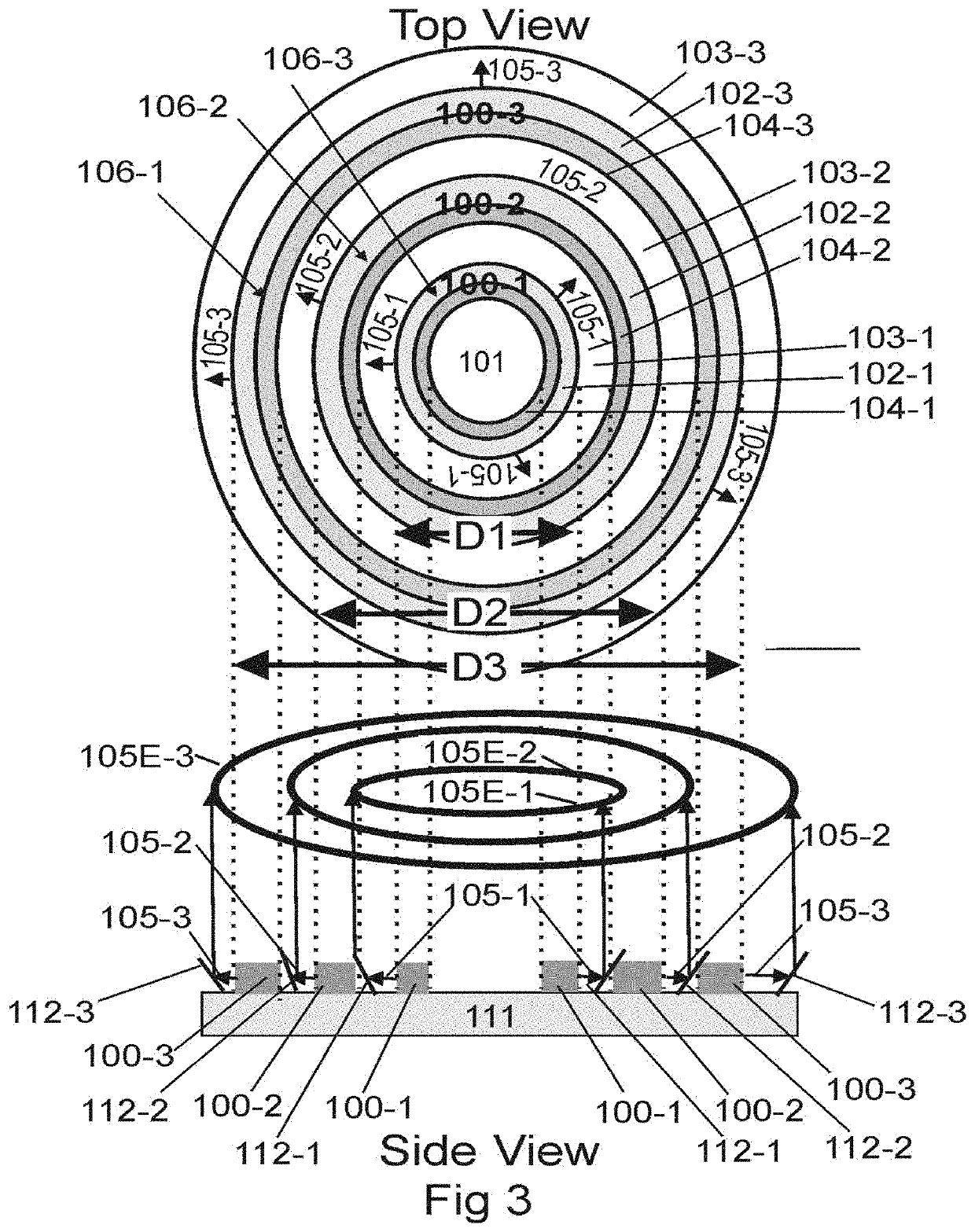
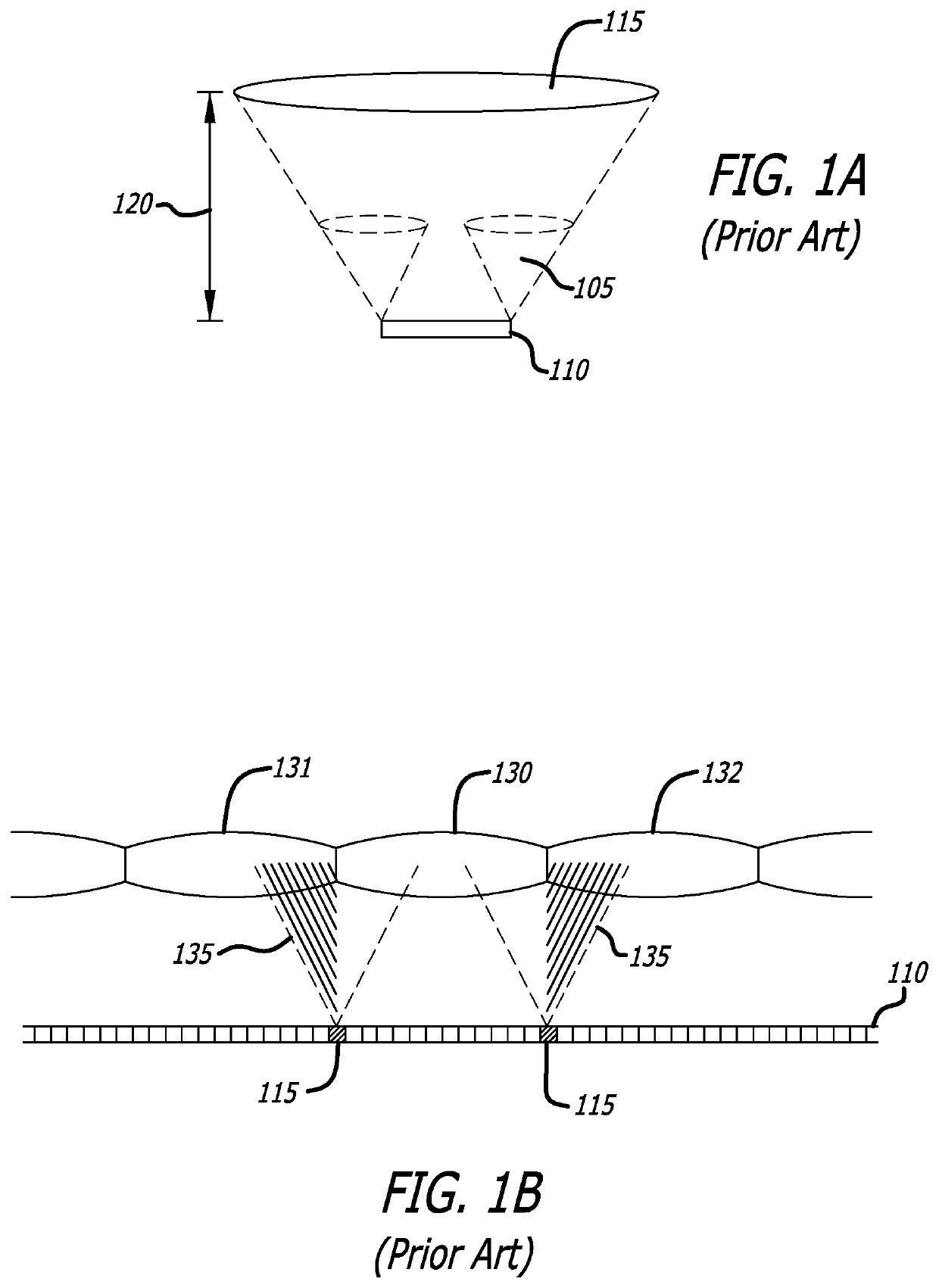
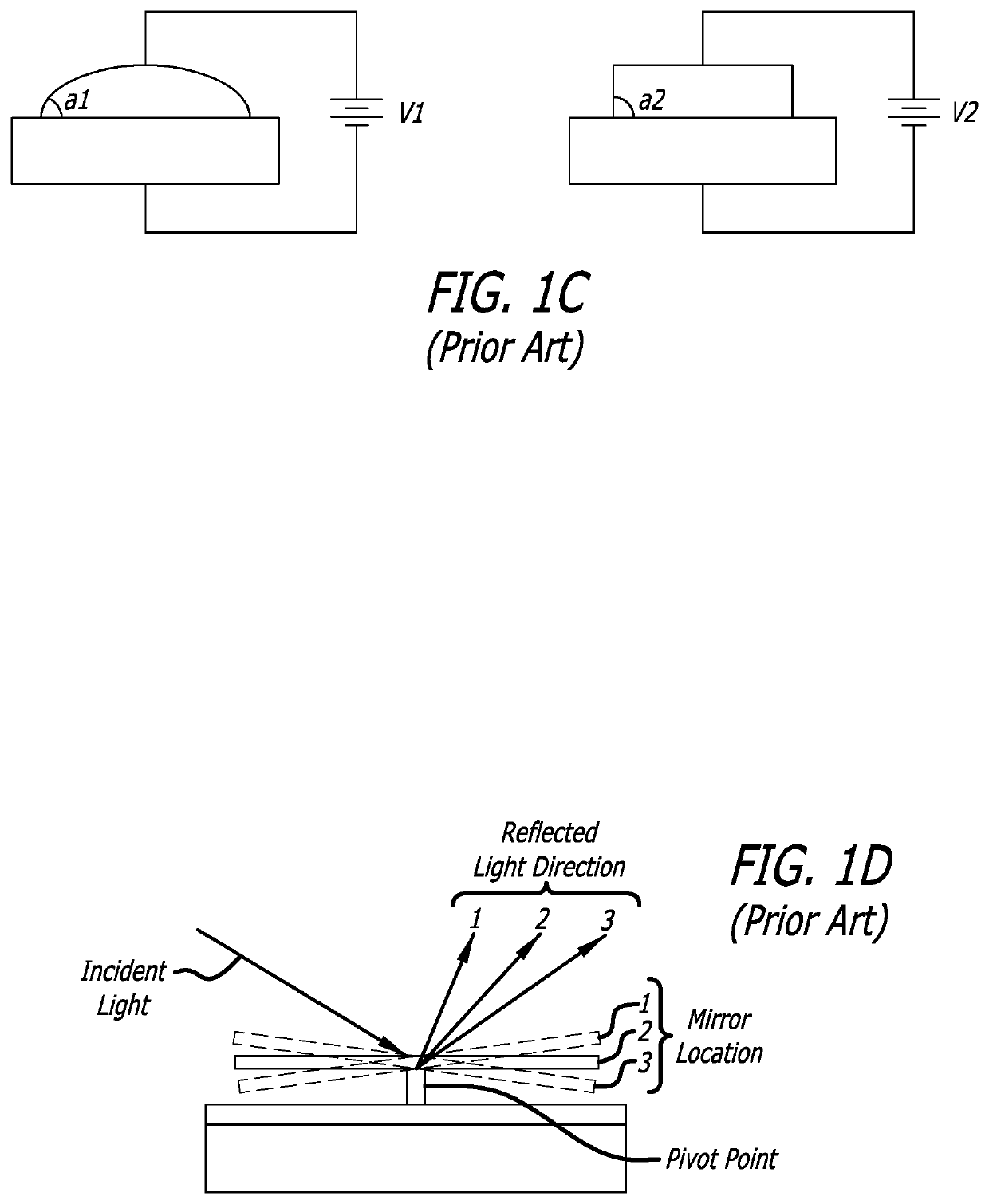
Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
73 results about "Waveguide (optics)" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
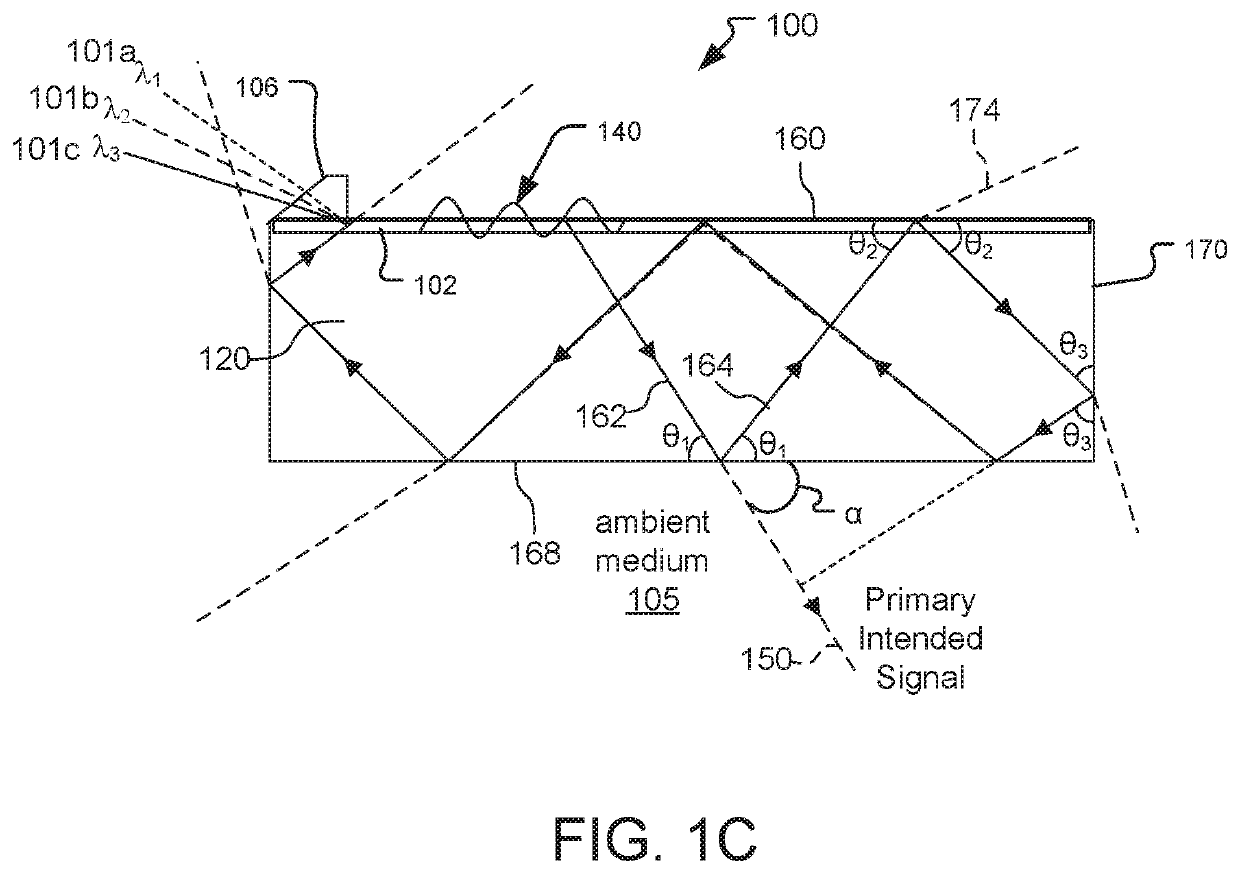
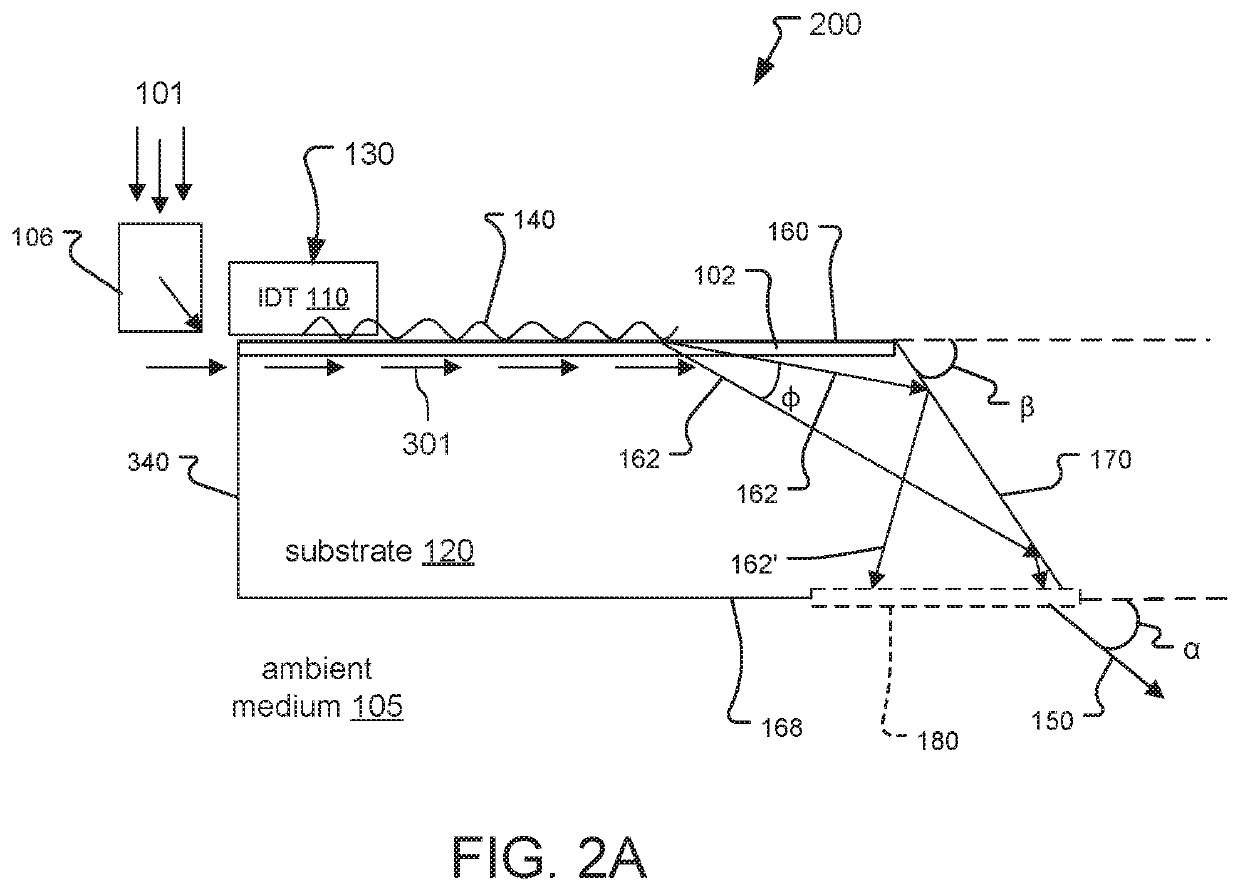
An optical waveguide is a physical structure that guides electromagnetic waves in the optical spectrum. Common types of optical waveguides include optical fiber and rectangular waveguides. Optical waveguides are used as components in integrated optical circuits or as the transmission medium in local and long haul optical communication systems.
