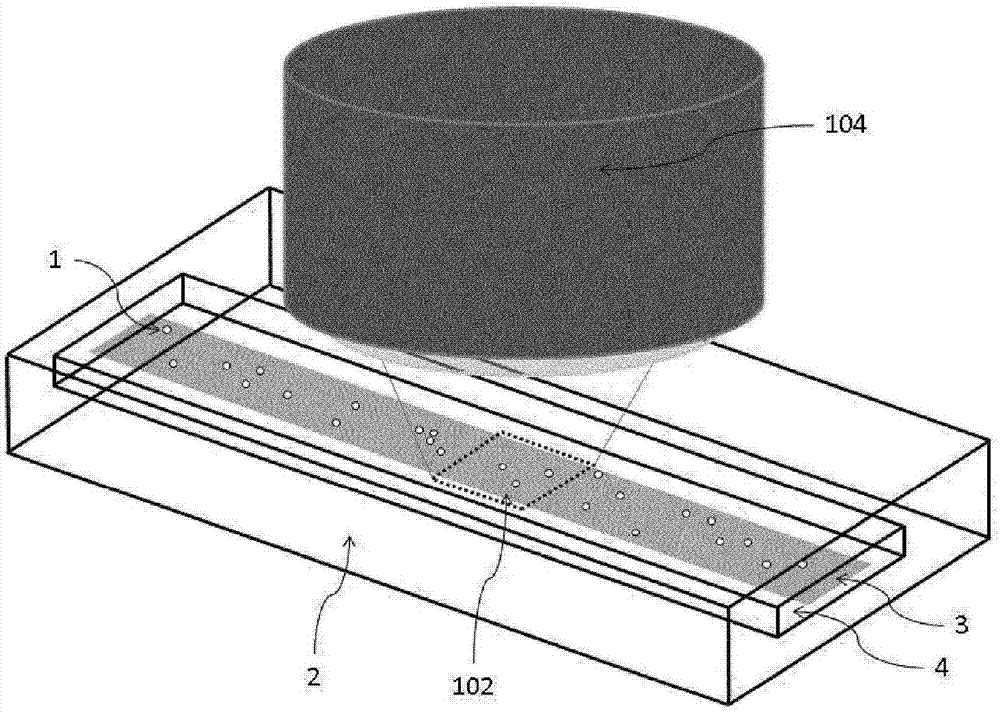
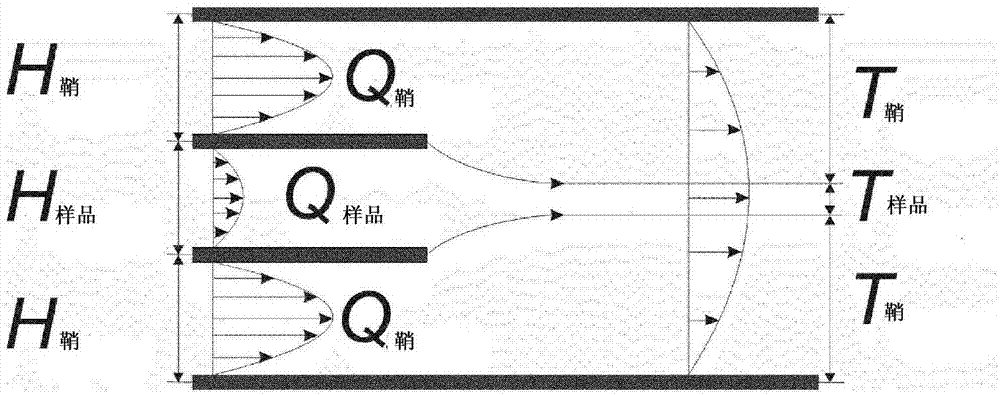
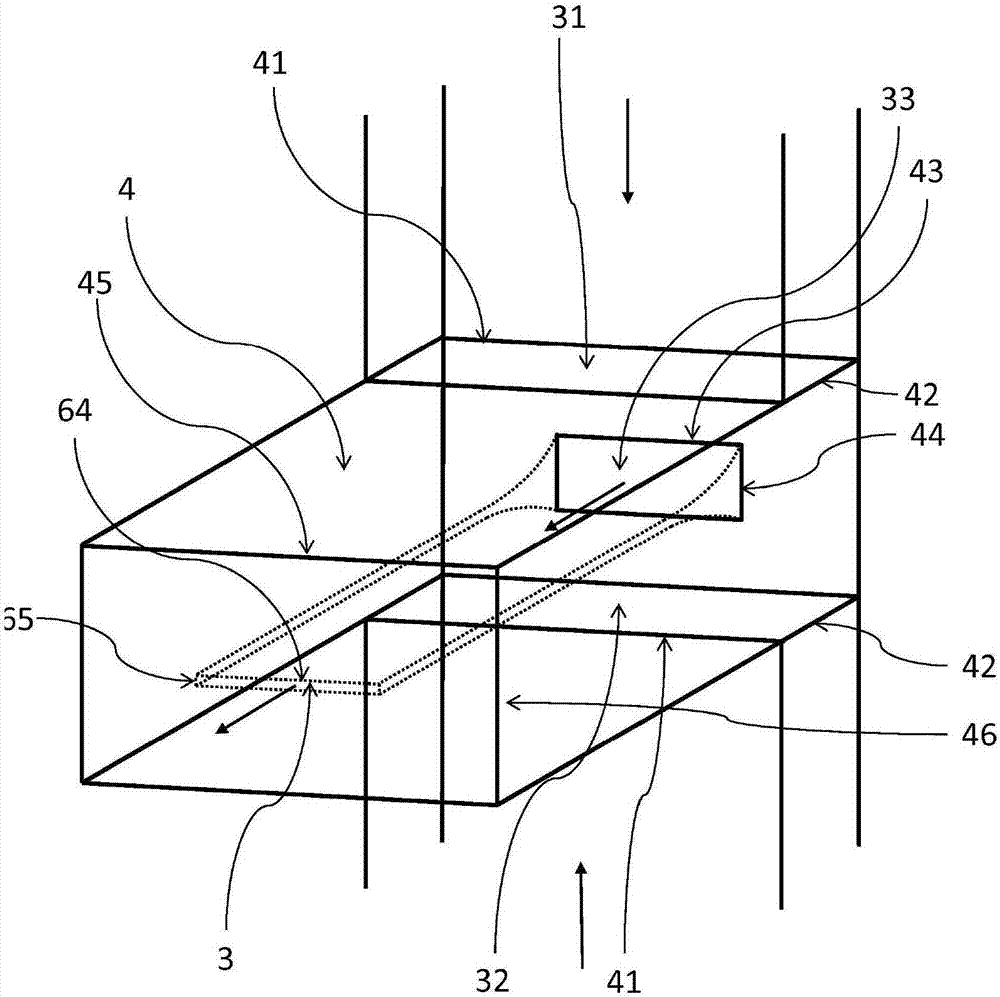
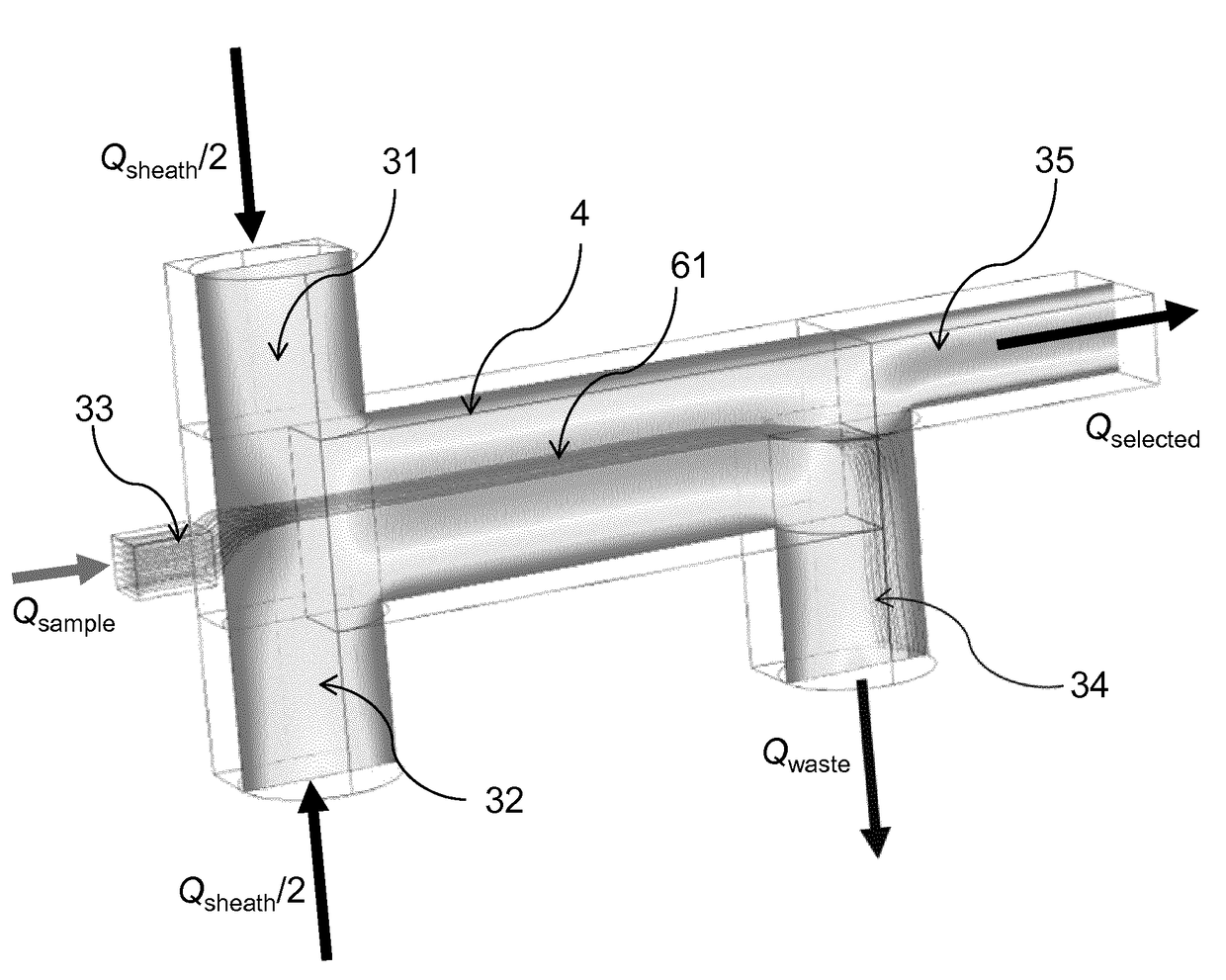
Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
41 results about "Hydrodynamic focusing" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
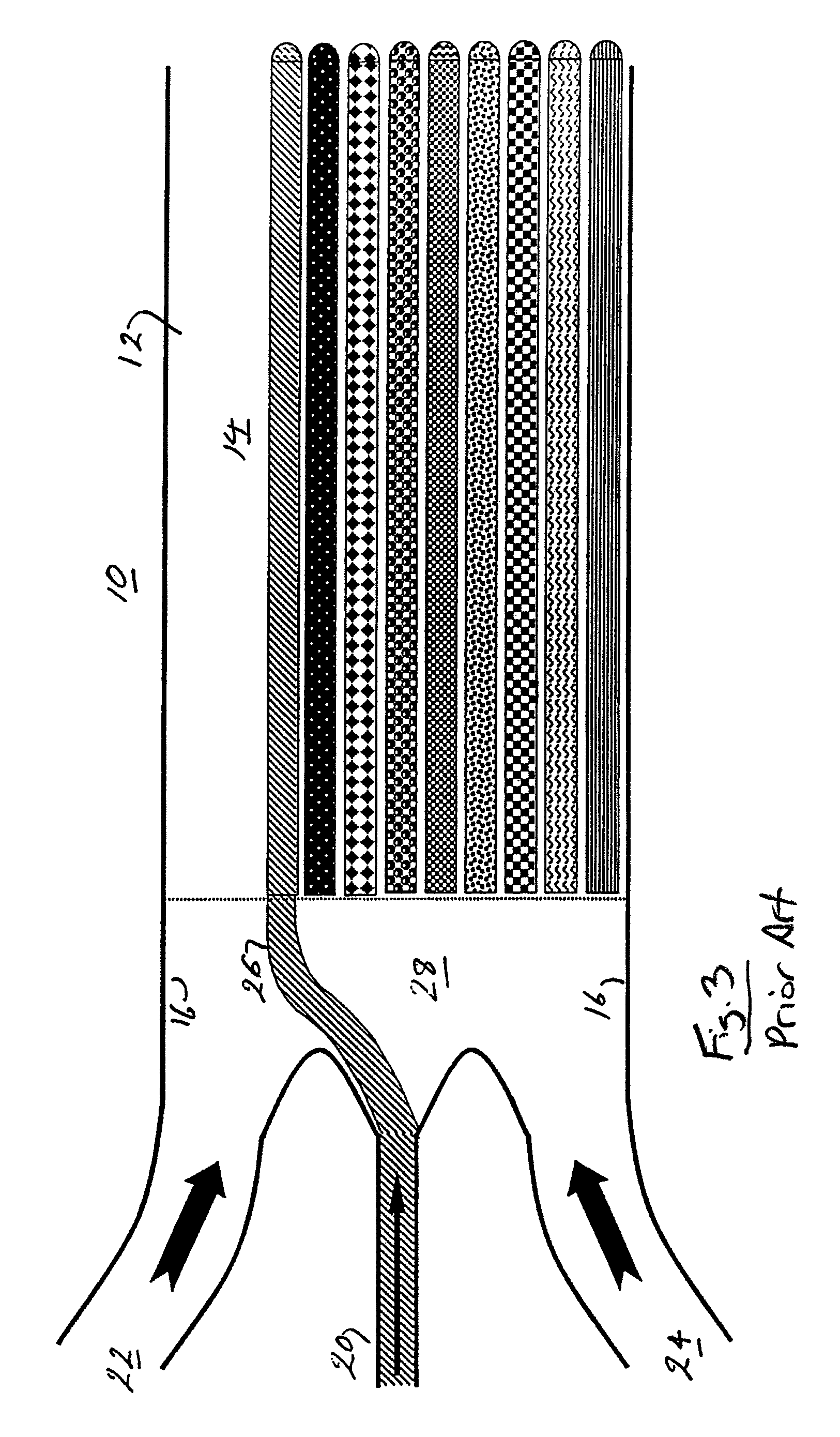
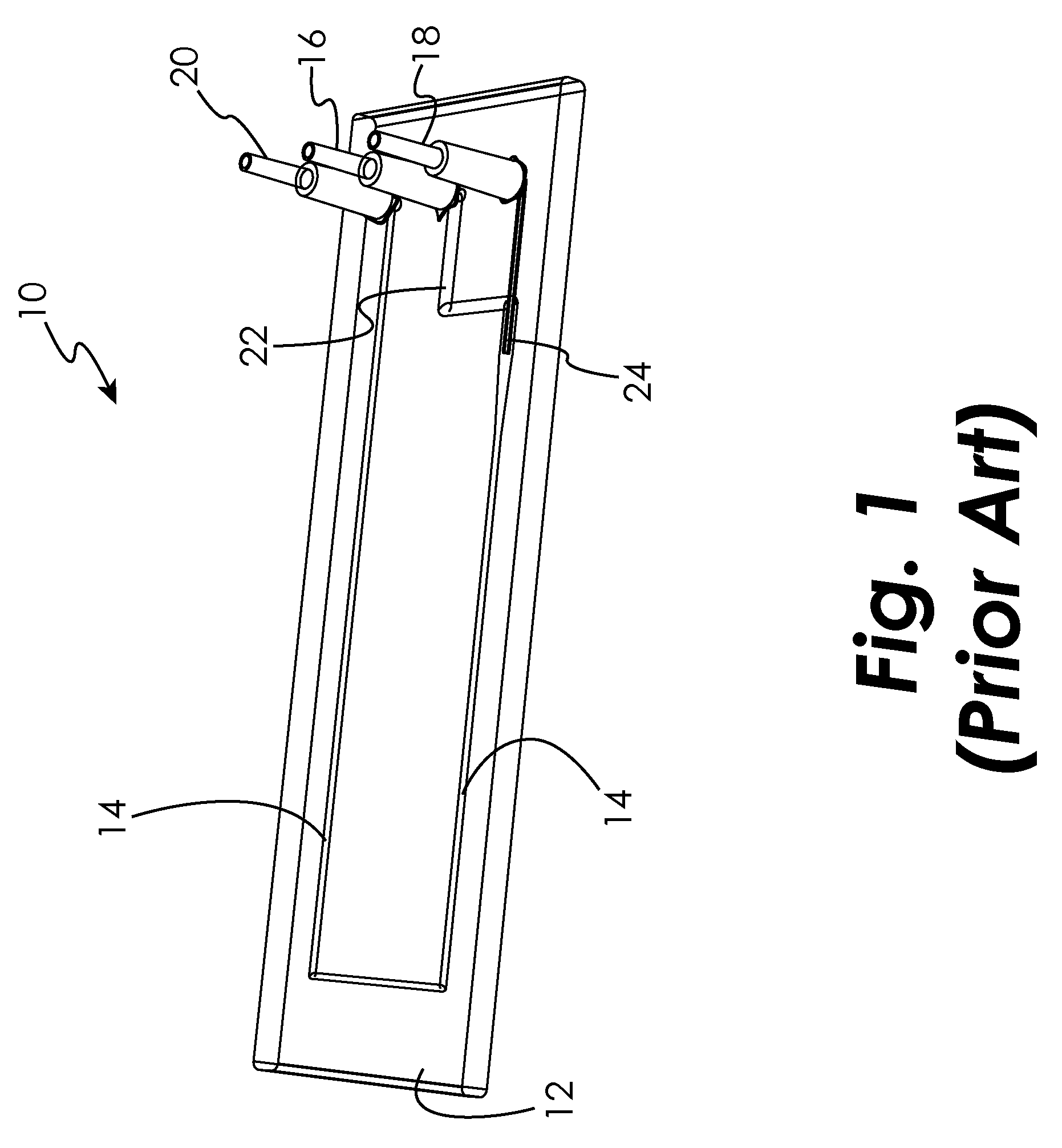
Hydrodynamic focusing is a technique used to provide more accurate results from flow cytometers or Coulter counters for determining the size of bacteria or cells.
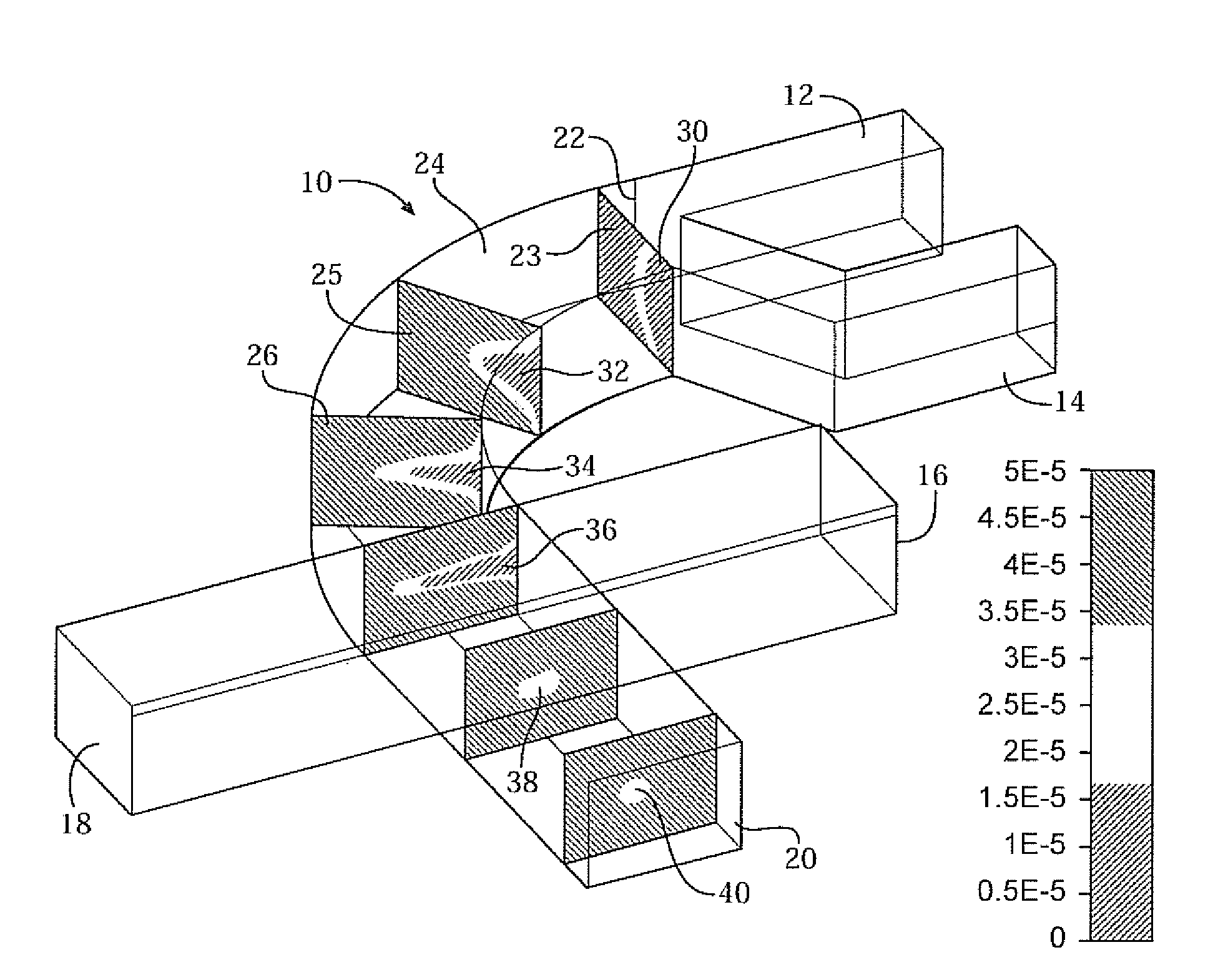
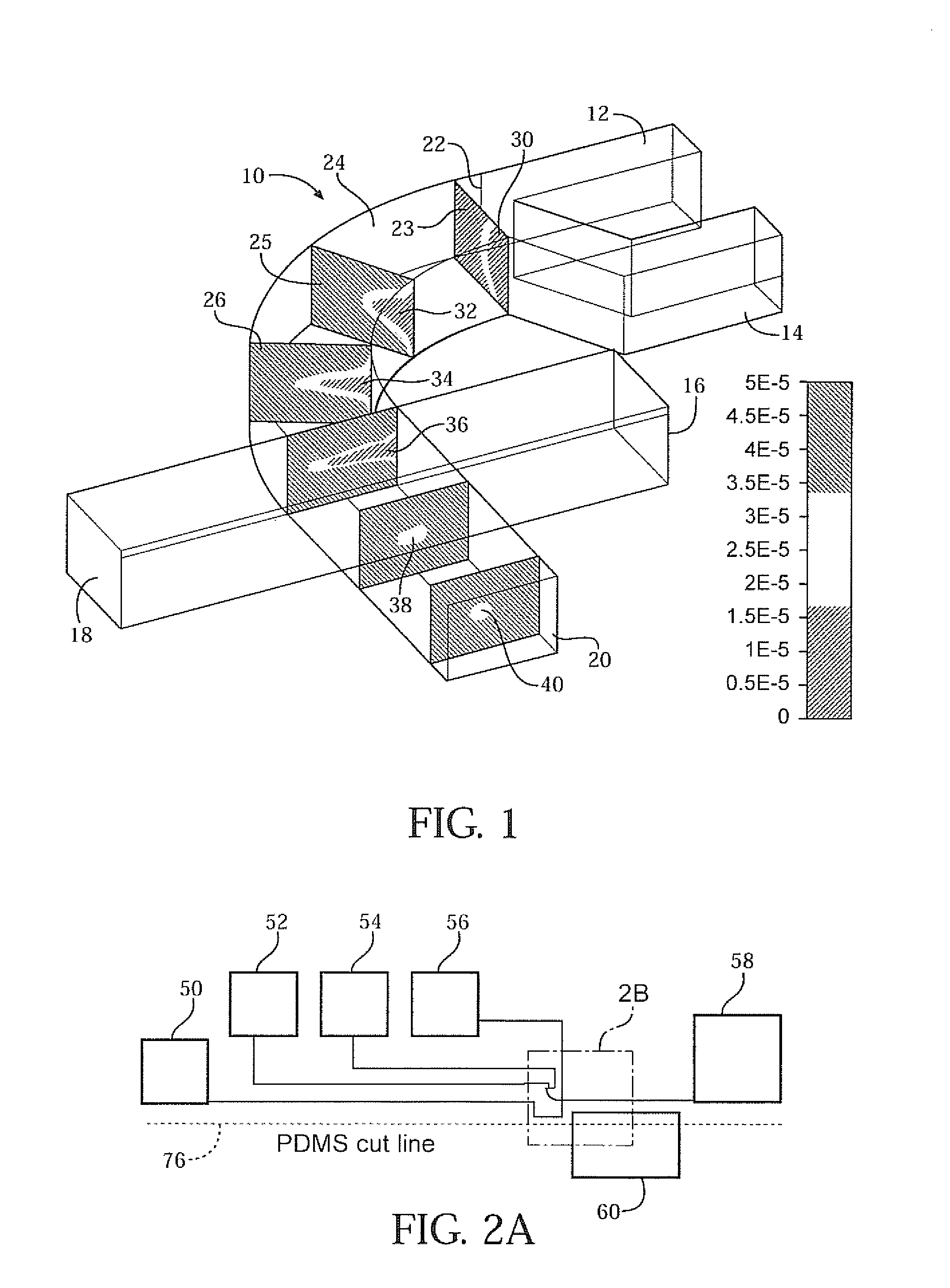
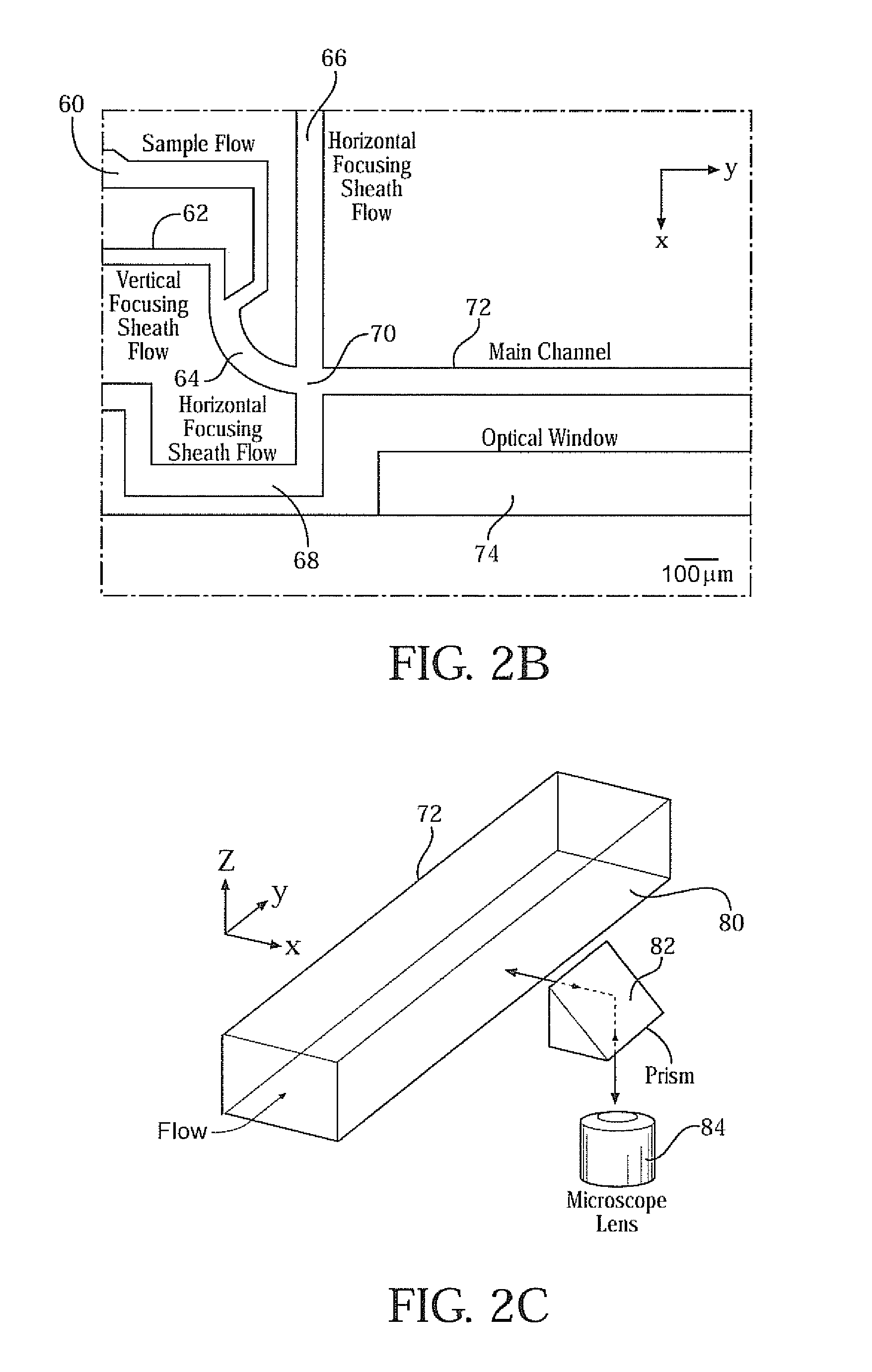
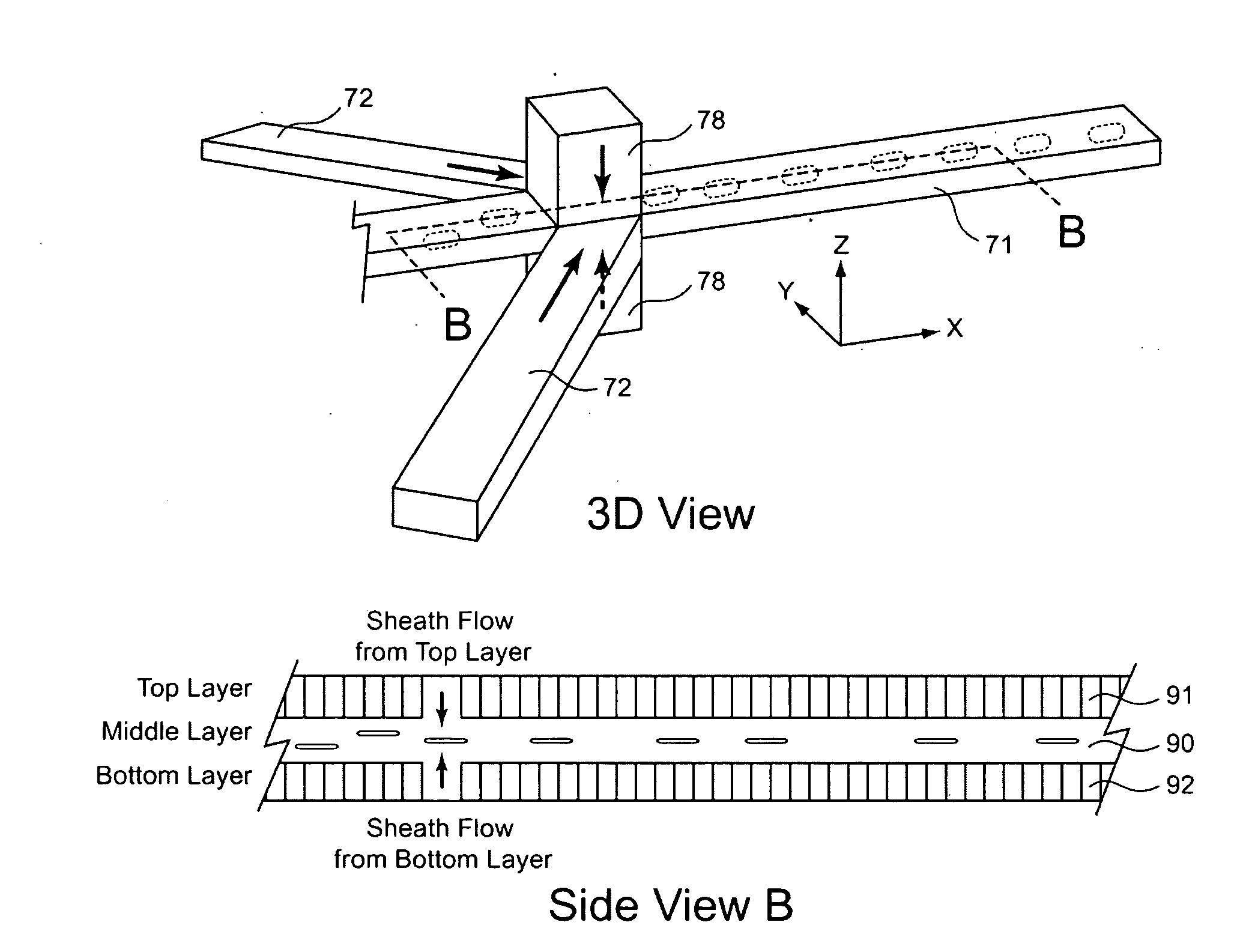
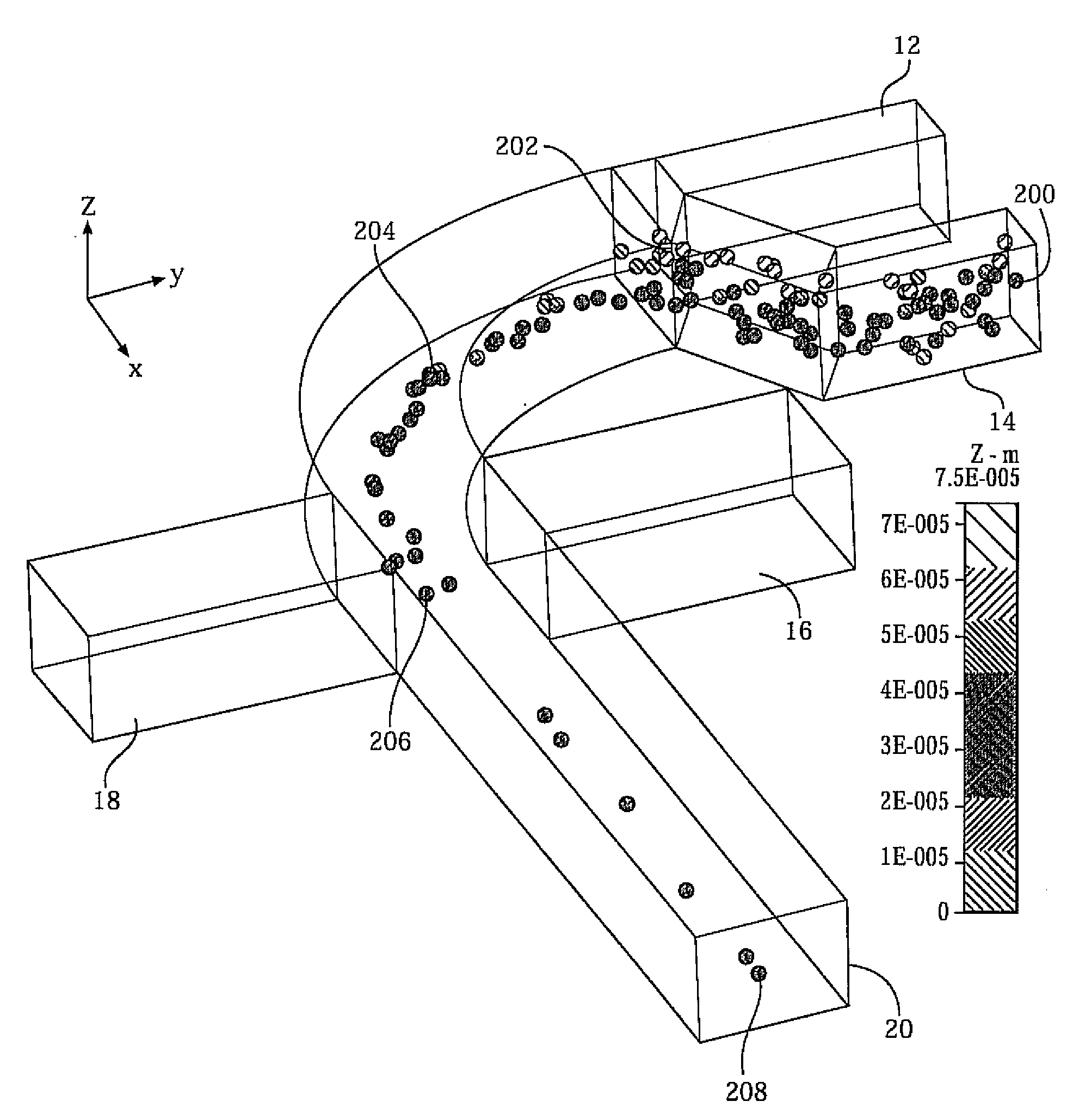
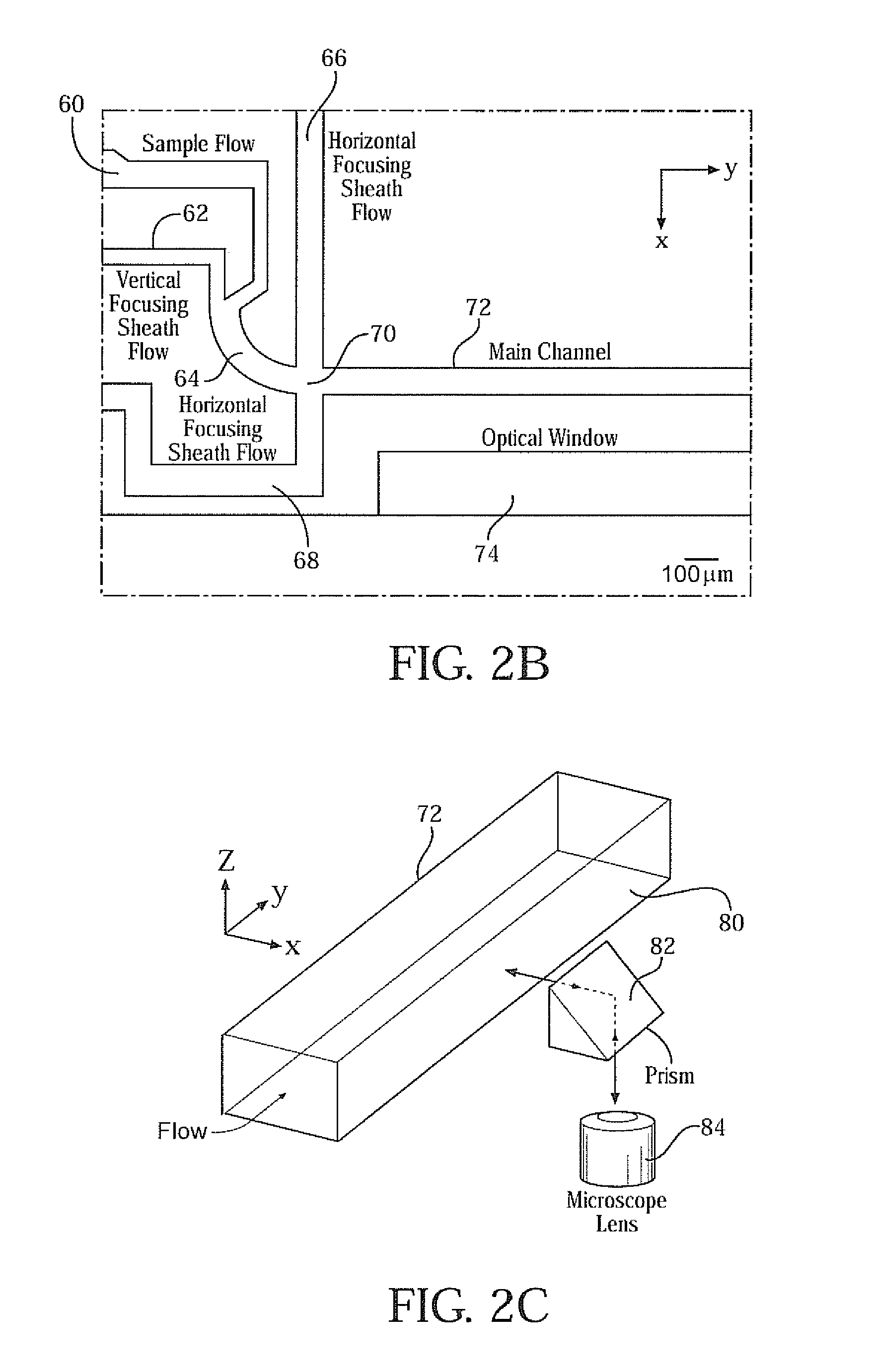
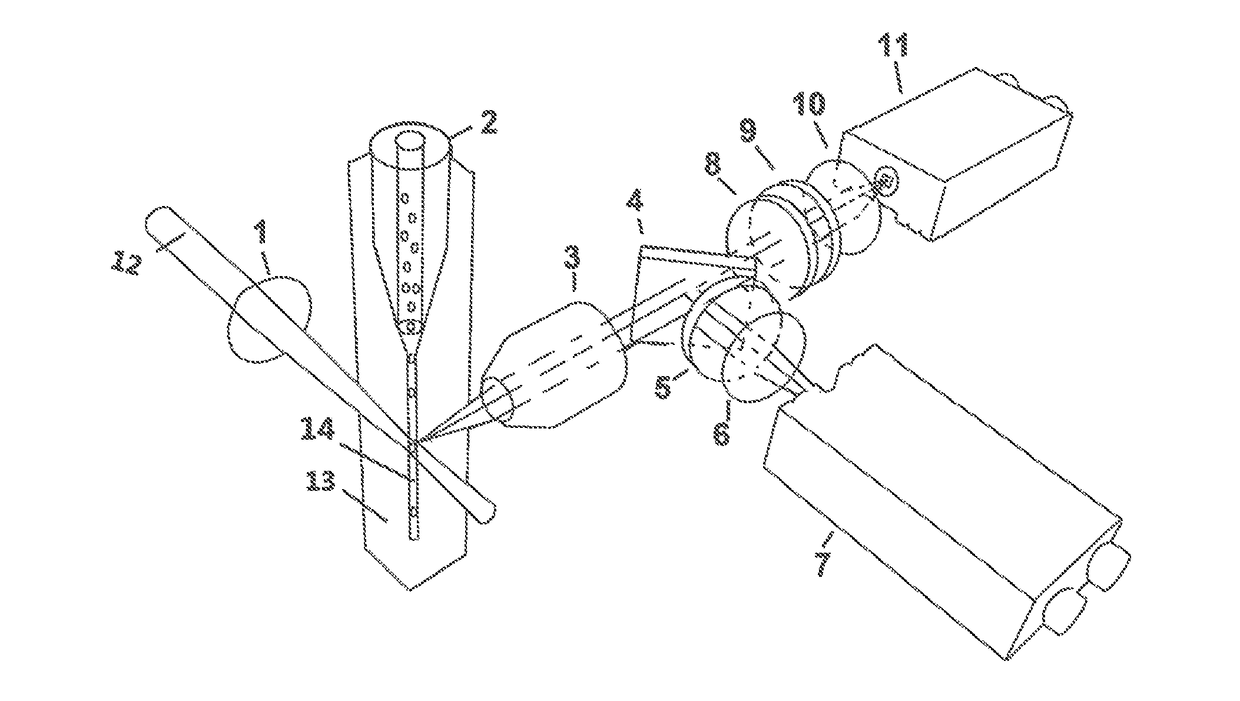
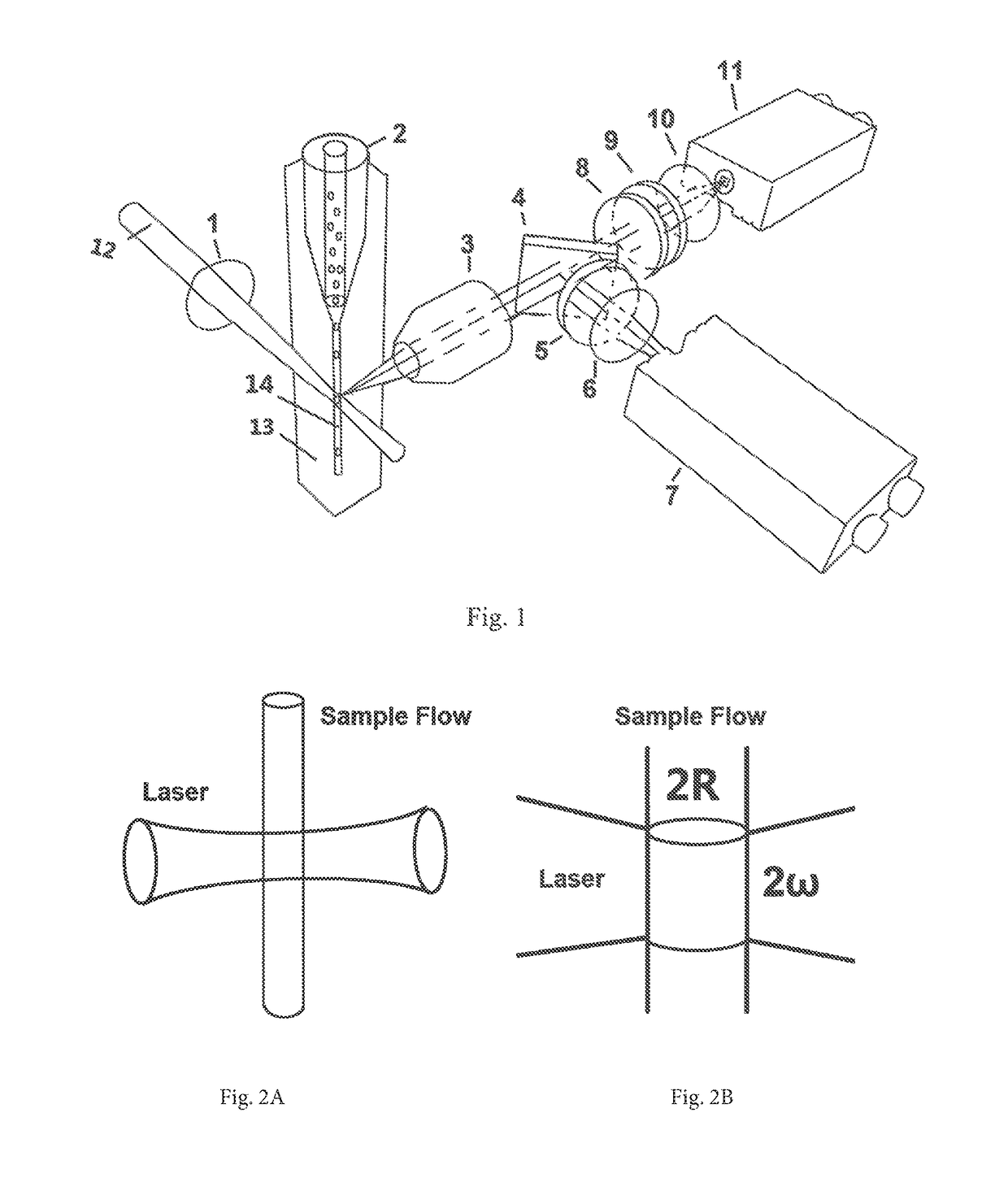
Three-dimensional (3D) hydrodynamic focusing using a microfluidic device
InactiveUS20120196314A1Reliable single molecule sensitivityFocusBioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsOut of planePhysics
A microfluidic device comprises inlets for a sample flow and an out-of-plane focusing sheath flow, and a curved channel section configured to receive the sample flow and out-of-plane focusing sheath and to provide hydrodynamic focusing of the sample flow in an out-of-plane direction, the out-of-plane direction being normal to a plane including the curved channel. Examples of the invention also include improved flow cytometers.
