Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
419 results about "Spanning tree" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
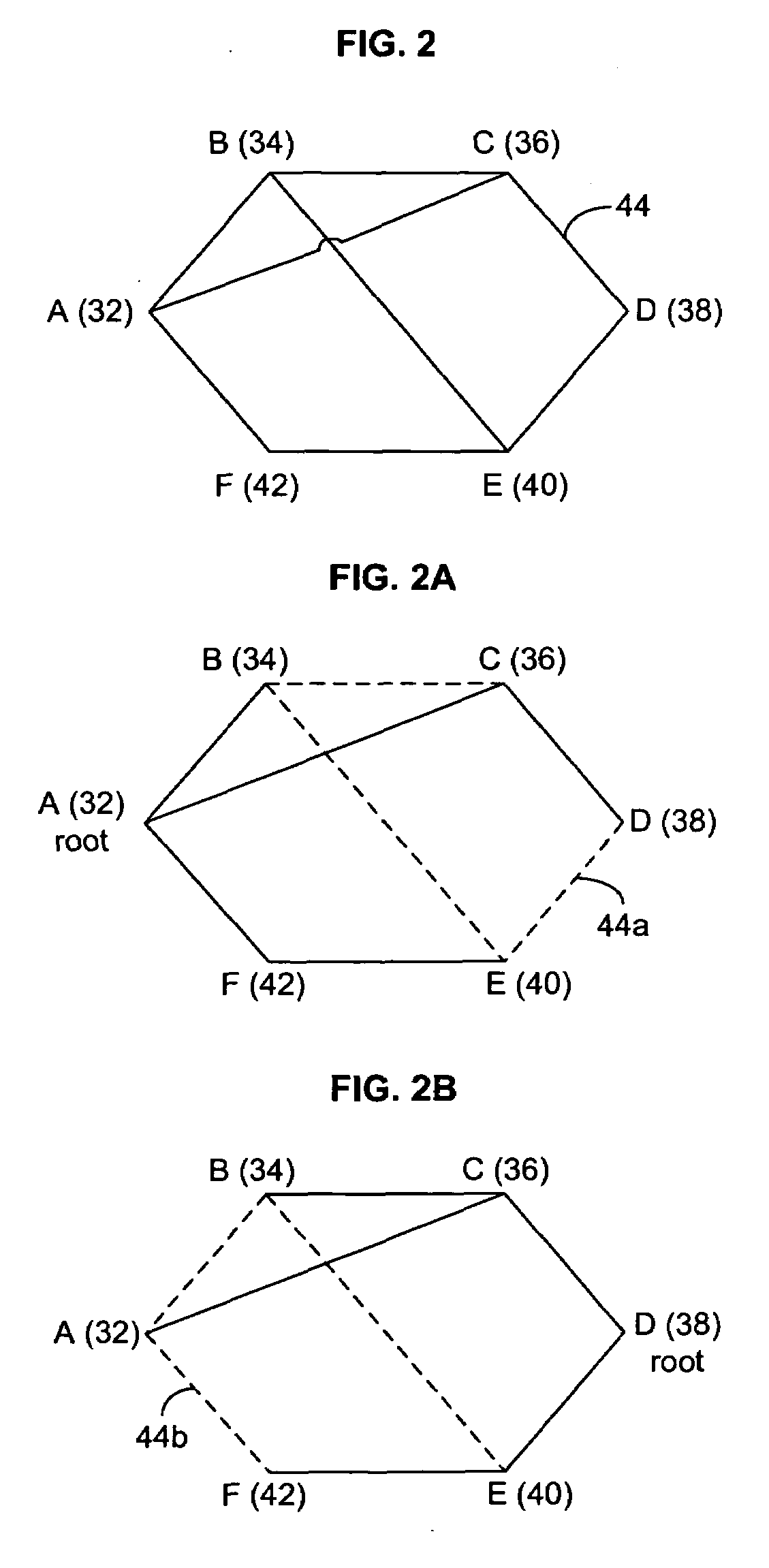
In the mathematical field of graph theory, a spanning tree T of an undirected graph G is a subgraph that is a tree which includes all of the vertices of G, with minimum possible number of edges. In general, a graph may have several spanning trees, but a graph that is not connected will not contain a spanning tree (but see Spanning forests below). If all of the edges of G are also edges of a spanning tree T of G, then G is a tree and is identical to T (that is, a tree has a unique spanning tree and it is itself).
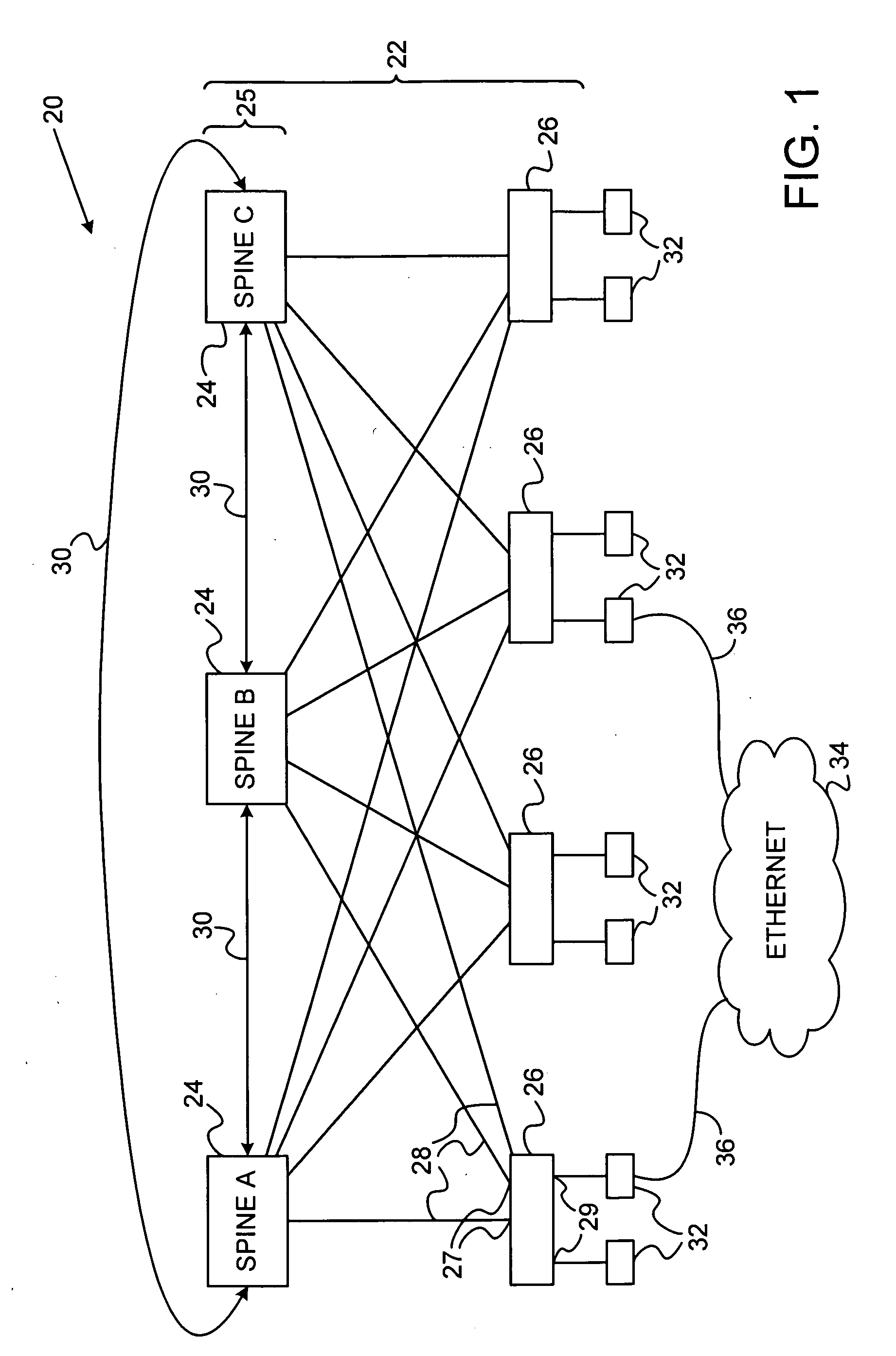
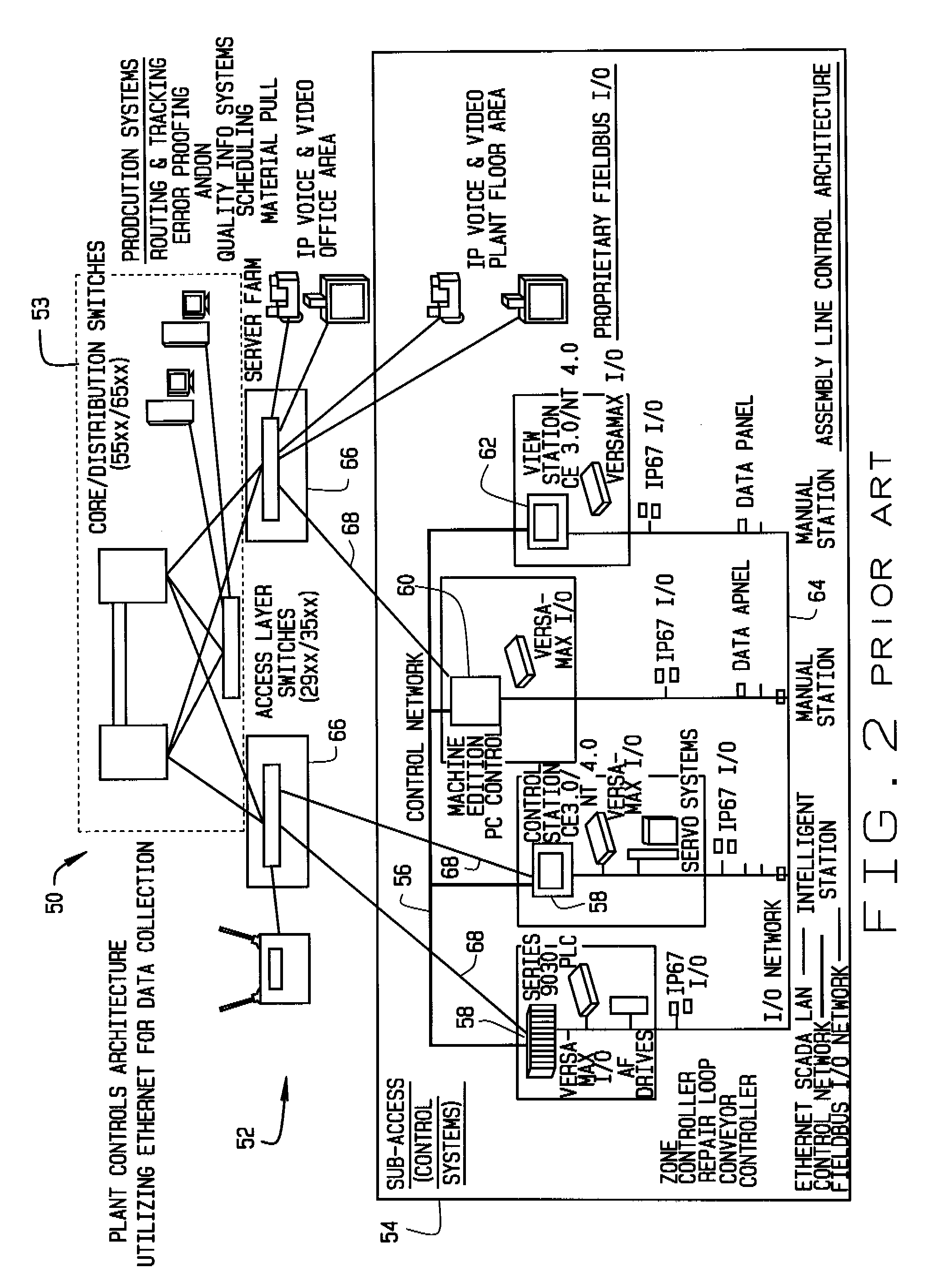
Spanning tree root selection in a hierarchical network
Communication apparatus includes a hierarchical network of switches, which includes at least a first plurality of spine switches, interconnected by a control channel, and a second plurality of edge switches having internal ports coupled to communicate via respective links with the spine switches and external ports for connecting to client devices. The spine switches are configured to detect, via the control channel, a partitioning of the hierarchical network into first and second partitions, including respective first and second numbers of the spine switches, wherein the first number is greater than the second number, and to assign respective priorities to the spine switches responsively to the first and second numbers so as to cause the larger of the partitions to be elected as a spanning tree root.
Owner:MELLANOX TECHNOLOGIES LTD
Network routing protocol power saving method for network elements
ActiveUS20140192677A1Energy efficient ICTData switching by path configurationDistance-vector routing protocolPath network
Methods and apparatus relating to network routing protocols to support power savings in network elements. A most utilized link path network topology for a computer network is discovered using a routing protocol such as a Spanning Tree, link-state, or distance vector routing protocol. In view of the most utilized link path network topology, links are identified as candidates for power management under which a power state of the link and associated network ports are managed to save power under applicable link conditions, such as low utilization. Link power-state change conditions are detected, and in response a corresponding change to the power state of a link is effected by changing the power-state of the network ports at the ends of the link. Power state changes include putting a link into a reduced power state, taking a link offline, and powering a link back up.
Owner:INTEL CORP
Technique for efficiently managing bandwidth registration for multiple spanning tree options
ActiveUS20070263554A1Efficient managementGreat opportunityData switching by path configurationData streamComputer network
A technique efficiently manages bandwidth (BW) registration for multiple spanning tree options in a computer network. According to the novel technique, an entry bridge determines multiple spanning tree paths to other bridges of the network (namely, one or more available spanning trees rooted at one or more bridges of the network) and determines a utilized (registered) BW on each of those paths. Upon receiving a request to initiate BW registration for a data flow to a destination end point, e.g., from an application source end point, the entry bridge selects one of the spanning tree paths to utilize for the data flow. Selection of the spanning tree path from among the multiple available paths may be based on (i) available bandwidth of the paths, (ii) a shortest of the paths, and (iii) a lowest bridge identifier ID for the bridge root for the path. The entry bridge sends a registration message for the data flow towards the destination end point along the selected spanning tree path. If successful, the data flow is transmitted on the selected path. If not, the entry bridge attempts to register the data flow on a next best alternate spanning tree, e.g., until a successful registration or until a determination that no further alternate spanning trees exist.
Owner:CISCO TECH INC
Network management method
InactiveUS20070274234A1Reliable monitoringGood estimateData switching by path configurationNetwork managementLogical network
The present invention provides a method in which the physical connection information and the logical network configuration information are kinked to the status of spanning tree, and the status of spanning tree is displayed with the physical connection and the logical network configurations. The method can provide the better recognition about not only intended the physical and logical configurations but the status of spanning tree to a network administrator. Therefore, the network administrator can integrally recognize the status of the network and the failure in the network will be analyzed easily to recover the network to normal state in shorter time.
Owner:FUJITSU LTD
Methods and devices for improving the multiple spanning tree protocol
ActiveUS20060198323A1Reduce the amount of calculationEasy loadingData switching by path configurationMedia access controlLearning network
The present invention provides improved unicast routing, multicast routing and unicast load sharing as compared with conventional methods. Preferred implementations of the invention provide improvements to IEEE 802.1Q. According to preferred aspects of the invention, each bridge is the root of its own multiple spanning tree instance (“MSTI”). Preferred implementations of the invention require no learning of media access control (“MAC”) addresses on the backbone of a network. Some methods of the invention can resolve spanning tree asymmetries. Preferred implementations of the invention require a very low computational load for control protocols.
Owner:CISCO TECH INC
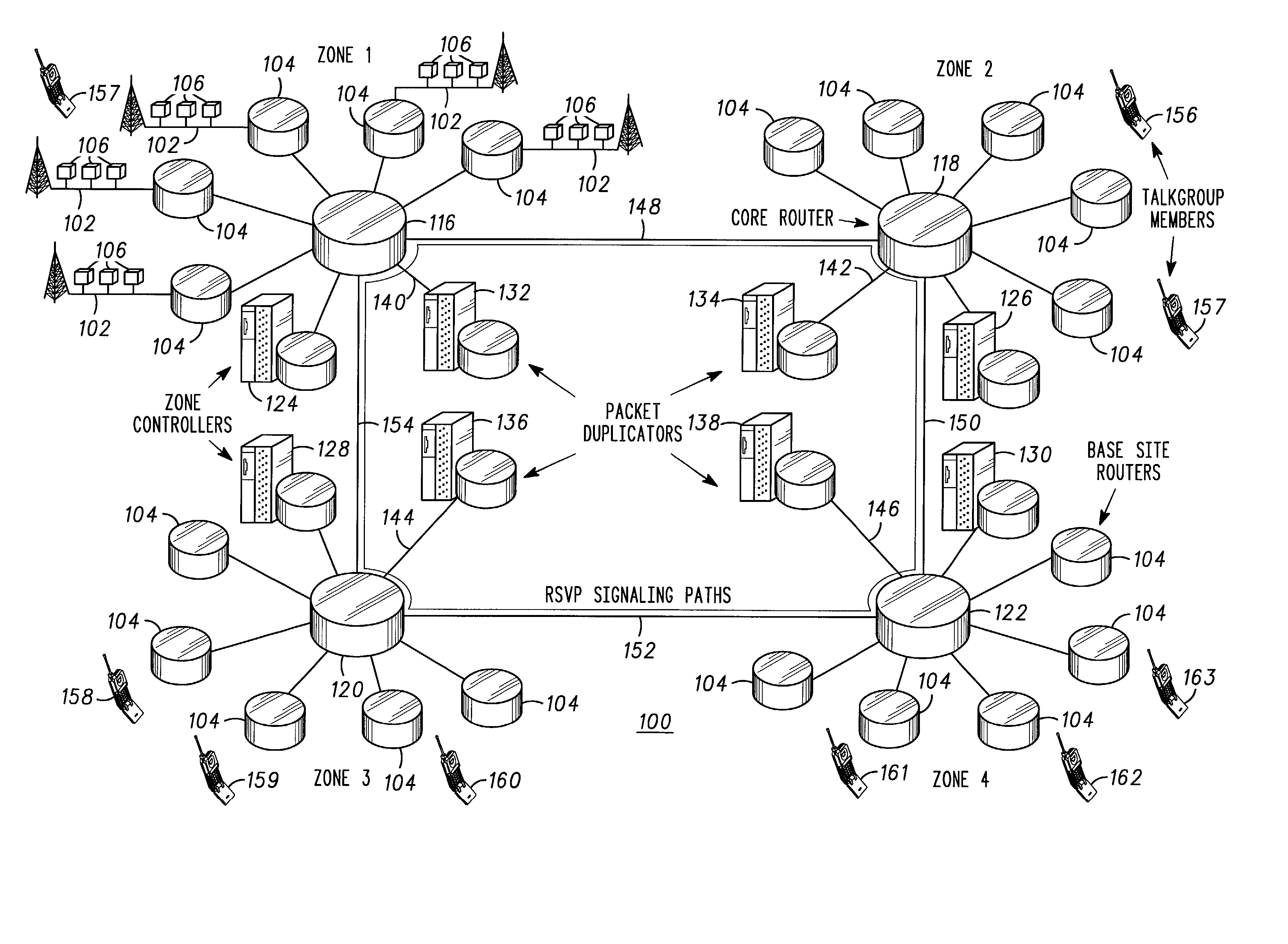
Multicast IP zones for fast spanning tree convergence in wide-area packet network systems
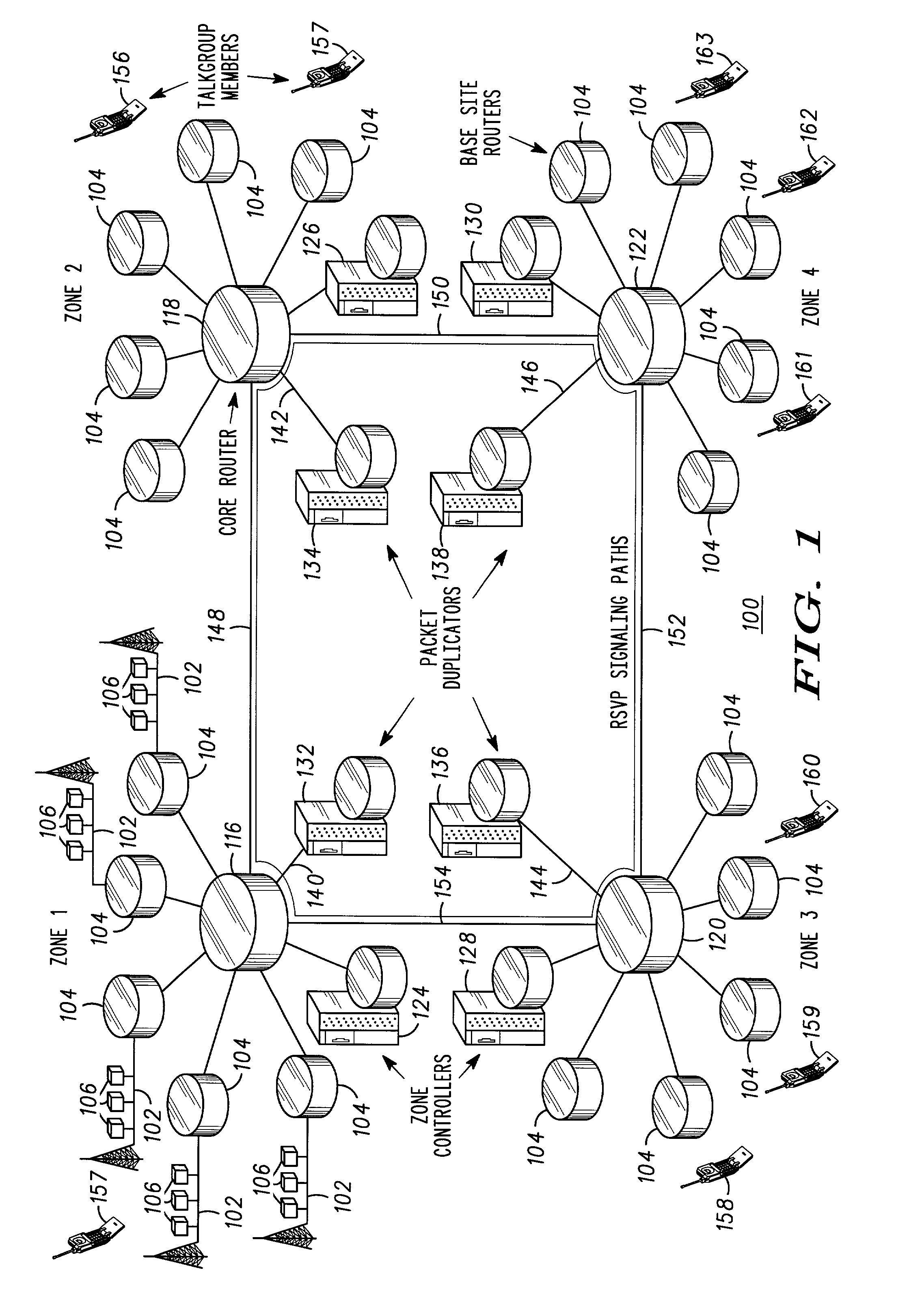
ActiveUS7009972B2Special service provision for substationTime-division multiplexCommunications systemMulticast address
System and methods for confining multicast routing trees to within single zones of a multi-zone communication systems, thereby enabling faster convergence of the trees relative to trees spanning multiple zones. Separate multicast routing trees are established using different multicast addresses in a source zone and one or more listening zones. Packets for a call distributed by routers (104, 116) of a packet network within the source zone via a source zone multicast address are received by a source zone packet duplicator (132). The source zone packet duplicator forwards the packets, via routers (116, 118, 120, 122) of the packet network using unicast routing, to various listening zone packet duplicators (136, 138). The listening zone packet duplicators, upon receiving the packets, separately distribute the packets within their respective zones via the packet network using different multicast addresses of the listening zones. The source zone and listening zones may be redefined during the call as the source changes or moves to different zones.
