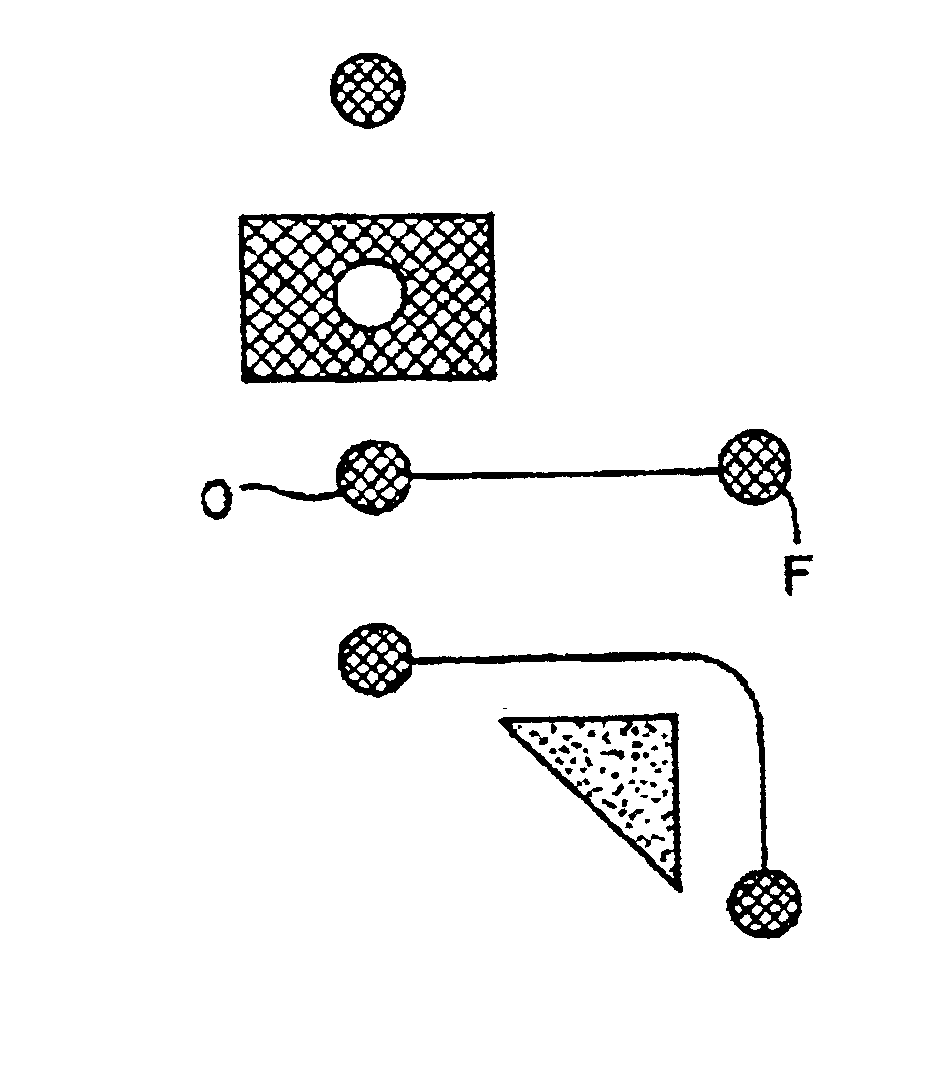
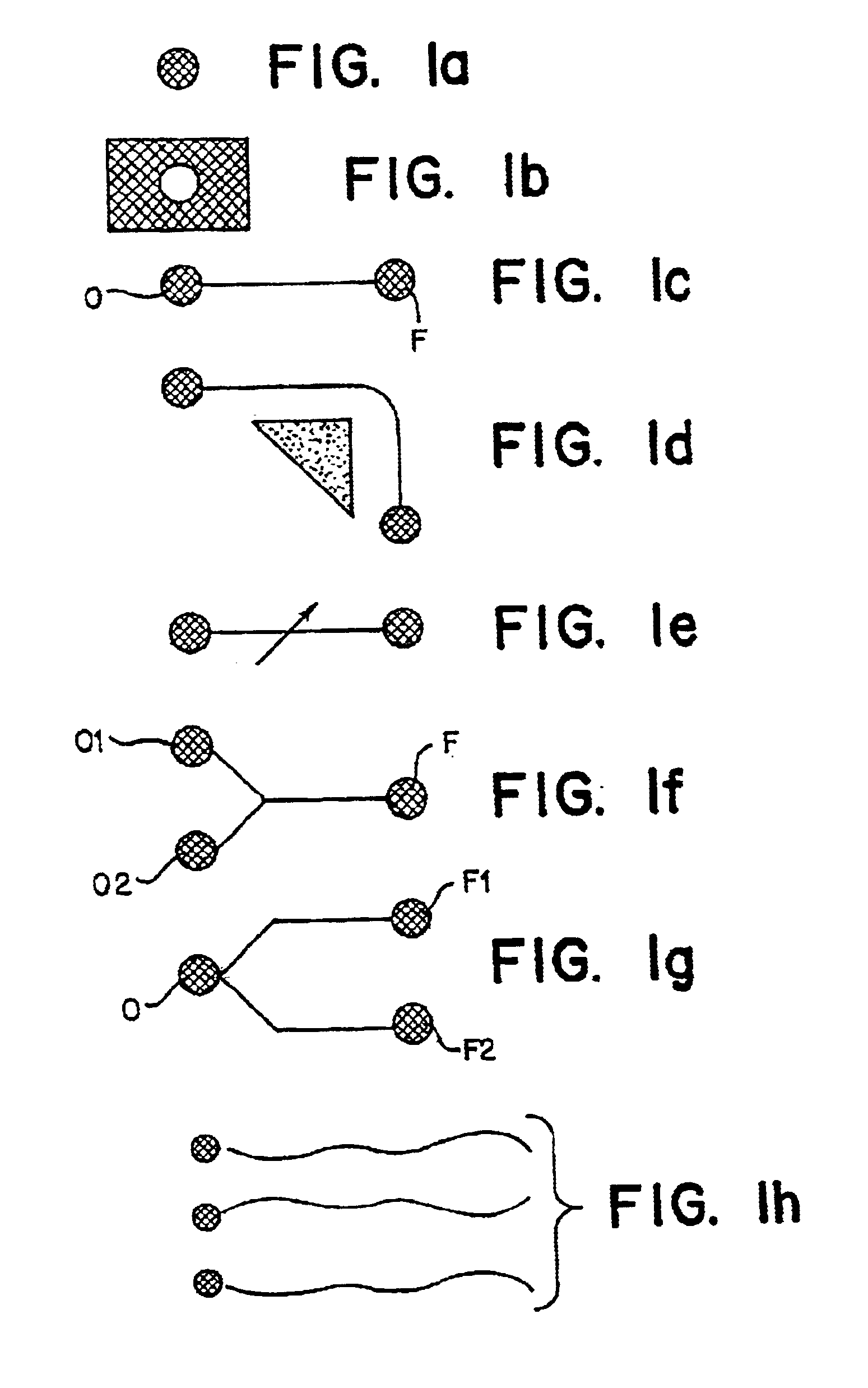
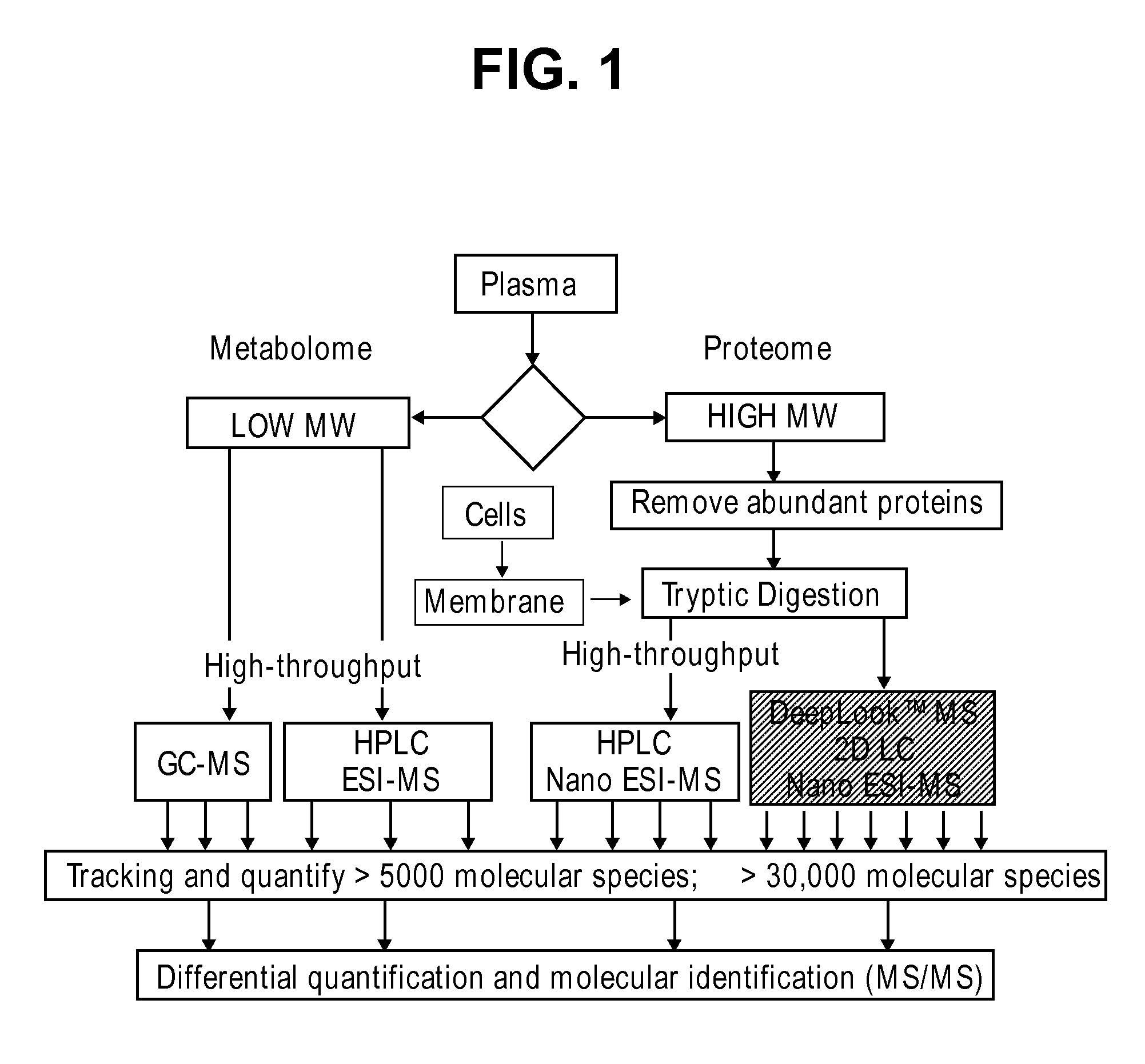
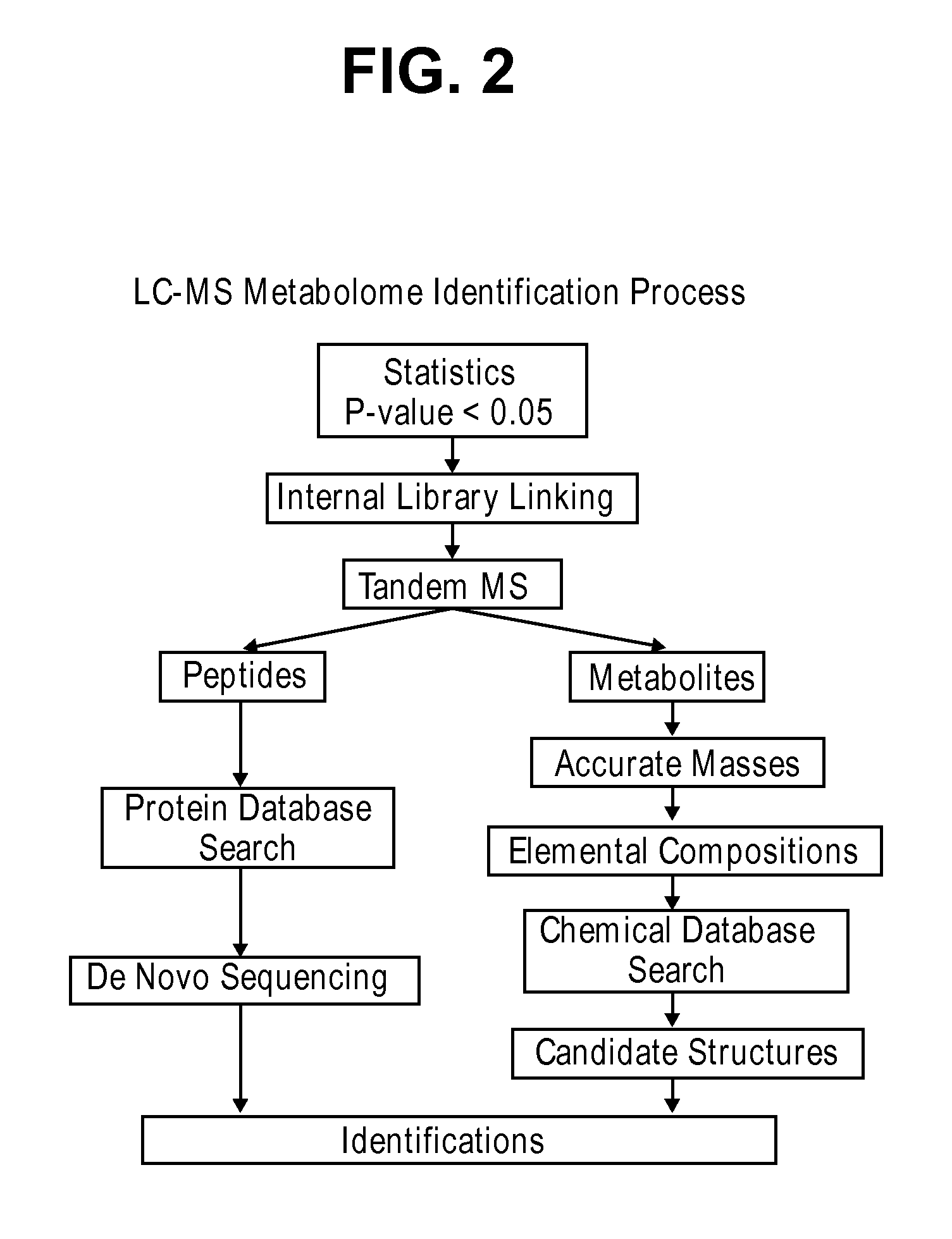
Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
166 results about "Cytometry" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
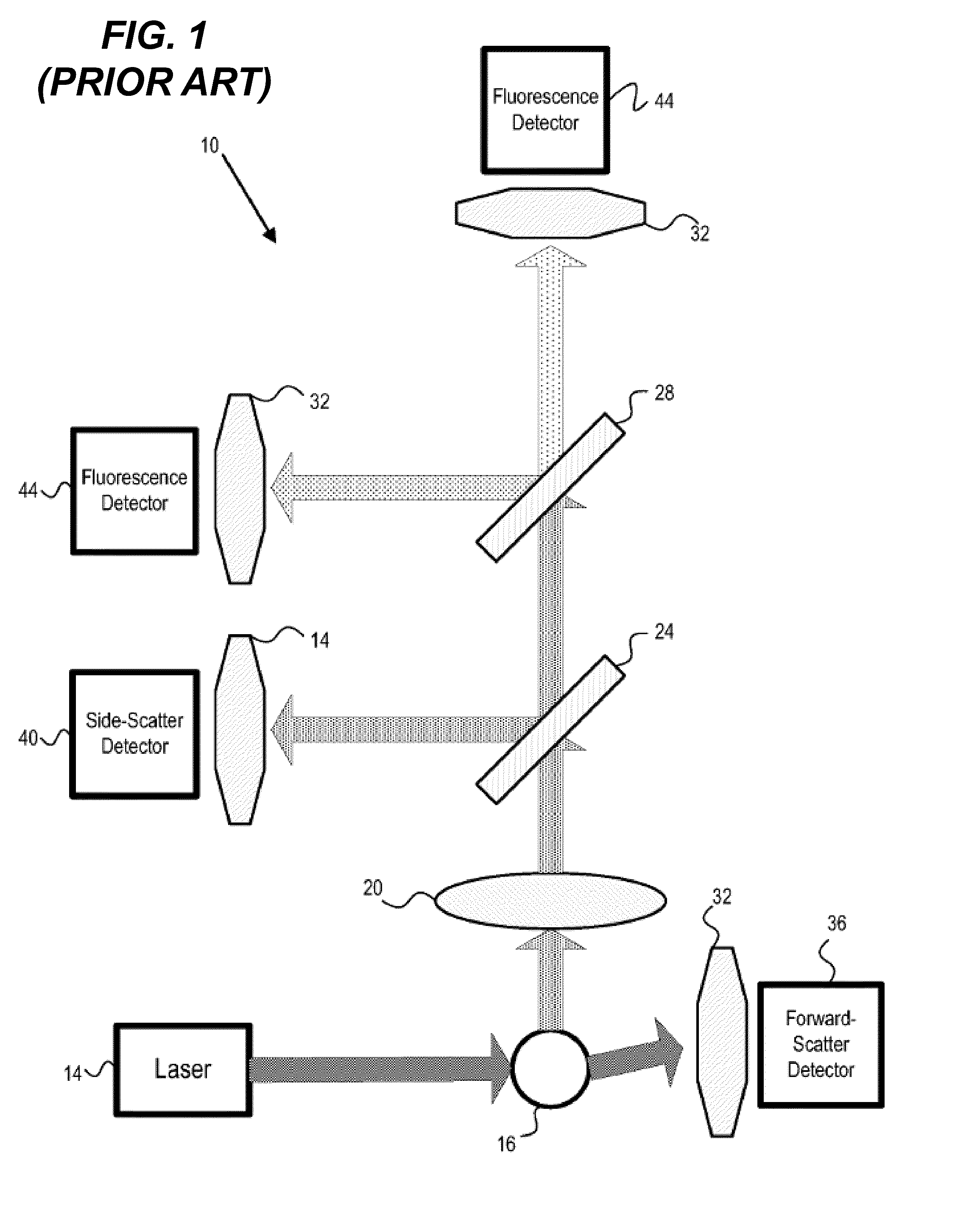
Cytometry is the measurement of the characteristics of cells. Variables that can be measured by cytometric methods include cell size, cell count, cell morphology (shape and structure), cell cycle phase, DNA content, and the existence or absence of specific proteins on the cell surface or in the cytoplasm. Cytometry is used to characterize and count blood cells in common blood tests such as the complete blood count. In a similar fashion, cytometry is also used in cell biology research and in medical diagnostics to characterize cells in a wide range of applications associated with diseases such as cancer and AIDS.
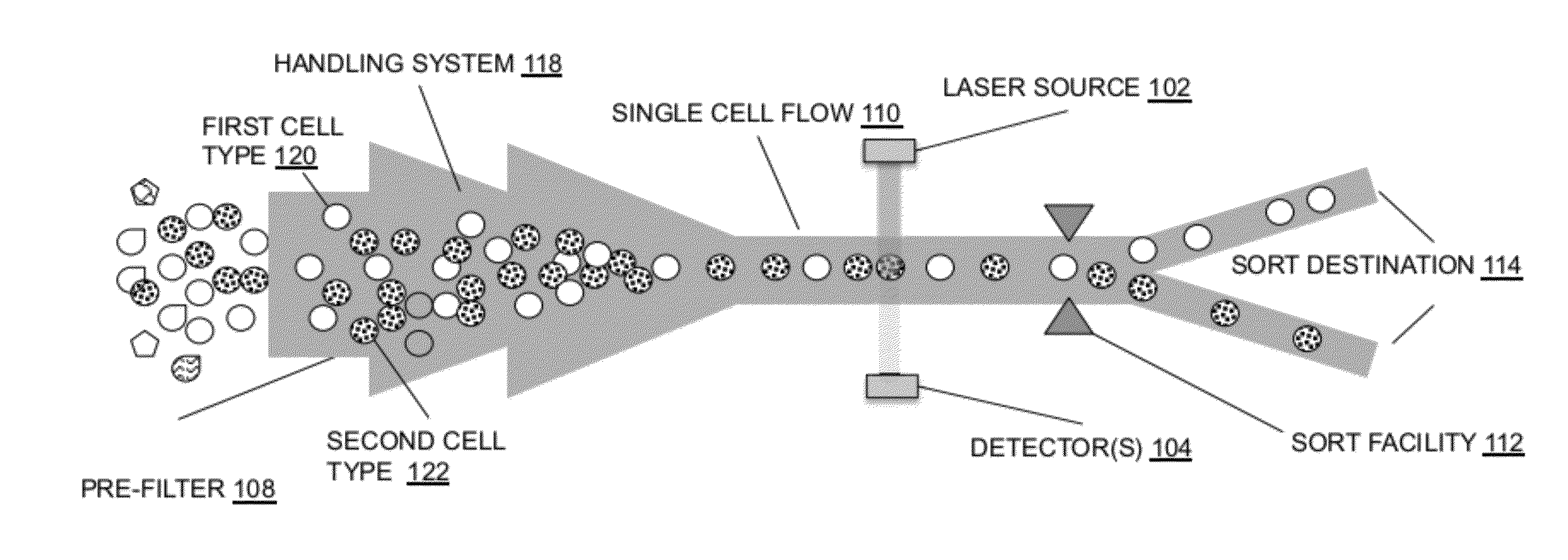
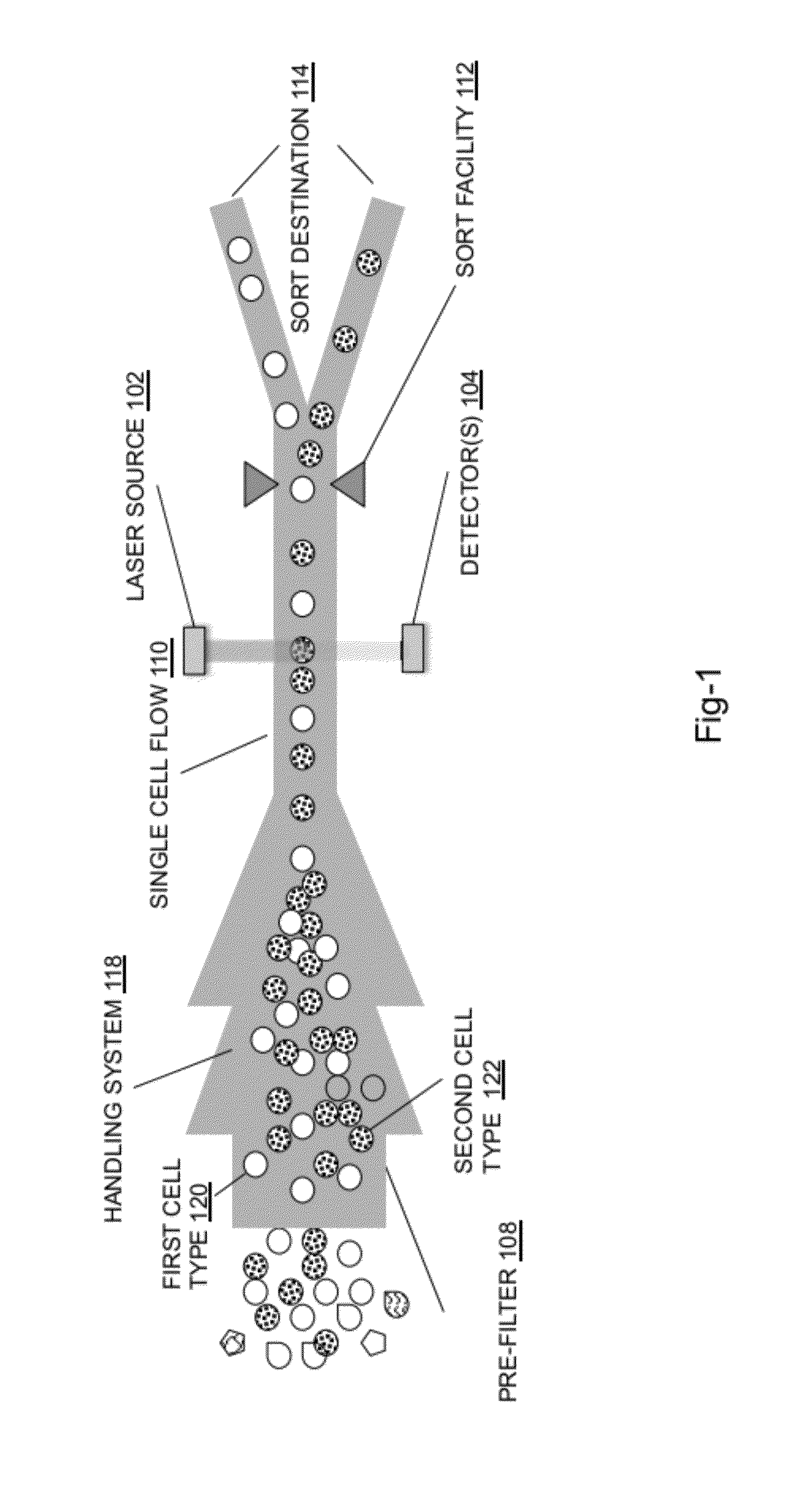
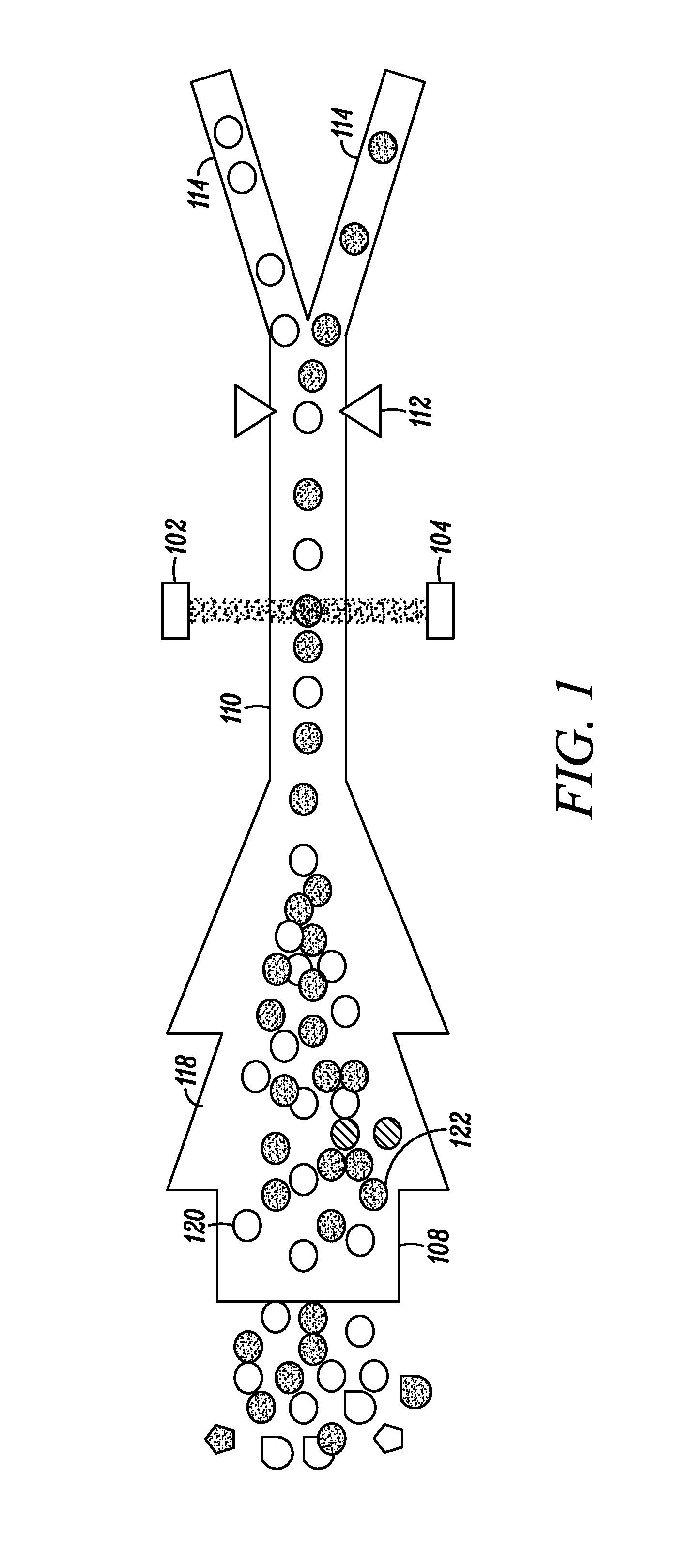
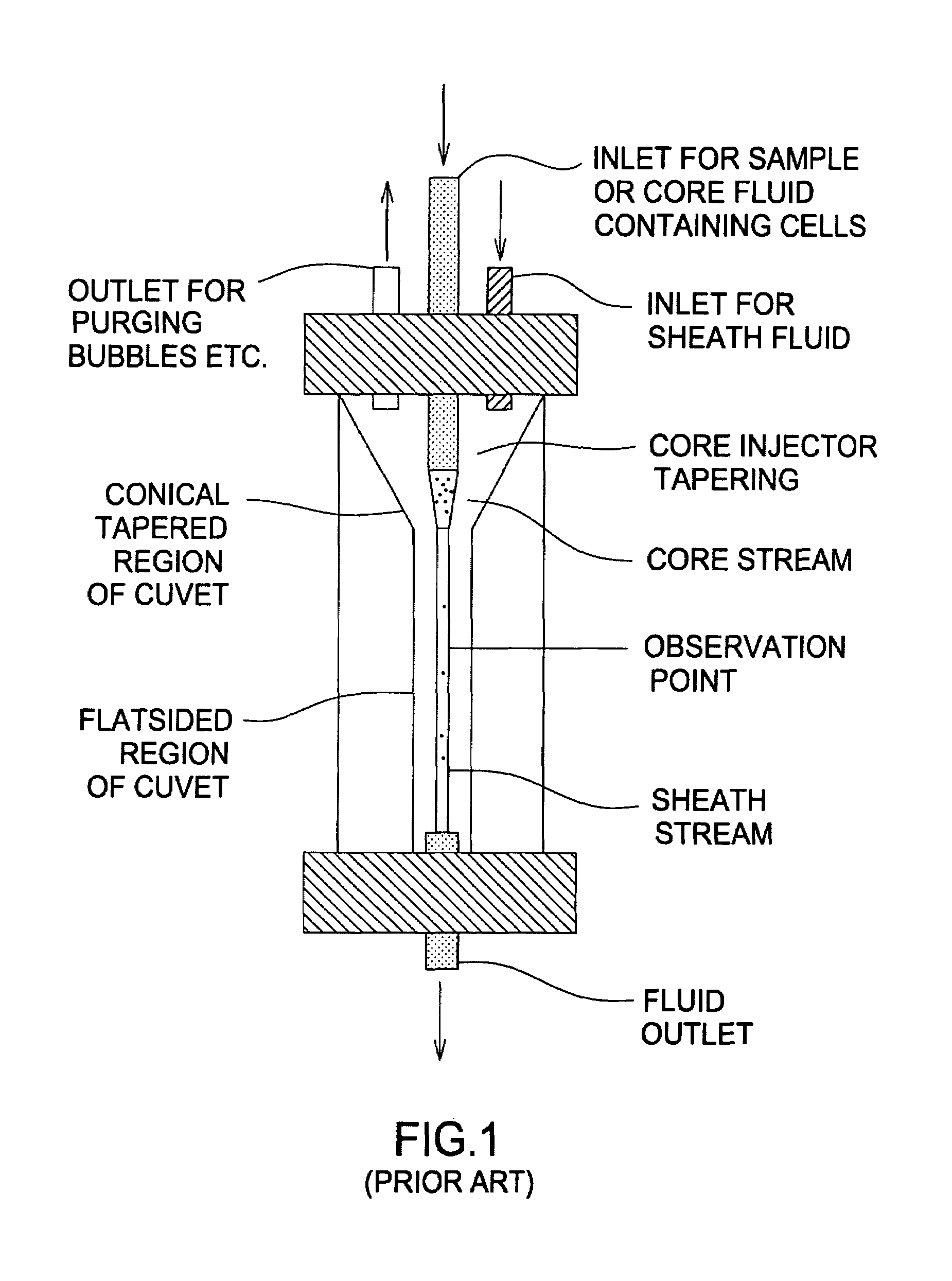
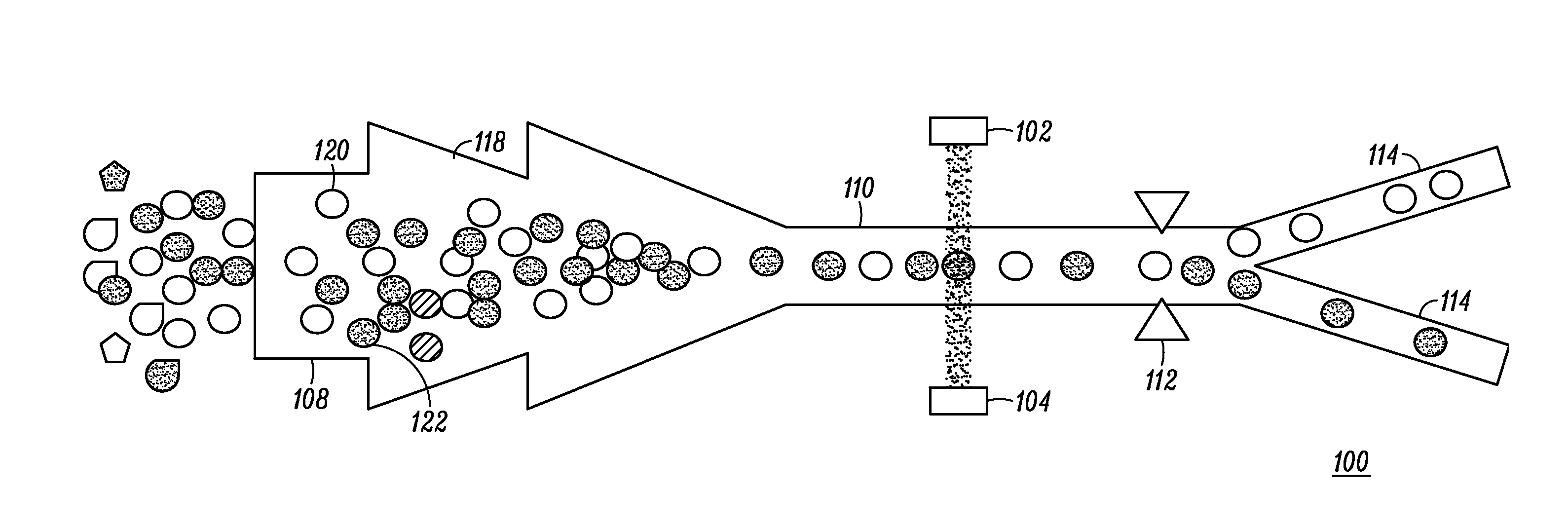
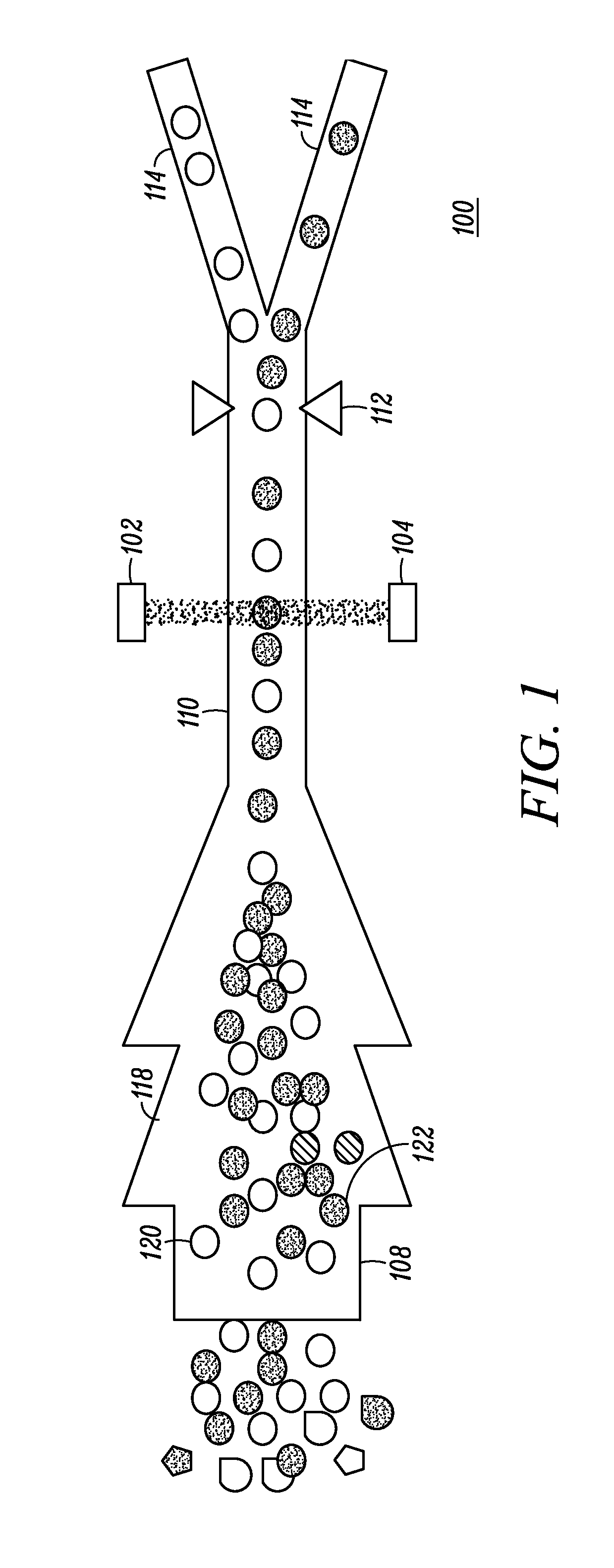
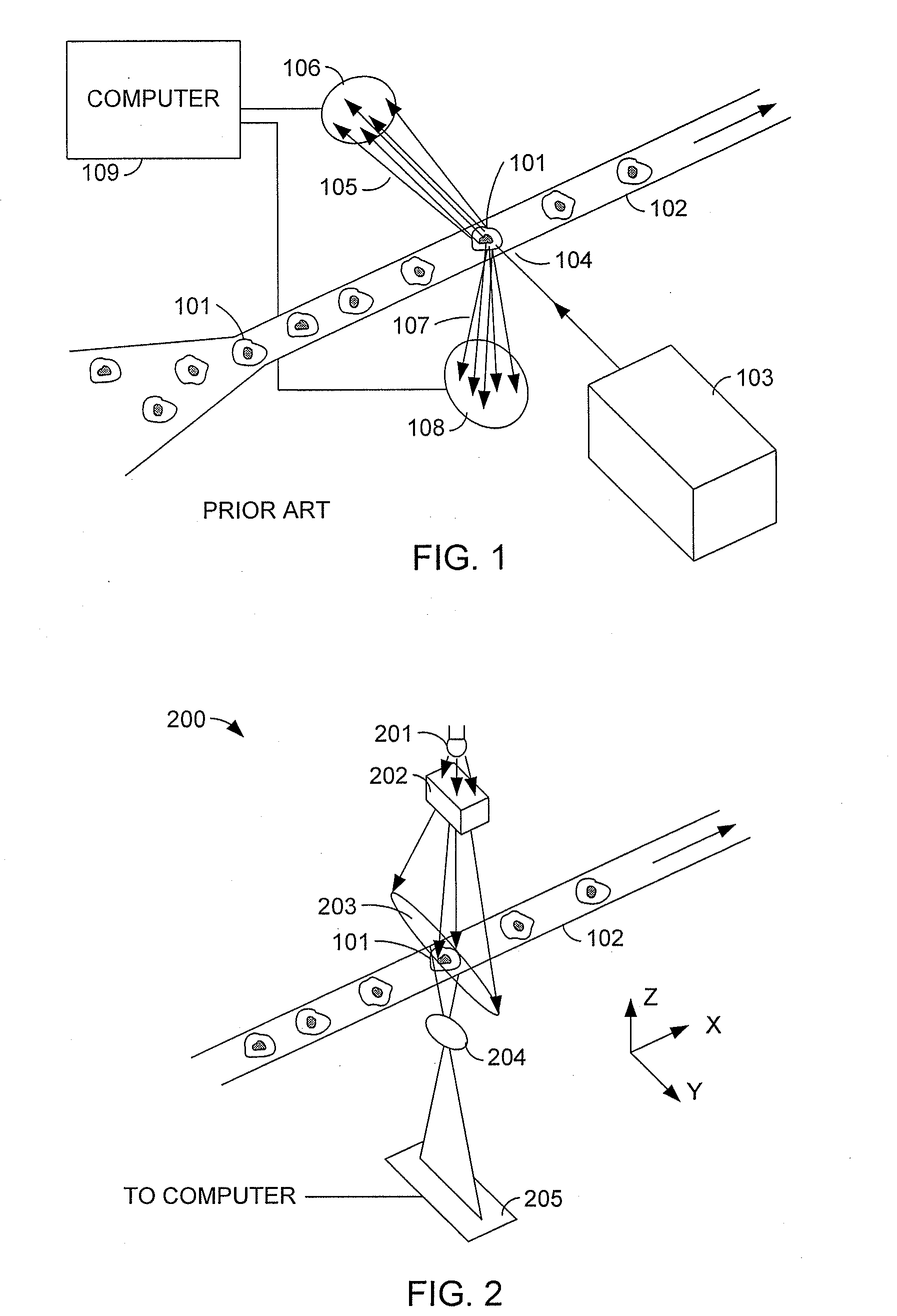
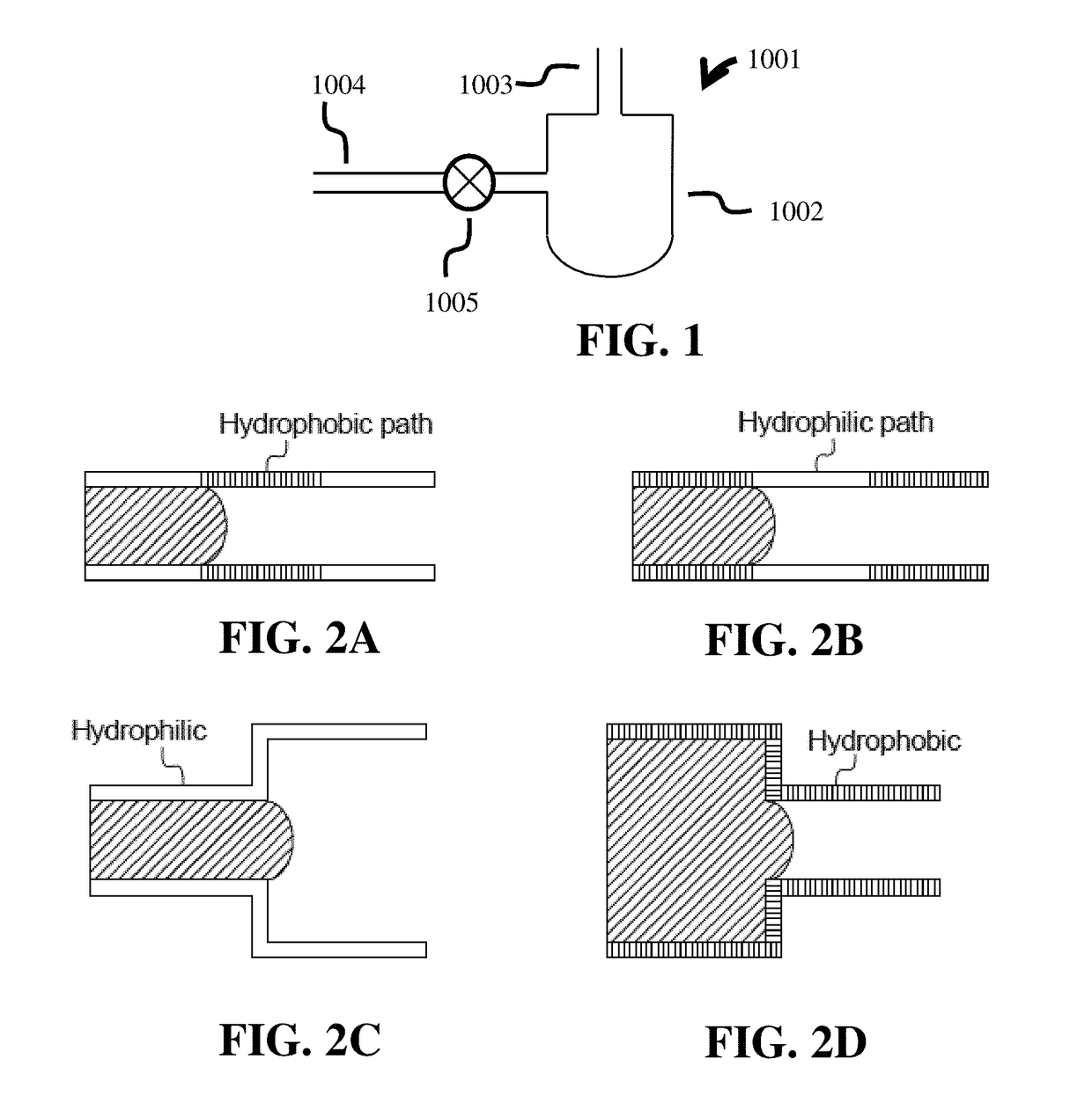
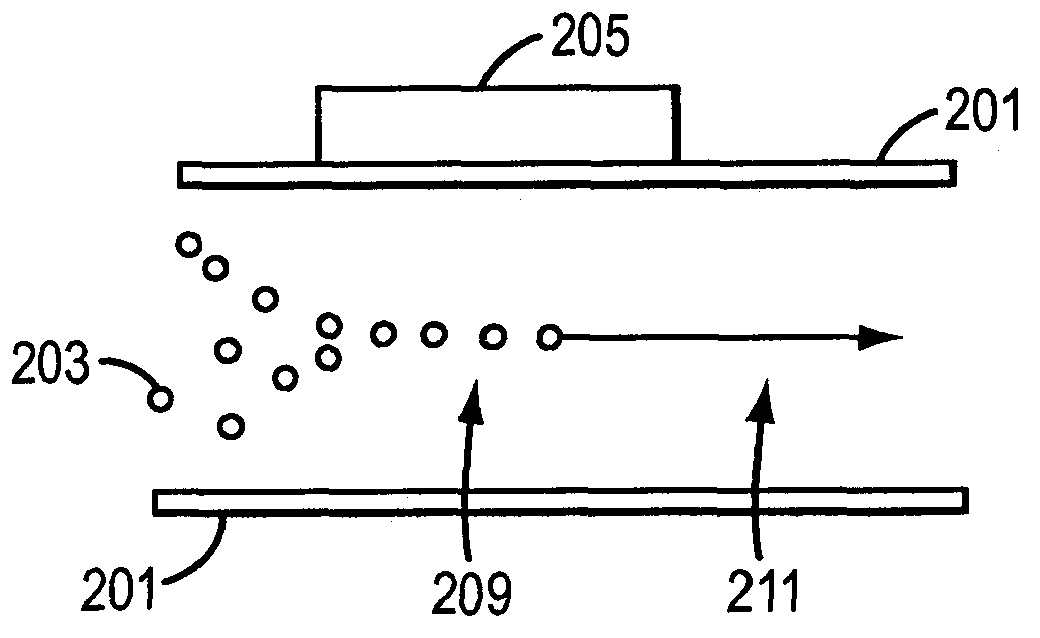
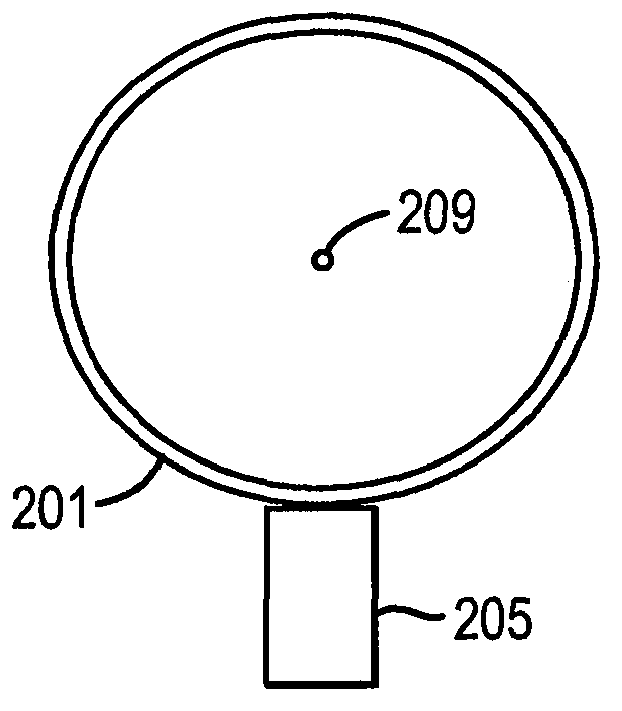
