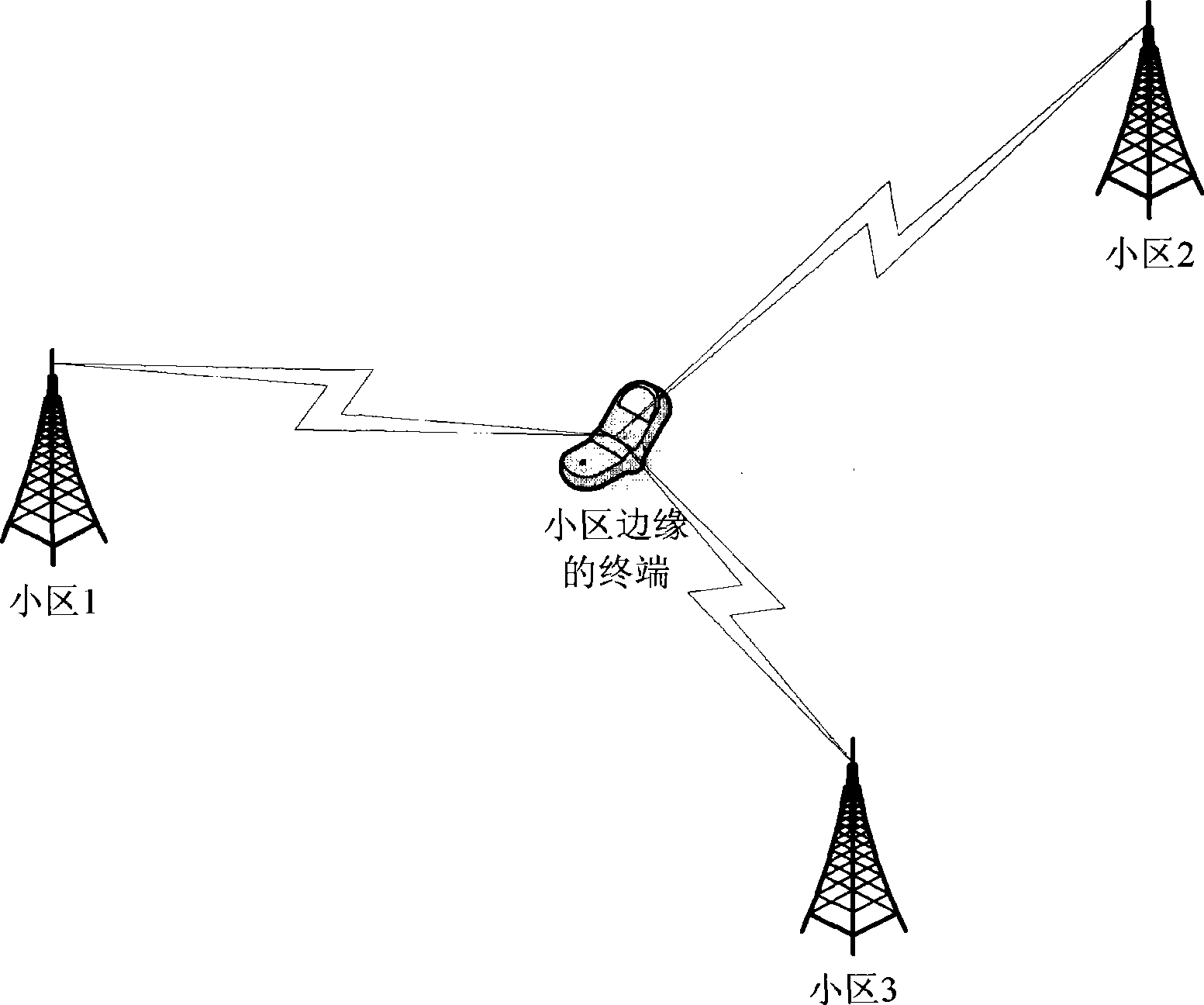
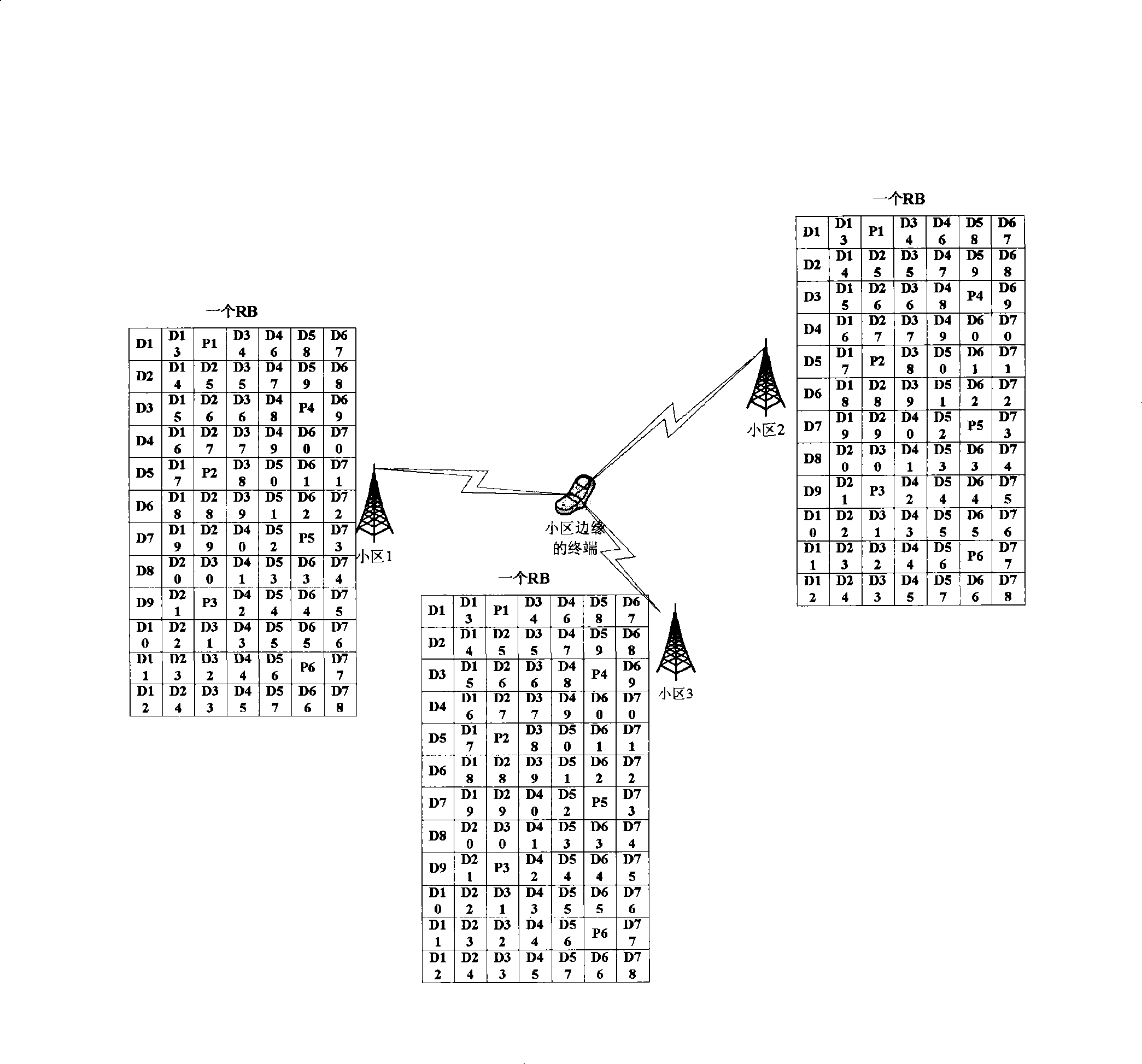
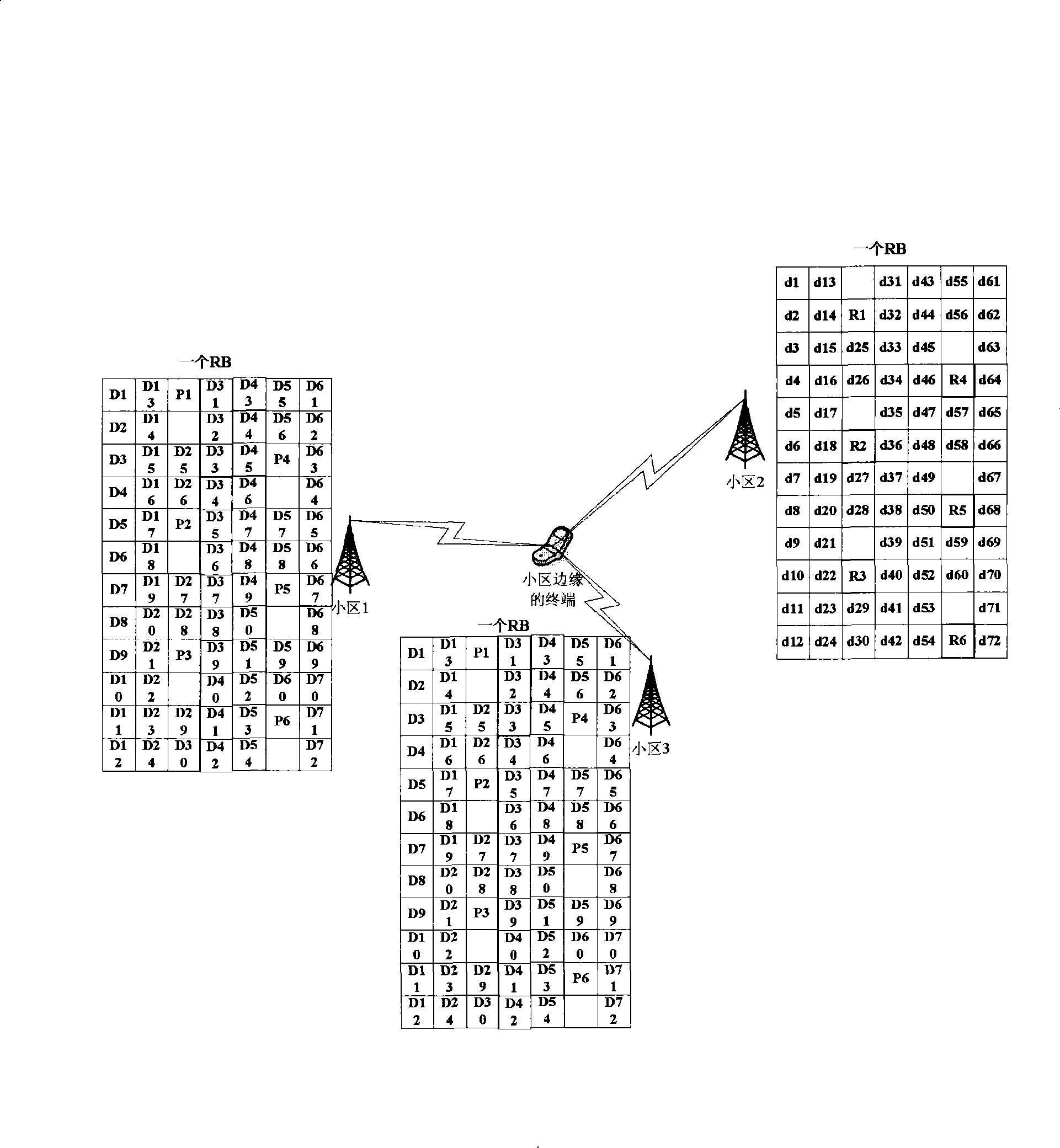
Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
790 results about "Multicast transmission" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
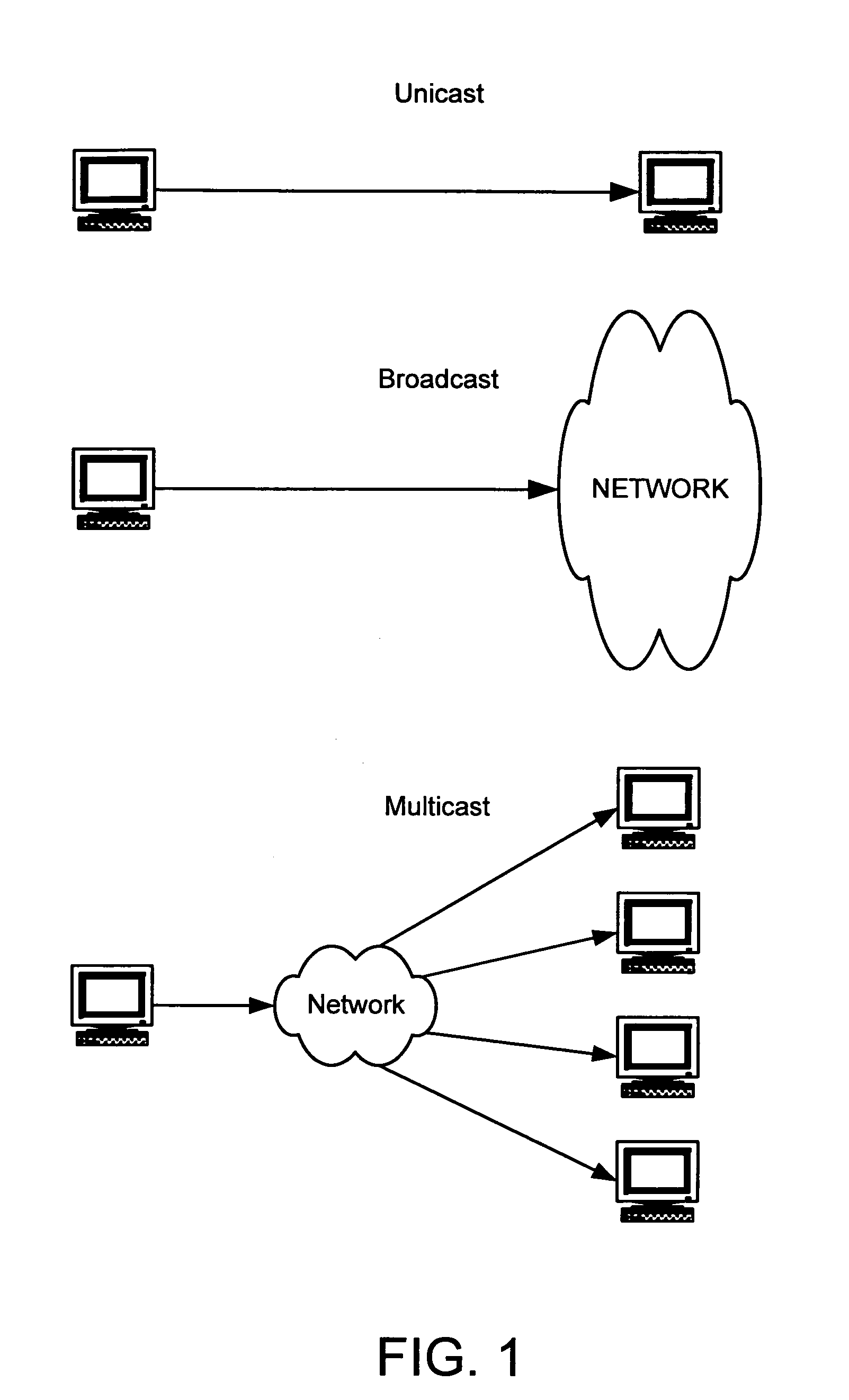
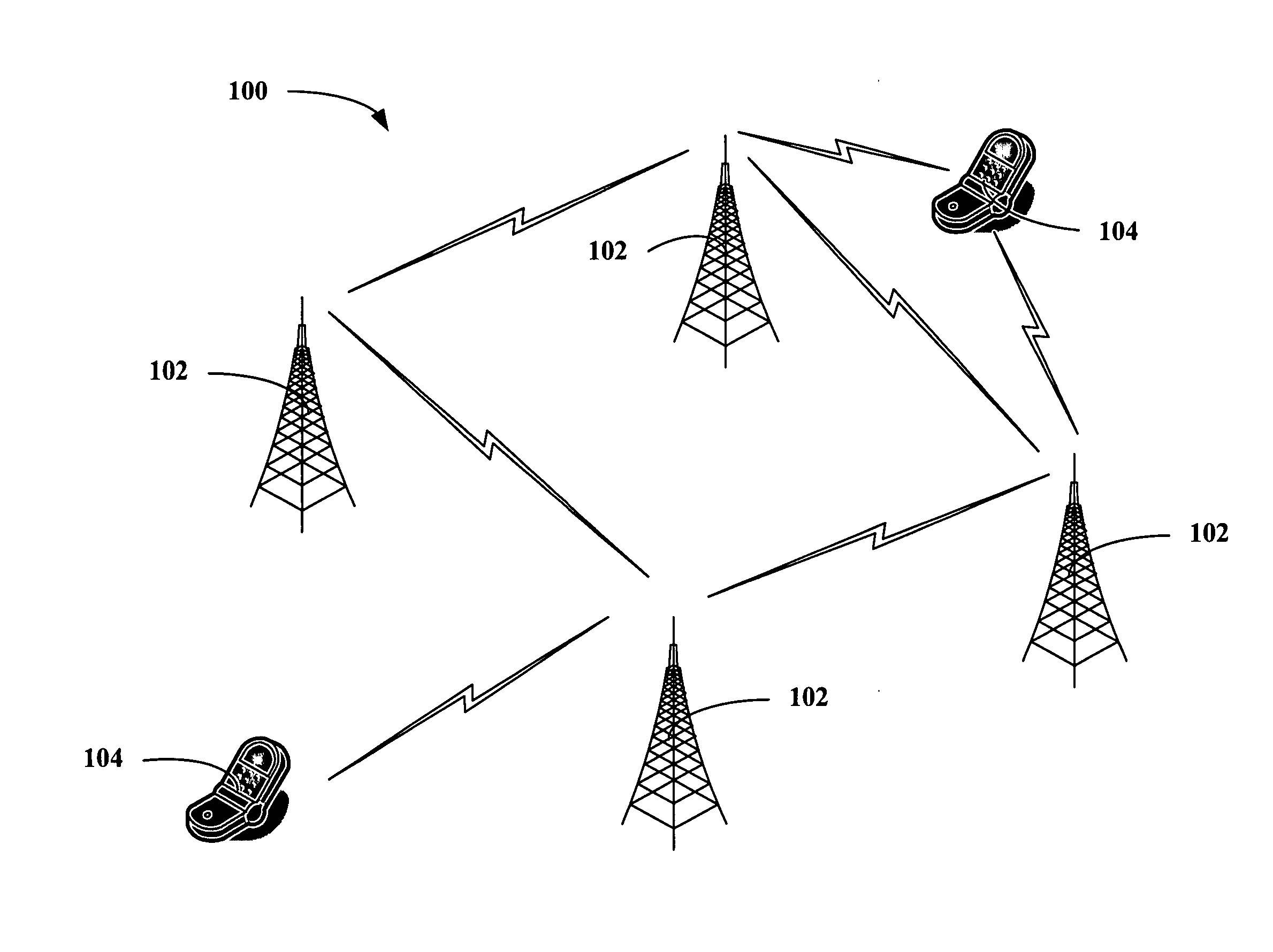
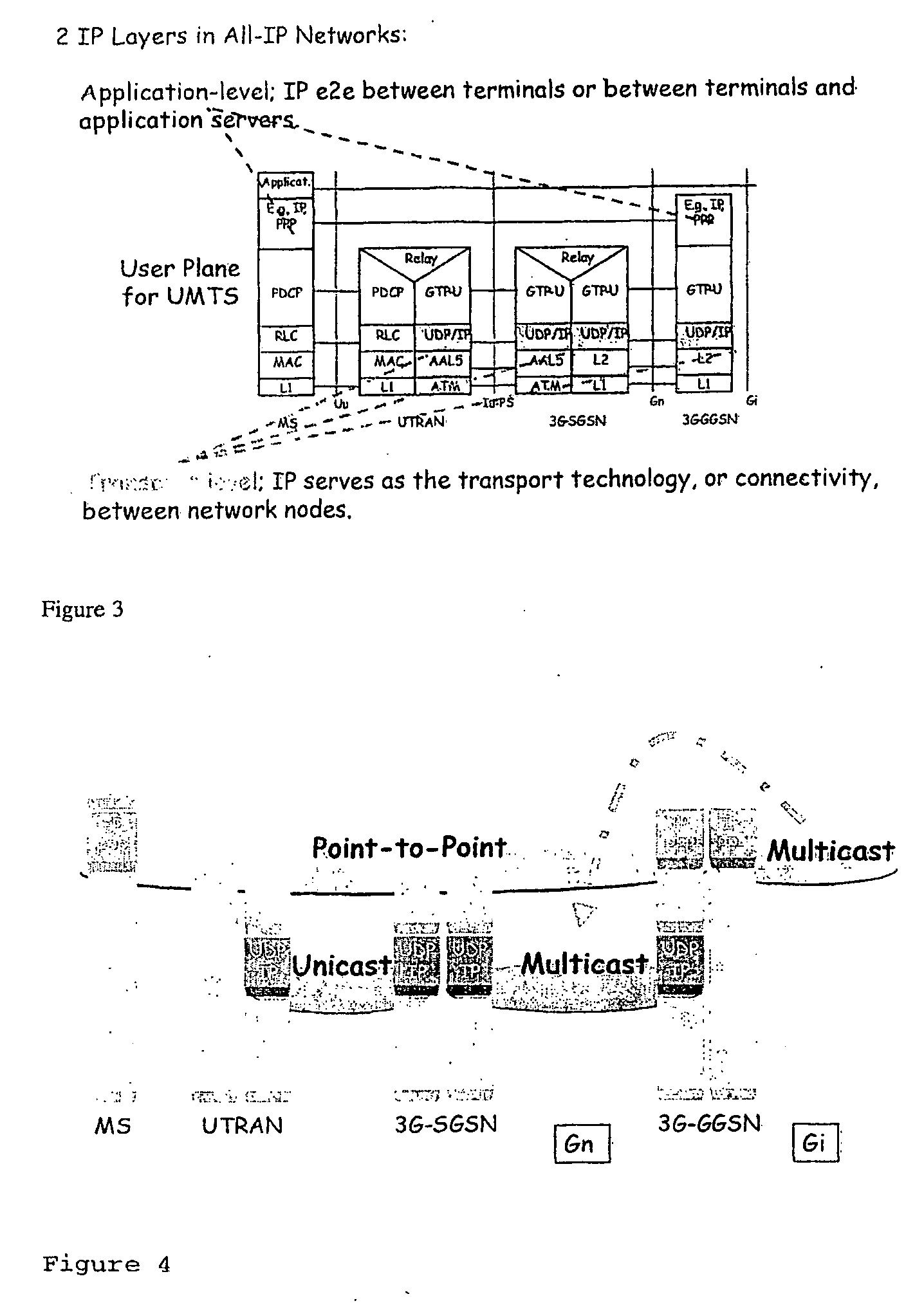
In computer networking, multicast is group communication where data transmission is addressed to a group of destination computers simultaneously. Multicast can be one-to-many or many-to-many distribution.
