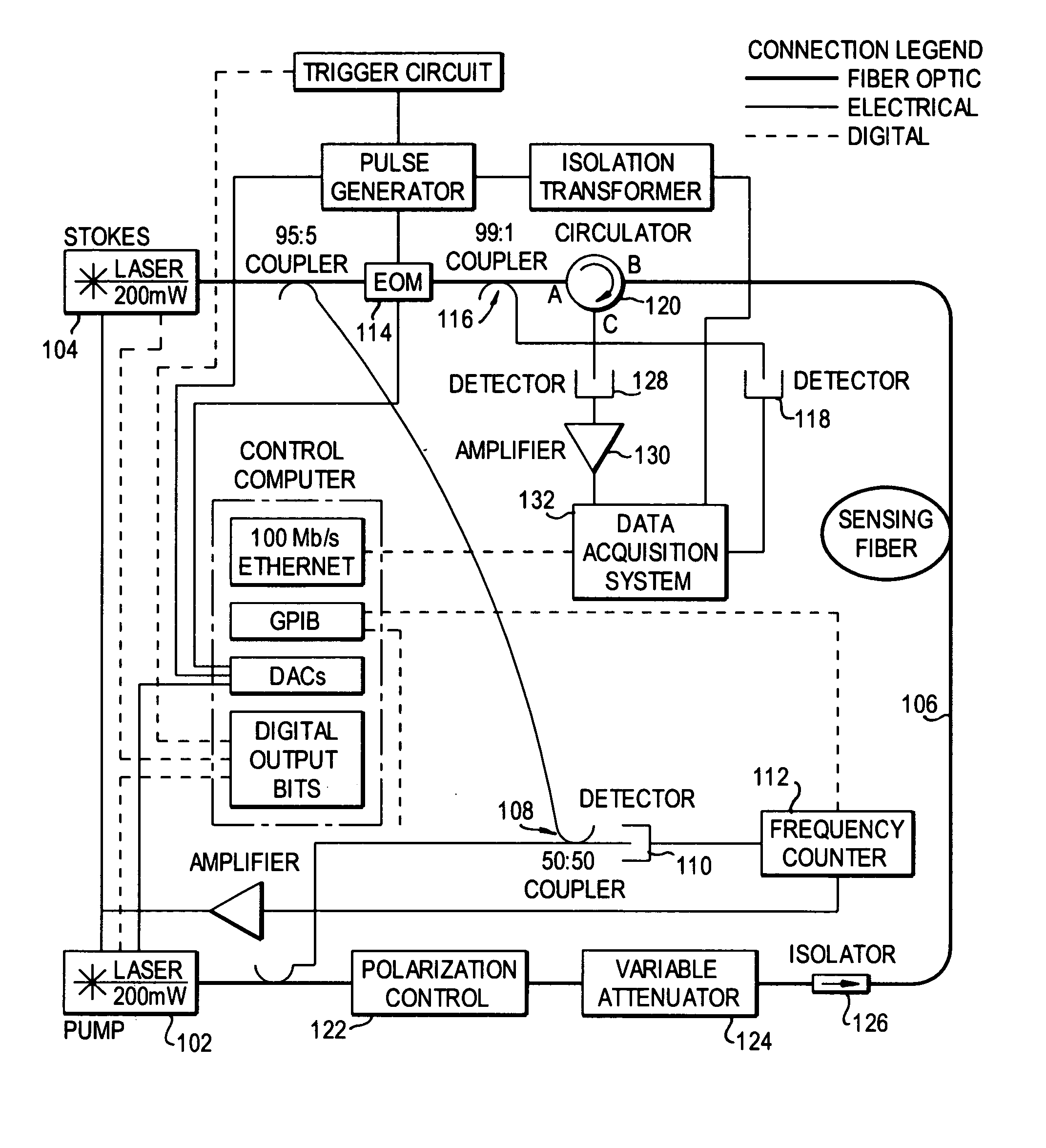
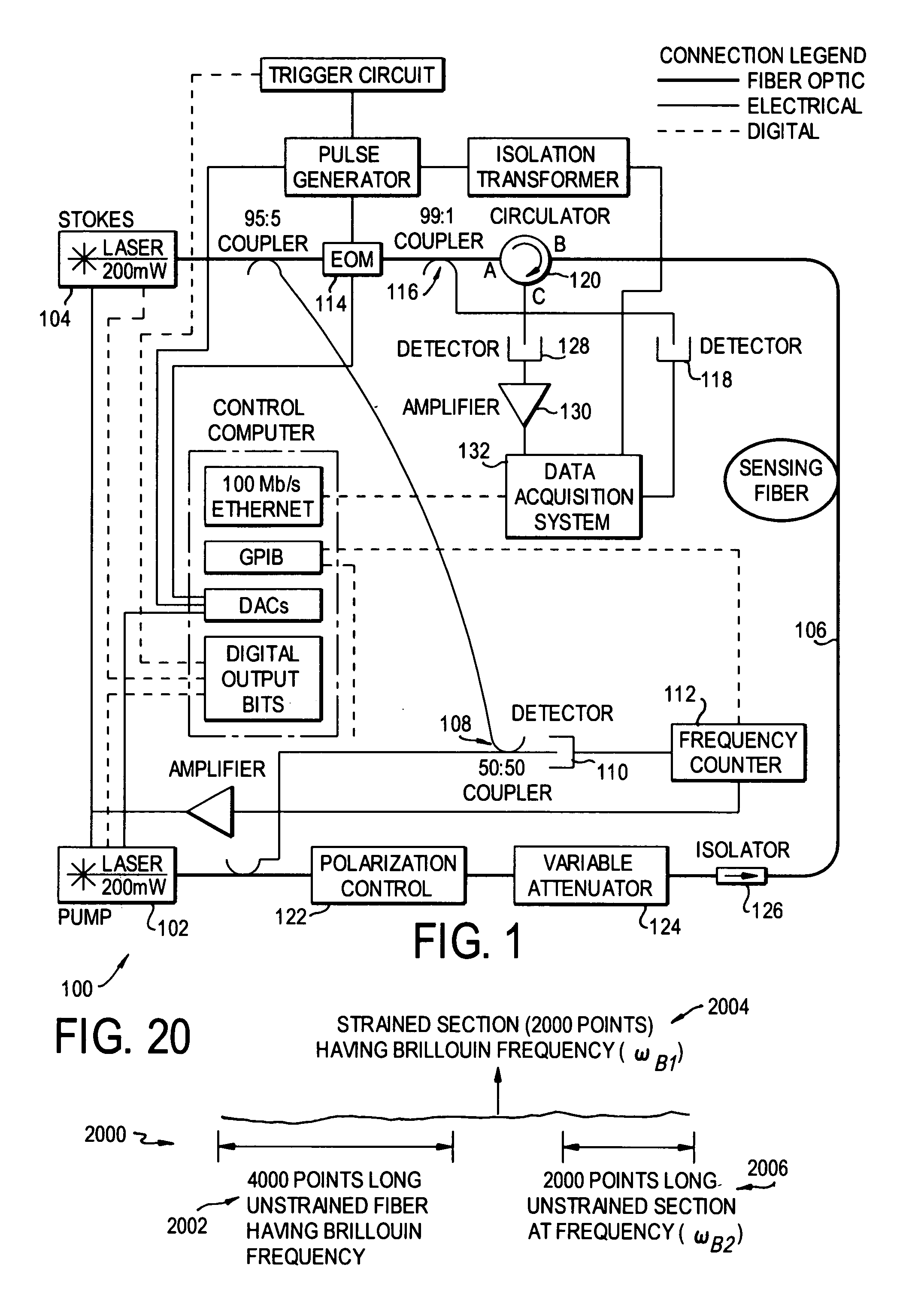
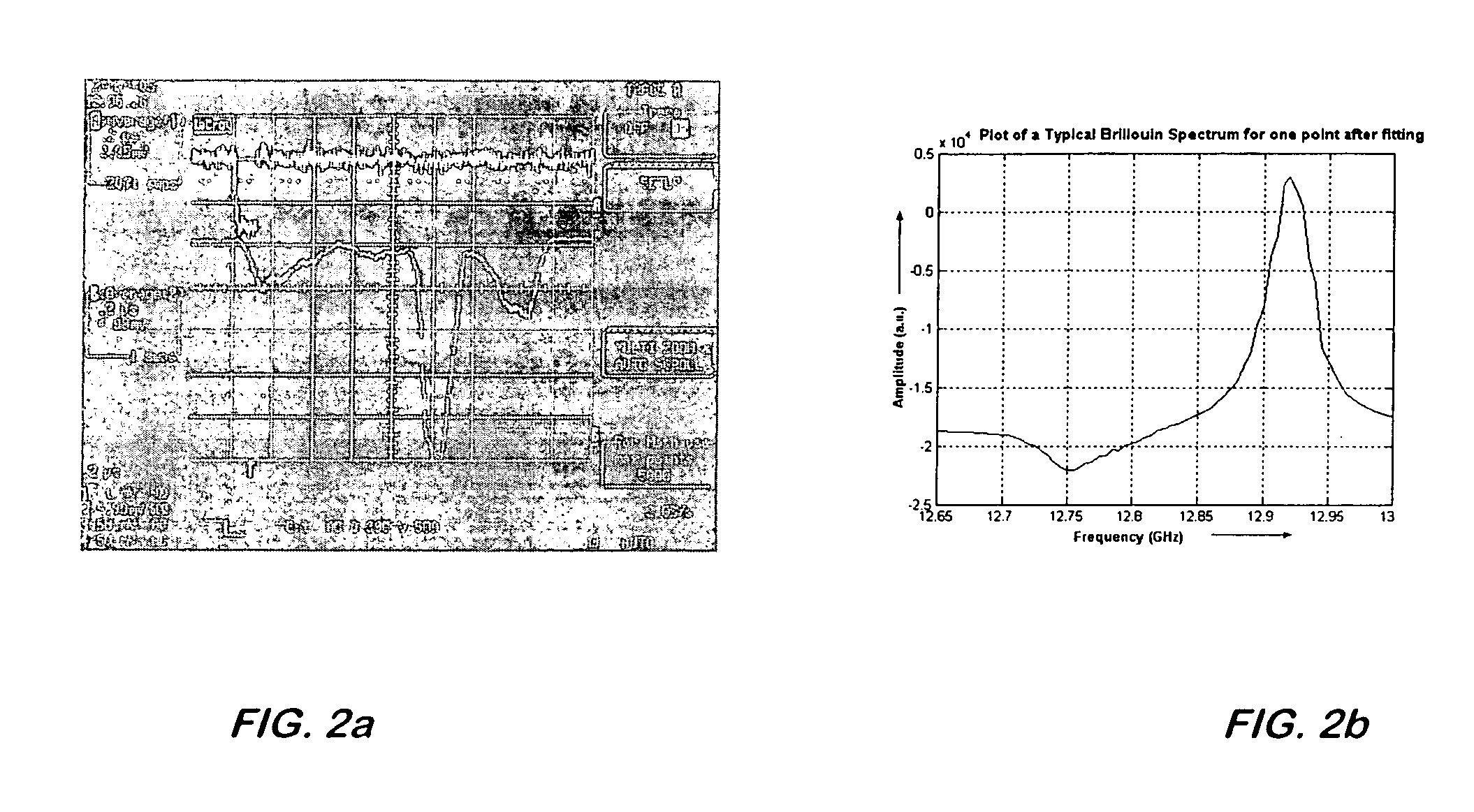
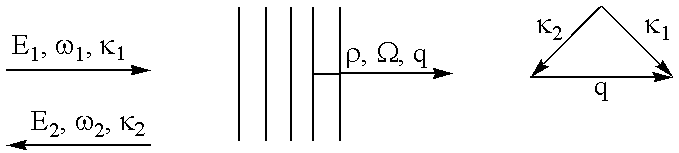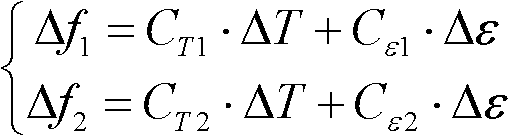Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
985 results about "Brillouin scattering" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
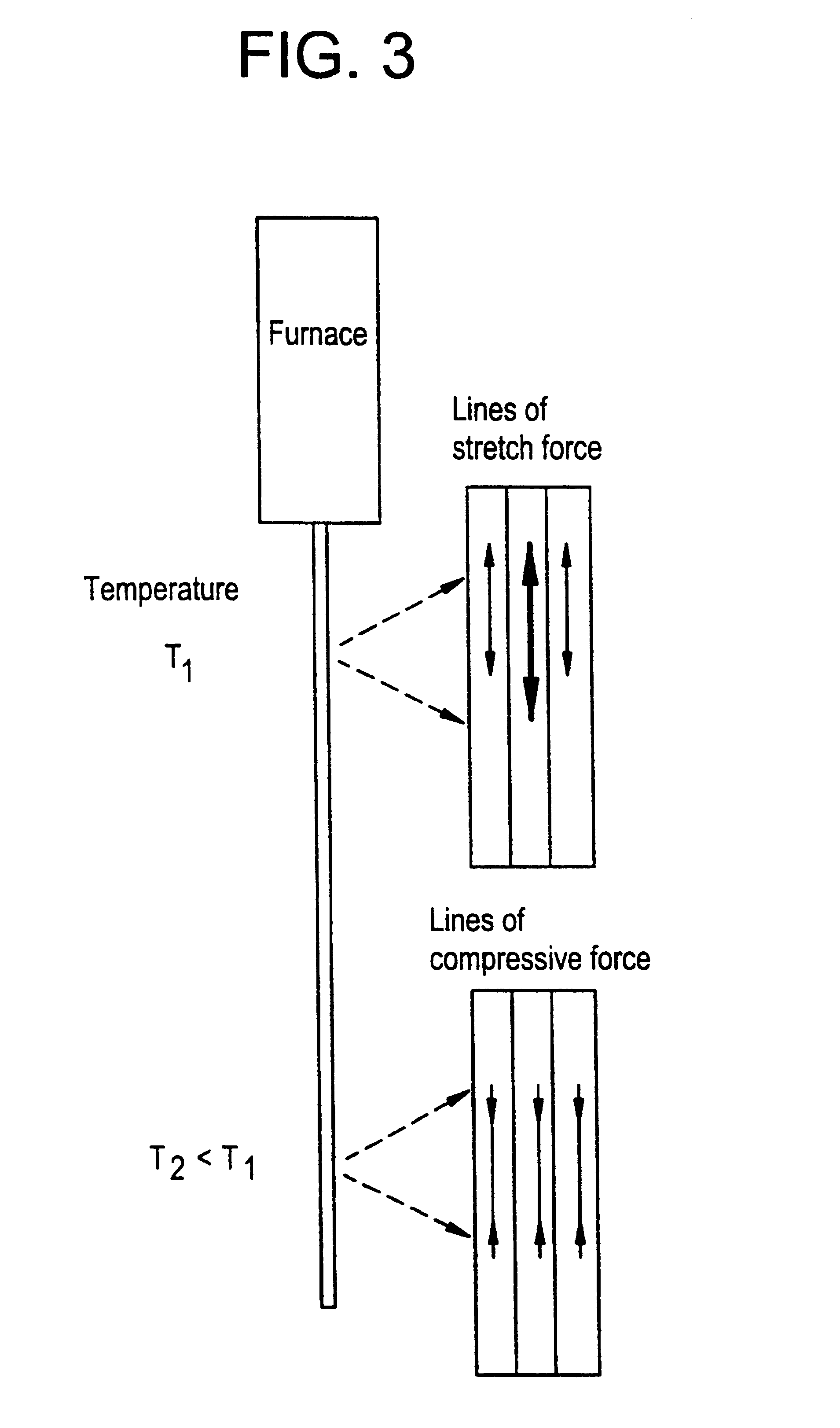
Brillouin scattering, named after Léon Brillouin, refers to the interaction of light with the material waves in a medium. It is mediated by the refractive index dependence on the material properties of the medium; as described in optics, the index of refraction of a transparent material changes under deformation (compression-distension or shear-skewing).
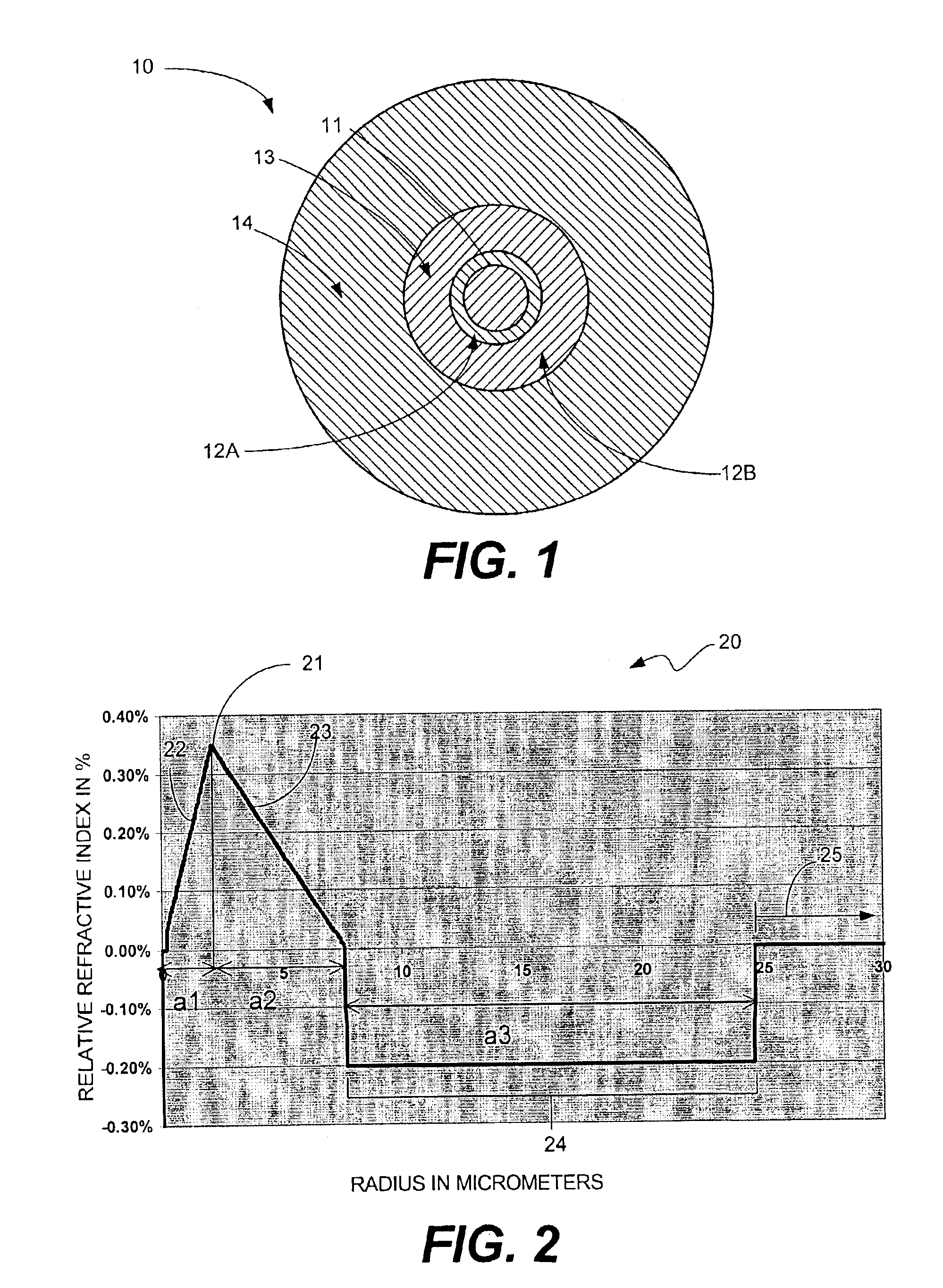
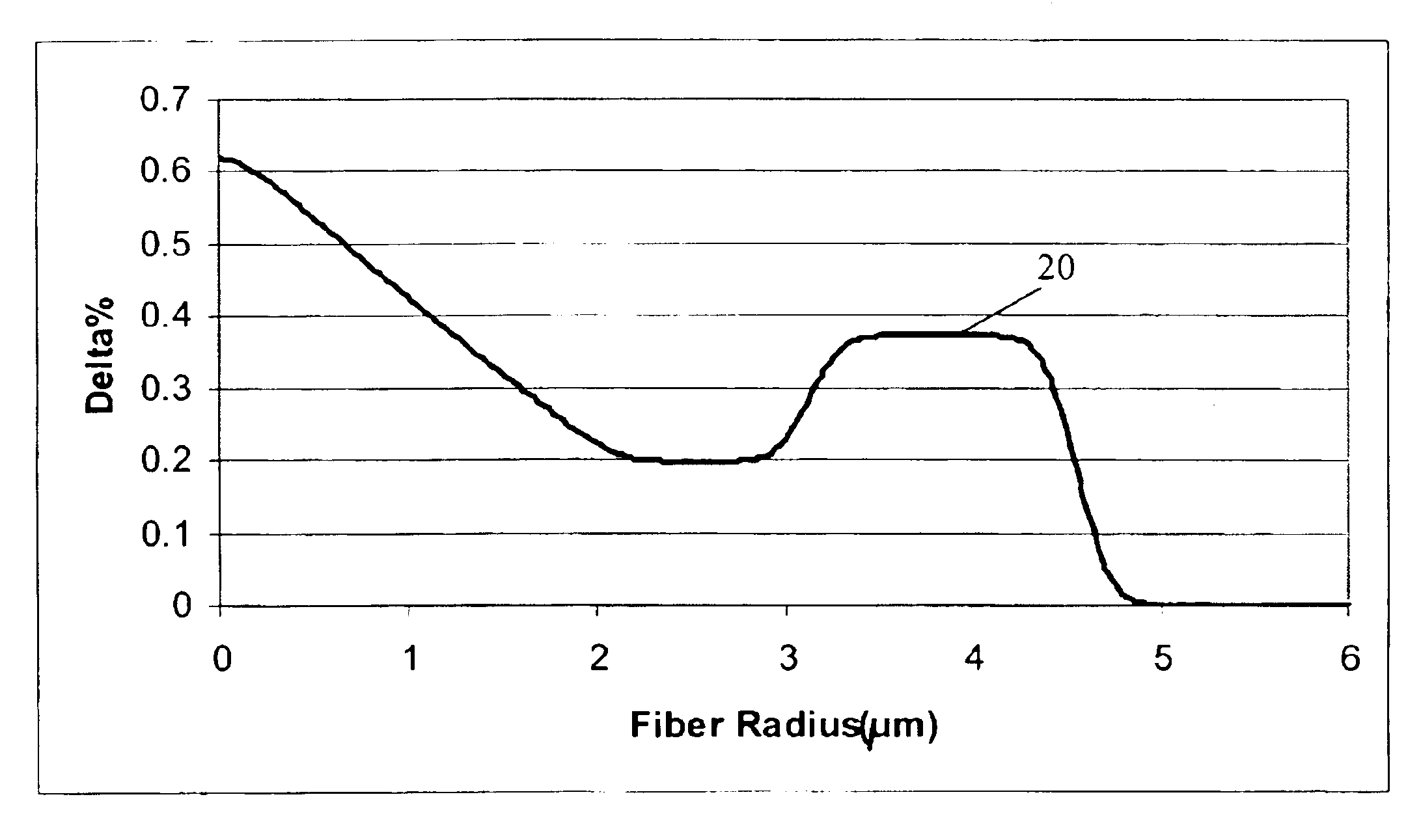
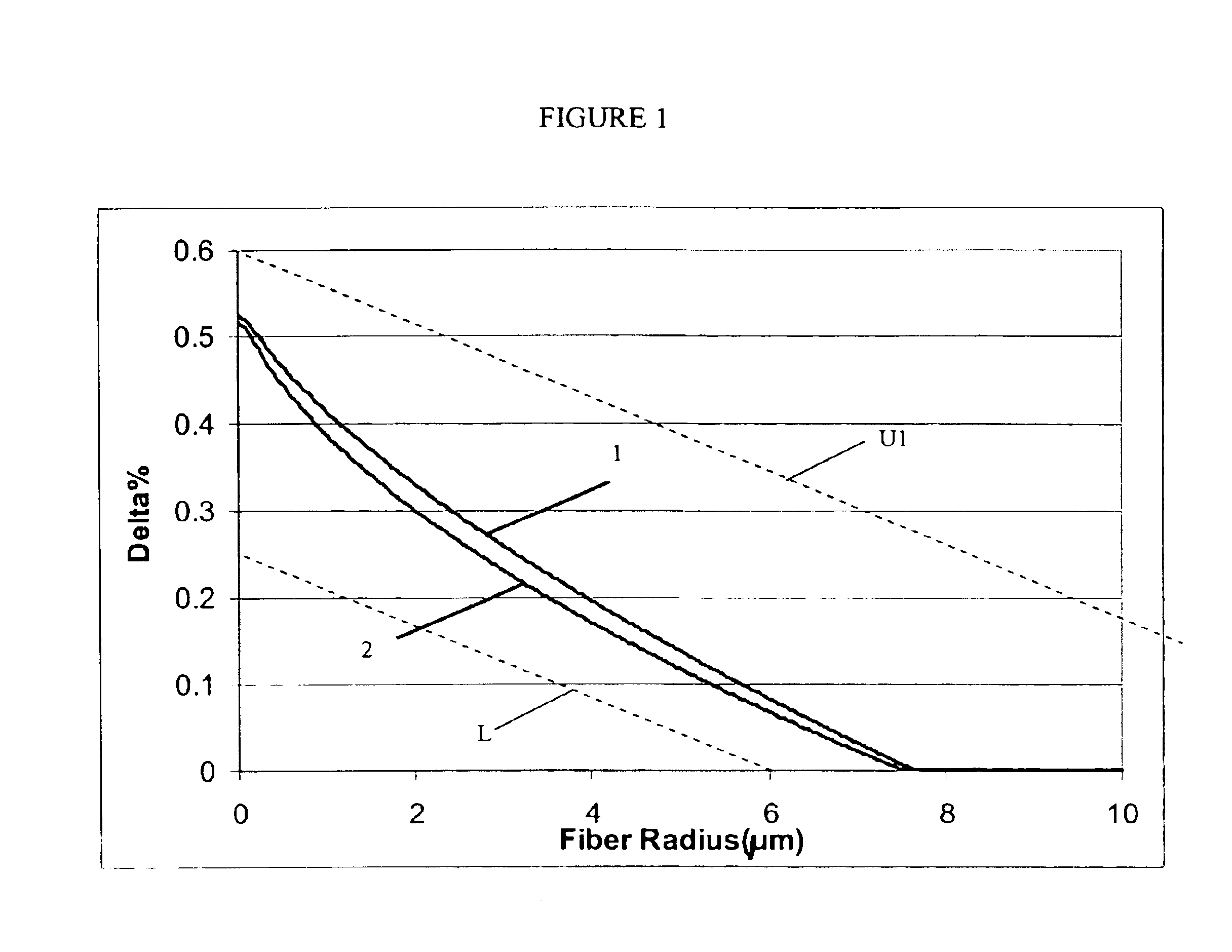
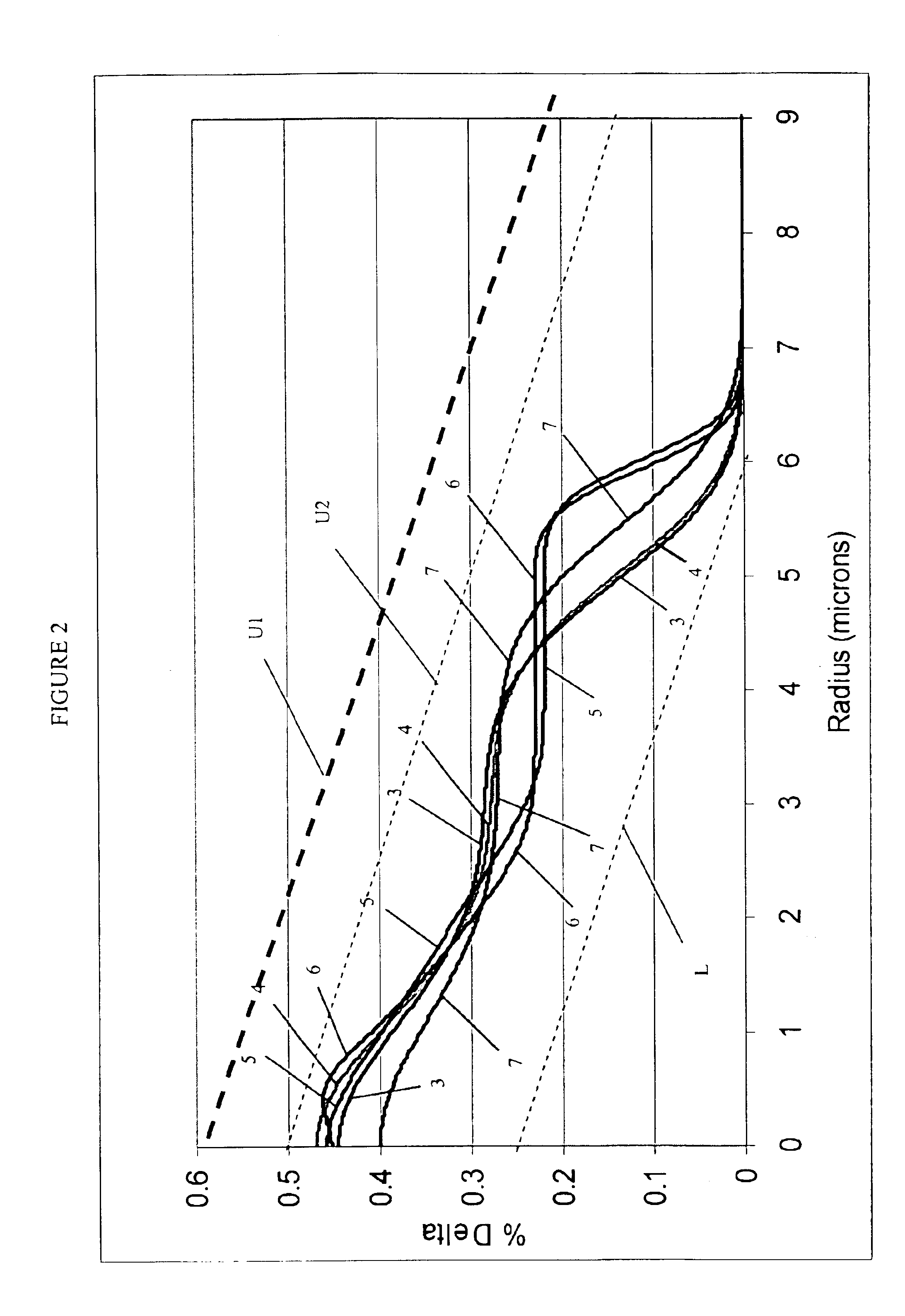
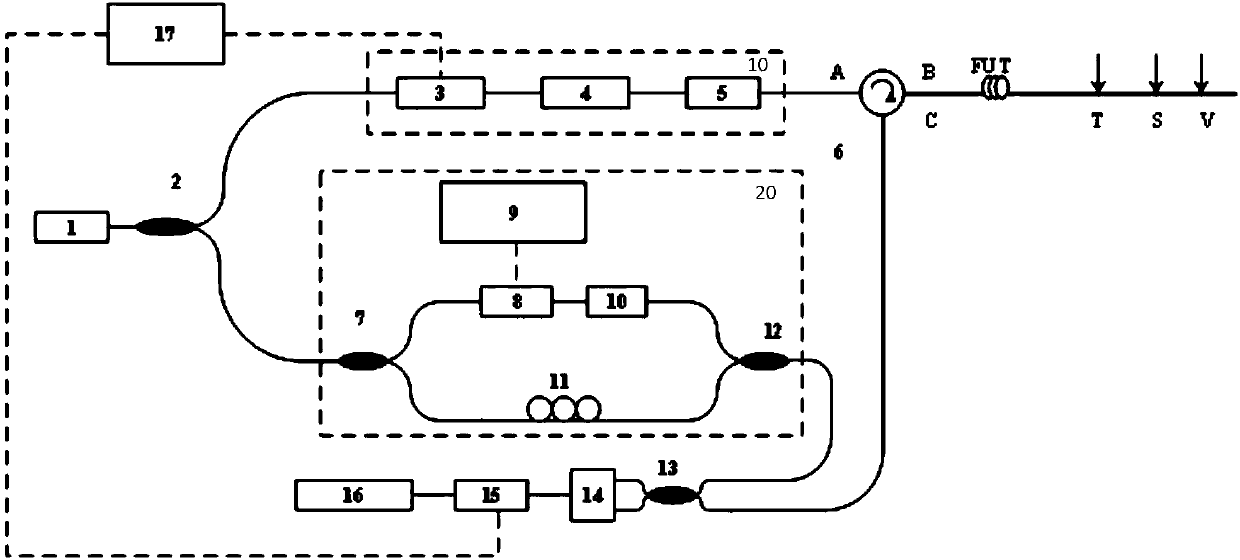
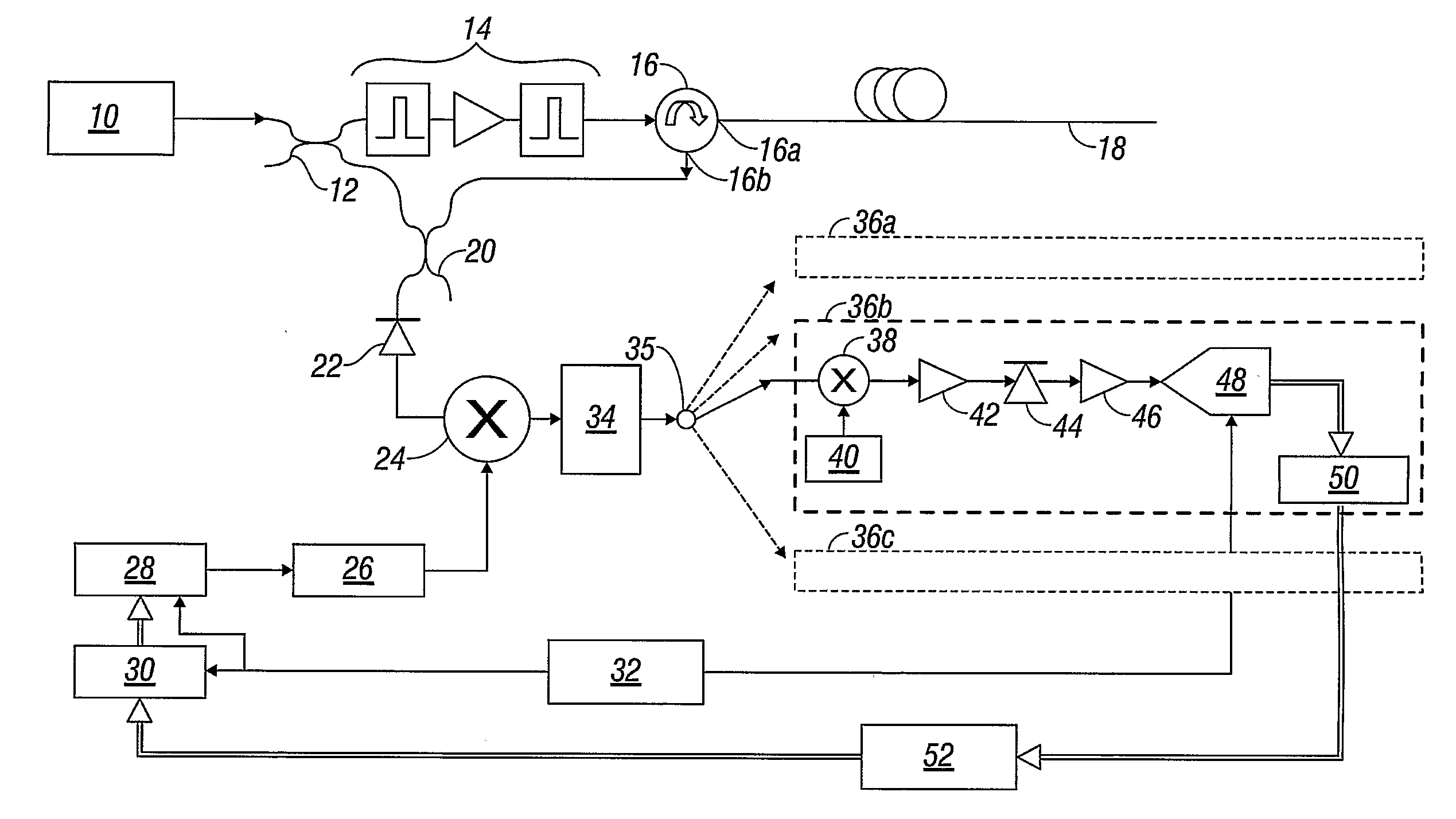
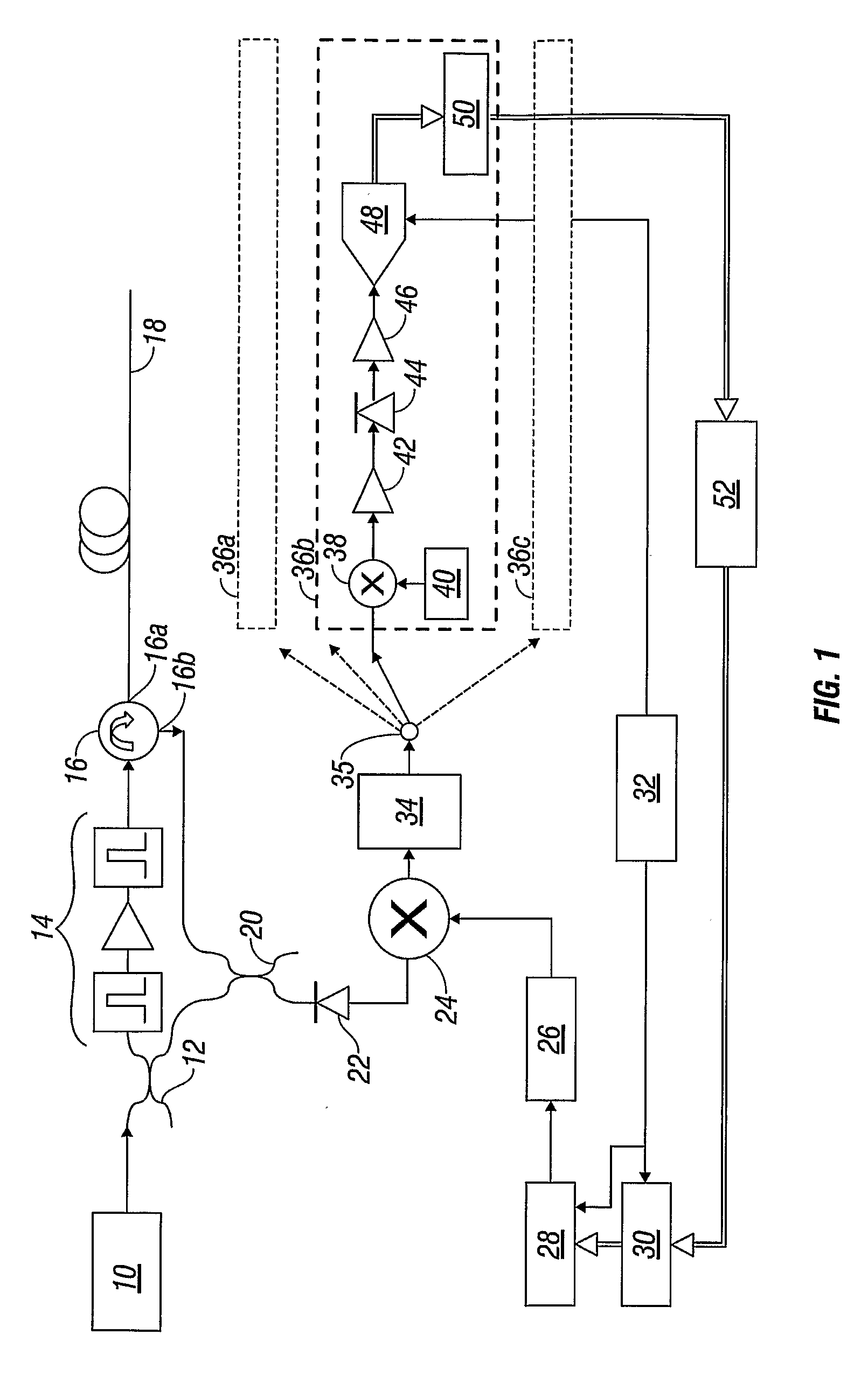
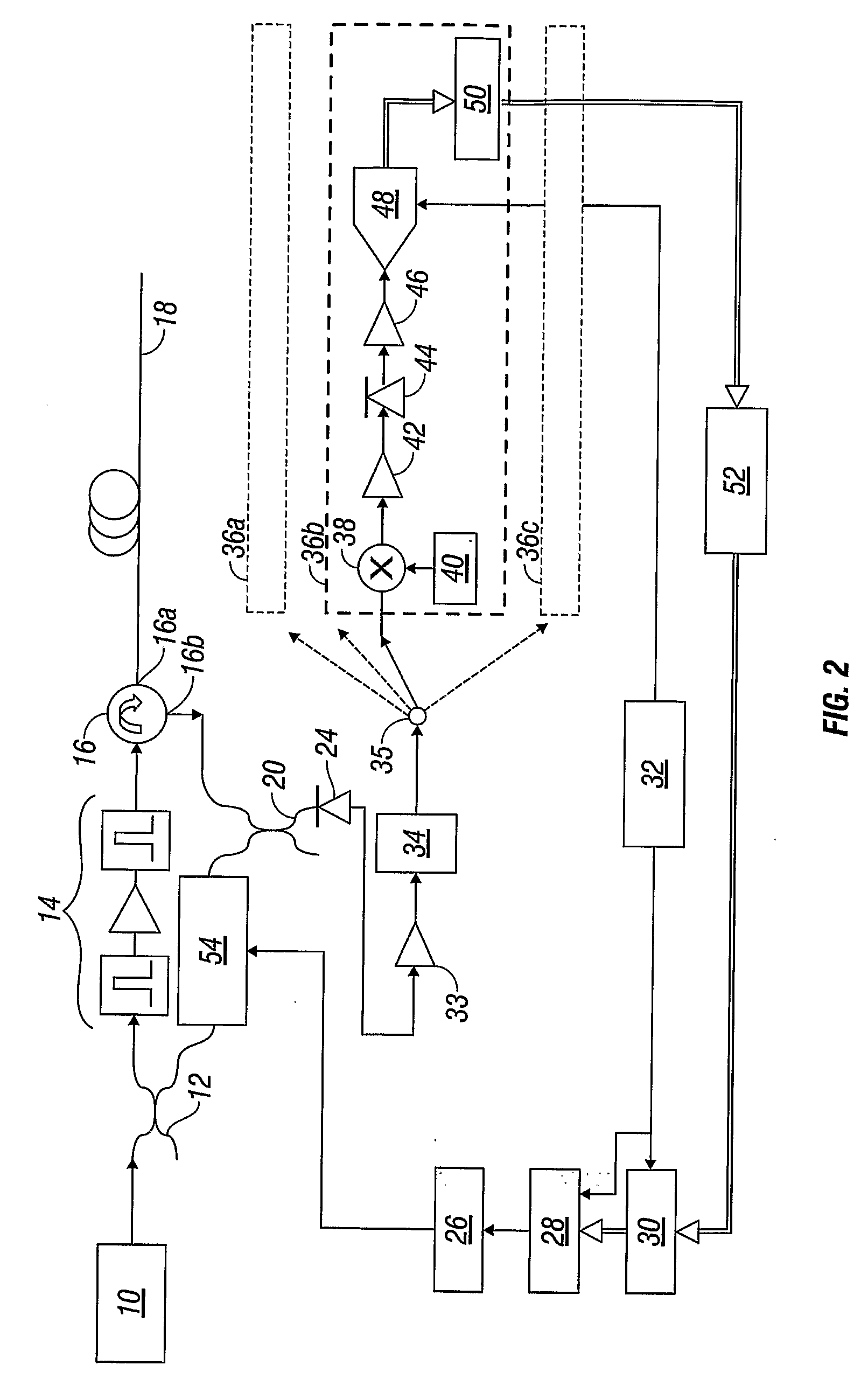
Super-large-effective-area (SLA) optical fiber and communication system incorporating the same
ActiveUS6904218B2Increase the effective areaLow cutoff wavelengthOptical fibre with multilayer core/claddingOptical waveguide light guideFiberUltrasound attenuation
