Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
431 results about "Exposure period" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
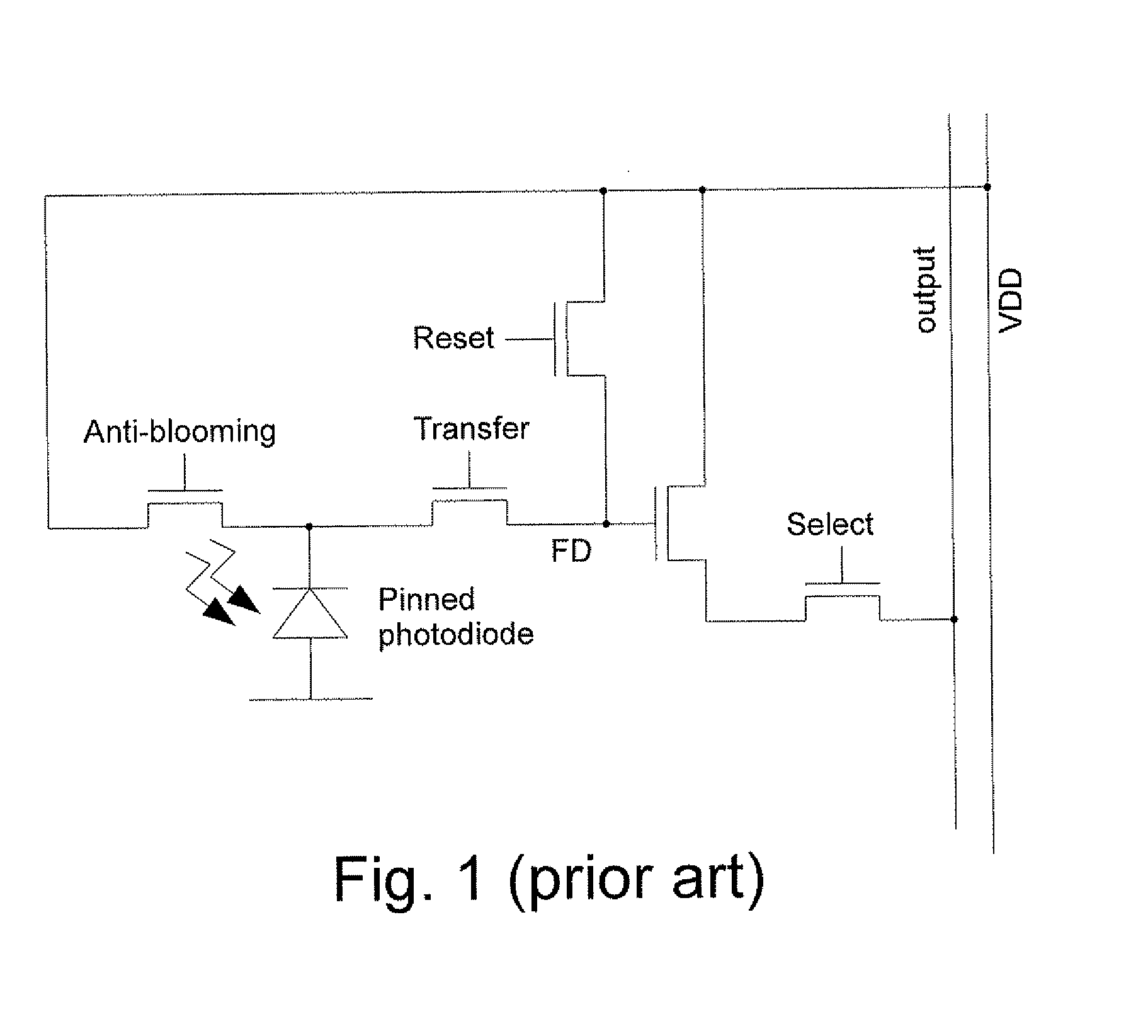
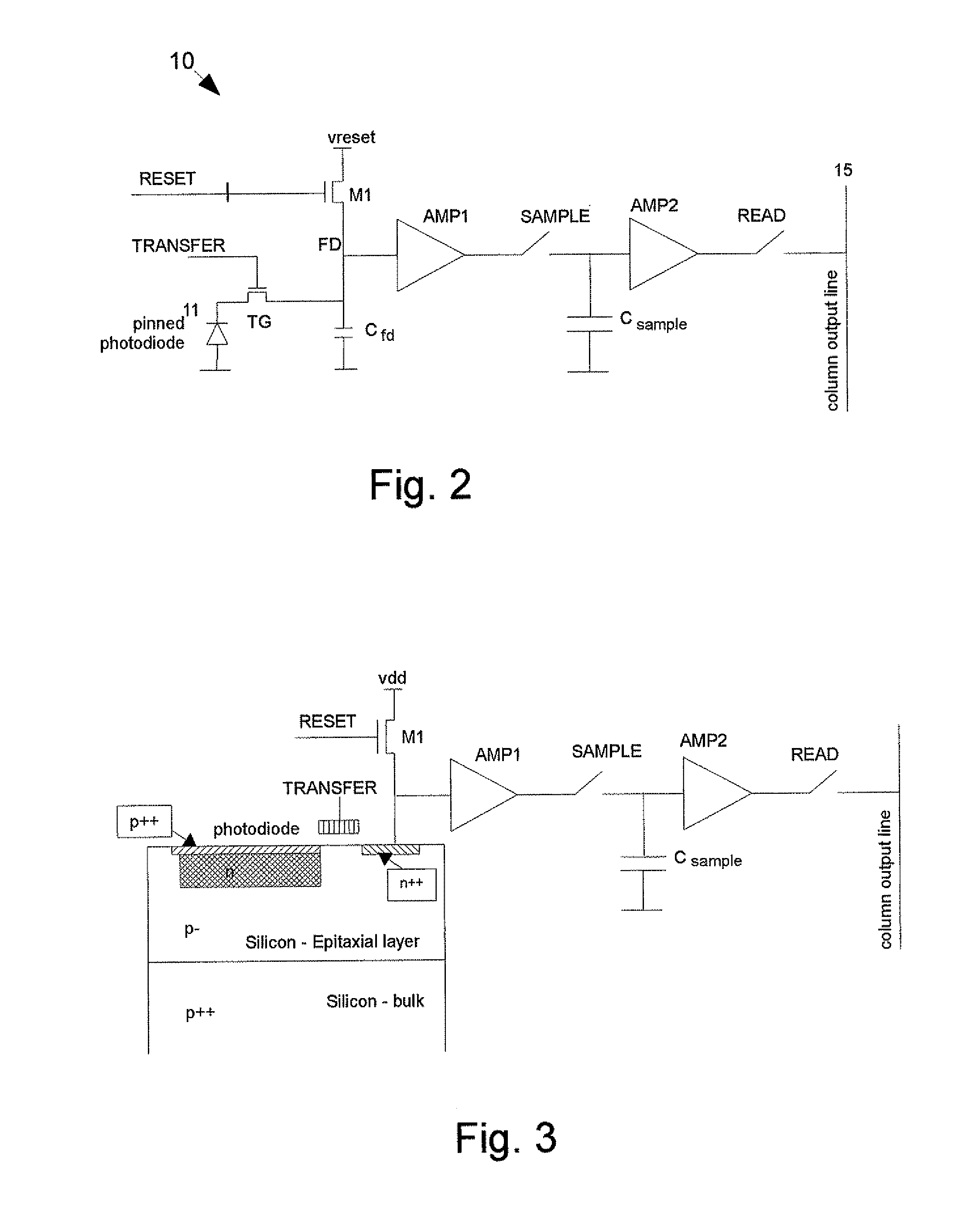
Exposure Period. Expressed in terms of a continuous variable, such as the time equipment is operating, or as a function of a discrete variable, such as the number of demands (also called cycles in some tests) imposed on a piece of equipment.
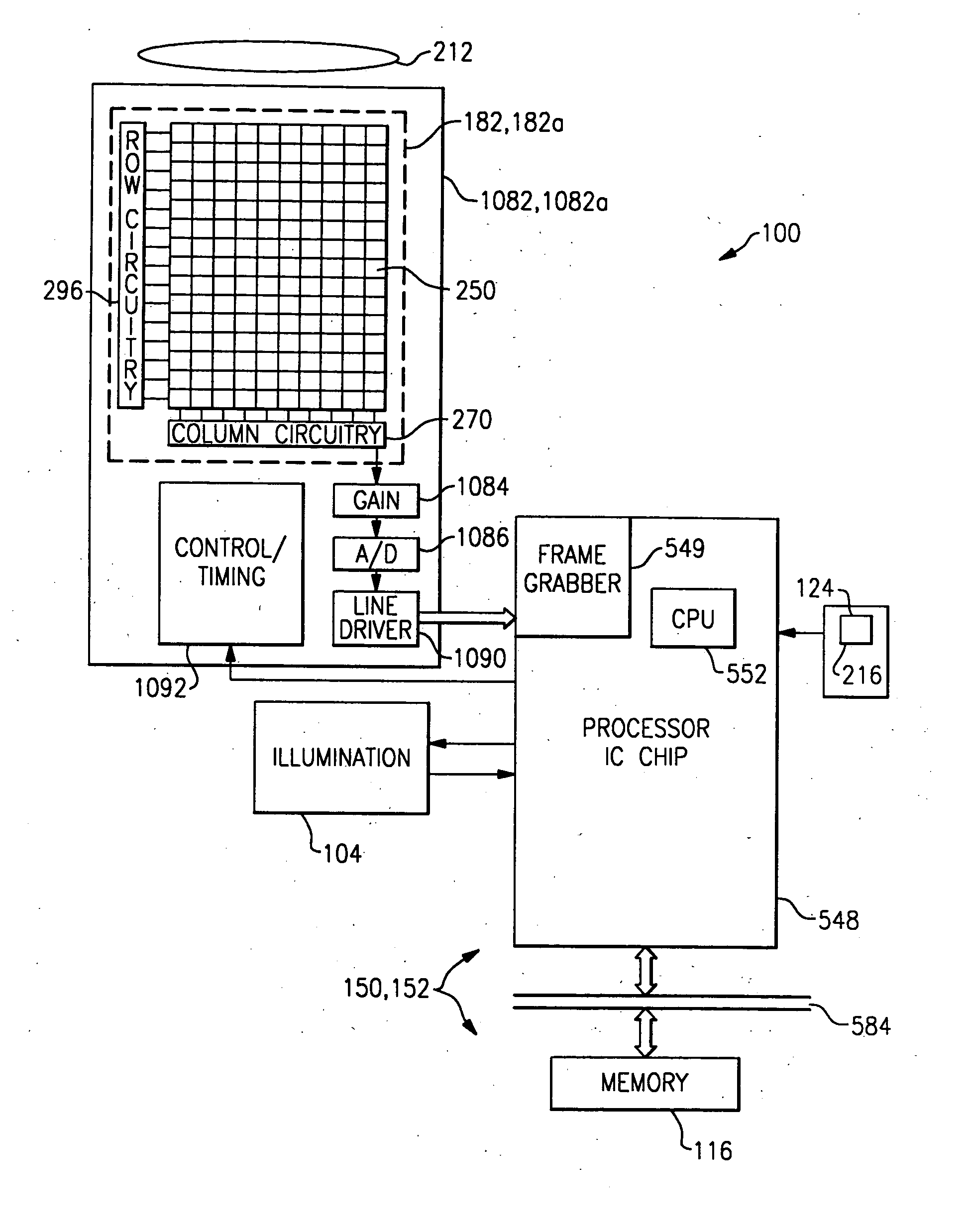
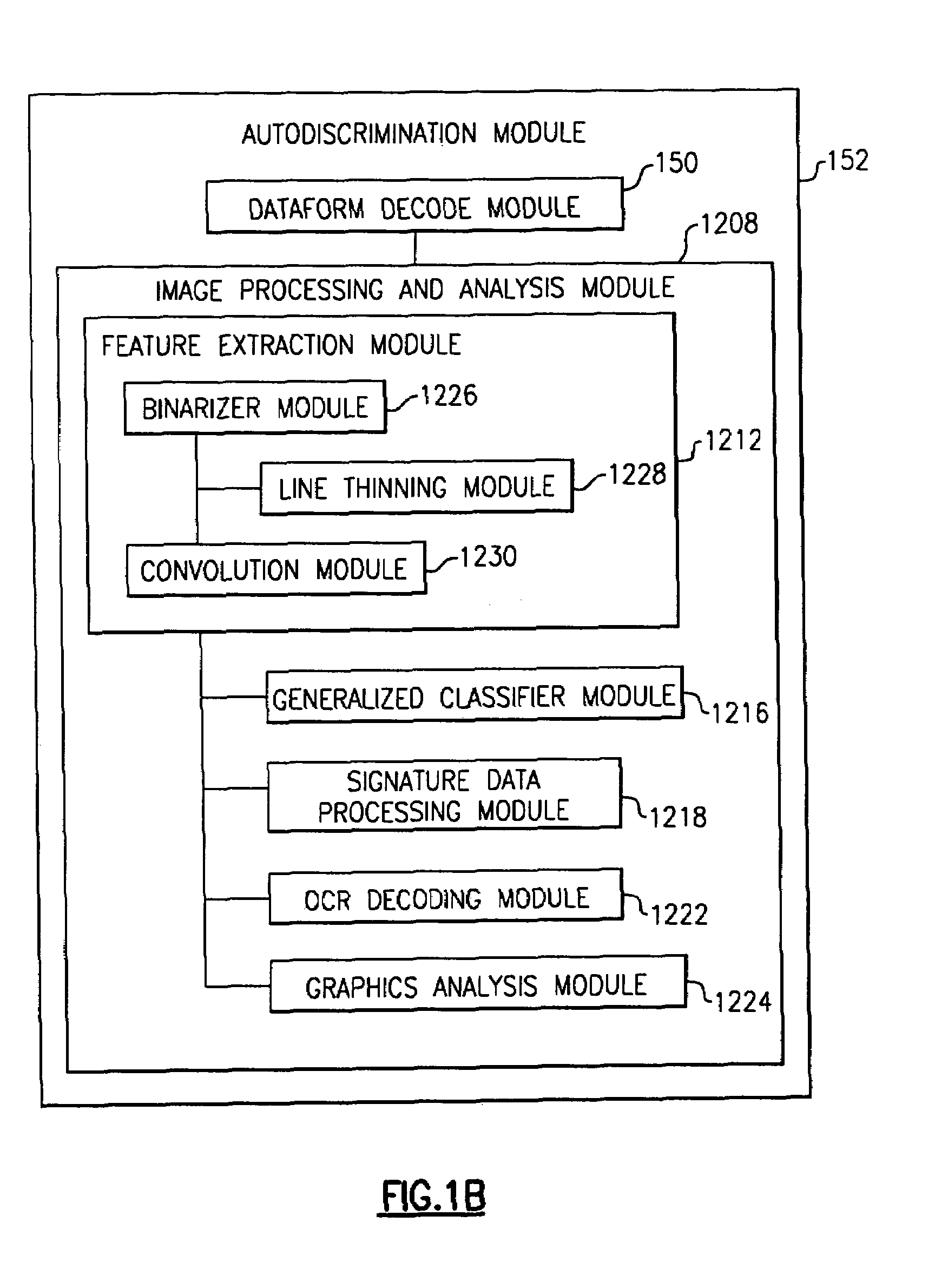
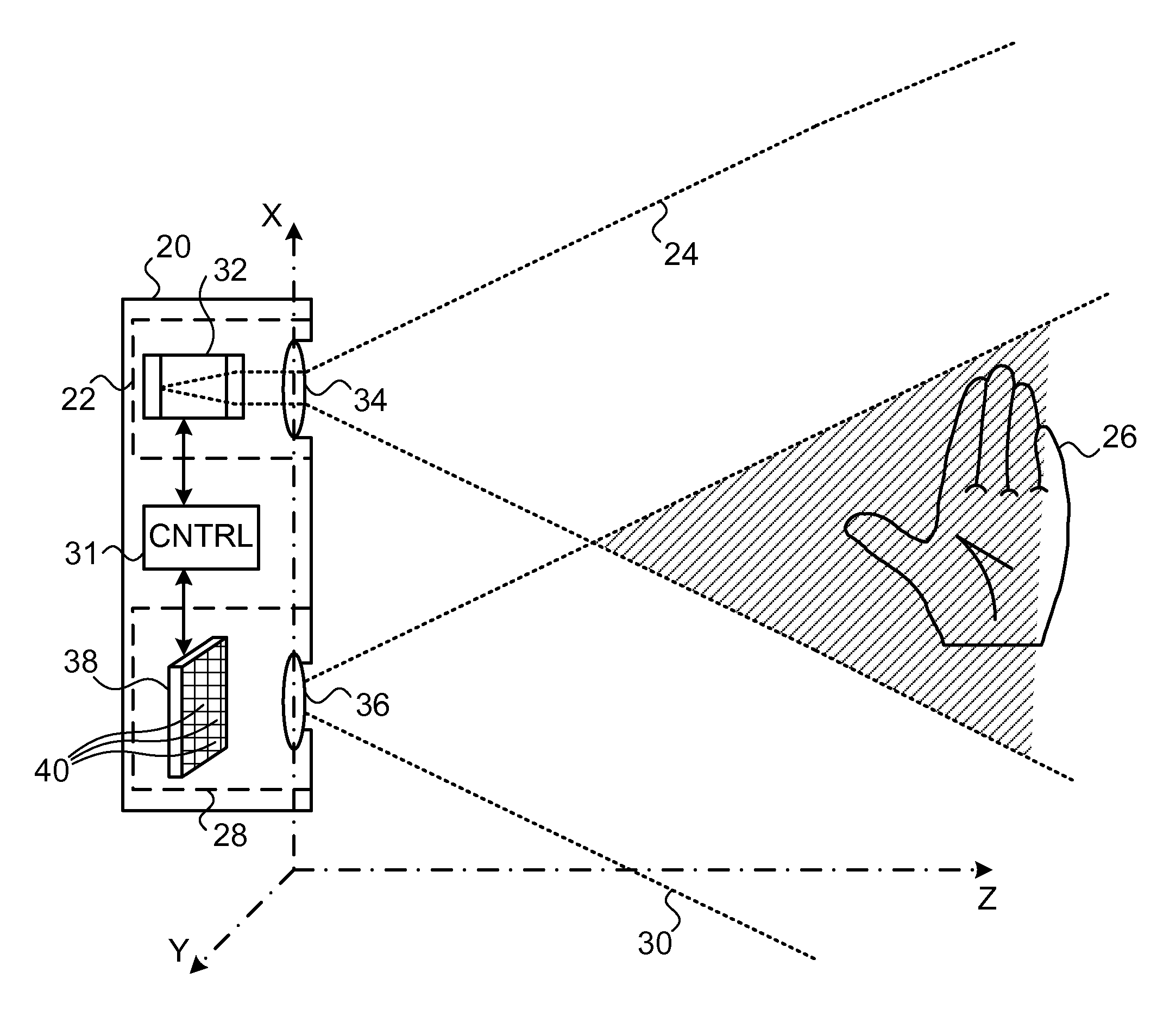
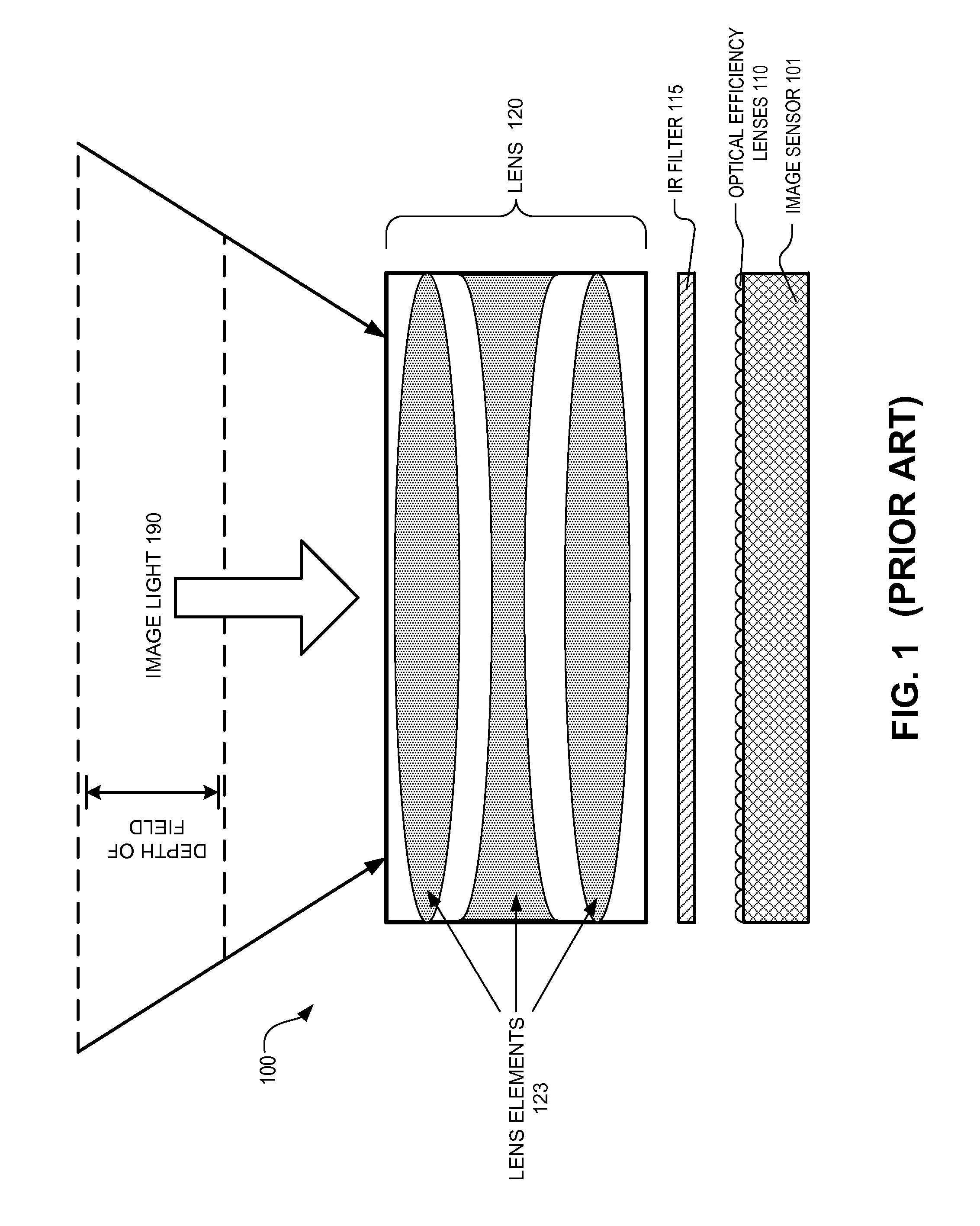
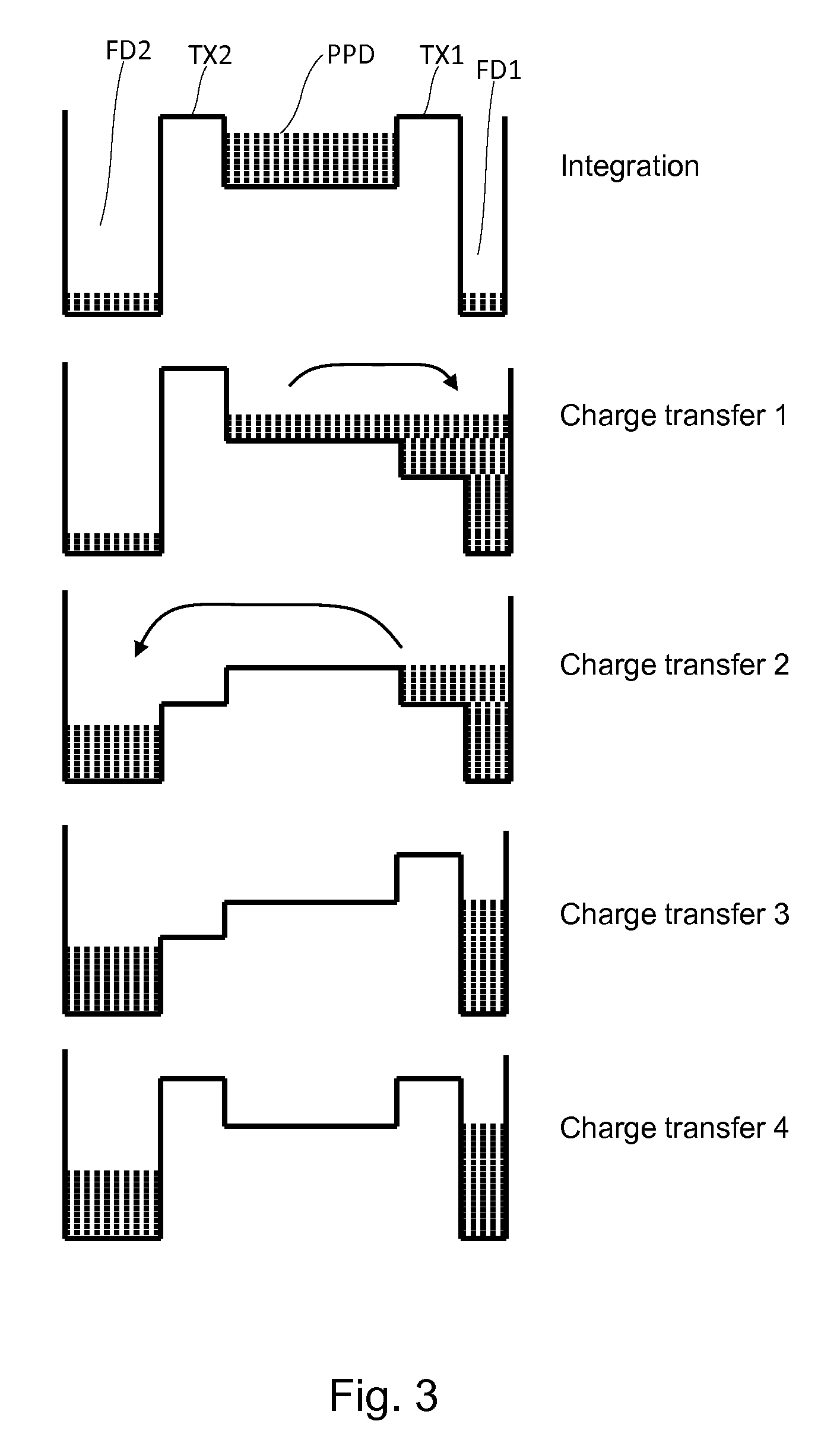
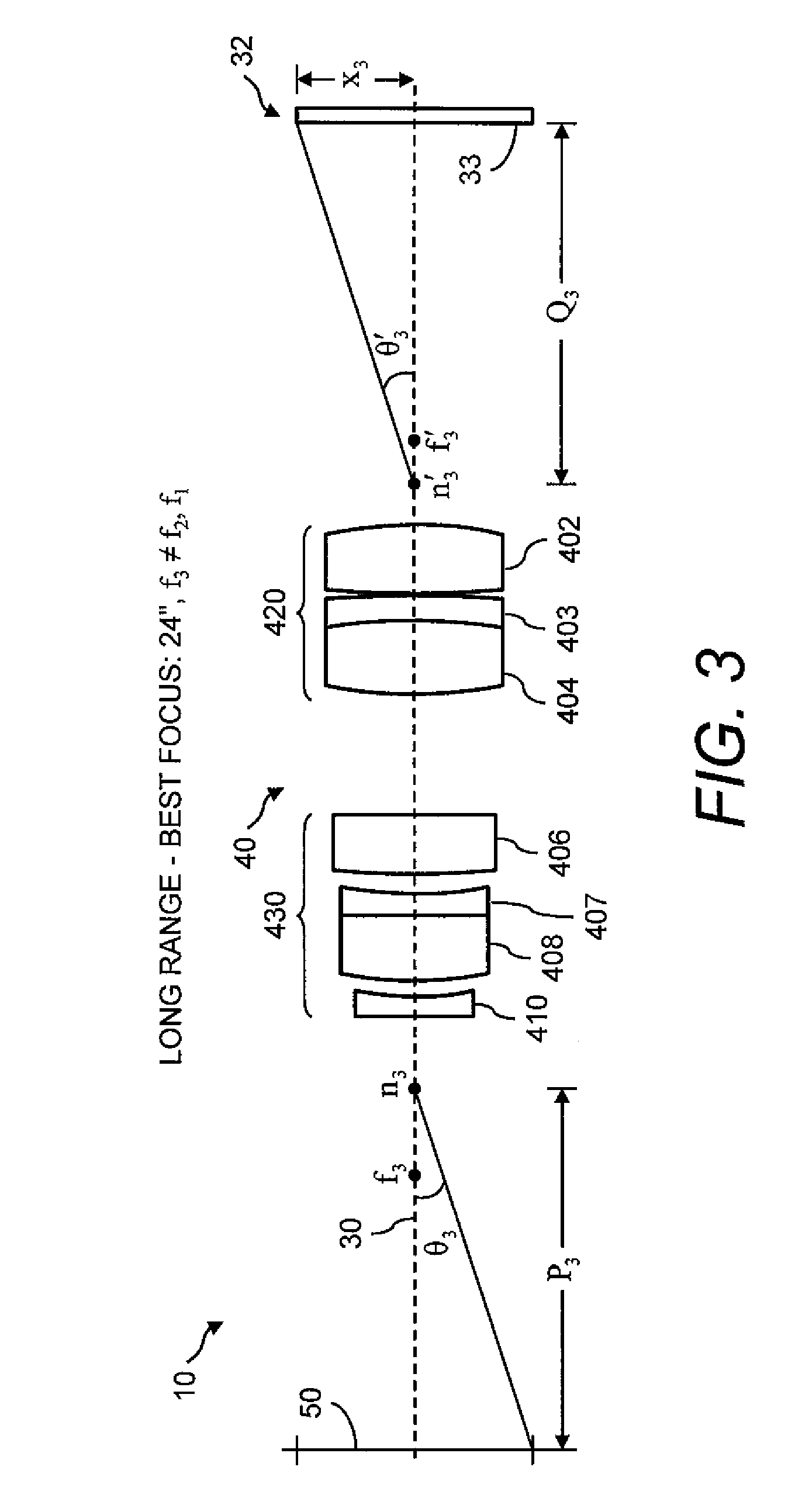
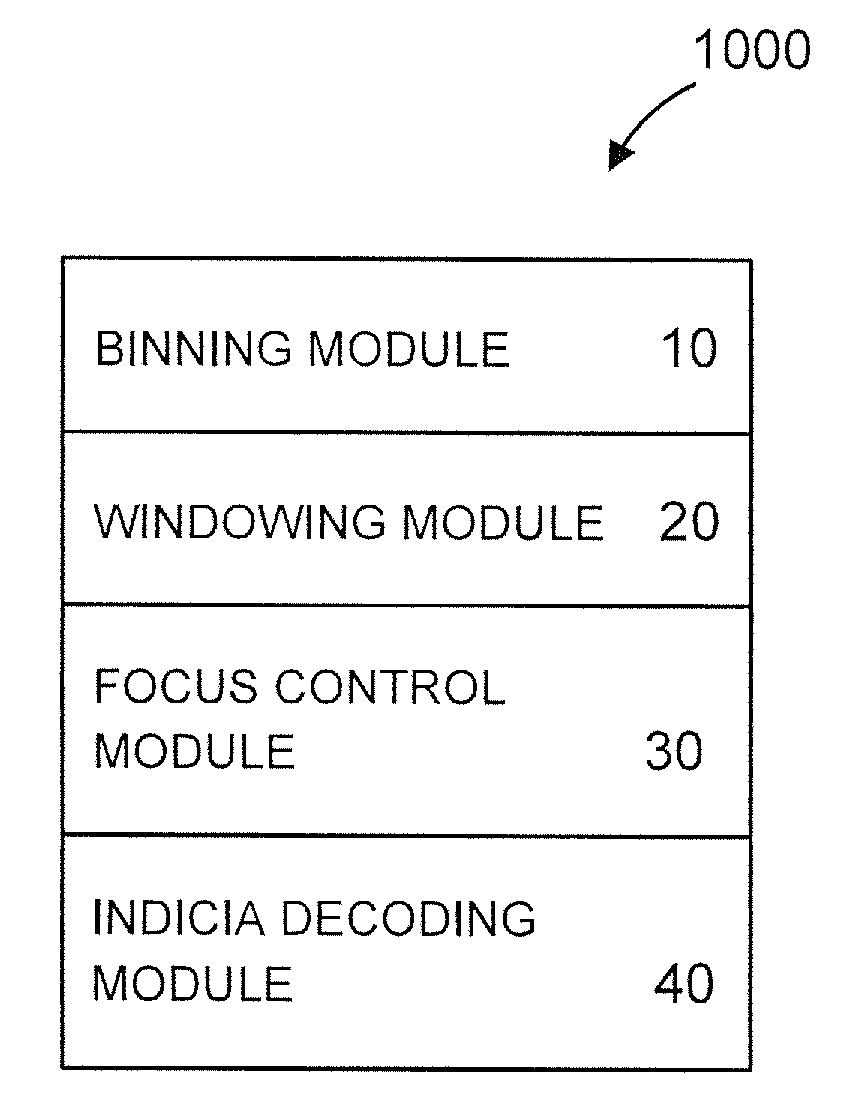
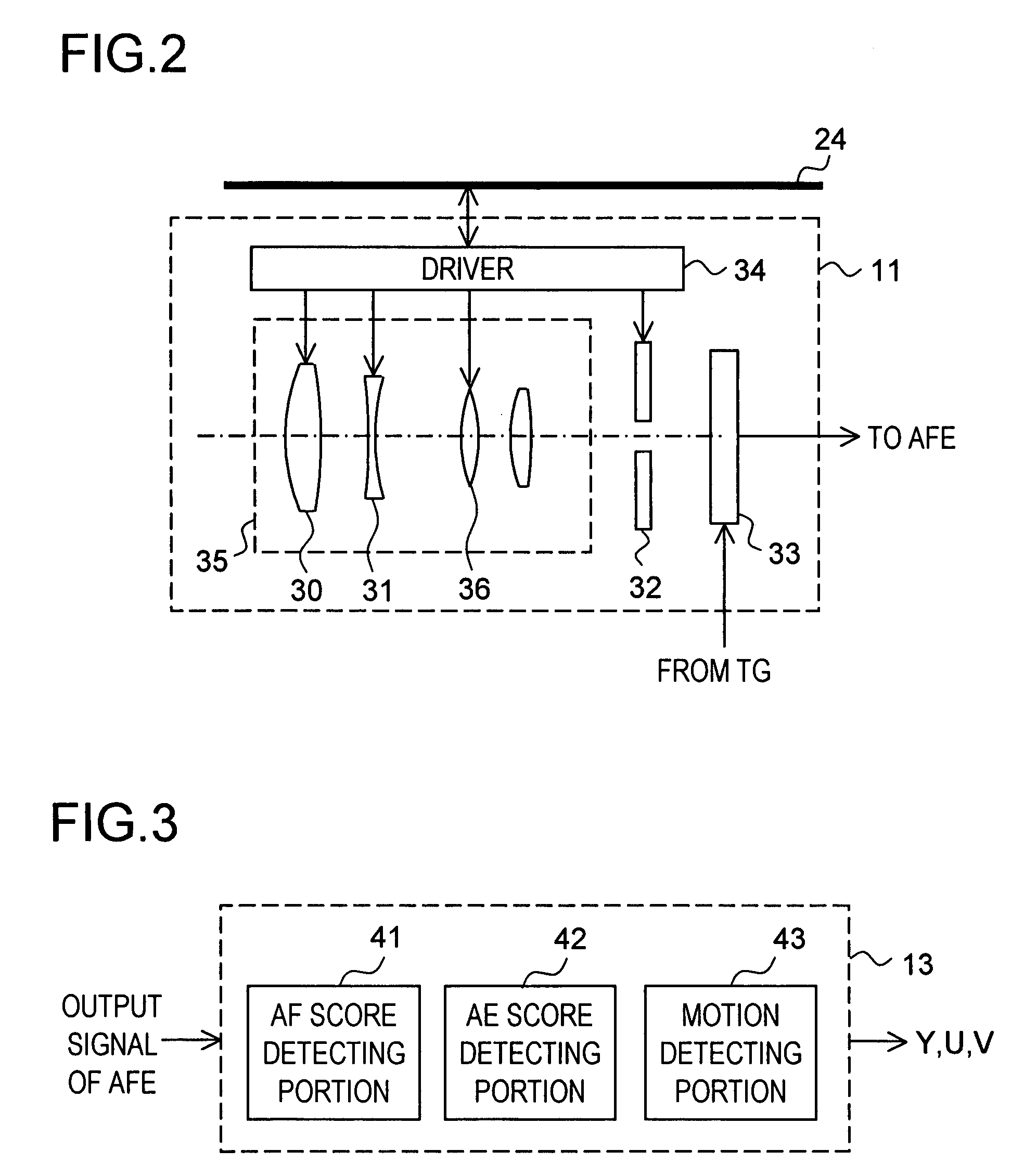
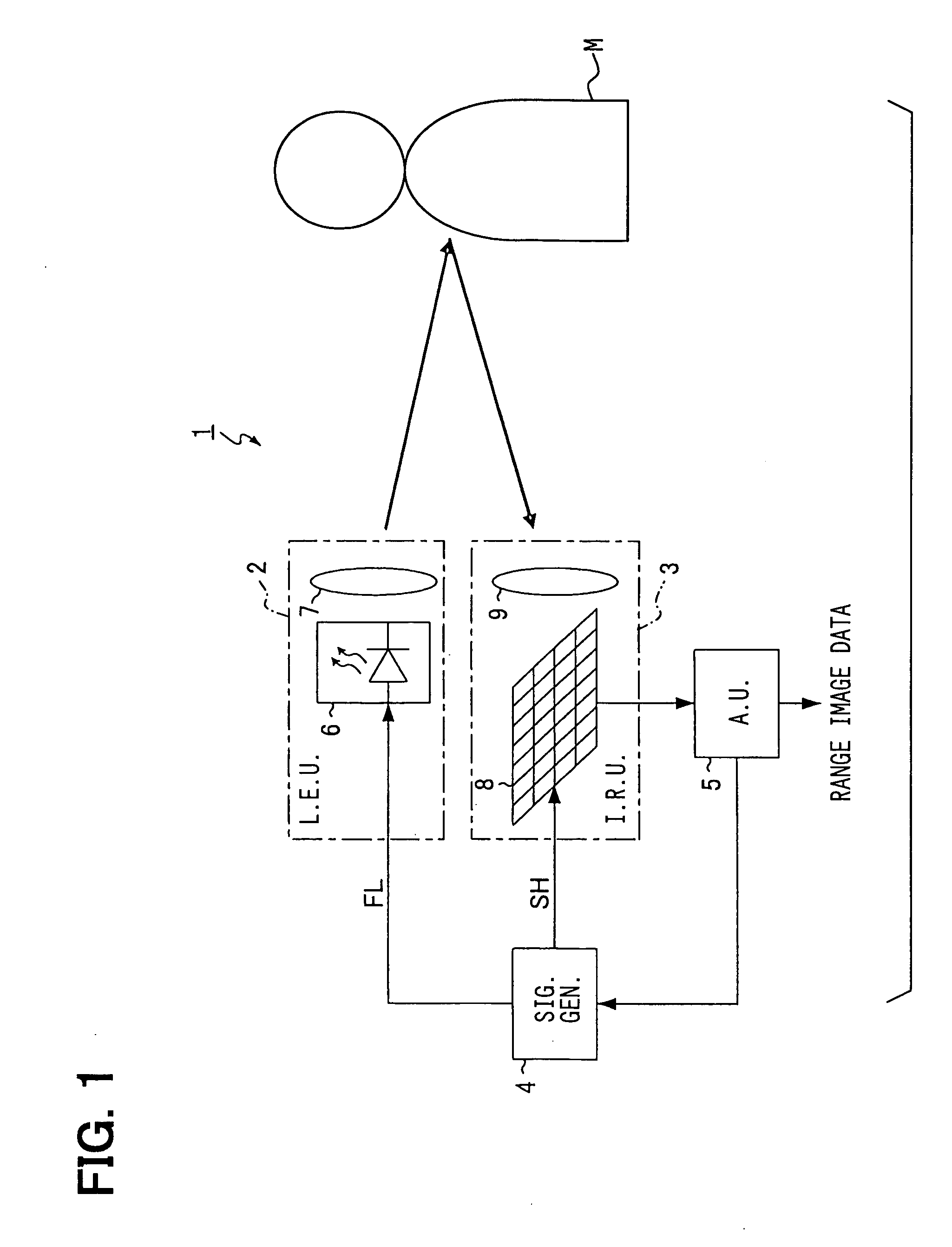
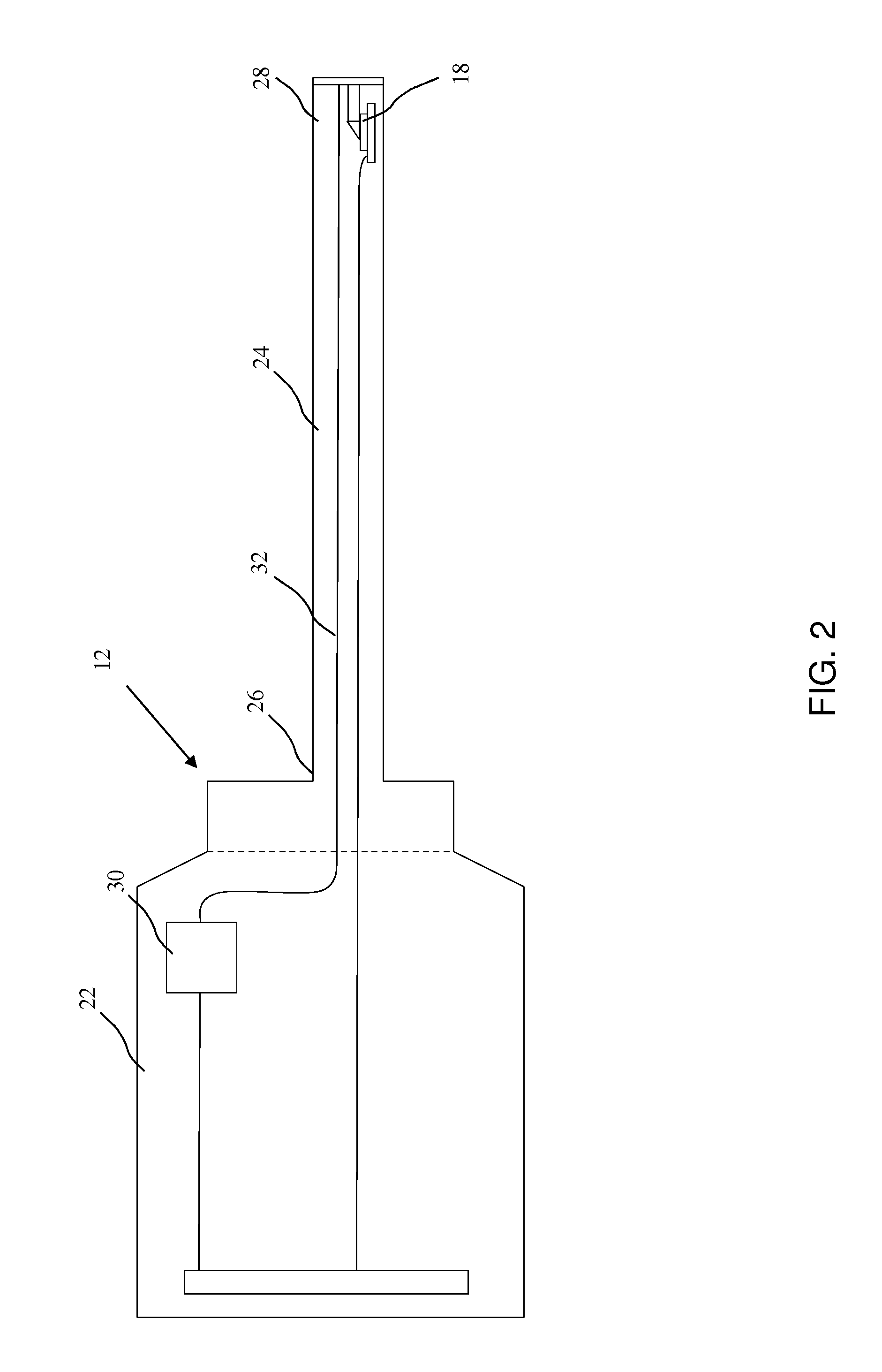
Bar code reading device with global electronic shutter control
ActiveUS20060202036A1Minimize degradationTelevision system detailsTransmission systemsSensor arrayElectronic shutter
The invention features an image reader and a corresponding method for capturing a sharp distortion free image of a target, such as a one or two-dimensional bar code. In one embodiment, the image reader comprises a two-dimensional CMOS based image sensor array, a timing module, an illumination module, and a control module. The time during which the target is illuminated is referred to as the illumination period. The capture of the image by the image sensor array is driven by the timing module that, in one embodiment, is able to simultaneously expose substantially all of the pixels in the array. The time during which the pixels are collectively activated to photo-convert incident light into charge defines the exposure period for the sensor array. In one embodiment, at least a portion of the exposure period occurs during the illumination period.
Owner:HAND HELD PRODS
Digital camera using multiple image sensors to provide improved temporal sampling
InactiveUS20080211941A1Keep for a long timeImprove spatial resolutionTelevision system detailsSignal generator with multiple pick-up deviceImage resolutionExposure period
A method and apparatus for capturing image data from multiple image sensors and generating an output image sequence are disclosed. The multiple image sensors capture data with one or more different characteristics, such as: staggered exposure periods, different length exposure periods, different frame rates, different spatial resolution, different lens systems, and different focal lengths. The data from multiple image sensors is processed and interleaved to generate an improved output motion sequence relative to an output motion sequence generated from an a single equivalent image sensor.
Owner:MONUMENT PEAK VENTURES LLC
Laser digitizer system for dental applications
InactiveUS7184150B2The process is fast and accurateImprove imaging effectImpression capsTeeth fillingExposure periodDigital converter
A intra-oral laser digitizer system provides a three-dimensional visual image of a real-world object such as a dental item through a laser digitization. The laser digitizer captures an image of the object by scanning multiple portions of the object in an exposure period. The intra-oral digitizer may be inserted into an oral cavity (in vivo) to capture an image of a dental item such as a tooth, multiple teeth or dentition. The captured image is processed to generate the three-dimension visual image.
