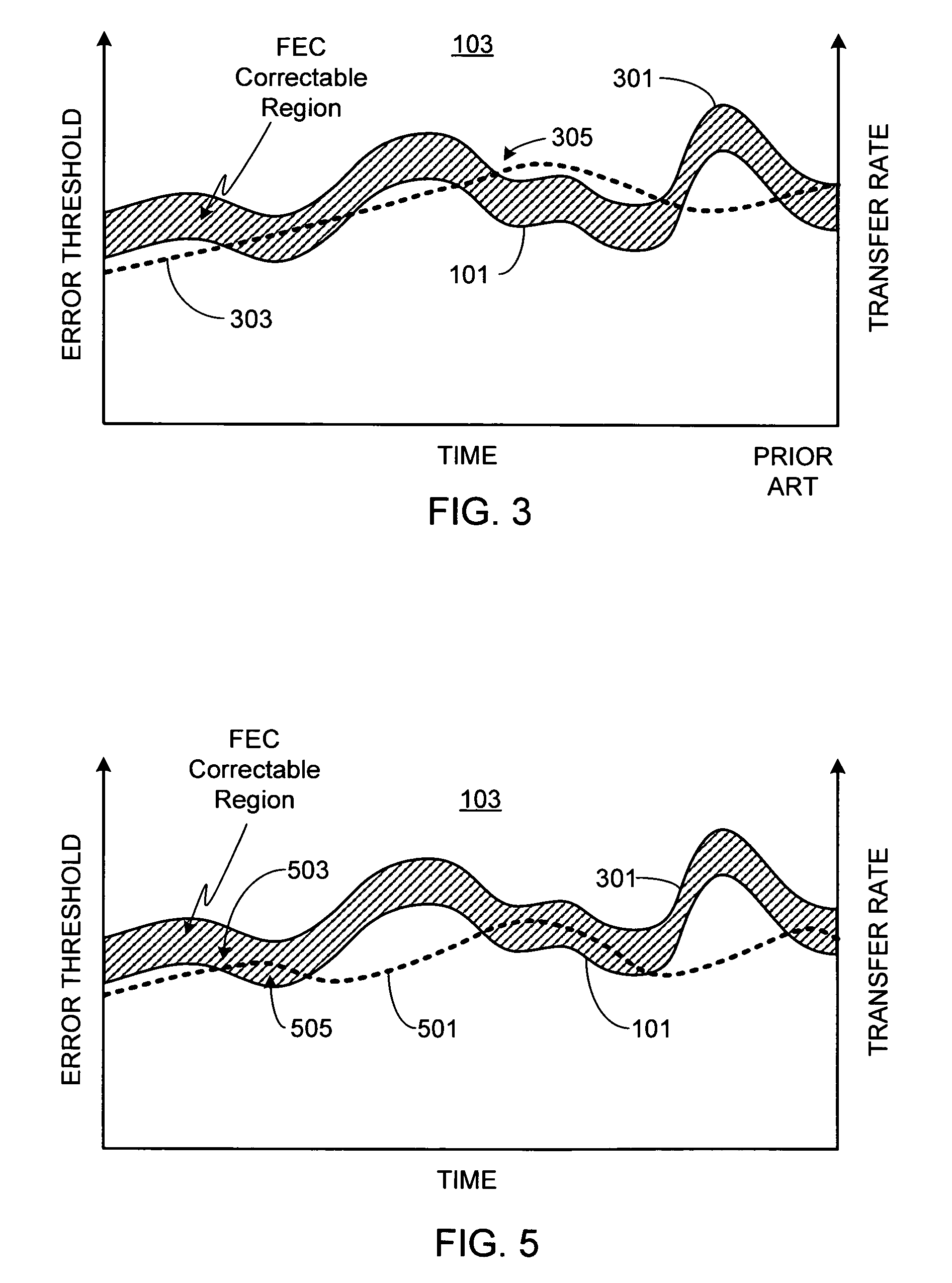
InactiveUS20060150055A1Useful resultError detection/prevention using signal quality detectorReceiver specific arrangementsTelecommunications linkThe Internet
A method and apparatus for optimizing the data transfer rate over a transport layer (i.e., communication link) such as the Internet is provided. Initially the data is prepared for transmission by a transfer rate controller, then the data is encoded by a Forward Error Correction (FEC) encoder. After the data has been transferred over the transport layer, the quality of the data transfer link is assessed by an FEC decoder that determines if any errors occurred during data transfer and if errors are detected, the magnitude of the errors (i.e., FEC-correctable packets, FEC-uncorrectable packets). This information is used to generate a feedback message which is used by the transfer rate controller to adjust and optimize the data transfer rate for the link quality as determined at that point in time. By continually monitoring and assessing link quality and providing feedback to the transfer rate controller, the transfer rate can be continually adapted to the varying link quality. In addition to generating feedback used by the transfer rate controller to optimize data transfer rate, the FEC decoder can generate feedback that is used by the FEC encoder to optimize the FEC algorithm. If desired, feedback from the FEC decoders within the link layer demodulator and / or feedback from the receiver can be used to augment the feedback generated by the FEC decoder.
Owner:TERAYON COMM SYST
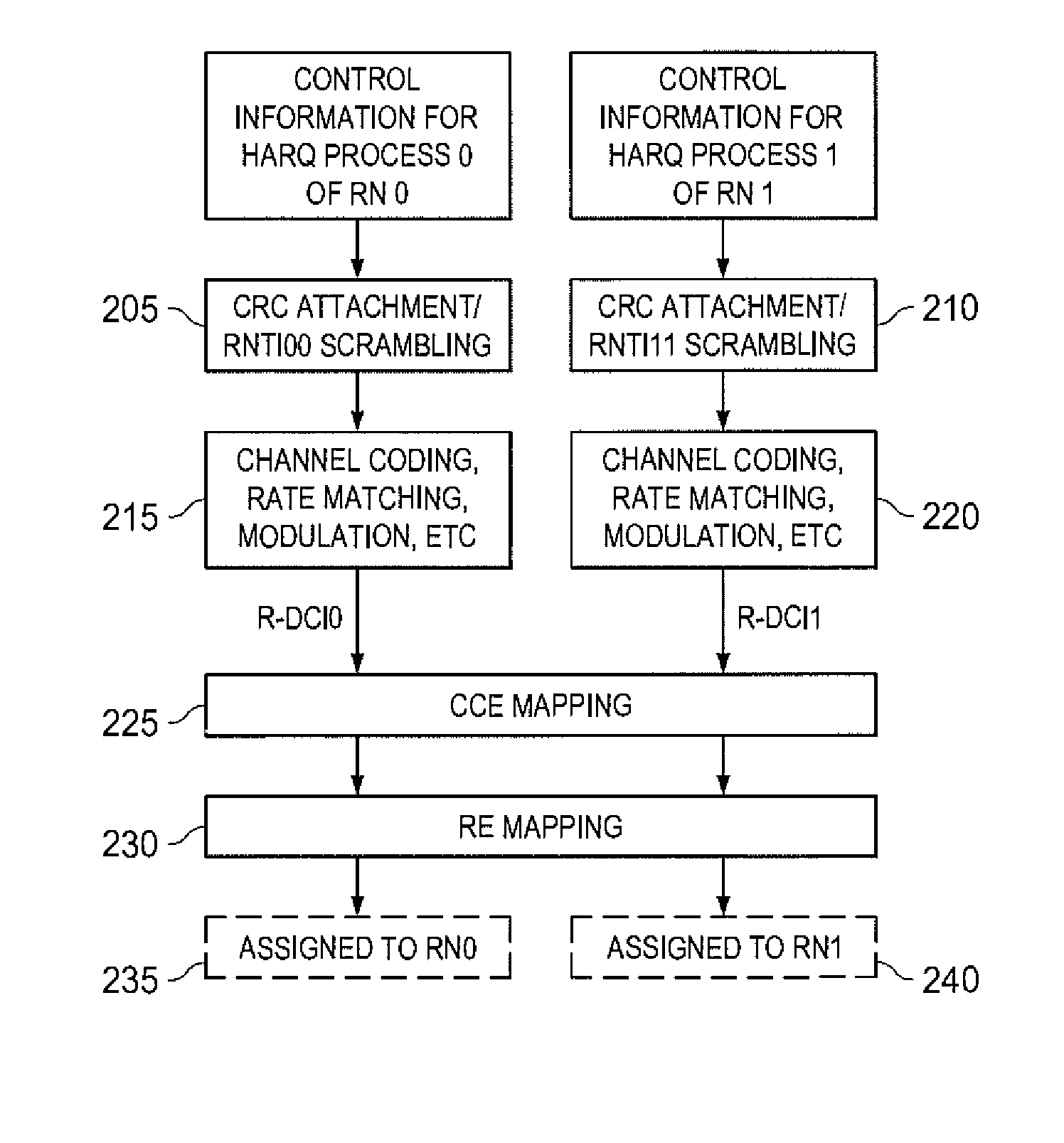
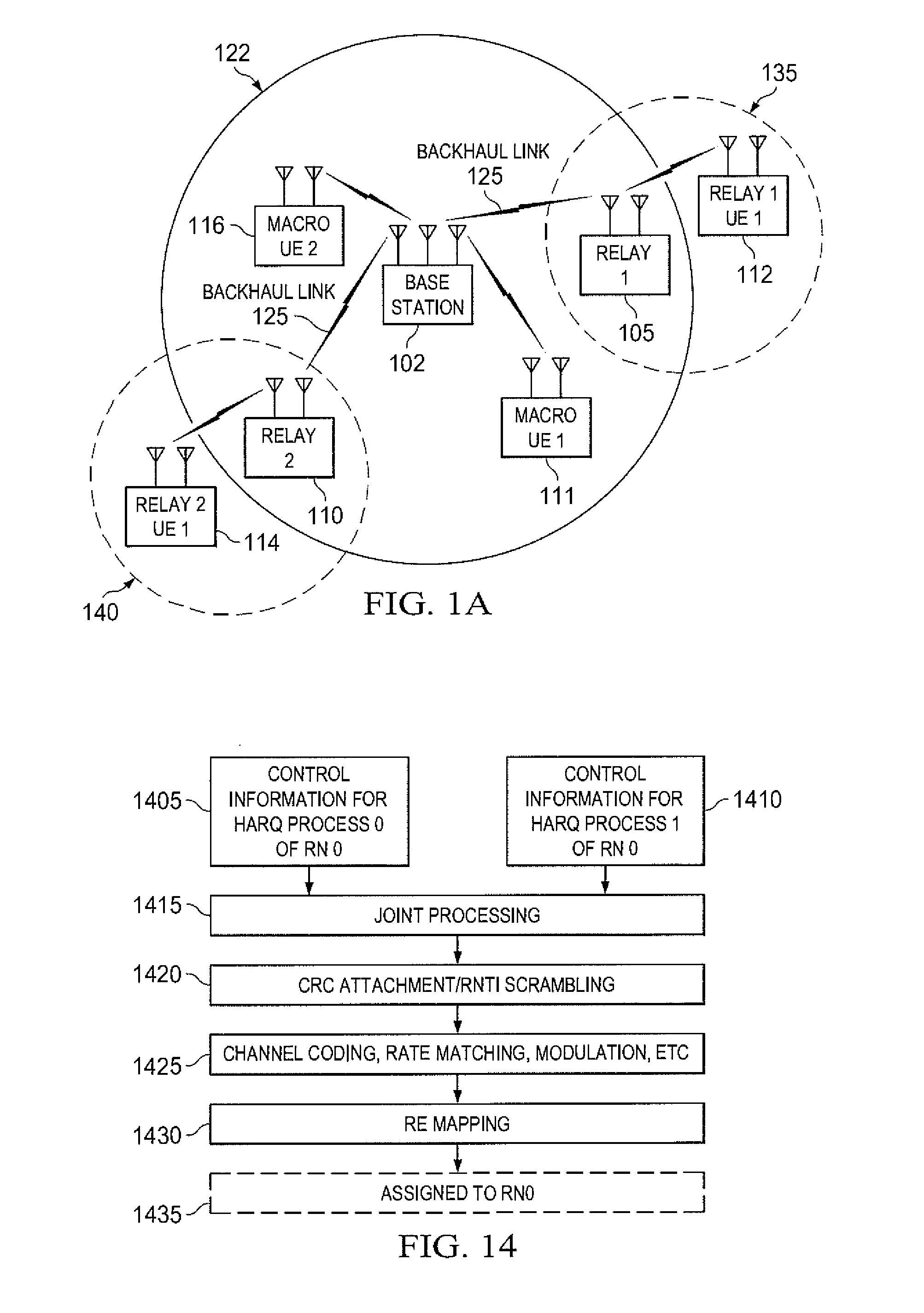
Control design for backhaul relay to support multiple HARQ processes
ActiveUS20100275083A1Error prevention/detection by using return channelError correction/detection using convolutional codesHybrid automatic repeat requestBase station
A wireless communication network includes a base station and a relay station. The relay station is configured to relay communications between the base station and at least one subscriber station. The base station is configured to communicate with the subscriber station via the relay station. The base station further is configured to transmit, in a subframe, a plurality of transport blocks for a plurality of Hybrid Automatic Repeat Request (HARQ) processes to the relay station. Each transport block corresponds to a different HARQ process.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
