Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
5719 results about "Projection image" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
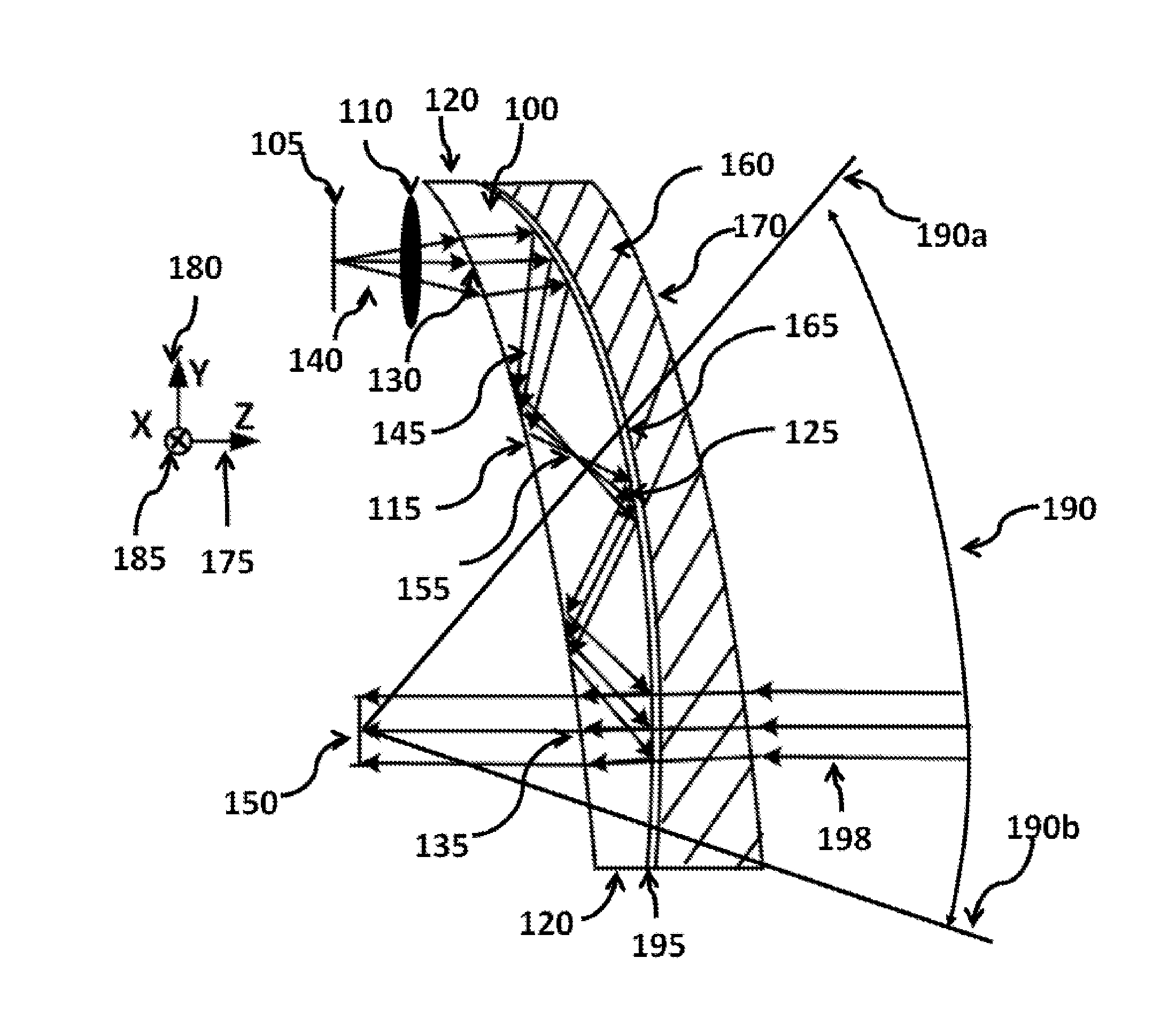
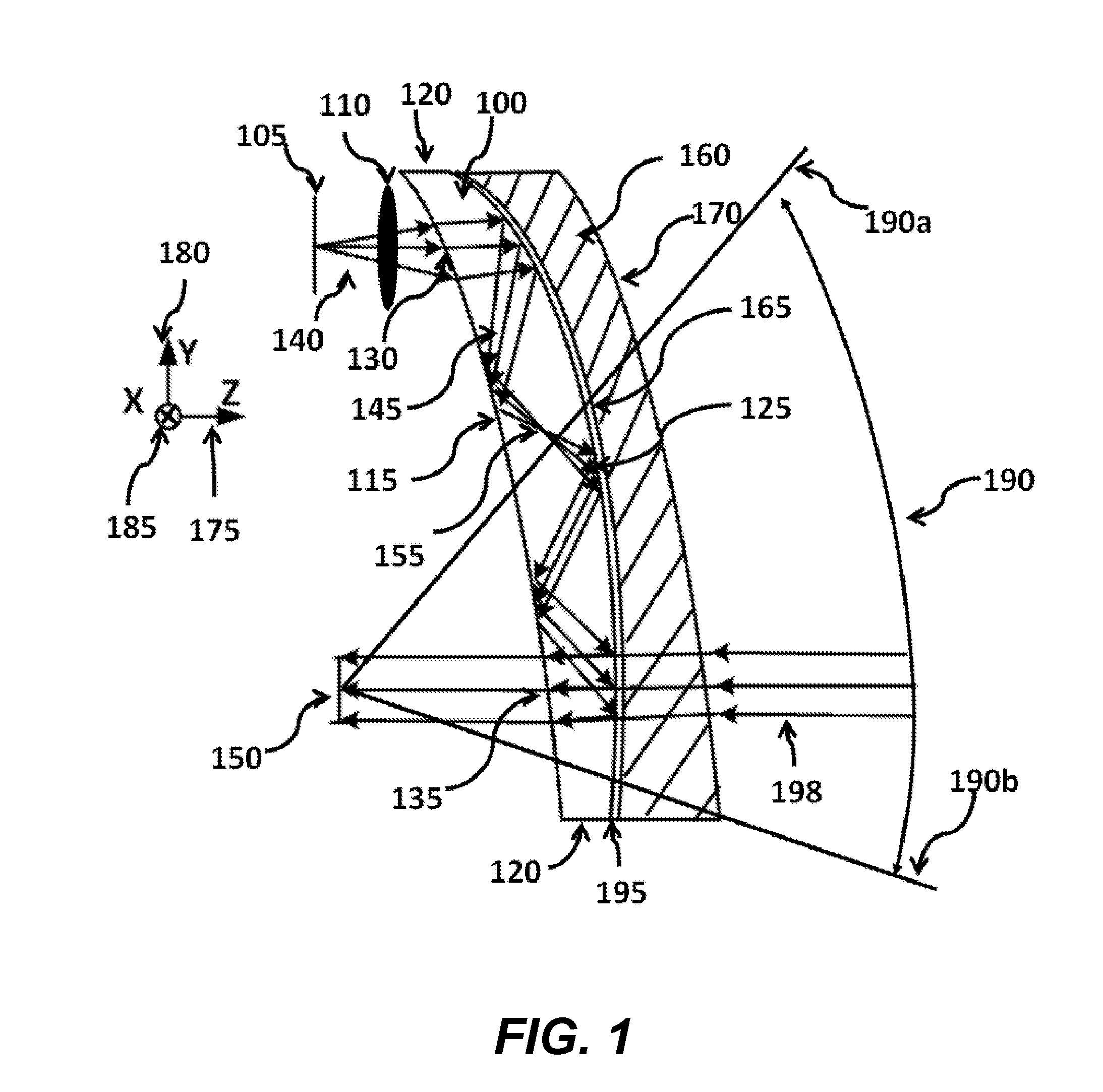
Ergonomic head mounted display device and optical system
Optical systems such as image display systems include a freeform optical waveguide prism and a freeform compensation lens spaced therefrom by a gap of air or index cement. The compensation lens corrects for aberrations which the optical waveguide prism will introduce in light or images from an ambient real-world environment. The optical waveguide prism receives actively projected images at an entry location, and emits the projected images at an exit location after internally reflecting the images along an optical path therein. The image display system may include an image source and coupling optics. The approach permits design of an optical viewing device, for example in optical see-through HMDs, achieving an eyeglass-form appearance and a wide see-through field of view (FOV).
Owner:MAGIC LEAP INC
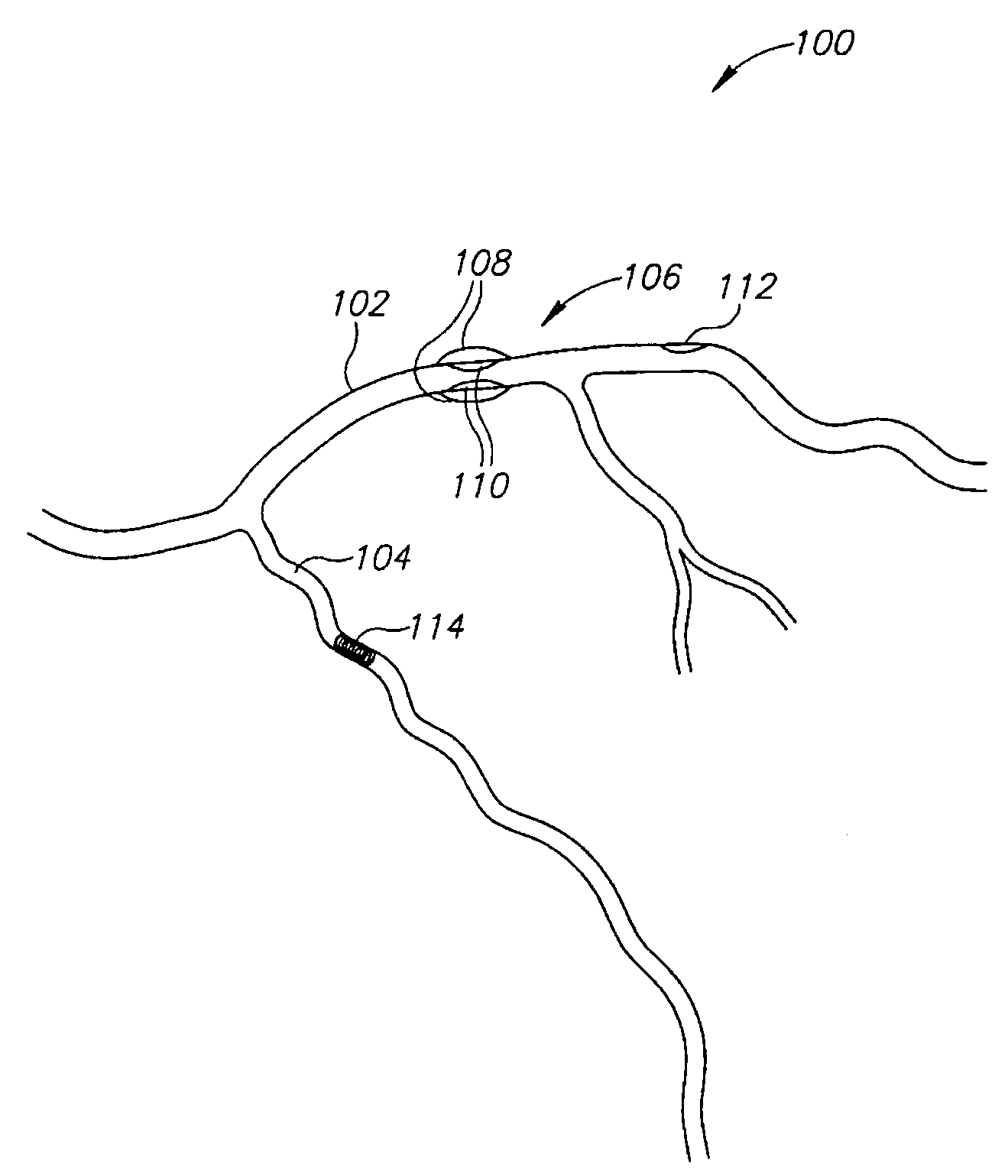
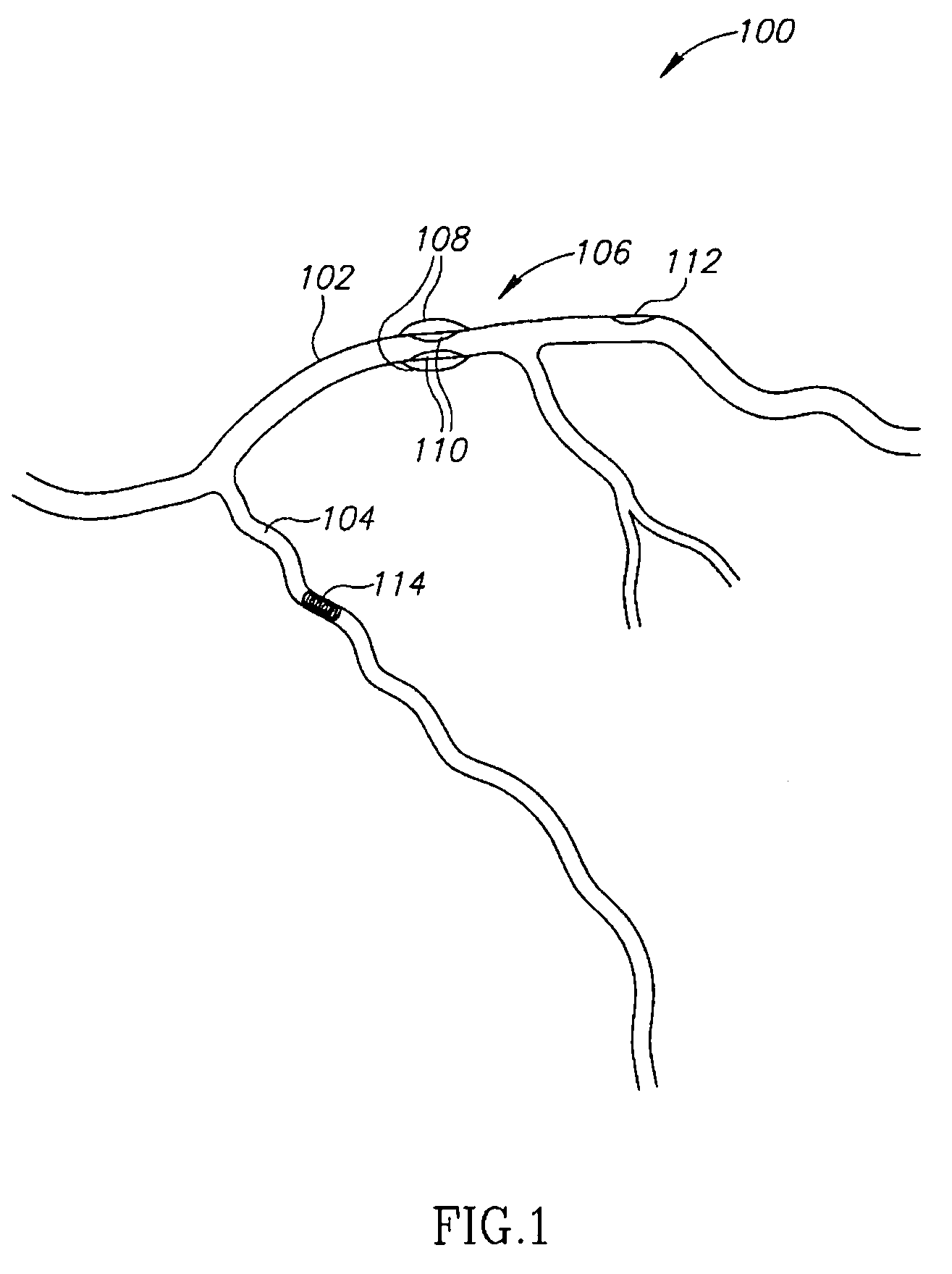
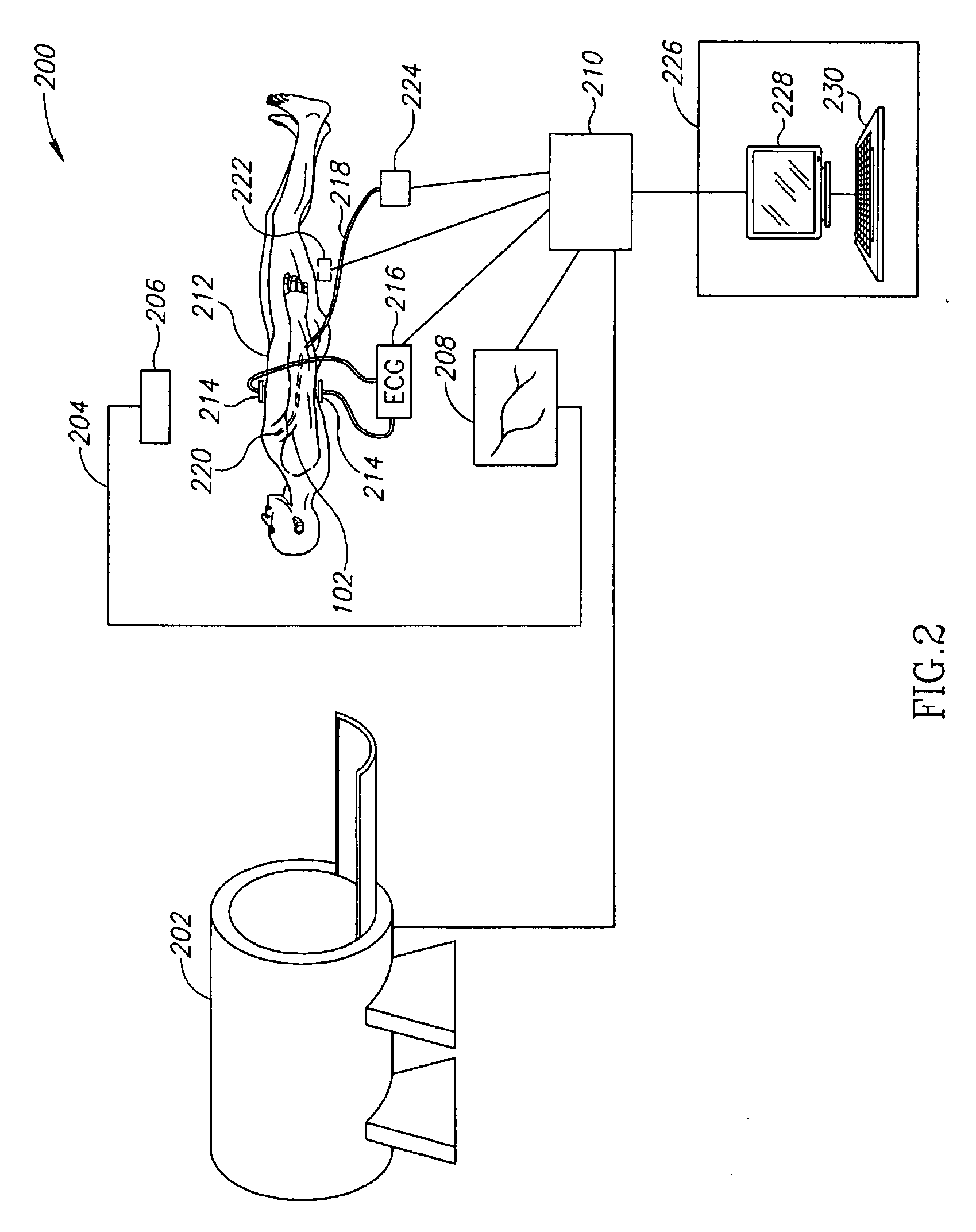
Vascular image processing
InactiveUS20060036167A1The effect is accurateUltrasonic/sonic/infrasonic diagnosticsCatheterImaging processingData set
A method of estimating a position of a foreign object in the body, comprising: (a) providing a 3D data set of at least one blood vessel; (b) acquiring at least one 2D projection image of the vessel including the object; (c) registering the 2D projection image of the vessel to the 3D data set; and (d) using the registration to estimate a 3D position of said object restricted to be in a blood vessel, according to said 3D data set.
Owner:SHINA SYST
Interaction between objects and a virtual environment display
InactiveUS20050245302A1Enhanced interactionBlurring distinctionInput/output for user-computer interactionDigital data processing detailsProjection imageHuman–computer interaction
An interactive table has a display surface on which a physical object is disposed. A camera within the interactive table responds to infrared (IR) light reflected from the physical object enabling a location of the physical object on the display surface to be determined, so that the physical object appear part of a virtual environment displayed thereon. The physical object can be passive or active. An active object performs an active function, e.g., it can be self-propelled to move about on the display surface, or emit light or sound, or vibrate. The active object can be controlled by a user or the processor. The interactive table can project an image through a physical object on the display surface so the image appears part of the object. A virtual entity is preferably displayed at a position (and a size) to avoid visually interference with any physical object on the display surface.
Owner:MICROSOFT TECH LICENSING LLC
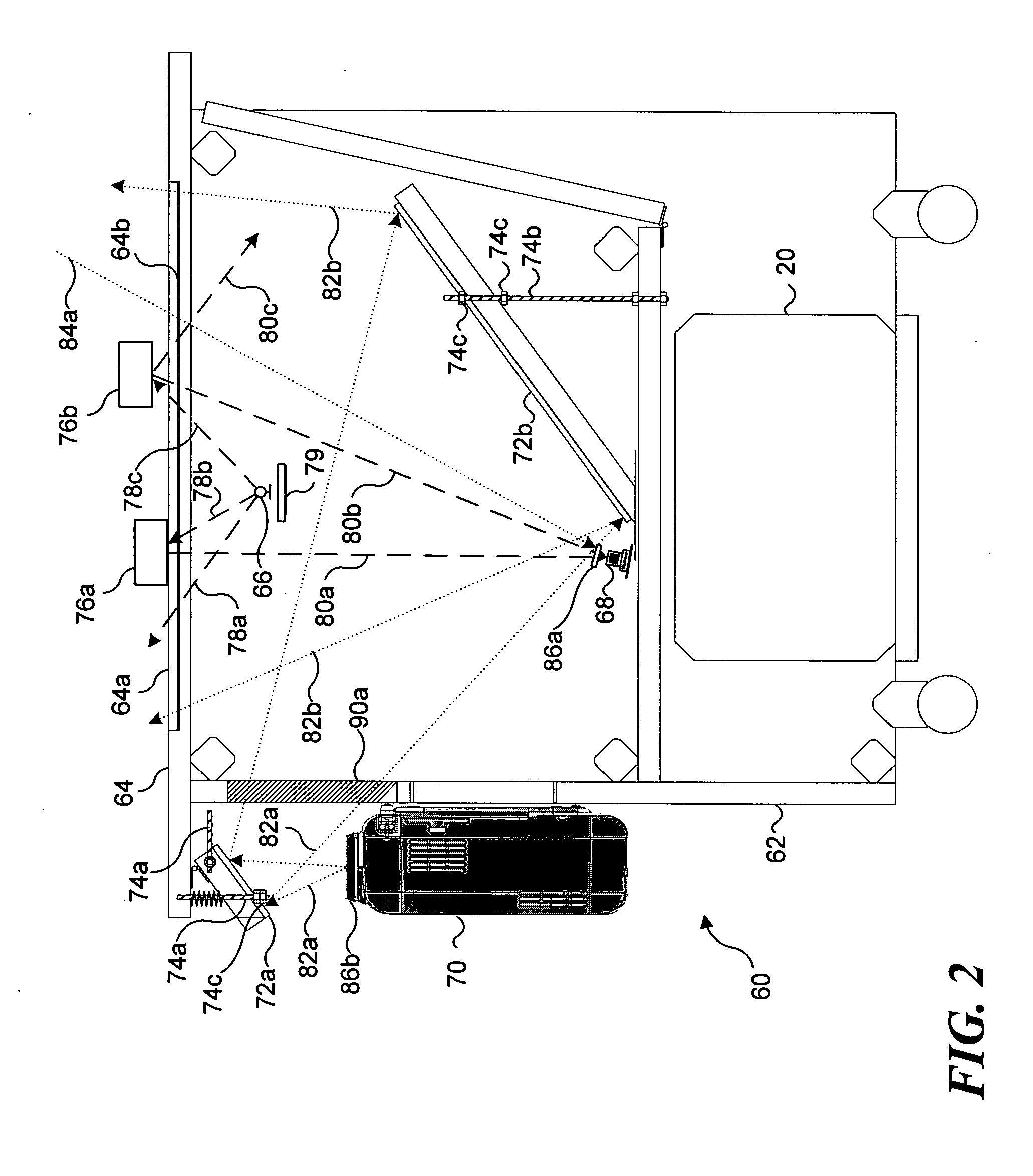
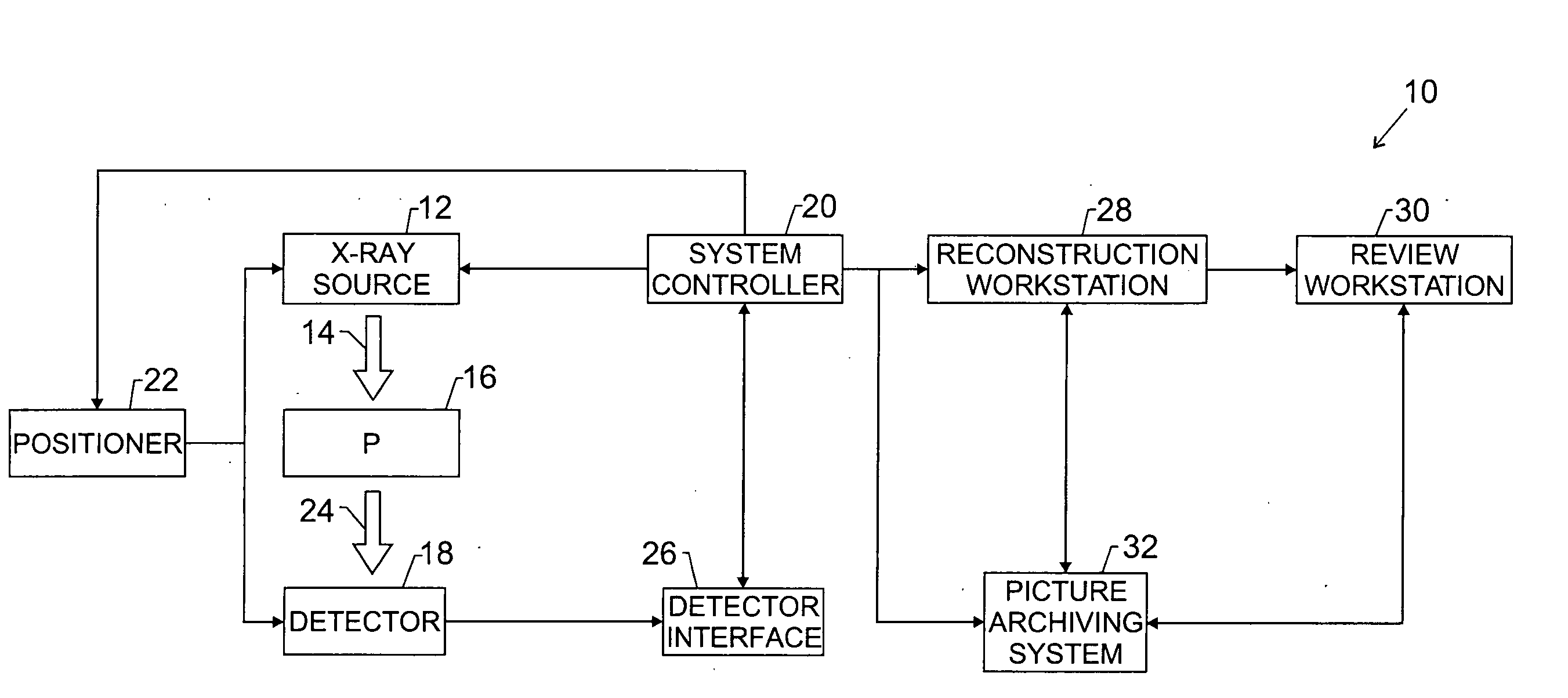
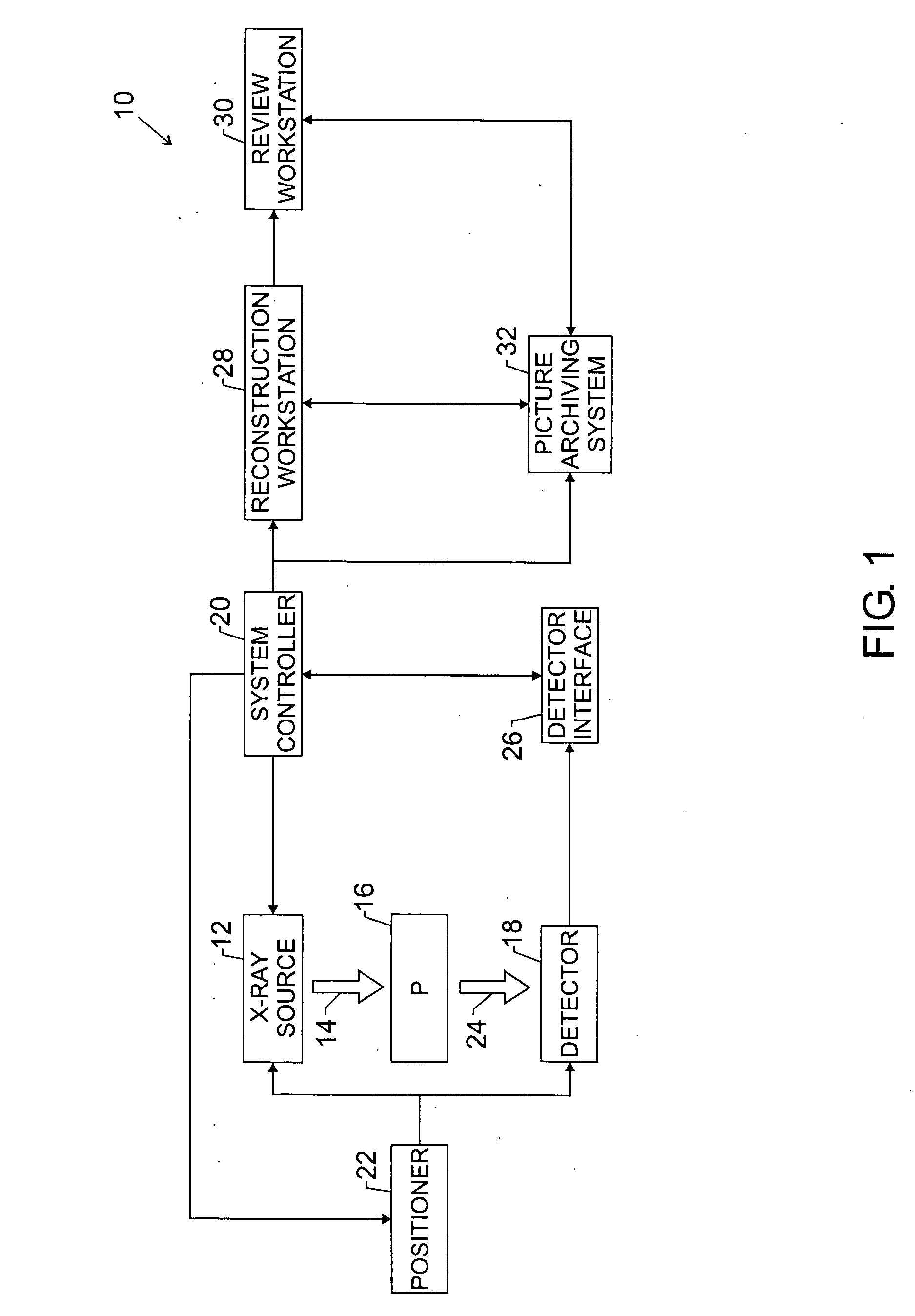