Owner:D4D TECH LP
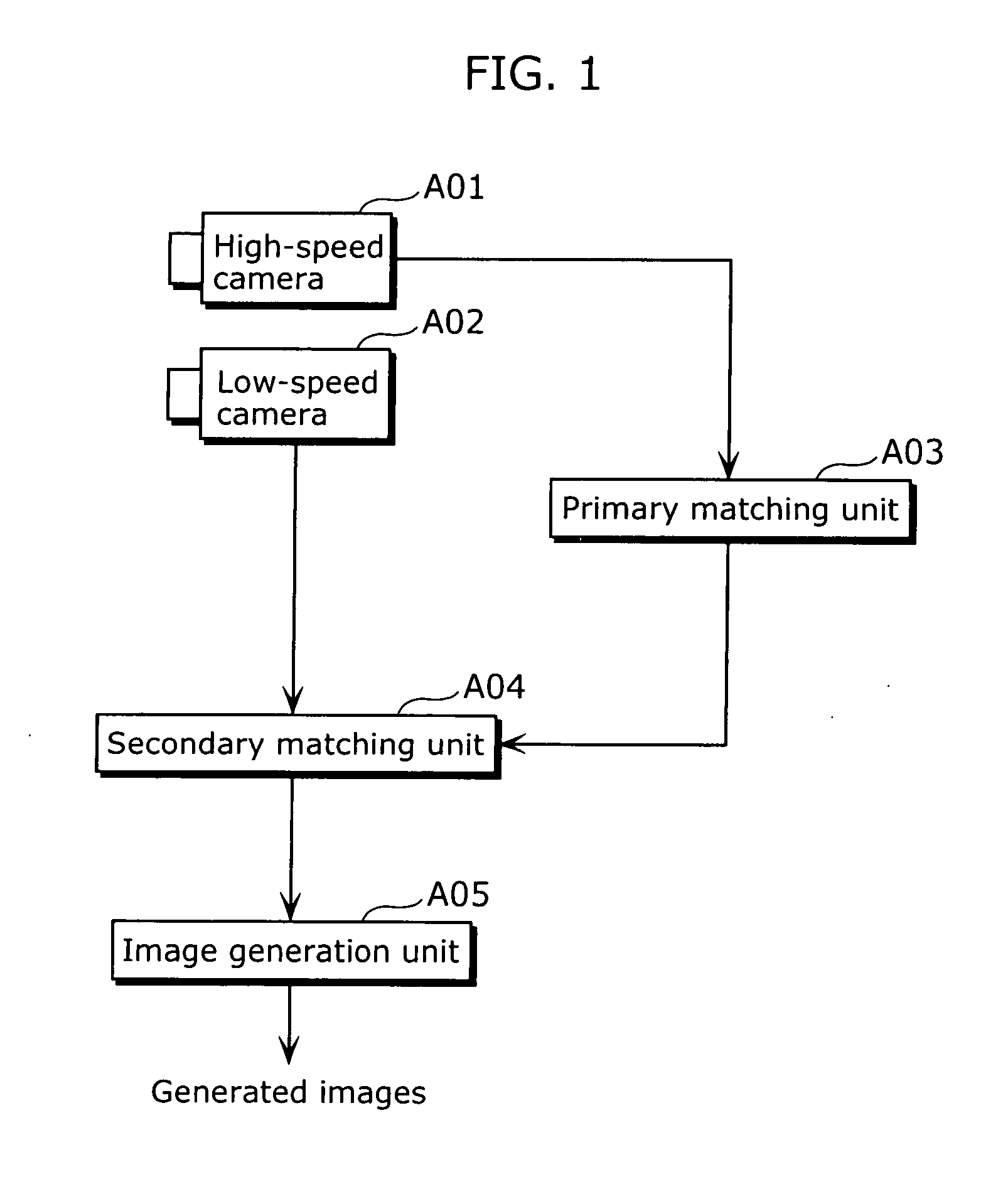
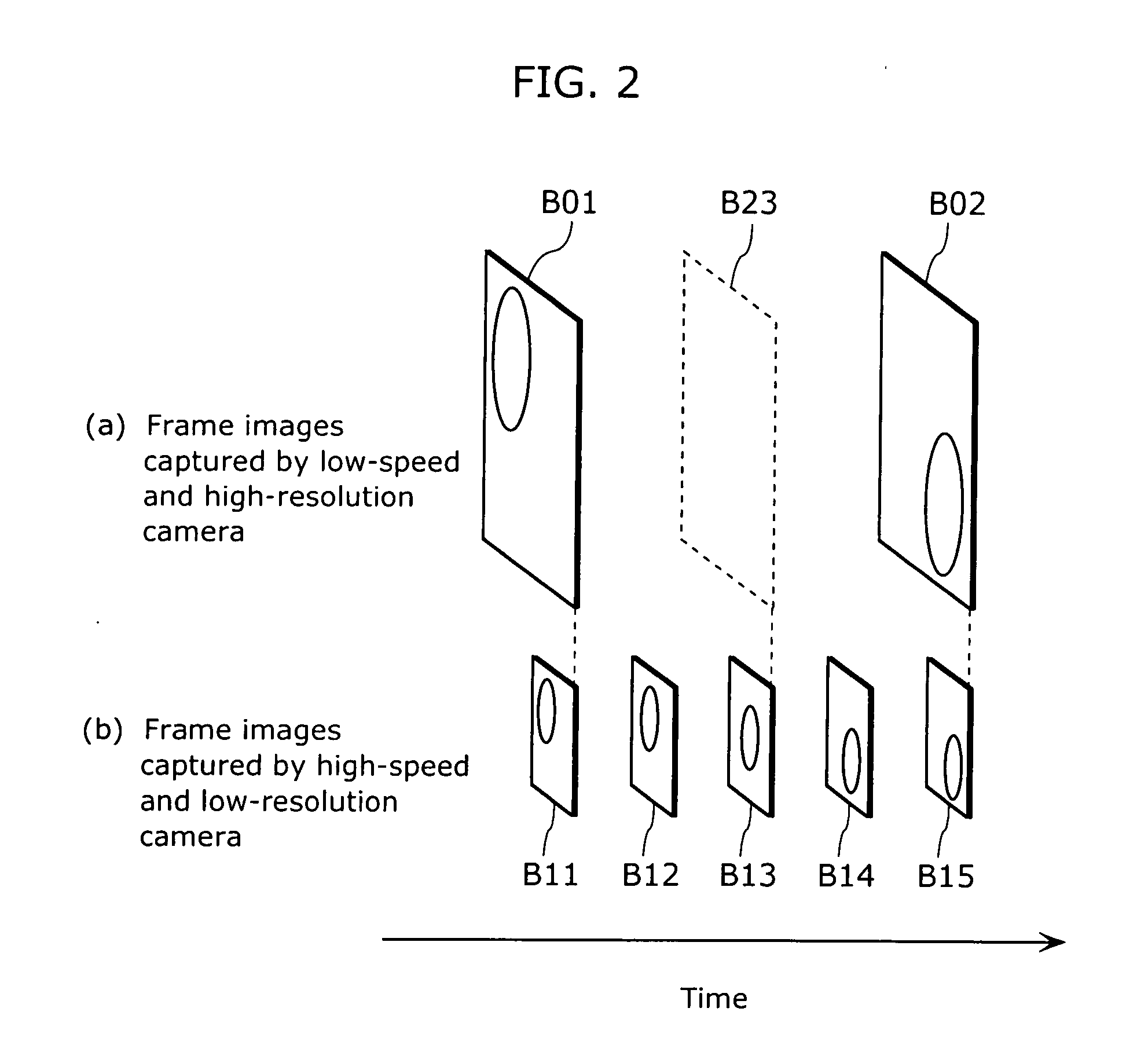
Image generation apparatus and image generation method
InactiveUS20070189386A1Maintain good propertiesReliable generationTelevision system detailsImage analysisComputer graphics (images)Image resolution
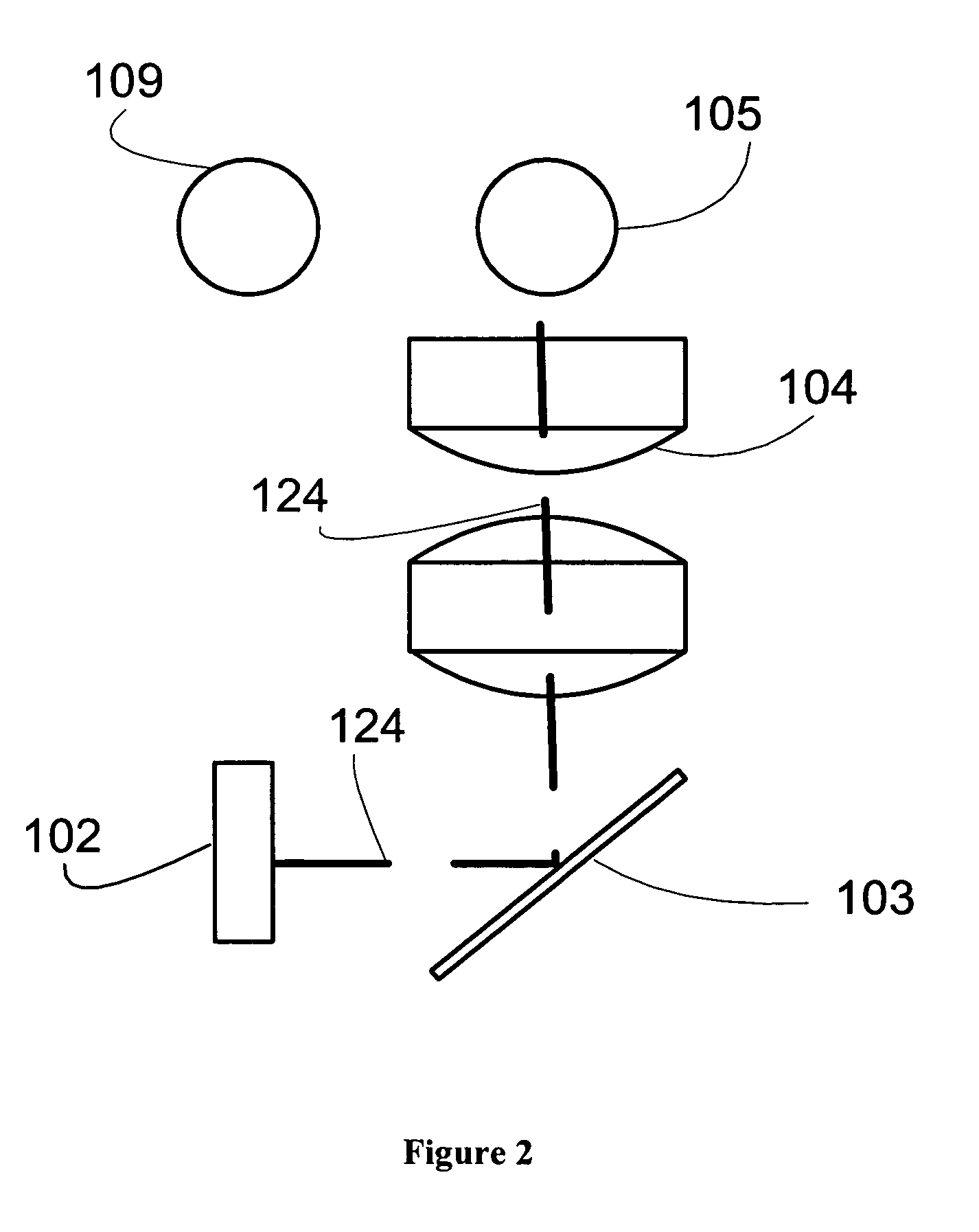
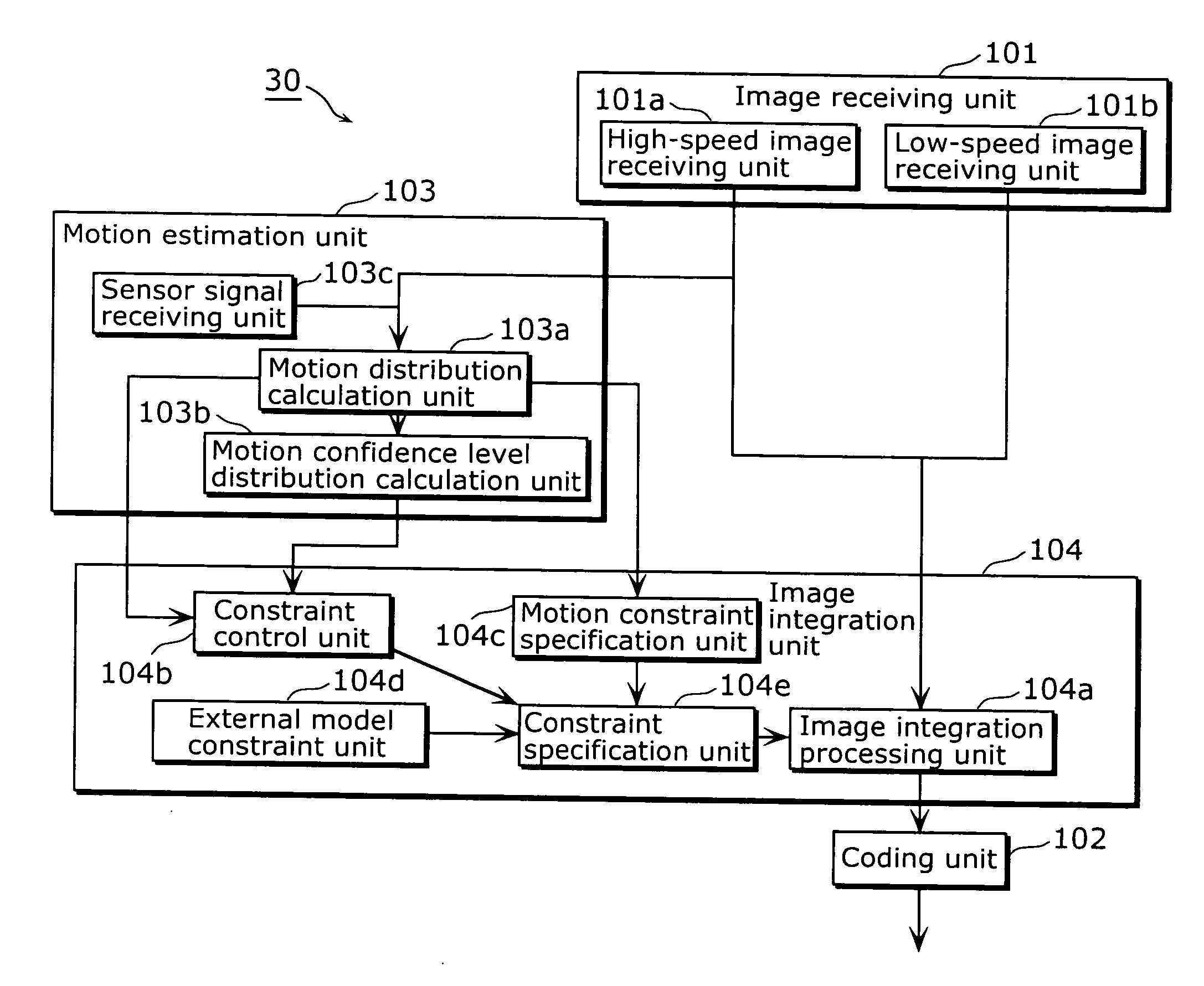
The image generation apparatus includes: an image receiving unit which receives a first video sequence including frames having a first resolution and a second video sequence including frames having a second resolution which is higher than the first resolution, each frame of the first video sequence being obtained with a first exposure time, and each frame of the second video sequence being obtained with a second exposure time which is longer than the first exposure time; and an image integration unit which generates, from the first video sequence and the second video sequence, a new video sequence including frames having a resolution which is equal to or higher than the second resolution, at a frame rate which is equal to or higher than a frame rate of the first video sequence, by reducing a difference between a value of each frame of the second video sequence and a sum of values of frames of the new video sequence which are included within an exposure period of the frame of the second video sequence.
Owner:SOVEREIGN PEAK VENTURES LLC
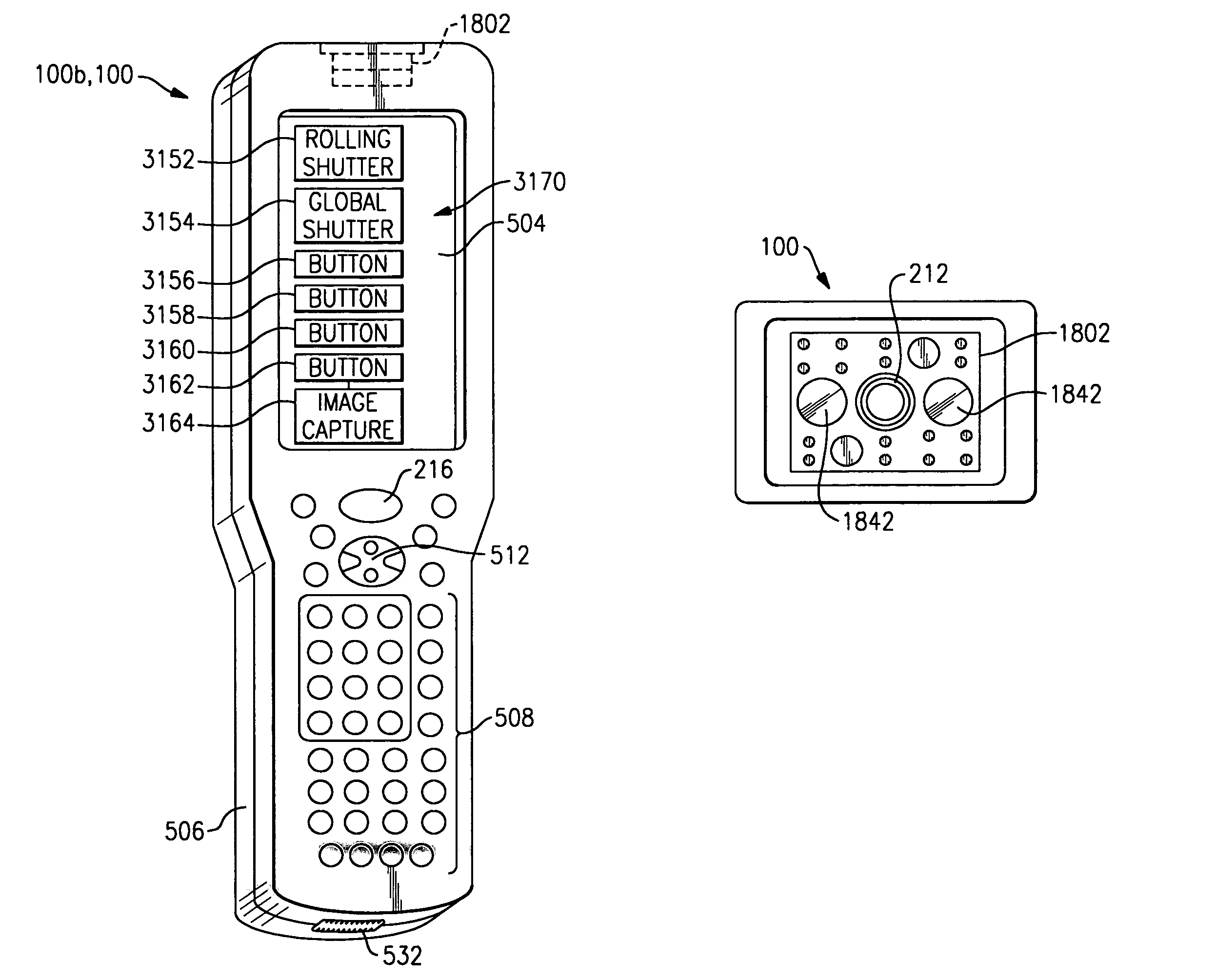
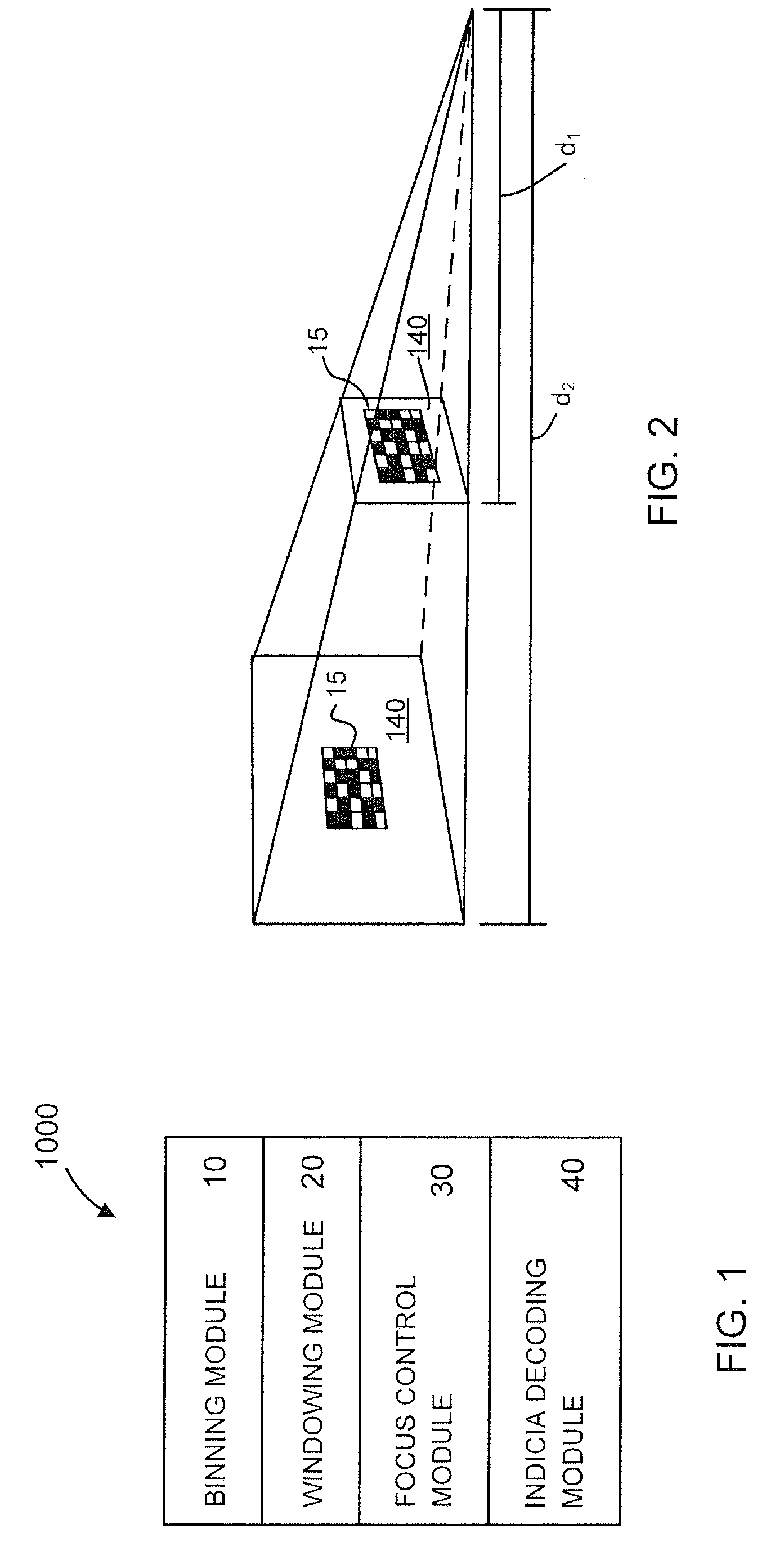
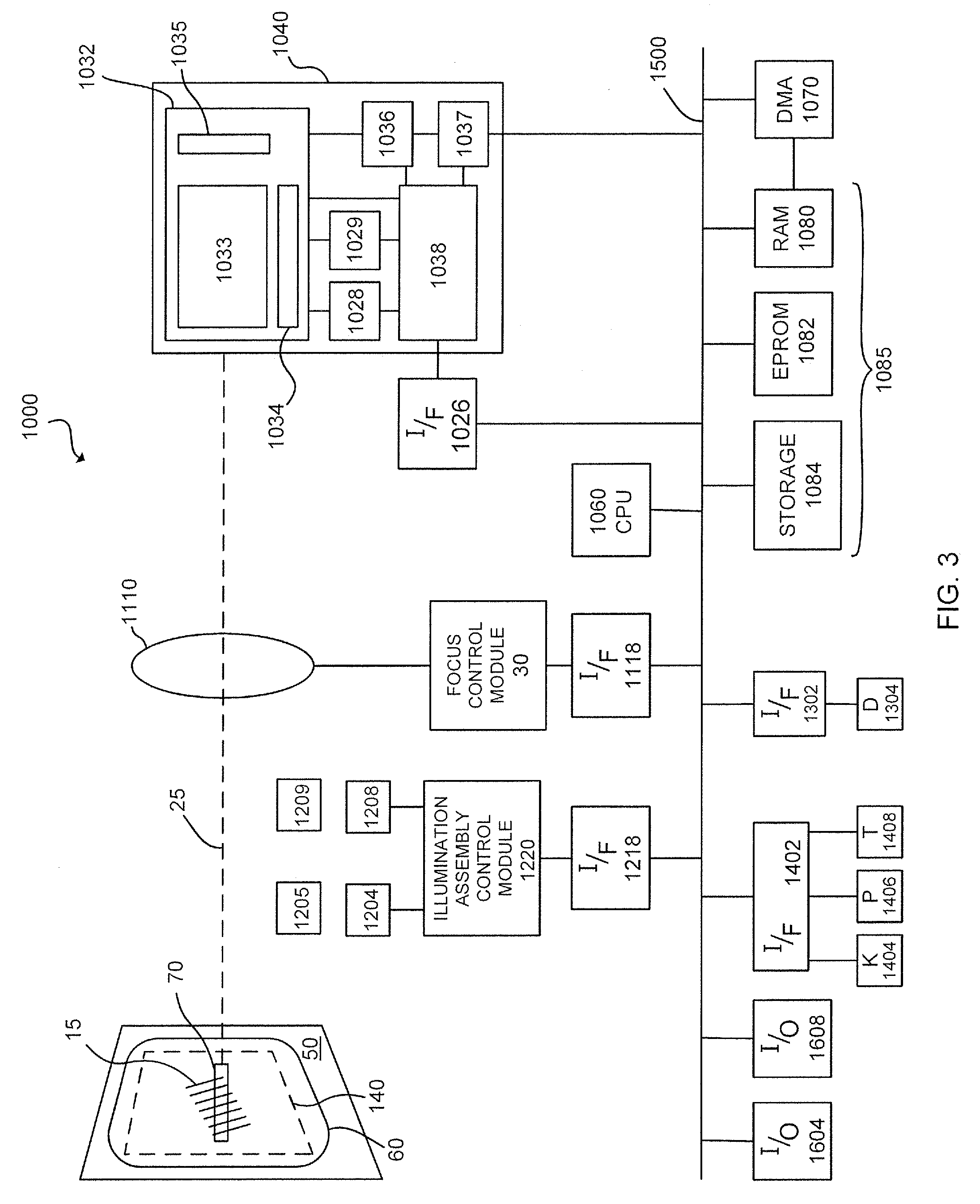
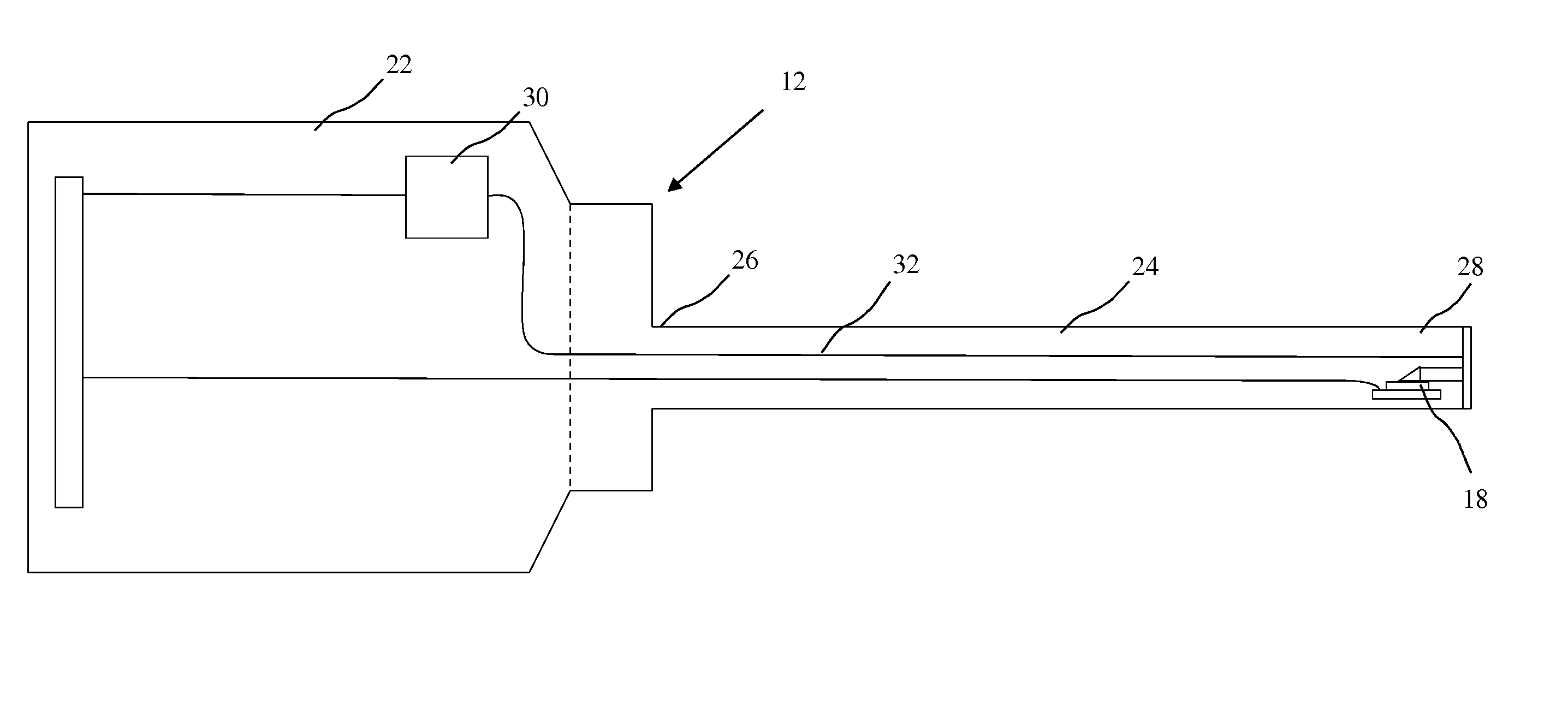
Indicia reading terminal having multiple setting imaging lens
ActiveUS7918398B2Visual representatino by photographic printingExposure controlSensor arrayCamera lens
An indicia reading terminal can include a multiple setting imaging lens assembly and an image sensor having an image sensor array. In one embodiment, an indicia reading terminal in an active reading state can cycle through a set of different lens settings, expose pixels of an image sensor array during an exposure period when each new lens setting is achieved, and attempt to decode decodable indicia represented in frames of image data captured corresponding to each exposure period. In one embodiment, movement of an imaging lens assembly lens element can be provided with use of a hollow stepper motor.
