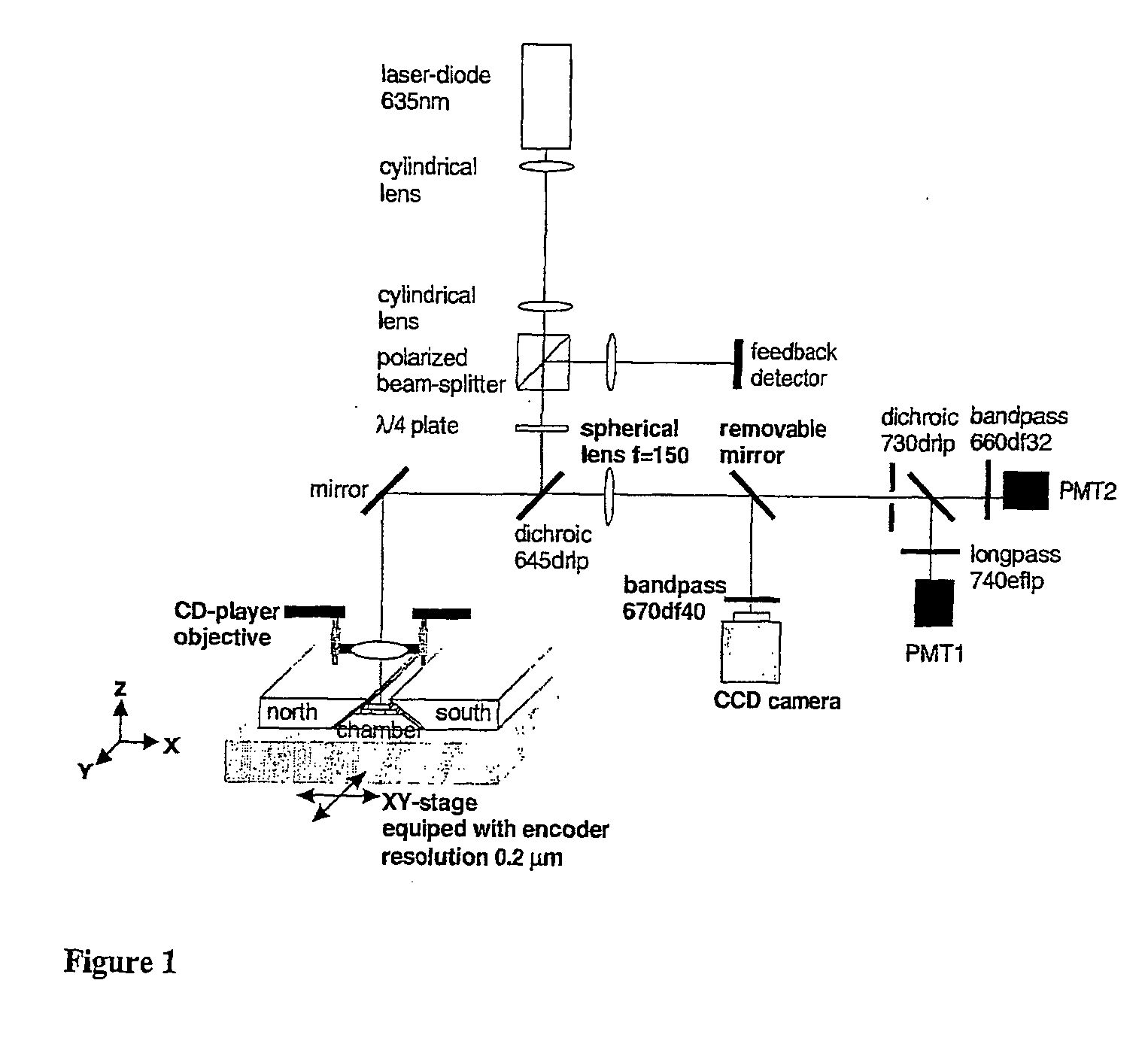
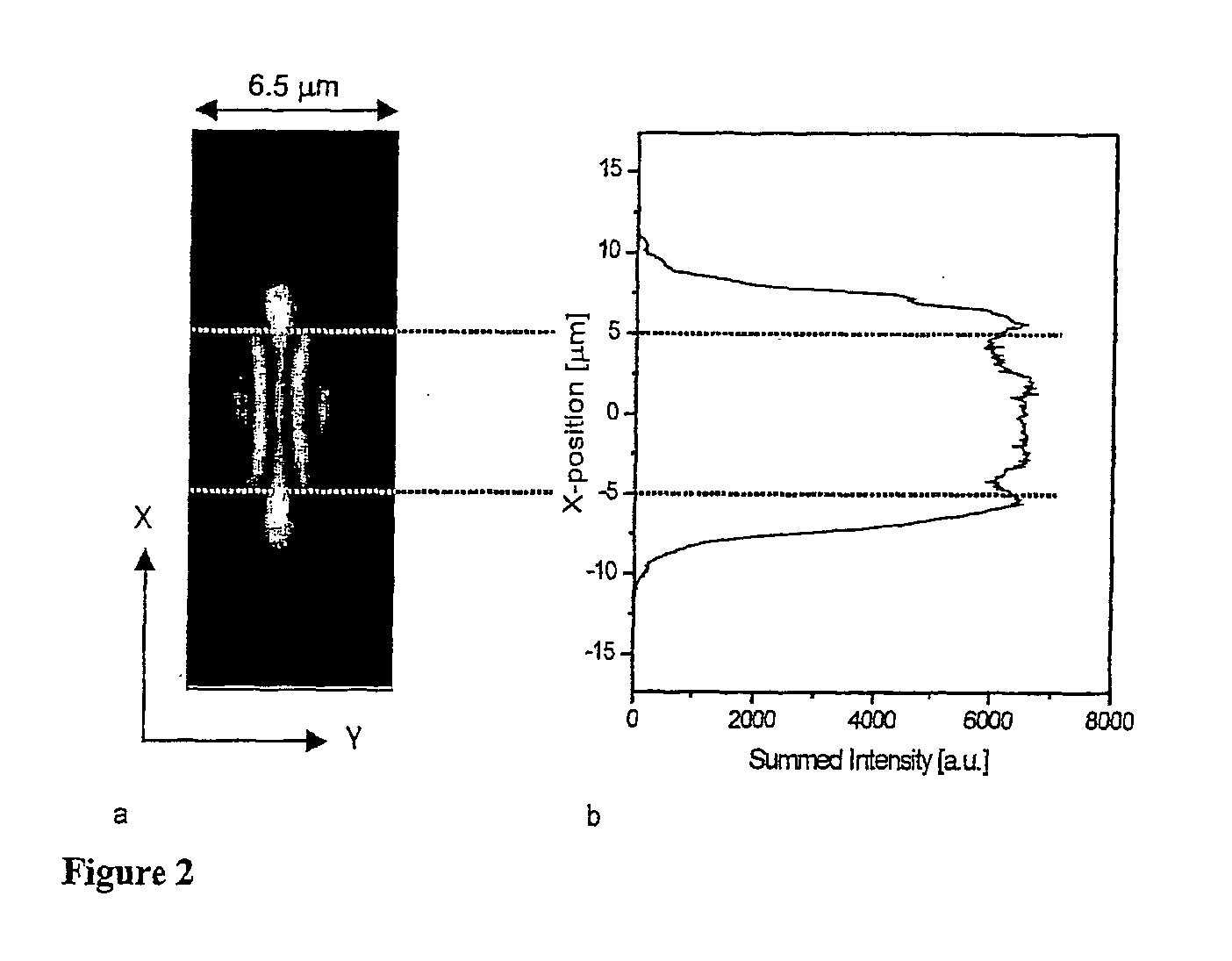
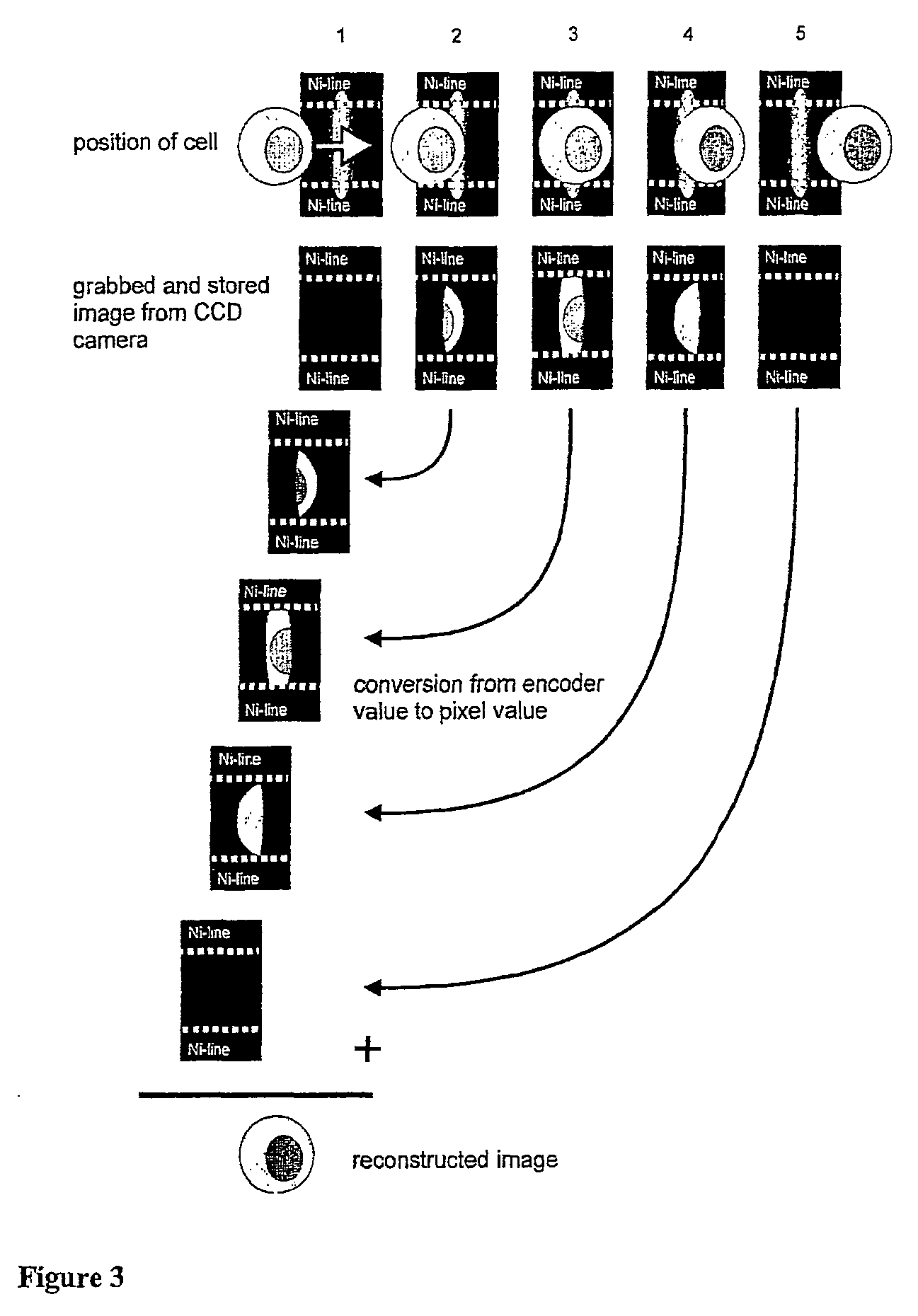
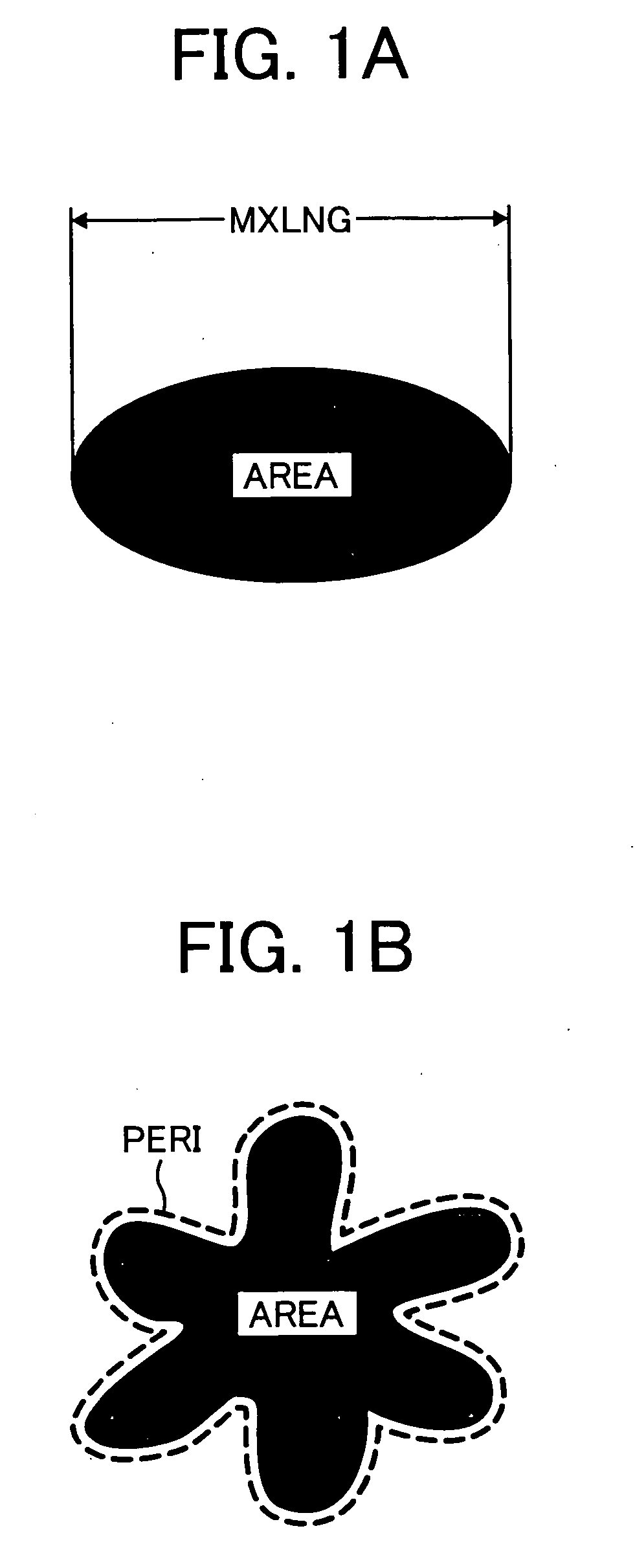
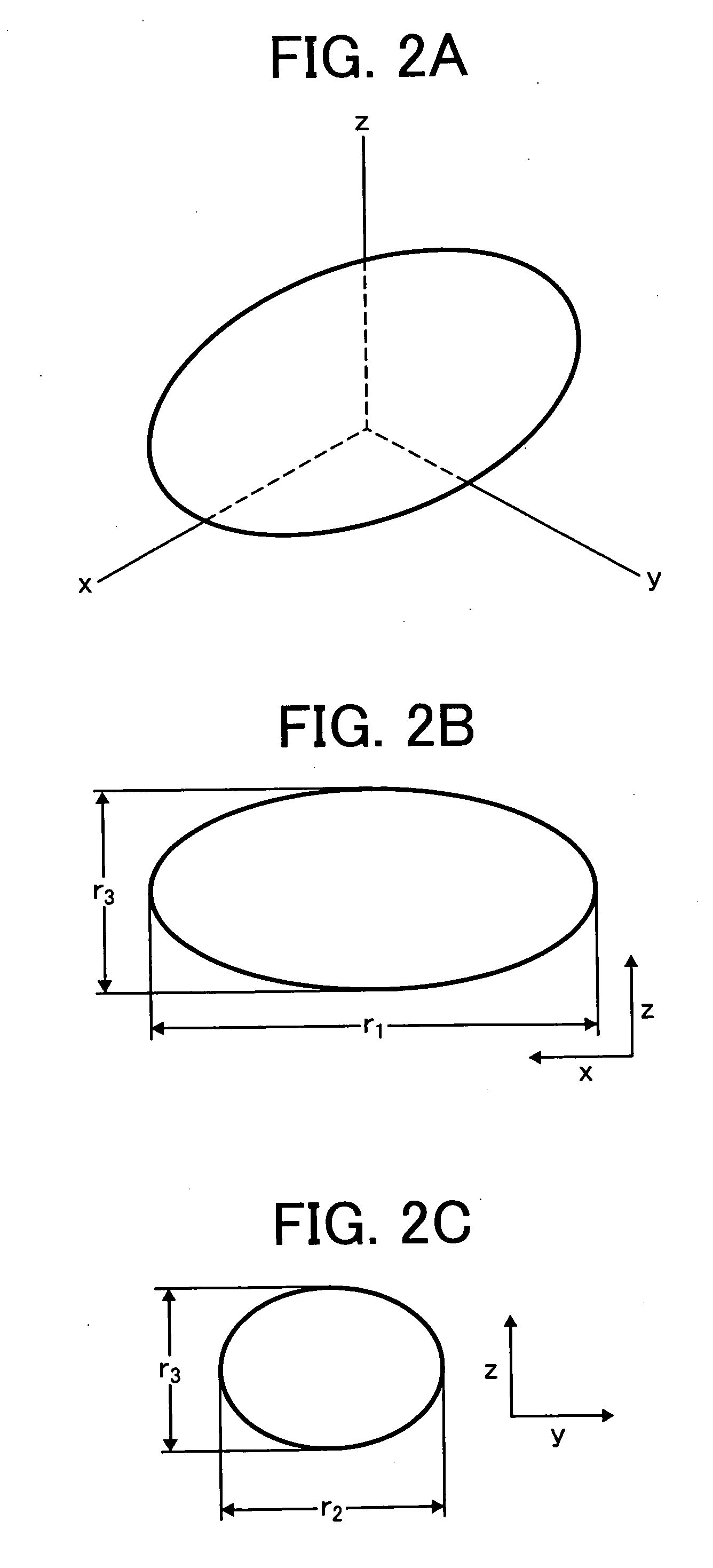
Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
405results about How to "High imaging" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
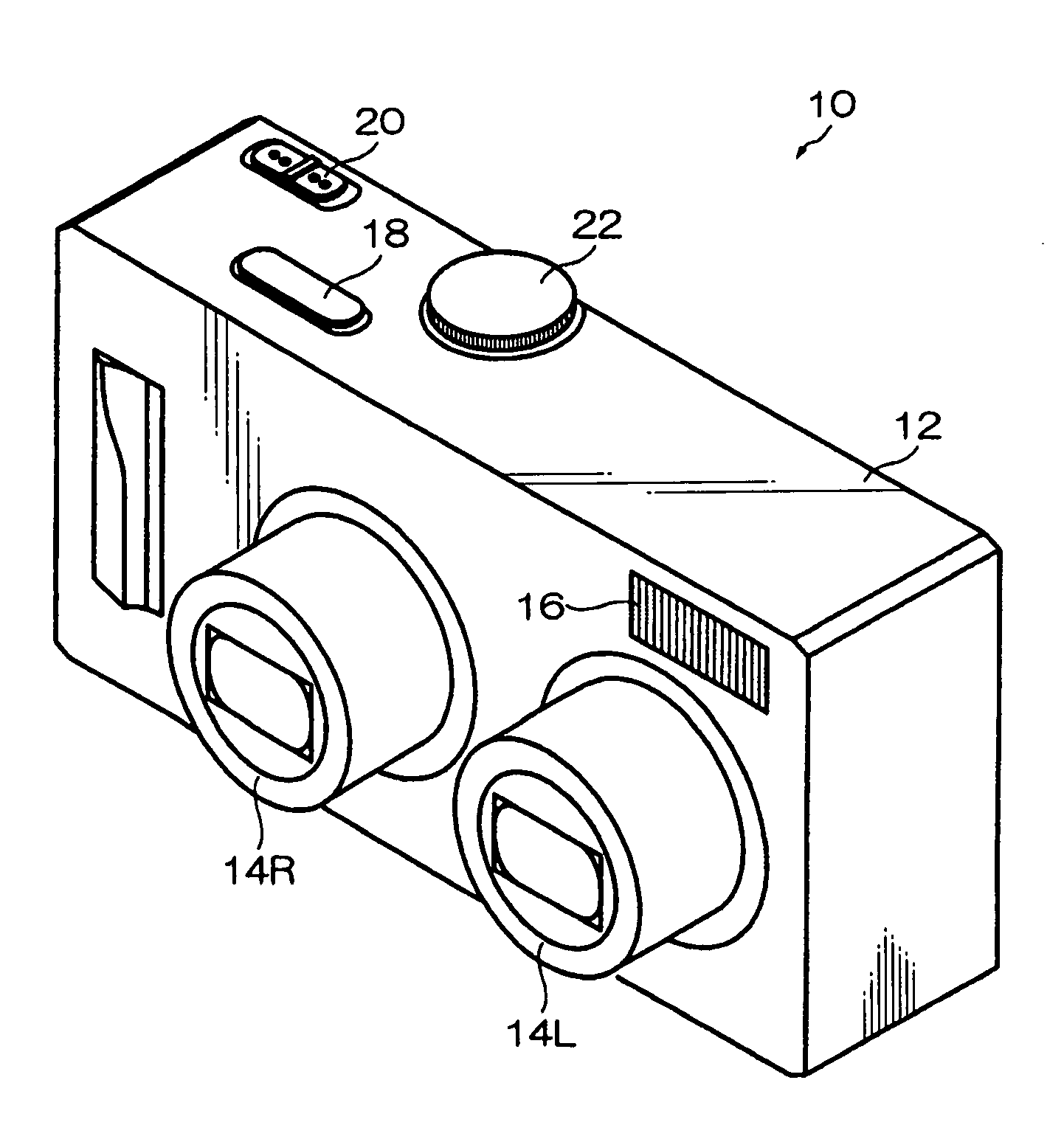
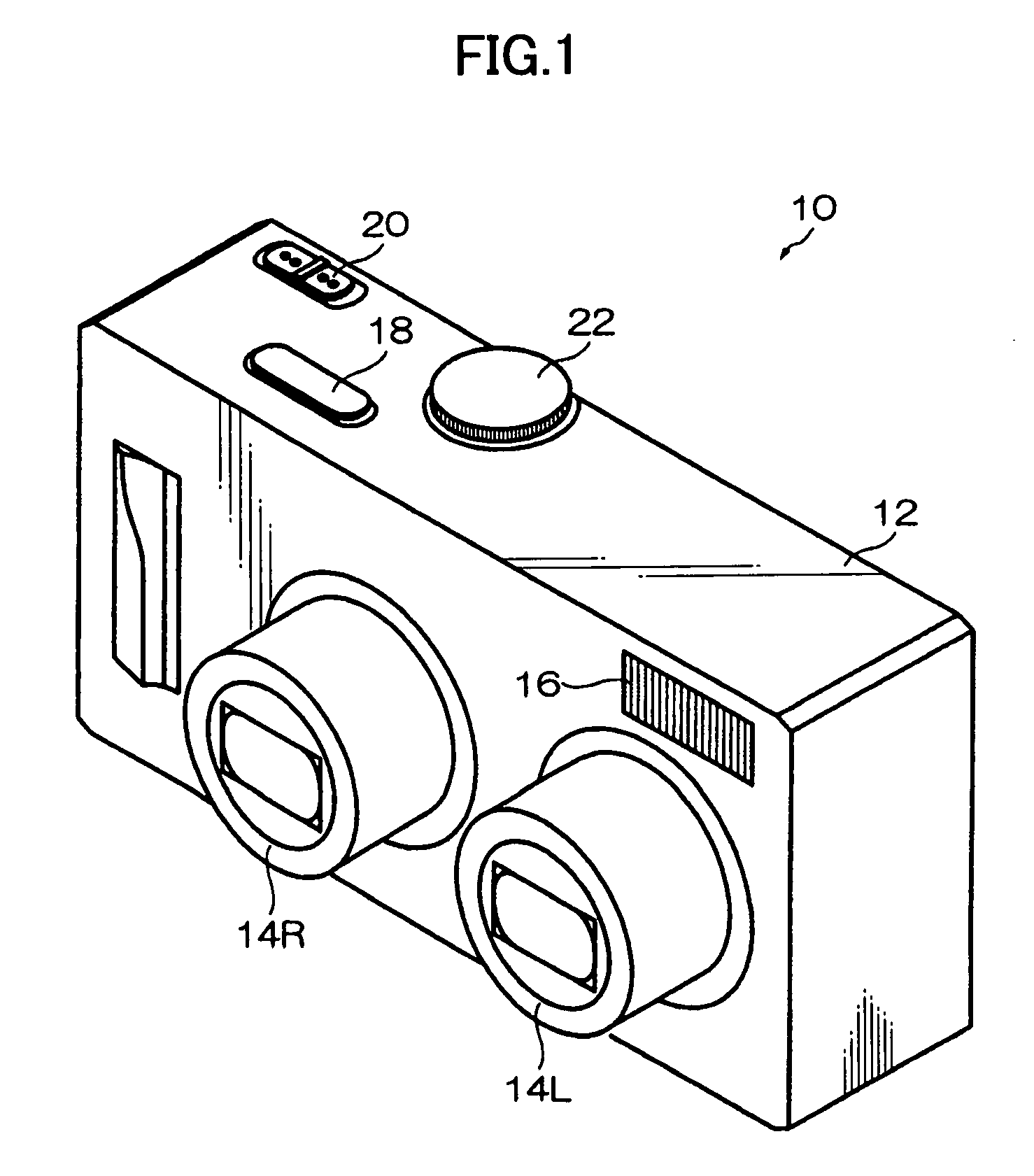
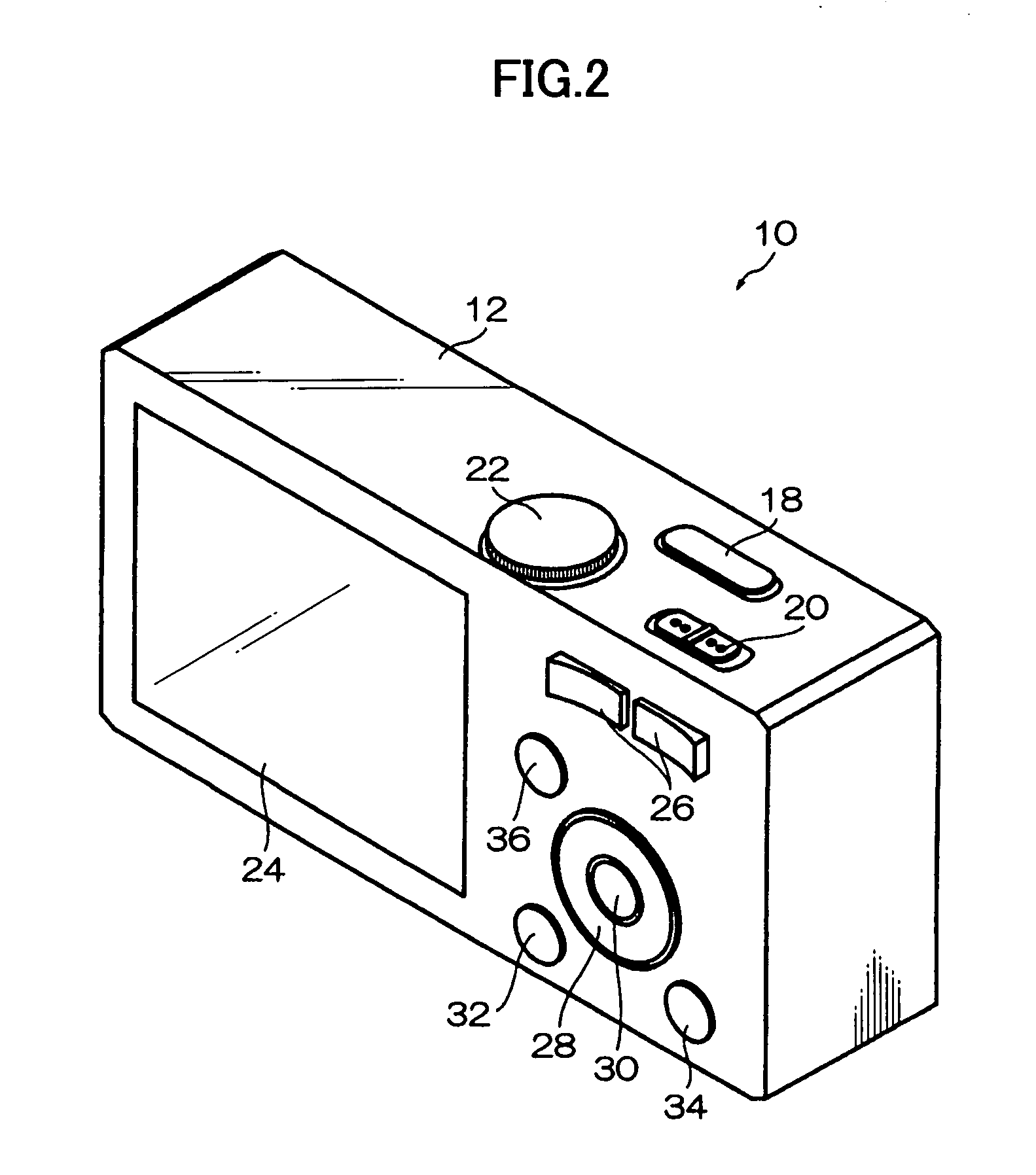
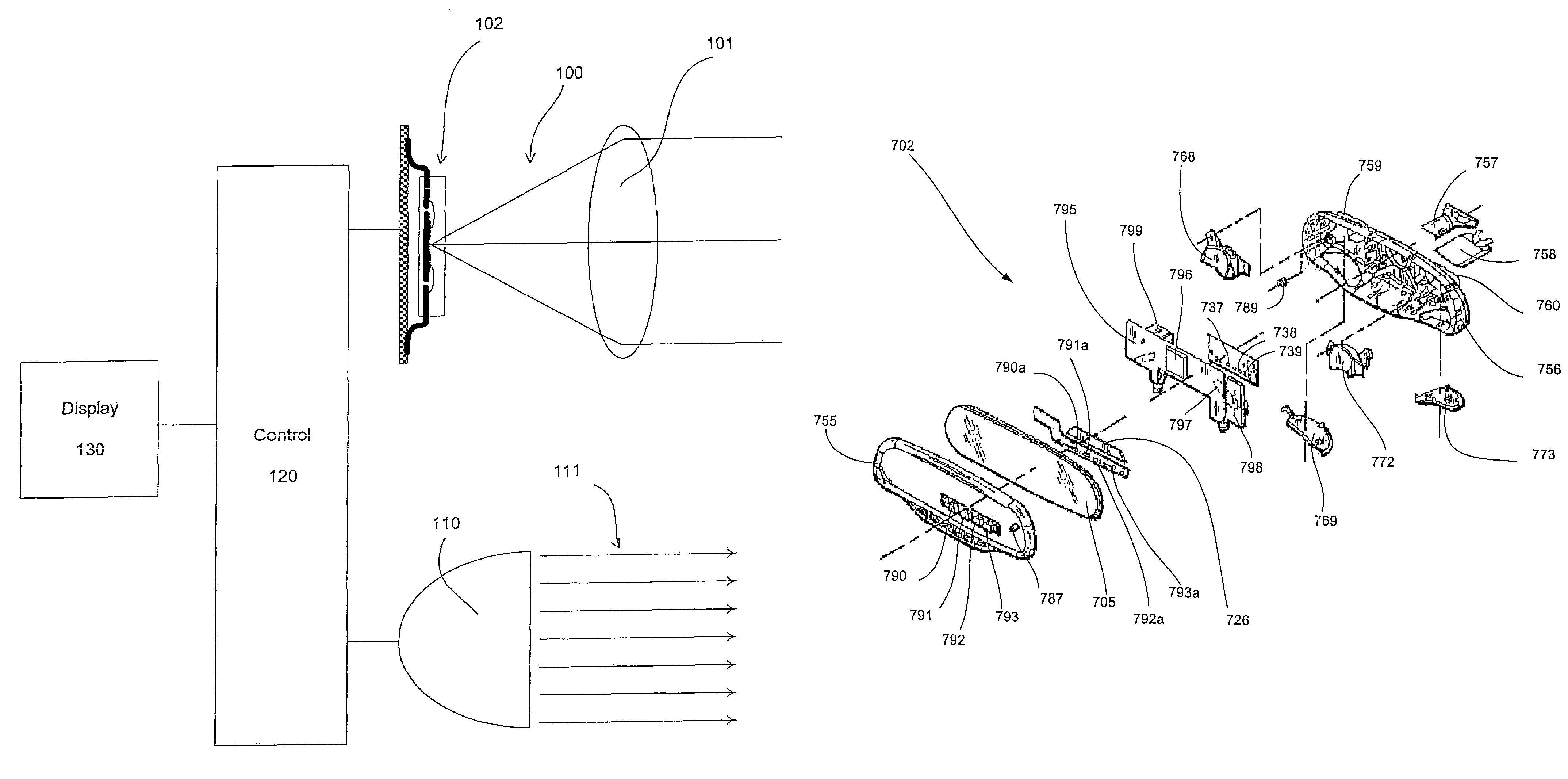
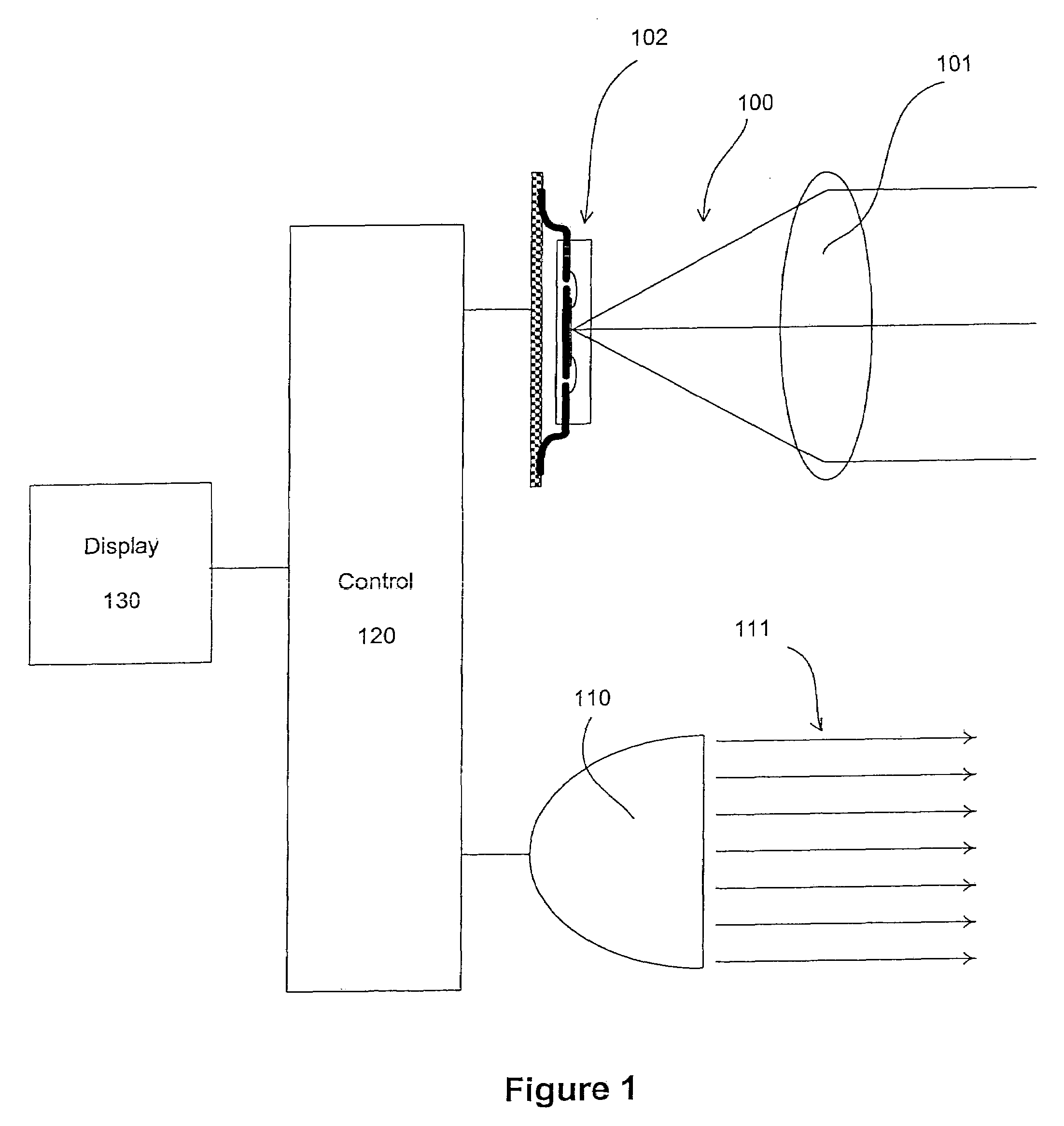
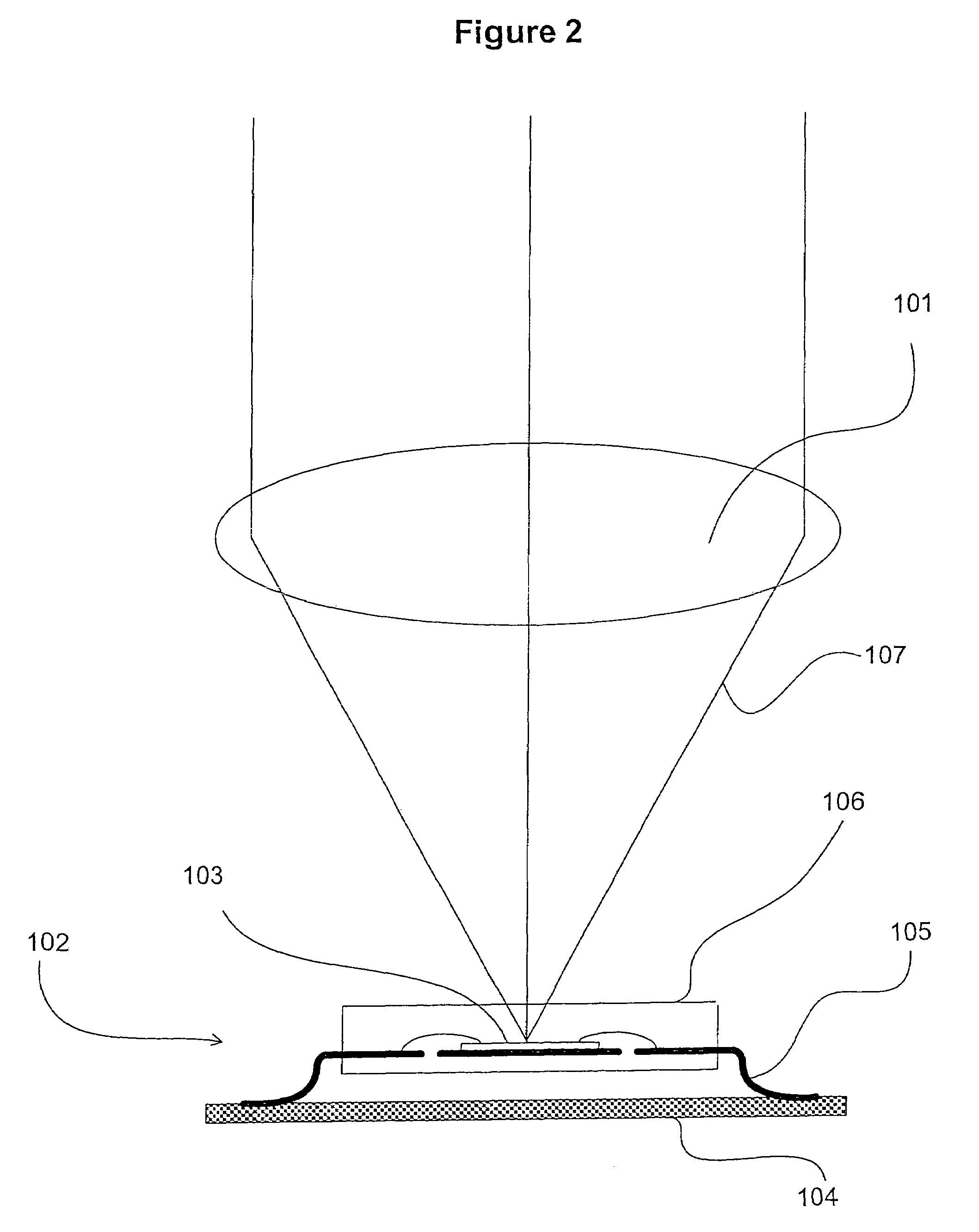
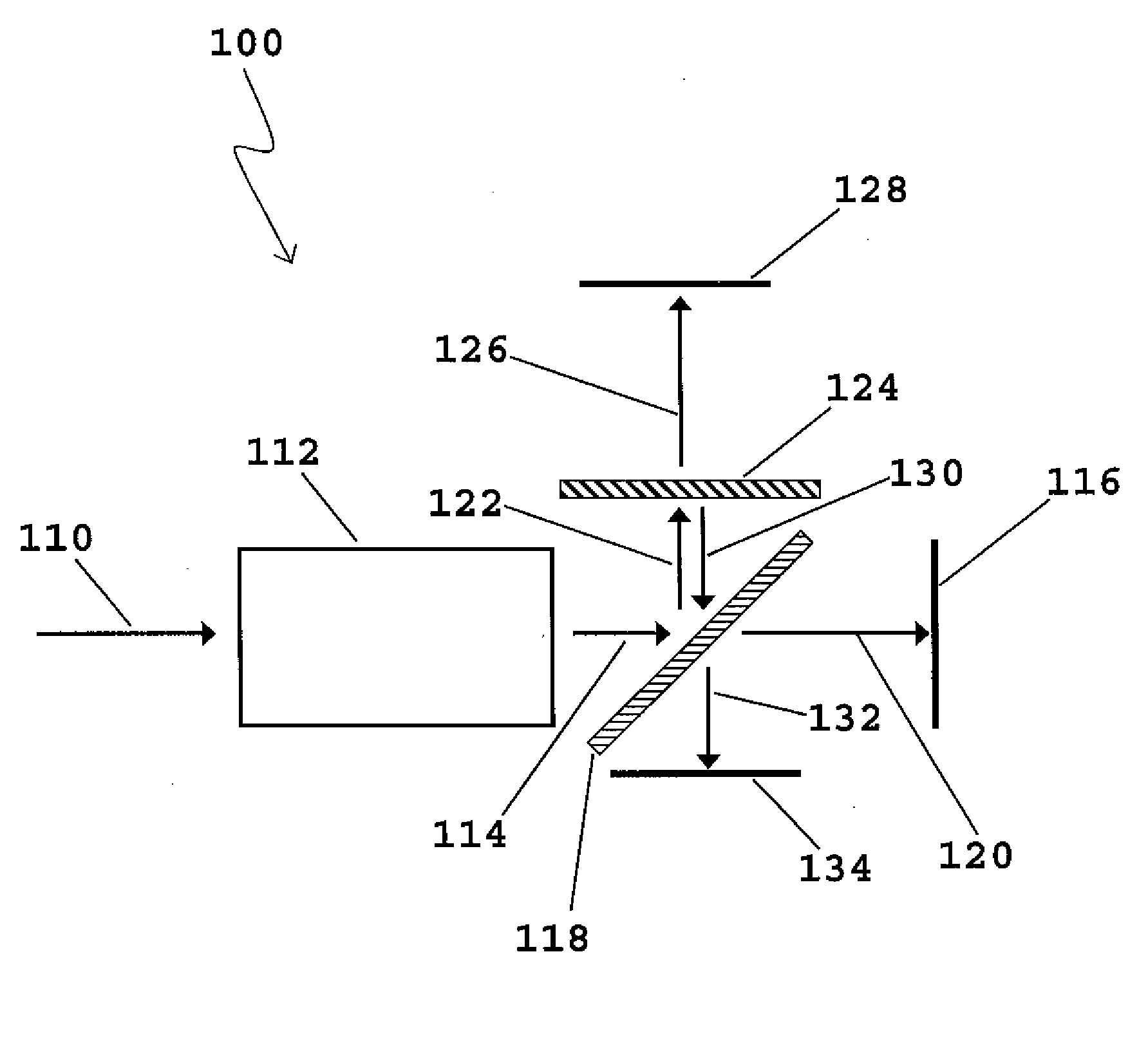
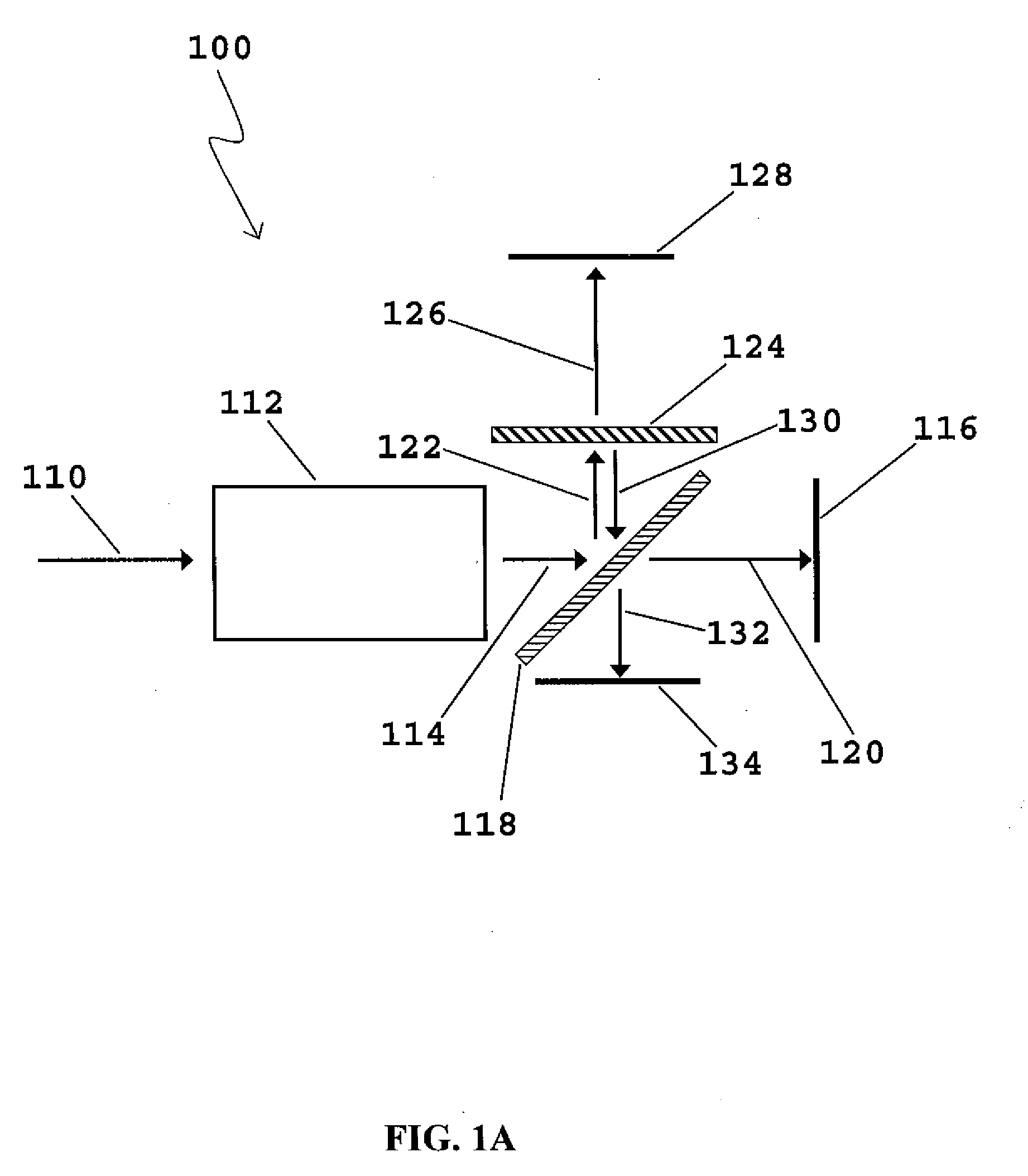
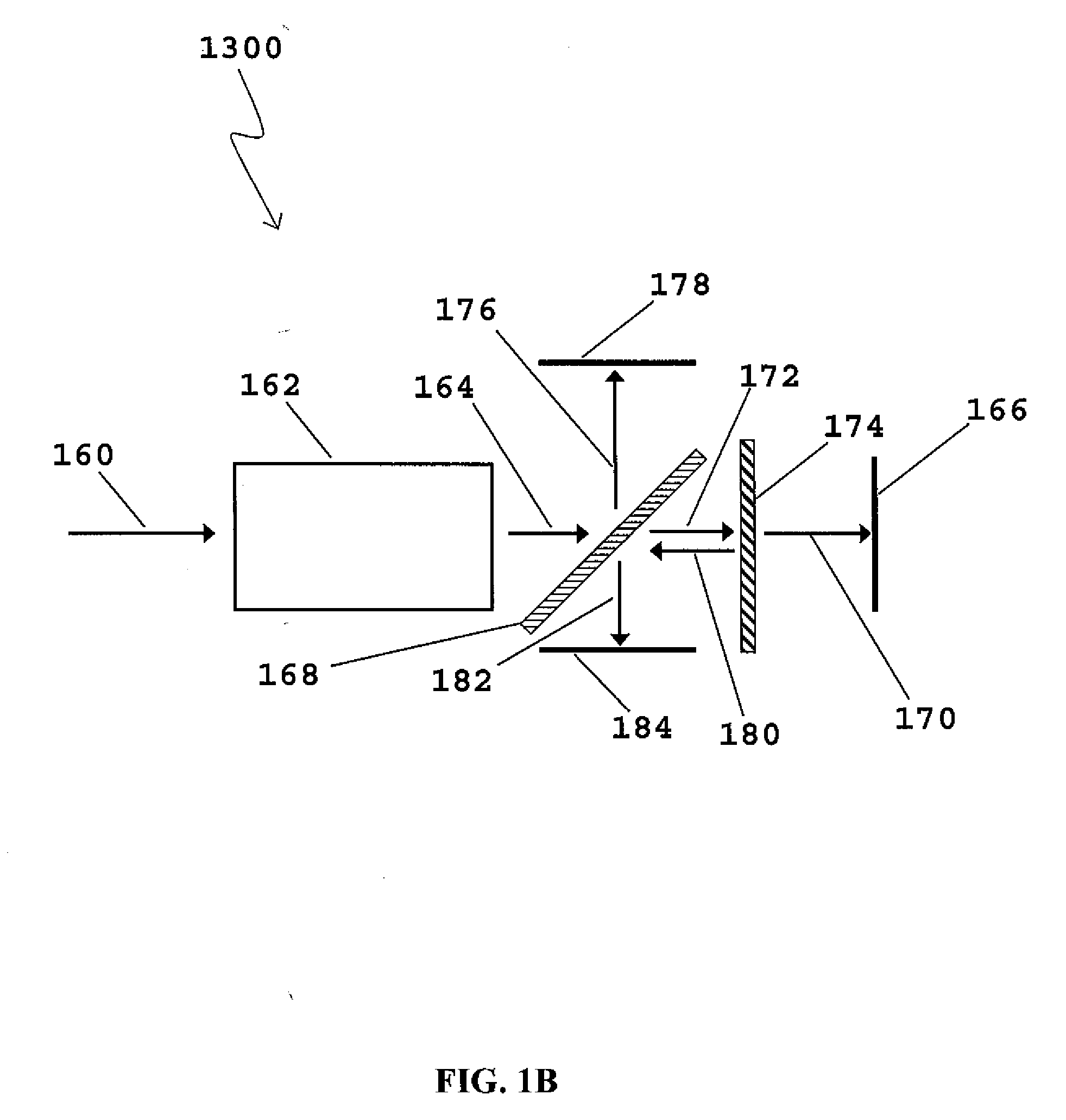
Photographing apparatus
ActiveUS20080131107A1Quality improvementSimply obtainedCharacter and pattern recognitionElectric digital data processingComputer graphics (images)Direction information
Photographing apparatus having a plurality of photographic optical systems, comprises: an attitude detecting device which detects an attitude of the apparatus body; a physical relationship information obtaining device which obtains information on physical relationship among the photographic optical systems setting; and a shooting direction information obtaining device which obtains information on the shooting direction of each of the photographic optical systems. The images photographed by each of the photographic optical systems may be corrected based on information on the attitude of the apparatus body, information on the physical relationship among the photographic optical systems, and information on the shooting direction of each of the photographic optical systems. Thereby it enables to easily correct tilt and the like of the images.
Owner:FUJIFILM CORP
Pixel image enhancement system and method
InactiveUS6038348ALow costReduce memoryCharacter and pattern recognitionPictoral communicationDisplay deviceOutput device
A pixel image enhancement system which operates on color or monochrome source images to produce output cells the same size as the source pixels but not spatially coincident or one-to-one correspondent with them. By operating upon a set of input pixels surrounding each output cell with a set of logic operations implementing unique Boolean equations, the system generates "case numbers" characterizing inferred-edge pieces within each output cell. A rendering subsystem, responsive to the case numbers and source-pixel colors, then produces signals for driving an output device (printer or display) to display the output cells, including the inferred-edge pieces, to the best of the output device's ability and at its resolution.