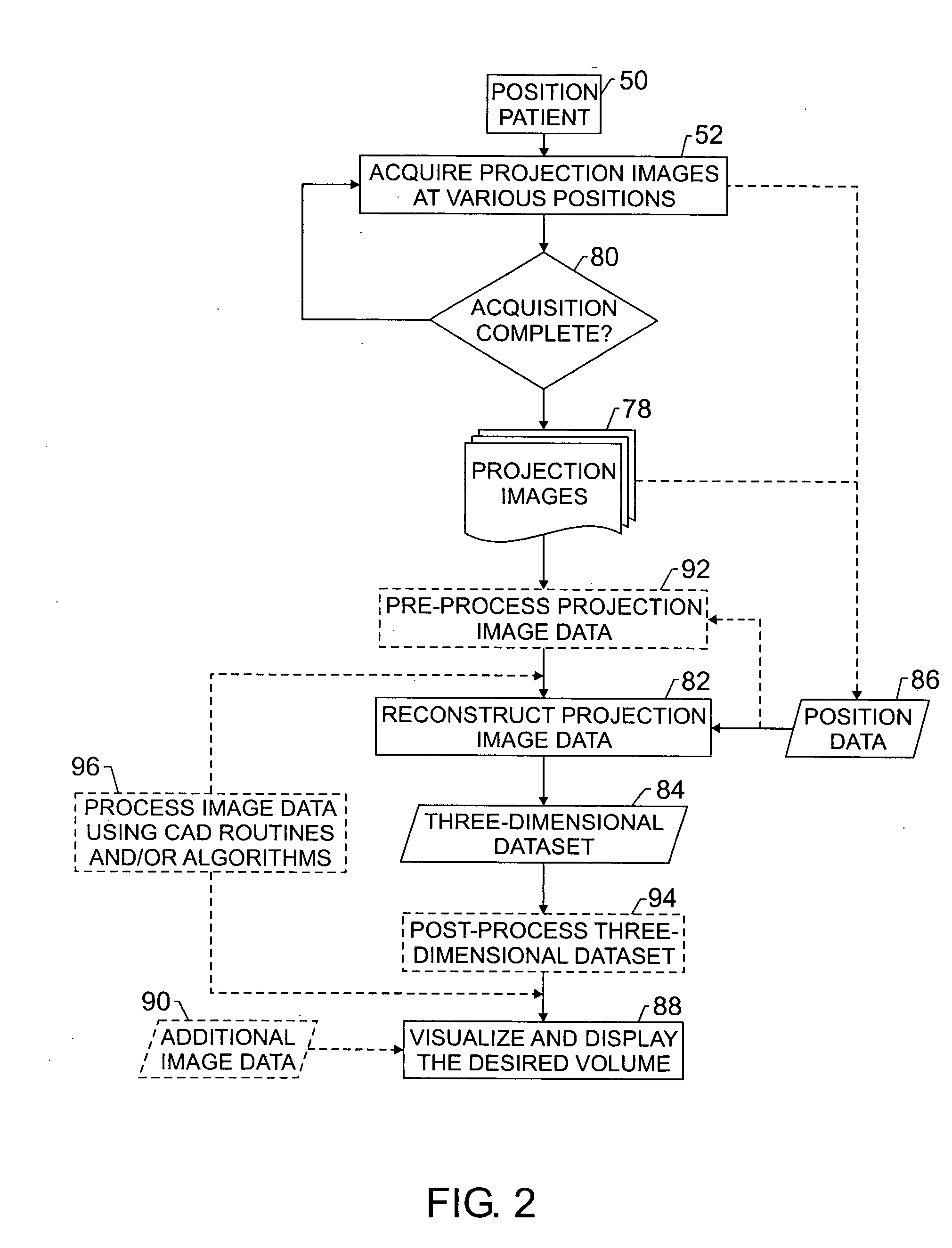
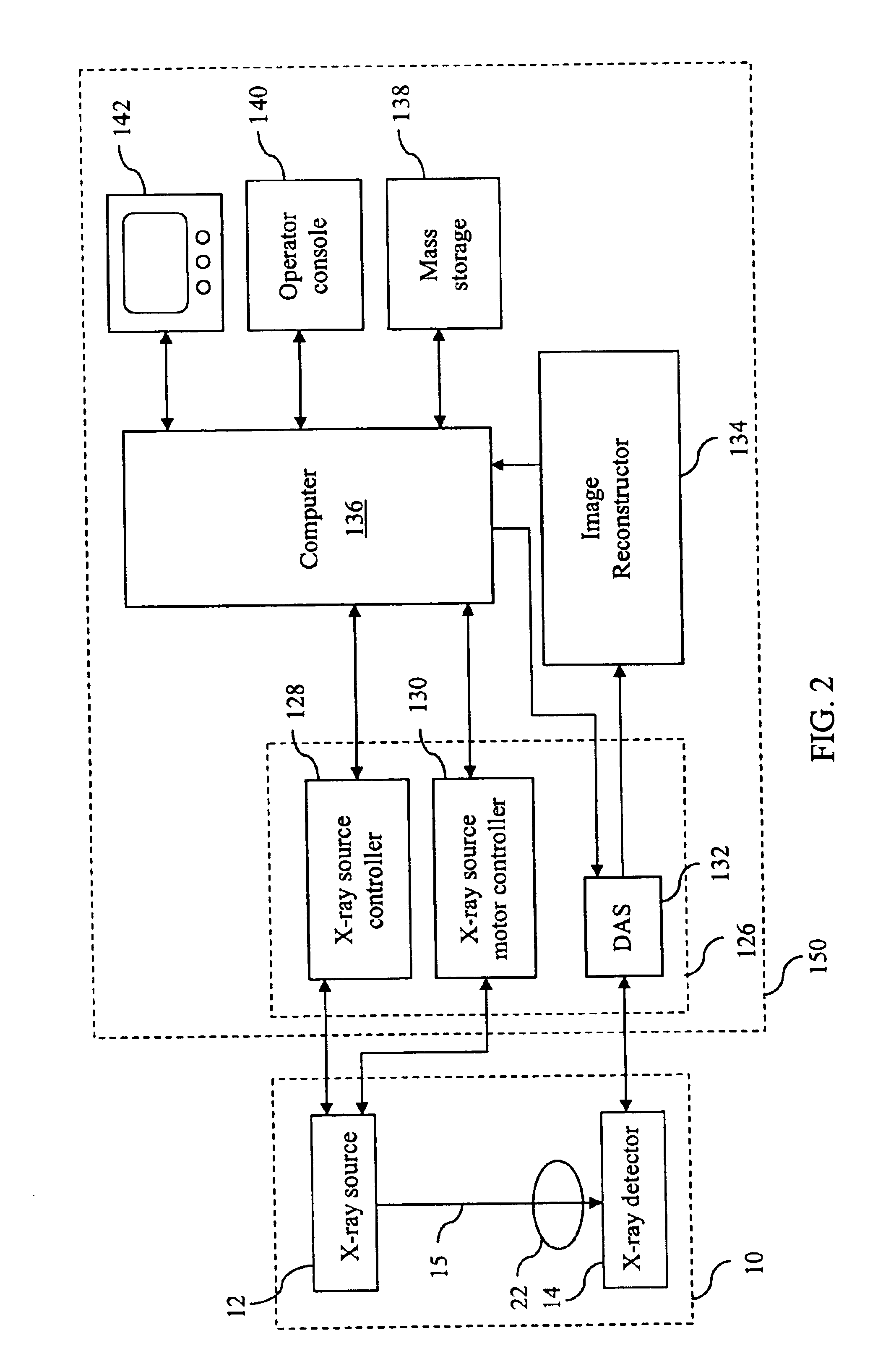
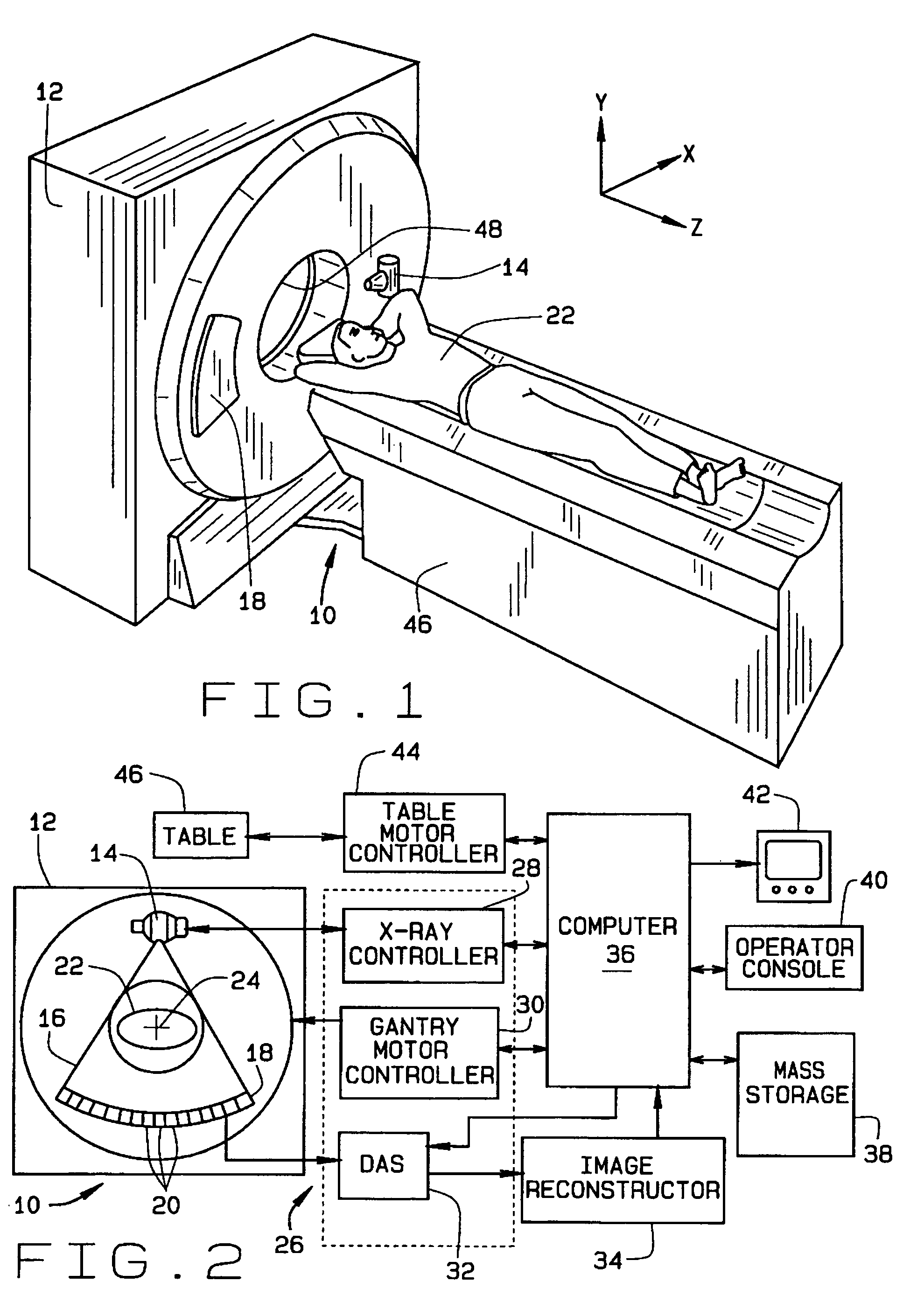
Enhanced X-ray imaging system and method
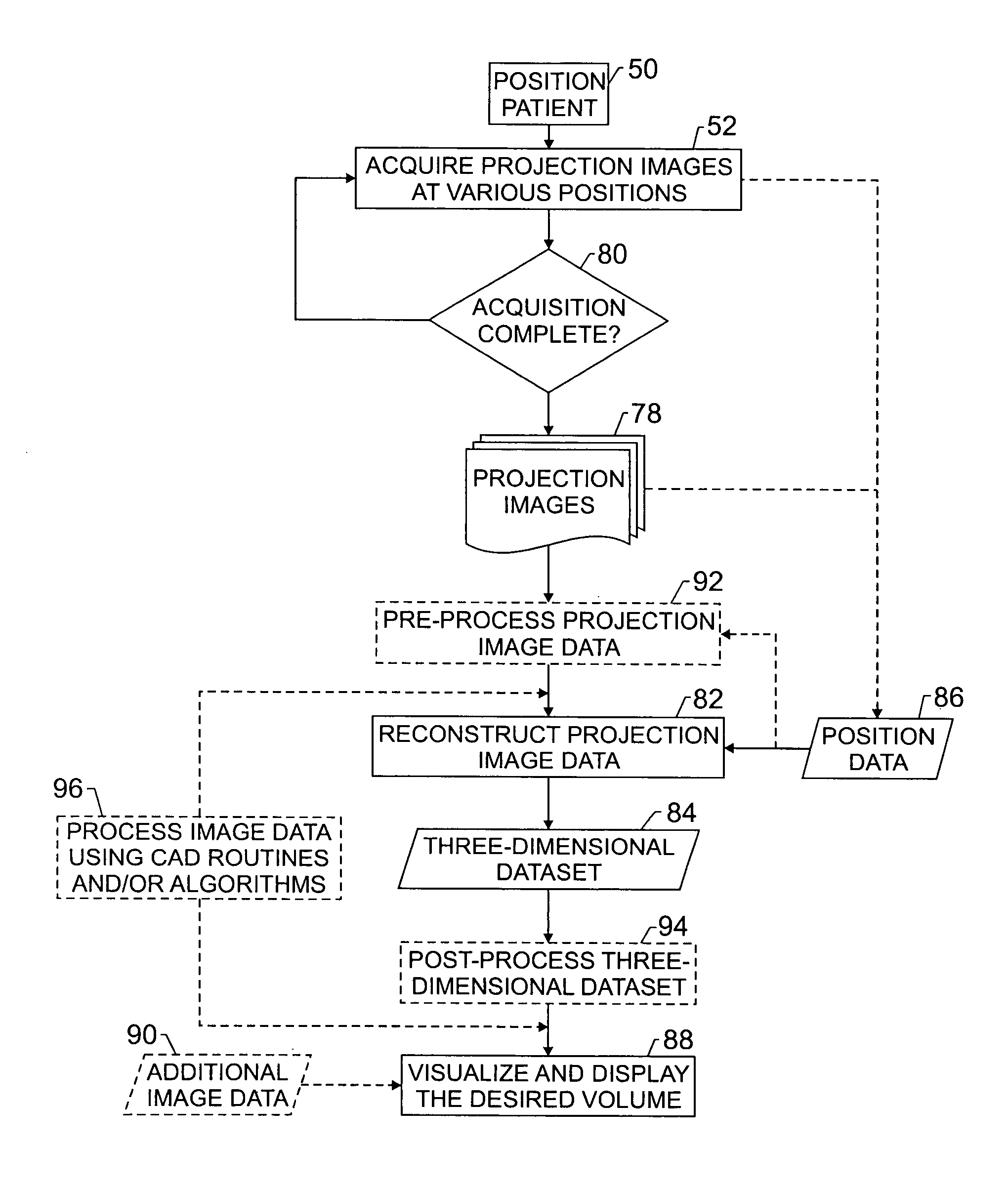
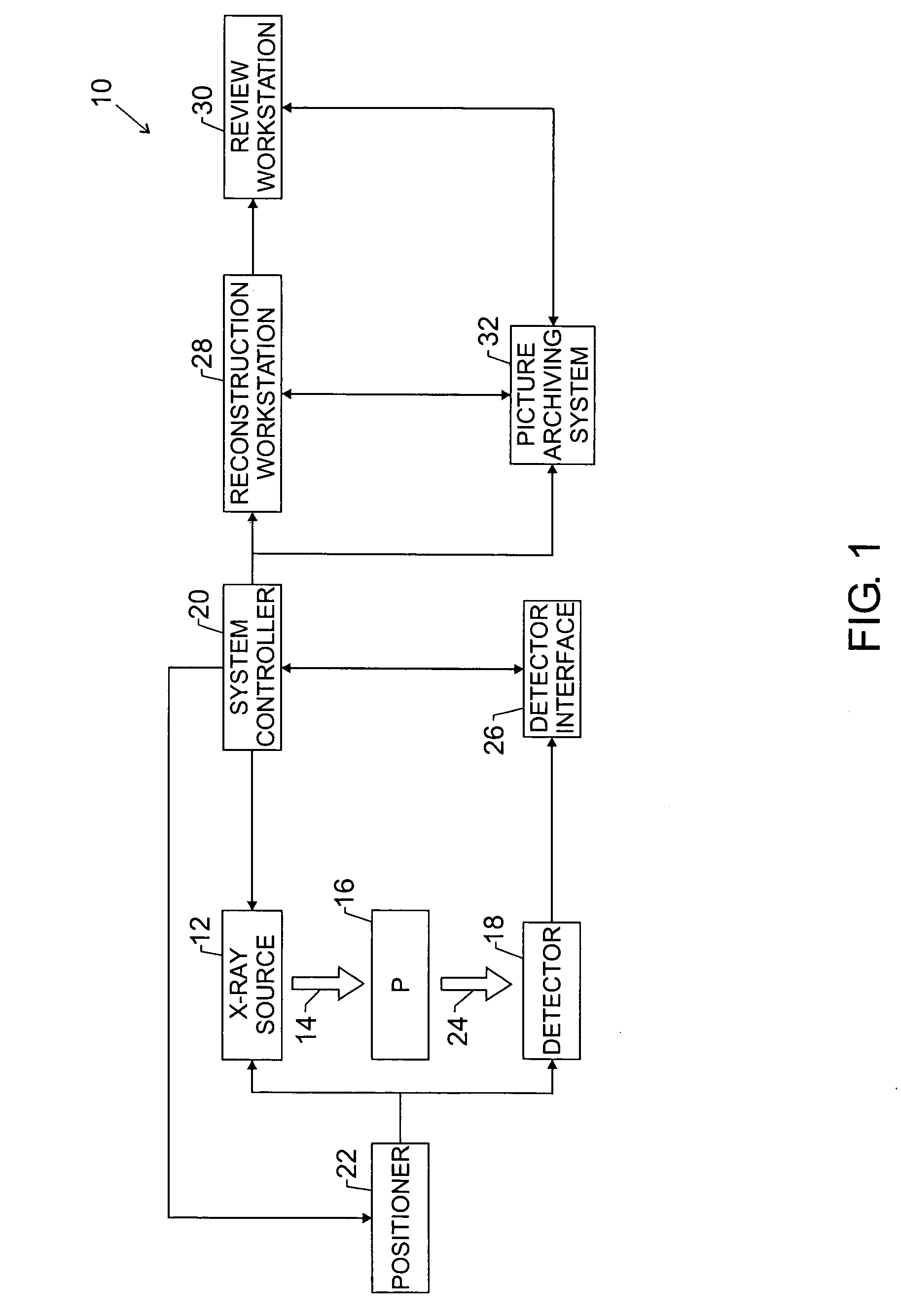
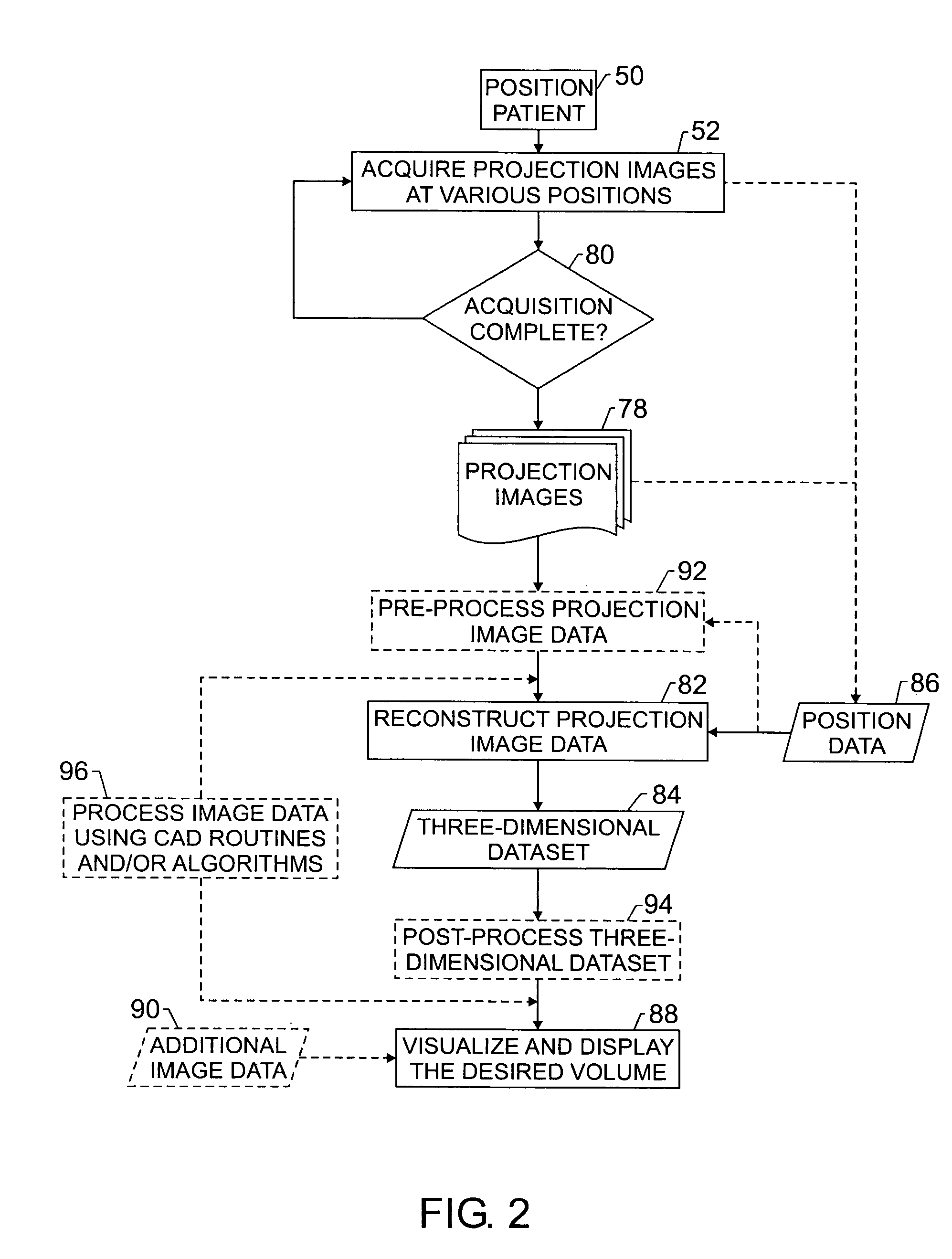
Techniques are provided for generating three-dimensional images, such as may be used in mammography. In accordance with these techniques, projection images of an object of interest are acquired from different locations, such as by moving an X-ray source along an arbitrary imaging trajectory between emissions or by individually activating different X-ray sources located at different locations relative to the object of interest. The projection images may be reconstructed to generate a three-dimensional dataset representative of the object from which one or more volumes may be selected for visualization and display. Additional processing steps may occur throughout the image chain, such as for pre-processing the projection images or post-processing the three-dimensional dataset.
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
Enhanced X-ray imaging system and method
Techniques are provided for generating three-dimensional images, such as may be used in mammography. In accordance with these techniques, projection images of an object of interest are acquired from different locations, such as by moving an X-ray source along an arbitrary imaging trajectory between emissions or by individually activating different X-ray sources located at different locations relative to the object of interest. The projection images may be reconstructed to generate a three-dimensional dataset representative of the object from which one or more volumes may be selected for visualization and display. Additional processing steps may occur throughout the image chain, such as for pre-processing the projection images or post-processing the three-dimensional dataset.
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
View projection matrix based high performance low latency display pipeline
InactiveUS8013904B2Easy to shipEasy to implementTelevision system detailsPicture reproducers using projection devicesHat matrixImaging processing
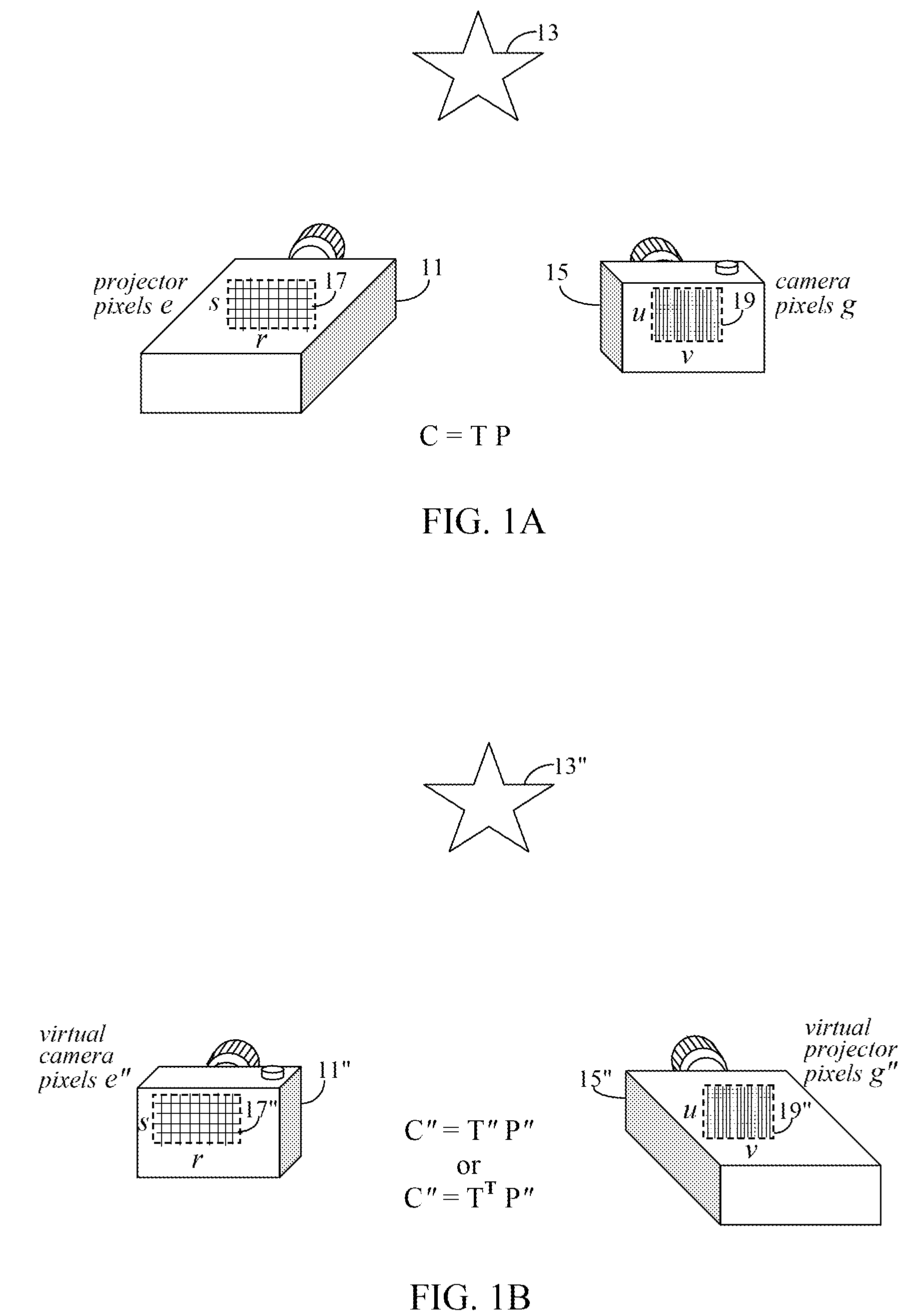
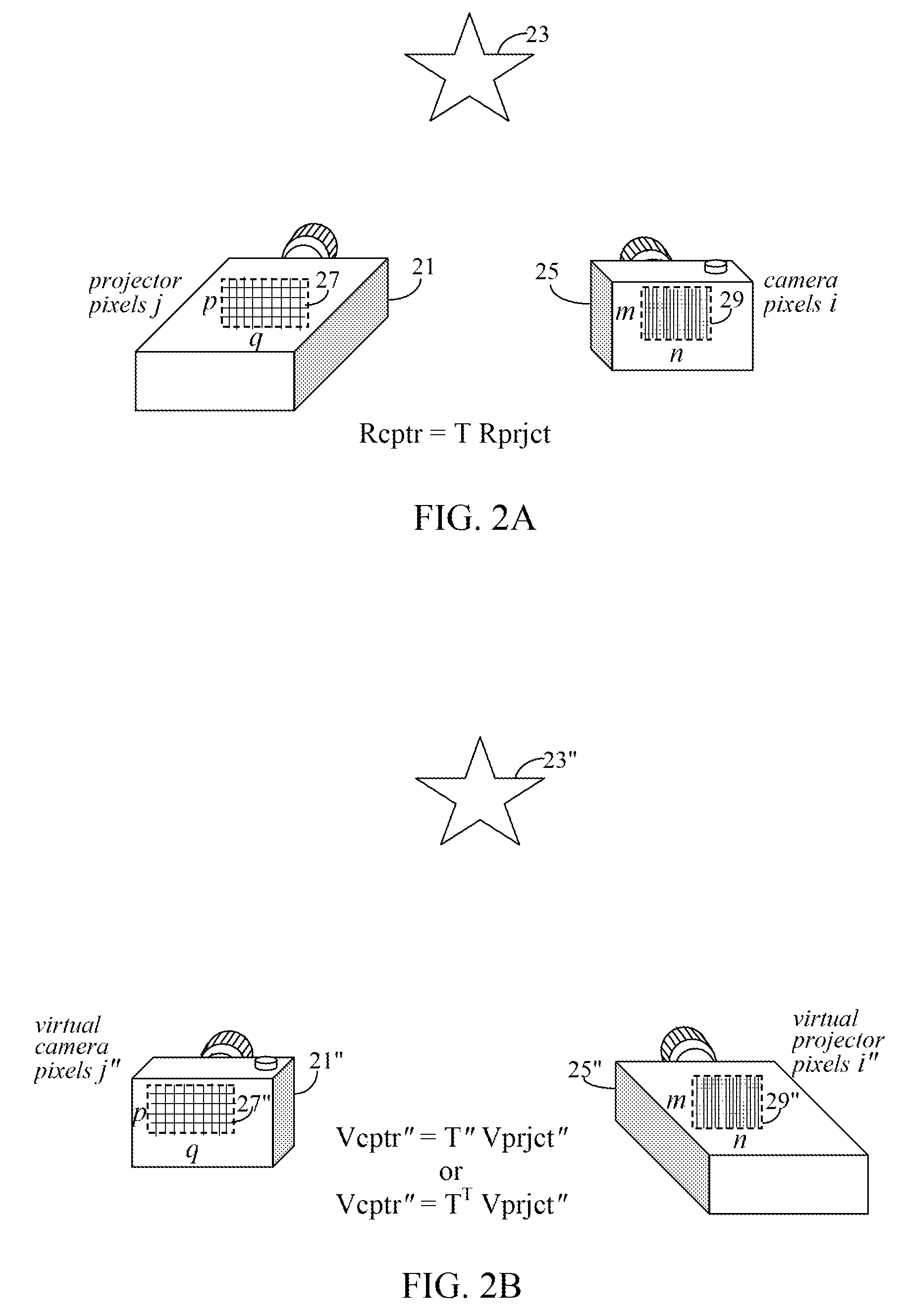
A projection system uses a transformation matrix to transform a projection image p in such a manner so as to compensate for surface irregularities on a projection surface. The transformation matrix makes use of properties of light transport relating a projector to a camera. A display pipeline of user-supplied image modification processing modules are reduced by first representing the processing modules as multiple, individual matrix operations. All the matrix operations are then combined with, i.e., multiplied to, the transformation matrix to create a modified transformation matrix. The created transformation matrix is then used in place of the original transformation matrix to simultaneously achieve both image transformation and any pre and post image processing defined by the image modification processing modules.