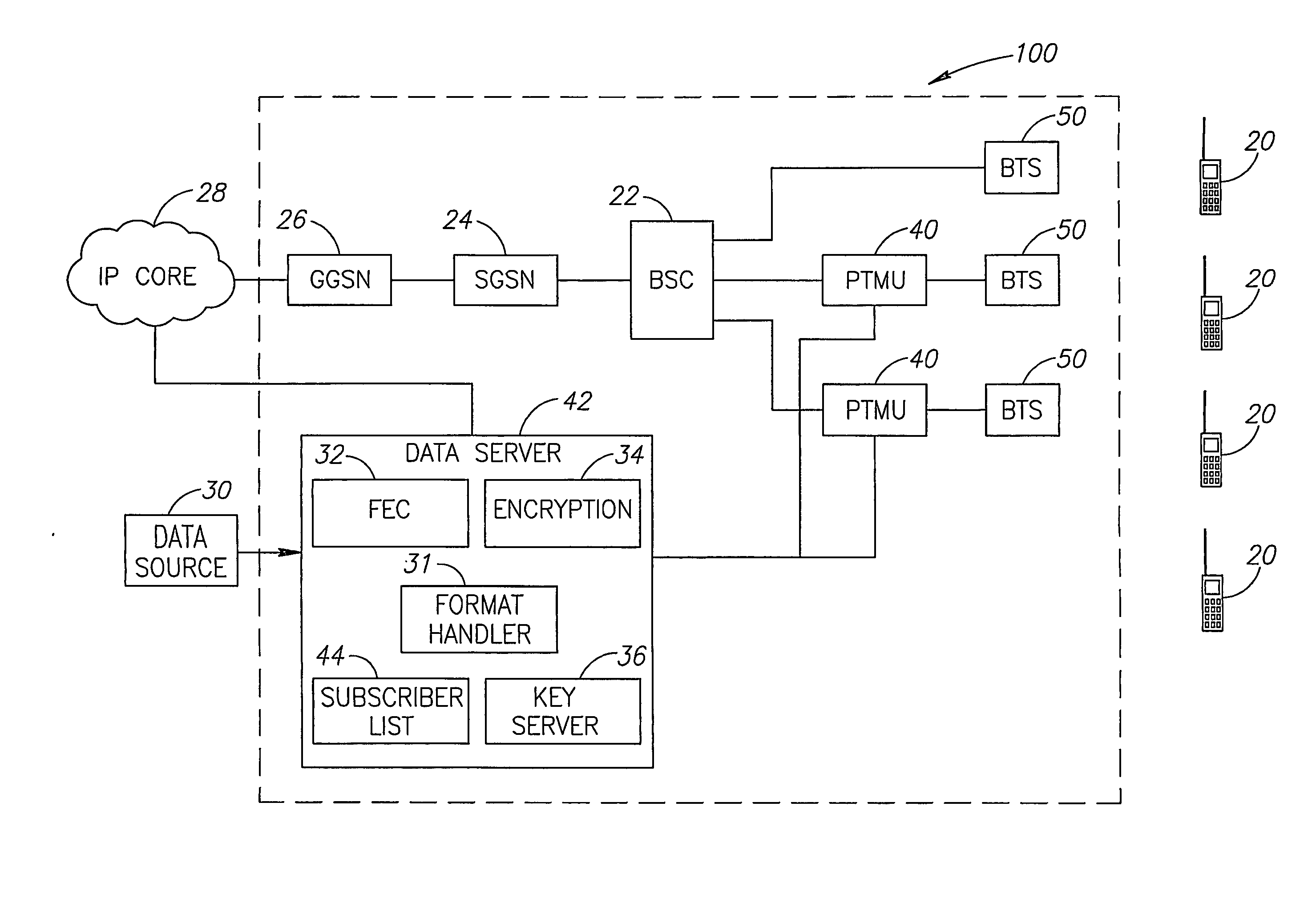
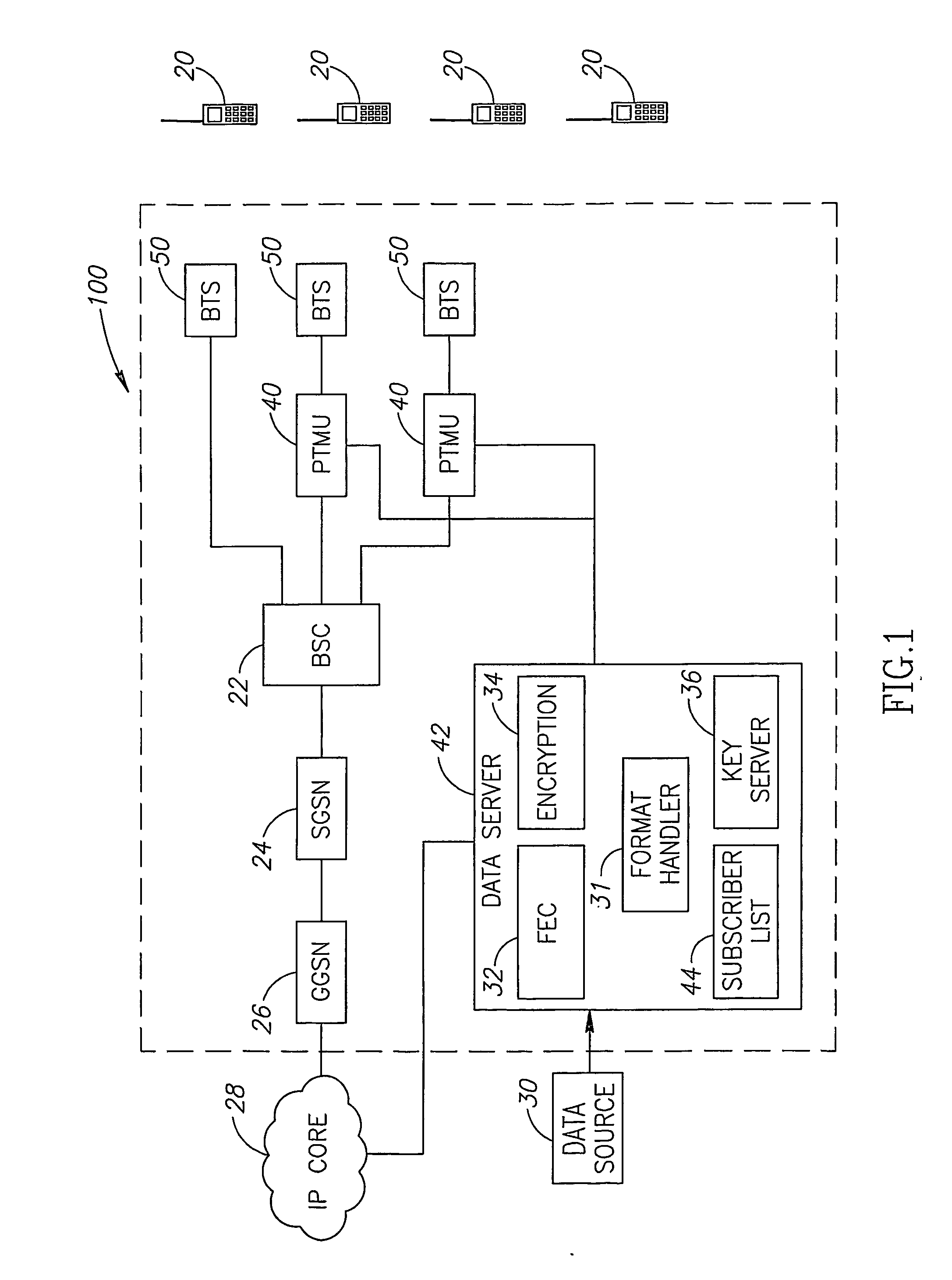
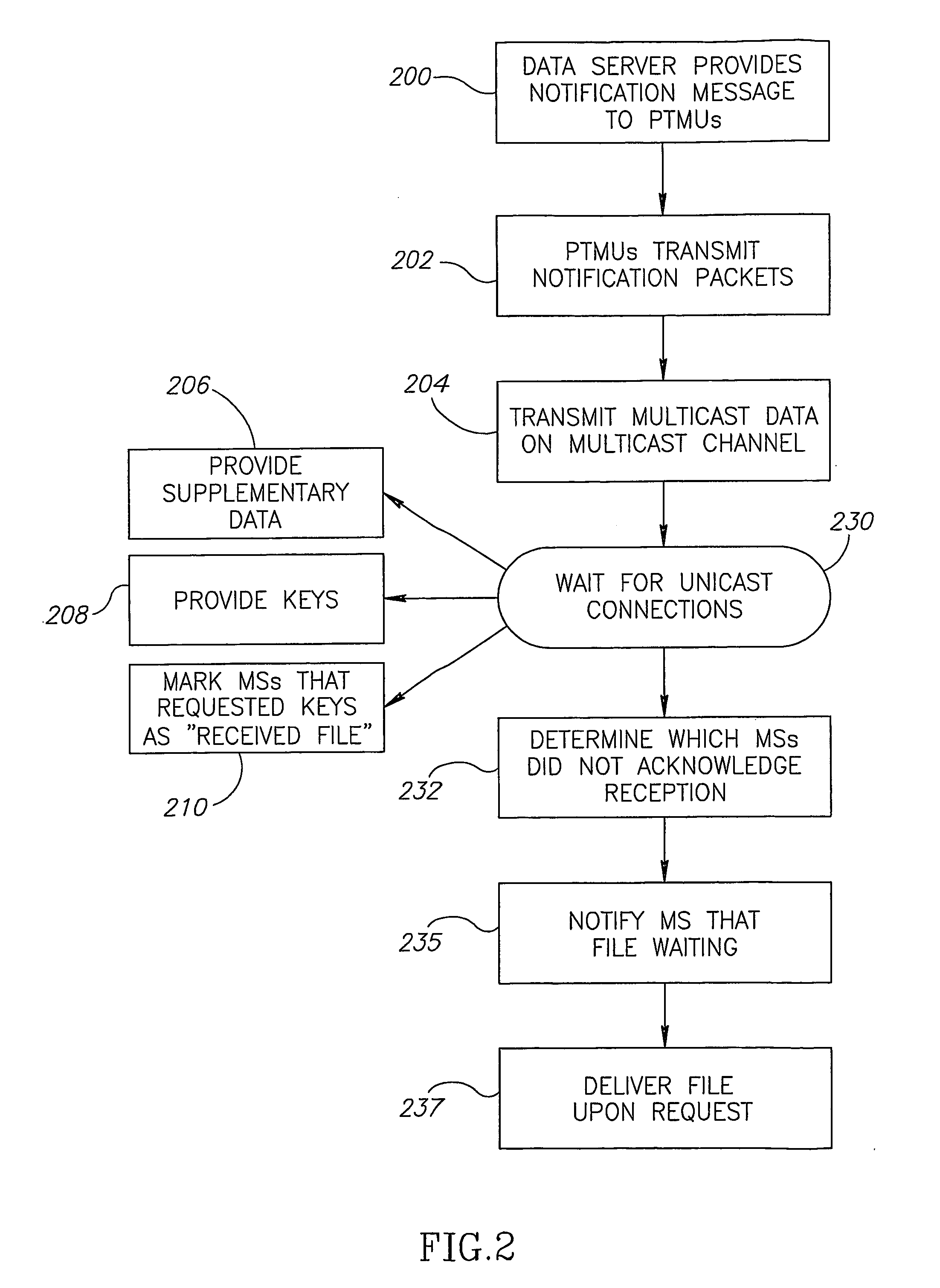
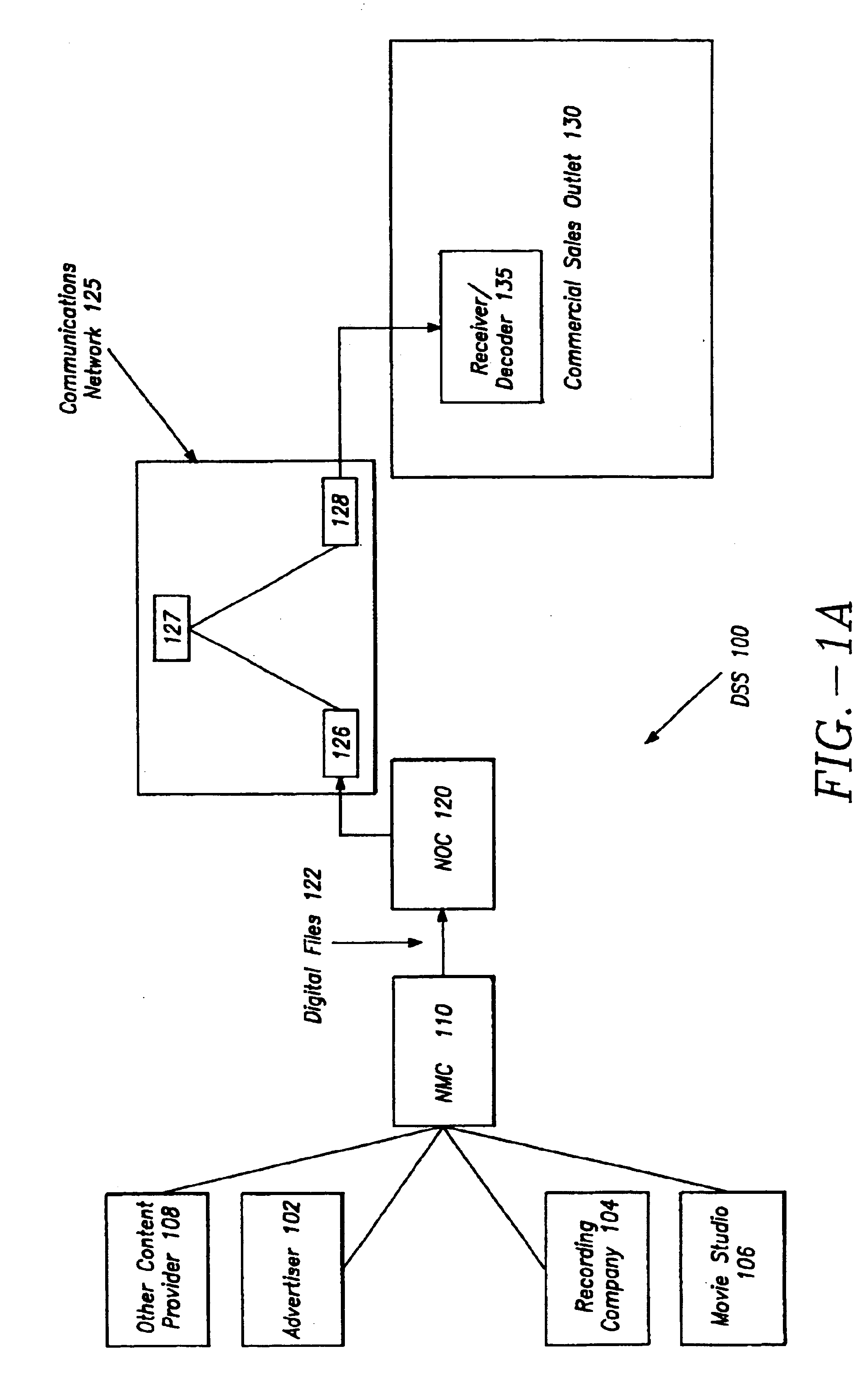
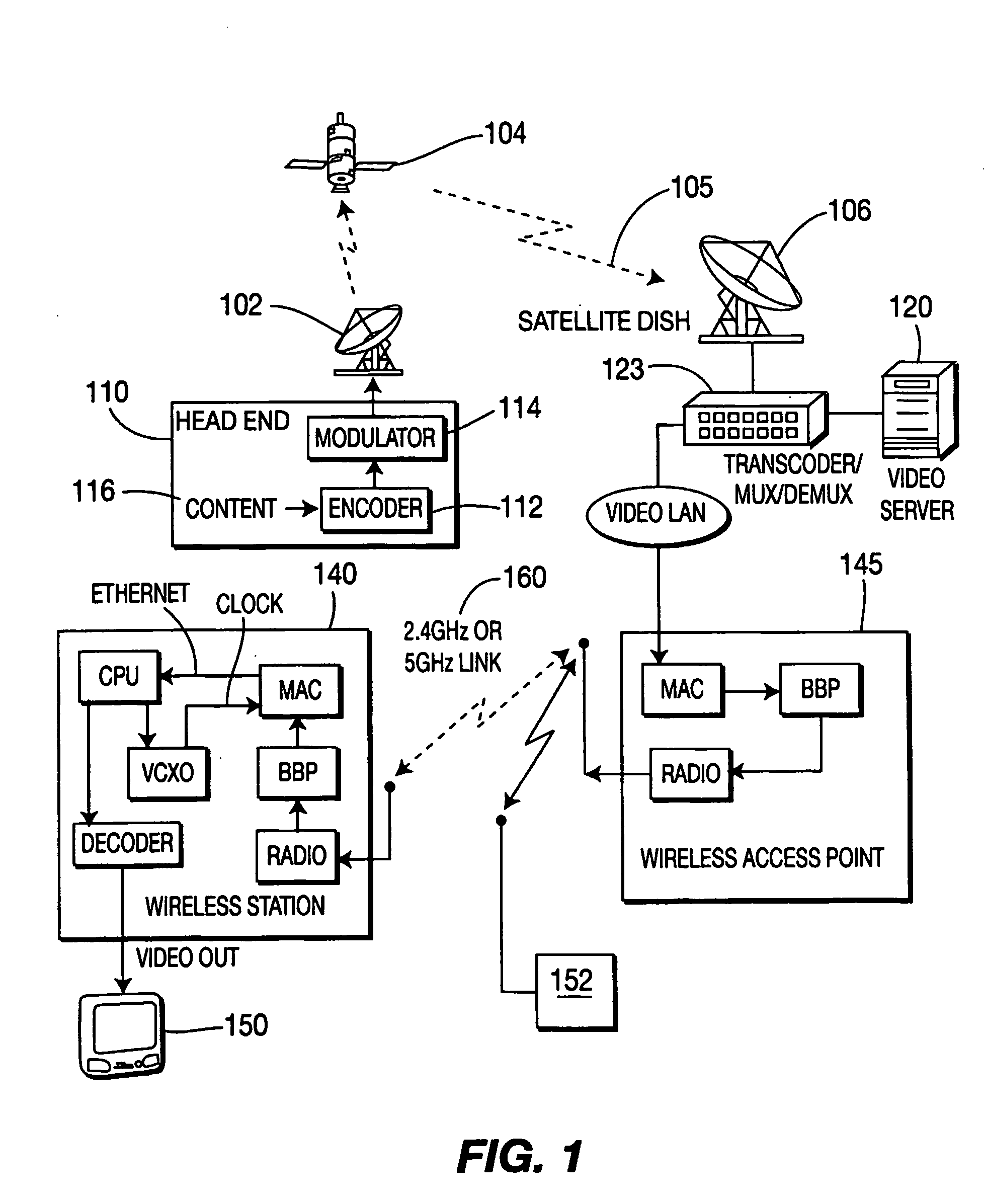
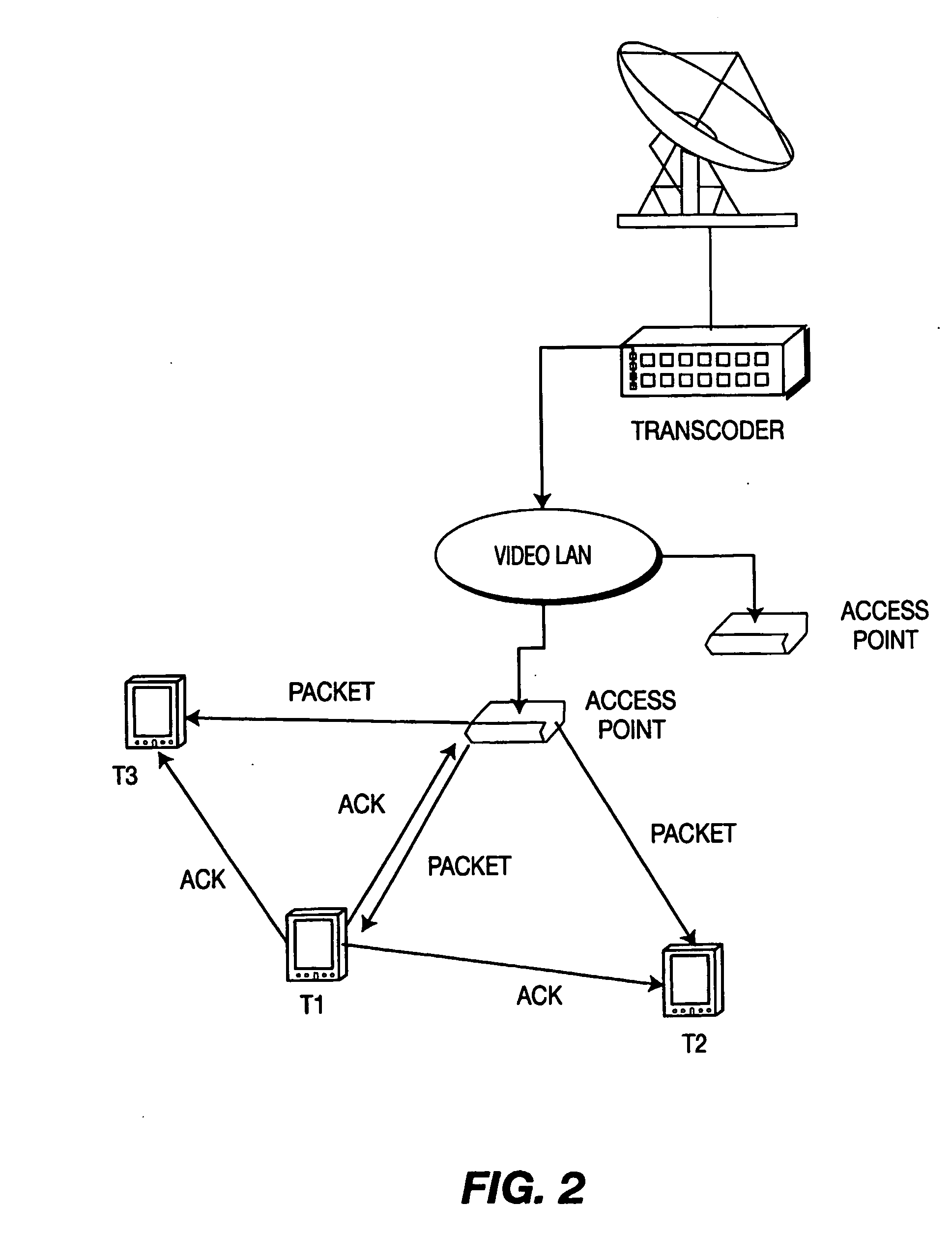
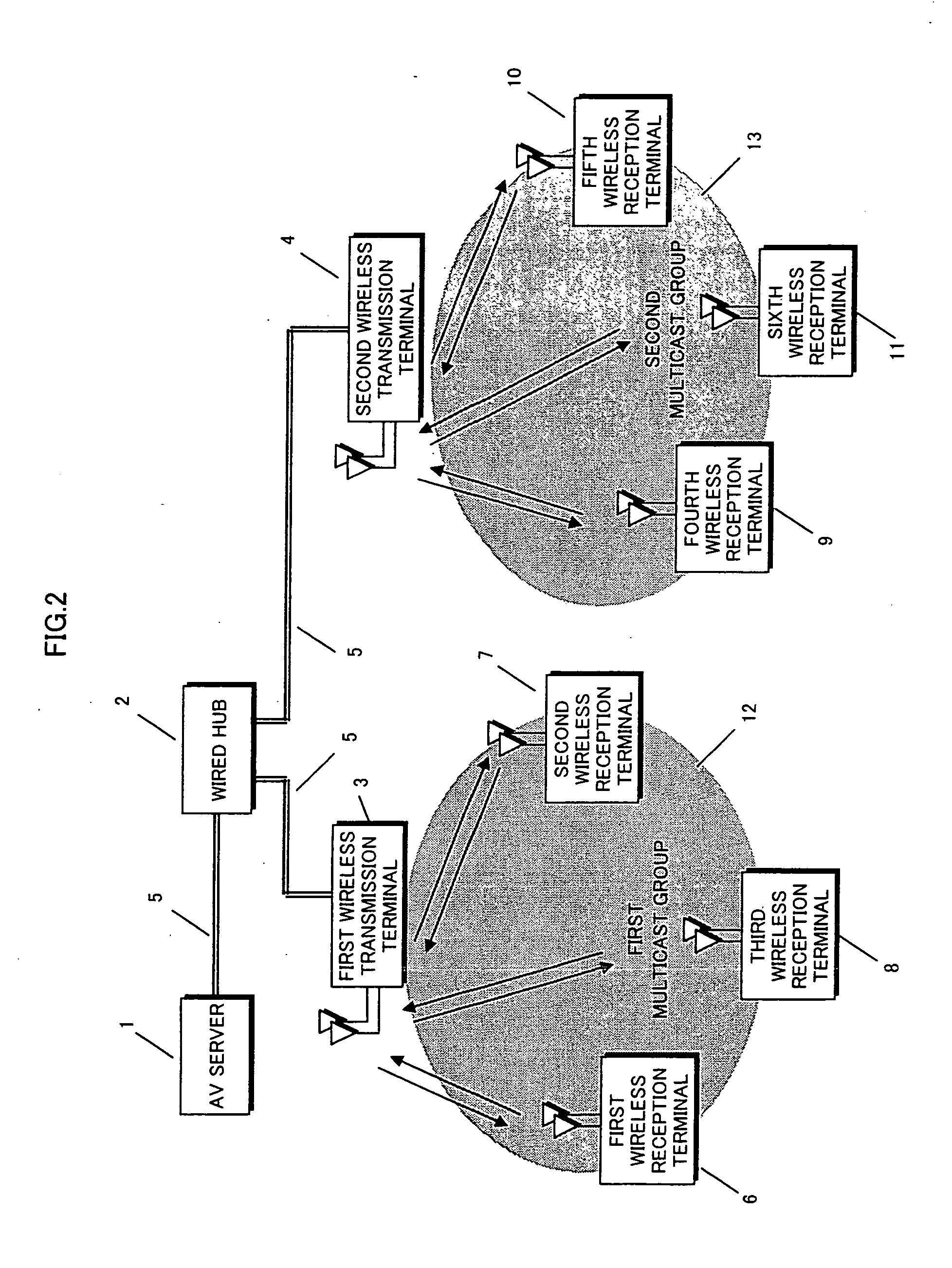
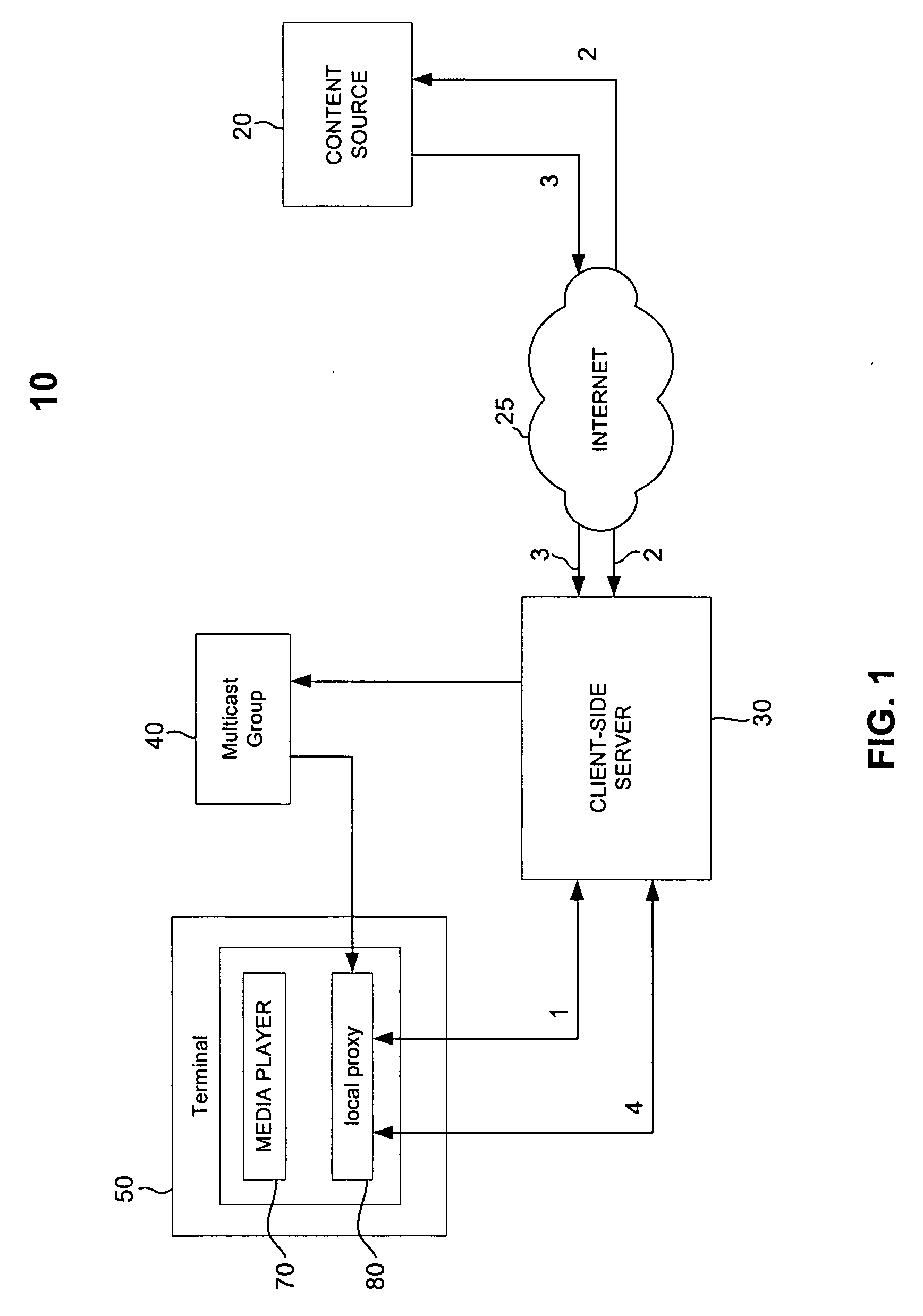
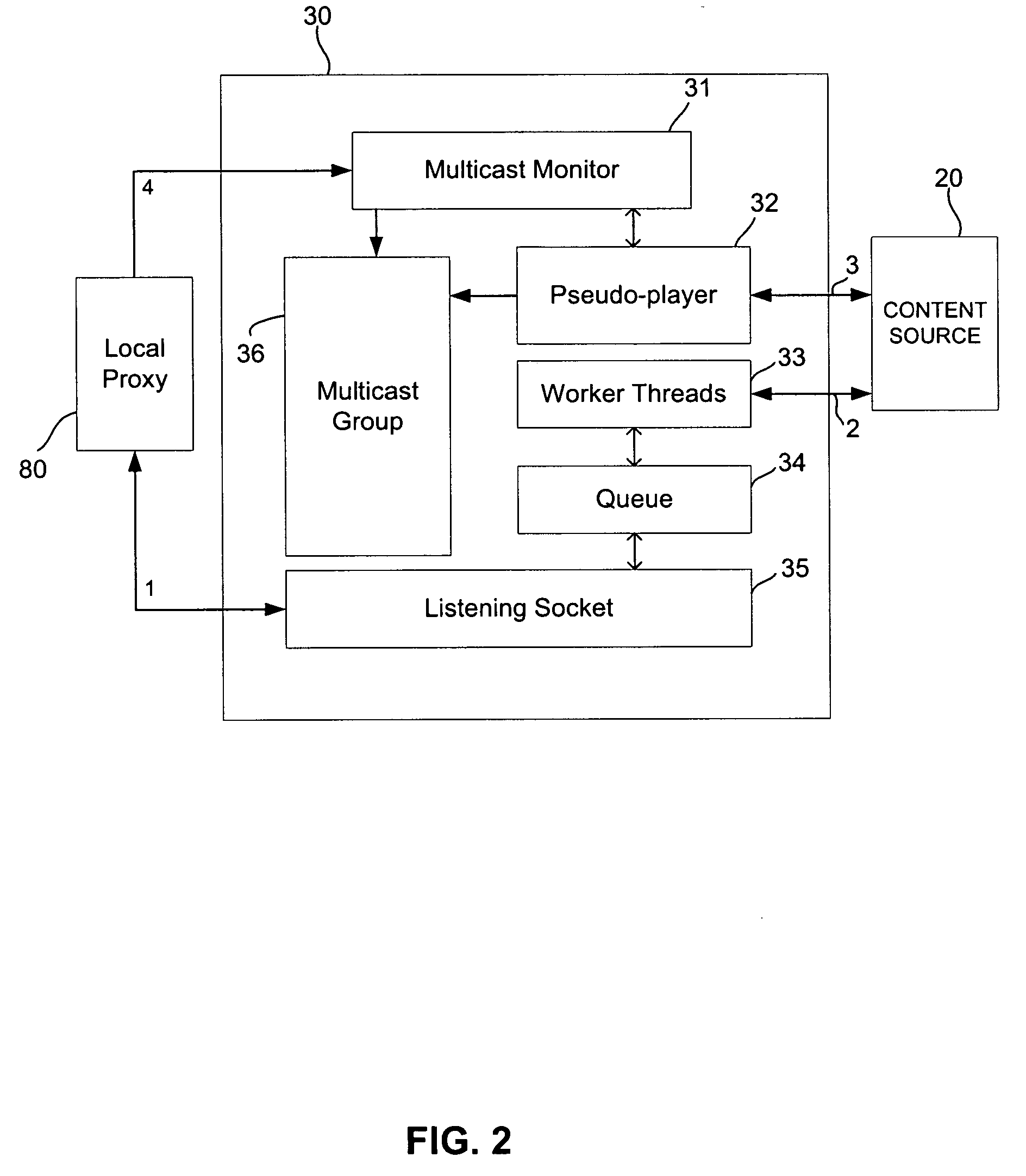
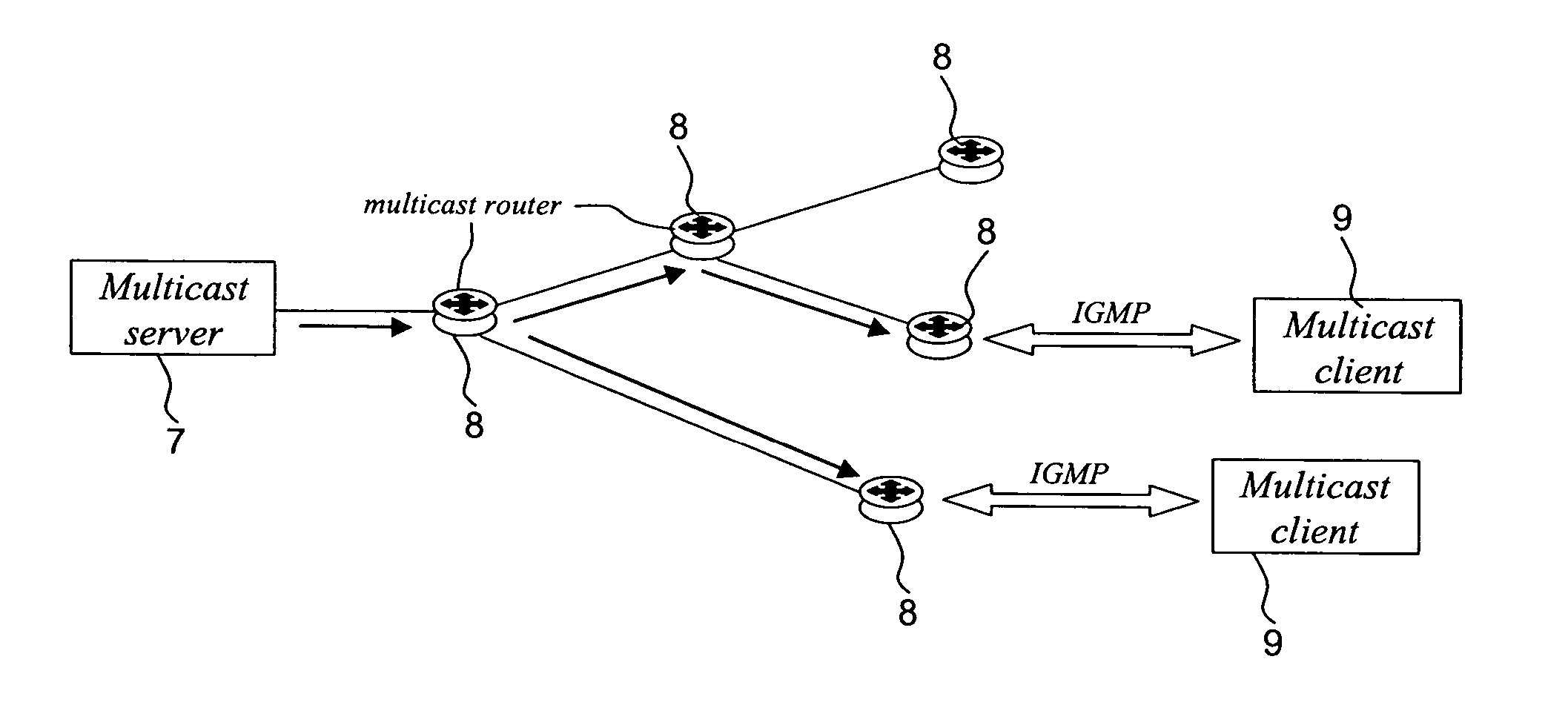
Distribution Of Multicast Data To Users
InactiveUS20070211720A1Reduce semaphoreLow costSpecial service provision for substationBroadcast systems characterised by addressed receiversComputer networkData file
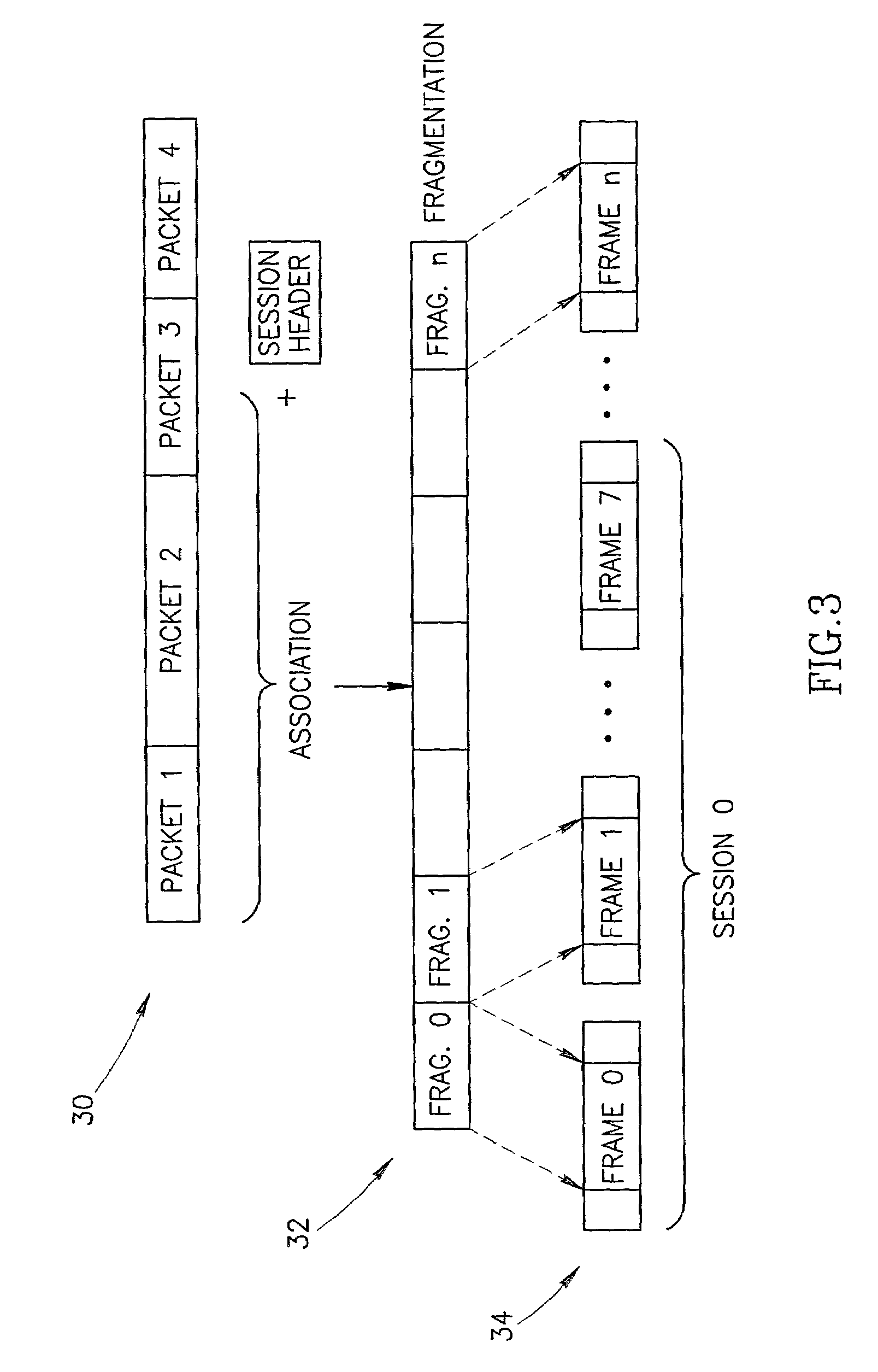
A method of multicasting a data file. The method includes transmitting a notification on an upcoming multicast transmission to a plurality of receivers (20) designated to receive the multicast transmission, tuning by at least one of the plurality of receivers (20) to one or more multicast channels, responsive to the notification, transmitting a data file, from a data server (42), on the one or more multicast channels, without the data server (42) receiving acknowledgements from the receivers (20) on whether they received the notification, determining receivers (20) designated to receive the multicast transmission that did not receive at least a portion of the data file; and attempting to deliver the data file to the determined receivers (20).