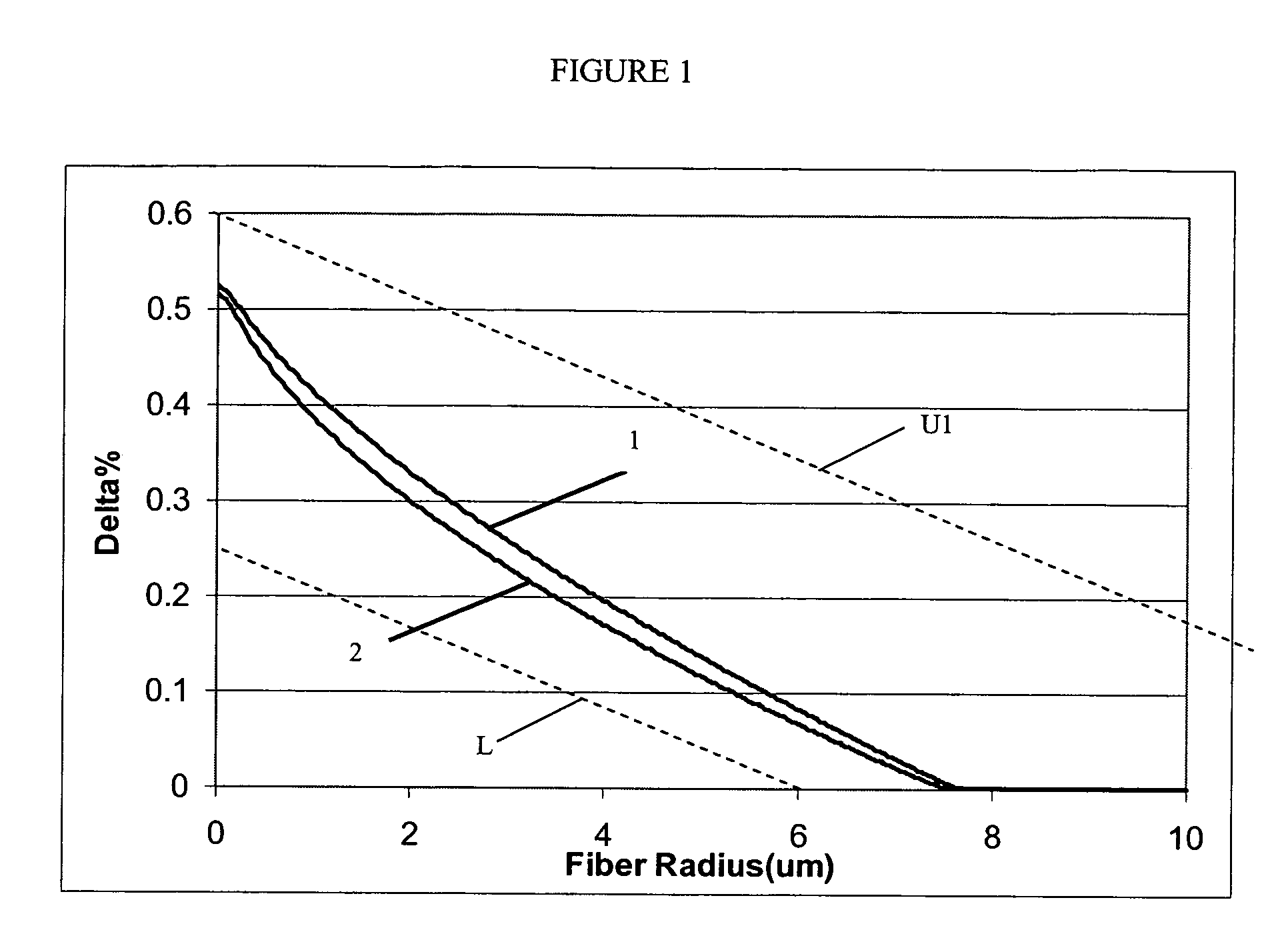
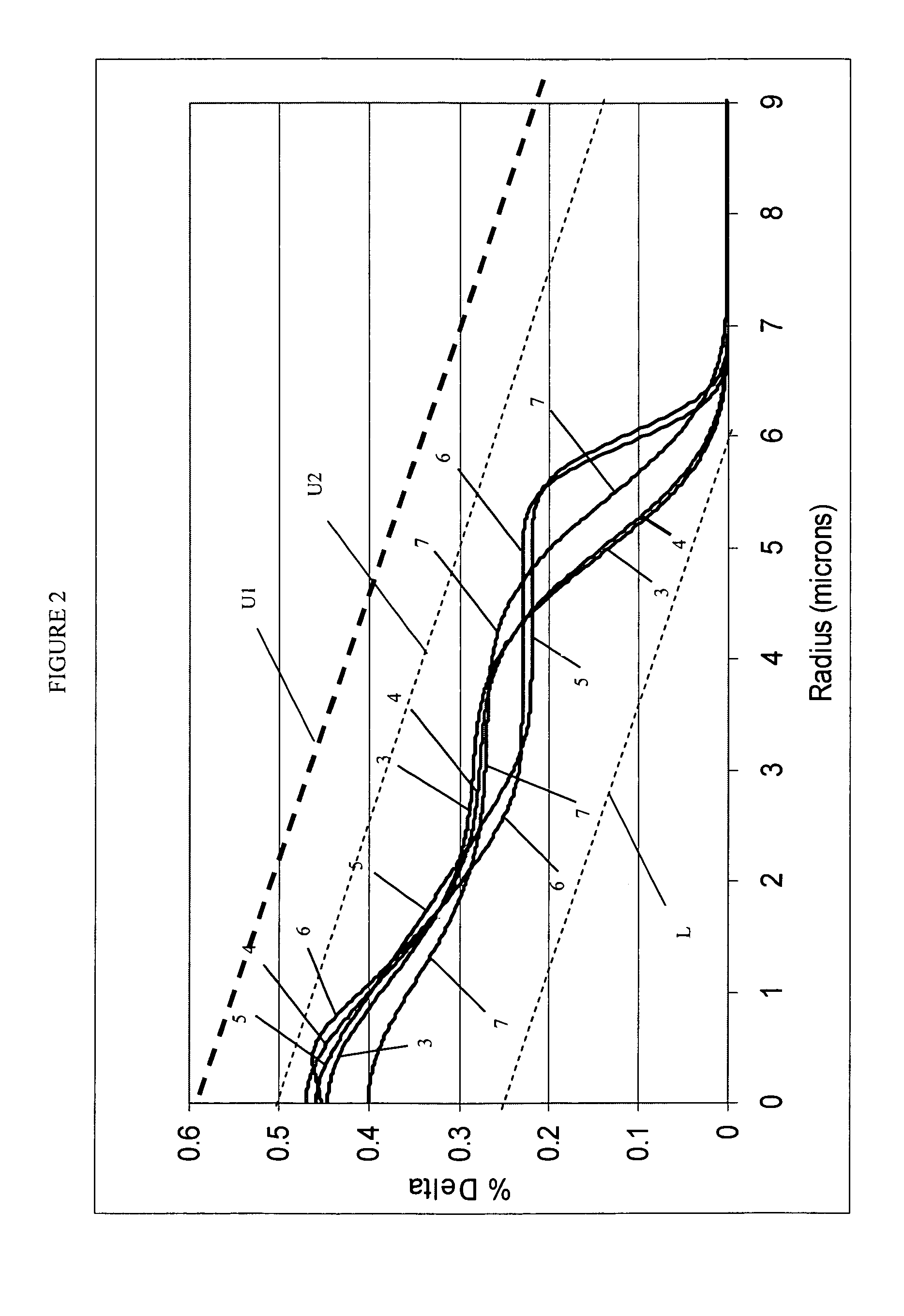
A super-large-effective-area (SLA) optical fiber that is suitable for communicating over a wide wavelength range and that, because of its large effective area, suppresses nonlinear effects that typically result from interaction between signal channels. The effective area, Aeff, of the SLA fiber of the present invention preferably is equal to or greater than approximately 80 μm2 at a wavelength window around 1310 nm. The cutoff wavelength of the SLA fiber of the present invention preferably is less than 1310 nm. Thus, the SLA fiber of the present invention has a very large effective area and a very low cutoff wavelength. In accordance with the present invention, a variety of SLA fibers are provided that all have very large effective areas and desirable transmission properties. The large effective areas of the SLA fibers of the present invention enable nonlinear effects to be suppressed, as well as Stimulated Brillouin Scattering in analog transmission. The large effective areas also enable attenuation to be reduced. The result of suppressing nonlinear effects and reducing attenuation enable signals to be transmitted over long distances and over a broad bandwidth.