Owner:PENN STATE RES FOUND
Hydrodynamic focusing for analyzing rectangular microbeads
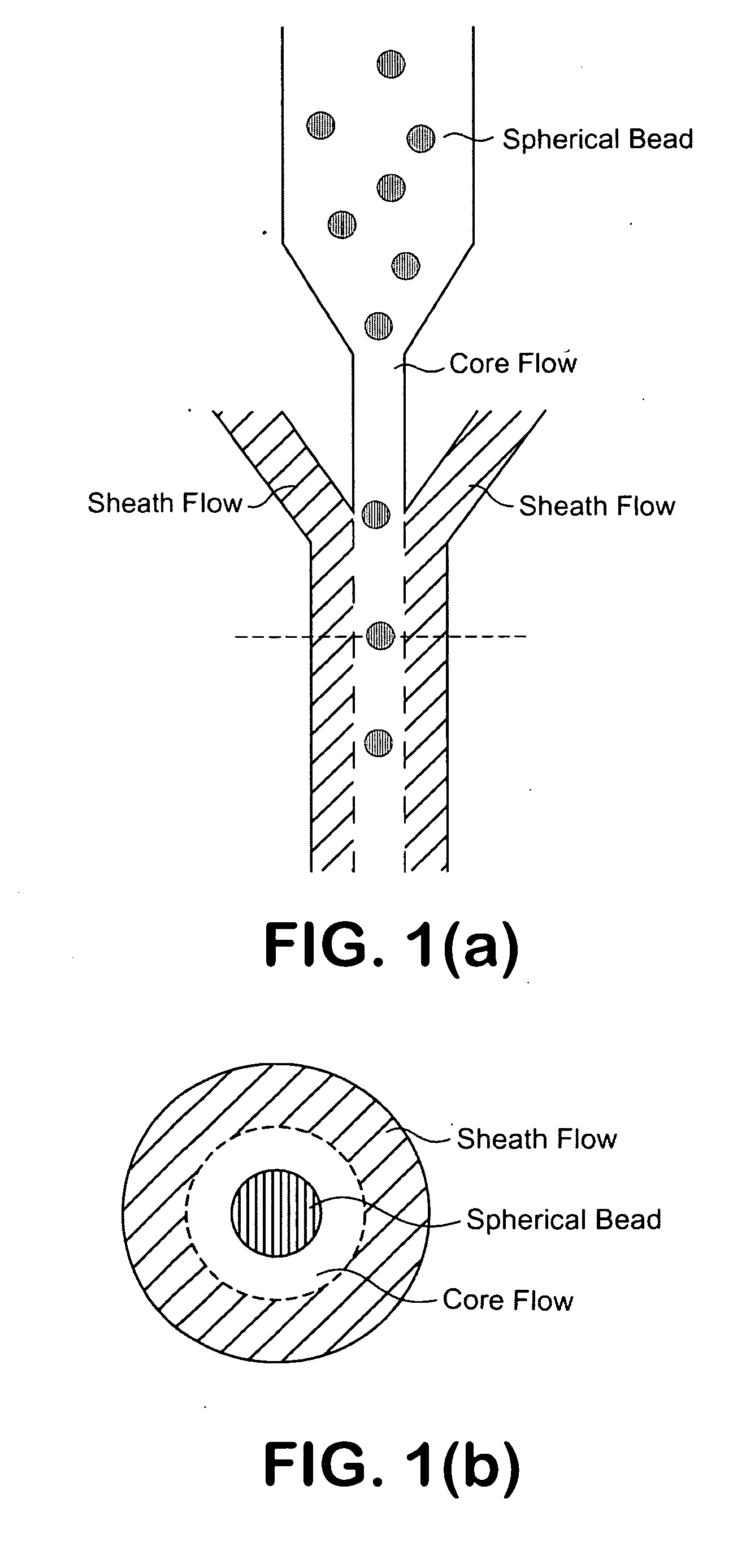
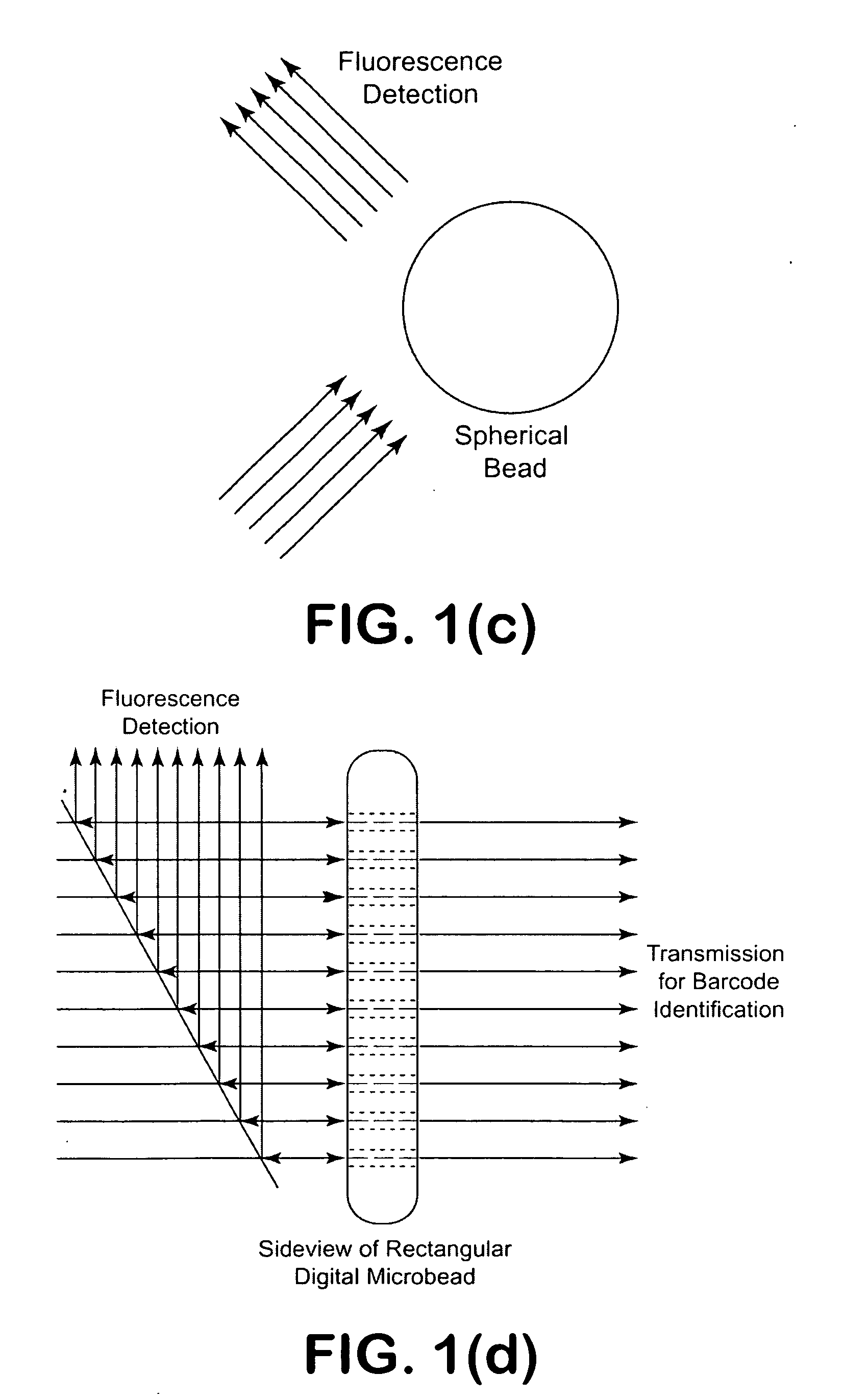
InactiveUS20090201504A1Improve liquidityNo cloggingVolume/mass flow measurementMaterial analysis by optical meansBarcodeEngineering
A microfluidic apparatus having a one-dimensional or two-dimensional hydrodynamic flow system to control stable and proper digitally coded bead orientation through the optical detection area of a bioanalysis system. The hydrodynamic system include one core flow, which carries the rectangular barcode beads, and sheath flows, on the sides of or about or around the outer periphery of the core flow, pull the core flow into a proper orientation. The sheath flows, at much higher flow speed but lower volume flow rate, can be pushed or pulled by vacuum, gravity, or pressure. By this method, the coded bead will align themselves in line and flow reliably, without wobbling or flipping, in the core flow channel through the detection zone. By adjusting the relative flow rate of core flow and sheath flows, the coded beads flow reliably in the flow system, thus it can be decoded and detected by an optical system accurately.
