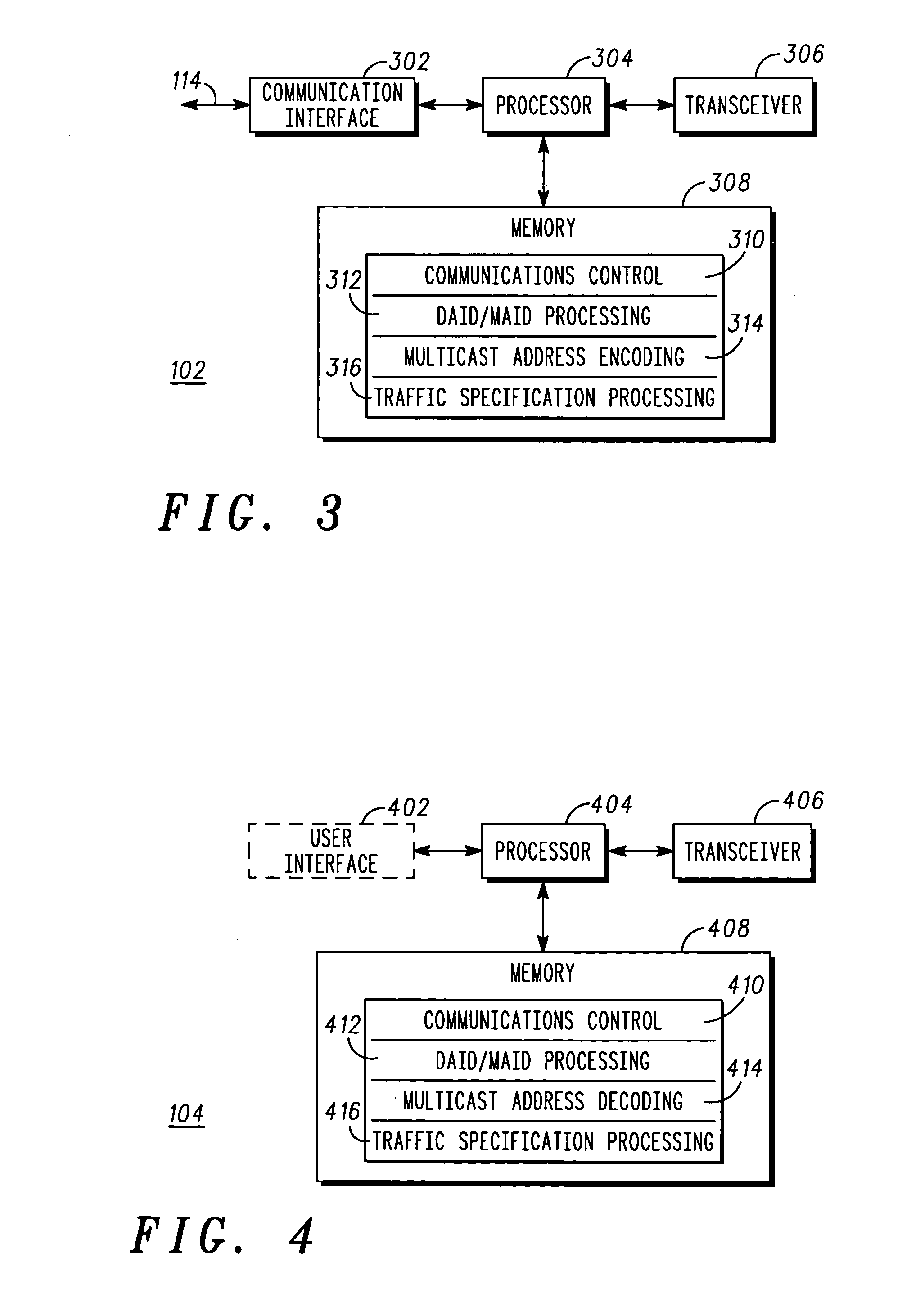
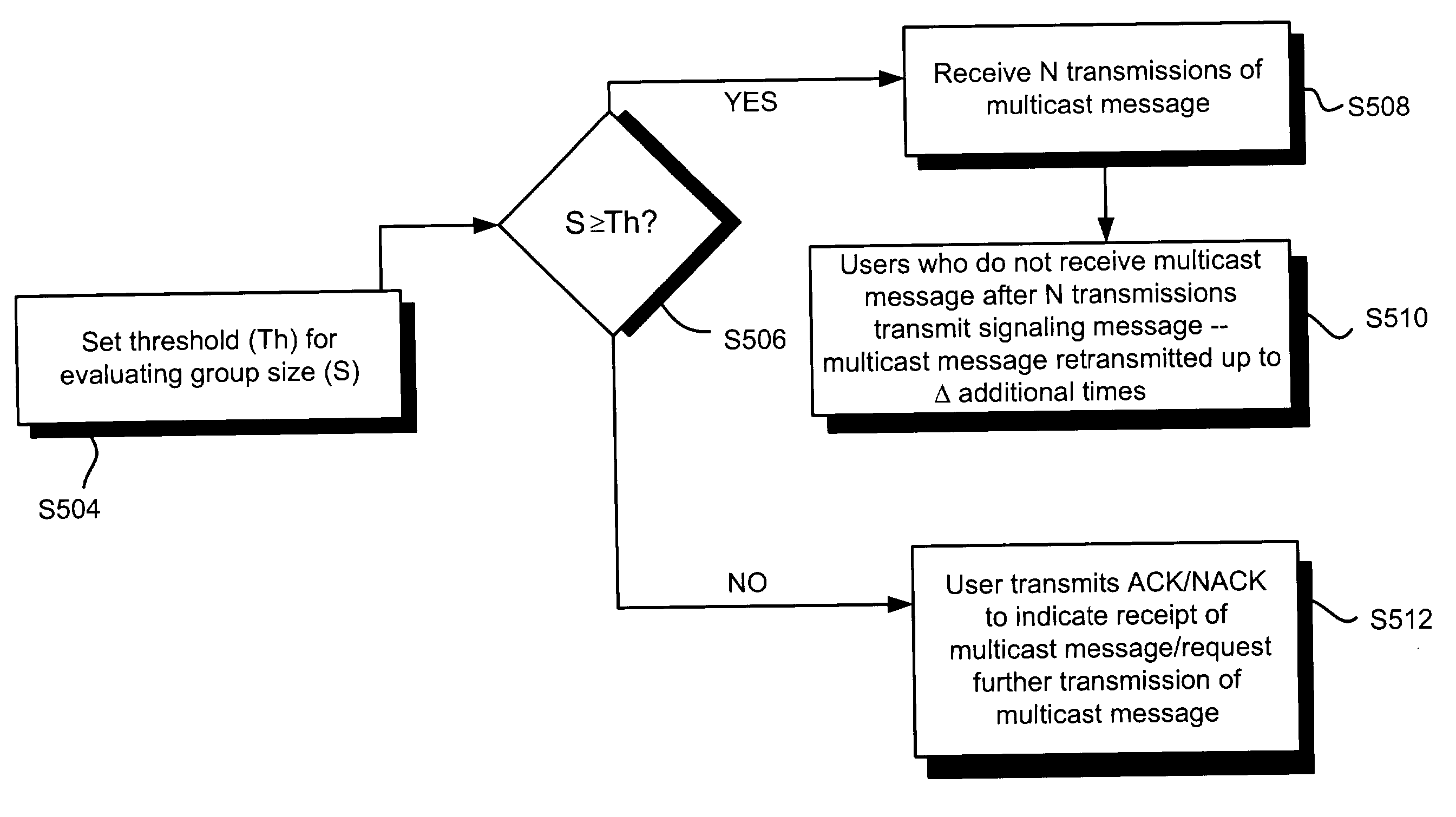
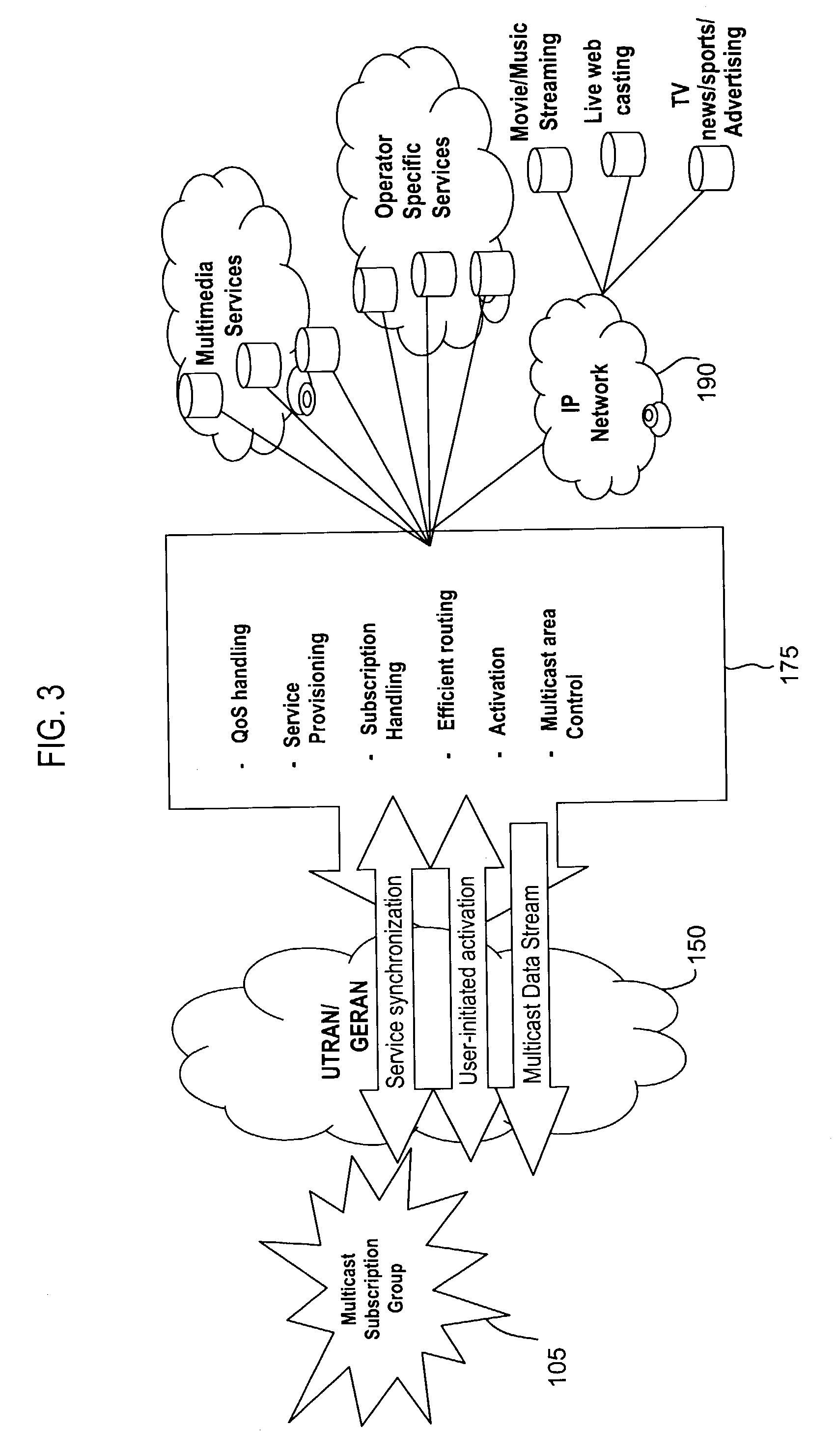
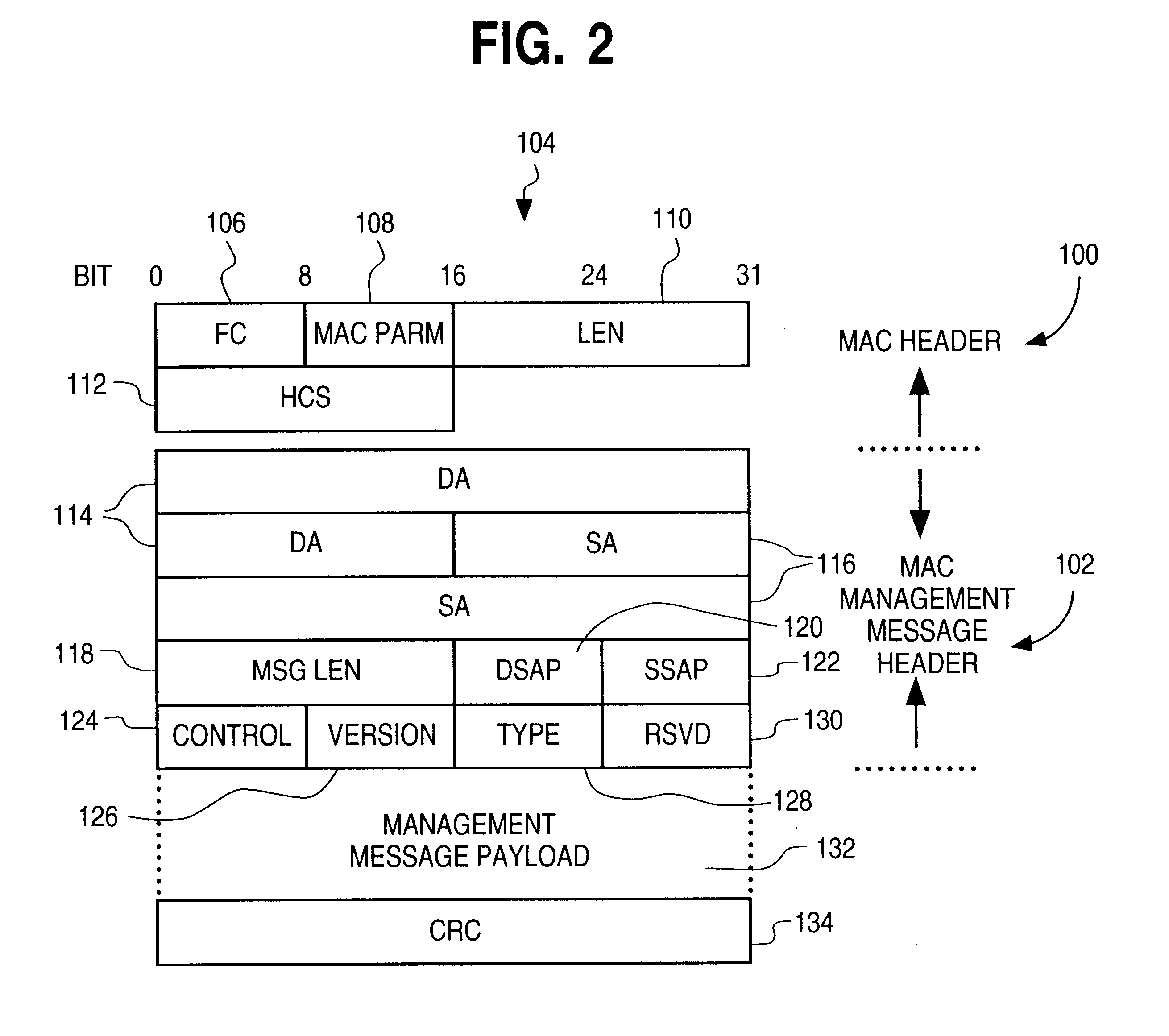
Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
974 results about "Multicast message" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
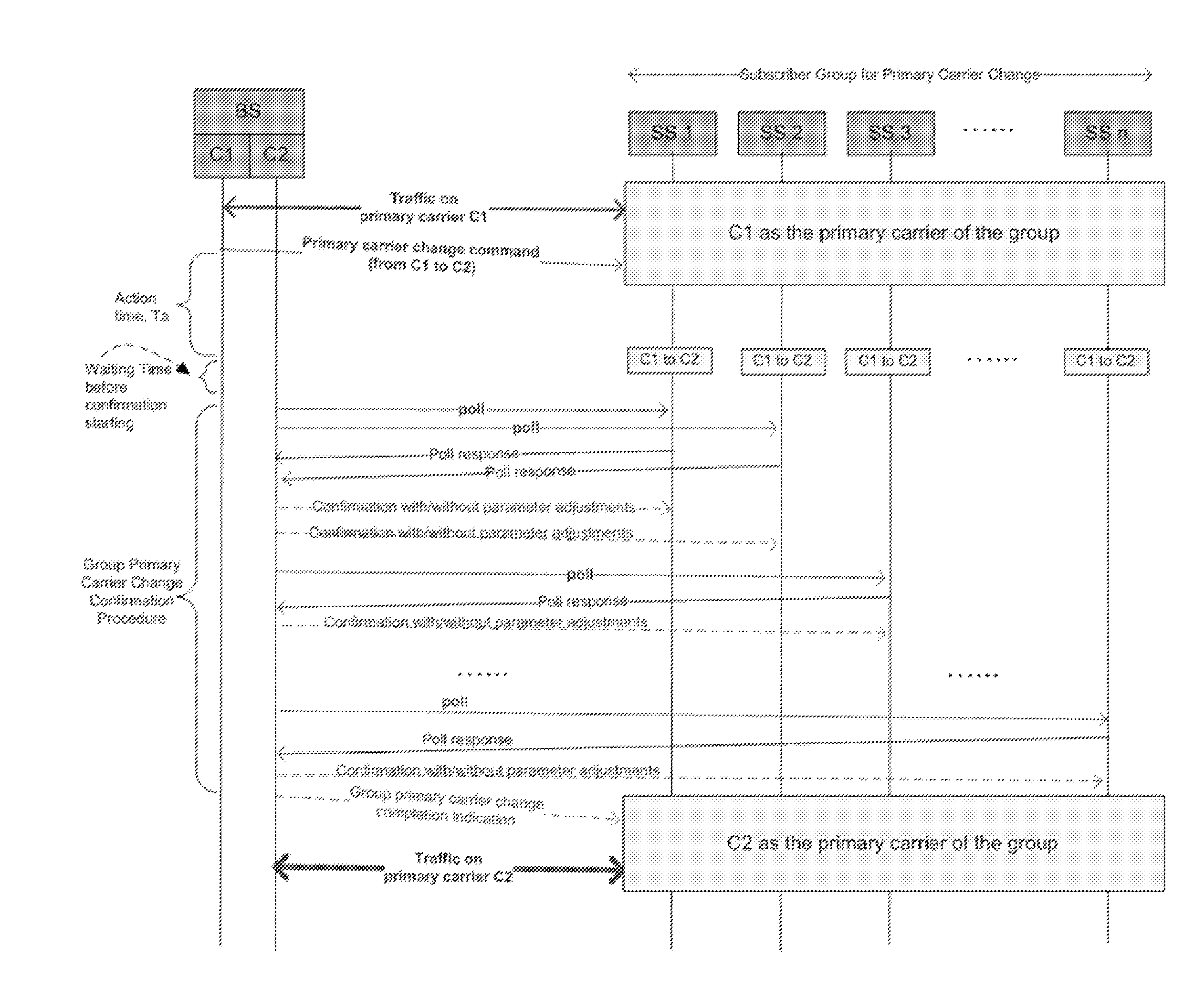
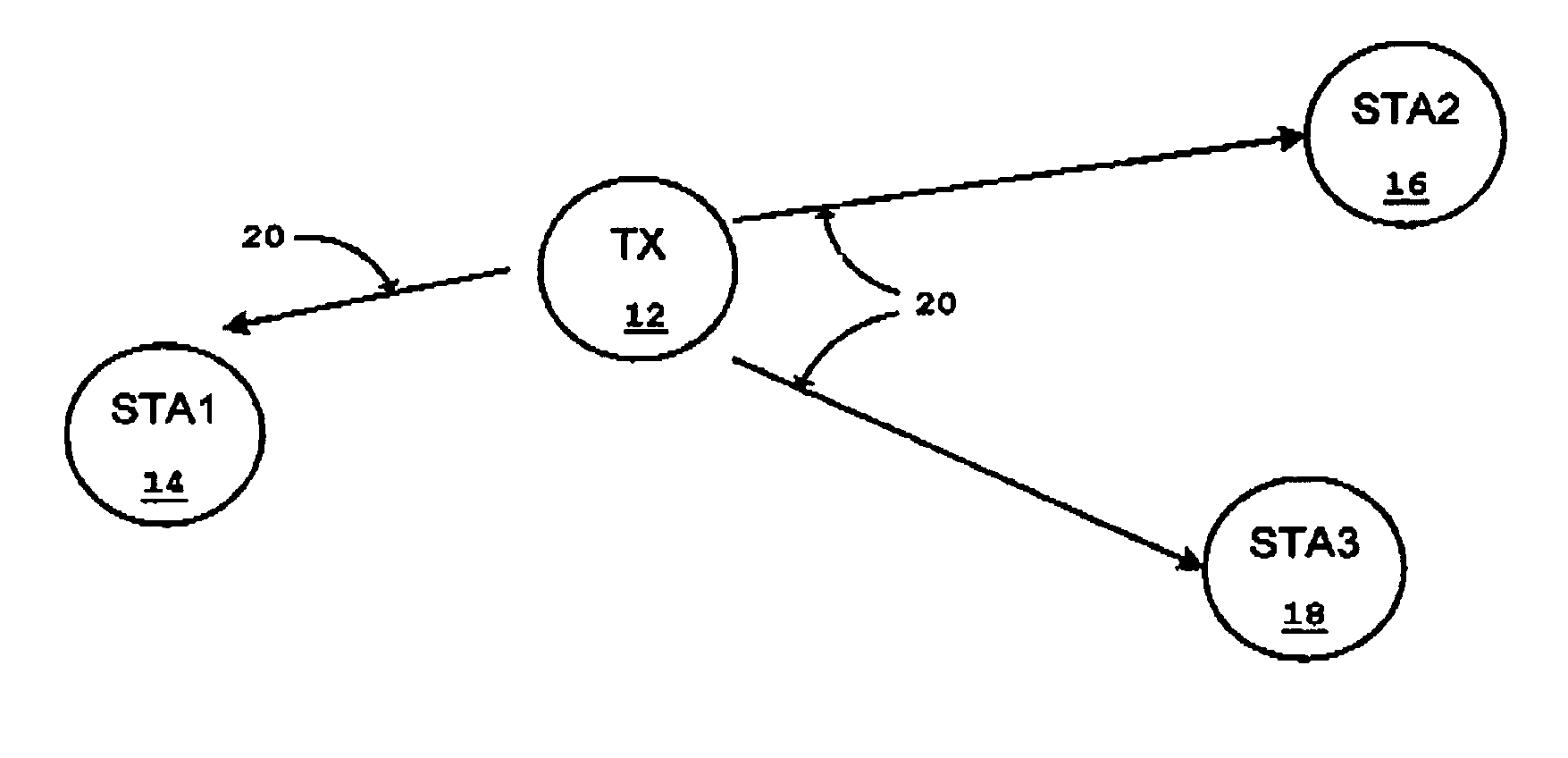
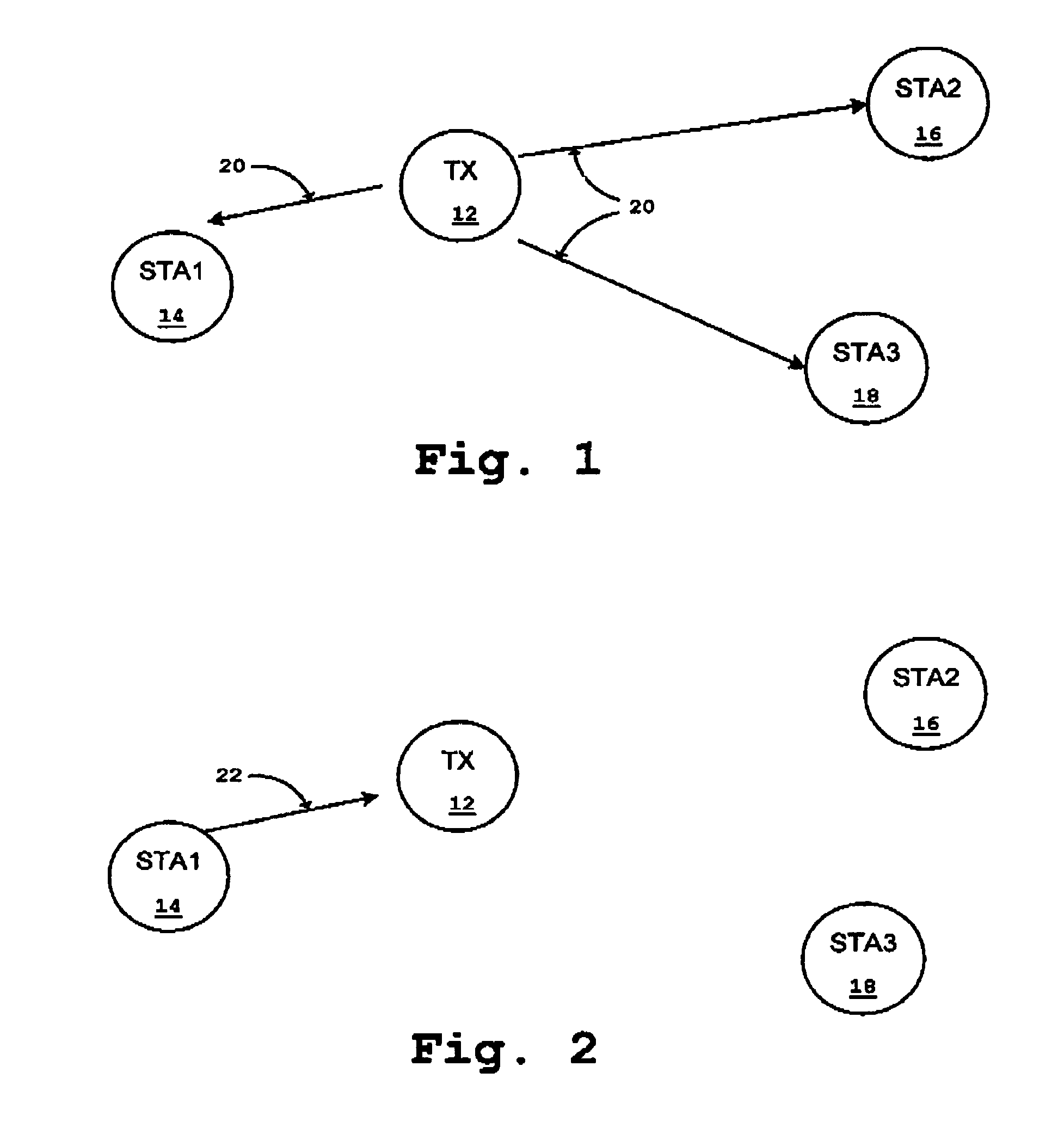
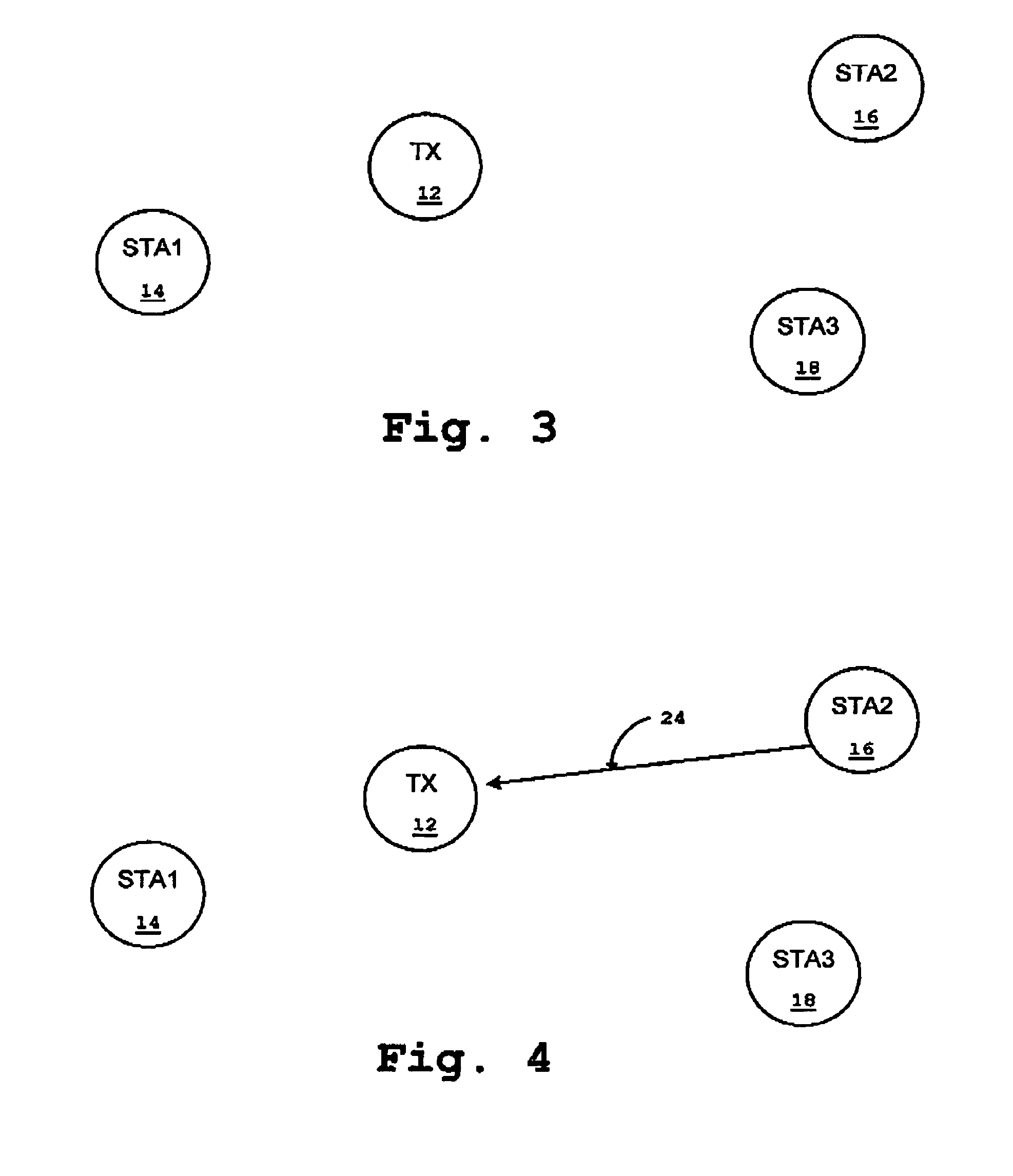
Essentially, a multicast is a message that originates with a single user and is received by multiple end points around the network. In a sense, a multicast is somewhat like sending a single email out to various email addresses.