Owner:HAND HELD PRODS
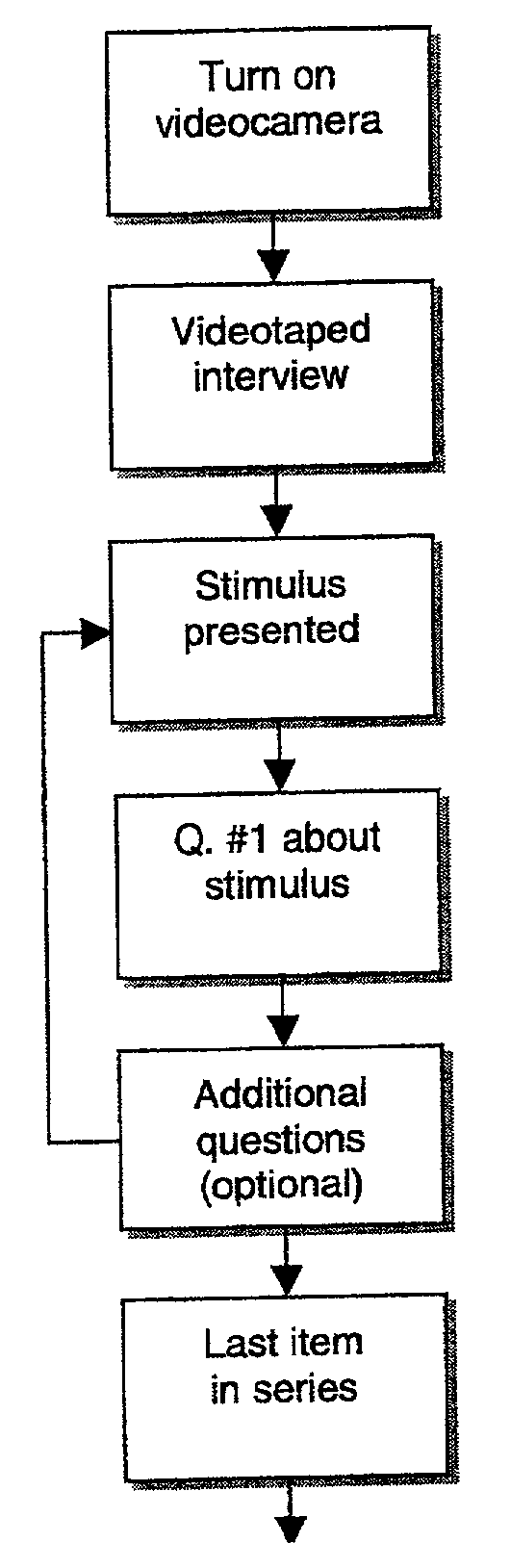
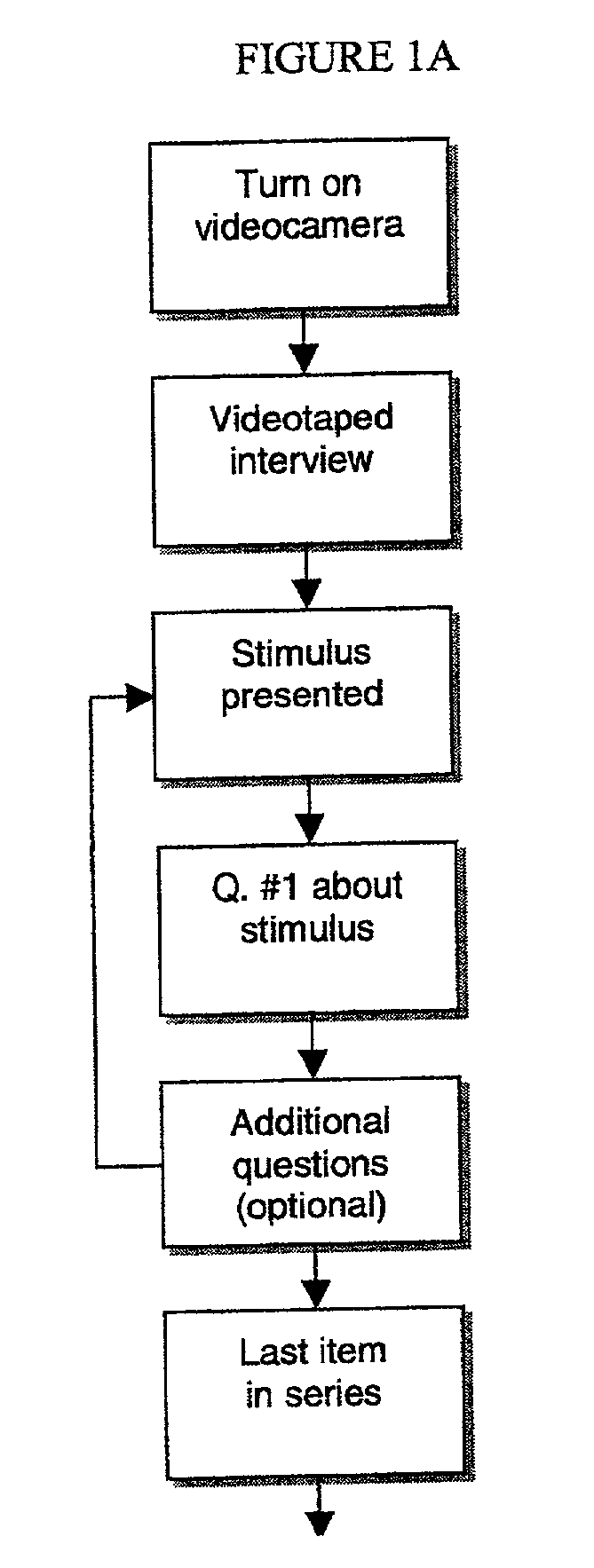
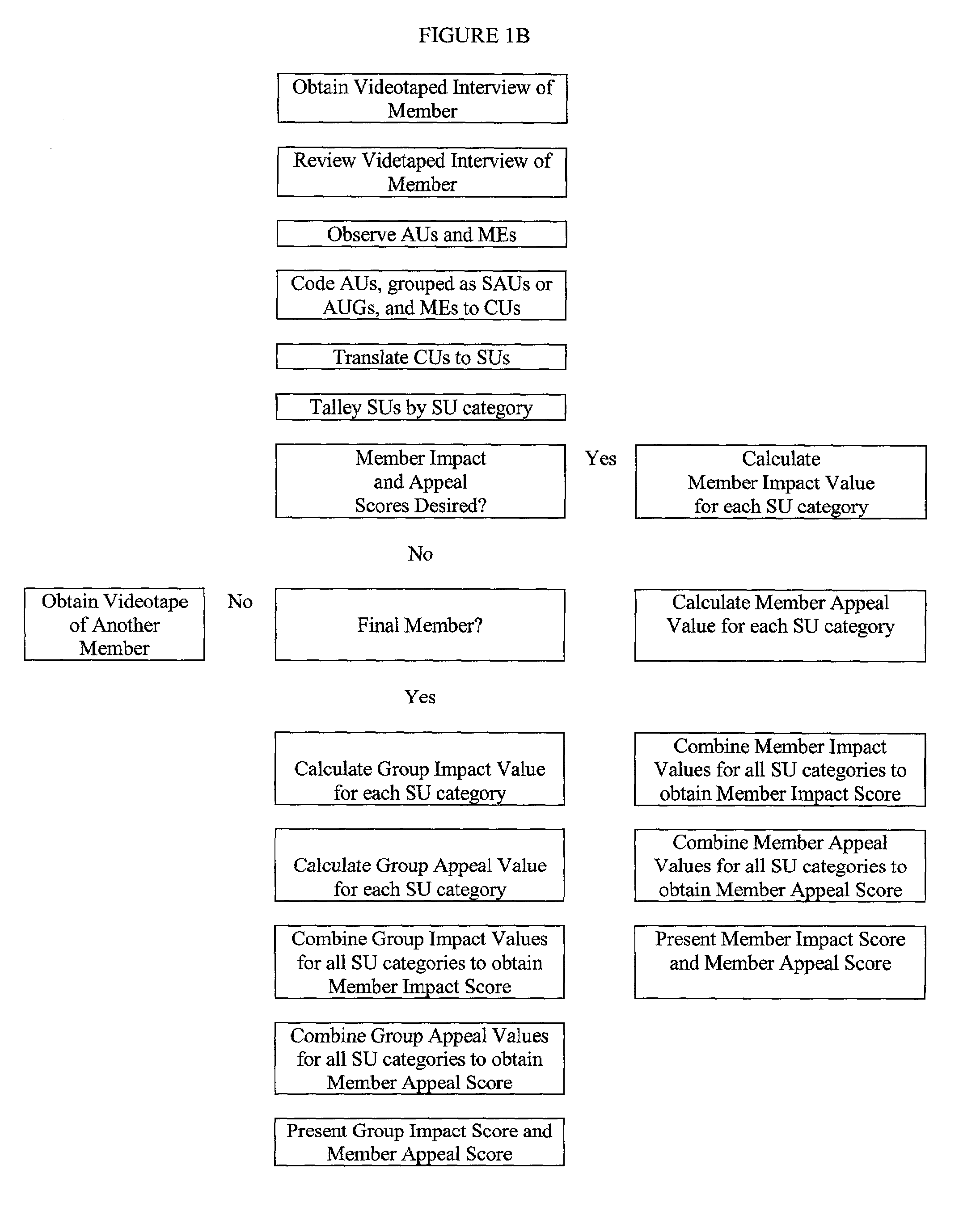
Method of facial coding monitoring for the purpose of gauging the impact and appeal of commercially-related stimuli
A method of assessing consumer reaction to a marketing stimulus, involving the steps of (a) exposing a sample population to a marketing stimulus for a period of time, (b) interviewing members of the sample population immediately after exposure of the members to the marketing stimulus, (c) videotaping any facial expressions and associated verbal comments of individual members of the sample population during the exposure period and interview, (d) reviewing the videotaped facial expressions and associated verbal comments of individual members of the sample population to (1) detect the occurrence of action units, (2) detect the occurrence of a smile, (3) categorize any detected smile as duchenne or social smile, (4) detect the occurrence of any verbal comment associated with a detected smile, and (5) categorize any associated verbal comment as positive, neutral or negative, (e) coding a single action unit or combination of action units to a coded unit, (f) associating coded units with any contemporaneously detected smile, (g) translating the coded unit to a scored unit, (h) tallying the scored unit by scoring unit category, (i) repeating steps (d) through (h) throughout the exposure period, (j) repeating steps (d) through (h) for a plurality of the members of the sample population, (k) calculating an impact value for each scoring unit category by multiplying the tallied number of scored units for each scoring unit category by a predetermined impact factor for that scoring unit category, (l) calculating an appeal value for each scoring unit category by multiplying the tallied number of scored units for each scoring unit category by a predetermined appeal factor for that scoring unit category, (m) combining the impact values obtained for each scoring unit category to obtain an impact score, (n) combining the appeal values obtained for each scoring unit category to obtain an appeal score, and (o) representing the appeal and impact scores with an identification of the corresponding marketing stimulus to which the members were exposed.
