Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
450 results about "Multicast network" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Multicast is communication between a single sender and multiple receivers on a network. Typical uses include the updating of mobile personnel from a home office and the periodic issuance of online newsletters. Together with anycast and unicast, multicast is one of the packet types in the Internet Protocol Version 6 (IPv6).
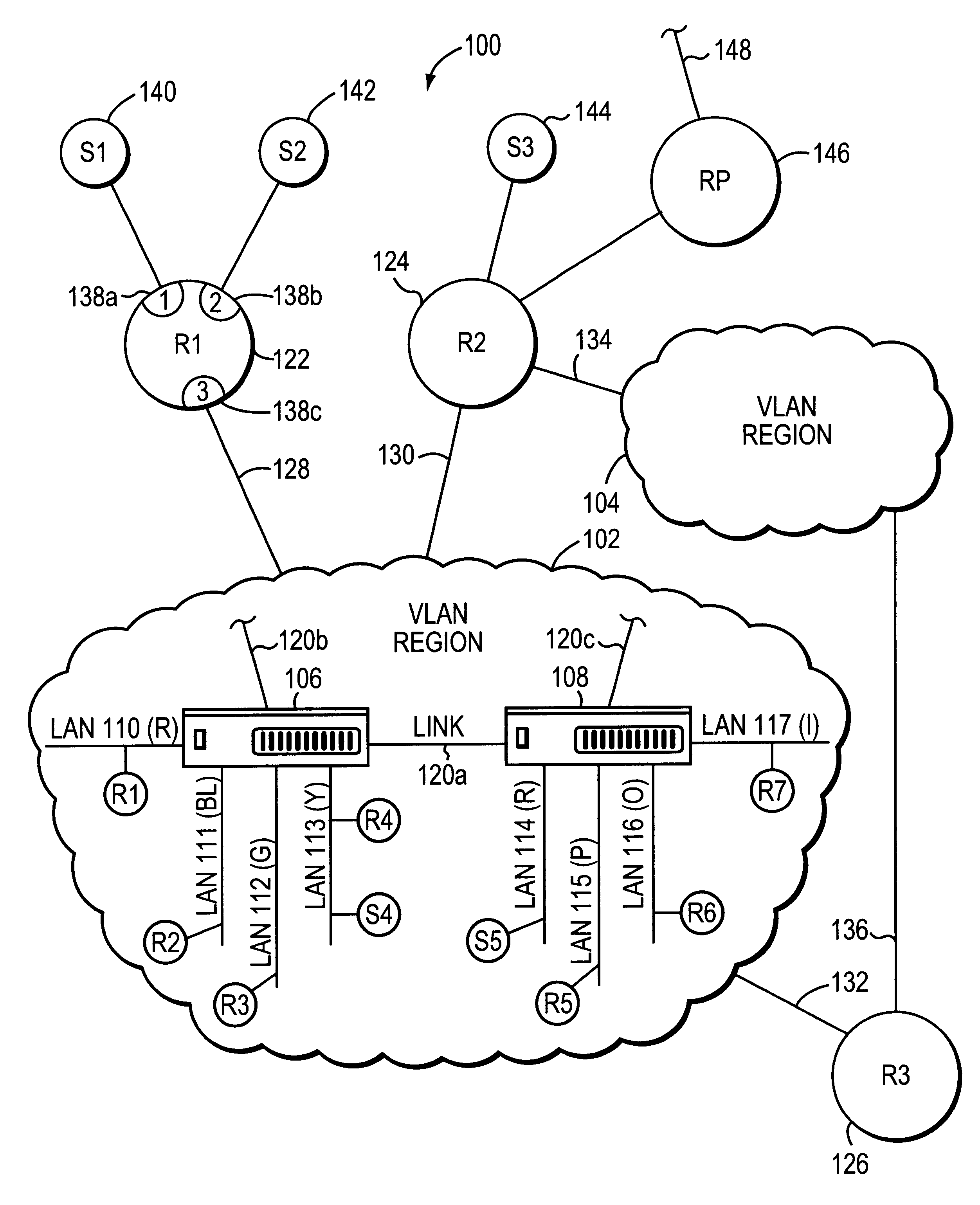
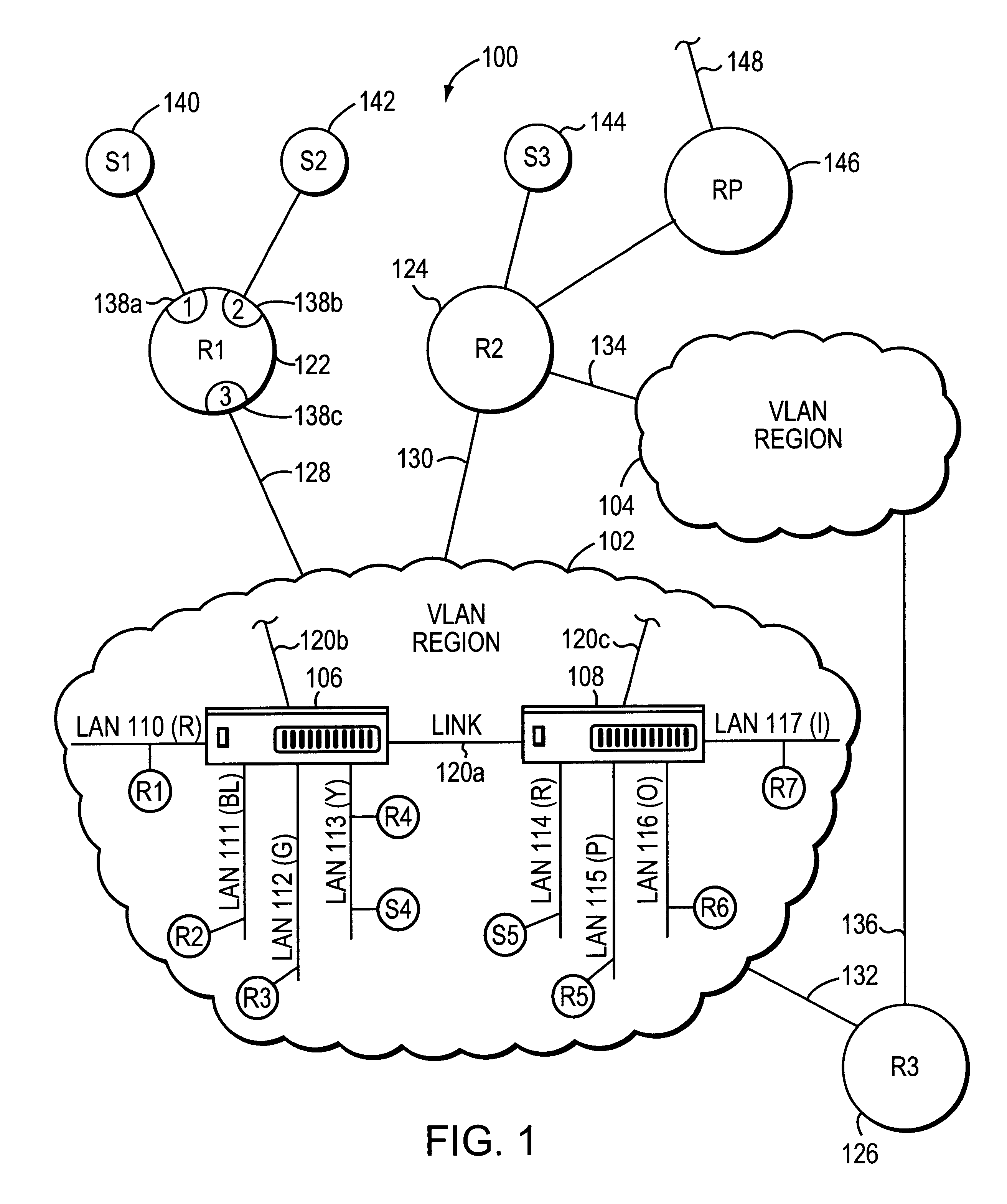
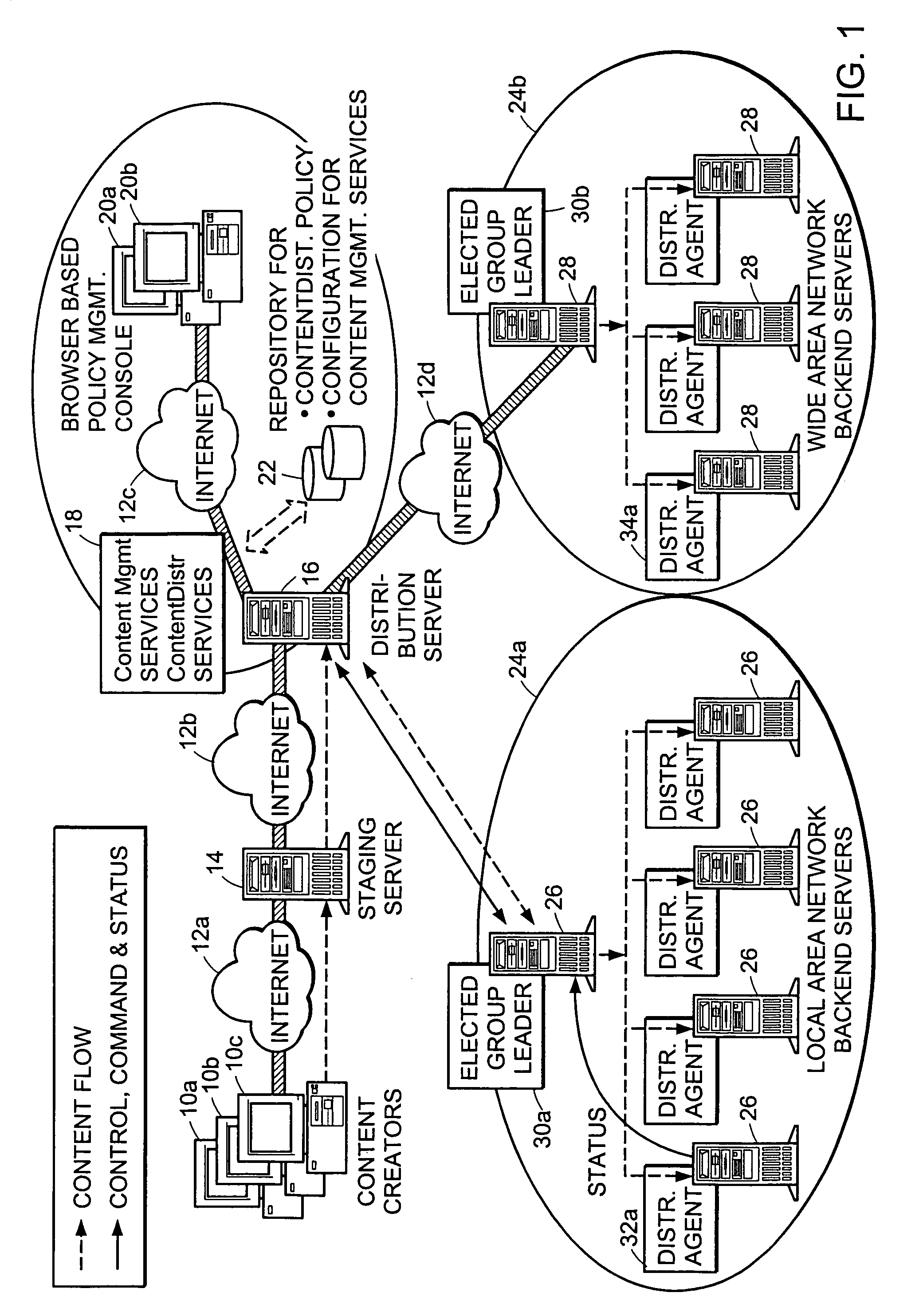
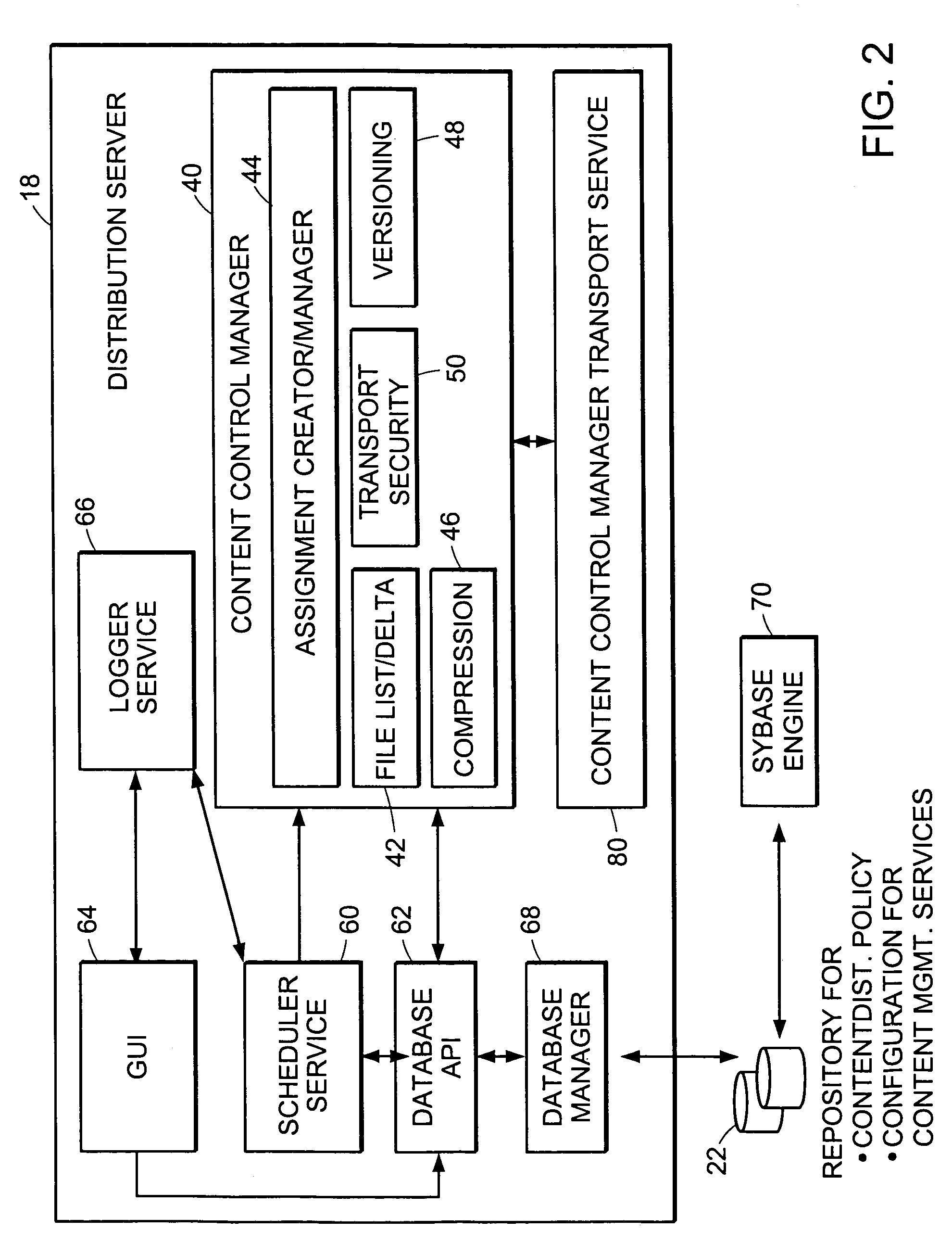
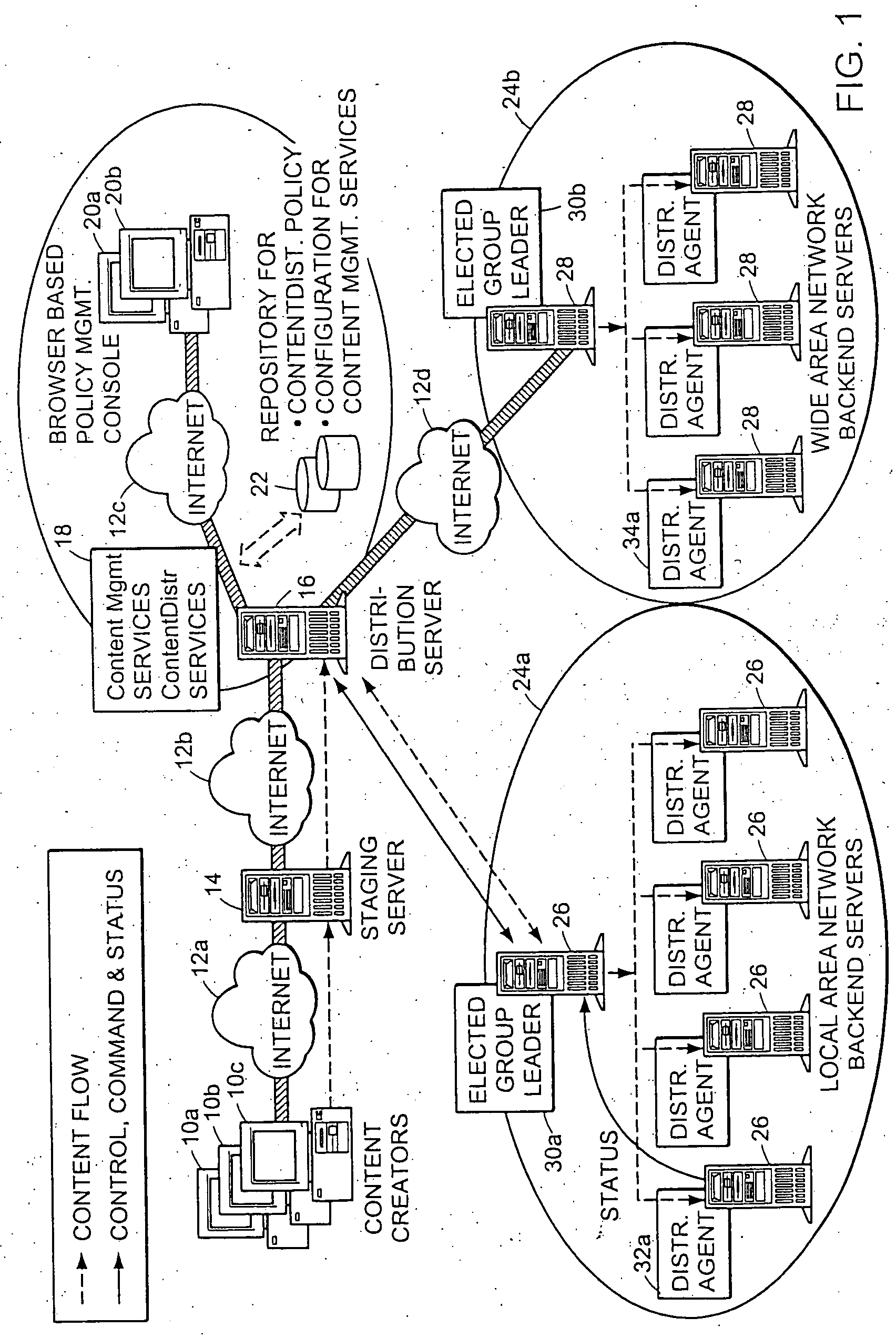
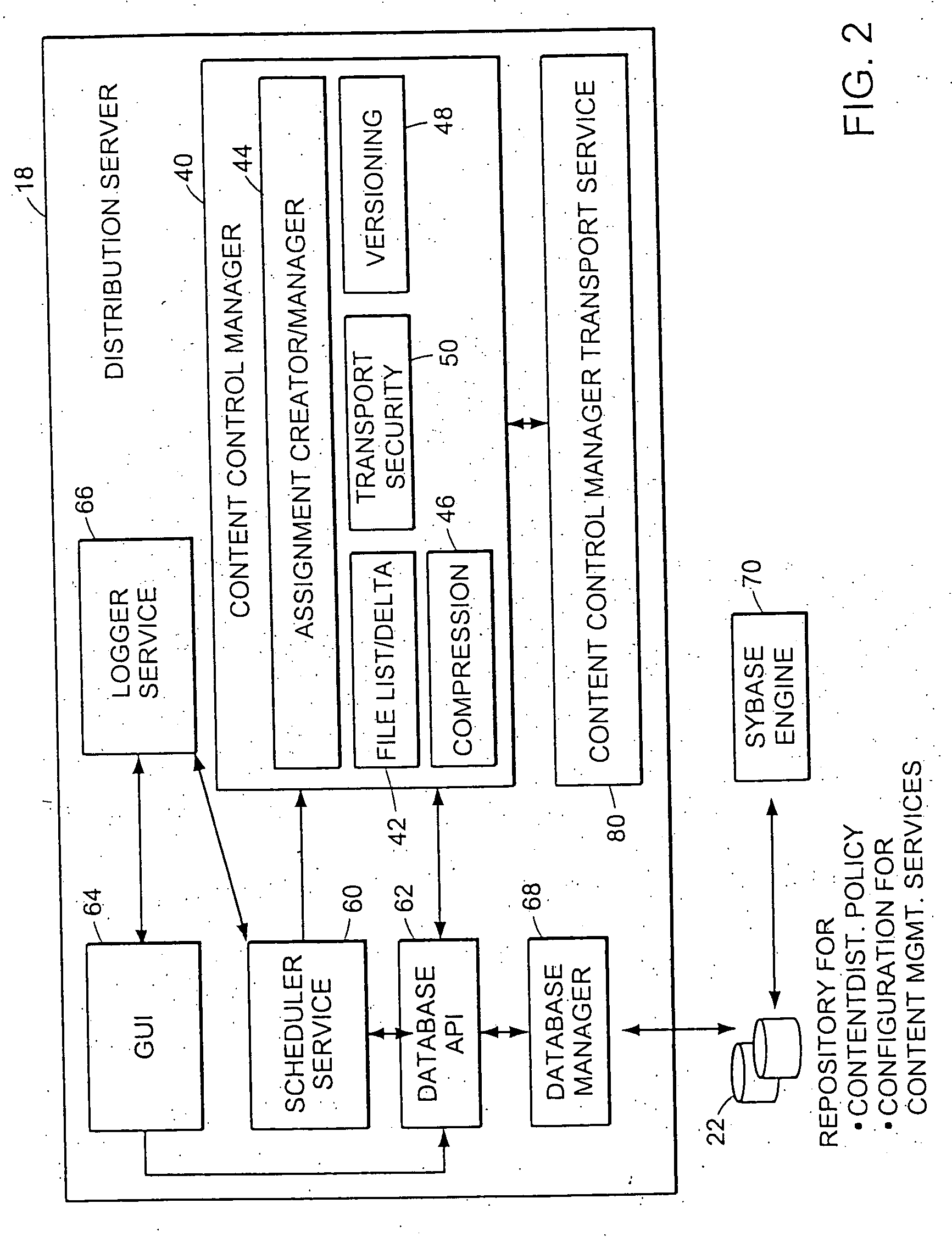
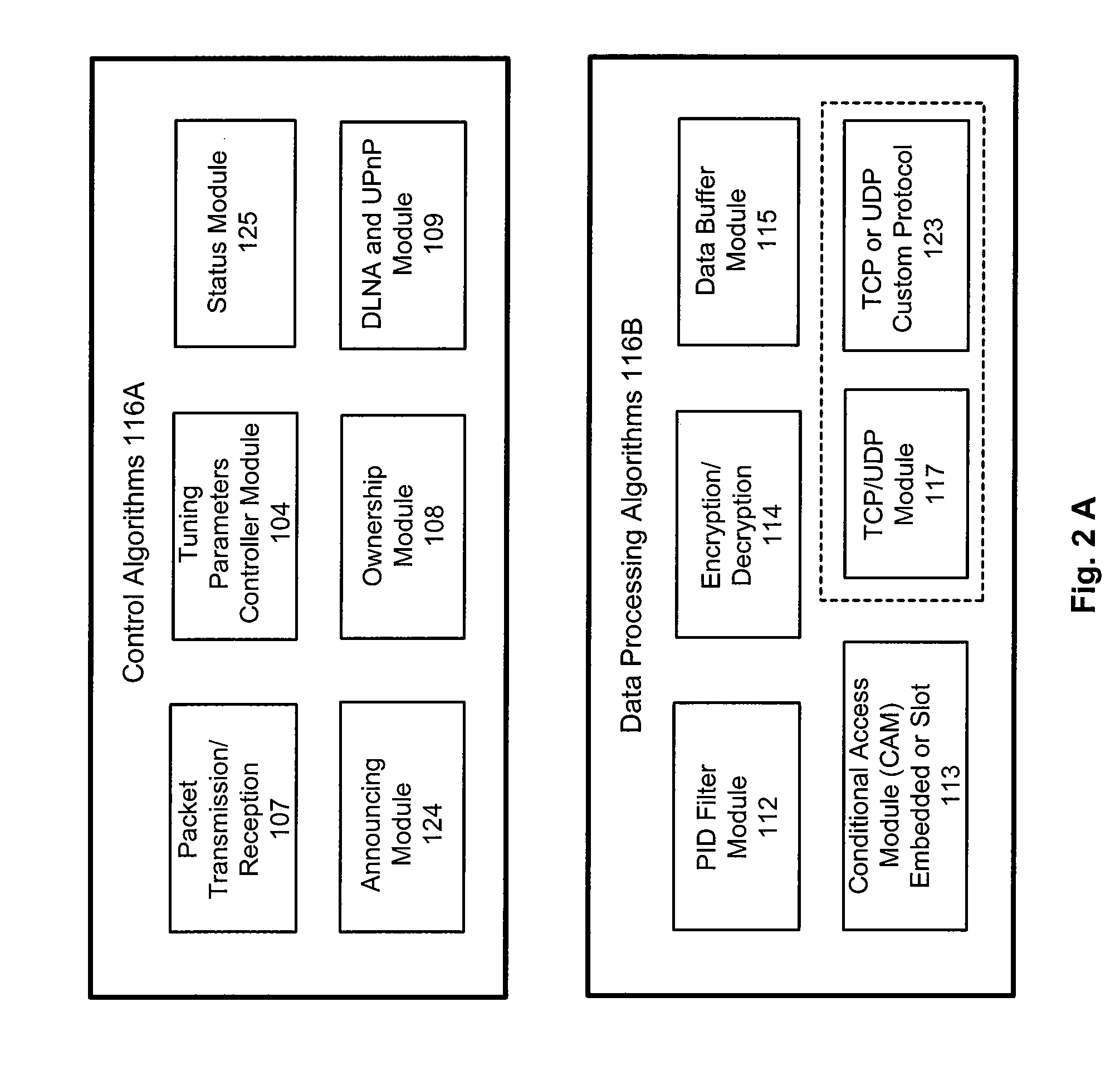
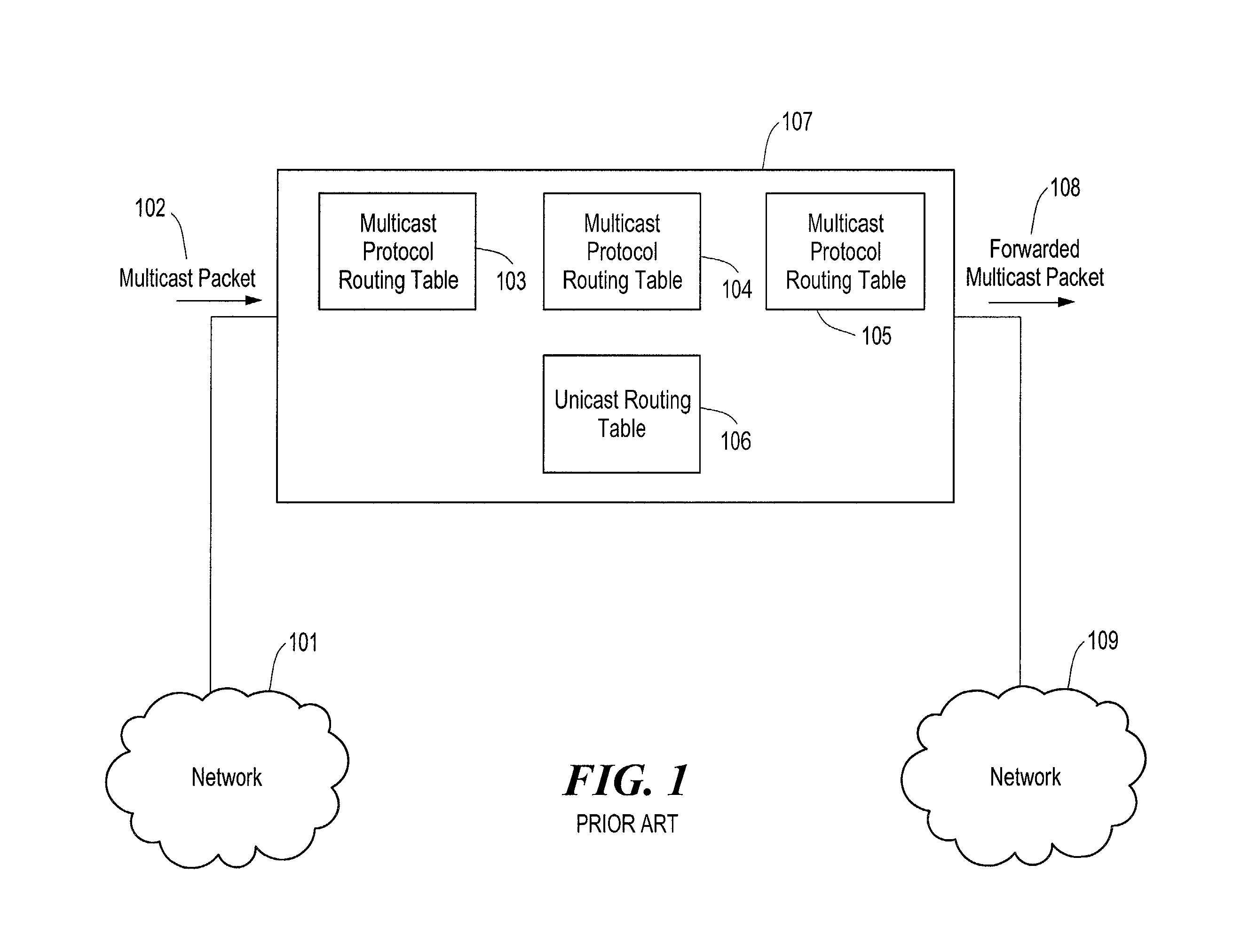
System and method for distributing multicasts in virtual local area networks
InactiveUS6839348B2Effective distributionEfficiently distributedSpecial service provision for substationTime-division multiplexVirtual LANIP multicast
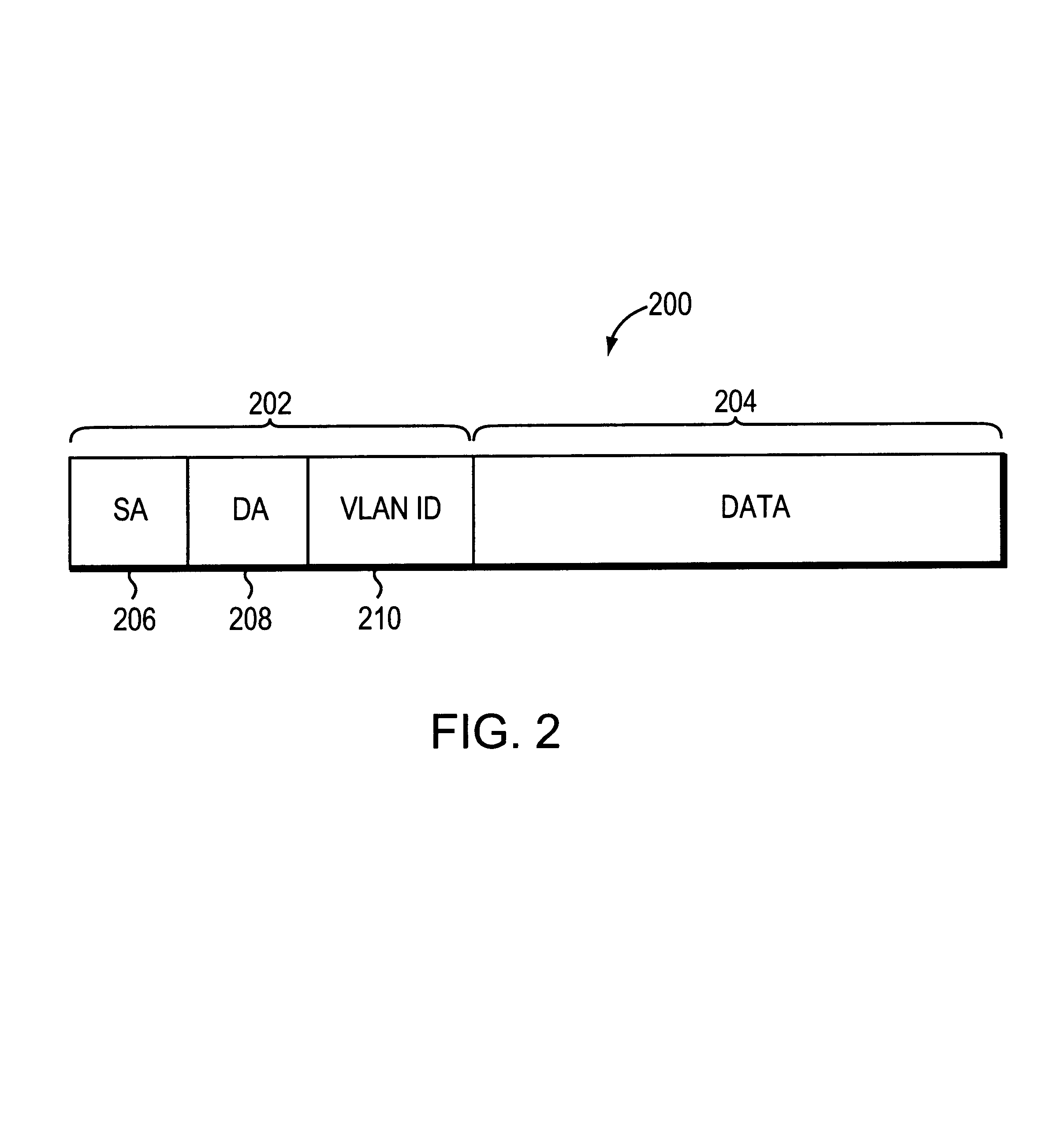
The invention relates to a system and method for efficiently distributing multicast messages within computer networks configured to have one or more virtual local area network (VLAN) domains. A multicast network device (MND), having a plurality of interfaces, includes a multicast controller for efficiently distributing multicast messages among subscribing entities associated with various VLAN domains. The multicast controller, which is in communicating relationship with the interfaces, includes a VLAN assignment engine for assigning responsibility for the VLAN domains to the extent there are multiple MNDs. The multicast controller also accesses a multicast tag source to establish a plurality of novel VLAN tags for efficiently distributing multicast messages, including a sub-regional Multicast VLAN Identifier (MVLAN-ID) that encompasses all of the VLAN domains for which the respective MND is responsible, and one or more color-limited MVLAN-IDs that encompass all of the VLAN domains for which the MND is responsible except for one. The multicast controller then tags multicast messages with its sub-regional or a color-limited MVLAN-ID depending on whether the message is considered internal or external by the respective MND. The tagged messages are then forwarded for distribution to the subscribers associated with the various VLAN domains.
