Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
5754 results about "Frame rate" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
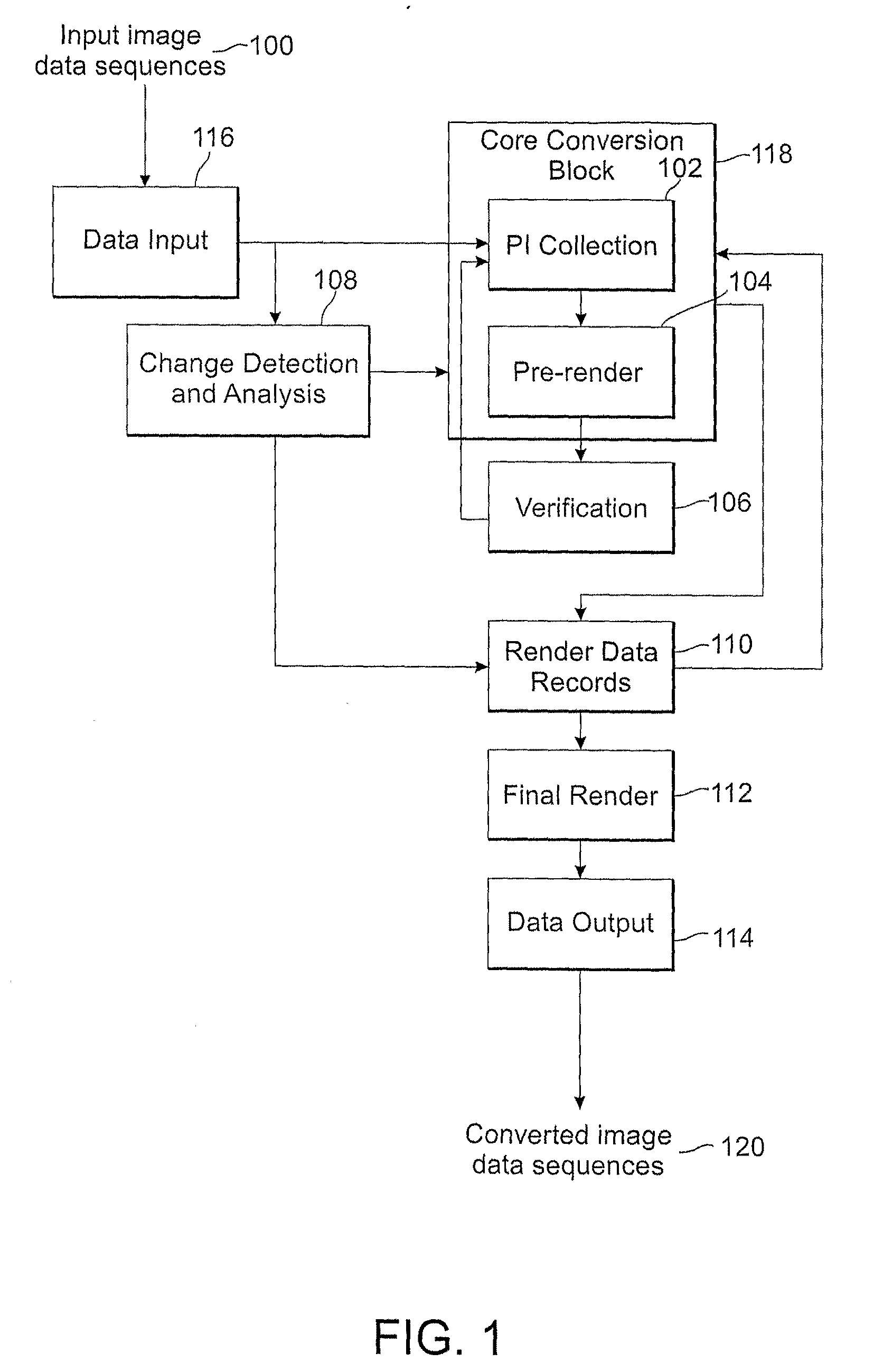
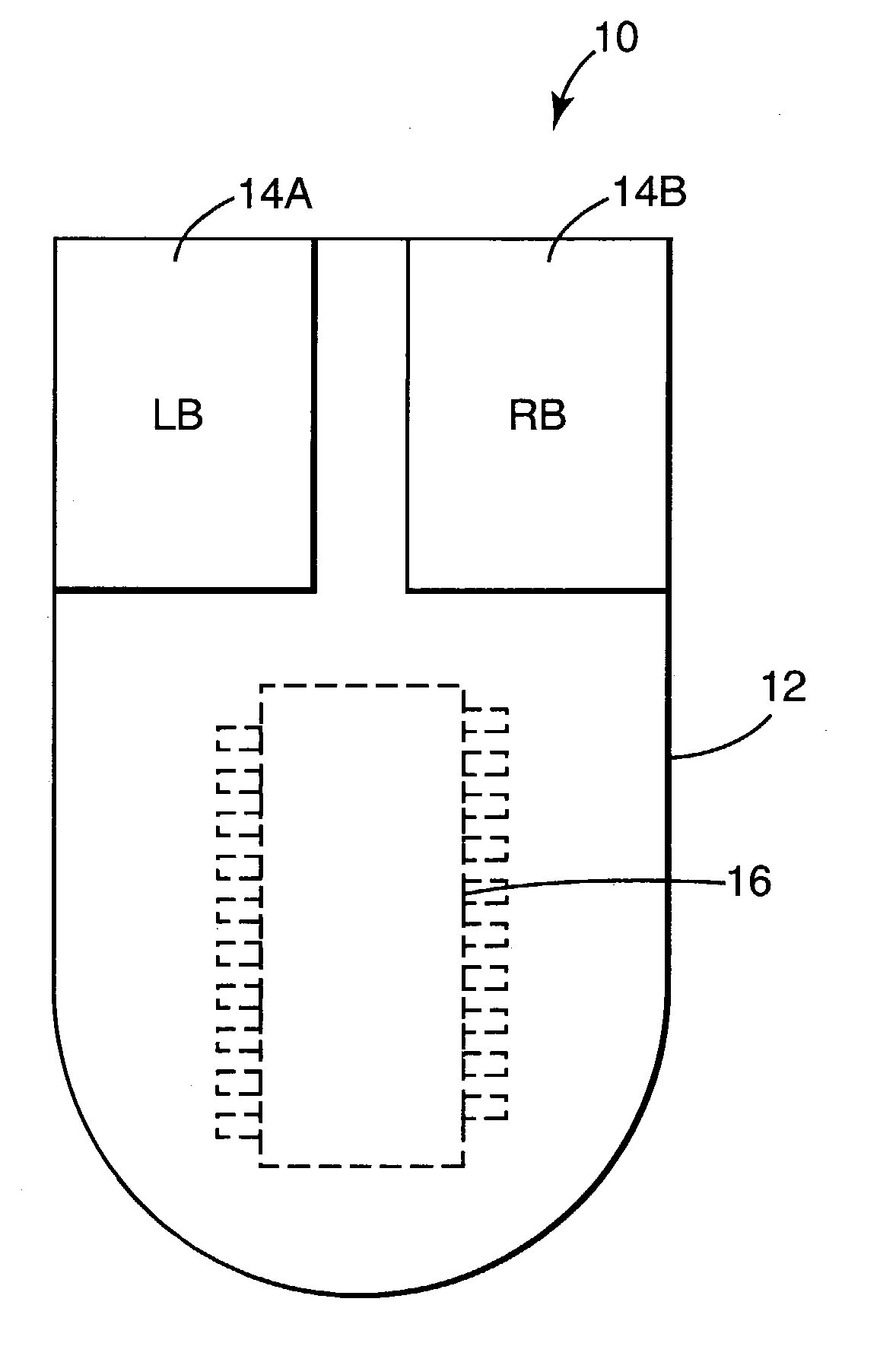
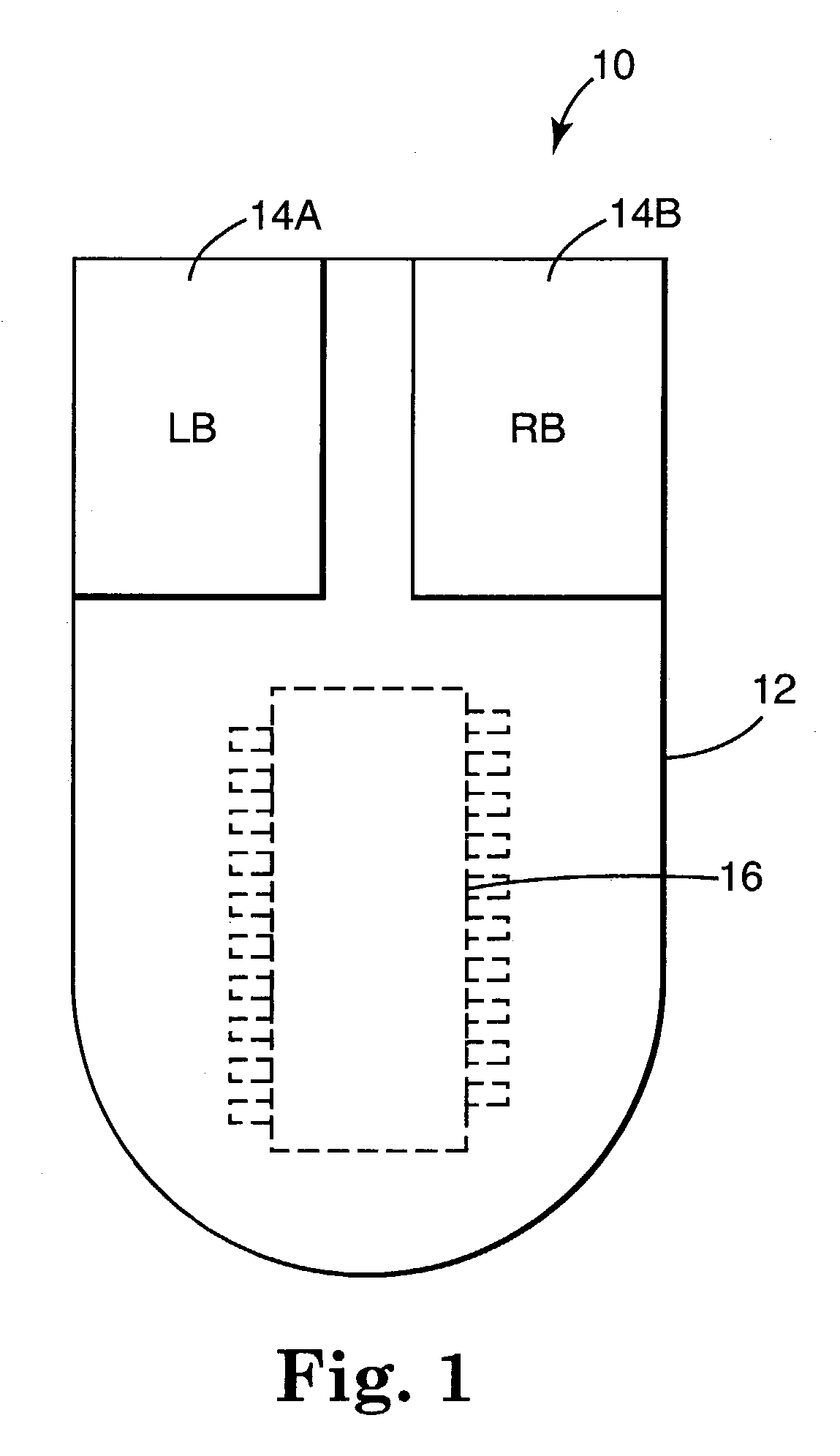
Frame rate (expressed in frames per second or FPS) is the frequency (rate) at which consecutive images called frames appear on a display. The term applies equally to film and video cameras, computer graphics, and motion capture systems. Frame rate may also be called the frame frequency, and be expressed in hertz.
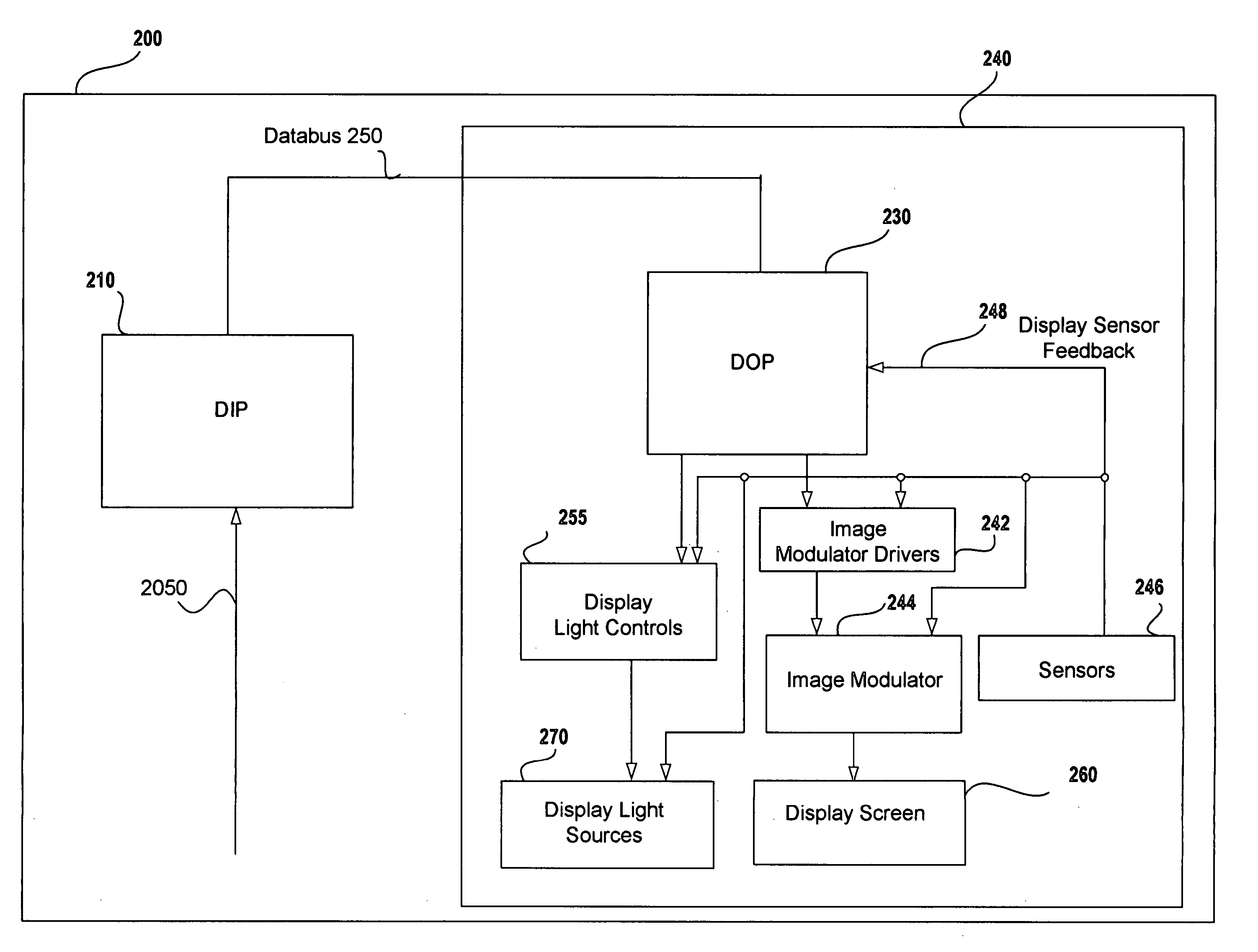
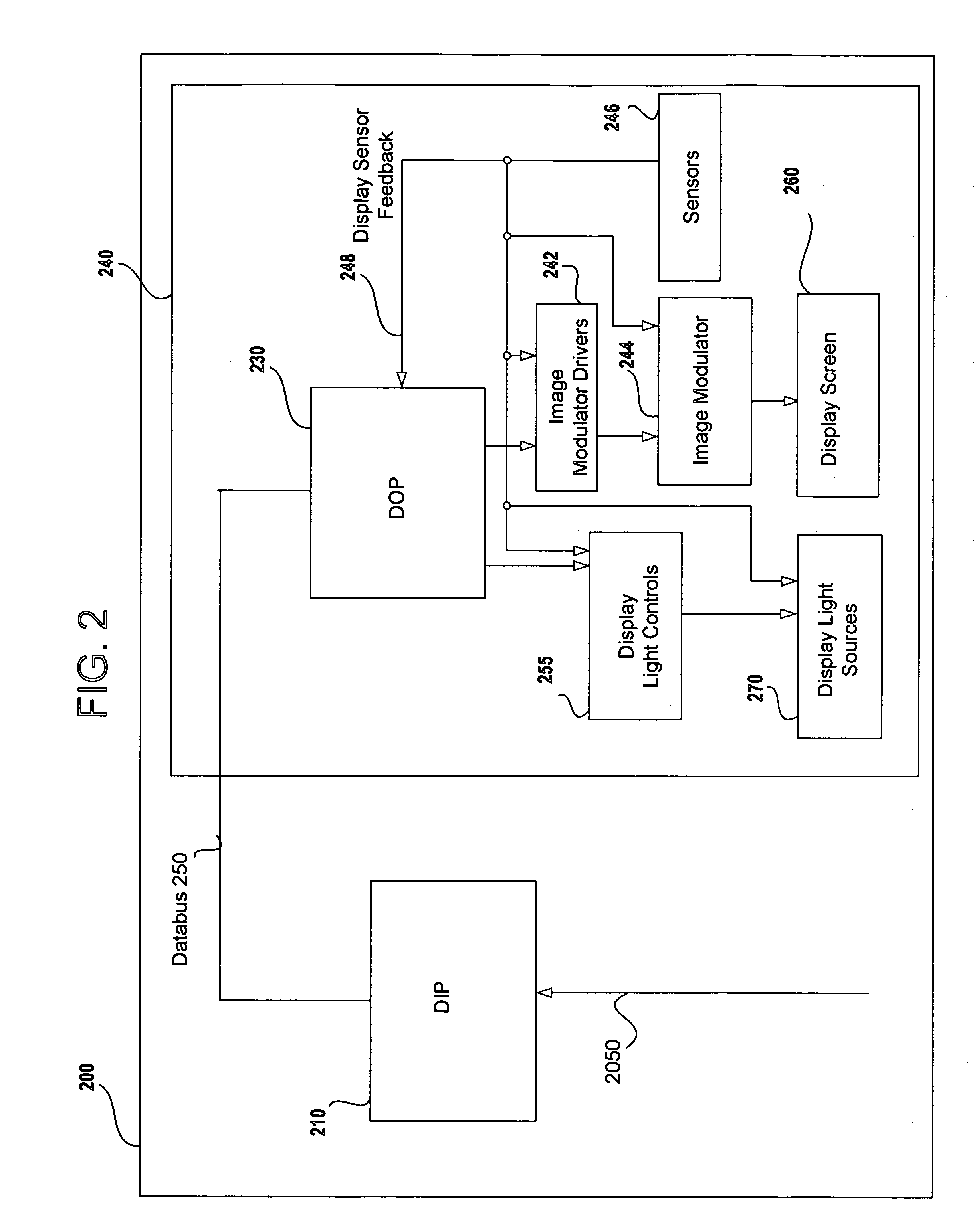
Field sequential light source modulation for a digital display system
ActiveUS20070035707A1Improve display qualityHigh resolutionTelevision system detailsStatic indicating devicesData streamImaging processing
A digital display system consists of an image modulator and multiple light modulators. An image processing system processes an incoming data stream, scans processed data to an image modulator and controls for the light modulators. Other user inputs and sensors are used to affect the processing and controls. The timing for scanning the processed data into the image modulators is controlled along with the intensity and wavelength of the light modulators. The display system may implement a spatial and temporal image processing, digital shutter controls, rolling shutter controls, sequential color output, adaptive dynamic sensor feedback, frame rate matching, motion compensated field sequencing and a variety of other techniques to produce a high quality display output. The resulting display has improved image consistency, enhanced color gamut, higher dynamic range and is better able to portray high motion content.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
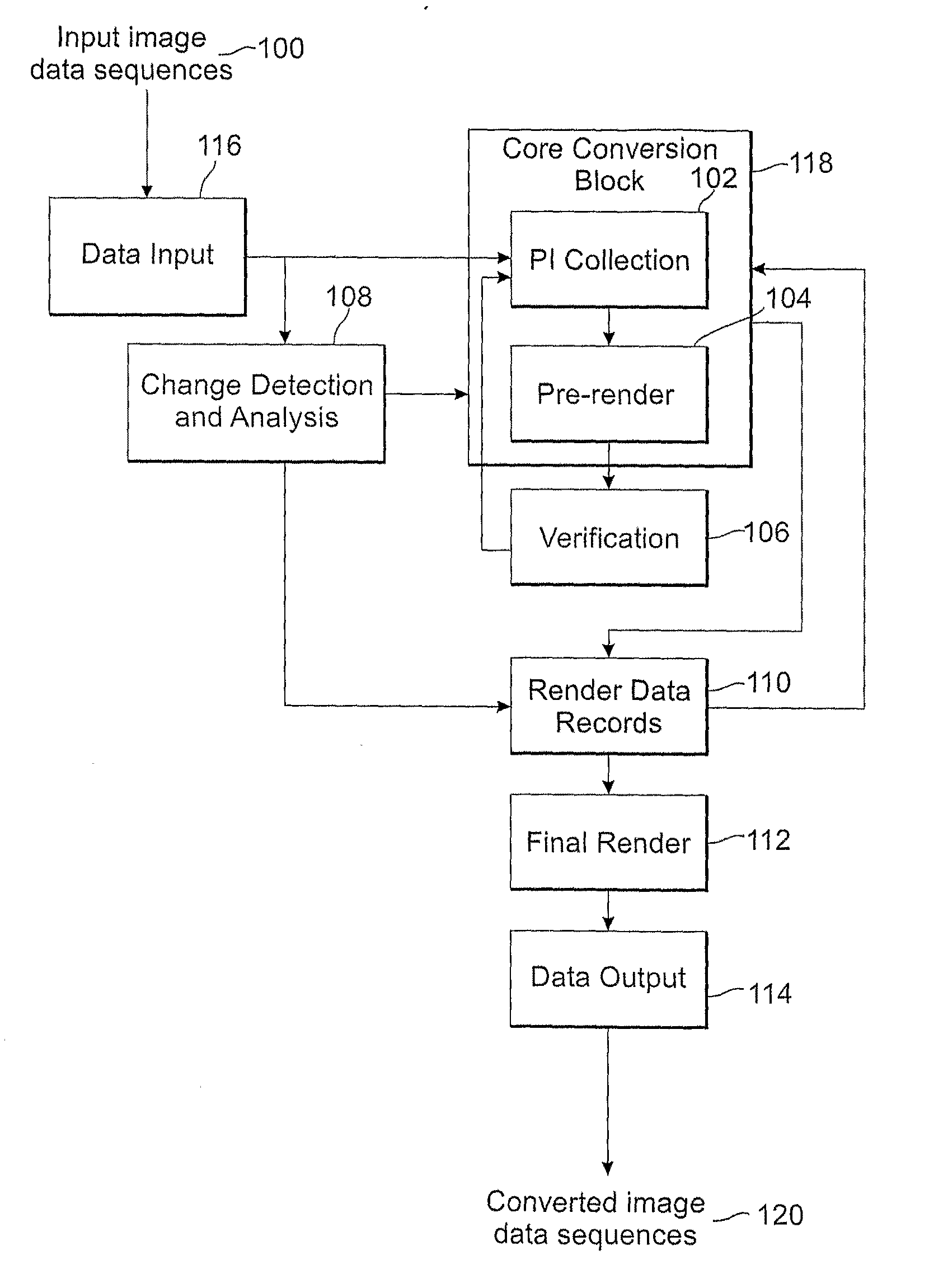
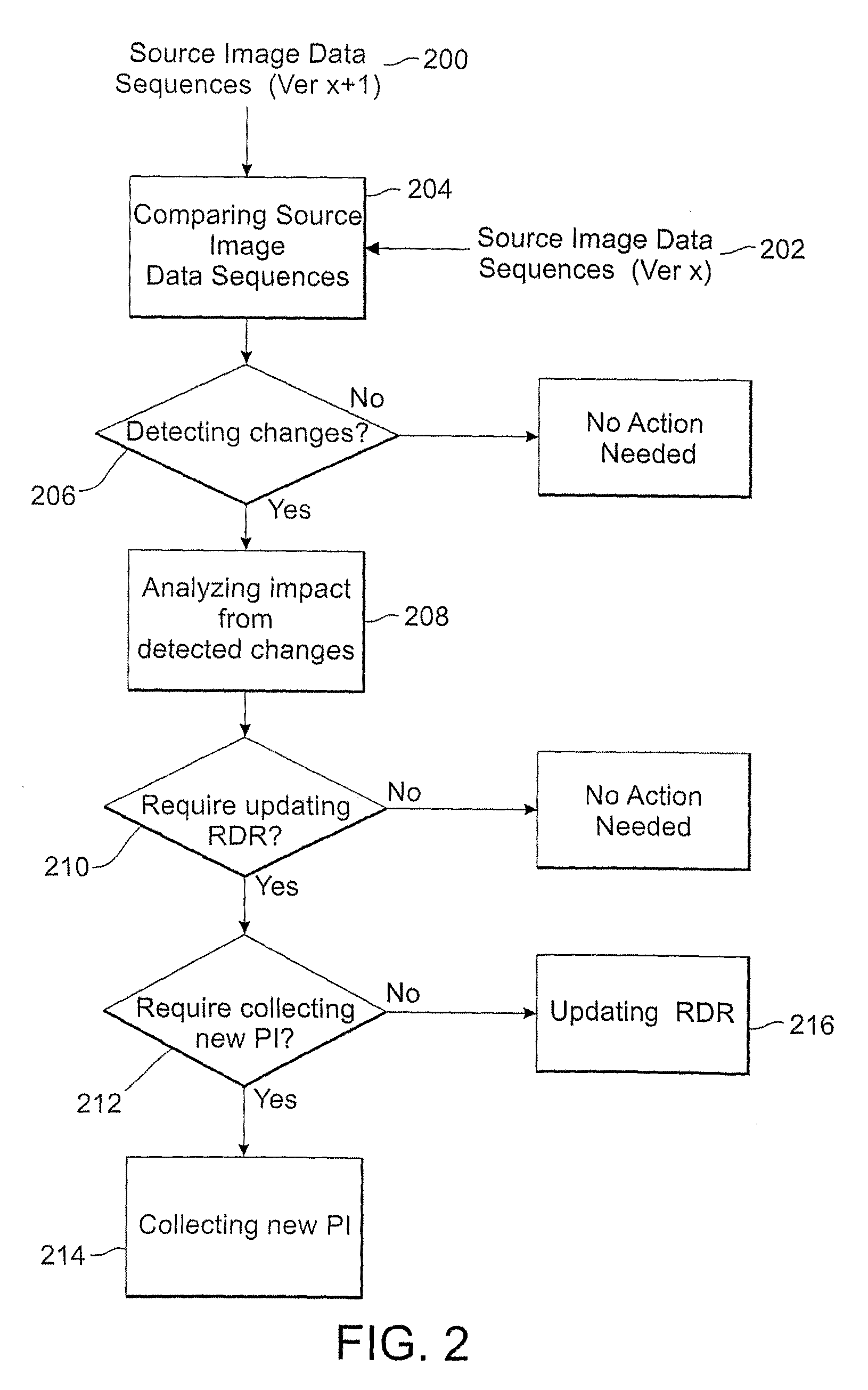
Methods and systems for converting 2d motion pictures for stereoscopic 3D exhibition
ActiveUS20090116732A1Improve image qualityImprove visual qualityPicture reproducers using cathode ray tubesPicture reproducers with optical-mechanical scanningImaging quality3d image
The present invention discloses methods of digitally converting 2D motion pictures or any other 2D image sequences to stereoscopic 3D image data for 3D exhibition. In one embodiment, various types of image data cues can be collected from 2D source images by various methods and then used for producing two distinct stereoscopic 3D views. Embodiments of the disclosed methods can be implemented within a highly efficient system comprising both software and computing hardware. The architectural model of some embodiments of the system is equally applicable to a wide range of conversion, re-mastering and visual enhancement applications for motion pictures and other image sequences, including converting a 2D motion picture or a 2D image sequence to 3D, re-mastering a motion picture or a video sequence to a different frame rate, enhancing the quality of a motion picture or other image sequences, or other conversions that facilitate further improvement in visual image quality within a projector to produce the enhanced images.