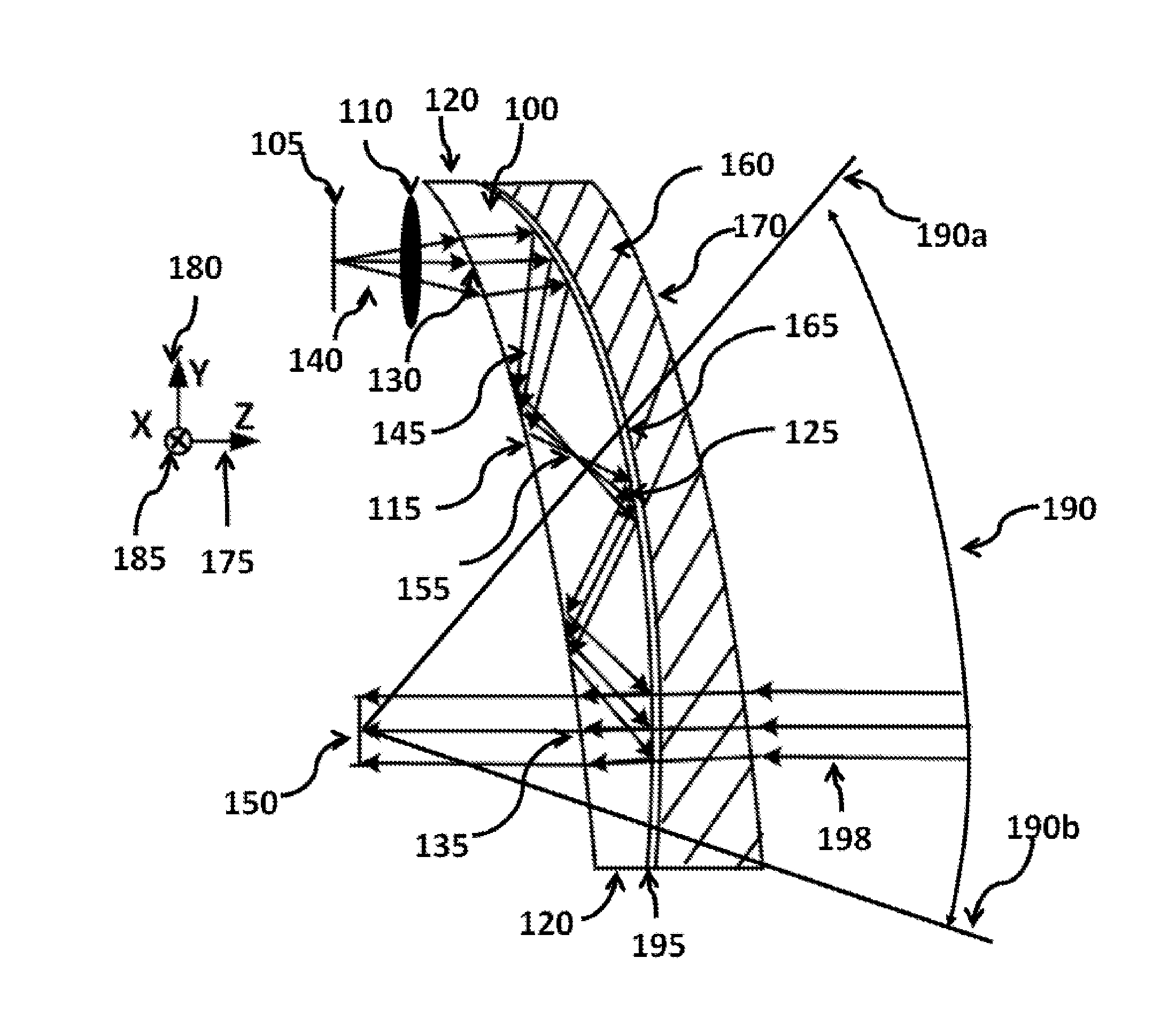
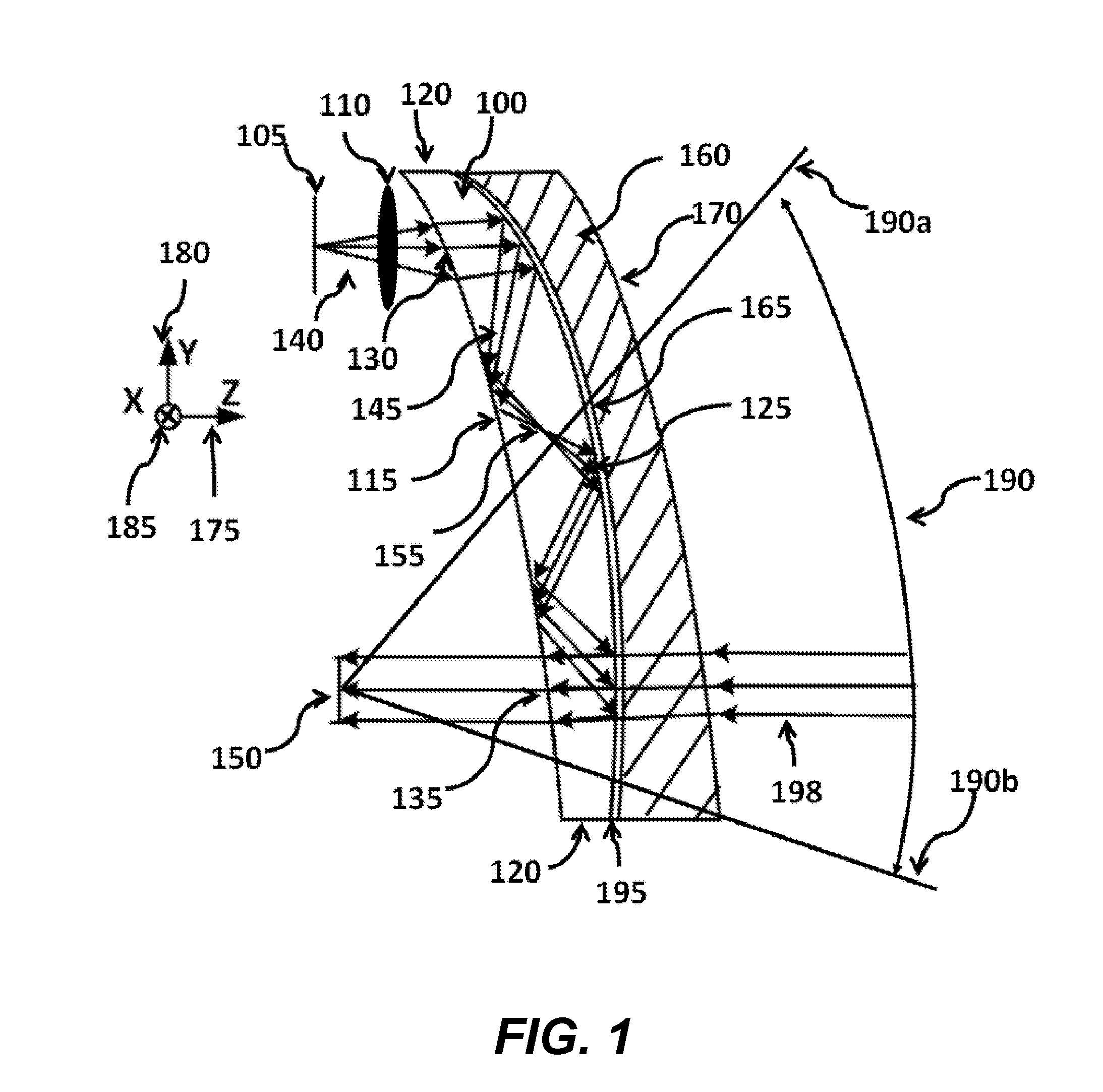
Ergonomic head mounted display device and optical system
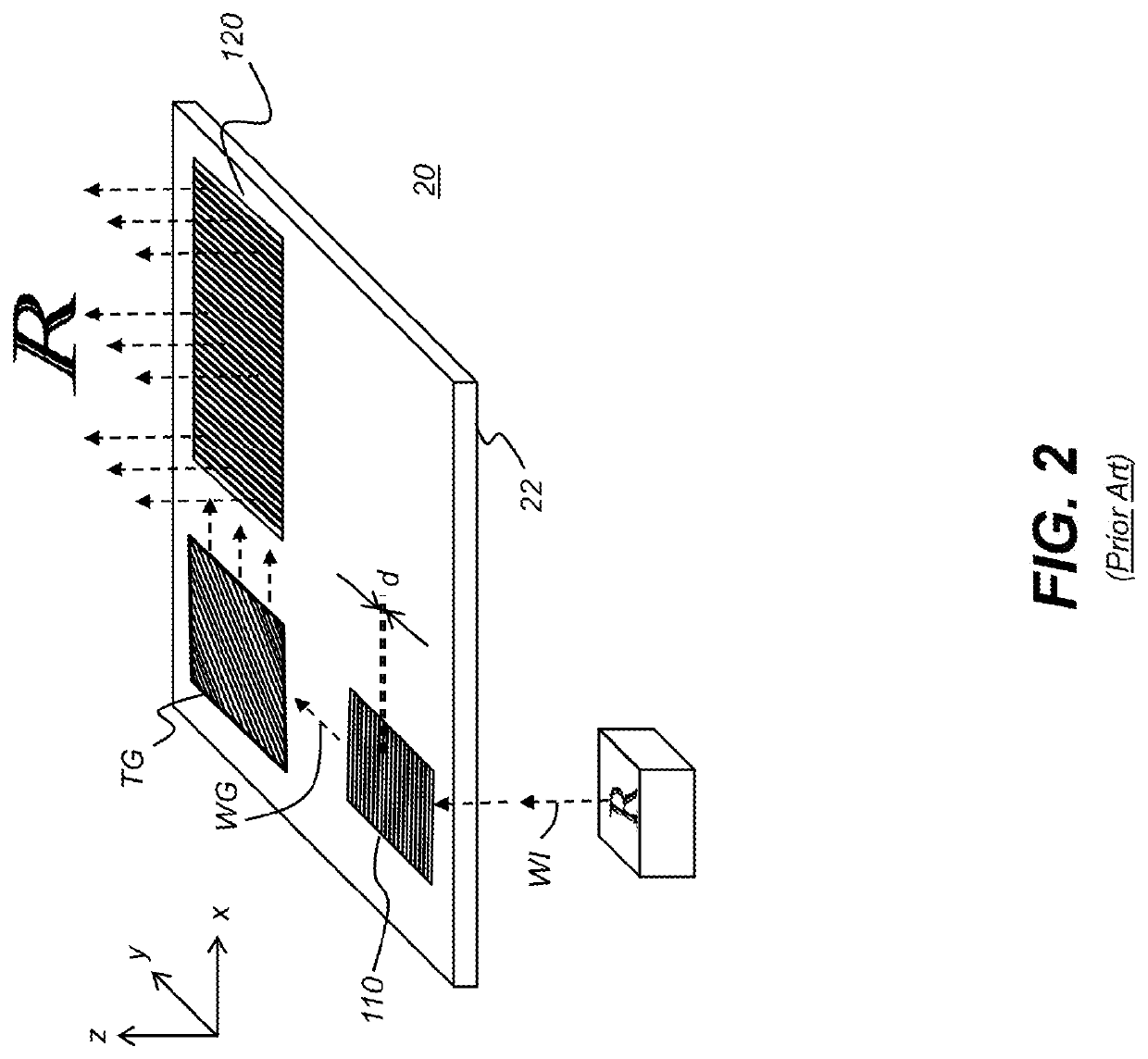
Optical systems such as image display systems include a freeform optical waveguide prism and a freeform compensation lens spaced therefrom by a gap of air or index cement. The compensation lens corrects for aberrations which the optical waveguide prism will introduce in light or images from an ambient real-world environment. The optical waveguide prism receives actively projected images at an entry location, and emits the projected images at an exit location after internally reflecting the images along an optical path therein. The image display system may include an image source and coupling optics. The approach permits design of an optical viewing device, for example in optical see-through HMDs, achieving an eyeglass-form appearance and a wide see-through field of view (FOV).
Owner:MAGIC LEAP INC
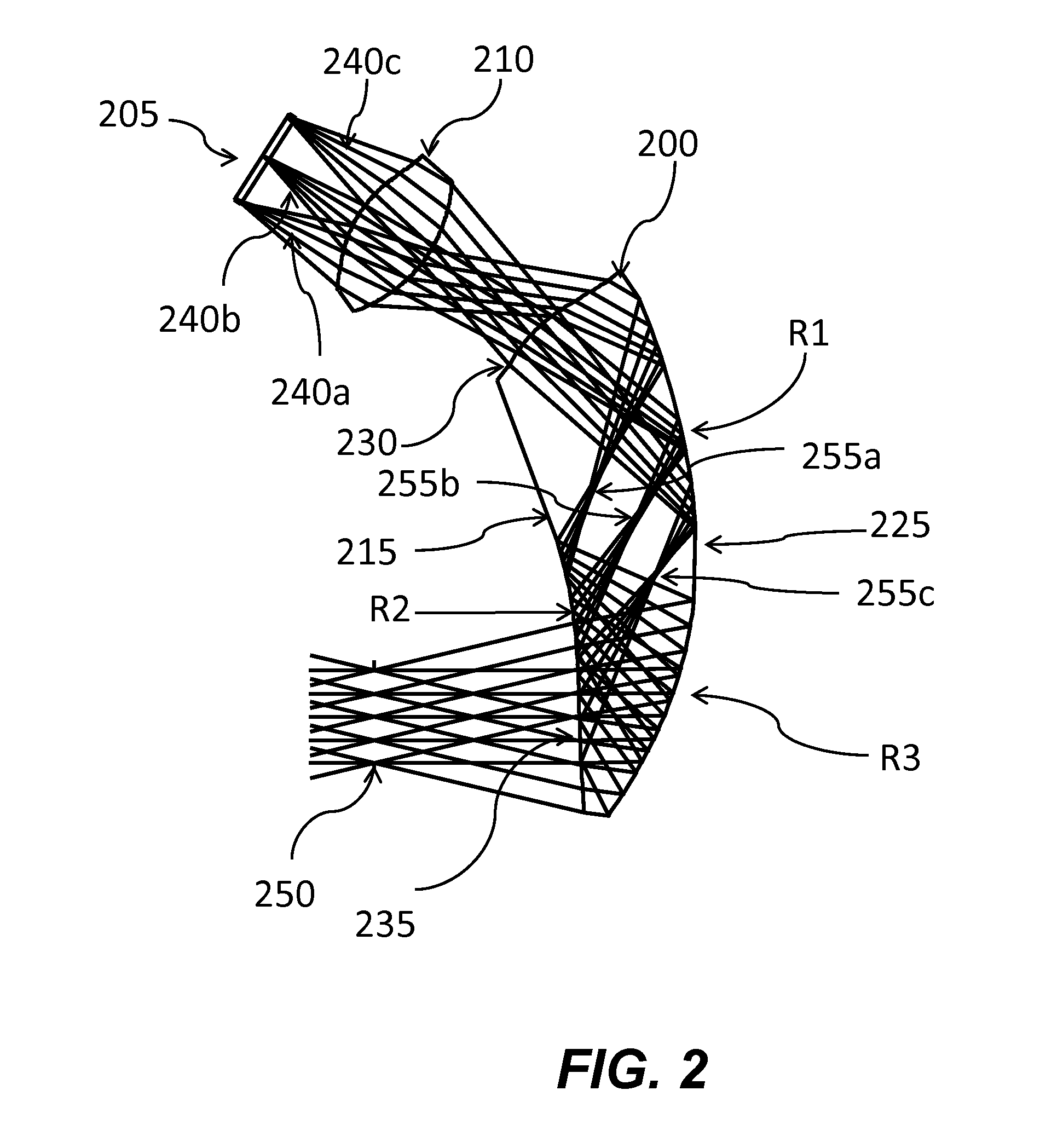
Wearable heads up displays
ActiveUS10545346B2Cathode-ray tube indicatorsInput/output processes for data processingHead-up displayGrating
An optical display, including a first waveguide having a first set of surfaces, an input grating, a fold grating, and an output grating; an image input image node assembly; and a prismatic relay optics is provided. The prismatic relay optics may be configured to be optomechanically connected to the waveguide and the input image node assembly. The optical display is may also be configured to operate alone or as integrated with a headpiece to be used as a HUD. The HUD may have a first and a second configuration wherein the waveguide is decoupled or coupled.
Owner:DIGILENS
Linear optical sampling method and apparatus
ActiveUS20050185255A1High sensitivityHigh temporal resolutionAnalogue/digital conversionElectric signal transmission systemsImage resolutionEngineering
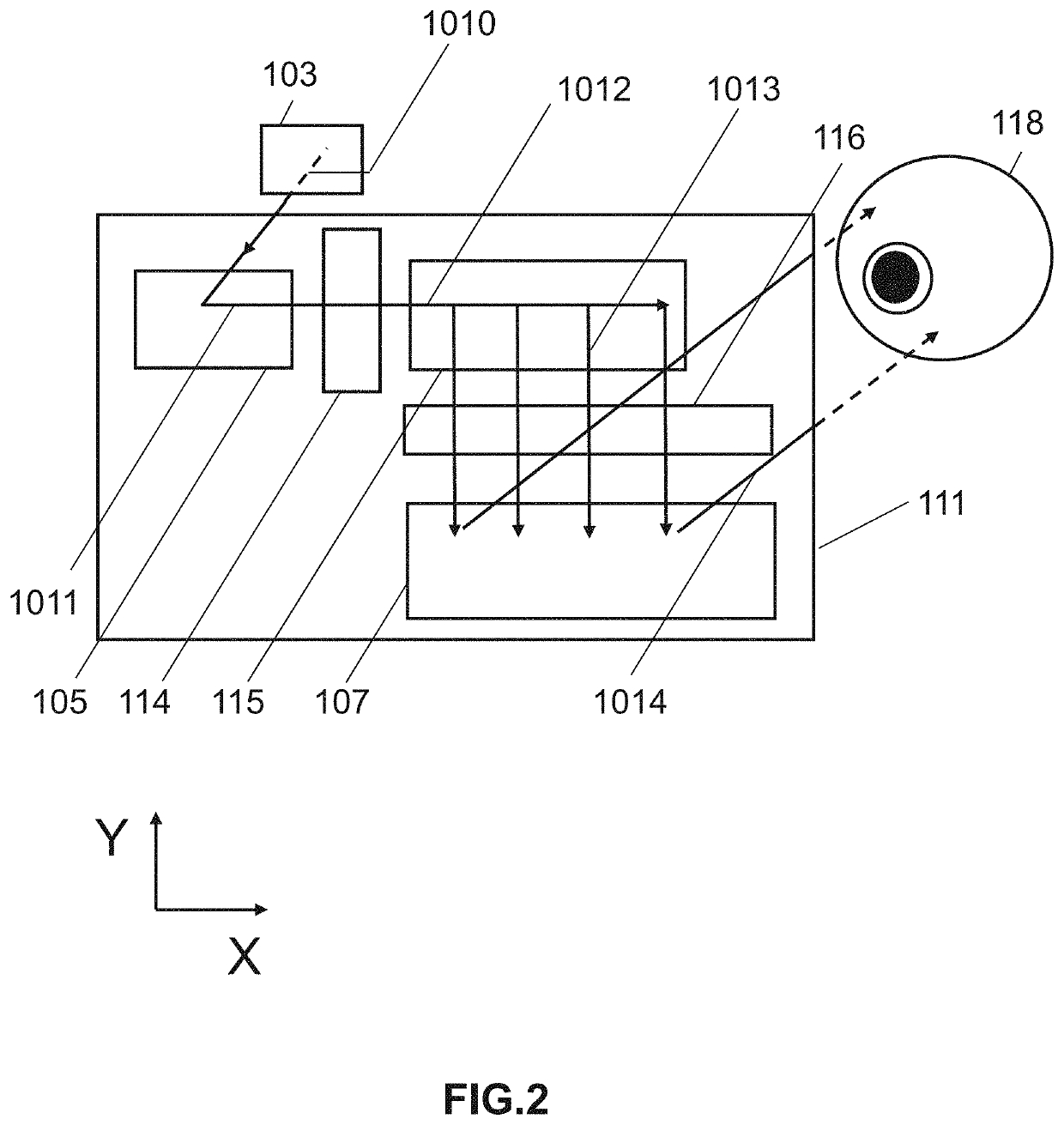
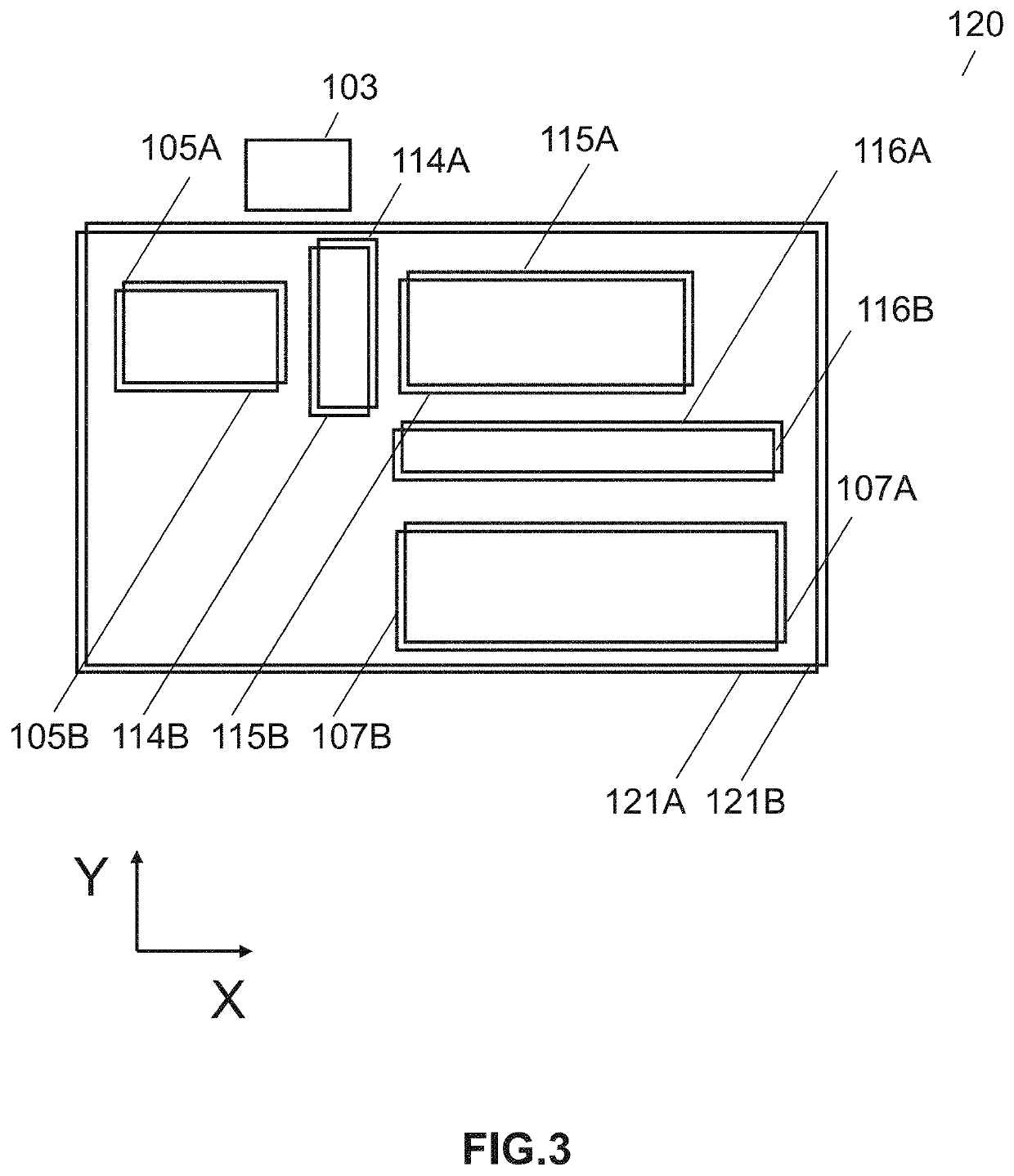
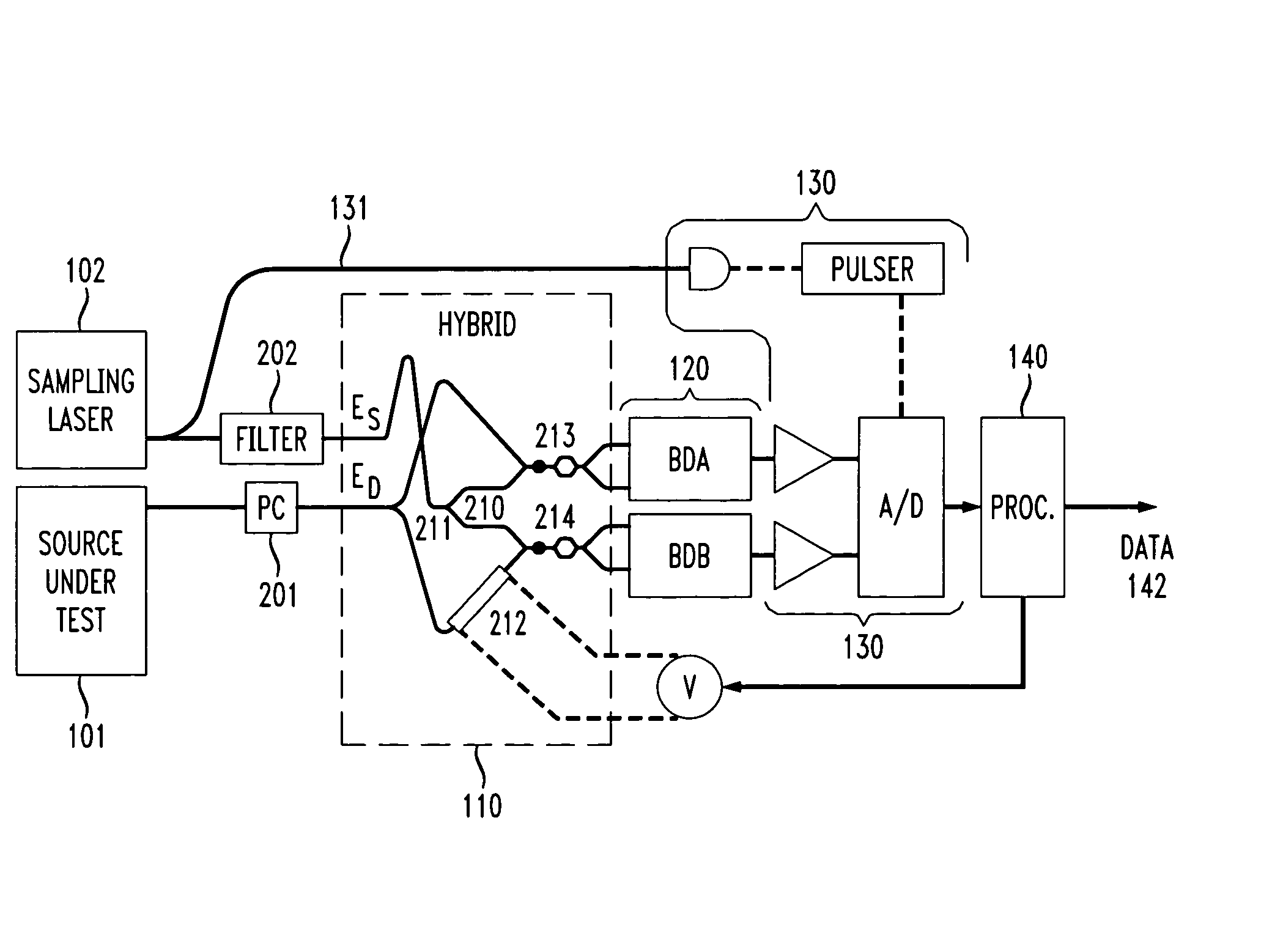