System for identifying and sorting living cells
ActiveUS20120122084A1Bioreactor/fermenter combinationsMaterial analysis using sonic/ultrasonic/infrasonic wavesFlow cellIr absorption
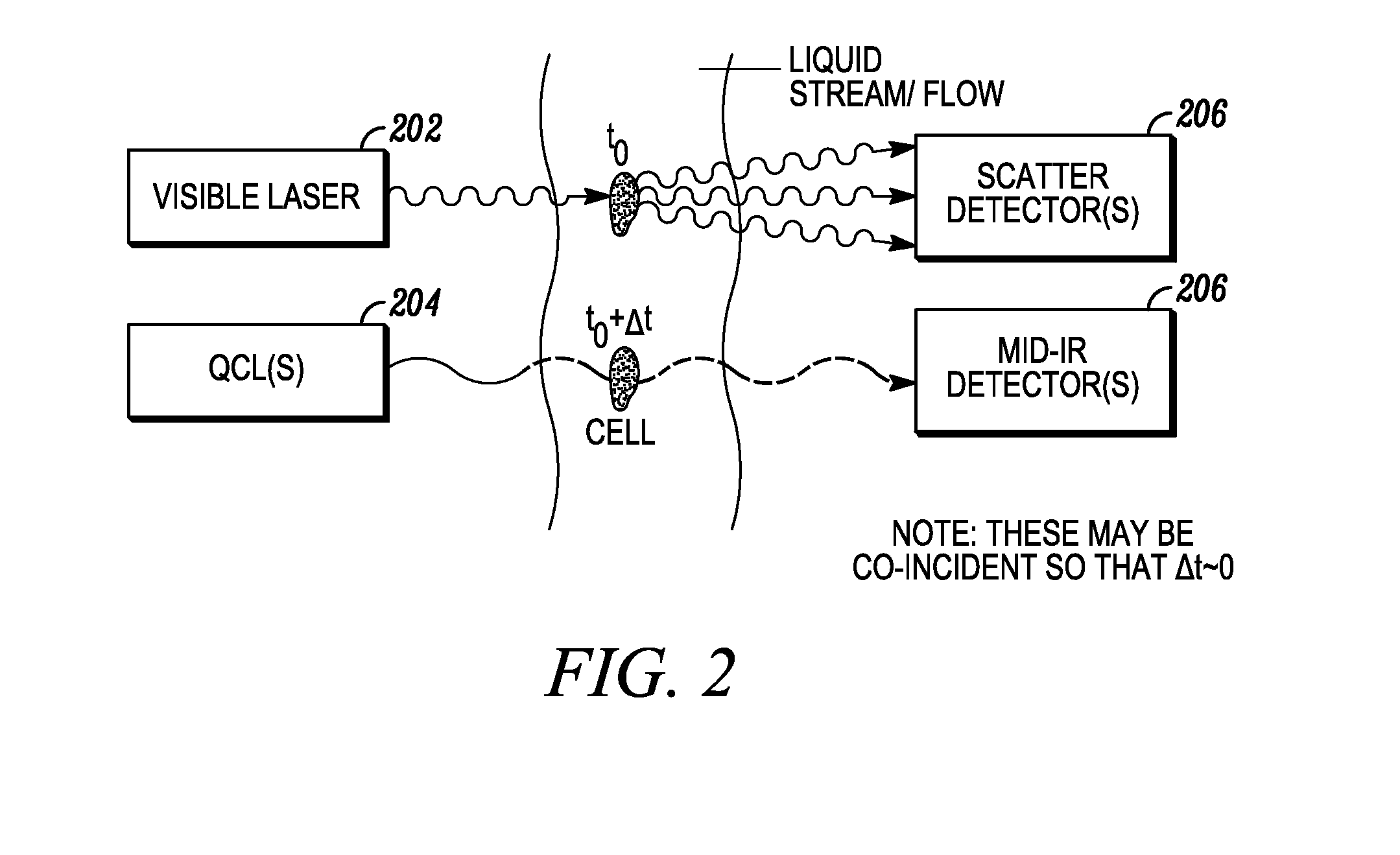
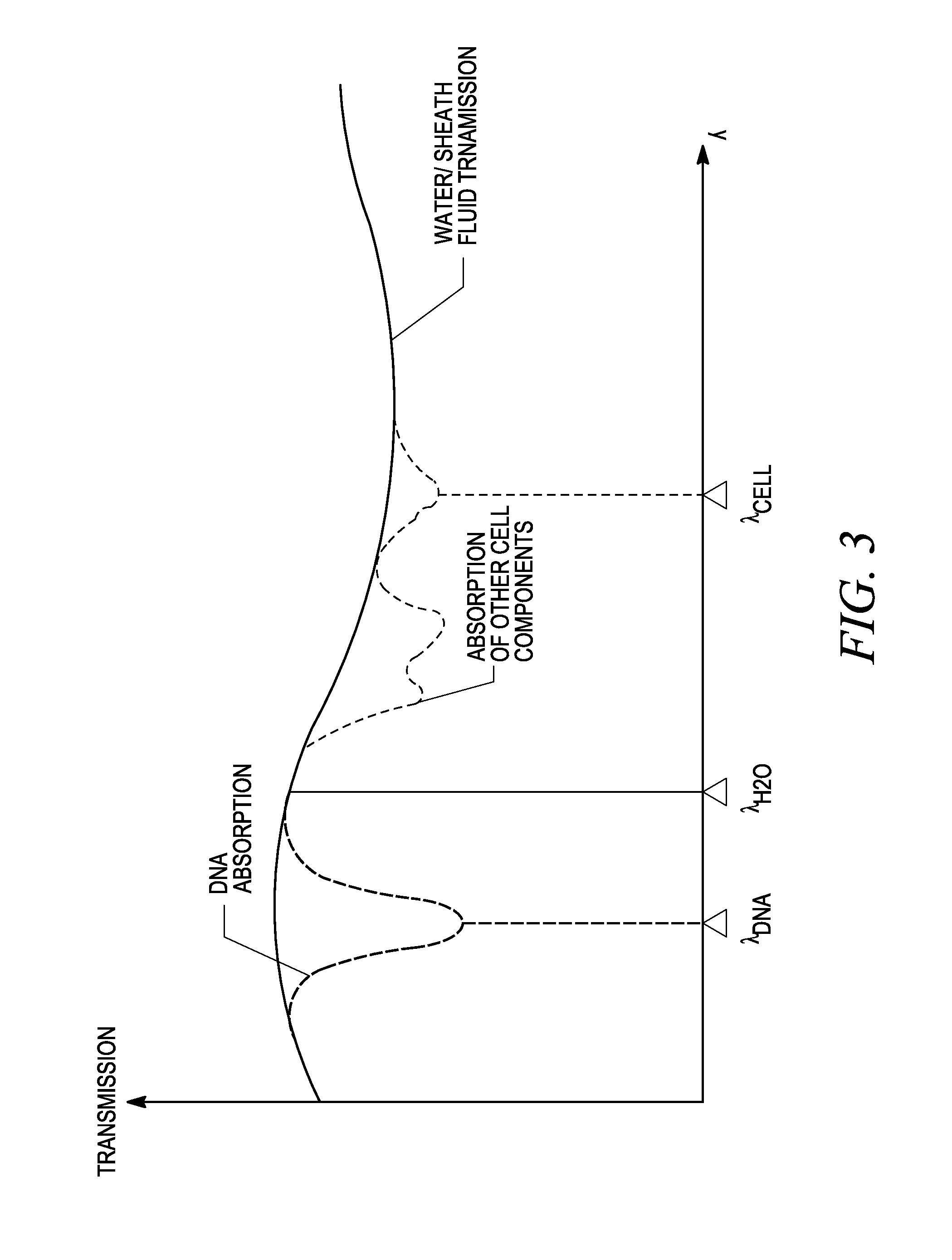
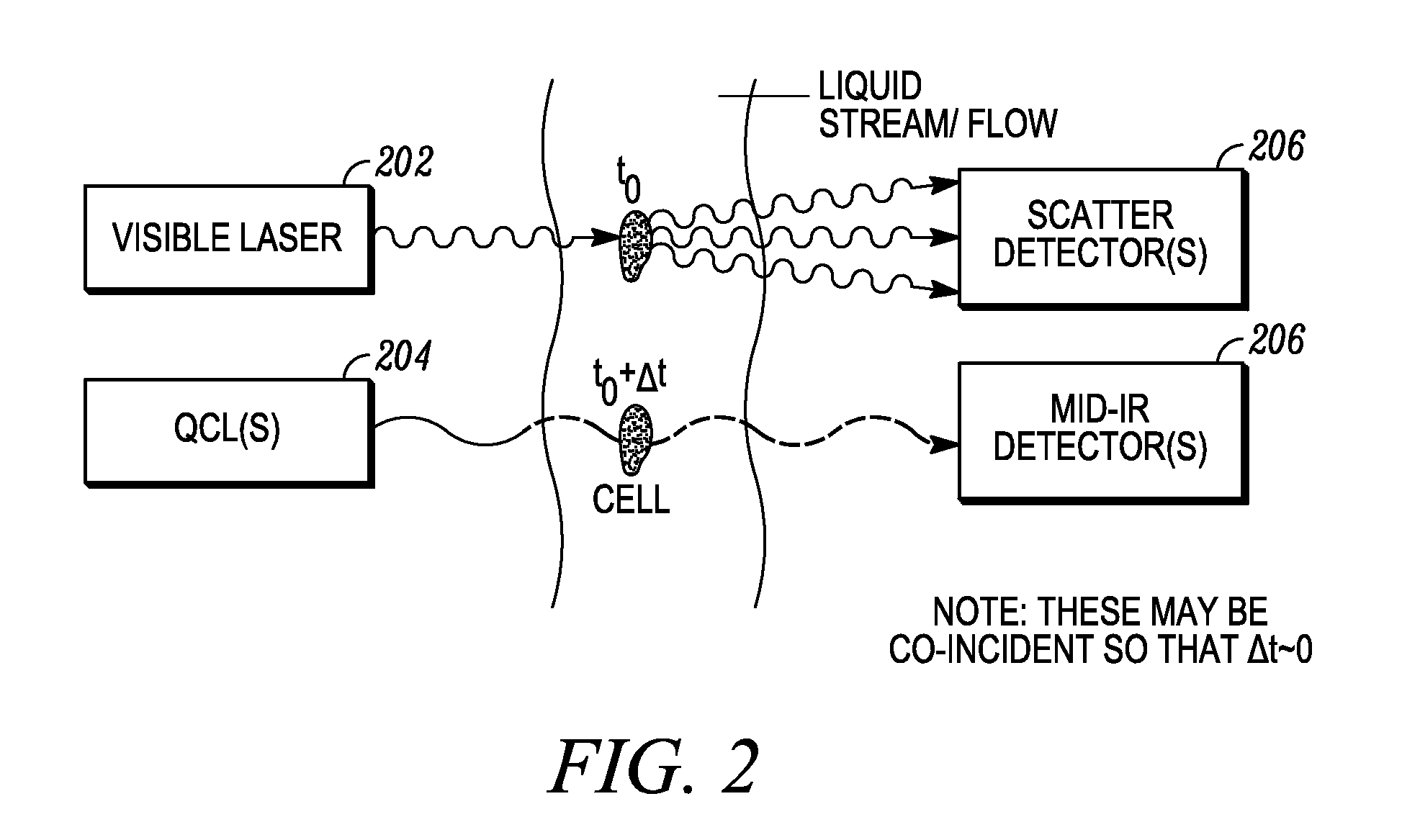
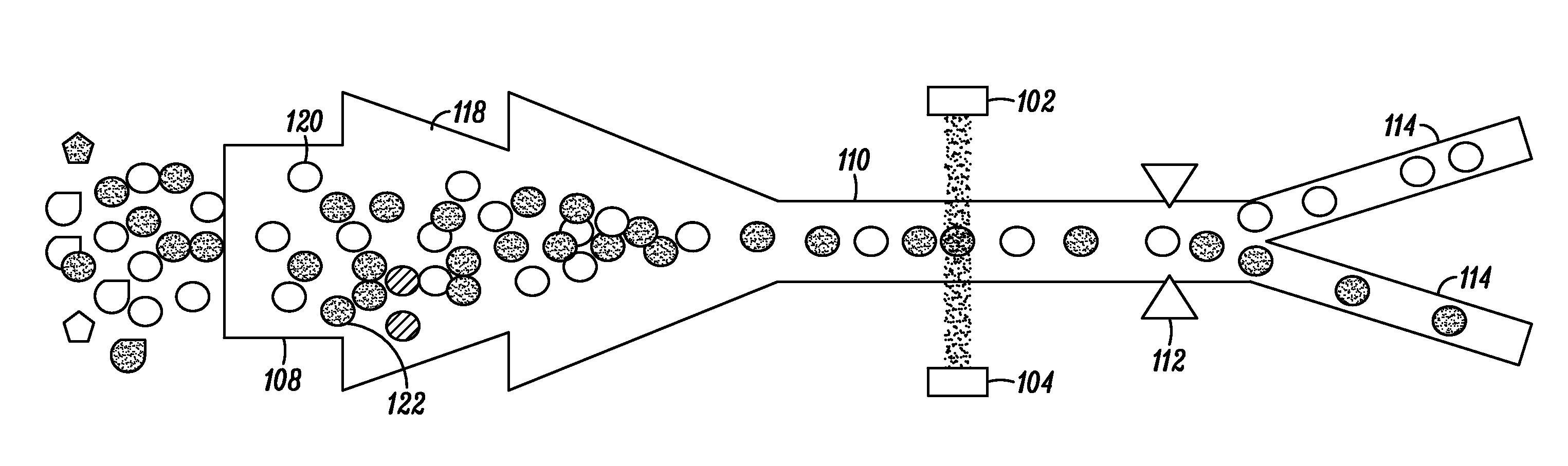
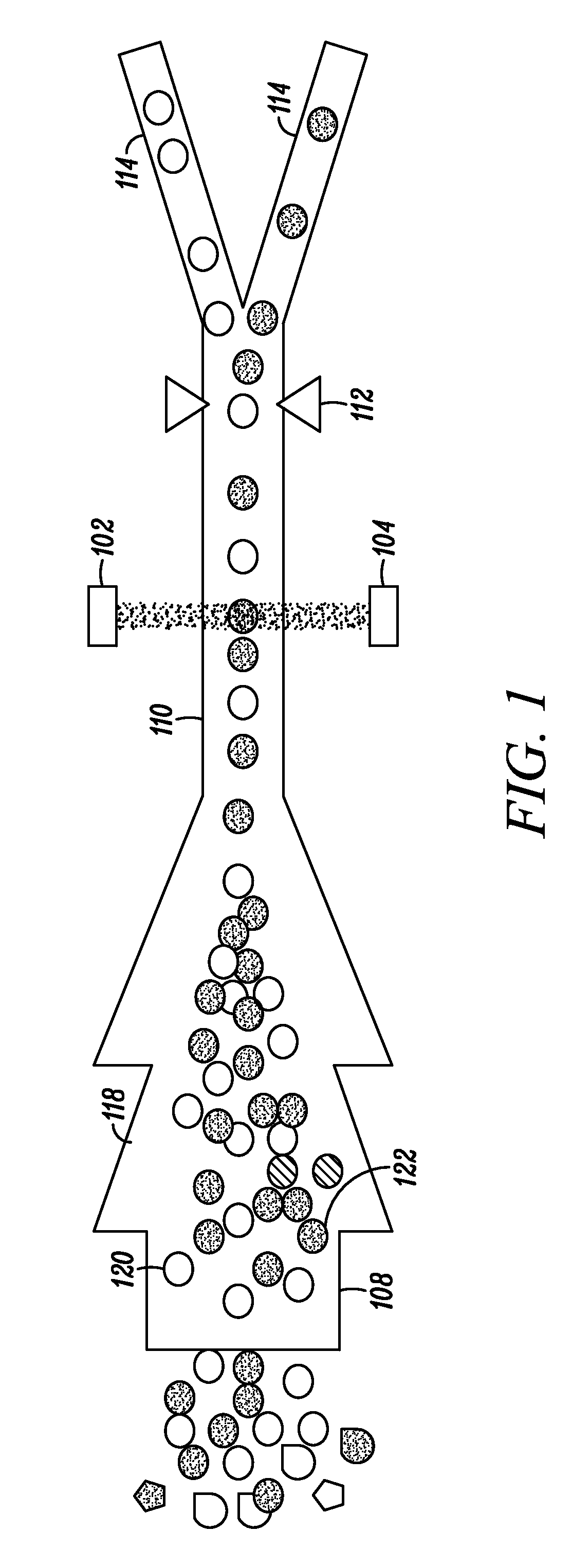
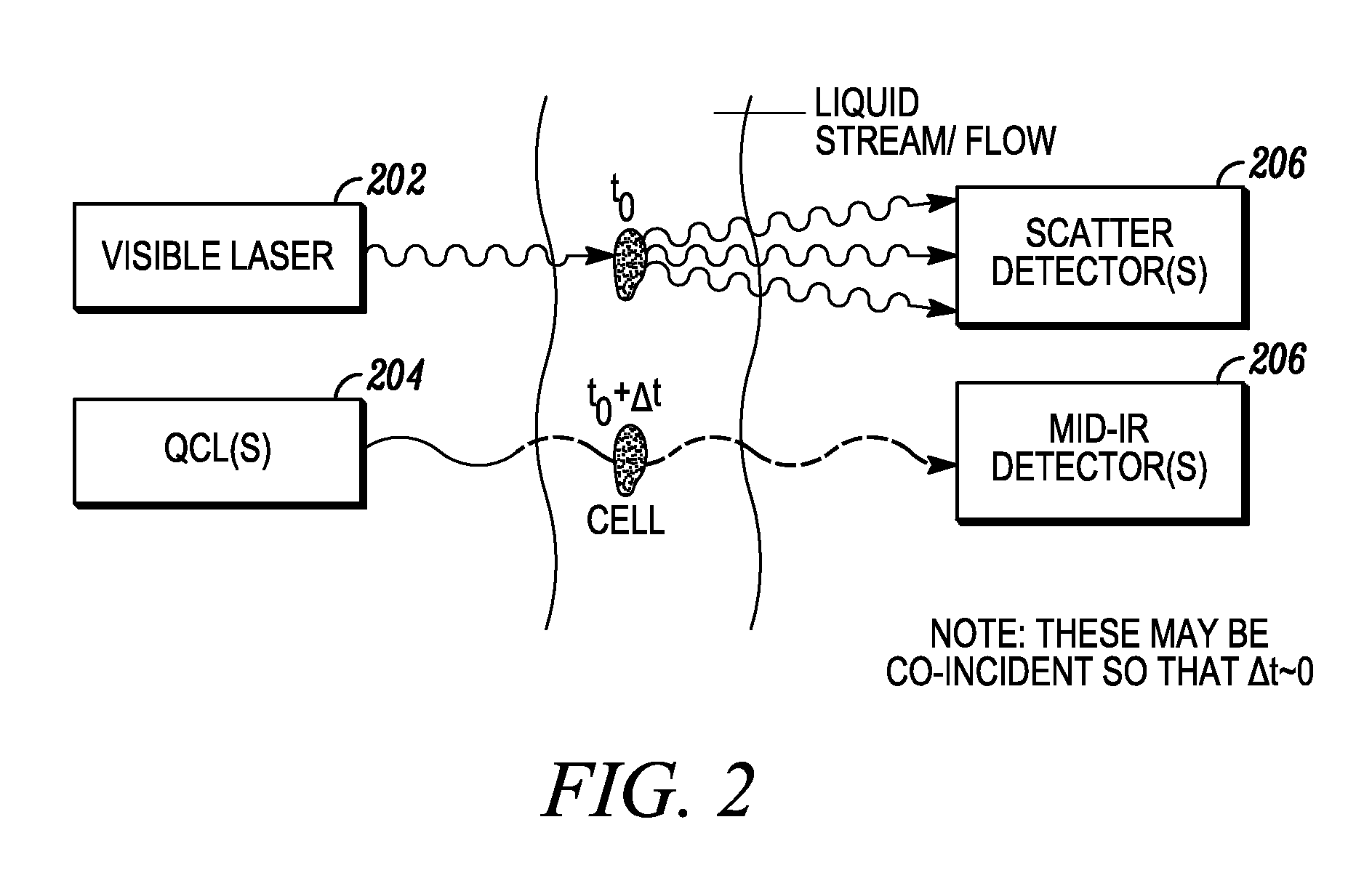
In embodiments of the present invention, a system and method of cytometry may include presenting a single sperm cell to at least one laser source configured to deliver light to the sperm cell in order to induce bond vibrations in the sperm cell DNA, and detecting the signature of the bond vibrations. The bond vibration signature is used to calculate a DNA content carried by the sperm cell which is used to identify the sperm cell as carrying an X-chromosome or Y-chromosome. Another system and method may include flowing cells past at least one QCL source one-by-one using a fluid handling system, delivering QCL light to a single cell to induce resonant mid-IR absorption by one or more analytes of the cell, and detecting, using a mid-infrared detection facility, the transmitted mid-infrared wavelength light, wherein the transmitted mid-infrared wavelength light is used to identify a cell characteristic.