Owner:MOTOROLA SOLUTIONS INC
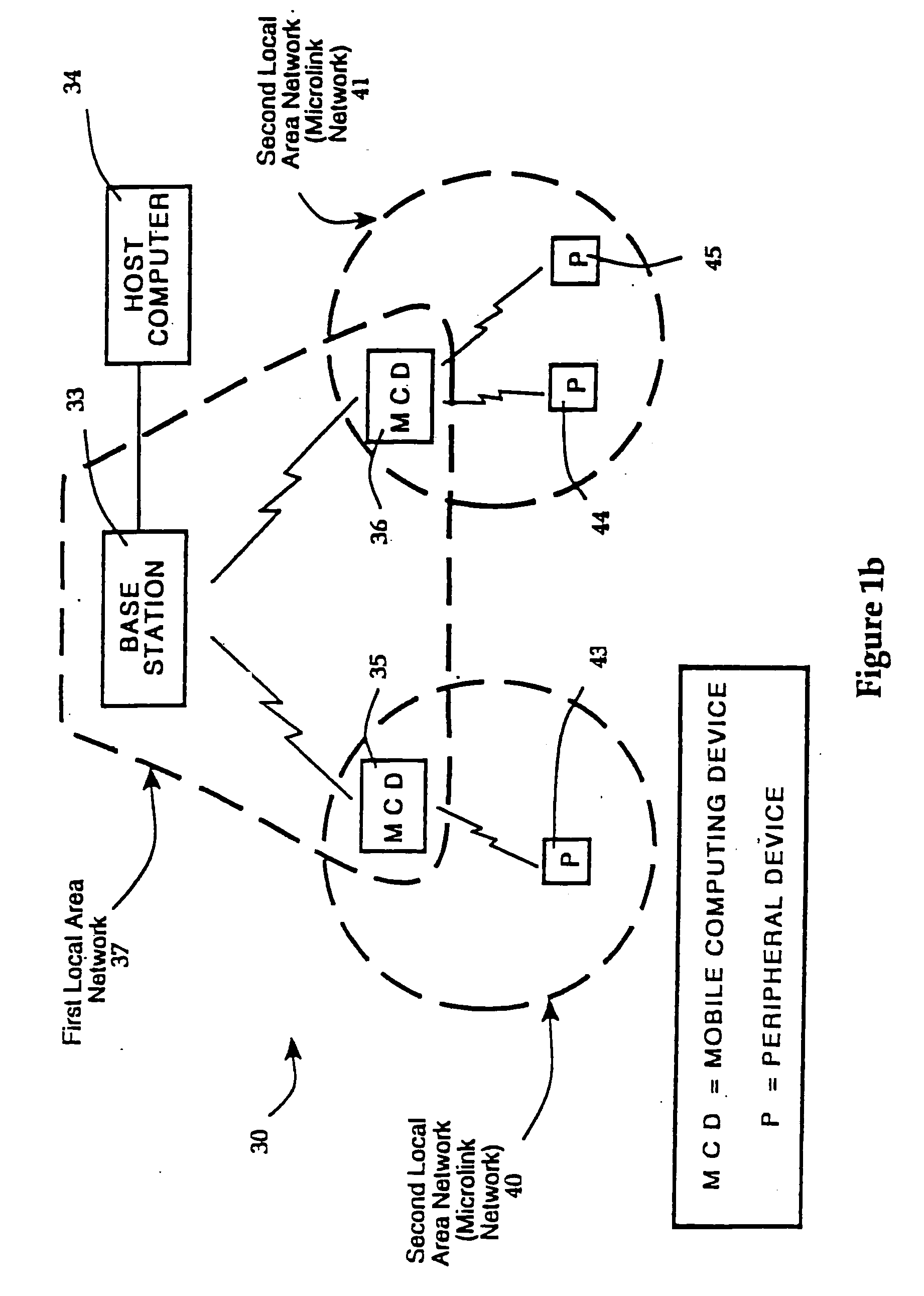
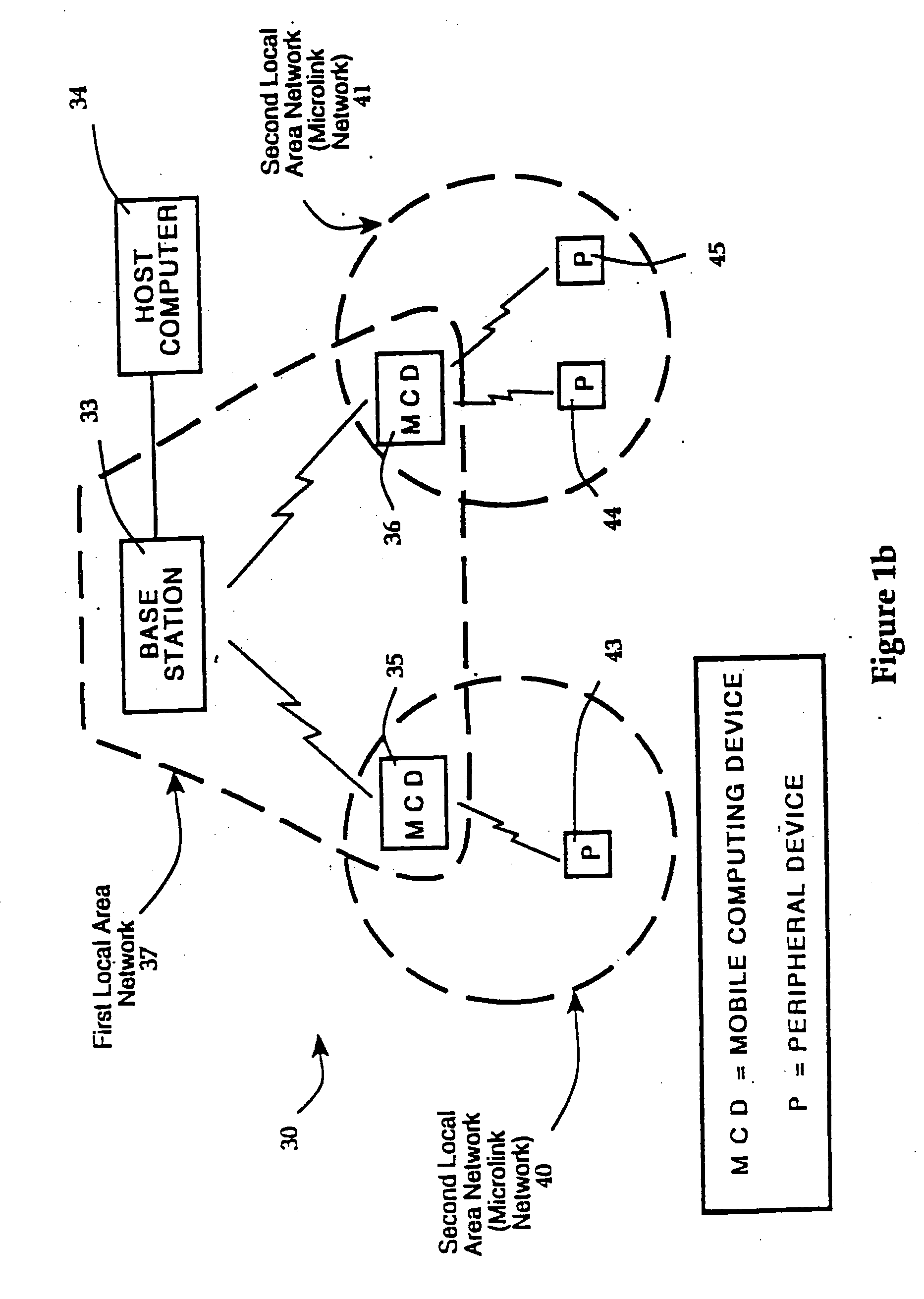
Hierarchical communication system providing intelligent data, program and processing migration
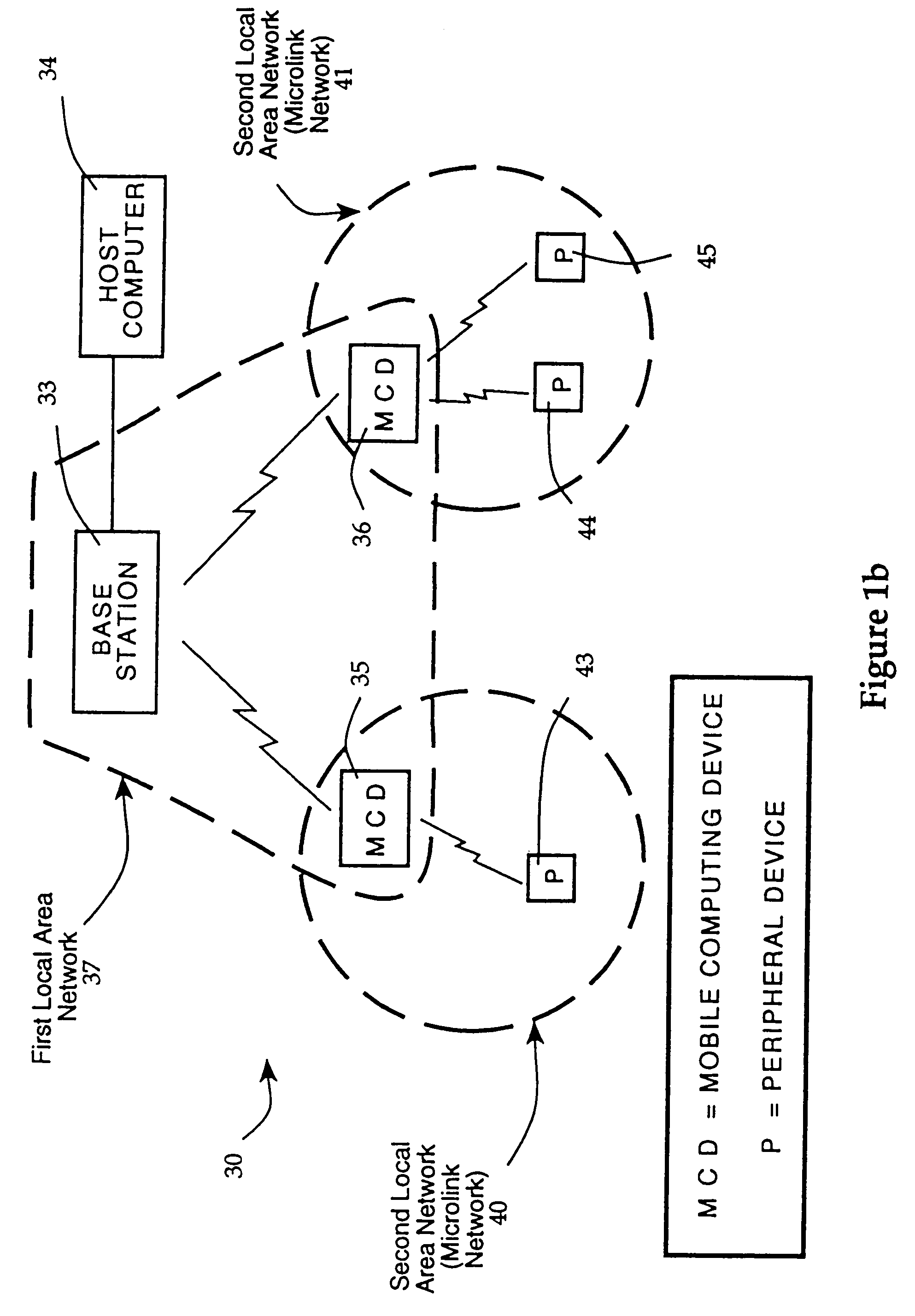
InactiveUS6970434B1Reduce traffic problemsReduce communicationPower managementError prevention/detection by using return channelCommunications systemTelecommunications link
A hierarchical communication system, arranged in a spanning tree configuration, is described in which wired and wireless communication networks exhibiting substantially different characteristics are employed in an overall scheme to link portable or mobile computing devices. Copies of data, program code and processing resources are migrated from their source toward requesting destinations based on request frequency, communication link costs and available local storage and / or processing resources. Each appropriately configured network device acts as an active participant in network migration. In addition, portable two-dimensional (2-D) code reading terminals are configured to wirelessly communicate compressed 2-D images toward stationary access servers that identify the code image through decoding and through comparison with a database of images that have previously been decoded and stored.
Owner:AVAGO TECH WIRELESS IP SINGAPORE PTE
Ethernet switch and system
ActiveUS7194003B2Multiple digital computer combinationsNetworks interconnectionQuality of serviceVirtual LAN
An Ethernet switch includes a plurality of ports, wherein the switch is configured to be operable within a temperature range of at least between approximately 0° C. and approximately 60° C. The switch is further configured to be operable within a non-condensing humidity range of at least between approximately 10% and approximately 95%. The switch is further configured to support at least one of a Virtual Local Area Network (VLAN), a Quality of Service (QoS), a Remote Monitoring (RMON), and a Spanning Tree, and the switch is configured to be upgradeable using a plug in device.
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO CO GE FANUC AUTOMATION +1
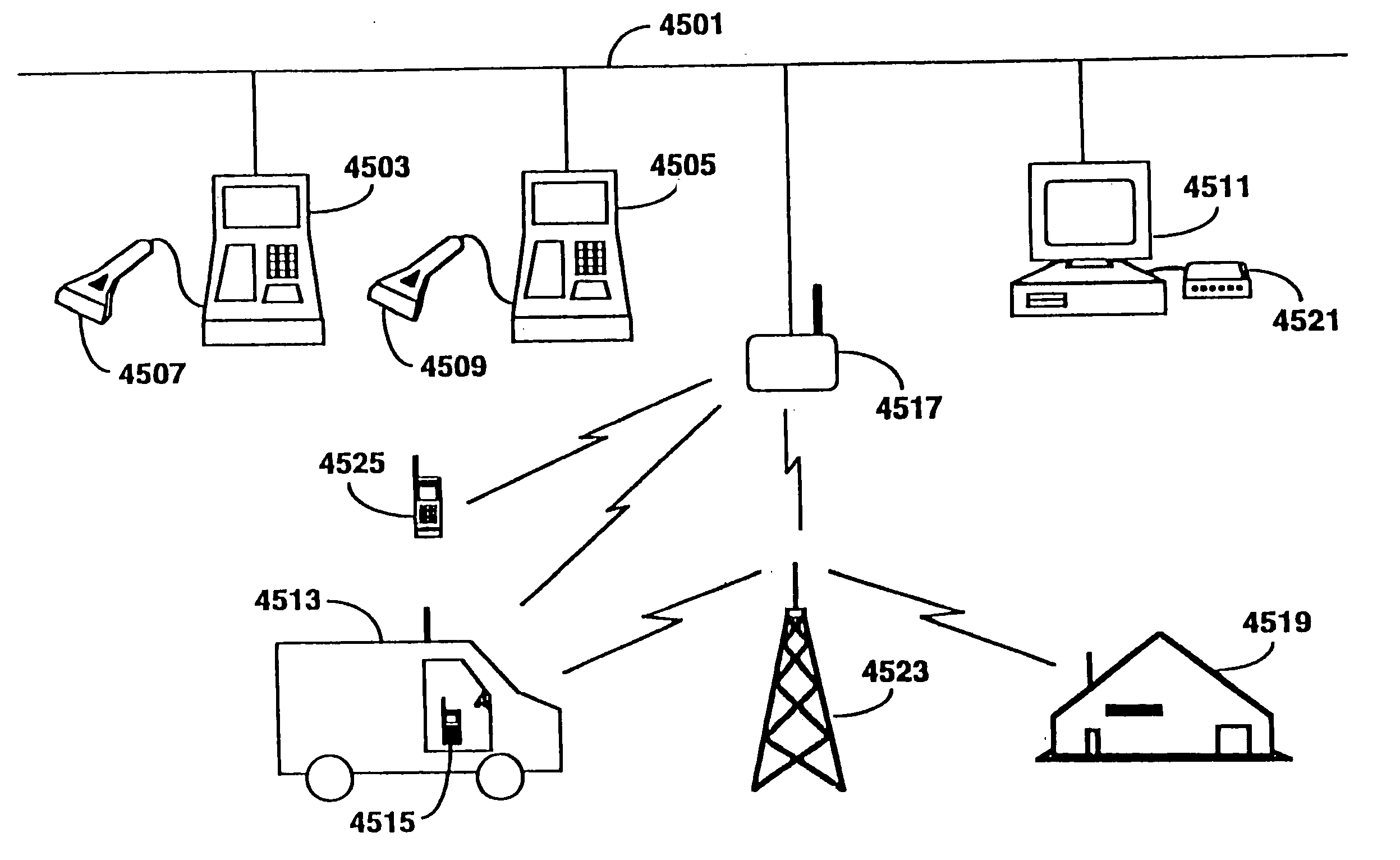
Hierarchical data collection network supporting packetized voice communications among wireless terminals and telephones
InactiveUS20040264442A1Efficient communication pathwayEfficient communicationDevices with card reading facilityError preventionVoice communicationThe Internet
A packet-based, hierarchical communication system, arranged in a spanning tree configuration, is described in which wired and wireless communication networks exhibiting substantially different characteristics are employed in an overall scheme to link portable or mobile computing devices. The network accommodates real time voice transmission both through dedicated, scheduled bandwidth and through a packet-based routing within the confines and constraints of a data network. Conversion and call processing circuitry is also disclosed which enables access devices and personal computers to adapt voice information between analog voice stream and digital voice packet formats as proves necessary. Routing pathways include wireless spanning tree networks, wide area networks, telephone switching networks, internet, etc., in a manner virtually transparent to the user. A voice session and associate call setup simulates that of conventional telephone switching network, providing well-understood functionality common to any mobile, remote or stationary terminal, phone, computer, etc.
Owner:AVAGO TECH INT SALES PTE LTD
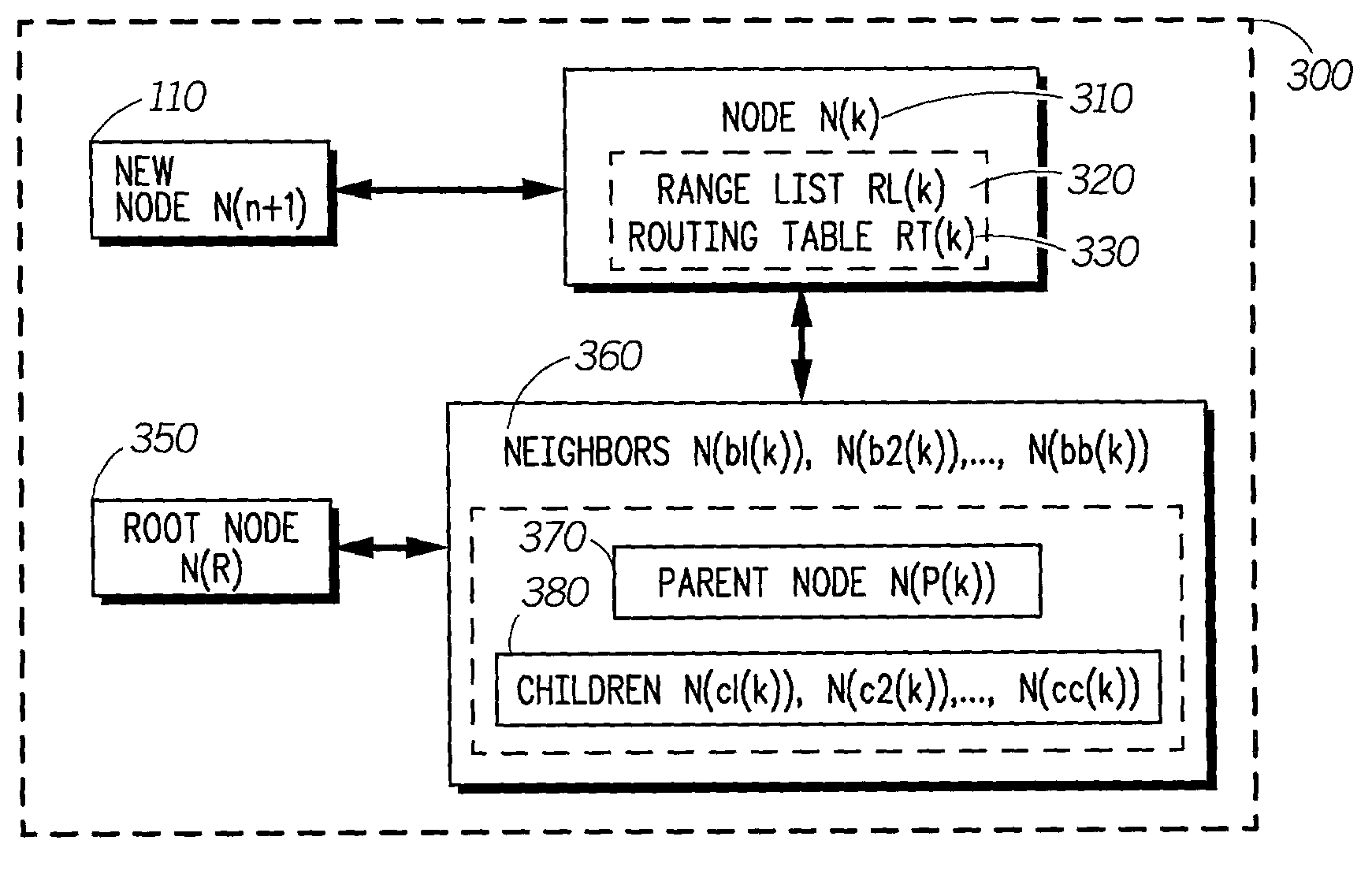
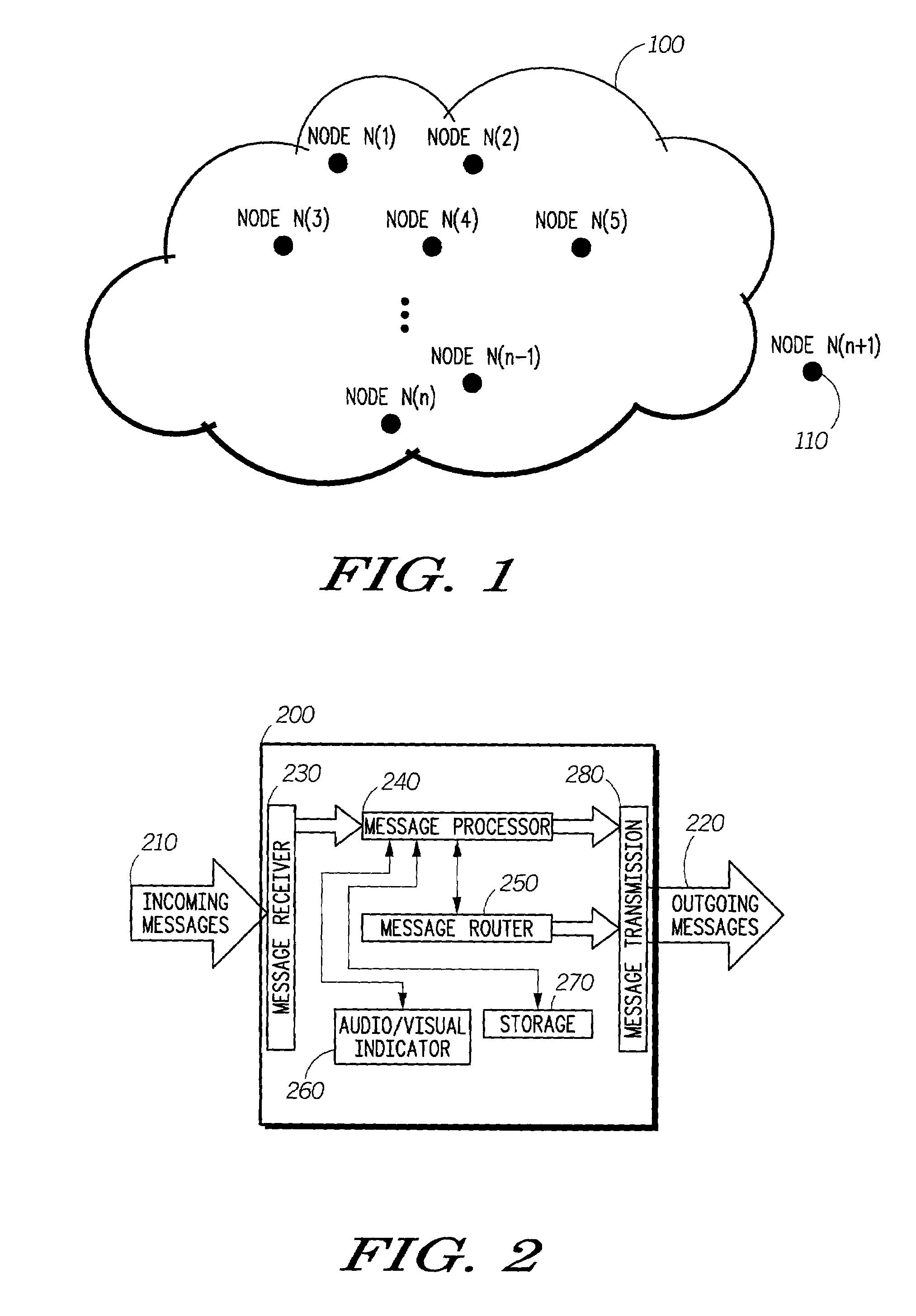
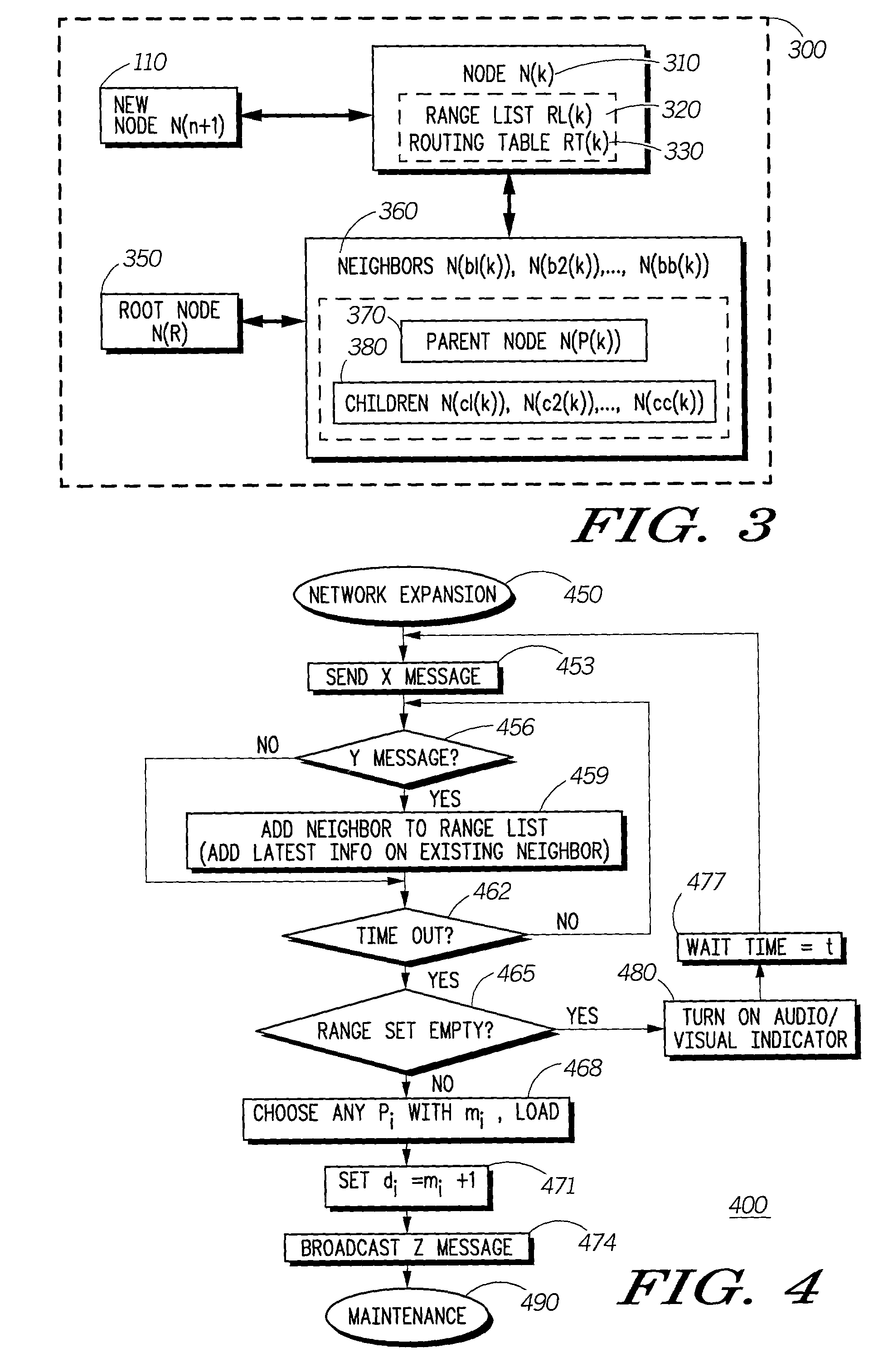
Protocol for self-organizing network using a logical spanning tree backbone
InactiveUS6982960B2Data switching by path configurationRadio/inductive link selection arrangementsNetworking protocolMaintenance phase
A network protocol for low-cost, low-power devices coupled to a self-organizing wireless network using a spanning tree backbone architecture is described. In this protocol, physical and logical network construction and maintenance operations, which supports efficient data routing in the network, are performed. The construction phase in conjunction with the maintenance phase insures the self-organizing capability of the network. At the same time, the maintenance operations provide a self-healing mechanism so that the network can recover from node failures and a self-updating mechanism so that the network can expand as more nodes enter the system. Also, the logical backbone hierarchy will facilitate multi-hop communication. The construction of a logical layered spanning tree backbone architecture from an underlying physical topology allows seamless data communication routing between all nodes in the network.