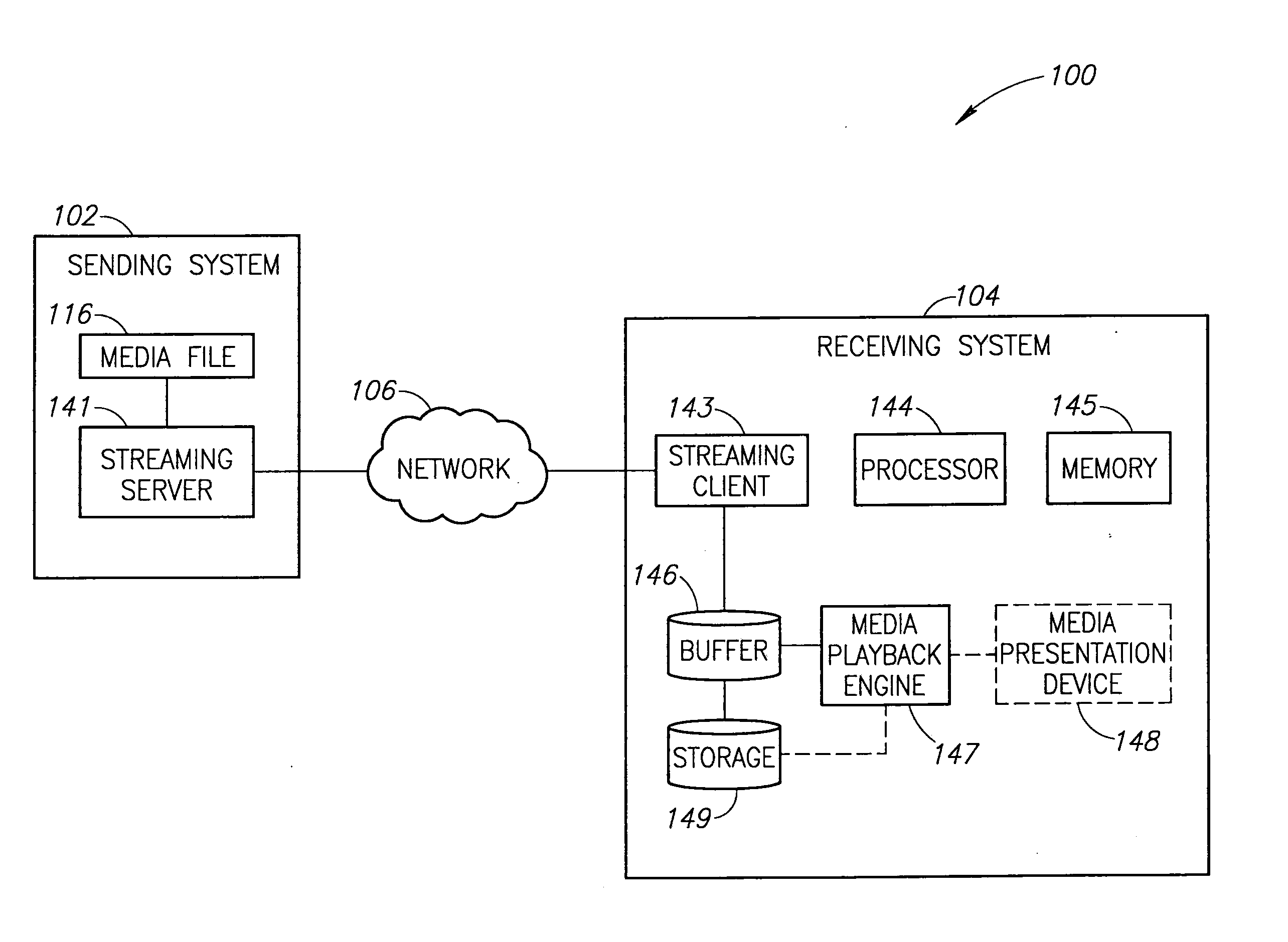
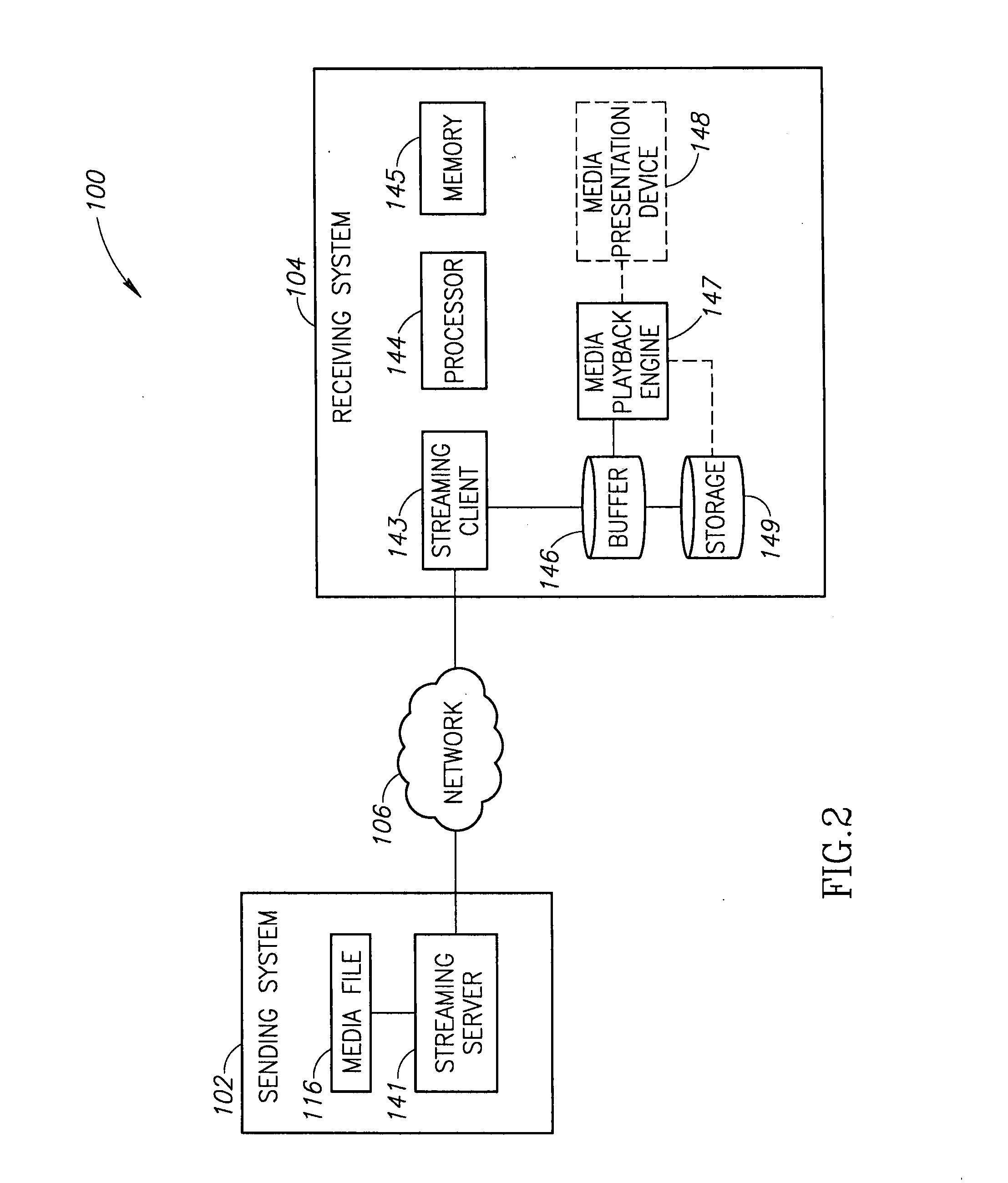
System and method for progressive download using surplus network capacity
ActiveUS20100198943A1Data processing applicationsReceiver specific arrangementsReceiver systemMedia content
Systems and methods for providing the progressive download of media content using techniques that preferentially identify and use periods of surplus network capacity to maintain the content delivery. A buffer of a receiving system is maintained and pre-filled with enough content to bridge playback intervals where a network is unable to deliver content as fast as it is played out. Content delivery does not impact other users' applications and use of the network and its resources since content is only sent when surplus network capacity exists in the network. When no surplus network capacity is available, a user requesting content may be given the option to continue the delivery in the background so that the content may be played at a later time. The user may then resume their playback experience once the content has been completely delivered using surplus network capacity as it becomes available.
Owner:OPANGA NETWORKS
Power headroom reporting for non-scheduled uplink component carriers
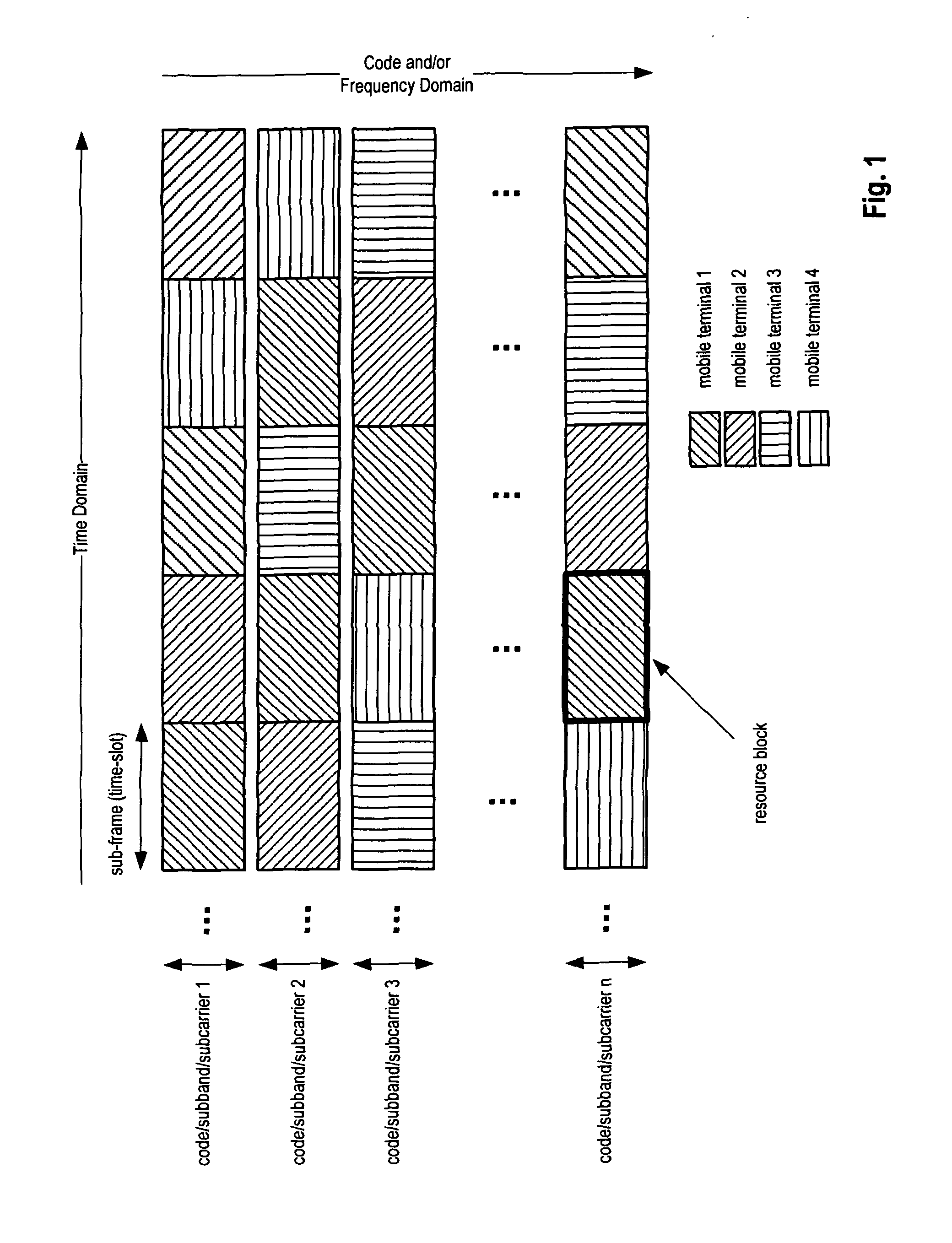
ActiveUS20130010720A1Efficient and robust (de)activationMinimize signaling overheadPower managementEnergy efficient ICTTransmitted powerResource block
This invention relates to a proposal for power headroom reporting for uplink component carriers for which no uplink resource allocation is scheduled by the eNodeB. The user equipment (UE) calculates a virtual power headroom for the non-scheduled uplink component carrier, based on a virtual uplink resource assignment pre-configured by the UE and eNodeB. According to one embodiment the maximum transmit power of the UE is set to a pre-configured fixed value. Alternatively, the maximum transmit power is calculated by the UE considering the power reduction, while the uplink transmission power is set to zero. The virtual power headroom is then transmitted to the eNodeB, which in turn can infer therefrom the pathloss and / or power-per-resource-block for the non-scheduled uplink component carrier and may also infer the power reduction used by the UE. This allows a more accurate scheduling of future uplink transmissions on said non-scheduled uplink component carrier.
