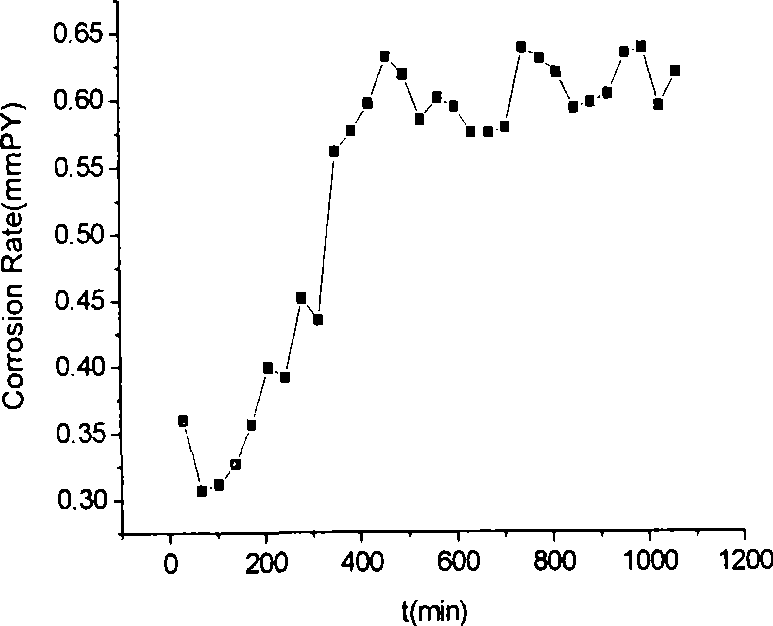
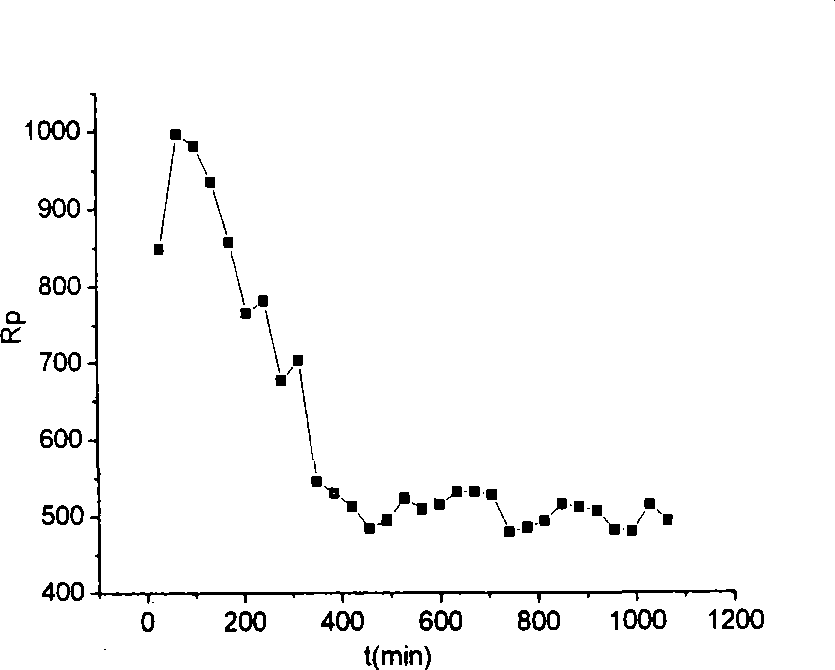
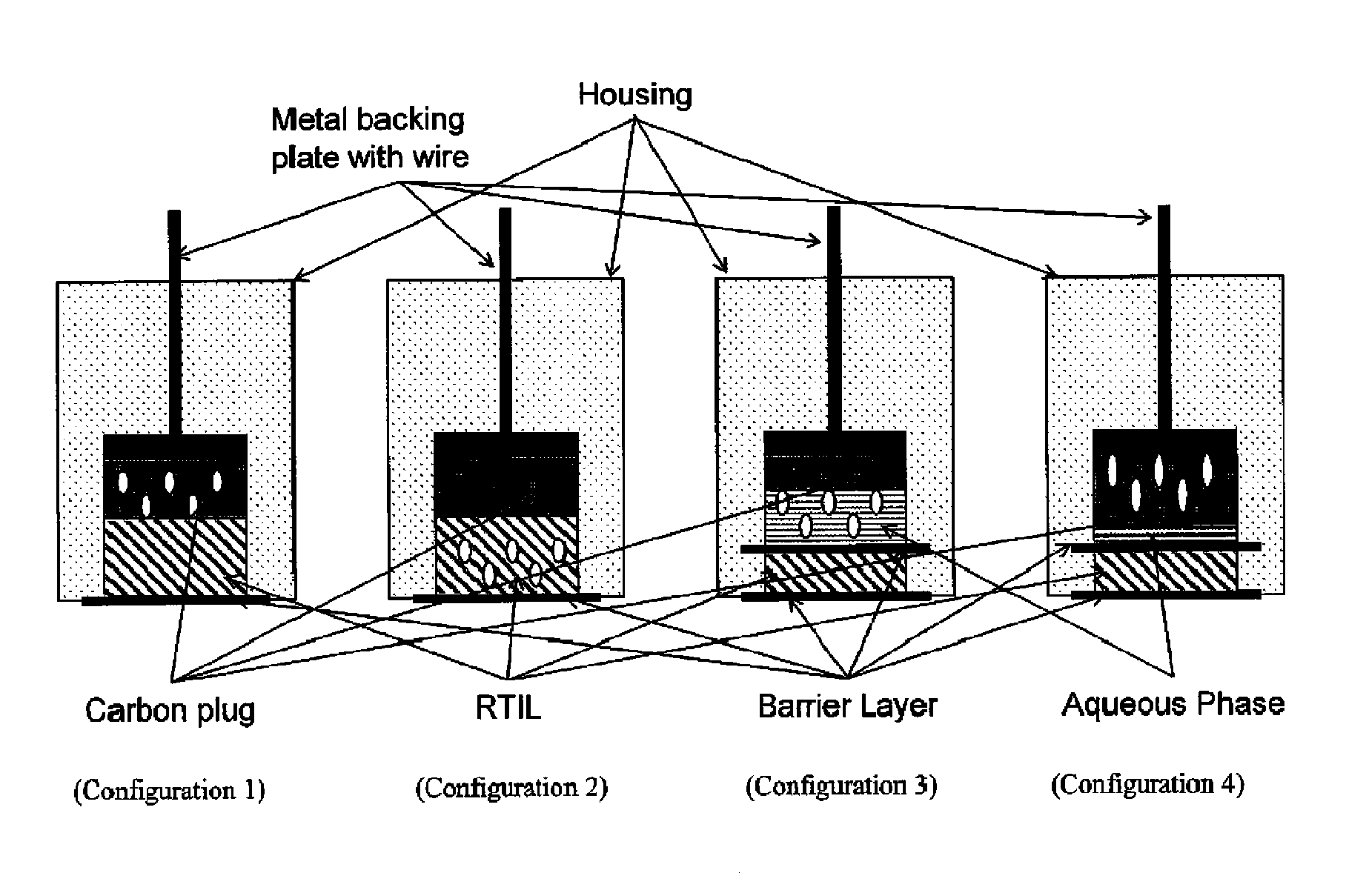
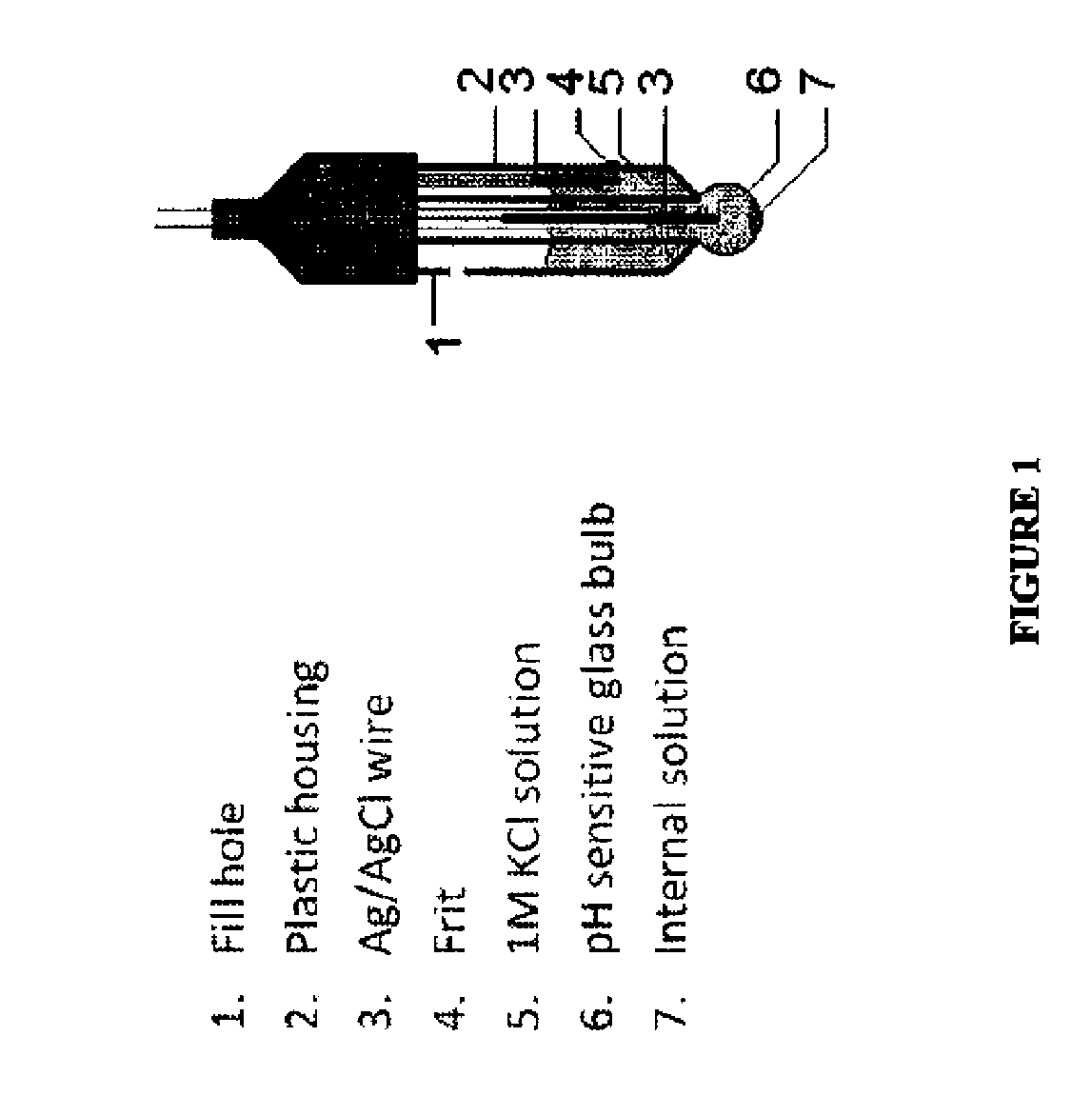
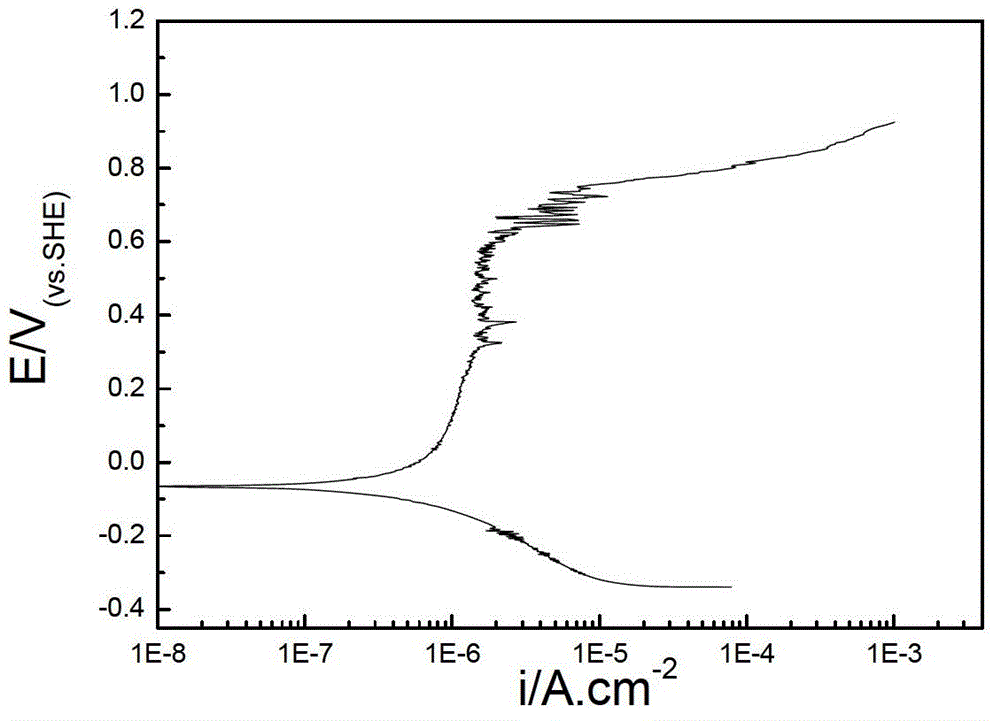
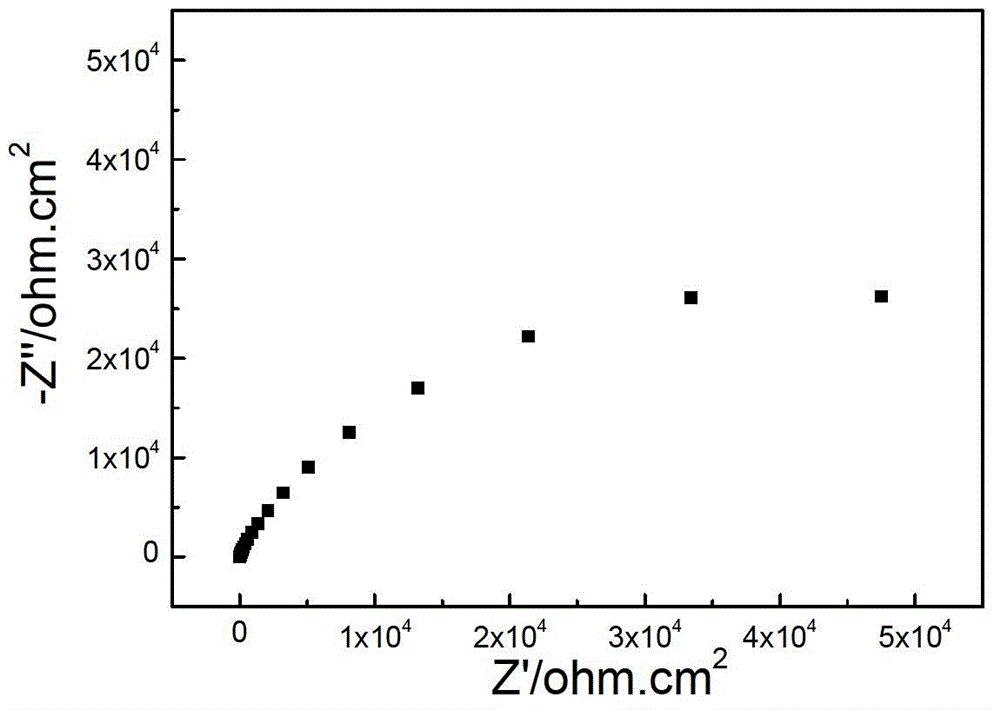
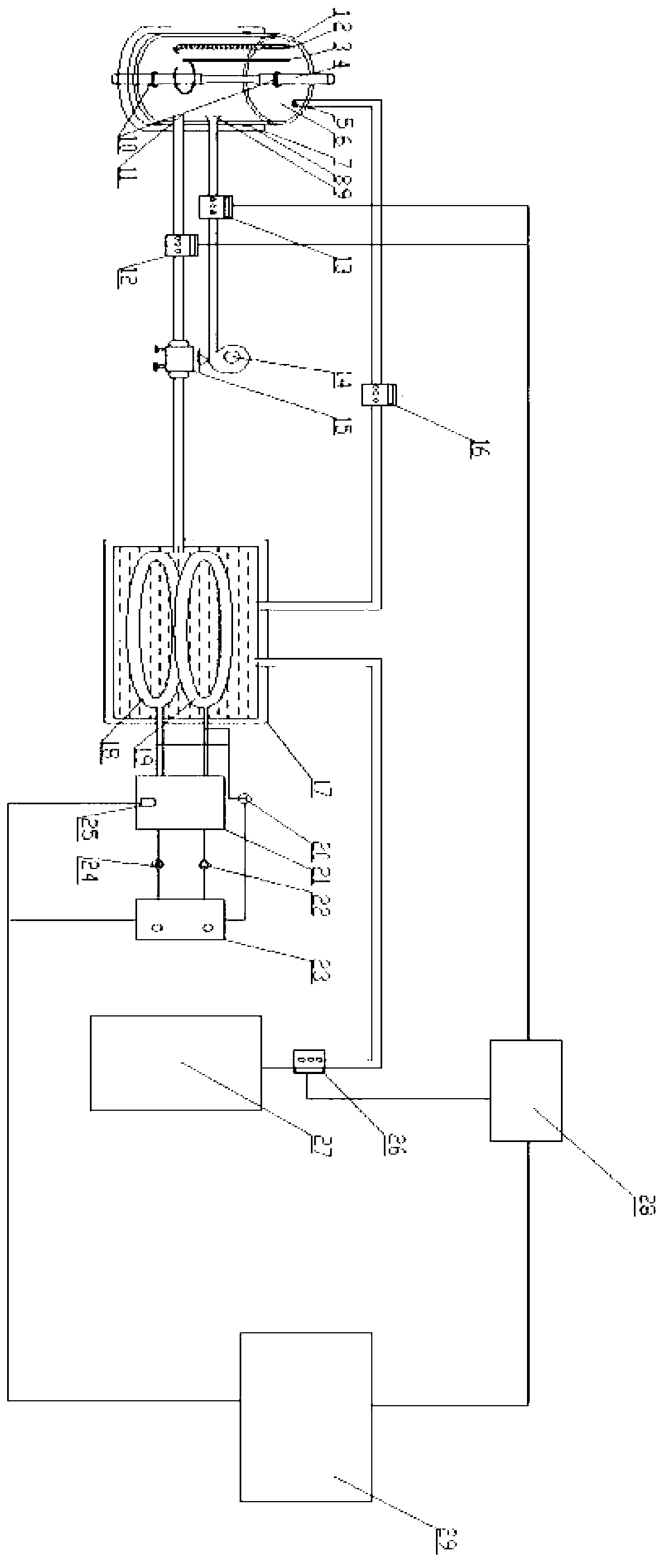
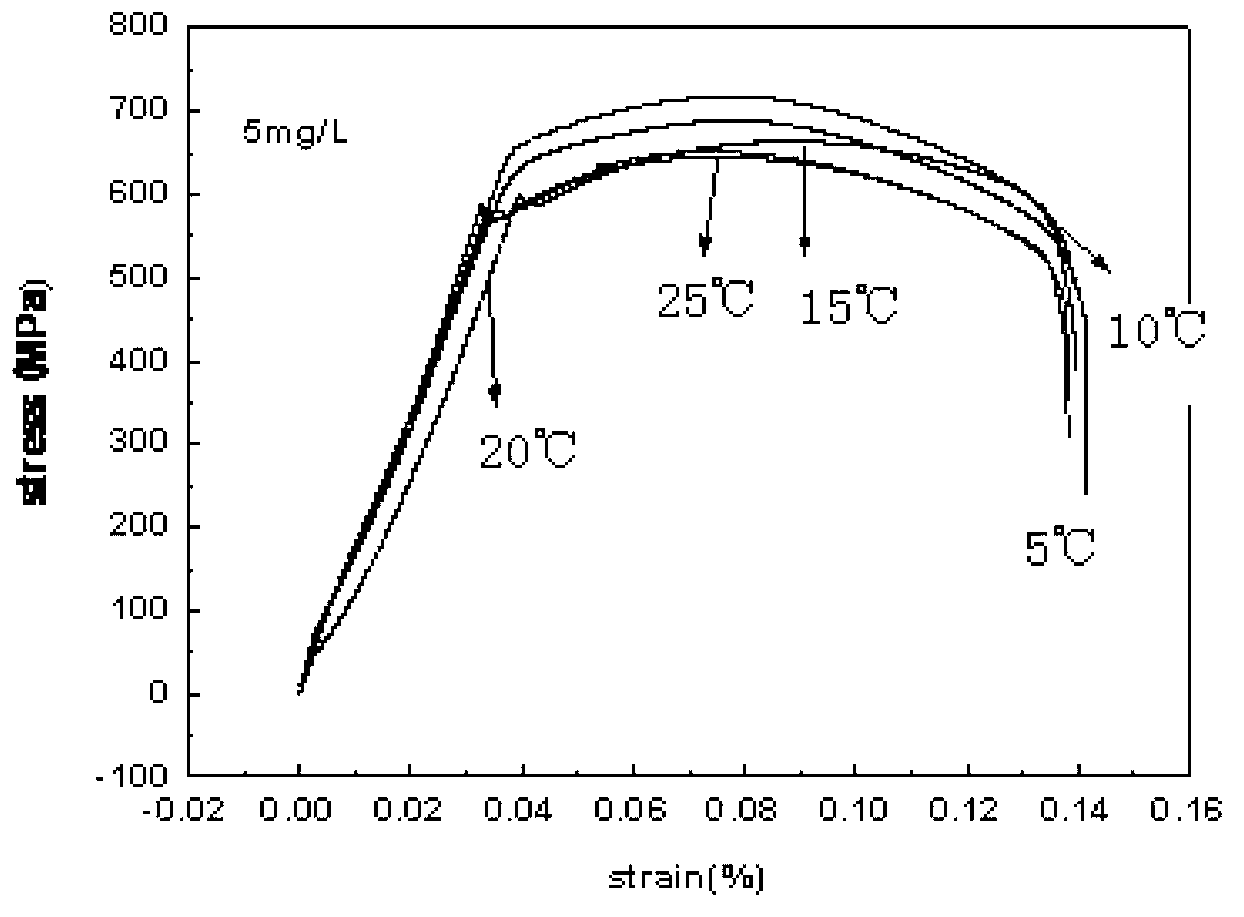
Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
247 results about "Salt bridge" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
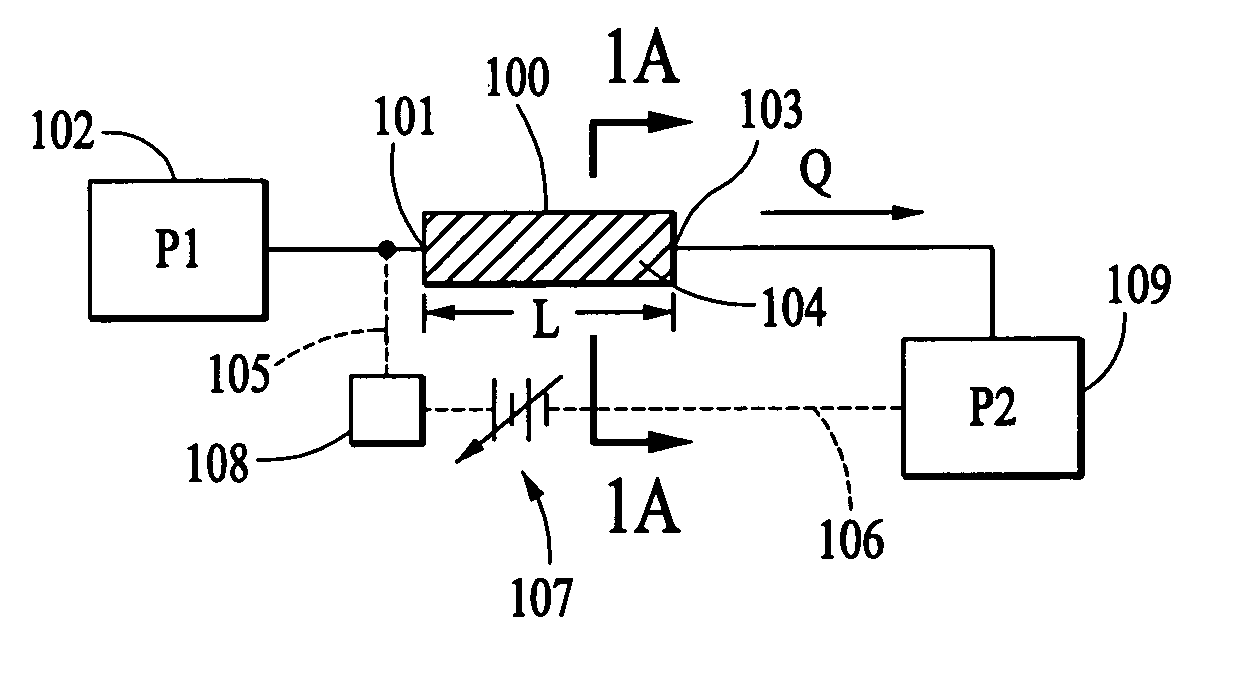
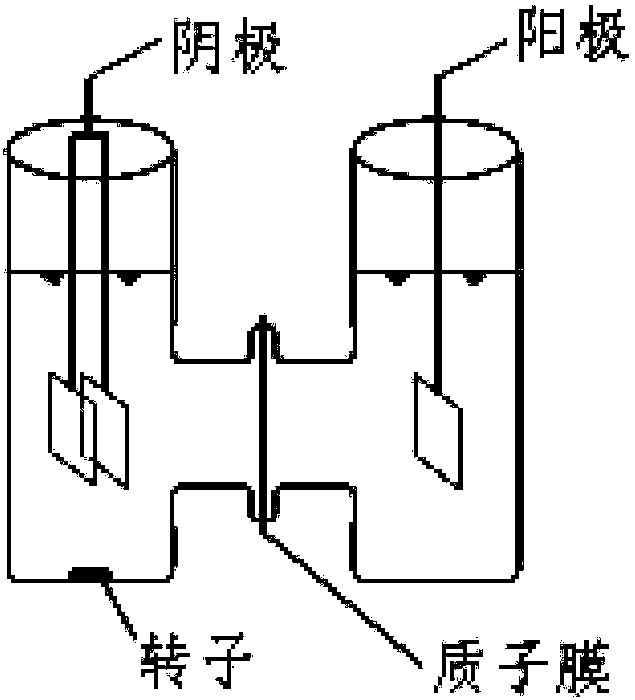
A salt bridge, in electrochemistry, is a laboratory device used to connect the oxidation and reduction half-cells of a galvanic cell (voltaic cell), a type of electrochemical cell. It maintains electrical neutrality within the internal circuit, preventing the cell from rapidly running its reaction to equilibrium. If no salt bridge were present, the solution in one half cell would accumulate negative charge and the solution in the other half cell would accumulate positive charge as the reaction proceeded, quickly preventing further reaction, and hence production of electricity.