Owner:NORTHWESTERN UNIV +1
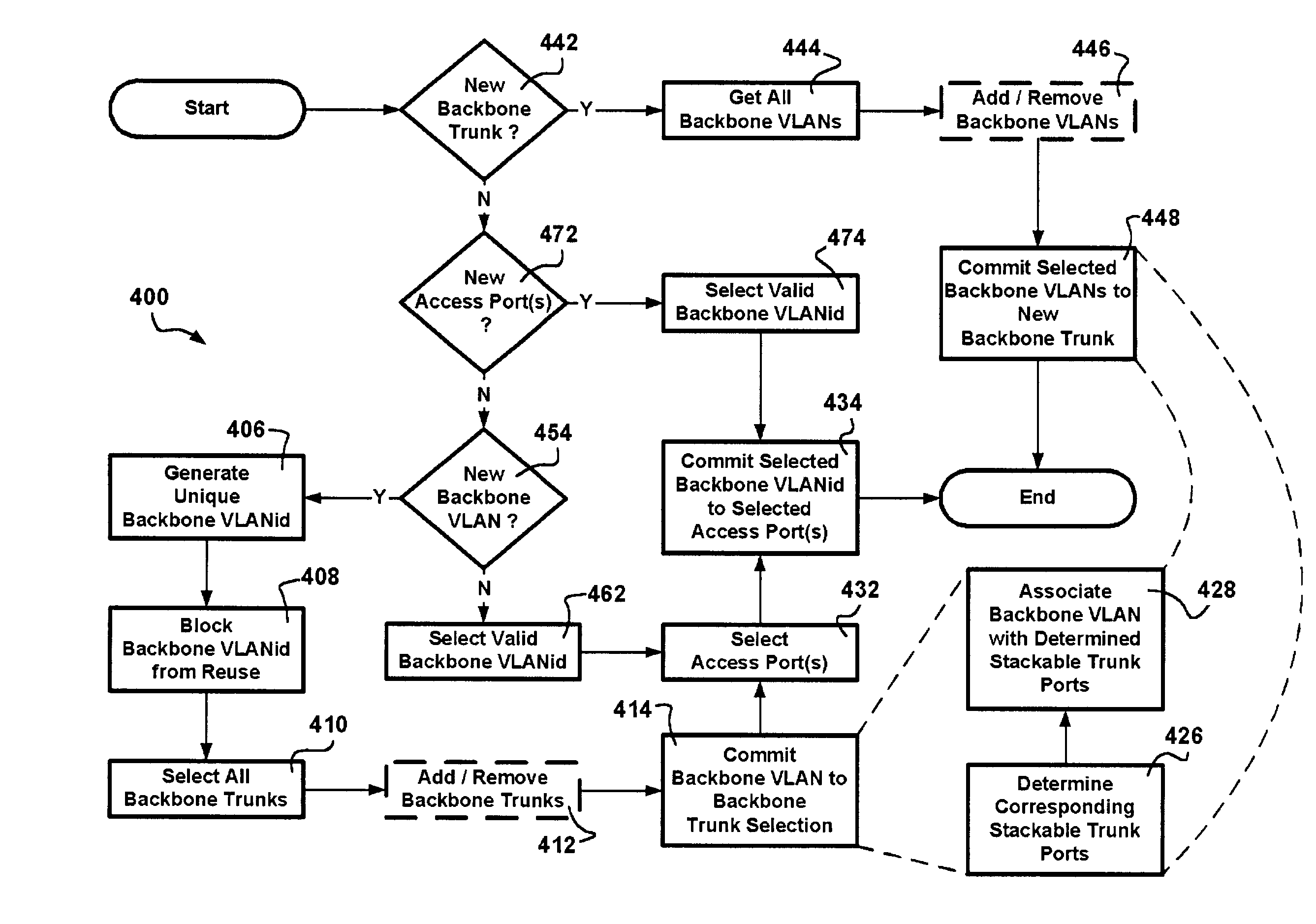
Stackable virtual local area network provisioning in bridged networks
ActiveUS7453888B2Shorten the timeReduce operating costsNetworks interconnectionTraffic capacityVirtual LAN
A method and human-machine interface for backbone Virtual Local Area Network (VLAN) provisioning in bridged networking environments are provided. The method includes steps of provisioning backbone VLAN support on every backbone data transport trunk and by extension of every stackable data trunk port in the associated data transport network. The human-machine interface enables an operator to expediently effect VLAN provisioning abstracting the intricacies of the data transport network over which VLAN services are provisioned. Advantages are derived from backbone VLAN provisioning independent of an underlying in-use active spanning-tree topology. In particular backbone VLANs are provisioned over spanning-tree stand-by designated backbone data transport trunk links and therefore preprovisioned in the case of spanning-tree re-configuration. Customer VLANs are mapped onto backbone VLANs ensuring data traffic differentiation, and providing standard VLAN identifier portability. Operator VLAN provisioning tasks are lessened via provisions for the selection of all backbone / stackable data transport trunk links / ports in the data transport network in effecting VLAN identifier associations therebetween.
Owner:WSOU INVESTMENTS LLC
System and method for spanning tree cross routes
InactiveUS20070110024A1Easy to routeData switching by path configurationWireless communicationRouting tableNetwork packet
A spanning tree cross-route protocol for establishing mesh-like cross routes in an underlying wireless spanning tree topology. A cross route spans branches of the tree topology to provide a more optimal route between any two nodes in the wireless network. The cross route can span multiple spanning trees. Each mesh node maintains a cross route table. When a packet is received, the node determines whether there is an entry for the destination node in the cross route table. If there is an entry for the destination node in the cross route table, the packet is forwarded via the cross route; otherwise, the packet is forwarded via the spanning tree.
Owner:CISCO TECH INC
Automatically maximizing network link utilization using virtual networks
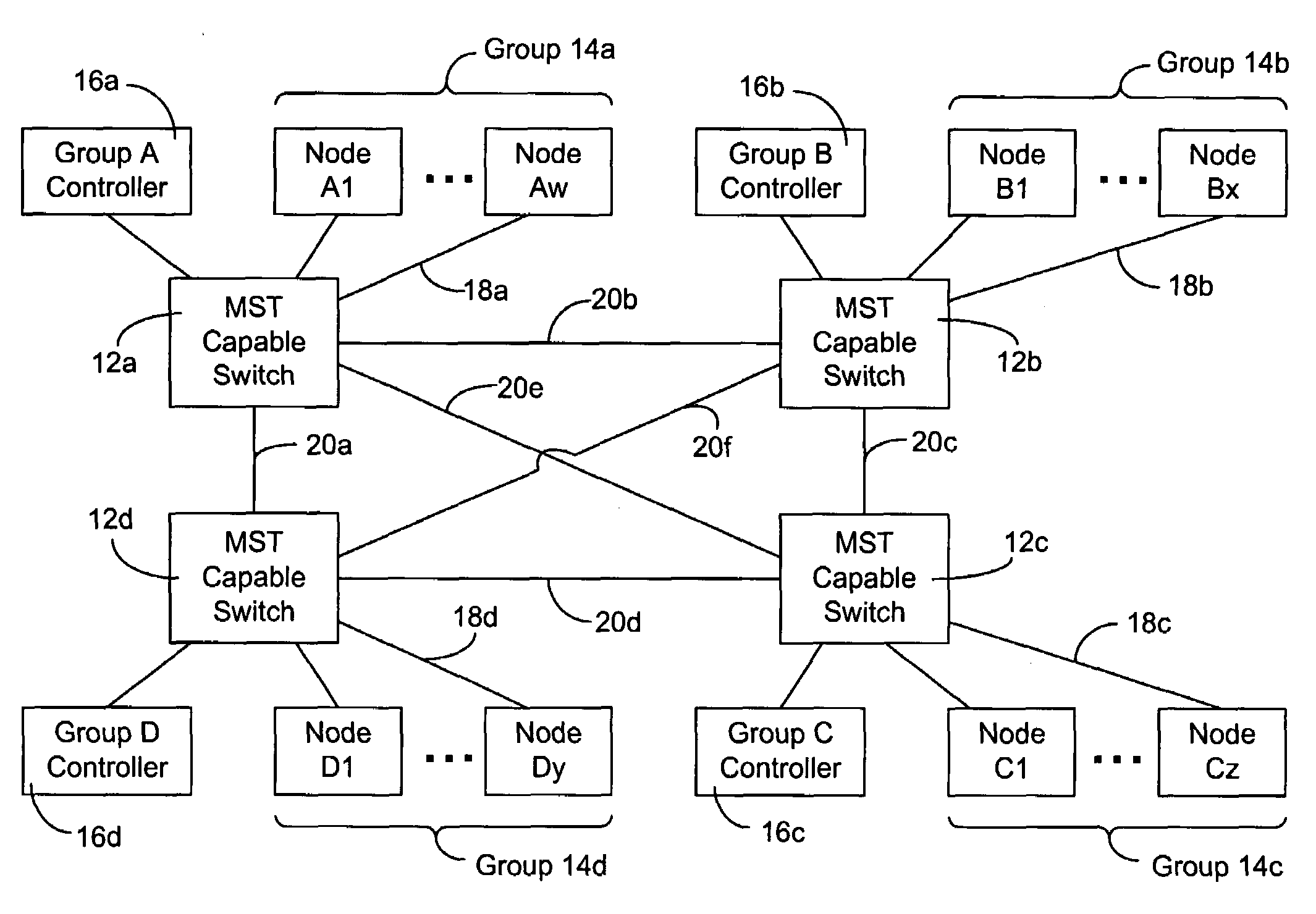
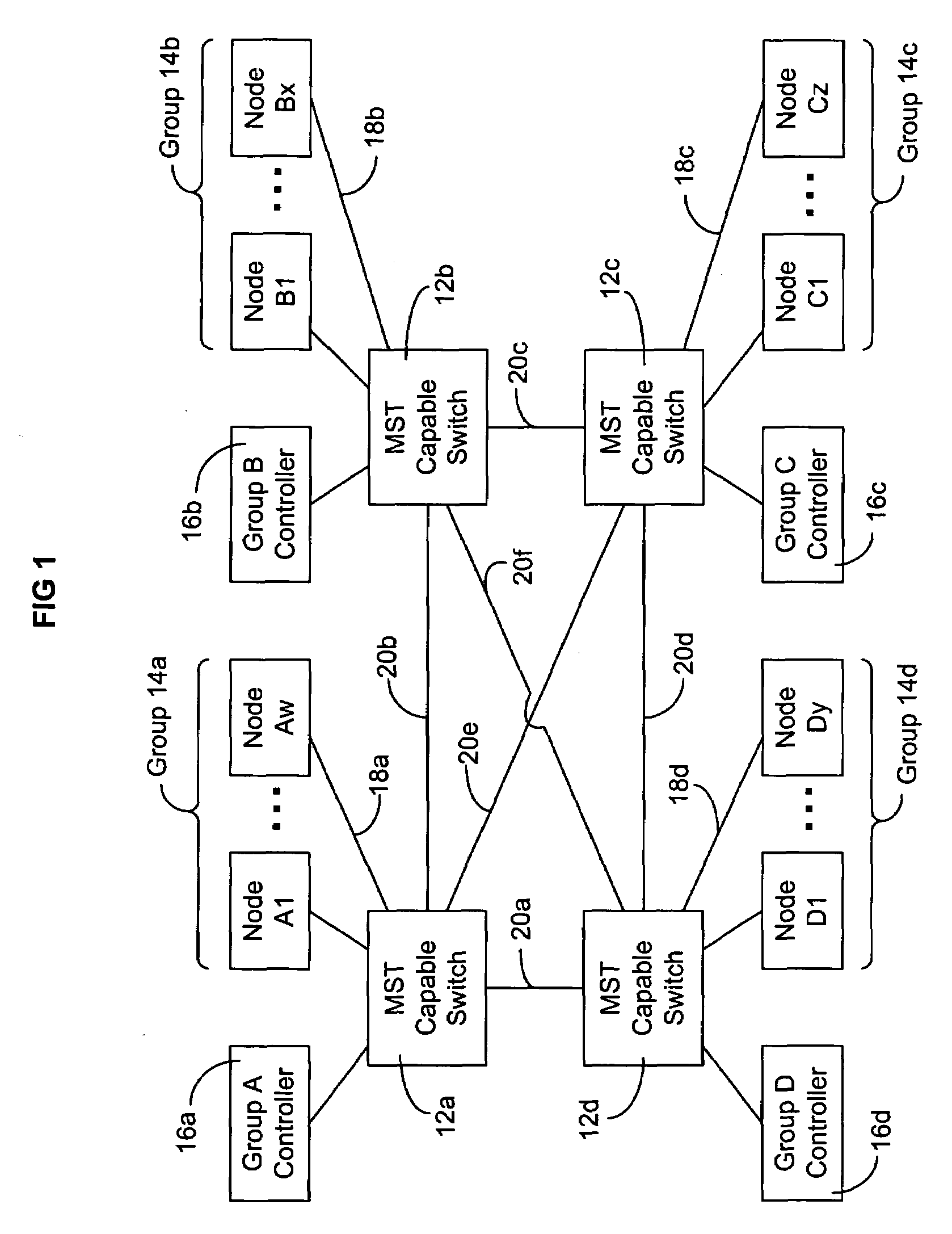
A system and method for automatically configuring a network so that each switch in the network is aware of the Multiple Spanning Tree Instances (MSTI) of each other switch and the Virtual Local Area Network (VLAN) that each switch uses. This is achieved through the use of controllers connected to each switch. A master switch is elected and the master switch monitors messages to determine if a switch should be using an alternative MISTI. If so, the master switch instructs a switch to use an alternative MSTI. Either a switch or a node connected to the switch may determine which VLAN to use in sending messages, subject to configuration from the controller of the master switch. Messages are periodically sent by each controller to educate other controllers to aid in learning which node is part of a group connected to a switch, the switch in turn connected to a controller.
Owner:SANDVINE CORP
Method for efficient content distribution using a peer-to-peer networking infrastructure
ActiveUS20050216559A1Effective distributionImprove the corresponding efficiencyMultiple digital computer combinationsTransmissionContent distributionTime sensitive
Disclosed is a method for efficiently distributing content by leveraging the use of a peer-to-peer network infrastructure. In a network of peers, a handful peers can receive content from centralized servers. These peers can then flood this content out to more clients who in turn can send the content along to others. Ultimately, a request for content can be fulfilled by locating the closest peer and obtaining the content from that peer. In one embodiment the method can be used to distribute content by creating content distribution groups of one or more client computing devices and redirecting requests for content from the server to the content distribution group. A further contemplated embodiment efficiently streams time sensitive data through the use of a spanning tree architecture of peer-to-peer clients. In yet another embodiment the present invention provides for more efficient use of bandwidth for shared residential broadband connections.
Owner:MICROSOFT TECH LICENSING LLC
Spanning tree root selection in a hierarchical network
InactiveUS8000336B2Error preventionFrequency-division multiplex detailsControl channelNetwork communication
Communication apparatus includes a hierarchical network of switches, which includes at least a first plurality of spine switches, interconnected by a control channel, and a second plurality of edge switches having internal ports coupled to communicate via respective links with the spine switches and external ports for connecting to client devices. The spine switches are configured to detect, via the control channel, a partitioning of the hierarchical network into first and second partitions, including respective first and second numbers of the spine switches, wherein the first number is greater than the second number, and to assign respective priorities to the spine switches responsively to the first and second numbers so as to cause the larger of the partitions to be elected as a spanning tree root.
Owner:MELLANOX TECHNOLOGIES LTD
Roaming Network Stations Using A Mac Address Identifier To Select New Access Point
There is disclosed a method of helping mobile stations such as voice over IP devices to roam between wireless access points, by each access point transmitting the MAC address of a spanning tree algorithm root switch of the local network domain. This MAC address is used by mobile stations to detect if two access points are in a common network domain.
Owner:STMICROELECTRONICS (RES & DEV) LTD
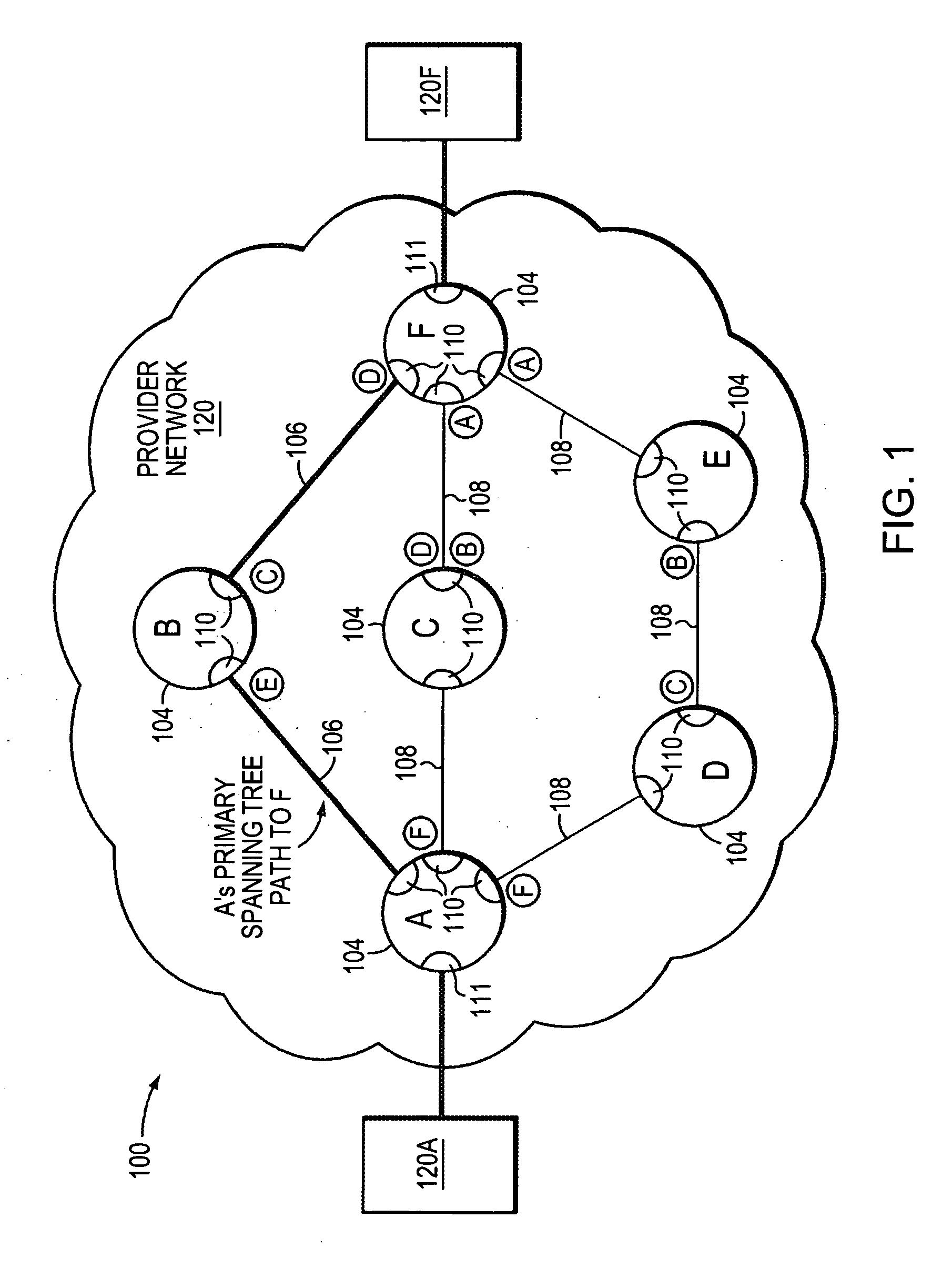
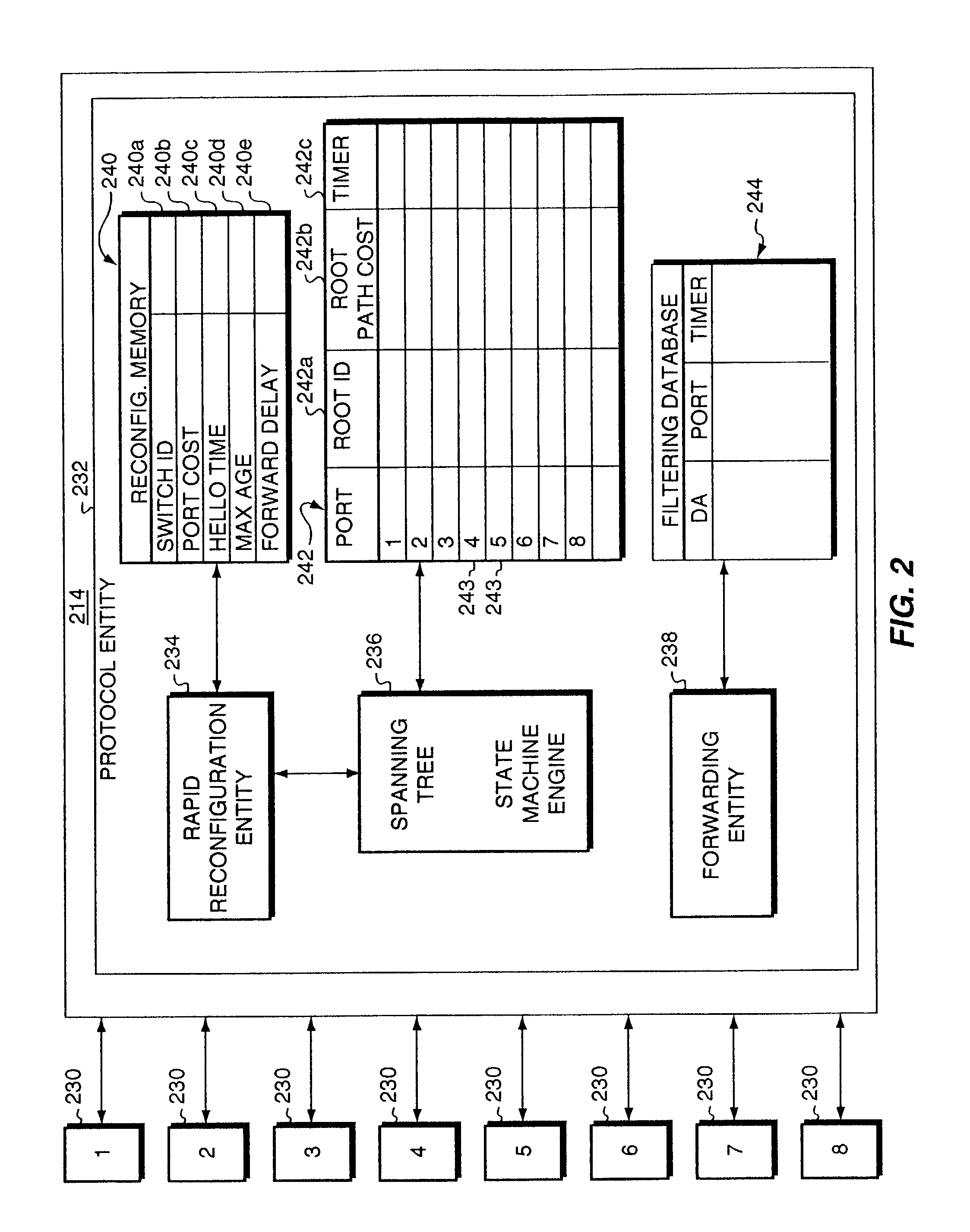
Method and apparatus for rapidly reconfiguring bridged networks using a spanning tree algorithm
InactiveUS6976088B1Shorten the timeDigital computer detailsNetworks interconnectionVirtual LANMulticast message
A method that rapidly reconfigures a computer network having a plurality of devices executing the spanning tree algorithm. First, one or more devices are configured and arranged so that one port, providing connectivity to the root, is in the forwarding state and the remaining ports, providing connectivity to the root, are in the blocked state. Next, one or more of the blocked ports are designated as back-up ports. Upon detection of a failure at the active forwarding port, one of the back-up ports immediately transitions from blocked to forwarding, thereby becoming the new active port for the device. Following the transition to a new active port, dummy multicast messages are transmitted, each containing the source address of an entity directly coupled to the affected device or downstream thereof. By examining the dummy multicast messages, other devices in the network learn to use to the new forwarding port of the affected device. Rapid reconfiguration of the network is also provided upon detection of a new or repaired link or device representing a better path toward the root. The method is also compatible with networks supporting virtual local area network (VLAN) designations and allows load balancing among different VLANs.
Owner:CISCO TECH INC
Hierarchical data collection network supporting packetized voice communications among wireless terminals and telephones
InactiveUS20050013266A1Modulated-carrier systemsDevices with card reading facilityVoice communicationThe Internet
A packet-based, hierarchical communication system, arranged in a spanning tree configuration, is described in which wired and wireless communication networks exhibiting substantially different characteristics are employed in an overall scheme to link portable or mobile computing devices. The network accommodates real time voice transmission both through dedicated, scheduled bandwidth and through a packet-based routing within the confines and constraints of a data network. Conversion and call processing circuitry is also disclosed which enables access devices and personal computers to adapt voice information between analog voice stream and digital voice packet formats as proves necessary. Routing pathways include wireless spanning tree networks, wide area networks, telephone switching networks, internet, etc., in a manner virtually transparent to the user. A voice session and associate call setup simulates that of conventional telephone switching network, providing well-understood functionality common to any mobile, remote or stationary terminal, phone, computer, etc.
Owner:AVAGO TECH INT SALES PTE LTD
Virtual LAN creation device
InactiveUS20050152289A1Easy to useShorten the timeStar/tree networksNetworks interconnectionVirtual LANNetwork topology
A spanning tree creation unit creates a plurality of spanning trees based on the network topology, and registers the spanning trees to a spanning tree information table. A spanning tree selection unit selects a spanning tree wherein communication resources will be used most effectively, out of the plurality of spanning trees registered to the spanning tree information table. A node setup unit sets the mapping information which expresses correspondence between the requested virtual LAN and the selected spanning tree in each node.