Owner:FURAKAWA ELECTRIC NORTH AMERICA INC
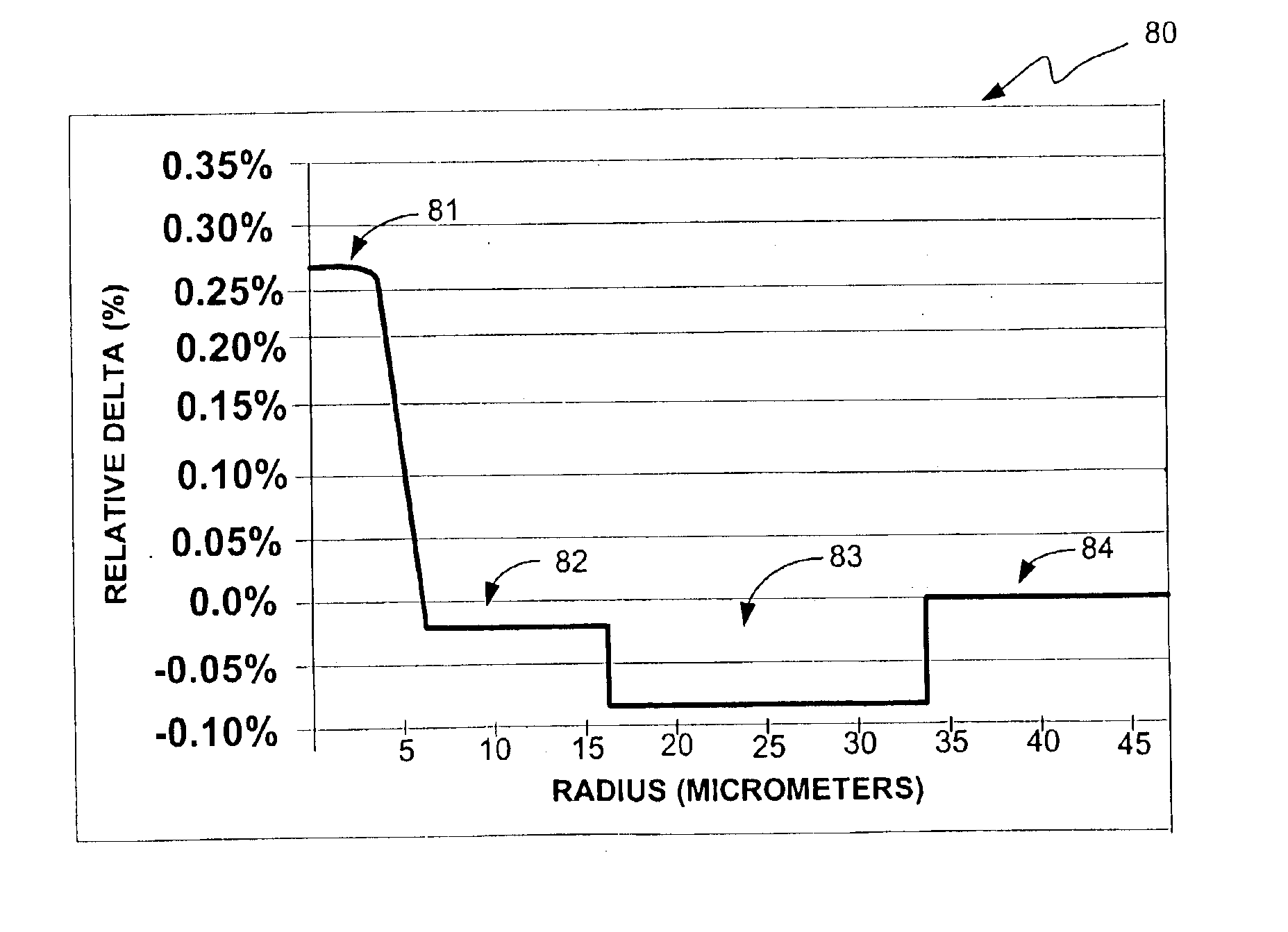
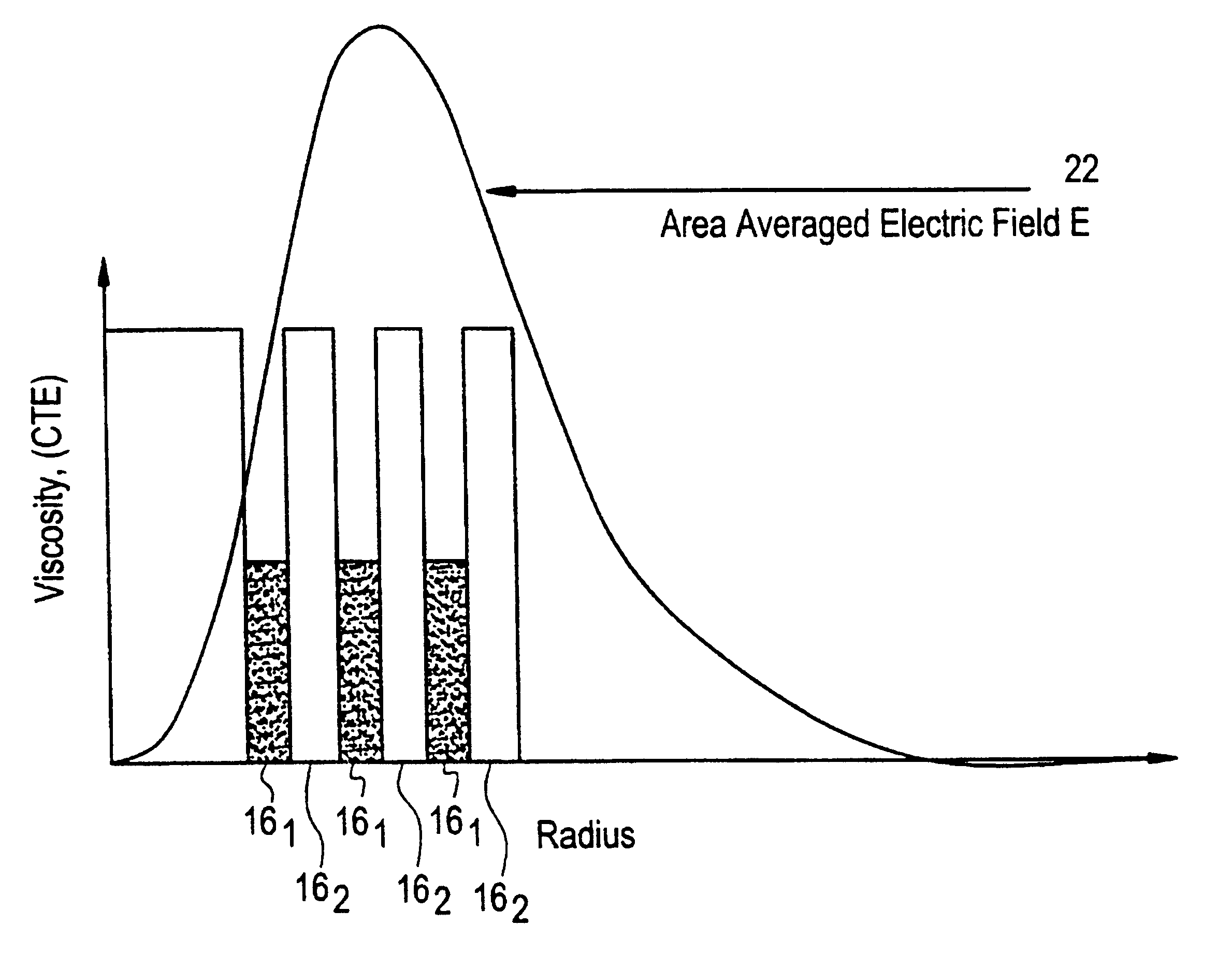
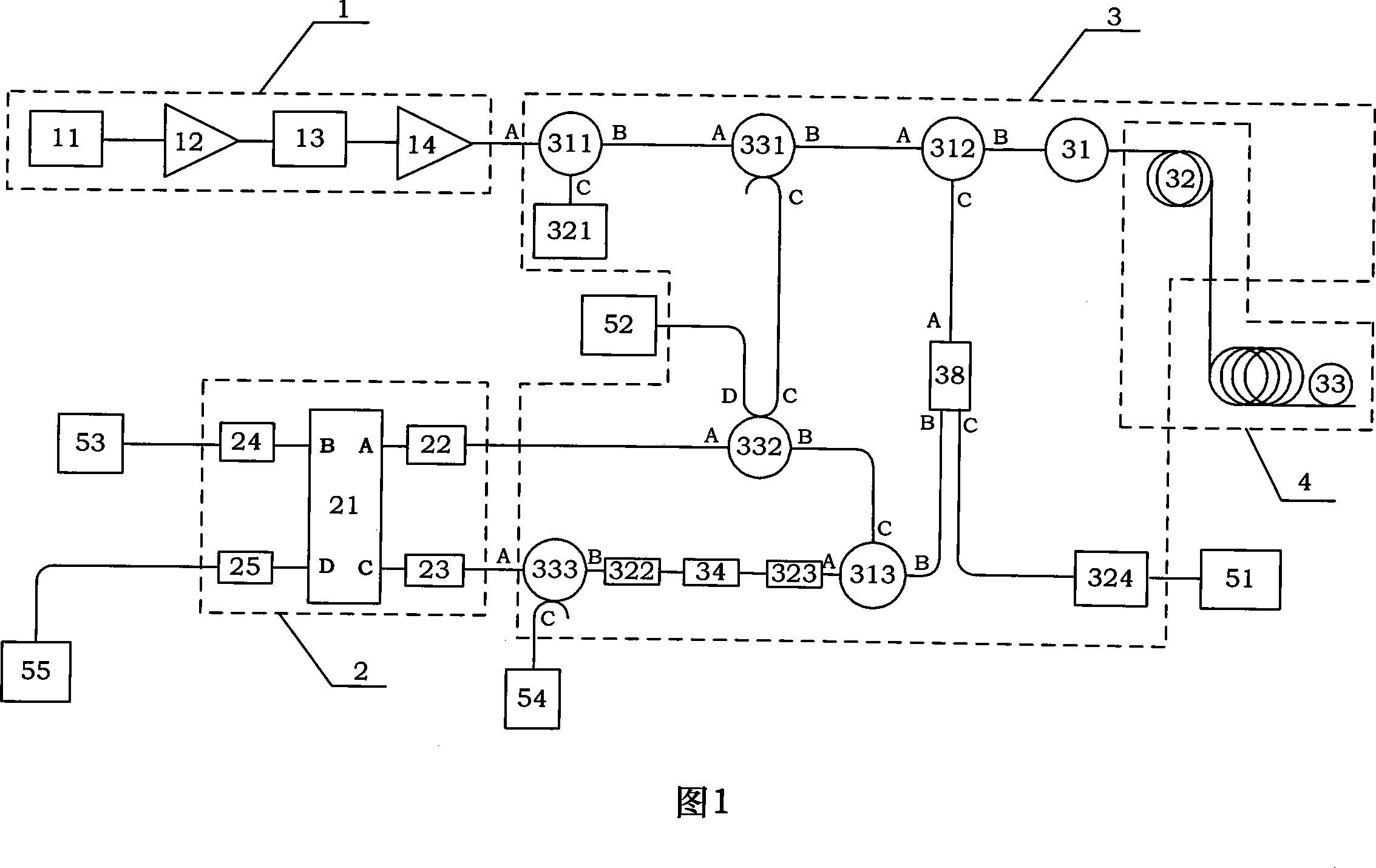
Suppression of stimulated Brillouin scattering in optical fiber
InactiveUS6542683B1Optical fibre with multilayer core/claddingGlass fibre drawing apparatusFiberDopant
Suppression of stimulated Brillouin scattering (SBS) by broadening the energy spectrum of participating SBS photons and / or phonons is achieved in an optical fiber having a core with both radially nonuniform viscosity and CTE profiles provided by alternating layers of glass modifying dopants such as phosphorous and fluorine. The nonuniform thermal expansion and viscosity profiles impart a residual, permanent, nonuniform stress in the fiber. The SBS suppressing effect provided by the nonuniform stress can be controlled and enhanced by applying a uniform or nonuniform tensile force to the fiber as it is being drawn. A preform for the fiber is also disclosed.
Owner:CORNING INC
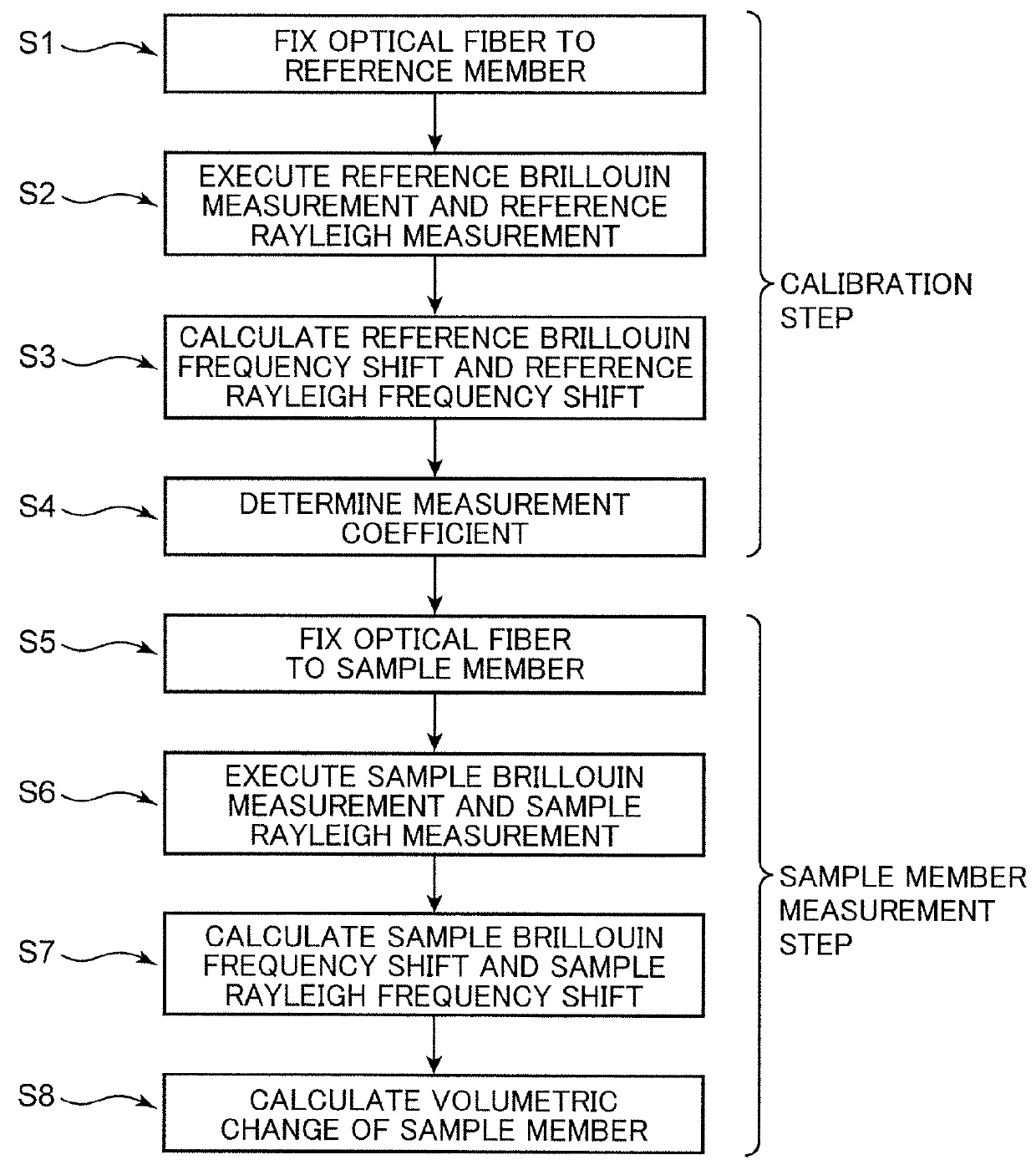
Method for measuring volumetric changes of object
ActiveUS9360304B2Accurate measurementOptical detectionUsing optical meansRayleigh scatteringRayleigh Light Scattering
Under a known pressure is externally applied to a reference member to which an optical fiber is fixed, test light is allowed to enter the optical fiber, and at least one of a reference Brillouin measurement for determining a reference Brillouin frequency shift amount based on the Brillouin scattering phenomenon, and a reference Rayleigh measurement for determining a reference Rayleigh frequency shift amount based on the Rayleigh scattering phenomenon is performed. A Brillouin measurement coefficient or a Rayleigh measurement coefficient is determined from these calculation results. An optical fiber is fixed to a sample member, the volumetric change of which is unknown, and the same sample Brillouin measurement or sample Rayleigh measurement is performed to determine the frequency shift amount. The volumetric change of the sample member is determined from the sample Brillouin or the sample Rayleigh frequency shift amount, and from the Brillouin or the Rayleigh measurement coefficient.
Owner:RES INST OF INNOVATIVE TECH FOR THE EARTH +1
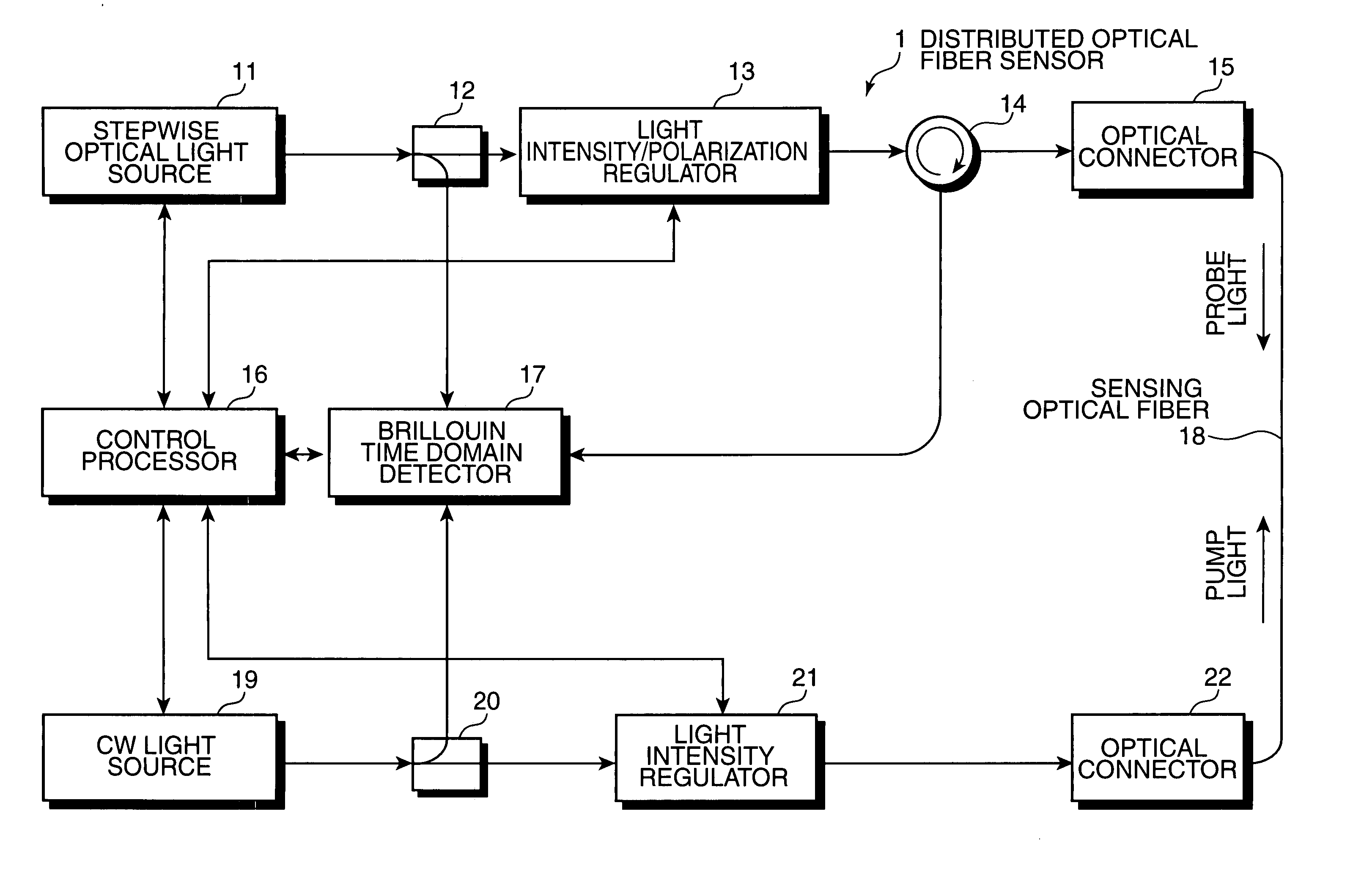
Distributed Optical Fiber Sensor
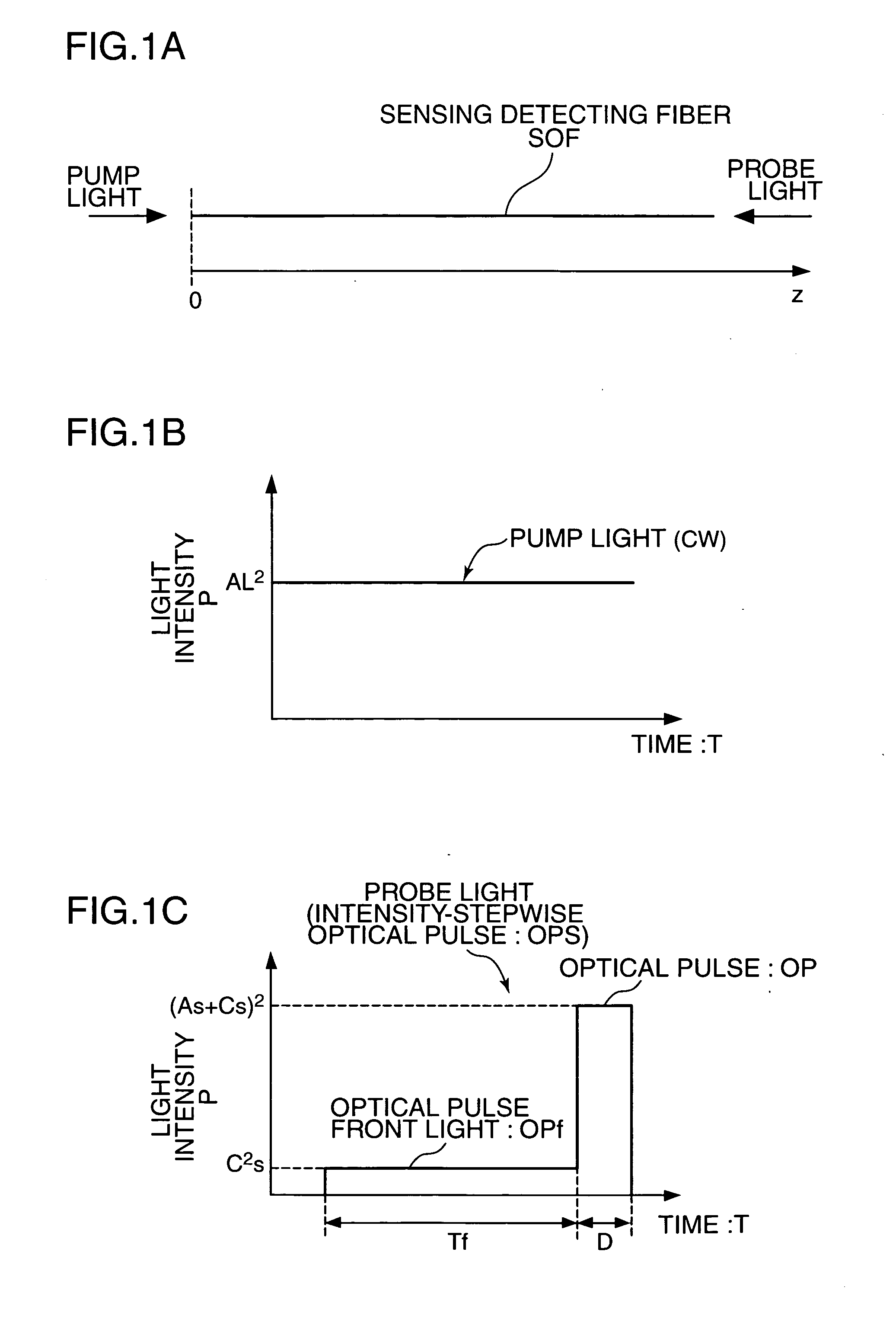
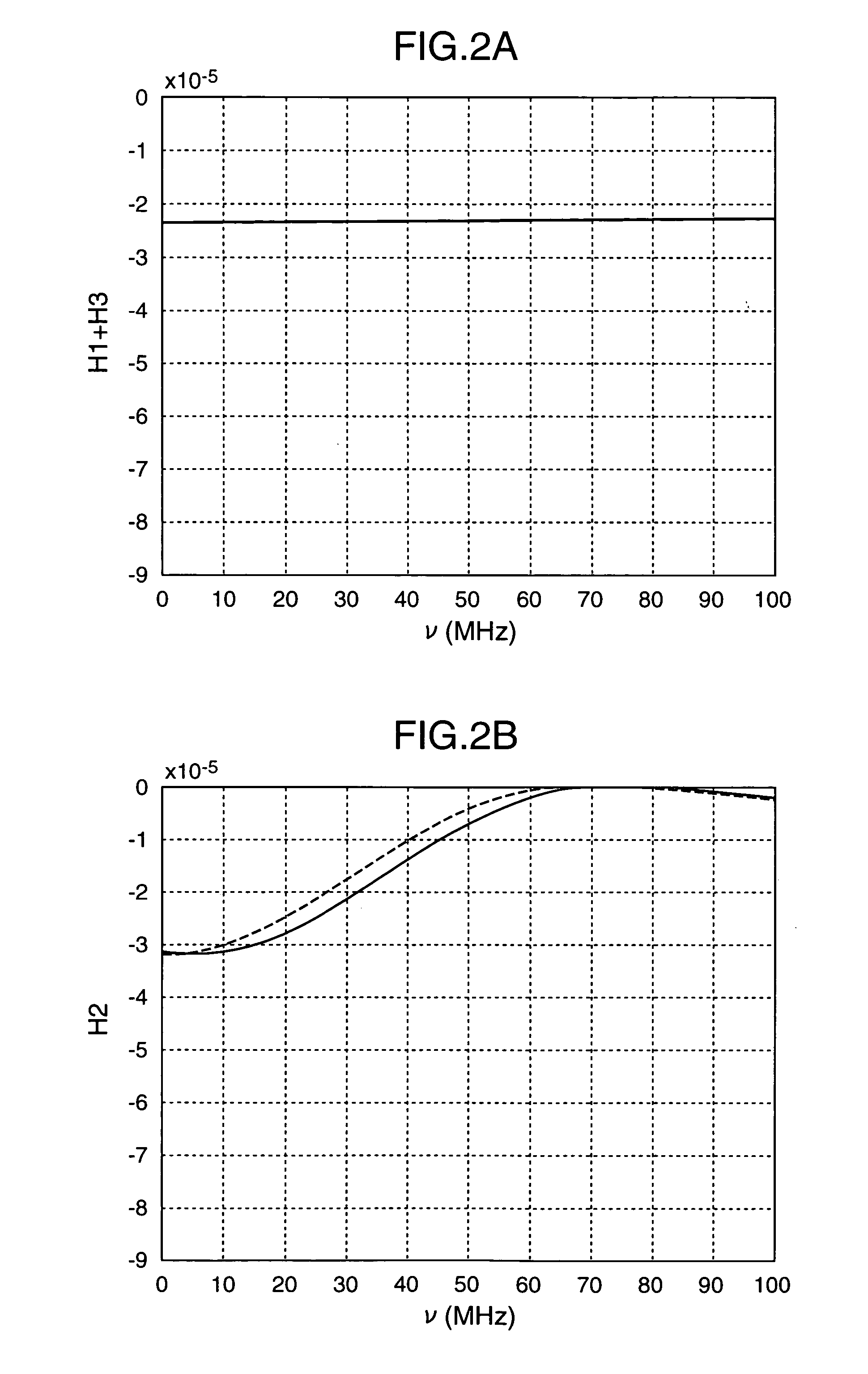
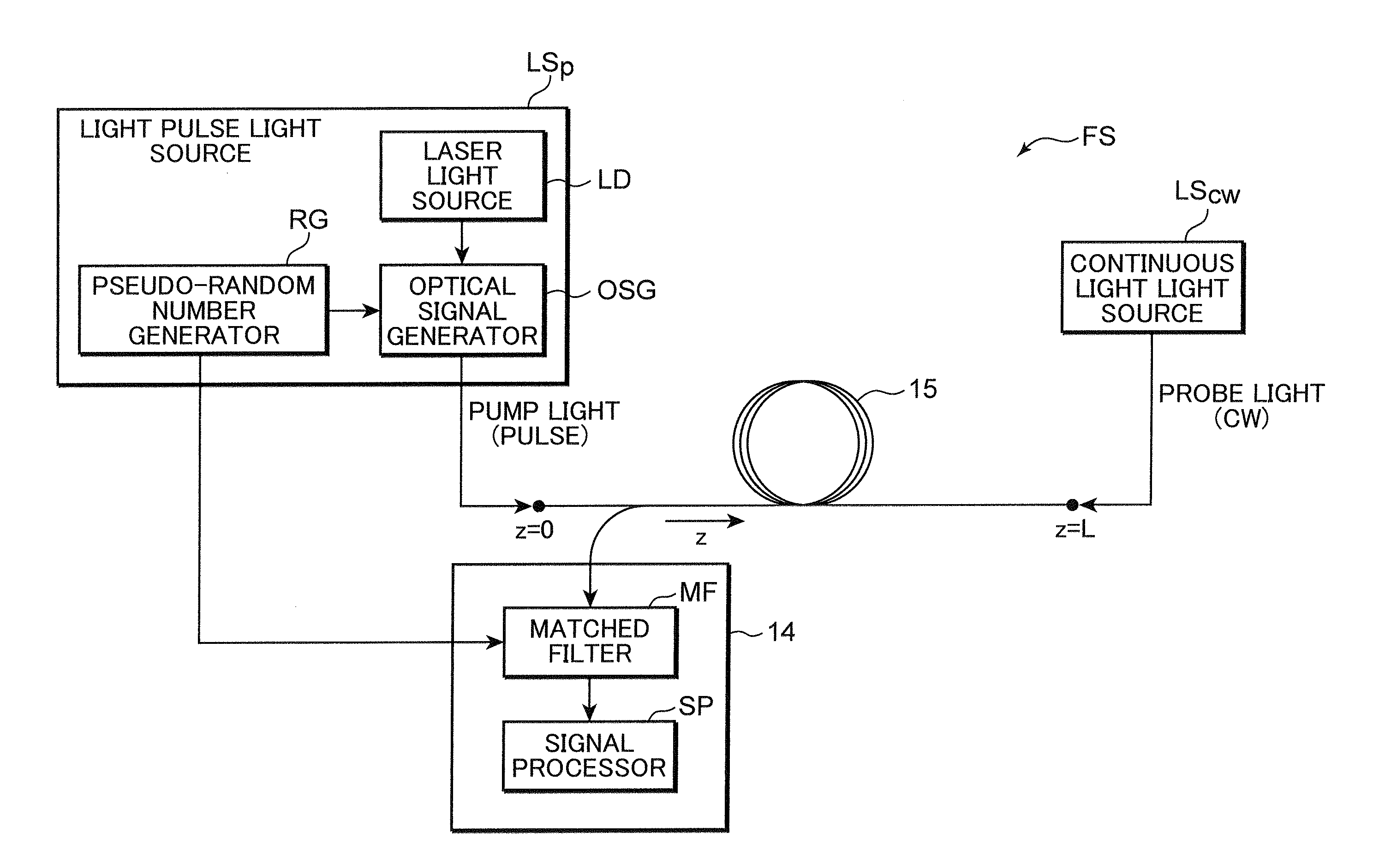
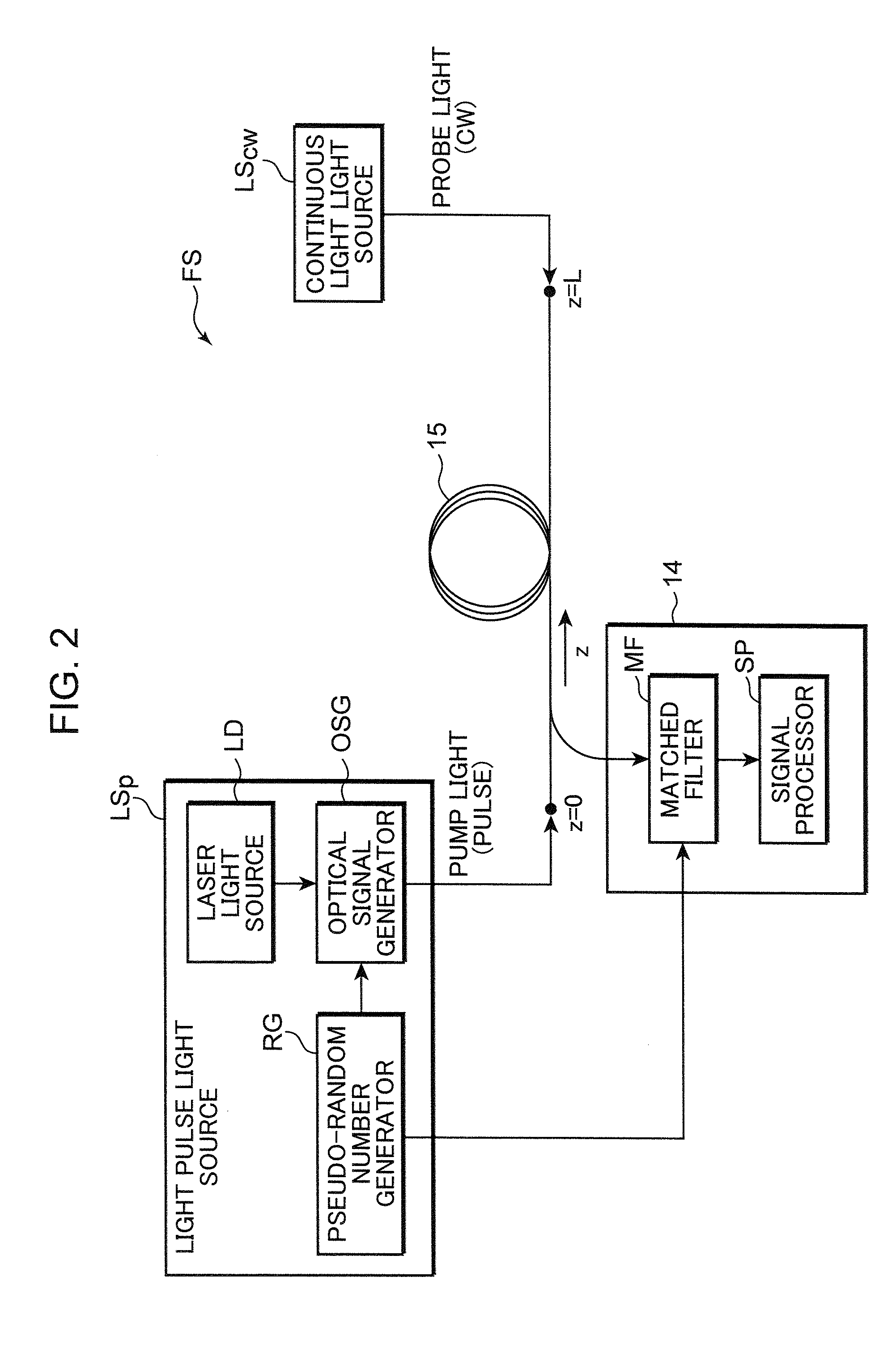
A distributed optical fiber sensor uses a Brillouin scattering phenomenon to avoid manual adjustment and to measure strain and / or temperature with high accuracy and high spatial resolution. A stepwise optical light source generates an optical pulse having a stepwise distribution of intensity to increase toward the center, and a continuous light source generates continuous light on. The optical pulse is incident on a sensing optical fiber as probe light and the continuous light is incident as pump light to cause a Brillouin scattering phenomenon between the probe light and the pump light. A Brillouin time domain detector determines a Brillouin loss or gain spectrum from the light emerging from the sensing optical fiber and attributed to the Brillouin scattering phenomenon, and measures strain in and / or temperature of the sensing optical fiber in the longitudinal direction thereof based on the determined Brillouin loss or gain spectrum.