Owner:RUNCOM TECH LTD
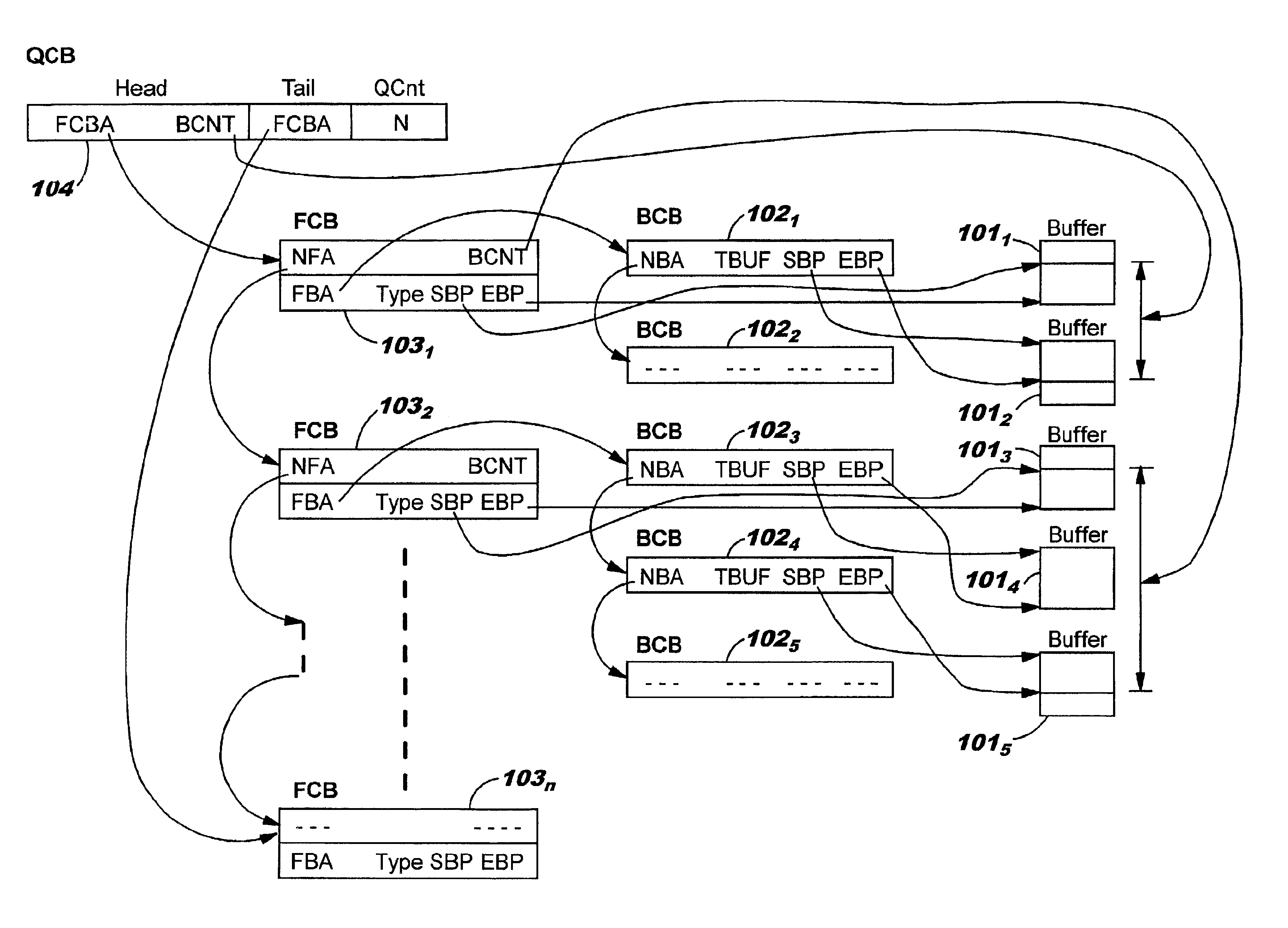
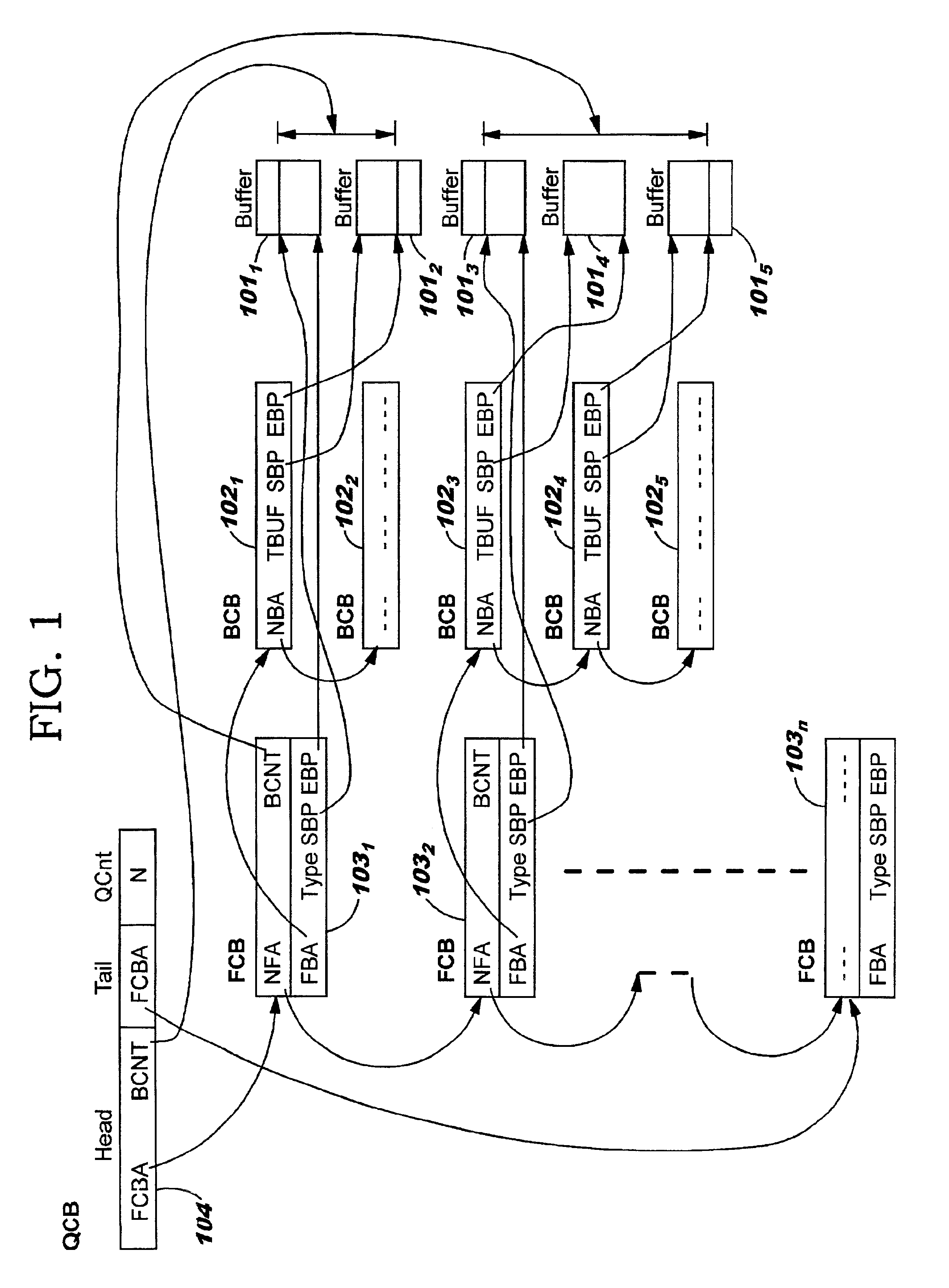
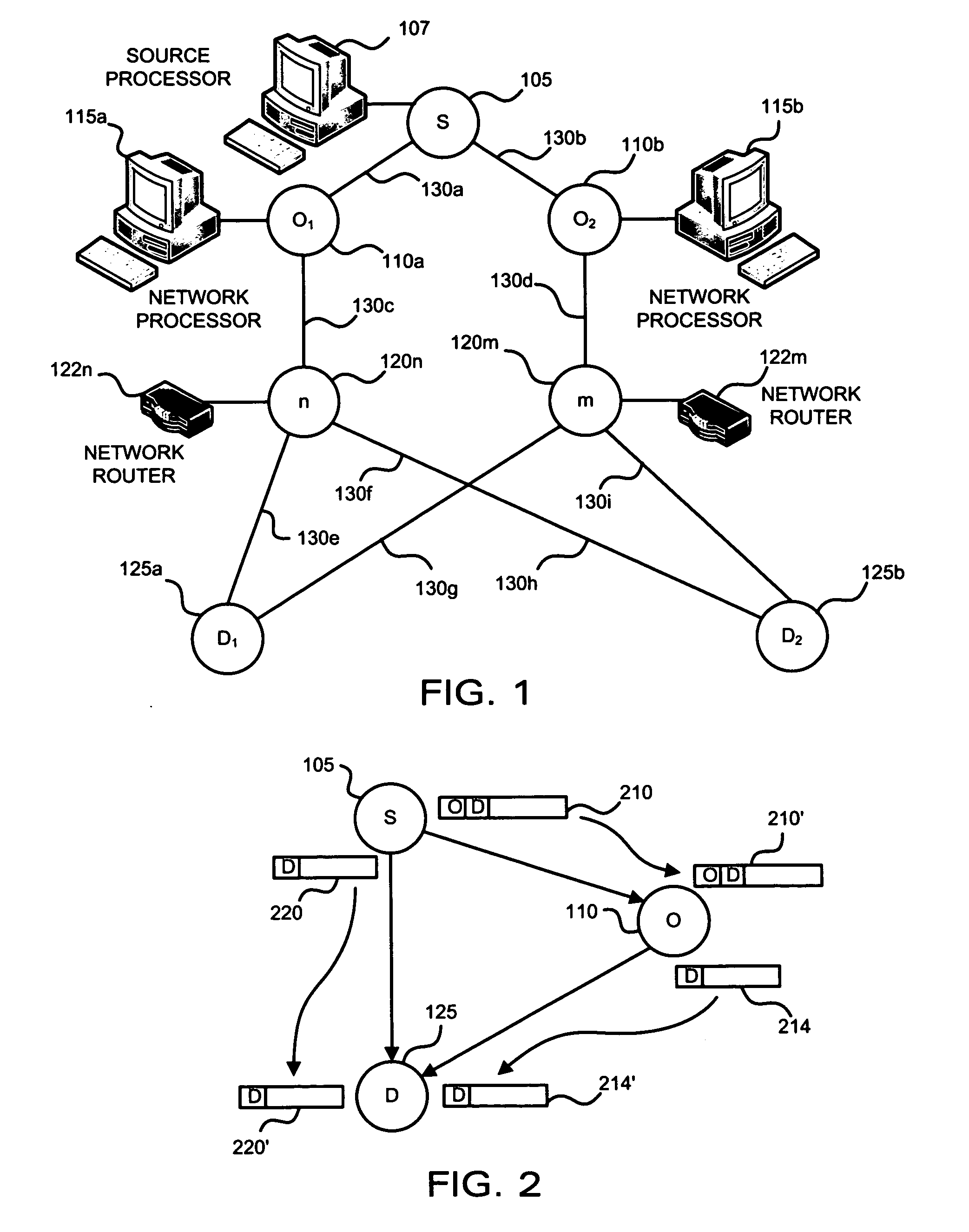
Data structures for efficient processing of multicast transmissions
InactiveUS6836480B2Reduce memory requirementsEliminate needSpecial service provision for substationTime-division multiplexArray data structureTransport system
Data structures, a method, and an associated transmission system for multicast transmission on network processors in order both to minimize multicast transmission memory requirements and to account for port performance discrepancies. Frame data for multicast transmission on a network processor is read into buffers to which are associated various control structures and a reference frame. The reference frame and the associated control structures permit multicast targets to be serviced without creating multiple copies of the frame. Furthermore this same reference frame and control structures allow buffers allocated for each multicast target to be returned to the free buffer queue without waiting until all multicast transmissions are complete.
Owner:ACTIVISION PUBLISHING
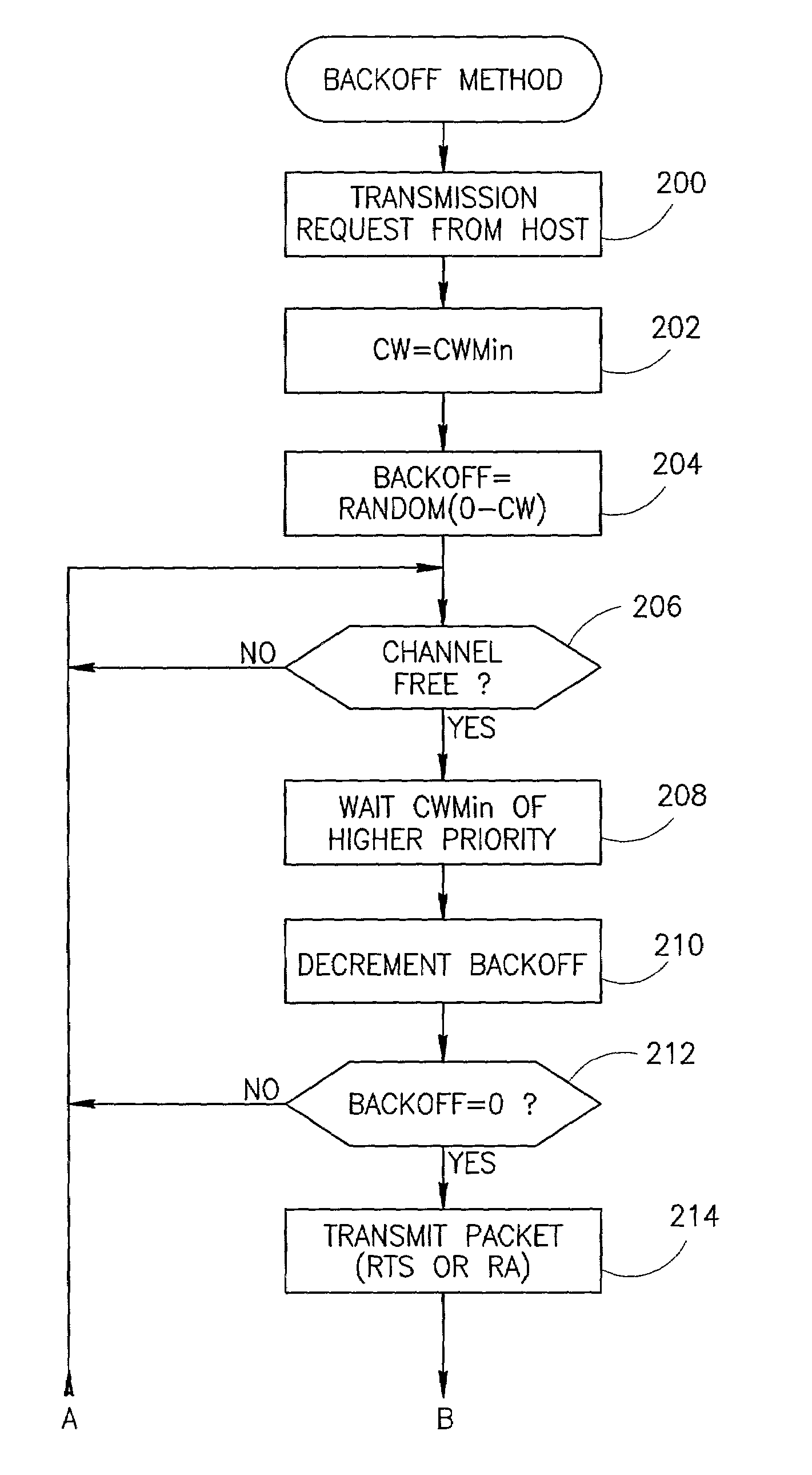
Channel access method for powerline carrier based media access control protocol
InactiveUS7570656B2Efficient and reliableEfficient mechanismError prevention/detection by using return channelNetwork traffic/resource managementCarrier signalMulticast transmission
A novel and useful media access control (MAC) protocol that is intended for use over noisy shared media channels. The MAC protocol provides layer 2 functionality over a network using a shared medium including a backoff mechanism for CSMA / CA channel access, link addressing that reduces the overhead of long MAC addresses, a flooding scheme having controlled exposure for broadcast transmissions, multicast transmissions using selective ACKs, implementation of traffic prioritization using an adaptive backoff scheme, a second layer repeater establishment process and multi-packet transport for short packets and fragmentation for long packet transport.
Owner:ITRAN COMM
WLAN access point with extended coverage area
ActiveUS20060025178A1Reduce bitrateImprove link qualityNetwork topologiesSubstation equipmentExtended coverageHigh bandwidth
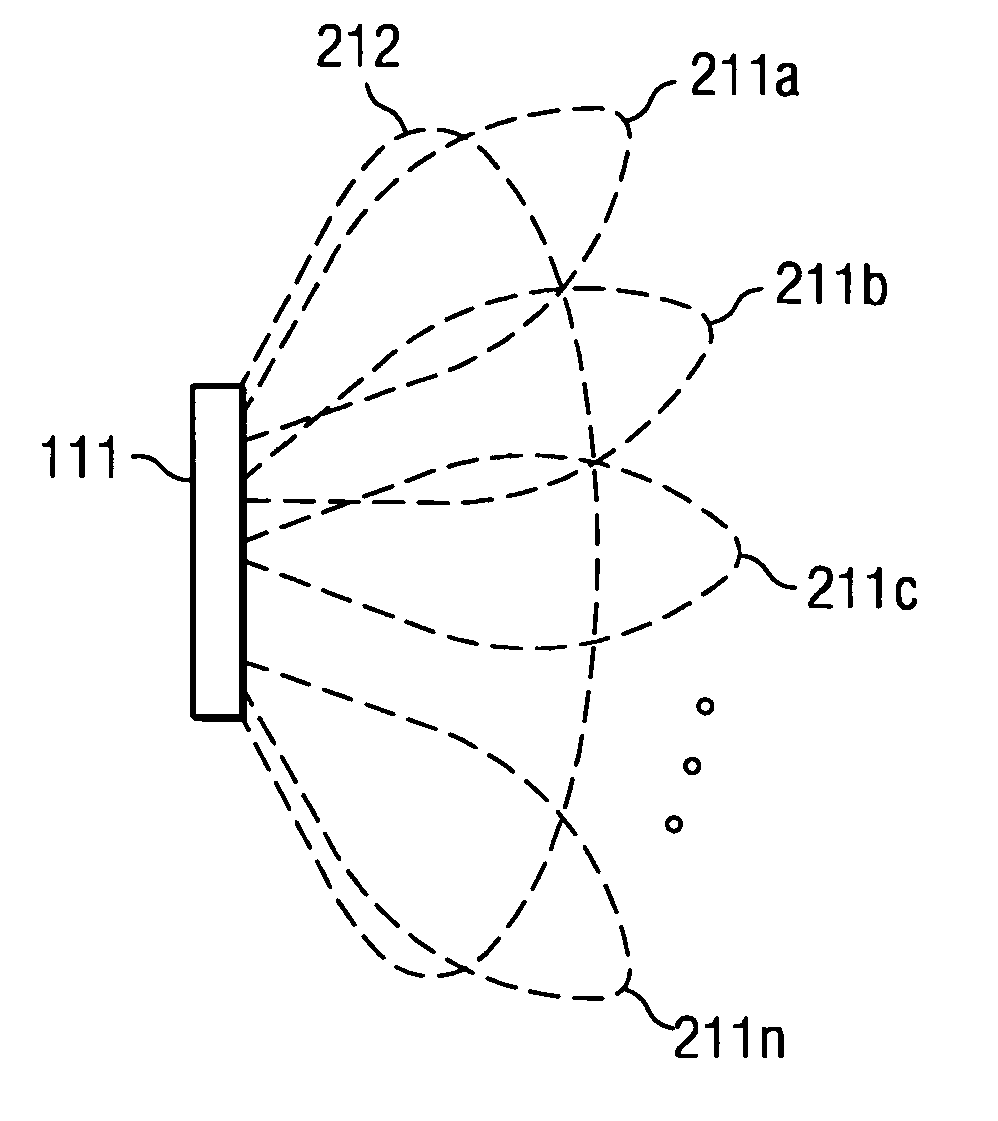
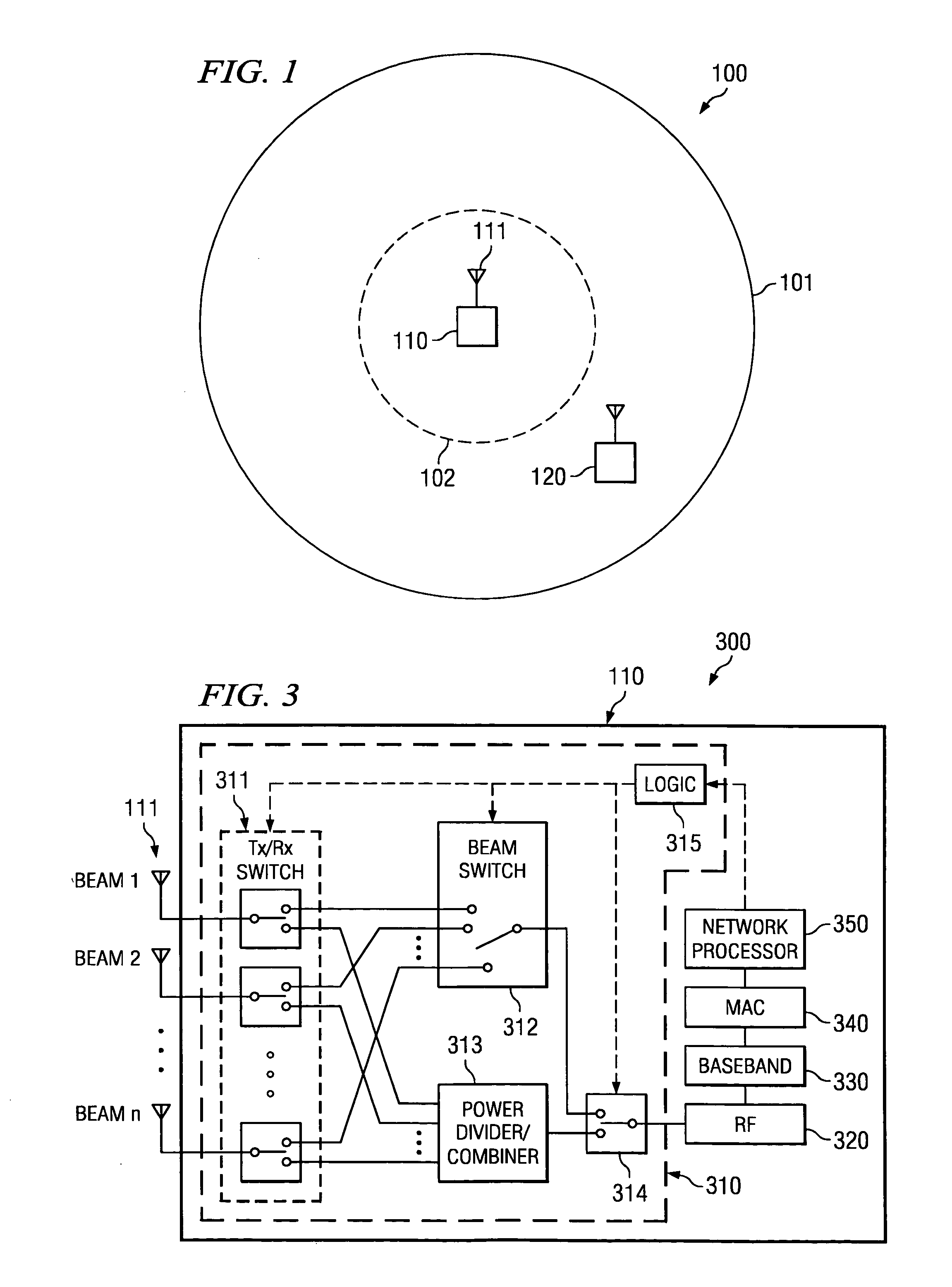
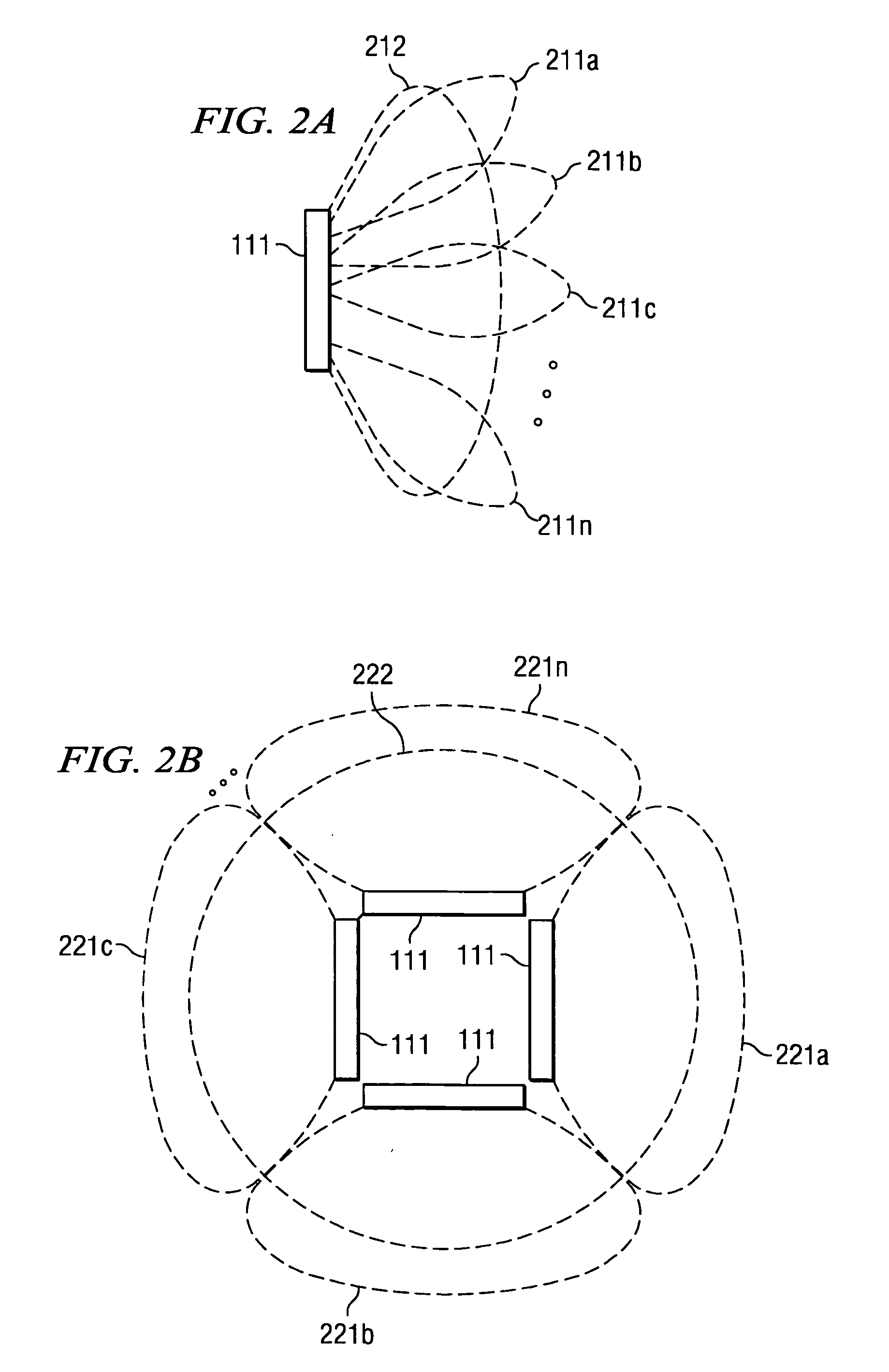
Disclosed are systems and methods which provide high bandwidth data communication with respect to a large coverage area using smart antenna and / or directional antenna (referred to herein as multi-beam antenna) technology. Circuitry may be provided at a WLAN AP to provide selection of particular antenna beams used in the downlink and / or uplink, control of multicast transmission, control of unicast transmission, and to provide antenna pattern shaping techniques. Embodiments implement multi-beam antenna technology with little or no hardware modifications to AP circuitry. Other embodiments implement multi-beam technology using radio front-end and / or radio hardware modifications to AP circuitry. Various diversity techniques may be implemented, such as selection diversity, maximum ratio combining, and equal gain combing. To provide desired antenna pattern shaping, phase offsets with respect to a signal as transmitted in each antenna beam may be employed.