Owner:CISCO TECH INC
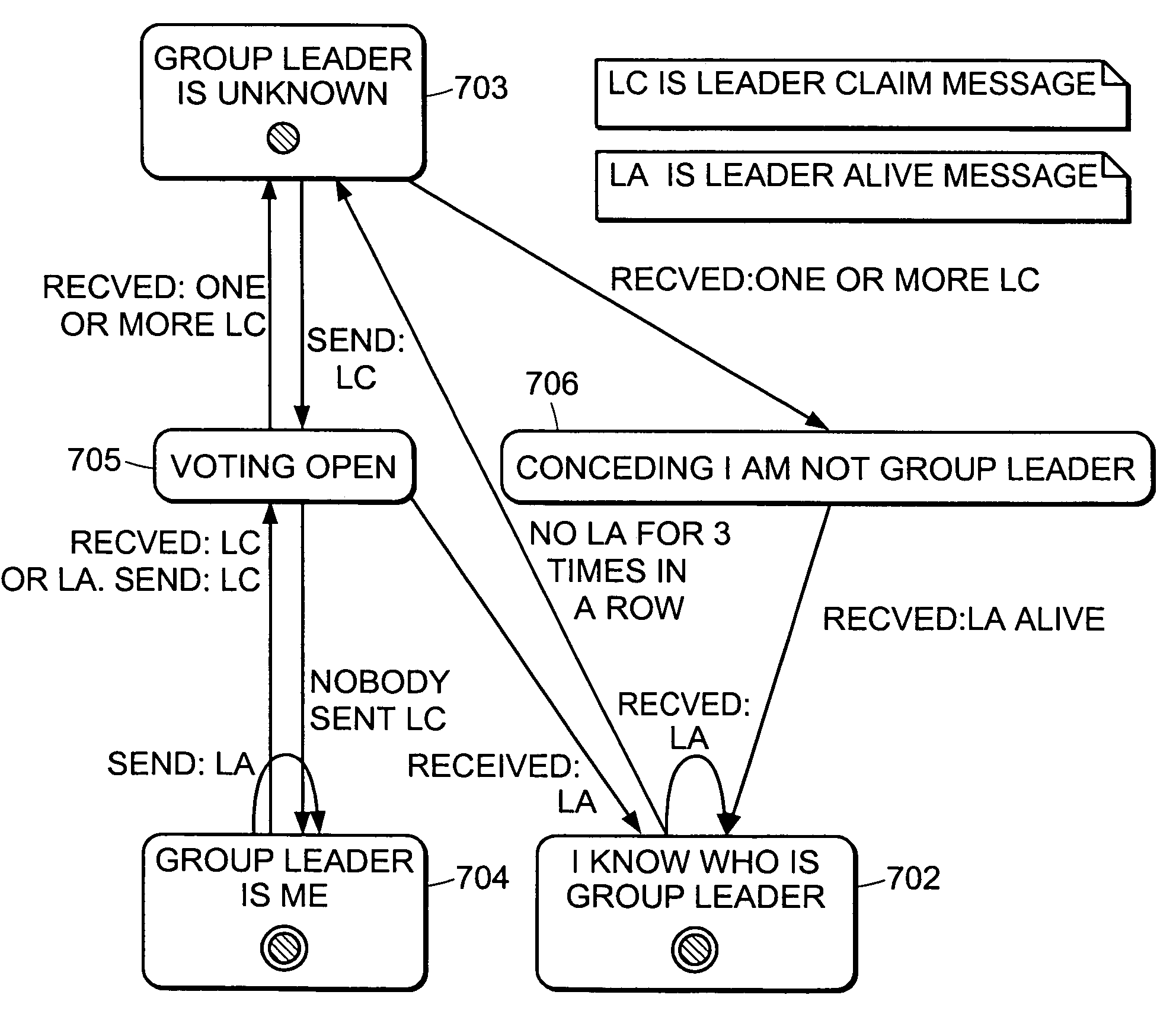
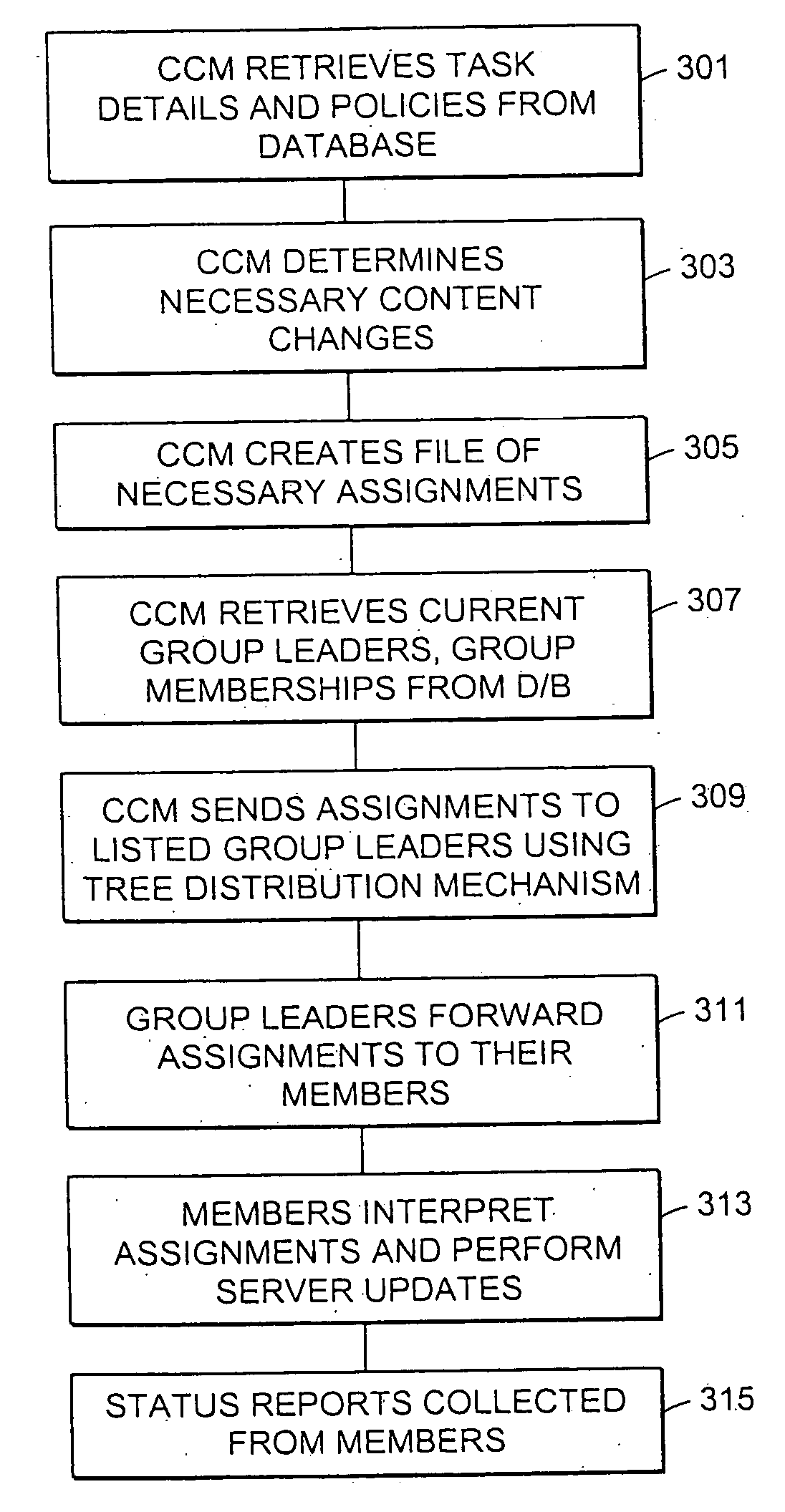
Method and apparatus for election of group leaders in a distributed network
InactiveUS6993587B1Effective controlEffective distributionMultiple digital computer combinationsTransmissionData fileMulticast network
The present invention provides a system and apparatus for efficient and reliable, control and distribution of data files in large-scale distributed networks. The members of a group of servers in a multicast network elect a group leader whenever a new group leader is required, as when the prior group leader become unavailable, as detected by absence of a periodic heartbeat message published by the leader. The election is carried out by a system of voting by each candidate whereby each candidate has a priority calculated from its configuration, and the server with the highest priority is configured to claim the leadership faster than the other candidates. As part of the claim, each candidate multicasts its priority. Each candidate that receives a multicast claim for leadership from another candidate compares its own priority against the claimant and only votes for itself if its own priority is higher. After a preconfigured period of hearing no other claimants with higher priority, the candidate with the highest priority becomes the new leader.
Owner:NETWORK APPLIANCE INC
Method and apparatus for election of group leaders in a distributed network
InactiveUS20050198359A1Effective controlEffective distributionMultiple digital computer combinationsTransmissionGroup controllerData file
A system and apparatus for control and distribution of data files in large-scale distributed networks. Members of a group of servers in a multicast network elect a group leader whenever a new group leader is required, as detected by absence of a periodic message published by the leader. Election is carried out by a system of voting by each candidate whereby each candidate has a priority calculated from its configuration, and the server with the highest priority is configured to claim the leadership faster than the other candidates. As part of the claim, each candidate multicasts its priority. Each candidate that receives a multicast claim for leadership from another candidate compares its own priority against the claimant and only votes for itself if its own priority is higher. After a preconfigured period of hearing no other claimants with higher priority, the candidate with the highest priority becomes the new leader.
Owner:NETWORK APPLIANCE INC
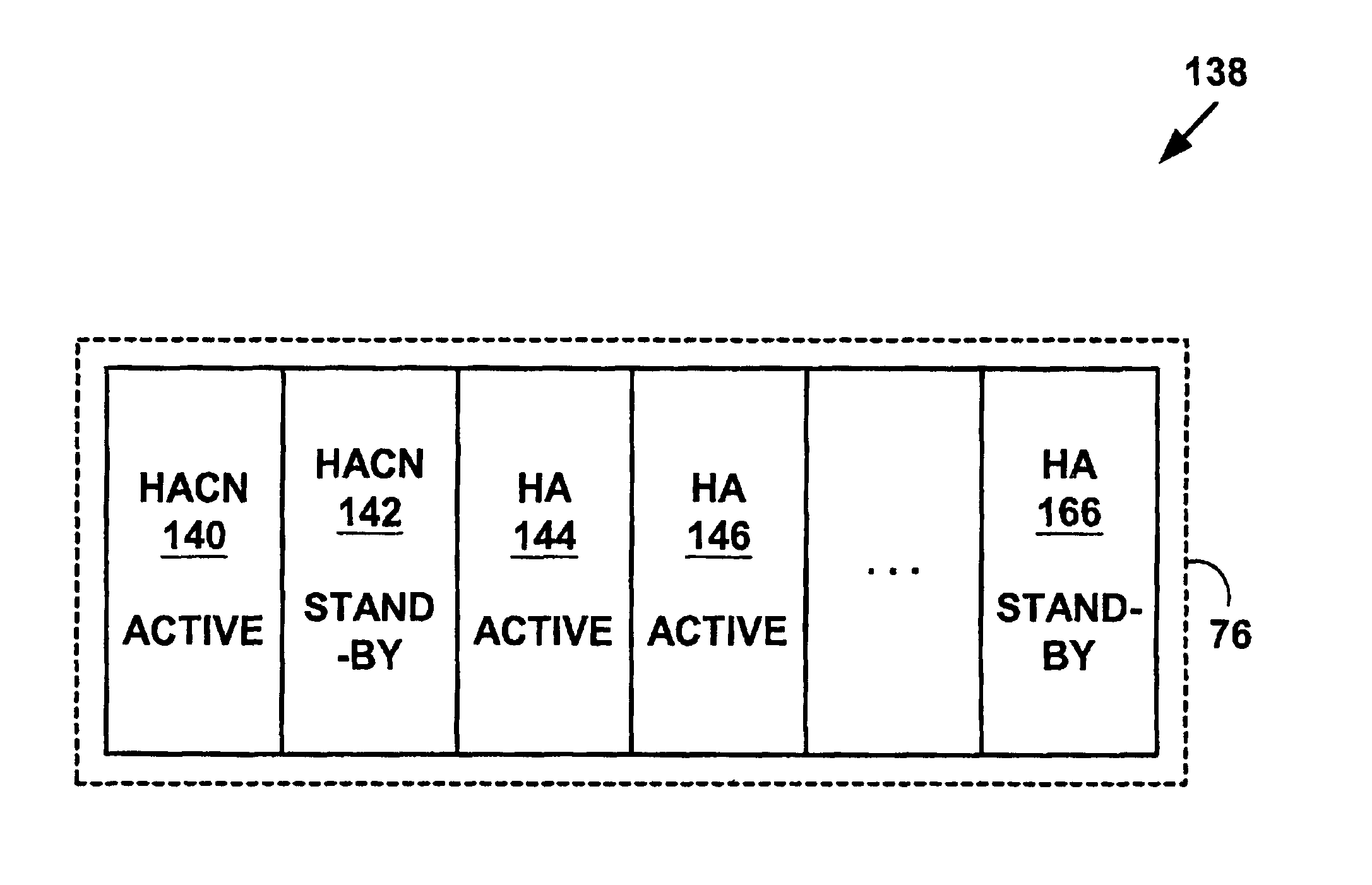
Method and system for mobile IP home agent redundancy by using home agent control nodes for managing multiple home agents
InactiveUS7080151B1Reduce failed callImprove user satisfactionMultiprogramming arrangementsCommmunication supplementary servicesComputer networkMulticast network
A method and system for Mobile Internet Protocol (IP) device redundancy. As mobile devices roam away from a home network and change a connective status, mobility binding records are sent to a multicast network address on the home network. The multicast network address multicasts the mobility binding records to other active Mobile IP home agent control nodes, standby home agent control nodes and standby home agents on the home network. The method and system allows standby home agent control nodes or standby home agents to be transparently switched for active home agent control nodes or active home agents that fail without downloading or uploading large numbers of mobility binding records after a failure. The method and system may also help reduce failed calls (e.g., data sessions including Voice over IP (VoIP), H.323, etc.), network congestion and improve user satisfaction in Mobile IP systems.
Owner:UTSTARCOM INC
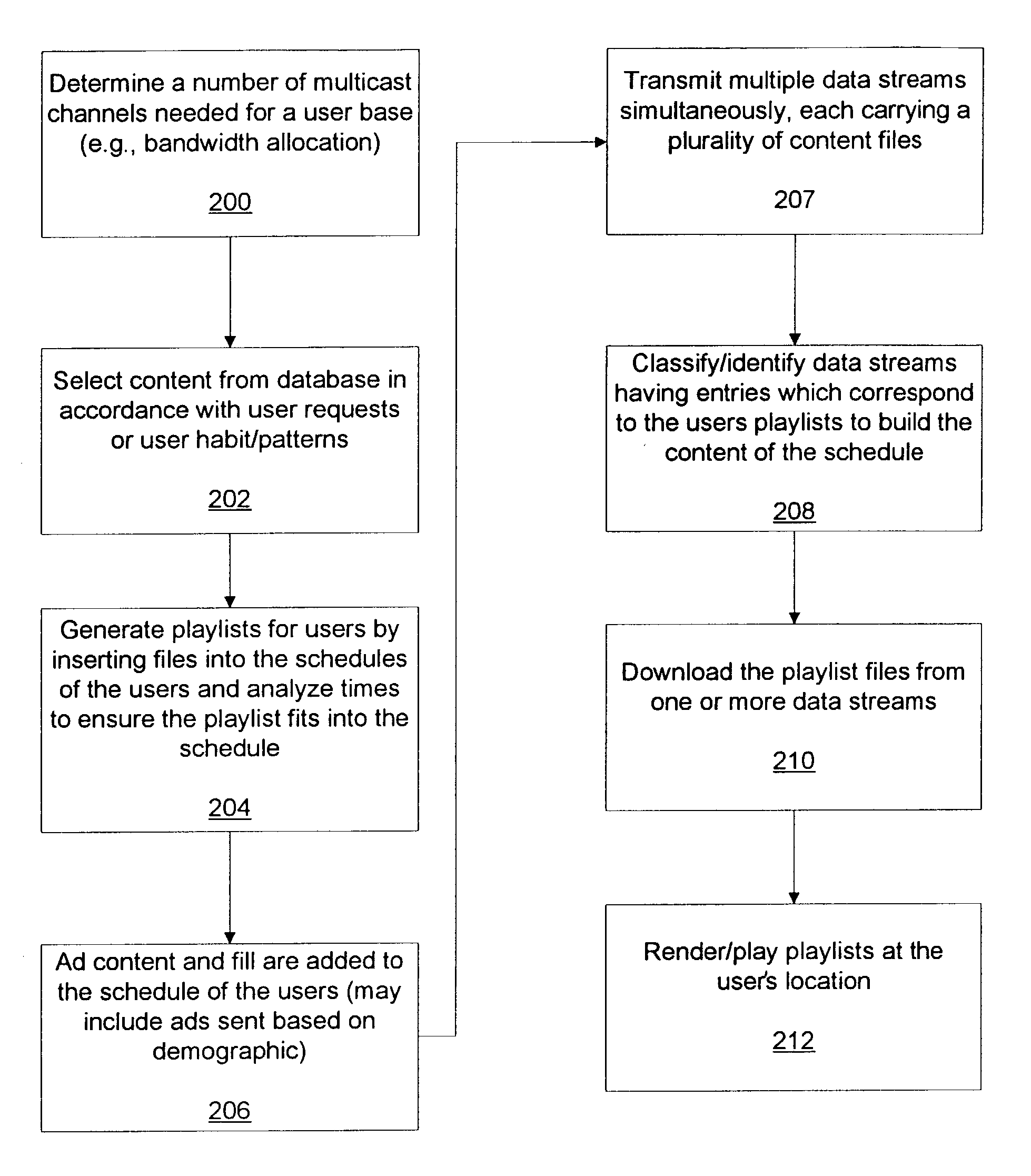
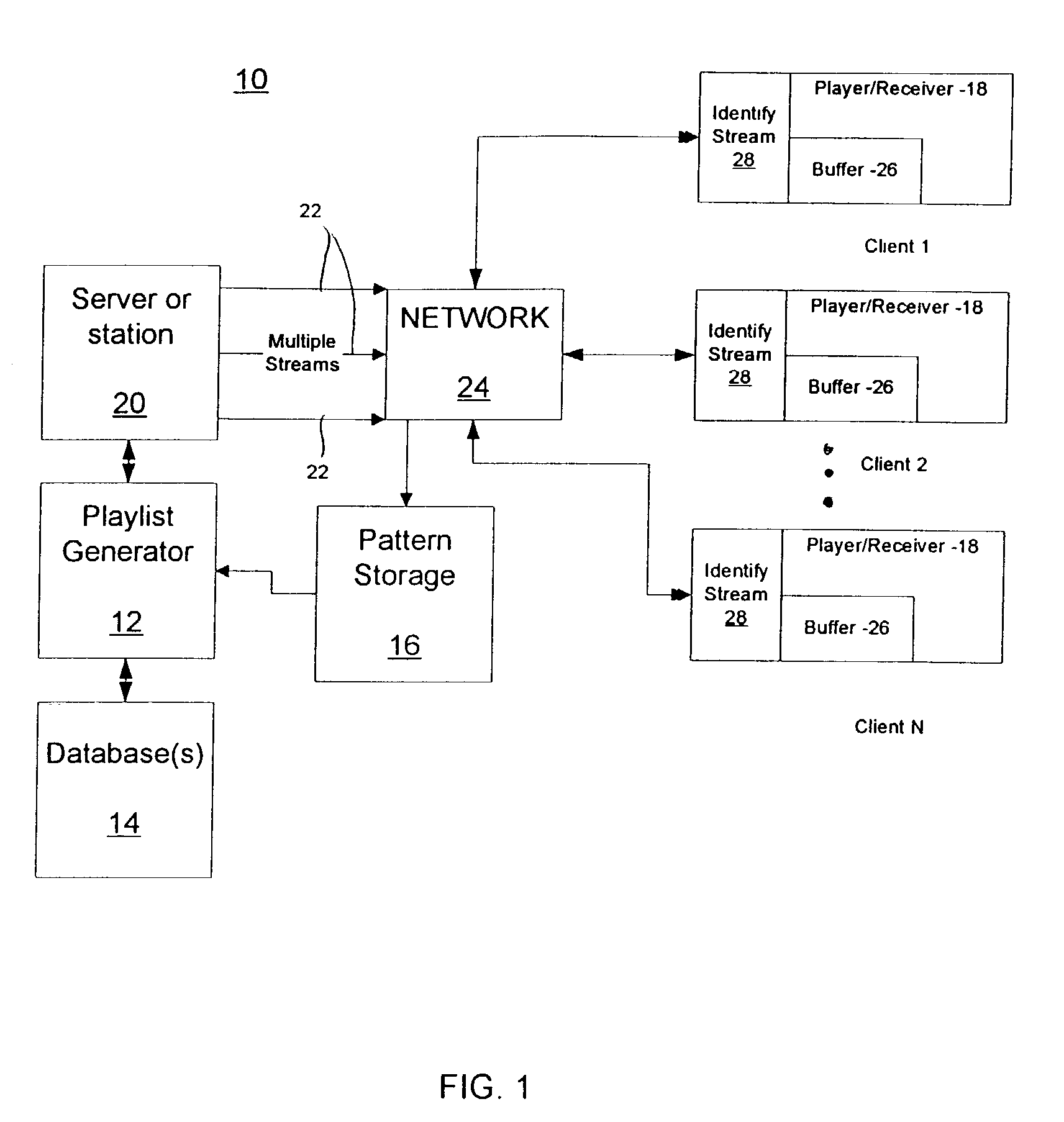
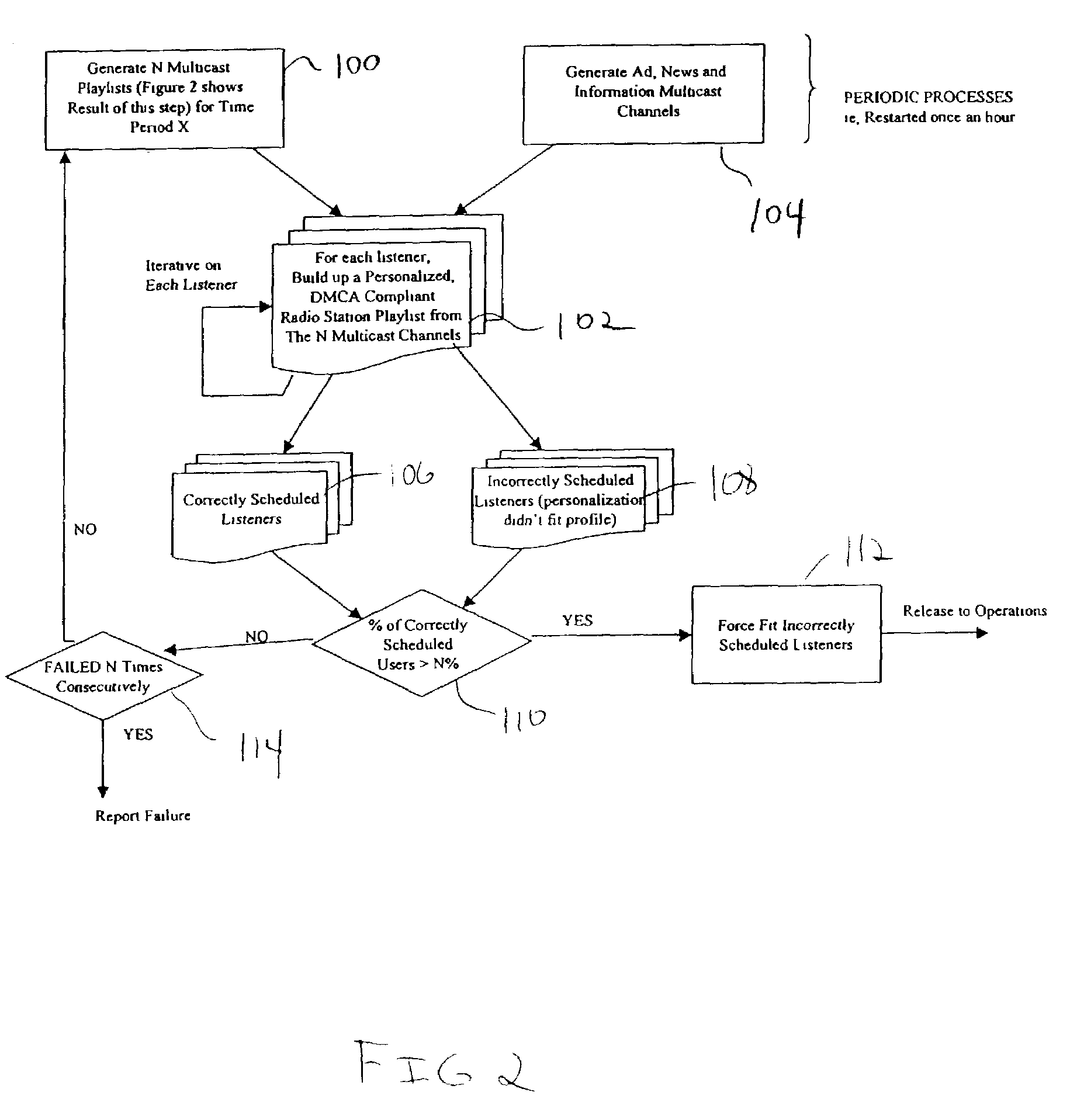
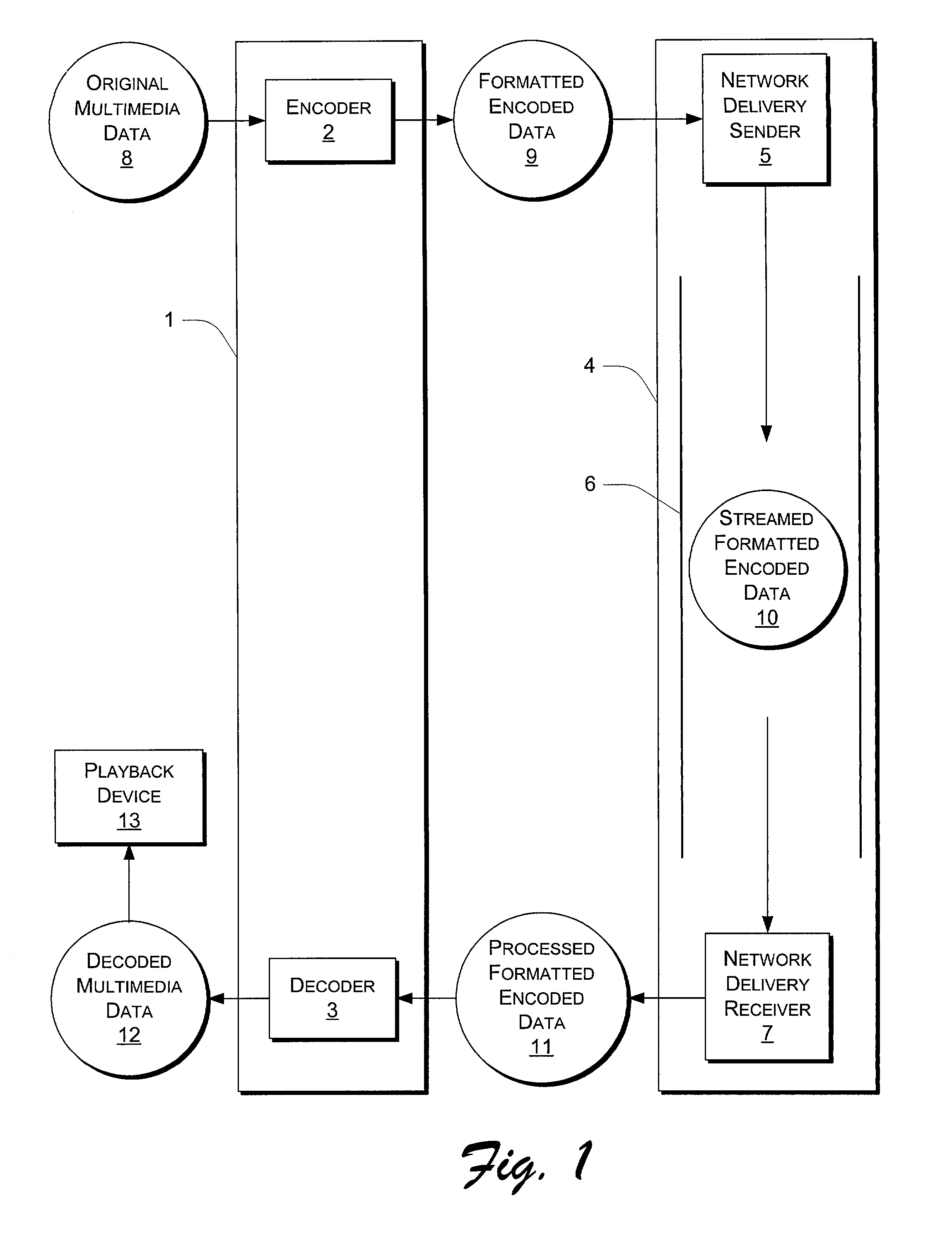
Streaming media delivery on multicast networks for network and server bandwidth minimization and enhanced personalization
InactiveUS7020710B2Receiver side switchingBroadcast transmission systemsPersonalizationComputer network
A system for personalizing received transmissions includes a content source that provides multiple transmission streams over a transmission media. A plurality of receivers is included wherein each receiver selects portions of one or more of the transmission streams in accordance with a playlist for each user. The receiver renders the portions of the received transmissions in accordance with a schedule.
Owner:THOMSON LICENSING SA
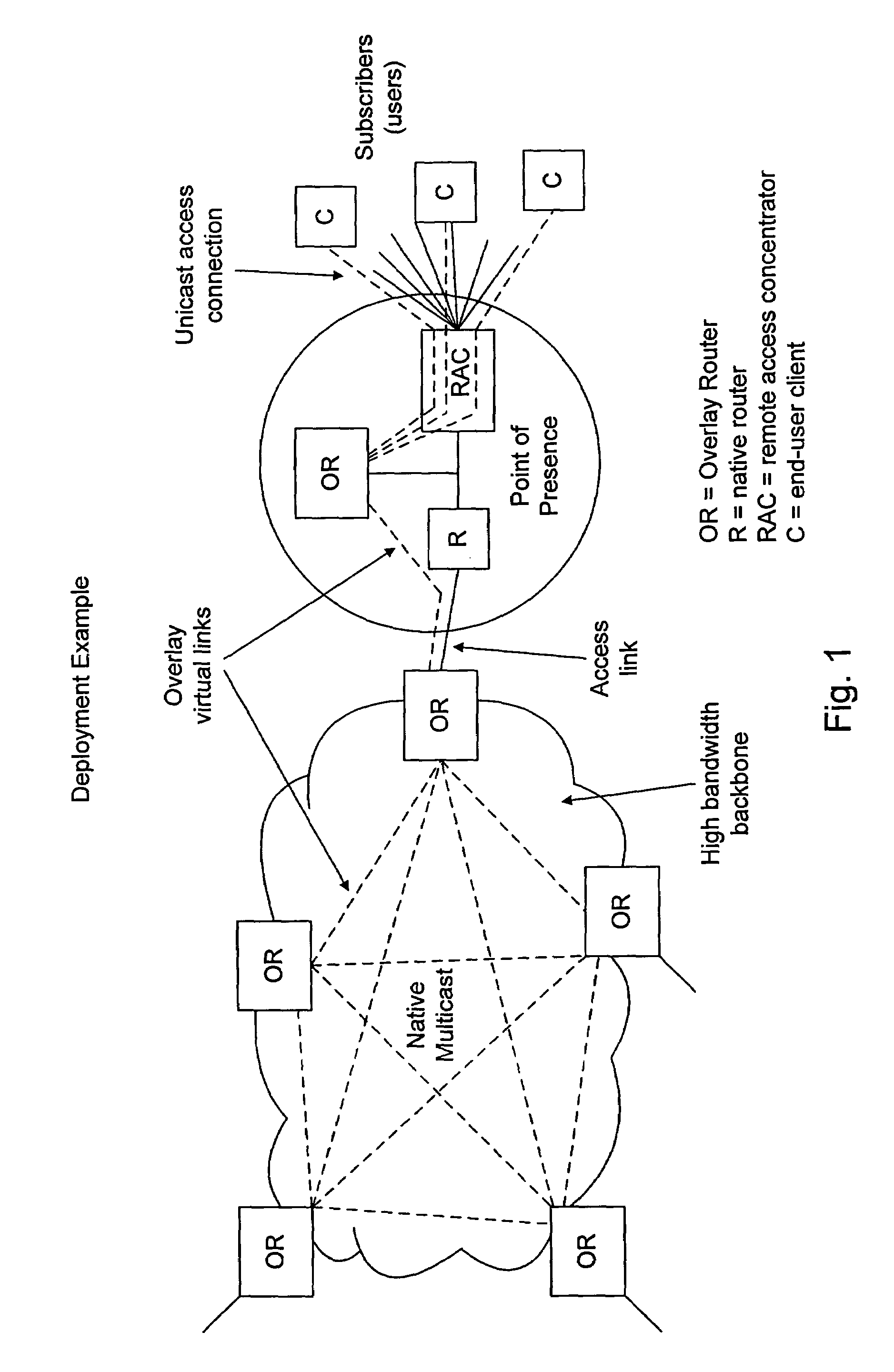
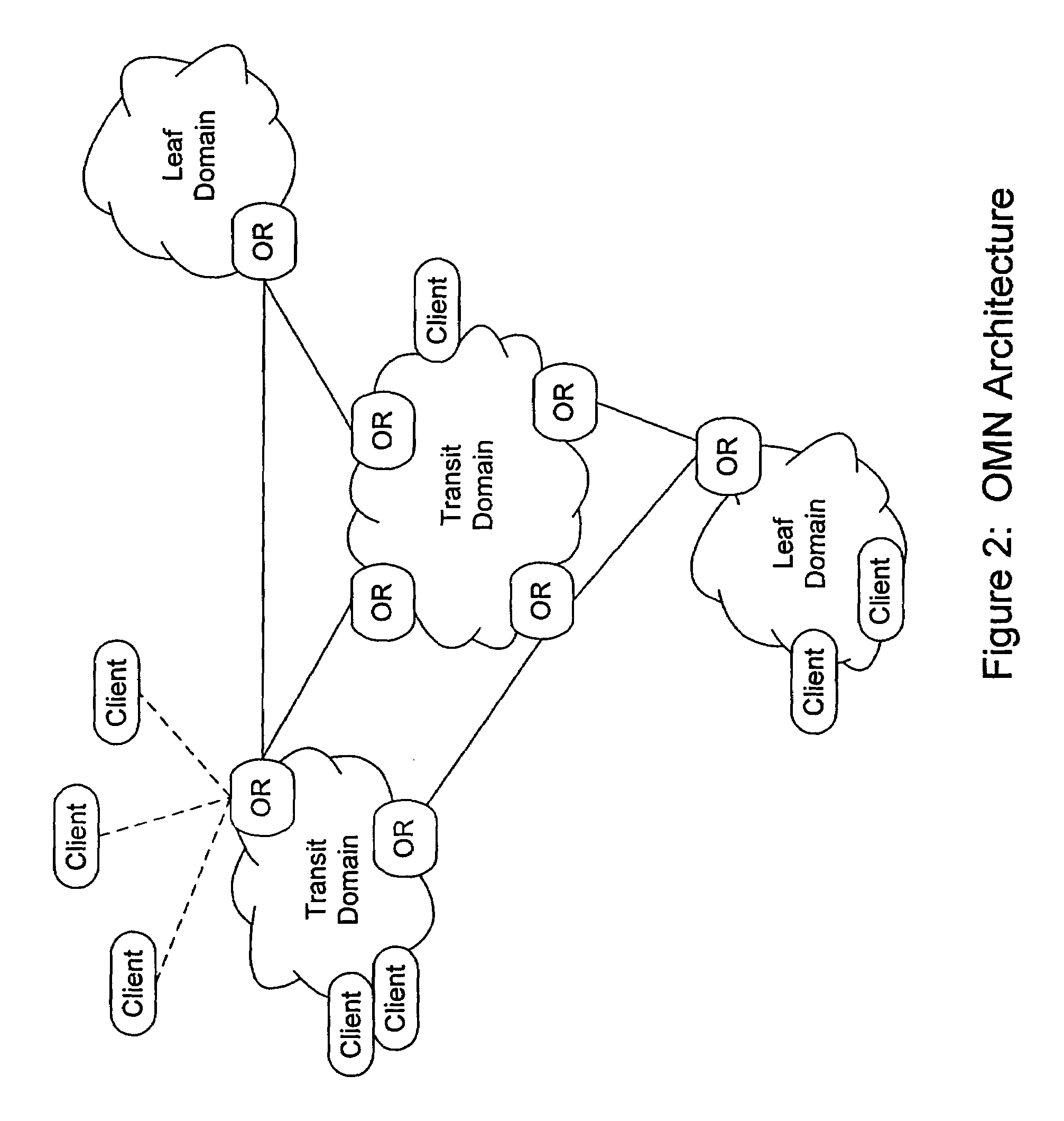
Performing multicast communication in computer networks by using overlay routing
InactiveUS7133928B2Efficient managementSpecial service provision for substationDigital computer detailsRouting tableMulticast network
An overlay protocol and system for allowing multicast routing in the Internet to be performed at the application level. The overlay protocol uses “native” Internet multicast and multicast routing protocols to route information, according to overlay routing tables. Overlay groups are mapped to native multicast groups to exploit native multicasting in regional or local forwarding domains. Use of the overlay protocol allows overlay distribution to be handled in a more intelligent and bandwidth-managed fashion. Overlay routers are placed at each of several local area networks, Internet service provider's point of presence, enterprise, or other cohesively-managed locations. The overlay computers are configured according to bandwidth and security policies, and perform application-level multicast distribution across the otherwise disjoint multicast networks by using the overlay routing. The result is an overlay multicast network that is effectively managed according to local network management policies. Application-level control can be applied to the transferred data at the overlay routers.
