Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
2458 results about "High dynamic range" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
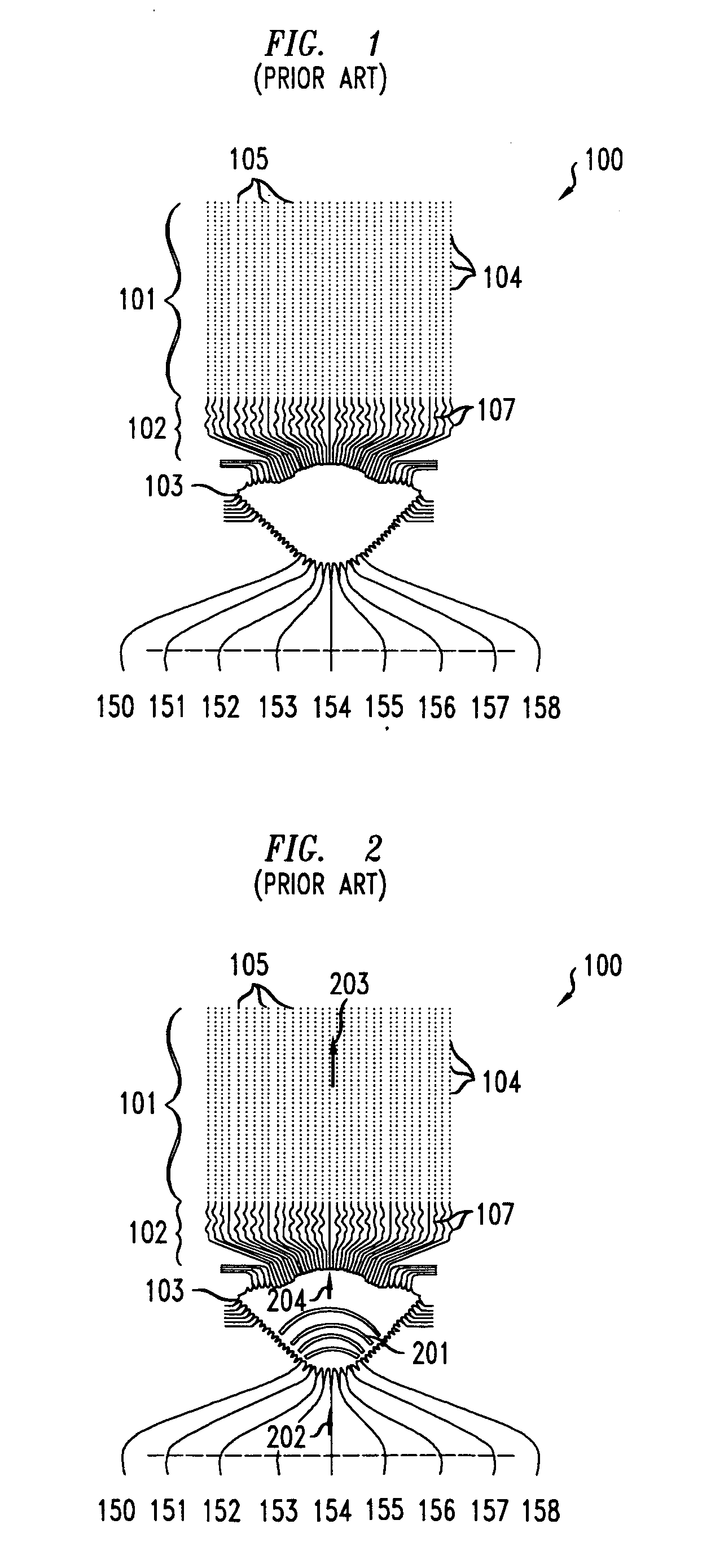
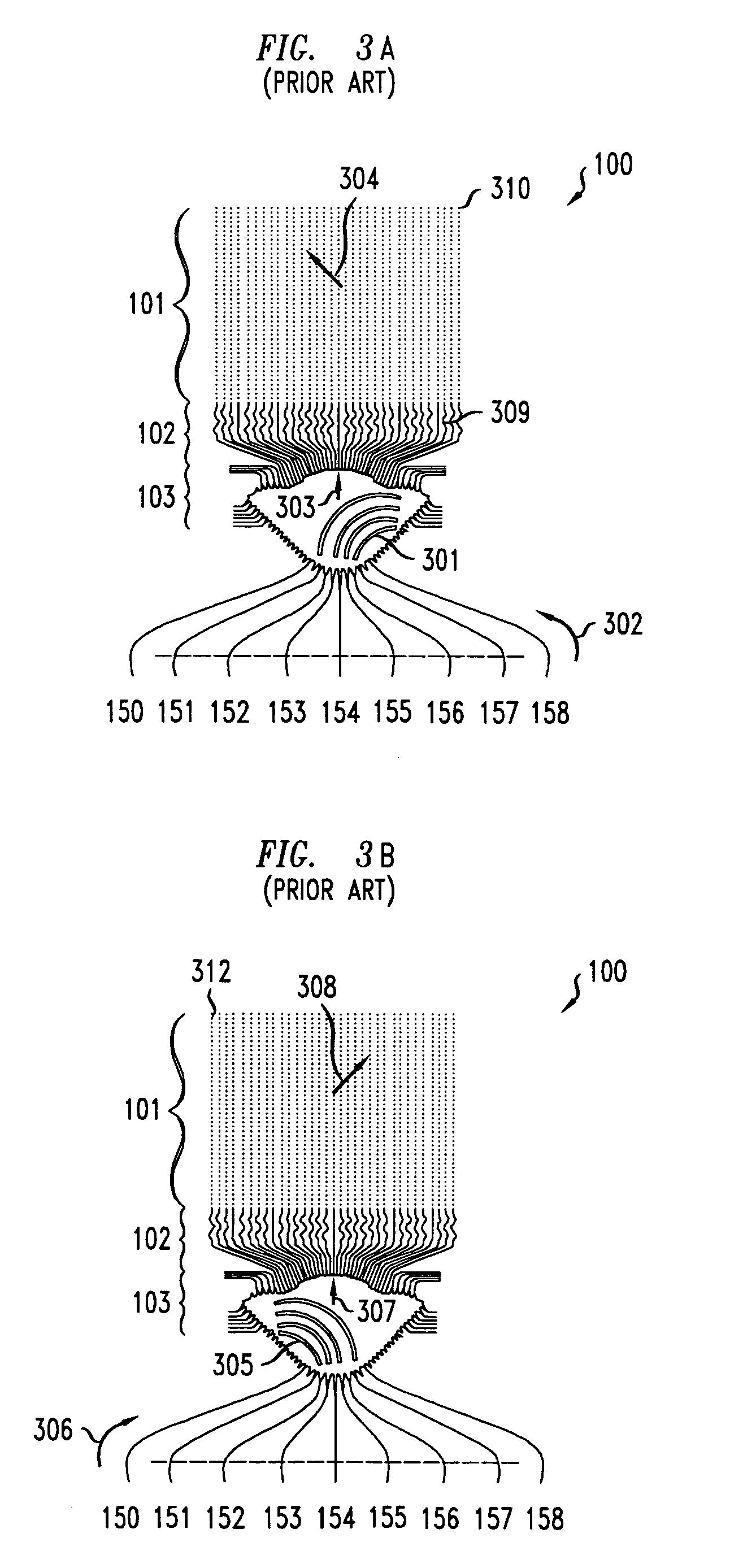
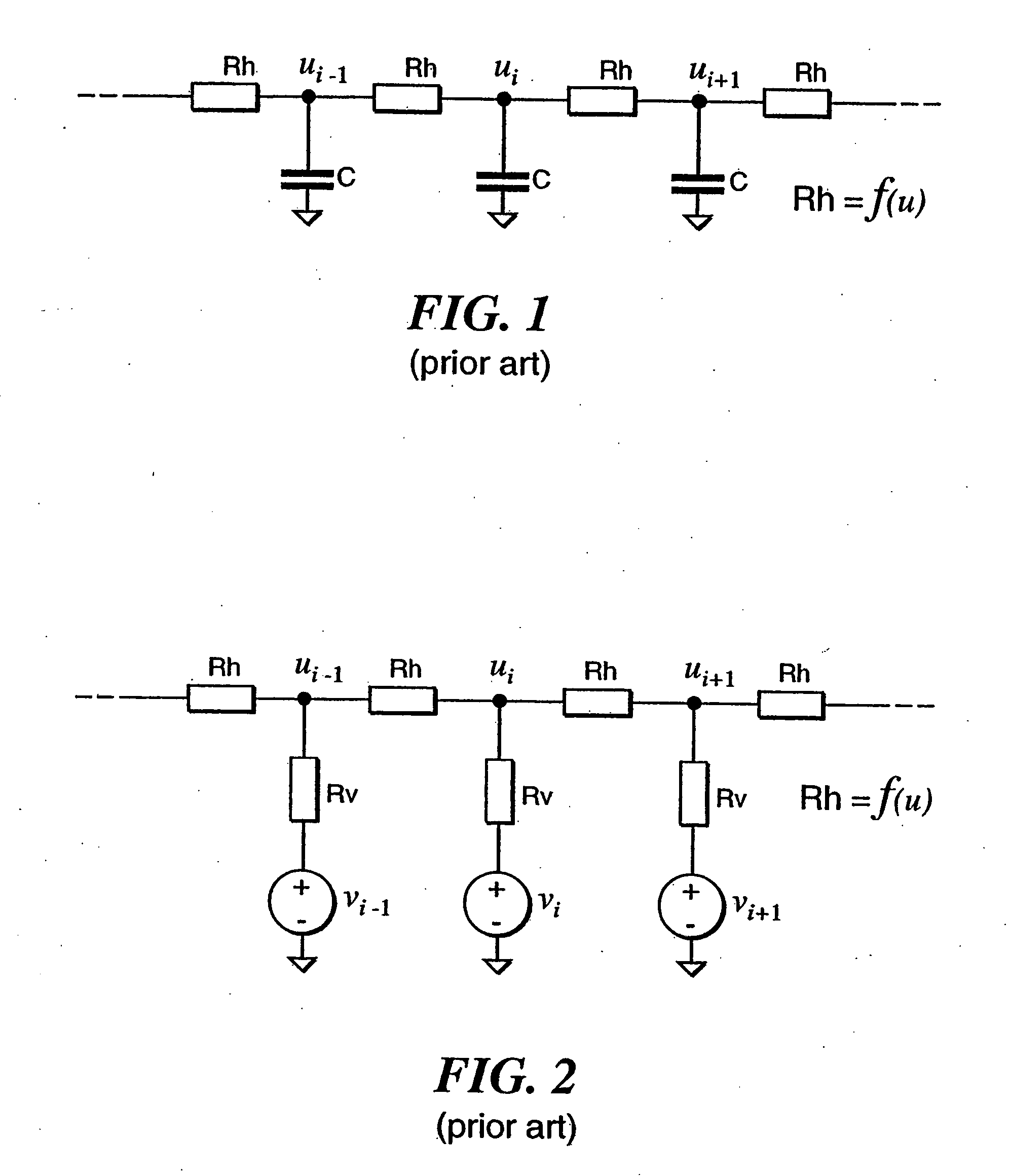
High dynamic range (HDR) is a dynamic range higher than what is considered to be standard dynamic range. The term is often used in discussing display devices, photography, 3D rendering, and sound recording including digital imaging and digital audio production. The term may apply to an analog or digitized signal, or to the means of recording, processing, and reproducing such signals.
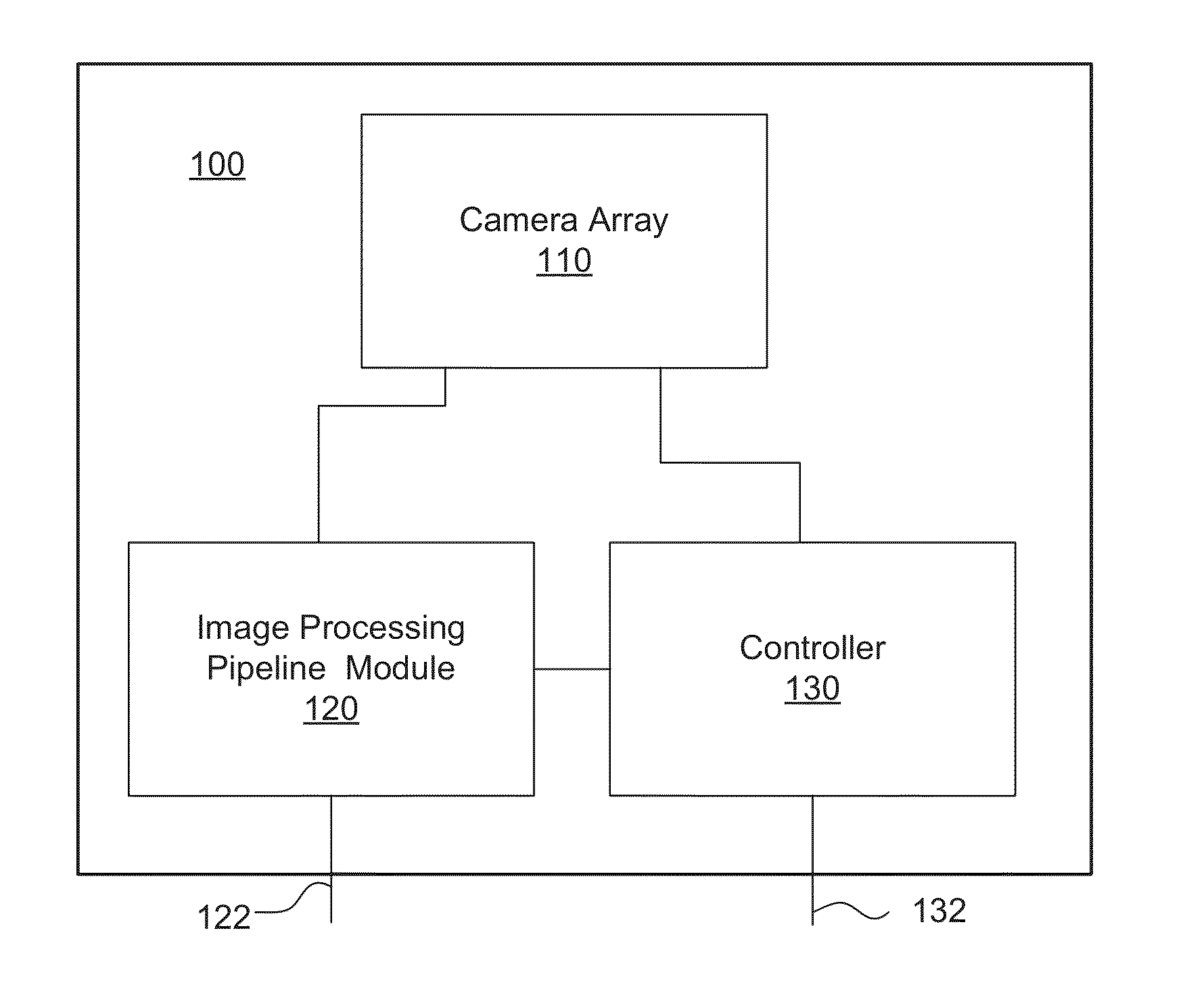
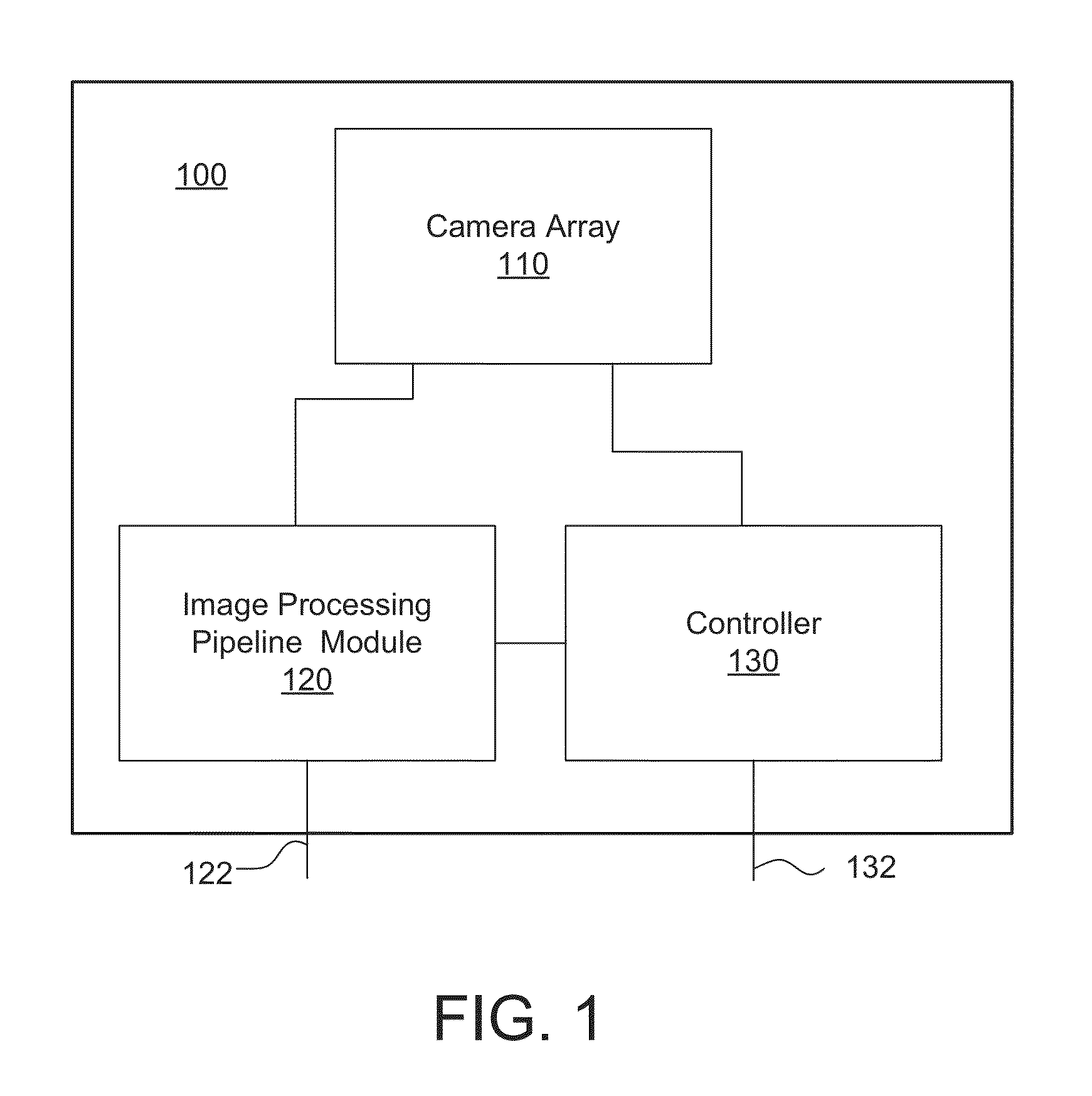
System and method for effectively rendering high dynamic range images
InactiveUS6993200B2High imagingEffectively renderingImage enhancementImage analysisComputer graphics (images)Image conversion
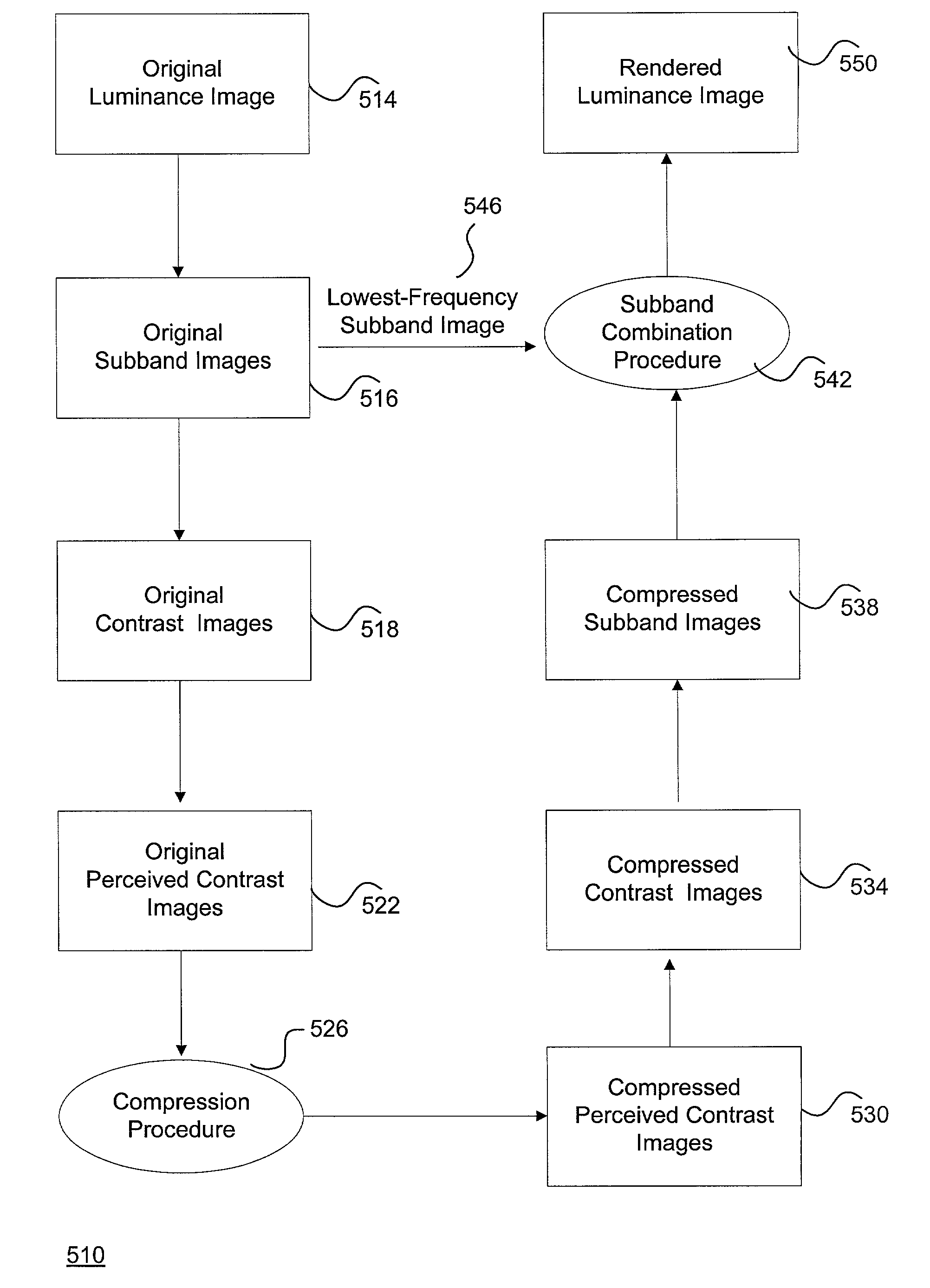
A system and method for rendering high dynamic range images includes a rendering manager that divides an original luminance image into a plurality of original subband images. The rendering manager converts the original subband images into original contrast images which are converted into original perceived contrast images. The rendering manager performs a compression procedure upon the original perceived contrast images to produce compressed perceived contrast images. The rendering manager converts the compressed perceived contrast images into compressed contrast images which are converted into compressed subband images. The rendering manager performs a subband combination procedure for combining the compressed subband images together with a lowest-frequency subband image to generate a rendered luminance image. The rendering manager may combines the rendered luminance image with corresponding chrominance information to generate a rendered composite image.
Owner:SONY CORP +1
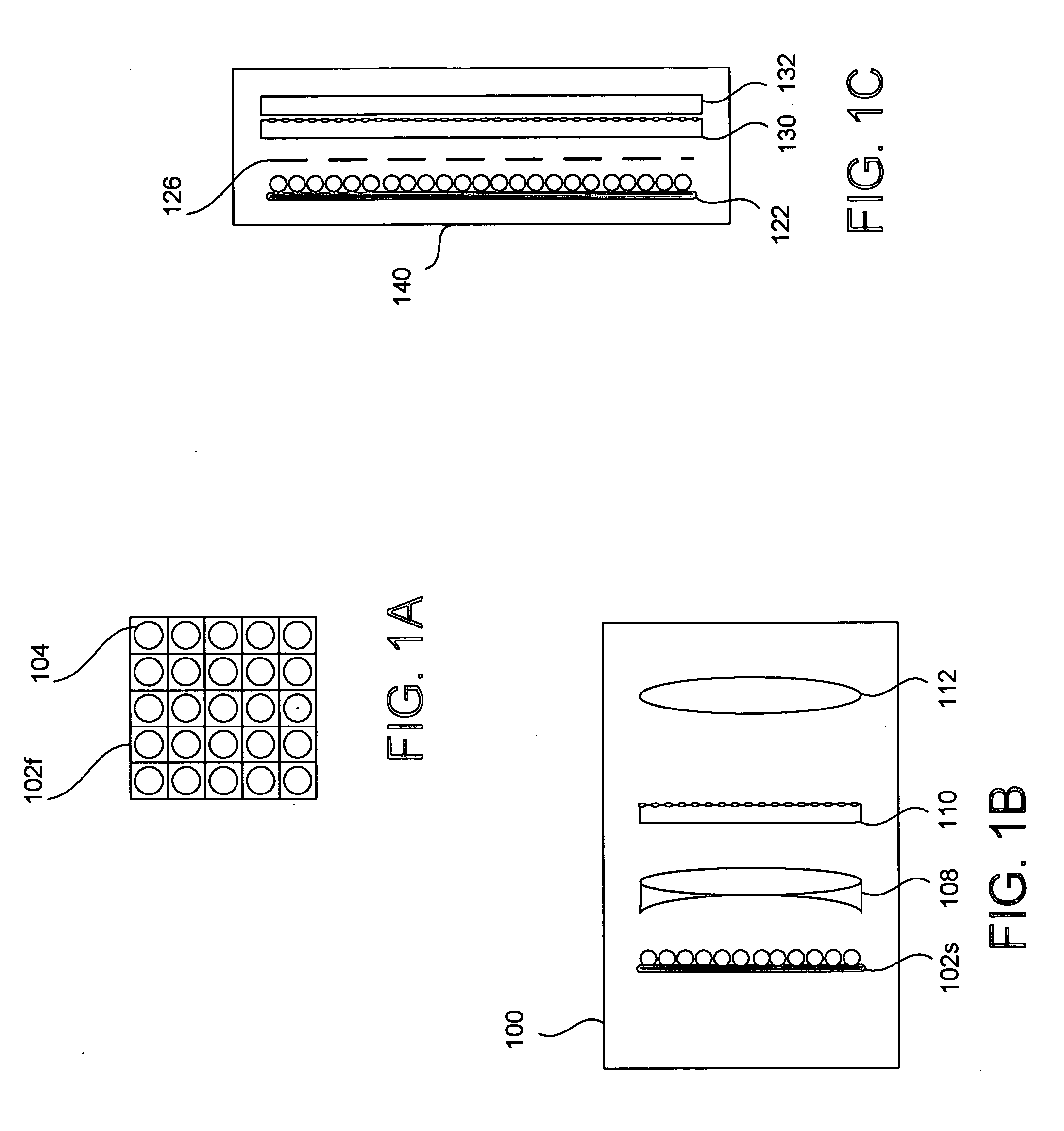
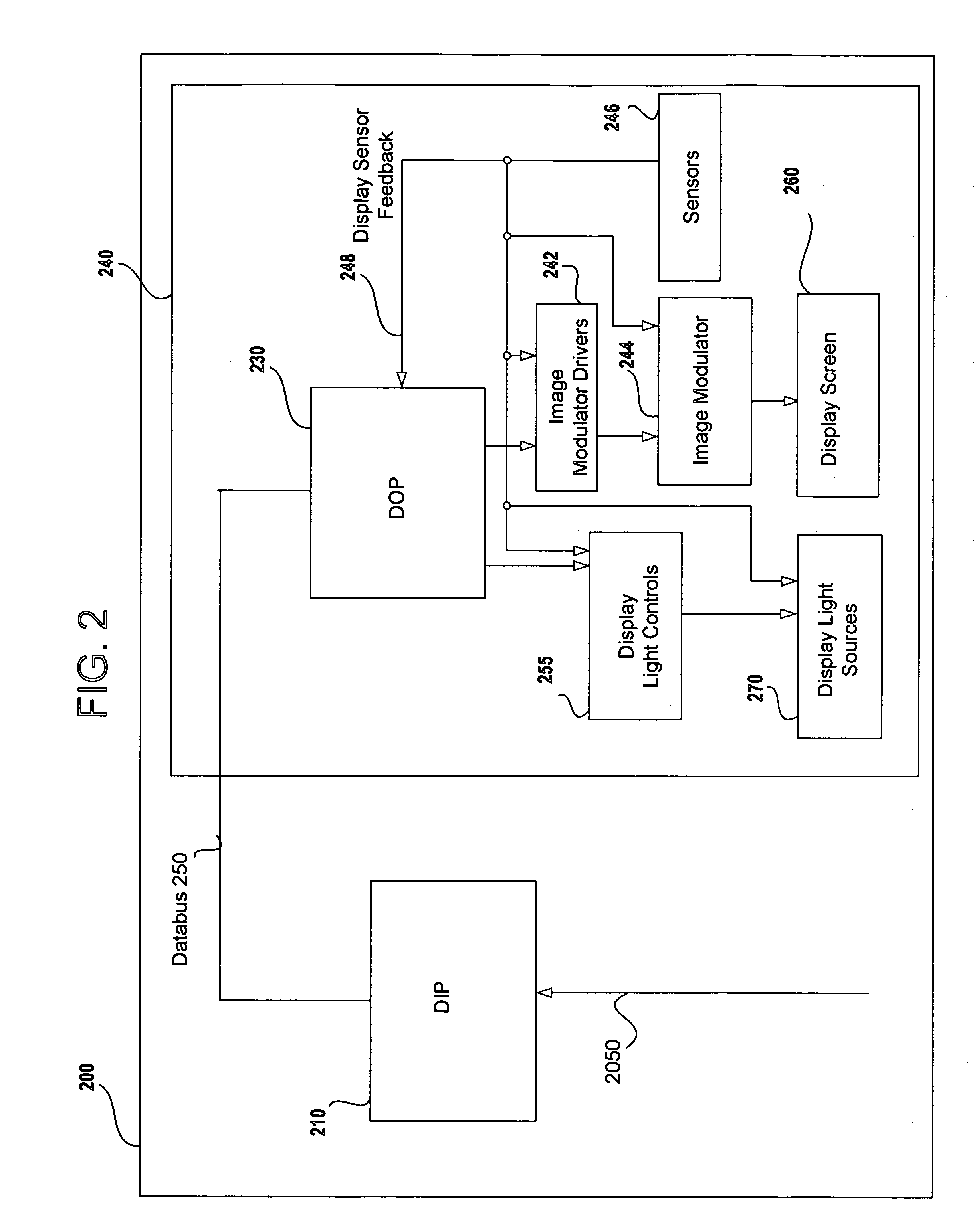
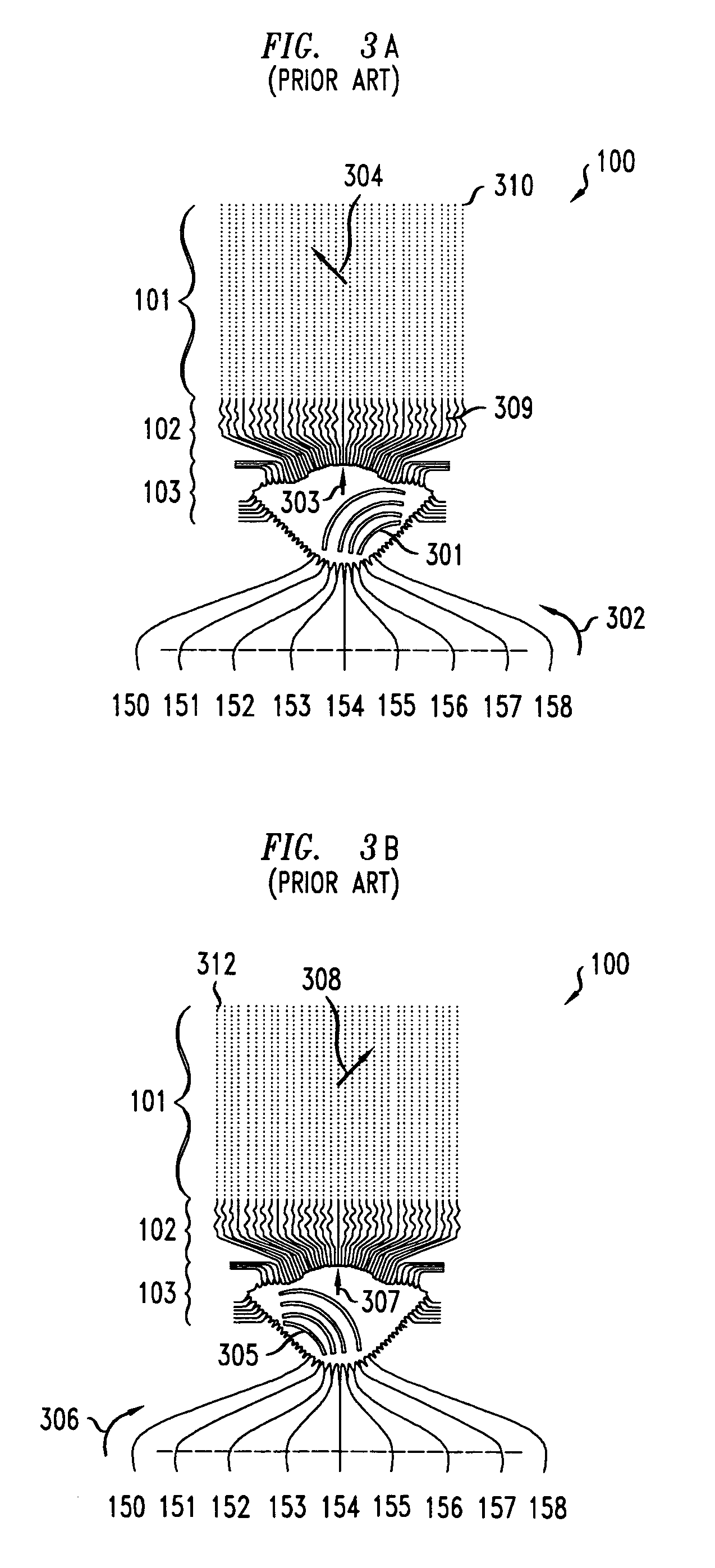
Field sequential light source modulation for a digital display system
ActiveUS20070035707A1Improve display qualityHigh resolutionTelevision system detailsStatic indicating devicesData streamImaging processing
A digital display system consists of an image modulator and multiple light modulators. An image processing system processes an incoming data stream, scans processed data to an image modulator and controls for the light modulators. Other user inputs and sensors are used to affect the processing and controls. The timing for scanning the processed data into the image modulators is controlled along with the intensity and wavelength of the light modulators. The display system may implement a spatial and temporal image processing, digital shutter controls, rolling shutter controls, sequential color output, adaptive dynamic sensor feedback, frame rate matching, motion compensated field sequencing and a variety of other techniques to produce a high quality display output. The resulting display has improved image consistency, enhanced color gamut, higher dynamic range and is better able to portray high motion content.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
Phased array metamaterial antenna system
ActiveUS6958729B1Reduce sidelobeIncrease amplitude performanceSimultaneous aerial operationsRadiating elements structural formsSolid substratePhased array
An efficient, low-loss, low sidelobe, high dynamic range phased-array radar antenna system is disclosed that uses metamaterials, which are manmade composite materials having a negative index of refraction, to create a biconcave lens architecture (instead of the aforementioned biconvex lens) for focusing the microwaves transmitted by the antenna. Accordingly, the sidelobes of the antenna are reduced. Attenuation across microstrip transmission lines may be reduced by using low loss transmission lines that are suspended above a ground plane a predetermined distance in a way such they are not in contact with a solid substrate. By suspending the microstrip transmission lines in this manner, dielectric signal loss is reduced significantly, thus resulting in a less-attenuated signal at its destination.
