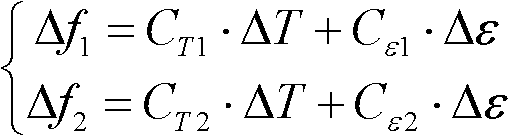Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
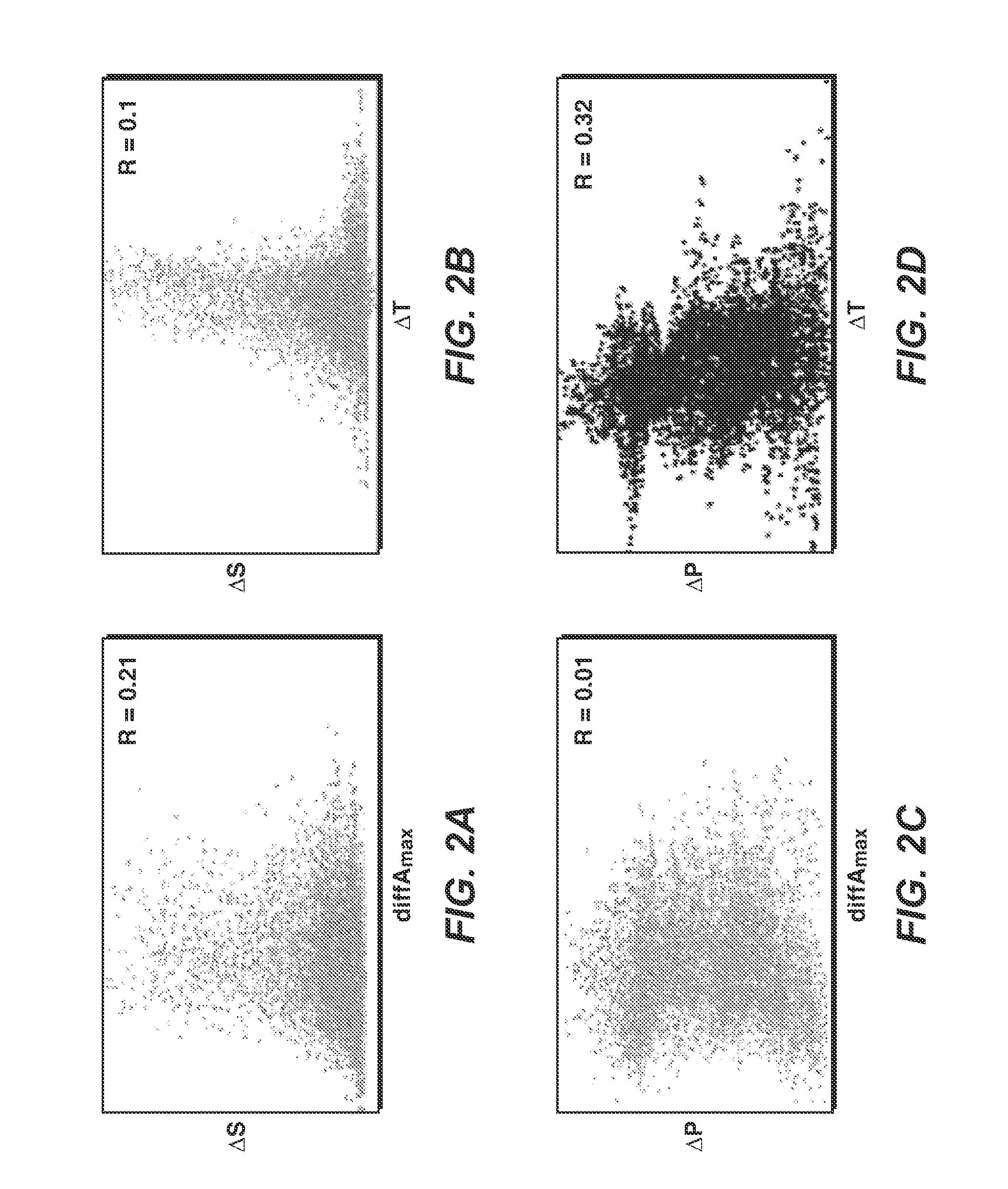
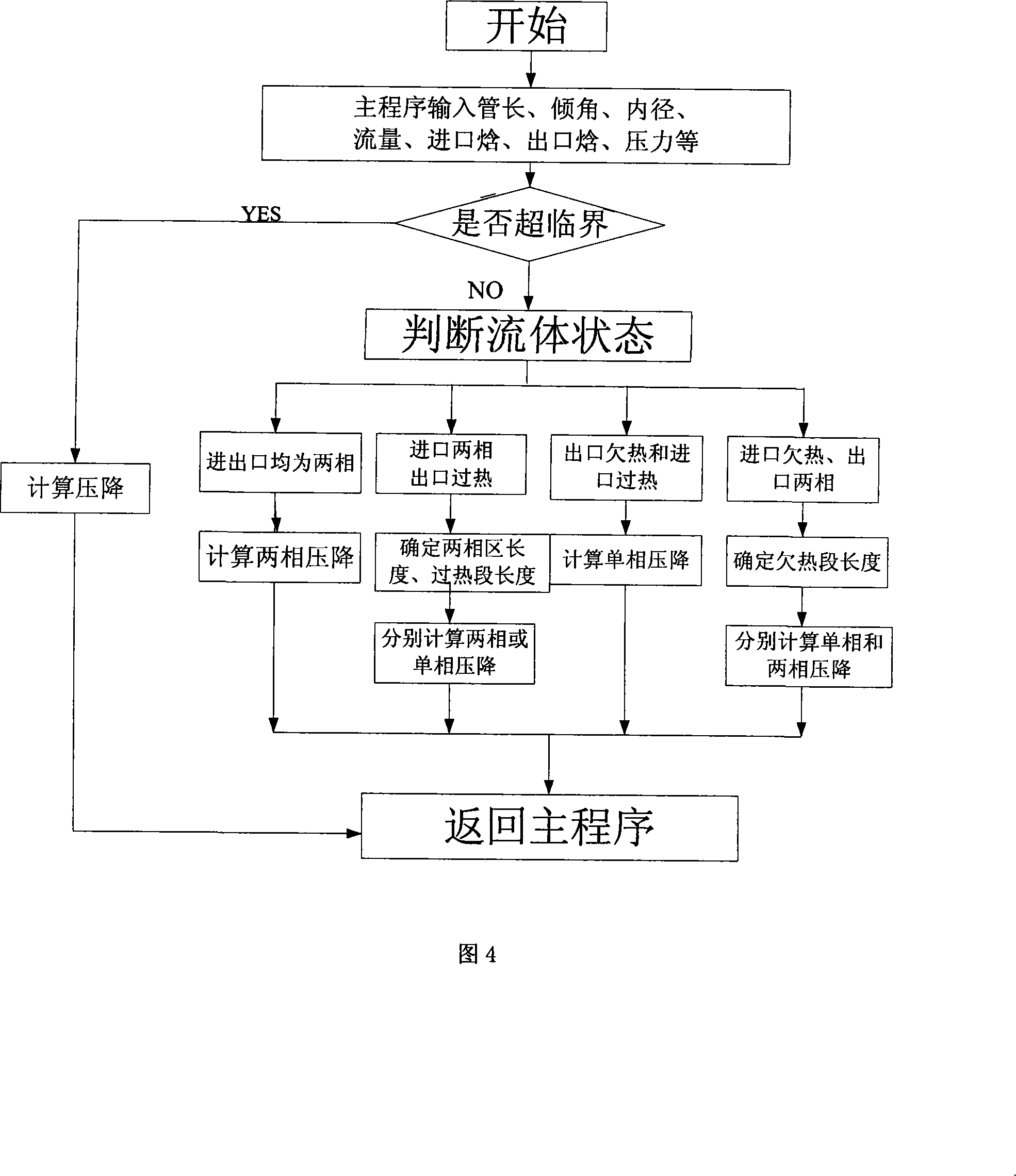
575 results about "Stress change" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Physiological Effects of Stress from Change. Stress can lead to numerous physiological changes. When you experience stress, your body releases many chemicals and hormones, such as cortisol and adrenaline, which prepare you for fight or flight.
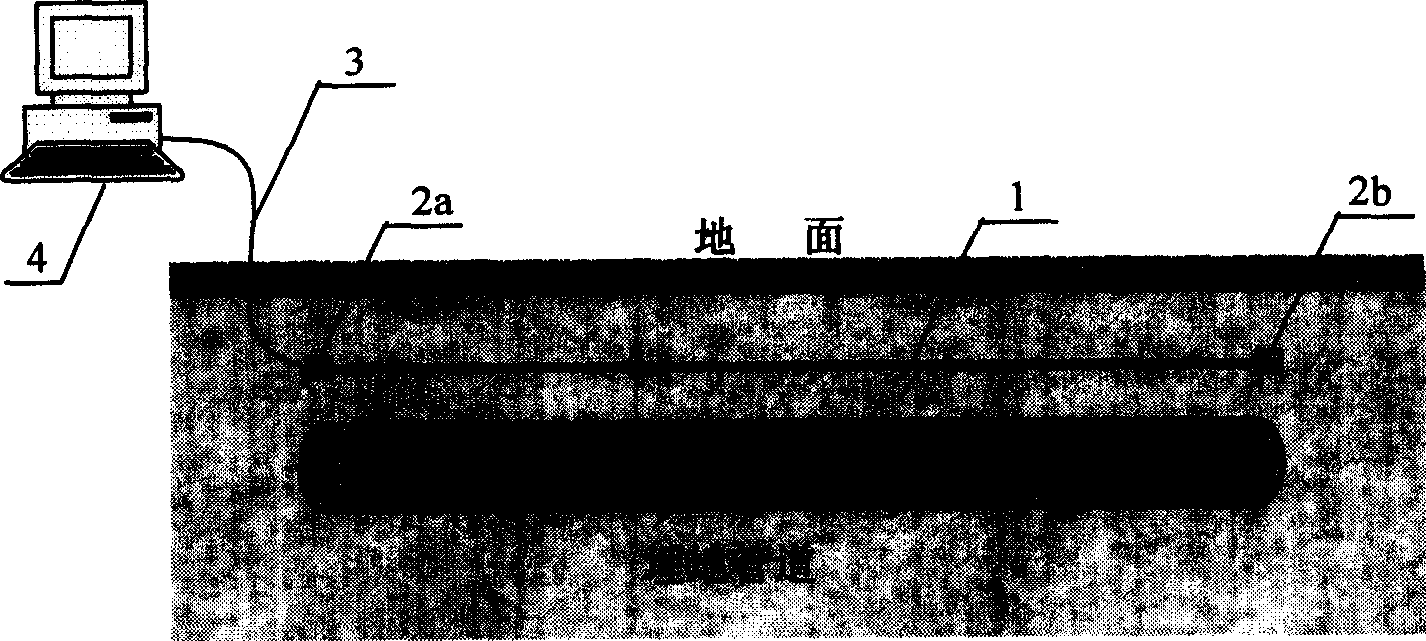
Interference distributed fibre-optical pipe leakage real-time monitoring method and device
InactiveCN1598516AQuick responseStrong electrical insulationFluid-tightness measurementPipeline systemsFiberMonitoring system
The invention discloses a distributed optical fiber oil channel leakage monitoring method and device based on interference theory. The monitoring system needs to lay an optical cable along the channel, and forms a fiber micro oscillation sensor with the fiber in the cable. When the channel has leakage, it will generate leakage noise, thus the fiber micro oscillator sensor can measures the micro oscillation and stress change around the channel, and it can fix on the leakage position quickly and accurately. The device is made up of