Owner:MAXWELL SENSORS
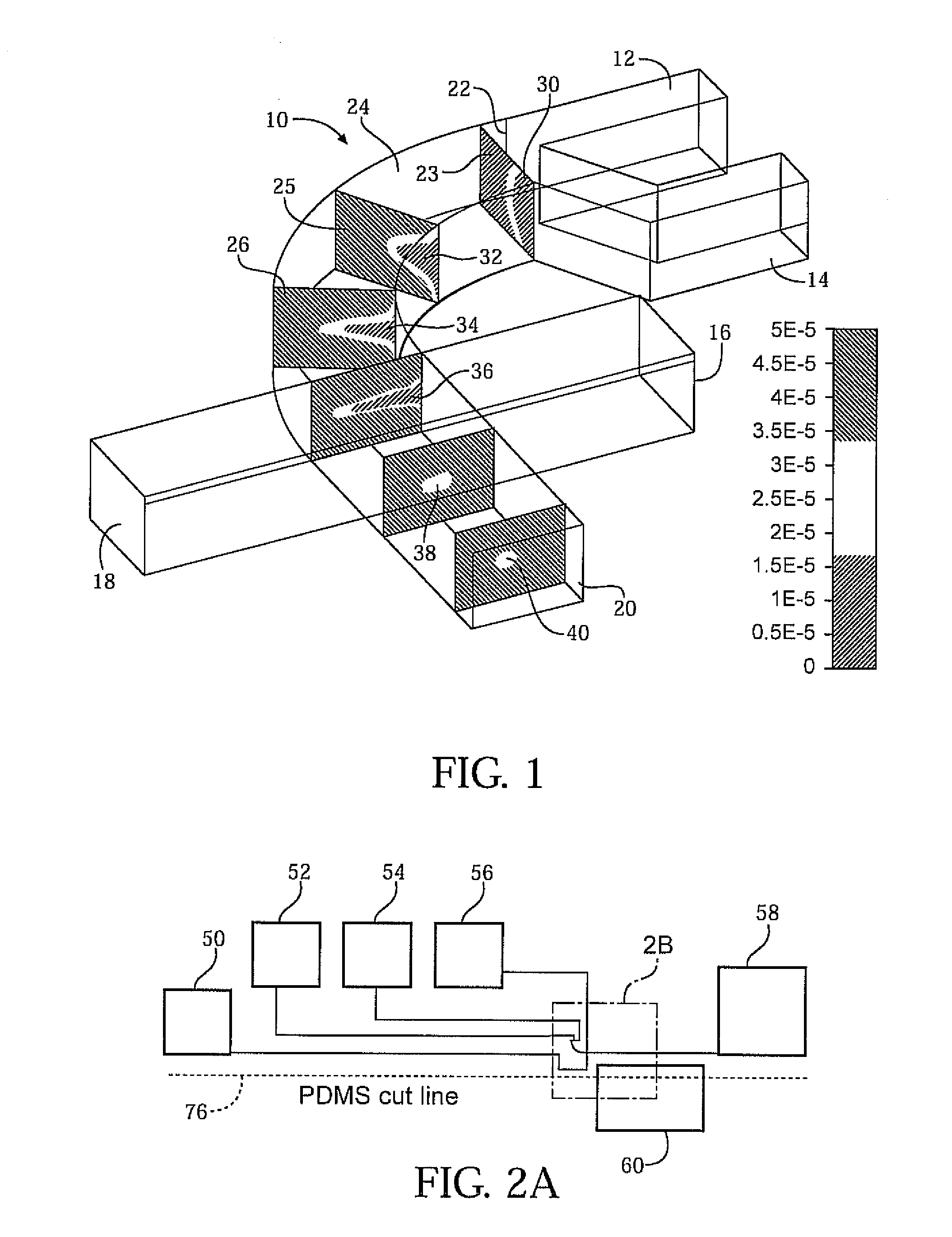
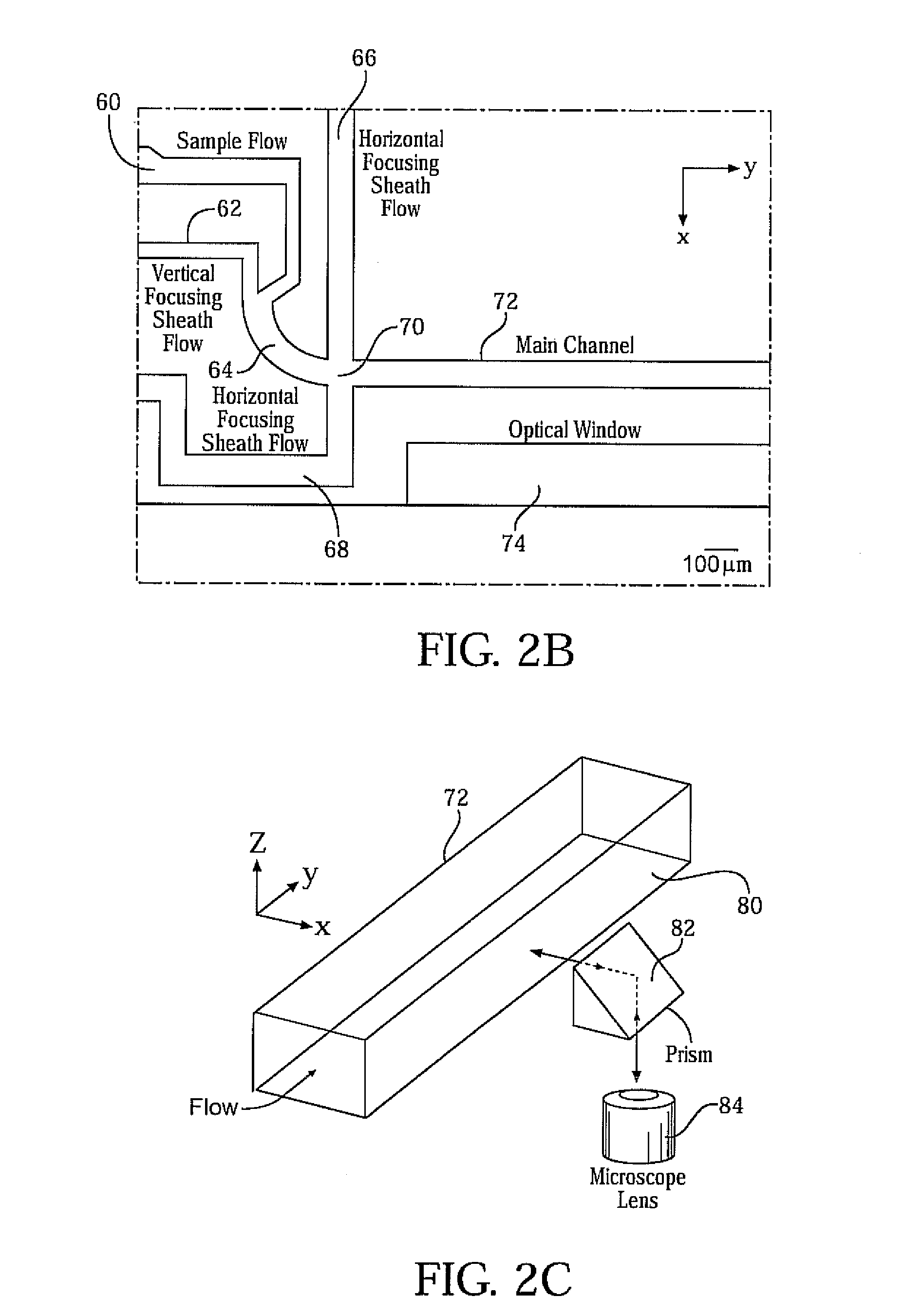
Microfluidic apparatus, systems, and methods for performing molecular reactions
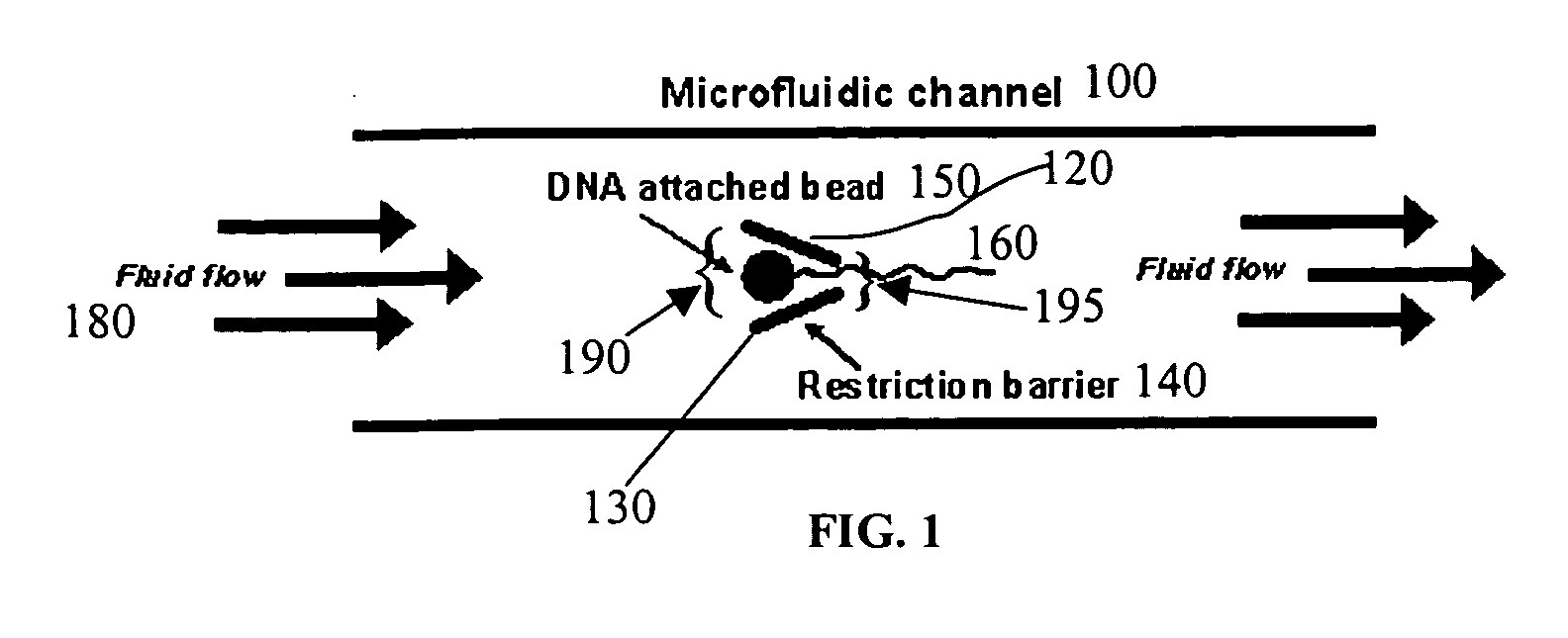
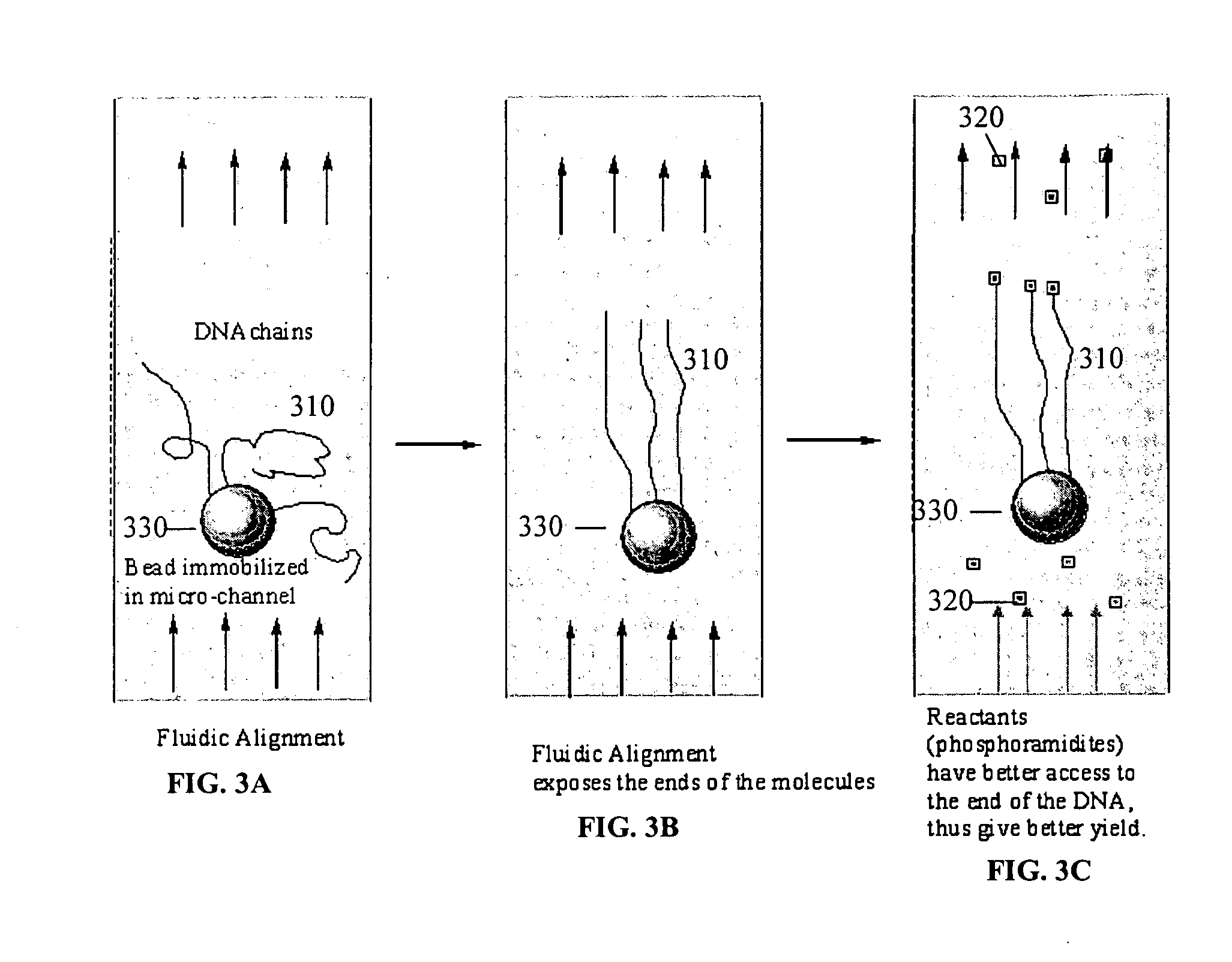
ActiveUS20050221333A1Radiation pyrometryMicrobiological testing/measurementMolecular bindingNucleic acid sequencing
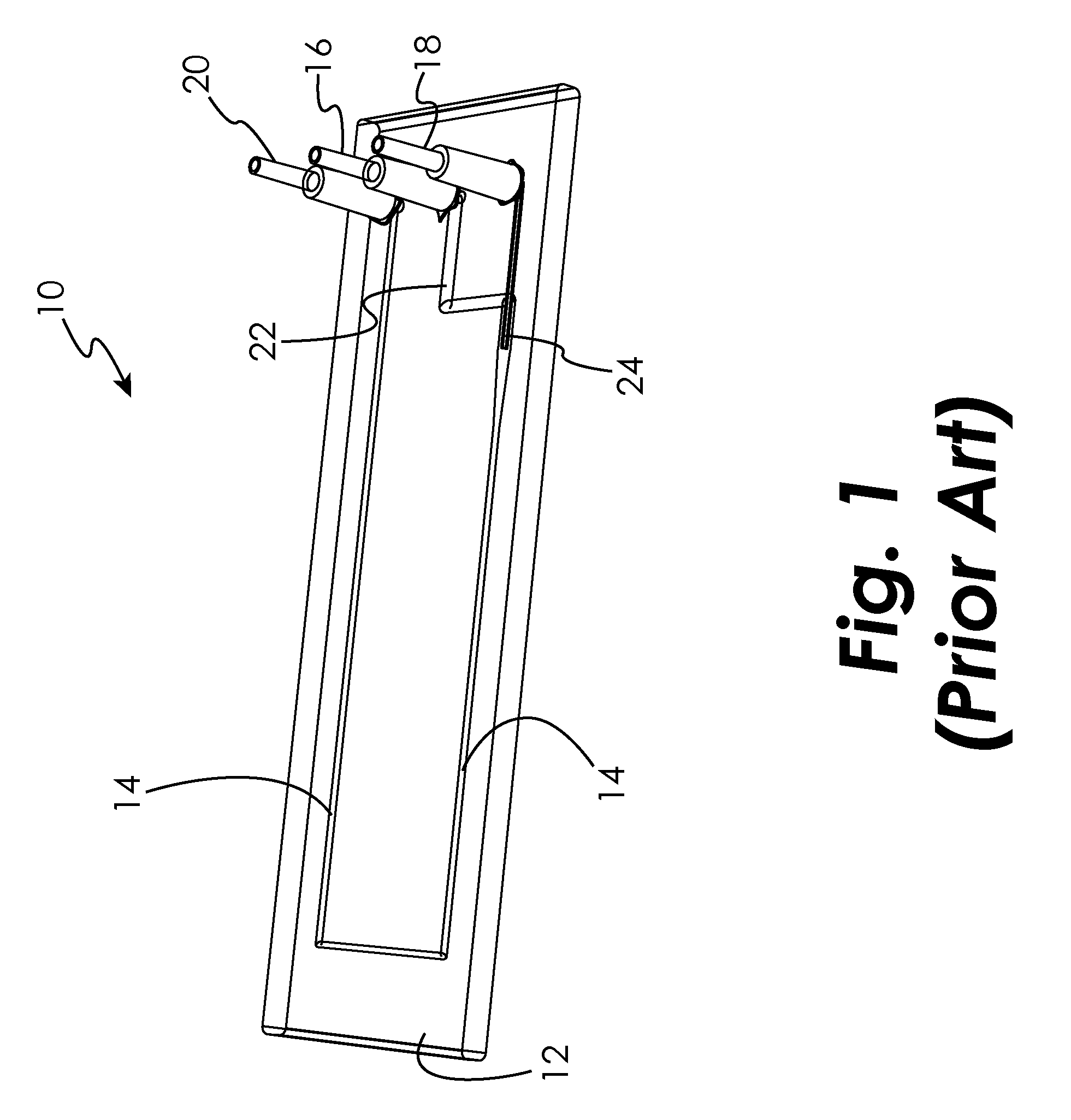
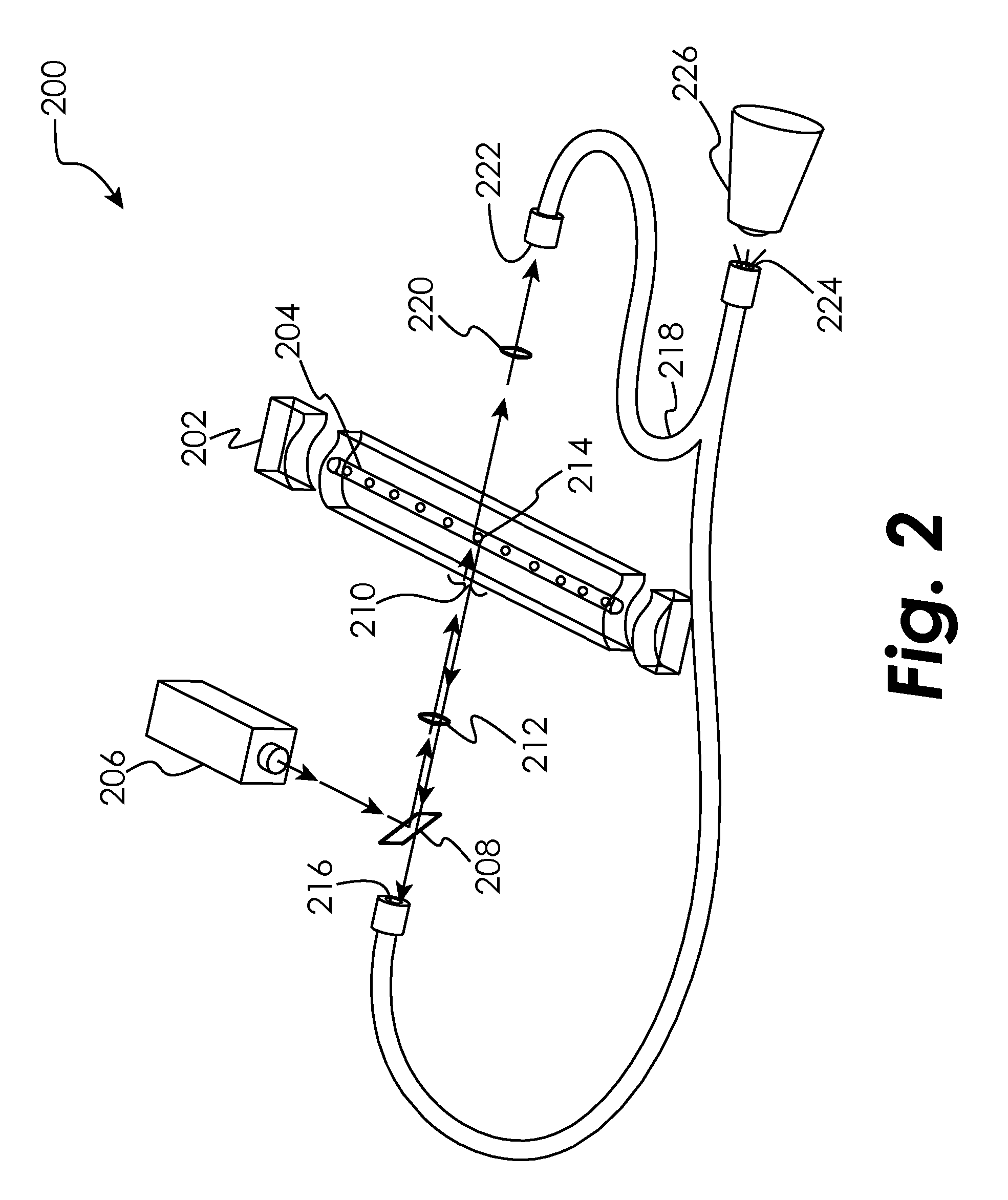
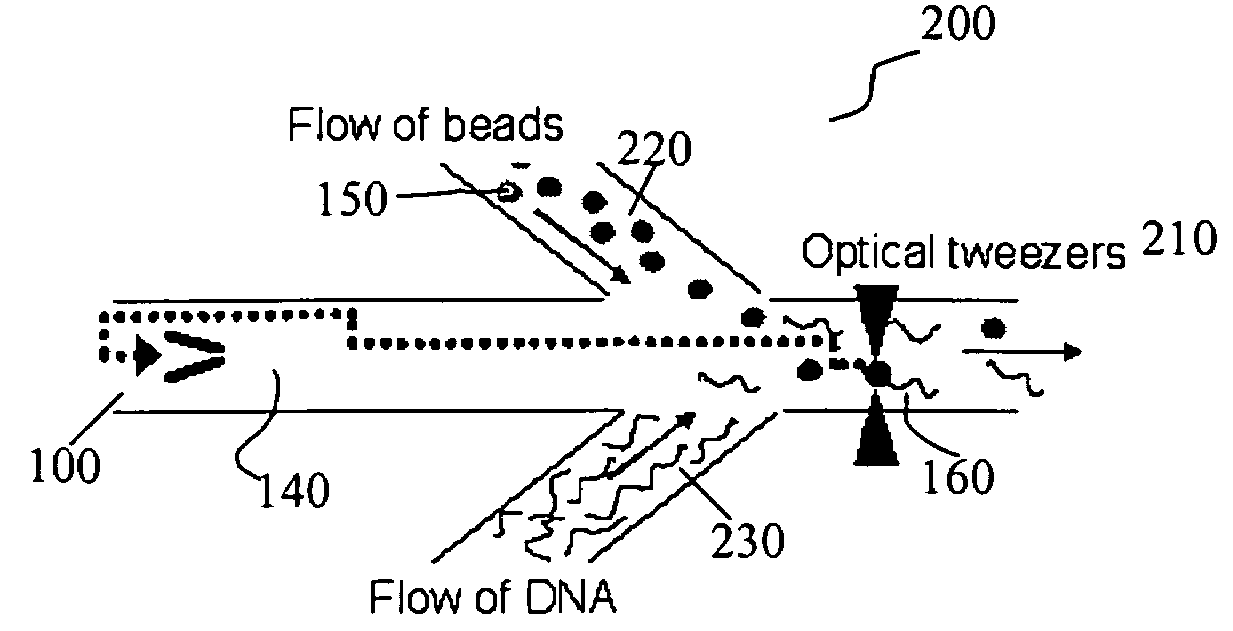
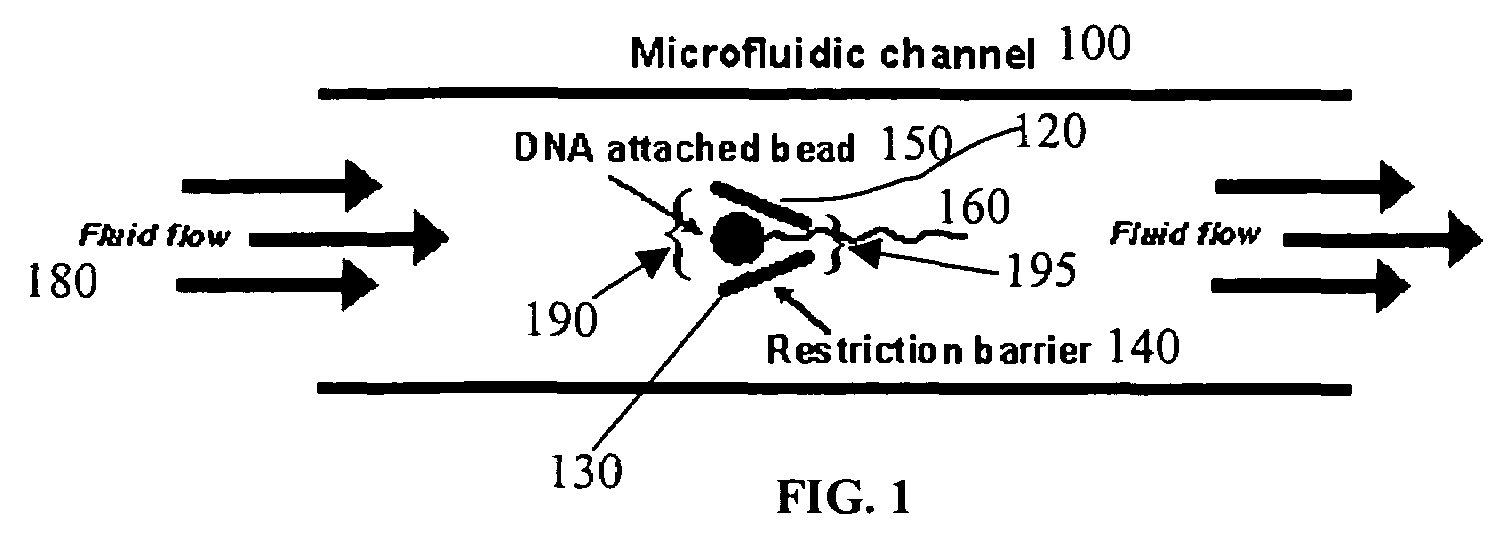
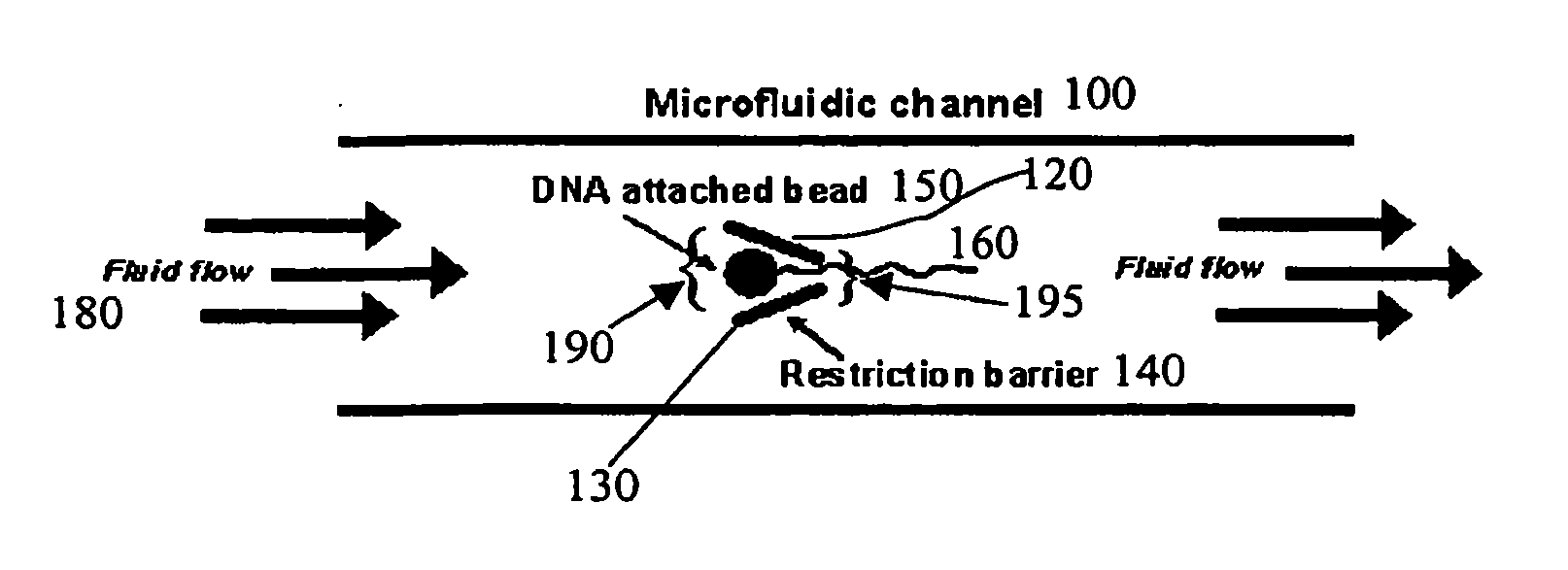
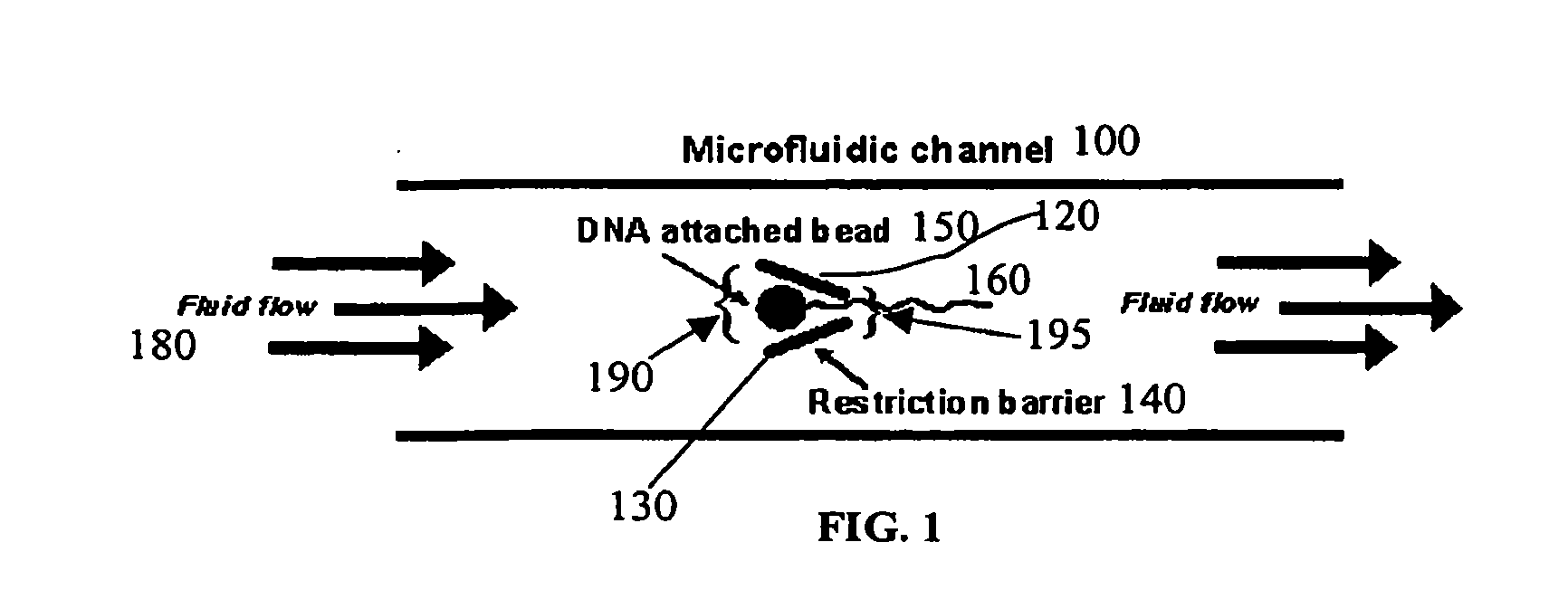
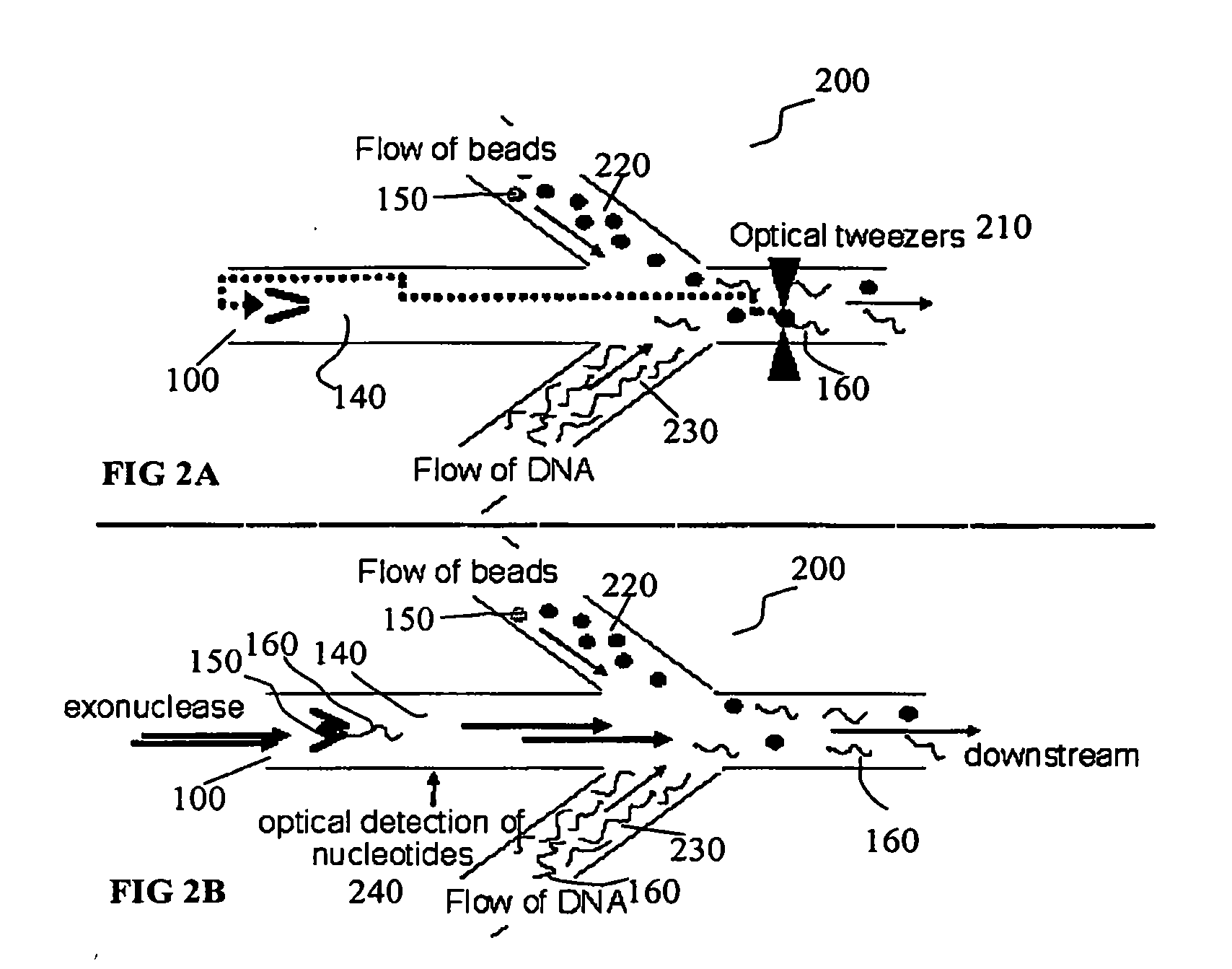
Disclosed herein are methods, apparatuses, and systems for performing nucleic acid sequencing reactions and molecular binding reactions in a microfluidic channel. The methods, apparatuses, and systems can include a restriction barrier to restrict movement of a particle to which a nucleic acid is attached. Furthermore, the methods, apparatuses, and systems can include hydrodynamic focusing of a delivery flow. In addition, the methods, apparatuses, and systems can reduce non-specific interaction with a surface of the microfluidic channel by providing a protective flow between the surface and a delivery flow.
Owner:INTEL CORP
Three-dimensional (3D) hydrodynamic focusing using a microfluidic device
InactiveUS20090066936A1Reliable single molecule sensitivityFocusOptical radiation measurementBioreactor/fermenter combinationsOut of planePhysics
A microfluidic device comprises inlets for a sample flow and an out-of-plane focusing sheath flow, and a curved channel section configured to receive the sample flow and out-of-plane focusing sheath and to provide hydrodynamic focusing of the sample flow in an out-of-plane direction, the out-of-plane direction being normal to a plane including the curved channel.
Owner:PENN STATE RES FOUND
Microfluidic device
ActiveUS20110008767A1Facilitate cytometry analysisBioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsParticle flowAcoustic energy
The present disclosure relates to microfluidic devices adapted for facilitating cytometry analysis of particles flowing therethrough. In certain embodiments, the microfluidic devices allow light collection from multiple directions. In certain other embodiments, the microfluidic devices use spatial intensity modulation. In certain other embodiments, the microfluidic devices have magnetic field separators. In certain other embodiments, the microfluidic devices have the ability to stack. In certain other embodiments, the microfluidic devices have 3-D hydrodynamic focusing to align sperm cells. In certain other embodiments, the microfluidic devices have acoustic energy couplers. In certain other embodiments, the microfluidic devices have phase variation producing lenses. In certain other embodiments, the microfluidic devices have transmissive and reflective lenses. In certain other embodiments, the microfluidic devices have integrally-formed optics. In certain other embodiments, the microfluidic devices have non-integral geographically selective reagent delivery structures. In certain other embodiments, the microfluidic devices have optical waveguides incorporated into their flow channels. In certain other embodiments, the microfluidic devices have optical waveguides with reflective surfaces incorporated into their flow channels. In certain other embodiments, the microfluidic devices have virus detecting and sorting capabilities. In certain other embodiments, the microfluidic devices display a color change to indicate use or a result.
