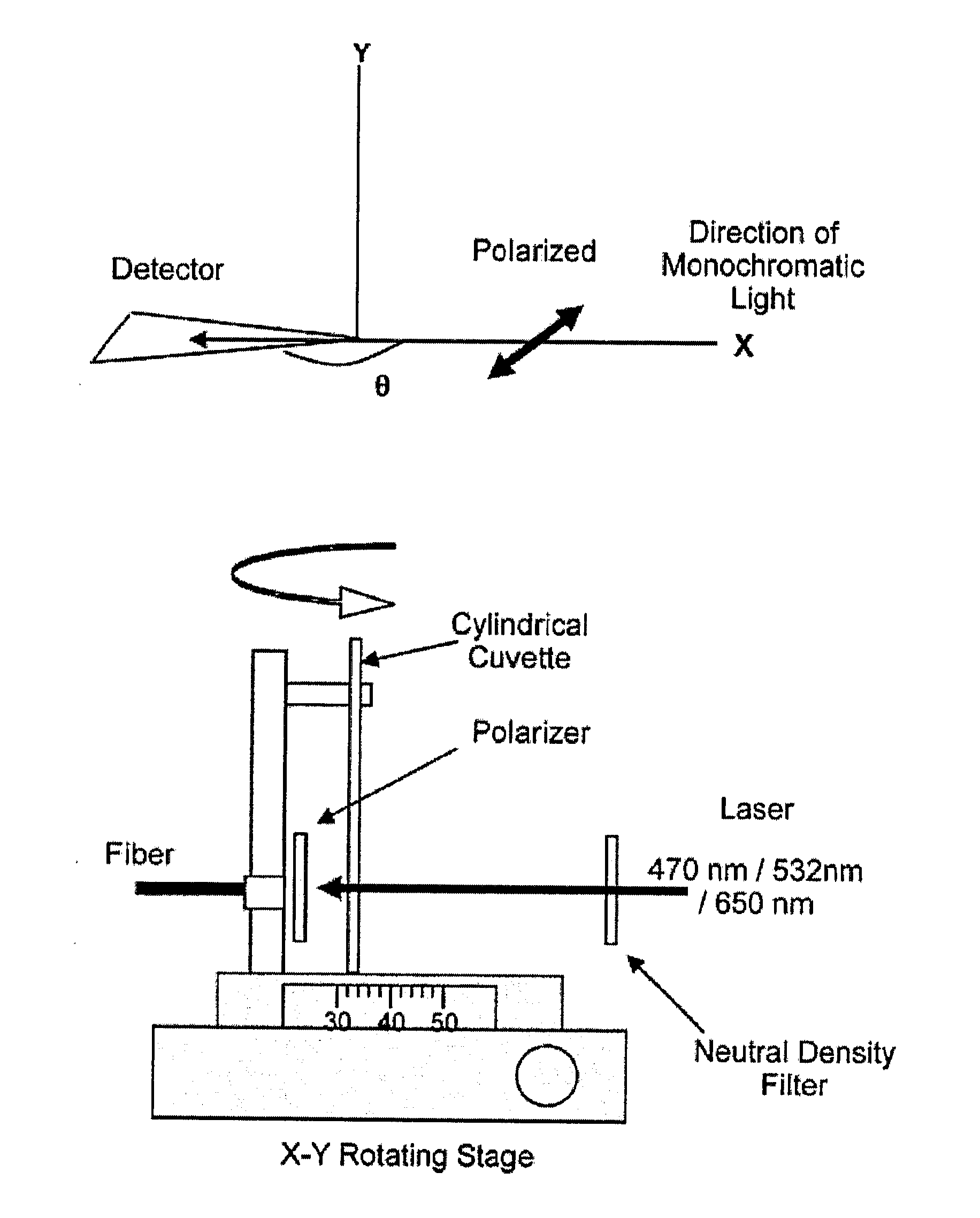
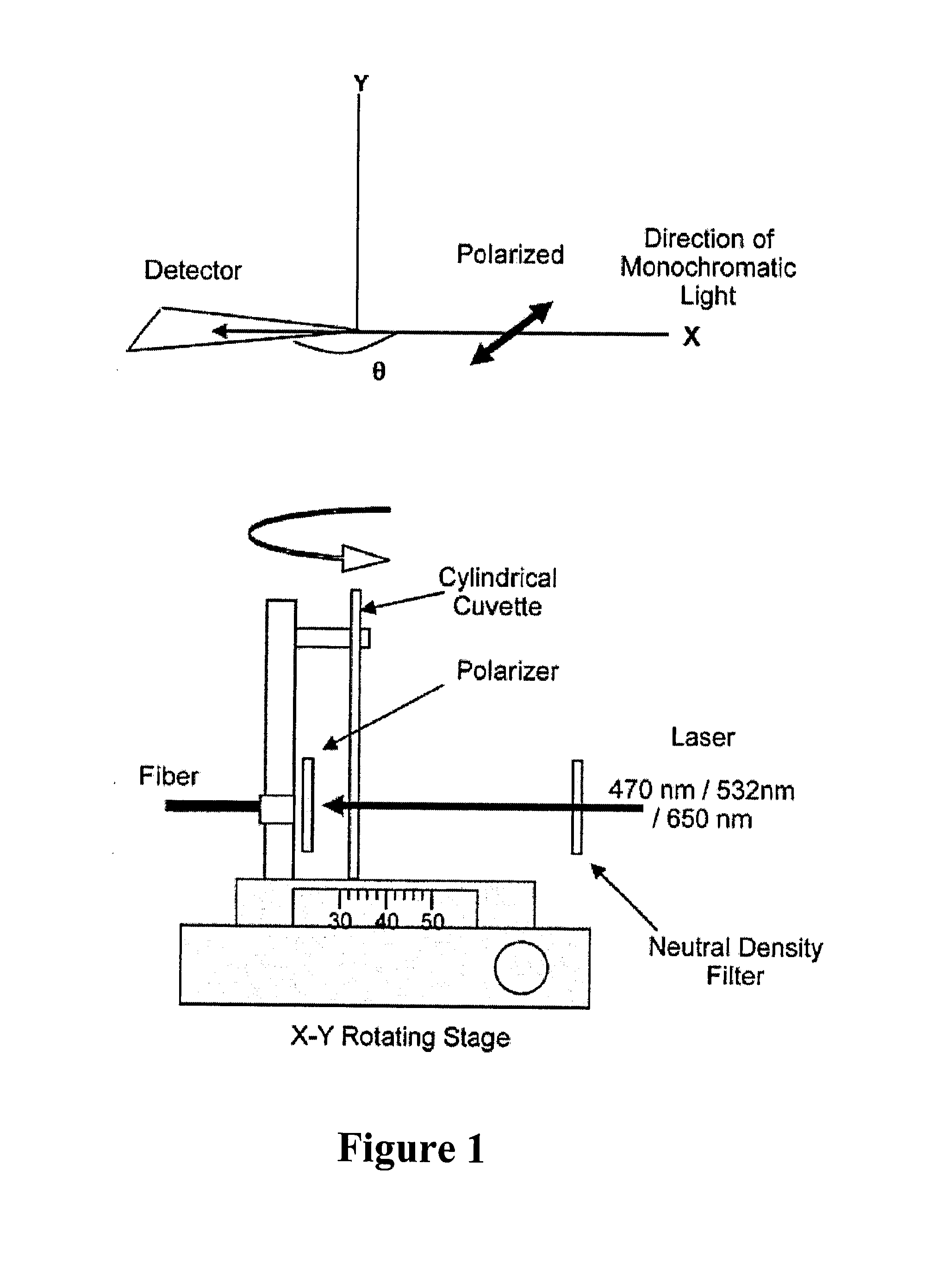
Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
724 results about "Scattering effect" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Updated March 26, 2018. The Compton effect (also called Compton scattering) is the result of a high-energy photon colliding with a target, which releases loosely bound electrons from the outer shell of the atom or molecule.