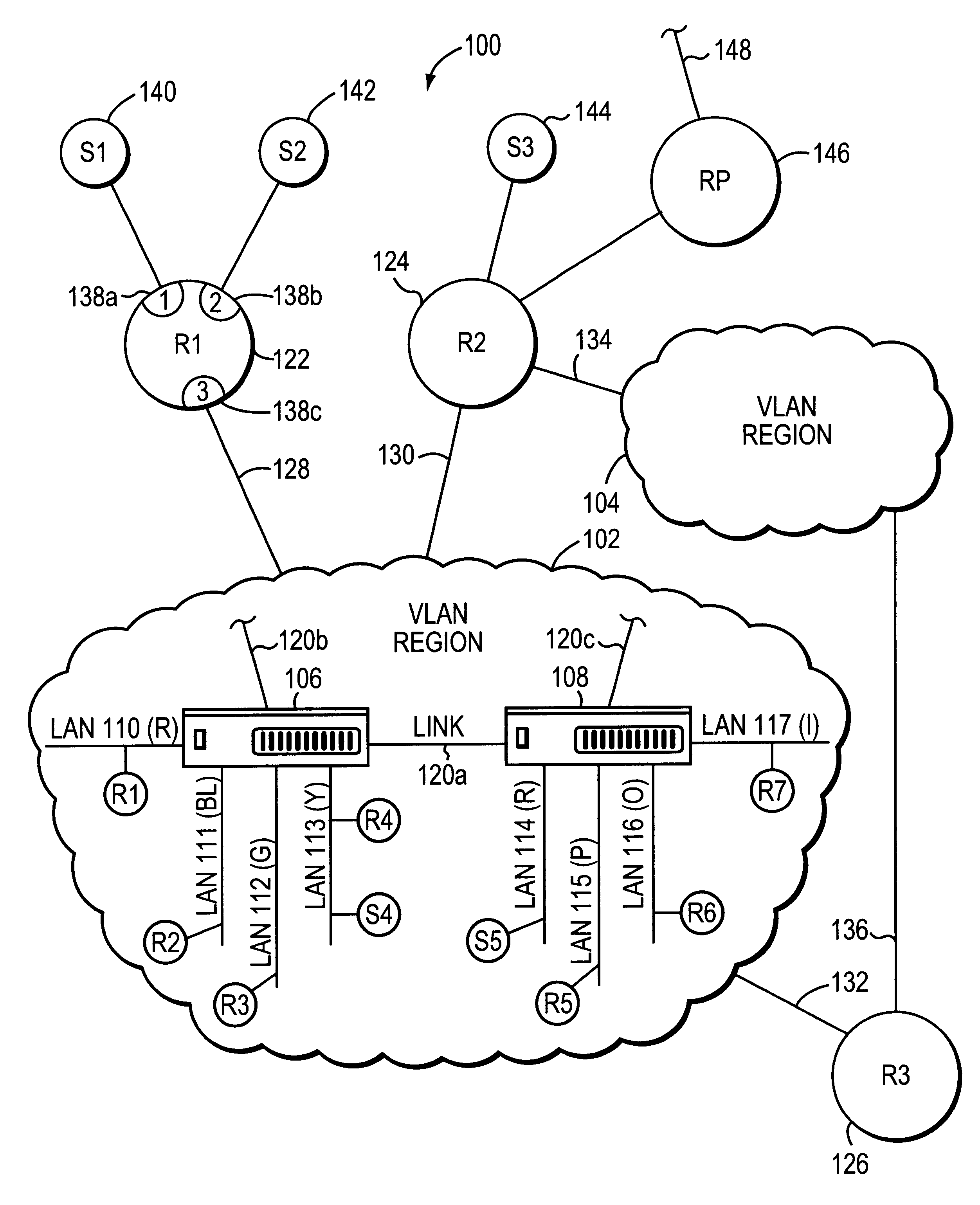
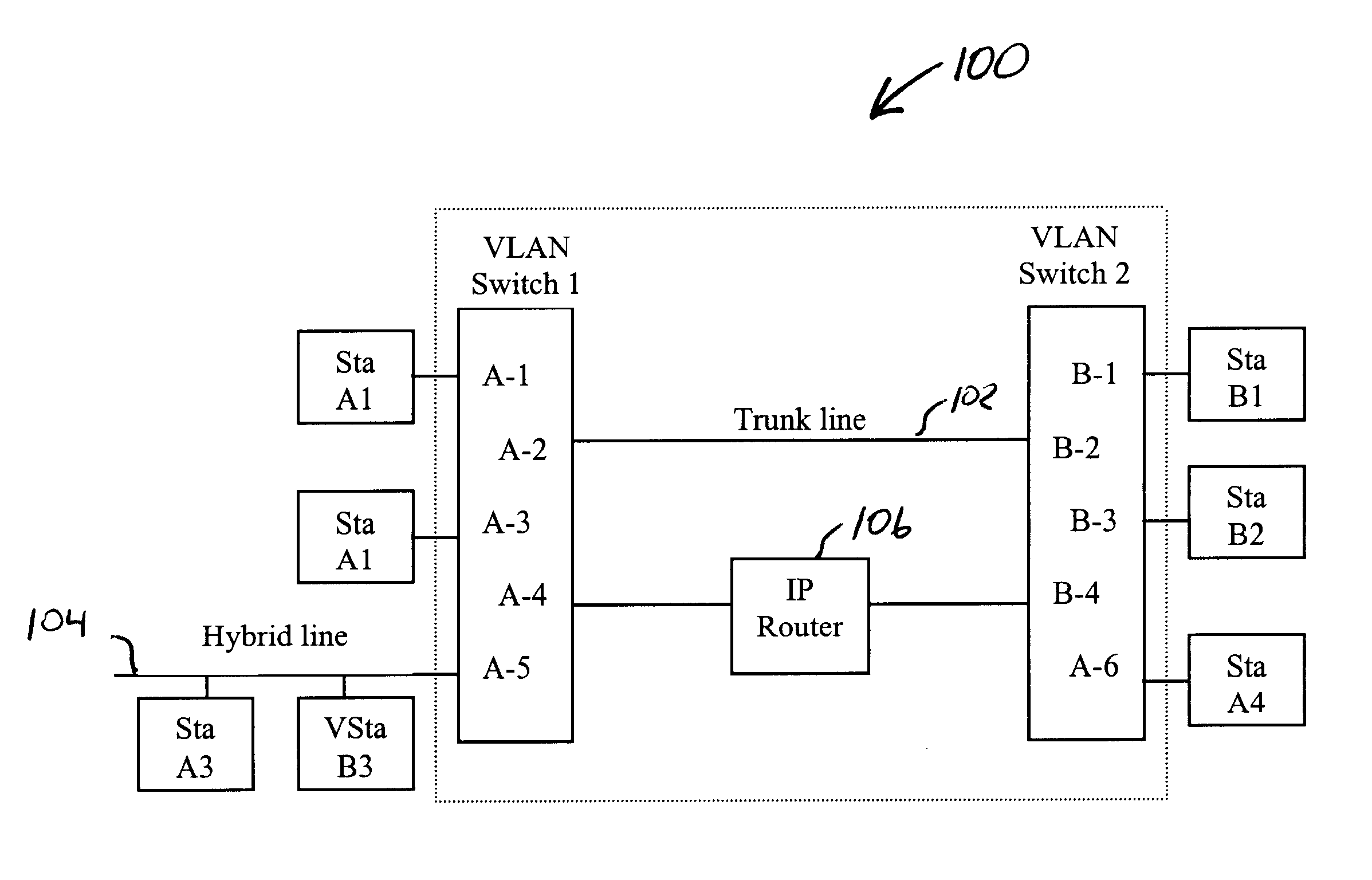
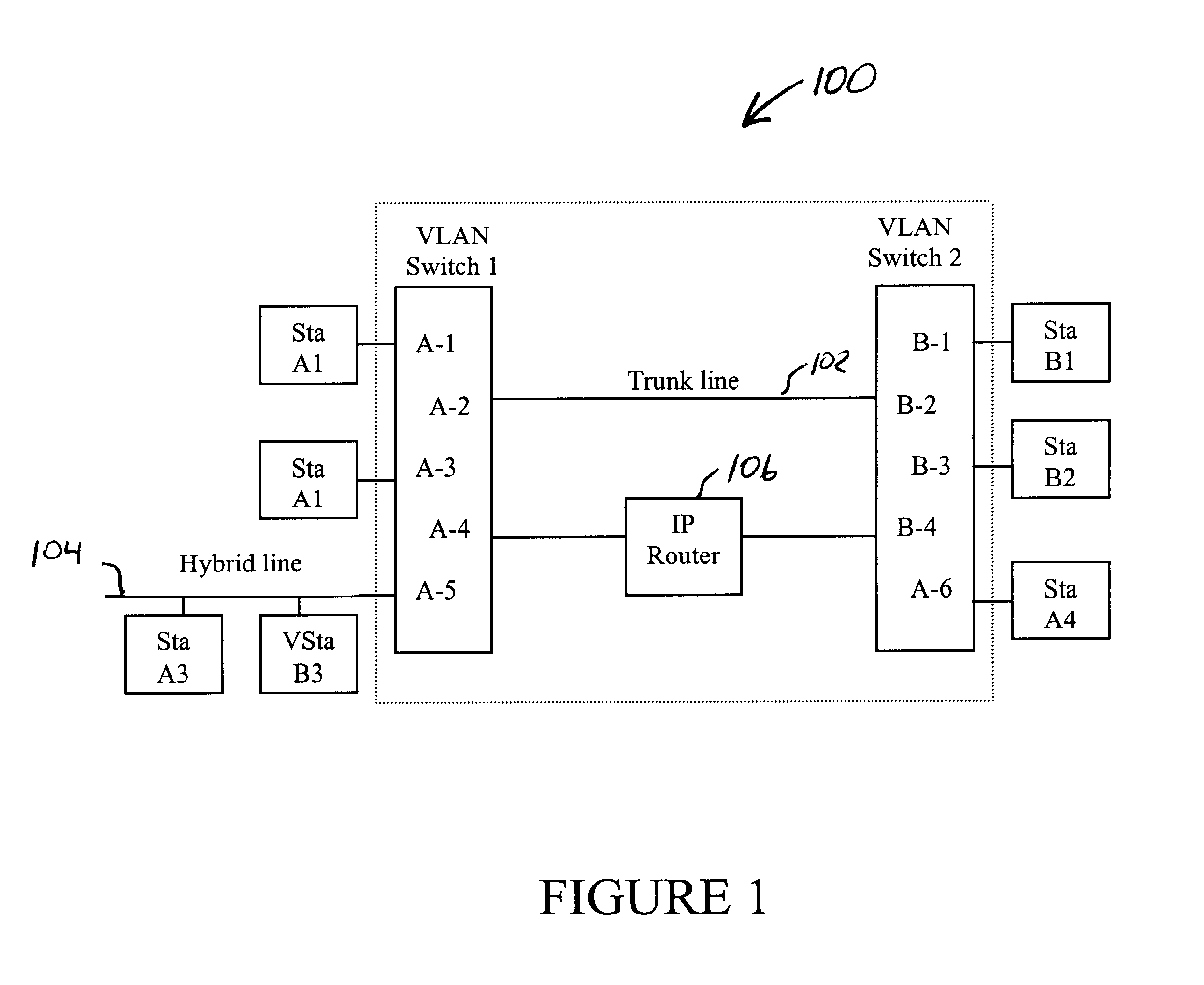
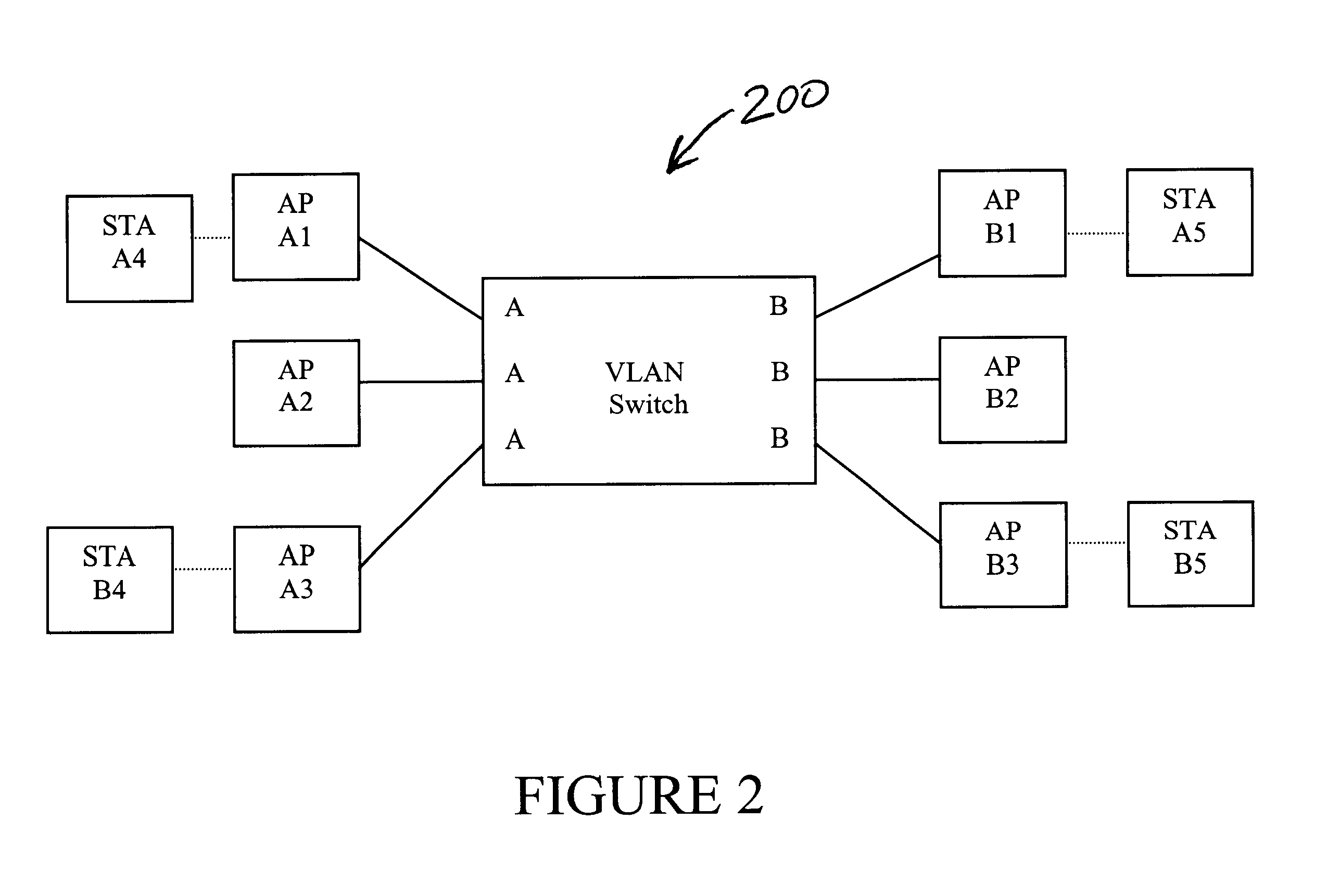
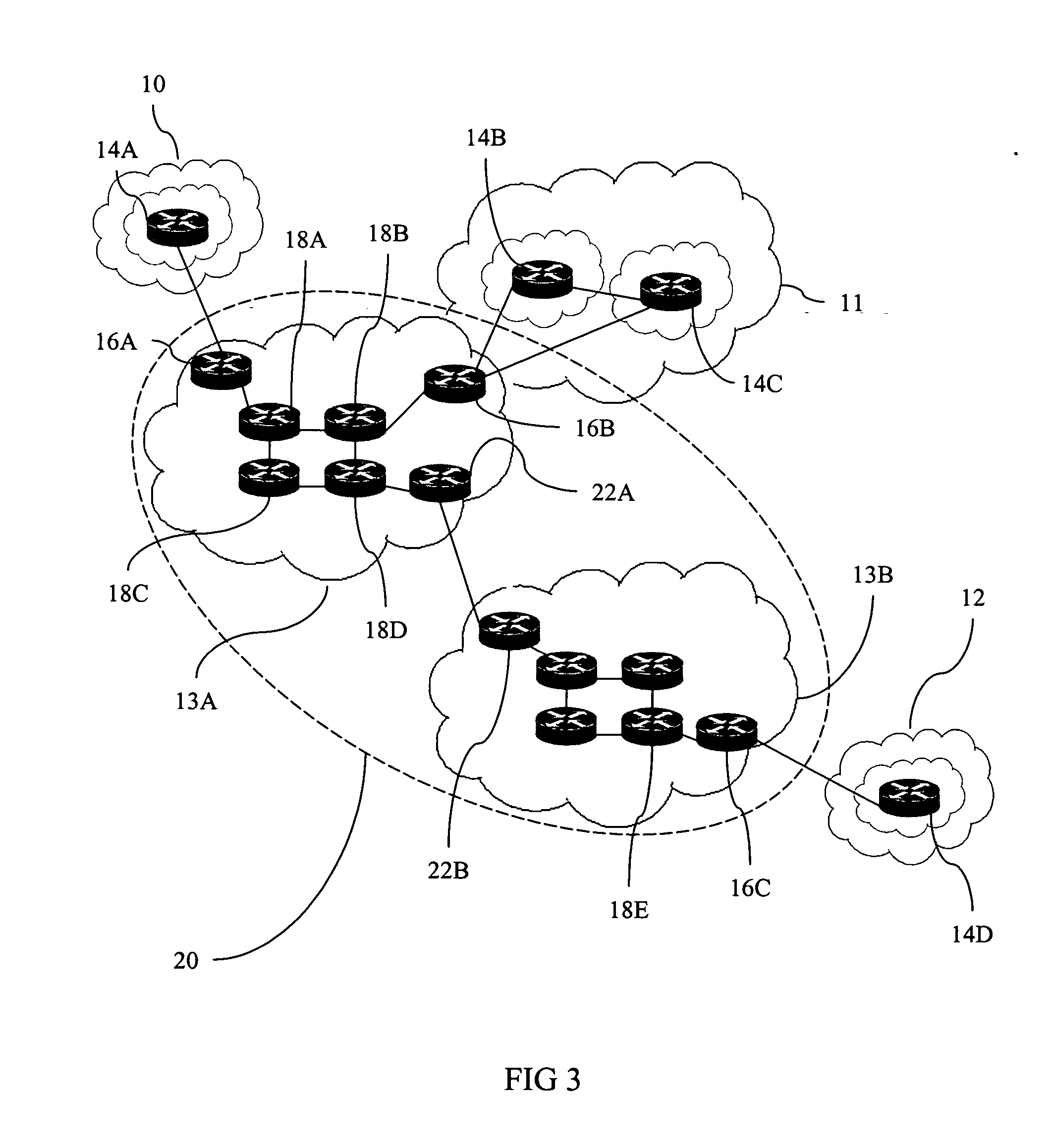
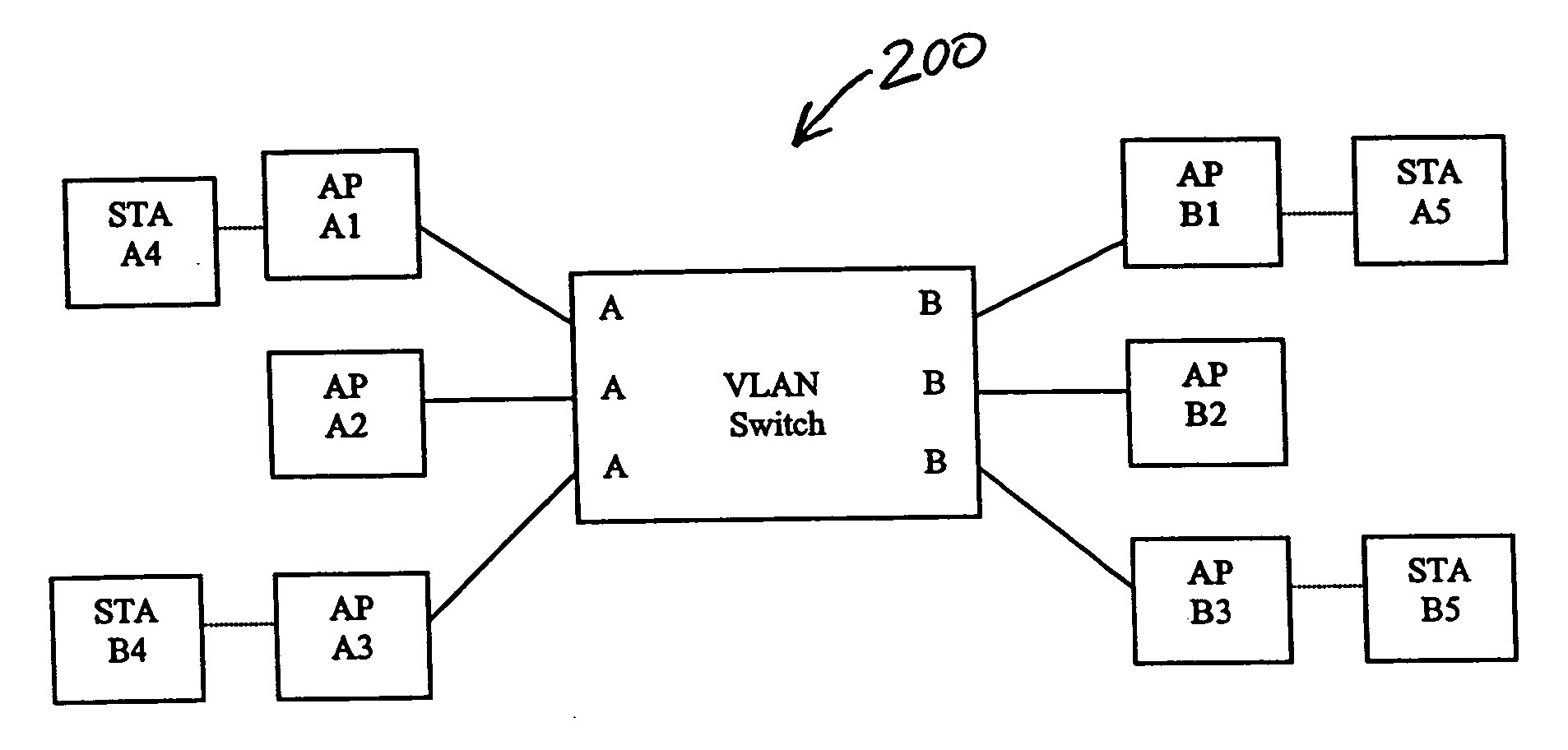
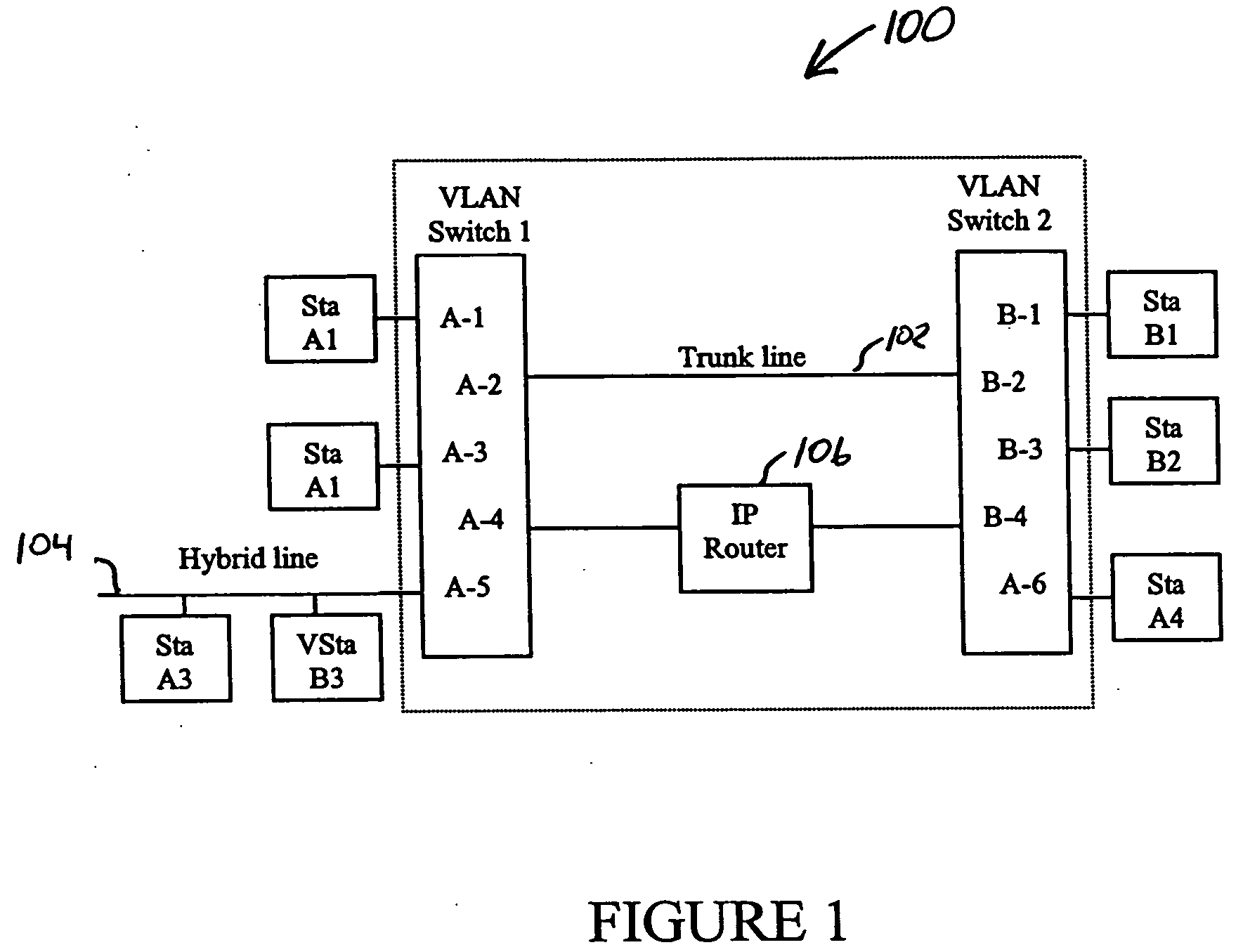
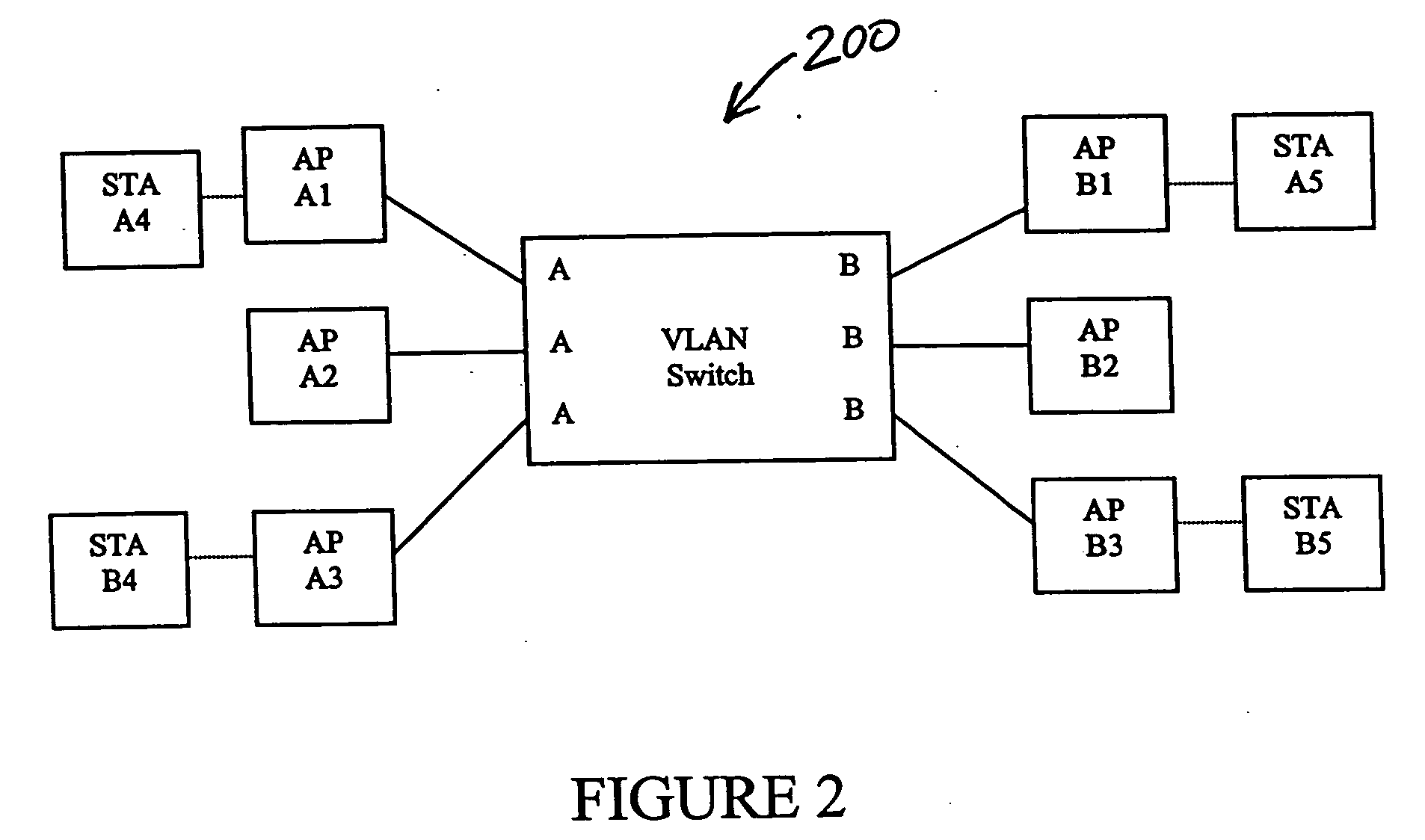
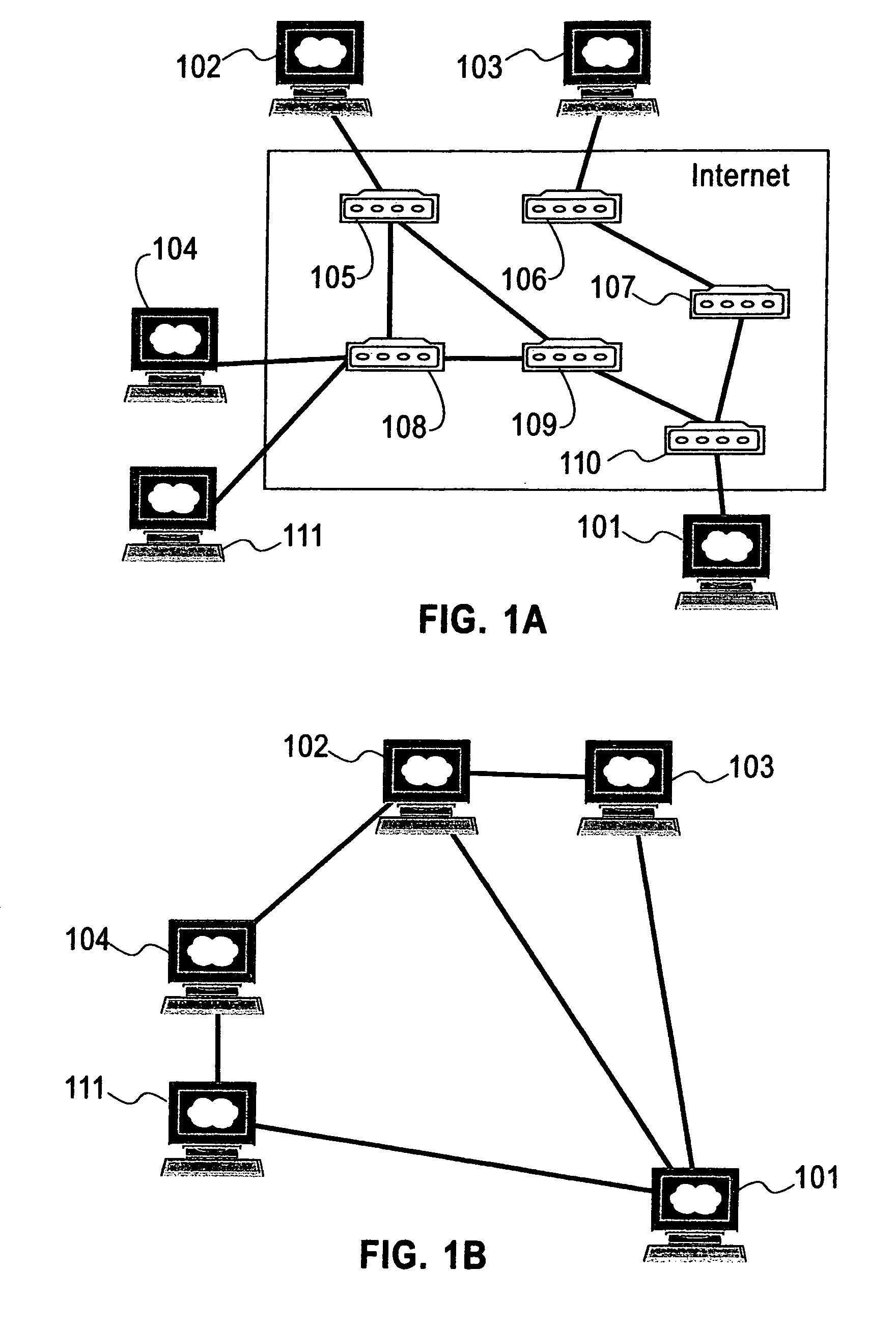
System and method for distributing multicasts in virtual local area networks
InactiveUS6839348B2Effective distributionEfficiently distributedSpecial service provision for substationTime-division multiplexVirtual LANIP multicast
The invention relates to a system and method for efficiently distributing multicast messages within computer networks configured to have one or more virtual local area network (VLAN) domains. A multicast network device (MND), having a plurality of interfaces, includes a multicast controller for efficiently distributing multicast messages among subscribing entities associated with various VLAN domains. The multicast controller, which is in communicating relationship with the interfaces, includes a VLAN assignment engine for assigning responsibility for the VLAN domains to the extent there are multiple MNDs. The multicast controller also accesses a multicast tag source to establish a plurality of novel VLAN tags for efficiently distributing multicast messages, including a sub-regional Multicast VLAN Identifier (MVLAN-ID) that encompasses all of the VLAN domains for which the respective MND is responsible, and one or more color-limited MVLAN-IDs that encompass all of the VLAN domains for which the MND is responsible except for one. The multicast controller then tags multicast messages with its sub-regional or a color-limited MVLAN-ID depending on whether the message is considered internal or external by the respective MND. The tagged messages are then forwarded for distribution to the subscribers associated with the various VLAN domains.