Owner:SONY CORP +1
Microfluidic apparatus, Raman spectroscopy systems, and methods for performing molecular reactions
ActiveUS7442339B2Radiation pyrometryMicrobiological testing/measurementMolecular bindingNucleic acid sequencing
Disclosed herein are methods, apparatuses, and systems for performing nucleic acid sequencing reactions and molecular binding reactions in a microfluidic channel. The methods, apparatuses, and systems can include a restriction barrier to restrict movement of a particle to which a nucleic acid is attached. Furthermore, the methods, apparatuses, and systems can include hydrodynamic focusing of a delivery flow. In addition, the methods, apparatuses, and systems can reduce non-specific interaction with a surface of the microfluidic channel by providing a protective flow between the surface and a delivery flow.
Owner:INTEL CORP
Multidimensional hydrodynamic focusing chamber
ActiveUS20150064694A1Bioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsHydrodynamic focusingBiophysics
Owner:BIO RAD LAB INC
Three-dimensional (3D) hydrodynamic focusing using a microfluidic device
InactiveUS8120770B2High sensitivityEasy to manufactureOptical radiation measurementBioreactor/fermenter combinationsOut of planePhysics
A microfluidic device comprises inlets for a sample flow and an out-of-plane focusing sheath flow, and a curved channel section configured to receive the sample flow and out-of-plane focusing sheath and to provide hydrodynamic focusing of the sample flow in an out-of-plane direction, the out-of-plane direction being normal to a plane including the curved channel.
Owner:PENN STATE RES FOUND
Two-Fluid Hydrodynamic Printing
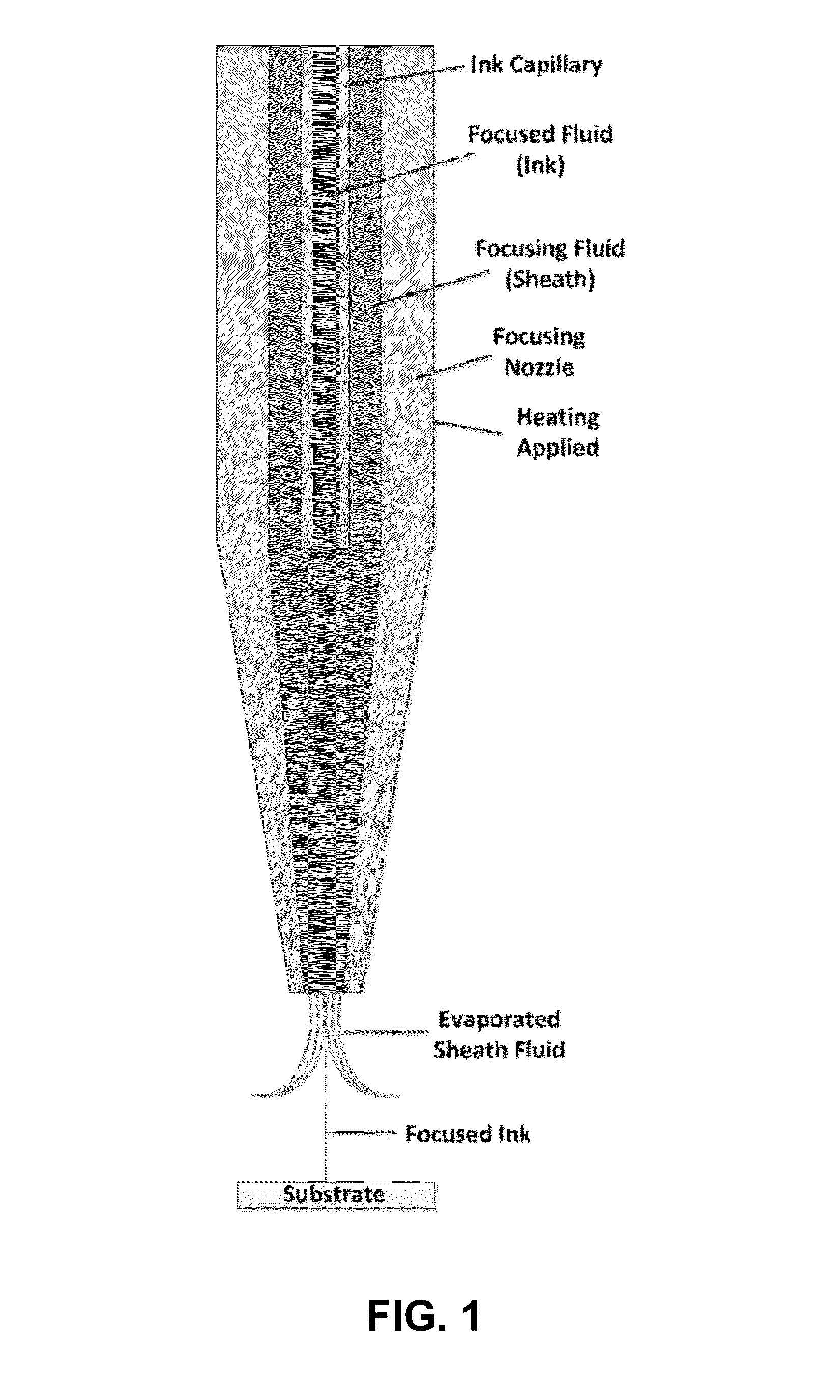
ActiveUS20160129634A1Manufacturing platforms/substratesFilament/thread formingEngineeringPrinted electronics
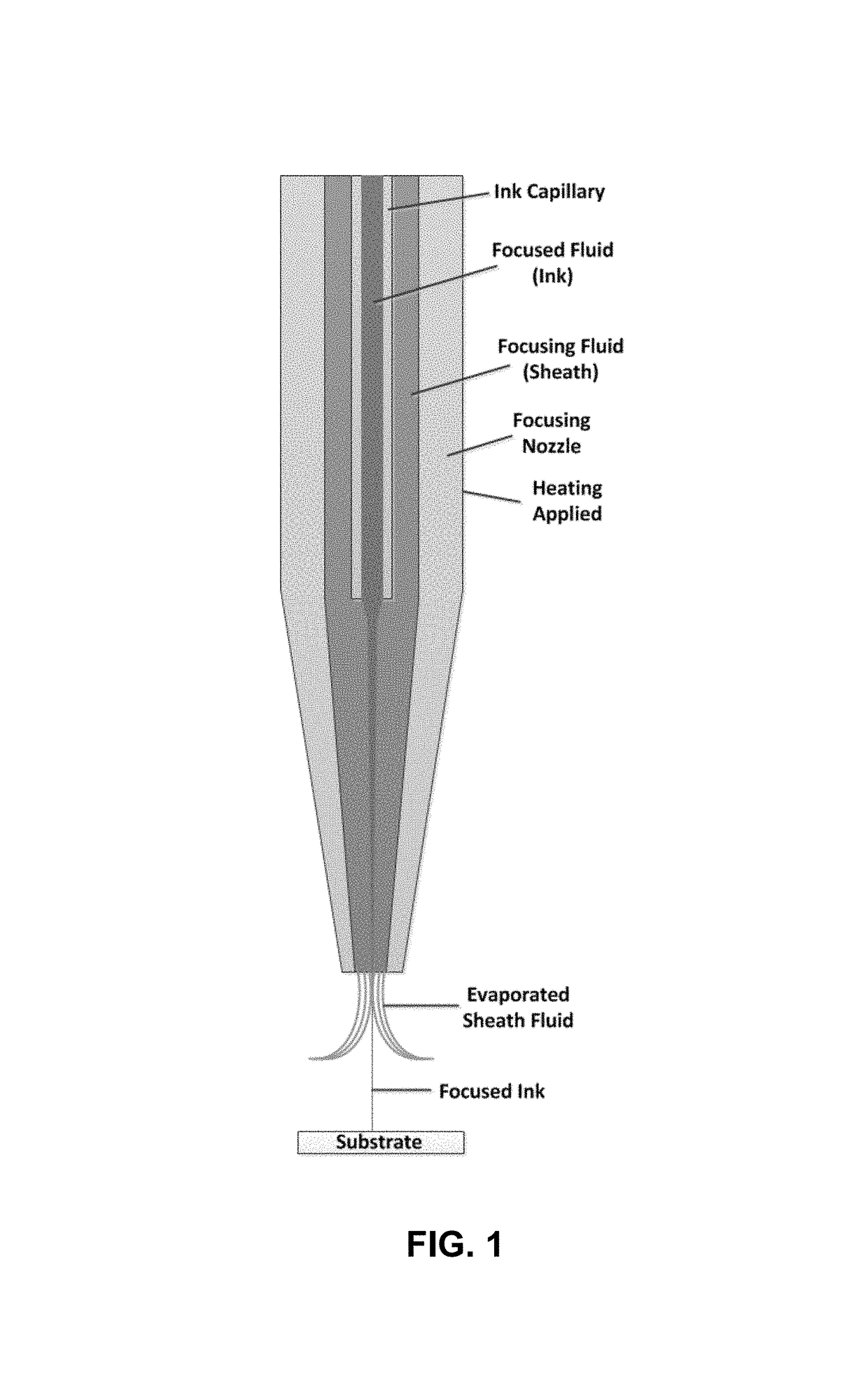
Hydrodynamic focusing of two fluid steams provides a novel micro printing technology for printed electronics and other high performance applications.
Owner:NAT TECH & ENG SOLUTIONS OF SANDIA LLC
Three-dimensional (3D) hydrodynamic focusing using a microfluidic device
InactiveUS8941826B2High sensitivityEasy to manufactureBioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsOut of planePhysics
A microfluidic device comprises inlets for a sample flow and an out-of-plane focusing sheath flow, and a curved channel section configured to receive the sample flow and out-of-plane focusing sheath and to provide hydrodynamic focusing of the sample flow in an out-of-plane direction, the out-of-plane direction being normal to a plane including the curved channel. Examples of the invention also include improved flow cytometers.
Owner:PENN STATE RES FOUND
Microfluidic apparatus, systems, and methods for performing molecular reactions
InactiveUS20100151454A1Microbiological testing/measurementMaterial analysis by optical meansMolecular bindingNucleic acid sequencing
Disclosed herein are methods, apparatuses, and systems for performing nucleic acid sequencing reactions and molecular binding reactions in a microfluidic channel. The methods, apparatuses, and systems can include a restriction barrier to restrict movement of a particle to which a nucleic acid is attached. Furthermore, the methods, apparatuses, and systems can include hydrodynamic focusing of a delivery flow. In addition, the methods, apparatuses, and systems can reduce non-specific interaction with a surface of the microfluidic channel by providing a protective flow between the surface and a delivery flow.