Owner:NEUBREX
Distributed optical fiber sensor
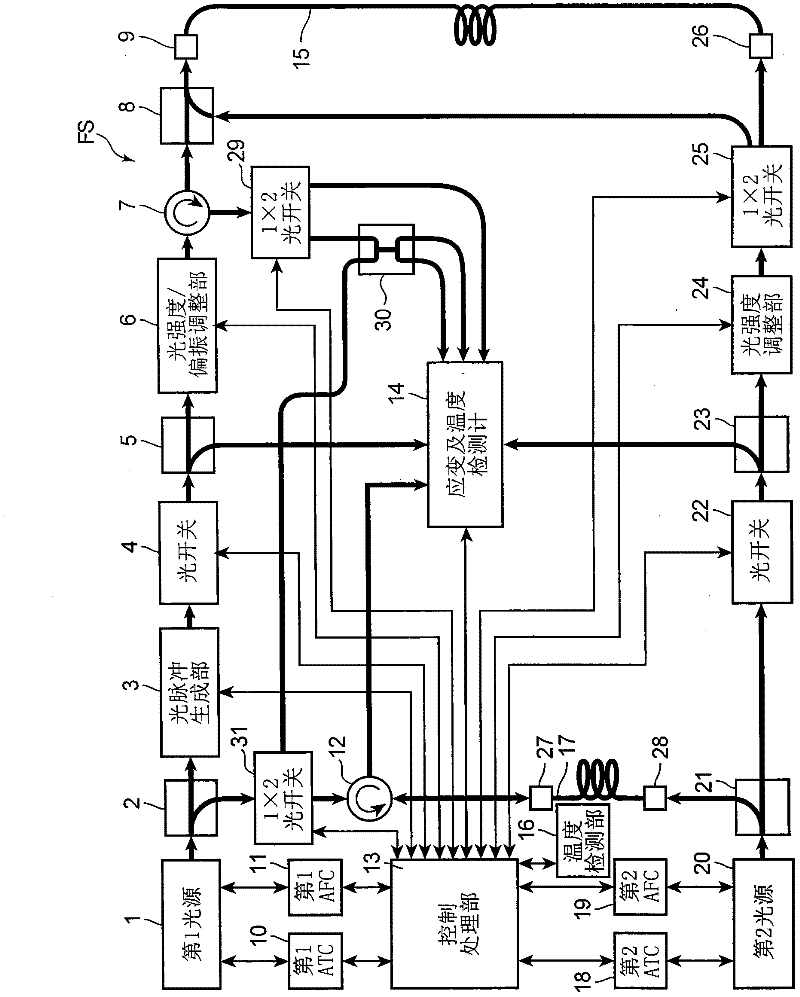
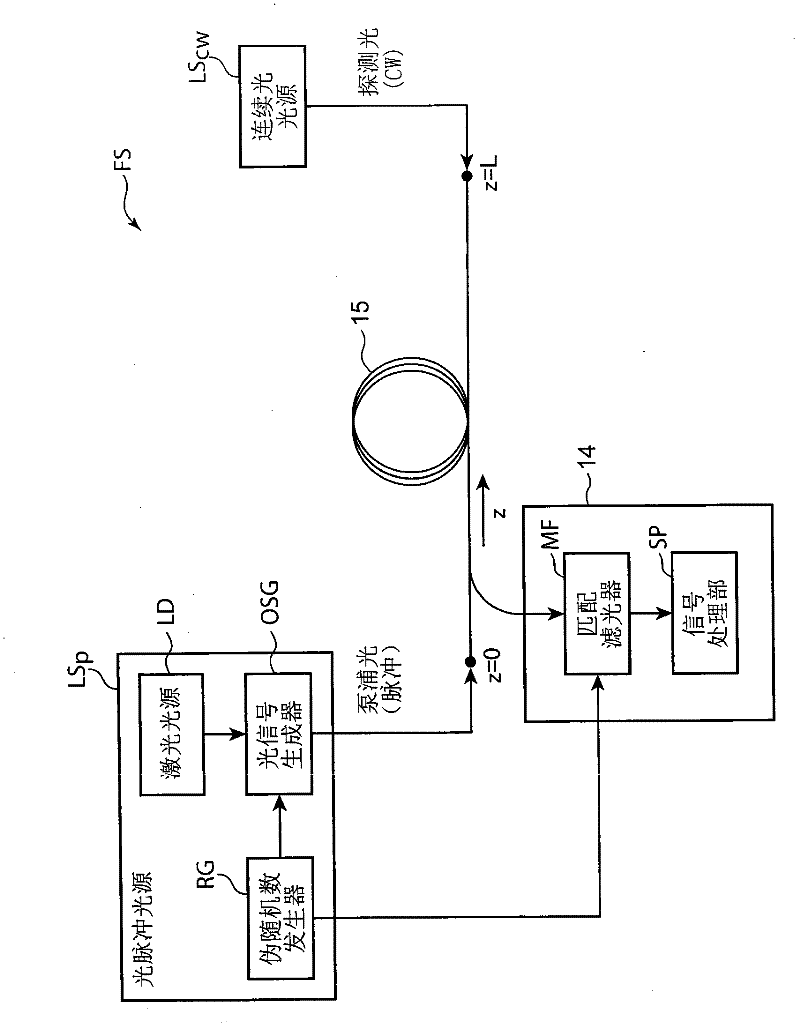
ActiveUS20110228255A1Improve spatial resolutionPolarisation-affecting propertiesForce measurementRayleigh scatteringRayleigh Light Scattering
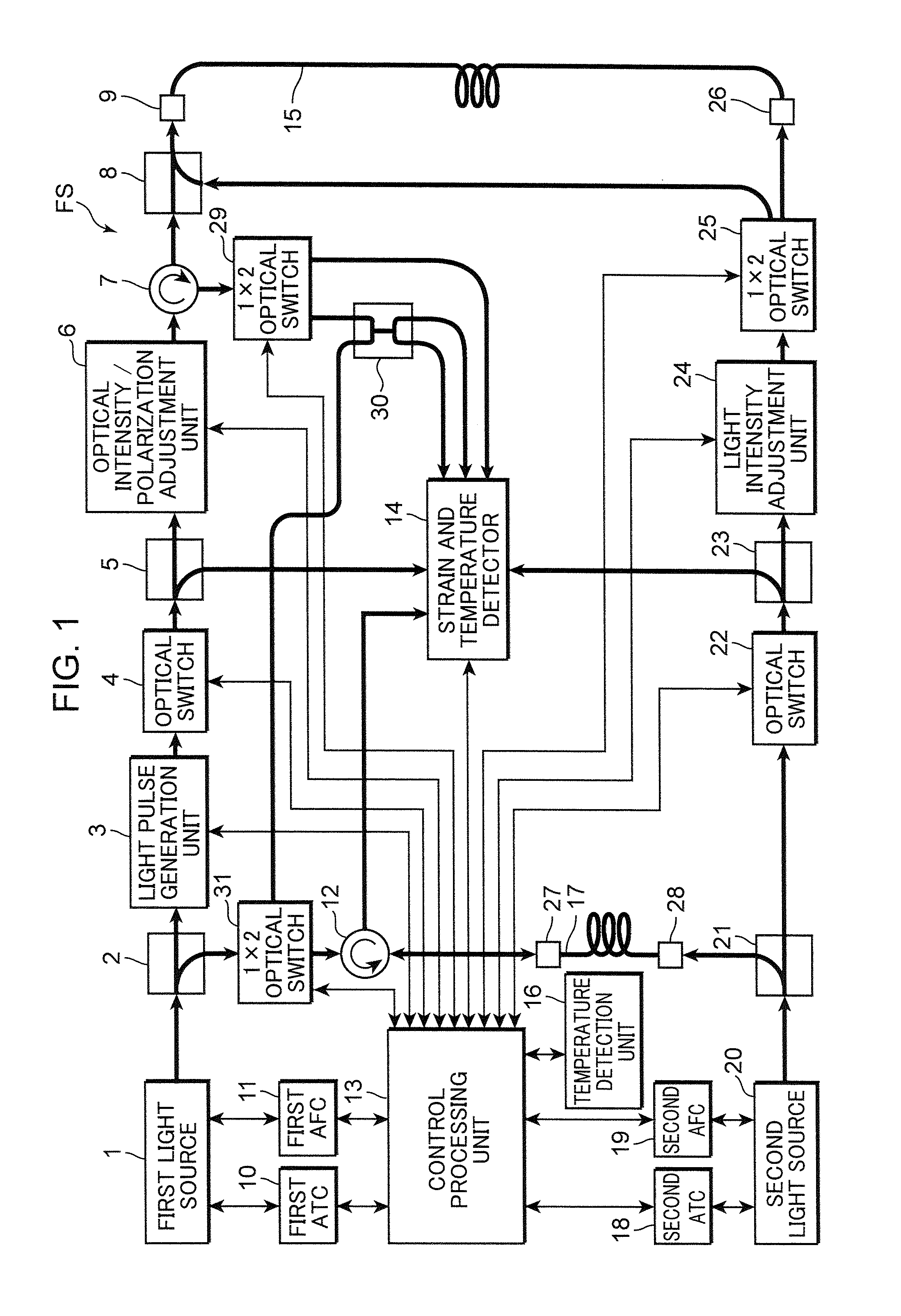
The present invention provides a distributed optical fiber sensor capable of measuring the strain and temperature of an object to be measured simultaneously and independently with high spatial resolution. A distributed optical fiber sensor FS is a distributed optical fiber sensor which uses an optical fiber 15 as a sensor, and a strain and temperature detector 14 measures a Brillouin frequency shift amount caused by a strain and a temperature generated in the optical fiber 15 by using a Brillouin scattering phenomenon, measures a Rayleigh frequency shift amount caused by the strain and temperature generated in the optical fiber 15 by using a Rayleigh scattering phenomenon, and calculates the strain and temperature generated in the optical fiber 15 from the measured Brillouin frequency shift amount and Rayleigh frequency shift amount.
Owner:NEUBREX
Ultra-remote distributed fiber raman and brillouin photons sensor
InactiveCN101162158AAvoid lossHigh strengthThermometers using physical/chemical changesUsing optical meansFiberPhotonic sensor
The invention discloses super-far distributed fiber Raman and Brillouin photon sensors; by using the stimulated Raman scattering effect of fiber, the self Raman scattering effect of fiber, the Brillouin scattering effect of fiber and the light time-field reflection principle, distributed fiber Raman photon temperature sensors, distributed fiber Brillouin photon strain sensors and distributed fiber Raman amplifier are integrated together. Fiber consumption is overcome by using the gain of amplifier, and strengths of self Raman scattering light and Brillouin scattering light in fiber is enhanced, the signal to noise ratio of the system of distributed fiber Raman photon sensor and distributed fiber Brillouin photon strain sensor is enhanced, meanwhile, the transmission distances of distributed fiber Raman photon sensor and distributed fiber Brillouin photon strain sensor are increased, finally, the temperature and stress measuring accuracy is enhanced.
Owner:WEIHAI BEIYANG PHOTOELECTRIC INFORMATION TECH
Dynamic strain distributed fiber optic sensor
InactiveUS20060285850A1Short measurement timeQuick measurementRadiation pyrometryMaterial analysis by optical meansConstant frequencySpectral width
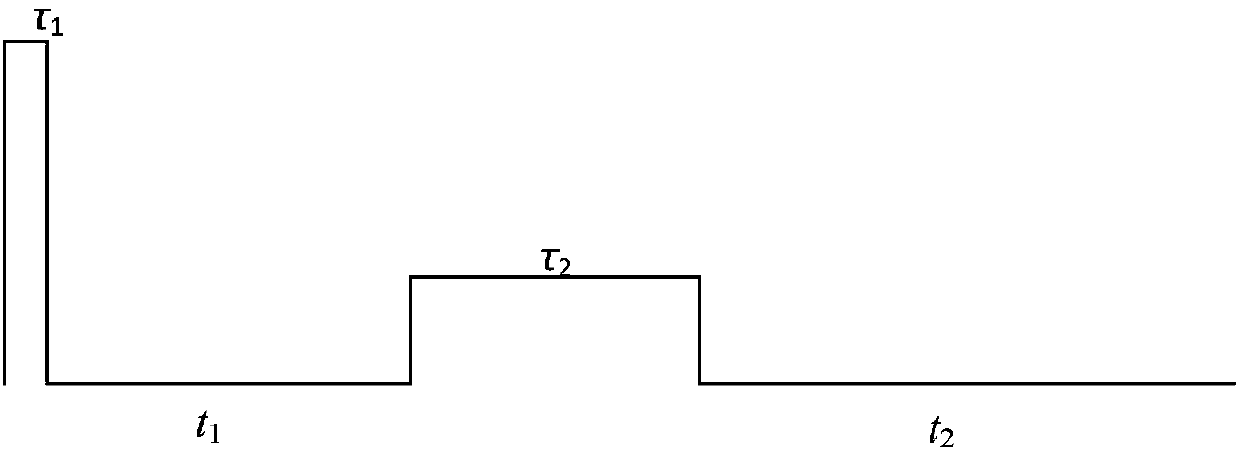
A distributed fiber optic sensor simultaneously interrogates the sensing fiber with two counter propagating light beams. One beam is set to a constant frequency. The second beam is modified to contain a “comb” of frequencies, with each frequency component in the comb offset by a predetermined amount. Each of the frequency components in the comb, herein referred to as teeth, is able to interact with the counter-propagating beam through the Brillouin scattering process. With proper selection of the comb characteristics such as the number of teeth, the frequency spacing of teeth, the spectral width of teeth, and the relative amplitude of the teeth, a representation of the Brillouin spectrum at each point in the fiber can be obtained simultaneously with a single pass through the fiber.
Owner:UNIVERSITY OF NEW BRUNSWICK
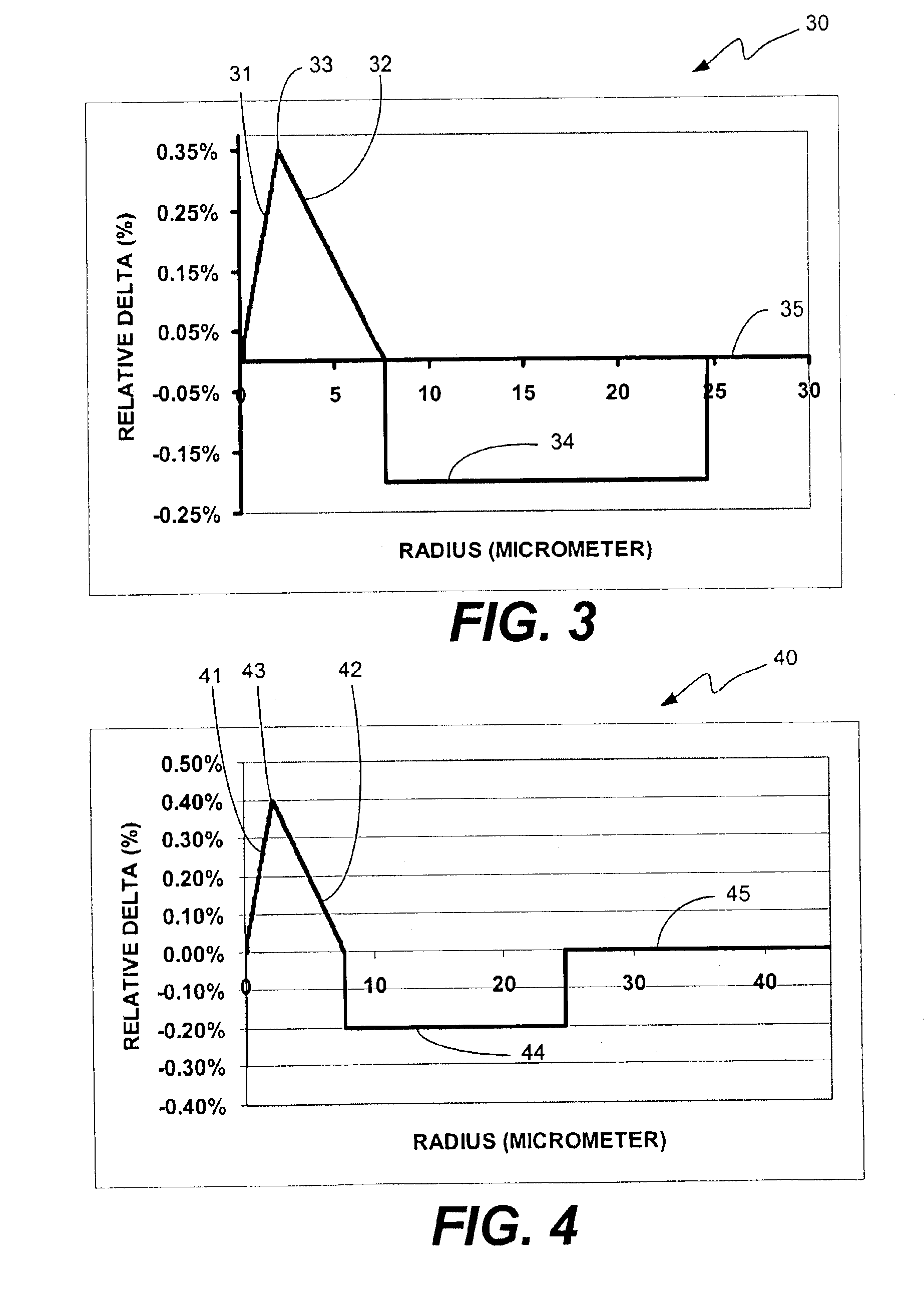
Large effective area high SBS threshold optical fiber
ActiveUS20040218882A1Laser using scattering effectsOptical fibre with graded refractive index core/claddingFiberZero-dispersion wavelength
An optical waveguide fiber having a high threshold for stimulated Brillouin scattering. The optical fiber preferably has large optical effective area, and further preferably has a low zero dispersion wavelength.