Owner:FUJITSU LTD
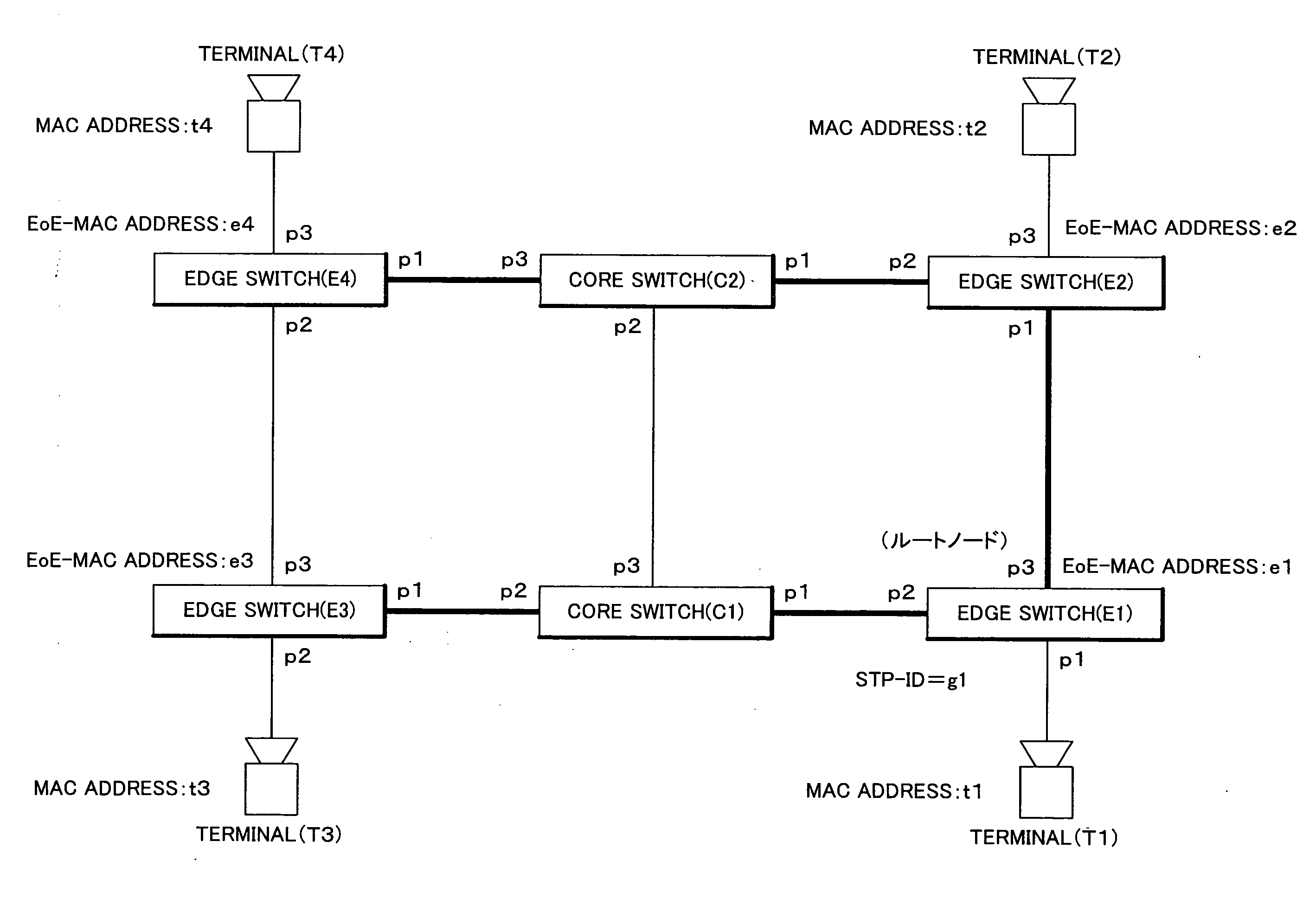
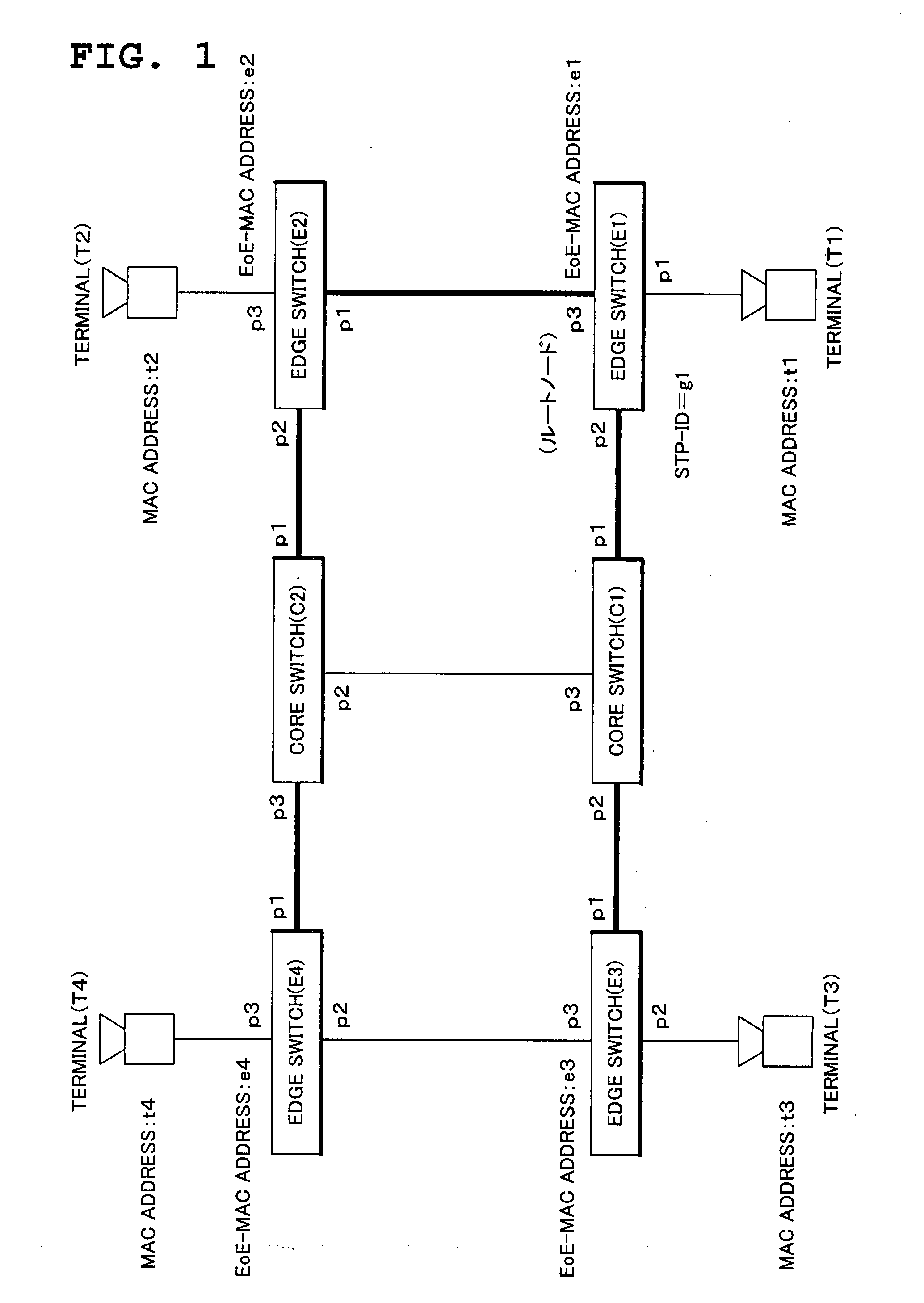
Node, Network, Correspondence Relationship Generation Method and Frame Transfer Program
InactiveUS20080165705A1Improve throughputAvoid concentrationData switching by path configurationLearning unitThroughput
Provided in the EoE technique are the node, the network, the correspondence relationship generating method and the frame transfer program to avoid traffic concentration on a specific link to improve throughput of the network as a whole by realizing optimum path transfer. The frame switching unit includes the frame analysis unit for analyzing an input frame kind and the like, the table search unit for obtaining frame rewriting information and output port information, the forwarding table storage unit for managing an output port of a frame, the MAC learning unit for executing MAC address learning, the EoE-MAC learning unit for learning a relationship between a MAC address and an EoE-MAC address, the STP control unit for executing processing of a spanning tree, and the like.
Owner:NEC CORP
Method for achieving dynamic multicast spanning tree path adjustment based on OpenFlow
InactiveCN103346969AOptimizing Multicast Transmission EfficiencyShort response timeData switching networksOpenFlowComputer science
The invention provides a method for achieving dynamic multicast spanning tree path adjustment based on OpenFlow. An OpenFlow technology is utilized to solve the problems in a multicast service of a host entering or leaving a multicast set, multicast spanning tree path dynamic adjustment and distributed multicast spanning tree strategies. According to the OpenFlow technology, a traditional packet forwarding process completely controlled by a router or a switch is converted into the process together completely by the OpenFlow switch and the controller, and therefore separation of forwarding logics and specific forwarding operation is achieved.