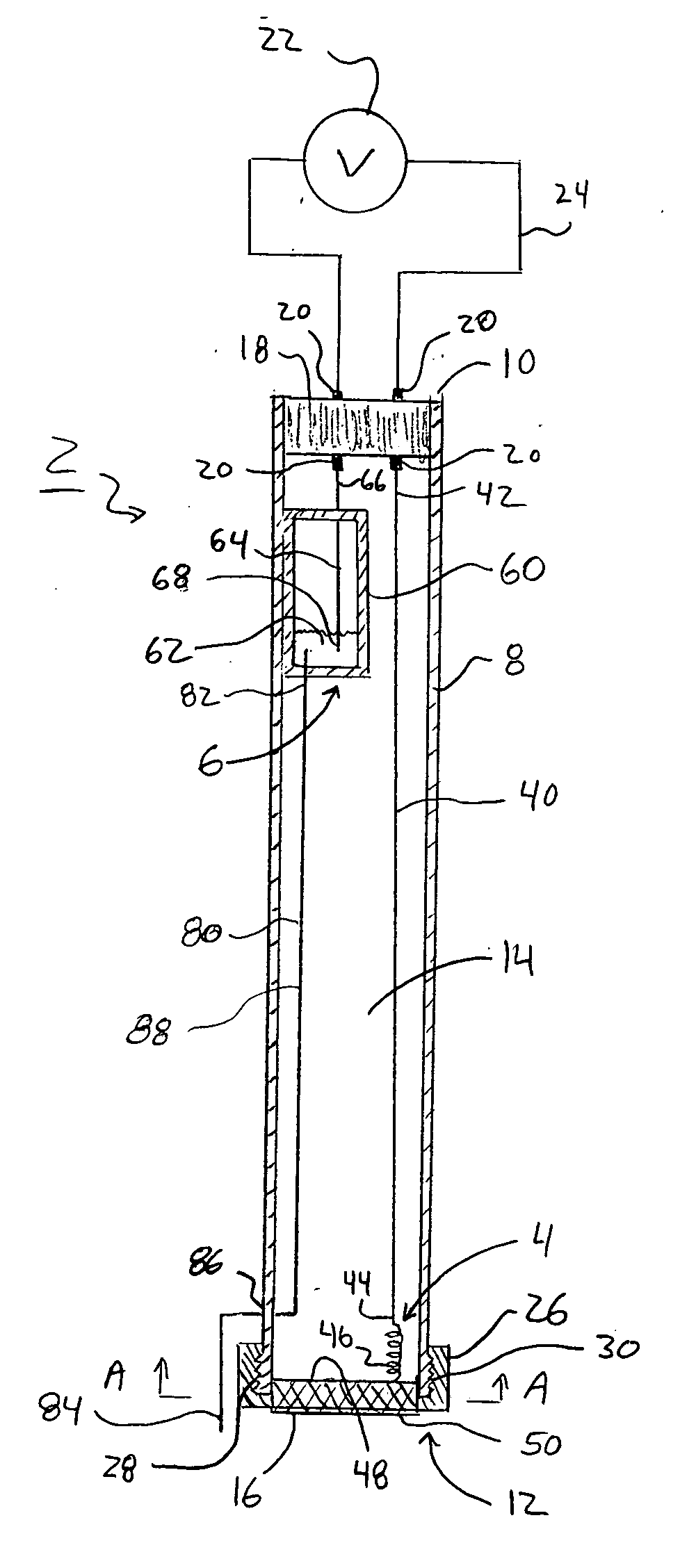
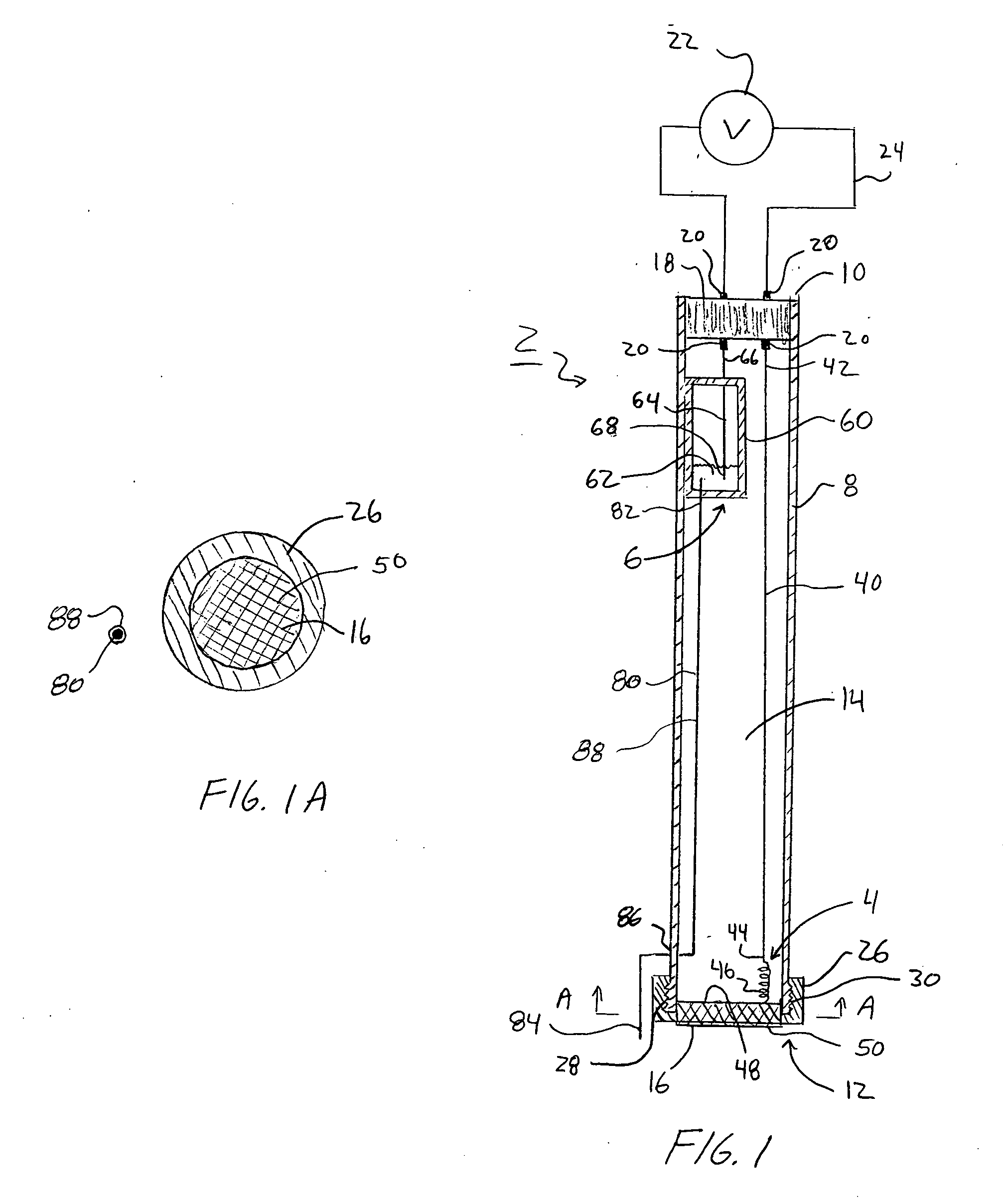
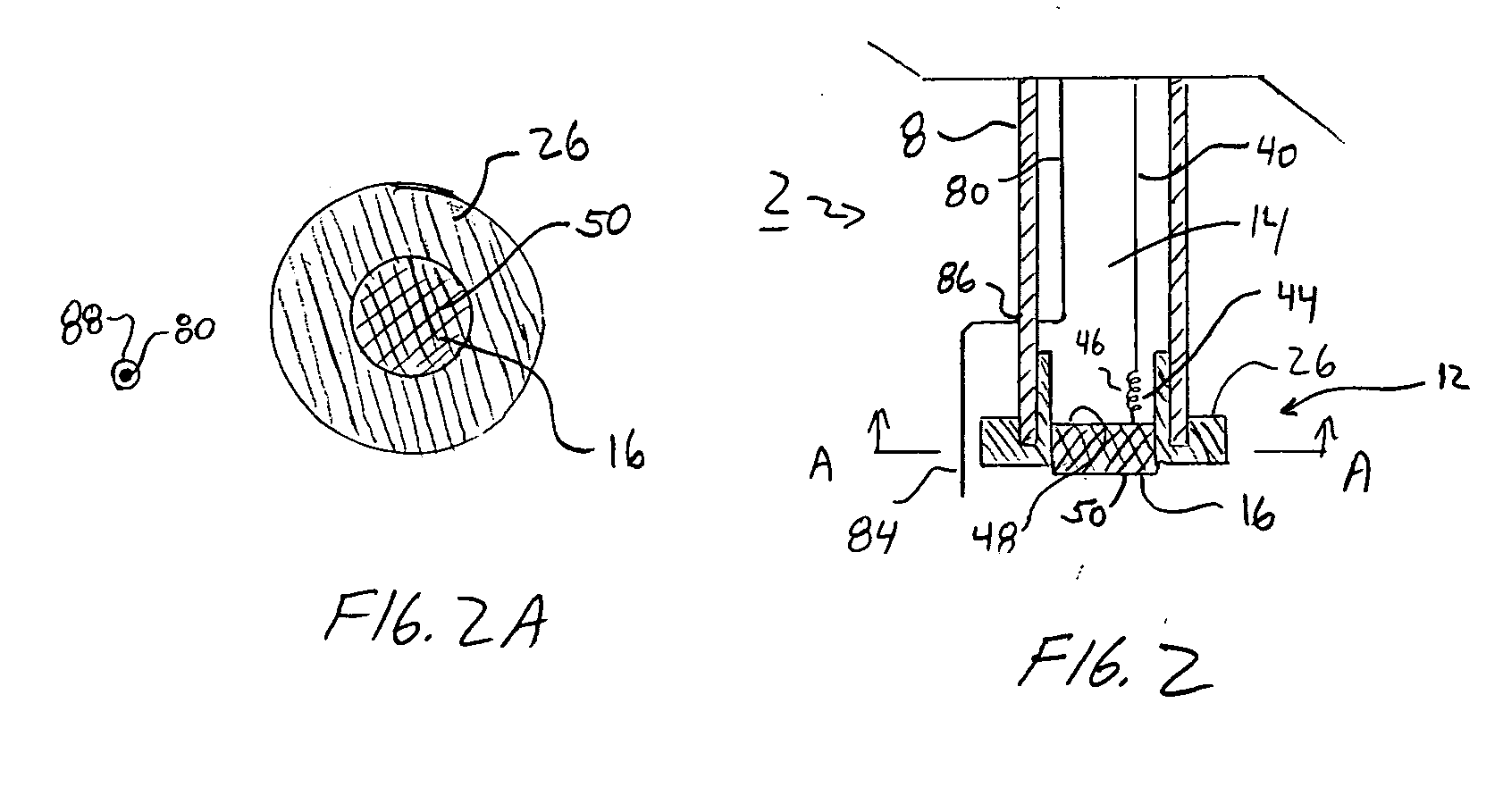
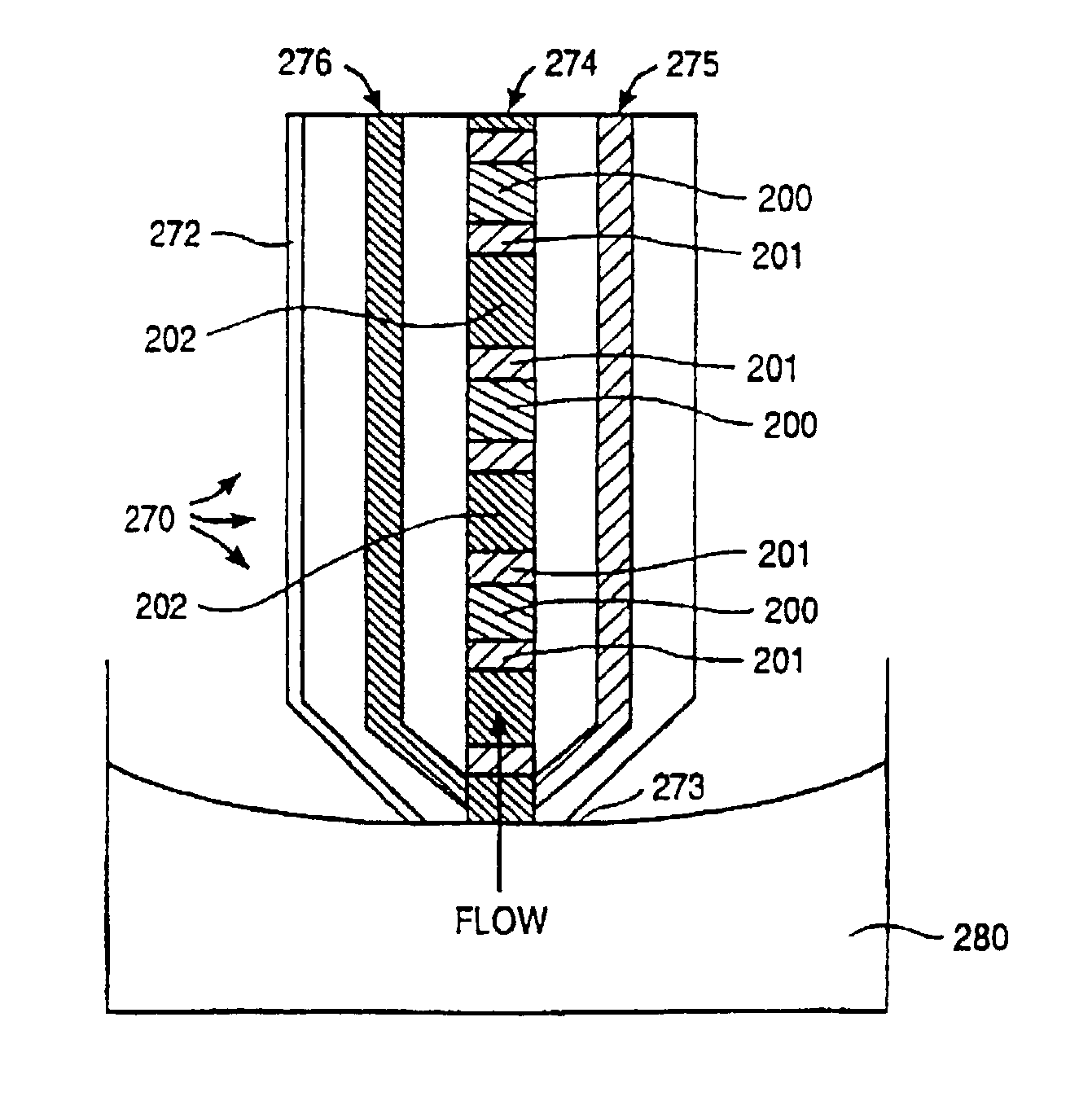
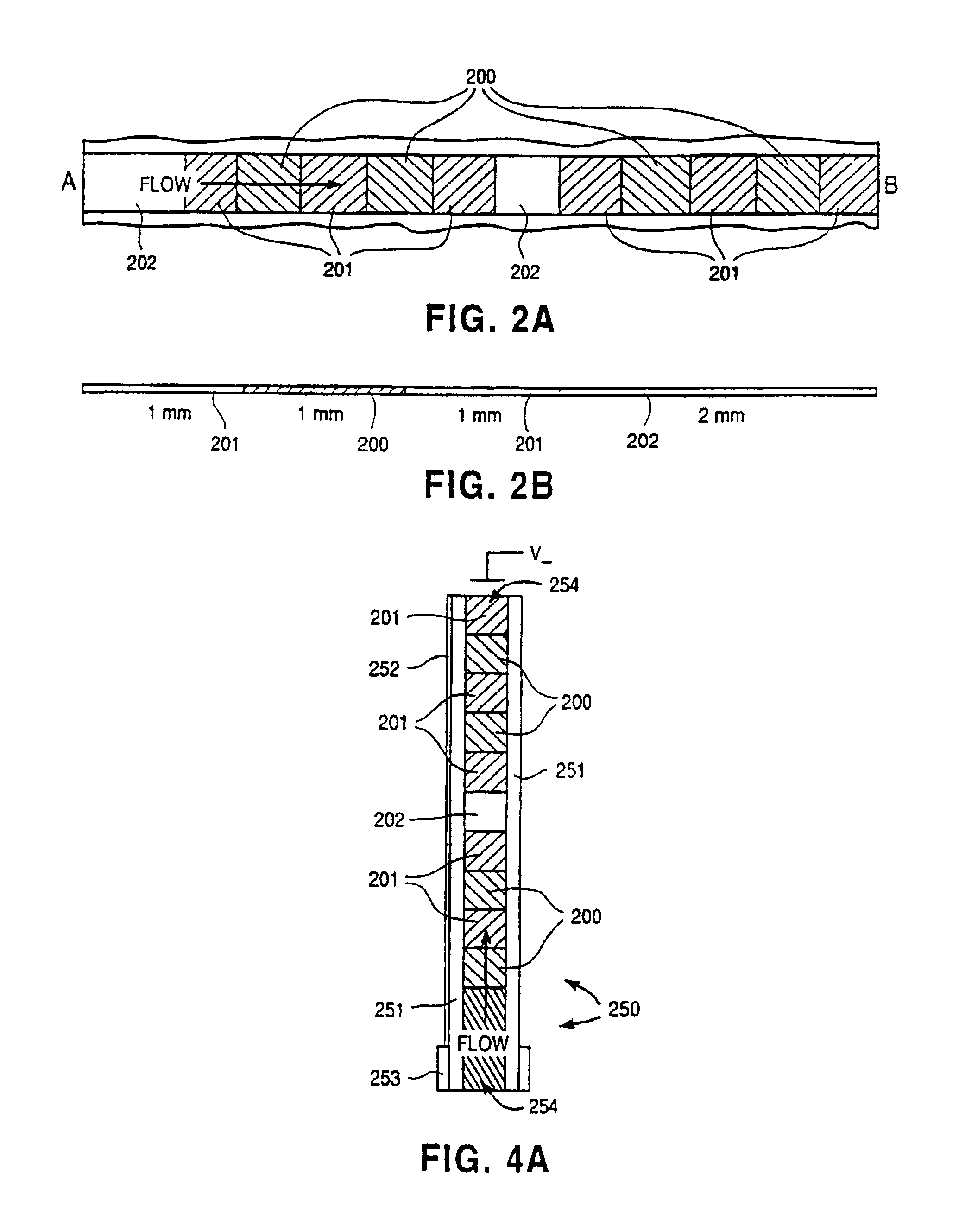
Electroosmotic flow controller
ActiveUS20070000784A1Rapid and accurate flow controlEasy to makeSludge treatmentVolume/mass flow measurementElectricitySalt bridge
Electroosmotic flow controllers and methods of fluid flow control are described. The invention uses an electroosmotically generated flow component in conjunction with a pressure driven flow component to modulate fluid flow. The devices and methods of the invention may include salt bridges for making electrical connection between a power supply and a channel filled with a porous dielectric material and a fluid. Embodiments including flow controllers and flow splitters are described as is their use in a variety of fluid handling applications.