Owner:SUNDARARAJAN NARAYANAN +6
Ultrasensitive SERS flow detector
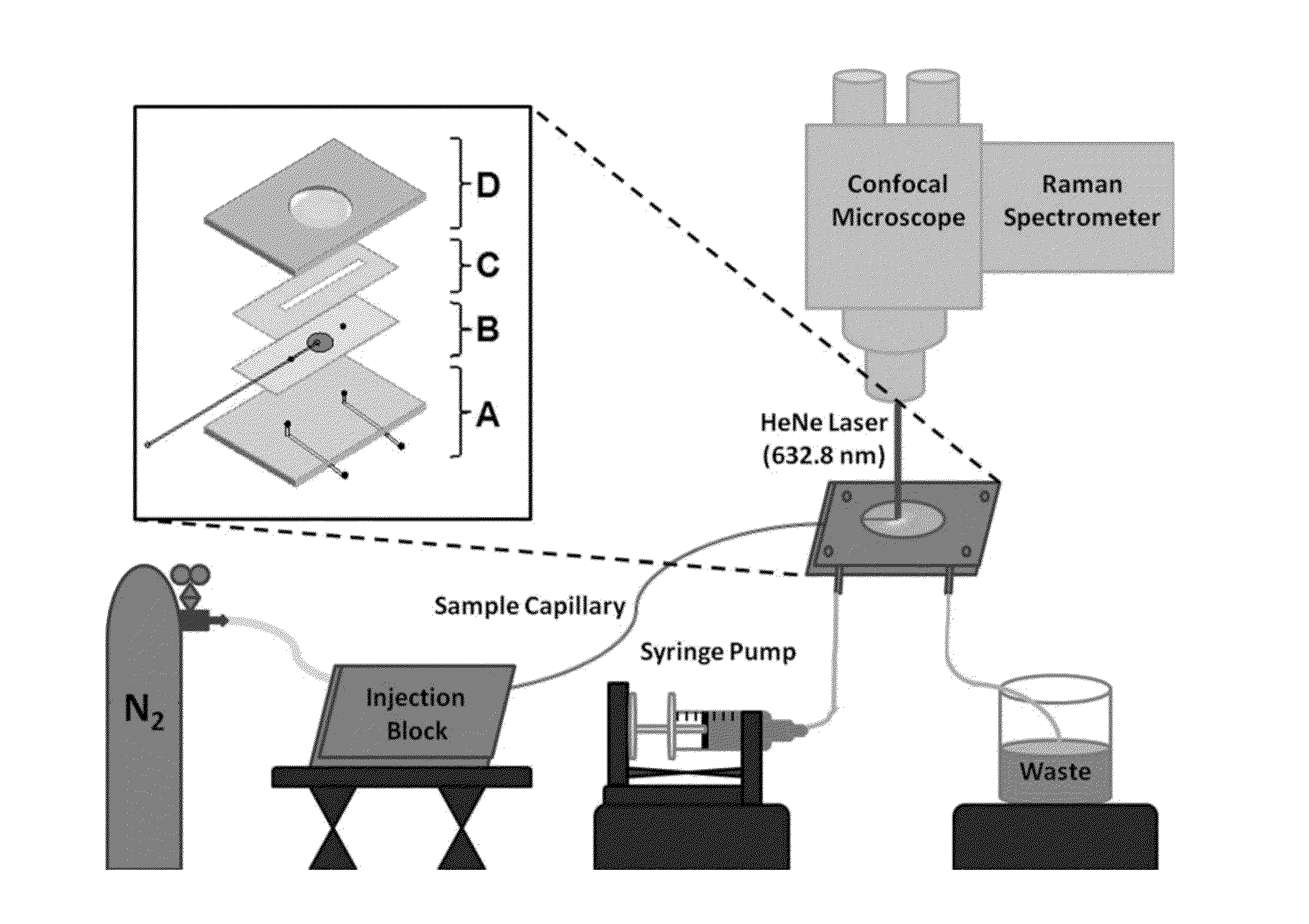
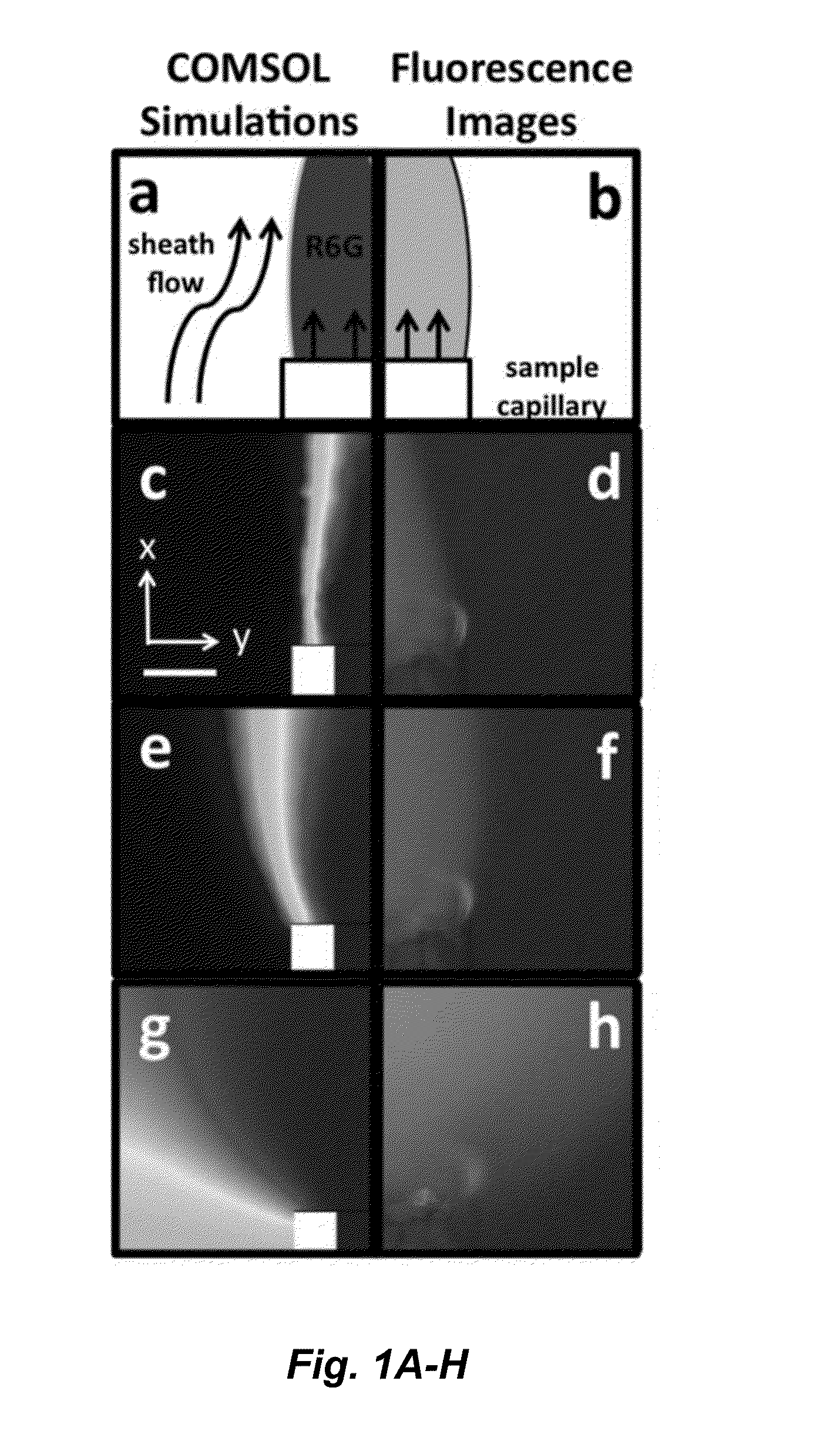
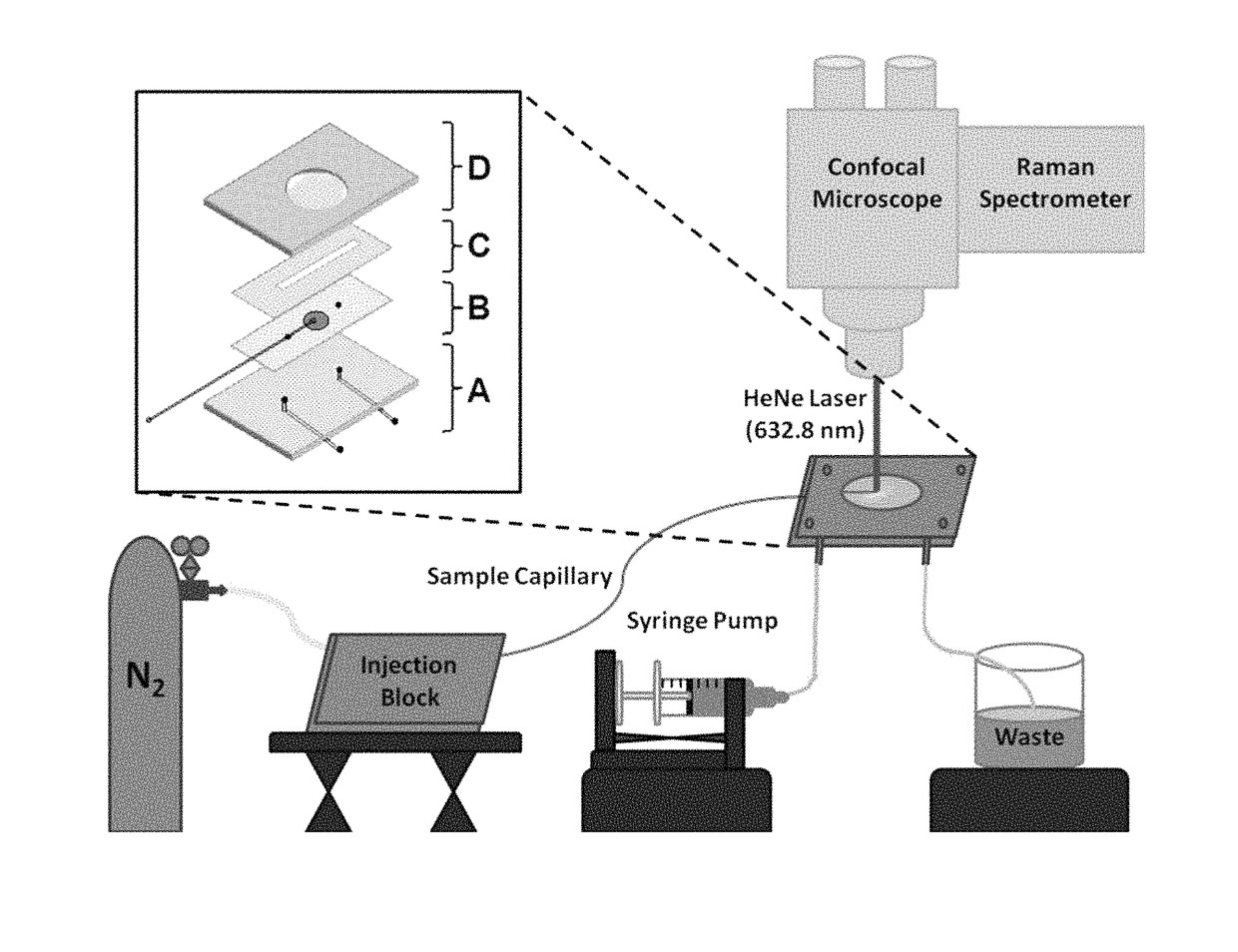
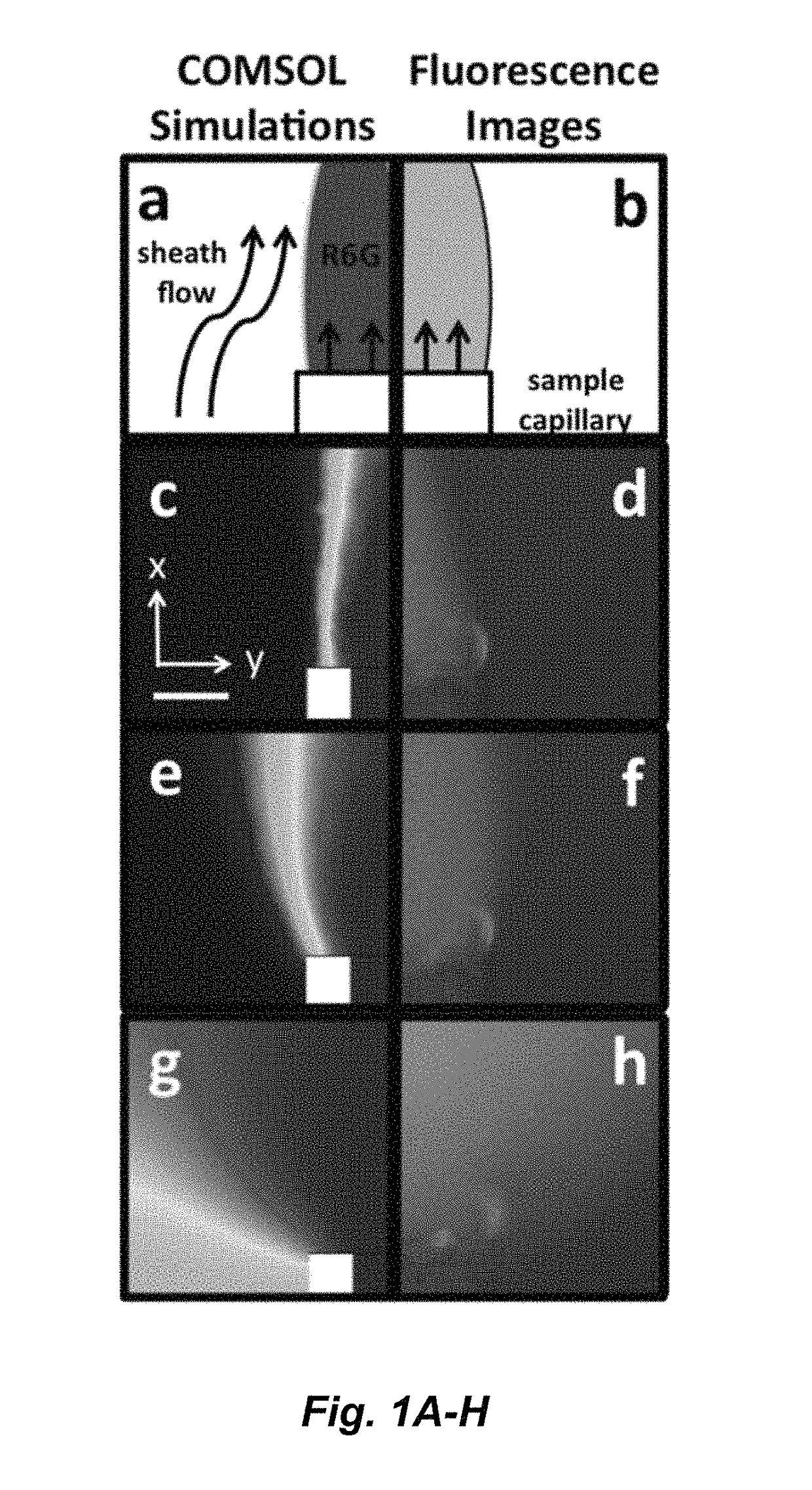
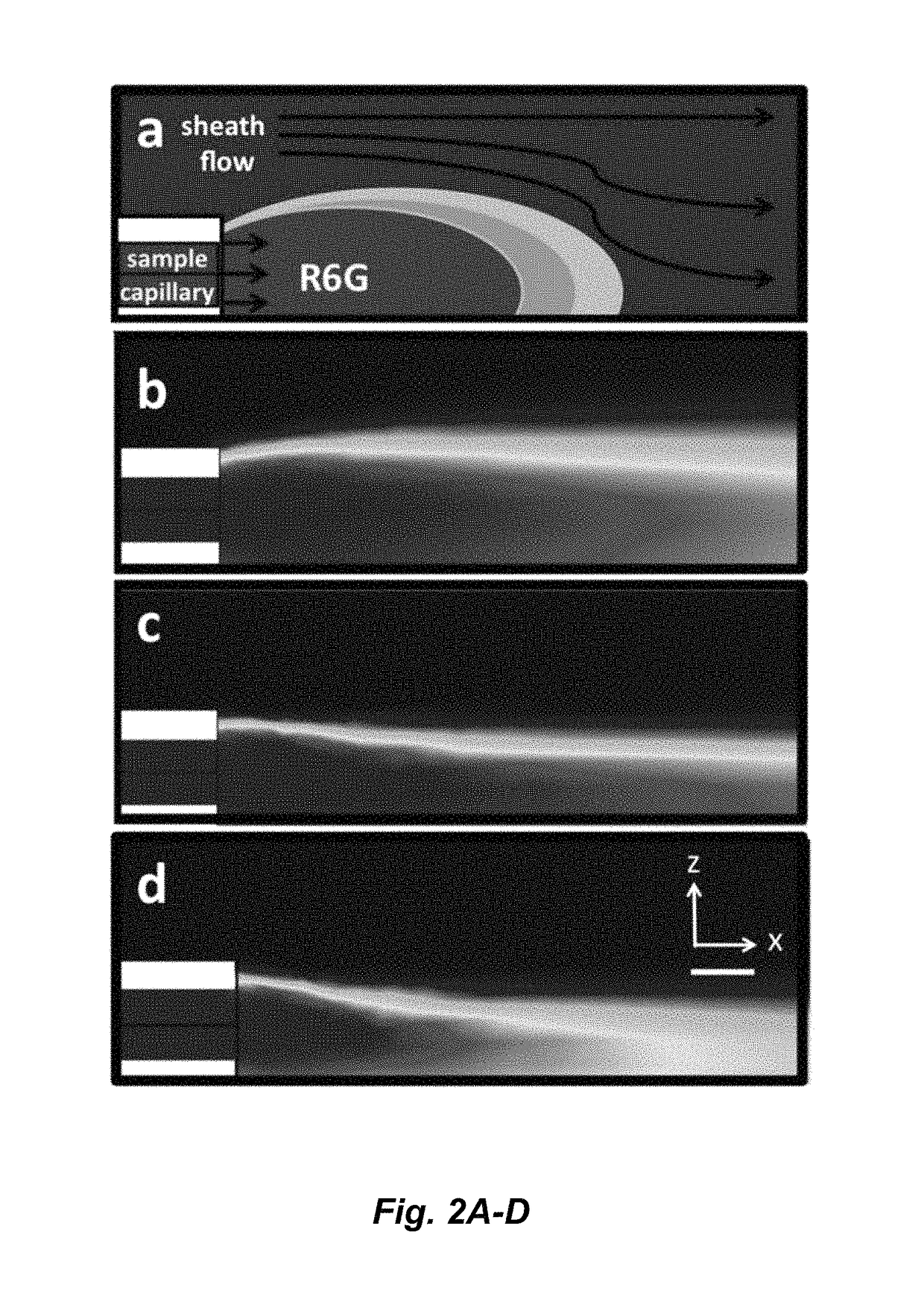
ActiveUS20150338348A1Enhanced signalShort acquisition timeRadiation pyrometryRaman scatteringDesorptionFlow injection analysis
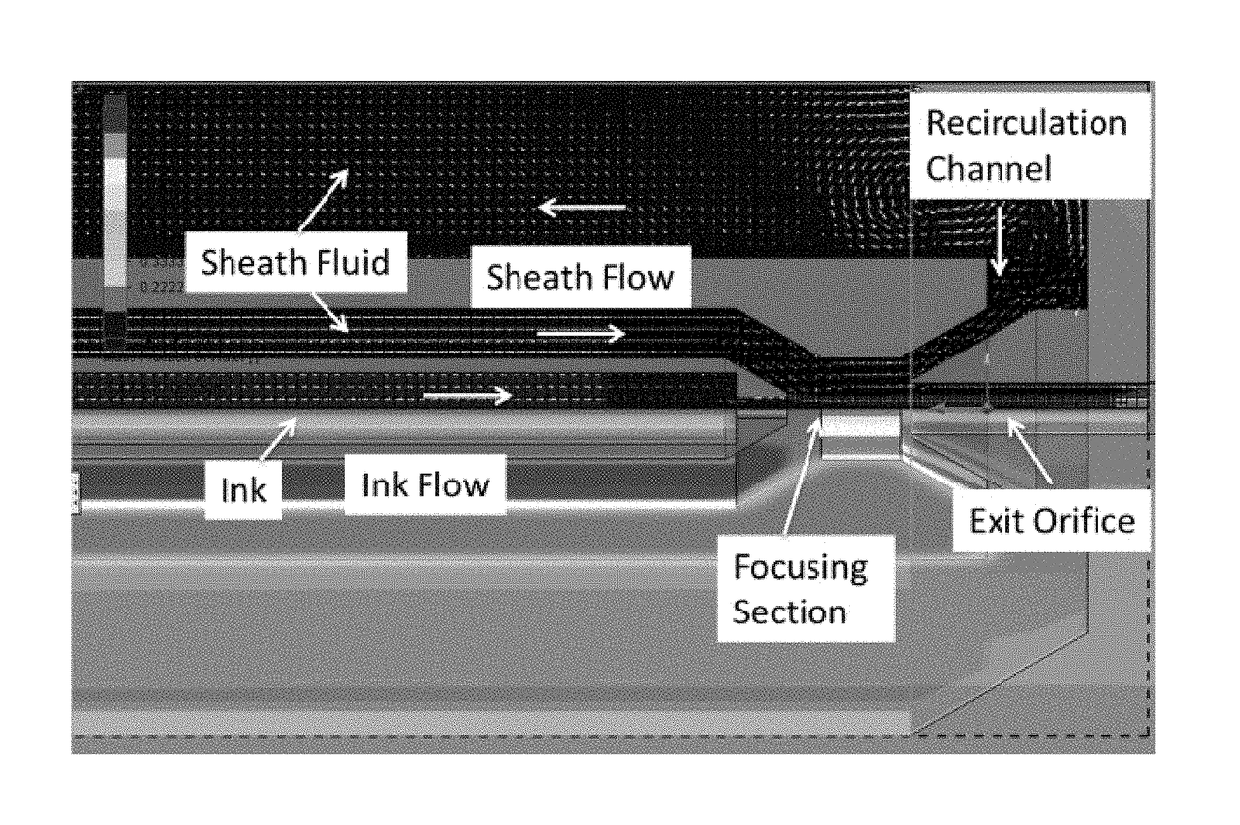
The invention provides an apparatus and methods for label-free, chemical specific detection in flow for high throughput characterization of analytes in applications such as flow injection analysis, electrophoresis, and chromatography. A surface-enhanced Raman scattering (SERS) flow detector capable of ultrasensitive optical detection on the millisecond time scale has been developed. The device employs hydrodynamic focusing to improve SERS detection in a flow channel where a sheath flow confines analyte molecules eluted from a capillary over a planar SERS-active substrate. Increased analyte interactions with the SERS substrate significantly improve detection sensitivity. Raman experiments at different sheath flow rates showed increased sensitivity compared with the modeling predictions, indicating increased adsorption. At low analyte concentrations, rapid analyte desorption is observed, enabling repeated and high-throughput SERS detection. The flow detector offers substantial advantages over conventional SERS-based assays such as minimal sample volumes and high detection efficiency.
Owner:UNIV OF NOTRE DAME DU LAC
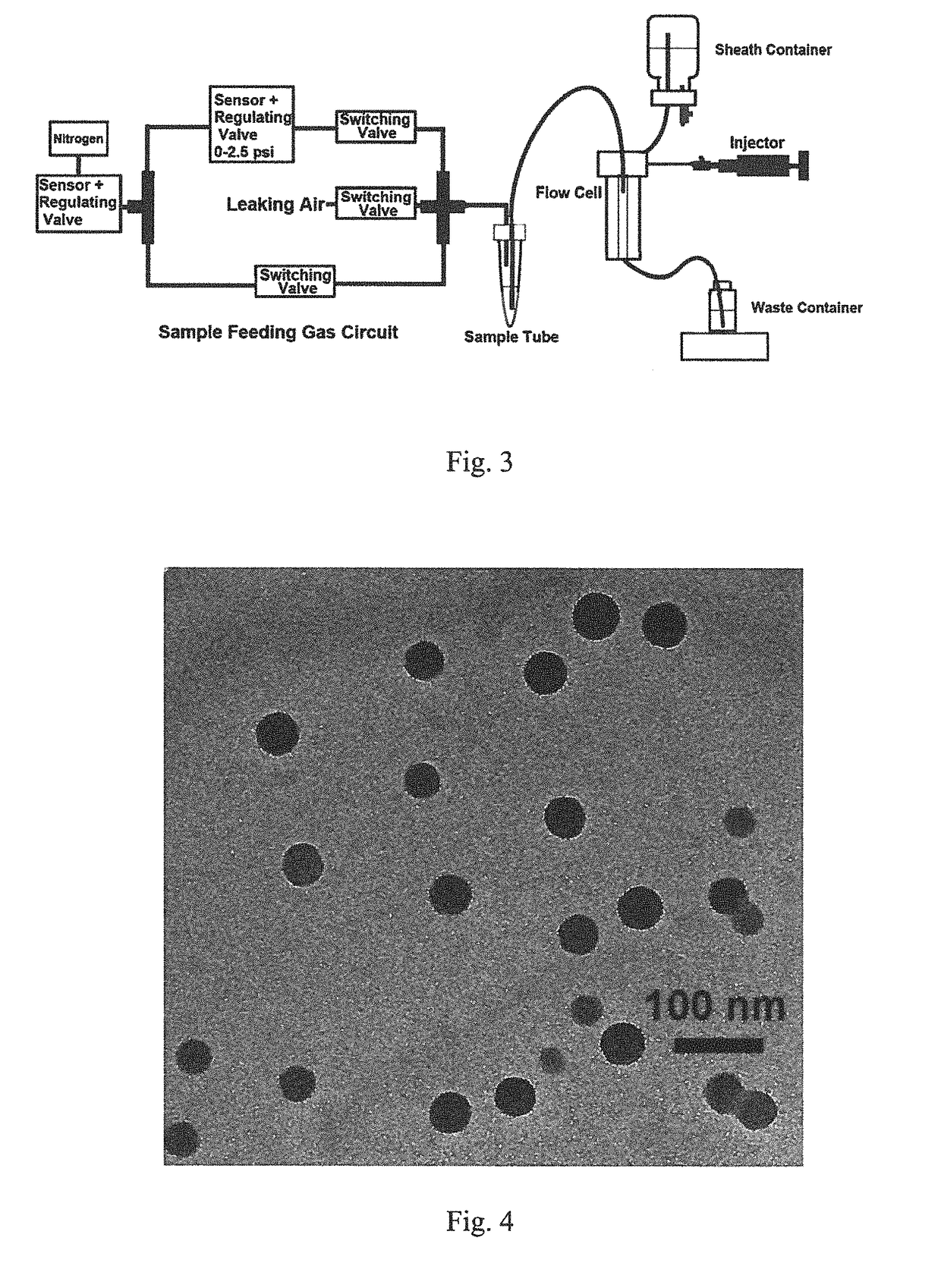
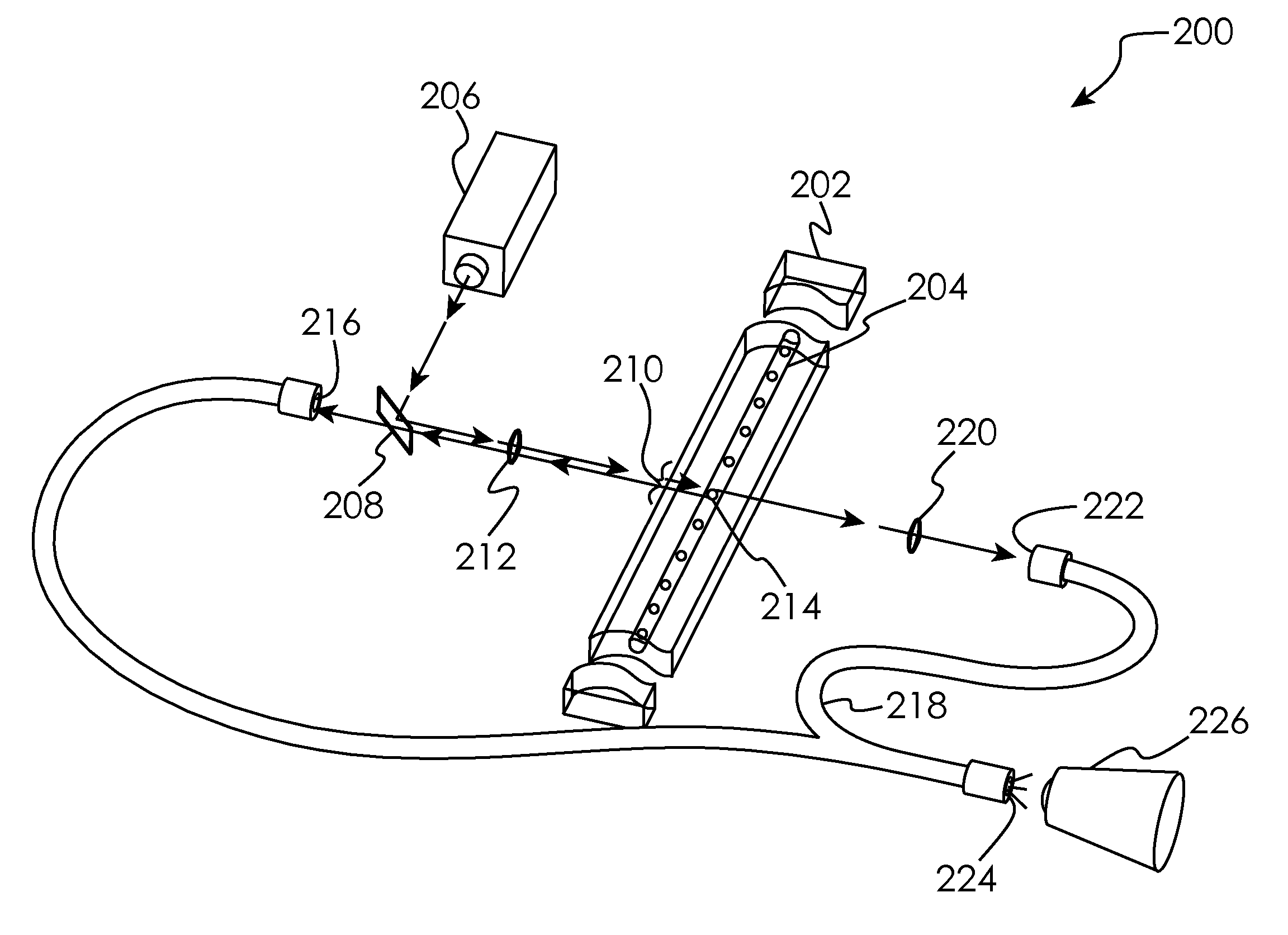
Flow cell facilitating precise delivery of reagent to a detection surface using evacuation ports and guided laminar flows, and methods of use
ActiveUS7858372B2Difficult to manufacture and break easilySmall array addressing microfluidic devicesAnalysis using chemical indicatorsWithdrawing sample devicesFlow cellChemical physics
The present invention is a flow cell and method for use in microfluidic analyses that presents highly discrete and small volumes of fluid to isolated locations on a two-dimensional surface contained within an open fluidic chamber defined by the flow cell that has physical dimensions such that laminar style flow occurs for fluids flowing through the chamber. This process of location specific fluid addressing within the flow cell is facilitated by combining components of hydrodynamic focusing with site specific cell evacuation. The process does not require the use of physical barriers within the flow cell or mechanical valves to control the paths of fluid movement.