Owner:CISCO TECH INC
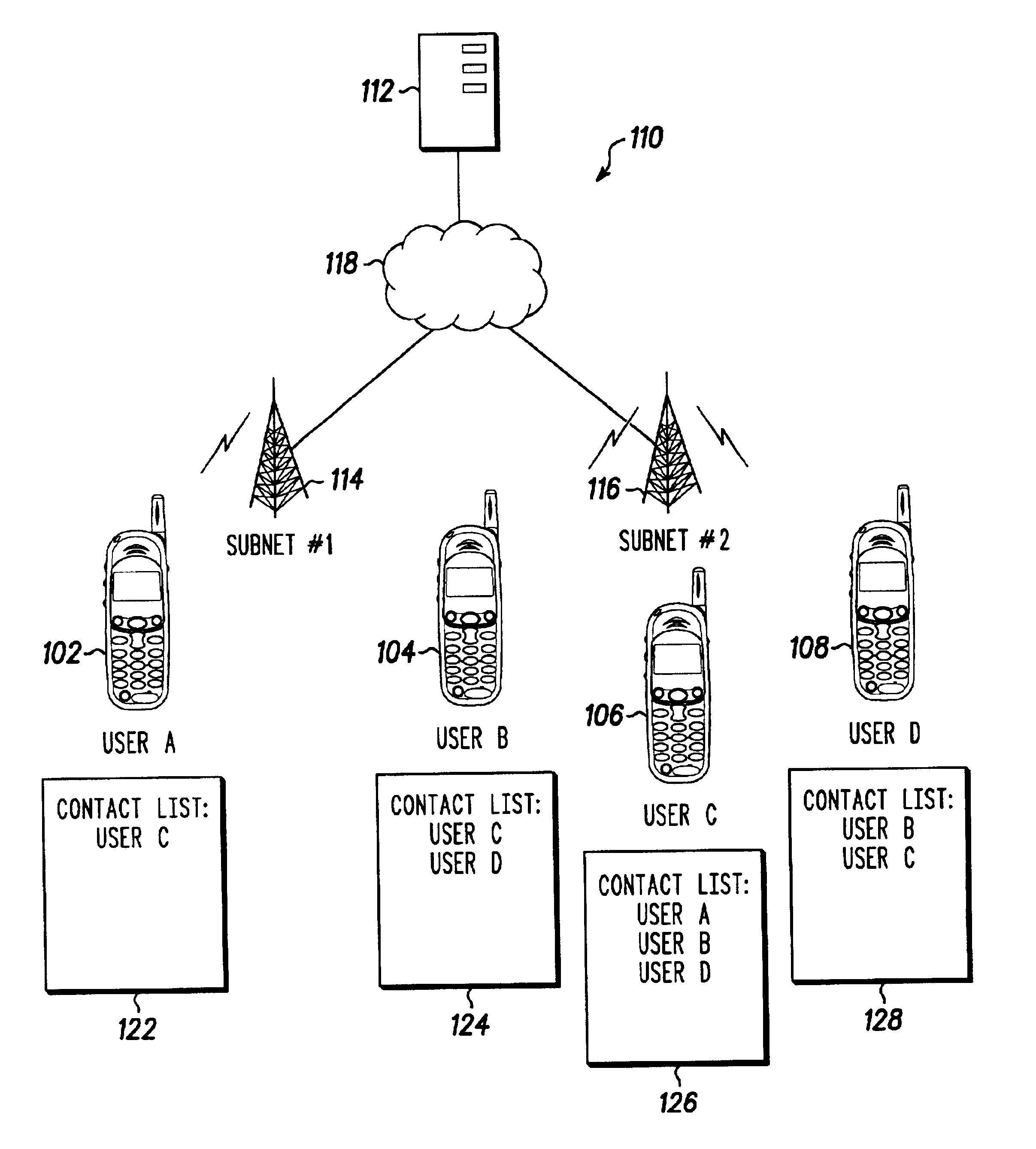
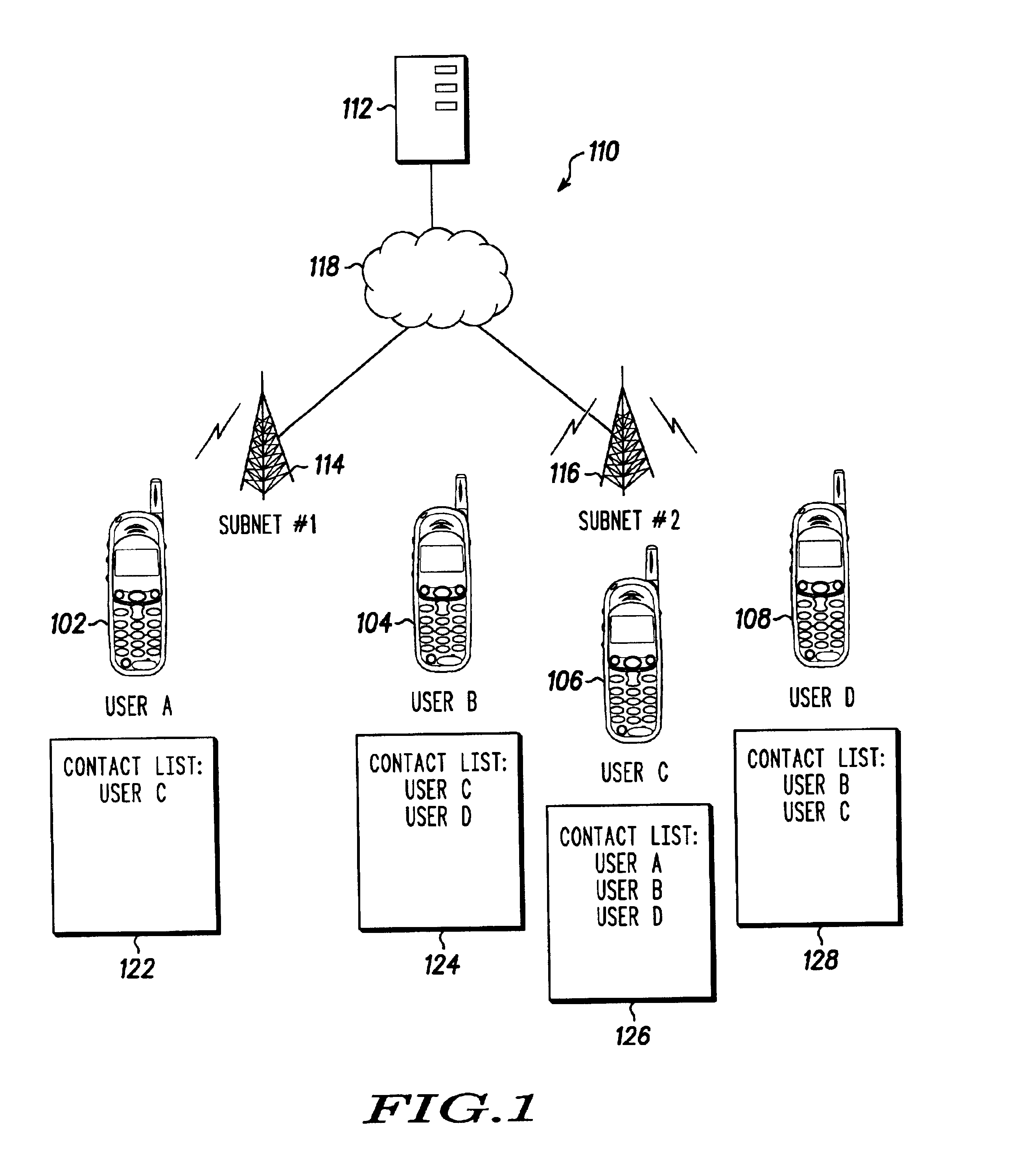
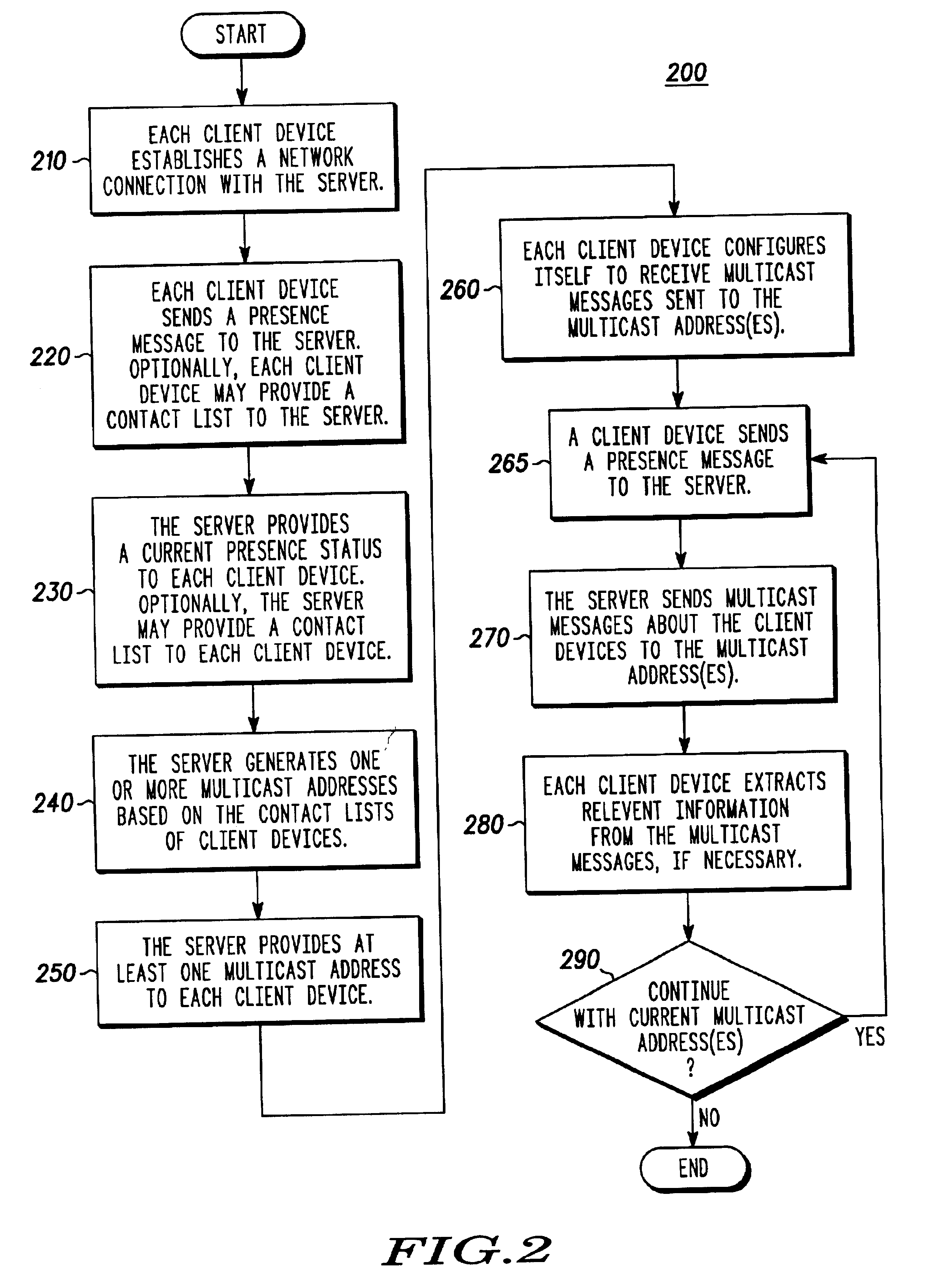
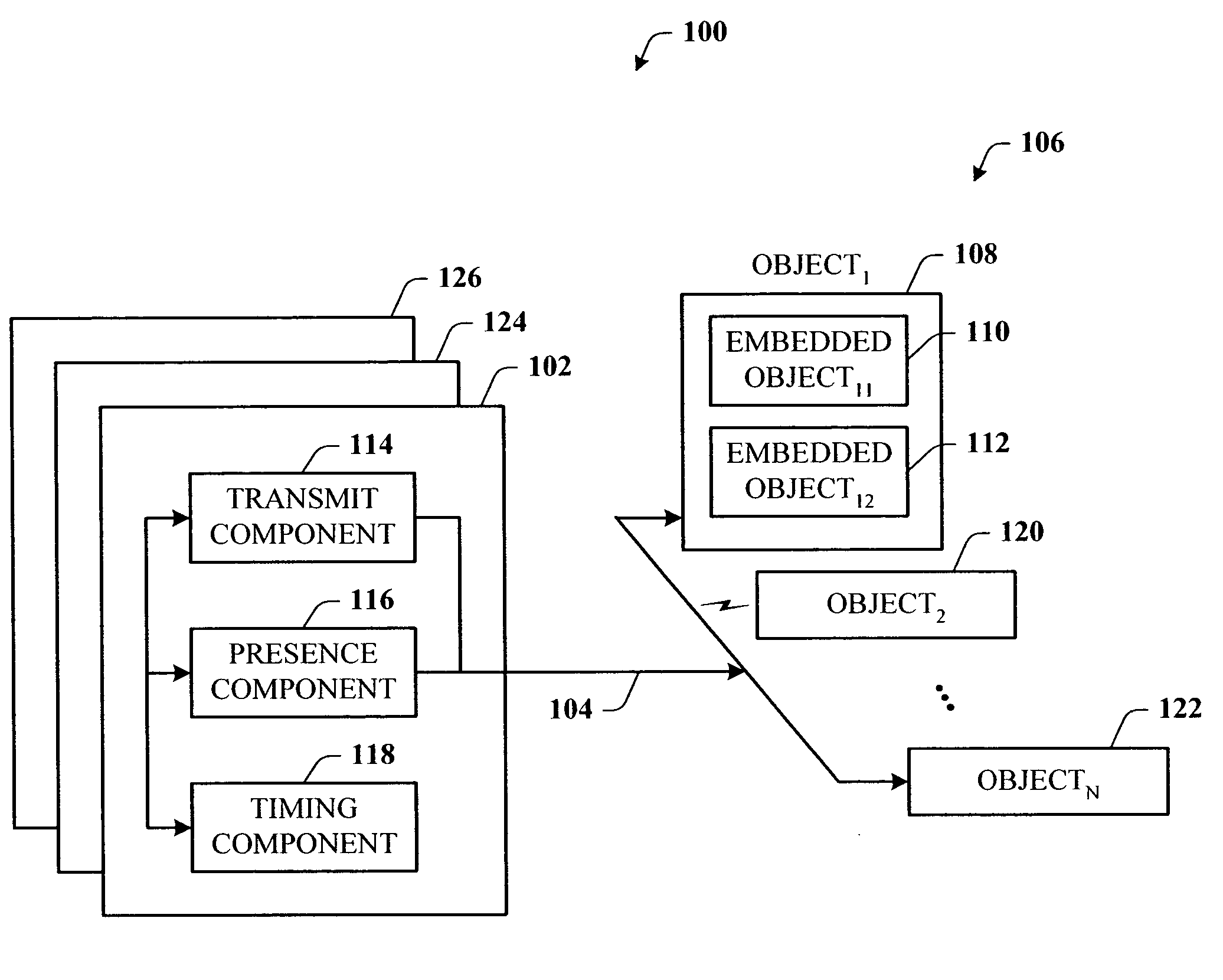
Multicast distribution of presence information for an instant messaging system
InactiveUS6993327B2Special service provision for substationSpecial service for subscribersMulticast addressContact list
The present invention is a system, method and network (110) for multicast distribution of presence information to a plurality of communication devices (102, 104, 106, 108). A contact list (122, 124, 126, 128), associated with each communication device, identifies one or more of the other communication devices. The network provides one or more multicast addresses based on the contact lists of the communication devices to the plurality of communication devices. The network also sends multicast messages identified by the one or more multicast addresses to the plurality of communication devices. Each multicast address identifies a group of multicast devices among the plurality of communication devices, and the multicast messages include presence information about the group of multicast devices. A portion of the plurality of communication devices receives the multicast messages identified by the one or more multicast addresses and extracts the presence information about the group of multicast devices from the multicast messages.
Owner:GOOGLE TECH HLDG LLC
Mobile virtual LAN
InactiveUS6847620B1Not burdened with associated computational overheadNetwork topologiesWireless network protocolsCommunications systemVirtual LAN
A communication system in which multiple protocols and proxy services are executed by an access point. In one embodiment of the invention, GVRP and GMRP registrations are combined in a single packet when a wireless device roams to a different VLAN. In addition, outbound GVRP and GMRP multicast messages are handled by an access point (also referred to as a GVRP and GMRP “gateway”) such that the wireless device is not burdened with the associated computational overhead. In a further embodiment, a wireless device may dynamically switch between a VLAN-aware state and a VLAN-unaware state depending on the nature of a detected access point. For example, if a relevant access point supports GVRP, the wireless device may operate as a VLAN terminal. If a wireless device is not attached to an access point with a matching VLAN ID, the wireless device sends and receives VLAN tagged frames. If a wireless device configured with a VLAN ID is attached to an access point with a matching VLAN ID, or if the wireless device is attached to a non-VLAN access point, then the wireless device may send and receive raw / untagged frames. In addition to the gateways described below, the ability of a wireless device to detect when it can send untagged frames is considered novel. In another embodiment of the invention, a special ID that is different than the native VLAN ID for a switch port is used for VLAN-unaware devices. This allows such devices that do not issue tagged frames to belong to a single VLAN ID.
Owner:AVAGO TECH INT SALES PTE LTD
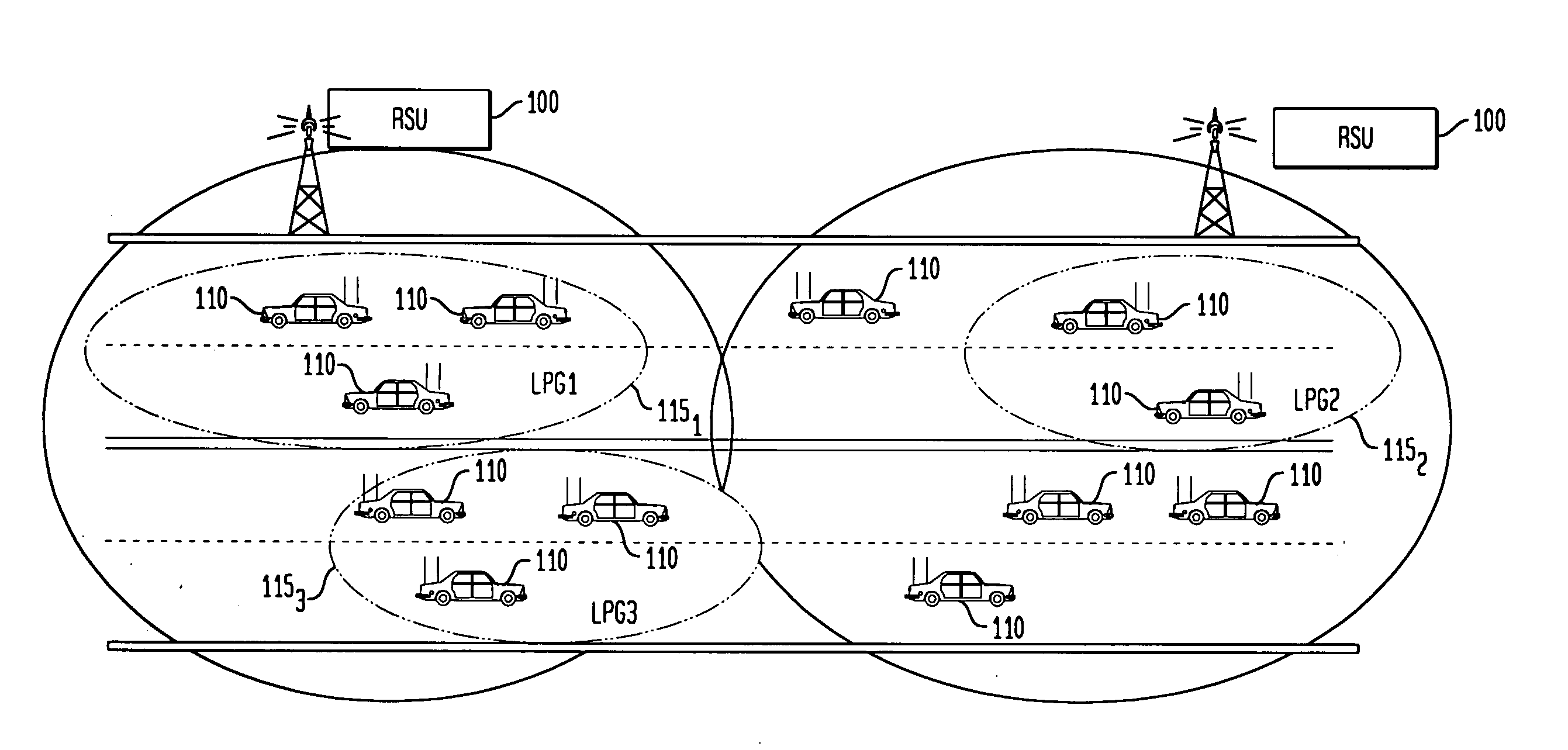
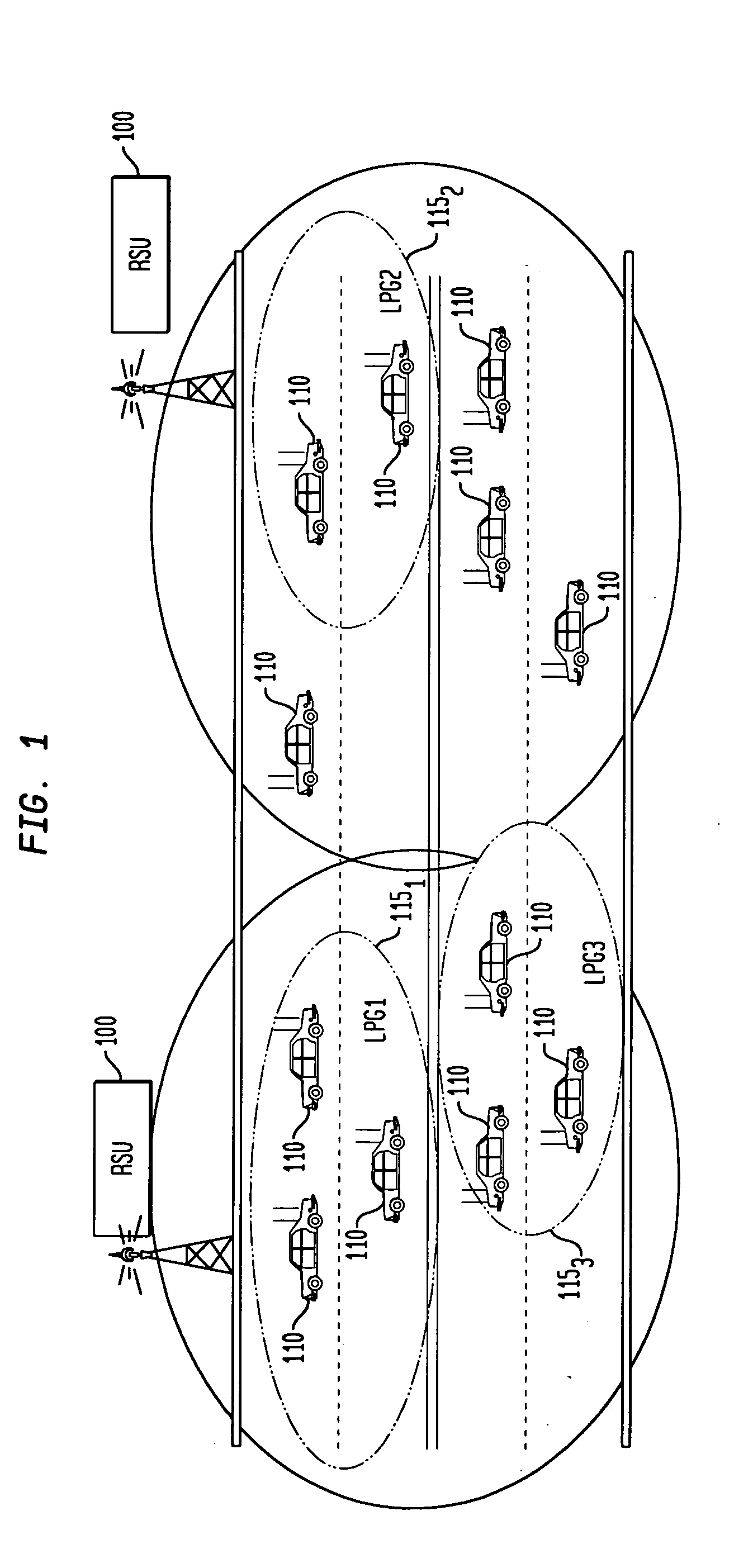
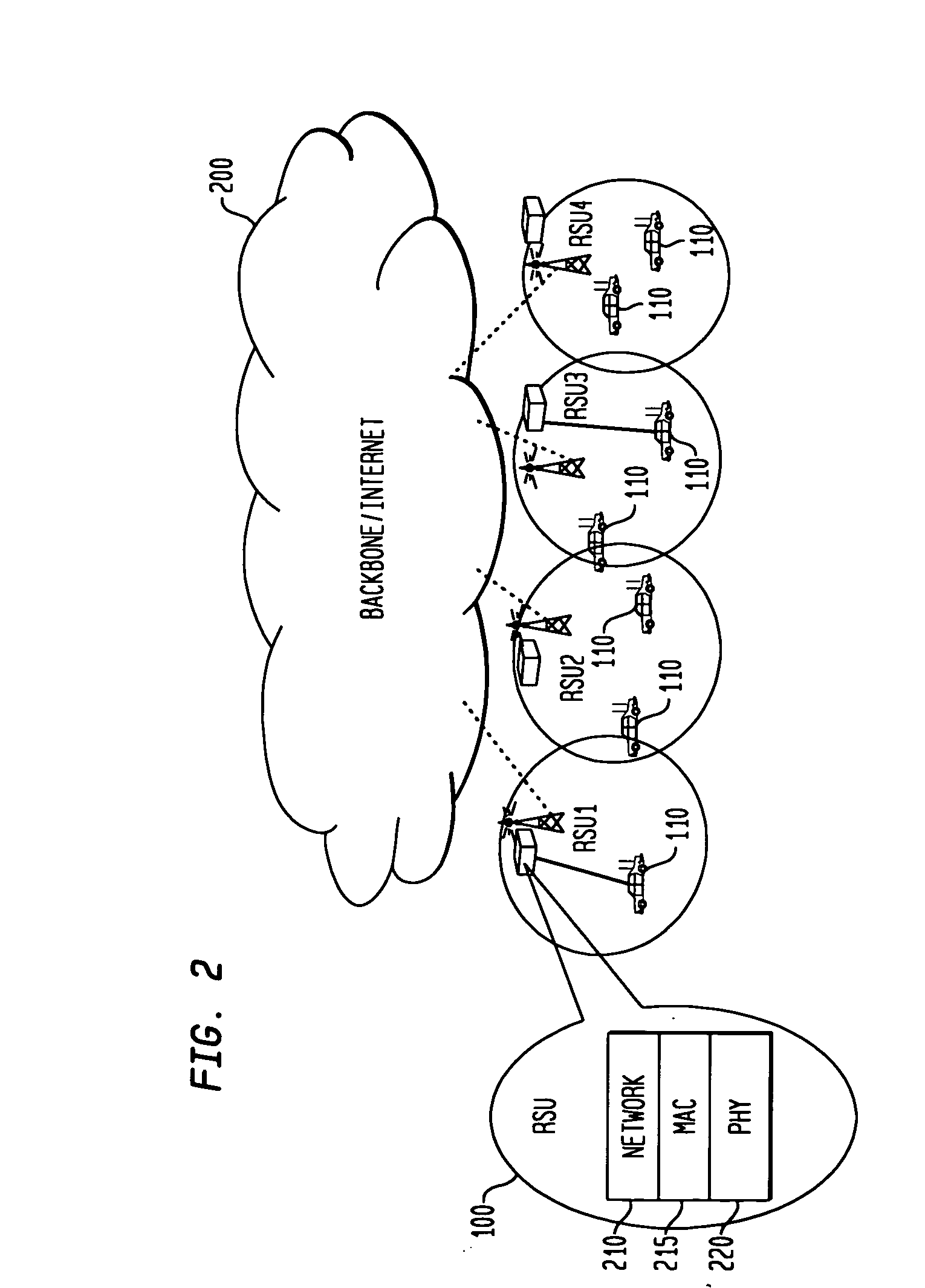
Method and communication device for routing unicast and multicast messages in an ad-hoc wireless network
ActiveUS20080095163A1Network topologiesBroadcast transmission systemsWireless mesh networkRouting table
A method and communication device for routing unicast and multicast messages. The method for routing a unicast message includes receiving a first control packet including routing parameters from a group header node, updating a routing table based upon the routing parameters, receiving a second control packet including additional routing parameters from a group node, updating the routing table based upon the additional routing parameters and generating a forwarding table from the routing table when both of the updated steps are completed. The unicast message is routed based upon the forwarding table. A method for routing a multicast message comprises receiving the multicast message, determining if a multicast group destination for the multicast message is in a multicast forwarding table (MFT), determining if the multicast message has been previously forwarded and forwarding the multicast message if the message was not previously forwarded and the multicast group destination is in the MFT.
Owner:TOYOTA INFOTECH CENT U S A +1
Method and apparatus for providing multicast messages across a data communication network
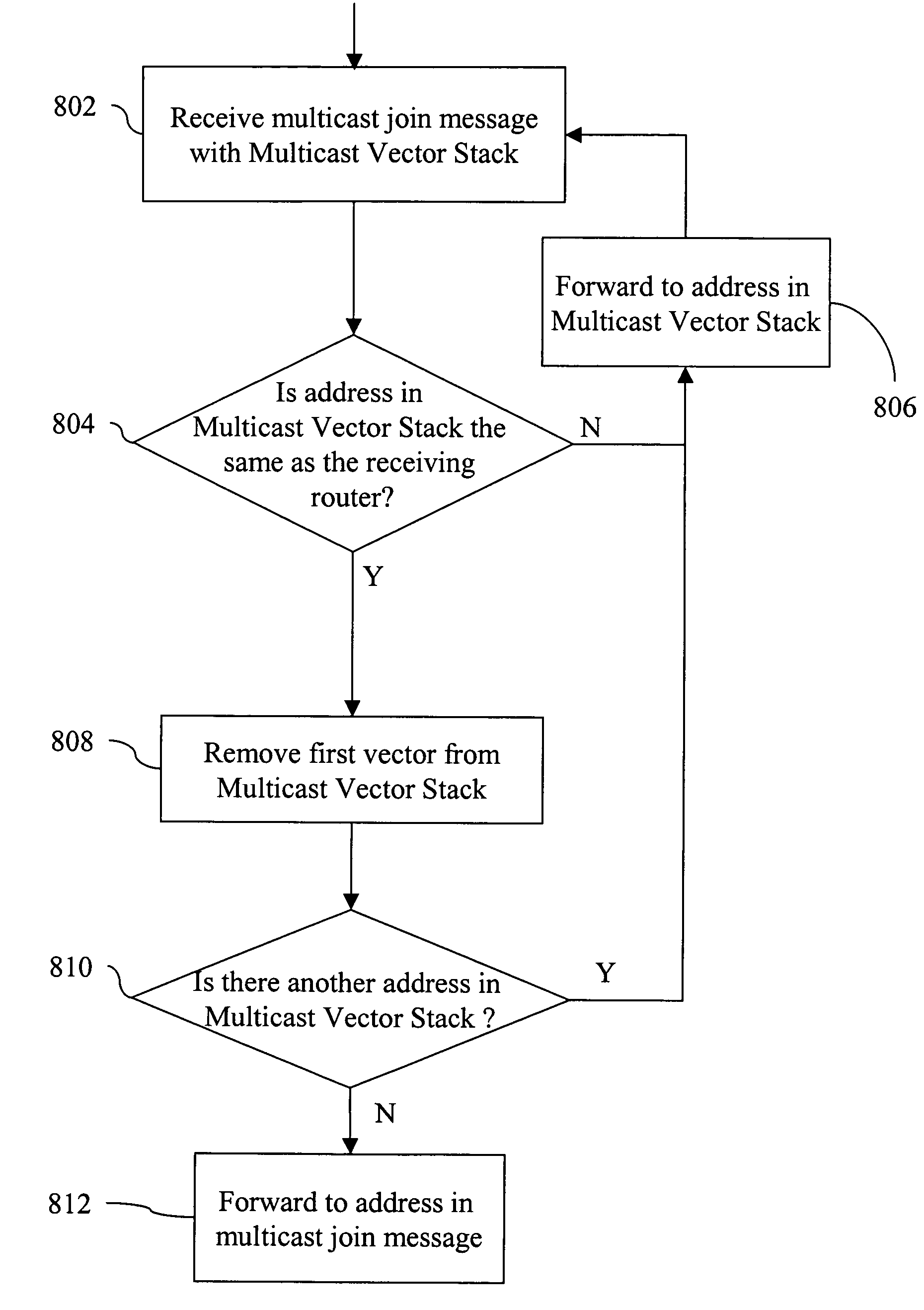
ActiveUS7925778B1Digital computer detailsData switching by path configurationComputer networkMulticast message
A method and apparatus for providing multicast messages across a data communication network, the method comprising receiving a multicast message and adding to the multicast message a vector stack including at least one address of a router to which the multicast message is to be sent. The multicast message and the vector stack are then forwarded. At the first router indicated by the vector stack, the next address to which the multicast message is to be sent is read. This is repeated as necessary until the multicast message is received by the final address in the vector stack. The multicast message is then routed to the address indicated in the original multicast message.
Owner:CISCO TECH INC
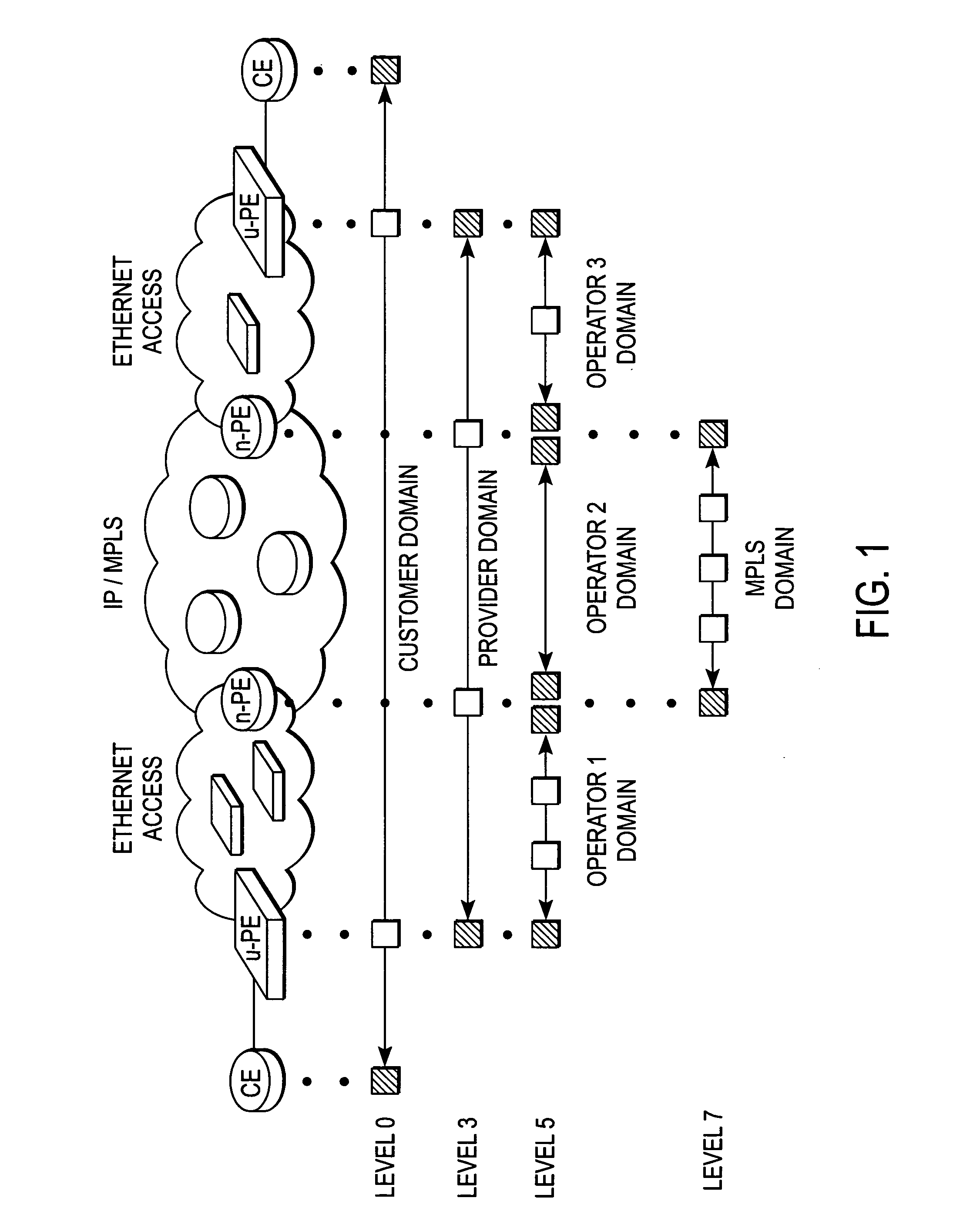
Address resolution mechanism for ethernet maintenance endpoints
A method of operation for a node of an Ethernet access network includes issuing a multicast message on the Ethernet access network by a maintenance end point (MEP) of the node. The multicast message contains a name of a target MEP. The node is further operable to receive a unicast reply message from the target MEP, the unicast message reply containing a MEP identifier (MEP-ID) and a MEP Media Access Control (MAC) address of the target MEP. It is emphasized that this abstract is provided to comply with the rules requiring an abstract that will allow a searcher or other reader to quickly ascertain the subject matter of the technical disclosure. It is submitted with the understanding that it will not be used to interpret or limit the scope or meaning of the claims.