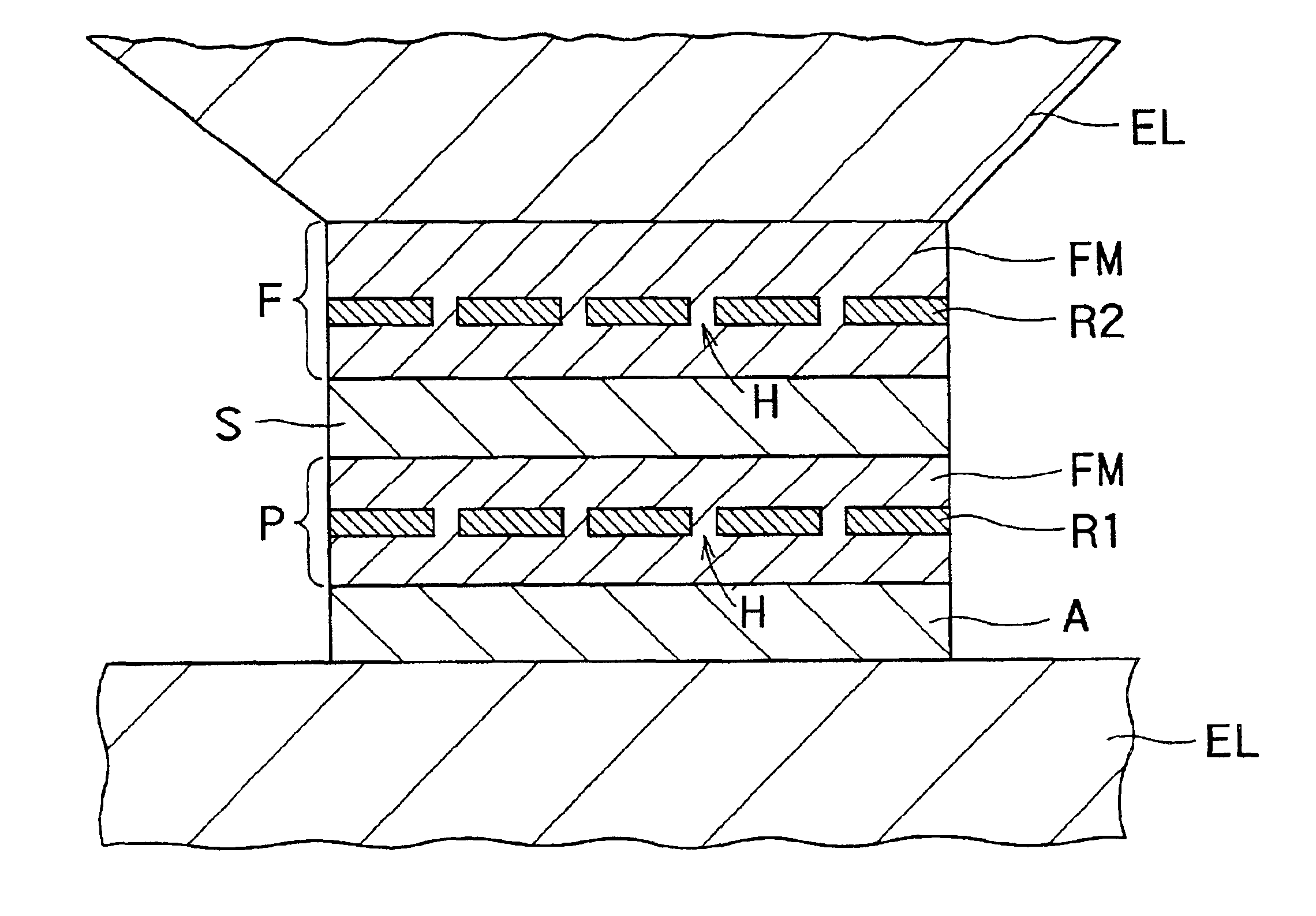
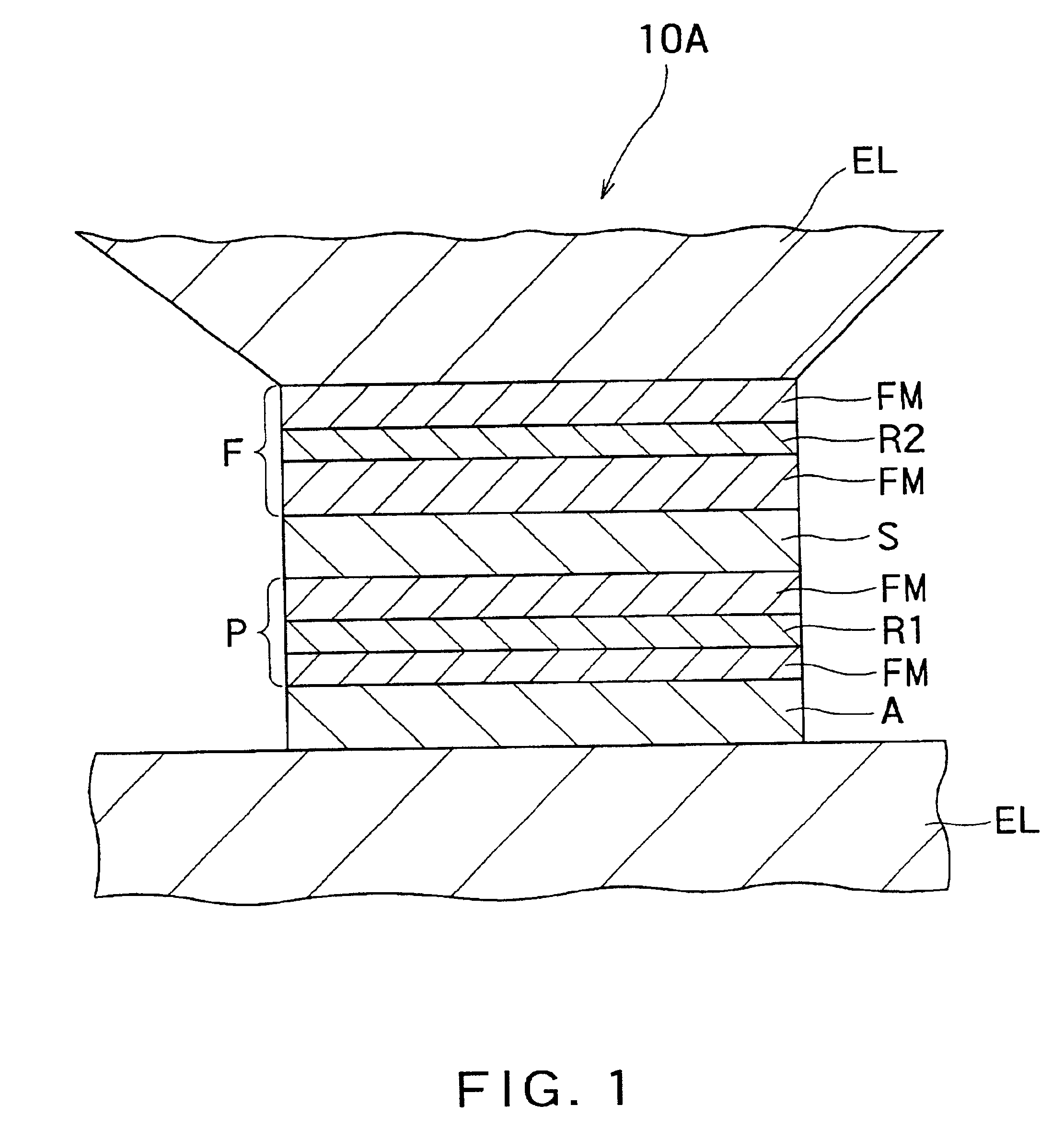
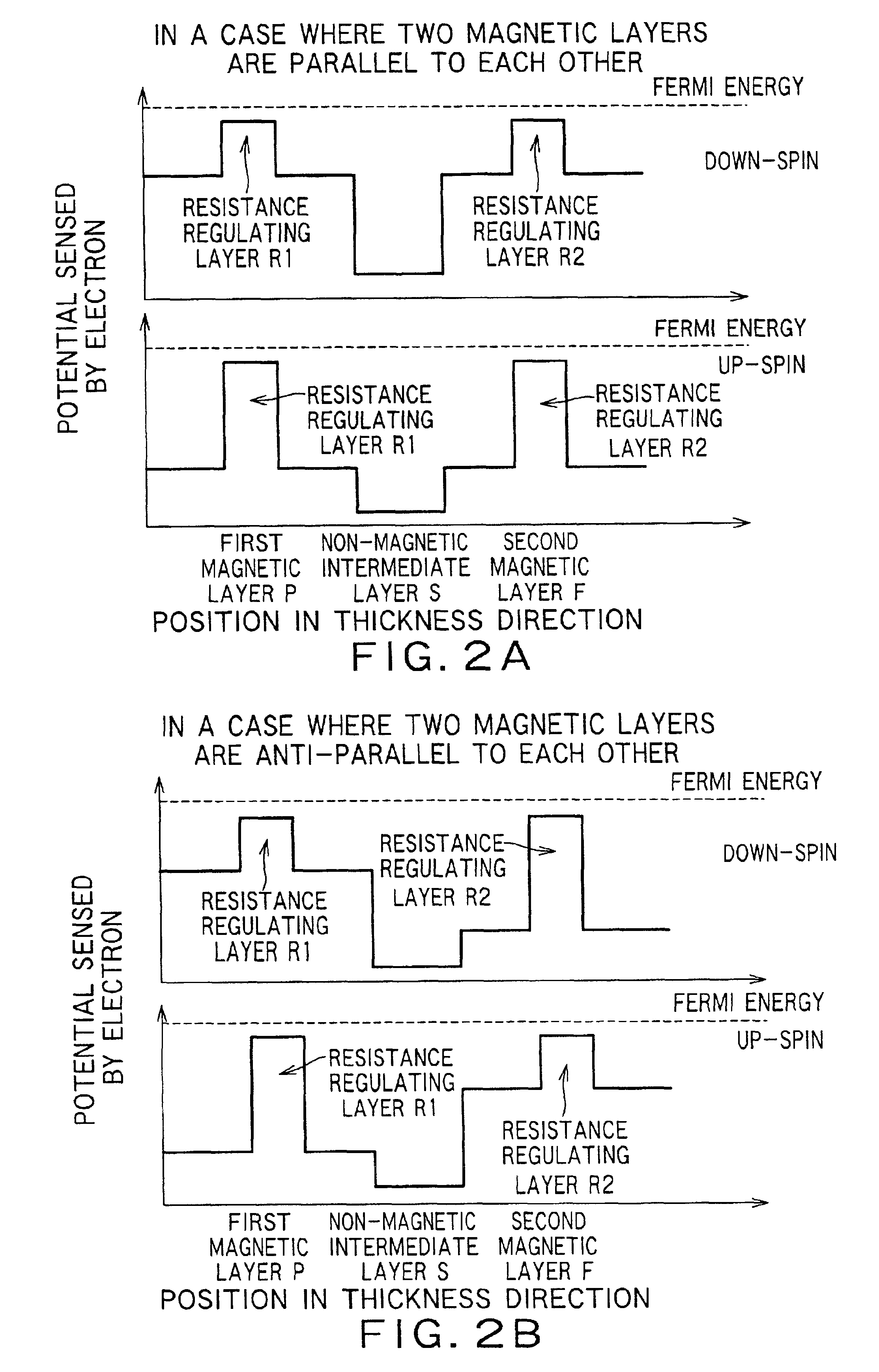
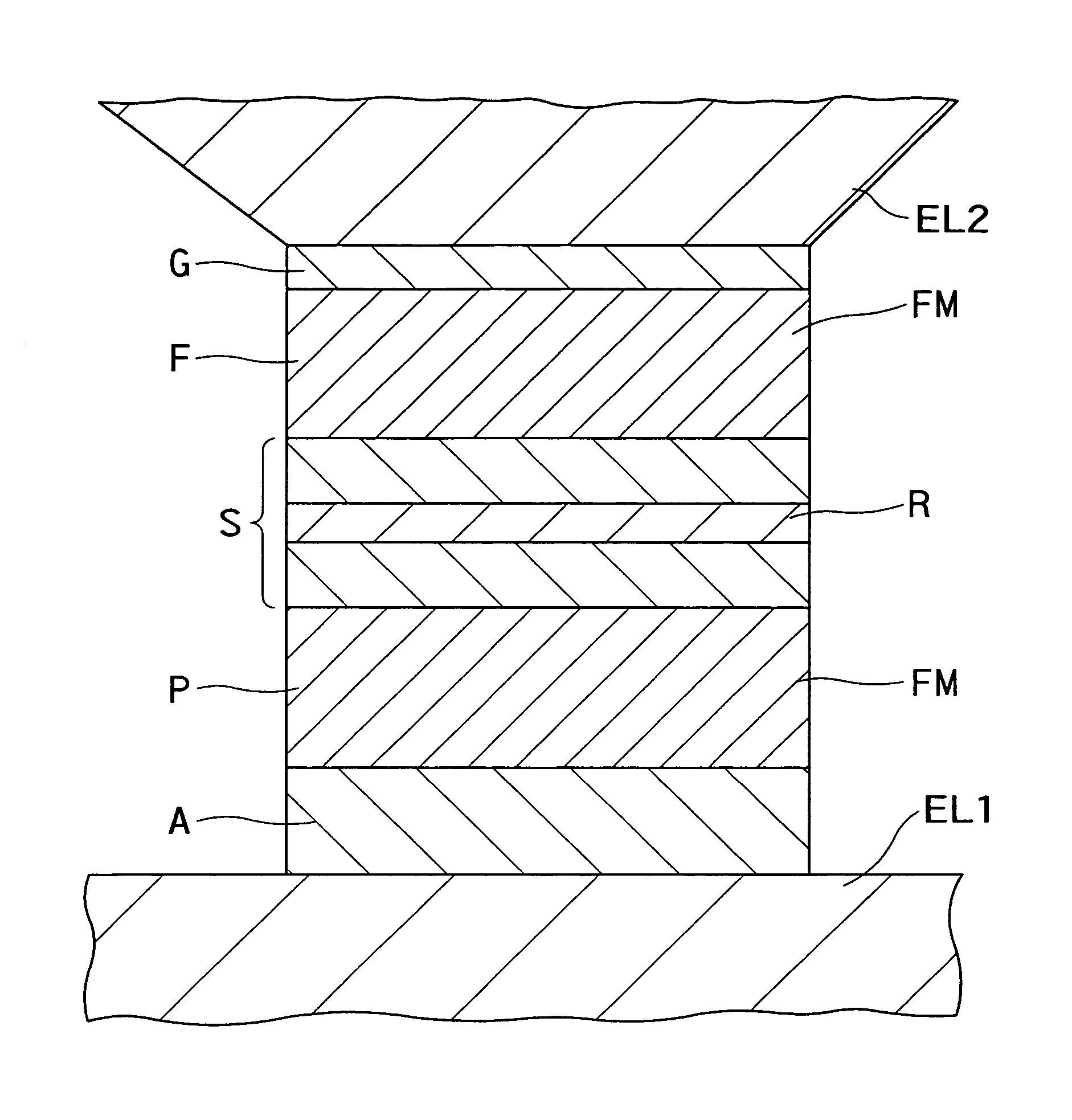
Magnetoresistance effect element, magnetic head and magnetic recording and/or reproducing system
InactiveUS6937446B2Efficient use ofControl quantityNanomagnetismMagnetic measurementsBorideScattering effect
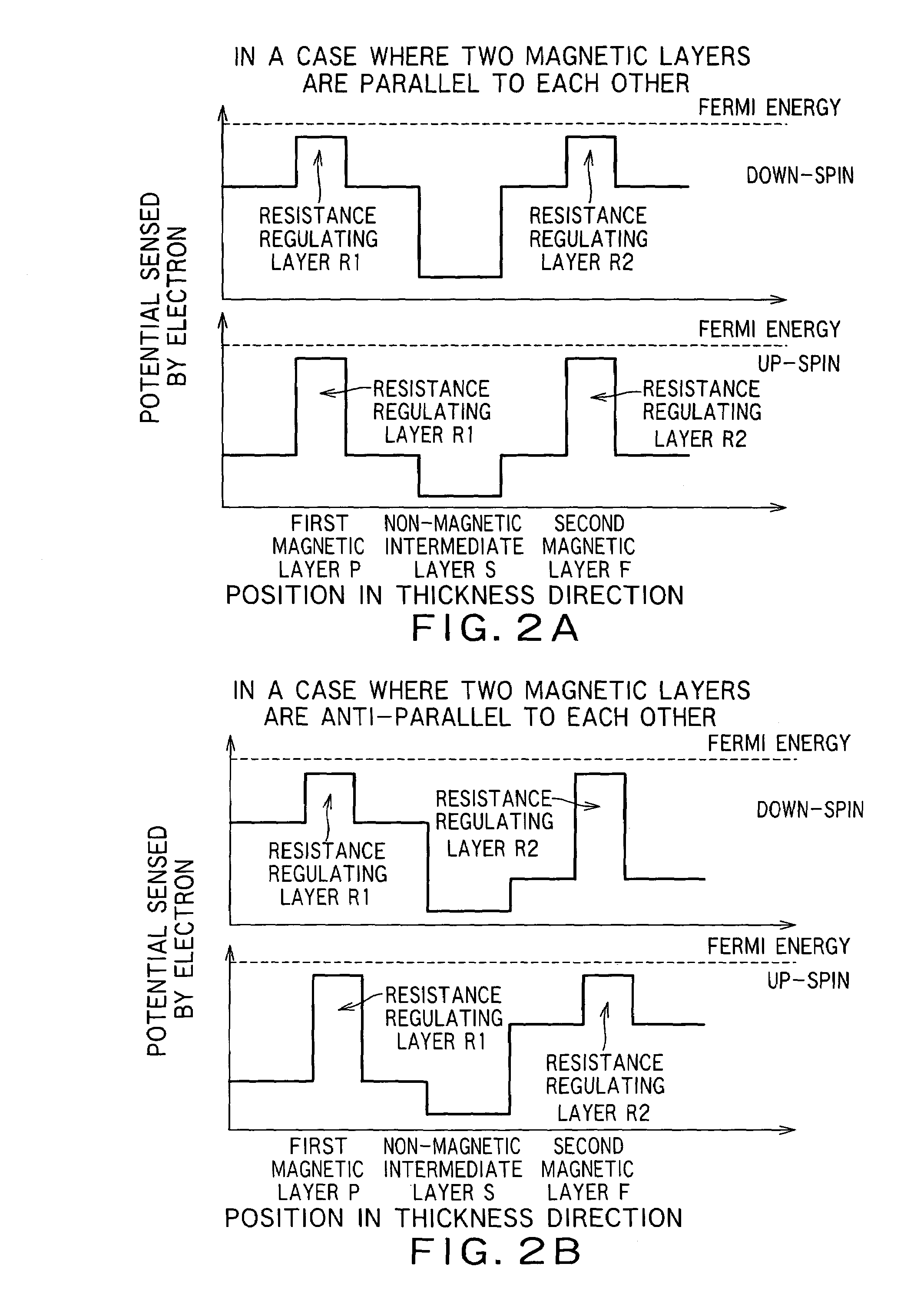
There is provided a practical magnetoresistance effect element which has an appropriate value of resistance, which can be sensitized and which has a small number of magnetic layers to be controlled, and a magnetic head and magnetic recording and / or reproducing system using the same. In a magnetoresistance effect element wherein a sense current is caused to flow in a direction perpendicular to the plane of the film, a resistance regulating layer is provided in at least one of a pinned layer, a free layer and an non-magnetic intermediate layer. The resistance regulating layer contains, as a principal component, an oxide, a nitride, a fluoride, a carbide or a boride. The resistance regulating layer may be a continuous film or may have pin holes. Thus, it is possible to provide a practical magnetoresistance effect element which has an appropriate value of resistance, which can be sensitized and which has a small number of magnetic layers, while effectively utilizing the scattering effect depending on spin.
Owner:KK TOSHIBA