Owner:IMAX CORP
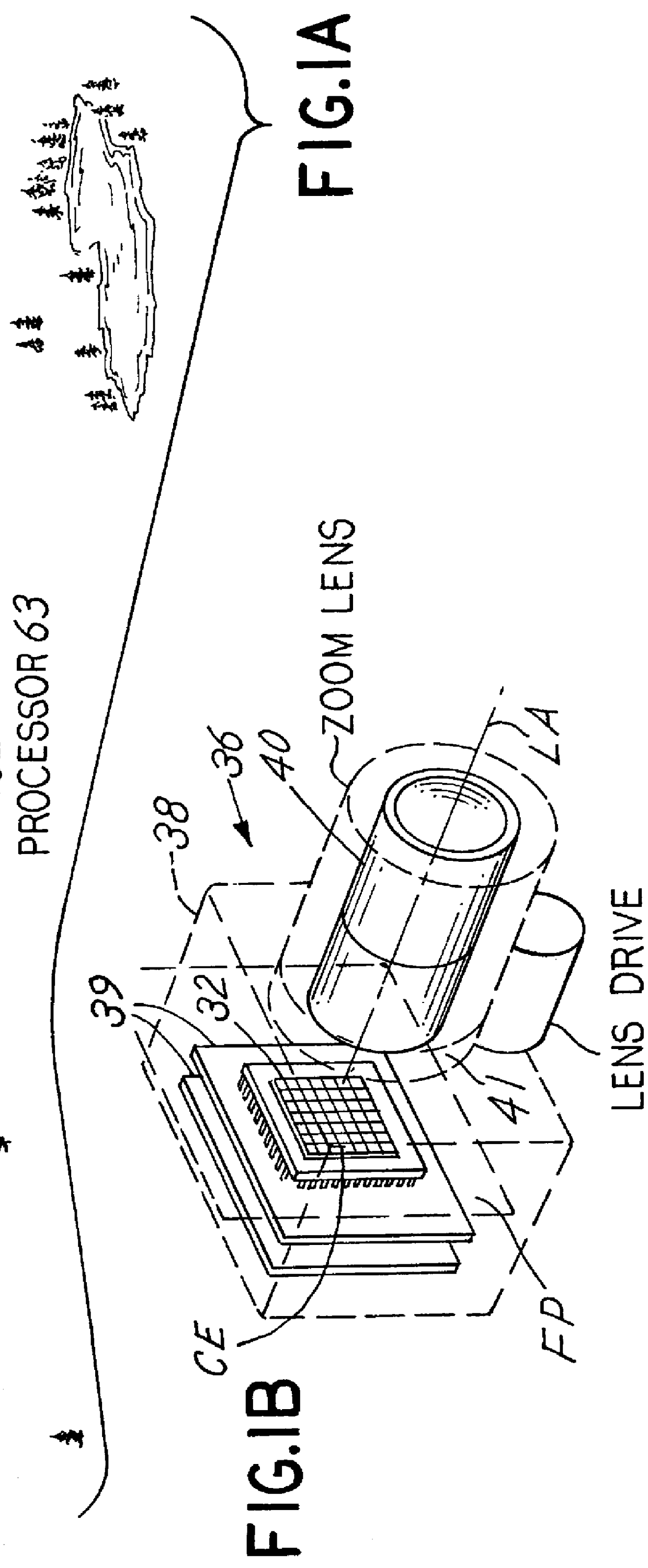
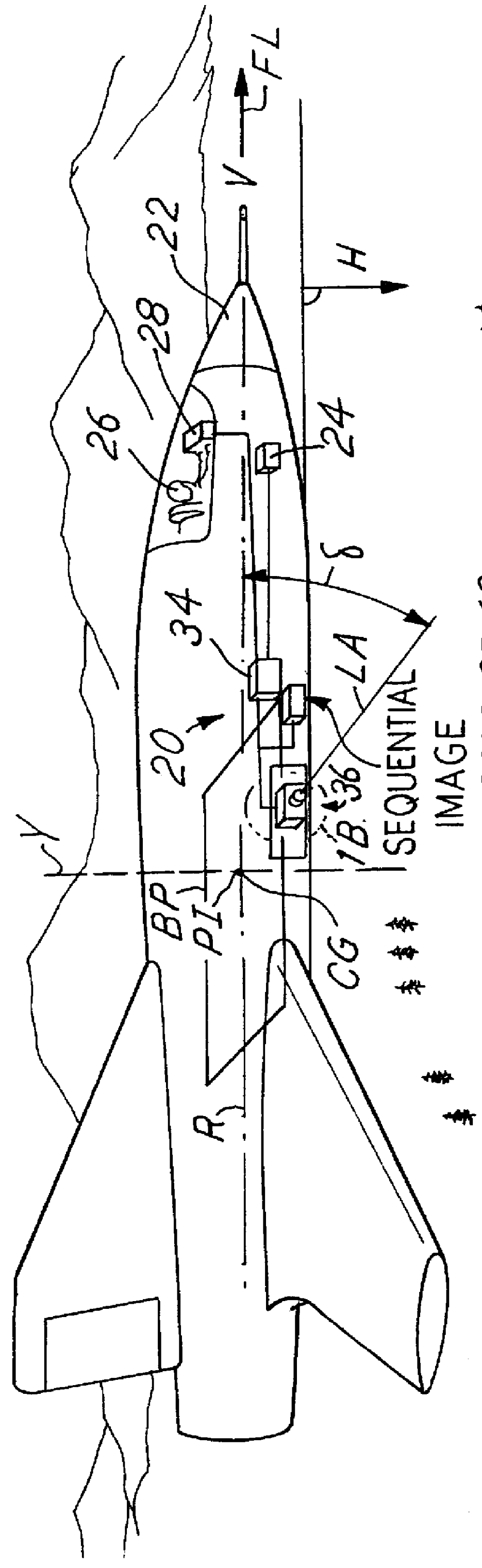
Autonomous electro-optical framing camera system with constant ground resolution, unmanned airborne vehicle therefor, and methods of use
InactiveUS6130705AReduce vibrationIncrease flexibilityTelevision system detailsOptical rangefindersCamera imageImage resolution
An aerial reconnaissance system generates imagery of a scene that meets resolution or field of view objectives automatically and autonomously. In one embodiment, a passive method of automatically calculating range to the target from a sequence of airborne reconnaissance camera images is used. Range information is use for controlling the adjustment of a zoom lens to yield frame-to-frame target imagery that has a desired, e.g., constant, ground resolution or field of view at the center of the image despite rapid and significant aircraft altitude and attitude changes. Image to image digital correlation is used to determine the displacement of the target at the focal plane. Camera frame rate and aircraft INS / GPS information is used to accurately determine the frame to frame distance (baseline). The calculated range to target is then used to drive a zoom lens servo mechanism to the proper focal length to yield the desired resolution or field of view for the next image. The method may be performed based on parameters other than range, such as aircraft height and stand off distance.
Owner:THE BF GOODRICH CO
Methods for driving video electro-optic displays
ActiveUS20080291129A1Reduce power consumptionStatic indicating devicesOptical propertyDisplay device
Video displays using relatively low frame rates of about 10 to about 20 frames per second, but having acceptable video quality are described. The displays may use bistable media, and may be driven such that the medium, when driven, changes its optical properties continuously during the driving of each frame. The displays may use an electro-optic medium such that the frame period is from about 50 to about 200 percent of the switching time of the electro-optic medium at the driving voltage used.
Owner:E INK CORPORATION
Liquid Crystal Display Device and Driving Method Thereof
ActiveUS20080284719A1Increase contrastImprove image qualityStatic indicating devicesSolid-state devicesLiquid-crystal displayDisplay device
In a display device including a backlight and a display panel, the area of the backlight is divided into a plurality of unit regions; the display panel includes pixels which are larger in number than the unit regions; a frame rate of image data input to the device is converted to perform display while part of the unit regions in which black is displayed is in a non-light emission state; and the driving frequency of the backlight is converted in accordance with the display.
Owner:SEMICON ENERGY LAB CO LTD
Providing multiple video signals from single sensor
ActiveUS20080084486A1Simple technologyTime requiredTelevision system detailsColor television detailsComputer scienceFrame rate
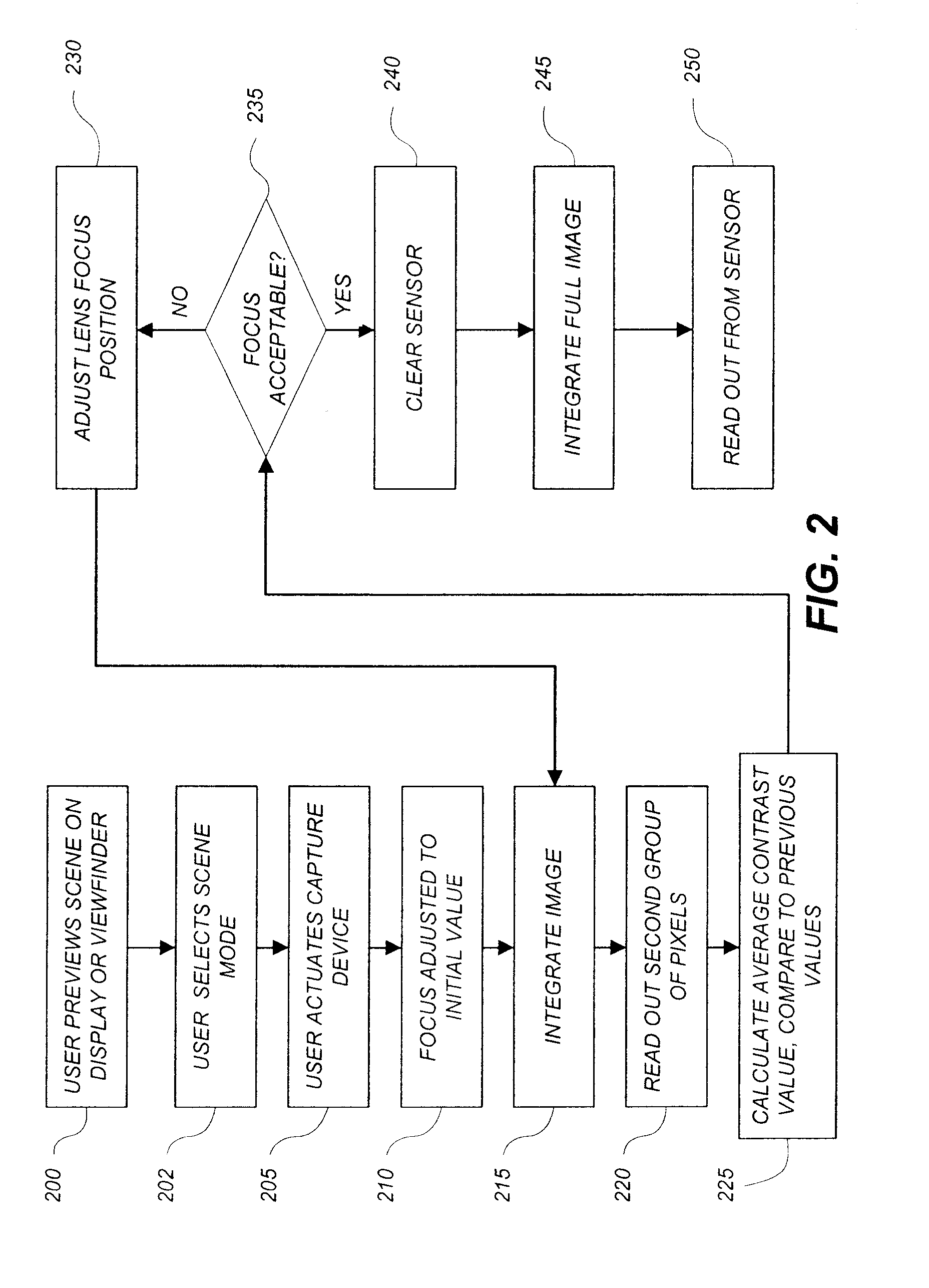
A method for using a capture device to capture at least two video signals corresponding to a scene, includes: providing a two-dimensional image sensor having a plurality of pixels; reading a first group of pixels from the image sensor at a first frame rate to produce a first video signal of the image scene; reading a second group of pixels from the image sensor at a second frame rate for producing a second video signal; and using at least one of the video signals for adjusting one or more of the capture device parameters.
Owner:OMNIVISION TECH INC
Digital camera using multiple image sensors to provide improved temporal sampling
InactiveUS20080211941A1Keep for a long timeImprove spatial resolutionTelevision system detailsSignal generator with multiple pick-up deviceImage resolutionExposure period
A method and apparatus for capturing image data from multiple image sensors and generating an output image sequence are disclosed. The multiple image sensors capture data with one or more different characteristics, such as: staggered exposure periods, different length exposure periods, different frame rates, different spatial resolution, different lens systems, and different focal lengths. The data from multiple image sensors is processed and interleaved to generate an improved output motion sequence relative to an output motion sequence generated from an a single equivalent image sensor.
Owner:MONUMENT PEAK VENTURES LLC
Frame synchronization in an ethernet NTP time-keeping digital cinema playback system
ActiveUS20050283820A1Highly accurateHighly stableTelevision system detailsAnalogue secracy/subscription systemsVideo decodingEthernet
In a digital cinema network of NTP-timekeeping devices in which one of the devices decodes video information, the scheduling of future instructions takes into account the differences between the nominal and actual frame rates of the video decoding device and the network's NTP latency.
Owner:DOLBY LAB LICENSING CORP
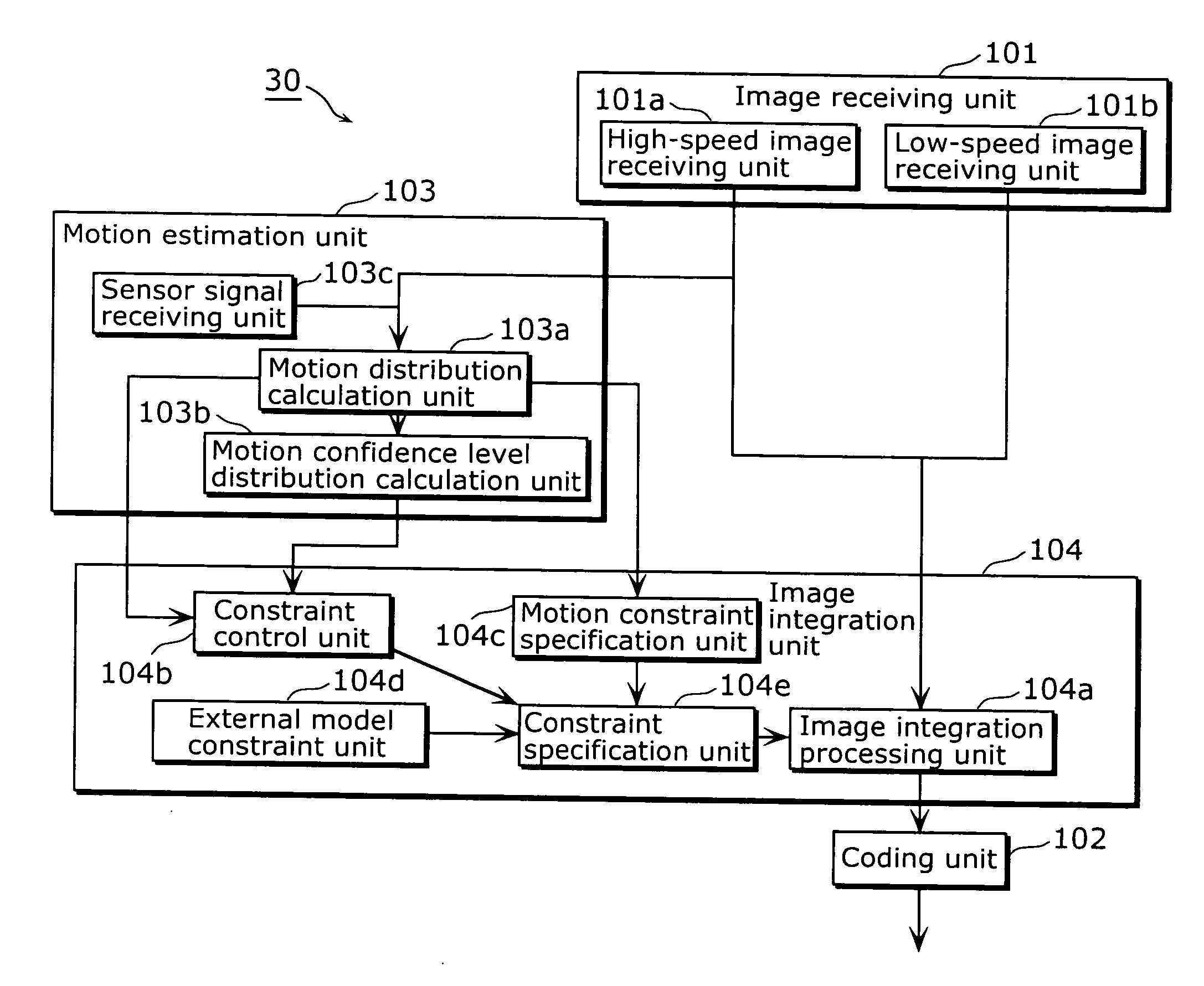
Image generation apparatus and image generation method
InactiveUS20070189386A1Maintain good propertiesReliable generationTelevision system detailsImage analysisComputer graphics (images)Image resolution
The image generation apparatus includes: an image receiving unit which receives a first video sequence including frames having a first resolution and a second video sequence including frames having a second resolution which is higher than the first resolution, each frame of the first video sequence being obtained with a first exposure time, and each frame of the second video sequence being obtained with a second exposure time which is longer than the first exposure time; and an image integration unit which generates, from the first video sequence and the second video sequence, a new video sequence including frames having a resolution which is equal to or higher than the second resolution, at a frame rate which is equal to or higher than a frame rate of the first video sequence, by reducing a difference between a value of each frame of the second video sequence and a sum of values of frames of the new video sequence which are included within an exposure period of the frame of the second video sequence.