Owner:SEIKO EPSON CORP
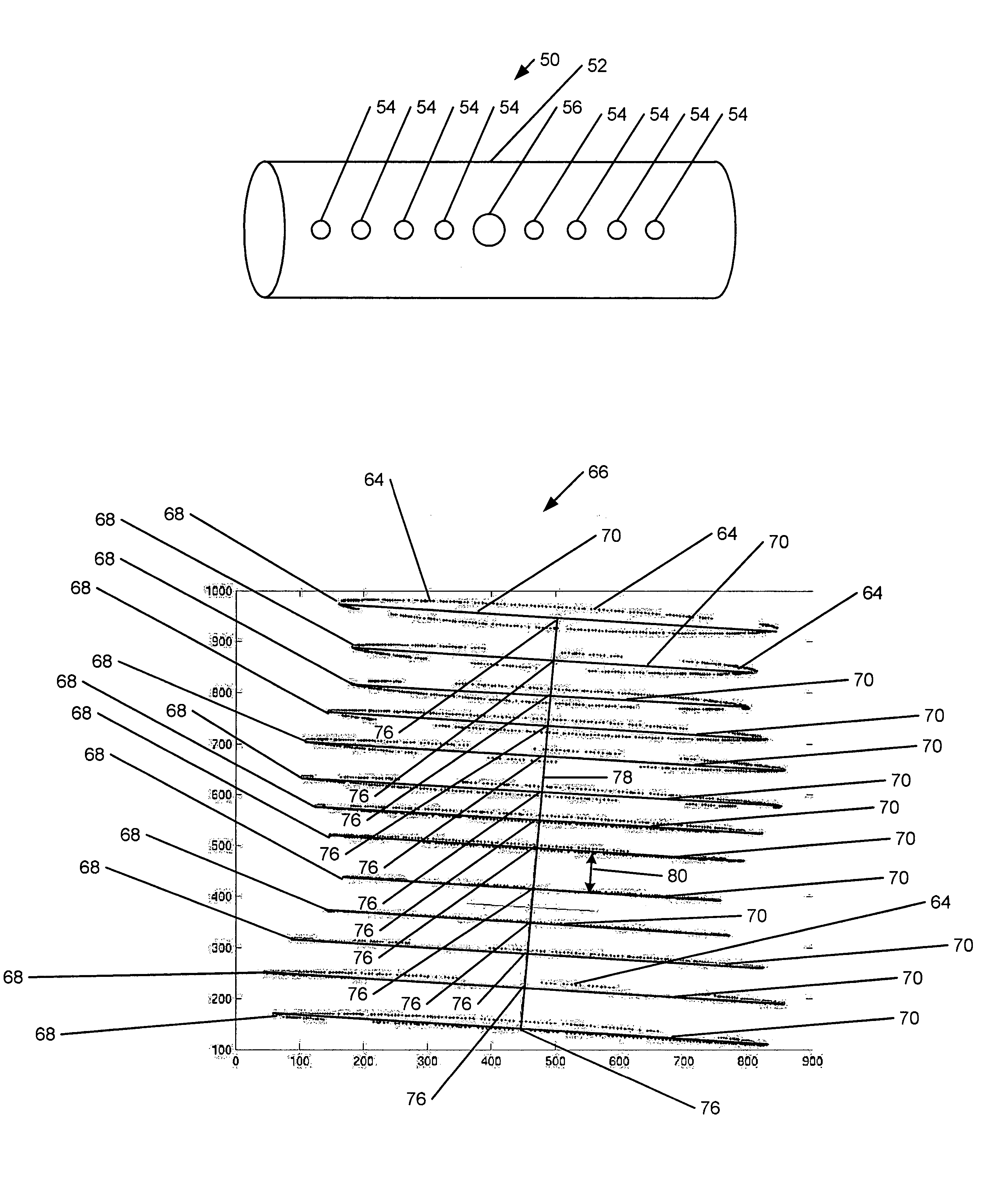
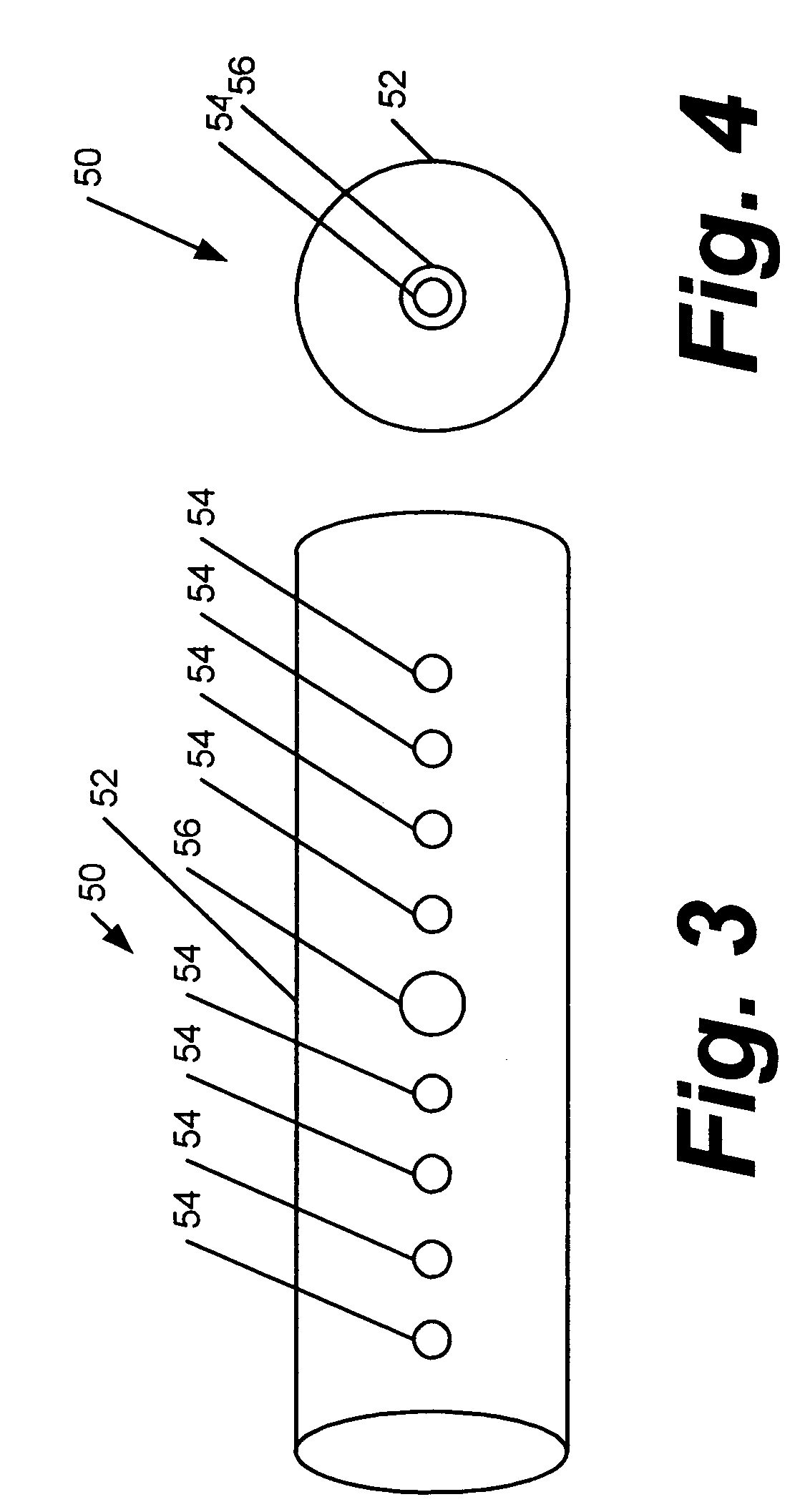
Method for reconstructing a three-dimensional image volume and x-ray devices
InactiveUS7711083B2Improve executionMaterial analysis using wave/particle radiationRadiation/particle handlingVoxelProjection image
Owner:SIEMENS HEALTHCARE GMBH
Small memory footprint light transport matrix capture
ActiveUS8106949B2Easy to shipEasy to implementTelevision system detailsTelevision system scanning detailsImaging processingProjection image
A projection system uses a transformation matrix to transform a projection image p in such a manner so as to compensate for surface irregularities on a projection surface. The transformation matrix makes use of properties of light transport relating a projector to a camera. A display pipeline of user-supplied image modification processing modules are reduced by first representing the processing modules as multiple, individual matrix operations. All the matrix operations are then combined with, i.e., multiplied to, the transformation matrix to create a modified transformation matrix. The created transformation matrix is then used in place of the original transformation matrix to simultaneously achieve both image transformation and any pre and post image processing defined by the image modification processing modules.
Owner:SEIKO EPSON CORP
Method and system for registering 3D models of anatomical regions with projection images of the same
Owner:APN HEALTH +1
System, method and computer-accessible medium for providing a panoramic cone beam computed tomography (CBCT)
InactiveUS20150213633A1Image enhancementReconstruction from projectionProjection imageCone beam computed tomography
Exemplary devices, procedures and computer-readable mediums for providing a projection image associated with at least one target. The projection image can be formed from a plurality of locations of a source arrangement. At each source location, a plurality of panoramic projection images associated with a target can be acquired. At least two of the panoramic projection images can be obtained at view angles which are different from one another. These panoramic projection images can be stitched together or otherwise combined. A resulting image can then be generated using a computed tomography procedure based on the stitched or combined projection images that are generated at the plurality of location.
Owner:THE TRUSTEES OF COLUMBIA UNIV IN THE CITY OF NEW YORK
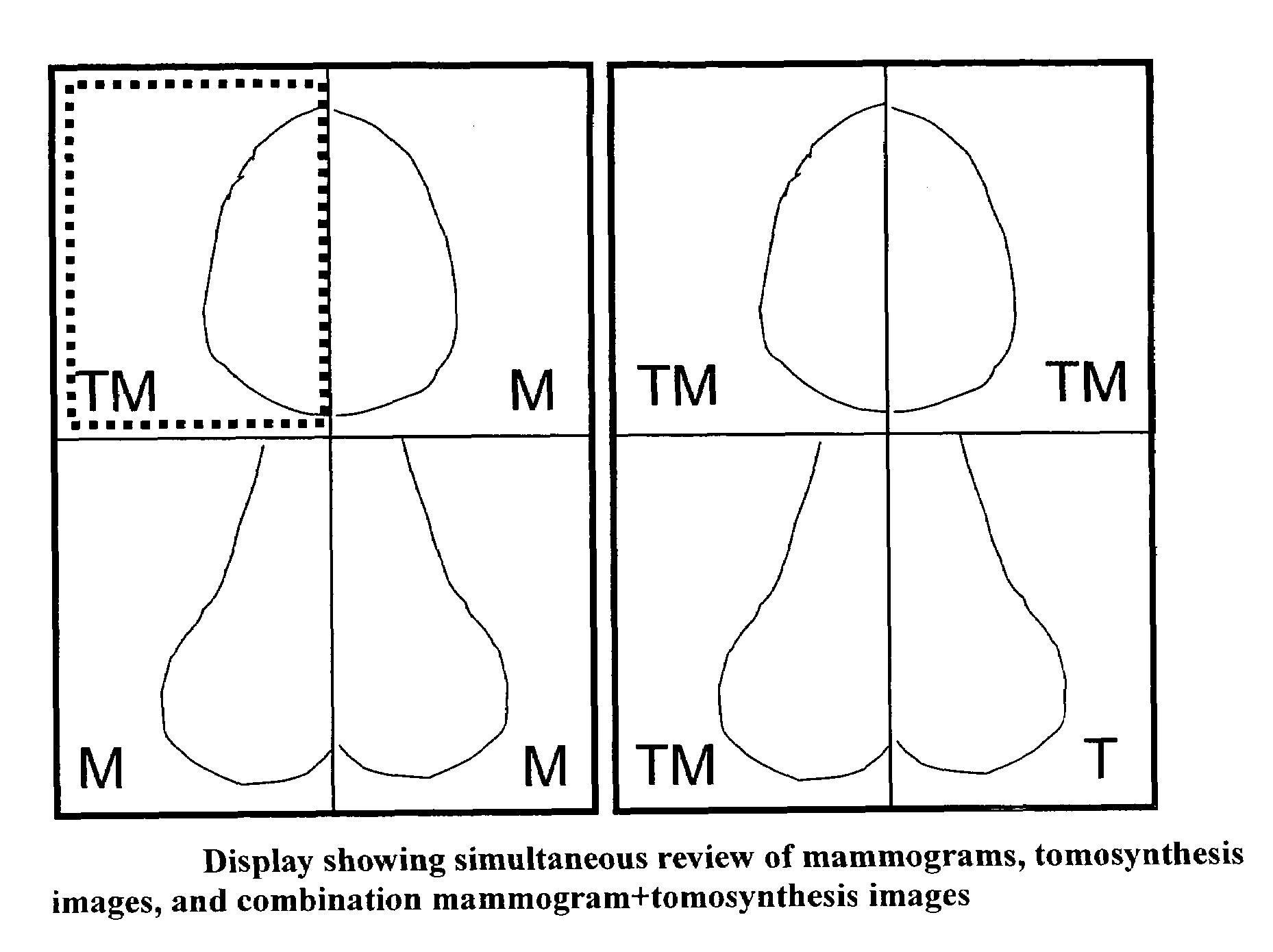
Image Handling and display in X-ray mammography and tomosynthesis