Owner:CISCO TECH INC
Method and apparatus for providing multicast messages within a virtual private network across a data communication network
InactiveUS20060088031A1Data switching by path configurationStore-and-forward switching systemsPrivate networkNetsniff-ng
A method and apparatus for providing multicast messages across a data communication network, the method comprising the computer-implemented steps of: receiving a multicast join message; adding to the multicast join message a next hop and an address of a router to which the multicast message is to be sent; forwarding the multicast message based on the next hop address.
Owner:CISCO TECH INC
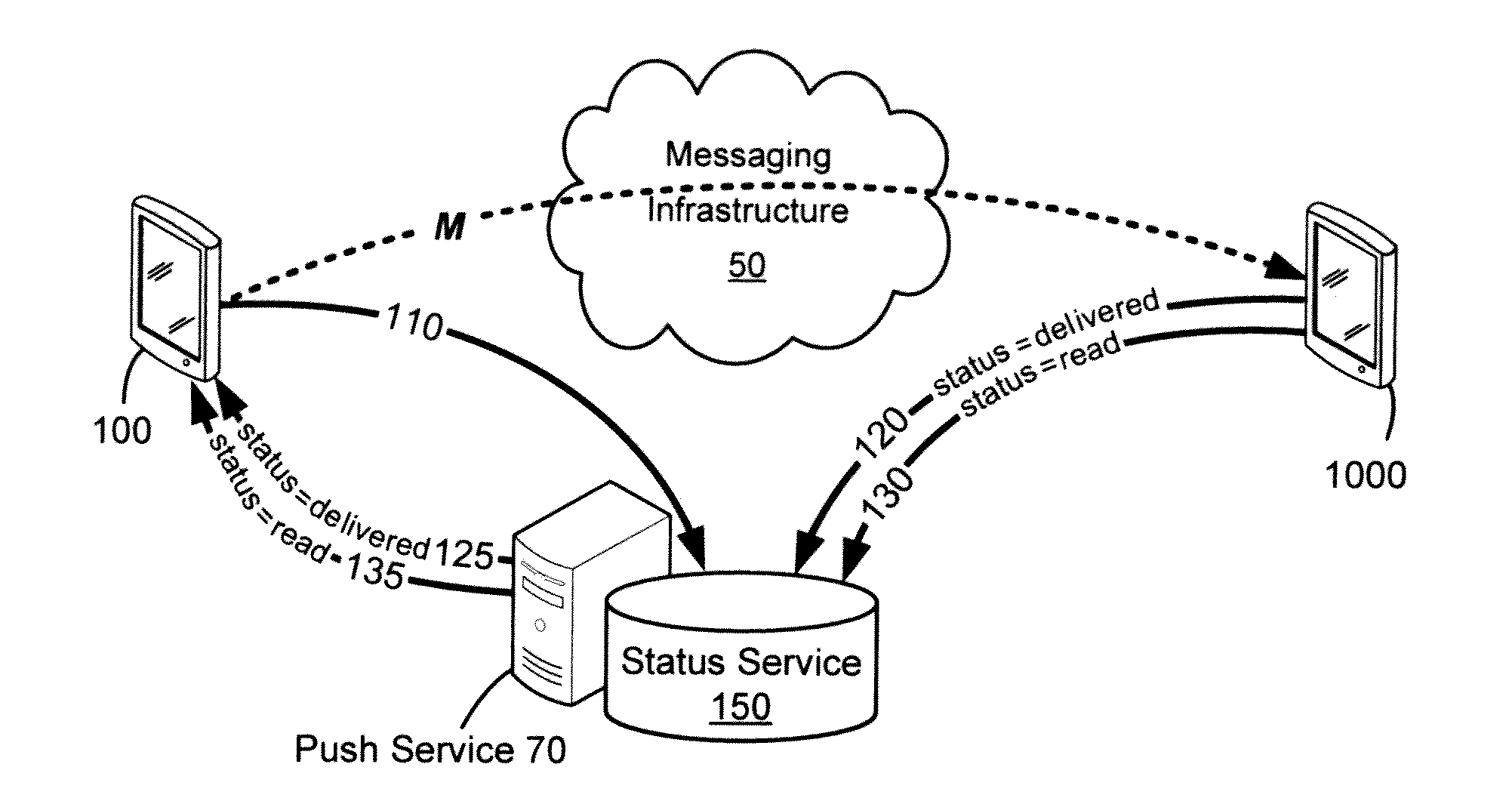
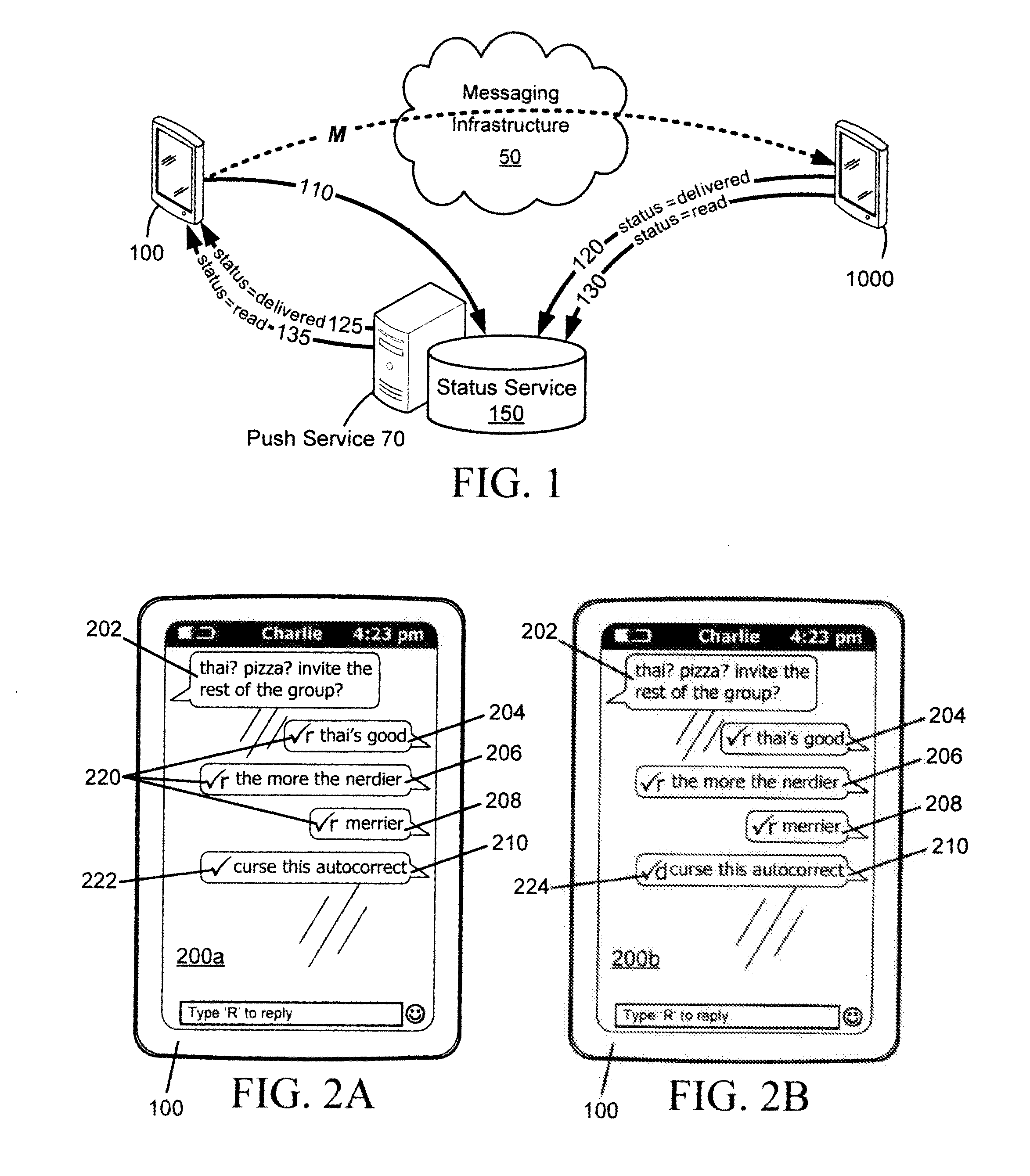
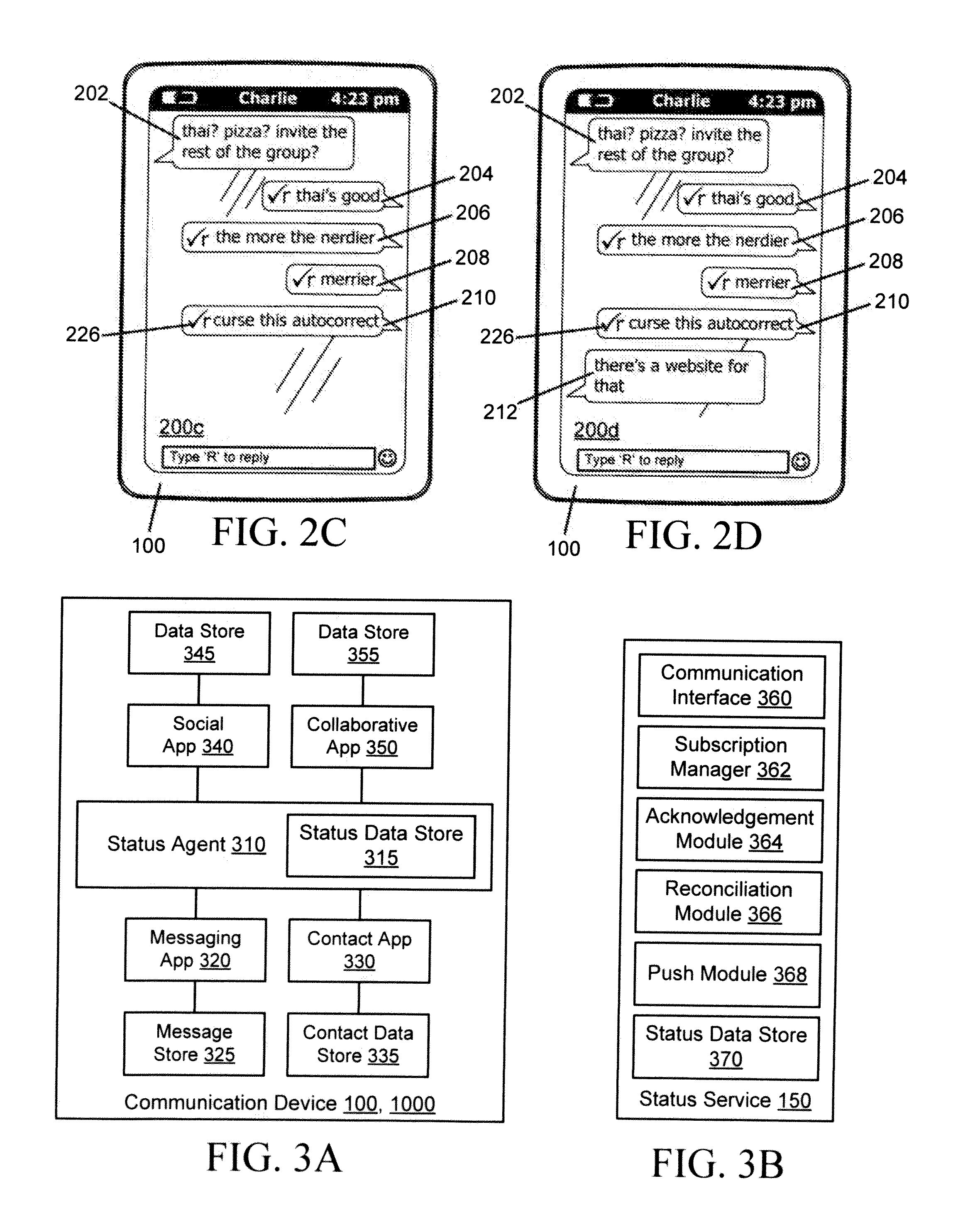
Delivery and management of status notifications for group messaging
ActiveUS20120231770A1Special service for subscribersCommmunication supplementary servicesMessage passingCommunication device
Systems and methods are provided for managing and delivering status notifications relating to multicast messages transmitted from a sending communication device to multiple recipient communication devices. Each communication device is provided with a status agent for detecting transmission of messages to a recipient device and receipt of messages from a sending device. Upon transmission, the status agent notifies a status service of the outbound message. Upon receipt of the multicast message by one of the recipients or upon the message being marked read, the recipient status agent notifies the status service. The status service then notifies the status agent of the sending device that the message has been received or read by that recipient, so that the sending device's status agent can notify a corresponding messaging application. The status service operates to reconcile outbound message notifications and received or read status updates for multicast messages.
Owner:MALIKIE INNOVATIONS LTD
Desynchronized network access in m2m networks
ActiveUS20120231828A1Power managementSynchronisation arrangementUplink transmissionSynchronous network
Systems, methods, and instrumentalities are disclosed to desynchronize transmissions in group-based operations. A group user equipment (UE), e.g., a UE that is a member of a group of UEs, may be in an inactive mode. The group UE may receive a multicast message indicating that the group UE may enter an active mode. For example, the group UE may use the active mode for periodic reporting of its monitoring activity to the network. The multicast message may indicate a mechanism for the group UE to use to send an uplink transmission to the network. The group UE may send the uplink transmission to the network at a transmission time indicated by the mechanism. The transmission time may be desynchronized from other UEs in the group.
Owner:INTERDIGITAL PATENT HLDG INC
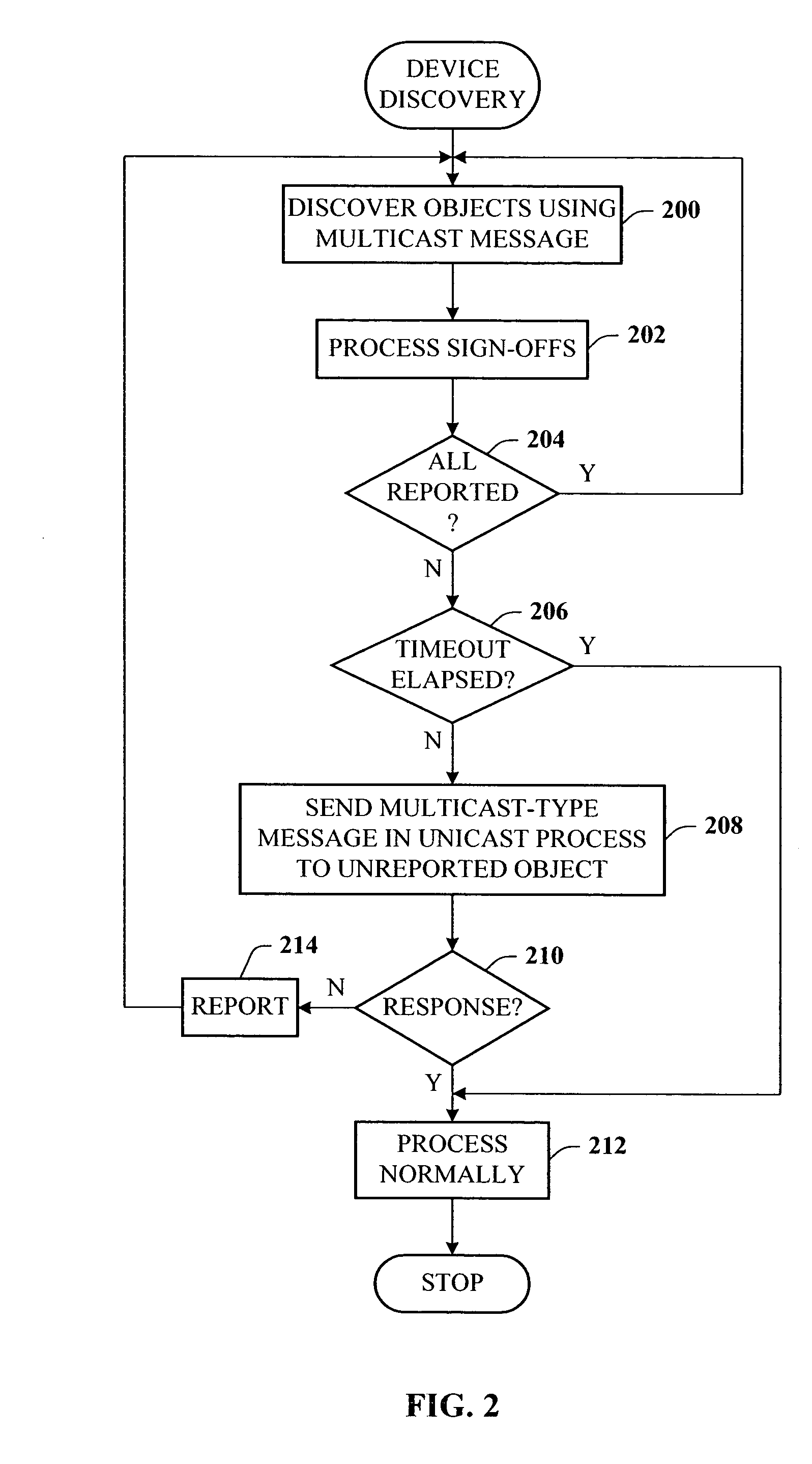
Presence tracking for datagram based protocols with search
InactiveUS20050108331A1Reduce network trafficEasy searchMultiple digital computer combinationsSecuring communicationClient-sideBroadcast multicast
A presence tracking architecture for datagram-based protocols. A client application seeking to know the presence or lack thereof of a device and / or service utilizes a standard protocol in a non-intuitive way to trigger notification of the device and / or service before any associated timeout expires. At first presence, a multicast message is broadcast to notify all devices. Subsequently, on-demand notification may be requested by a client application by sending directly (e.g., in unicast) to the device before its timeout has expired a message that is normally only sent in multicast. If capable, the device can then respond normally with a unicast message indicating it is on-line. If the response is not received, the device and / or service is determined to be off-line.
Owner:MICROSOFT TECH LICENSING LLC
Method and apparatus for electing a leader node in a computer network
InactiveUS7421578B1Data switching by path configurationSecuring communicationTime segmentKey signature
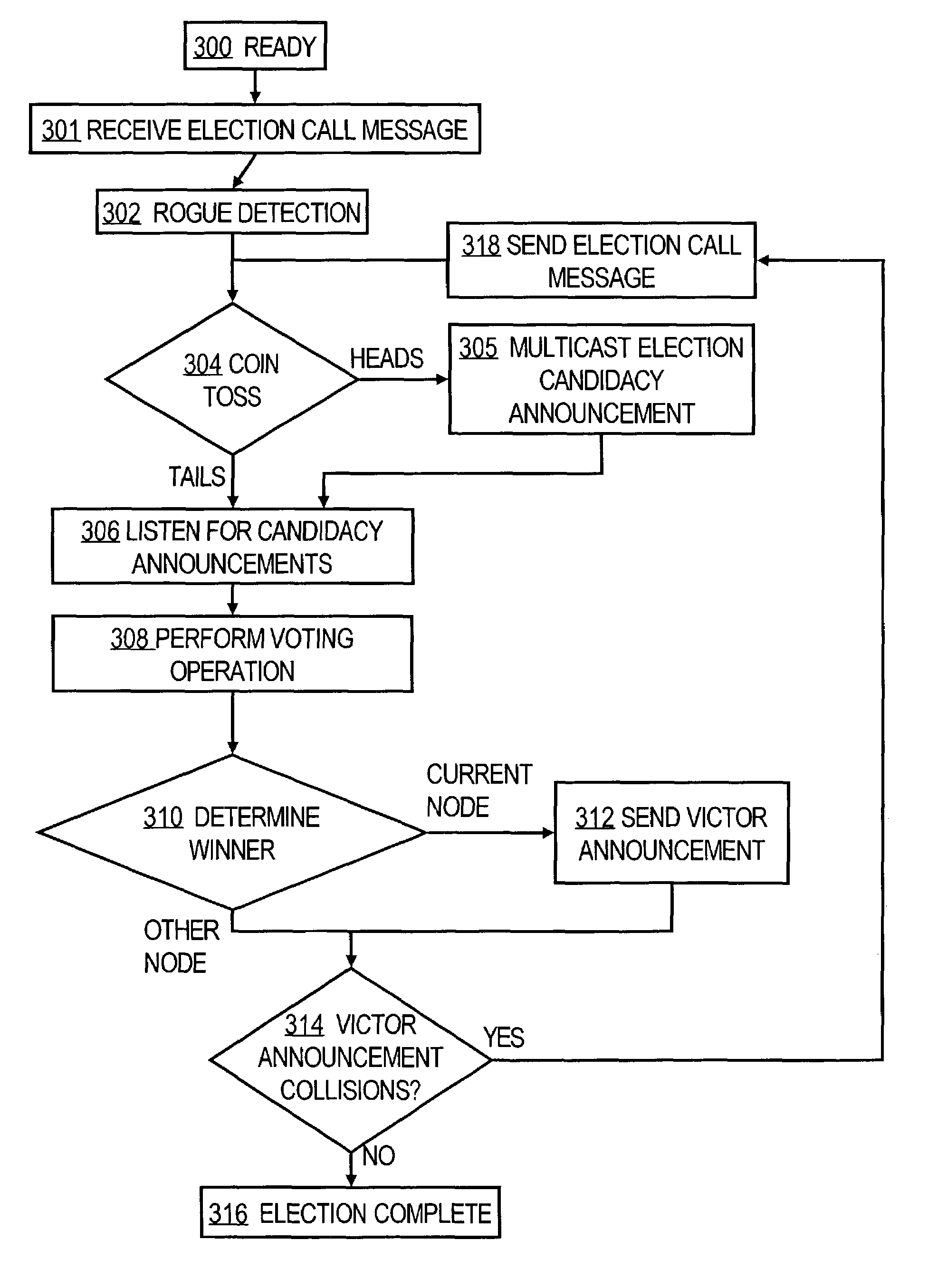
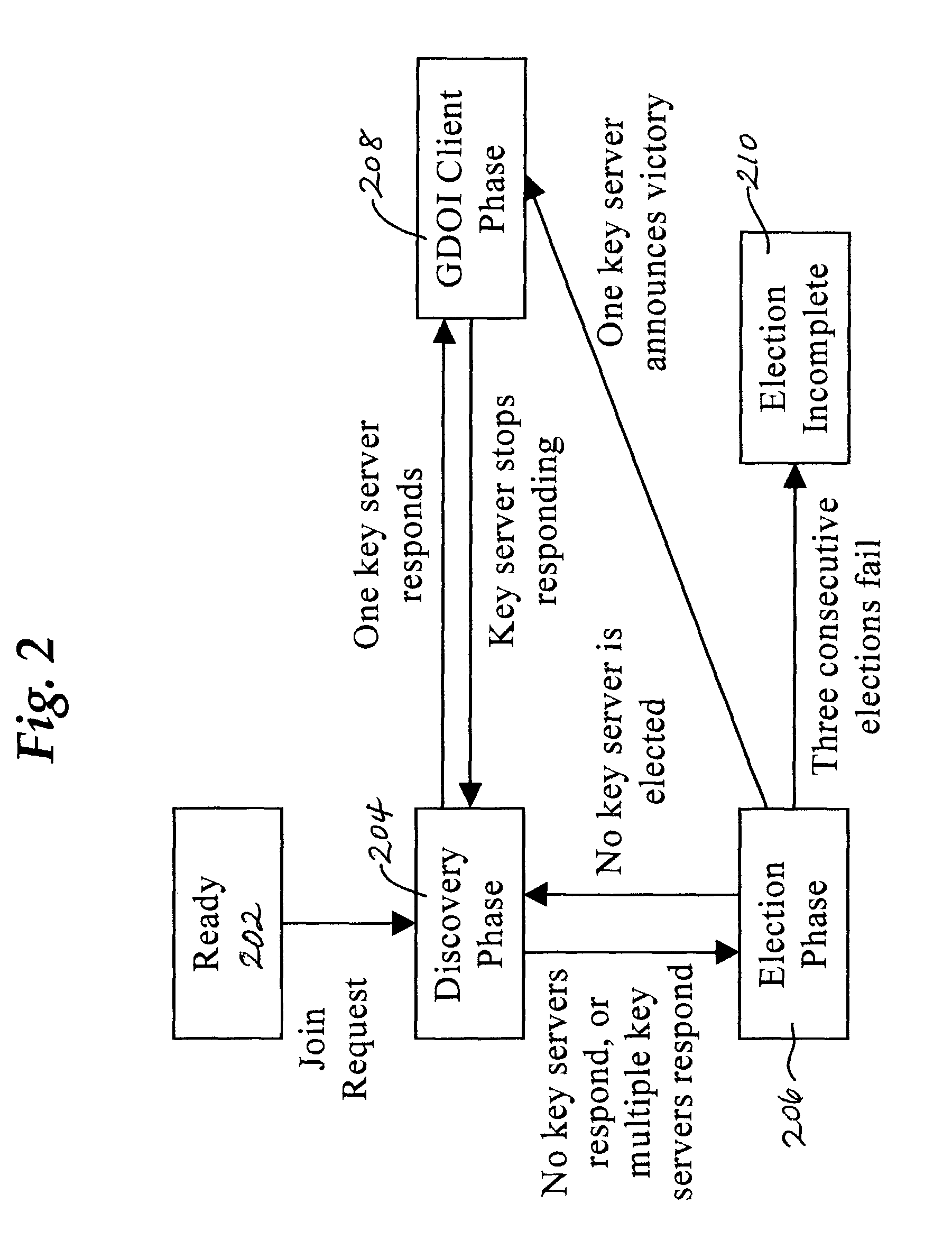
A method performed by a first computer node for selecting a leader node to provide service to a plurality of other nodes in a multicast group, wherein each of the nodes communicates using multicast messages, comprises issuing a first election call message; receiving candidacy announcement messages from one or more leader candidate nodes in a specified time period; selecting a victor from among all leader candidate nodes from which candidacy announcement messages are received; receiving one or more victor announcement messages from one or more leader victor nodes for a second specified time period; resolving zero or more collisions among the victor announcement messages to result in selecting the leader node. One embodiment provides a dynamic secure protocol for electing a key server, such as a key server that is suited for use with a group key exchange protocol such as the Group Domain of Interpretation (GDOI). Public key signatures may be used to secure message exchanges and to provide for authentication of network nodes in a multicast group.
Owner:CISCO TECH INC
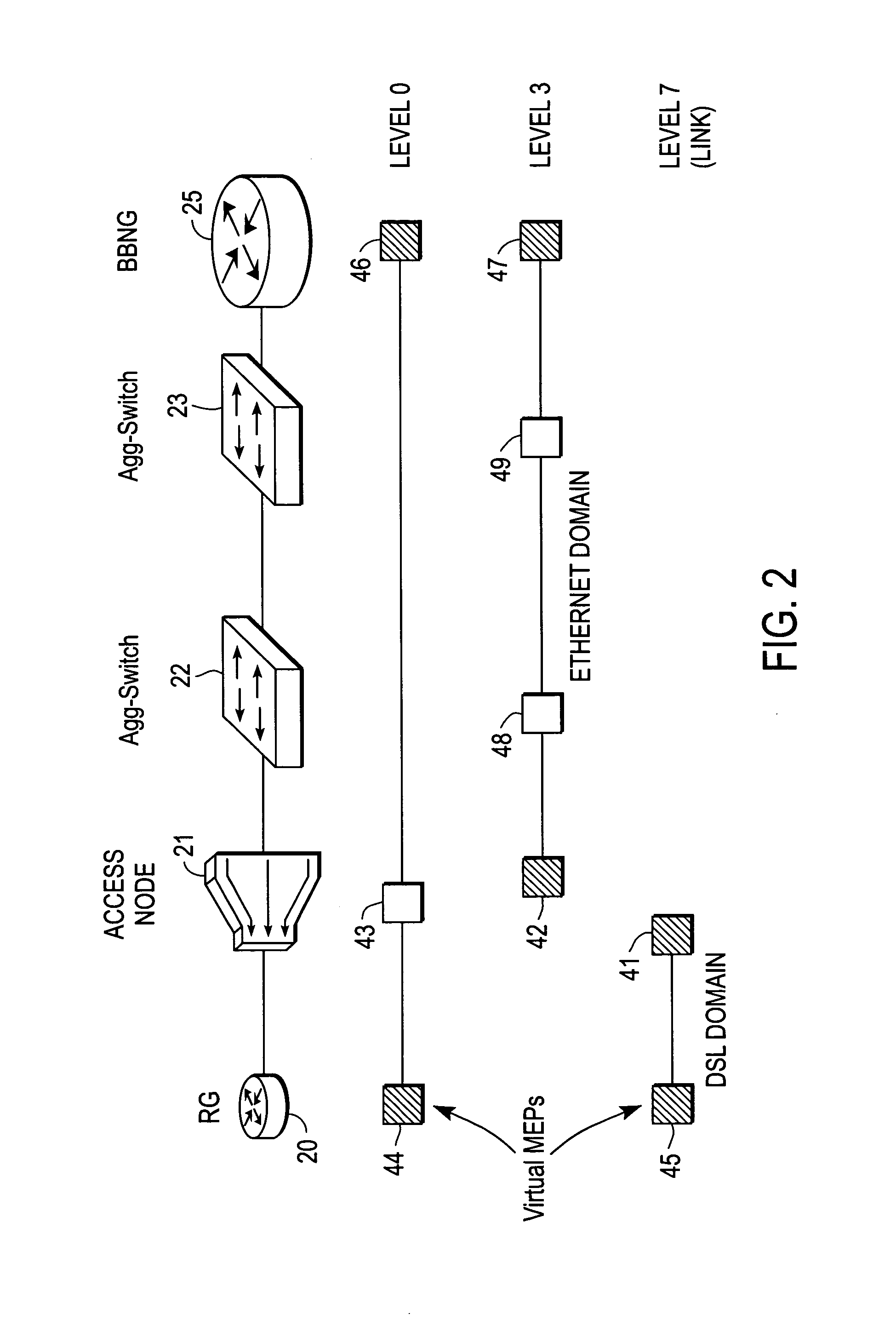
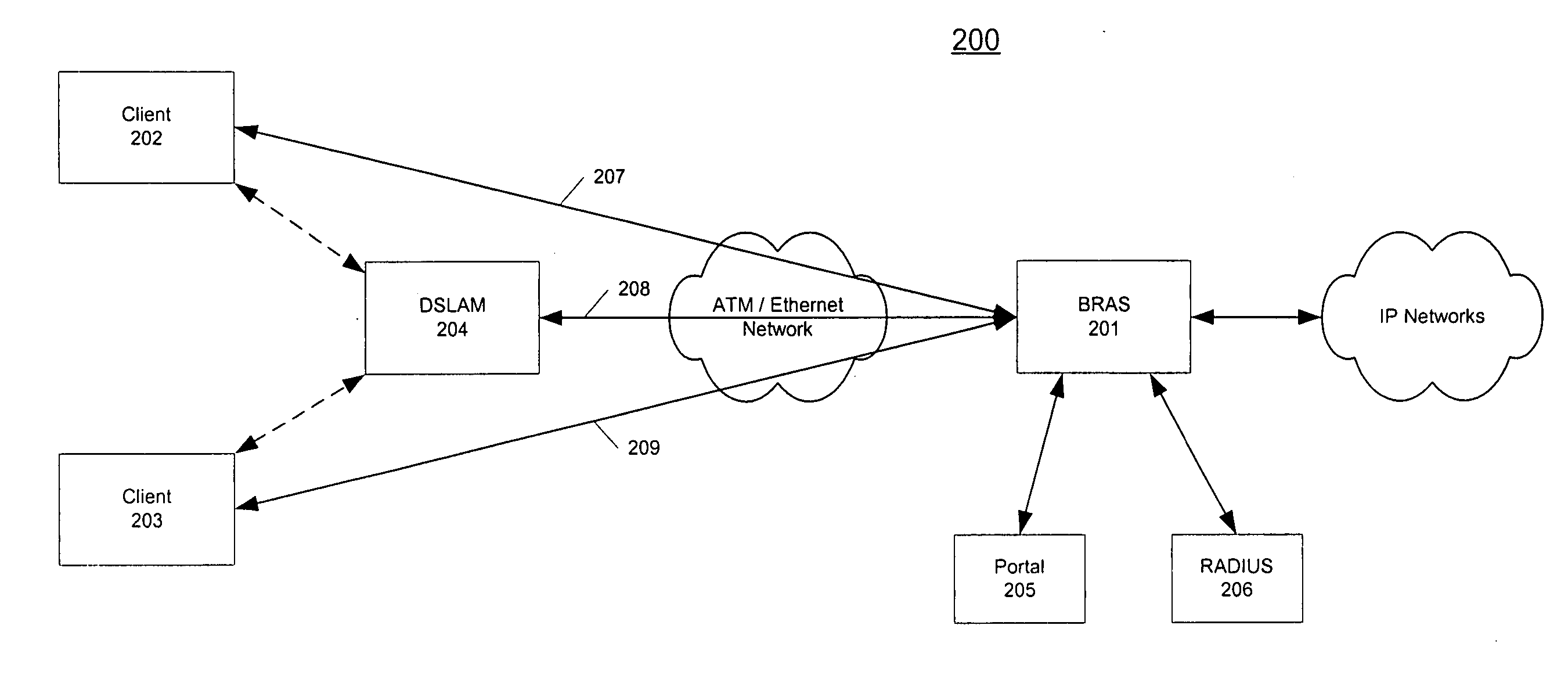
Protocol for messaging between a centralized broadband remote aggregation server and other devices
ActiveUS20050152370A1Special service provision for substationData switching by path configurationAccess networkMultiplexer
Protocols for messaging between a centralized network management system and other entities are described. According to one embodiment, in response to a request of a subscriber for joining a multicast group received at a centralized aggregation server, the centralized aggregation server transmits a port subscriber announcement (PSA) message to substantially all subscriber access multiplexers over an access network. The PSA message includes an identifier (ID) of the subscriber. In response to the PSA message, a subscriber access multiplexer having a subscriber matching the ID of the subscriber in the PSA message identifies a user port corresponding to the subscriber and applies a local service policy to the identified user port. Subsequent multicast messages destined to the subscriber are delivered by the subscriber access multiplexer to the subscriber based on the local service policy corresponding to the receiving subscriber without having the aggregation server handling the service policy of the receiving subscriber. Other methods and apparatuses are also described.