Back light unit including a diffuser with various diffusion effects
InactiveUS6861789B2Improve the scattering effectImprove uniformityStatic indicating devicesIncadescent envelopes/vesselsDiffusionScattering effect
A backlight unit is disposed beneath a display panel. The backlight unit includes an illumination means, which is used to provide a light source, and a diffuser positioned between the illumination means and the display panel, which is used to scatter the light generated by the illumination means. The diffuser, which is composed of liquid crystal particles and polymer, has a plurality of regions. The region thatis closer to the illumination means has greater scattering effect. In addition, the region with the greatest scattering effect has a shape corresponding to the illumination means.
Owner:INNOLUX CORP
Tailoring material composition for optimization of application-specific switchable holograms
InactiveUS7175780B1Improve efficiencyOptical qualityLiquid crystal compositionsThin material handlingCrystallographyChemical composition
The process described herein offers the optimizing of performance parameters of holograms, such as reducing scattering effects in a polymer-dispersed liquid crystal optical element. In the process, an interfacial tension agent is added to a polymer-dispersed liquid crystal material. The polymer-dispersed liquid crystal material has at least one acrylic acid monomer, at least one type of liquid crystal material, a photoinitiator dye, and a co-initiator. The polymer-dispersed liquid crystal material is subjected to a polymerization. The interfacial tension agent reduces the size of liquid crystal droplets formed within the polymer-dispersed liquid crystal optical element during polymerization.
Owner:LEIDOS
Ultra-remote distributed fiber raman and brillouin photons sensor
InactiveCN101162158AAvoid lossHigh strengthThermometers using physical/chemical changesUsing optical meansFiberPhotonic sensor
The invention discloses super-far distributed fiber Raman and Brillouin photon sensors; by using the stimulated Raman scattering effect of fiber, the self Raman scattering effect of fiber, the Brillouin scattering effect of fiber and the light time-field reflection principle, distributed fiber Raman photon temperature sensors, distributed fiber Brillouin photon strain sensors and distributed fiber Raman amplifier are integrated together. Fiber consumption is overcome by using the gain of amplifier, and strengths of self Raman scattering light and Brillouin scattering light in fiber is enhanced, the signal to noise ratio of the system of distributed fiber Raman photon sensor and distributed fiber Brillouin photon strain sensor is enhanced, meanwhile, the transmission distances of distributed fiber Raman photon sensor and distributed fiber Brillouin photon strain sensor are increased, finally, the temperature and stress measuring accuracy is enhanced.