Owner:COMP NETWORK INFORMATION CENT CHINESE ACADEMY OF SCI
Secured software patching and upgrade method for densely deployed networks having spanning-tree topology
InactiveUS20050028001A1Service provisioningDigital data processing detailsWireless sensor networkingSoftware upgrade
A method for secured software patching and upgrade in a distributed wireless sensor network (DSN) includes the steps of providing a spanning-tree network of communications nodes with at least one root node (CH) and at least one software upgrade repository (SR), receiving a software upgrade with the root node (CH), communicating the upgrade from the root node (CH) to the software upgrade repository (SR), and installing the upgrade from the software upgrade repository (SR) to all of the nodes on the same branch by authenticating a patch key and delivering the upgrade from the software upgrade repository (SR) to the nodes after authentication occurs. The communications nodes (1000) can be sensor devices each sensing, processing, transmitting, receiving, and actuating in a given geographical area.
Owner:MOTOROLA INC
Configuration of computer networks
InactiveUS20030097468A1Multiple digital computer combinationsTransmissionDistributed computingSpanning tree
Systems involving generations of a complex node respresentation of a PNNI peer group are provided. Use is made of a set of restrictive costs, such as a transition matrix, defining the restrictives costs of paths between pairs of border nodes of the peer group. The complex node representation generation method is based on the group evolution process of the logical group representation of a peer group, and use is also made of the spanning tree representation of a network. Complex node representations generated by the disclosed possible number of exception bypasses.
Owner:HEWLETT PACKARD DEV CO LP
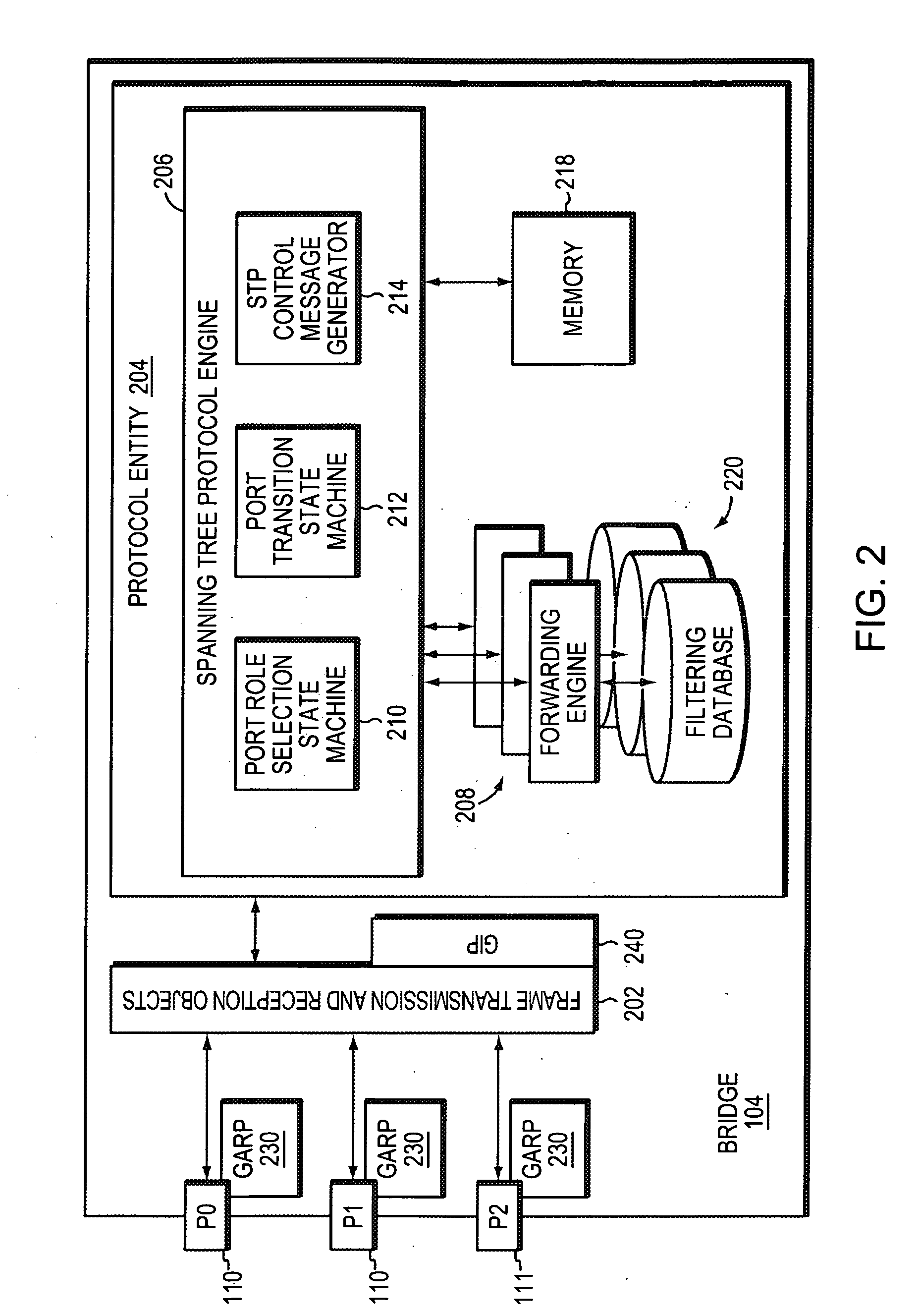
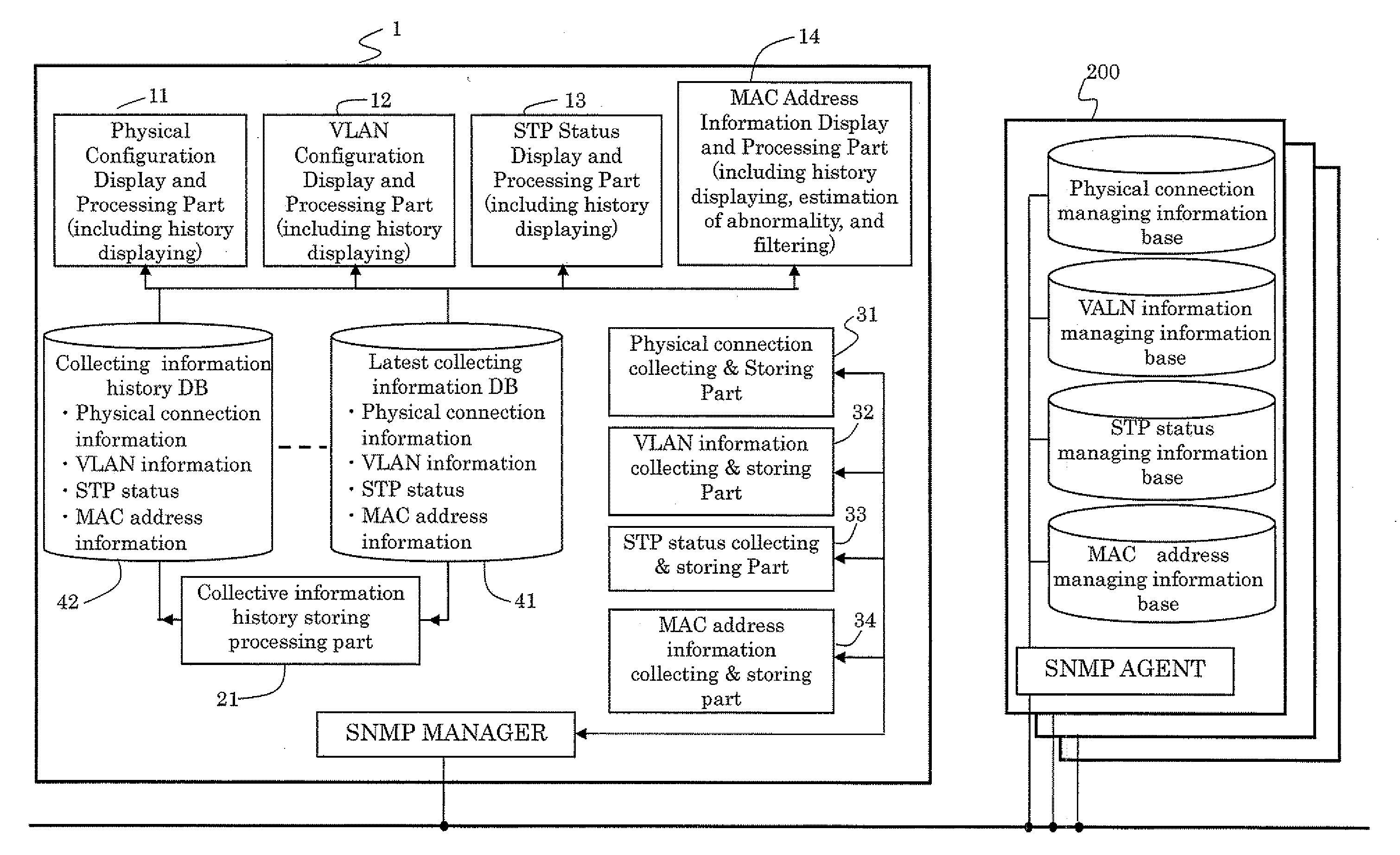
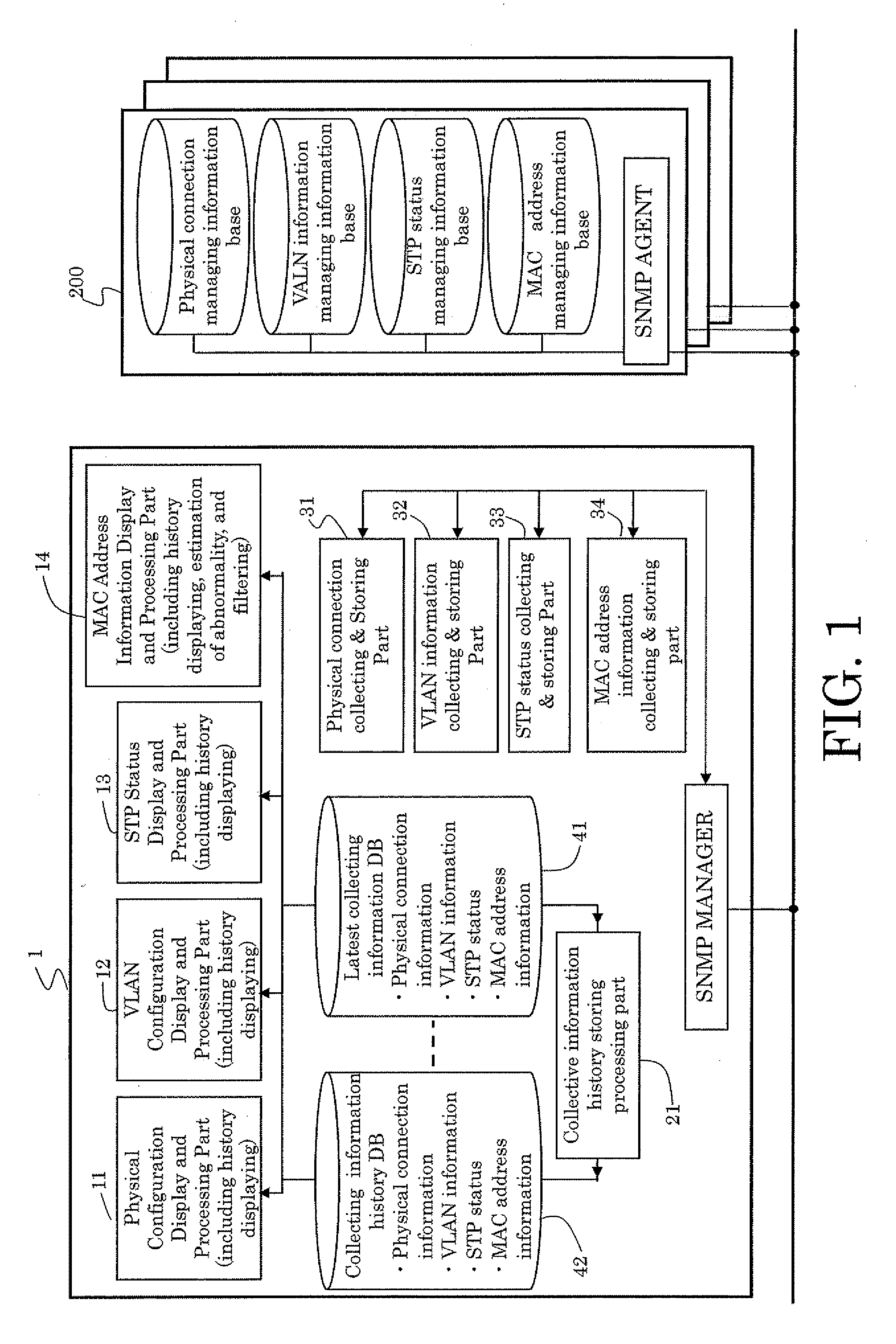
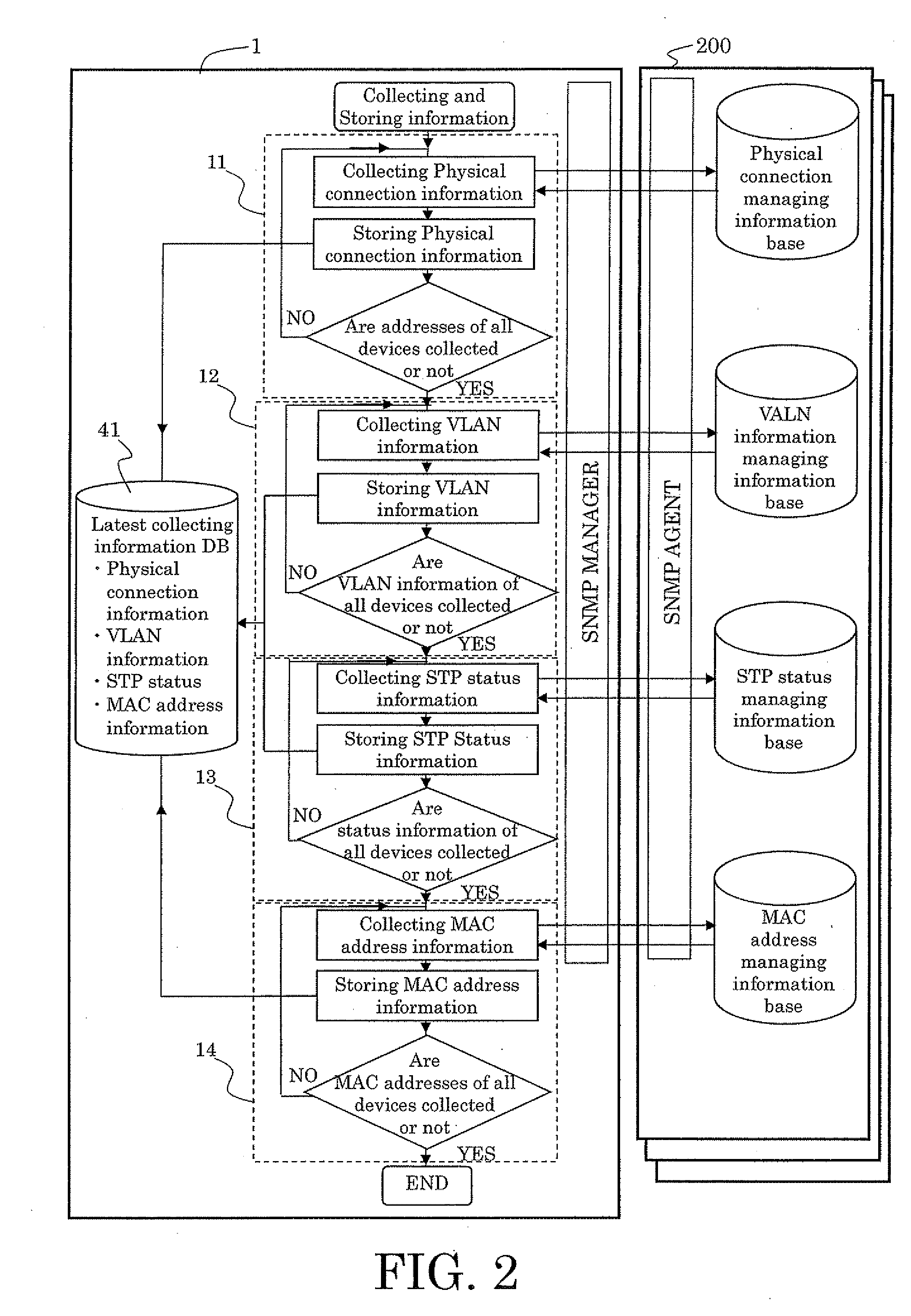
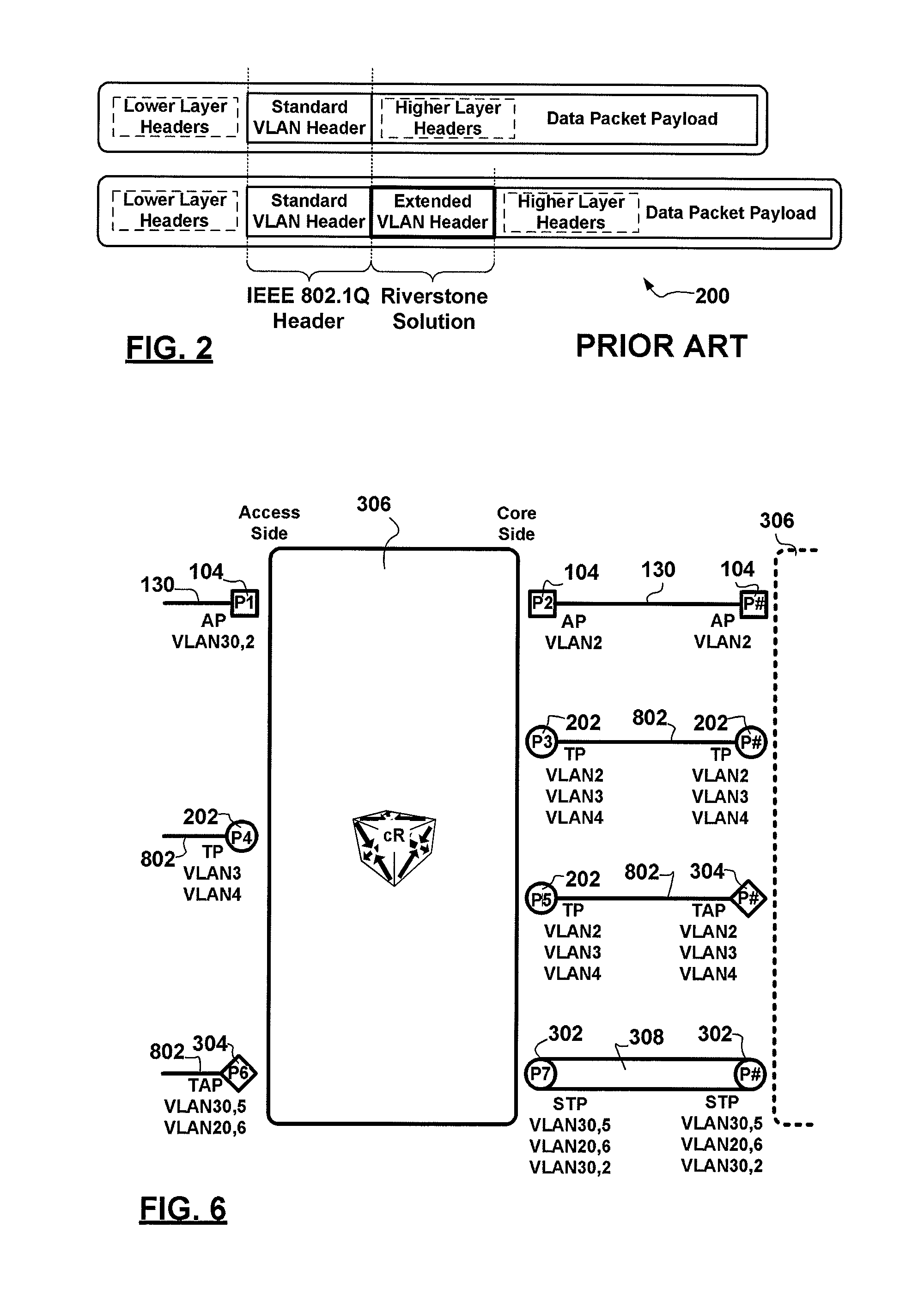
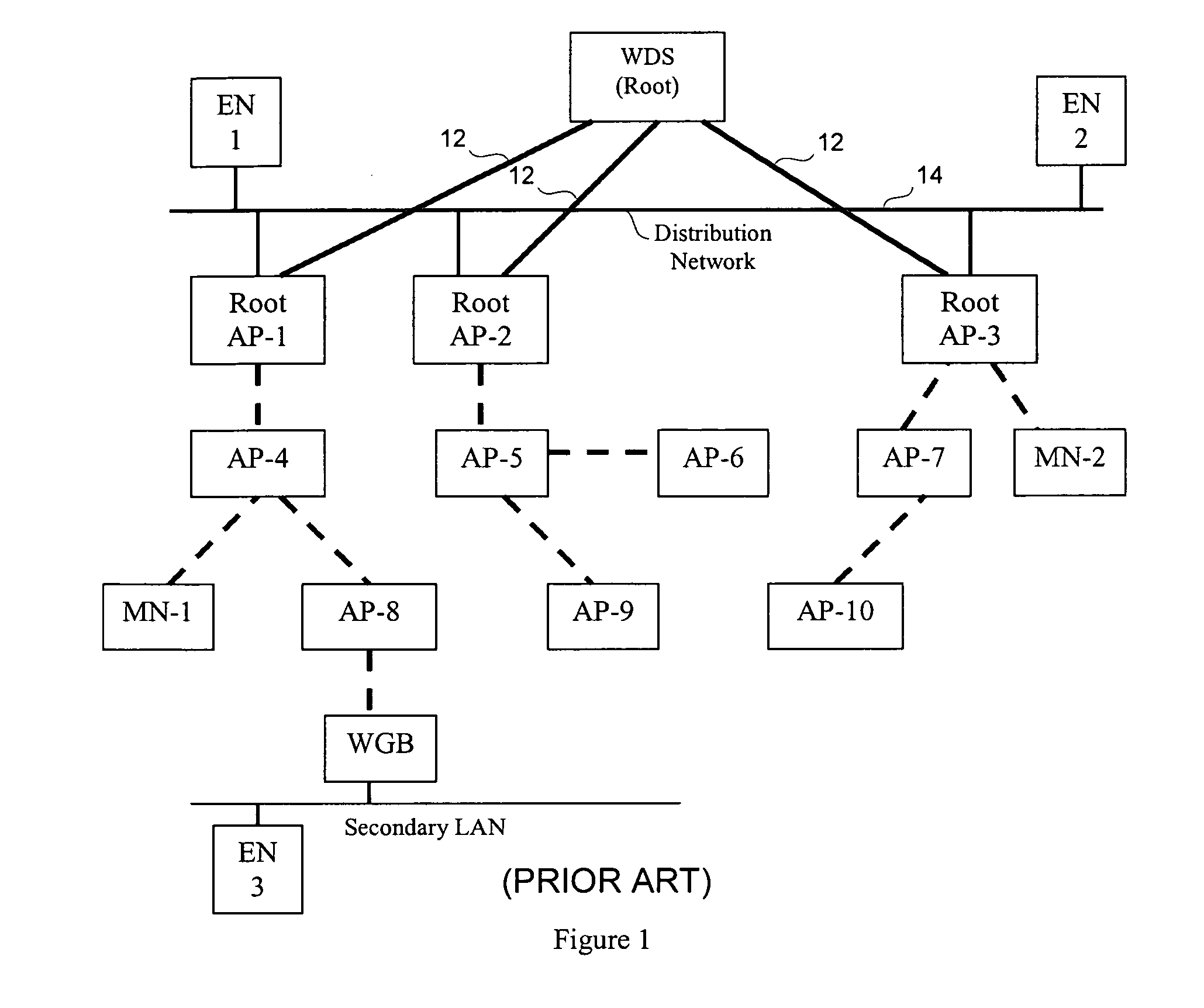
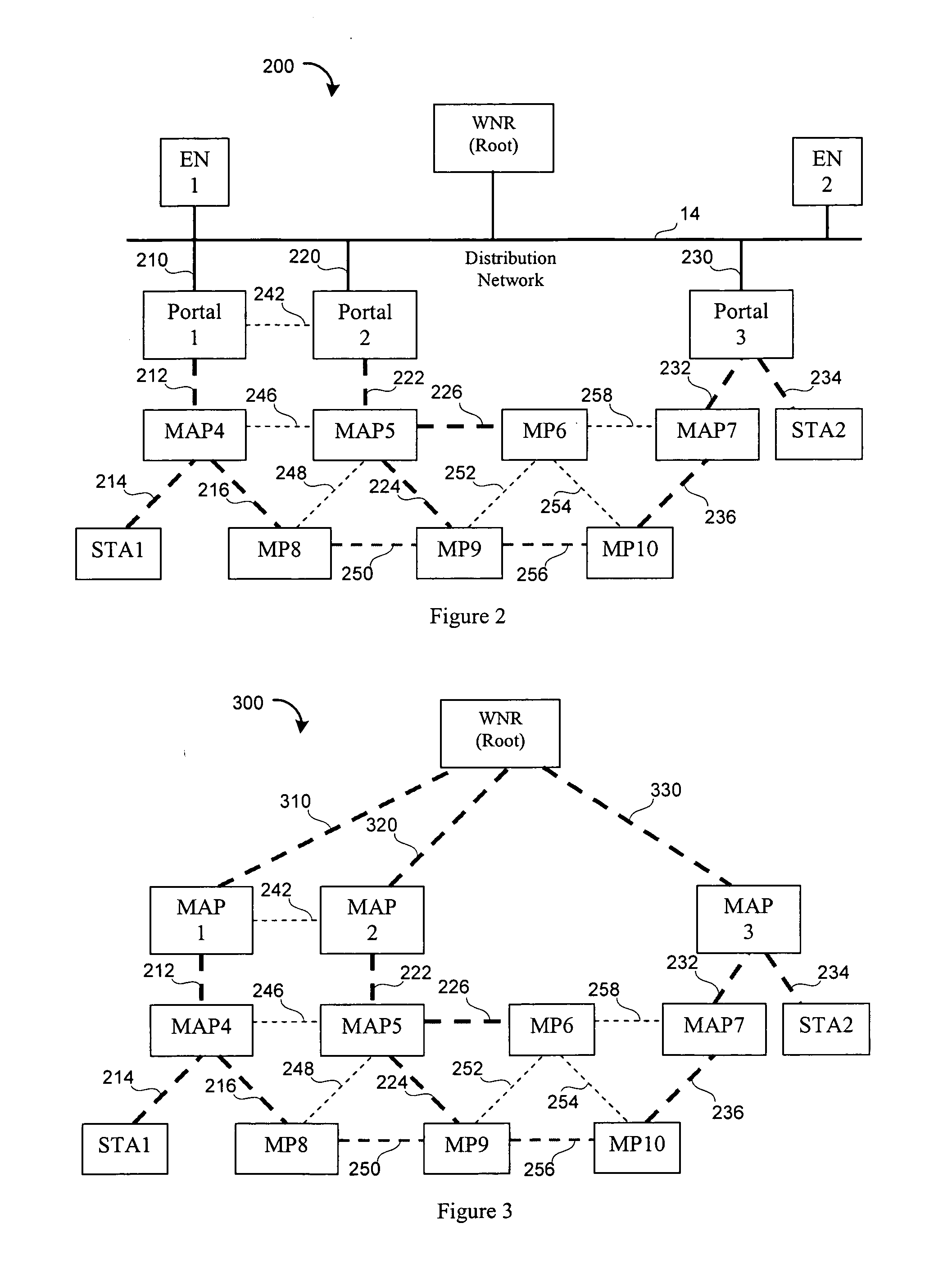
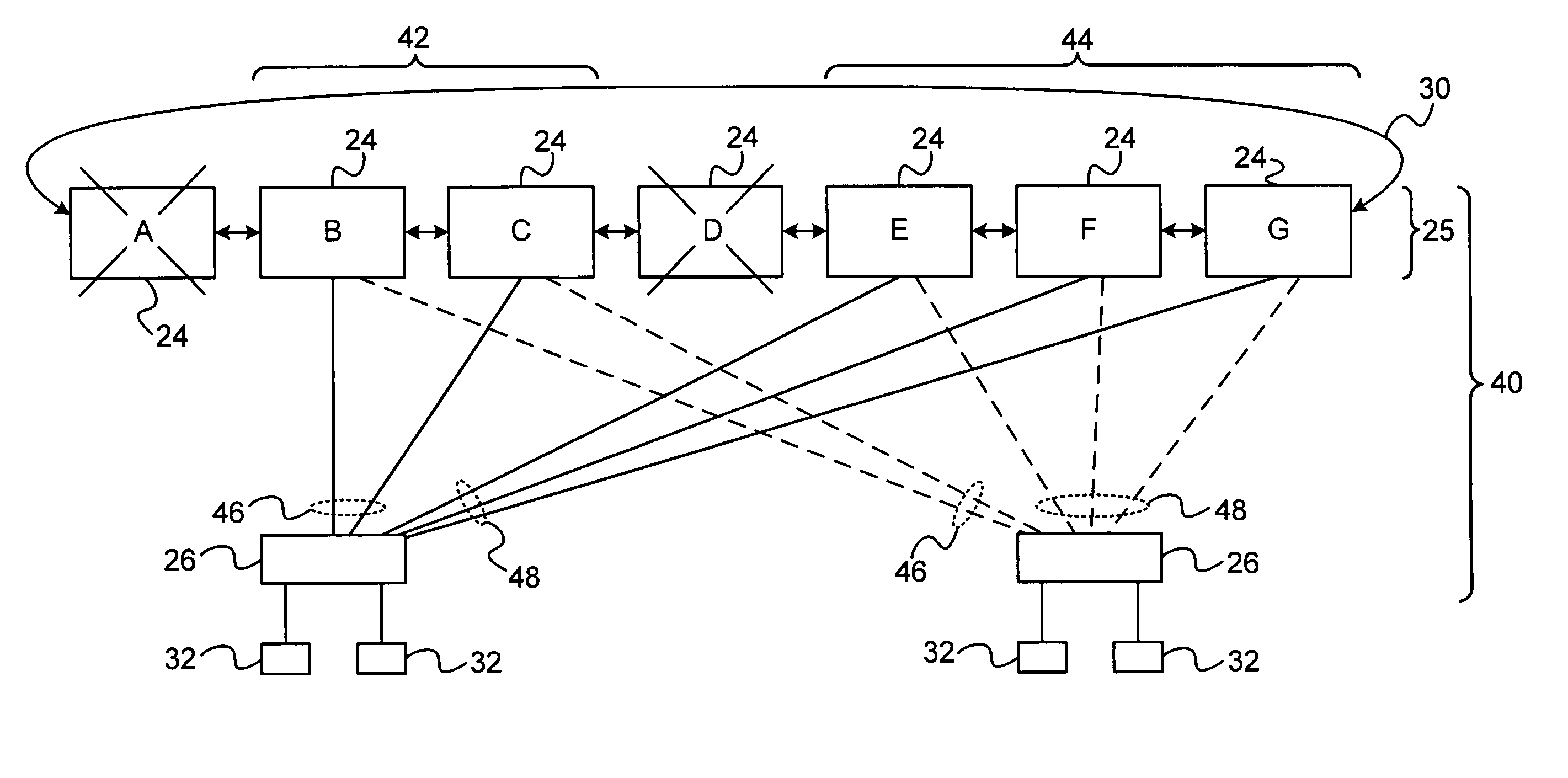
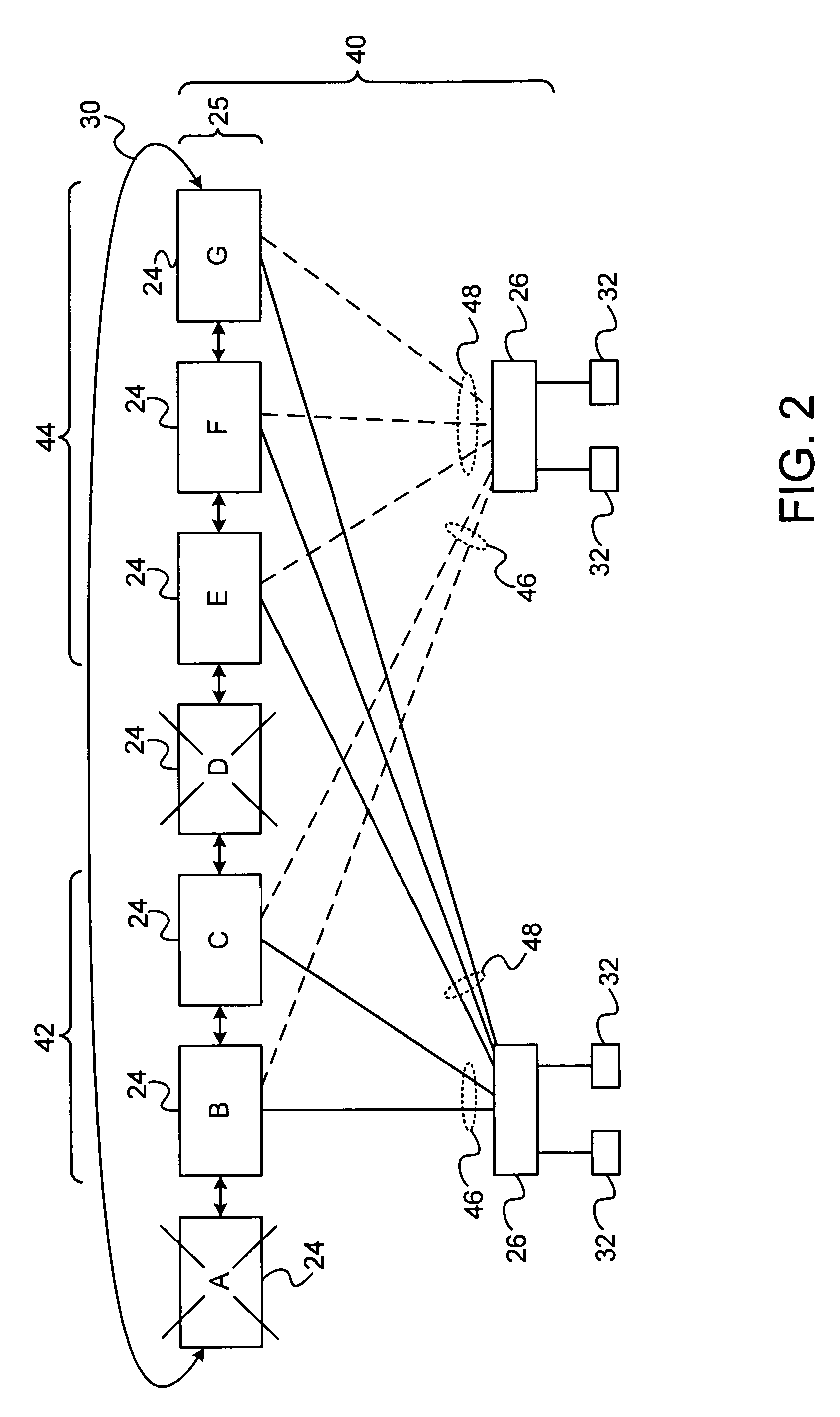
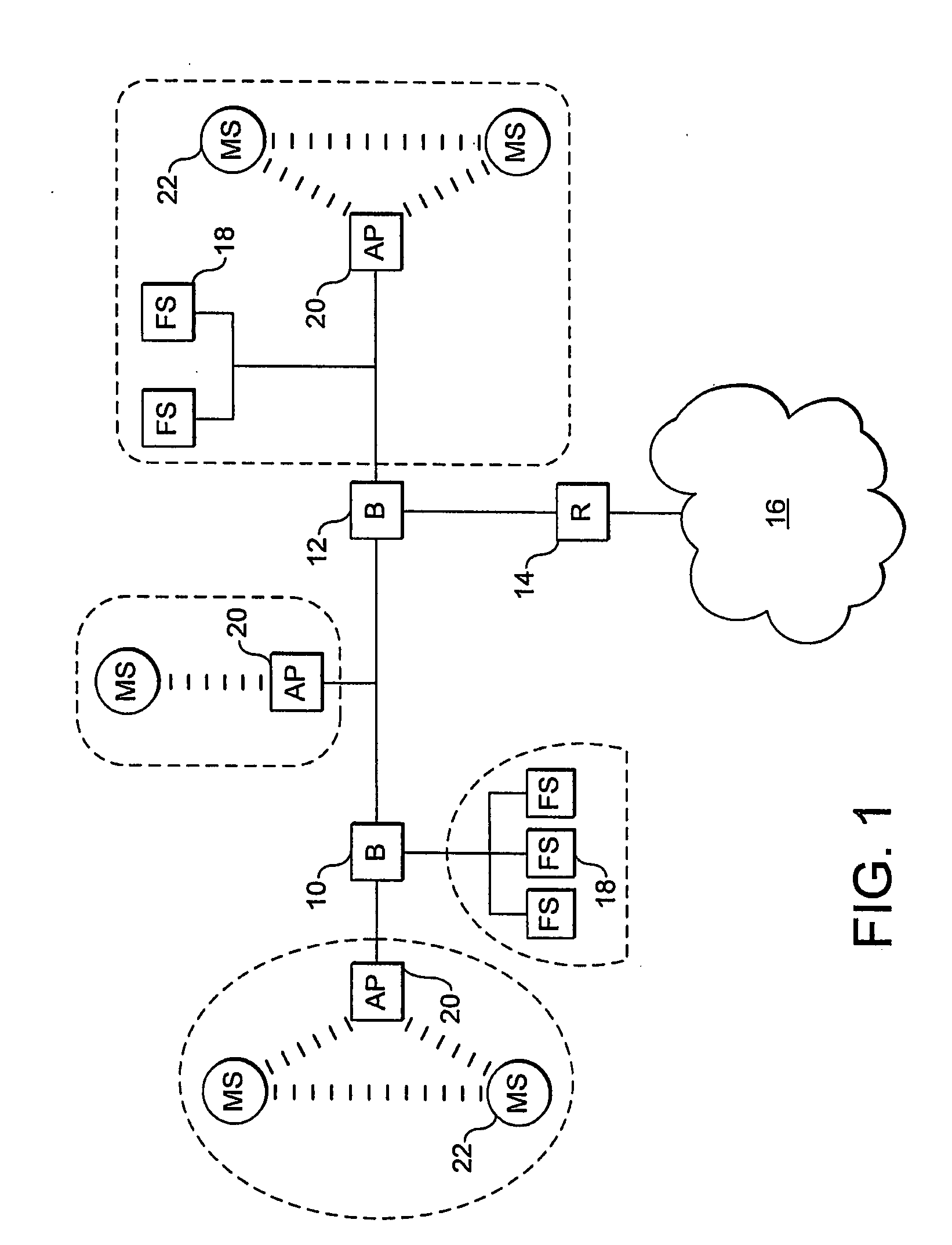
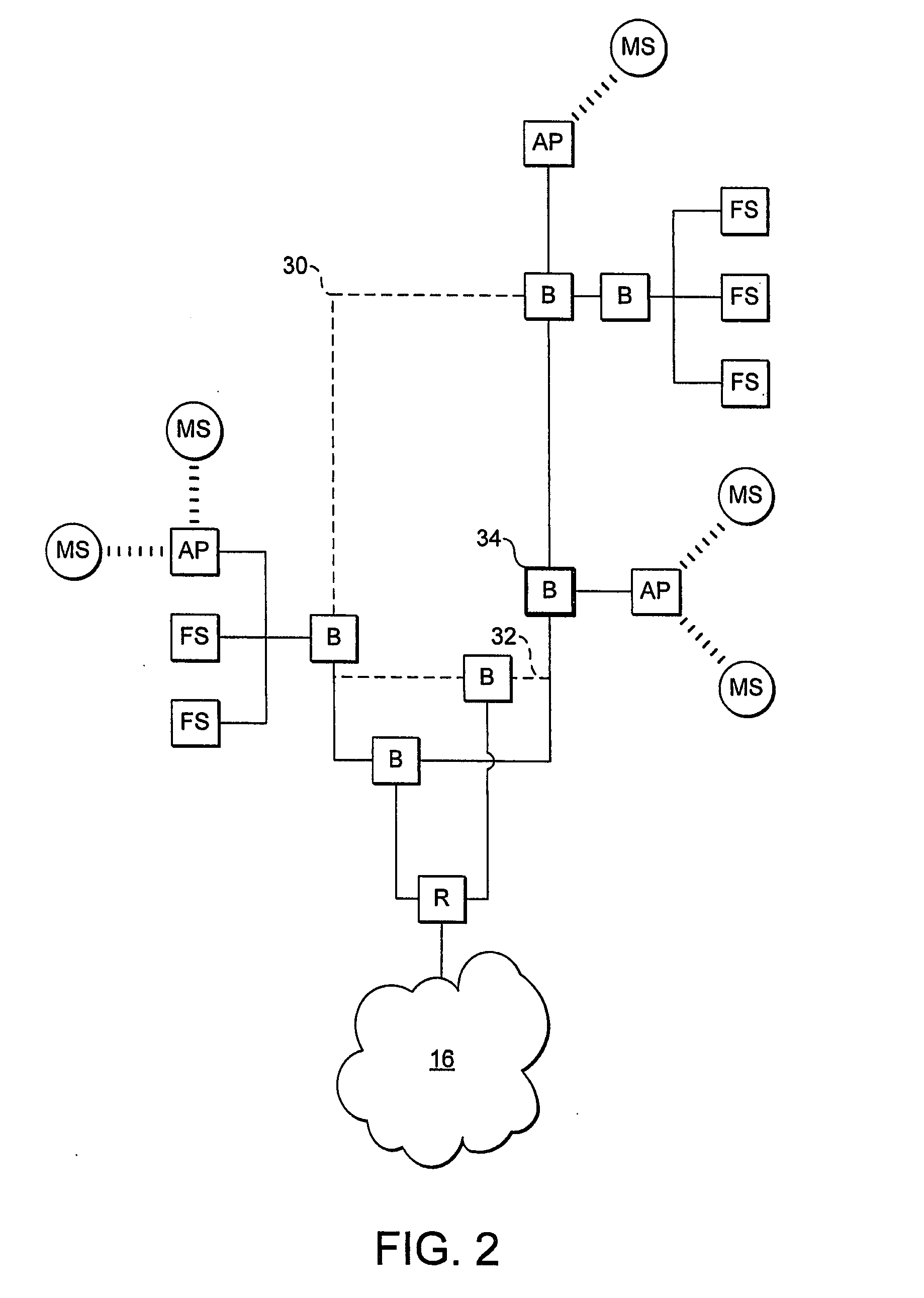
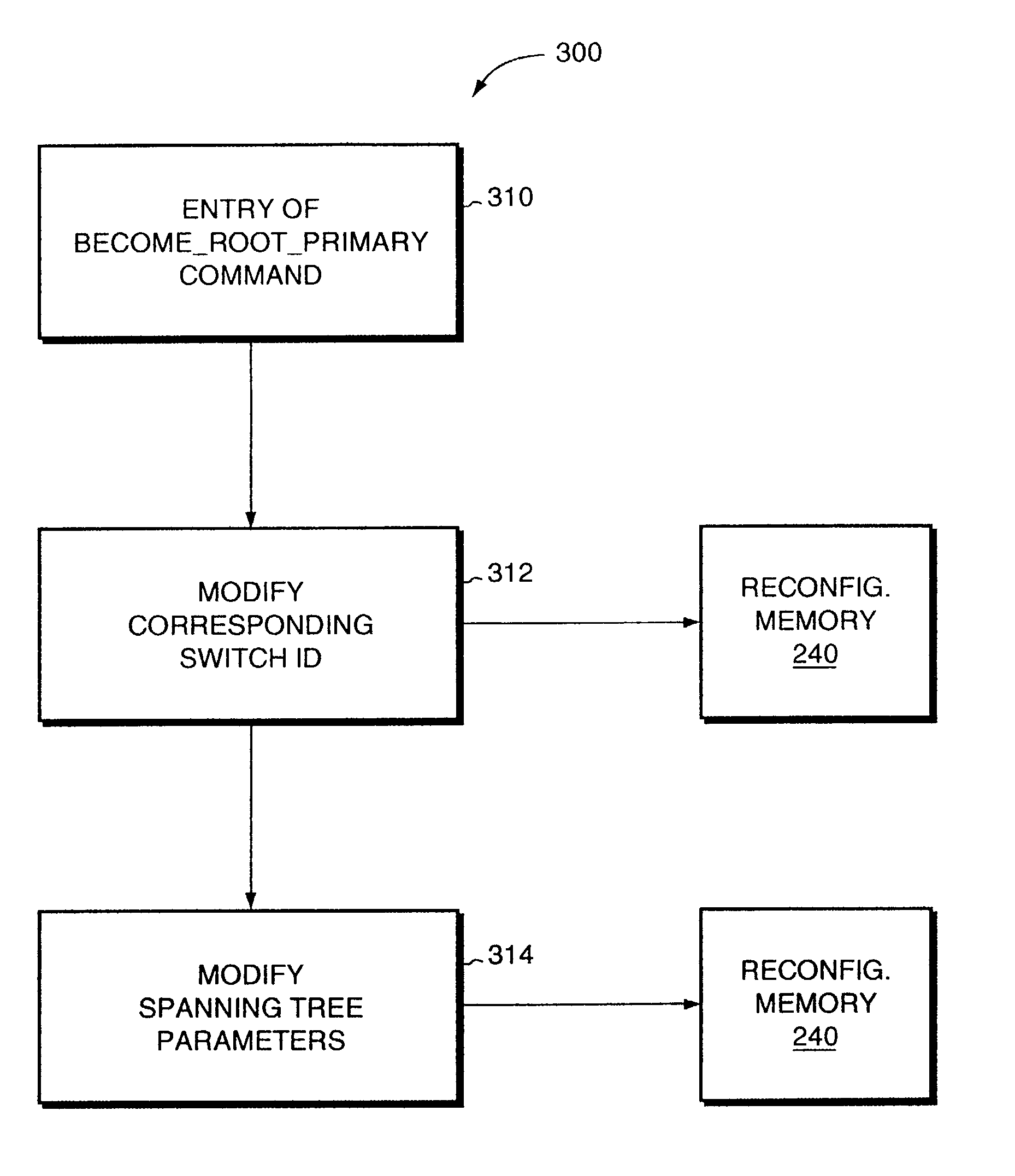
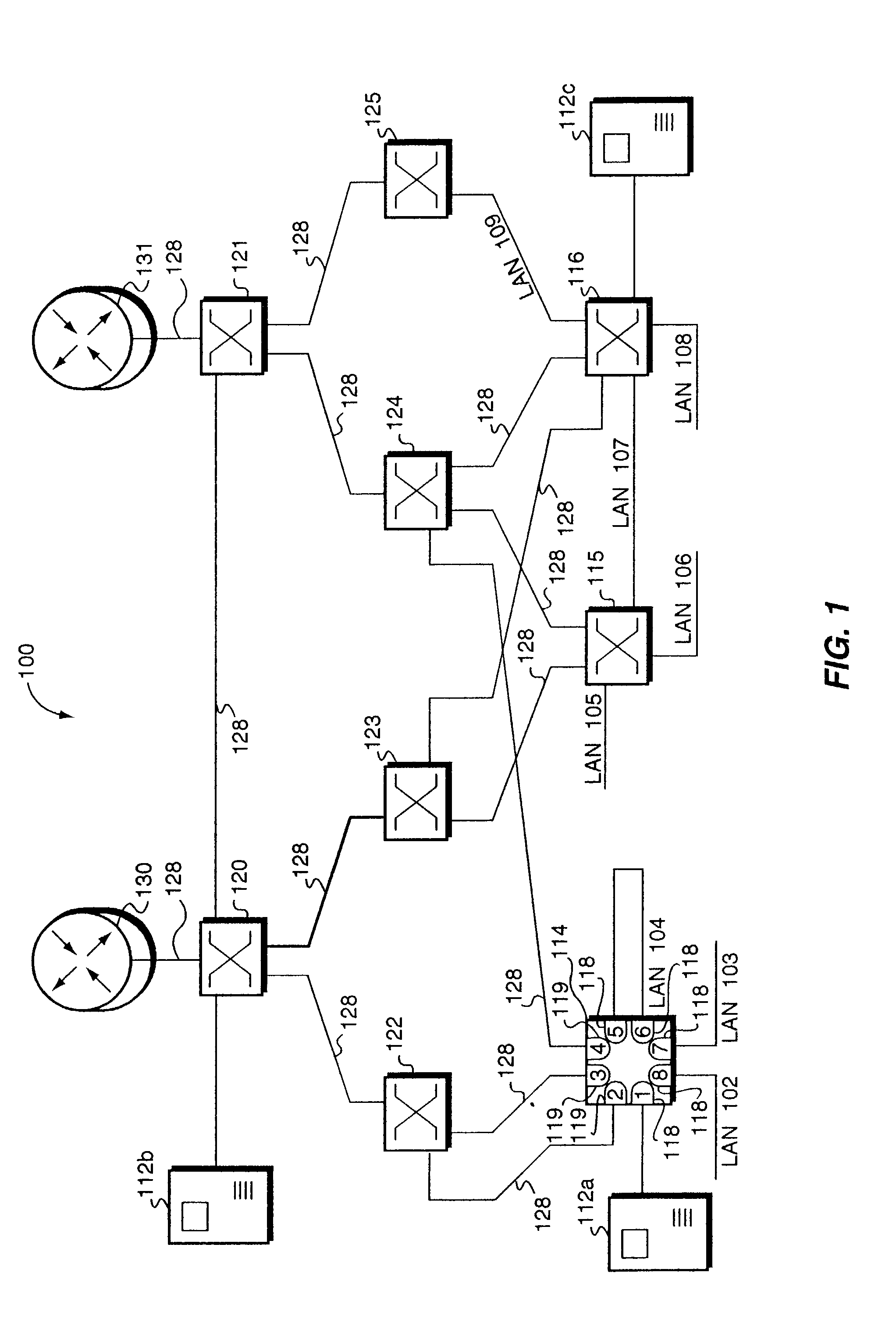
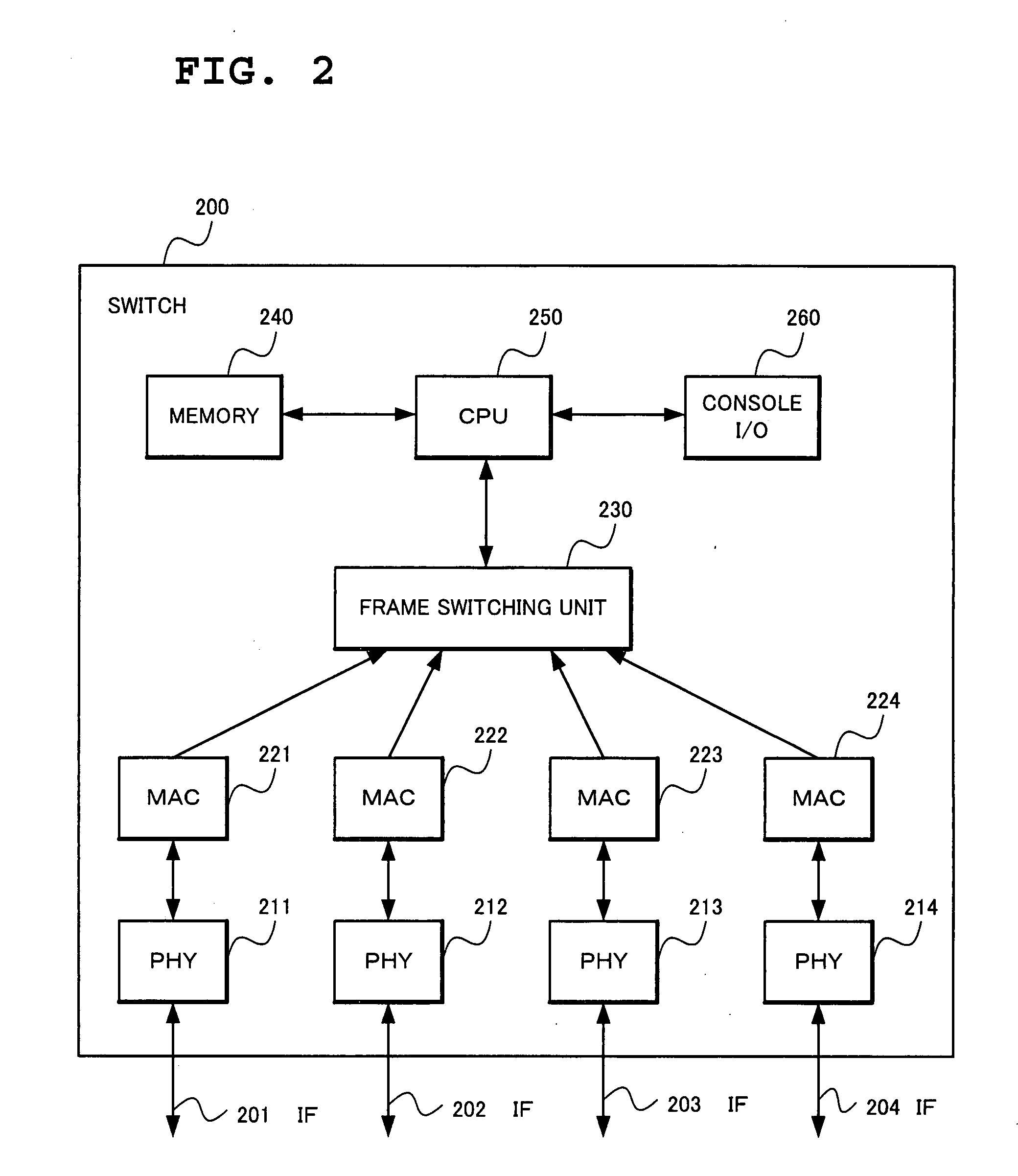
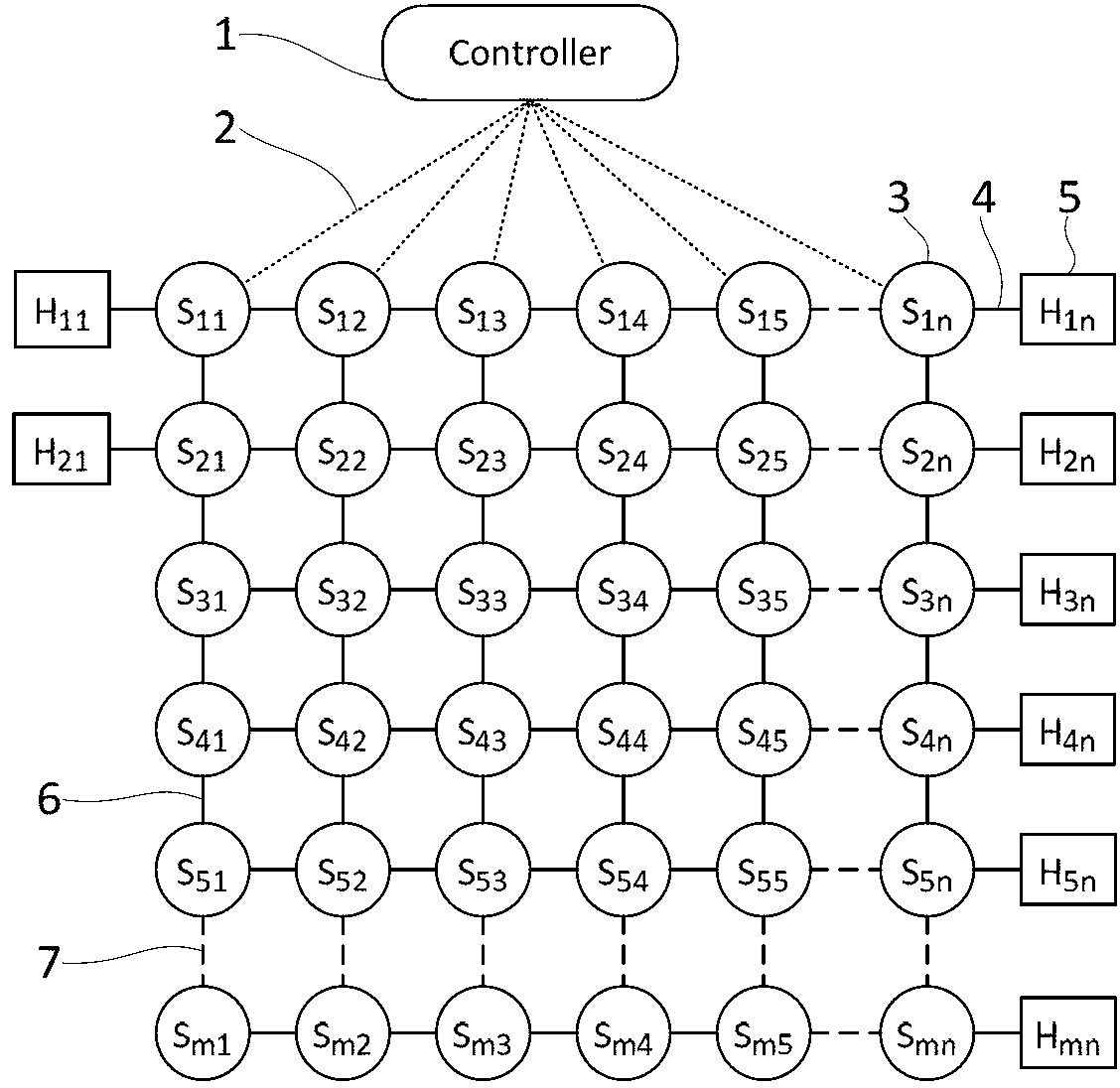
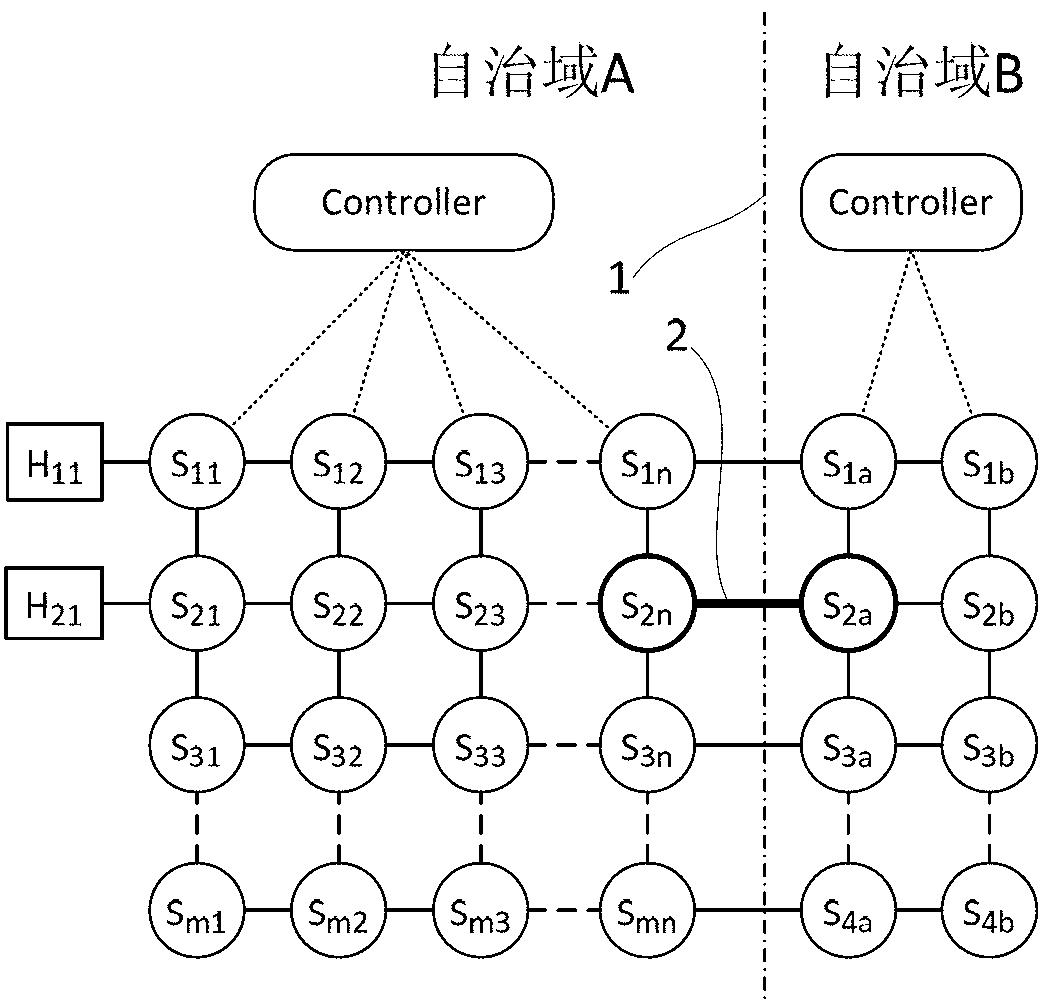
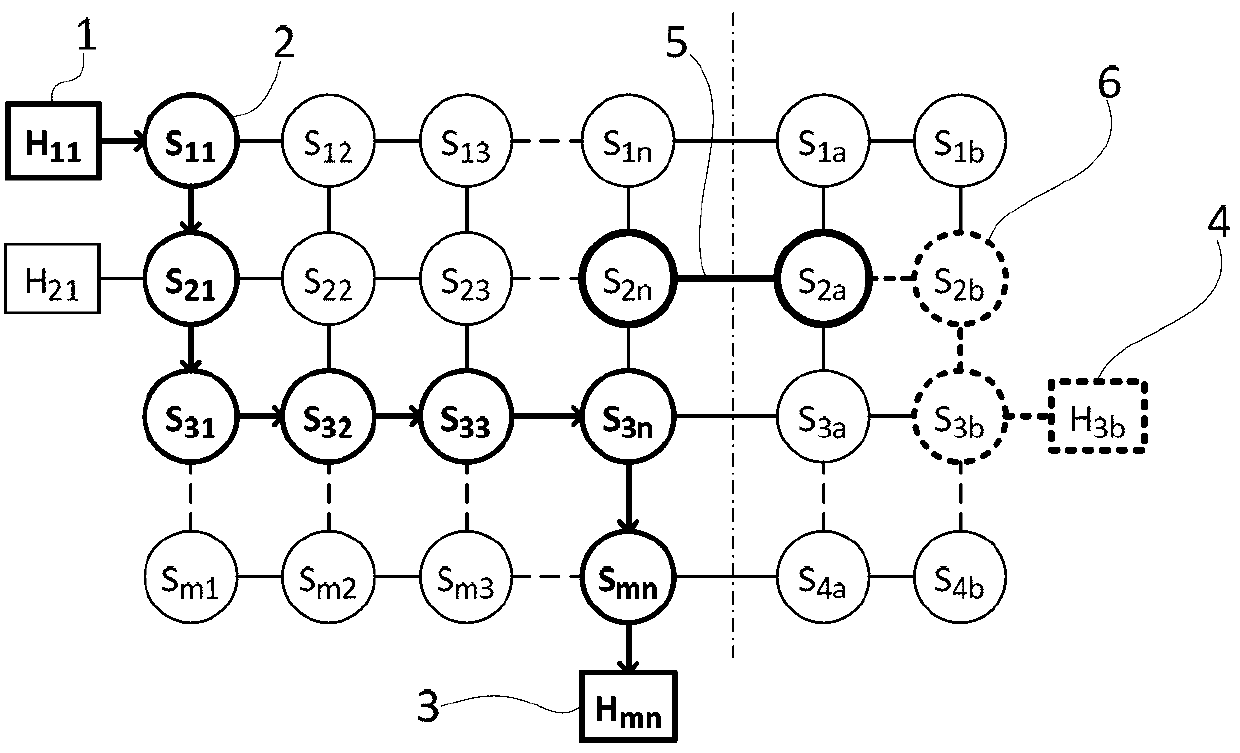
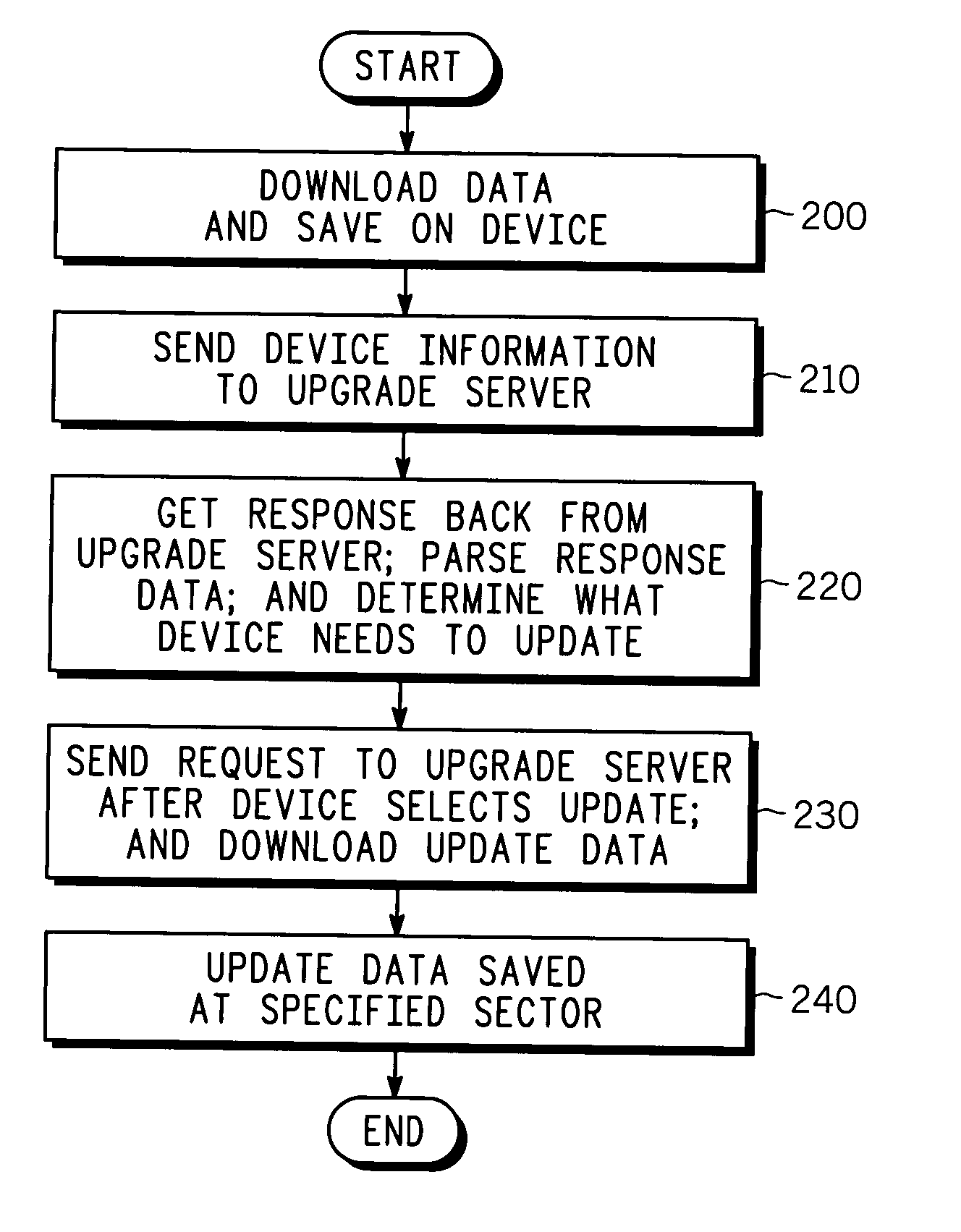
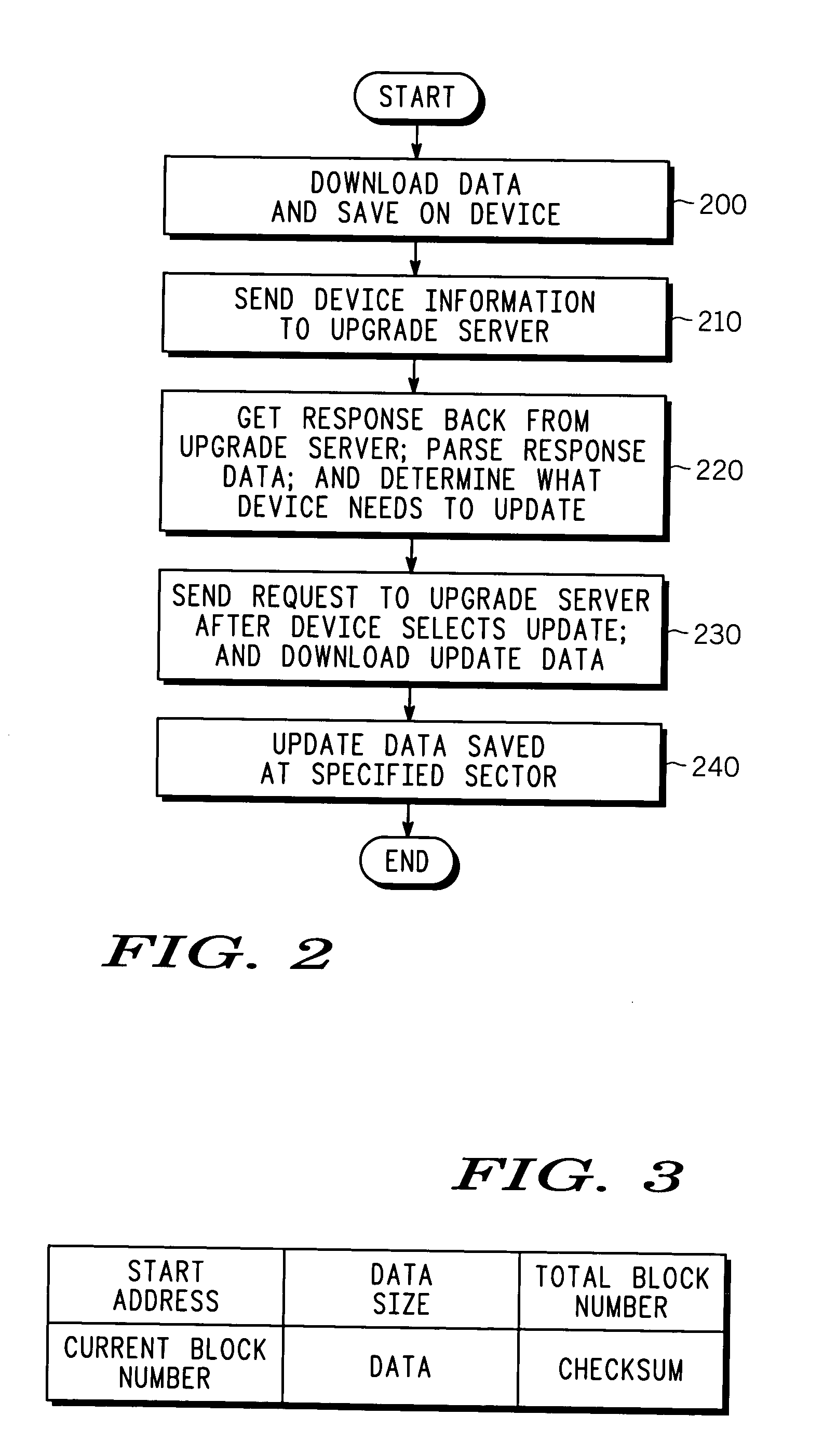
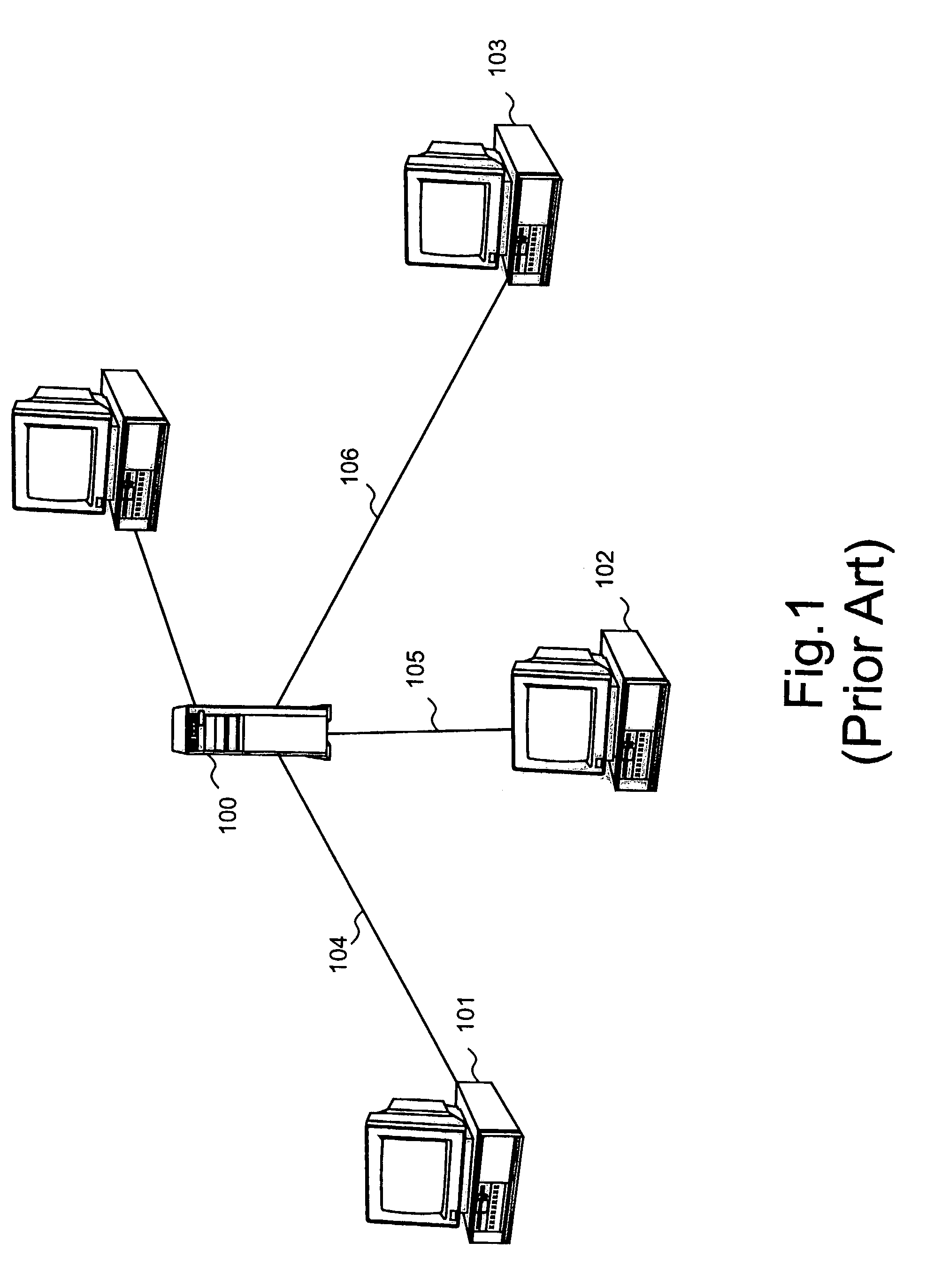
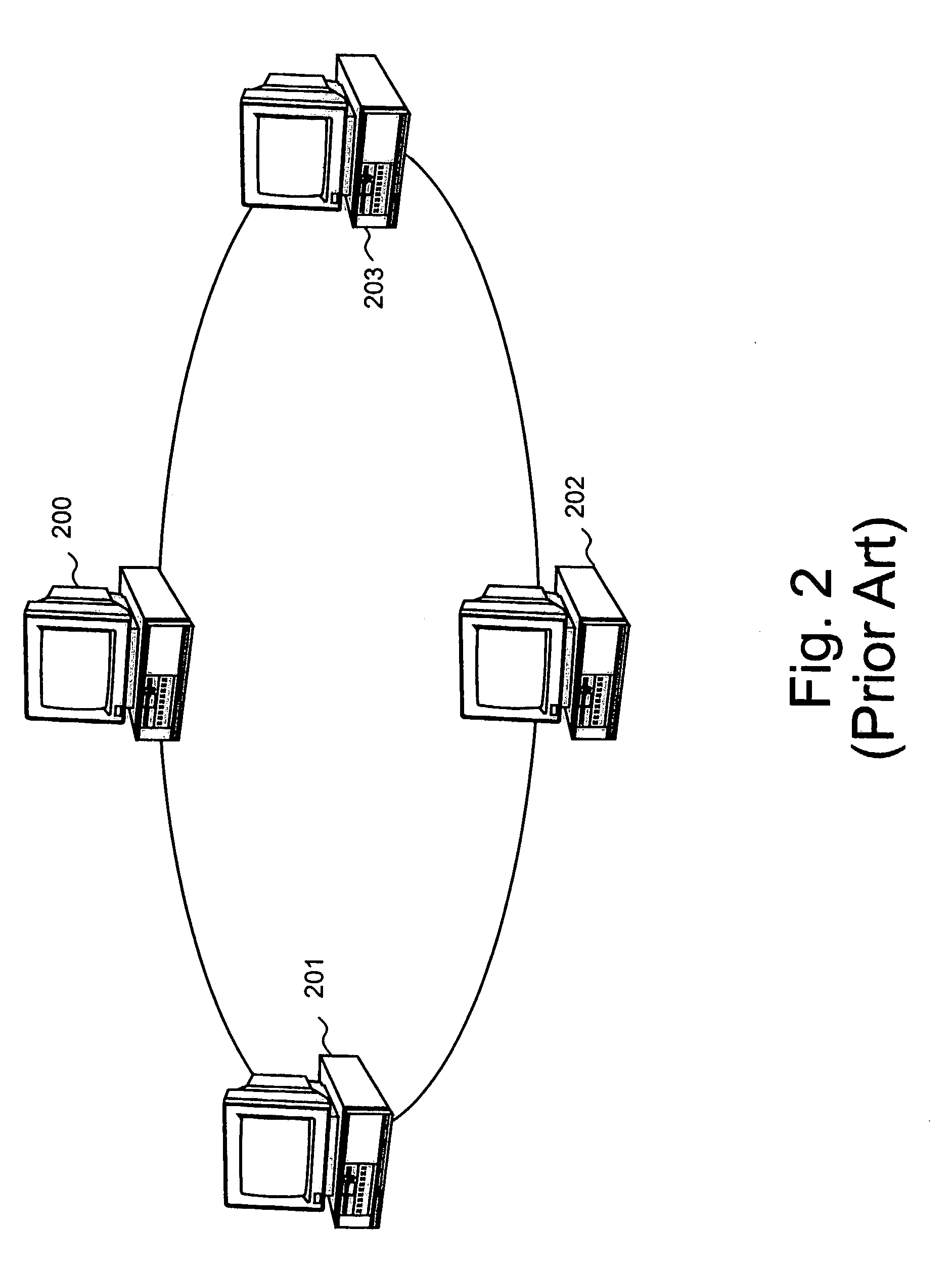
[topology loop detection mechanism]
InactiveUS20050076140A1Multiple digital computer combinationsNetworks interconnectionBroadcast radiationParallel computing
Broadcast storm due to topology loop may result from end-user mis-configurations, faulty ports, cabling problems, faulty spanning-tree algorithm implementations, and others. This loop detection mechanism helps detecting topology loops and eliminates them. It operates as a watchdog independent of the spanning-tree algorithm. The feature is aiming at enhancing the values of SO-LOS.