Owner:LUCENT TECH INC
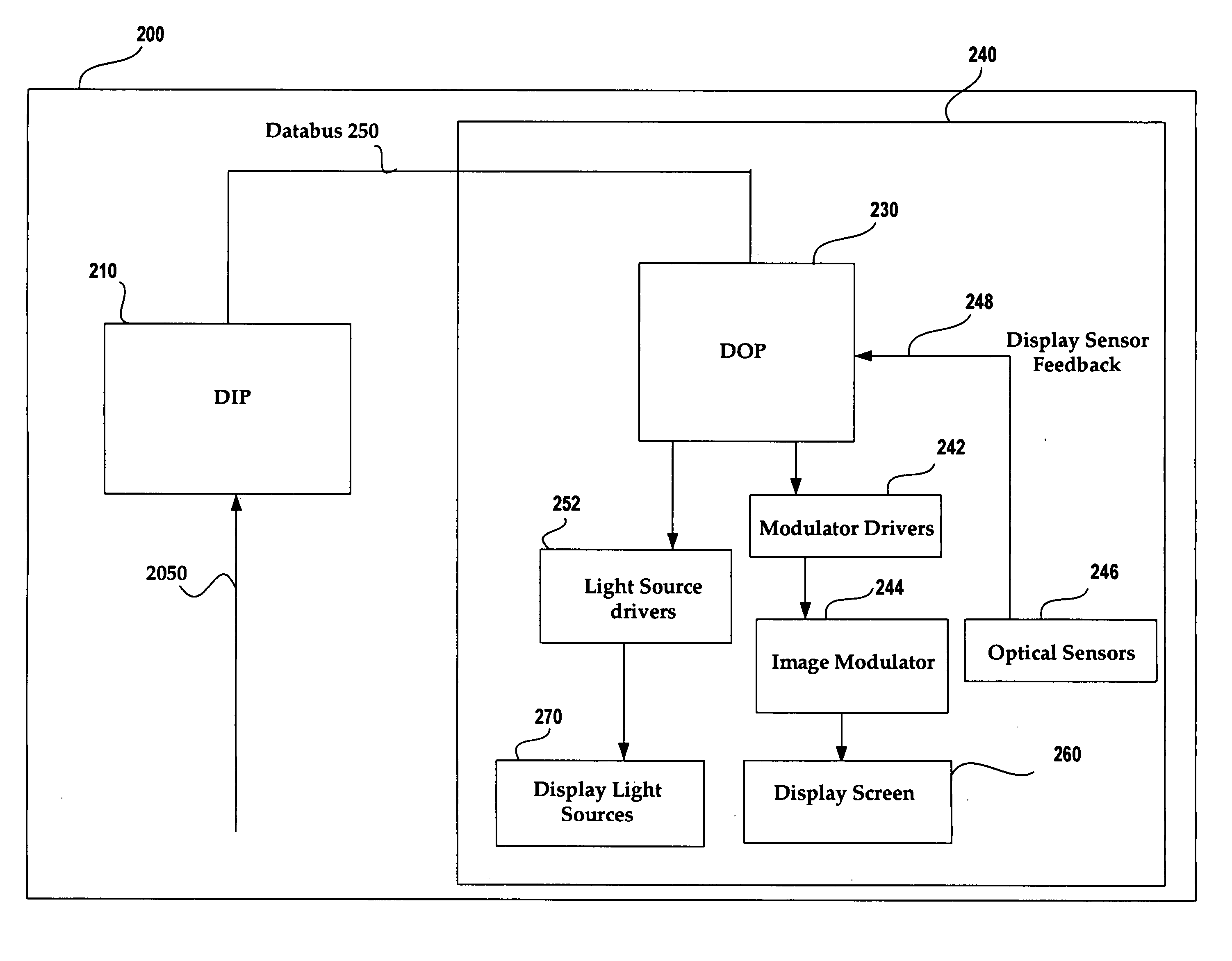
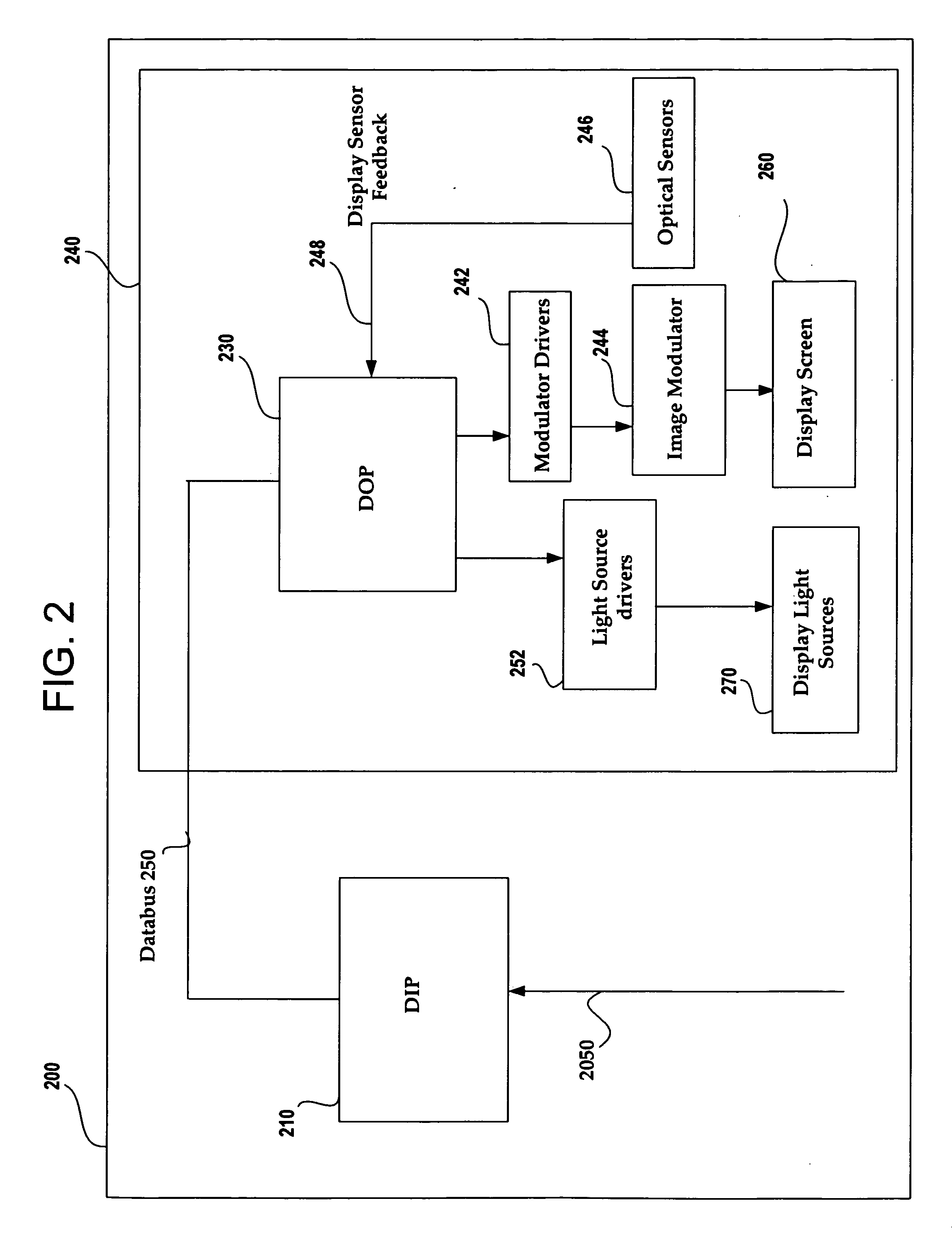
Image and light source modulation for a digital display system
ActiveUS20070035706A1Improve display qualityImprove consistencyTelevision system detailsProjectorsDisplay deviceSystem configuration
Image processing enhances display quality by controlling both the image modulator and the light sources to produce the best possible visual images. The image processing system utilizes a combination of user inputs, system configuration, design information, sensor feedback, pixel modulation information, and lighting control information to characterize the display environment on a per pixel basis. This per pixel characterization information is combined with one or more frames of the incoming real time display data. The image processing system processes each incoming pixel and produces a modified corresponding output pixel. Each pixel of each frame is processed accordingly. In addition to producing modified output pixels, the image processing system produces control information for the light sources. The light source control information can control individual lamps, tubes or LEDs, or can control a block or subset of the light sources. The resulting display has improved image consistency, enhanced color gamut, higher dynamic range and is better able to portray high motion content.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
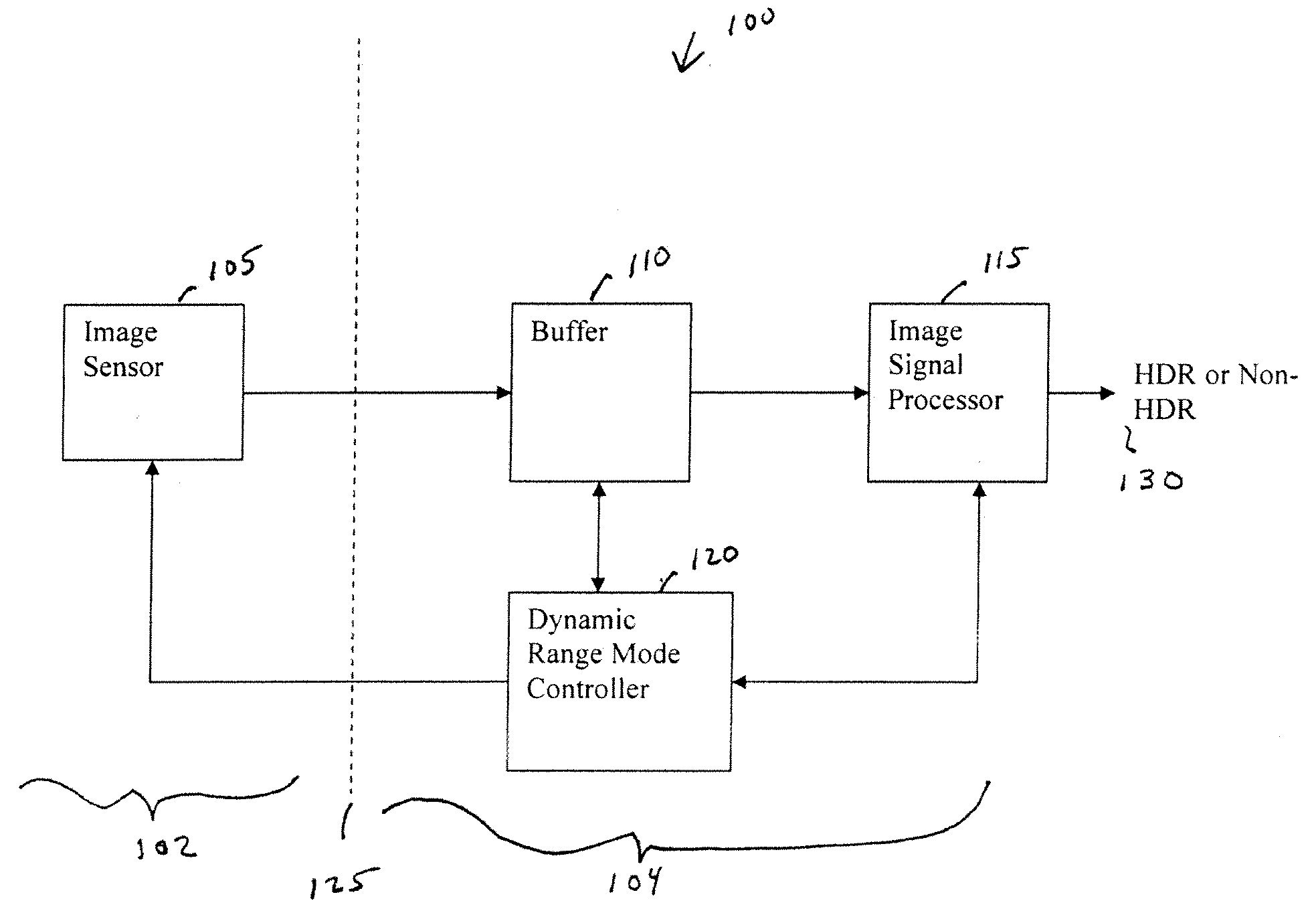
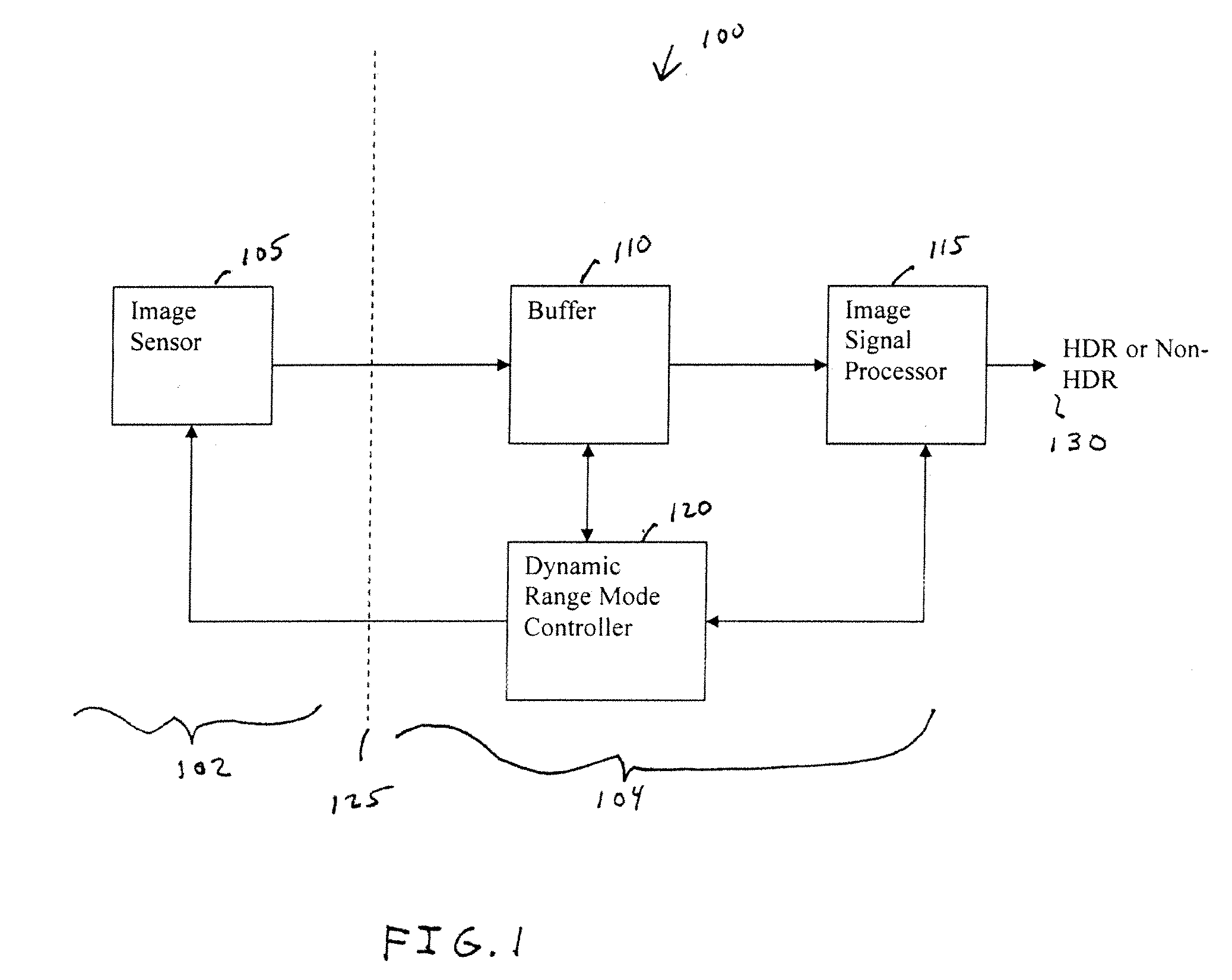
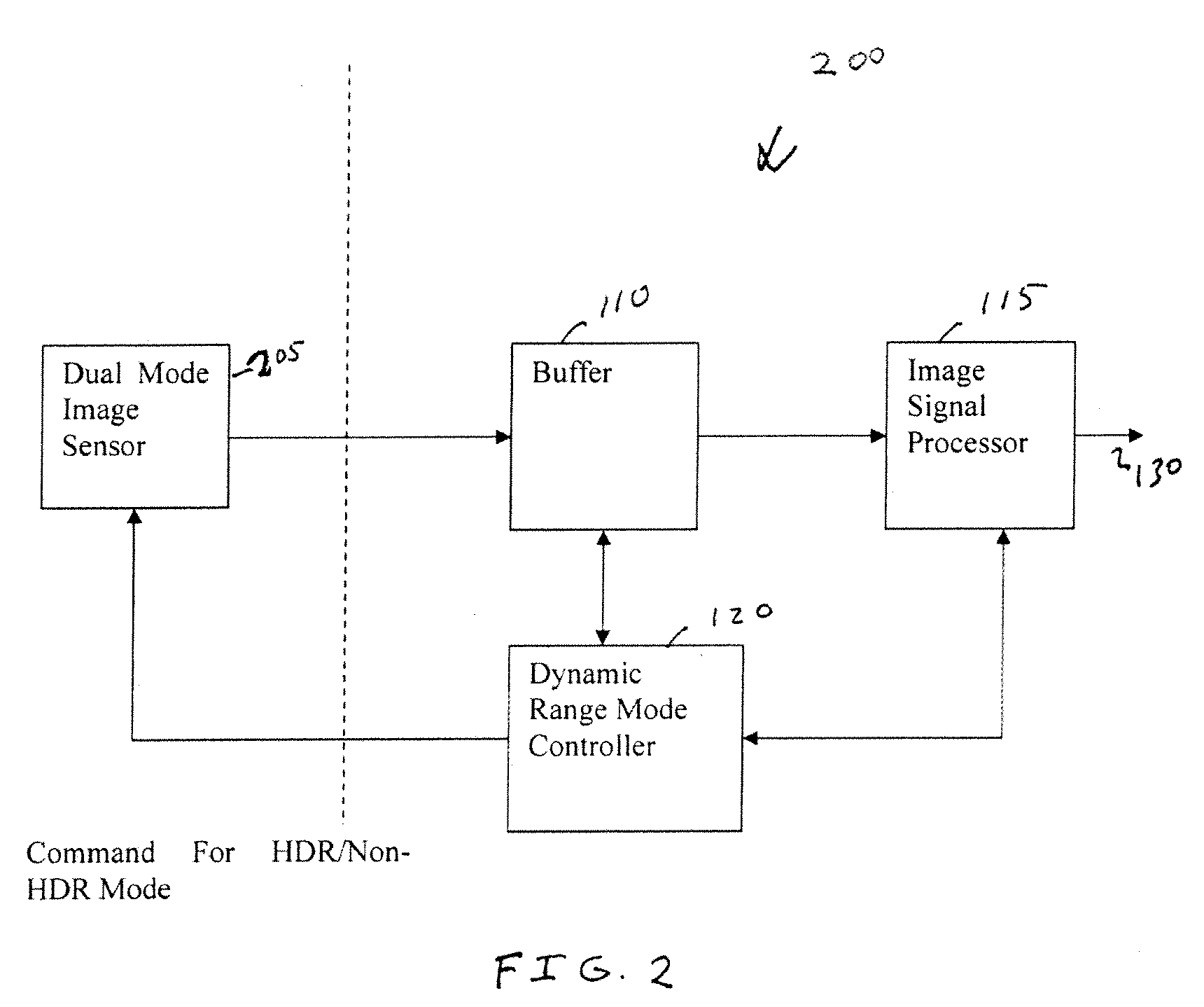
Dual mode camera solution apparatus, system, and method
InactiveUS20090086074A1Improve dynamic rangeTelevision system detailsTelevision system scanning detailsImaging processingDual mode
A camera solution includes an image sensor and an image processing and control system. At least two different operating modes are supported, with one of the modes having a higher dynamic range. Control of the dynamic range is provided at the system level. The system supports statically or dynamically selecting an operating mode that determines the dynamic range of a camera. In one implementation, the system supports the use of either a conventional image sensor that does not natively support a high dynamic range or a dual-mode image sensor.
Owner:OMNIVISION TECH INC
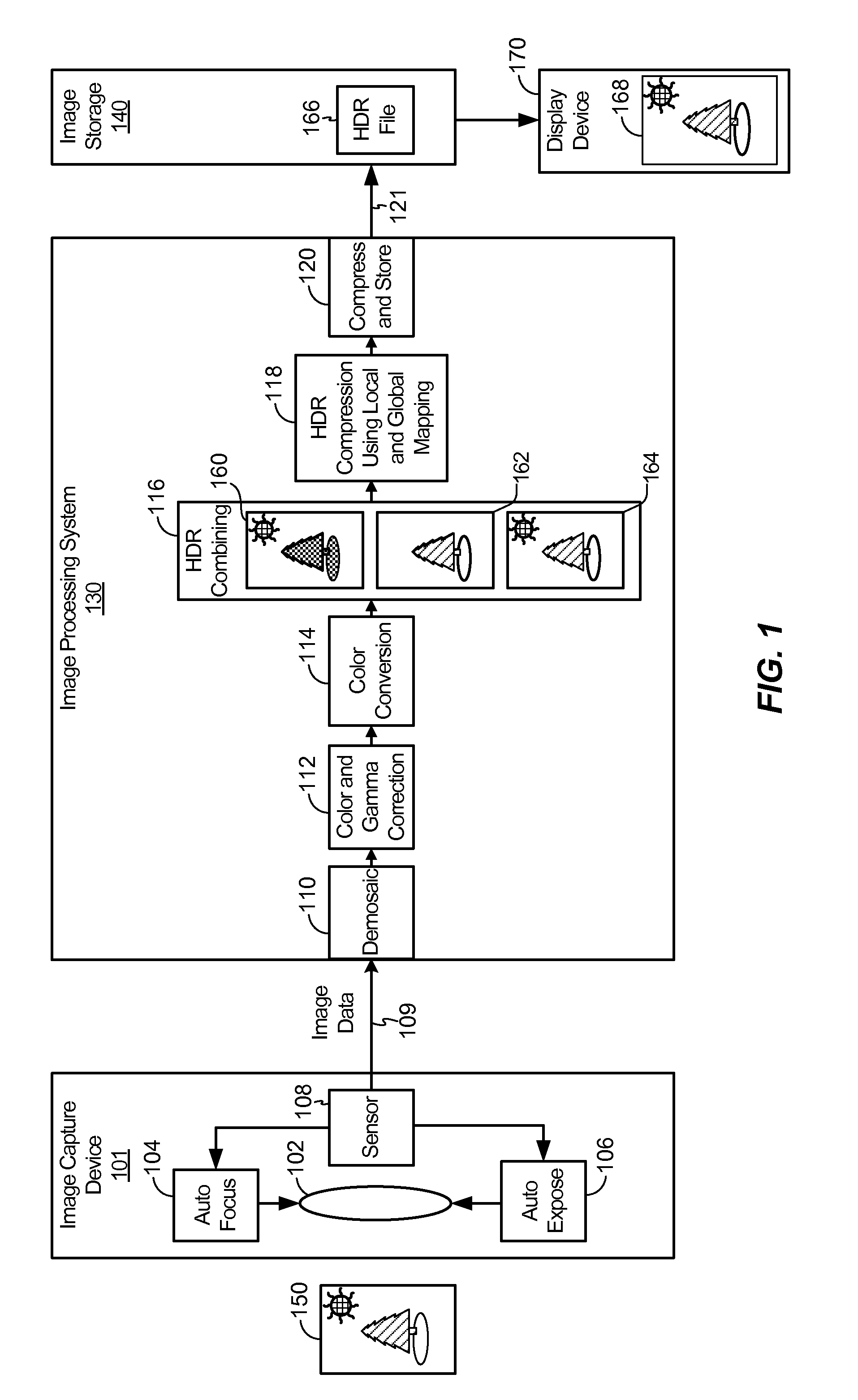
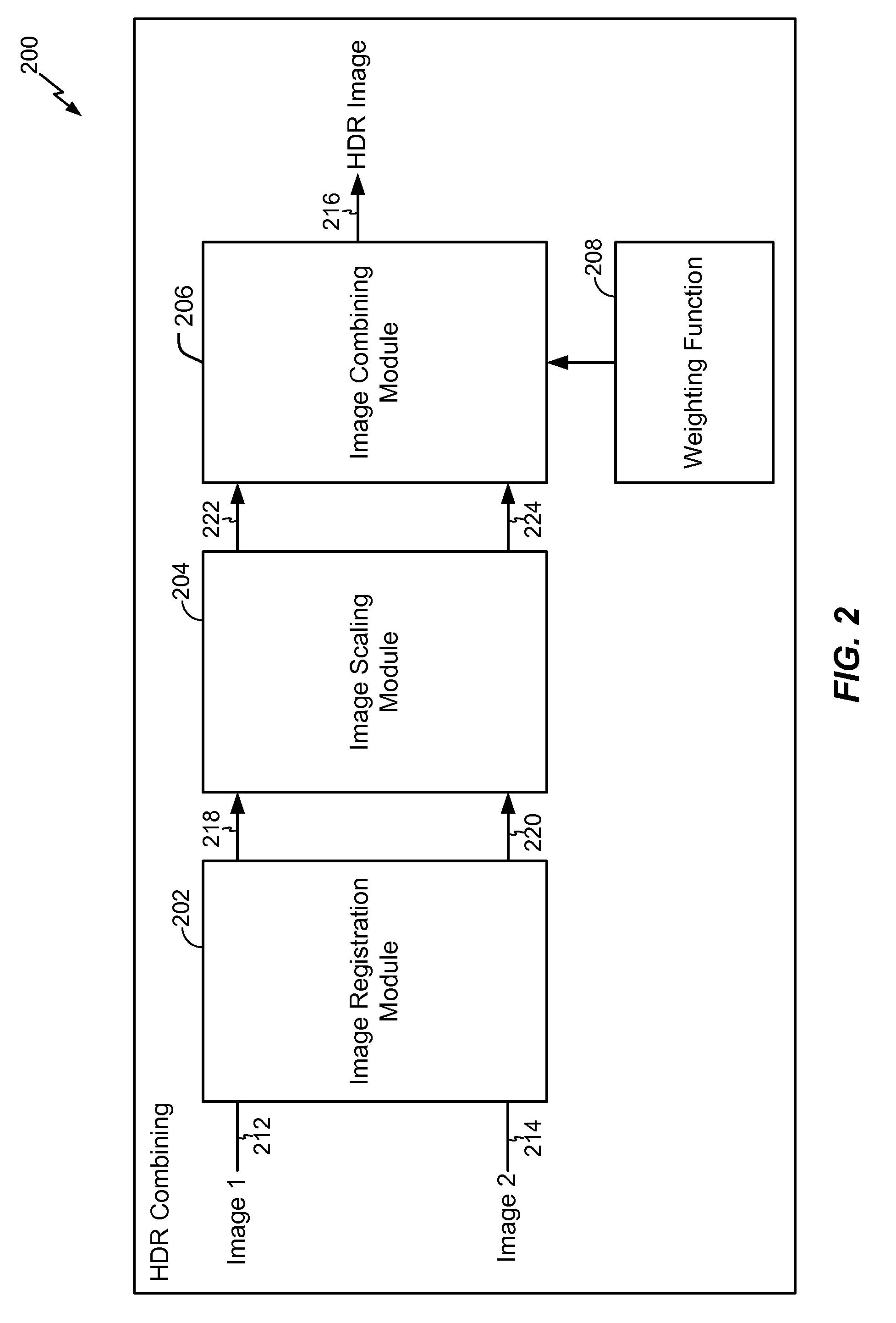
High dynamic range image combining
ActiveUS20100157078A1Enhance the imageTelevision system detailsImage enhancementImage basedHigh dynamic range
Systems and methods of high dynamic range image combining are disclosed. In a particular embodiment, a device includes a global mapping module configured to generate first globally mapped luminance values within a region of an image, a local mapping module configured to generate second locally mapped luminance values within the region of the image, and a combination module configured to determine luminance values within a corresponding region of an output image using a weighted sum of the first globally mapped luminance values and the second locally mapped luminance values. A weight of the weighted sum is at least partially based on a luminance variation within the region of the image.