Owner:HONG KONG APPLIED SCI & TECH RES INST
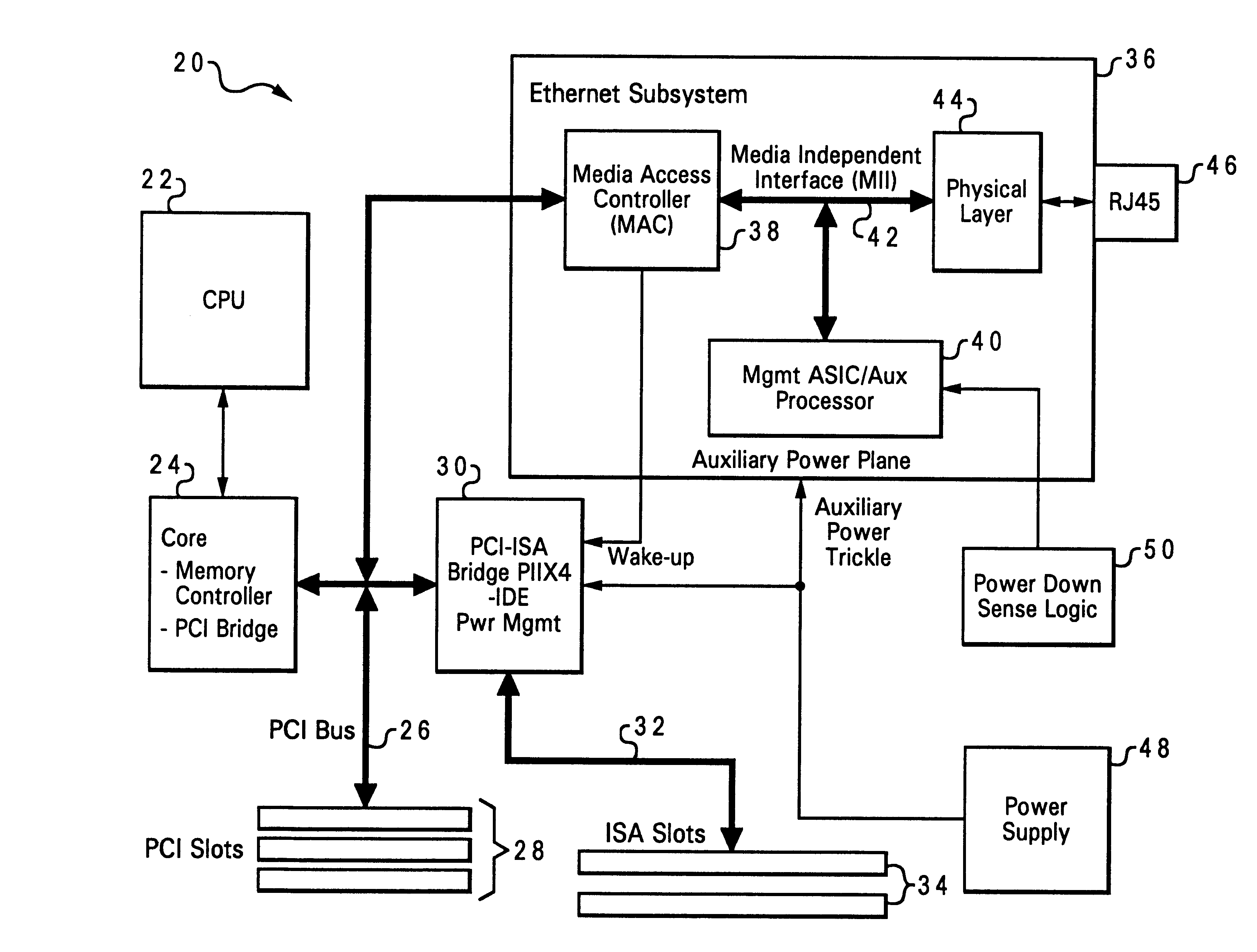
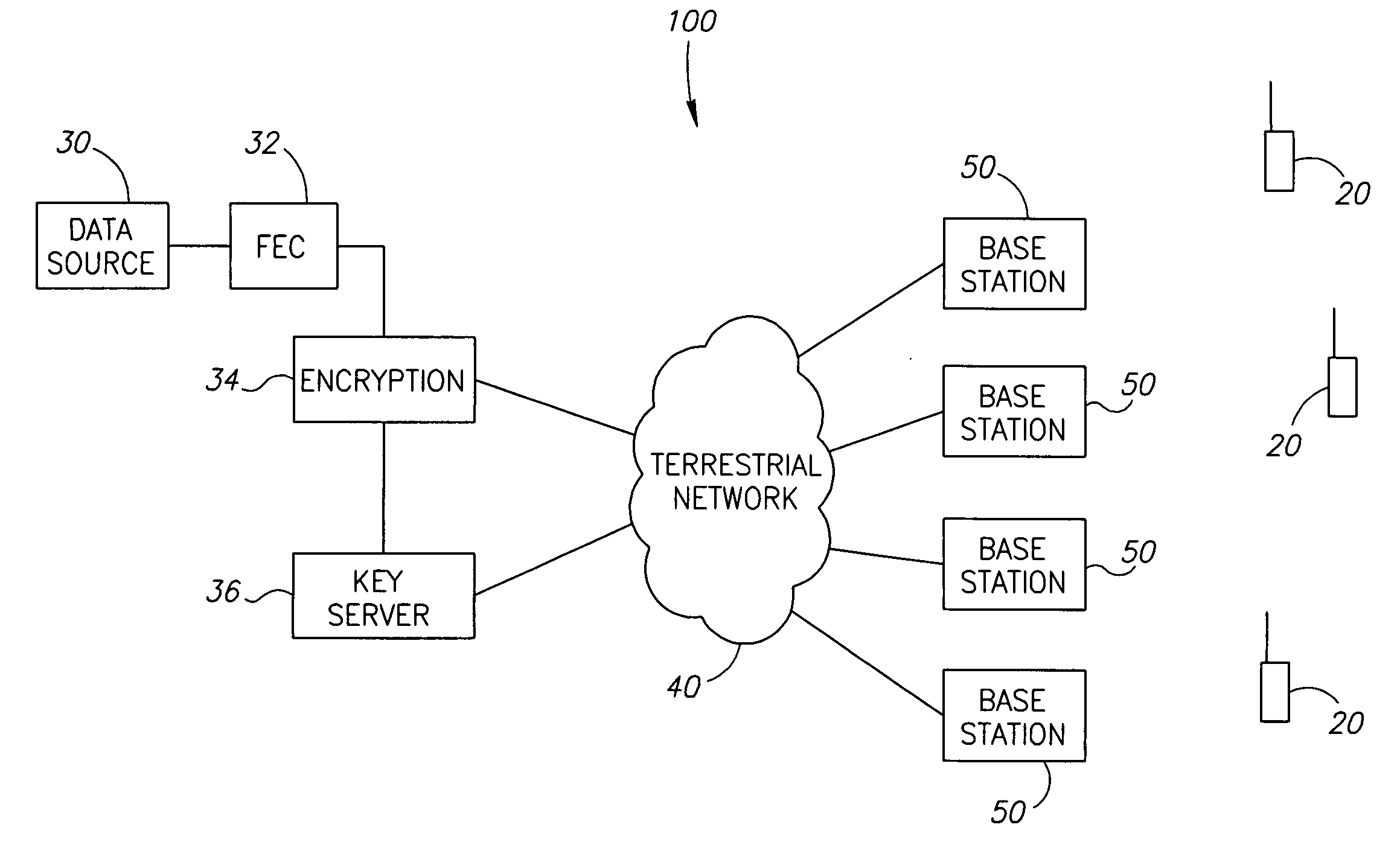
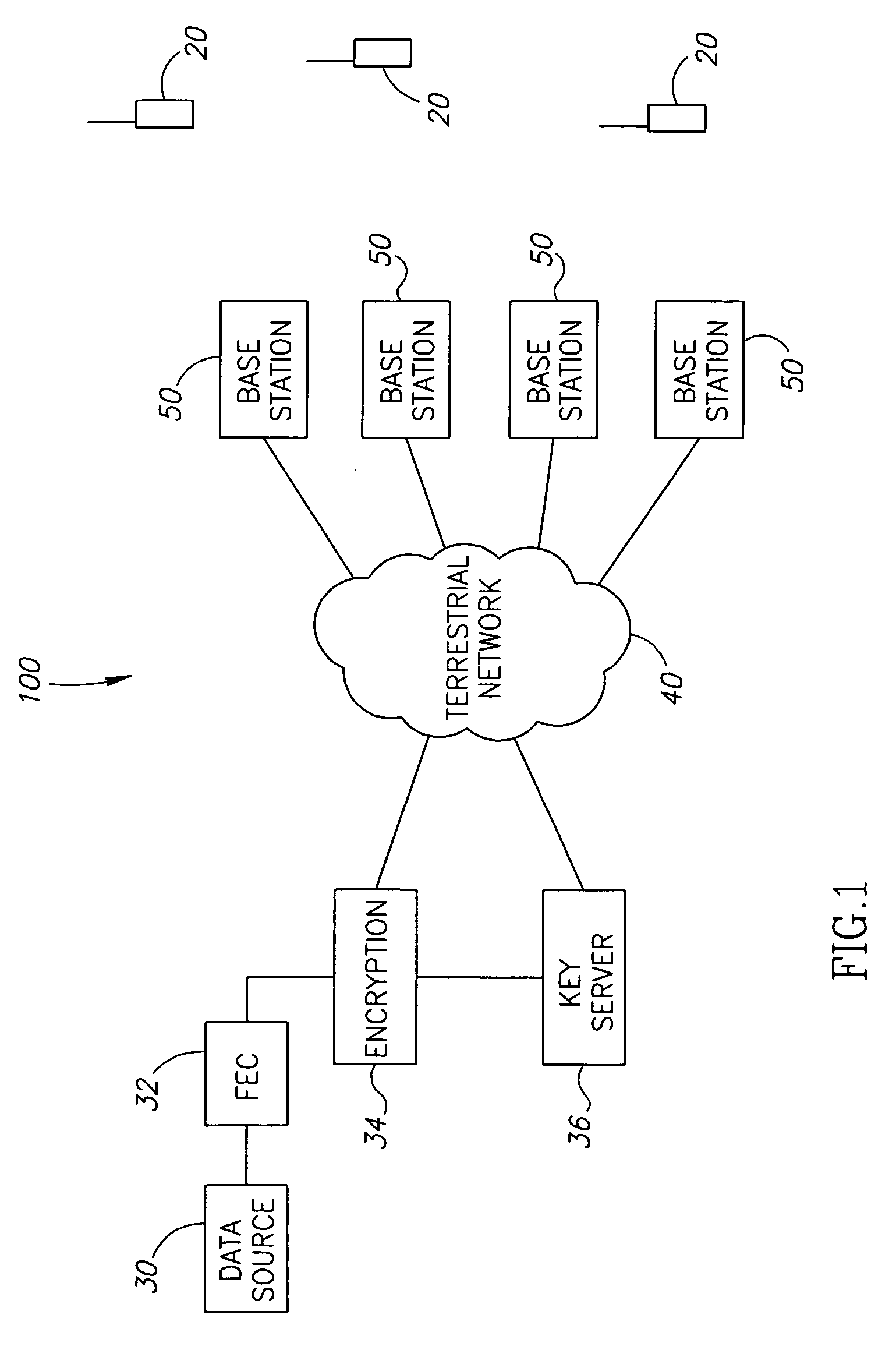
Alert mechanism for service interruption from power loss
A method of monitoring a computer system, by detecting a power interruption to the computer system, using power down sense logic, and generating an alert associated with the power interruption. When the computer system is networked, the alert is transmitted to a remote server. The power down sense logic sends a message to an auxiliary processor (which may be an application-specific integrated circuit, or ASIC), and the auxiliary processor creates a network transmission packet indicating that the computer system is losing power. The auxiliary processor may allow selection of a transmission mode such as uni-cast transmission, multi-cast transmission, or broadcast transmission. A common power supply provides a first power signal to the computer system, and a second power signal to the power down sense logic and auxiliary processor, and maintains the second power signal for a longer duration than the first power signal upon removal of a power source for the power supply, sufficient to carry out the sending of the message from the power down sense logic and the creating of the network alert.
Owner:LENOVO PC INT
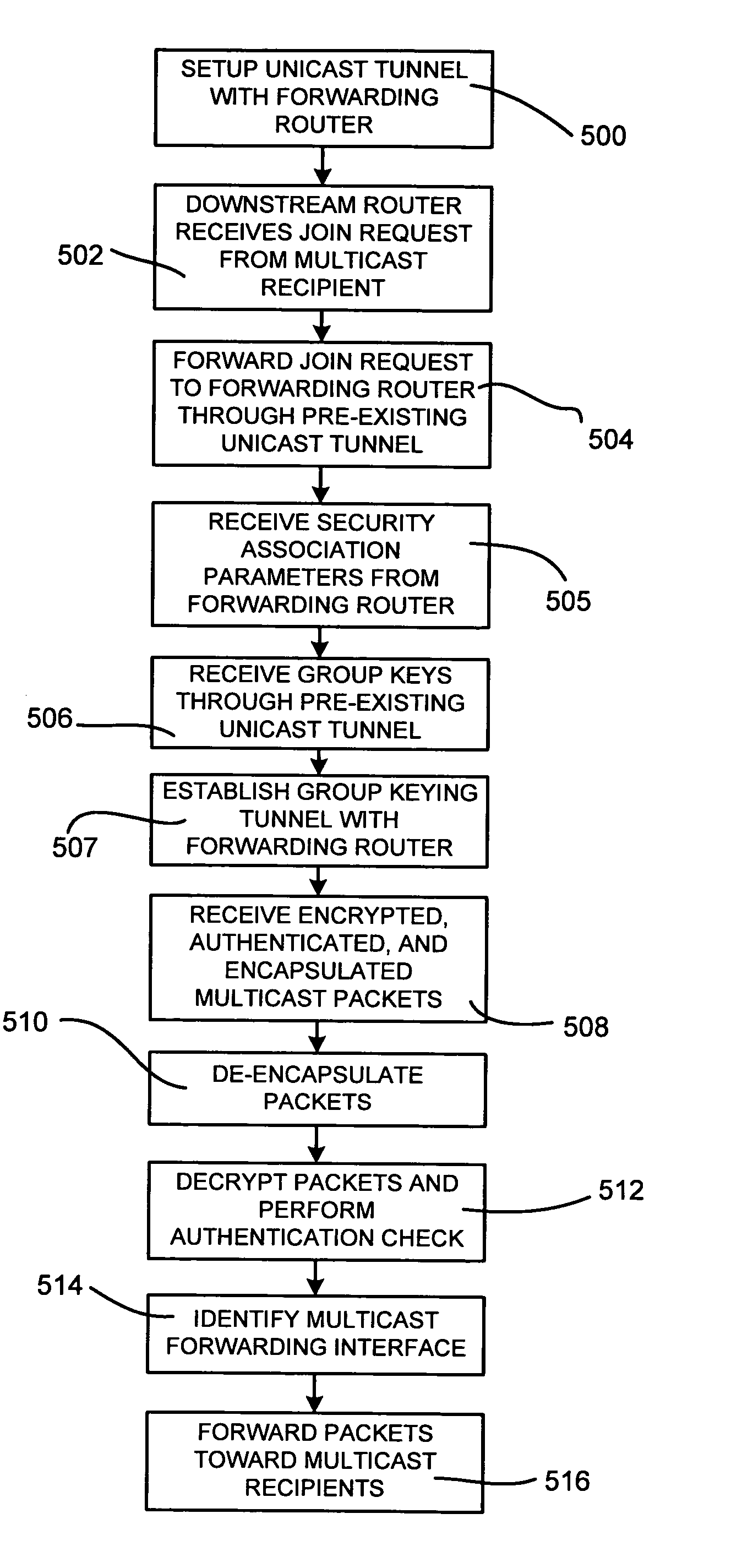
Secure transport of multicast traffic
ActiveUS20050138369A1Special service provision for substationMultiplex system selection arrangementsComputer networkSecure transmission
Secure tunneled multicast transmission and reception through a network is provided. A join request may be received from a second tunnel endpoint, the join request indicating a multicast group to be joined. Group keys may be transmitted to the second tunnel endpoint, where the group keys are based at least on the multicast group. A packet received at the first tunnel endpoint may be cryptographically processed to generate an encapsulated payload. A header may be appended to the encapsulated payload to form an encapsulated packet, wherein the header includes information associated with the second tunnel endpoint. A tunnel may be established between the first tunnel endpoint and the second tunnel endpoint based on the appended header. The encapsulated packet may be transmitted through the tunnel to the second tunnel endpoint. The second tunnel endpoint may receive the encapsulated packet. Cryptographic processing of the encapsulated packet may reveal the packet having a second header. The packet may then be forwarded on an interface toward at least one multicast recipient identified in the second header.
Owner:JUMIPER NETWORKS INC
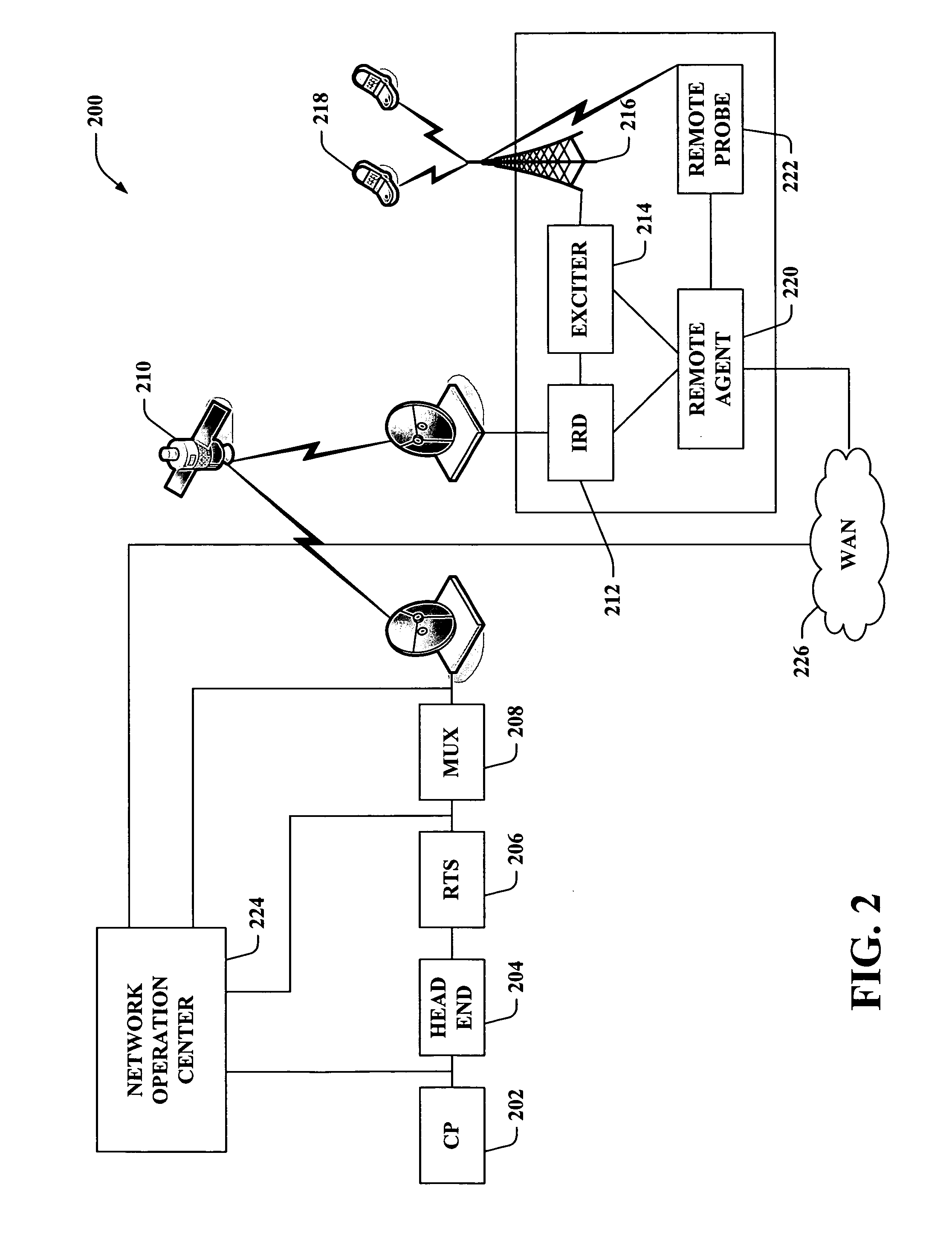
Method and apparatus for collecting information from a wireless device
InactiveUS20070117516A1Well formedNetwork traffic/resource managementBroadcast service distributionForward link onlyMulticast transmission
Systems and methodologies are described that facilitate remotely monitoring and / or controlling a media device that obtains broadcast and / or multicast transmission(s). According to various aspects, systems and methods are described that facilitate remotely controlling media device(s) that operate in connection with broadcast and / or multicast transmission(s) with limited or no reverse link (e.g., employing Forward Link Only (FLO) technology, . . . ). Such systems and methods may monitor various service issues, device performance, network performance, and the like.
Owner:QUALCOMM INC
Multicast transfer route setting method, and multicast label switching method for implementing former method
InactiveUS20060147204A1Increase computing speedLow costTransmission monitoringTransmission monitoring/testing/fault-measurement systemsSelection criterionLabel switching
A method of establishing a multicast transfer route is disclosed that can reduce the cost of entire route under a constraint on delay incurred between starting point and ending points. The method includes the steps of: computing the shortest route with respect to delay connecting the starting point and the plural ending points based on measurement result; computing delay from a node on the shortest route to each ending point and the greatest delay; removing, if the greatest delay satisfies a delay condition, the greatest-cost route from the shortest route in accordance with selection criteria effective for cost reduction; dividing the multicast transfer route into two route trees; and establishing separately computed route as a complementary route that complement the removed route for connecting the two route trees. A method of multicast label switching for realizing the above method is also disclosed. A multicast label switching route is established using hierarchical labels by establishing a common multicast label switching route using a first layer label and establishing plural partial multicast label switching routes for subgroup destinations using lower layer labels. A relay node recognizes the hierarchical labels thereby to label-switch using all hierarchical labels.
Owner:NIPPON TELEGRAPH & TELEPHONE CORP
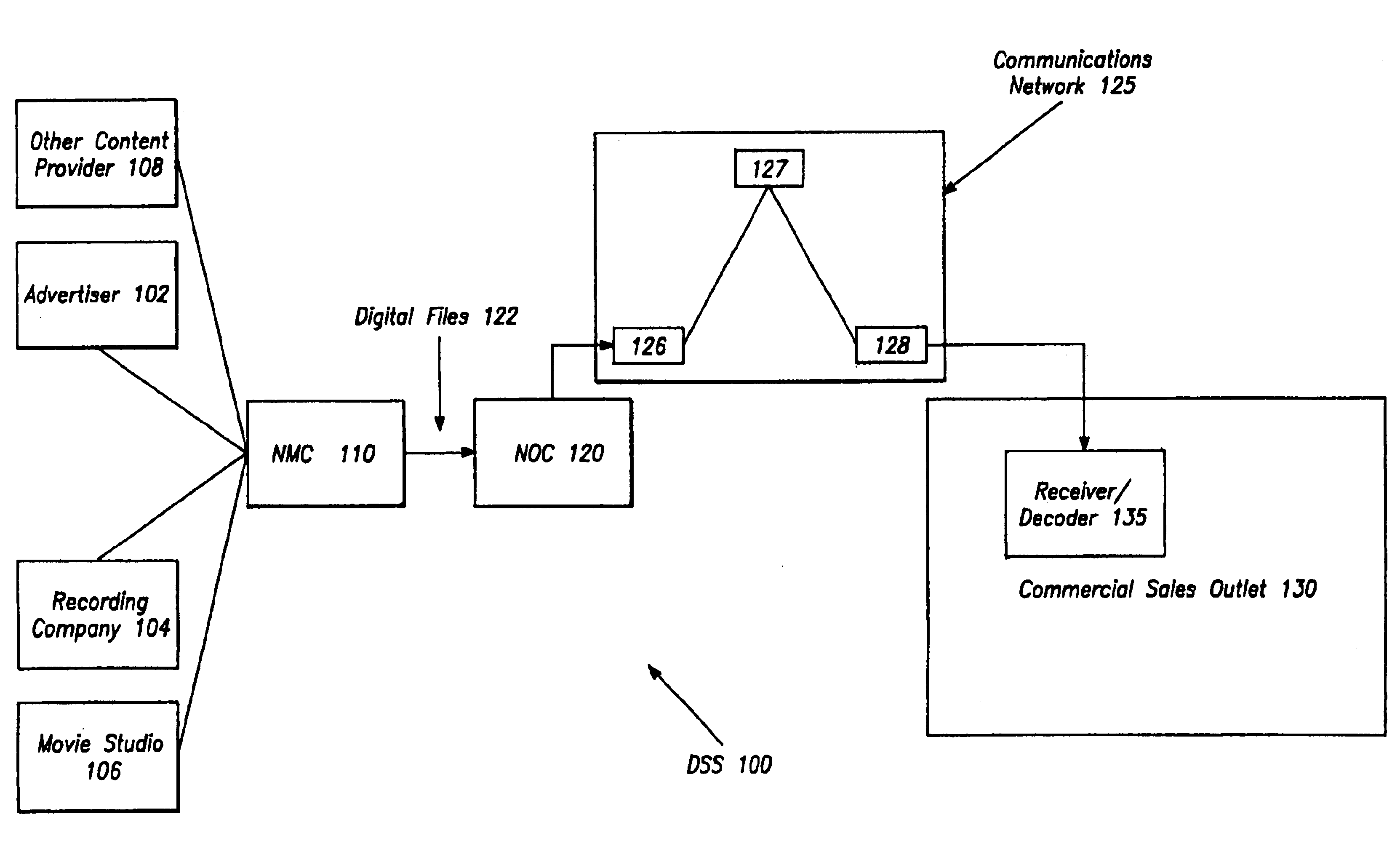
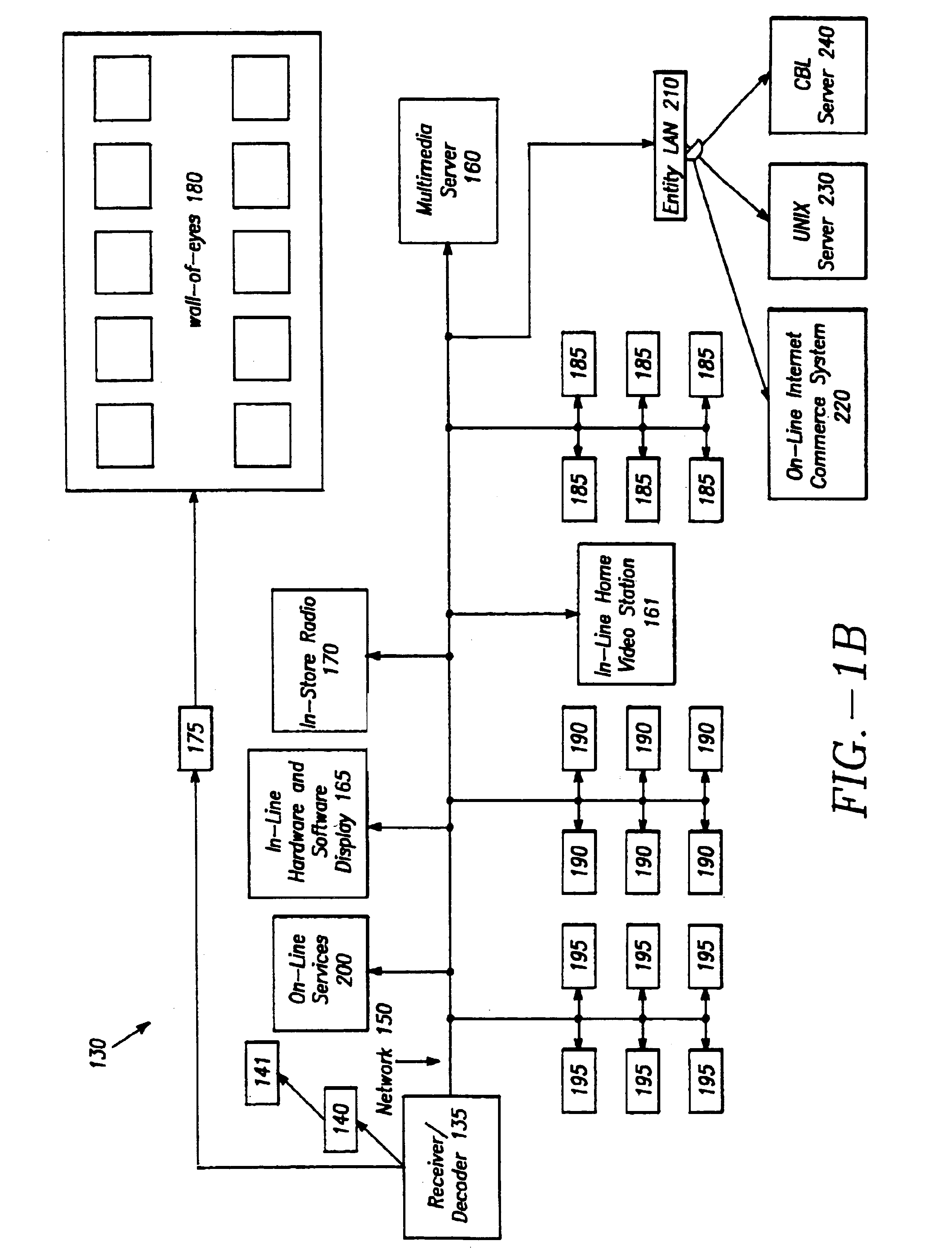
Method and apparatus for gathering statistical information about in-store content distribution
InactiveUS6944632B2Digital data processing detailsBuying/selling/leasing transactionsContent distributionMultimedia servers
Owner:THOMSON LICENSING SA
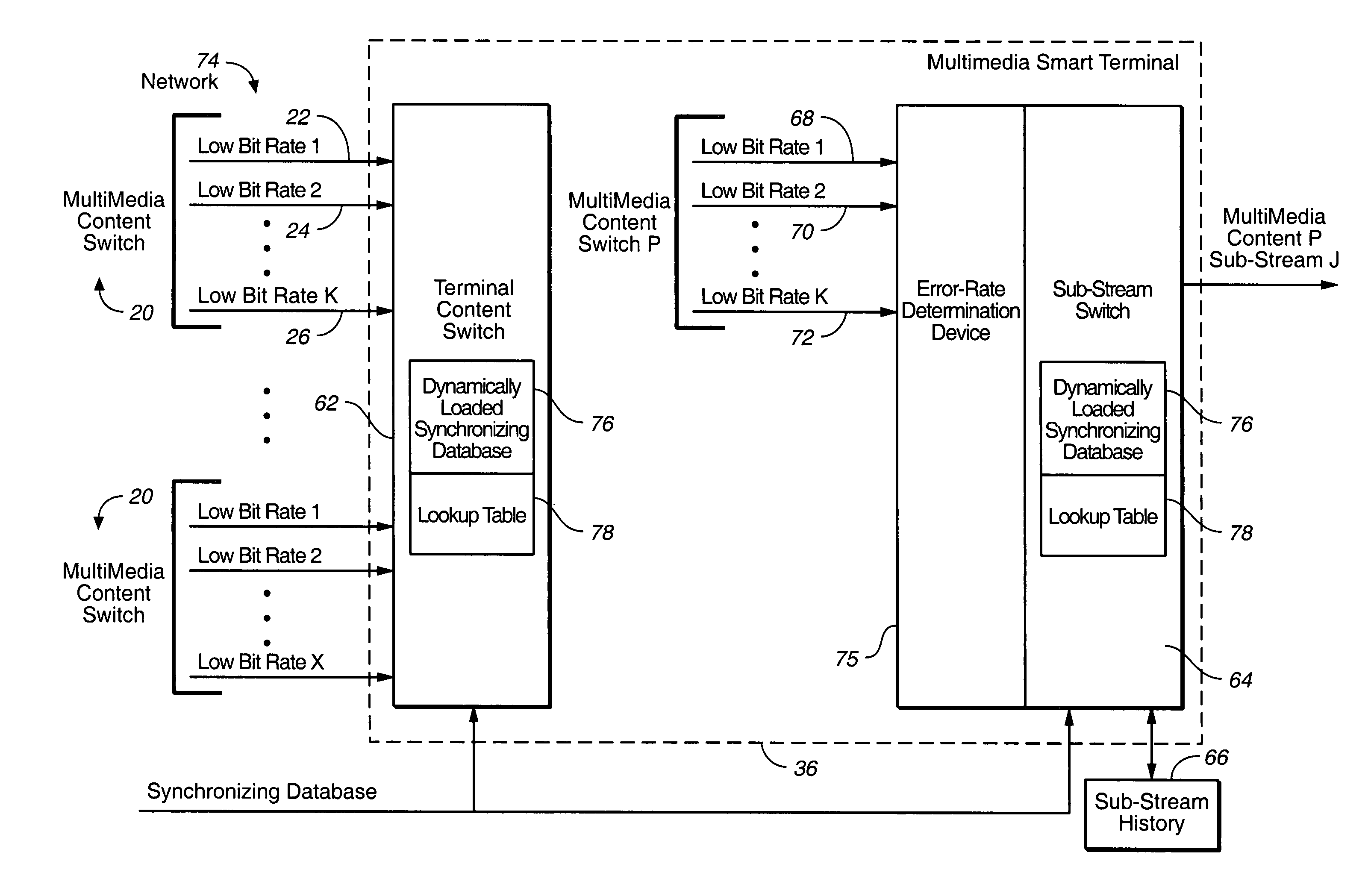
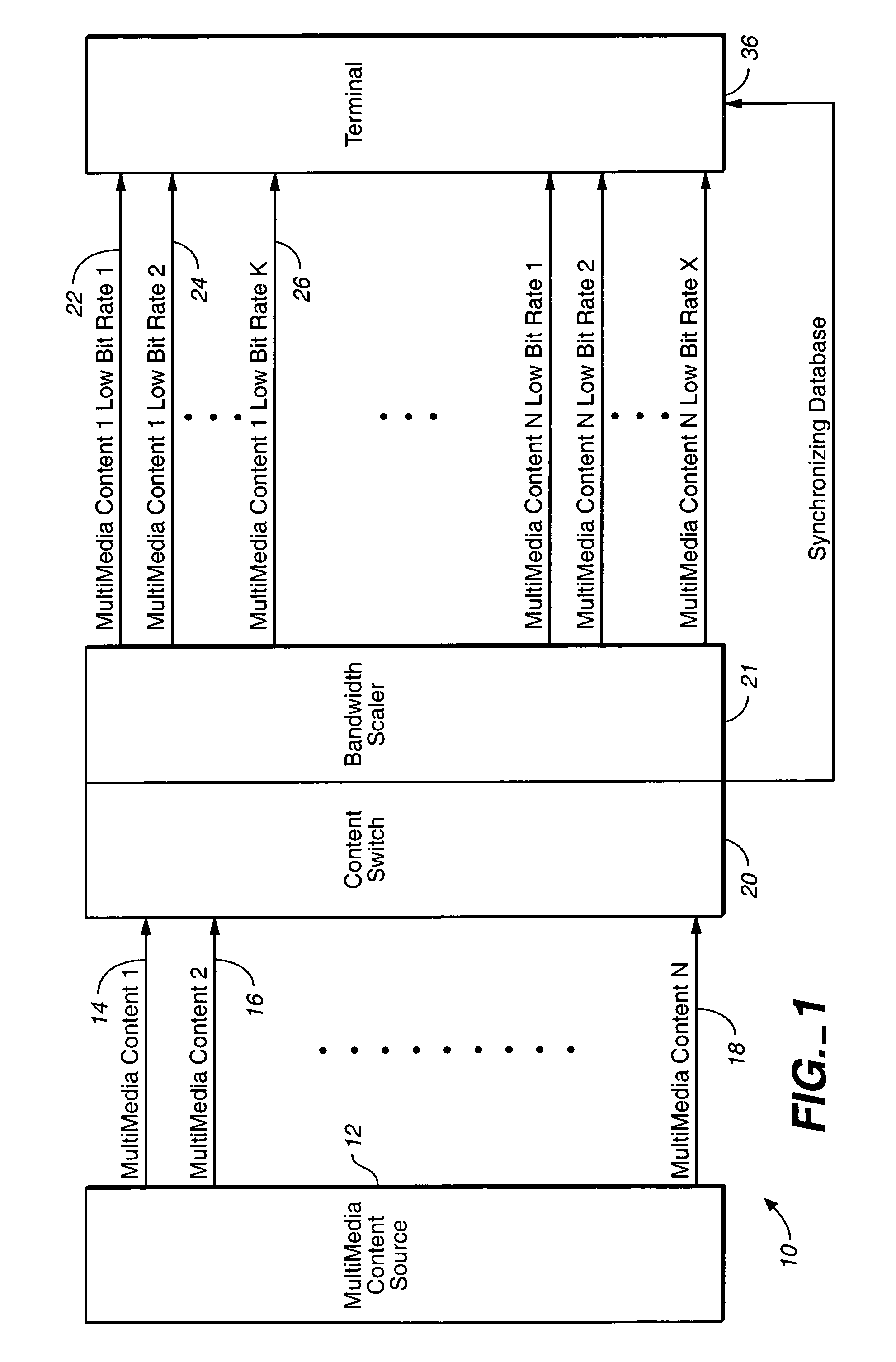
Multicasting transmission of multimedia information
InactiveUS7003794B2Easy to receiveSmooth transitionBroadcast transmission systemsTime-division multiplexComputer networkMulticast transmission
A multicasting system for reception of multimedia information comprising: a content switch coupled to a multimedia content source and at least one multimedia smart terminal. The multimedia content source includes a plurality of multimedia contents, wherein each multimedia content is supported by a primary multimedia stream transmitted over a primary dedicated channel having a primary bandwidth. At least one multimedia smart terminal is configured to receive from the content switch over a network each multimedia content as a secondary multimedia stream transmitted over a secondary channel having a secondary bandwidth. The content switch includes a bandwidth scaler configured to scale each primary multimedia stream to a plurality of secondary multimedia sub-streams that are substantially synchronized. The multimedia smart terminal includes a smart terminal sub-stream switch configured to switch among the plurality of secondary multimedia sub-streams in order to select a substantially optimum secondary multimedia sub-stream. The substantially optimum secondary multimedia sub-stream includes a substantially optimum relationship between an error rate level determined at the time of reception of a multimedia content and the quality of reception of a multimedia content.