Owner:BLAZING ENERGY CO LTD
Method and apparatus for determining a layer 2 path in a switched network
InactiveUS6944130B1Error preventionFrequency-division multiplex detailsComputer networkConcatenation
A method and apparatus that provide for a Layer 2 path determination are disclosed. In one embodiment of the invention, a Layer 3 path between a source device and destination device is first determined in order to identify contiguous pairs of Layer 3 devices. A subpath is then determined for each contiguous pair of Layer 3 devices based on VLAN and spanning tree information associated with the contiguous pair. The Layer 2 path is a concatenation of the subpaths of all the contiguous pairs in the Layer 3 path.
Owner:CISCO TECH INC
Method and apparatus for restricting the assignment of VLANs
Restricting the assignment of VLANs so that a unique VLAN or set of VLANs must be assigned to each link for a particular network circuit (NC) or group of NCs. NCs are prevented from being assignd a particular VLAN if the addition of the VLAN assignment will create a mix-match topology, which may either create a loop or prevent a loop from being able to be properly blocked without inadvertently blocking a link of another NC. Restriction of VLAN assignment allow a single conventional spanning tree to be run to ensure that there are no layer 2 forwarding loops exist while at the same time not inadvertently blocking the path of another NC.
Owner:CISCO TECH INC
Data frame routing method and network bridge
InactiveUS20120044837A1Reduce the numberRobust controlStar/tree networksPort forwardingComputer science
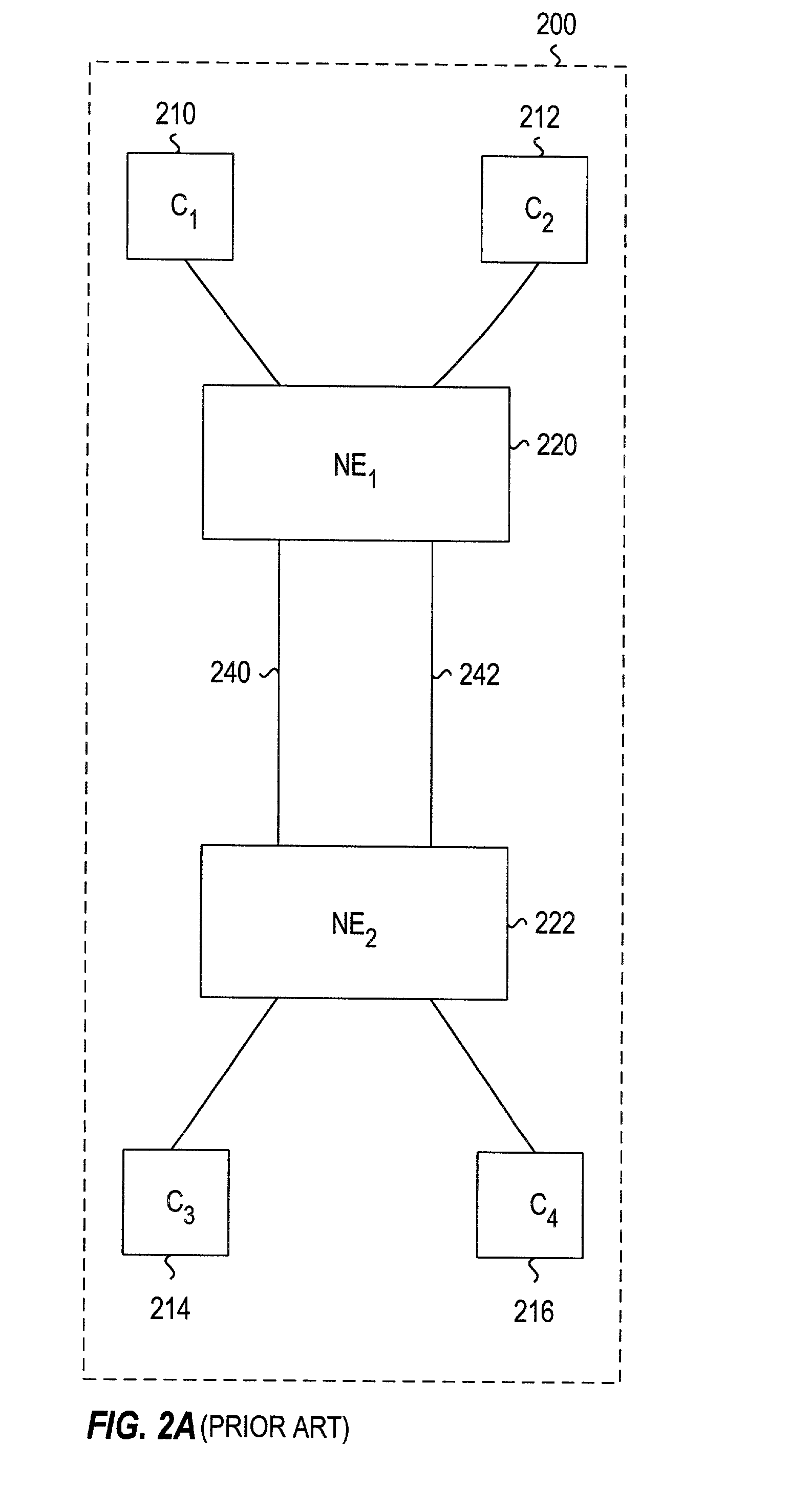
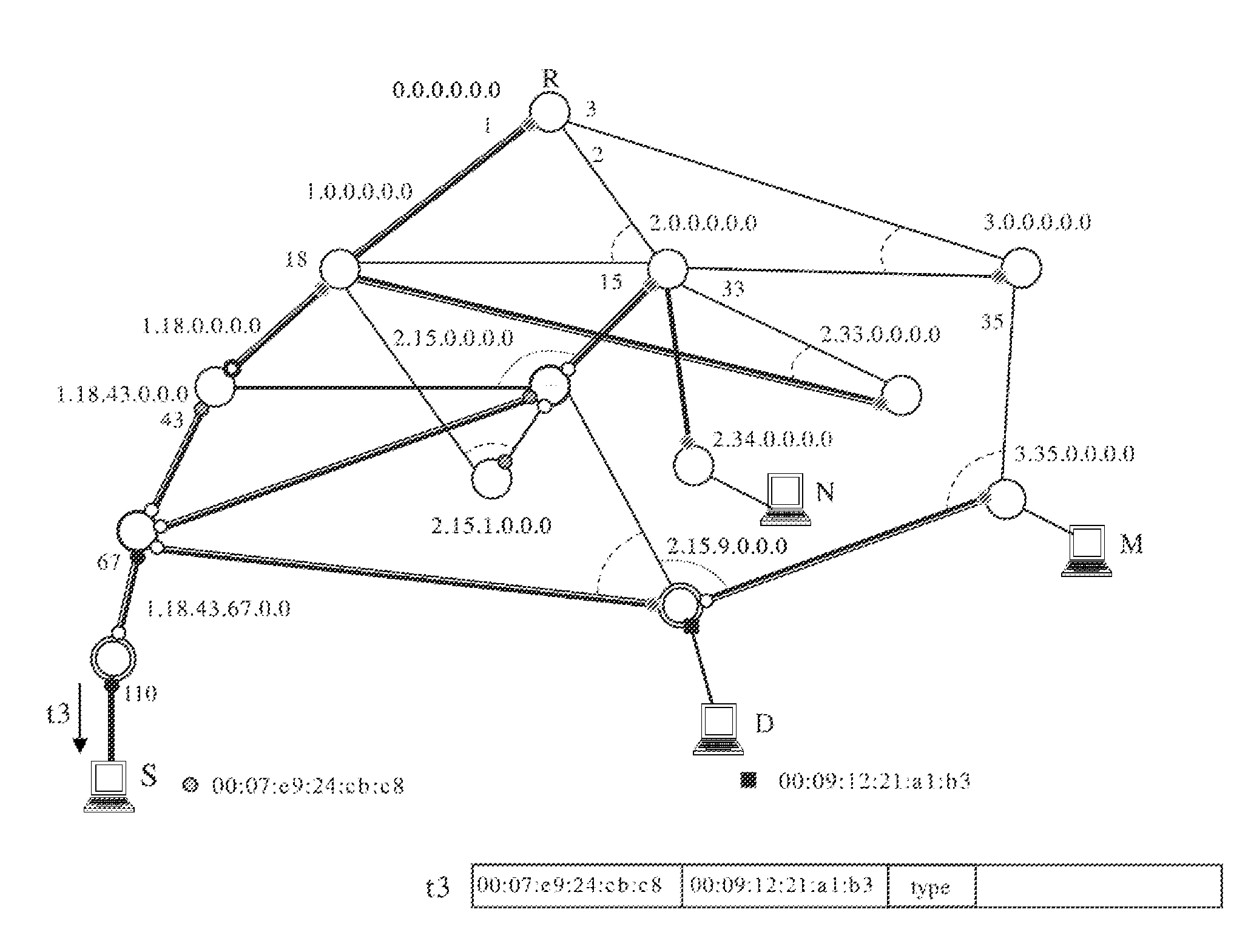
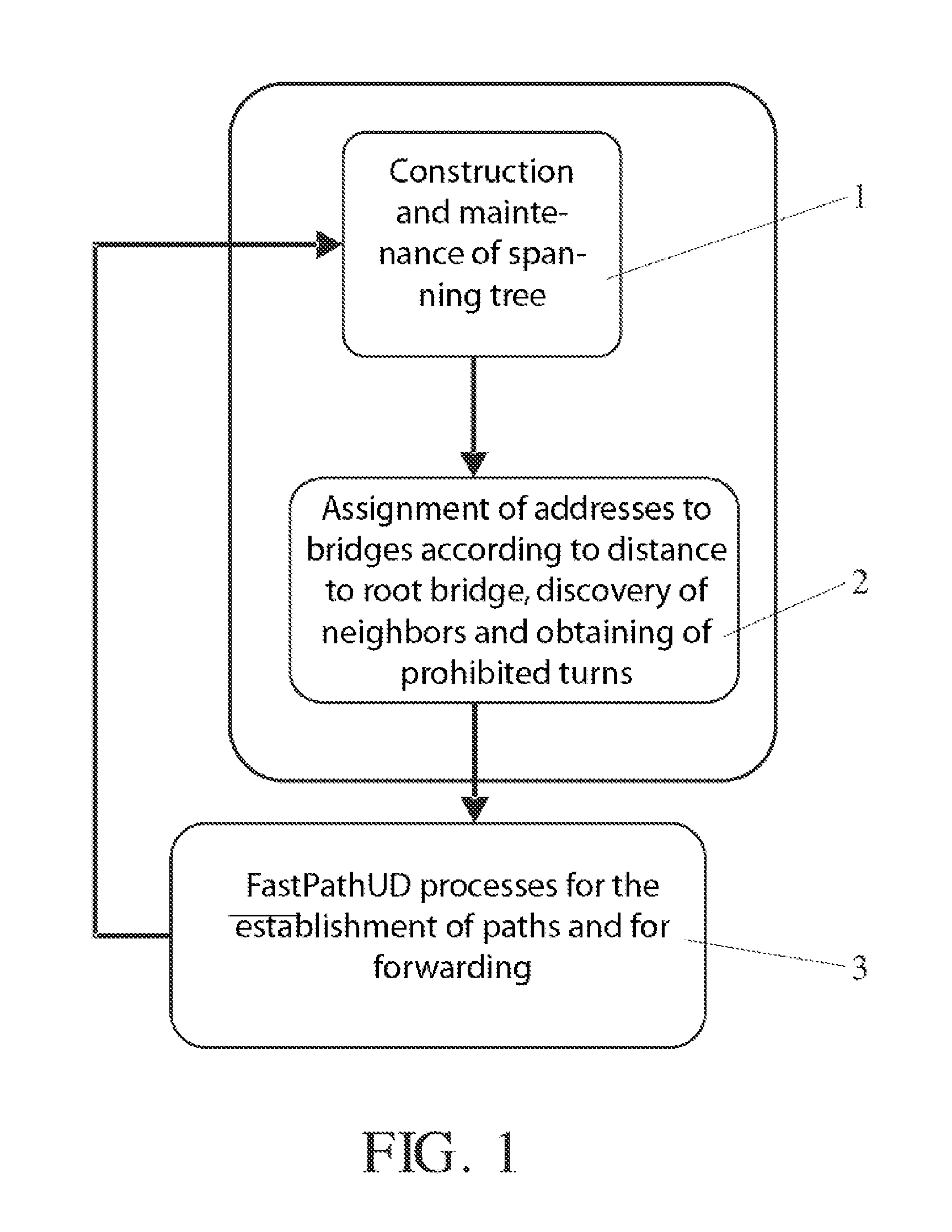
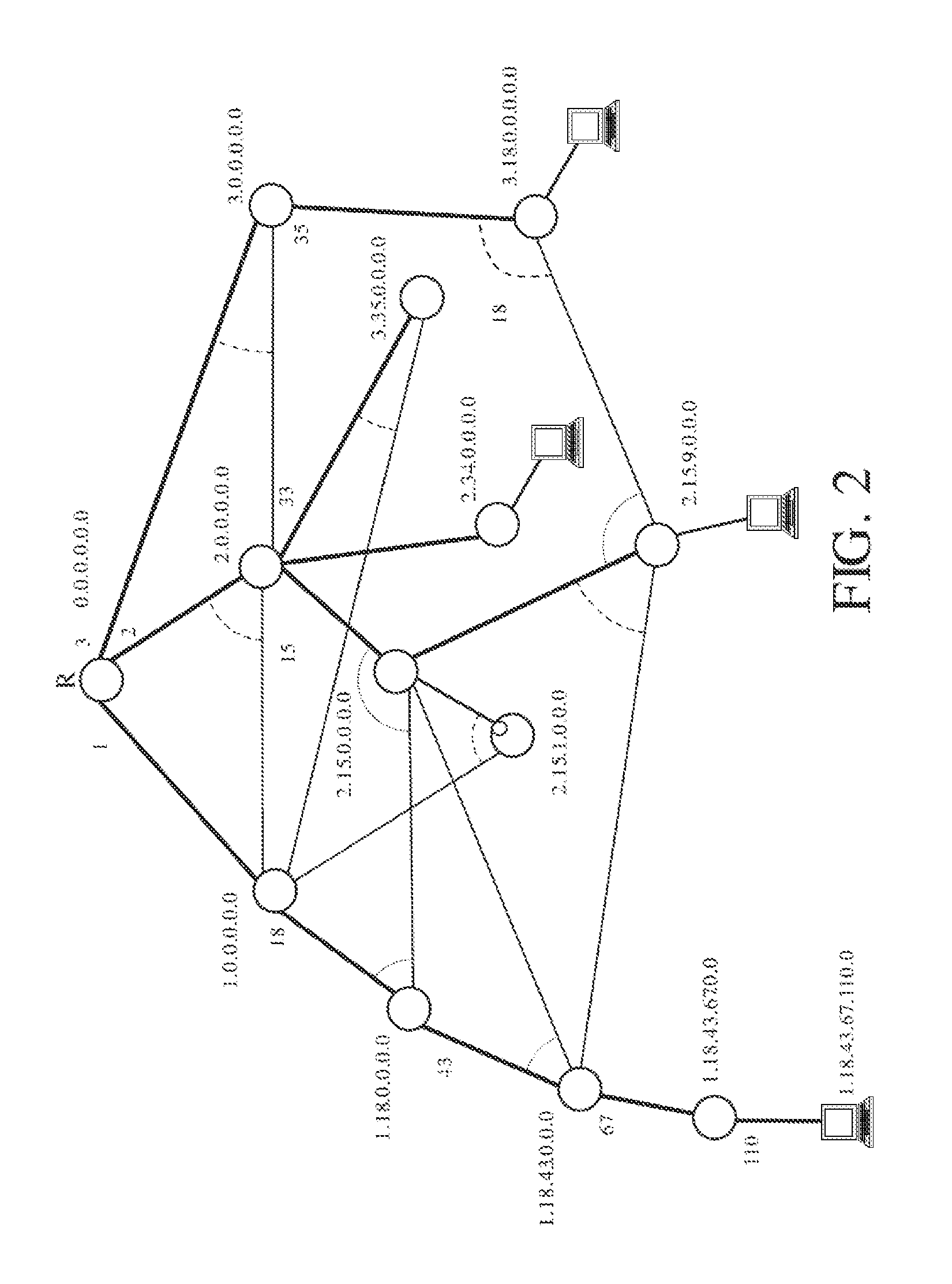
A method operates at the data link level. Each bridge associates, during a guard time, the port through which a frame is first received with a source MAC address until a unicast reply frame confirms the matching two-way path between the source and destination addresses. Any frame from the same source received through another different port is discarded. Each bridge forwards the received broadcast frames through the rest of the ports, except those involving prohibited (down-up) turns, and deviates (or optionally returns) the unicast frames with an unknown or aged destination address through the spanning tree. The protocol can operate with encapsulation in the border bridges or without encapsulation, using in this case the replacement of universal MAC addresses in the border bridges with local MAC addresses. The establishment and control of paths can optionally be performed proactively by the border bridges, especially the bridges connected to servers.