InactiveUS20080019581A1Easy to identifyImprove assessmentImage enhancementReconstruction from projectionTomosynthesisProjection image
A method and system for acquiring, processing, storing, and displaying x-ray mammograms Mp tomosynthesis images Tr representative of breast slices, and x-ray tomosynthesis projection images Tp taken at different angles to a breast, where the Tr images are reconstructed from Tp images
Owner:HOLOGIC INC
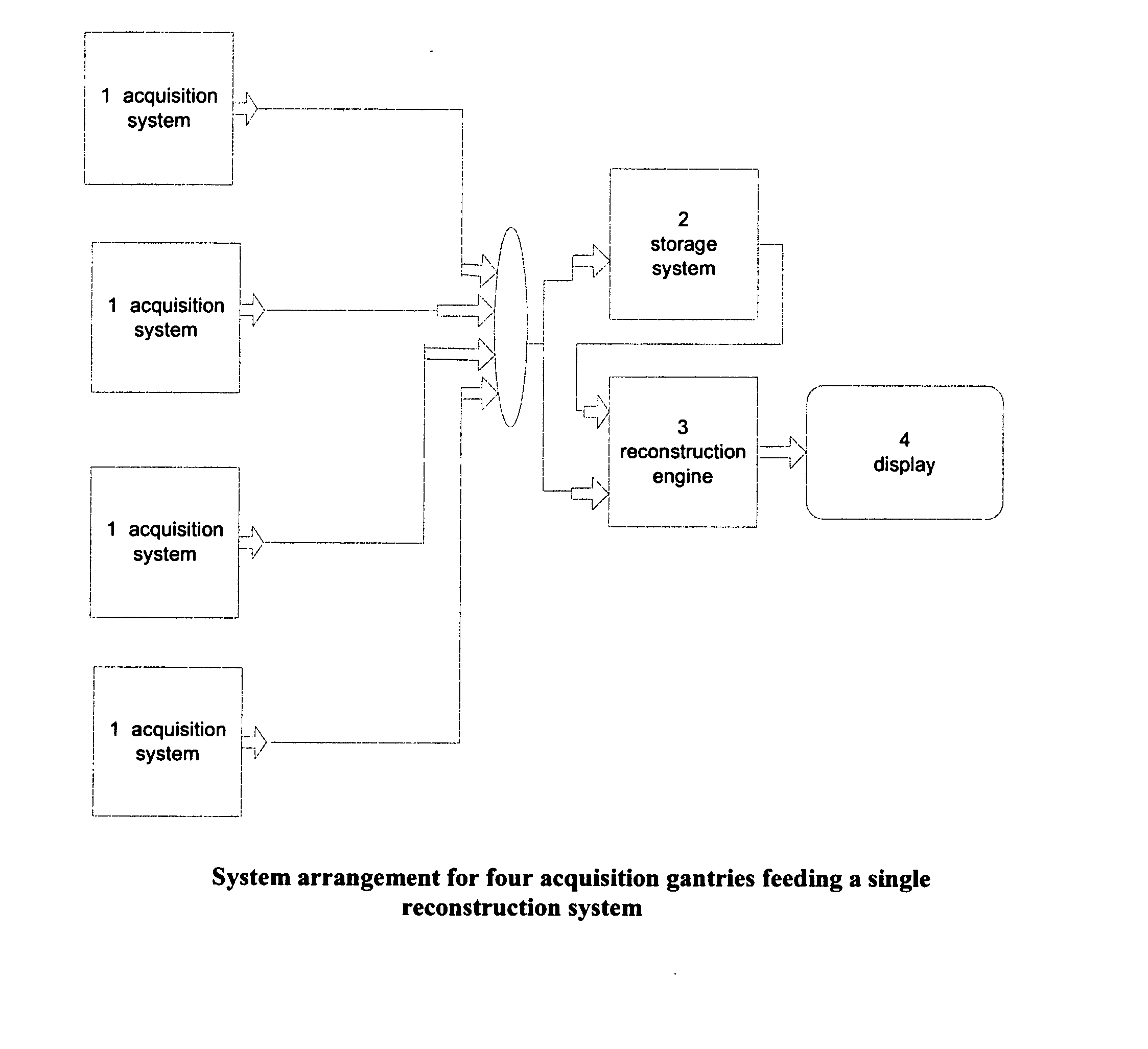
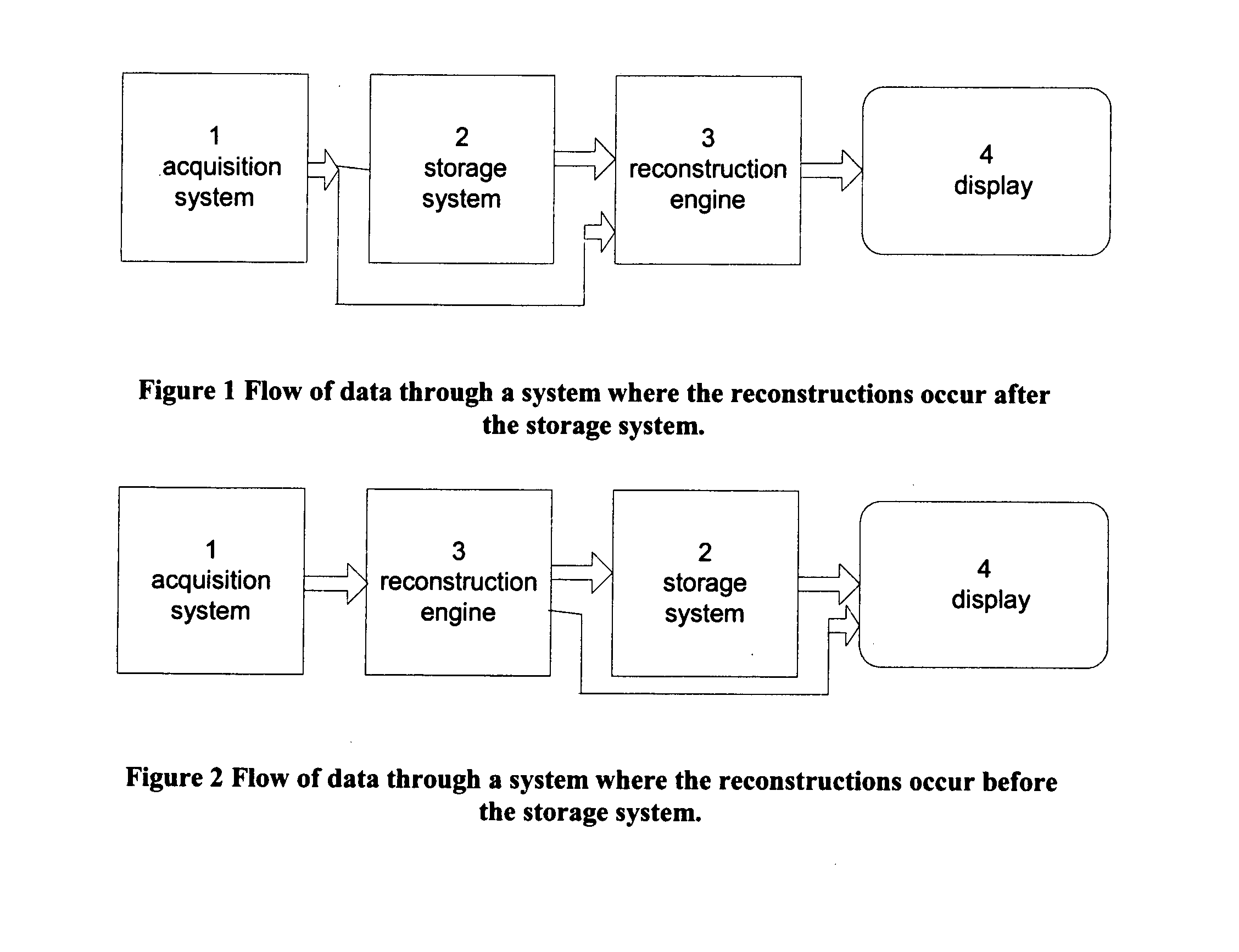
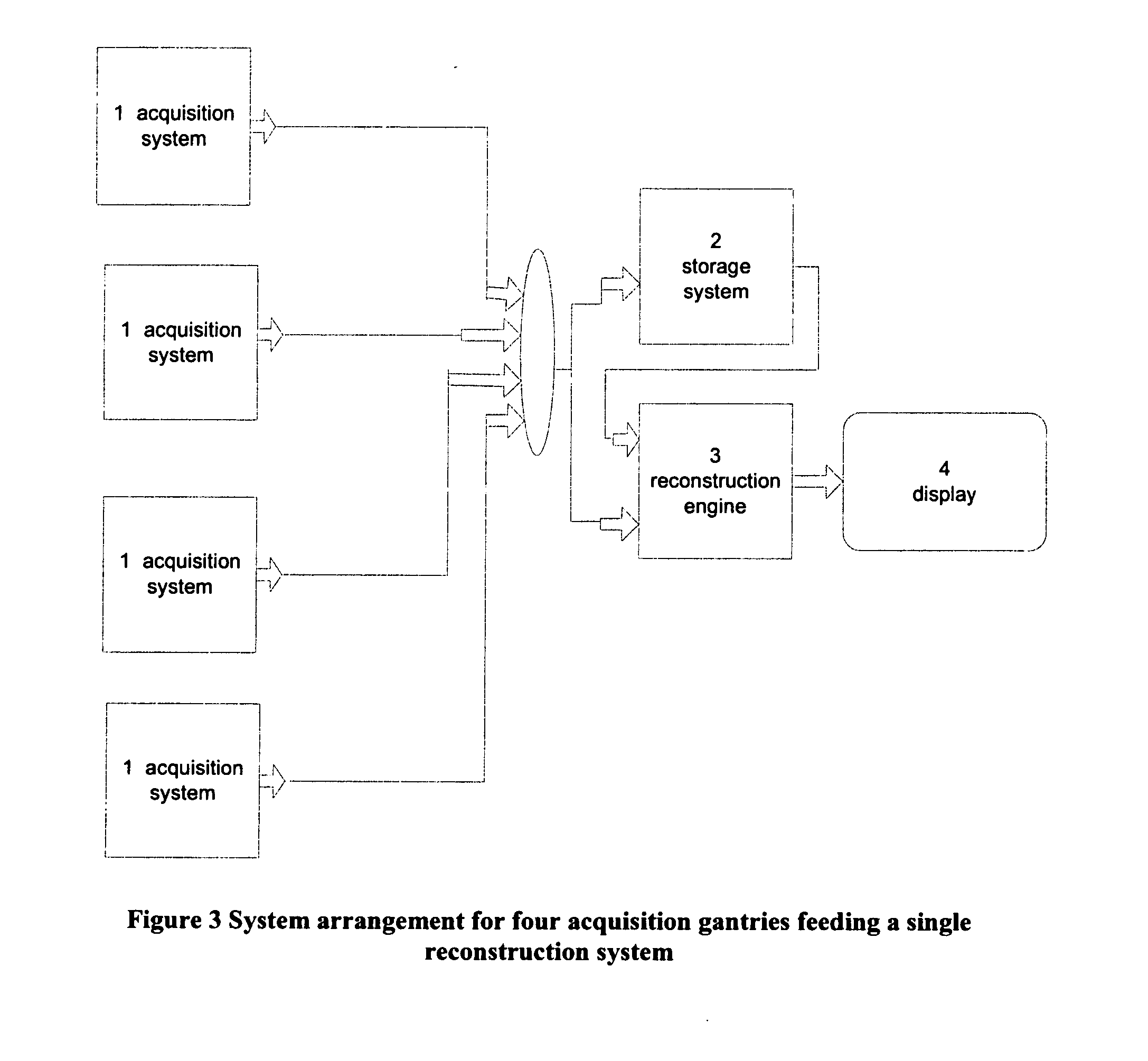
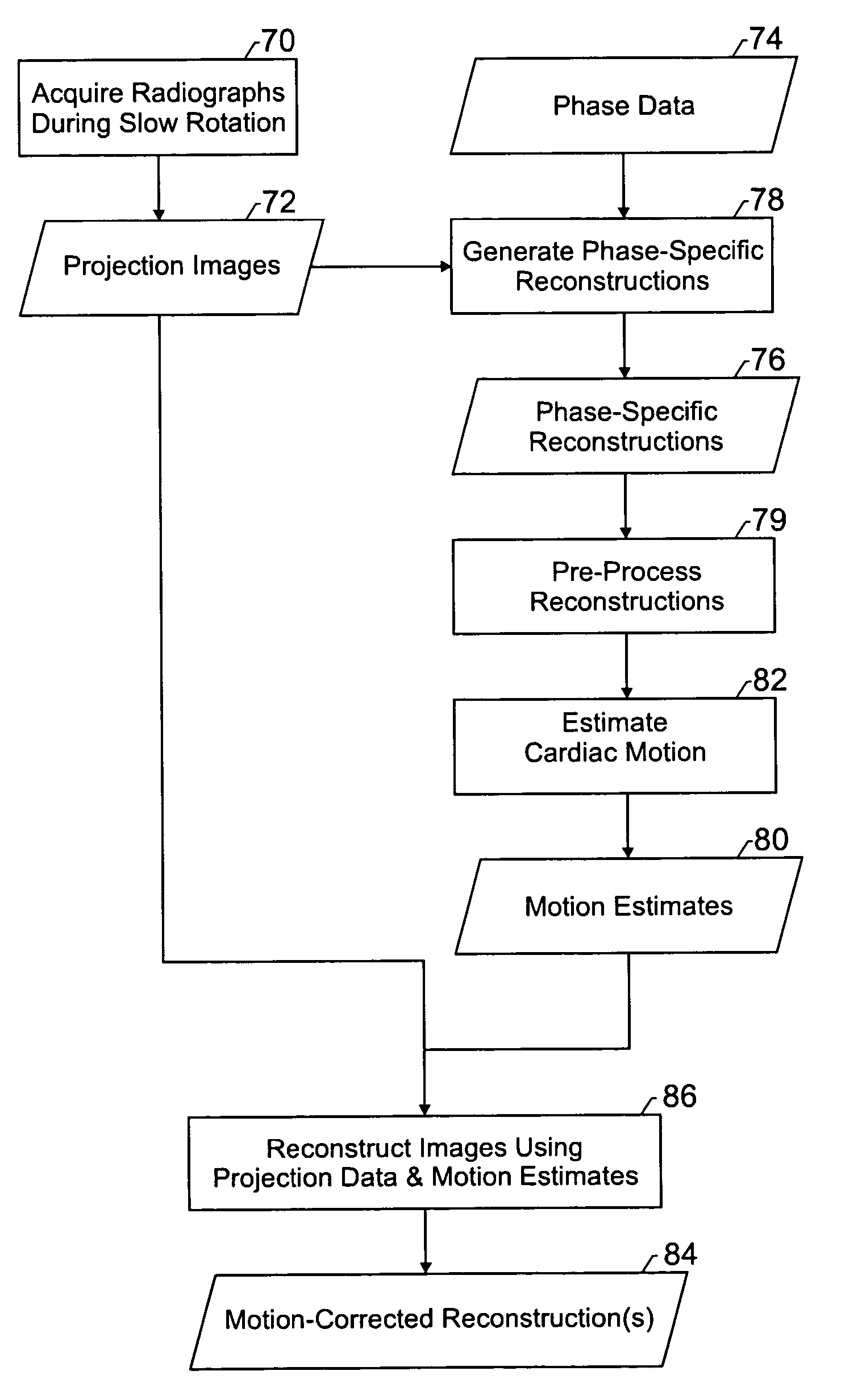
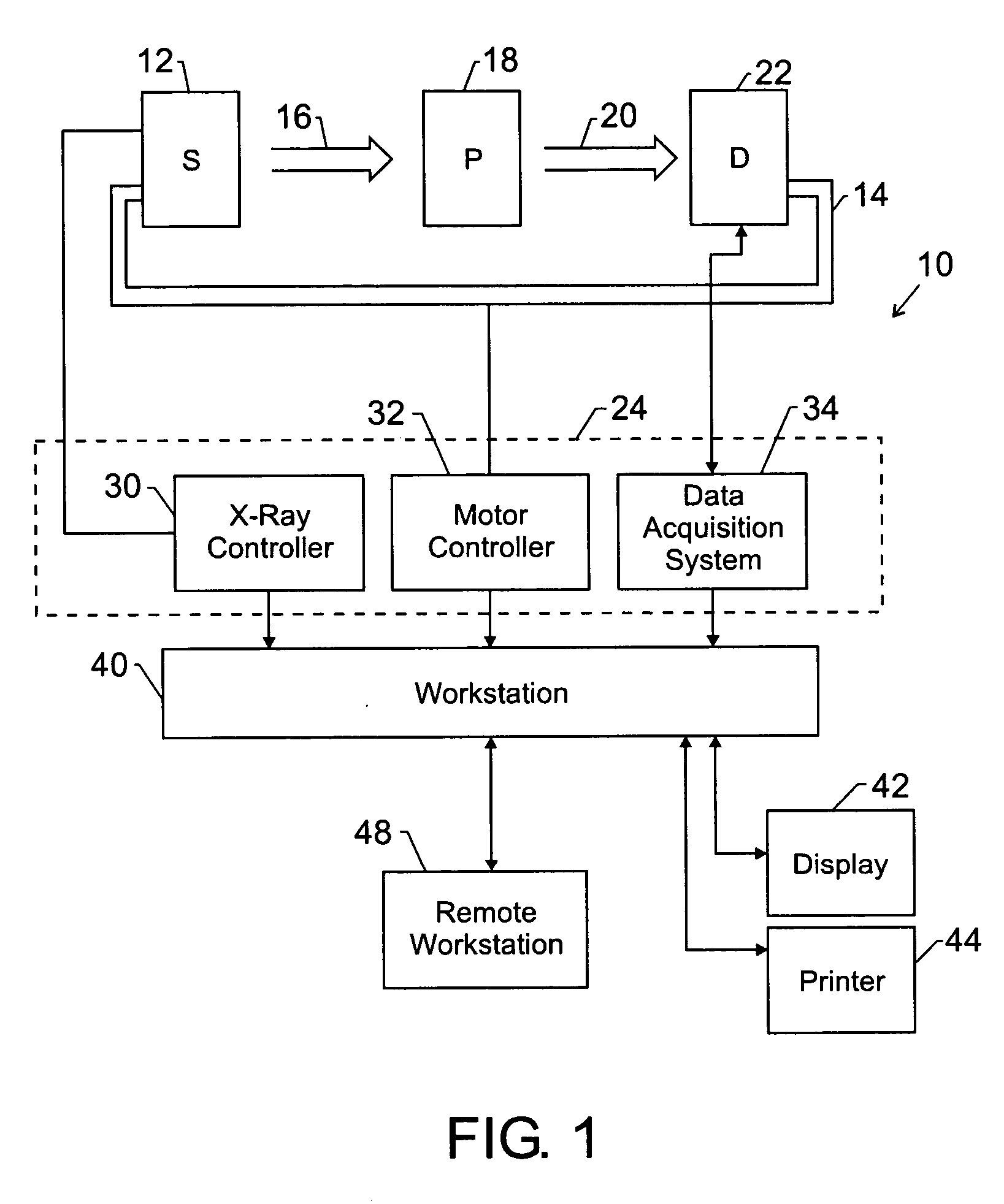
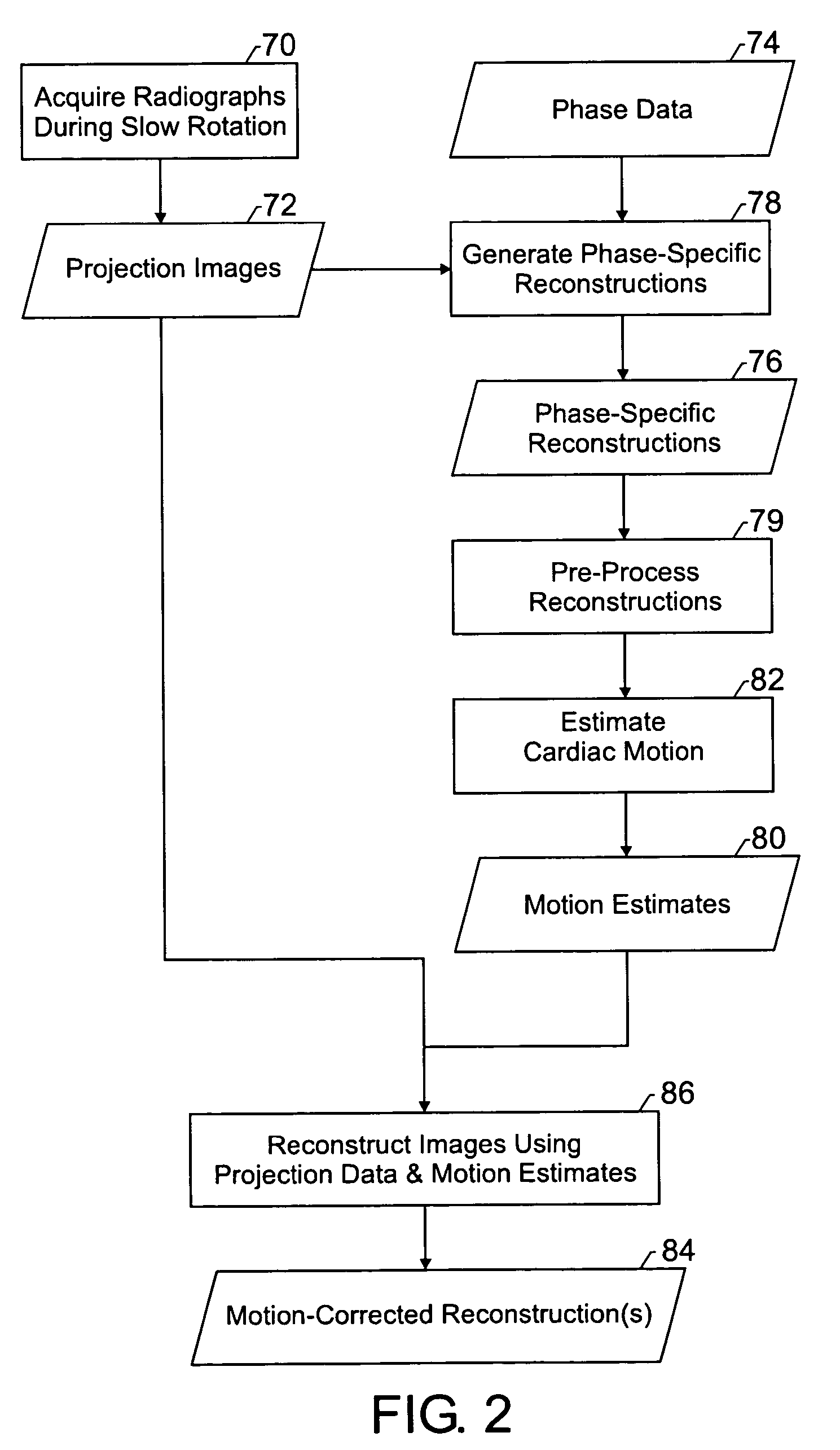
Method and apparatus for correcting motion in image reconstruction
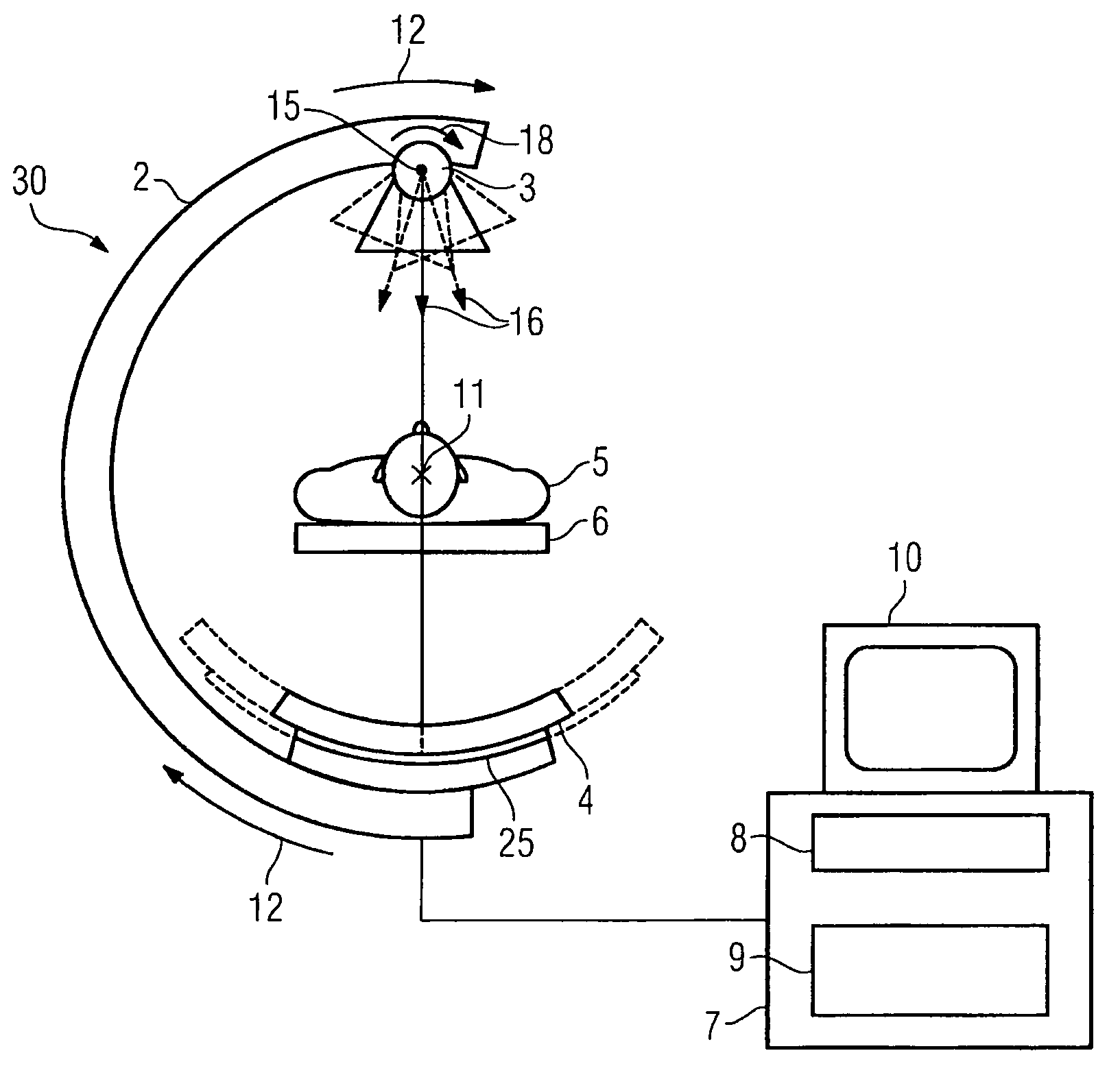
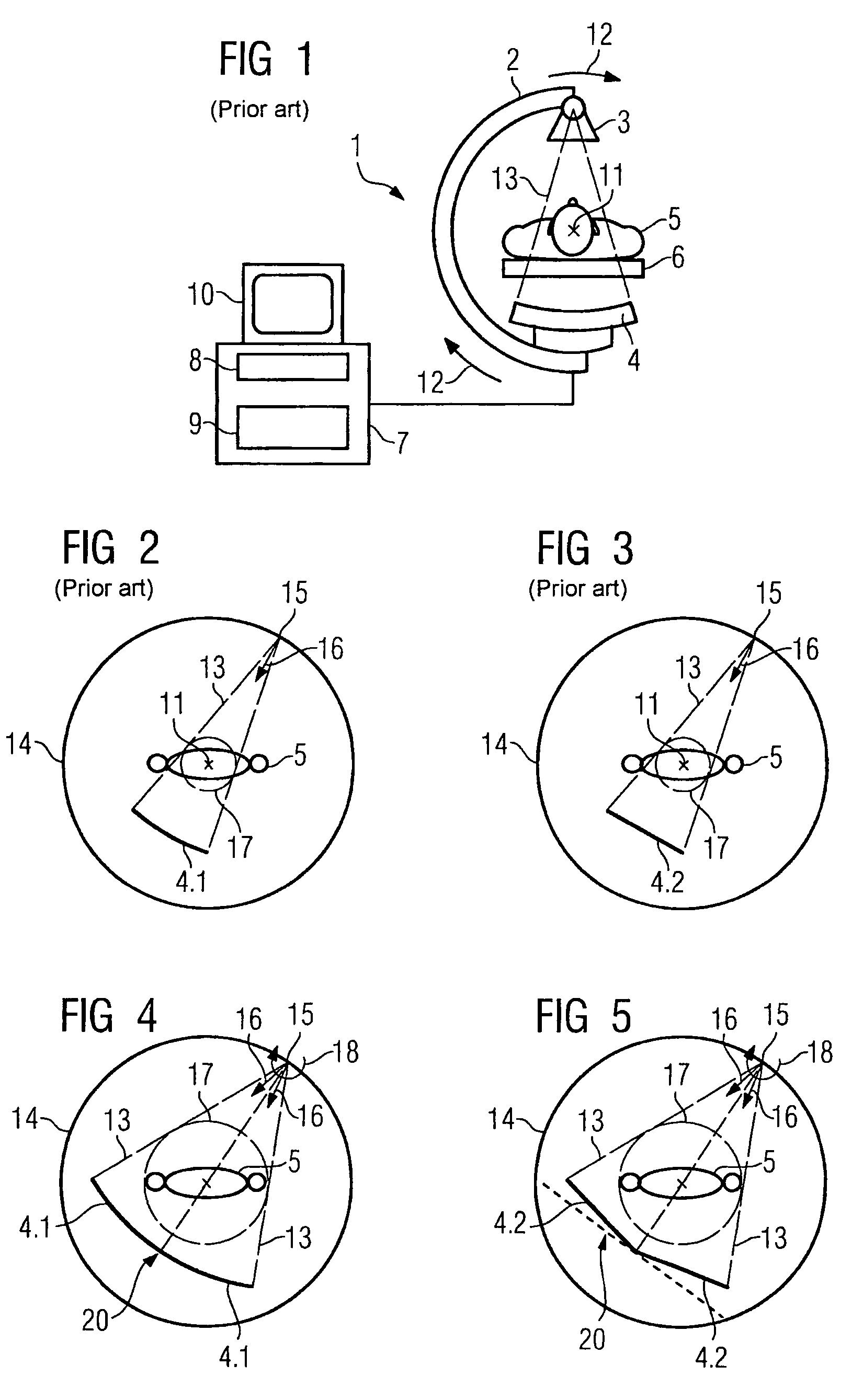
A plurality of projection images are acquired over an angular range during the slow rotation of a C-arm gantry having a source and detector. Phase-specific reconstructions are generated from the plurality of projections, wherein each phase-specific reconstruction is generated generally from projections acquired at or near the respective phase. In one embodiment, a plurality of motion estimates are generated based upon the phase-specific reconstructions. One or more motion-corrected reconstructions may be generated using the respective motion estimates and projections. The motion-corrected reconstructions may be associated to form motion-corrected volume renderings.
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
Computed tomography scanning
InactiveUS7356112B2Effect can be studiedContinuous acquisitionImage enhancementReconstruction from projectionProjection imageTherapeutic radiation
Artifacts in the reconstructed volume data of cone beam CT systems can be removed by the application of respiration correlation techniques to the acquired projection images. To achieve this, the phase of the patients breathing is monitored while acquiring projection images continuously. On completion of the acquisition, projection images that have comparable breathing phases can be selected from the complete set, and these are used to reconstruct the volume data using similar techniques to those of conventional CT. Any phase can be selected and therefore the effect of breathing can be studied. It is also possible to use a feature in the projection images such as the patient's diaphragm to determine the breathing phase. This feature in the projection images can be used to control delivery of therapeutic radiation dependent on the patient's breathing cycle, to ensure that the tumor is in the correct position when the radiation is delivered.