Owner:SUN PATENT TRUST
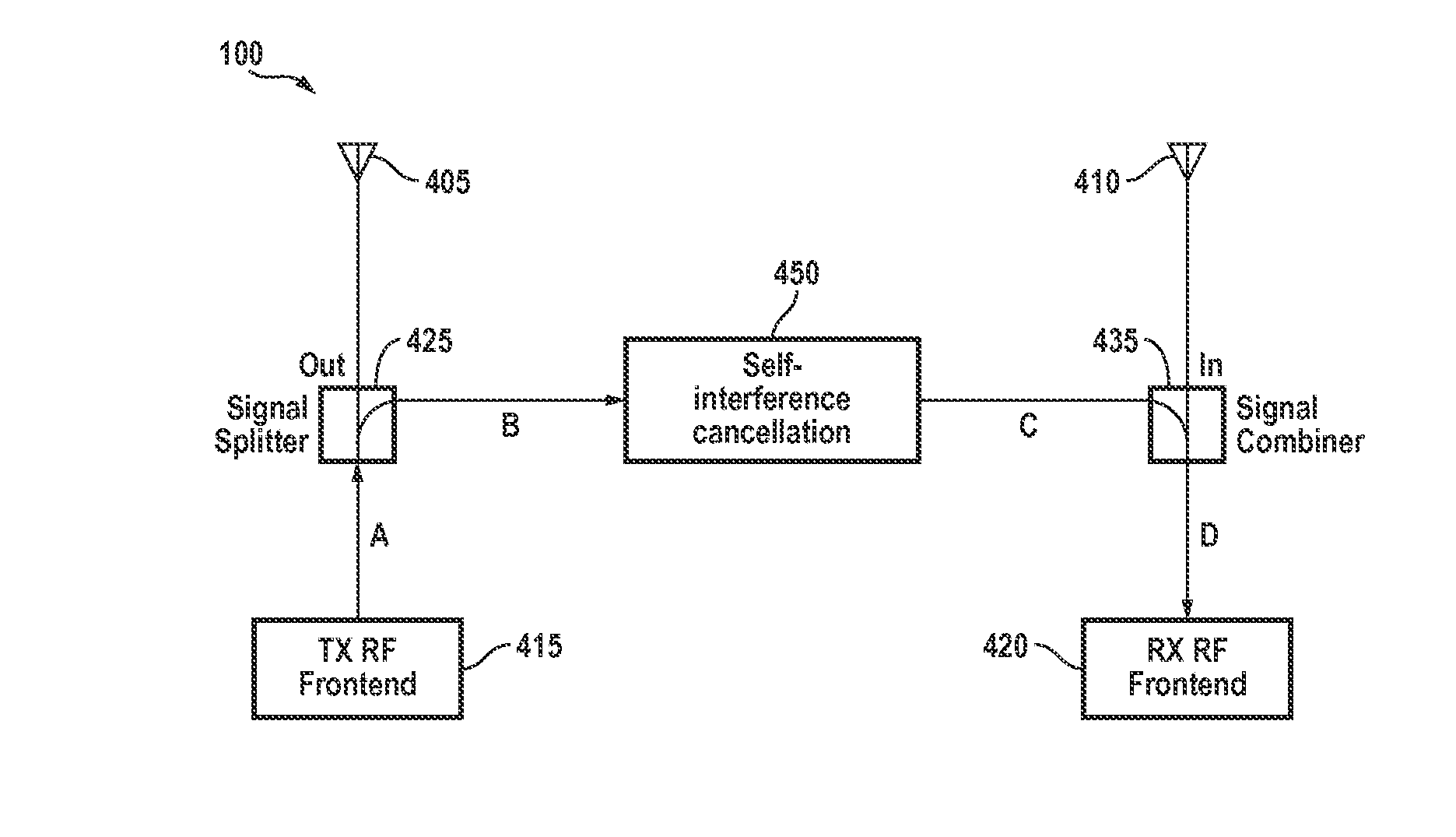
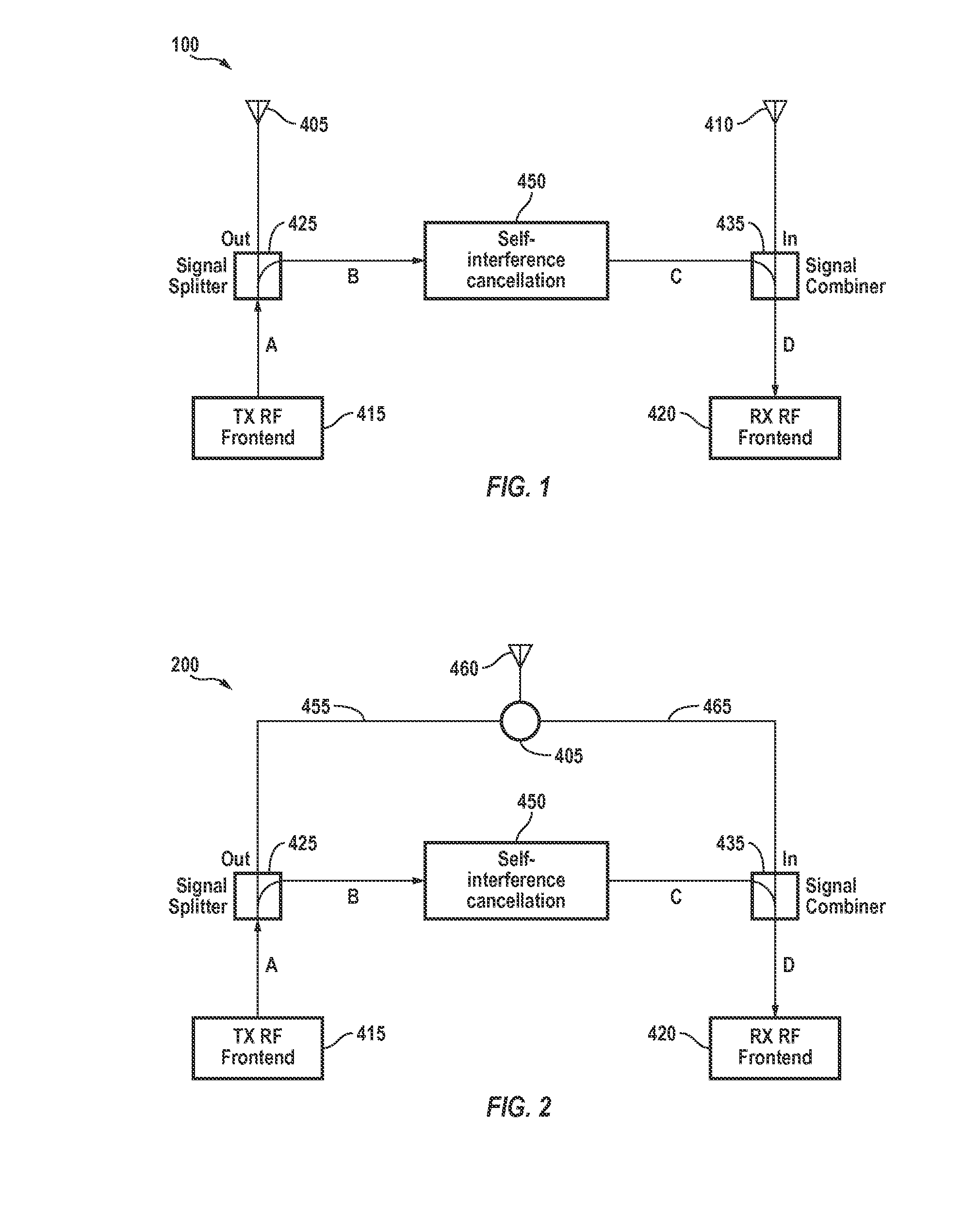
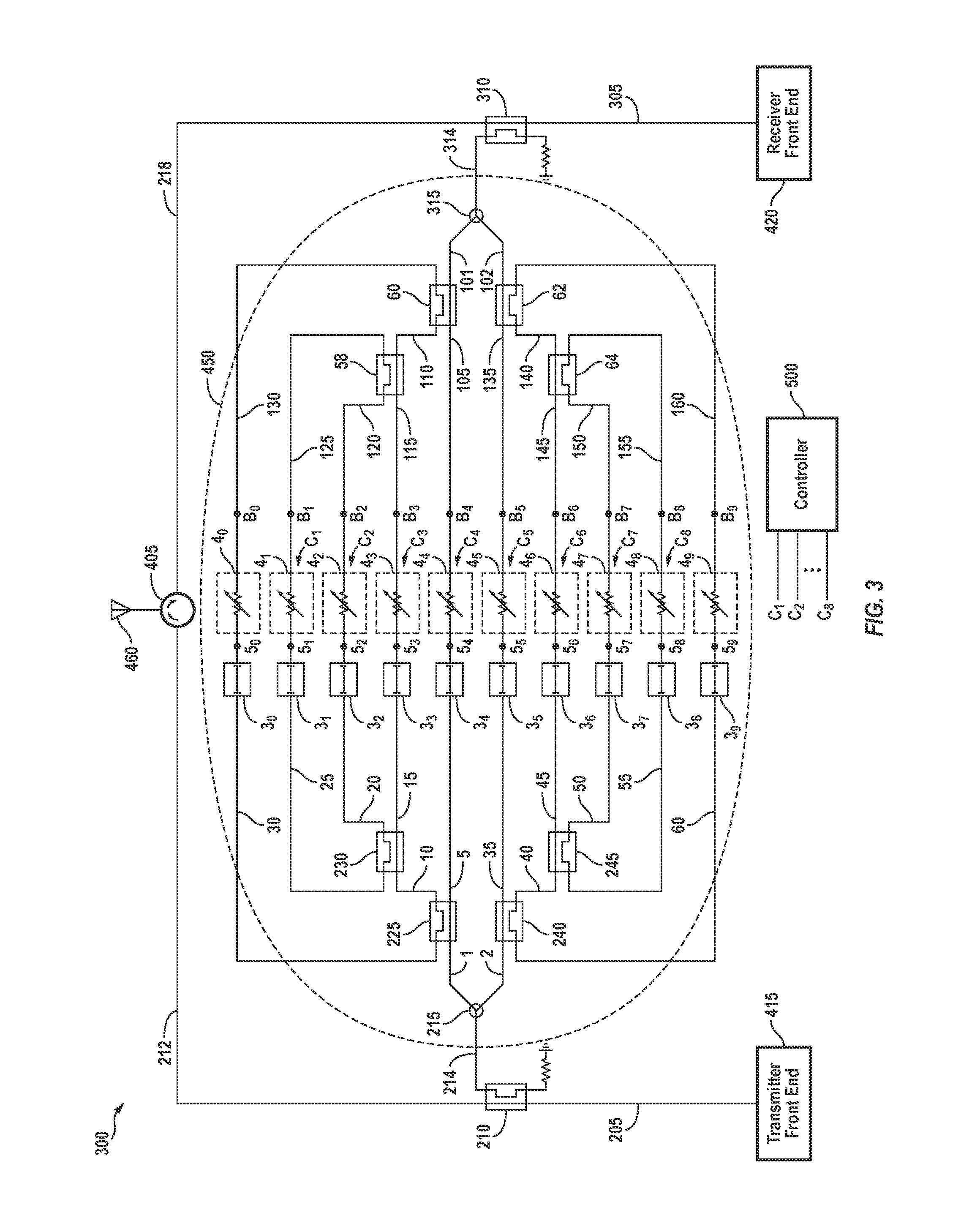
Signal cancellation using feedforward and feedback paths
ActiveUS20140219139A1Reducing self-interference signalTransmission control/equalisingReceiver specific arrangementsSelf interferenceSignal cancellation
A circuit that cancels a self-interference signal includes, in part, a pair of signal paths that are substantially in phase, each of which paths includes a passive coupler, a delay element and a variable attenuator. The circuit further includes, in part, a first group of P signal paths each of which is substantially in phase with the pair of paths, a second group of M signal paths each of which is substantially out-of-phase relative to the pair of signal paths, and at least a pair of feedback paths. Each of the P and M signal paths, as well as the feedback paths includes a delay element and a variable attenuator. Optionally, each of the M signal paths is optionally 180° out-of-phase relative to the pair of signal paths.
Owner:KUMU NETWORKS
Method and apparatus of receiving data in wireless communication system
InactiveUS20110194514A1Data efficientImprove system performanceModulated-carrier systemsTransmission path divisionCommunications systemControl channel
Owner:LG ELECTRONICS INC
Method and Apparatus of Transmitting Control Information in Wireless Communication System
ActiveUS20110141941A1Efficiently transmitting control informationImprove system performanceFrequency-division multiplex detailsModulated-carrier systemsCommunications systemCarrier signal
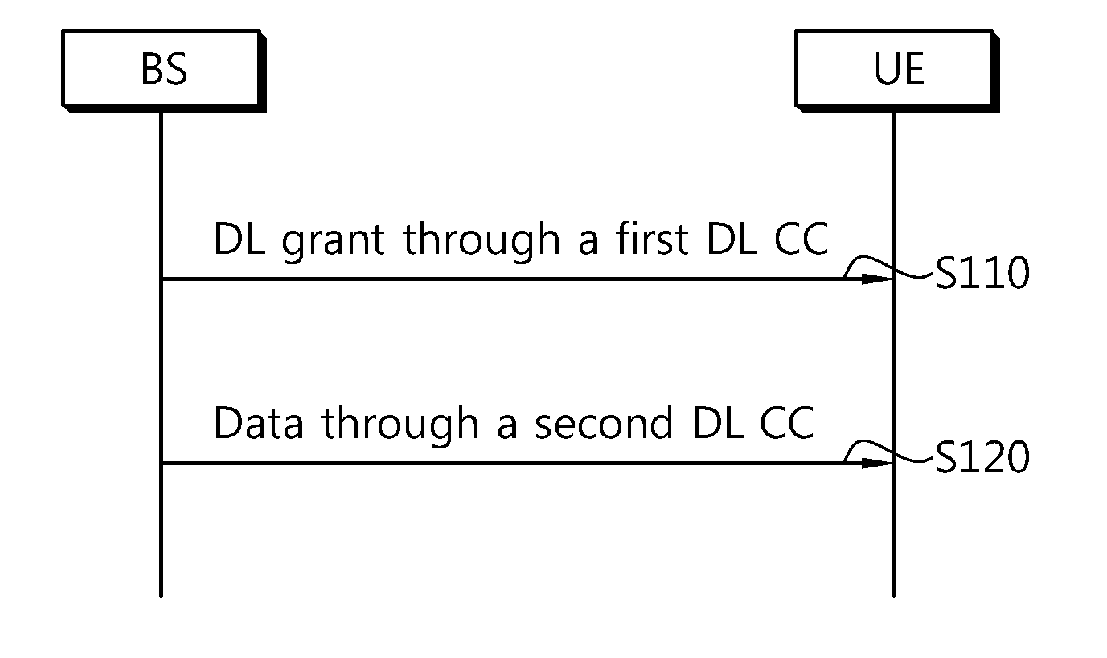
A method and an apparatus of transmitting control information in a wireless communication systema are provided. The method includes transmitting first control information and second control information through an uplink component carrier (UL CC), wherein the first control information is for a first downlink component carrier (DL CC), and the second control information is for a second DL CC.