Owner:SCIEX
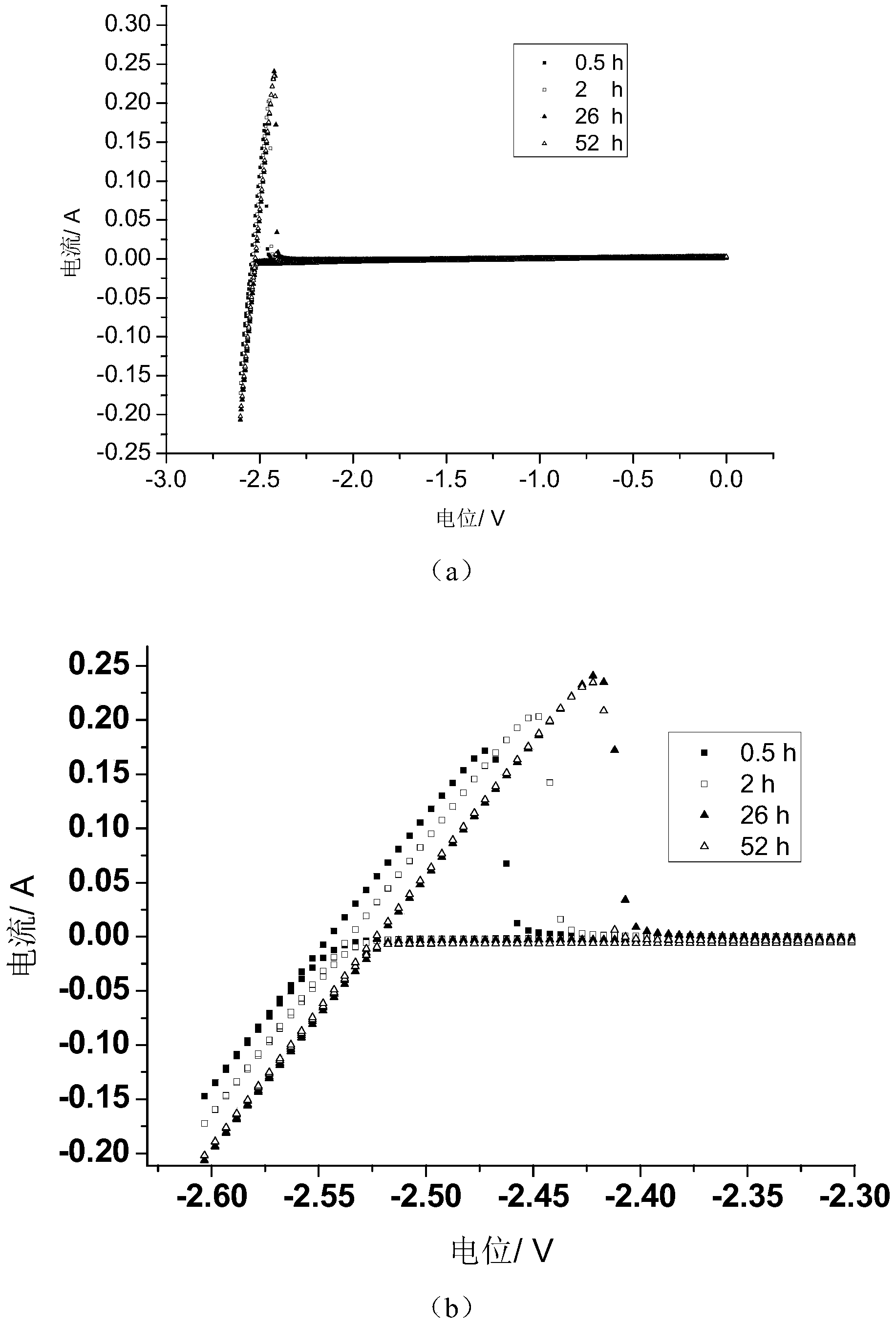
Method for testing electrochemical corrosion of welded pipe seam in high-stress state and sample of welded pipe seam
InactiveCN101608995ACorrosion Resistance EvaluationFix damageWeather/light/corrosion resistanceMaterial electrochemical variablesSalt bridgeAuxiliary electrode
The invention relates to a method for testing electrochemical corrosion of a welded pipe seam in a high-stress state, which utilizes an electronic universal testing machine, an electrolytic cell component comprising a working electrode, an auxiliary electrode, a reference electrode, a salt bridge and the like, and an electrochemical workstation. Under a load stress of between 0 and 800 MPa, the stress change caused by stress relaxation is corrected regularly by a constant potential method or a constant current method to test the circumferential tensile stress of the welded pipe seam and the circumferential tensile stress of the working electrode. A tensile sample is wide and thick at both ends and narrow and thin in the middle part and is provided with connection holes at both ends. A groove corrosion depth d1 and an average corrosion depth d2 of the working electrode are tested under different loads, so a groove corrosion susceptibility coefficient alpha, alpha=d1 / d2, of the working electrode in practical application can be obtained. The method has no stress relaxation, and the stress is convenient to regulate during test; the sample is free from generating plastic deformation or detachment under the load of high stress, and can be used for corrosion test under the condition of high stress; and the electrochemical workstation can be made full use for testing.
Owner:BAOSHAN IRON & STEEL CO LTD
Electrolytic extraction and detection method of nonmetallic inclusion in steel by utilizing organic solution
ActiveCN102213654AReduce and stabilize liquid junction potentialAvoid destructionElectrolysis componentsPreparing sample for investigationFiltrationSalt bridge
The invention relates to an electrolytic extraction and detection method of nonmetallic inclusion in steel by utilizing an organic solution. The method comprises the following process steps: (1) preparing electrolyte; (2) preparing and electrolyzing a steel sample: soaking the steel sample containing the inclusion into the electrolyte in an electrolytic cell; arranging a salt bath beside the electrolytic cell; erecting a salt bridge between the salt bath and the electrolytic cell; inserting a calomel electrode into the salt bath; inserting a calomel electrode in the salt bath; using the positive electrode of the steel sample, connected with a direct current stabilized power supply, as the anode, using a platinum wire as an electrolysis cathode, charging inert gas, particularly referring to argon; and (3) separating: pouring the electrolyte left after the electrolysis of the steel sample in the step (2) into a funnel which is filled with filter paper; arranging a vacuum filtration device which is loaded with a polytetrafluoroethylene membrane at the position tightly attached to the liquid down port of the funnel; separating the inclusion from the steel sample under the state that the vacuum filtration device is vacuumized; and transferring the polytetrafluoroethylene membrane which is distributed with the inclusion to a scanning electron microscope for detection. In the method provided by the invention, the inclusion can be extracted out of the steel without being damaged; and the three-dimensional shape of the inclusion is directly observed.
Owner:JIANGYIN XINGCHENG SPECIAL STEEL WORKS CO LTD
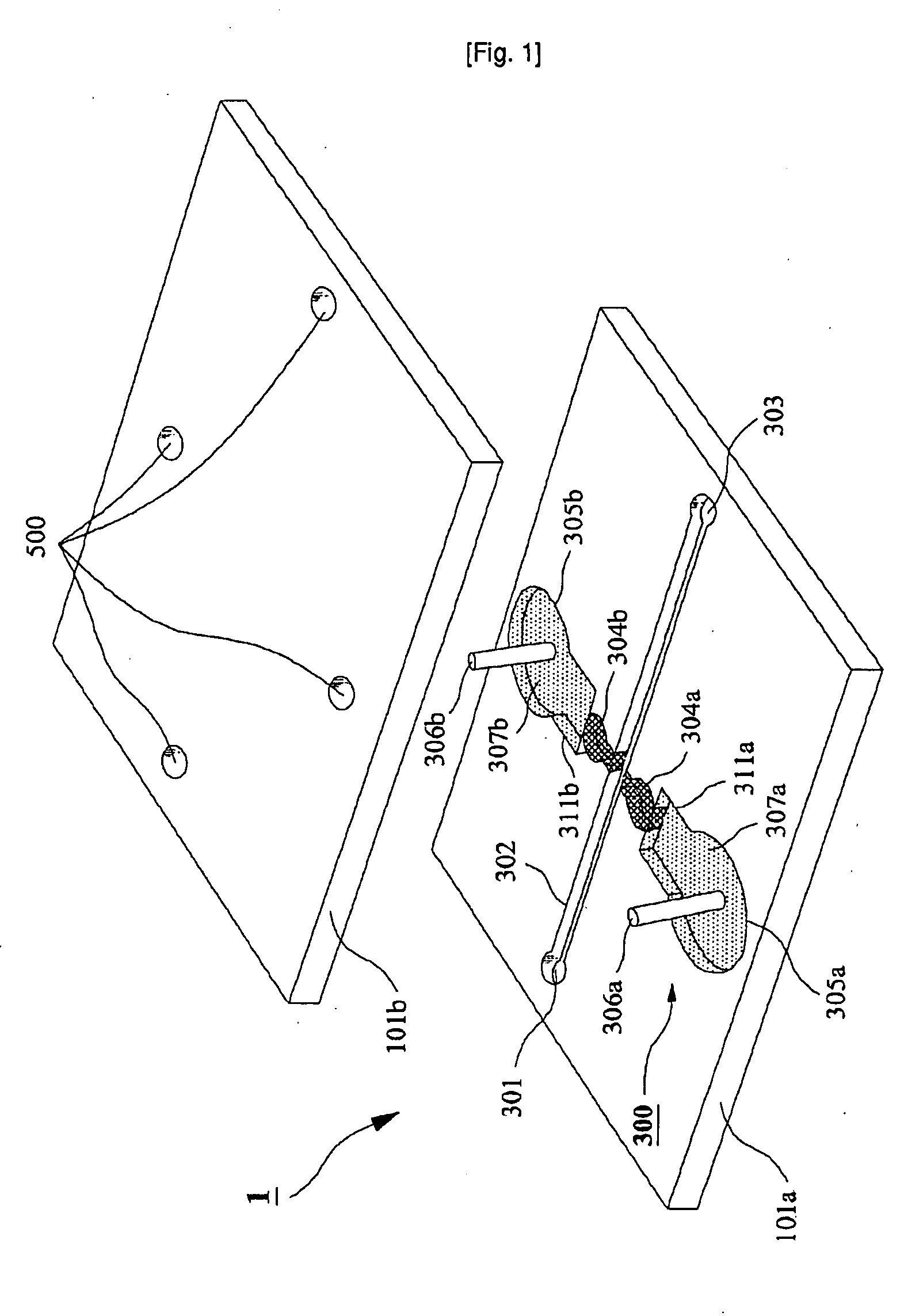
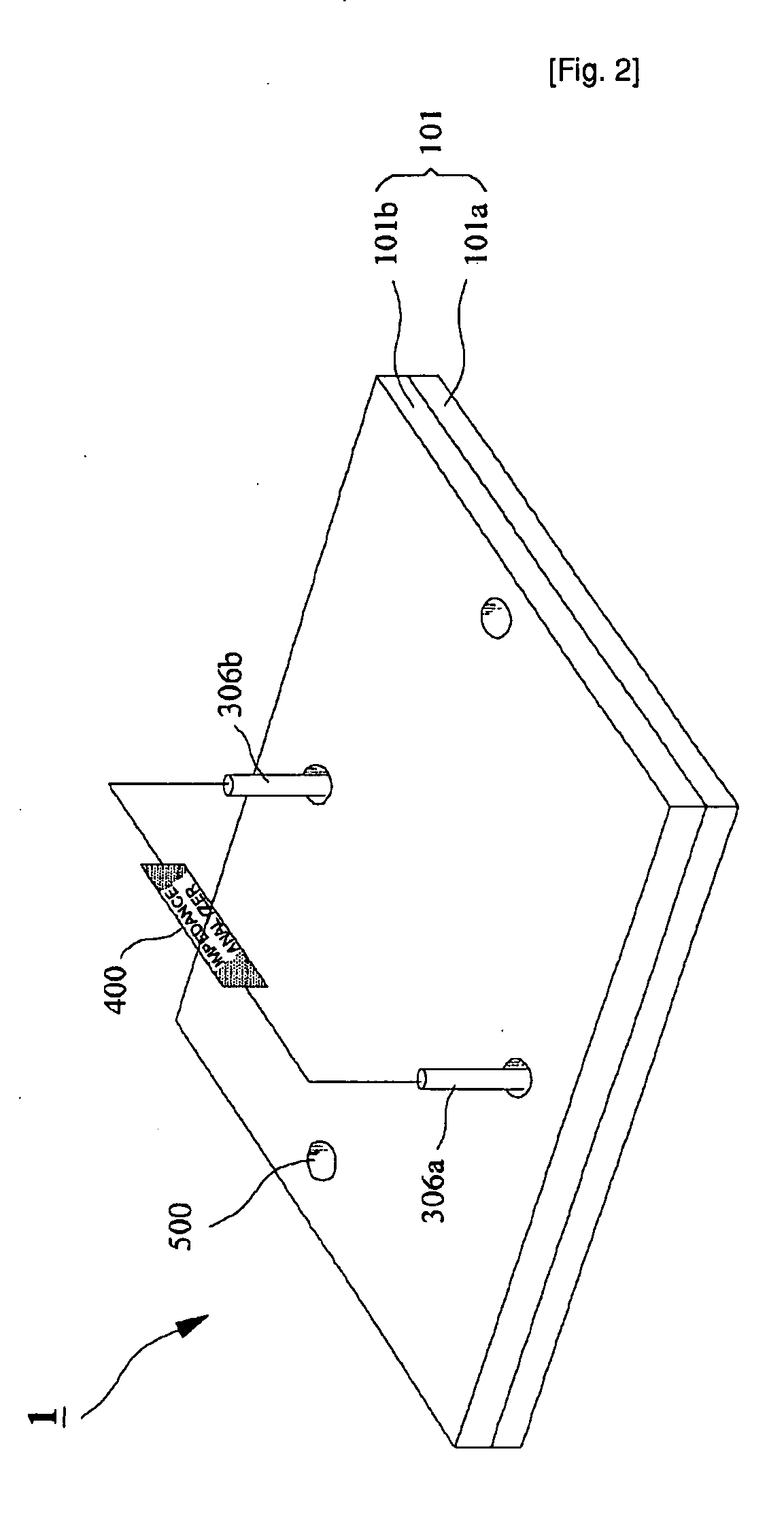
Microchip For Use In Cytometry, Velocimetry And Cell Sorting Using Polyelectrolytic Salt Bridges
InactiveUS20090104689A1Bioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsPolyelectrolyteElectrolysis
The present invention relates to a microchip using polyelectrolyte salt bridge for cytometry, velocimetry, and cell sorting. The microchip comprises; a) an inlet for solution to be analyzed, b) a microchannel which provides a moving passage for solution to be analyzed, c) at least one outlet for solution to be analyzed which has passed through the moving passage, d) at least one electrode system comprising a first and a second salt bridges connected to the microchannel (the two salt bridges face each other), and a first and a second reservoirs connected to said each salt bridge (the reservoir comprises electrode and standard electrolyte solution). The microchip detects analytes in the solution to be analyzed (for example, a cell) by detecting change of impedance. In detail, anion in the standard electrolyte solution, which is comprised in the first reservoir, moves from the first salt bridge to the second salt bridge across the microchannel. Impedance change occurs by interference of anion moving across the microchannel and the change can be detected by impedance analyzer connected to electrodes in the first and the second reservoirs.
Owner:SEOUL NAT UNIV R&DB FOUND
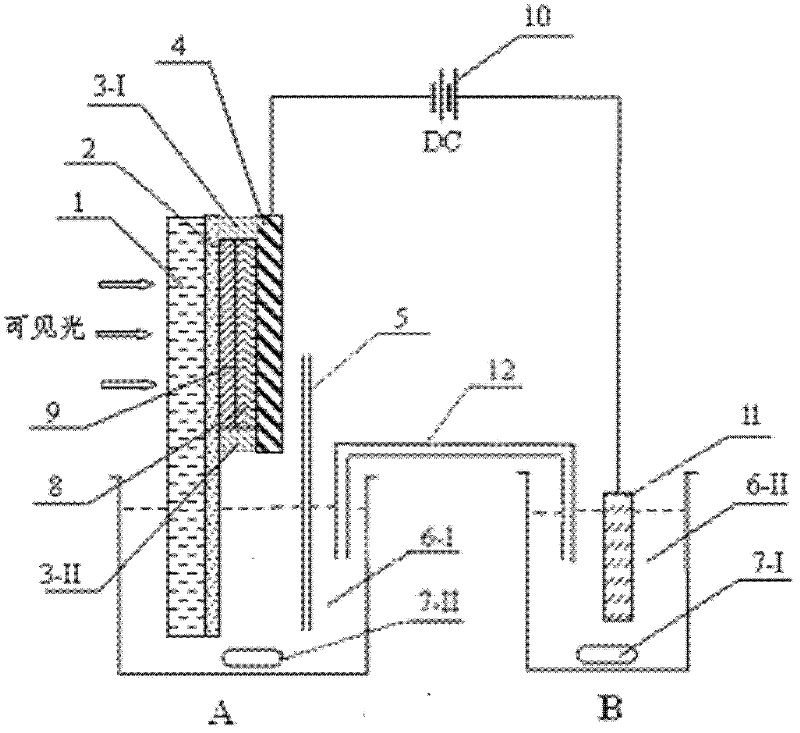
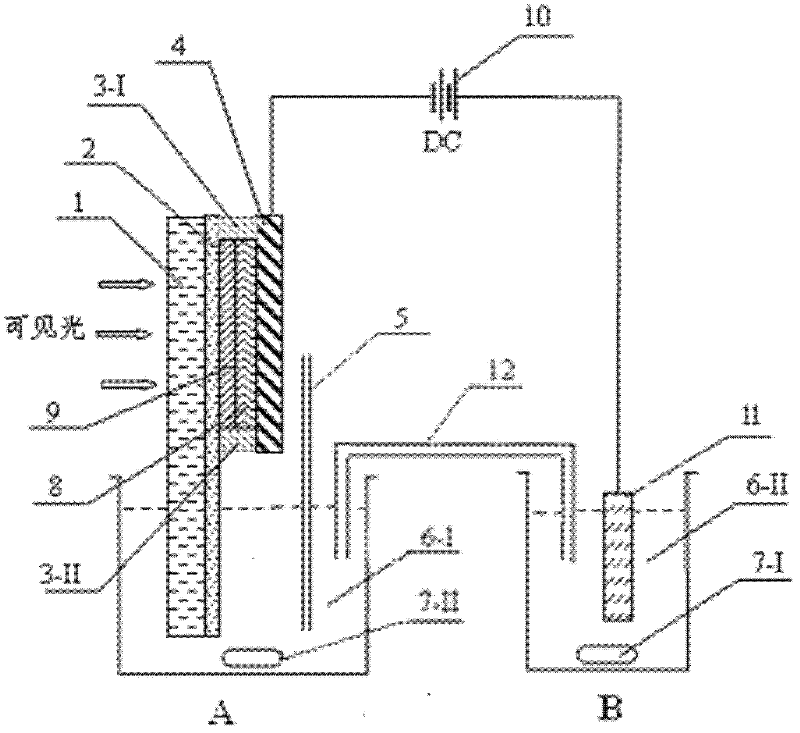
Method and device for removing organic matters from water by using double-pool double-effect visible light in response to photo-electro-Fenton reaction
InactiveCN102092820AImprove stabilityIncrease concentrationWater/sewage treatment by oxidationSalt bridgePotassium
The invention discloses a method and a device for removing organic matters from water by using double-pool double-effect visible light in response to a photo-electro-Fenton reaction. The device comprises a cathode pool, an anode pool, a saturated potassium chloride (KCl) salt bridge, a visible light response semiconductor membrane material anode, a carbon-iron composite material oxygen negative electrode, an air pump, a magnetic stirrer, a direct current stabilized voltage power supply and a visible light source, wherein an anode performs photoelectrocatalysis under the actions of visible light and anode bias voltage to remove organic pollutants from water; the carbon-iron composite material oxygen negative electrode performs cathode potential reduction on O2 under the conditions of external voltage and introduced air to produce hydrogen peroxide which is subjected to an electric Fenton reaction to generate active substances such as hydroxyl radicals and the like capable of effectively removing the organic matters from the water; electrons produced by a photoanode migrate towards an oxygen cathode under the action of anode bias voltage; the O2 is reduced by the electrons on the cathode to generate more H2O2; and the H2O2 produced on the cathode cannot migrate to the anode pool for consumption, so that higher H2O2 concentration is ensured, and the oxidation reaction of the organic matters by electric Fenton is ensured. The method and the device are suitable for treating various types of organic waste water.