Owner:BRUKER DALTONIK GMBH & CO KG
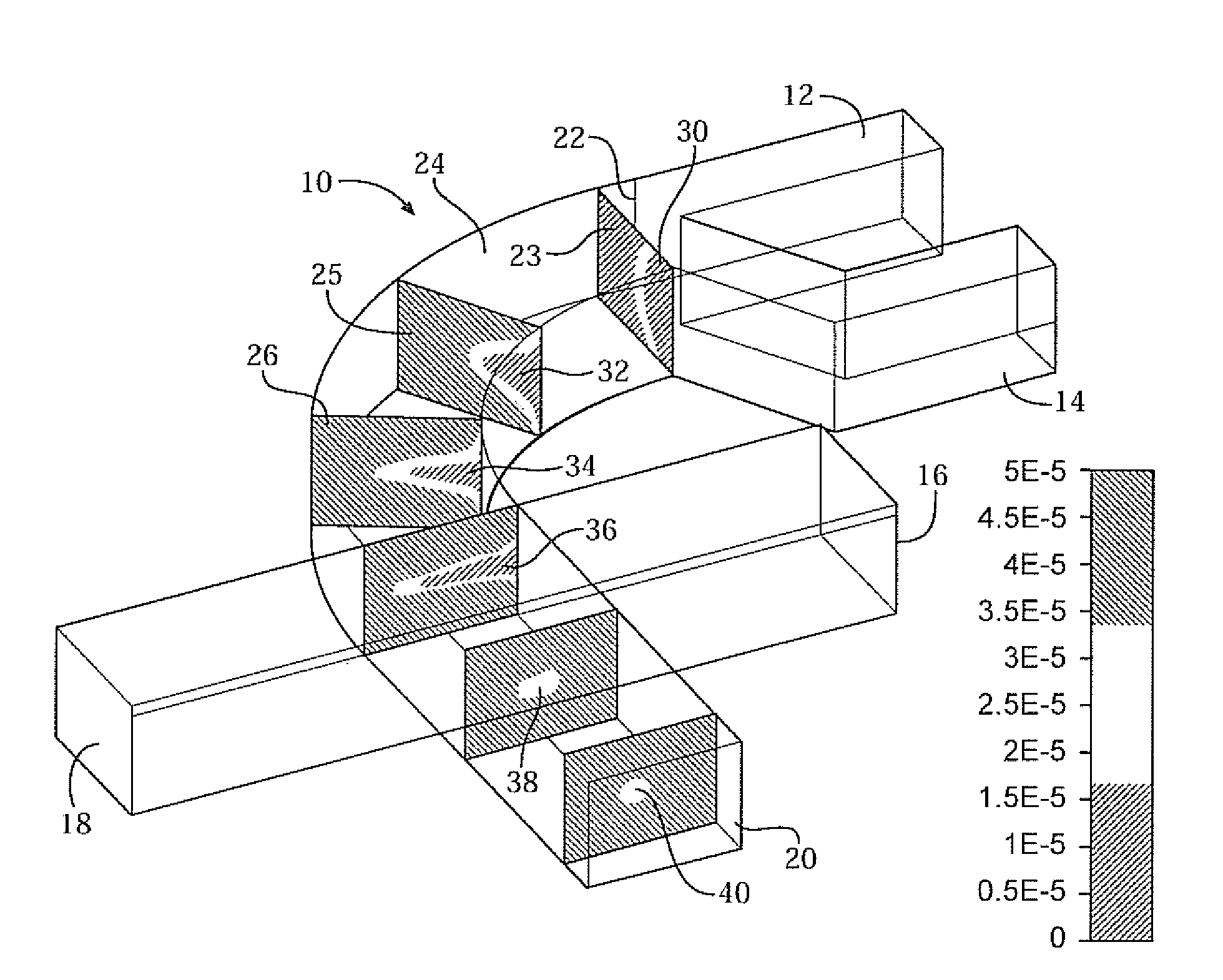
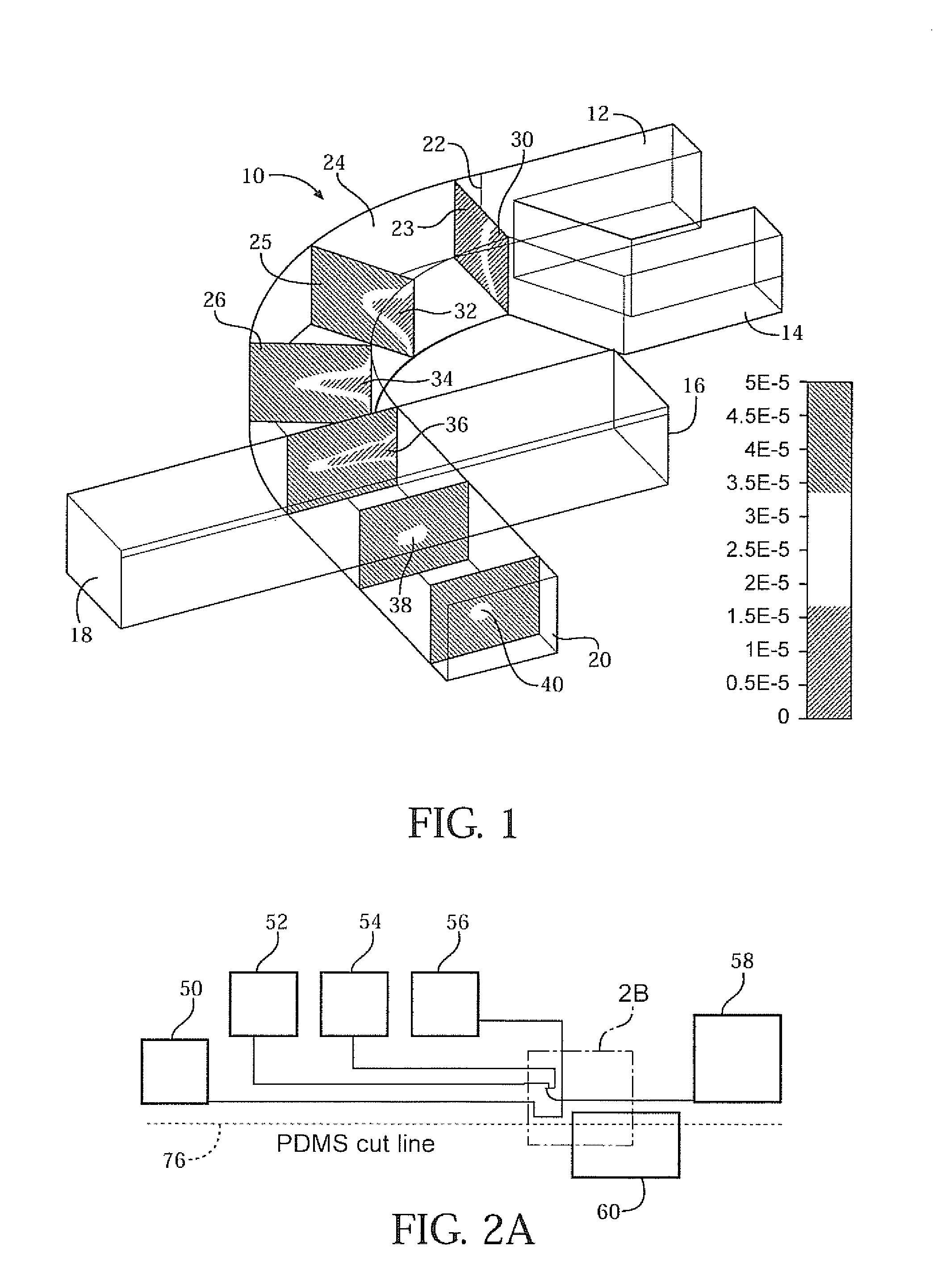
Hydrodynamic focusing apparatus and methods
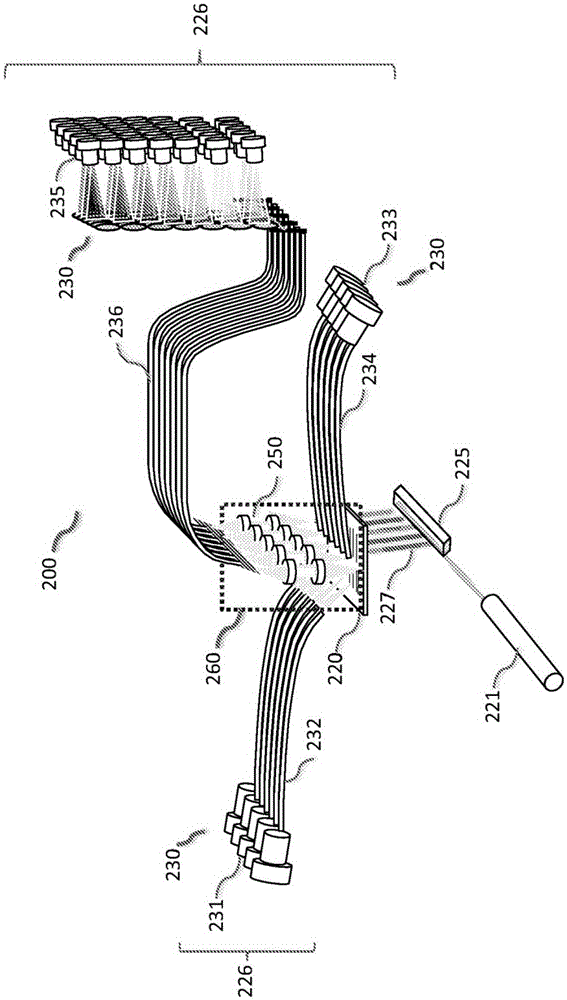
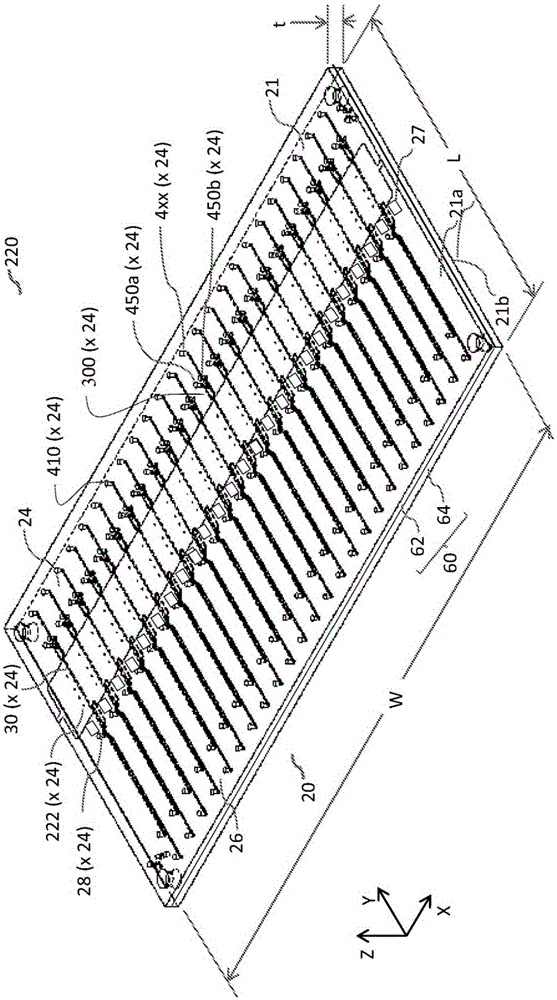
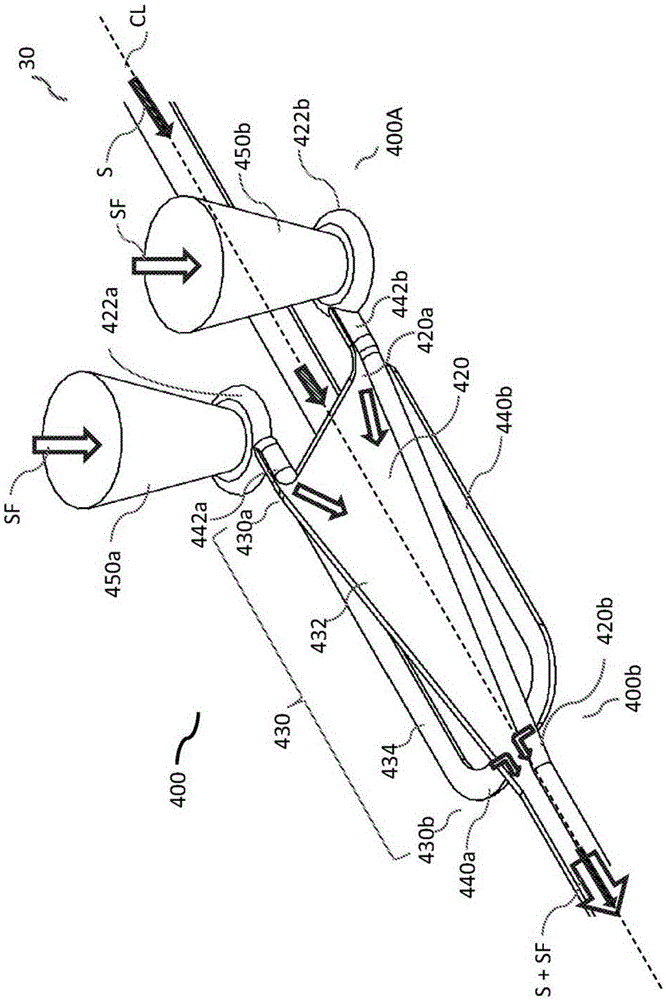
A microfluidic chip having a micro channel for processing a sample is provided. The micro channel may focus the sample by using focusing fluid and a core stream forming geometry. The core stream forming geometry may include a lateral fluid focusing component and one or more vertical fluid focusing components. A microfluidic chip may include a plurality micro channels operating in parallel on a microfluidic chip.
Owner:CYTONOMEST
Method, device and system for hydrodynamic flow focusing
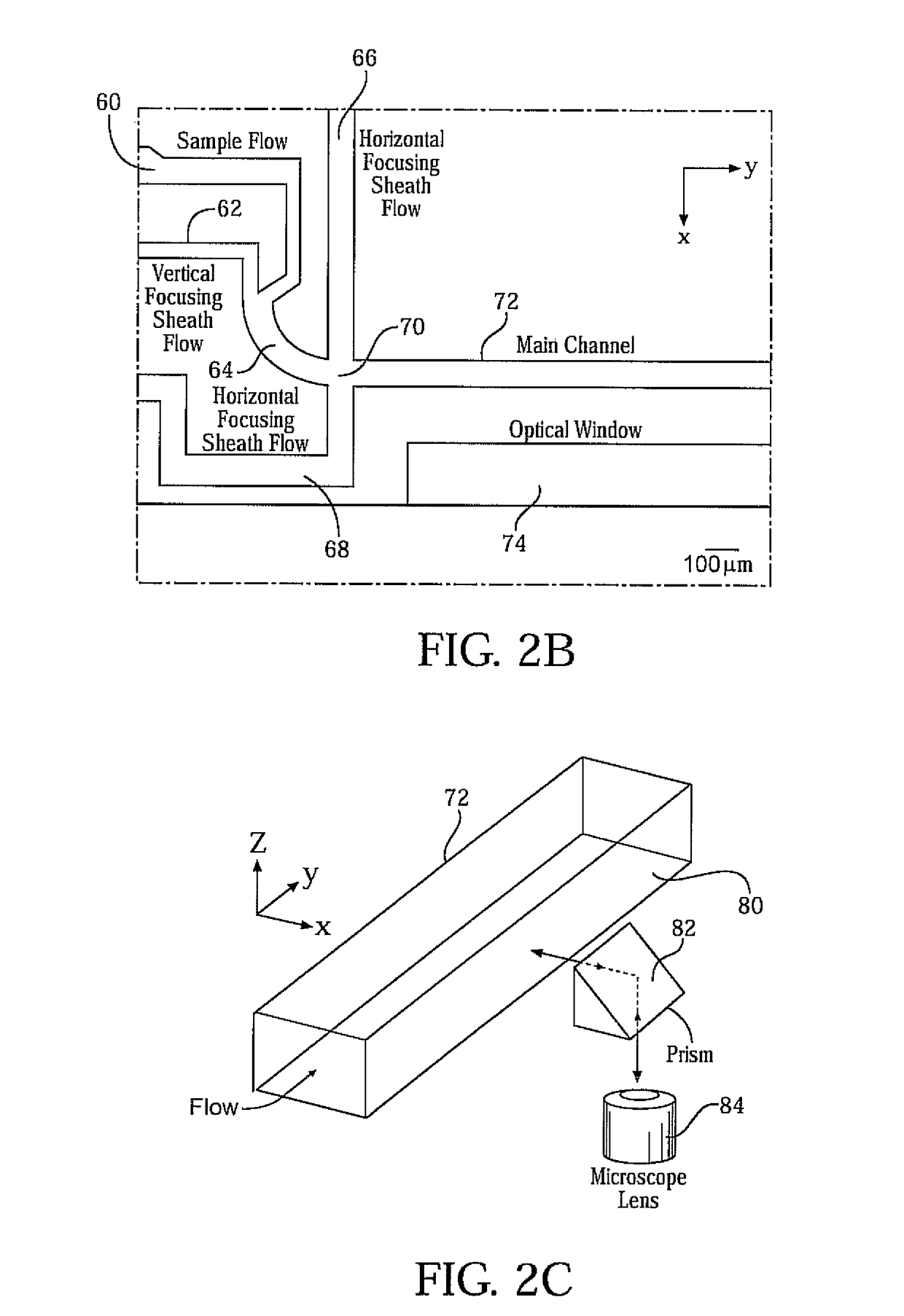
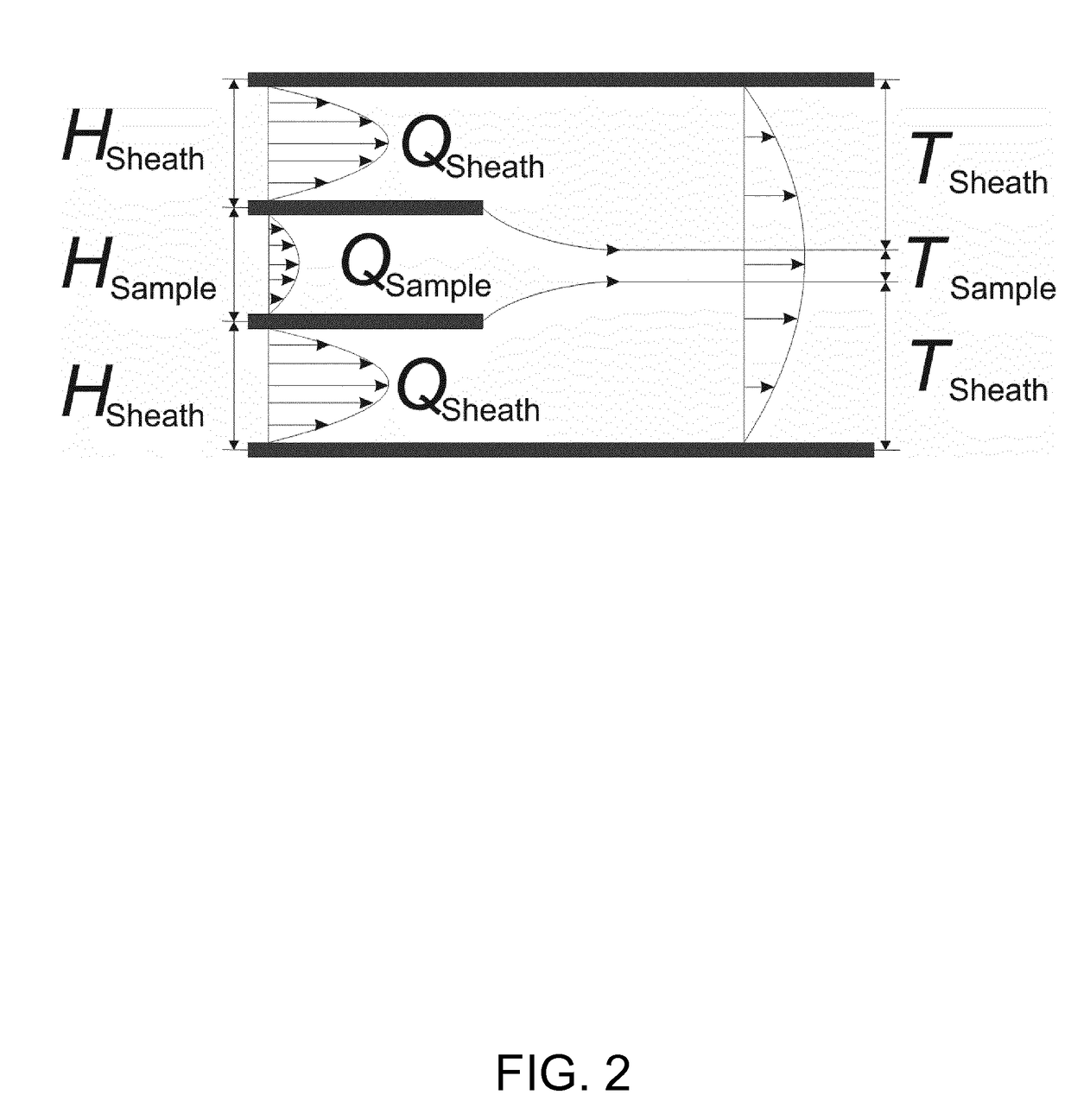
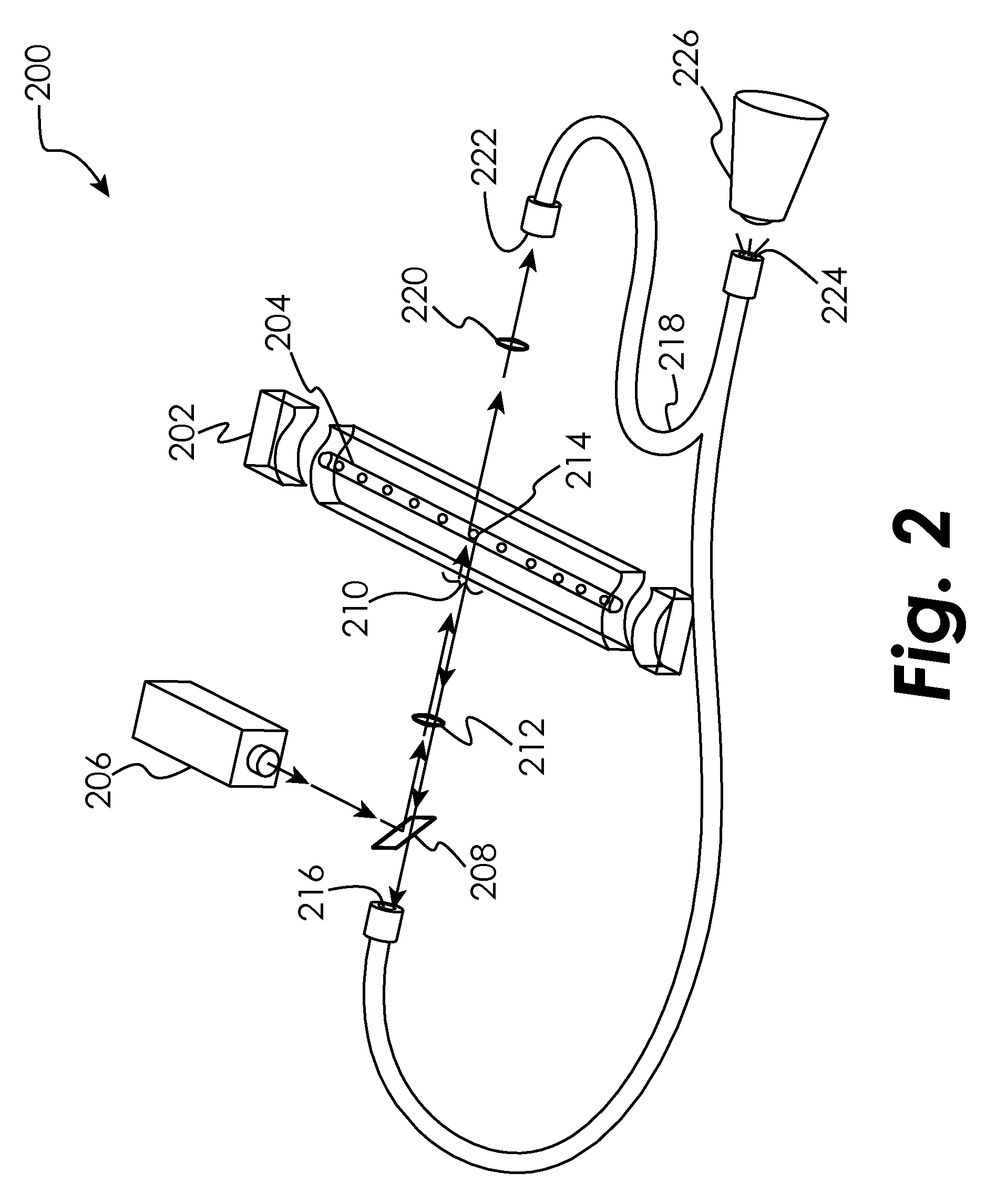
In a method for hydrodynamic focusing of a laminar and planar sample fluid flow, a system is provided for analysis and / or sorting of microscopic objects in the sample fluid comprising an optical objective for optical inspection of the microscopic objects. Microscopic objects are conveyed in the laminar flow of the sample fluid, and two laminar and planar flow of sheath fluids are provided. The flow of the sample fluid is hydrodynamically focused at an optical inspection zone of the system by the sheath fluids. Focusing of the flow of the sample fluid is controlled such that all of the microscopic objects in the sample fluid are caused to be conveyed in a common flow direction in one single plane at the inspection zone of the system, and the microscopic objects in the fluid are optically inspected through the optical objective.
Owner:FOSS ANALYTICAL AS
Method, device and system for hydrodynamic flow focusing
InactiveUS20170299492A1Large widthHigh resolutionBiological particle analysisLaboratory glasswaresPlanar flowMechanics
In a method for hydrodynamic focusing of a laminar and planar sample fluid flow, a system is provided for analysis and / or sorting of microscopic objects in the sample fluid comprising an optical objective for optical inspection of the microscopic objects. Microscopic objects are conveyed in the laminar flow of the sample fluid, and two laminar and planar flow of sheath fluids are provided. The flow of the sample fluid is hydrodynamically focused at an optical inspection zone of the system by the sheath fluids. Focusing of the flow of the sample fluid is controlled such that all of the microscopic objects in the sample fluid are caused to be conveyed in a common flow direction in one single plane at the inspection zone of the system, and the microscopic objects in the fluid are optically inspected through the optical objective.