Owner:LG ELECTRONICS INC
Base station, communication terminal, transmission method, and reception method
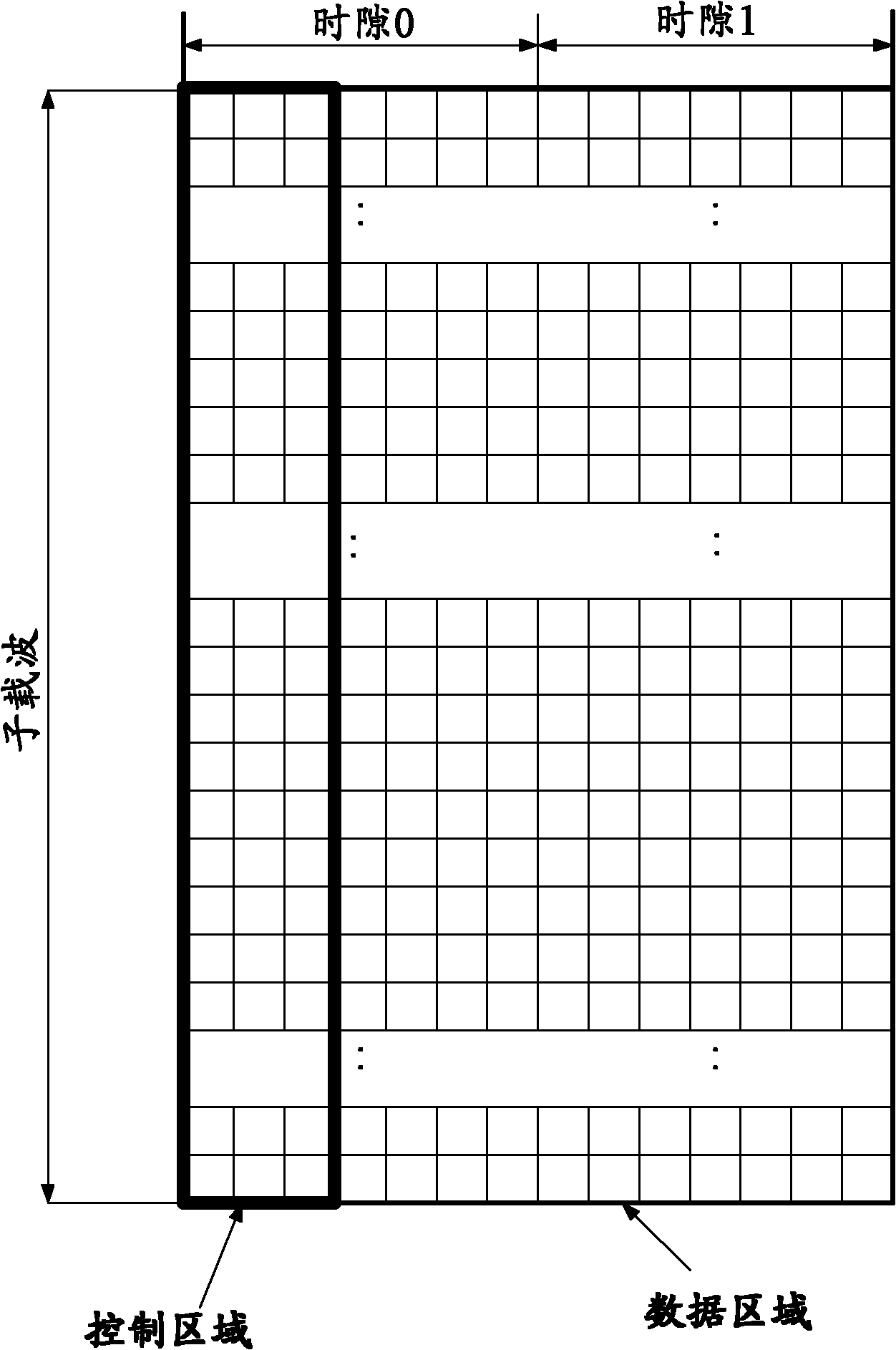
ActiveUS20100103901A1Guaranteed normal transmissionTransmission path divisionMultiplex communicationUser deviceBroadcast domain
A base station includes a scheduler configured to perform frequency scheduling for each subframe; a control channel generating unit configured to generate a control channel including common control information to be mapped to radio resources distributed across a system frequency band and specific control information to be mapped to one or more resource blocks allocated to each selected user device; and a transmission signal generating unit configured to generate a transmission signal by time-division-multiplexing the common control information and the specific control information according to scheduling information from the scheduler. The common control information includes a format indicator representing one of preset options that indicates the number of symbols occupied by the common control information in one subframe. The common control information includes information units with a predetermined data size. The number of the information units is less than or equal to a specified multiplicity included in broadcast information.
Owner:NTT DOCOMO INC
Hierarchical communication system providing intelligent data, program and processing migration
InactiveUS6970434B1Reduce traffic problemsReduce communicationPower managementError prevention/detection by using return channelCommunications systemTelecommunications link
A hierarchical communication system, arranged in a spanning tree configuration, is described in which wired and wireless communication networks exhibiting substantially different characteristics are employed in an overall scheme to link portable or mobile computing devices. Copies of data, program code and processing resources are migrated from their source toward requesting destinations based on request frequency, communication link costs and available local storage and / or processing resources. Each appropriately configured network device acts as an active participant in network migration. In addition, portable two-dimensional (2-D) code reading terminals are configured to wirelessly communicate compressed 2-D images toward stationary access servers that identify the code image through decoding and through comparison with a database of images that have previously been decoded and stored.
Owner:AVAGO TECH WIRELESS IP SINGAPORE PTE
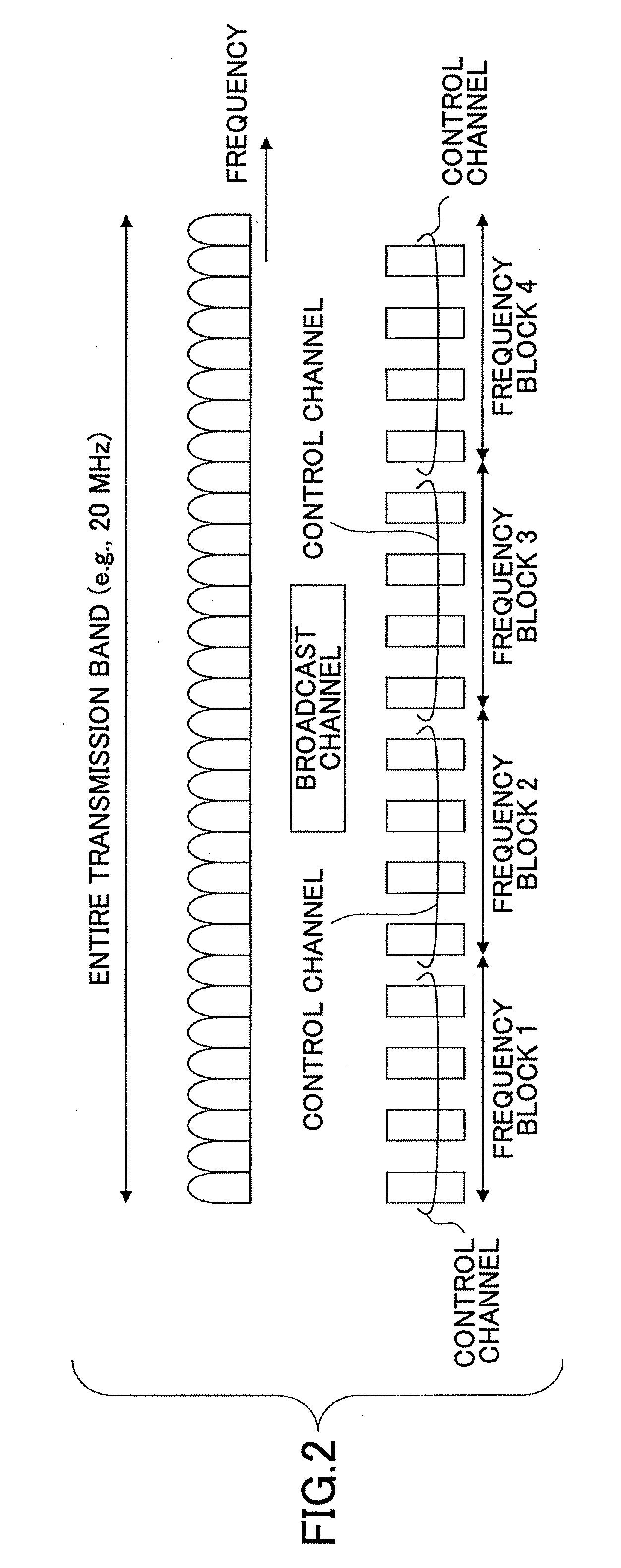
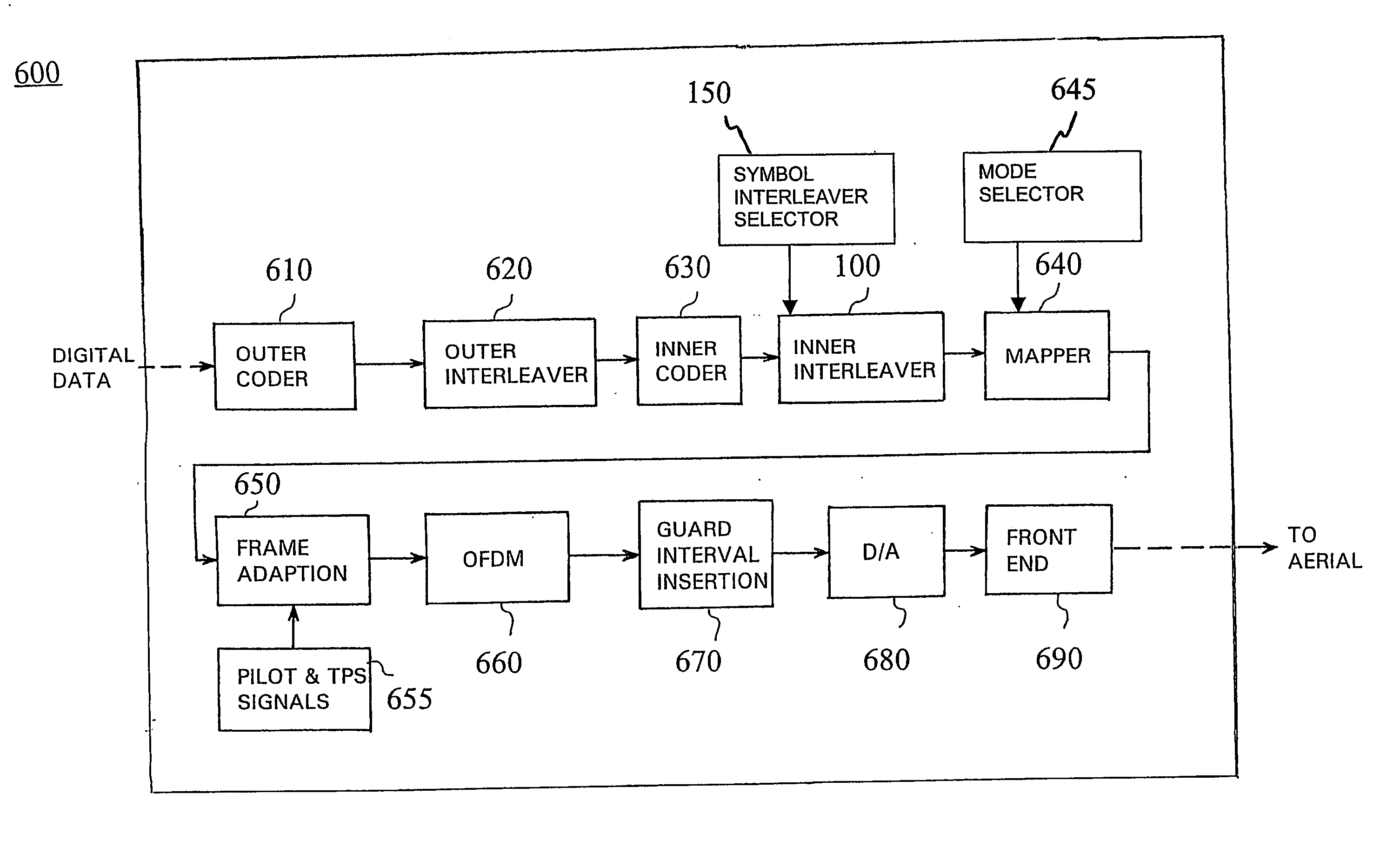
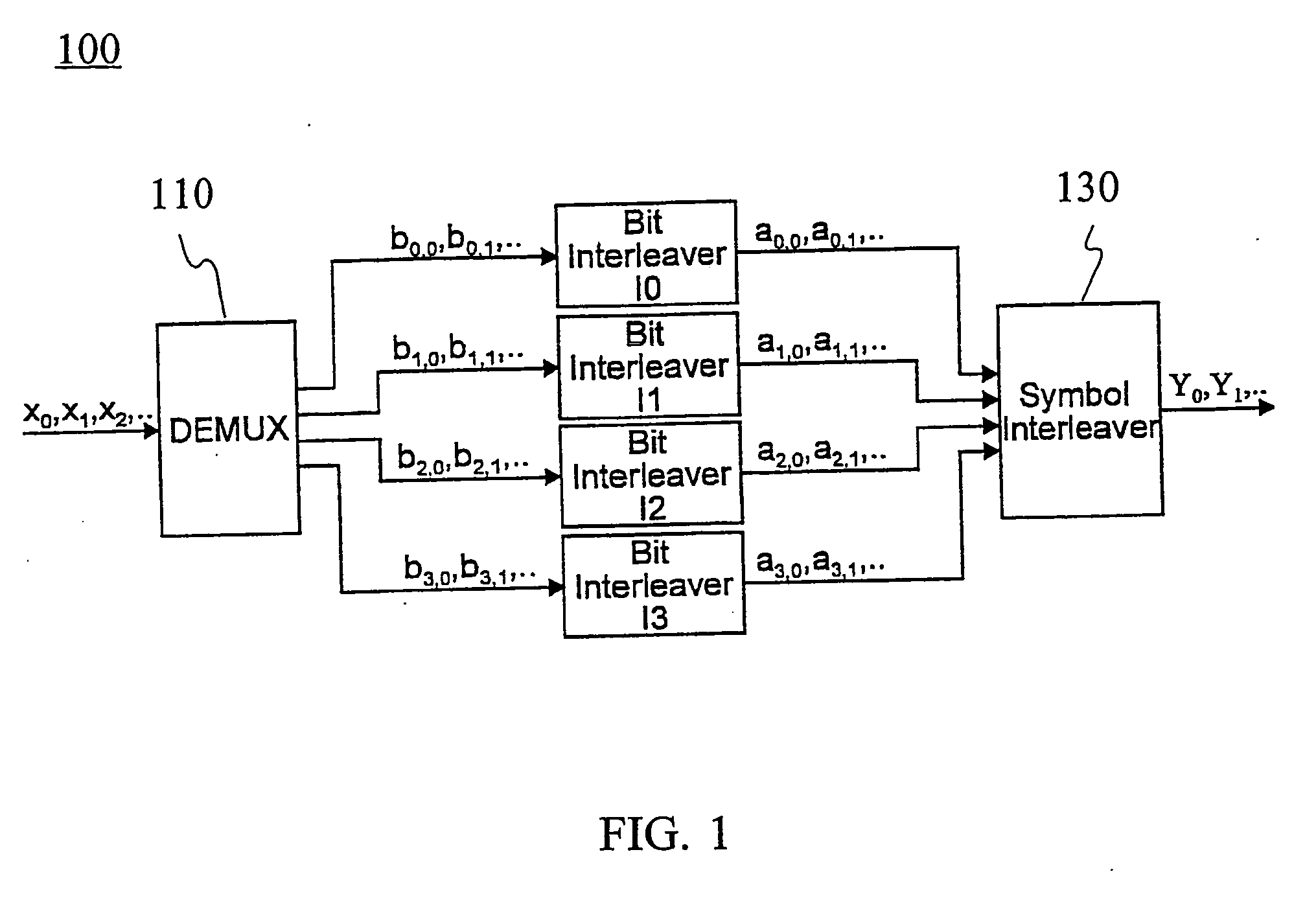
Symbol interleaving
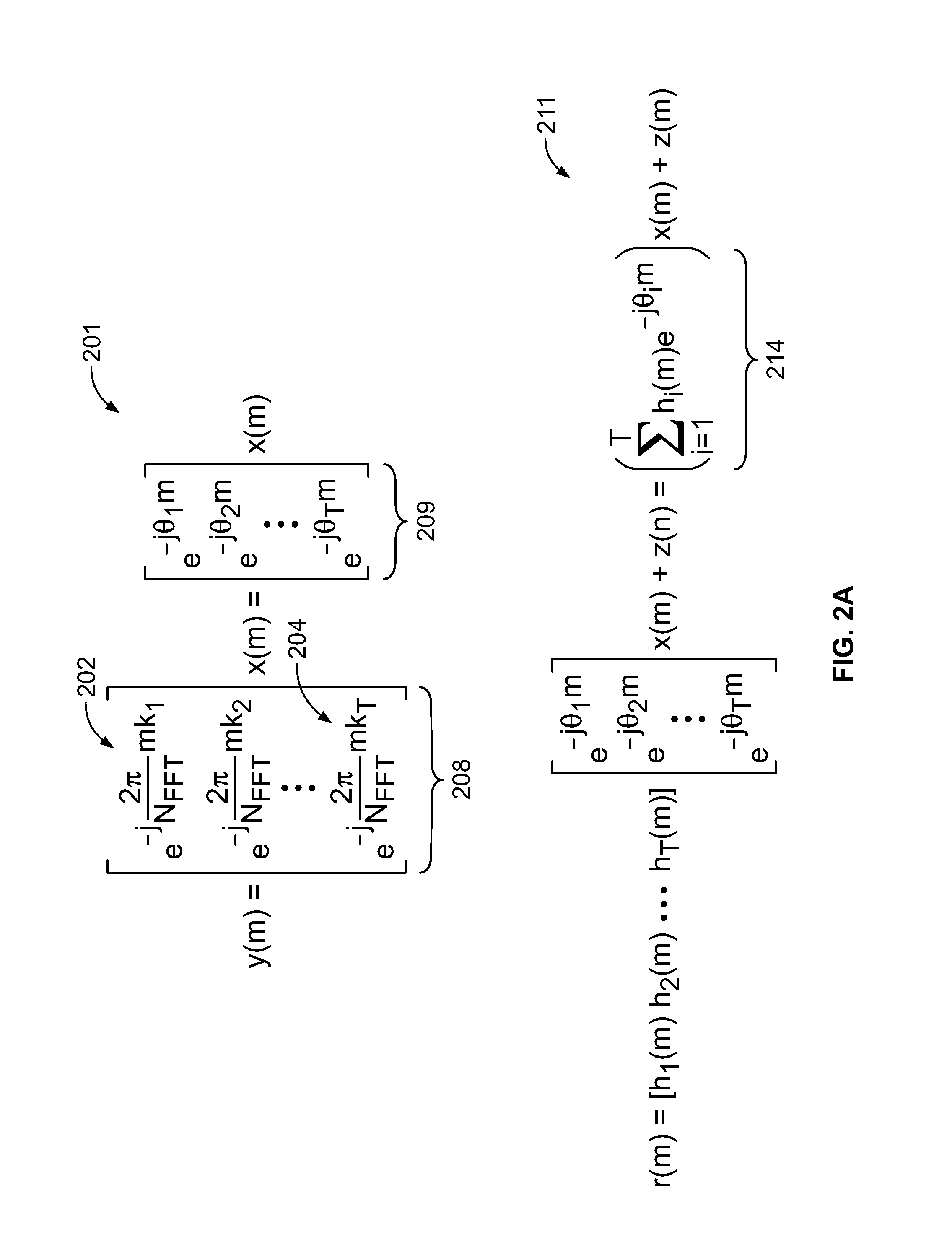
ActiveUS20060062314A1Receiver specific arrangementsSecret communicationDigital dataSymbol interleaving
The invention relates to a method for communicating digital data using an orthogonal frequency division multiplexing (OFDM) transmission system (10) including at least one transmitter (600, 601) and receivers (700, 701). The method comprises selecting a mode of operation in a transmitter among at least one mode, each mode of operation being associated with a number of active carriers for payload data transmission, selecting a symbol interleaver in the transmitter from a set of symbol interleavers for symbol interleaving in said selected mode of operation, applying symbol interleaving in the transmitter on blocks of data units, mapping the interleaved data units onto the active carriers of said selected mode of operation, receiving the interleaved data units in the receiver, recognizing in the receiver the symbol interleaver used in the data transmission, selecting a de-interleaver in the receiver to correspond to the recognized symbol interleaver, and de-interleaving in the receiver the received data units using the selectedde-interleaver.