Owner:HUAZHONG NORMAL UNIV
Medical type all-solid potassium ion selectivity sensor and preparation method thereof
InactiveCN102636532ASimple structureSimple processMaterial electrochemical variablesHigh volume manufacturingSalt bridge
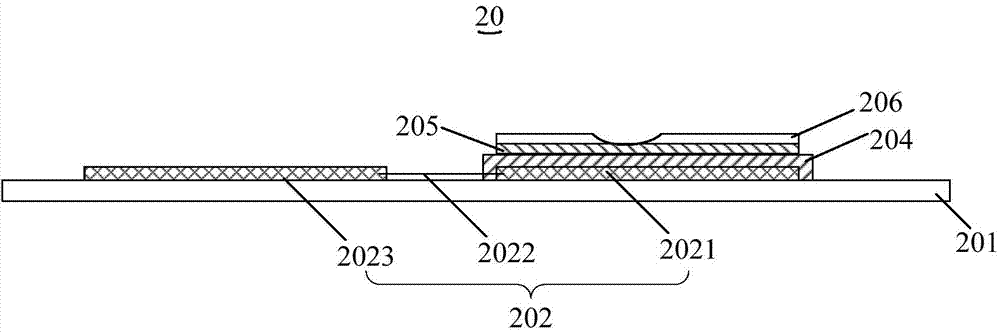
The invention discloses a medical type all-solid potassium ion selectivity sensor and a preparation method thereof. The medical type all-solid potassium ion selectivity sensor comprises a substrate, two potassium ion selectivity working electrodes which are completely the same in structure and arranged side by side, an insulating layer and a salt bridge. Without a constant-potential reference electrode in the conventional sense, one of the two potassium ion selectivity working electrodes is used to be matched with a potassium standard solution to realize the function of a reference electrode, the complexity in preparation of the whole sensor is greatly reduced. Each of the two same potassium ion selectivity working electrodes comprises a conductive layer, a reaction electrode, a contact electrode and a potassium ion sensitive film. According to the invention, since the constant-potential traditional reference electrode and the electrolyte layer of a common solid-state electrode are not needed, the preparation process and flow of the all-solid potassium ion selectivity sensor are greatly simplified; and moreover, the all-solid potassium ion selectivity sensor has accurate and quick response, and is small and light, convenient to carry and suitable for large-scale production.
Owner:NANJING UNIV OF TECH
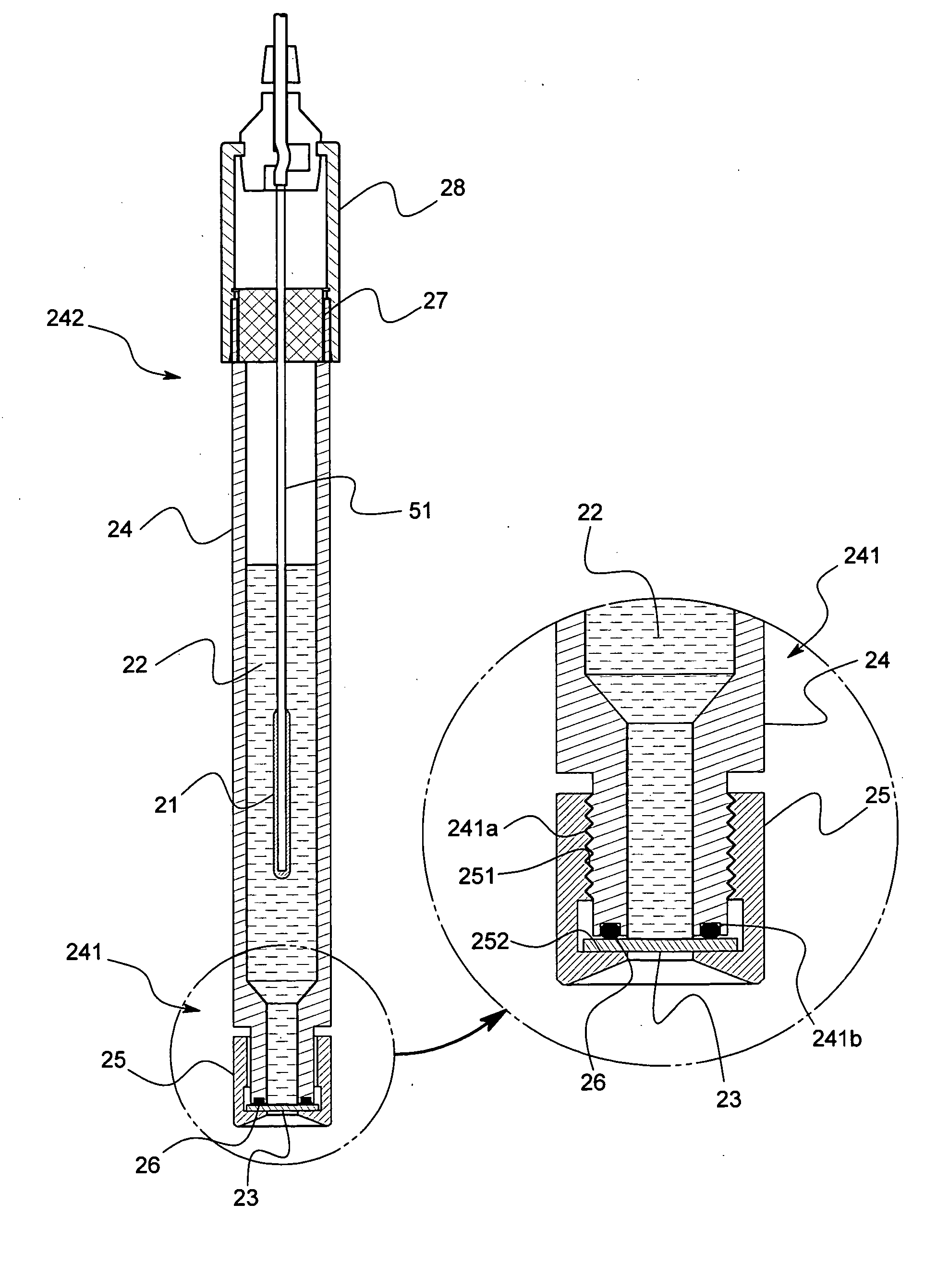
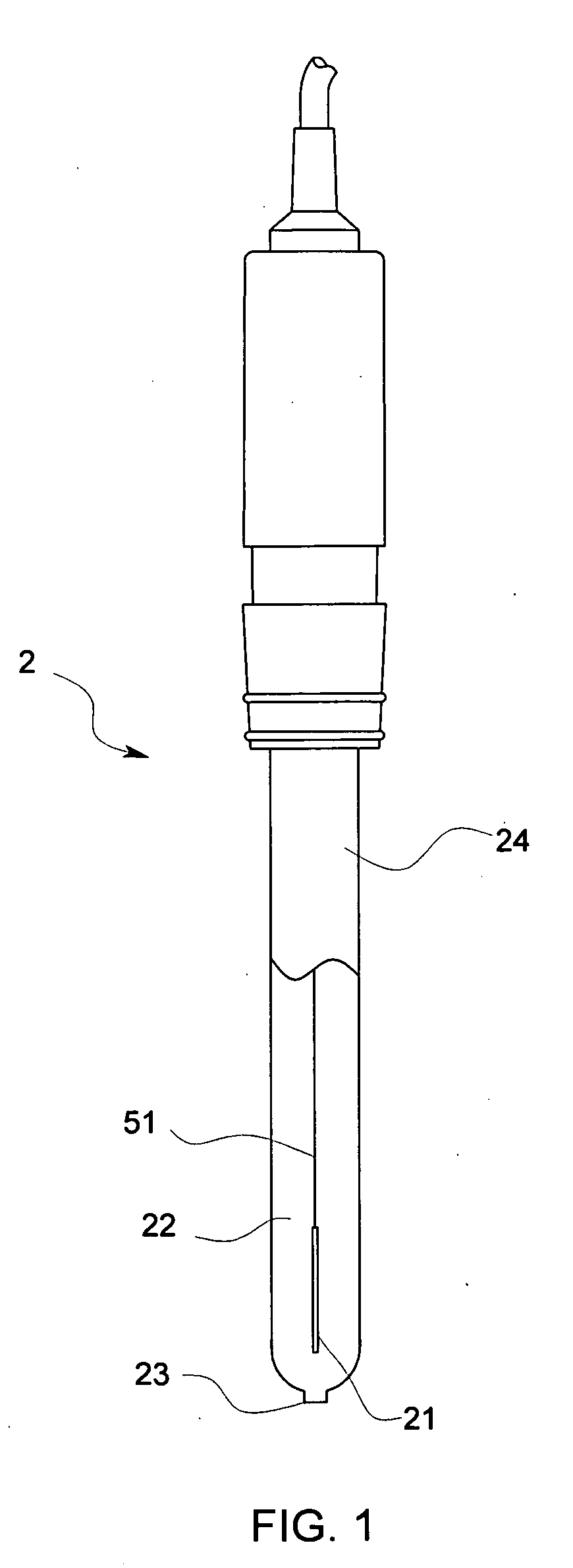
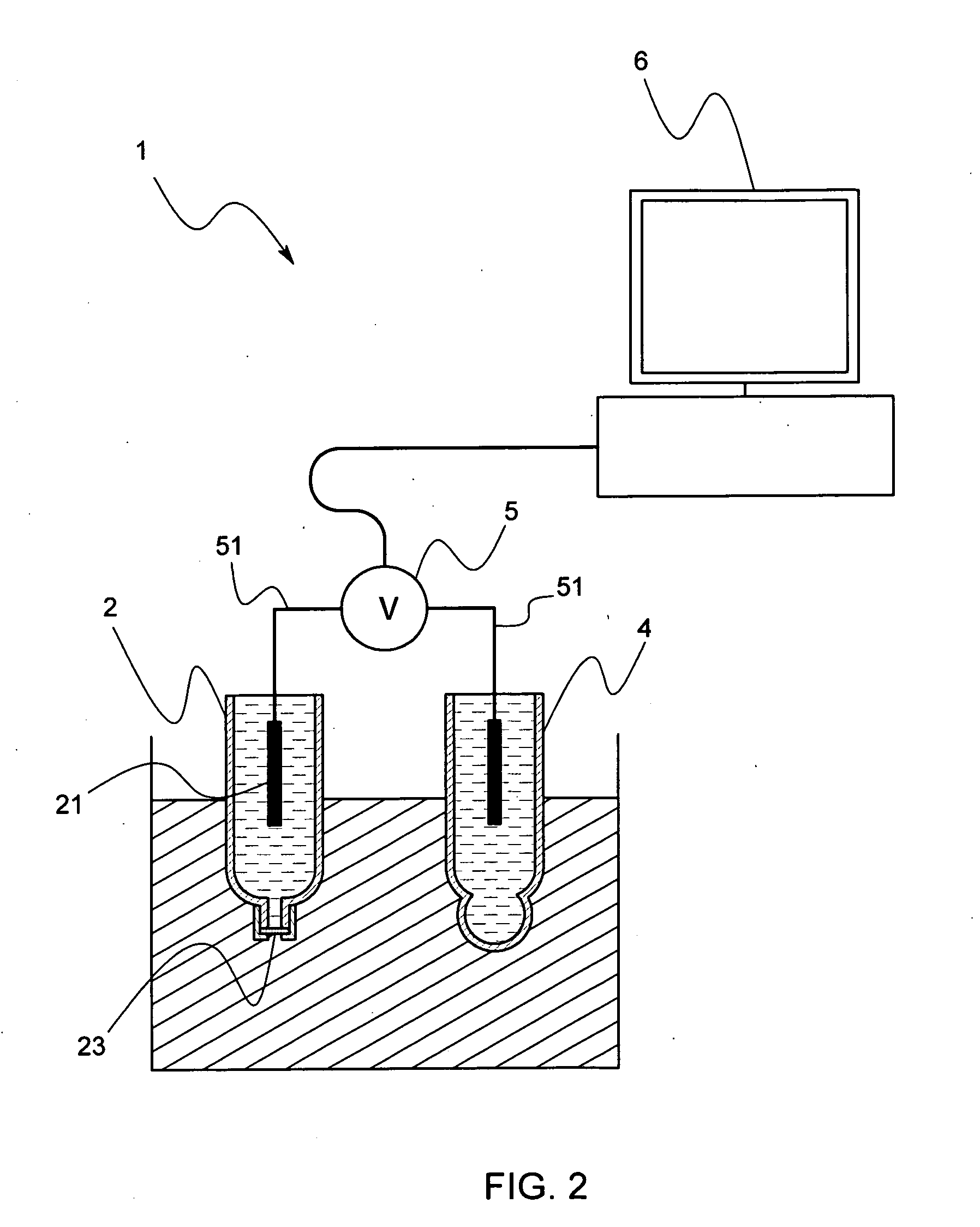
Reference electrode, salt bridge and ionic concentration measuring device by the use of reference electrode and salt bridge
ActiveUS20080000771A1Increased durabilityImprove accuracyWeather/light/corrosion resistanceVolume/mass flow measurementSalt bridgePotential difference
Owner:KYOTO UNIV +1
Preparation method of anti-pollution composite nanofiltration membrane
ActiveCN110052179AEasy to separateWater flux effectSemi-permeable membranesHydrophilic polymersSalt bridge
The invention provides a preparation method of an anti-pollution composite nanofiltration membrane. The preparation method includes subjecting a polysulfone ultrafiltration membrane to primary interfacial polymerization by a first aqueous phase solution and an oil phase solution, pouring a second aqueous phase solution containing nonionic hydrophilic polymers onto the surface of the ultrafiltration membrane to conduct secondary interfacial polymerization, removing the second aqueous phase solution, conducting heat treatment, and taking out the membrane for washing to obtain the composite nanofiltration membrane. The preparation method has the advantages that the nonionic hydrophilic polymers containing ether bonds in main chains are embedded in a polyamide layer through the secondary interfacial polymerization, the surface of the modified membrane is smooth, and the surface roughness is lowered; through introduction of nonionic hydrophilic groups, the number of residual carboxyl groupson the surface can be remarkably decreased, pollutant adsorption and salt bridge effect can be effectively reduced, and the anti-pollution performance of the nanofiltration membrane is improved; theoperation process is simple and convenient, and the preparation method is convenient for industrial production and has a broad application prospect in anti-pollution modification of the composite nanofiltration membrane.
Owner:WANHUA CHEM GRP CO LTD +1
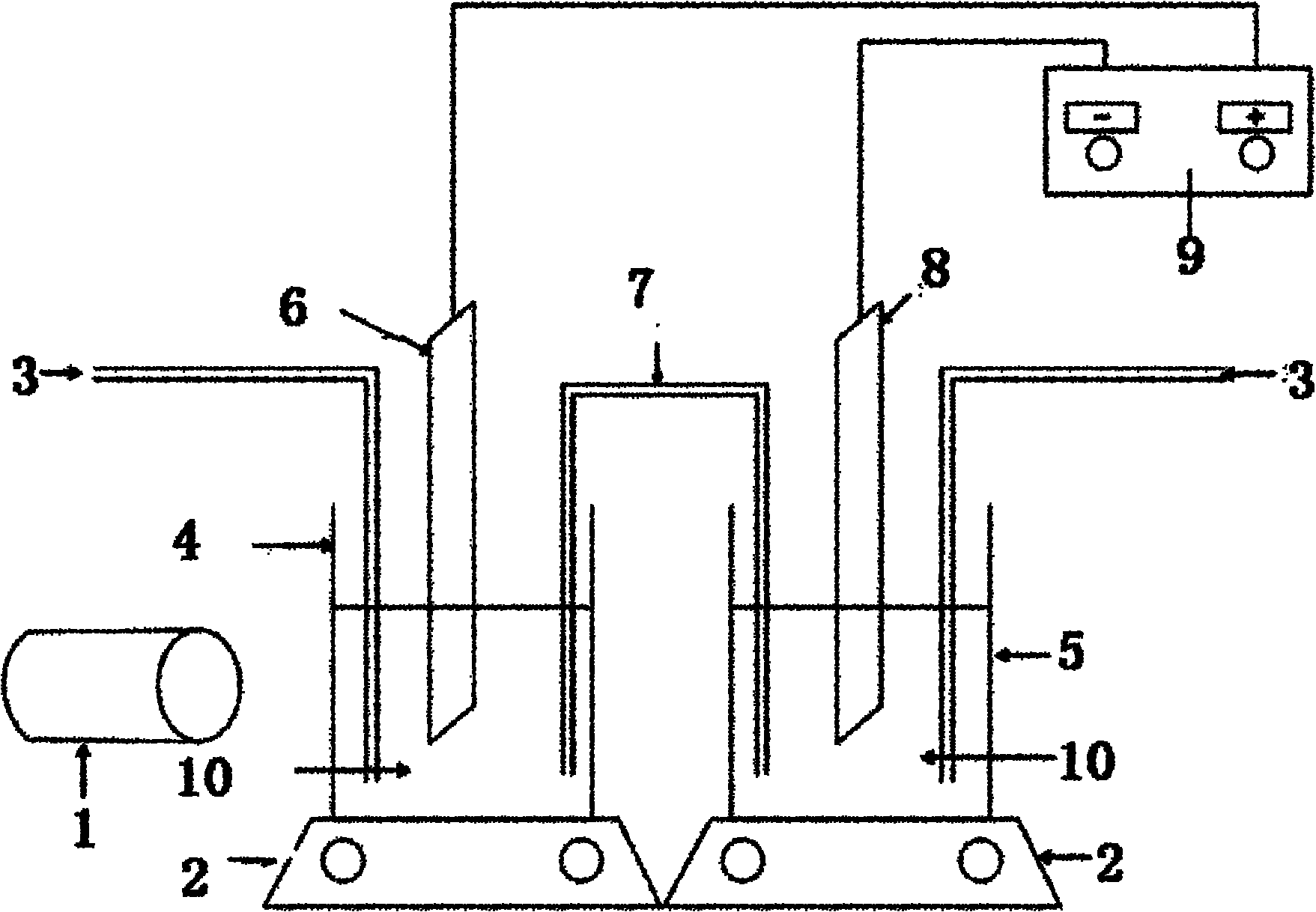
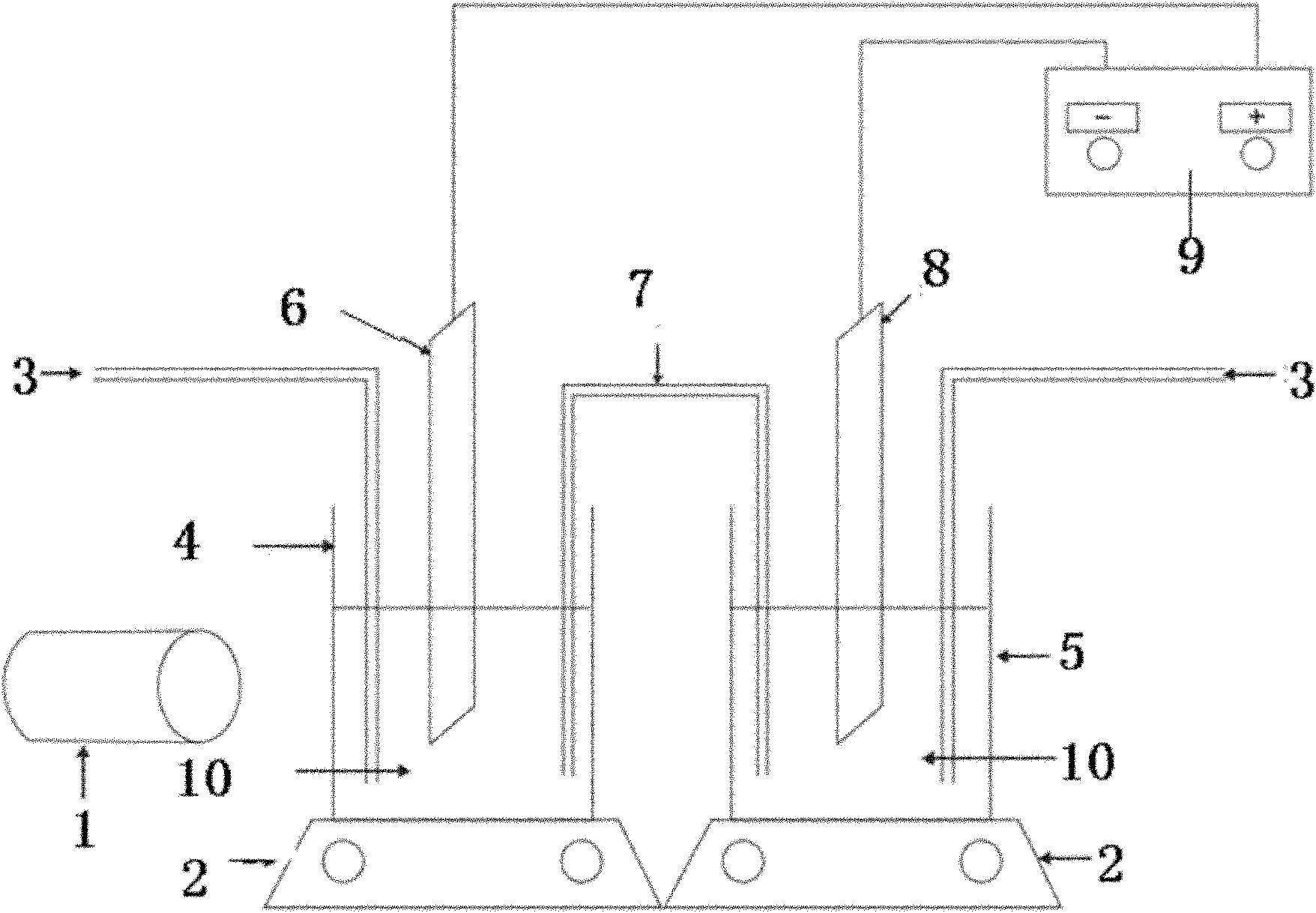
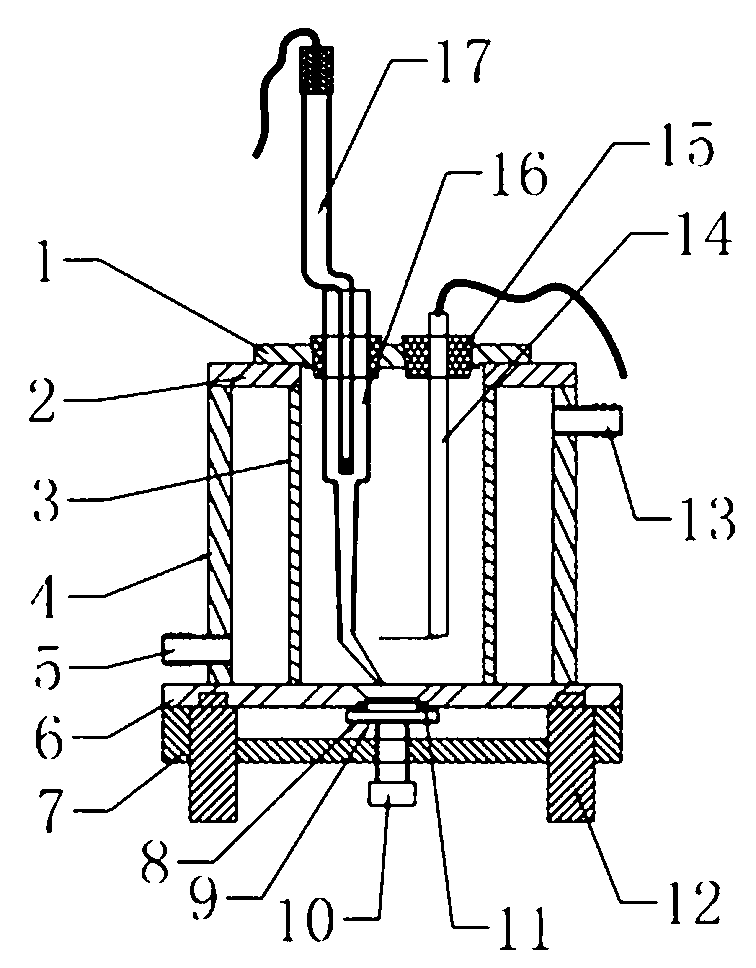
Electrolytic cell with controllable temperature used for electrochemical measurement
InactiveCN102937616AEasy to disassemble and replacePrevent rust and corrosionMaterial electrochemical variablesAdhesiveSalt bridge
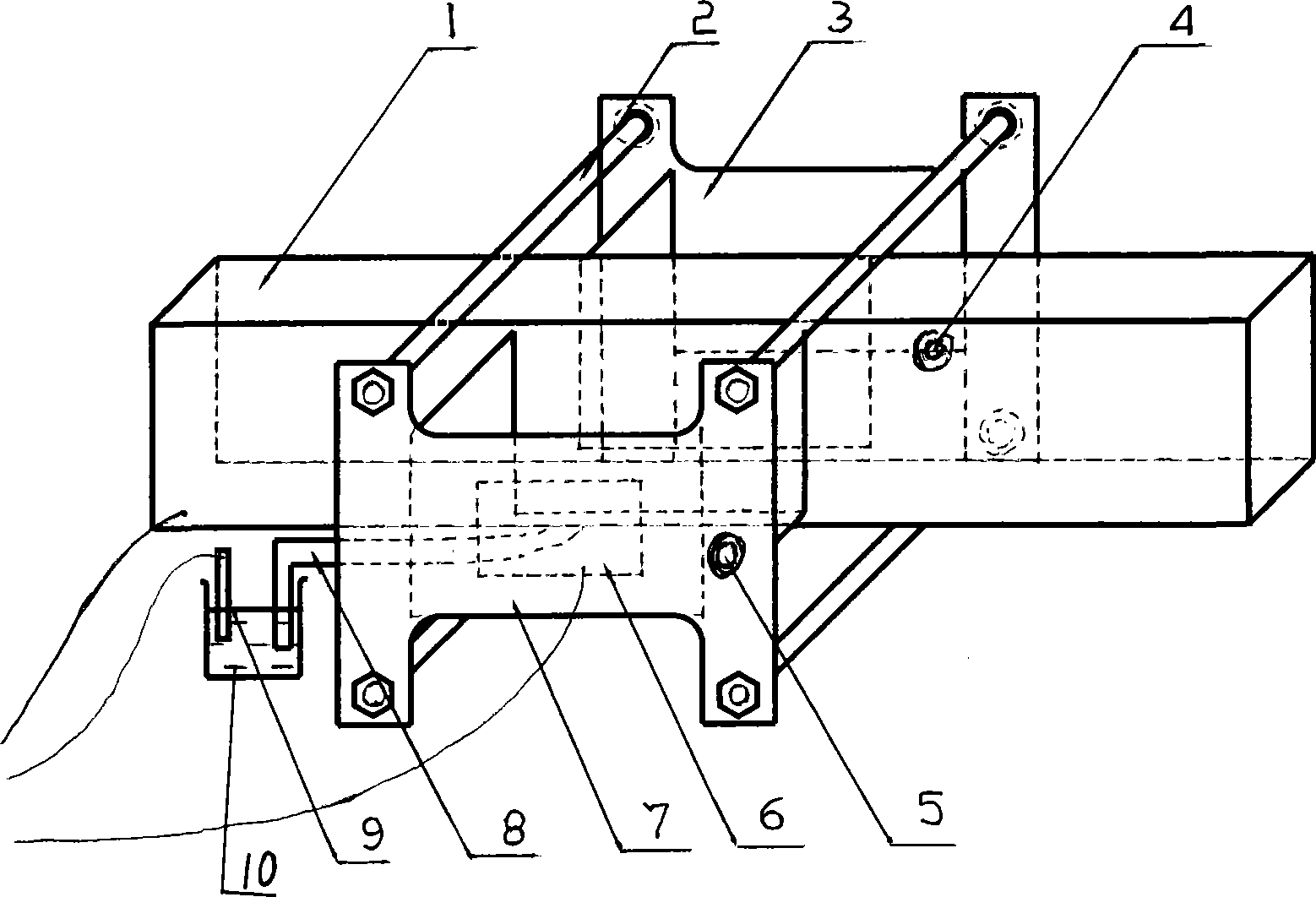
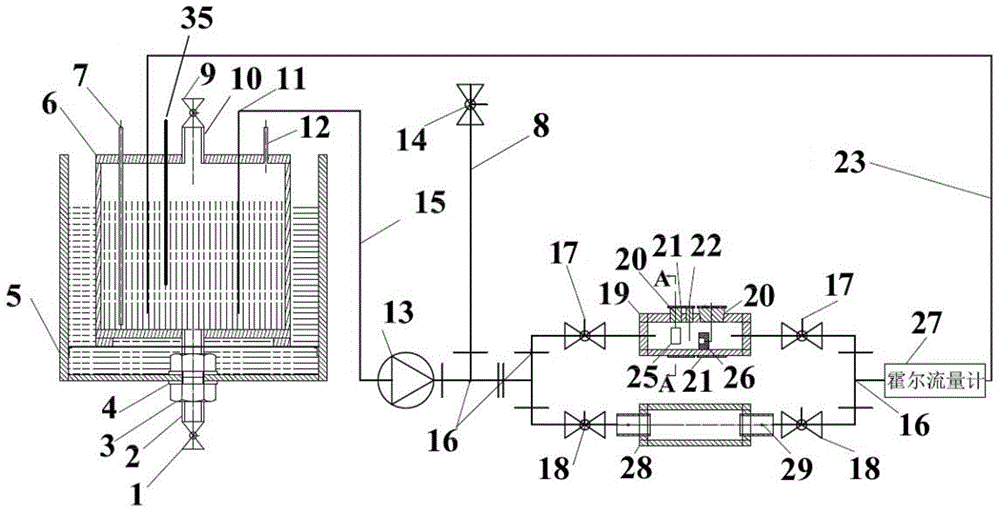
The invention provides an electrolytic cell with a controllable temperature used for electrochemical measurement. The electrolytic cell comprises an upper cover (1), a sleeve top board (2), a electrolytic cell container (3), a circulating water sleeve pipe (4), a water inlet (5), a sleeve bottom board (2), a fixed support plate (7), a working electrode (8), a gasket (9), a fastening bolt (10), a sealing ring (11), container legs (12), a water outlet (13), a platinum electrode (14), a rubber plug (15), a salt bridge (16), a reference electrode (17), etc. Only need to align a sample to a central hole of the sleeve bottom board and screw a nut to make the sample contacted and sealed with the sealing ring, with no need of welding and sealing the sample, the electrolytic cell can directly measure electrochemical properties of the samples, and is convenient for replacing the sample. Temperature of the electrolyte can be controlled by externally connecting circulating water, so that interference electrochemical signals caused by eddy current produced by electric heating can be prevented. The whole container is made of corrosion resistant organic glass members; and the connecting parts are adhered with organic glass adhesives, so that the electrolytic cell is convenient in preparation and has long service life.