Owner:TELEFON AB LM ERICSSON (PUBL)
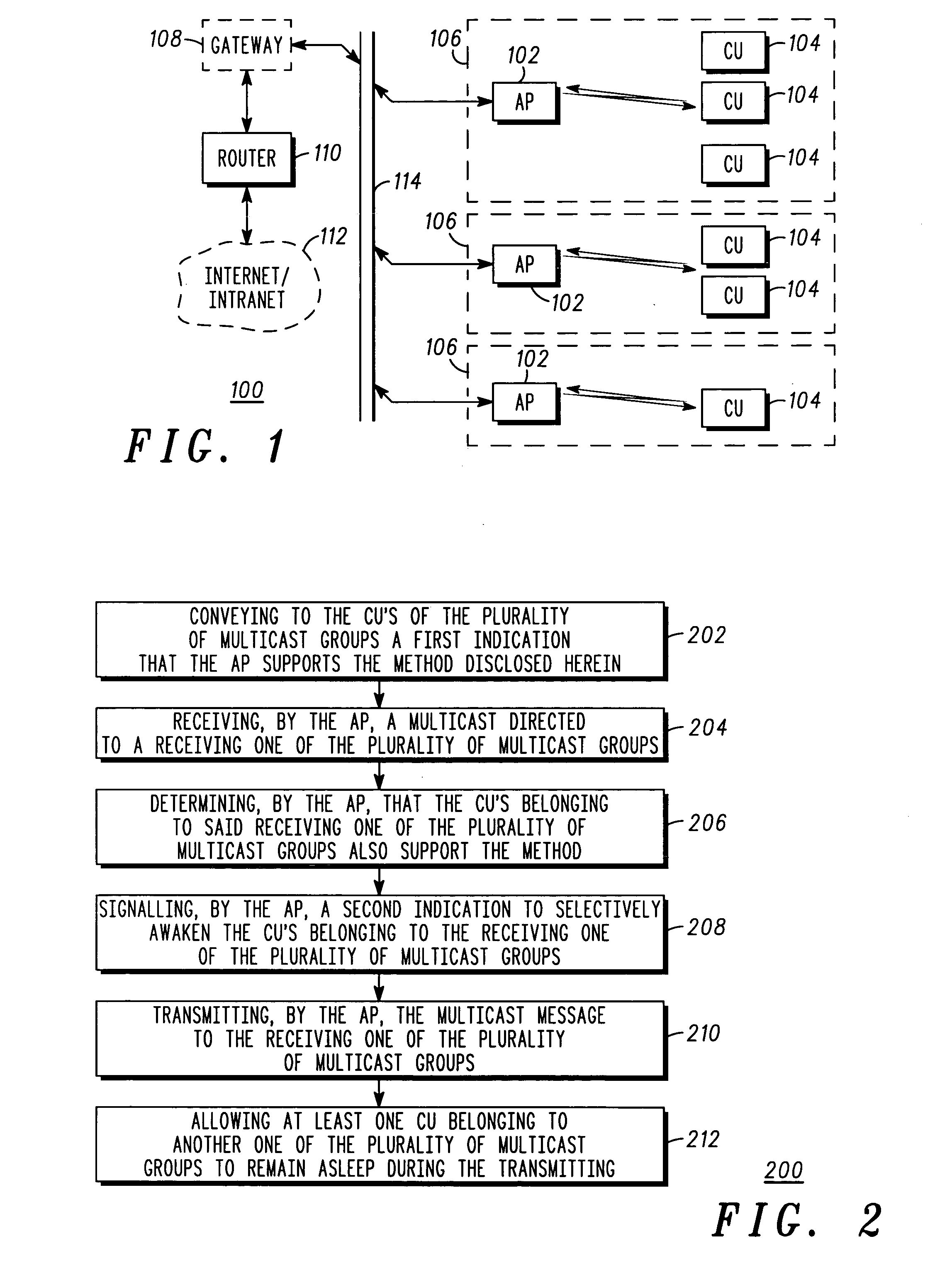
Method and apparatus for sending a multicast message
InactiveUS20050276237A1Special service provision for substationBroadcast transmission systemsComputer networkCommunication unit
An access point (102) conveys (202) to communication units (104) of a plurality of multicast groups, a first indication that the access point supports a method for sending a multicast message. The access point receives (204) a multicast message directed to a receiving one of the plurality of multicast groups, and determines (206) that the communication units belonging to the receiving one of the plurality of multicast groups also support the method. The access point signals (208) a second indication to selectively awaken the communication units belonging to the receiving one of the plurality of multicast groups, and transmits (210) the multicast message to the receiving one of the plurality of multicast groups in a manner that allows (212) at least one communication unit not belonging to the receiving one of the plurality of multicast groups to remain asleep during the transmitting.
Owner:GOOGLE TECH HLDG LLC
Transmission methods for communication systems supporting a multicast mode
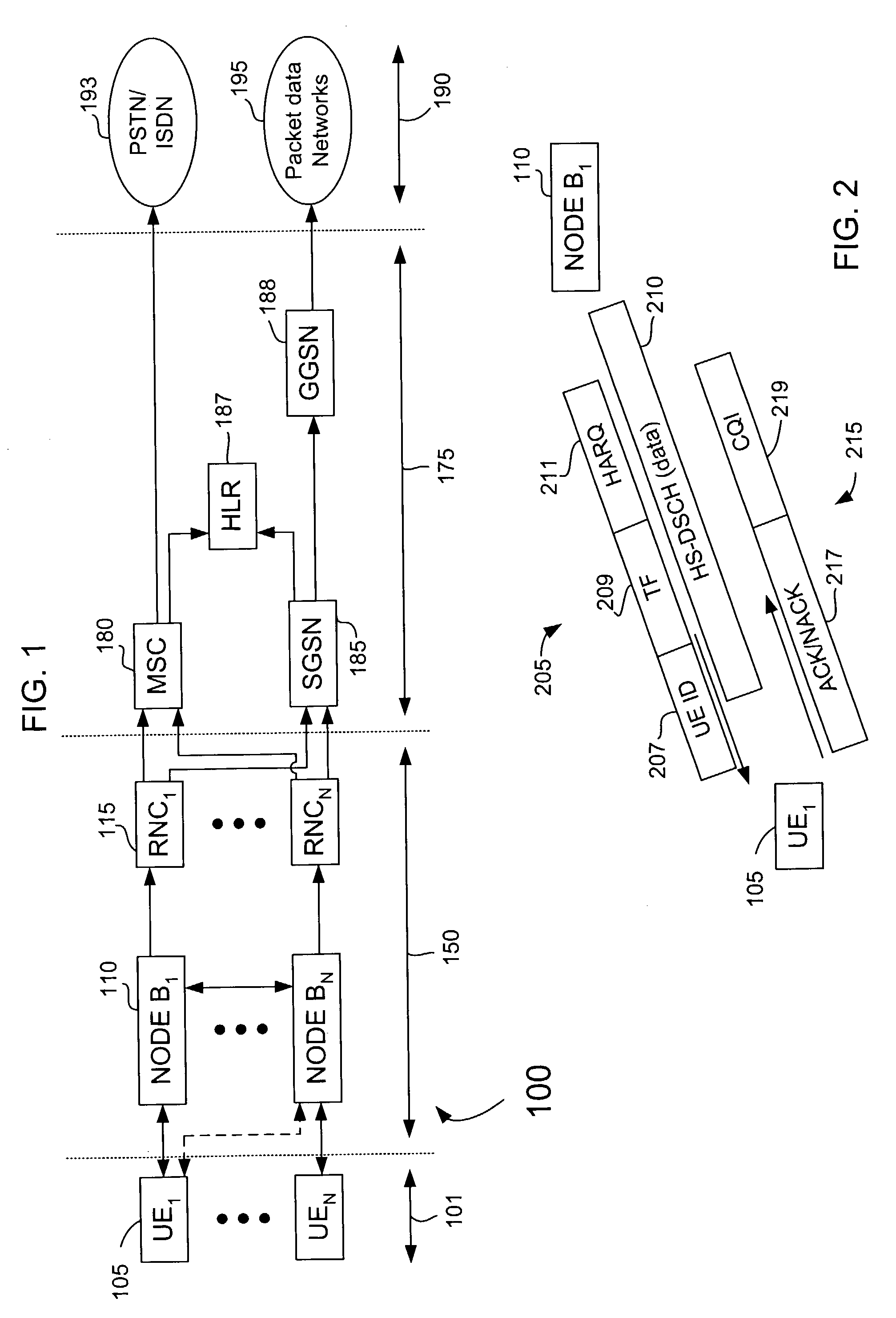
InactiveUS20040184471A1Special service provision for substationError prevention/detection by using return channelCommunications systemMulticast message
Transmission methods for multicast messages and for signaling message responses thereto in communication systems supporting a multicast mode provide that a number of retransmissions of a multicast message may be changed based on a number of receivers of the message. Signaling messages to the multicast message may be transmitted in response to a fixed number of multicast message transmissions, and receivers that have not received the multicast message after the fixed number of transmissions may request further retransmissions up to an additional given number of times. Further, signaling messages may be transmitted at different times or staggered based on a radio condition of the receivers. For example, a first multicast message may be transmitted, and responses from groups of receivers may be listened to for a given period, after which one of a next multicast message and a portion of the first multicast message may be transmitted to the groups.
Owner:ALCATEL-LUCENT USA INC +1
Method for building MAC (Media Access Control) address table and provider edge device
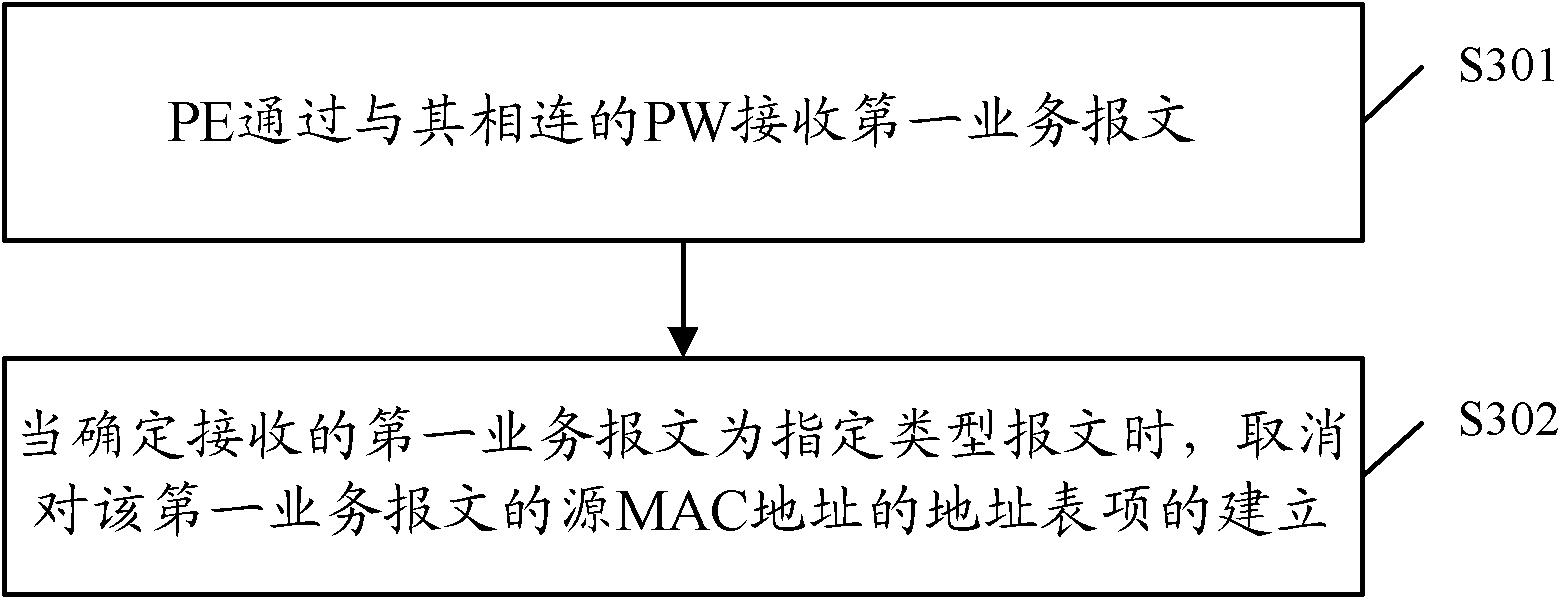
ActiveCN102164091AReduce in quantityReduce capacityData switching networksAddress Resolution ProtocolMedia access control
The invention discloses a method for building an MAC (Media Access Control) address table and a provider edge device. In the method, a PE (Provider Edge Device) receives a first service message by a PW (Pseudo Wire) connected with the PE; when the first received service message is confirmed to be a specific-type message, the building of the address table entry of the source MAC address of the first service message is cancelled, wherein the specific-type message is an unknown unicast message, a multicast message or the broadcasting message of a non-free ARP (Address Resolution Protocol) message. According to the scheme provided by the embodiment of the invention, the amount of the address table entries built by the PE is reduced so as to reduce the volume of the MAC address table.
Owner:BEIJING XINWANG RUIJIE NETWORK TECH CO LTD
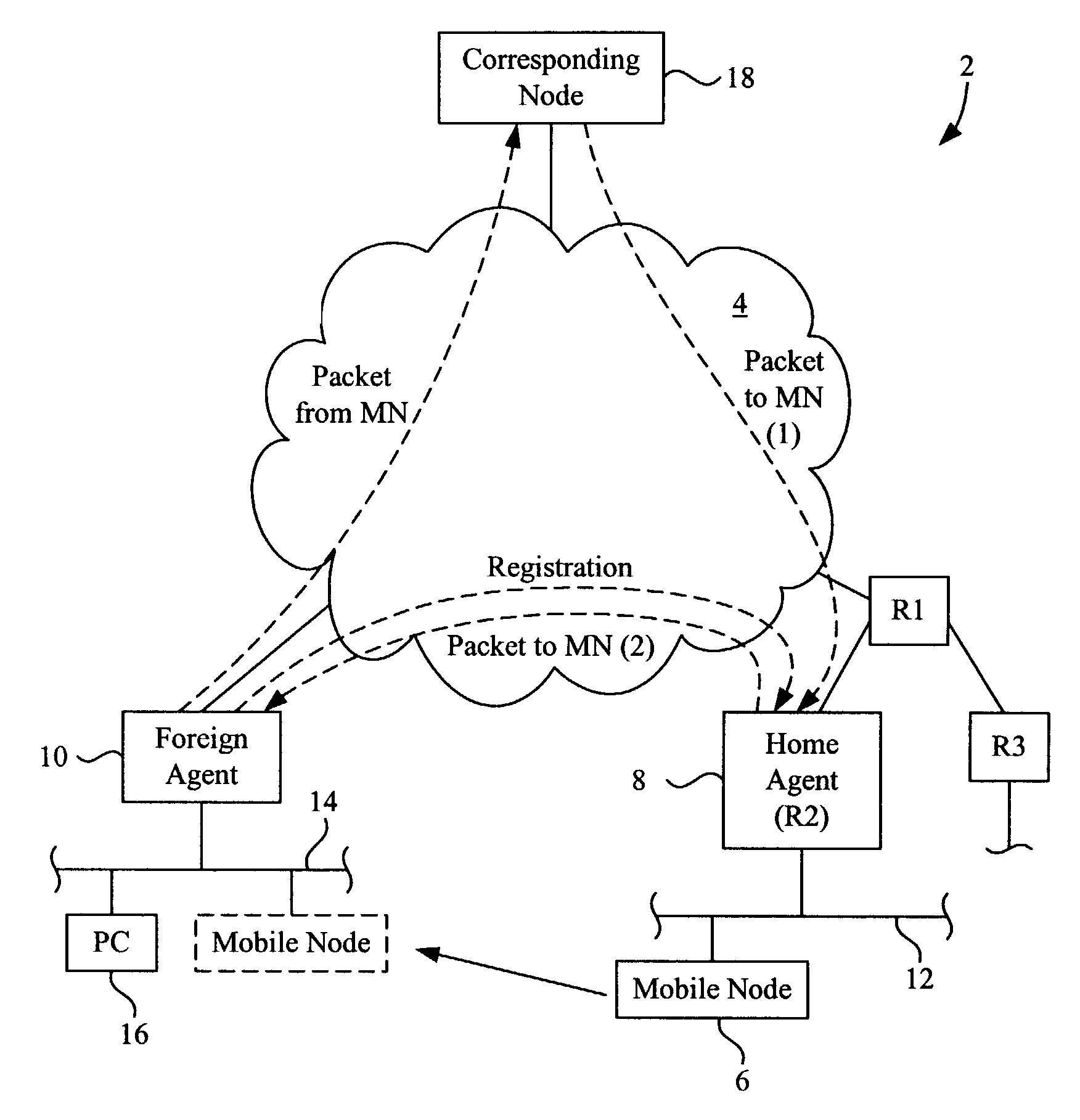
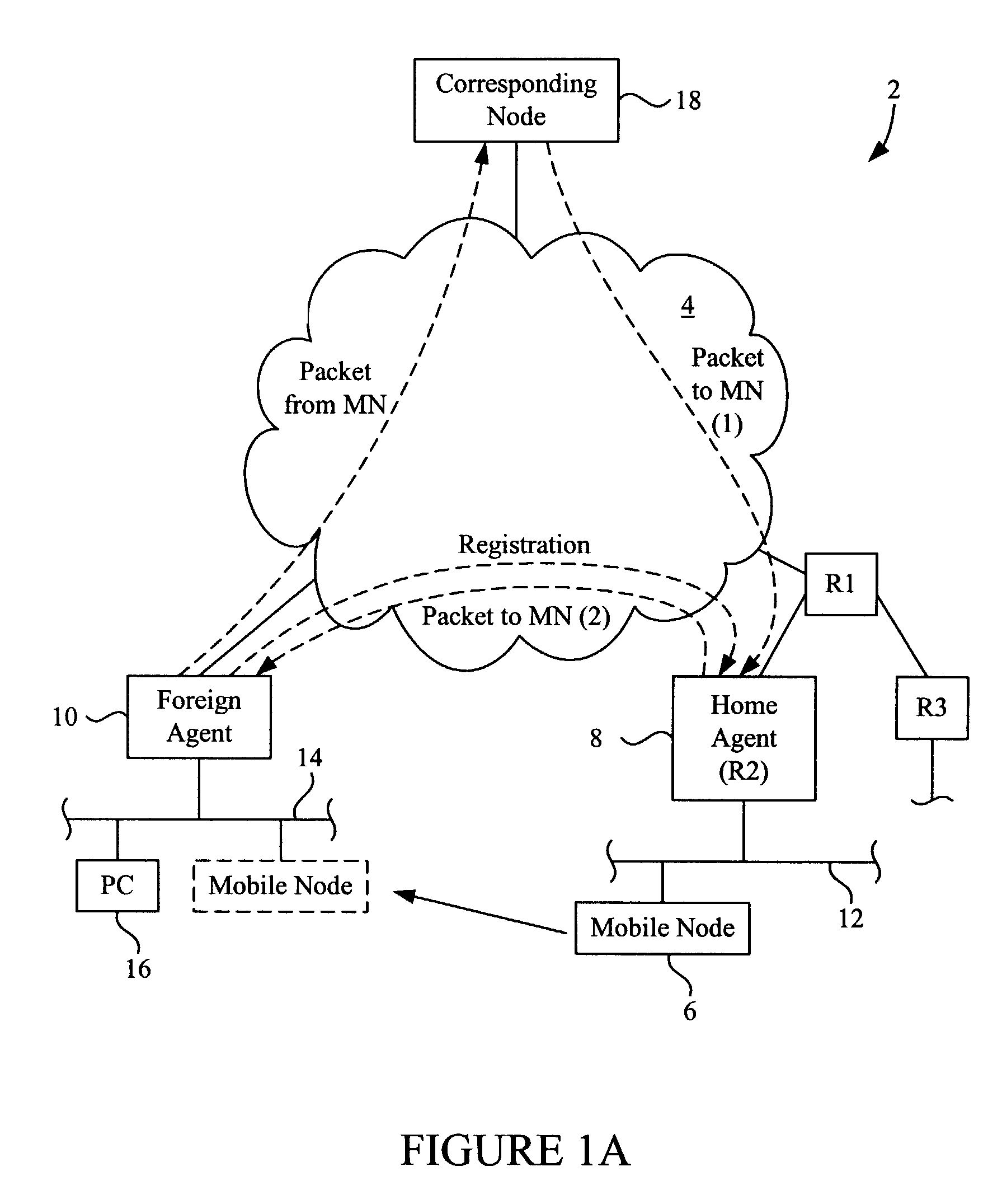
Methods and apparatus for implementing home agent redundancy
InactiveUS7227863B1Time-division multiplexData switching by path configurationComputer networkMobile IP
Methods and apparatus for maintaining Mobile IP operation in a Home Agent are disclosed. In a Home Agent, a Mobile Node is registered and a registration entry is created in a mobility binding table for the Mobile Node. A multicast message is then sent to a virtual router group to which the Home Agent belongs and with which the Home Agent shares a virtual IP address. The multicast message notifies the virtual router group of the registration. A similar process may be performed when a Mobile Node is de-registered. When an active or non-active Home Agent is initialized, it sends a multicast mobility binding table request to the redundancy group indicating that bindings are requested. The Home Agent may then receive bindings in response to the request and update its mobility binding table with the received bindings.
Owner:CISCO TECH INC
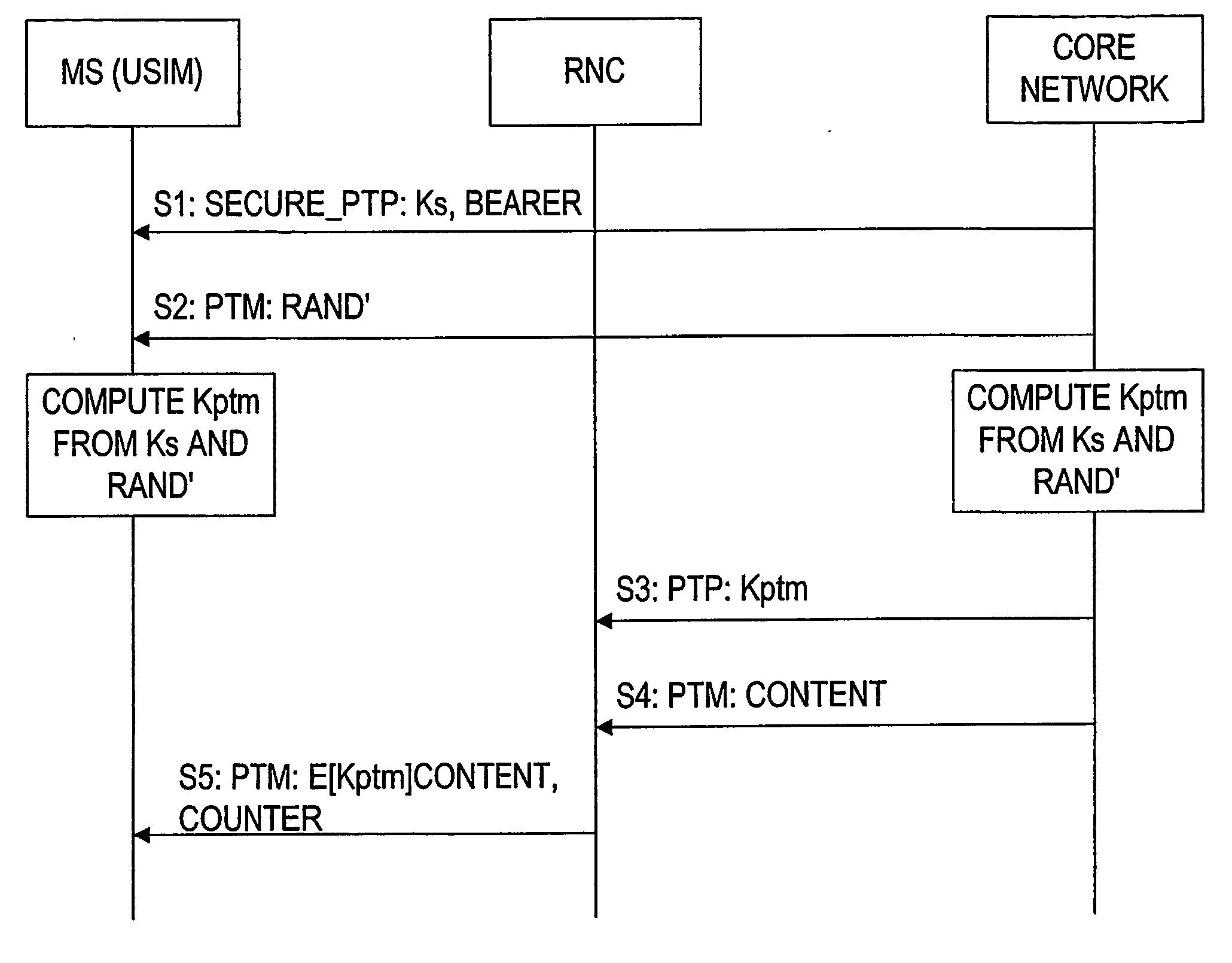
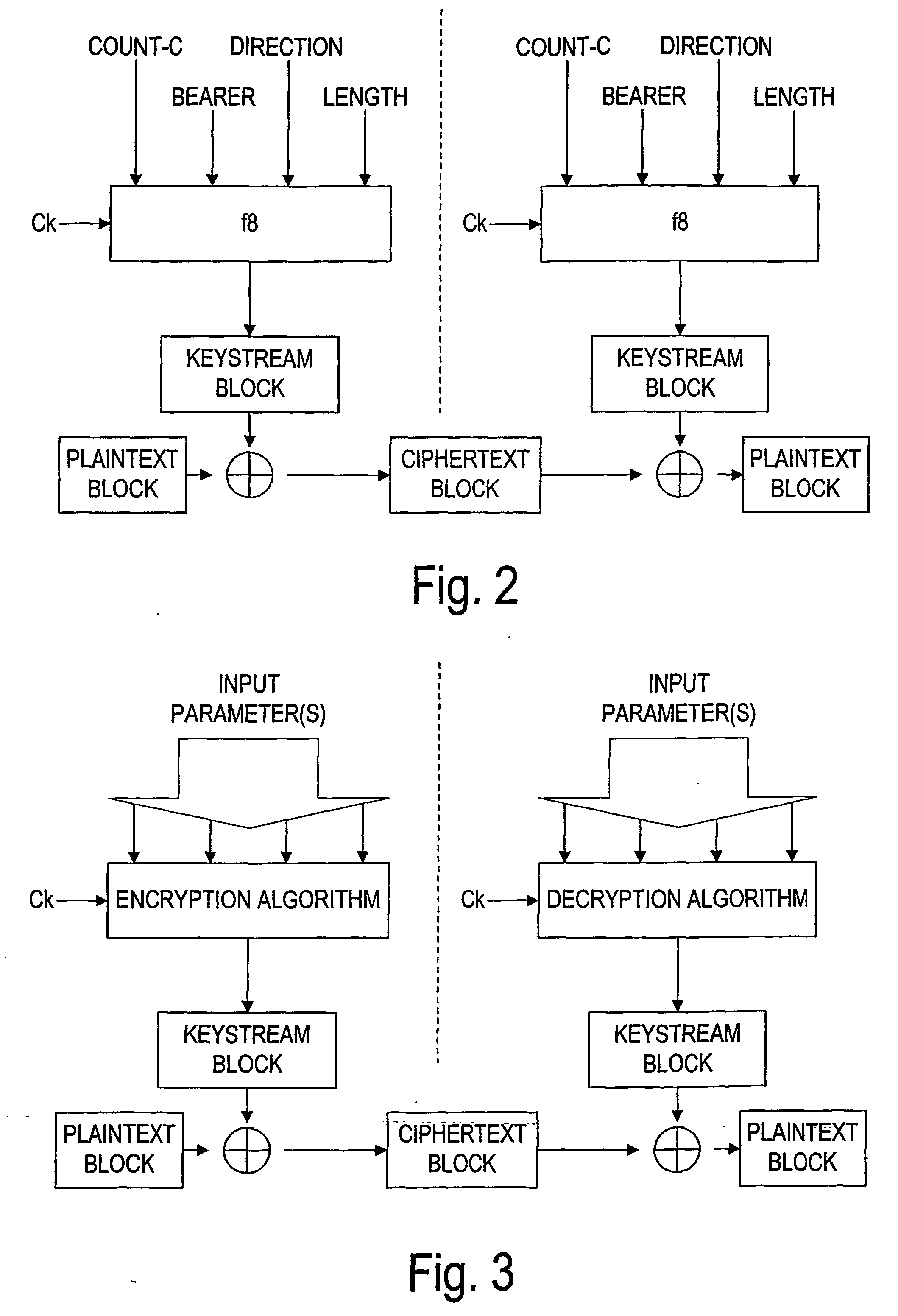
Ciphering as a part of the multicast concept
ActiveUS20050015583A1Improve securityEliminate generationSpecial service provision for substationKey distribution for secure communicationService controlControl equipment
The invention proposes a method for transmitting a message to a plurality of user entities in a network by using a multicast service, comprising the steps of encrypting a multicast message by using ciphering, and sending the encrypted multicast message to the plurality of user entities simultaneously. The invention also proposes a corresponding multicast service control device and a corresponding user entity.
Owner:NOKIA TECHNOLOGLES OY
Method and apparatus for optimized centralized critical control architecture for switchgear and power equipment
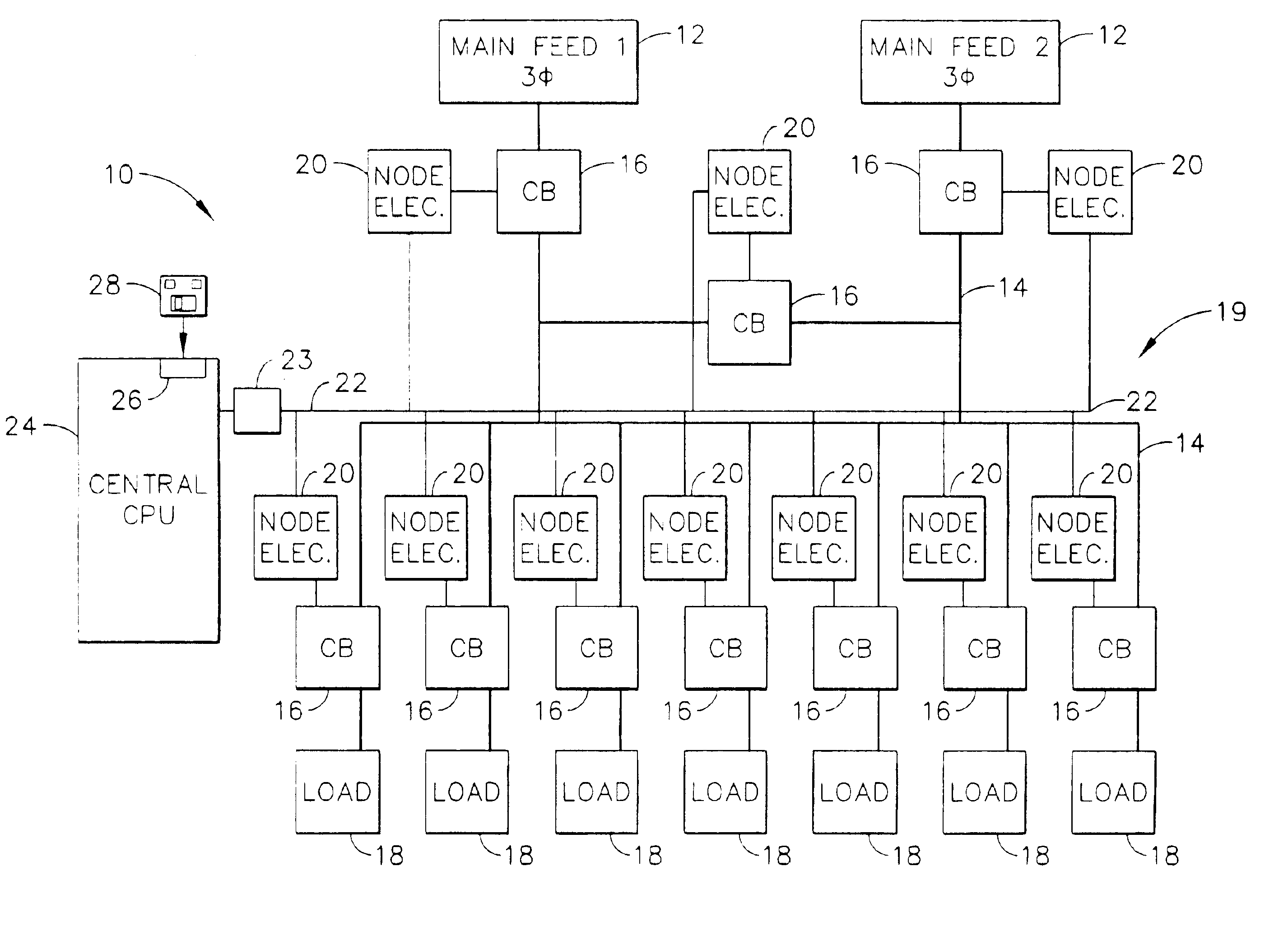
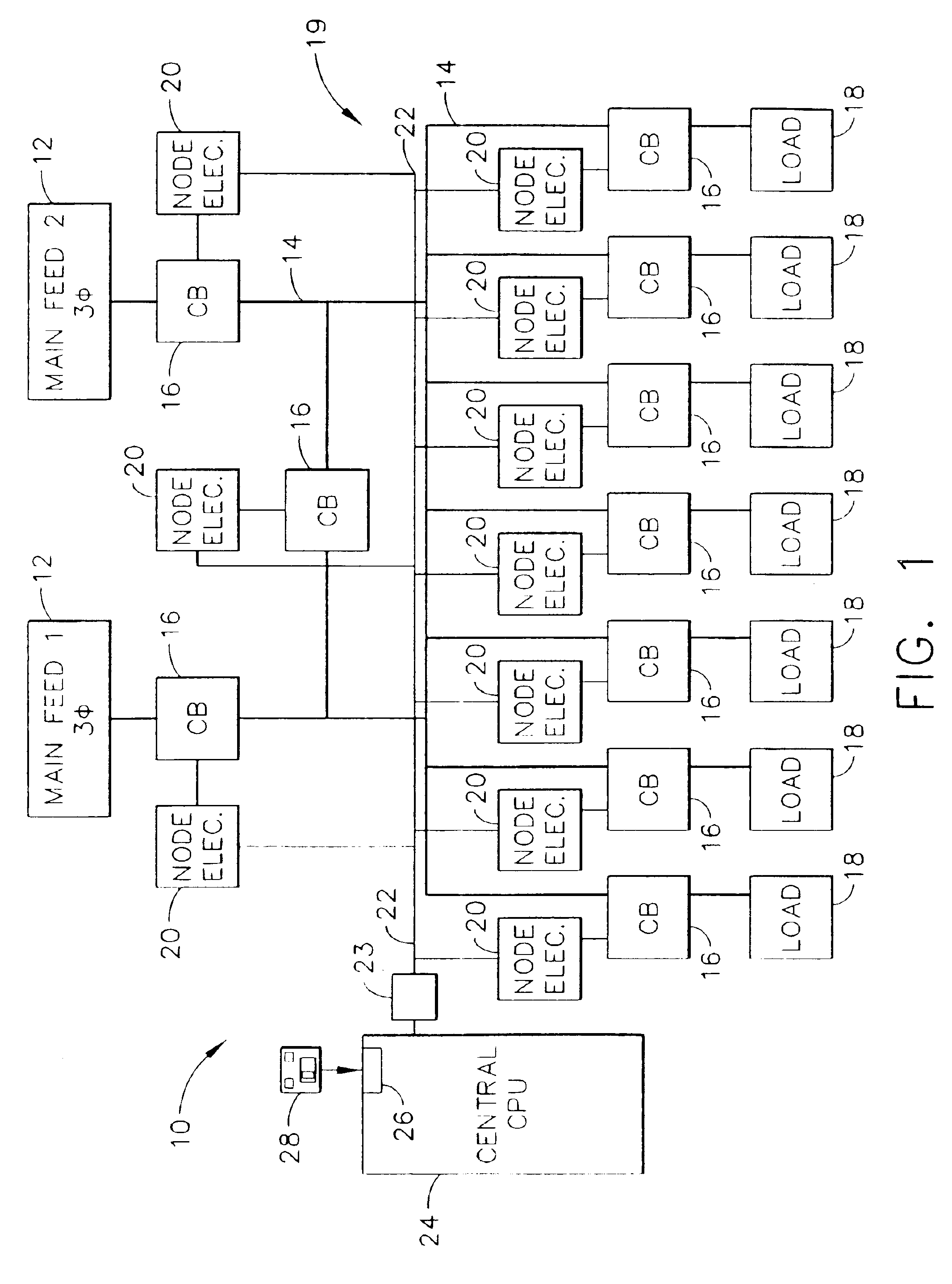
InactiveUS6892115B2Selective ac load connection arrangementsLevel controlElectricityDistribution power system
A method of monitoring and controlling a power distribution system is provided. The power distribution system includes a plurality of circuit breakers, a plurality of node electronic units, and wherein each associated circuit breaker is electrically coupled with each respective node electronic unit. The system also includes at least one digital network, and at least one central control processing unit (CCPU) wherein each CCPU includes a first power system global information set, and each CCPU is communicatively coupled to the plurality of node electronic units. The method includes transmitting at least one digital message from each node electronic unit to each CCPU over a respective network, determining an operational state of the power distribution system from the digital message, and transmitting at least one multicast message from each CCPU to each node electronic unit such that the circuit breakers are operable from each CCPU.