Owner:GOOGLE LLC
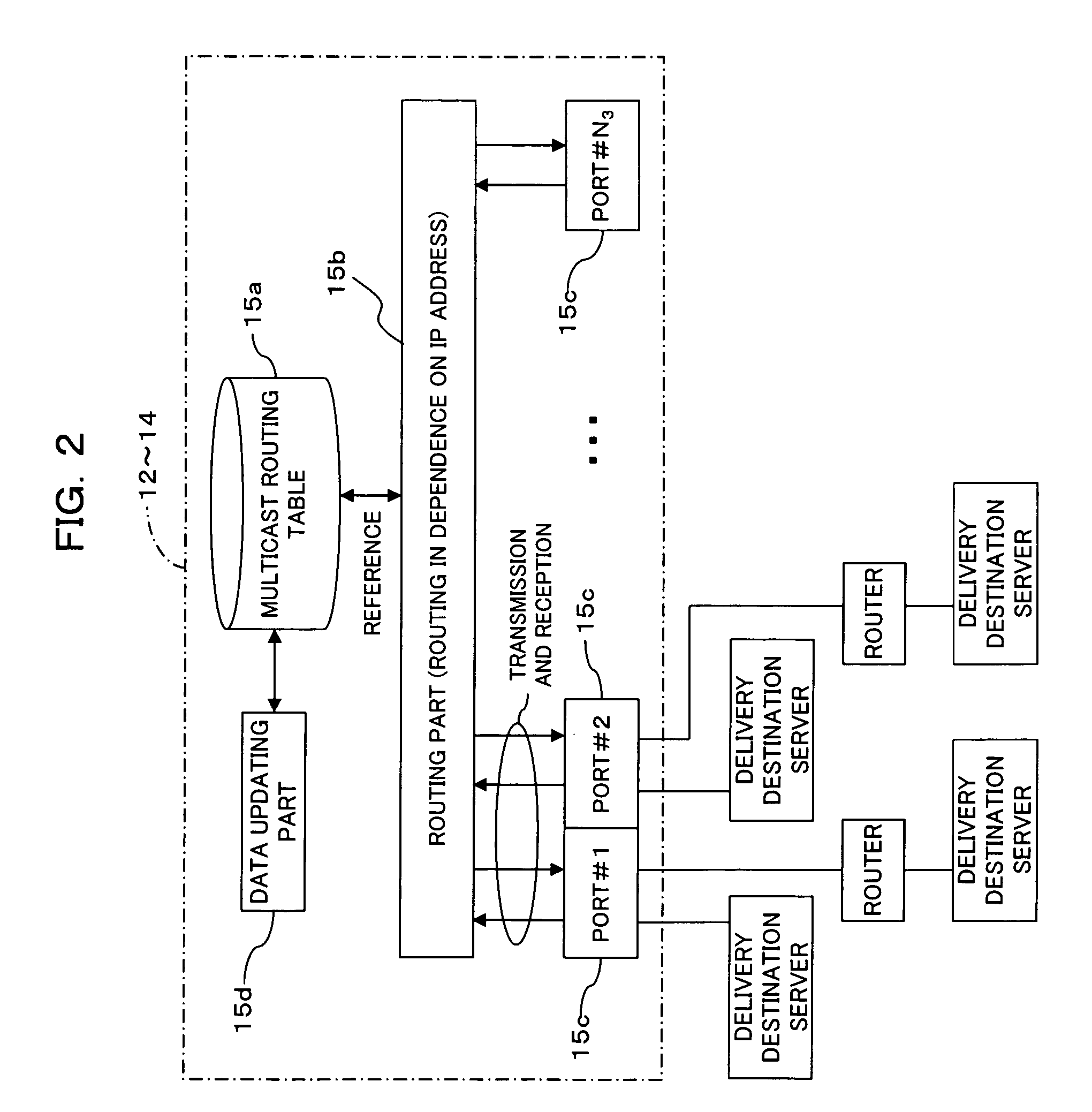
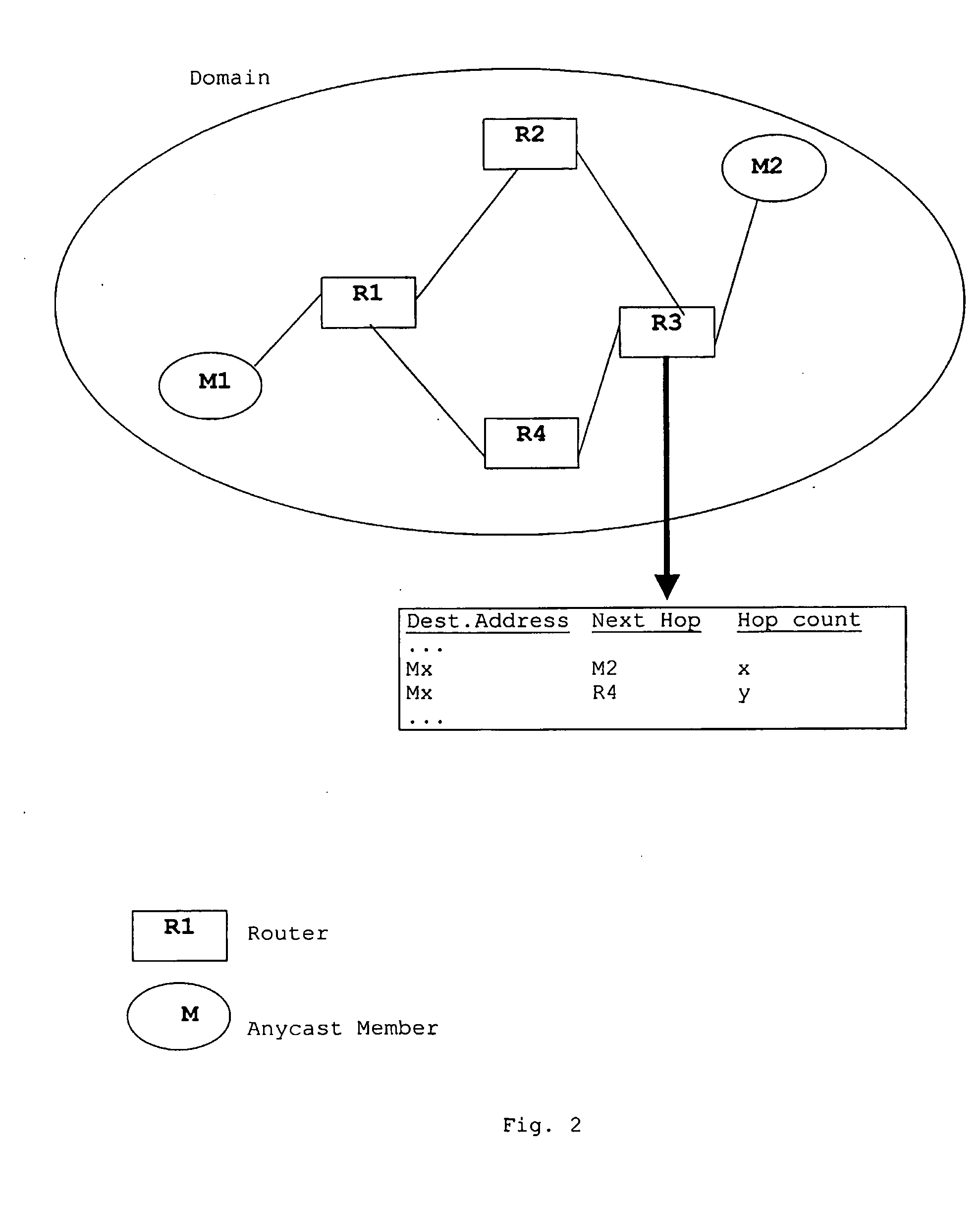
Multicast network unit, multicast network system, and multicast method
InactiveUS20050190765A1Easy to manageAvoid delaySpecial service provision for substationTime-division multiplexComputer networkMulticast network
A multicast network system is provided with a multicast network unit that delivers data between independent multicast network domains. The multicast network unit includes an extraction part for extracting a multicast delivery destination address from received data, a holder part for holding conversion data where the multicast delivery destination address corresponds to a delivery source address, and a judgment part for judging whether the multicast delivery destination address is held and outputting the result of a judgment. The multicast network unit also includes a filtering part which, when the result of the judgment is holding, converts the multicast delivery source address to an arbitrary delivery destination address and, when it is non-holding, discards the received data. The multicast network unit further includes a transmitter part for transmitting data containing the converted multicast address to the domain.
Owner:FUJITSU LTD
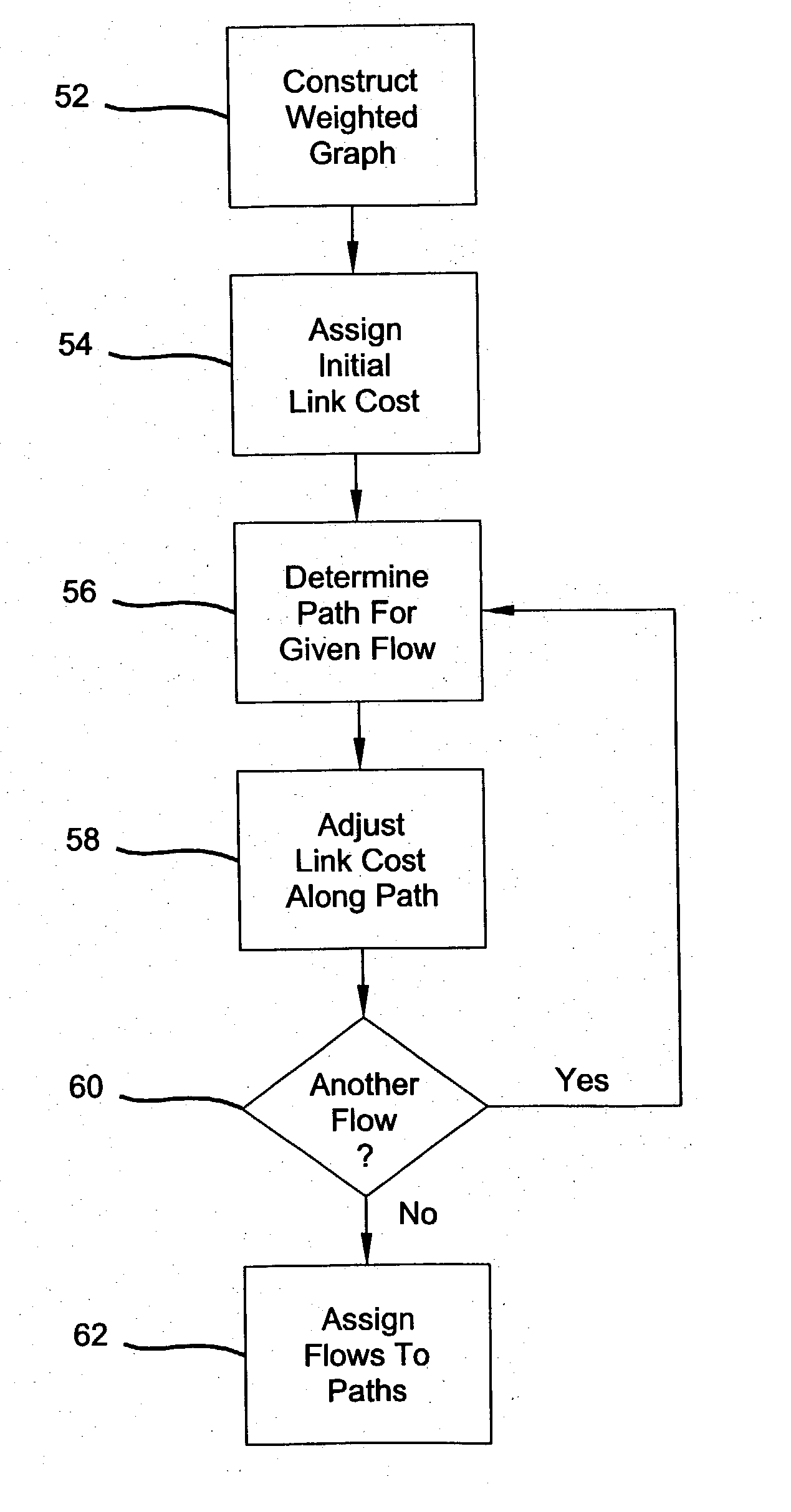
Static dense multicast path and bandwidth management
Improved algorithms are provided for performing path management for a plurality of select data transmission sessions in a multicast network. The algorithms include: constructing a weighted graph which represents topology of the network; assigning load correlated costs to network links; and computing least cost paths for each of the data transmission sessions which accounts for global bandwidth utilization.
Owner:PANASONIC CORP
Method and system for a Unicast endpoint client to access a multicast internet protocol (IP) session
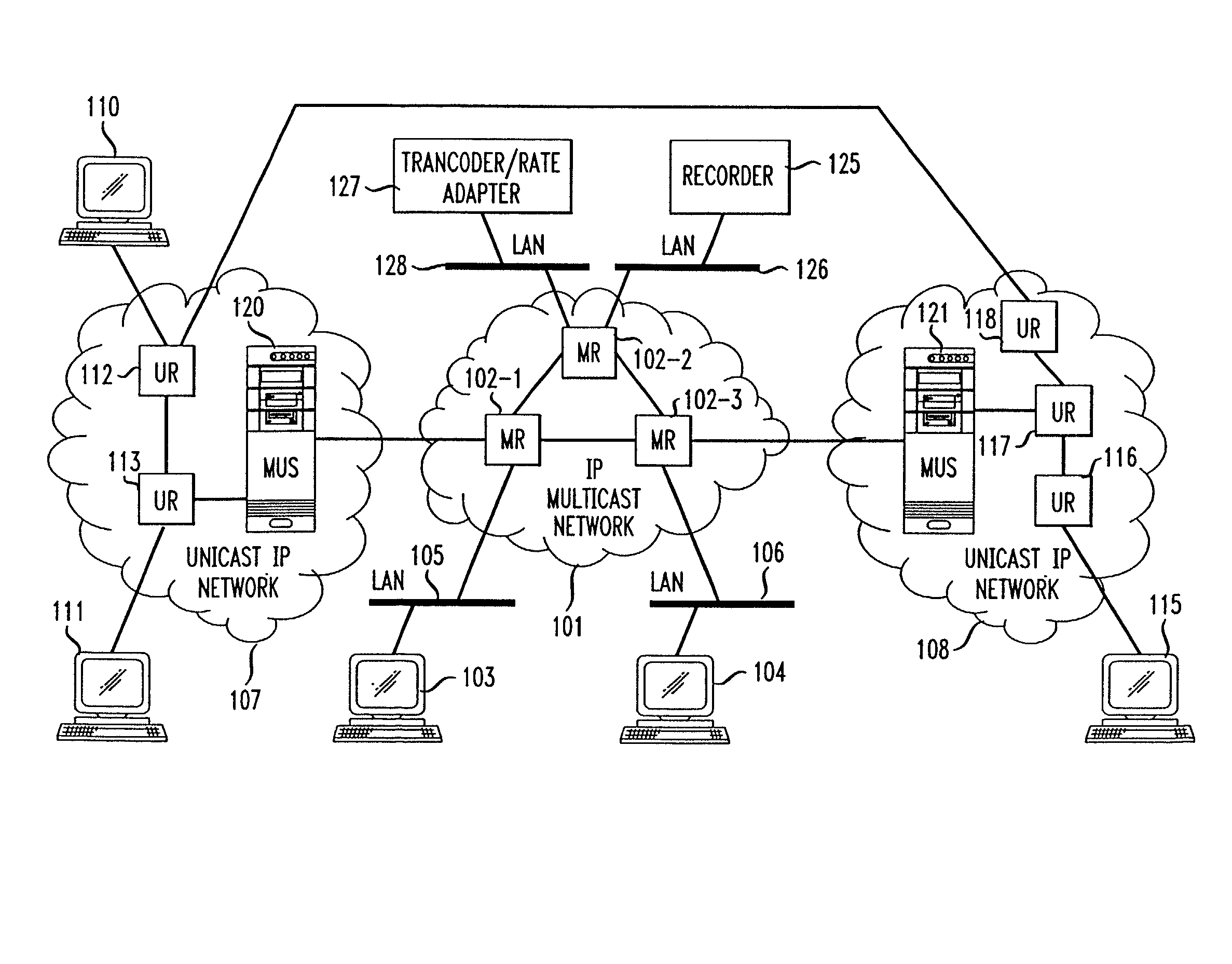
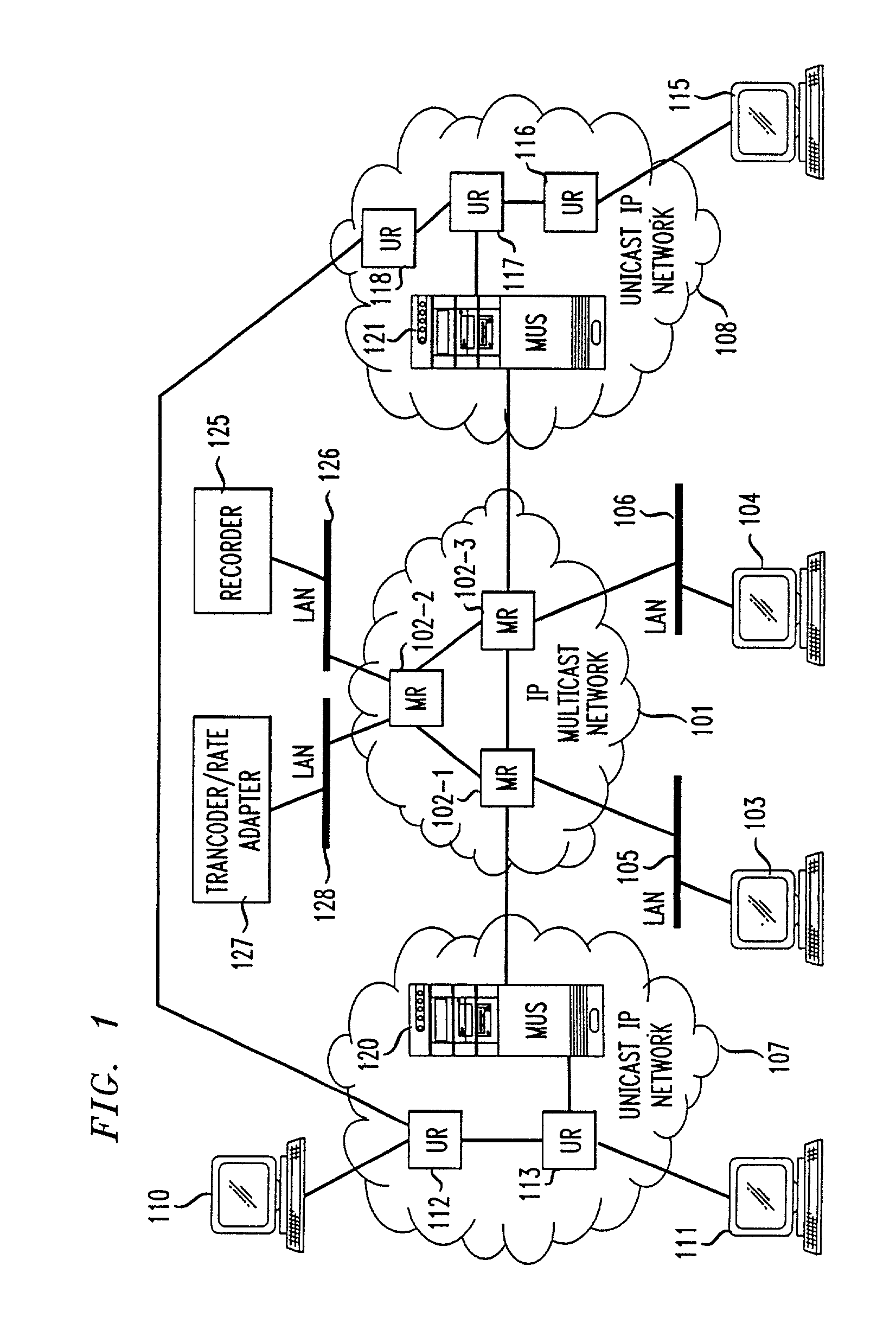
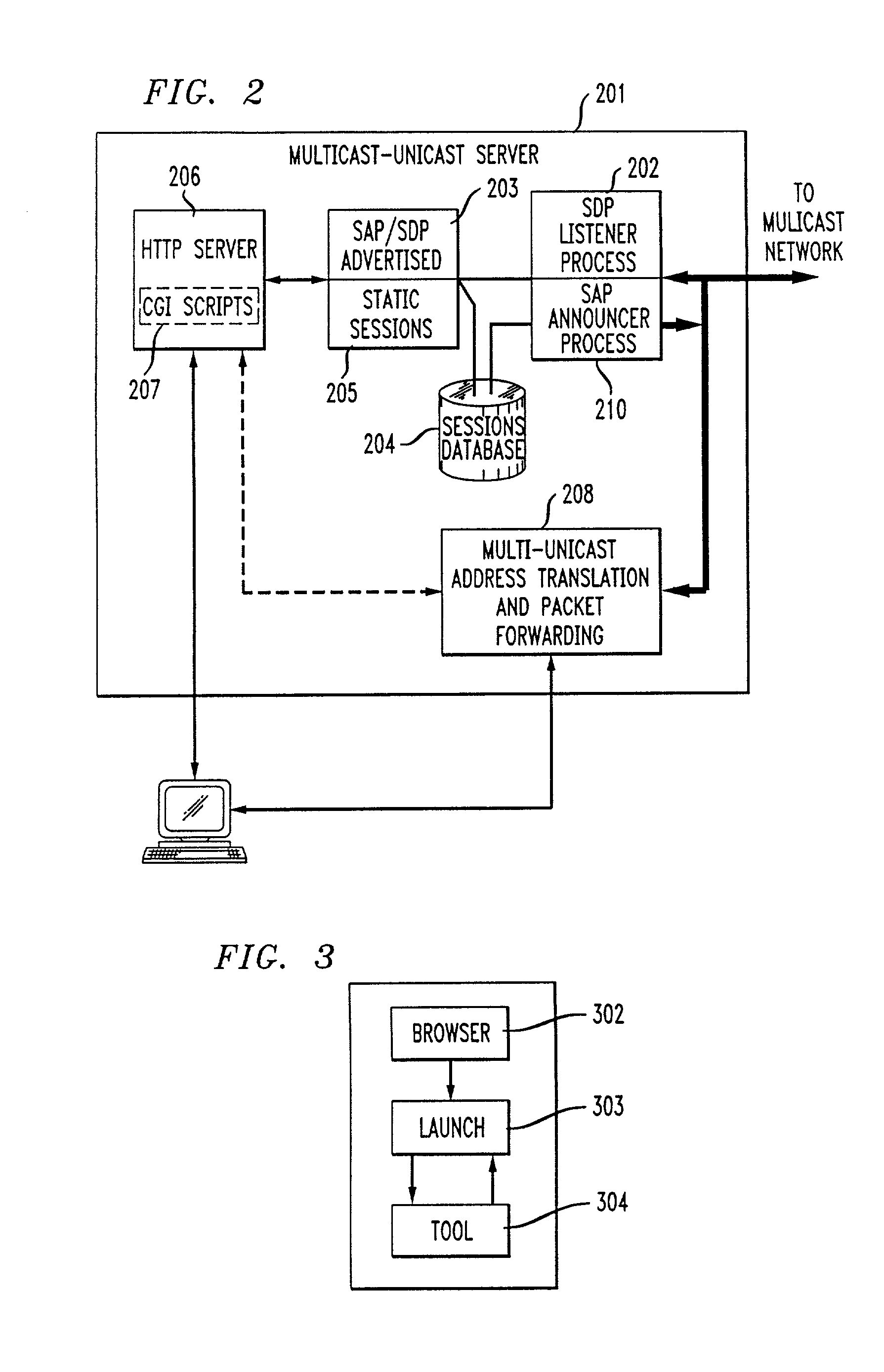
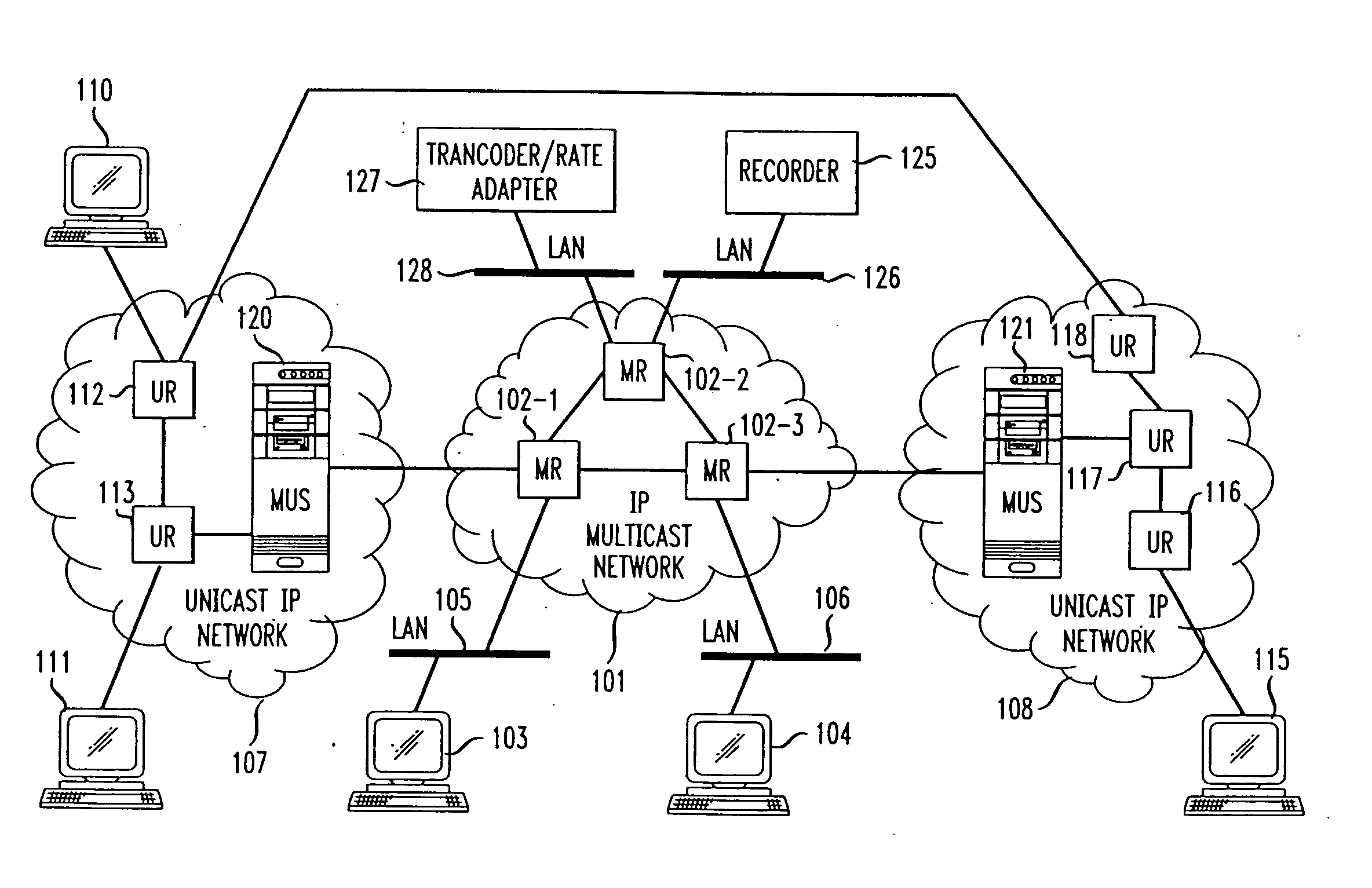
InactiveUS7031326B1Information obtainTime-division multiplexData switching by path configurationMedia typeNetwork packet
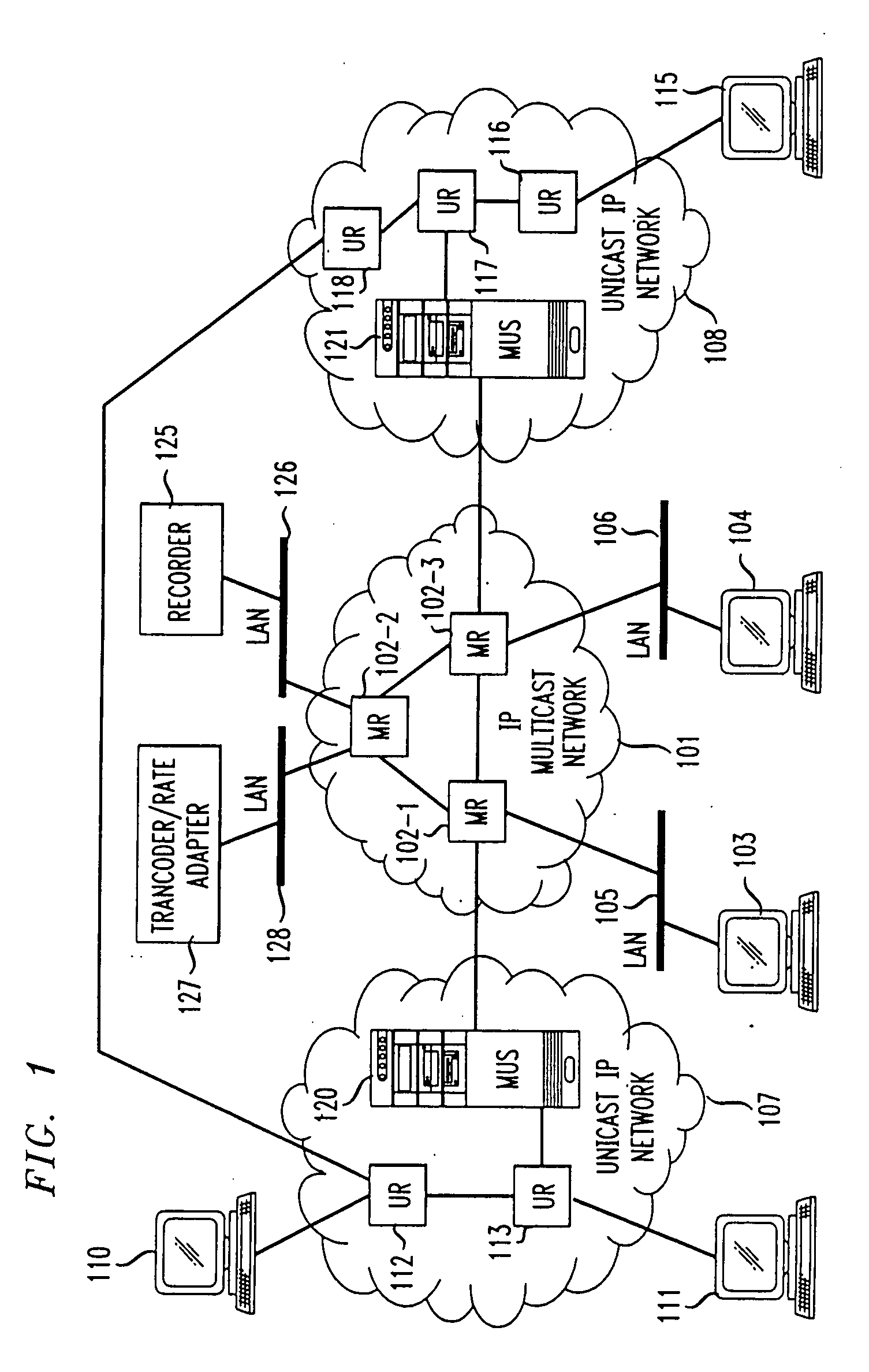
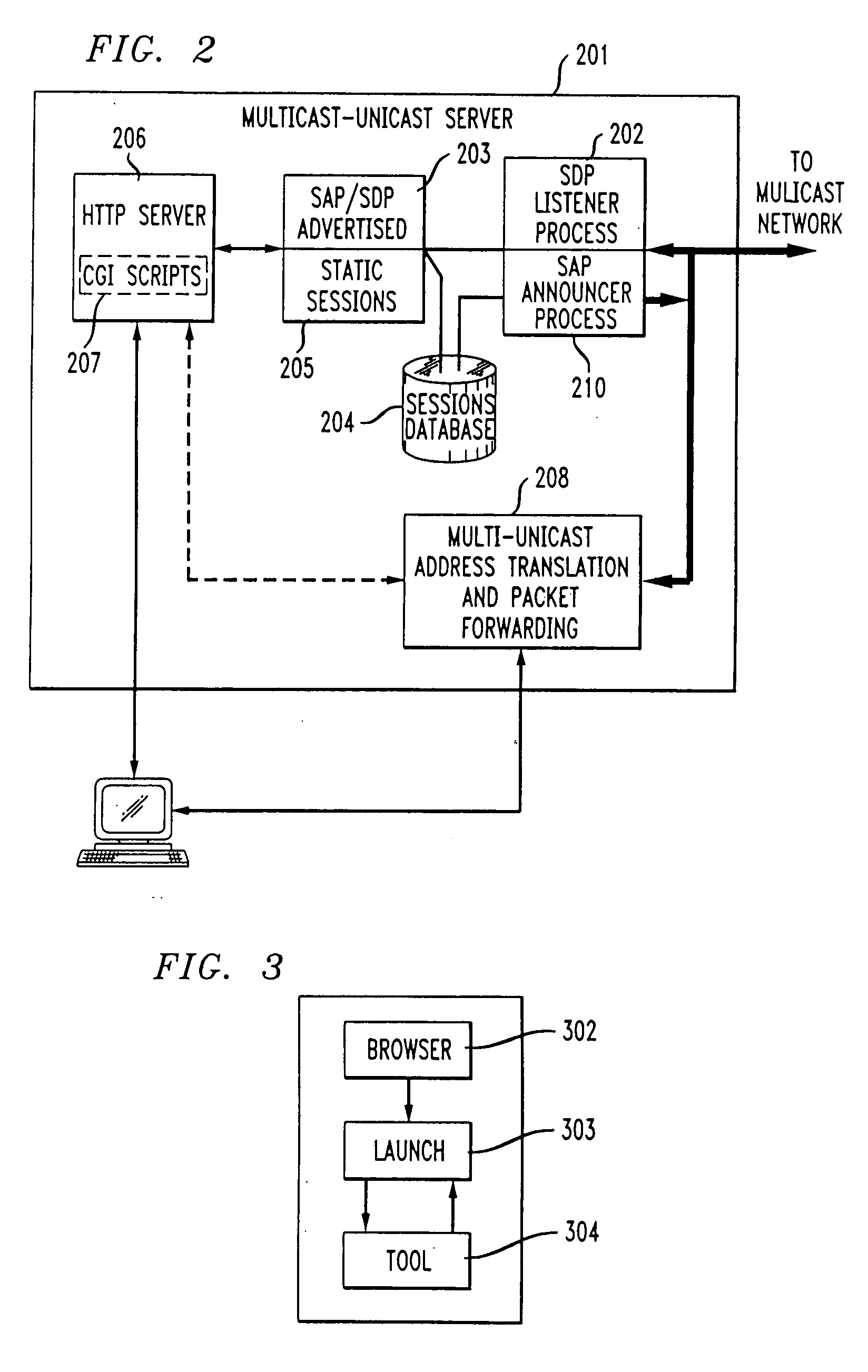
Unicast endpoint clients (110, 111, 115) on an IP Unicast network (107, 108) are provided access to Multicast sessions on an IP Multicast network (101) through a Multicast-Unicast gateway server (120, 121). The server obtains information about sessions on the Multicast network and makes such information available to a Unicast client on the Unicast network upon request by the client. Upon being presented with a list describing the subject matter of each session, the user at the Unicast client selects the session to which he or she wants to join, which causes the Multicast-Unicast server to join the appropriate session on behalf of the requesting client for each media type in which the joining client wants to be a participant. The server then sets a bi-directional Unicast User Datagram Protocol (UDP) stream between itself and the client. All packets then received by the server from the Unicast client are address-translated to the appropriate Multicast session address. In addition, all packets received by the server on the Multicast session address are address-translated and sent to the Unicast client. The Unicast client is then able to participate in the Multicast session as both a sender and a receiver of packets to and from other Unicast and Multicast clients which are active during the session. Further, the Unicast client is capable of creating a new session, recording a session in the network for later retrieval and playback, and creating and accessing low bandwidth versions of existing sessions.