Owner:CSR TECH INC
Dental Optical Coherence Tomograph
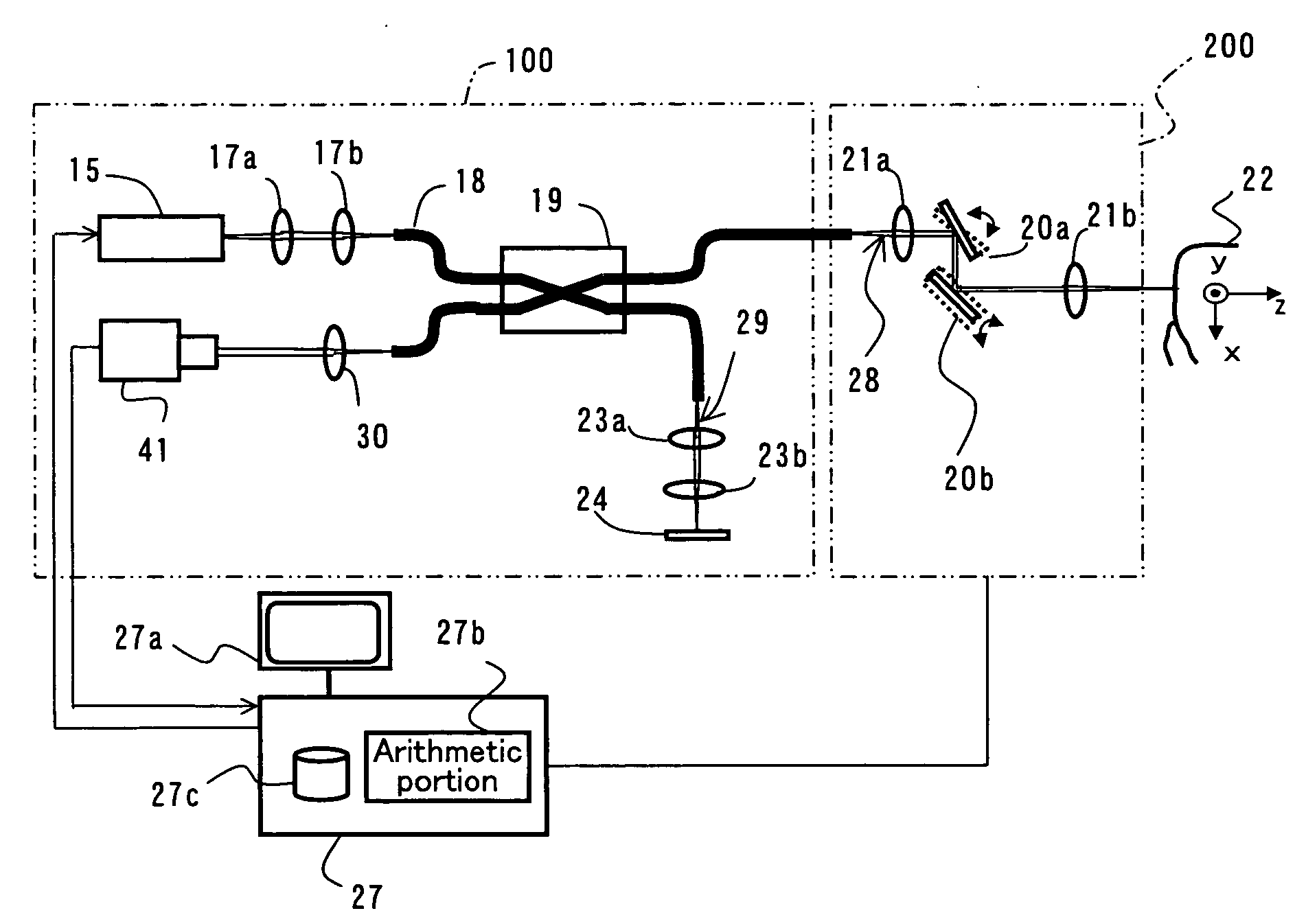
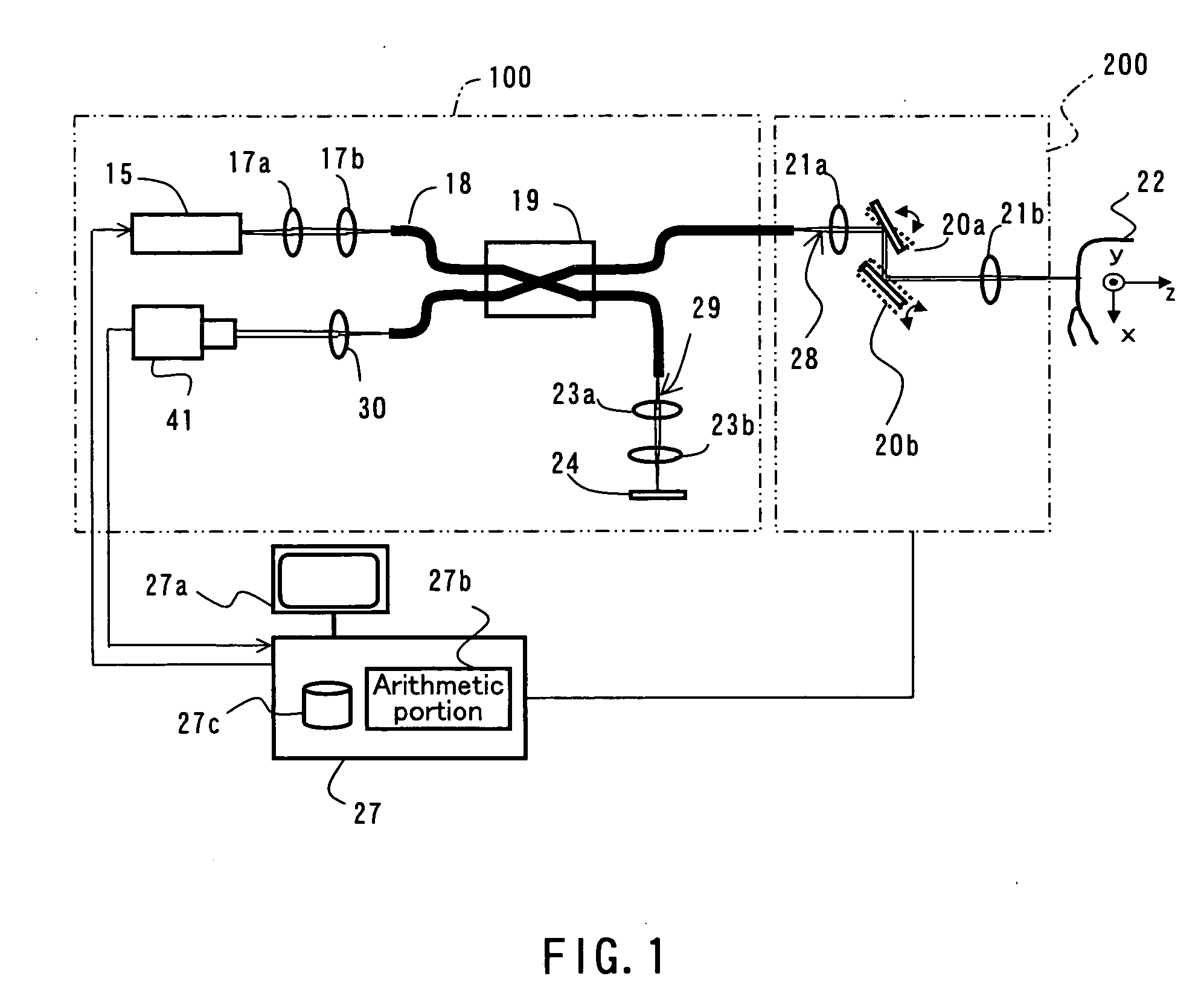
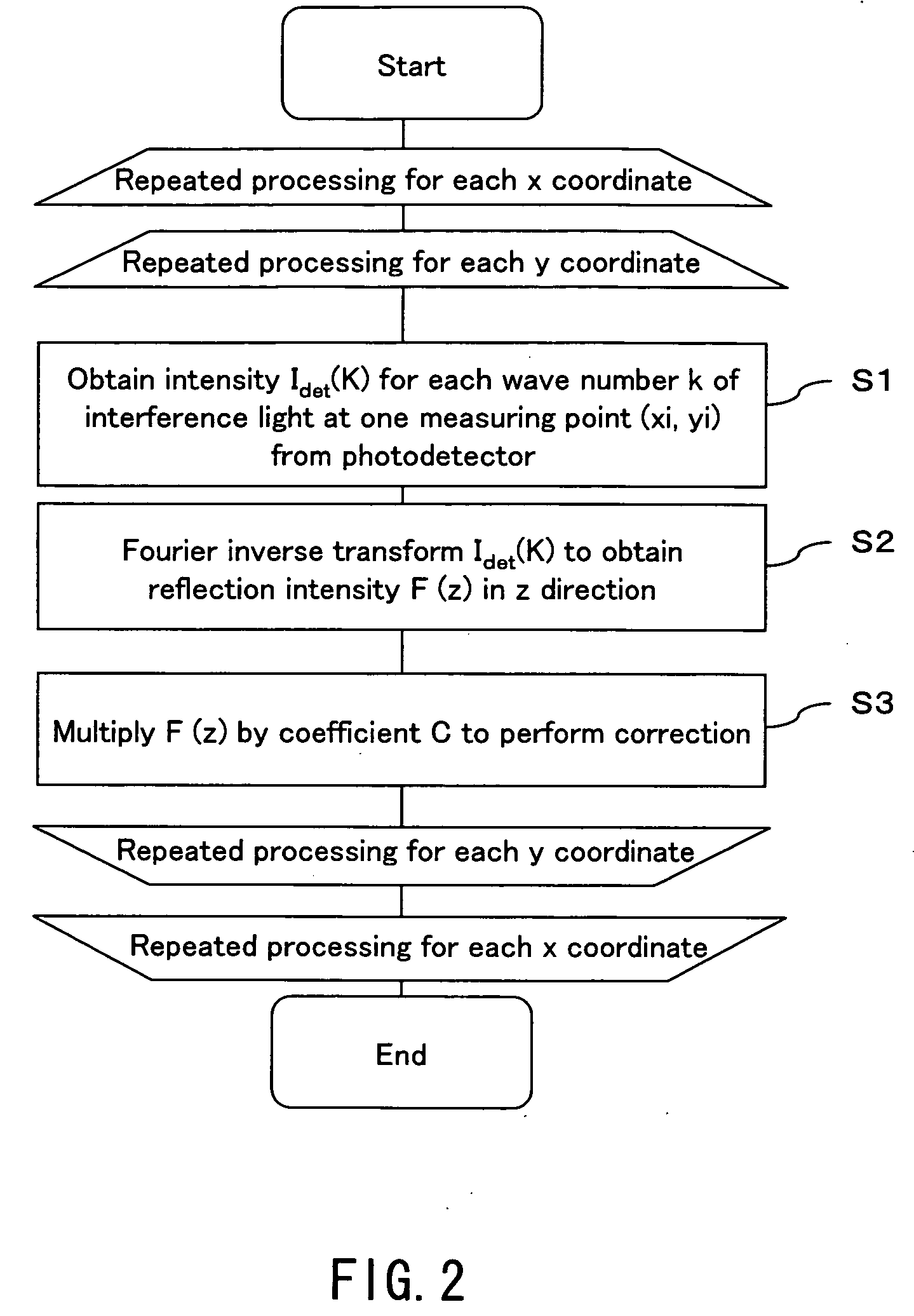
InactiveUS20090079993A1Simple structureHigh imagingInterferometersMaterial analysis by optical meansBiological bodyFourier transform on finite groups
A dental optical coherence tomography apparatus for measuring tissue in a stomatognathic region of a living body or an artificial composition in the stomatognathic region as a measured object includes: a variable wavelength light source (15); a light splitting portion (19) that splits light-source light emitted from the variable wavelength light source (15) into reference light (29) and measuring light (28); an interference portion (19) that causes the measuring light (28) and the reference light (29) to interfere with each other, thereby generating interference light; a photodetection portion (41) that measures the interference light; and an arithmetic portion (27b) that generates an image of a measured object (22) by Fourier transforming or inverse Fourier transforming the intensity of the interference light, whose wavelength changes with time, that has been detected by the photodetection portion for each of the wavelengths. Accordingly, an optical coherence tomography apparatus applicable to dental measurement can be provided.
Owner:SHOFU INC
Method and apparatus for obtaining high dynamic range images
InactiveUS20050099504A1High imagingTelevision system detailsTelevision system scanning detailsLight sensingBrightness perception
The application provides techniques for obtaining a relatively high dynamic range image of a scene using a relatively low dynamic range image sensor exposed to incident light from the scene for capturing an image. The image sensor has a multiplicity of light-sensing elements in an array and each light sensing element has a particular one of a plurality of sensitivity levels to incident light in accordance with a predetermined sensitivity pattern for the array of light-sensing elements and has a response function. Each light sensing element is responsive to incident light from the scene for producing a captured image brightness value at a corresponding one of a multiplicity of pixel positions of a pixel position array. Each one of the multiplicity of pixel positions corresponds to a particular one of the plurality of sensitivity levels of the light sensing elements.
Owner:THE TRUSTEES OF COLUMBIA UNIV IN THE CITY OF NEW YORK +1
Vehicle vision system with high dynamic range
ActiveUS7683326B2High imagingHigh dynamic rangeTelevision system detailsSolid-state devicesSelf adaptiveAdaptive control
A vehicular vision system is disclosed comprising a high dynamic range. The systems and methods are advantages for rear vision, collision avoidance, obstacle detection, adaptive cruise control, rain sensing, exterior light control, and lane departure warning, as well as other applications where a given scene may comprise objects having widely varying brightness values.
Owner:GENTEX CORP +1
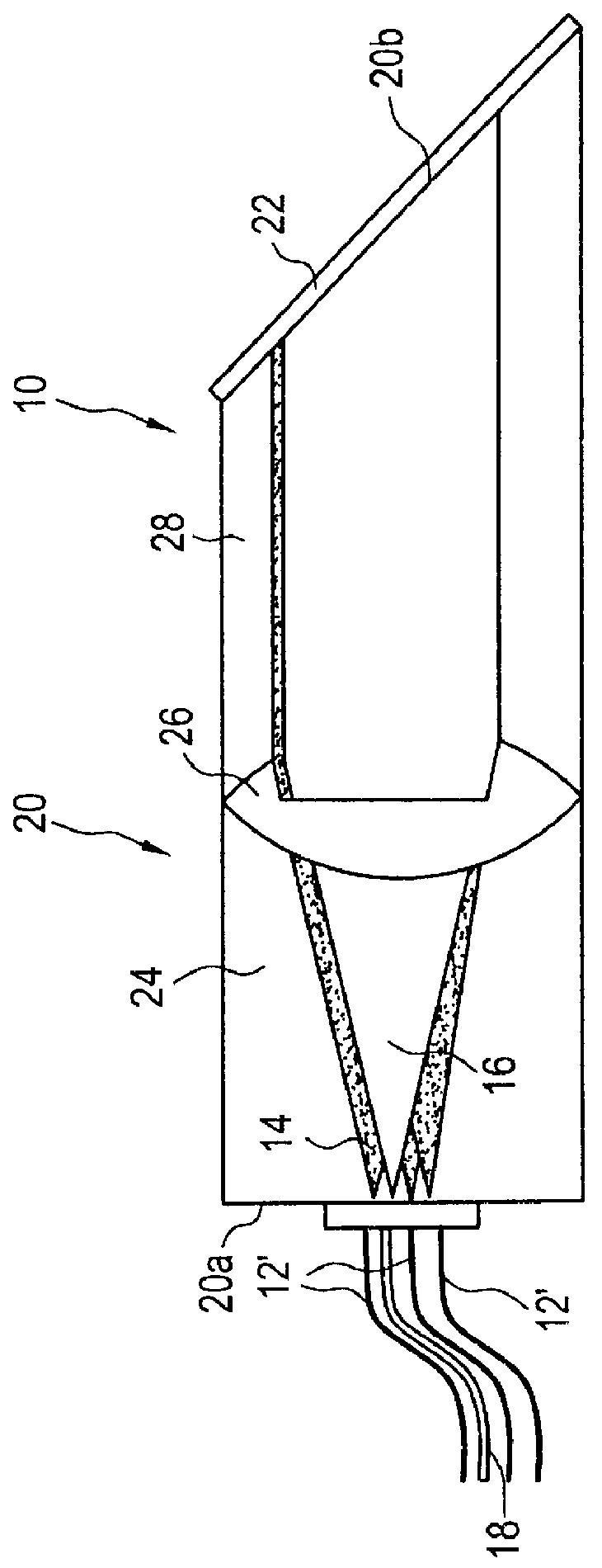
Integrated bi-directional axial gradient refractive index/diffraction grating wavelength division multiplexer
InactiveUS6011884AIncreased durabilityImprove the environmentLaser detailsCoupling light guidesMultiplexingMultiplexer
A wavelength division multiplexer is provided that integrates an axial gradient refractive index element with a diffraction grating to provide efficient coupling from a plurality of input optical sources (each delivering a single wavelength to the device) which are multiplexed to a single polychromatic beam for output to a single output optical receiver. The device comprises: (a) means for accepting optical input from at least one optical source, the means including a planar surface; (b) a coupler element comprising (1) an axial gradient refractive index collimating lens having a planar entrance surface onto which the optical input is incident and (2) a homogeneous index boot lens affixed to the axial gradient refractive index collimating lens and having a planar but tilted exit surface; (c) a diffraction grating, such as a Littrow diffraction grating, on the tilted surface of the homogeneous index boot lens which combines a plurality of spatially separated wavelengths from the optical light; and (d) means to output at least one multiplexed, polychromatic output beam, the means including a planar surface. The device may be operated in the forward direction as a multiplexer or in the reverse direction as a demultiplexer.
Owner:AUXORA
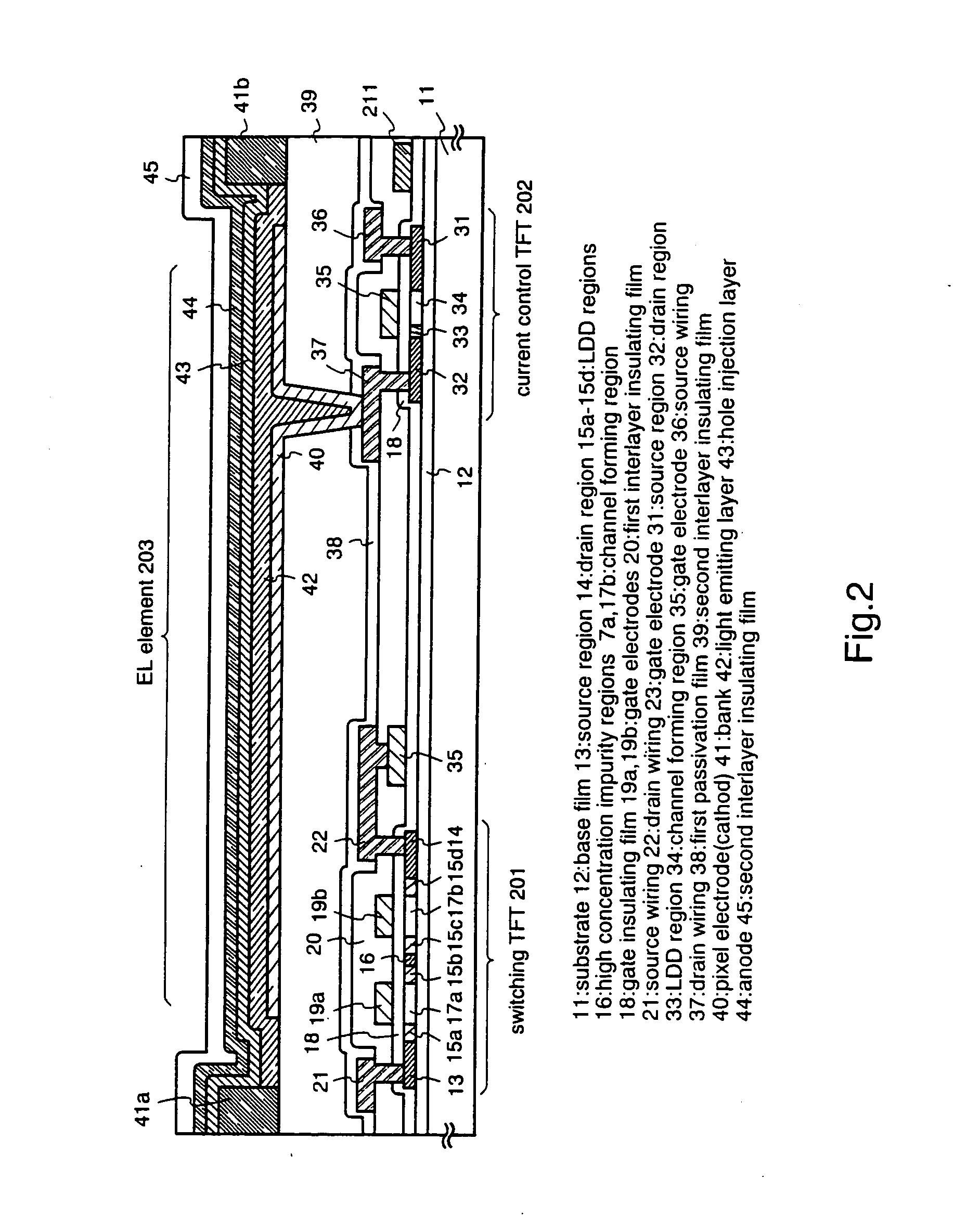
EL display device and a method of manufacturing the same
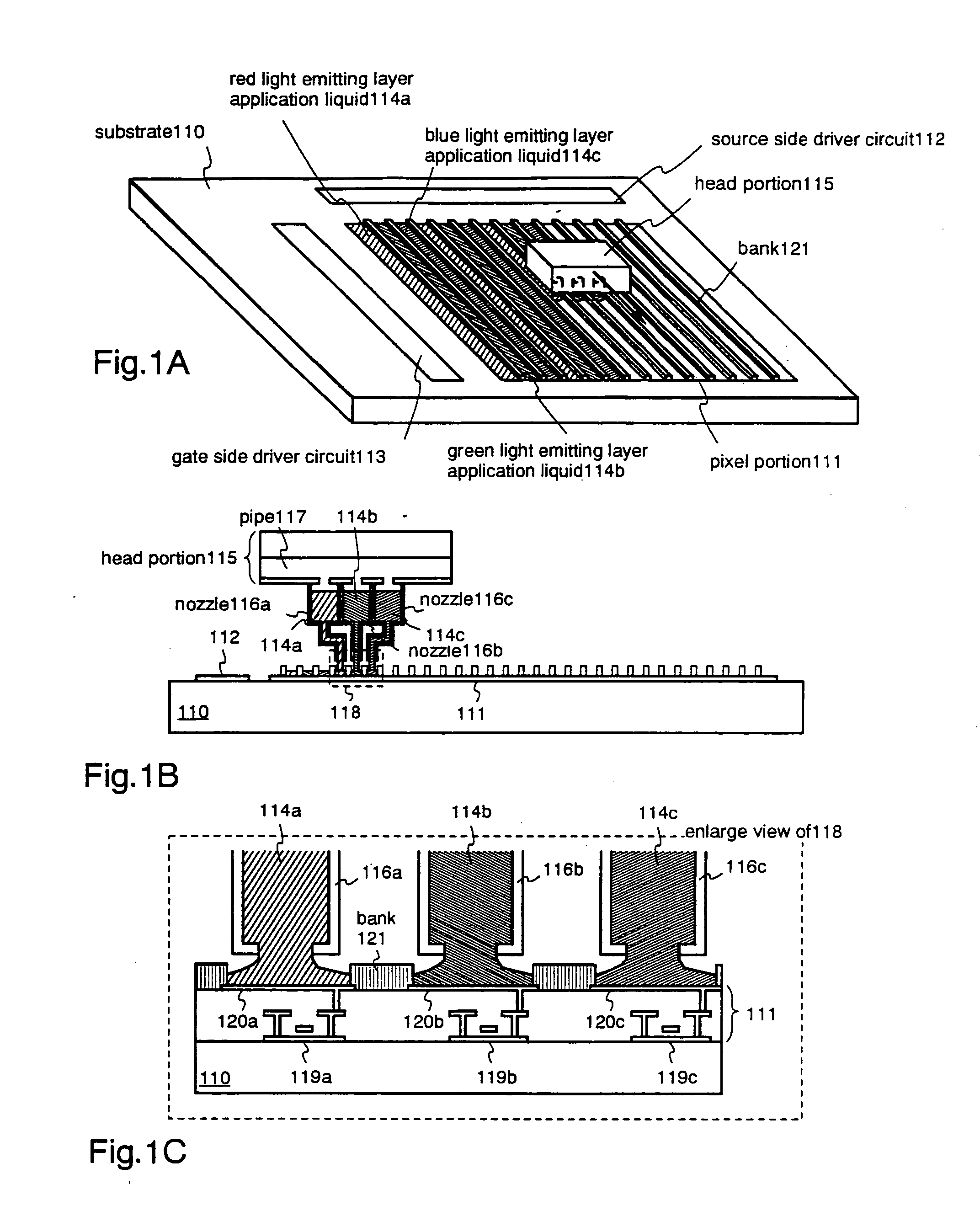
InactiveUS20050012445A1High throughputHigh imagingDischarge tube luminescnet screensElectroluminescent light sourcesDisplay devicePolymer
To provide a high throughput film deposition means for film depositing an organic EL material made of polymer accurately and without any positional shift. A pixel portion is divided into a plurality of pixel rows by a bank, and a head portion of a thin film deposition apparatus is scanned along a pixel row to thereby simultaneously apply a red light emitting layer application liquid, a green light emitting layer application liquid, and a blue light emitting layer application liquid in stripe shapes. Heat treatment is then performed to thereby form light emitting layers luminescing each of the colors red, green, and blue.
Owner:SEMICON ENERGY LAB CO LTD
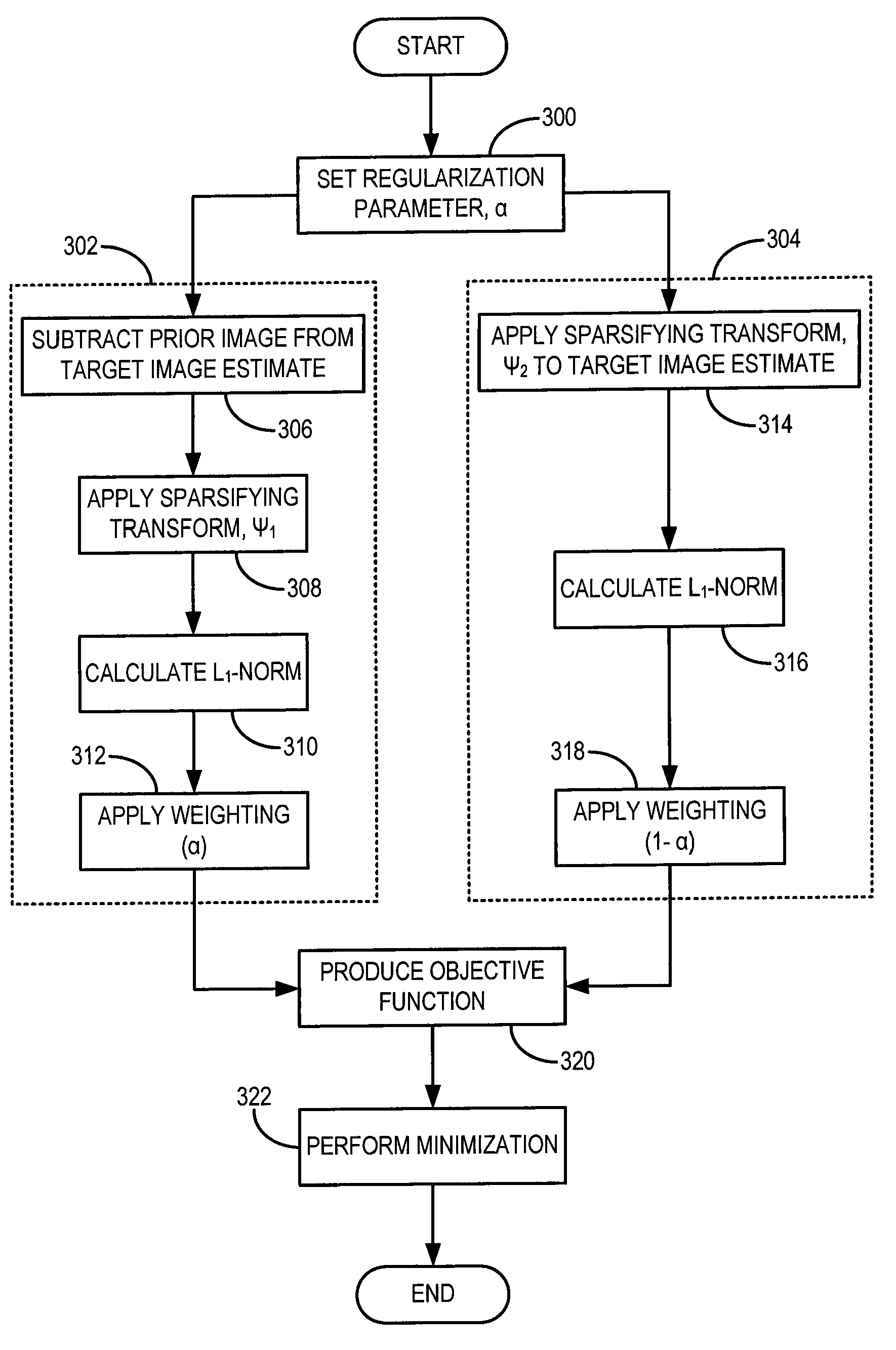
Method for dynamic prior image constrained image reconstruction
ActiveUS20090161933A1Improve signal-to-noise ratioHigh resolutionReconstruction from projectionCharacter and pattern recognitionDiagnostic Radiology ModalityTemporal resolution
A method for reconstructing a high quality image from undersampled image data is provided. The image reconstruction method is applicable to a number of different imaging modalities. Specifically, the present invention provides an image reconstruction method that incorporates an appropriate prior image into the image reconstruction process. Thus, one aspect of the present invention is to provide an image reconstruction method that requires less number of data samples to reconstruct an accurate reconstruction of a desired image than previous methods, such as, compressed sensing. Another aspect of the invention is to provide an image reconstruction method that produces a time series of desired images indicative of a higher temporal resolution than is ordinarily achievable with the imaging system. For example, cardiac phase images can be produced with high temporal resolution (e.g., 20 milliseconds) using a CT imaging system with a slow gantry rotation speed.