Owner:ABB (SCHWEIZ) AG
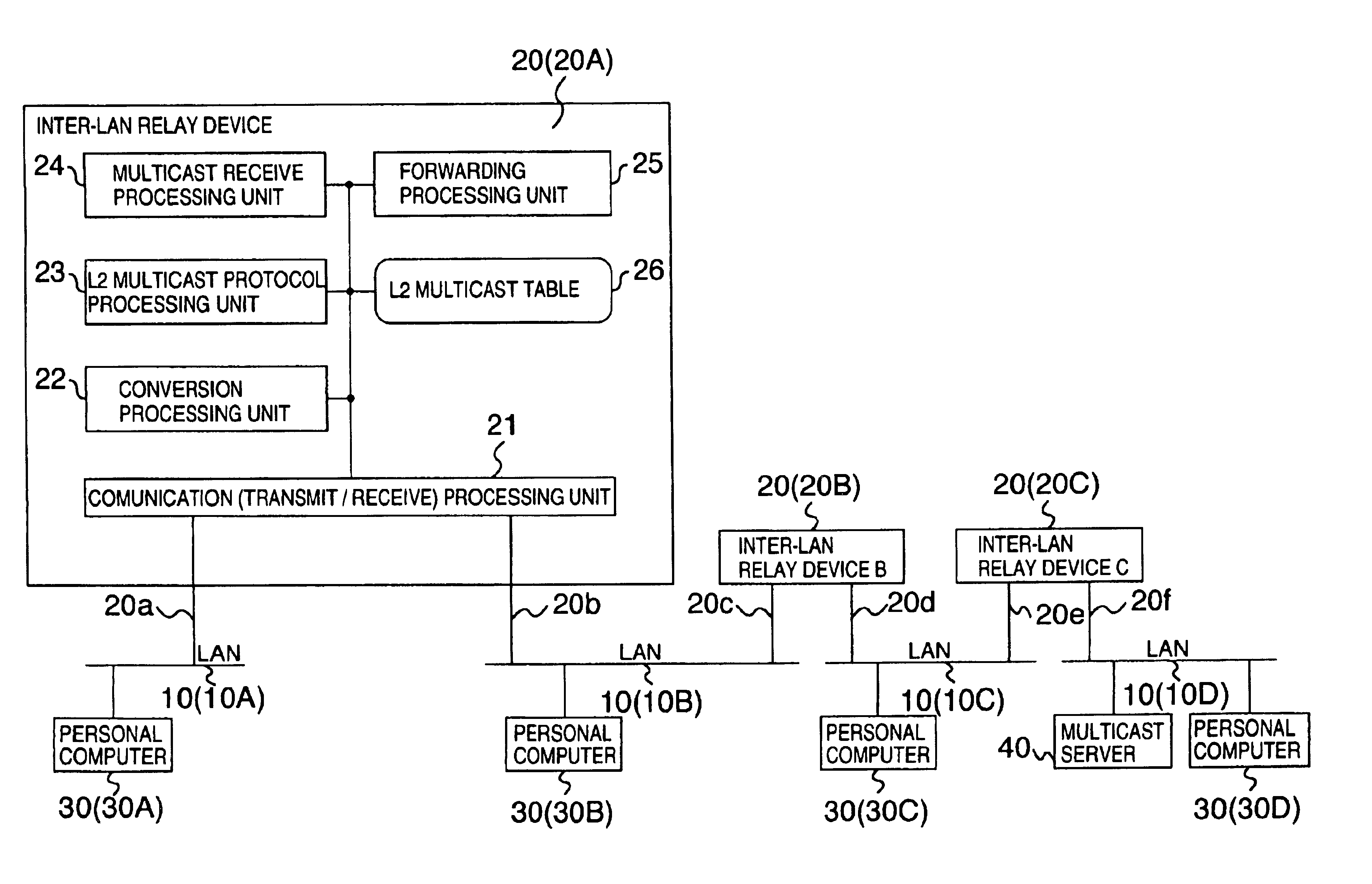
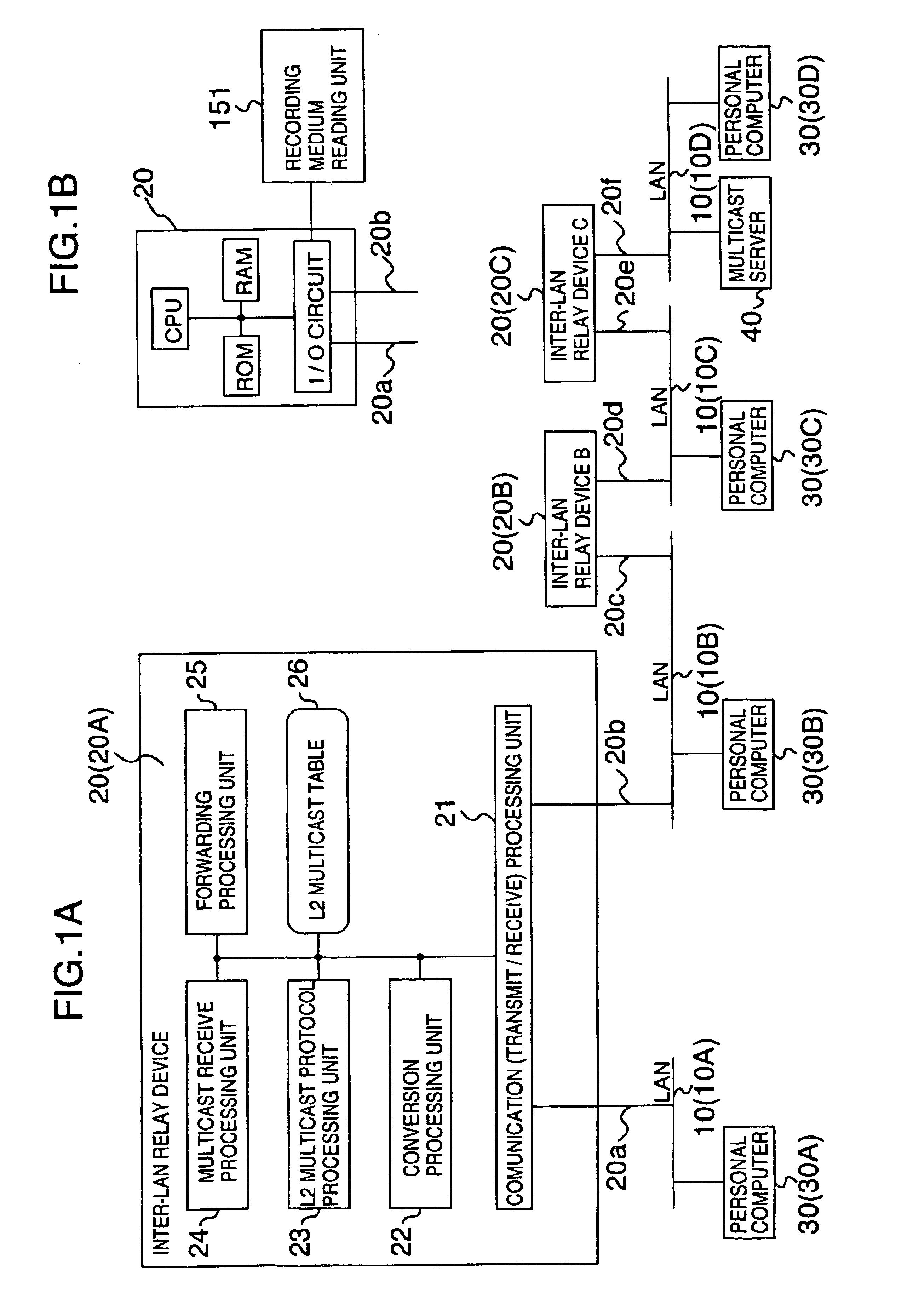
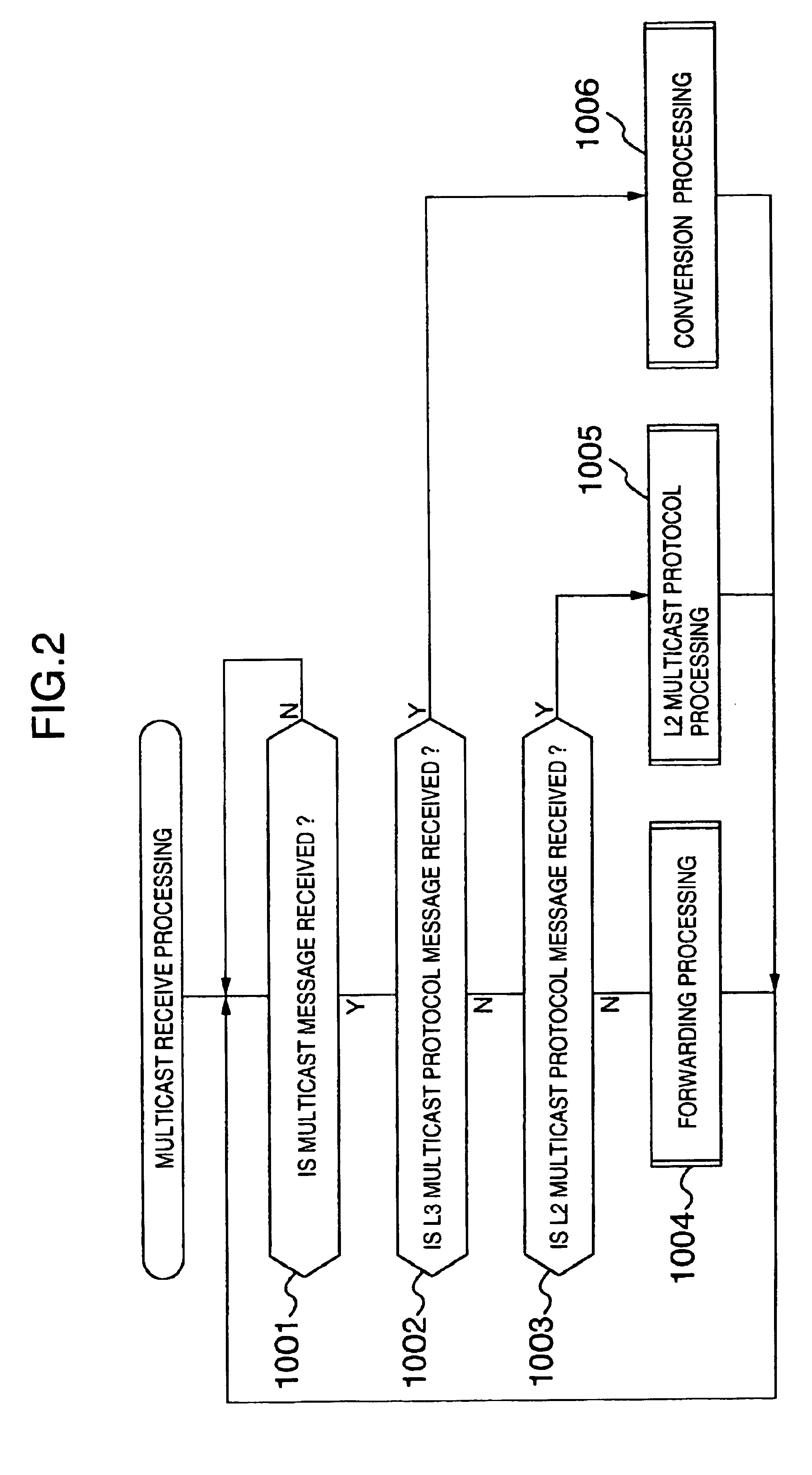
Information relay device and method with multicast protocol conversion function and information network system using the same
InactiveUS6853639B1Easy to installSpecial service provision for substationData switching by path configurationGeneral purposeInformation networks
An information relay device connected between a plurality of logical or physical networks for performing an operation for relay of information between the networks is provided with a transmit / receive processing unit for receiving a general purpose multicast message from one of the plurality of networks and transmitting a multicast message to at least one of the plurality of networks, and a protocol conversion processing unit for converting, in the case where the general purpose multicast message received by the transmit / receive processing unit is a multicast protocol message of a certain level layer, the multicast protocol message of the certain level layer into a multicast protocol message of another level layer.
Owner:HITACHI LTD
Mobile virtual LAN
InactiveUS20050180345A1Not burdened with associated computational overheadNetwork topologiesWireless network protocolsCommunications systemVirtual LAN
A communication system in which multiple protocols and proxy services are executed by an access point. In one embodiment of the invention, GVRP and GMRP registrations are combined in a single packet when a wireless device roams to a different VLAN. In addition, outbound GVRP and GMRP multicast messages are handled by an access point (also referred to as a GVRP and GMRP “gateway”) such that the wireless device is not burdened with the associated computational overhead. In a further embodiment, a wireless device may dynamically switch between a VLAN-aware state and a VLAN-unaware state depending on the nature of a detected access point. For example, if a relevant access point supports GVRP, the wireless device may operate as a VLAN terminal. If a wireless device is not attached to an access point with a matching VLAN ID, the wireless device sends and receives VLAN tagged frames. If a wireless device configured with a VLAN ID is attached to an access point with a matching VLAN ID, or if the wireless device is attached to a non-VLAN access point, then the wireless device may send and receive raw / untagged frames. In addition to the gateways described below, the ability of a wireless device to detect when it can send untagged frames is considered novel. In another embodiment of the invention, a special ID that is different than the native VLAN ID for a switch port is used for VLAN-unaware devices. This allows such devices that do not issue tagged frames to belong to a single VLAN ID.
Owner:AVAGO TECH INT SALES PTE LTD
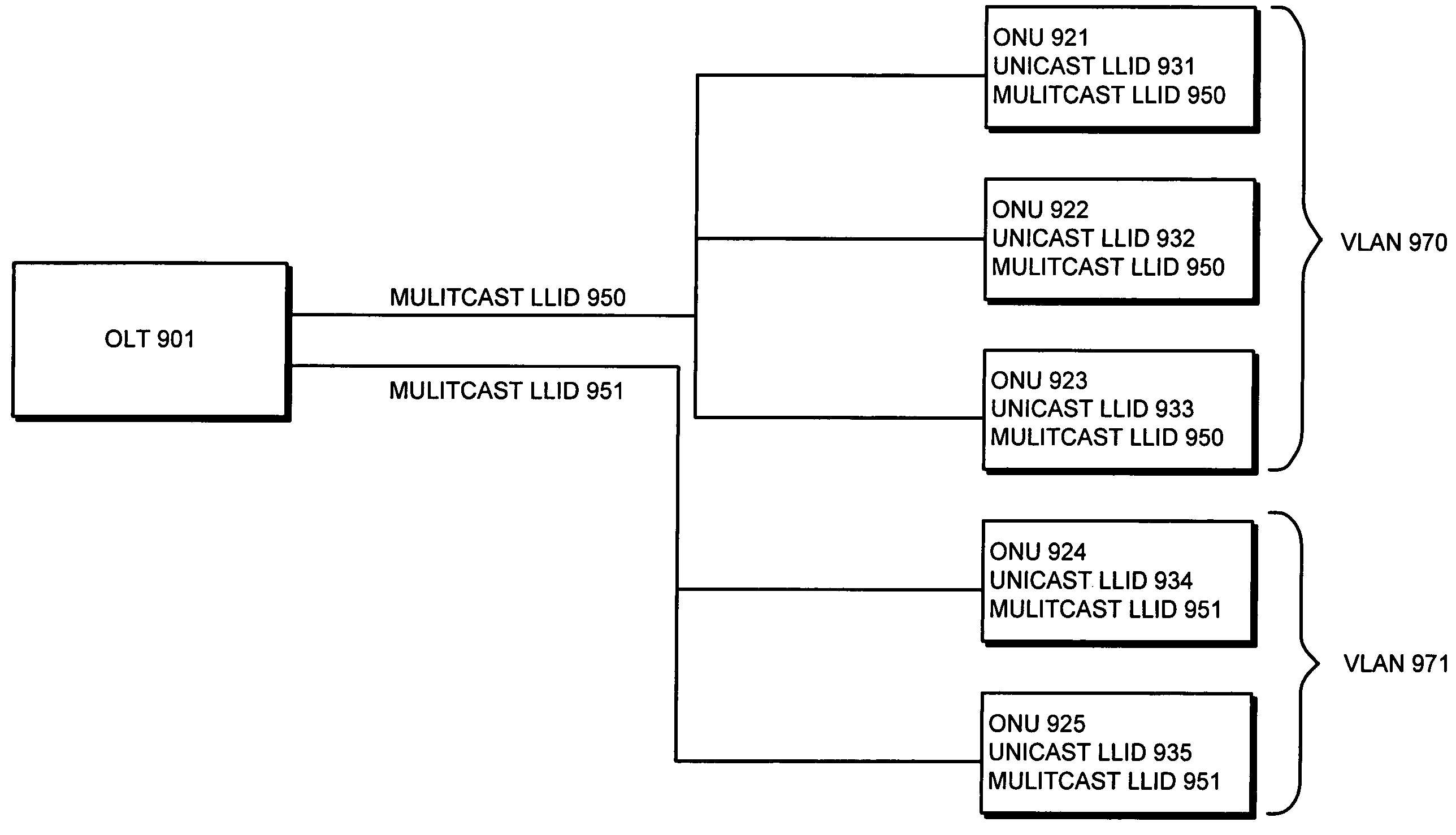
Method and apparatus for bandwidth-efficient multicast in ethernet passive optical networks
InactiveUS20050100036A1Facilitates bandwidth-efficient multicastMultiplex system selection arrangementsTime-division multiplexBroadcastingOptical coupler
One embodiment of the present invention provides a system that facilitates bandwidth-efficient multicast in EPONs. The system includes a central node and at least one remote node. Downstream data from the central node is broadcast through a passive optical coupler to remote nodes. In the other direction, upstream data from a remote node is transmitted through the passive optical coupler to the central node in a unicast manner. During operation, the system first selects a common multicast LLID to represent a number of remote nodes that comprise a multicast group. Upon receiving a multicast message destined to the multicast group, the system sends the multicast message along with the multicast LLID for the multicast group, whereby the multicast message is broadcast through the passive optical coupler in the downstream direction. This allows each remote node belonging to the multicast group to receive the multicast message by matching the multicast LLID.
Owner:AVAGO TECH INT SALES PTE LTD
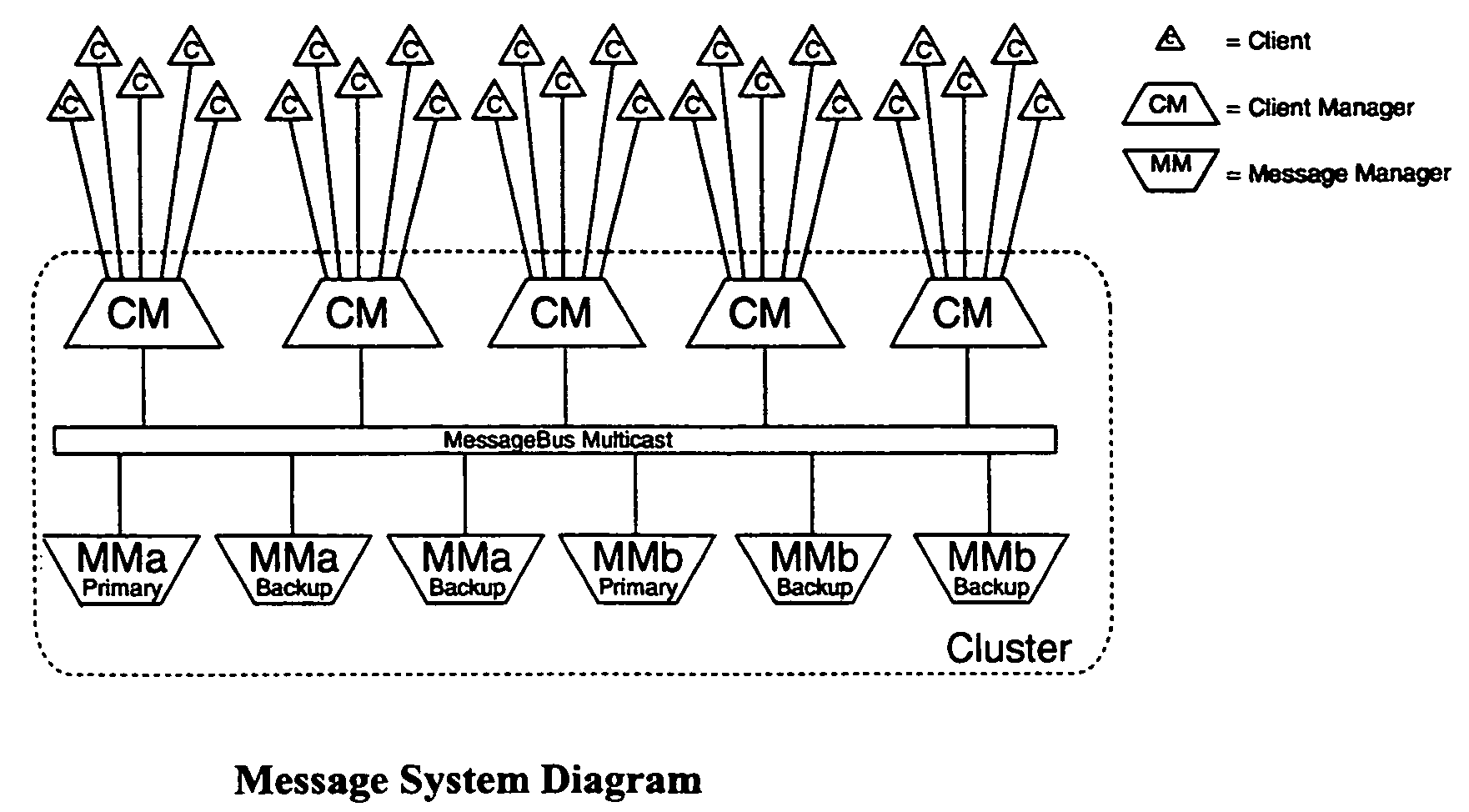
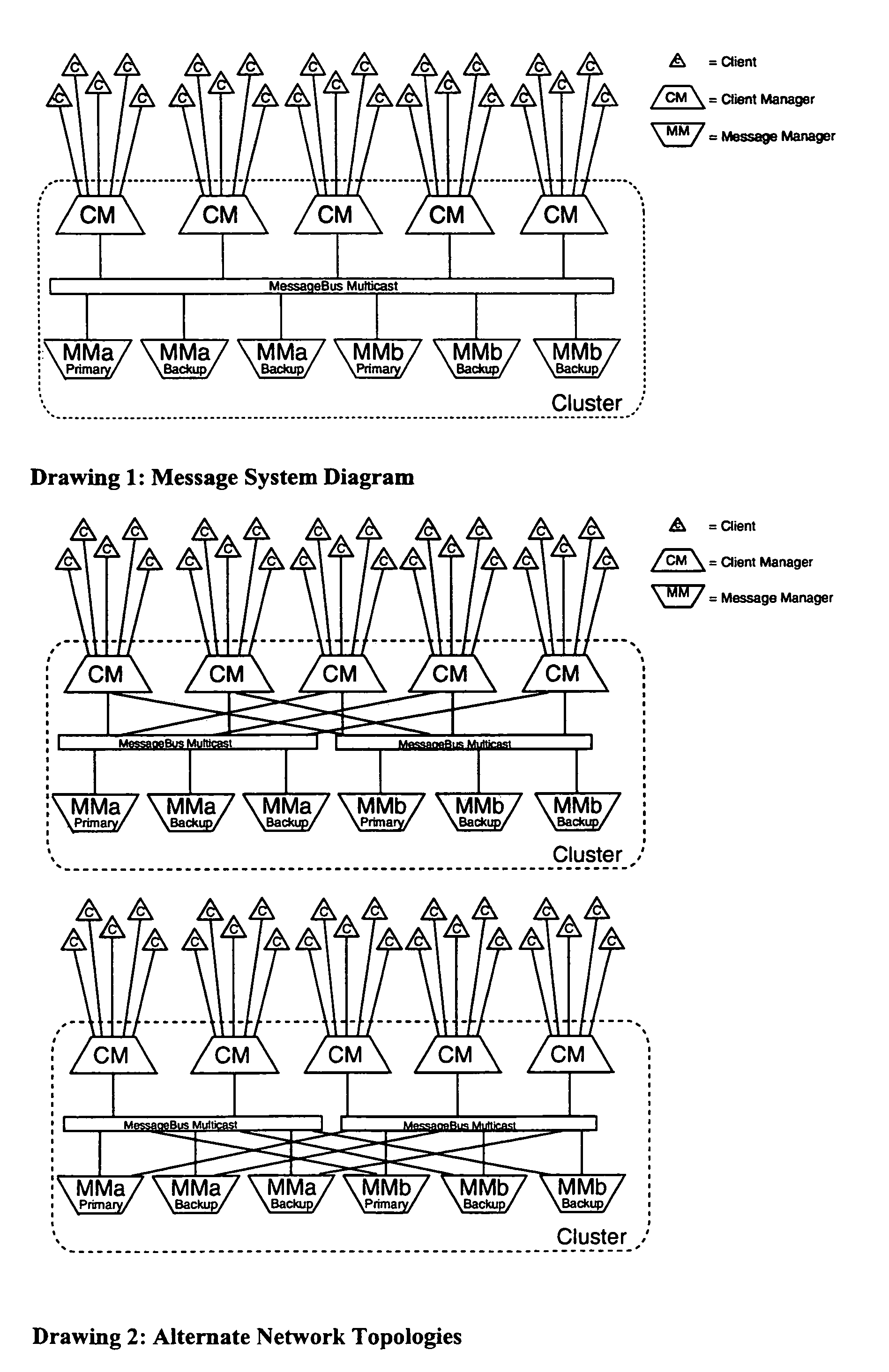
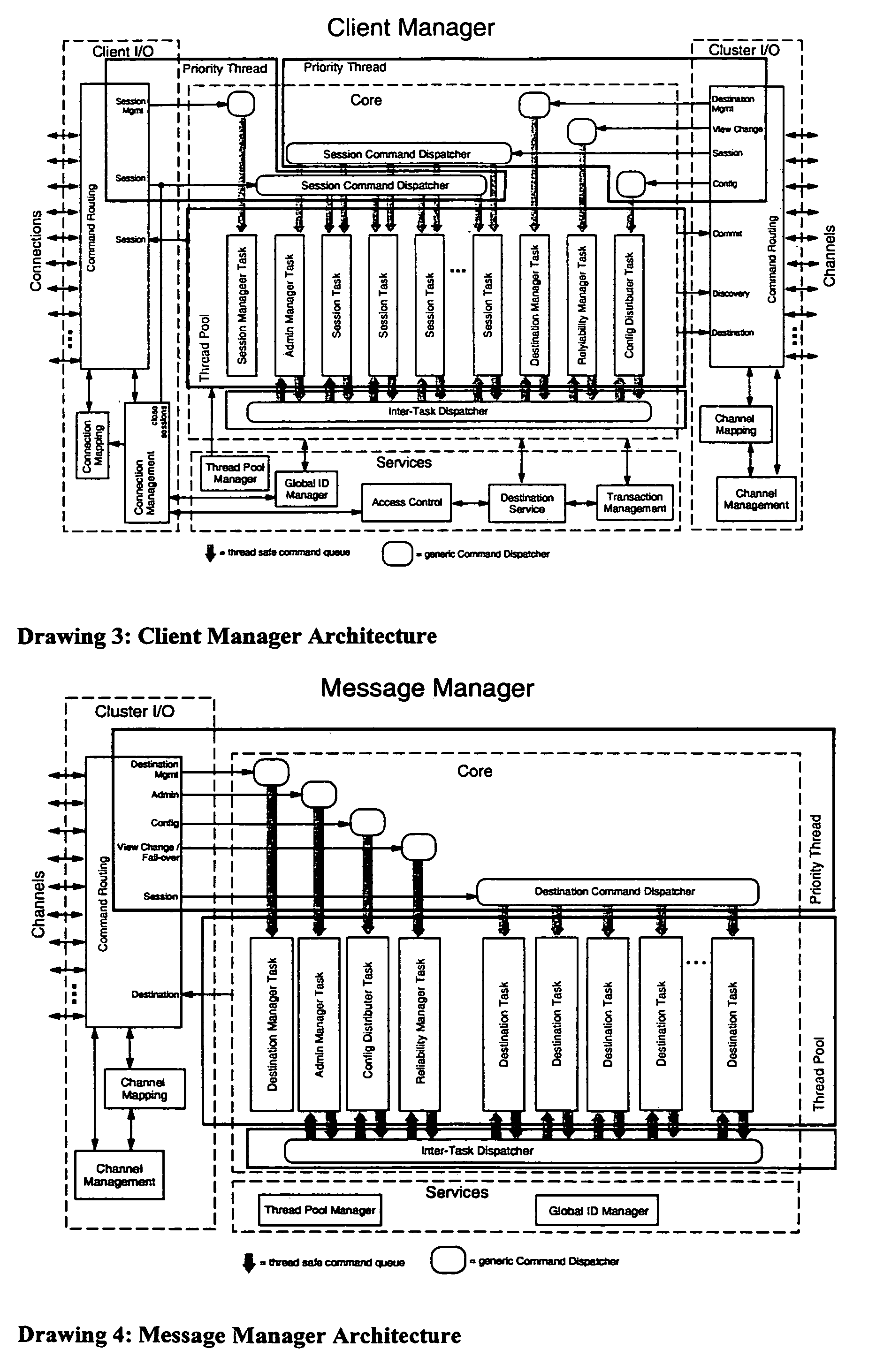
Scaleable message system
InactiveUS7177917B2Improve scalabilityOvercomes drawbackMultiprogramming arrangementsMultiple digital computer combinationsClient-sideMulticast communication
A message system for delivering data in the form messages between message clients comprises a server cluster with a group of client manager nodes and a group of independent message manager nodes. The client manager nodes have the function of managing client connections, whereas the message manager are configured to store and distribute messages. The system further comprising communication channel means in the form of a multicast messagebus for providing a multicast communication channel between said at least one client manager node and said at least one message manager node. The system guarantees delivery of a message by storing it until a receiver is ready to consume it.