Owner:AMERICAN TELEPHONE & TELEGRAPH CO
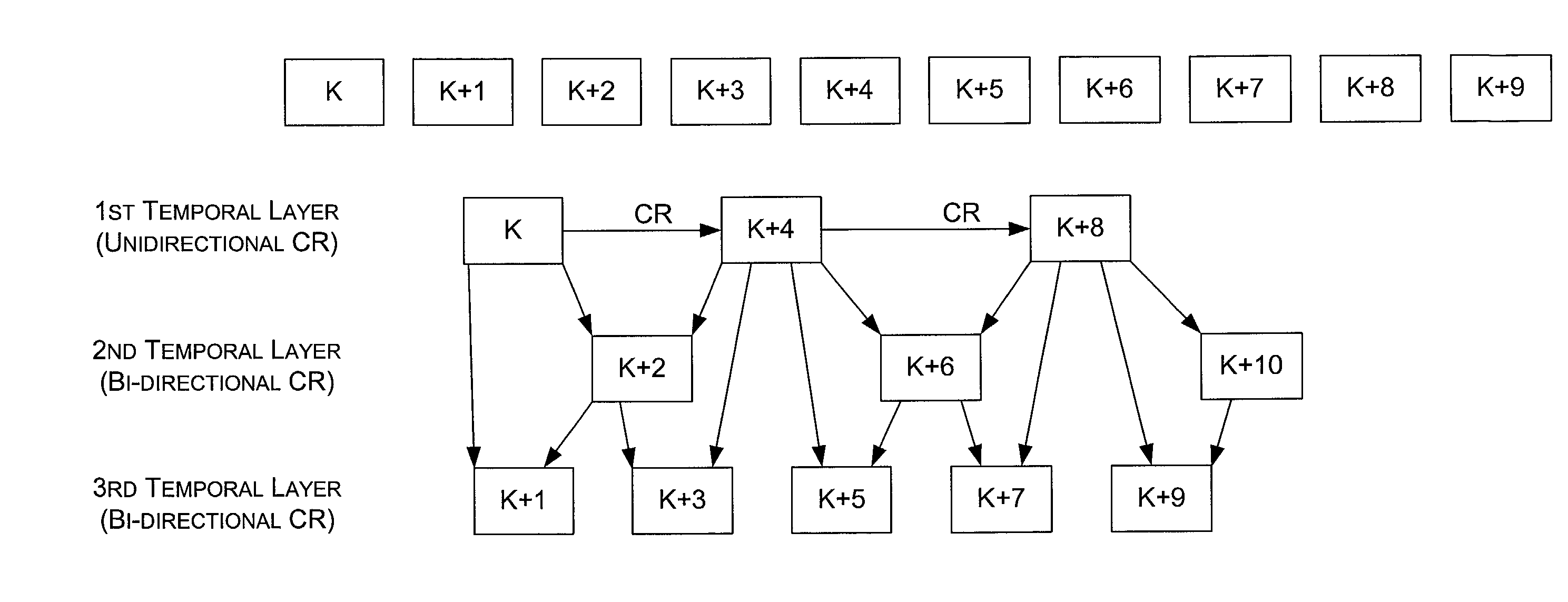
Multimedia compression system with additive temporal layers
InactiveUS7082164B2Easy to compressFrame rate scalabilityPicture reproducers using cathode ray tubesPicture reproducers with optical-mechanical scanningDecompositionMulticast network
A multimedia compression system for generating frame rate scaleable data in the case of universally scaleable data. Universally scaleable data is scaleable across all of the relevant characteristics of the data (e.g., frame rate, resolution, and quality for video). The scaleable data generated by the compression system includes multiple additive layers for each characteristic across which the data is scaleable. For video, the frame rate layers are additive temporal layers, the resolution layers are additive base and enhancement layers, and the quality layers are additive index planes of embedded codes. Various techniques can be used for generating these layers (e.g., Laplacian pyramid decomposition or wavelet decomposition for generating the resolution layers; tree structured vector quantization or tree structured scalar quantization for generating the quality layers). The system further provides for embedded inter-frame compression in the context of frame rate scalability, and non-redundant layered multicast network delivery of the scaleable data.
Owner:MICROSOFT TECH LICENSING LLC
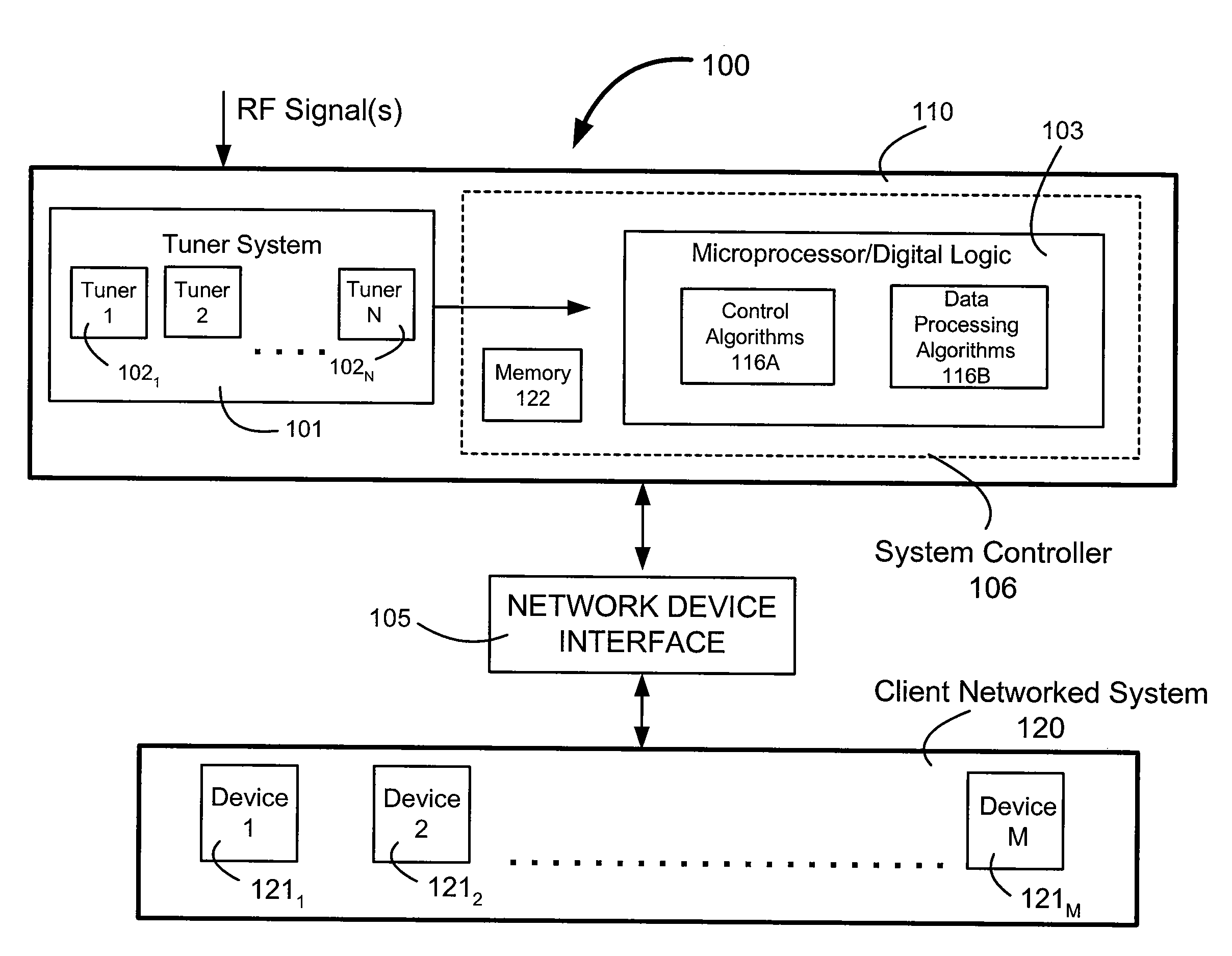
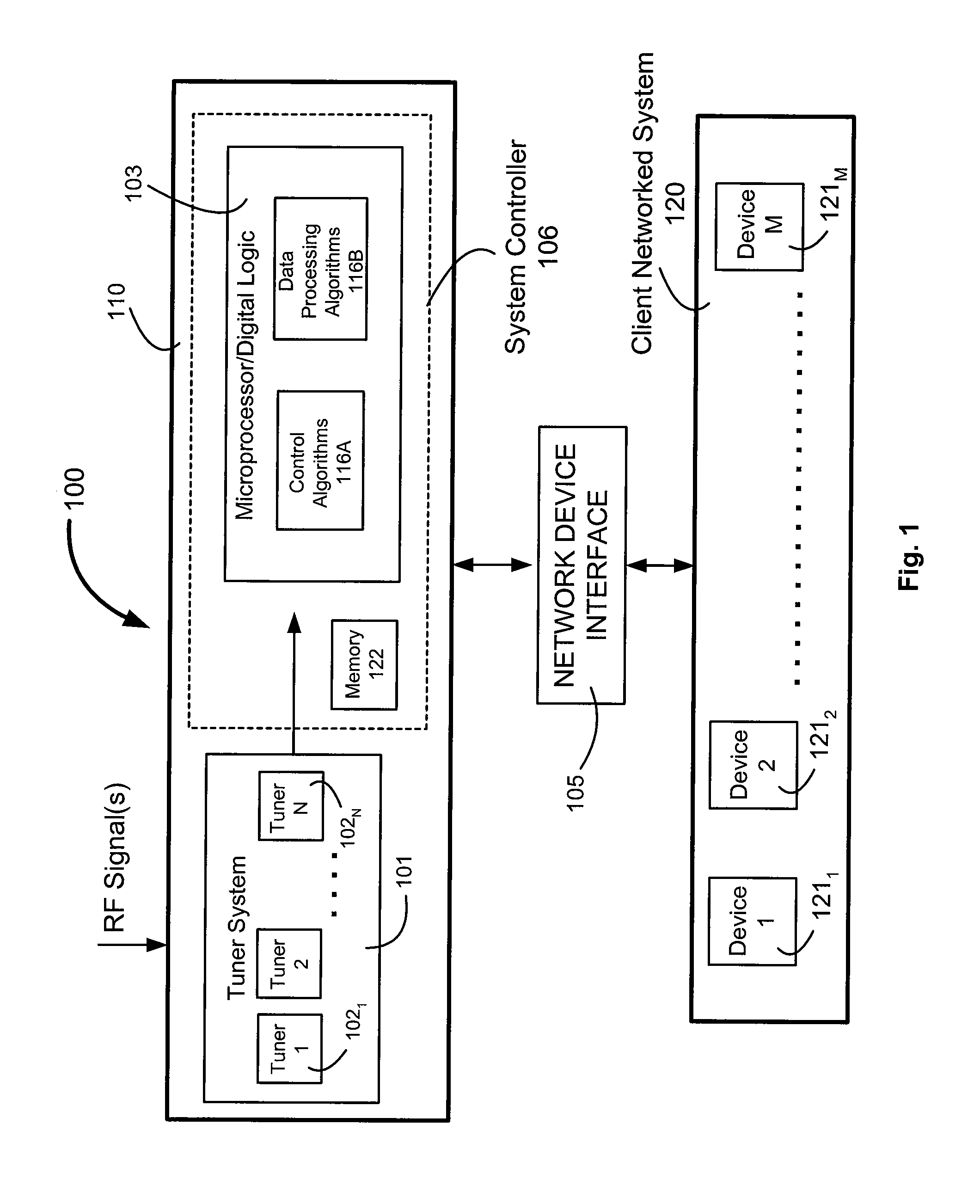
Networked digital tuners
InactiveUS20080127277A1Broadcast specific applicationsBroadcast-related systemsDigital tuningNetwork connection
A network bridging system, which receives RF (radio frequency) broadcast digital audio / video and encapsulates and routes selected broadcast content across a Local-Area-Network (LAN). The system includes multiple tuners that allow multiple client devices to access the broadcast content simultaneously through a network connection. It serves as a standalone Ethernet server and does not require a connection to a PC. The broadcast content, encapsulated in unicast or multicast network packets, is shared among multiple users concurrently.
Owner:PIONEER RES CENT USA
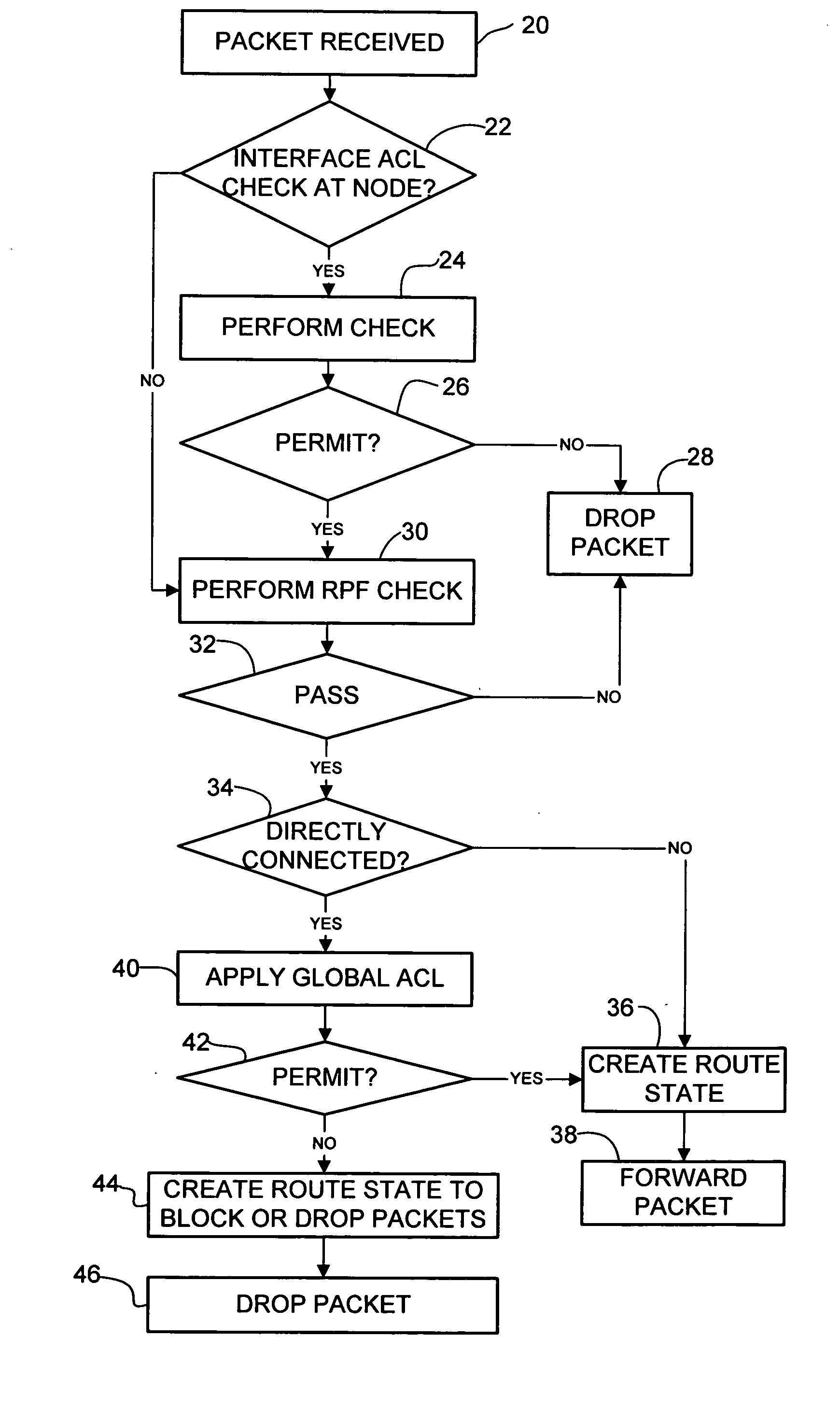
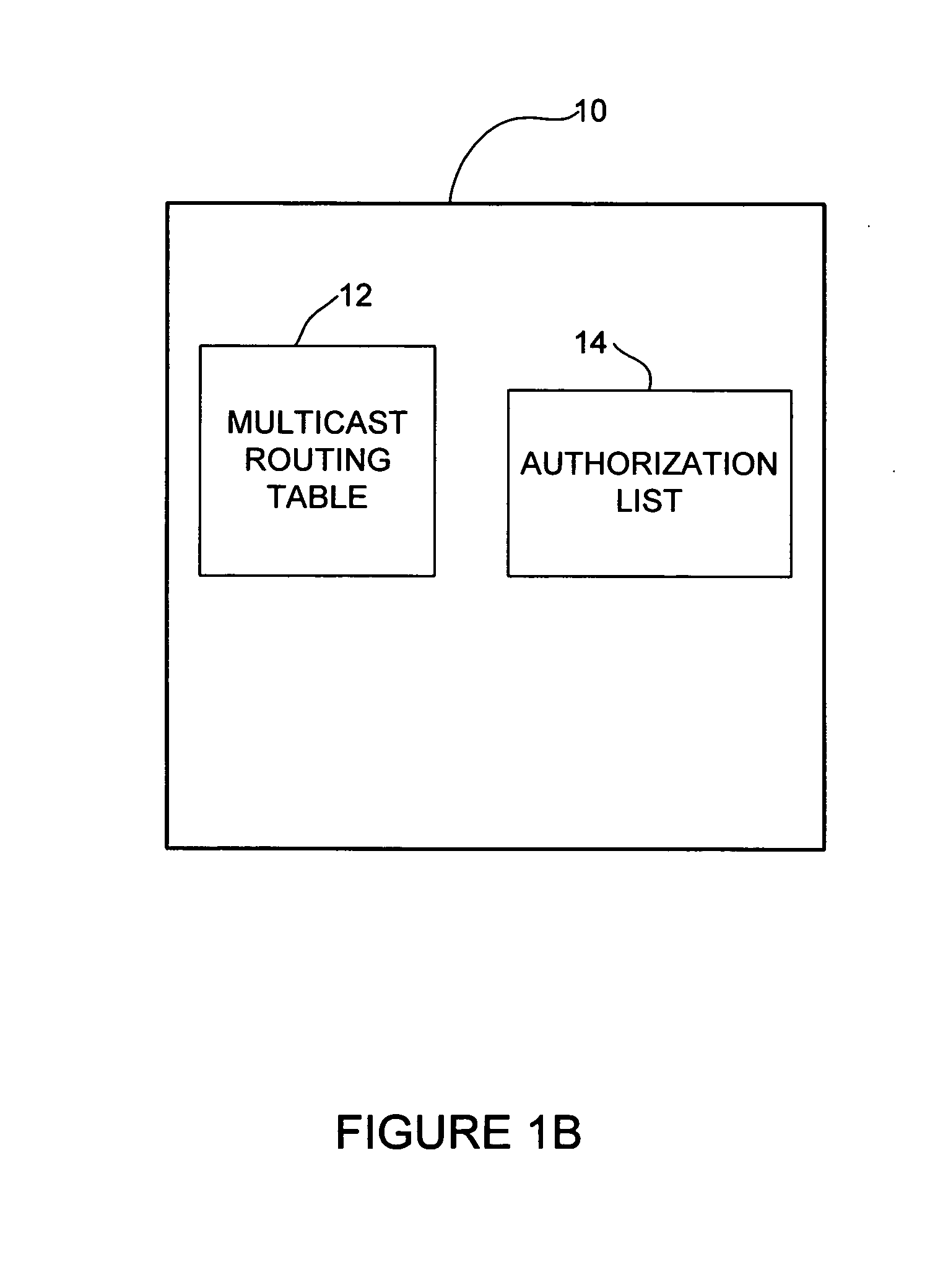
Method and system for filtering traffic from unauthorized sources in a multicast network
ActiveUS20070211722A1Special service provision for substationData switching by path configurationComputer networkRouting table
A method and system for filtering traffic in a multicast network are disclosed. Multicast packets are received at a network device which has a multicast routing table and a list containing nodes or interfaces authorized for transmitting multicast traffic into the network at the network device. The method includes determining if the network device is directly connected to a source of the multicast packet and only if the network device is directly connected to the source of the multicast packet, checking the list to determine if the source is an authorized source and dropping or blocking multicast packets from the source if the source is not an authorized source. The method further includes processing multicast packets from the source according to the multicast routing table.
Owner:CISCO TECH INC
Static dense multicast path and bandwidth management
Improved algorithms are provided for performing path management for a plurality of select data transmission sessions in a multicast network. The algorithms include: constructing a weighted graph which represents topology of the network; assigning load correlated costs to network links; and computing least cost paths for each of the data transmission sessions which accounts for global bandwidth utilization.
Owner:PANASONIC CORP
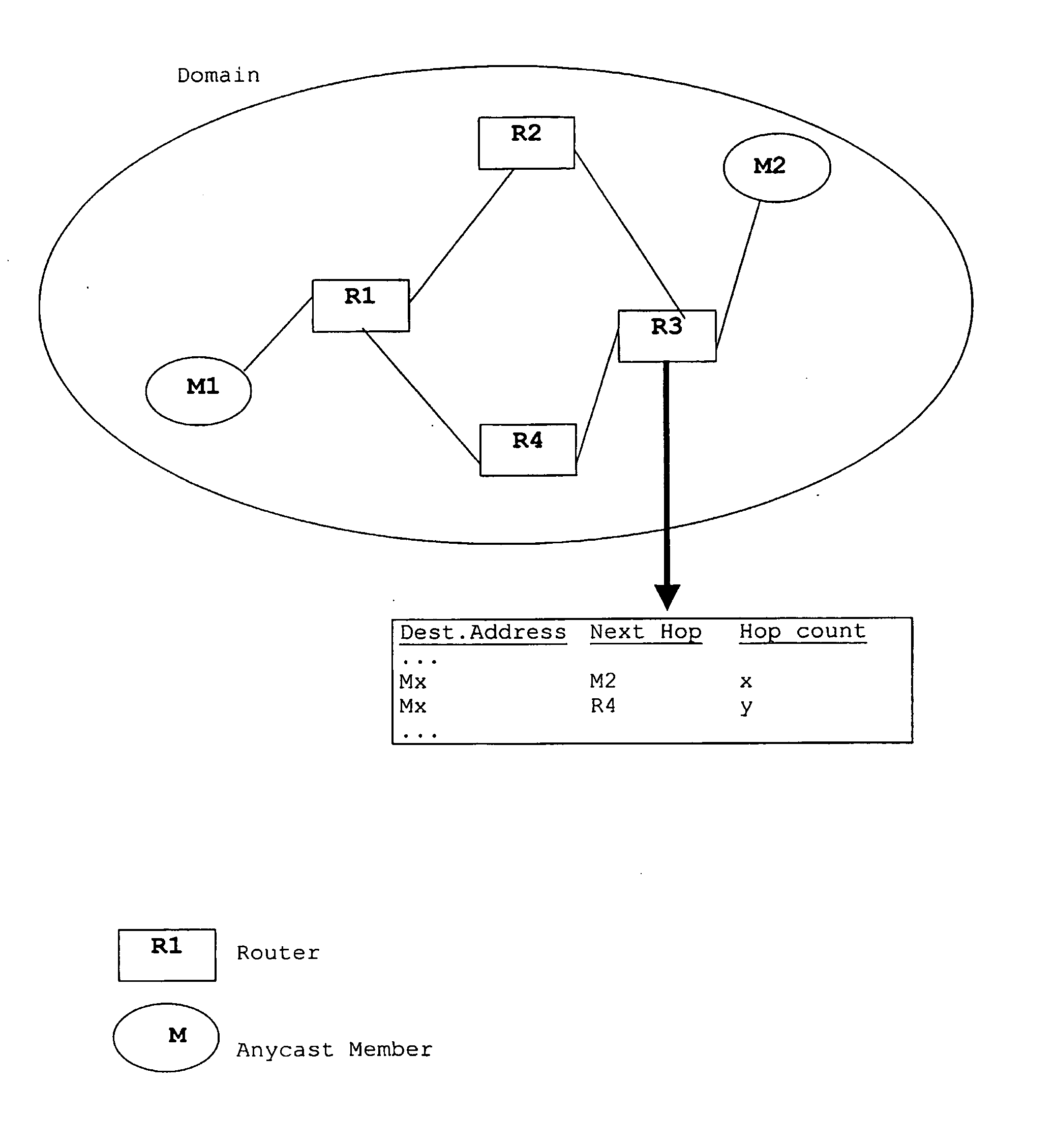
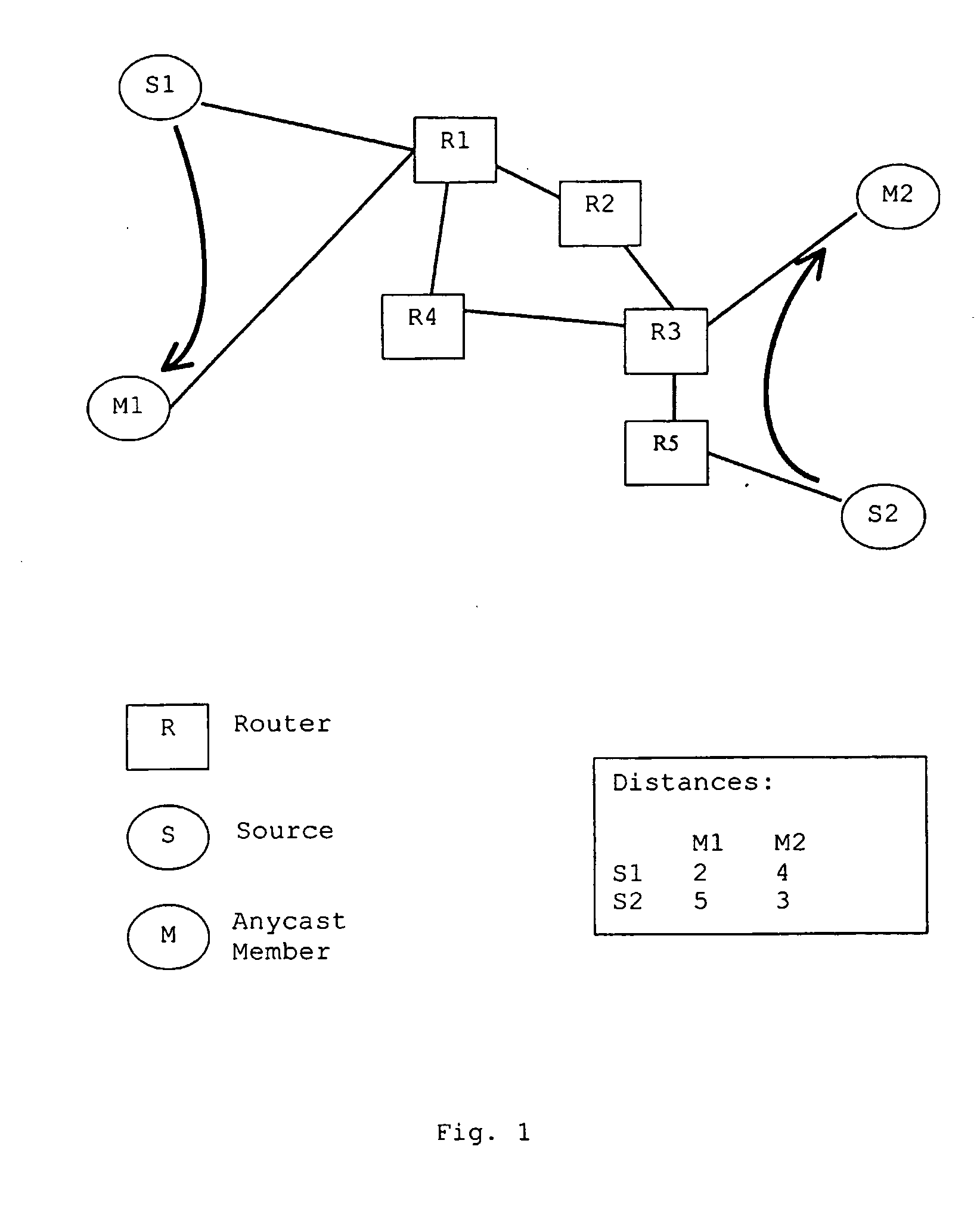
Method and system for multiple hosts anycast routing
ActiveUS20050044141A1Anycast routing can be enhancedSpecial service provision for substationData switching by path configurationMulticast addressMulticast network
Conventional anycast networks provide a service which allows a sender to access the nearest of a group of receivers sharing a common anycast address. In contrast thereto, multicast networks establish data communications between a sender and all receivers confined by a group having the same multicast address. Thus, the networks providing both anycast and multicast routing only allow for accesses by a sender to one receiver being specified according to the employed anycast protocol or to a plurality of receivers forming a multicast group. In order to provide accesses by a sender to a specified number of nearest receivers, the present invention provides a method and a system for multiple hosts anycast routing in a network. An indicator specifying the number of nearest receivers to be set up for data communications with a sender is included in an anycast address or associated thereto as an extension. On the basis of the indicator, a corresponding number of anycast members of an anycast group identified by the anycast address are contacted / allocated for data communications with the sender.