distributed fiber micro oscillation sensor, guiding fiber and micro oscillation detector. The technology not only can detect the leakage, but also can detect the event which can cause the leakage, and it can send out alarm and accurate localization. The device has high sensitivity and localization precise, and the disturbance ability is strong, and it is reliable.
Owner:TIANJIN UNIV
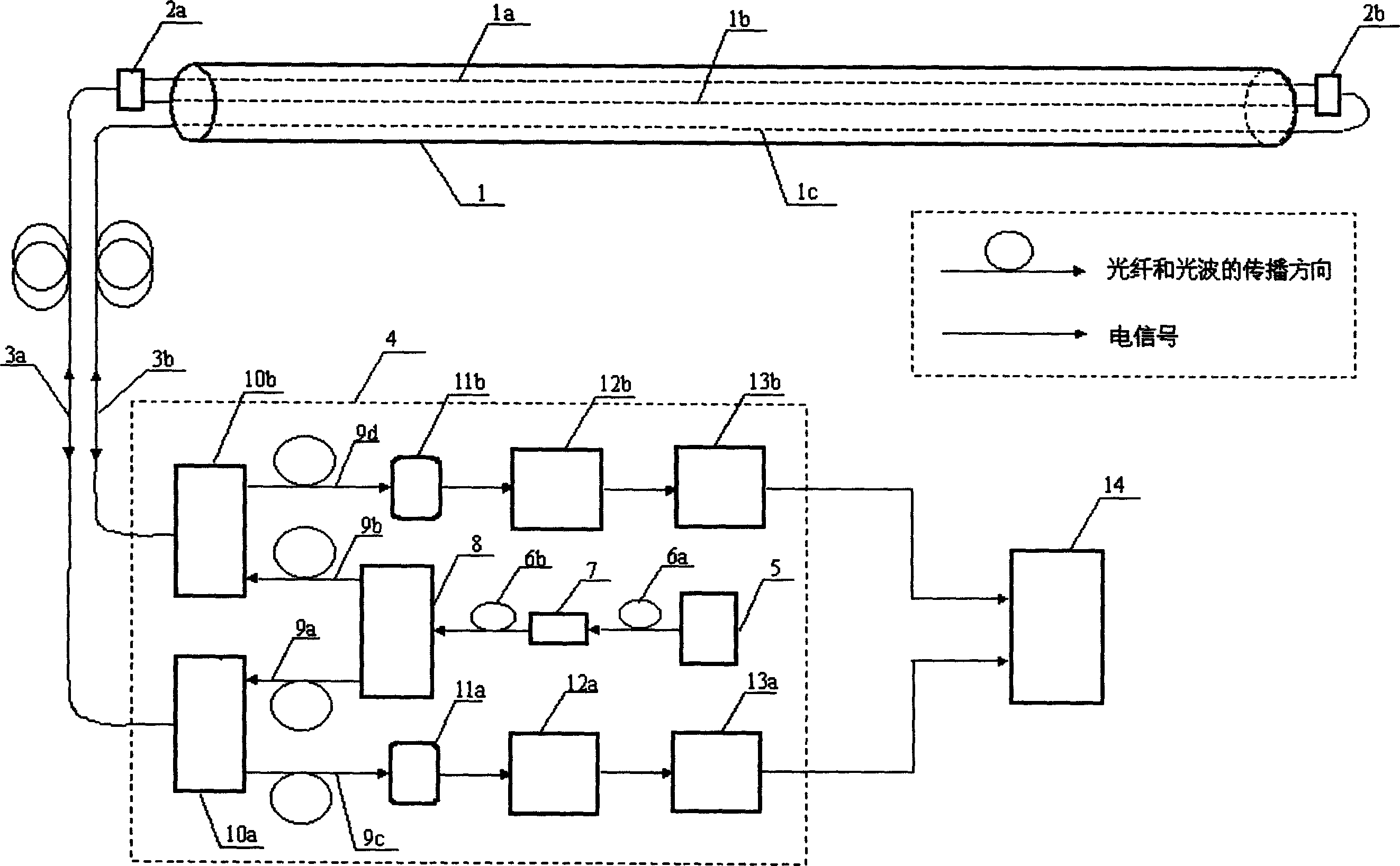
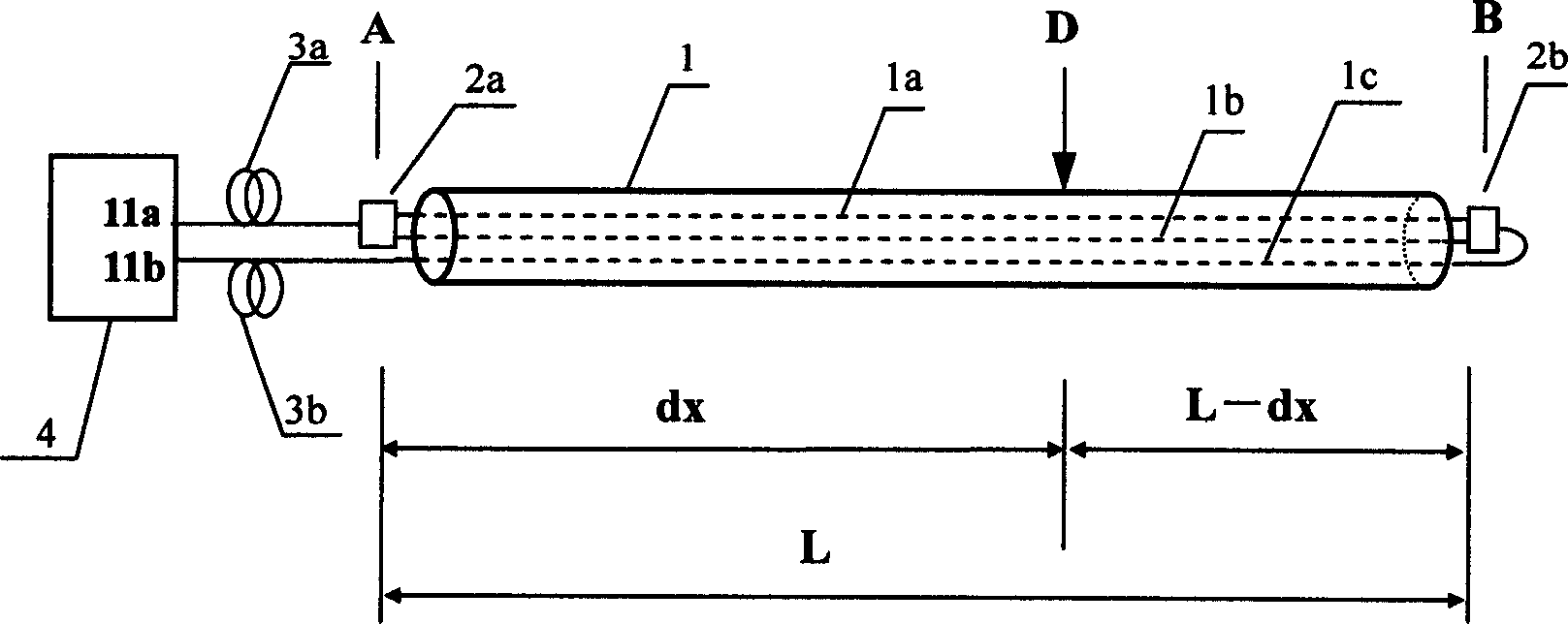
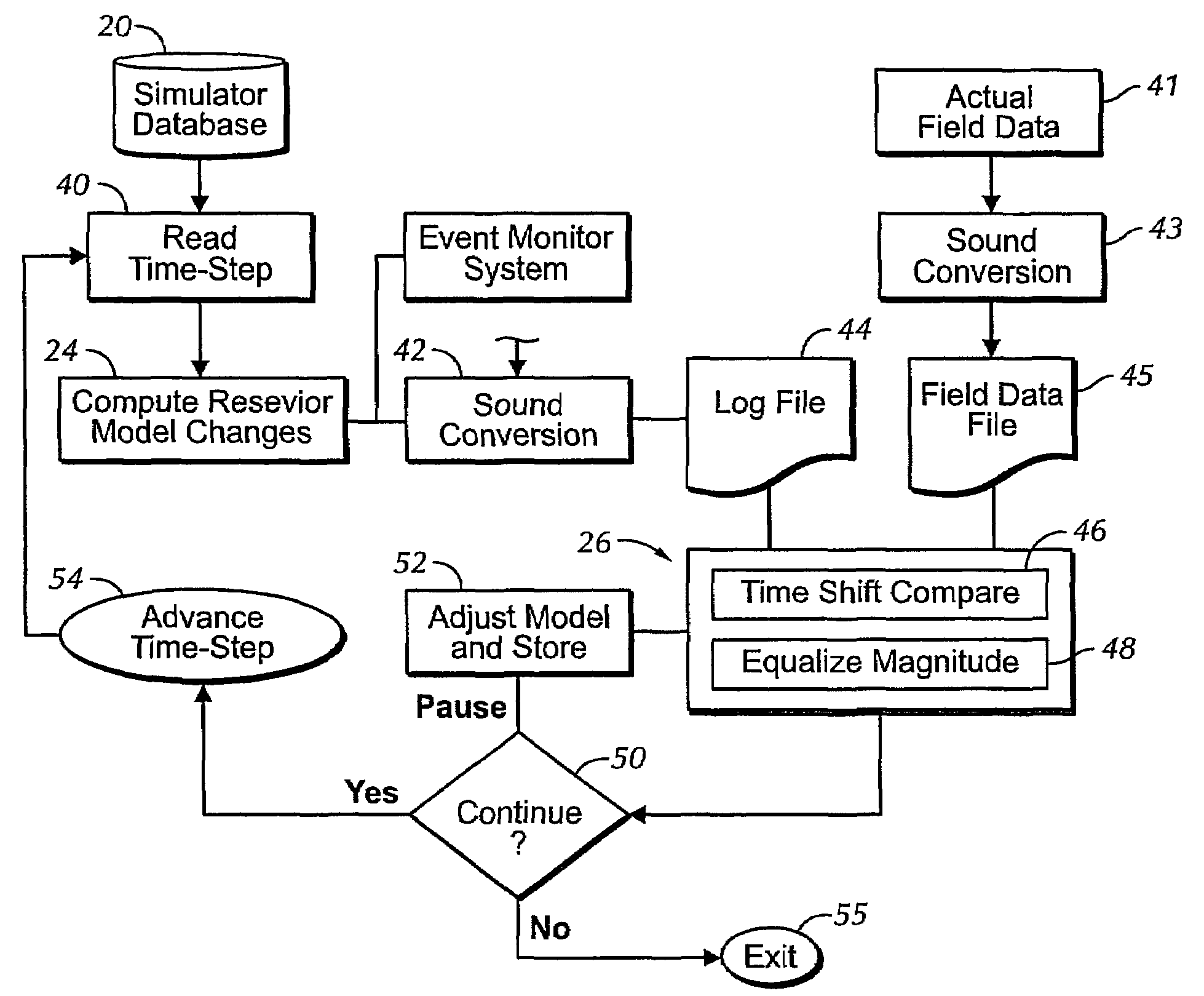
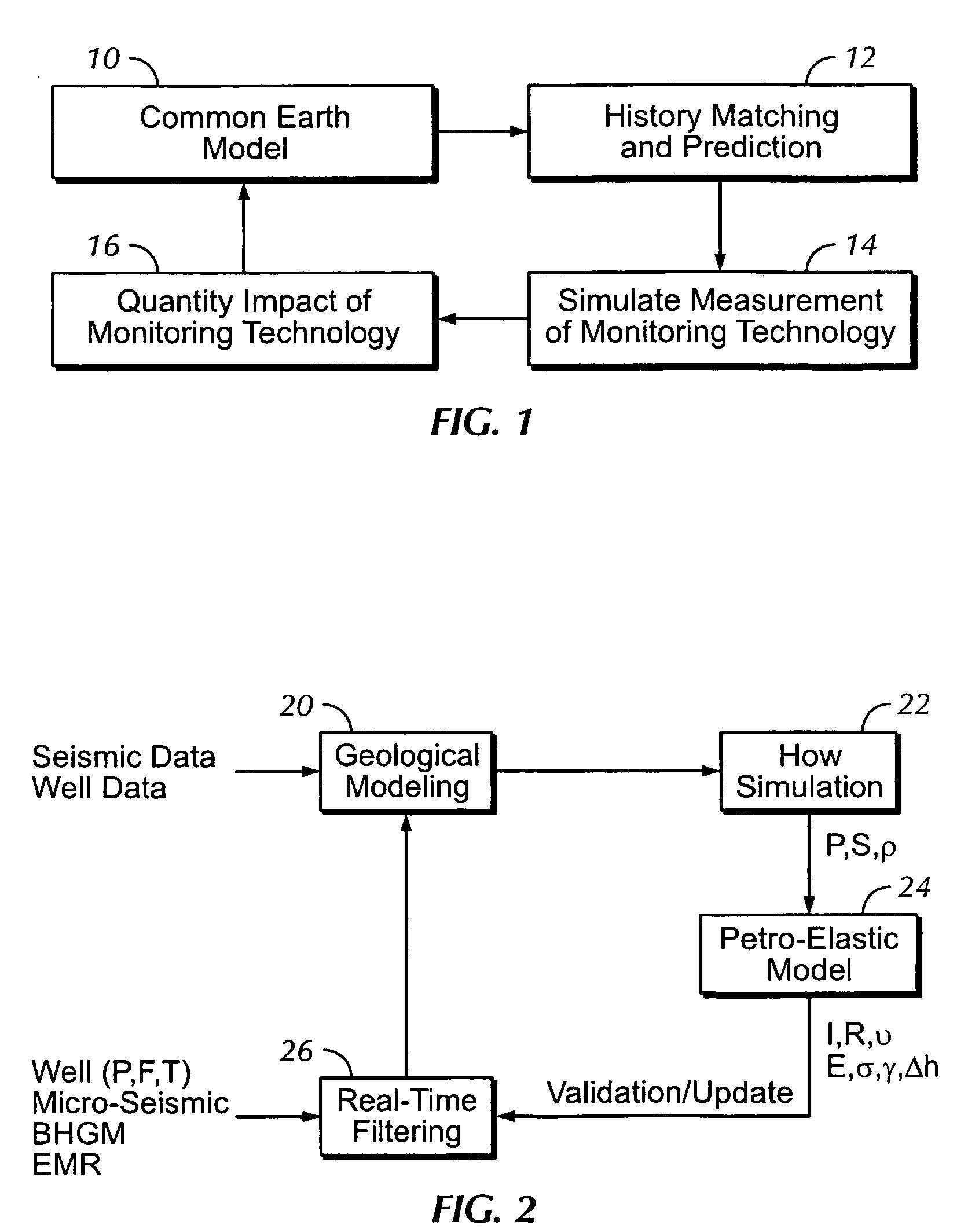
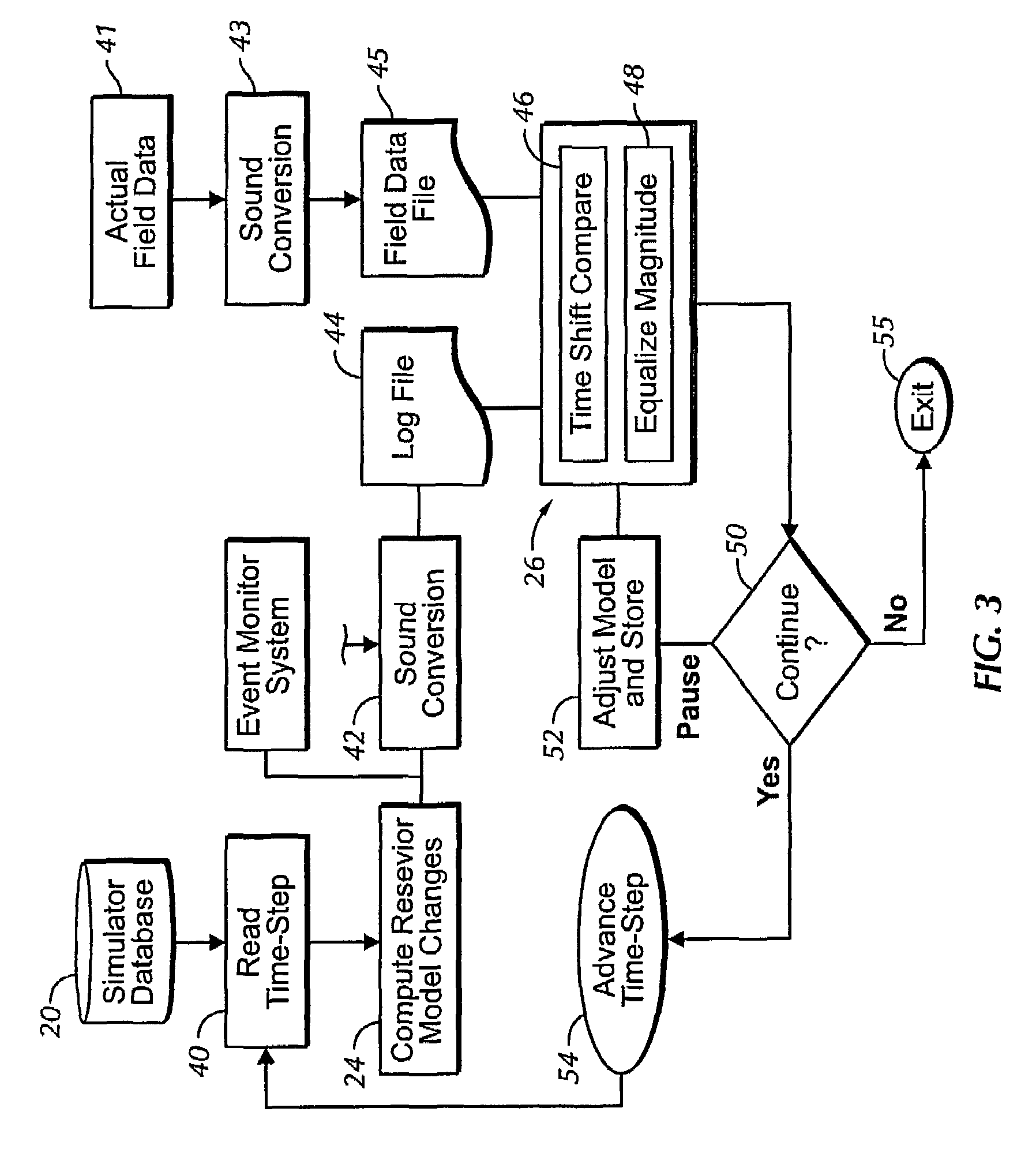
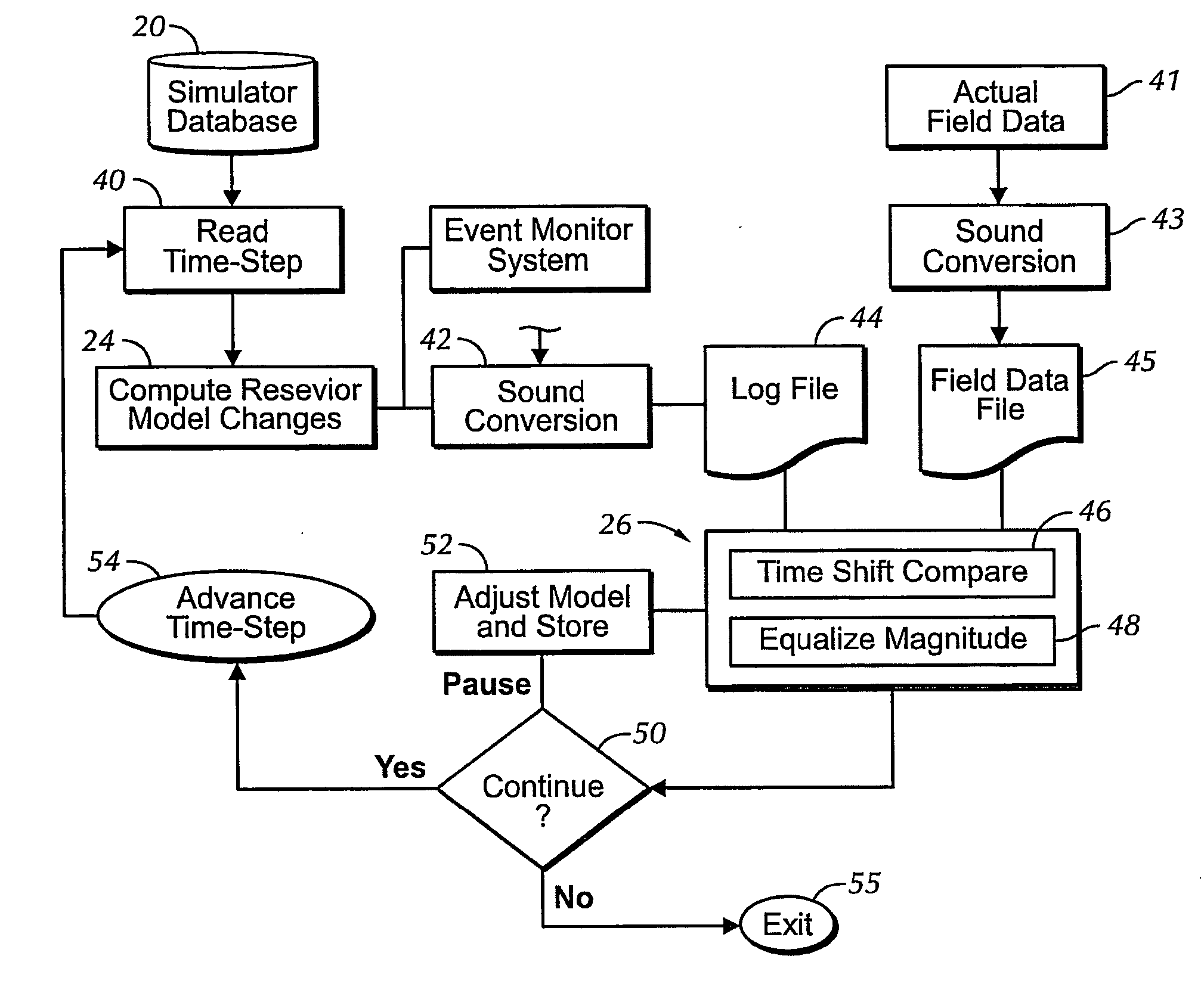
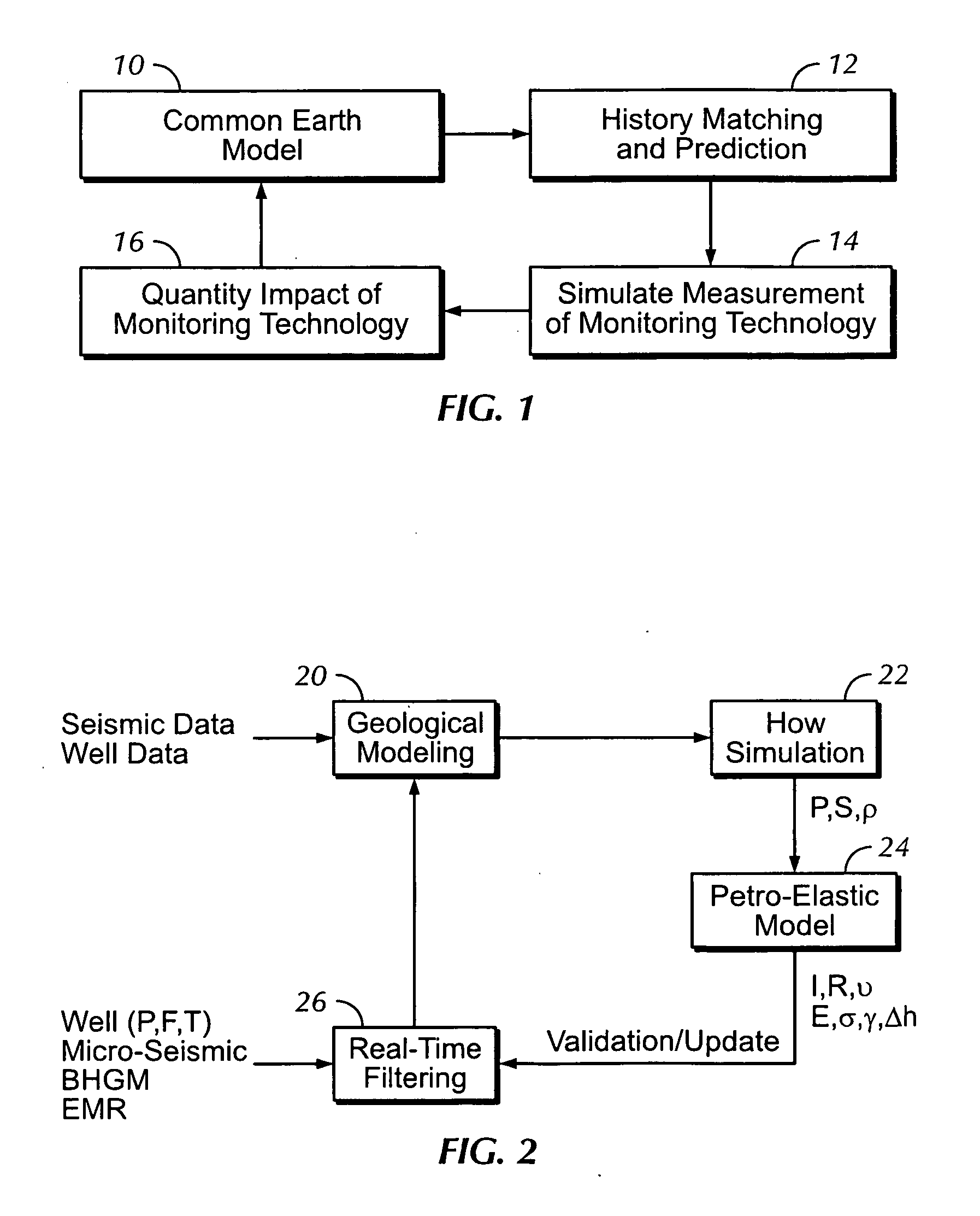
Sound enabling computerized system for real time reservoir model calibration using field surveillance data
ActiveUS7620534B2Digital data processing detailsVolume/mass flow measurementHydrocotyle bowlesioidesComputerized system
A computer-based system generates digital and audio responses to changes in fluid and rock properties of a producing hydrocarbon reservoir for surveillance analysis. The system calibrates observed changes against directly-measured field data in order to optimize the reservoir model. The changes may include, for example, stress changes in rock, impedance changes in rock, and fluid density changes.