Owner:SENSORY LOGIC
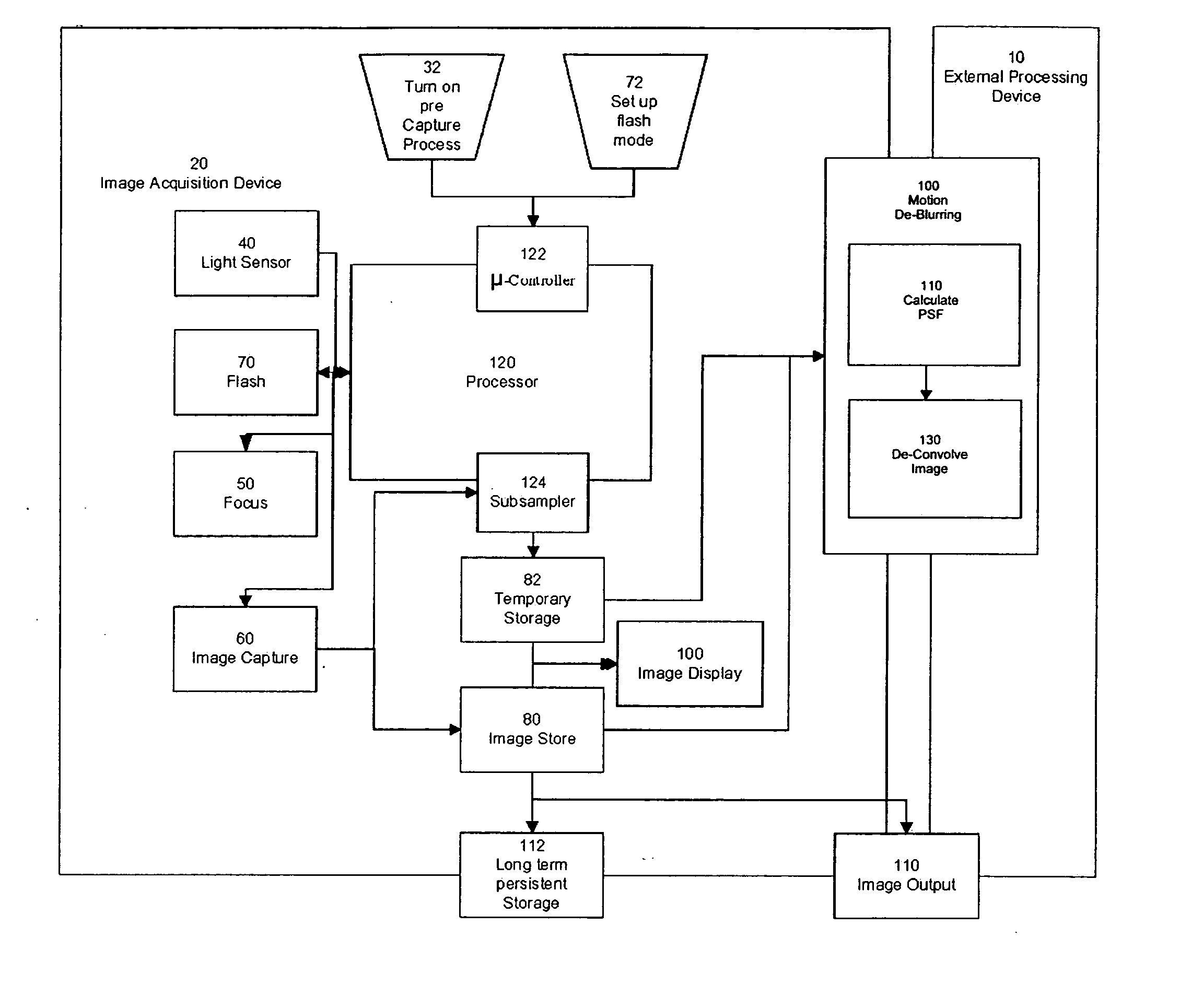
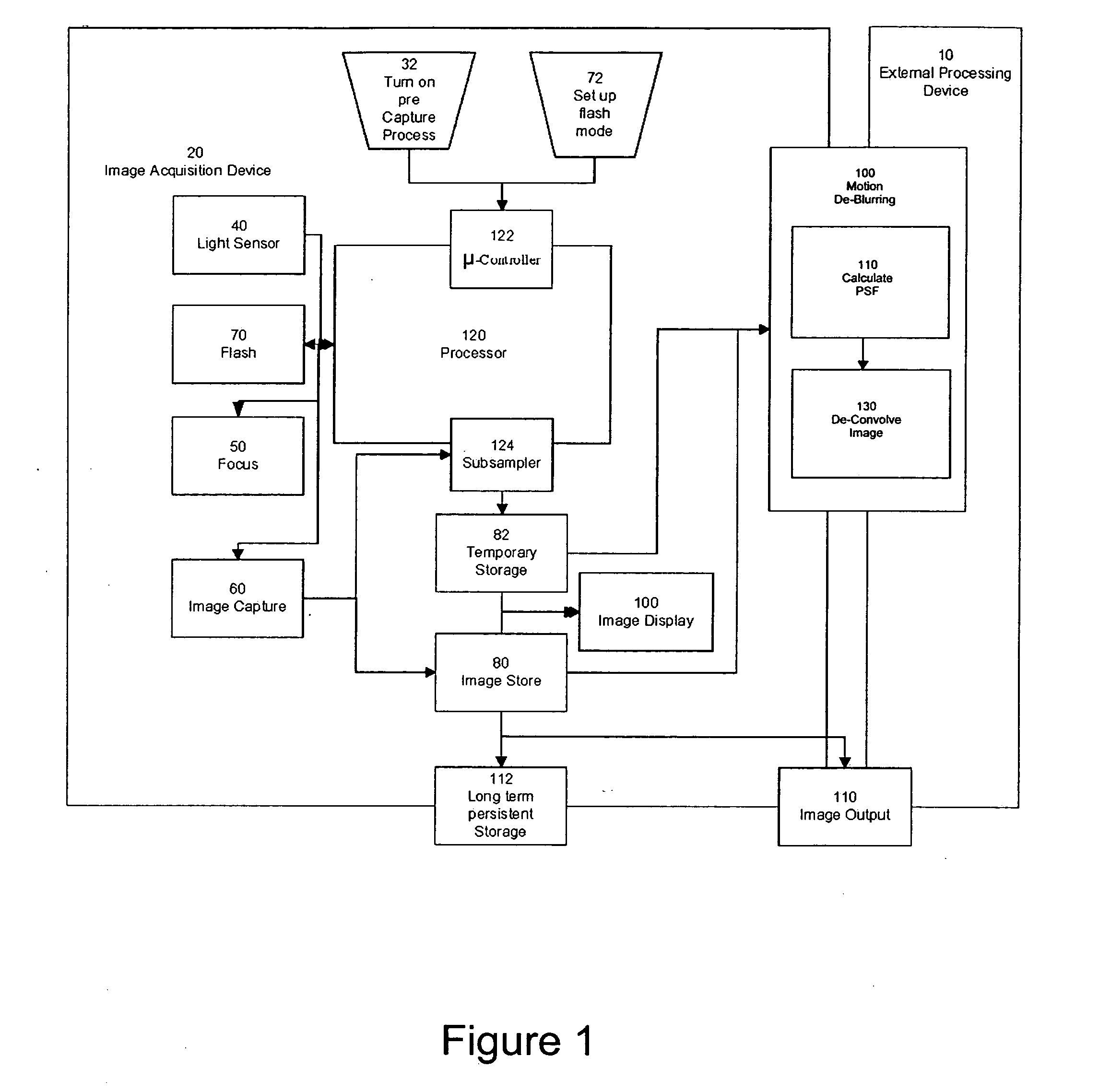
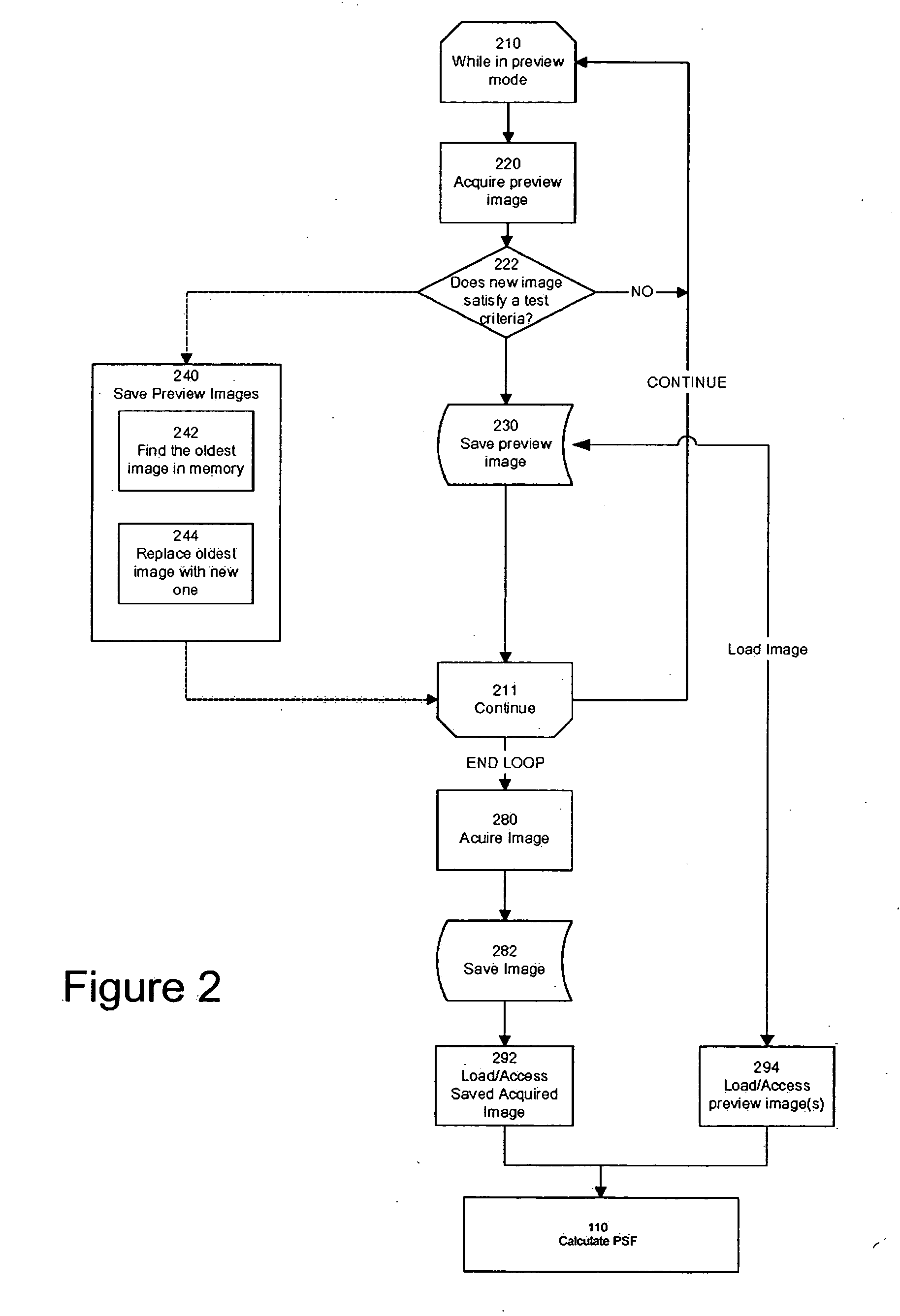
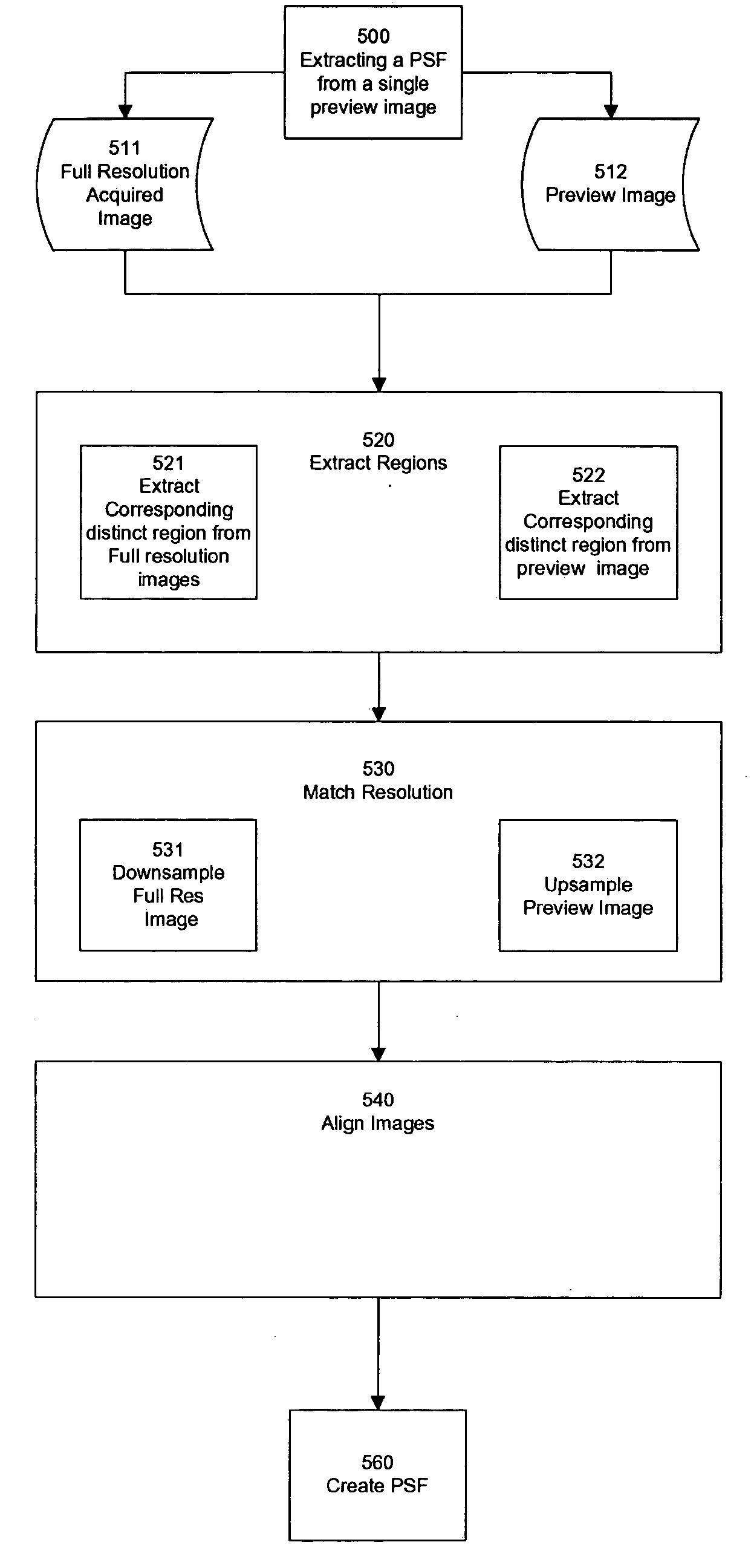
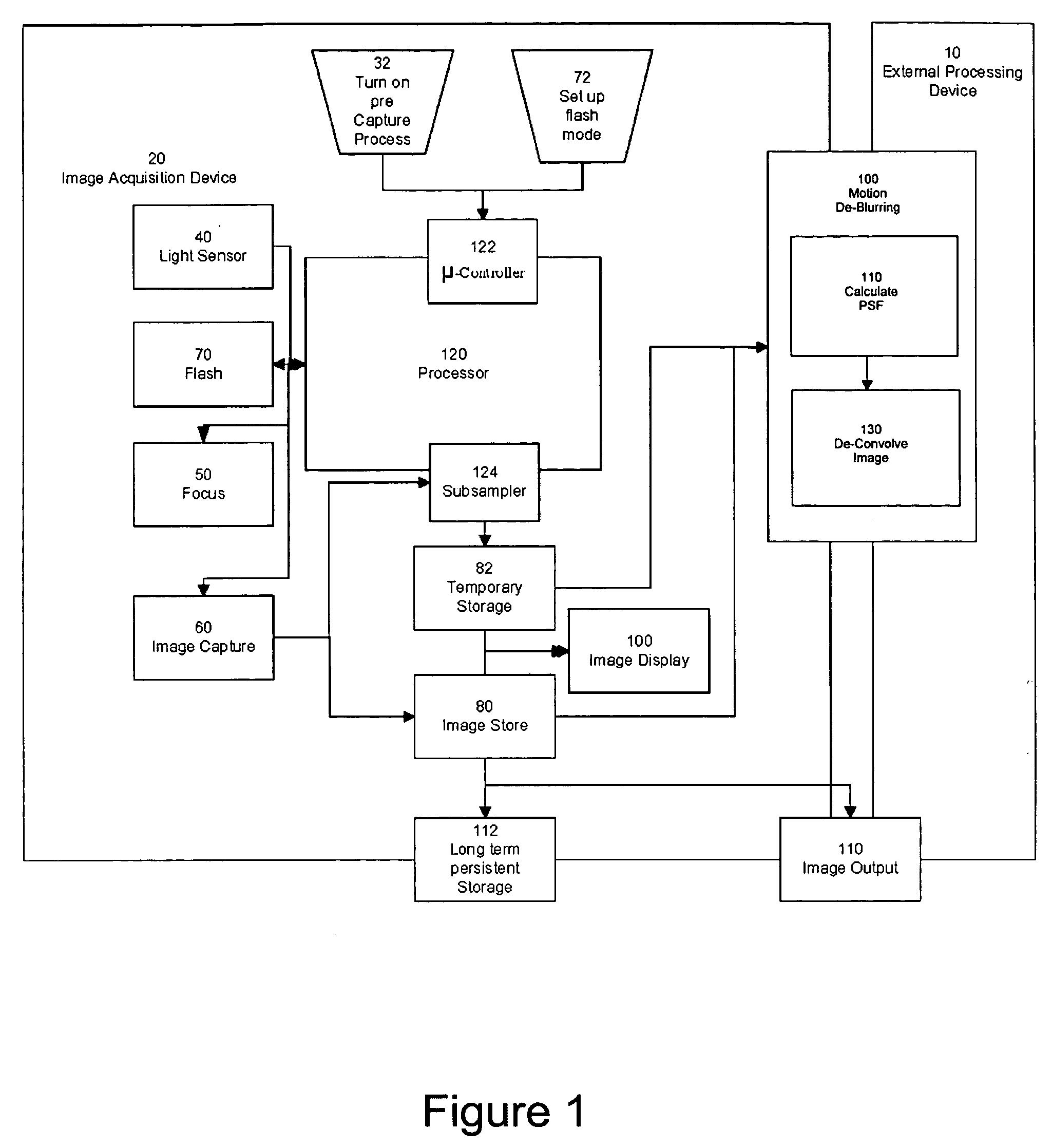
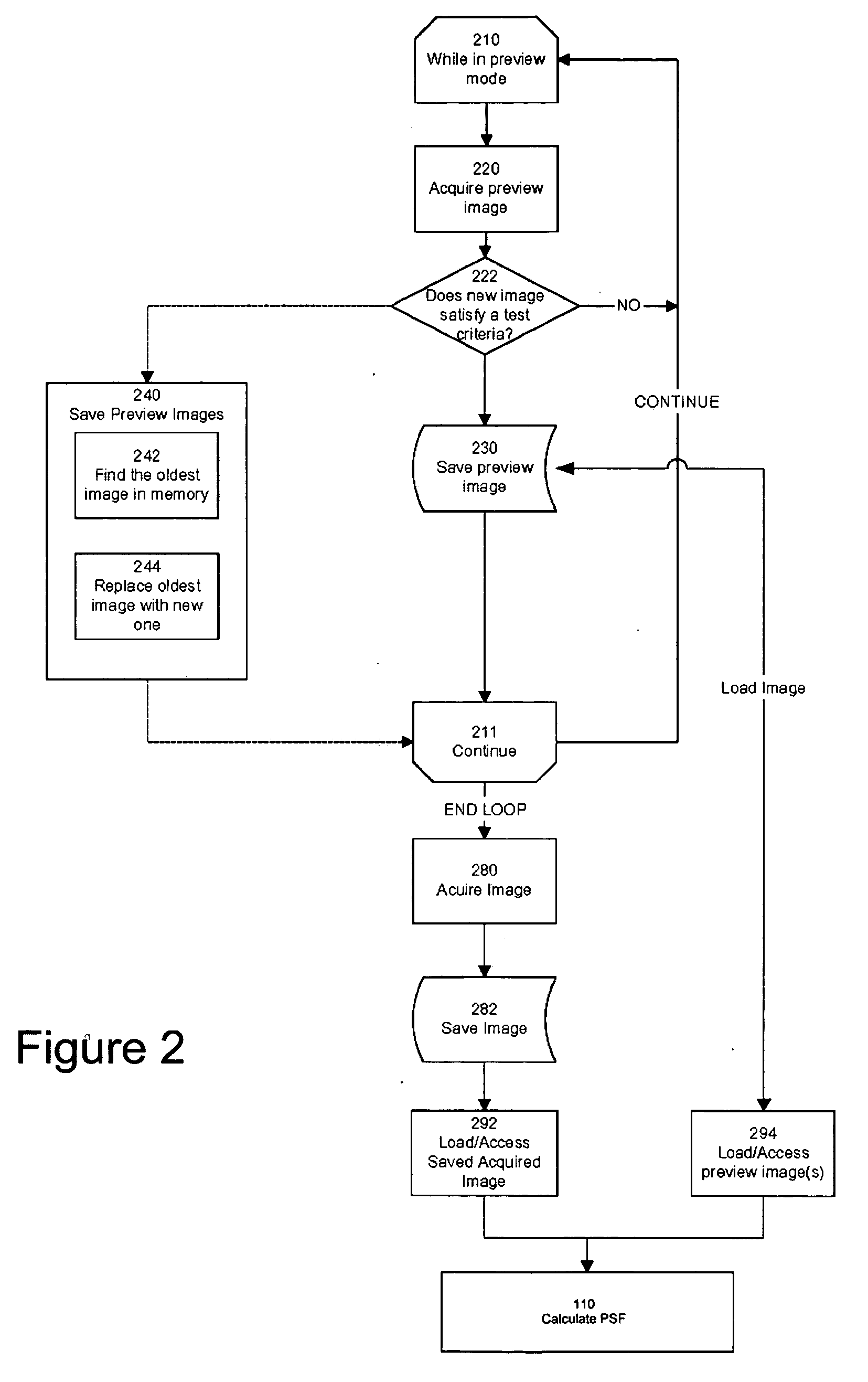
Method of determining PSF using multiple instances of a nominally similar scene
InactiveUS20060098890A1Image enhancementTelevision system detailsPoint spread functionExposure period
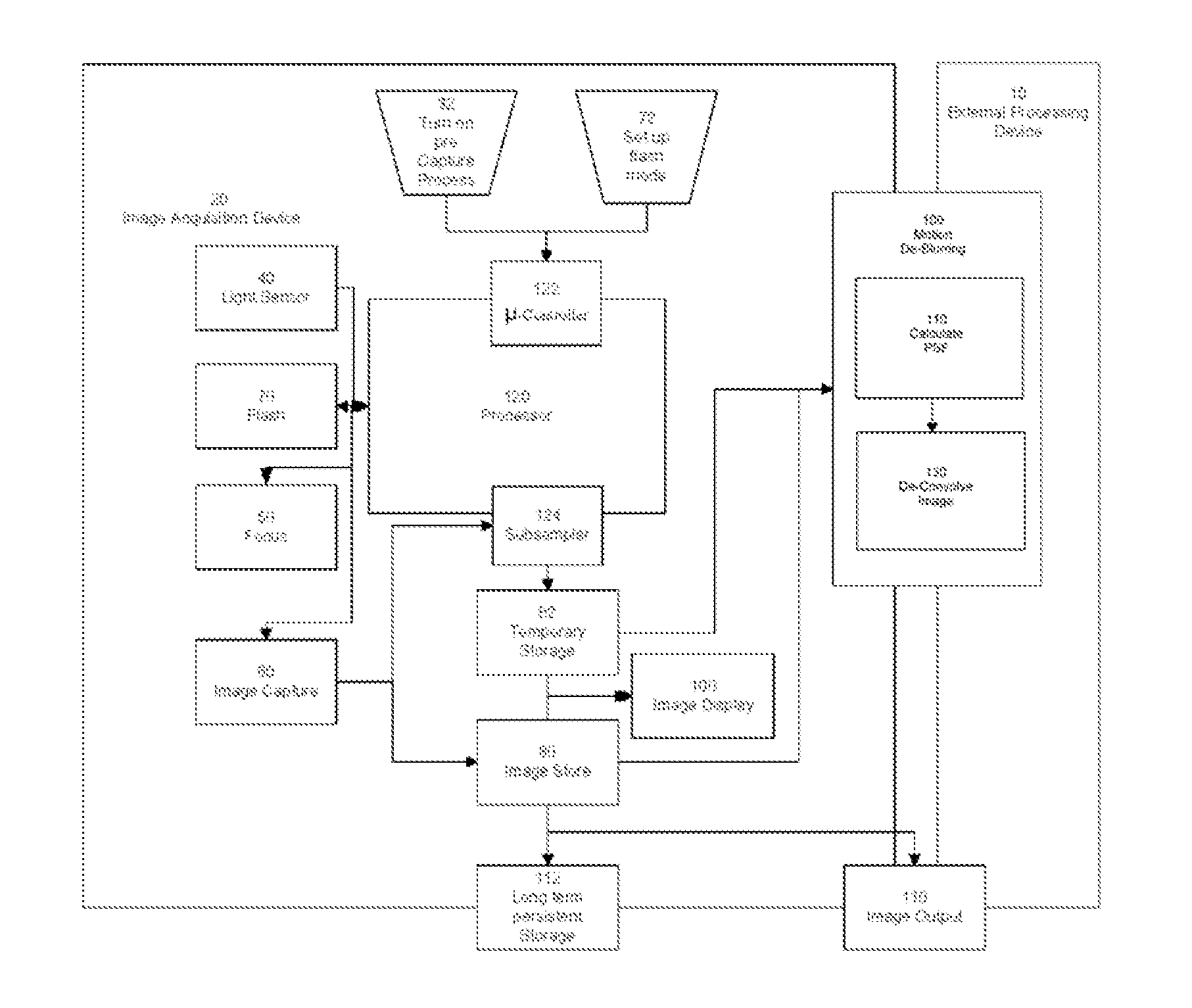
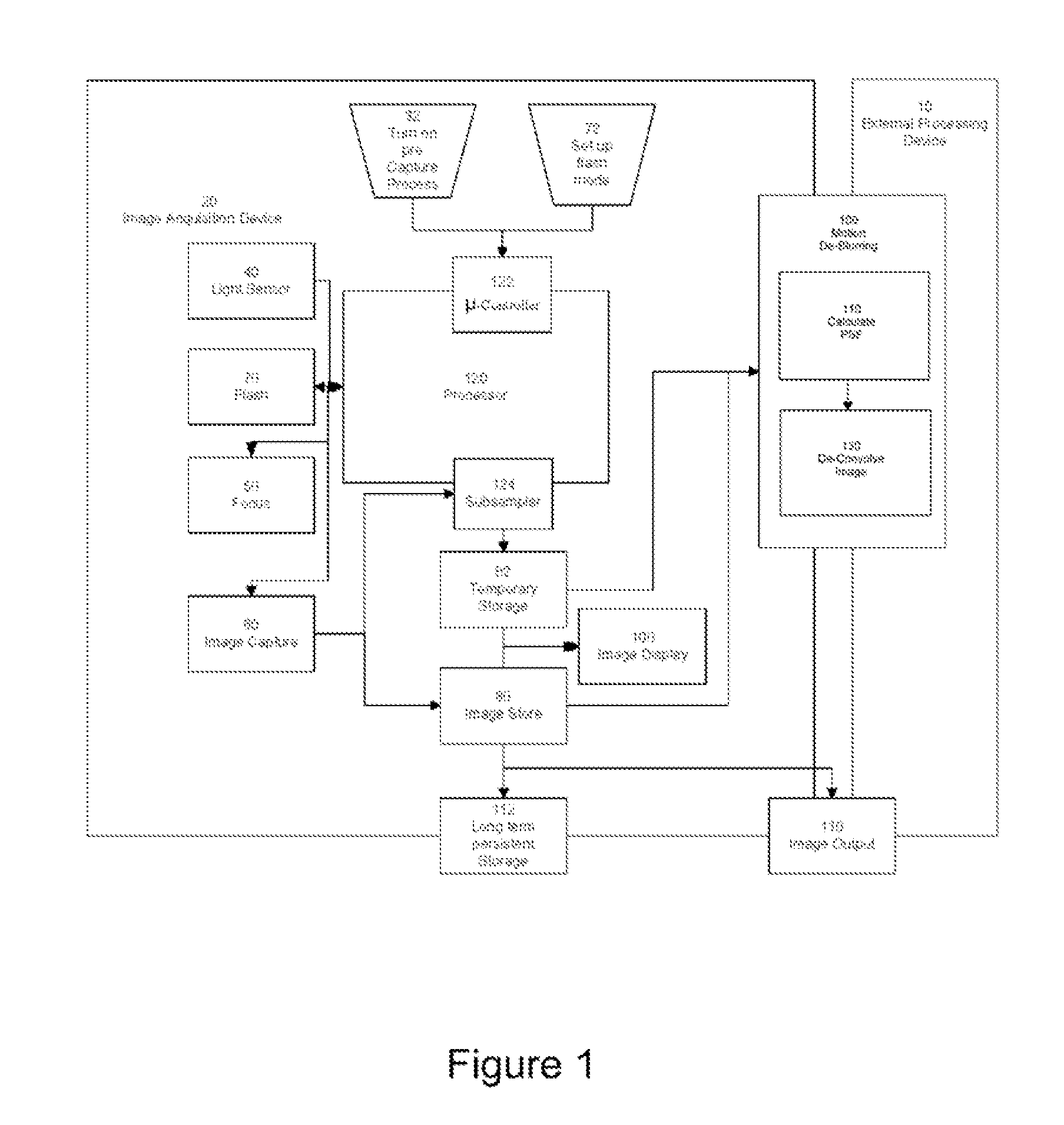
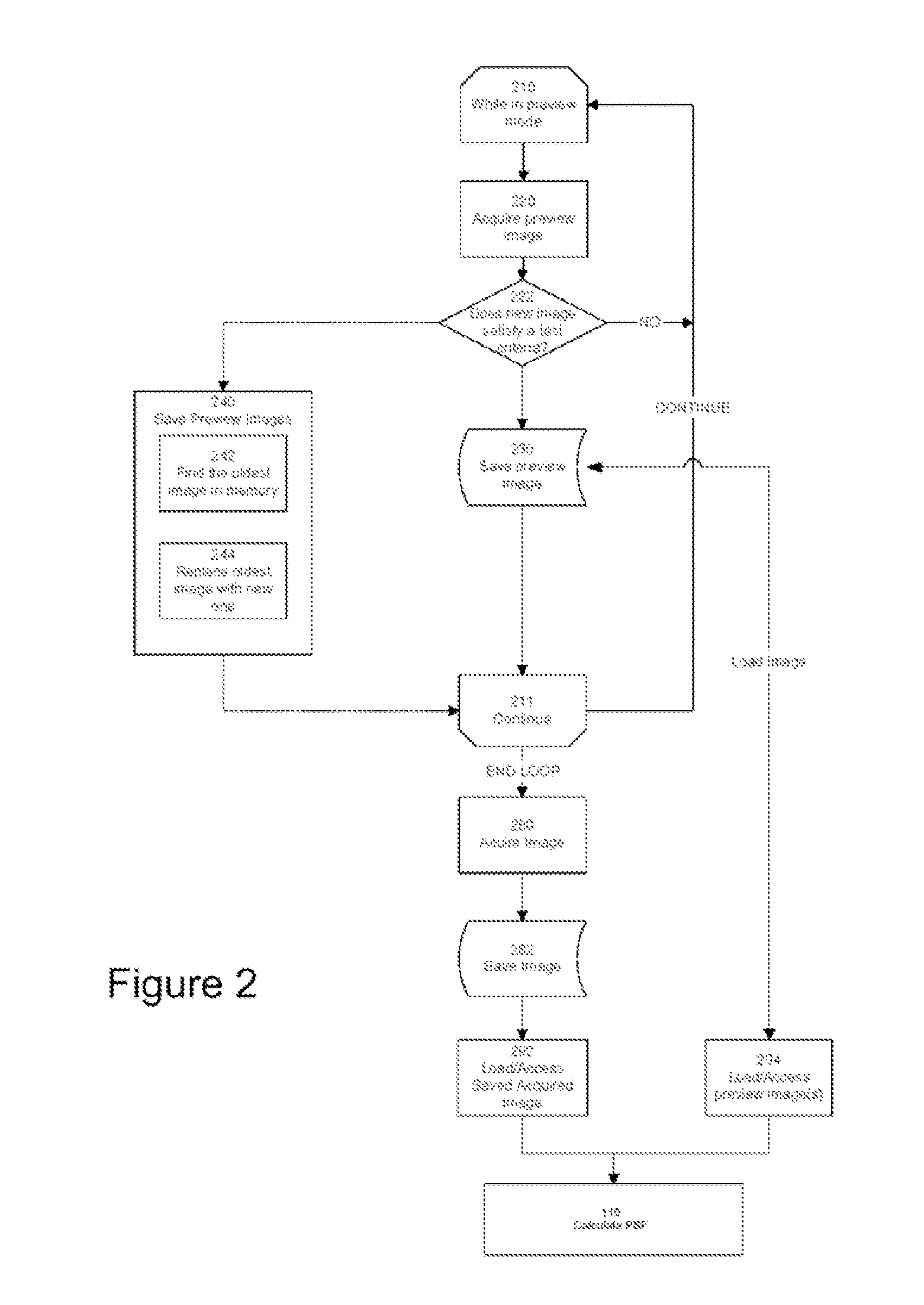
A digital image acquisition system includes a portable apparatus for capturing digital images and a digital processing component for detecting, analyzing and informing the photographer regarding motion blur, and for reducing camera motion blur in an image captured by the apparatus. The digital processing component operates by comparing the image with at least one other image, for example a preview image, of nominally the same scene taken outside the exposure period of the main image. In one embodiment the digital processing component identifies at least one feature in a single preview image which is relatively less blurred than the corresponding feature in the main image, calculates a point spread function (PSF) in respect of such feature, and de-convolves the main image using the PSF. In another embodiment, the digital processing component calculates a trajectory of at least one feature in a plurality of preview images, extrapolates such feature on to the main image, calculates a PSF in respect of the feature, and de-convolves the main image using the PSF. In another embodiment the digital processing unit after determining the degree of blur notifies the photographer of the existing blur or automatically invokes consecutive captures.