Owner:RUNCOM TECH LTD
System and method of source based multicast congestion control
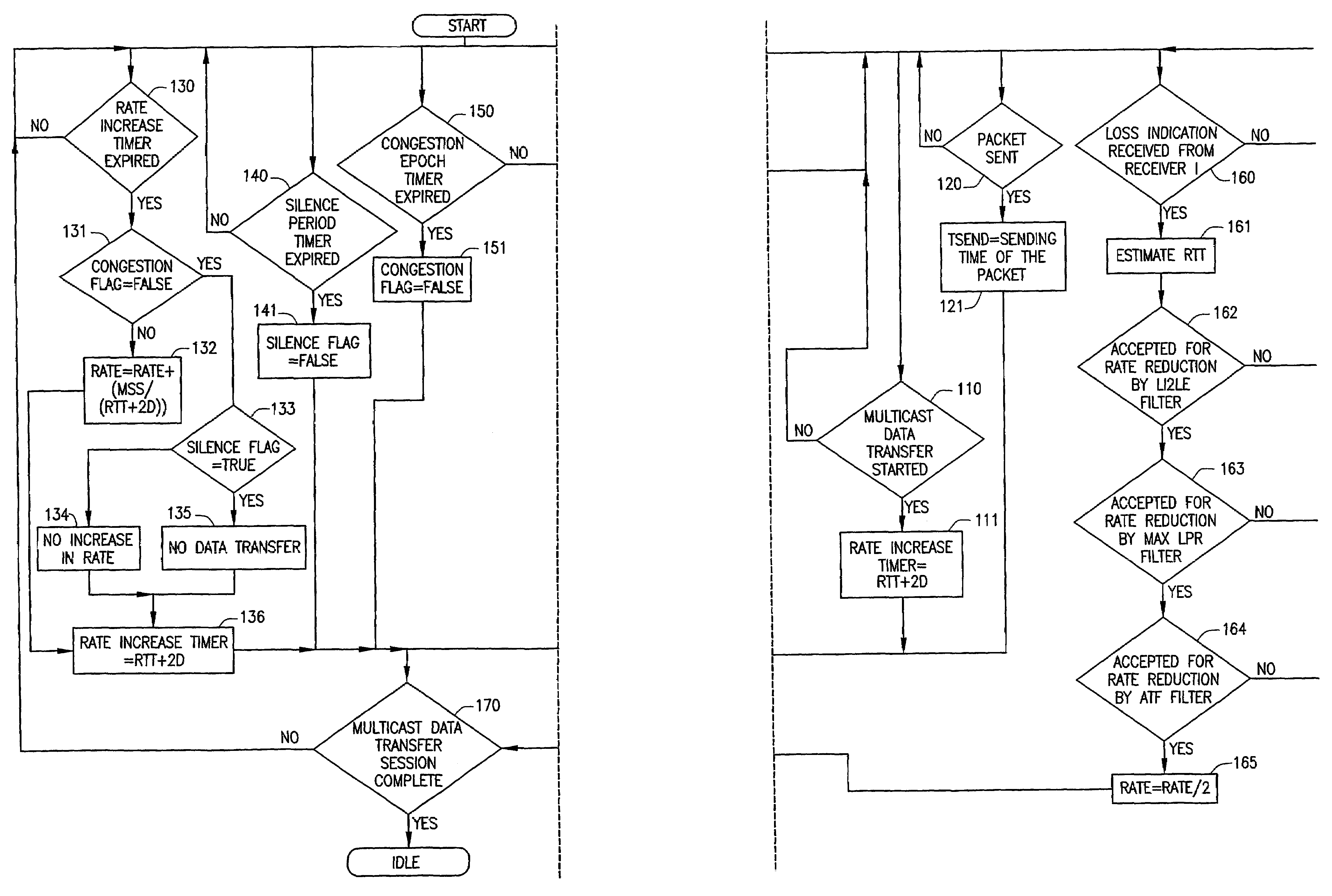
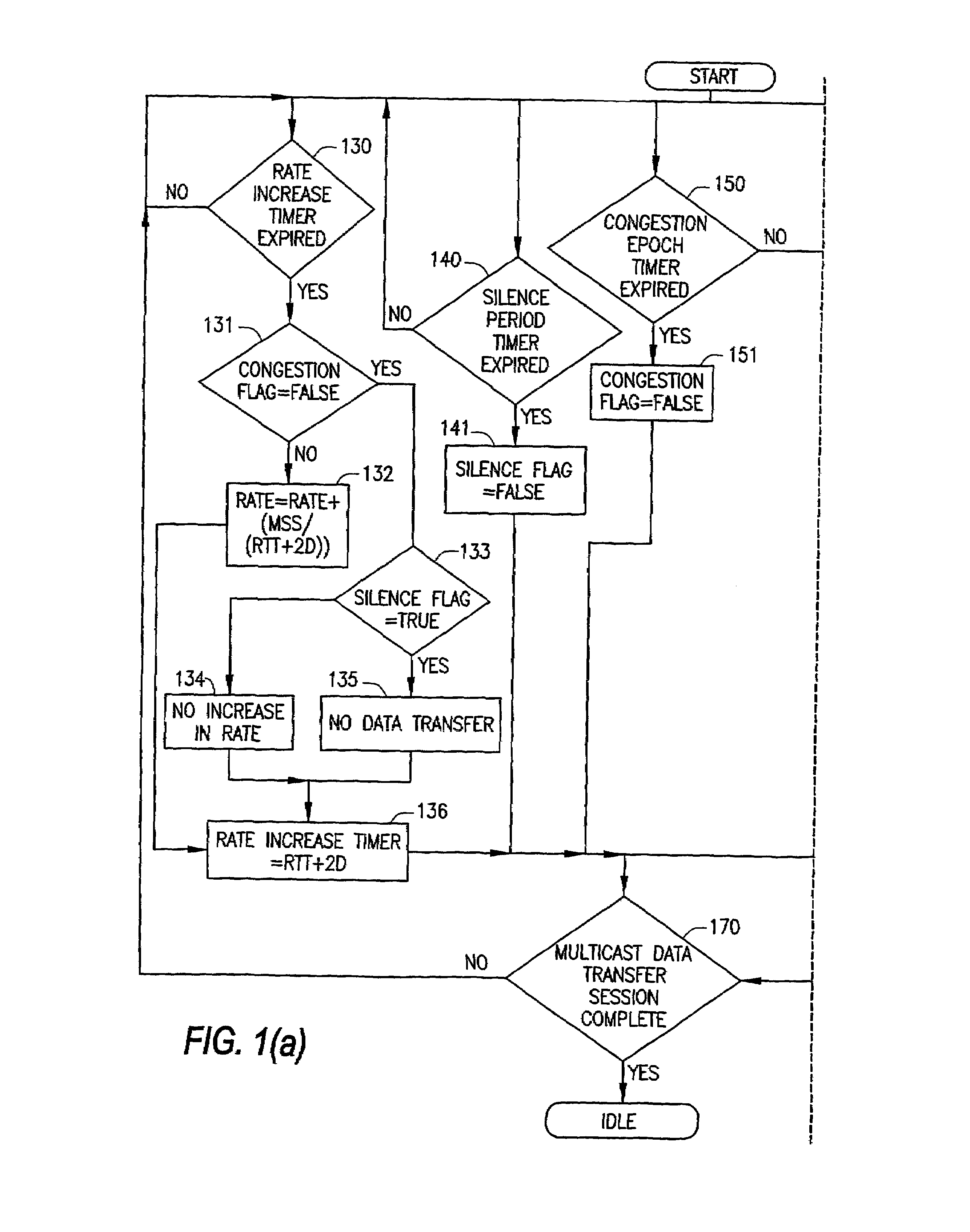
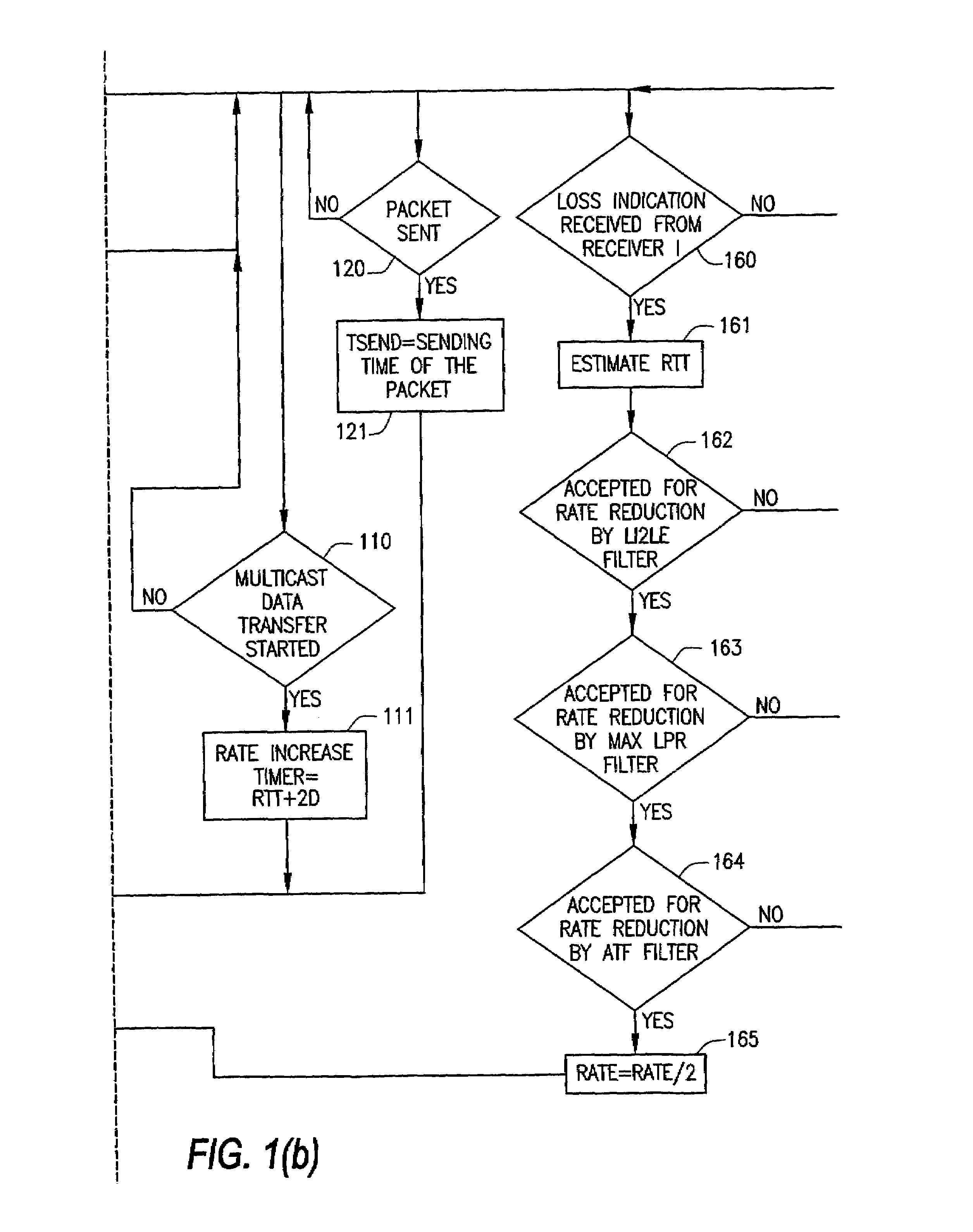
InactiveUS7020714B2Control congestionIncrease multiplicative decrease moduleSpecial service provision for substationEnergy efficient ICTComputer networkMulticast congestion control
The present invention provides for a method of congestion control for multicast transmission that is entirely managed at the source of the transmission. The various types of filters as well as round trip time estimators (130) that are used in the invention to determine when the rate of the multicast transmission should be reduced to alleviate congestion. The source of the transmission adjusts the rate of transmission based on loss indications that the receivers would otherwise transmit.
Owner:RENESSELAER POLYTECHNIC INST
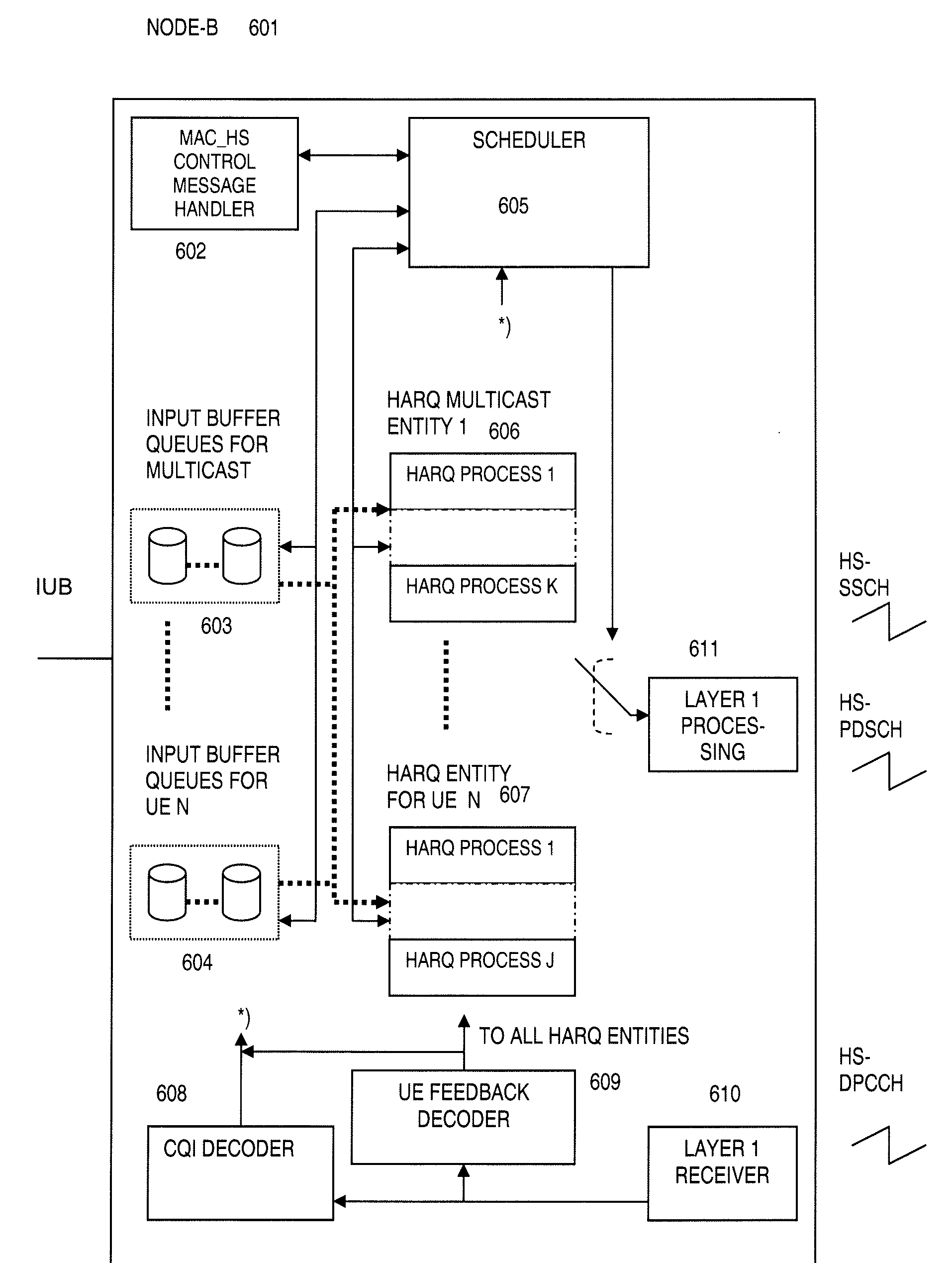
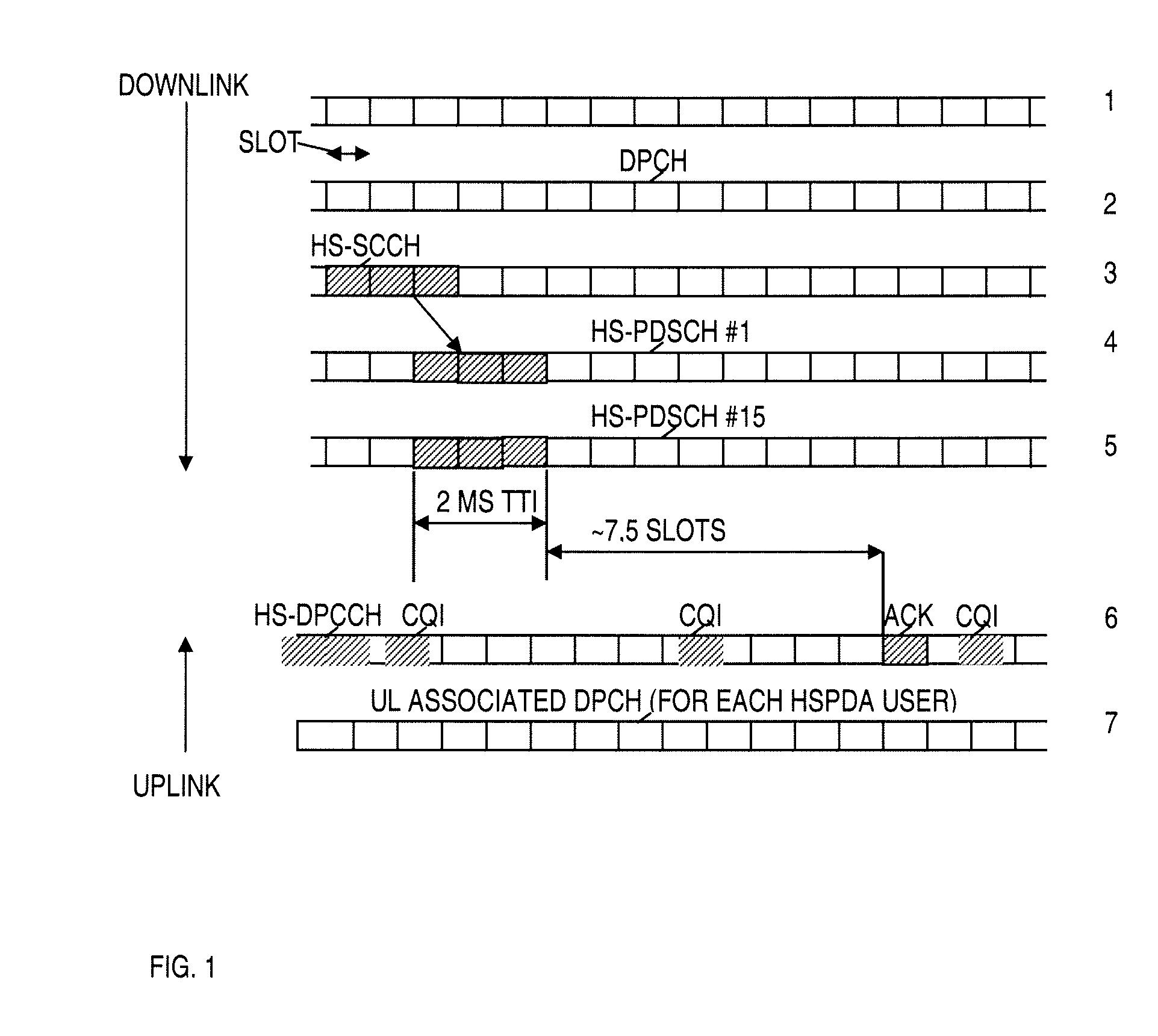
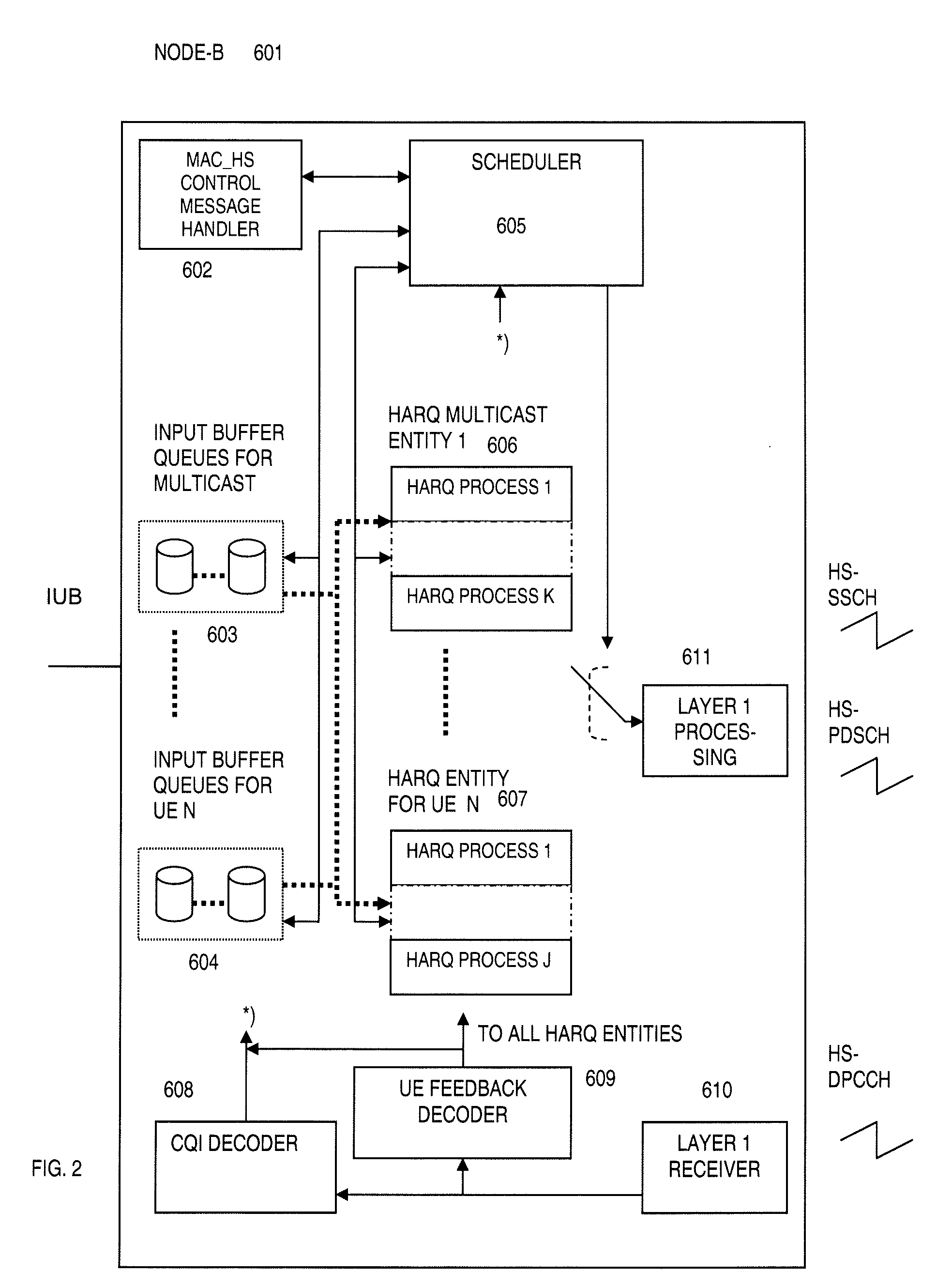
Broadcast AMD Multicast On High Speed Downlink Channels
InactiveUS20090207771A1Efficiently streamedAssess restrictionBroadcast transmission systemsDPCCHControl channel
A high speed downlink packet access base station (HSPDA Node B) and a method therefore working in acknowledged mode (AM), the base station being adapted for unicast transmission on a physical downlink shared channel (HS-DSCH), by preceding announcement on a shared control channel (HS-SCCH) which shared control channel may be decoded by a given user entity using its own identity (UE-ID), each user entity (UE) being adapted for transmitting an acknowledge (ACK) or non-acknowledge (NACK) message pertaining to the reception of the given transmission on an uplink dedicated physical control channel (HS-DPCCH) pertaining to a given HARQ process of a given individual user entity. The base station is performing multicast transmissions (11, 401) on the physical downlink shared channel (HS-DSCH) by preceding announcement on the shared control channel (HS-SCCH) coded with a multicast identity (MU-ID) of a reserved address space, which downlink shared channel (HS-SCCH) may be decoded simultaneously by a plurality of user entities, wherein each user entity is using the multicast identity (MU-ID) instead of the user entity's respective user identity. A user entity and a method therefore have moreover been provided.
Owner:TELEFON AB LM ERICSSON (PUBL)
Multicast over unicast in a network
ActiveUS20070002858A1Quality improvementSpecial service provision for substationData switching by path configurationUser deviceComputer science
A method is described for receiving a multicast in user devices in a network issuing a request to join a multicast group, identifying multicast data packets associated with the multicast group, monitoring transmissions of the multicast data packets to determine whether the identified multicast data packets are being transmitted in an already established unicast session and establishing a unicast session and processing multicast data packets if an already established unicast session does not exist A method is described for receiving a multicast transmission in user devices in a network establishing a unicast session with a dedicated terminal, identifying multicast data packets associated with a multicast group, monitoring transmissions of the multicast data packets and processing the multicast data packets by the dedicated terminal. Additonally, an apparatus is described for accepting a request to join a multicast group, for identifying multicast data packets associated with the multicast group, establishing a unicast session, for encapsulating said multicast data packets in a unicast frame and for forwarding the unicast frame via the unicast session.
Owner:THOMSON LICENSING SA
Secure multicast transmission
InactiveUS20070028099A1Reduce amountReduce loadSpecial service provision for substationKey distribution for secure communicationComputer hardwareSecure multicast
A method of multicasting data. The method includes providing a data block for multicasting, generating a plurality of segments that represent the data block, such that a receiver needs to receive fewer than all the generated segments in order to reconstruct the data block, encrypting at least a portion of the generated segments, so as to generate encrypted data units encrypted with a plurality of different keys or encryption methods and transmitting the encrypted data units over one or more multicast channels.