Owner:NOKIA TECHNOLOGLES OY
Method and system of resource position indication and channel blind detection, and apparatus thereof
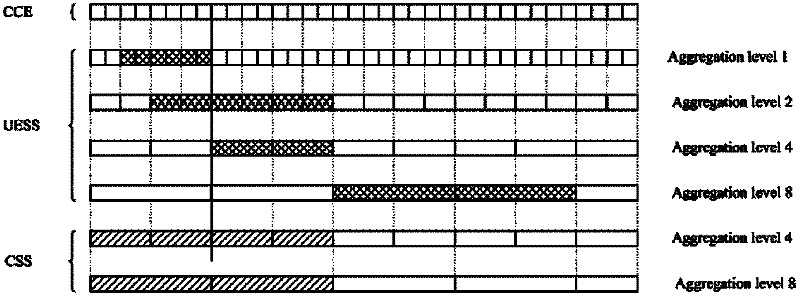
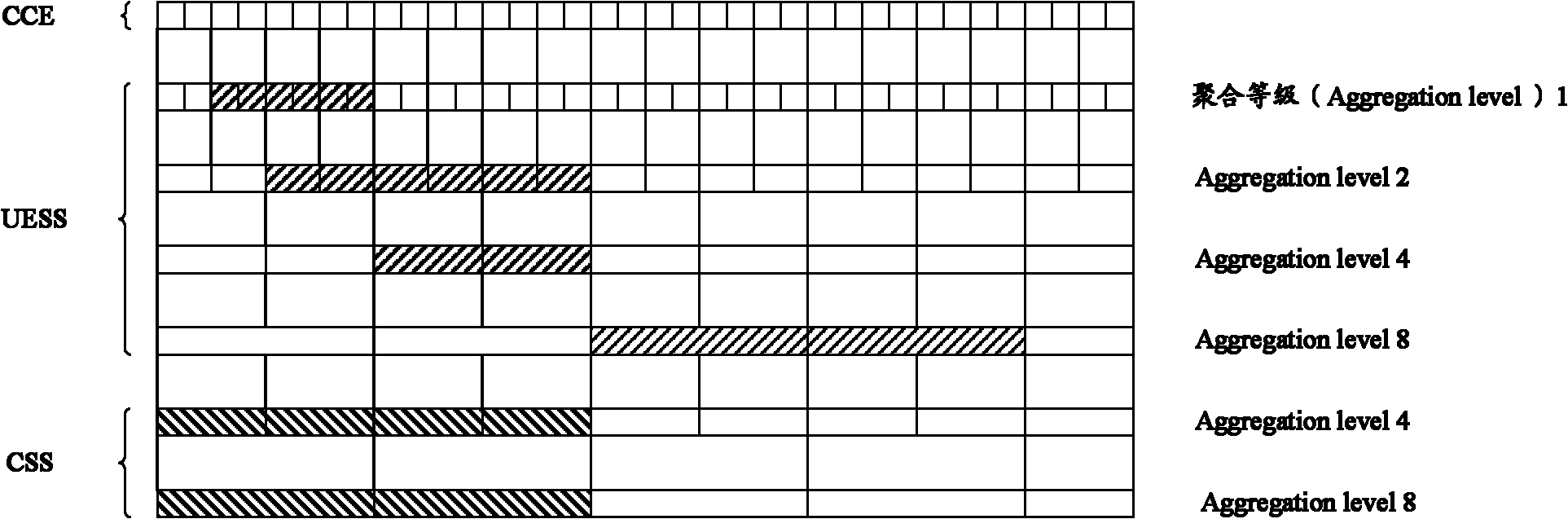
ActiveCN102202324ASolve the problem that PDCCH cannot be received correctlyReceiver specific arrangementsSignal allocationTelecommunicationsControl channel
An embodiment of the invention discloses a method and a system of resource position indication and channel blind detection, and an apparatus thereof, which relate to the wireless communication technology field. Through using the method, a physical downlink control channel (PDCCH) can be correctly received by a terminal. In the invention, a base station sends resource position information of common search space (CSS) and UE-specific search space (UESS) of PDCCH to the terminal. Blind detection is performed by the terminal according to the resource positions of CSS and UESS of PDCCH.
Owner:DATANG MOBILE COMM EQUIP CO LTD
Apparatus, method and computer program product to request a data rate increase based on ability to transmit at least one more selected data unit
ActiveUS20070073895A1High data rateNetwork traffic/resource managementMultiple digital computer combinationsReal-time computingComputer program
A method includes, in response to selection of a transport block to be transmitted through a wireless channel at a current data rate, performing at least the following: selecting a size for a data unit that can be scheduled for transmission; identifying one of a number of potential transport blocks, the identified potential transport block having a corresponding transport block size large enough to hold at least the selected size of the data unit and the transport block size of the currently selected transport block; determining whether the identified potential transport block is available for transmission; and transmitting a request for an increase in the current data rate in response to the identified potential transport block being available for transmission.
Owner:NOKIA TECHNOLOGLES OY
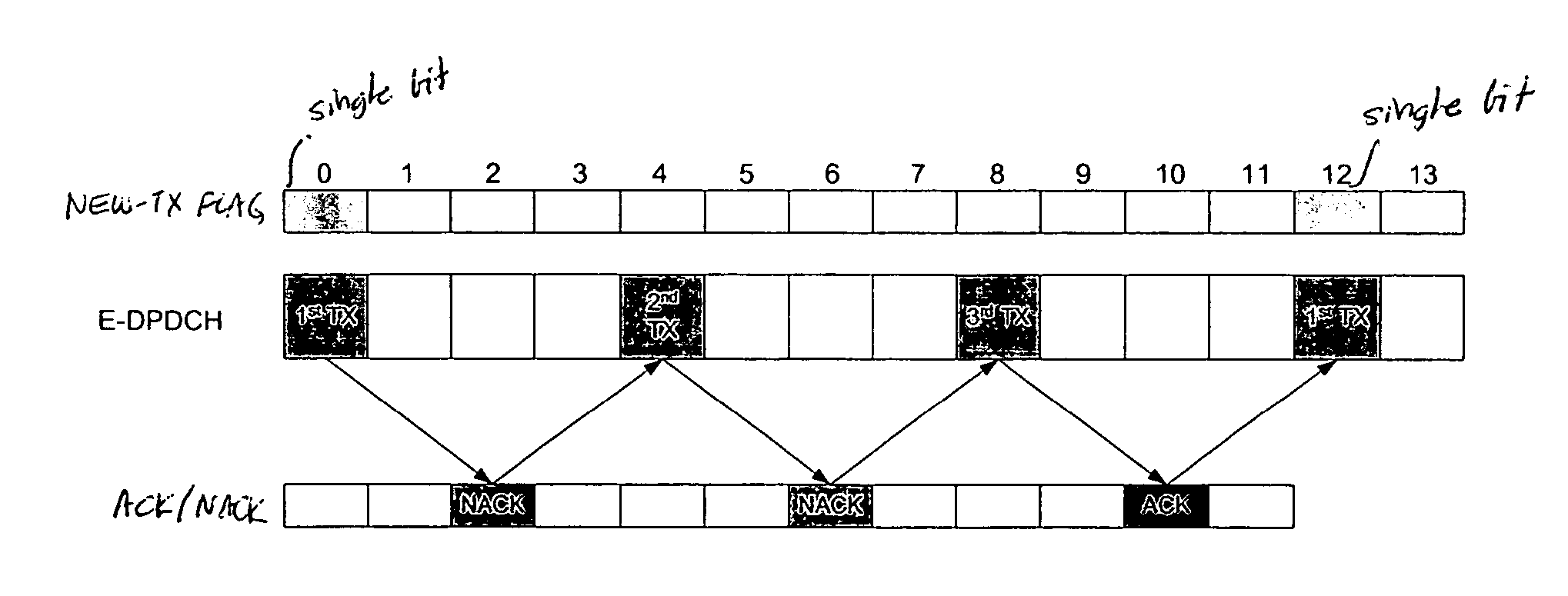
Method of increasing the capacity of enhanced data channel on uplink in a wireless communications systems
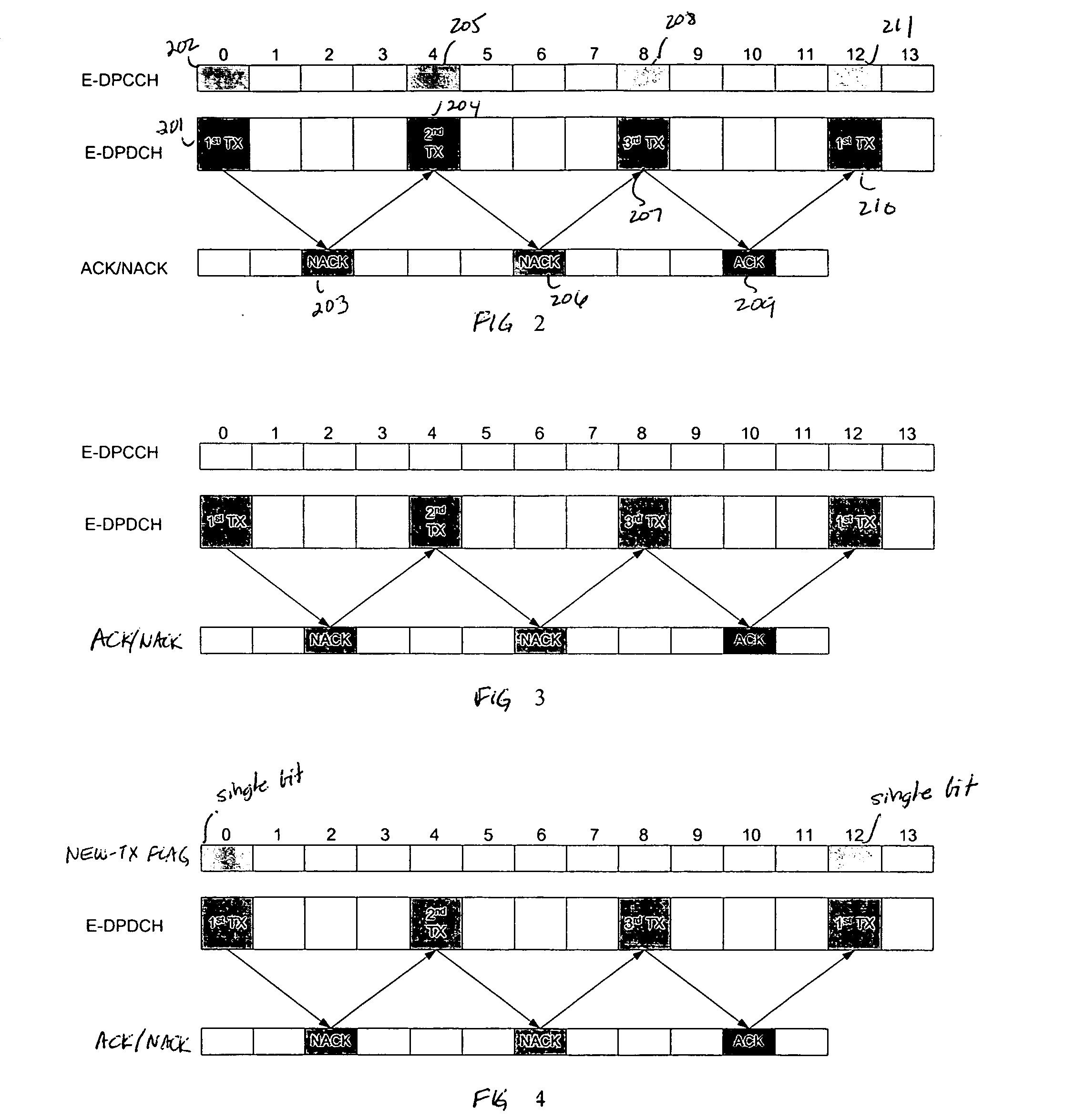
InactiveUS20070025345A1Power is requiredIncrease capacityNetwork traffic/resource managementAssess restrictionCommunications systemDPDCH
In a UMTS wireless communication system, when the packet size on the enhanced dedicated physical data channel (E-DPDCH) on the uplink from a UE to a NodeB reaches a converged default packet size, the corresponding dedicated physical control channel (E-DPCCH) is turned off. The NodeB uses the default packet size to decode the frame received on the E-DPDCH using each possible redundancy version. Alternatively, the E-DPCCH is turned off and a new transmission flag is transmitted by the UE only when a new frame is transmitted by the UE. NodeB then uses the presence or absence of that flag in conjunction with the absence of E-DPCCH to determine which redundancy version is to be assumed in decoding the frame received on E-DPDCH.