Owner:WEIHAI BEIYANG PHOTOELECTRIC INFORMATION TECH
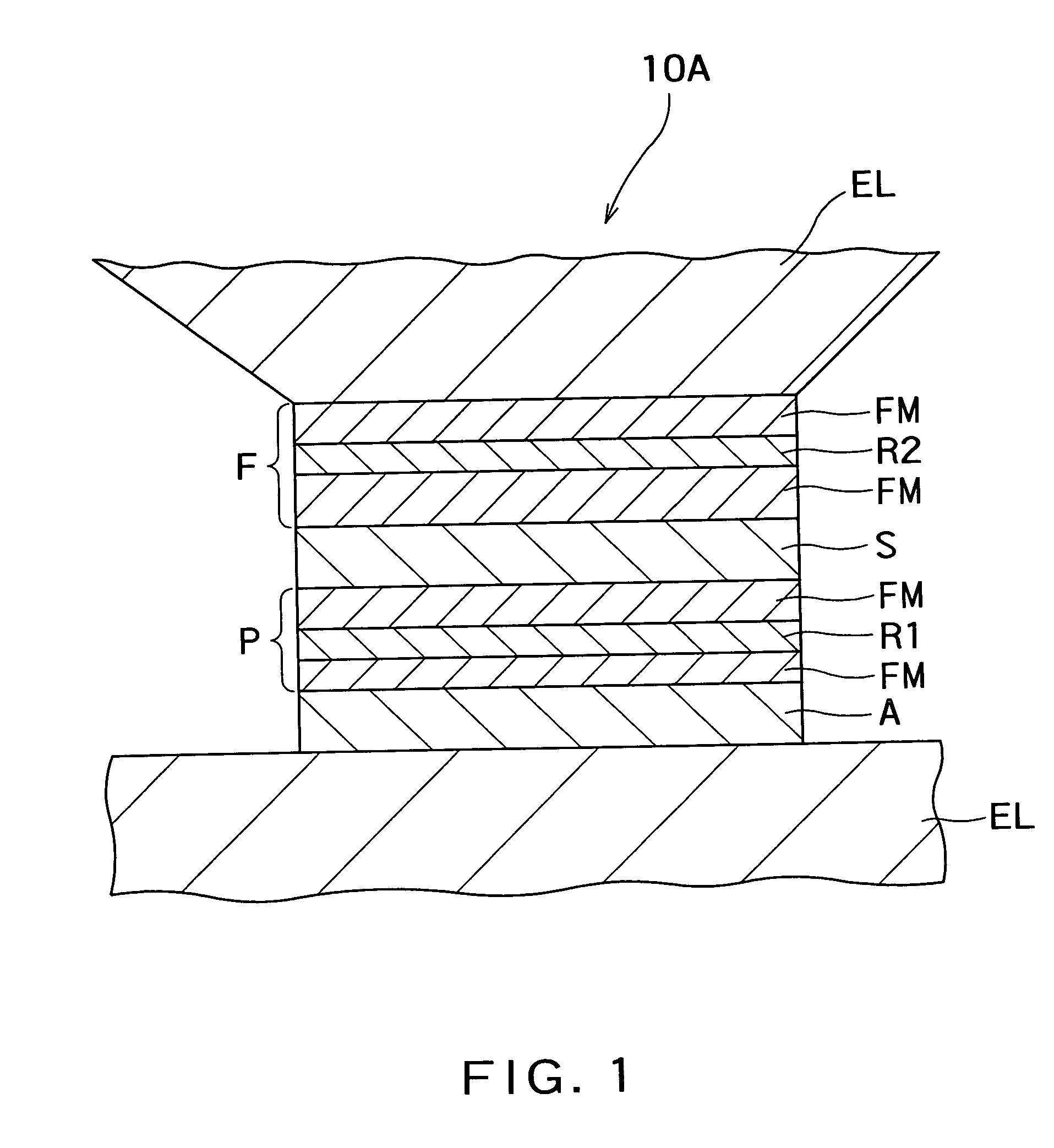
Magnetoresistance effect element, magnetic head and magnetic recording and/or reproducing system
InactiveUS7046489B2Efficient use ofControl quantityNanomagnetismMagnetic measurementsBorideScattering effect
There is provided a practical magnetoresistance effect element which has an appropriate value of resistance, which can be sensitized and which has a small number of magnetic layers to be controlled, and a magnetic head and magnetic recording and / or reproducing system using the same. In a magnetoresistance effect element wherein a sense current is caused to flow in a direction perpendicular to the plane of the film, a resistance regulating layer is provided in at least one of a pinned layer, a free layer and an non-magnetic intermediate layer. The resistance regulating layer contains, as a principal component, an oxide, a nitride, a fluoride, a carbide or a boride. The resistance regulating layer may be a continuous film or may have pin holes. Thus, it is possible to provide a practical magnetoresistance effect element which has an appropriate value of resistance, which can be sensitized and which has a small number of magnetic layers, while effectively utilizing the scattering effect depending on spin.
Owner:KK TOSHIBA
Structure and method to fabricate high performance MTJ devices for spin-transfer torque (STT)-RAM
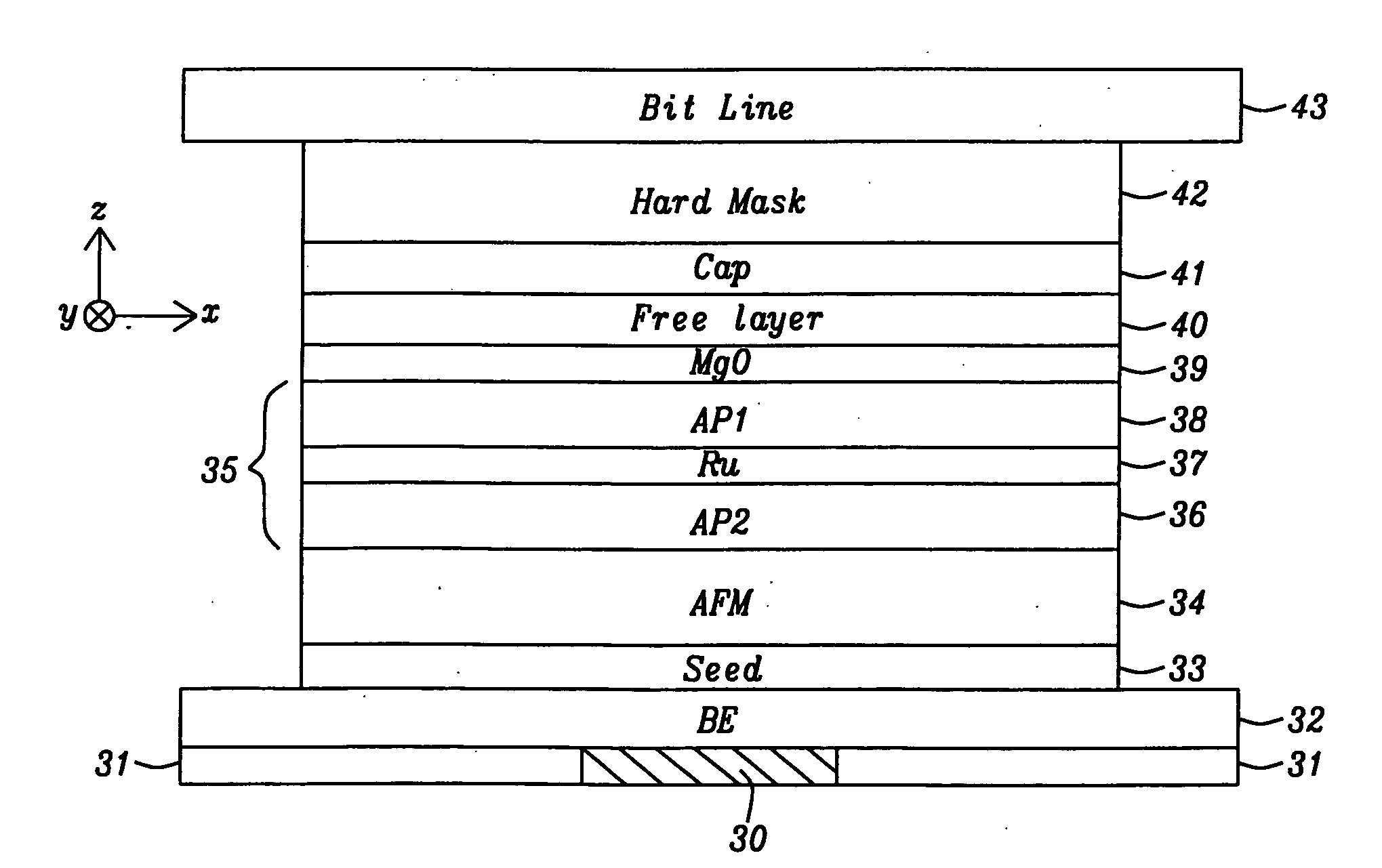
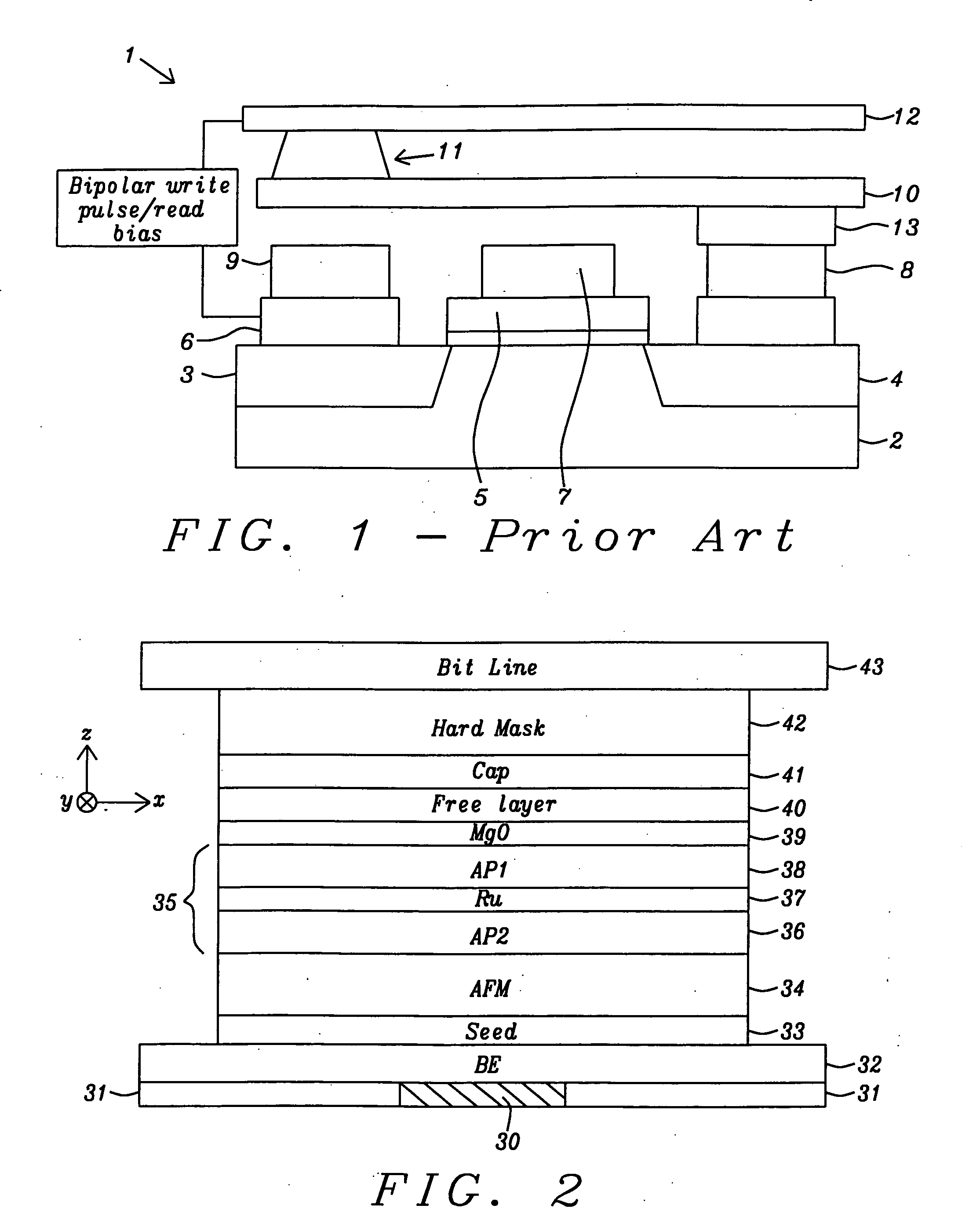
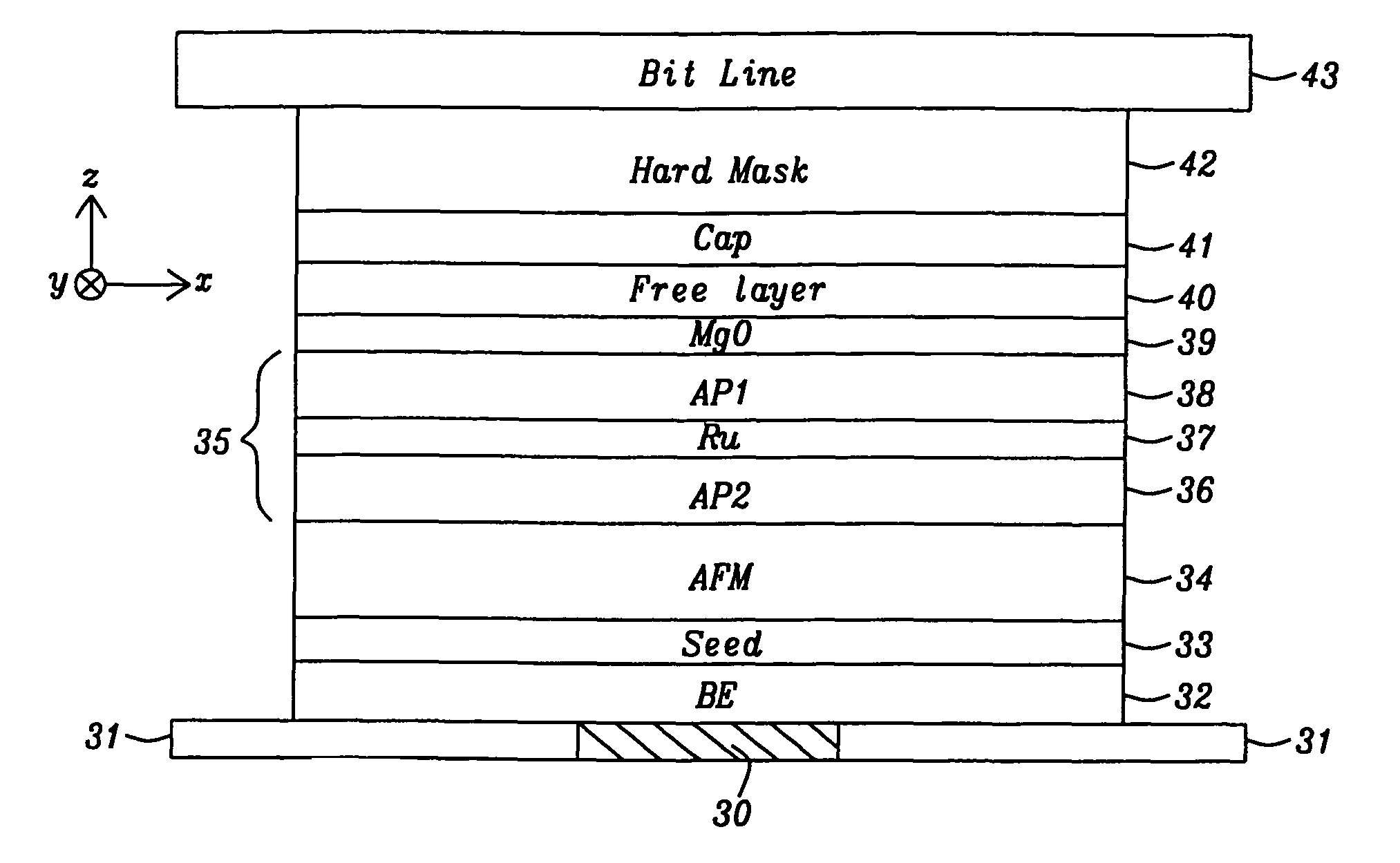
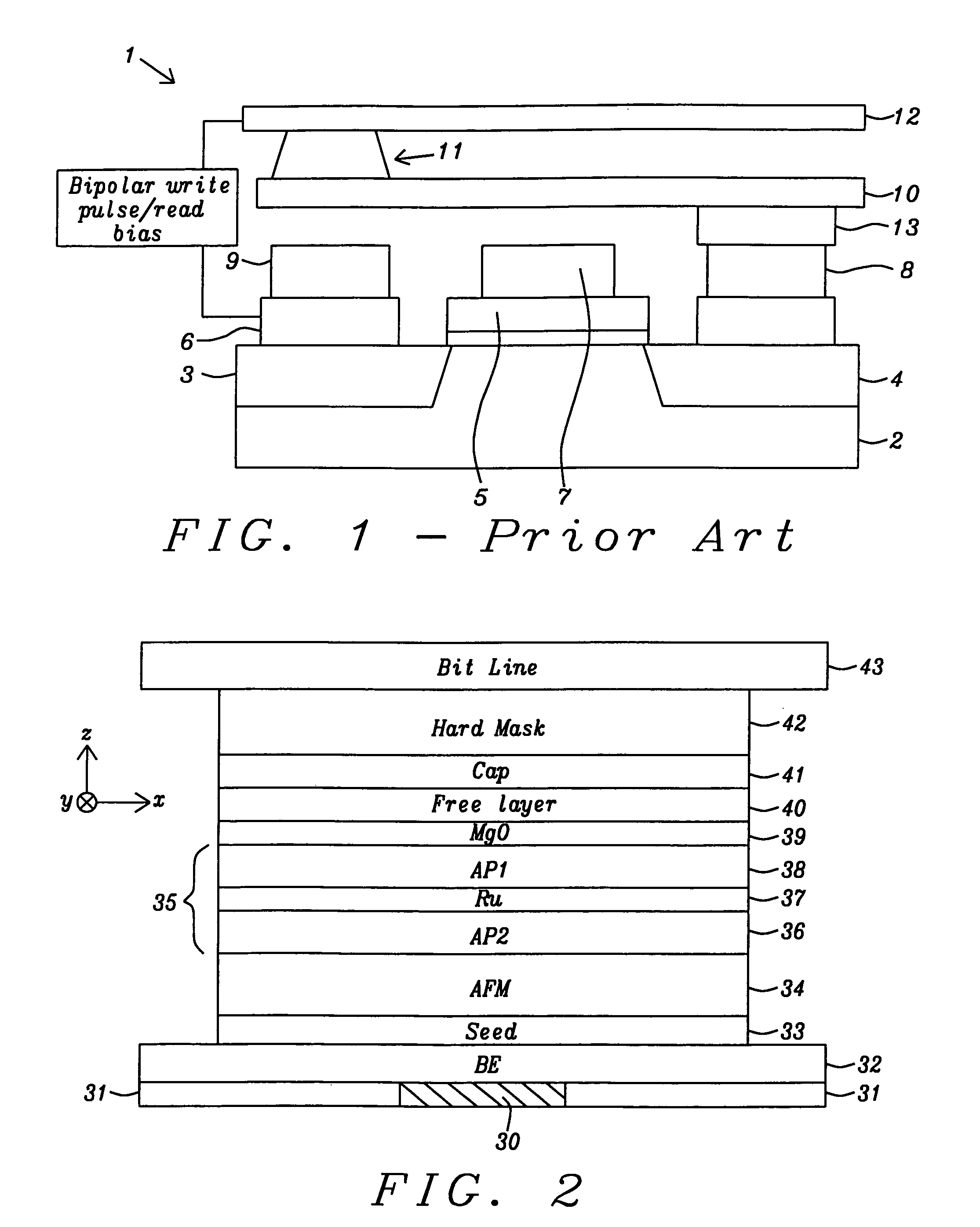
ActiveUS20100065935A1Facilitate magnetization switchingNegatively affectingNanomagnetismSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingSpin-transfer torqueEngineering