Owner:BEIJING UNIV OF CHEM TECH
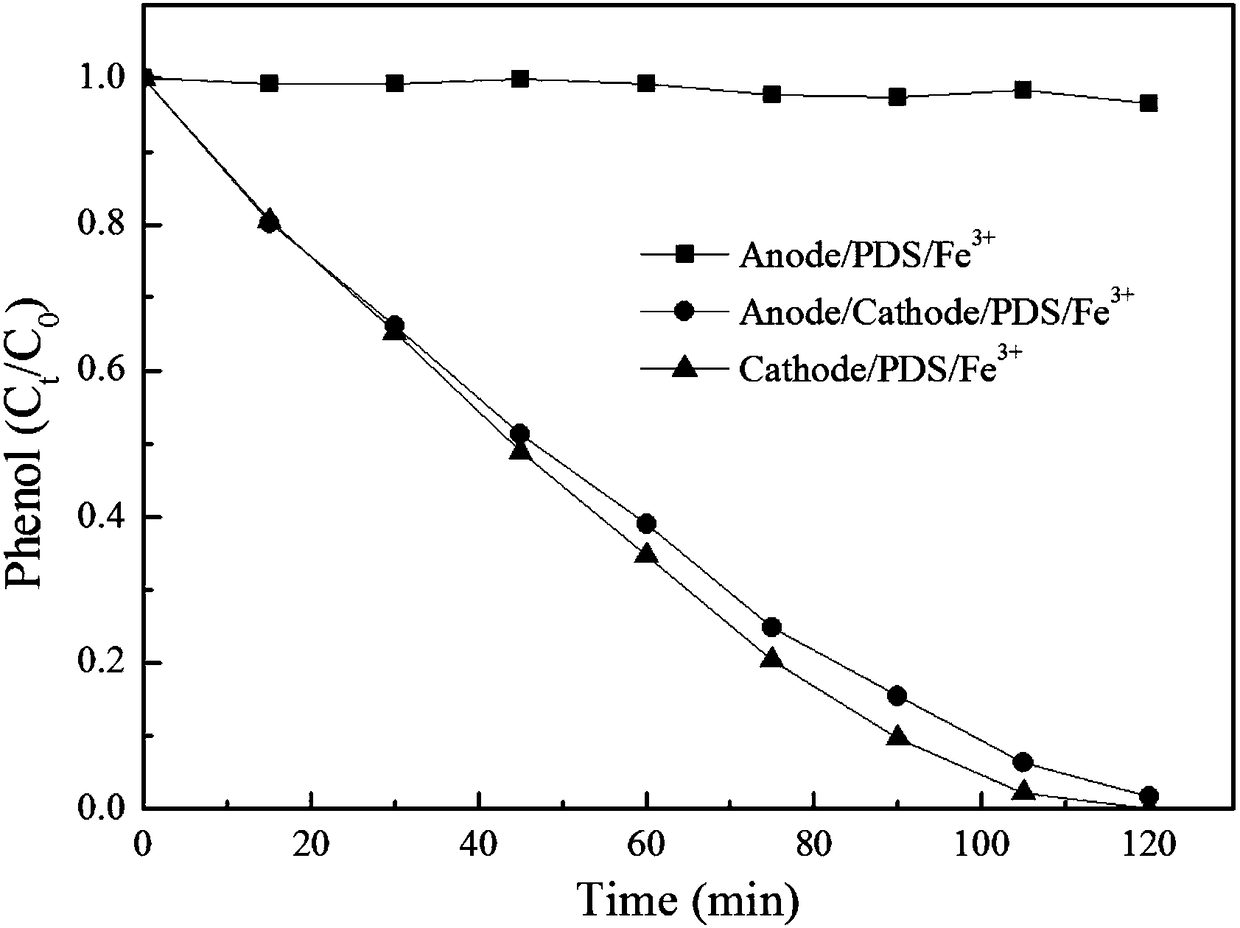
Method for electrochemically coordinating persulfate to remove organic pollutants in wastewater
ActiveCN108726640AEfficient removalReduce concentrationWater contaminantsWater/sewage treatment apparatusPersulfateSalt bridge
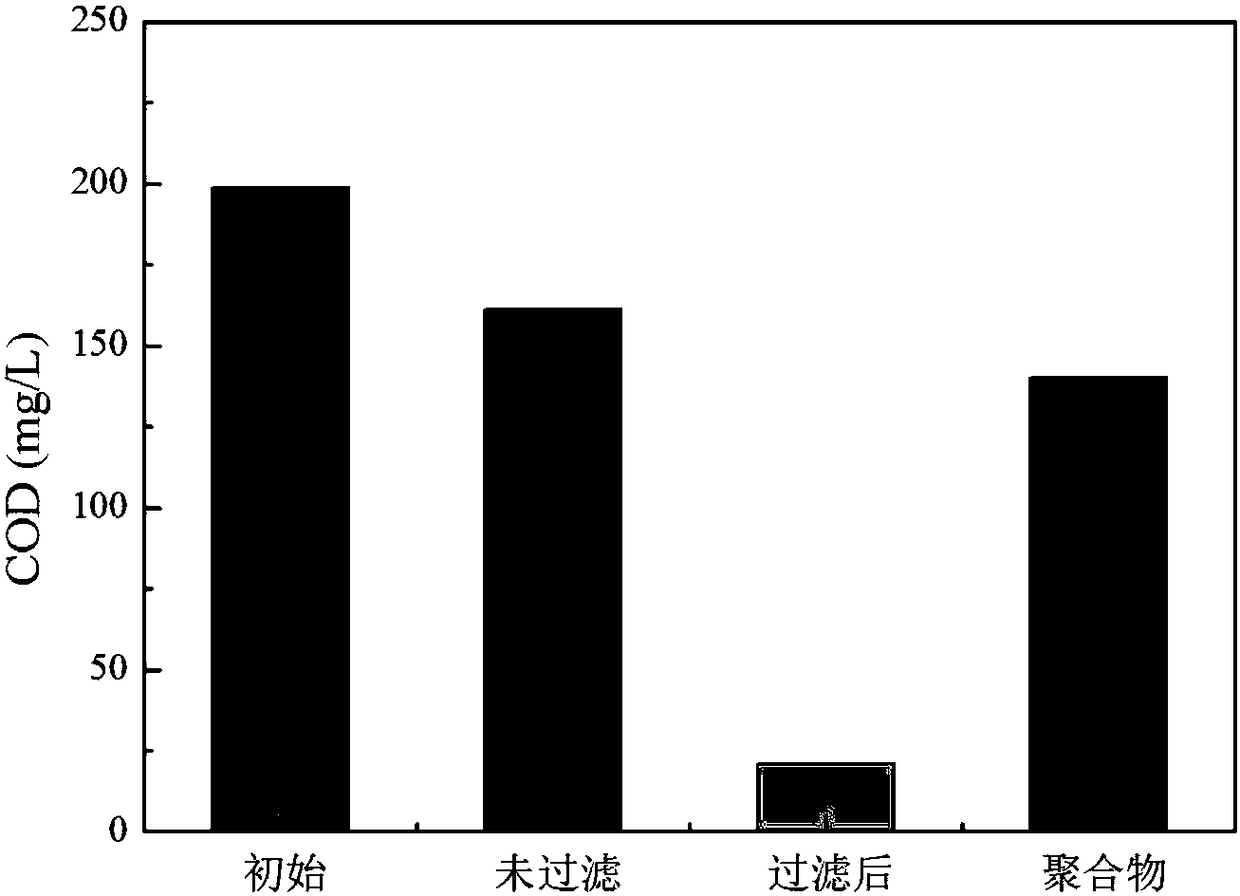
The invention discloses a method for electrochemically coordinating persulfate to remove organic pollutants in wastewater. The method comprises the following steps: separating cathode liquor from anode liquor through a salt bridge or a proton membrane, wherein the cathode liquor is prepared from persulfate, transition metal ions and wastewater containing the organic pollutants; then adjusting a pHvalue of the cathode liquor to 0 to 10 and electrifying to treat for 0.5 to 12 hours under low current density after stirring; performing solid-liquid separation on the cathode liquor and separatingto obtain the liquid, namely wastewater with the organic pollutants removed. According to the method disclosed by the invention, the organic pollutants can polymerize to form solid precipitate in an electrolytic process of a cathode chamber; after reaction is finished, solid-liquid separation is performed on reaction liquid; thus, target organic pollutants, COD and TOC in the wastewater can be effectively removed; meanwhile, the method has the advantages of high efficiency, energy conservation, simpleness and convenience in operation and the like.
Owner:HUAZHONG UNIV OF SCI & TECH
Process for treating sewage by bipolar oxidizing and electrochemical method
InactiveCN1396121ACompact structureLarge specific surface areaWater/sewage treatment by electrochemical methodsElectrolysisSalt bridge
A dual-electrode oxidizing and electrochemical process for treating the industrial sewage is discloosed. A 3D membrane gas-diffusion electrode is used as the electrolytic cathode. An ion exchange membrane or a salt bridge is used to partition the cathode area from the anode area. The electrically catalytic electrolysis is performed to generate H2O2 which can be used to decompose the organic pollutants. Its advantages are high efficiency and low energy consumption.
Owner:SHANGHAI JIAO TONG UNIV
Electrochemical in-situ measurement electrolytic cell device
InactiveCN101451941AAvoid Galvanic CorrosionWon't interfereWeather/light/corrosion resistanceInvestigating abrasion/wear resistanceSalt bridgeMetallic materials
The invention relates to an electrolytic cell device of electrochemistry electrochemistry for performing corrosion fatigue crack propagation experiment on metal materials, belonging to the technical field of material corrosion research, mainly comprising a front trough solid, a rear trough solid, a three point bending specimen, a bolt, a water outlet, a water inlet, an auxiliary electrode, a salt bridge, a reference electrode and a conical flask; the front trough solid and the rear trough solid are symmetrical halfbody structures, which fix the electrolytic cell in a box shaped structure on two sides of the three point bending specimen through a thru bolt. A groove placing auxiliary electrode is arranged at the center of the front plate inner side of the front trough solid. One end of the salt bridge communicates with the auxiliary electrode and the work electrode through etching solution, and the other end is connected with the reference electrode through the conical flask full of saturated potassium chloride solution. A left posterior lateral plate and a right posterior lateral plate have the same height and the same width with a left front lateral plate and a right front lateral plate, which is a symmetrical shape and structure, having simple and practical structure, multiple measurable functions, long service life, high measuring precision and good accuracy.
Owner:725TH RES INST OF CHINA SHIPBUILDING INDAL CORP
Device for providing a means for internal calibration in an electrochemical sensor
ActiveUS8877037B2Enhance electronic communicationLimit chemical interactionMaterial nanotechnologyMachining electrodesElectrochemical gas sensorIonic strength
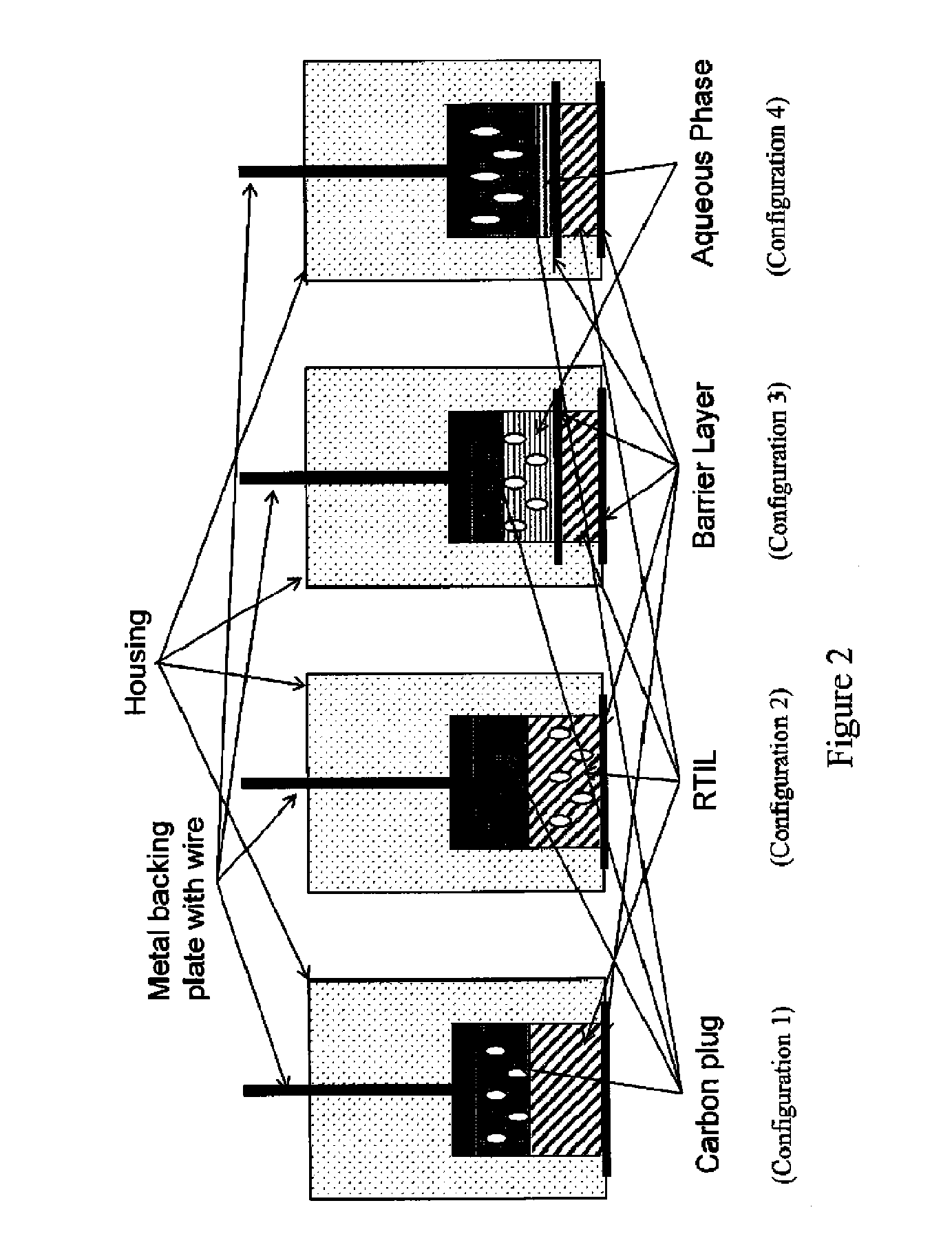
Internally calibrated pH and other analyte sensors based on redox agents provide more accurate results when the redox active reference agent is in a constant chemical environment, yet separated from the solution being analyzed in such a way as to maintain electrical contact with the sample. Room temperature ionic liquids (RTIL) can be used to achieve these results when used as a salt bridge between the reference material and the sample being analyzed. The RTIL provides the constant chemical environment and ionic strength for the redox active material (RAM) and provides an electrolytic layer that limits or eliminates direct chemical interaction with the sample. A broad range of RAMs can be employed in a variety of configurations in such “Analyte Insensitive Electrode” devices.