Owner:SOVEREIGN PEAK VENTURES LLC
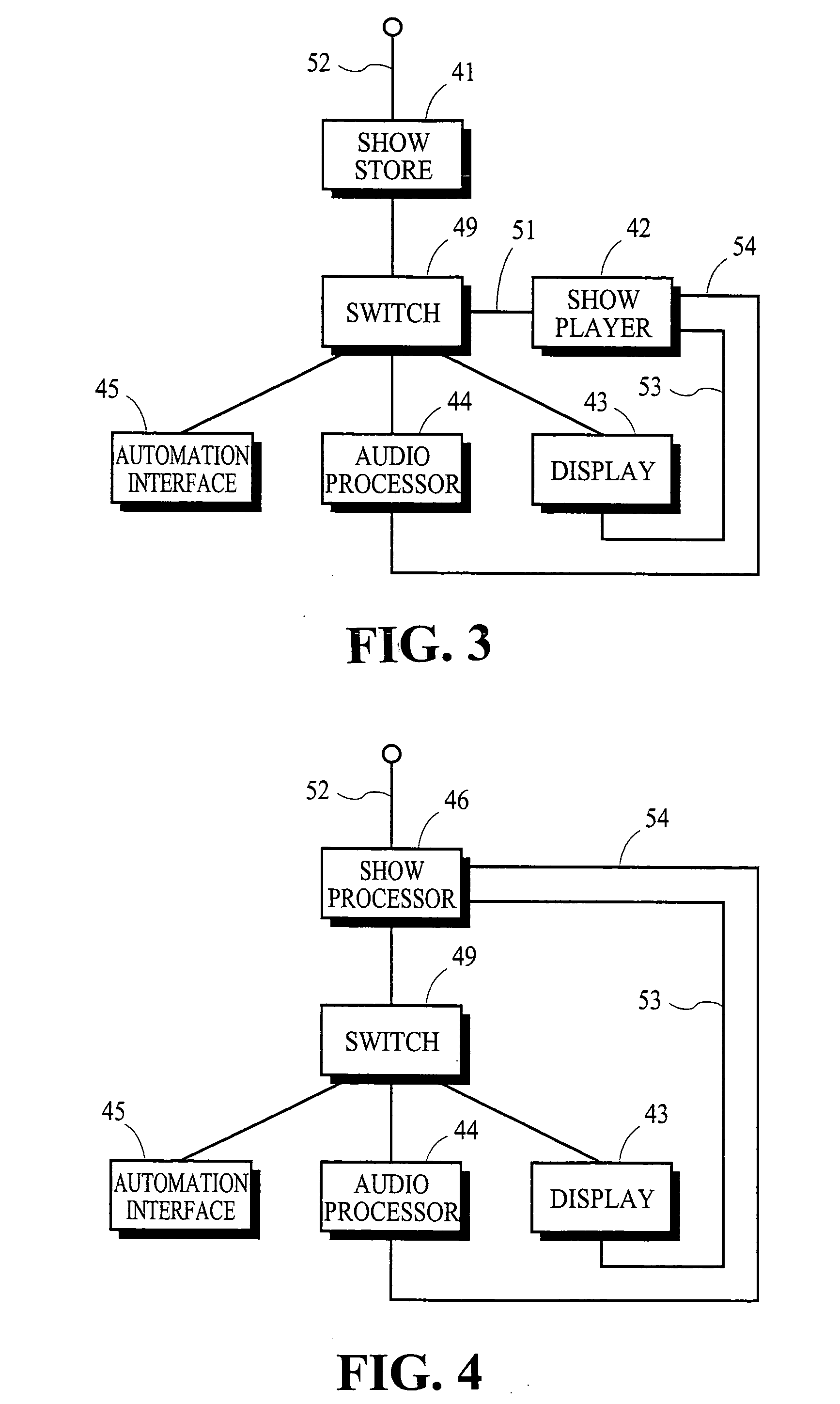
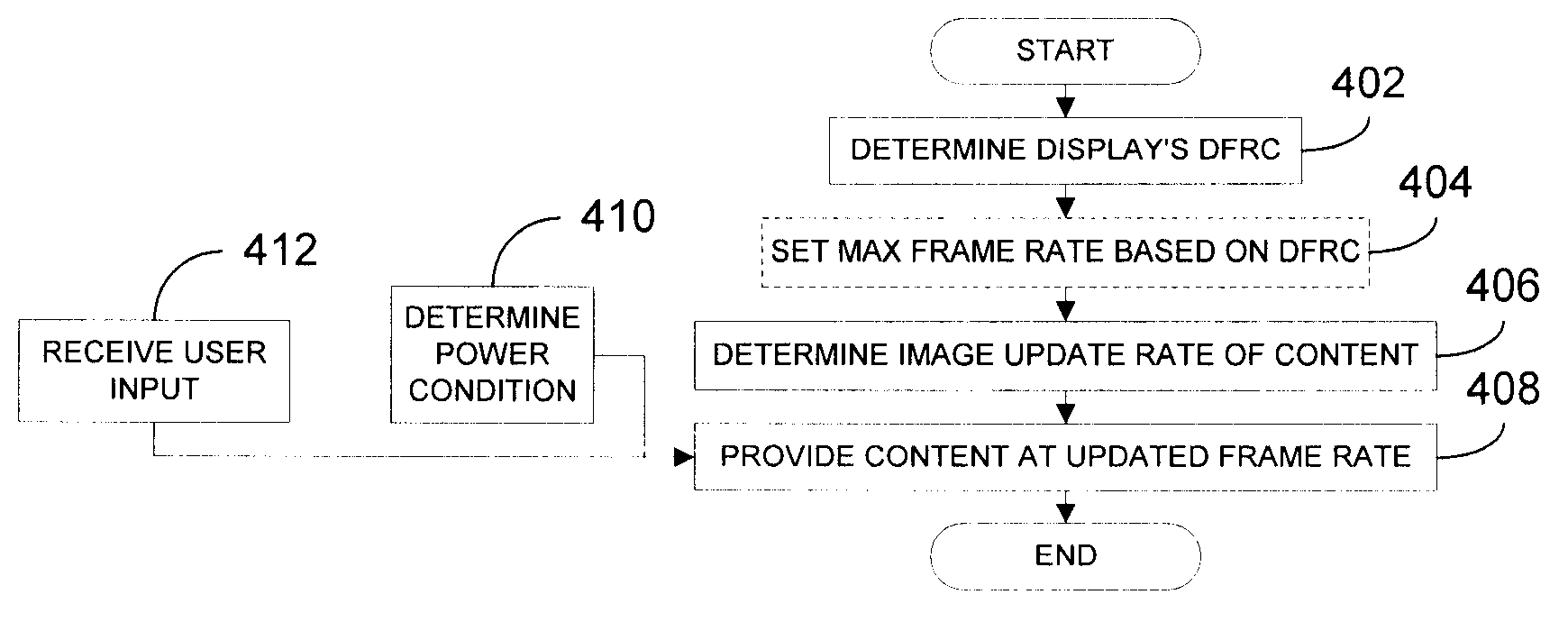
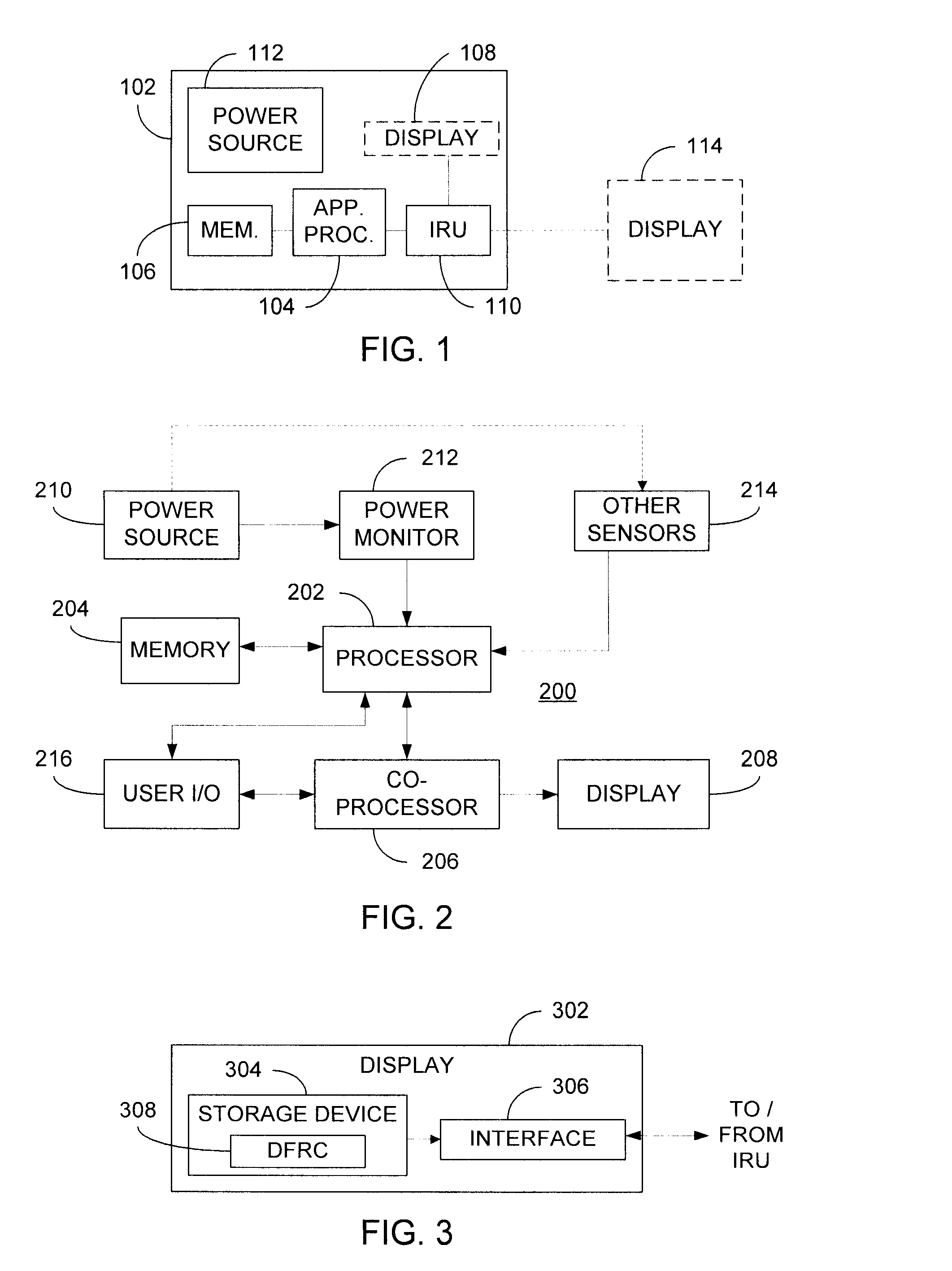
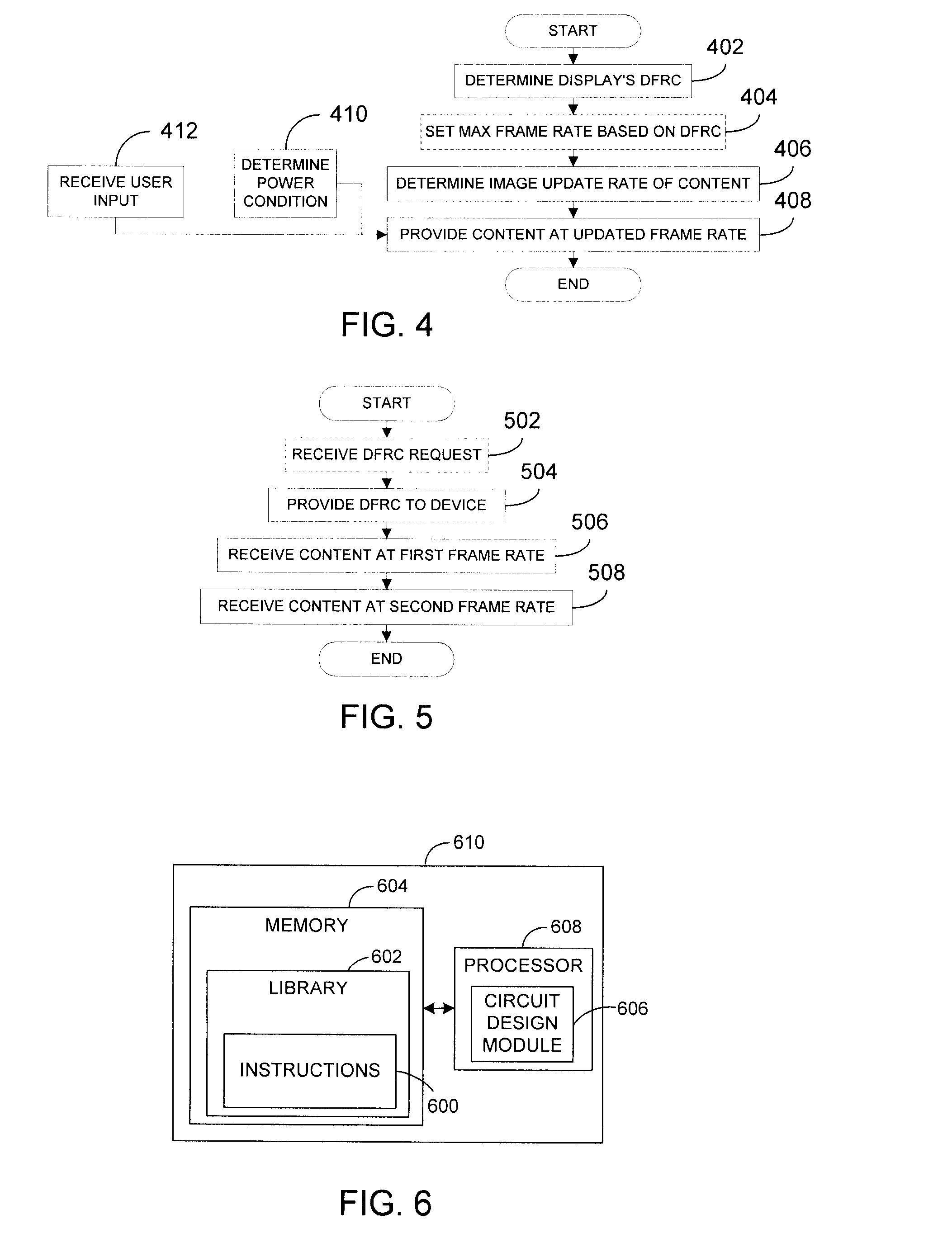
Dynamic frame rate adjustment
InactiveUS20080055318A1Television system detailsStatic indicating devicesComputer graphics (images)Display device
An image rendering unit (IRU) of a device determines the dynamic frame rate capabilities (DFRCs) of a display and an image frame rate of content to be displayed. Preferably, the DFRCs are stored in a storage device deployed within the display itself. Based on the DFRCs and the image frame rate for the content, the IRU determines an updated frame rate and thereafter provides the content to the display at the updated frame rate. Where control of power consumption is desired, selection of a reduced frame rate can effect a power savings. In this manner, the present invention provides flexible control over display frame rates and / or power consumption of the device.
Owner:ATI TECH INC
Digital camera having variable duration burst mode
ActiveUS20120257071A1Capacity be still finiteTelevision system detailsColor television detailsData processing systemDigital image
A digital camera for having a variable time duration burst capture mode, comprising: an image sensor; an optical system; a data processing system; a frame buffer memory; and a program memory. The program memory stores instructions including: specifying a first frame rate; initiating an image capture sequence; storing a sequence of digital images captured at the first frame rate in the frame buffer memory; determining whether the frame buffer memory has been filled to a predetermined capacity. If the frame buffer memory has been filled to the predetermined capacity, the program memory further includes instructions for specifying a second frame rate, wherein the second frame rate is lower than the first frame rate; designating a set of stored digital images that can be overwritten; and storing a sequence of digital images captured at the second frame rate in the frame buffer memory, overwriting the designated set of stored digital images.
Owner:APPLE INC
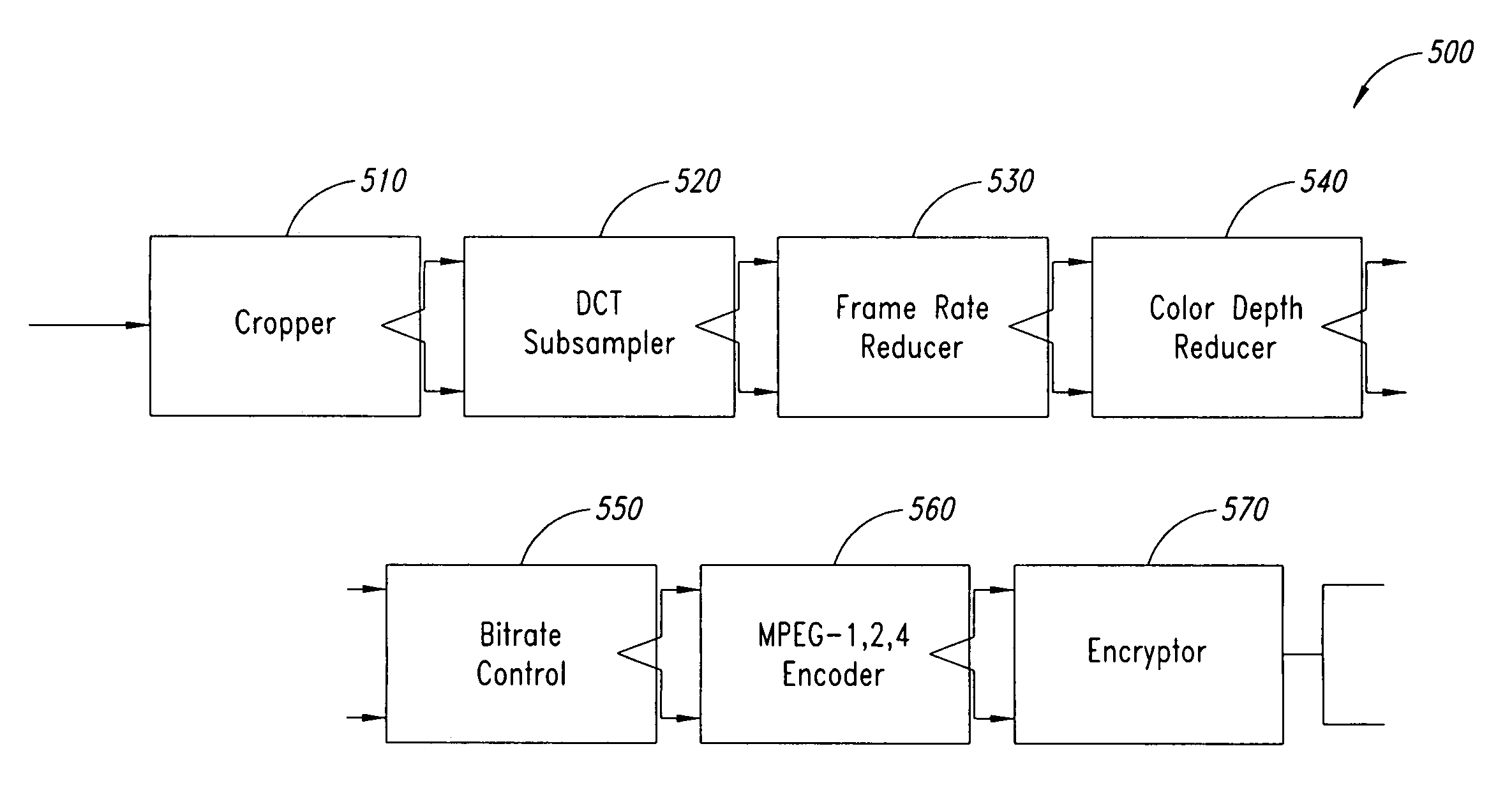
Methods for transforming streaming video data
InactiveUS7339993B1Reduces input bandwidthReduce bandwidth usagePicture reproducers using cathode ray tubesPicture reproducers with optical-mechanical scanningData streamImage resolution
A method for forming an output stream of data includes determining an output resolution for the output stream of data, determining an output frame rate for the output stream of data, determining an output color depth for the output stream of data, retrieving a first frame of data, a second frame of data, and a third frame of data from an input stream of data, the input stream of data having an input resolution, an input frame rate, and an input color depth, subsampling the first frame of data, the second frame of data, and the third frame of data to respectively form a first subsampled frame of data, a second subsampled frame of data, and a third subsampled frame of data, when the output resolution is lower than the input resolution, dropping the second subsampled frame of data, when the output frame rate is lower than the input frame rate, reducing color depth for the first subsampled frame of data and the second subsampled frame of data to respectively form a first reduced frame of data and a second reduced frame of data, when the output color depth is smaller than the input color depth, and converting the first reduced frame of data and the second reduced frame of data into the output stream of data.
Owner:ADAPTIVE STREAMING INC
System for transforming streaming video data
InactiveUS7143432B1Decreased bit depthAttenuation bandwidthPicture reproducers using cathode ray tubesPicture reproducers with optical-mechanical scanningImage resolutionComputer graphics (images)
According to one embodiment, a circuit configured to form an output video stream includes a resolution modification circuit configured to receive a plurality of video frames from a frame buffer, and configured to modify resolution of the plurality of video frames, when the desired resolution for the output video stream is different than a resolution of the input video stream, the plurality of frames of data derived from an input video stream, a frame reducing circuit coupled to the resolution reducing circuit configured to reduce a number of video frames in the plurality of video frames from the resolution reducing circuit, when a desired frame rate for the output video stream is different than a frame rate of the input video stream, a depth reduction circuit coupled to the frame reducing circuit configured to reduce bit depth of the plurality of video frames from the frame reducing circuit, when a desired bit depth for the output video stream is different than a bit depth of the input video stream, and a rate reduction circuit coupled to the depth reduction circuit, configured to scale the plurality of video frames from the depth reduction circuit, in response to a desired bit rate for the output video stream, and an encoder coupled to the rate reduction circuit, configured to encode the plurality of video frames from the rate reduction circuit into the output video stream is also contemplated.