Owner:FOSS ANALYTICAL AS
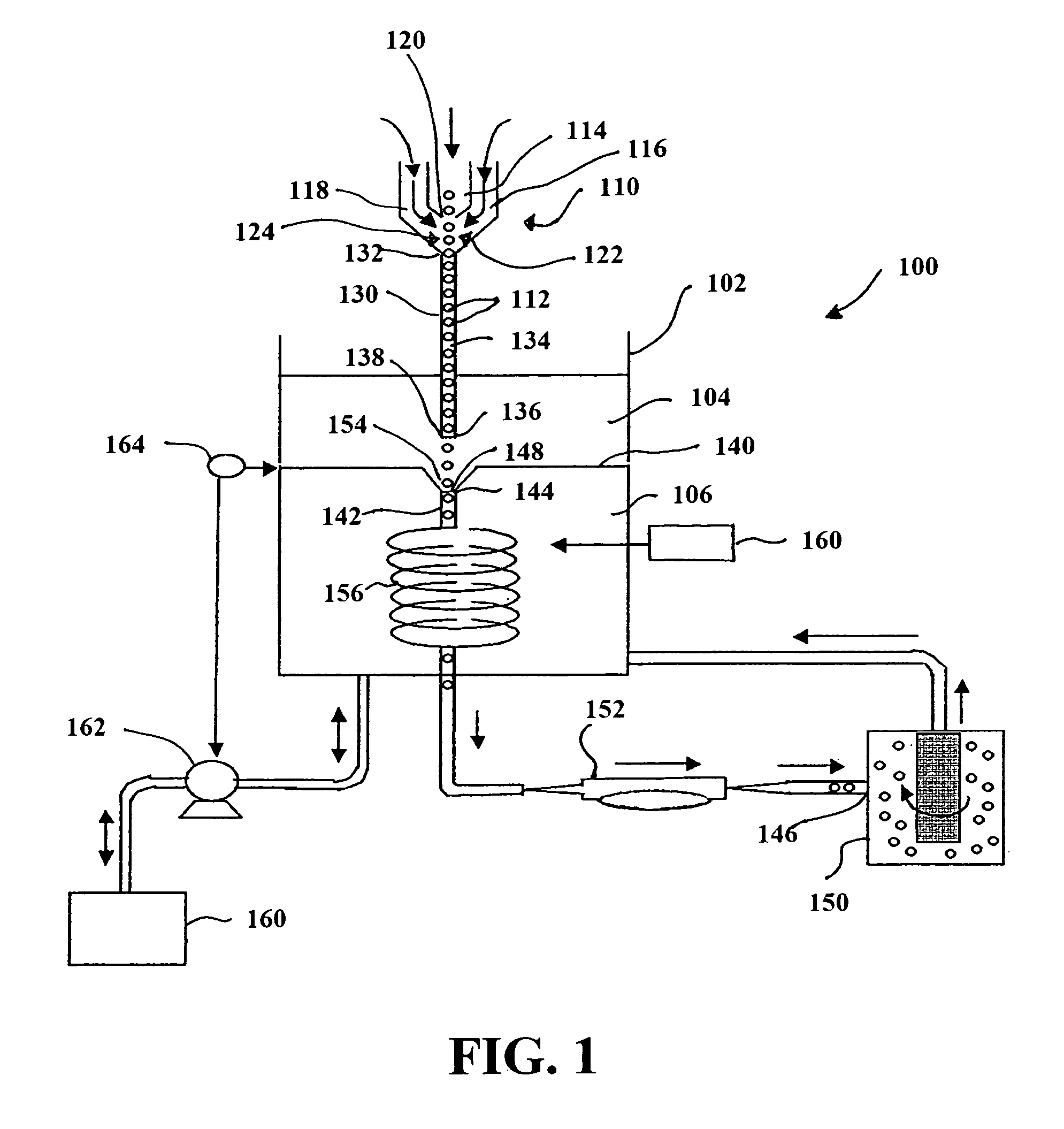
Method for detecting nano-particles
ActiveUS20150233812A1Nanoparticle analysisInvestigating moving fluids/granular solidsNanoparticleGold particles
Disclosed is a method for detecting nano-particles, comprising the steps of (1) compressing a sample liquid to be tested into a sample liquid flow by hydrodynamic focusing using a sheath fluid; (2) irradiating a measuring light to the sample liquid flow, wherein a single nano-particle in the sample liquid flow is irradiated by the measuring light for a duration of 0.1-10 milliseconds; (3) defining the area in which the measuring light irradiates the sample liquid flow as a detecting area, and collecting light signals emitted from the area irradiated by the measuring light by a lens imaging system, and allowing the light signals collected by the lens imaging system to pass a field stop, so as to filter out the light signals outside the detecting area and enrich the light signals from the detecting area; and (4) subjecting the light signals enriched by the field stop to optoelectronic signal conversion. The method can achieve detection for nano-particles with a low refractive index and a particle size of 24-1000 nm as well as nano-scale gold particles with a particle size of 6.7-150 nm.
Owner:NANOFCM INC
Methods of screening chemotherapeutic agents and treating cancer
ActiveUS20130295198A1Increase in amount of cytotoxicityExpand the populationHeavy metal active ingredientsBiocideCancer cellCytotoxicity
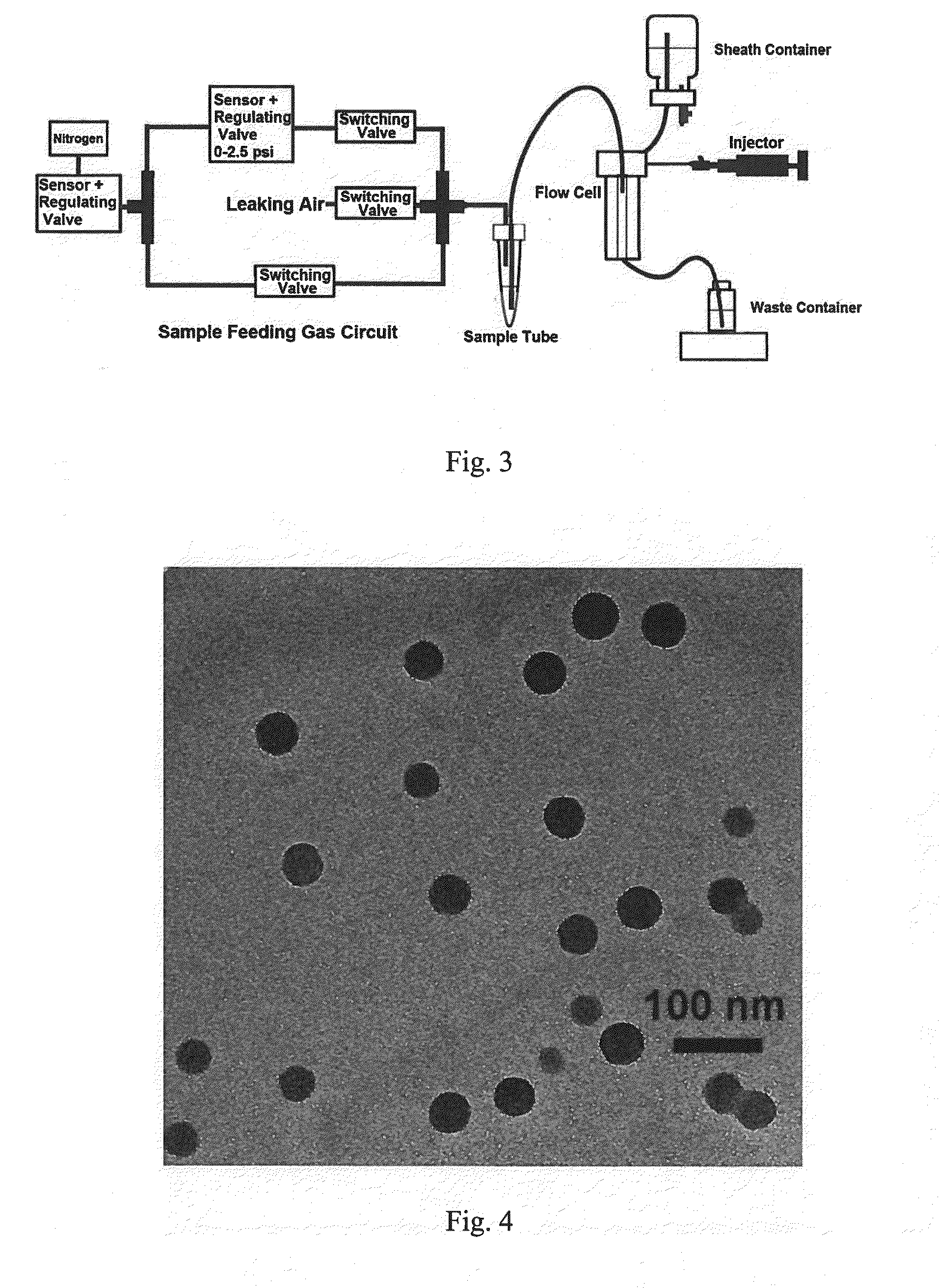
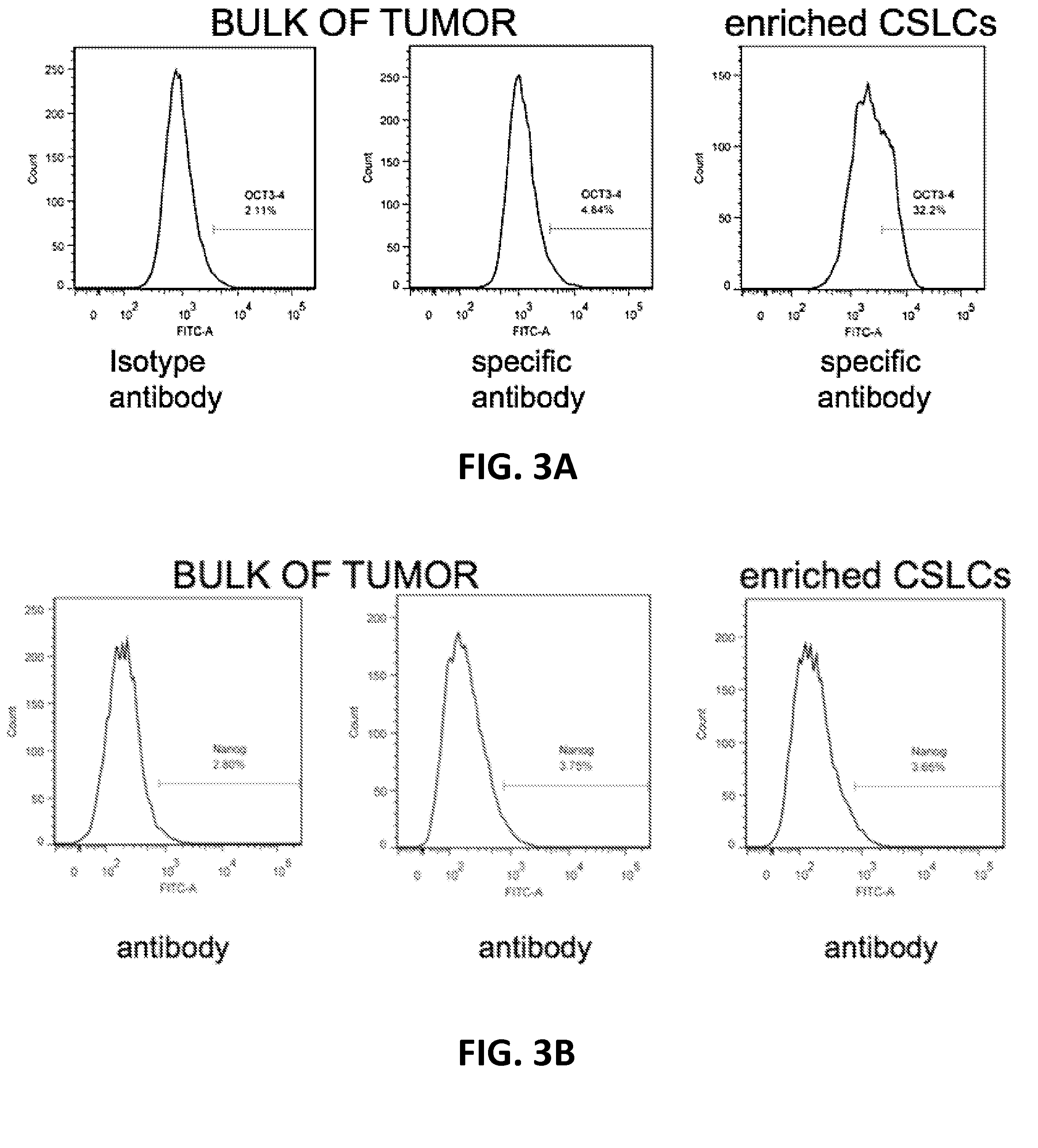
Methods for selecting chemotherapeutic agents for treating a cancer are provided that include the steps of providing a cancer cell sample having a population of bulk cancer cells and a population of cancer stem-like cells, culturing a first portion of the cancer cell sample in a hydrodynamic focusing bioreactor under microgravity conditions and for a period of time to selectively enhance the population of cancer stem-like cells and selectively kill the population of bulk cancer cells, contacting the cancer stem-like cells with one or more chemotherapeutic agents, and then selecting the one or more chemotherapeutic agents for treating the cancer if there is an increase in an amount of cytotoxicity. Methods for treating a cancer are also provided in which the identified chemotherapeutic agents are administered to a subject. Further provided are methods for identifying a test compound useful for treating a cancer.
Owner:MARSHALL UNIV RES
Method for detecting nano-particles using a lens imaging system with a field stop
ActiveUS9739700B2Nanoparticle analysisInvestigating moving fluids/granular solidsNanoparticleGold particles
Disclosed is a method for detecting nano-particles, comprising the steps of (1) compressing a sample liquid to be tested into a sample liquid flow by hydrodynamic focusing using a sheath fluid; (2) irradiating a measuring light to the sample liquid flow, wherein a single nano-particle in the sample liquid flow is irradiated by the measuring light for a duration of 0.1-10 milliseconds; (3) defining the area in which the measuring light irradiates the sample liquid flow as a detecting area, and collecting light signals emitted from the area irradiated by the measuring light by a lens imaging system, and allowing the light signals collected by the lens imaging system to pass a field stop, so as to filter out the light signals outside the detecting area and enrich the light signals from the detecting area; and (4) subjecting the light signals enriched by the field stop to optoelectronic signal conversion. The method can achieve detection for nano-particles with a low refractive index and a particle size of 24-1000 nm as well as nano-scale gold particles with a particle size of 6.7-150 nm.
Owner:NANOFCM INC
Apparatus and method for encapsulating pancreatic cells
InactiveUS8093038B2High yieldLong-term viabilityBioreactor/fermenter combinationsPowder deliveryFiltrationCentrifugation
An apparatus and method for coating micron-sized or sub-micron-sized particles such as living cells. The coating apparatus includes an encapsulation chamber enclosing a two-layer water-oil system for coating each islet cell with an aqueous polymeric coat. Islets together with an aqueous polymer solution are fed by a feed device that utilizes the principle of hydrodynamic focusing in order to ensure encapsulation of individual islets. The polymer in the aqueous coat is subsequently crosslinked by being exposed to laser light to produce structurally stable microcapsules of controllable thickness of the order of tens of microns. Encapsulated islets are removed from the encapsulation chamber by a valveless pump and recovered by filtration or centrifugation.
Owner:ILLINOIS INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGY
Micro-channel structure used for two-dimensional hydrodynamic focusing and microfluid chip
ActiveCN105149019AWith two-dimensional focusing functionLaboratory glasswaresFlow resistivityEngineering
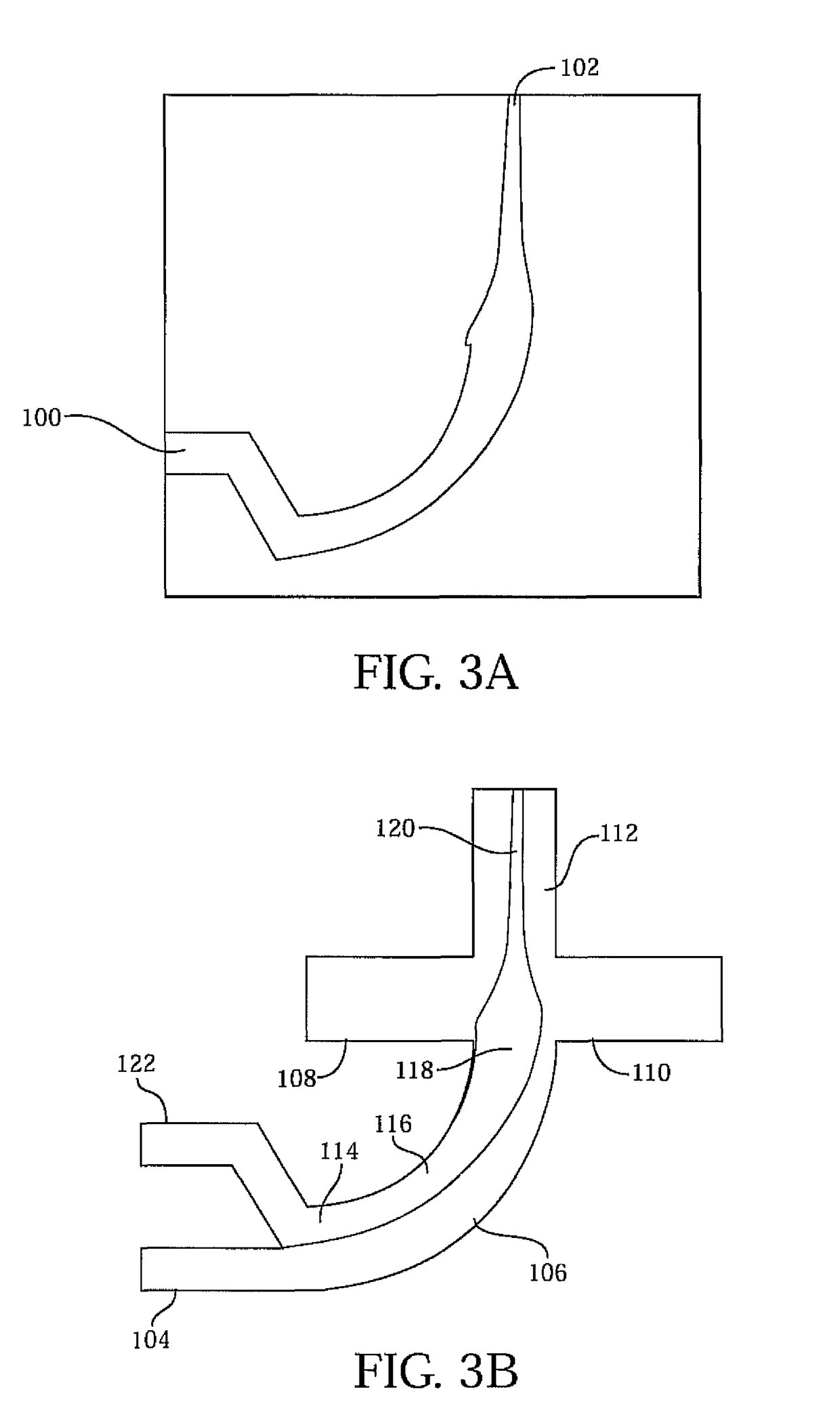
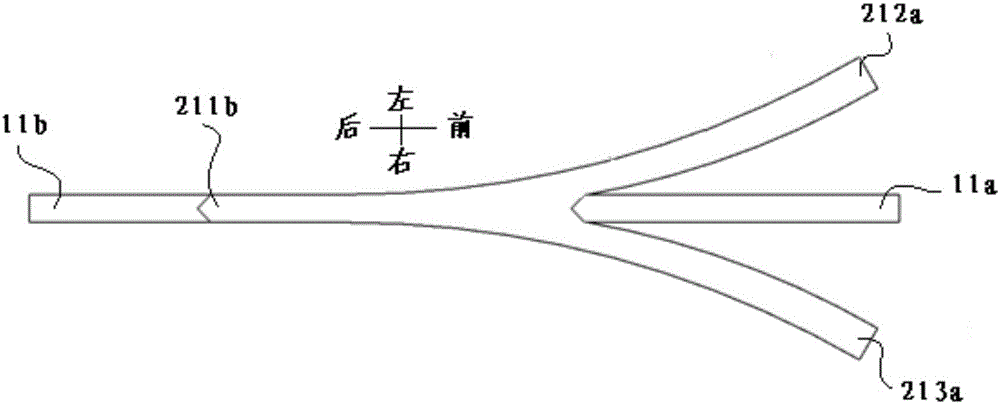
The invention discloses a micro-channel structure used for two-dimensional hydrodynamic focusing and a microfluid chip. The micro-channel structure comprises a first sample flow channel, a second sample flow channel, an upper-layer longitudinal focused flow channel, a lower-layer longitudinal focused flow channel, a left transverse focused flow channel and a right transverse focused flow channel, wherein the first sample flow channel and the second sample flow channel are respectively located at the front and the back and are mutually communicated, the upper-layer longitudinal focused flow channel and the lower-layer longitudinal focused flow channel are respectively stacked on the top and the bottom of the first sample flow channel, the left transverse focused flow channel and the right transverse focused flow channel are respectively arranged on at the left and right sides of the second sample flow channel, the rears end of the upper-layer and lower-layer longitudinal focused flow channels are both communicated with the first sample flow channel, and the rears end of the left and right transverse focused flow channels are both communicated with the second sample flow channel. The micro-channel structure used for two-dimensional hydrodynamic focusing has a two-dimensional focusing function, controllable focusing effect and the advantages of low flow resistance, a wide application scope of flow velocity, etc.