A STT-RAM MTJ is disclosed with a MgO tunnel barrier formed by a NOX process, a CoFeB / FeSiO / CoFeB composite free layer with a middle nanocurrent channel layer to minimize Jc0, and a Ru capping layer to enhance the spin scattering effect and increase dR / R. Good write margin is achieved by modifying the NOX process to afford a RA less than 10 ohm-μm2 and good read margin is realized with a dR / R of >100% by annealing at 330° C. or higher to form crystalline CoFeB free layers. The NCC thickness is maintained in the 6 to 10 Angstrom range to reduce Rp and avoid Fe(Si) granules from not having sufficient diameter to bridge the distance between upper and lower CoFeB layers. A FeSiO layer may be inserted below the Ru layer in the capping layer to prevent the Ru from causing a high damping constant in the upper CoFeB free layer.
Owner:TAIWAN SEMICON MFG CO LTD
Structure and method to fabricate high performance MTJ devices for spin-transfer torque (STT)-RAM
A STT-RAM MTJ is disclosed with a MgO tunnel barrier formed by a NOX process, a CoFeB / FeSiO / CoFeB composite free layer with a middle nanocurrent channel layer to minimize Jc0, and a Ru capping layer to enhance the spin scattering effect and increase dR / R. Good write margin is achieved by modifying the NOX process to afford a RA less than 10 ohm-μm2 and good read margin is realized with a dR / R of >100% by annealing at 330° C. or higher to form crystalline CoFeB free layers. The NCC thickness is maintained in the 6 to 10 Angstrom range to reduce Rp and avoid Fe(Si) granules from not having sufficient diameter to bridge the distance between upper and lower CoFeB layers. A FeSiO layer may be inserted below the Ru layer in the capping layer to prevent the Ru from causing a high damping constant in the upper CoFeB free layer.
Owner:TAIWAN SEMICON MFG CO LTD
Pixel for a fringe field switching reflective and transflective liquid crystal display
InactiveUS20050030451A1Reduced masking stepReduce manufacturing costTransistorDiffusing elementsLiquid-crystal displayScattering effect