Owner:PARKER INTANGIBLES LLC
Heterogeneous membrane electrodes
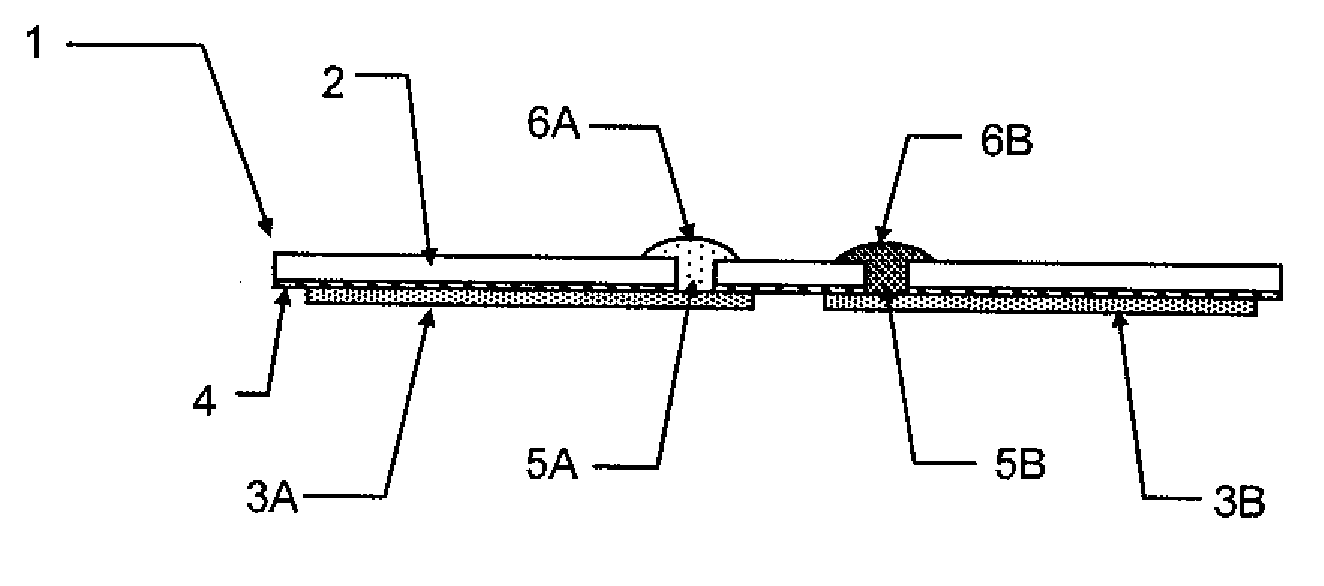
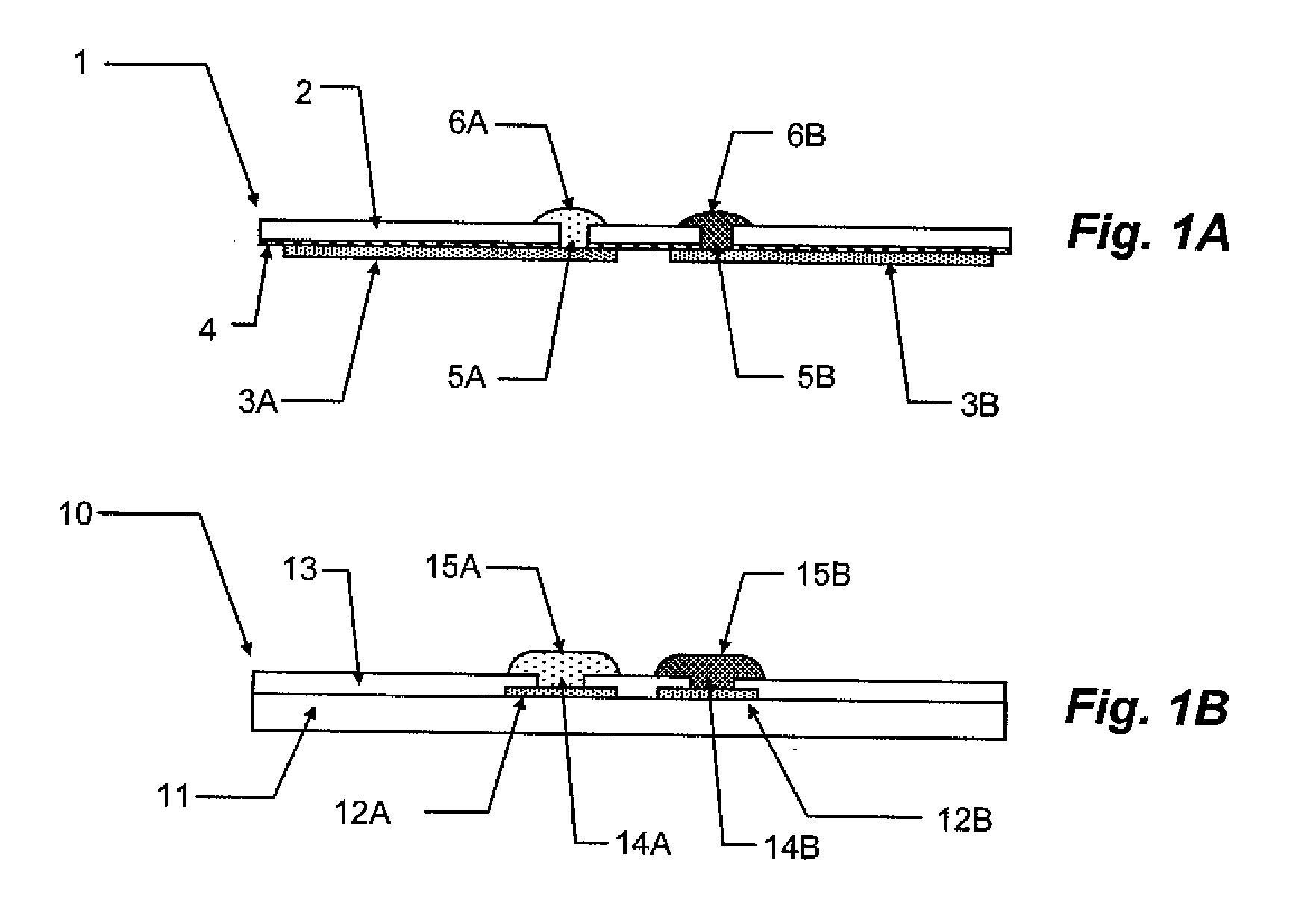
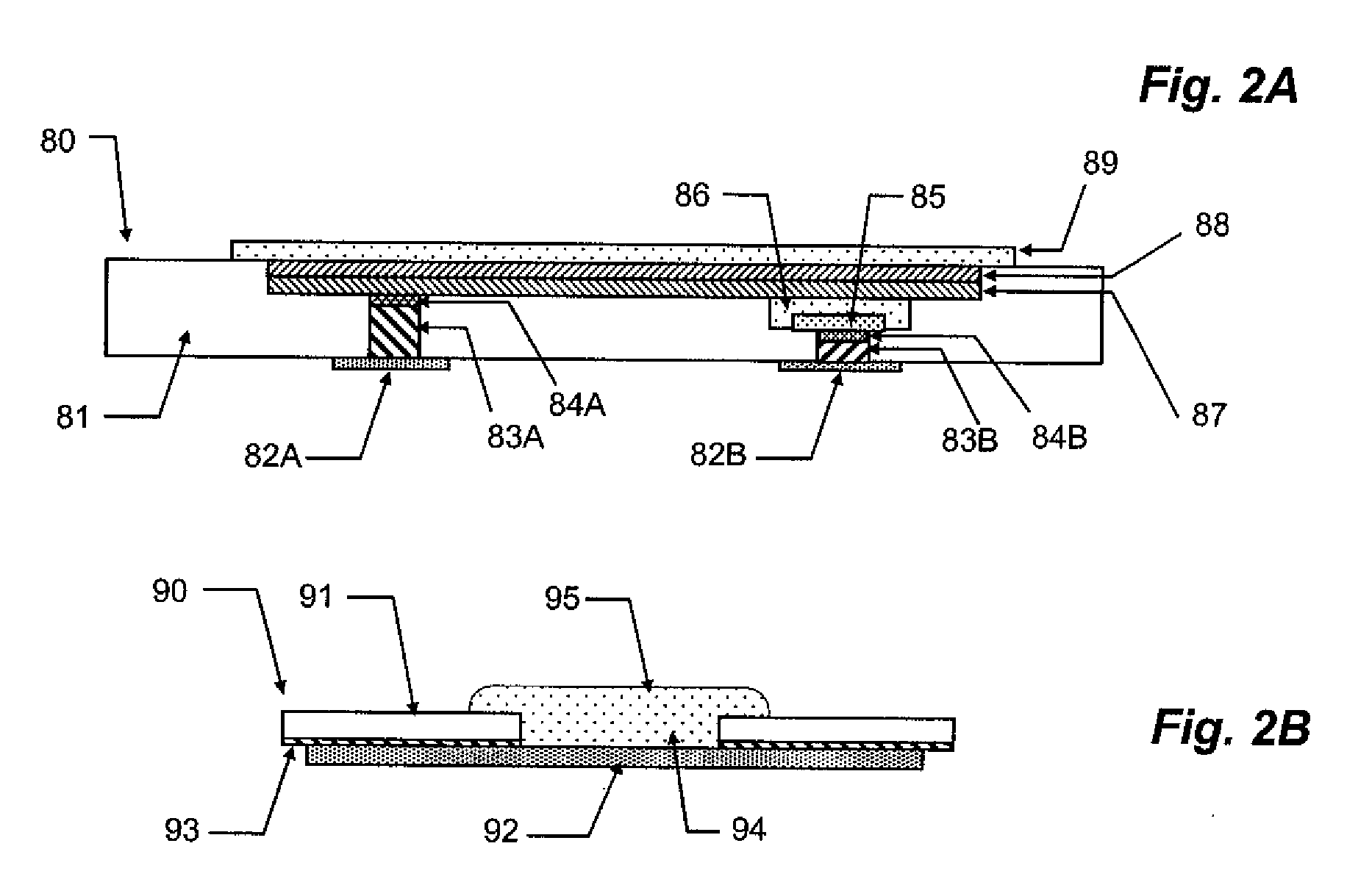
InactiveUS20100252428A1Rapid gasFast shippingLaboratory glasswaresSpecial surfacesElectrical conductorWater vapor
The present invention relates to planar electrochemical sensors with membrane coatings used to perform chemical analyses. The object of this invention is to provide unit-use disposable sensors of very simple and inexpensive construction, preferably with only a single membrane coating on an electrode. The invented devices are potentiometric salt-bridge reference electrodes and dissolved gas sensors constructed with a heterogeneous membrane coating of a conductor. The heterogeneous membrane, which is an intimate admixture of a hydrophobic and a hydrophilic compartment, concurrently supports constrained transport of non-volatile species through its hydrophilic compartment and rapid gas and water vapor transport through its hydrophobic compartment.
Owner:SIEMENS HEALTHCARE DIAGNOSTICS INC
Method for preparing methanol from carbon dioxide by photoelectric catalytic reduction
InactiveCN102605385AImprove reduction efficiencyImprove utilization efficiencyElectrolysis componentsEnergy inputSalt bridgePhotochemistry
The invention relates to a method for preparing methanol from carbon dioxide by photoelectric catalytic reduction. The methanol is prepared by a dye sensitization photoelectric catalytic unit which is composed of a titanium dioxide membrane electrode component and a positive electrode, wherein the titanium dioxide membrane electrode component comprises a glass substrate, a nano titanium dioxide membrane, a dye sensitization membrane, an electrolyte and a counter electrode; and the counter electrode of the component and the positive electrode are respectively connected with a constant voltage DC source. The method comprises the following steps: respectively putting a catalytic reduction area in the titanium dioxide membrane electrode component and the positive electrode into a container A containing distilled water and a container B; introducing carbon dioxide into the container A; connecting the container A and the container B with a U-shaped salt bridge; and reducing the carbon dioxide in the container A in the dye sensitization area under the irradiation of visible light to generate the methanol. The invention has the following advantages: the photocatalysis response range of titanium dioxide is widened to the visible light area, thereby enhancing the solar energy utilization efficiency; the sandwich structure prevents the dye from degradation, and enhances the service life of the unit; and the constant voltage DC source enhances the carbon dioxide reduction efficiency.
Owner:TIANJIN UNIVERSITY OF TECHNOLOGY
Implantable voltaic cell
InactiveUS20100004521A1Avoid biological contaminationMedical devicesCatheterElectrical resistance and conductanceSalt bridge
The invention provides a voltaic cell for implantation into the body of a subject that oxidizes oxidizable biological material to generate current to do work. The voltaic cell comprises a biologically inert shell having an inner compartment containing a cathodic environment and an anodic environment on the outer surface of the shell that is in contact with bodily fluid. A connector connects the anodic environment to the cathodic environment and has a component that provides resistance between the anodic and cathodic environments. The shell contains at least one salt bridge disposed within the shell that permits passage of small ions between the inner compartment and the bodily fluid, thereby completing the circuit. The invention also provides devices such as a glucometer which continuously detects glucose and transmits a signal to an external device which provides an output, such as blood glucose level. Methods of using the same are also provided.
Owner:EPPS SPENCER J G
Corrosion testing device for metal inside gaps under stripped coatings
InactiveCN103630480AReal-time monitoring of physical and chemical propertiesReal-time monitoring of microenvironmental changesWeather/light/corrosion resistanceSmall sampleSalt bridge
The invention relates to a corrosion testing device for metal inside gaps under stripped coatings. The corrosion testing device comprises a bottom board and a cover board which is placed on the bottom board and is fixed with the bottom board, wherein a gap is formed between the cover board and the bottom board, a solution area is located on one side of the cover board and is communicated with the gap, and salt bridges are arranged on the other side of the cover board at equal intervals and used for being connected with outside reference electrodes. An auxiliary electrode and a composite micro electrode are respectively installed on corresponding positions one two sides of each salt bridge, one ends of each auxiliary electrode and each composite micro electrode are both communicated with solution inside the gap, and the other ends of each auxiliary electrode and each composite micro electrode are respectively connected with a measurement meter through copper conducting wires. More than two small sample placing areas are installed on the bottom board, and the positions of the small sample placing areas correspond to the auxiliary electrodes one to one. By means of the corrosion testing device, different gap depth electrochemical measurement of the metal in gaps can be conducted, and simultaneously changes of microenvironments in gaps can be monitored in real time. Besides, the corrosion testing device has the advantages of small size, simple structure, convenient operation, high measurement accuracy, and the like.
Owner:INST OF METAL RESEARCH - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Sodium ion sensor and preparation method thereof
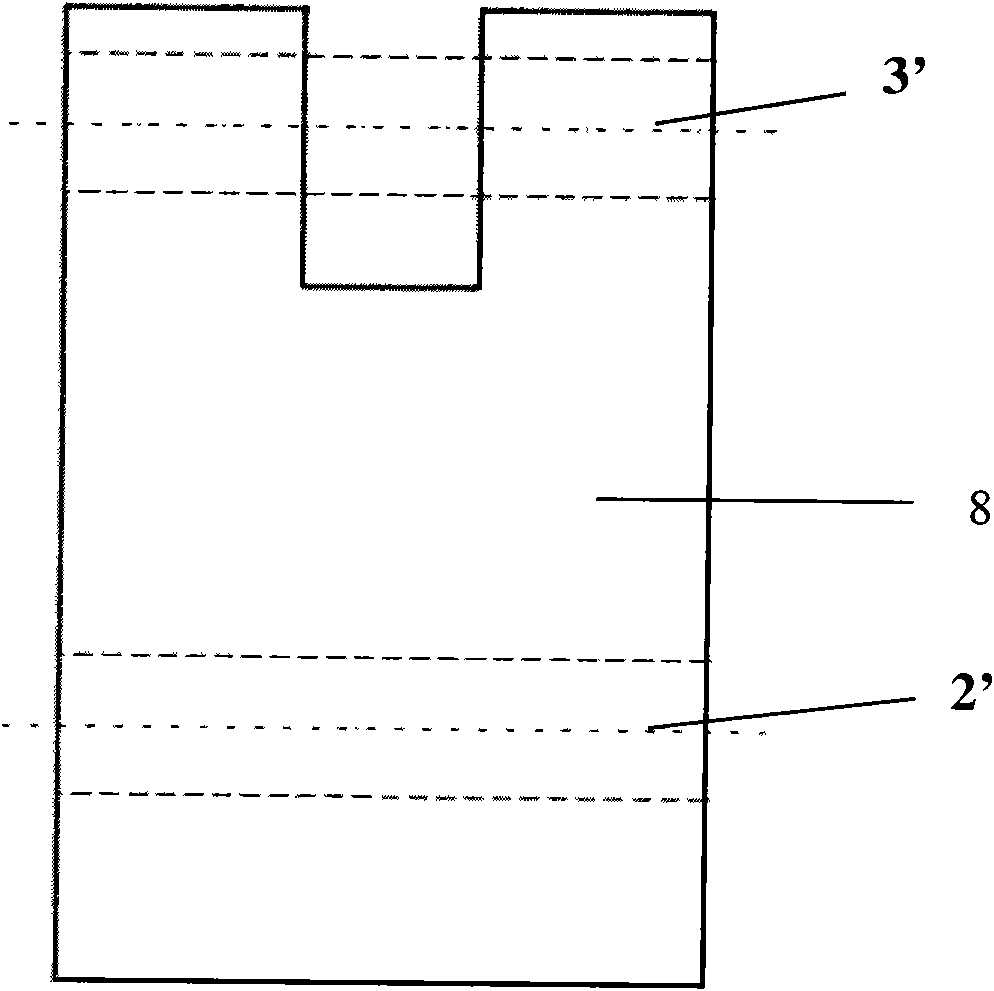
InactiveCN104330449AAchieve integrationMiniaturizationMaterial electrochemical variablesSalt bridgeIon sensitive
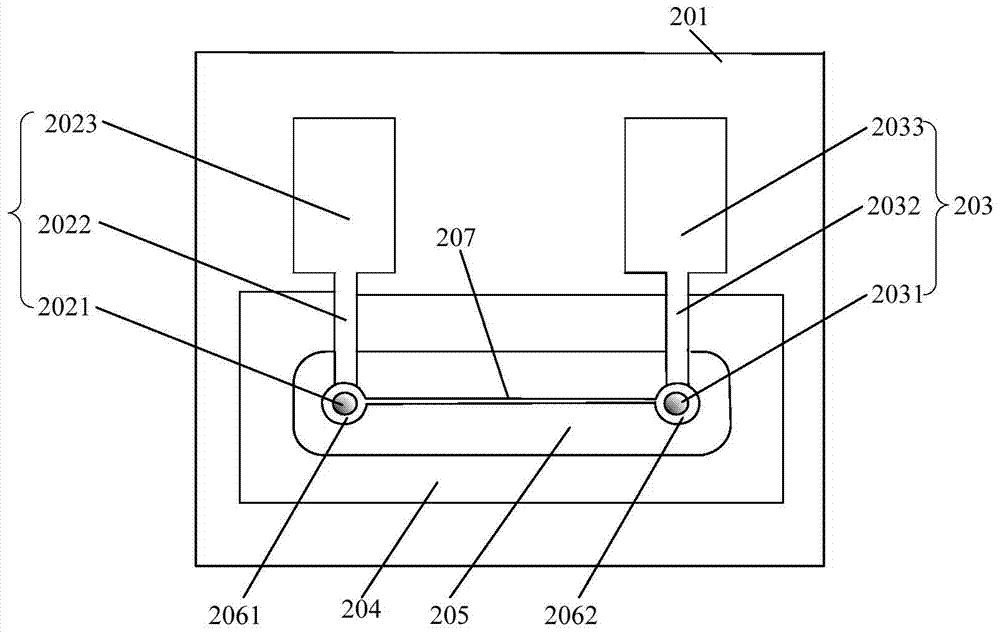
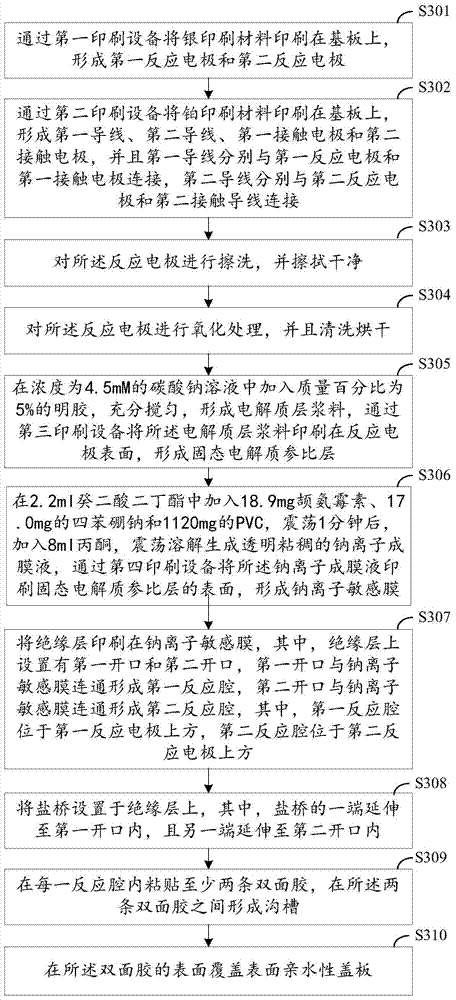
The invention discloses a sodium ion sensor and a preparation method thereof. The sodium ion sensor comprises a substrate, a first sodium ion selection electrode, a second sodium ion selection electrode, a solid electrolyte reference layer, a sodium ion sensitive film, an insulating layer and a salt bridge, wherein the first sodium ion selection electrode comprises a first reaction electrode arranged on the substrate; the second sodium ion selection electrode comprises a second reaction electrode arranged on the substrate; the solid electrolyte reference layer covers the first reaction electrode and the second reaction electrode; the sodium ion sensitive film is arranged on the solid electrolyte reference layer; the insulating layer is arranged on the sodium ion sensitive film; a first opening and a second opening are formed in the insulating layer; the first opening is communicated with the sodium ion sensitive film to form a first reaction cavity; the second opening is communicated with the sodium ion sensitive film to form a second reaction cavity; the salt bridge is arranged on the insulating layer; one end of the salt bridge extends to the inside of the first reaction cavity; and the other end of the salt bridge extends to the inside of the second reaction cavity. Through the manner, the sodium ion sensor disclosed by the invention can be miniaturized, so that the sodium ion sensor is convenient to carry and convenient to operate.