Owner:CORNING INC
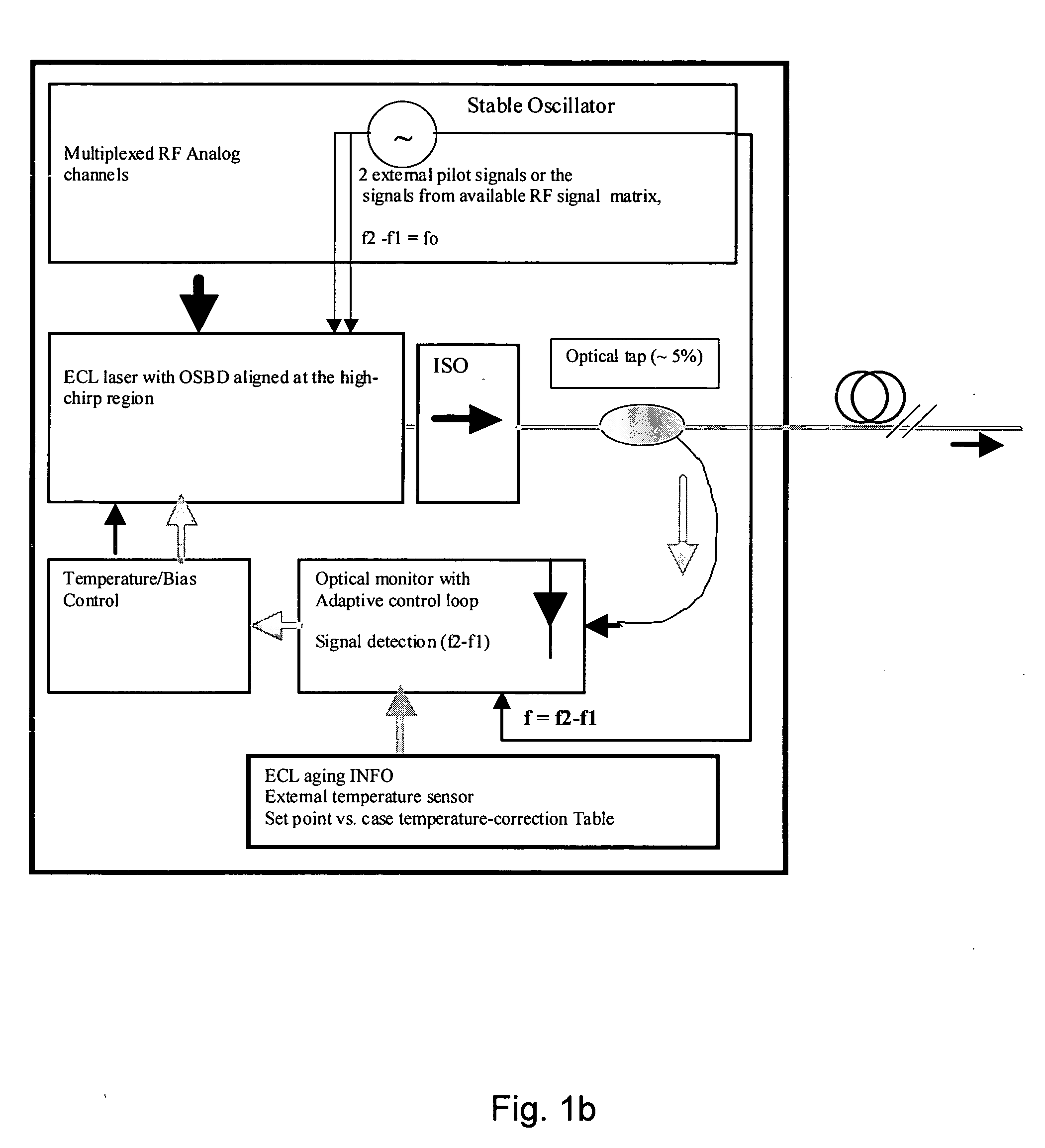
Analog transmitter using an external cavity laser (ECL)
InactiveUS20050220458A1Improve the level ofElimination of electronic ditheringLaser optical resonator constructionSemiconductor laser arrangementsNarrow rangeExternal cavity laser
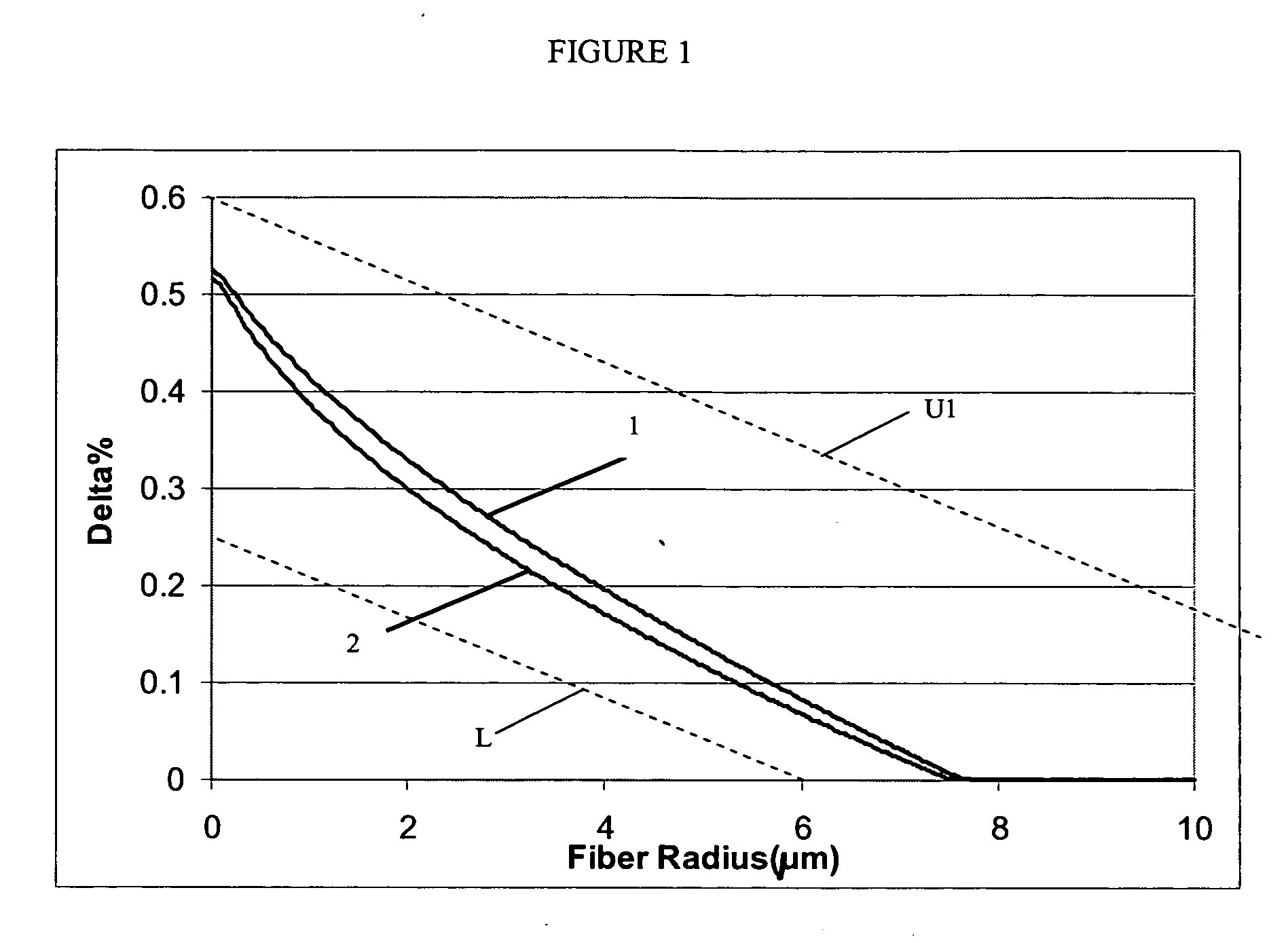
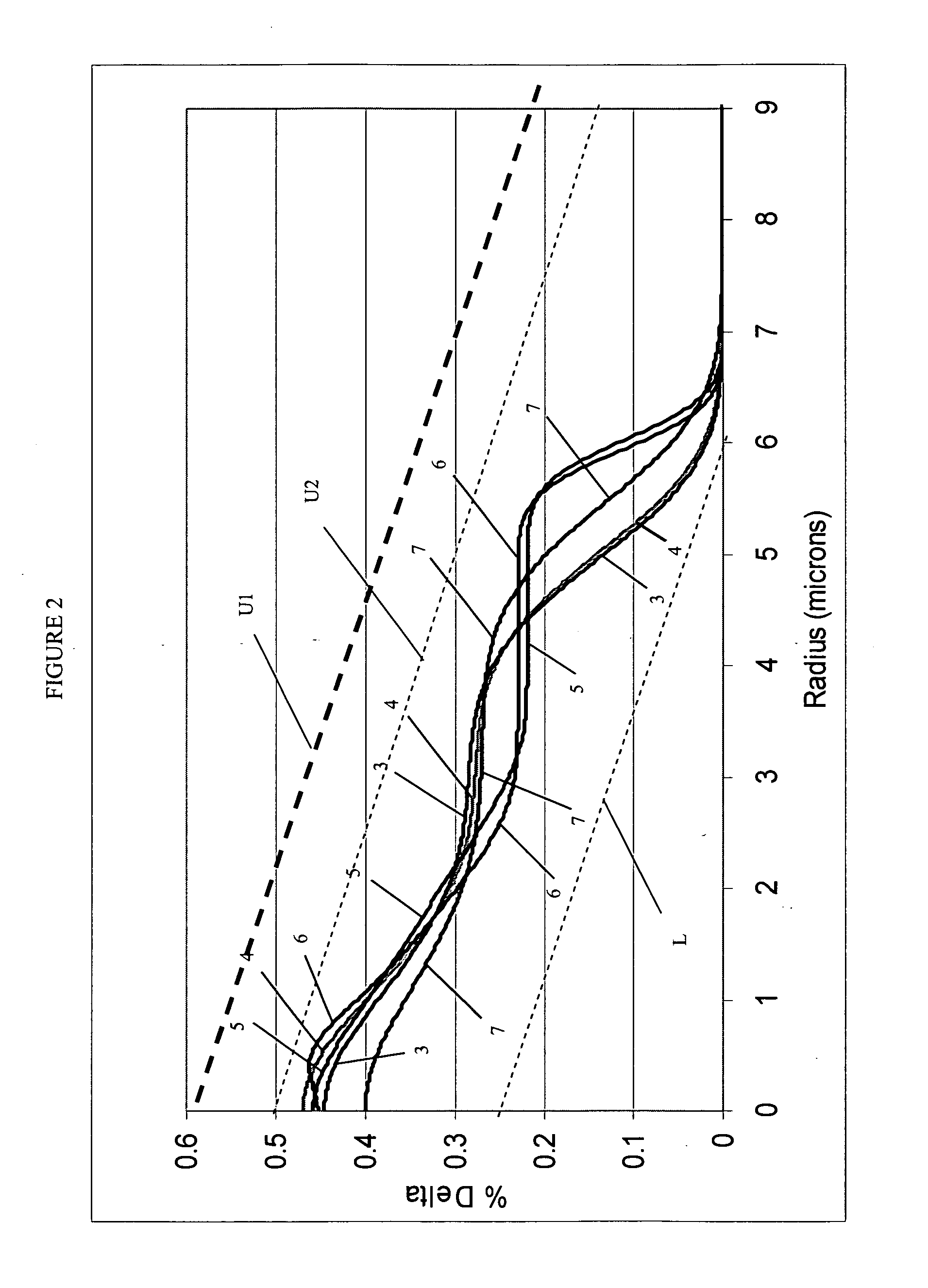
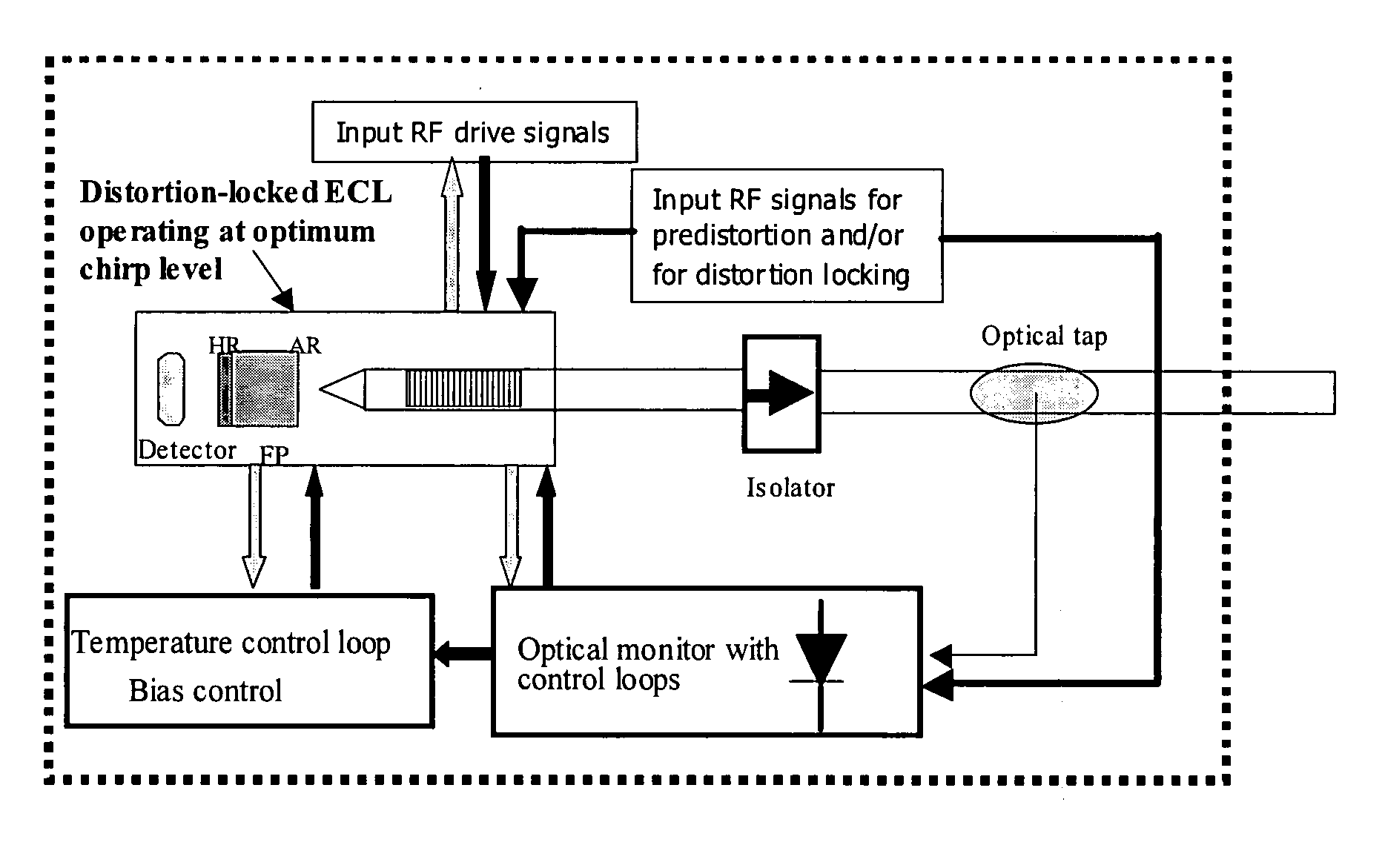
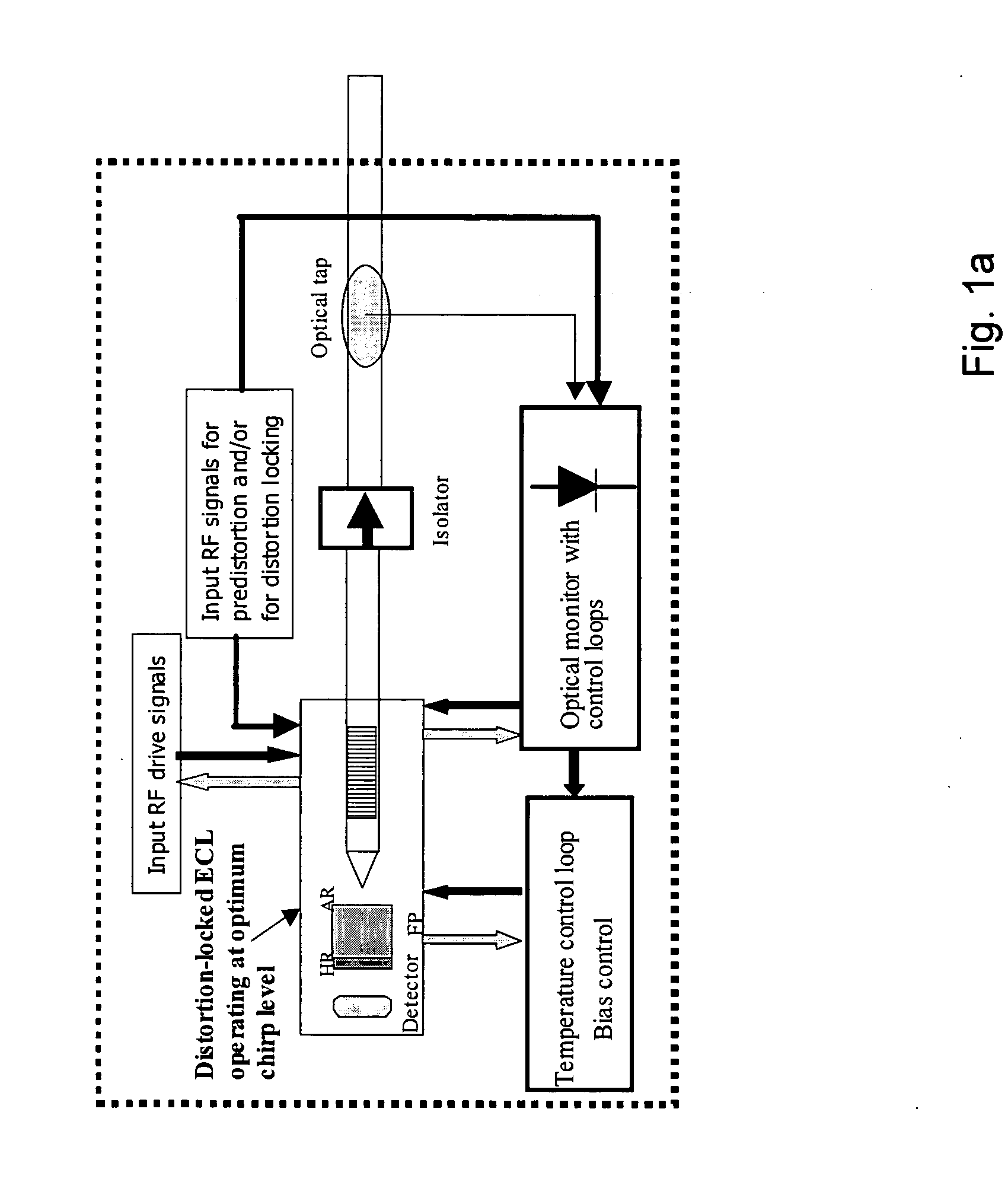
The present invention relates to an analog transmitter using an external cavity laser (ECL) in which specific characteristics of the ECL are enhanced and exploited to improve 2nd and 3rd order distortion while increasing the threshold for the occurrence of deleterious stimulated Brillouin scattering (SBS). The performance of the ECL shows a substantial reduction in distortion occurring over certain narrow ranges of operating temperatures. Optical, electronic, thermal and / or mechanical methods are described that cause this “distortion dip” to be moved to, or created at, stable regions of ECL operation, away from mode hops. Methods are also described that allow the distortion dip to be moved to, or created at, ECL operating regions in which sufficiently high chirp occurs, thereby reducing SBS. Transmitters and other devices employing these and related techniques are also described.
Owner:EMCORE INC +1
Fiber amplifier system for suppression of modal instabilities and method
ActiveUS20150138630A1Avoids and minimizes modal instabilitySame performanceLaser detailsFibre transmissionInstabilitySignal beam
Apparatus and method for suppressing modal instabilities (MI) in fiber-amplifier systems. In some embodiments, thermal effects drive the MI process, and in some such embodiments, the present invention provides a plurality of options for mitigating these thermal effects. In some embodiments, the present invention provides a hybrid fiber with a smaller core in the initial length where the thermal loads are highest, followed by a larger-core fiber. In some embodiments the length of the smaller-core section is chosen to keep the core heat-per-unit-length of the second section below a critical value for the onset of MI. In some embodiments, the hybrid fiber of the present invention avoids modal instabilities while yielding almost the same performance as compared to conventional fibers with regard to minimizing fiber nonlinearities such as Stimulated Brillouin Scattering (SBS). In some embodiments, the hybrid fiber outputs a signal beam with at least 1 kW of power.
Owner:LOCKHEED MARTIN CORP
Optical fiber transmission system with polarization multiplexing to reduce stimulated brillouin scattering
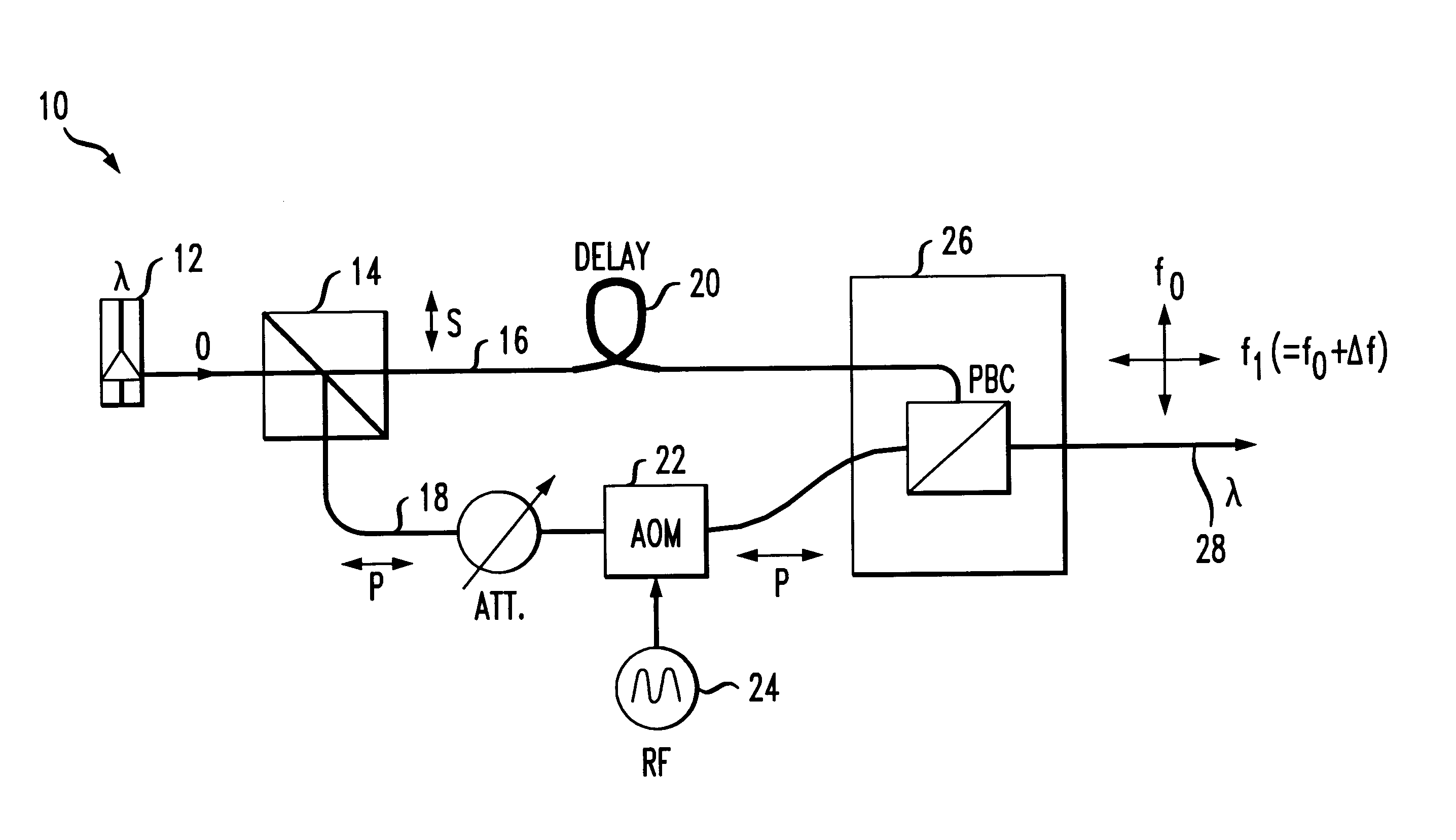
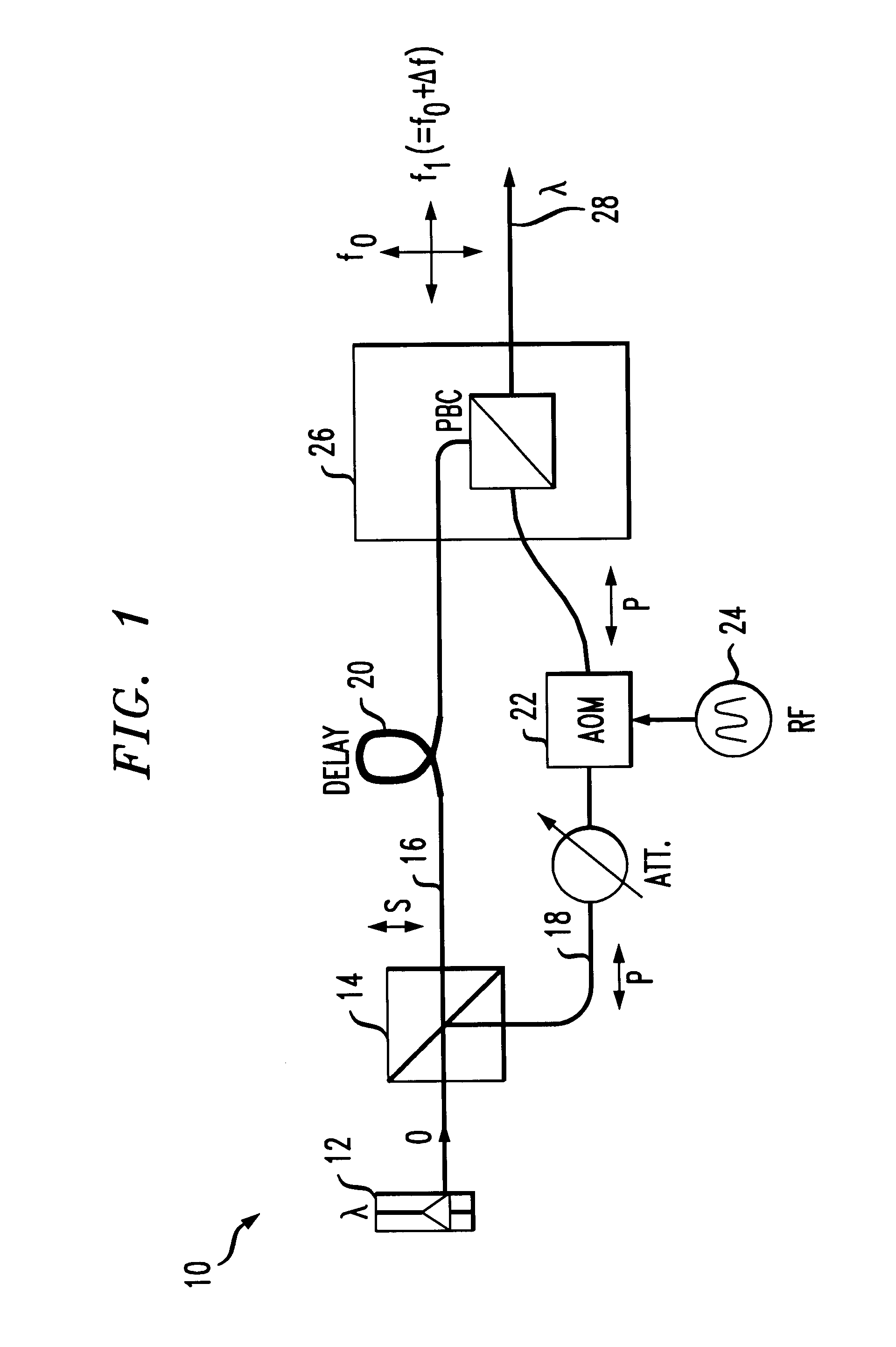
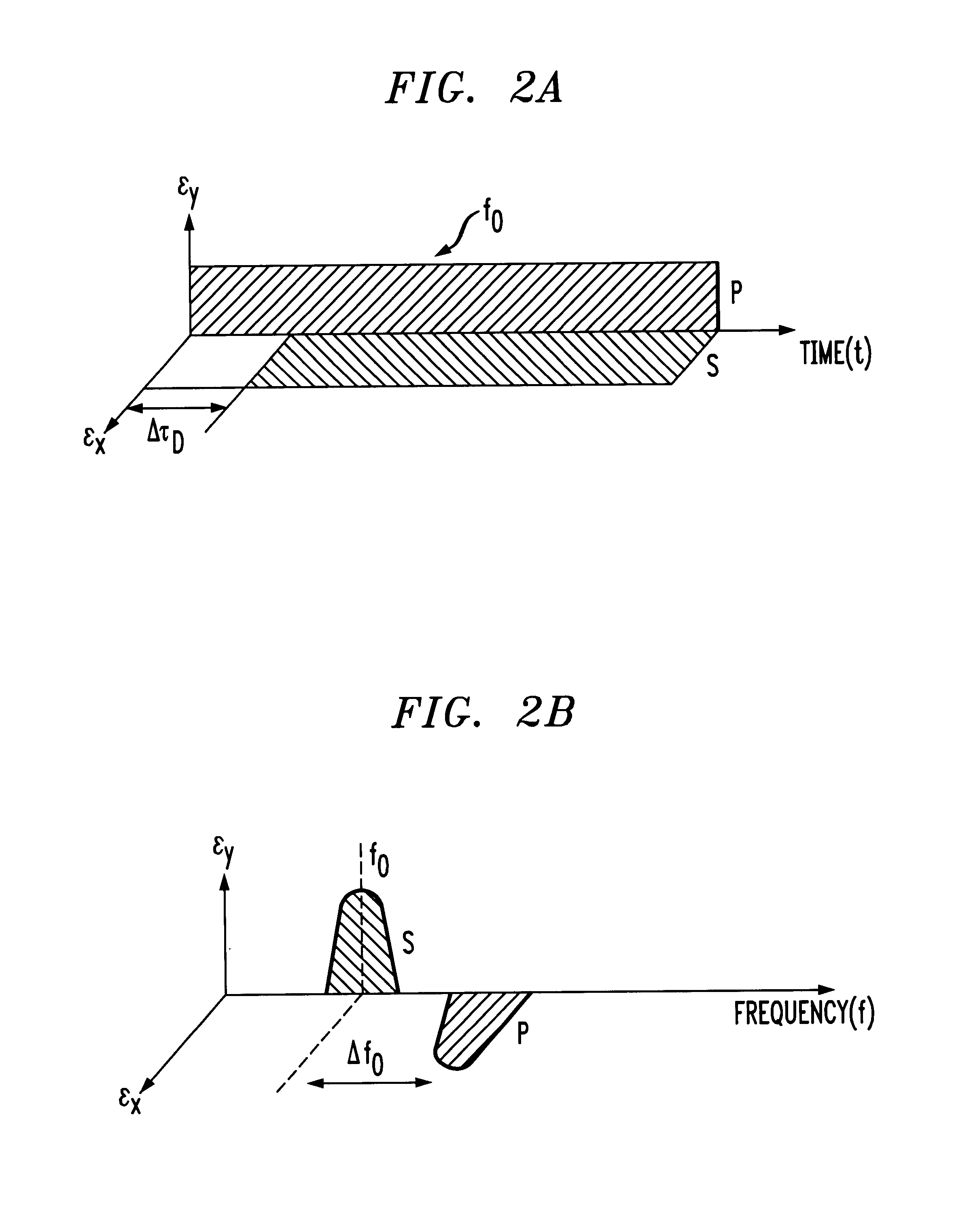
InactiveUS6850712B1Lower Level RequirementsReduce impactLaser detailsPolarisation multiplex systemsLine widthTime delays
A technique for suppressing stimulated Brillouin scattering SBS along an optical fiber signal path utilizes polarization modulation at the transmitter to split the launched power into orthogonal polarization states. By reducing the power along each polarization, SBS will be reduced. Linewidth broadening of the optical source is achieved by introducing: (1) a incoherence between the polarization states (using a time delay along the signal path of one polarization state); and (2) a frequency shift between the polarization states (using an acousto-optic modulator along the signal path of the remaining polarization state).