Owner:WISCONSIN ALUMNI RES FOUND
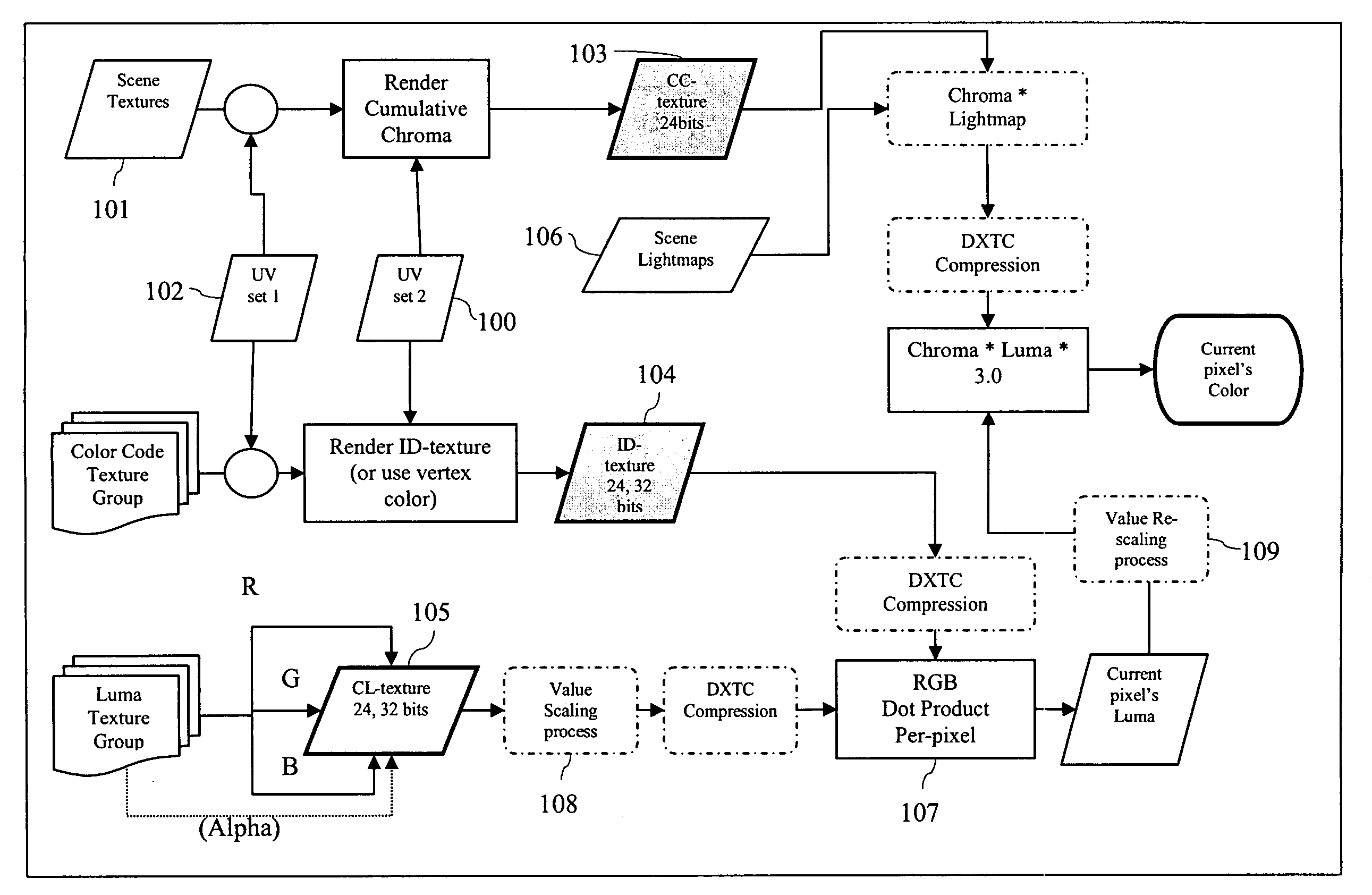
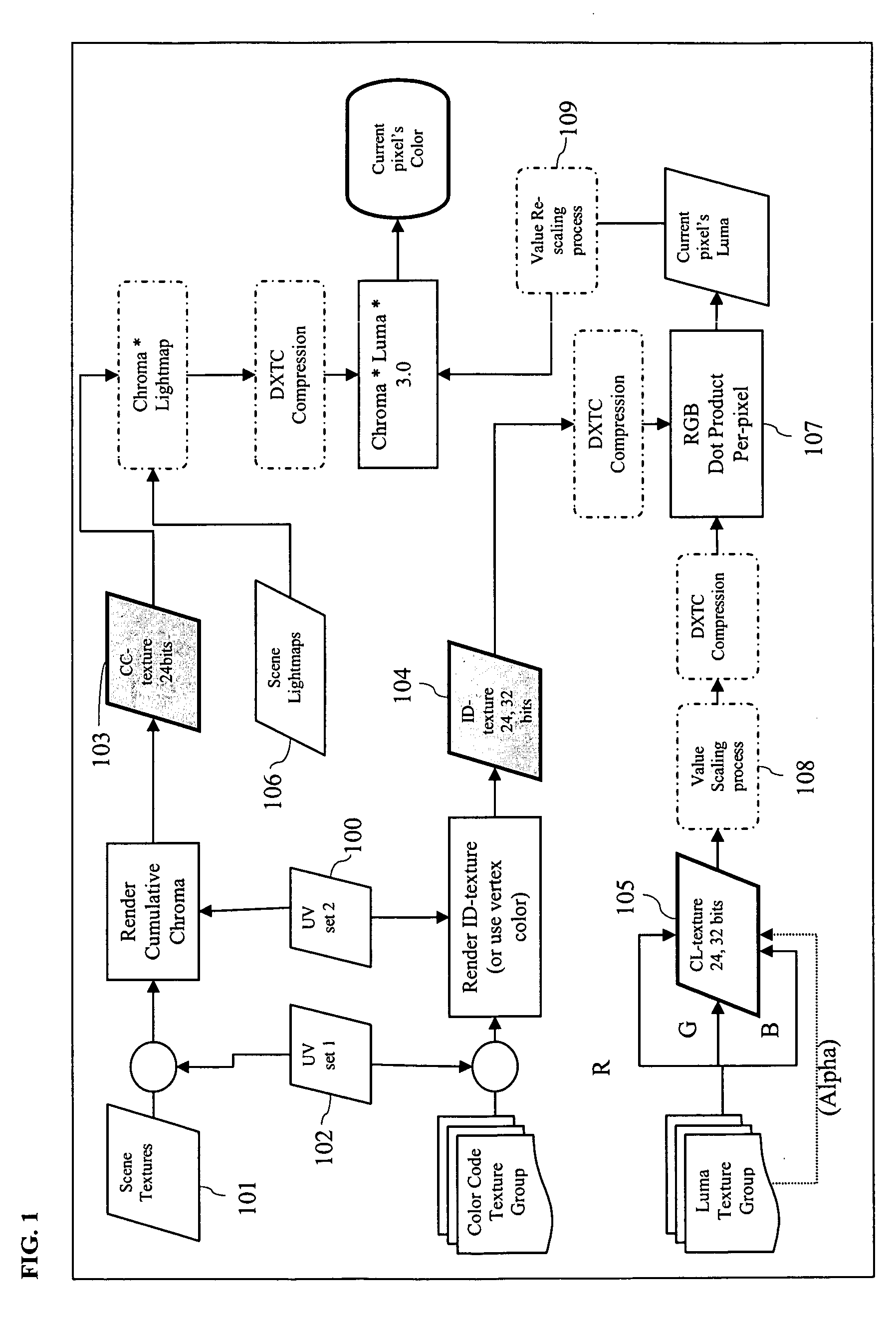
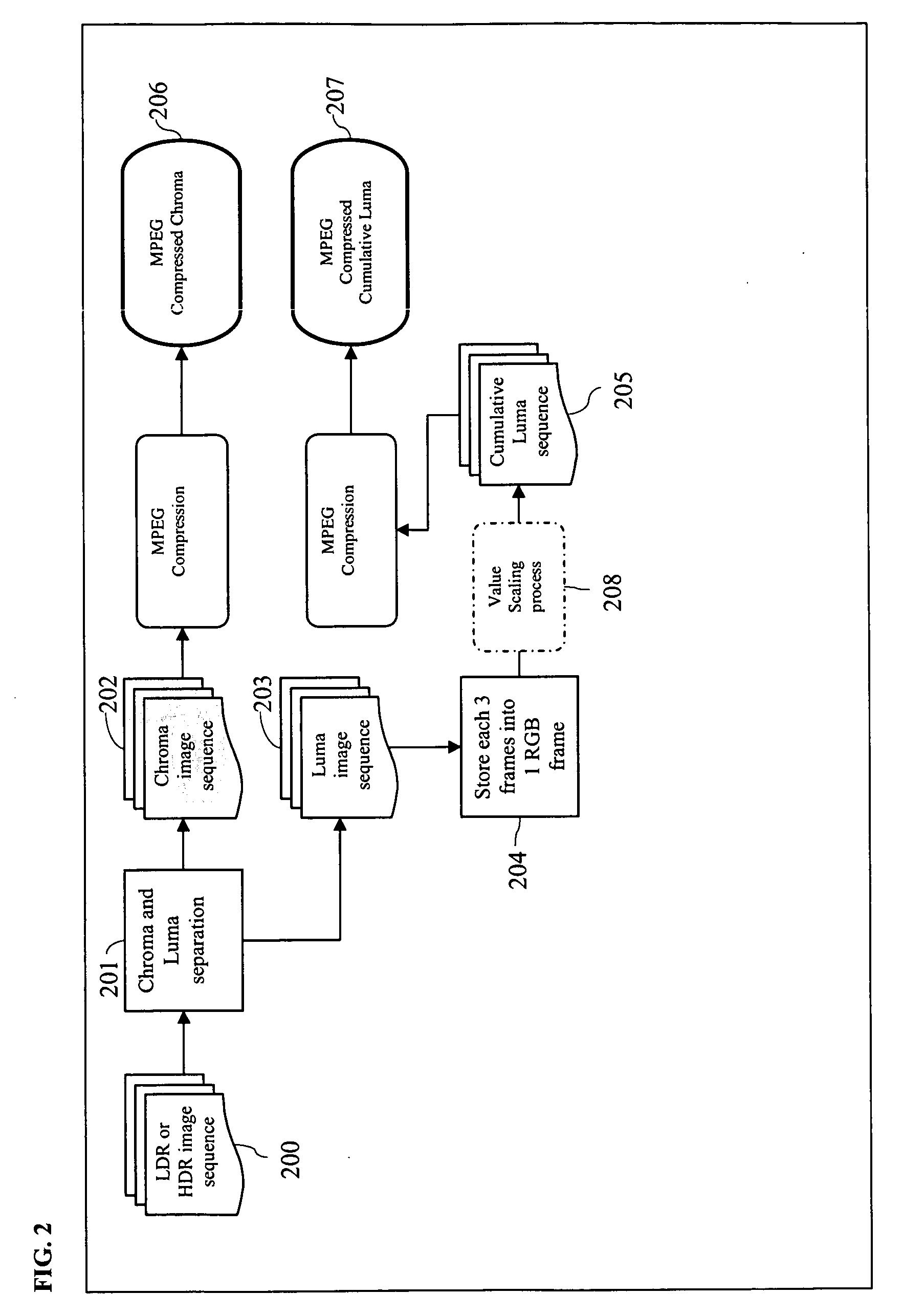
Multi-compatible low and high dynamic range and high bit-depth texture and video encoding system
ActiveUS20090046207A1Simple and efficient and practicalHigh imagingColor signal processing circuitsBrightness and chrominance signal processing circuitsVideo encodingComputer science
A method of processing image data includes generating image data including luminance and chrominance data representing a selected object, separating the luminance and chrominance data, storing the separated luminance and chrominance data in corresponding separate spaces in memory, and separately compressing the stored luminance and chrominance data.
Owner:TRELLIS EURO SRL
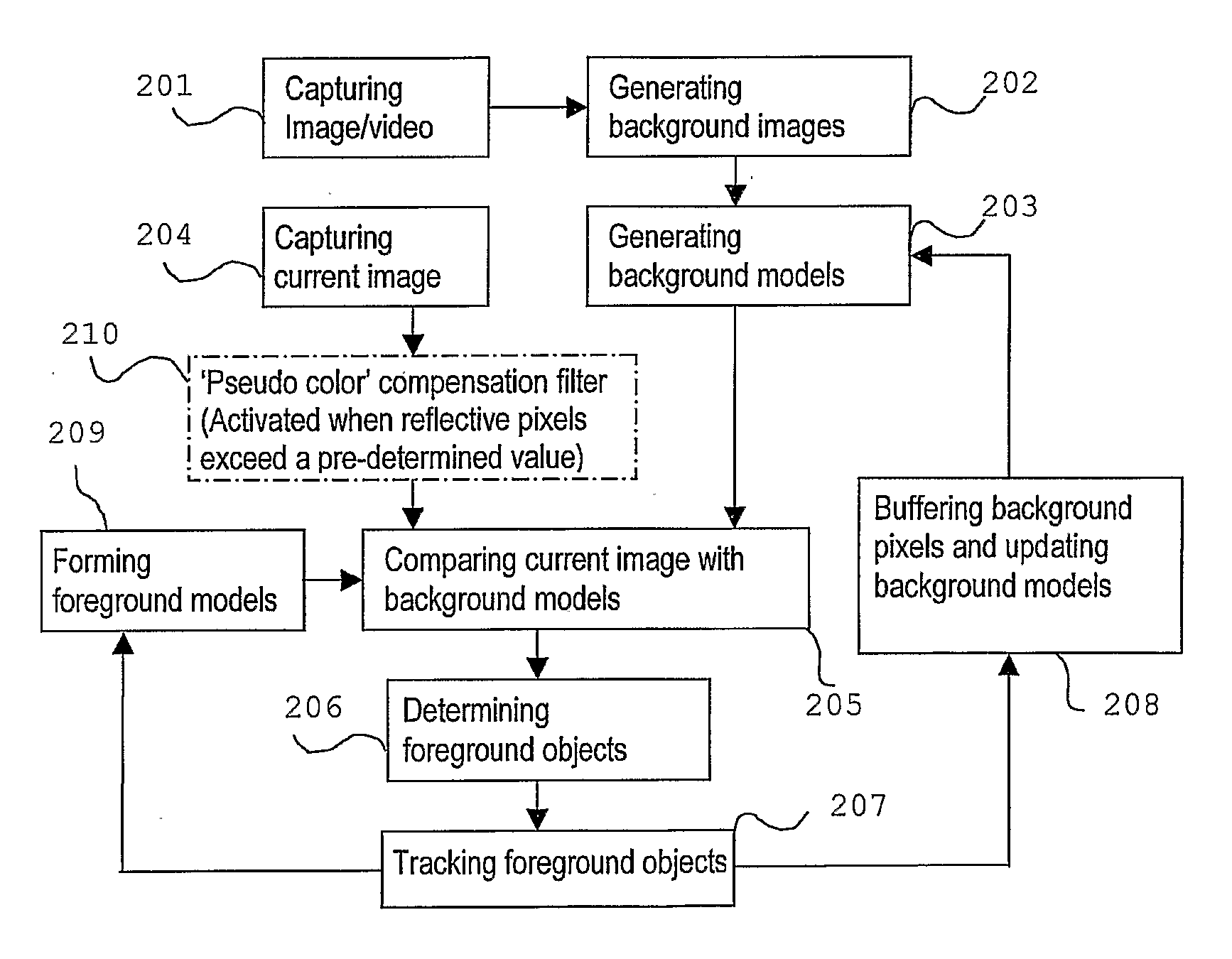
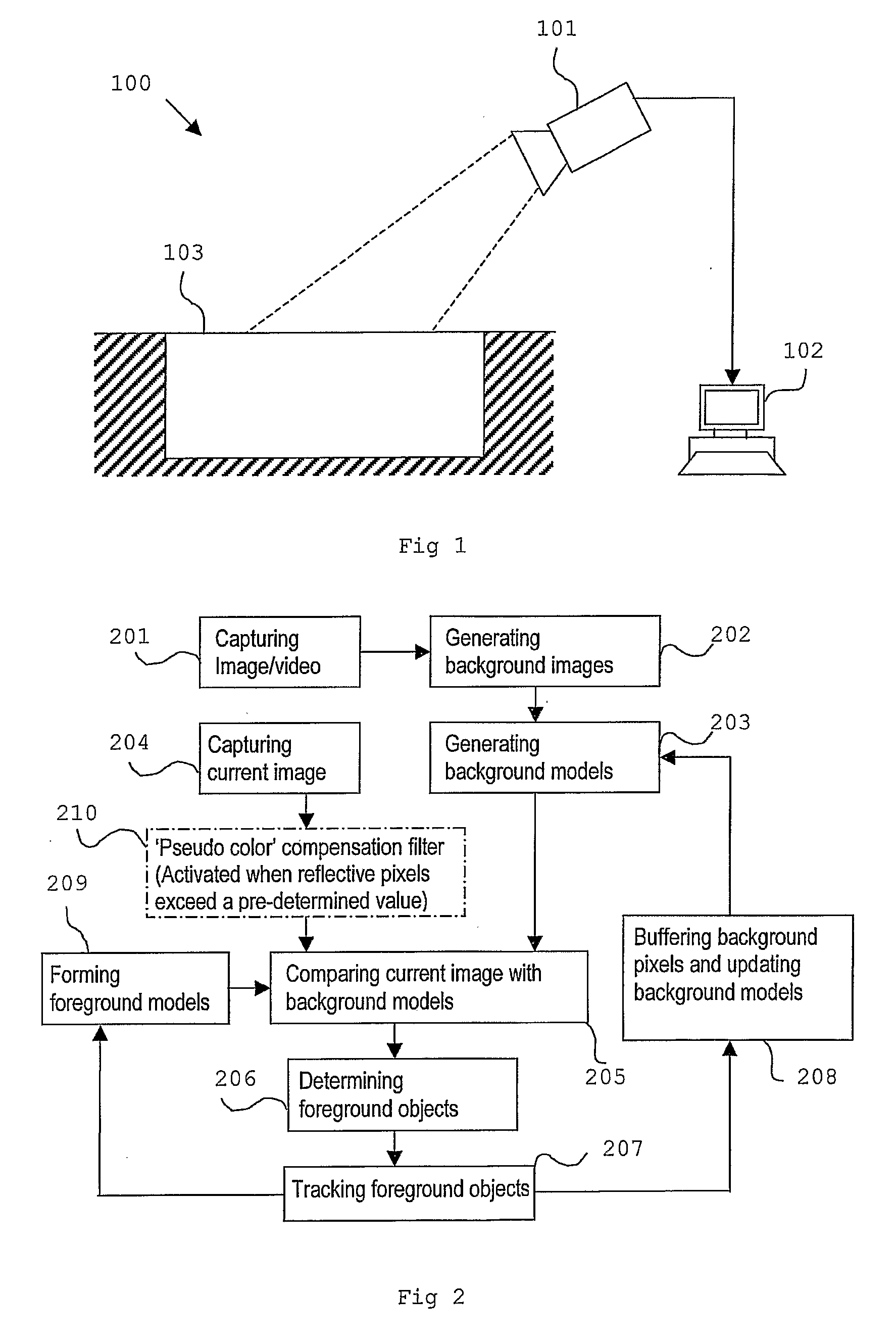
Method for Detecting Desired Objects in a Highly Dynamic Environment by a Monitoring System
ActiveUS20070273765A1Accurate shadeAccurate color informationImage analysisCharacter and pattern recognitionMonitoring systemBackground image
At least one image of the environment is taken using either an image capturing device of the monitoring system. Based on the image of the environment, at least one background image is generated. The background image, which comprises a plurality of pixels, is divided into pixel blocks. In each pixel block, at least one data cluster is formed using at least one feature of the pixels in the pixel block. The data cluster formed in each pixel block is described as a data distribution having a mean value and a standard deviation from the mean value. After generating the background image, a subsequent image is taken by the monitoring system. Each pixel of the subsequent image is compared with the data cluster of the block of the background image correspond to the pixel, and a first discrepancy value is generated accordingly. The pixel of the subsequent image is further compared with the data distribution of at least another pixel block which is adjacent to the pixel block of the background image corresponding to the pixel, and a second discrepancy value is generated as a result of this comparison. Based on the first and second discrepancy value, the pixel of the subsequent image is determined to be either a background pixel or a foreground pixel. After all the pixels in the subsequent image have been determined as either a background or a foreground pixel, a binary map is generated. The connected foreground pixels in the binary map are marked to form a foreground object, which is the detected objected in the environment according to the invention.
Owner:AGENCY FOR SCI TECH & RES
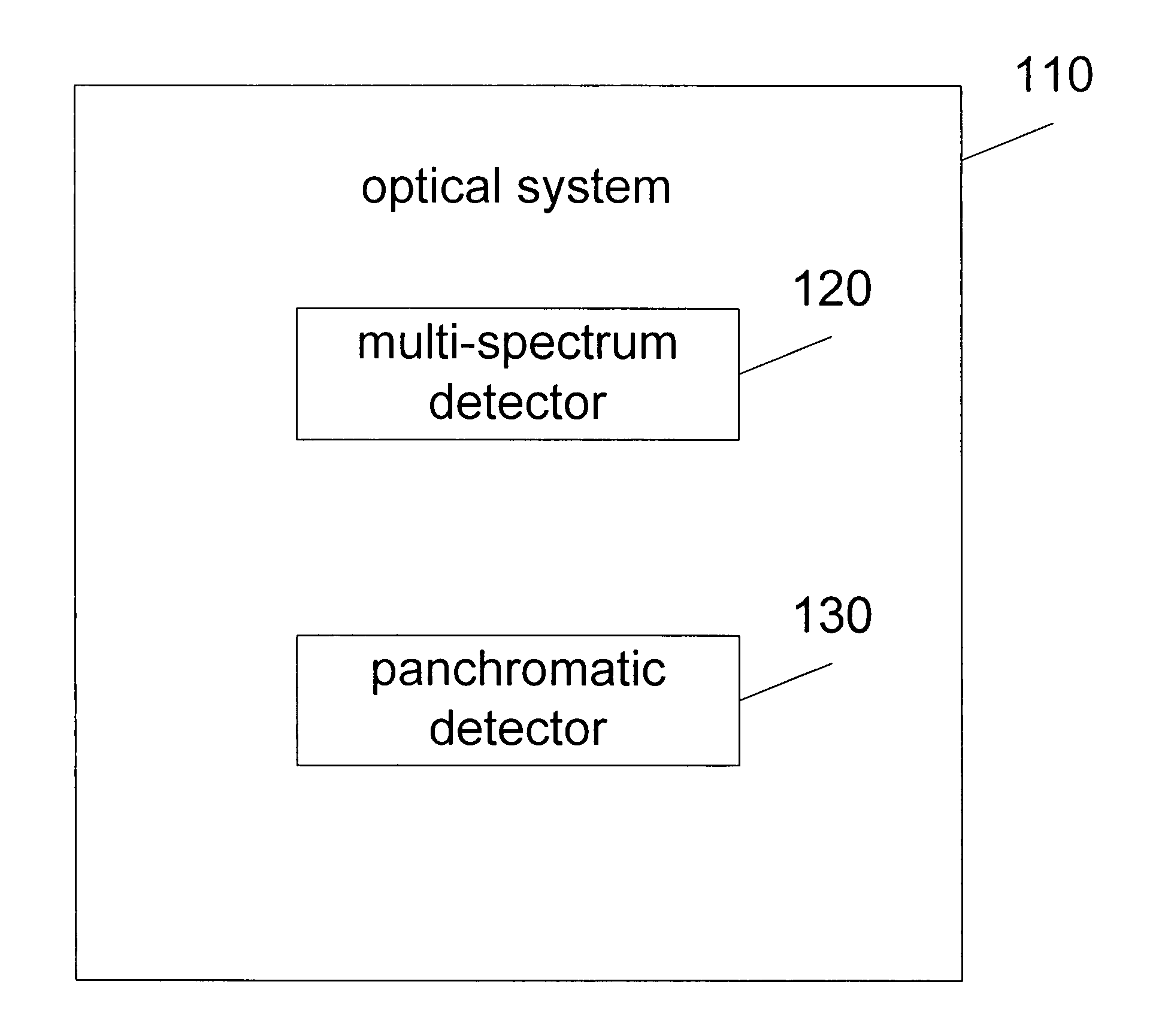
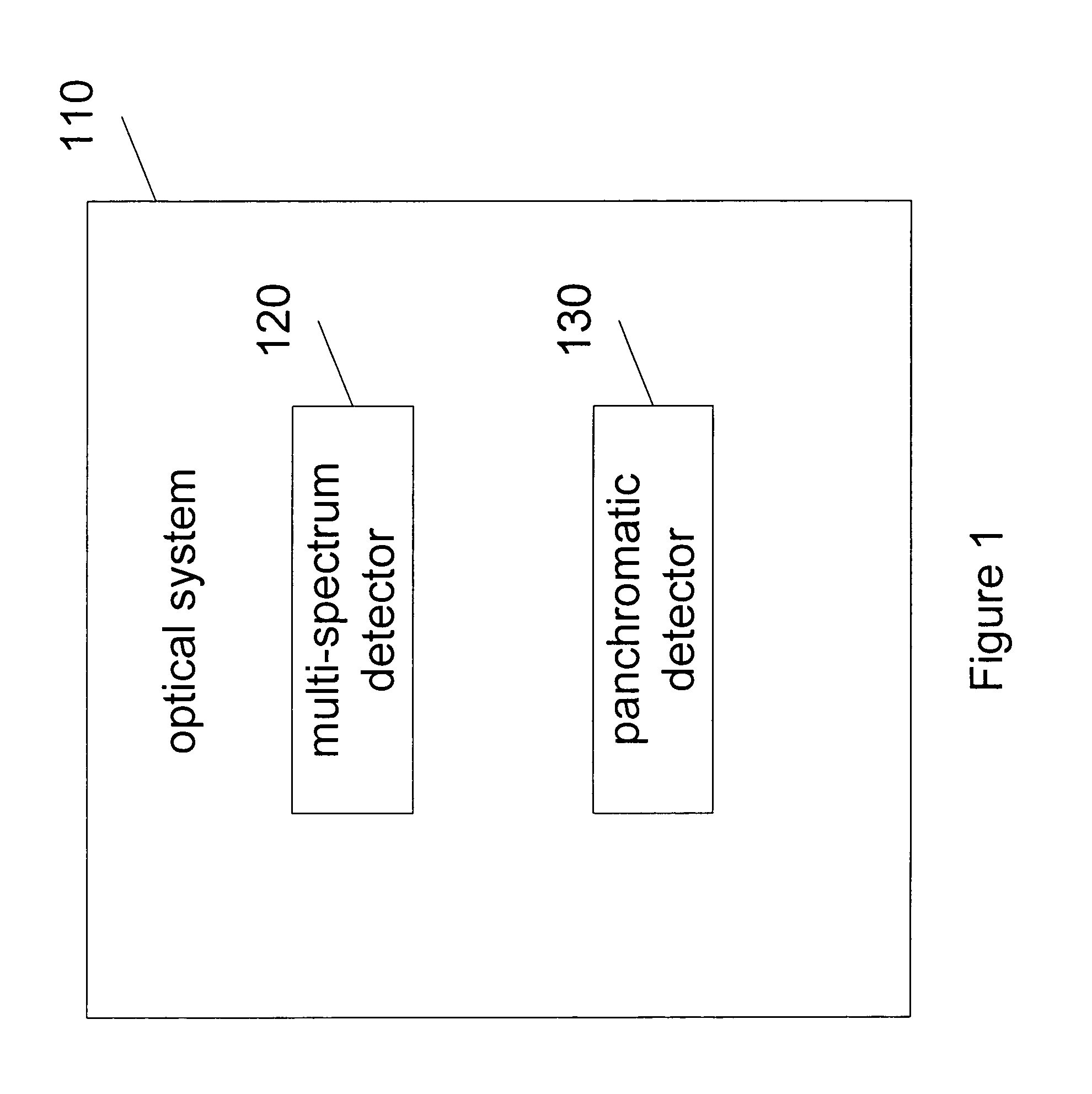
Synthetic panchromatic imagery method and system
ActiveUS7298922B1Quality improvementHigh imagingImage enhancementImage analysisMultispectral imageSpectral weight
Method and system for generating synthetic panchromatic imagery. A method for making a multi-spectral image includes capturing a panchromatic image of an imaging target. Additionally, the method includes capturing at least a first spectral image of the imaging target in a first spectral bandwidth, and capturing at least a second spectral image of the imaging target in a second spectral bandwidth. Also, the method includes determining at least a first spectral weight and a second spectral weight for the first spectral image and the second spectral image respectively. Additionally, the method includes generating a synthetic panchromatic image, determining a registration offset between the synthetic panchromatic image and the captured panchromatic image, warping the first spectral image and the second spectral image, and generating a multi-spectral image.