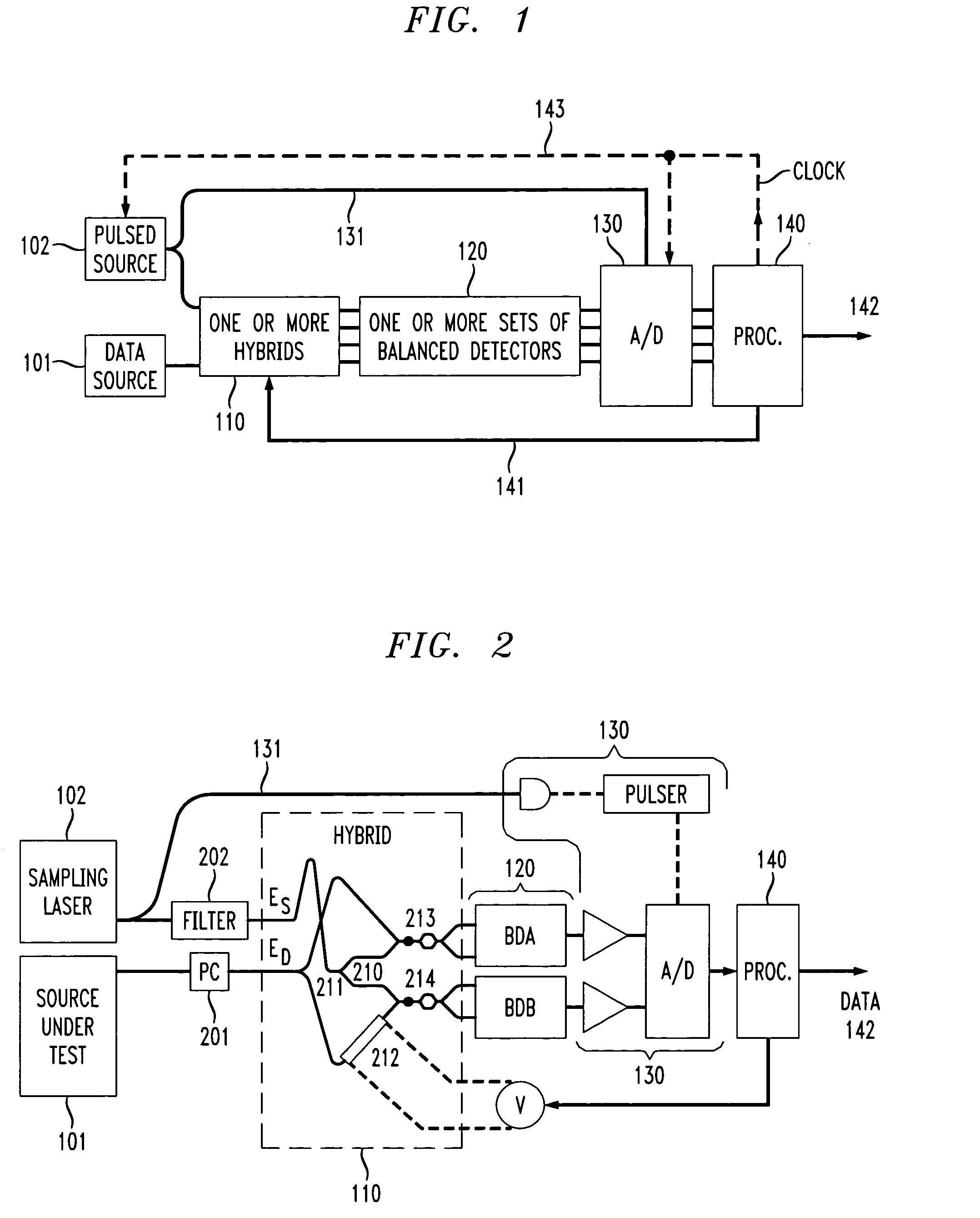
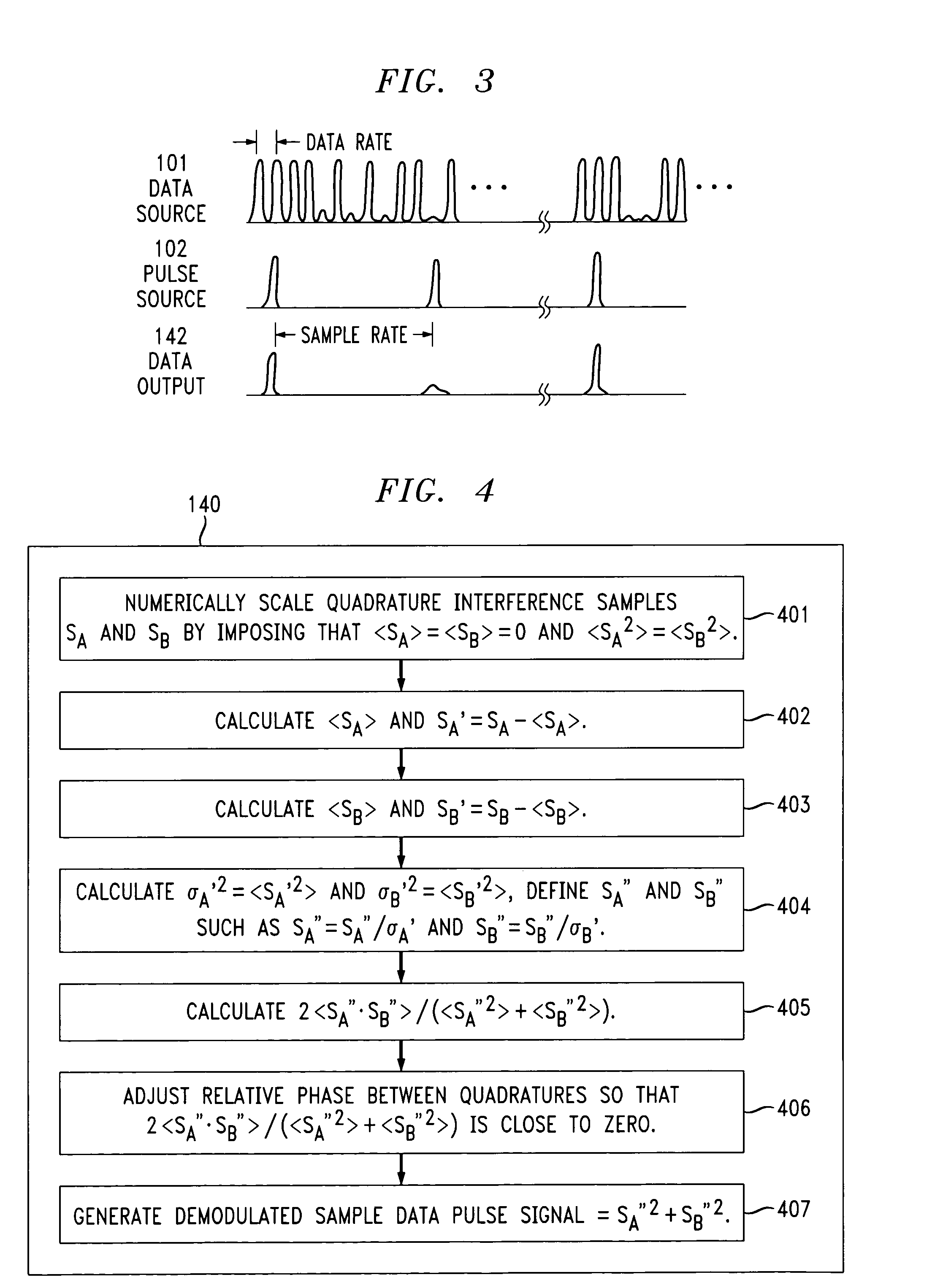
A linear optical sampling apparatus, temporally samples a modulated optical signal using the amplitude of the interference of its electric field with the electric field of a laser pulse. The apparatus includes a 90° optical hybrid that combines the optical signal and laser pulse in order to generate two quadratures interference samples SA and SB. A processor compensates for optical and electrical signal handling imperfections in the hybrid, balanced detectors, and A / D converters used in the optical sampling apparatus. The processor numerically scales the two quadratures interference samples SA and SB over a large collection of samples by imposing that the average <SA>=<SB>=0 and <SA2>=<SB2> and then minimizes 2<SA·SB> / (<SA2>+<SB2>)=cos(φB−φA)). This is done by adjusting the phase between the two quadratures (ideally either −π / 2 or +π / 2) so that cos(φB−φA)) is zero. The processor then generates a demodulated sample signal using the quadratures interference samples SA and SB. According to one feature, the hybrid sets the relative phase between two quadratures of their interferometric component so that the phase sensitivity inherent to linear optics is removed. A variety of hybrid arrangements is disclosed that can be implemented using integrated waveguide technology. The apparatus enables sampling of picosecond pulses up to 640 Gb / s with high sensitivity and temporal resolution.
Owner:ALCATEL-LUCENT USA INC +1
Compact optics for concentration and illumination systems
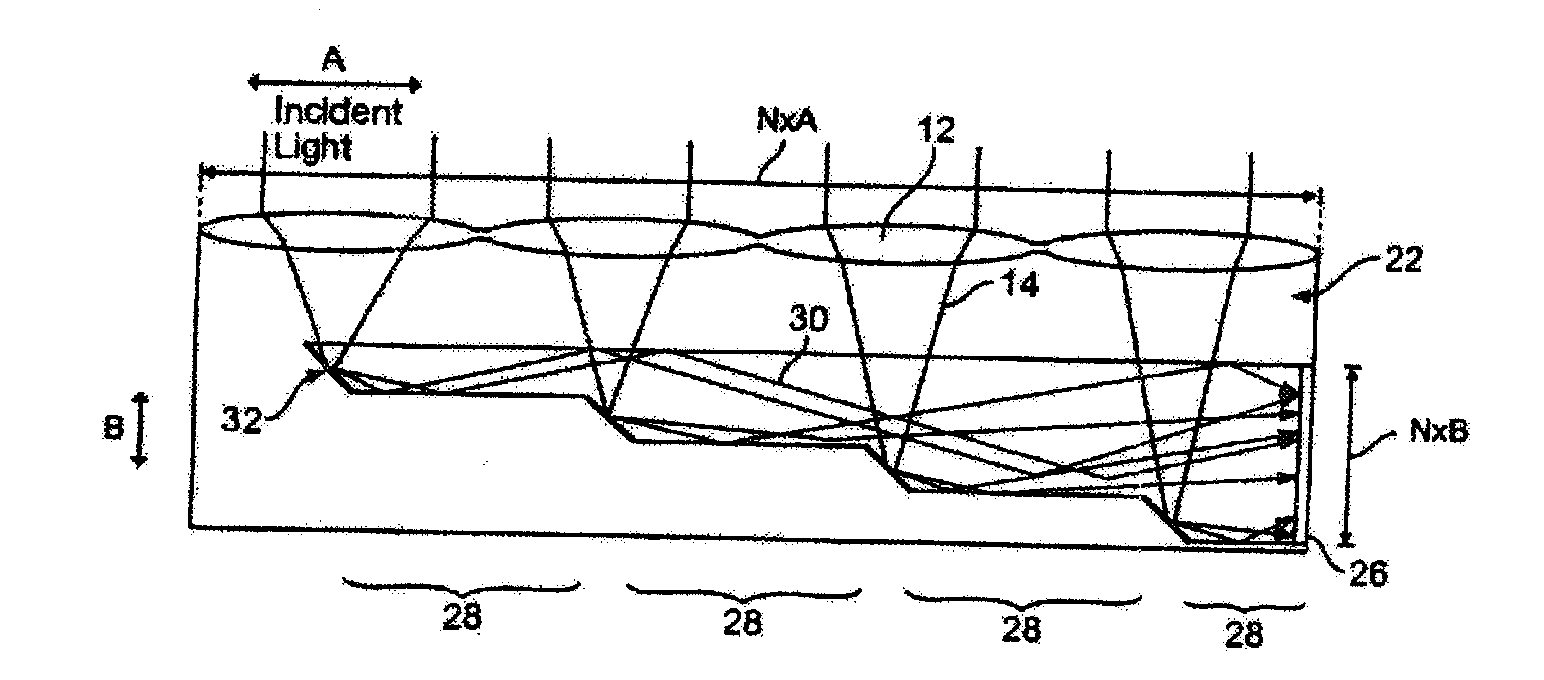
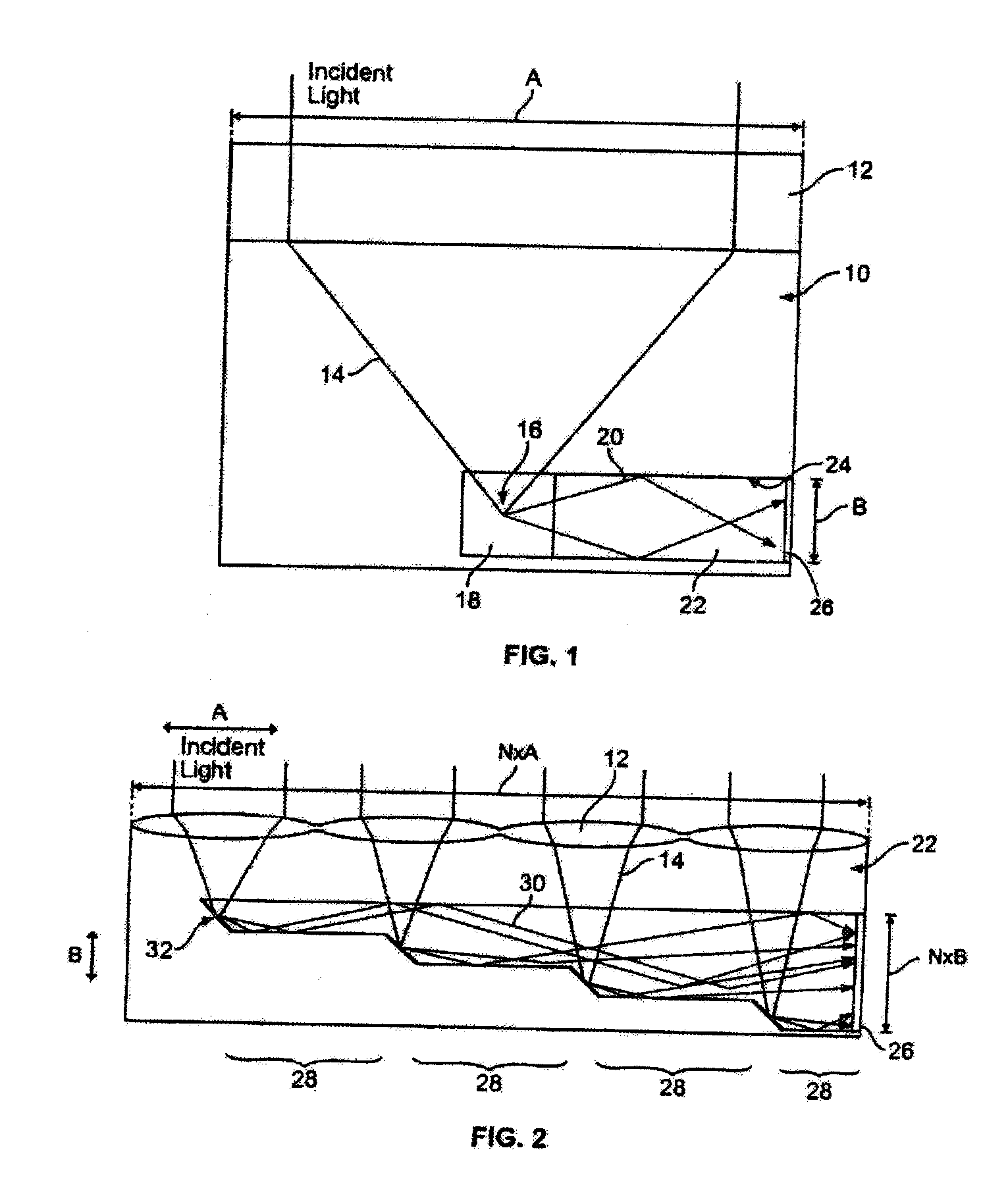
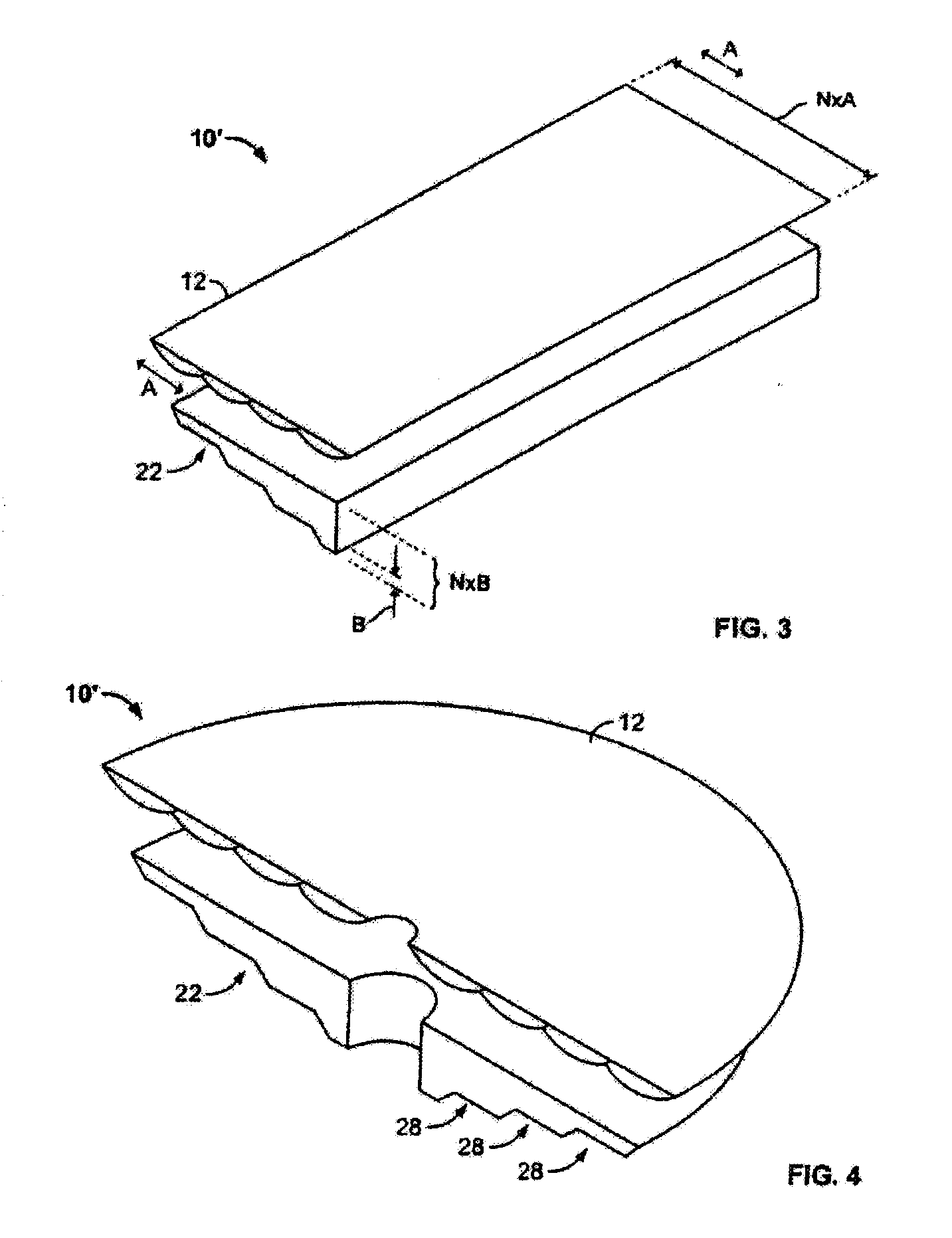
An optical concentrator having a concentrating element for collecting input light, a redirecting element for receiving the light and also for redirecting the light, and a waveguide including a plurality of incremental portions enabling collection and concentration of the light onto a receiver. Other systems replace the receiver by a light source so the optics can provide illumination.