Owner:TAIWAN SEMICON MFG CO LTD
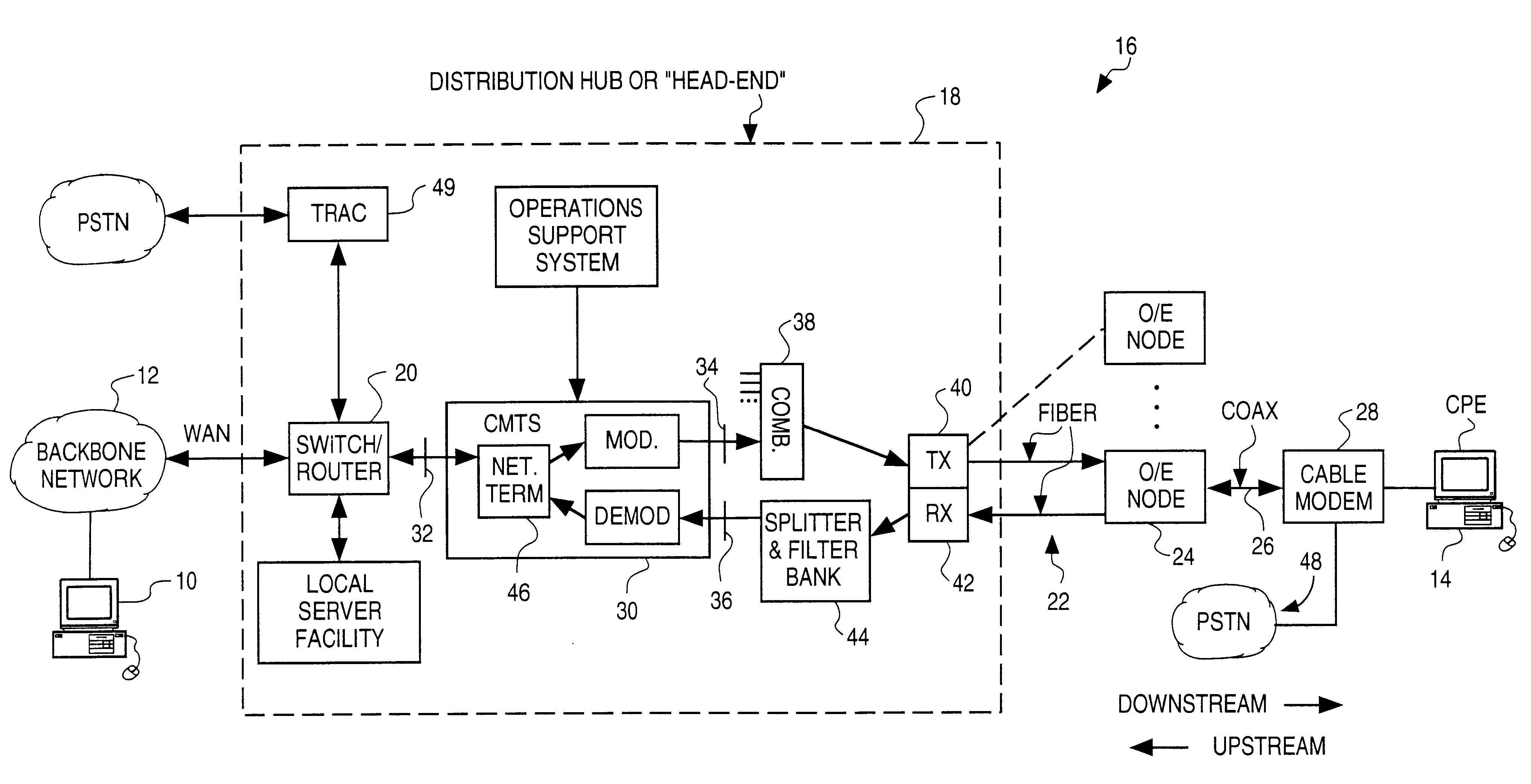
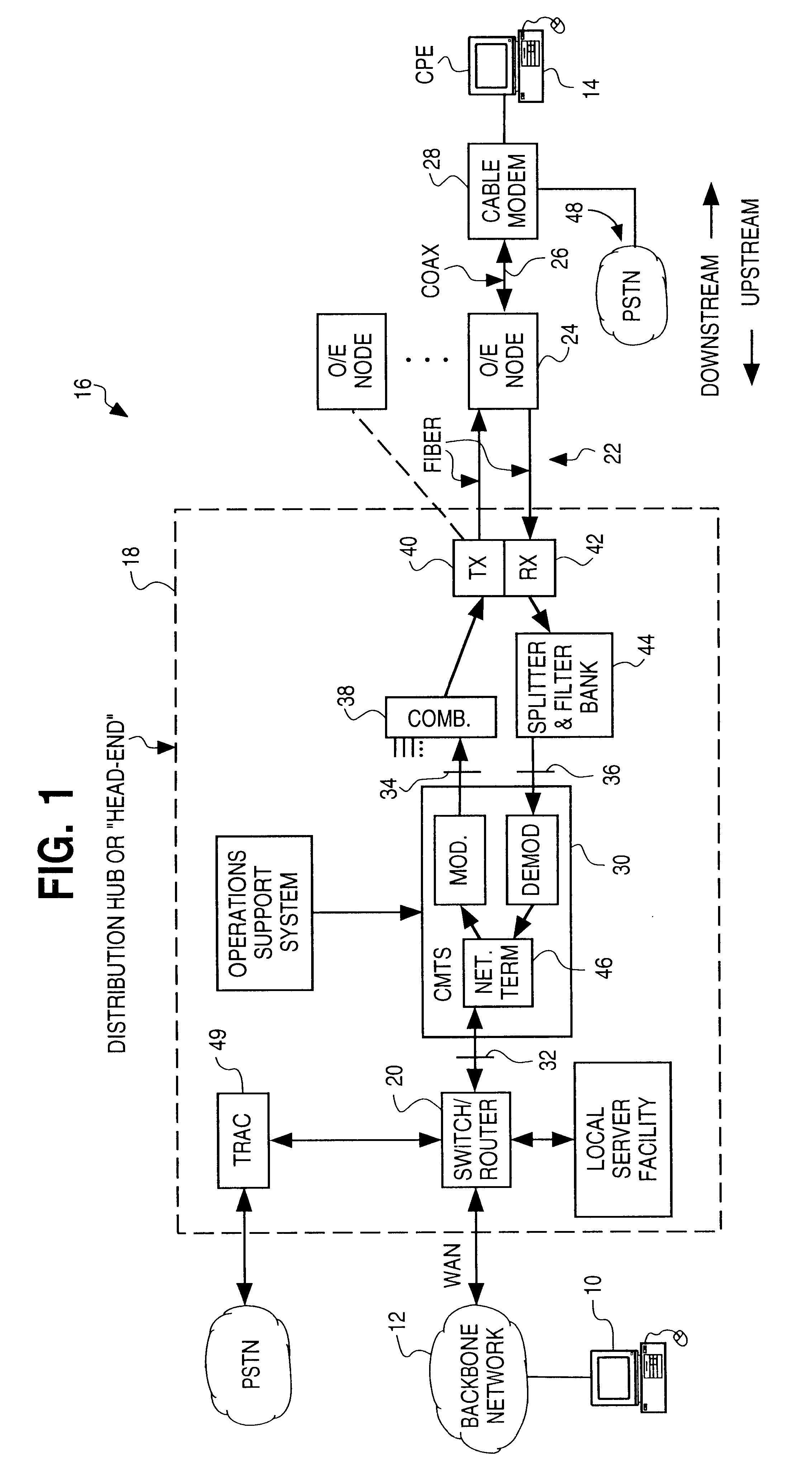
Upstream channel multicast media access control (MAC) address method for data-over-cable systems
A head-end in a data-over-cable system transmits a multicast message in a downstream channel to all the cable modems in a particular MAC layer. The message includes an address field that contains an upstream channel multicast MAC address that identifies a particular channel, and is used to send a multicast message for which only cable modems transmitting in the upstream direction in that channel are to respond. When the message is received by the cable modems, the cable modems compare the upstream channel multicast MAC address with addresses stored in a memory. If a match is found, indicating that the cable modem happens to transmit in the upstream direction in the particular channel, it processes the message. If no match is found, the message is discarded. The upstream channel multicast MAC address helps noise avoidance or redundancy problems associated with a particular channel to be quickly remedied, and avoids the head-end from having to send out a large number of unicast messages in order to communicate with all the modems sharing a given upstream channel.
Owner:HEWLETT-PACKARD ENTERPRISE DEV LP
Method for multicast delivery with designated acknowledgment
InactiveUS7013157B1Maintain compatibilityImprove reliabilityTime-division multiplexMultiple digital computer combinationsComputer networkMulticast message
A packet format for multicast messages which designates a single receiver to send an acknowledgment to the multicast message. The designated receiver responds to the multicast message with an acknowledgment. If the designated receiver does not respond to the multicast message, the message is resent. The resent message may designate a different receiver for acknowledging the message.
Owner:CISCO TECH INC
Method and system for providing acknowledged broadcast and multicast communication
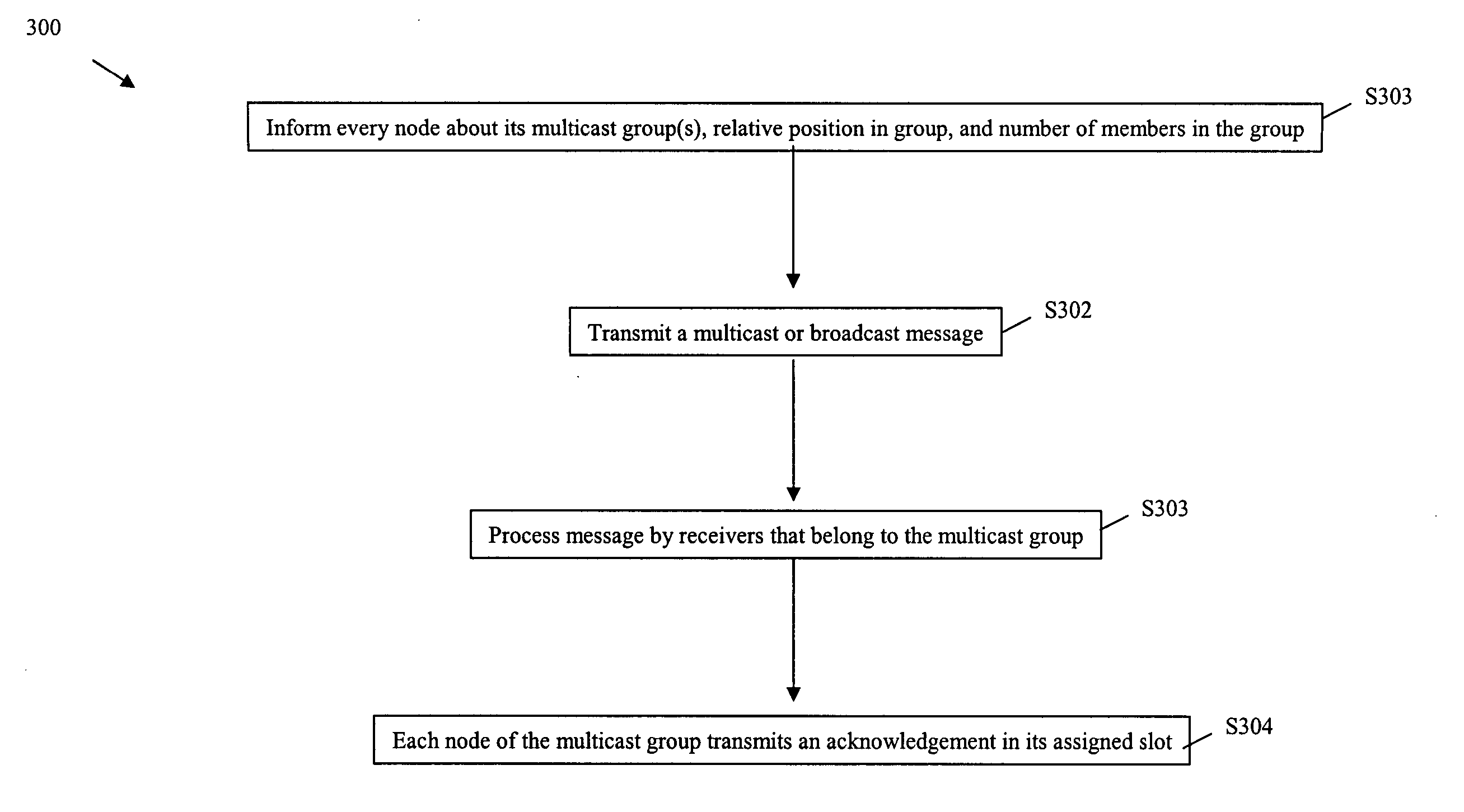
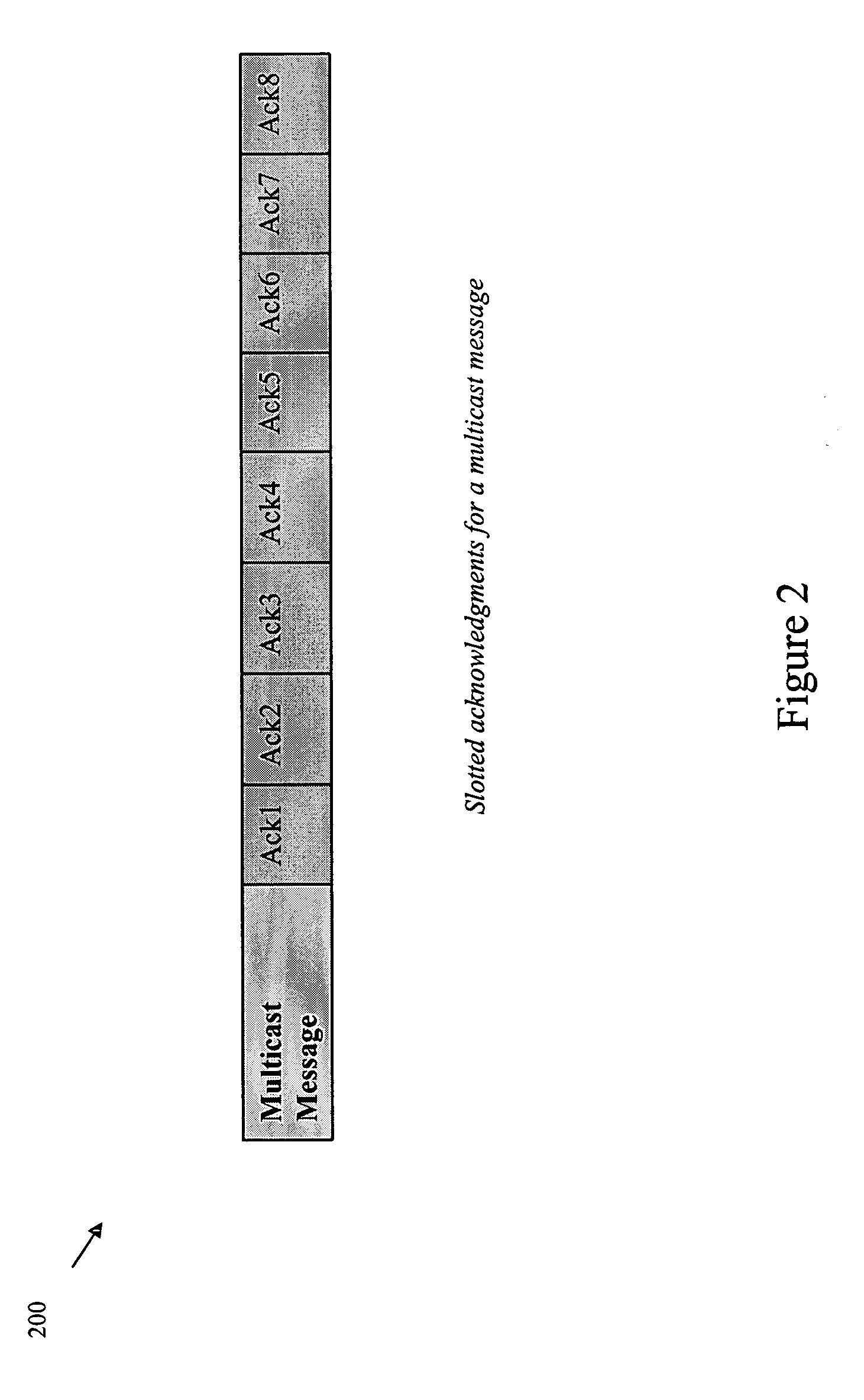
ActiveUS20070076739A1Shorten the timeEasy to receiveError preventionTransmission systemsComputer networkMulticast communication
A method and system to acknowledge a multicast message includes informing each node in a network about each multicast group to which it belongs, a relative position in each multicast group to which it belongs, and a group size of each multicast group to which it belongs, transmitting the multicast message, and transmitting, by each node in the multicast group, an acknowledgment in an assigned slot, which is determined by the relative position.
Owner:ROBERT BOSCH GMBH
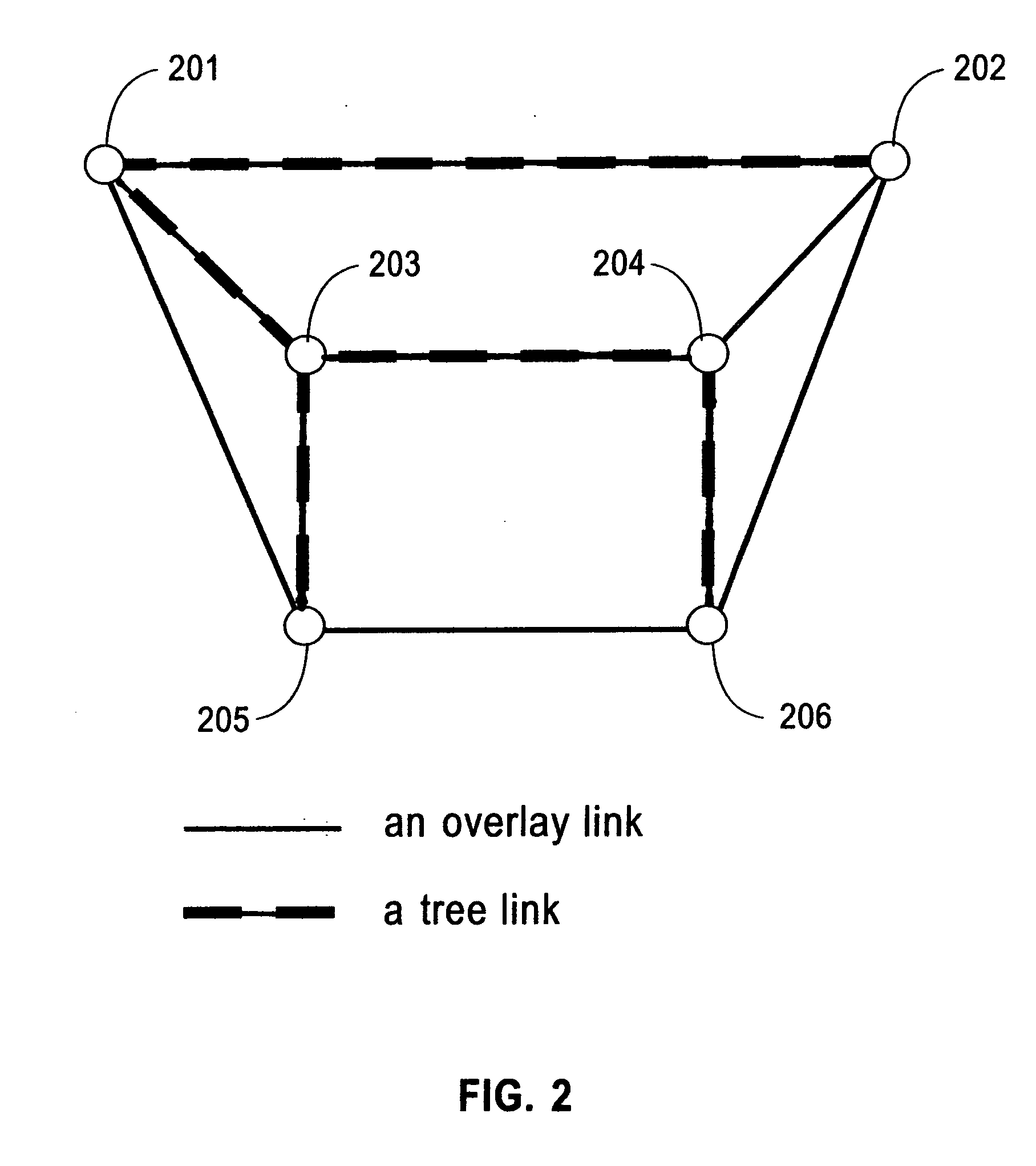
Apparatus, system, and method for reliable, fast, and scalable multicast message delivery in service overlay networks
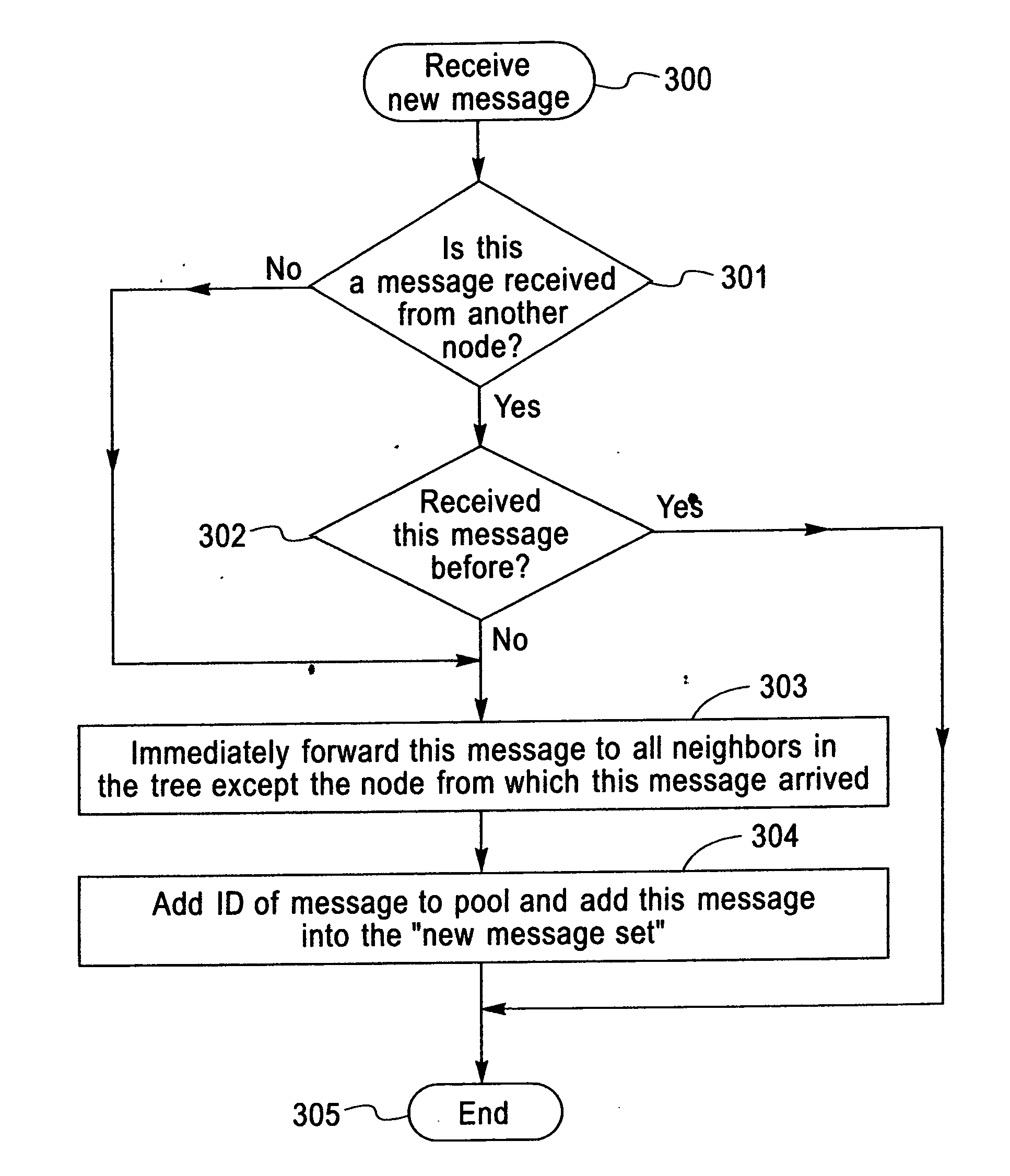
InactiveUS20070110063A1Reduce overheadIncrease delayTime-division multiplexData switching by path configurationOverlay networkMulticast message
A method to organize nodes into an overlay network and to disseminate multicast messages within this overlay both through an efficient tree embedded in the overlay and through gossips exchanged between overlay neighbors. Regardless of the size of the system, this invention incurs a constant low overhead on each node.
Owner:IBM CORP
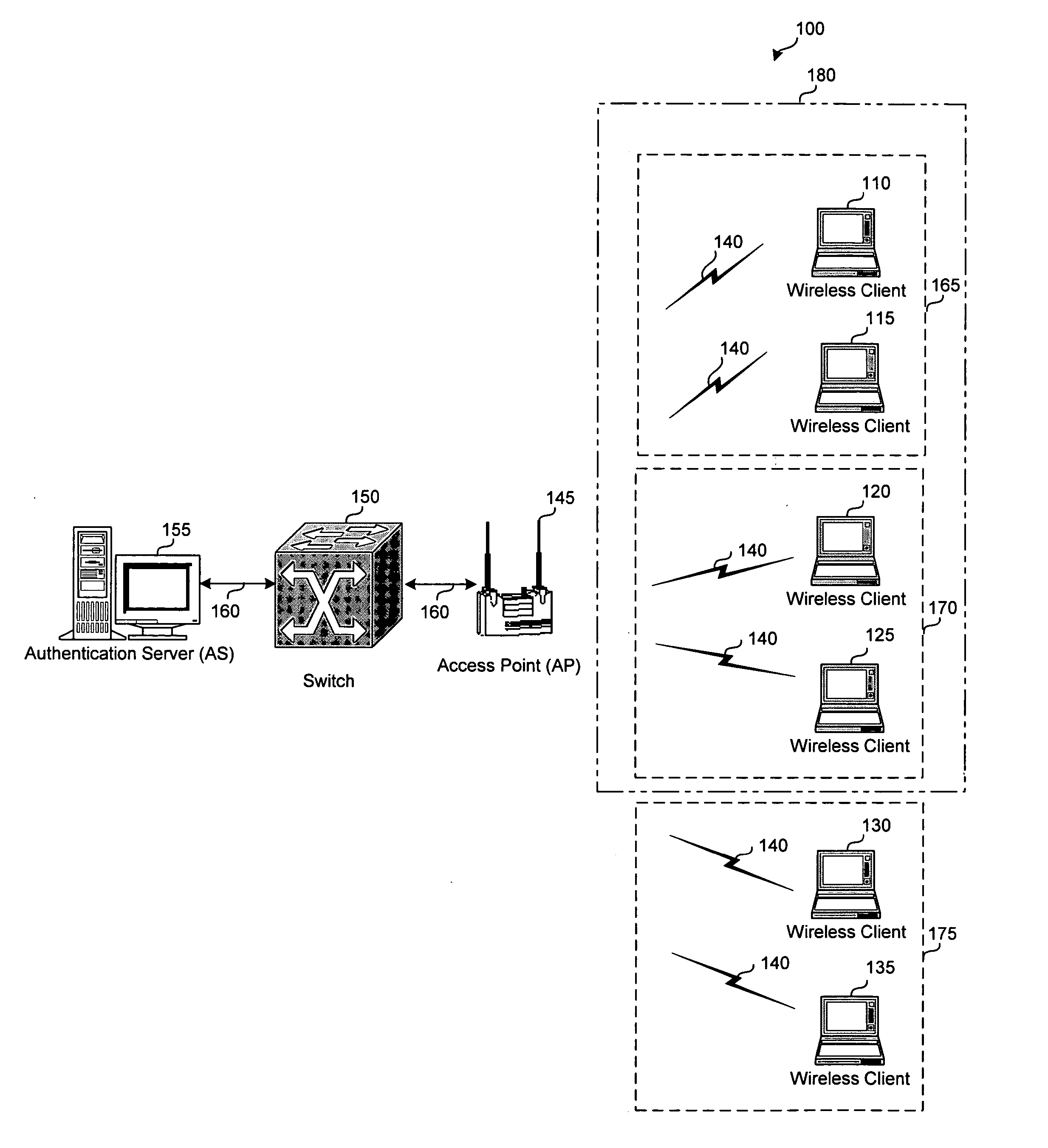
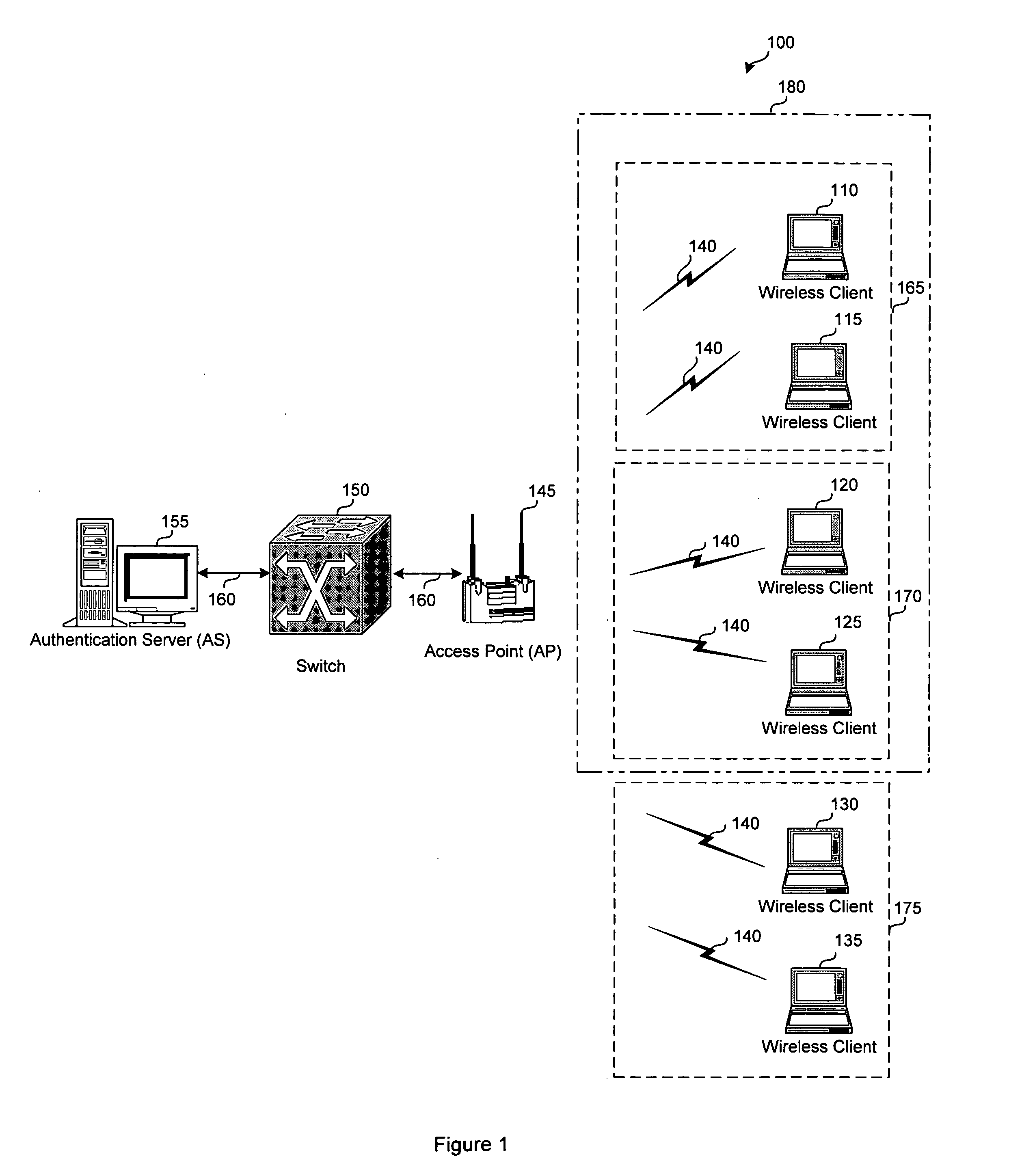
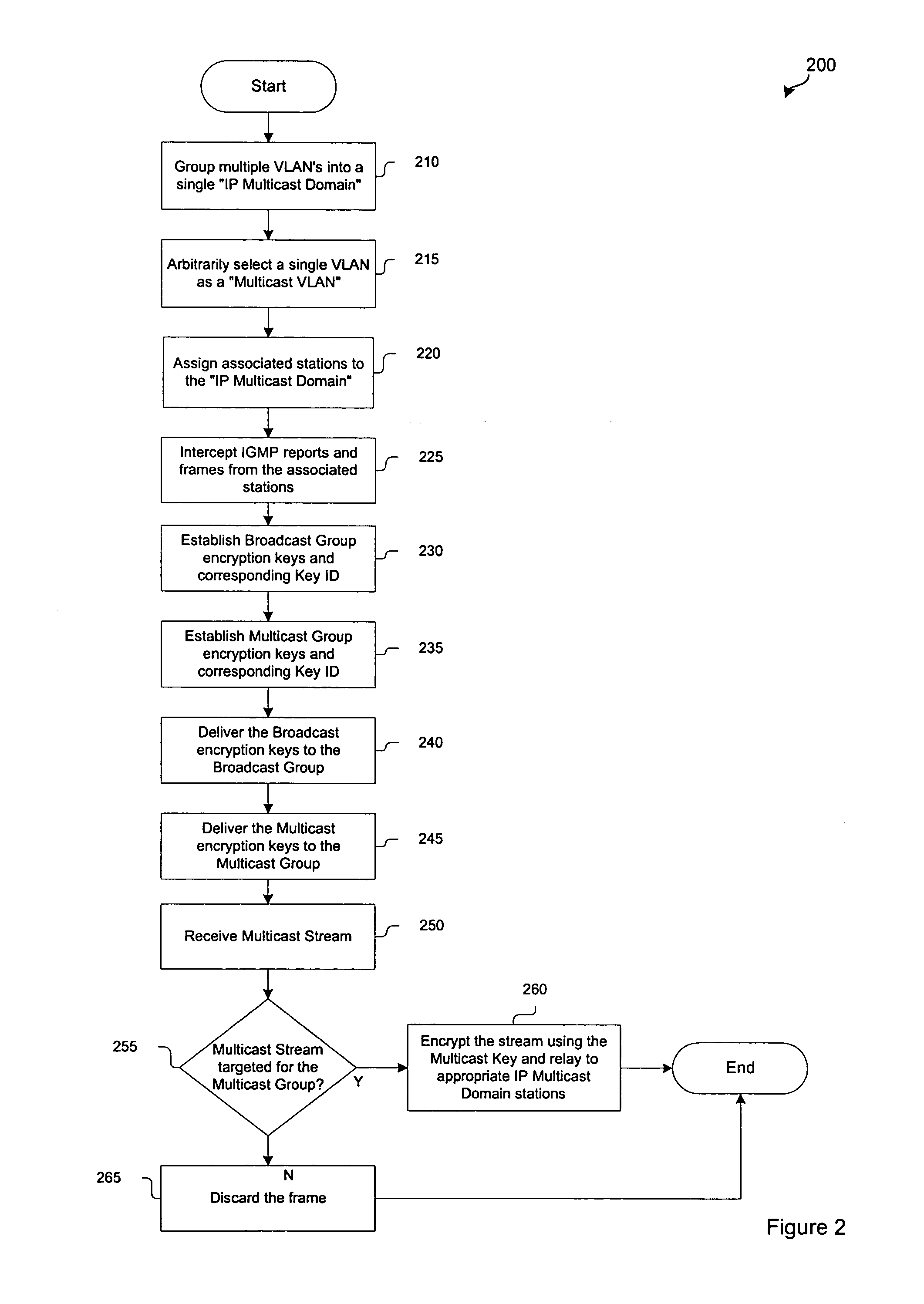
System and method for grouping multiple VLANs into a single 802.11 IP multicast domain
ActiveUS20050025160A1Special service provision for substationBroadcast with distributionVirtual LANIP multicast
A system and method for identifying and grouping multiple virtual local area networks into a single multicast domain is provided. The system and method may be configured to designate a virtual local area network within as a multicast virtual local area network to streamline the delivery of multicast messages via a network. A station may be configured with multiple group keys so that it can receive messages from multiple broadcast or multicast domains.