Owner:ELEKTA AB
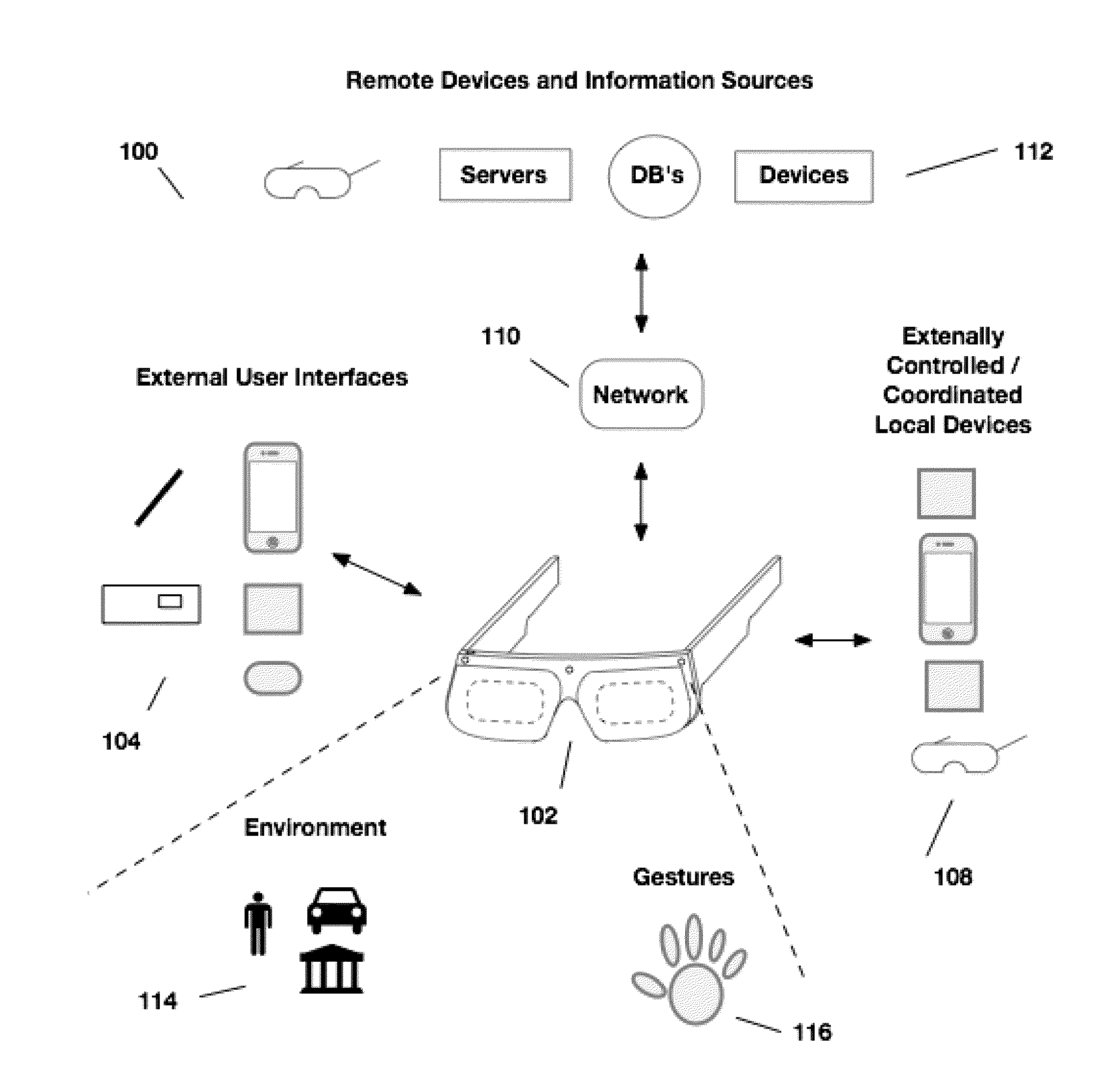
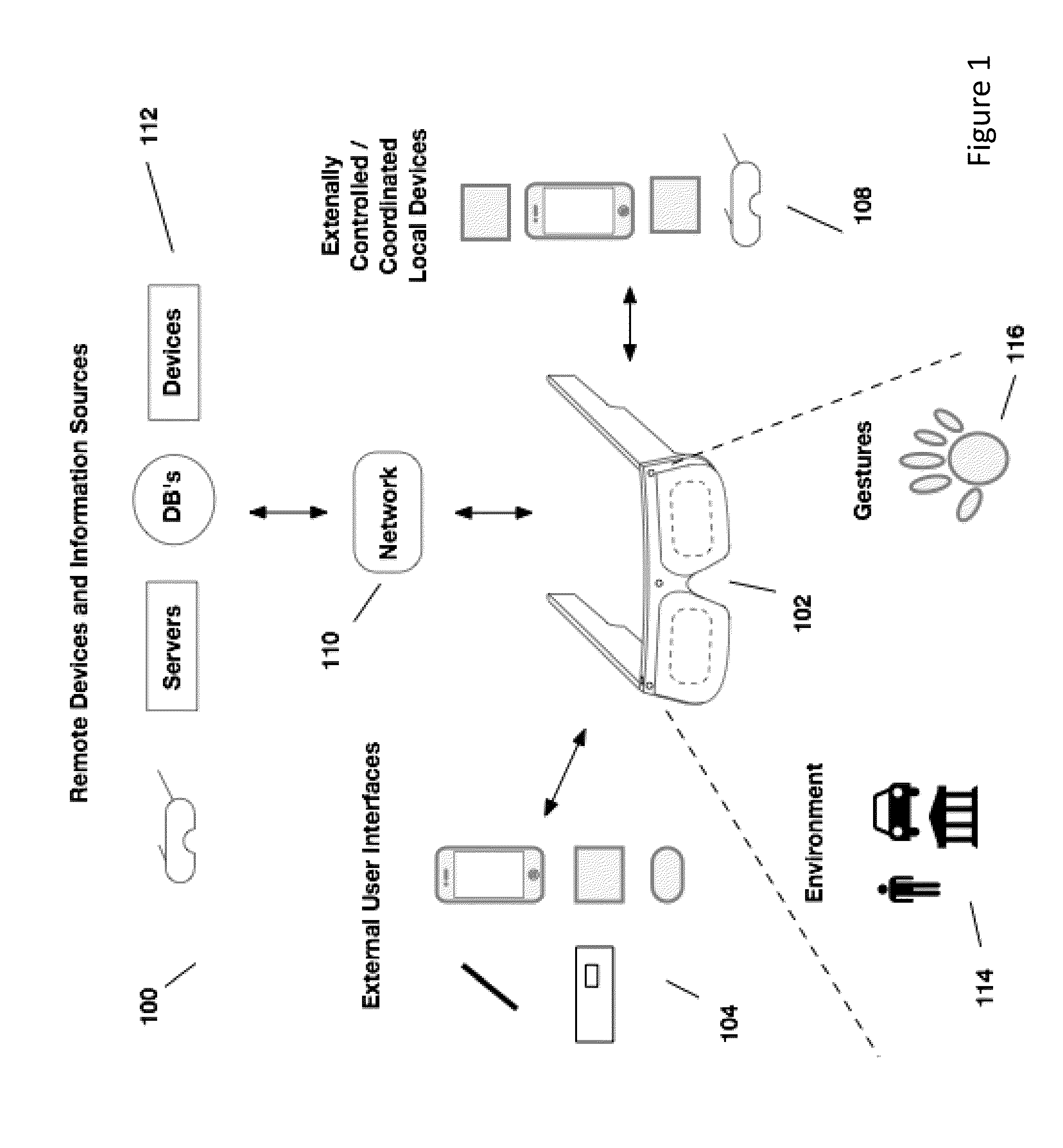
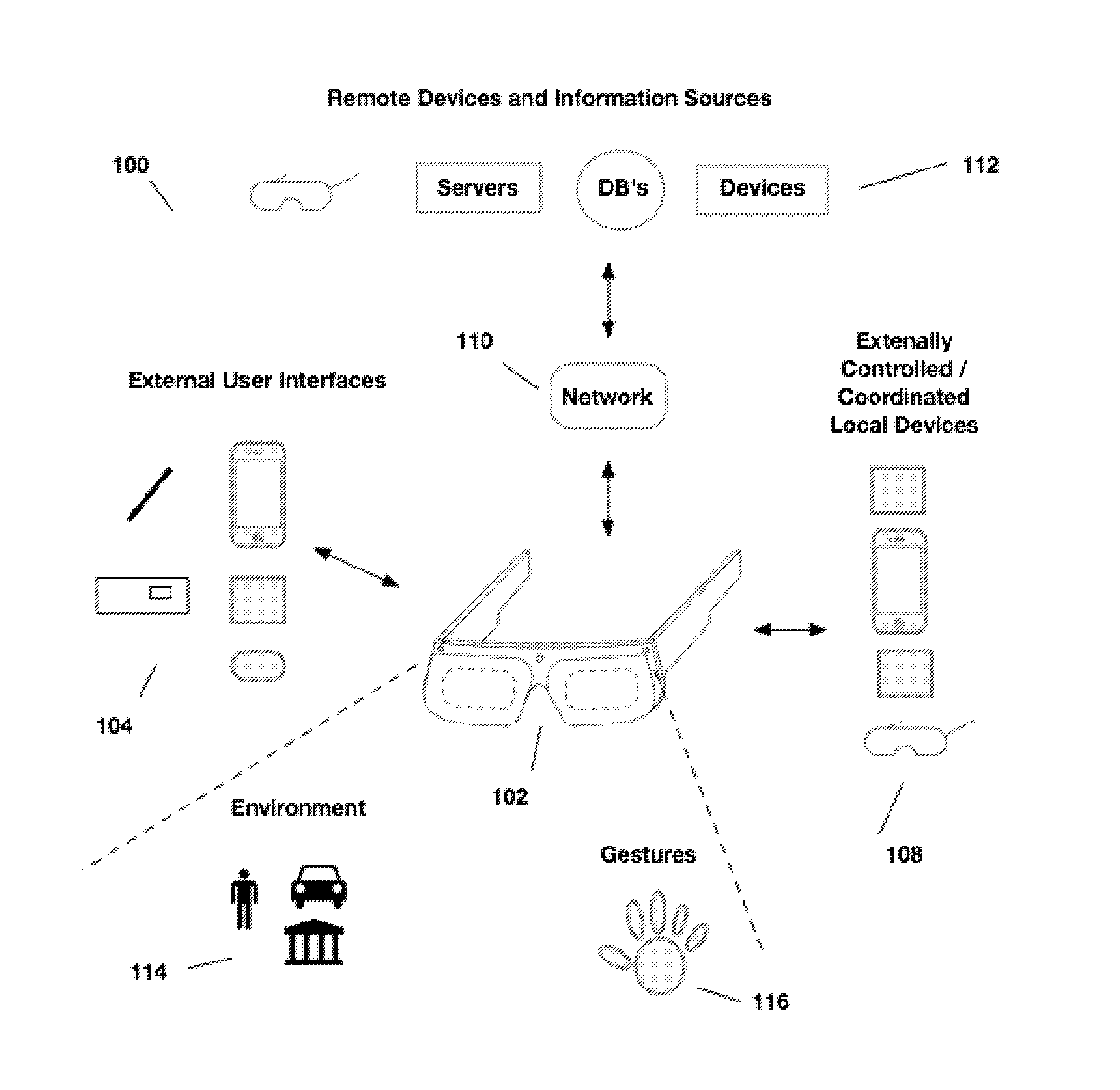
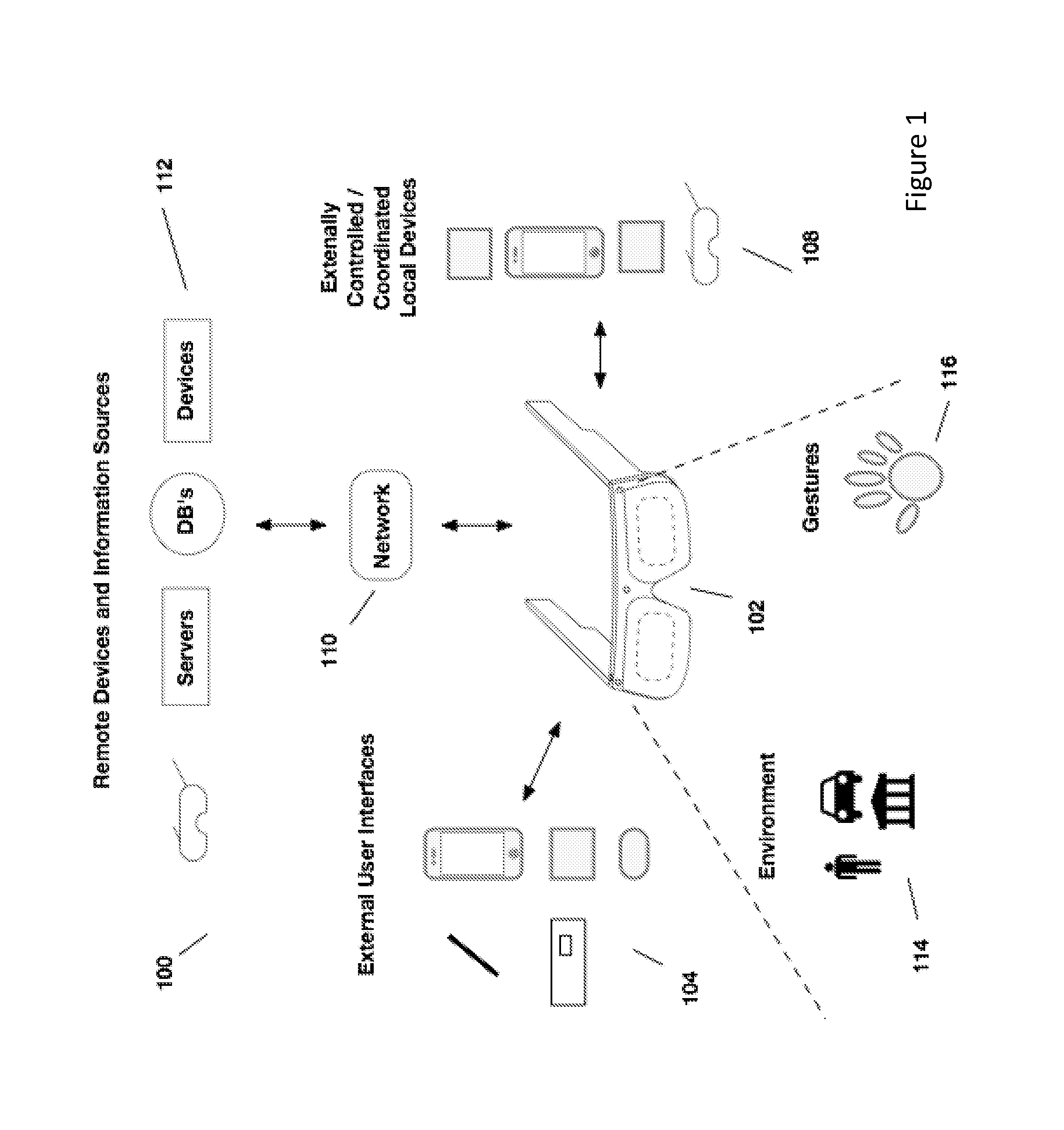
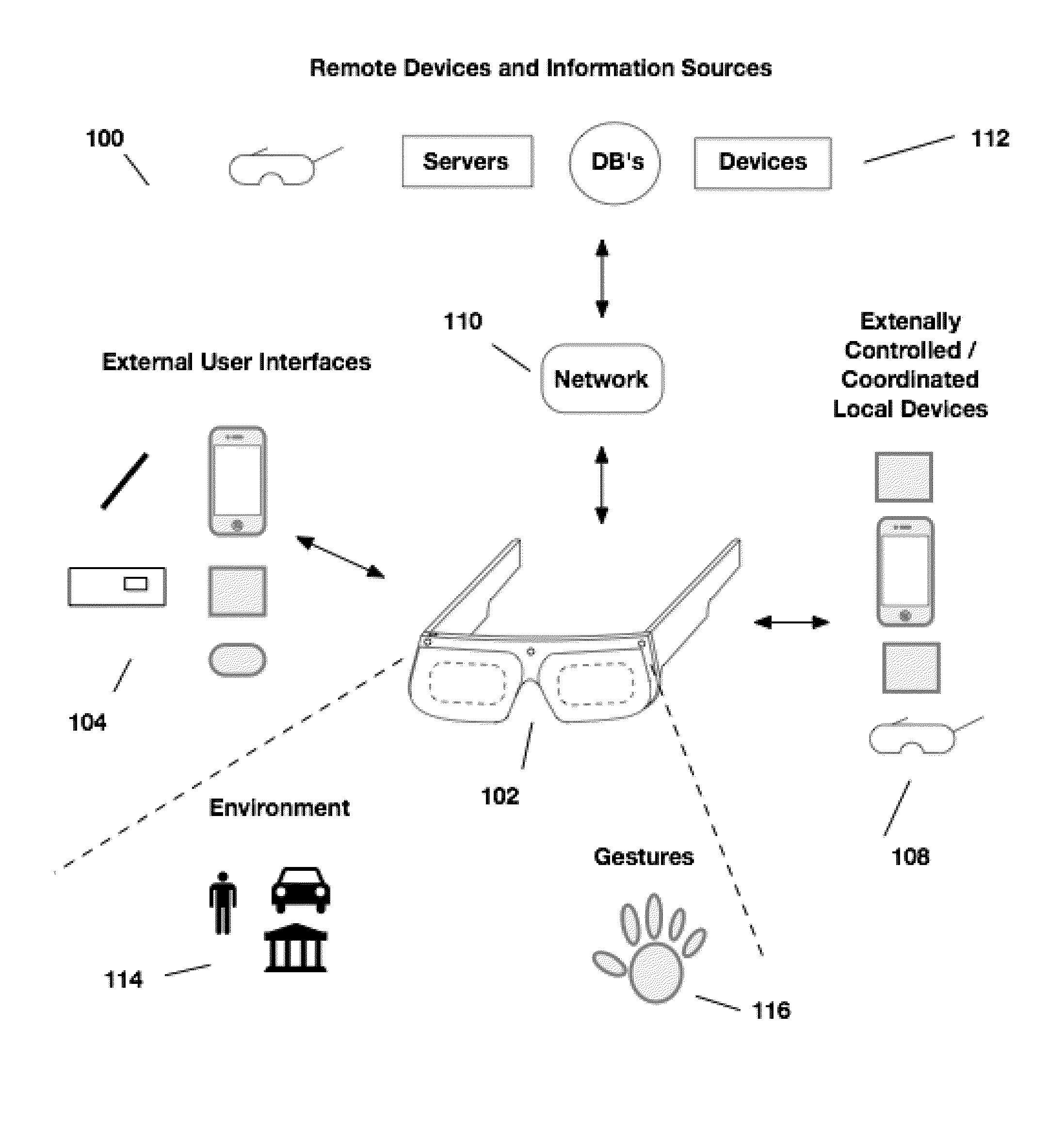
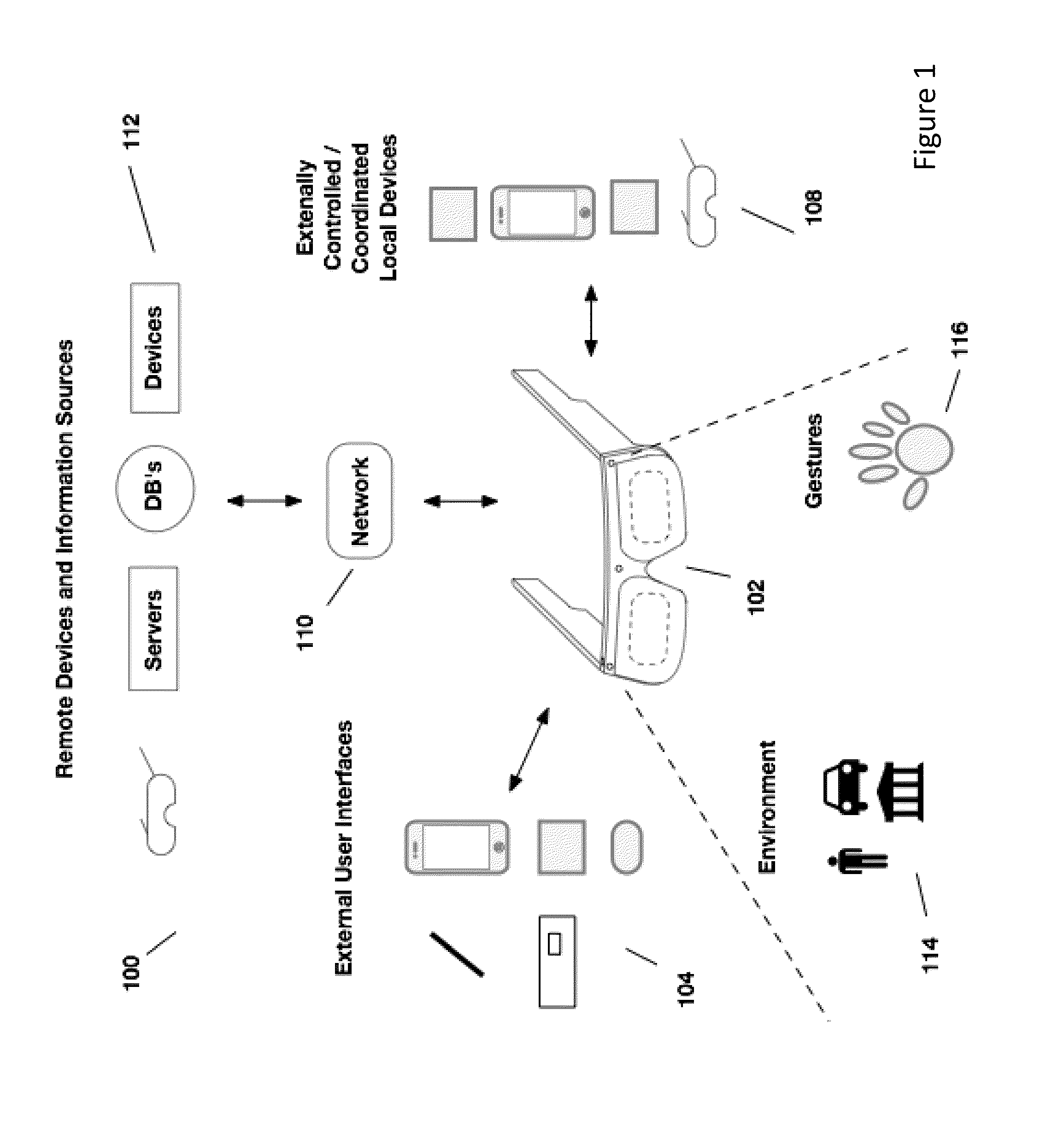
External user interface for head worn computing
InactiveUS20160025977A1Cathode-ray tube indicatorsDetails for portable computersComputer graphics (images)User interface
Owner:OSTERHOUT GROUP INC
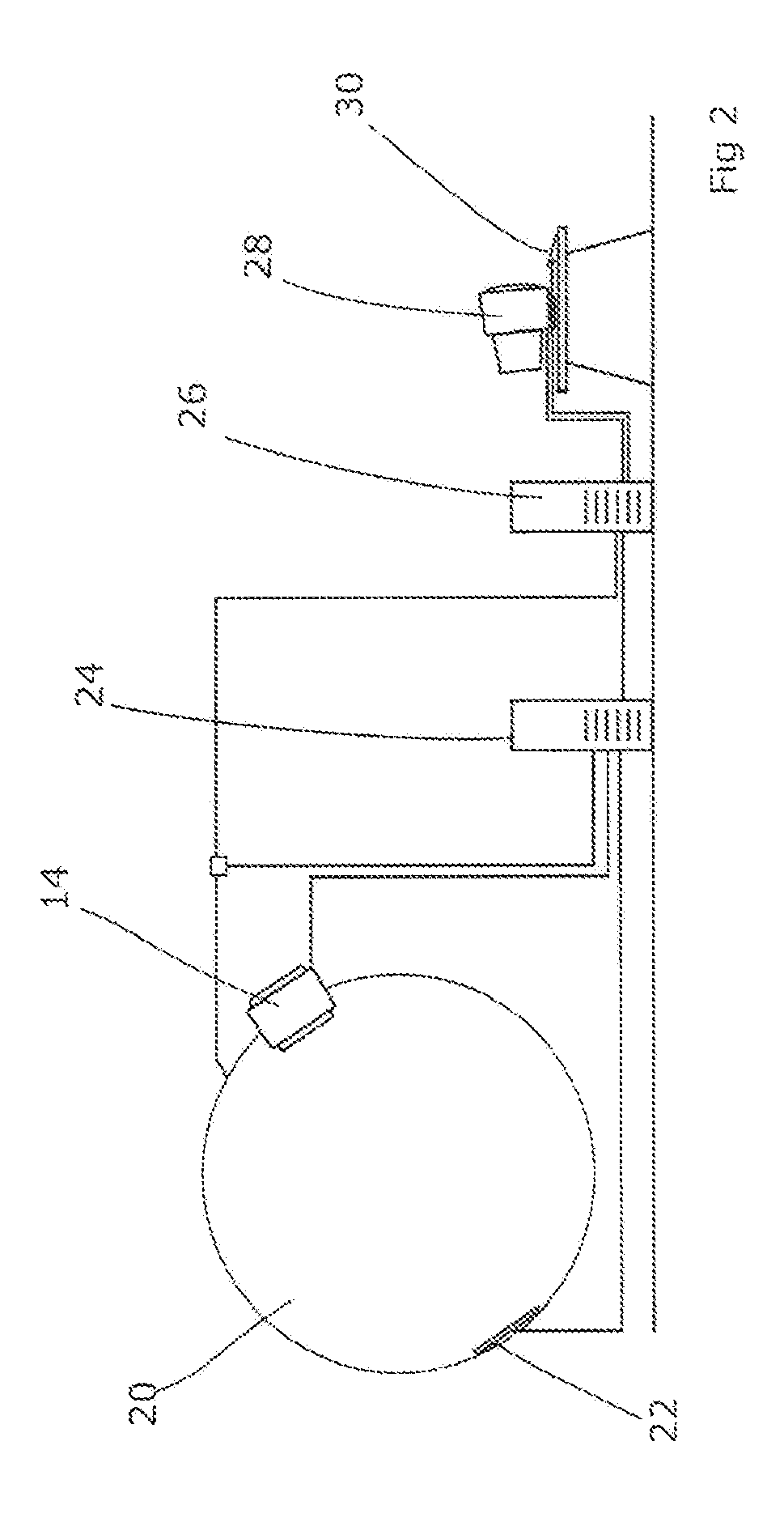
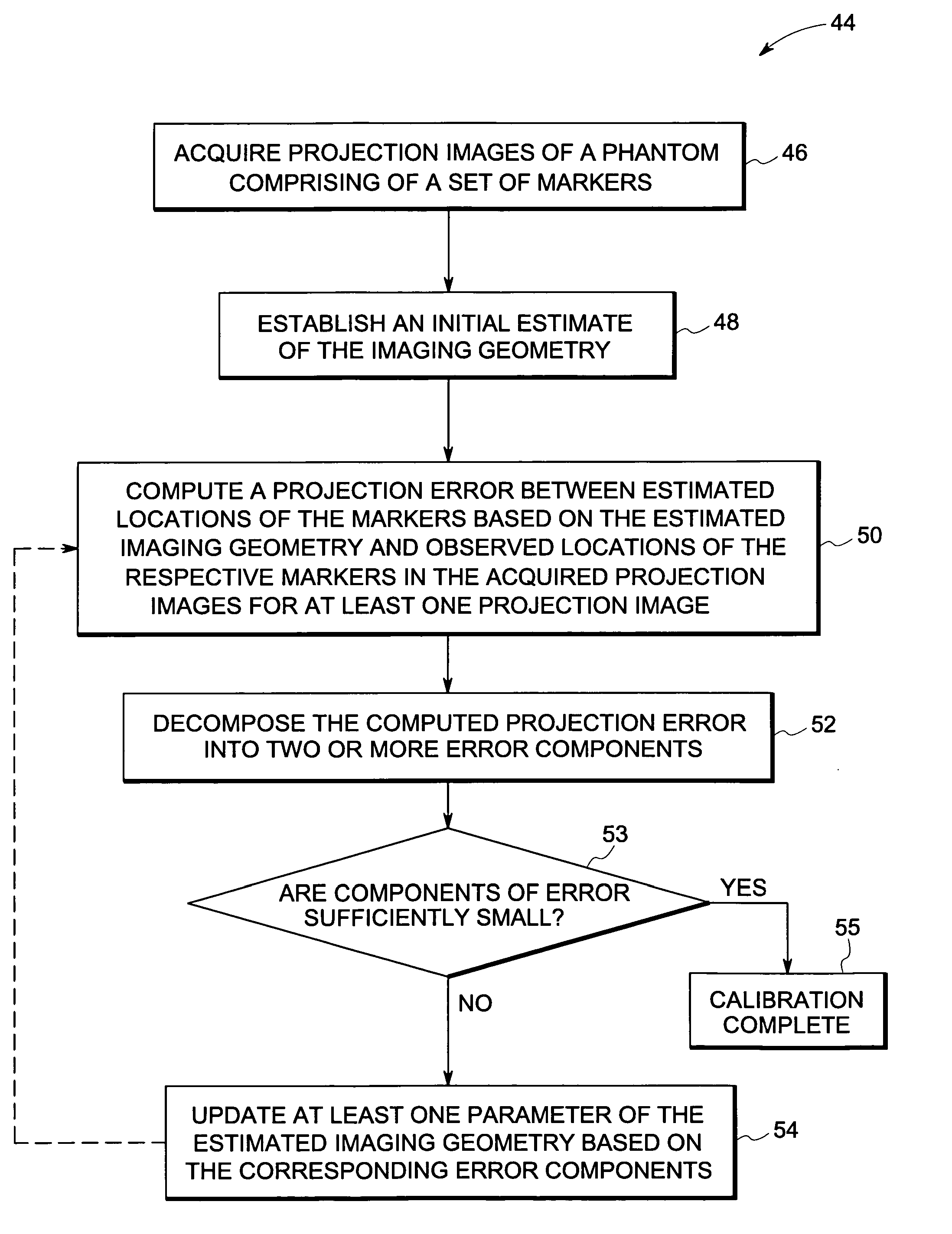
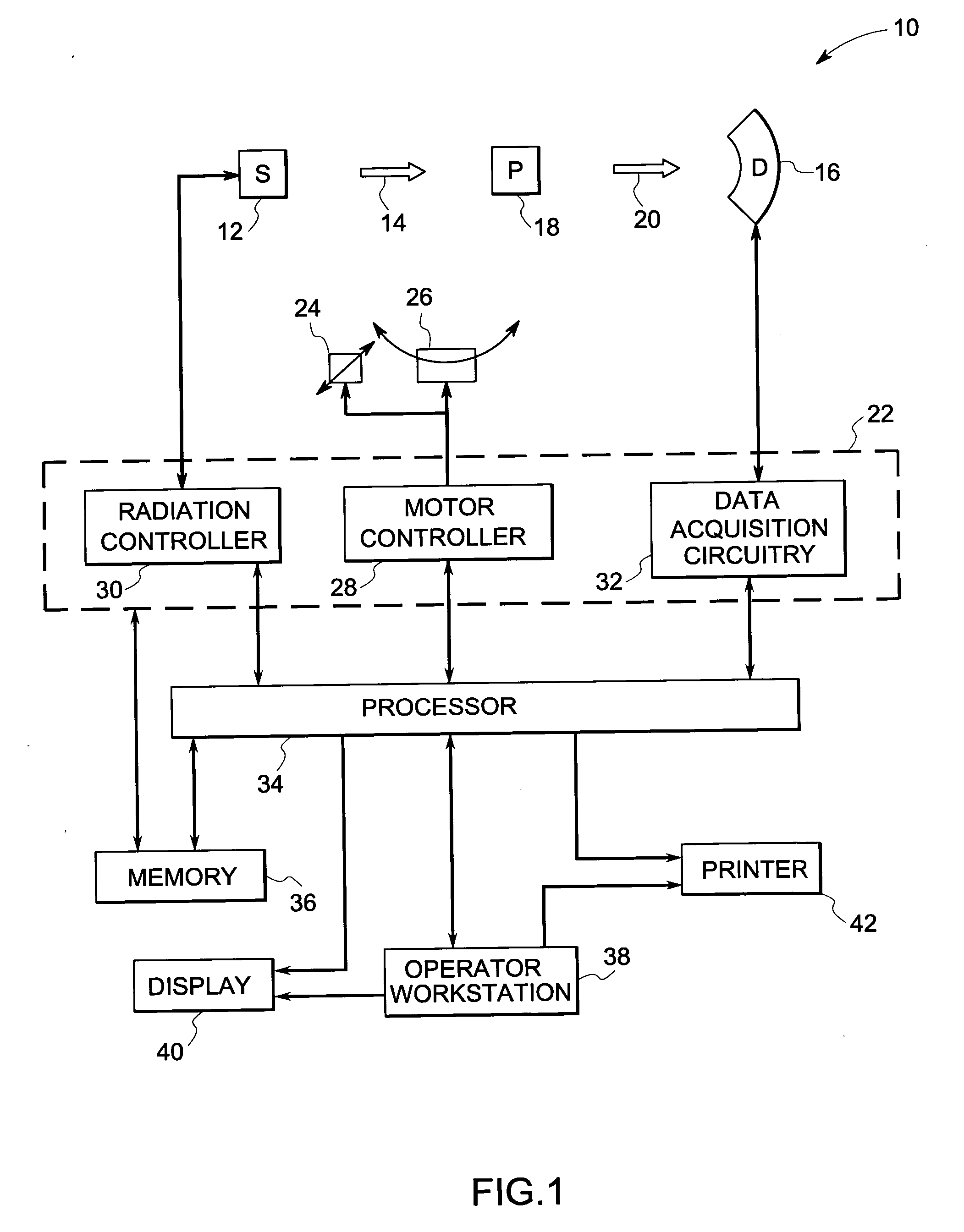
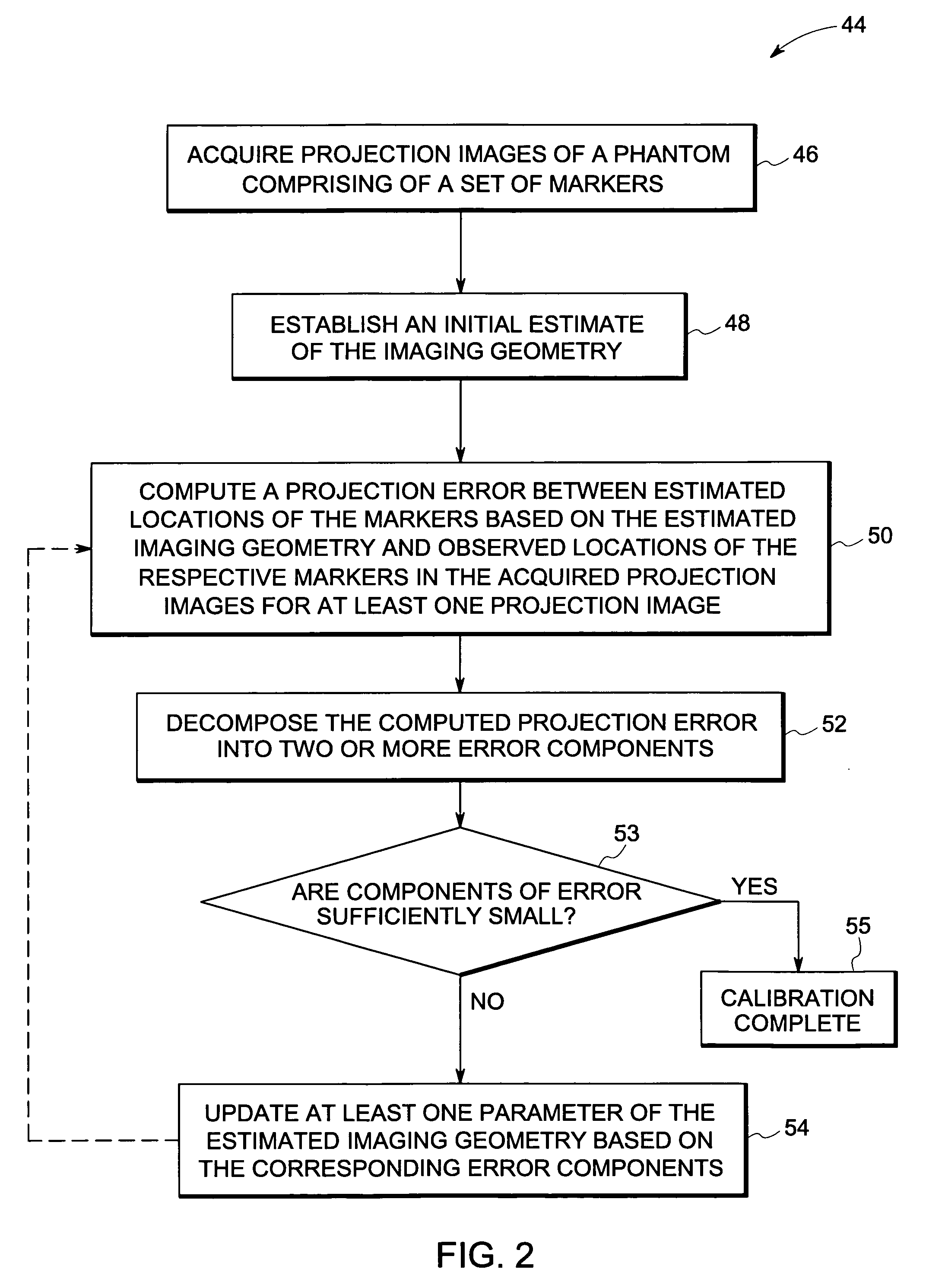
Method and device for geometry analysis and calibration of volumetric imaging systems
ActiveUS20070122020A1Enhance the imageImprove accuracyReconstruction from projectionMaterial analysis using wave/particle radiationVolumetric imagingProjection image
A technique is provided for geometrical analysis and calibration of a volumetric imaging system. The technique includes computing a projection error between estimated locations of a set of markers of a phantom based on a estimated imaging geometry and observed locations of the respective markers for at least one projection image, decomposing the computed projection error into one or more error components corresponding to respective geometric parameters of the imaging geometry, and updating at least one parameter of the estimated imaging geometry based on the one or more error components.
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
Radiographic tomosynthesis image acquisition utilizing asymmetric geometry
InactiveUS6885724B2High sensitivityImprove image qualityTomosynthesisX/gamma/cosmic radiation measurmentSoft x rayTomosynthesis
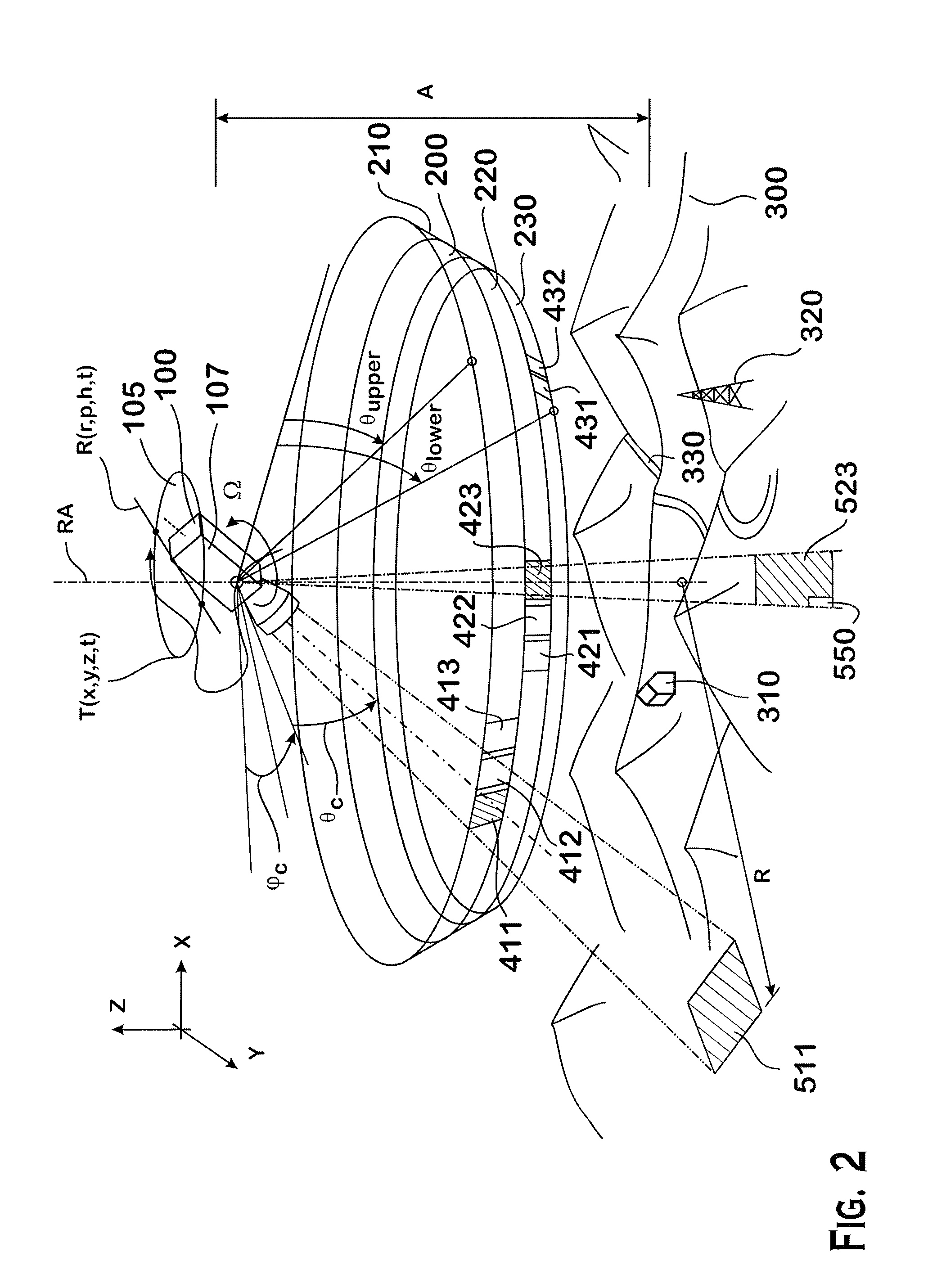
Systems and methods that utilize asymmetric geometry to acquire radiographic tomosynthesis images are described. Embodiments comprise tomosynthesis systems and methods for creating a reconstructed image of an object from a plurality of two-dimensional x-ray projection images. These systems comprise: an x-ray detector; and an x-ray source capable of emitting x-rays directed at the x-ray detector; wherein the tomosynthesis system utilizes asymmetric image acquisition geometry, where θ1≠θ0, during image acquisition, wherein θ1 is a sweep angle on one side of a center line of the x-ray detector, and θ0 is a sweep angle on an opposite side of the center line of the x-ray detector, and wherein the total sweep angle, θasym, is θasym=θ1+θ0. Reconstruction algorithms may be utilized to produce reconstructed images of the object from the plurality of two-dimensional x-ray projection images.