Owner:ARAMCO SAUDI
Sound enabling computerized system for real time reservoir model calibration using field surveillance data
ActiveUS20070255500A1Digital data processing detailsVolume/mass flow measurementReliable computingComputerized system
A computer-based system generates digital and audio responses to changes in fluid and rock properties of a producing hydrocarbon reservoir for surveillance analysis. The system calibrates observed changes against directly-measured field data in order to optimize the reservoir model. The changes may include, for example, stress changes in rock, impedance changes in rock, and fluid density changes.
Owner:ARAMCO SAUDI
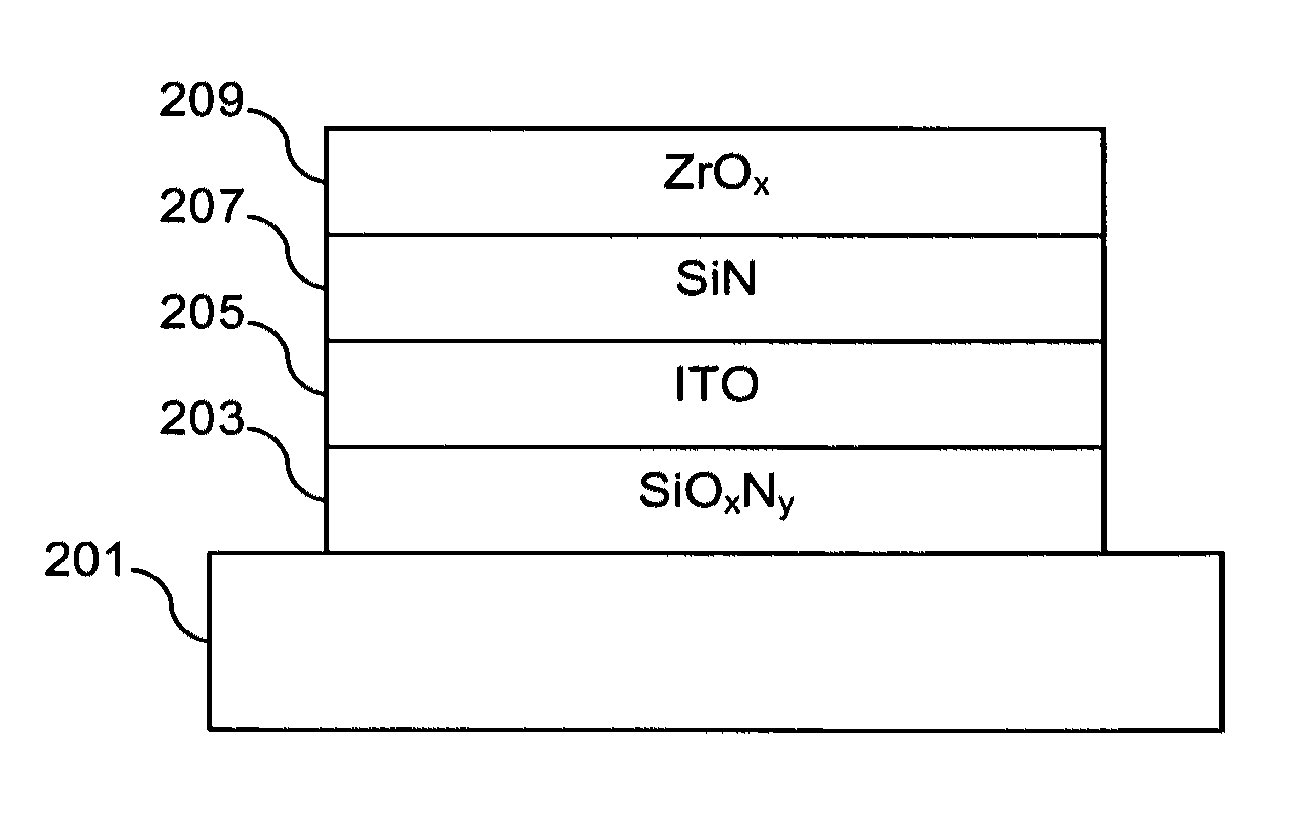
System and/or method for heat treating conductive coatings using wavelength-tuned infrared radiation
ActiveUS20120048722A1Reduce the impactSimple technologyMuffle furnacesVacuum evaporation coatingDownstream processingConductive coating
Certain example embodiments relate to systems and / or methods for preferentially and selectively heat treating conductive coatings such as ITO using specifically tuned near infrared-short wave infrared (NIR-SWIR) radiation. In certain example embodiments, the coating is preferentially heated, thereby improving its properties while at the underlying substrate is kept at low temperatures. Such techniques are advantageous for applications on glass and / or other substrates, e.g., where elevated substrate temperatures can lead to stress changes that adversely effect downstream processing (such as, for example, cutting, grinding, etc.) and may sometimes even result in substrate breakage or deformation. Selective heating of the coating may in certain example embodiments be obtained by using IR emitters with peak outputs over spectral wavelengths where the conductive coating (or the conductive layer(s) in the conductive coating) is significantly absorbing but where the substrate has reduced or minimal absorption.
Owner:GUARDIAN GLASS LLC
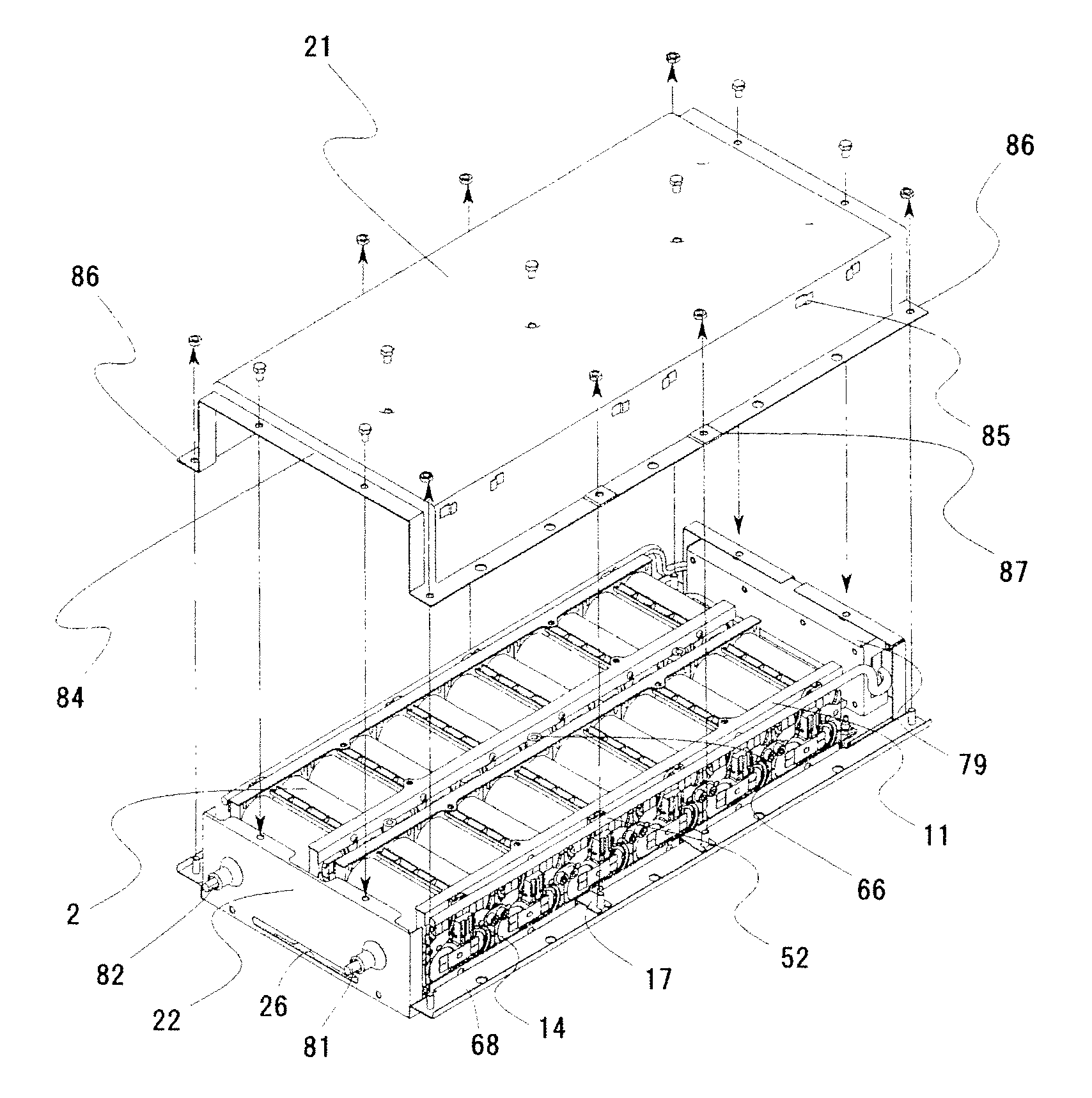
Secondary battery module
InactiveUS20080057393A1Improve vibration resistanceImprove the immunityPrimary cell to battery groupingSecondary cellsEngineeringStress change
The present invention provides a secondary battery module which is excellent in vibration resistance. A battery module 20 has assembled battery blocks 11 each constituted by screw-fixing the assembled batteries 2 to the block bases 3, 4 supporting a lower portion thereof and the two block reinforcing plates 5 supporting an upper portion thereof, the six assembled batteries 2 are sandwiched by and fixed firmly to the block bases 3, 4 and the block reinforcing plates 5. The assembled batteries 2 do not move freely even if vibration is added to the battery module 20. Because the elastic sheet 9 is laid between the block bases 3, 4 and the assembled batteries 2, since a space derived due to variance in size accuracy of frames 12 which hold and fix the unit cells 11 and derived due to variance in size accuracy of the block bases 3, 4 can be removed, and vibration resistance can be enhanced. To thermal stress change caused due to combination of different materials, influence thereof can be reduced by laying the elastic sheet 9.
Owner:HITACHI AUTOMOTIVE SYST LTD
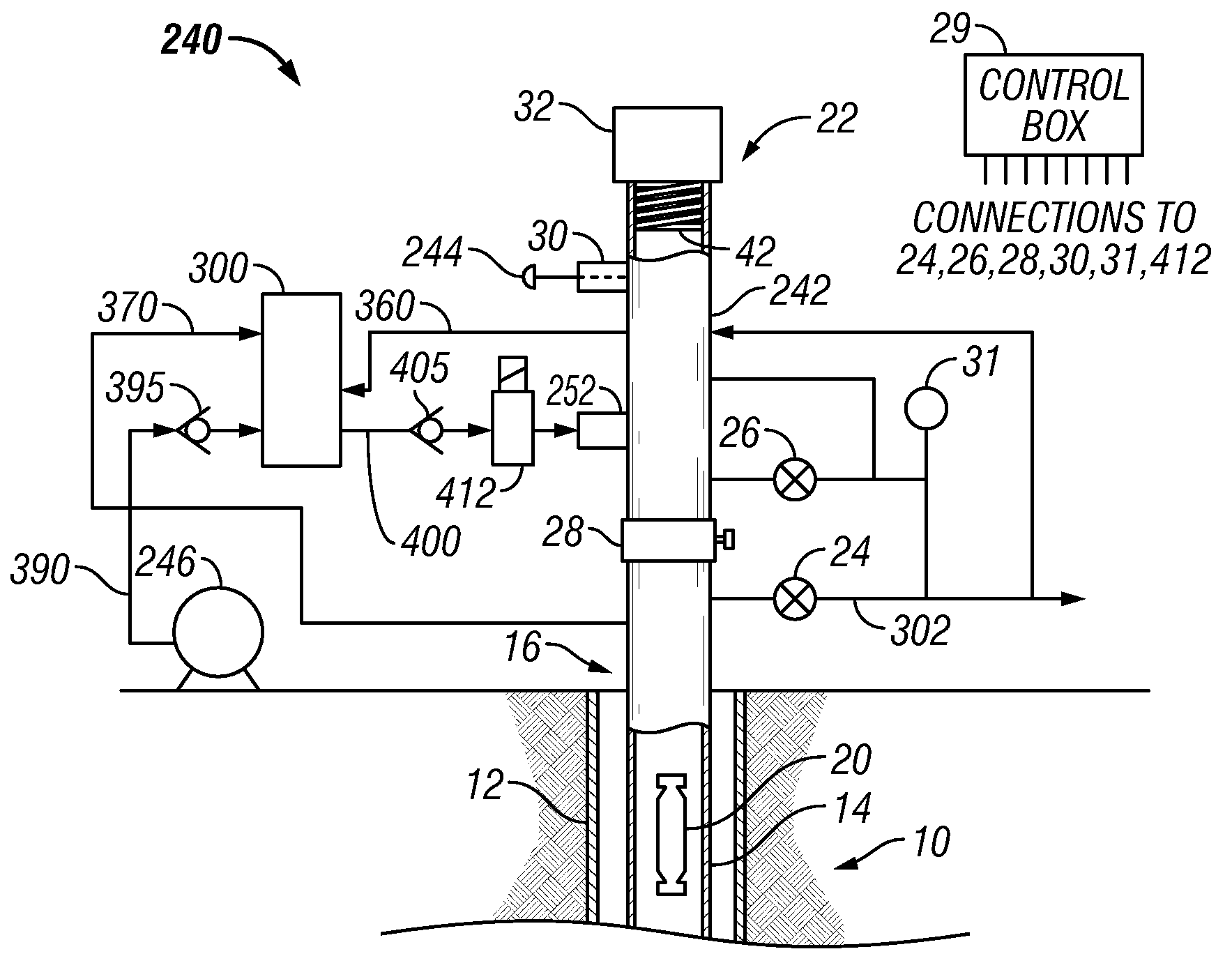
Devices and Methods for Utilizing Pressure Variations as an Energy Source
ActiveUS20080308270A1Travel can be limitedPump componentsCleaning apparatusEnvironmental effectDifferential pressure
The present disclosure relates to a pump mechanism driven by differential pressure conditions and method for delivery of materials. In one embodiment, the pump mechanism may be used to deliver treatment chemical to a plunger apparatus or directly to a wellbore by exploiting pressure conditions found at a well. In certain embodiments, the pump mechanism is able to balance high pressure conditions available within a petroleum formation against low pressure conditions present in a common flow line serving the well. In so balancing these pressures, the pump mechanism is able to automatically tune itself to the needs of the well, ensuring continued operation over a wider range of operating conditions. The pump mechanism has the further advantages of lower operation costs and less environmental impact as compared with existing pumps. The pump mechanism can be used in connection with a chemical applicator which can be used to apply chemical into, onto, or below, a plunger or plunger / dispenser apparatus used in plunger lift operations, or to apply chemical directly down the well. It is emphasized that this abstract is provided to comply with the rules requiring an abstract which will allow a searcher or other reader to quickly ascertain the subject matter of the technical disclosure. It is submitted with the understanding that it will not be used to interpret or limit the scope or meaning of the claims. 37 CFR 1.72(b)
Owner:CONOCOPHILLIPS CO
Distributed optical fiber Brillouin sensing device and method thereof for detecting temperature and strain synchronously
InactiveCN102607621AHigh measurement accuracyEasy to implementThermometers using physical/chemical changesUsing optical meansFrequency shiftLinearity
The invention relates to a distributed optical fiber Brillouin sensing device for detecting temperature and strain synchronously and a method for detecting the temperature and the strain synchronously by use of the device. The method is based on the linear relation among the frequency shift change of the spontaneous Brillouin scattering in the optical fiber, external temperature change and external strain change, a compound sensing optical fiber is formed by two different types of sensing optical fibers, and the variation of the temperature and the strain can be distinguished at the same time through different responses of the two optical fibers to the external temperature change and the external stress change. According to the device and the method, the temperature change and the strain change in a sensing area can be detected at the same time, and the detection precision of an optical fiber distributed sensor based on spontaneous Brillouin scattering can be improved.