Owner:QUALCOMM INC
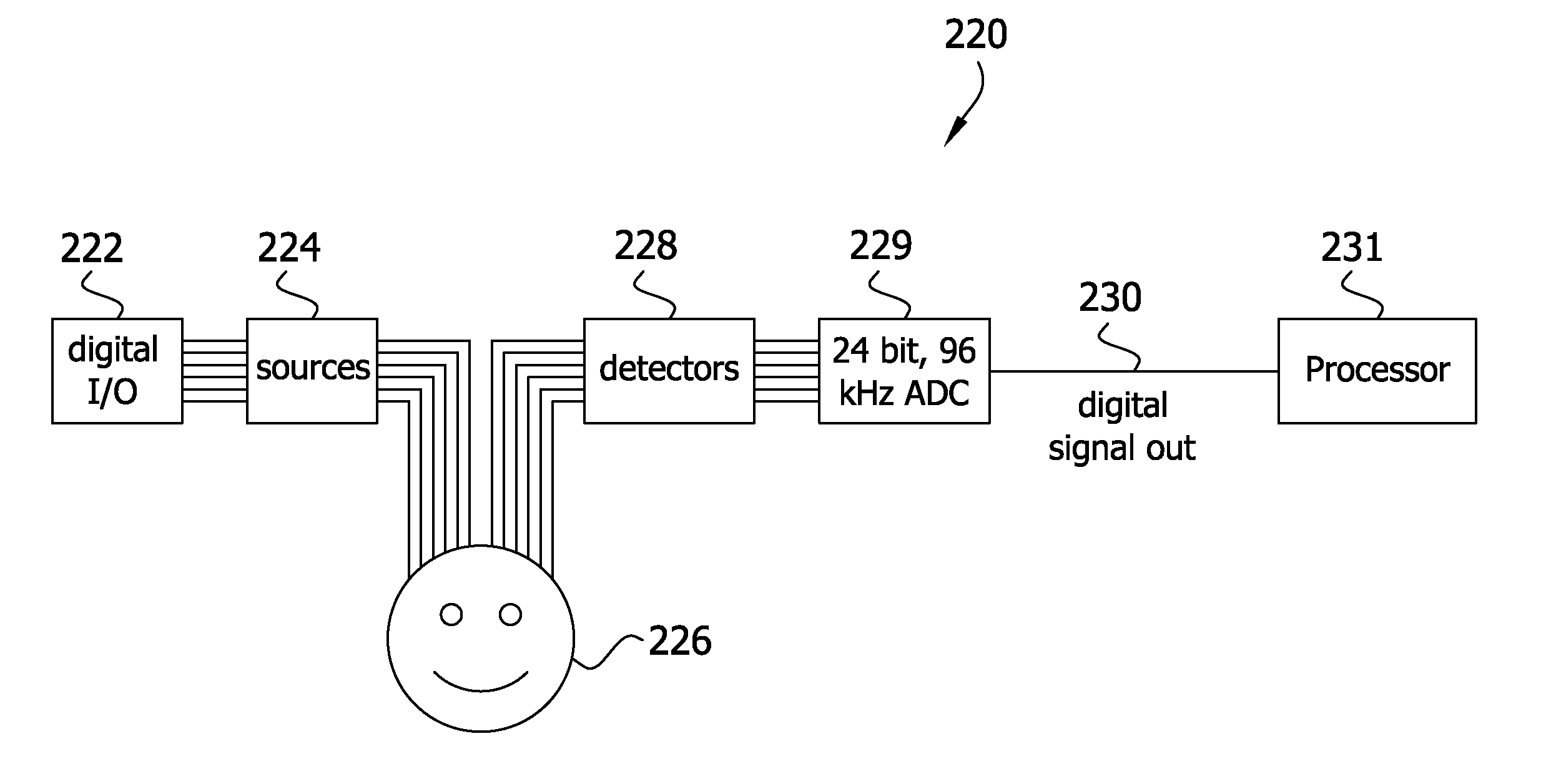
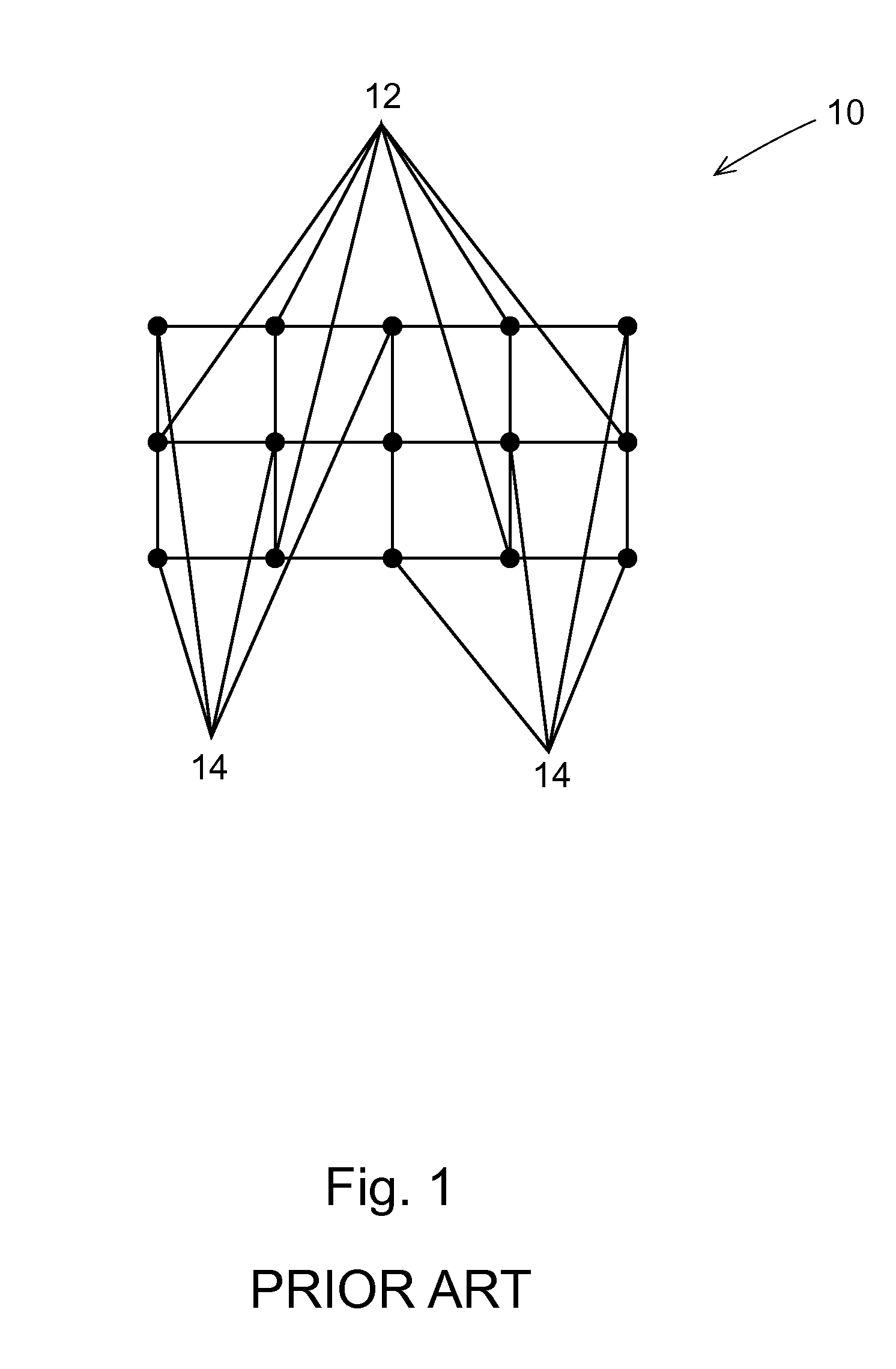
High performance imaging system for diffuse optical tomography and associated method of use
ActiveUS7983740B2High bandwidthImprove performanceDiagnostics using tomographySensorsOptical tomographyImaging quality
A high performance imaging system for diffuse optical tomography is disclosed. A dense grid utilizing sources, e.g., light emitting diodes (“LEDs”), that achieve high performance at high speed with a high dynamic range and low inter-channel crosstalk are complemented by a system of discrete, isolated receivers, e.g., avalanche photodiodes (“APDs”). The source channels have dedicated reconfigurable encoding control signals, and the detector channels have reconfigurable decoding, allowing maximum flexibility and optimal mixtures of frequency and time encoding and decoding. Each detector channel is analyzed by dedicated, isolated, high-bandwidth receiver circuitry so that no channel gain switching is necessary. The resulting improvements to DOT system performance, e.g., increased dynamic range and decreased crosstalk, enable higher density imaging arrays and provide significantly enhanced DOT image quality. A processor can be utilized to provide sophisticated three dimensional modeling as well as noise reduction.
Owner:WASHINGTON UNIV IN SAINT LOUIS
Systems and methods for extending dynamic range of imager arrays by controlling pixel analog gain
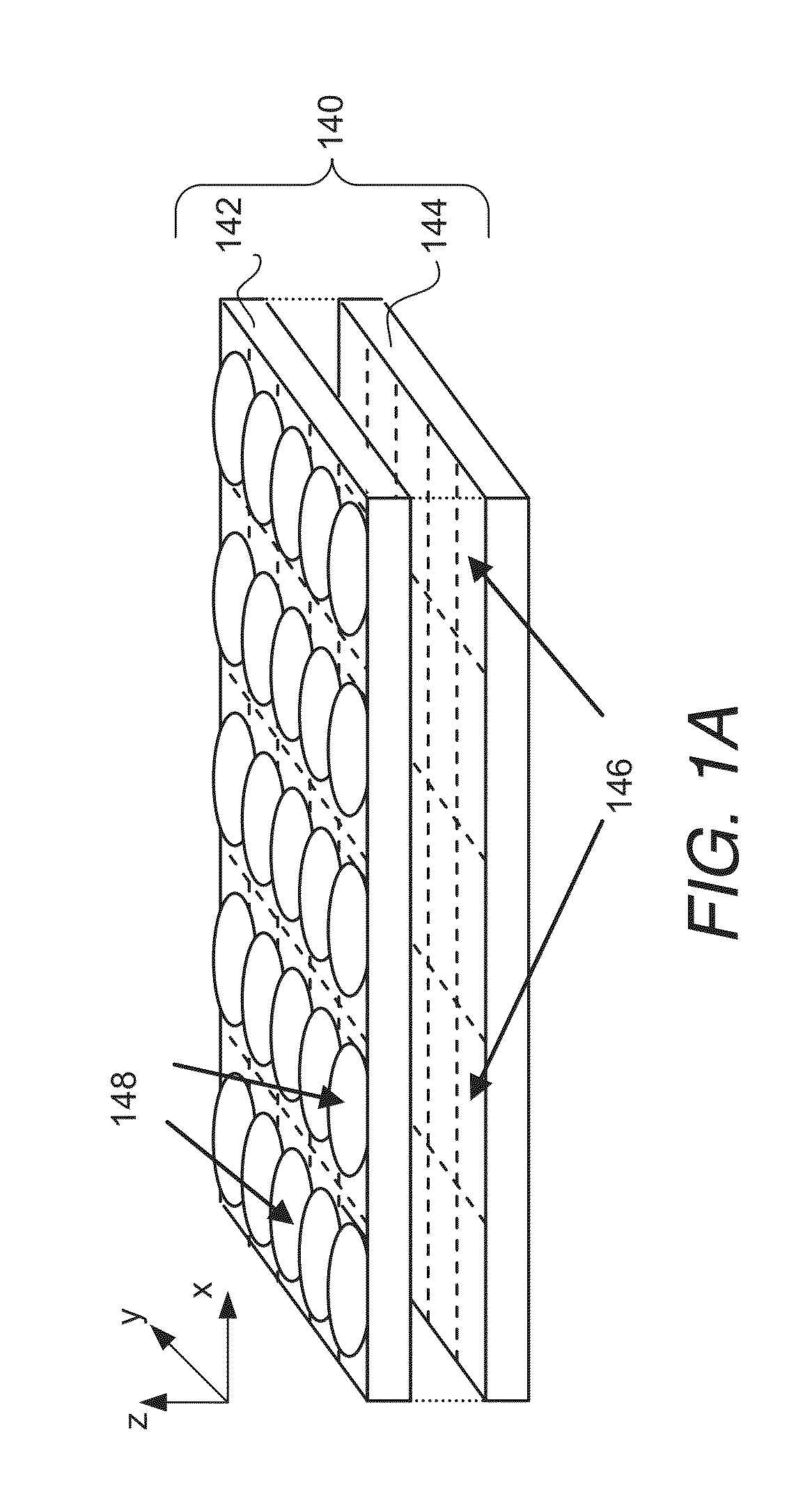
InactiveUS20130147979A1Improve dynamic rangeAdvanced image informationTelevision system detailsSolid-state device signal generatorsAnalog front-endDigital image data
Array cameras and imager arrays configured to capture high dynamic range light field image data and methods of capturing high dynamic range light field image data in accordance with embodiments of the invention are disclosed. Imager arrays in accordance with many embodiments of the invention include multiple focal planes with associated read out and sampling circuitry. The sampling circuitry controls the conversion of the analog image information into digital image data. In certain embodiments, the sampling circuitry includes an Analog Front End (AFE) and an Analog to Digital Converter (ADC). In several embodiments, the AFE is used to apply different amplification gains to analog image information read out from pixels in a given focal plane to provide increased dynamic range to digital image data generated by digitizing the amplified analog image information. The different amplifications gains can be applied in a predetermined manner or on a pixel by pixel basis.
Owner:FOTONATION CAYMAN LTD
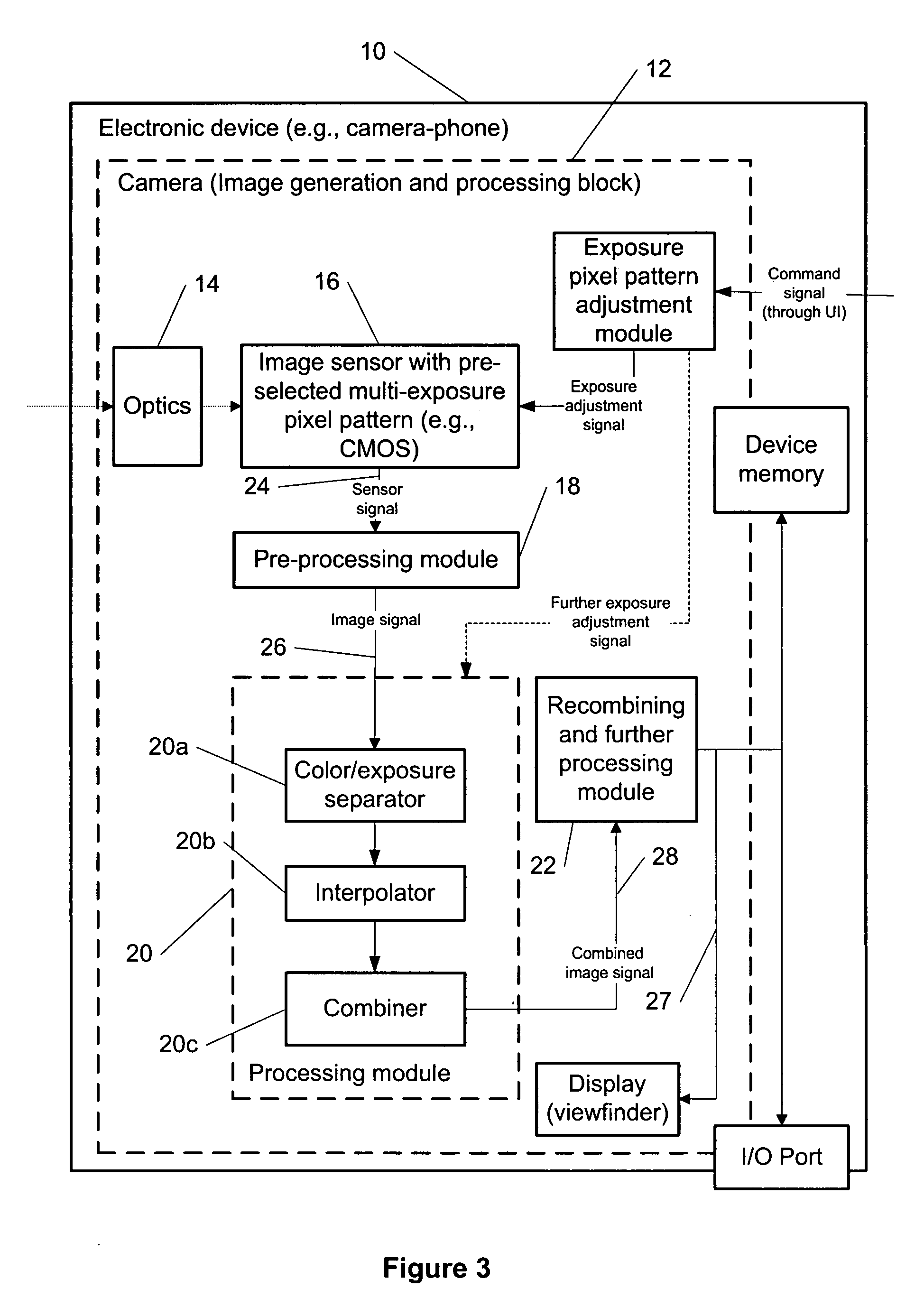
Multi-exposure pattern for enhancing dynamic range of images
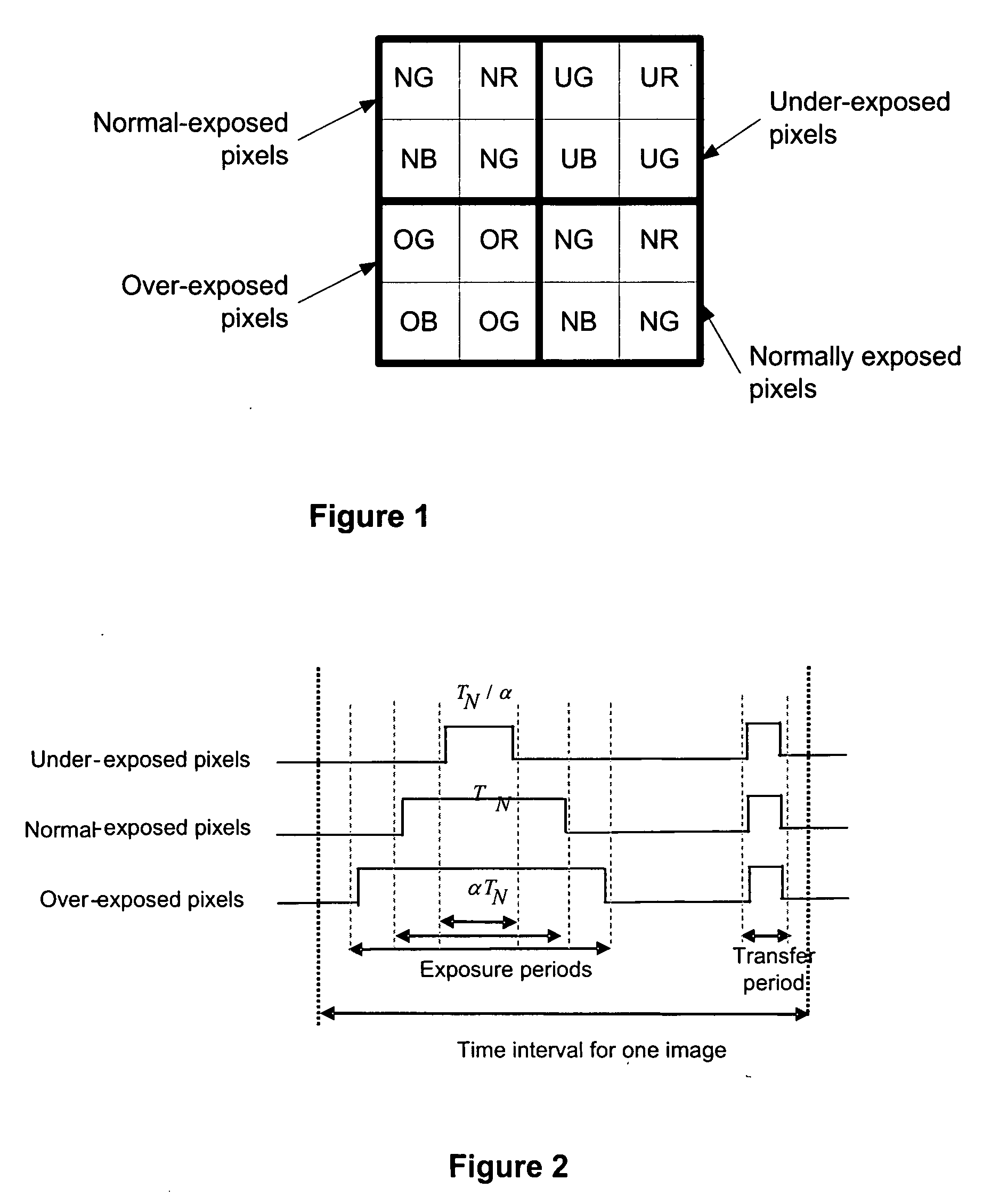
ActiveUS20090091645A1Extended imaging rangeTelevision system detailsTelevision system scanning detailsViewfinderComputer science
The specification and drawings present a new method, apparatus and software product for enhancing a dynamic range of an image with a multi-exposure pixel pattern taken by an image sensor of a camera for one or more color channels, wherein a plurality of groups of pixels of the image sensor have different exposure times (e.g., pre-selected or adjusted by a user through a user interface using a viewfinder feedback, or adjusted by a user through a user interface after taking and storing RAW image, etc.). Processing of the captured image for constructing an enhanced image of the image for each of the one or more color channels can be performed using weighted combination of exposure times of pixels having different pre-selected exposure times according to a predetermined criterion.
Owner:NOKIA TECHNOLOGLES OY
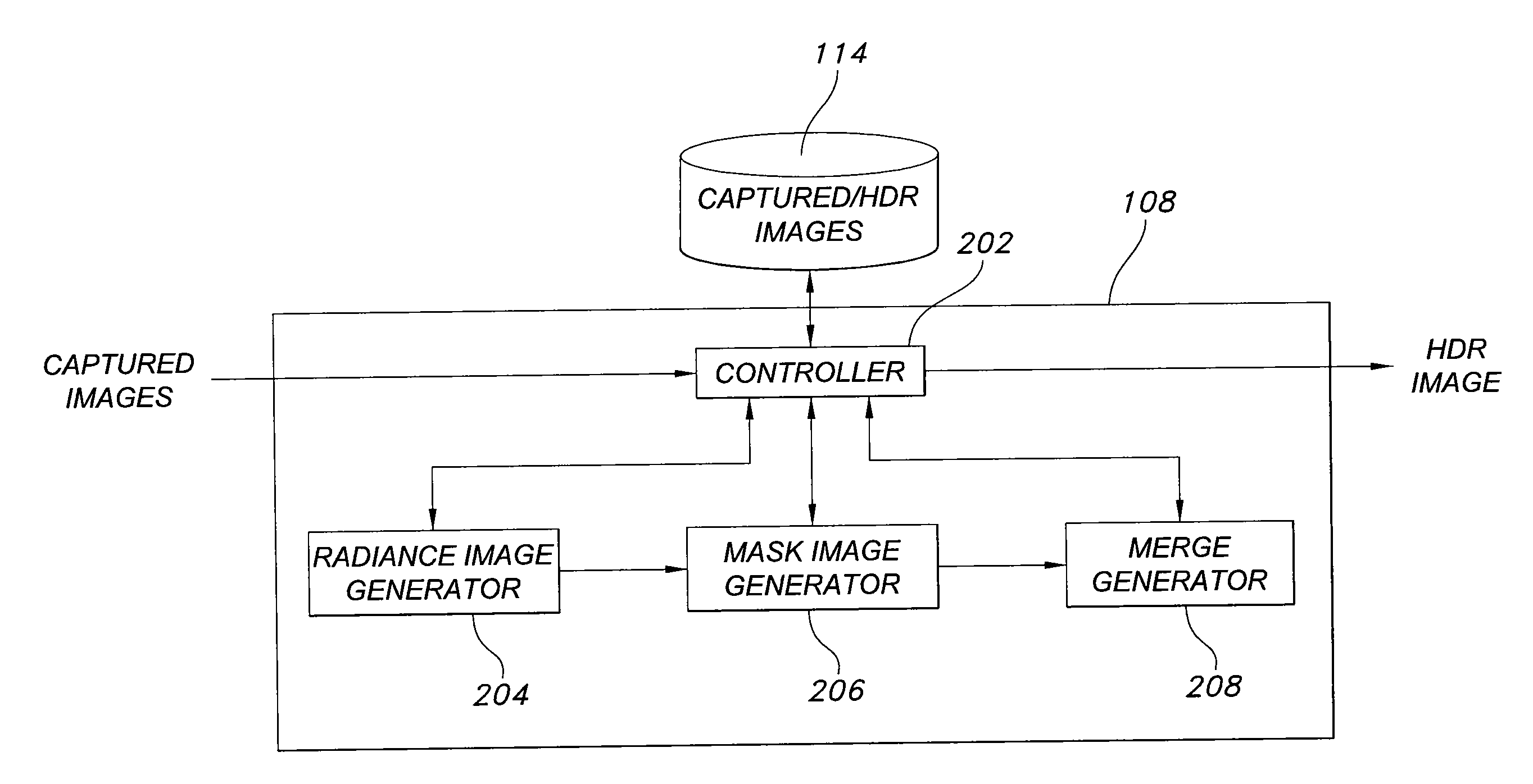
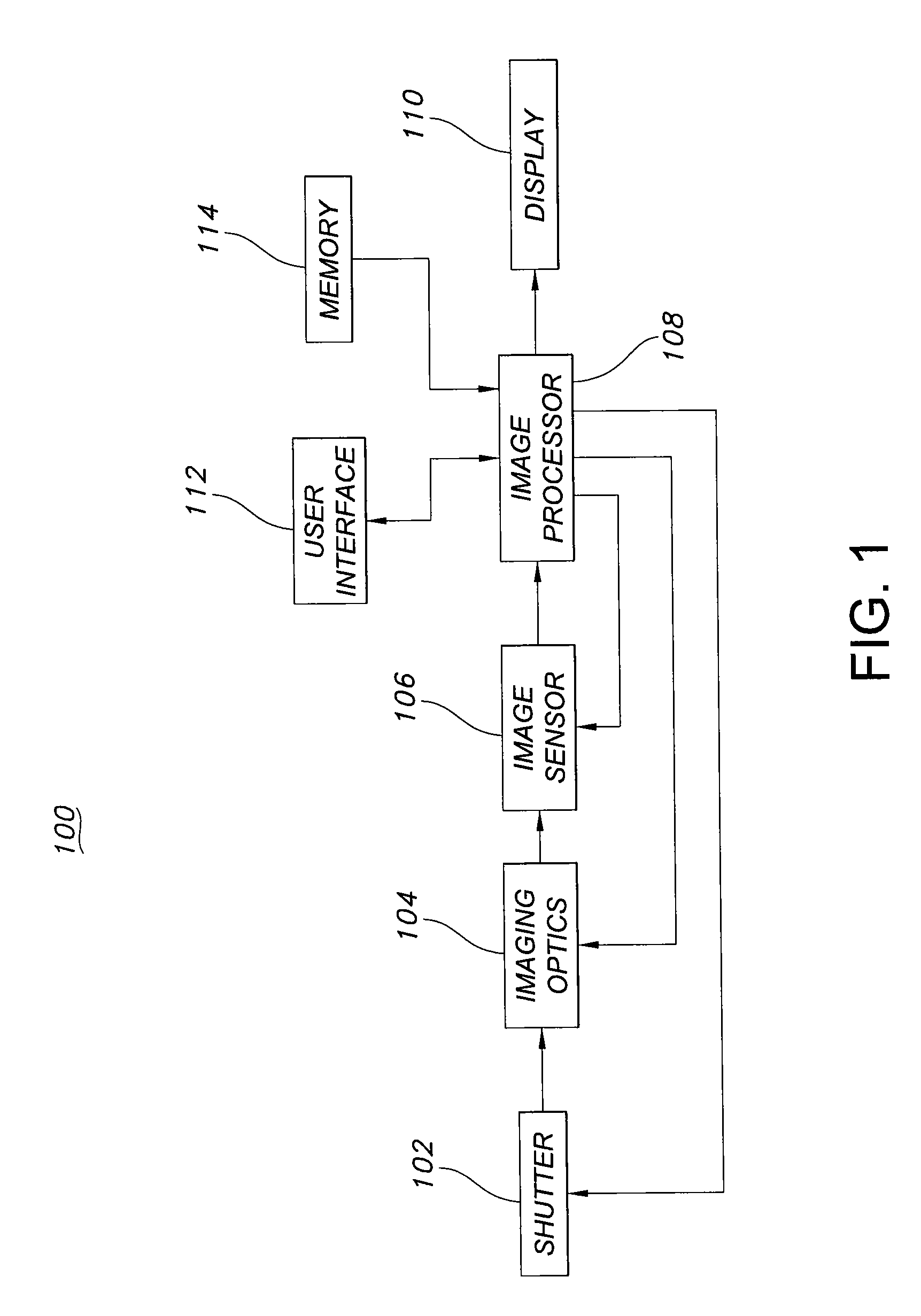
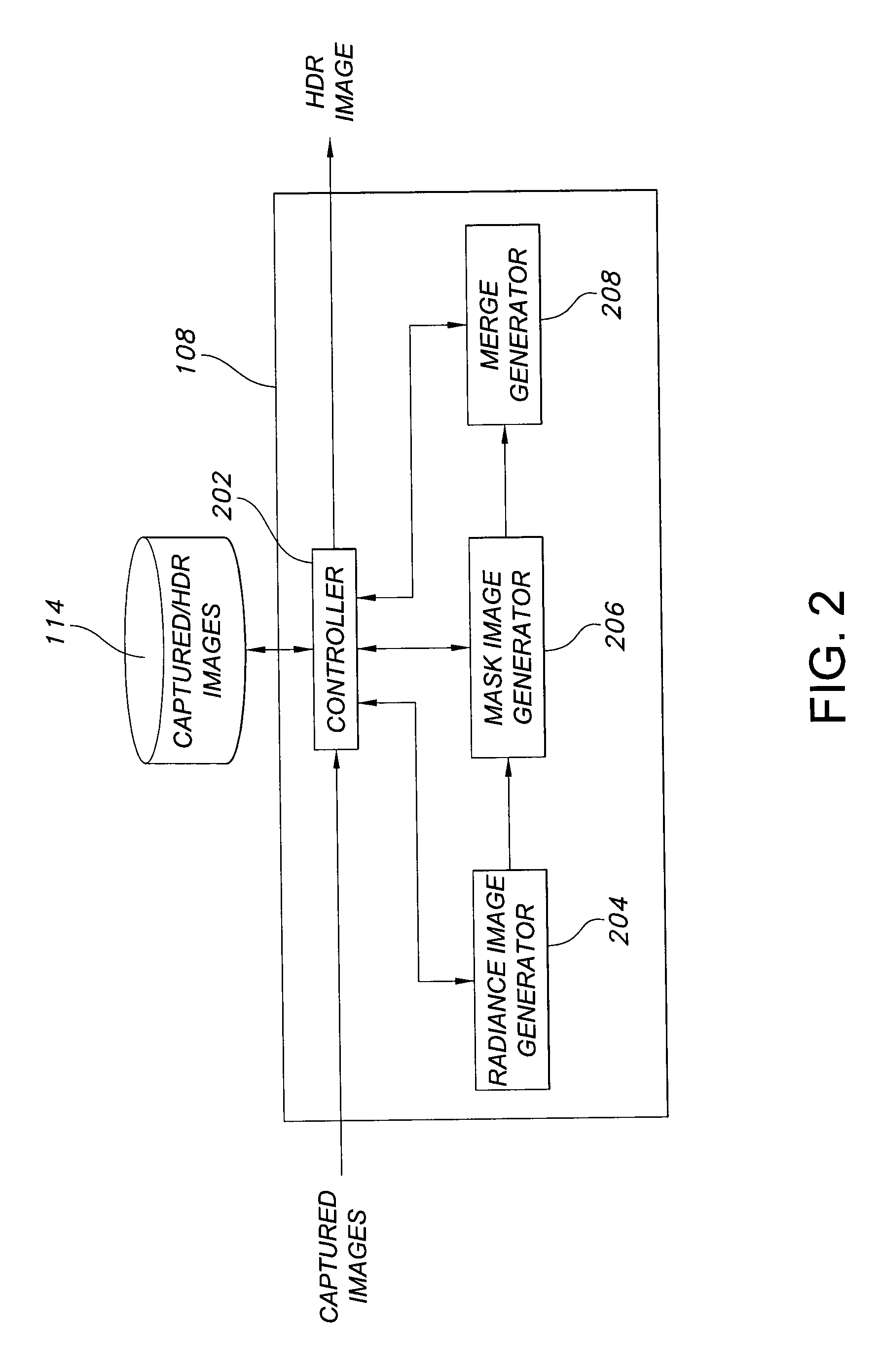
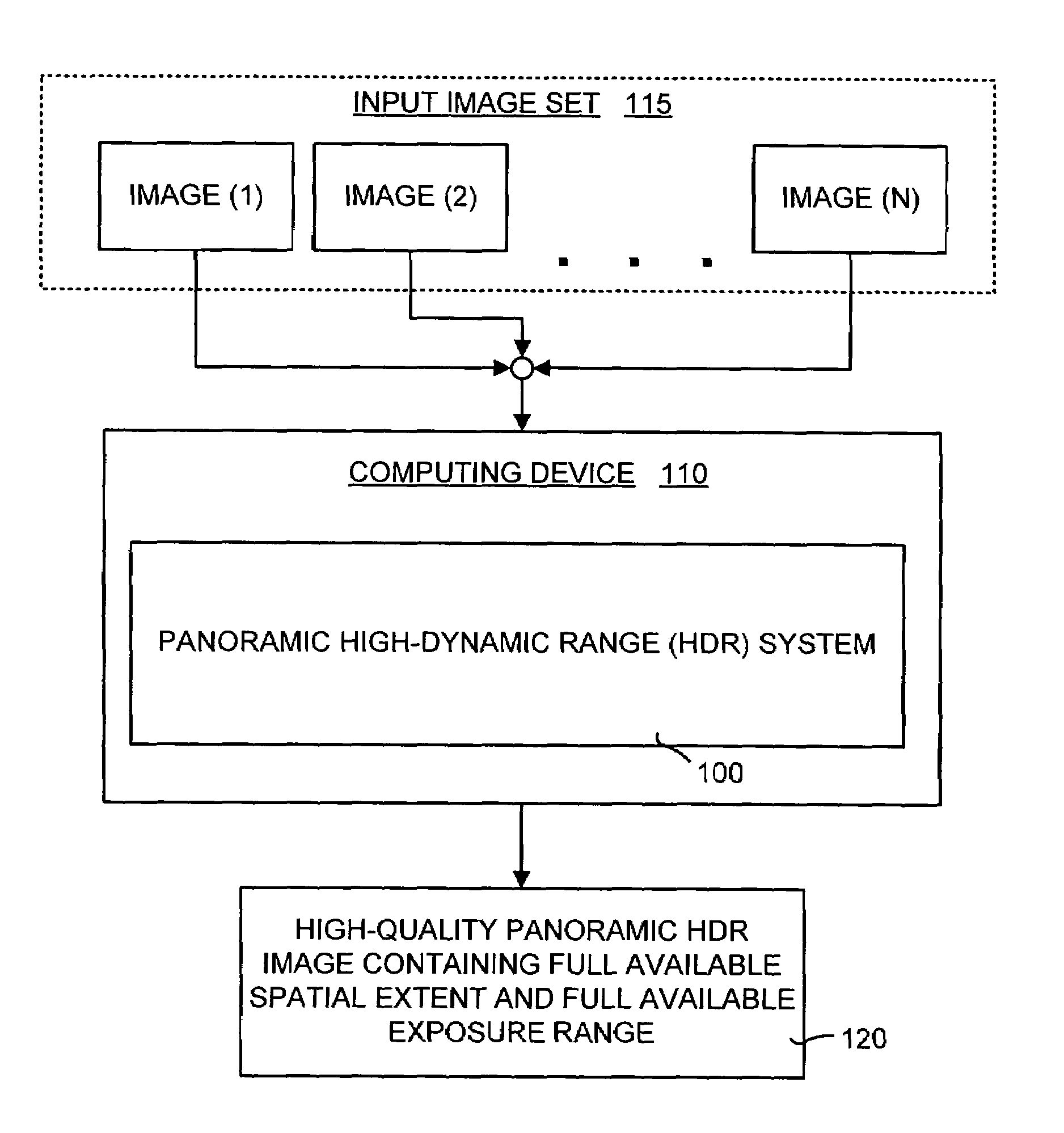
Method of capturing high dynamic range images with objects in the scene
Methods, image processors and imaging devices for capturing a high dynamic range (HDR) image. Multiple images of a scene are captured at respectively different exposure settings. A further image of an object placed in the scene is captured at one exposure setting. A first radiance image is formed from the multiple images. A second radiance image is formed from the further image. The first radiance image and the second radiance image are merged to form the HDR image.