Owner:深圳市希莱恒医用电子有限公司
Ion selective electrode
InactiveUS20070144919A1Weather/light/corrosion resistanceVolume/mass flow measurementElectrical conductorSalt bridge
An ion selective electrode (ISE) includes an electrode body or housing having an ion selective membrane located at one end thereof and an indicator electrode formed at or adjacent to the ion selective membrane. A sealed vessel is disposed inside the electrode body, the sealed vessel holding an electrically conductive solution and a reference electrode conductor, wherein a portion of the reference electrode conductor is submerged in the electrically conductive solution. The ISE includes a conductive member having a proximal end and a distal end, wherein the proximal end of the conductive member terminates inside the sealed vessel and the distal end terminates outside the housing. The construction of the ISE keeps the reference electrode separate from the indicator electrode. Electrons are passed to the reference electrode via the conductive member obviating the need for a salt bridge. Importantly, no reference electrode is needed that connects to the inner membrane surface. The ISE operates on the double capacitor mechanism which is fundamentally different from the conventional Nernst redox reactions described in the prior art.
Owner:KUANG LU CHENG TRUST
Biological membrane electrode and UASB (Upflow Anaerobic Sludge Blanket) coupled reactor
ActiveCN103964572AHigh removal rateIncreased degradation rateTreatment with anaerobic digestion processesChemical oxygen demandSalt bridge
The invention relates to a sewage treatment device and particularly relates to a biological membrane electrode and UASB (Upflow Anaerobic Sludge Blanket) coupled reactor comprising a reactor cylinder, a biological membrane electrode system, an electrochemical testing system and a cathode potential testing device, wherein the reactor cylinder internally and sequentially comprises a water distribution plate and the biological membrane electrode system from bottom to top; a sludge bed region is arranged between the biological membrane electrode system and a three-phase separator; the biological membrane electrode system comprises an anode and a cathode; the cathode potential testing device comprises a reference electrode, a salt bridge and sealed electrolyte, wherein the salt bridge is used for communicating the sludge bed region near the cathode and the sealed electrolyte, one end of the reference electrode is connected with the sealed electrolyte, and the other end of the reference electrode is connected with the electrochemical testing system. The biological membrane electrode and UASB coupled reactor provided by the invention is used for promoting the oxidative metabolism of microorganisms to organic pollutants and increasing the COD (Chemical Oxygen Demand) removal rate through the coupling effect of a micro electric field and the microorganisms; meanwhile, the micro electric field can be used for promoting the transfer of electrons in the system and increasing the degradation rate of the pollutants.
Owner:宜兴市产品质量监督检验所
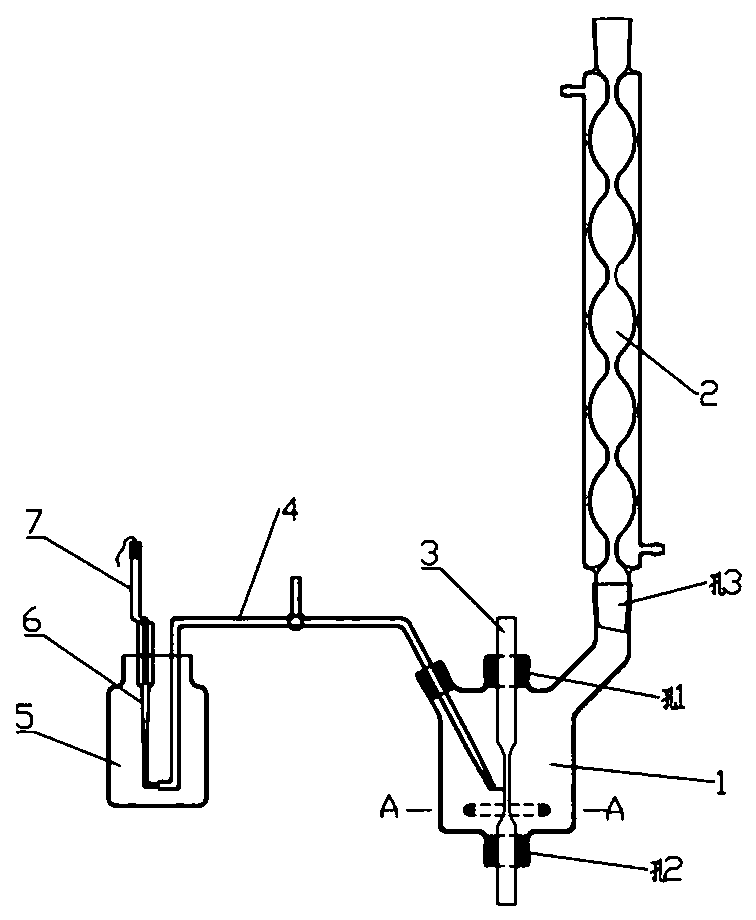
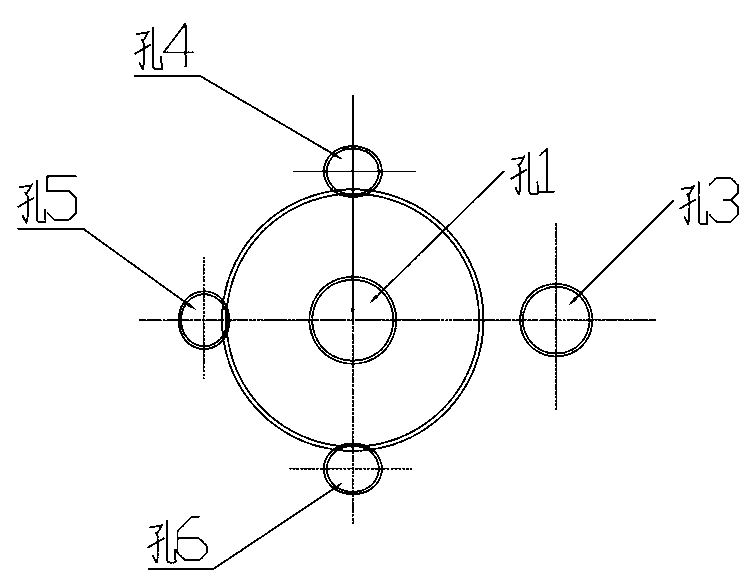
Stress corrosion test apparatus
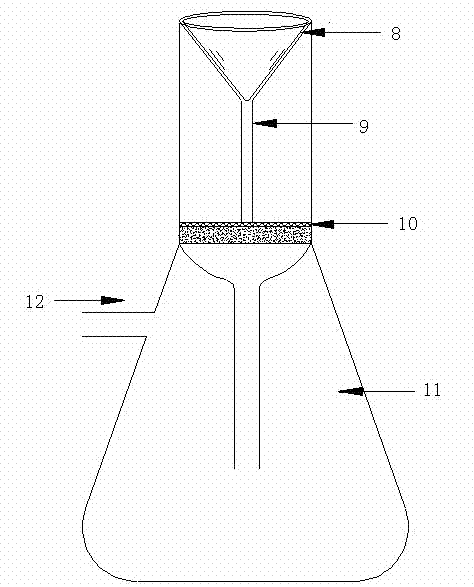
InactiveCN102937569ATemperature controlWeather/light/corrosion resistanceMaterial strength using tensile/compressive forcesSalt bridgeTransformer
The invention discloses a stress corrosion test apparatus. The apparatus comprises a stress corrosion container (1), a spherical condenser (2), a tensile test specimen (3), a salt bridge 1 (4), a wide-mouth bottle (5), a salt bridge 2 (6), a reference electrode (7), a platinum electrode, a computer (8), an electrochemical workstation (9), a electric stove wire (10), a thermoelectric thermometer (11), a temperature controller (12), an alternating-current transformer (13), etc. The apparatus can provide tensile tests capable of being used for metals in a corrosive medium with controllable temperature and capable of being externally applied corrosion current. The temperature of the corrosion medium is controlled by the electric stove wire and a temperature-control system. The reference electrode, the platinum electrode and the tensile test specimen constitute a voltage circuit and a current circuit respectively to control the corrosion potential and current additionally applied on the test specimen or generated on a monitoring sample. A normal temperature reference electrode rather than a high temperature reference electrode can be used for the measurement of the potential by connecting the reference electrode, the wide-mouth bottle and the stress corrosion container with the salt bridges.
Owner:BEIJING UNIV OF CHEM TECH
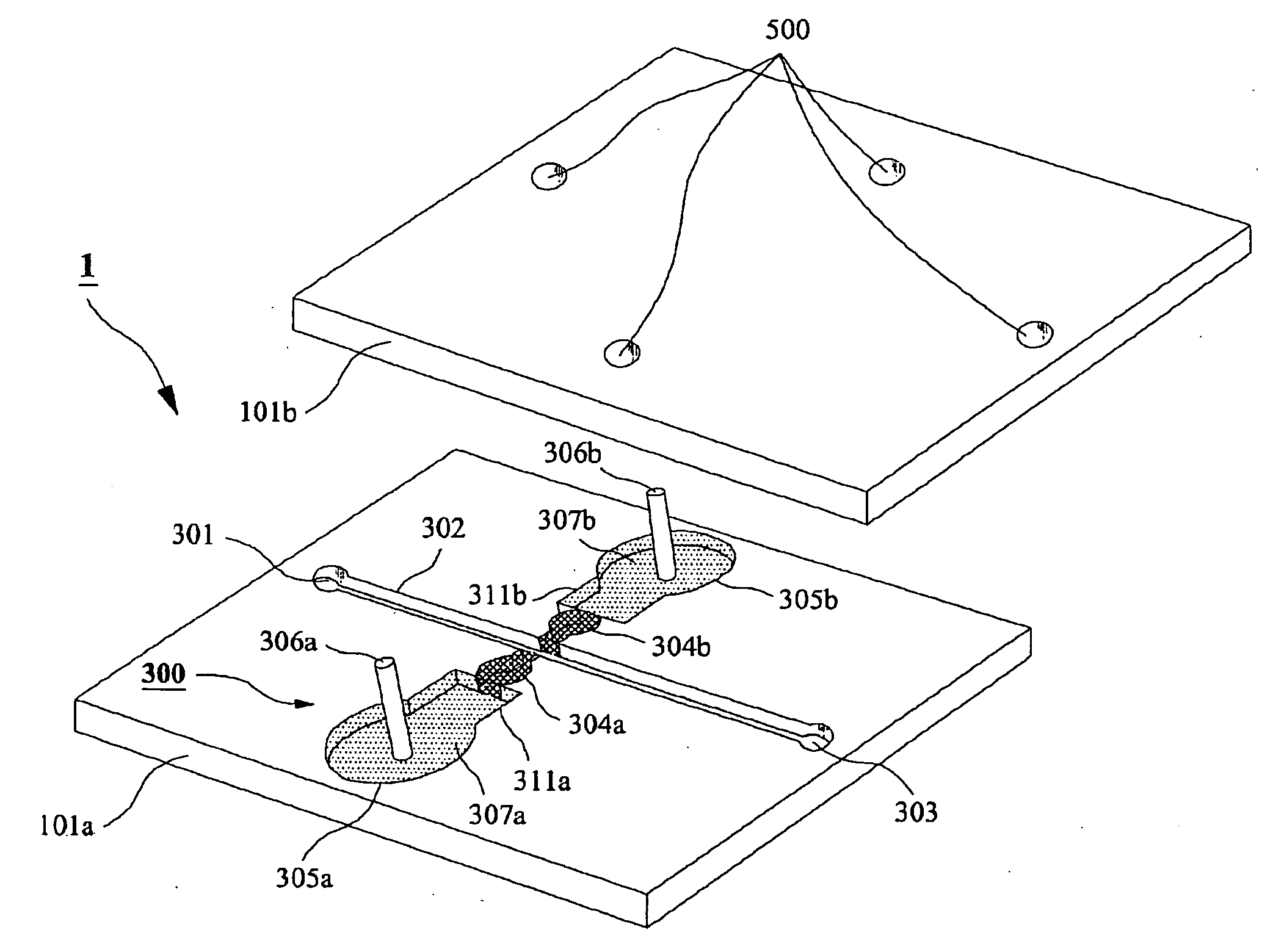
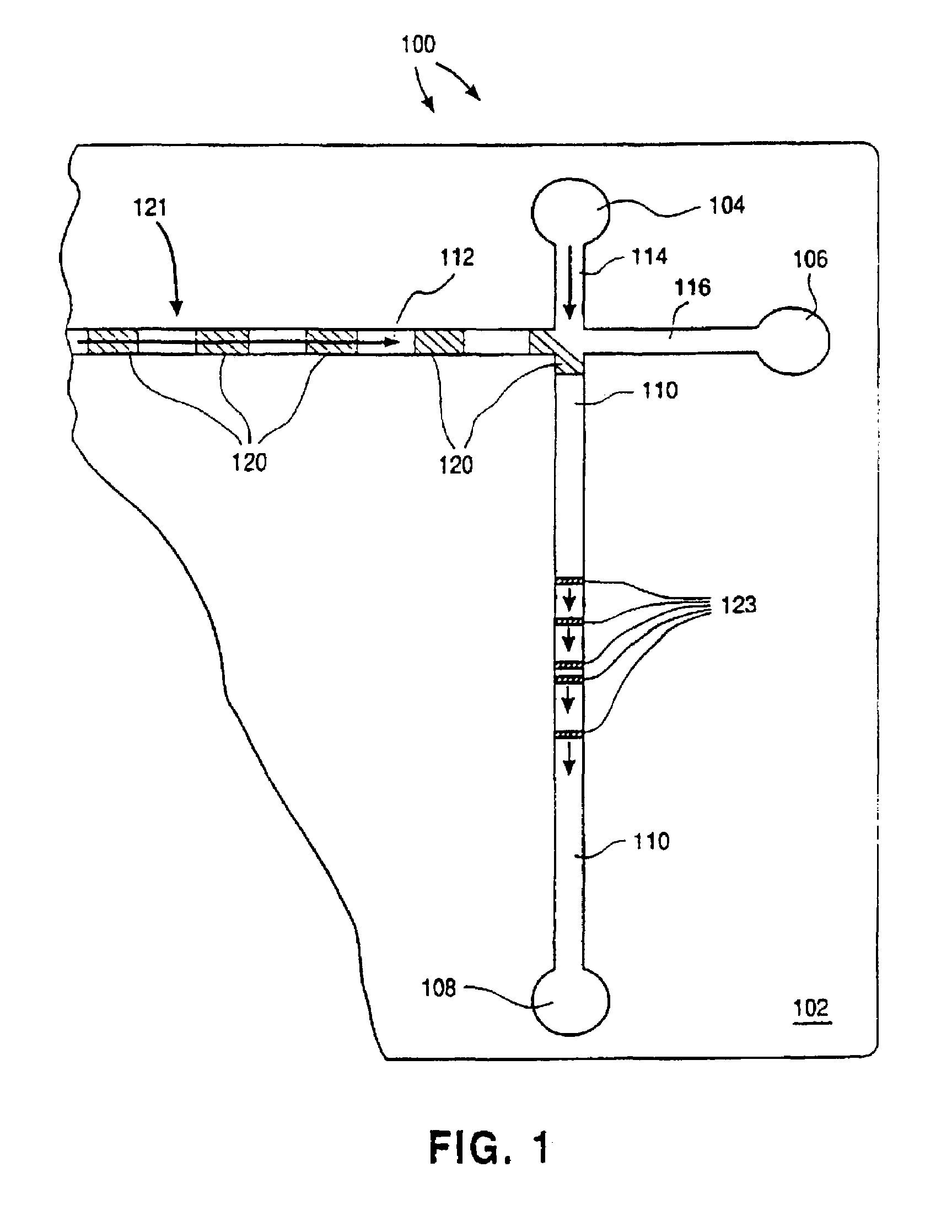
Electropipettor and compensation means for electrophoretic bias
InactiveUS7001496B2Easy to introduceEasily introducedSludge treatmentVolume/mass flow measurementFritSalt bridge
A channel (140) is divised into portions (142, 144). The sidewalls of each channel portion (142, 144) have surface charges of opposite polarity. The two channel portions (142, 144) are physically connected together by a salt bridge (133), such as a glass frit or gel layer. The salt bridge (133) separates the fluids in channel (140) from an ionic fluid reservoir (135). To impart electroosmotic and electrophoretic forces along the channel (140) between parts A and B, respectively. Additionally, a third electrode (137) is placed in the reservoir (135).
Owner:CAPLIPER LIFE SCI INC
Long-life reference electrode suitable for deep-sea high-hydrostatic pressure environment
ActiveCN102944594AHigh strengthStable saturated chloride ion concentrationMaterial electrochemical variablesSalt bridgeAutomatic control
The invention provides a long-life reference electrode suitable for a deep-sea high-hydrostatic pressure environment. The long-life reference electrode comprises a housing, an inner electrode core, a salt bridge and a diaphragm, wherein the inner electrode core, the salt bridge and the diaphragm are arranged in the housing from top to bottom. The long-life reference electrode is characterized in that the salt bridge comprises saturated potassium chloride sol-gel and potassium chloride particles uniformly dispersed in the saturated potassium chloride sol-gel; the diaphragm is a supermicroporous ceramic column; an upper end of the inner electrode core is provided with an epoxy sealing filler; the upper end of the inner electrode core is connected to an electrode lead which passes through the epoxy sealing filler and is drawn out of the housing; a lower end of the inner electrode core contacts with an upper end of the salt bridge; a lower end of the salt bridge contacts with one side of the diaphragm which is the supermicroporous ceramic column; and the other side of the diaphragm is connected to the external world. The long-life reference electrode can satisfy electrochemical measurement requirements in a deep-sea high-hydrostatic pressure environment, can be widely used for corrosion signal monitoring and detection, electrochemical protection and equipment probe automatic control of marine structures, deep sea petroleum pipes and deep sea detection equipment.
Owner:HARBIN ENG UNIV
Corrosion test device for simulating environment alternation
InactiveCN103175774AThe main structure is simpleReliable principleWeather/light/corrosion resistanceTemperature controlRubber ring
The invention belongs to the field of corrosion technologies, and relates to a corrosion test device for simulating environment alternation; small holes are respectively formed in the top of an upper barrel of an electrolytic tank and in the middle of the bottom of a lower barrel of the electrolytic tank in a digging manner; a tensile sample passes through the small holes and is sealed by a sealing rubber ring; a reference electrode is arranged in a salt bridge; a water outlet is formed in the other side of the upper barrel of the electrolytic tank, and a water inlet is formed in one side of the lower barrel of the electrolytic tank; a cold water pipe is arranged at the upper part in a corrosive solution tank; a hot water pipe is arranged at the lower part in the corrosive solution tank; the corrosive solution tank is respectively connected with the lower barrel and the upper barrel of the electrolytic tank; an air inlet is formed in the water inlet of the lower barrel of the electrolytic tank, and is connected with an air blower; a temperature control device is formed by connecting a condensing device, a heating device, a temperature sensor, an electronic temperature induction switch and a temperature controller; and a data acquisition device is arranged in the temperature controller. The corrosion test device is simple in main body structure, reliable in principle, low in preparation cost, good in test effect, easy in control of environmental parameters and environment-friendly.
Owner:725TH RES INST OF CHINA SHIPBUILDING INDAL CORP
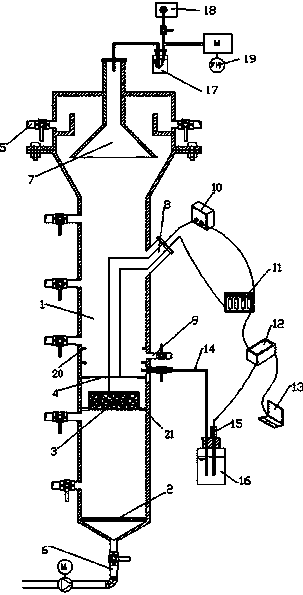
Simple stimulation apparatus for corrosion and electrochemistry tests in low speed pipeline
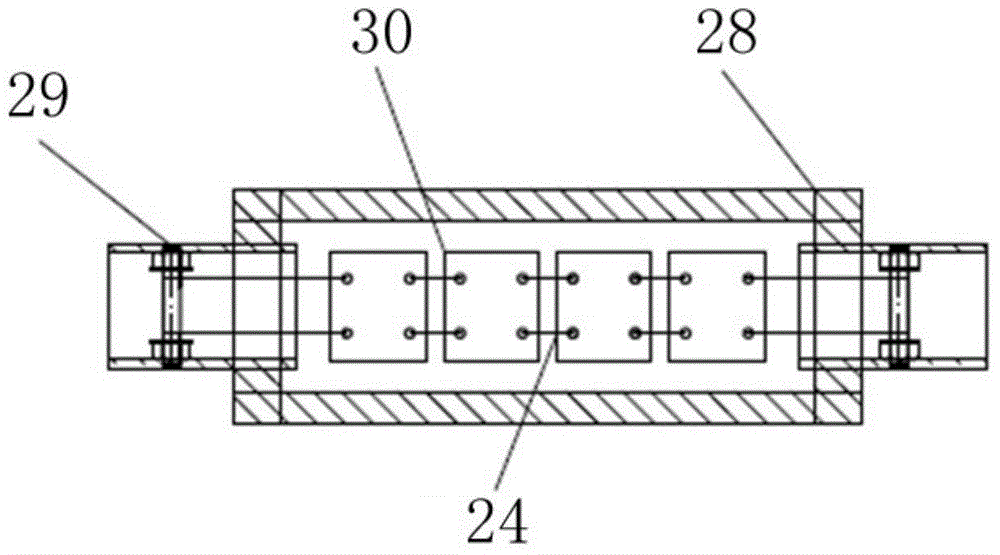
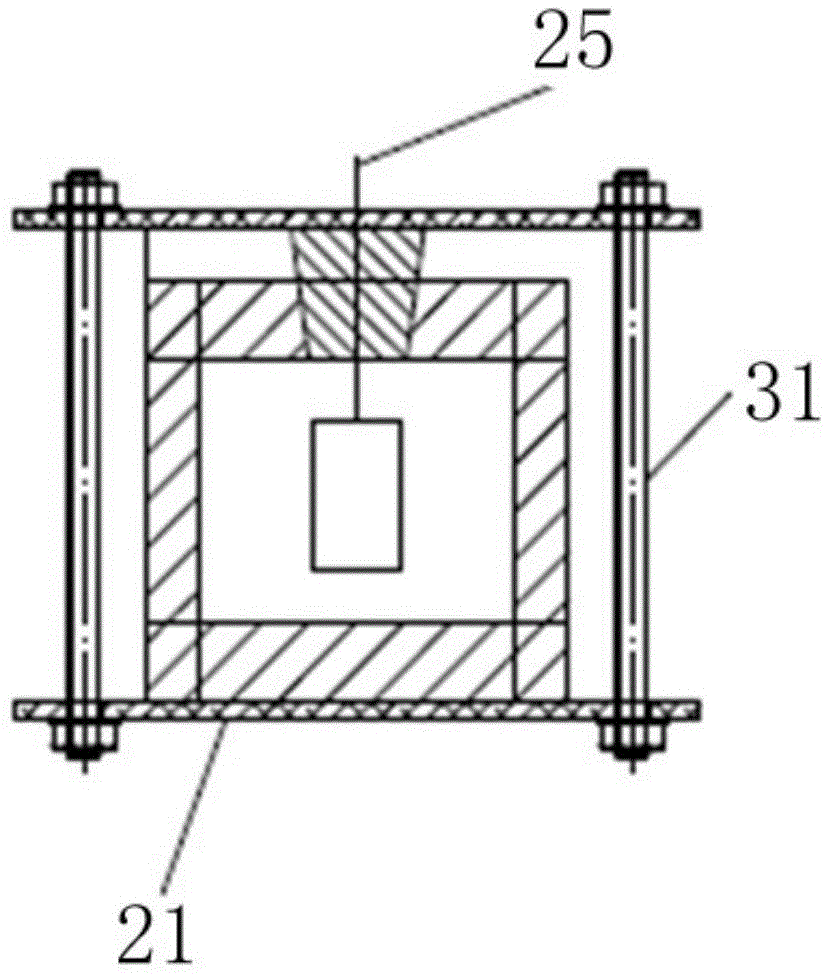
ActiveCN104880502AEasy to makeLow costMaterial analysis by electric/magnetic meansElectricityTest flow
The invention discloses a simple stimulation apparatus for corrosion and electrochemistry tests in a low speed pipeline. The apparatus can realize electrochemical test in a pipeline with the flow speed being smaller than 1m / s in below 75DEG C closed environment with different corrosion media and corrosion simulation acceleration corrosion test in a pipeline with the flow speed being smaller than 3m / s. The apparatus comprises a corrosion solution storage container, a solution circulating and metering system, a simulation pipeline internal corrosion sample chamber and an electrochemical test device. The corrosion solution container is mainly used for storing a large amount of a solution, the solution circulating and metering system comprises a variable frequency magnetic pump and a flow meter, and the flow meter can determine the test flow speed; and the simulation pipeline internal corrosion sample chamber stimulates six o'clock direction corrosion and other tests in a sample stimulation pipeline, and an electrochemical test chamber comprises an electrochemical test interface, a reference electrode and an outside salt bridge. The apparatus has the advantages of great reduction of leakage of hydrogen sulfide and a solution thereof, improvement of the safety of test personnel and environment, convenient and accurate stimulation of corrosion and electrochemical parameter determination in the pipeline under practical conditions, and wide test application range.