Owner:ALCATEL-LUCENT USA INC +1
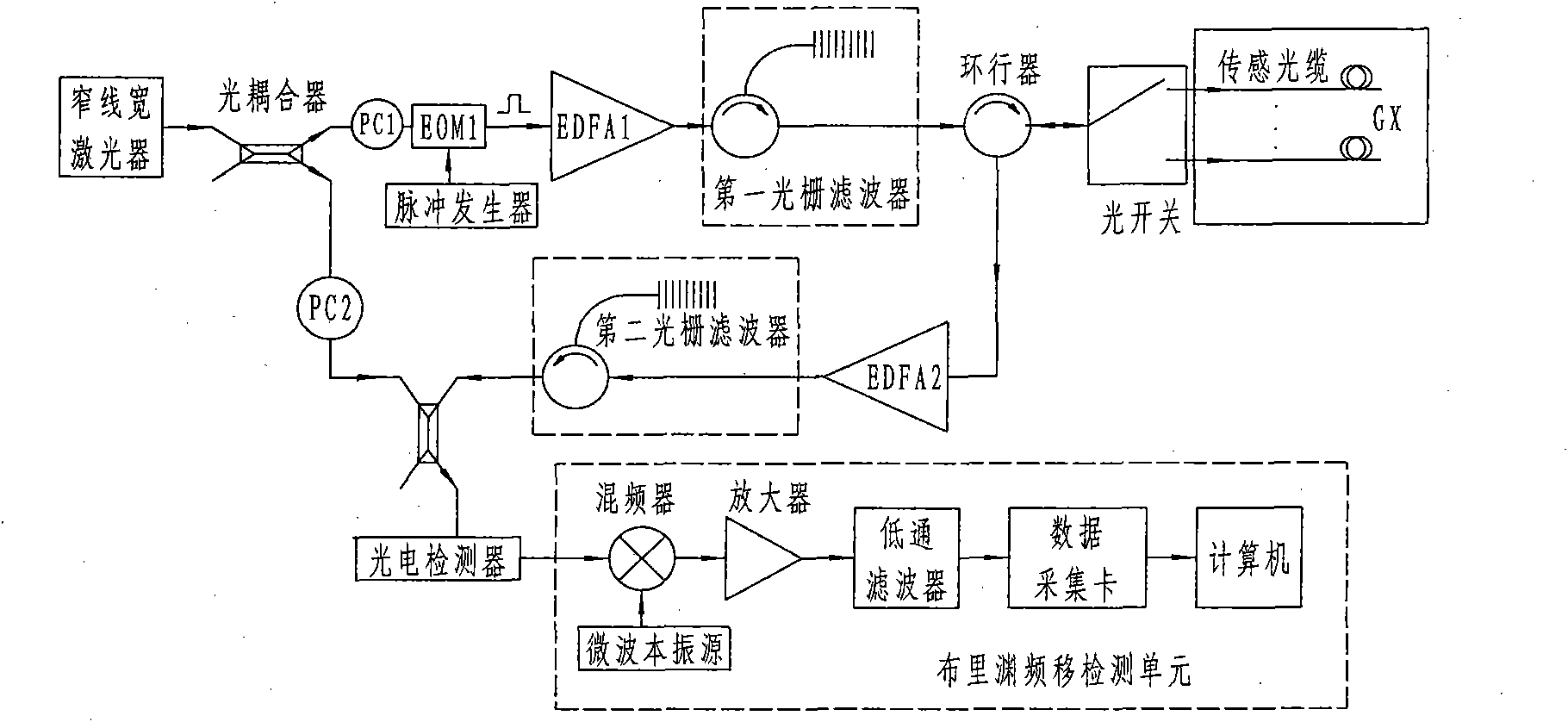
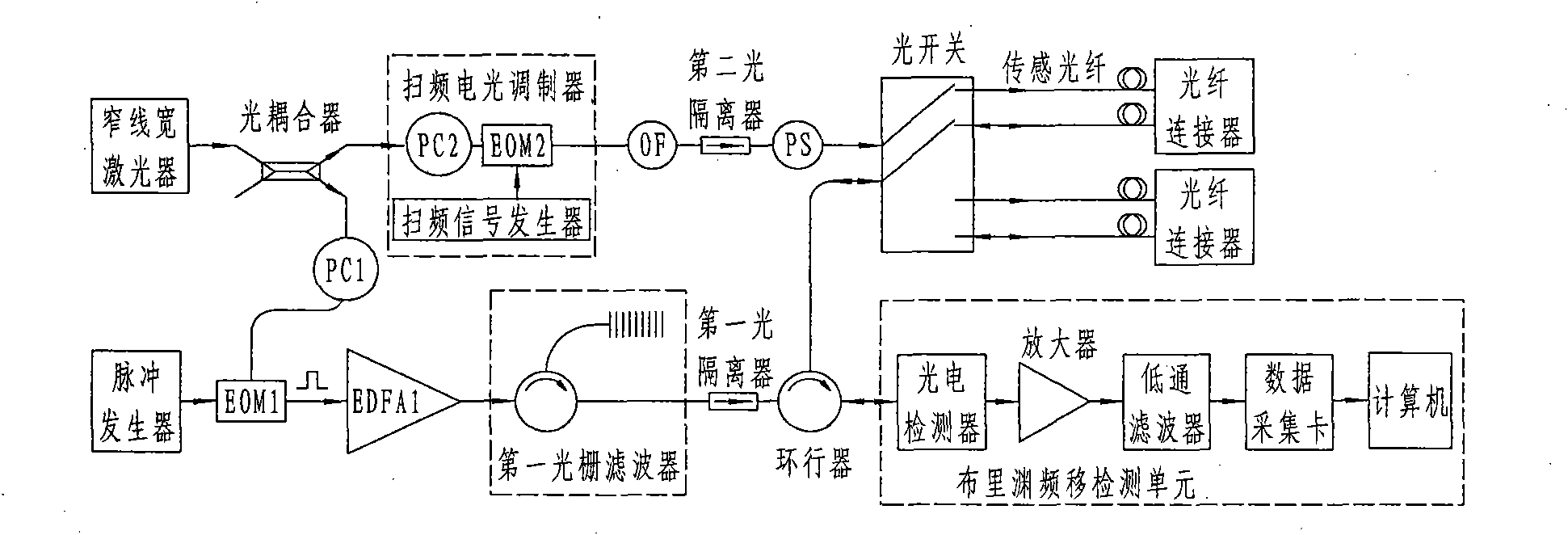
Method for measuring sea water temperature profile based on optical fiber Brillouin scattering principle
InactiveCN101825499AHigh mechanical strengthImprove tensile propertiesThermometers using physical/chemical changesContinuous measurementLine width
The invention discloses a method for a measuring sea water temperature profile based on an optical fiber Brillouin scattering principle. A Brillouin optical time domain reflection principle-based measurement system consists of a narrow line-width laser, an optical coupler, a pulse generator, an optical modulator, a circulator, an optical switch, a photoelectric detector, a Brillouin frequency shift detection unit and a sensing optical cable. The sensing optical cable used by the invention has a small size and sea water corrosion resistance, and is convenient to use. The measurement system has high reliability and high measuring sensitivity, can provide continuous temperature field distribution of the sea water profile, and is particularly suitable for real-time continuous measurement of the sea water temperature profile.
Owner:NORTH CHINA ELECTRIC POWER UNIV (BAODING)
Large effective area high SBS threshold optical fiber
ActiveUS6952519B2Suitable performanceLaser using scattering effectsOptical fibre with graded refractive index core/claddingFiberZero-dispersion wavelength
An optical waveguide fiber having a high threshold for stimulated Brillouin scattering. The optical fiber preferably has large optical effective area, and further preferably has a low zero dispersion wavelength.
Owner:CORNING INC
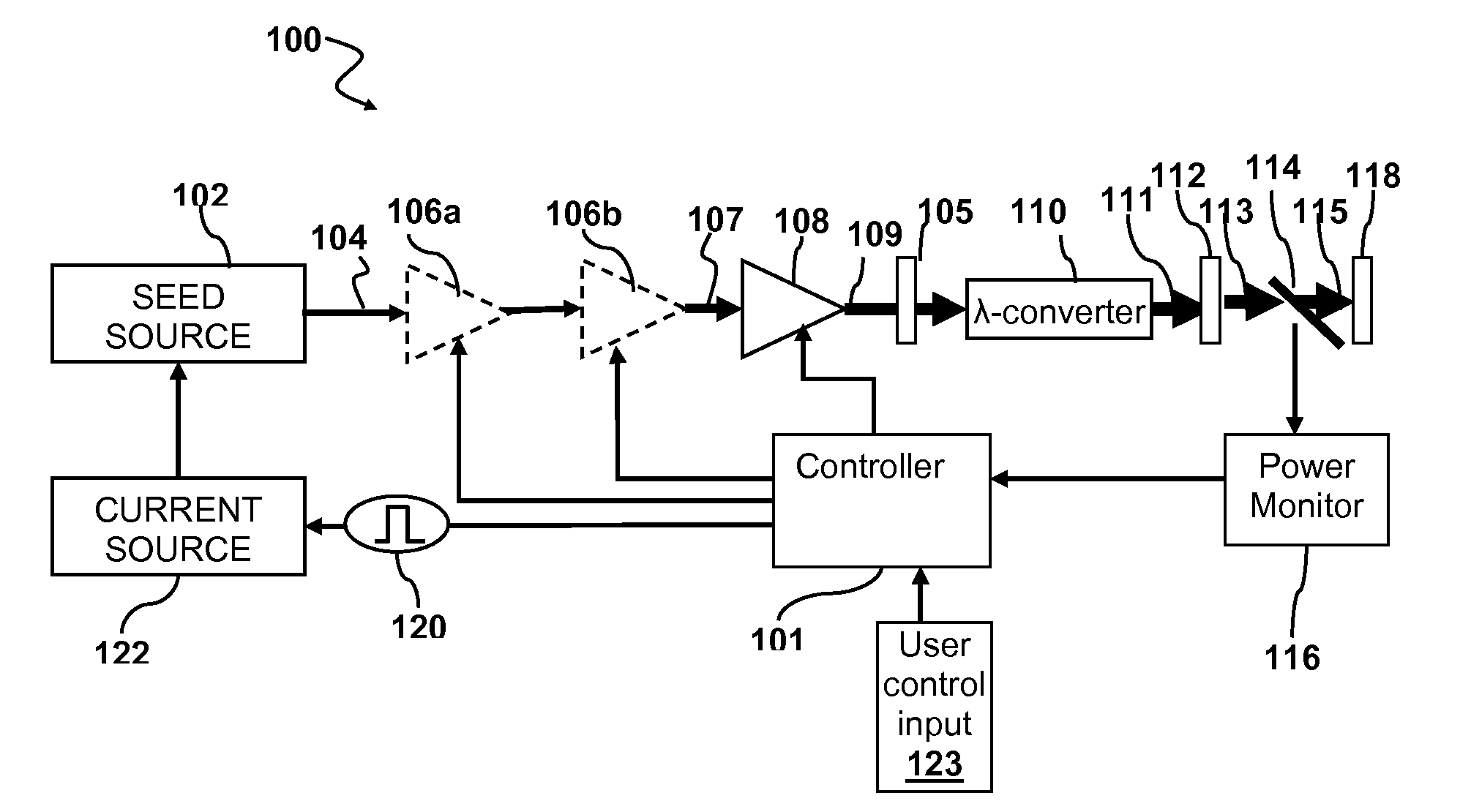
Fiber mopa system without stimulated brillouin scattering
ActiveUS20090010288A1Shorten fiber lengthIncreasing mode areaLaser using scattering effectsOptical resonator shape and constructionNanosecondSeeds source
Methods and systems for increasing the threshold for stimulated Brillouin scattering are described. A seed source may generate one or more chirped seed pulses characterized by a pulse duration τ, and a frequency chirp. The pulse duration τ may be greater than about 2 nanoseconds. A photonic crystal amplifier amplifies the seed pulses to produce one or more amplified pulses characterized by a peak power P greater than about 1 kilowatt. The pulse duration τ, frequency chirp, and the photonic crystal fiber may be selected such that a threshold for stimulated Brillouin scattering (SBS) in the photonic crystal fiber is greater than the peak power P.
Owner:DISCO CORP
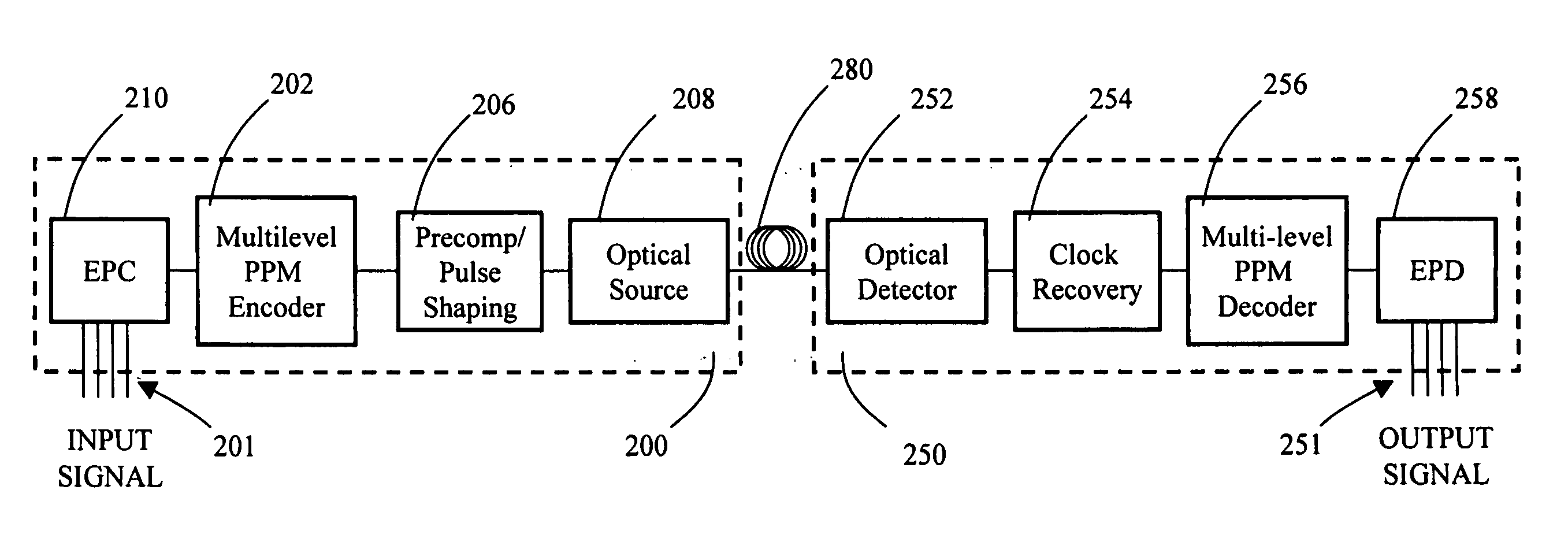
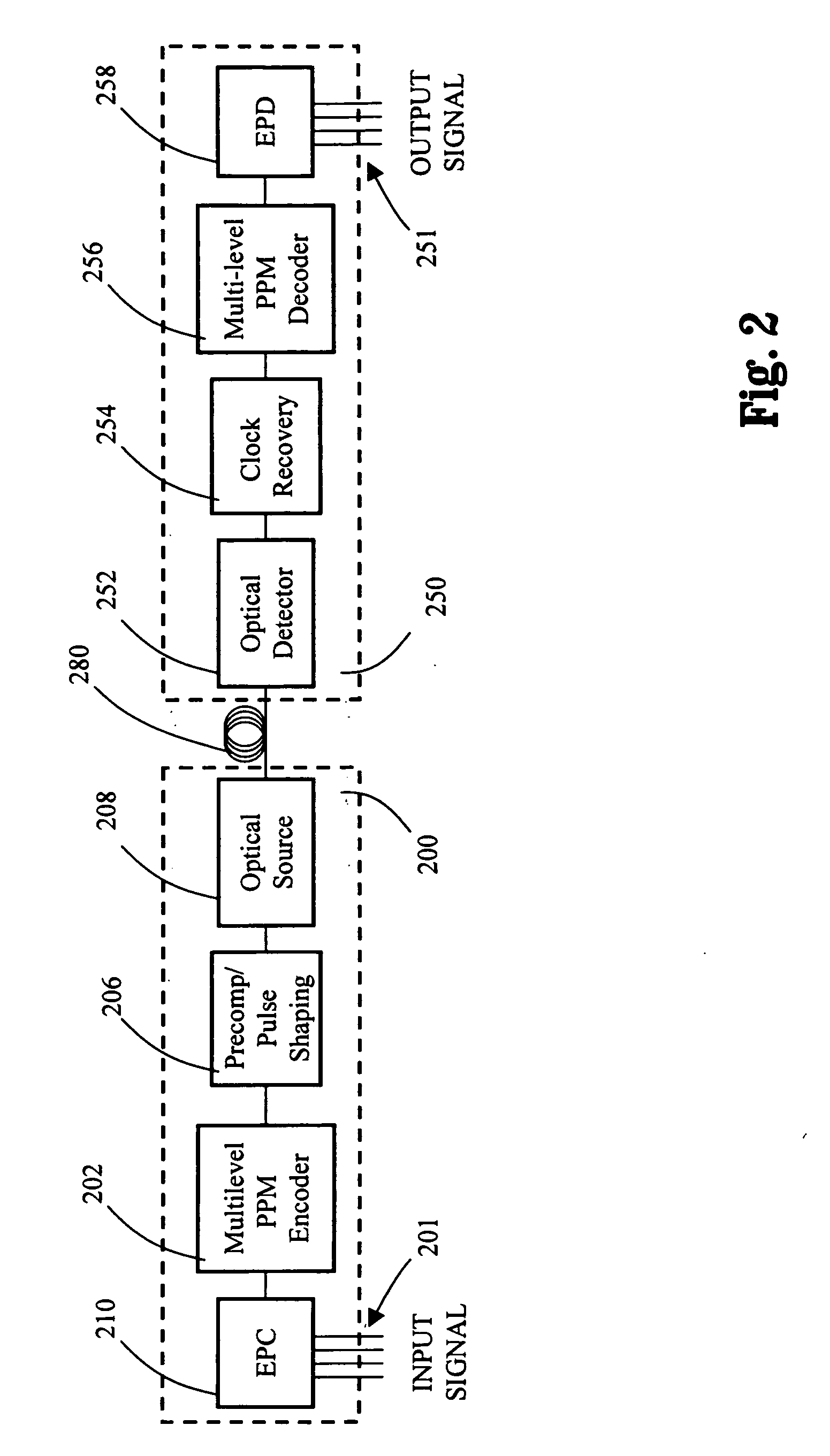
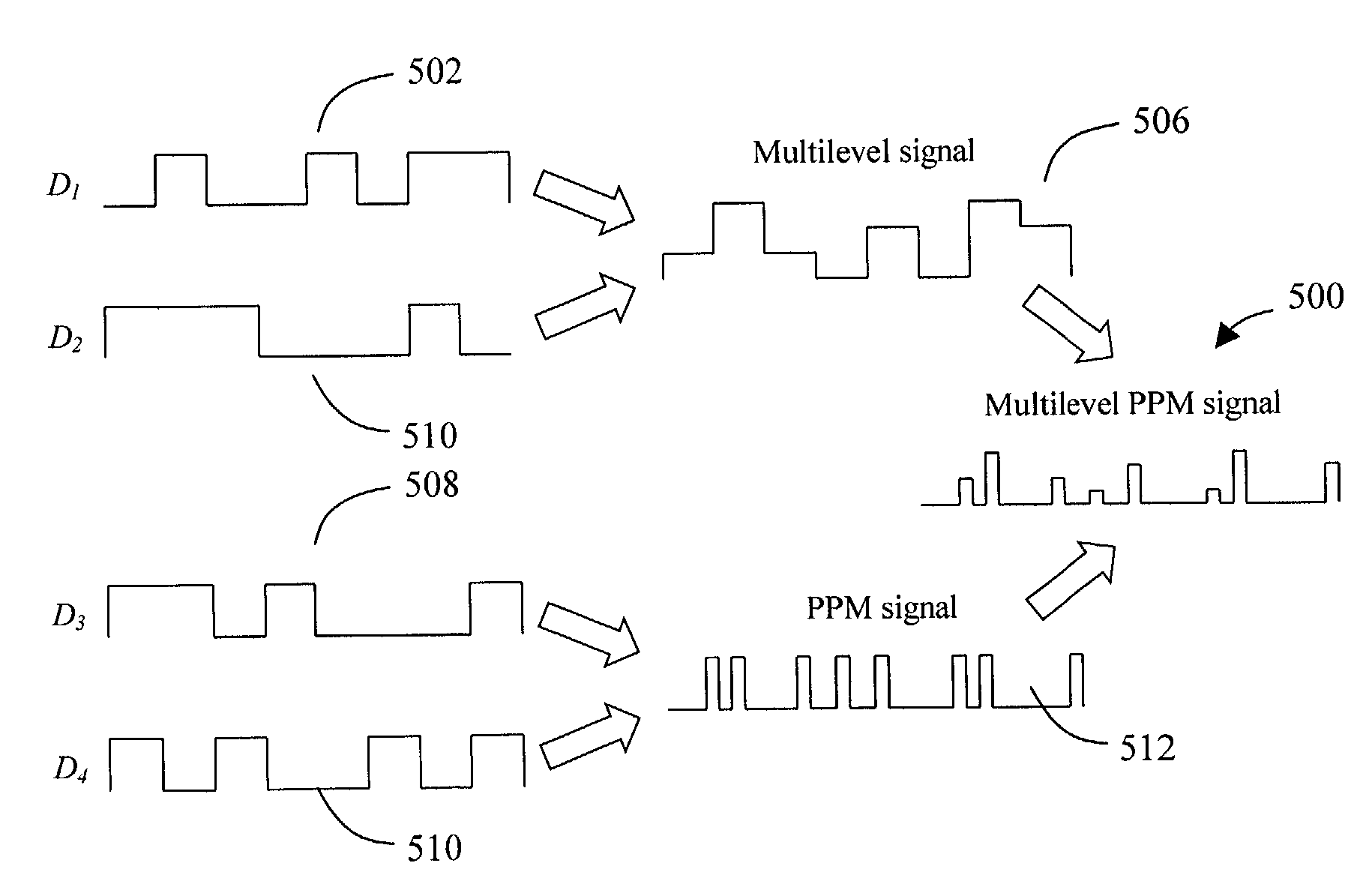
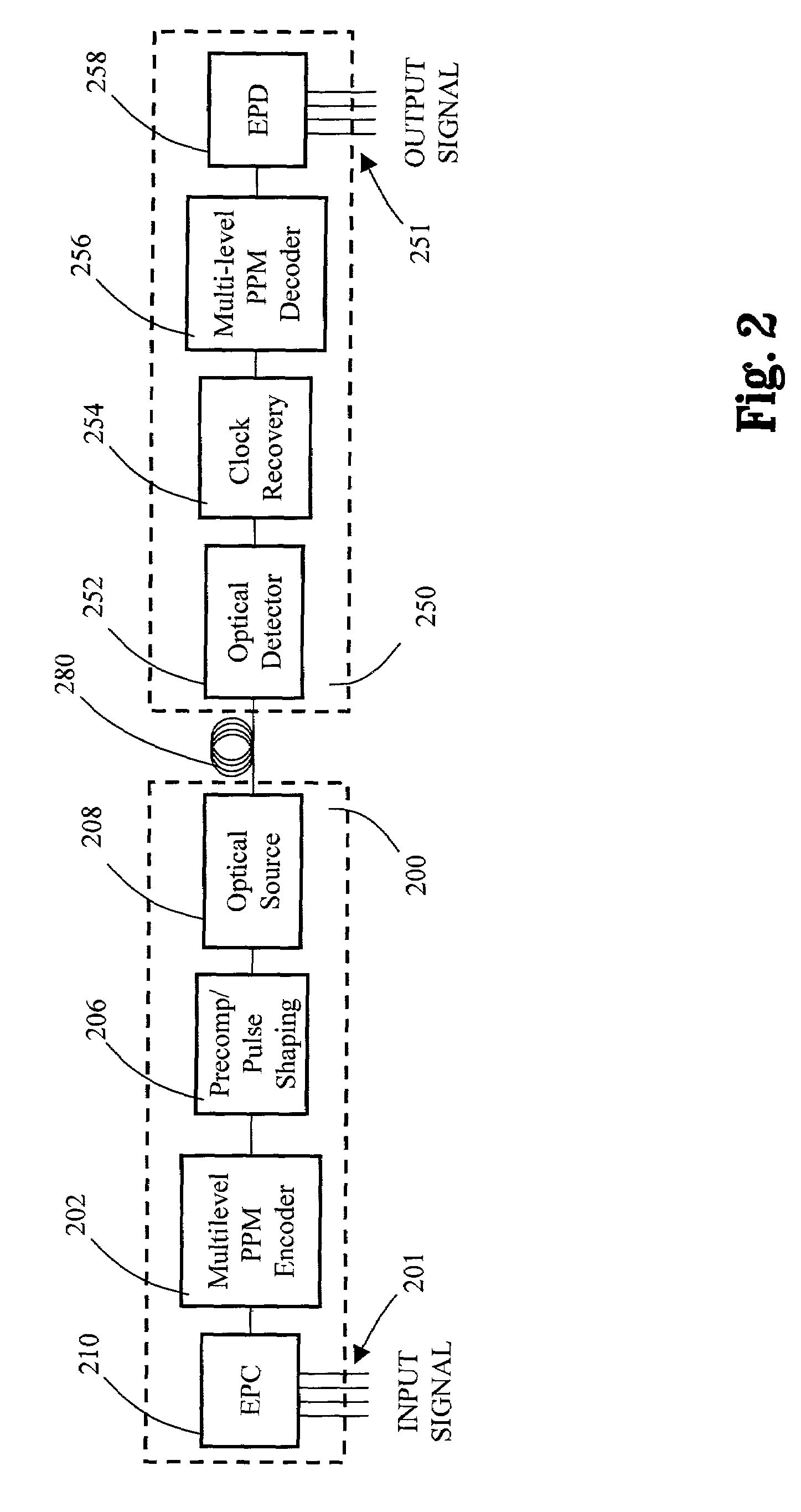
Multilevel pulse position modulation for efficient fiber optic communication
InactiveUS20070092265A1Increasing aggregate data rateReduce transmit powerModulated-carrier systemsElectromagnetic transmittersTransmitted powerStimulate raman scattering
Decreasing the average transmitted power in an optical fiber communication channel using multilevel amplitude modulation in conjunction with Pulse Position Modulation (PPM). This multilevel PPM method does not entail any tradeoff between decreased power per channel and channel bandwidth, enabling a lower average transmitted power compared to On / Off Keying (OOK) with no reduction in aggregate data rate. Therefore, multilevel PPM can be used in high-speed Dense Wavelength Division Multiplexed (DWDM) systems where the maximum number of channels is traditionally limited by nonlinear effects such as self-phase modulation (SPM), cross-phase modulation (XPM), four-wave mixing (FWM), stimulated Brillouin scattering (SBS), and stimulated Raman scattering (SRS). This modulation technique can enable an increased number of channels in DWDM systems, thereby increasing aggregate data rates within those systems.
Owner:INTERSIL INC
Distributed optical fiber Brillouin sensing device and method thereof for detecting temperature and strain synchronously
InactiveCN102607621AHigh measurement accuracyEasy to implementThermometers using physical/chemical changesUsing optical meansFrequency shiftLinearity
The invention relates to a distributed optical fiber Brillouin sensing device for detecting temperature and strain synchronously and a method for detecting the temperature and the strain synchronously by use of the device. The method is based on the linear relation among the frequency shift change of the spontaneous Brillouin scattering in the optical fiber, external temperature change and external strain change, a compound sensing optical fiber is formed by two different types of sensing optical fibers, and the variation of the temperature and the strain can be distinguished at the same time through different responses of the two optical fibers to the external temperature change and the external stress change. According to the device and the method, the temperature change and the strain change in a sensing area can be detected at the same time, and the detection precision of an optical fiber distributed sensor based on spontaneous Brillouin scattering can be improved.
Owner:SHANGHAI INST OF OPTICS & FINE MECHANICS CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Distributed optical fiber sensing system for measuring temperature, strain and vibration simultaneously
ActiveCN107917738ADemodulation frequencyReduce intensityConverting sensor output opticallyMultiplexingRayleigh scattering
The invention discloses a distributed optical fiber sensing system for measuring temperature, strain and vibration simultaneously. Based on an Optical Time Domain Reflectometry (ODTR) multiplexing technology, optical time-division multiplexing unequal-width dipulse serves as detection light, coherent detection technologies of Brillouin scattering signals and Rayleigh scattering signals are merged,and a set of distributed optical fiber sensing system which can conduct single-ended measuring on the temperature, strain and vibration is achieved; meanwhile, the measuring range of the vibration frequency can reach the MHz level, and the problems are solved that a traditional ODTR system can only measure the temperature strain or the static strain while cannot timely respond to the dynamic change, or it is hard to measure the temperature strain and the static strain simultaneously, or the measurable range of the vibration frequency is limited by the length of sensing optical fiber. The distributed optical fiber sensing system can conduct single-ended measuring, and is simple in structure, easy to implement, and good in application prospect.
Owner:NANJING UNIVERSTIY SUZHOU HIGH TECH INST
Large effective area high SBS threshold optical fiber
ActiveUS7082243B2Suitable performanceGlass making apparatusOptical fibre with multilayer core/claddingFiberZero-dispersion wavelength
An optical waveguide fiber having a high threshold for stimulated Brillouin scattering. The optical fiber preferably has large optical effective area, and further preferably has a low zero dispersion wavelength.
Owner:CORNING INC
Optical fiber distributed temperature and stress sensing device
InactiveCN101158592AAddress cross-sensitivity issuesSolving Measurement Range IssuesForce measurement by measuring optical property variationThermometers using physical/chemical changesObservational errorDiscriminator
The invention discloses a sensing device of optical fiber distribution type temperature and stress and mainly comprises a light source module (1), a frequency discriminator module (2), and a thermo tank module (3), which are all connected with one another by polarization-preserving fiber. The invention is a direct detection method which is based on optical fiber Raman scattering used as a carrier wave of temperature information, brillouin scattering used as a carrier wave of stress, rayleigh scattering used for measuring relative frequency of a outgoing laser beam to a frequency discriminator and Fabry-Perot etalon used for discriminating frequency and distributing sensing temperature and stress. The invention has the advantages of simple structure, fine stability, avoidance of outgoing power of the light source during coherent detection, outgoing frequency of the light source. Instability of acoustic modulation or electro-optic modulation frequency is directly referred to measure errors and the direct detection technology of the frequency discrimination is not sensitive to frequency drift of the light source and fluctuation of signal intensity.