Owner:BANYAN ENERGY INC
Optical switching apparatus and method for fabricating
InactiveUS20030035614A1Coupling light guidesOptical waveguide light guideCross connectionOptical beam deflection
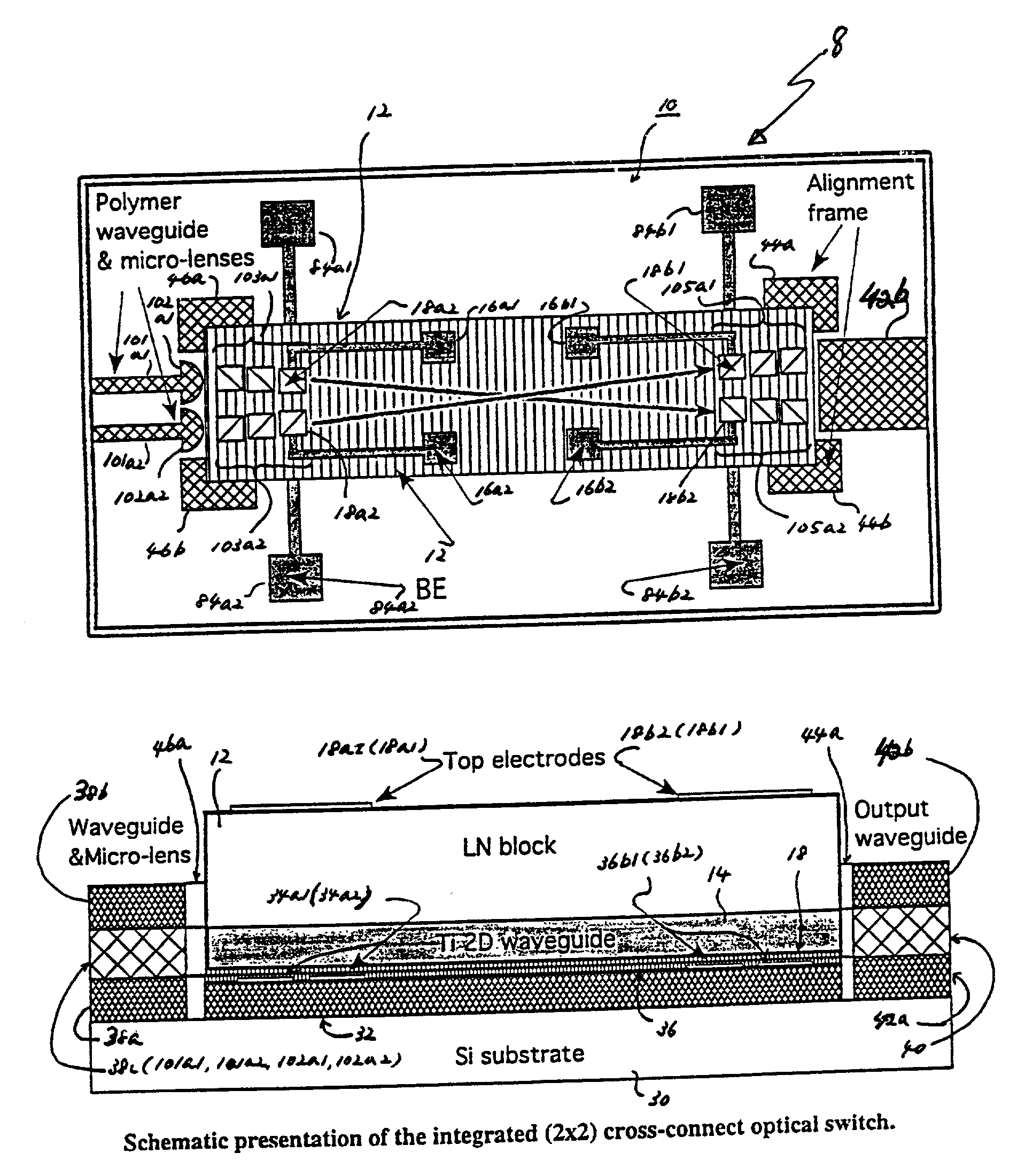
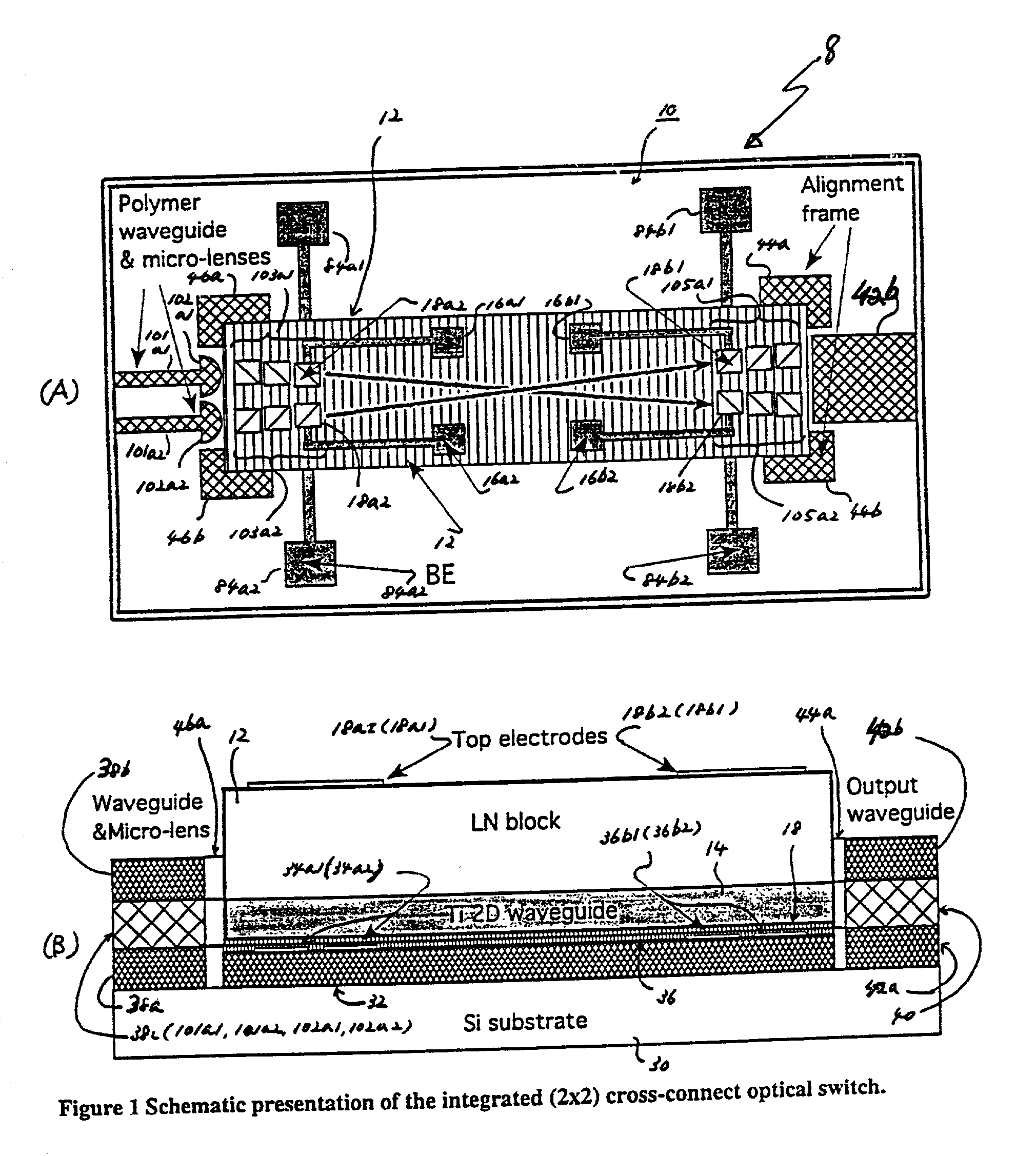
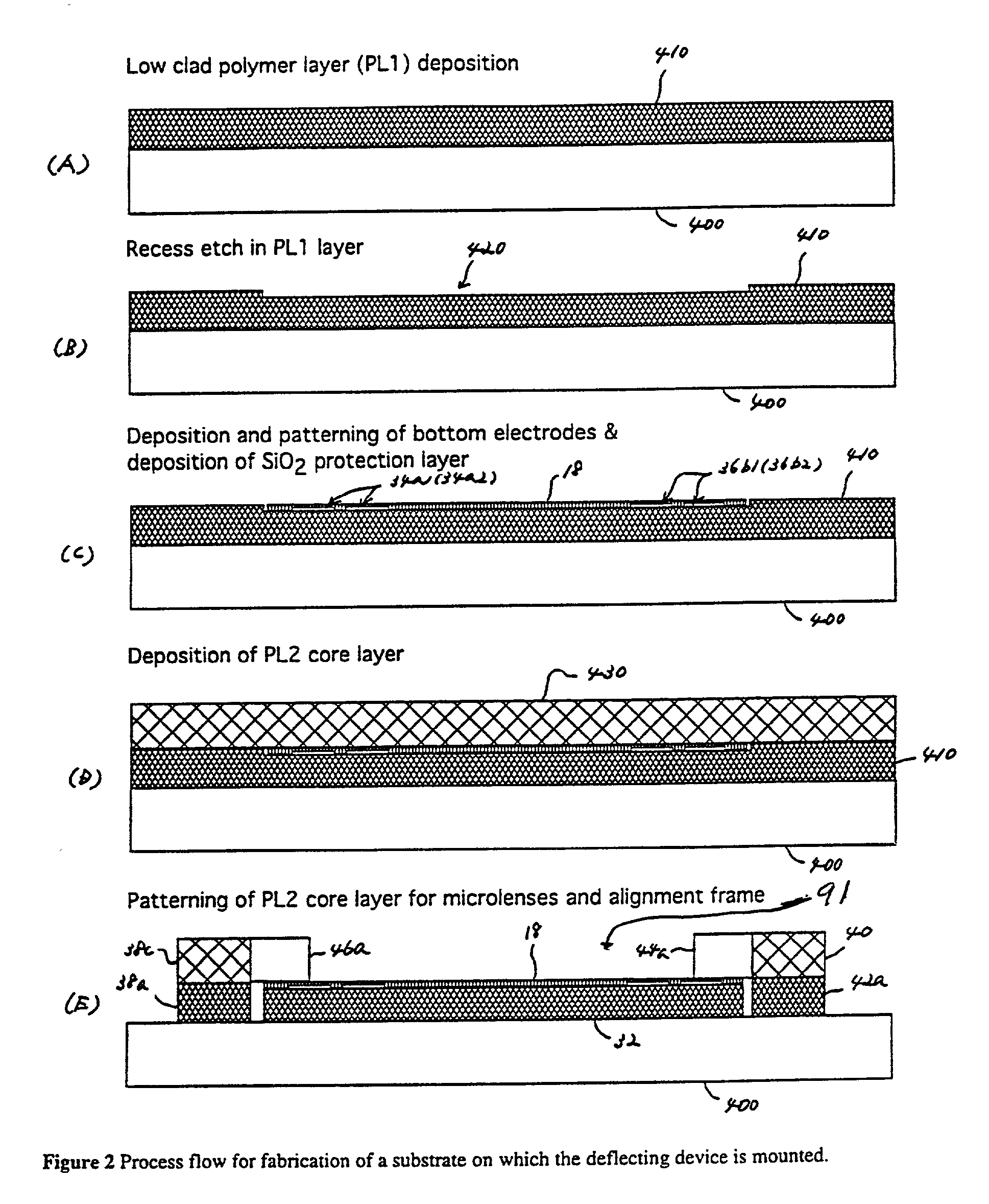
A hybrid integration process for fabrication of an optical cross-connect switching apparatus. The switching element is based on the deflection of light beam in electro-optic materials by applying electric field across electrodes of an appropriate configuration. The integration process includes fabrication of a substrate (e.g. silicon substrate) with 2D imaging optics from polymeric materials (or silica), fabrication of the light deflecting element, and assembly of the deflecting element on the substrate with imaging optics. The fabrication of the light deflecting element includes fabrication of a LN (lithium niobate) block. The LN block assembled in an optical switching apparatus includes a two-dimensional waveguide formed on a surface of the LN block and an electrode on a surface of the LN block.
Owner:FUJITSU LTD
Double-sided imaging light guide
ActiveUS20200278543A1Improve artMechanical apparatusPlanar/plate-like light guidesLight guideLight beam
An imaging light guide has waveguide for conveying image-bearing light beams from an image source to an eyebox within which a virtual image can be viewed. First and second in-coupling diffractive optics direct first and second sets of the image-bearing light beams into the waveguide along different first and second paths. First and second turning diffractive optics disposed along the respective paths expand the image-bearing light beams of the first and second sets in a first dimension and direct the expanded image-bearing light beams of the first and second sets to first and second out-coupling diffractive optics. The first and second out-coupling diffractive optics further expand the image-bearing light beams of the two sets in a second dimension and direct the further expanded image-bearing light beams of the two sets from the waveguide toward the eyebox.
Owner:VUZIX
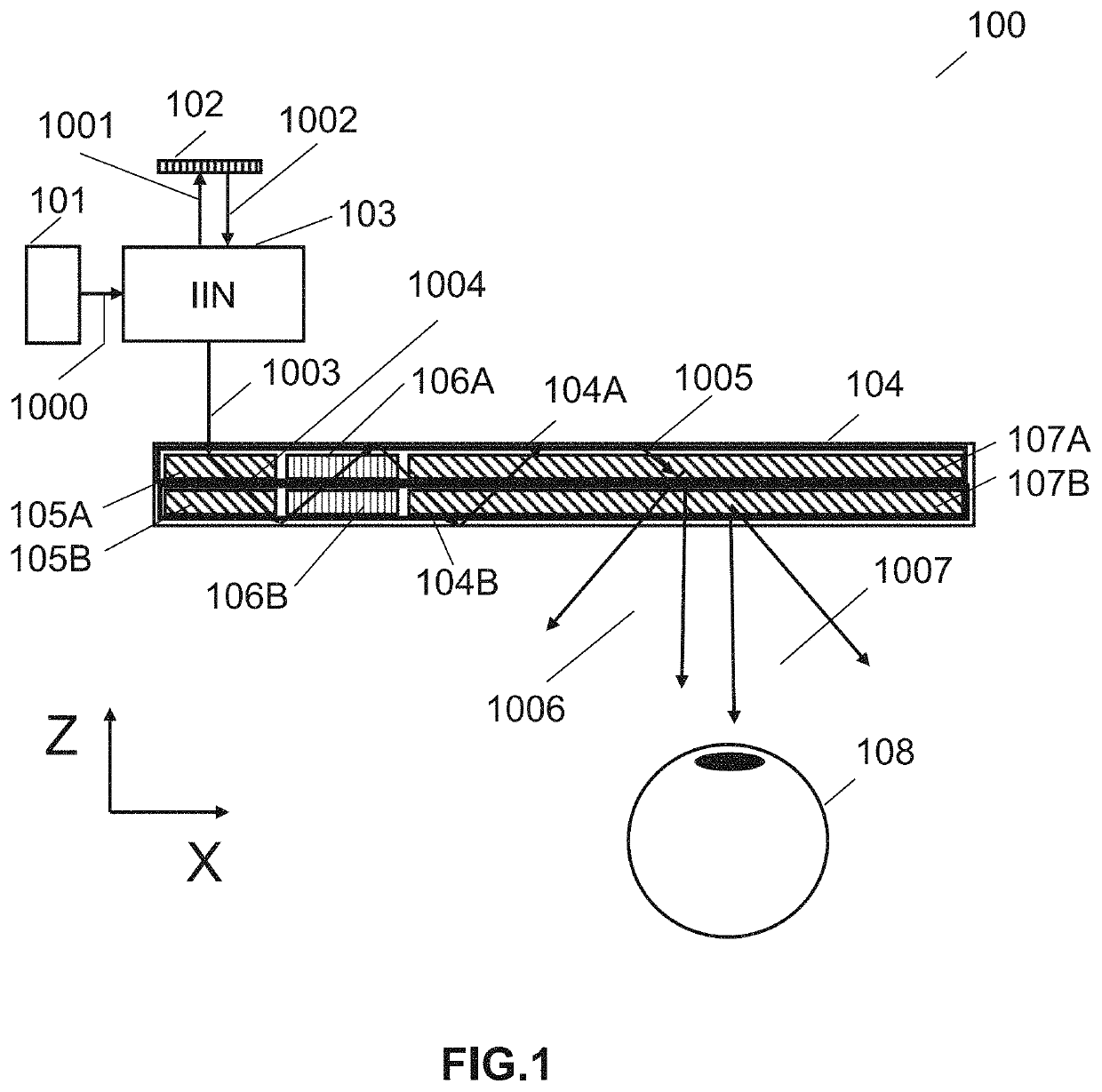
Optical waveguide and near-to-eye display system
PendingCN111679362AImprove energy utilizationDiffraction gratingsOptical light guidesLight beamWaveguide (optics)
The embodiment of the invention relates to the technical field of optics, and in particular relates to an optical waveguide and a near-to-eye display system. The optical waveguide provided by the embodiment of the invention comprises a waveguide substrate, a coupling-in region, a coupling-out region and a light return region; the coupling-in region, the coupling-out region and the light return region are arranged on the waveguide substrate; the coupling-in region is used for coupling in a light beam with image information; the coupling-out region is used for coupling out the light beam with the image information; the light return region is used for reversely returning the light beam with the image information to the coupling-out region; the coupling-out region comprises at least three sideedges; at least one side edge of the coupling-out region is provided with the light return region; when an image light beam is propagated to the edge of the coupling-out region, part of the image light beam can be reversely propagated back to the coupling-out region due to the action of the light return region and then is coupled out to human eyes through the coupling-out region, and therefore the energy utilization rate of the two-dimensional expansion diffraction optical waveguide is increased.
Owner:SHENZHEN LOCHN OPTICS TECH CO LTD
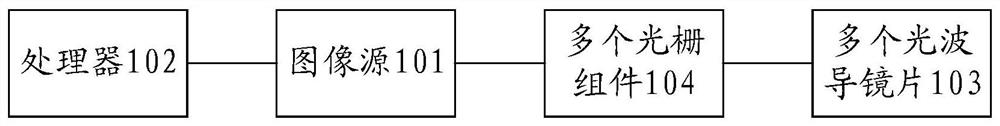
Image display method, near-to-eye display equipment and device
The invention provides an image display method, near-to-eye display equipment and device, and relates to the technical field of optics. The image display method comprises the steps that a first FOV corresponding to each optical waveguide lens in multiple optical waveguide lenses of the near-to-eye display equipment is determined, and a second FOV of the near-to-eye display equipment is composed of first FOVs of the multiple optical waveguide lenses; for each optical waveguide lens, a grating parameter of a grating assembly of the optical waveguide lens is determined according to the first FOV; when an image source is displayed, incident light corresponding to the image source is diffracted according to the grating parameters, a plurality of first images are obtained, and the field angle of the image source is a second FOV; and the plurality of first images are spliced to obtain the second image corresponding to the image source, so that the plurality of first FOVs have no overlapped part by optimizing the grating parameters, the second image is ensured to have no ghosting, the uniformity of the second image is improved, and the eye movement range of the near-eye display equipment is expanded.
Owner:HANGZHOU HIKVISION DIGITAL TECH
Diffractive optical elements with mitigation of rebounce-induced light loss and related systems and methods
ActiveUS20200033604A1Reduce generationMechanical apparatusCoupling light guidesProjection opticsTotal internal reflection
Display devices include waveguides with in-coupling optical elements that mitigate re-bounce of in-coupled light to improve overall in-coupling efficiency and / or uniformity. A waveguide receives light from a light source and / or projection optics and includes an in-coupling optical element that in-couples the received light to propagate by total internal reflection in a propagation direction within the waveguide. Once in-coupled into the waveguide the light may undergo re-bounce, in which the light reflects off a waveguide surface and, after the reflection, strikes the in-coupling optical element. Upon striking the in-coupling optical element, the light may be partially absorbed and / or out-coupled by the optical element, thereby effectively reducing the amount of in-coupled light propagating through the waveguide. The in-coupling optical element can be truncated or have reduced diffraction efficiency along the propagation direction to reduce the occurrence of light loss due to re-bounce of in-coupled light, resulting in less in-coupled light being prematurely out-coupled and / or absorbed during subsequent interactions with the in-coupling optical element.
Owner:MAGIC LEAP
SAW modulators and light steering methods
ActiveUS10795235B2Piezoelectric/electrostrictive device manufacture/assemblyImpedence networksTransducerEngineering
An electro-holographic light field generator device is disclosed. The light field generator device has an optical substrate with a waveguide face and an exit face. One or more surface acoustic wave (SAW) optical modulator devices are included within each light field generator device. The SAW devices each include a light input, a waveguide, and a SAW transducer, all configured for guided mode confinement of input light within the waveguide. A leaky mode deflection of a portion of the waveguided light, or diffractive light, impinges upon the exit face. Multiple output optics at the exit face are configured for developing from each of the output optics a radiated exit light from the diffracted light for at least one of the waveguides. An RF controller is configured to control the SAW devices to develop the radiated exit light as a three-dimensional output light field with horizontal parallax and compatible with observer vertical motion.
Owner:CHARLES STARK DRAPER LABORATORY
Optical waveguide pulse coupler and manufacturing method thereof
InactiveCN103558665ARealization of pulse-coupled kinetic processesCoupling light guidesGlass compositesNerve network
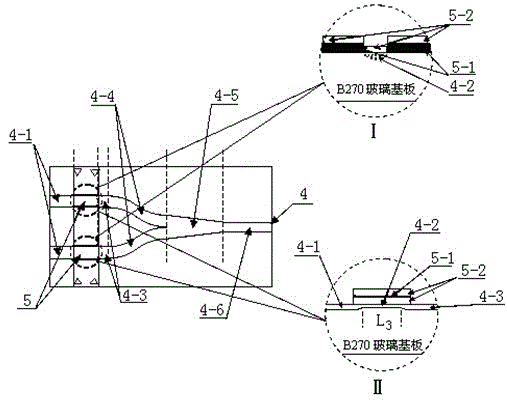
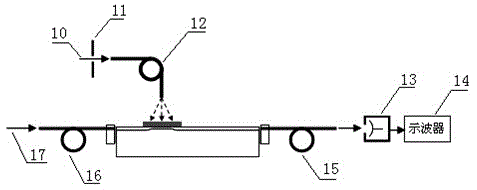
The invention relates to an optical waveguide pulse coupler and a manufacturing method thereof. The unsaturation light blocking effect of As2S8-B270 glass composite waveguide is used for achieving coupling response on input effect electric pulse signals, and an optics reversal phase asymmetric input waveguide branch mode coupling effect is used for providing threshold value limitation. The optics corpuscular property shown by the unsaturation light blocking effect and the optics undulatory property shown by branch waveguide mode coupling are combined in an organic mode on an optical waveguide carrier, a full-optical mode is used for achieving a pulse coupling kinetics process between input effect electric pulses and output synchronization electric pulses, and a full-optical method is used for achieving the pulse coupling kinetics process which meets the requirement of a pulse coupled neural network (PCNN).
Owner:UNIV OF SHANGHAI FOR SCI & TECH
Two-dimensional grating, optical waveguide and AR glasses
The embodiment of the invention relates to the technical field of optics, in particular to a two-dimensional grating, an optical waveguide and AR glasses. The embodiment of the invention provides a two-dimensional grating, an optical waveguide and AR glasses. The two-dimensional grating comprises at least one period, on one hand, the proportion of the long side size to the short side size of the two-dimensional grating in each period increases the diversity of the light beam expansion propagation direction, and on the other hand, the grating structure and the size can be freely designed in each period, so that the design diversity is increased, the designed grating structure is applied to the optical waveguide and the AR glasses, and the problems of exit pupil uniformity and view field uniformity in the optical waveguide and the AR glasses are solved.