Owner:APTINA IMAGING CORP
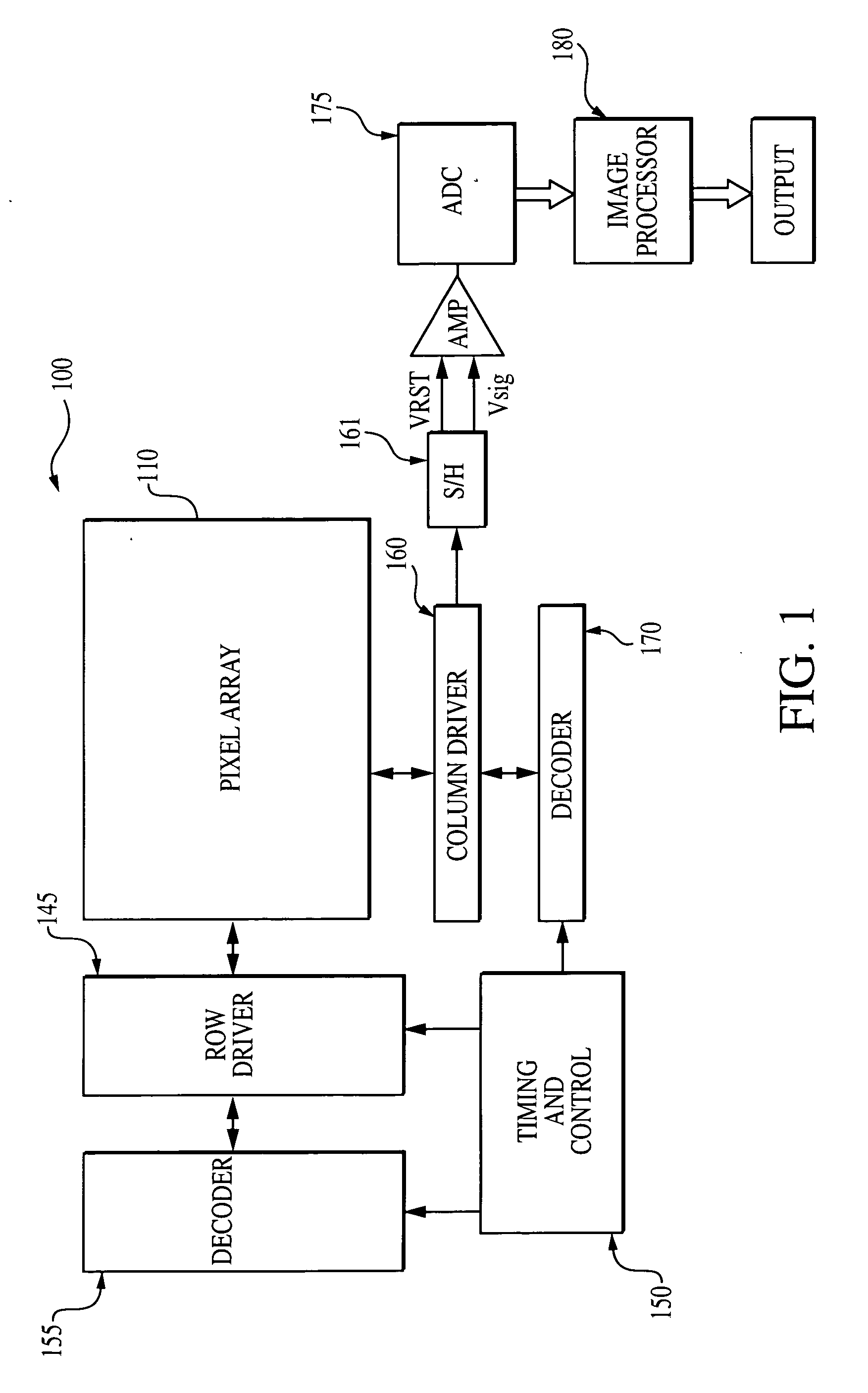
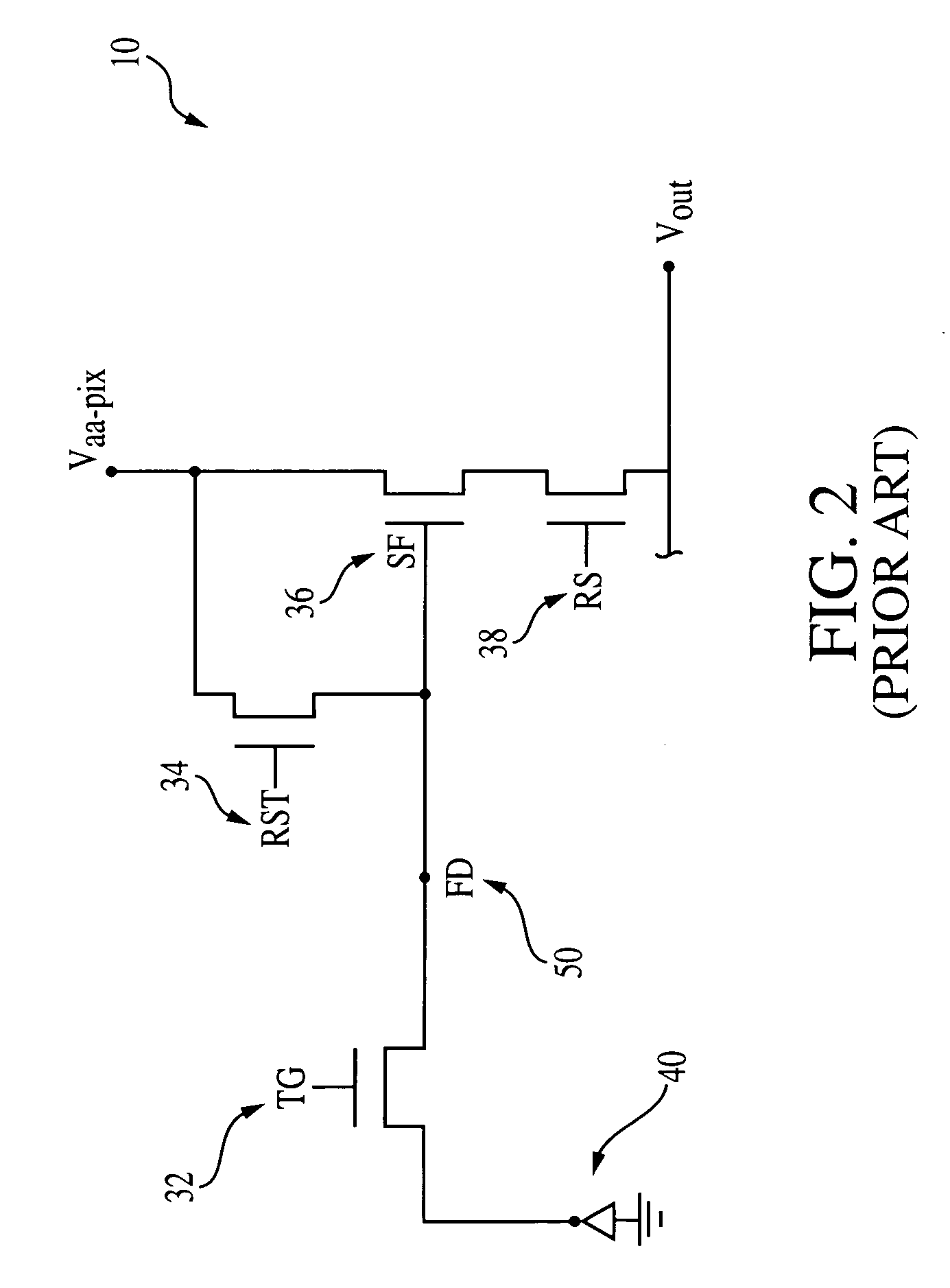
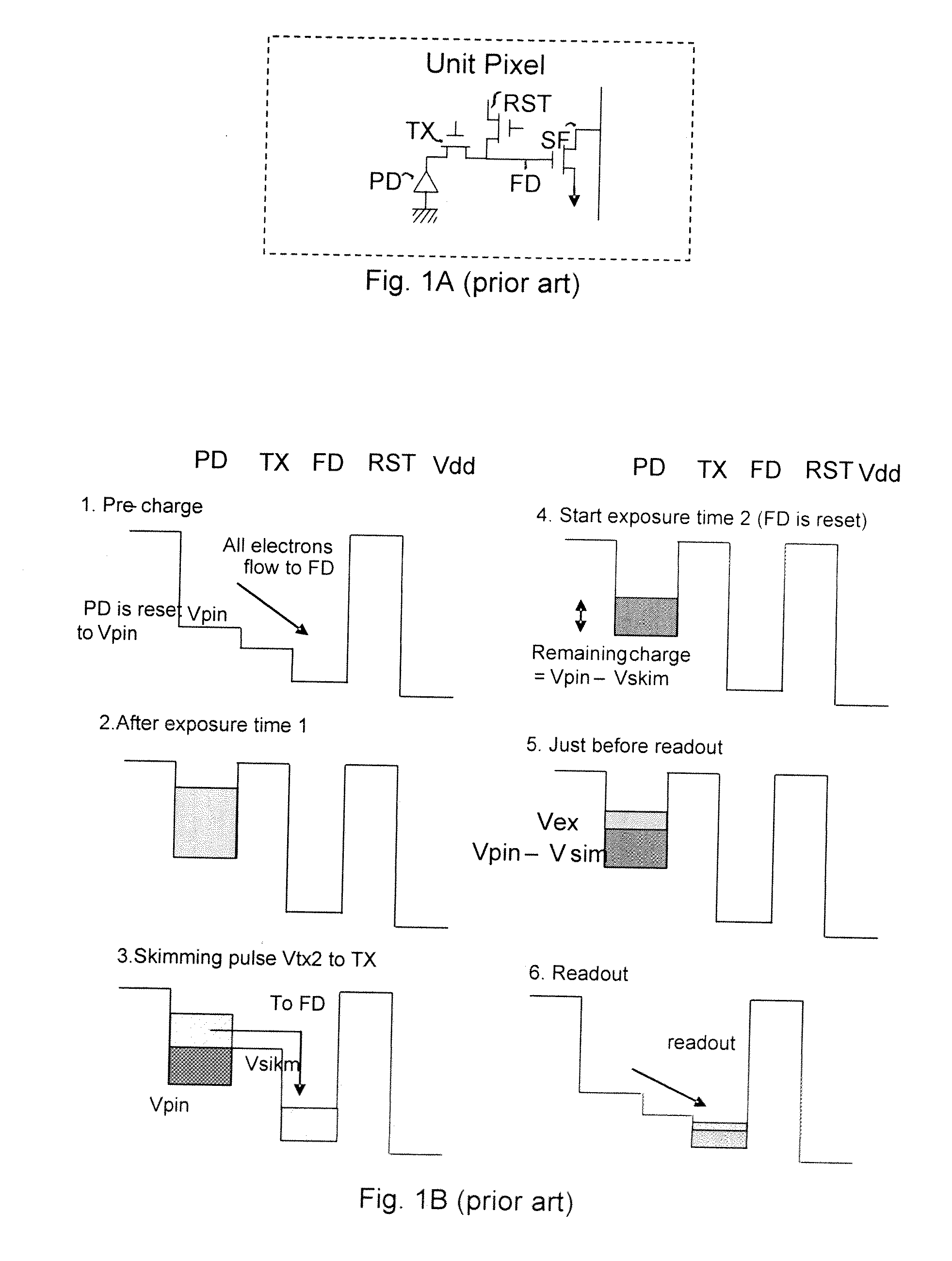
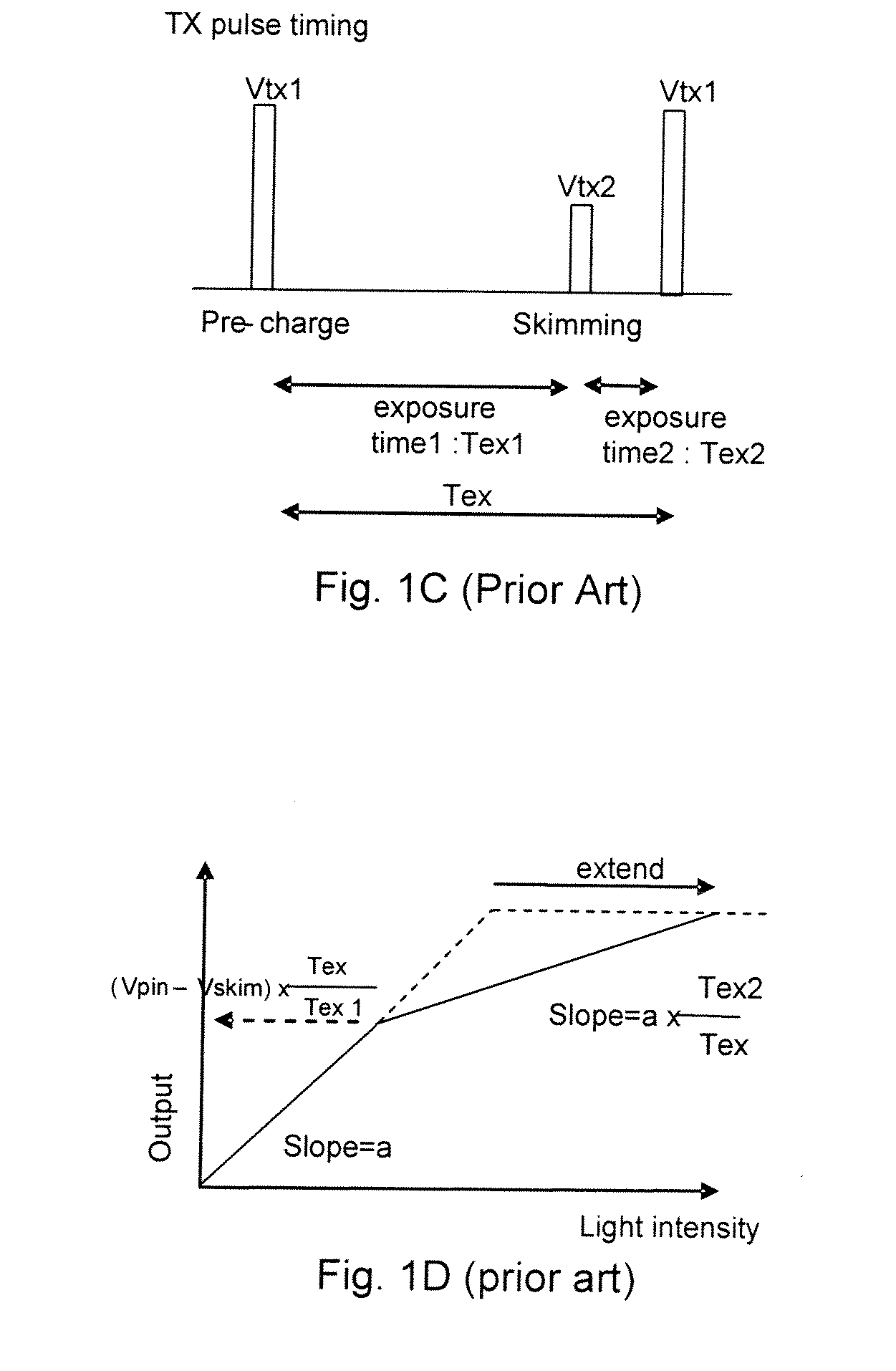
High dynamic range pixel amplifier
ActiveUS20050224843A1Increase capacitanceReduce capacitanceTelevision system detailsTelevision system scanning detailsCapacitanceEngineering
A pixel cell with increased dynamic range is formed by providing a floating diffusion region having a variable capacitance, controlled by at least one gate having source and drain regions commonly connected to the floating diffusion region. The gate has an intrinsic capacitance which, when the gate is activated, is added to the capacitance of the floating diffusion region, providing a low conversion gain readout. When the gate is off, the floating diffusion region capacitance is minimized, providing a high conversion gain readout. The gate may also be selectively switched to mid-level. At mid-level, a mid-level conversion gain, which is between the high and low conversion gains, readout is provided, but the gate still provides some capacitance to prevent the floating diffusion region from saturating.
Owner:APTINA IMAGING CORP
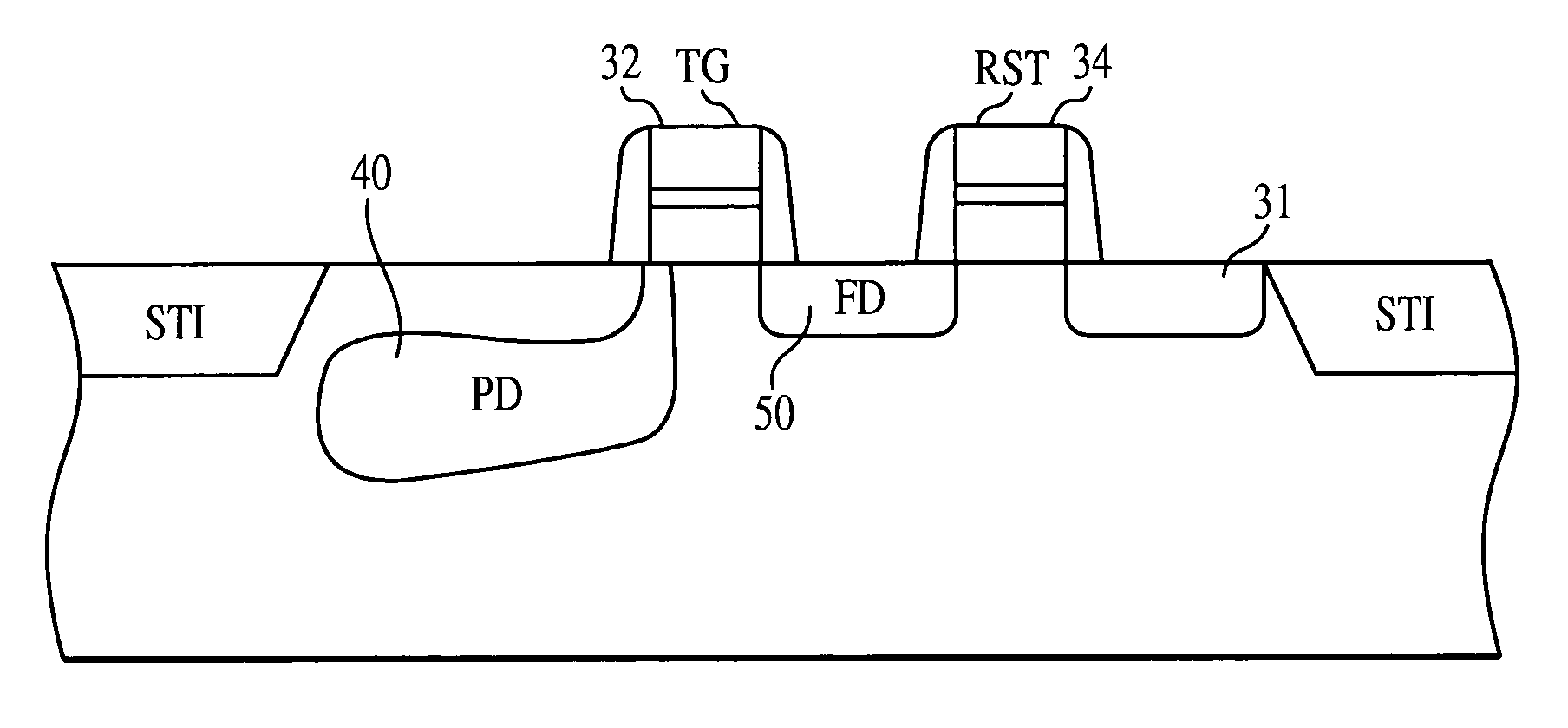
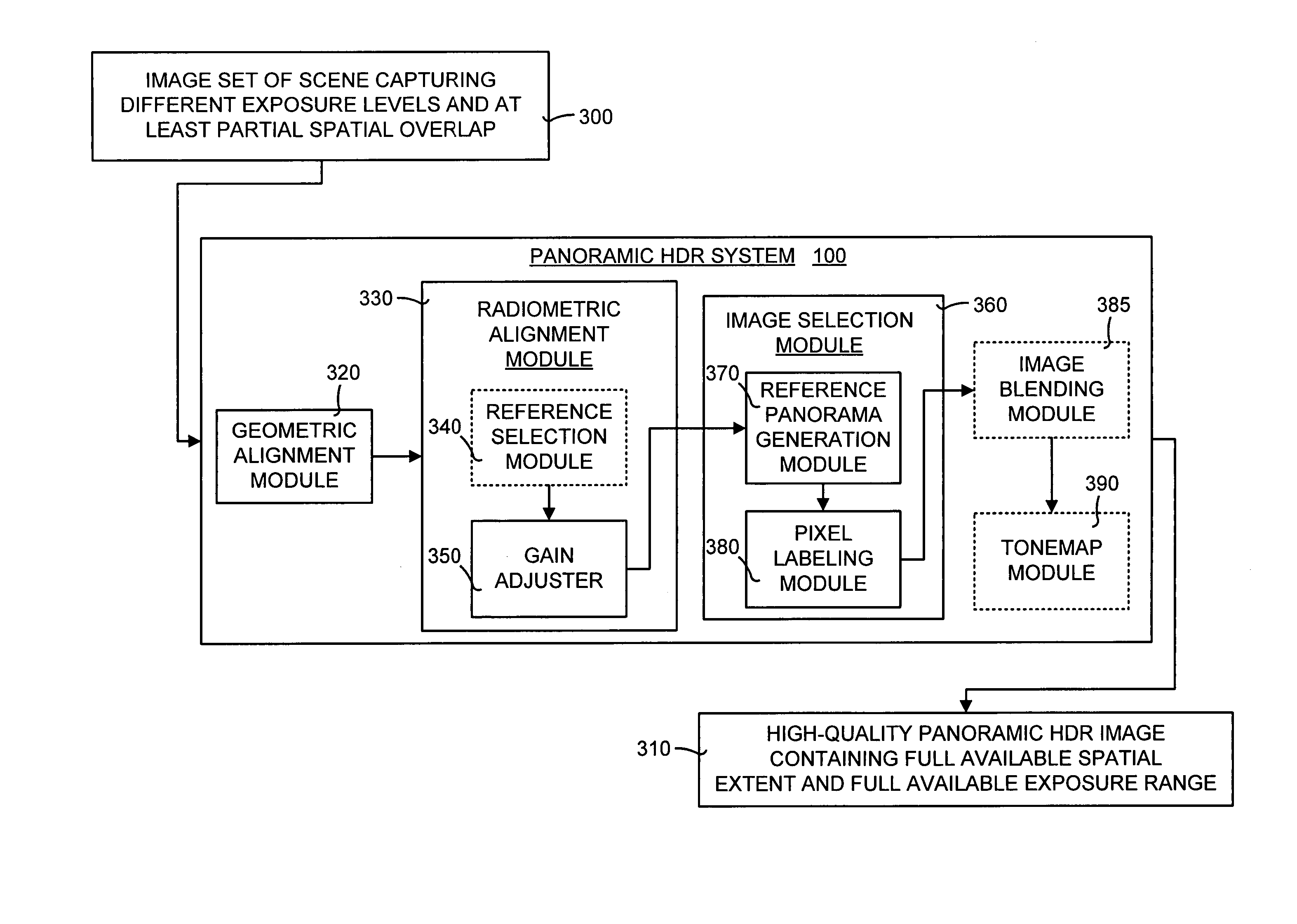
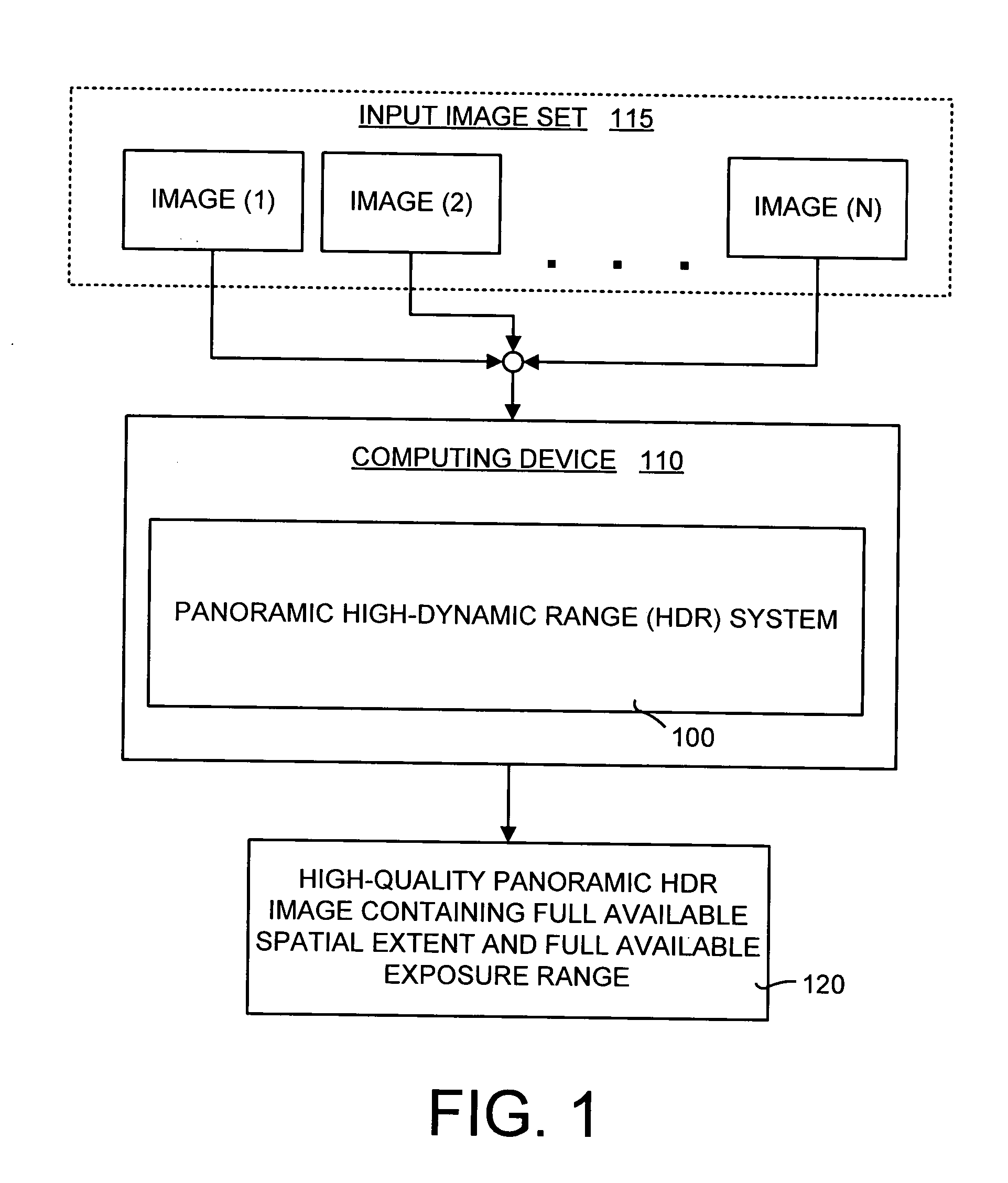
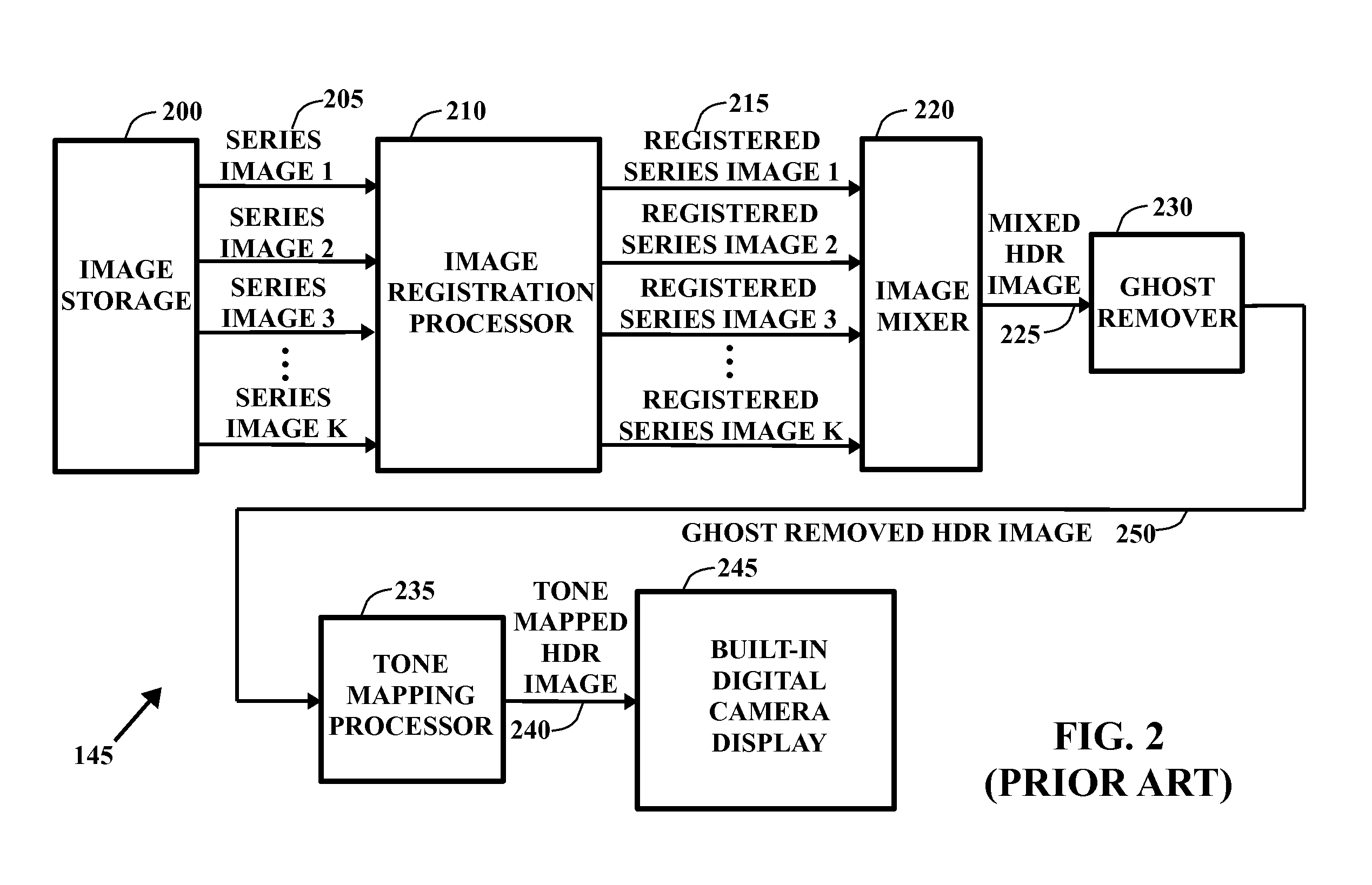
Method and system for combining multiple exposure images having scene and camera motion
ActiveUS20060177150A1Quality improvementImprove signal-to-noise ratioImage enhancementTelevision system detailsSignal-to-noise ratio (imaging)Radiance
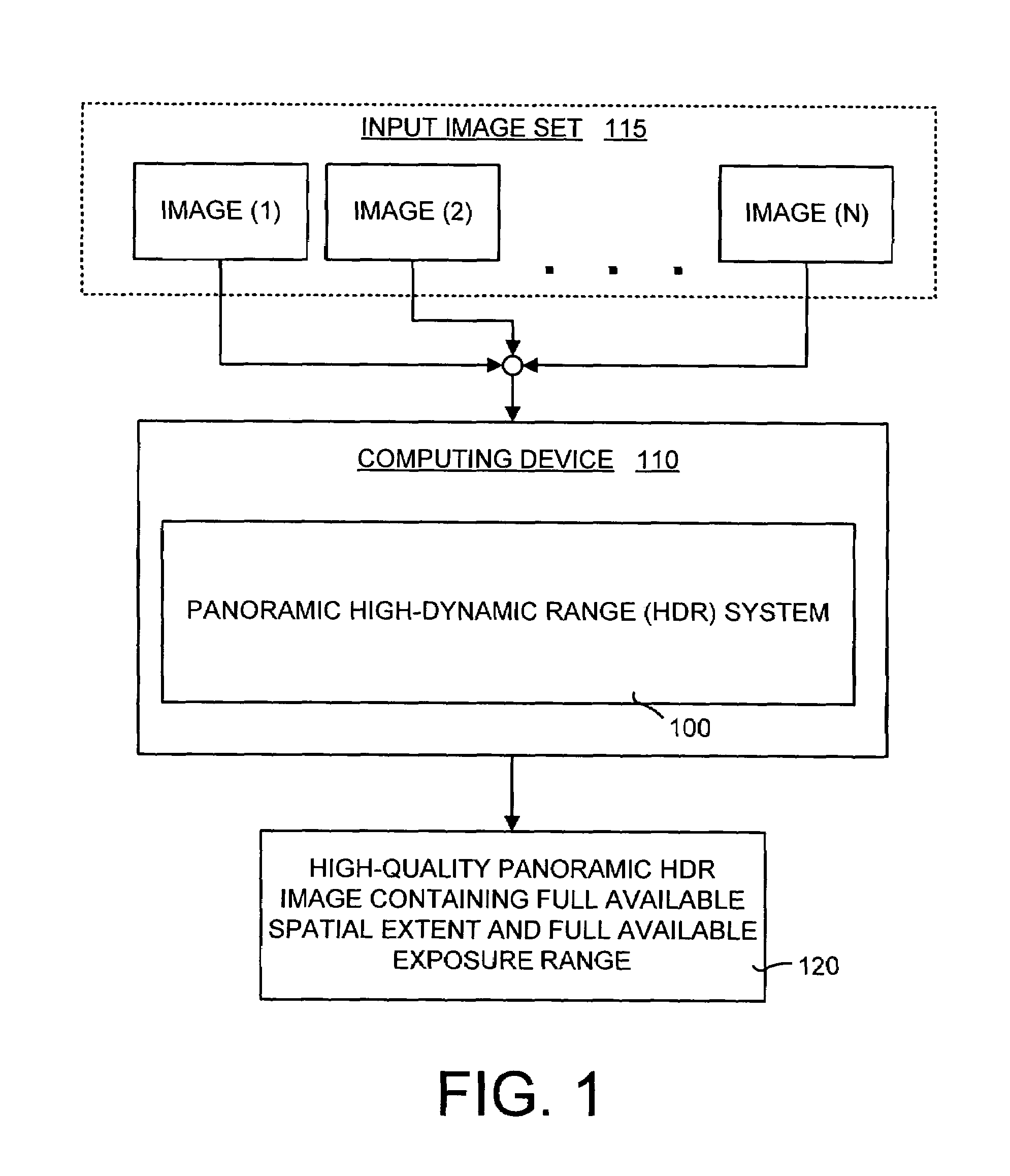
A panoramic high-dynamic range (HDR) image method and system of combining multiple images having different exposures and at least partial spatial overlap wherein each of the images may have scene motion, camera motion, or both. The major part of the panoramic HDR image method and system is a two-pass optimization-based approach that first defines the position of the objects in a scene and then fills in the dynamic range when possible and consistent. Data costs are created to encourage radiance values that are both consistent with object placement (defined by the first pass) and of a higher signal-to-noise ratio. Seam costs are used to ensure that transitions occur in regions of consistent radiances. The result is a high-quality panoramic HDR image having the full available spatial extent of the scene along with the full available exposure range.
Owner:MICROSOFT TECH LICENSING LLC
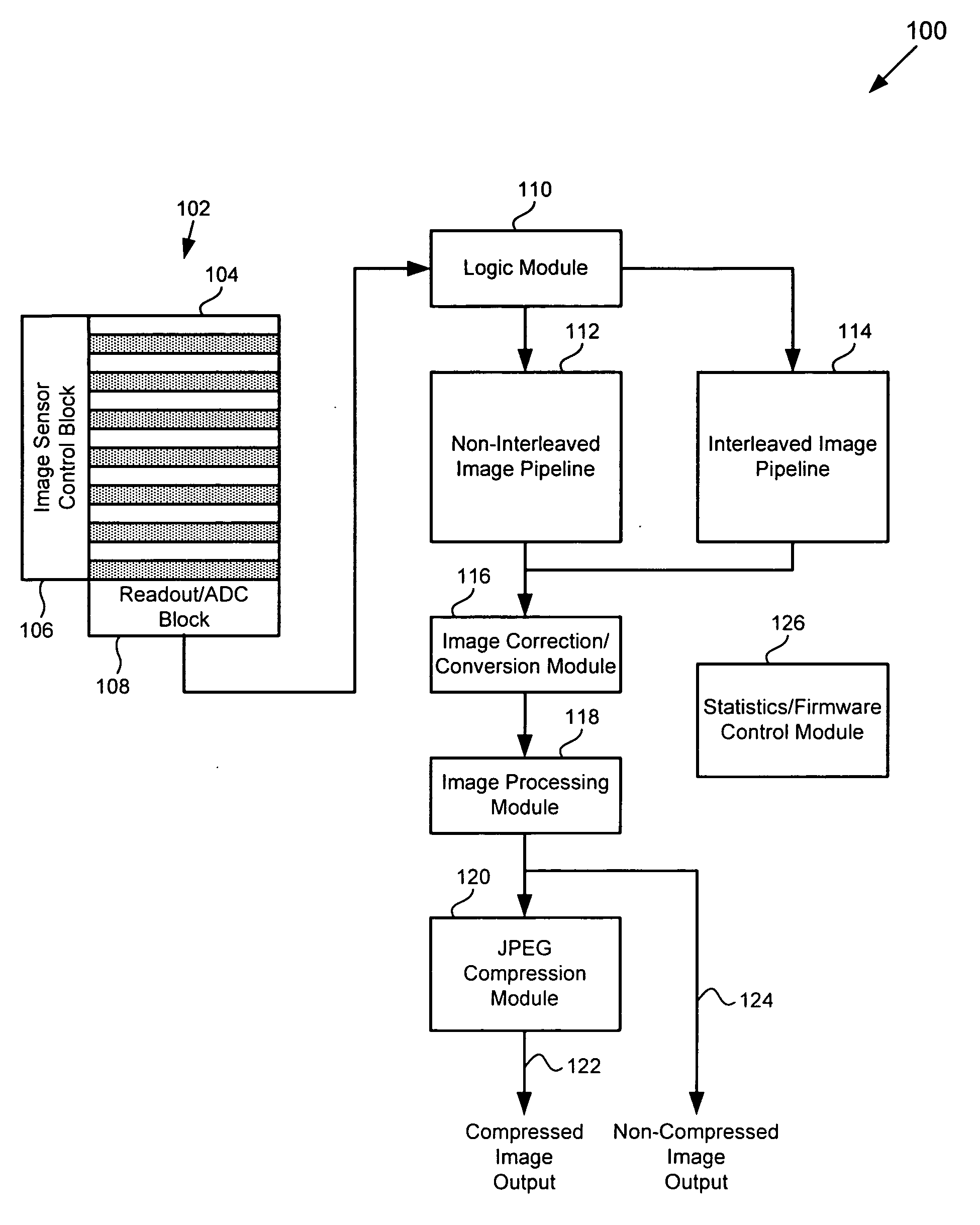
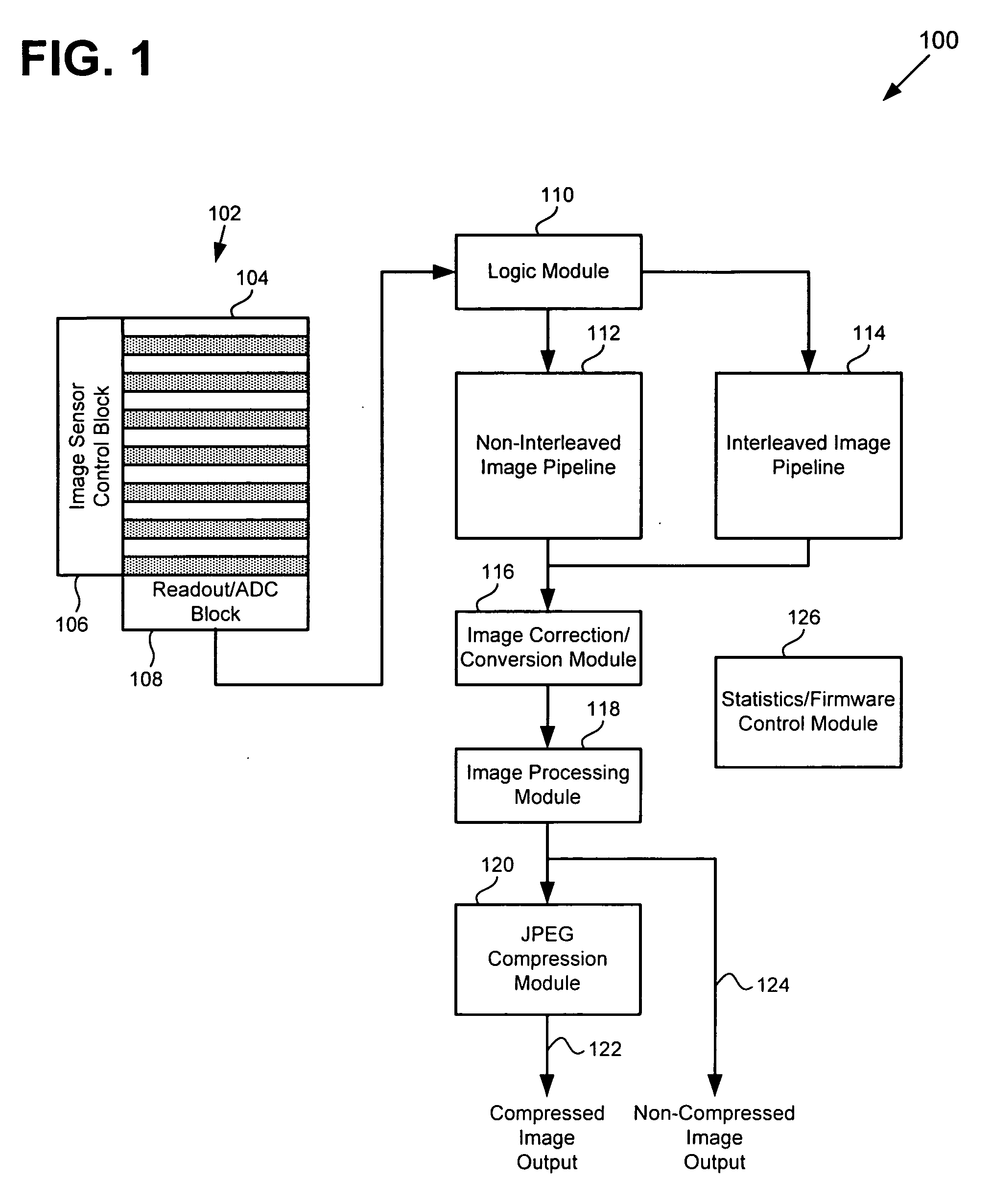