Owner:ADAPTIVE STREAMING INC
Solid-state image pickup device and method for driving the same
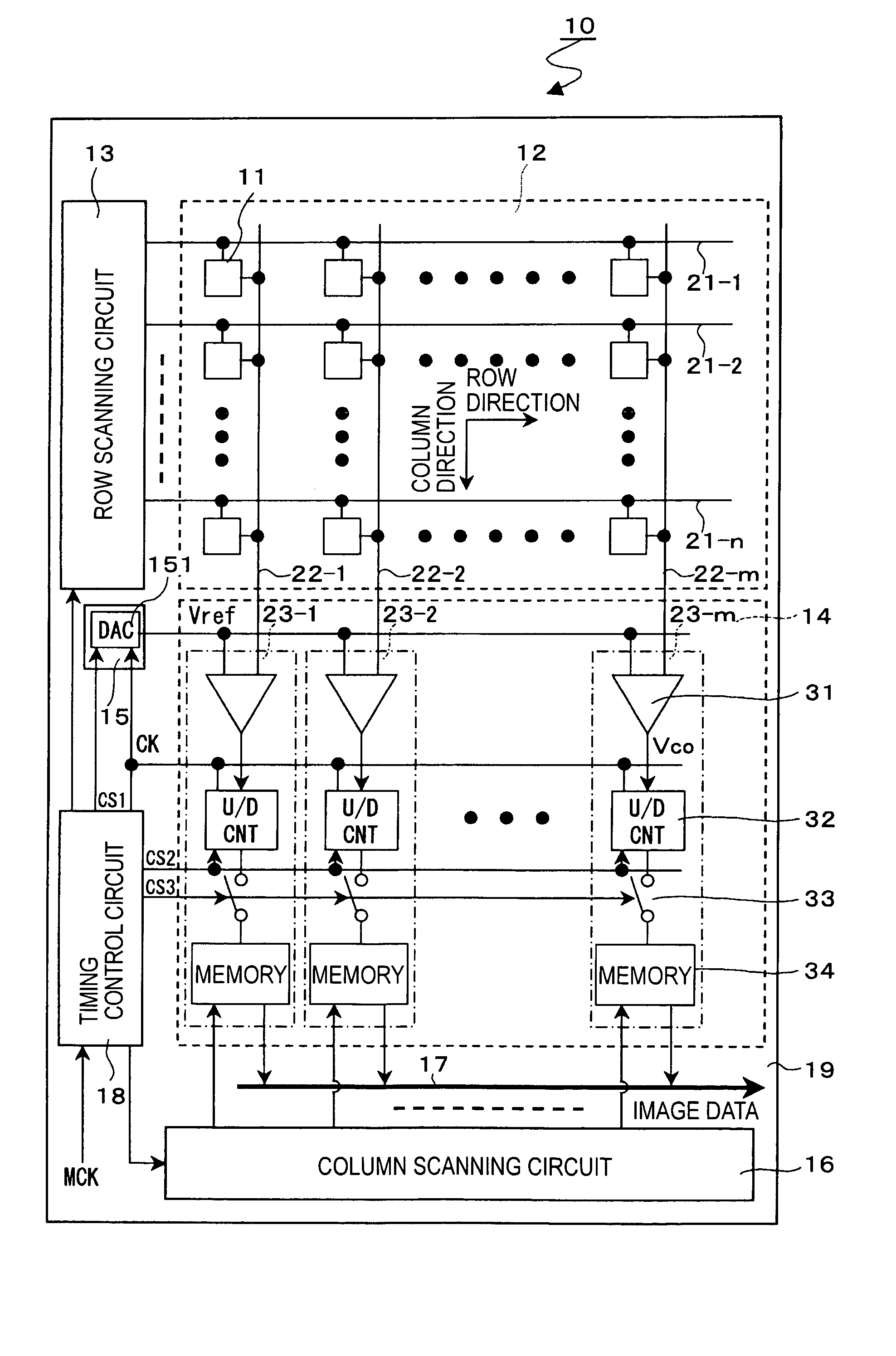
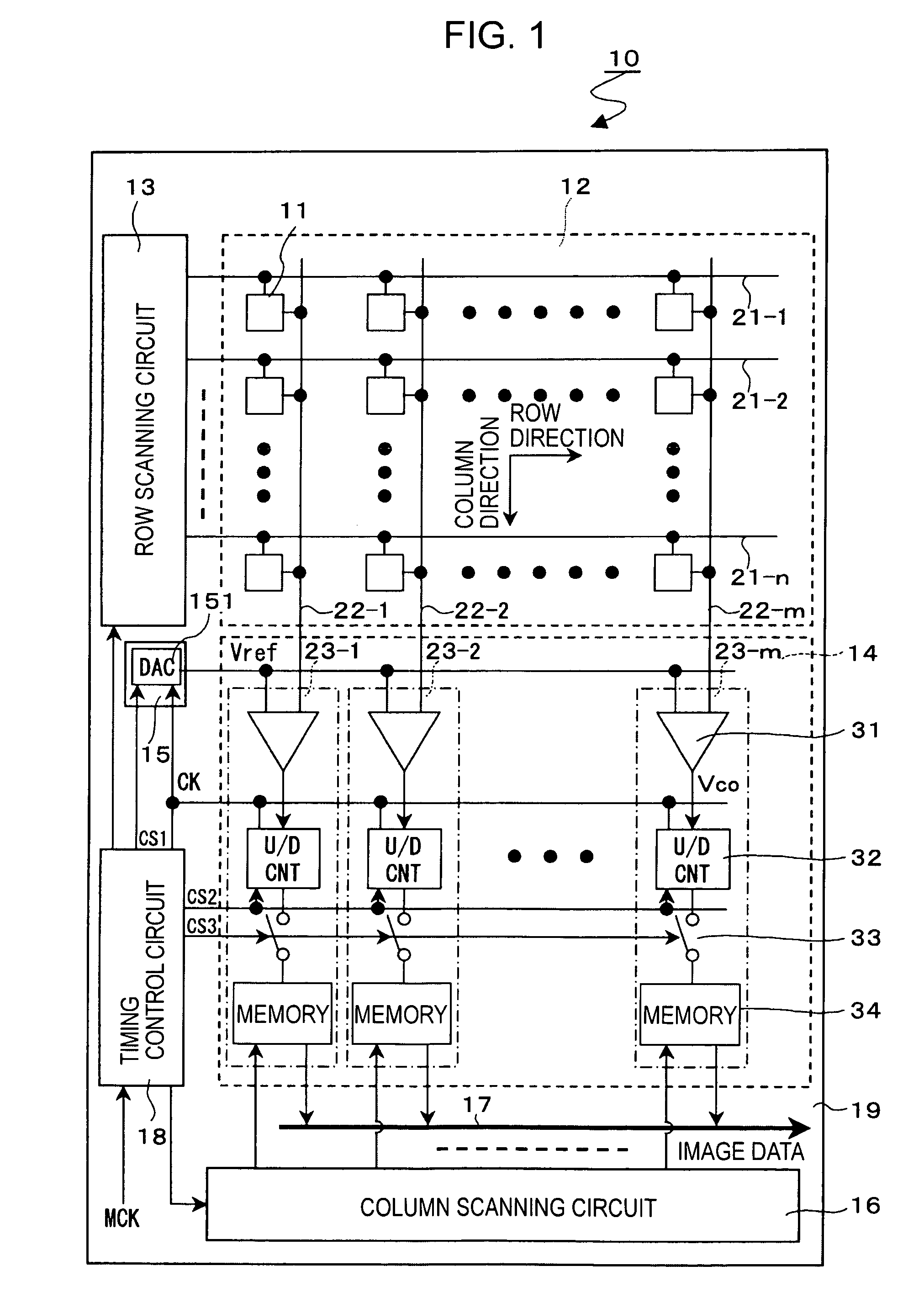
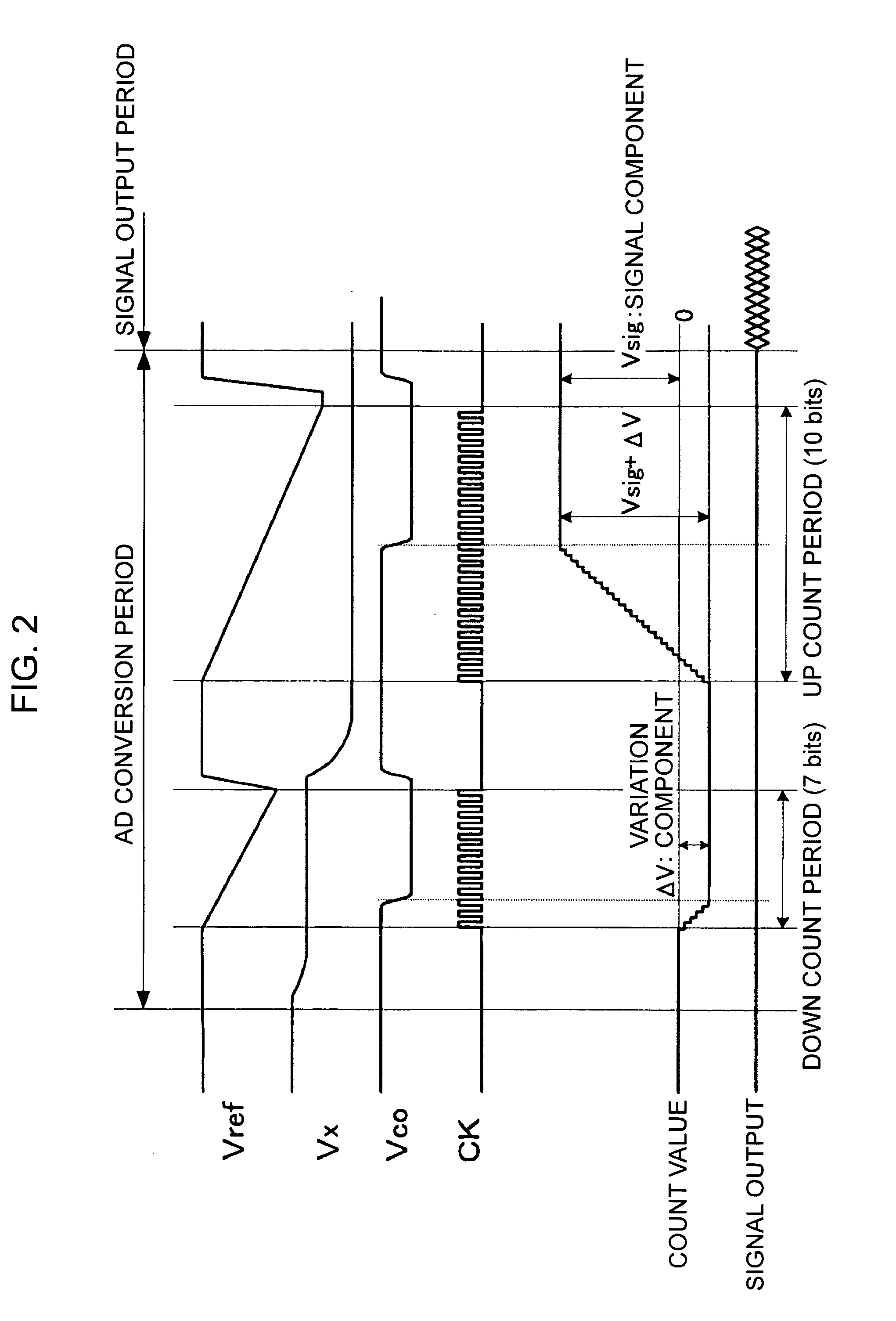
InactiveUS20050195304A1Reduce sensitivityIncrease frame rateAnalogue/digital conversionTelevision system detailsCMOSComputer science
A CMOS image sensor includes column-parallel ADCs. Each of the ADCs includes a comparator and an up / down counter. With this configuration, digital values of pixels in a plurality of rows can be added without using additional circuits, such as an adder and a line memory device, and the frame rate can be increased while maintaining constant sensitivity.
Owner:SONY CORP
Handheld video transmission and display
InactiveUS20060114987A1Easy to handleReduce drainageTelevision conference systemsPicture reproducers using cathode ray tubesDigital videoComputer graphics (images)
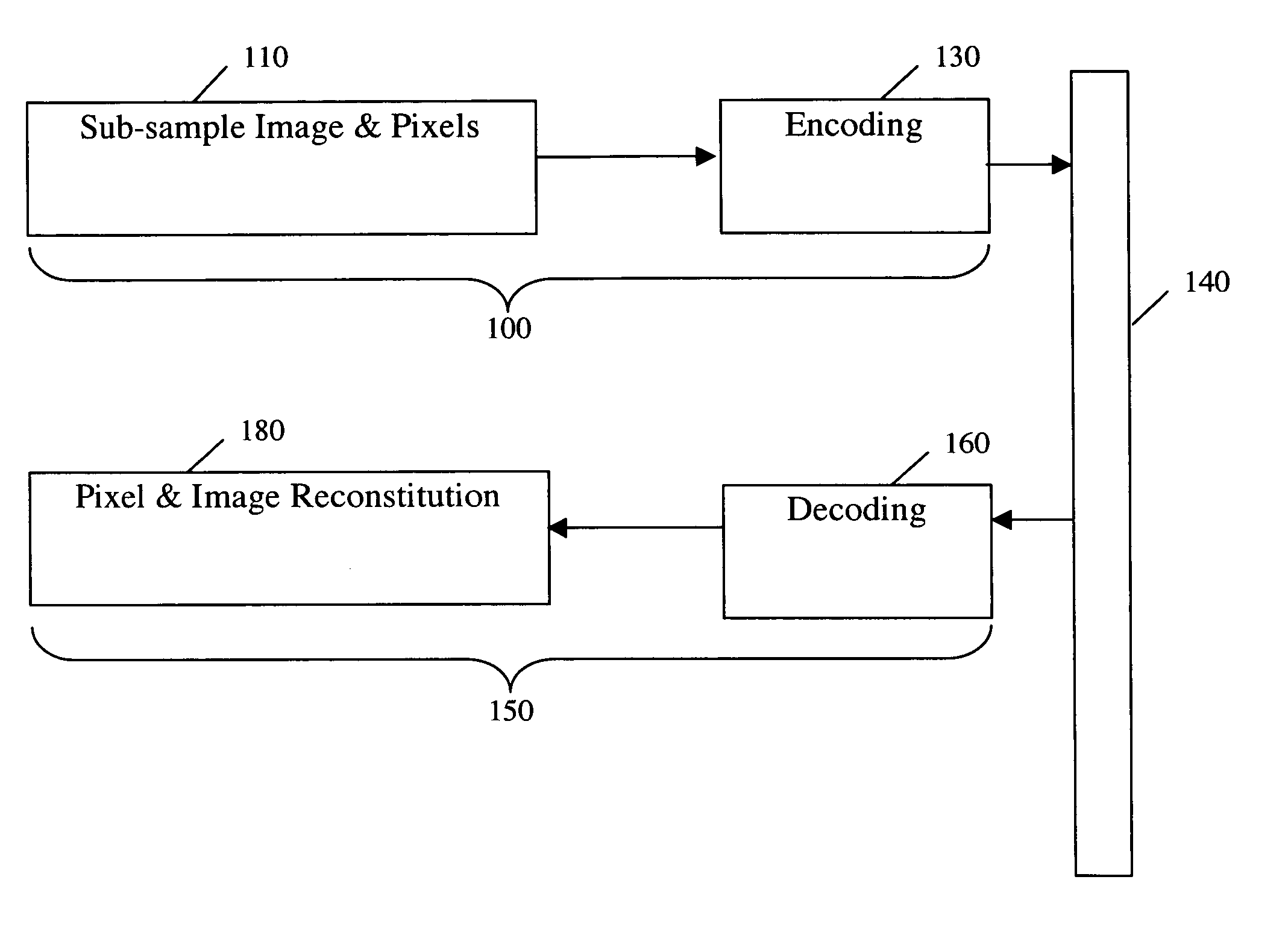
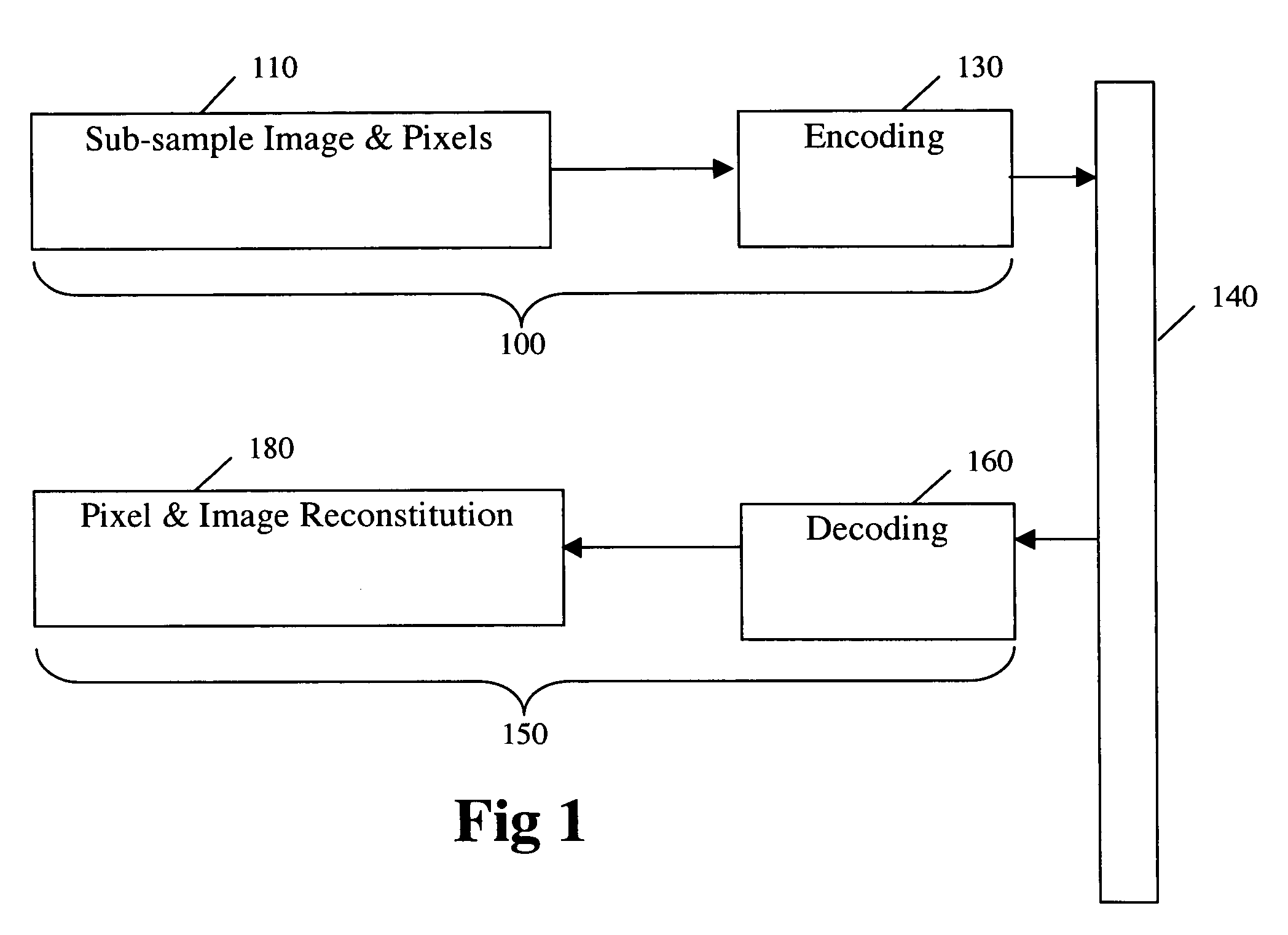
Methods, medium, and handheld, wireless devices which compress, enhance, encode, transmit, decompress and display digital video images in real time. Real time wireless videoconferences connect multiple handheld video devices. Real time compression is achieved by sub-sampling each frame of a video signal, filtering the pixel values, and encoding. Real time transmission is achieved due to high levels of effective compression. Real time decompression is achieved by decoding and decompressing the encoded data to display high quality images. A receiver can alter various setting including but not limited to the format for the compression, image size, frame rate, brightness and contrast. A zoom control can be used select a portion of interest of video being transmitted or being played back.
Owner:MUSICQUBED INNOVATIONS LLC
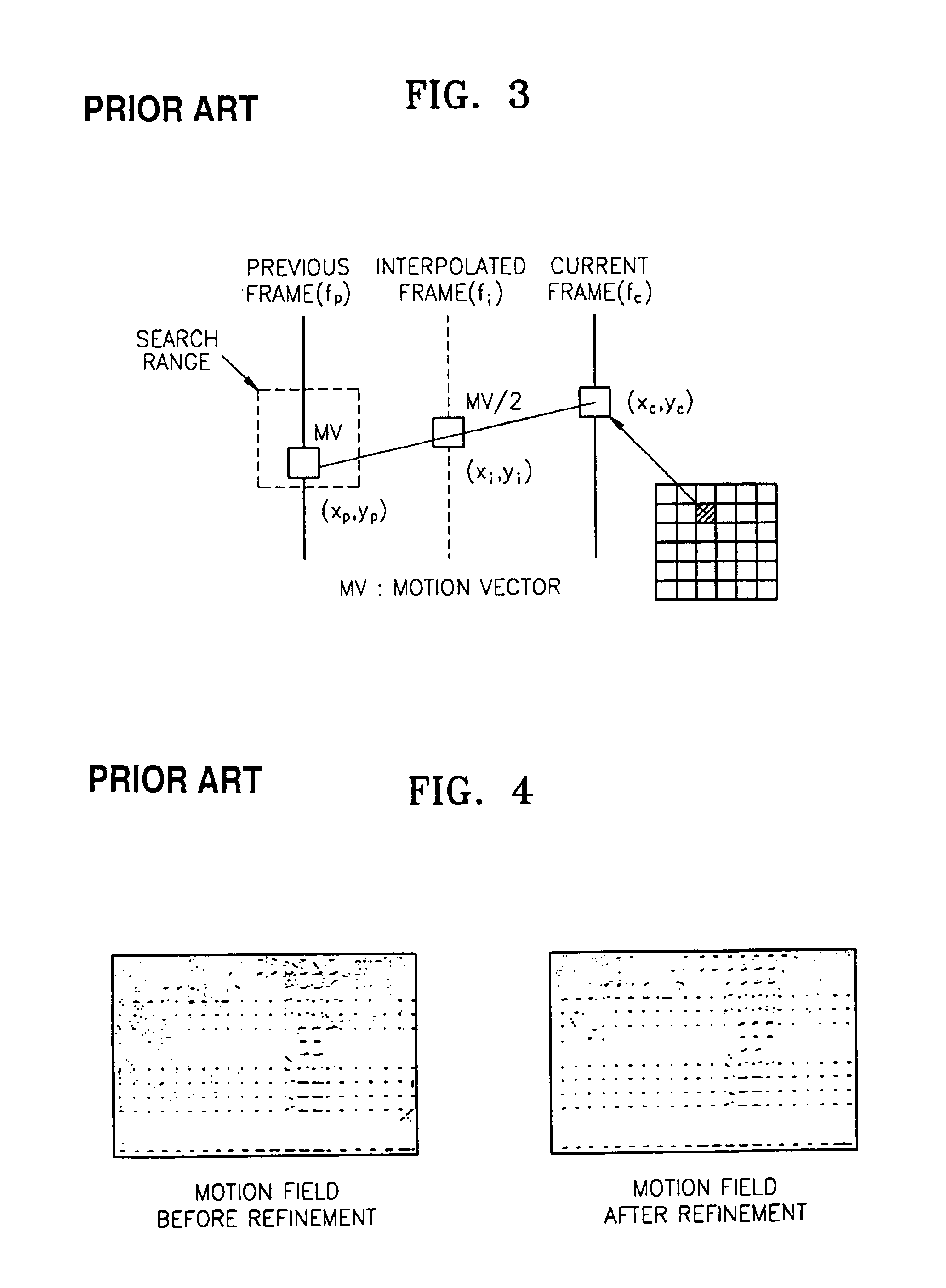
Format converter using bi-directional motion vector and method thereof
InactiveUS6900846B2Improve picture qualityEasy to implementTelevision system detailsPicture reproducers using cathode ray tubesMotion vectorComputer science
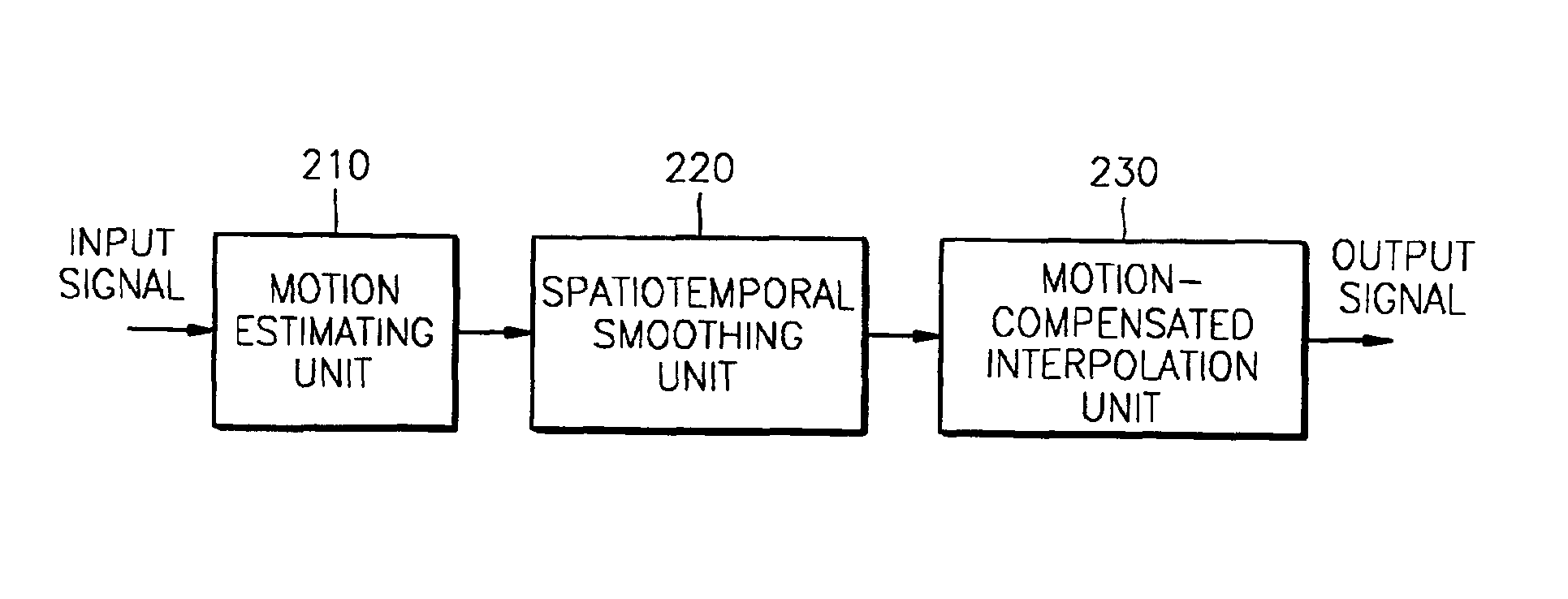
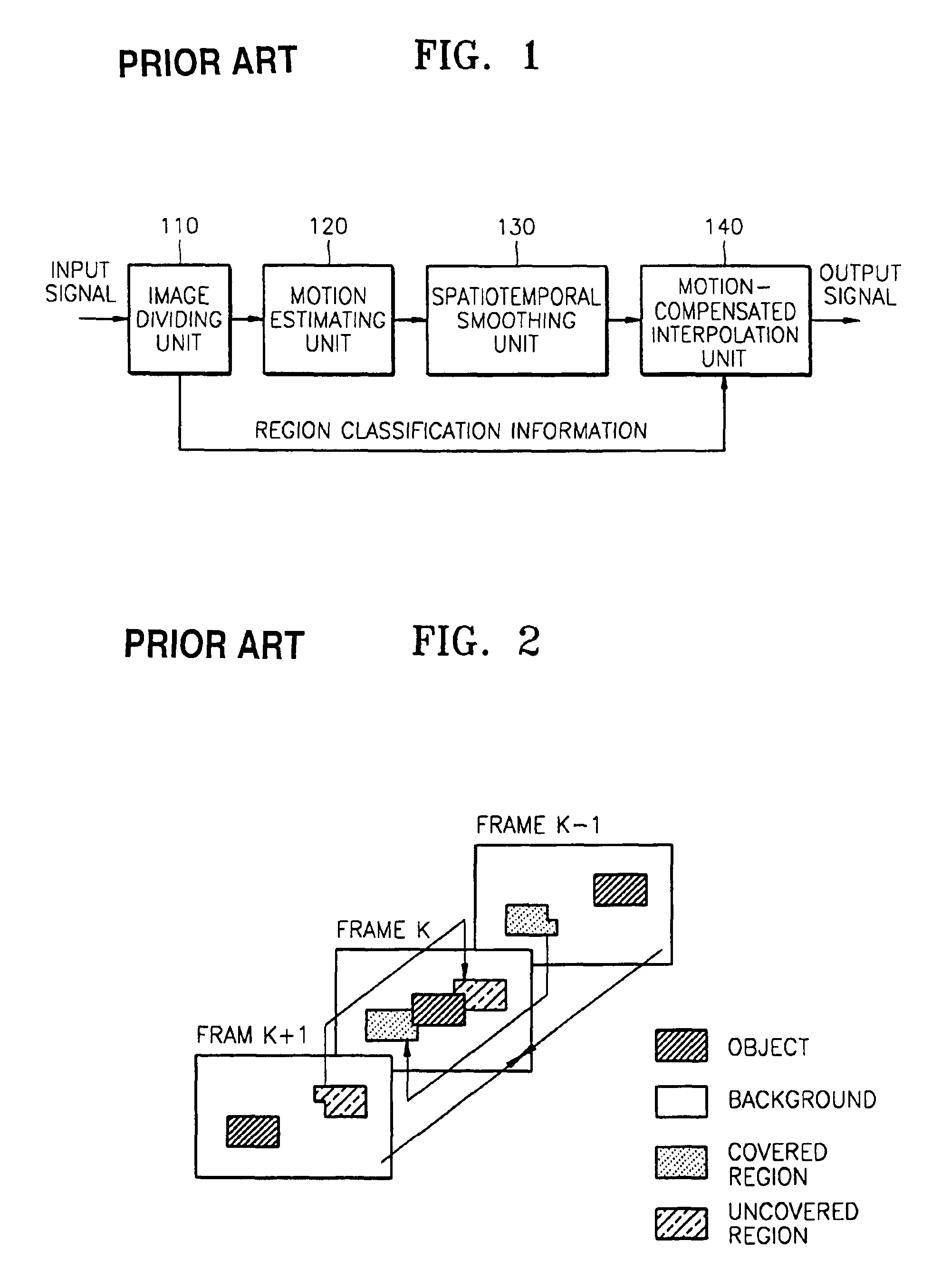
A format converter which performs frame rate conversion and de-interlacing using a bi-directional motion vector and a method thereof are provided. The method includes the steps of (a) estimating a bi-directional motion vector between the current frame and the previous frame from a frame to be interpolated; setting the motion vector of a neighboring block that has the minimum error distortion, among motion vectors estimated in step (a), as the motion vector of the current block; and (c) forming a frame to be interpolated with the motion vector set in step (b).