Owner:SHENZHEN LOCHN OPTICS TECH CO LTD
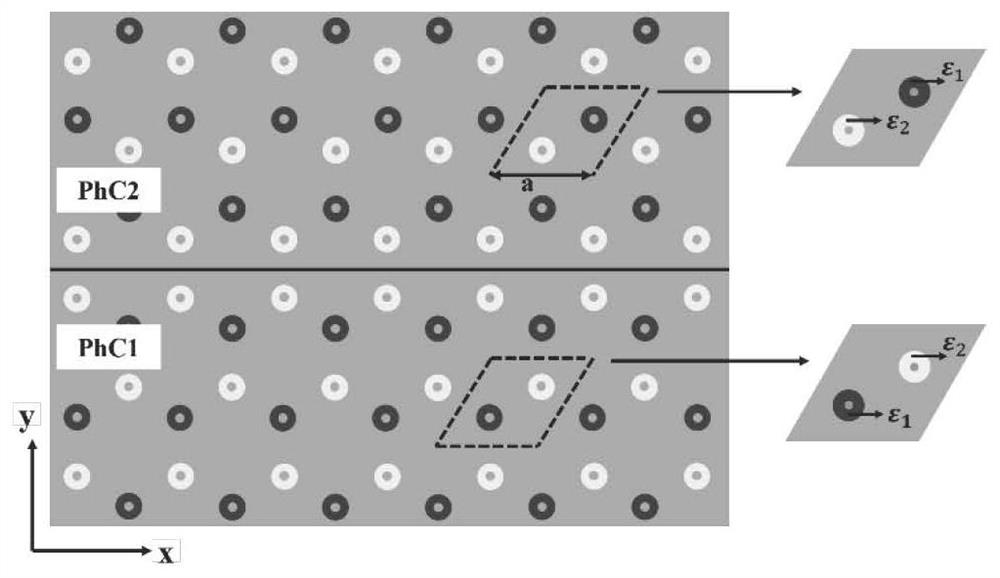
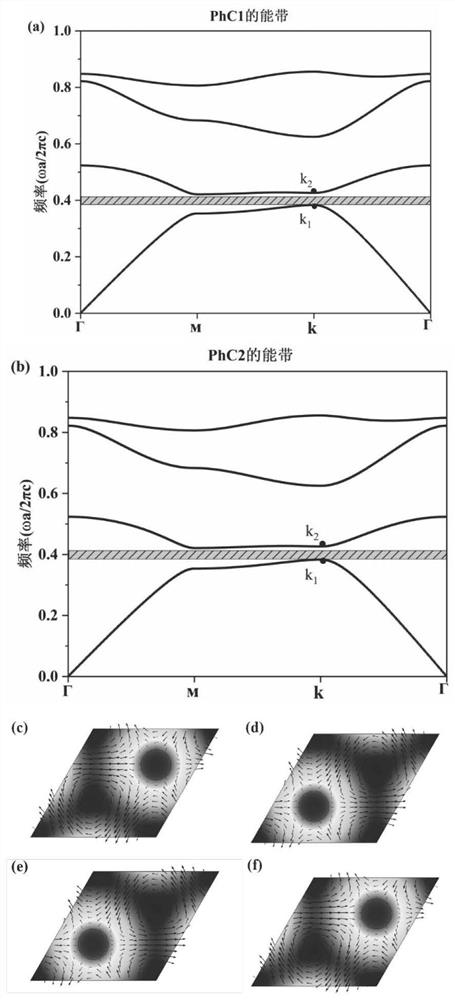
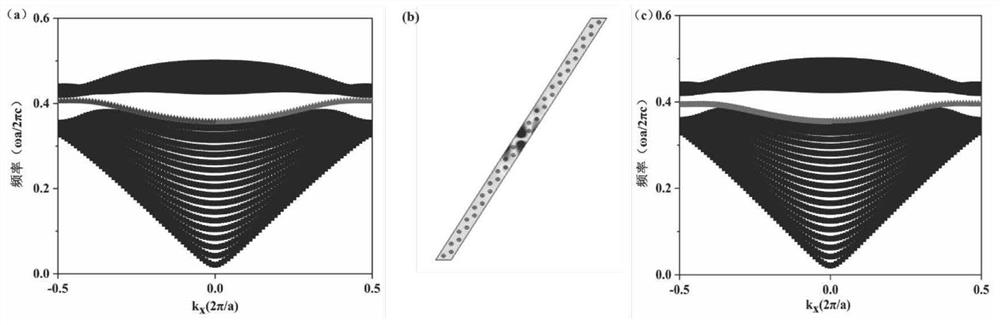
Topological photonic crystal composite structure for realizing one-way transmission of light waves based on energy band inversion
ActiveCN111965736ARealize one-way transmissionOptical light guidesPhotonic crystalCommunications system
The invention belongs to quantum optics and optical communication systems, and particularly relates to a topological photonic crystal composite structure for realizing one-way transmission of light waves based on energy band inversion. A topological photonic crystal composite structure for realizing unidirectional transmission of light waves based on energy band inversion comprises two kinds of two-dimensional photonic crystals PhC1 and PhC2 with the same crystal lattice and the same type, and unidirectional transmission of light is realized on an interface of the two kinds of two-dimensionalphotonic crystals. According to the invention, the structure can realize unidirectional transmission of TM mode light, is immune to defects and impurities, and can provide a new thought for designinga novel optical waveguide for an efficient optical transmission problem.
Owner:TAIYUAN UNIV OF TECH
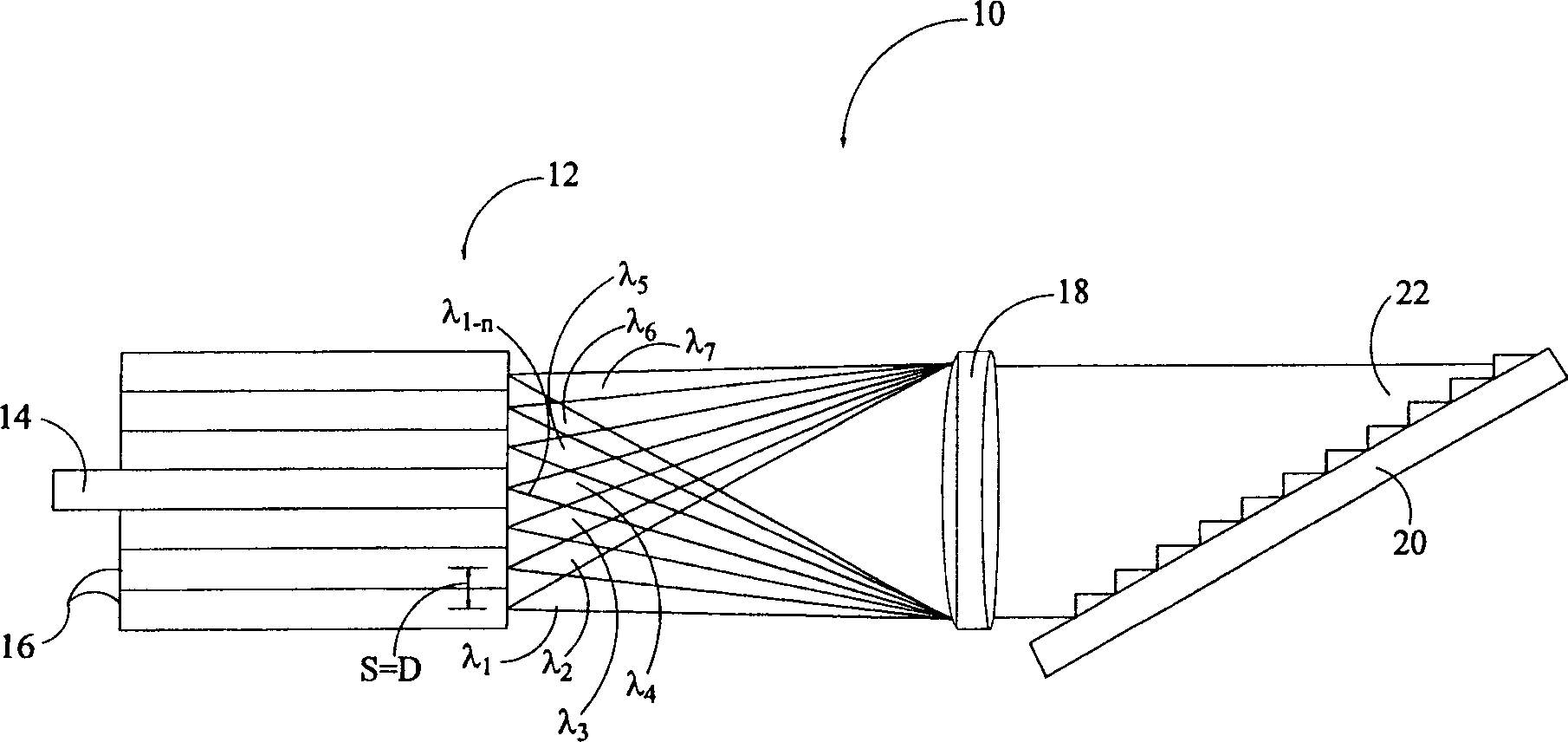
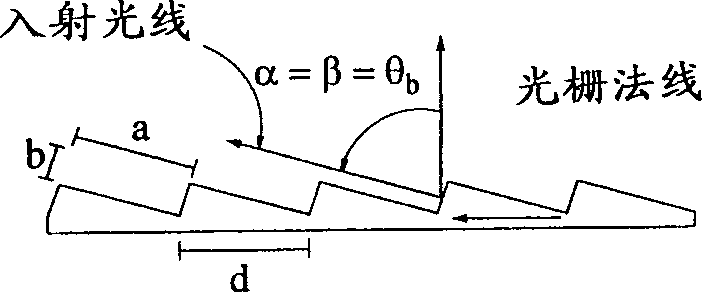
Dense wavelength division multiplexer/demultiplexer based on echelle grating
InactiveCN1377474ASmall form factorHigh resolutionDiffraction gratingsCoupling light guidesGratingEngineering
A dense wavelength division multiplexer / demultiplexer ("DWDM") (10) for use in an optical communication system, comprising a propagating multiple multiplexed with selected channel spacing into a single optical a multiplexed optical waveguide (14) of the optical channel of the signal (λiest; 1-n), a collimation / focusing optical component (18) optically coupled to the multiplexed optical waveguide at a selective focal length, an optically coupled to the collimation / focusing A reflective echelle grating (20) of an optical component (18), wherein the echelle grating (20) has a groove spacing (d) and a blaze angle (θb) capable of providing multiplexed optical signals (λ1- n) of the channel spacing (d). A linear array of single-channel waveguides (16), each propagating a single channel in the near-infrared wavelength region, is optically coupled to collimating / focusing optics, each single-channel waveguide (16) having a center and a propagating termination, and propagating The distance between the terminals and the collimating / focusing optics is equal to the focal length, while the distance between the centers of adjacent branching waveguides is the selected channel spacing (D). Fiber optic harnesses are used to connect the multiplexers operating in the Littrow configuration.
Owner:JOHN ZINK CO LLC
Concentric cylindrical circumferential laser
ActiveUS20210104861A1Laser optical resonator constructionActive medium shape and constructionModal gainOptical limiting
The present disclosure relates to a three-dimensional cylindrical cavity-type laser system capable of supporting circumferential radial emission. A cylindrical ring waveguide provides optical confinement in the radial and axial dimensions thereby supporting a plurality of radial modes, one of a plurality of axial modes and a plurality of degenerate azimuthal modes. These modes constitute a set of traveling wave modes which propagate around the cylindrical ring waveguide possessing various degrees of optical confinement as quantified by their respective Q-factors. Index tailoring is used to tailor the radial refractive index profile and geometry of the waveguide to support radial modes possessing Q-factors capable of producing efficient radial emission, while gain tailoring is used to define a gain confining region which offsets modal gain factors of the modal constituency to favor a preferred set of modes supporting efficient radial emission out of the total modal constituency supported by the resonator. Under appropriate pump actuation the selected modes produce circumferential laser radiation with the output surface comprising of the entire outer perimeter of the cylindrical ring waveguide. The design is applicable toward both micro-resonators and resonators much larger than the optical wavelength, enabling high output powers and scalability. The circumferential radial laser emission can be concentrated by positioning the cylindrical ring laser inside a three-dimensional conical mirror thereby forming a laser ring of light propagating in the axial dimension away from the surface of the laser, which can be subsequently collimated for focused using conventional optics.
Owner:LACOMB RONALD +1
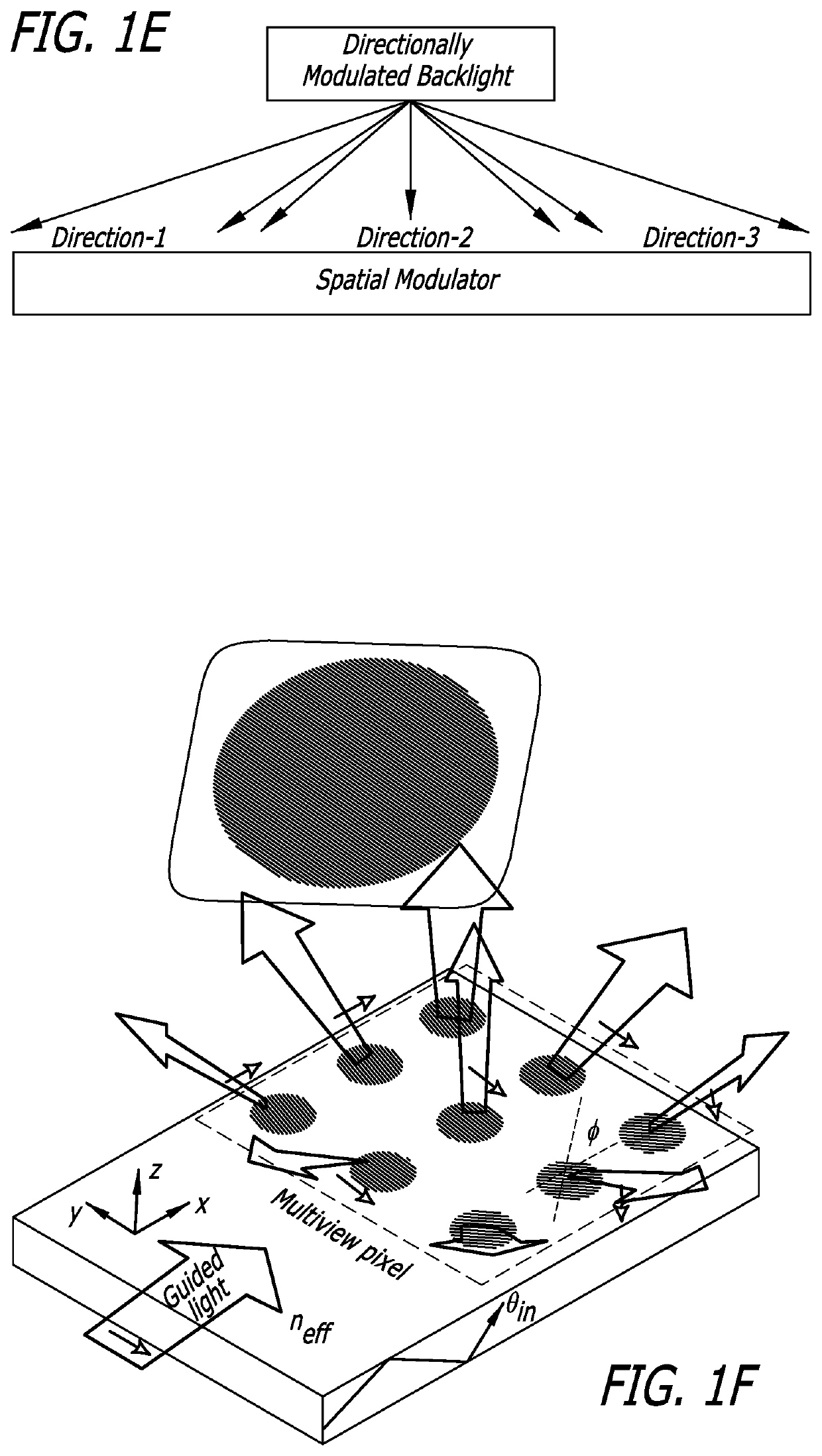
Non-telecentric emissive micro-pixel array light modulators and methods of fabrication thereof
Emissive micro-pixel spatial light modulators with non-telecentric emission are introduced. The individual light emission from each multi-color micro-scale emissive pixel is directionally modulated in a unique direction to enable application-specific non-telecentric emission pattern from the micro-pixel array of the emissive spatial light modulator. Design methods for directionally modulating the light emission of the individual micro-pixels using micro-pixel level optics are described. Monolithic wafer level optics methods for fabricating the micro-pixel level optics are also described. An emissive multi-color micro-pixel spatial light modulator with non-telecentric emission is used to exemplify the methods and possible applications of the present invention: ultra-compact image projector, minimal cross-talk 3D light field display, multi-view 2D display, and directionally modulated waveguide optics for see-through near-eye displays.
Owner:OSTENDO TECH INC
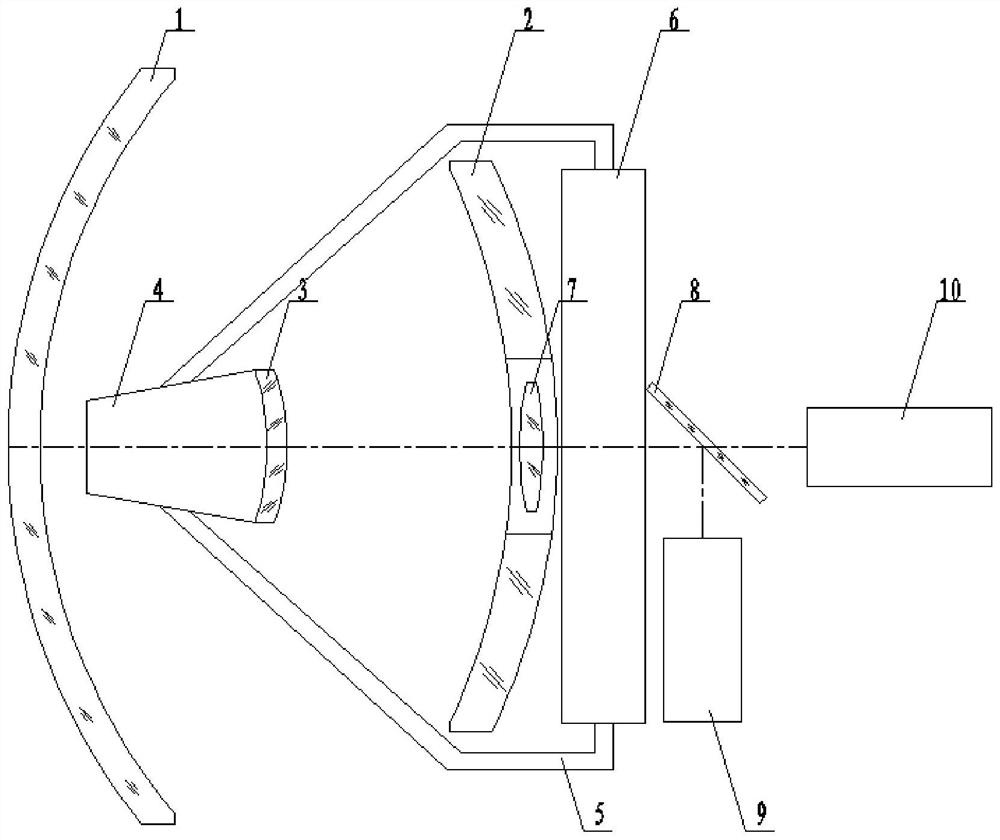
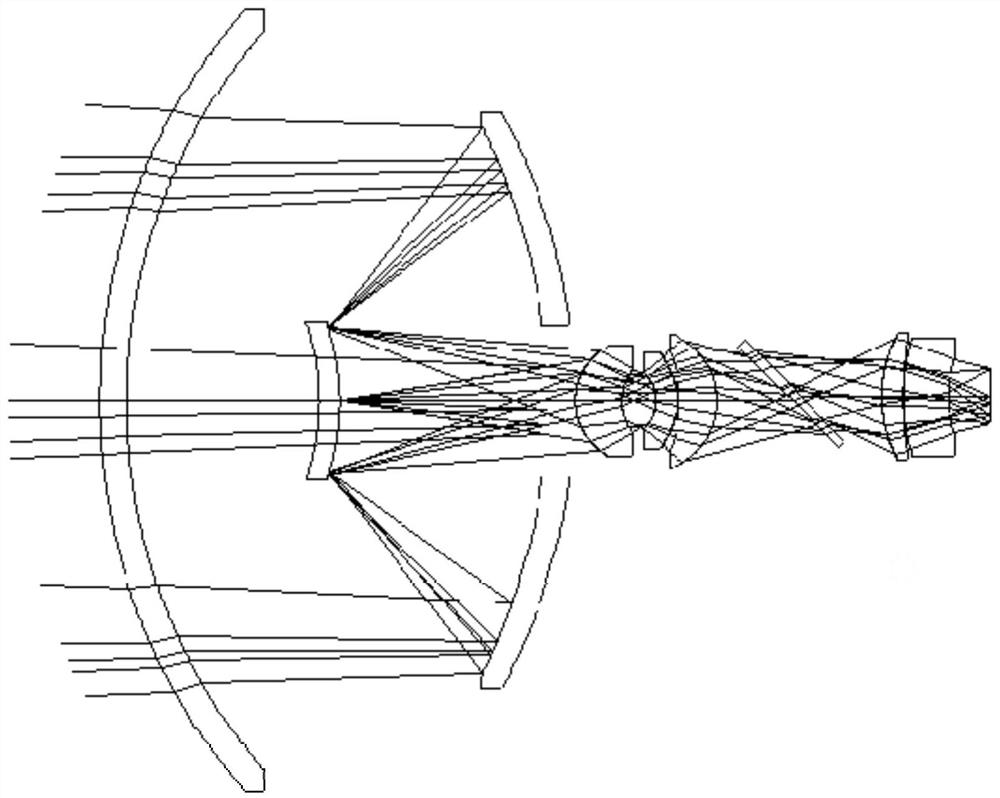
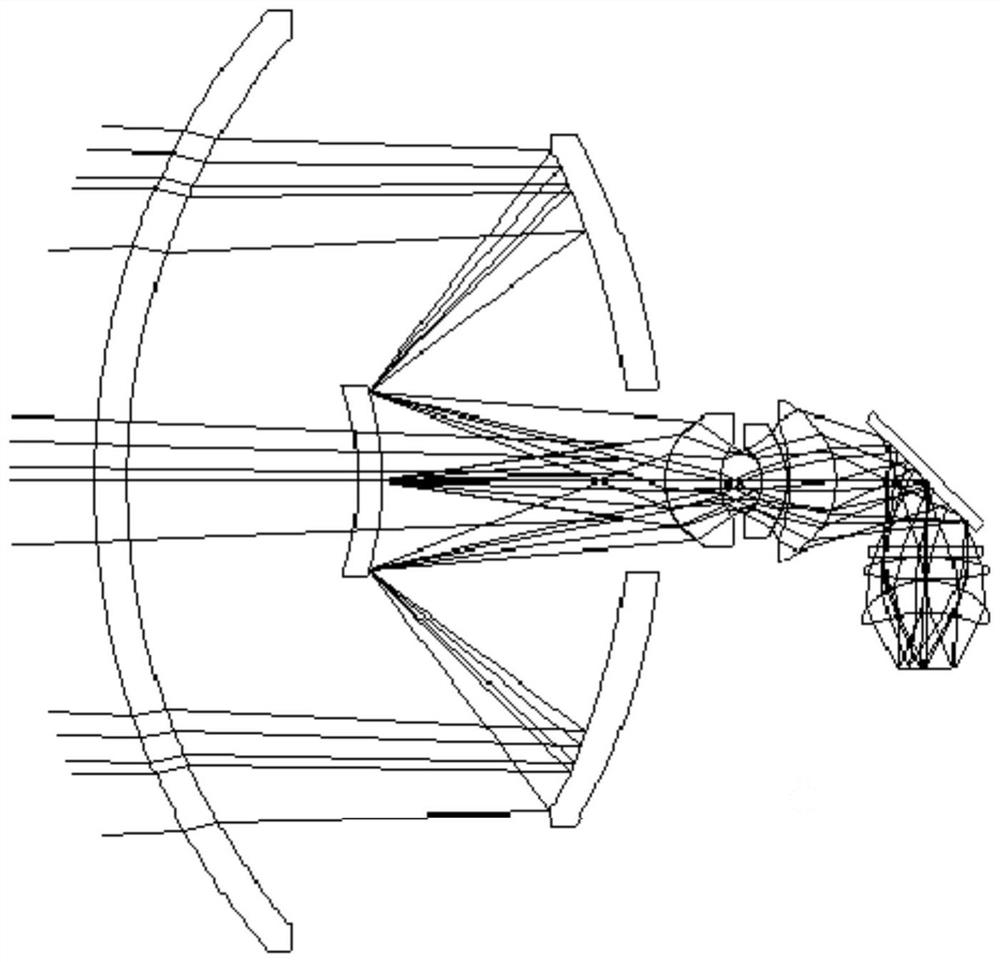
Infrared, laser and millimeter wave common-caliber three-mode seeker optical system
InactiveCN112068311AReduce loadIncreasing the thicknessDirection controllersOptical elementsTransceiverImaging quality
The invention belongs to the technical field of optics, and discloses an infrared, laser and millimeter wave common-caliber three-mode seeker optical system. The system is composed of a hood, a primary mirror, a secondary mirror, a feed source, a waveguide, a millimeter wave transceiver module, an infrared channel, a laser channel and the like. The hood and the secondary mirror are designed to beequal in thickness, and the thickness values of the hood and the secondary mirror are optimized and calculated to ensure the lowest loss of millimeter waves. The secondary mirror is plated with a wide-spectrum medium reflecting film to reflect infrared and laser and transmit millimeter waves. The primary mirror is made of aluminum alloy, and the reflecting surface of the primary mirror is a paraboloid. The millimeter wave feed source is located between the secondary mirror and the hood, and the millimeter wave transceiver module is located at the rear end of the primary mirror and connected with the feed source through four waveguides. The infrared channel and the laser channel are located at the rear end of the primary mirror. Only the millimeter wave feed source is arranged at the secondary mirror so that the load can be reduced, and the stability of the system imaging quality can be effectively enhanced.