Owner:1087 SYST
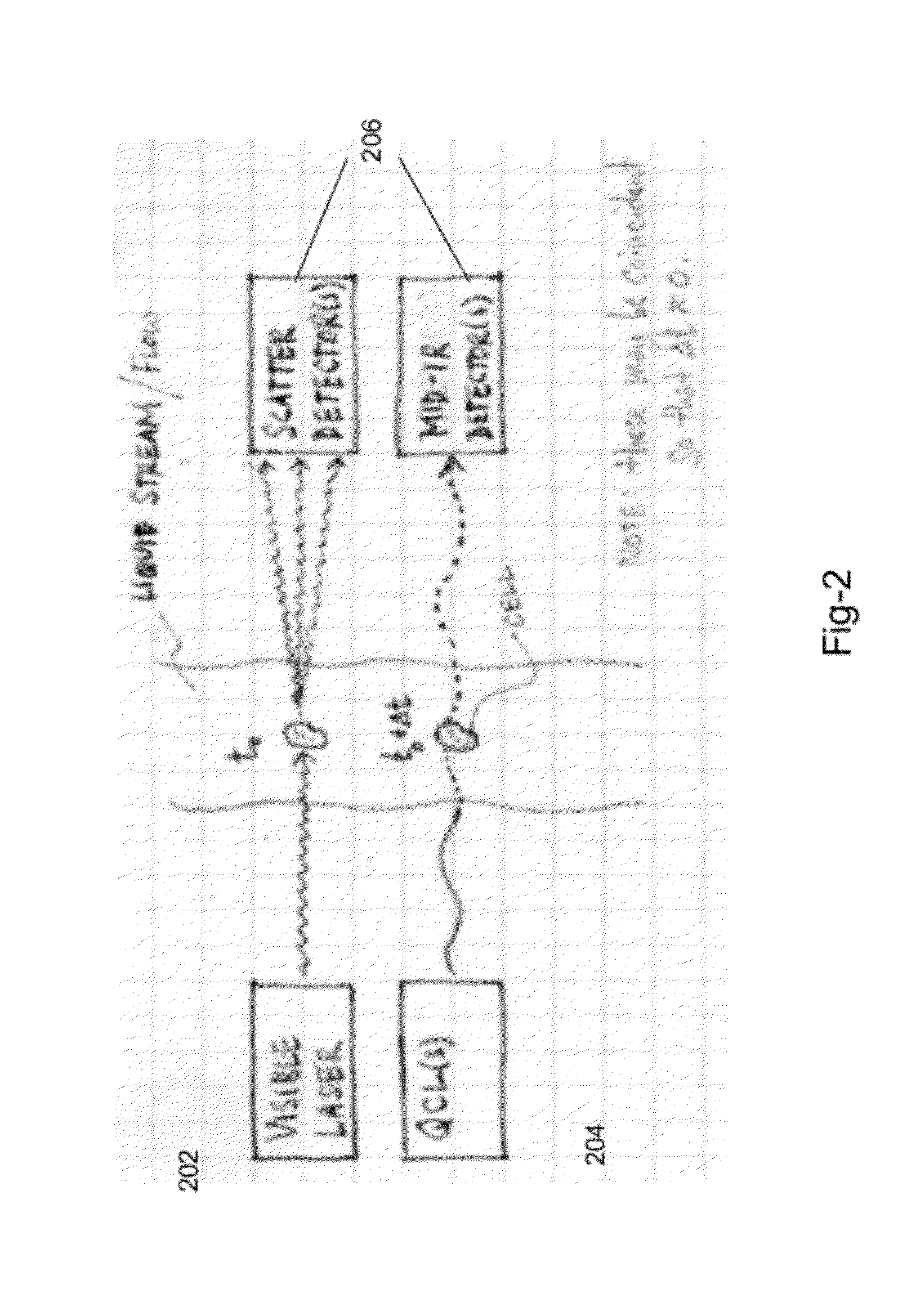
Cytometry system with quantum cascade laser source, acoustic detector, and micro-fluidic cell handling system configured for inspection of individual cells
InactiveUS20120225475A1Bioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsAnalyteCell handling
This disclosure concerns a cytometry system including a handling system that presents single cells to at least one quantum cascade laser (QCL) source. The QCL laser source is configured to deliver light to a cell within the cells in order to induce resonant mid-IR vibrational absorption by one or more analytes, leading to local heating that results in thermal expansion and an associated shockwave. An acoustic detection facility that detects the shockwave emitted by the single cell.
Owner:1087 SYST
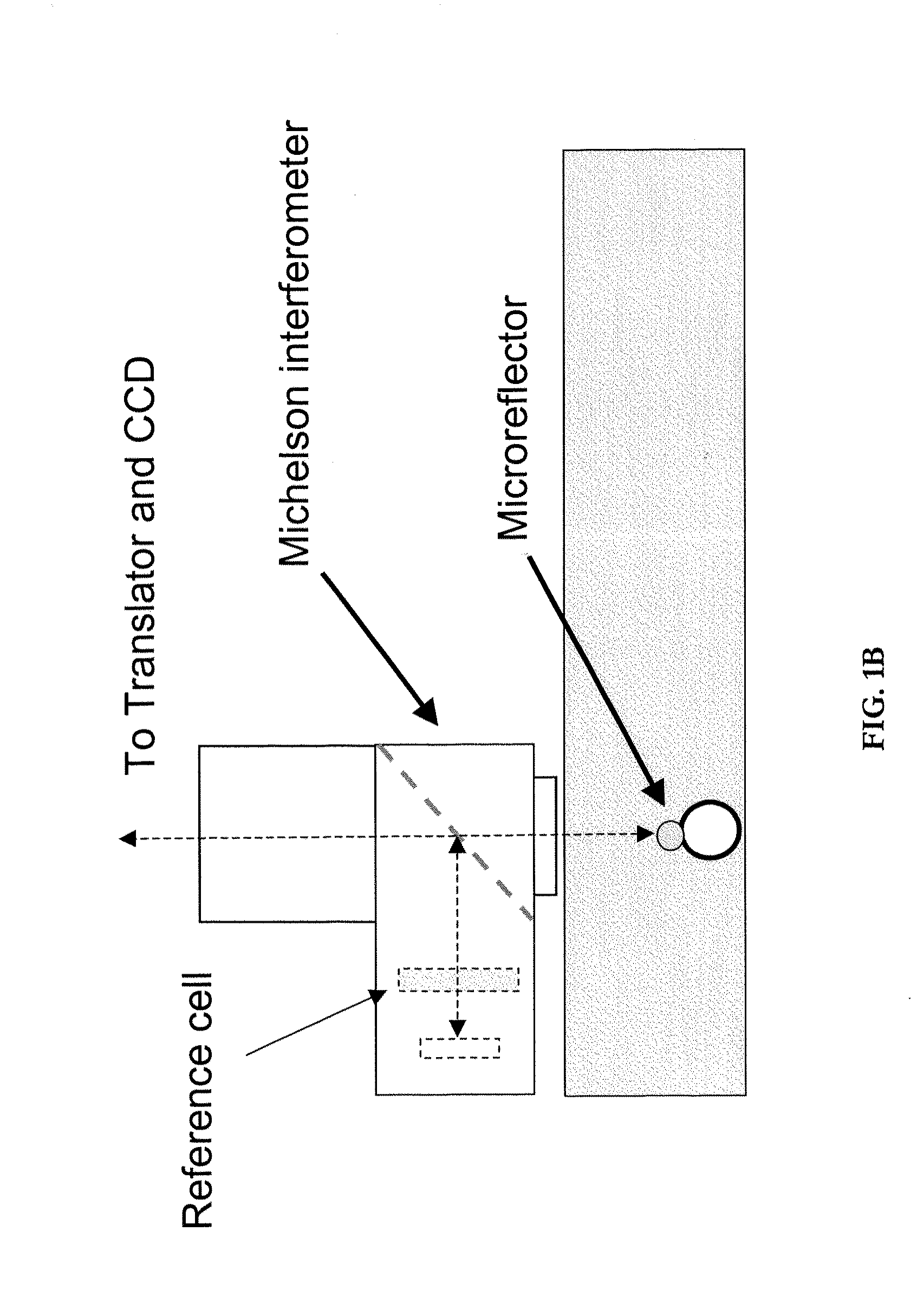
Optical cytometry
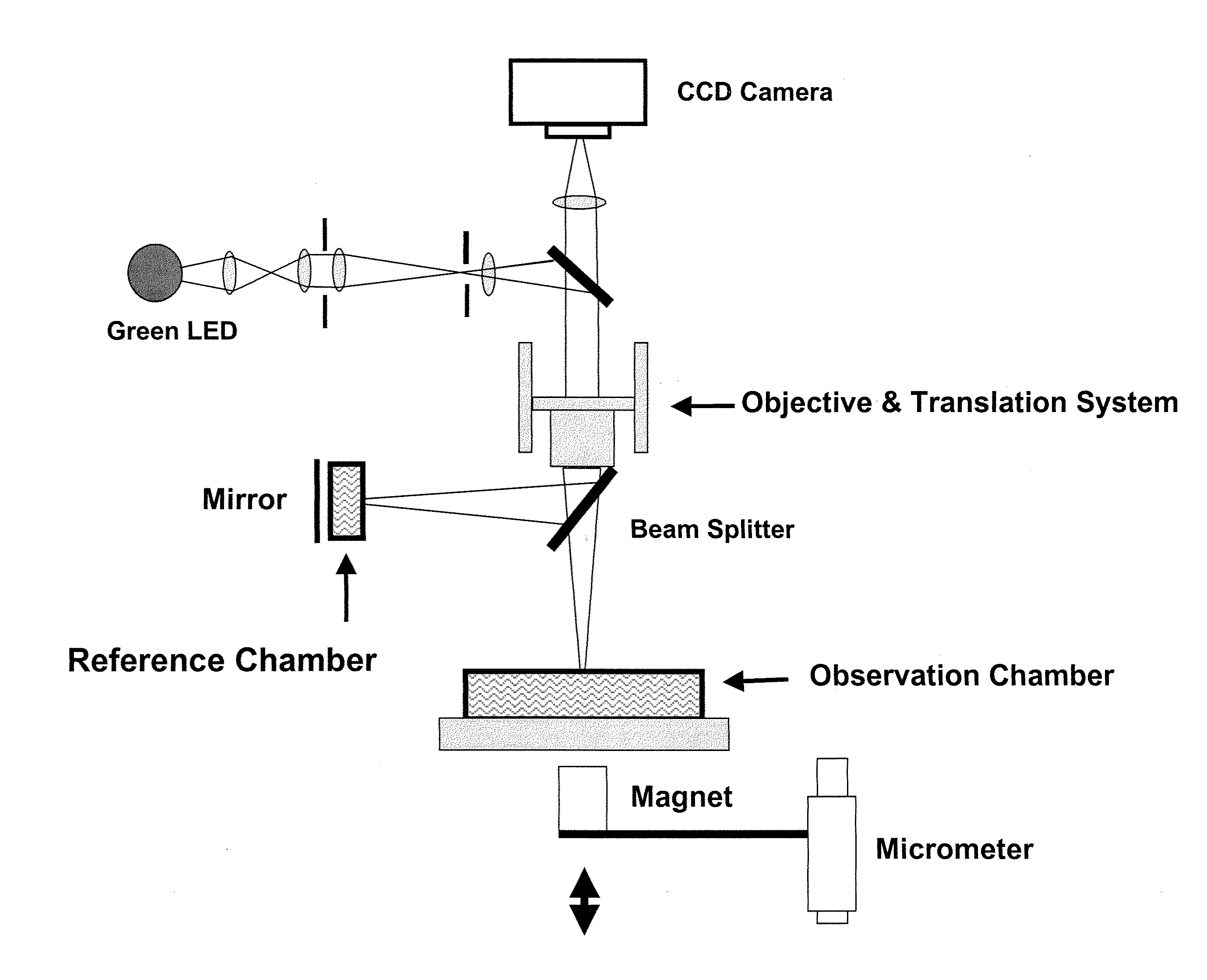
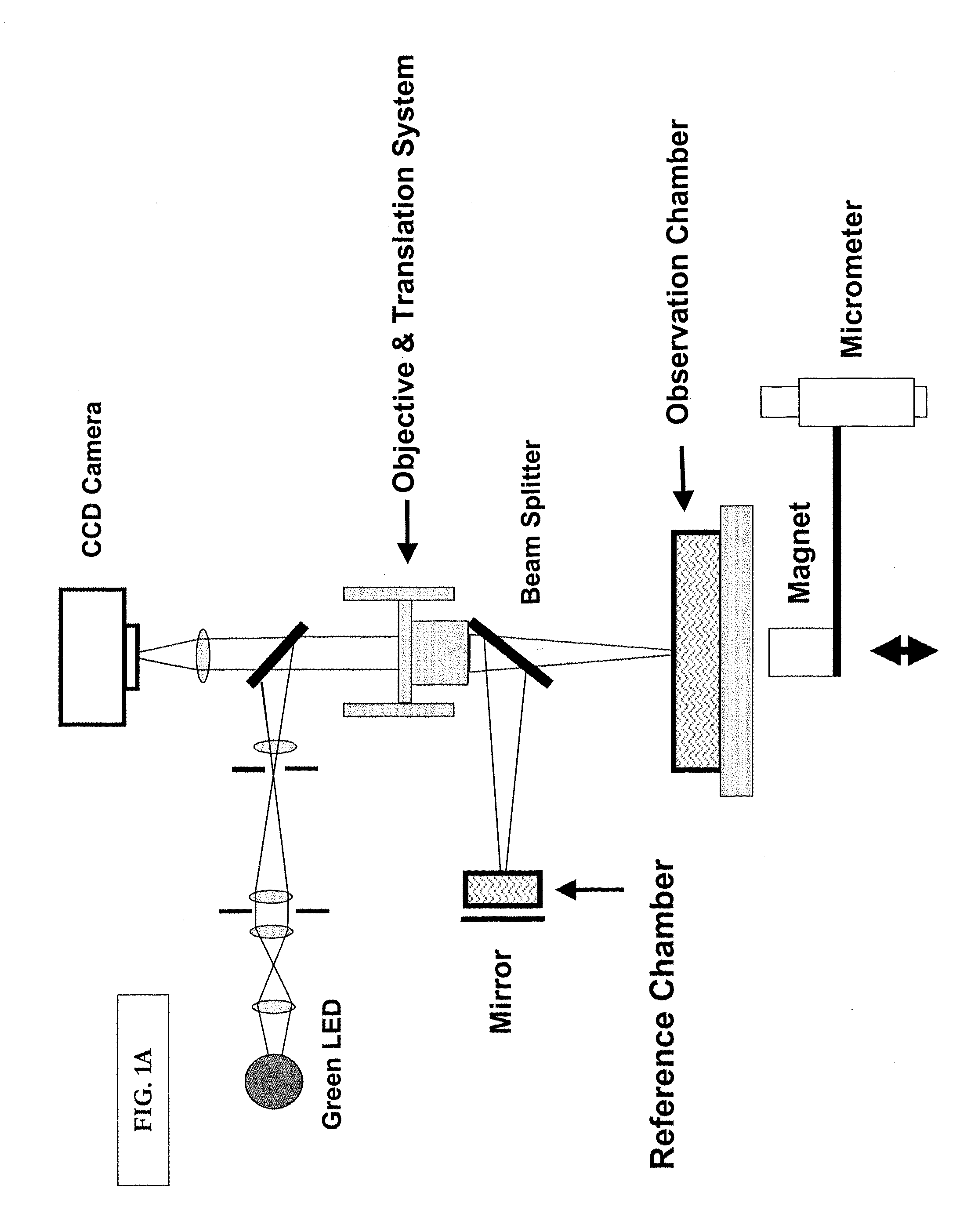
The present invention provides optical systems and methods for determining a characteristic of a cell, such as cell type, cellular response to a biochemical event, biological state and the like. The methods typically involve using interferometry to observe membrane properties in a cell and then use this information to determine one or more characteristics of a cell. The methods of the invention are useful for applications such as drug screening as well as diagnostic techniques.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA
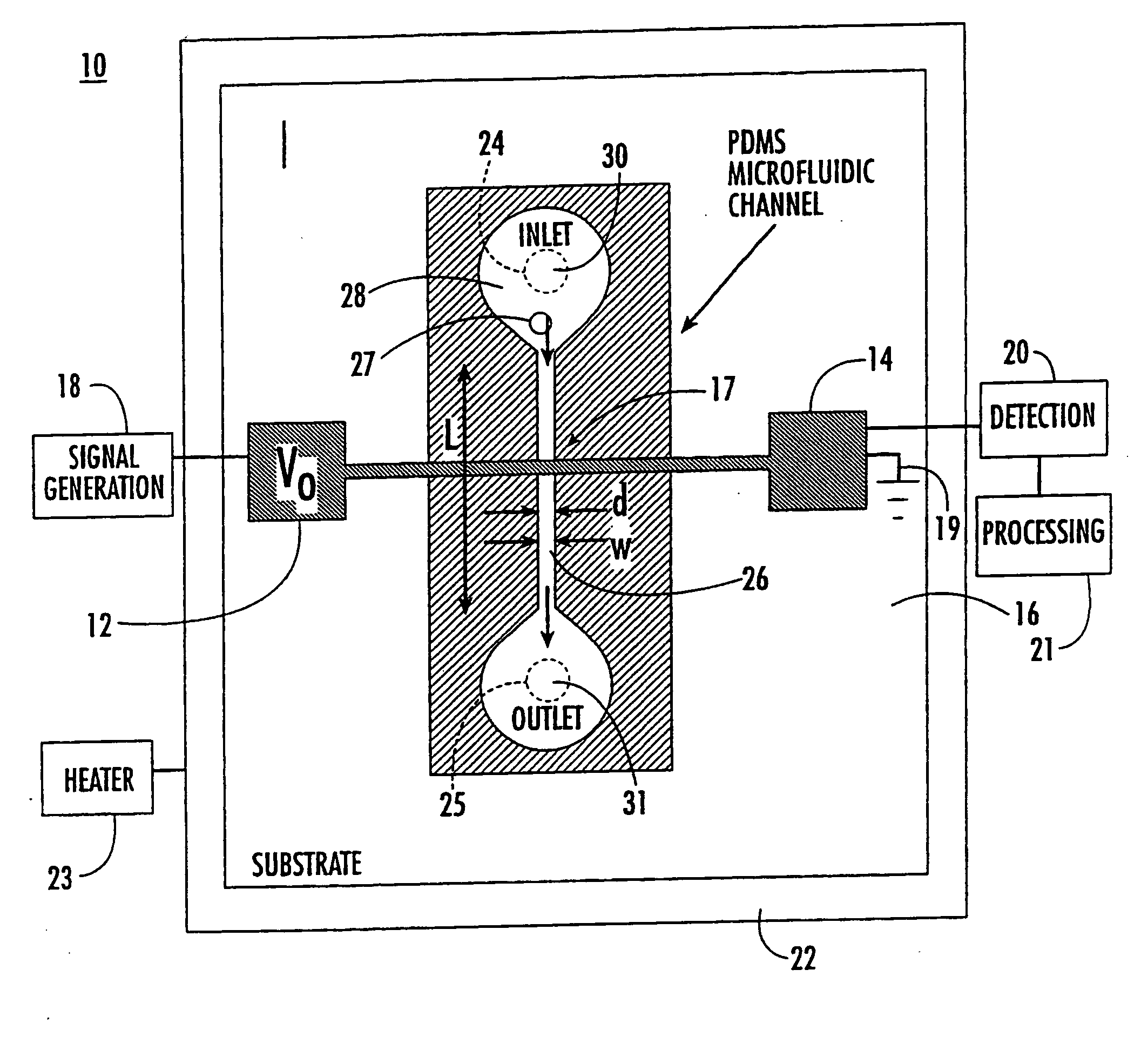
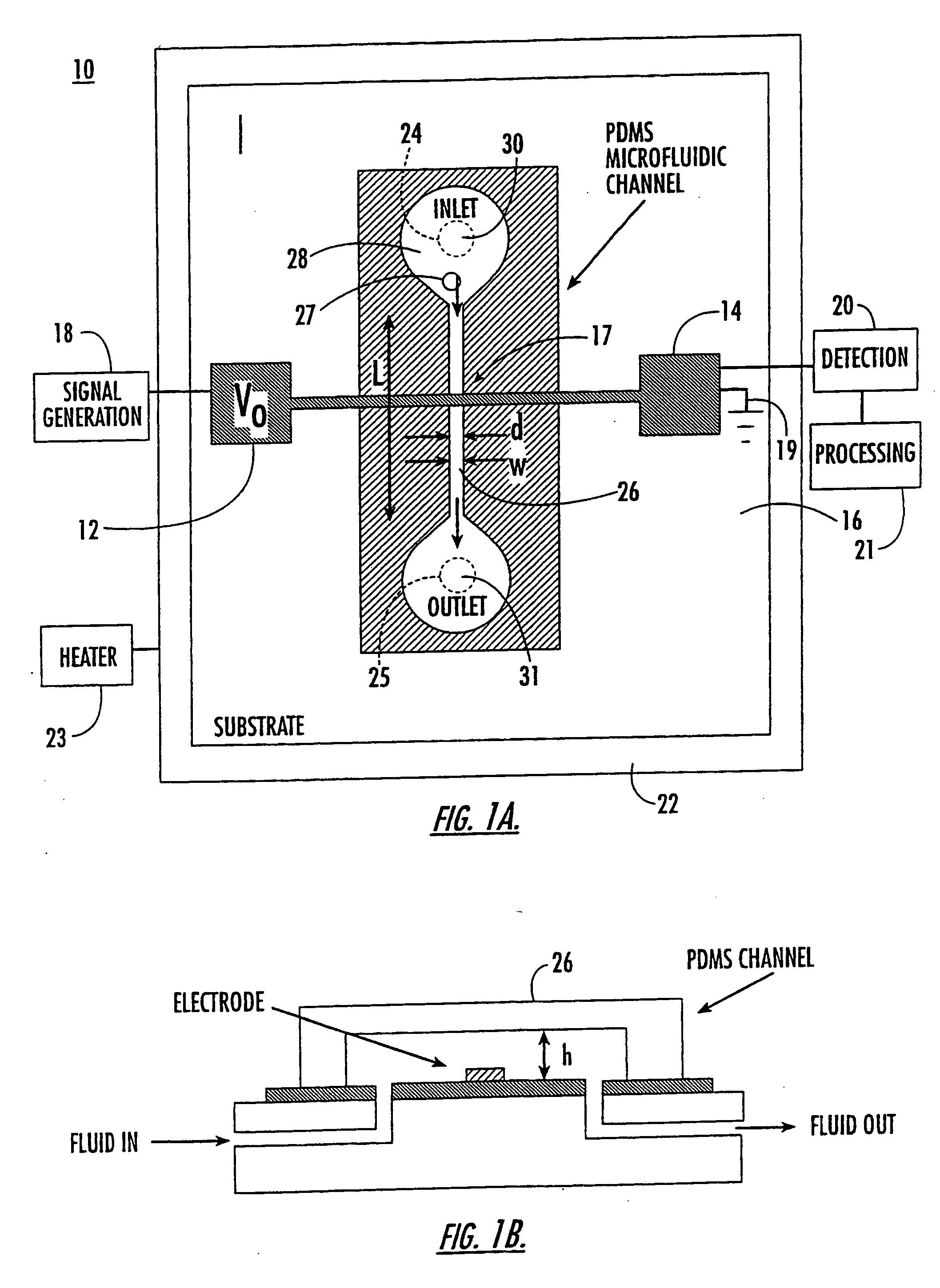
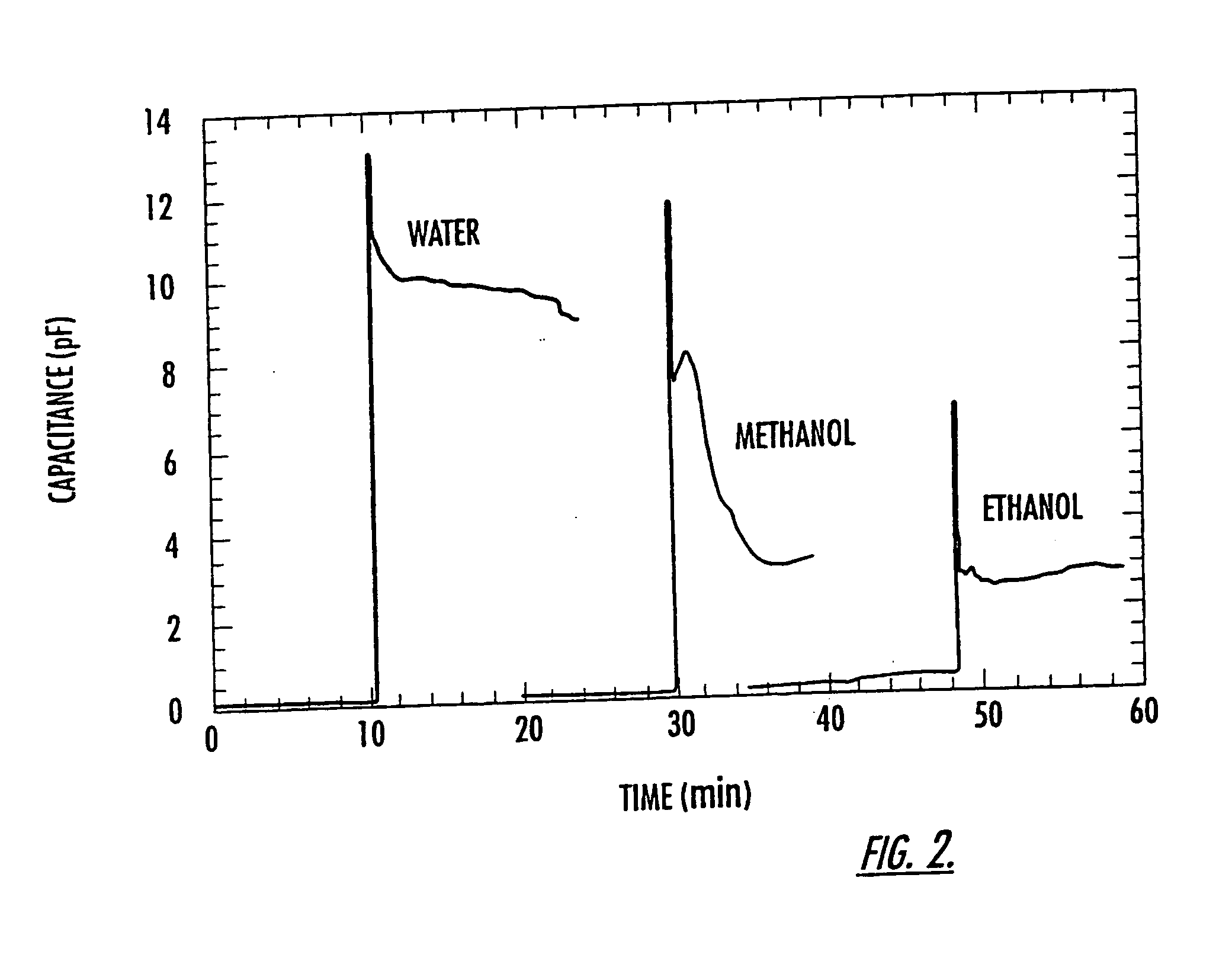
Microfluidic and nanofluidic electronic devices for detecting changes in capacitance of fluids and methods of using
InactiveUS20070238112A1Simpler and faster and less-expensiveMaterial nanotechnologyBioreactor/fermenter combinationsCapacitanceCell Cycle Kinetics
The present invention (also identified as “Capacitance cytometry”) relates to microfluidic and nanofluidic devices for detecting or measuring an electrical property of a fluid (liquid or aerosol), a single molecule, particle, or cell in fluid. In a particular embodiment, the devices detect or measure changes in capacitance of a fluid, molecule, particle or cell as it passes through the device. The invention relates to detection and measurement of single molecules, particularly biological molecules, and to methods of sequencing polynucleotide molecules (RNA or DNA) by detecting differentially labeled single nucleotides. Single molecule detection applications include DNA or RNA sequencing, detection of SNPs, protoemics, and particle sizing. The device can be used to determine cell DNA content, to analyze cell-cycle kinetics of cell populations, and to assay for abnormal changes in cell DNA content. Nano-microfluidic devices of this invention also have utility as detectors in molecular sorting systems and for detecting pathogens.