Owner:SHANGHAI INST OF OPTICS & FINE MECHANICS CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Device and method for measuring permeability coefficient of rock material under action of seepage-stress coupling
InactiveCN101915724AReduce volatilityHigh degree of automationPermeability/surface area analysisMaterial weighingMeasurement deviceCoupling
The invention discloses a device for measuring the permeability coefficient of rock material under the action of seepage-stress coupling, which comprises a triaxial pressure chamber balance system, a permeability coefficient acquisition system and a data acquisition and processing system, wherein the triaxial pressure chamber balance system loads samples axially or laterally through different stress paths; the permeability coefficient acquisition system is connected with the triaxial pressure chamber balance system so as to realize the determination for the quality of penetrating fluid of rock material sample; and the data acquisition and processing system regularly acquires the quality of penetrating fluid of rock material, calculates penetration flow and permeability coefficient, and draws a relationship curve of the permeability coefficient and time, and simultaneously, the data acquisition and processing system also forms a data format of the quality, the penetration flow and the permeability coefficient for storage and display. Such a measurement device can measure the permeability coefficient, as time and stress change, under different stress loading paths, has simple operation and reliable result, and can display the result visually. The invention also discloses a measurement method adopting the measurement device.
Owner:HOHAI UNIV
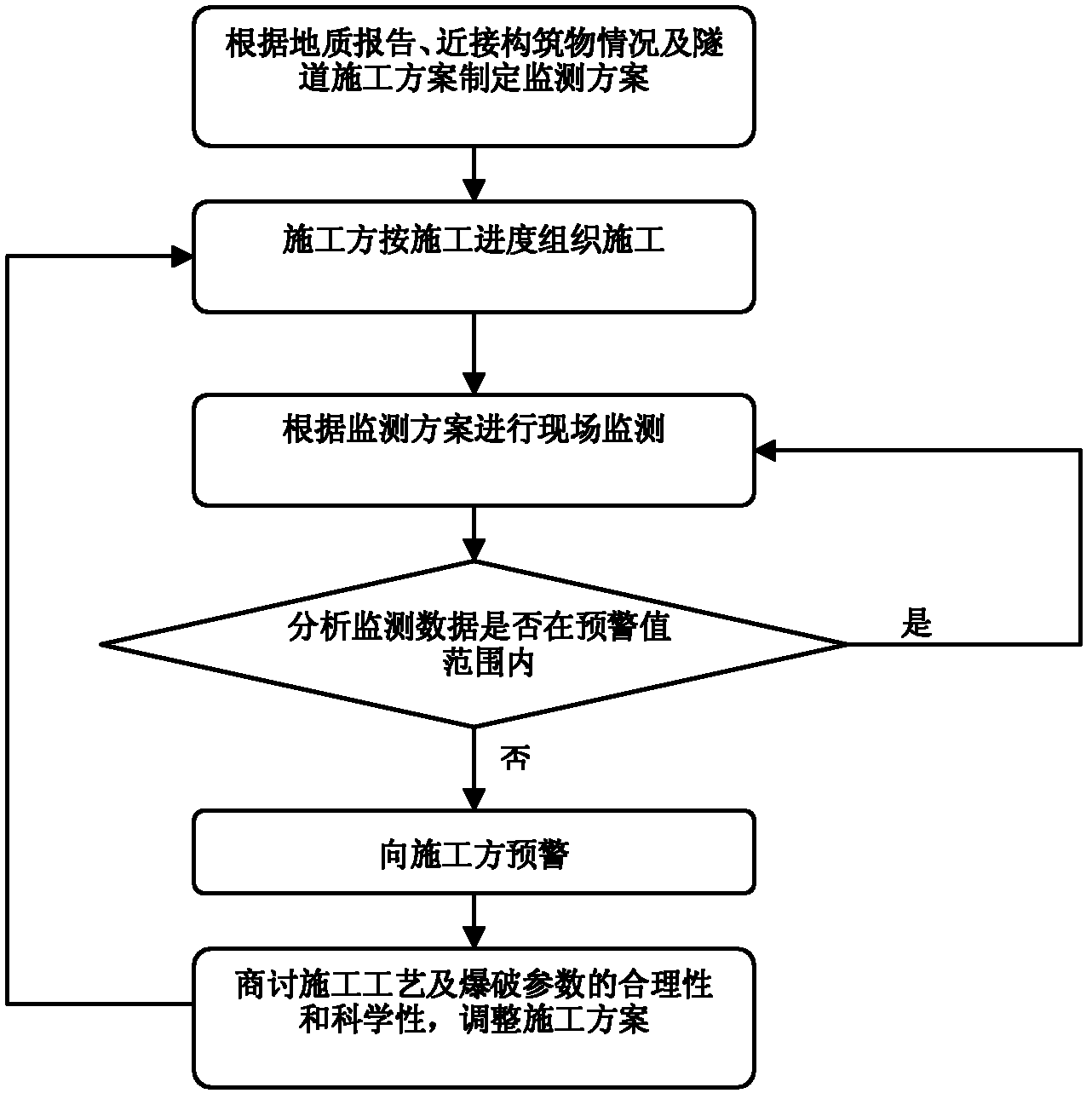
Monitoring method for influence on adjacent existing structures from tunnel excavation
The invention discloses a monitoring method for an influence on adjacent existing structures from tunnel excavation, comprising the following steps: (1), making a monitoring plan according to a geologic report, adjacent existing structure conditions and a construction plan for a tunnel; (2), organizing construction works by the construction party according to the construction progress; (3), performing field monitoring according to the monitoring plan; (4), organizing the monitored data and performing a simulation analysis on the monitored data, and judging whether the data is in the range of the pre-warning value; (5), pre-warning the construction party; (6), assessing the rationality and scientificity of the construction technology, and adjusting the construction plan. The invention establishes a monitoring method with a set of perfect system, and sets monitoring index values, and selects and arranges monitoring points, and monitors vertical deformations of the baseboards of the adjacent existing structures, stress changes of surrounding rocks in disturbed areas, shock vibrations of tunnel blasting, cracks of existing structures and walls, leveling for the baseboard and so on, and establishes communication between the construction and monitored information to form a positive cycling for quality controls on engineering constructions.
Owner:UNIV OF SHANGHAI FOR SCI & TECH
Method for measuring welding residual stress
InactiveCN101539506AReduce additional stressIntegrity guaranteedUsing mechanical meansMaterial analysisThick plateWelding residual stress
The invention relates to a method for measuring welding residual stress-a partial layer-by-layer blind hole removing method for measuring the residual stress on the basis of a blind hole method, which proposes to measure the residual stress in a component by using the partial layer-by-layer blind hole removing method. After materials of certain depth on both the front side and the opposite side of a component to be measured are partially removed, the blind hole method is used for measuring the residual stress. The method is a semi-destructive residual stress measuring method, can be used for carrying out multi-point measurement and measuring the residual stress in the component with severe stress change and has convenient operation and high measuring efficiency. Proved by a thick plate carbon steel welding residual stress measuring test, the method has more accurate measuring results.
Owner:XI AN JIAOTONG UNIV
Method for testing electrochemical corrosion of welded pipe seam in high-stress state and sample of welded pipe seam
InactiveCN101608995ACorrosion Resistance EvaluationFix damageWeather/light/corrosion resistanceMaterial electrochemical variablesSalt bridgeAuxiliary electrode
The invention relates to a method for testing electrochemical corrosion of a welded pipe seam in a high-stress state, which utilizes an electronic universal testing machine, an electrolytic cell component comprising a working electrode, an auxiliary electrode, a reference electrode, a salt bridge and the like, and an electrochemical workstation. Under a load stress of between 0 and 800 MPa, the stress change caused by stress relaxation is corrected regularly by a constant potential method or a constant current method to test the circumferential tensile stress of the welded pipe seam and the circumferential tensile stress of the working electrode. A tensile sample is wide and thick at both ends and narrow and thin in the middle part and is provided with connection holes at both ends. A groove corrosion depth d1 and an average corrosion depth d2 of the working electrode are tested under different loads, so a groove corrosion susceptibility coefficient alpha, alpha=d1 / d2, of the working electrode in practical application can be obtained. The method has no stress relaxation, and the stress is convenient to regulate during test; the sample is free from generating plastic deformation or detachment under the load of high stress, and can be used for corrosion test under the condition of high stress; and the electrochemical workstation can be made full use for testing.
Owner:BAOSHAN IRON & STEEL CO LTD
Reliability acceleration test method of electronic products
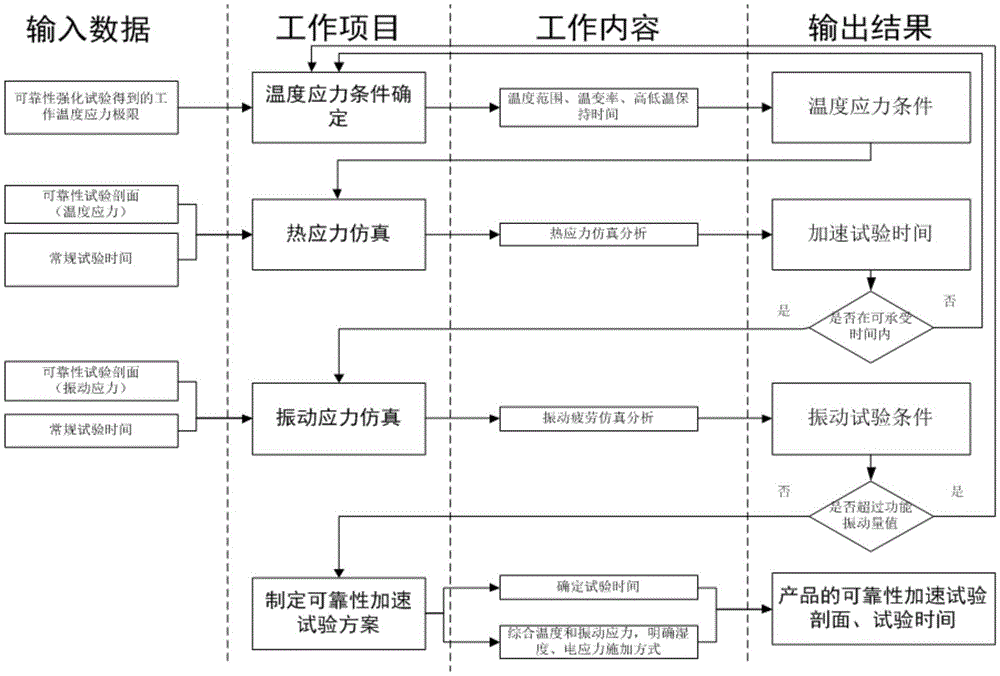
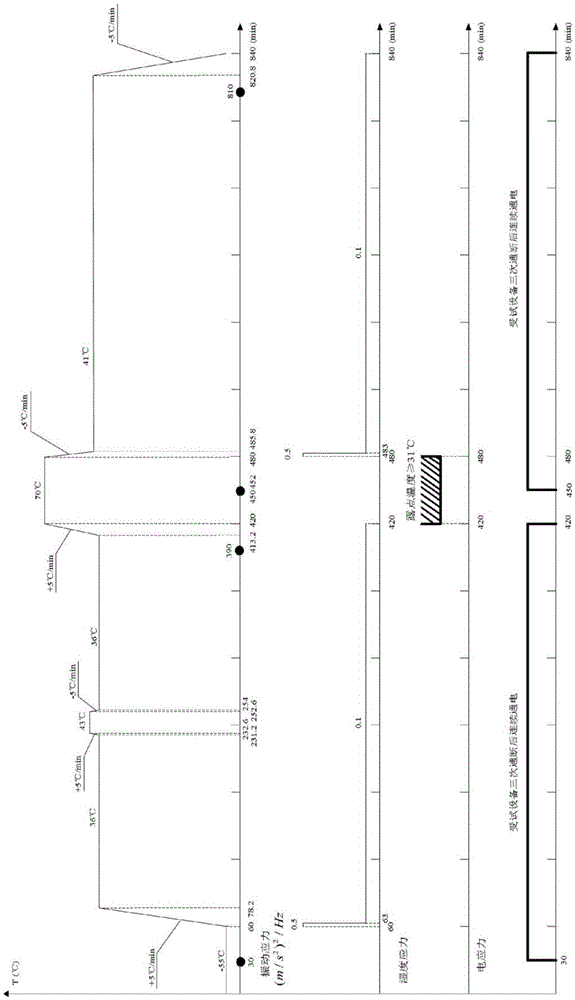
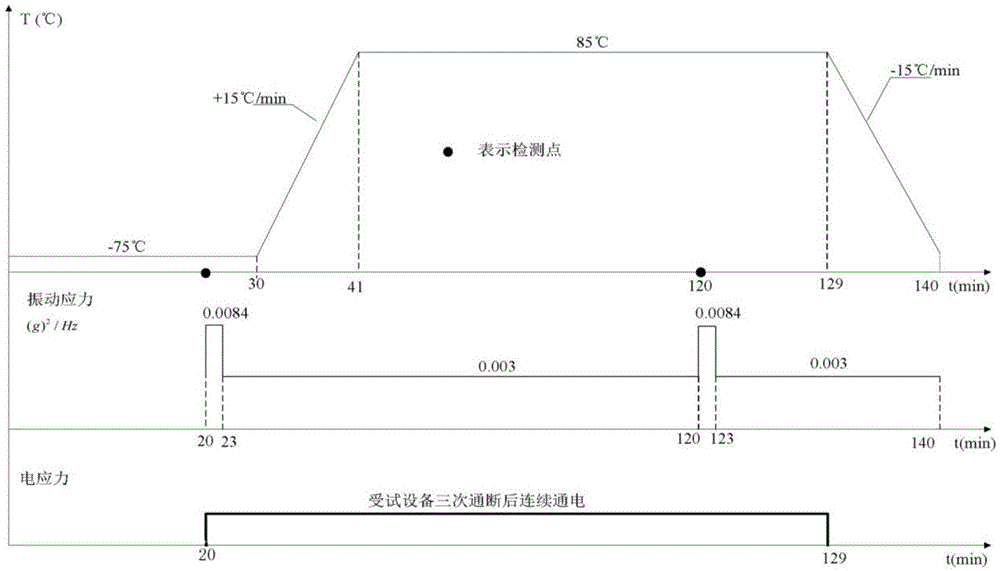
ActiveCN105572498ASolve engineering problems that are difficult to test and identify indicatorsSynthetic Stress Conditions for Growth TestsEnvironmental/reliability testsTemperature stressAcceleration factor
The invention discloses a reliability acceleration test method of electronic products, and belongs to the field of reliability designing and testing. The method comprises steps of firstly presetting an acceleration test temperature change curve boundary according to working stress limit obtained via a routine test for reliability of an electronic product, carrying out simulating calculation of temperature acceleration factors, and modifying and determining initial acceleration test temperature stress change curves; and secondly, calculating vibration acceleration factors according to the initial acceleration test temperature stress change curves and a test profile of the routine test for the reliability of the original electronic product, calculating acceleration test vibration stress change curves according to the vibration acceleration factors, and according to the acceleration test vibration stress change curves, determining the final temperature stress change curves and determining acceleration test time. According to the invention, by following the thought of testing and examining working stress of a product and properly increasing test stress level, test time is shortened; a reliability test of the electronic product can be accelerated; and diversity and controllability of the acceleration factors are achieved.
Owner:XIAN AIRCRAFT DESIGN INST OF AVIATION IND OF CHINA
Low loss ultrasound transducers
InactiveUS20070080609A1Minimize attenuationPiezoelectric/electrostriction/magnetostriction machinesMechanical vibrations separationUltrasonic sensorAlloy
An ultrasound transducer is constructed to be under damped at higher overtone frequencies by reducing losses through one or more of the following: even pressure shaped surfaces on masses, reversed drive to at least one piezoelectric ceramic, an ultrasonically formed metallic bond between the transducer's front mass and the radiating surface, high current carrying strain relieved electrodes, fine grain structure masses, low internal friction masses and radiating materials, and zero bias stress change due to temperature variations. Improved methods and construction details for bonding the higher overtone frequency transducer to quartz are disclosed and include: front masses with cross-hatched or concentric circle patterns and invar front masses or an invar transition mass that is bonded to the quartz.
Owner:CLEANING TECH GROUP
Method for Determining the Fluid/Pressure Distribution of Hydrocarbon Reservoirs from 4D Seismic Data
A method including analyzing seismic data relating to a producing hydrocarbon reservoir is disclosed. The seismic data includes first and second sets of seismic data obtained at different times. An interval composed substantially of hard rock is identified in the hydrocarbon reservoir. 4D seismic attributes for the region are calculated. Rock physics relationships are applied to seismic data related to the interval according to the permeability associated therewith. A fluid saturation change or a pressure change of the interval is inferred based on outputs of the first or second sets of rock physics relationships and the calculated 4D attributes for the interval. The inferred fluid saturation change or pressure change of the interval is outputted.
Owner:EXXONMOBIL UPSTREAM RES CO
Method for finite element optimization of bolt pretightening force and bolt structural design
InactiveCN102831263ANumerical optimization method worksImprove accuracySpecial data processing applicationsLoad stepElement analysis
The invention relates to a method for finite element optimization of bolt pretightening force and bolt structural design. A two-dimensional FEA (finite element analysis) modified model and the method are applicable to structural modeling of different bolts. By considering various types of nonlinear factors such as complex contact, friction, pretightening in threaded connection, three-dimensional spiral thread structures are simplified effectively by the planar FEA modified model while calculation precision is guaranteed. The pretightening force and an external force are loaded step by step by inputting component parameters and material attributes and integrating nonlinear factor relationships. A curve of maximum stress changing along with the external force and a curve of changing of maximum stress inside the thread along with the pretightening force are defined according to stress status in the thread area. The optimal pretightening force of threaded connection is determined by judging whether contact faces are separated or not. Optimal bolt structural design and optimal parameters are calculated according to maximum external force borne by the bolt structure and the required pretightening force of the bolt structure. The method is also applicable to rectangular or other nonstandard threaded bolt structures.