Owner:BAMBOO MEDIACASTING
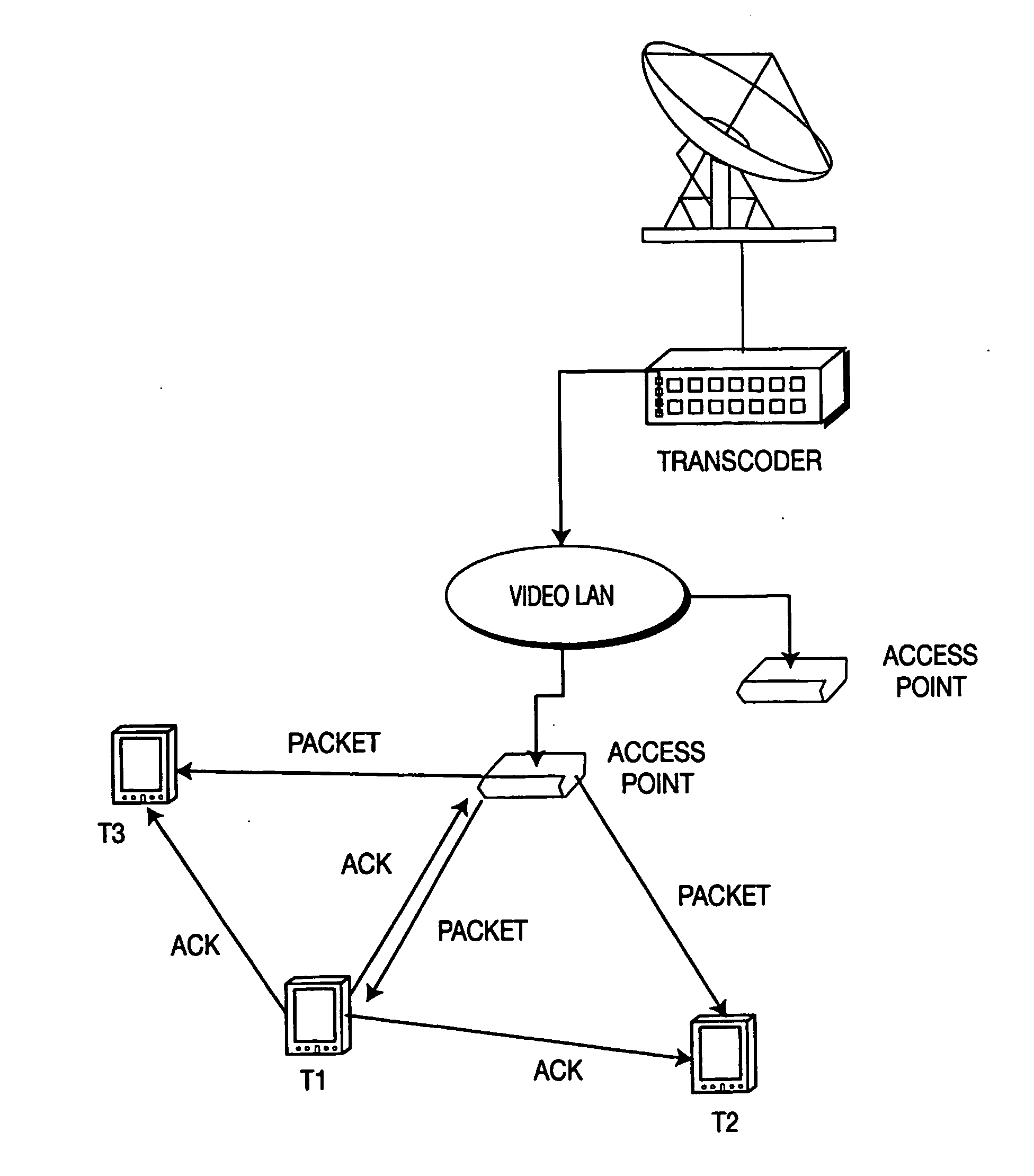
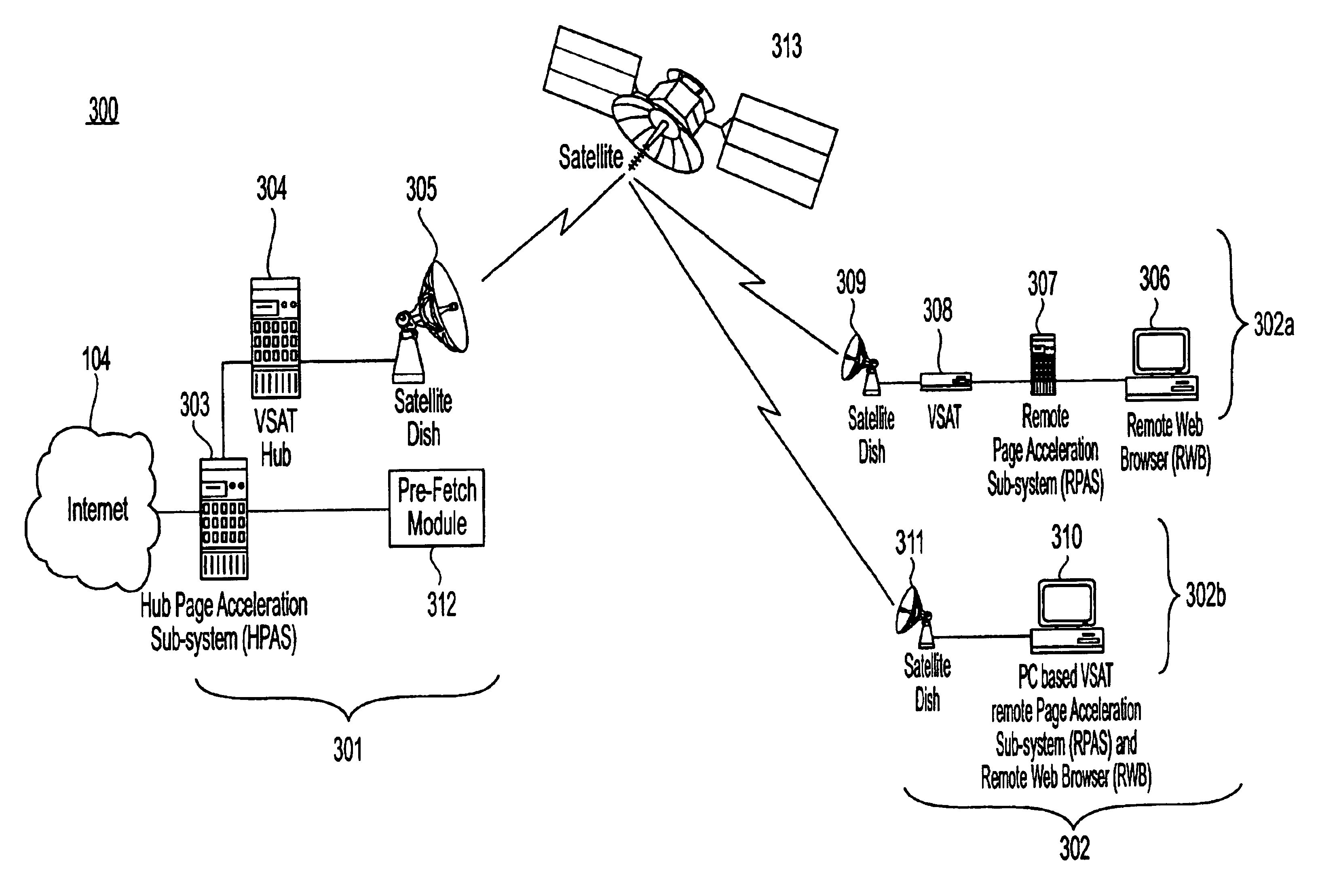
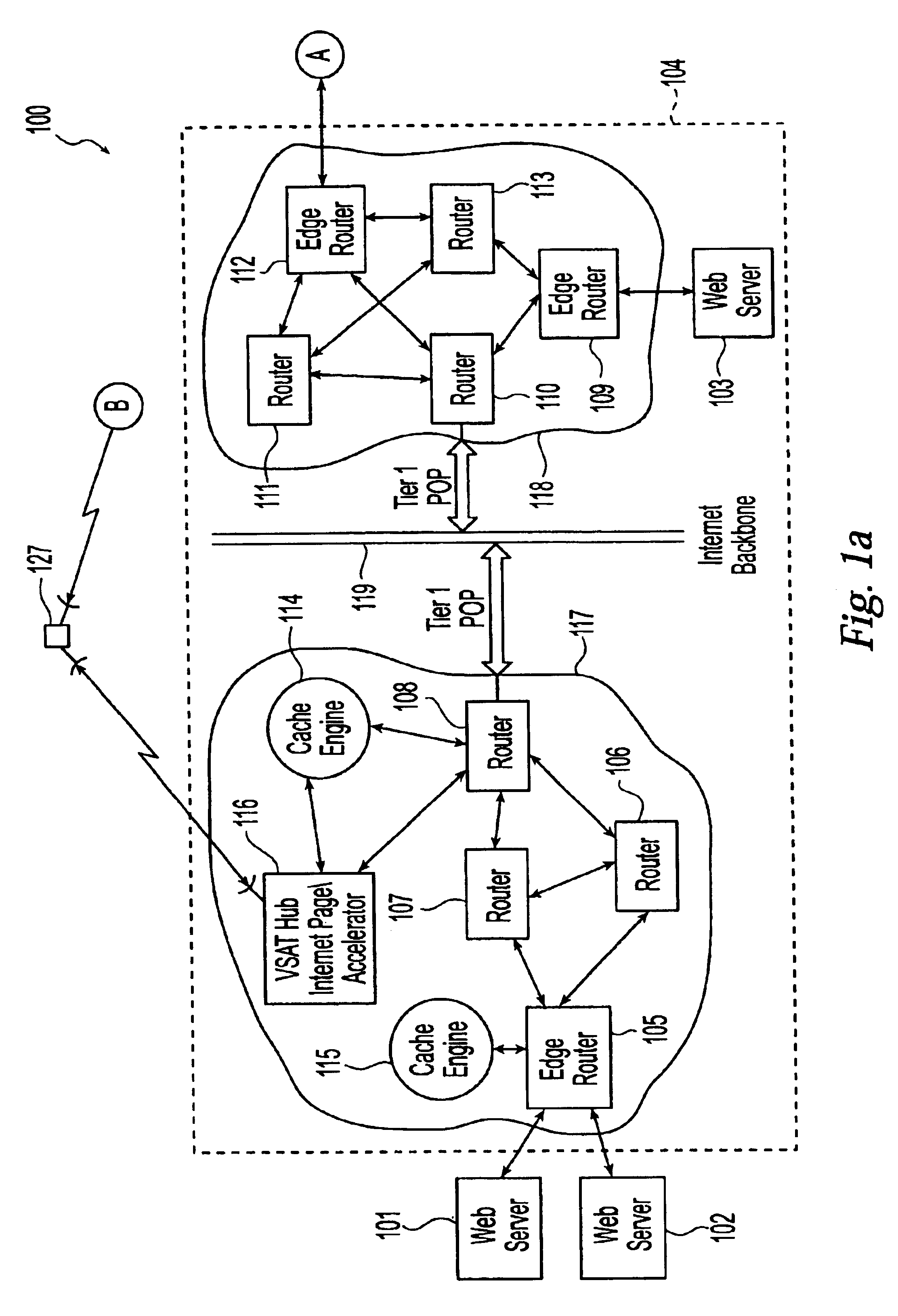
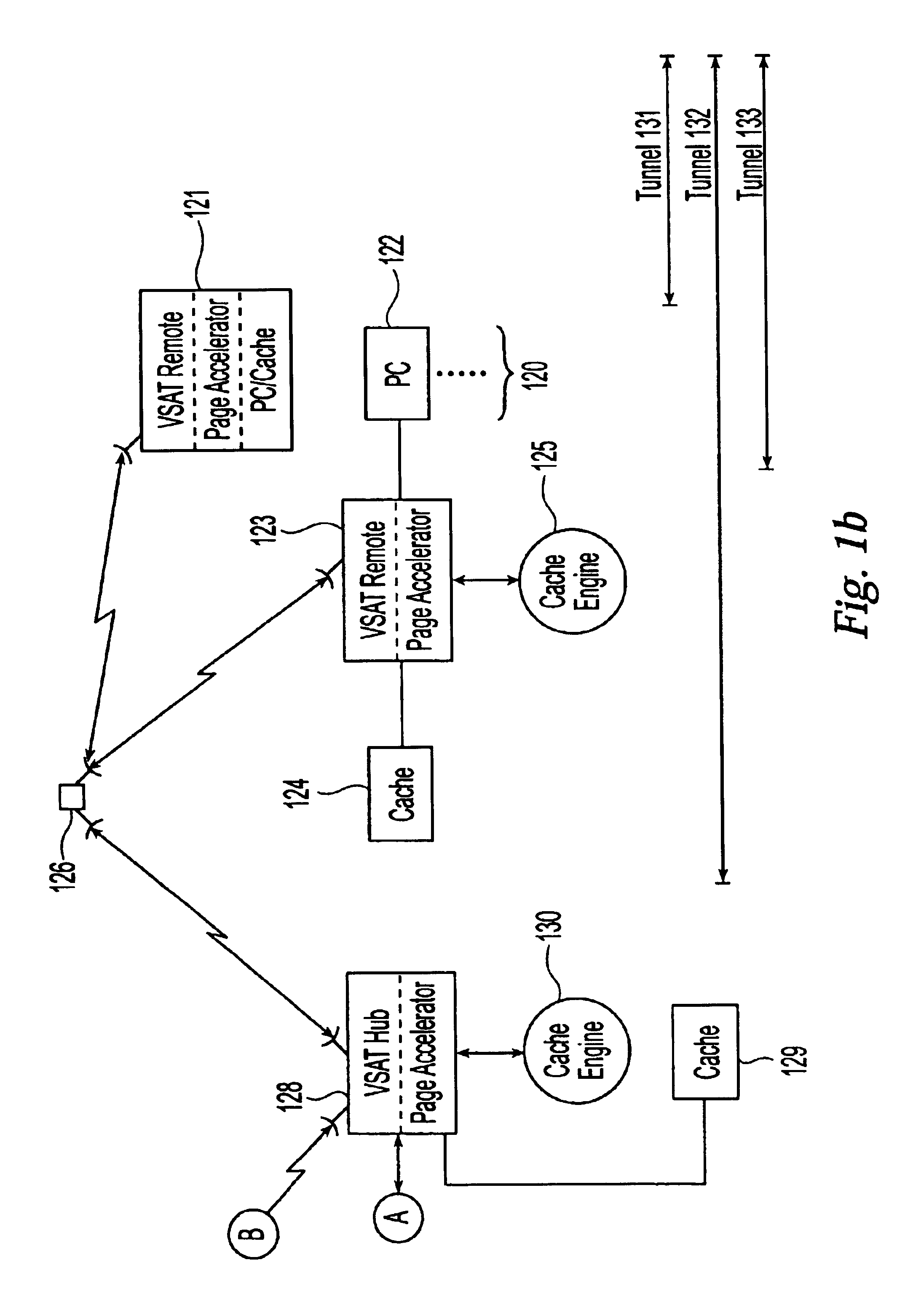
System and method for internet page acceleration including multicast transmissions
InactiveUS6947440B2Reducing latency experiencedLow experience requirementSpecial service provision for substationNetwork topologiesDistributed cacheThe Internet
A broadband communication system with improved latency is disclosed. The system employs distributed caching techniques to assemble data objects at locations proximate to a source to avoid latency over delayed links. The assembled data objects are then multicast to one or more remote terminals in response to a request for the objects, thus reducing unnecessary data flow across the satellite link.
Owner:GILAT SATELLITE NETWORKS
Methods for energy-efficient unicast and multicast transmission in a wireless communication system
ActiveUS20140204825A1Improve reception qualityTransmission path divisionBroadcast transmission systemsCommunications systemUser equipment
A method for time multiplexing subframes on a serving cell to a user equipment, wherein one set of subframes operate with the legacy LTE transmission format and one set of subframes operate with an evolved transmission format comprising reduced density CRS transmission without a PDCCH control region.
Owner:TEXAS INSTR INC
Radio Transmission Method
InactiveUS20080192661A1Improve reliabilityImprove utilization efficiencyError prevention/detection by using return channelData switching by path configurationMulticast packetsWireless security
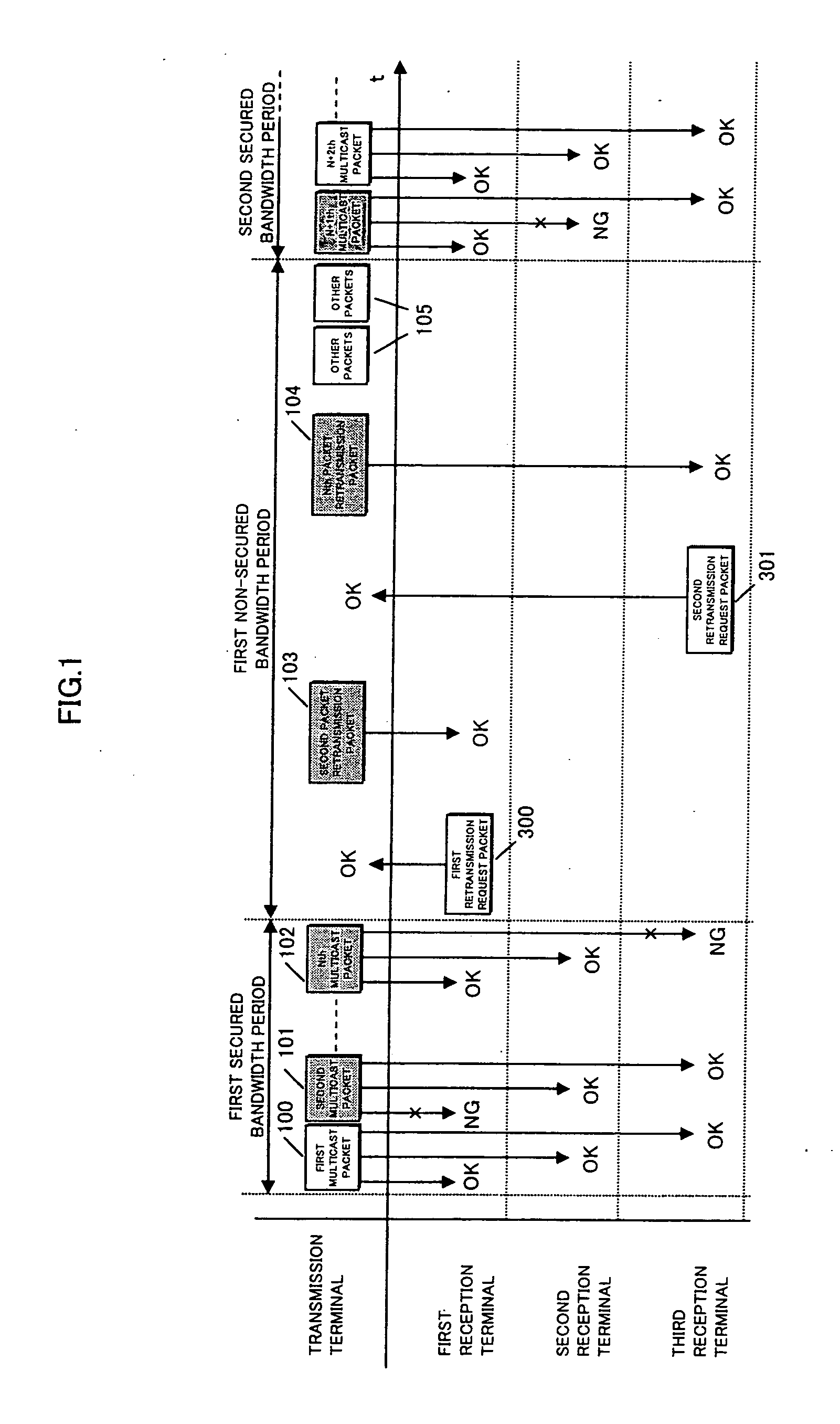
Retransmission control and retransmission are performed at a lower priority than the transmission of multicast packets from a transmission apparatus to two or more reception apparatuses. A communication apparatus performs wireless multicast transmission to reliable transmit packets. In a transmission side terminal, sequence numbers are attached at a layer higher than the Mac layer to each of secured-bandwidth or priority control-type Mac layer multicast packets, and in a plurality of reception side terminals, missing packets are detected using the sequence numbers, and bandwidth other than the secured bandwidth or lower priority packets are used to perform retransmission requests. The transmission terminal retransmits data using bandwidth other than the secured bandwidth or lower priority packets, thereby enabling favorable reception of audio, video and data when transmitting the audio, video and data in real-time to the reception terminals using wireless secured bandwidth-type or priority control-type Mac layer multicast transmission.
Owner:PANASONIC CORP
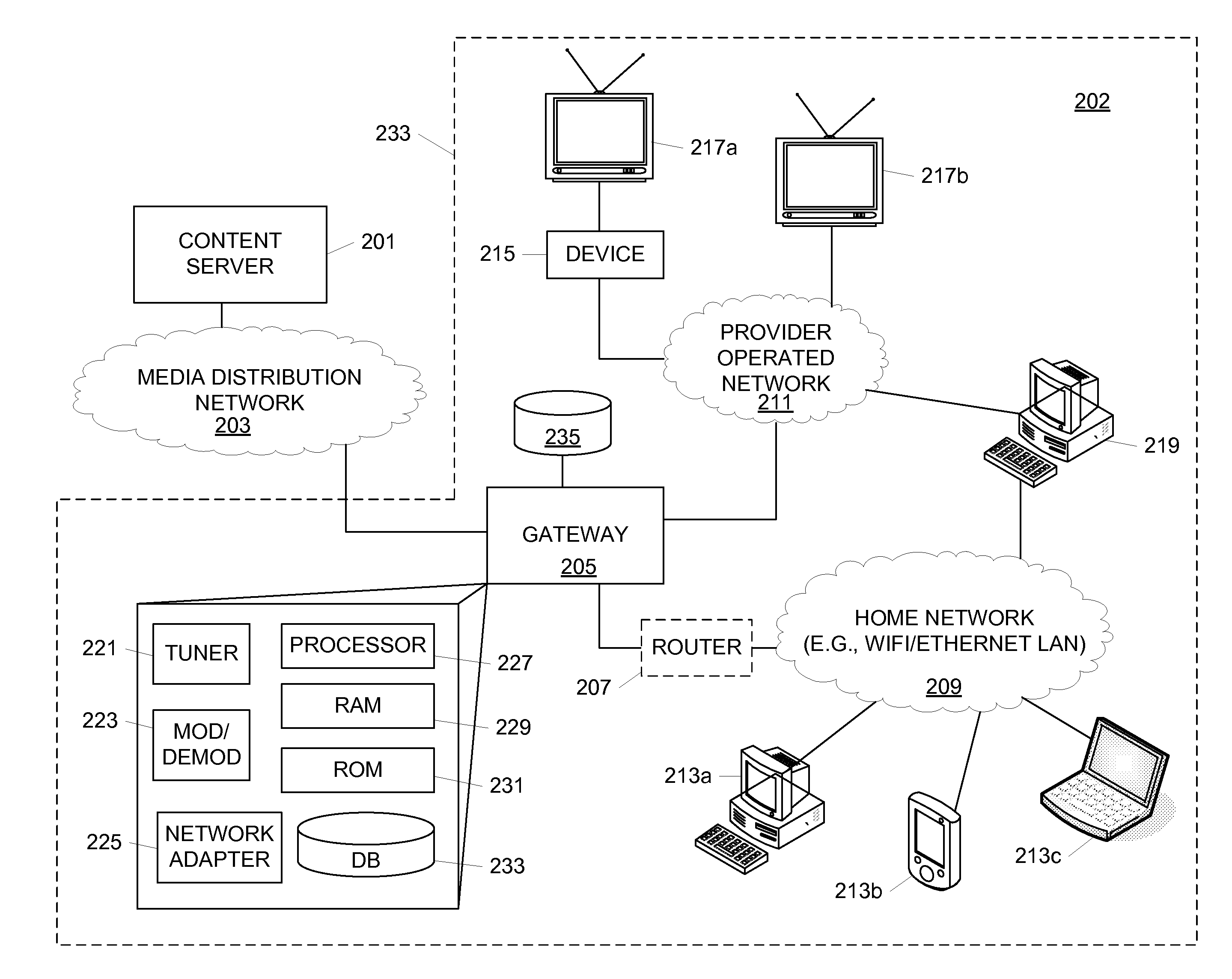
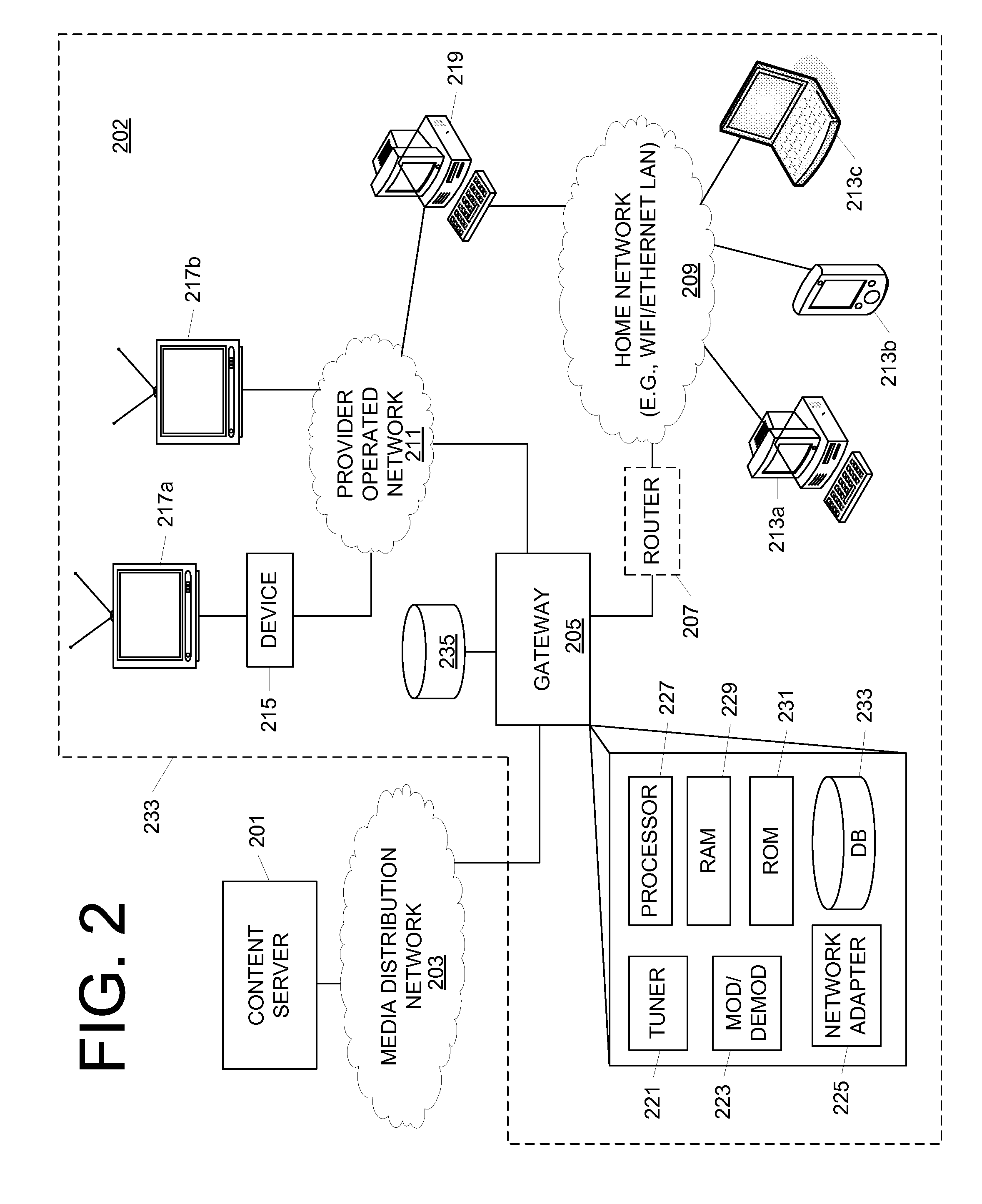
Quality of Service for Distribution of Content to Network Devices
ActiveUS20120173746A1Prevent excess lagQuality assuranceMultiple digital computer combinationsTransmissionQuality of serviceComputer compatibility
A gateway device configured to receive IP video content may select and use transmission methods that maintain a certain quality of service for delivering the content. A transmission method may be selected based on a network to which the client device is connected. The gateway device may select a network through which the content is to be delivered depending on a variety of factors including bandwidth availability, client compatibility, quality of service provided and the like. A gateway device may further be configured to convert multicast transmissions to unicast, to provide dynamic storage of content for pre-positioning and other purposes and / or to provide other functions.