Owner:THE TRUSTEES FOR PRINCETON UNIV
Array cytometry
InactiveUS6958245B2Easy to disassembleMinimize Faradaic processImmobilised enzymesBioreactor/fermenter combinationsParticulatesSilicon oxide
A method and apparatus for the manipulation of colloidal particulates and biomolecules at the interface between an insulating electrode such as silicon oxide and an electrolyte solution. Light-controlled elektrokinetic assembly of particles near surfaces relies on the combination of three functional elements, the AC electric field-induced assembly of planar aggregates; the patterning of the electrolyte / silicon oxide / silicon interface to exert spatial control over the assembly process; and the real-time control of the assembly process via external illumination. The present invention provides a set of fundamental operations enabling interactive control over the creation and placement of planar arrays of several types of particles and biomolecules and the manipulation of array shape and size. The present invention enables sample preparation and handling for diagnostic assays and biochemical analysis in an array format, and the functional integration of these operations. In addition, the present invention provides a procedure for the creation of material surfaces with desired properties and for the fabrication of surface-mounted optical components. This invention is also for a method and apparatus to direct the lateral motion and induce the assembly into planar arrays of cells on semiconductor surfaces in response to temporally and spatially varying electric fields and to projected patterns of illumination.
Owner:BIOARRAY SOLUTIONS
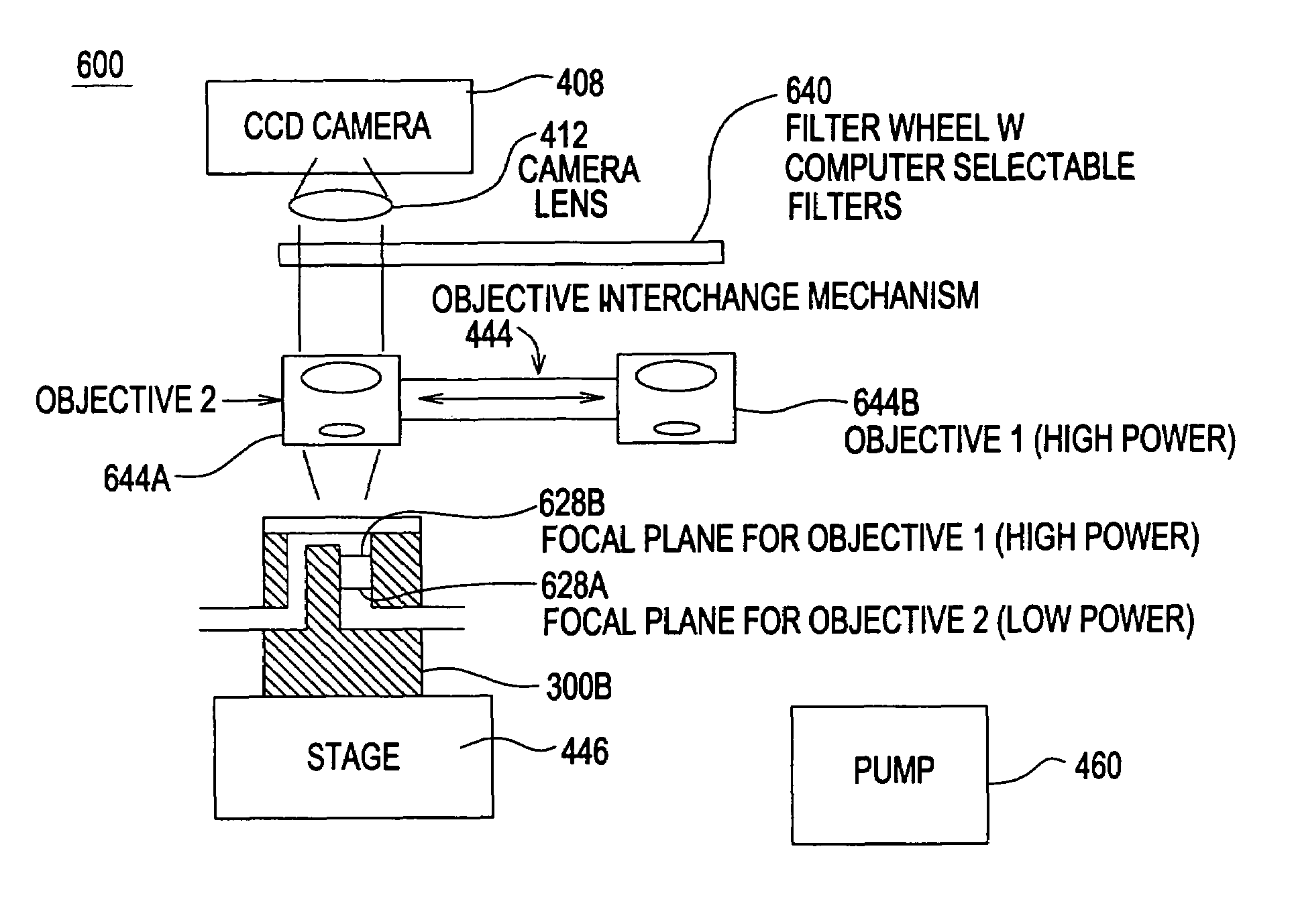
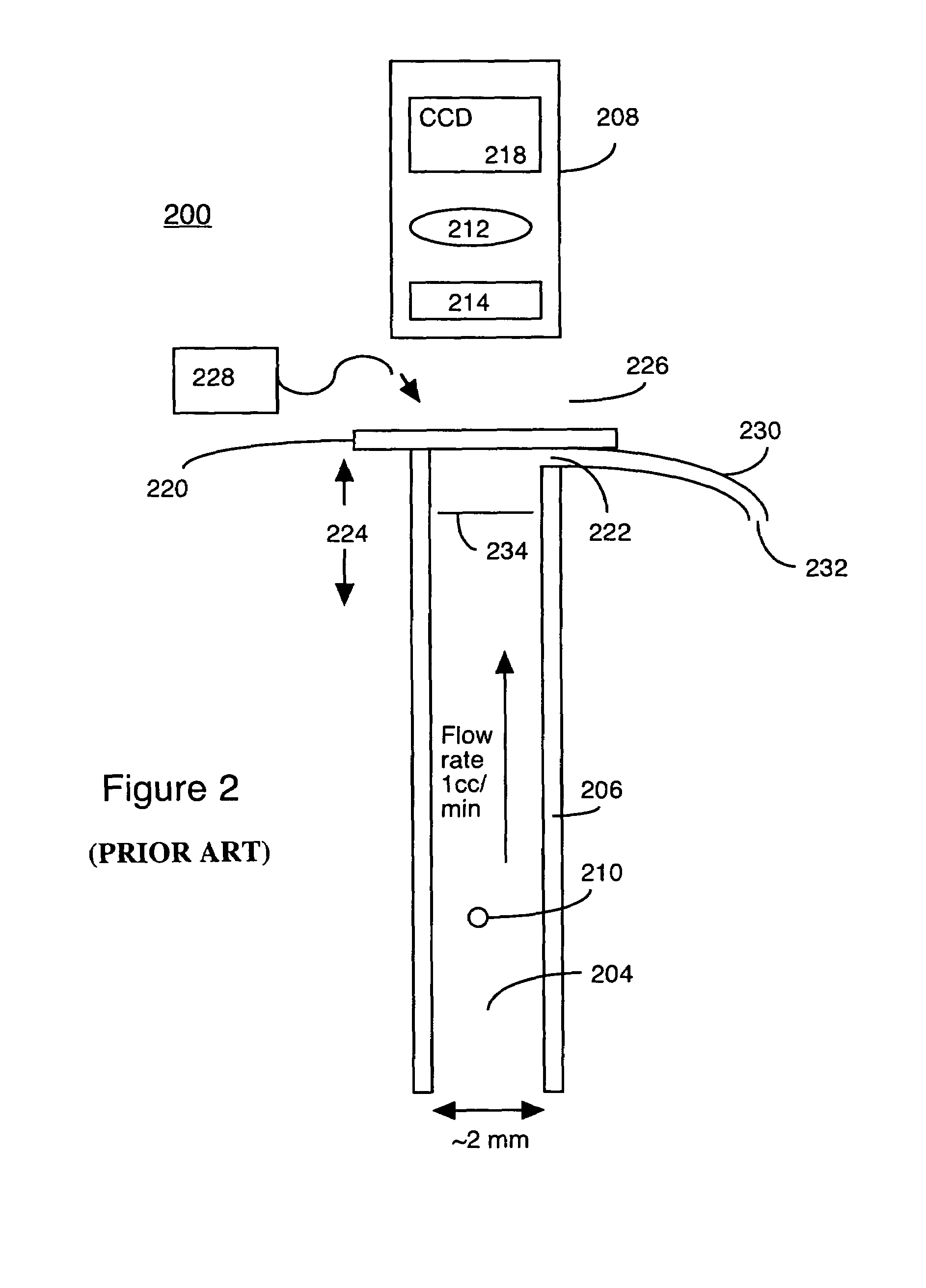
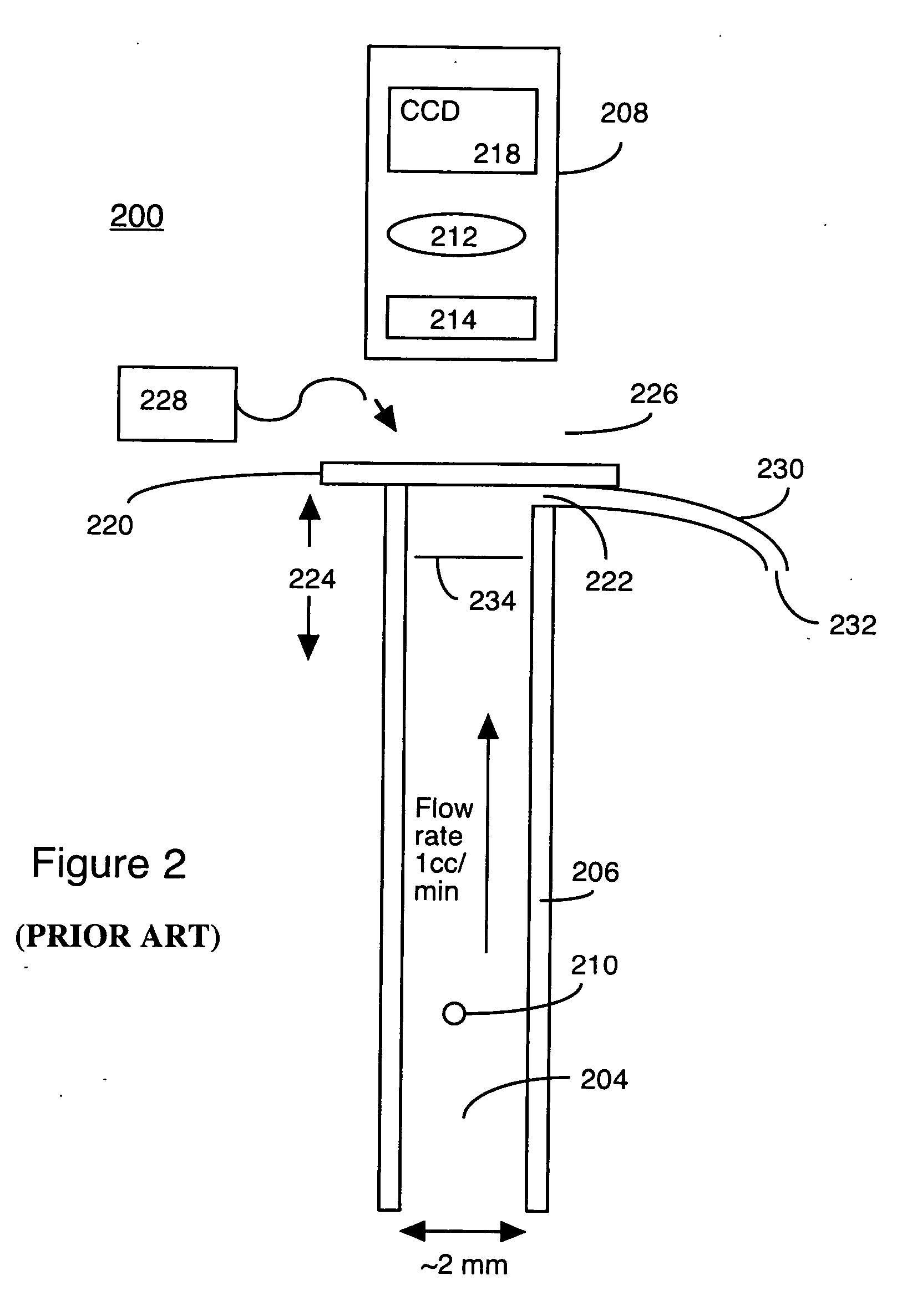
High resolution imaging fountain flow cytometry
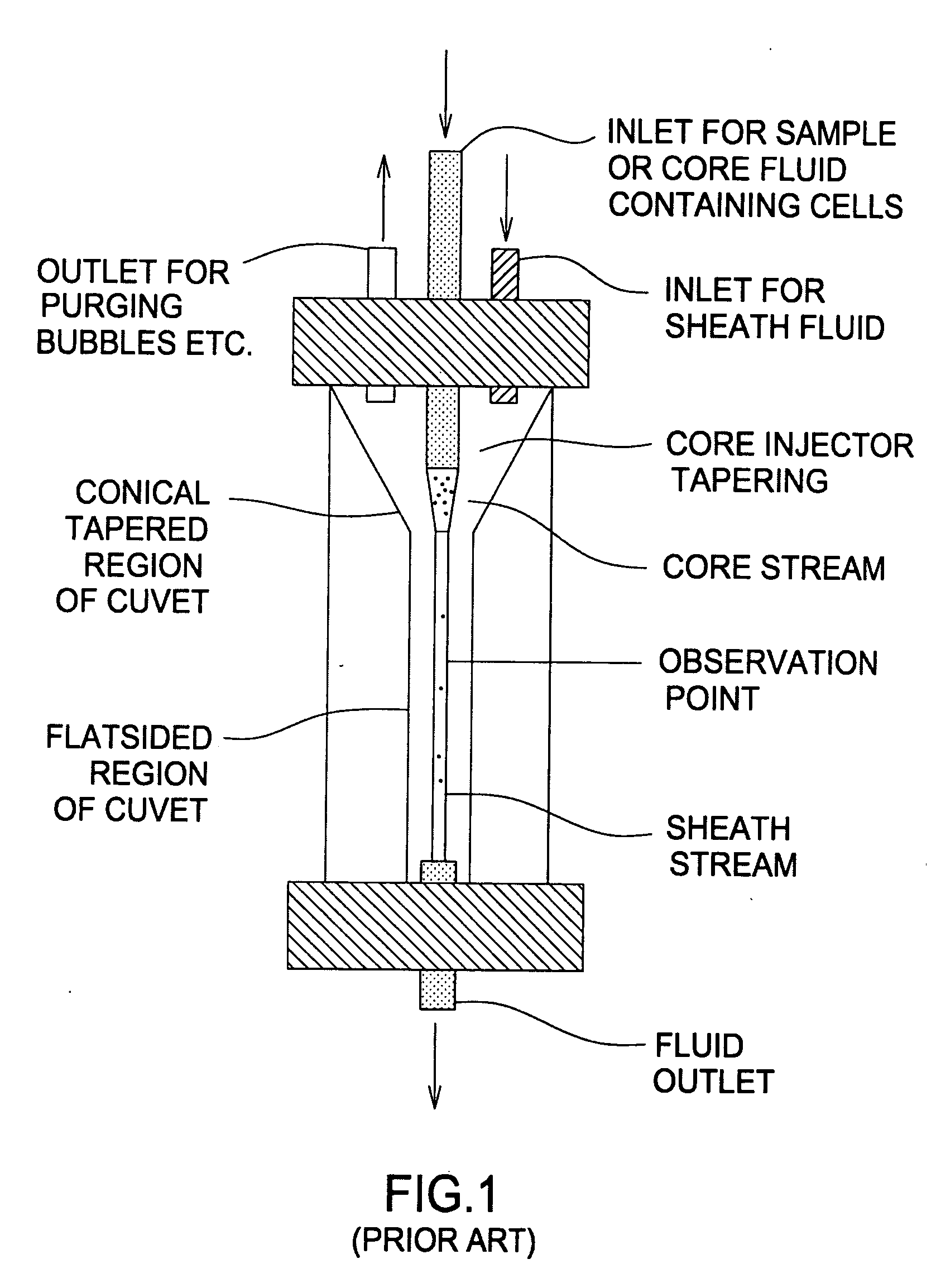
InactiveUS7161665B2Improve throughputHigh resolutionWithdrawing sample devicesMaterial analysis by optical meansHigh resolution imagingFlow cell
An imaging fountain flow cytometer allows high resolution microscopic imaging of a flowing sample in real time. Cells of interest are in a vertical stream of liquid flowing toward one or more illuminating elements at wavelengths which illuminate fluorescent dyes and cause the cells to fluoresce. A detector detects the fluorescence emission each time a marked cell passes through the focal plane of the detector. A bi-directional syringe pump allows the user to reverse the flow and locate the detected cell in the field of view. The flow cell is mounted on a computer controlled x-y stage, so the user can center a portion of the image on which to zoom or increase magnification. Several computer selectable parfocal objective lenses allow the user to image the entire field of view and then zoom in on the detected cell at substantially higher resolution. The magnified cell is then imaged at the various wavelengths.
Owner:UNIVERSITY OF WYOMING
Array cytometry
InactiveUS7056746B2Easy to disassembleMinimize Faradaic processSequential/parallel process reactionsOrganic chemistry methodsParticulatesEngineering
A method and apparatus for the manipulation of colloidal particulates and biomolecules at the interface between an insulating electrode such as silicon oxide and an electrolyte solution. Light-controlled electrokinetic assembly of particles near surfaces relies on the combination of three functional elements: the AC electric field-induced assembly of planar aggregates; the patterning of the electrolyte / silicon oxide / silicon interface to exert spatial control over the assembly process; and the real-time control of the assembly process via external illumination. The present invention provides a set of fundamental operations enabling interactive control over the creation and placement of planar arrays of several types of particles and biomolecules and the manipulation of array shape and size. The present invention enables sample preparation and handling for diagnostic assays and biochemical analysis in an array format, and the functional integration of these operations. In addition, the present invention provides a procedure for the creation of material surfaces with desired properties and for the fabrication of surface-mounted optical components. This invention is also for a method and apparatus to direct the lateral motion and induce the assembly into planar arrays of cells on semiconductor surfaces in response to temporally and spatially varying electric fields and to projected patterns of illumination.