Owner:章伊华
Water-cooled wall on-line safe evaluation method
InactiveCN101216164AHigh precisionReduce occupancySteam boilersSteam boilers componentsInstabilityEngineering
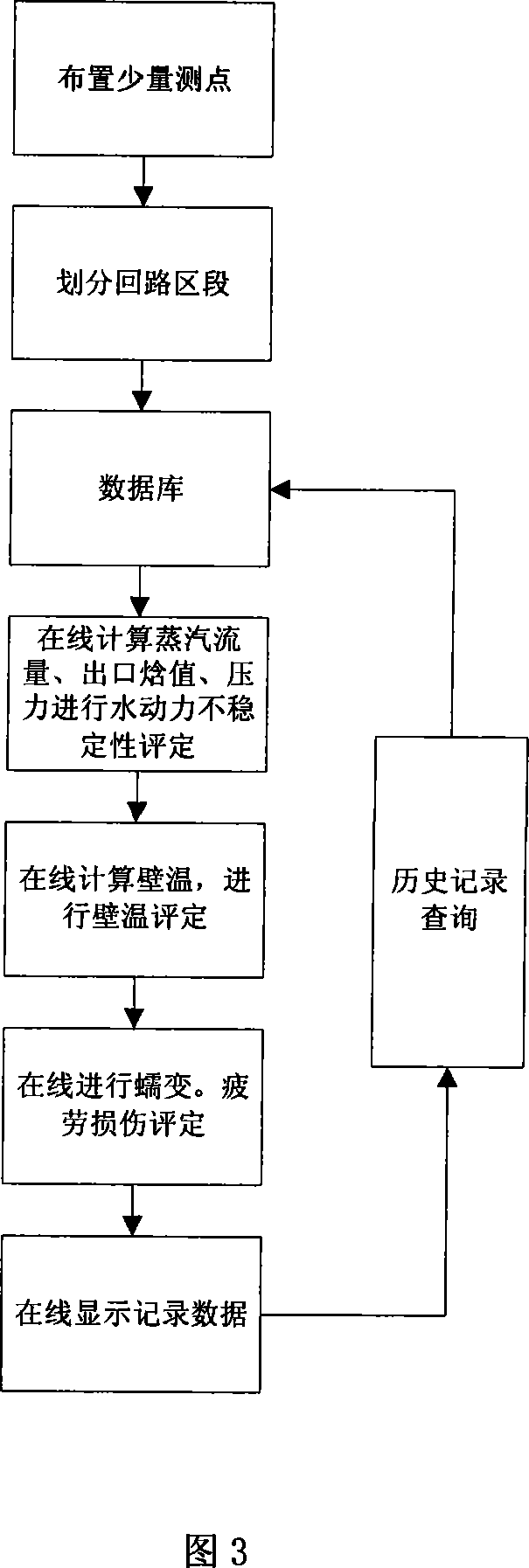
The invention relates to an on-line safety evaluation method for water-cooled walls. The method comprises the following steps: arranging a small amount of test points in the pipeline section with typical flow heat transfer in each radiation zone, combining with the existing test points at the entrance and exit outside the furnace, calculating and checking the characteristic parameters of the inner wall of the water-cooled wall of the station boiler, inputting to a computer for calculation, performing the on-line real-time calculation of the Parameters such as pipeline flow, entrance and exit pressures, enthalpy value, lengthwise furnace inner wall temperature of each pipeline section and stress change value, to judge whether the dangerous factors exist, such as hydrodynamic instability, over-temperature and creep fatigue, displaying the calculation results in real time, recording the data as judgment basis of safe operation of the water-cooled wall. The invention realizes the optimal operation of equipment, manages the repair and maintenance based on the operational state, and ensures the state maintenance and repair of equipment.
Owner:XI AN JIAOTONG UNIV
Testing device and method for monitoring steel wire rope-friction pad dynamic micro-friction state
ActiveCN103954553AReal-time measurement of dynamic tension evolutionSimple structureUsing mechanical meansMaterial analysisEngineeringDynamic Tension
The invention discloses a testing device and a testing method for monitoring steel wire rope-friction pad dynamic micro-friction state. The testing device comprises a base frame, a loading system, a micro-slip system and a state monitoring system, wherein the loading system comprises a weight loading system, a hydraulic loading system and a steel wire rope; the micro-slip system comprises a support system, a drive system and a friction transmission system; the state monitoring system comprises a dynamic tension monitoring system, a pad stress measuring system, a friction force measuring system and a micro-slip monitoring system. By utilizing the testing device and the testing method, dynamic alternating tension can be applied to the steel wire rope and dynamic micro-friction can be applied between the steel wire rope and a friction pad simultaneously, and dynamic tension evolution of the steel wire ropes at both sides of the friction pad, micro-slip amplitudes of different sections of a contact arc of the steel wire rope and the friction pad, stress change of the friction pad near the contact zone of the steel wire rope and the friction pad and dynamic friction force between the steep wire rope and the friction pad can be measured in real time.
Owner:CHINA UNIV OF MINING & TECH
Resonance type micro accelerometer
InactiveCN101303365ASensitivity effectsHigh sensitivityTelevision system detailsImpedence networksCapacitanceAccelerometer
The invention relates to the technical field of micro mechanical electronics, in particular to a resonance micro accelerometer with high sensitivity, which solves the problem that the measuring sensitivity of traditional resonance accelerometers based on stress change is easy to be affected by interior residual stress and other factors. The accelerometer comprises a glass substrate, a mass block, two DETF resonators and a sensitive capacitor. The resonators are arranged in parallel / row and opposite to the side of the sensitive capacitor. The sensitive capacitor comprises a plurality of plate capacitors, polar plates at one side of which are fixed to the tuning forks by an articulated beam and polar plates at the other side of which are fixed by a supporting and connecting beam; the mass block is arranged between the two resonators, and a pair of symmetrical micro levers are arranged between the mass block and the two resonators respectively; the micro levers at the two sides of the mass block are symmetrical corresponding to the mass block, and one end of the micro level is fixed on the mass block and the other end on the supporting and connecting beam of the plate capacitor. The accelerometer of the invention has the advantages of reasonable structure, low volume, high sensitivity, good detecting effect and good development prospect.