Owner:FOTONATION LTD
Bar code reading device with global electronic shutter control
ActiveUS7568628B2Minimize degradationTelevision system detailsTransmission systemsSensor arrayElectronic shutter
The invention features an image reader and a corresponding method for capturing a sharp distortion free image of a target, such as a one or two-dimensional bar code. In one embodiment, the image reader comprises a two-dimensional CMOS based image sensor array, a timing module, an illumination module, and a control module. The time during which the target is illuminated is referred to as the illumination period. The capture of the image by the image sensor array is driven by the timing module that, in one embodiment, is able to simultaneously expose substantially all of the pixels in the array. The time during which the pixels are collectively activated to photo-convert incident light into charge defines the exposure period for the sensor array. In one embodiment, at least a portion of the exposure period occurs during the illumination period.
Owner:HAND HELD PRODS
Synchronization of projected illumination with rolling shutter of image sensor
Imaging apparatus includes an illumination assembly, including a plurality of radiation sources and projection optics, which are configured to project radiation from the radiation sources onto different, respective regions of a scene. An imaging assembly includes an image sensor and objective optics configured to form an optical image of the scene on the image sensor, which includes an array of sensor elements arranged in multiple groups, which are triggered by a rolling shutter to capture the radiation from the scene in successive, respective exposure periods from different, respective areas of the scene so as to form an electronic image of the scene. A controller is coupled to actuate the radiation sources sequentially in a pulsed mode so that the illumination assembly illuminates the different, respective areas of the scene in synchronization with the rolling shutter.
Owner:APPLE INC
Imaging apparatus and imaging method
InactiveUS20060157760A1Blocking phenomenonQuality improvementTelevision system detailsColor television detailsEngineeringExposure period
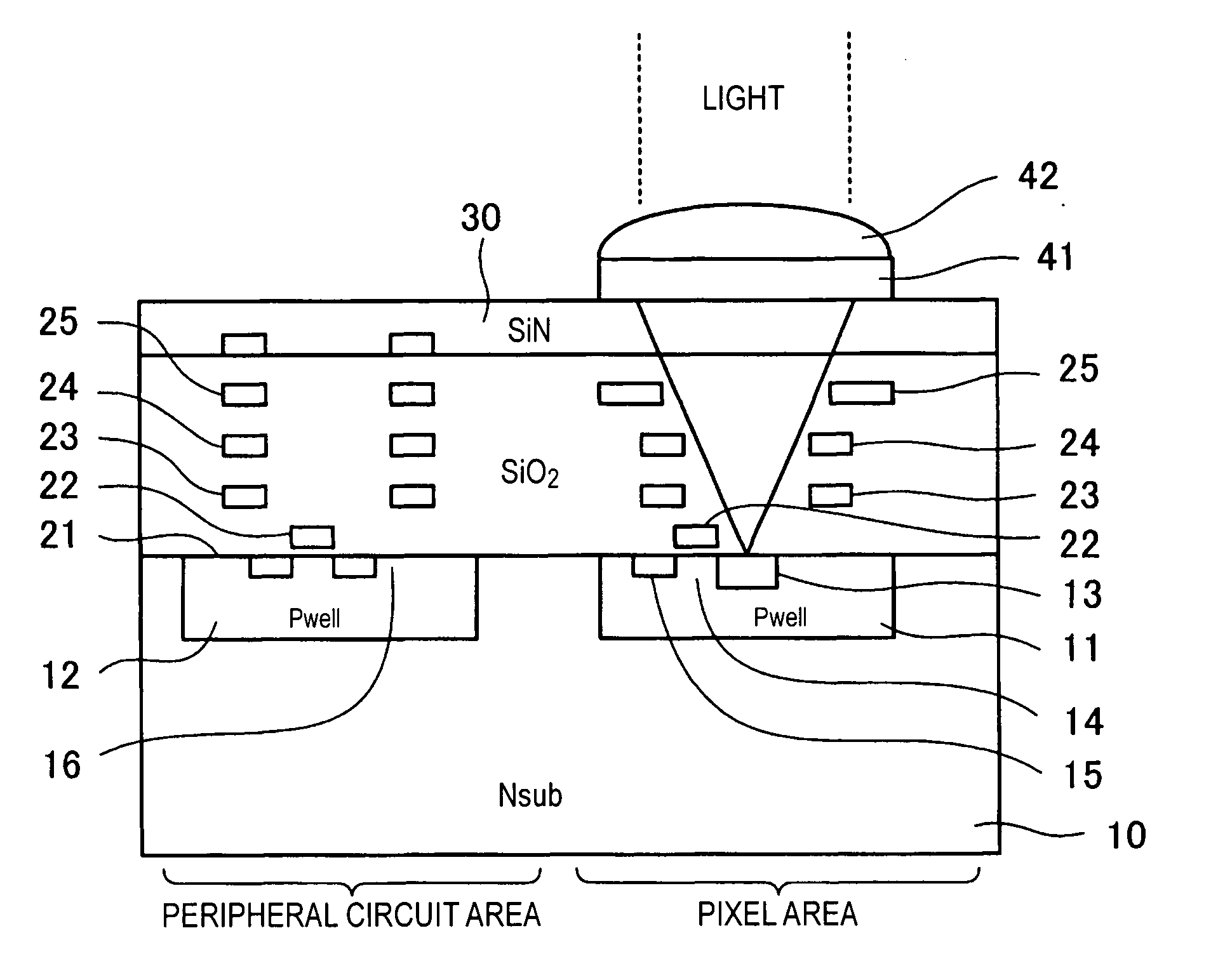
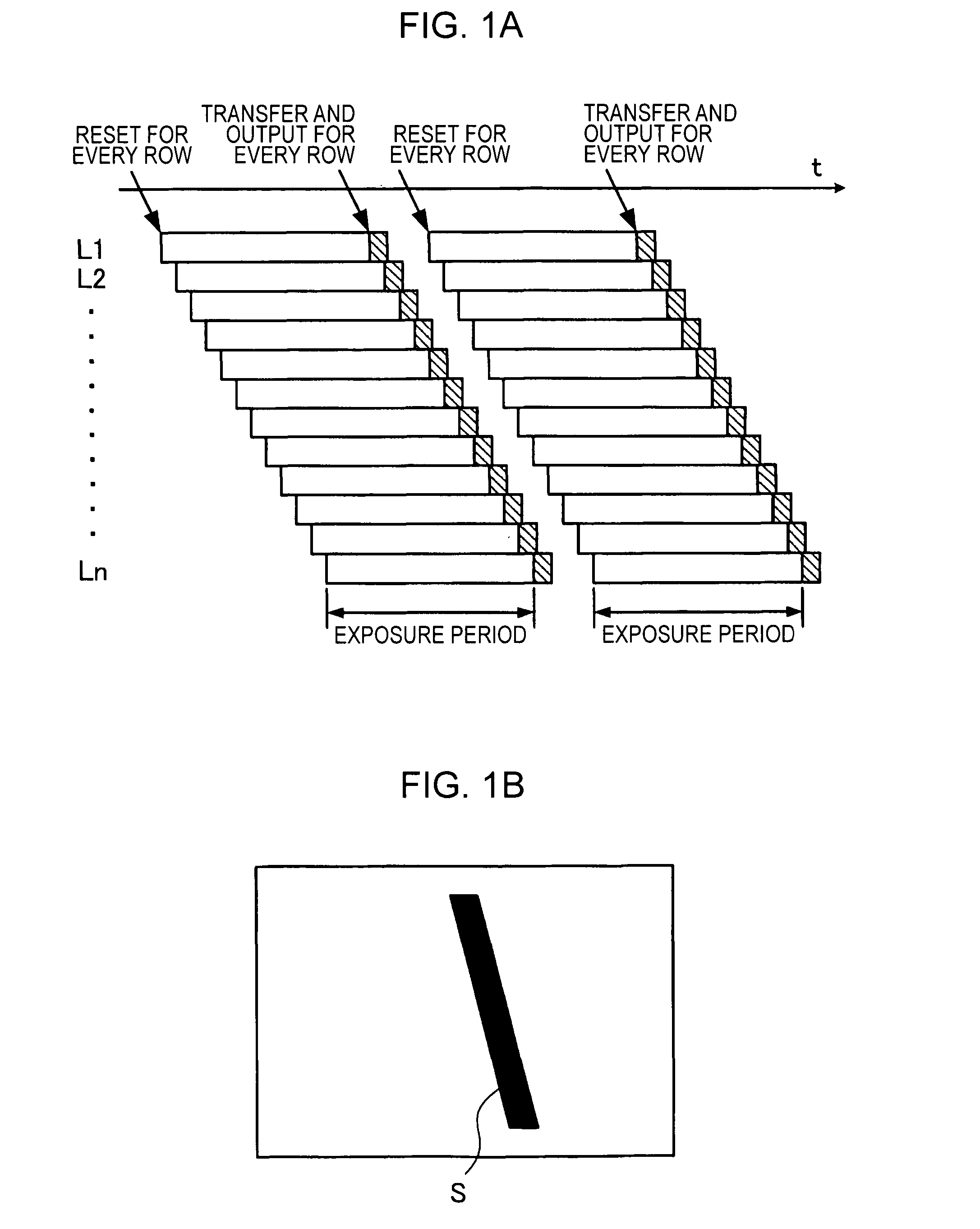
An imaging apparatus using a solid-state image sensor that reads out a signal of each pixel by an XY address method to capture an image includes a mechanical shutter configured to block light incident on a light receiving surface of the solid-state image sensor; and control means for simultaneously resetting the pixel signals for all rows in the solid-state image sensor to start exposure to the solid-state image sensor, closing the mechanical shutter after a predetermined exposure period is elapsed, and sequentially reading out the pixel signals for every row of the solid-state image sensor with the mechanical shutter being closed.
Owner:THOMSON LICENSING SA
Image Pickup Apparatus, Image Processing Method, and Computer Program
ActiveUS20080012969A1High-quality image dataTelevision system detailsTelevision system scanning detailsImaging processingExposure control
An image pickup apparatus includes an image pickup device that has high-sensitivity pixel devices receiving a relatively large amount of light and low-sensitivity pixel devices receiving a relatively small amount of light, an exposure control unit independently controlling exposure periods of the high-sensitivity pixel devices and the low-sensitivity pixel devices, and an image generation unit performing image generation on the basis of an output signal of the image pickup device. The image generation unit compares a high-sensitivity pixel evaluation image generated using data output from the high-sensitivity pixel devices with a low-sensitivity pixel evaluation image generated using data output from the low-sensitivity pixel devices by obtaining a difference or ratio between pixel values of corresponding pixels in the two evaluation images, and performs different types of image processing for a region composed of pixels each having a small difference and a region composed of pixels each having a large difference.
Owner:SONY SEMICON SOLUTIONS CORP
Digital camera using multiple image sensors to provide improved temporal sampling
InactiveUS7978239B2Television system detailsSignal generator with multiple pick-up deviceImage resolutionExposure period
A method and apparatus for capturing image data from multiple image sensors and generating an output image sequence are disclosed. The multiple image sensors capture data with one or more different characteristics, such as: staggered exposure periods, different length exposure periods, different frame rates, different spatial resolution, different lens systems, and different focal lengths. The data from multiple image sensors is processed and interleaved to generate an improved output motion sequence relative to an output motion sequence generated from an a single equivalent image sensor.
Owner:MONUMENT PEAK VENTURES LLC
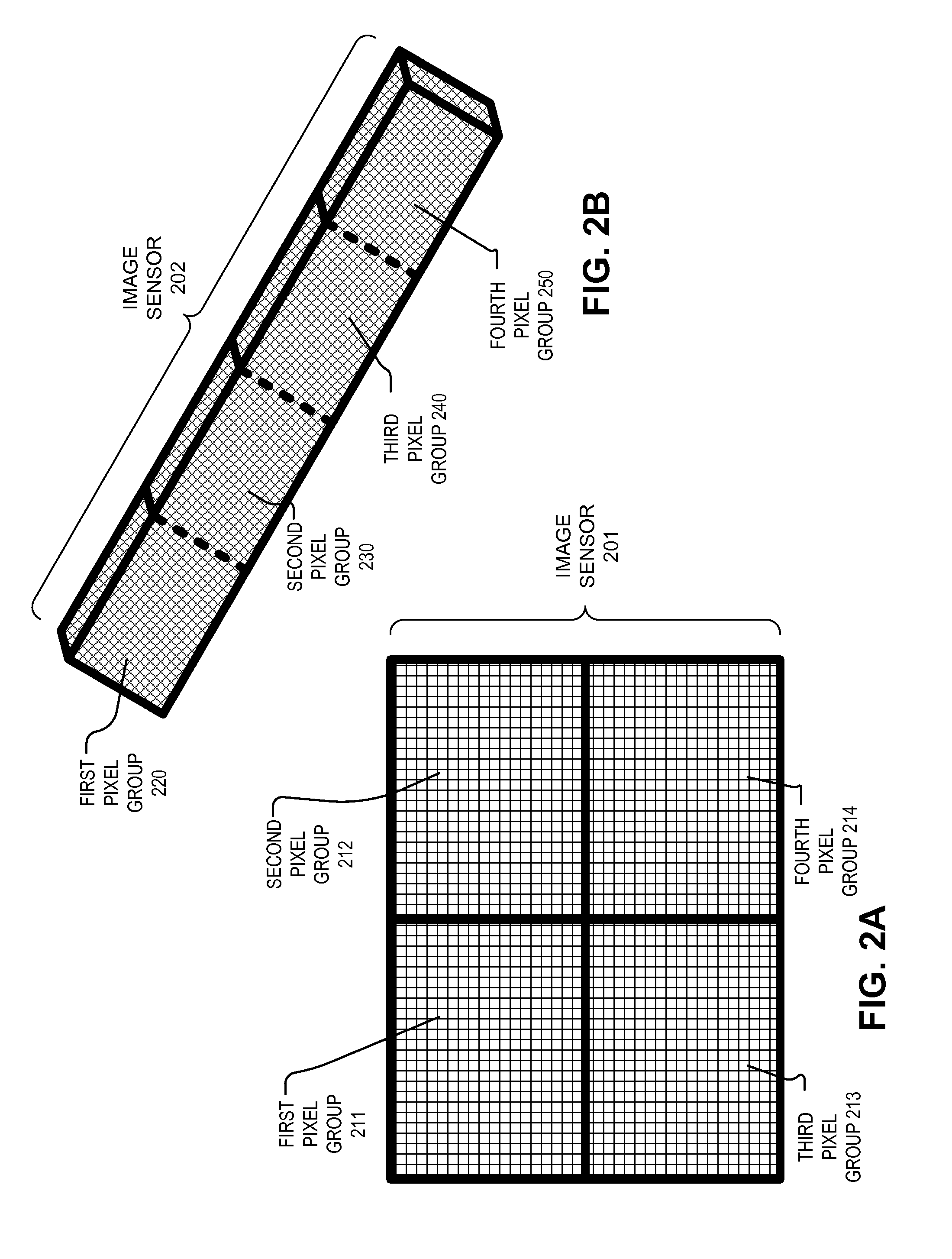
Imaging device with a plurality of pixel arrays
ActiveUS20140078333A1Television system detailsColor television detailsExposure periodComputer vision
An imaging device includes a first pixel array arrange to capture a first image and a second pixel array arranged to capture a second image. The first pixel array and the second pixel array face substantially a same direction. The imaging device also includes shutter control circuitry which is coupled to the first pixel array to initiate a first exposure period of the first pixel array to capture the first image. The shutter control circuitry is also coupled to the second pixel array to initiate a second exposure period of the second pixel array to capture the second image. The imaging device also includes processing logic coupled to receive first pixel data of the first image and coupled to receive second pixel data of the second image. The processing logic is configured to generate at least one image using the first pixel data and the second pixel data.
Owner:GOOGLE LLC
Pixel structure with multiple transfer gates
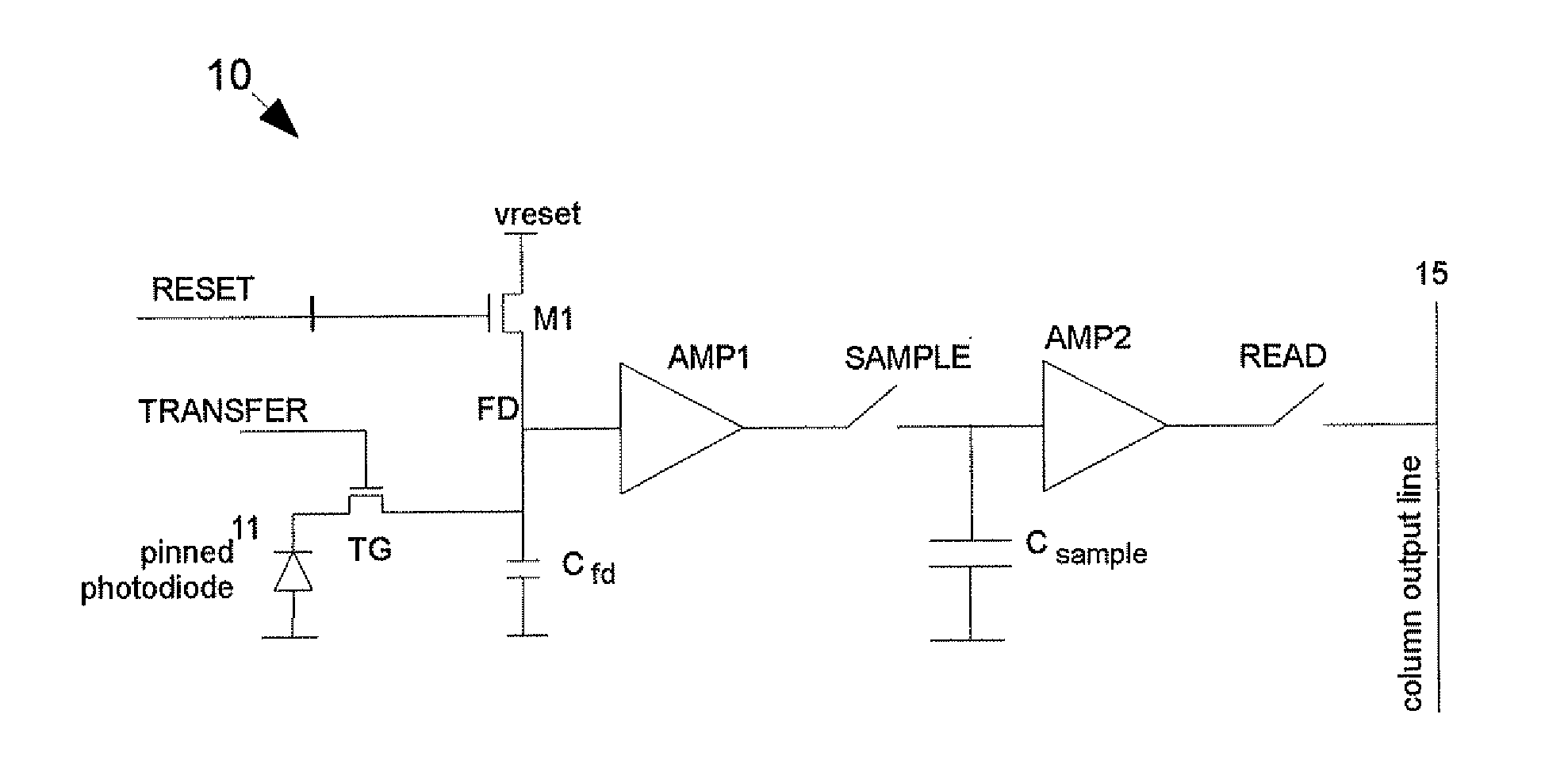
ActiveUS20120002089A1Improve dynamic rangeComplex implementationTelevision system detailsTelevision system scanning detailsEngineeringExposure period
A pixel structure comprises a photo-sensitive element for generating charge in response to incident light. A first transfer gate is connected between the photo-sensitive element and a first charge conversion element. A second transfer gate is connected between the photo-sensitive element and a second charge conversion element. An output stage outputs a first value related to charge at the first charge conversion element and outputs a second value related to charge at the second charge conversion element. A controller controls operation of the pixel structures and causes a pixel structure. The controller causes the pixel structure to: acquire charges on the photo-sensitive element during an exposure period; transfer a first portion of the charges acquired during the exposure period from the photo-sensitive element to the first charge conversion element via the first transfer gate; and transfer a second portion of the charges acquired during the exposure period from the photo-sensitive element to the second charge conversion element via the second transfer gate.