Owner:LOCKHEED MARTIN CORP
Devices and methods to image objects
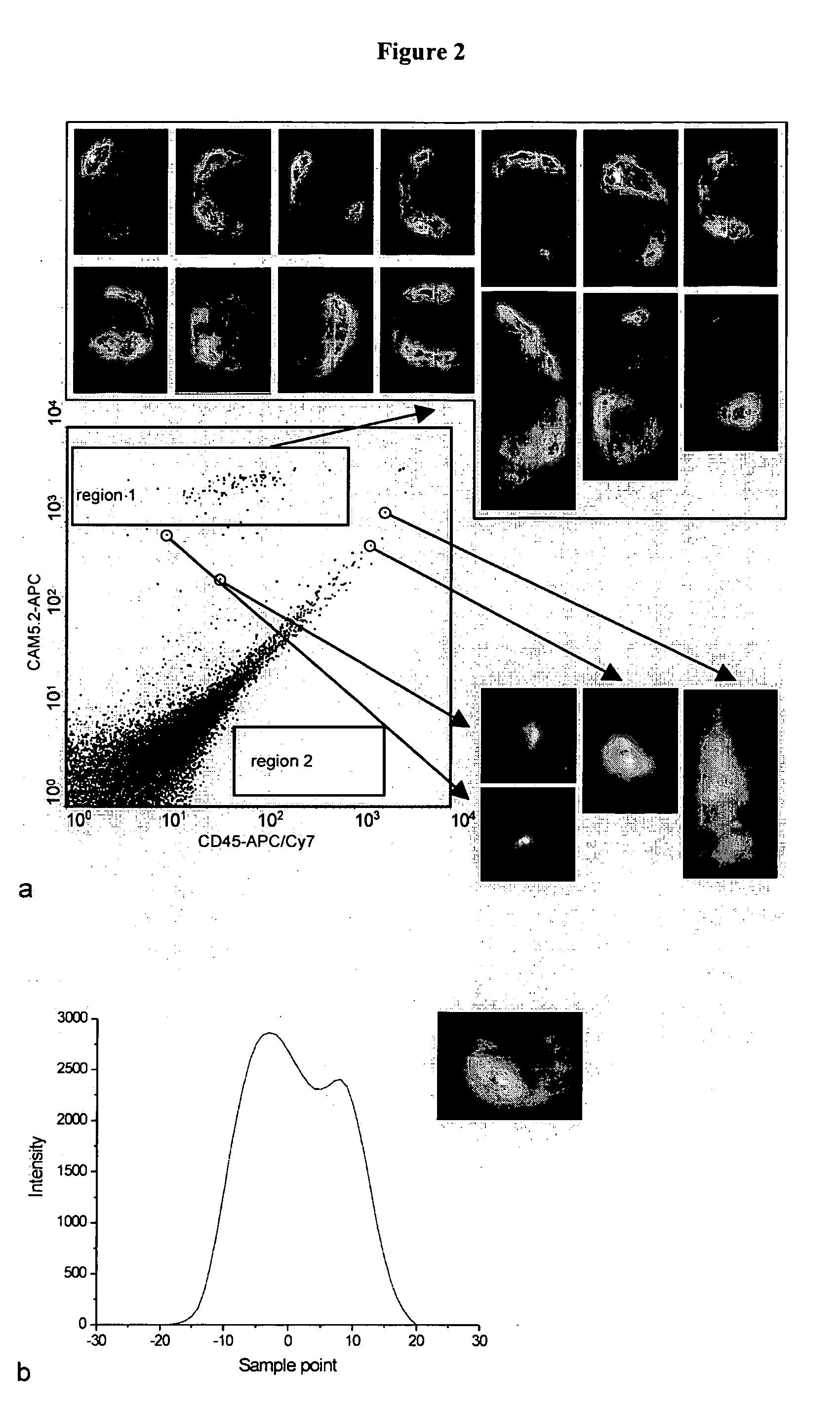
ActiveUS20050003464A1Improve detectionExtensive analysisBioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsImage analysisImage object
Devices and methods for automated collection and image analysis are disclosed that enable identification or classification of microscopic objects aligned or deposited on surfaces. Such objects, e.g. detectably labeled rare target cells, are magnetically or non-magnetically immobilized and subjected to automated laser scanning to generate sequential digitized x-y sub-images or partial images of target and non-target objects that are combined to form reconstructed full images, thereby allowing detection, enumeration, differentiation and characterization of imaged objects on the basis of size, morphology and immunophenotype.
Owner:MENARINI SILICON BIOSYSTEMS SPA
Integrated bi-directional dual axial gradient refractive index/diffraction grating wavelength division multiplexer
InactiveUS6137933AIncreased durabilityImprove the environmentCoupling light guidesExit surfaceWavelength-division multiplexing
A wavelength division multiplexer / demultiplexer is provided that integrates axial gradient refractive index elements with a diffraction grating to provide efficient coupling from a plurality of input optical sources (each delivering a single wavelength to the device) which are multiplexed to a single polychromatic beam for output to a single output optical source. The device comprises: (a) means for accepting an optical input from at least one optical source, the means including a planar surface; (b) a first coupler element comprising (1) a first axial gradient refractive index collimating lens having a planar entrance surface onto which the optical input is incident and (2) a first homogeneous index boot lens affixed to the first collimating lens and having a planar exit surface from which optical light exits; (c) a diffraction grating formed on the planar exit surface which combines a plurality of angularly separated diffracted wavelengths from the optical light; (d) a reflecting element for reflecting the plurality of diffracted wavelengths; (e) a second coupler element comprising (1) a second homogeneous index boot lens having a planar entrance surface onto which said plurality of diffracted wavelengths is incident and (2) a second axial gradient refractive index collimating lens affixed to the second homogeneous index boot lens; and (f) means for outputting at least one multiplexed, polychromatic output beam to an optical receiver, the means including a planar back surface. The device may be operated in either the forward or the reverse direction.
Owner:AUXORA
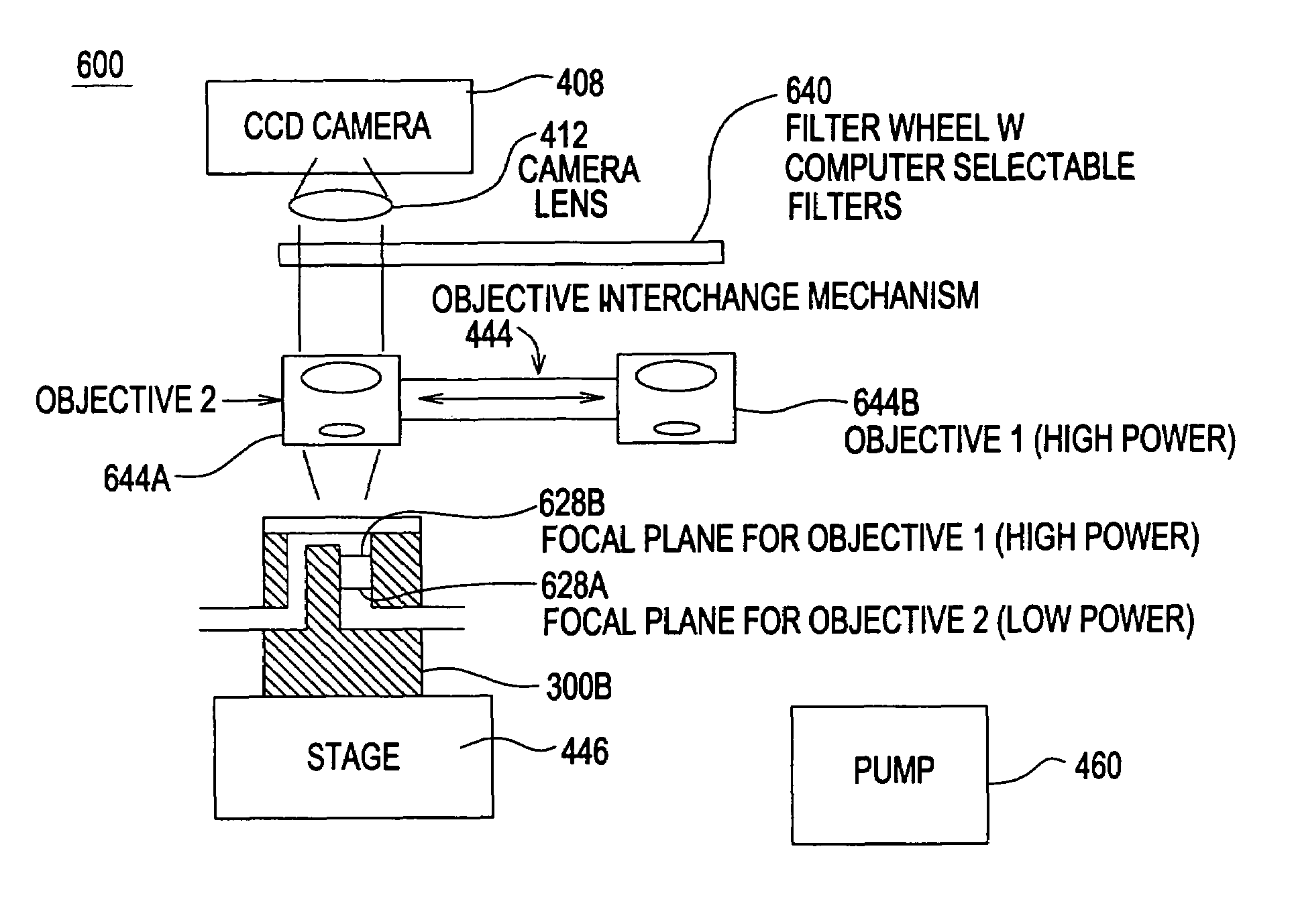
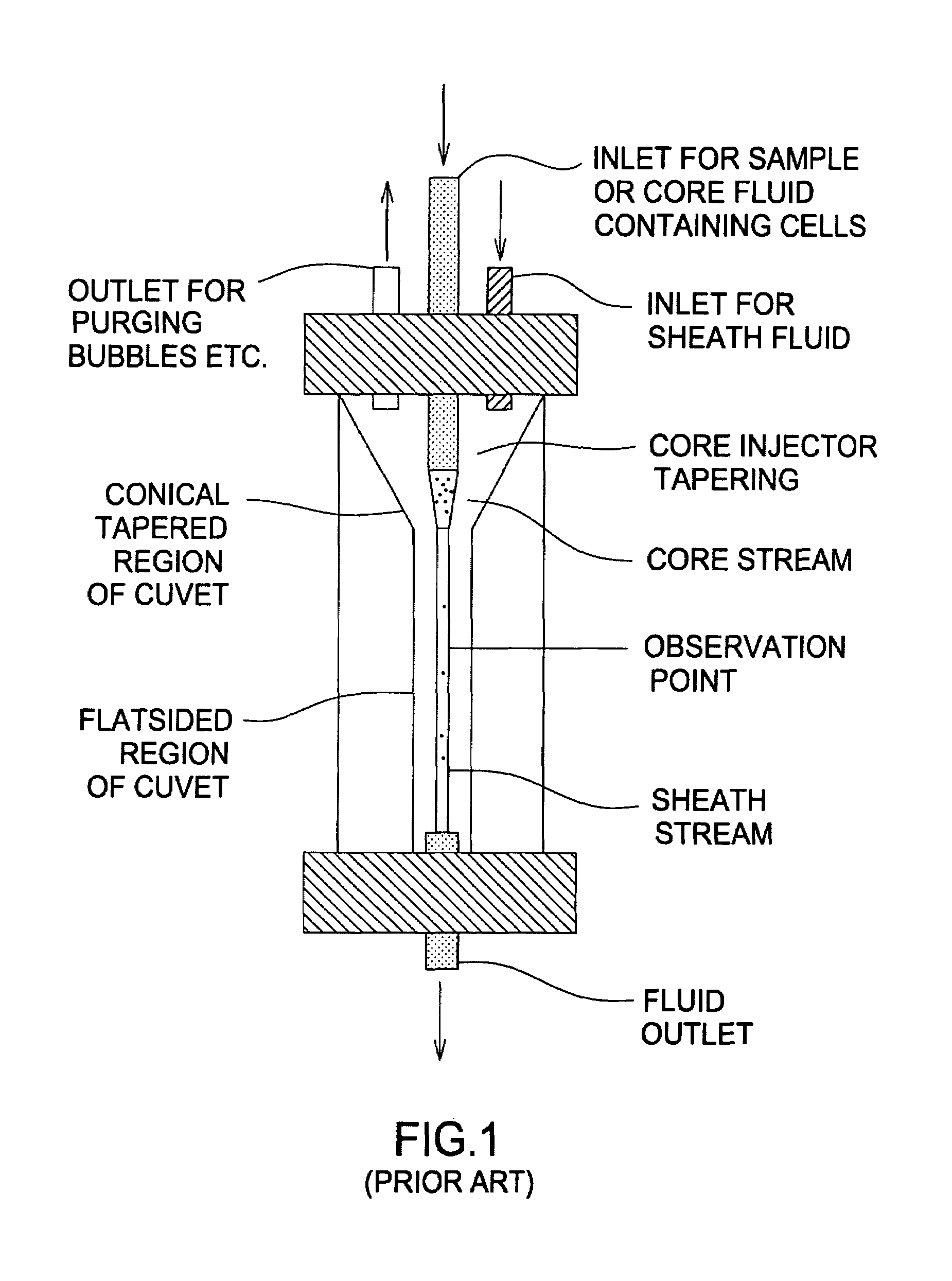
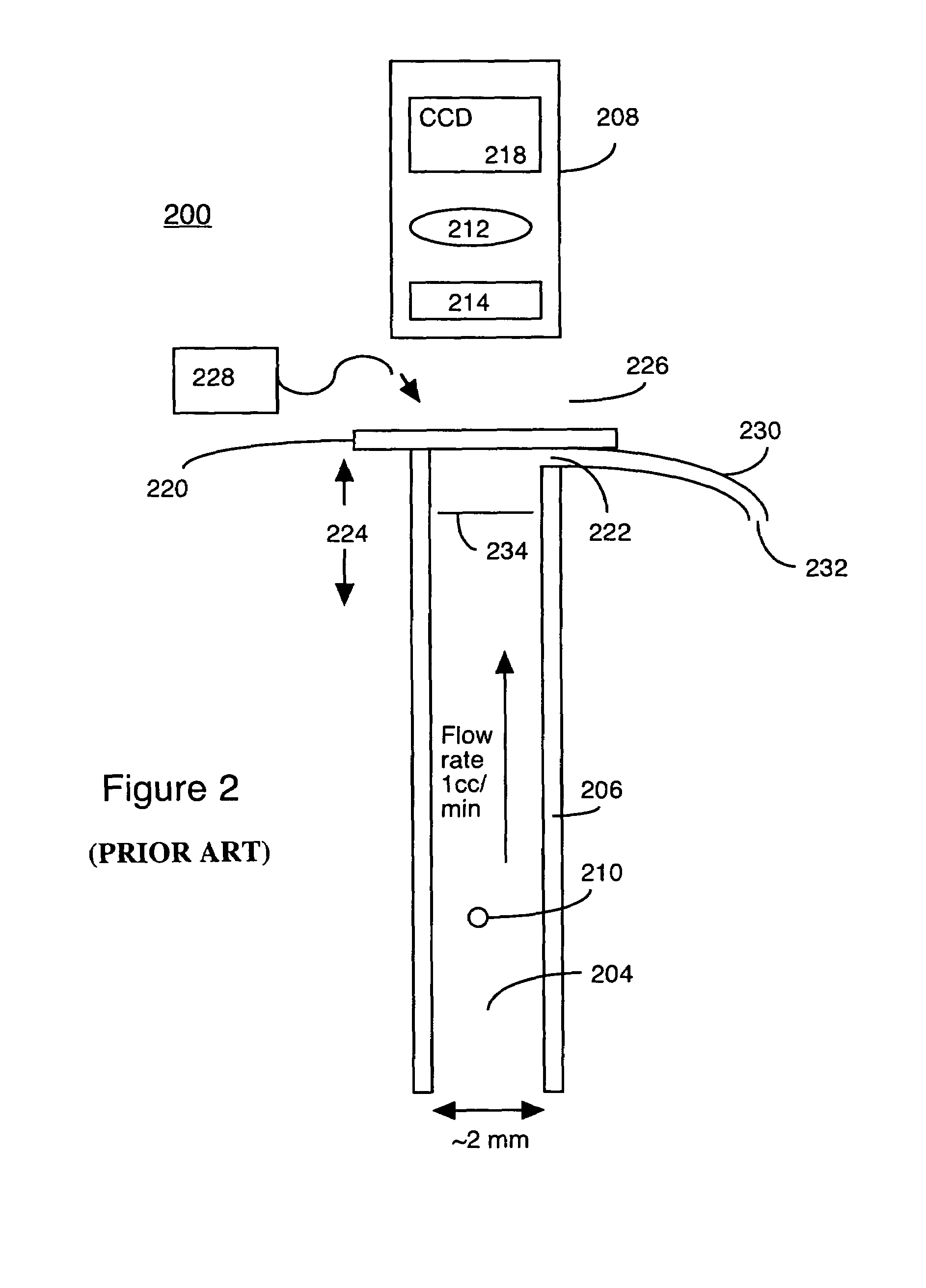
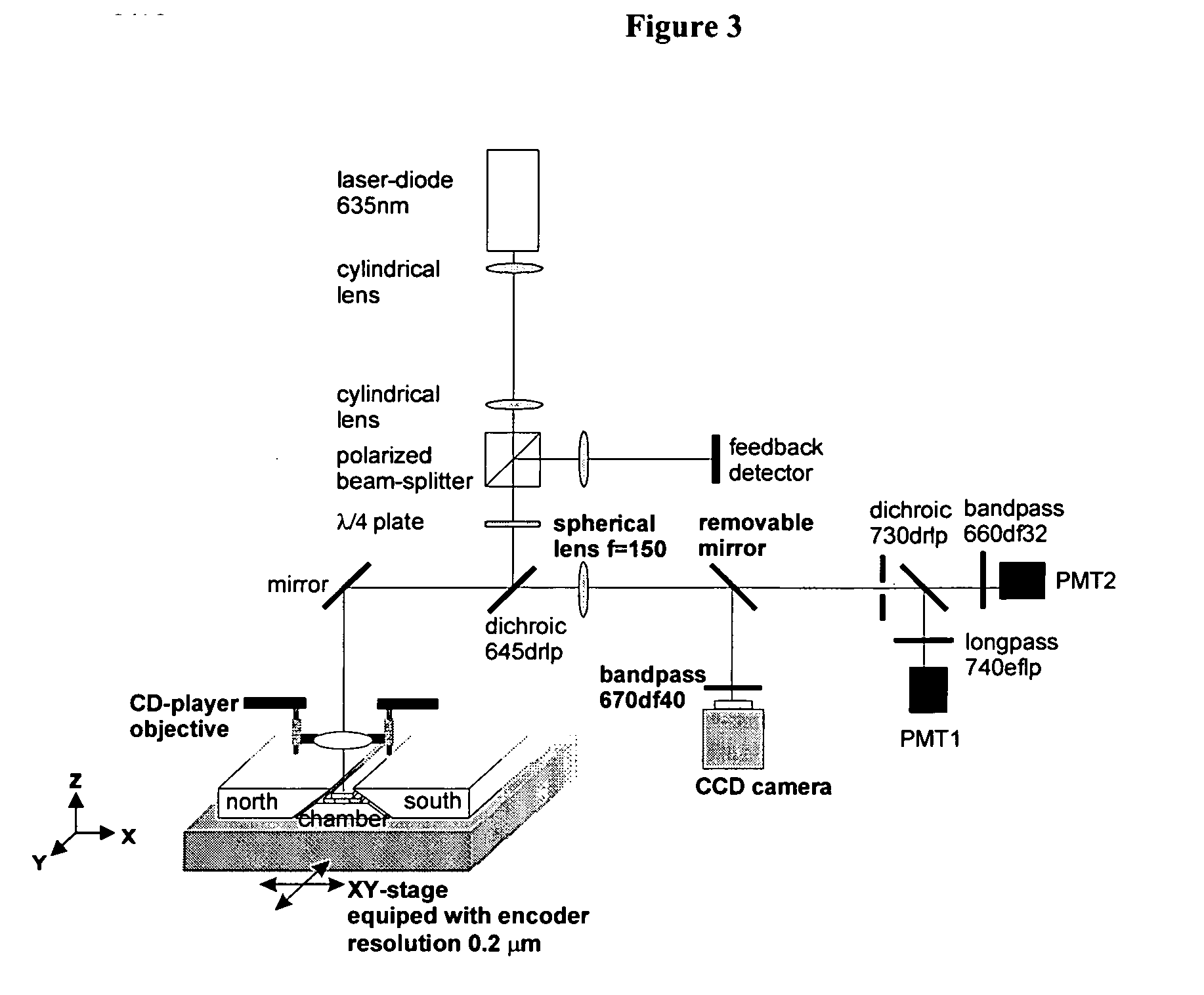
High resolution imaging fountain flow cytometry
InactiveUS7161665B2Improve throughputHigh resolutionWithdrawing sample devicesMaterial analysis by optical meansHigh resolution imagingFlow cell
An imaging fountain flow cytometer allows high resolution microscopic imaging of a flowing sample in real time. Cells of interest are in a vertical stream of liquid flowing toward one or more illuminating elements at wavelengths which illuminate fluorescent dyes and cause the cells to fluoresce. A detector detects the fluorescence emission each time a marked cell passes through the focal plane of the detector. A bi-directional syringe pump allows the user to reverse the flow and locate the detected cell in the field of view. The flow cell is mounted on a computer controlled x-y stage, so the user can center a portion of the image on which to zoom or increase magnification. Several computer selectable parfocal objective lenses allow the user to image the entire field of view and then zoom in on the detected cell at substantially higher resolution. The magnified cell is then imaged at the various wavelengths.
Owner:UNIVERSITY OF WYOMING
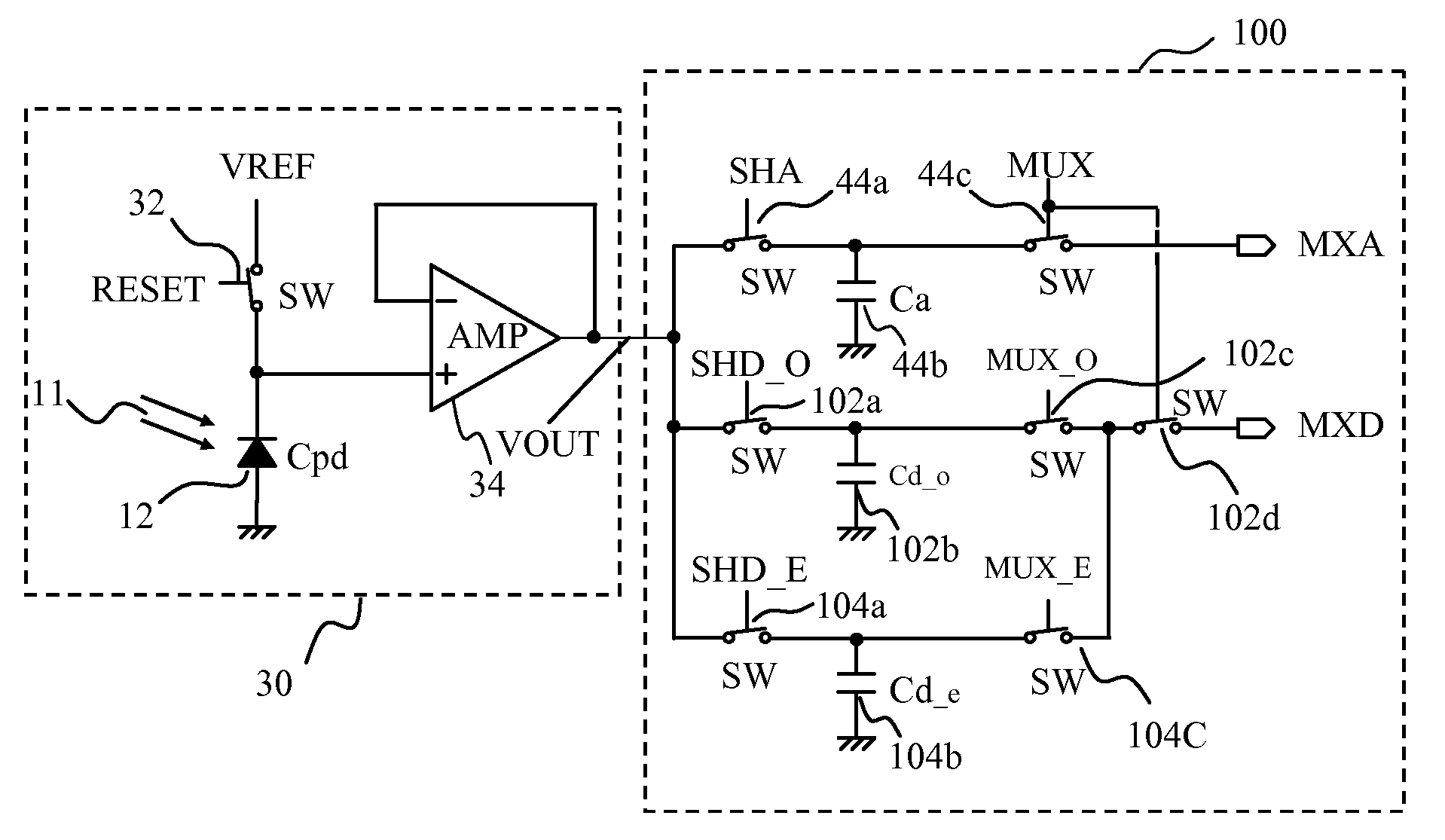
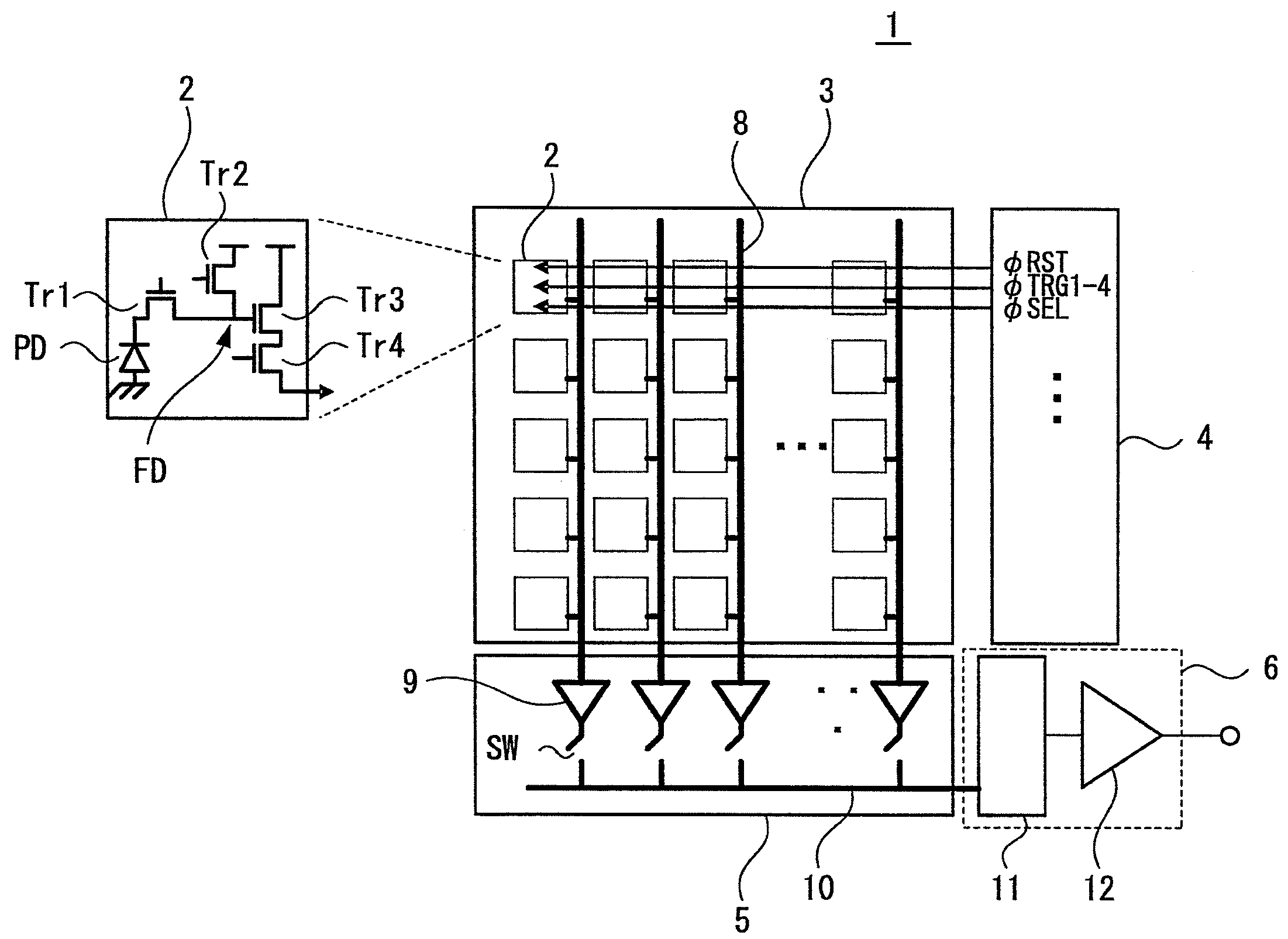
Multi-resolution Image Sensor Array with High Image Quality Pixel Readout Circuitry
InactiveUS20090091648A1Improve performanceImprove image qualityTelevision system detailsTelevision system scanning detailsSensor arrayCMOS sensor
A configurable, compact multi-resolution linear image sensor array is disclosed. The multi-resolution image sensor array employs a spatial array of photoelectric sites with each site having an image output terminal and a cluster of switched photo-detector elements. To effect a high quality snapshot operation mode for a high pixel count array, a transfer control switch is added bridging each photo-detector element and its correspondingly connected negative input terminal of an operational amplifier to form an active pixel sensor circuit. To minimize a reset kTC noise associated with numerous traditional active pixel sensor circuits, an in-pixel KTC noise-correlated correlated multiple sampling (CMS) circuitry is also proposed to replace an otherwise traditional correlated double sampling (CDS) circuitry.