Owner:GE MEDICAL SYST GLOBAL TECH CO LLC
External user interface for head worn computing
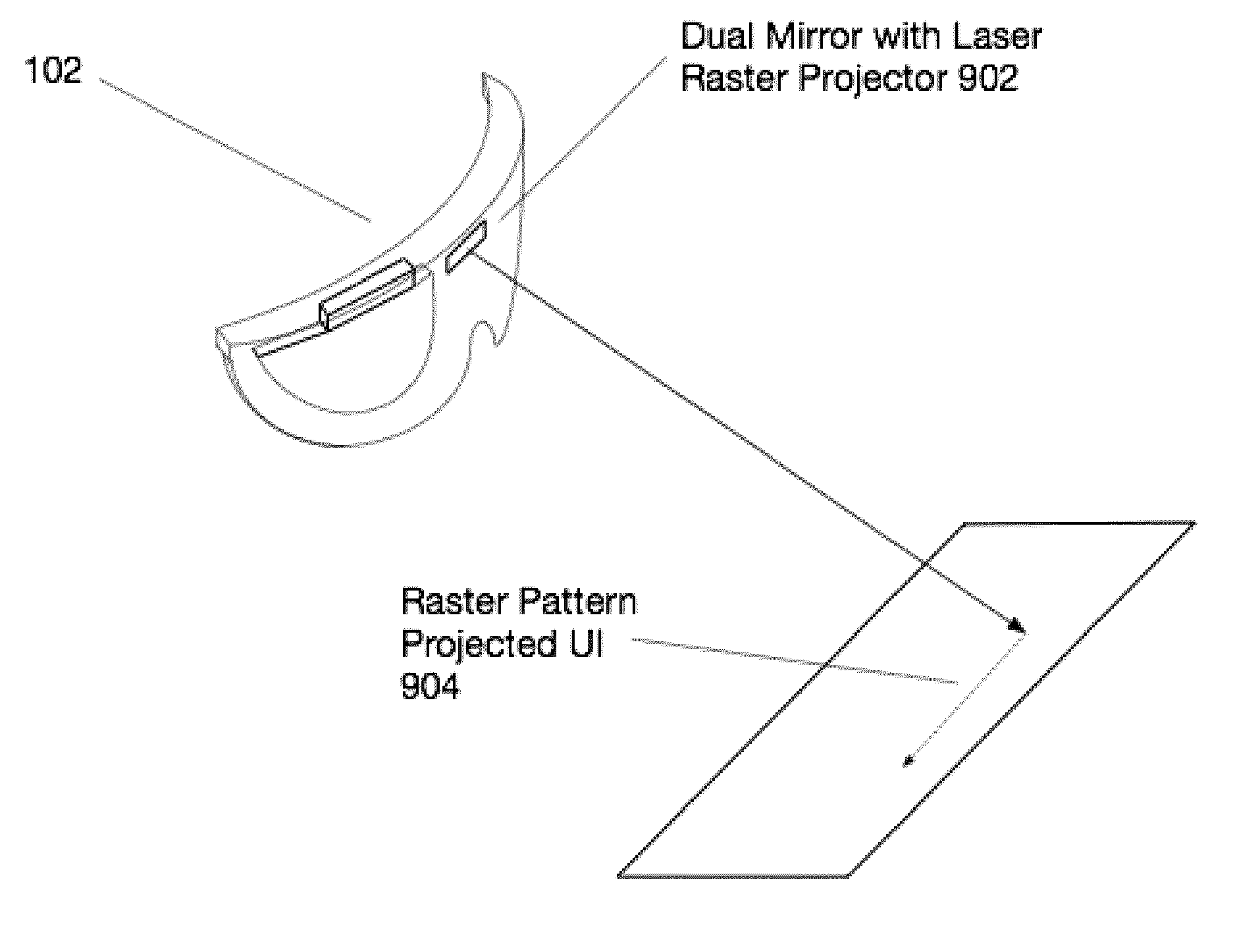
InactiveUS20160027211A1Image analysisPicture reproducers using projection devicesLaserUser interface
Aspects of the present invention relate to the projection of imagery from a head-worn computer, wherein a projector with x-y control and a laser are mounted in the head-worn computer and positioned to project a raster style interactive user interface image onto a nearby surface.
Owner:OSTERHOUT GROUP INC
External user interface for head worn computing
InactiveUS20160025980A1Character and pattern recognitionCathode-ray tube indicatorsHuman–computer interactionUser interface
Aspects of the present invention relate to the projection of imagery from a head-worn computer, wherein a projector with x-y control and a laser are mounted in the head-worn computer and positioned to project a raster style interactive user interface image onto a nearby surface.
Owner:OSTERHOUT GROUP INC
System and method for processing specimens and images for optical tomography
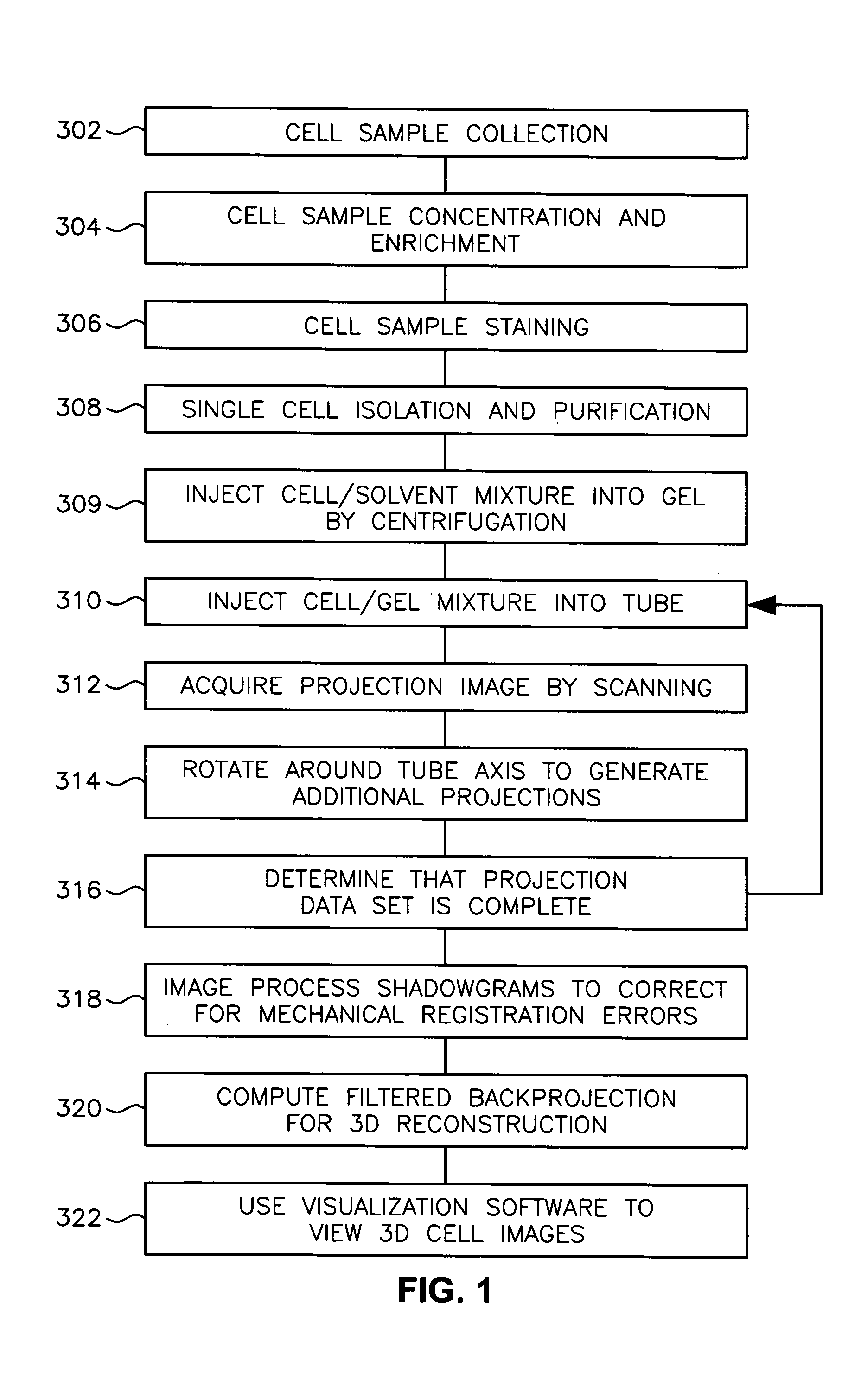
ActiveUS20050085721A1Beam/ray focussing/reflecting arrangementsMaterial analysis by optical meansBiological cellOptical tomography
A scanning method for scanning samples of biological cells using optical tomography includes preparing, acquiring, reconstructing and viewing three-dimensional images of cell samples. Concentration and enrichment of the cell sample follows. The cell sample is stained. Cells are isolated from the cell sample and purified. A cell / solvent mixture is injected into a gel by centrifugation. A cell / gel mixture is injected into a capillary tube until a cell appears centered in a field of view using a step flow method. An optical imaging system, such as a fixed or variable motion optical tomography system acquires a projection image. The sample is rotated about a tube axis to generate additional projections. Once image acquisition is completed, the acquired shawdowgrams or image projections are corrected for errors. A computer or other equivalent processor is used to compute filtered backprojection information for 3D reconstruction.
Owner:UNIV OF WASHINGTON +1
External user interface for head worn computing
InactiveUS20160027414A1Character and pattern recognitionCathode-ray tube indicatorsNatural user interfaceHuman–computer interaction
Aspects of the present invention relate to the projection of imagery from a head-worn computer, wherein a projector with x-y control and a laser are mounted in the head-worn computer and positioned to project a raster style interactive user interface image onto a nearby surface.
Owner:OSTERHOUT GROUP INC
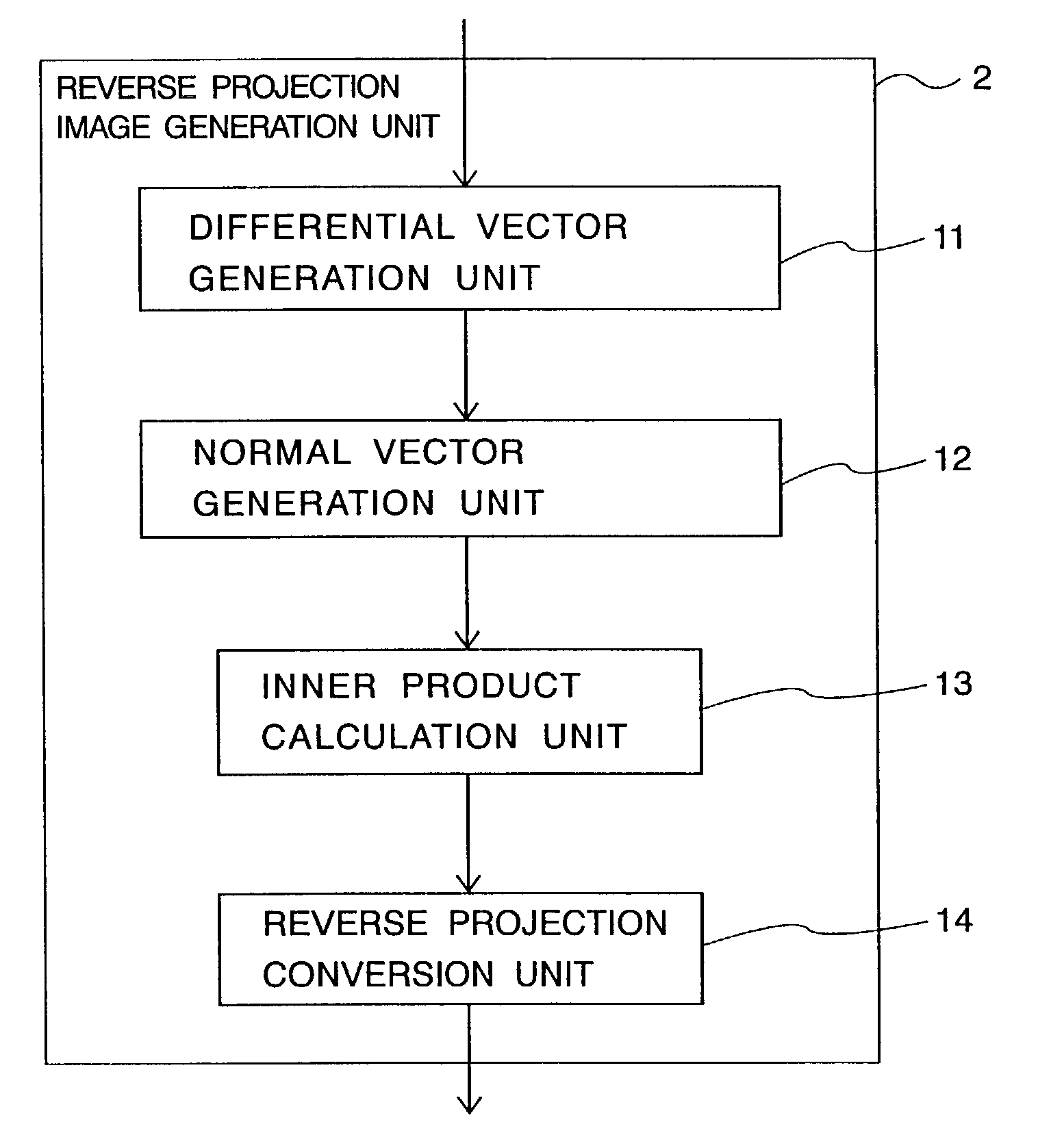
Image processing apparatus and method
ActiveUS7095432B2Small amount of calculationImage enhancementImage analysisImaging processingProjection image
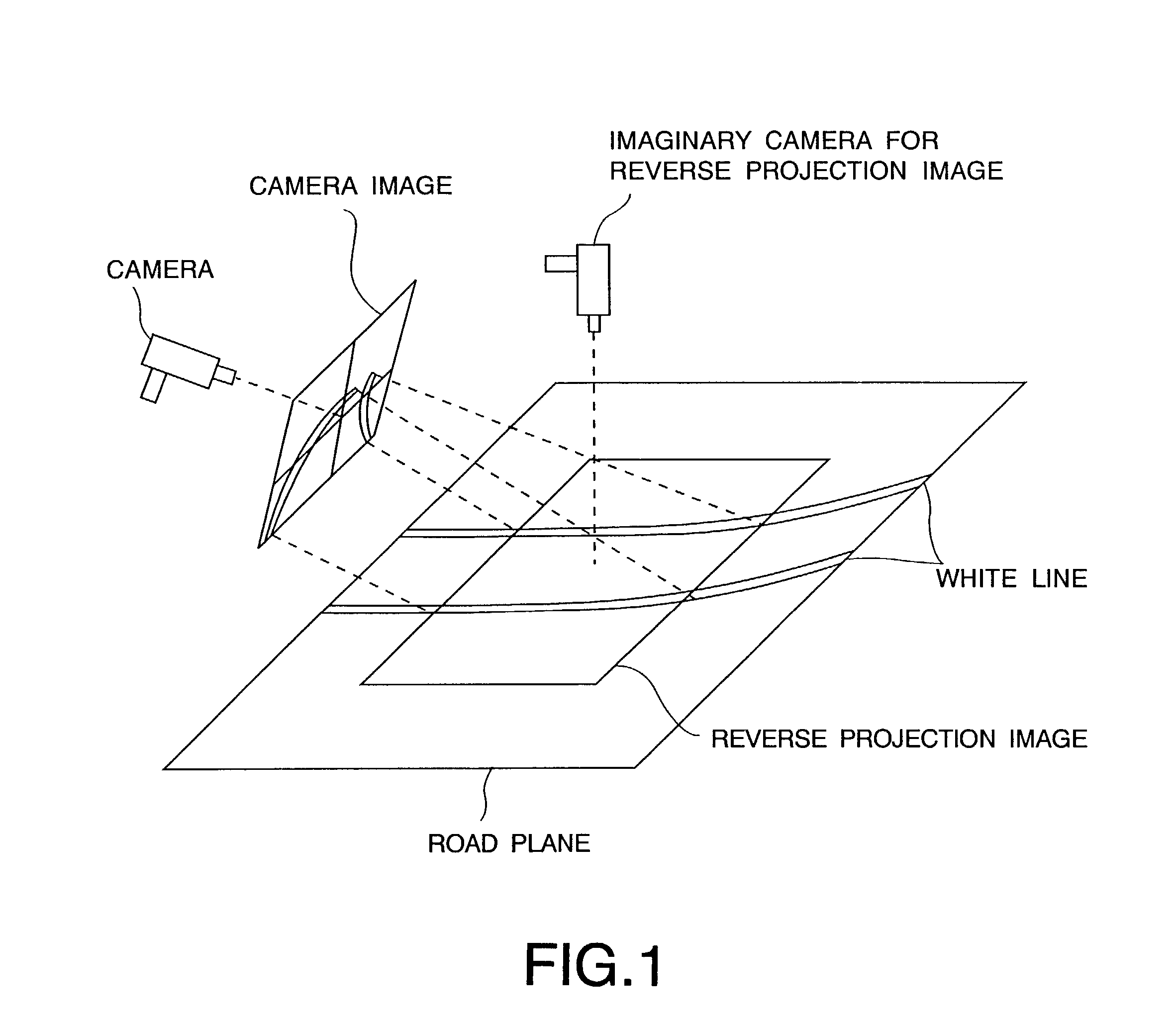
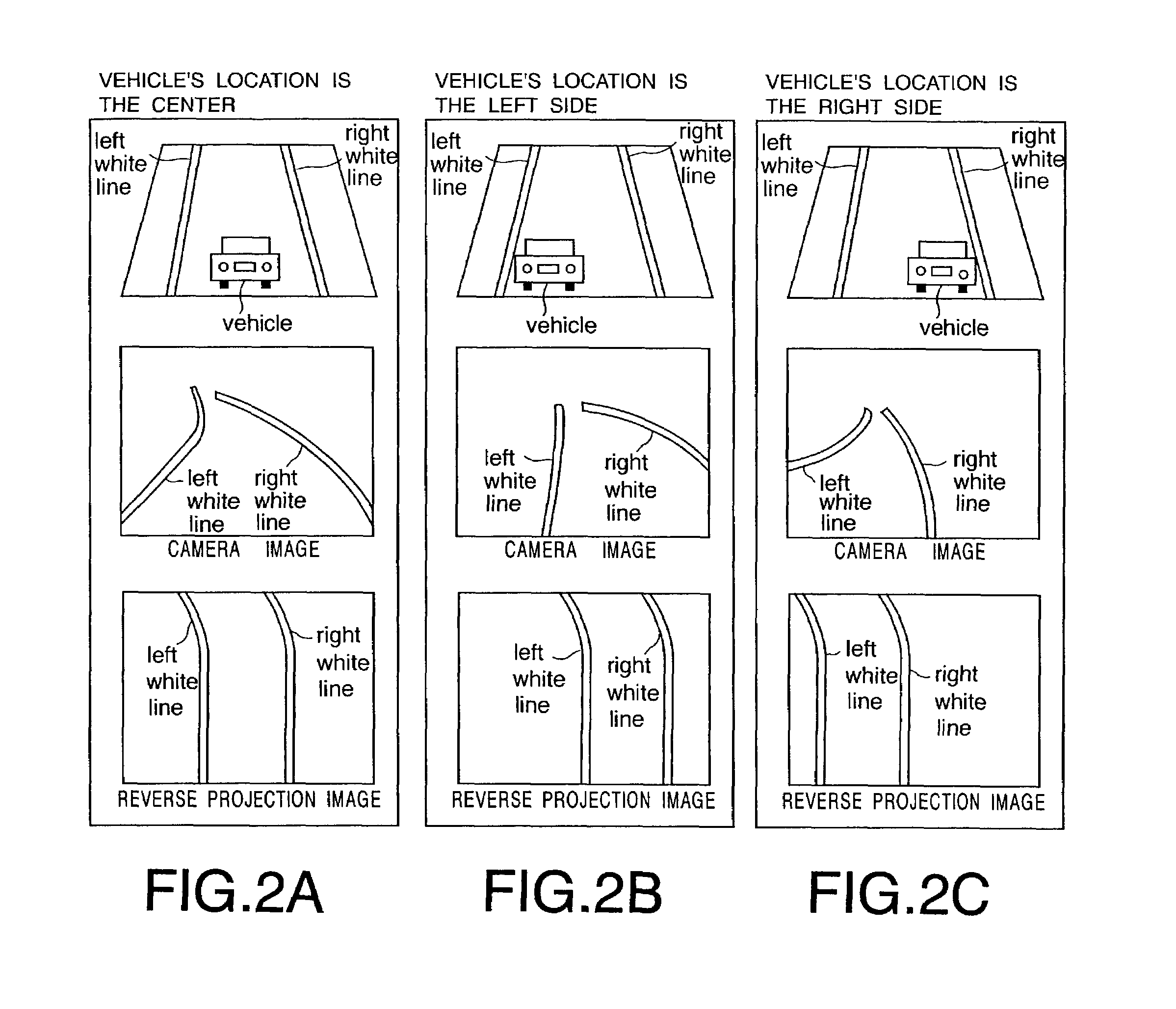
An image input unit inputs a plurality of images in a time series. Each input image includes a boundary line extending toward a vanishing point on a plane. A reverse projection image generation unit generates a reverse projection image of each input image by projecting information related to each input image onto the plane. A boundary line detection unit detects the boundary line from the reverse projection image by identifying a boundary line candidate on each reverse projection image.
Owner:KK TOSHIBA
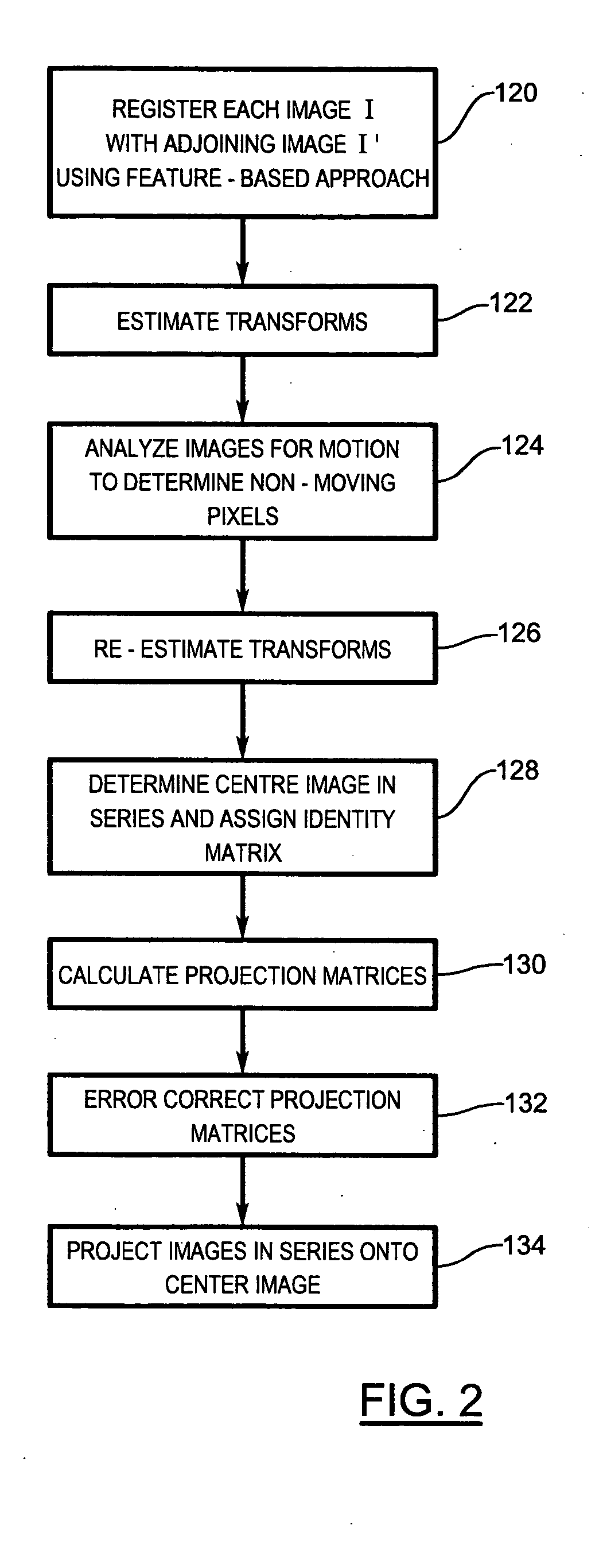
System and method for creating a panorama image from a plurality of source images
InactiveUS20050063608A1Fast and efficientTelevision system detailsImage enhancementProjection imagePanorama
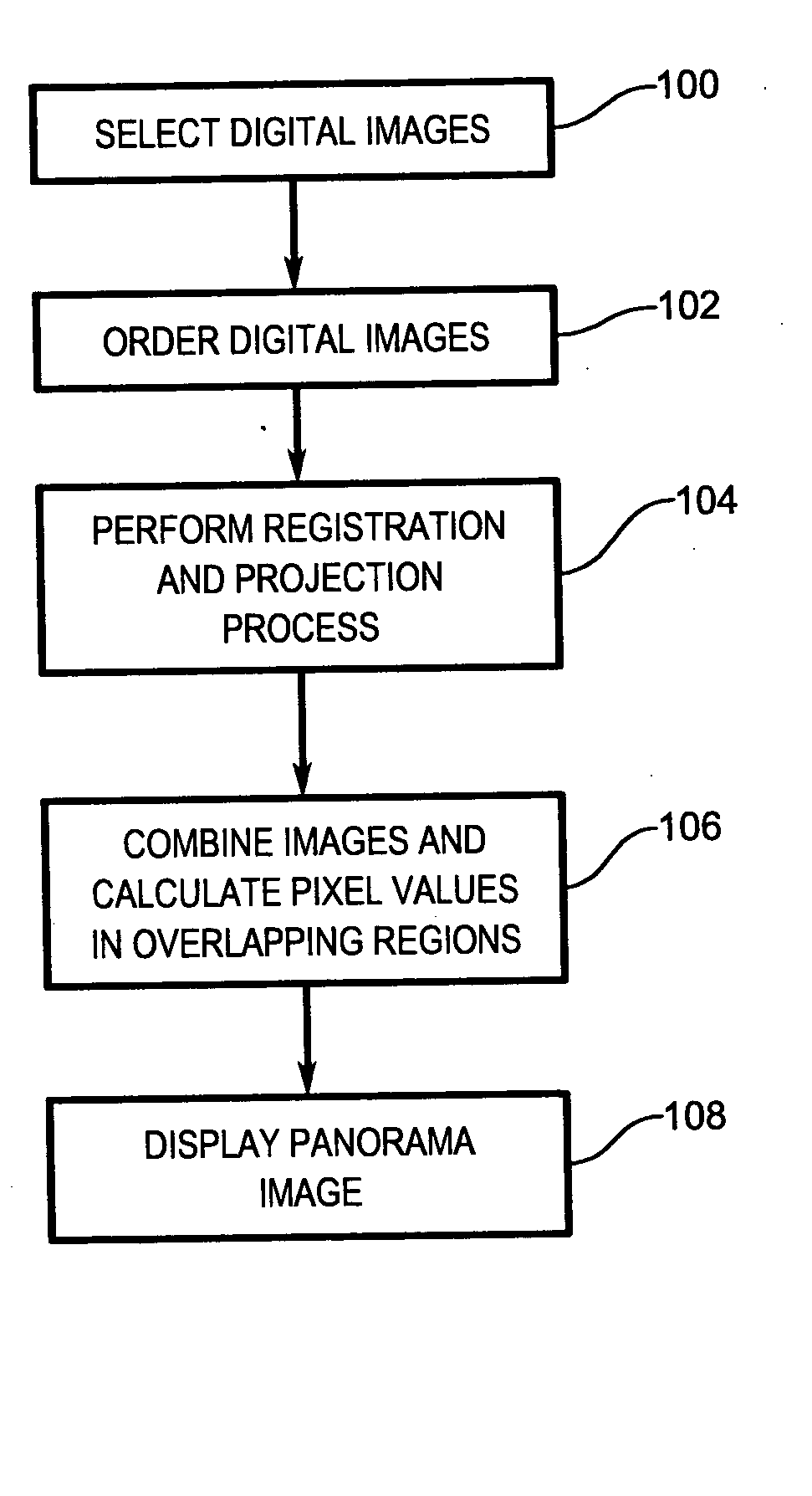
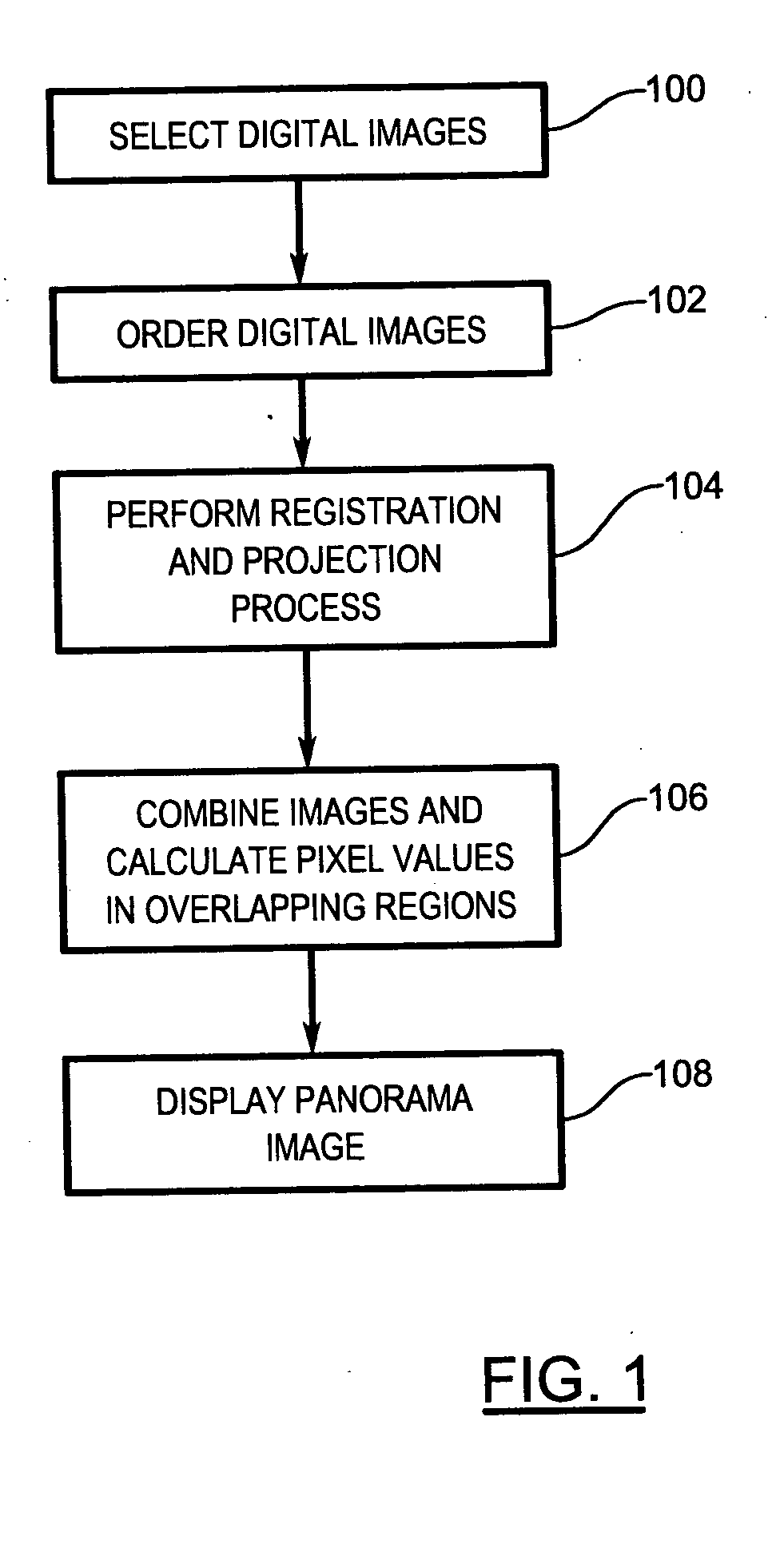
A system and method of creating a panorama image from a series of source images includes registering adjoining pairs of images in the series based on common features within the adjoining pairs of images. A transform between each adjoining pair of images is estimated using the common features. Each image is projected onto a designated image in the series using the estimated transforms associated with the image and with images between the image in question and the designated image. Overlapping portions of the projected images are blended to form the panorama image.