Owner:TSINGHUA UNIV
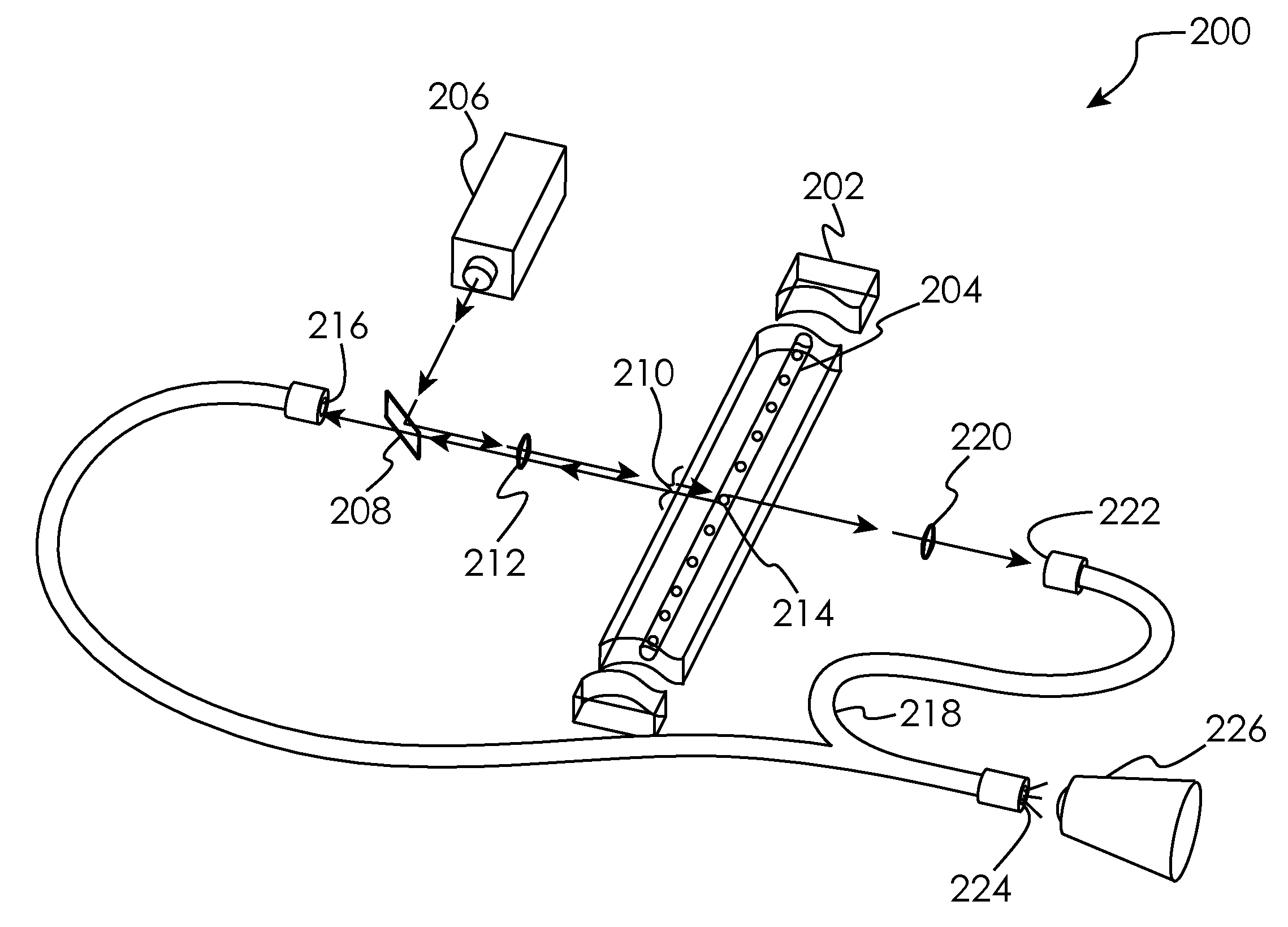
Hydrodynamic focusing apparatus used for diffraction imaging flow cytometer
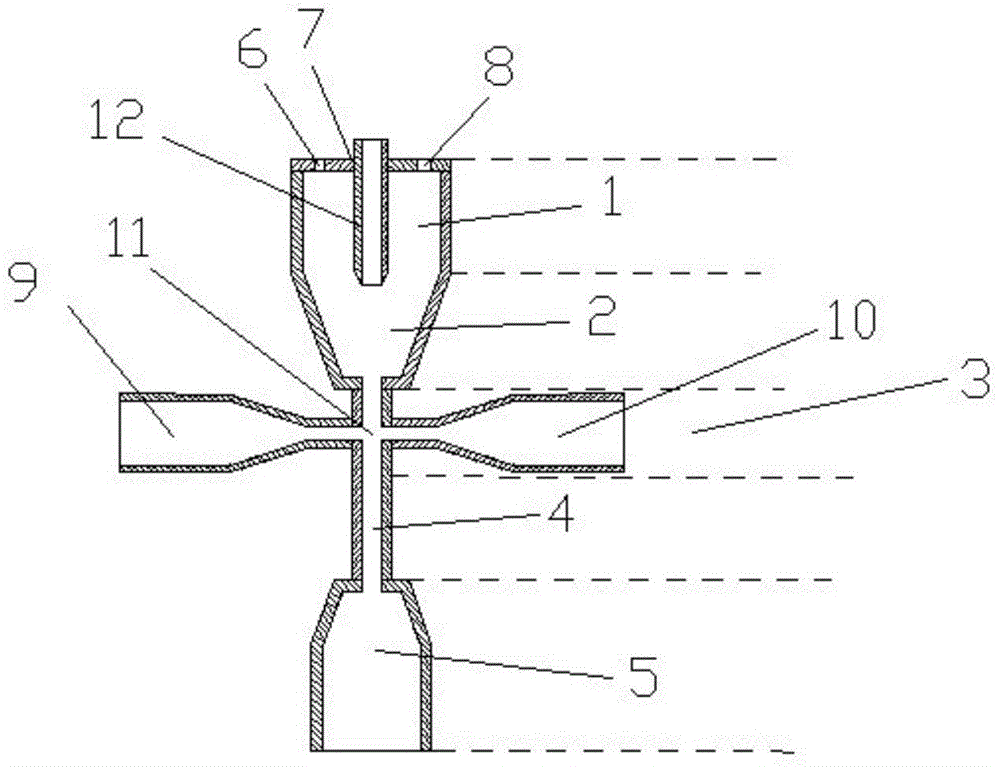
InactiveCN104034648AEasy to processIncrease contrastHydrodynamic testingIndividual particle analysisEngineeringContrast ratio
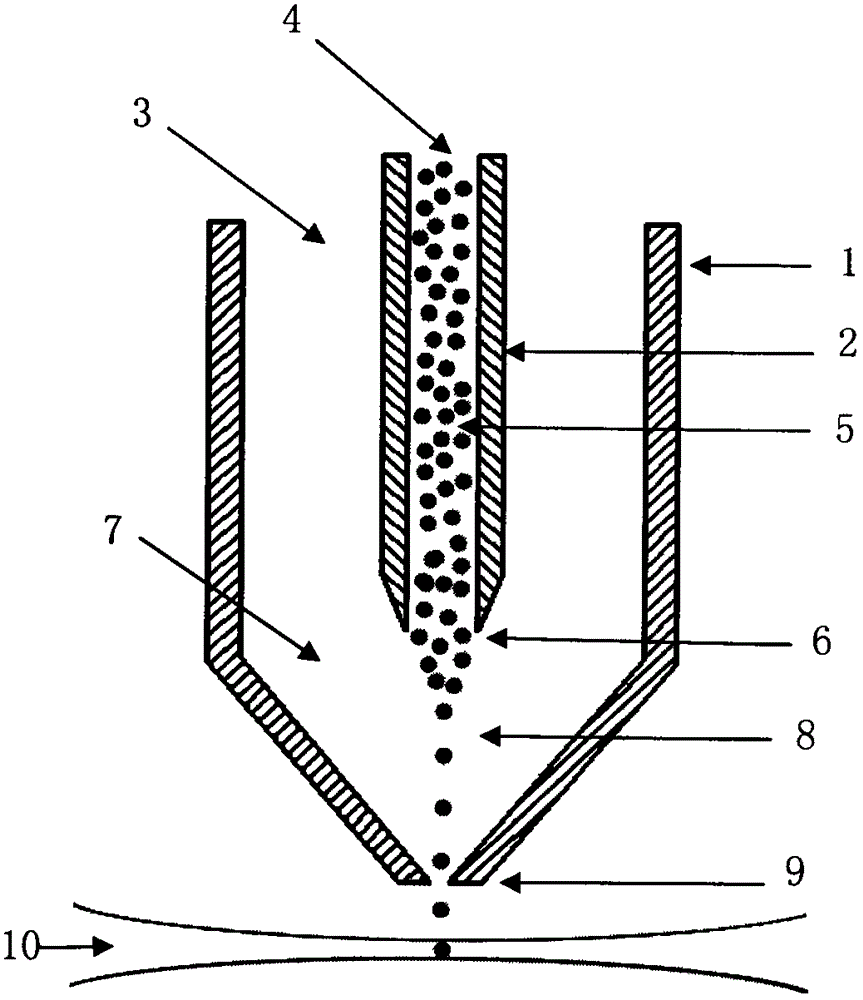
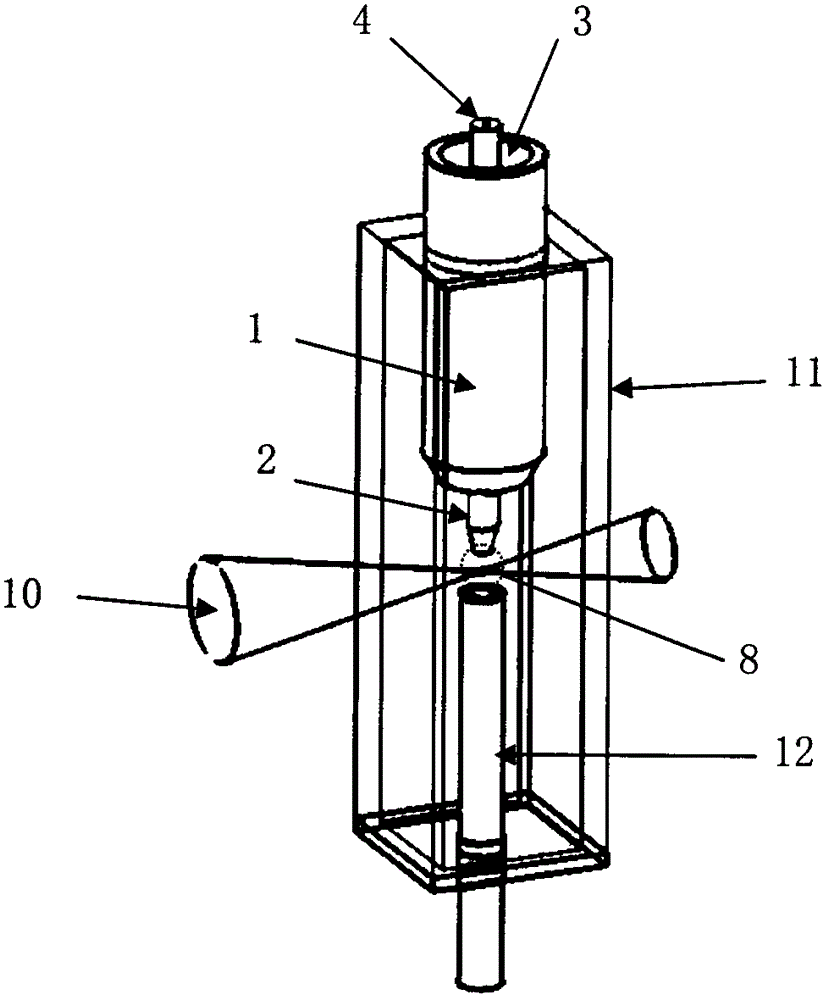
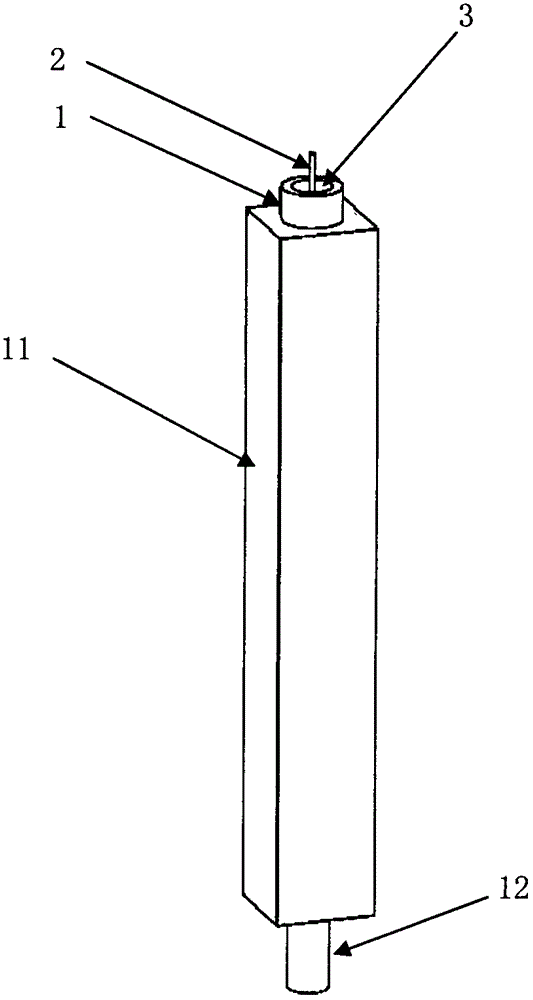
The invention provides a hydrodynamic focusing apparatus used for a diffraction imaging flow cytometer. The hydrodynamic focusing apparatus comprises a sheath flow tube, a nuclear flow tube and a fluid chamber made of an optically transparent material, wherein the upper part of the sheath flow tube is located out of the upper port of the fluid chamber, the lower part of the sheath flow tube is embedded into the upper port of the fluid chamber, the lower part of the nuclear flow tube axially penetrates the center of the sheath flow tube from the upper port of the sheath flow tube and is located in the fluid chamber, the upper part of the nuclear flow tube is located out of the upper port of the sheath flow tube, and the lower port of the fluid chamber is provided with a liquid discharging pipe. The cross section of a liquid flow channel in the fluid chamber is a polygon, the outer wall of each edge is a plane, and the fluid chamber is prepared from the optically transparent material through bonding or sintering. According to the invention, processing of the sheath flow tube and the nuclear flow tube is simple; the hydrodynamic focusing apparatus can realize hydrodynamic focusing of nuclear flow in a great flow velocity adjusting range and obtain a stable layer fluid with accurately controllable nuclear flow position and flow velocity, so a high-contrast diffraction image of a to-be-measured particle can be obtained eventually.
Owner:天津炜辐医疗科技有限公司
Apparatus for microfluidic flow cytometry analysis of a particulate containing fluid
PendingUS20200316603A1Good flexibilityFocusLaboratory glasswaresIndividual particle analysisEngineeringAc impedance
An apparatus for microfluidic flow cytometry analysis of a particulate containing fluid An apparatus for microfluidic flow cytometry analysis of a particulate containing fluid comprises a hydrodynamic focussing apparatus for providing a focused stream of particulate containing fluid; and a microfluidic chip. The chip has a plurality of layers and comprises a microfluidic channel that extends through the chip substantially orthogonal to a plane of the layers of the chip, and is in fluid communication with the hydrodynamic focusing apparatus for receipt of a focused steam of particulate containing fluid. The chip also comprises a detection zone comprising at least one pair of electrodes in electrical communication with the microfluidic channel. At least one pair of electrodes comprise an excitation electrode coupled to an AC signal source and a detection electrode configured to detect AC impedance changes in the microfluidic channel between the electrodes resulting from particles passing between the electrodes in the microfluidic channel. Methods of sorting mammalian sperm cells according to sex is also described.
Owner:CELLIX
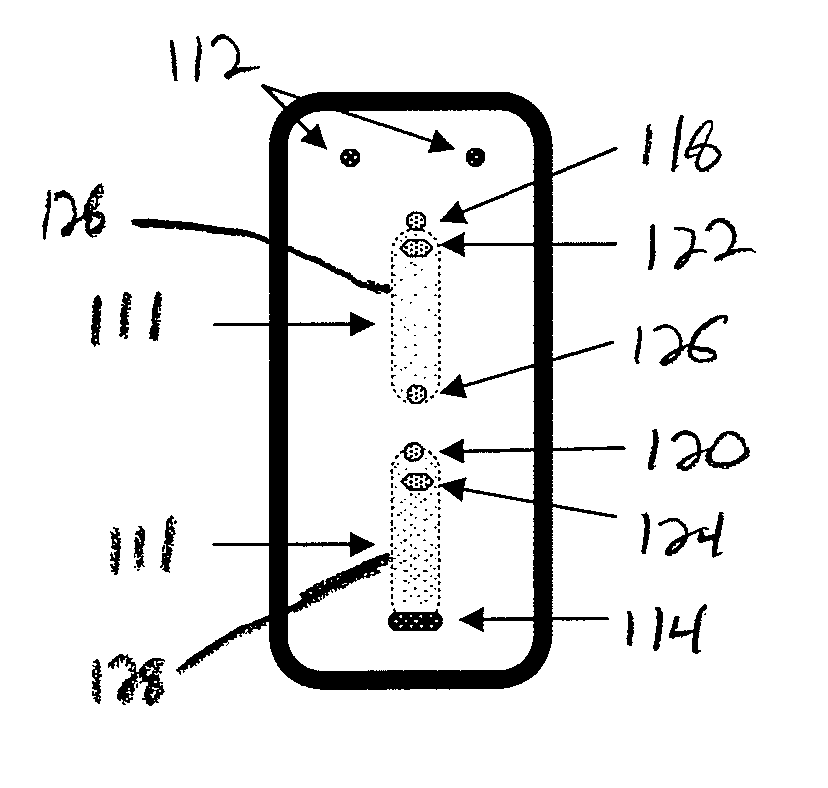
Hydrodynamic Isolation Method and Apparatus
ActiveUS20080268544A1Difficult to manufactureDifficult to break easilyAnalysis using chemical indicatorsWithdrawing sample devicesFlow cellPhysical Barrier
The present invention is a flow cell and method for use in microfluidic analyses that presents highly discrete and small volumes of fluid to isolated locations on a two-dimensional surface contained within an open fluidic chamber defined by the flow cell that has physical dimensions such that laminar style flow occurs for fluids flowing through the chamber. This process of location specific fluid addressing within the flow cell is facilitated by combining components of hydrodynamic focusing with site specific cell evacuation. The process does not require the use of physical barriers within the flow cell or mechanical valves to control the paths of fluid movement.
Owner:BRUKER DALTONIK GMBH & CO KG
Micro-channel structure and micro-fluid chip for achieving two-dimensional fluid power accumulation by using single-way sheath liquid
The invention discloses a micro-channel structure and a micro-fluid chip with the micro-channel structure for achieving two-dimensional fluid power accumulation by using a single-way sheath liquid. The micro-channel structure comprises a sample flow channel, an upper longitudinal accumulated flow channel, a lower longitudinal accumulated flow channel and two transverse accumulated flow channels, wherein the upper longitudinal accumulated flow channel is arranged above the sample flow channel in an overlapped manner; the lower longitudinal accumulated flow channel is arranged below the sample flow channel in the overlapped manner; the two transverse accumulated flow channels are respectively arranged on the left side and right side of the sample flow channel; the width of each transverse accumulated flow channel is gradually reduced from back to front in a liquid flowing direction; and the maximum width of each transverse accumulated flow channel is greater than that of the sample flow channel. According to the micro-channel structure for achieving two-dimensional fluid power accumulation by using the single-way sheath liquid, disclosed by the embodiment of the invention, two-dimensional accumulation of a sample flow can be achieved, the sample flow can be prevented from being dispersed by the sheath liquid, the liquid flow can be kept stable, and the two-dimensional accumulation effect of the sample flow can be ensured.
Owner:TSINGHUA UNIV
Multi-mode precisely-focused electrical impedance flow cytometry detection device and preparation method thereof
InactiveCN111735854AReduce complexityReduce usageMaterial resistanceElectrical impedanceFlow cytometry
The invention discloses a multi-mode precisely-focused electrical impedance flow cytometry detection device and a preparation method thereof. The device comprises a non-conductive body, and a hydrodynamic focusing flow channel, an ultrasonic focusing flow channel, an electrical impedance detection flow channel and an outlet flow channel are sequentially arranged in the body in the direction from the fluid inlet to the fluid outlet. The hydrodynamic focusing flow channel comprises a sample flow channel in the middle and a sheath fluid flow channel wrapping the sample flow channel; the sample flow channel is communicated with the sample inlet, the sheath fluid flow channel is communicated with the sheath fluid inlet through the sheath fluid flow inlet flow channel, a piezoelectric element isarranged on the outer side of the ultrasonic focusing flow channel, electrical impedance detection electrodes are arranged at the two ends of the electrical impedance detection flow channel, and double-nozzle 3D printing is adopted in the preparation method. According to the invention, the problem of congestion of a sample particle blocking point is solved, the targets of high focusing speed andaccurate focusing position are realized, rapid, accurate and effective focusing is carried out on cells, and the difficulty of signal processing is reduced.
Owner:SOUTHEAST UNIV
Ultrasensitive SERS flow detector
ActiveUS9804093B2Surface-enhanced RamanPrevent escapeRaman scatteringIndividual particle analysisDesorptionFlow injection analysis
The invention provides an apparatus and methods for label-free, chemical specific detection in flow for high throughput characterization of analytes in applications such as flow injection analysis, electrophoresis, and chromatography. A surface-enhanced Raman scattering (SERS) flow detector capable of ultrasensitive optical detection on the millisecond time scale has been developed. The device employs hydrodynamic focusing to improve SERS detection in a flow channel where a sheath flow confines analyte molecules eluted from a capillary over a planar SERS-active substrate. Increased analyte interactions with the SERS substrate significantly improve detection sensitivity. Raman experiments at different sheath flow rates showed increased sensitivity compared with the modeling predictions, indicating increased adsorption. At low analyte concentrations, rapid analyte desorption is observed, enabling repeated and high-throughput SERS detection. The flow detector offers substantial advantages over conventional SERS-based assays such as minimal sample volumes and high detection efficiency.
Owner:UNIV OF NOTRE DAME DU LAC
Microfluidic device
ActiveUS8891084B2Bioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsParticle flowAcoustic energy
The present disclosure relates to microfluidic devices adapted for facilitating cytometry analysis of particles flowing therethrough. In certain embodiments, the microfluidic devices allow light collection from multiple directions. In certain other embodiments, the microfluidic devices use spatial intensity modulation. In certain other embodiments, the microfluidic devices have magnetic field separators. In certain other embodiments, the microfluidic devices have the ability to stack. In certain other embodiments, the microfluidic devices have 3-D hydrodynamic focusing to align sperm cells. In certain other embodiments, the microfluidic devices have acoustic energy couplers. In certain other embodiments, the microfluidic devices have phase variation producing lenses. In certain other embodiments, the microfluidic devices have transmissive and reflective lenses. In certain other embodiments, the microfluidic devices have integrally-formed optics. In certain other embodiments, the microfluidic devices have non-integral geographically selective reagent delivery structures. In certain other embodiments, the microfluidic devices have optical waveguides incorporated into their flow channels. In certain other embodiments, the microfluidic devices have optical waveguides with reflective surfaces incorporated into their flow channels. In certain other embodiments, the microfluidic devices have virus detecting and sorting capabilities. In certain other embodiments, the microfluidic devices display a color change to indicate use or a result.
Owner:SONY CORP +1
Flow chamber of flow cytometer
InactiveCN104634719ADecrease the stable laminar flow diameterImprove detection accuracyIndividual particle analysisLight spotAtmospheric pressure
The invention discloses a flow chamber of a flow cytometer, and relates to the field of flow cytometers. By adopting the flow chamber, the problems that when the sample feeding rate of a sample flow of an existing flow cytometer is increased, to-be-tested cells or micro-particles are deviated from the central position of an irradiation light spot to cause that the irradiation energy is non-uniform, signal changes are increased, and data quality is reduced, and thus the detection precision of the cytometer is reduced can be solved. The flow chamber comprises an inlet area, a converging area, an adjusting area, a detection area and an auxiliary area, wherein the inlet area is provided with a main sheath liquid inlet, a sample flow inlet and an air pressure adjusting opening, the adjusting area is provided with two adjusting area inlets and a comprehensive adjusting area, main sheath liquid enters the inlet area from the sheath liquid inlet, the sample flow enters the converging area from a sample flow pipe, and the main sheath liquid and the sample flow are converged into a steady laminar flow in the converging area by using hydrodynamic focusing characteristics and then sequentially enter the comprehensive adjusting area, the detection area and the auxiliary area. According to the flow chamber disclosed by the invention, relatively high detection precision can be achieved at both high and low sample flow sample feeding rates, particularly, the nuclear flow diameter obtained after the sample flow is converged can be reduced at a high sample flow sample feeding rate, and high precision can be achieved.
Owner:CHANGCHUN INST OF OPTICS FINE MECHANICS & PHYSICS CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Two-fluid hydrodynamic printing
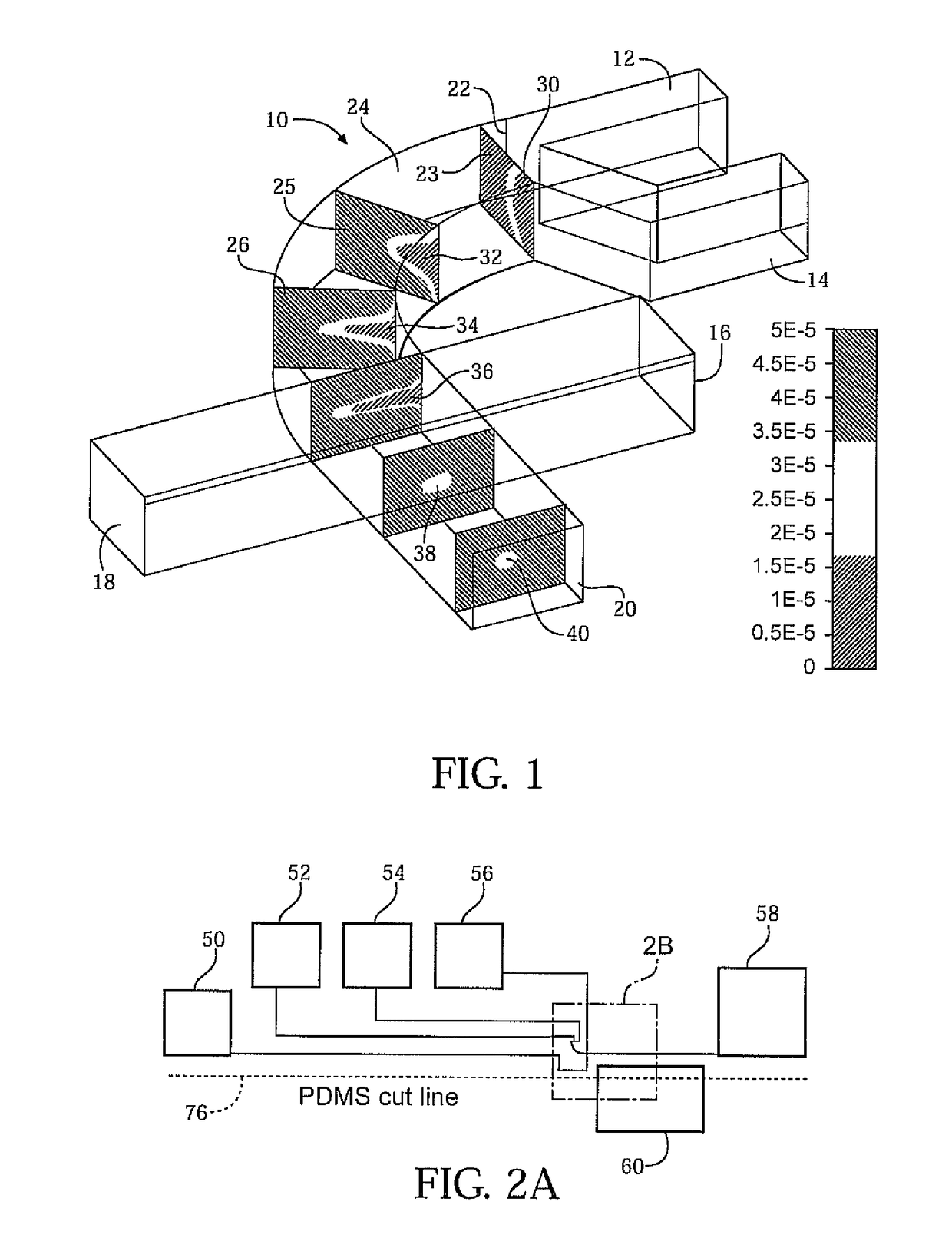
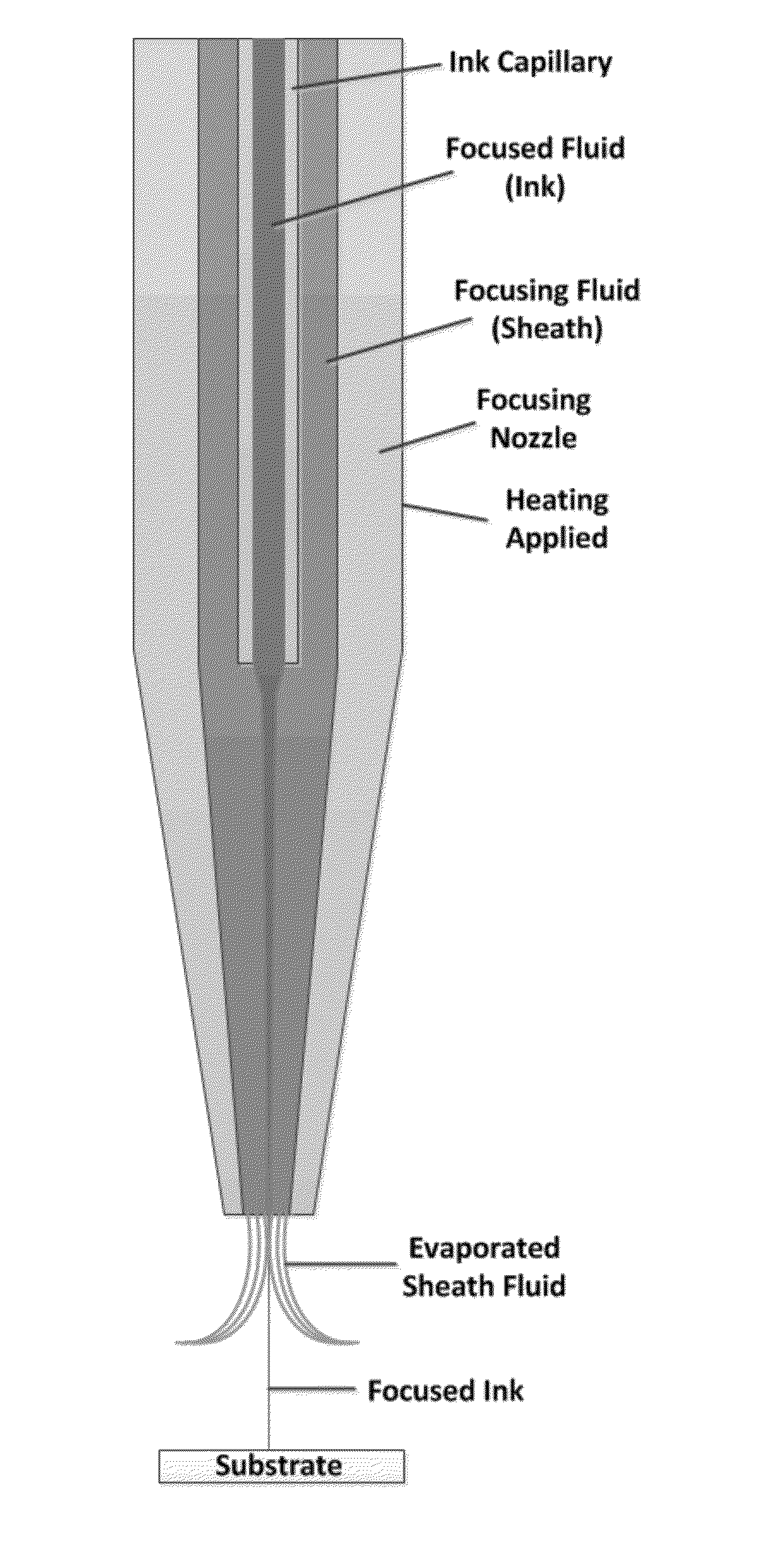
ActiveUS10130961B2Manufacturing platforms/substratesManufacturing recyclingEngineeringPrinted electronics
Hydrodynamic focusing of two fluid steams provides a novel micro printing technology for printed electronics and other high performance applications.
Owner:NAT TECH & ENG SOLUTIONS OF SANDIA LLC
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com