Owner:BIOARRAY SOLUTIONS
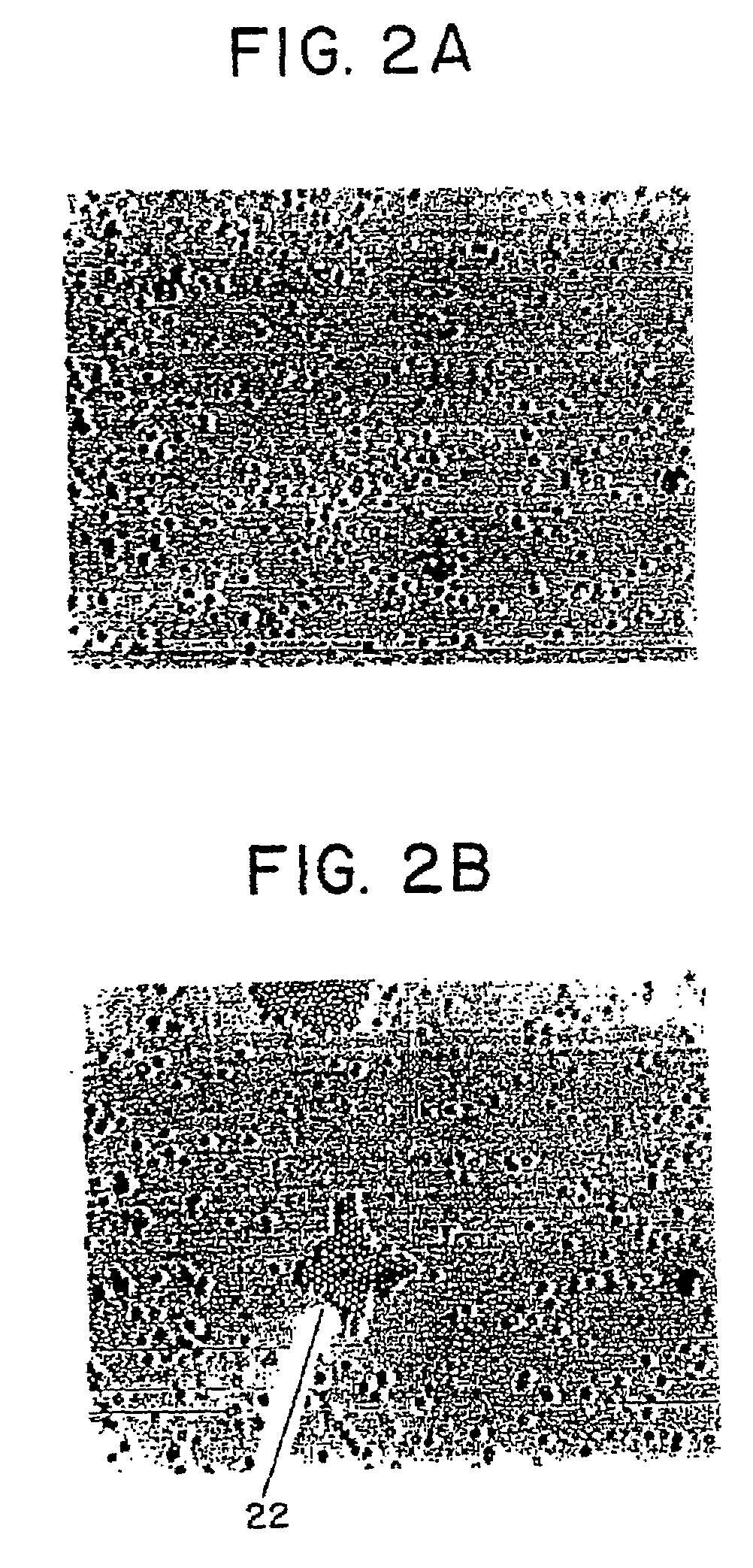
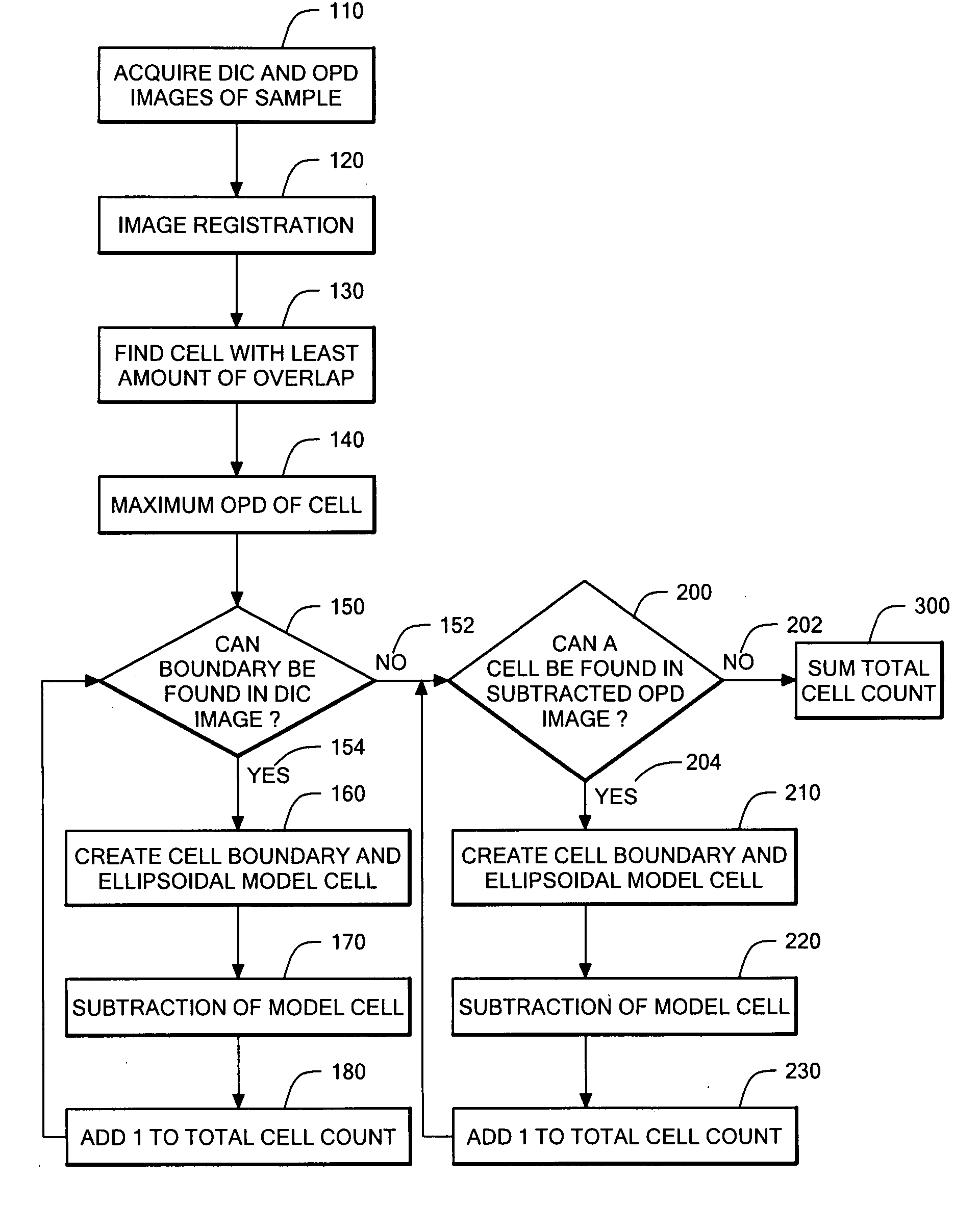
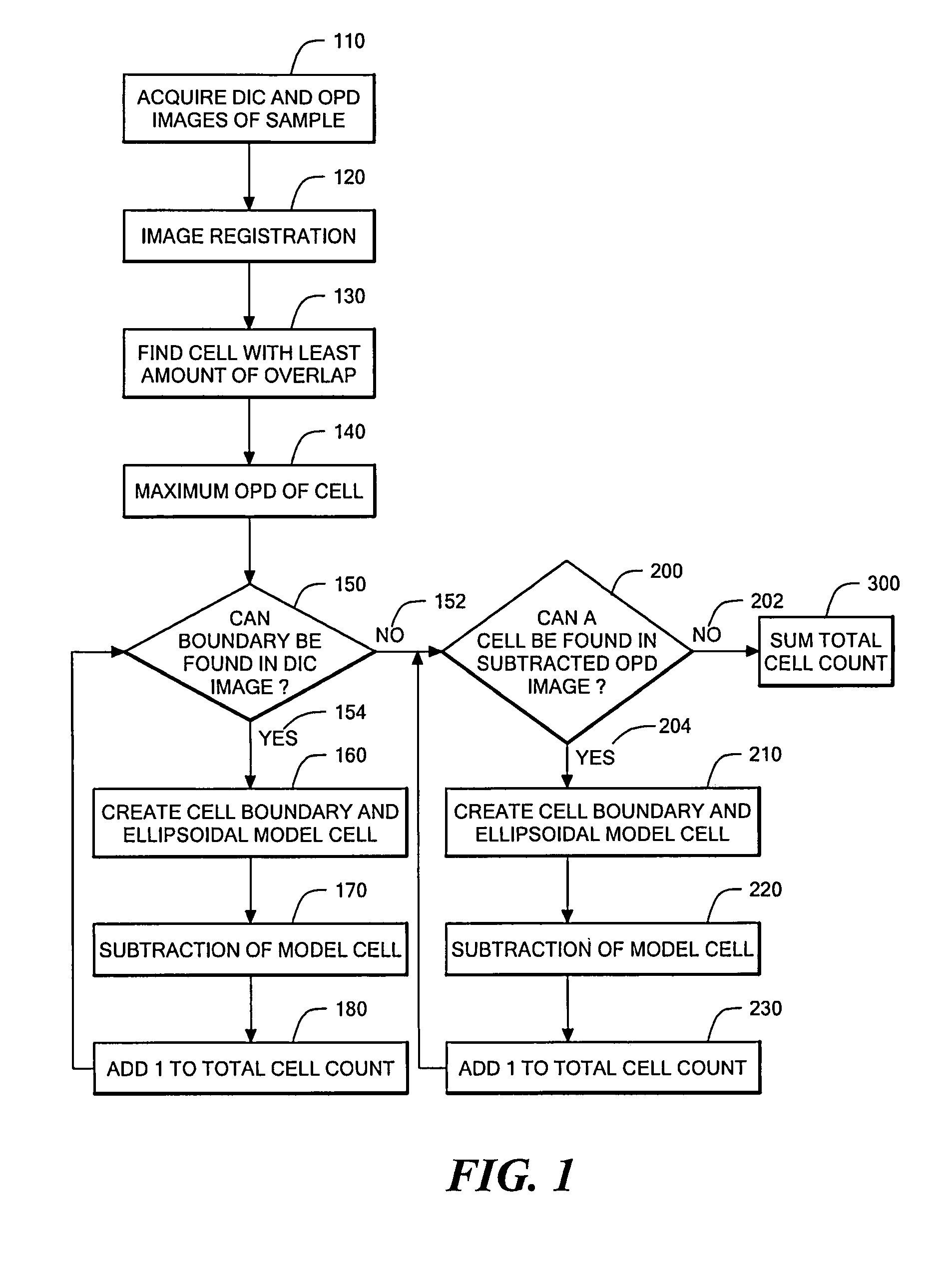
Phase subtraction cell counting method
InactiveUS20080032325A1Enough timeAccurate countMicrobiological testing/measurementCharacter and pattern recognitionMicroscopic imageDevelopmental stage
A method and device are provided for counting cells in a sample of living tissue, such as an embryo. The method involves obtaining a microscopic image of the unstained tissue that reveals cell boundaries, such as a differential interference contrast (DIC) image, and an optical quadrature microscopy (OQM) image which is used to prepare an image of optical path length deviation (OPD) across the cell cluster. The boundaries of individual cells in the cell cluster are modeled as ellipses and used, together with the maximum optical path length deviation of a cell, to calculate ellipsoidal model cells that are subtracted from the OPD image. The process is repeated until the OPD image is depleted of phase signal attributable to cells of the cell cluster, and the cell count is obtained from the number of cells subtracted. The method is capable of accurately and non-invasively counting the number of cells in a living embryo at the 2-30 cell stage, and can be employed to assess the developmental stage and health of human embryos for fertility treatments.
Owner:NORTHEASTERN UNIV
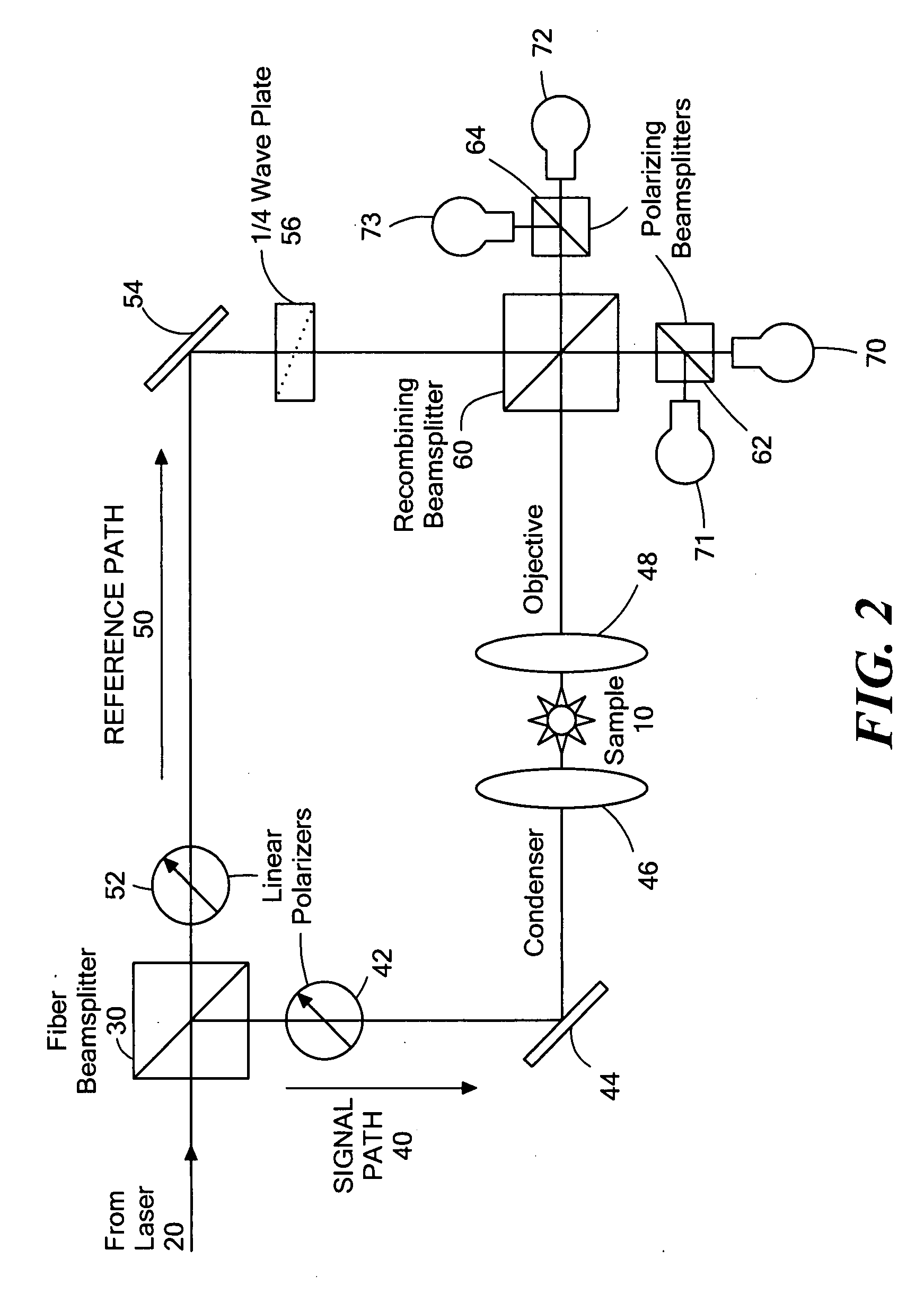
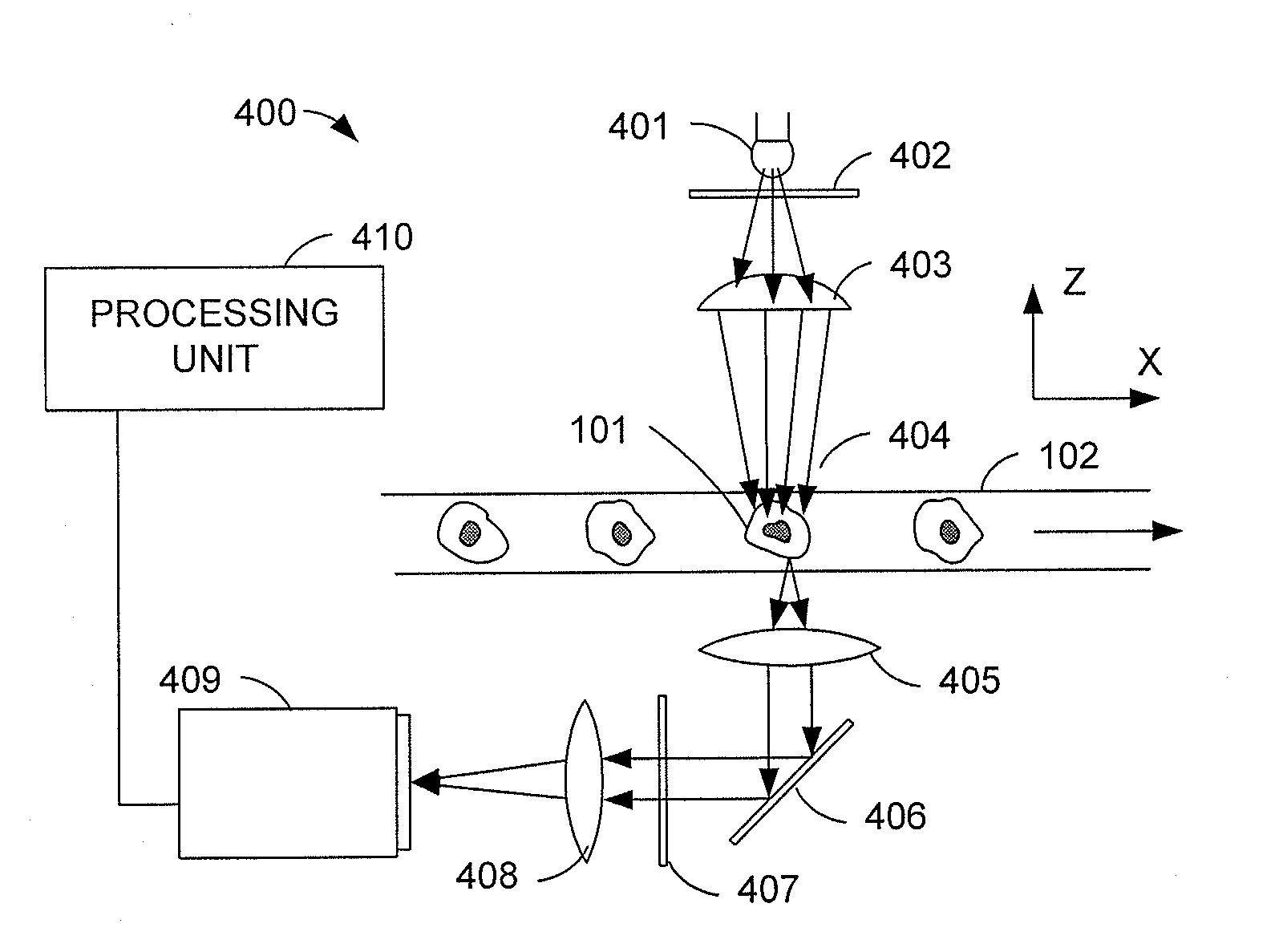
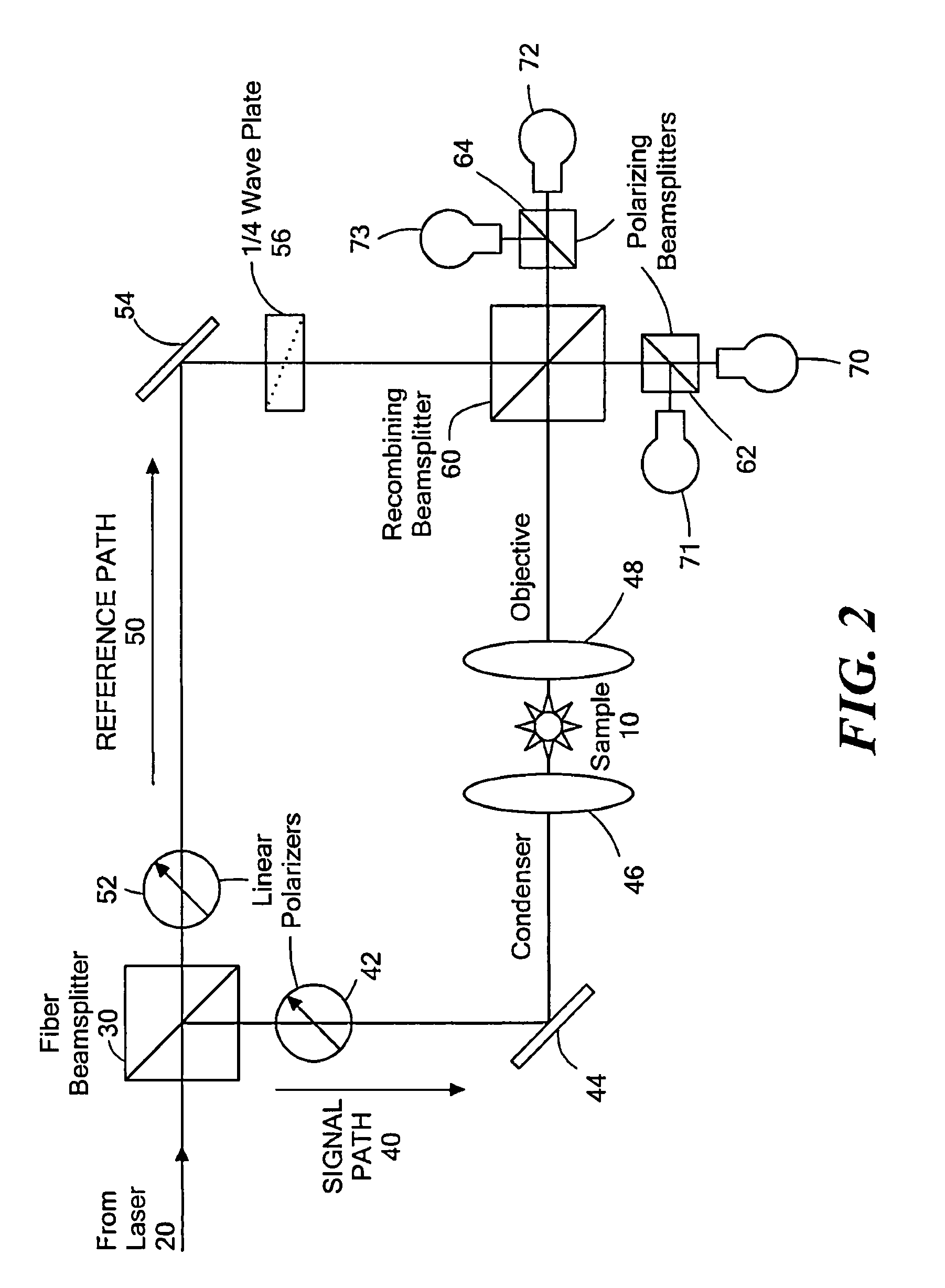
Cytometry system with interferometric measurement
ActiveUS20130252237A1Reduce light energyEasy to handleBioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsSignal-to-noise ratio (imaging)Phase difference
This disclosure concerns methods and apparatus for interferometric spectroscopic measurements of particles with higher signal to noise ratio utilizing an infrared light beam that is split into two beams. At least one beam may be directed through a measurement volume containing a sample including a medium. The two beams may then be recombined and measured by a detector. The phase differential between the two beams may be selected to provide destructive interference when no particle is present in the measurement volume. A sample including medium with a particle is introduced to the measurement volume and the detected change resulting from at least one of resonant mid-infrared absorption, non-resonant mid-infrared absorption, and scattering by the particle may be used to determine a property of the particle. A wide range of properties of particles may be determined, wherein the particles may include living cells.
Owner:1087 SYST
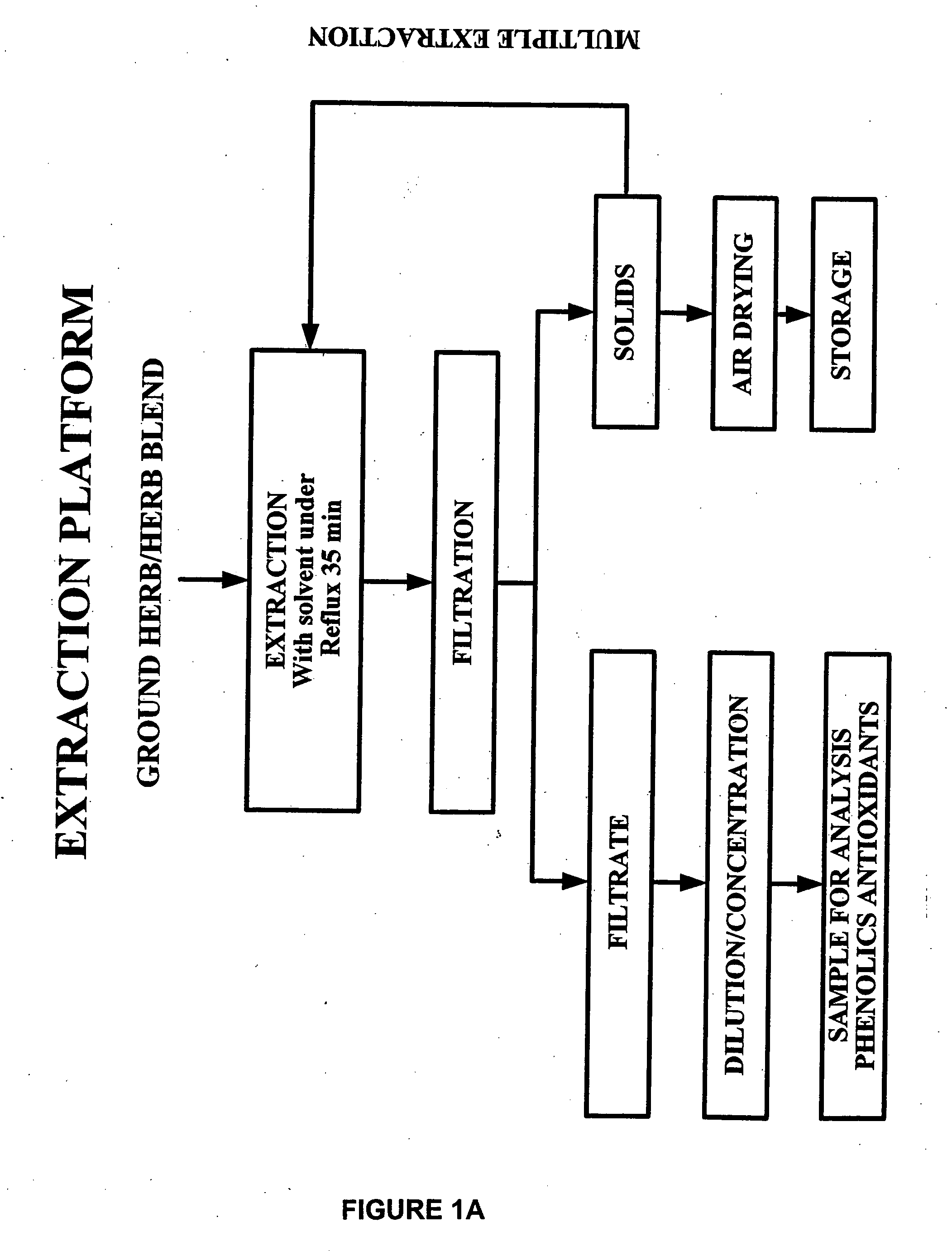
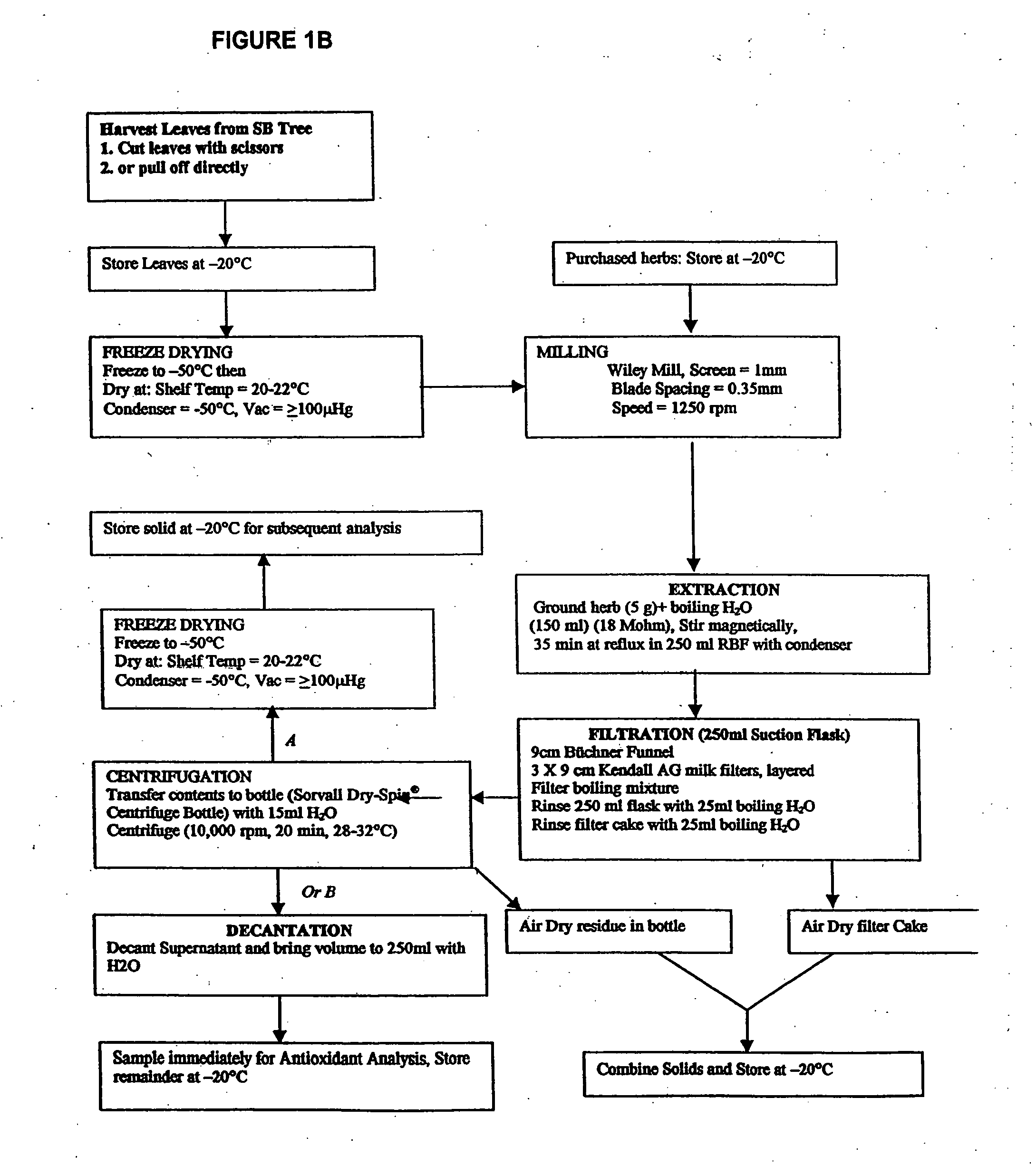
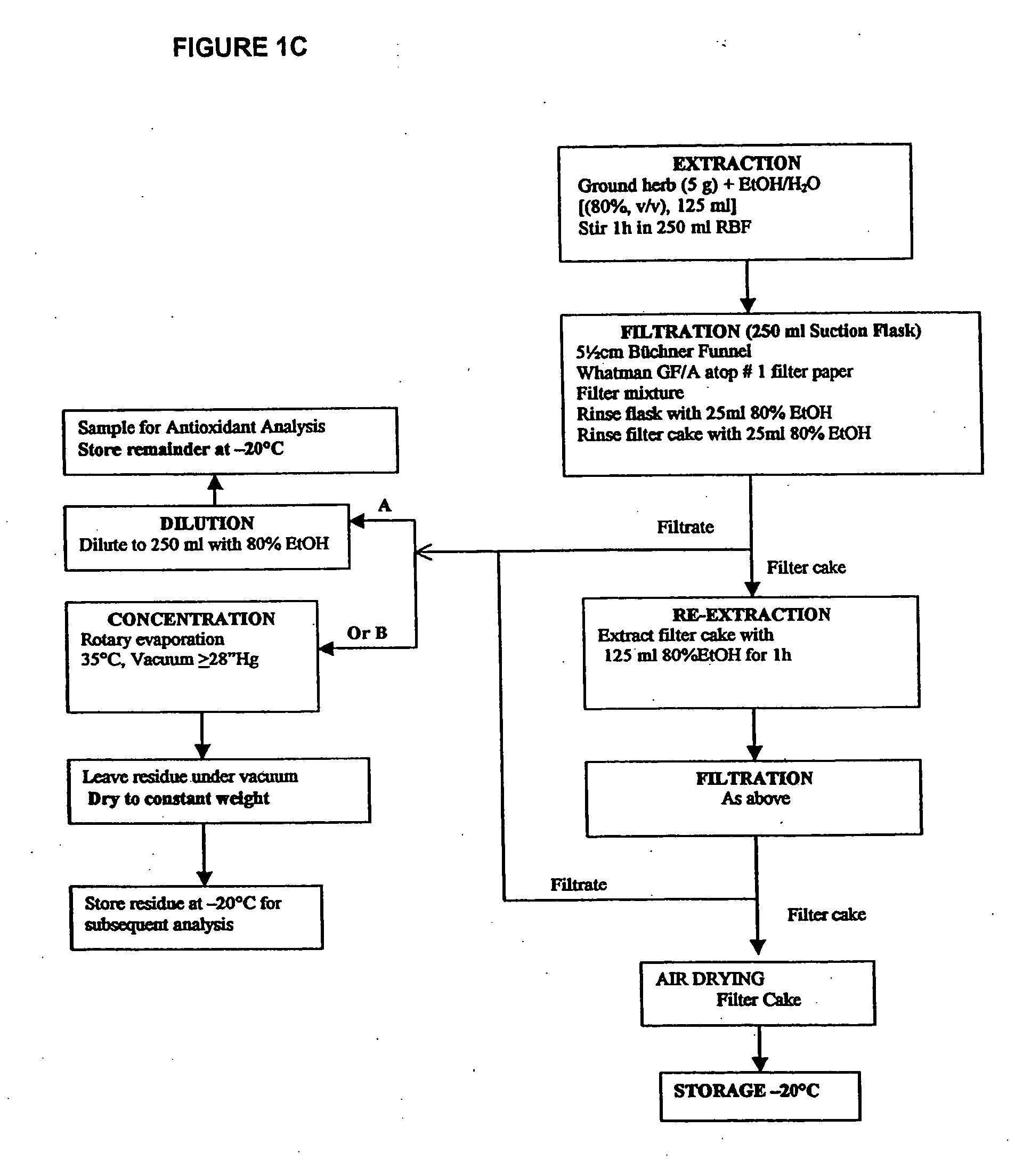
Compositions of botanical extracts for treating malignancy-associated changes
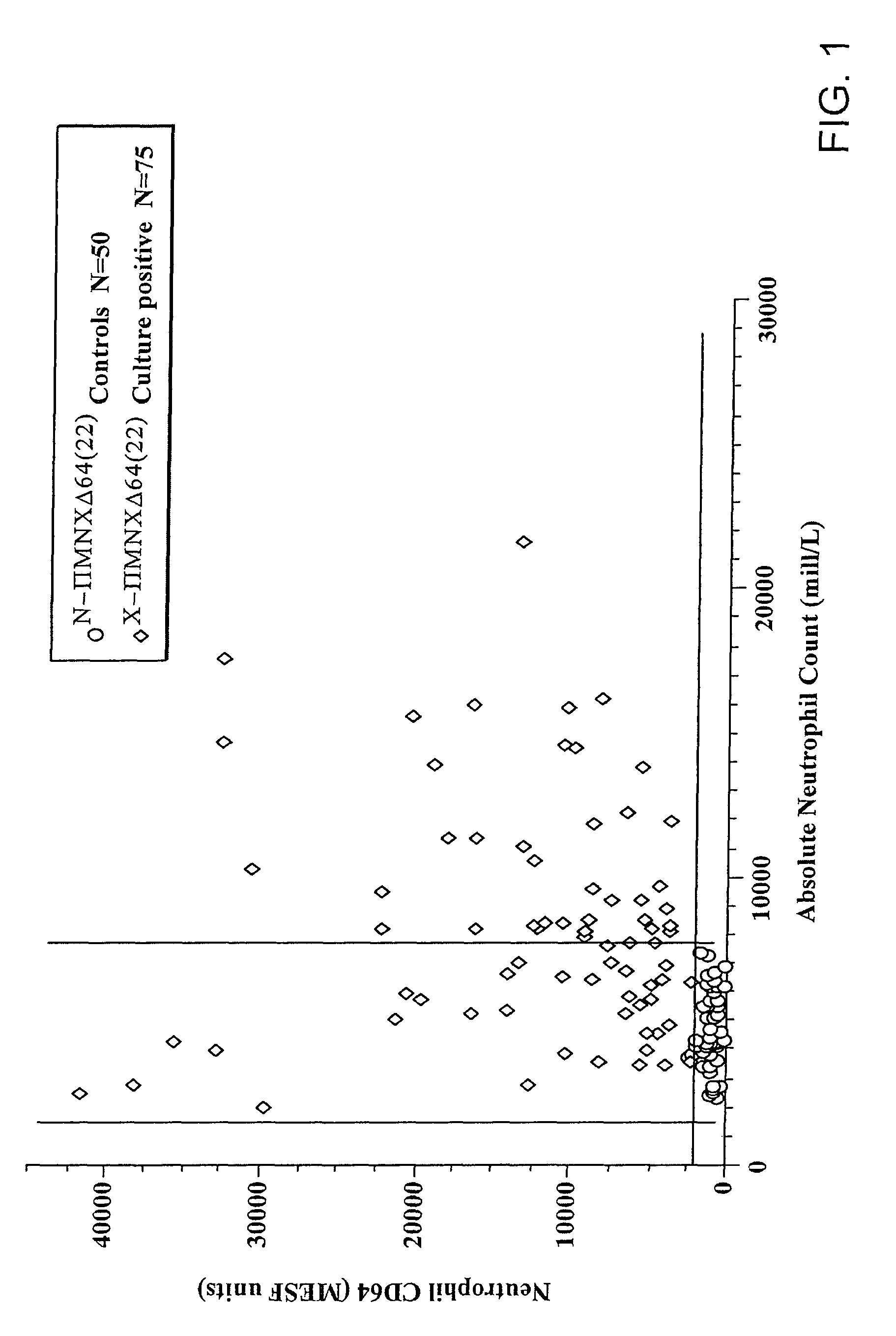
InactiveUS20050196409A1Low toxicityHigh sensitivityBiocideMicrobiological testing/measurementSalvia miltiorrhizaCytometry
Methods for diagnosis of malignancy associated changes (MAC) using Automated Quantitative Cytometry (AQC) and treatment using compositions, extracts and compounds comprising botanical extracts. Use of such compounds in the prevention and therapy of cancer diagnosed by the AQC MAC test are also provided as well as methods for treatment using the compositions of this invention. Compositions comprising therapeutically effective amounts of two or more of an extract of Ganoderma lucidum, an extract of Salvia miltiorrhiza and an extract of Scutellaria barbata and optionally a therapeutically effective amount of an extract of Hippophae rhamnoides are provided. Novel synergistic effects of the use of these compounds in combination therapy are disclosed. Compositions further comprising therapeutically effective amounts of at least one chemotherapeutic agent are also provided.