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
Methods and systems for game video recording and virtual reality replay
ActiveUS9473758B1Reduce rateReduce resolutionTelevision system detailsElectronic editing digitised analogue information signalsVideo sharingImage resolution
Methods and systems for processing computer game videos for virtual reality replay are disclosed. The method, when executed by a processor, comprises first receiving a video recorded using a virtual camera array during a game play of a source computer game. Next, upscaling the received video to a higher resolution, and interpolating neighboring video frames of the upscaled video for insertion into the upscaled video at a server. Finally, generating a spherical video from the interpolated video for replay in a virtual reality environment. The virtual camera array includes multiple virtual cameras each facing a different direction, and the video is recorded at a frame rate and a resolution lower than those of the source computer game. The spherical videos are provided on a video sharing platform. The present invention solves the chicken-and-egg problem of mass adoption of virtual reality technology by easily generating VR content from existing computer games.
Owner:SLIVER VR TECH INC
Apparatus for controlling a screen pointer with a frame rate based on velocity
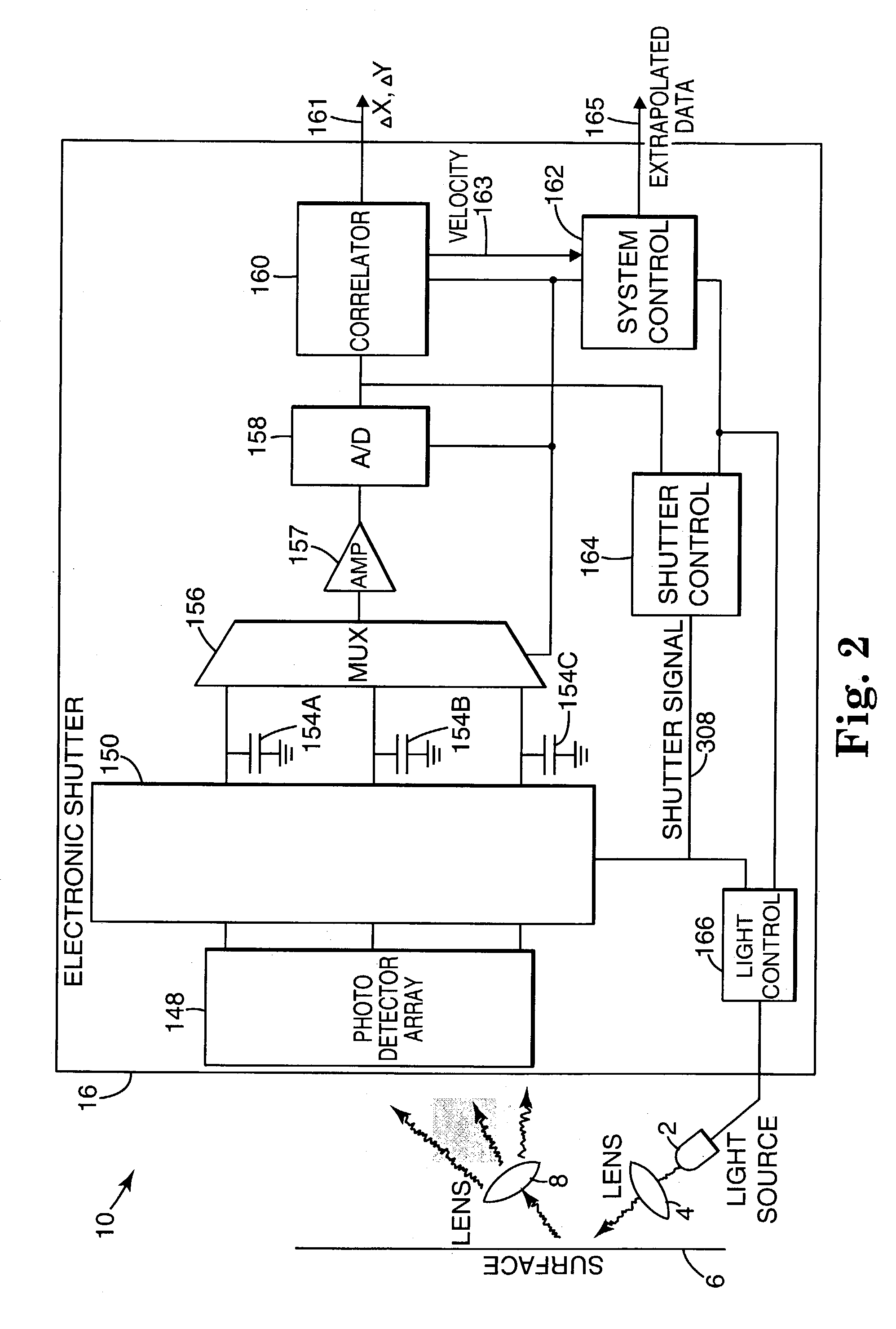
ActiveUS6995748B2Input/output for user-computer interactionEnergy efficient ICTRelative motionDigital image
An apparatus for controlling the position of a screen pointer for an electronic device having a display screen includes a light source for illuminating an imaging surface, thereby generating reflected images. An optical motion sensor generates digital images from the reflected images at a first frame rate. The motion sensor is configured to generate movement data based on the digital images. The movement data is indicative of relative motion between the imaging surface and the apparatus. The motion sensor is configured to modify the first frame rate to one of a plurality of alternate frame rates based on a current relative velocity between the imaging surface and the apparatus.
Owner:ELAN MICROELECTRONICS CORPORATION
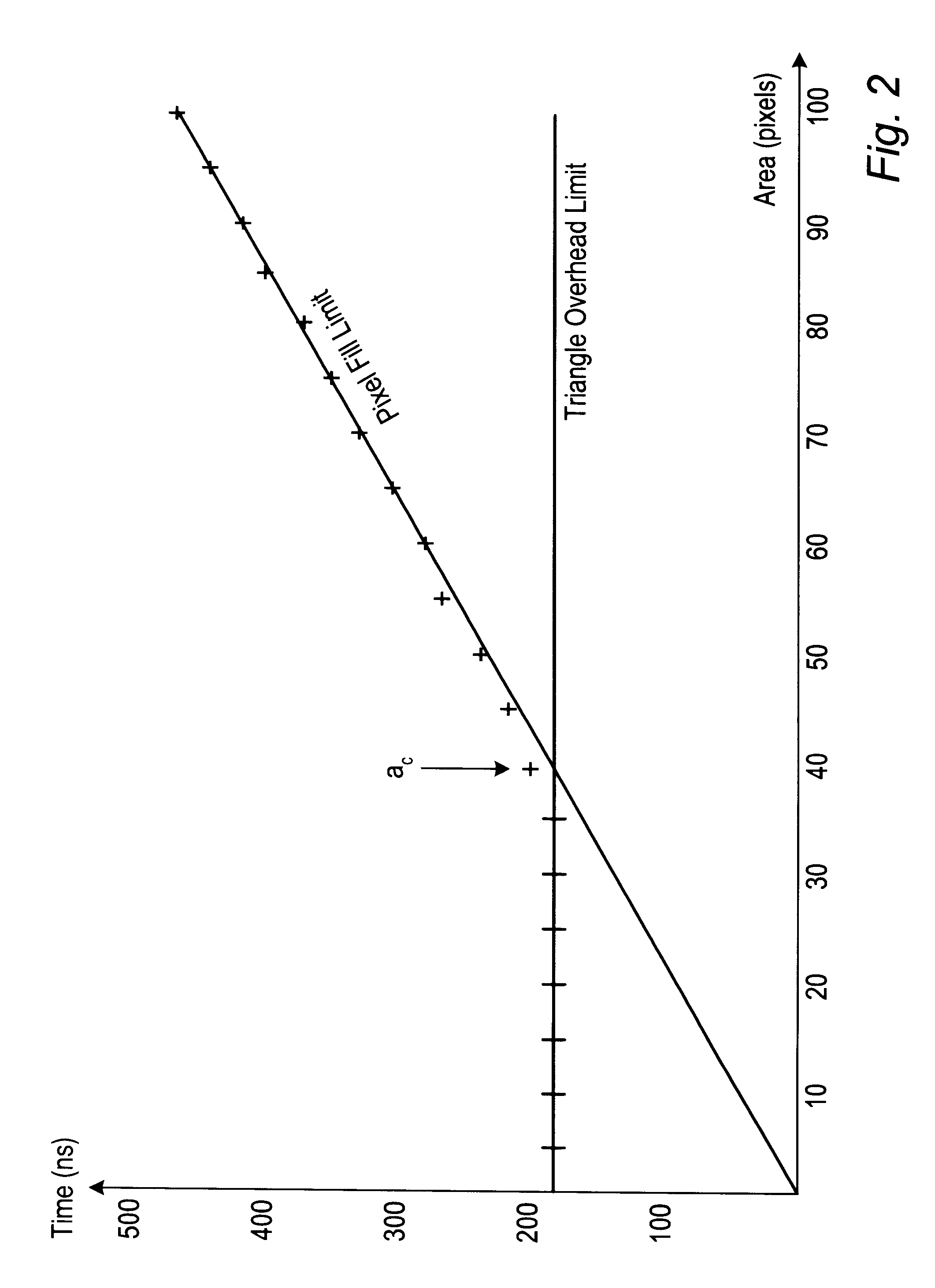
Estimating graphics system performance for polygons
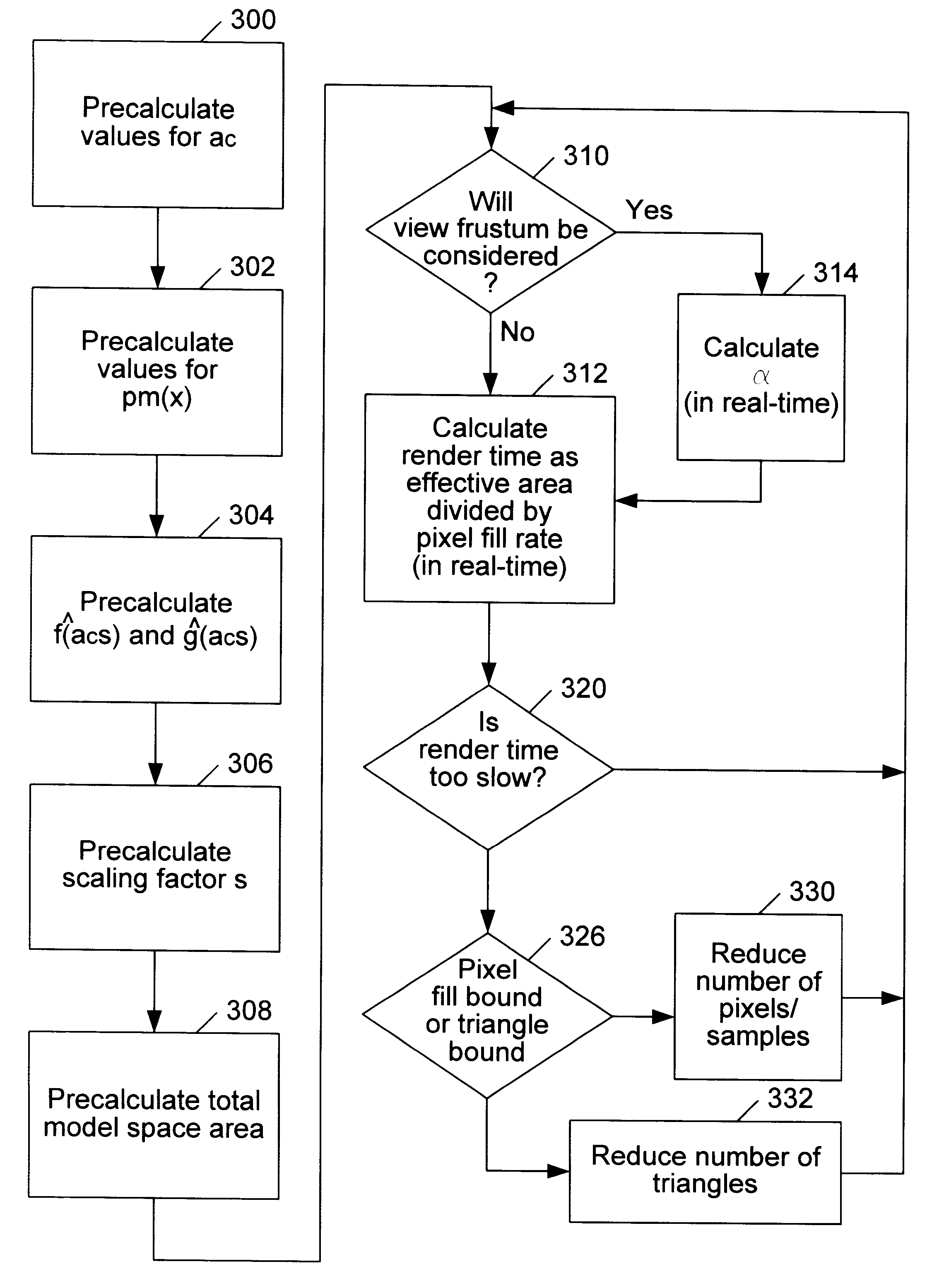
InactiveUS6313838B1Cathode-ray tube indicatorsImage data processing detailsComputational scienceGraphic system
A method for estimating rendering times for three-dimensional graphics objects and scenes is disclosed. The rendering times may be estimated in real-time, thus allowing a graphics system to alter rendering parameters (such as level of detail and number of samples per pixel) to maintain a predetermined minimum frame rate. Part of the estimation may be performed offline to reduce the time required to perform the final estimation. The method may also detect whether the objects being rendered are pixel fill limited or polygon overhead limited. This information may allow the graphics system to make more intelligent choices as to which rendering parameters should be changed to achieve the desired minimum frame rate. A software program configured to efficiently estimate rendering times is also disclosed.
Owner:ORACLE INT CORP
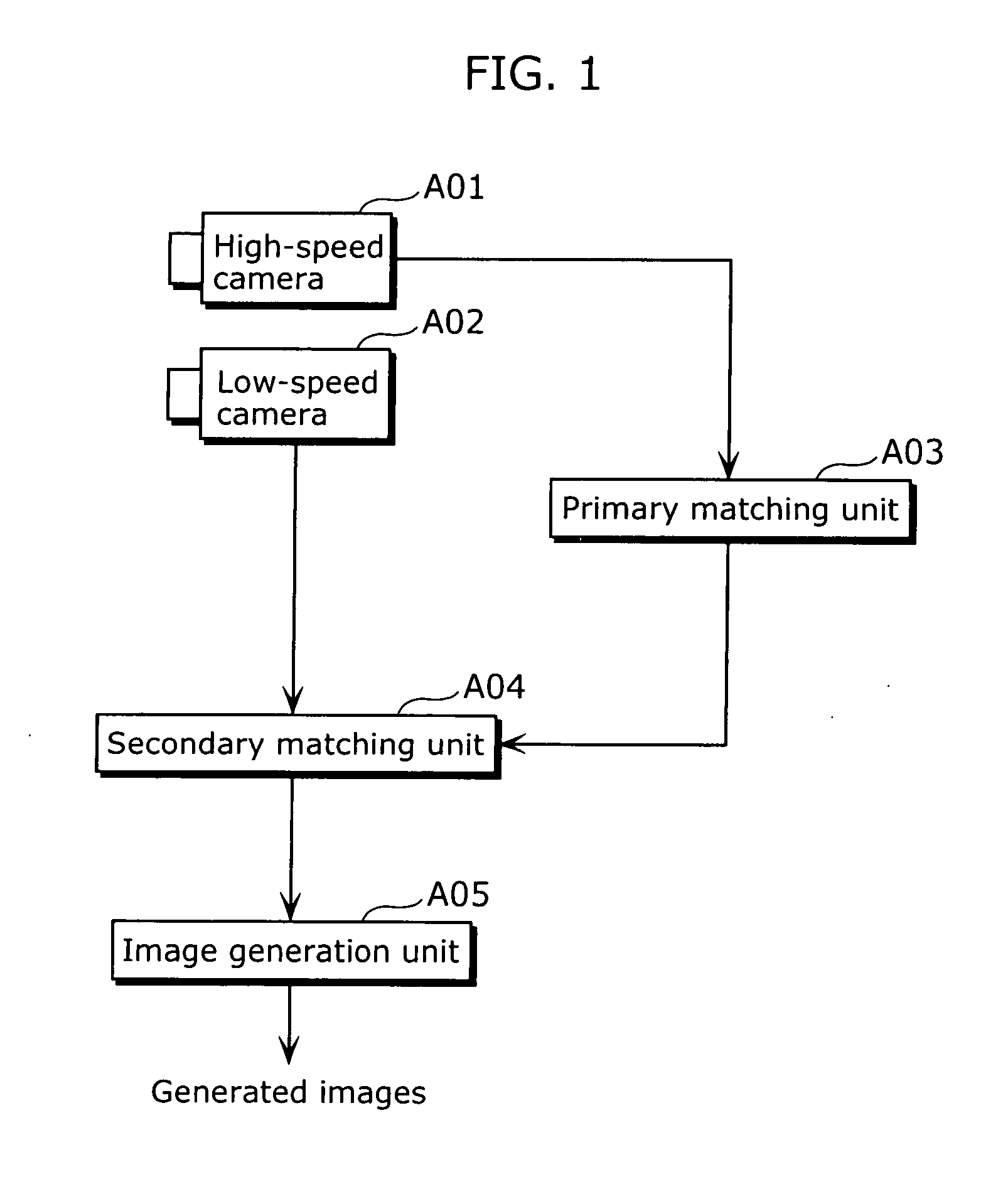
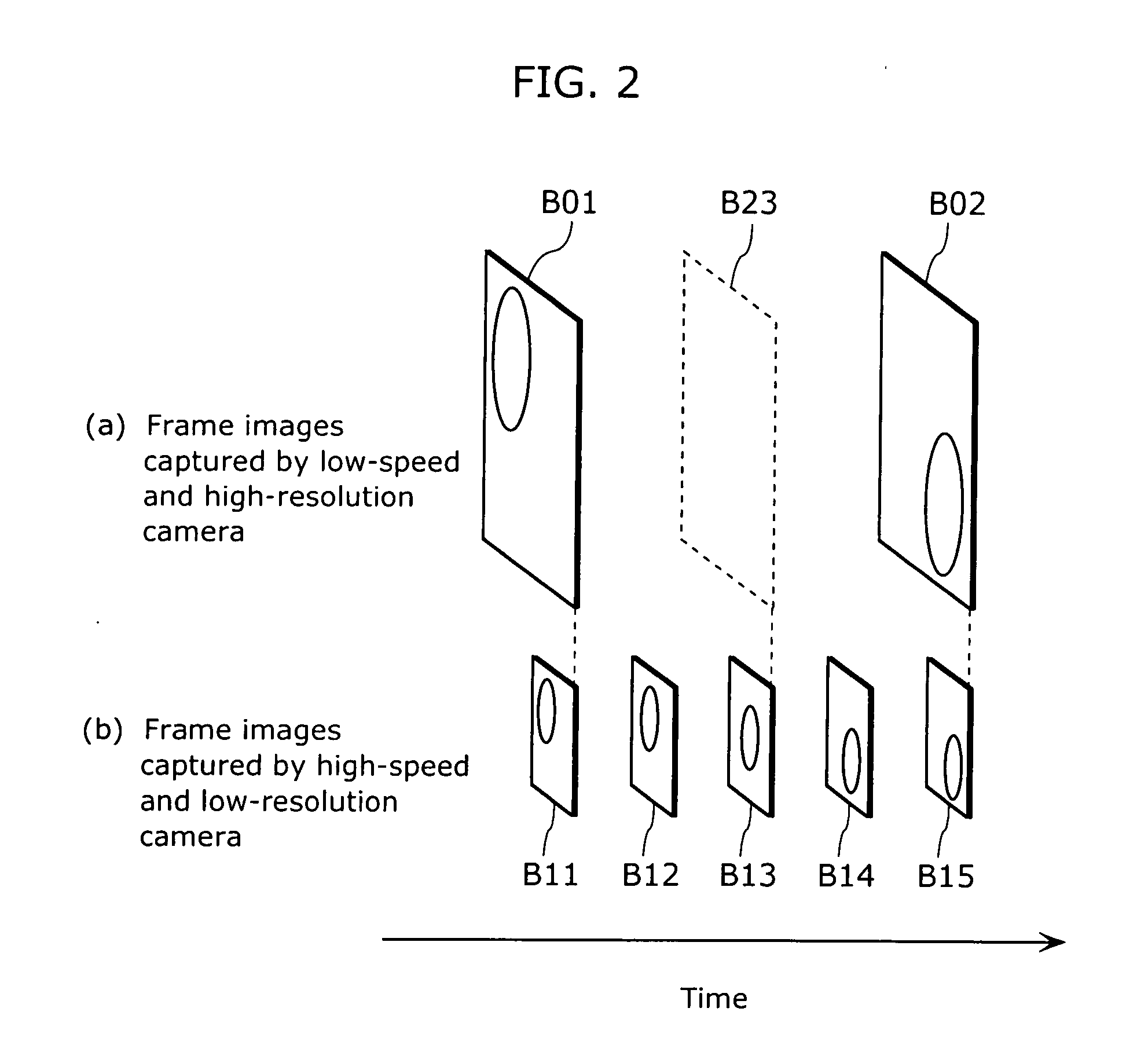
Digital camera for capturing a sequence of full and reduced resolution digital images and storing motion and still digital image data
InactiveUS7110025B1Reduce operating rateTelevision system detailsColor television detailsDigital videoComputer graphics (images)
A method for simultaneously recording motion and still images, includes the steps of: capturing a motion image sequence and accompanying audio of a scene with a digital video camera adapted to record both motion and higher resolution still images; simultaneously capturing a still image sequence having a higher resolution and lower frame rate than the motion capture sequence; compressing the motion image sequence using interframe compression and the accompanying audio and storing the compressed motion image and audio data; and compressing the still images using intraframe coding and storing the compressed still image data.