By employing an ultra-micro scattering layer with a top surface in a nano-scale roughness resulted from the crystallization or the property of the material within the ultra-micro scattering layer in a pixel for a fringe field switching liquid crystal display, the mask steps to manufacture the liquid crystal display and the cost therefore are reduced. The nano-scale roughness of the top surface on the ultra-micro scattering layer results in larger scattering angle and smooth distribution for the scattering effect. Accordingly, the reflectivity will not vary violently with the viewing angle, and excellent anti-glare effect is obtained also.
Owner:WISTRON OPTRONICS CORP
Skin preparation for external use characterized by containing sugar derivative of alpha, alpha-trehalose
ActiveUS20070003502A1Prevent and improve rough skinPrevent and improve and suntanAntibacterial agentsCosmetic preparationsScattering effectSugar derivatives
The present invention has an object to provide an external dermatological formulation having satisfactory blood flow-promoting effect, antiinflammatory effect, antibacterial effect, moisturizing effect, whitening effect, UV-absorbing effect, UV-scattering effect, antioxidant effect, hair growing effect, hair nourishing effect, emusifying effect, astringent effect, wrinkle-reducing effect, cell-activating effect and / or transdermal absorption-promoting effect with a satisfactory safety and skin feeling; The object is solved by providing an external dermatological formulation comprising a saccharide derivative of α,α-trehalose and one or more members selected from substances having any one of blood flow-promoting effect, antiinflammatory effect, antibacterial effect, moisturizing effect, whitening effect, UV-absorbing effect, UV-scattering effect, antioxidant effect, hair growing efect, hair nourishing effect, emulsifying effect, astringent effect, wrinkle-reducing effect, cell-activating effect and transdermal absorption-promoting effect.