Owner:INST OF METAL RESEARCH - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Card type potassium ion sensor and method for preparing card type potassium ion sensor
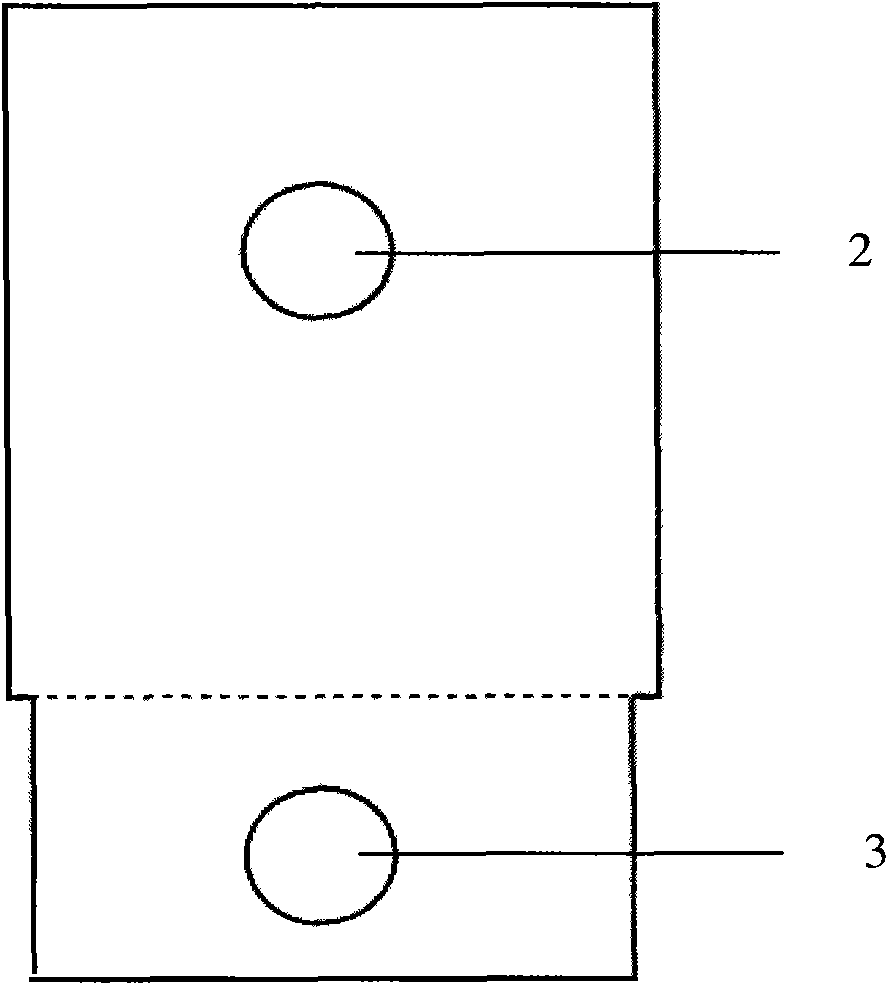
ActiveCN103424451AAchieve integrationMiniaturizationMaterial analysis by electric/magnetic meansInsulation layerSalt bridge
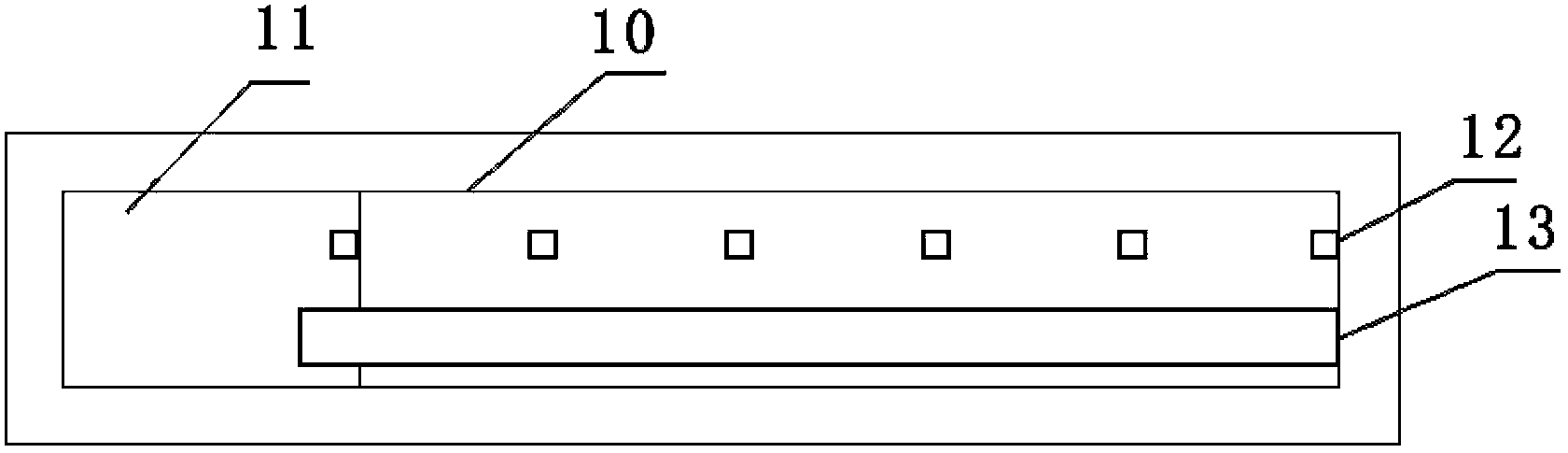
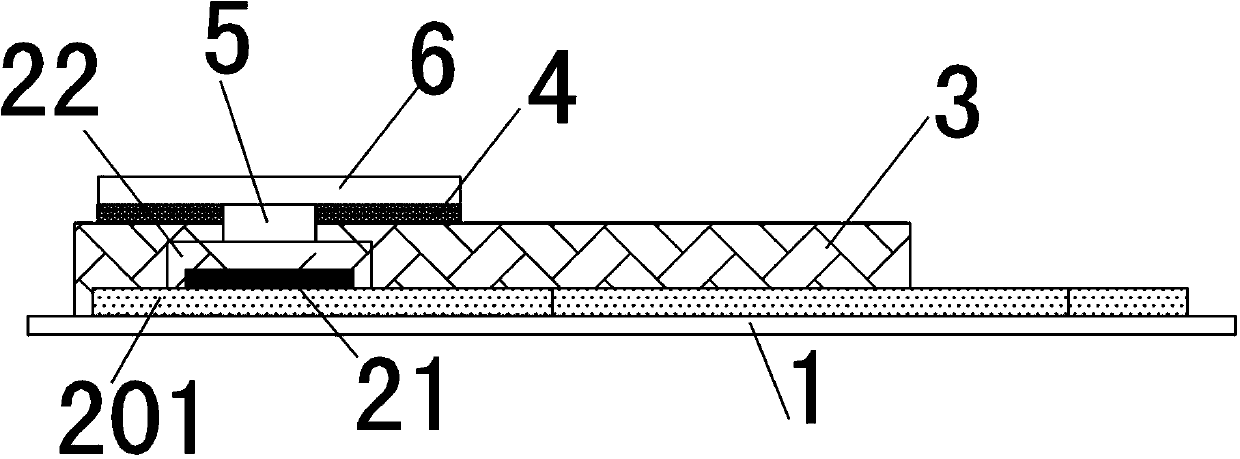
The invention relates to the technical field of electrochemical sensors, in particular to a card type potassium ion sensor and a method for preparing the card type potassium ion sensor. The sensor comprises a base plate (1), two potassium ion selective electrodes (2) arranged on the base plate (1) in parallel, an insulation layer (3) and a salt bridge (4). Each potassium ion selective electrode (2) comprises an electrode substrate system (20), an electrolyte layer (21) and a potassium ion sensitive membrane (22), wherein each electrode substrate system (20) is composed of a reaction electrode (201), a contact electrode (202) and a conductive wire (203), the reaction electrodes (201) and the contact electrodes (202) are arranged on the base plate (1), and the conductive wires (203) are connected with the reaction electrodes (201) and the contact electrodes (202). The electrolyte layers (21) are arranged on the reaction electrodes (201) of the electrode substrate systems (20), and the potassium ion sensitive membranes (22) surround the electrolyte layers (21). The sensor is convenient to carry, and has the advantages of being easy to operate, rapid in response and stable in work.
Owner:深圳市希莱恒医用电子有限公司
Silver/silver chloride reference electrode and manufacturing method of reference electrode
ActiveCN104297311AImprove stabilityPerformance unchangedMaterial electrochemical variablesSalt bridgeChloride
The invention discloses a silver / silver chloride reference electrode and a manufacturing method of the reference electrode. The silver / silver chloride reference electrode comprises an electrode sleeve, a composite metal wire electrode (2) and reference salt (3), wherein the electrode sleeve comprises an electrode shell and a salt bridge (4) which are connected together; the material of the salt bridge (4) is borosilicate glass; the silver / silver chloride reference electrode is fully sealed; the composite metal wire electrode (2) comprises a section A, a section B, a section C and a section D which are sequentially connected with one another. The manufacturing method of the silver / silver chloride reference electrode comprises the steps of filling salt and sealing. The reference electrode is simple to manufacture, low in cost, high in reproducibility, high in stability, high in reversibility, fast in response to signal, easy to store, free of pollution to research system and in particular suitable for industrial production. The reference electrode is suitable for researching electrochemical properties of a chloride mixed fuse salt system at the temperature of 350-650 DEG C.
Owner:SHANGHAI INST OF APPLIED PHYSICS - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Multi-term ion biochemical analysis dry plate and preparation method thereof
InactiveCN105353018AShort response timeHigh measurement accuracyMaterial analysis by electric/magnetic meansSalt bridgeOsmosis
The invention relates to a multi-term ion biochemical analysis dry plate and a preparation method thereof, which belong to the technical field of a blood gas biochemical sensor, and the multi-term ion biochemical analysis dry plate is used for detecting sodion, potassium ions, calcium ions, chloride ions and carbon dioxide concentration in body fluid. The dry plate comprises a supporting layer, a sodion selective electrode, a potassium ions selective electrode, a calcium ions selective electrode, a chlorine ions selective electrode, a carbon dioxide selection electrode, a reference electrode, an interface layer, a salt bridge and a top. The salt bridge is sealed between the interface layer and the top, sodion, potassium ions, calcium ions, chloride ions, the carbon dioxide selection electrode and the reference electrode are respectively bounded to the supporting layer, the interface layer and the top for assembly to obtain the dry plate. When a test is carried out, a reference liquid and a test liquid are mutually conducted through osmosis of the salt bridge. The dry plate can simultaneously measure the sodion, the potassium ions, the calcium ions, the chloride ions and the carbon dioxide concentration in the liquid to-be-measured, has the advantages of simple operation, fast response speed and small volume, has the characteristics of simple preparation operation and low production cost, and is suitable for industrial production.
Owner:吴国清
Heterogeneous membrane electrodes
ActiveUS7767068B2Low costRapid gasLaboratory glasswaresMaterial electrochemical variablesElectrical conductorSalt bridge
The present invention relates to planar electrochemical sensors with membrane coatings used to perform chemical analyses. The object of this invention is to provide unit-use disposable sensors of very simple and inexpensive construction, preferably with only a single membrane coating on an electrode. The invented devices are potentiometric salt-bridge reference electrodes and dissolved gas sensors constructed with a heterogeneous membrane coating of a conductor. The heterogeneous membrane, which is an intimate admixture of a hydrophobic and a hydrophilic compartment, concurrently supports constrained transport of non-volatile species through its hydrophilic compartment and rapid gas and water vapor transport through its hydrophobic compartment.
Owner:SIEMENS HEALTHCARE DIAGNOSTICS INC
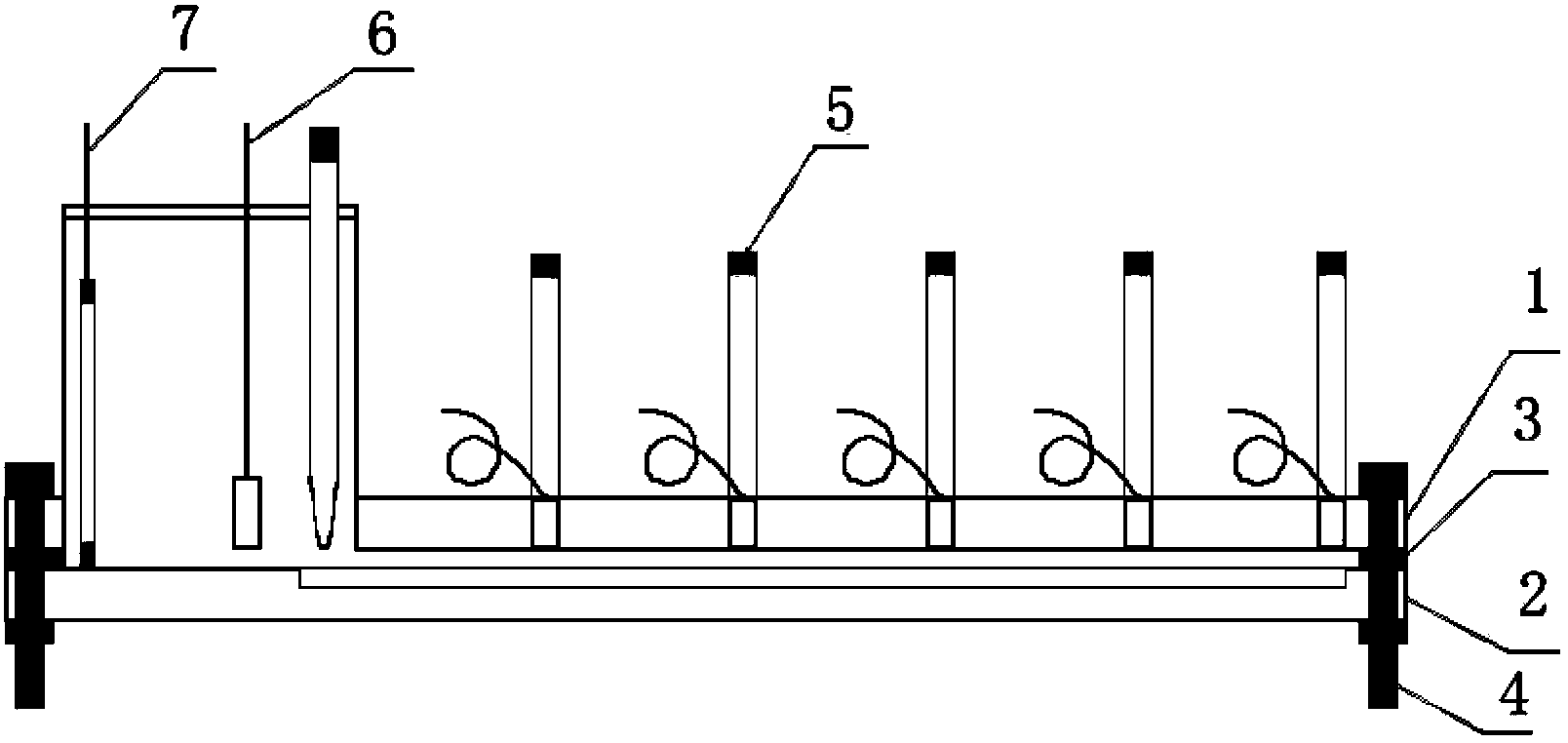
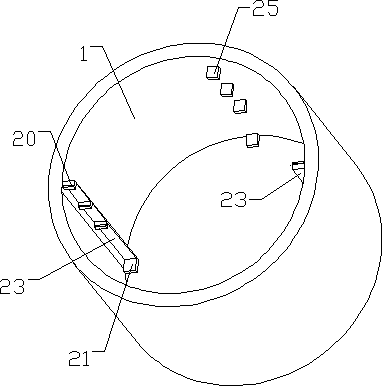
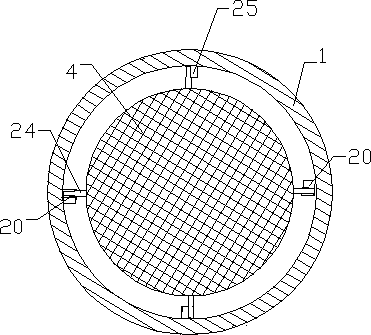
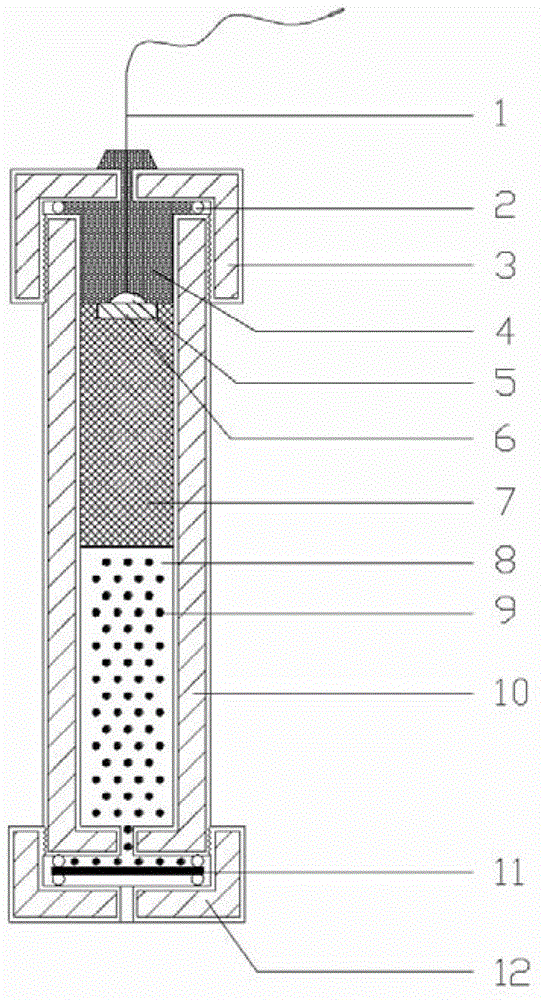
Online detection device and method of battery electrode level in lead-acid storage battery inner chemosynthesis process
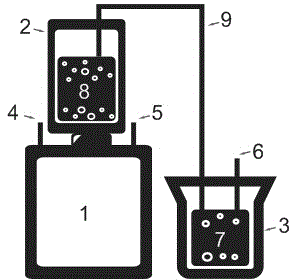
The invention discloses an online detection device and a method of battery electrode level in lead-acid storage battery inner chemosynthesis process; the detection device consists of an acid kettle, a beaker, a screw A, a screw B, and a mercury sulfate electrode C; a sulfuric acid chemosynthesis solution is contained in the acid kettle; a sulfuric acid solution is contained in the beaker; the two sulfuric systems are connected via a salt bridge; the mercury sulfate electrode C is placed in the sulfuric acid solution; A-C end and B-C end are respectively connected with an electric potential measuring device. The detection steps are as follows: taking an assembled non-chemically synthesized lead-acid storage battery, inserting the screw A and the screw B on the bridge, sealing the edges with sealants; assembling the acid kettle with the battery, then adding acid; standing the battery for 1 hour after injected the acid, implementing the chemosynthesis according to the inner chemosynthesis technology; then inserting the salt bridge into the acid kettle and the beaker, and connecting a data collector for collecting data. In condition of not dissecting the battery, the electrode level in lead-acid storage battery inner chemosynthesis process can be precisely detected online, thus being convenient for understanding the chemosynthesis information, and researching the research technology.
Owner:HARBIN INST OF TECH
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com