Owner:TELEFON AB LM ERICSSON (PUBL)
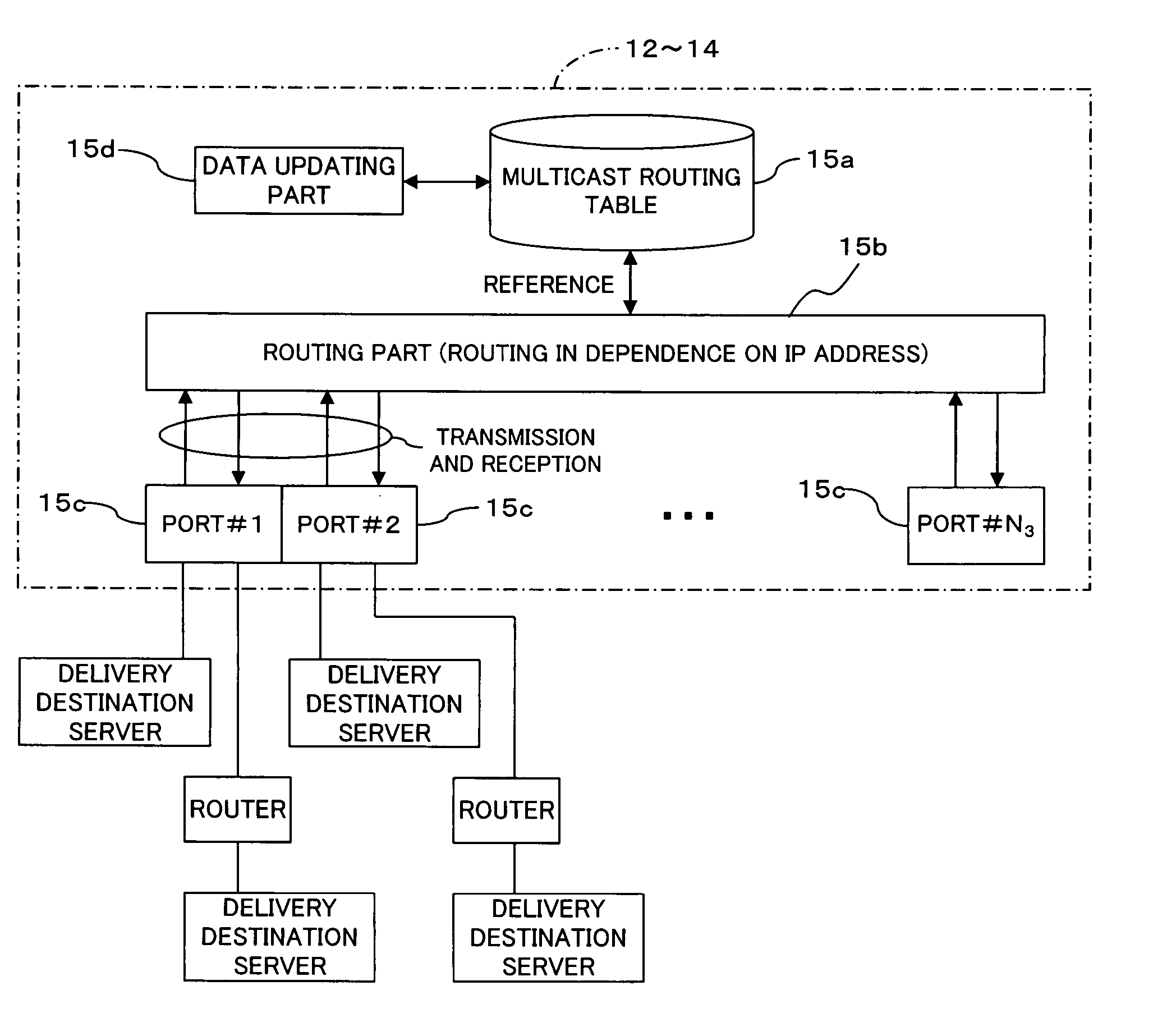
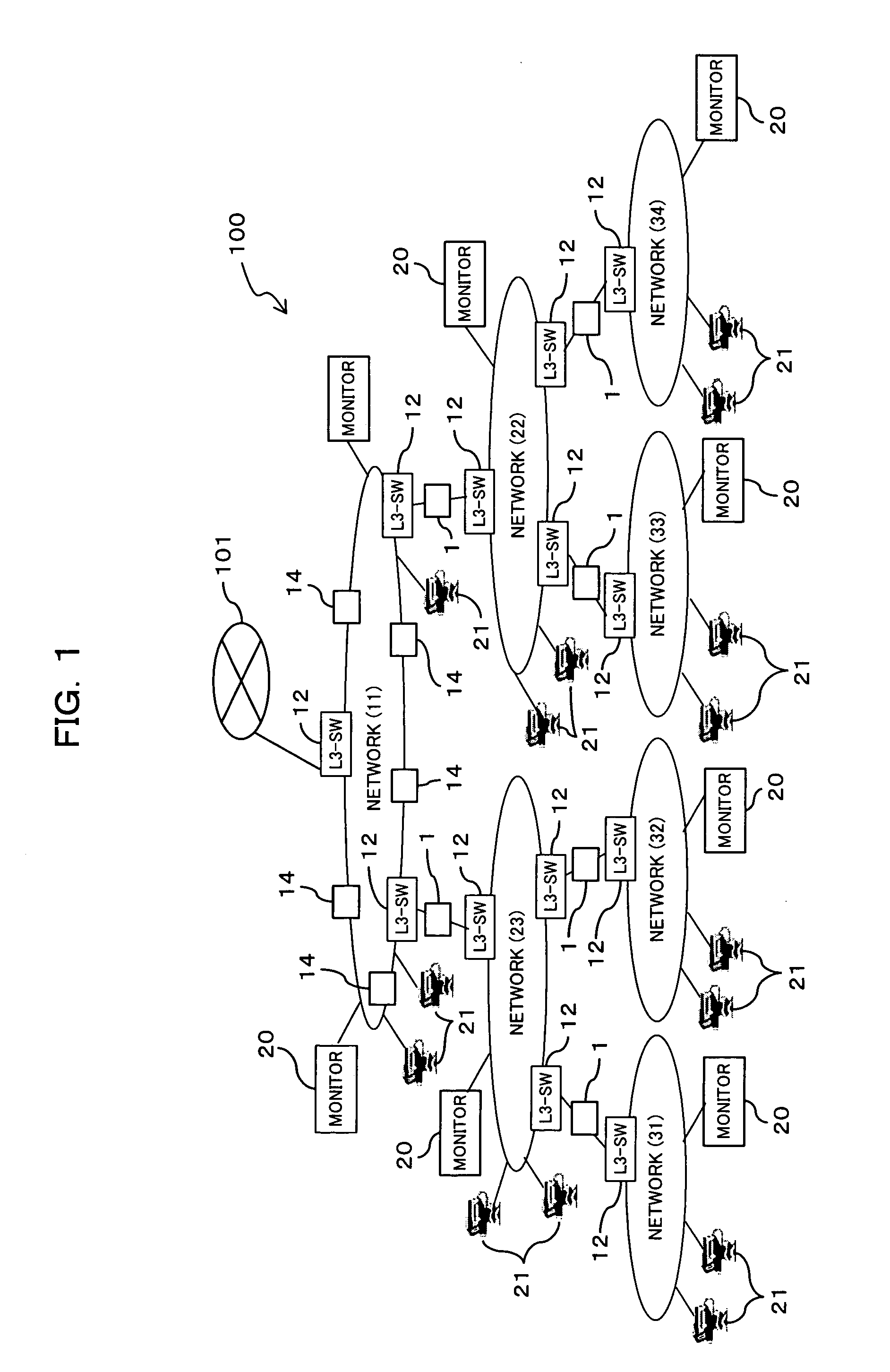
Multicast network monitoring method and multicast network system to which the method is applied
InactiveUS20080002591A1Quick checkAccurate extractionError preventionTransmission systemsComputer networkMulticast network
Disclosed is a multicast network system including a multicast network which provides a plurality of relay nodes, and a monitoring server and a plurality of acknowledgment agents connected to the multicast network. The monitoring server includes an acknowledgment request message generating and sending unit that generates and sends an acknowledgment request message storing an acknowledgment probability to the plurality of acknowledgment agents; a collecting unit that collects acknowledgment messages from acknowledgment agents; and a collection number comparing unit that compares the number of acknowledgment messages collected by the acknowledgment message collecting unit with the expected number of acknowledgment messages obtained from the acknowledgment probability and the total number of acknowledgment agents. The acknowledgment agent has an acknowledgment message sending unit that determines whether an acknowledgment is needed for the acknowledgment request message based on the acknowledgment probability stored in the acknowledgment request message to send an acknowledgment message.
Owner:FUJITSU LTD
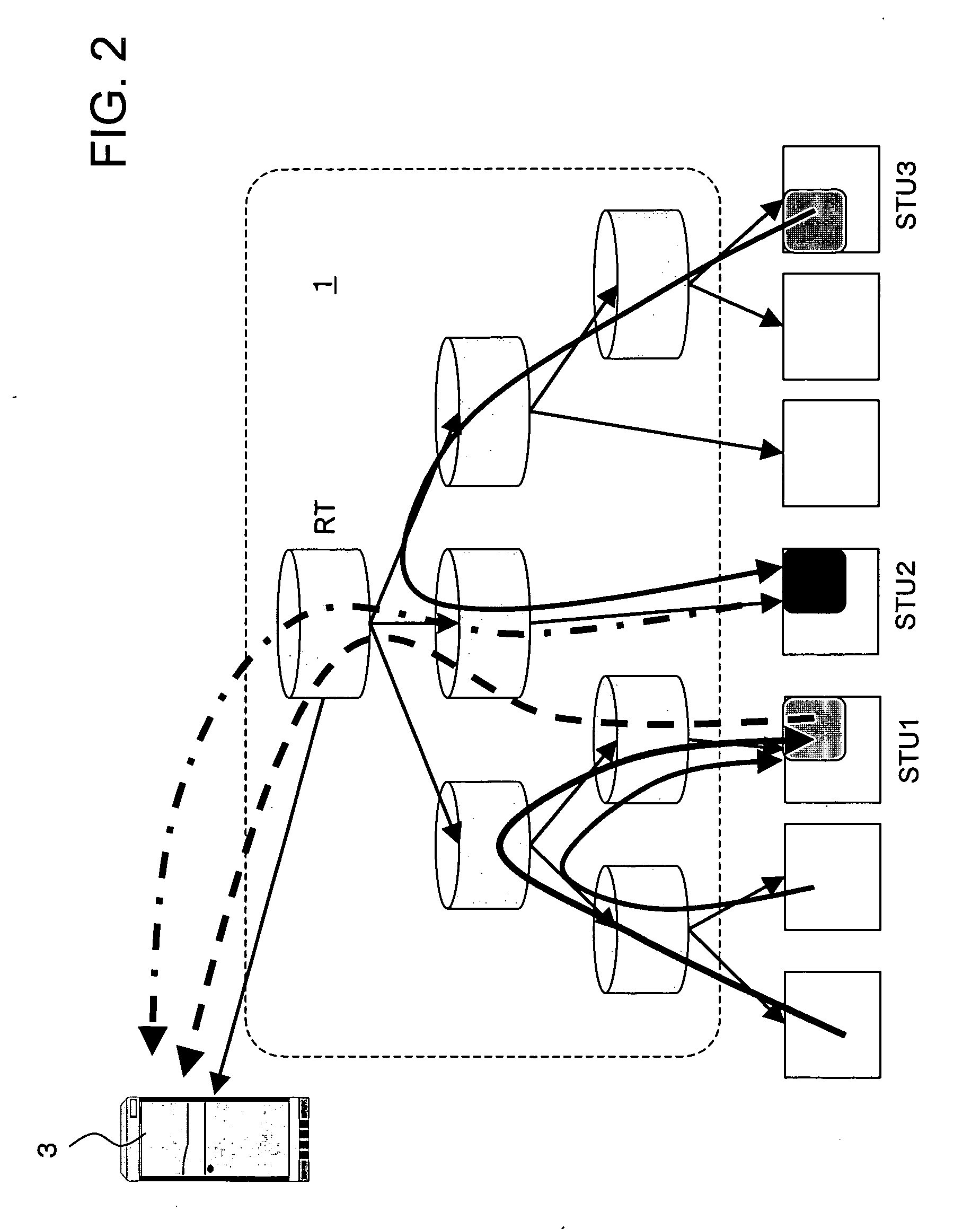
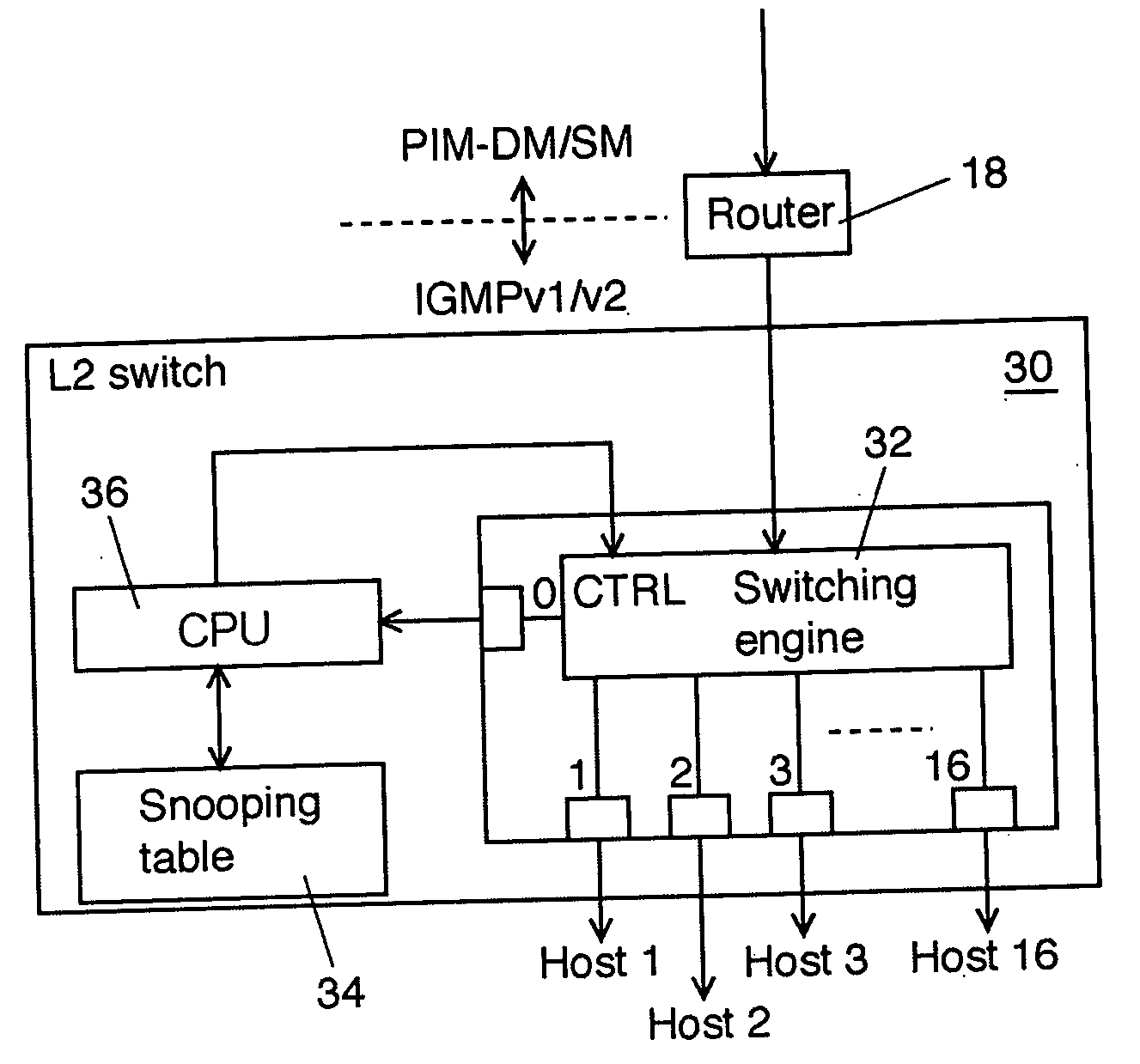
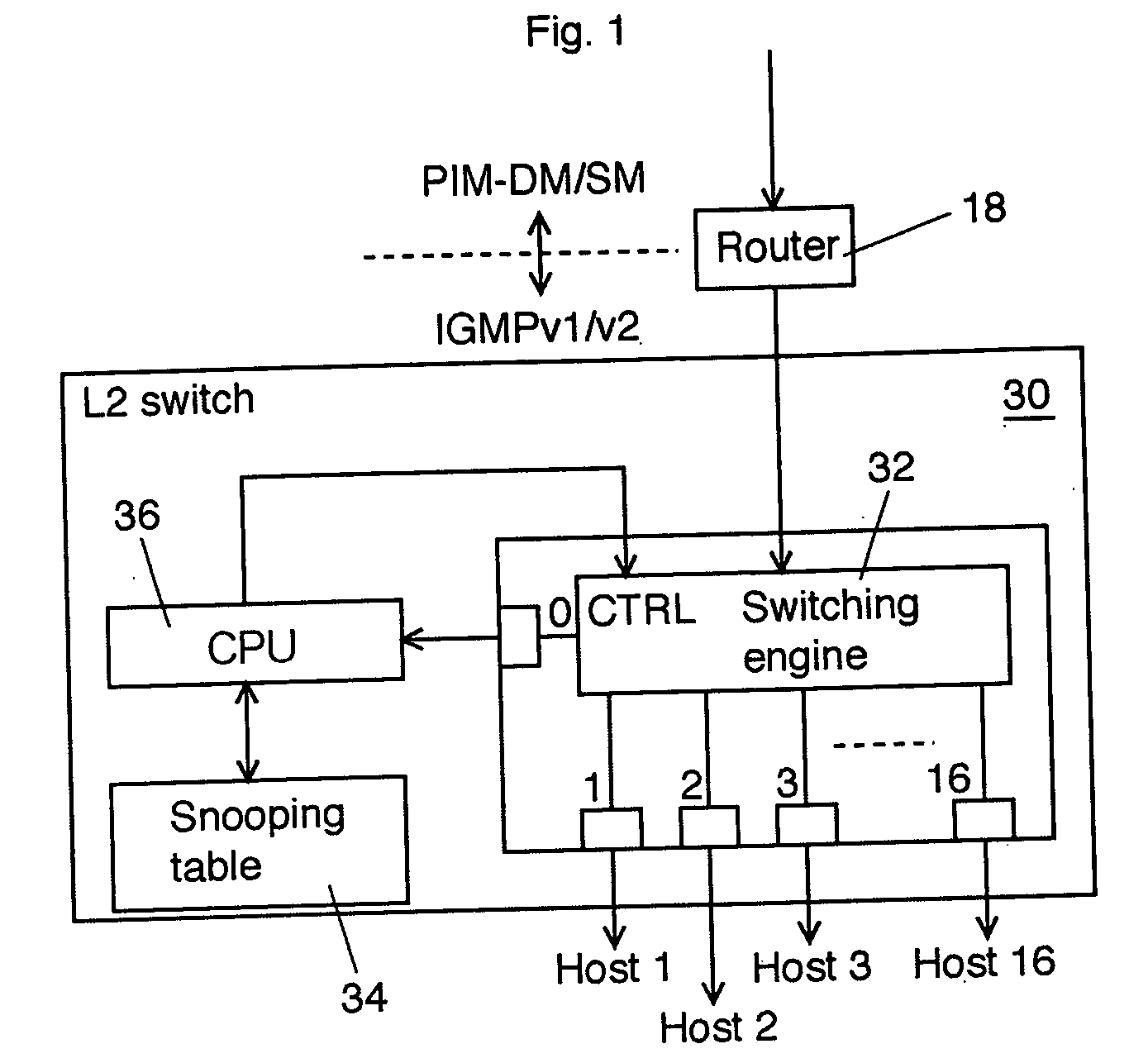
L2 switch and control method therof
InactiveUS20050041680A1Prevent DoS attacksSpecial service provision for substationTime-division multiplexMulticast networkData source
An L2 switch disposed between a multicast network and one or more user systems includes a switching engine having an input port to receive multicasted data from the multicast network and a plurality of output ports, the switching engine capable of delivering at least a part of the multicasted data from at least one of a plurality of data sources in the multicast network to one or more data-destination ports of the plurality of output ports; a transfer table to store corresponding relations between the at least one of the plurality of data sources and the one or more data-destination ports of the plurality of output ports; and a switching controller to update the transfer table according to a predetermined message that passes through the switching engine and to control the delivering of the multicasted data of the switching engine by referring to the transfer table. The switching controller limits a number of the plurality of data sources to be assigned to each output port of the switching engine within a predetermined number and refuses to update the transfer table for a delivery request that exceeds the predetermined number.
Owner:KDDI CORP
Method and system for a Unicast endpoint client to access a Multicast internet protocol (IP) session
InactiveUS20060039388A1Information obtainTime-division multiplexData switching by path configurationClient-sideMulticast network
Unicast endpoint clients (110, 111, 115) on an IP Unicast network (107, 108) are provided access to Multicast sessions on an IP Multicast network (101) through a Multicast-Unicast gateway server (120, 121). The server obtains information about sessions on the Multicast network and makes such information available to a Unicast client on the Unicast network upon request by the client. Upon being presented with a list describing the subject matter of each session, the user at the Unicast client selects the session to which he or she wants to join, which causes the Multicast-Unicast server to join the appropriate session on behalf of the requesting client for each media type in which the joining client wants to be a participant. The server then sets a bi-directional Unicast User Datagram Protocol (UDP) stream between itself and the client. All packets then received by the server from the Unicast client are address-translated to the appropriate Multicast session address. In addition, all packets received by the server on the Multicast session address are address-translated and sent to the Unicast client. The Unicast client is then able to participate in the Multicast session as both a sender and a receiver of packets to and from other Unicast and Multicast clients which are active during the session. Further, the Unicast client is capable of creating a new session, recording a session in the network for later retrieval and playback, and creating and accessing low bandwidth versions of existing sessions.
Owner:AMERICAN TELEPHONE & TELEGRAPH CO
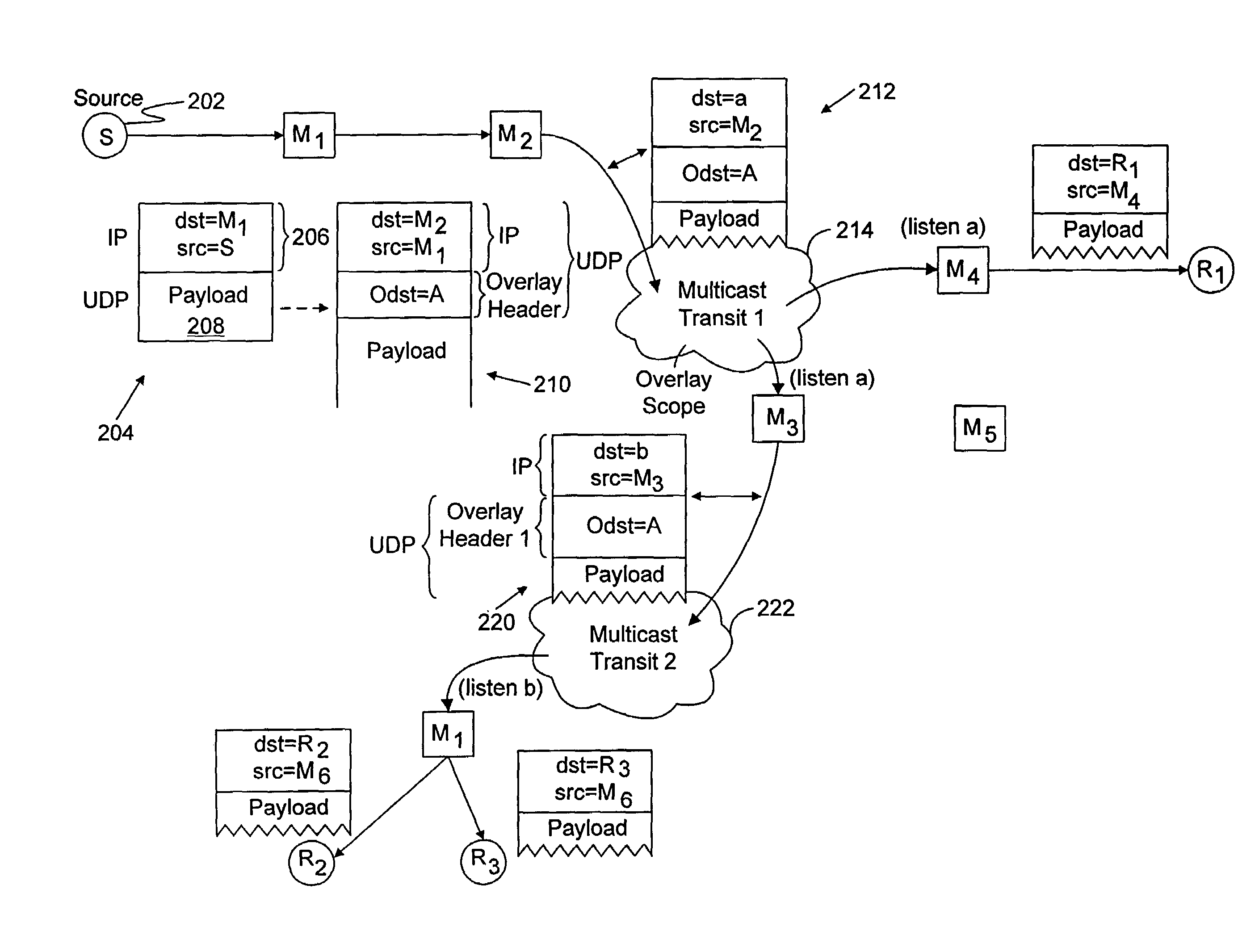
Multicast multipathing in an IP overlay network
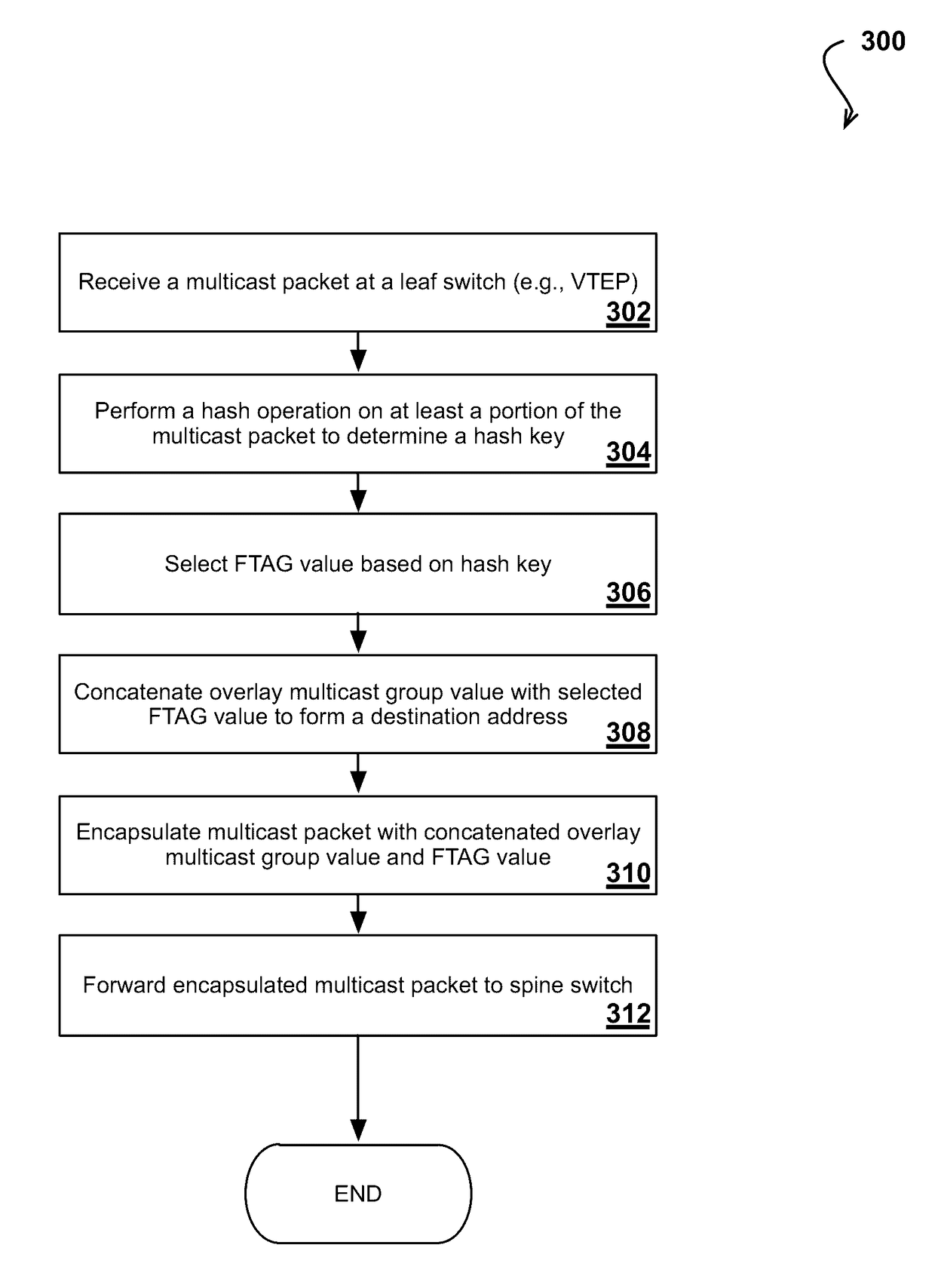
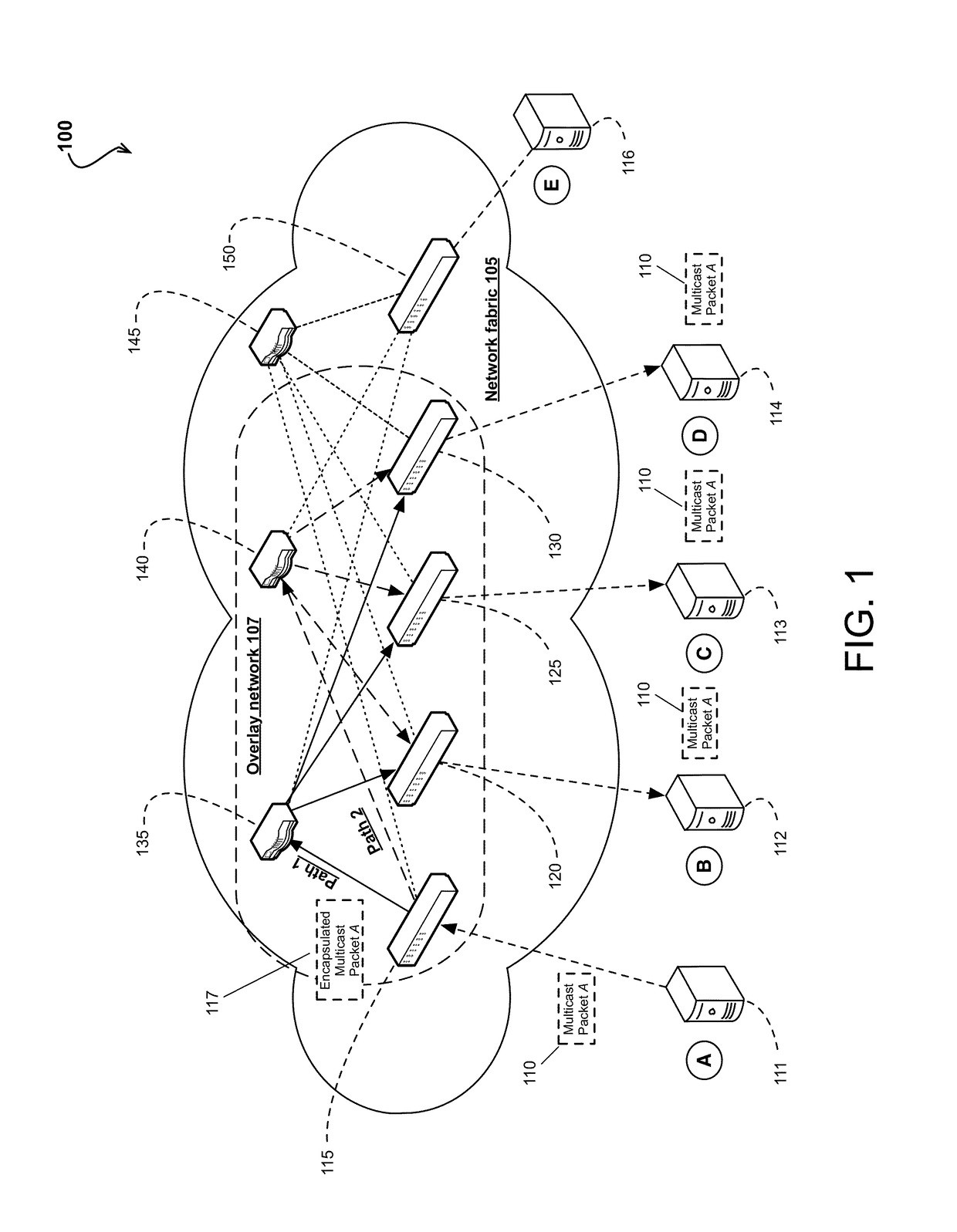
ActiveUS9654385B2Special service provision for substationNetworks interconnectionIP multicastMulticast network
The subject technology addresses the need in the art for improving utilization of network bandwidth in a multicast network environment. More specifically, the disclosed technology addresses the need in the art for extending multipathing to tenant multicast traffic in an IP overlay network, which enables the network to fully utilize available bandwidth for multicast traffic. In some examples, nodes in the overlay network may be connected by virtual or logical links, each of which corresponds to a path, perhaps through many physical links, in the underlying network.