Owner:CMOS SENSOR
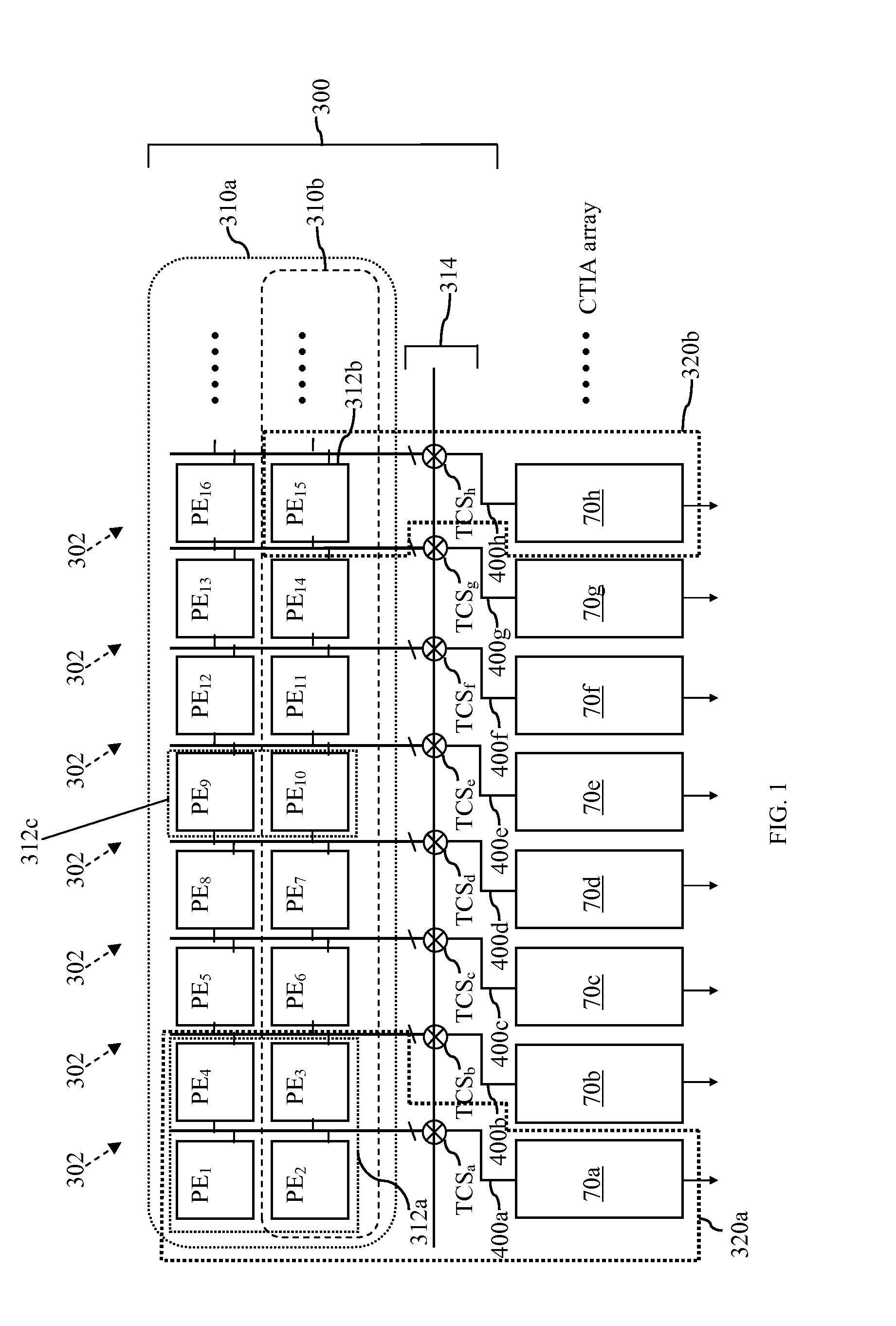
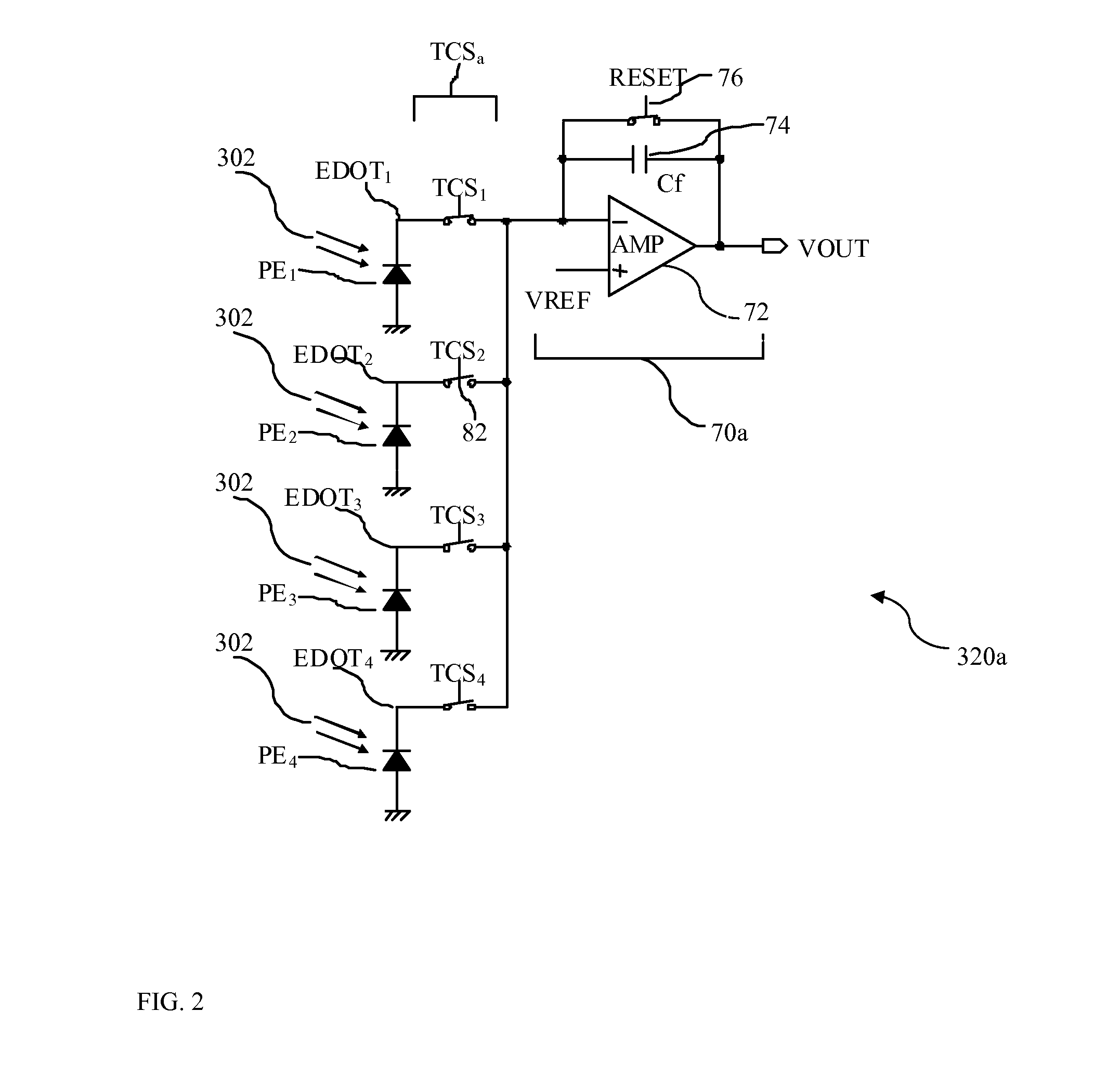
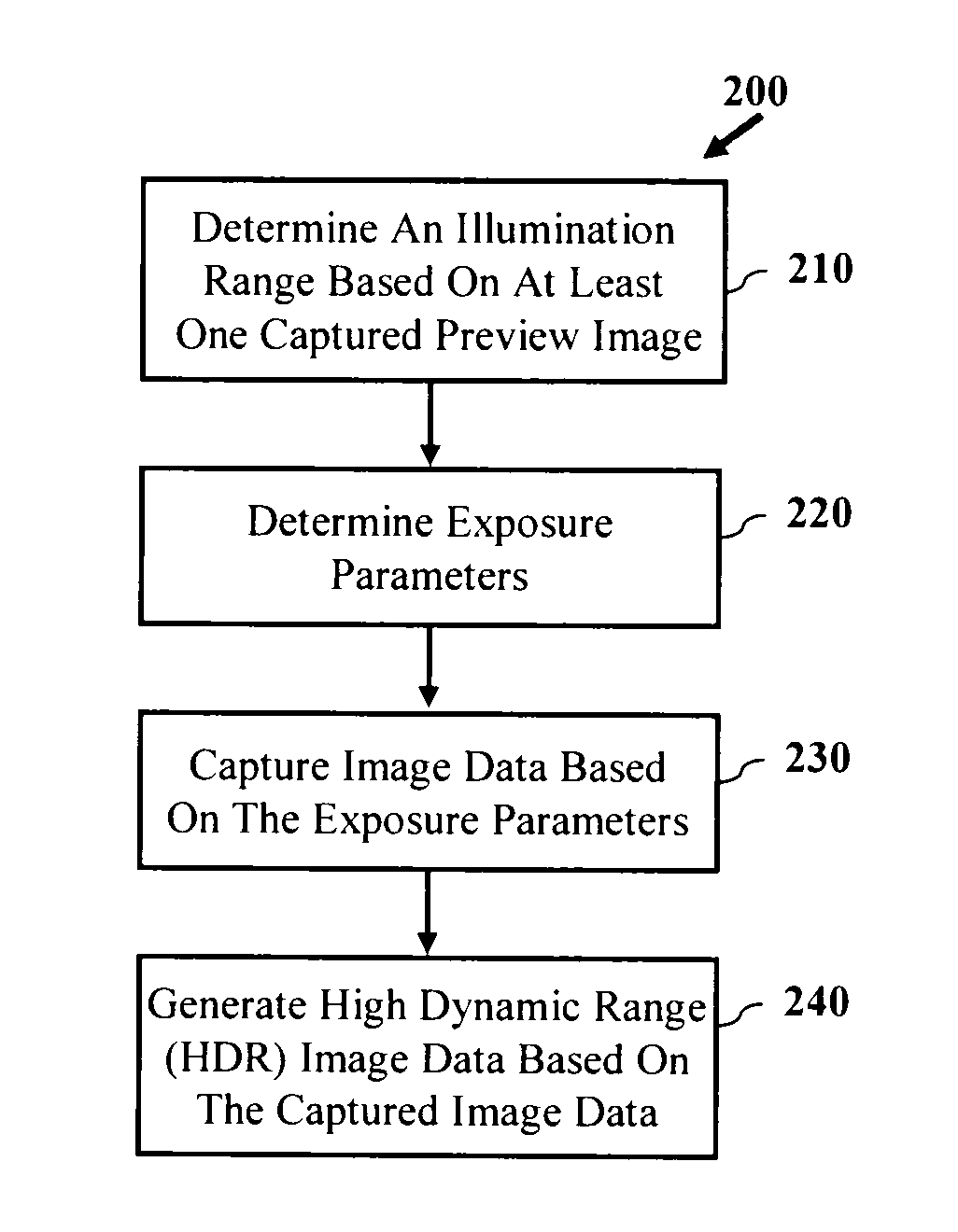
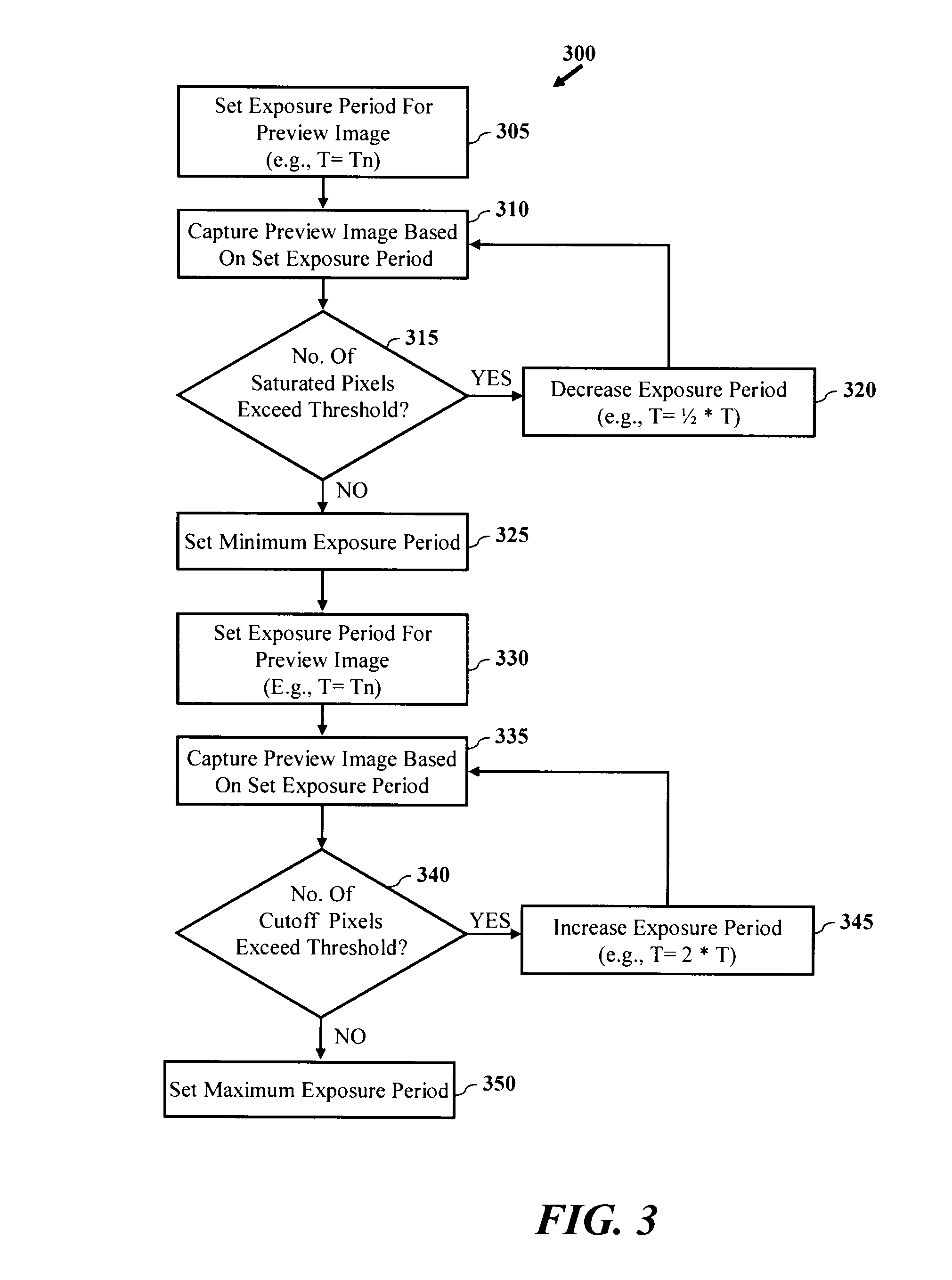
Exposure control for high dynamic range image capture
InactiveUS20100259636A1High dynamic range (HDR) image dataHigh imagingTelevision system detailsColor television detailsImage sensorExposure period
A device and methods are provided for producing a high dynamic range (HDR) image of a scene are disclosed and claimed. In one embodiment, method includes setting an exposure period of an image sensor of the digital camera and capturing image data based on the exposure period. The method may further include checking the image data to determine whether the number of saturated pixels exceeds a saturation threshold and checking the image data to determine whether the number of cutoff pixels exceeds a cutoff threshold. The method may further include generating a high dynamic range image based on image data captured by the digital camera, wherein the high dynamic range image is generated based on a minimum number of images to capture a full dynamic range of the scene.
Owner:QUALCOMM INC
Determining Material Stiffness Using Multiple Aperture Ultrasound
ActiveUS20130218012A1High resolutionHigh imagingOrgan movement/changes detectionInfrasonic diagnosticsDiseaseSonification
Changes in tissue stiffness have long been associated with disease. Systems and methods for determining the stiffness of tissues using ultrasonography may include a device for inducing a propagating shear wave in tissue and tracking the speed of propagation, which is directly related to tissue stiffness and density. The speed of a propagating shear wave may be detected by imaging a tissue at a high frame rate and detecting the propagating wave as a perturbance in successive image frames relative to a baseline image of the tissue in an undisturbed state. In some embodiments, sufficiently high frame rates may be achieved by using a ping-based ultrasound imaging technique in which unfocused omni-directional pings are transmitted (in an imaging plane or in a hemisphere) into a region of interest. Receiving echoes of the omnidirectional pings with multiple receive apertures allows for substantially improved lateral resolution.
Owner:MAUI IMAGING
Fixing device, and image forming apparatus using the fixing device
InactiveUS7702271B2High imagingHigh quality tonerElectrographic process apparatusImage formationEngineering
Owner:RICOH KK
Toner, developer, image forming method, and toner container
ActiveUS20070015077A1Quality improvementHigh color reproductionDevelopersElectrographic processes using charge patternPolyesterParticulates
A toner is provided manufactured by a method having the steps: dispersing toner constituents including a resin, in an aqueous medium containing a particulate resin, wherein the resin has a polyester skeleton formed by a ring-opening addition reaction of a cyclic ester with a first compound having an active hydrogen group; and a developer and an image forming method using the toner, and a toner container containing the toner.
Owner:RICOH KK
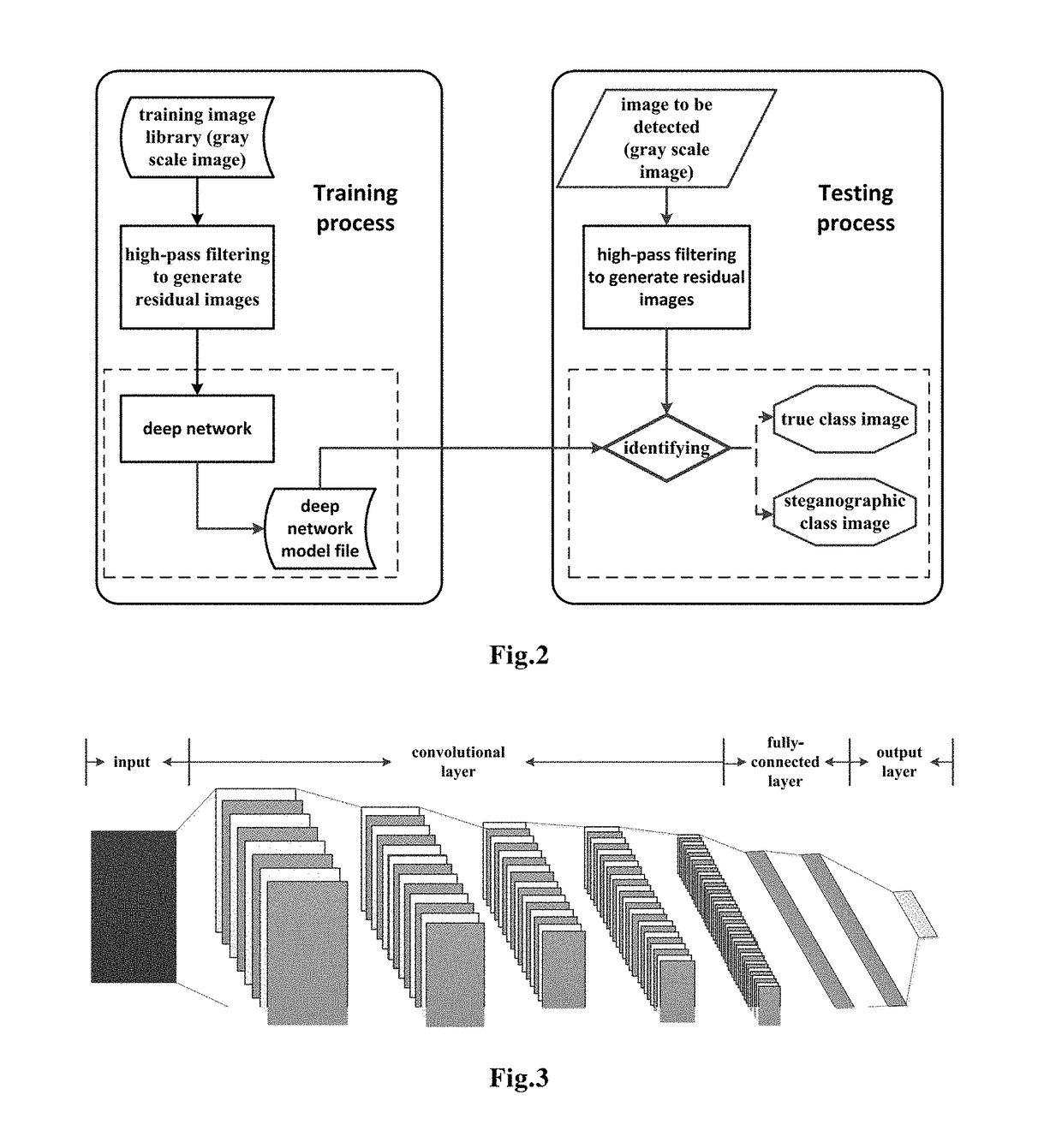
Image Steganalysis Based on Deep Learning
ActiveUS20180068429A1Highly universal image steganalysis modelAccurate identificationImage enhancementImage analysisSteganalysisFeature learning
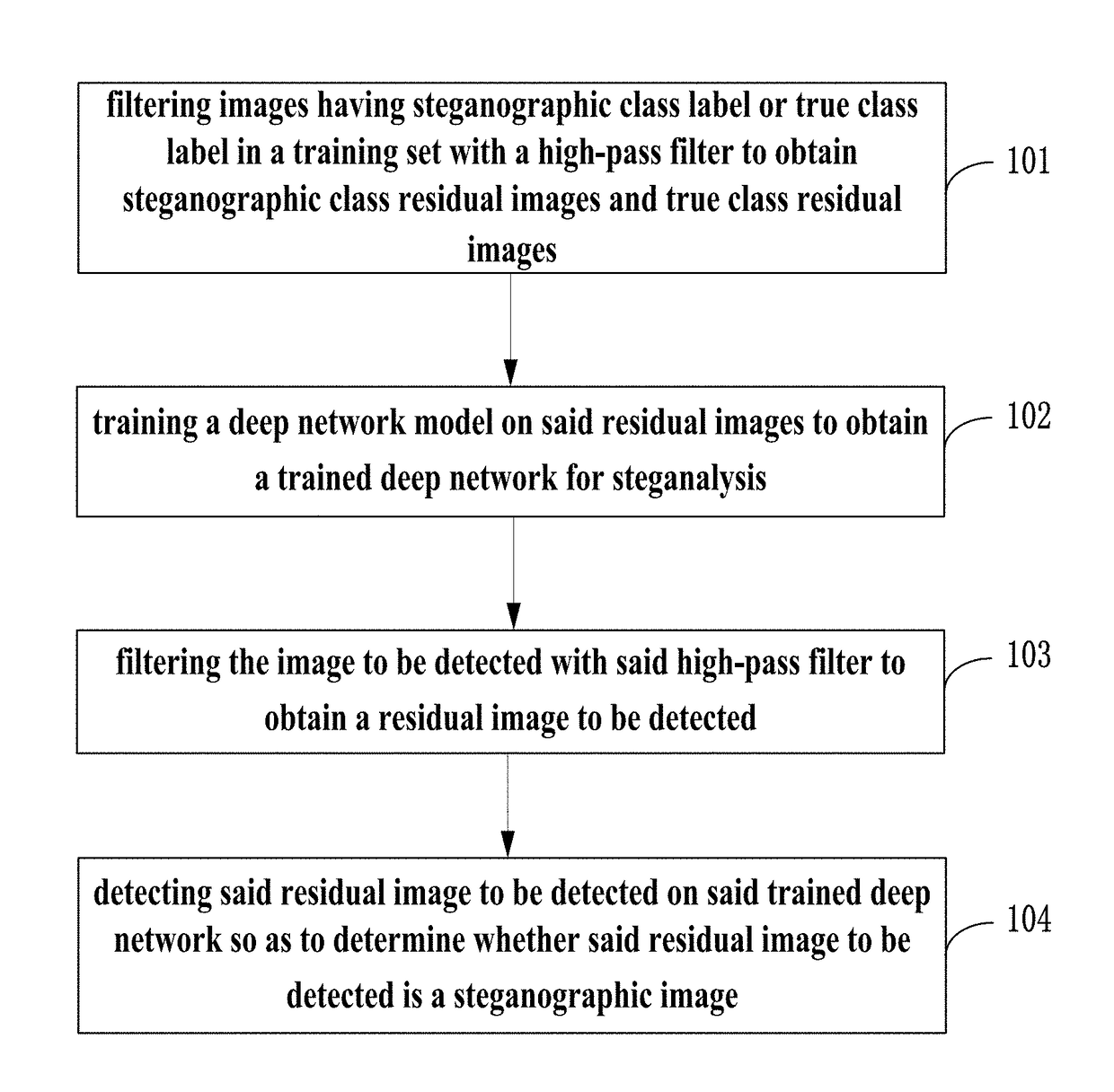
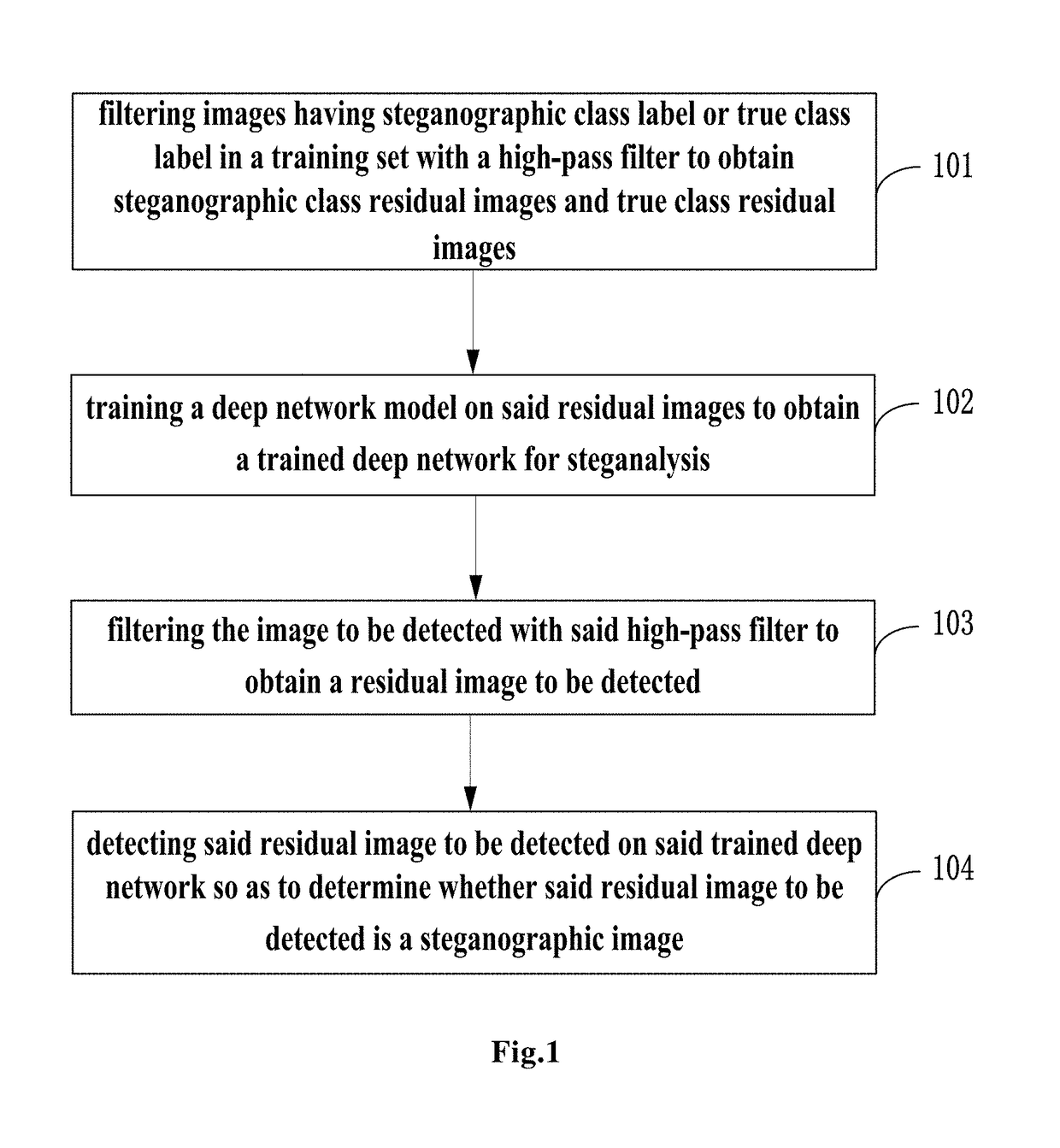
The present invention provides a method for detecting image steganography based on deep learning, which comprises: filtering images having steganographic class label or true class label in a training set with a high-pass filter to obtain a training set including steganographic class residual images and true class residual images; training a deep network model on said training set to obtain a trained deep model for steganalysis; filtering the image to be detected with said high-pass filter to obtain a residual image to be detected; detecting said residual image to be detected on said deep model so as to determine whether said residual image to be detected is a steganographic image. The method for detecting image steganography in the present invention can create an automatic blind steganalysis model through feature learning and can identify steganographic images accurately.