CMOS imager system with interleaved readout for providing an image with increased dynamic range
ActiveUS20070285526A1Improve dynamic rangeReduce Motion ArtifactsTelevision system detailsTelevision system scanning detailsCMOSPattern generation
There is provided a CMOS imager system for providing a viewable image having increased dynamic range including an image sensor including a number of sets of pixels. Each set of pixels is configured to receive one of a number of exposures and to generate image data corresponding to the received exposure in the interleaved mode. The image sensor is configured to operate in either an interleaved mode or a non-interleaved mode and to output the image data generated by each set of pixels as a frame of interleaved image data in the interleaved mode. The imager system further includes an interleaved image pipeline in communication with the image sensor, where the interleaved image pipeline is configured to receive the interleaved image data from the image sensor, combine the image data generated by each set of pixels corresponding to one of the exposures to form the viewable image.
Owner:IMPERIUM IP HLDG +1
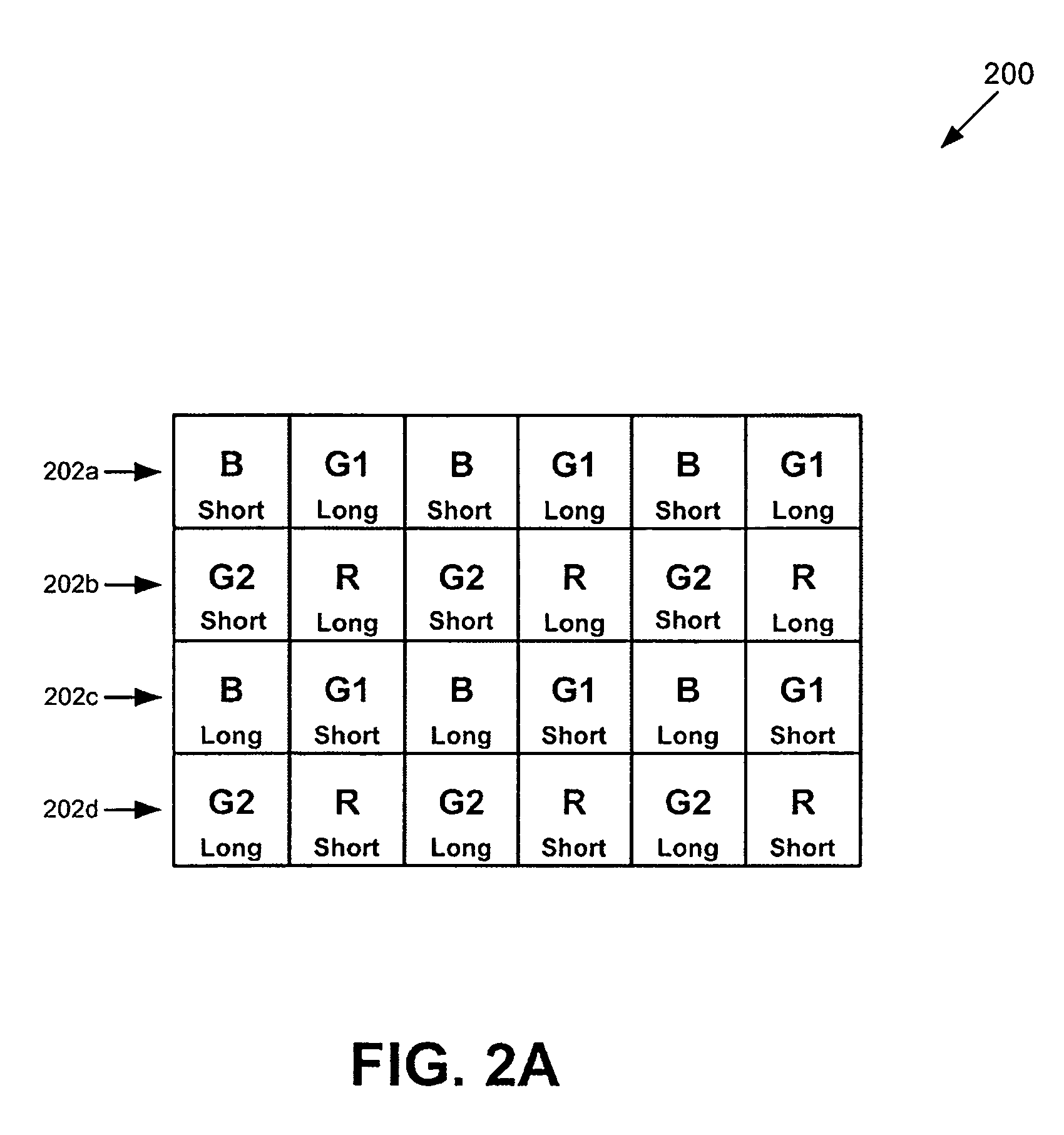
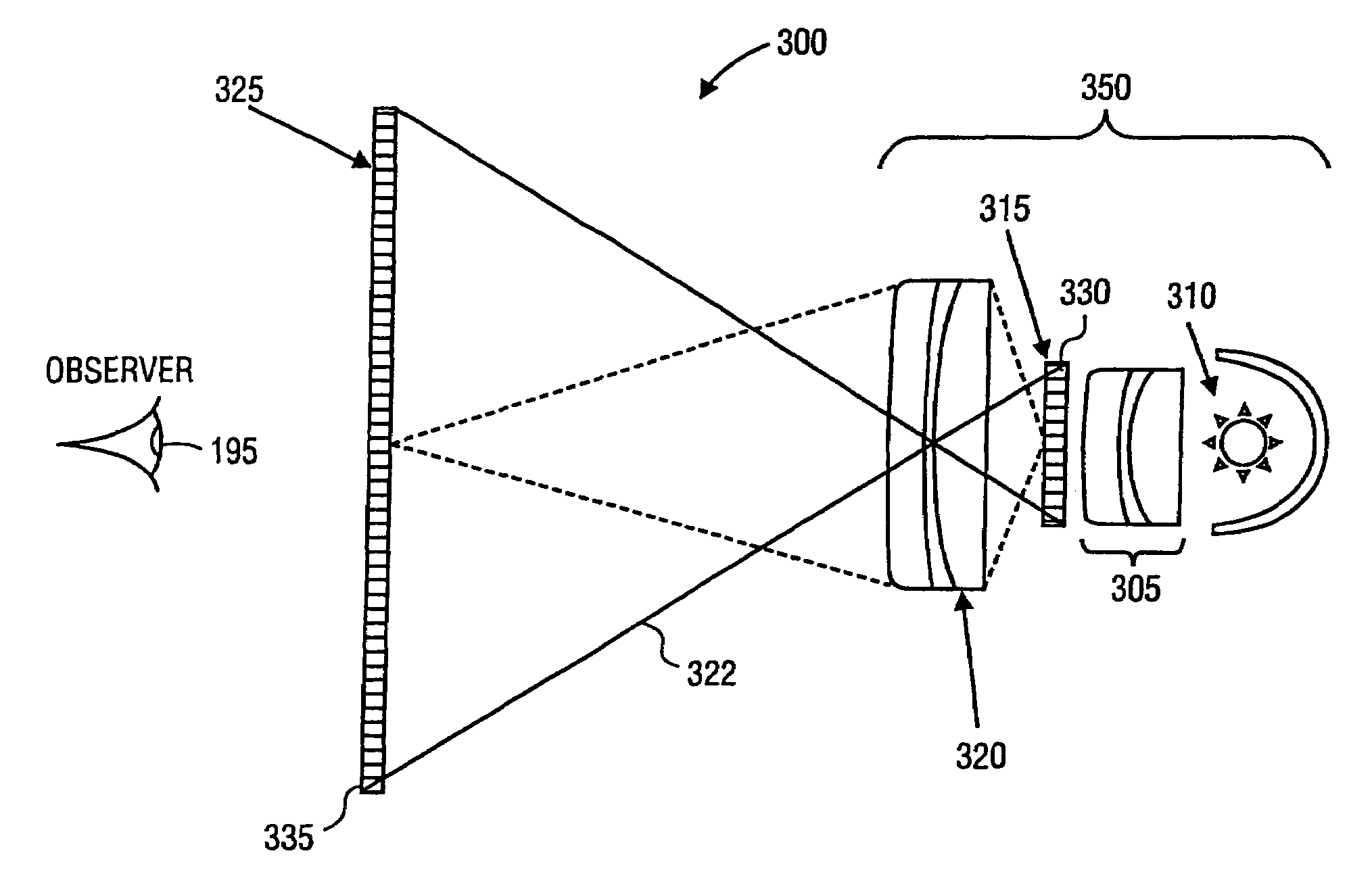
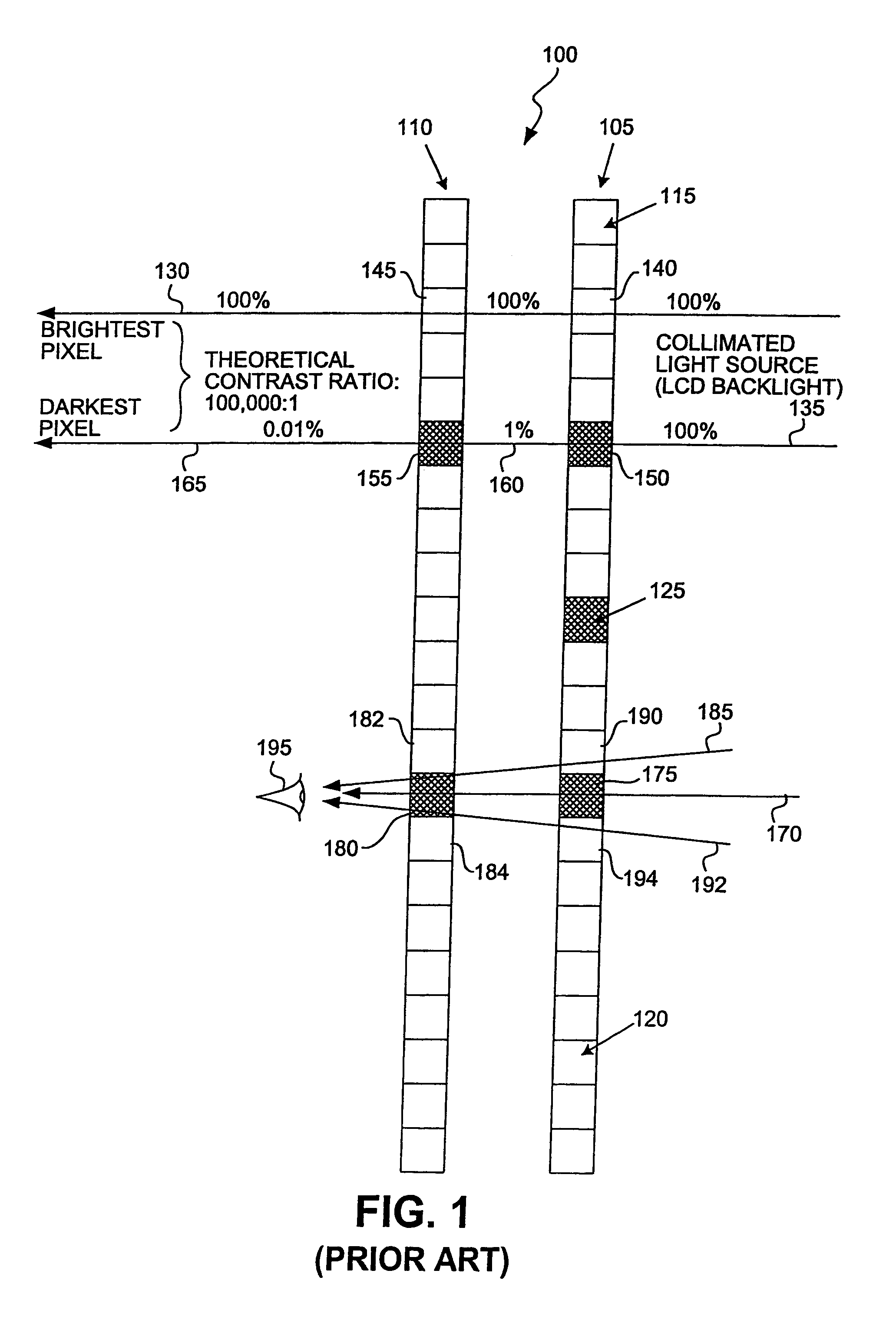
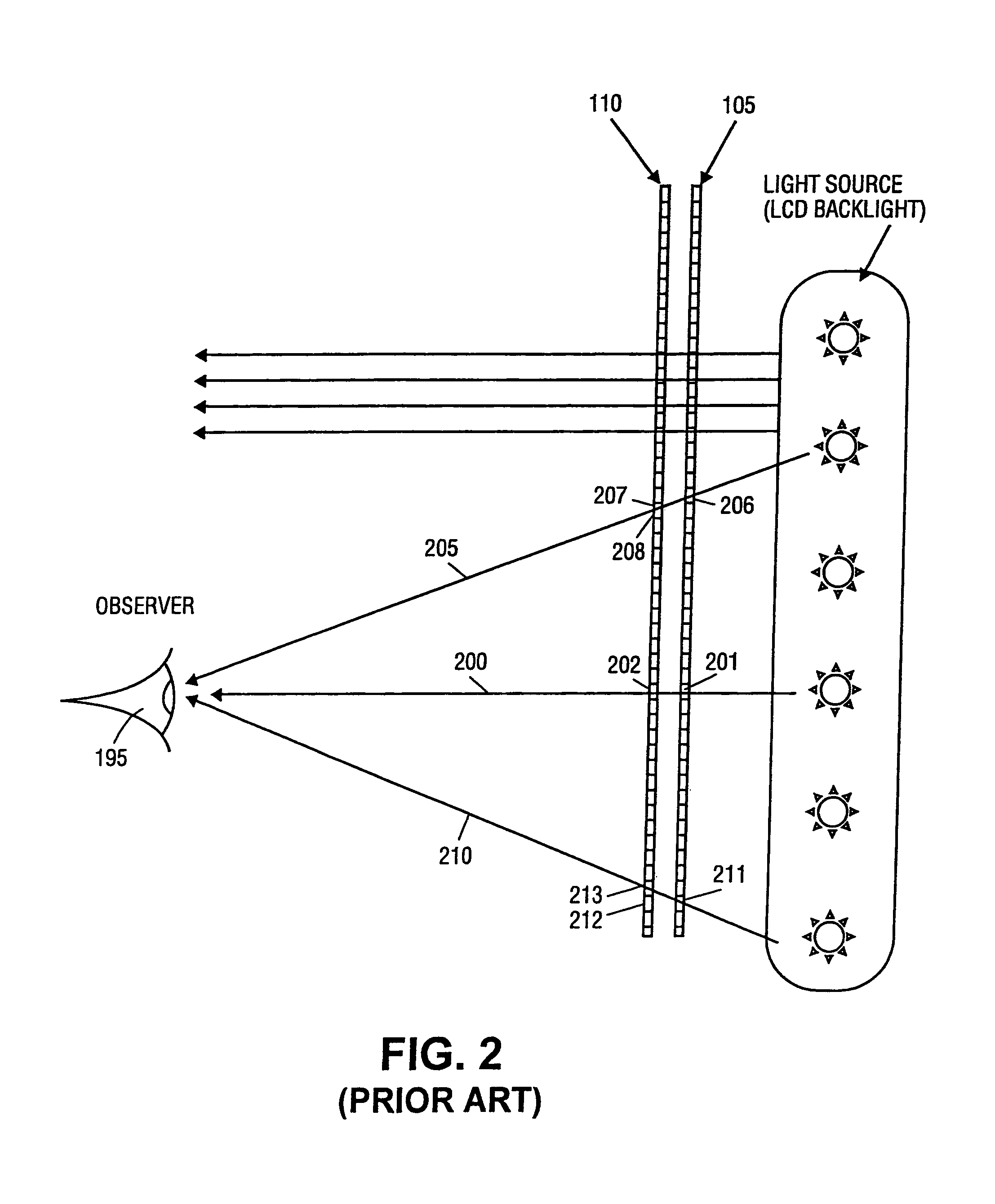
High Dynamic Range Displays Using Filterless LCD(s) For Increasing Contrast And Resolution
ActiveUS20110279749A1Increase contrastImprove black levelCathode-ray tube indicatorsSteroscopic systemsFiltrationDisplay device
A display provides increased contrast and resolution via first LCD panel energized to generate an image and a second LCD panel configured to increase contrast of the image. The second panel is an LCD panel without color filters and is configured to increase contrast by decreasing black levels of dark portions of images (making them blacker or darker) using polarization rotation and filtration. Preferably, the second LCD panel is of higher resolution than the first LCD panel. The panels may be directly illuminated or edge lit, and may be globally or locally dimmed monochrome or multi primary lights that may also include individual control of color intensities for each image or frame displayed. The panels may be placed in any order, but preferably are arranged such that active layers in each panel are as close together as possible. Brightness is maintained by the combination of reusing polarization between the panels and by not going through more than one set of color filters. Improved contrast is a result of using multiple light modulators in series.