Owner:GENYOUS BIOMED INT
Serial-line-scan-encoded multi-color fluorescence microscopy and imaging flow cytometry
InactiveUS20100238442A1Improved signal-to-noise ratioRaman/scattering spectroscopyPhotometryHigh resolution imagingSerial line
A system for performing high-speed, high-resolution imaging cytometry utilizes a line-scan sensor. A cell to be characterized is transported past a scan region. An optical system focuses an image of a portion of the scan region onto at least one linear light sensor, and repeated readings of light falling on the sensor are taken while a cell is transported though the scan region. The system may image cells directly, or may excite fluorescence in the cells and image the resulting light emitted from the cell by fluorescence. The system may provide a narrow band of illumination at the scan region. The system may include various filters and imaging optics that enable simultaneous multicolor fluorescence imaging cytometry. Multiple linear sensors may be provided, and images gathered by the individual sensors may be combined to construct an image having improved signal-to-noise characteristics.
Owner:BIO RAD LAB INC
Cytometer
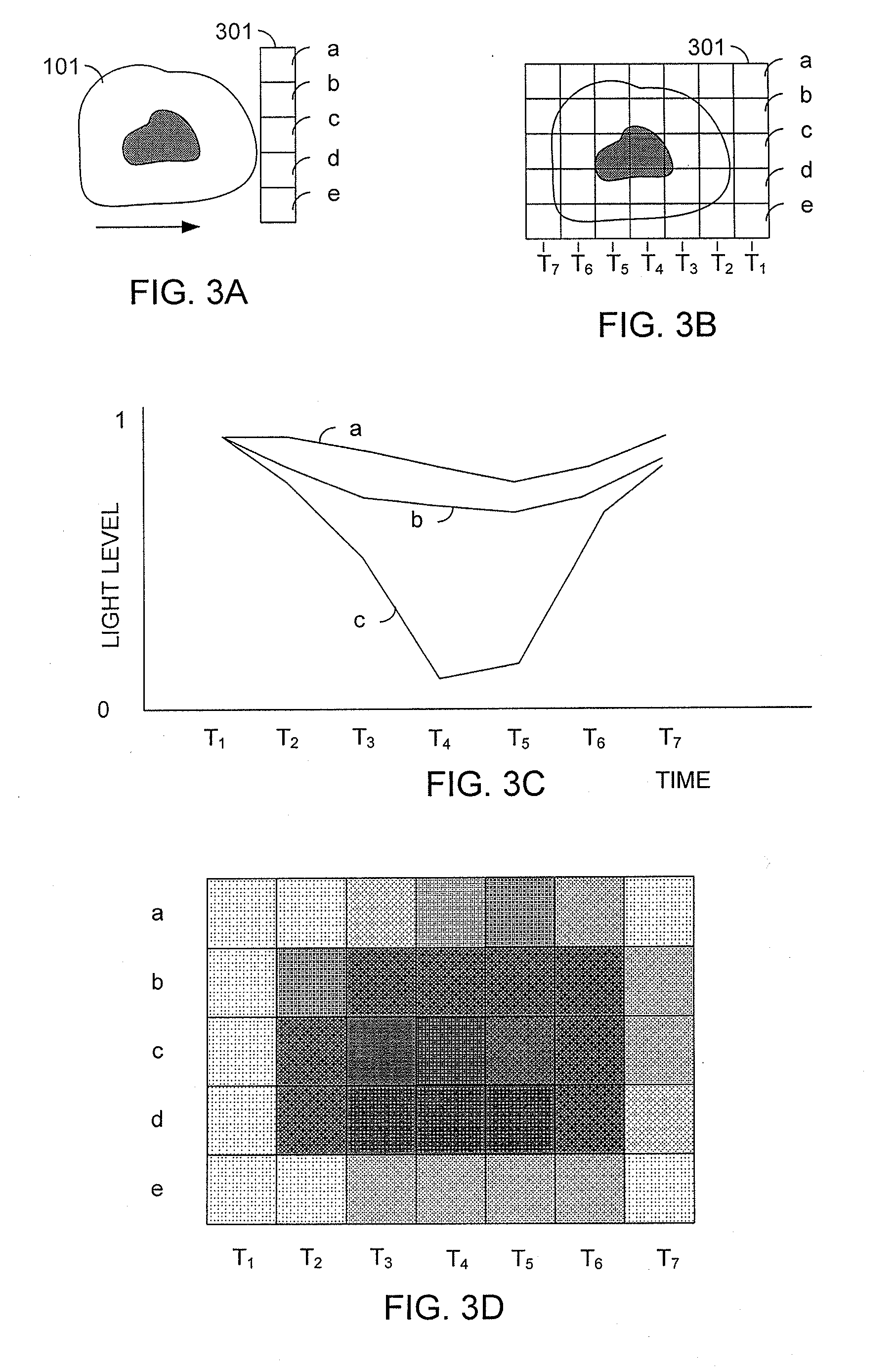
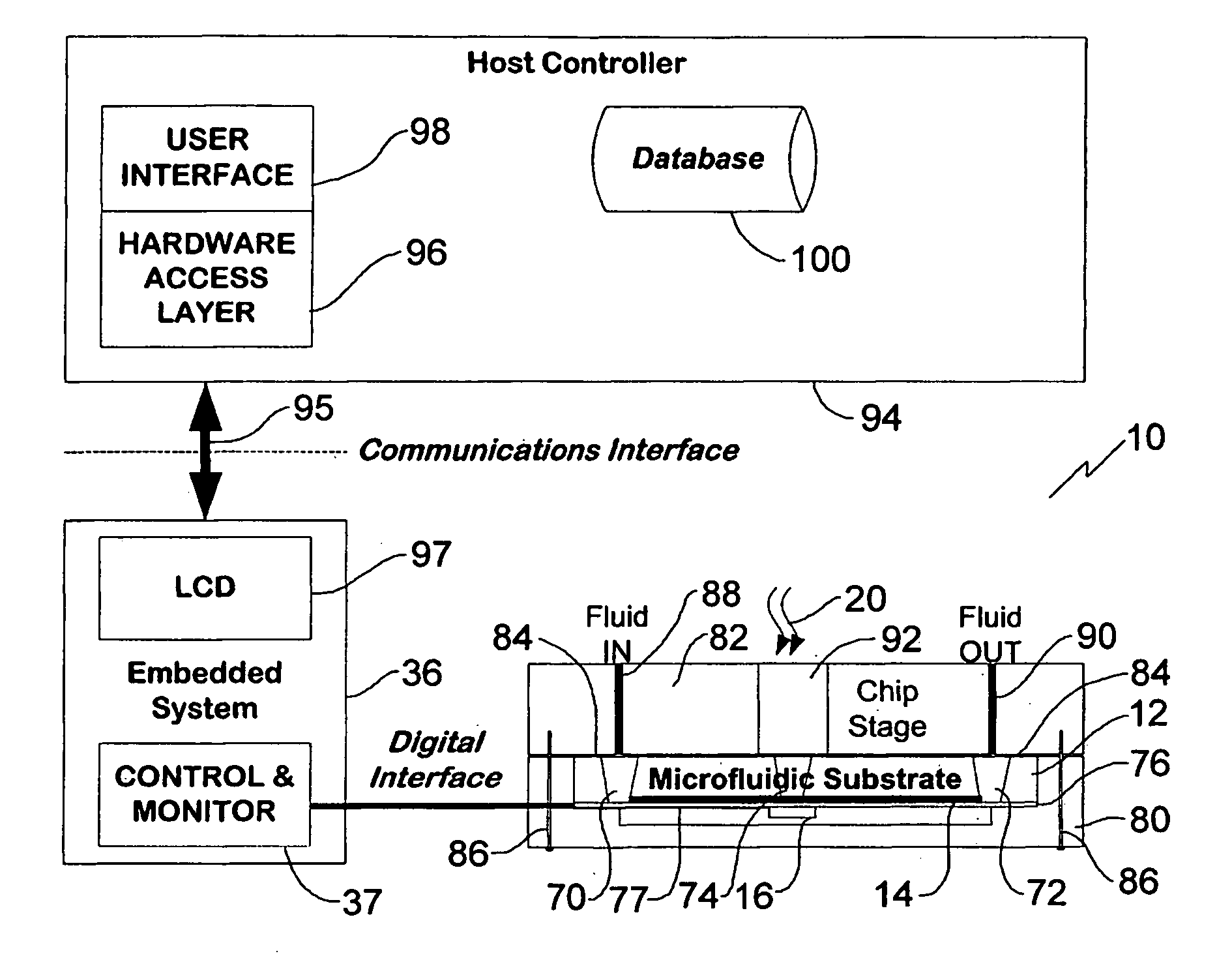
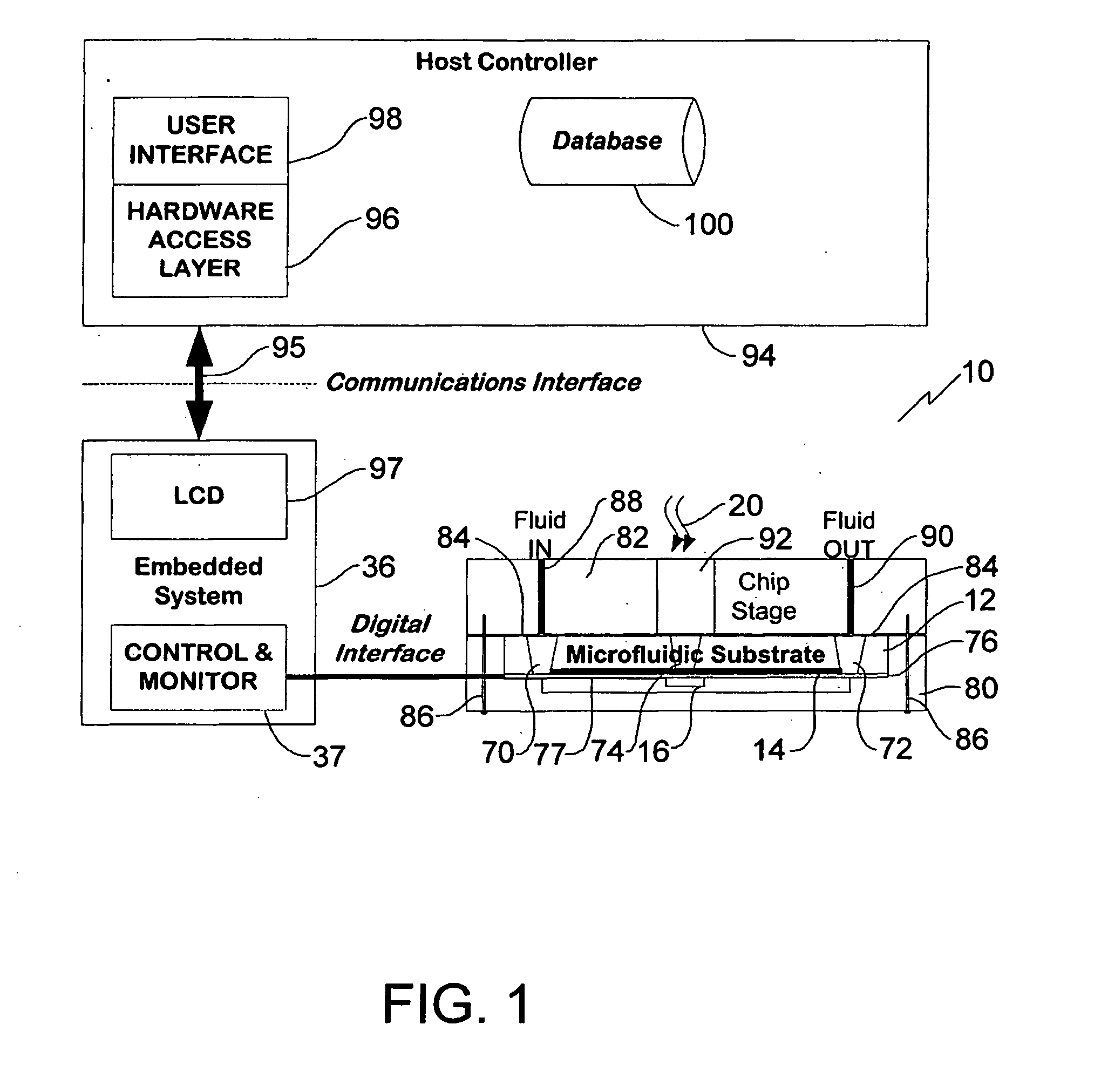
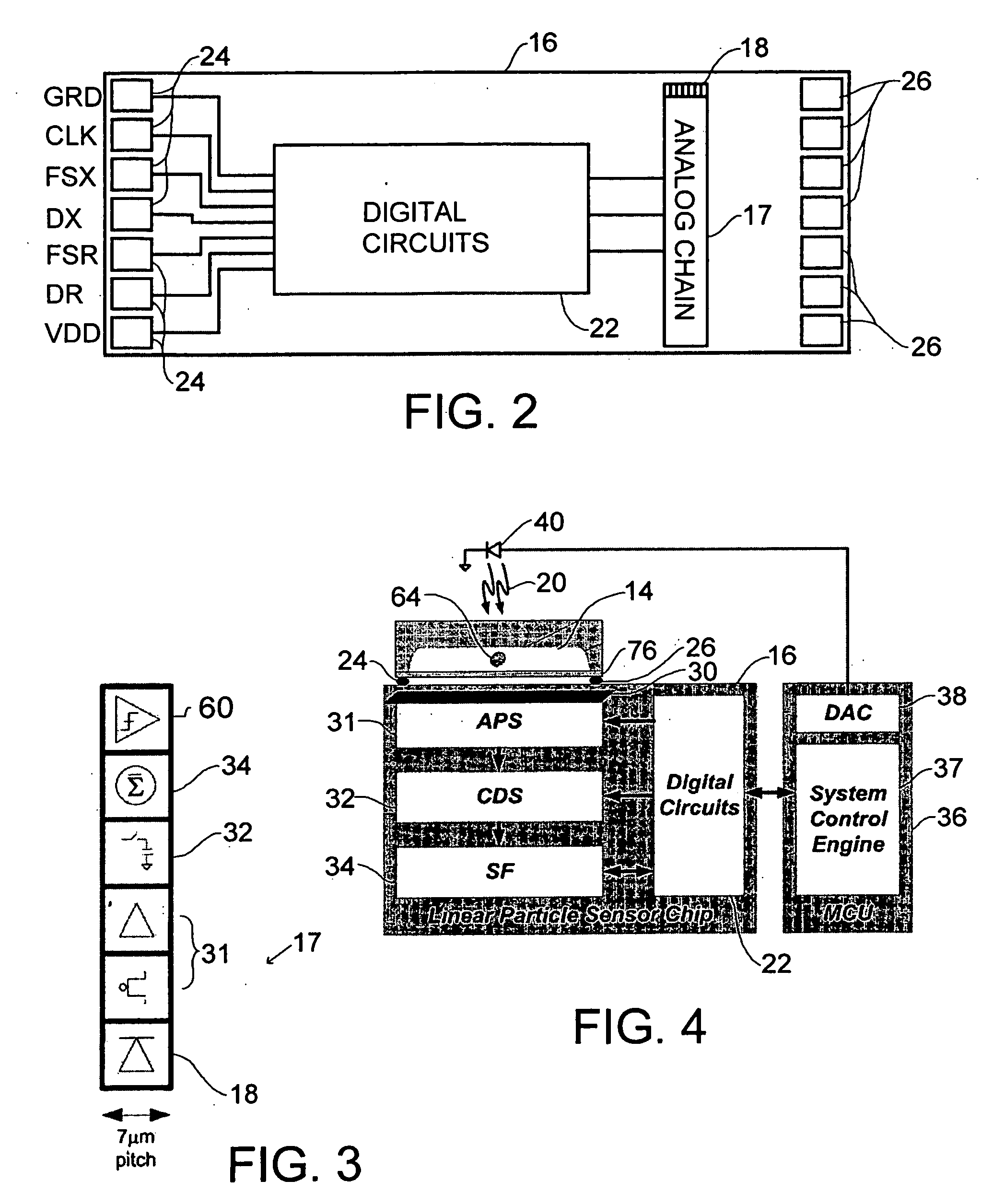
A real-time digital cytometer on a chip system utilizing a custom near field CMOS active pixel intelligent sensor that is flip-chip attached to a fluidic microchannel etched in a thin glass substrate. The CMOS active pixel sensor, fabricated using a 0.18 micron process, is a mixed signal chip comprising a sixteen pixel linear adaptive spatial filter coupled to a digital serial interface. This near field hybrid digital sensor topology obviates the need for both high resolution analog to digital conversion as well as conventional microscopy for the realization of real time optical cytometry. The custom sensor based design approach affords efficient scaling into a tiled multi-channel sensing configuration. The complete system, supported by a handheld graphical user interface and control module, demonstrates a viable micro total analysis sub-system for sample preparation and analysis which can support a wide range of applications ranging from cytometry to cell growth kinetics and analysis and various forms of fluid and droplet metering on an integrated and compact microfluidic platform.
Owner:UTI LLP
Combined inspection system including mid-ir vibrational spectroscopy and a fluorescent cytometry facility
InactiveUS20120196356A1Bioreactor/fermenter combinationsMaterial analysis using sonic/ultrasonic/infrasonic wavesAnalyteSpectroscopy
This disclosure concerns a cytometry system including a handling system that presents single cells to at least one quantum cascade laser (QCL) source. The QCL laser source configured to deliver light to a cell within the cells in order to induce resonant mid-infrared absorption by one or more analytes of the cell. The system includes a laser source that excites at least one fluorophore present in the cell or on the surface of the cell and a fluorescence detector that measures the fluorescence intensity of the fluorophore. A mid-infrared detection facility detects the transmitted mid-infrared wavelength light, wherein the transmitted mid-infrared wavelength light and the fluorescence intensity are used to identify at least one cell characteristic.
Owner:1087 SYST
High resolution imaging fountain flow cytometry
InactiveUS20050036139A1Improve throughputHigh sensitivityWithdrawing sample devicesMaterial analysis by optical meansHigh resolution imagingFlow cell
An imaging fountain flow cytometer allows high resolution microscopic imaging of a flowing sample in real time. Cells of interest are in a vertical stream of liquid flowing toward one or more illuminating elements at wavelengths which illuminate fluorescent dyes and cause the cells to fluoresce. A detector detects the fluorescence emission each time a marked cell passes through the focal plane of the detector. A bi-directional syringe pump allows the user to reverse the flow and locate the detected cell in the field of view. The flow cell is mounted on a computer controlled x-y stage, so the user can center a portion of the image on which to zoom or increase magnification. Several computer selectable parfocal objective lenses allow the user to image the entire field of view and then zoom in on the detected cell at substantially higher resolution. The magnified cell is then imaged at the various wavelengths.
Owner:UNIVERSITY OF WYOMING
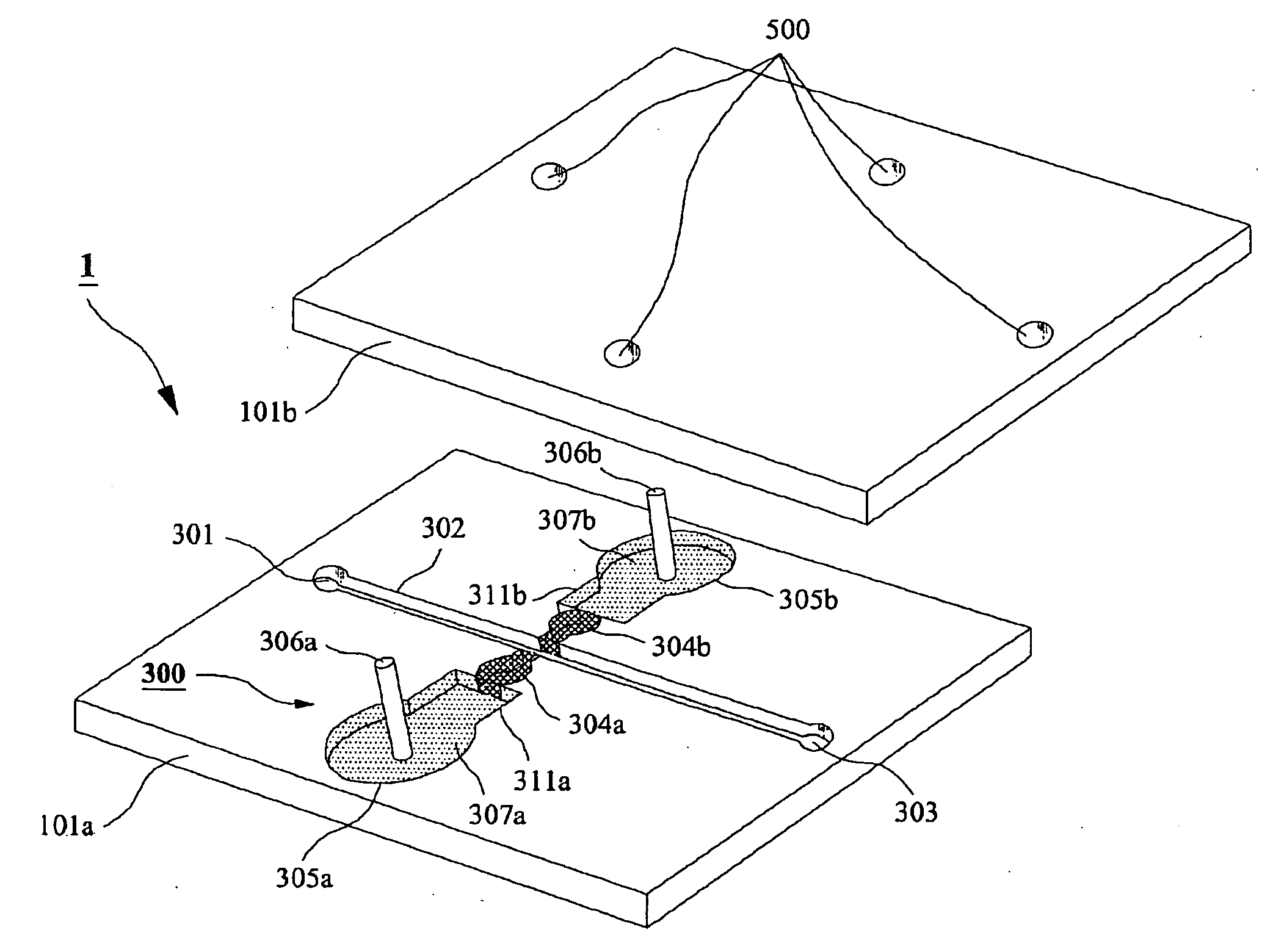
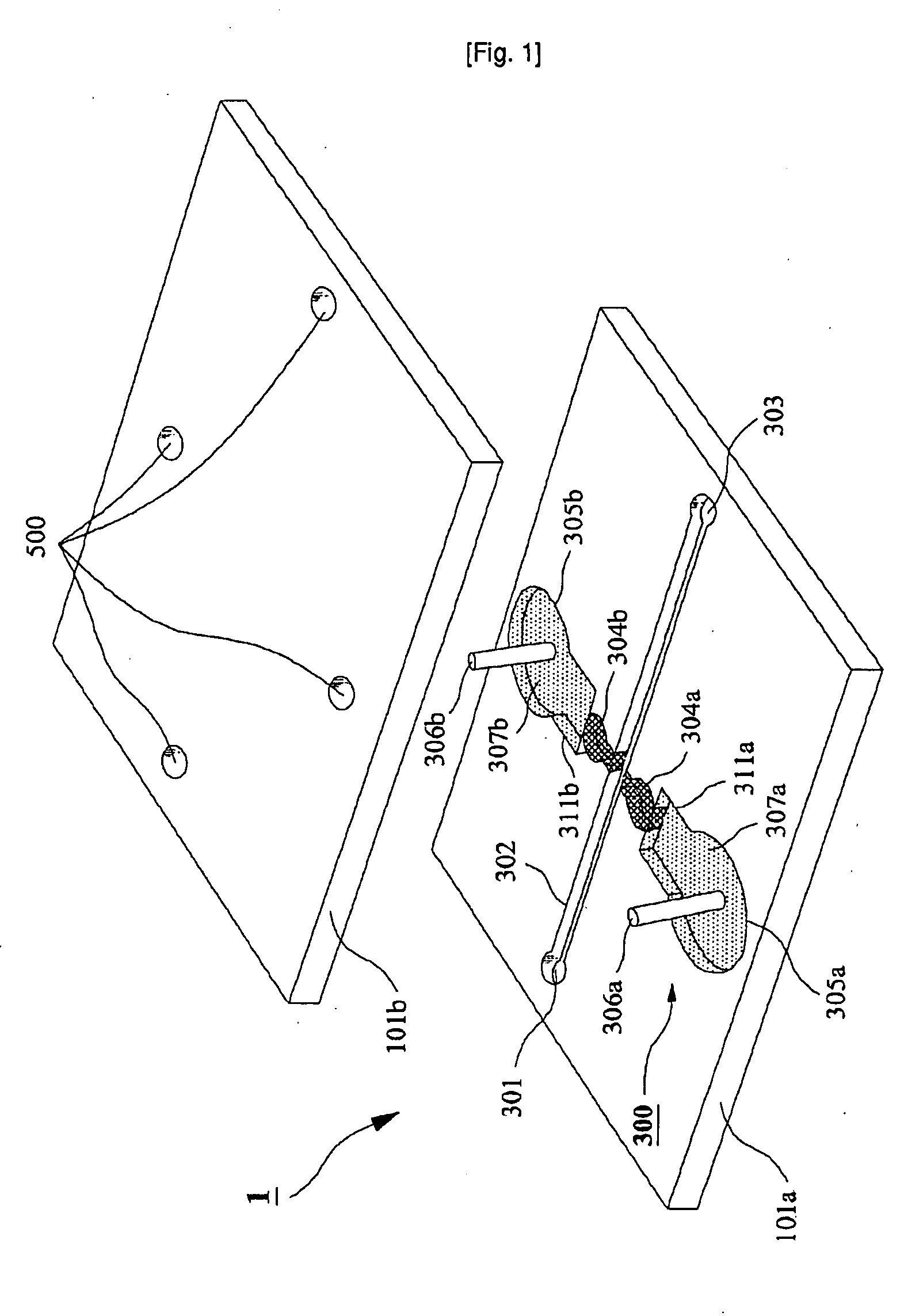
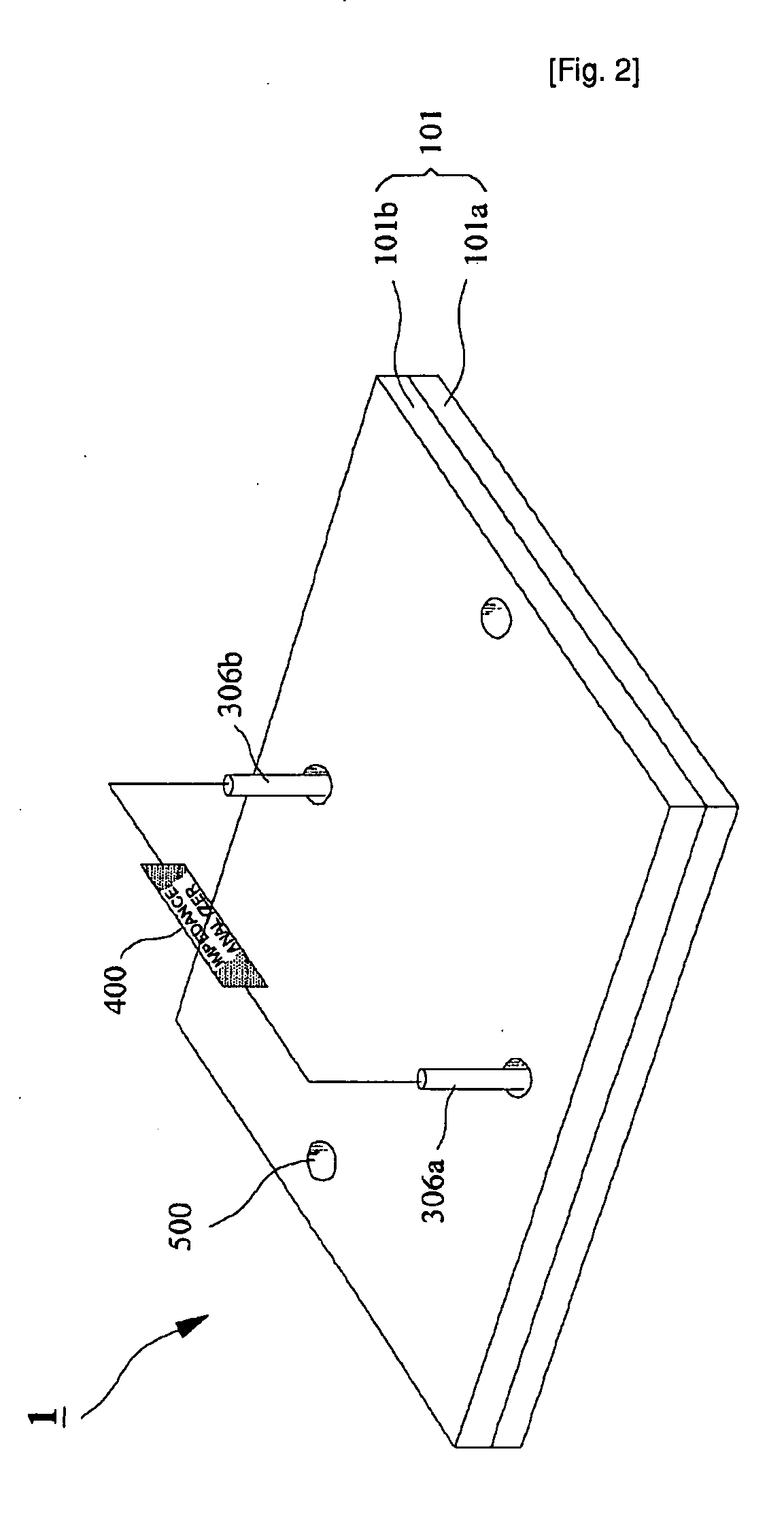
Microchip For Use In Cytometry, Velocimetry And Cell Sorting Using Polyelectrolytic Salt Bridges
InactiveUS20090104689A1Bioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsPolyelectrolyteElectrolysis
The present invention relates to a microchip using polyelectrolyte salt bridge for cytometry, velocimetry, and cell sorting. The microchip comprises; a) an inlet for solution to be analyzed, b) a microchannel which provides a moving passage for solution to be analyzed, c) at least one outlet for solution to be analyzed which has passed through the moving passage, d) at least one electrode system comprising a first and a second salt bridges connected to the microchannel (the two salt bridges face each other), and a first and a second reservoirs connected to said each salt bridge (the reservoir comprises electrode and standard electrolyte solution). The microchip detects analytes in the solution to be analyzed (for example, a cell) by detecting change of impedance. In detail, anion in the standard electrolyte solution, which is comprised in the first reservoir, moves from the first salt bridge to the second salt bridge across the microchannel. Impedance change occurs by interference of anion moving across the microchannel and the change can be detected by impedance analyzer connected to electrodes in the first and the second reservoirs.