Owner:LUCENT TECH INC
Method and apparatus of monitoring pdcch in wireless communication system
InactiveUS20110143796A1Effective monitoringImprove system performanceModulated-carrier systemsTransmission path divisionCommunications systemControl channel
A method and an apparatus of monitoring a physical downlink control channel (PDCCH) in a wireless communication system, carried in a user equipment (UE), are provided. The method includes receiving a PDCCH map, and monitoring a set of PDCCH candidates based on the PDCCH map.
Owner:LG ELECTRONICS INC
Method and apparatus for estimating a channel quality indicator (CQI) for multiple input multiple output (MIMO) systems
ActiveUS8644262B1Effective valueMultiplex system selection arrangementsSpecial service provision for substationSignal-to-noise ratio (imaging)Transport system
Systems and methods are provided for determining a channel quality indicator (CQI) in a transmission system associated with a diversity transmission scheme. A plurality of independent diversity branches are identified in the diversity transmission scheme. Each one of the independent diversity branches may correspond to a different portion of the effective channel and may include any suitable combination of frequency, time, and / or spatial components of the effective channel or of any wired or wireless paths or combinations of the same. An effective Signal-to-Noise Ratio (SNR) value is computed for each one of the identified independent diversity branches. The computed effective SNR values are combined for the identified independent diversity branches to generate a CQI value.
Owner:NXP USA INC
Method and apparatus for providing channel quality feedback in an orthogonal frequency division multiplexing communication system
ActiveUS20070098098A1Receivers monitoringTransmission path divisionCommunications systemRadio access network
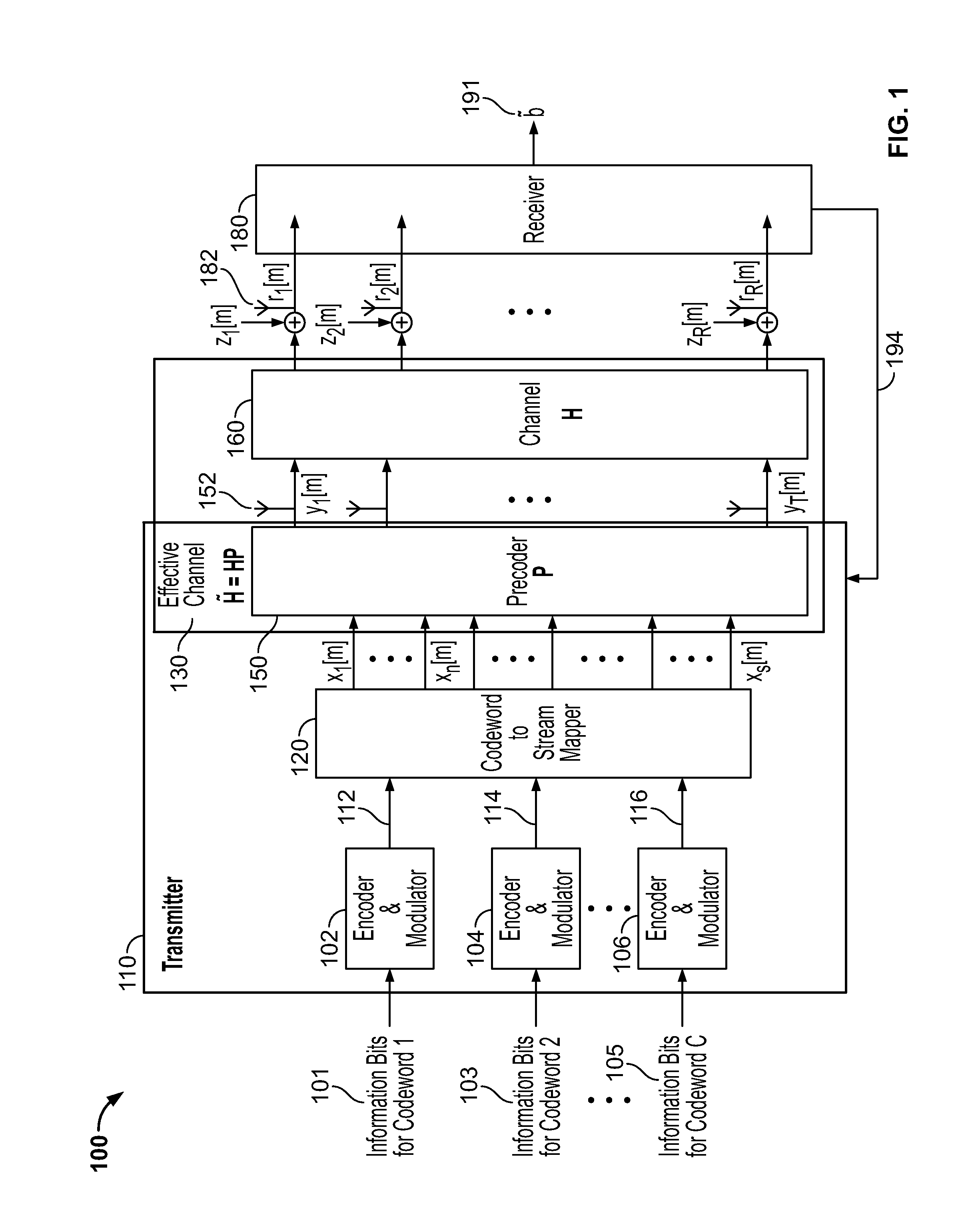
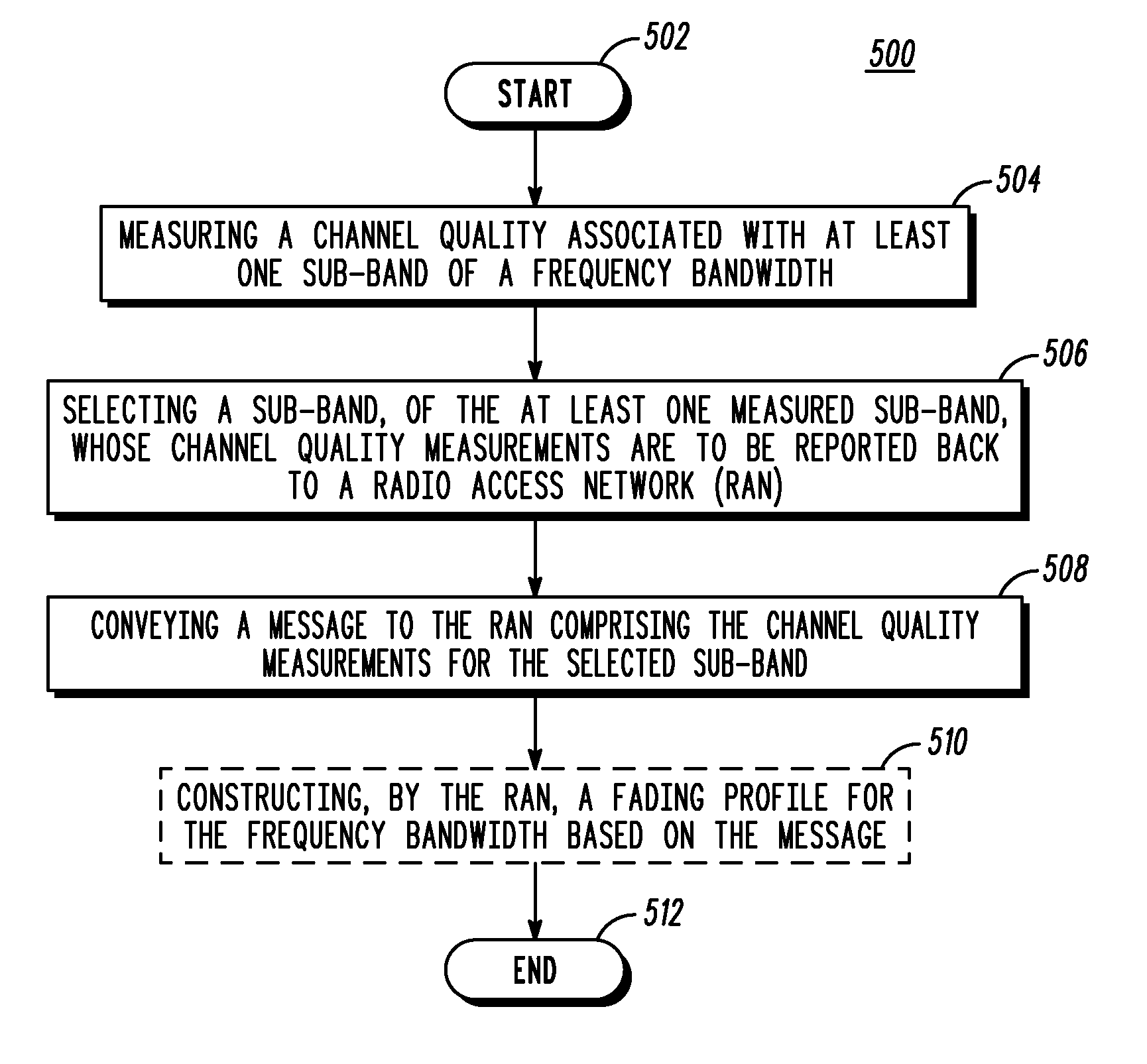
In an Orthogonal Frequency Division Multiplexing communication system, a user equipment reports channel quality information that is sufficient to construct a fading profile of a frequency bandwidth and that does not consuming the overhead resulting from the reporting of CQI for every sub-band of the frequency bandwidth. In the communication system, the frequency bandwidth may be represented by multiple sub-band levels, wherein each sub-band level comprises a division of the frequency bandwidth into a number of sub-bands different from the number of sub-bands of the other sub-band levels. The user equipment measures a channel quality associated with each sub-band of a sub-band level of the multiple sub-band levels, selects a sub-band of the sub-band level based on the measured channel qualities, and reports channel quality information associated with the selected sub-band to a radio access network.