Owner:CMOSIS
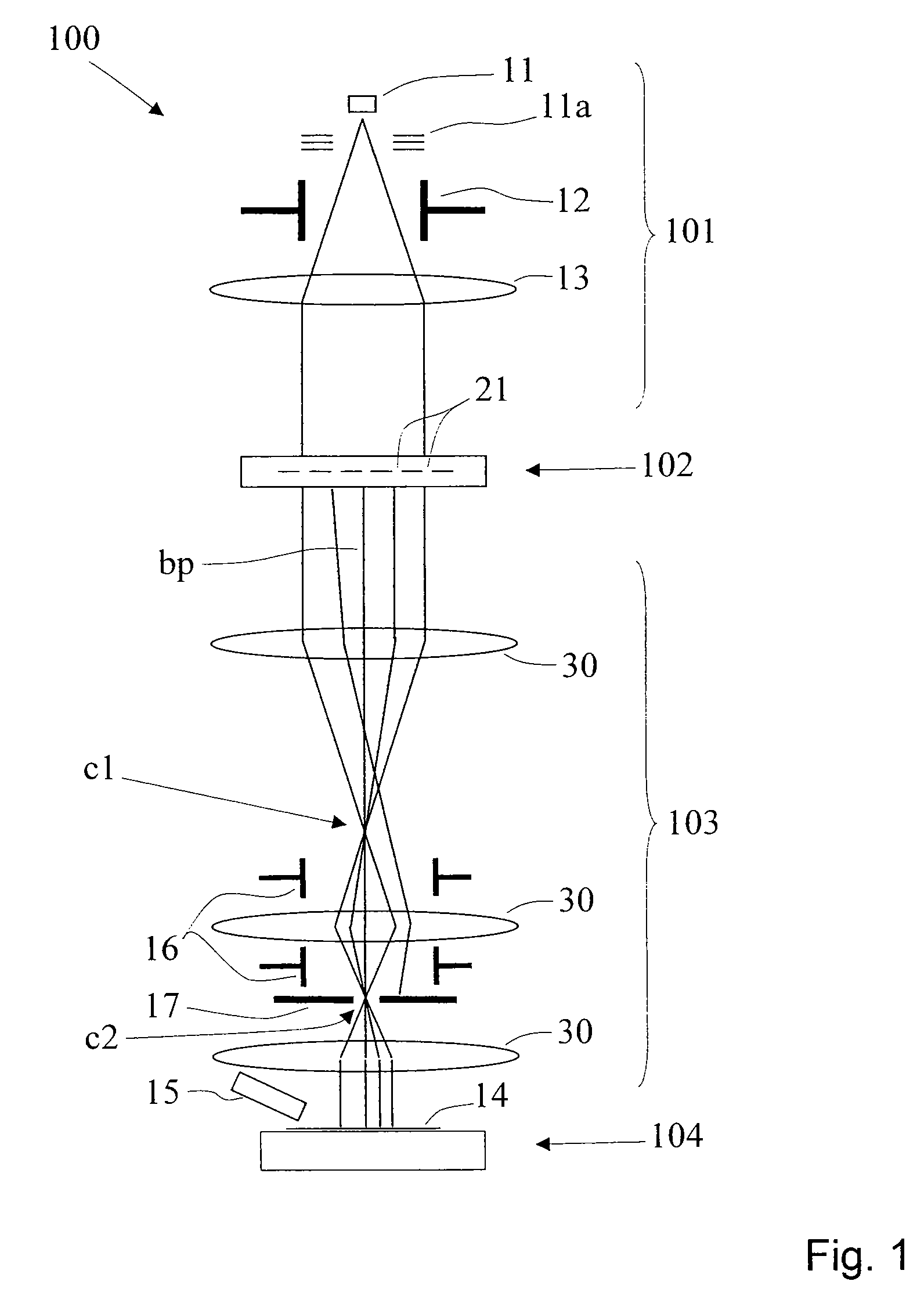
Method for maskless particle-beam exposure
ActiveUS7777201B2Improve throughputEasy to implementThermometer detailsMaterial analysis using wave/particle radiationParticle beamClassical mechanics
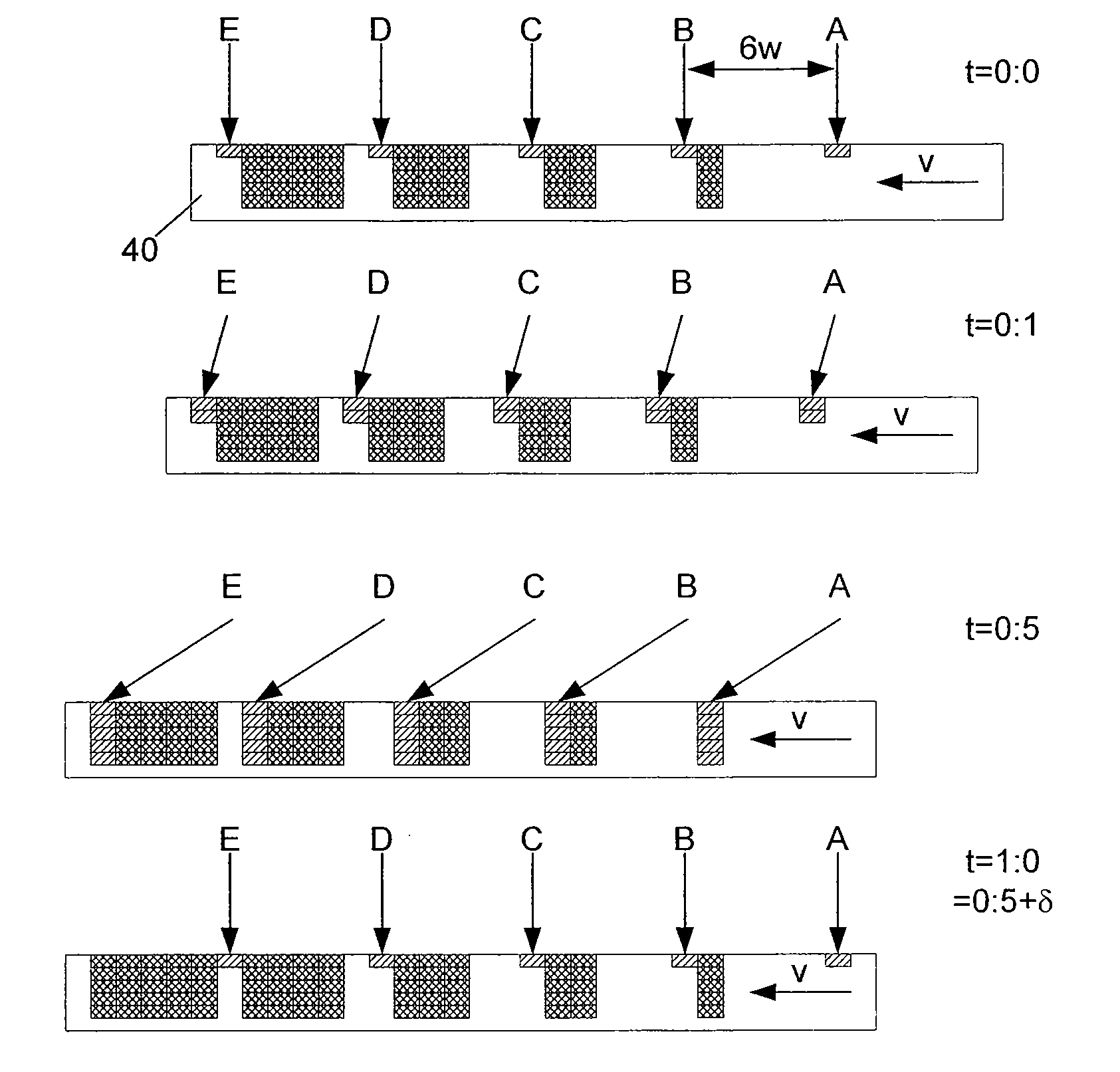
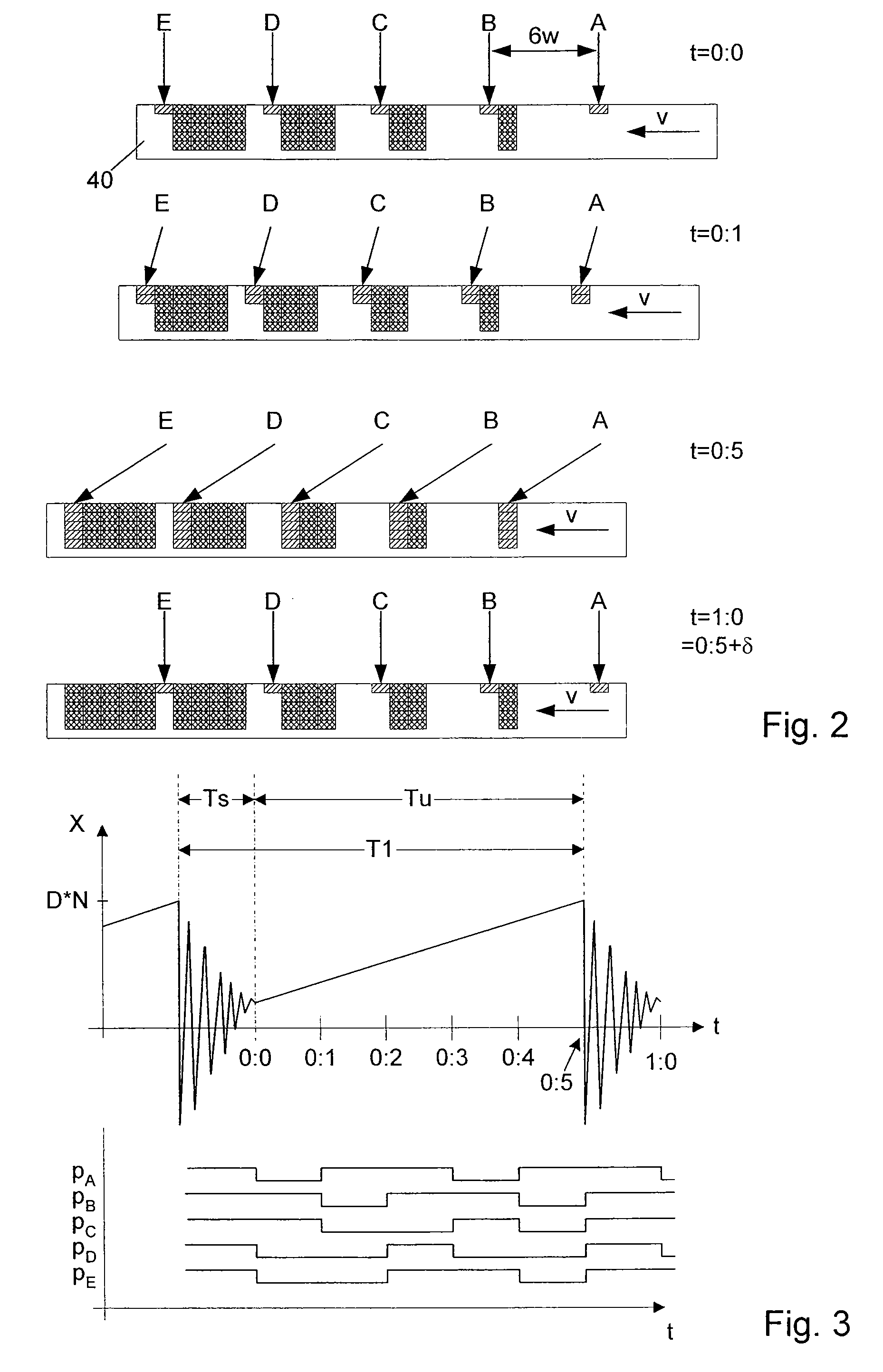
For maskless irradiating a target with a beam of energetic electrically charged particles using a pattern definition means with a plurality of apertures and imaging the apertures in the pattern definition means onto a target which moves (v) relative to the pattern definition means laterally to the axis, the location of the image is moved along with the target, for a pixel exposure period within which a distance of relative movement of the target is covered which is at least a multiple of the width (w) of the aperture images as measured on the target, and after said pixel exposure period the location of the beam image is changed, which change of location generally compensates the overall movement of the location of the beam image.
Owner:IMS NANOFABTION
Indicia reading terminal having multiple setting imaging lens
ActiveUS20090072038A1Visual representatino by photographic printingExposure controlCamera lensExposure period
An indicia reading terminal can include a multiple setting imaging lens assembly and an image sensor having an image sensor array. In one embodiment, an indicia reading terminal in an active reading state can cycle through a set of different lens settings, expose pixels of an image sensor array during an exposure period when each new lens setting is achieved, and attempt to decode decodable indicia represented in frames of image data captured corresponding to each exposure period. In one embodiment, movement of an imaging lens assembly lens element can be provided with use of a hollow stepper motor.
Owner:HAND HELD PRODS
Method and apparatus for initiating subsequent exposures based on determination of motion blurring artifacts
InactiveUS20060098237A1Television system detailsCharacter and pattern recognitionReal time analysisPoint spread function
A digital image acquisition system includes a portable apparatus for capturing digital images and a digital processing component for detecting, analyzing, invoking subsequent image captures and informing the photographer regarding motion blur, and for reducing camera motion blur in an image captured by the apparatus. The digital processing component operates by comparing the image with at least one other image, for example a preview image, of nominally the same scene taken outside the exposure period of the main image. In one embodiment the digital processing component identifies at least one feature in a single preview image which is relatively less blurred than the corresponding feature in the main image, calculates a point spread function (PSF) in respect of such feature, and initiates a subsequent capture if determined that the motion blur exceeds a certain threshold. In another embodiment the digital processing determines the degree of blur by analyzing the motion blur in the captured image itself, and initiates a subsequent capture if determined that the motion blur exceeds a certain threshold. Such real time analysis may use the auto focusing mechanism to qualitatively determine the PSF.
Owner:FOTONATION LTD
Methods, systems, and computer program products for imperceptibly embedding structured light patterns in projected color images for display on planar and non-planar surfaces
Methods, systems, and computer program products for imperceptibly embedding structured light patterns in projected color images for display on planar and non-planar surfaces are disclosed. According to one method, an image exposure period for detecting an embedded structured light patterns in a projected image is selected based on analysis of pixel polarities for different pixel intensities of a pixel color. Pixel intensities for the color are varied in the user image so that pixel polarities encode the structured light patterns during image exposure period. The user image is projected with the structured light patterns onto the surface. Depth information is continuously acquired and used to adjust display of the user image.
Owner:THE UNIV OF NORTH CAROLINA AT CHAPEL HILL
Indicia reading terminal including frame processing
There is described an indicia reading terminal that can be operative to process a frame of image data for attempting to decode a decodable indicia. A frame can be a frame that is among a succession of frames for subjecting to processing subsequent to and during a time a trigger signal is active. Such a succession of frames can include zero or more binned frames, zero or more unbinned frames, zero or more windowed frames, and zero or more unwindowed full frames. An indicia reading terminal can also include a variable focus imaging lens. Control of the variable focus imaging lens can be provided so that during an exposure period for a binned frame the variable focus imaging lens is set to a short range focus setting and further so that during an exposure period for a windowed frame the variable focus imaging lens is set to a long range focus setting.
Owner:HAND HELD PRODS
Pixel array with global shutter
ActiveUS20090256060A1Reduce in quantityOptimize layoutTransistorTelevision system detailsAudio power amplifierExposure period
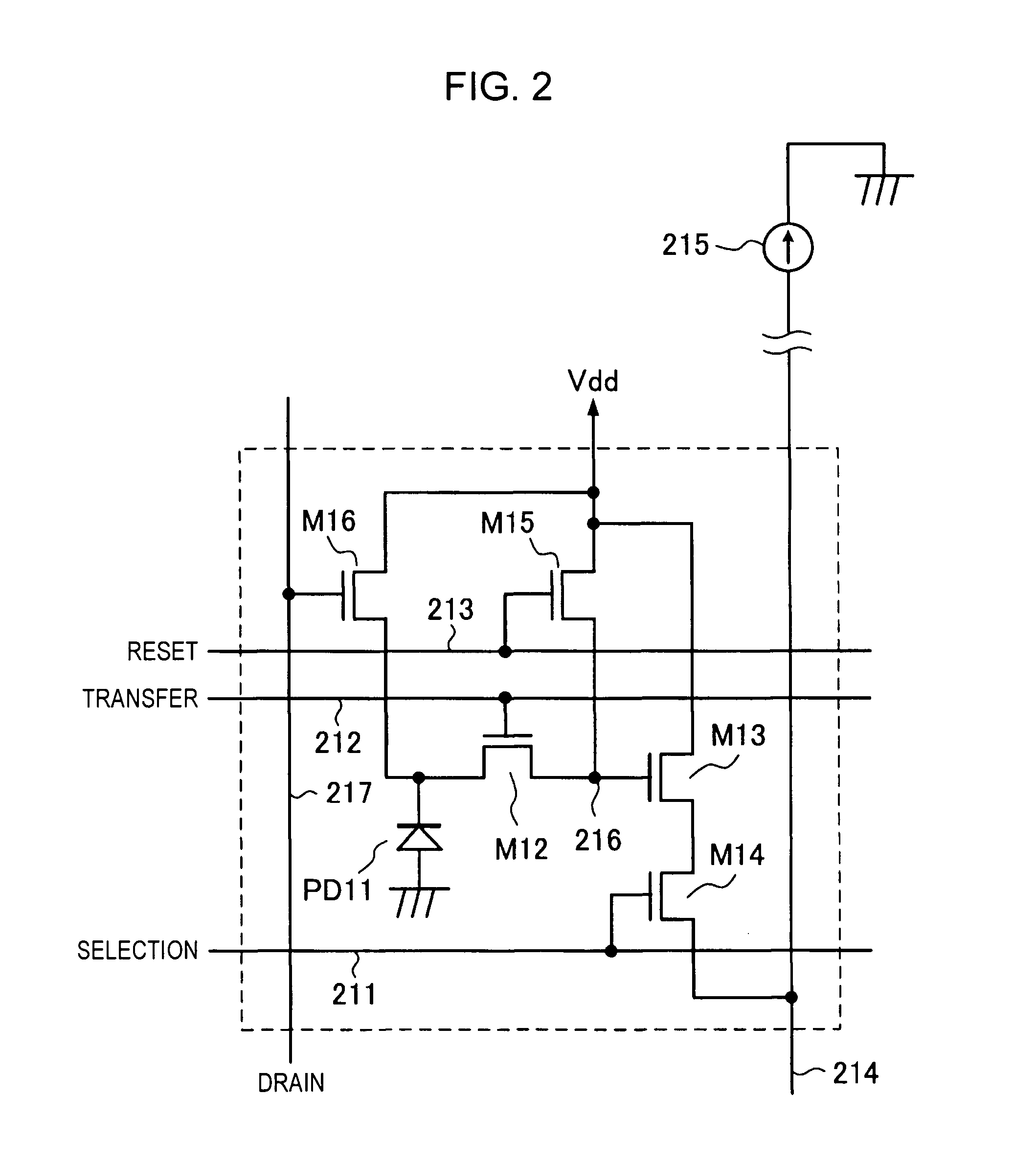
A pixel comprises a photo-sensitive element for generating charges in response to incident radiation and a sense node. A transfer gate is positioned between the photo-sensitive element and the sense node for controlling transfer of charges to the sense node. A reset switch is connected to the sense node for resetting the sense node to a predetermined voltage. A first buffer amplifier has an input connected to the sense node. A sample stage is connected to the output of the first buffer amplifier and is operable to sample a value of the sense node. A second buffer amplifier has an input connected to the sample stage. Control circuitry operates the reset switch and causes the sample stage to sample the sense node while the photo-sensitive element is being exposed to radiation. An array of pixels is synchronously exposed to radiation. Sampled values for a first exposure period can be read while the photo-sensitive element is exposed for a second exposure period.
Owner:CMOSIS
Methods, systems, and computer program products for imperceptibly embedding structured light patterns in projected color images for display on planar and non-planar surfaces
Methods, systems, and computer program products for imperceptibly embedding structured light patterns in projected color images for display on planar and non-planar surfaces are disclosed. According to one method, an image exposure period for detecting an embedded structured light patterns in a projected image is selected based on analysis of pixel polarities for different pixel intensities of a pixel color. Pixel intensities for the color are varied in the user image so that pixel polarities encode the structured light patterns during image exposure period. The user image is projected with the structured light patterns onto the surface. Depth information is continuously acquired and used to adjust display of the user image.
Owner:THE UNIV OF NORTH CAROLINA AT CHAPEL HILL
Imaging apparatus and imaging control method
The imaging apparatus includes an image sensor for obtaining a picture image from an optical image that is projected to the image sensor through an optical system, an image moving portion for moving the optical image on the image sensor, a motion detecting portion for detecting a movement on the picture image of a moving subject that appears in the optical image, and a control portion for controlling, during an exposure period after a predetermined operation, the image moving portion in the direction of canceling the movement of the moving subject on the image sensor due to a movement of the moving subject in the real space, based on a movement of the moving subject detected in advance. The control portion sets length of the exposure period based on the movement of the moving subject detected in advance.
Owner:XACTI CORP
Laser digitizer system for dental applications
A intra-oral laser digitizer system provides a three-dimensional visual image of a real-world object such as a dental item through a laser digitization. The laser digitizer captures an image of the object by scanning multiple portions of the object in an exposure period. The intra-oral digitizer may be inserted into an oral cavity (in vivo) to capture an image of a dental item such as a tooth, multiple teeth or dentition. The captured image is processed to generate the three-dimension visual image.
Owner:D4D TECH LP
Apparatus, method, and program for generating range-image-data
ActiveUS20050162638A1Reduce distanceHigh reception levelOptical rangefindersSolid-state devicesExposure periodLight emission
First image data including a first pixel value according to the intensity of background light is obtained by means of only exposure. Second image data including a second pixel value according to the intensity of the light reflected or scattered by an object is obtained by so controlling light emission and exposure as to receive part of the reflected or scattered light over the whole exposure period. The part of the reflected or scattered light corresponds to the flat period of emitted pulsed light. Third image data including a third pixel value according to the distance to the object is obtained by so controlling light emission and exposure as to receive the part of the reflected or scattered light for a time according to the distance. The first pixel value is subtracted from each of the second and third pixel values so that the influence of the background light can be excluded. The ratio between the subtraction results is calculated so that the influences of factors that vary the intensity of the reflected or scattered light can be cancelled.