Owner:CISCO TECH INC
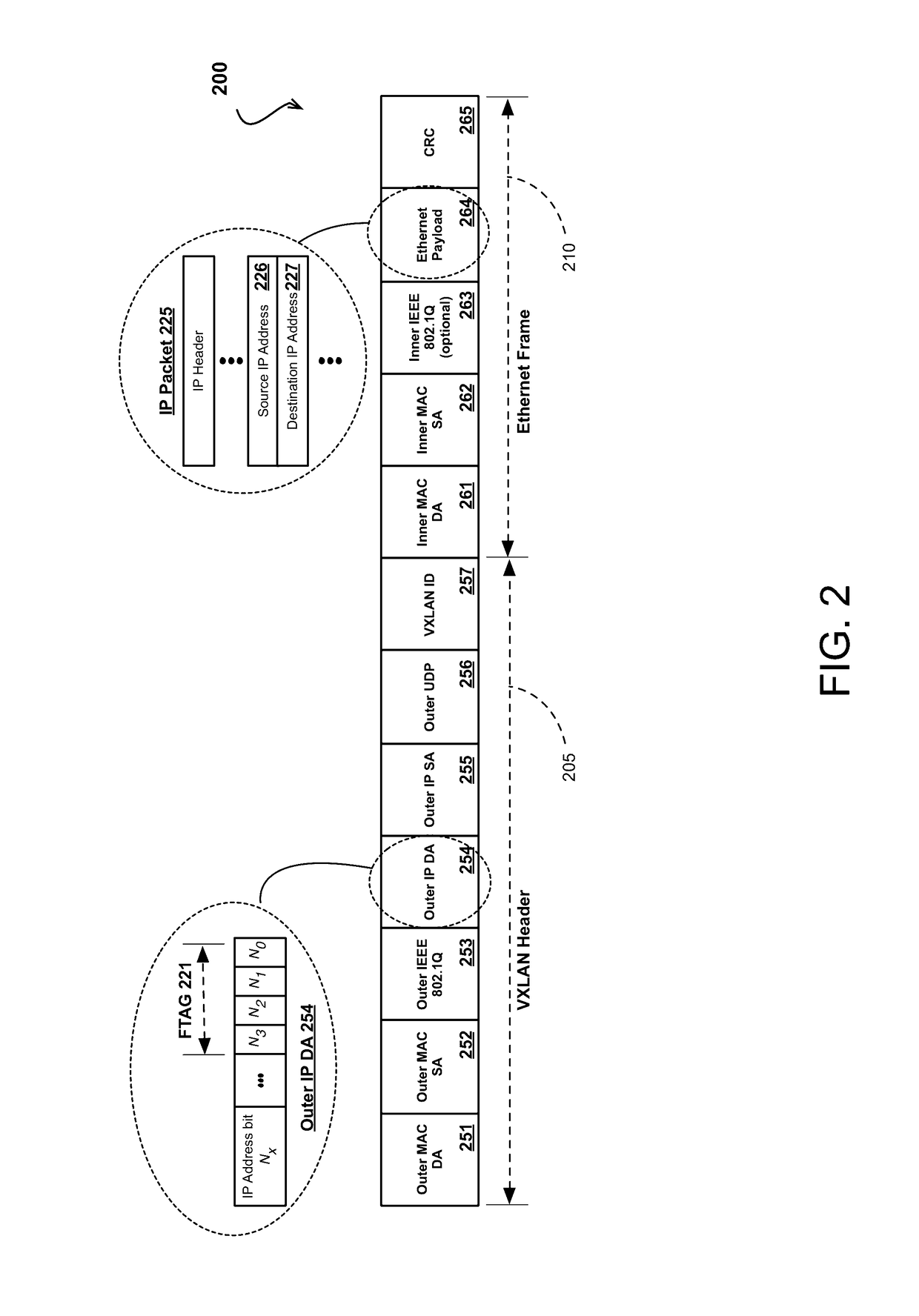
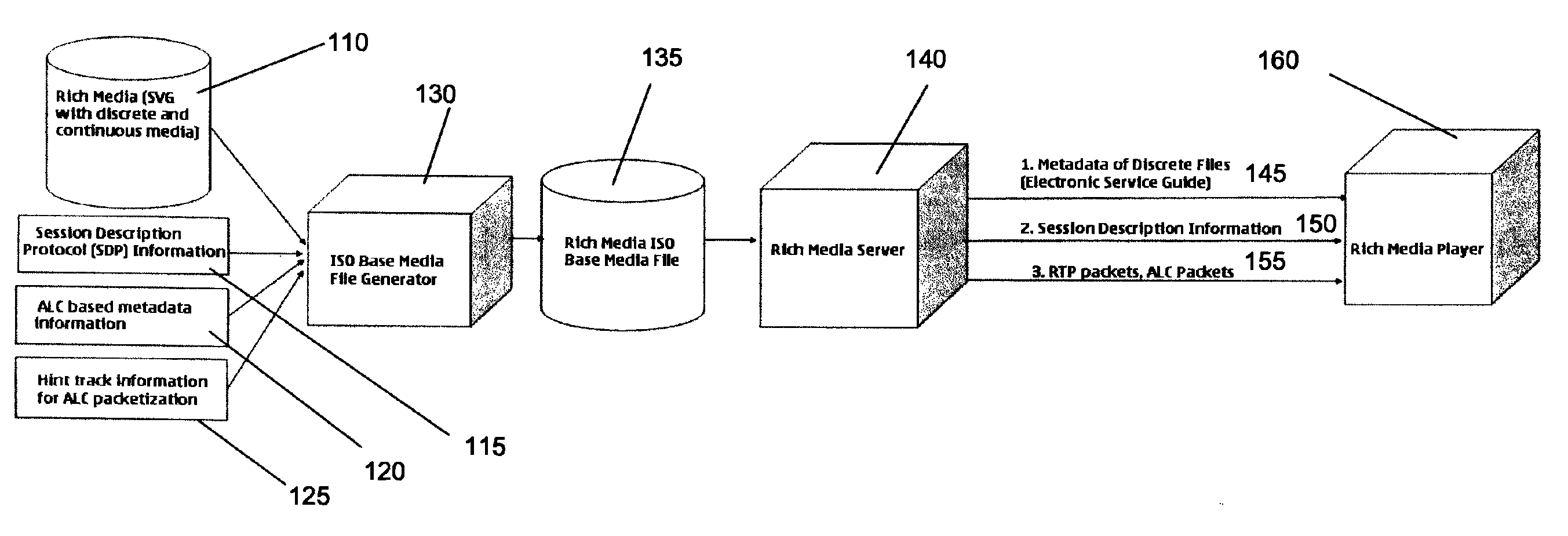
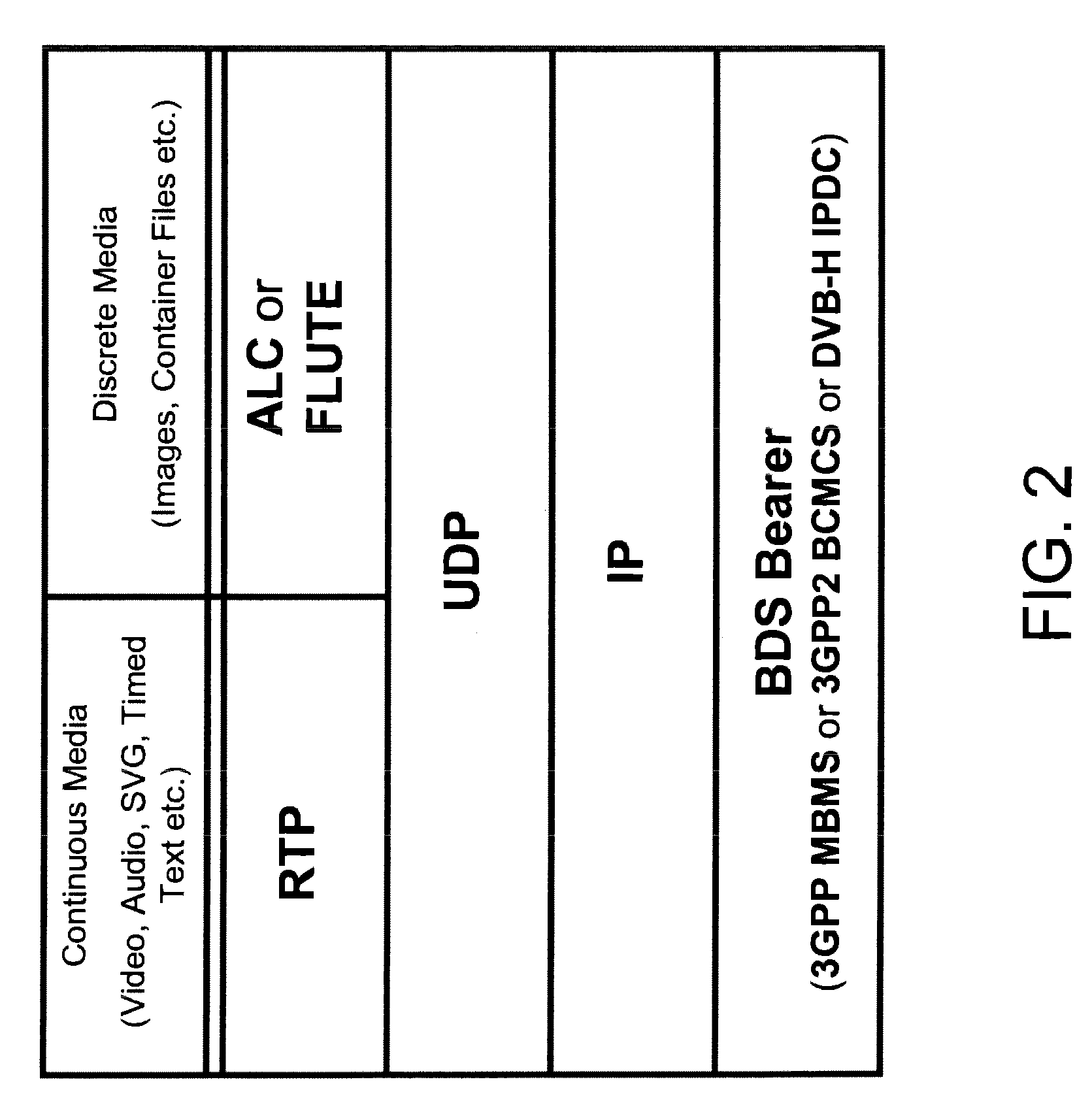
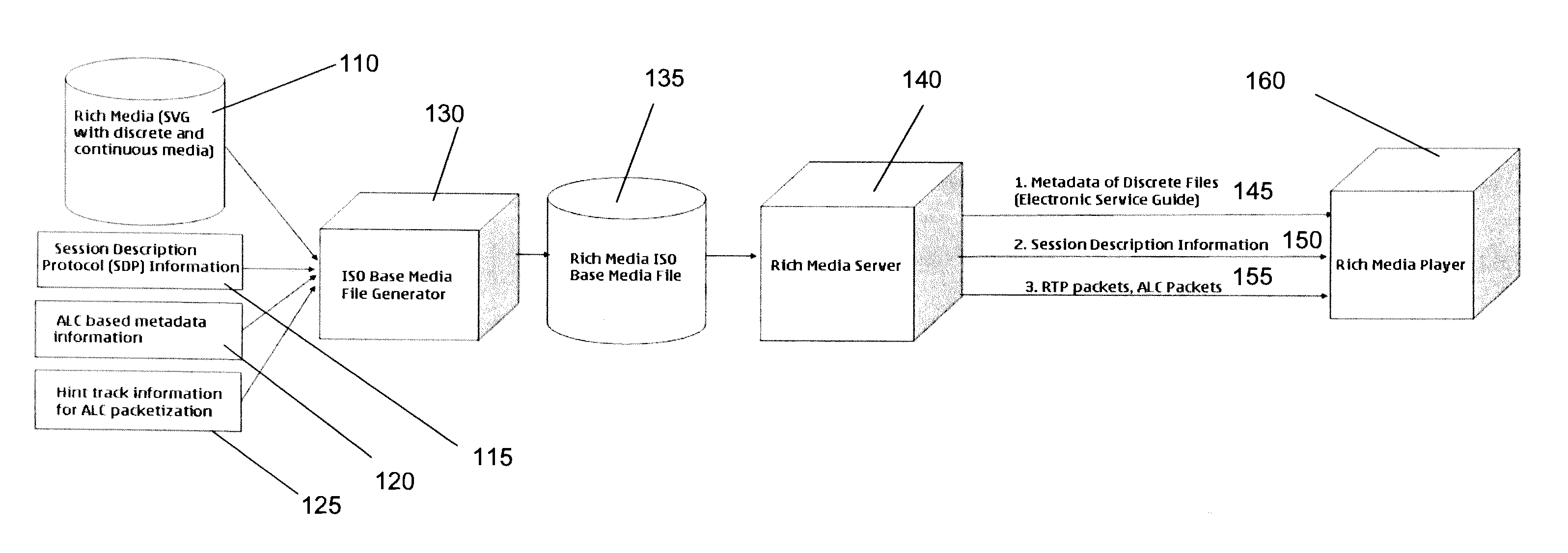
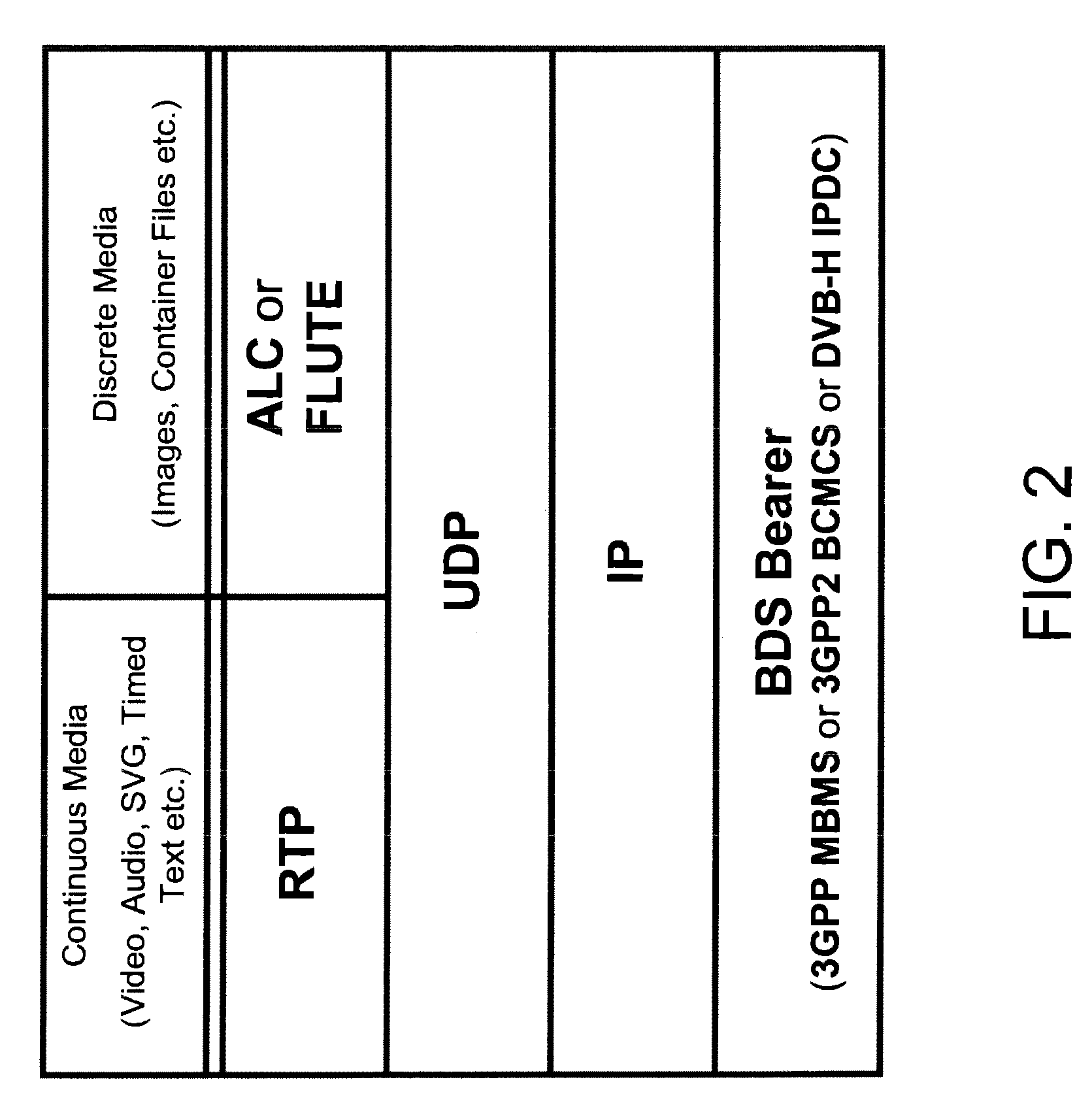
Extensions to rich media container format for use by mobile broadcast/multicast streaming servers
InactiveUS7917644B2Facilitates greater leveragePulse modulation television signal transmissionNetwork traffic/resource managementData feedCartoon animation
An extension to the ISO Base Media File Format to support ALC as a broadcast protocol. The present invention also provides for the extension of the ESG to include metadata specific to the transport of SVG over mobile broadcast / multicast networks. A “BMFDP hint track” is introduced in the container file format, with the required file metadata being in these hint tracks. The present invention can be used in applications such as the preview of long cartoon animations, interactive Mobile TV services, live enterprise data feeds, live chat services, and karaoke programs.
Owner:CORE WIRELESS LICENSING R L
Transmitting data to a group of receiving devices
ActiveUS20060034202A1Multiplex system selection arrangementsSpecial service provision for substationVisibilityCommunications system
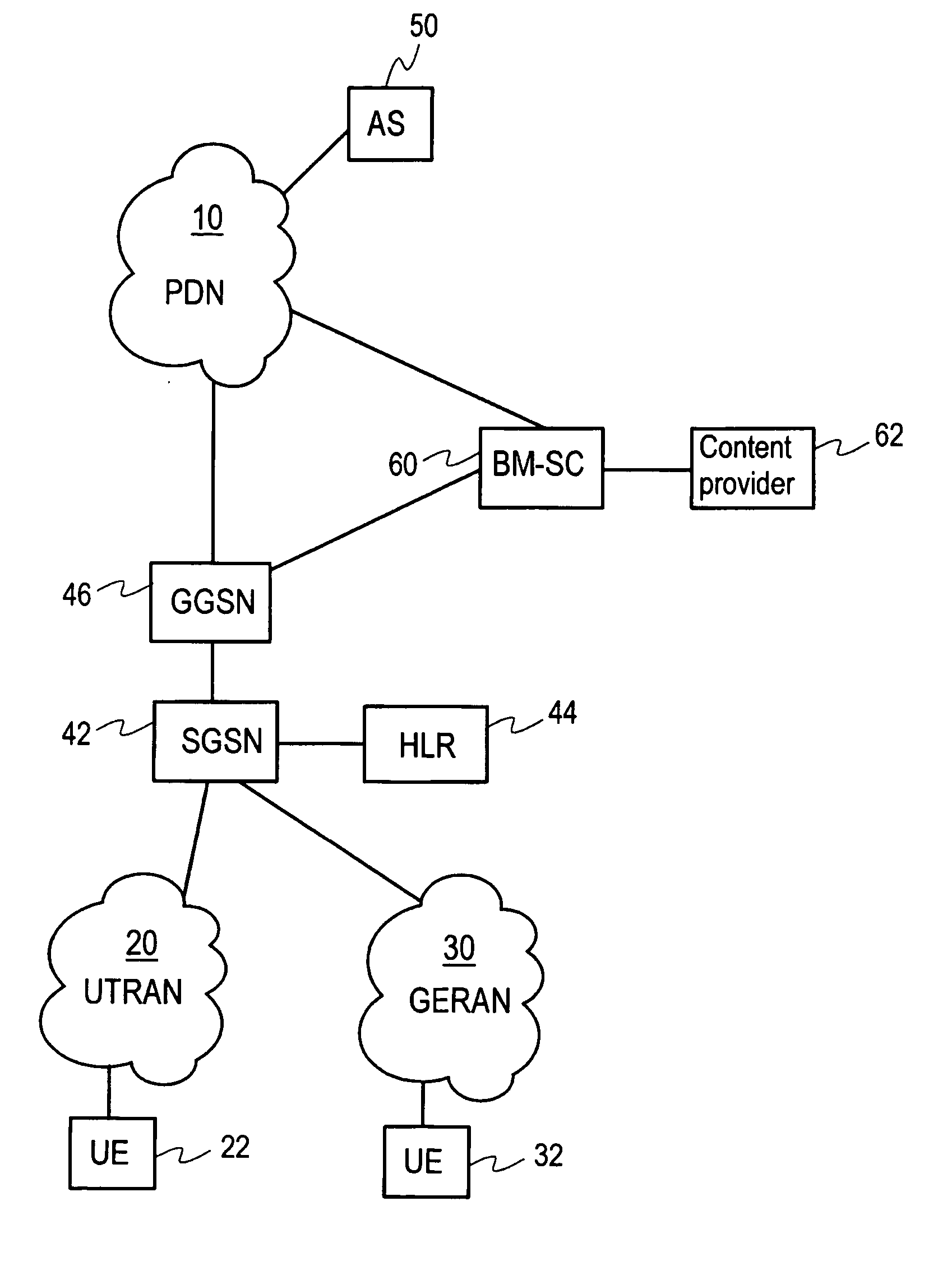
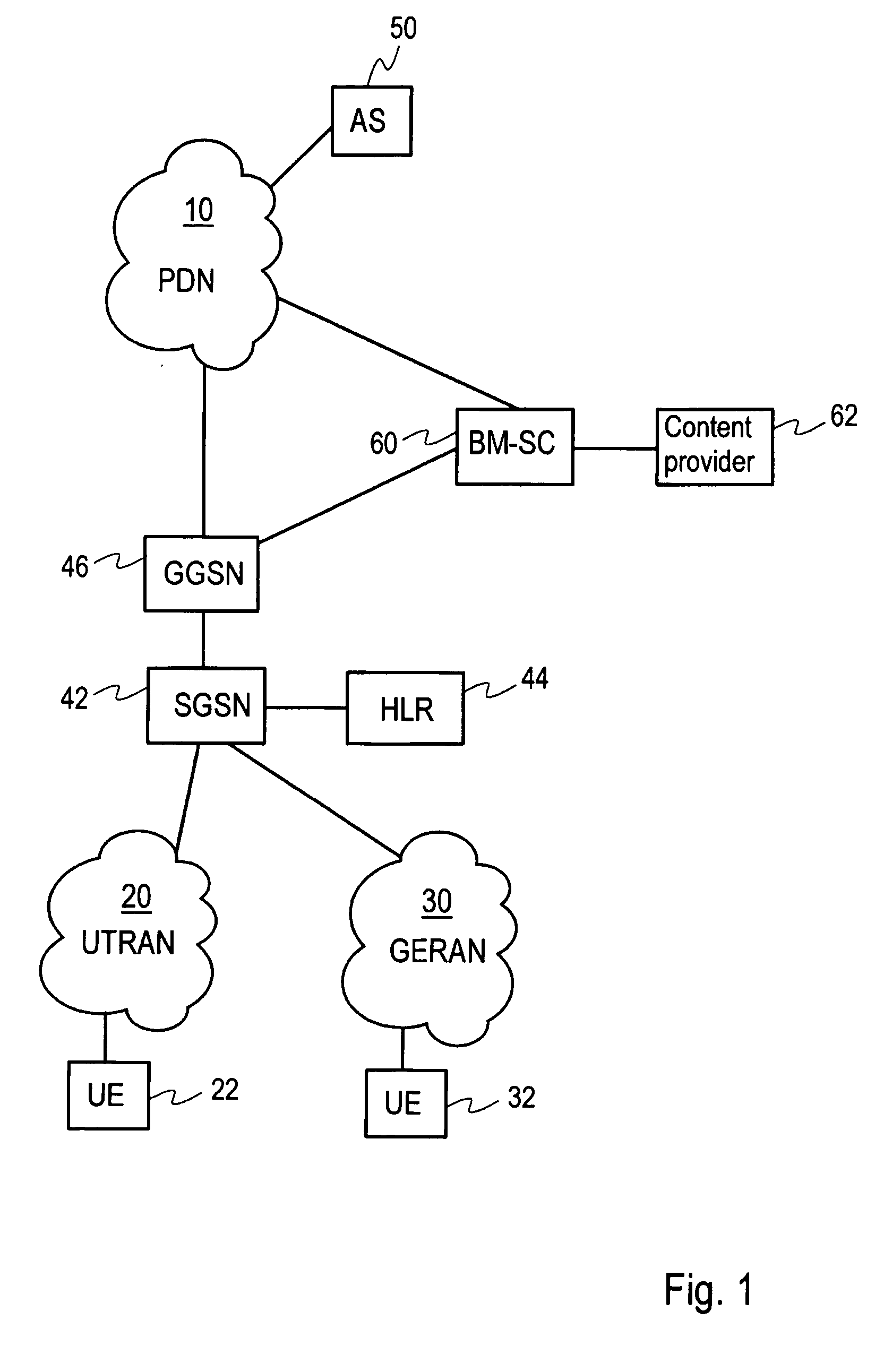
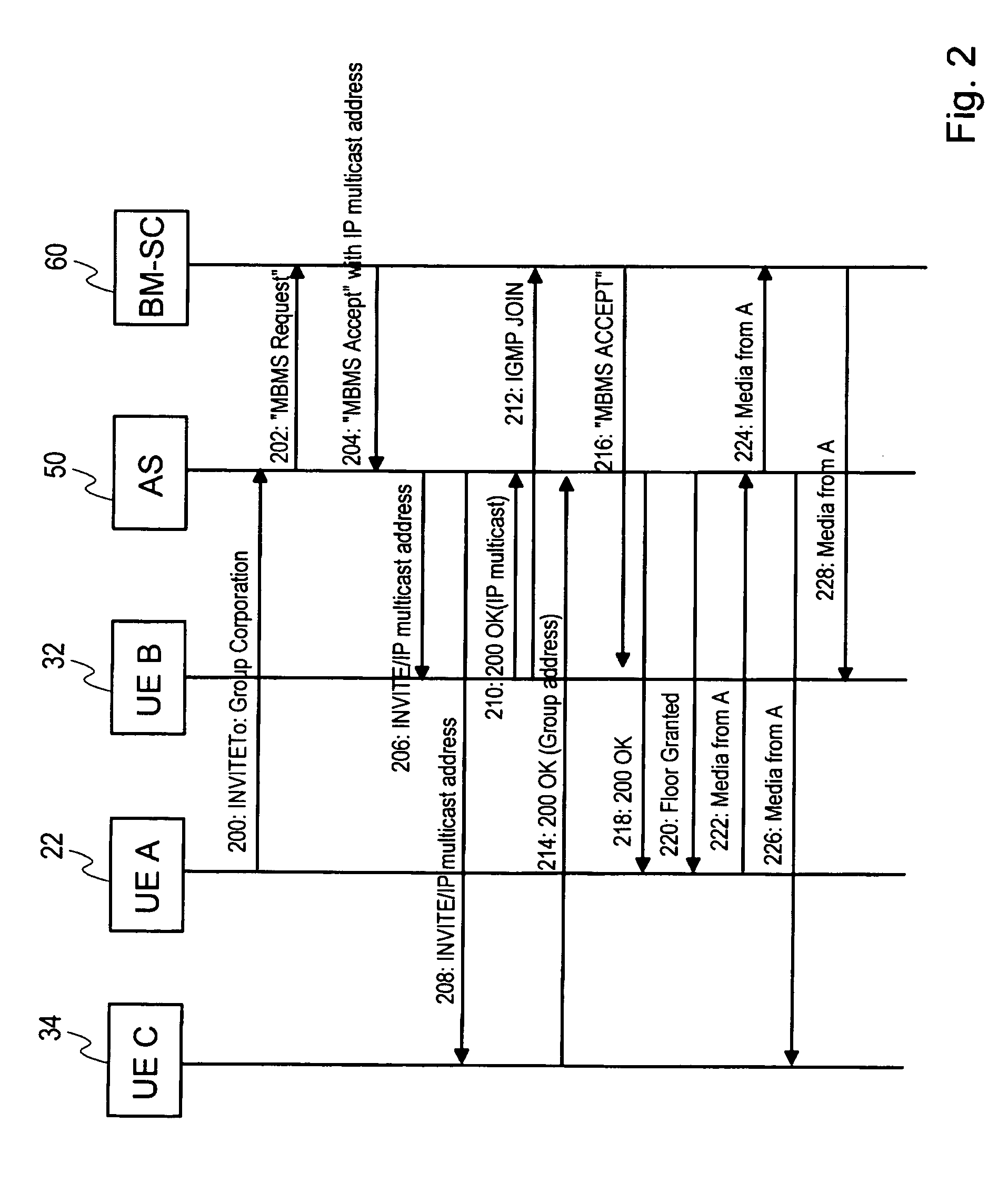
A data transmission method transmits data to a group of receiving communication devices in a communication system comprising at least one cellular network. The method includes defining, by an application server situated beyond a cellular network, a group of receiving communication devices in the cellular network, the application server having no visibility to locations of receiving devices in the cellular network. The method also includes receiving, in a broadcast / multicast network entity configured to provide broadcast and multicast services in the cellular network, data to be transmitted from the application server to the group. The method also includes transmitting the data from the broadcast / multicast network entity to the group using broadcast and / or multicast transmission. Furthermore, a network entity in a cellular network and a communication system are provided configured to implement the method.
Owner:CALLAHAN CELLULAR L L C
Method and system of monitoring the receipt of multicast traffic
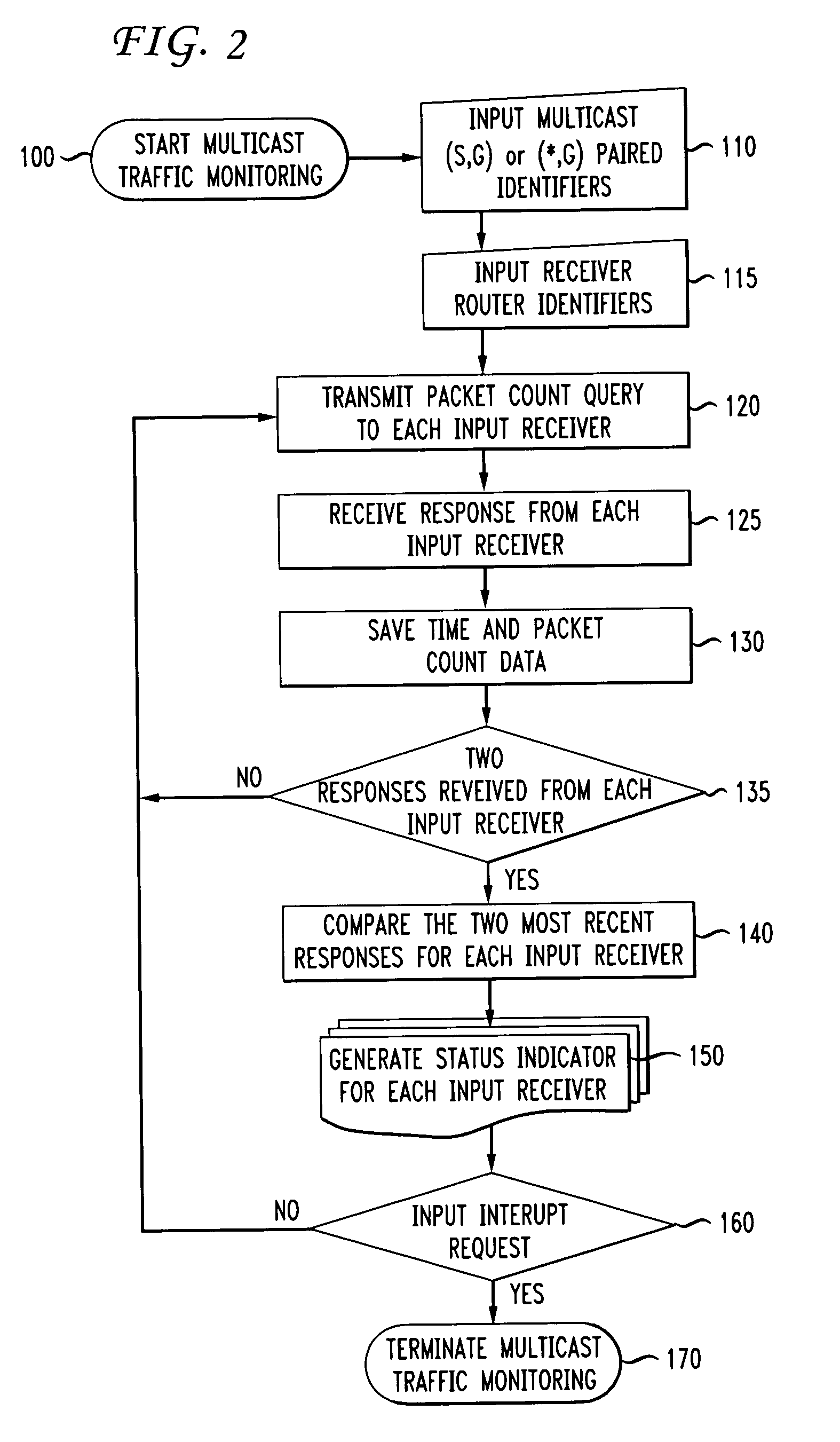
ActiveUS7180856B1Avoid data lossError preventionTransmission systemsTraffic capacityMulticast network
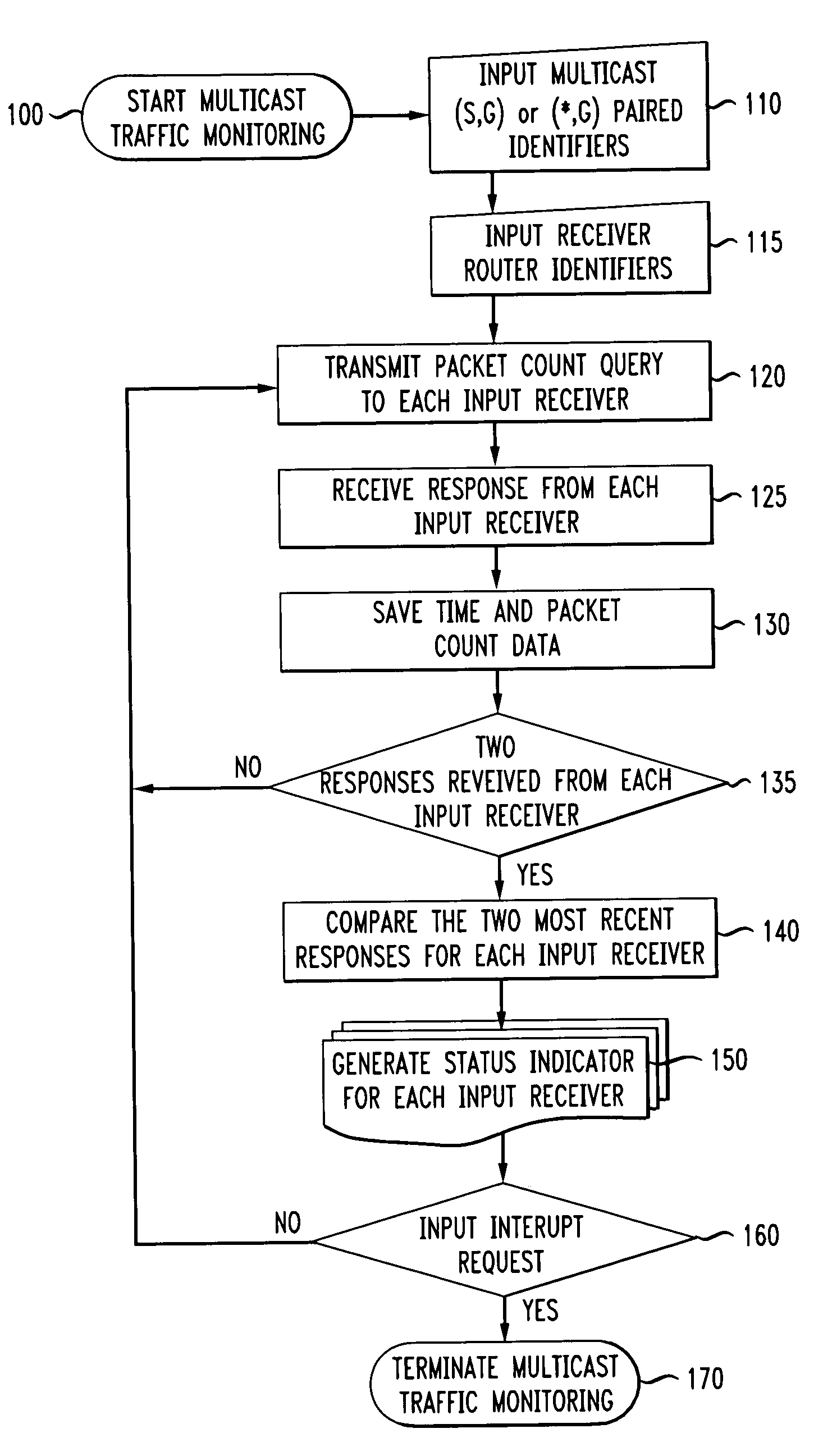
A method of and system for monitoring traffic in a multicast network including determining at a first time a first packet count representing a quantity of packets associated with a multicast group transmitted from at least one source, and received by a router, determining at a second time a second packet count representing a quantity of packets associated with the multicast group, transmitted from the at least one source, and received by the router, the second time being after the first time, comparing the second packet count to the first packet count, and initiating an alarm in response to the second packet count being less than a predetermined value greater than the first packet count. A status for multiple routers can be obtained, comprising a difference between the quantity of the first and second packet counts, and indicating a warning in response to at least one of the plurality of router status being less than the predetermined value.