Owner:GOOGLE TECH HLDG LLC
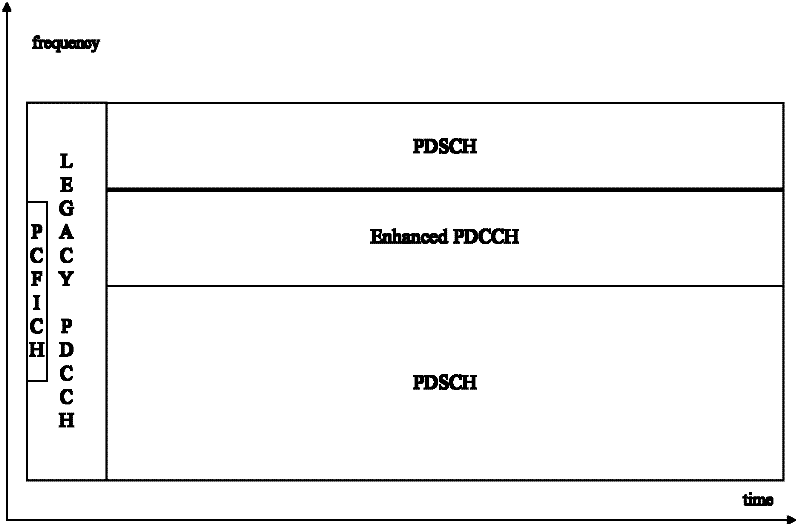
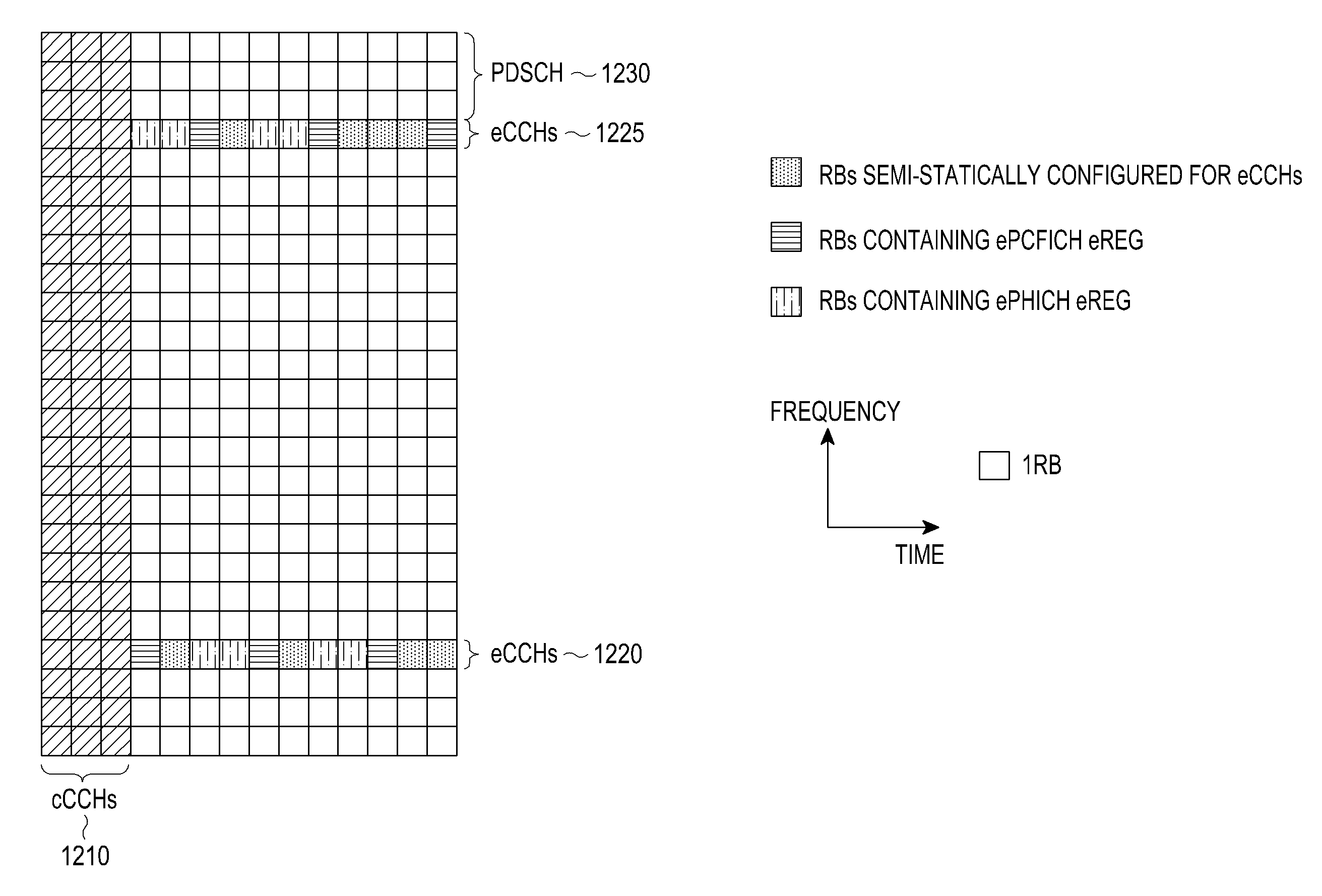
Extension of physical downlink control channels in a communication system
ActiveUS20130039299A1Transmission path divisionReceiver specific arrangementsCommunications systemResource element
Methods and apparatuses are described for a User Equipment (UE) to receive enhanced Control CHannels (eCCHs), including enhanced Physical Downlink Control CHannels (ePDCCHs), transmitted in a set of Resource Blocks (RBs) over a Transmission Time Interval (TTI). A method includes transmitting a first control signal to a first UE over a first number of Resource Elements (Res) in a subset of the RBs and over a first number of the transmission symbols in the TTI; transmitting a second control signal to a second UE over a second number of the REs in the subset of the RBs and over a second number of the transmission symbols in the TTI; and transmitting a reference signal of the first type over a third number of the REs in the subset of the RBs and over a third number of the transmission symbols in the TTI.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
System and Method for Signaling Configuration of Sounding Reference Signals
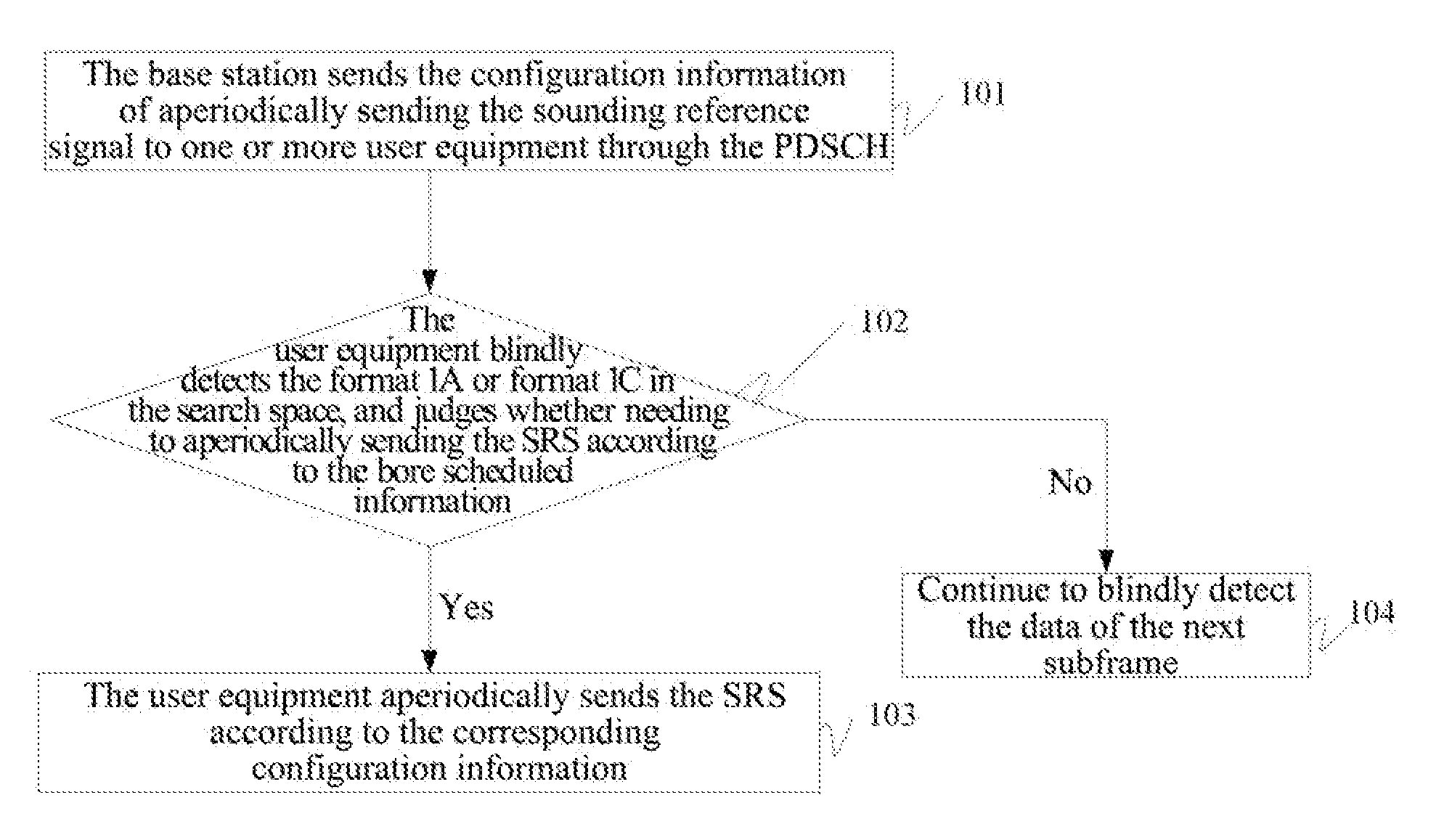
ActiveUS20130028134A1Increase profitIncrease flexibilityTransmission path divisionReceiver specific arrangementsSounding reference signalComputer science
The present invention discloses a method for a signaling configuration of a sounding reference signal. The method includes: a base station notifying a user equipment to aperiodically send the sounding reference signal, and sending configuration information of aperiodically sending the sounding reference signal (SRS) down to the user equipment. The present invention also discloses a base station for a signaling configuration of a sounding reference signal and a user equipment for a signaling configuration of a sounding reference signal. The present invention can realize that the user equipment aperiodically sends the SRS, which improves the utilization ratio of SRS resources and increases the flexibility of resource scheduling.
Owner:ZTE CORP
Control channel signaling using code points for indicating the scheduling mode
ActiveUS20100290419A1Small sizeSignaling overheadTransmission path divisionReceiver specific arrangementsCode pointMode control
The invention relates to a control channel signal for use in a mobile communication system providing at least two different scheduling modes. Further the invention relates to a scheduling unit for generating the control channel signal and a base station comprising the scheduling unit. The invention also relates to the operation of a mobile station and a base station for implementing a scheduling mode using the control channel signal proposed by the invention. In order to facilitate the use of different scheduling schemes for user data transmission while avoiding an additional flag for indicating the scheduling mode in the control signaling, the invention proposes the use of code points in existing control channel signal fields. Further, the invention proposes a specific scheduling mode for use in combination with the proposed new control channel signal according to the invention. According to this scheduling mode control channel information is only provided for retransmissions, while initial transmissions are decoded using blind detection.
Owner:PANASONIC INTELLECTUAL PROPERTY CORP OF AMERICA
Method and apparatus for transmitting/receiving feedback information in a wireless packet data communication system
ActiveUS20080101498A1Reduce overheadReceiver specific arrangementsDiversity/multi-antenna systemsAccess networkCommunications system
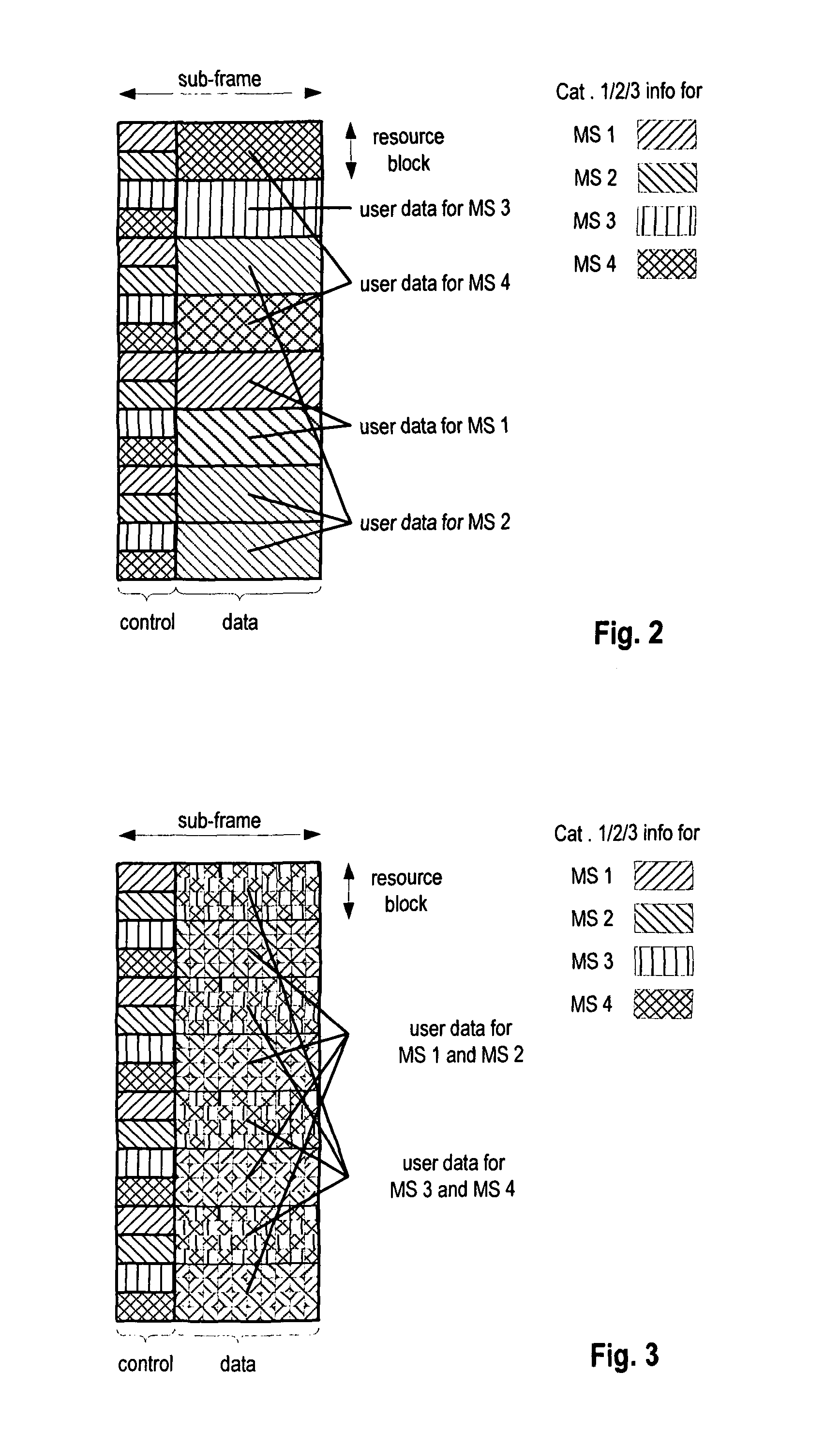
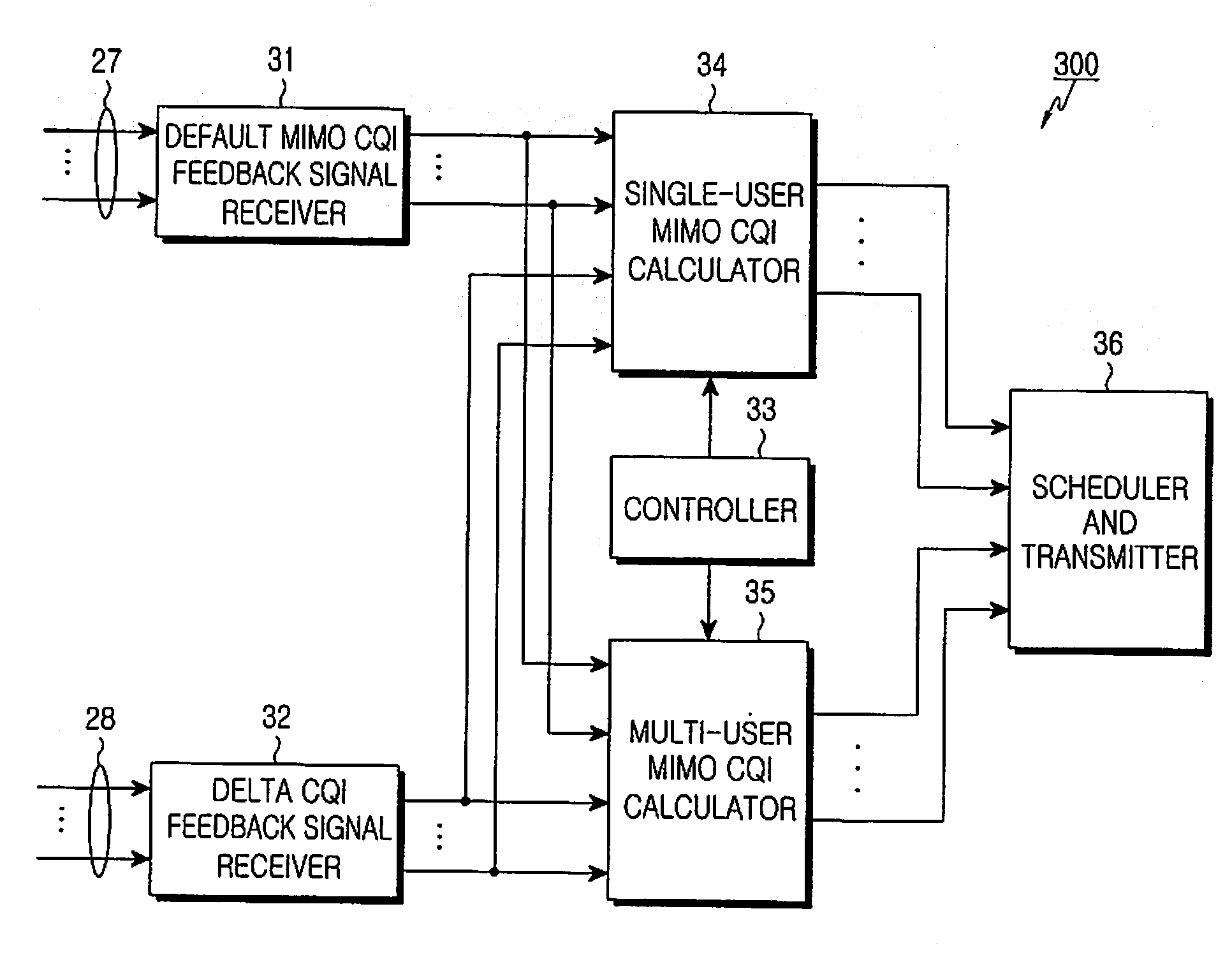
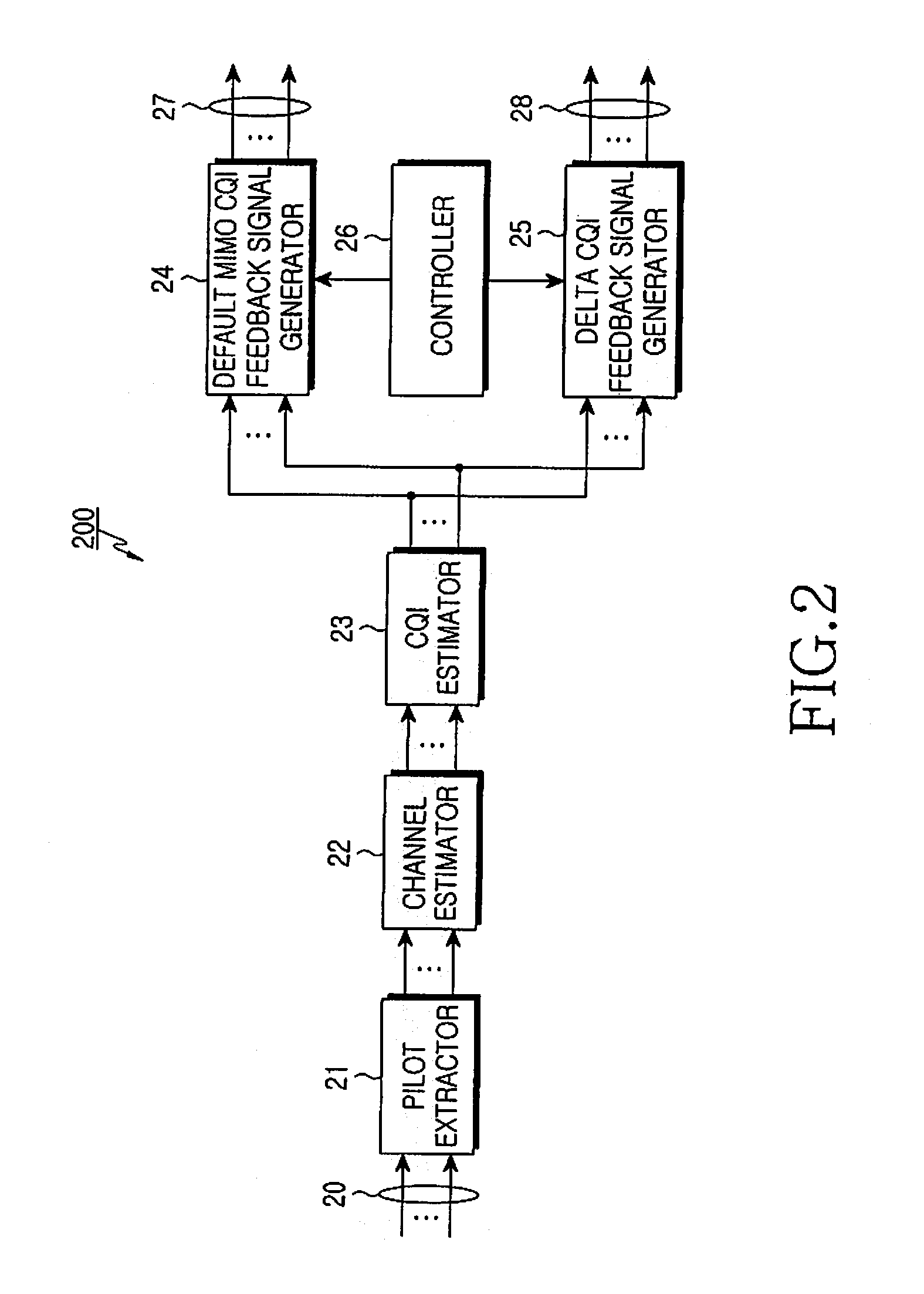
A Channel Quality Indicator (CQI) expression and feedback method prevents an excessive increase in the CQI feedback overhead while supporting both Single-User MIMO and Multi-User MIMO operations. When a default MIMO operation is set to Single-User MIMO or Multi-User MIMO, an access network can receive MIMO CQI feedback optimized for the corresponding MIMO operation. However, when a scheduler has selected an alternative MIMO operation other than the default MIMO operation, the access network calculates a CQI necessary for the alternative MIMO operation based on the default MIMO CQI feedback for the default MIMO operation and the DELTA CQI feedback for the alternative MIMO operation. In this manner, the invention enables the best operation in the default MIMO operation by providing a correct CQI, and enables the second best operation in the alternative MIMO operation. With use of the invention, the access network can dynamically select the Single-User MIMO and Multi-User MIMO operations, contributing to an increase in the resource management efficiency.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