Owner:MONUMENT PEAK VENTURES LLC
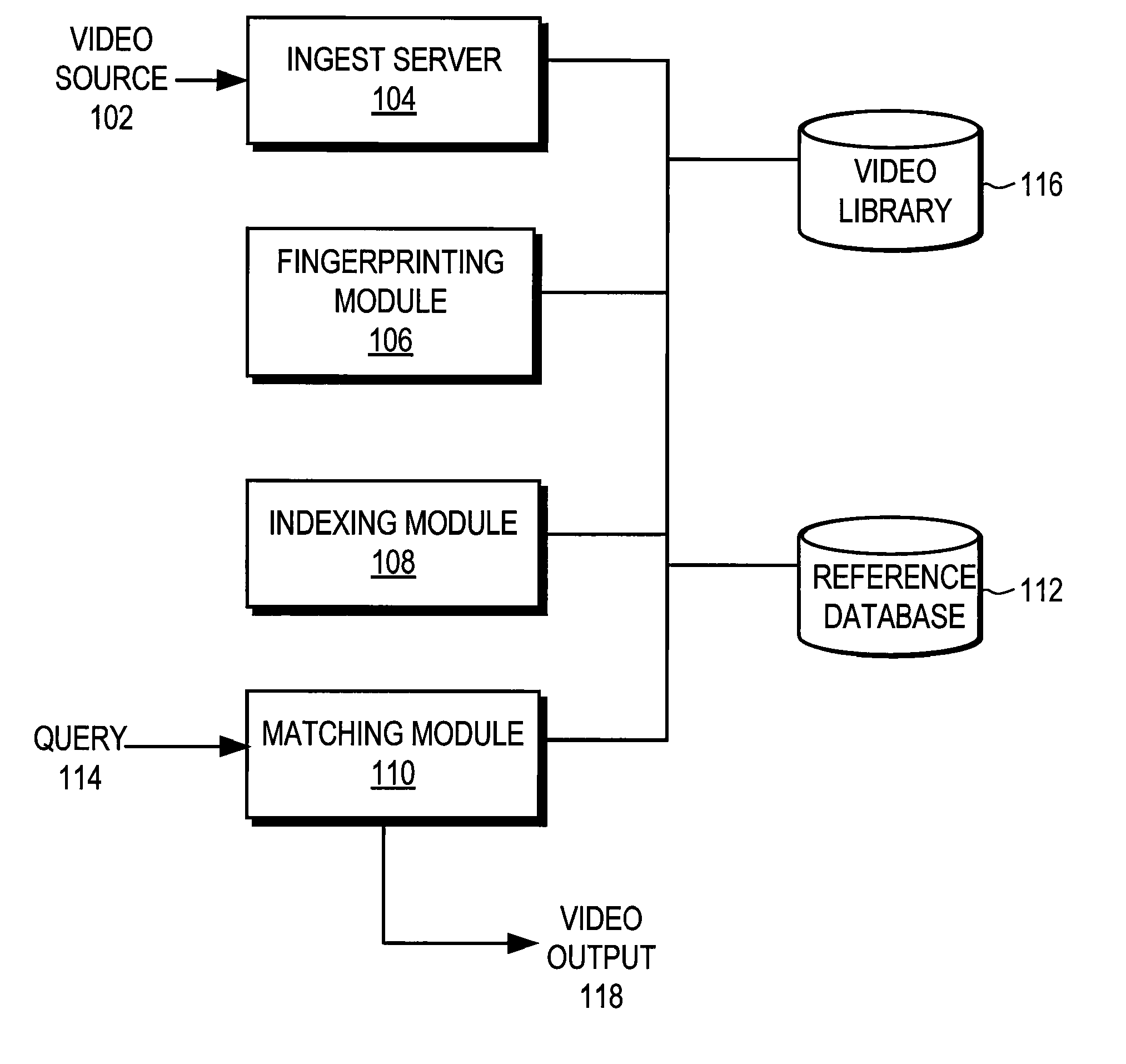
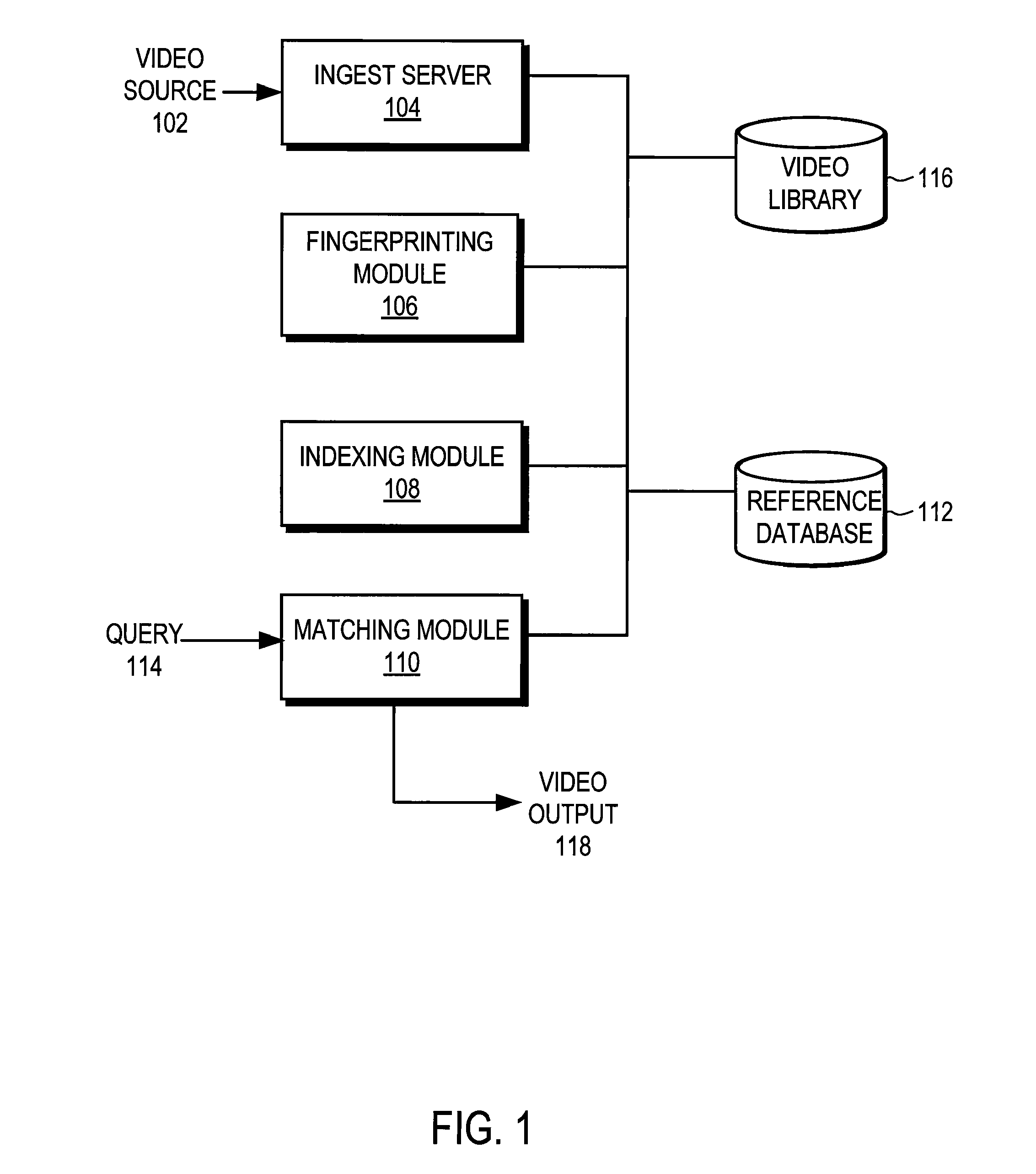
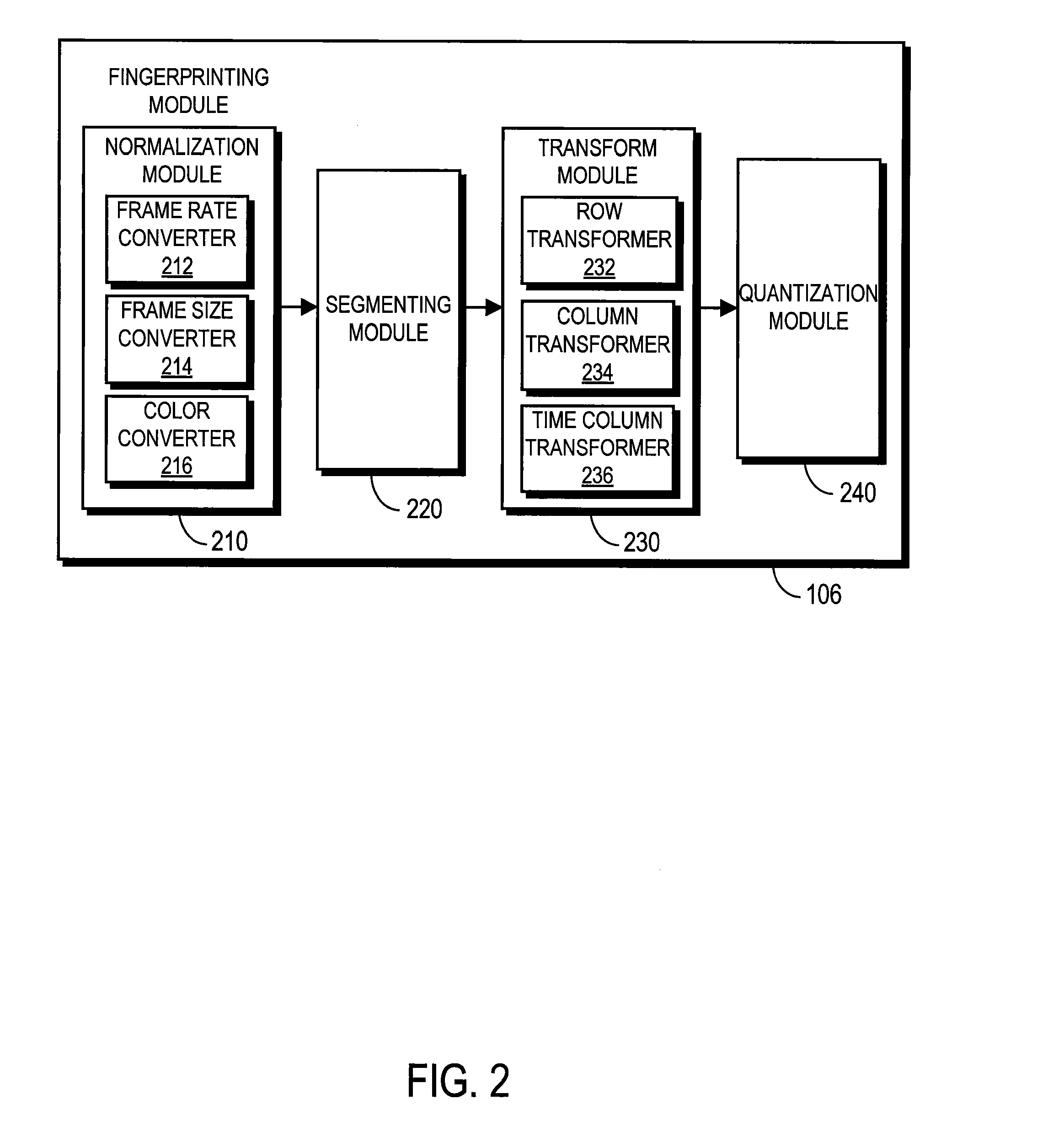
Endpoint based video fingerprinting
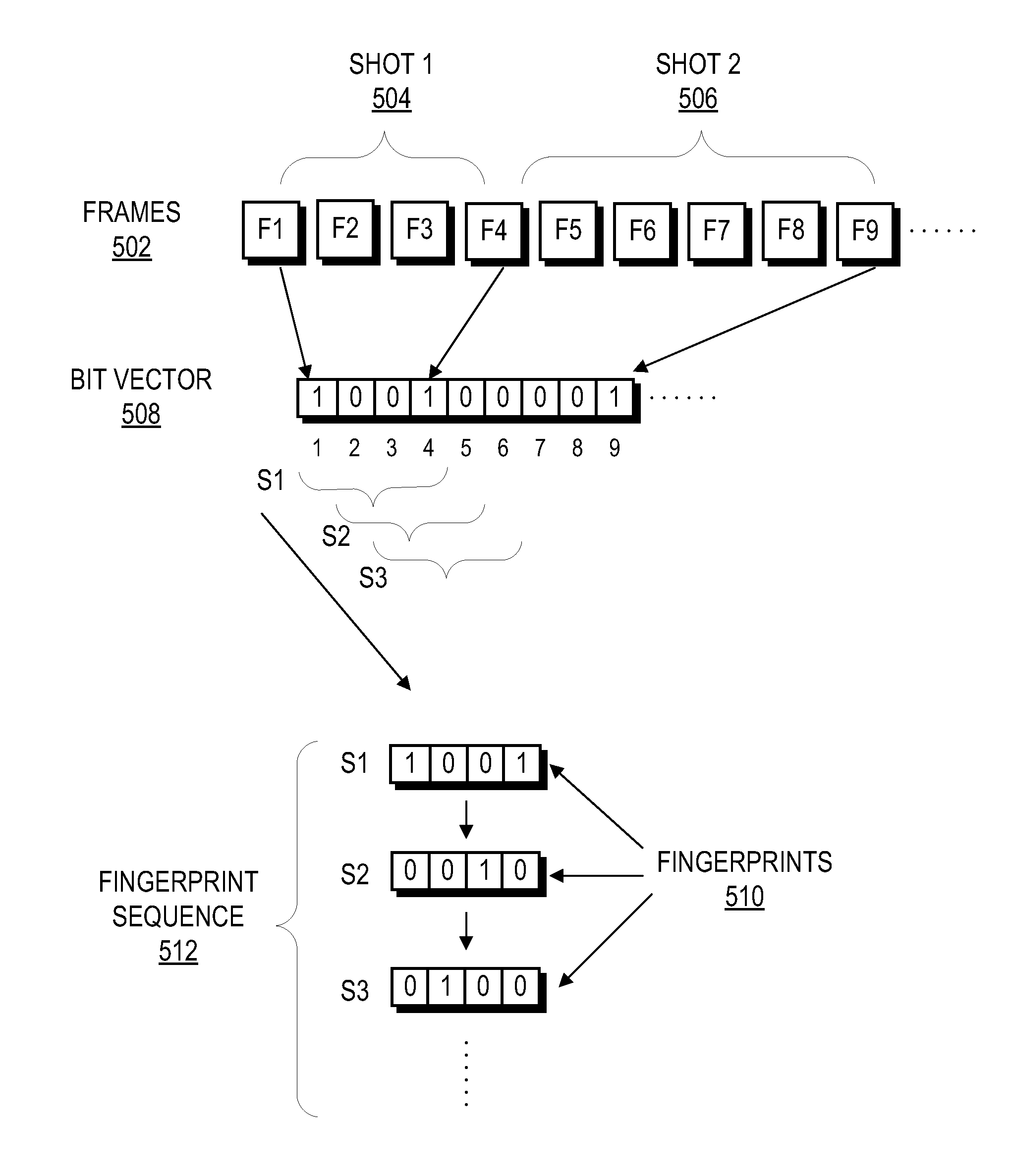
ActiveUS8611422B1Quickly and efficiently identifyImprove the display effectPicture reproducers using cathode ray tubesPicture reproducers with optical-mechanical scanningFrame sequenceComputer graphics (images)
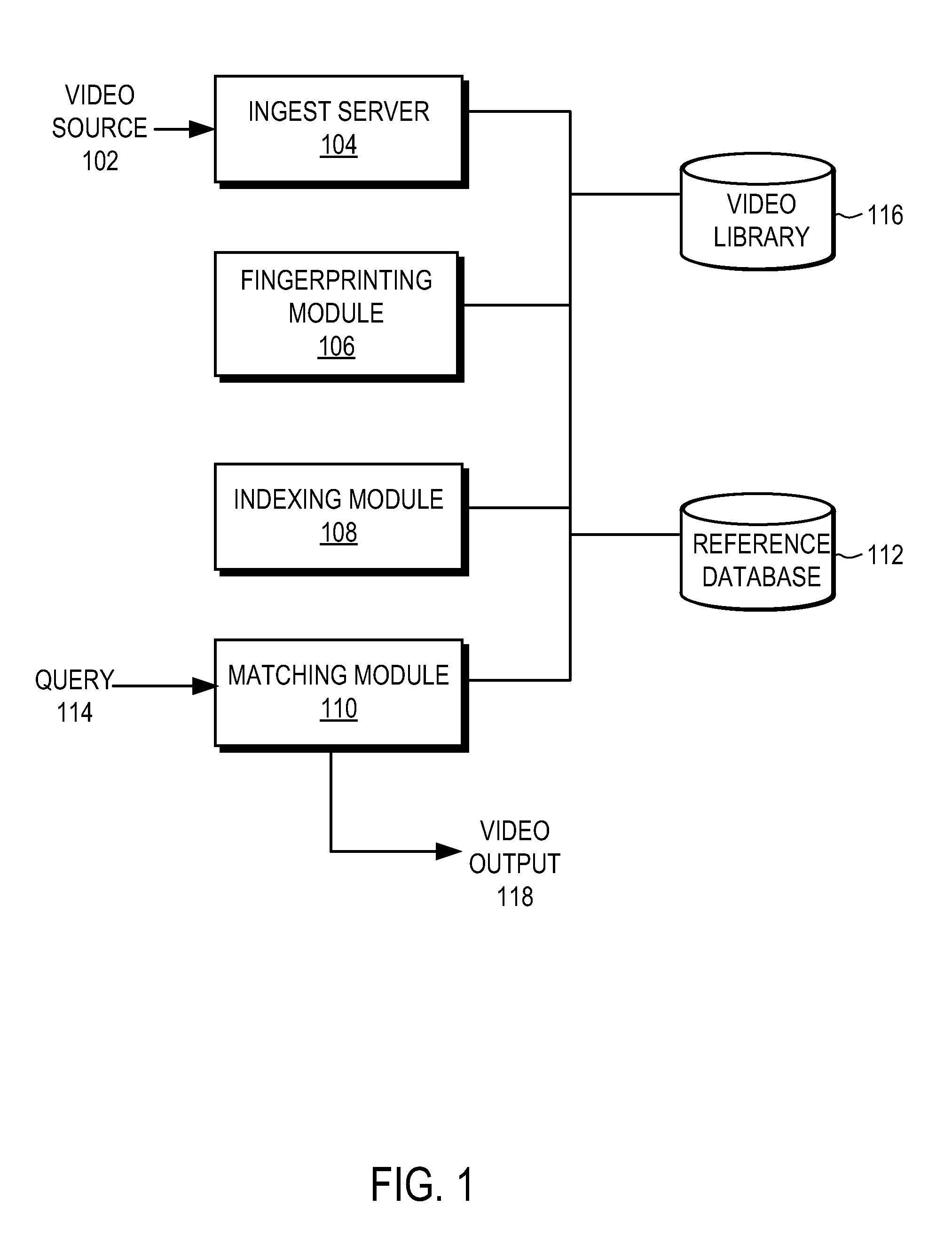
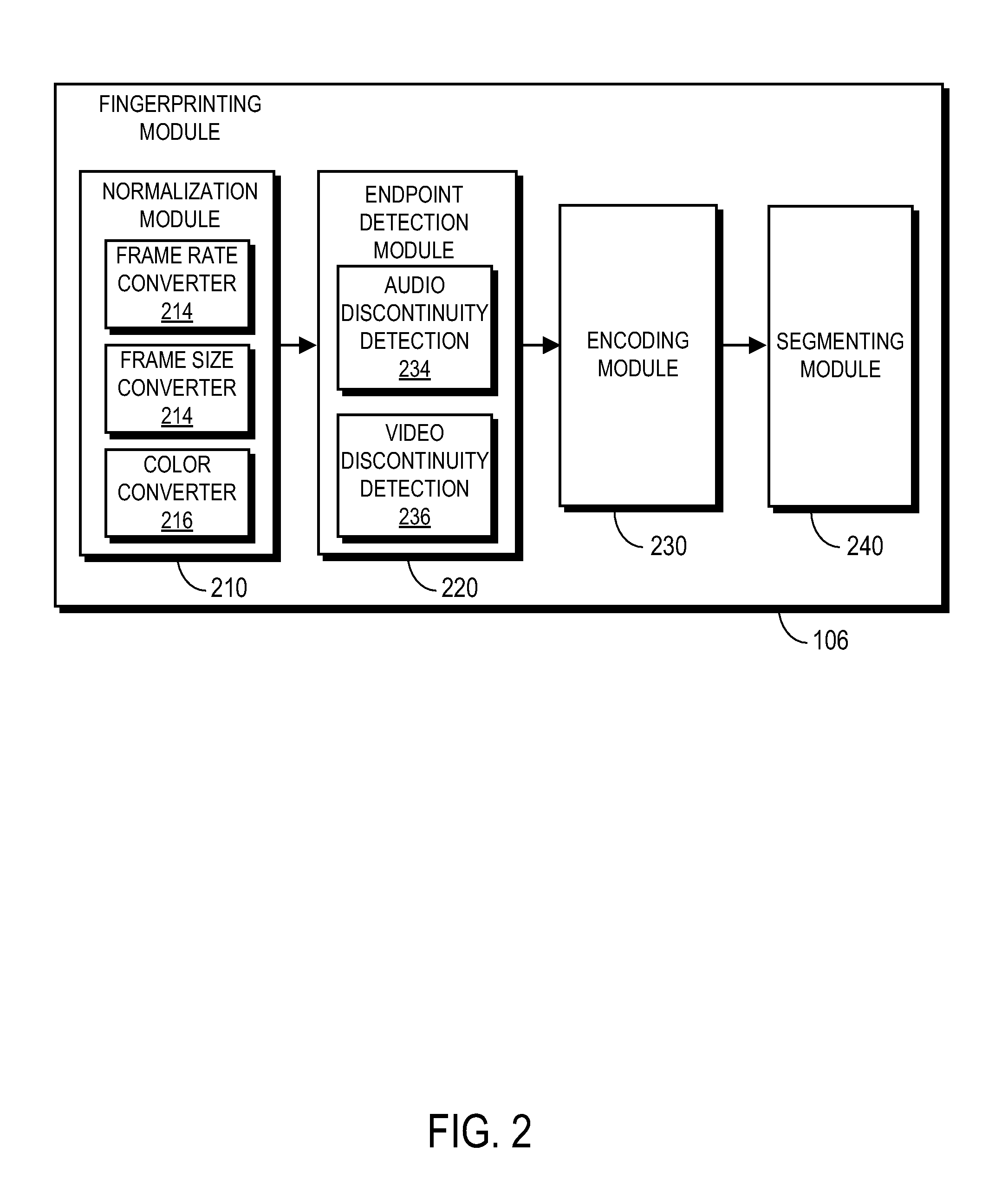
A method and system generates and compares fingerprints for videos in a video library. The video fingerprints provide a compact representation of the temporal locations of discontinuities in the video that can be used to quickly and efficiently identify video content. Discontinuities can be, for example, shot boundaries in the video frame sequence or silent points in the audio stream. Because the fingerprints are based on structural discontinuity characteristics rather than exact bit sequences, visual content of videos can be effectively compared even when there are small differences between the videos in compression factors, source resolutions, start and stop times, frame rates, and so on. Comparison of video fingerprints can be used, for example, to search for and remove copyright protected videos from a video library. Furthermore, duplicate videos can be detected and discarded in order to preserve storage space.