Owner:AMERICAN TELEPHONE & TELEGRAPH CO
Method and system for controlling the multicast source
ActiveUS20070115975A1Reduce managementReduce maintenance costsSpecial service provision for substationError preventionNetwork terminationControl system
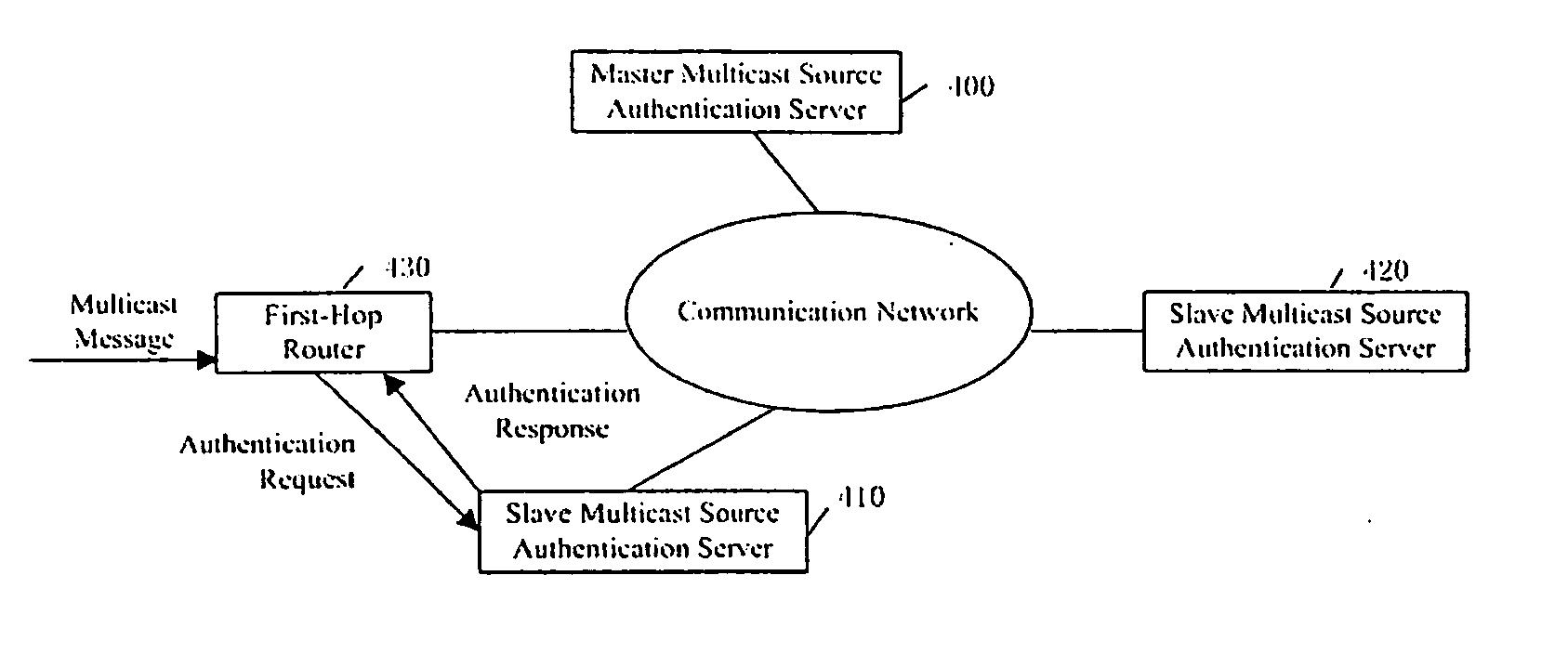
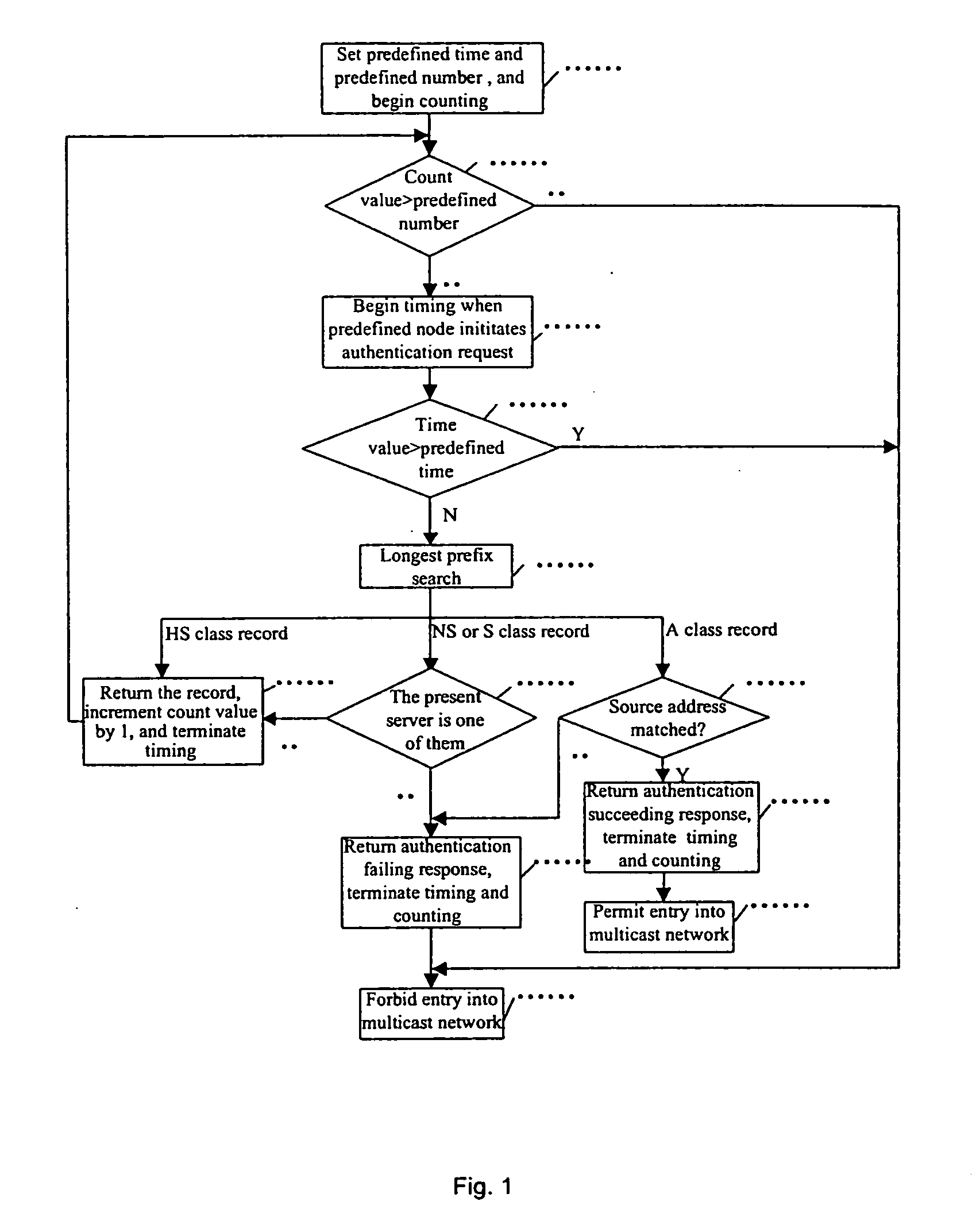
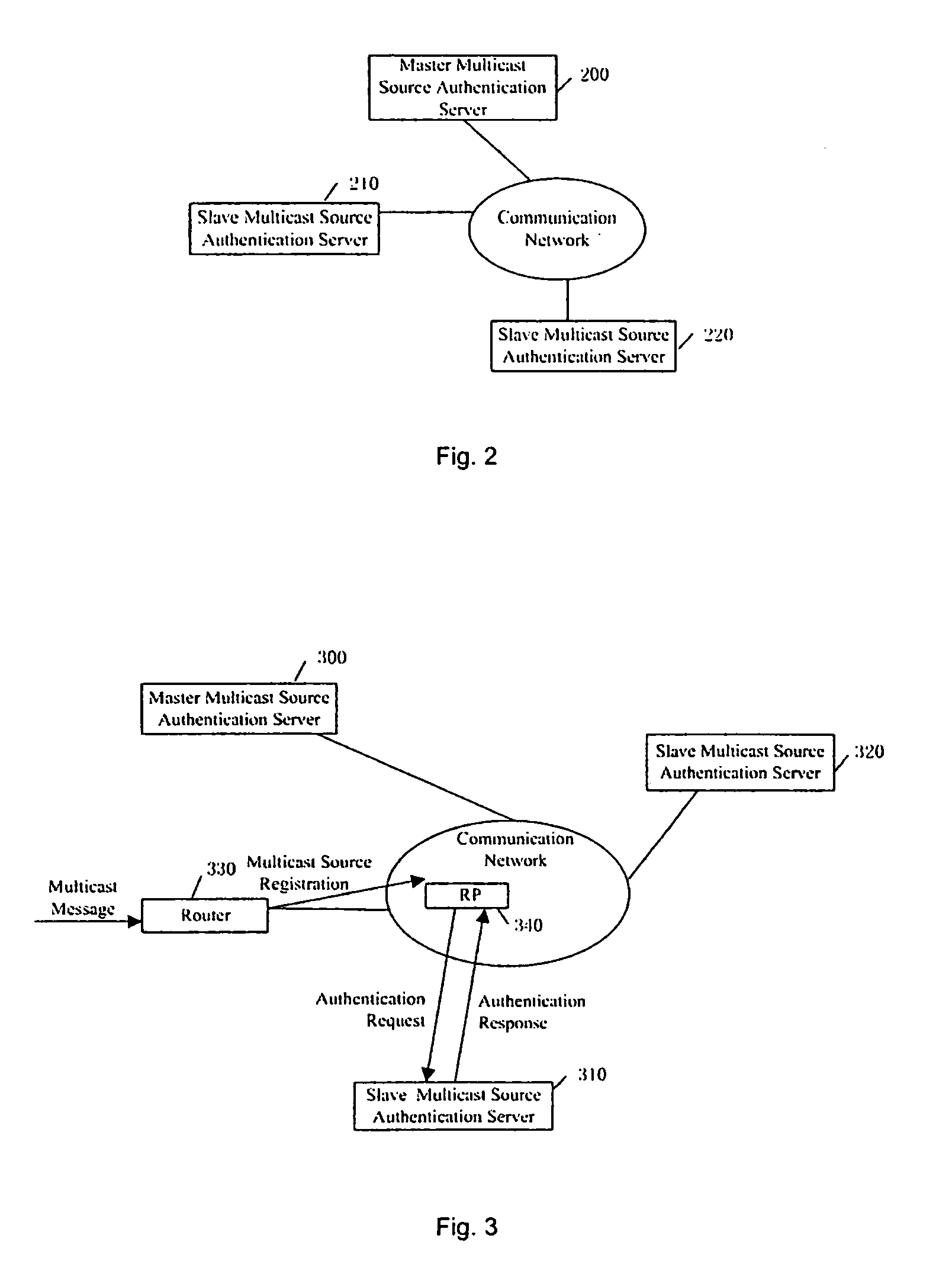
The present invention provides a multicast source control method, which comprises: creating multicast source authentication information; a management platform of the multicast source authentication information dynamically updating said multicast source authentication information in accordance with restriction on multicast source; controlling multicast message sent from the multicast source in accordance with said multicast source authentication information. The present invention also provides a multicast source control system comprising a master multicast source authentication server, a group of slave multicast source authentication servers, and a predefined node. With the present invention, multicast sources can be performed a control management at the earliest time through initiating authentication requests for multicast sources by the predefined node; the network terminal resources are saved through deploying hierarchical distributed multicast source authentication servers to manage different multicast address fields; without manual intervention, the master and slave multicast source authentication servers interact for authentication information periodically and in real time, such that automatic and real time management of multicast sources can be implemented; and thereby the object of reducing management and maintenance cost as well as improving manageability and operability of the multicast network is attained.
Owner:CHENGDU HUAWEI TECH
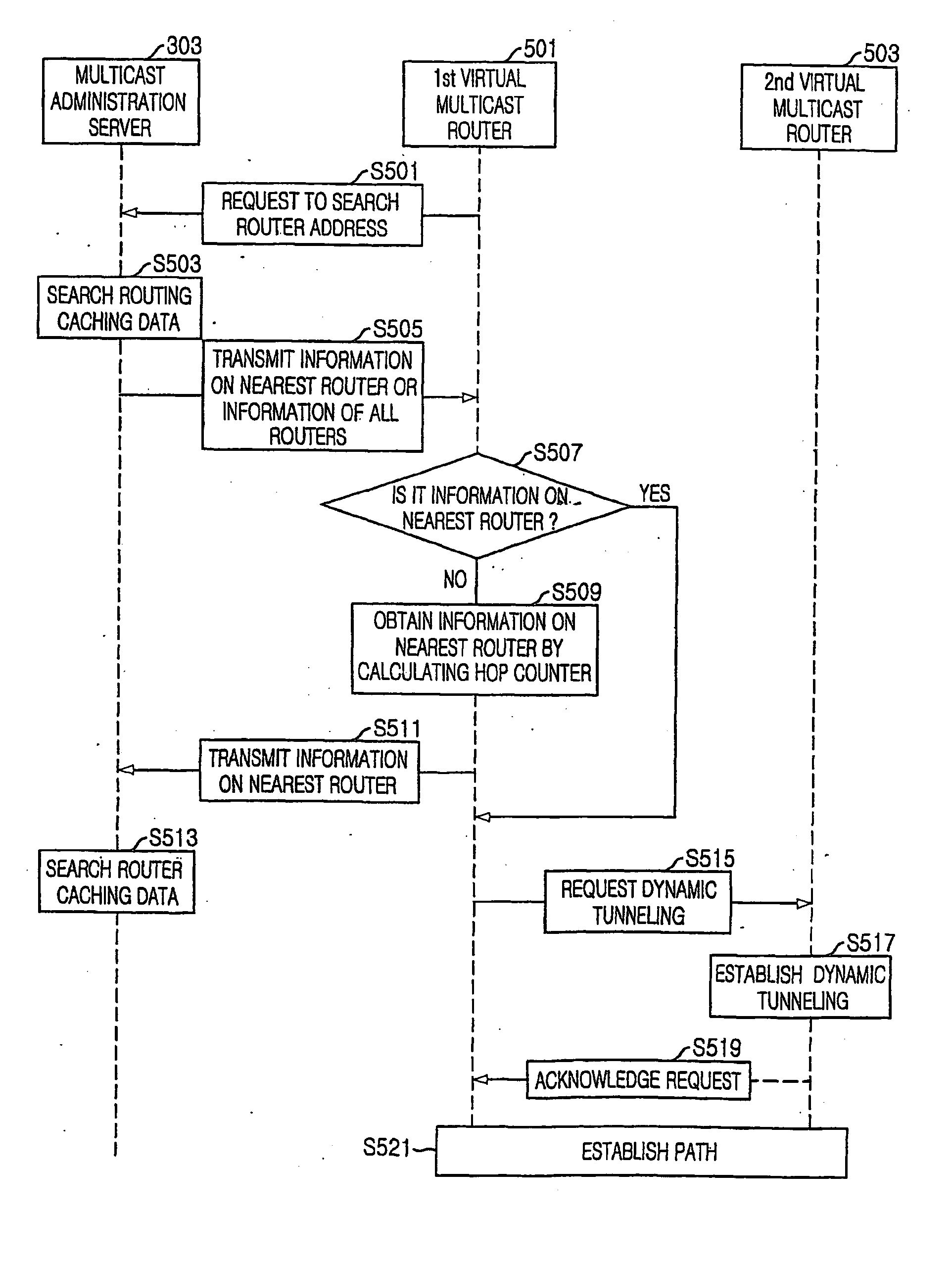
Method and system for virtual multicast networking
InactiveUS20050076207A1Special service provision for substationDigital computer detailsIp addressMulticast network
Method and system for virtual multicast networking, which can provide multicasting application service on non-multicast network that does not support multicast, are provided. A virtual multicast networking system for providing virtual multicast network on network environment where a multicast data source network to which multicast data source server is connected is linked through backbone network to non-multicast network that does not support multicast and to which a client is connected, the virtual multicast networking system includes: virtual multicast router system, included in the non-multicast network, for routing or relaying multicast data through tunnelling to multicast router or the nearest virtual multicast router system; multicast agent system, mounted on the client, for receiving the multicast data through tunnelling to the nearest virtual multicast router system, and transmitting the received multicast data to application program mounted on the client; and multicast management system, included in the multicast data source network, for managing the IP address of the virtual multicast router system and transmitting the IP address information of the virtual multicast router system to the virtual multicast router system or the multicast agent system.
Owner:ZOOINNET +2
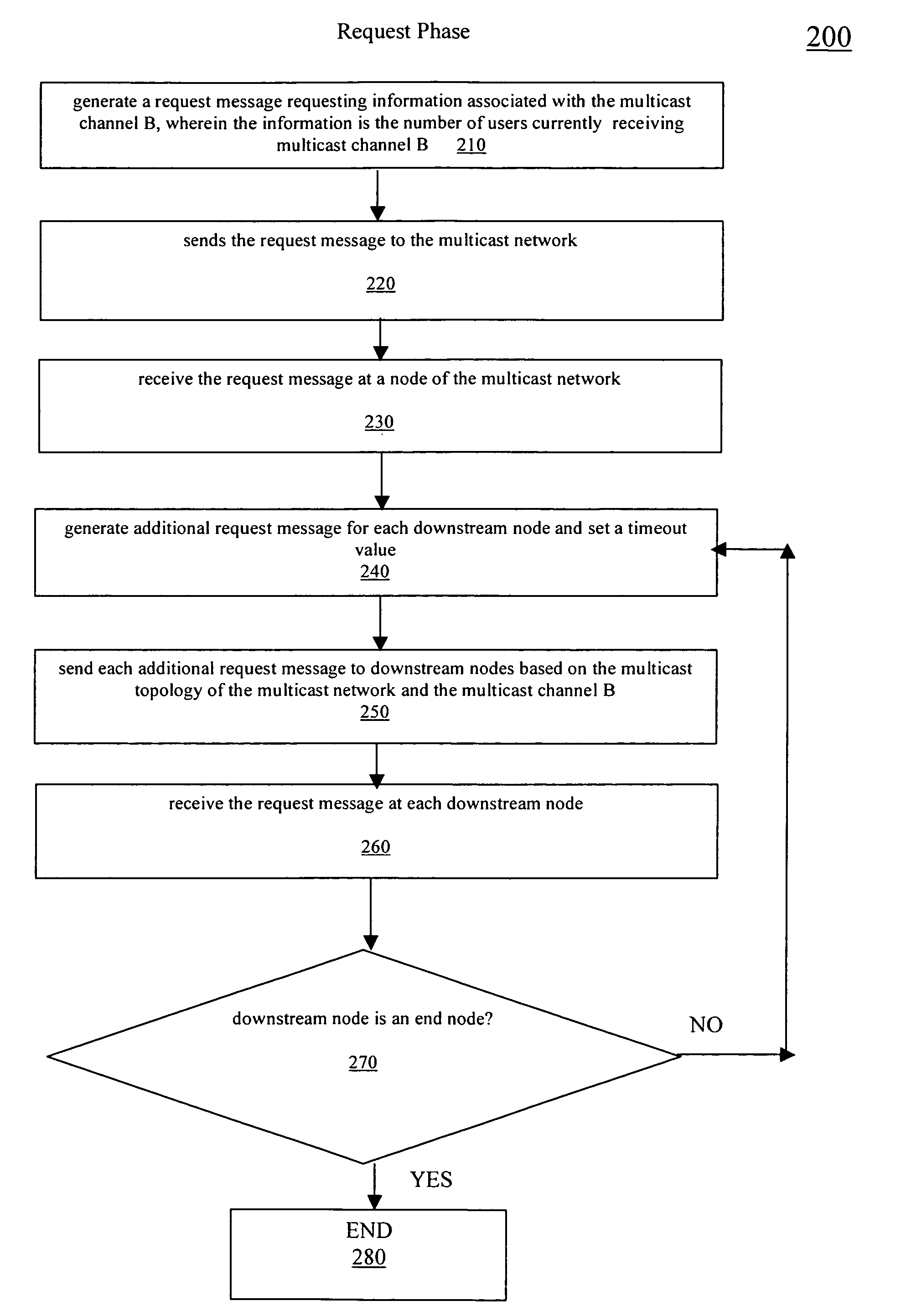
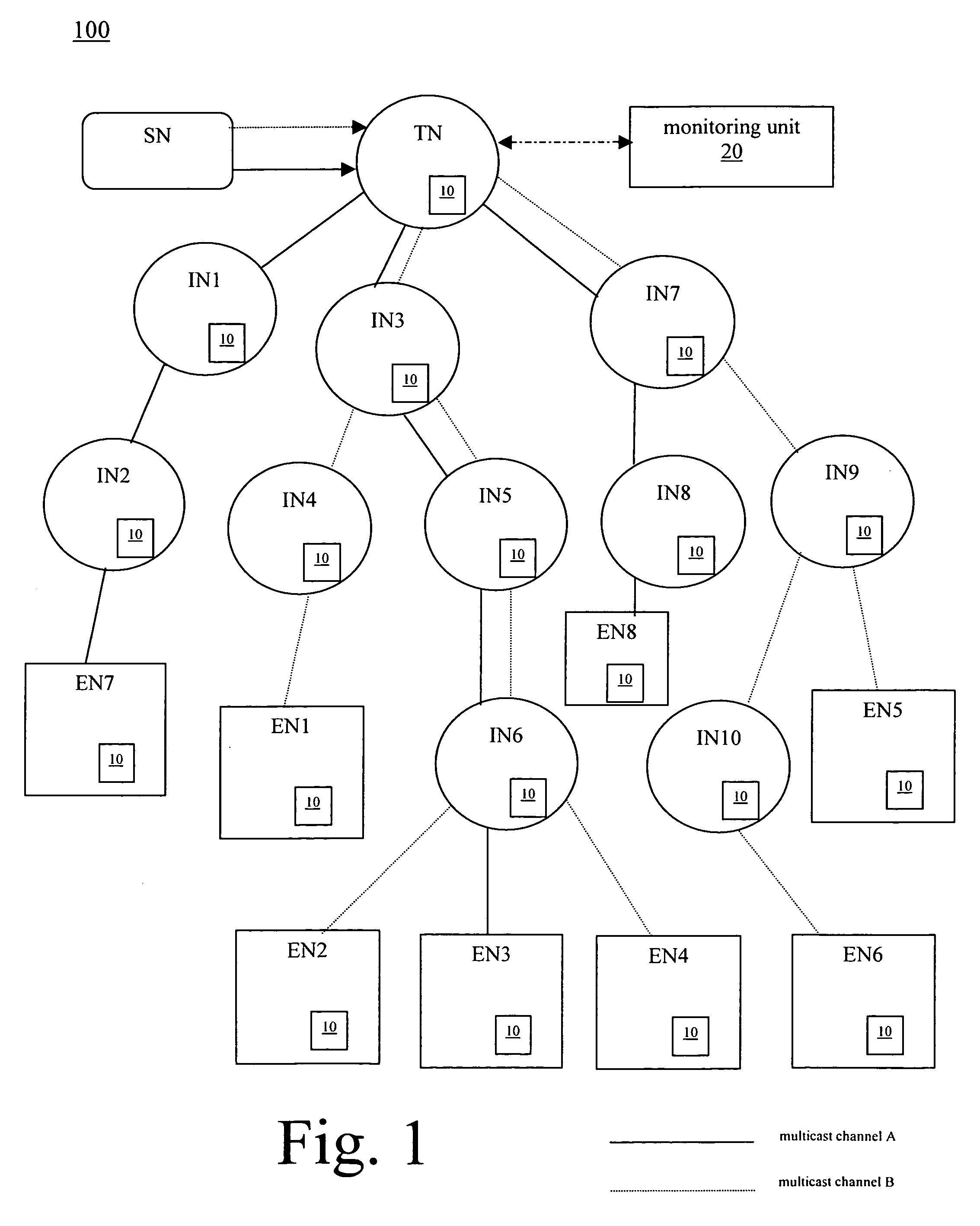
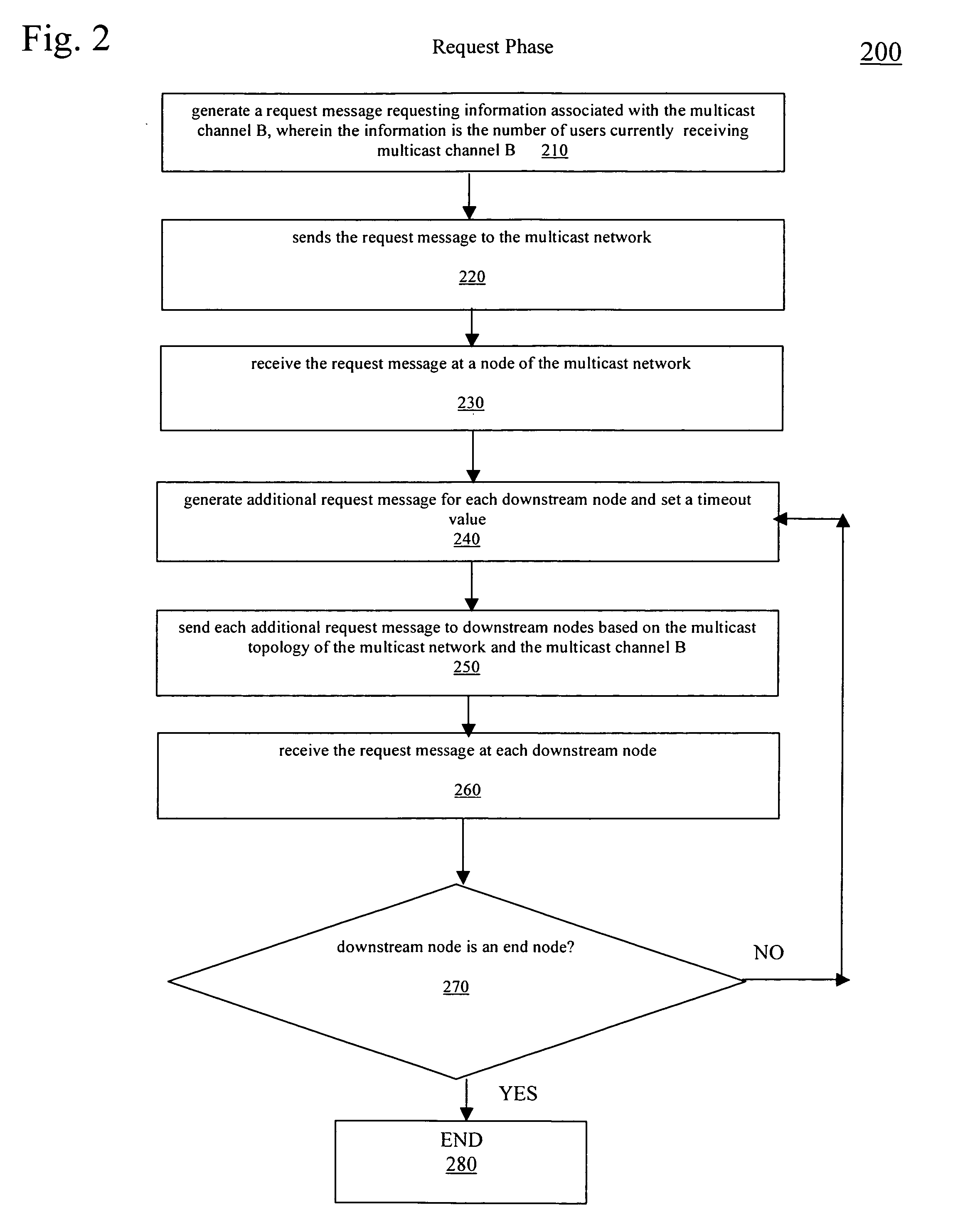
Method and apparatus for determining information associated with a particular multicast channel in a multicast network
ActiveUS20060239289A1Multiplex system selection arrangementsBroadcast transmission systemsComputer networkMulticast network
A method and apparatus for determining information associated with a particular multicast channel in a multicast network are disclosed. In accordance with the method, a request message requesting information associated with the particular multicast channel is generated and sent to the multicast network. Further, the request message is propagated downstream in a recursive manner via a multicast topology of the multicast network. A response to the request message is propagated upstream via the multicast topology to generate a response message including requested information associated with the particular multicast channel. The information may comprise number of users receiving the particular multicast channel.
Owner:SYNAMEDIA LTD
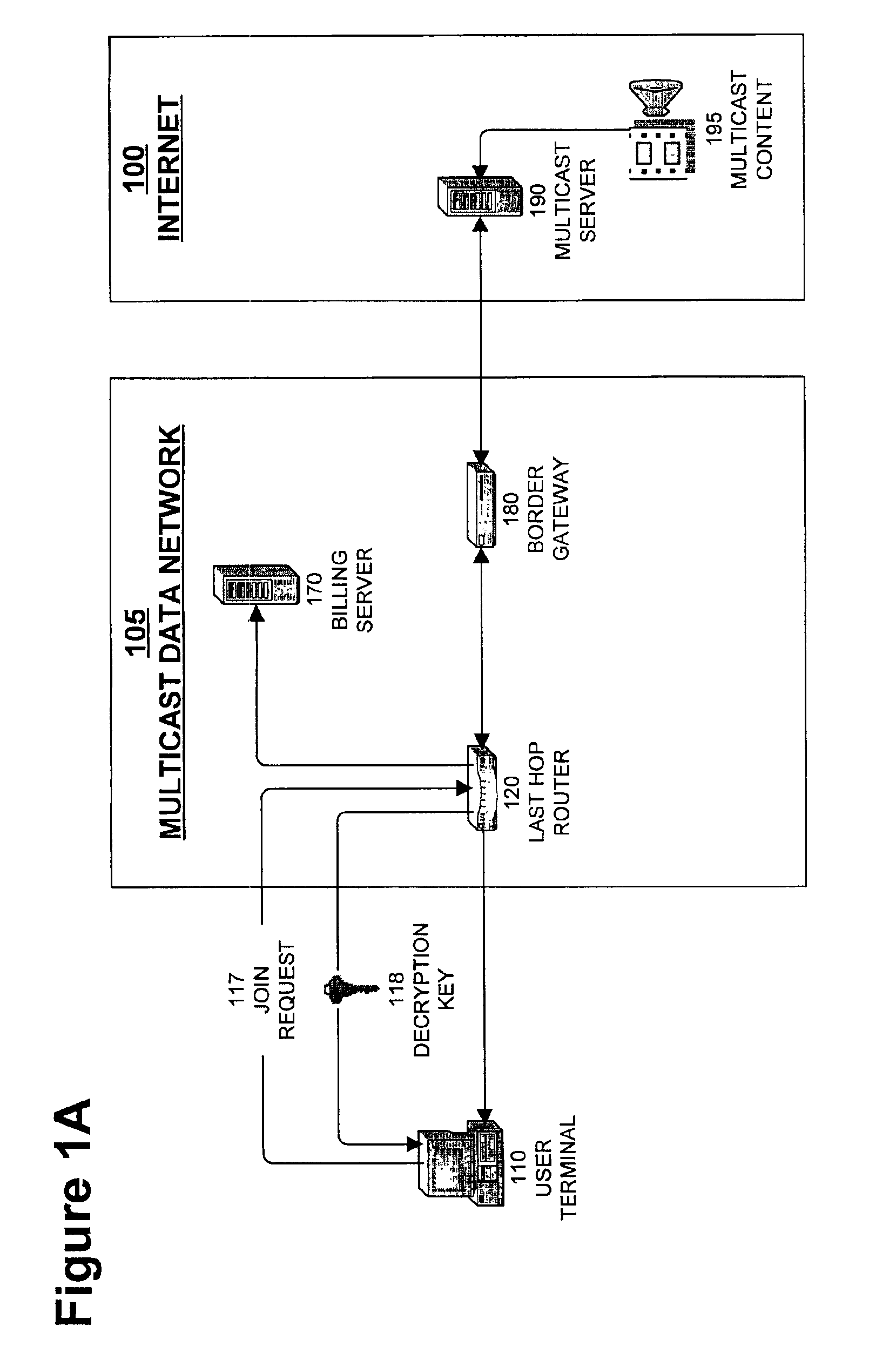
Charging mechanism for multicasting
InactiveUS6965883B2Special service provision for substationTicket-issuing apparatusComputer networkStart time
An apparatus for calculating a cost of receiving multicast data from a multicast session. A multicast network includes at least one multicast service, each multicast service including at least one multicast session. The apparatus receives a request to establish a connection to the multicast session, stores a start time for the connection and an end time for the connection and, after termination of the connection, calculates the cost of receiving the multicast data The apparatus can receive a subsequent request to extend the connection, the subsequent request specifying a new end time for the connection, and store the new end time for the connection. Alternatively, the apparatus can receive a subsequent request to terminate the connection, the subsequent request specifying a new end time that precedes the end time for the connection, and store the new end time for the connection.
Owner:NOKIA TECHNOLOGLES OY
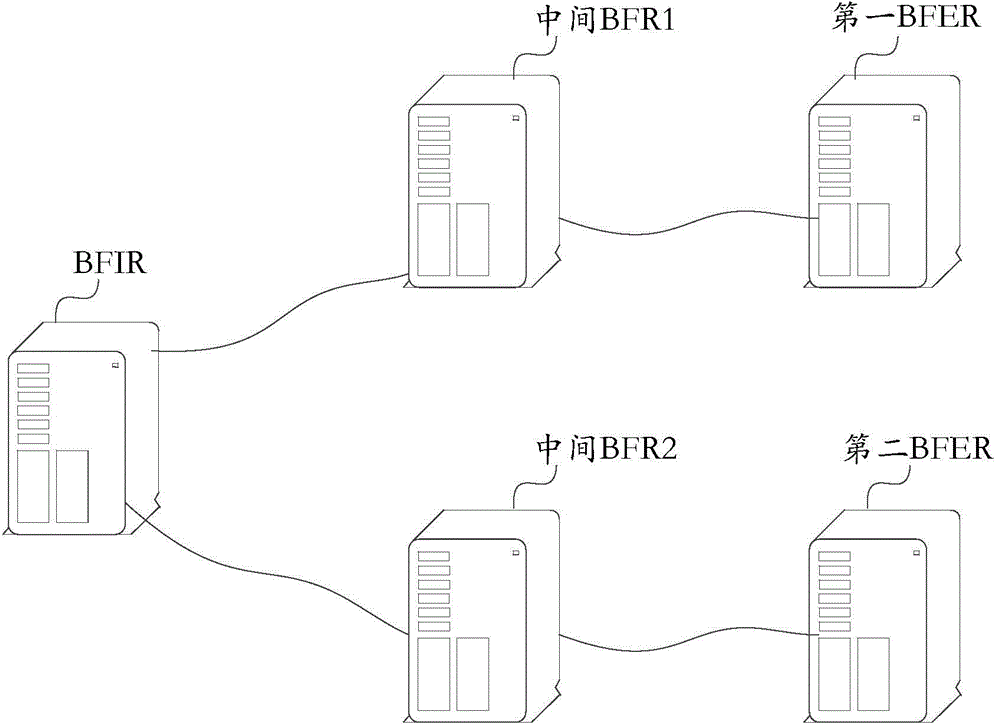
Bit-forwarding ingress router, bit-forwarding router and operation administration maintenance detection method
ActiveCN105812197ASave resourcesImprove detection efficiencySpecial service provision for substationMulticast networkEgress router
The invention provides a bit-forwarding ingress router (BFIR), a bit-forwarding router (BFR) and an operation administration maintenance (OAM) detection method and belongs to the multicast network field. An OAM request message from the BFIR is received through a first BFR; a target BFR corresponding to the OAM request message is determined by the first BFR to be the first BFR according to the OAM request message; a first OAM response message is acquired by the first BFR according to the ID of the BFIR, and the first OAM response message is sent to the BFIR. Through the method and the device, a problem that a transmission fault generated in a transmission process of a multicast message can not be diagnosed or processed by the BFIR can be solved, connectivity detection can be facilitated through the OAM message, and detection on multiple bit-forwarding egress routers (BFER) can be realized.