Owner:DOLBY LAB LICENSING CORP
Multiple exposure high dynamic range image capture
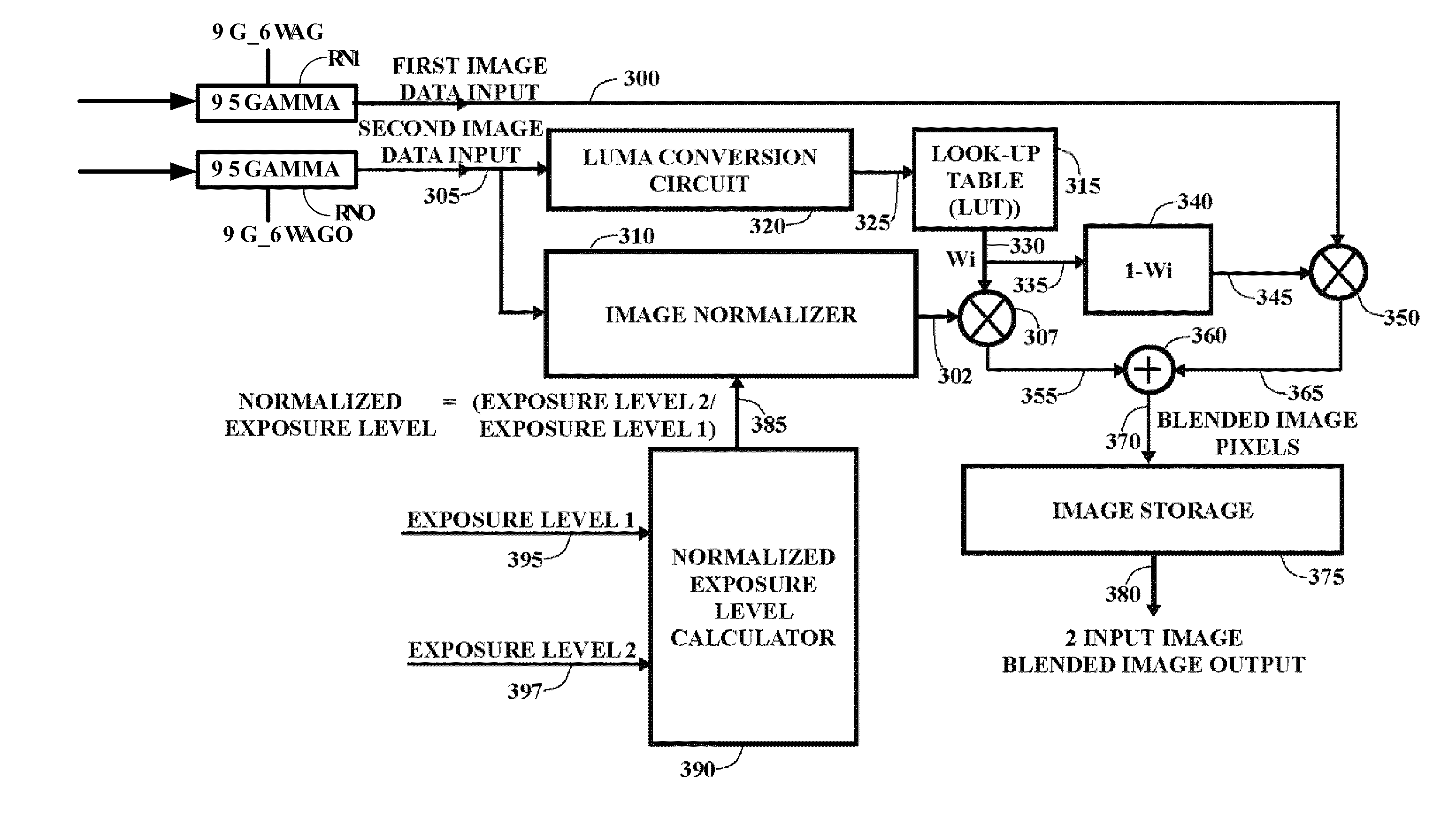
ActiveUS20110254976A1Increase influenceIncrease valueTelevision system detailsColor signal processing circuitsDisplay deviceExposure level
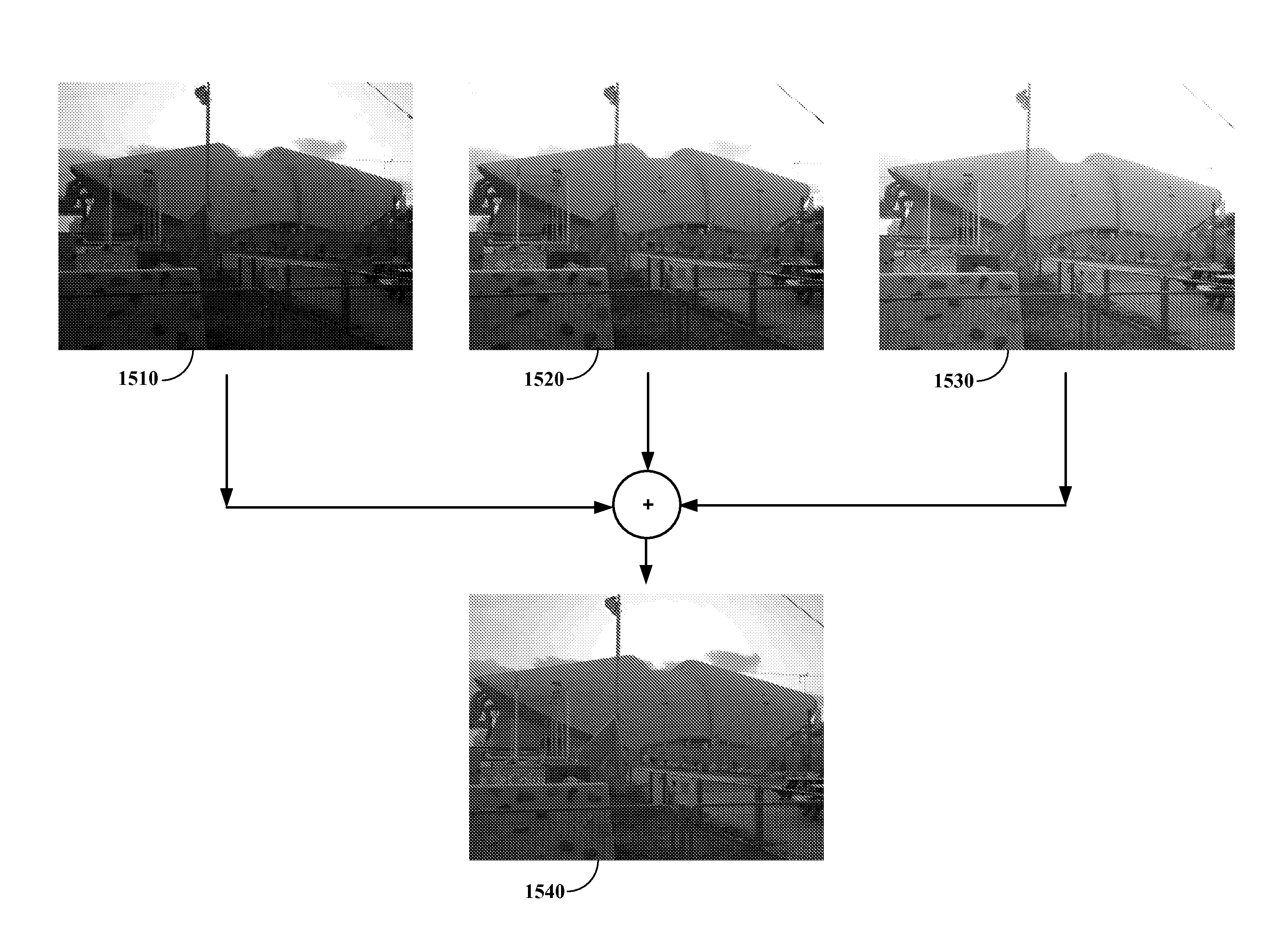
Techniques for creating a High Dynamic Range (HDR) image within a consumer grade digital camera from a series of images of a scene captured at different exposure levels, and displaying the HDR image on the camera's built-in display are provided. The approach employs mixing images of the series to incorporate both scene shadow and highlight details, and the removing of “ghost” image artifacts appearing in the mixed HDR image resulting from movement in the scene over the time the series images are captured. The low computational resource utilization of the image mixing and ghost removal processing operations, along with the ability to commence image mixing and ghost removal prior to the acquisition of all series images, can significantly reduce the time required to generate and display a tone mapped HDR image.
Owner:QUALCOMM INC
Phased array metamaterial antenna system
ActiveUS20050225492A1Low Sidelobe PerformanceReduce sidelobeRadiating elements structural formsWaveguidesSolid substratePhased array
An efficient, low-loss, low sidelobe, high dynamic range phased-array radar antenna system is disclosed that uses metamaterials, which are manmade composite materials having a negative index of refraction, to create a biconcave lens architecture (instead of the aforementioned biconvex lens) for focusing the microwaves transmitted by the antenna. Accordingly, the sidelobes of the antenna are reduced. Attenuation across microstrip transmission lines may be reduced by using low loss transmission lines that are suspended above a ground plane a predetermined distance in a way such they are not in contact with a solid substrate. By suspending the microstrip transmission lines in this manner, dielectric signal loss is reduced significantly, thus resulting in a less-attenuated signal at its destination.
Owner:LUCENT TECH INC
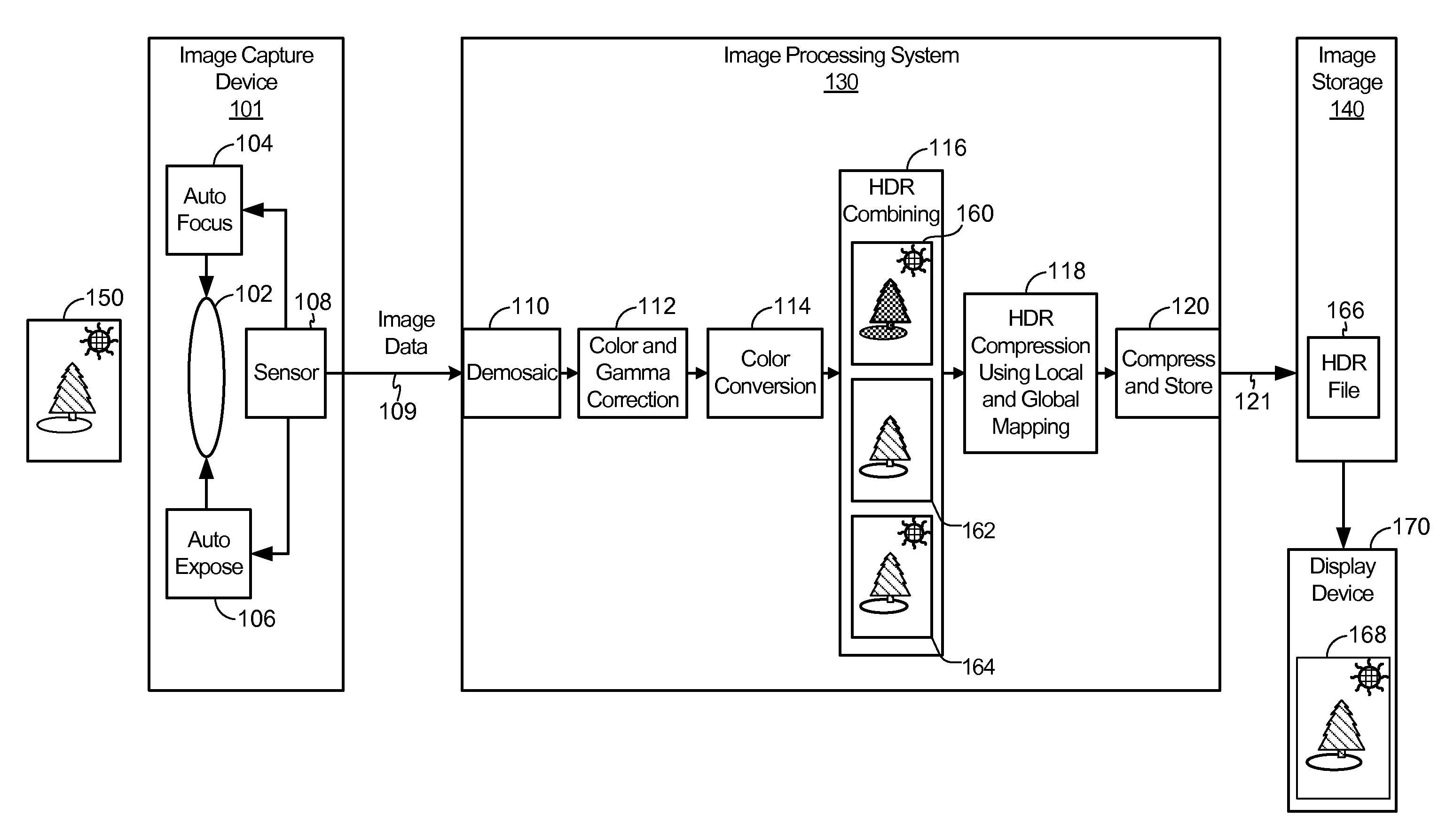
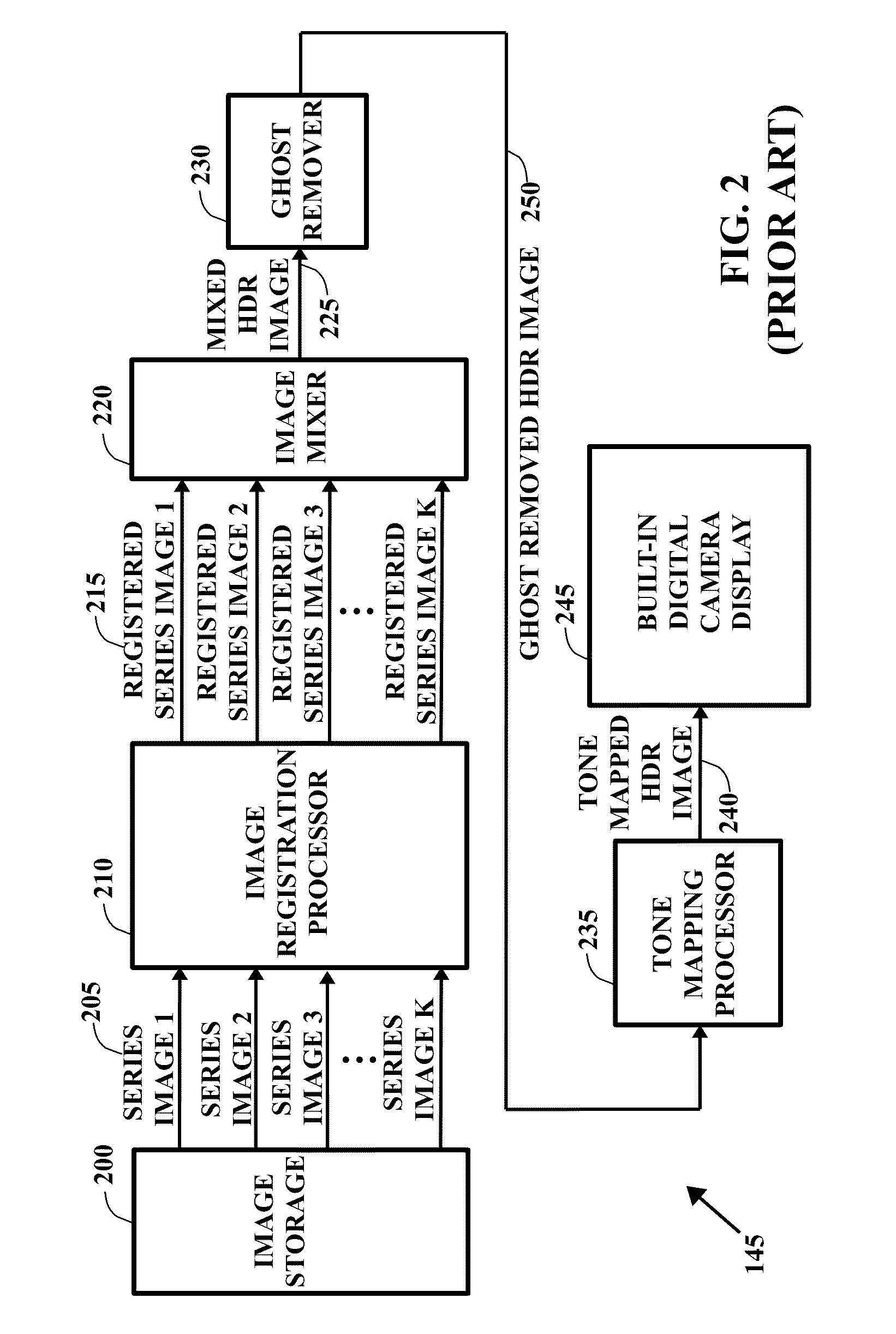
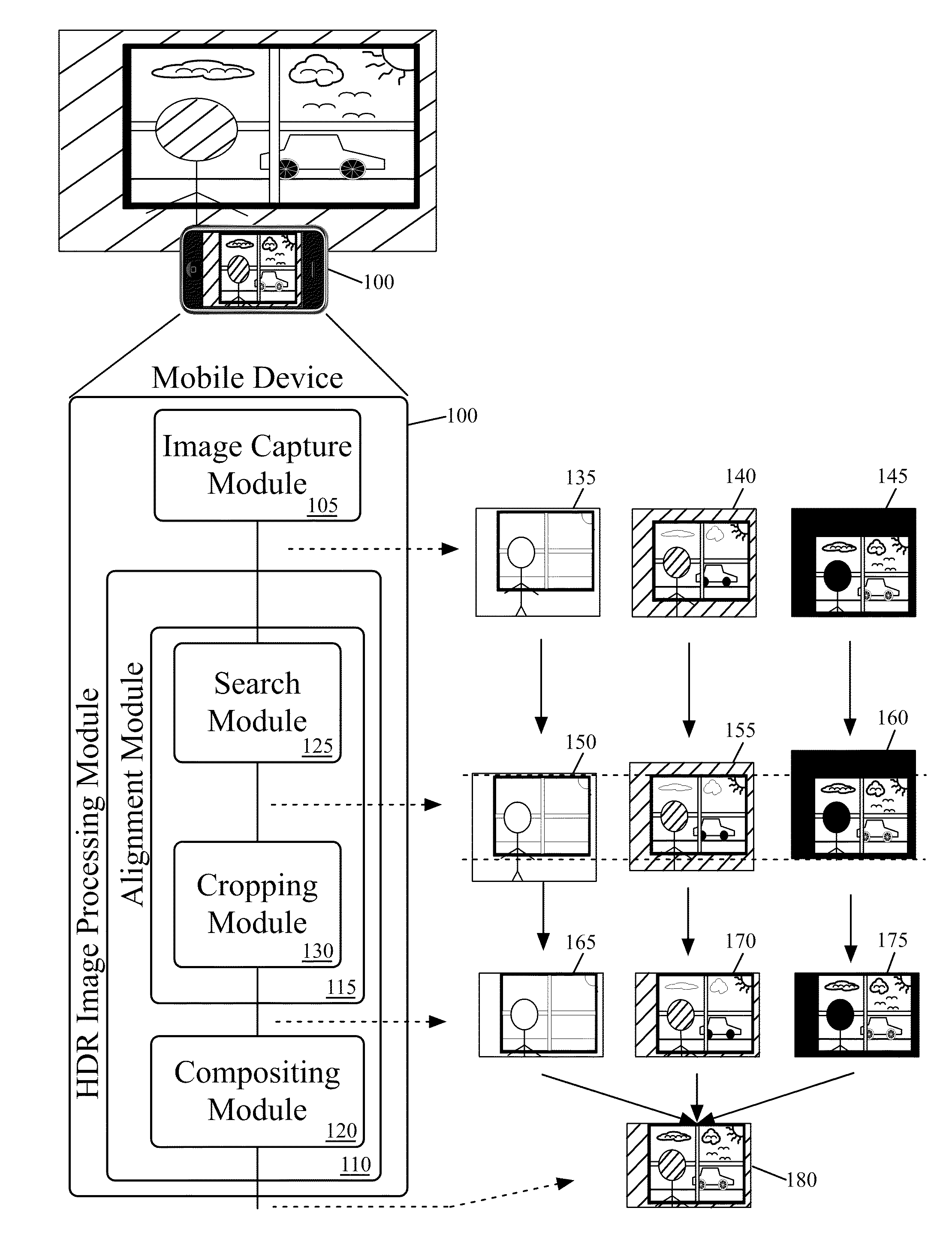
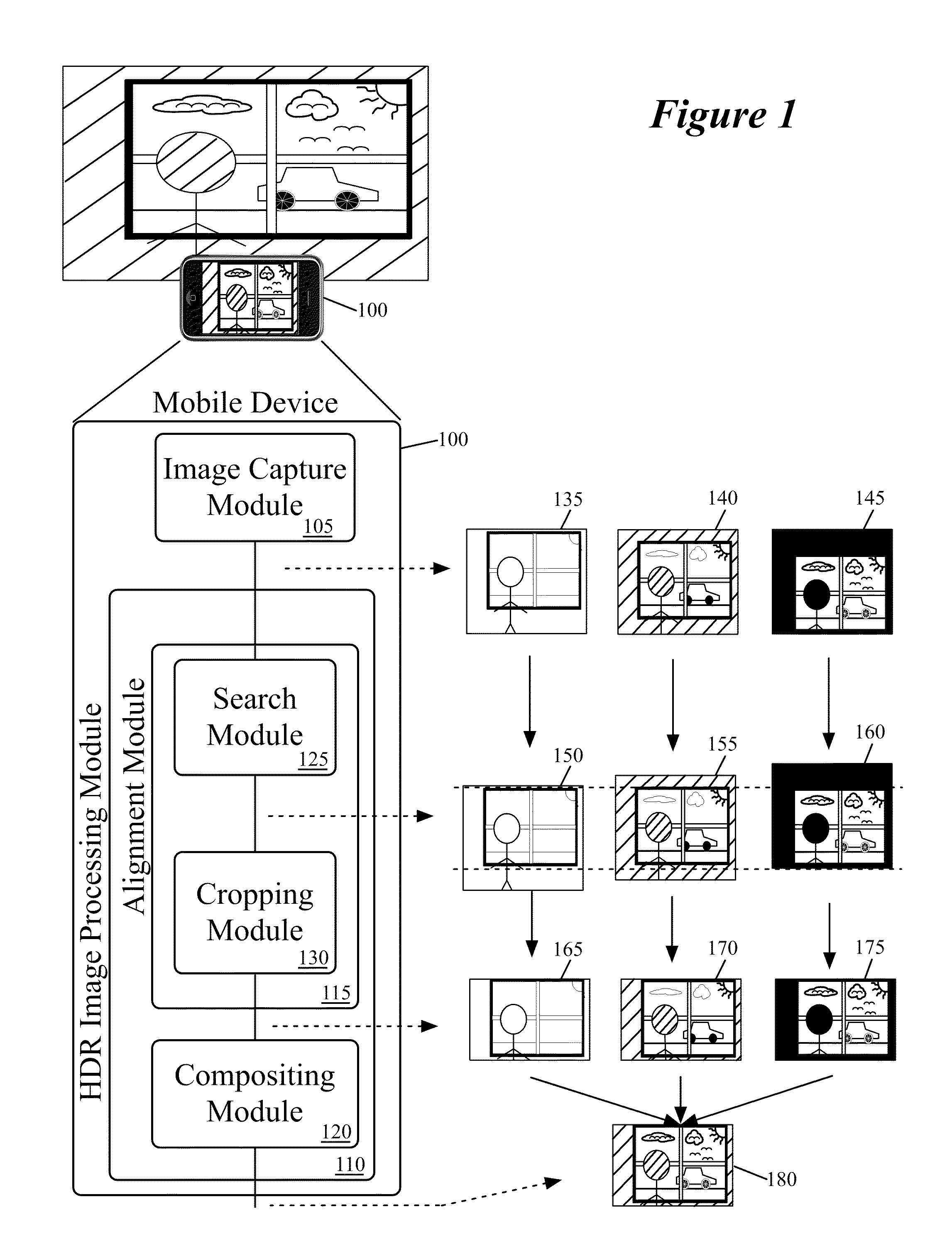
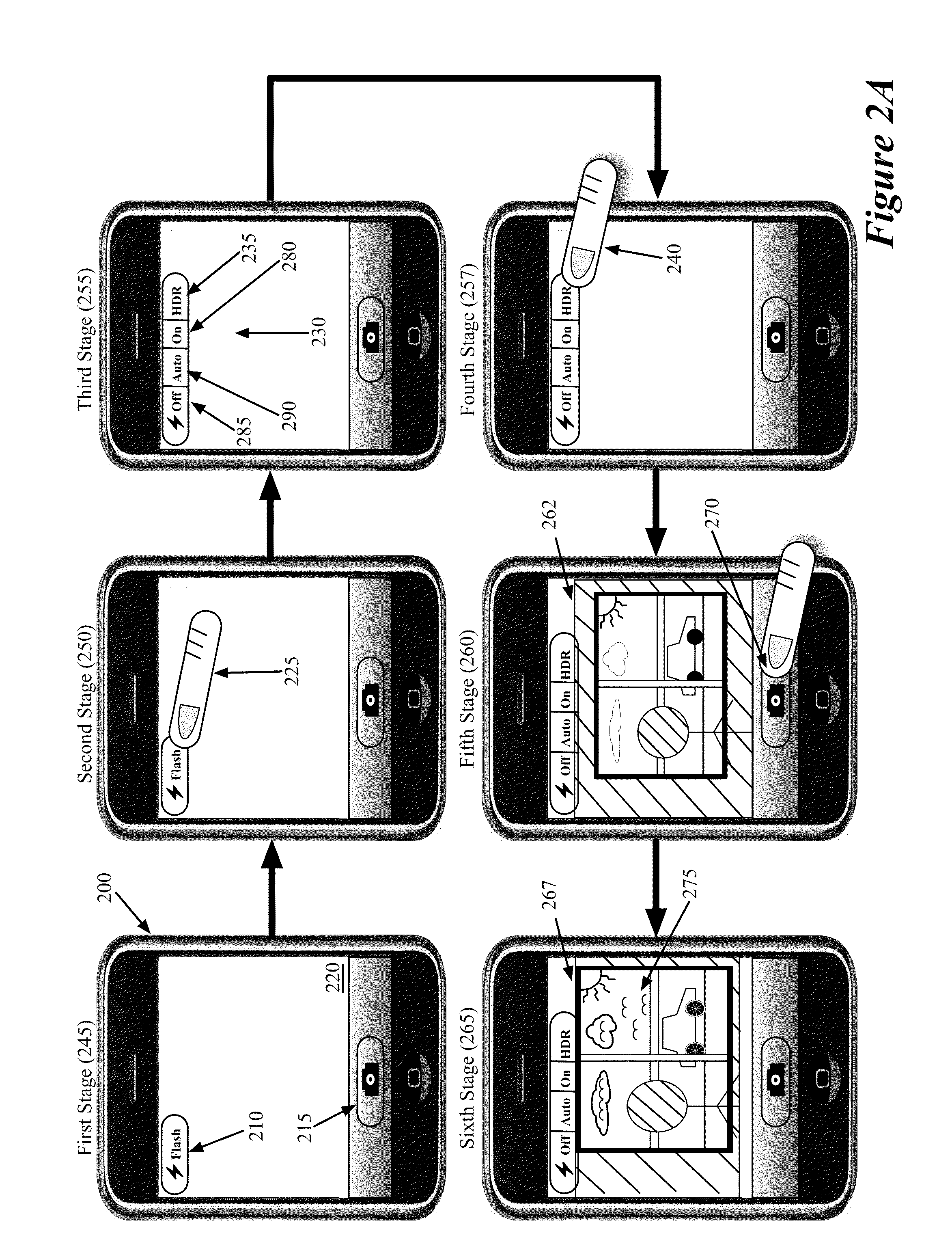
Capturing and Rendering High Dynamic Range Images
ActiveUS20120002082A1Speed up speed upQuick snapImage enhancementTelevision system detailsImaging processingComputer graphics (images)
Some embodiments of the invention provide a mobile device that captures and produces images with high dynamic ranges. To capture and produce a high dynamic range image, the mobile device of some embodiments includes novel image capture and processing modules. In some embodiments, the mobile device produces a high dynamic range (HDR) image by (1) having its image capture module rapidly capture a succession of images at different image exposure durations, and (2) having its image processing module composite these images to produce the HDR image.