Owner:ZHONGBEI UNIV
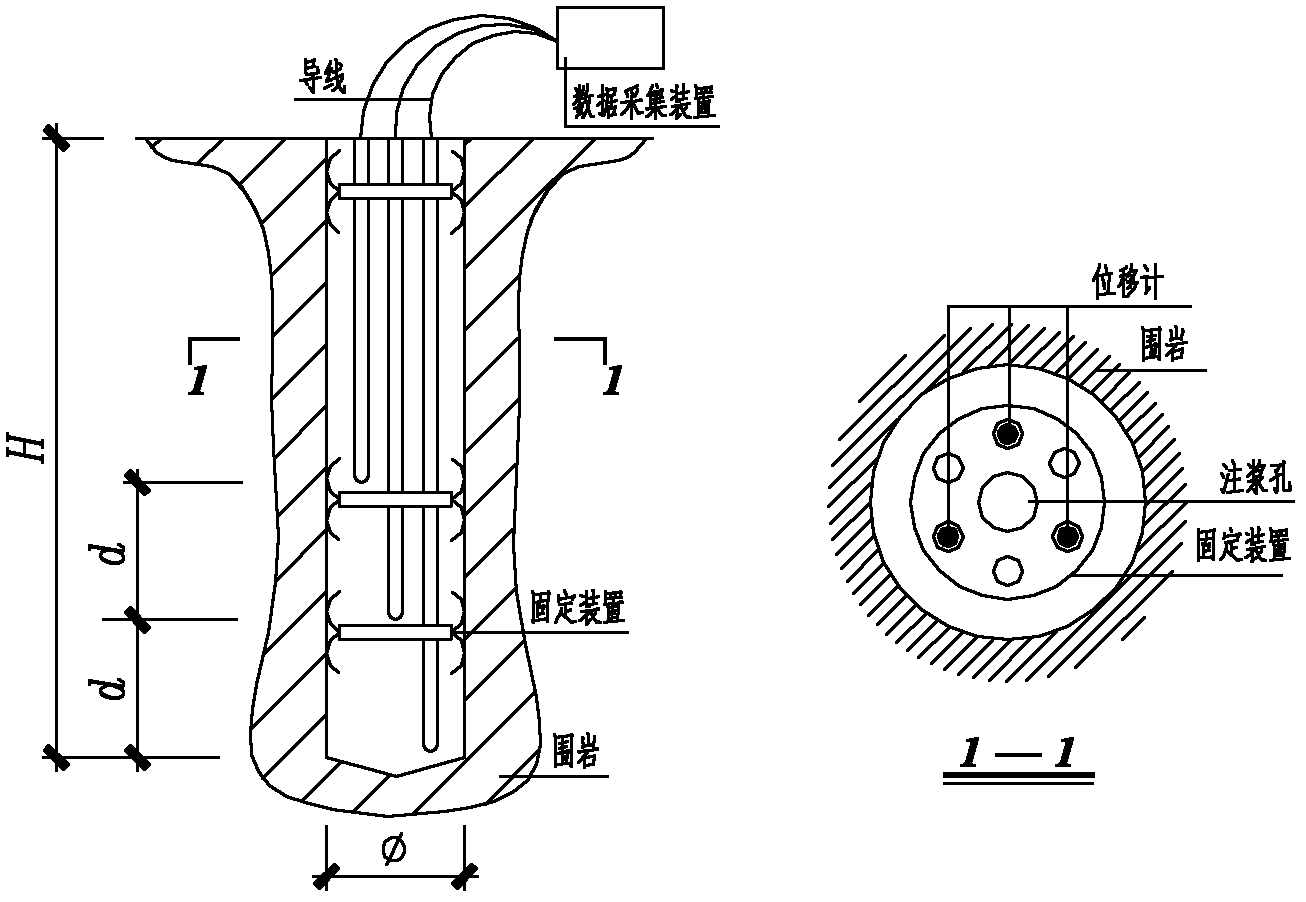
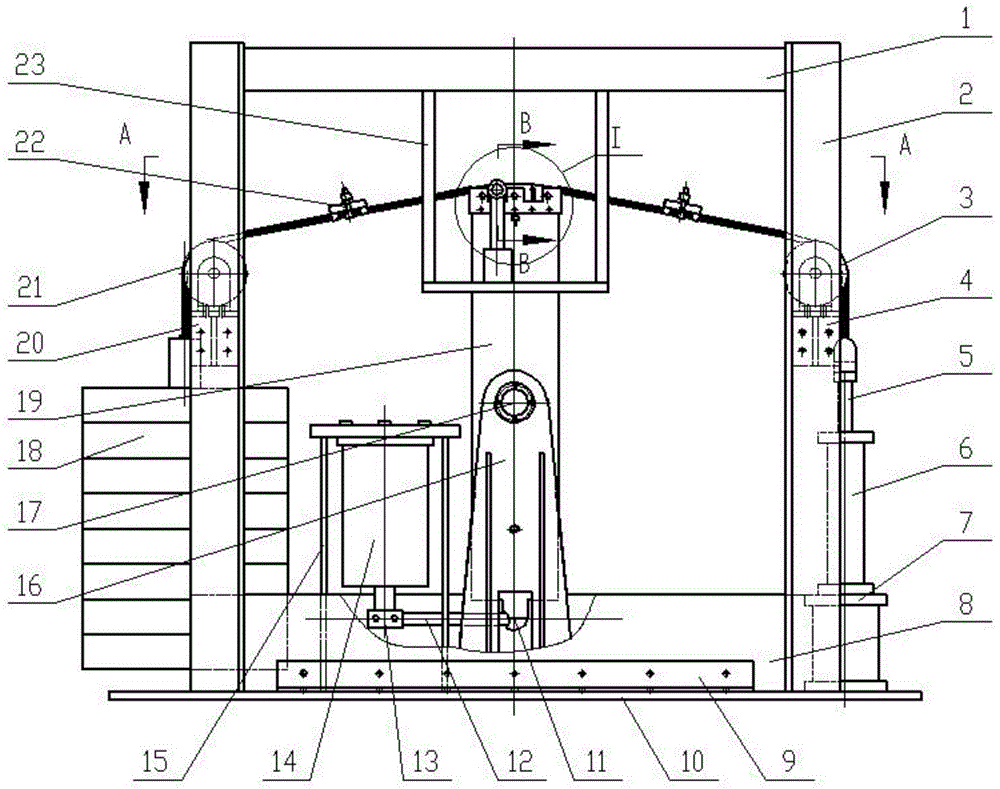
Measurement method for stress change of rocks during TBM tunneling
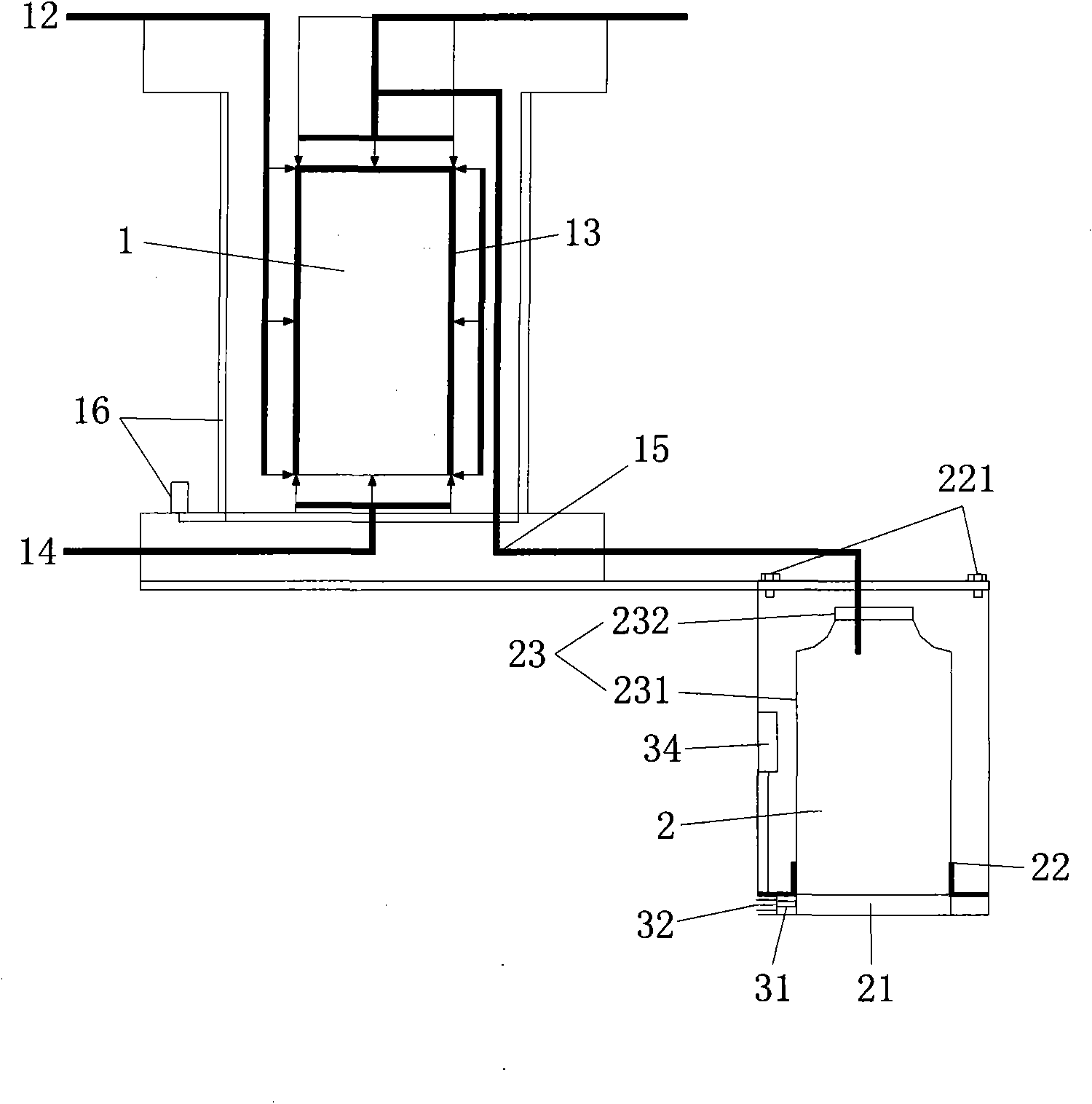
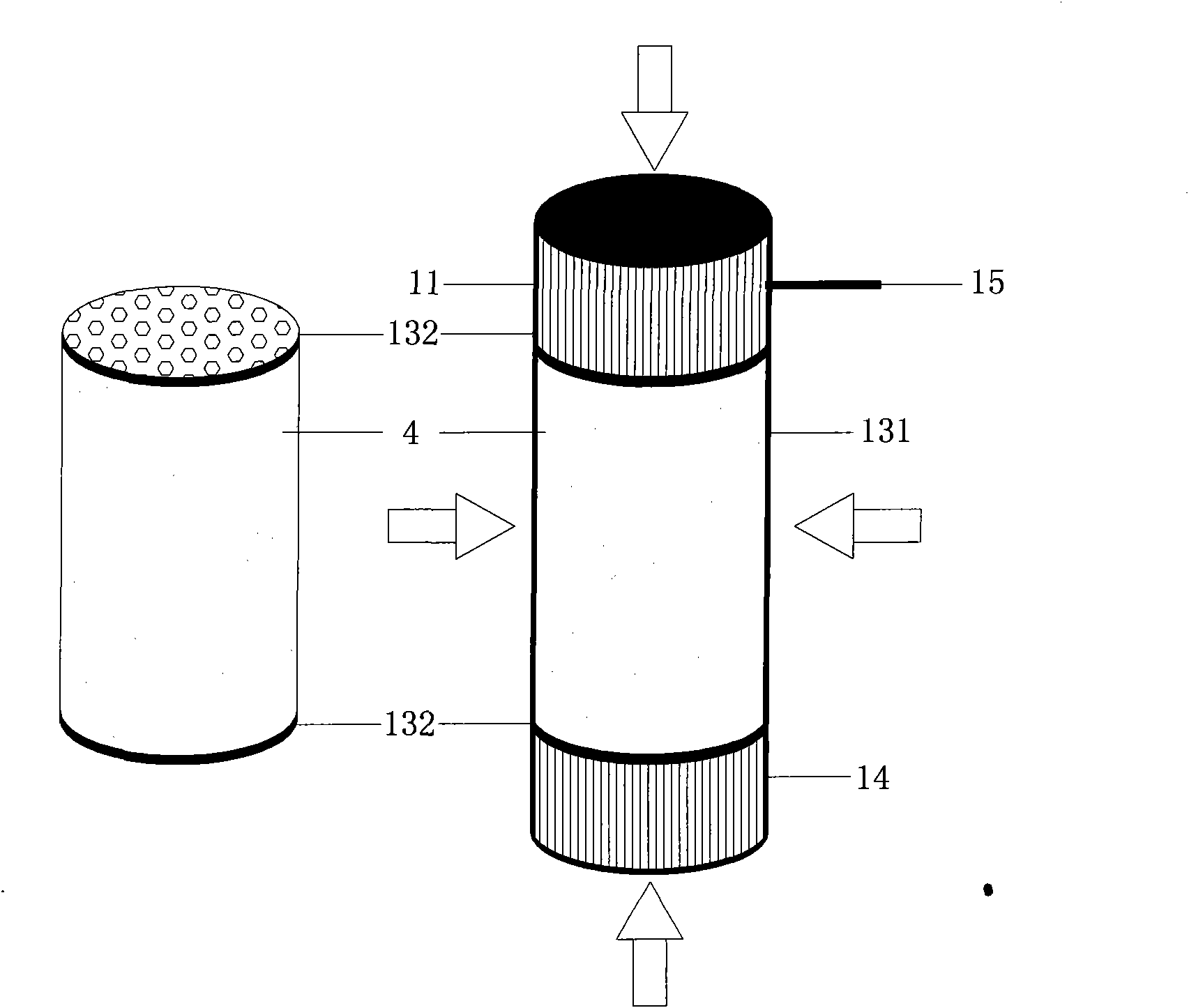
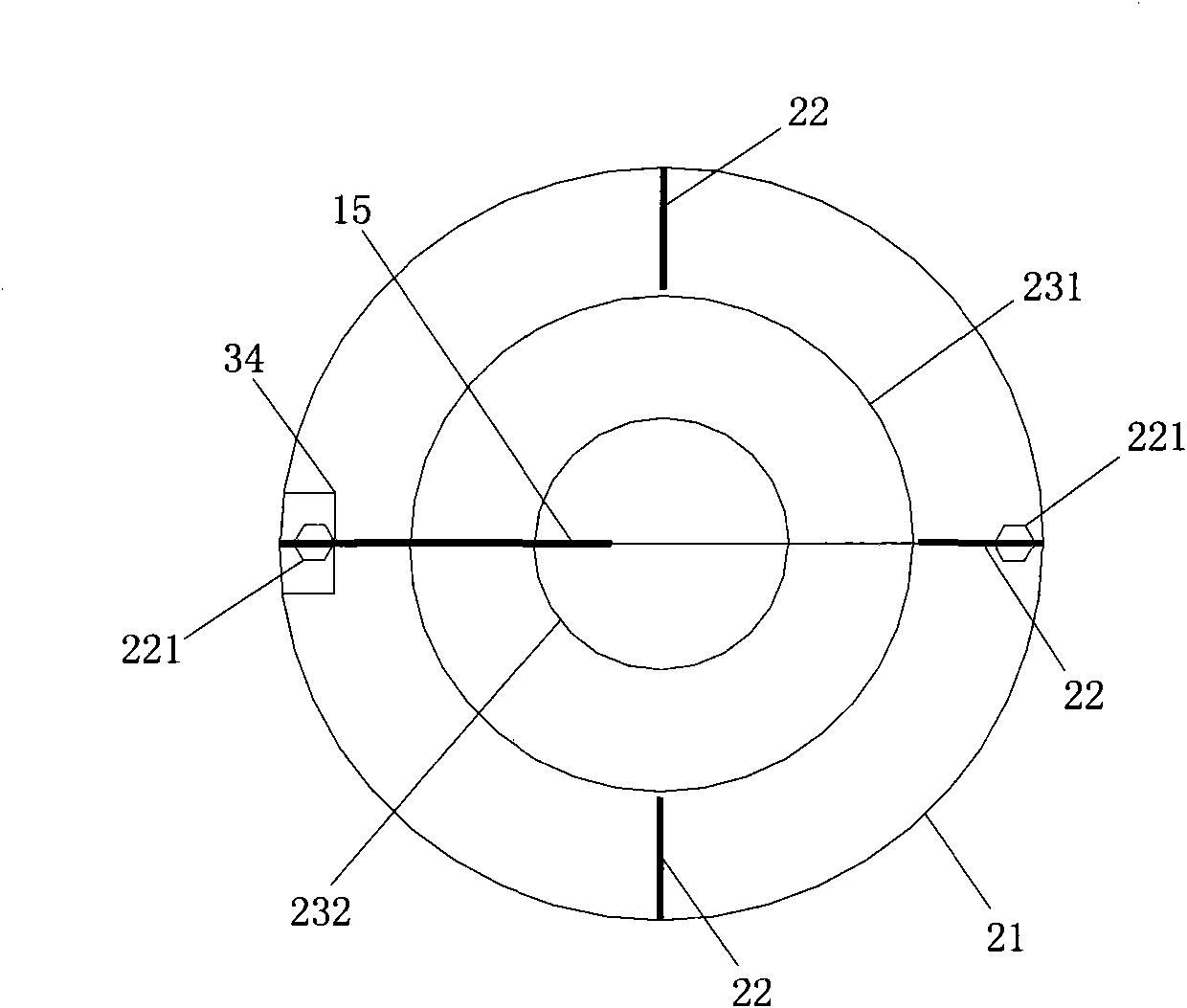
ActiveCN101922985AReflect the extent of damageEnsure stabilityForce measurementGreek letter epsilonStress change
The invention relates to a measurement method for stress change of rocks during TBM tunneling. The technical problems to be solved in the invention are as follows: providing the measurement method for stress change of rocks during TBM tunneling, measuring the three-dimensional stress change of some point in rock of a TBM evacuation hole section, judging the damaged range of the rock, and optimizing supporting design to ensure the overall stability of a grotto and the safety of stuff. The technical scheme for solving the problem is as follows: the measurement method for stress change of rocks during TBM tunneling comprises the following steps: a, determining the embedding position and the quantity of measure points of a hollow inclusion stressometer; b, digging an auxiliary hole or using an existing grotto to drill a TBM hole section to be evacuated and embedding the hollow inclusion stressometer; c, performing TBM tunneling, monitoring and recording the stress change of the hollow inclusion stressometer; d, determining the elastic modulus and Poisson ratio of rock of a section to be measured; and e, working out an equation, i.e. E epsilon k=Ak1sigmax+ Ak2sigmay + Ak3sigmaz + Ak4tauxy + Ak5tauyz + Ak6tauzx, solving the six components, namely sigmax, sigmay, sigmaz, tauxy, tauyz and tauxz of ground stress. The measurement method is mainly used for the supporting optimization design of construction time of tunnels and the like and the estimation of overall stability of grottos.
Owner:POWERCHINA HUADONG ENG COPORATION LTD
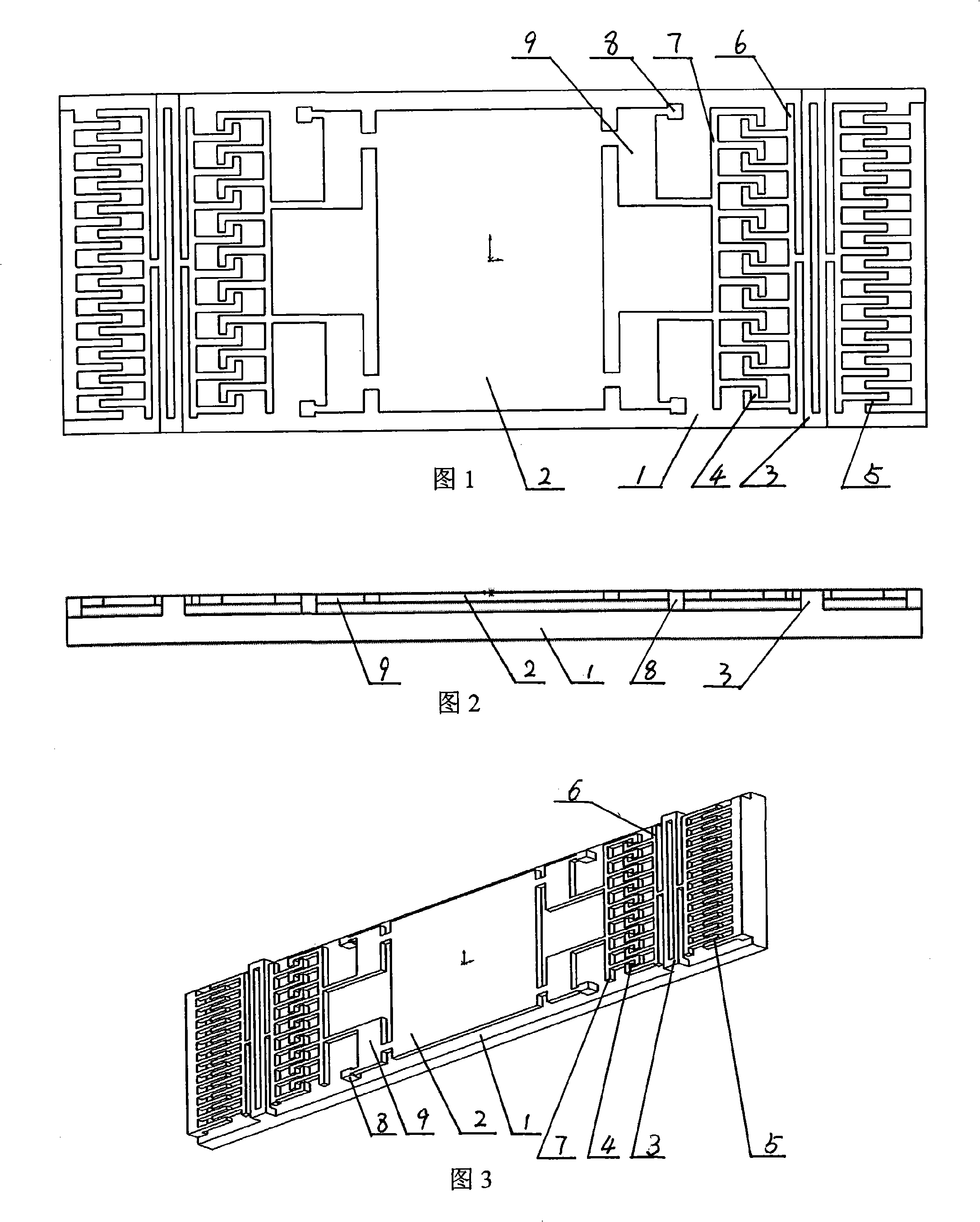
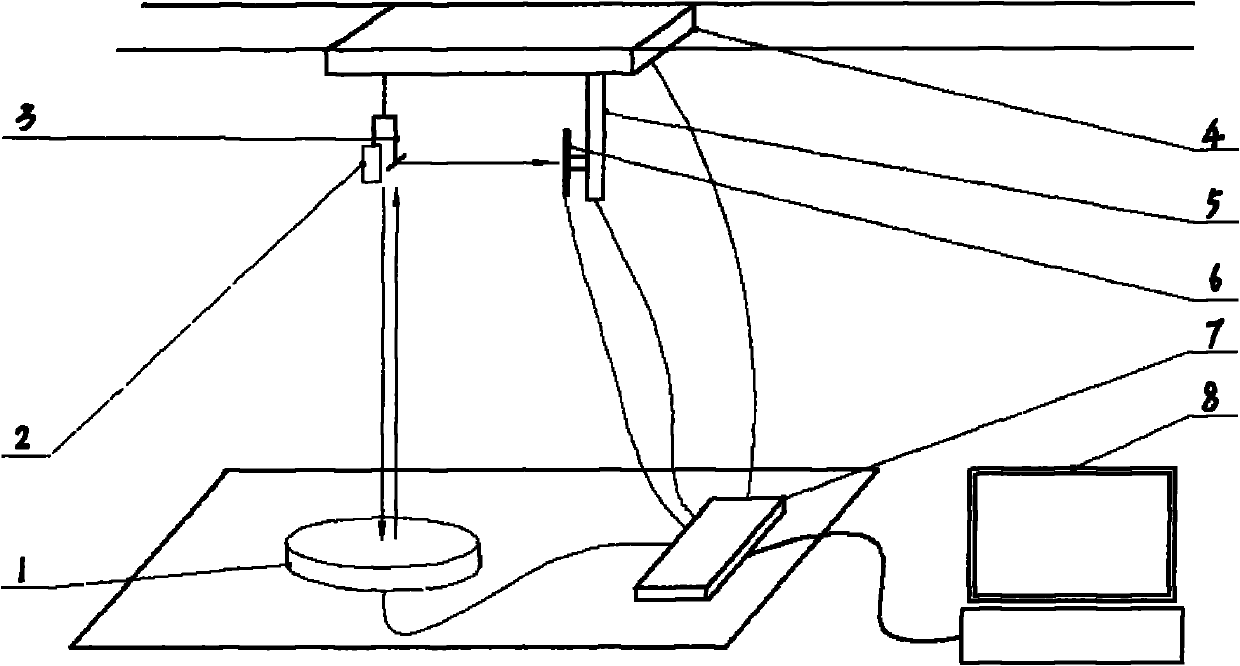
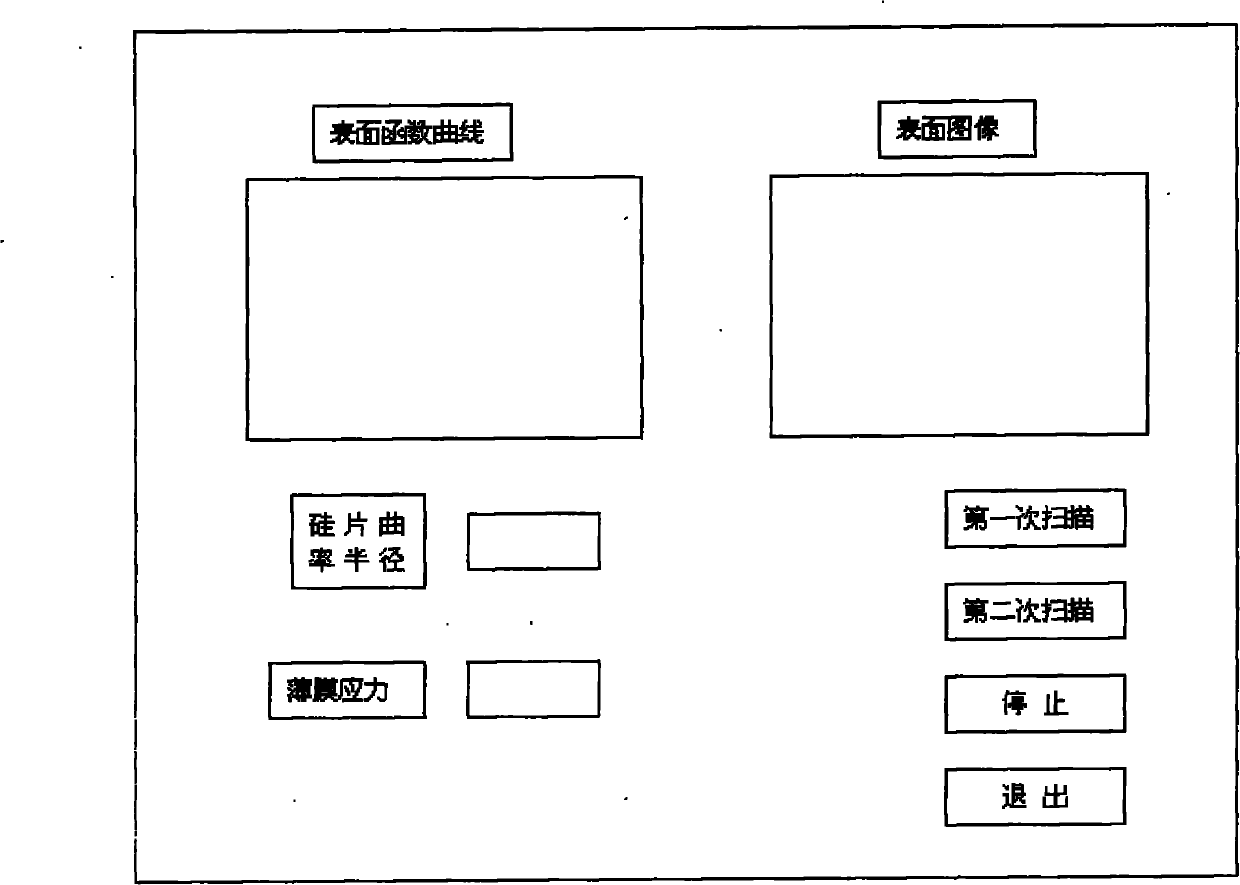
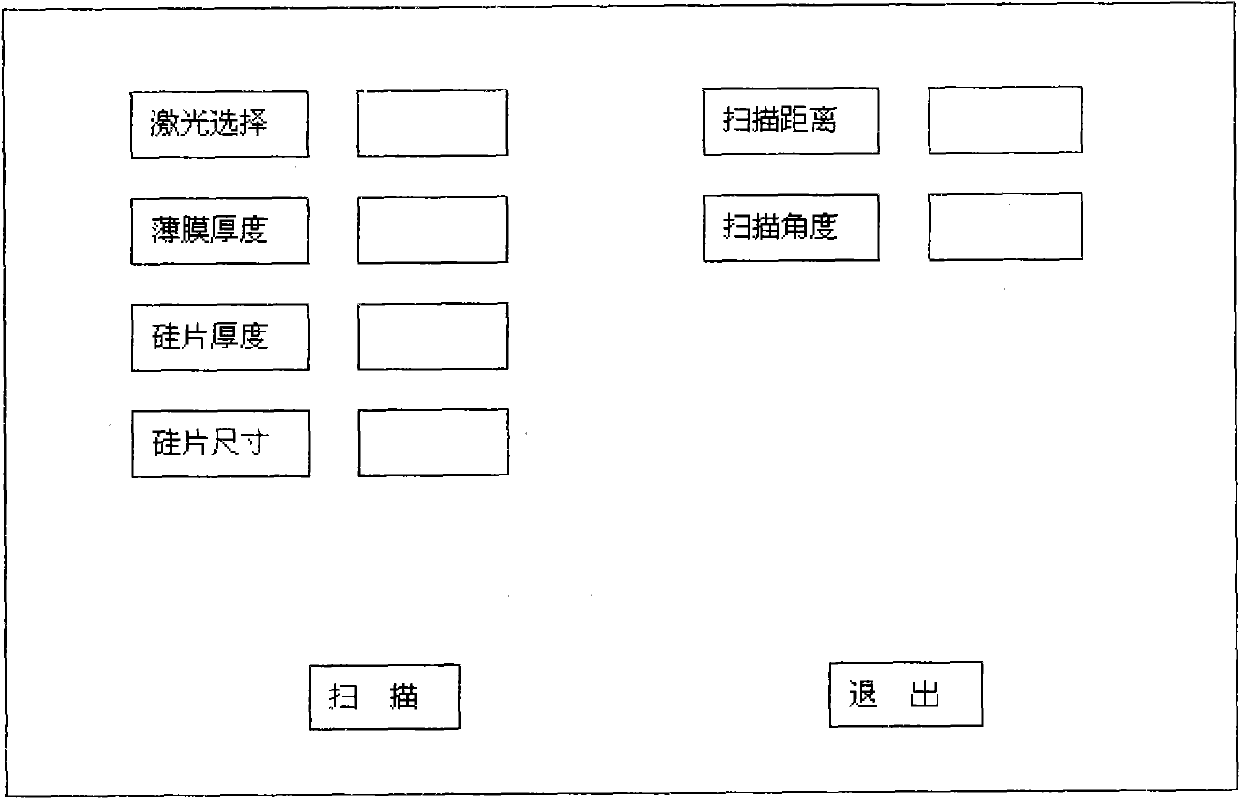
Film stress measuring equipment and film stress measuring method
InactiveCN102023068AUnderstand situationExtension functionForce measurement by measuring optical property variationUsing optical meansStress measuresData acquisition
The invention relates to film stress measuring equipment and a film stress measuring method. In a cuboid equipment case, a laser LED, an optical reflector, a linear sliding rail, a detector and another linear sliding rail all are connected with the top face of the equipment case; the linear sliding rail is arranged below and vertically connected with another sliding rail; a tray and an analog / digital (A / D) data acquisition card are arranged on the internal bottom face of the equipment case; and the tray, the A / D data acquisition card, the linear sliding rail, the detector and the other linear sliding rail are all connected with a computer outside the equipment case through a circuit. In the equipment, a light sensitive electrical detector is used for automatically tracking light path deflection and acquiring a light path deflection displacement signal, a micro step motor is used to control and rotate the tray to quickly generate a silicon chip accurate region curvature and stress change color drawing that helps to get the condition of a thin film on the surface of an entire silicon chip, two-dimensional and three-dimensional images of the surface of the thin film can be obtained, a friendly interface can be written in VC++ language, and it is possible to further expand program functions.