Owner:HUAWEI TECH CO LTD
A robust point to point based stream scheduling method
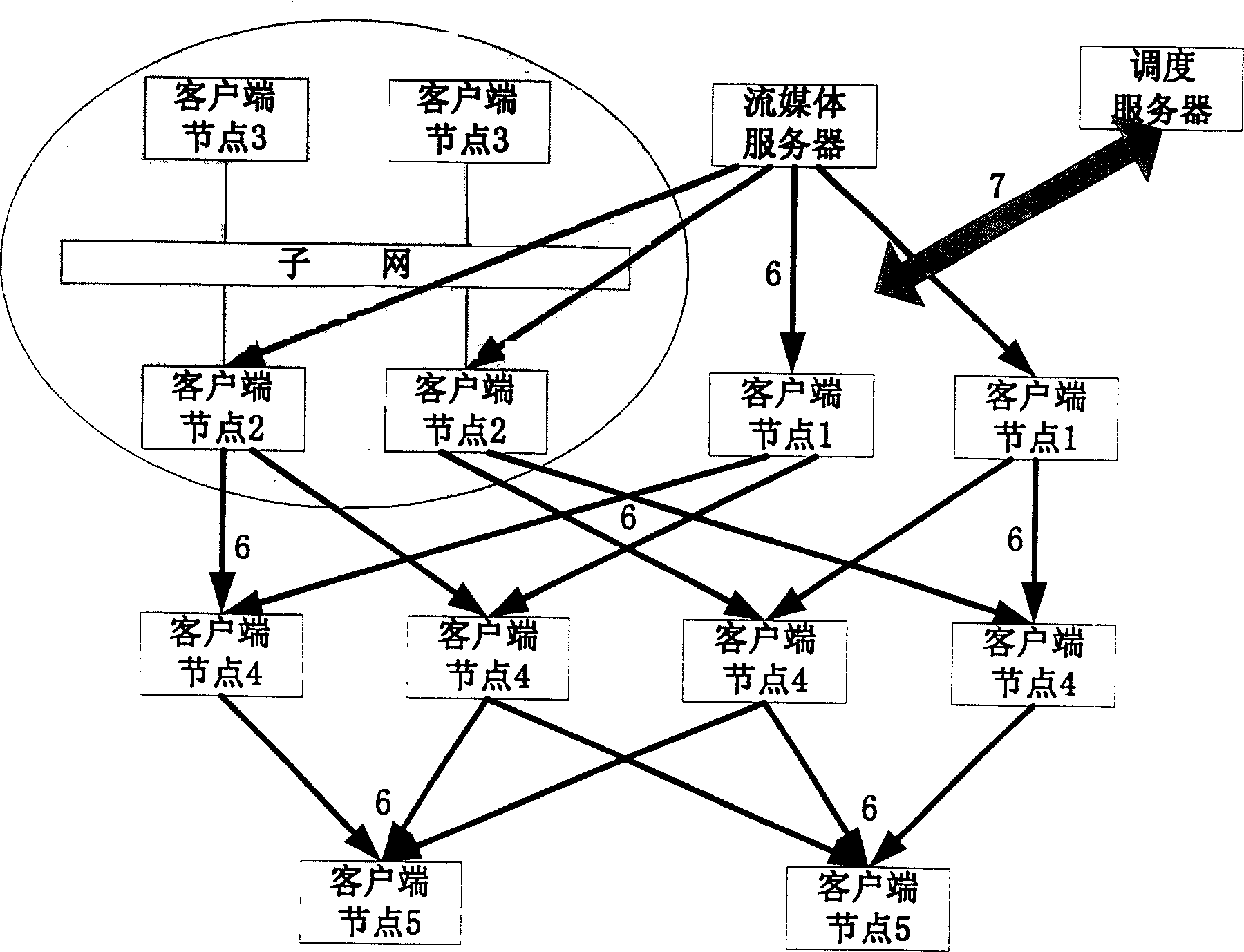
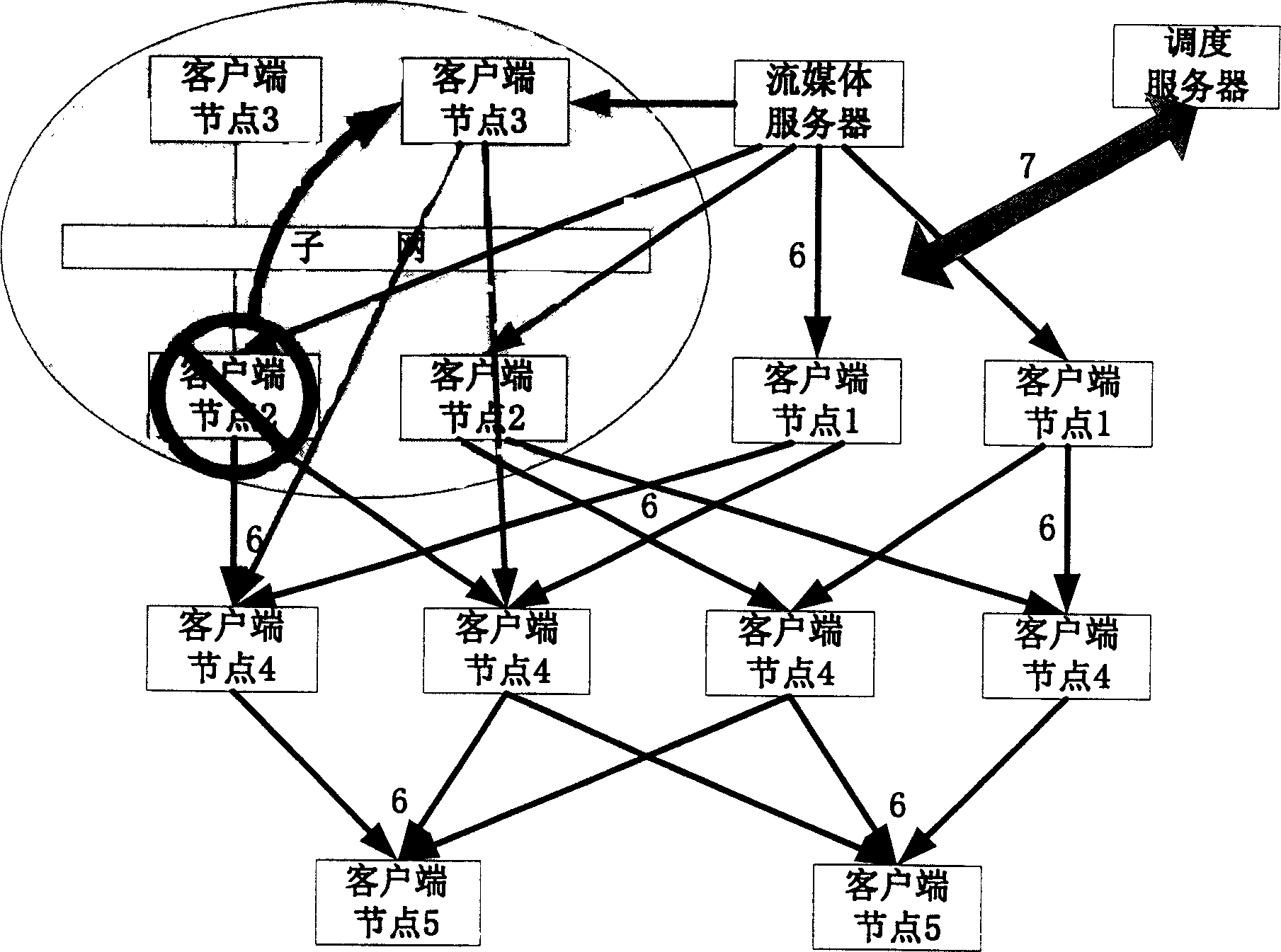
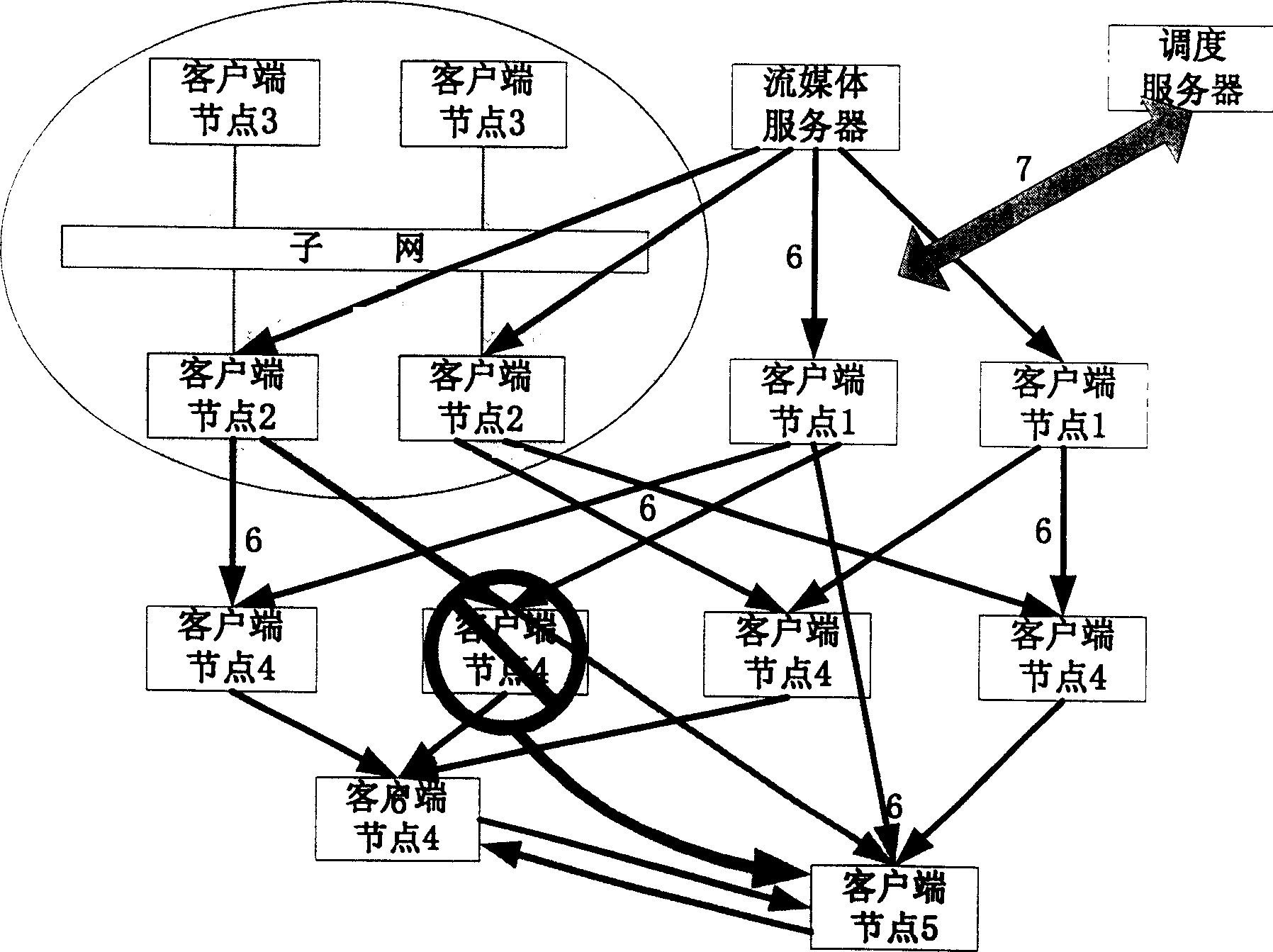
InactiveCN1604569ASave bandwidthReduce correlationData switching networksMulticast networkMedia server
This invention belongs to information transmission technique field and relates to a robust flow dispatching method based on point to point. The method is to integrate dispatching server, flow media server and customer terminal points into one living broadcast network gives different definitions to functions in network of each customer points and gives different functions to each customer points in the network. The entrance and exit of the new customer point make changes of the network topological structure and realizes the flow dispatching through network topological form dynamic update and monitoring and part of changing customer point.
Owner:TSINGHUA UNIV
System, device, and method for receiver access control in a multicast communication network
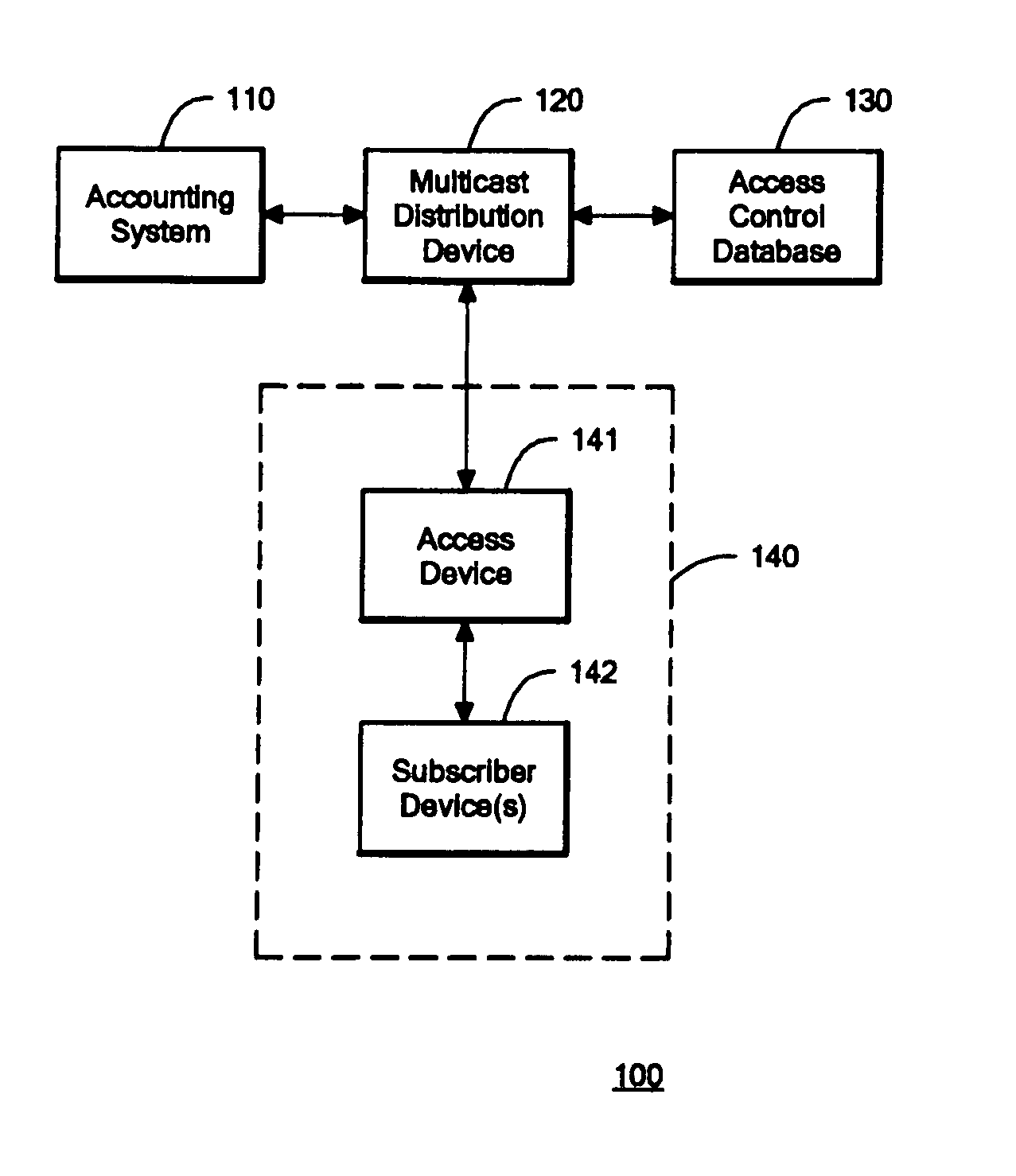
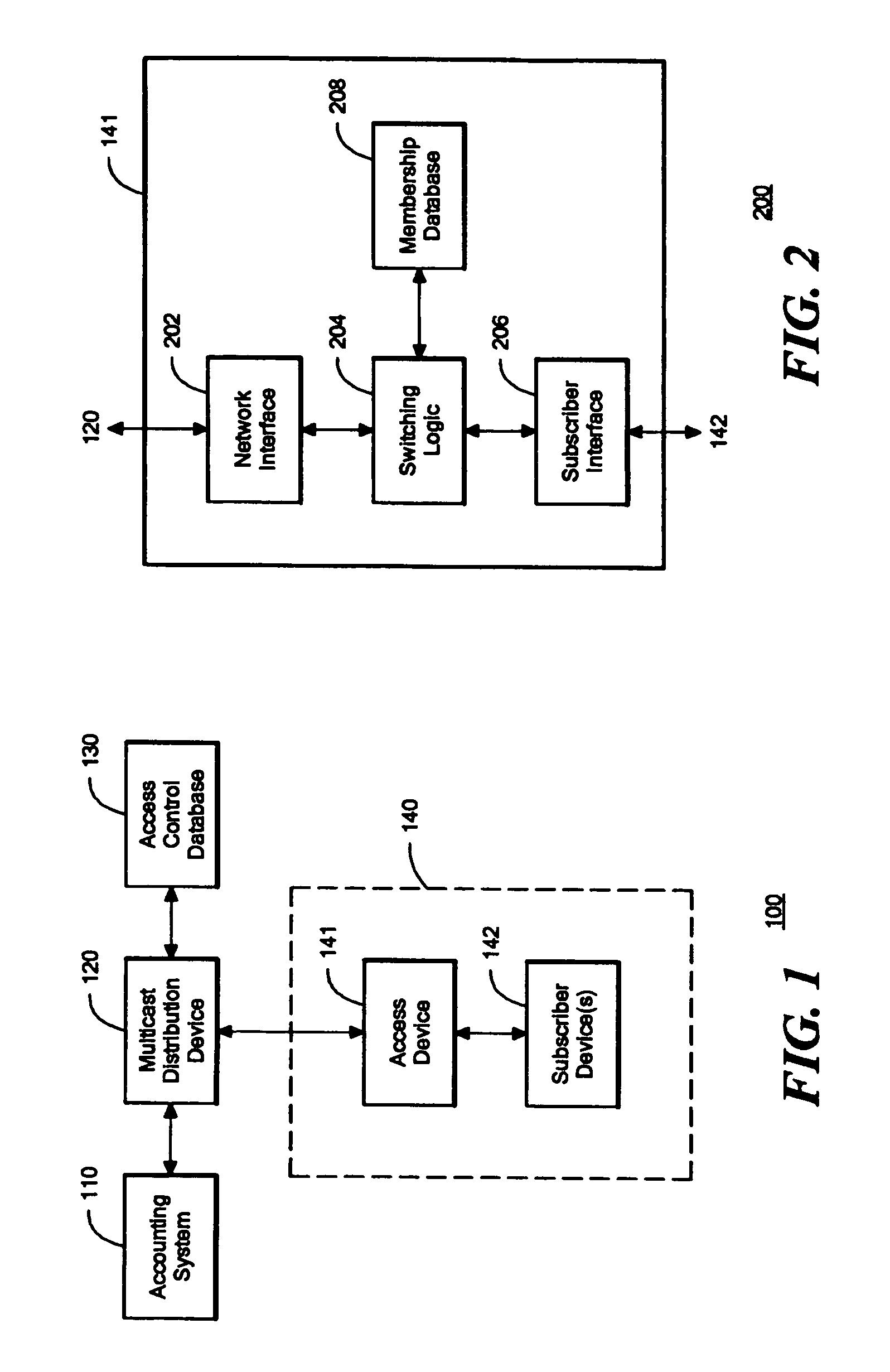
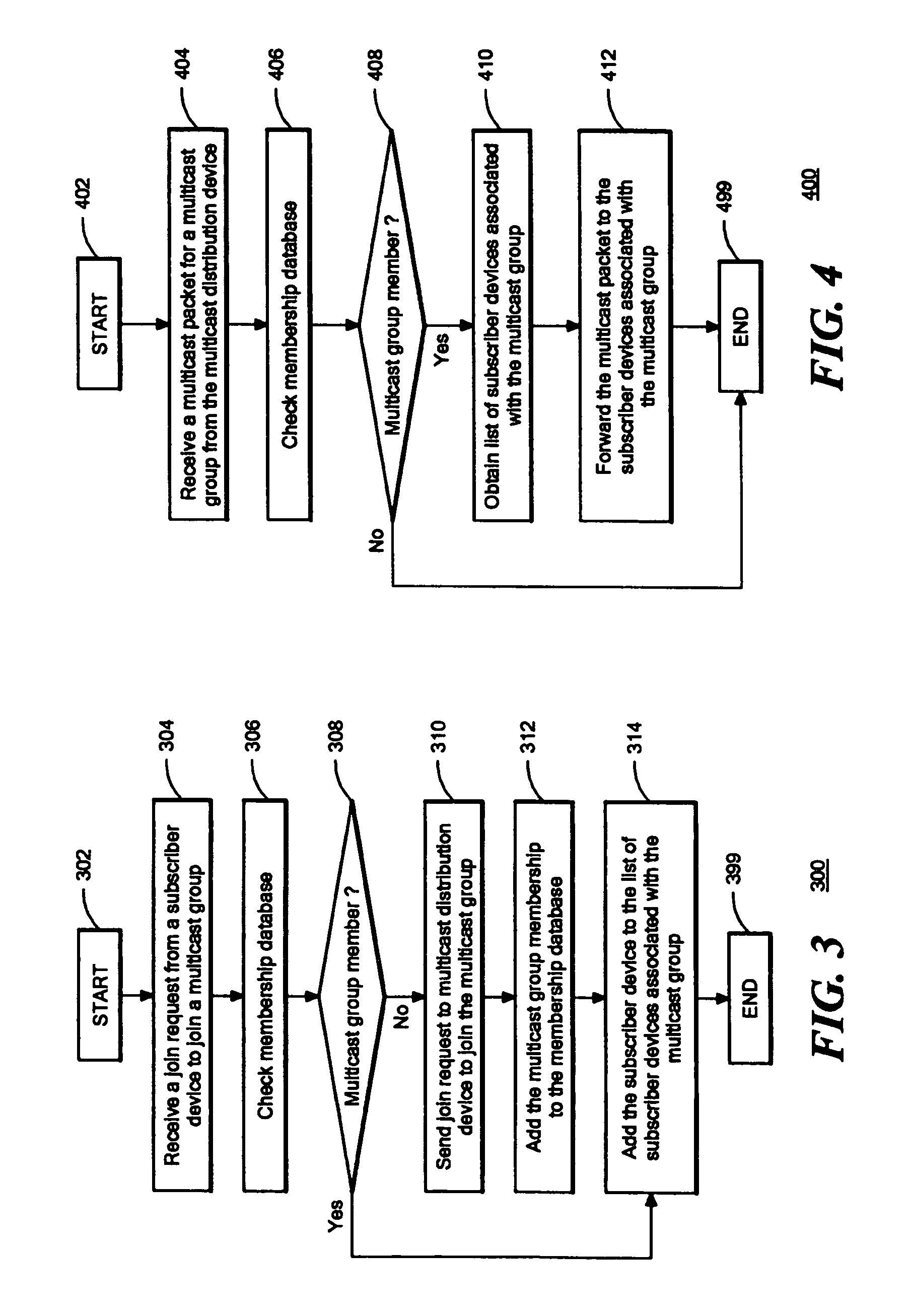
InactiveUS7454518B1Multiple digital computer combinationsData switching networksMulticast networkProtocol for Carrying Authentication for Network Access
A system, device, and method for receiver access control in a multicast communication network treats each subscriber location as a separate subnetwork having one and only one multicast receiver. An access device is situated at each subscriber location. Each access device connects to a separate port of a multicast distribution device. Each subscriber device accesses the multicast network through the access device that is situated at its subscriber location. Each access device acts as a proxy for its respective subscriber devices by joining and leaving multicast groups on behalf of the subscriber devices and acting as the sole multicast receiver for the subscriber location. The access devices run a multicast group management protocol for joining and leaving various multicast groups, and therefore the access devices appear to the multicast distribution device as the ultimate multicast receivers for multicast information. The access devices maintain group membership information their respective subscriber devices and distribute multicast information to their respective subscriber devices accordingly.
Owner:AVAYA INC
Extensions to rich media container format for use by mobile broadcast/multicast streaming servers
InactiveUS20070180133A1Facilitates great leverageFacilitates greater leveragePulse modulation television signal transmissionNetwork traffic/resource managementData feedCartoon animation
An extension to the ISO Base Media File Format to support ALC as a broadcast protocol. The present invention also provides for the extension of the ESG to include metadata specific to the transport of SVG over mobile broadcast / multicast networks. A “BMFDP hint track” is introduced in the container file format, with the required file metadata being in these hint tracks. The present invention can be used in applications such as the preview of long cartoon animations, interactive Mobile TV services, live enterprise data feeds, live chat services, and karaoke programs.
Owner:CORE WIRELESS LICENSING R L
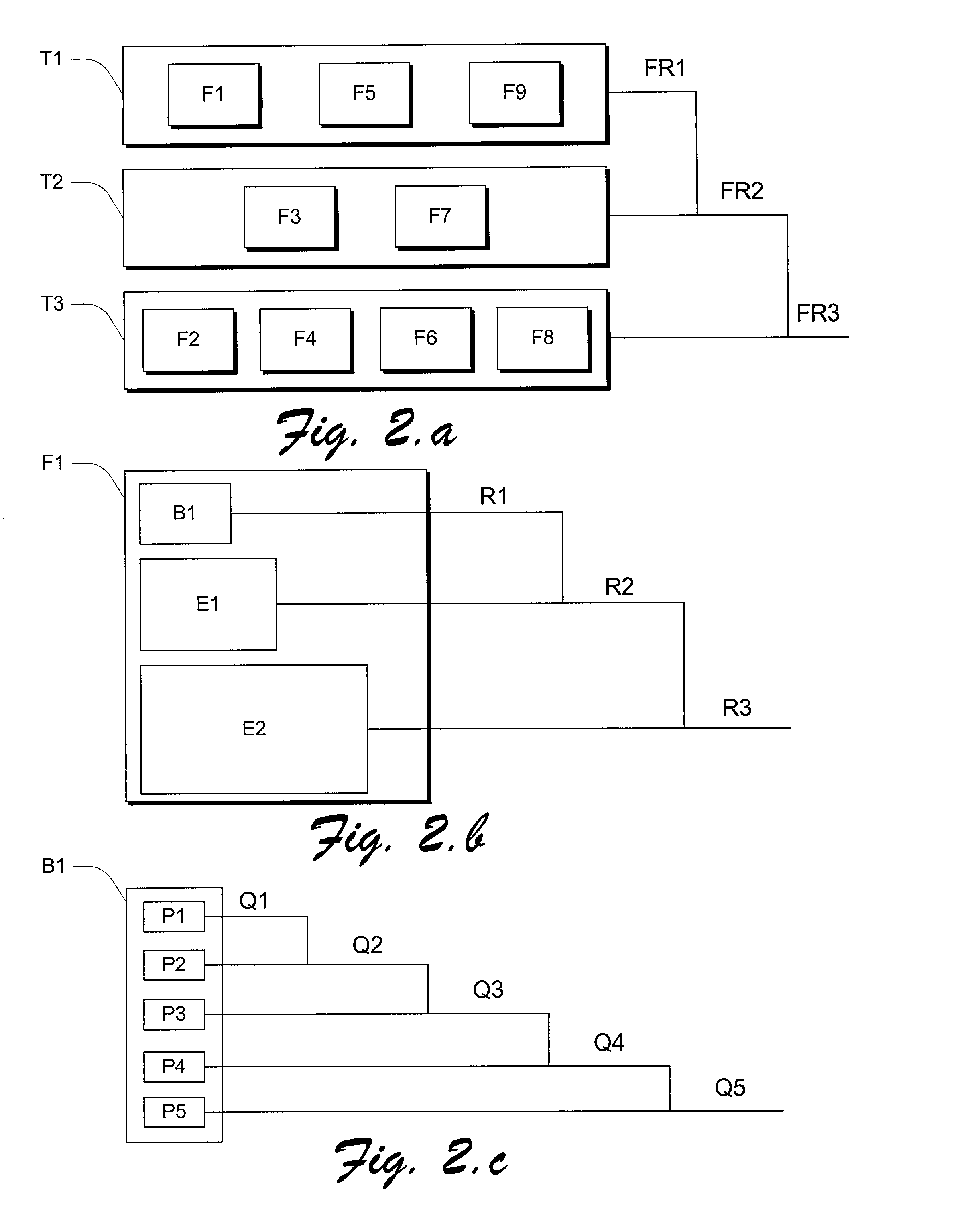
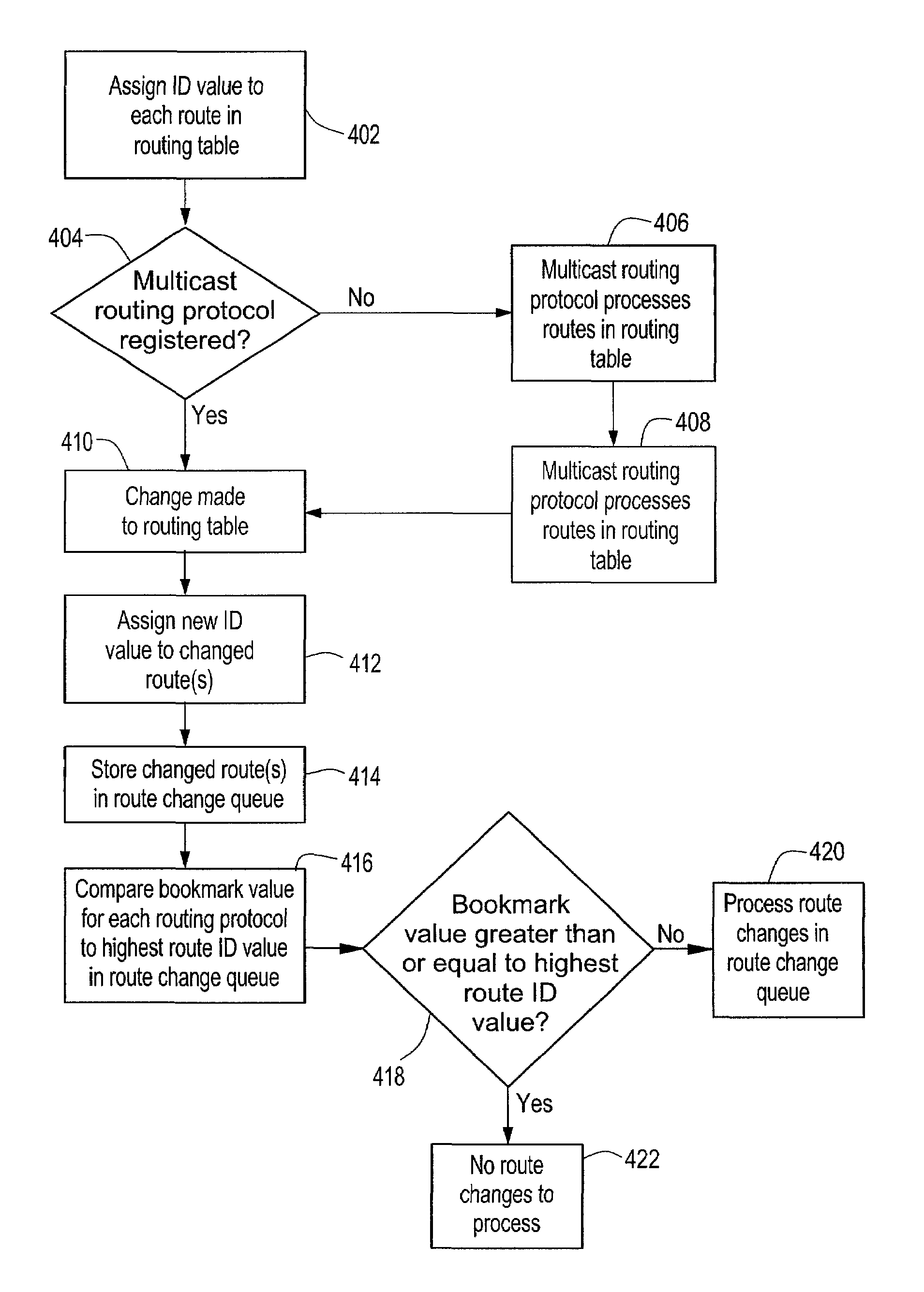
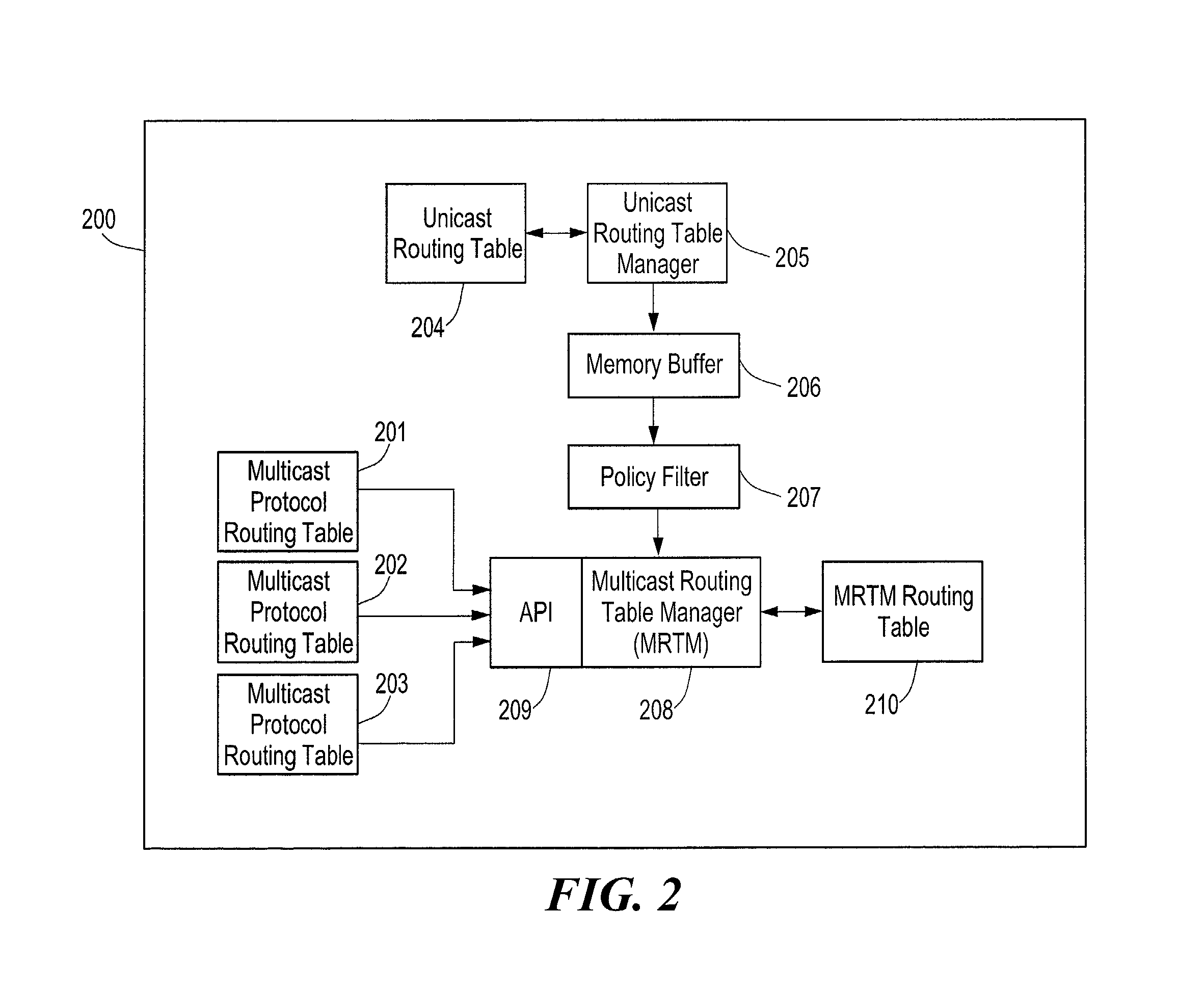
Method for synchronization of multicast routing table changes with a plurality of multicast routing protocols
InactiveUS7007100B1Data switching by path configurationMultiple digital computer combinationsProtocol processingRouting table
A multicast network device, such as a route may support a plurality of multicast routing protocols. A single multicast routing table may be provided to store the multicast routes for each multicast routing protocol and a selected set of unicast routes from a unicast routing table. In order to synchronize route changes in the multicast routing table with the plurality of multicast routing protocols, a route ID value is assigned to each route in the multicast routing table. Each multicast routing protocol is assigned a bookmark in a route change queue, where the bookmark is assigned the route ID value of the last route processed by the multicast routing protocol. When a route is changed, the route is assigned a new route ID value and stored in the route change queue. A multicast routing protocol may determine if a route change has occurred by comparing its bookmark to the highest route ID value in the route change queue.
Owner:AVAYA MANAGEMENT LP
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com