Owner:SEIKO EPSON CORP
Image handling and display in X-ray mammography and tomosynthesis
Owner:HOLOGIC INC
Method and apparatus for calibrating volumetric computed tomography systems
InactiveUS7016456B2Simplified determinationMaterial analysis using wave/particle radiationRadiation/particle handlingProjection imageX-ray
The present invention provides a method for determining a geometry of a scanning volumetric computed tomographic (CT) system having a rotation axis, a rotational plane, an x-ray source and a detector. The method includes scanning a phantom having a series of spatially separated discrete markers with the scanning volumetric computed tomographic system, wherein the markers are configured on a supporting structure of the phantom so as to permit separate identification of each marker in a collection of projection images. The method further includes locating images of the markers in each projection, using the located marker images to assign marker locations to tracks, and using the assigned tracks, determining a relative alignment between the detector, the source, and the rotation axis of the scanning volumetric computed tomographic system.
Owner:GE MEDICAL SYST GLOBAL TECH CO LLC
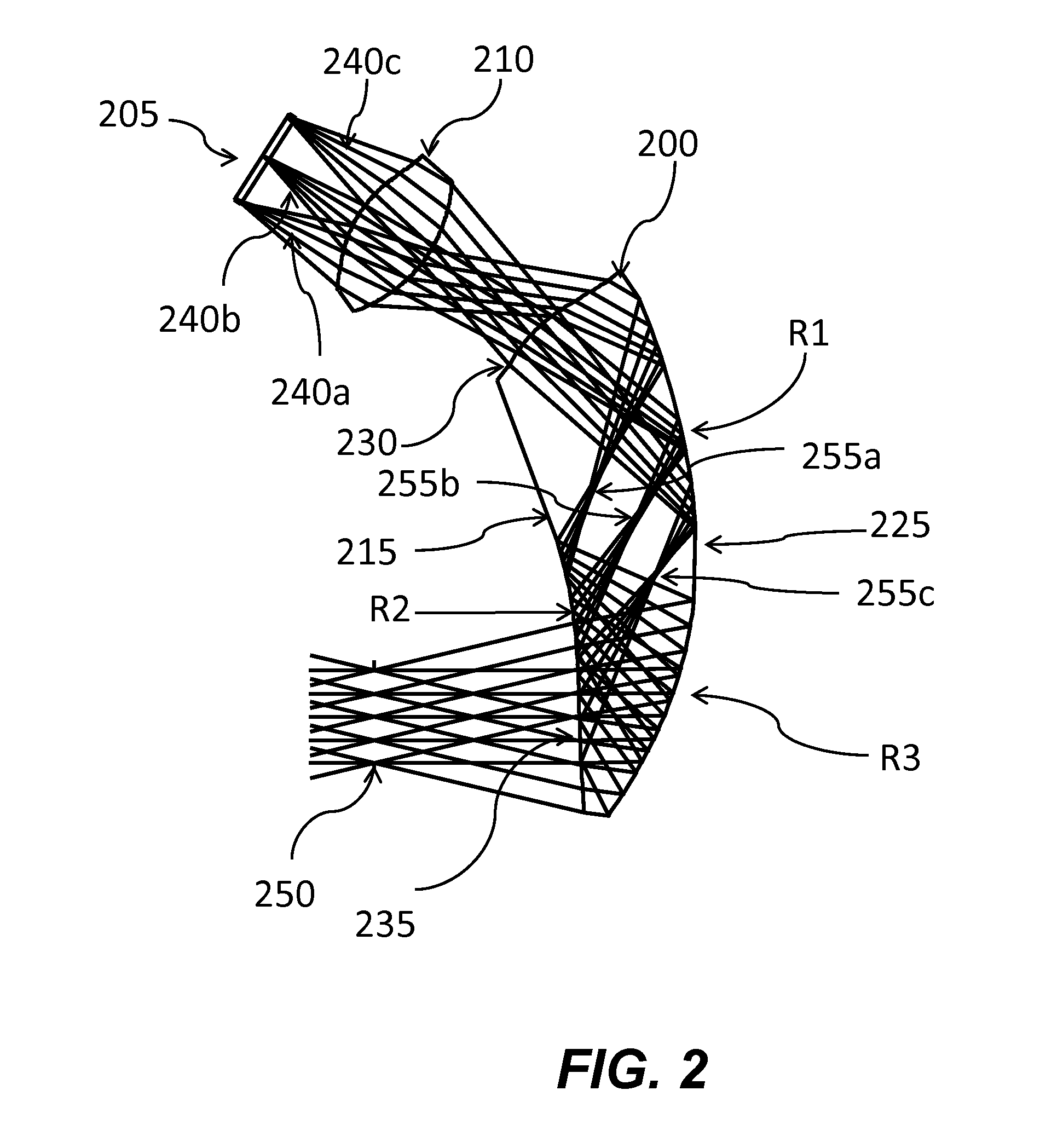
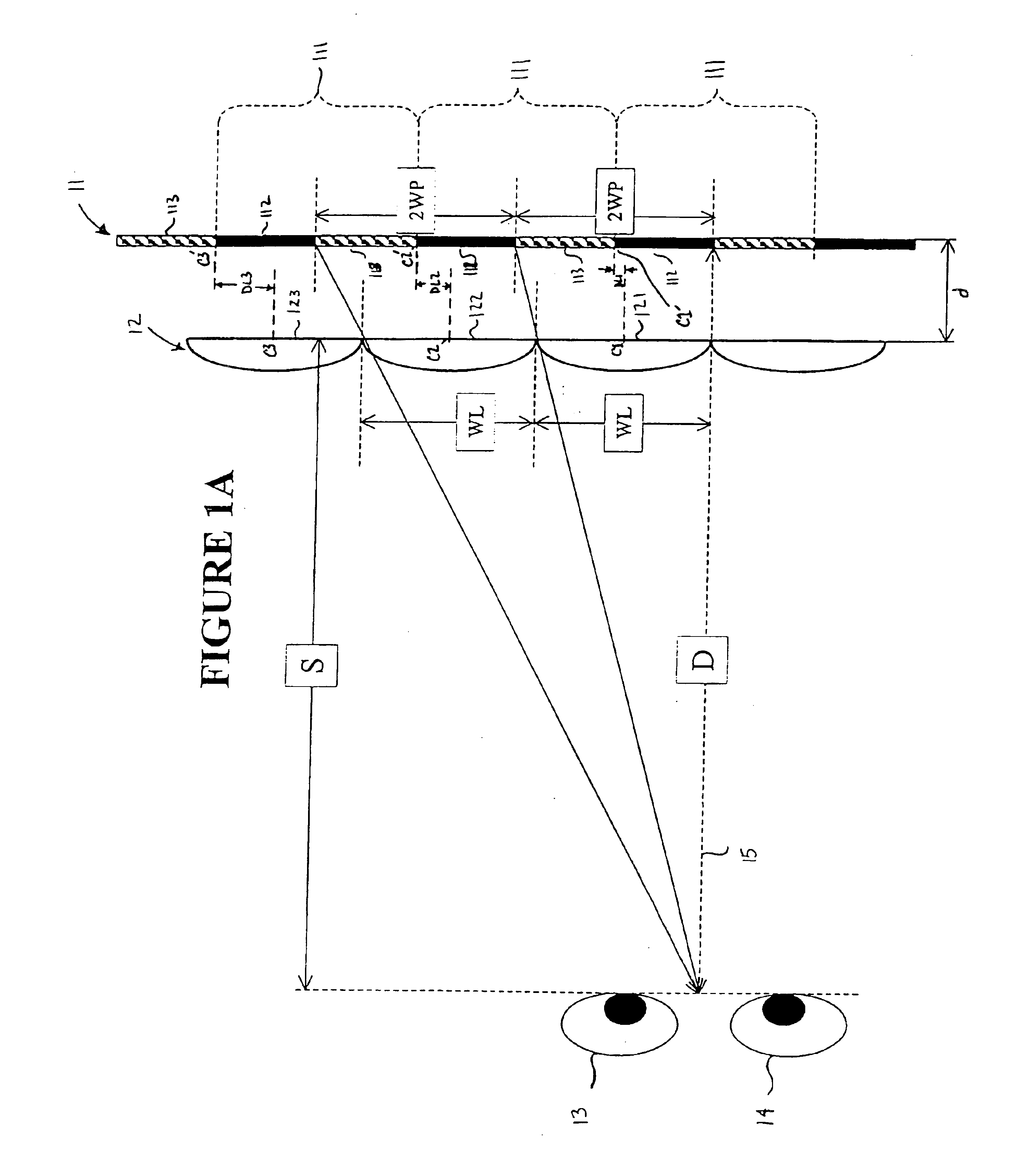
Autostereoscopic display
An autostereoscopic display and method of displaying multidimensional images involves a first lenticular array preferably of cylindrical lenses positioned between a viewer and a pixel array, and a second lenticular array also preferably of cylindrical lenses positioned between the first lenticular array and the viewer. The pixel array includes several pixel groups that project images through corresponding groups of first lenses within the first lenticular array. A pitch of the lenses within the second lenticular array differs from a pitch of the lenses in the first lens groups within the first lenticular array. The display can be manufactured or retrofit with the first and second lenticular arrays. By use of the first lenticular array, light from plural color pixels may be focussed to a single point so that color subpixels arranged in a direction transverse to the direction of the cylindrical lenses of the first lenticular array may be focussed to a single point on the secondary lenticular array and then as a single image to the user.
Owner:MEMS OPTICAL
Methods and apparatus for back-projection and forward-projection
ActiveUS20050152590A1Few computational resourceAddressing slow performanceReconstruction from projectionMaterial analysis using wave/particle radiationVoxelProjection image
The invention provides improvements in reconstructive imaging of the type in which a volume is reconstructed from a series of measured projection images (or other two-dimensional representations) generated by projection of a point x-ray source (or other radiation source), positioned at a distinct focus, through the volume to a plane at which the respective projection image is acquired (“detector plane”). In one aspect, the improvements are with respect to back-projecting a two-dimensional representation lying in the detector plane (representing, for example, a difference between an originally-acquired measured projection image and a subsequently-generated estimate thereof) to generate three-dimensional representation (which can be used, for example, to update an estimate of the volume). According to this aspect, for each of one or more slices of the 3D representation parallel to the projection plane and for each distinct focus at which a projection is generated, the following steps are performed in connection with the back-projection: (i) warping the first 2D representation to generate a second 2D representation by applying to the first 2D representation a selected linear mapping, where that selected linear mapping would map, in order to match dimensions of the respective slice within the 3D representation, a region defined by projection, at the respective focus, of comers of that slice onto the detector plane, and (ii) incrementing values of each of one or more voxels of the respective slice by an amount that is a function of a value of a correspondingly indexed pixel of the second 2D representation. A related aspect provides improvements with respect to forward-projecting, as well as in iterative (and non-iterative) methodologies that incorporate both back-projection and forward-projection.
Owner:PME IP
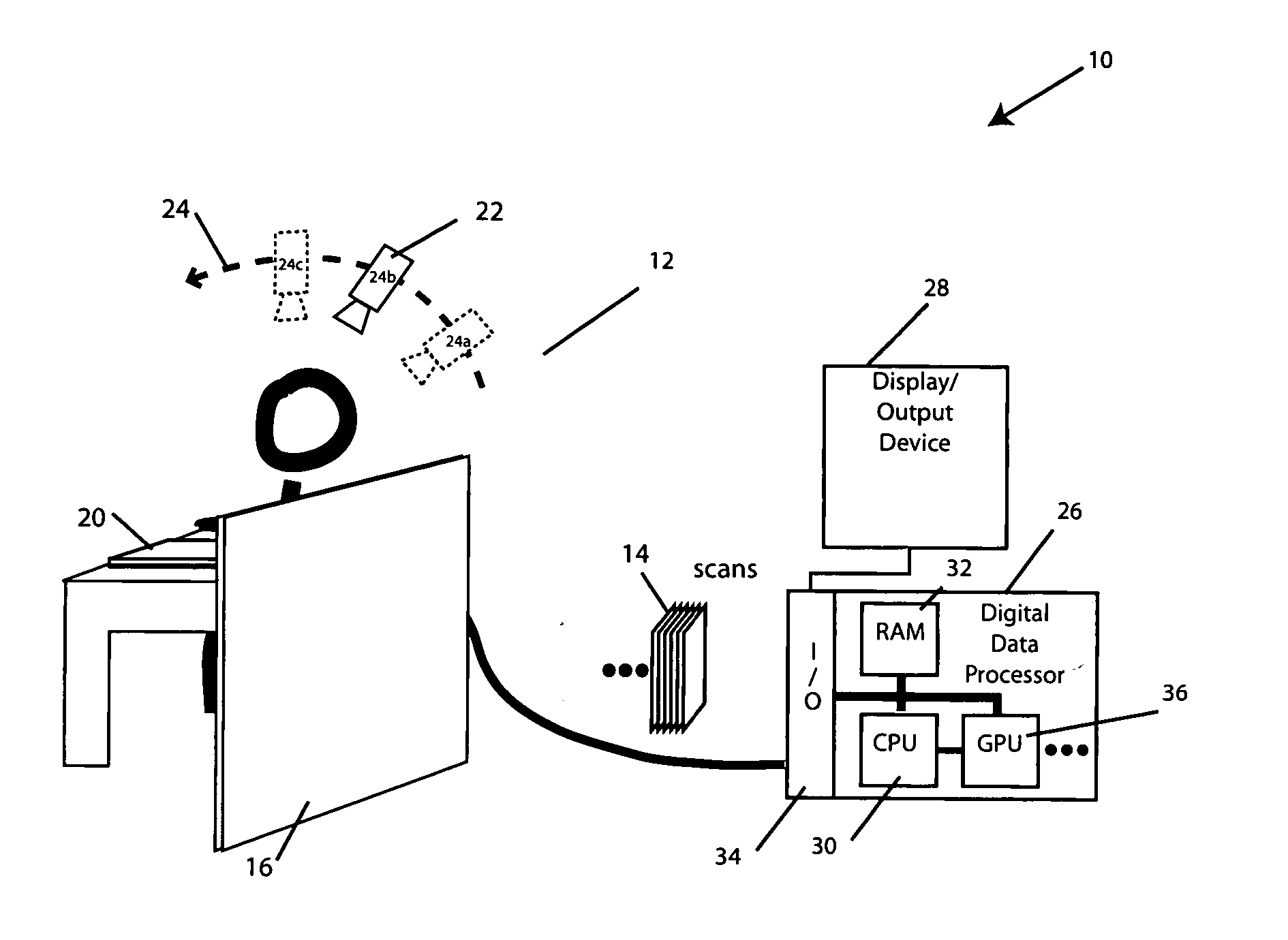
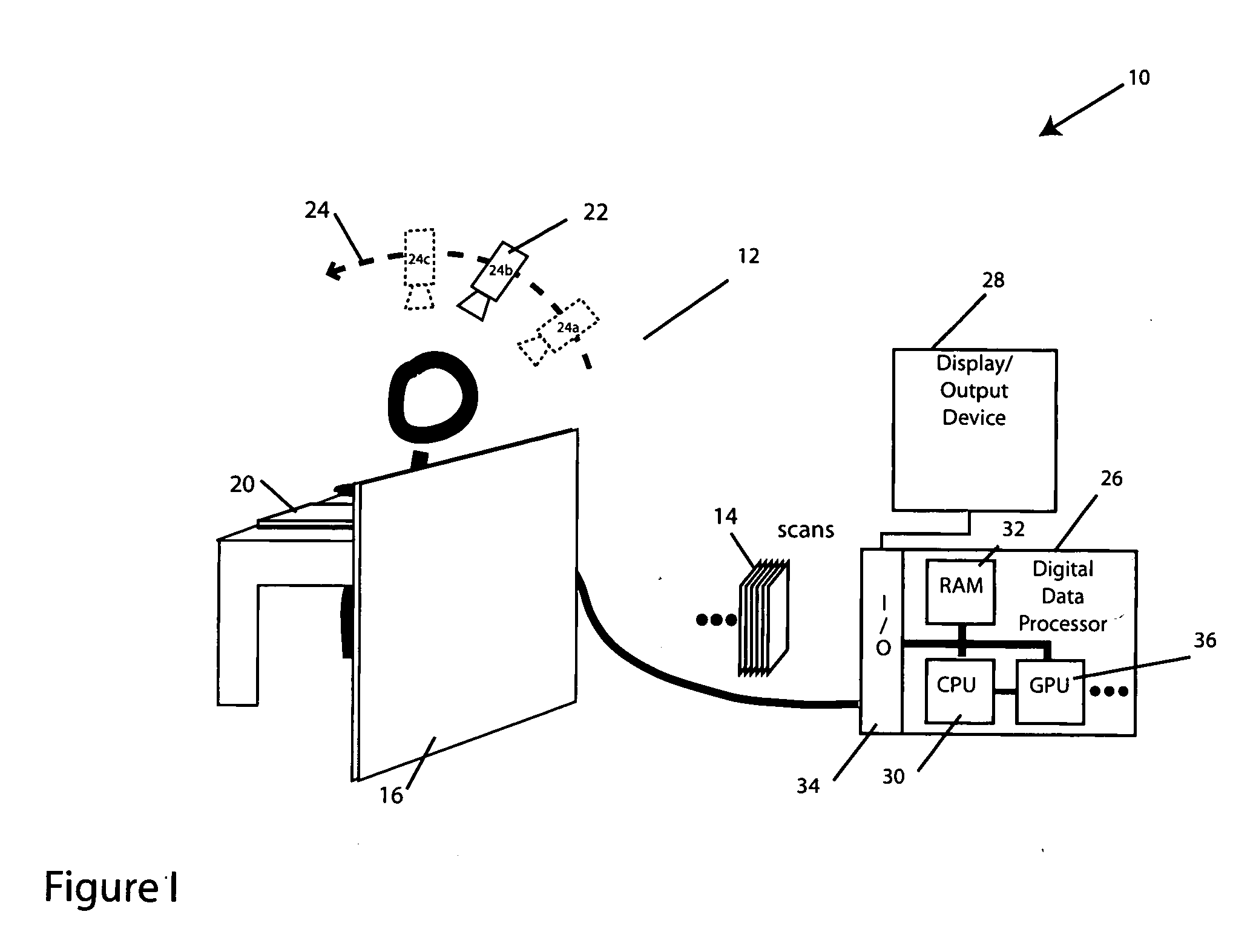
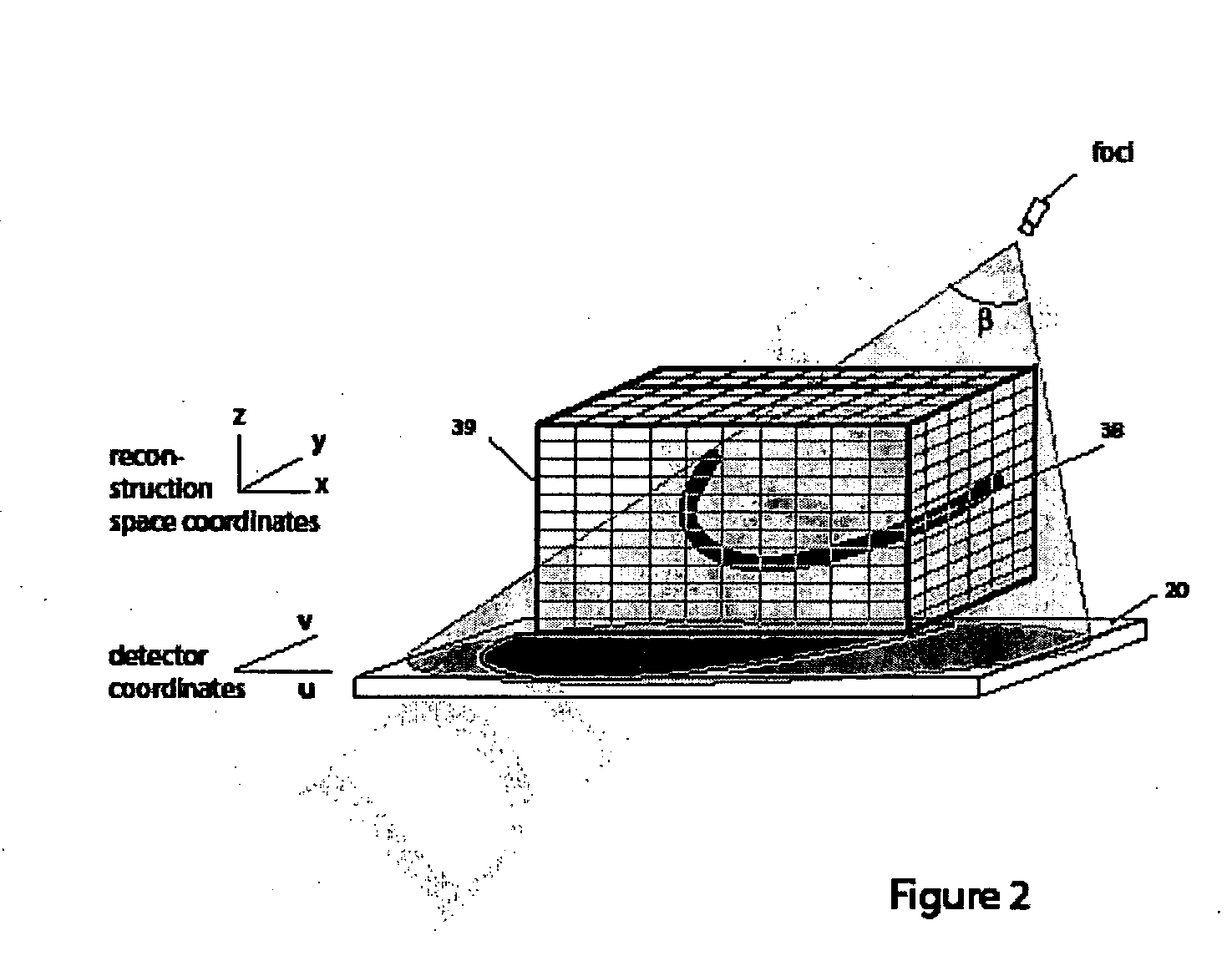
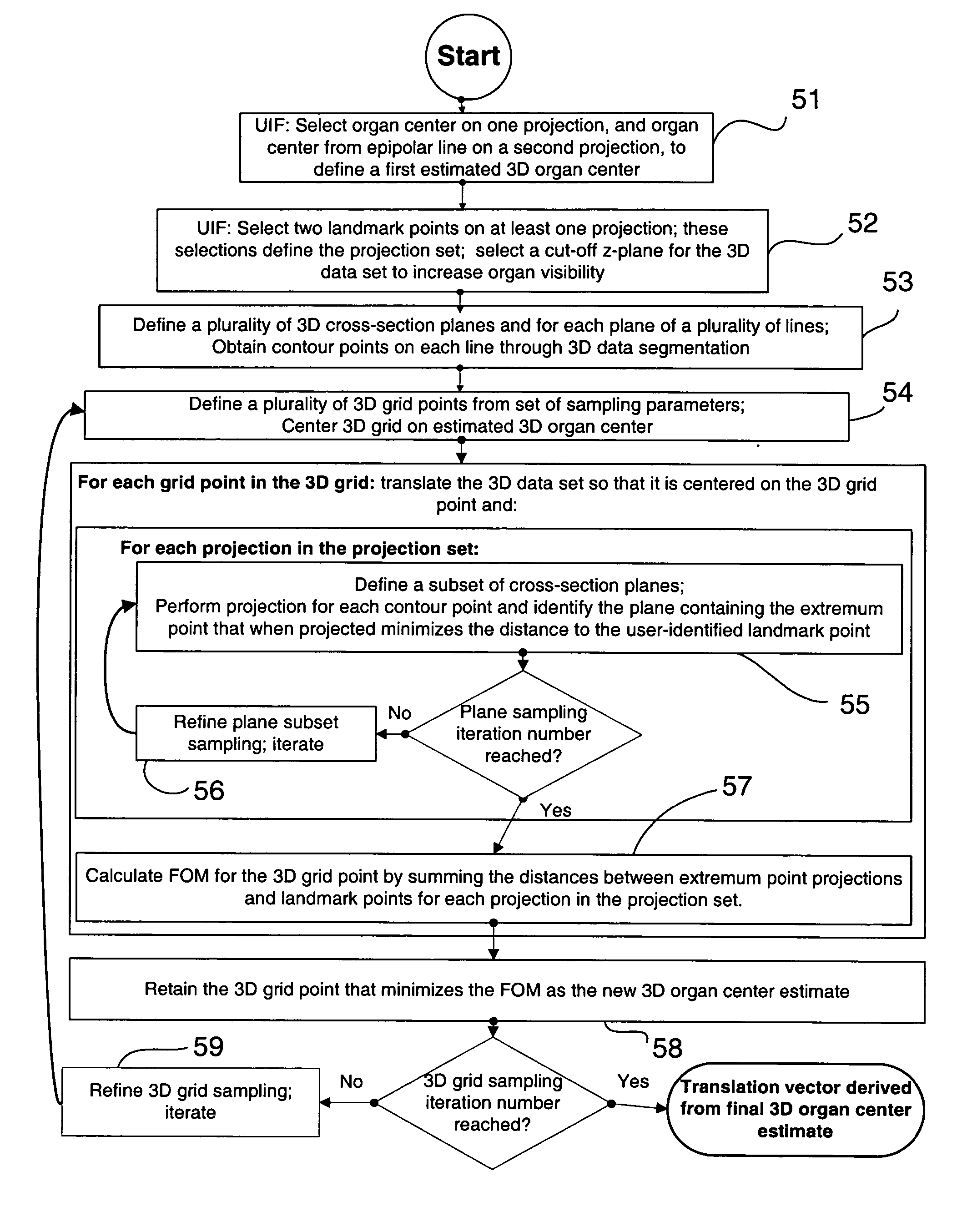
Registration of three dimensional image data with patient in a projection imaging system
A method for determining a translation of a three-dimensional pre-operative image data set to obtain a registration of the three-dimensional image data with a patient positioned in a projection imaging system. In one embodiment the user identifies an initial three-dimensional organ center from projections and extreme contour landmark points of the object on a set of projections. A set of contour points for the image object in each of a plurality of three-dimensional cross-section planes; is obtained and the points projecting nearest to the user-identified landmark points are selected. A three-dimensional grid having a predetermined number of intervals at a predetermined interval spacing centered at the user-identified organ center is defined. The three-dimensional image data contour points as centered onto each grid point are projected for evaluation and selection of the grid point leading to contour points projecting nearest to the user-identified landmark points. This selection leads to the iterative definition of a series of improved estimated three-dimensional organ centers, and associated translation vectors. Registration of a three dimensional image data to the patient positioned in a projection imaging system will allow, among other things, overlay of a visual representation of a pre-operative image object onto a projection image plane that can serve as a visual tool and a surgical navigation aid. In particular, the position and orientation of a medical device can be shown with respect to the three-dimensional image data and thus enable quicker, safer, and less invasive navigation of the medical device to and within an organ of interest.