Owner:COMCAST CABLE COMM LLC
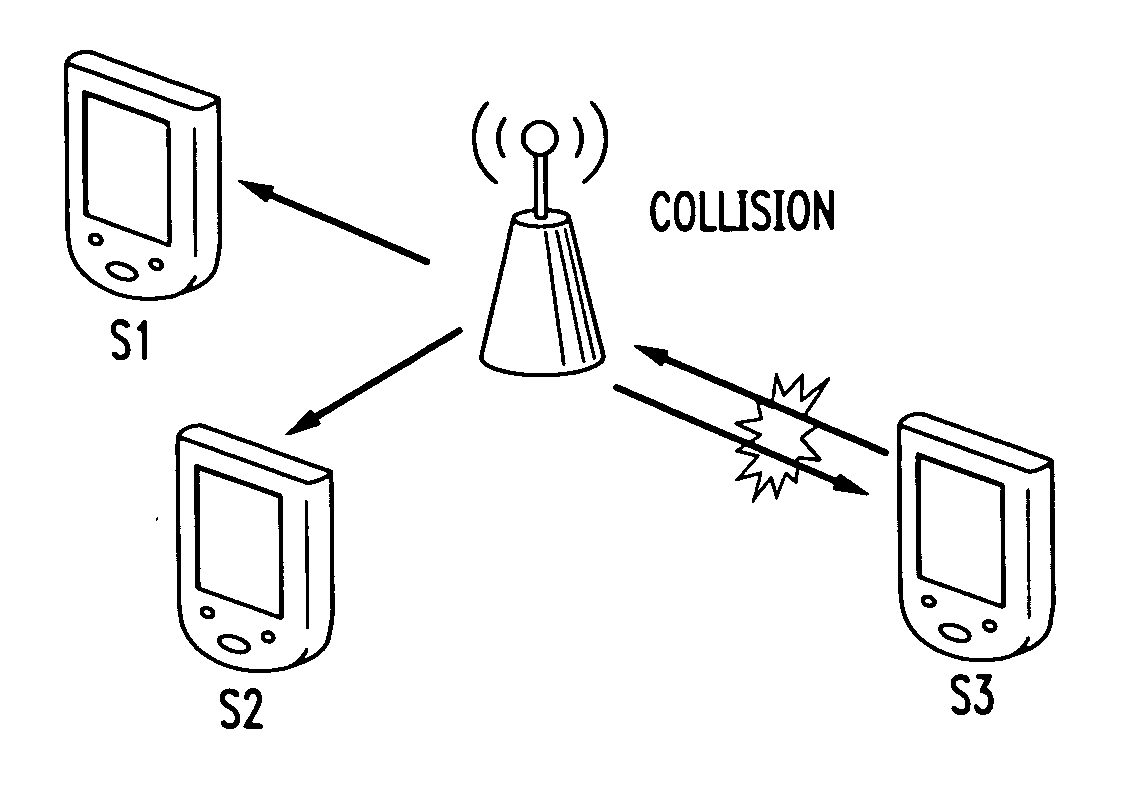
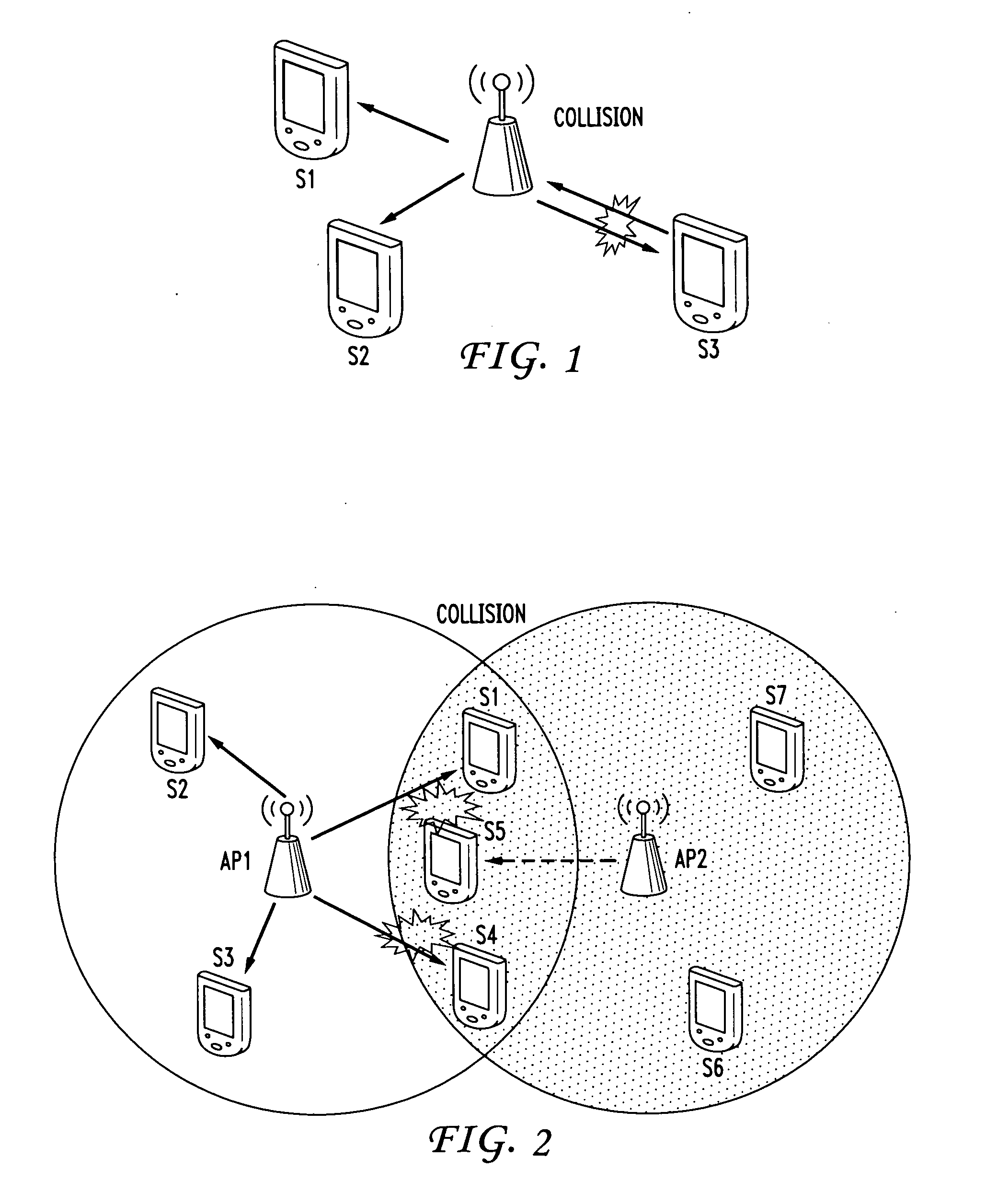
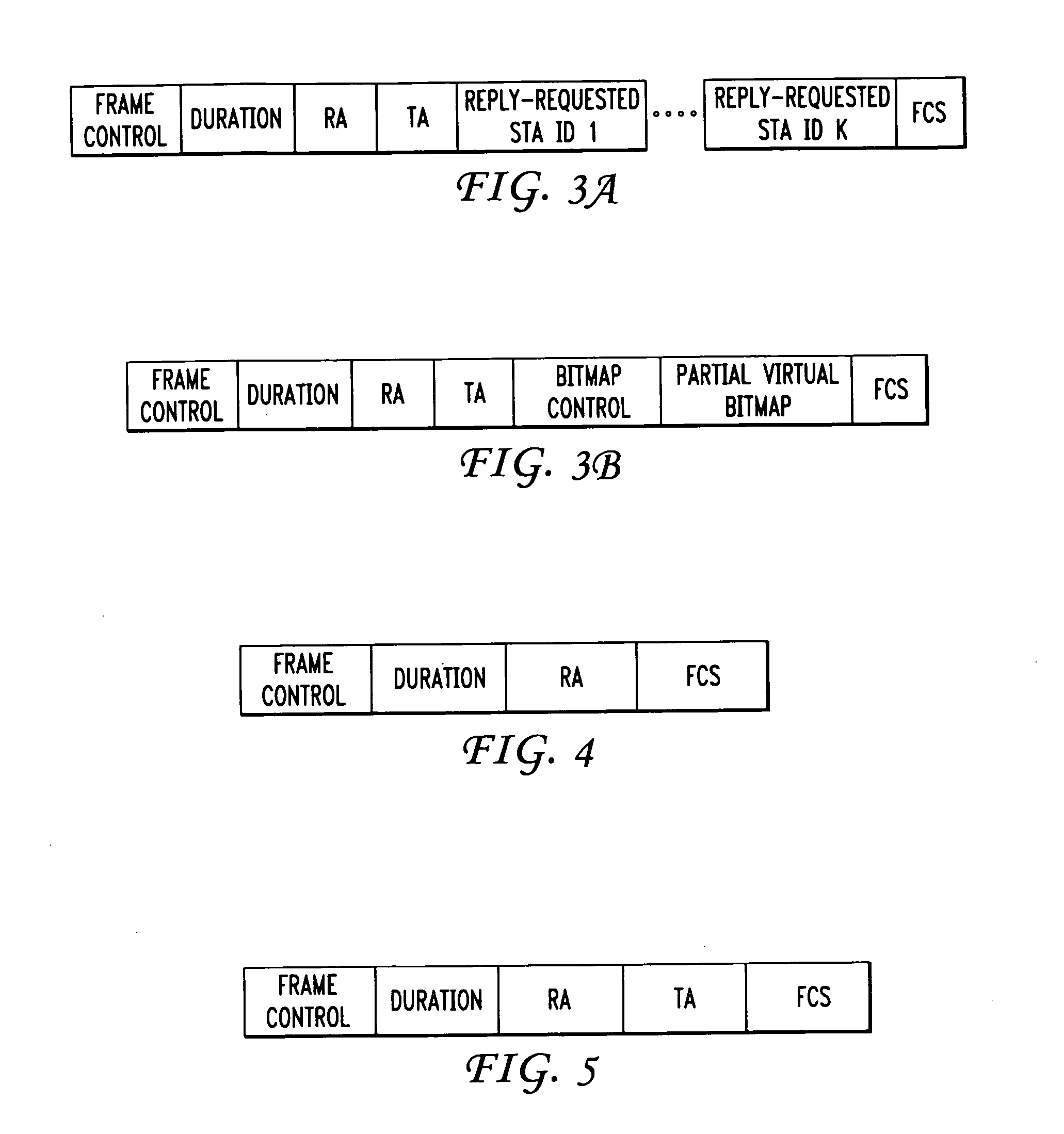
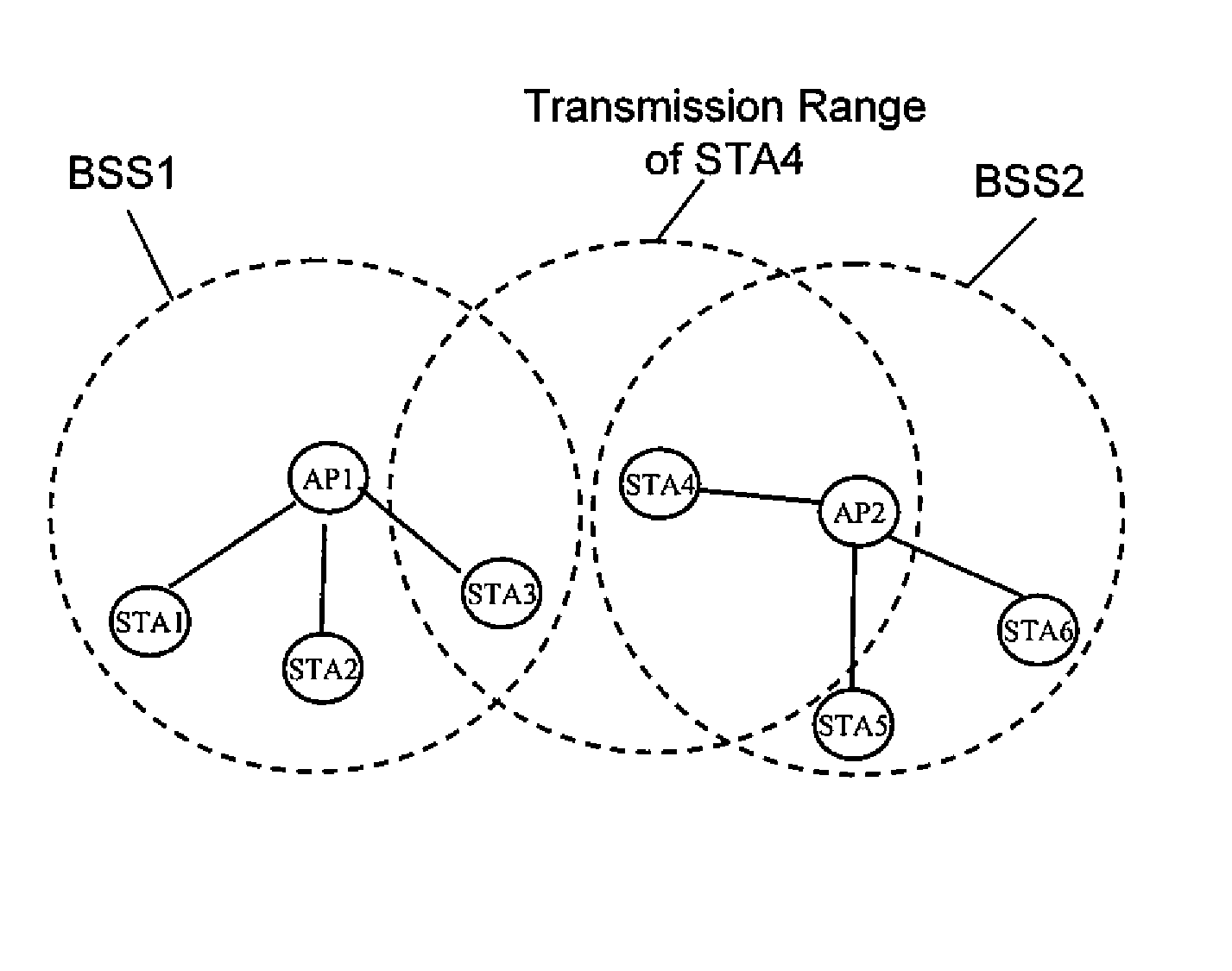
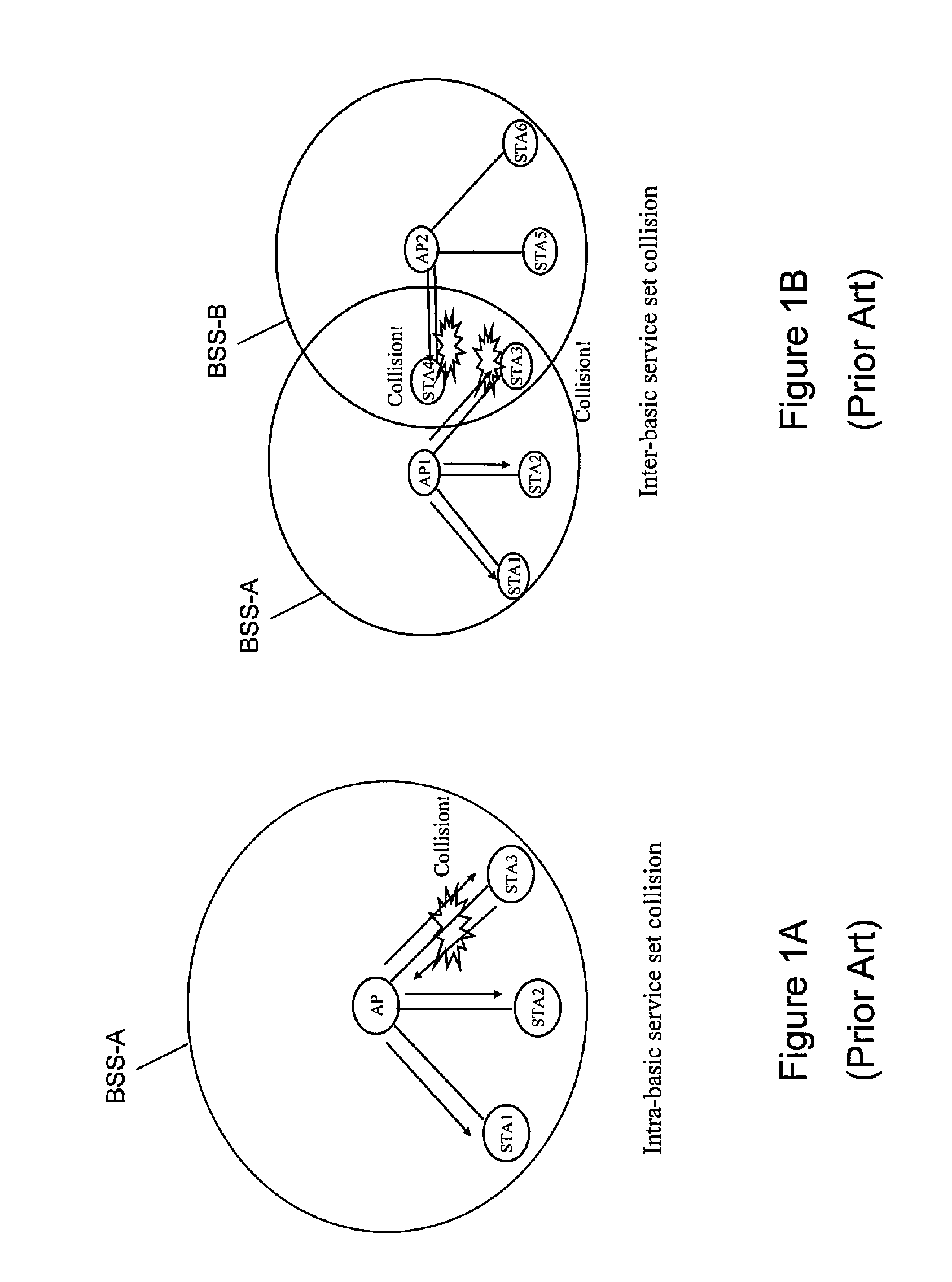
Collision mitigation for multicast transmission in wireless local area networks
InactiveUS20110064013A1Reduce the probability of collisionProtect normal transmissionError preventionNetwork topologiesLocal area networkMulticast transmission
A method and apparatus are described including multicasting a medium reservation message, receiving responses to the medium reservation message and determining if a ratio of the received responses to an expected number of responses exceeds a threshold. Also described are a method and apparatus including receiving a medium reservation message, determining if the medium reservation message specifies this receiver in a list of receivers from which a response is requested, determining if a medium is idle and transmitting the response to the medium reservation message responsive to the second determination.
Owner:MAGNOLIA LICENSING LLC
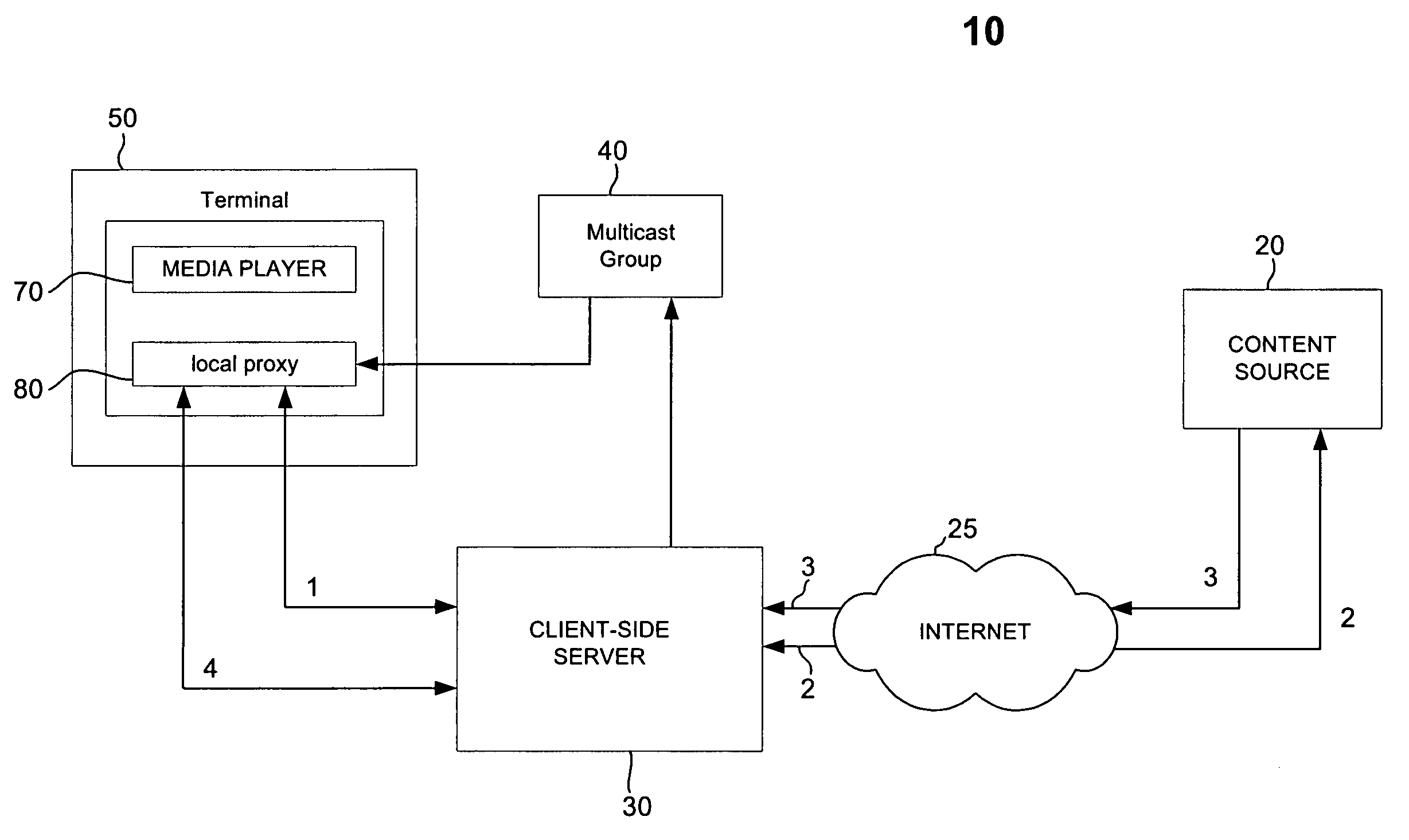
Network architecture for data transmission
ActiveUS20050198097A1Reduce bandwidth requirementsMultiple digital computer combinationsSelective content distributionContent distributionNetwork architecture
A content distribution network with client side multicasting properties that operates with a reduced bandwidth is provided. The arequested content, such as multimedia content, is provided in a format suitable for transmission over existing unicast communication links and is then changed to a multicast format for local distribution. This allows an application provider to transmit a single unicast stream of content to a client-side media server in a local area network (LAN) and then distribute it to multiple interested users within the LAN using a multicasting transmission format. This significantly reduces bandwidth requirements by providing a single unicast transmission to a LAN rather than supply each user within the LAN with a dedicated content stream.
Owner:BLOOMBER FINANCE LP
Robust unicast/broadcast/multicast communication protocol
ActiveUS20100165963A1Reduce in quantityLoop networksWireless commuication servicesBasic serviceMulticast communication
Methods and apparatus for implementing a robust unicast / broadcast / multicast protocol are provided. In one aspect, a method of avoiding collision of intra-basic service set unicast, broadcast or multicast transmissions notifies stations in the basic service set of a reserved transmit opportunity for a unicast, broadcast or multicast transmission. Transmissions from at least one station in the basic service set are deferred until after the reserved unicast, broadcast or multicast transmit opportunity.
Owner:STMICROELECTRONICS SRL
Multicast control technique using MPLS
InactiveUS20060268934A1Improve management efficiencyEasy to startTime-division multiplexData switching by path configurationMulticast addressMulti protocol
In this invention, an idea of the reverse direction label switched path (RLP) in Multi-Protocol Label Switching (MPLS) is applied to the multicast transmission to improve the management transmission in the multicast transmission, and to easily carry out an additional connection and disconnection. Specifically, in the reverse direction symmetric routing Label switched Path (LP), a virtual label in addition to an input label and an output label is used for the reverse direction routing. However, in this invention, instead of the virtual label, a multicast address to which a client terminal, which is connected to a head of the path on the reverse direction routing, and corresponds to a leaf in the multicast tree, is connected, is registered, as a multicast index, in routers on the path. Then, when receiving a multicast packet including a label and a multicast address, an output label corresponding to the received label is identified, thereby a destination link is identified.
Owner:FUJITSU LTD
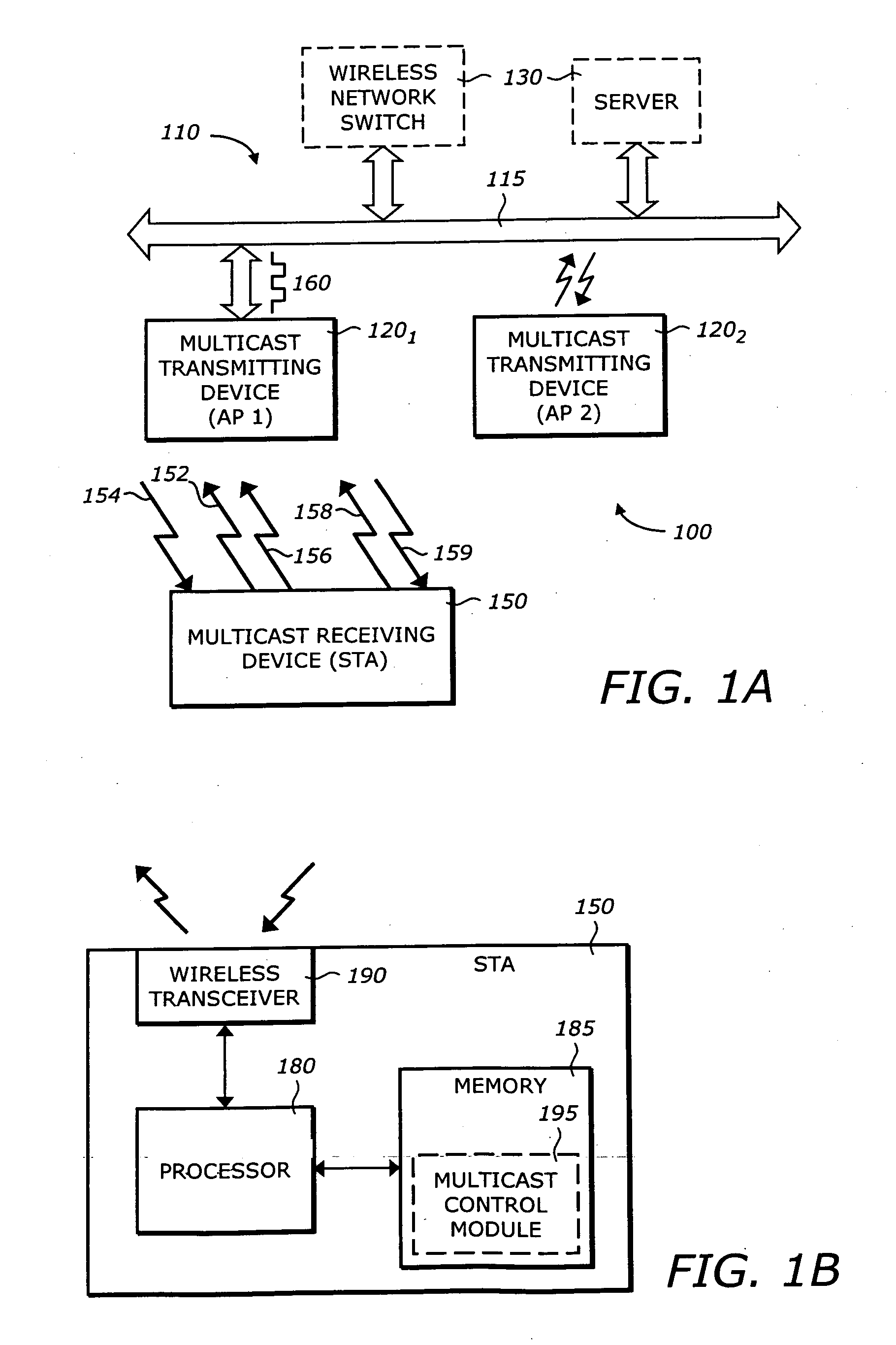
System and method for reliable multicast transmissions over shared wireless media for spectrum efficiency and battery power conservation
According to one embodiment of the invention, wireless spectrum and battery power conservation is achieved through an adaptable multicast group communication scheme. This involves a method for controlling the multicast transmission rate based on a first operation of receiving information from a multicast receiving device that is a member of a multicast group. Based on this information and potentially other information from other member devices, the modulation and coding rate for the multicast group is altered.
Owner:HEWLETT-PACKARD ENTERPRISE DEV LP +1
Multicast in point-to-point packet-switched oriented networks
ActiveUS20040233907A1Efficient use ofReducing transmission resourceSpecial service provision for substationData switching by path configurationMultiplexingTelecommunications network
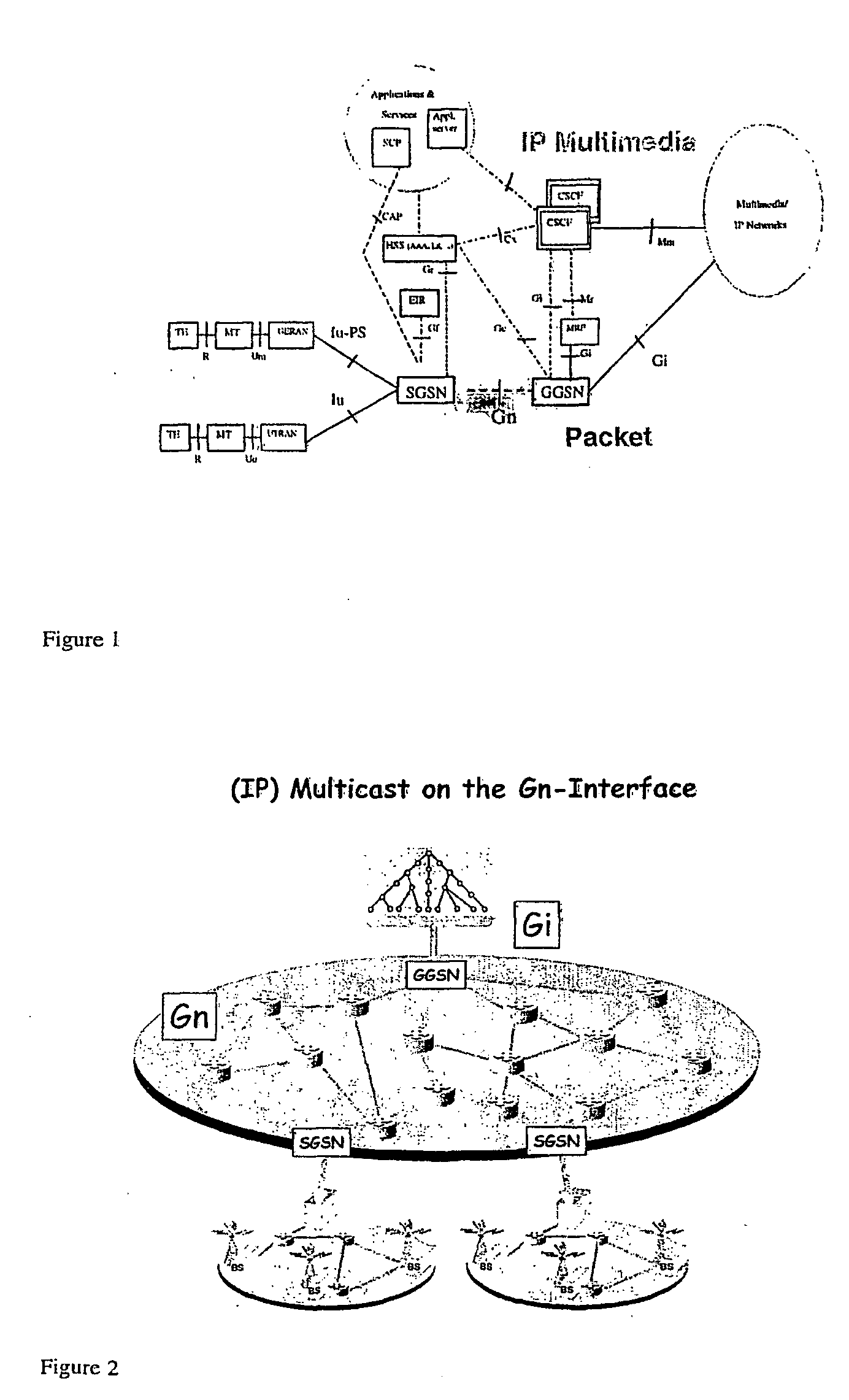
The invention relates to a method, network node, router, serving node and system for performing multicast in a point-to-point packet-switched oriented telecommunication network. The basic idea is to introduce pre-configured multicast transmission for parts of a network. This is done by creating pre-configured transport multicast group tunnels between a router and a serving node in order to transport the multicast data. Further the present invention describes the possibility of multiplexing of the multicast data streams on a pre-configured transport multicast group tunnel. In particular the invention is applicable for multicasting in networks, like UMTS with a scarce number of resources, in the IP network between the SGSN and GGSN for example on the Gn interface.