Owner:DENSO CORP
Time of flight system capable of increasing measurement accuracy, saving power and/or increasing motion detection rate and method thereof
ActiveUS20110304842A1High measurement accuracySave powerOptical rangefindersElectrical apparatusExposure periodUltimate tensile strength
A light source is used for emitting an invisible light toward an object. The object reflects the invisible light and reflected light is formed, and a sensor is used for receiving the reflected light. A processor is coupled to the sensor for recording a time interval of the invisible light traveling from the light source to the object and reflected from the object to the sensor. Then, the processor estimates a measurement distance of the object according to the time interval, and adjusts an emission period of the light source, an exposure period of the sensor, intensity of the invisible light, and / or main sensing range of the sensor according to the measurement distance.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
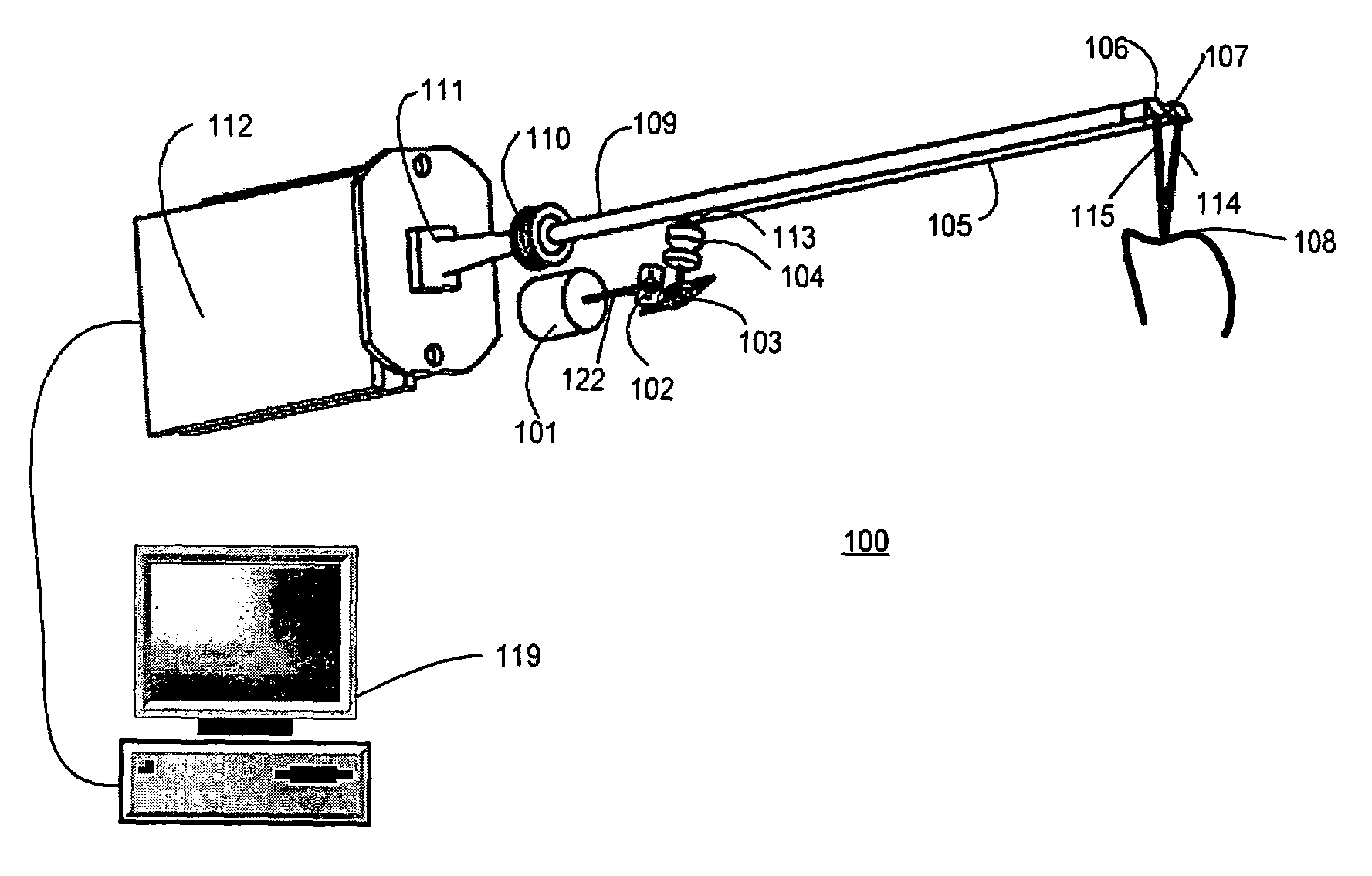
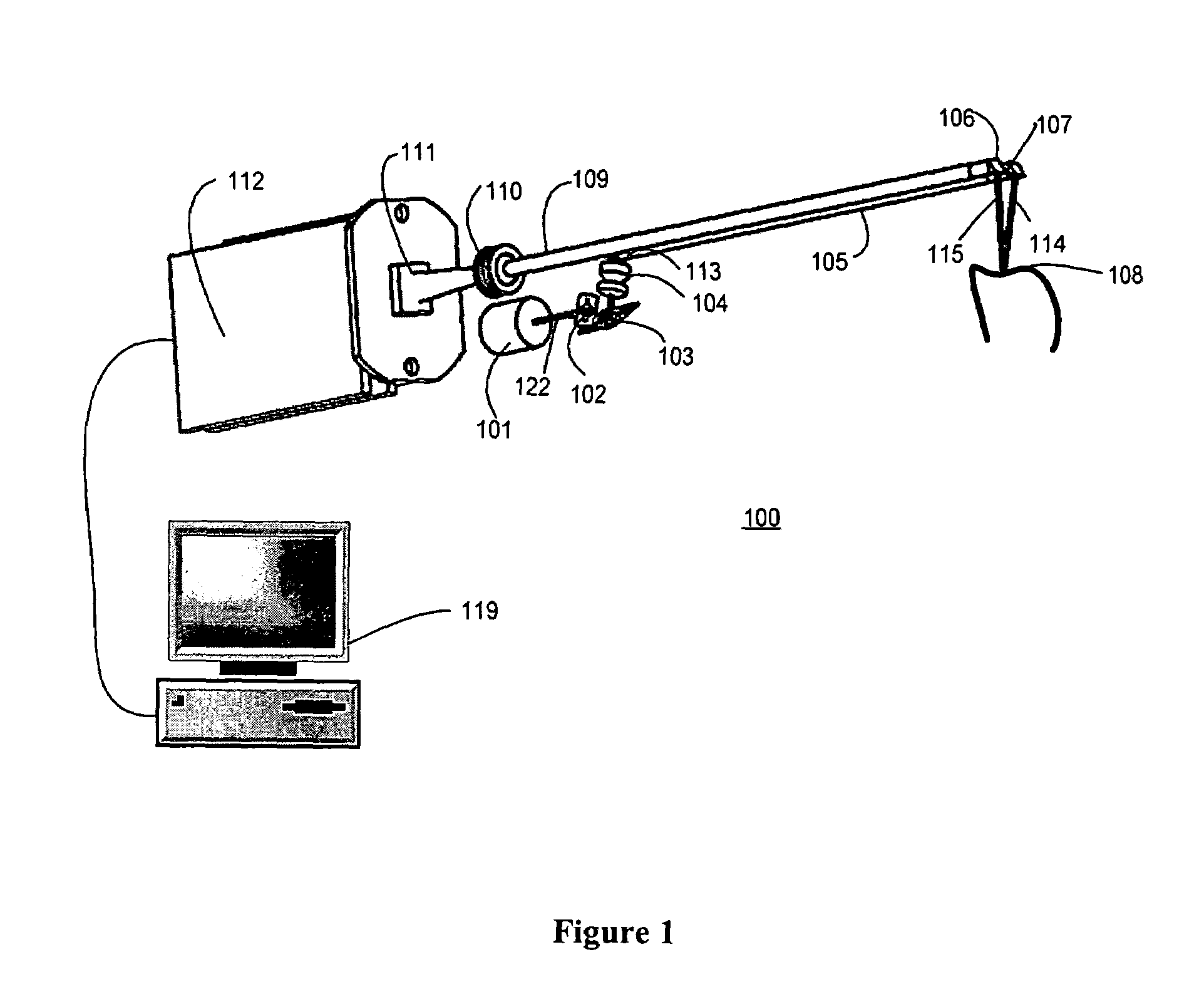
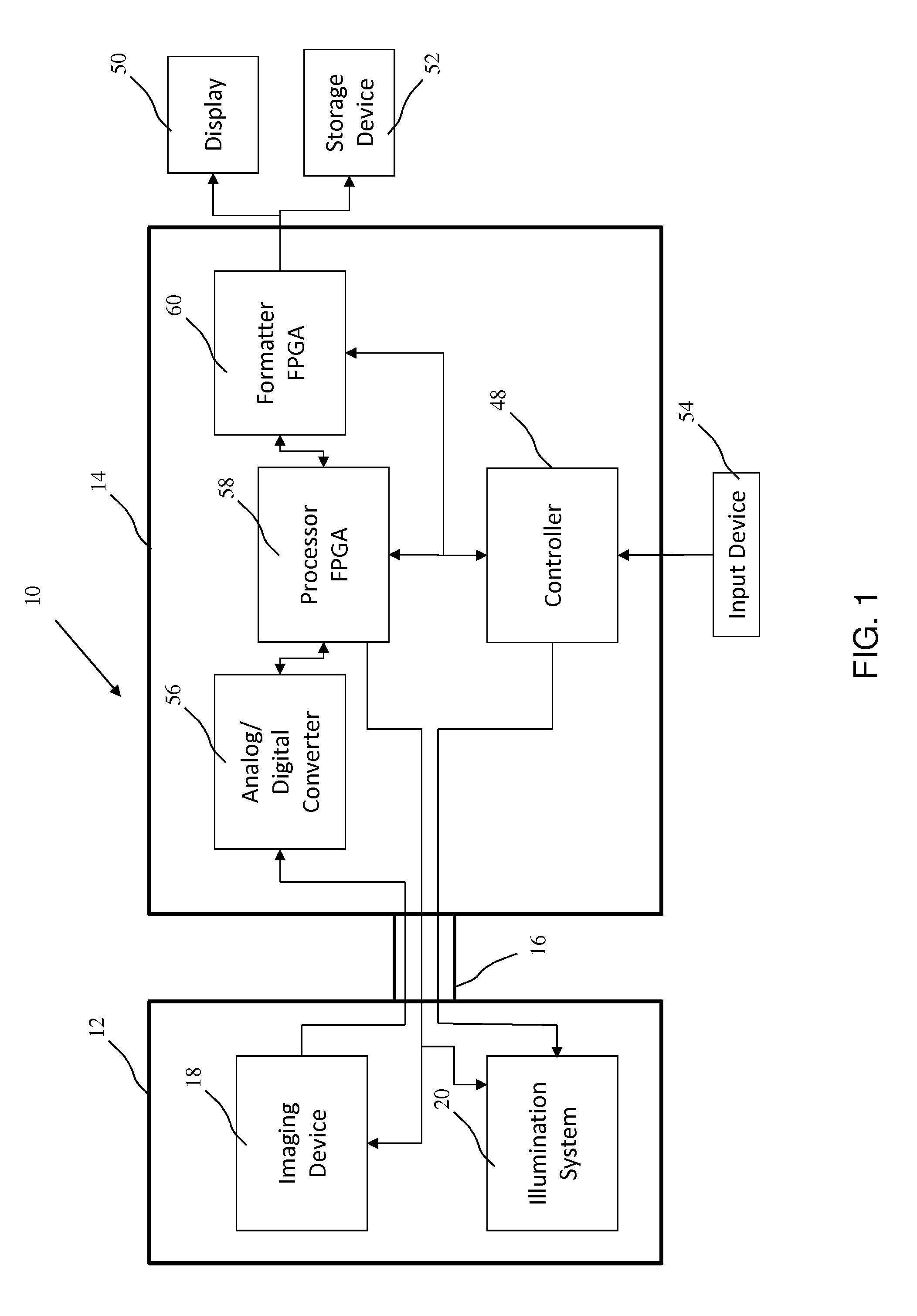
Endoscopic camera illumination system and method
An endoscopic camera system having an imaging device for taking images during an exposure period at a predetermined number of frames per second; an illumination system for providing light for the imaging device; and an illumination controller that supplies a drive current to the illumination system, the illumination controller altering the drive current to the illumination system so light is only provided for a portion of each image frame corresponding to the exposure period and for a second portion of each frame outside of the exposure period.
Owner:ARTHREX
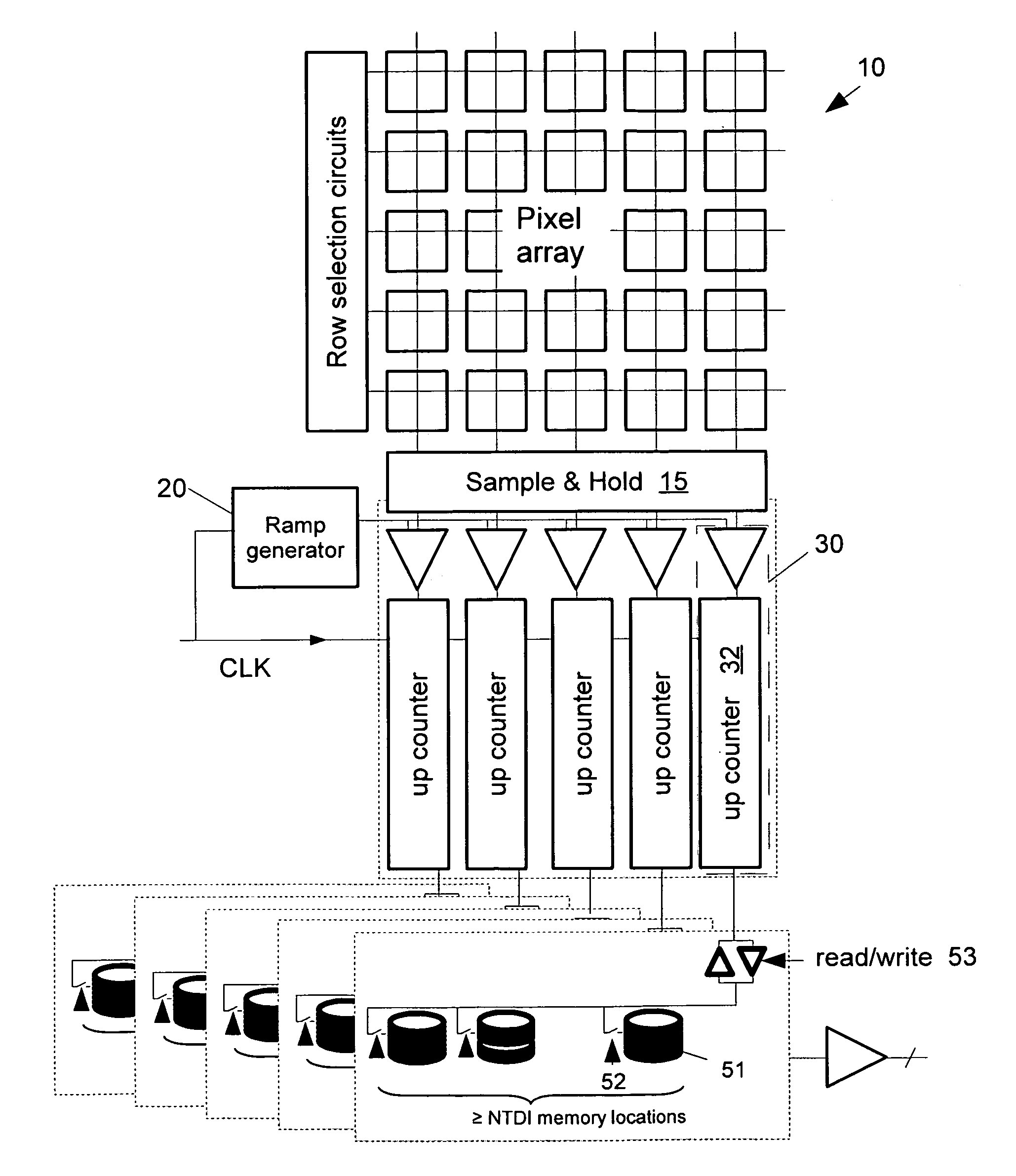
Analog-to-digital conversion in pixel arrays
ActiveUS7880662B2Improve accuracyAvoid the needAnalogue/digital conversionTelevision system detailsExposure periodAnalog signal
An analog-to-digital converter (ADC) generates an output digital value equivalent to the difference between two analog signal values. The ADC 30 receives a first analog signal level, a second analog signal level and a ramp signal. A counter 32 is operable to count in a single direction. A control stage is arranged to enable the counter 32 based on a comparison 19 of the ramp signal with the first analog signal and the second analog signal. A digital value accumulated by the counter during a period when it is enabled forms the output. The ADC can perform the conversion during a single cycle of the ramp signal. The counter 32 can be loaded with a starting digital value representing an exposure level accumulated during a previous exposure period. Techniques are described for reducing the conversion time.
Owner:CMOSIS
Method of Determining PSF Using Multiple Instances of a Nominally Scene
A digital image acquisition system includes a portable apparatus for capturing digital images and a digital processing component for detecting, analyzing and informing the photographer regarding motion blur, and for reducing camera motion blur in an image captured by the apparatus. The digital processing component operates by comparing the image with at least one other image, for example a preview image, of nominally the same scene taken outside the exposure period of the main image. In one embodiment the digital processing component identifies at least one feature in a single preview image which is relatively less blurred than the corresponding feature in the main image, calculates a point spread function (PSF) in respect of such feature, and de-convolves the main image using the PSF. In another embodiment, the digital processing component calculates a trajectory of at least one feature in a plurality of preview images, extrapolates such feature on to the main image, calculates a PSF in respect of the feature, and de-convolves the main image using the PSF. In another embodiment the digital processing unit after determining the degree of blur notifies the photographer of the existing blur or automatically invokes consecutive captures.
Owner:FOTONATION LTD
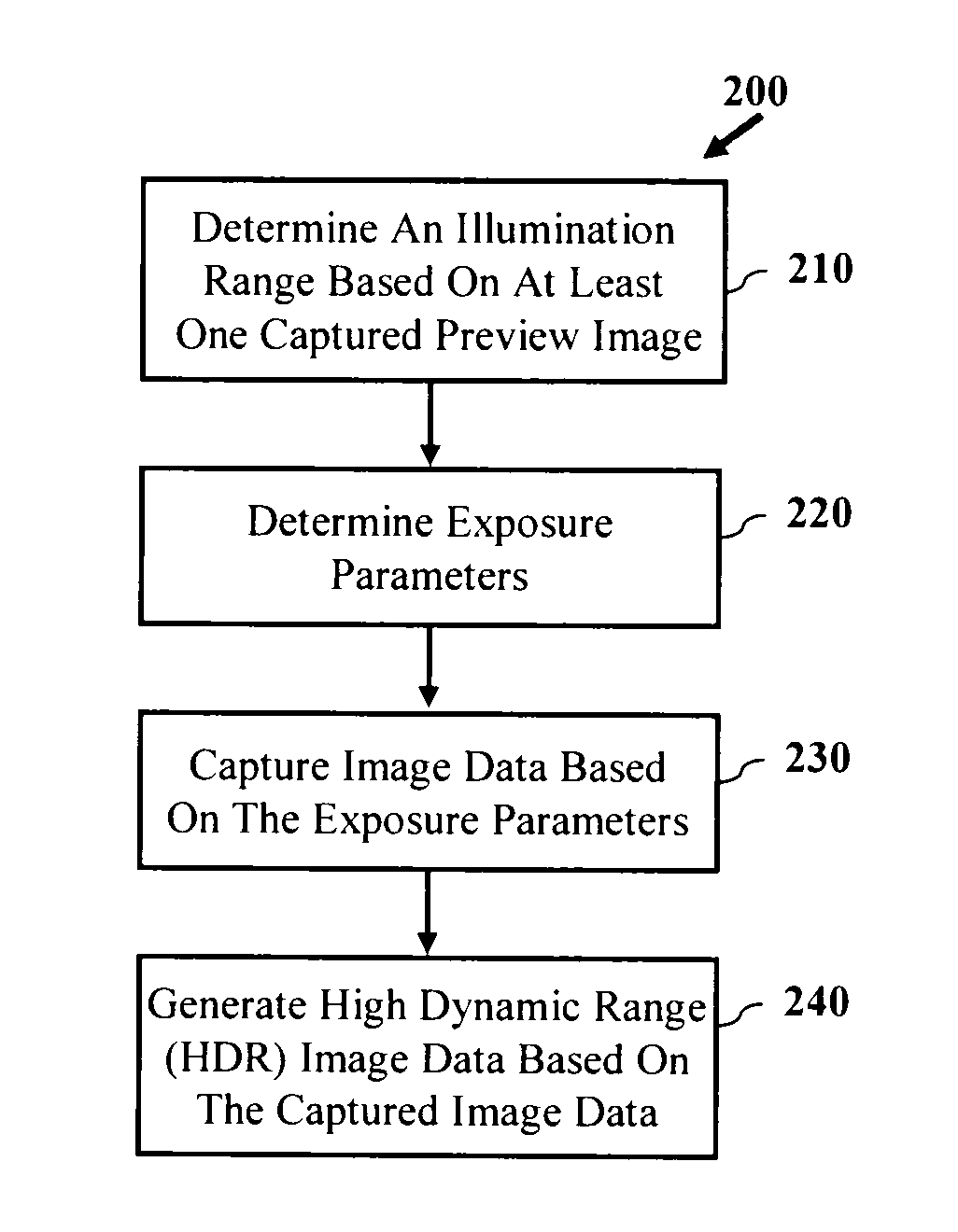
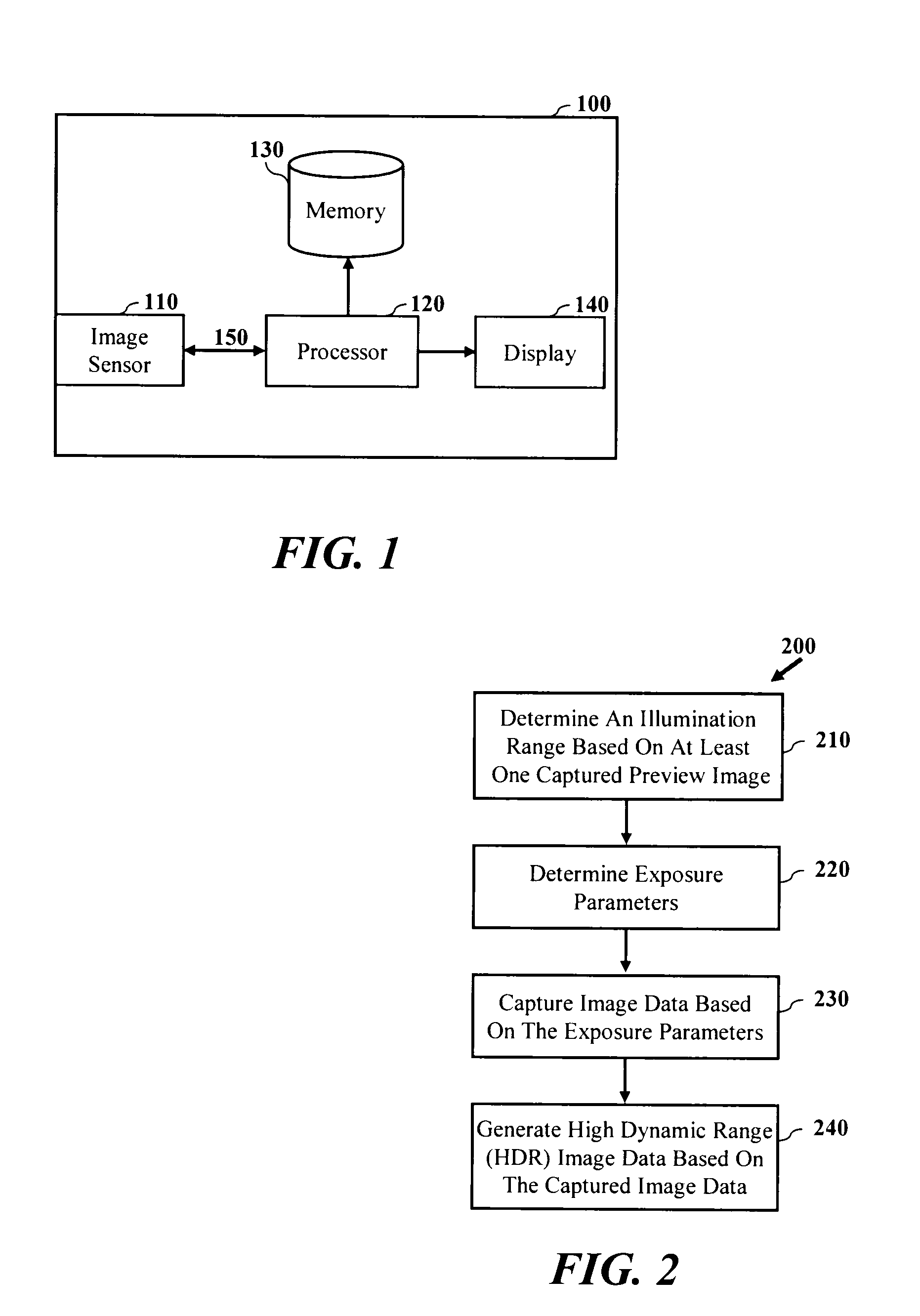
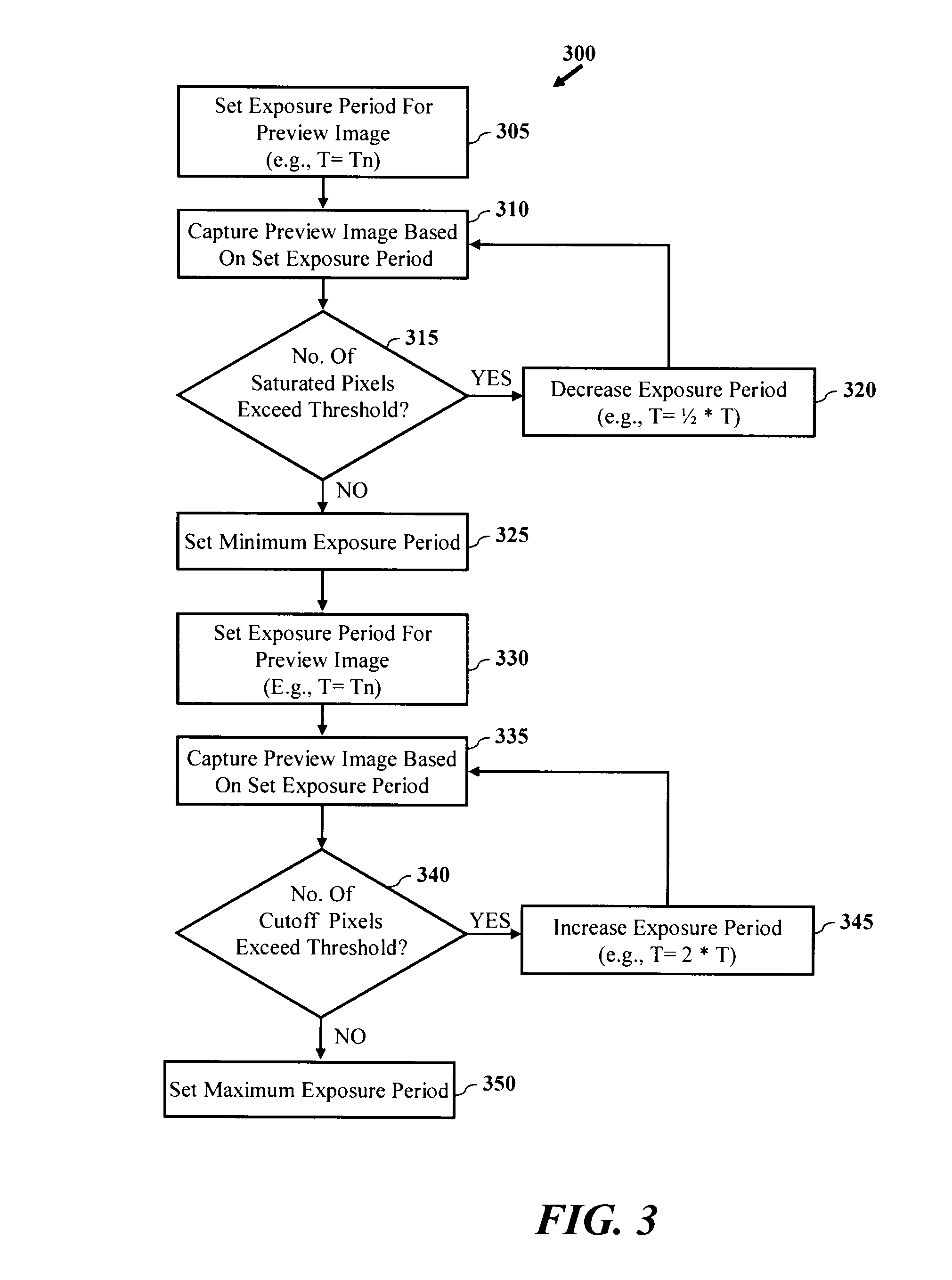
Exposure control for high dynamic range image capture
InactiveUS20100259636A1High dynamic range (HDR) image dataHigh imagingTelevision system detailsColor television detailsImage sensorExposure period
A device and methods are provided for producing a high dynamic range (HDR) image of a scene are disclosed and claimed. In one embodiment, method includes setting an exposure period of an image sensor of the digital camera and capturing image data based on the exposure period. The method may further include checking the image data to determine whether the number of saturated pixels exceeds a saturation threshold and checking the image data to determine whether the number of cutoff pixels exceeds a cutoff threshold. The method may further include generating a high dynamic range image based on image data captured by the digital camera, wherein the high dynamic range image is generated based on a minimum number of images to capture a full dynamic range of the scene.
Owner:QUALCOMM INC
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com