Owner:SEOUL NAT UNIV R&DB FOUND
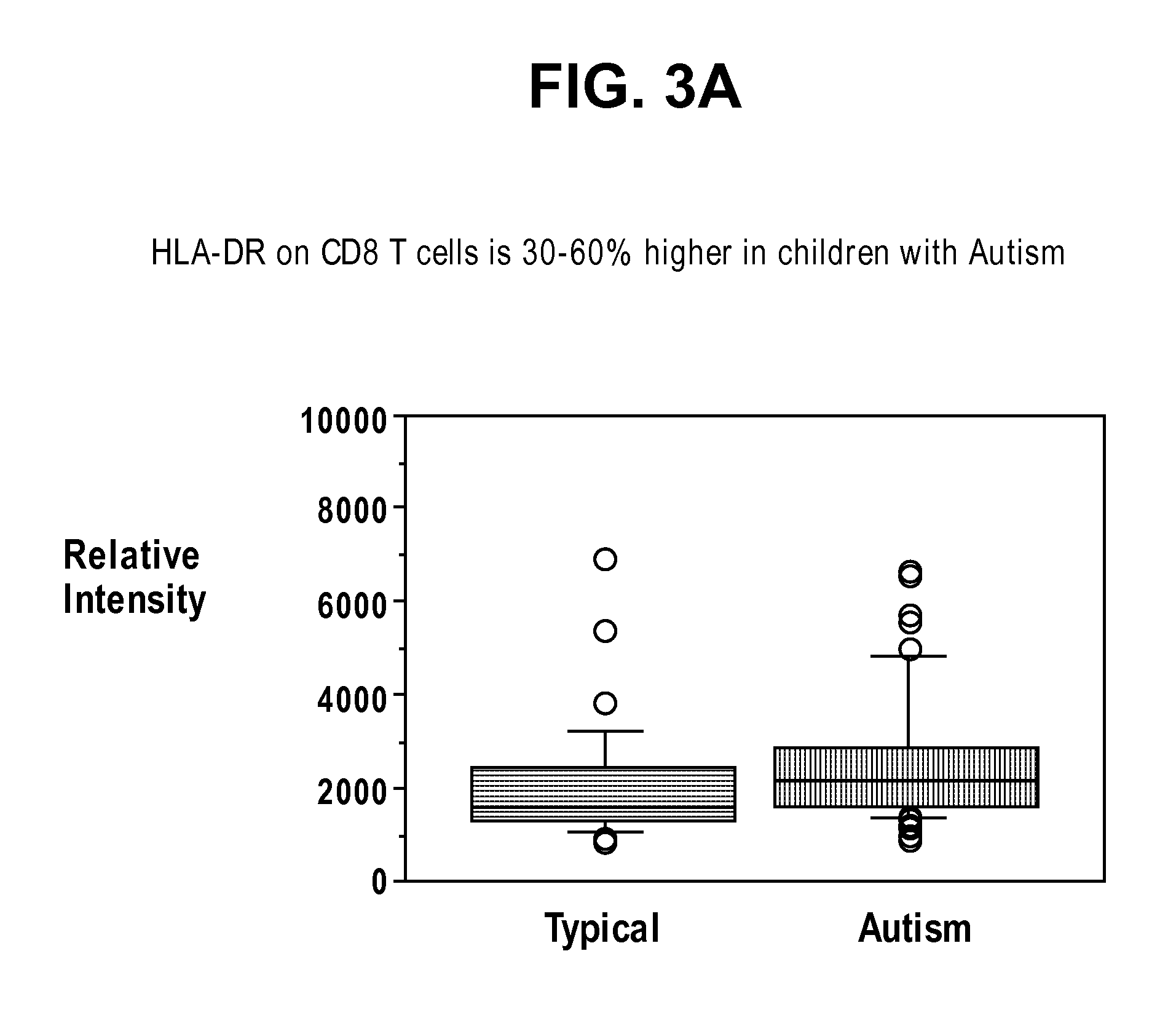
Biomarkers for diagnosing an autism spectrum disorder
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA
Phase subtraction cell counting method
InactiveUS8428331B2Enough timeAccurate countMicrobiological testing/measurementCharacter and pattern recognitionDevelopmental stageMicroscopic image
A method and device are provided for counting cells in a sample of living tissue, such as an embryo. The method involves obtaining a microscopic image of the unstained tissue that reveals cell boundaries, such as a differential interference contrast (DIC) image, and an optical quadrature microscopy (OQM) image which is used to prepare an image of optical path length deviation (OPD) across the cell cluster. The boundaries of individual cells in the cell cluster are modeled as ellipses and used, together with the maximum optical path length deviation of a cell, to calculate ellipsoidal model cells that are subtracted from the OPD image. The process is repeated until the OPD image is depleted of phase signal attributable to cells of the cell cluster, and the cell count is obtained from the number of cells subtracted. The method is capable of accurately and non-invasively counting the number of cells in a living embryo at the 2-30 cell stage, and can be employed to assess the developmental stage and health of human embryos for fertility treatments.
Owner:NORTHEASTERN UNIV
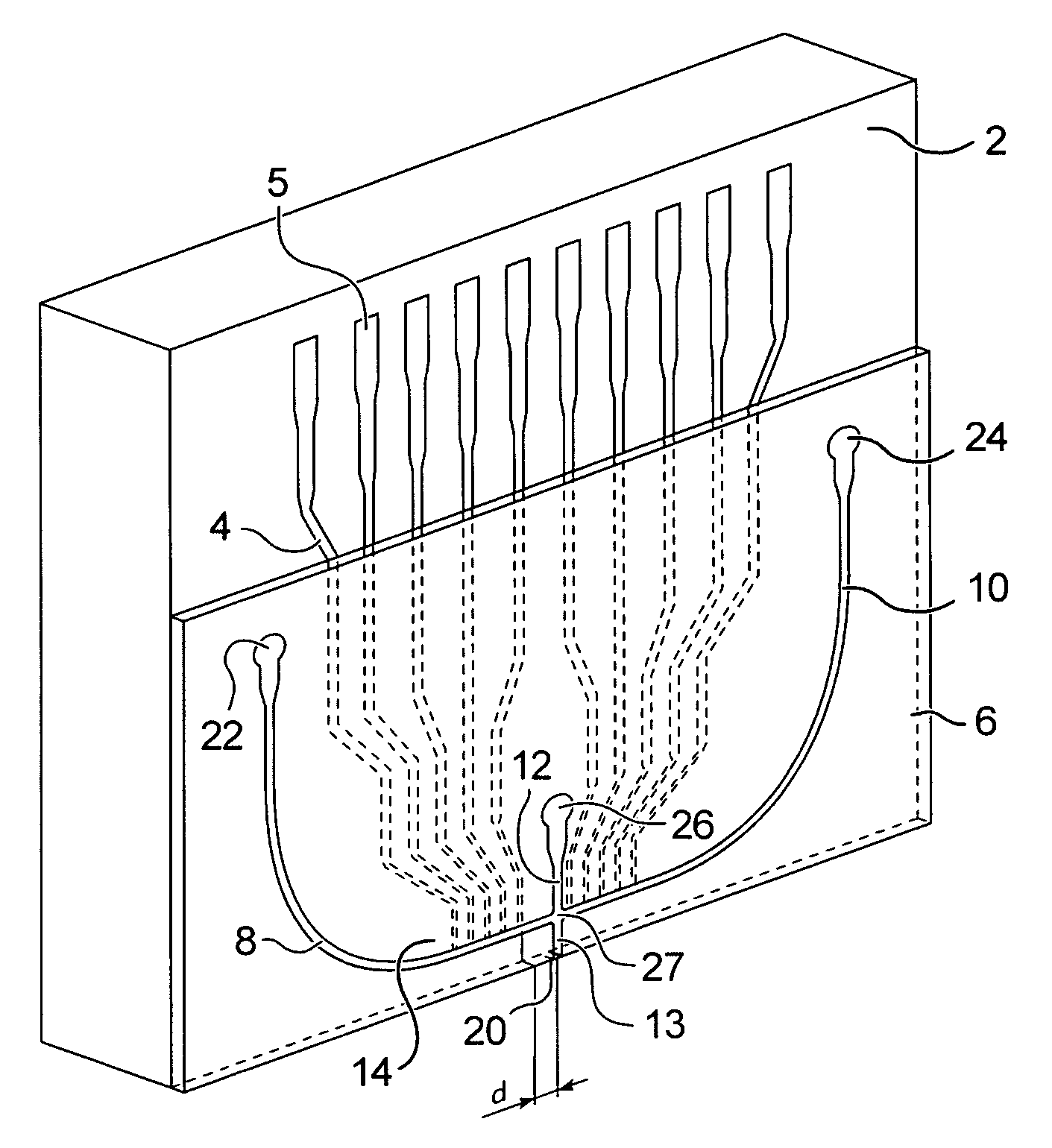
Dispensing Device For Microfluidic Droplets Especially For Cytometry
InactiveUS20080286751A1High precisionImprove abilitiesBioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsMain channelCytometry
The invention relates to a dispensing device for droplets comprising a first channel (8, 10), known as main channel, for circulation of a first fluid flow, a second channel (12, 13) for circulation of fluid, which forms with the first channel an intersection zone (27) and terminates in an ejection orifice (20), means (4) for measuring a physical property particles or cells in the first channel (18), and means for engendering a pressure wave in the second channel (12, 13).
Owner:COMMISSARIAT A LENERGIE ATOMIQUE ET AUX ENERGIES ALTERNATIVES
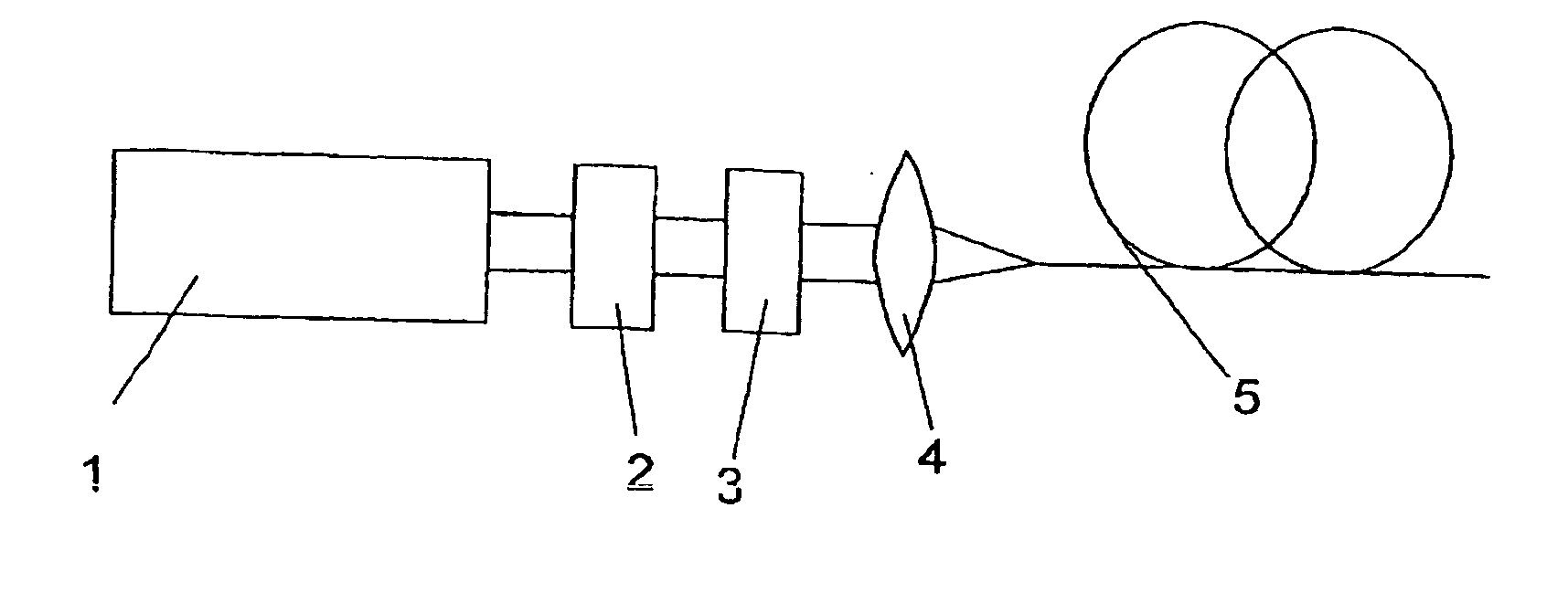
Method and optical arrangement for the generation of a broadband spectrum
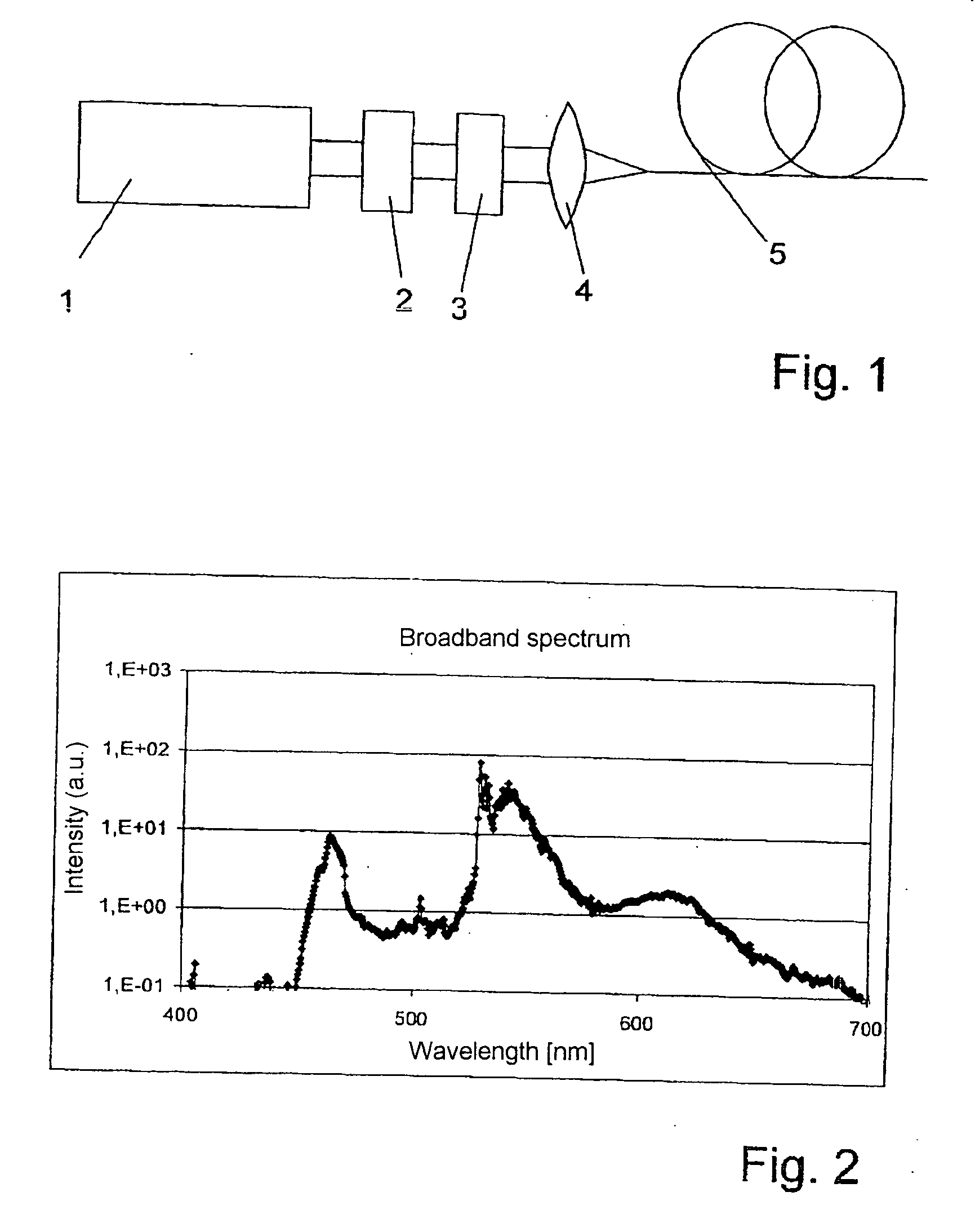
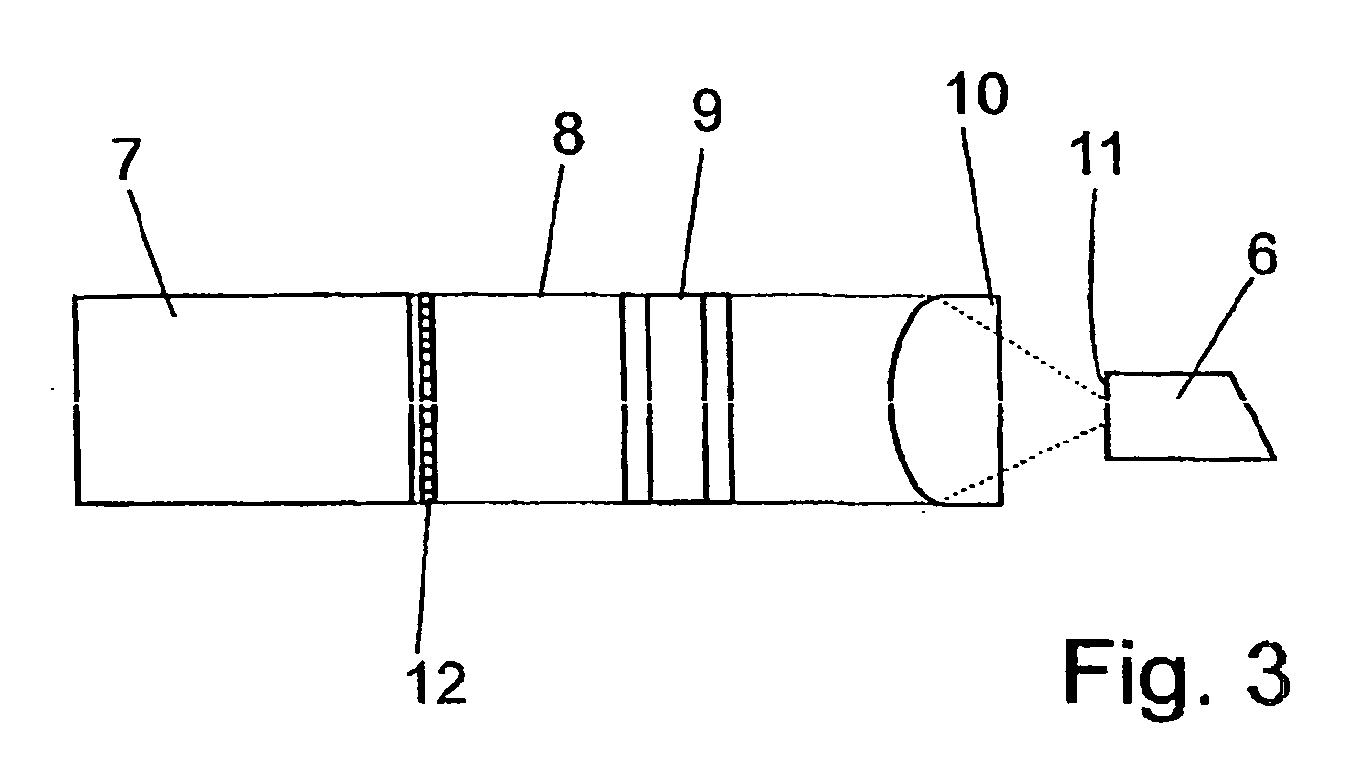
InactiveUS20060002437A1Easy to operateEasy constructionLaser detailsNon-linear opticsPicosecond laserPicosecond laser pulse
The invention is directed to a method and an optical arrangement for the generation of a broadband spectrum in which wavelength regions are selected in an application-oriented manner already during spectrum generation in order to provide increased laser power. A passively mode-coupled solid-state laser provides picosecond laser pulses with an infrared output wavelength which is transformed to a secondary wavelength in the visible spectral range by nonlinear optical processes. The picosecond laser pulses are coupled into a nonlinear optical fiber which is optically adapted to the secondary wavelength with respect to dispersion and nonlinear characteristics, so that a radiation output interval comprising a visible wavelength region is selectively generated. The broadband spectrum has high brilliance and can be used, for example, in spectroscopy, microscopy, cytometry or for array readers.