Owner:西安应用光学研究所
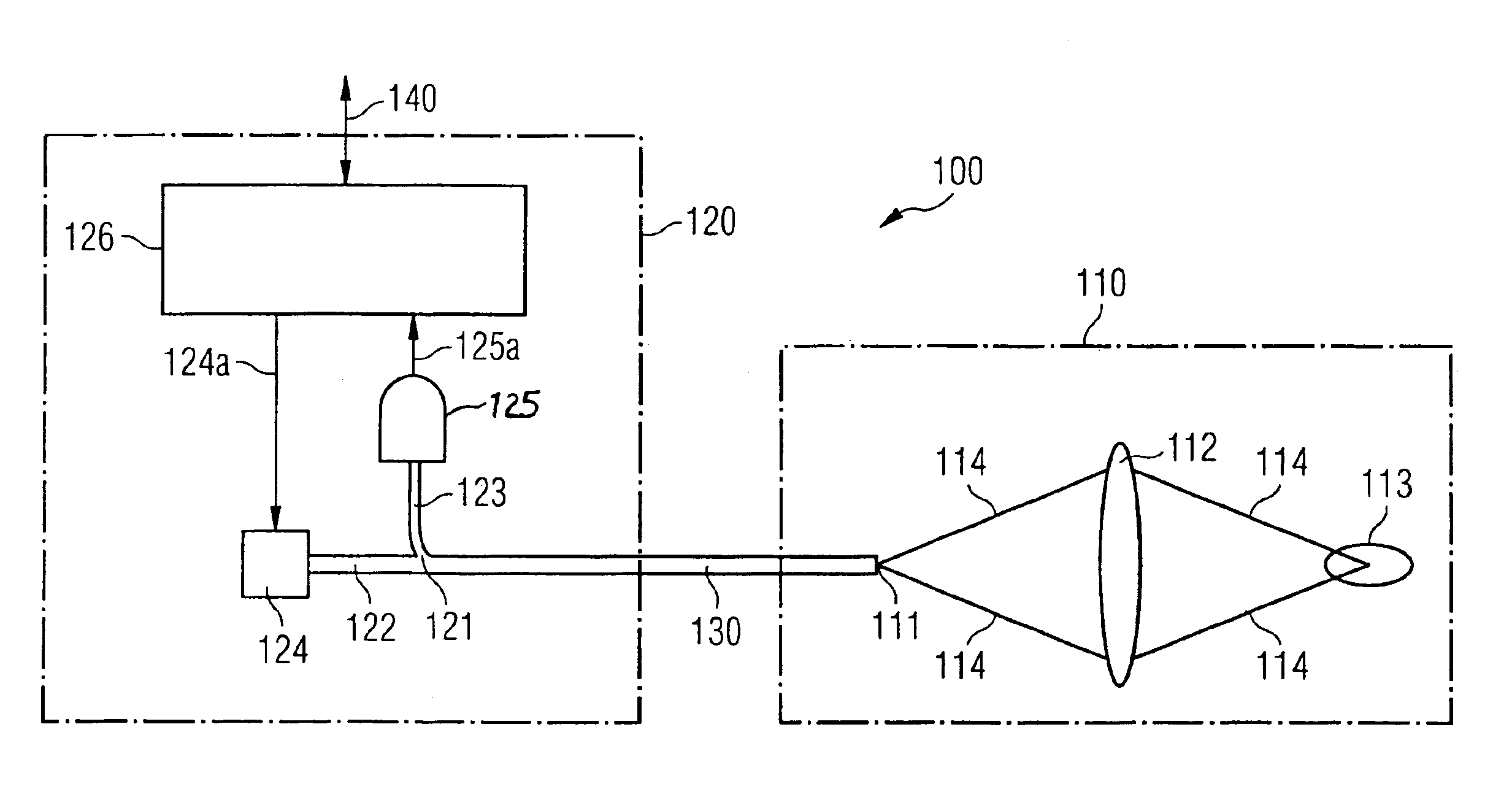
Optical spacer switch and insertion head, automatic insertion machine and method for inserting components on substrates by using the optical spacer switch
InactiveUS6882768B2Increase capacityHigh insertionUsing optical meansCoupling light guidesOptical ModuleComputer module
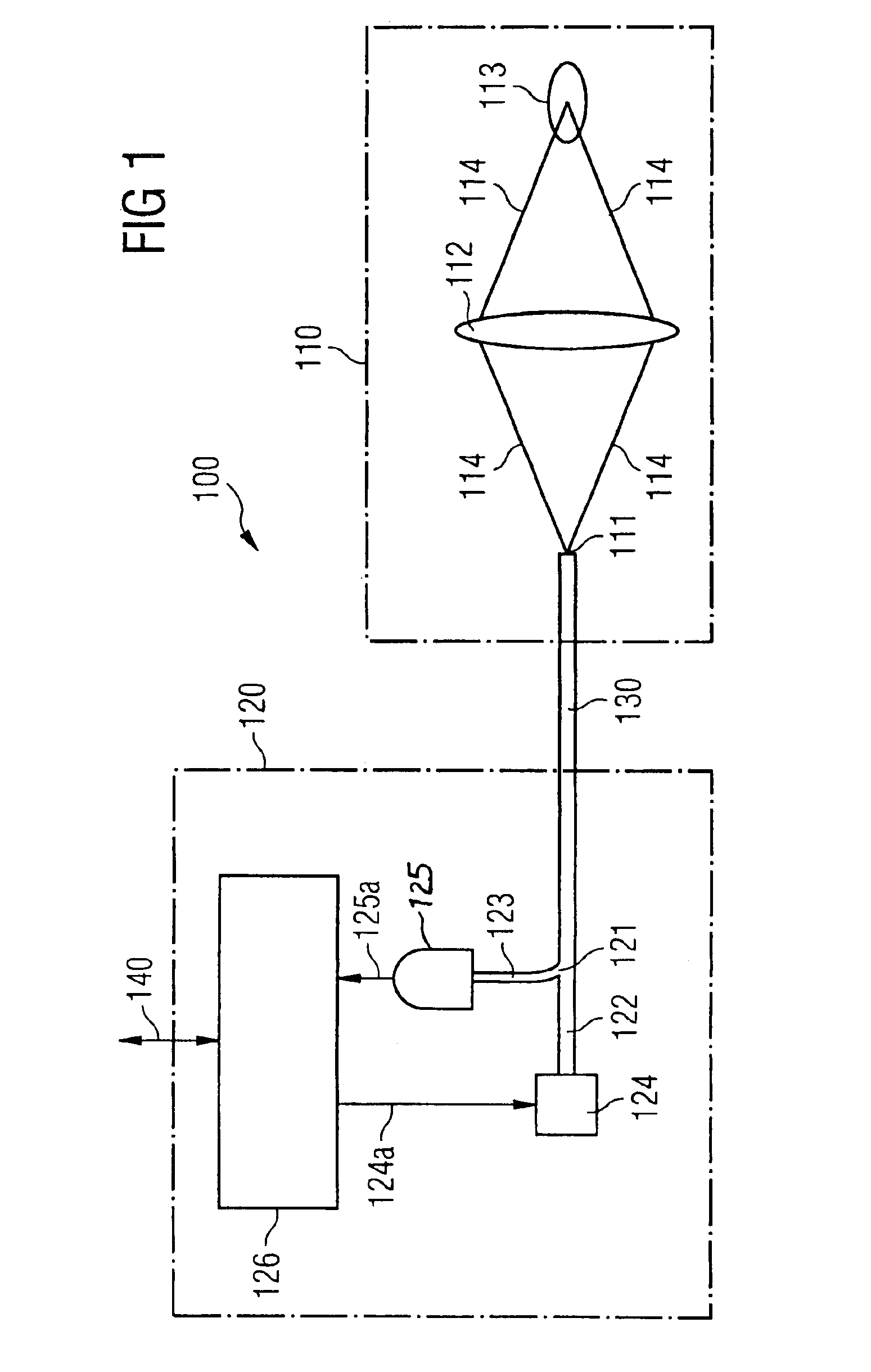
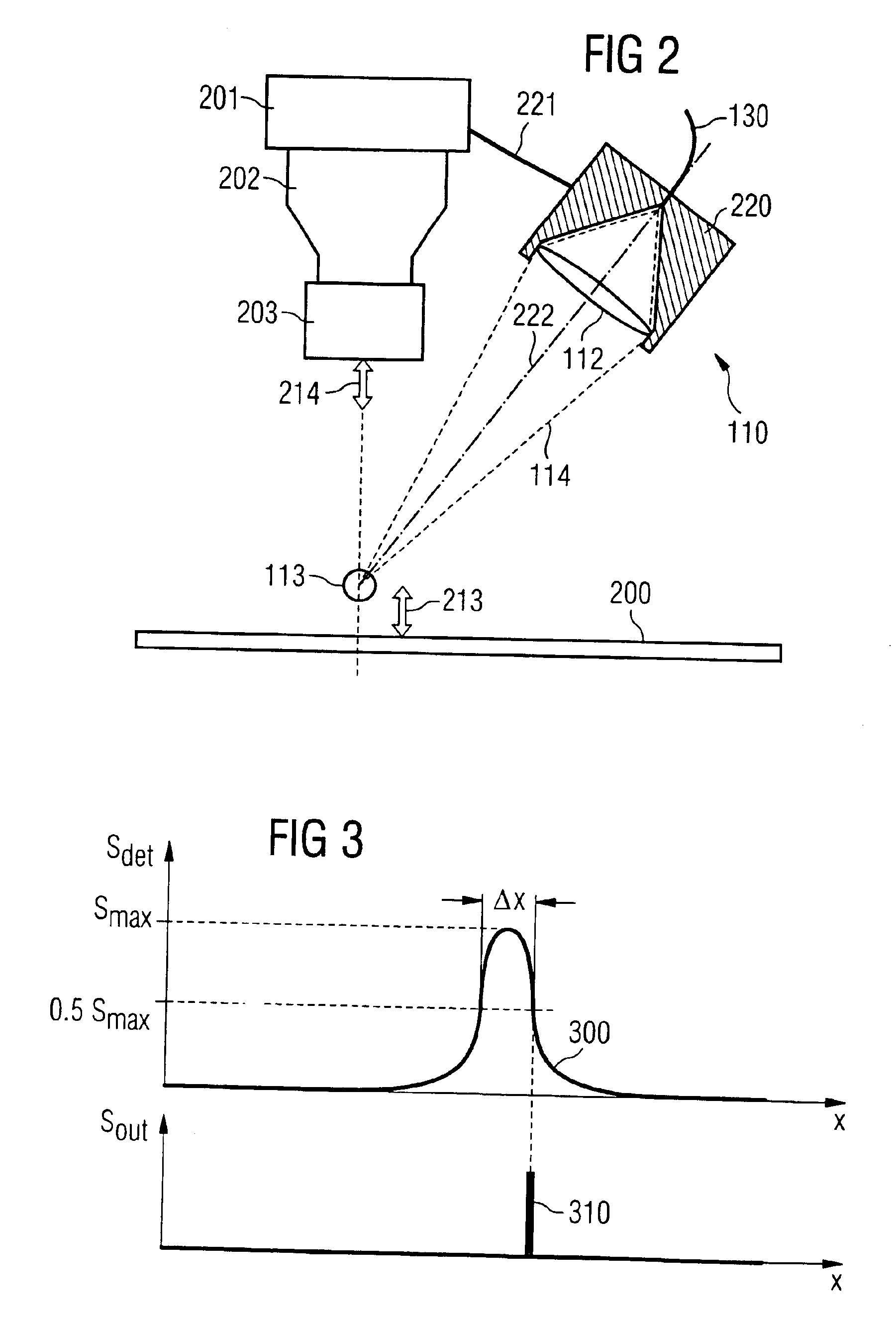
A confocal spacer switch for a fast, non-contacting determination of the spacing includes a point-shaped element that simultaneously transmits and receives light, imaging optics that form an image of the light-emitting element on a switching range and a light detection device that is coupled to the light-receiving element and emits a signal if an at least partially reflecting object enters the switching range and reflected light falls onto on the light-receiving element. The light-emitting and the light-receiving element preferably is realized with an optical waveguide end. As a result, the optical spacer switch can be divided into two modules that are connected via the optical waveguide, wherein a purely optical module can be realized in a compact and lightweight manner. A method for inserting components on substrates, uses the spacer switch, for which the insertion speed of the components is reduced immediately prior to inserting them. Thus, the impact of the component with the substrate is reduced, for an on the whole fast insertion operation.
Owner:ASMPT GMBH & CO KG
Light source device based on fluorescent crystal pump light waveguide
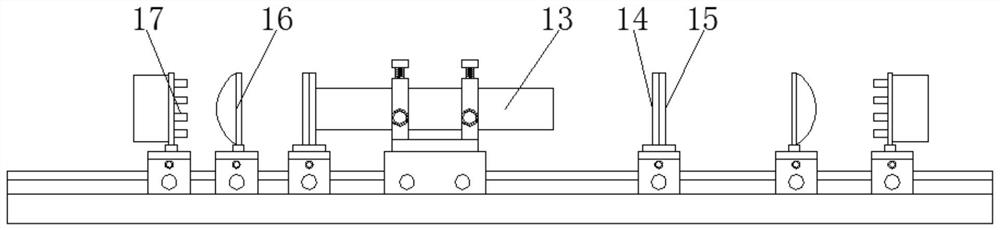
PendingCN113507031ALow costEasy to useLaser cooling arrangementsSolid state laser constructional detailsFluorescenceEngineering
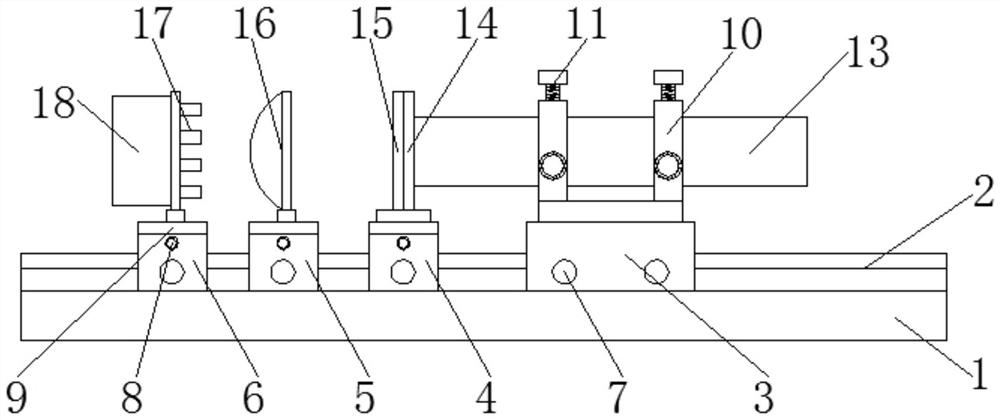
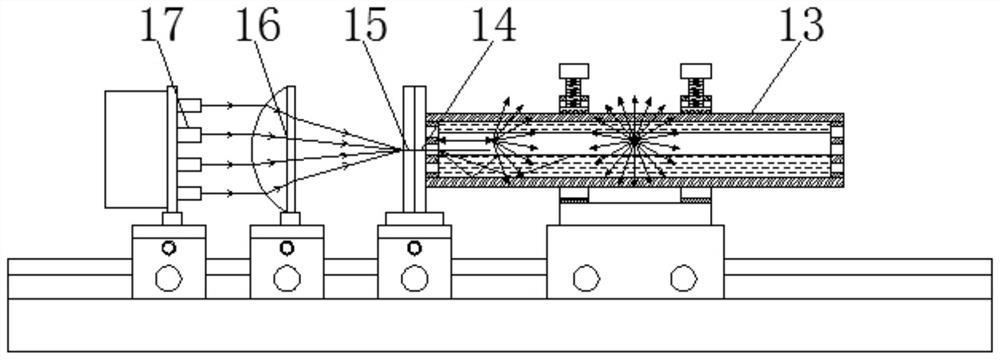
The invention provides a light source device based on a fluorescent crystal pump light waveguide, and relates to the technical field of optics. The light source device based on the fluorescent crystal pump light waveguide comprises a base, a sliding rail is fixedly arranged at the upper end of the base, and a first sliding base, a second sliding base, a third sliding base and a fourth sliding base are arranged at the upper end of the sliding rail in a sliding mode. Locking devices are fixedly arranged on the side portions of the first sliding base, the second sliding base, the third sliding base and the fourth sliding base, two fixing rings are fixedly arranged at the upper end of the first sliding base, and three adjusting bolts are fixedly arranged on each fixing ring. According to the light source device based on the fluorescent crystal pumping light waveguide, light emitted by pumping laser can be converted into low-cost blue-green light, the low-cost blue-green light is converted into yellow-green light for use, and therefore the cost of generating the yellow-green light is effectively reduced, and use is convenient.