Owner:CISCO TECH INC
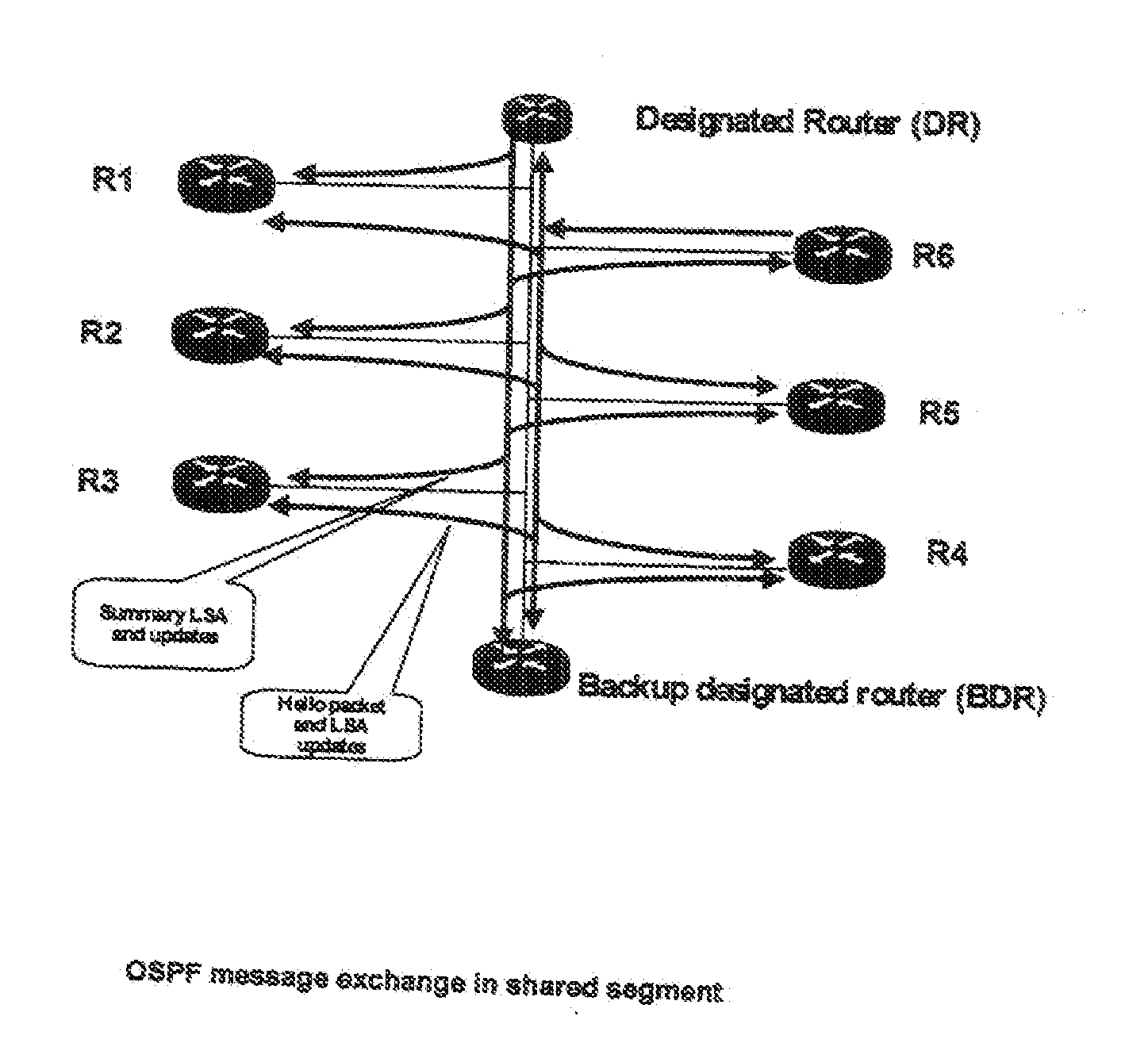
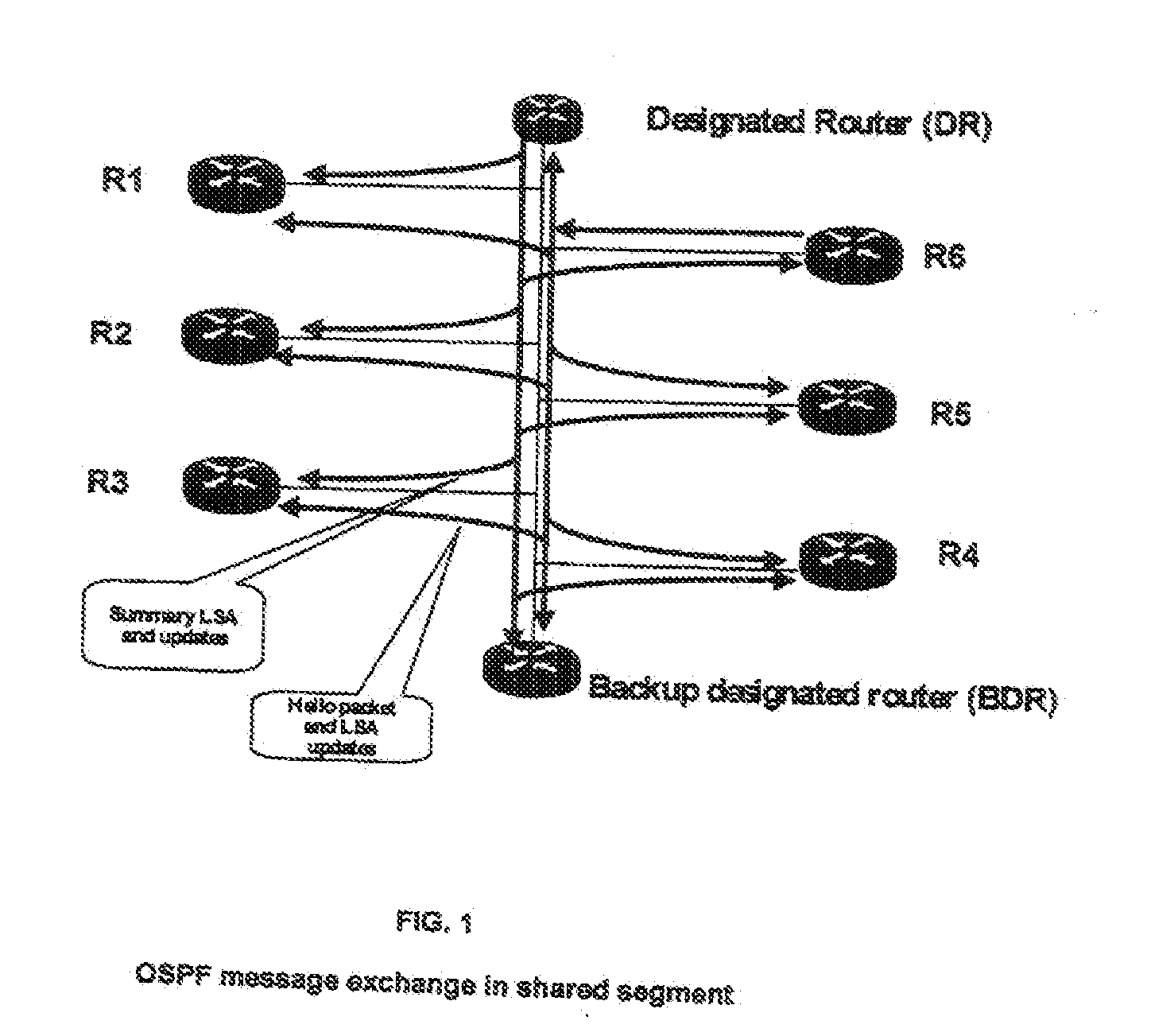
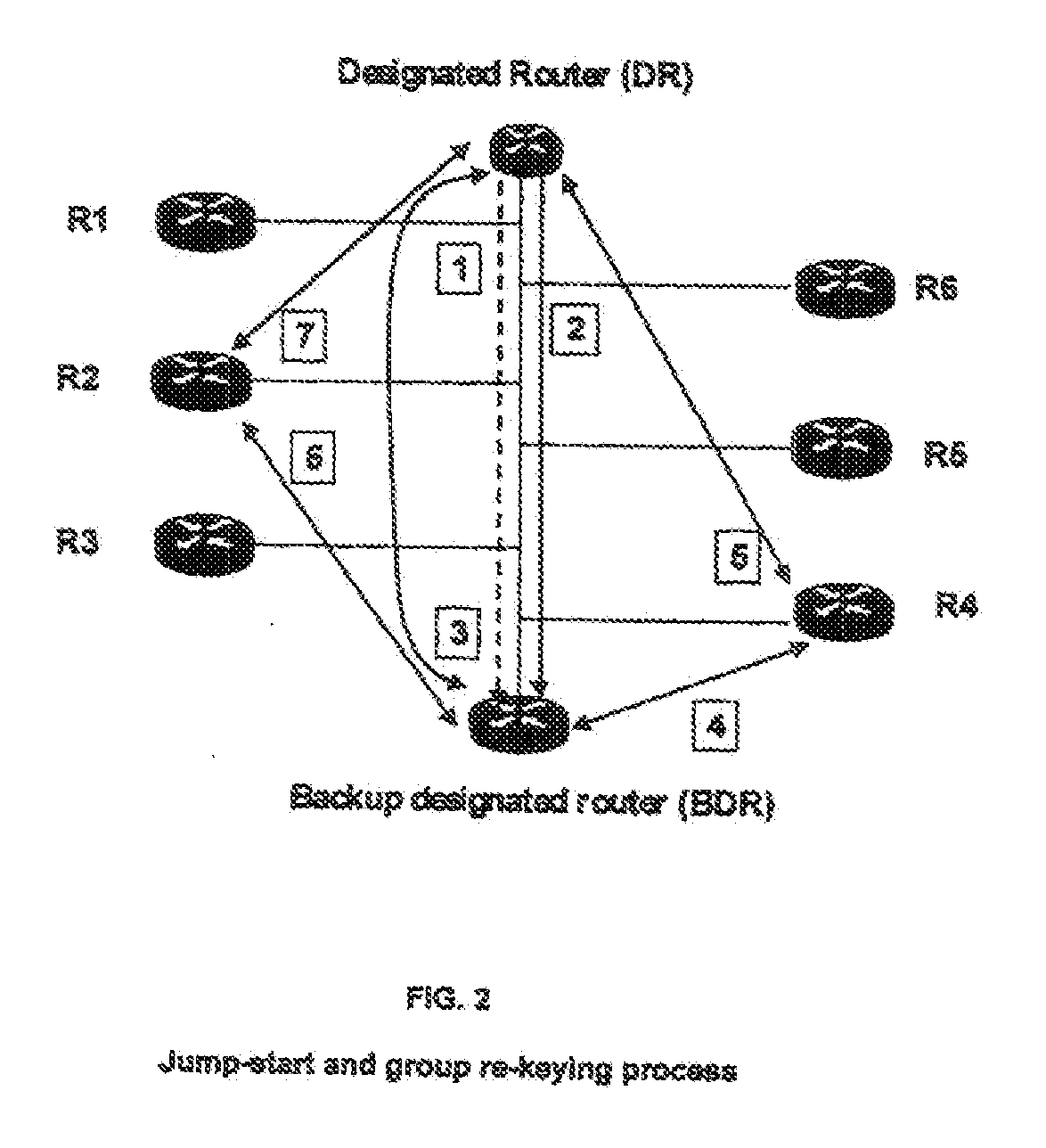
System and method for nodes communicating in a shared network segment
InactiveUS20100284402A1Keep for a long timeData switching by path configurationProtocol ApplicationOpen Shortest Path First
The invention provides a method and system for a network which includes a plurality of nodes, preferably routers, a shared network segment for communication between the nodes, and several multicast channels in the shared network segment on which the nodes, preferably routers, can send multicast messages to the other nodes. A specific multicast channel is provided on which the nodes can send specific start multicast messages to other nodes, wherein a node which starts a protocol application, preferably a routing protocol application such as Open Shortest Path First (OSPF) protocol, is adapted to send a multicast start message on the specific multicast channel. Another node, preferably a router, receiving this start message is adapted to validate the authenticity of the start message and to send a response message.
Owner:AI CORE TECH LLC +1
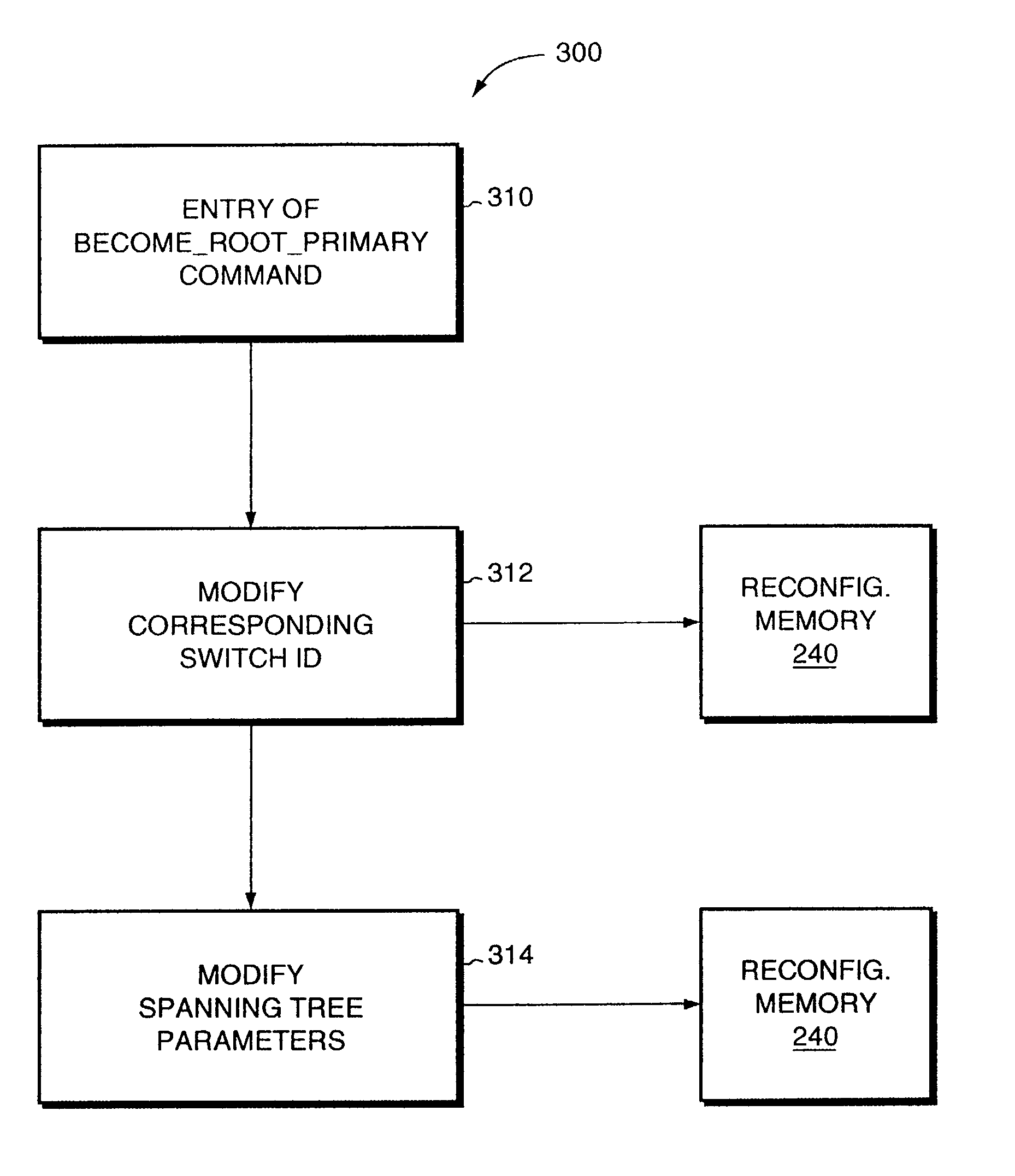
Method and apparatus for rapidly reconfiguring bridged networks using a spanning tree algorithm
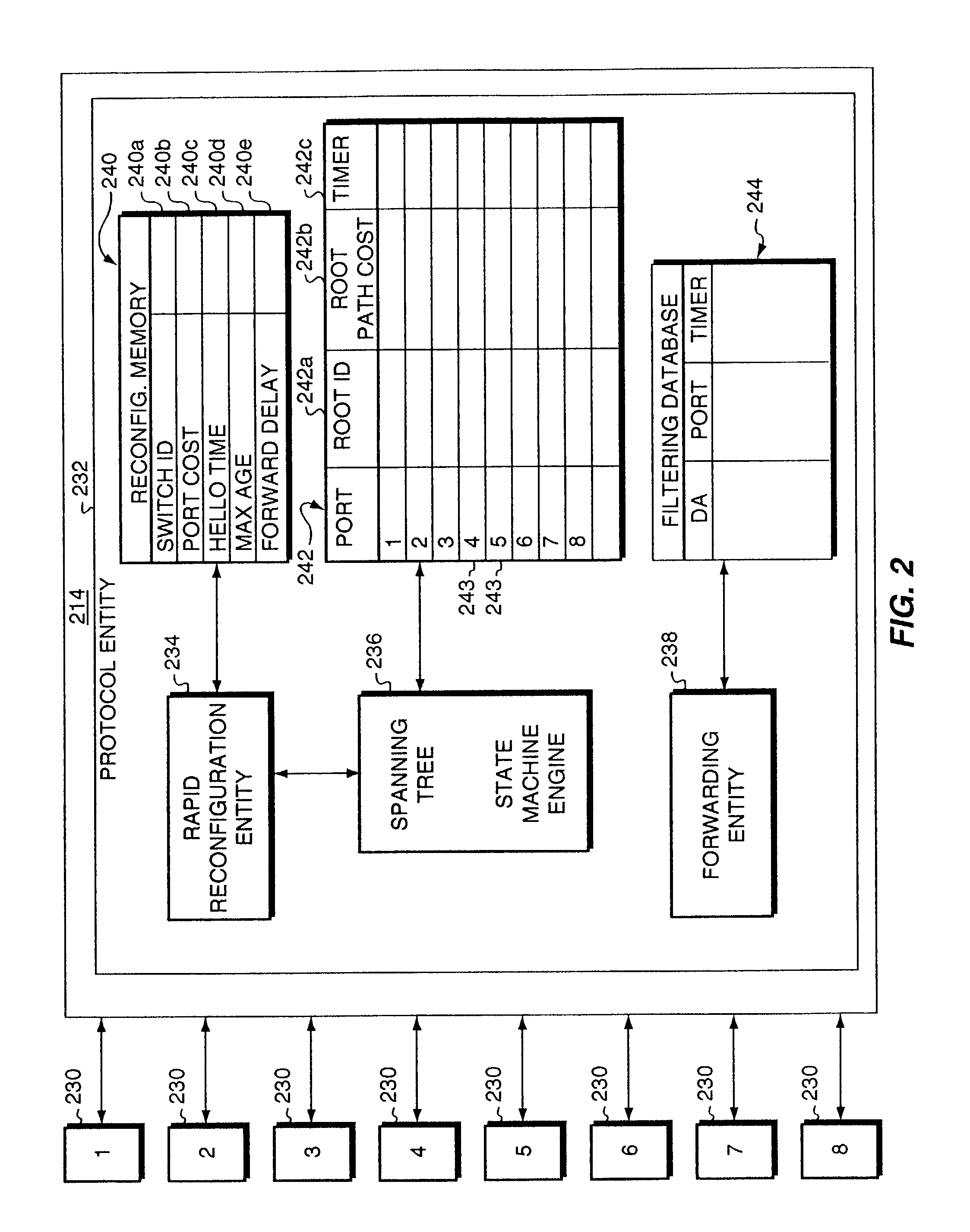
InactiveUS6976088B1Shorten the timeDigital computer detailsNetworks interconnectionVirtual LANMulticast message
A method that rapidly reconfigures a computer network having a plurality of devices executing the spanning tree algorithm. First, one or more devices are configured and arranged so that one port, providing connectivity to the root, is in the forwarding state and the remaining ports, providing connectivity to the root, are in the blocked state. Next, one or more of the blocked ports are designated as back-up ports. Upon detection of a failure at the active forwarding port, one of the back-up ports immediately transitions from blocked to forwarding, thereby becoming the new active port for the device. Following the transition to a new active port, dummy multicast messages are transmitted, each containing the source address of an entity directly coupled to the affected device or downstream thereof. By examining the dummy multicast messages, other devices in the network learn to use to the new forwarding port of the affected device. Rapid reconfiguration of the network is also provided upon detection of a new or repaired link or device representing a better path toward the root. The method is also compatible with networks supporting virtual local area network (VLAN) designations and allows load balancing among different VLANs.
Owner:CISCO TECH INC
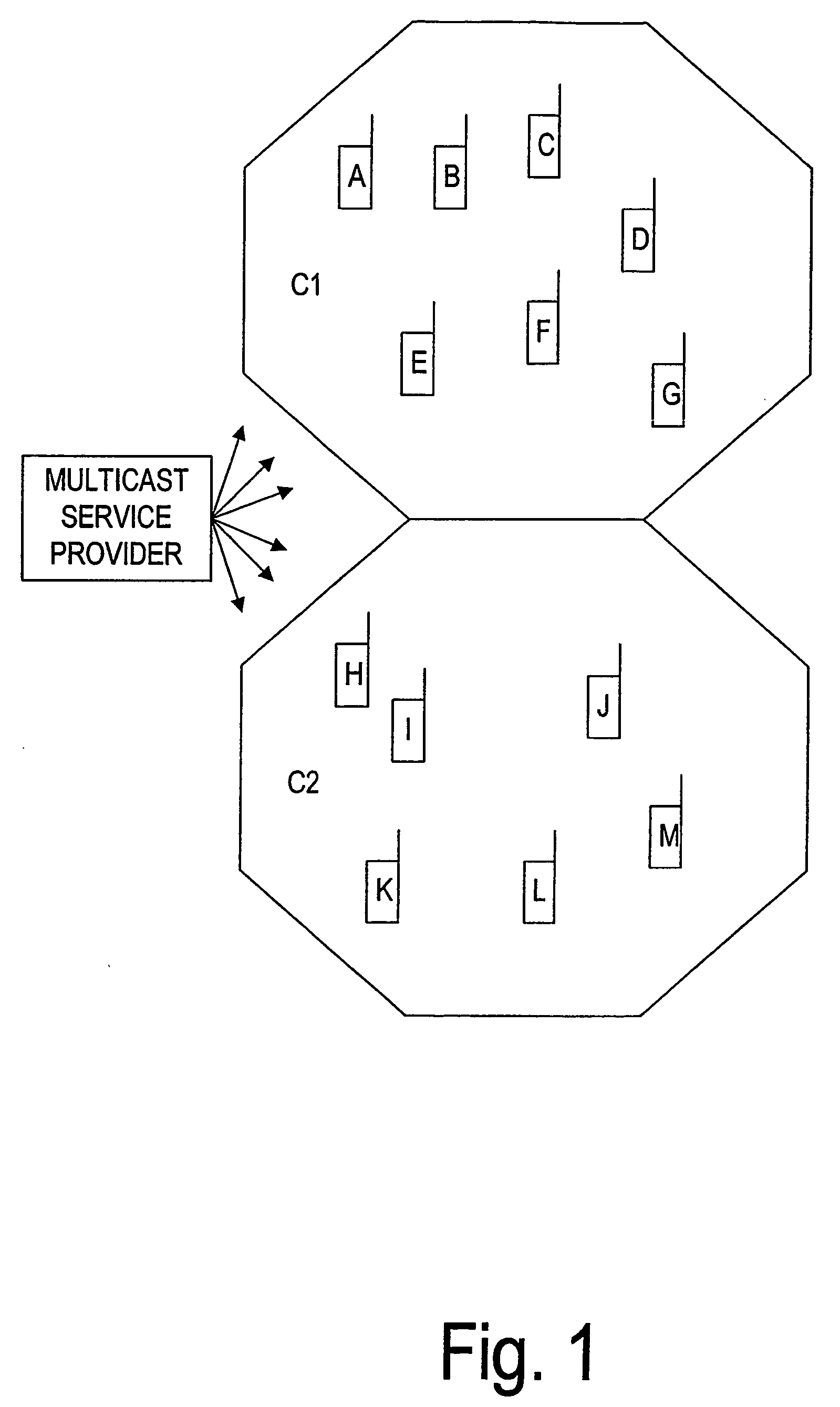
Method and system for multicasting messages to select mobile recipients
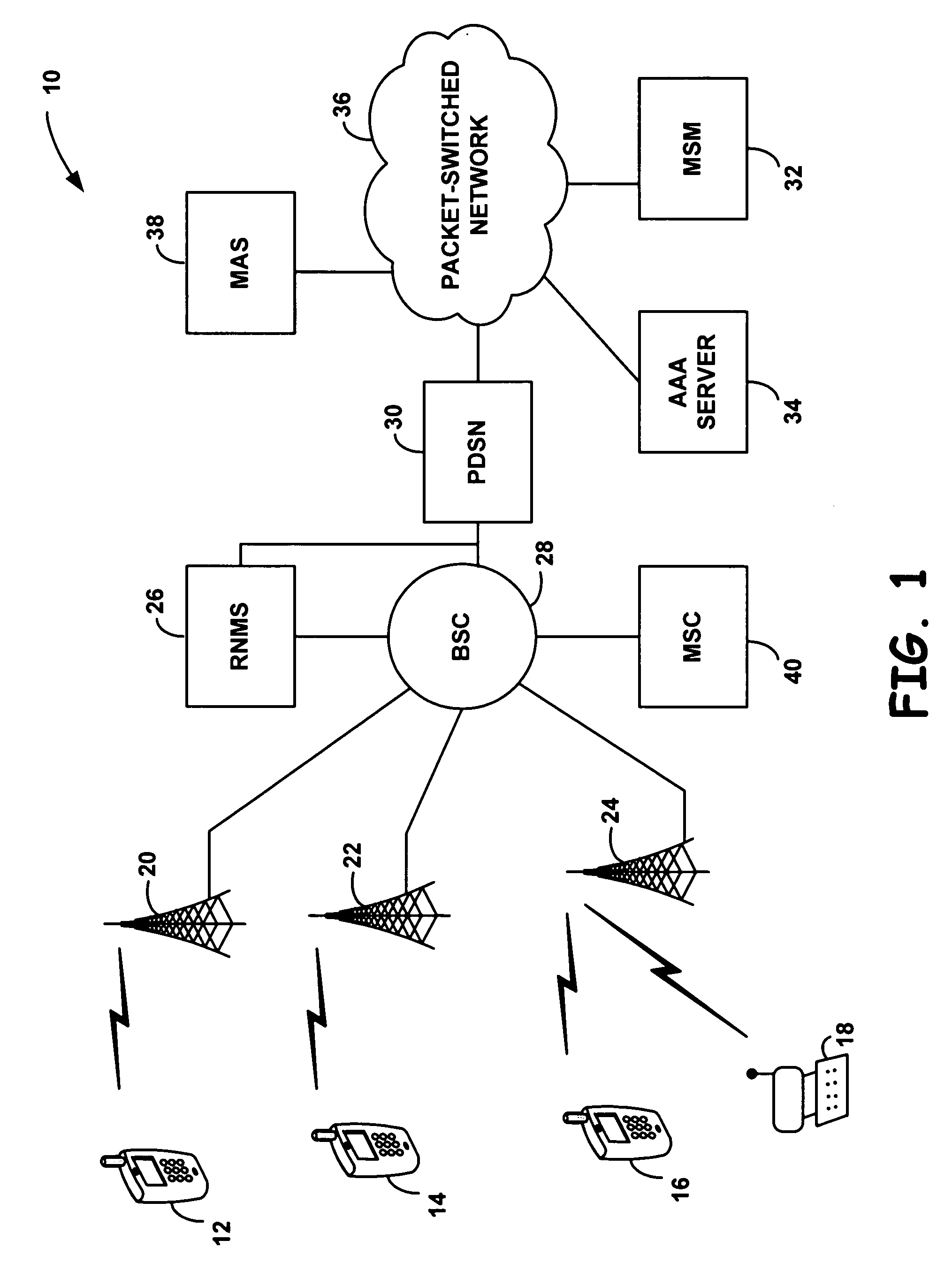
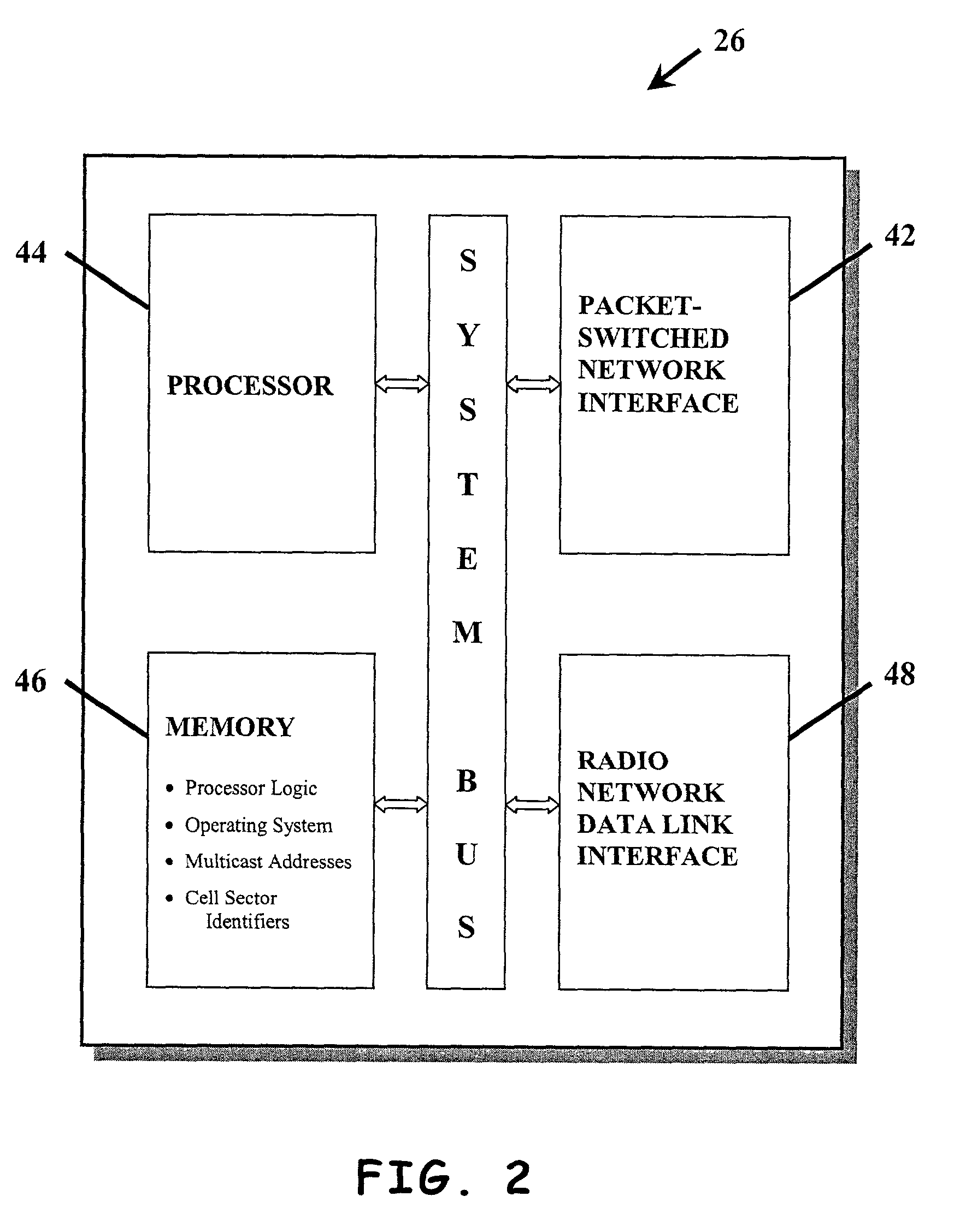
ActiveUS7075904B1Easy to receiveOptimization mechanismSpecial service provision for substationSpecial service for subscribersCommunications systemRadio networks
A method and system for multicasting or broadcasting a message to a specific group of mobile stations or to a specific group of cell sectors in a cellular wireless communication system. The method may include maintaining a record of which mobile stations are in a particular multicast group, and may include maintaining a record of which cell sectors are currently serving one or more members of the multicast group. The records may be maintained at one or more network entities, such as a radio network multicast router / server and / or hosts on a packet-switched network. By sending multicast messages, such as IP messages, to only those cell sectors currently serving members of a multicast group, network resources may be conserved.
Owner:SPRINT SPECTRUM LLC
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com