Owner:徐建康
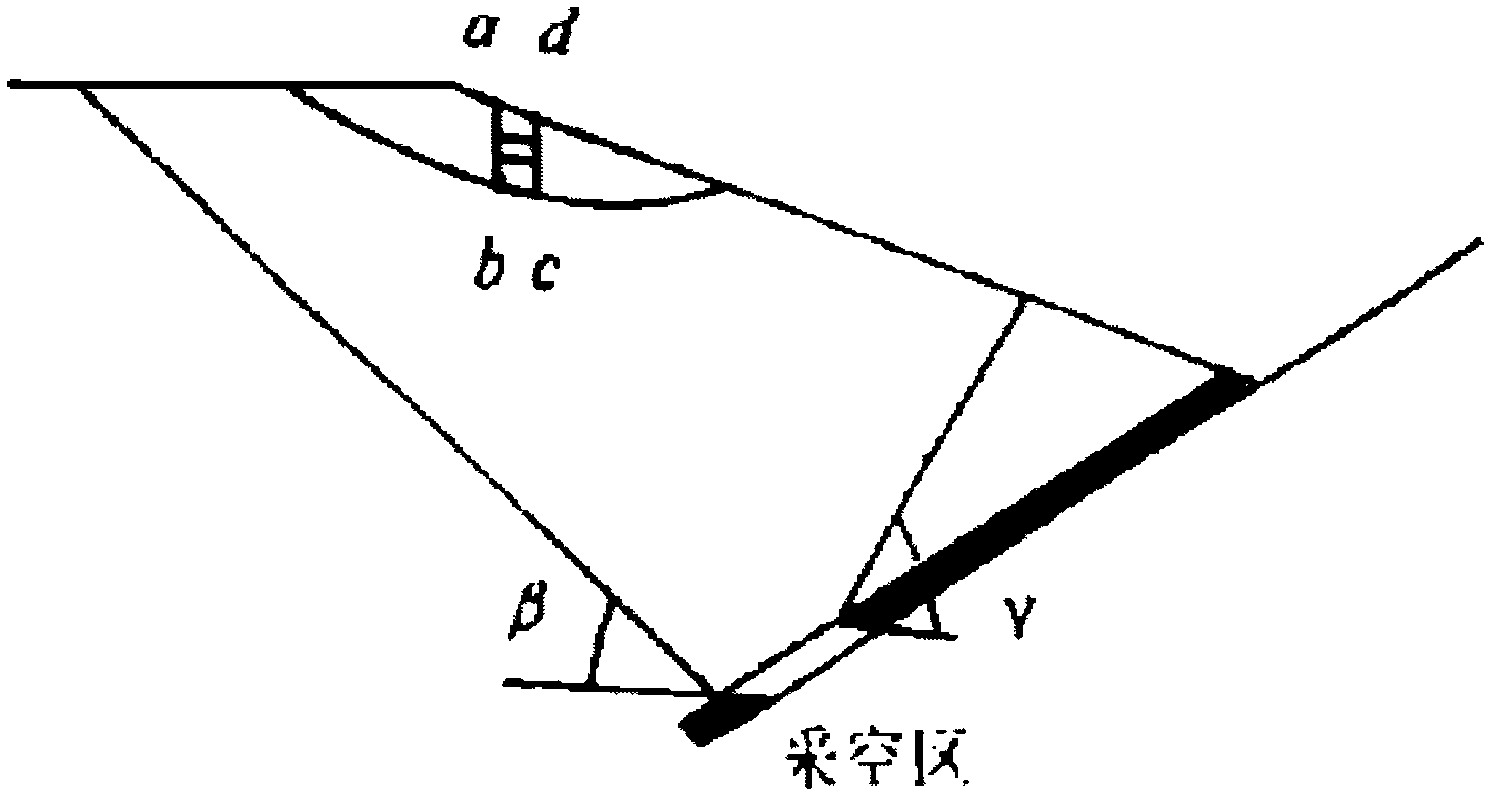
A Method for Evaluating the Stability of Slope Rock Mass
For the combined underground and open-pit mining methods, according to the spatial correspondence of the mining area, some of the two mining influence domains overlap each other, resulting in the interaction and superposition of the mining effects, thus forming a composite dynamic system. Therefore, the slope The deformation mechanism of rock mass is more complex. Underground mining has three effects on the overlying rock mass in the area of influence, that is, the change of the overlying rock layer, the reduction of the overall strength and the change of the stress field in the area of influence. The latter is due to underground excavation changing the stress distribution state of the original rock. Within its influence domain, the stress values and behaviors at different spatial locations are different, so the damage to the overlying rock mass by underground excavation is zonal, and this zonal stress change will occur with subsequent excavation different processes of change. This change process will directly affect the stability state of the slope rock mass, that is, the occurrence of this stress restricts or changes the stability state of the slope mass. Therefore, in the stability analysis of slope rock mass, this main influencing factor should be taken into consideration. However, in the past, when dealing with such problems, the analysis method under the influence of single open-pit mining was approximately applied, and the results were somewhat different from the actual situation; the present invention deduces a slope rock mass stability evaluation on the basis of theoretical analysis Methods to provide scientific basis for the follow-up mining design and safety production of such mines.
Owner:NORTH CHINA UNIVERSITY OF TECHNOLOGY
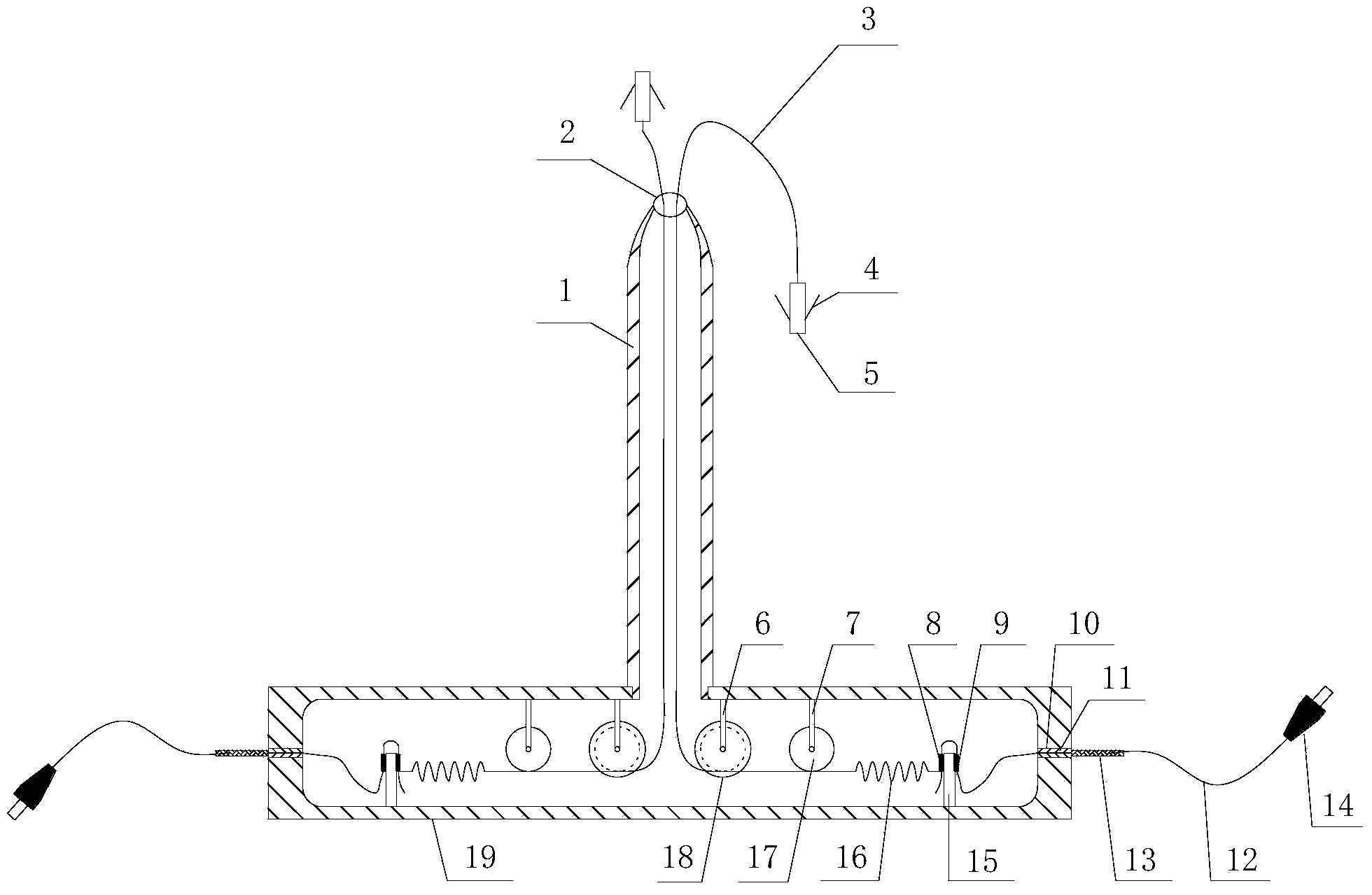
Monitoring device and monitoring method for mining FBG (fiber bragg grating) roof separation layer
ActiveCN103528530ARealize online measurementTimely warningMining devicesTesting machinesGratingBoundary values
The invention provides a monitoring device and a monitoring method for a mining FBG roof separation layer. The device comprises a vertical measurement barrel and a packaging casing, wherein fixed pulleys, tape pulleys and constant-strength cantilever beams are symmetrically arranged in the packaging casing; a steel wire rope penetrates through the tape pulleys and the fixed pulleys and penetrates out from a steel wire rope guide hole in the top part of the vertical measurement barrel; one end of the steel wire rope is connected with an anchor head; a shallow part measurement point and a deep part measurement point are distributed inside a drill hole; the anchor head is pushed to the measurement points in the drill hole; when the stress of the steel wire rope changes, the stress change is displayed through wavelength values of an FBG A and an FBG B; a wavelength demodulation device is used for demodulating the wavelength values into digital signals, the digital signals are sent to a computer for real-time processing, and a separation layer numerical value is combined for drawing a separation layer quantity changing curve and a set separation layer boundary value; whether the separation layer exists is judged; and the data change of the roof separation layer is monitored in real time. Temperature compensation is performed with a differential form, on-line measurement of the roof separation layer is realized, the reliability and the accuracy are high, an early warning signal can be issued, and roof fall accidents can be avoided.
Owner:CHINA UNIV OF MINING & TECH
Intrusion protection using stress changes
ActiveUS20110089506A1More cost-effectiveConvenient restAcceleration measurement using interia forcesSemiconductor/solid-state device detailsSmart cardEngineering
The invention relates to a integrated circuit comprising an electronic circuit integrated on a substrate (5), and further comprising protections means for protection of the electronic circuit (25). The protection means comprise: i) a first strained encapsulation layer (10) being provided on a first side of the substrate (5), wherein the first strained encapsulation layer (10) has a strain (S1) in a direction parallel to the substrate (5), and ii) disabling means (20) arranged for at least partially disabling the electronic circuit (25) under control of a strain change in the substrate (5). The invention further relates to a method of manufacturing such integrated circuit, and to a system comprising such integrated circuit. Such system is selected from a group comprising: a bank-card, a smart-card, a contact-less card and an RFID. All embodiments of the integrated circuit in accordance with the invention provide essentially an alternative tamper protection to the data stored or present in the electronic circuit therein. A first main group of embodiments concerns an integrated circuit wherein tamper protection is obtained by detecting a strain change during tampering and subsequently disabling the electronic circuit. A second main group of embodiments concerns an integrated circuit wherein tamper protection is obtained by designing a stack of strained encapsulation layers, such that tampering causes releasing of strain and thereby mechanical disintegrate (break, delaminate, etc) of the integrated circuit, and thus disabling the electronic circuit.
Owner:NXP BV
Method for testing residual stress of steel rail
The invention relates to a method for testing residual stress of a steel rail. The method is characterized by comprising the following steps of using a steel rail with the length of 1m, taking one point (namely a center position) 500mm away from the end of the steel rail, drawing a line which is arranged at the point in the circumferential direction vertical to the axis of the steel rail, sequentially and alternatively taking 14 points from the center point of the rail bottom to the center of the rail head in the linear direction, attaching each point with a strain sheet, measuring the initial value of the residual stress of each point by a static stress-strain gage, using the line drawn on the steel rail as a center line, cutting steel rail into 20mm thin sheets at each 10mm part of the two ends of the center line in the direction vertical to the axis of the steel rail, and then measuring the final value of the residual stress of each point by the static stress-strain gage. The method has the advantages that by adopting the multi-point testing, the stress distribution conditions of the rail bottom, the rail waist, the rail head and other parts are acknowledged, the stress change of each point is analyzed, then the pressing amount of a rolling machine is corrected, and the distribution of the residual stress is adjusted, so the steel rail is qualified.
Owner:INNER MONGOLIA BAOTOU STEEL UNION
Vibration resistant secondary battery module
InactiveUS7955729B2Improve vibration resistanceImprove the immunitySecondary cellsCell lids/coversEngineeringStress change
The present invention provides a secondary battery module which is excellent in vibration resistance. A battery module 20 has assembled battery blocks 11 each constituted by screw-fixing the assembled batteries 2 to the block bases 3, 4 supporting a lower portion thereof and the two block reinforcing plates 5 supporting an upper portion thereof, the six assembled batteries 2 are sandwiched by and fixed firmly to the block bases 3, 4 and the block reinforcing plates 5. The assembled batteries 2 do not move freely even if vibration is added to the battery module 20. Because the elastic sheet 9 is laid between the block bases 3, 4 and the assembled batteries 2, since a space derived due to variance in size accuracy of frames 12 which hold and fix the unit cells 11 and derived due to variance in size accuracy of the block bases 3, 4 can be removed, and vibration resistance can be enhanced. To thermal stress change caused due to combination of different materials, influence thereof can be reduced by laying the elastic sheet9.