Power control for reverse packet data channel in CDMA systems
ActiveUS7299402B2Enabling detectionPower managementError prevention/detection by using return channelTransmitted powerControl signal
A method of reverse link power control for a reverse packet data channel in a wireless communication system allows a mobile station to autonomously change its data transmission rate. The mobile station transmits packet data over a reverse packet data channel having a data rate variant transmit power level that varies based on a transmit data rate on the packet data channel. The mobile station further transmits control signals over a reverse control channel associated with the reverse packet data channel. The transmit power level of the reverse control channel is such that the transmit power level does not vary with the transmit data rate on the packet data channel. The radio base station measures the strength of the received signals on the reverse control channel, compares the measured strength to a power control set point, and generates a power control signal responsive to the comparison of the control signal to the power control set point.
Owner:TELEFON AB LM ERICSSON (PUBL)
Apparatus and method for transmitting and receiving forward shared control channel in a mobile communication system
ActiveUS20080225964A1Receiver specific arrangementsCode division multiplexPrecodingTelecommunications
A method is provided for transmitting a downlink shared control channel including a control signal necessary for restoring a transmission data signal in a mobile communication system that transmits a data signal using multiple antennas. It is determined whether the transmission data signal is coded with two or more codewords before being transmitted. One of a first element index of a sub-codebook configured only with a one codeword-dedicated precoding in a precoding codebook and a second element index of a sub-codebook configured only with a more-than-two codeword- dedicated precoding is selected, according to the determination result. A control channel is generated by including the selected element index in the precoding information. The generated control channel is mapped to a particular resource block and the mapped control channel is transmitted to a particular reception apparatus.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
Device and method for transmitting downlink control information in a wireless communication system
ActiveUS20100111107A1Modulated-carrier systemsReceiver specific arrangementsComputer hardwareCommunications system
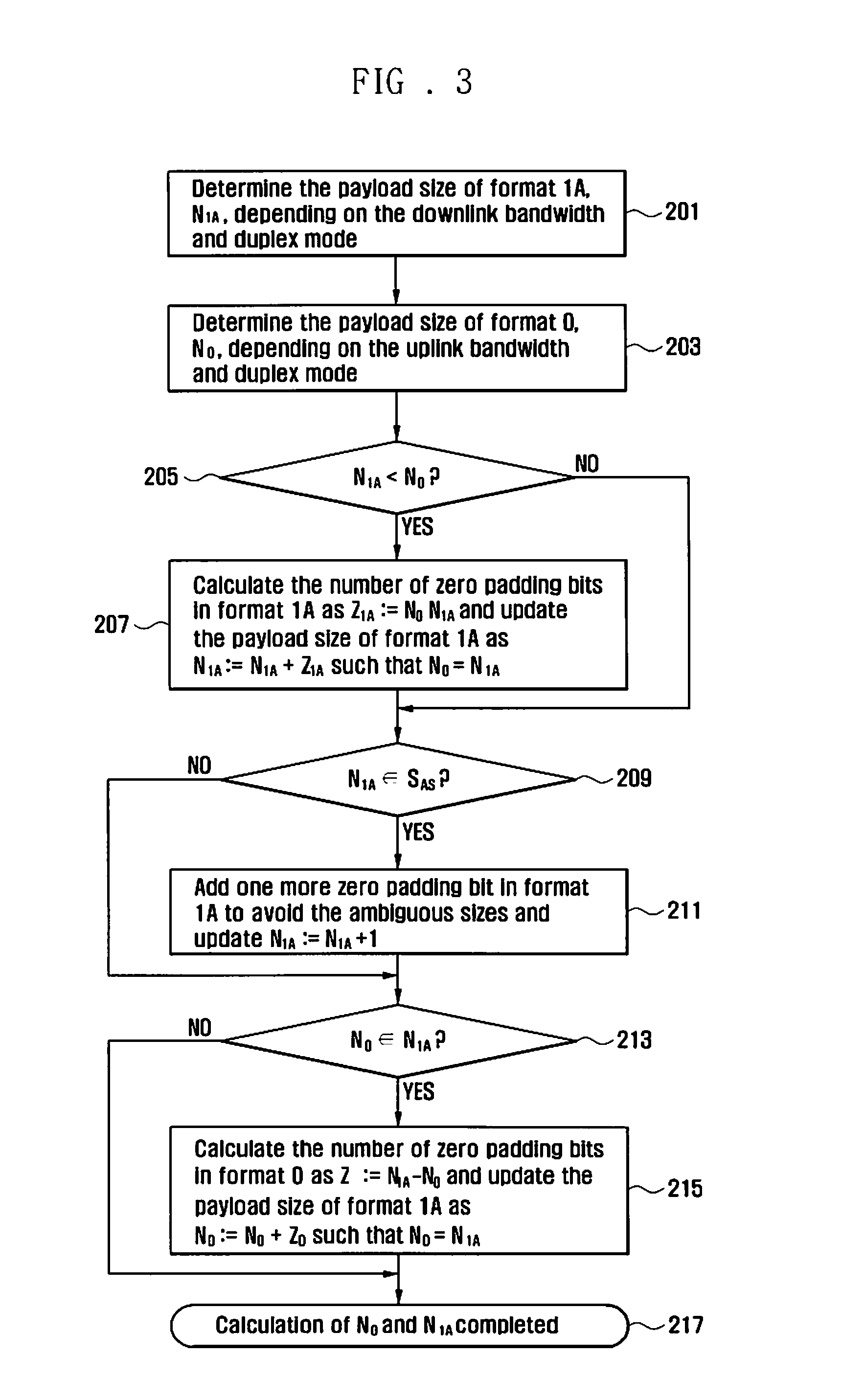
A Downlink Control Information (DCI) processing device and method for a wireless communication system that encodes / decodes downlink control information based on a payload size of DCI format. The method includes determining a payload size of a first DCI format; and determining a payload size of a second DCI format by appending padding bits to the second DCI format until the payload size of the second DCI format is not an ambiguous size and is not equal to the payload size of the first DCI format.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
Channel change procedures in a wireless communications network
ActiveUS20070213012A1Solve the real problemNetwork topologiesTime-division multiplexTelecommunicationsCurrent channel
A method, apparatus, and computer program product are disclosed for wireless communications networks, such as WiMedia networks, to solve problems of channel congestion, searching for candidate channels to select, and achieving reliable channel changes that will be recognized by other devices in the network. A wireless communications device selects a channel finding technique in a first stage, based on whether the device has any active connections in a current channel. The device then performs the selected channel finding technique with a plurality of channels to find a candidate channel. Then the initiating device sends a request to at least one remote device to change its channel from the current channel to the candidate channel during a time slot within a repeating time interval. If the request is successful, the initiating device receives an acceptance of the request from the remote device. Then in a second stage, the initiating device selects a channel changing technique based on whether the device has any active connections in the current channel. The initiating device then executes the selected channel changing technique to change a channel from the current channel to the candidate channel, thereby establishing the desired new connection across the candidate channel with the remote device.
Owner:III HLDG 3
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com