Owner:UNIV DE ALCALA DE HENARES +1
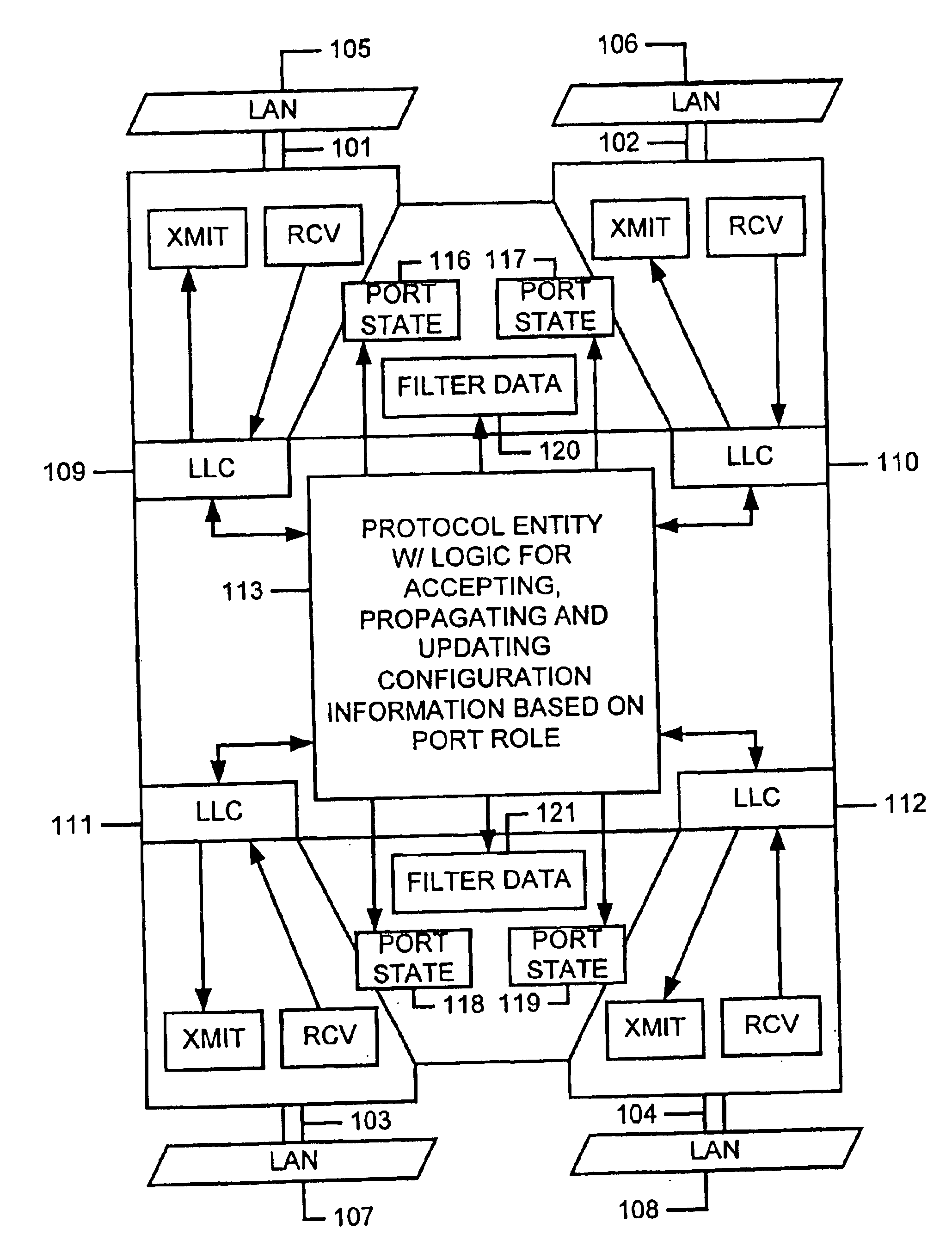
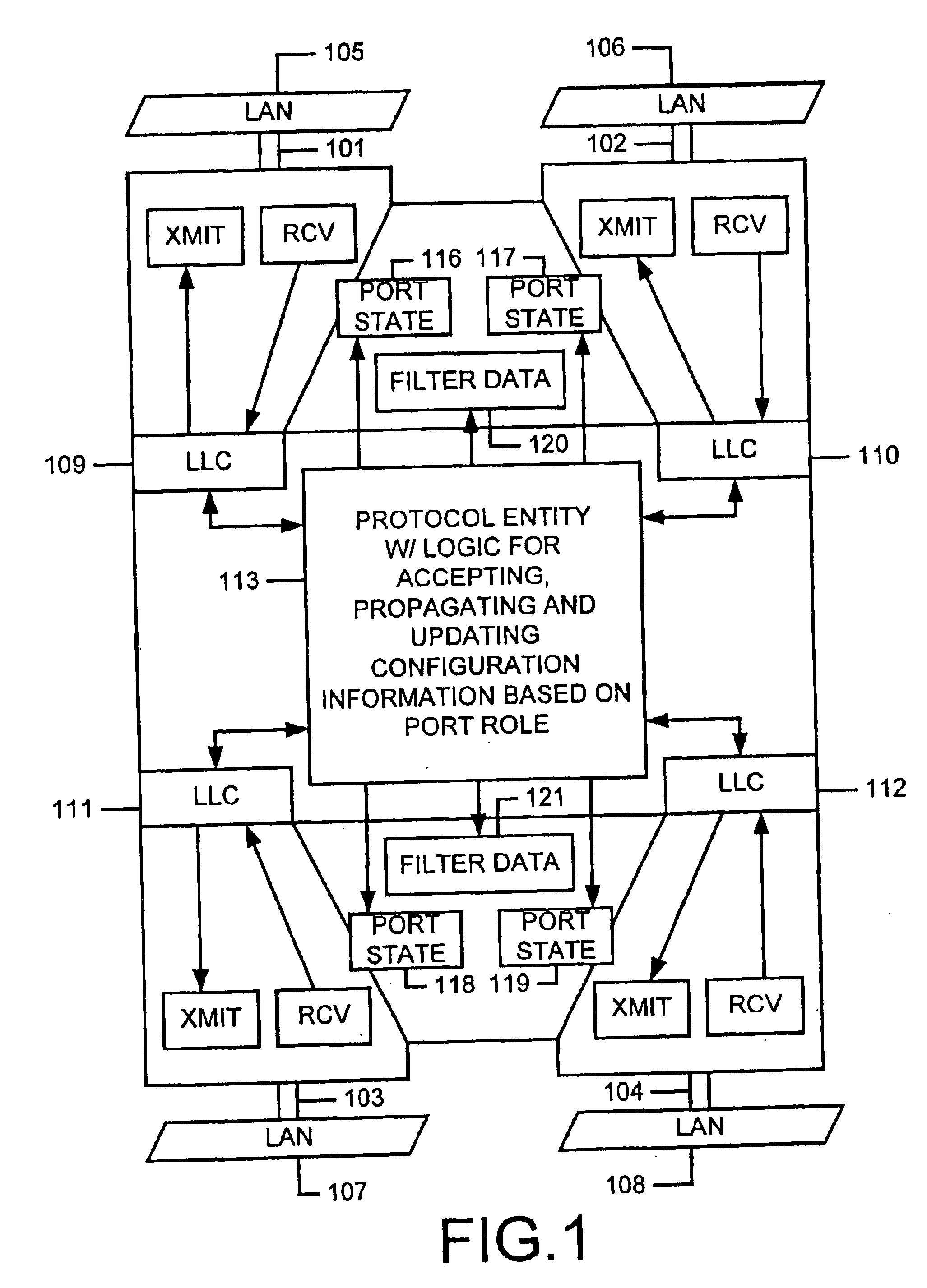
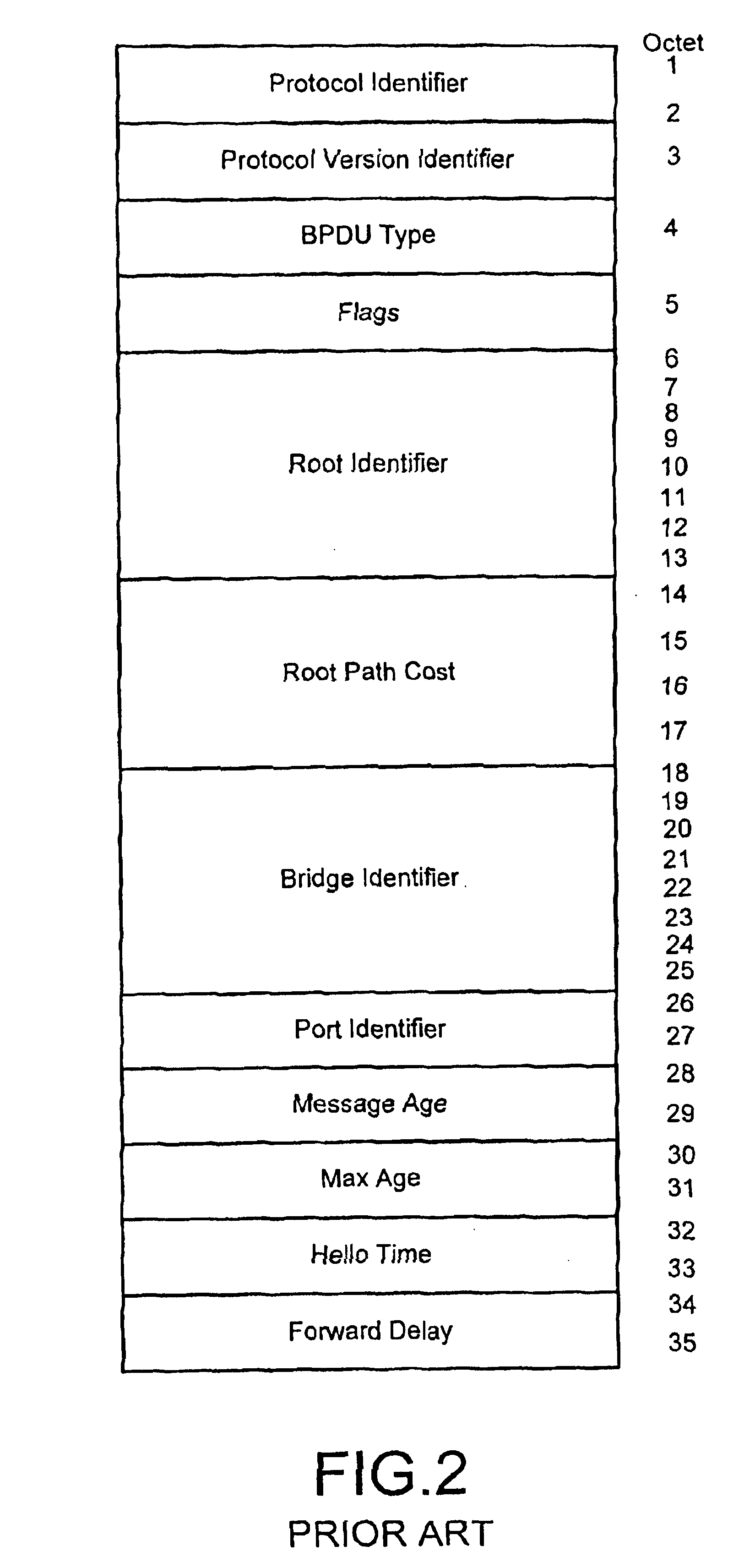
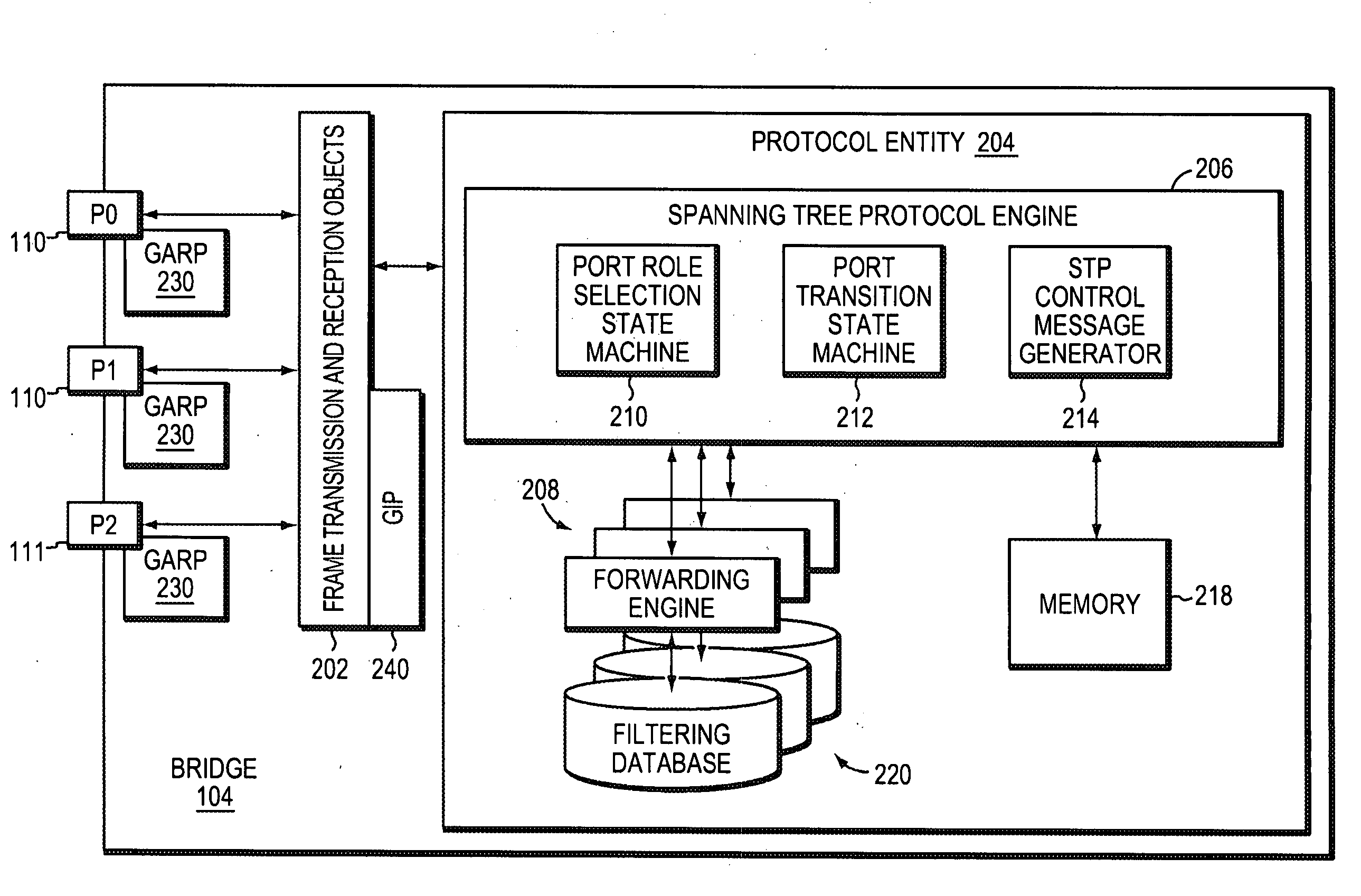
Spanning tree with rapid propagation of topology changes
InactiveUS6882630B1Spread quicklyBad newsNetworks interconnectionInformation propagationProtocol entity
Modifications to the spanning tree algorithm allow bad news to propagate quickly by providing that protocol entities on bridges process inferior information sent by the designated bridge for each LAN. In addition, bridges use per port hello timers to stimulate information propagation, setting it to suit local link characteristics. No changes to the format of bridge protocol data units (BPDUs) as specified in the IEEE Standard 802.1D are required, and the algorithm for computing the topology of the network remains unchanged. Techniques have been adopted for expiring information and recomputing the spanning tree upon detection of link failure, upon receipt of a message having a message age greater than its accompanying maximum age, or if the port hello time algorithm detects a loss of link. Rules for propagating information are provided allowing rapid propagation of changes. Finally, techniques for burning out information in a configuration message are adopted.
Owner:HEWLETT-PACKARD ENTERPRISE DEV LP
Link inference in large networks based on incomplete data
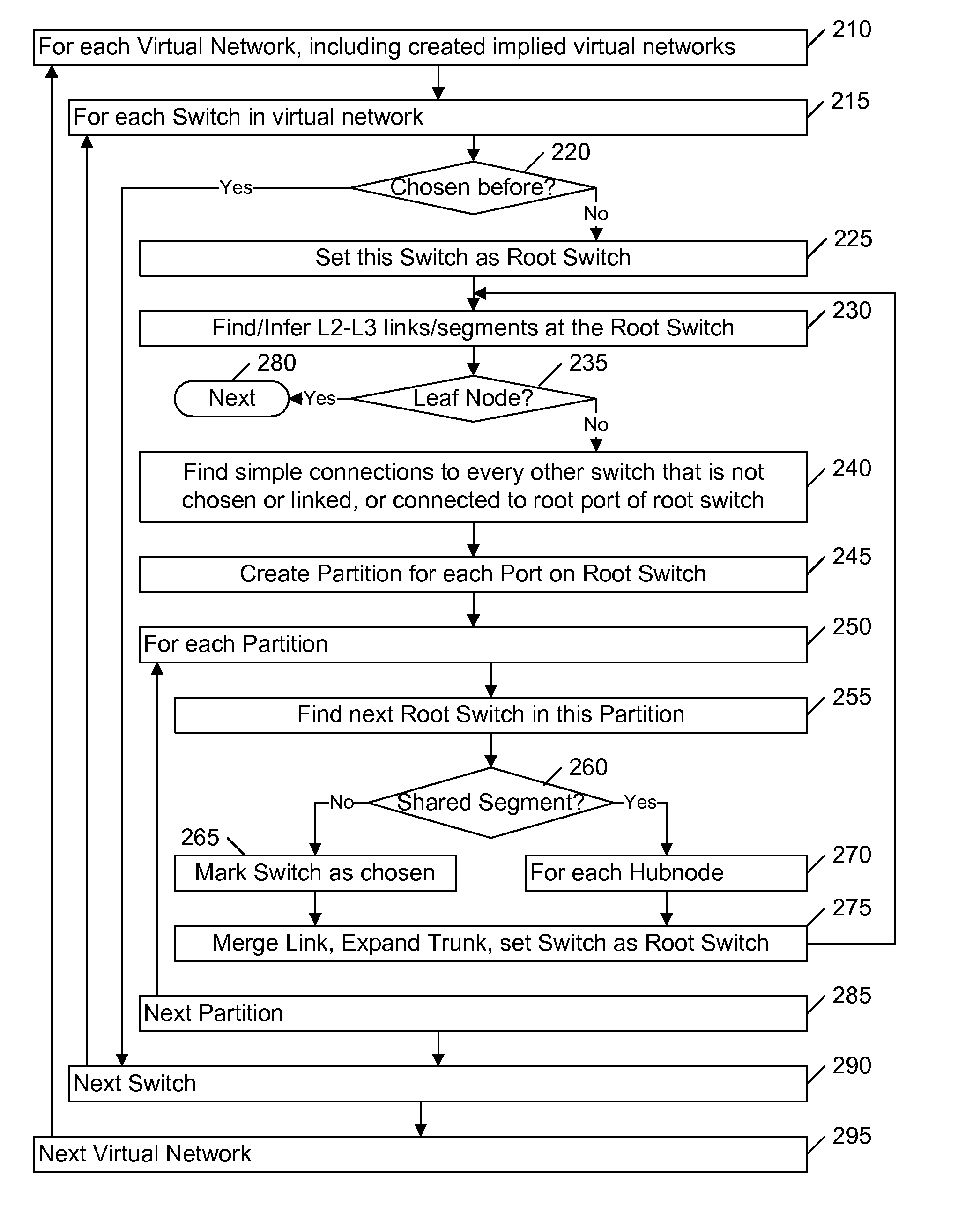
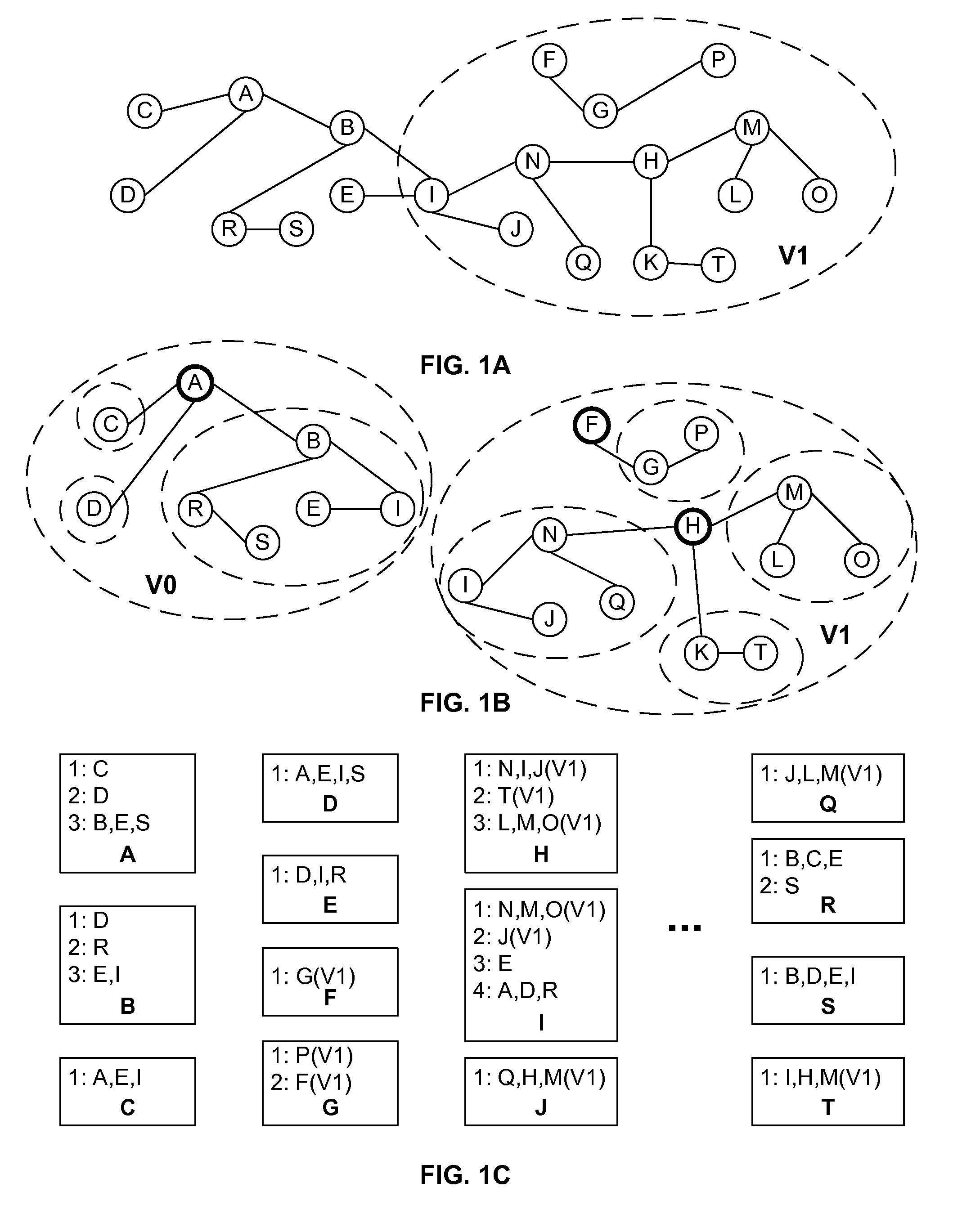
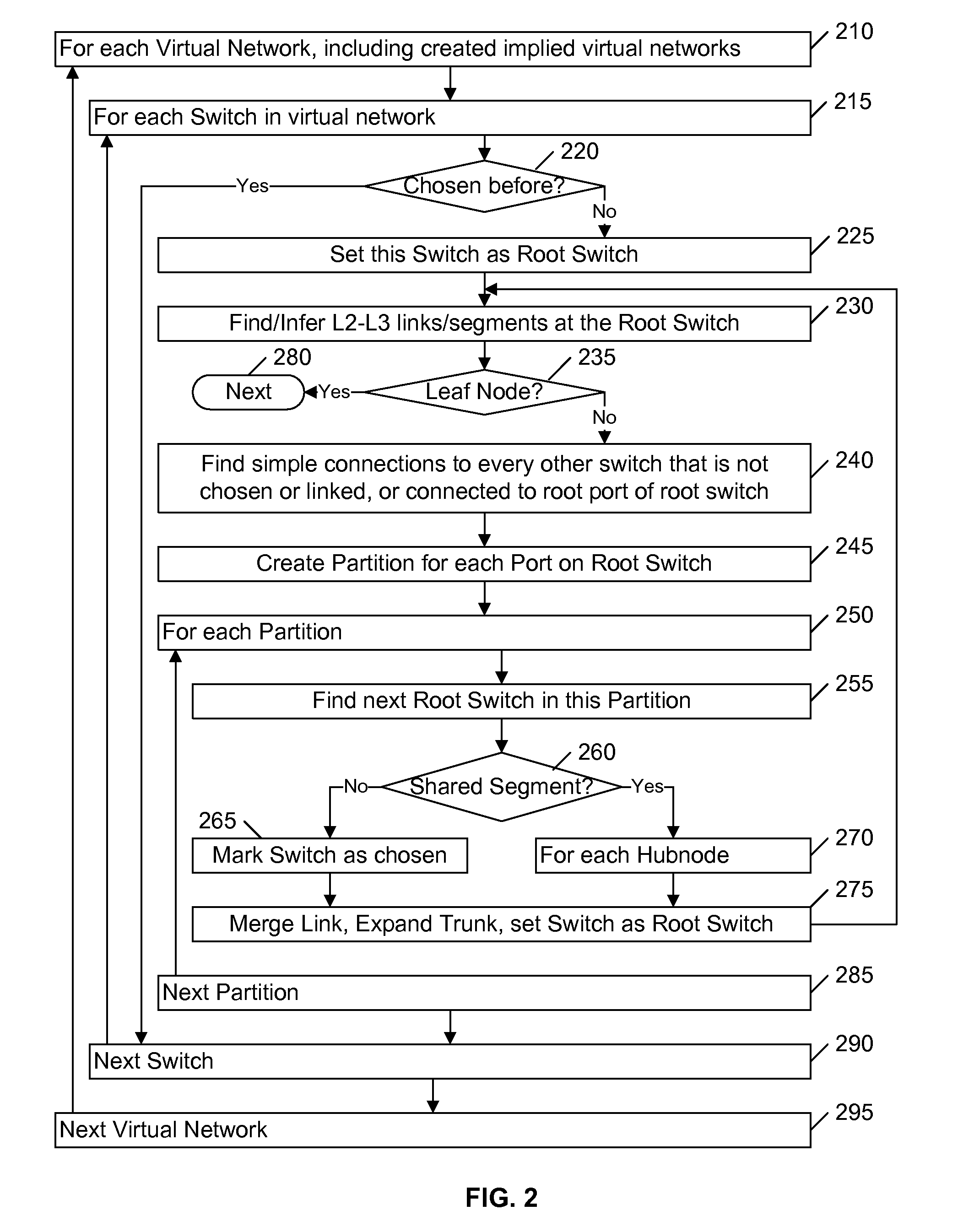
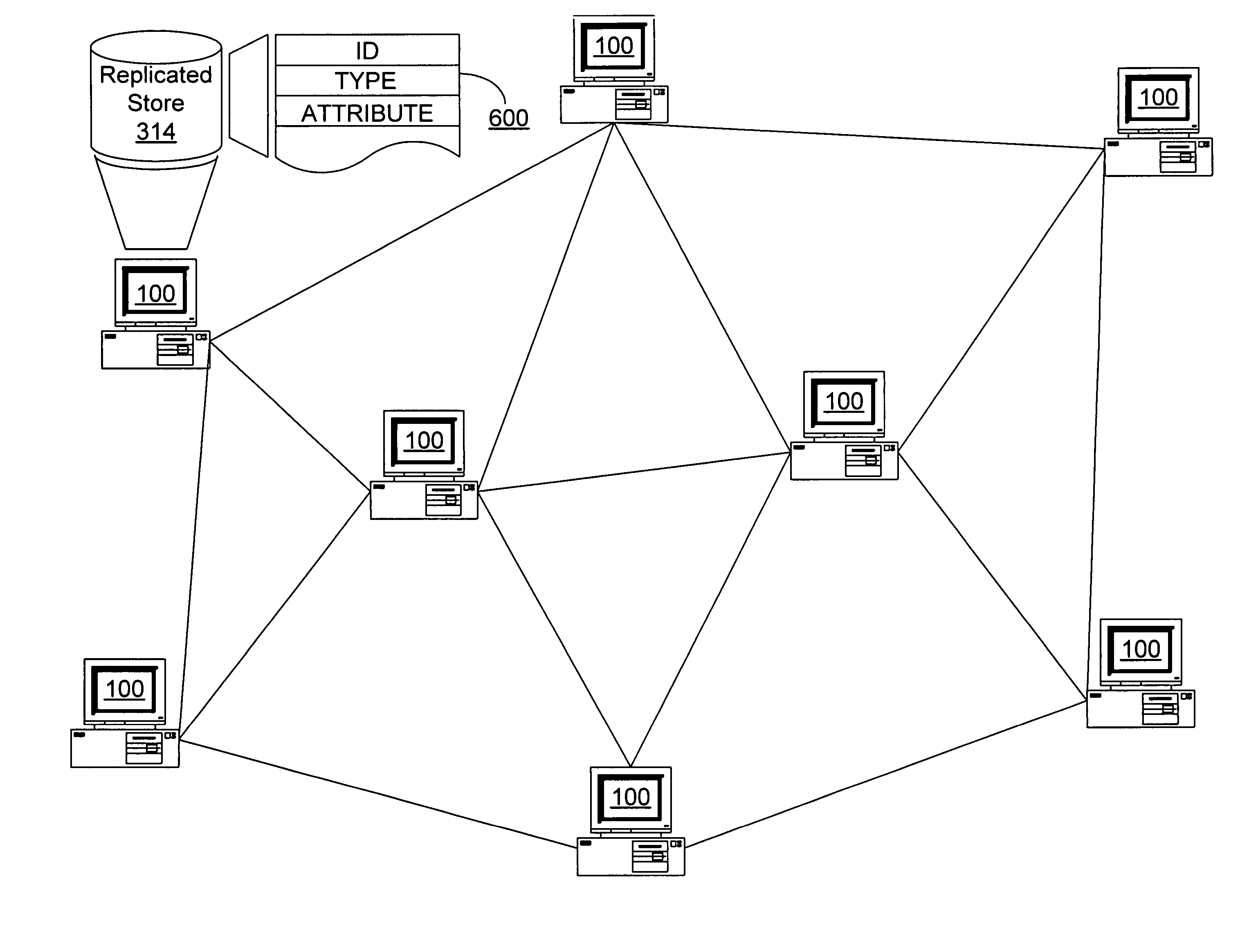
ActiveUS8089904B2Efficient implementationFirmly connectedData switching by path configurationNetwork connectionsTheoretical computer scienceLarge networks
A network is partitioned into a set of independent partitions, and the topology of each partition is determined, then merged to form a topology of the entire network. Preferably, the partitioning is hierarchical, wherein the network is partitioned to form individual VLAN partitions, and each of the VLAN partitions is further partitioned based on the nodes that are simply connected to each port of one or more selected root switches within the VLAN partition. Simple connections to each port are efficiently determined based on an aggregate address forwarding table associated with each node. Ancillary information, such as spanning tree or CDP data, may be used to facilitate efficient partitioning and / or to validate inferences that are made with incomplete information.
Owner:RIVERBED TECH LLC
Network supporting roaming, sleeping terminals
InactiveUS7536167B2Minimize collisionHighly versatileEnergy efficient ICTPower managementTransceiverCommunications system
Improved apparatus for a radio communication system having a multiplicity of mobile transceiver units selectively in communication with a plurality of base transceiver units which, in turn, communicate with one or more host computers for storage and manipulation of data collected by bar code scanners or other collection means associated with the mobile transceiver units. A network controller and an adapter which has a simulcast and sequential mode provide selective interface between host computers and base transceivers. A scheme for routing data through the communication system is also disclosed wherein the intermediate base stations are organized into an optimal spanning-tree network to control the routing of data to and from the RF terminals and the host computer efficiently and dynamically. Additionally, redundant network and communication protocol is disclosed wherein the network utilizes a polling communication protocol which, under heavy loaded conditions, requires that a roaming terminal wishing to initiate communication must first determine that the channel is truly clear by listing for an entire interpoll gap time. In a further embodiment, a criterion used by the roaming terminals for attaching to a given base station reduces conflicts in the overlapping RF regions of adjacent base stations.
Owner:AVAGO TECH WIRELESS IP SINGAPORE PTE +1
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com

















![[topology loop detection mechanism] [topology loop detection mechanism]](https://images-eureka-patsnap-com.libproxy1.nus.edu.sg/patent_img/a0af4b77-5473-47d3-b77d-fe366477b852/US20050076140A1-20050407-D00000.png)
![[topology loop detection mechanism] [topology loop detection mechanism]](https://images-eureka-patsnap-com.libproxy1.nus.edu.sg/patent_img/a0af4b77-5473-47d3-b77d-fe366477b852/US20050076140A1-20050407-D00001.png)
![[topology loop detection mechanism] [topology loop detection mechanism]](https://images-eureka-patsnap-com.libproxy1.nus.edu.sg/patent_img/a0af4b77-5473-47d3-b77d-fe366477b852/US20050076140A1-20050407-D00002.png)