Owner:APPLE INC
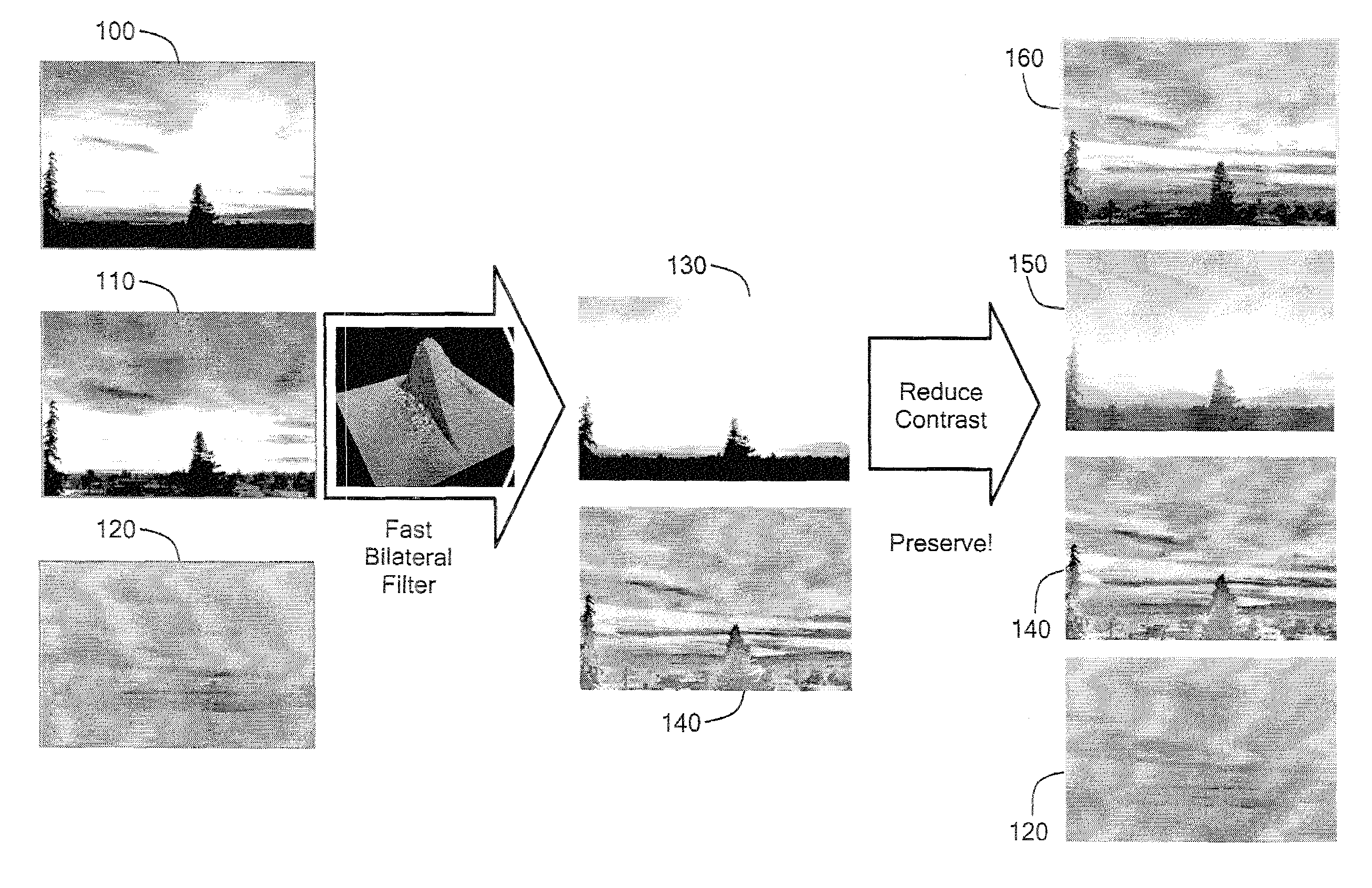
Method of performing fast bilateral filtering and using the same for the display of high-dynamic-range images
ActiveUS7146059B1Reduce image contrastKeep detailsImage enhancementImage analysisNonlinear filterDecomposition
A method of performing bilateral filtering and using the method for displaying high-dynamic-range images is presented. The method reduces the contrast of the image while preserving detail of the image. The presently disclosed method incorporates a two-scale decomposition of the image into a base layer encoding large-scale variations, and a detail layer. The base layer has its contrast reduced, thereby preserving detail. The base layer is obtained using an edge-preserving bilateral filter. The bilateral filter is a non-linear filter, where the weight of each pixel is computed using a Gaussian in the spatial domain multiplied by an influence function in the intensity domain that decreases the weight of pixels with large intensity differences. The bilateral filtering is accelerated by using a piecewise-linear approximation in the intensity domain and appropriate subsampling.
Owner:MASSACHUSETTS INST OF TECH
Method and system for combining multiple exposure images having scene and camera motion
ActiveUS7239805B2Quality improvementImprove signal-to-noise ratioImage enhancementTelevision system detailsSignal-to-noise ratio (imaging)Radiance
A panoramic high-dynamic range (HDR) image method and system of combining multiple images having different exposures and at least partial spatial overlap wherein each of the images may have scene motion, camera motion, or both. The major part of the panoramic HDR image method and system is a two-pass optimization-based approach that first defines the position of the objects in a scene and then fills in the dynamic range when possible and consistent. Data costs are created to encourage radiance values that are both consistent with object placement (defined by the first pass) and of a higher signal-to-noise ratio. Seam costs are used to ensure that transitions occur in regions of consistent radiances. The result is a high-quality panoramic HDR image having the full available spatial extent of the scene along with the full available exposure range.
Owner:MICROSOFT TECH LICENSING LLC
Multiple exposure high dynamic range image capture
ActiveUS20110211732A1Increase influenceIncrease valueTelevision system detailsColor signal processing circuitsDisplay deviceImage Artifact
Techniques for creating a High Dynamic Range (HDR) image within a consumer grade digital camera from a series of images of a scene captured at different exposure levels, and displaying the HDR image on the camera's built-in display are provided. The approach employs mixing images of the series to incorporate both scene shadow and highlight details, and the removing of “ghost” image artifacts appearing in the mixed HDR image resulting from movement in the scene over the time the series images are captured. The low computational resource utilization of the image mixing and ghost removal processing operations, along with the ability to commence image mixing and ghost removal prior to the acquisition of all series images, can significantly reduce the time required to generate and display a tone mapped HDR image.
Owner:QUALCOMM INC
Method and apparatus for acquiring HDR flash images
InactiveUS20070025717A1Minimize the numberQuality improvementTelevision system detailsImage enhancementComputer visionComputer science
A method generates a high dynamic range image by first acquiring a set of images of a scene illuminated by different lighting conditions. The set of images are then combined to generate a high dynamic range image.
Owner:MITSUBISHI ELECTRIC RES LAB INC
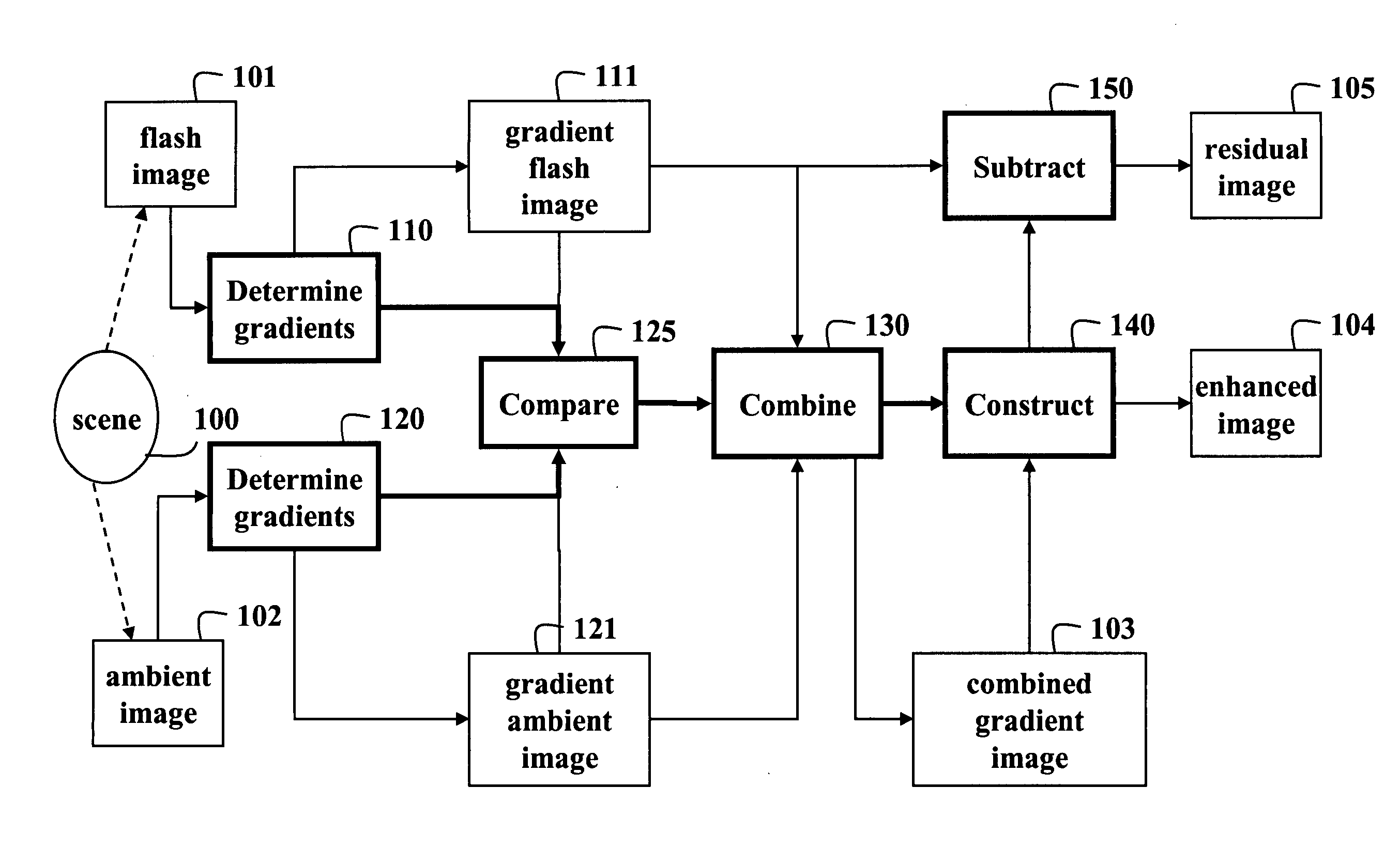
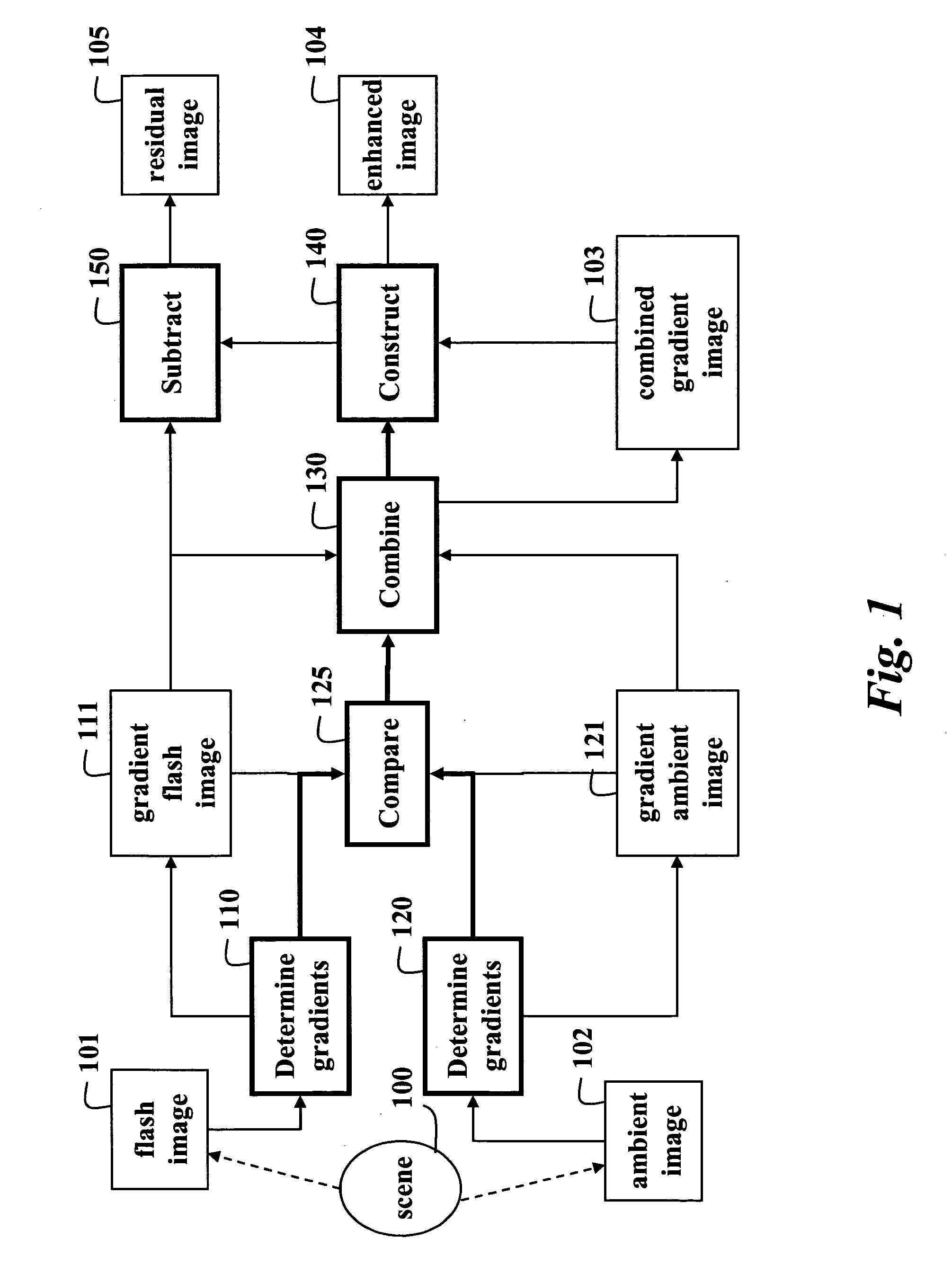
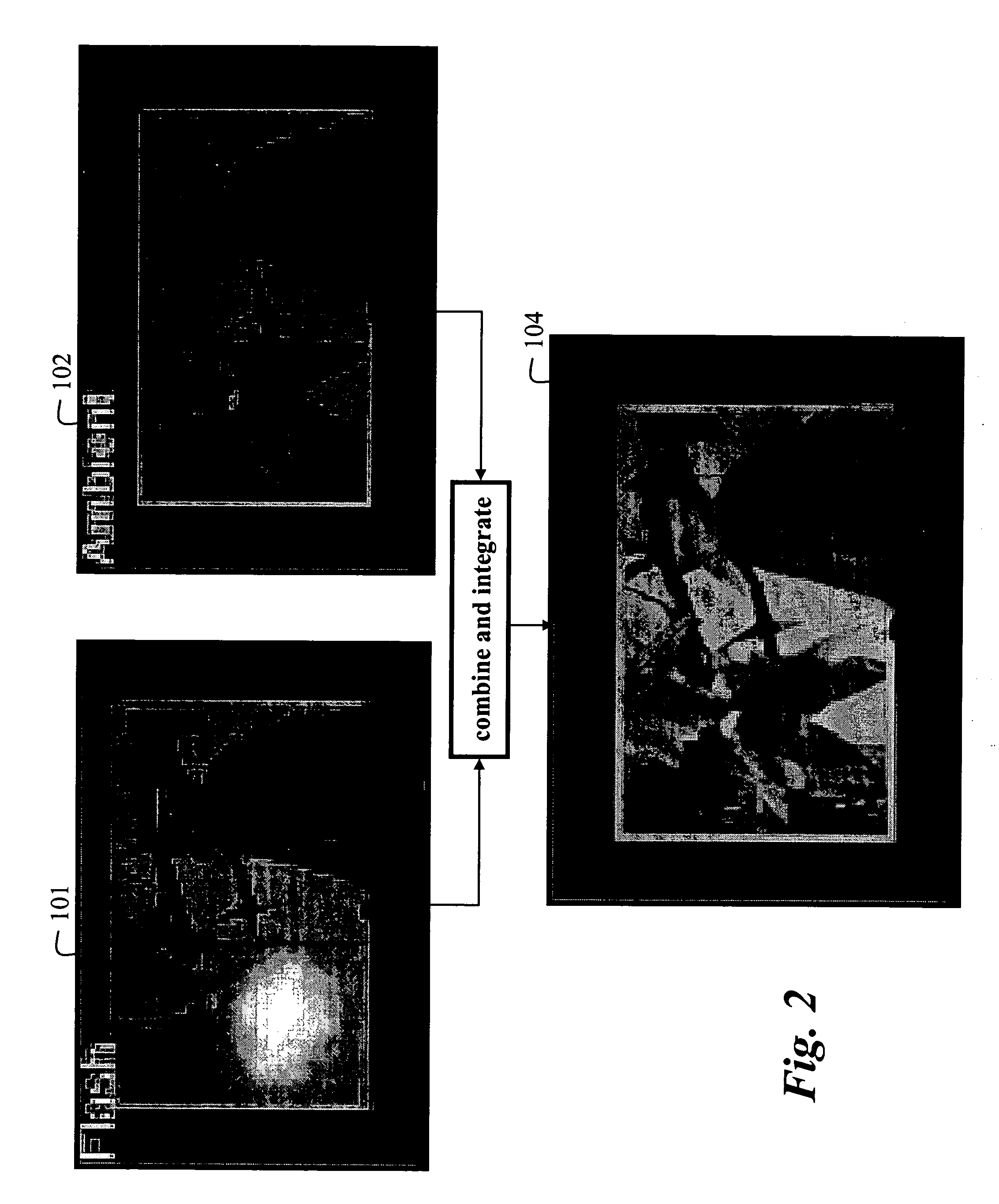
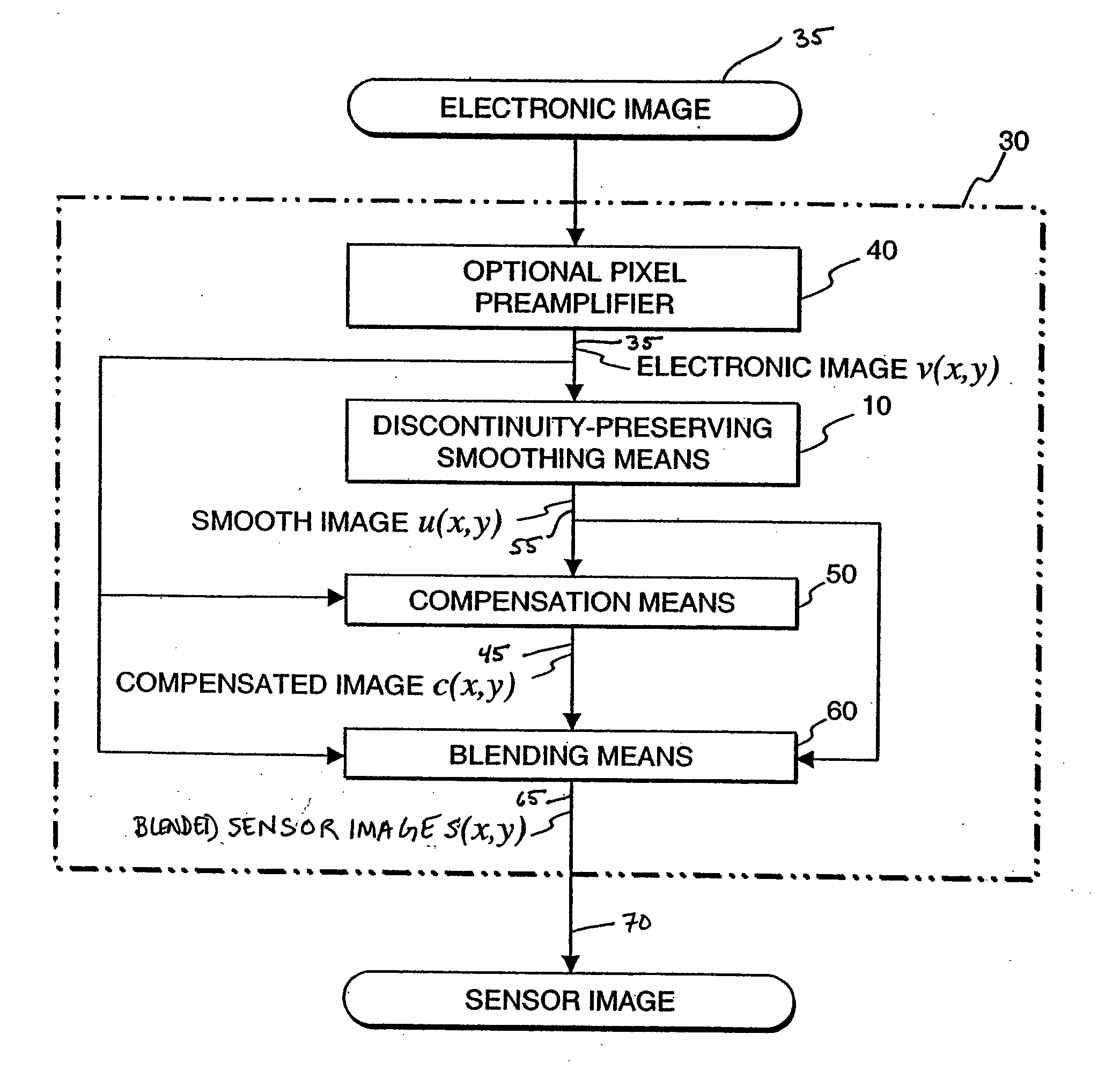
Method for improving digital images and an image sensor for sensing the same
ActiveUS20050089239A1Avoid smoothImage enhancementImage analysisImaging processingDynamic range compression
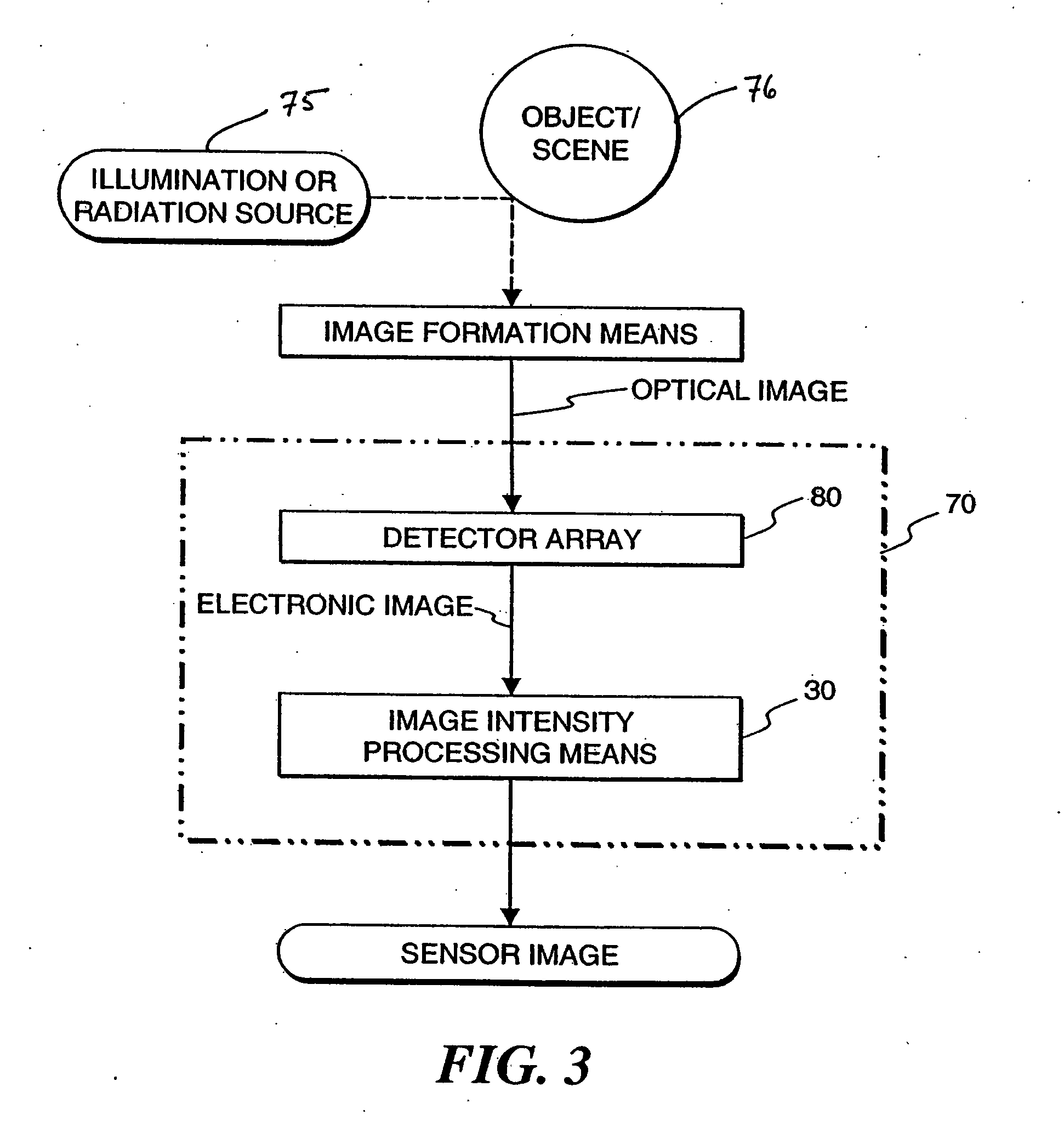
The present invention provides an image processing method. In one embodiment, the method provides discontinuity-preserving image smoothing and segmentation, noise reduction, reduction of image variations particularly those variations caused by illumination conditions, exposure compensation, and dynamic range compression. The present invention also provides an electronic image sensor that is able to detect high dynamic range optical images and produce electronic images with reduced dynamic range.
Owner:BRAJOVIC VLADIMIR
High dynamic range & depth of field depth camera
ActiveUS20130201288A1Add depthImprove dynamic rangeElectromagnetic wave reradiationSteroscopic systemsObject motionFrame time
In order to maximize the dynamic range and depth of field for a depth camera used in a time of flight system, the light source is modulated at a plurality of different frequencies, a plurality of different peak optical powers, a plurality of integration subperiods, a plurality of lens foci, aperture and zoom settings during each camera frame time. The different sets of settings effectively create subrange volumes of interest within a larger aggregate volume of interest, each having their own frequency, peak optical power, lens aperture, lens zoom and lens focus products consistent with the distance, object reflectivity, object motion, field of view, etc. requirements of various ranging applications.
Owner:LUMENTUM OPERATIONS LLC
Method and system to increase dynamic range of time-of-flight (TOF) and/or imaging sensors
InactiveUS7379100B2Television system detailsColor television detailsPhotovoltaic detectorsPhotodetector
Owner:MICROSOFT TECH LICENSING LLC
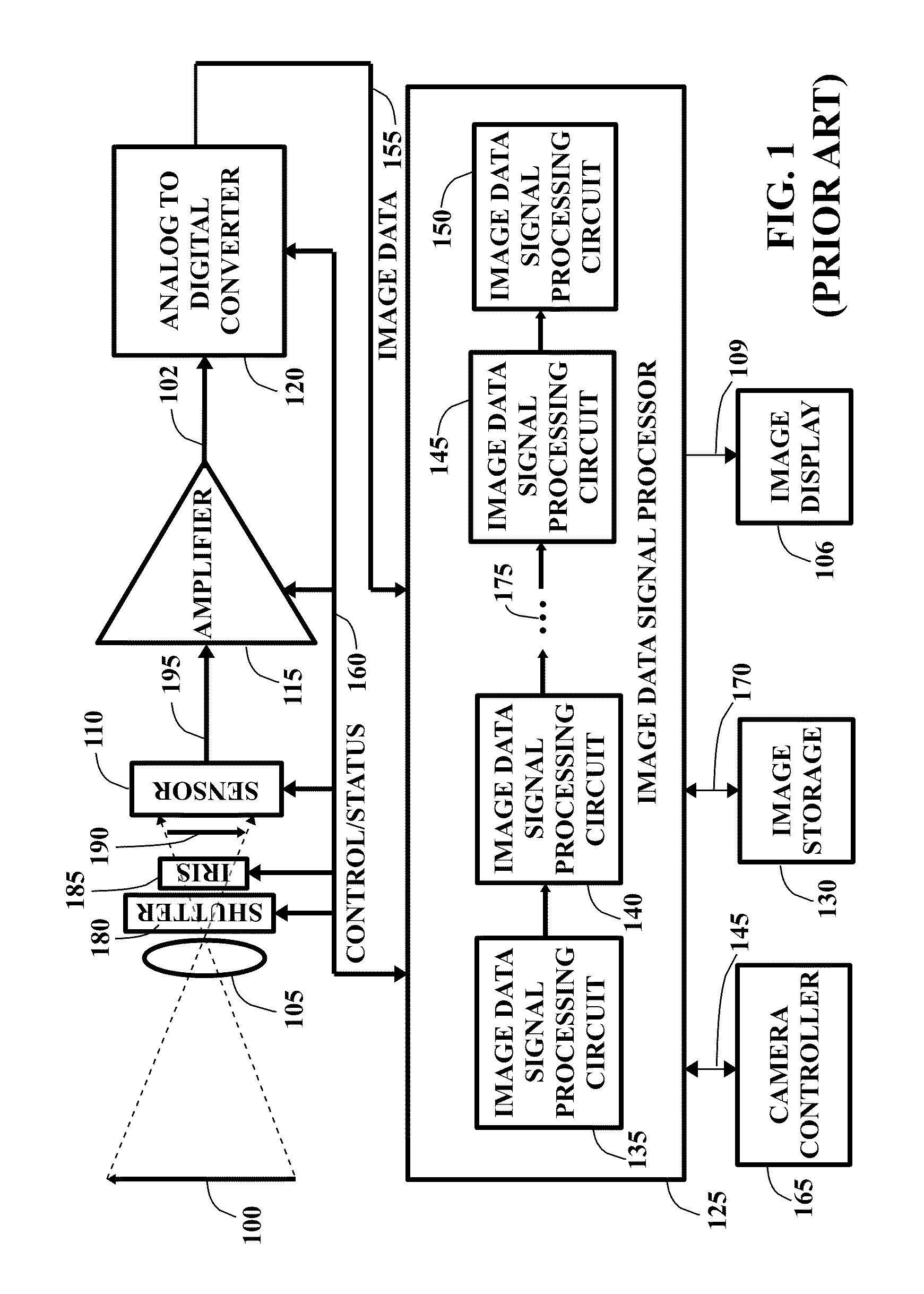
Image pickup apparatus
InactiveUS7098946B1Solving Lag ProblemsEasy to operateTelevision system detailsColor television detailsImage signalWide dynamic range
An image pickup apparatus having function for synthesizing image signals corresponding to a plurality of frames of different exposure amounts to generate wide dynamic range, synthesized image is provided with: at least two control means among a taking control means based on a normal taking mode, a taking control means based on a forced wide dynamic range taking mode, and a taking control means based on an automatic wide dynamic range taking mode for selectively generating wide dynamic range, synthesized image automatically on the basis of object information or information set for the image taking; and means for selectively setting one image taking mode out of the taking modes respectively corresponding to the two control means. It is thereby possible to take image by selecting one image taking mode from at least two taking modes among the normal taking mode, the forced wide dynamic range taking mode, and the automatic wide dynamic range taking mode.