Owner:GOOGLE LLC
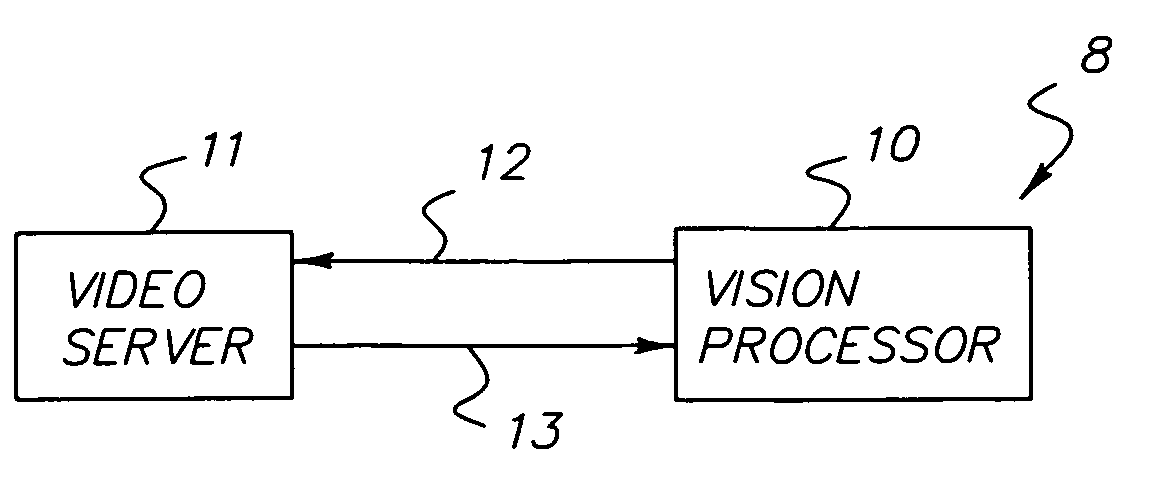
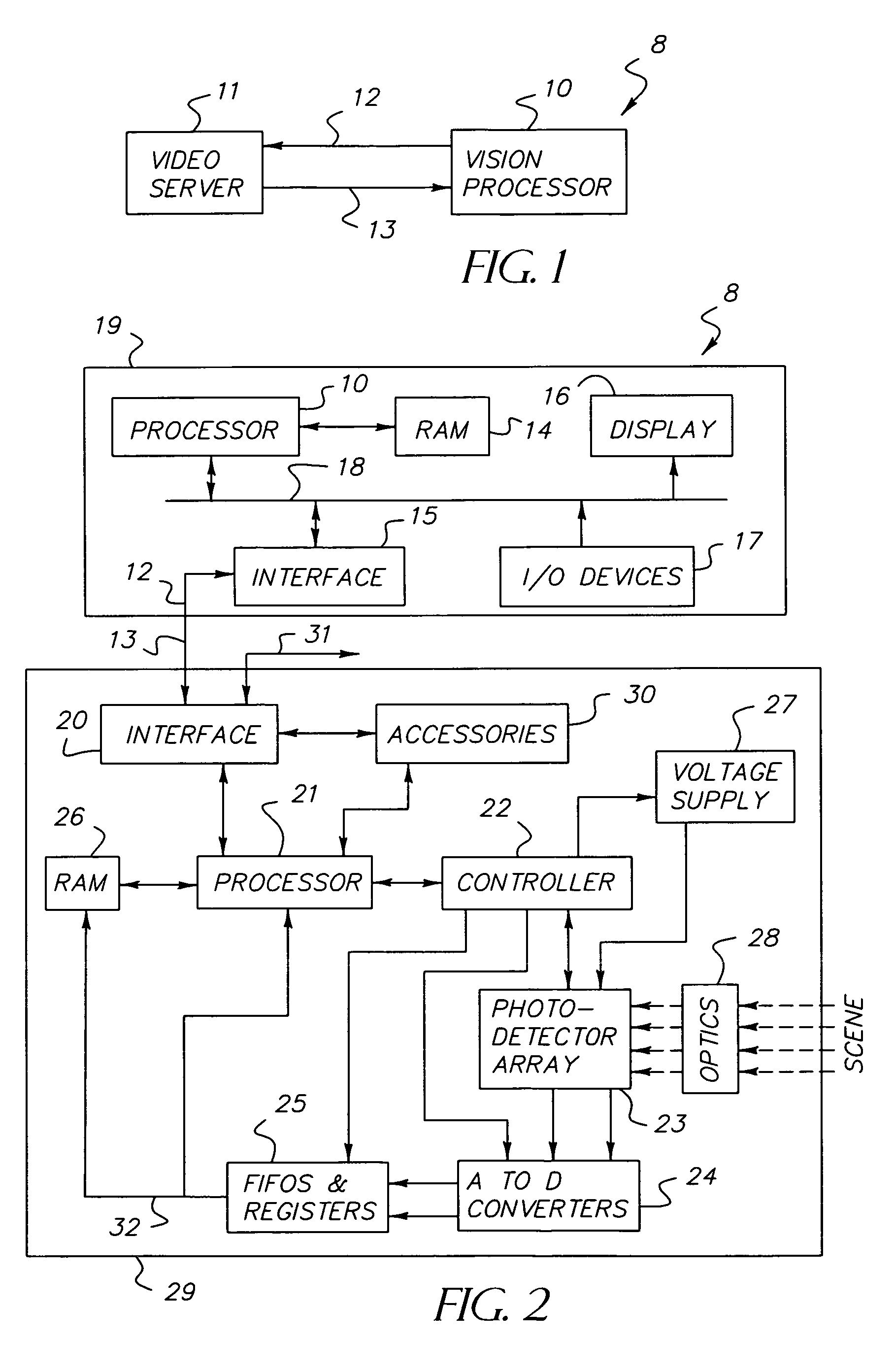
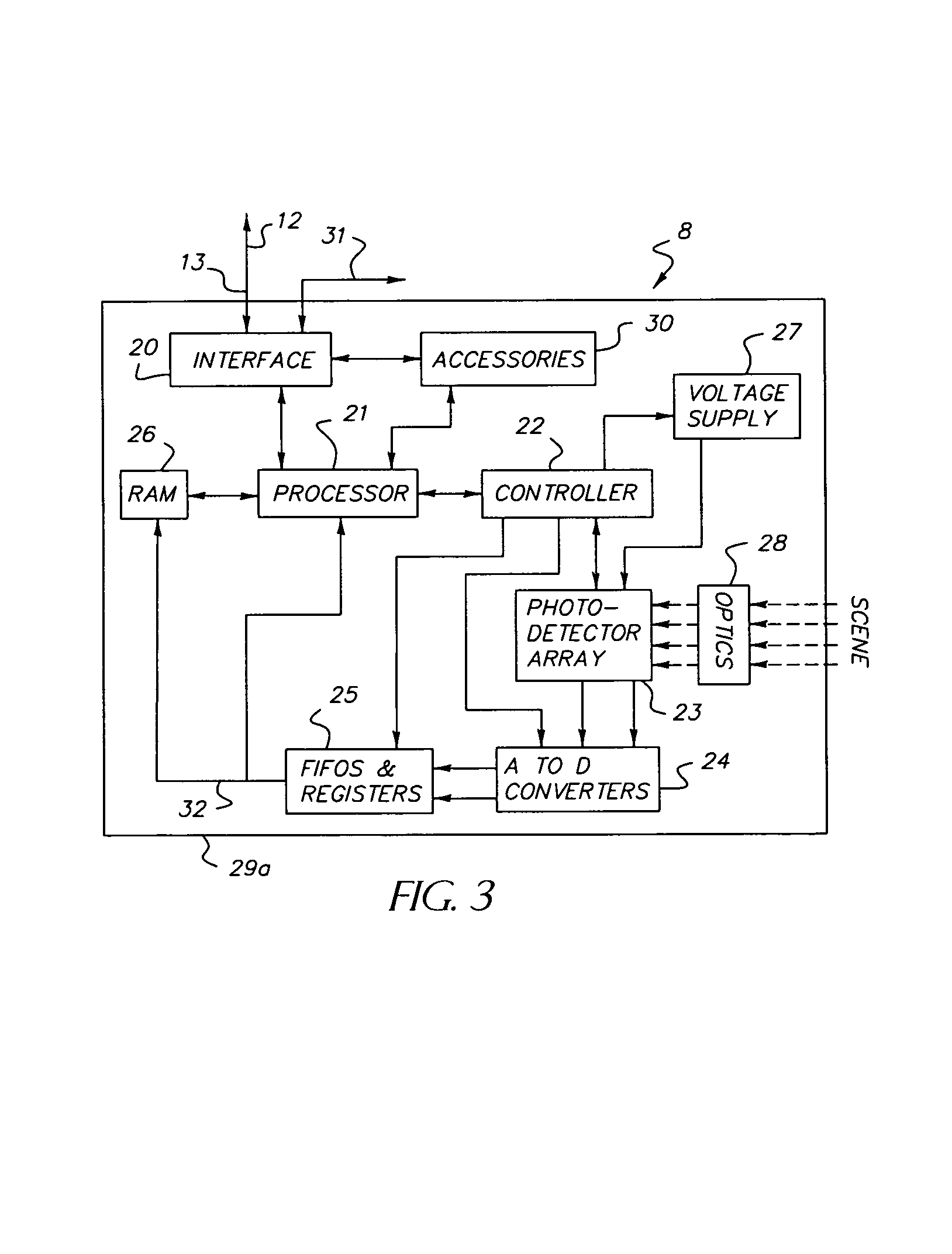
Dynamically reconfigurable vision system
InactiveUS7106374B1Efficiently usEffective resourcesTelevision system detailsTelevision system scanning detailsVision processingPhotodetector
A closed-loop vision system is disclosed that utilizes a concept known as Dynamically Reconfigurable Vision (DRV), which is adaptive image sensing driven by a computer or human operator's response to changing scenery. The system reduces the amount of irrelevant video information sensed and thus achieves more effective bandwidth and computational resource utilization, as compared to traditional vision systems. One or more reconfigurable photodetector arrays sensitive to either visible, infrared or ultraviolet radiation are present in the DRV system. These photodetector arrays feature on-chip means for spatial and temporal data reduction implemented through multiple independently controllable, time-correlated, frequently overlapping windows on the photodetector array that may be programmed according to their size, location, resolution, integration time, and frame rate. All photodetector array windows are dynamically reconfigurable in real time on a frame-by-frame basis. Furthermore, a DRV system is constructed in a client-server architecture in which a vision processor client passes window request command messages to the reconfigurable photodetector array server, which in turn delivers the requested video back to the client processor. The ability to simultaneously reconfigure, integrate, process, and readout multiple photodetector array video windows is an important characteristic of the DRV system.
Owner:COMPTEK AMHERST SYST INC
Three-dimensional wavelet based video fingerprinting
ActiveUS8094872B1Quickly and efficiently identifyImprove the display effectUser identity/authority verificationCharacter and pattern recognitionComputer graphics (images)Stop time
A method and system generates and compares fingerprints for videos in a video library. The video fingerprints provide a compact representation of the spatial and sequential characteristics of the video that can be used to quickly and efficiently identify video content. Because the fingerprints are based on spatial and sequential characteristics rather than exact bit sequences, visual content of videos can be effectively compared even when there are small differences between the videos in compression factors, source resolutions, start and stop times, frame rates, and so on. Comparison of video fingerprints can be used, for example, to search for and remove copyright protected videos from a video library. Further, duplicate videos can be detected and discarded in order to preserve storage space.
Owner:GOOGLE LLC
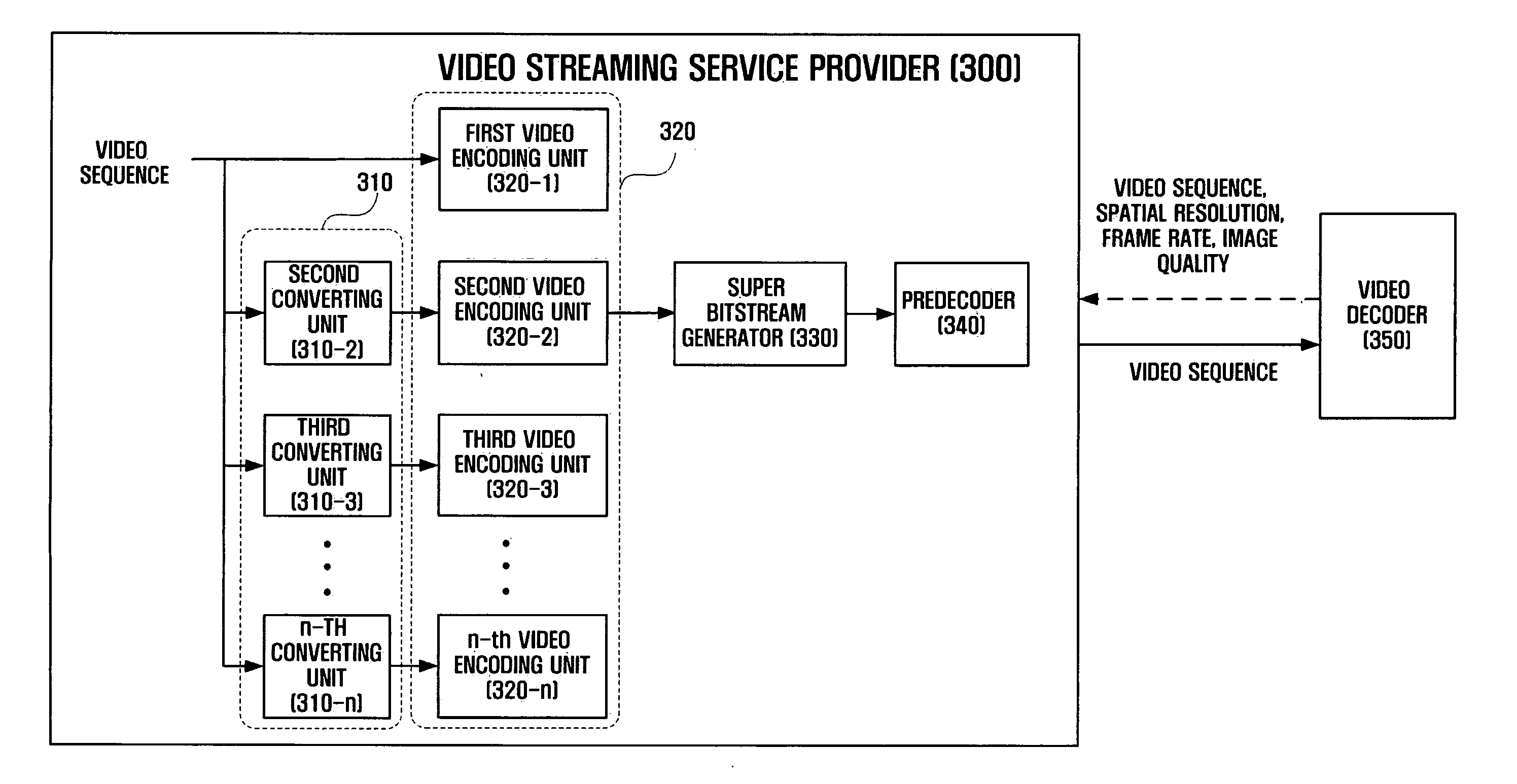
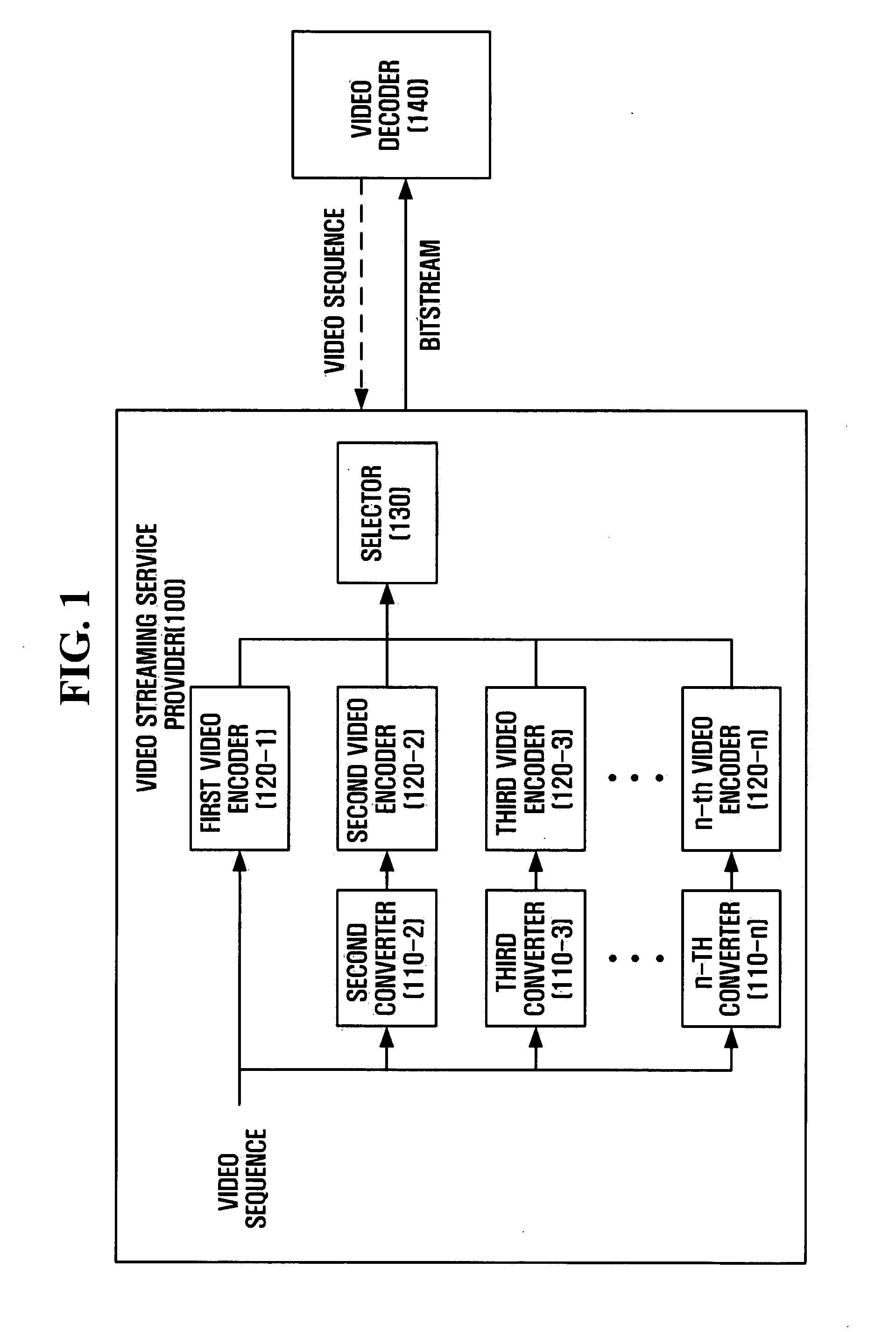
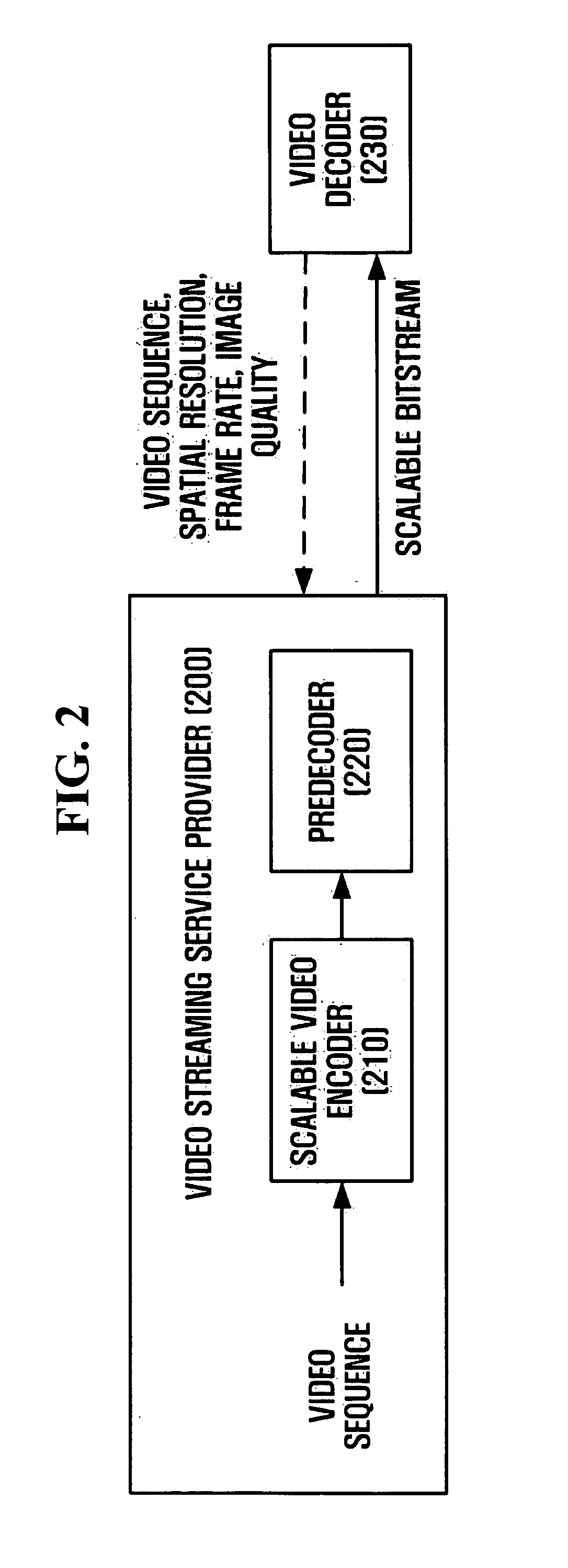
Method and apparatus for video coding, predecoding, and video decoding for video streaming service, and image filtering method
ActiveUS20050195899A1Improve efficiencyImprove image qualityPulse modulation television signal transmissionPicture reproducers using cathode ray tubesComputer graphics (images)Video encoding
A method and apparatus for video encoding, predecoding, and video decoding for video streaming services. The video encoding method includes encoding first and second video sequences into first and second bitstreams using scalable video coding, wherein at least one of resolution, frame rate, and image quality of the second video sequence is different from that of the first video sequence, and combining the first and second bitstreams into a super bitstream.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
High frequency array ultrasound system
ActiveUS20070239001A1Time indicationSynchronous motors for clocksPhased array transducerLinear arrays
A system for acquiring an ultrasound signal comprises a signal processing unit adapted for acquiring a received ultrasound signal from an ultrasound transducer having a plurality of elements. The system is adapted to receive ultrasound signals having a frequency of at least 20 megahertz (MHz) with a transducer having a field of view of at least 5.0 millimeters (mm) at a frame rate of at least 20 frames per second (fps). The signal processing can further produce an ultrasound image from the acquired ultrasound signal. The transducer can be a linear array transducer, a phased array transducer, a two-dimensional (2-D) array transducer, or a curved array transducer.
Owner:SUNNYBROOK HEALTH SCI CENT +1
Image capturing apparatus
InactiveUS20050052553A1Television system detailsTelevision system scanning detailsHigh velocityComputer science
A digital camera capable of capturing, displaying and recording images at appropriate frame rates is provided. When a current shooting scene mode is a non-sport mode, a current readout mode and a current display mode are set to a high-definition readout mode and a high-definition display mode, respectively, at the same time. Additionally, when a current operating mode is a moving image capturing mode, a current recording mode is also set to a high-definition recording mode at the same time. When the current shooting scene mode is a sport mode, on the other hand, the current readout mode and the current display mode are set to a high-speed readout mode and a high-speed display mode, respectively, at the same time. Additionally, when the current operating mode is the moving image capturing mode, the current recording mode is also set to a high-speed recording mode. The digital camera increases the image-capturing frame rate, the display frame rate and the recording frame rate in synchronism with each other in response to a change of the current shooting scene mode from the non-sport mode to the sport mode.
Owner:KONICA MINOLTA CAMERA
Adaptive optical image reader
InactiveUS20050056699A1Data augmentationExtension of timeCharacter and pattern recognitionExposure controlDigital imageDigital converter
A digital image reading system including an image sensor and a computer that is programmed to adjust the frame rate of the image sensor, and to obtain a maximum frame rate of the image sensor for obtaining an acceptable image. An algorithm for adjusting the frame rate evaluates image parameters and calculates new exposure times, gain values, and exposure settings to support a maximum frame rate of the image sensor. A process for obtaining an acceptable image with an image reader evaluates an image signal level and adjusts the frame rate if the signal level is outside of a predetermined range. The process adjusts the image sensor to run at a maximum operational frame rate. A digital image reading system including multiple separate digitizers for use in various read environments and under various read conditions.