Owner:JENOPTIK OPTICAL SYST
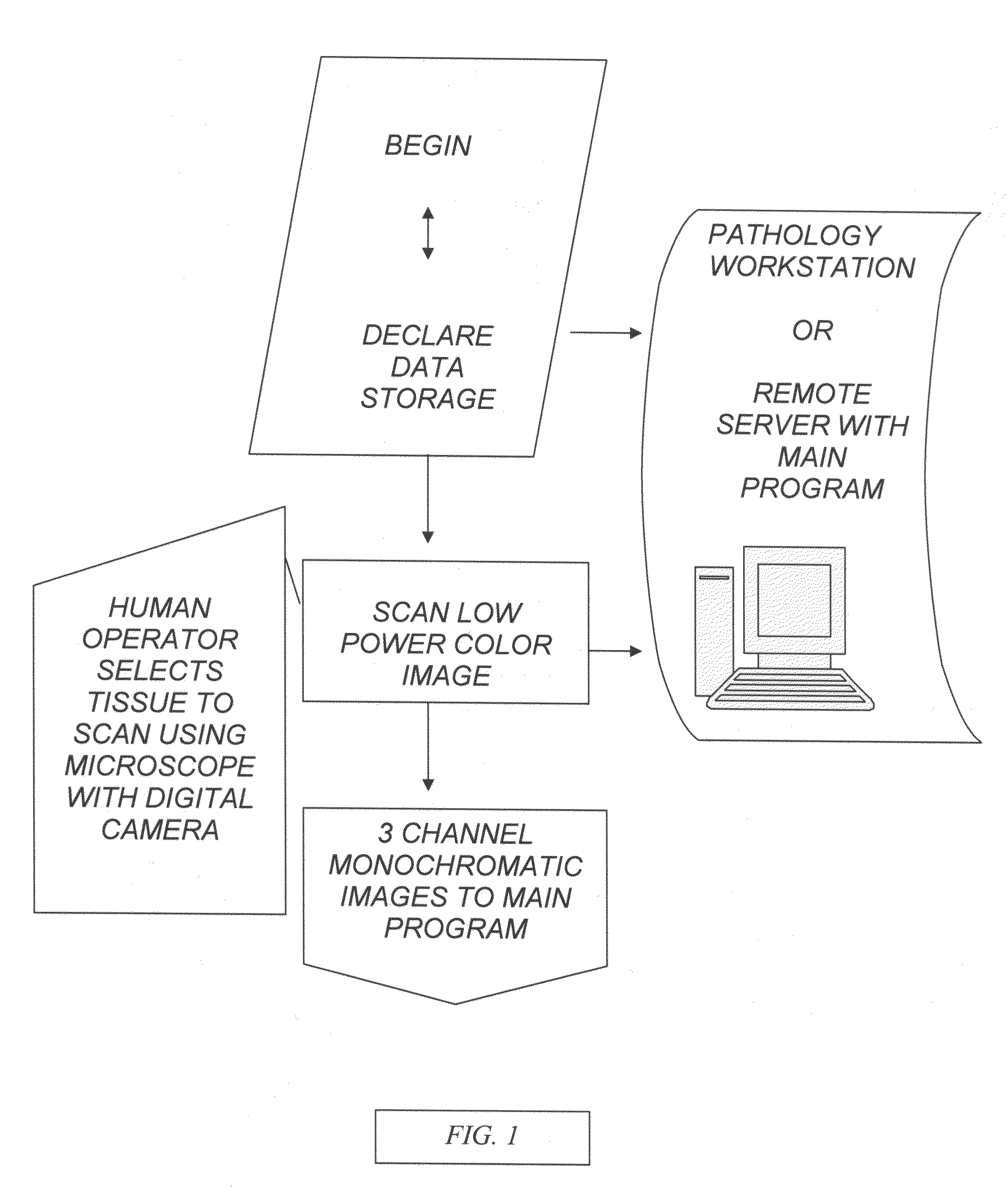
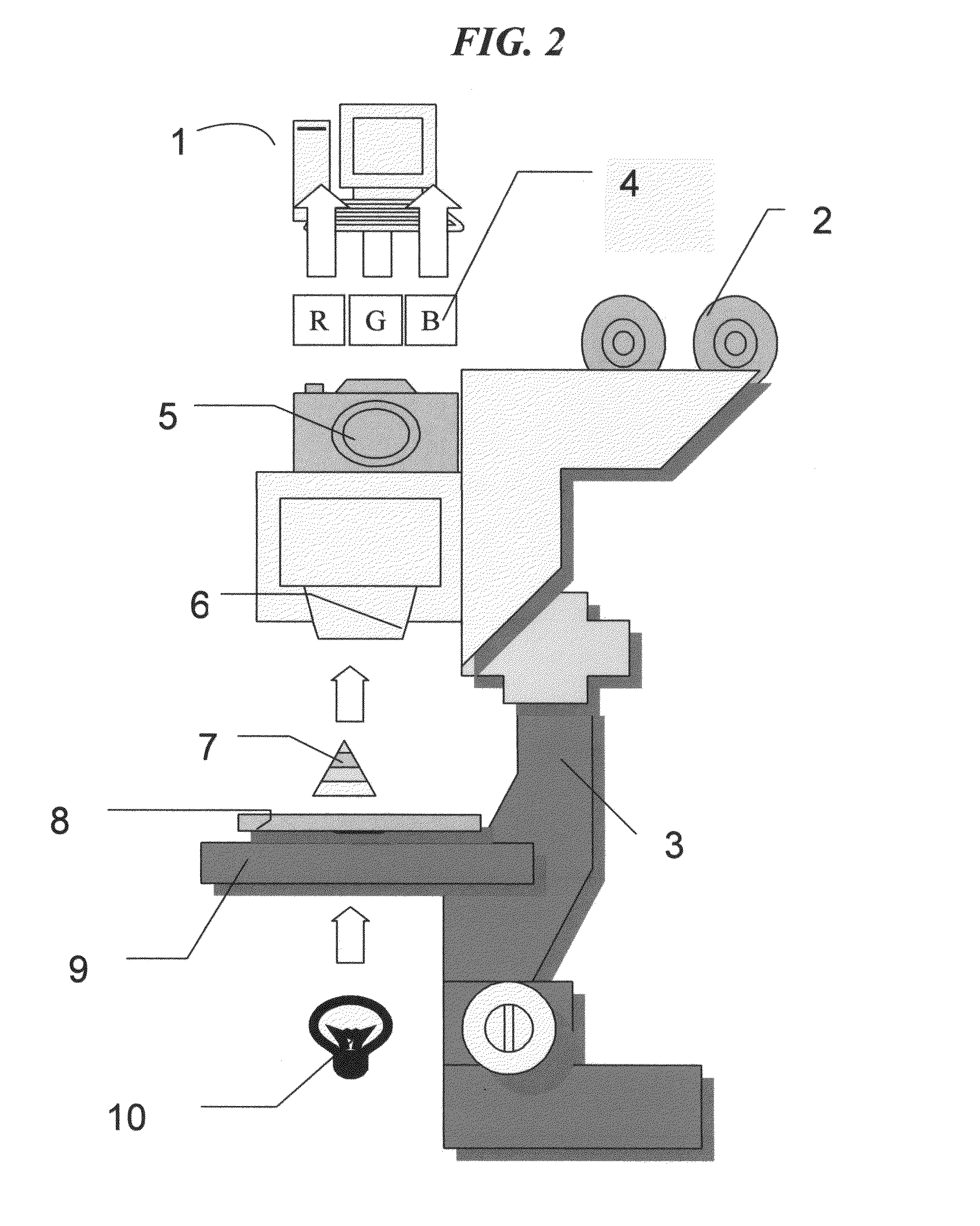
Virtual flow cytometry on immunostained tissue-tissue cytometer
InactiveUS7899624B2Bioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsColor imageCytometry
Owner:CUALING HERNANI D
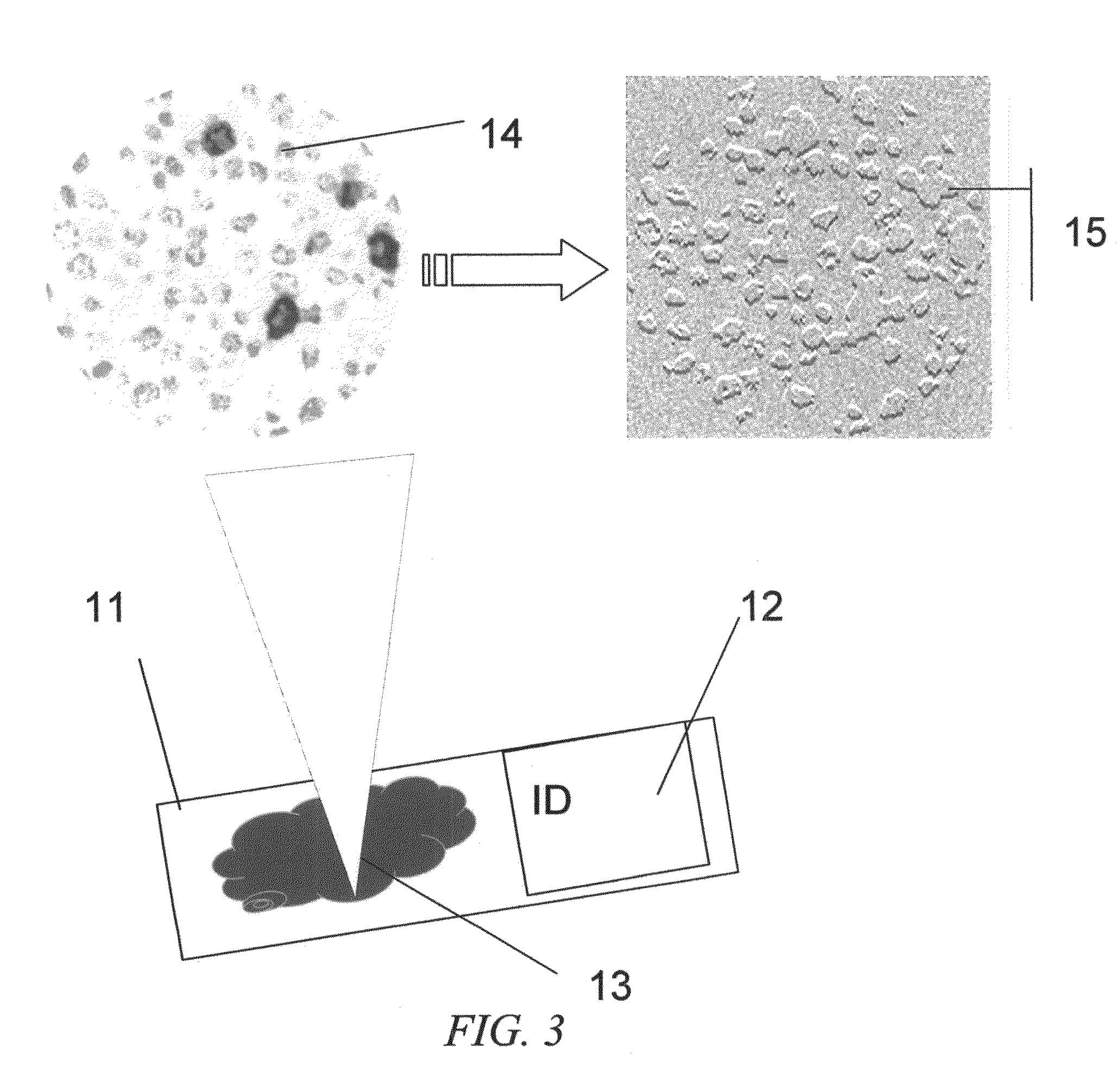
Methods of in vivo cytometry
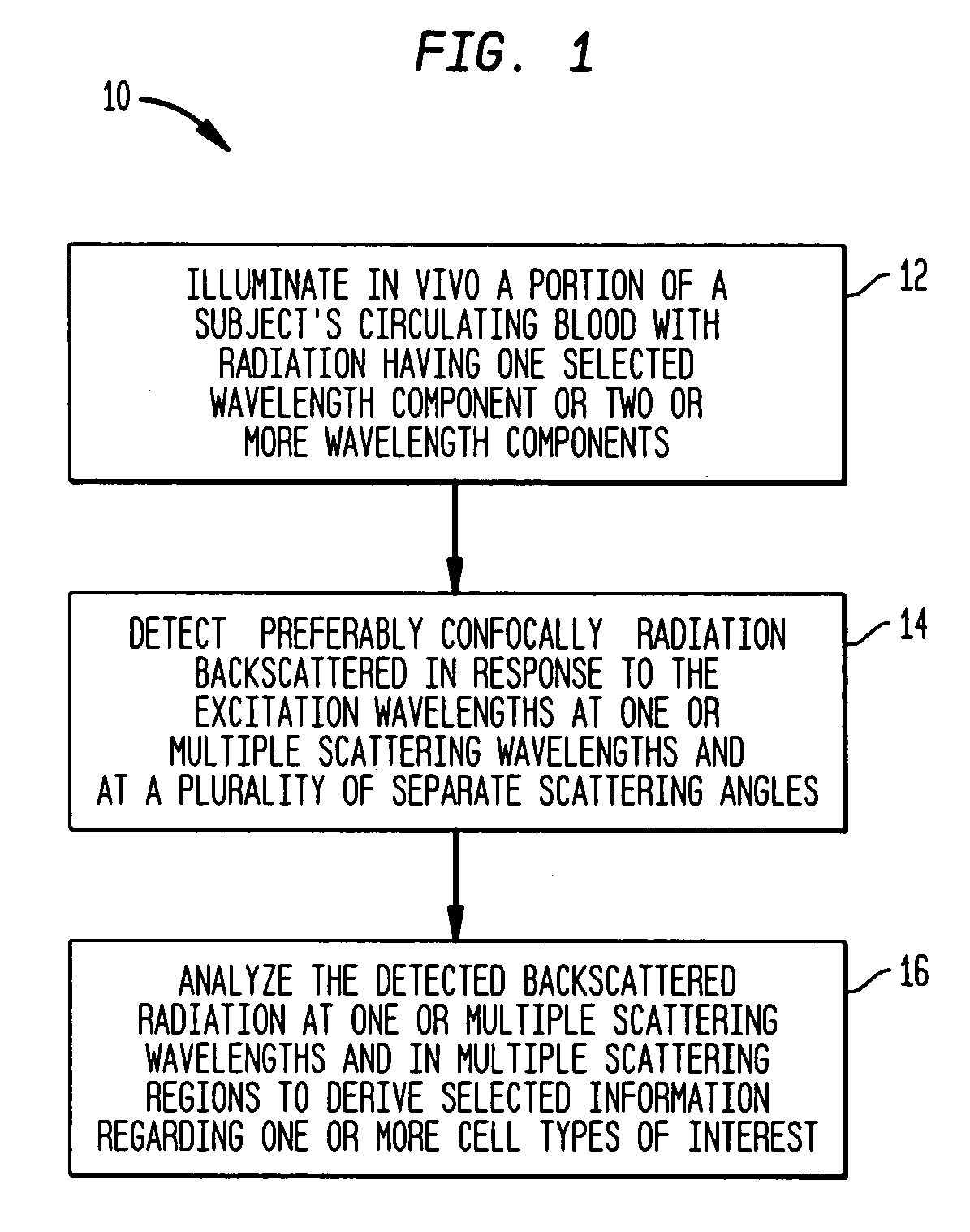
The present invention provides methods and systems for performing in-vivo flow cytometry to obtain desired information regarding one or more cell types of interest flowing through a subject's circulatory system. In one embodiment of the invention, a portion of the subject's circulating blood is illuminated with radiation having multiple wavelength components, and the backscattered radiation generated in response to the excitation radiation is detected at a plurality of scattering angles and analyzed to derive the desired information.
Owner:THE GENERAL HOSPITAL CORP
Fluidic cartridge for cytometry and additional analysis
ActiveUS20180052093A1Shaking/oscillating/vibrating mixersTransportation and packagingCytometryAnalysis sample
The disclosure relates to devices and methods for analyzing particles in a sample. In various embodiments, the present disclosure provides devices and methods for cytometry and additional analysis. In various embodiments, the present disclosure provides a cartridge device and a reader instrument device, wherein the reader instrument device receives, operates, and / or actuates the cartridge device. In various embodiments, the present disclosure provides a method of using a device as disclosed herein for analyzing particles in a sample.
Owner:CYTOCHIP INC
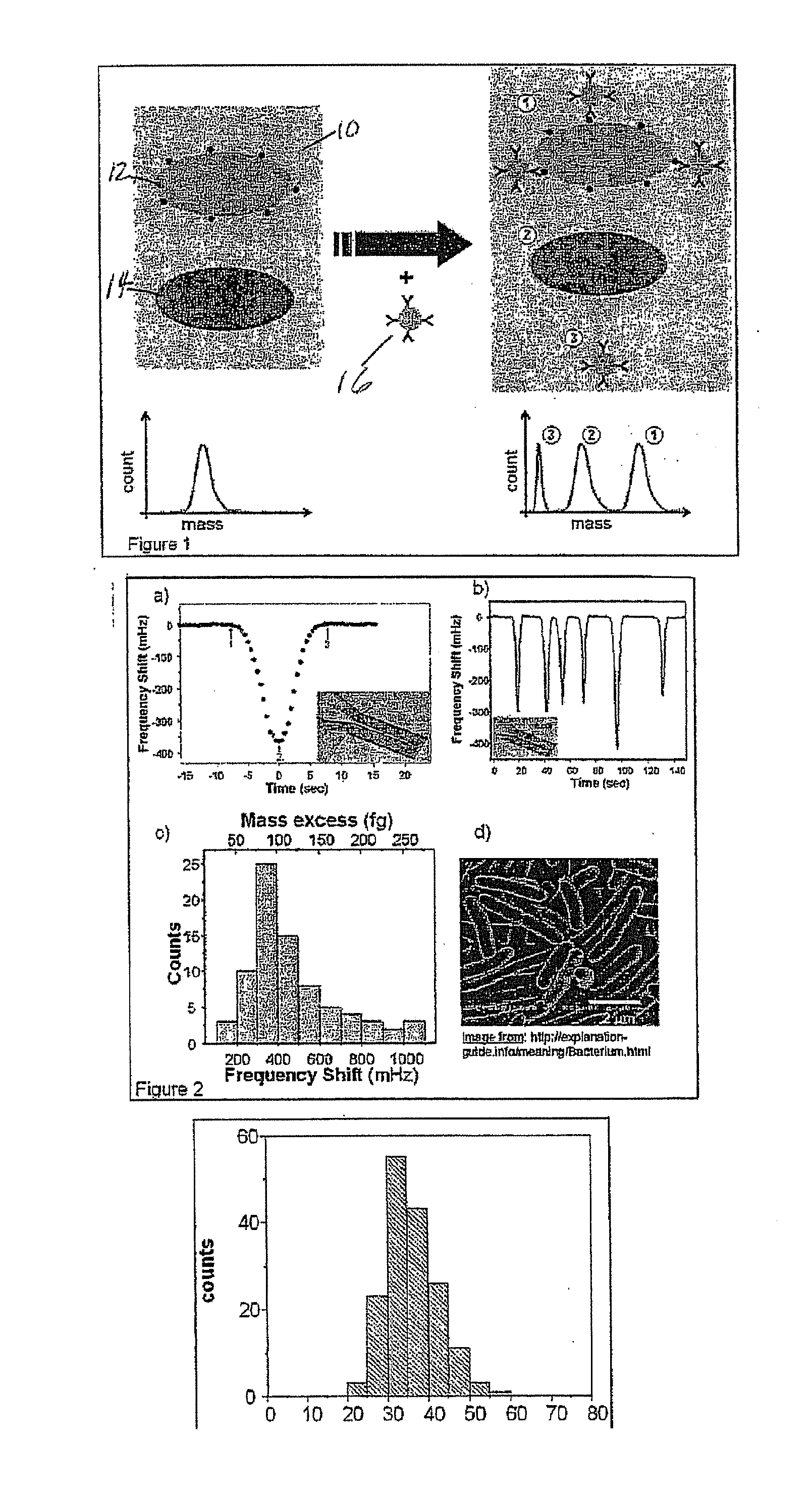
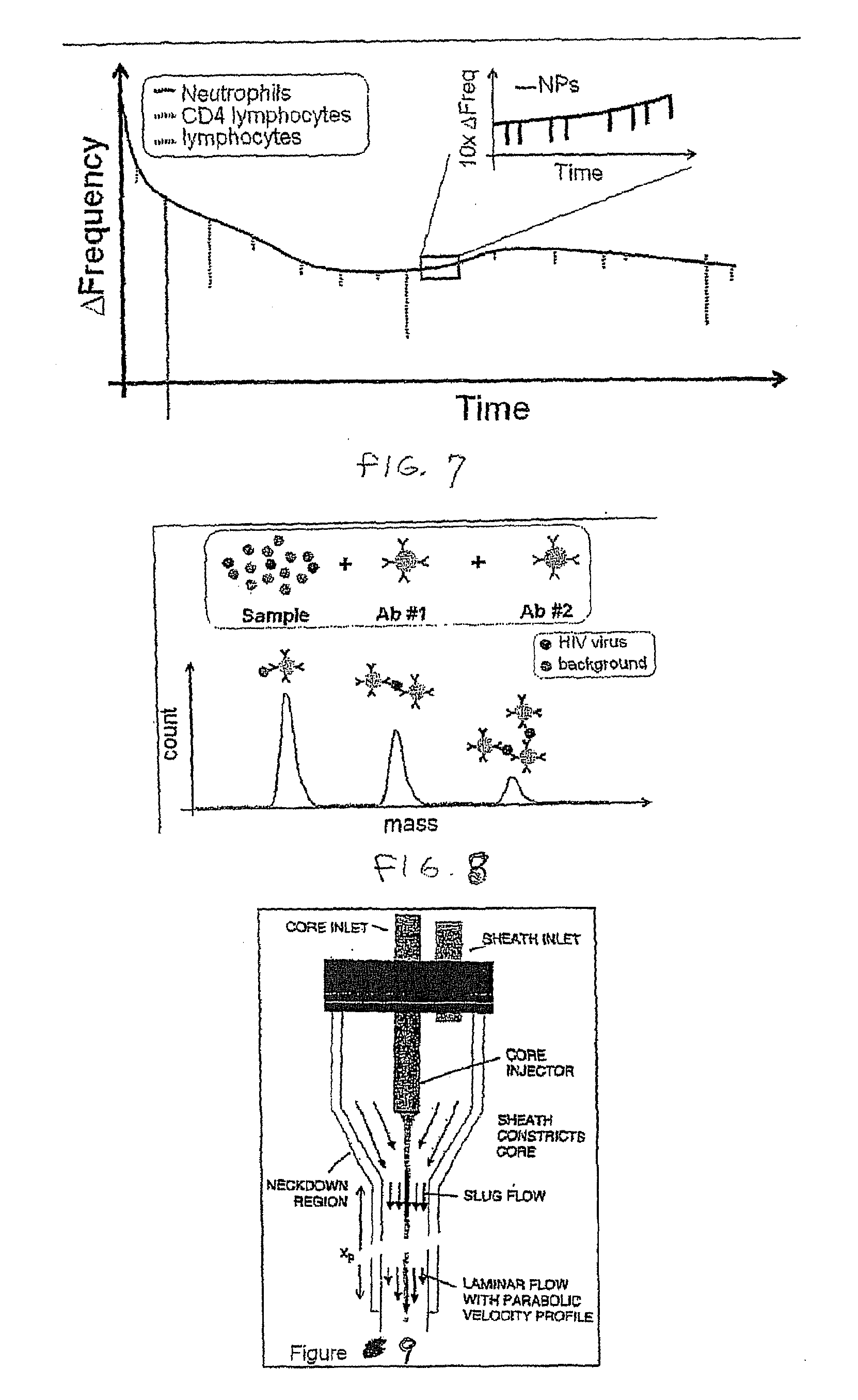
Flow cytometry methods and immunodiagnostics with mass sensitive readout
ActiveUS20100227310A1Packed tightlyImprove throughputMicrobiological testing/measurementBiological testingImmunodiagnosticsNanoparticle
Mass cytometry method. In one aspect, the method includes providing a sample having at least one cell type and mixing the sample with material such as nanoparticles functionalized with affinity molecules for the at least one cell type. The sample is transported through a suspended microchannel resonator to record a mass histogram and a cell count for the at least one cell type is determined from the histogram.
Owner:MASSACHUSETTS INST OF TECH
Flow-cytometry-based method for rapidly measuring heterotrophic bacteria in eutrophic lake
InactiveCN103926189AShorten the timeRapid detection quantityIndividual particle analysisEutrophicationStaining
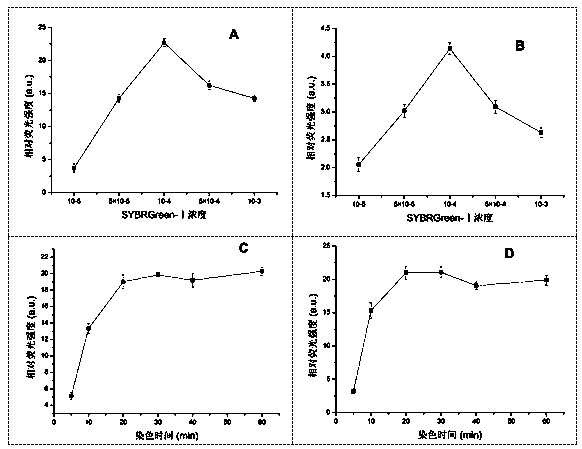
The invention aims to develop a flow-cytometry-based method for rapidly measuring heterotrophic bacteria in a eutrophic lake. The method is a flow-cytometry-based bacterium counting method. The method comprises the following steps of fixing a sample, performing ultrasonic processing, filtering, performing SYBR Green I dyeing, detecting the heterotrophic bacteria by utilizing a flow cytometer, and acquiring forward and lateral scattering light, an SYBR Green I green fluorescence signal and a chlorophyll a red fluorescence signal of autotrophic plankton, wherein the SYBR Green I green fluorescence signal is used for setting a threshold value; and eliminating the influence of the nannoplankton on bacterium detection by utilizing the forward and lateral scattering light, separating the plankton from abiological particles and cellular debris according to the intensity of the SYBR Green I green fluorescence signal, and separating the bacteria from phytoplankton according to the intensity of the chlorophyll a red fluorescence signal of the autotrophic plankton, thereby obtaining the accurate number of the heterotrophic bacteria. The method has the time-saving and labor-saving effects, the large-scale ecological survey can be developed, and the counting precision and accuracy of the bacteria are improved.
Owner:NANJING INST OF GEOGRAPHY & LIMNOLOGY
Five classifying full blood cell analysis method based on vision shape
InactiveCN1945326AIncrease the level of automationImprove accuracyMaterial analysis by optical meansCharacter and pattern recognitionRed blood cellVision based
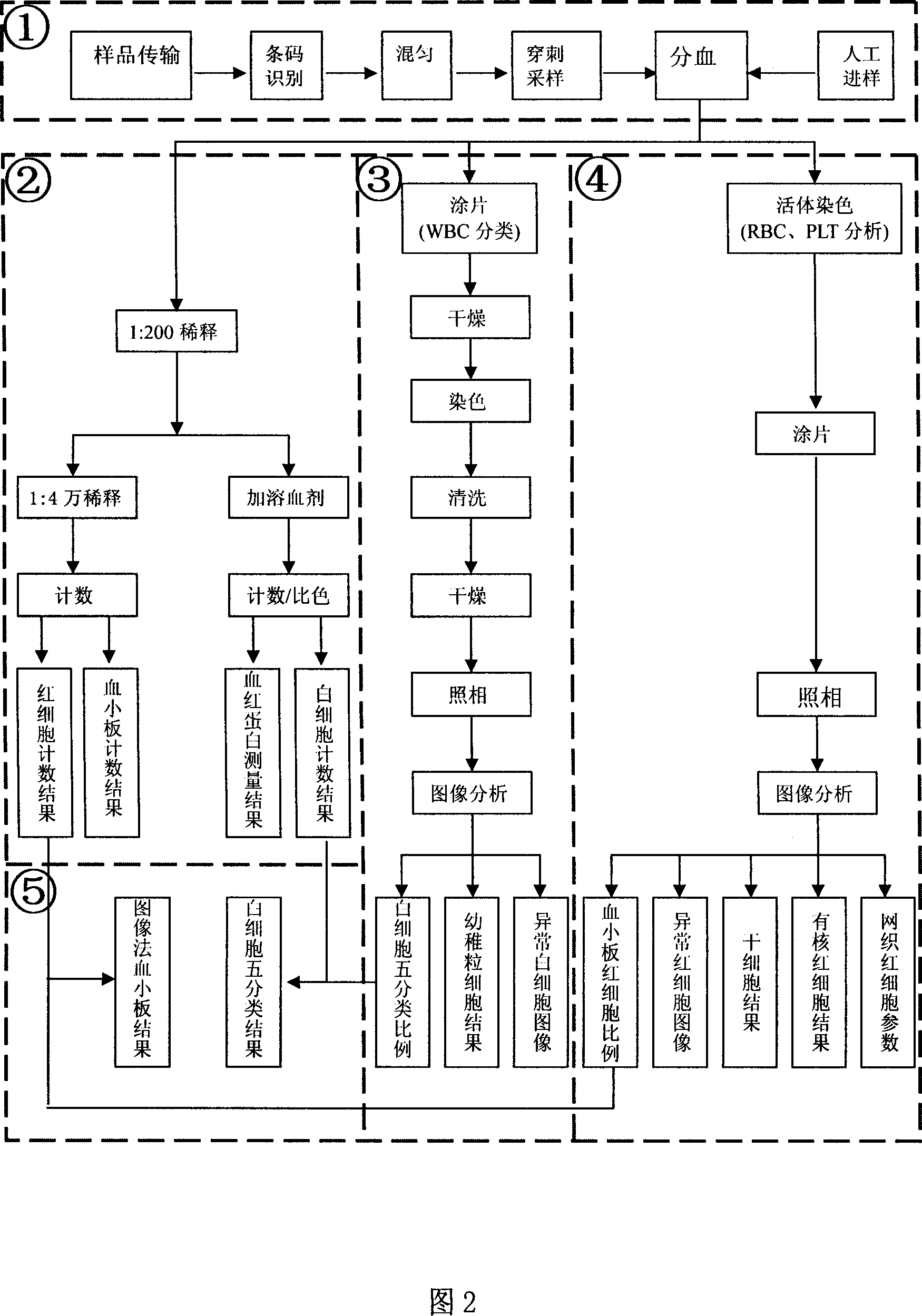
The five classifying whole blood cell analysis method based on visual shape includes analysis in two channels, including one conventional hemacytometry to obtain total number of blood cells, and one image recognizing technological channel to recognize and calculate blood cells of different categories. The results of these two channels are then used in further operation to obtain the numbers of different categories of blood cells. The present invention combines image recognizing technology with conventional hemacytometry, and has high accuracy and high automation.
Owner:TECOM SCI CORP
Apparatuses, systems, methods, and computer readable media for acoustic flow cytometry
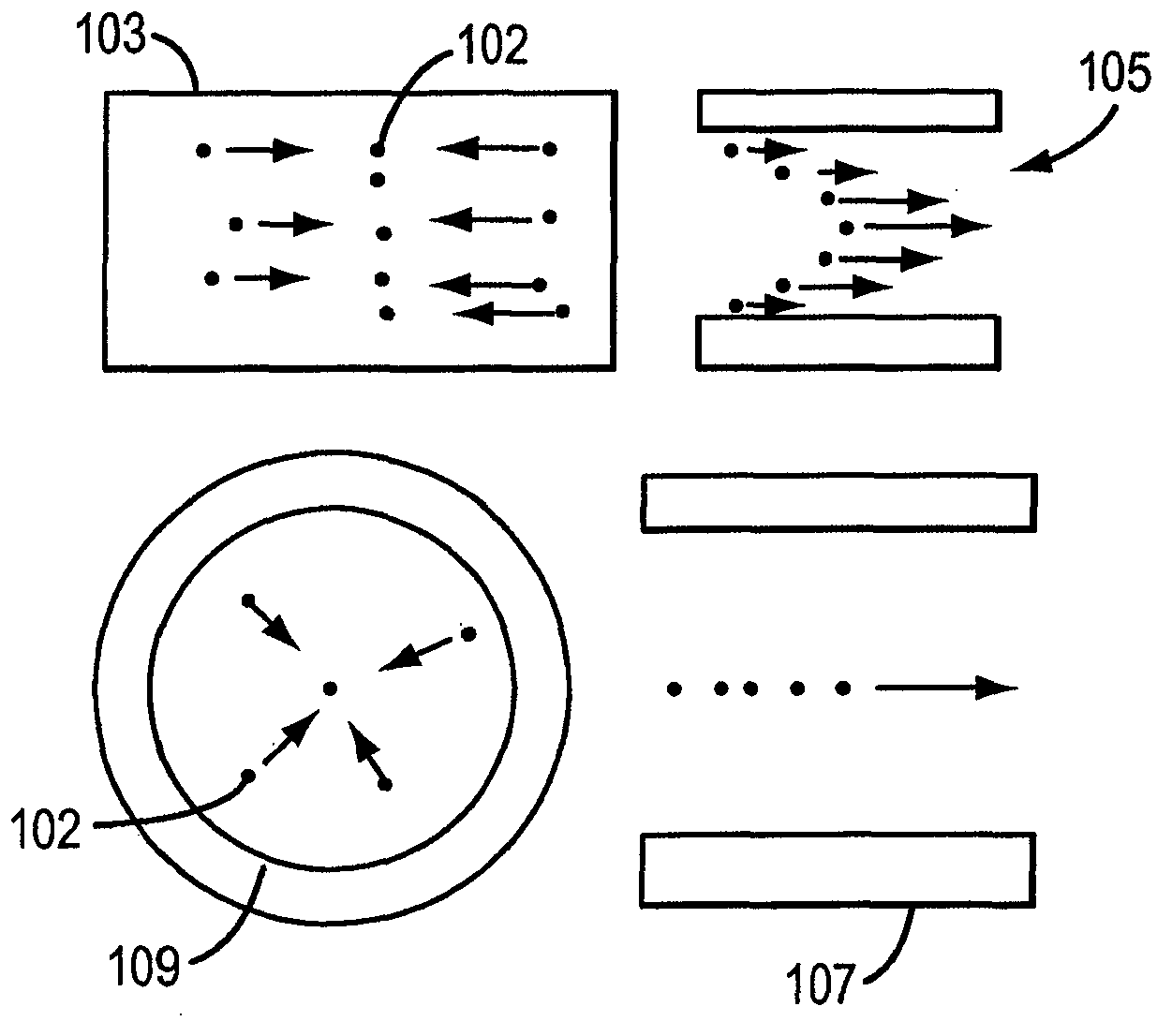
ActiveCN102762990AHigh Throughput AnalysisQuick analysisMaterial analysis by optical meansParticle flowTransducer
A flow cytometer includes a capillary having a sample channel; at least one vibration producing transducer coupled to the capillary, the at least one vibration producing transducer being configured to produce an acoustic signal inducing acoustic radiation pressure within the sample channel to acoustically concentrate particles flowing within a fluid sample stream in the sample channel; and an interrogation source having a violet laser and a blue laser, the violet and blue lasers being configured to interact with at least some of the acoustically concentrated particles to produce an output signal.
Owner:LIFE TECH CORP
Method for detecting the colon bacillus by combining magnetic nanoparticle enrichment with bi-color flow cytometry
InactiveCN101907556ASensitive detectionQuick checkIndividual particle analysisLuminescent compositionsMagnetite NanoparticlesColor flow
The invention relates to a detection method of colon bacillus, particularly discloses a method for detecting the colon bacillus by combining magnetic nanoparticle enrichment with bi-color flow cytometry. The method comprises the following steps of: firstly co-culturing nanoparticles and samples to be measured and enriching composites formed by the magnetic nanoparticles and the samples to be measured under the action of an externally applied magnetic field; then carrying out immune co-culture and secondary enrichment on colon bacillus antibodies labelled by fluorescent nanoparticles and the enriched samples to be measured; then dyeing the secondarily-enriched samples to be measured by using nucleic acid dyes; finally detecting and viewing the dyed samples to be measured by adopting the multi-parameter flow cytometry and a laser confocal microscope, and analyzing and judging detection results of the colon bacillus contained in the samples to be measured according to the number of detected objects with fluorescent double-positive signals. The detection method has the advantages of rapidness, accuracy, sensitivity, low false positive rate, and the like.
Owner:HUNAN UNIV
Diagnostic biomarkers for neurodevelopmental disorders
ActiveUS20070003922A1Microbiological testing/measurementDisease diagnosisClinical psychologyCytometry
The present invention provides methods of identifying biomarkers indicative of the presence of a neurodevelopmental disorder, including an autism spectrum disorder, in an individual, using cytometry and mass spectrometry. The invention further provides methods of using the identified biomarkers to diagnose the presence of a neurodevelomental disorder, including an autism spectrum disorder.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA
Gate-free flow cytometry data analysis
InactiveUS20130226469A1Big amount of dataQuick testDigital computer detailsIndividual particle analysisCytometryData analysis system
Systems, methods, and computer-readable media for determining parameters are provided, as are methods for determining differences in one or more biological response(s) by cell(s) to factor(s). Distances or difference scores are automatically calculated between test data and reference data from a flow cytometer.
Owner:PURDUE RES FOUND INC
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com