Owner:OLYMPUS CORP
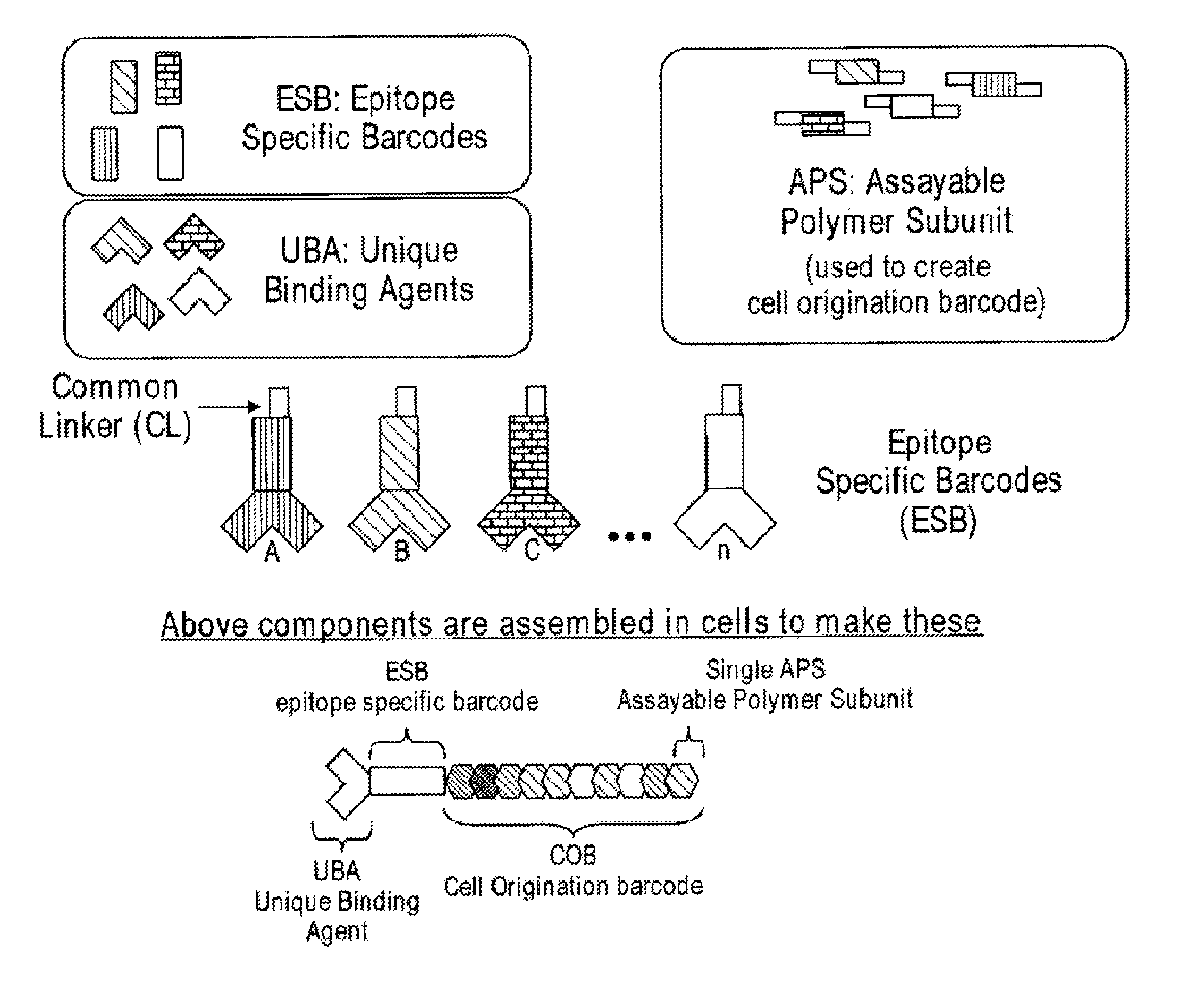
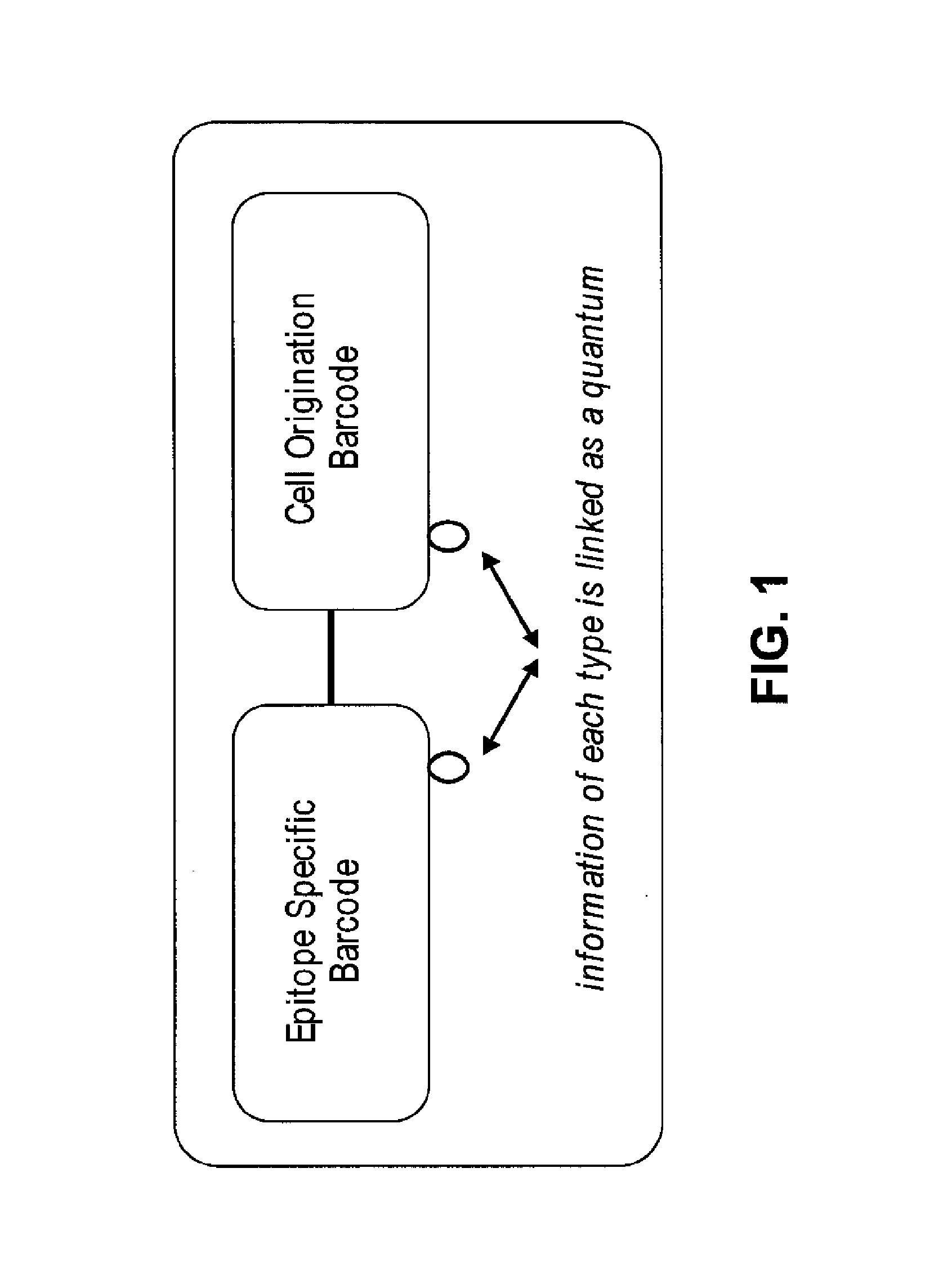
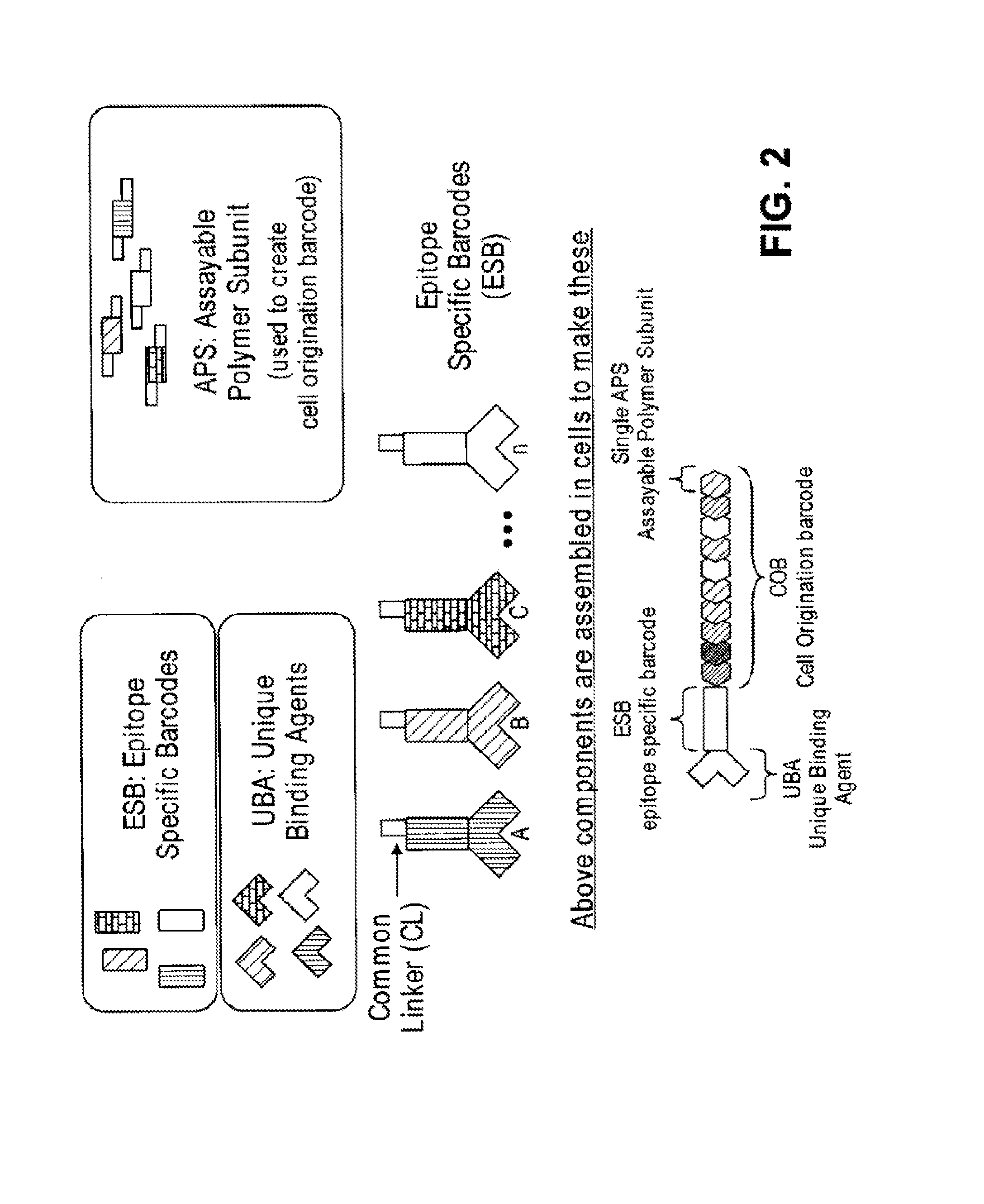
Increasing dynamic range for identifying multiple epitopes in cells
ActiveUS20150329852A1Nucleotide librariesMicrobiological testing/measurementEpitopeMolecular biology
Owner:ROCHE SEQUENCING SOLUTIONS INC
Dual-stage high-contrast electronic image display
InactiveUS7002533B2Lower ratioSimple and inexpensive methodTelevision system detailsColor television detailsDual stageSheet film
Electronic displays are provided which can reproduce image data with high contrast ratios and a gray scale range comparable to conventional X-ray film viewed on a light box. One such display includes a rear low-resolution LCD or DLP display which projects an image onto a high-resolution LCD display. In such embodiments, the mechanical and optical registration between the two displays is not critical. Therefore, modulation transfer function and distortion of the projection optics are not critical. Accordingly, the brightness of the inventive display can be maximized with high power lamps and high aperture projection optics. Because the display has a high dynamic range, the need for dynamic range compression algorithms is reduced.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
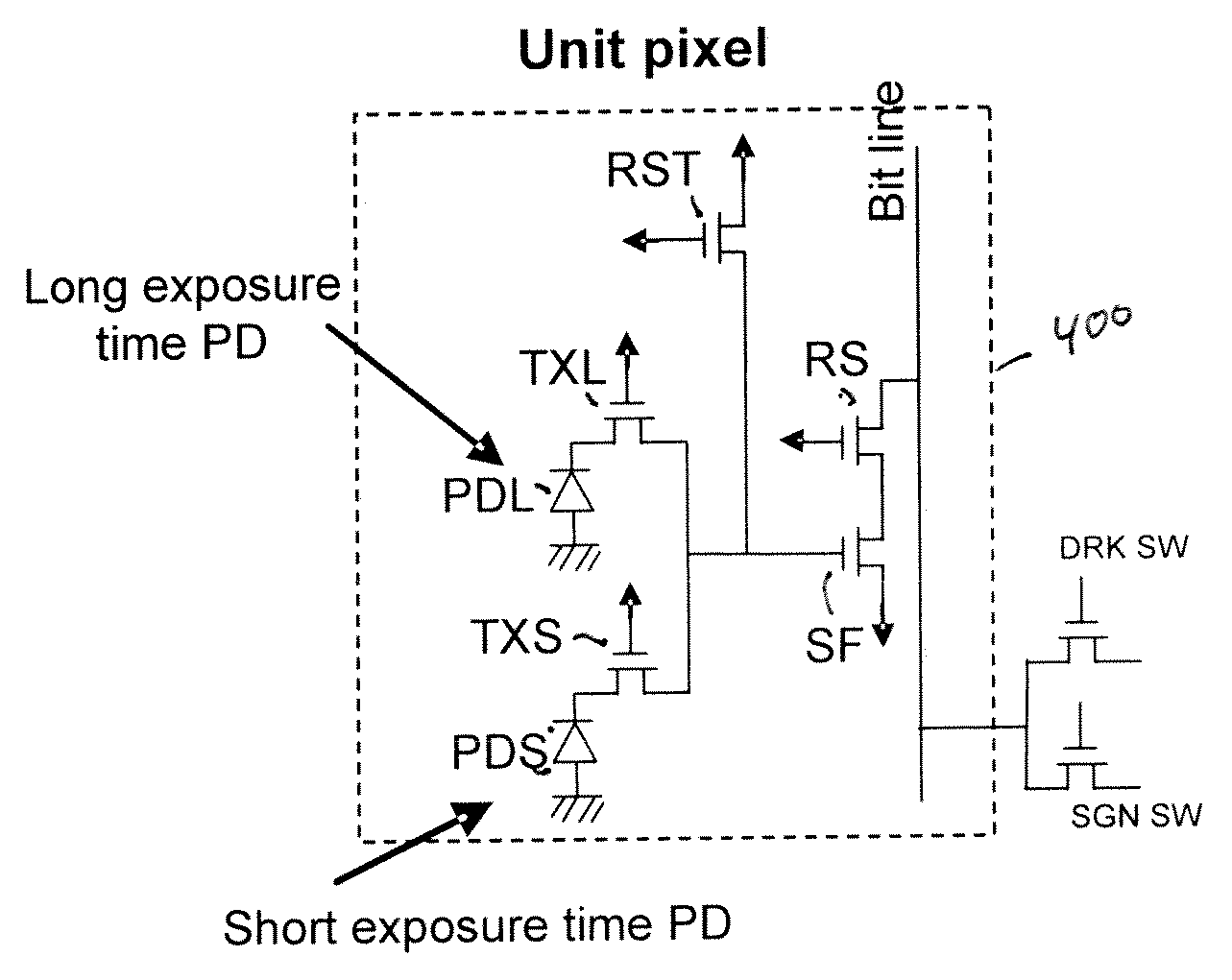
High dynamic range sensor with blooming drain
ActiveUS20090002528A1High sensitivityExtended imaging rangeTelevision system detailsColor signal processing circuitsEngineeringPhotodiode
An image sensor has at least two photodiodes in each unit pixel. A high dynamic range is achieved by selecting different exposure times for the photodiodes. Additionally, blooming is reduced. The readout timing cycle is chosen so that the short exposure time photodiodes act as drains for excess charge overflowing from the long exposure time photodiodes. To improve draining of excess charge, the arrangement of photodiodes may be further selected so that long exposure time photodiodes are neighbored along vertical and horizontal directions by short exposure time photodiodes. A micro-lens array may also be provided in which light is preferentially coupled to the long exposure time photodiodes to improve sensitivity.
Owner:OMNIVISION TECH INC
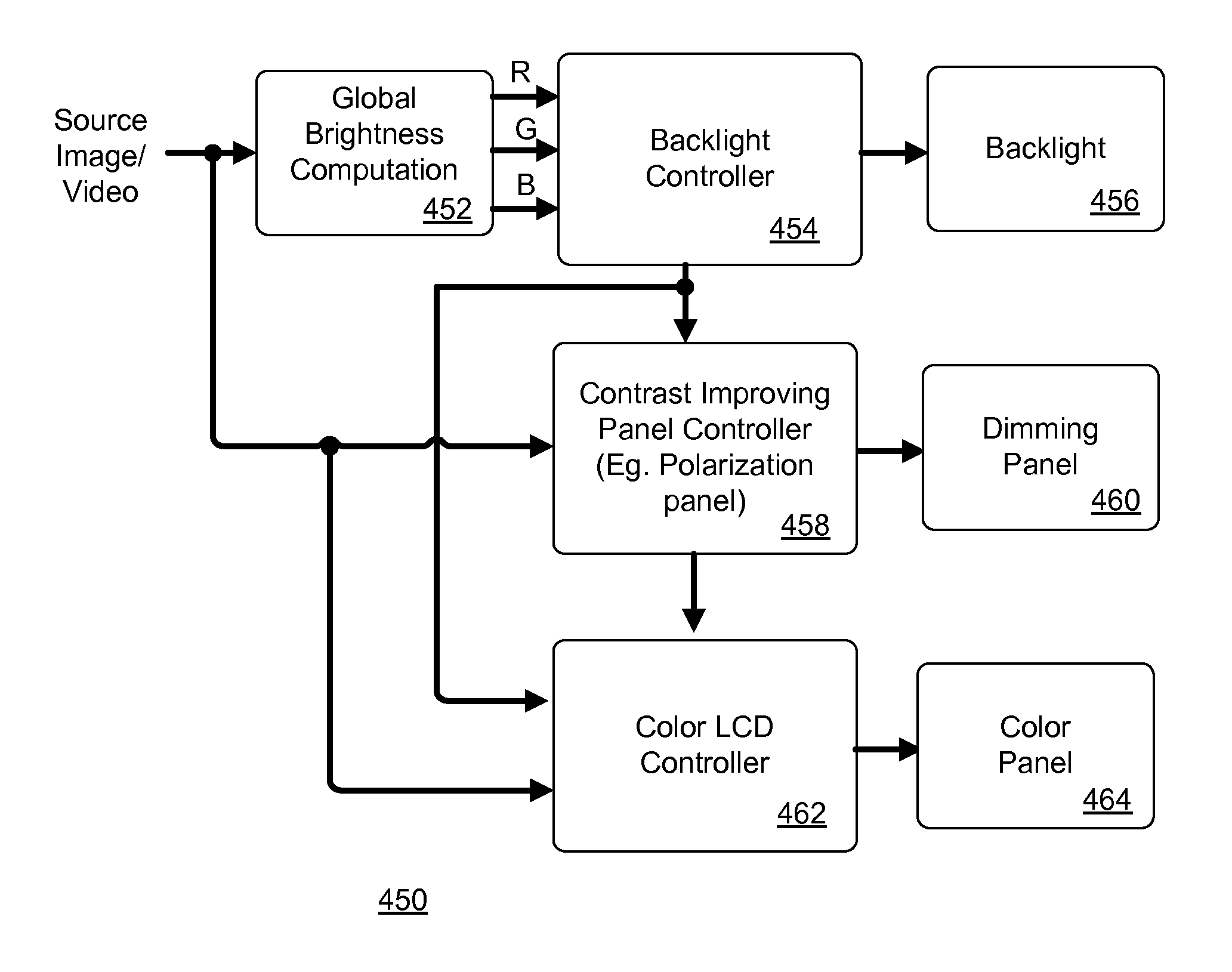
Systems and Methods for Accurately Representing High Contrast Imagery on High Dynamic Range Display Systems
ActiveUS20130106923A1Minimize number of Just Noticeable Difference (JND) stepEnhance the imageColor television detailsCathode-ray tube indicatorsParallaxImaging quality
A dual-panel display system is provided that comprises control modules and algorithms to select codeword pairs (CWs) to drive a first image-generating panel and a second contrast-improving panel. The first codewords is selected by considering some characteristics of the input image data (e.g., peak luminance) and to improve some image rendering metric (e.g., reduced parallax, reduced contouring, improved level precision). The first codeword may be selected to be the minimum first codeword within a set of codeword pairs that preserves the peak luminance required by the input image data. Also, the first codeword may be selected to minimize the number of Just Noticeable Difference (JND) steps in the final image to be rendered. The second codeword may be selected to similarly improve image quality according to a given quality metric.
Owner:DOLBY LAB LICENSING CORP
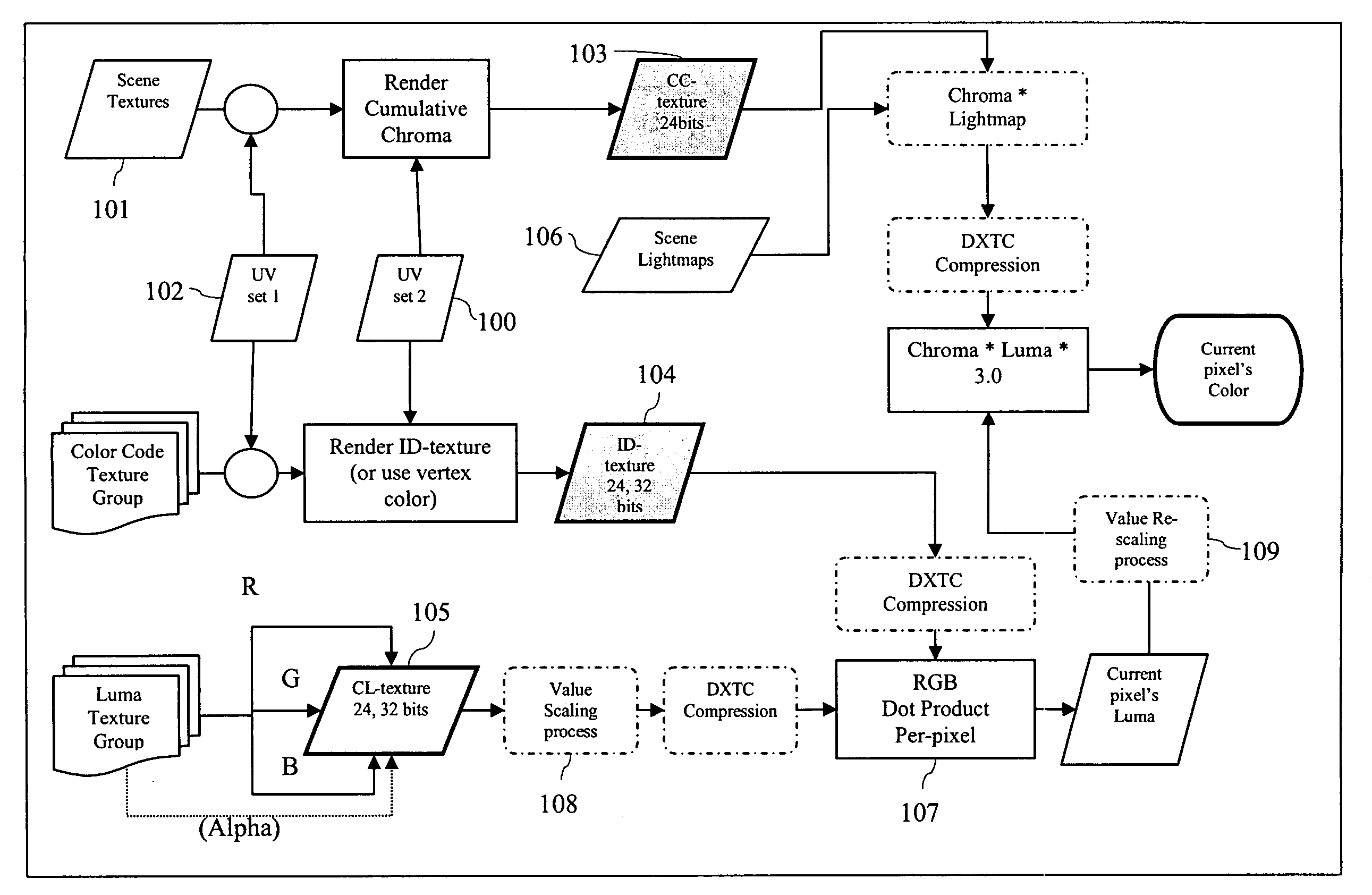
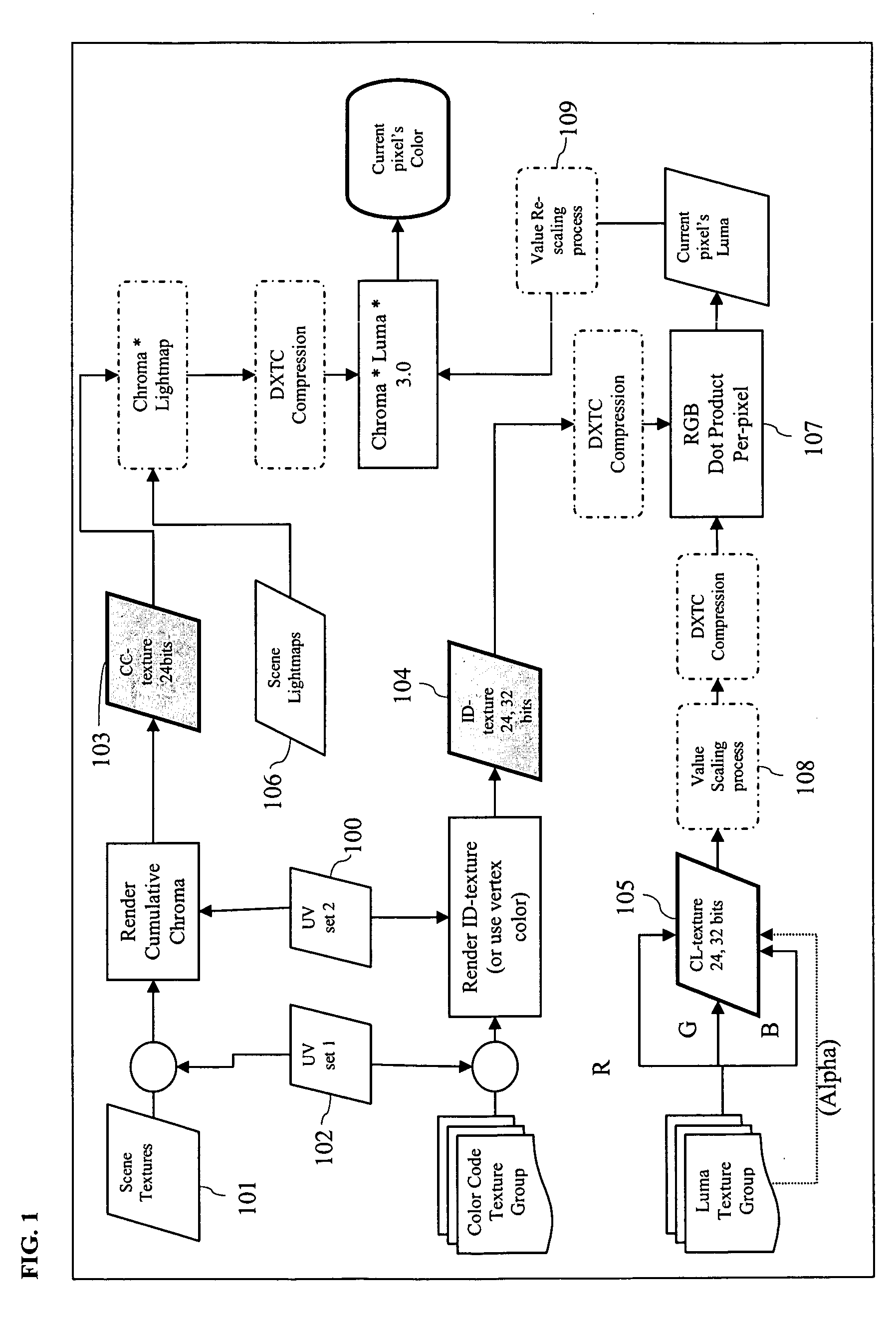
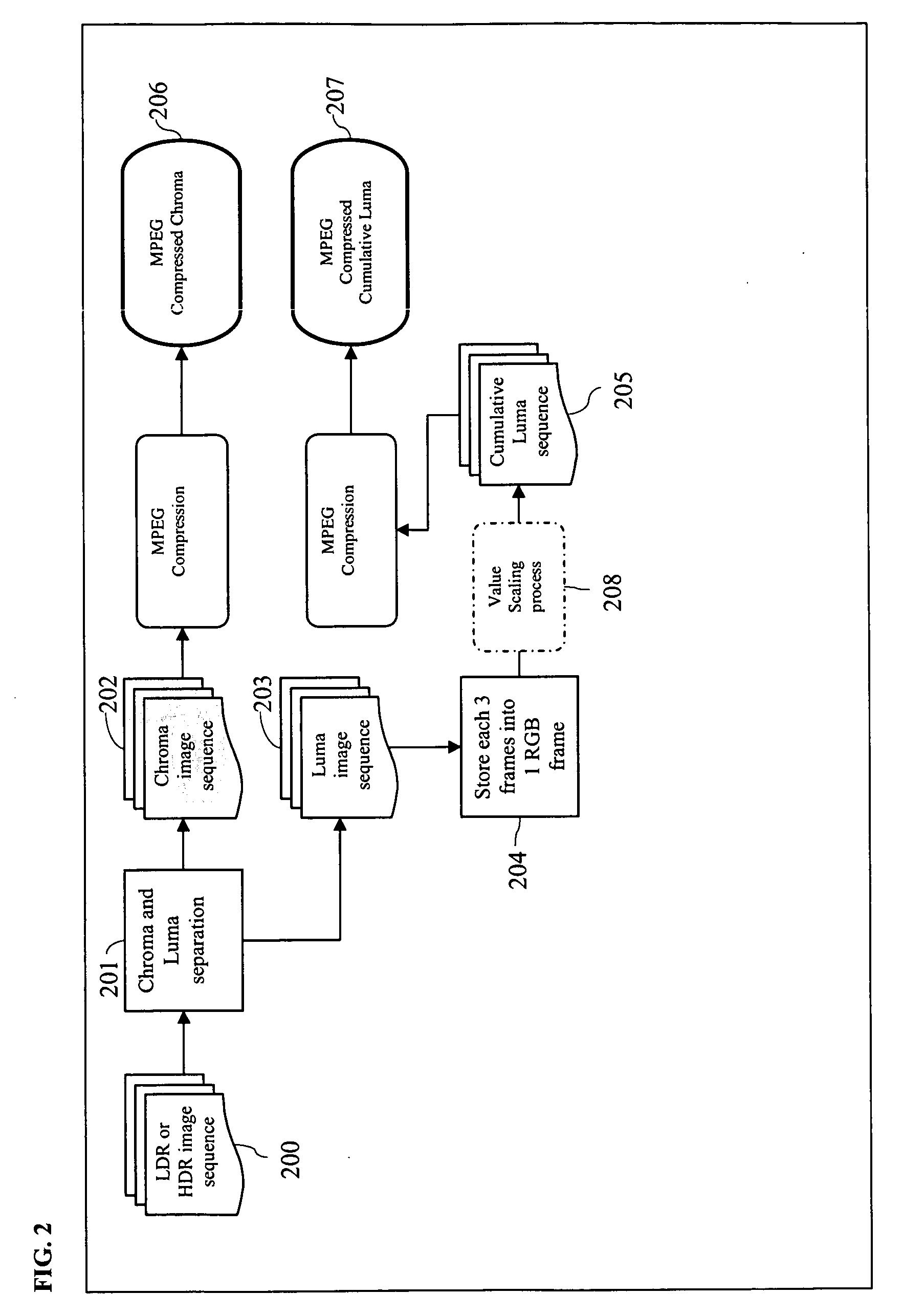
Multi-compatible low and high dynamic range and high bit-depth texture and video encoding system
ActiveUS20090046207A1Simple and efficient and practicalHigh imagingColor signal processing circuitsBrightness and chrominance signal processing circuitsVideo encodingComputer science
A method of processing image data includes generating image data including luminance and chrominance data representing a selected object, separating the luminance and chrominance data, storing the separated luminance and chrominance data in corresponding separate spaces in memory, and separately compressing the stored luminance and chrominance data.
Owner:TRELLIS EURO SRL
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com