Owner:STEREOTAXIS
Method, device, and system for computing a spherical projection image based on two-dimensional images
InactiveUS20140340427A1Television system detailsImage enhancementComputer graphics (images)Three-dimensional space
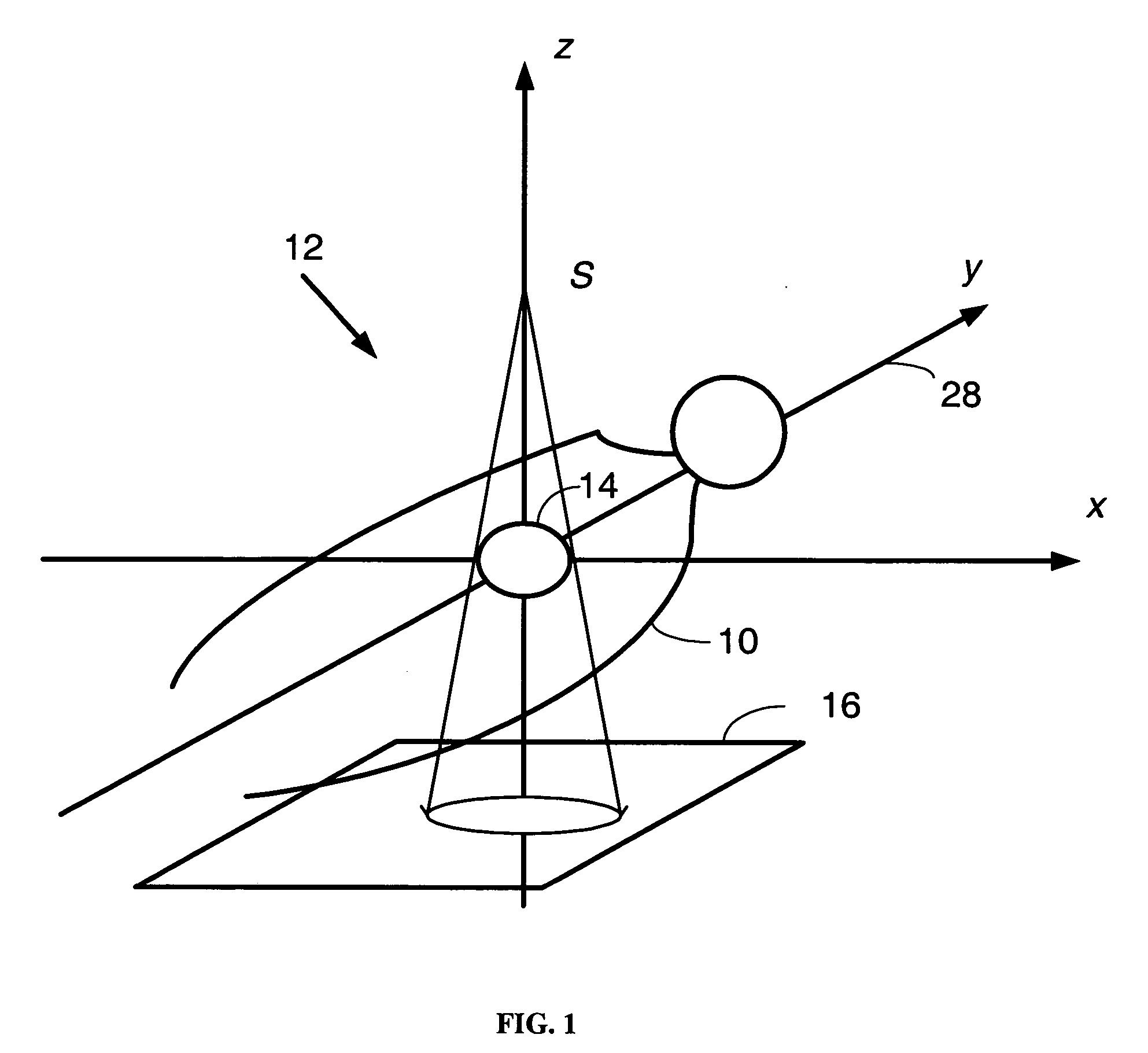
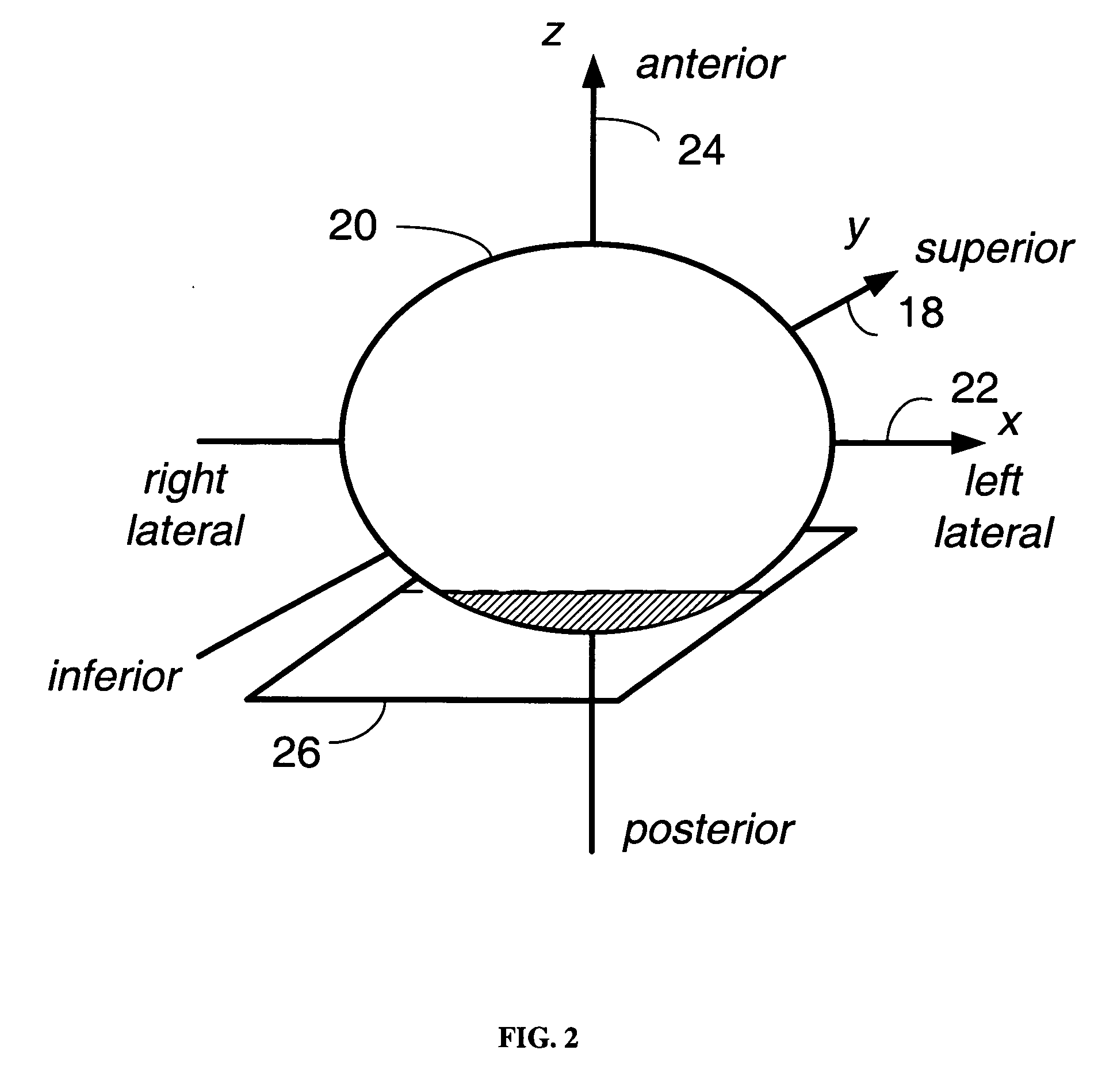
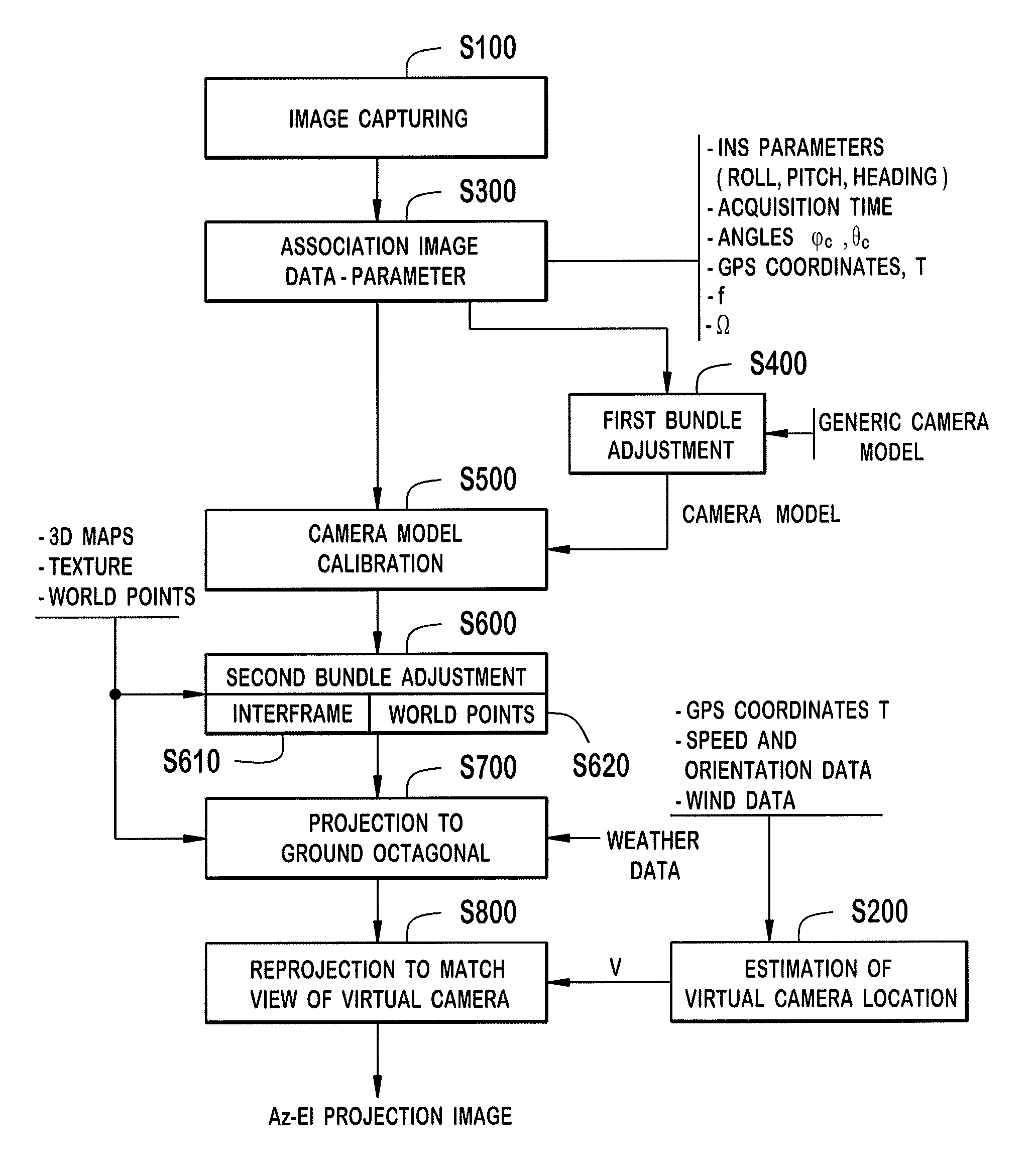
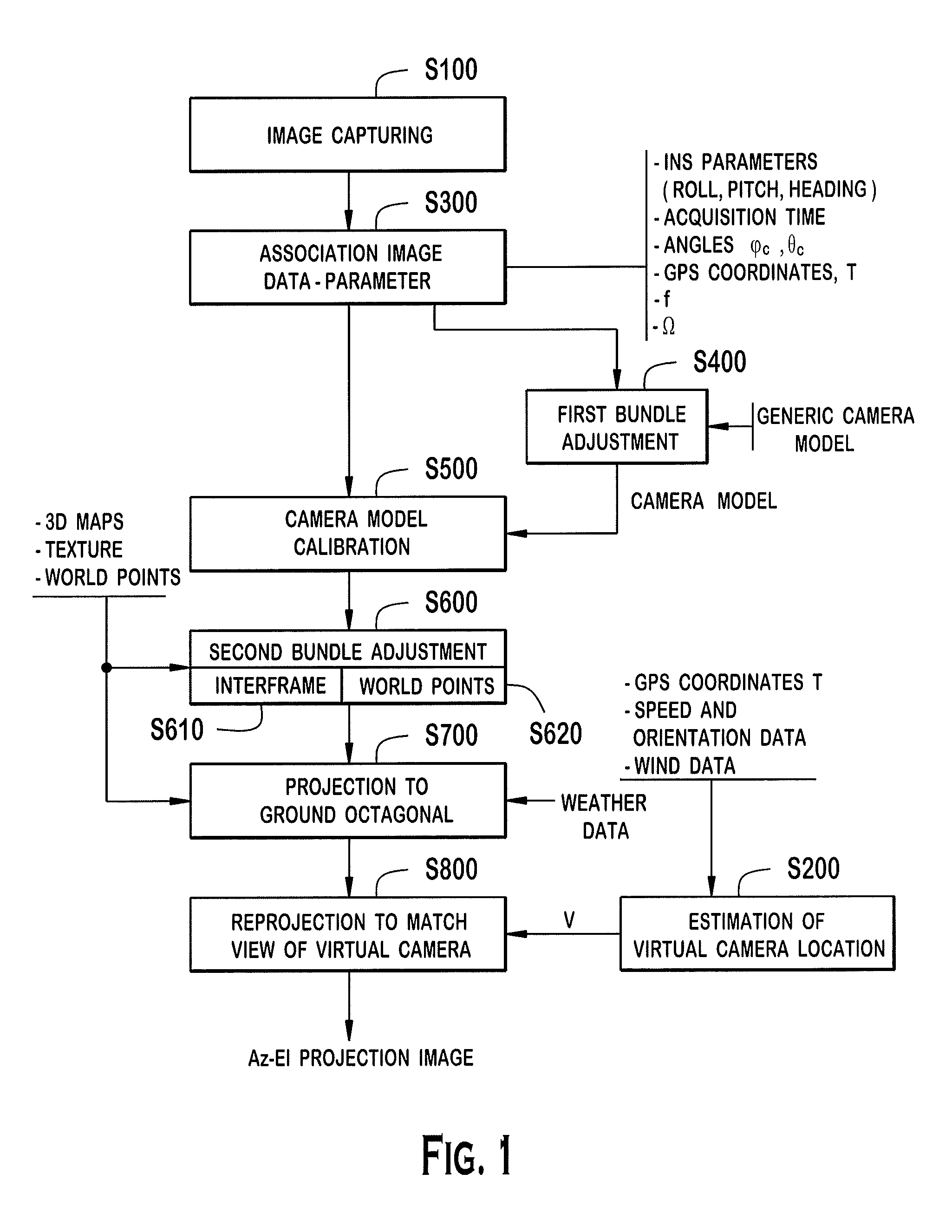
An image projection method for generating a panoramic image, the method including the steps of accessing images that were captured by a camera located at a source location, and each of the images being captured from a different angle of view, the source location being variable as a function of time, calibrating the images collectively to create a camera model that encodes orientation, optical distortion, and variable defects of the camera; matching overlapping areas of the images to generate calibrated image data, accessing a three-dimensional map, first projecting pixel coordinates of the calibrated image data into a three-dimensional space using the three-dimensional map to generate three-dimensional pixel data, and second projecting the three-dimensional pixel data to an azimuth-elevation coordinate system that is referenced from a fixed virtual to generate the panoramic image.
Owner:LOGOS TECH
Contrast-enhanced cone beam X-ray imaging, evaluation, monitoring and treatment delivery
ActiveUS20070269000A1Material analysis using wave/particle radiationRadiation/particle handlingVoxelData set
A method of imaging a patient's uncompressed region of interest using X-ray cone beam computed tomography or cone beam digital tomography comprises the step of introducing an effective amount of a contrast agent to the uncompressed region of interest. A system for imaging a patient's uncompressed region of interest using cone beam computed tomography (CBCT) or cone beam digital tomography (CBDT) comprises an X-ray source transmitting an X-ray to the uncompressed region of interest, an image acquisition system acquiring a plurality of two-dimensional projection images data for a CBCT or CBDT data set with at least one of the projection images acquired in 35 milliseconds or less, and a processor generating a three-dimensional computed tomography image data set resolving voxels with dimensions of 0.4 mm or less in at least two orthogonal directions.
Owner:VARIAN MEDICAL SYSTEMS +2
3D image acquisition apparatus and 3D image acquisition method
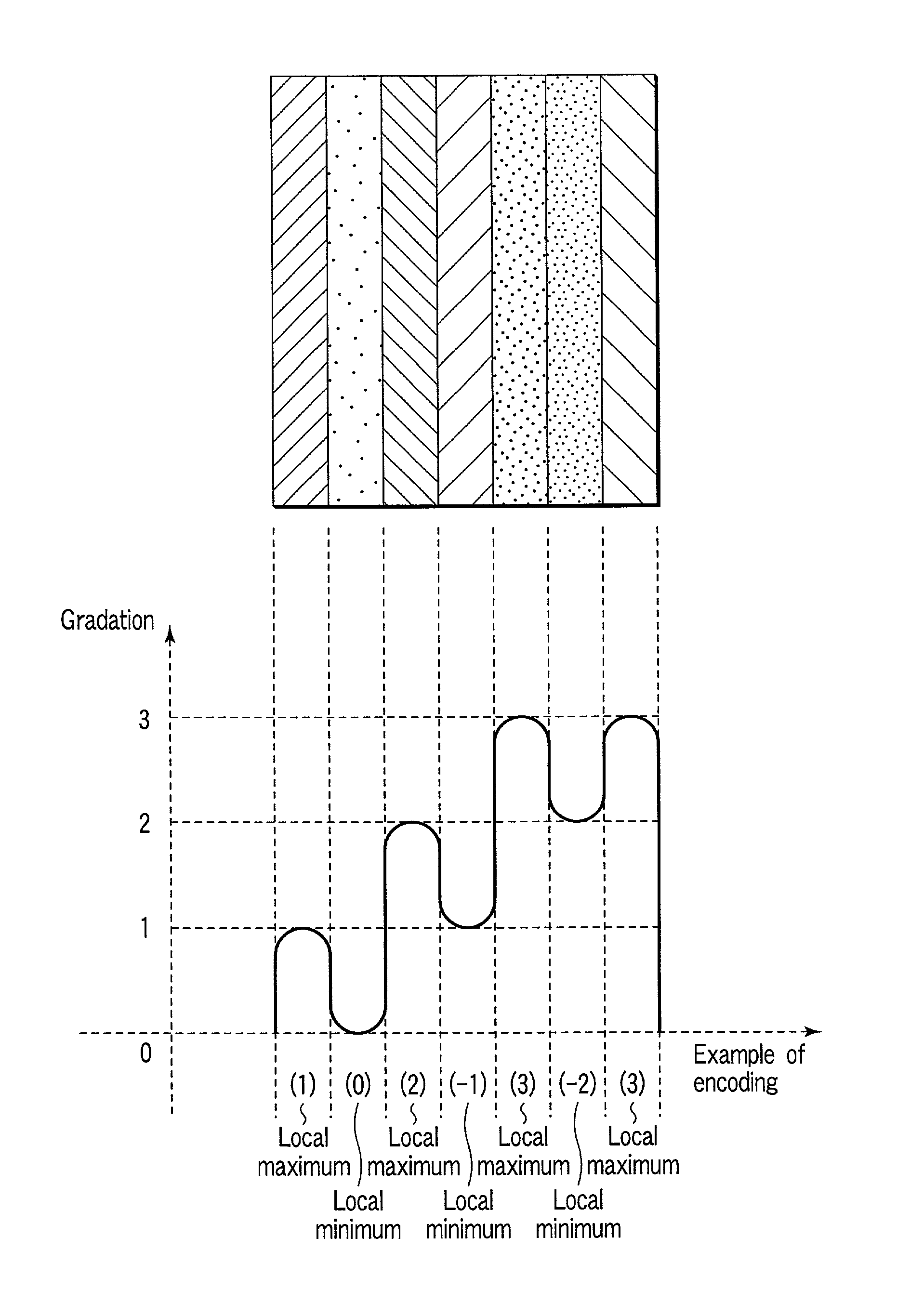
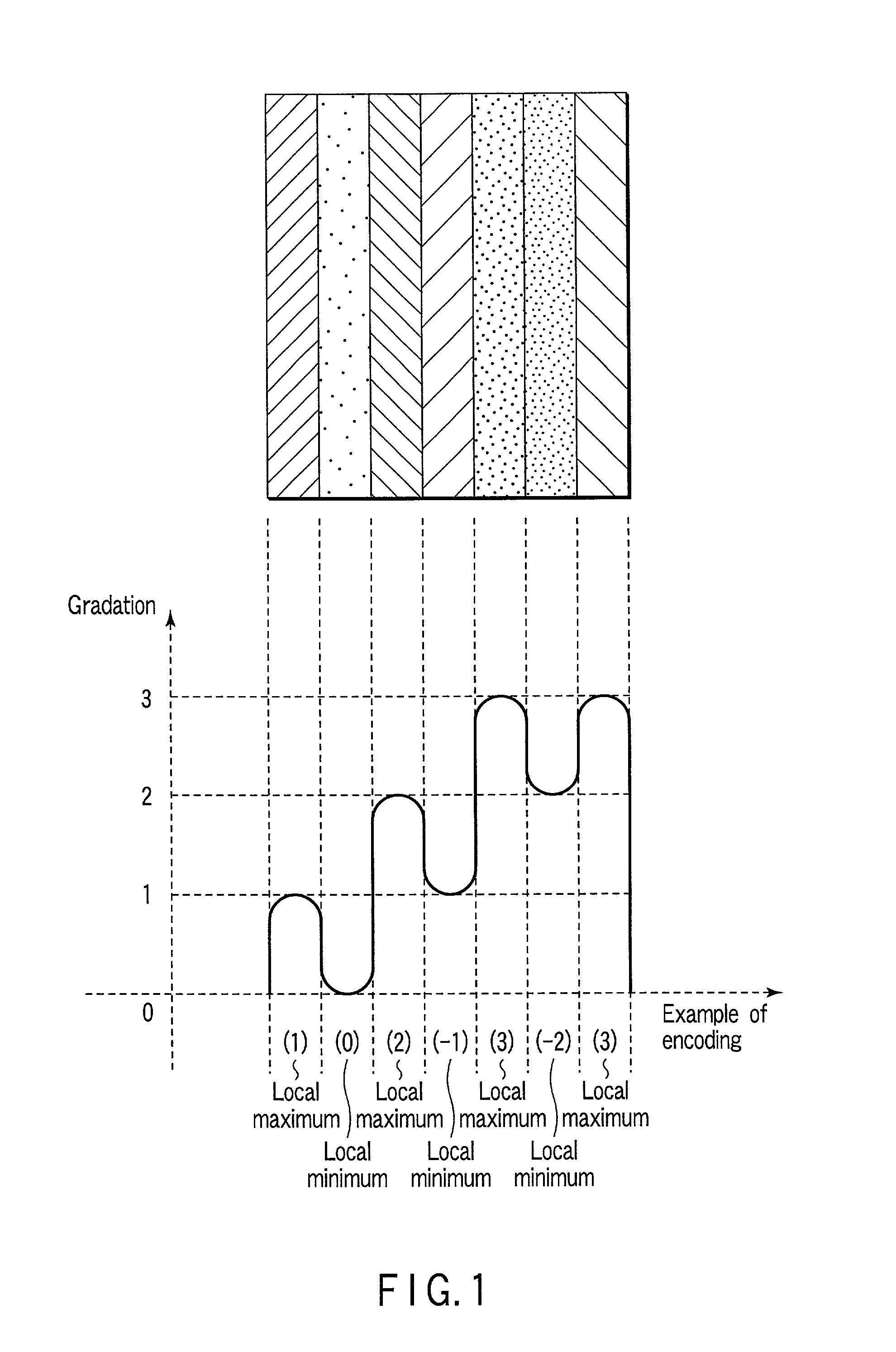
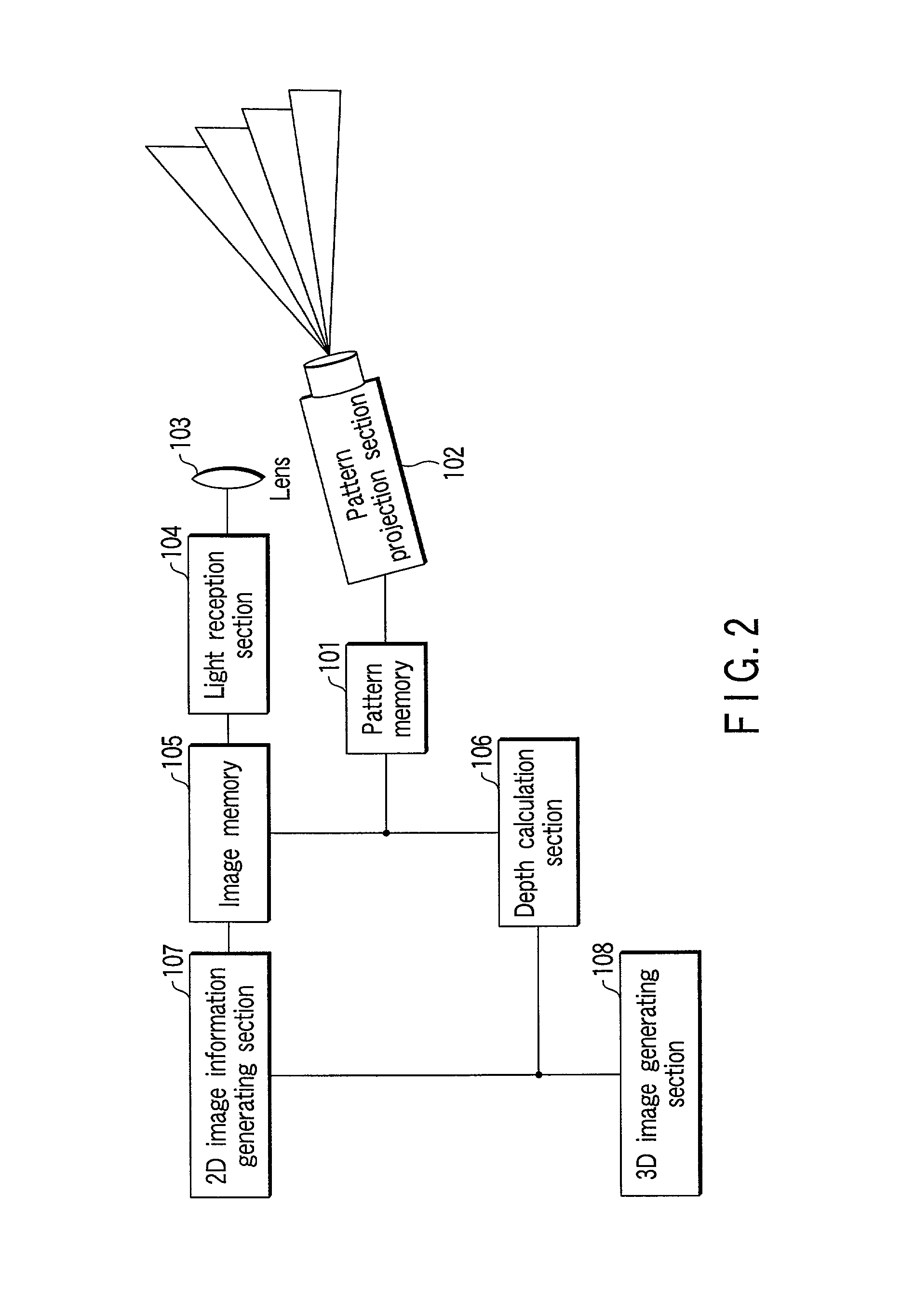
A 3D image acquisition apparatus comprises a pattern projection section which projects a pattern on an object to be measured, an imaging section which is disposed at a distance from the pattern projection section and images the object on which the pattern has been projected, and a depth calculation section which detects the projection pattern projected on the object on the basis of an image acquired by the imaging section, collates the detected pattern and the projected pattern, and calculates a depth of respective parts of the object on the basis of the correspondency of the collation. The projected pattern is stripes / matrix formed by alternately arranging areas with local maximum / minimum luminance values. Thus, stripes / matrix boundaries can be exactly extracted from the pattern projection image, and correct decoding is performed from the encoded projection image even where the object is not a white-based color one or a low-saturation color one.
Owner:OLYMPUS CORP
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com