Owner:HITACHI AUTOMOTIVE SYST LTD
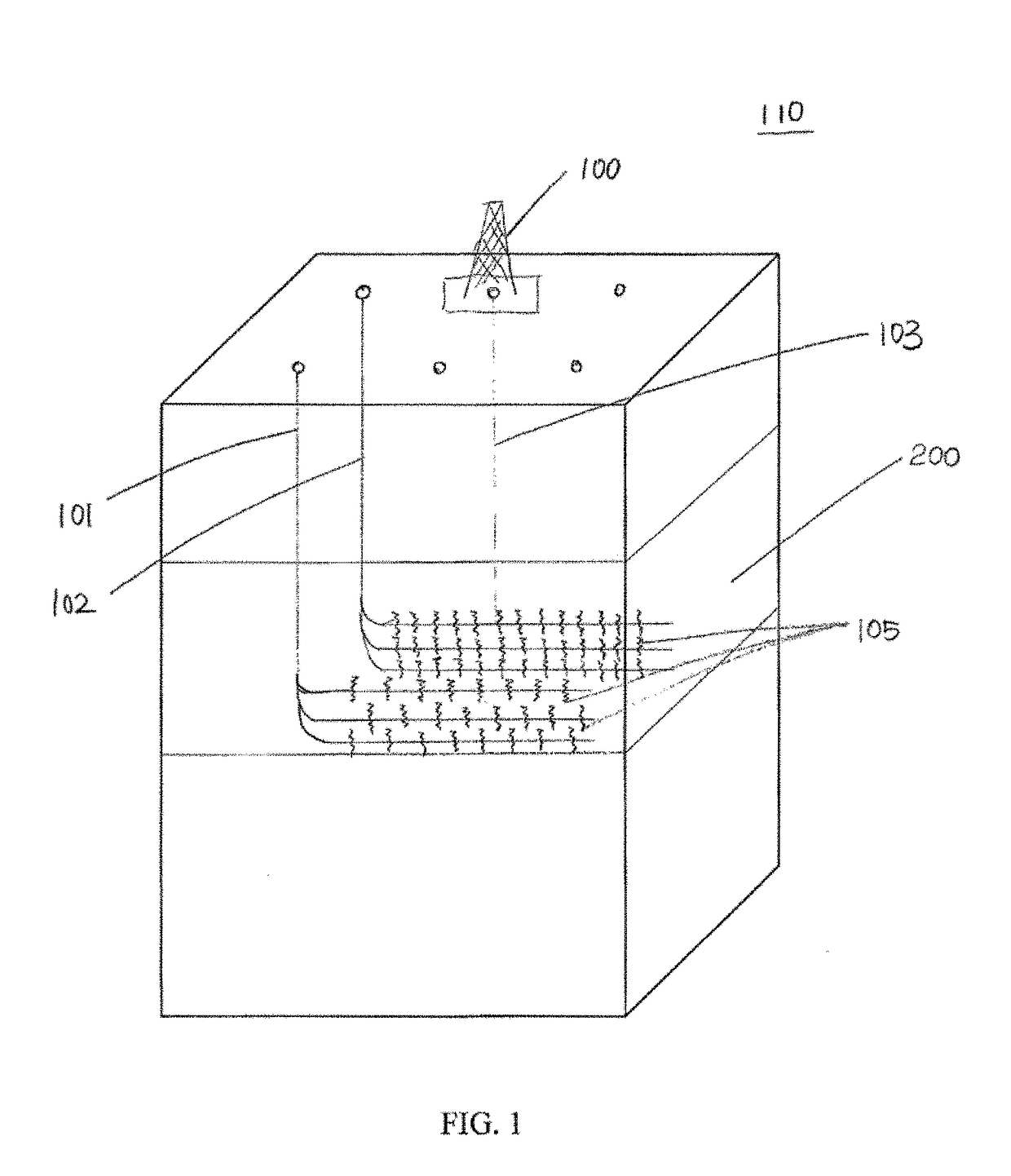
Method of geometric evaluation of hydraulic fractures by using pressure changes
ActiveUS9988900B2Improve certaintyLow costSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingFluid removalStress changeWellbore
A method of evaluating a geometric parameter of a first fracture emanating from a first wellbore penetrating a subterranean formation is provided. The method includes the steps of forming the first fracture in fluid communication with the first wellbore; forming a second fracture in fluid communication with a second wellbore; measuring a first pressure change in the second wellbore in proximity to the first wellbore; and determining the geometric parameter of the first fracture using at least the measured first pressure change in an analysis which couples a solid mechanics equation and a pressure diffusion equation.
Owner:STATOIL GULF SERVICES
Active pressure-bearing type positioning borehole stress meter and use method thereof
InactiveCN102914393ATimely judgment of changing rulesMonitor stress changesHydraulic/pneumatic force measurementInductorEngineering
The invention discloses an active pressure-bearing type positioning borehole stress meter and a use method thereof. The active pressure-bearing type positioning borehole stress meter comprises a columnar shell, wherein the columnar shell is full of grease oil; a piston is arranged at one end of the columnar shell; an elastic inductor is arranged at the other end of the columnar shell; a foil gauge is arranged on the elastic inductor; a rigid bearing piece is arranged on one side of the columnar shell; the rigid bearing piece is inserted into the columnar shell; the contact parts of the rigid bearing piece and the columnar shell are in sealing contact; and an angle sensor is fixed on the columnar shell. The active pressure-bearing type positioning borehole stress meter has an active pressure-bearing function, can timely judge a change rule of the stress, can dynamically quantitative monitor a stress change condition of a danger area during the whole process and can supply a reliable data to the forecasting and preventing for the impact danger. The stress change along a certain direction can be continuously observed according to a mounting position of the stress meter, so as to further confirm the direction of the force and conveniently and specifically prevent the rock burst.
Owner:SHANDONG UNIV OF SCI & TECH
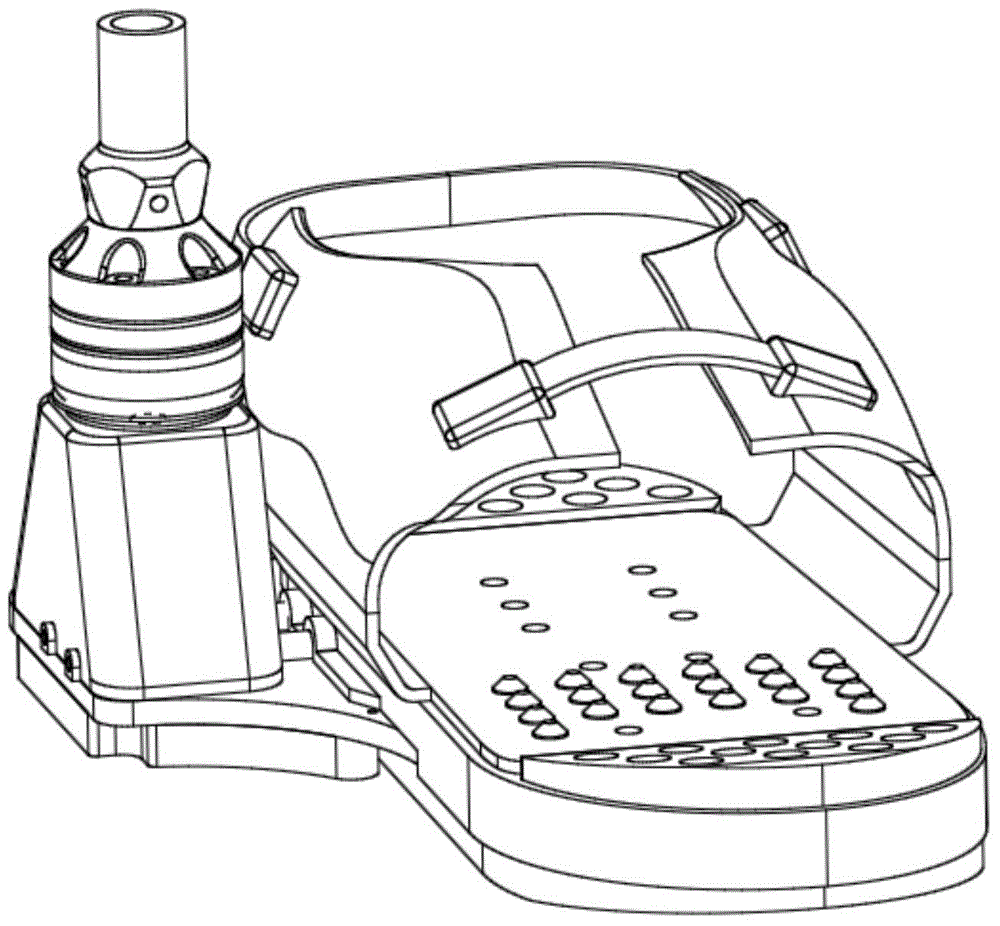
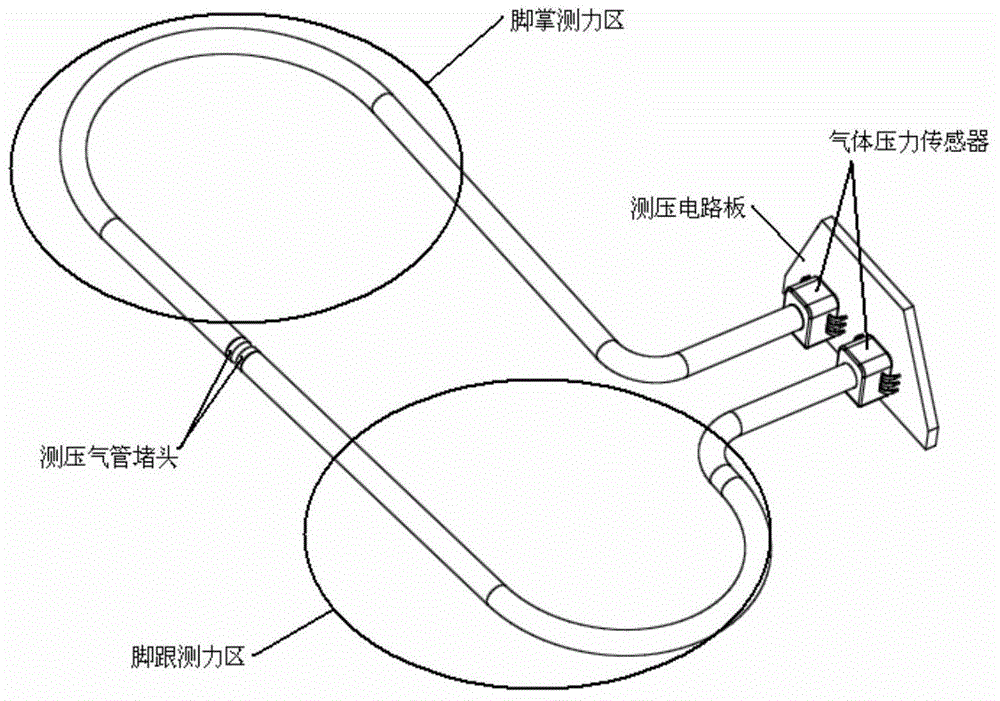
Force measuring and supporting structure
InactiveCN104905804AThe overall structure is simple and reliablePracticalDiagnostic recording/measuringSensorsHuman bodyCarrying capacity
The invention belongs to the technical field of a human body mechanics design, and specifically relates to a force measuring and supporting structure, for measuring stress change conditions of a front sole and a rear sole at the bottom of a human foot and supporting a matched device. Compared to the prior art, plantar stress is converted into change of air pressure in an air pipe, a force measuring effect is achieved through acquisition of gas pressure, the structure is simple and reliable, supporting of the matched device above an ankle joint and buffering of a load impact are taken into full consideration, and the practicality is high. When a person moves, plantar pressure forces the pressure measuring air pipe to be compressed and deformed, the internal air pressure is changed, a gas pressure sensor converts pressure signals into electric signals, and a monitoring system can determine the change condition of the plantar pressure according to the signals; and the structure of the ankle joint guarantees a higher carrying capacity, and takes full consideration of a buffering effect caused by motion to a force.
Owner:CHINA NORTH VEHICLE RES INST
LOW k POROUS SiCOH DIELECTRIC AND INTEGRATION WITH POST FILM FORMATION TREATMENT
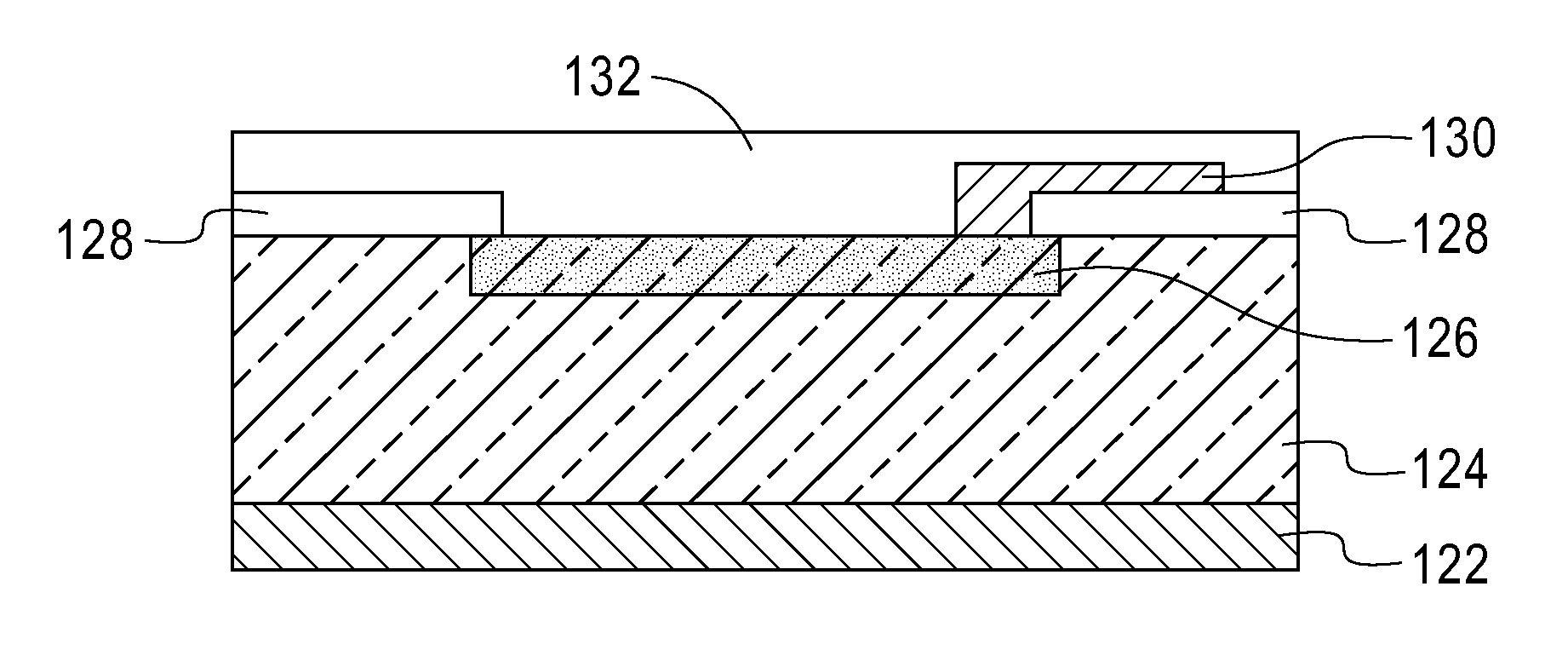
ActiveUS20120329287A1Reduce and minimize stress changeMinimize impactElectric discharge tubesSemiconductor/solid-state device detailsDielectricUnsaturated hydrocarbon
A porous SiCOH dielectric film in which the stress change caused by increased tetrahedral strain is minimized by post treatment in unsaturated Hydrocarbon ambient. The p-SiCOH dielectric film has more —(CHx) and less Si—O—H and Si—H bonding moieties. Moreover, a stable pSiOCH dielectric film is provided in which the amount of Si—OH (silanol) and Si—H groups at least within the pores has been reduced by about 90% or less by the post treatment. A p-SiCOH dielectric film is produced that is flexible since the pores include stabilized crosslinking —(CHx)— chains wherein x is 1, 2 or 3 therein. The dielectric film is produced utilizing an annealing step subsequent deposition that includes a gaseous ambient that includes at least one C—C double bond and / or at least one C—C triple bond.
Owner:TAIWAN SEMICON MFG CO LTD
Dense roadway group rock burst hazard prediction method
InactiveCN102392685ATimely determination of early disturbance responseMining devicesDynamic methodHigh energy
The invention discloses a dense roadway group rock burst hazard prediction method. The method includes the following steps: first acquiring the dynamic sensitive area of a coal bed in a dense roadway group area; then mounting roof dynamics monitors along a direction leading to a dense roadway group to carry out roof dynamics observation; before a dynamic area stress range related to coal mining gets close to the dense roadway group, mounting highly sensitive stressmeters in the sensitive area to observe stress change, and when the stress increment is abruptly changed, carrying out rock burst hazard monitoring. By means of an artificial blasting technique in the dense roadway group, the method acquires the coal-rock stratum disturbance-sensitive area, finding a vulnerable area; the roof dynamics method is adopted to acquire the tendency characteristics and range of dynamic stress and quantitatively describe the distribution rule of the dynamic stress; delicate physical quantity observation timely judges the early disturbance response of the dense roadway group, rock burst hazard process monitoring is carried out before high energy is released, and the hazard level is judged by means of indexes.
Owner:SHANDONG UNIV OF SCI & TECH
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com