Owner:INST OF AUTOMATION CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Devices and methods to image objects by time delay integration
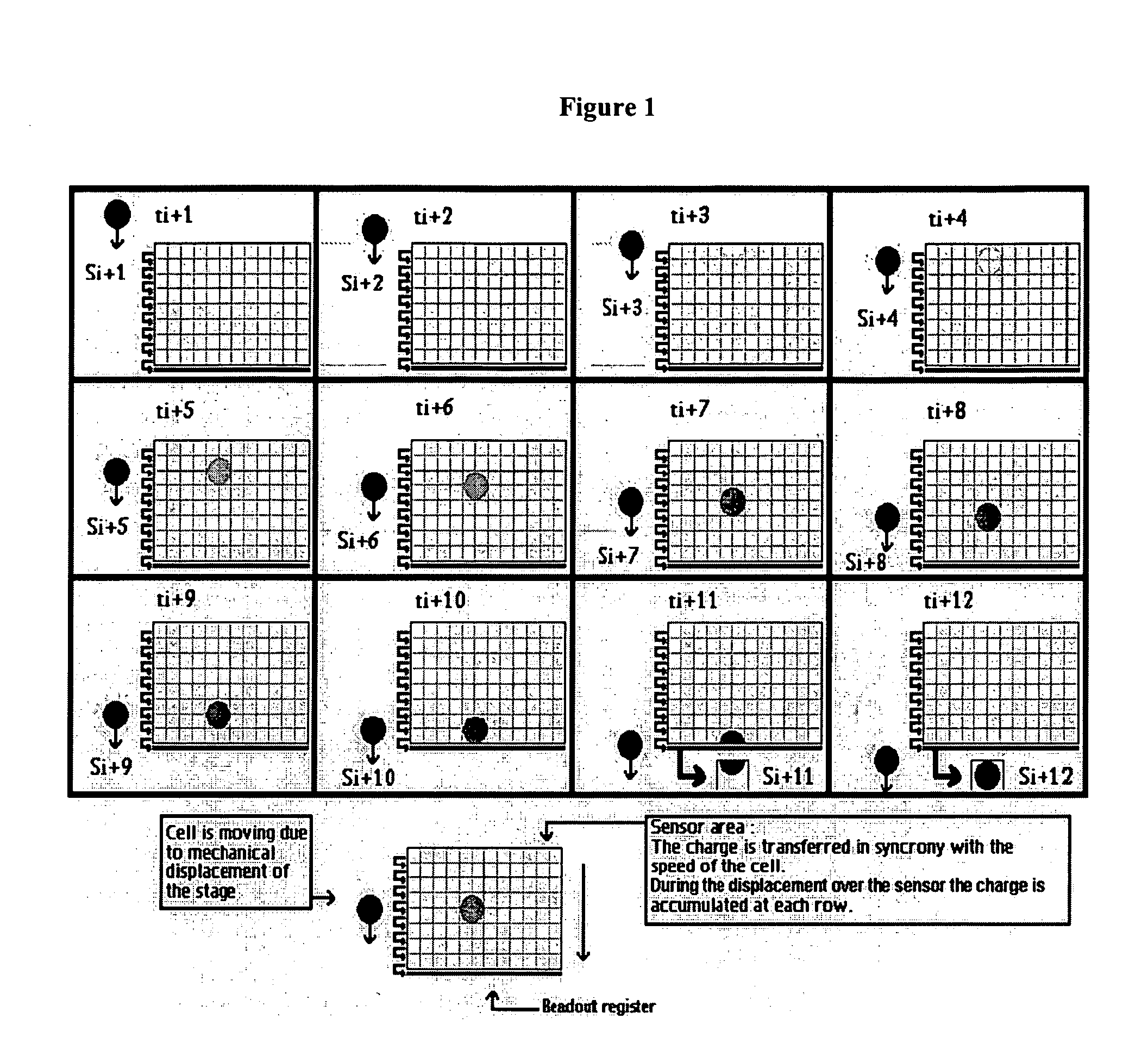
InactiveUS20060147901A1Improved detection and enumeration and classificationAvoid lostBioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsRare cellSignal-to-noise ratio (imaging)
Devices and methods for automated collection and image analysis are disclosed that enable identification or classification of microscopic objects aligned or deposited on surfaces. Such objects, e.g. detectably labeled rare target cells, are magnetically or non-magnetically immobilized and subjected to Time Delay Integration imaging (TDI). Incorporation of TDI technology into image cytometry analysis, like CellTracks®, makes it possible to image moving objects with very high sensitivity and signal-to-noise ratios. Implementation of TDI camera technology with dual excitation and multispectral imaging of enriched rare cells provides a rapid system for detection, enumeration, differentiation and characterization of imaged rare cells on the basis of size, morphology and immunophenotype.
Owner:JANSSEN DIAGNOSTICS LLC
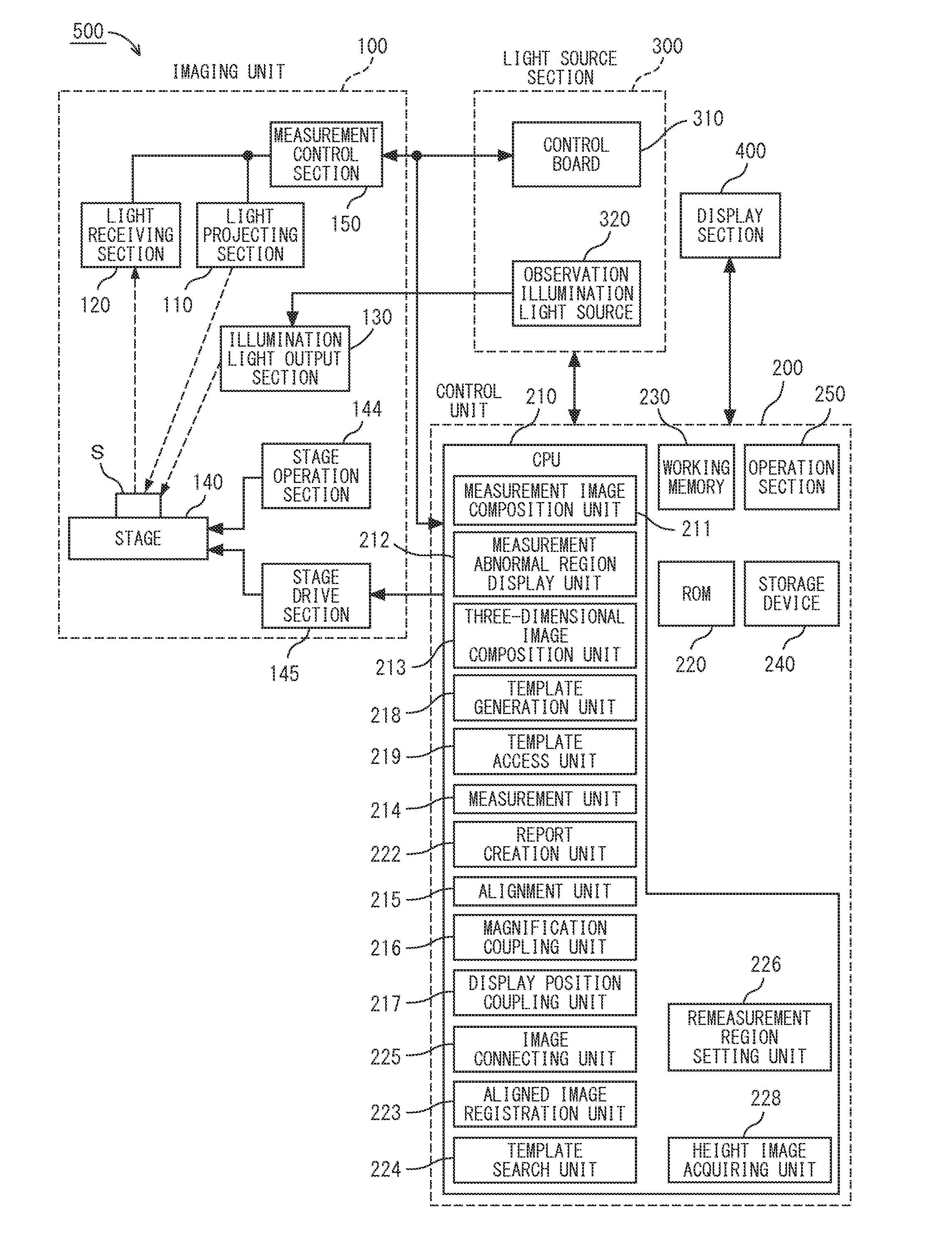
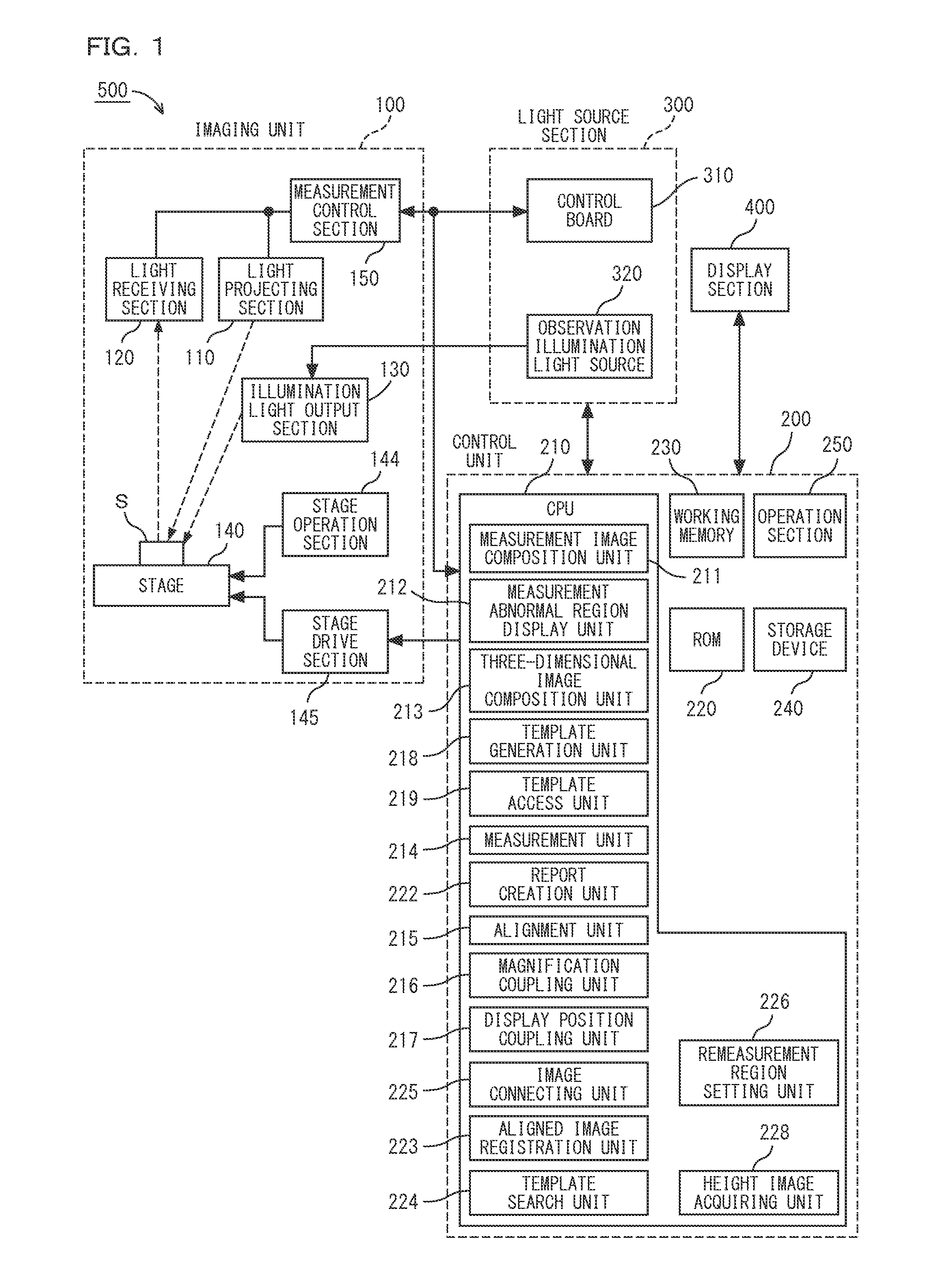
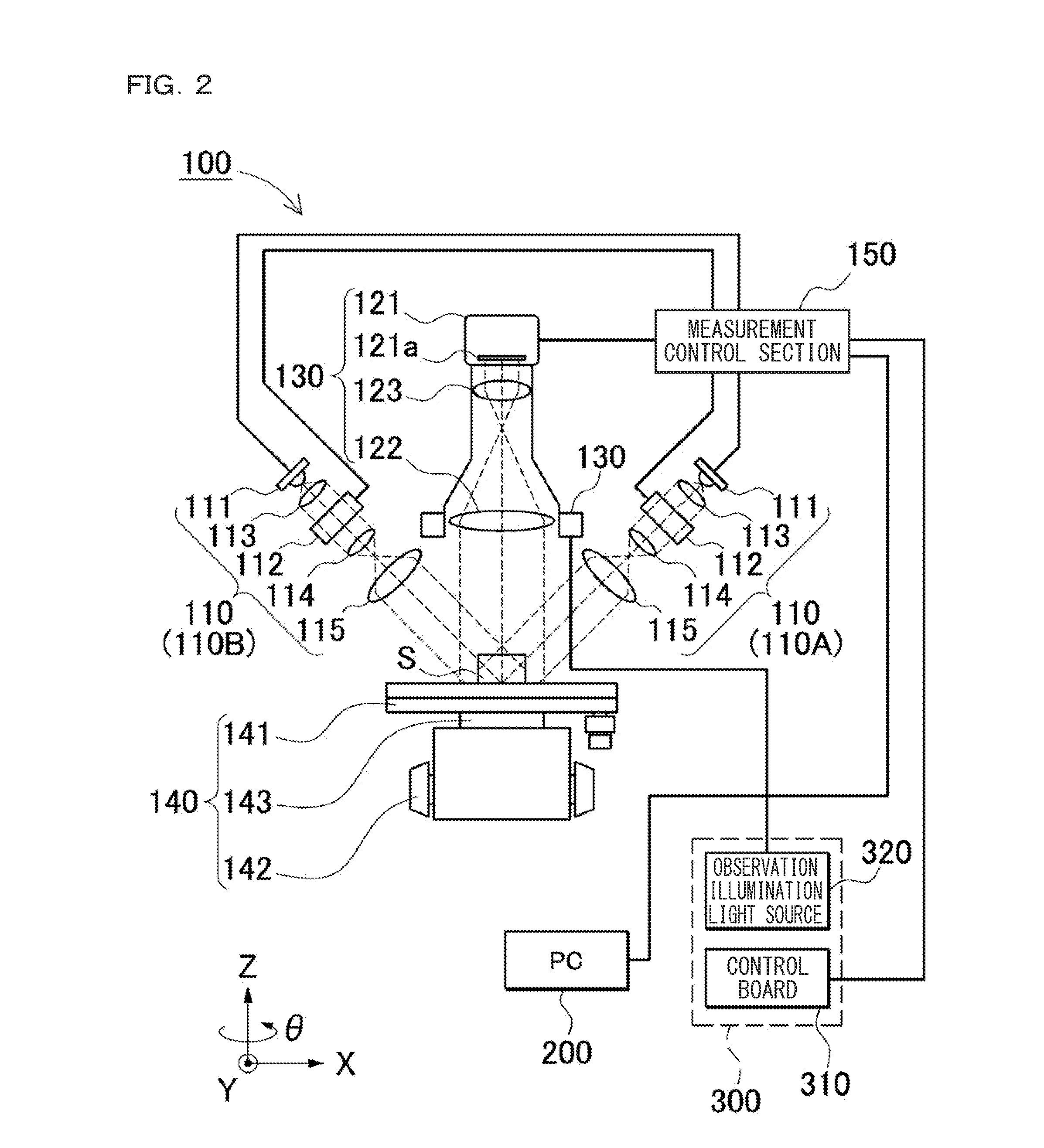
Measurement Microscope Device, Image Generating Method, Measurement Microscope Device Operation Program, And Computer-Readable Recording Medium
ActiveUS20140152794A1Wide visual field without causing deterioration in measurement accuracyImprove accuracyColor television detailsClosed circuit television systemsVisual field lossObservational error
An image with a wide visual field can be captured without causing deterioration in measurement accuracy. There are provided: a stage on which an object is placed; a display unit for displaying a height image or an observation image; a measurement unit for performing measurement on the height image; an image connecting unit configured to, by moving the stage and capturing a different region, acquire a plurality of height images, and connect the obtained plurality of height images and observation images to generate a connected image; a measurement error region display unit configured to superimpose and display a measurement error region, on an image of the object; and a measurement-image imaging condition setting unit for adjusting an imaging condition for a striped image required for generation of the height image to reduce the measurement error region.
Owner:KEYENCE
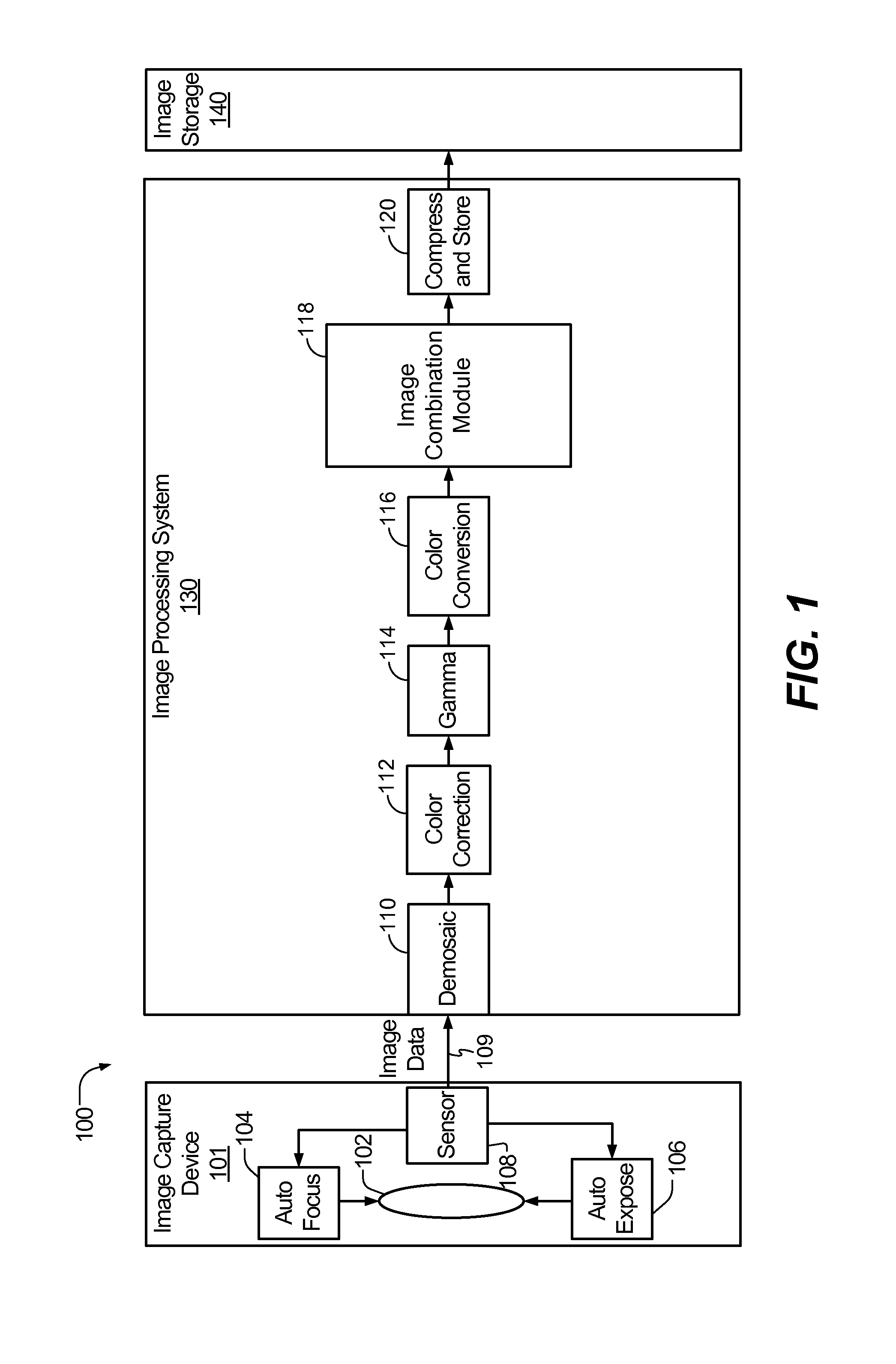
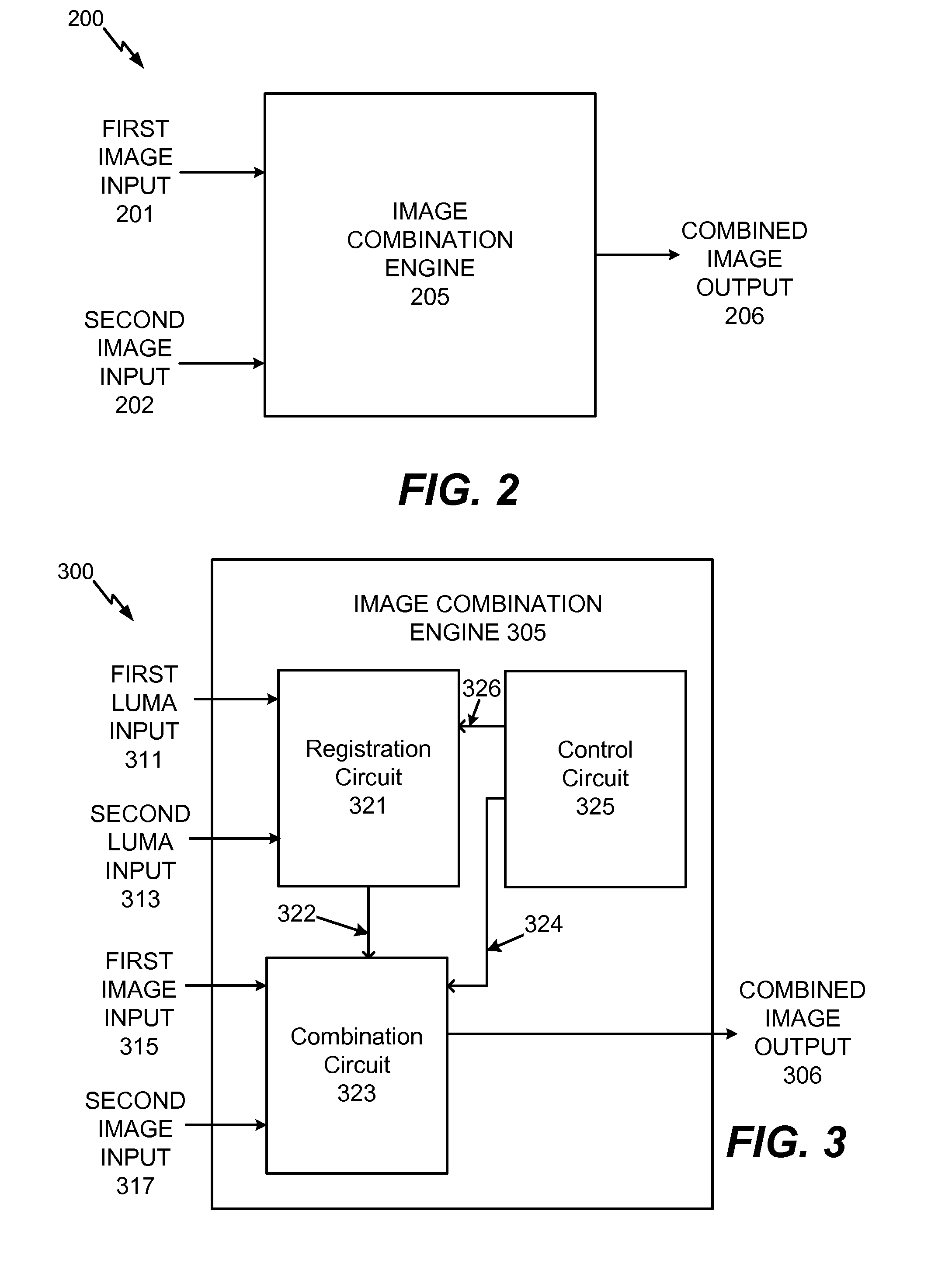
System and method to selectively combine images
InactiveUS20100157079A1Issue of imageReduce ghostingImage enhancementTelevision system detailsMotion vectorControl circuit
Systems and methods to selectively combine images are disclosed. In a particular embodiment, an apparatus includes a registration circuit configured to generate a set of motion vector data based on first image data corresponding to a first image and second image data corresponding to a second image. The apparatus includes a combination circuit to selectively combine the first image data and adjusted second image data that corresponds to the second image data adjusted according to the motion vector data. The apparatus further includes a control circuit to control the combination circuit to generate third image data.
Owner:QUALCOMM INC
Holography-based device, system and method for coded aperture imaging
A system and related method for coded aperture sensing, comprising: passing at least one scene wavefront from a target scene through at least one original coded aperture mask onto a focal plane array, producing a diffracted projection of the target scene; and processing the diffracted projection into a representation of the target scene by correlating a function of the diffracted projection with a function of a known array pattern of the at least one original coded aperture mask and by using at least one reconstructing wavefront for holographic reconstructing.