Owner:HAND HELD PRODS
Method for video/audio recording using unrestricted pre-event/post-event buffering with multiple bit and frame rates buffer files
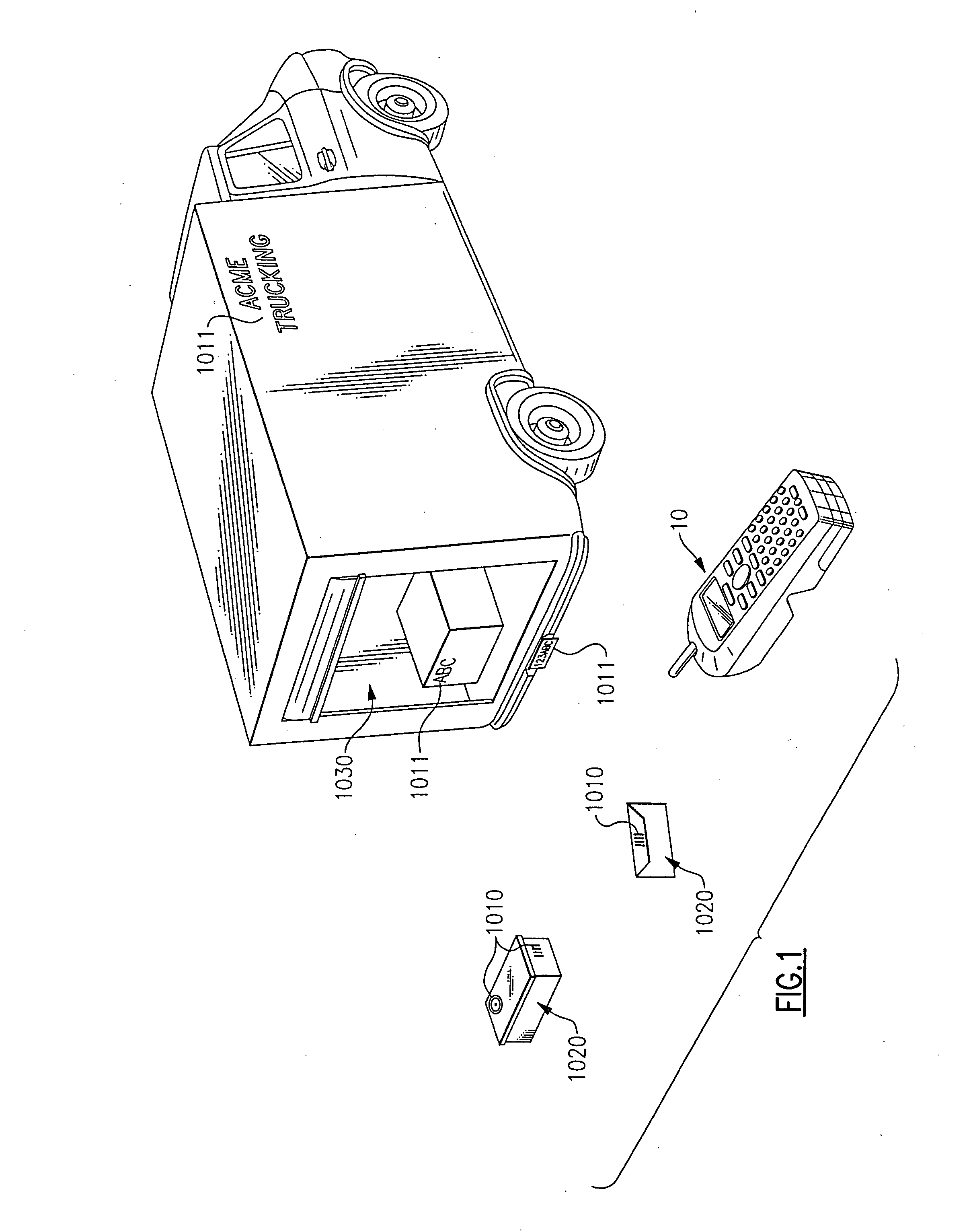
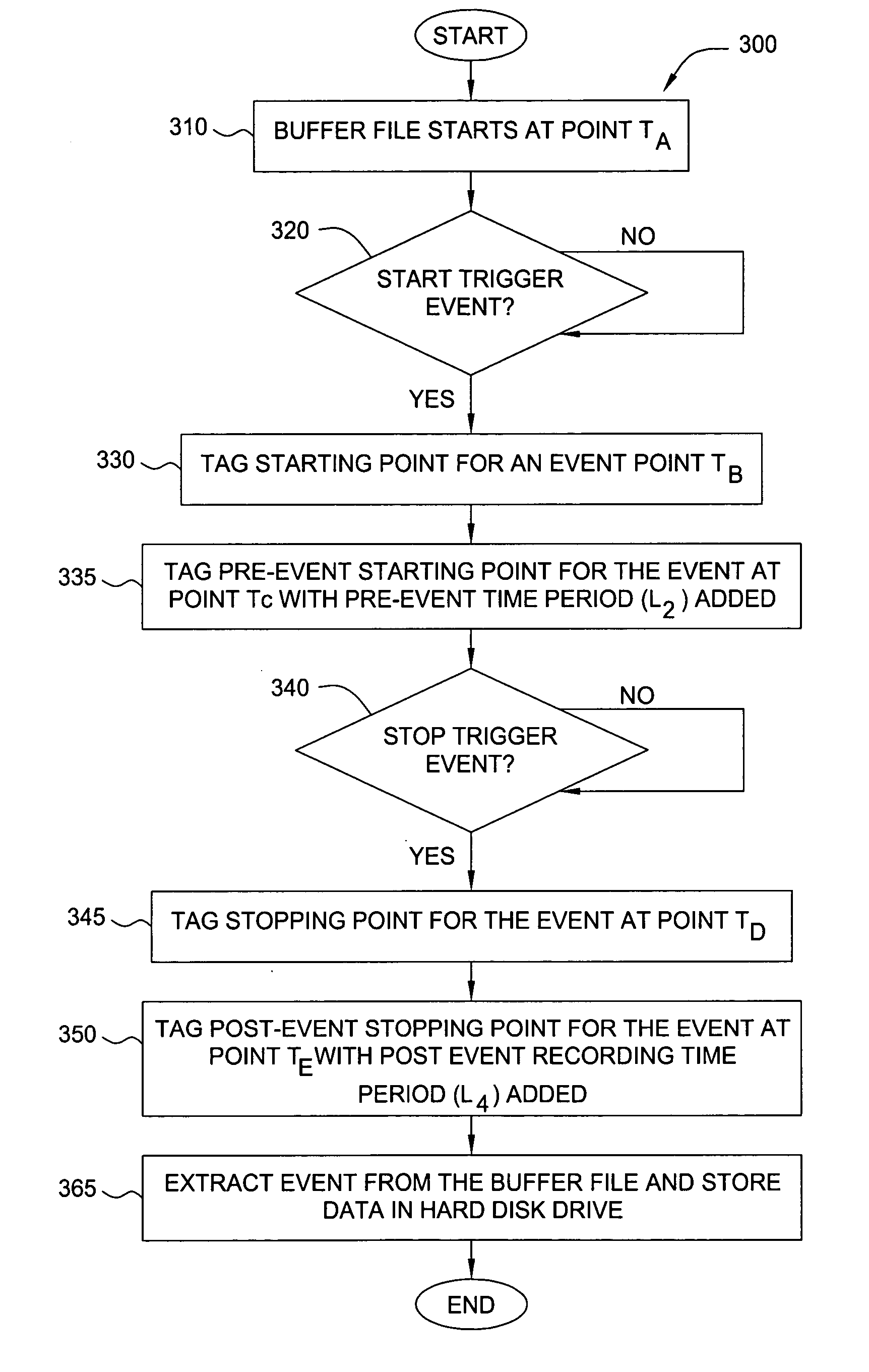
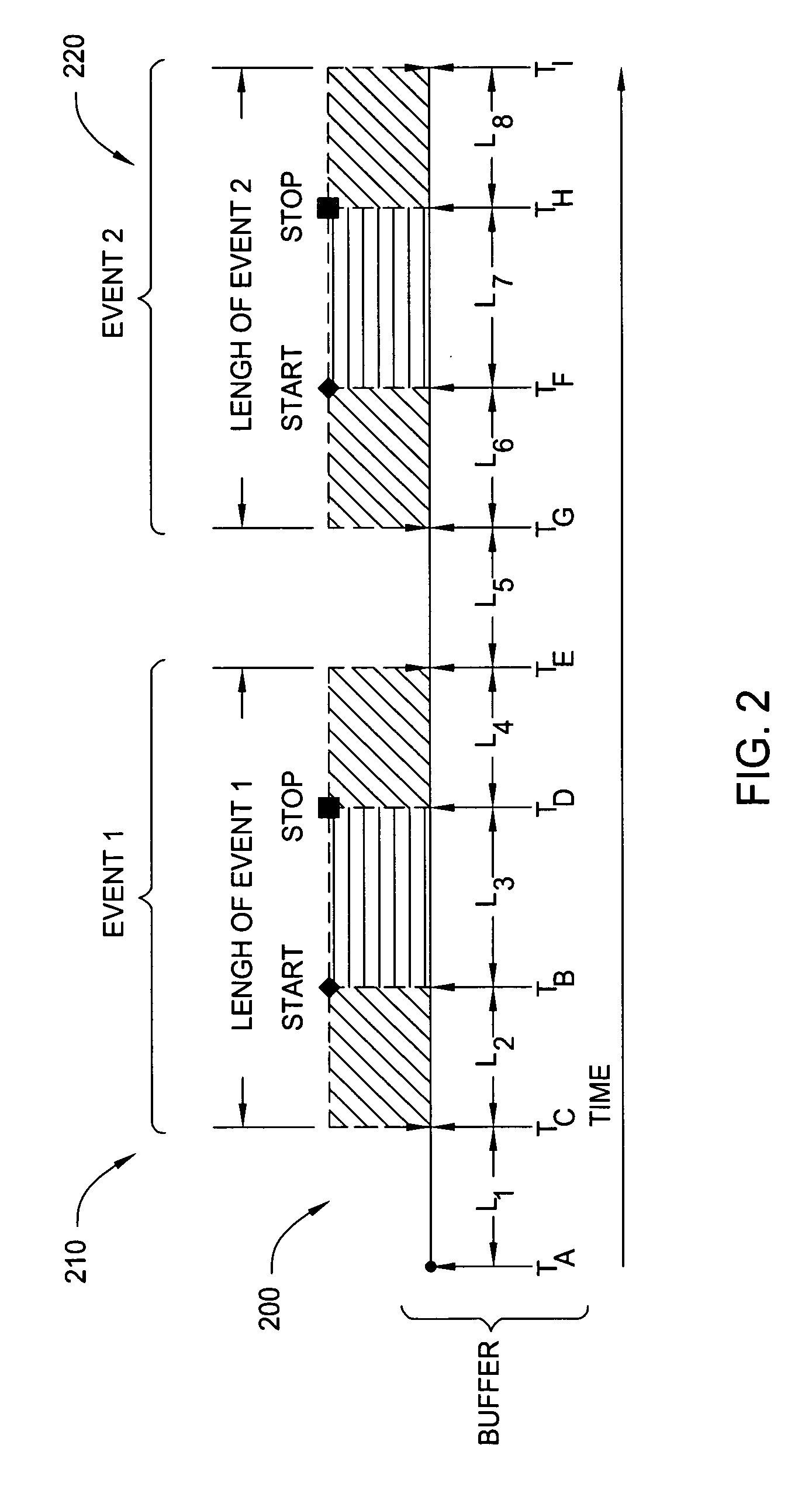
InactiveUS20070217761A1Television system detailsData buffering arrangementsDigital videoHard disc drive
Aspects of the present invention include method and apparatuses that may be utilized to more efficiently use available storage space for a digital video recording system in a law enforcement vehicle and final “backend storage systems.” In one embodiment of the present invention, video and audio data is recorded in one or more buffers when a triggering event is activated, while a digital video recording device accounts for specified pre-event time, a time period before a first triggering event has been activated, and a post-event time, a time period after a second triggering event has been activated. The system will tag the actual start and stop points of events in one or more buffers based on a first and a second triggering event and will then include the pre-event and post-event data along with specified data. The system will then extract the event from one or more buffer files and write the event into final video files to be stored in a hard disk drive. By recording the pre-event and post-event data in multiple buffer files and extracting the final result from selected buffer files based on the nature of the event type, the system ensures that storage device is effectively used and, in this way, useful information is recorded.
Owner:COBAN TECH
Video controller system with object display lists
InactiveUS20020145611A1Television system detailsMemory adressing/allocation/relocationGraphicsScan line
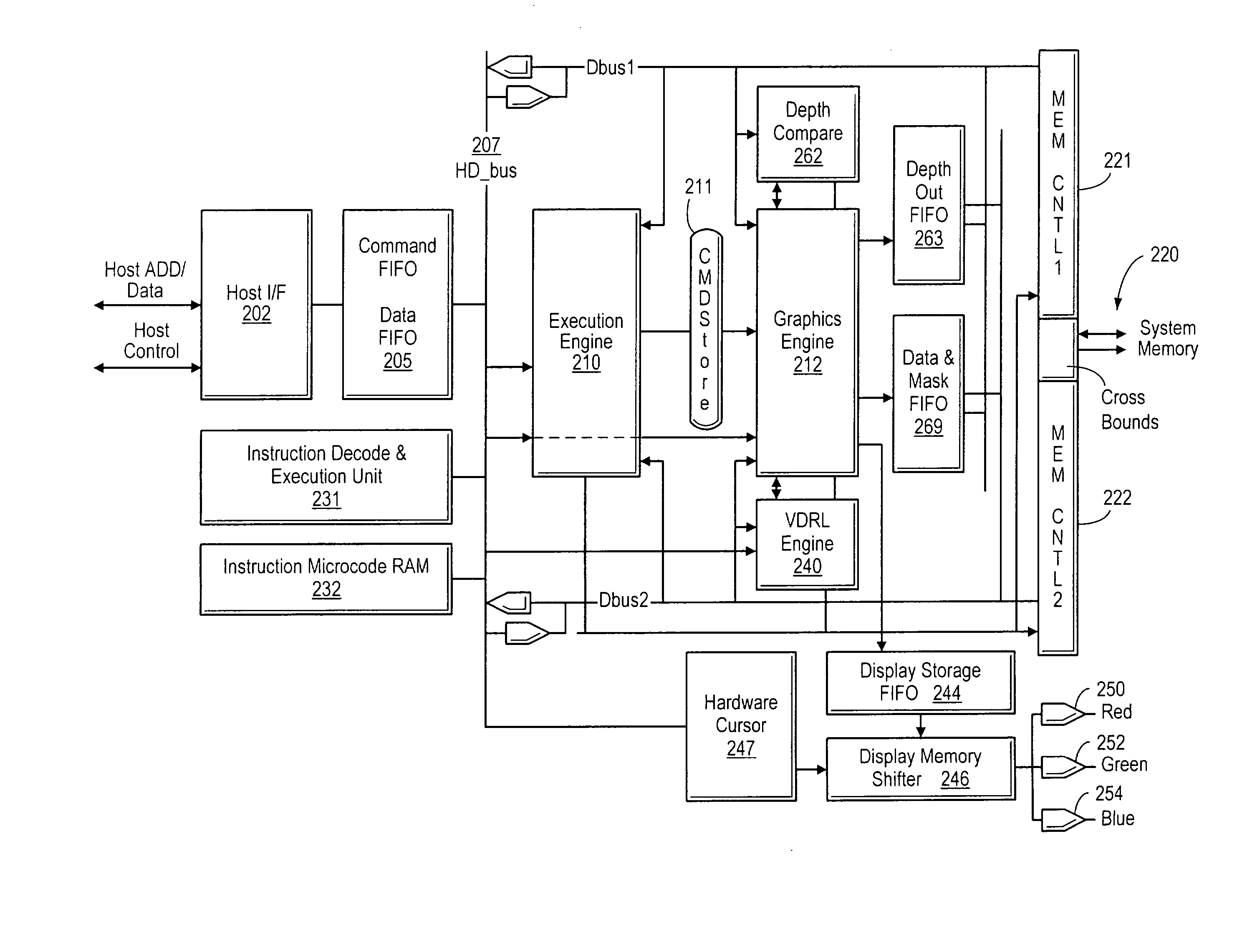
A graphics controller which performs display list-based video refresh operations that enable objects with independent frame rates to be efficiently assembled is disclosed. The graphics controller maintains a virtual display refresh list (VDRL) comprising a plurality of pointers to scan line segments in memory. The graphics controller also creates, maintains, and deletes draw display lists (DDLs) that comprise pointers to object display list subroutines (ODLs) that independently draw objects in memory. The ODLs may allocated one or more buffers in memory into which different frames of the objects are drawn. When an ODL has completed executing, the corresponding pointer in the DDL may be updated to point to the buffer location in memory that stores the newly completed object frame. The VDRL is maintained independently (and may be doubled-buffered) and is updated using the DDLs. Motion estimation may be performed by the graphics controller using the different frames of objects that are drawn into memory by the ODLs. The different object frames may also be animated by the graphics controller once they are drawn into memory. The object frames stored in memory may be compressed to conserve memory.
Owner:DIGIMEDIA TECH LLC
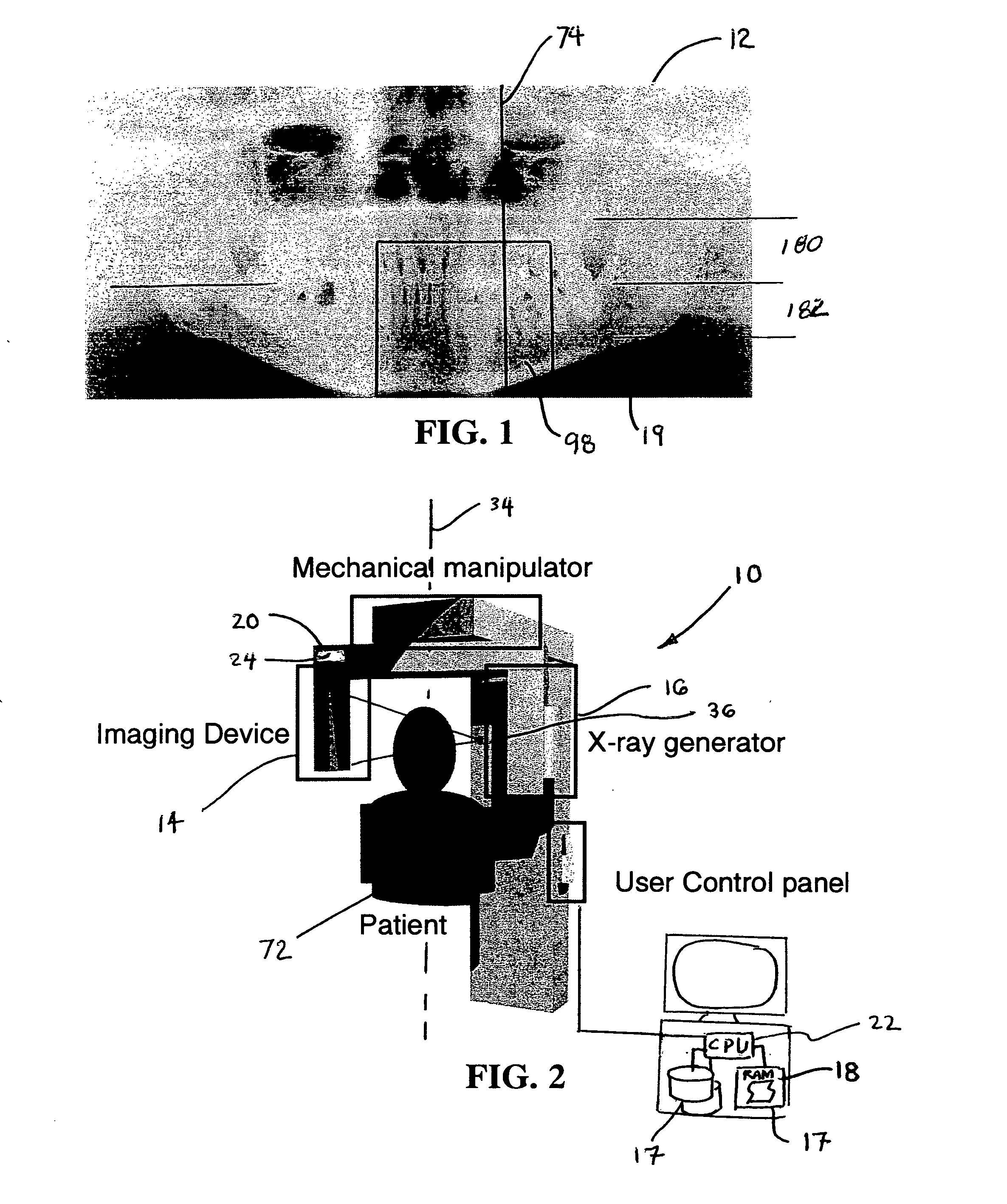
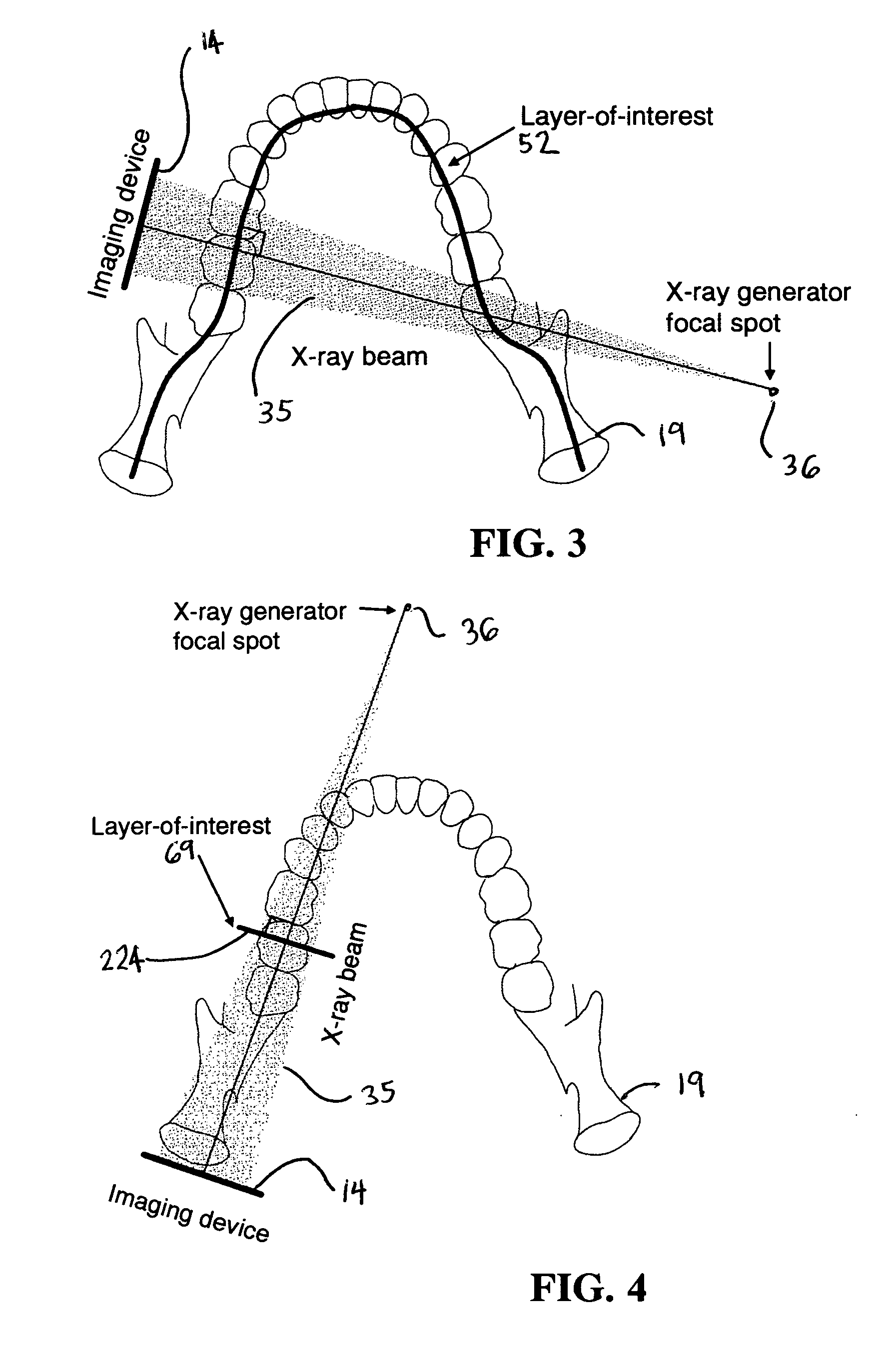
Dental extra-oral x-ray imaging system and method
ActiveUS20060203959A1Image producedImage enhancementTelevision system detailsRotational axisHard disc drive
A multi-layer dental panoramic and transverse x-ray imaging system includes an x-ray source; a digital imaging device capable of frame mode output with a sufficient frame rate; a mechanical manipulator having at least one rotational axis located in a position other than the focal point of the x-ray source; a position detection mechanism for detecting the camera position in 1D, 2D or 3D depending of the complexity of the trajectory; a final image reconstruction mechanism for reconstructing the final images out of the stored frames; a real time storage system such as RAM, hard drive or an drive array able to store all the frames captured during an exposure; and a digital processing unit capable of executing the reconstruction algorithm, such components being interconnected in operational arrangement. The system produces selectively dental panoramic x-ray images, dental transverse x-ray images and dental tomosynthetic 3D images from a frame stream produced by a high-speed, x-ray digital imaging device.
Owner:OY AJAT LTD
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com