Owner:BEIHANG UNIV
System and method for resolution enhancement of a distributed sensor
ActiveUS20050213869A1Reduce resolutionForce measurementMaterial analysis by optical meansFiberLine width
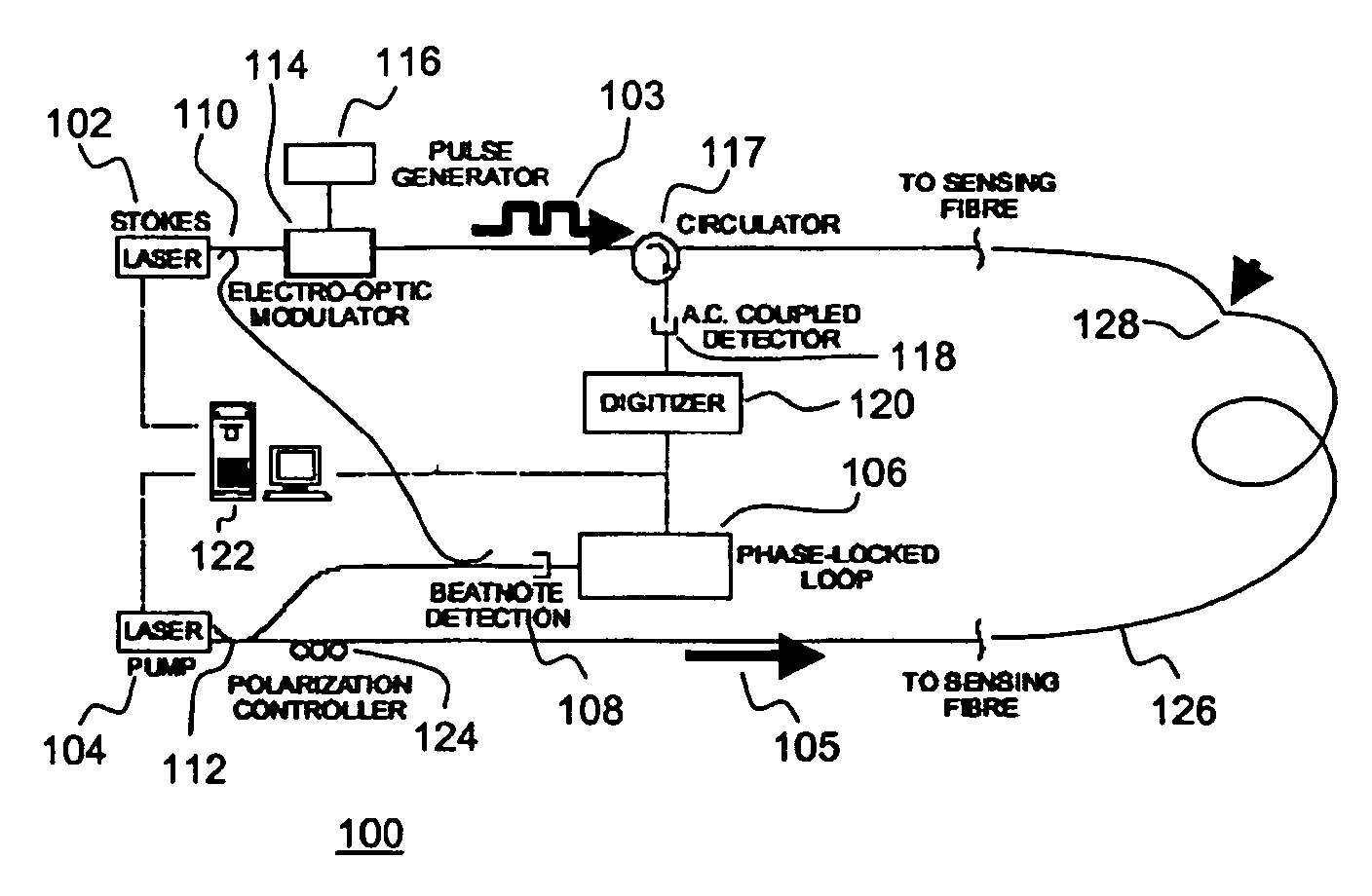
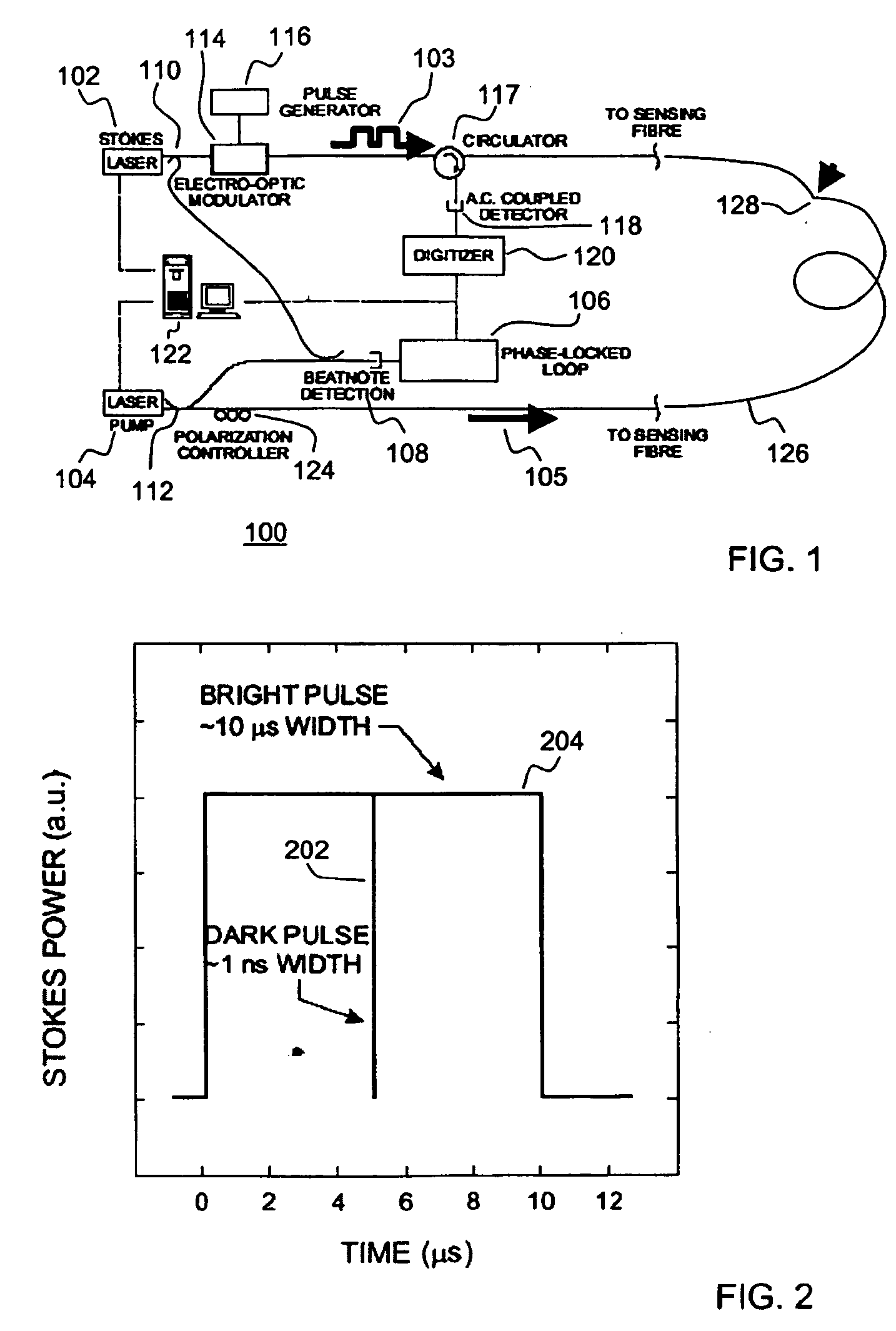
A Brillouin Optical Time-Domain Analysis (BOTDA) distributed sensor system and method use a continuous wave (cw) Stokes wave interrupted with a dark pulse for improved spatial resolution. The cw Stokes wave causes a continuous depletion of the pump wave. The dark pulse causes the depletion to stop for the duration of the pulse. Brillouin interactions are measured during the dark pulse. Very narrow dark pulses can be used because sufficient Stokes wave energy is maintained. The system produces a stronger time-domain signal and narrower linewidth Brillouin spectra than traditional techniques using a bright Stokes pulse. Narrower measurement pulses can be used leading to improved spatial resolution. A quasi-cw Stokes wave can be used to reduce the effect of stimulated Brillouin scattering (SBS) in long measurement fibers. The system can be used for distributed strain or temperature measurements.
Owner:DARKPULSE TECH INC
Method for simultaneously measuring distributed type temperatures and strain
ActiveCN103674084AReduce complexityReduce manufacturing costThermometers using physical/chemical changesUsing optical meansTime-domain reflectometerRayleigh scattering
The invention provides a method for simultaneously measuring distributed type temperatures and strain. A brillouin optical time domain reflectometer and a coherent light time domain reflectometer share the same optical path system and the same circuit system and serve as a sensing measurement system. The sensing measurement system works in a BOTDR mode and a COTDR mode in an alternate mode to measure a brillouin scattering spectrum and a Rayleigh scattering spectrum which are distributed along a single single-mode sensing optical fiber and detect the frequency shift of the brillouin scattering spectrum and the frequency shift of the Rayleigh scattering spectrum, a linear equation set in two unknowns about the temperature and the strain is set up according to the characteristic that the frequency shift of the two scattering spectra is in the linear relationship with the temperature and the strain, and the temperature and the strain of each position of the sensing optical fiber can be obtained by solving the equation set, and then the temperatures and the strain distributed along the whole sensing optical fiber can be obtained. According to the method, the complexity and the manufacturing cost of the system are greatly reduced, no special requirement for the brillouin frequency shift coefficient of the optical fiber exists, and the application range of the measurement system is enlarged.
Owner:NORTH CHINA ELECTRIC POWER UNIV (BAODING)
Distributed optical fiber sensor based on roman and brillouin scattering
InactiveUS20130020486A1Improve signal-to-noise ratioRealize measurementRadiation pyrometryForce measurementMechanical engineeringMaterials science
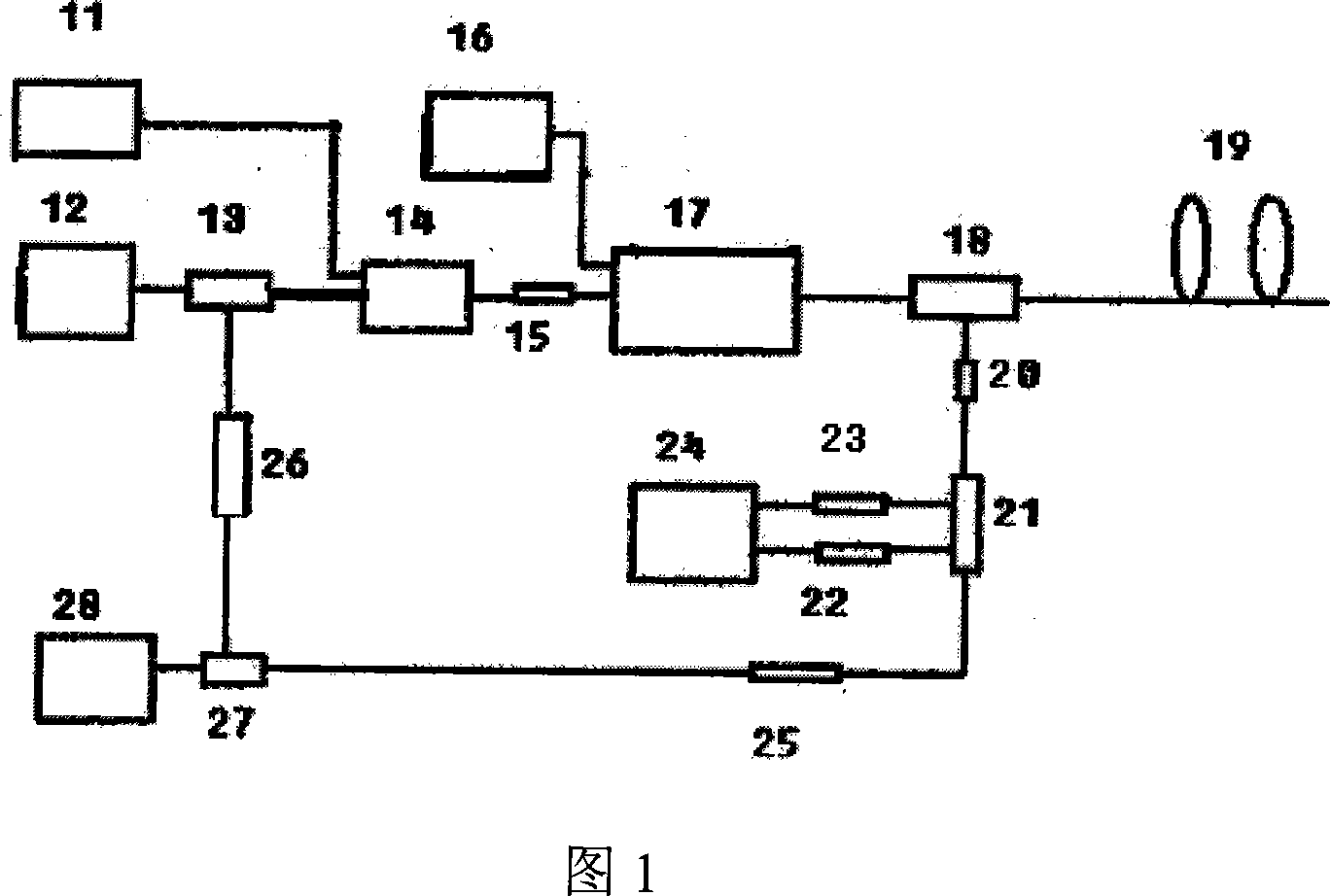
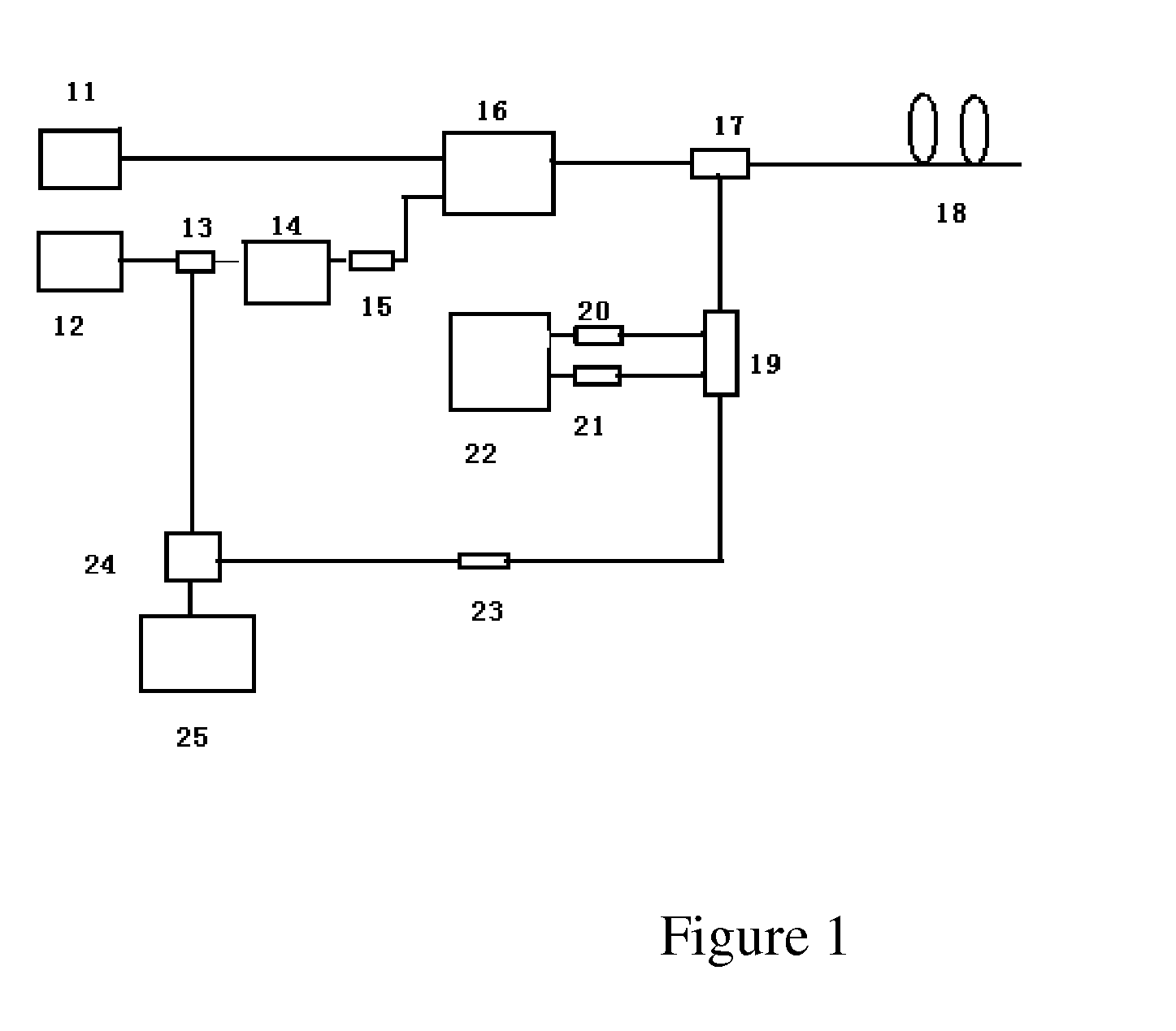
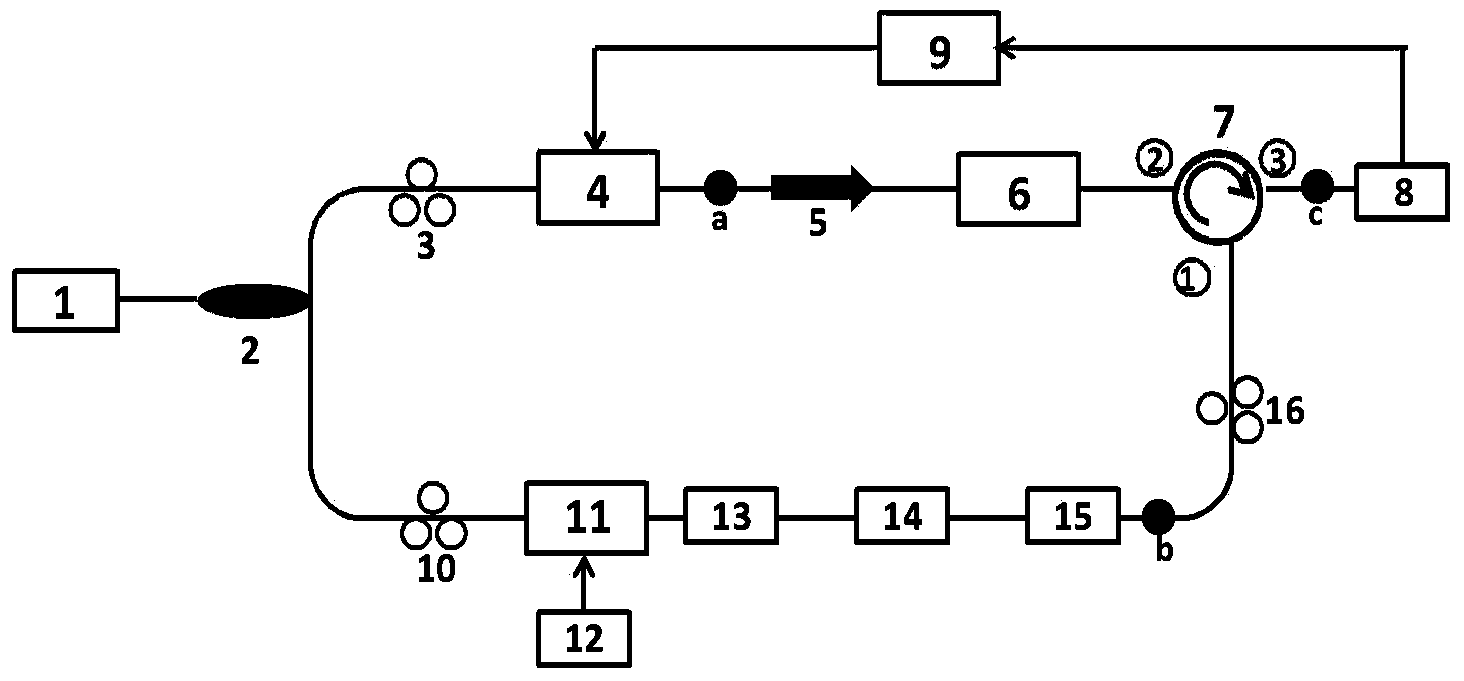
A distributed optical fiber sensor based on Raman and Brillouin scattering is provided. The distributed optical fiber sensor includes a semiconductor FP cavity pulsed wideband optical fiber laser (11), a semiconductor external-cavity continuous narrowband optical fiber laser (12), a wave separator (13), an electro-optic modulator (14), an isolator (15), an Er-doped optical fiber amplifier (16), a bidirectional coupler (17), an integrated wavelength division multiplexer (19), a first photoelectric receiving and amplifying module (20), a second photoelectric receiving and amplifying module (21), a direct detection system (22), a narrowband optical fiber transmission grating (23), a circulator (24) and a coherence detection module (25). The temperature and the strain can be measured simultaneously, and the signal-to-noise ratio of the system is enhanced.
Owner:CHINA JILIANG UNIV
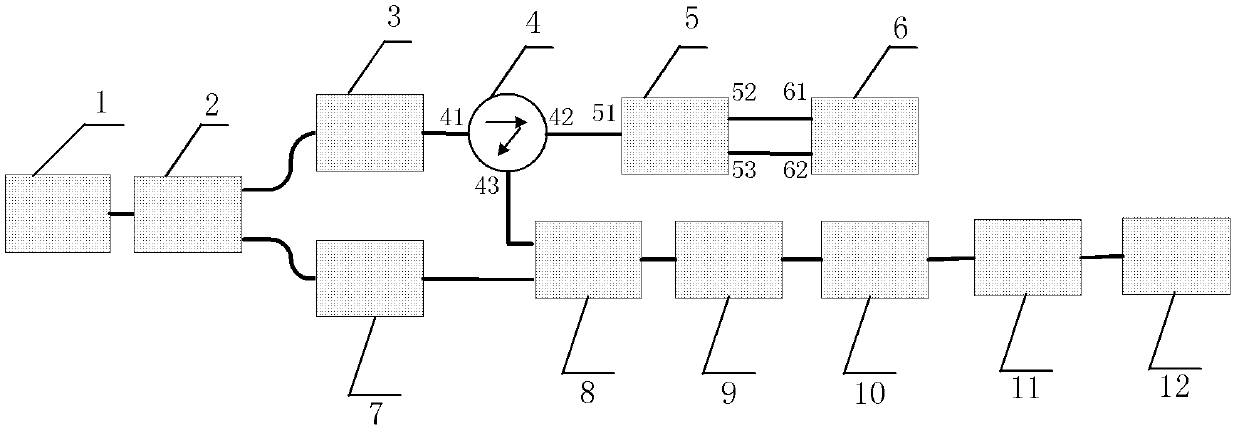
Reinforcement Element With Sensor Fiber, Monitoring System, And Monitoring Method
A reinforcement element, comprises at least one sensor fiber adapted for strain measurements based on stimulated Brillouin scattering within said sensor fiber. Furthermore, a system for monitoring strain within a structure comprises a reinforcement element comprising at least one sensor fiber adapted for strain measurements based on stimulated Brillouin scattering within said sensor fiber, a pump laser for coupling in laser radiation of a pump frequency into said at least one sensor fiber, a Stokes laser for coupling in laser radiation of a Stokes laser radiation into said at least one sensor fiber, wherein the pump frequency and the Stokes frequency are different from one another and wherein the frequency difference between the pump and Stokes frequencies is within the range of acoustical phonons within said sensor fiber, a sensor adapted to obtain a stimulated Brillouin backscattering signal, and a network analyzer adapted for determining the complex transfer function of the sensor fiber to determine a spatially resolved strain measurement.
Owner:GLOTZL GES FUR BAUMESSTECHN +2
Detecting method suitable for optical fiber distributed temperature and stress sensing device
InactiveCN101158591AAddress cross-sensitivity issuesSolve the problem of measuring range of large temperature 0~400℃Force measurement by measuring optical property variationThermometers using physical/chemical changesDiscriminatorRayleigh scattering
The invention discloses a detection method suitable for a sensing device of optical fiber distribution type temperature and stress. The sensing device of the optical fiber distribution type temperature and stress mainly comprises a light source module (1), a frequency discriminator module (2), and a thermo tank module (3), which are all connected with one another by polarization-preserving fiber. The detection method of the invention is a direct detection method which is based on optical fiber Raman scattering used as a carrier wave of temperature information, brillouin scattering used as a carrier wave of stress, rayleigh scattering used for measuring the relative frequency of a outgoing laser beam to the frequency discriminator and Fabry-Perot etalon used for discriminating frequency and distributing sensing temperature and stress. The invention has the advantages of simple structure, fine stability, avoidance of outgoing power of the light source during coherent detection, and outgoing frequency of the light source. Instability of acoustic modulation or electro-optic modulation frequency is directly referred to measure errors and the direct detection technology of frequency discrimination is not sensitive to the frequency drift of the light source and the fluctuation of signal intensity.
Owner:BEIHANG UNIV
Multilevel pulse position modulation for efficient fiber optic communication
InactiveUS7149256B2Reduce transmit powerIncreasing aggregate data rateAmplitude-modulated carrier systemsTransmission monitoringTransmitted powerStimulate raman scattering
Decreasing the average transmitted power in an optical fiber communication channel using multilevel amplitude modulation in conjunction with Pulse Position Modulation (PPM). This multilevel PPM method does not entail any tradeoff between decreased power per channel and channel bandwidth, enabling a lower average transmitted power compared to On / Off Keying (OOK) with no reduction in aggregate data rate. Therefore, multilevel PPM can be used in high-speed Dense Wavelength Division Multiplexed (DWDM) systems where the maximum number of channels is traditionally limited by nonlinear effects such as self-phase modulation (SPM), cross-phase modulation (XPM), four-wave mixing (FWM), stimulated Brillouin scattering (SBS), and stimulated Raman scattering (SRS). This modulation technique can enable an increased number of channels in DWDM systems, thereby increasing aggregate data rates within those systems.
Owner:INTERSIL INC
Distributed optical fiber sensor
ActiveCN102227615APolarisation-affecting propertiesForce measurementRayleigh scatteringRayleigh Light Scattering
Provided is a distributed optical fiber sensor capable of measuring the strain and temperature of an object to be measured simultaneously and independently with high spatial resolution. A distributed optical fiber sensor (FS) uses an optical fiber (15) as a sensor, wherein a distortion and temperature detector (14) measures the amount of Brillouin frequency shift due to the strain and temperature generated in the optical fiber (15) using a Brillouin scattering phenomenon, measures the amount of Rayleigh frequency shift due to the strain and temperature generated in the optical fiber (15) using a Rayleigh scattering phenomenon, and calculates the strain and temperature generated in the optical fiber (15) from the measured amount of Brillouin frequency shift and amount of Rayleigh frequency shift.