Owner:TELEFON AB LM ERICSSON (PUBL)
Multicast transmission in a cellular network
InactiveUS20060166653A1Avoiding allocation of resourceAvoid allocation problemsSpecial service for subscribersBroadcast service distributionAccess networkRadio access network
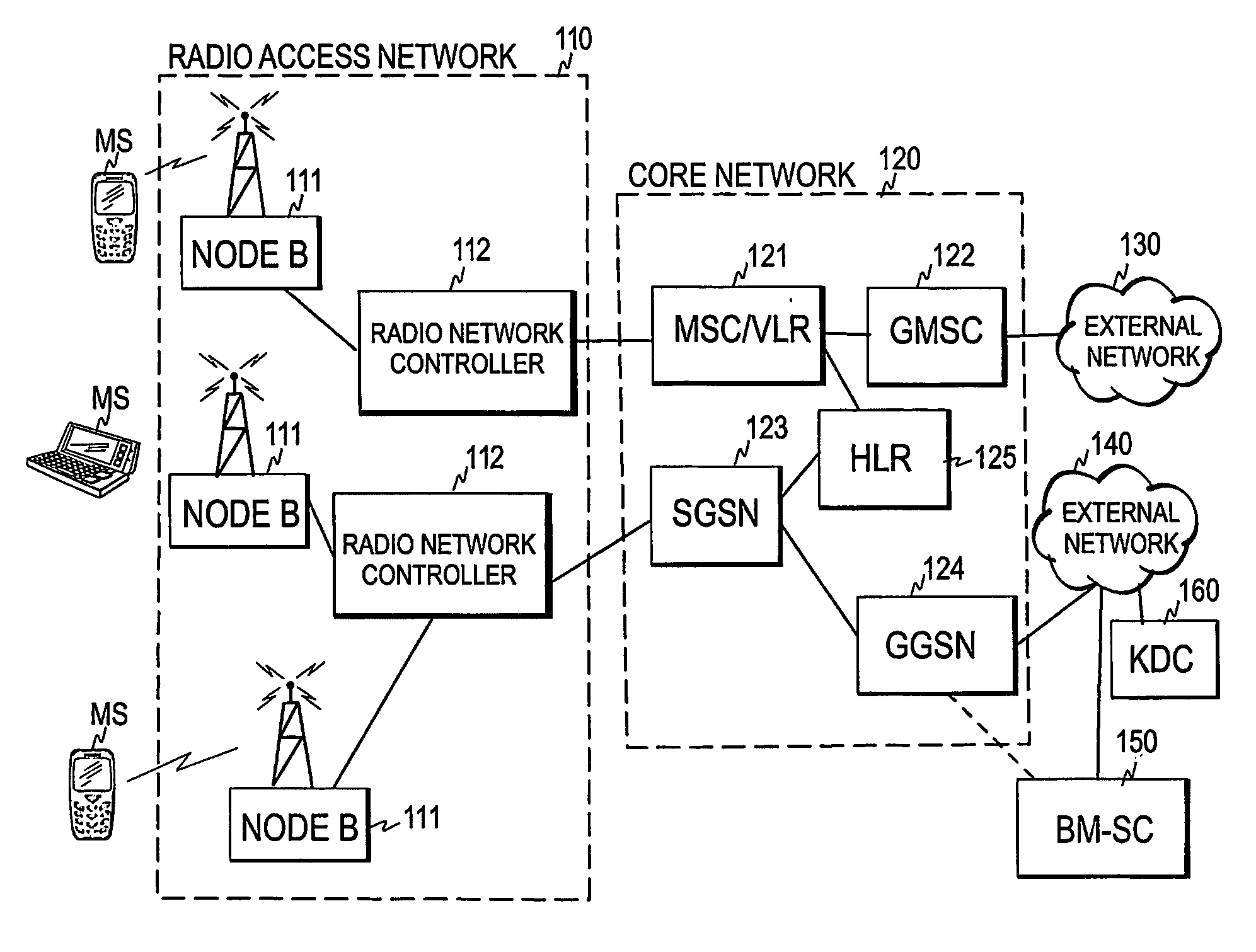
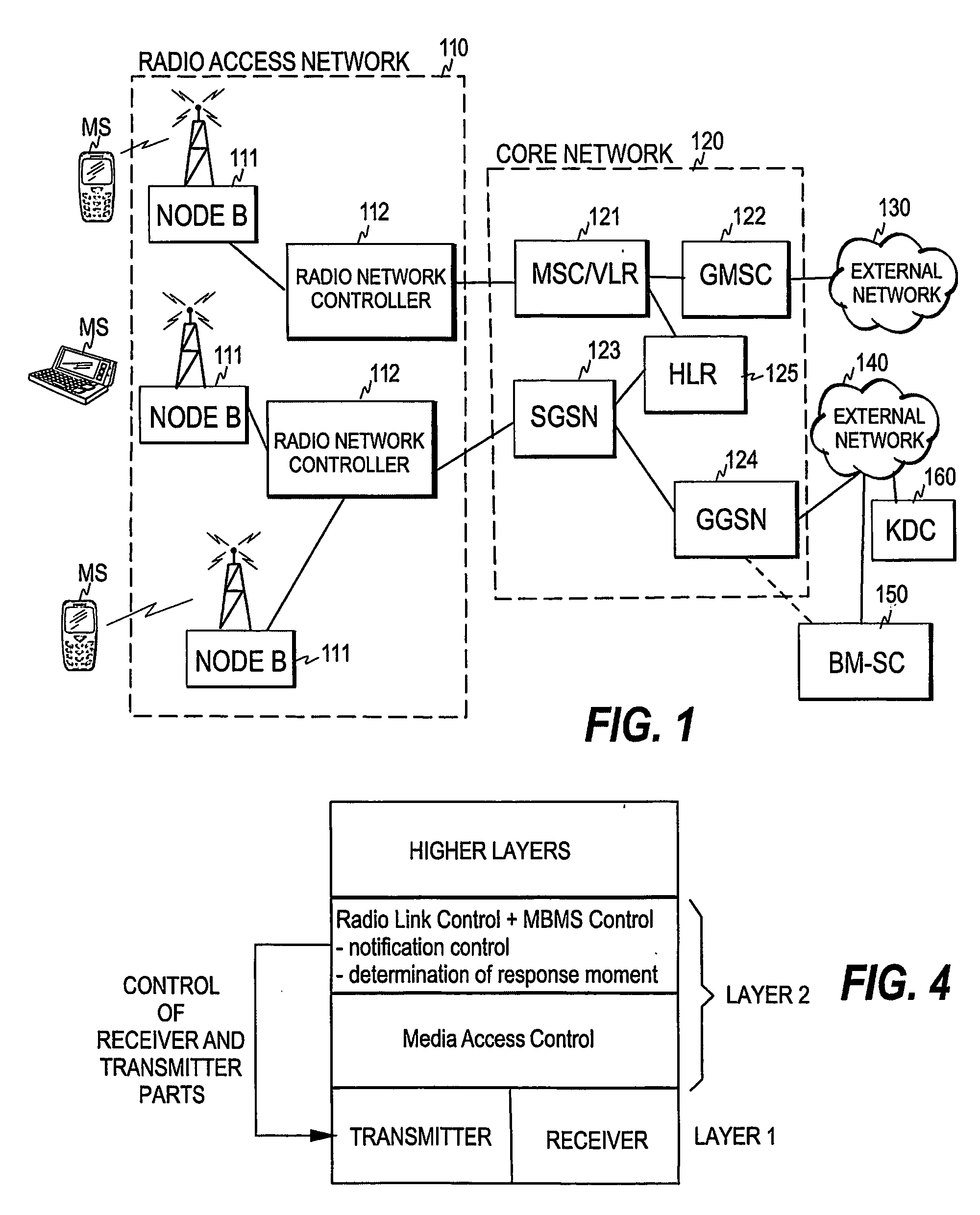
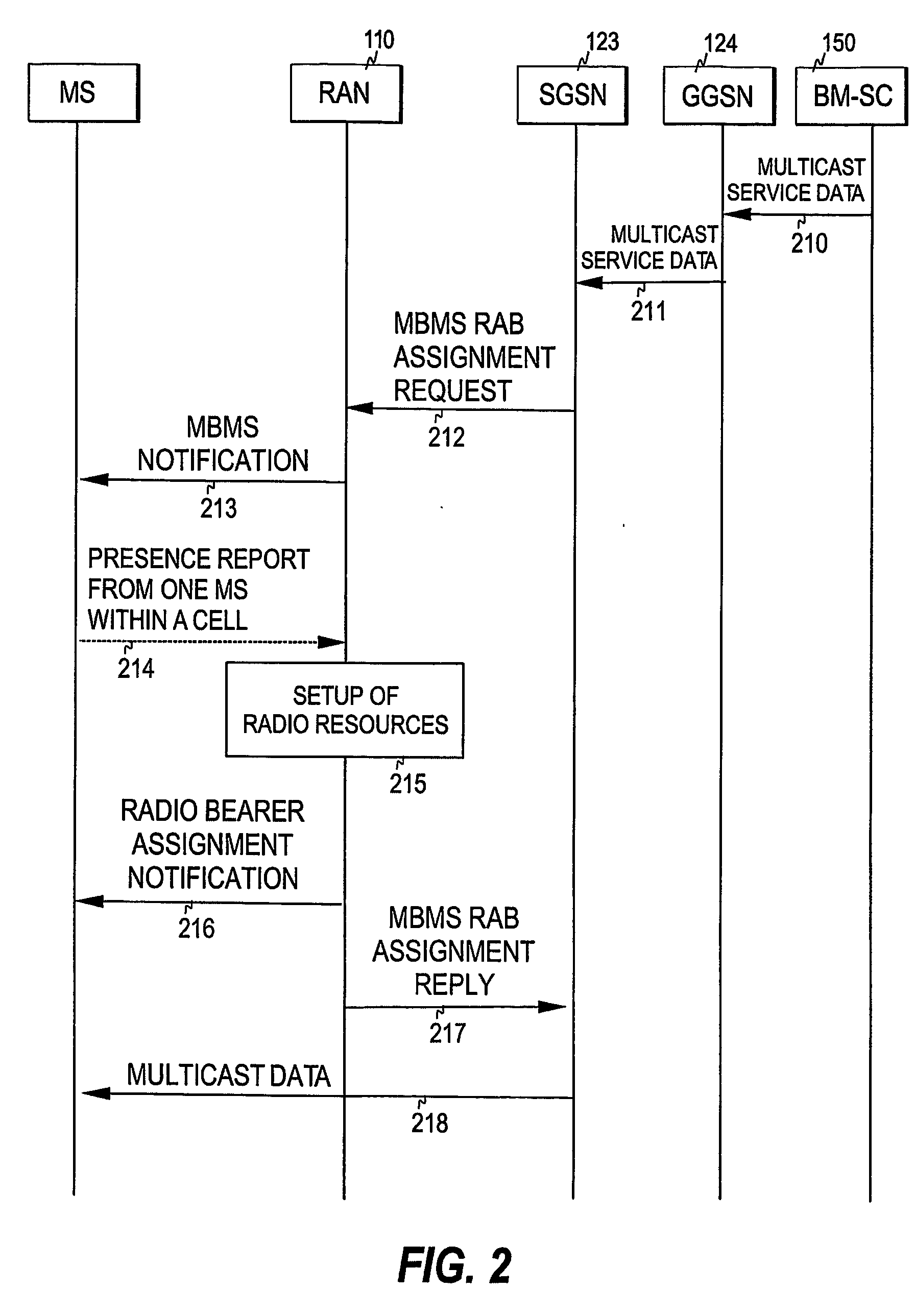
The invention relates to a mechanism for performing multicast transmission in a cellular network. In order to enable establishment of resources only in cells containing members of the multicast group and to avoid congestion on the uplink channel, a multicast service notification is transmitted to mobile stations, thereby informing members of the multicast group of an upcoming multicast session. The moment for a response to said multicast service notification is selected in the mobile stations and a presence report is sent from at least one of said mobile stations at the response moment of said at least one mobile station. The presence report or reports are received within a radio access network, and radio resources are established for multicast transmission in a cell of the cellular network when the presence report(s) received in said cell meet(s) predetermined criteria.
Owner:NOKIA CORP
Pilot transmission method for down collaboration multi-point transmission
ActiveCN101373999AReduce overheadEasy to receiveDiversity/multi-antenna systemsMulti-frequency code systemsMultiplexingResource block
The invention discloses a pilot frequency transmission method for downlink shared multicast transmission, which is used in a long term evolution advance (LTE-A) system. The system is allocated with a plurality of sets of pilot frequencies for downlink multicast transmission and multiplexing modes thereof; and each transmission point involved in downlink share transmits one of the pilot frequencies in a resource block carrying user data, the same set of pilot frequency occupies the same time and frequency sites in the resource block, and the different sets of pilot frequencies are discriminated via frequency division, time division or code division in the resource block. The inventive method needs not a receiving terminal to discriminate channels corresponding to the transmission points which are involved in the share and only needs to allocate one set or a plurality of sets of logic pilot frequencies for multicast transmission, thereby resulting in low cost of pilot frequencies, simple terminal reception and less downlink control signaling.
Owner:ZTE CORP
Transporting multicast over MPLS backbone using virtual interfaces to perform reverse-path forwarding checks
ActiveUS20060221975A1Special service provision for substationTime-division multiplexReverse path forwardingData set
A mechanism is provided in which multicast reverse path forwarding can be performed at a provider network egress edge router wherein core routers of the provider network are not configured to support multicast protocols or point-to-multipoint LSPs. An embodiment of the present invention provides for the creation of virtual interfaces in the egress edge router element during configuration of a multicast connection in response to a subscriber request. A virtual interface will be associated with an upstream ingress edge router element and that ingress edge router element is provided a label associated with the virtual interface. Such a label can then be included in datastream packets transmitted through the provider network. The label can then be used by reverse path forward checking at the egress edge router element to ascertain whether the multicast datastream is being received by the correct upstream interface (e.g., the virtual interface associated with the ingress edge router element). In such a manner, core network router elements of the provider's network need not be configured to process multicast transmissions as such, nor need the core router elements be configured to use the same network protocols as those used by the customer networks (e.g., customer networks can use IPv6 while the core network routers can use IPv4).
Owner:CISCO TECH INC
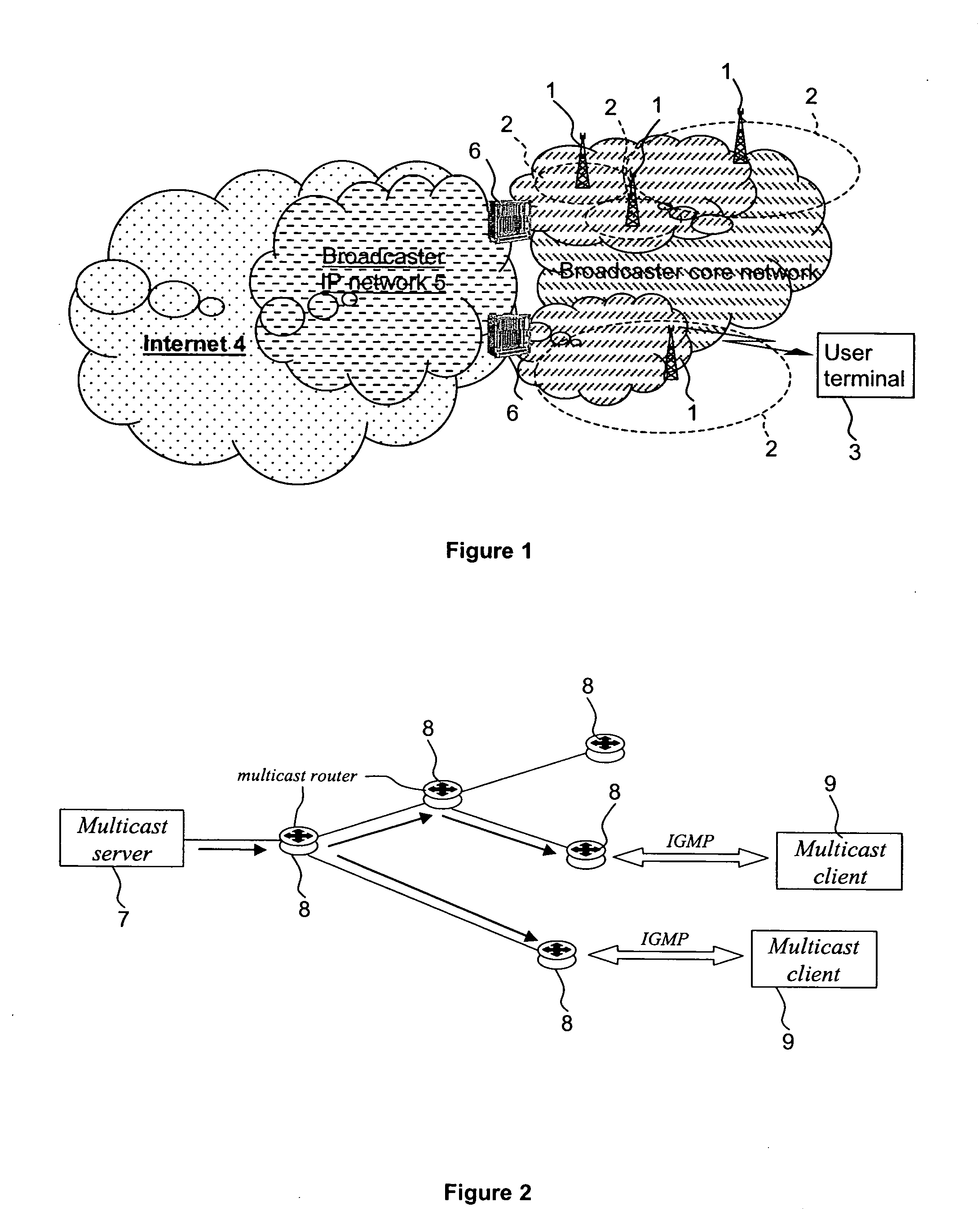
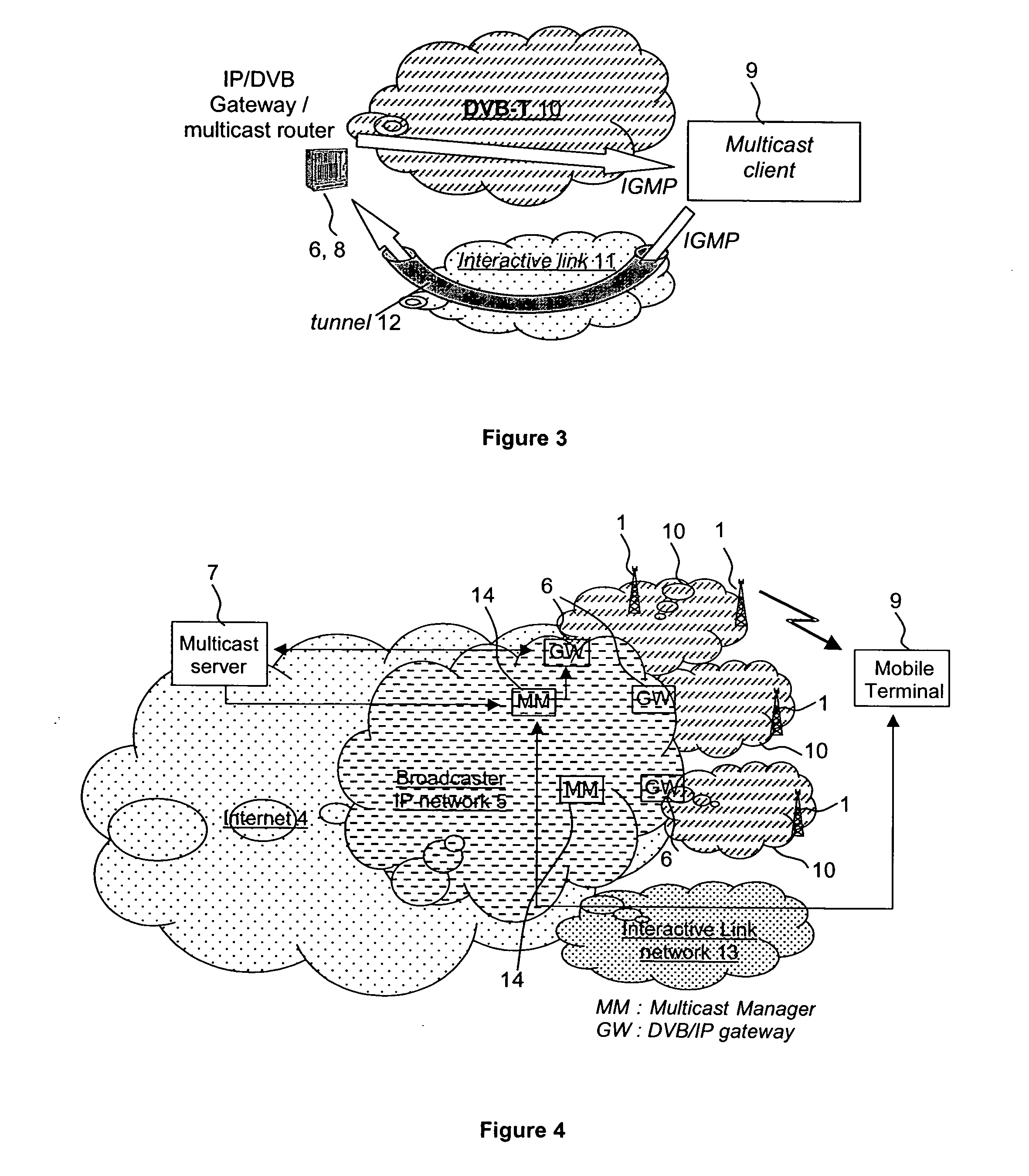
Ip multicast service over a broadcast channel
InactiveUS20050044142A1Special service provision for substationPulse modulation television signal transmissionBroadcast channelsIP multicast
A method of and apparatus for providing an Internet Protocol multicast service wherein multicast data is transmitted through multicast routers (8) to user stations (9) over a digital broadcast channel (especially DVB-T) together with digital broadcast signals, at least if a request has been received from a user station (9) for the multicast data,. The transmission of the multicast data by a multicast router is conditional upon the reception of a request for said multicast data from that multicast router by a plurality of the user stations (9). The number of requests from the user stations (9) has to be greater than a threshold number, which is a function of the available bandwidth for multicast transmission over the broadcast channel. Information concerning the requests for the multicast data by the user stations (9) is unavailable to the other user stations (9).
Owner:GOOGLE TECH HLDG LLC
Multipath routing optimization for unicast and multicast communication network traffic
InactiveUS20070133420A1Minimize cost functionError preventionFrequency-division multiplex detailsInternet trafficMulticast communication
Multiple paths in a communication network are provided between at least one source node and at least one destination node. The network arrangement may thus support either unicast transmission of data or multicast transmission. Measurements are made at nodes of the network to determine a partial network cost for data traversing the links in the multiple paths. An optimization procedure determines a distribution of the network traffic over the links between the at least one source node and the at least one destination node that incurs the minimum network cost.
Owner:UNIV OF MARYLAND
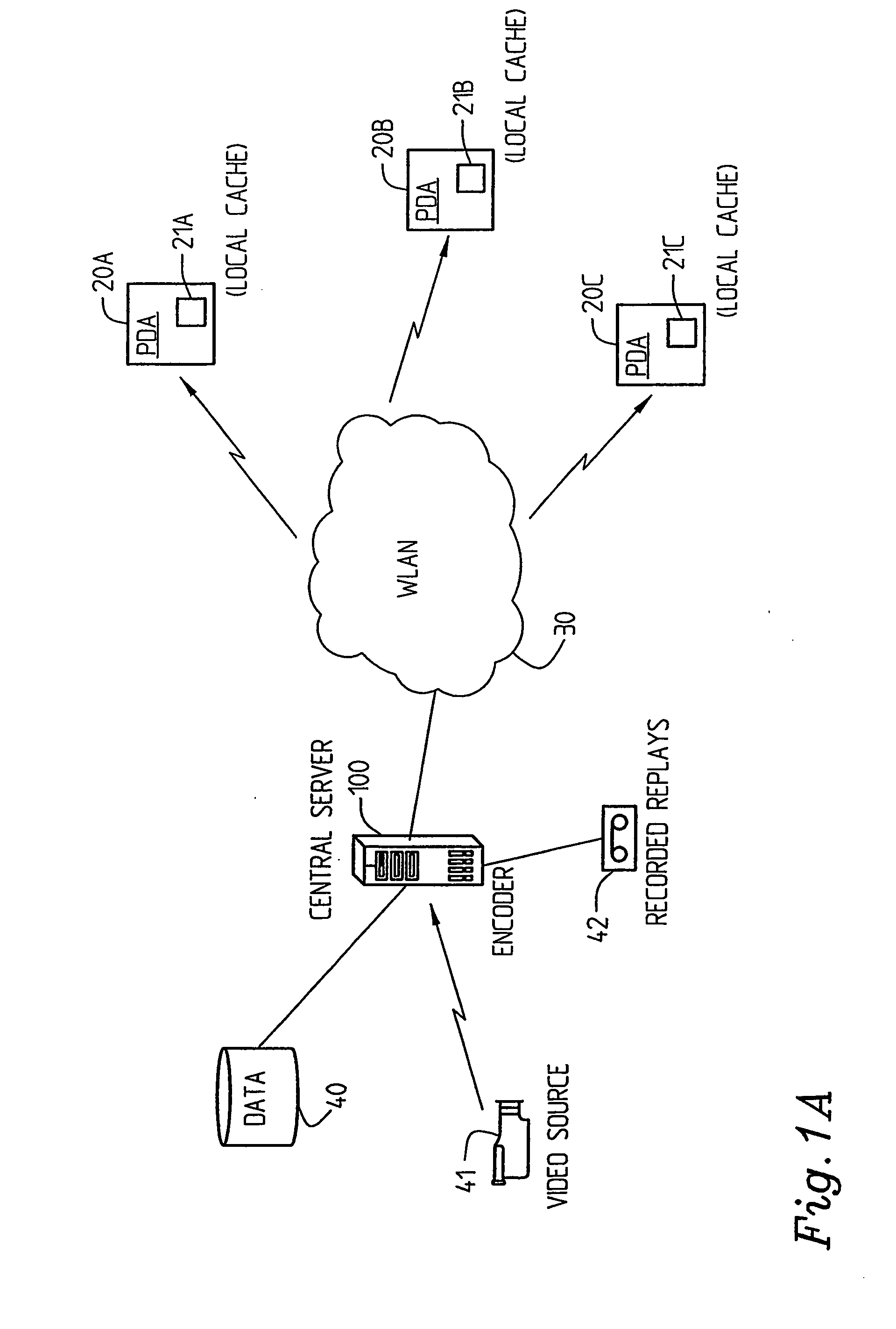
System and a method relating to communication of data
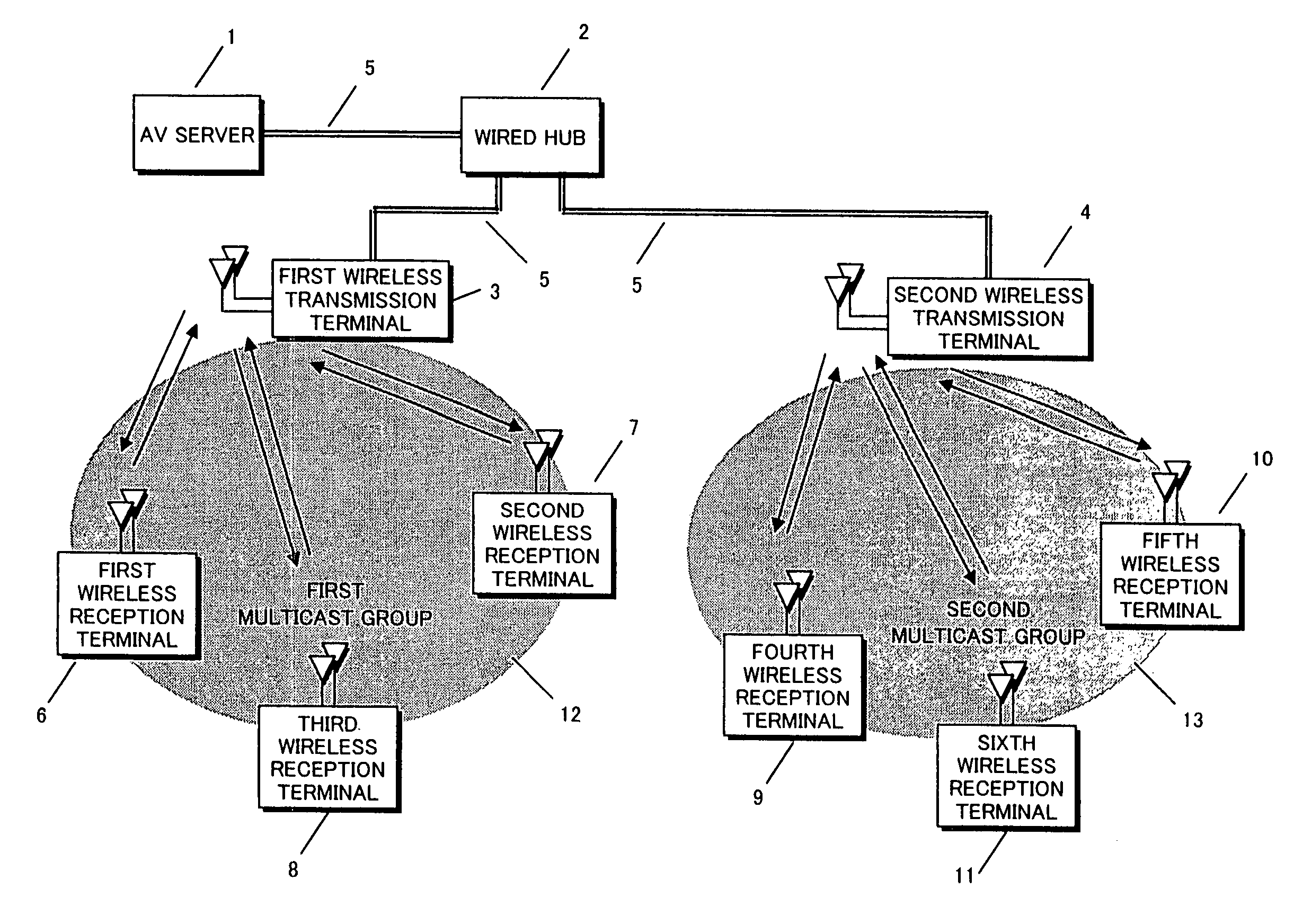
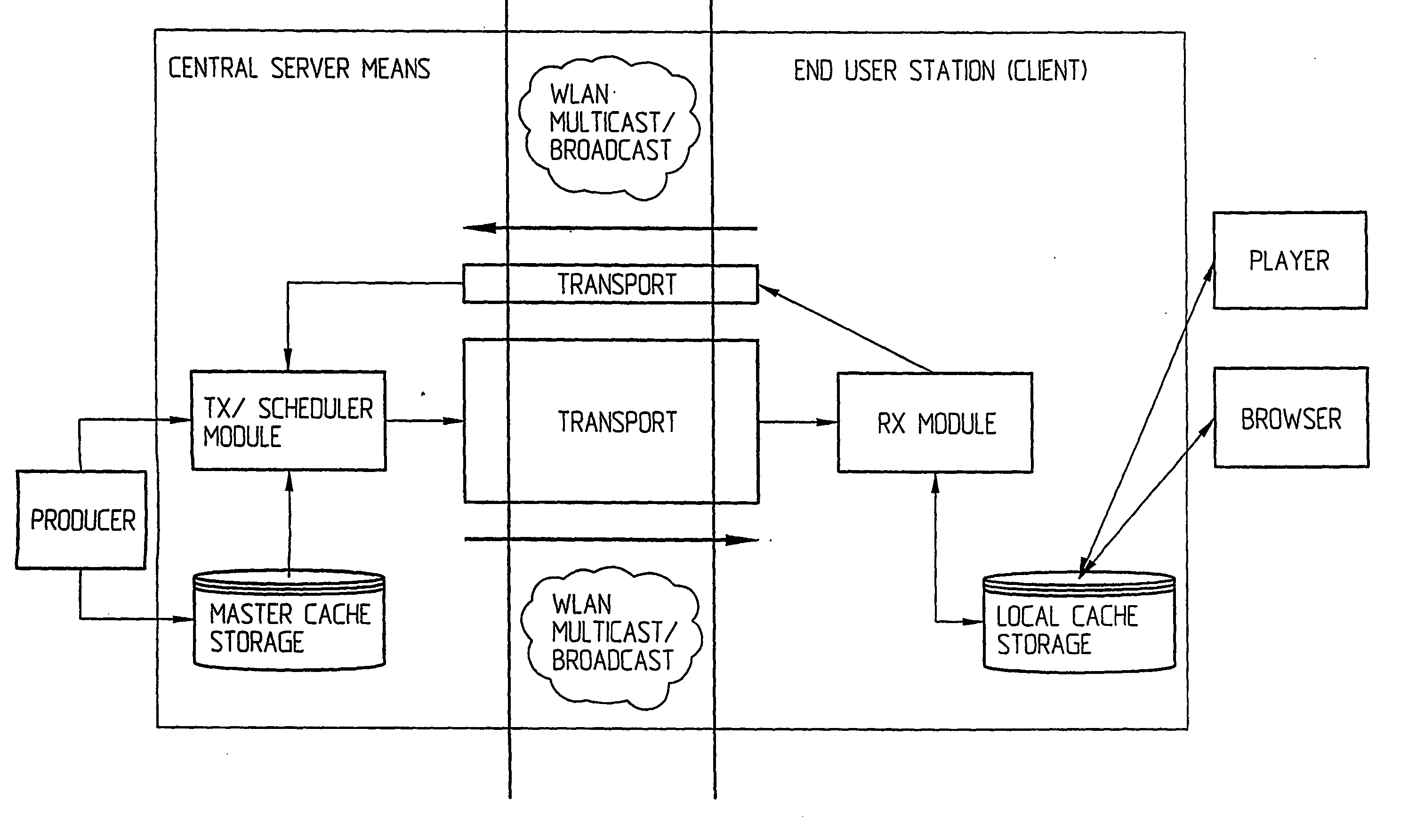
InactiveUS20050125533A1Special service provision for substationDigital data information retrievalData informationBroadcasting
The present inventions relates to a system for communication of data information, e.g. multimedia content, over a wireless network connecting a plurality of end user stations and supporting broadcast / multicast transmission. It comprises central server means with at least one central cache arrangement for storing at least selected parts of data information relevant for at least a segment of the wireless network, transmission scheduling means for transmission scheduling, central cache arrangement control means for, by using scheduling information, controlling a central cache arrangement push engine for multicast / broadcast pushing of information to end user stations within said at least one segment of the wireless network. The end user stations comprise or are associated with proprietary, local push content caching means for holding the pushed data information, and, upon request by the respective end user, selected data information may be presented to the end user in a customized manner via a user client from said local caching means.
Owner:TELEFON AB LM ERICSSON (PUBL)
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com