Owner:SHANDONG UNIV
Integrated Optical Fiber and Epsilon-Near-Zero Material
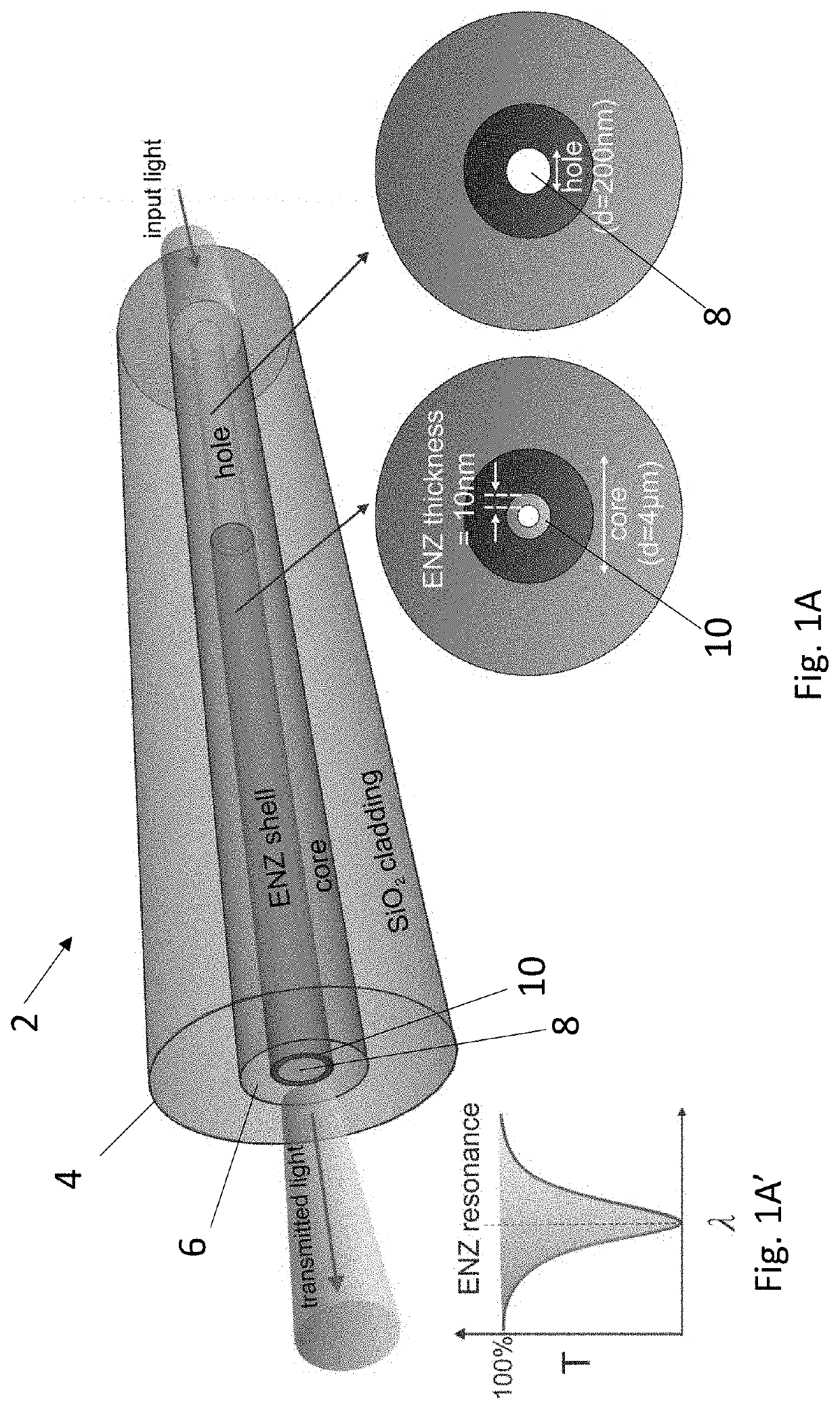
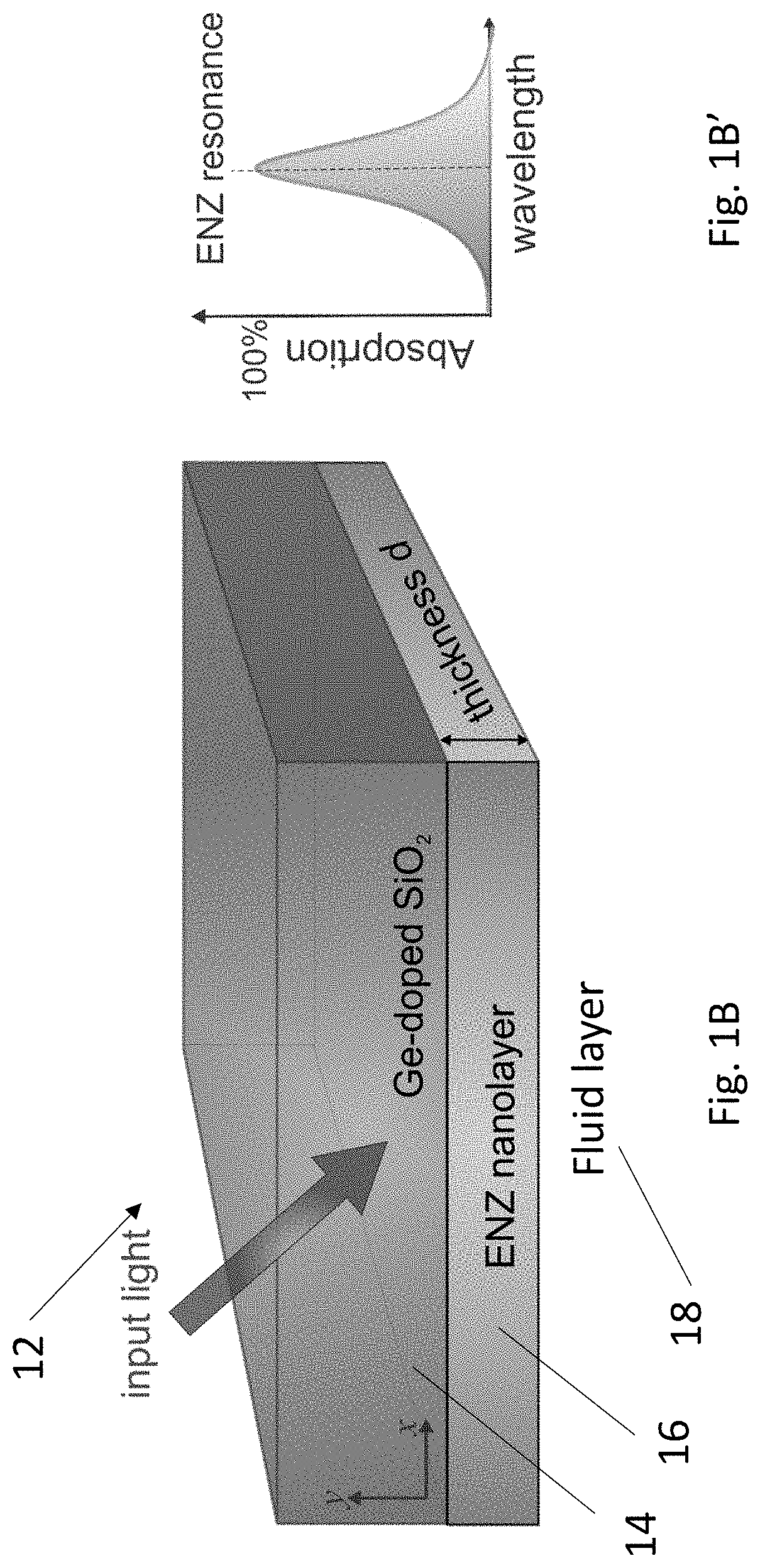
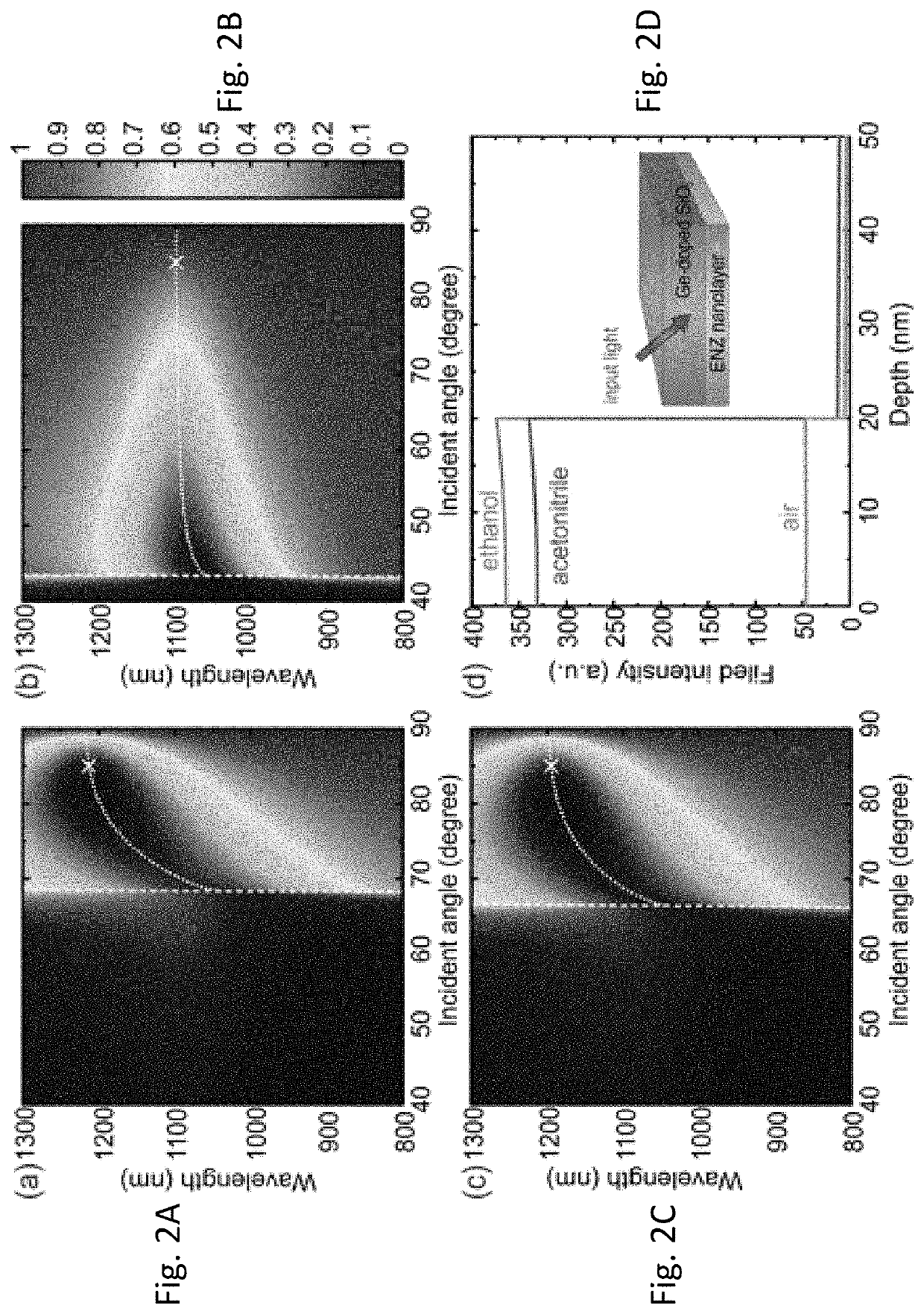
The present disclosure provides an optical waveguide design of a fiber modified with a thin layer of epsilon-near-zero (ENZ) material. The design results in an excitation of a highly confined waveguide mode in the fiber near the wavelength where permittivity of thin layer approaches zero. Due to the high field confinement within thin layer, the ENZ mode can be characterized by a peak in modal loss of the hybrid waveguide. Results show that such in-fiber excitation of ENZ mode is due to the coupling of the guided fundamental core mode to the thin-film ENZ mode. The phase matching wavelength, where the coupling takes place, varies depending on the refractive index of the constituents. These ENZ nanostructured optical fibers have many potential applications, for example, in ENZ nonlinear and magneto-optics, as in-fiber wavelength-dependent filters, and as subwavelength fluid channel for optical and bio-photonic sensing.
Owner:BAYLOR UNIVERSITY
Multi-channel waveguide with reduced crosstalk
ActiveUS20200319461A1Reduce optical cross-talkImprove artMechanical apparatusPlanar/plate-like light guidesLight beamEngineering
A waveguide apparatus for conveying a virtual image has first and second parallel planar surfaces. A first in-coupling diffractive optic on the first planar surface directs a first subset of image-bearing light beams into the waveguide and a second in-coupling diffractive optic on second planar surface directs a second subset of the image-bearing light beams into the waveguide. The first and second in-coupling diffractive optics are offset with respect to each other along the first and second parallel planar surfaces to independently direct the respective first and second subsets of the image-bearing light beams into the waveguide.
Owner:VUZIX
Method and system for variable optical thickness waveguides for augmented reality devices
PendingUS20220283371A1Quality improvementMechanical apparatusLight guides for lighting systemsEyepieceEngineering
An augmented reality device includes a projector, projector optics optically coupled to the projector, and an eyepiece optically coupled to the projector optics. The eyepiece includes an eyepiece waveguide characterized by lateral dimensions and an optical path length difference as a function of one or more of the lateral dimensions.
Owner:MAGIC LEAP
Grating structure, optical waveguide and near-to-eye display system
PendingCN111812760AEasy to adjust diffraction efficiencyGood diffraction efficiencyDiffraction gratingsOptical waveguide light guideWaveguide (optics)Materials science
The embodiment of the invention relates to the technical field of optics, and particularly relates to a grating structure, an optical waveguide and a near-to-eye display system. The embodiment of theinvention provides the grating structure which is applied to the optical waveguide and the near-to-eye display system. The grating structure comprises a grating body. A through hole is formed in the grating body, and compared with a cylindrical structure grating and a rhombus structure grating, the grating structure is more in adjustable parameters, high in design freedom degree and easy to adjustdiffraction efficiency of the grating so that the grating structure provided by the embodiment of the invention is better in diffraction efficiency.
Owner:SHENZHEN LOCHN OPTICS TECH CO LTD
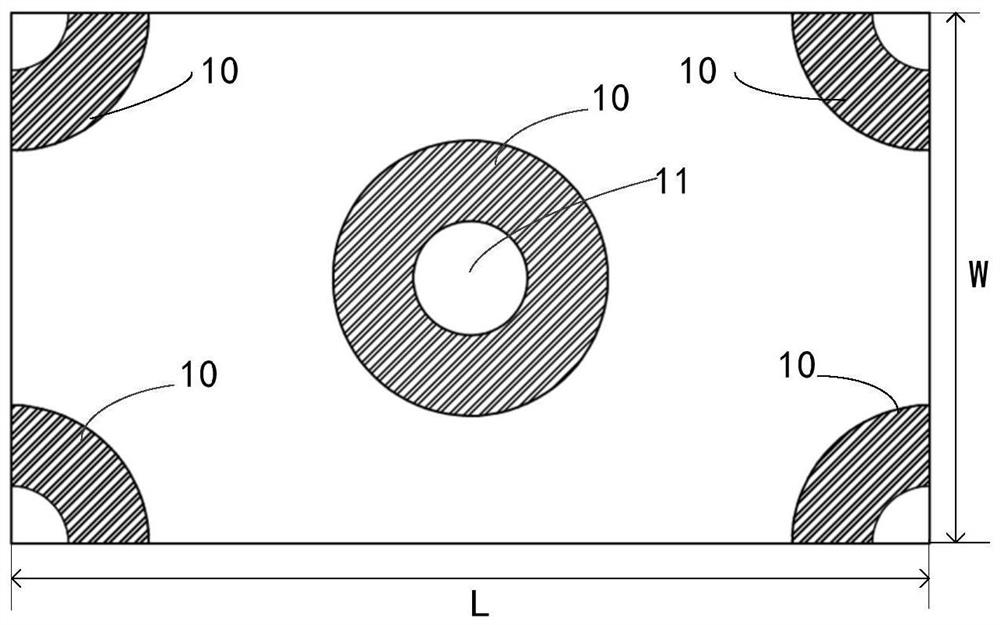
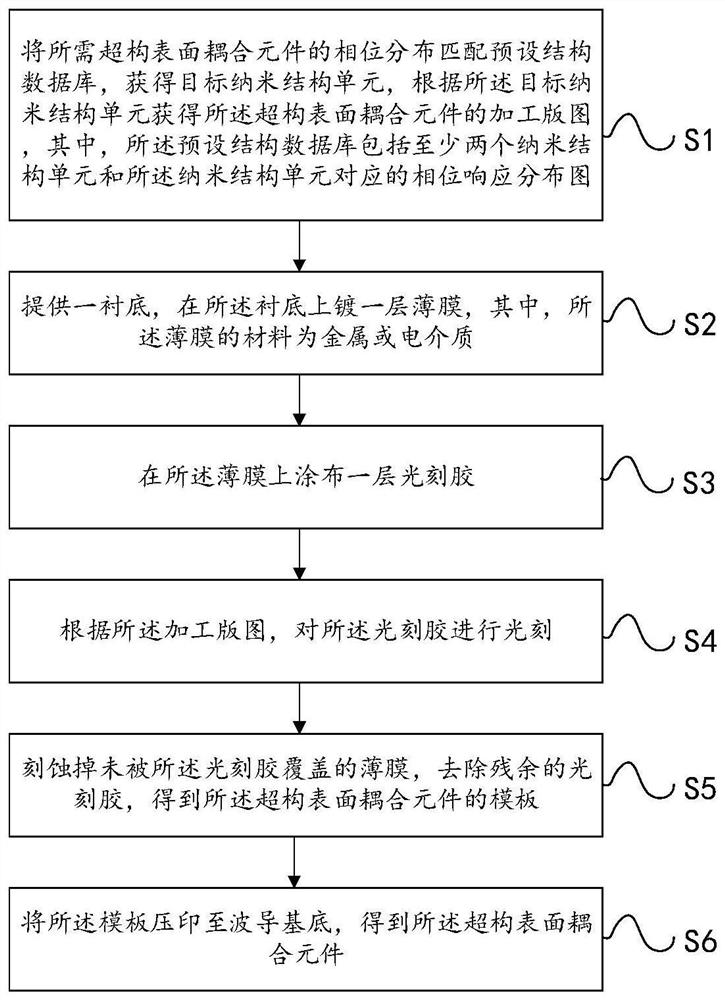
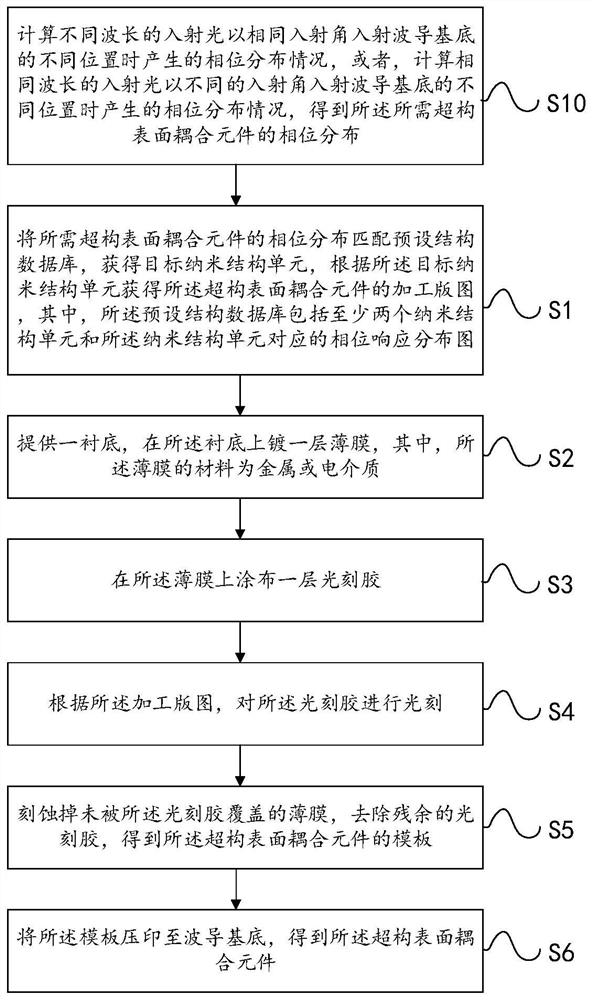
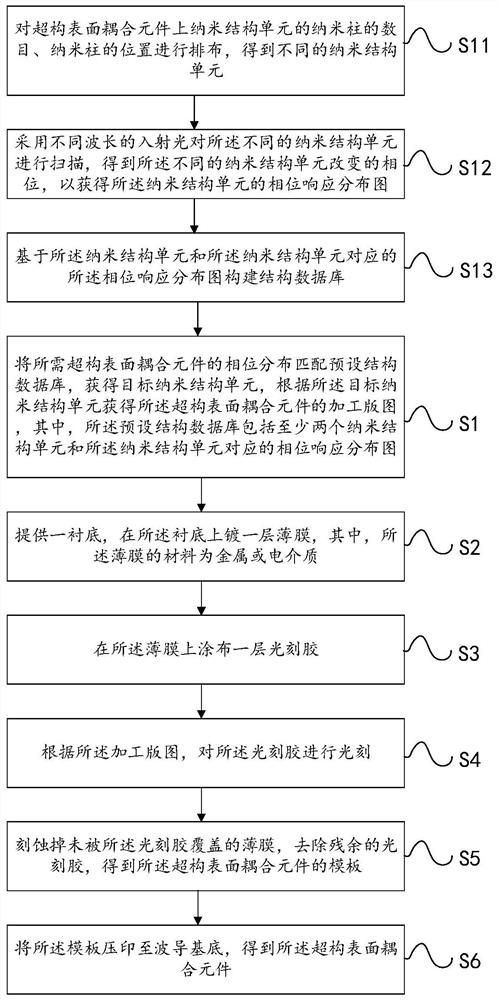
Manufacturing method of meta-structure surface coupling element
ActiveCN112394449AAchromaticReduce processing difficultyOptical waveguide light guideEtchingThin membrane
An embodiment of the invention relates to the technical field of optics, in particular to a manufacturing method of a meta-structure surface coupling element. The manufacturing method of the meta-structure surface coupling element provided by the embodiment of the invention comprises the following steps of: matching the phase distribution of a required meta-structure surface coupling element witha preset structure database to obtain a target nano-structure unit, and acquiring a processing layout of the meta-structure surface coupling element according to the target nano-structure unit, wherein the preset structure database comprises at least two nanostructure units and phase response distribution diagrams corresponding to the nanostructure units; providing a substrate, and plating a layerof metal or dielectric material film on the substrate; coating a layer of photoresist on the film; performing photoetching, etching and photoresist removing according to the processing layout to obtain a template of the meta-structure surface coupling element; and impressing the template to the waveguide substrate to obtain the meta-structure surface coupling element. The meta-structure surface coupling element manufactured through adopting the manufacturing method can be applied to an optical waveguide, achromatism can be achieved, and the machining difficulty is low.