Owner:APPLIED SCI INNOVATIONS
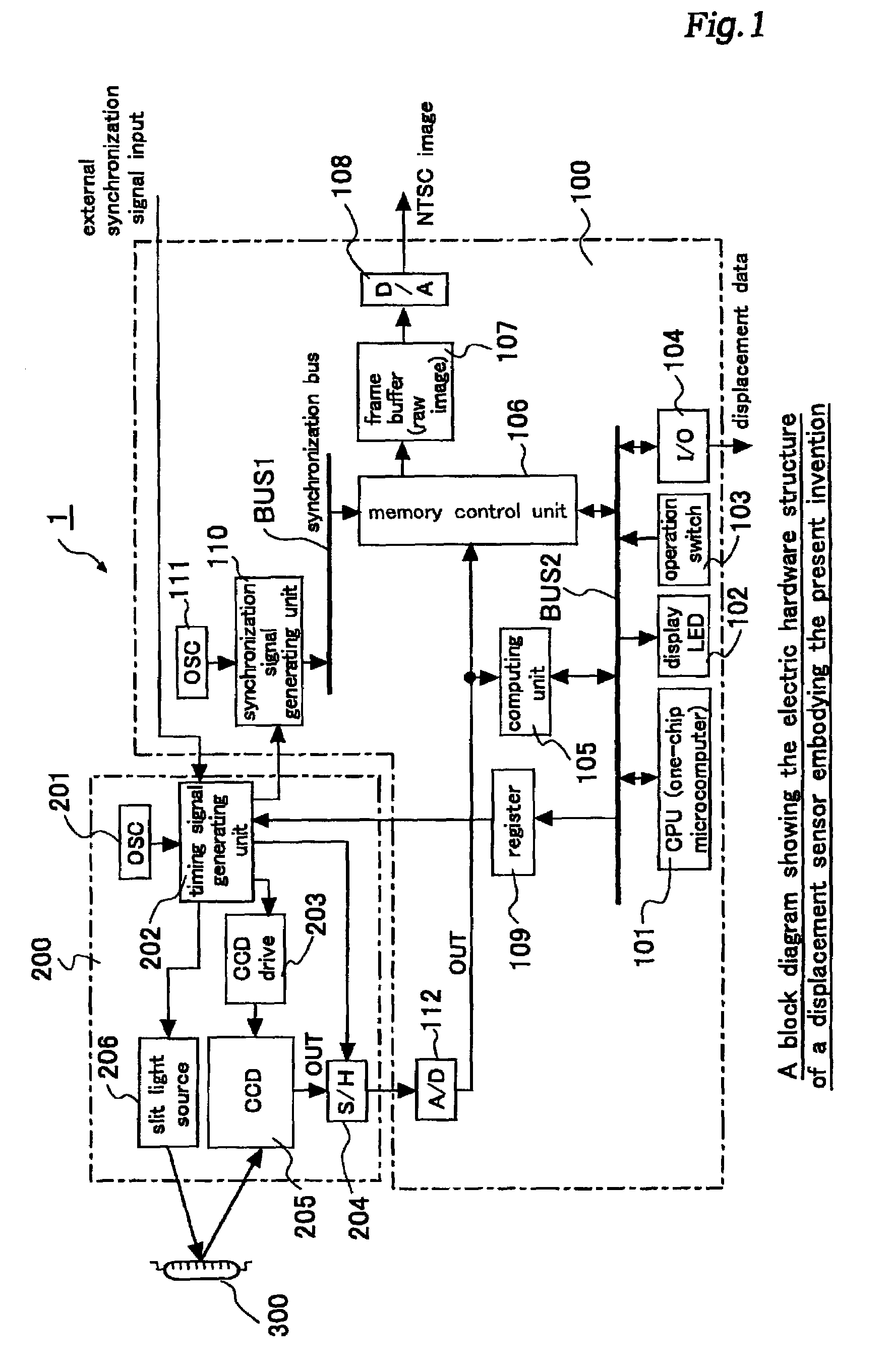
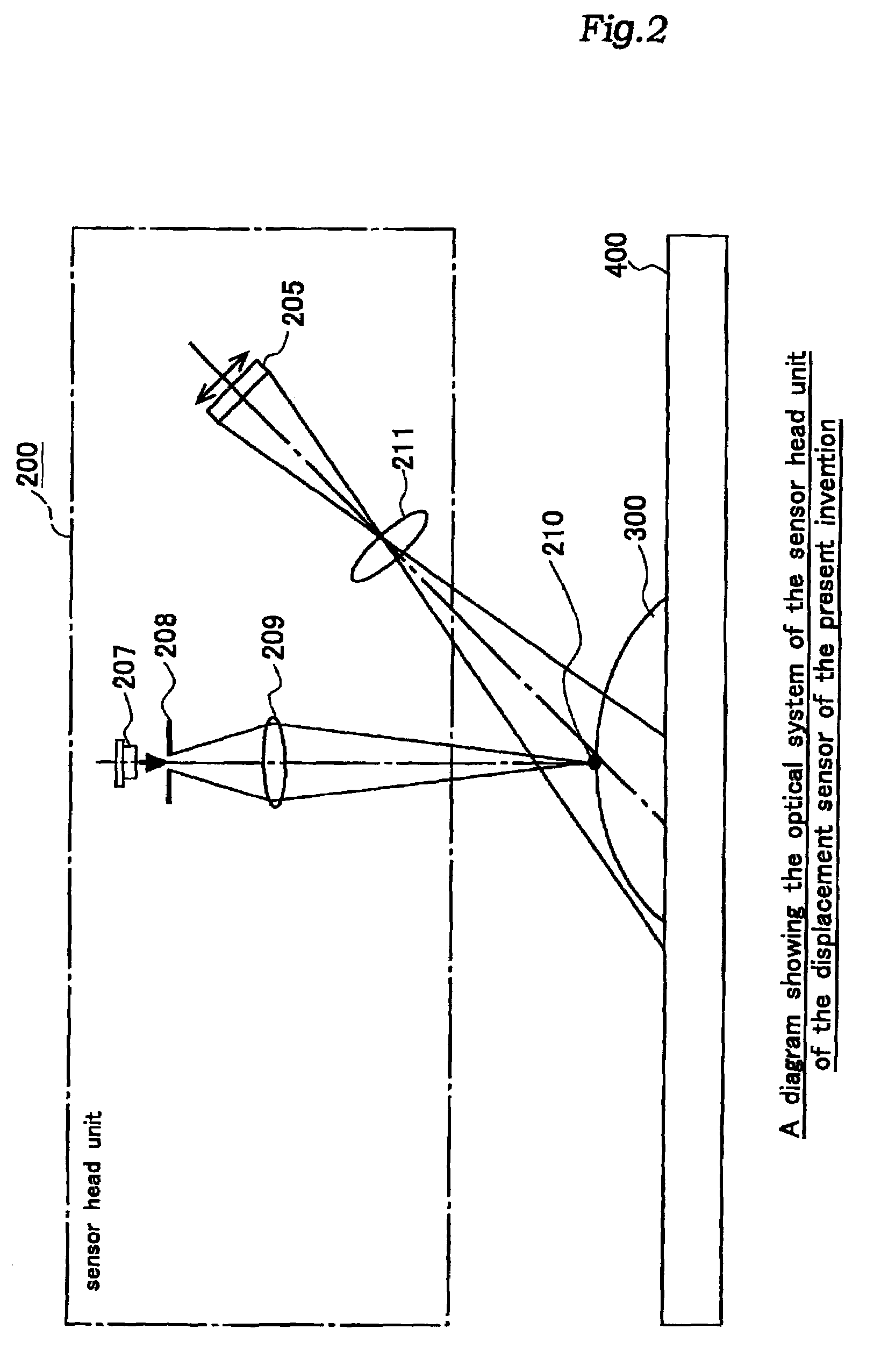
Displacement sensor
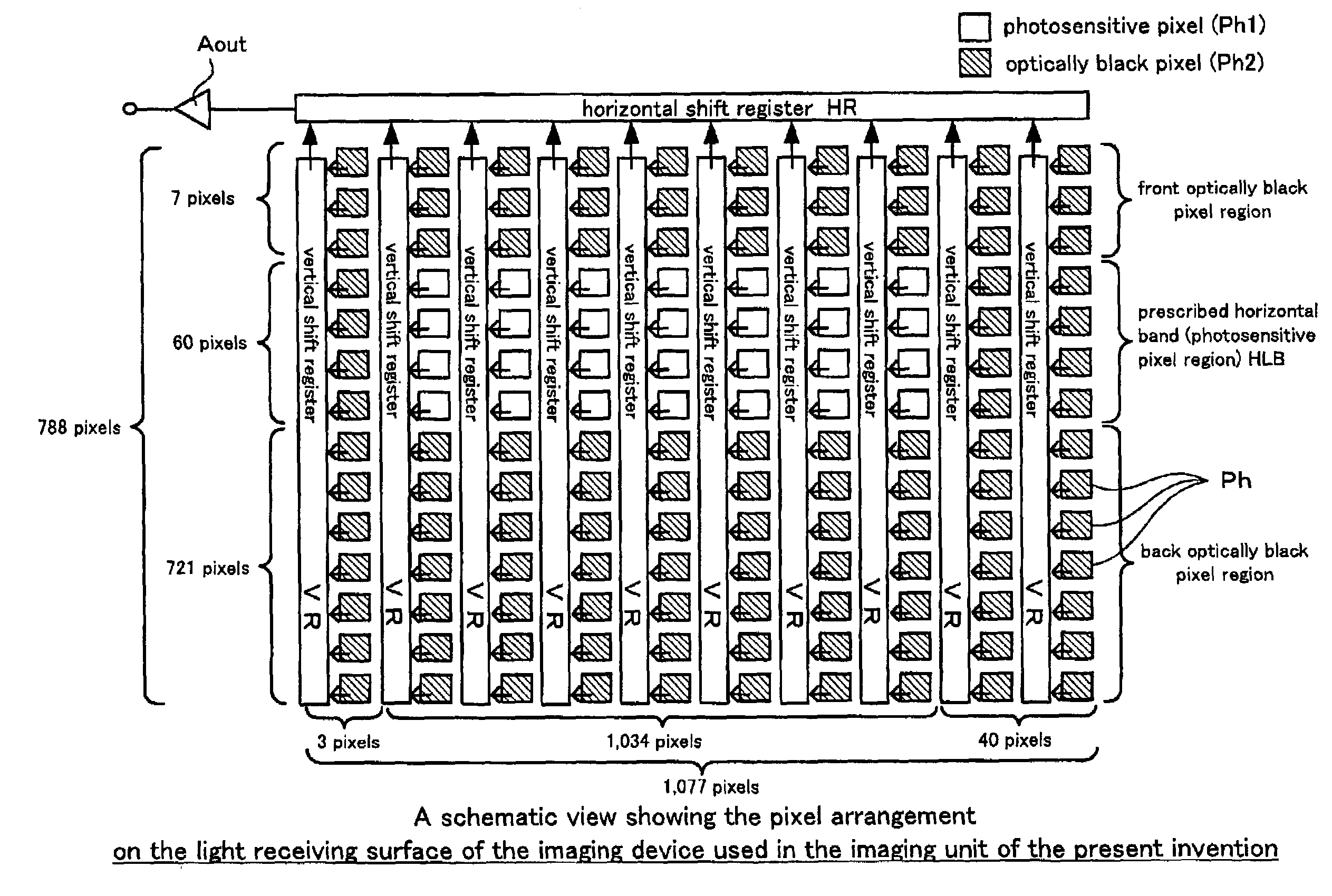
ActiveUS7151568B2Reduced period of timeHigh speedTelevision system detailsImage analysisShift registerVertical transfer
A displacement sensor comprising an imaging unit and an image processing unit. The imaging unit comprises a two dimensional imaging device and a drive control unit. The two dimensional imaging device includes a group of light receiving pixels arranged in a matrix so as to correspond to a field of view of a standard imaging unit, a plurality of vertical shift registers corresponding to different columns of the pixels, and a horizontal register for receiving the outputs of the vertical shift registers from top stages thereof, a photosensitive pixel region being defined in a prescribed horizontal band having a sufficiently narrower width than that would be provided by the total number of horizontal lines and interposed between a front optically black pixel region and a back optically black pixel region. The drive control unit controls, according to a commanded electric charge transfer protocol, a feeding of signal electric charges from each light receiving pixel to the vertical shift register of a corresponding column, a vertical transfer of signal electric charges in the vertical shift register of each column, and a horizontal transfer of signal electric charges in the horizontal shift register. The image processing unit comprises electric charge transfer protocol command means for giving an electric charge transfer protocol to the drive control unit of the imaging unit in dependence of a content of the image process.
Owner:ORMON CORPORATION
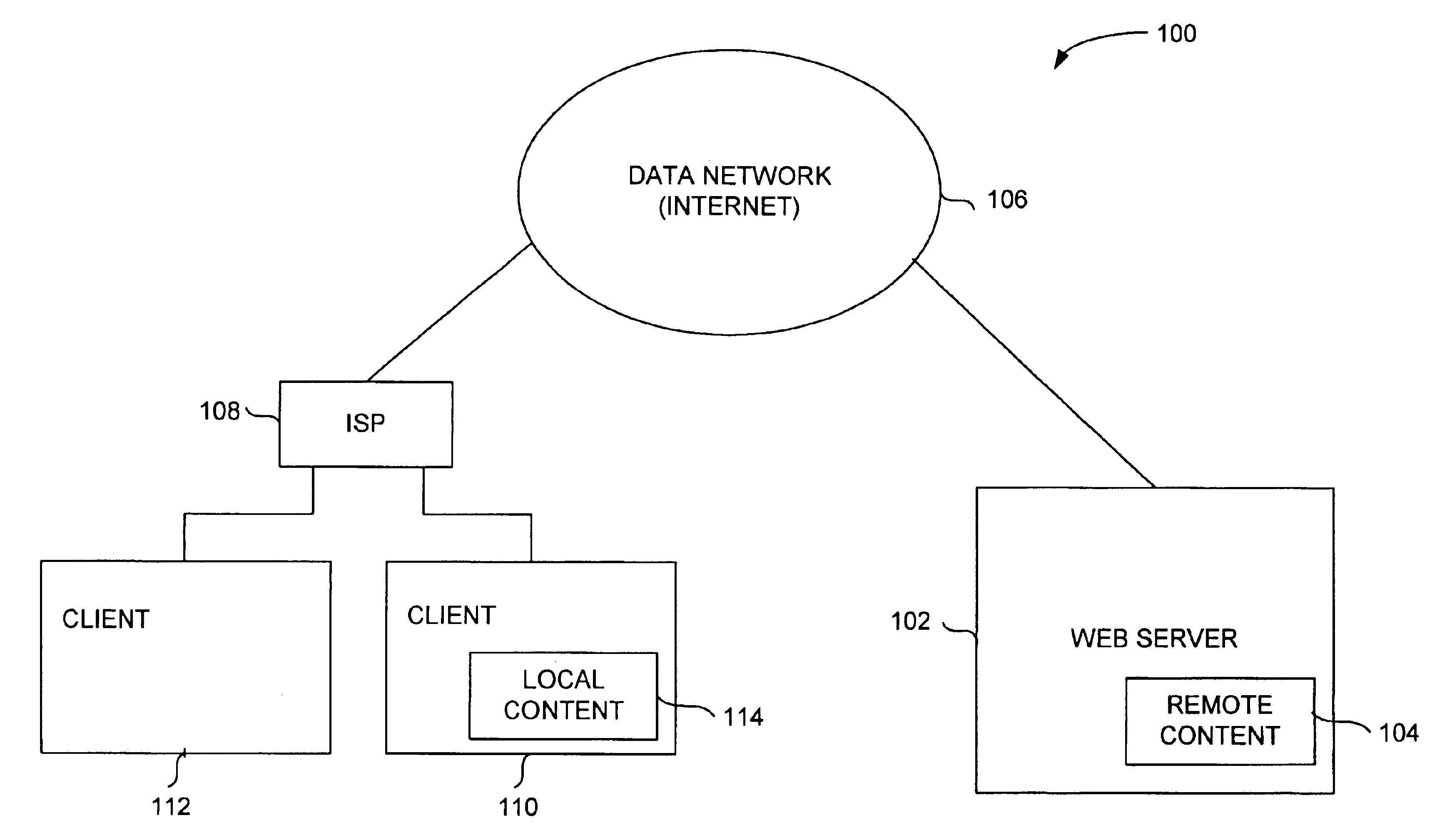
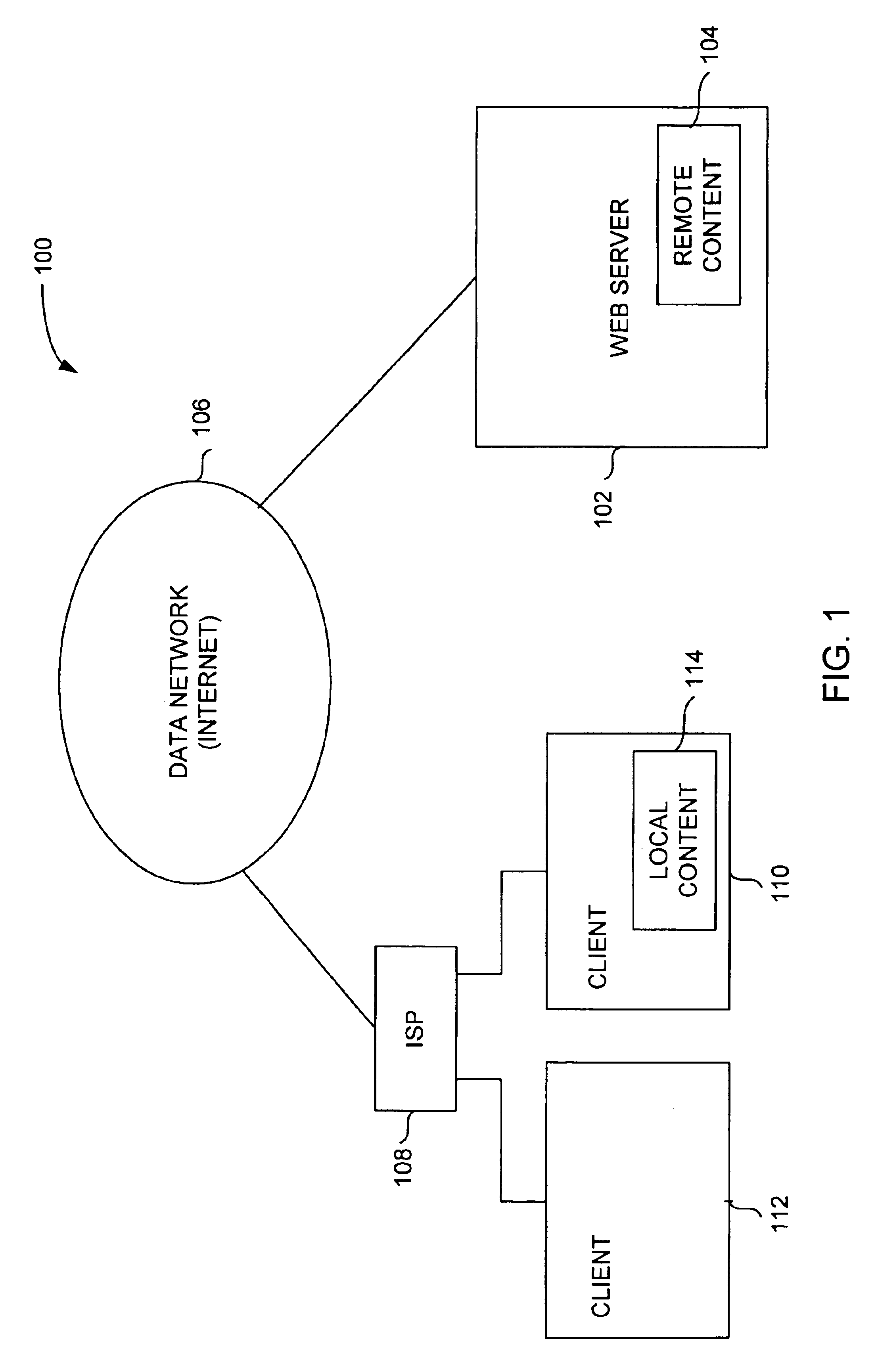
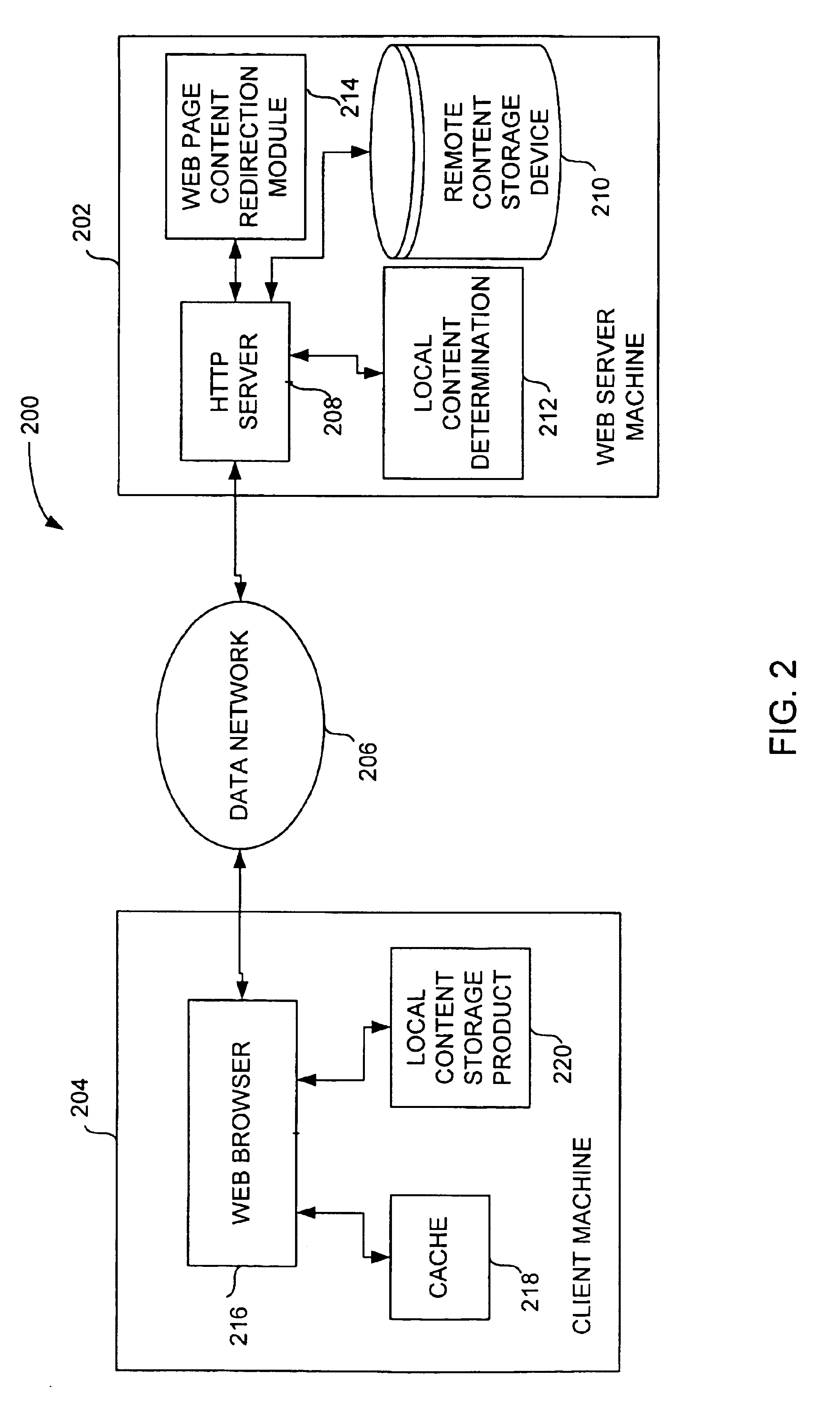
Method and system for providing local content for use in partially satisfying internet data requests from remote servers
InactiveUS6904455B1Reduce demandReduce the amount requiredDigital data information retrievalMultiple digital computer combinationsThe InternetClient-side
Improved techniques for data delivery from a server machine to client machines through a network are disclosed. The techniques reduce the demands on connection bandwidth between the client machines and the network, and thus enable media-rich data to be delivered with reduced amounts of network bandwidth. The techniques also reduce the bandwidth demands on network servers and overall network infrastructure.
Owner:YEN ROBERT C
Method for making transmission electron microscope grid
ActiveUS20090317926A1High imagingElectric discharge tubesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingOrganic solventCarbon nanotube
A method for making transmission electron microscope gird is provided. An array of carbon nanotubes is provided and drawing a carbon nanotube film from the array of carbon nanotubes. A substrate has a plurality of spaced metal girds attached on the substrate. The metal girds are covered with the carbon nanotube film and treating the carbon nanotube film and the metal girds with organic solvent. A transmission electron microscope (TEM) grid is obtained by removing remaining CNT film.
Owner:TSINGHUA UNIV +1
Wafer level image module
ActiveUS20070070511A1Quality improvementHigh imagingTelevision system detailsSolid-state devicesImaging qualityOptoelectronics
A wafer level image module includes a photo sensor for outputting an electrical signal upon receiving light, a lens set for focusing incident light onto the photo sensor, and an adjustment member disposed between the photo sensor and the lens set for controlling the distance between the photo sensor and the lens set to compensate the focus offset of the photo sensor for enabling the lens set to accurately focus the incident light onto the photo sensor in an in-focus manner so as to provide a high image quality.
Owner:VISERA TECH CO LTD +1
Whole beam image splitting system
ActiveUS20090244717A1Increase framerateHigh imagingTelevision system detailsPrismsPhysicsSensor plane
The present invention comprises methods and apparatuses for causing a single imaging lens system to simultaneously form multiple high resolution images on multiple imaging sensor planes. The images are preferably substantially identical, with no parallax error, except for different light levels so that the multiple images are of sufficient quality and similarity that they may be compared and / or combined (typically pixel-by-pixel) to create a single instantaneous high dynamic range (HDR) image. The invention may be used to create high-resolution HDR snapshots of moving subjects, as well as high-resolution HDR moving pictures (e.g. cinematographic films, movies, or other video) in which the subject and / or camera is moving. Alternatively, the images are substantially identical except for different focuses.
Owner:CONTRAST OPTICAL DESIGN & ENG
Solid-state imaging device and camera
InactiveUS20090213256A1Avoid error accumulationHigh signal sensitivityTelevision system detailsTelevision system scanning detailsPhotoelectric conversionLight signal
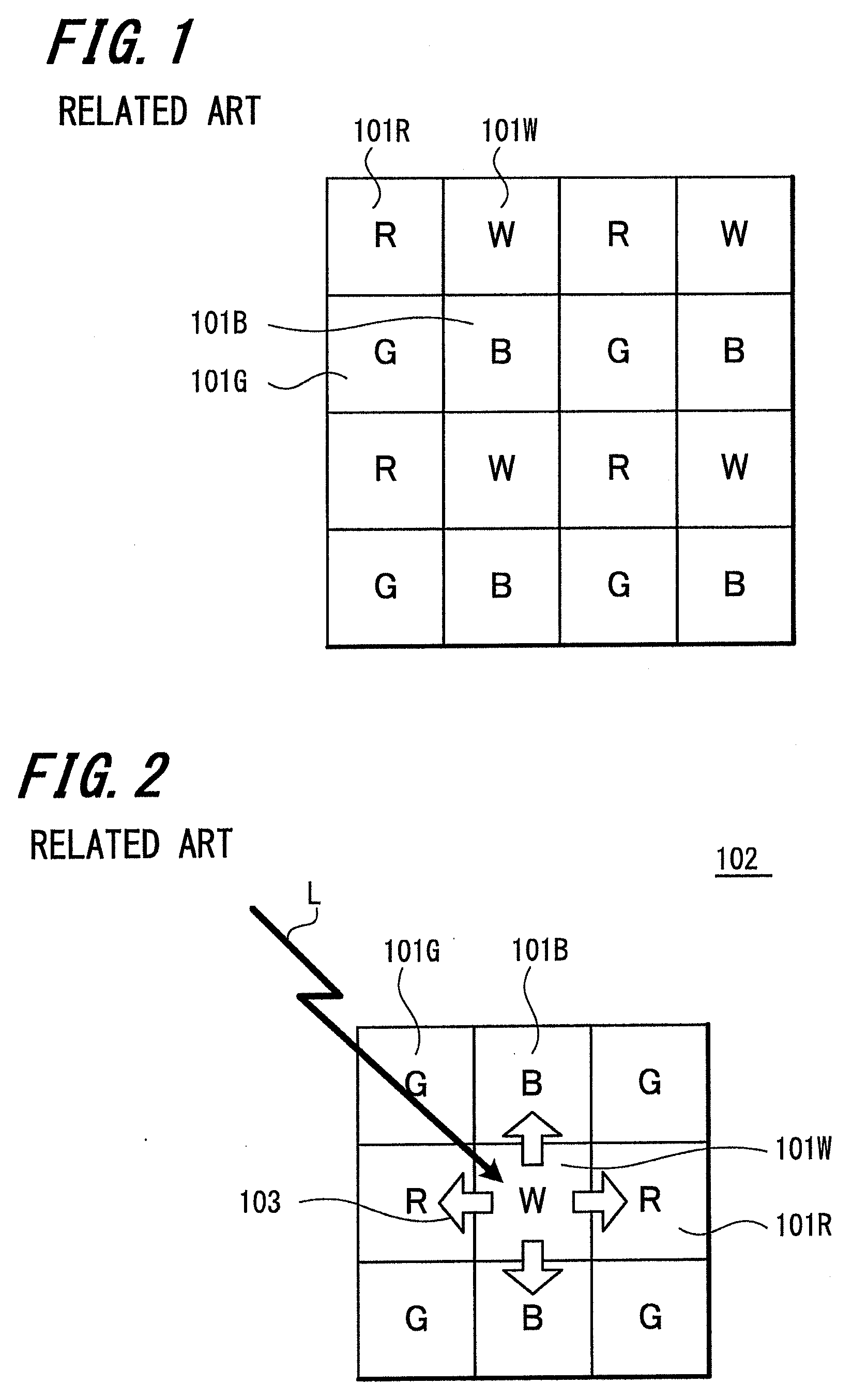
Disclosed is a solid-state imaging device which includes a group of elements, the group including at least color photoelectric conversion elements configured to convert light signals in first, second, and third wavelength ranges to electric signals, respectively, a white photoelectric conversion element configured to convert light signals in the wavelength range including the entire visible light range and a portion of the infrared light range to electric signals, and a light-shielded diode element configured to be shielded from light. A unit is formed by including the white photoelectric conversion element and the light-shielded diode element for one color photoelectric conversion element, and within the unit, the white photoelectric conversion element is electrically connected with the light-shielded diode element by way of an overflow path. A camera provided with the solid-state imaging device is also disclosed.
Owner:SONY SEMICON SOLUTIONS CORP
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com