Owner:NEUBREX
Broadband tunable single-passband microwave photon filter generating system
InactiveCN103955028AHigh out-of-band rejection ratioHigh Q valueCoupling light guidesContinuous lightOptical coupler
The invention discloses a broadband tunable single-passband microwave photon filter generating system. The system comprises a laser, an optical coupler, a polarization modulator, a dispersion displacement optical fiber, a photoelectric detector, a vector network analyzer, a strength modulator and an optical fiber; the laser is used for providing continuous light signals; the optical coupler is used for dividing the continuous light signals into the first path of light signals and the second path of light signals; the polarization modulator is used for modulating the polarization state of the first path of light signals; the dispersion displacement light fiber is used for performing stimulated Brillouin scattering on the detection light signals under the induction effect of pump light signals; the photoelectric detector is used for receiving the detection light signals which are processed in a stimulated Brillouin scattering mode and output by the dispersion displacement optical fiber and generating microwave signals; the vector network analyzer is used for receiving microwave signals output by the photoelectric detector, performing measurement frequency response on the microwave signals, and outputting the microwave signals to the a first polarization modulator at the same time; the strength modulator is used for modulating the polarization state of the first path of light signals and outputting the first path of light signals which are modulated; the optical fiber is used for filtering the first path of light signals which are modulated, and the first path of light signals serve as the pump light signals.
Owner:INST OF SEMICONDUCTORS - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Measuring brillouin backscatter from an optical fibre using a tracking signal
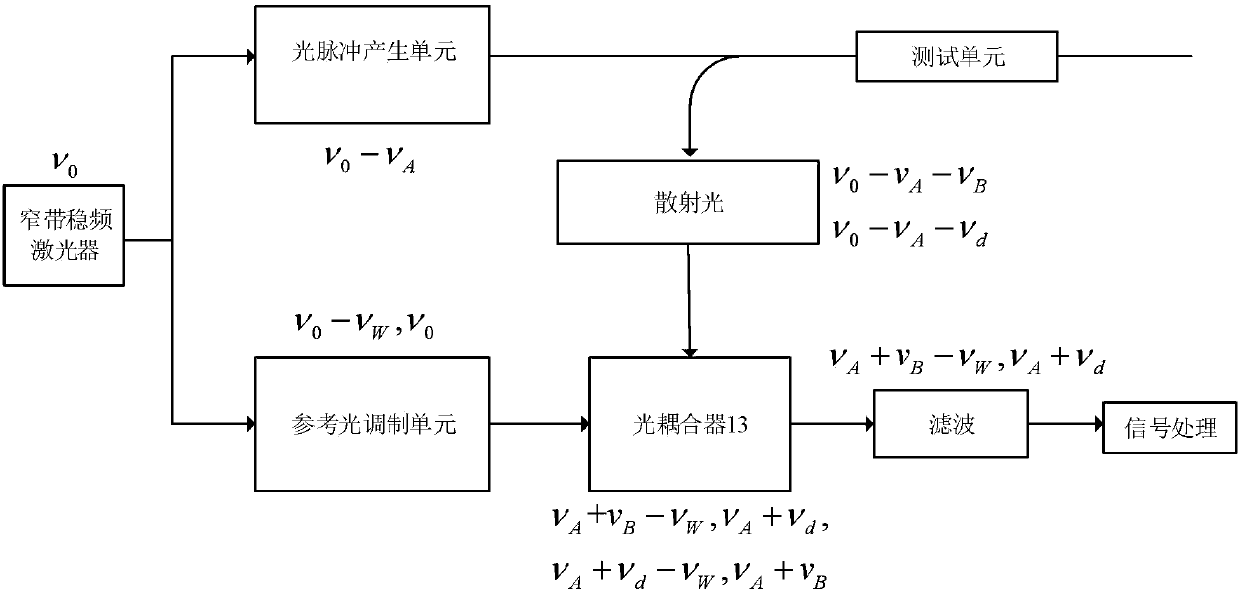
ActiveUS20100002226A1Narrow down the frequency rangeReduce the amount requiredReflectometers using simulated back-scatterConstructionsFrequency measurementsFrequency shift
A method for measuring Brillouin backscattering from an optical fibre (18), comprises frequency mixing a first signal with a frequency f B (t) representative of the Brillouin frequency shift in backscattered light received from a deployed optical fibre with a second signal at a frequency f i (t) that varies in time in the same manner as a Brillouin shift previously measured from the fibre to produce a difference signal with a difference frequency iF(t) that has a nominally constant value corresponding to the situation where the received light has a Brillouin shift that matches the previously measured shift. The difference signal is acquired and processed to determine properties of the Brillouin shift and corresponding physical parameters producing the shift. The frequency mixing can be carried out. optically or electrically. Techniques for acquisition of the difference signal include the use of parallel frequency measurement channels and fast rate digital sampling.
Owner:SCHLUMBERGER TECH CORP
Optical time domain reflectometer simultaneously sensing temperature and stress
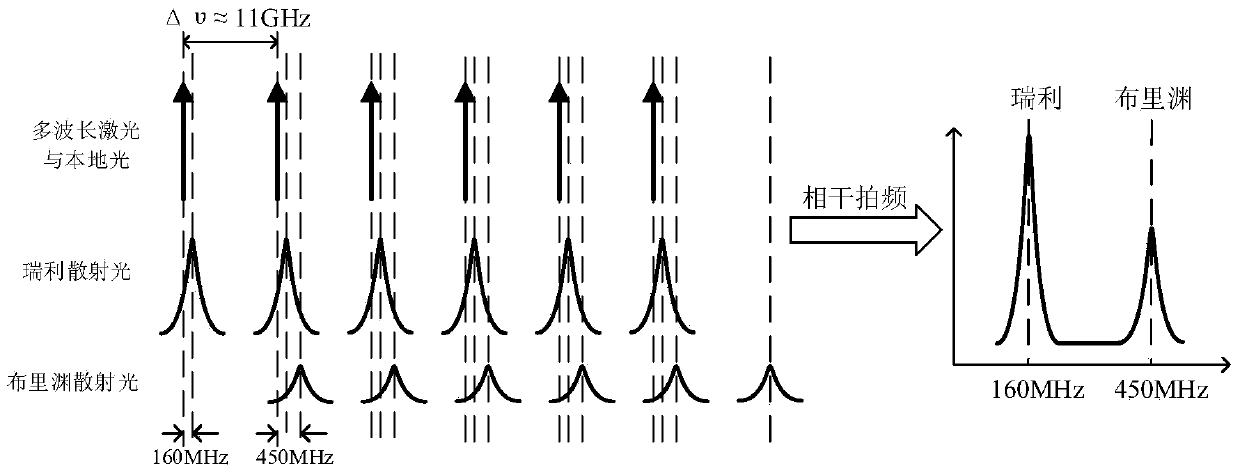
InactiveCN104180833AReduce the impact of noiseReduce the scattered light signal-to-noise ratioConverting sensor output opticallyFiberData acquisition
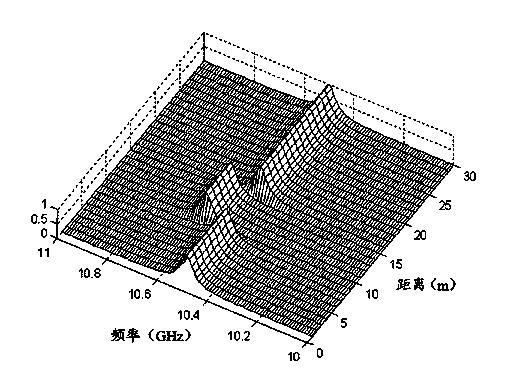
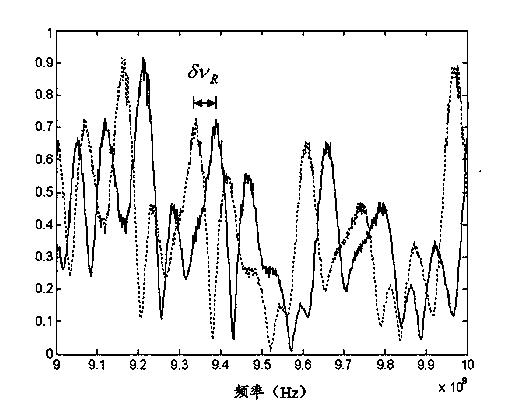
Disclosed is an optical time domain reflectometer simultaneously sensing temperature and stress. The system is based on parallel detection of Rayleigh and Brillouin scattered light and includes devices such as a multi-wavelength laser source, a light-pulse modulator, a balance detector, a microwave amplifier, a high-speed data acquisition card, a coupler and a circulator and the like. In the optical time domain reflectometer, the frequency interval of wavelengths of the multi-wavelength laser source is arranged to be in a range of 9-12 GHz, which is equivalent to a frequency shift quantity of Brillouin scattered light in a fiber. A heterodyne coherent detection method is used to carry out parallel detection on Rayleigh and Brillouin scattered spectra and temperature and stress information is demodulated through a Landau-Placzek ratio (LPR) and Brillouin frequency shift distribution; and at the same time, coherent Rayleigh noises are reduced and superposition of the scattered spectra improves the signal-to-noise ratio of the scattered light. The optical time domain reflectometer is capable of realizing simultaneous temperature and stress sensing of a distributed fiber sensing system, improving the signal-to-noise ratio of the scattered light and improving the sensing precision and distance.
Owner:SHANGHAI INST OF OPTICS & FINE MECHANICS CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
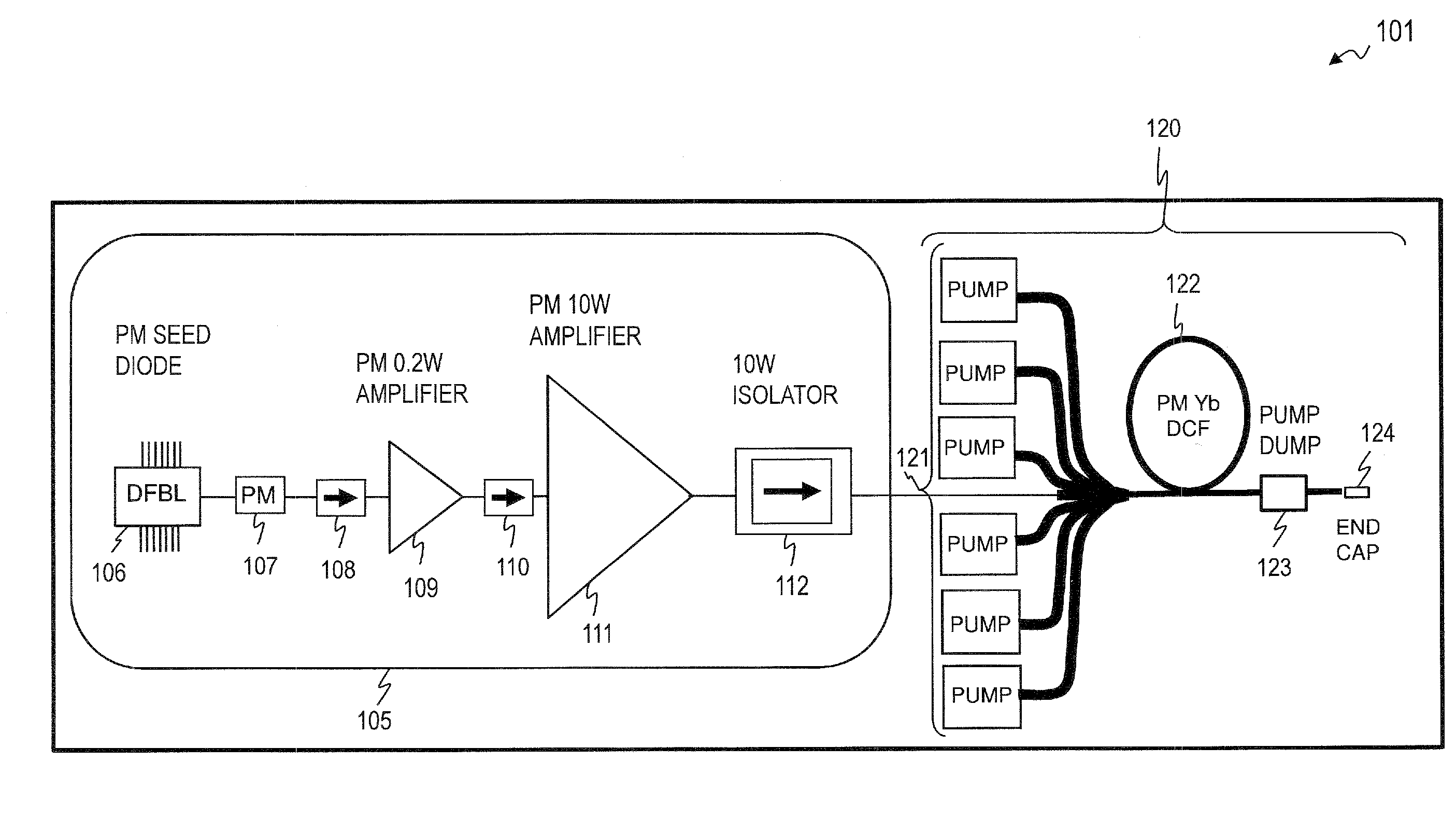
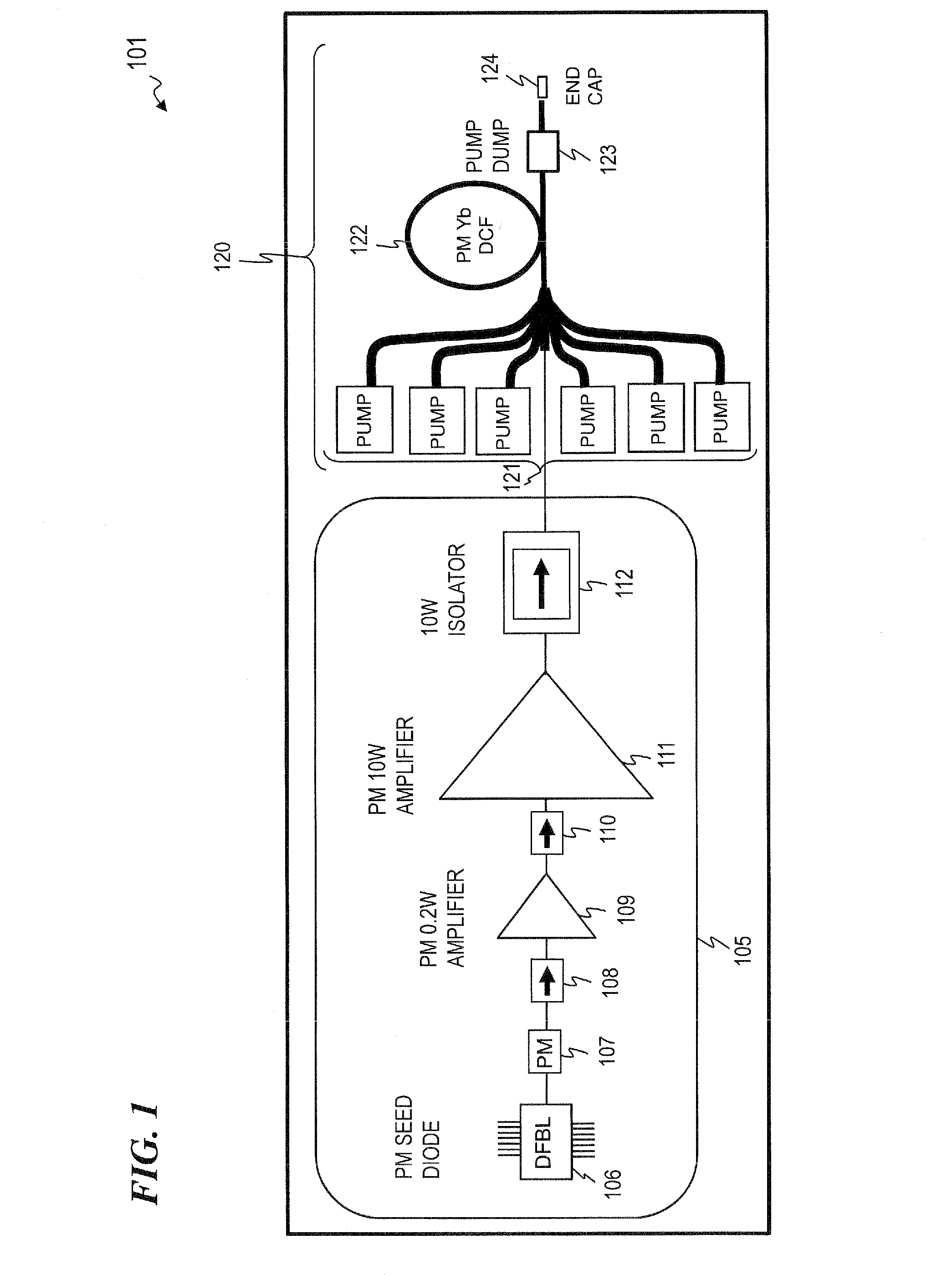
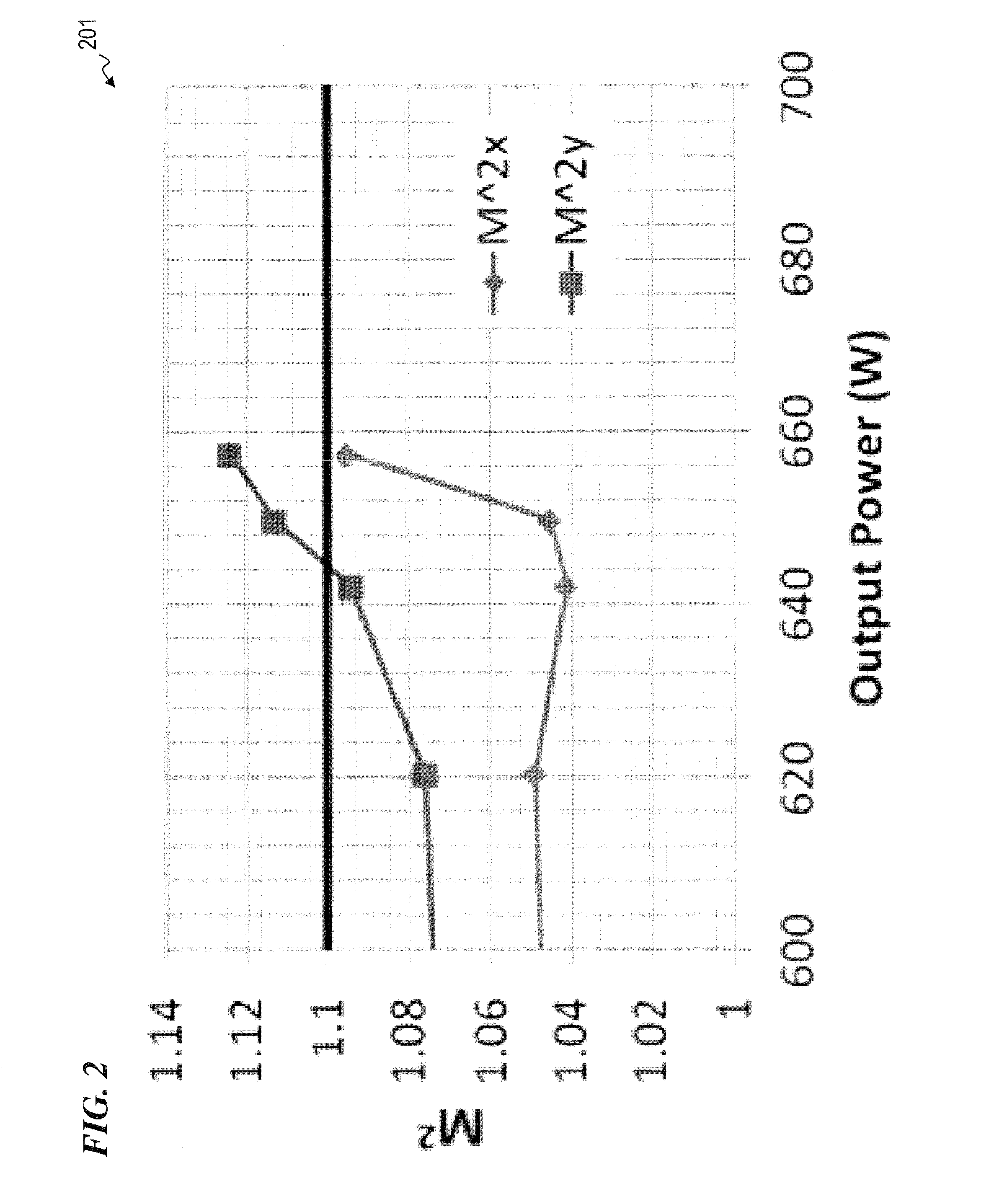
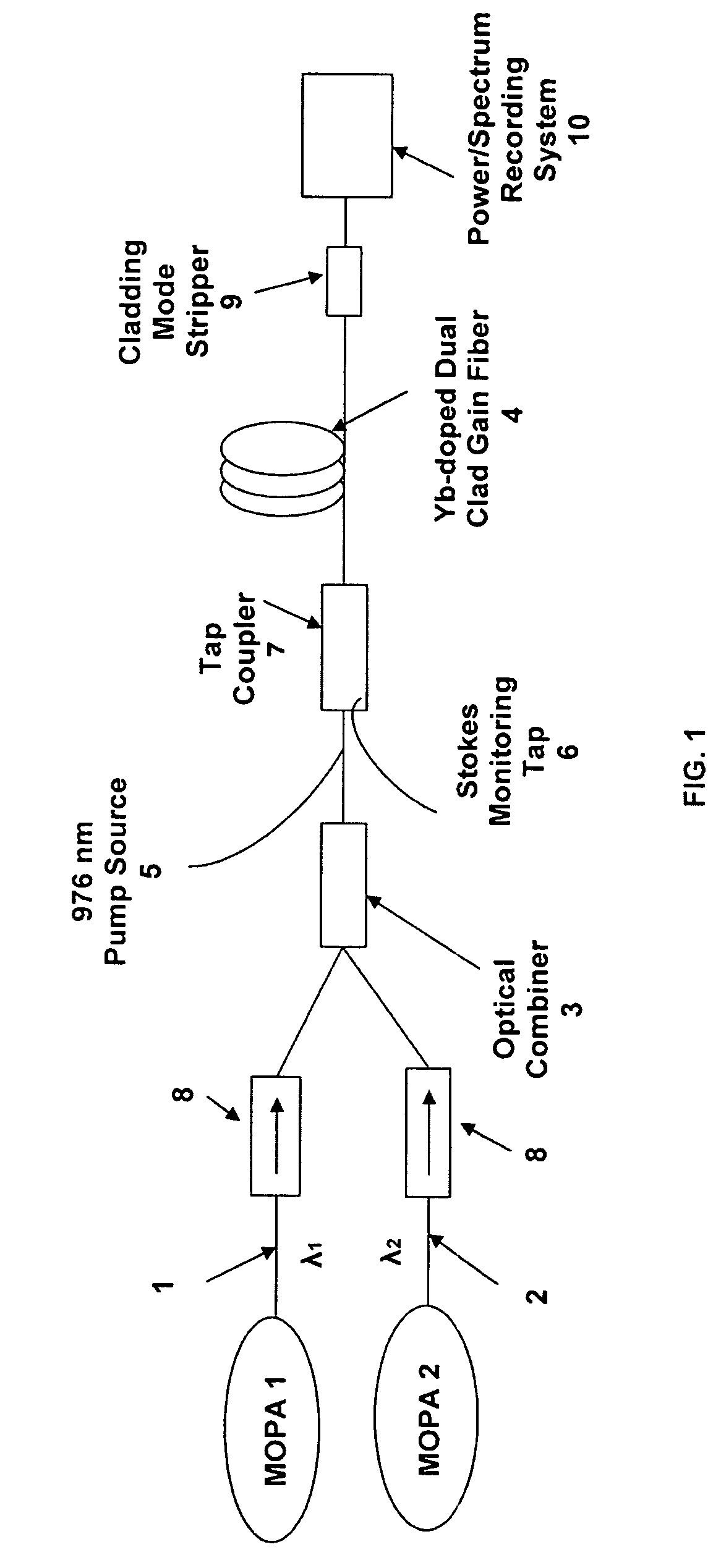
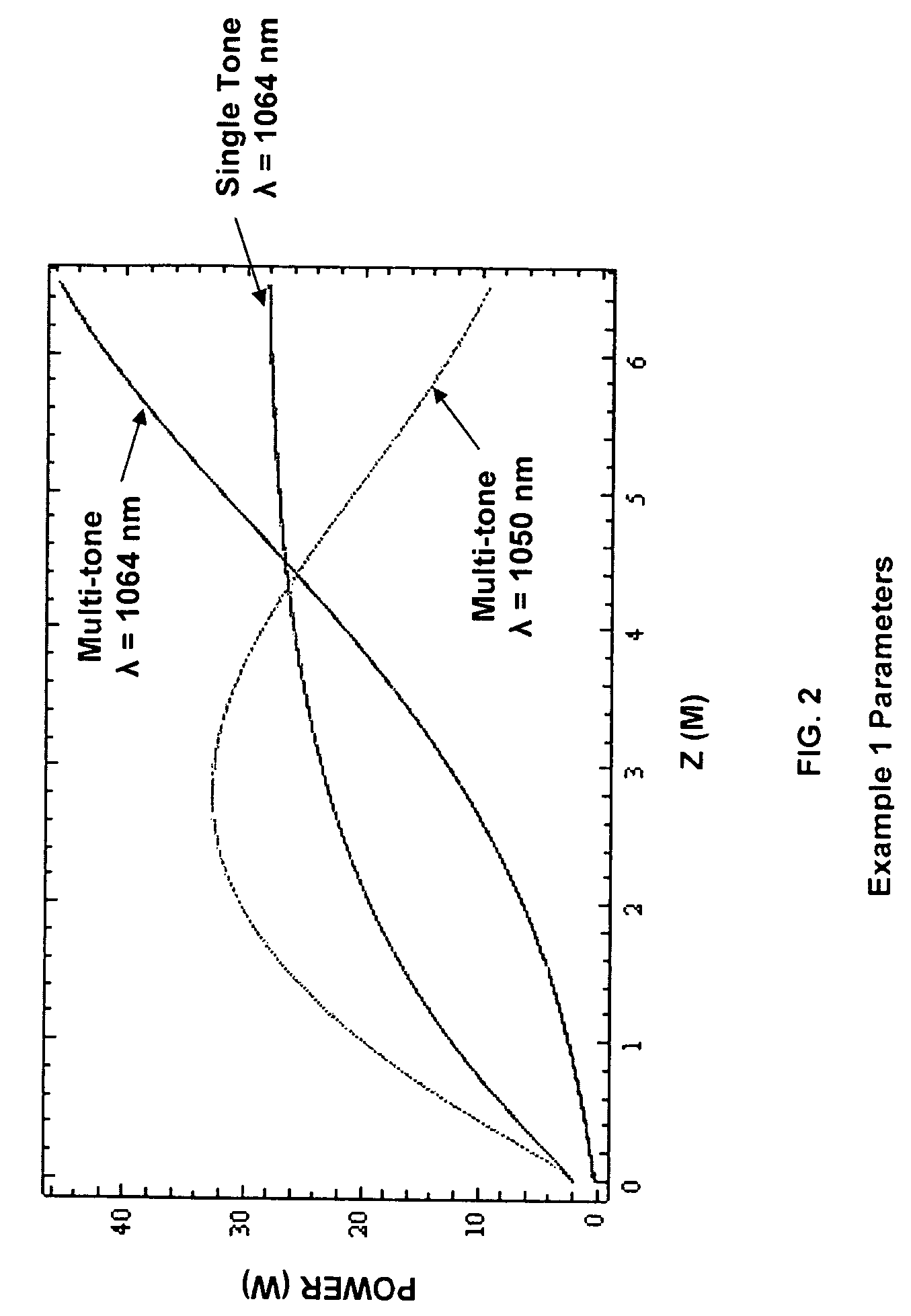
Multi-tone driven high-power narrow-linewidth rare earth doped fiber amplifier
A method to increase the output power of narrow-linewidth rare earth-doped fiber amplifiers by suppressing simulated Brillouin scattering. The fiber amplifier is seeded with two or more lasers having frequencies and input powers that are sufficiently different. The seed signal with the highest emission cross section (e.g., signal 2) initially experiences the greatest gain. If signal 2 is also given sufficiently greater input power than signal 1, it will be amplified to its maximum value before the seed signals have reached the midpoint of the gain fiber. Beyond that point, the signal having the lower emission and absorption cross sections (signal 1) and significantly lower input power will continue to experience gain by power transfer from both signal 2 and the pump light, attaining a power output well beyond what the maximum output would have been had the amplifier been illuminated with a single frequency beam. This technique effectively reduces the Stokes light of signal 1, whereby higher power narrow-linewidth optical fiber amplifiers may be realized.
Owner:THE UNITED STATES OF AMERICA AS REPRESETNED BY THE SEC OF THE AIR FORCE
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com