Owner:SHENZHEN LOCHN OPTICS HI-TECH CO LTD
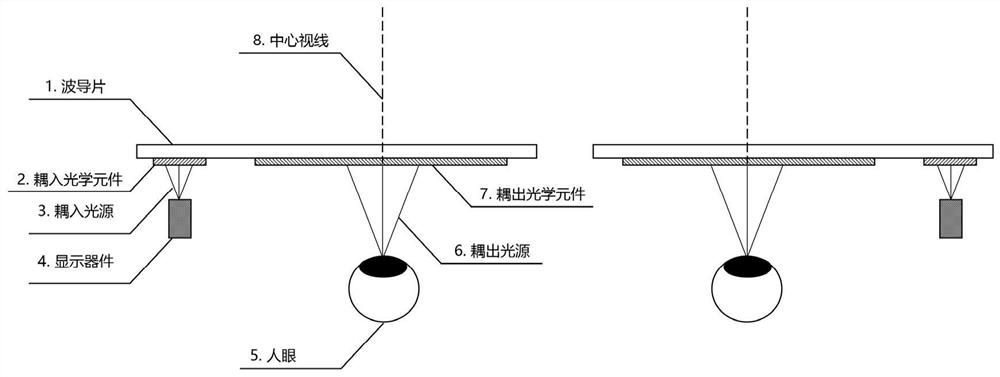
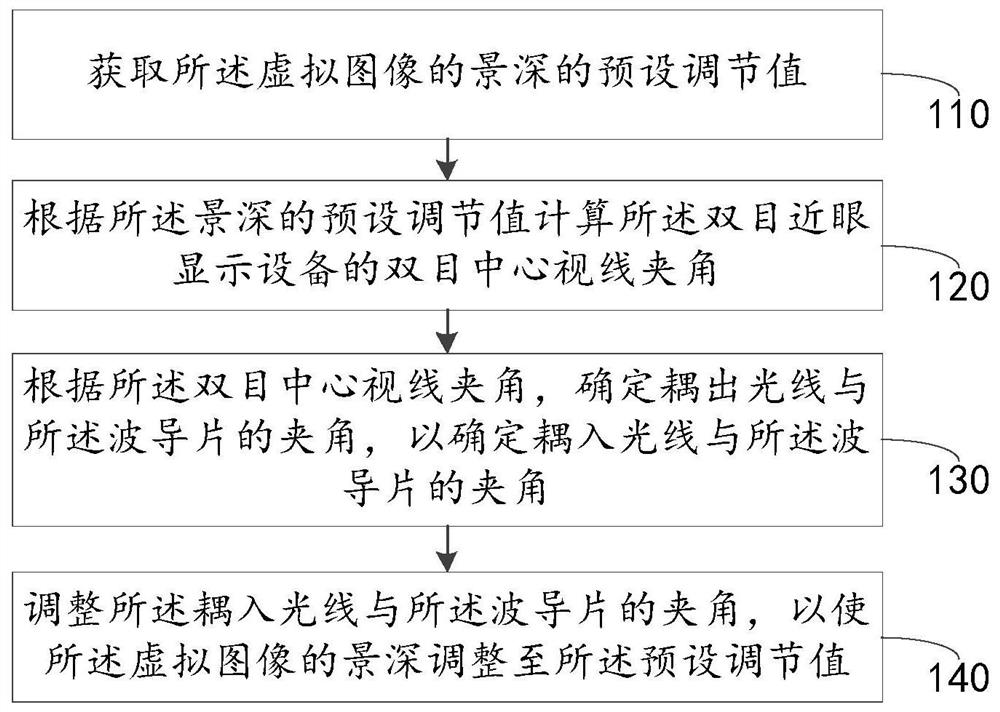
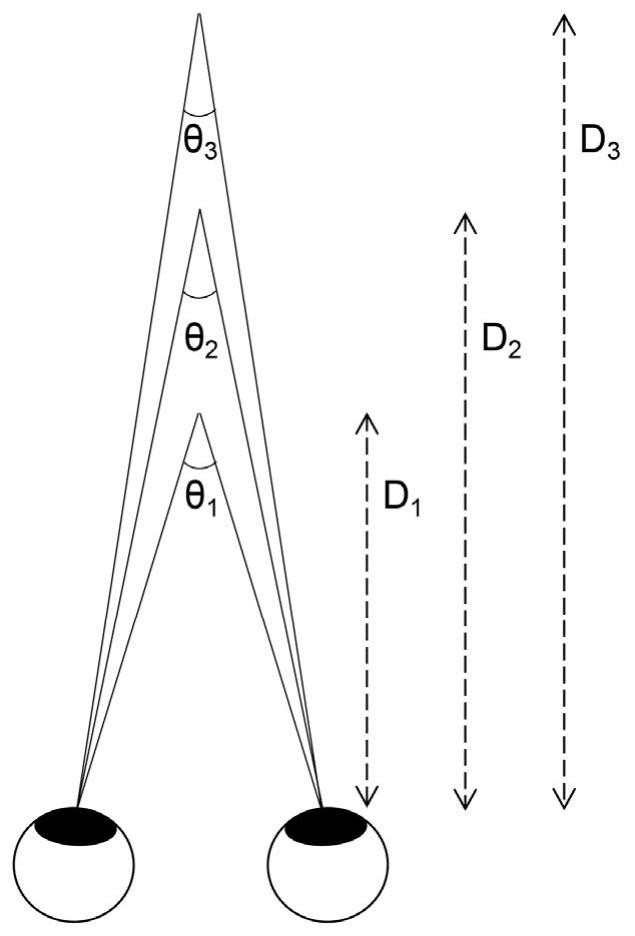
Depth-of-field adjusting method and device and binocular near-to-eye display equipment
The embodiment of the invention relates to the technical field of optics. The invention discloses a depth-of-field adjusting method and device capable of achieving multiple depths of field and binocular near-to-eye display equipment. The device comprises a display device used for outputting a display image and a waveguide sheet used for receiving the display image and outputting a virtual image visible to human eyes according to the display image. The display image is coupled into the waveguide sheet in the form of light; the virtual image is coupled out from the optical waveguide in the formof light. The method comprises the steps of firstly obtaining a preset adjustment value of the depth of field of a virtual image, calculating a binocular center sight included angle of the binocular near-to-eye display equipment according to the preset adjustment value, determining an included angle between coupled-out light and the waveguide sheet according to the binocular center sight includedangle to determine an included angle between coupled-in light and the waveguide sheet, and finally adjusting the included angle between the coupled-in light and the waveguide sheet to enable the depthof field of a virtual image to be adjusted to the preset adjustment value.
Owner:SHENZHEN LOCHN OPTICS HI-TECH CO LTD
Microfluidic device
ActiveUS8891084B2Bioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsParticle flowAcoustic energy
The present disclosure relates to microfluidic devices adapted for facilitating cytometry analysis of particles flowing therethrough. In certain embodiments, the microfluidic devices allow light collection from multiple directions. In certain other embodiments, the microfluidic devices use spatial intensity modulation. In certain other embodiments, the microfluidic devices have magnetic field separators. In certain other embodiments, the microfluidic devices have the ability to stack. In certain other embodiments, the microfluidic devices have 3-D hydrodynamic focusing to align sperm cells. In certain other embodiments, the microfluidic devices have acoustic energy couplers. In certain other embodiments, the microfluidic devices have phase variation producing lenses. In certain other embodiments, the microfluidic devices have transmissive and reflective lenses. In certain other embodiments, the microfluidic devices have integrally-formed optics. In certain other embodiments, the microfluidic devices have non-integral geographically selective reagent delivery structures. In certain other embodiments, the microfluidic devices have optical waveguides incorporated into their flow channels. In certain other embodiments, the microfluidic devices have optical waveguides with reflective surfaces incorporated into their flow channels. In certain other embodiments, the microfluidic devices have virus detecting and sorting capabilities. In certain other embodiments, the microfluidic devices display a color change to indicate use or a result.
Owner:SONY CORP +1
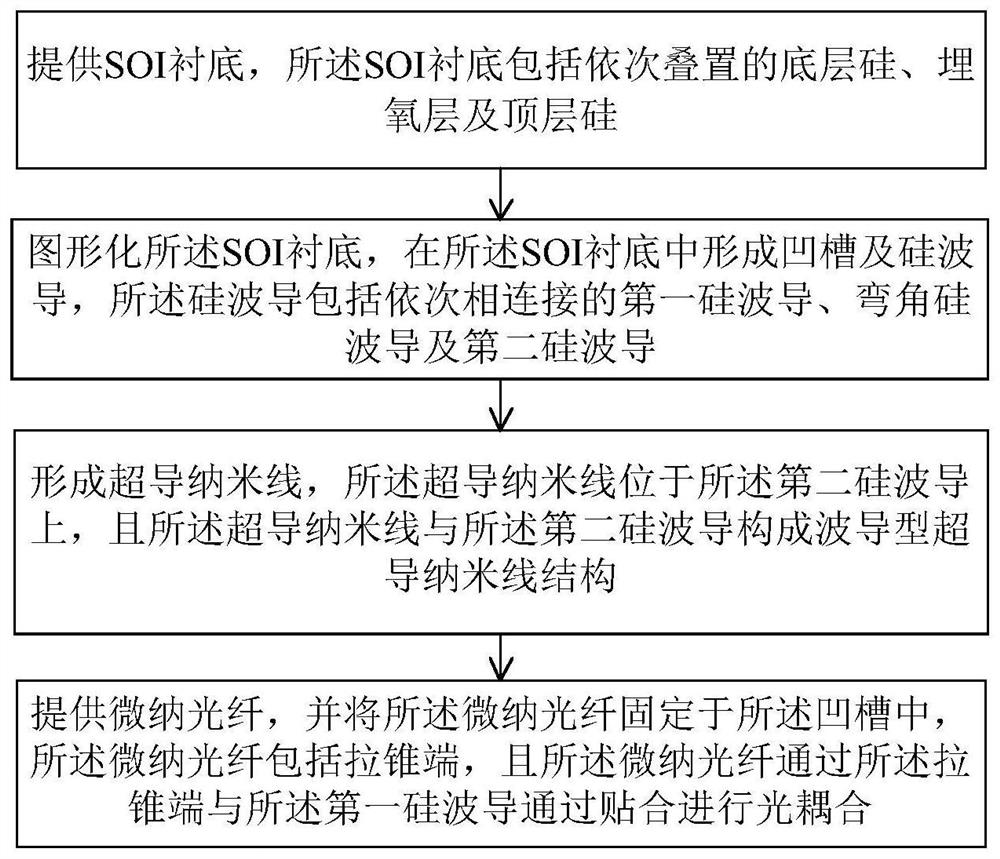
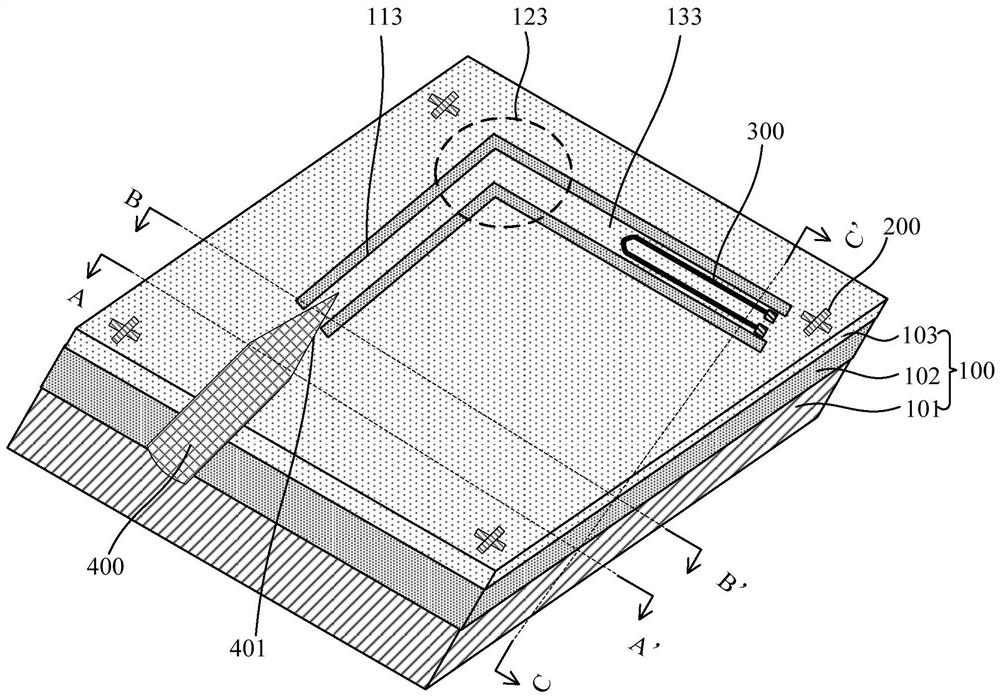
Micro-nano optical fiber-waveguide-superconducting nanowire single-photon detector and preparation method thereof
ActiveCN113204075AAchieve absorptionOptical coupling is easyNanosensorsCoupling light guidesNanowireWaveguide (optics)
The invention provides a micro-nano optical fiber-waveguide-superconducting nanowire single-photon detector and a preparation method thereof. A micro-nano optical fiber fixed in a V-shaped groove can realize high-precision optical coupling alignment with a waveguide, and the transition section, which becomes thin from thick, of the micro-nano optical fiber is suspended, so that light is prevented from leaking to a substrate, and the loss in the optical transmission process is further reduced; the waveguide type superconducting nanowire structure can completely absorb light on a chip; due to the design of the corner waveguide, an optical coupling area of the micro-nano optical fiber-waveguide can be completely separated from an optical detection area of the waveguide type superconducting nanowire structure, dark counting caused by background radiation propagating along the optical fiber can be effectively reduced, and the influence of the background dark counting on optical detection is reduced; according to the invention, a single-photon detector integrating high detection efficiency, high counting rate, low time jitter and low dark counting can be realized, and the detector is expected to play a role in the fields of light quantum information processing, quantum optics and the like.
Owner:SHANGHAI INST OF MICROSYSTEM & INFORMATION TECH CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Multi-channel optical fiber rotary junction
Exemplary apparatus, systems, methods of making, and methods of using a rotary junction are provided. A rotary junction having multiple channels is provided herein. The rotary junction has a first coupling optic and a second coupling optic where the rotating optical fiber or other waveguide comping from the first coupling optic passes through the second coupling optics.
Owner:CANON USA +1
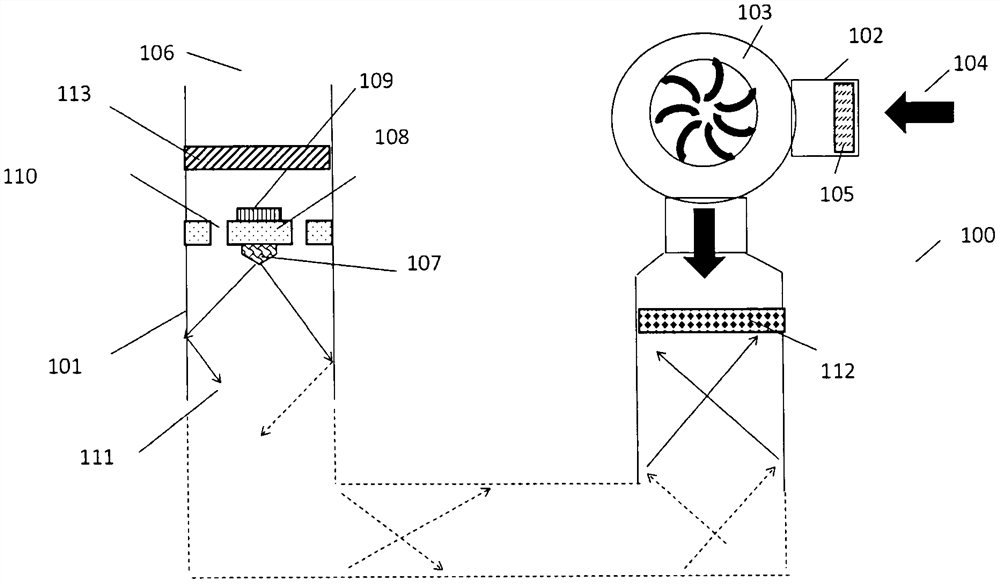
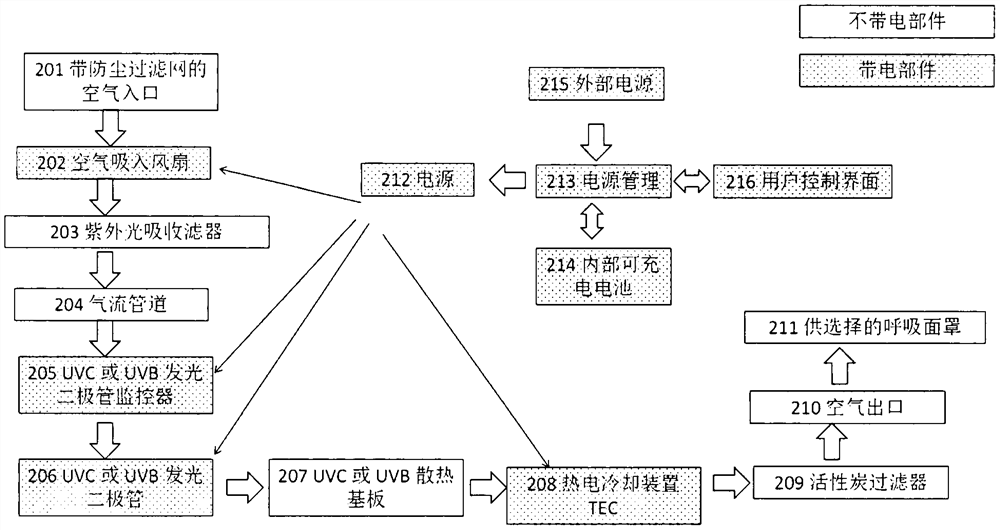
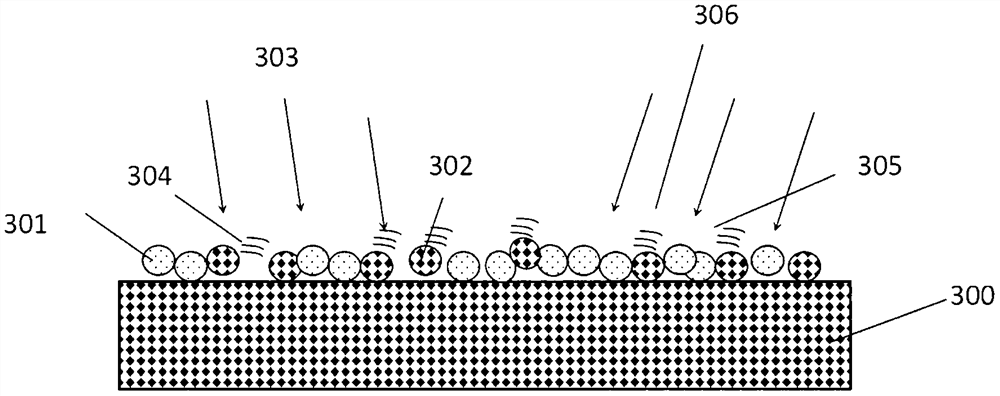
Air purification system
The invention provides a brand new air purification system. An airflow pipeline of the air purification system is made of a material which possesses low absorption and high reflectivity on UVC or UVB ultraviolet light, the airflow pipeline serves as a light wave reflection waveguide of the ultraviolet light, and meanwhile, a UVC and / or UVB light-emitting diode (LED) is arranged in the pipeline of the system. According to the design concept of the air purification system, the maximum ultraviolet irradiation dose is provided for biological aerosol possibly carried in air entering the system through organic combination of an air pipeline, ultraviolet optics and ultraviolet light-emitting diode heat dissipation, so that the biological activity of the biological aerosol is lost, and the purpose of purifying the air is achieved. The air purification system can be conveniently integrated into air supply systems of travel pillows, backpacks, handbags and various public and private transportation systems, and provides a pure air source for passengers (such as passengers on airplanes or trains) in a closed environment. The air purification system can be used for removing various harmful viruses (including COVID-19 and SARS viruses) in the air. In the flu season, the air purification system can also be used in offices; and the air purification system can also provide clean air for a user of the air purification system in the frequent pollination season.
Owner:肖军
Rod-like microstructure optical fiber
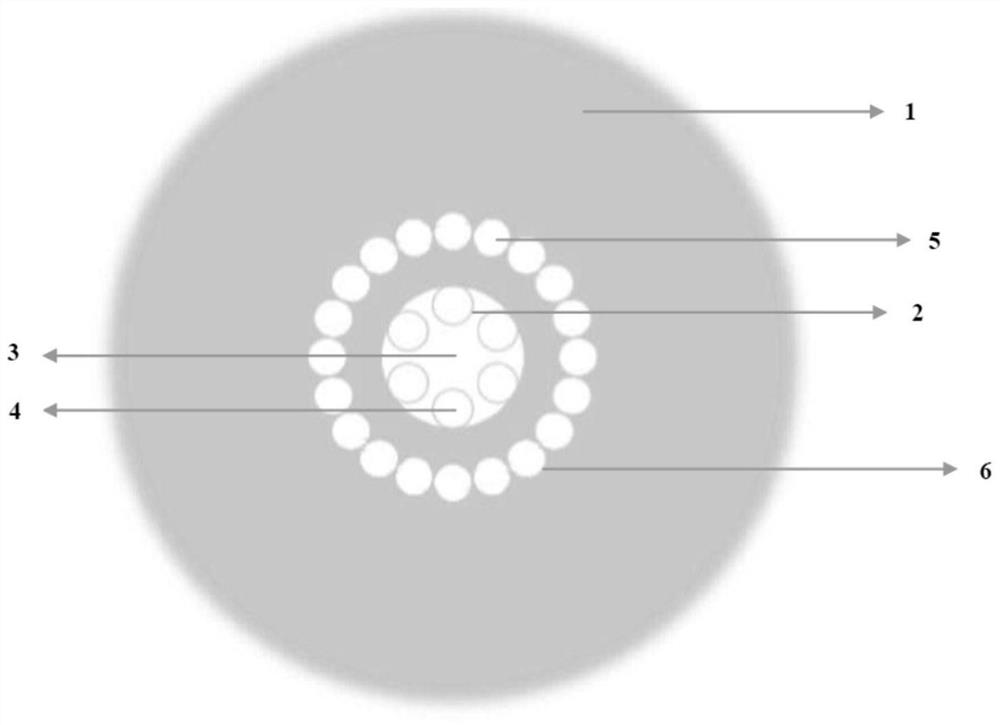
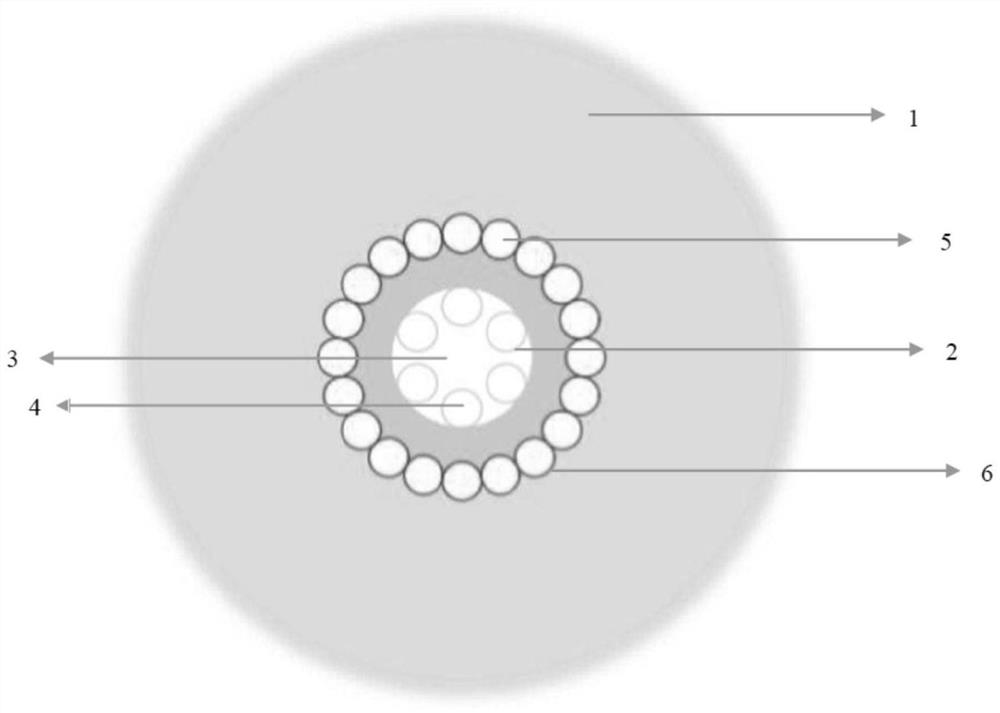
PendingCN112859236AAvoid damageStable waveguide systemCladded optical fibreOptical waveguide light guideWaveguide (optics)Microstructure
The invention discloses a rod-shaped microstructure optical fiber, and belongs to the technical field of optics and laser photoelectrons. An anti-resonance cladding, an air region, an outer cladding and a fiber core region are included. The anti-resonance cladding is formed by axially and parallelly enclosing a plurality of hollow-core capillaries into a circle, the inner part of the anti-resonance cladding is a fiber core region, the outer part of the anti-resonance cladding is an outer cladding, each hollow-core capillary of the anti-resonance cladding is parallelly connected with the inner side surface of the outer cladding, and the inner part of each hollow-core capillary is the air region; and gaps are formed among the hollow-core capillaries. The thickness of the outer cladding is millimeter-scale thickness, and the high mechanical strength can be achieved by omitting the process step of coating in a drawing process so that the optical fiber can provide a stable and perfect waveguide system which is not influenced by bending and an external stress. And more structures are additionally arranged in the external cladding so that different functions are realized.
Owner:BEIJING UNIV OF TECH
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com