Owner:HAYASHIBARA BIOCHEMICAL LAB INC
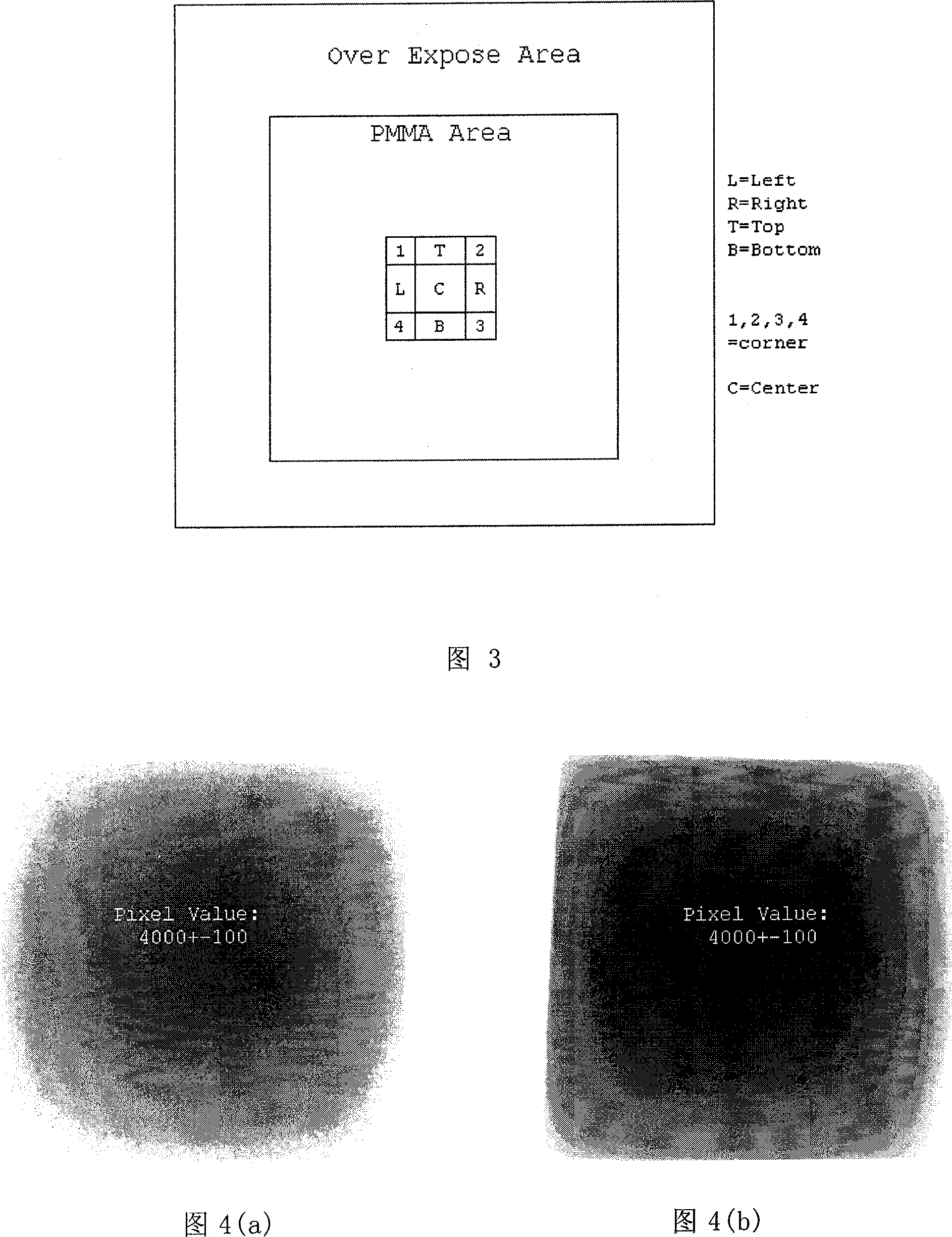
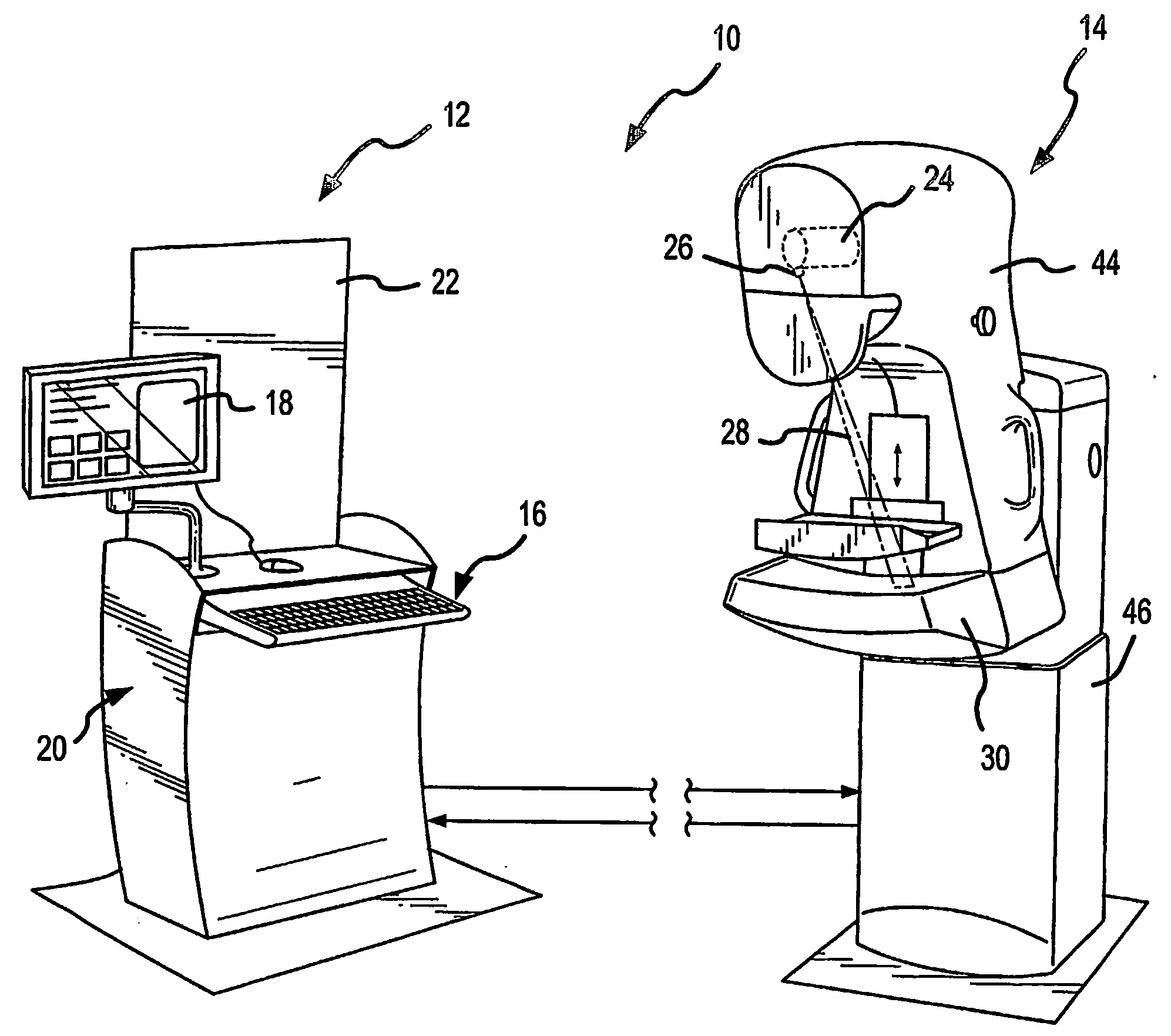
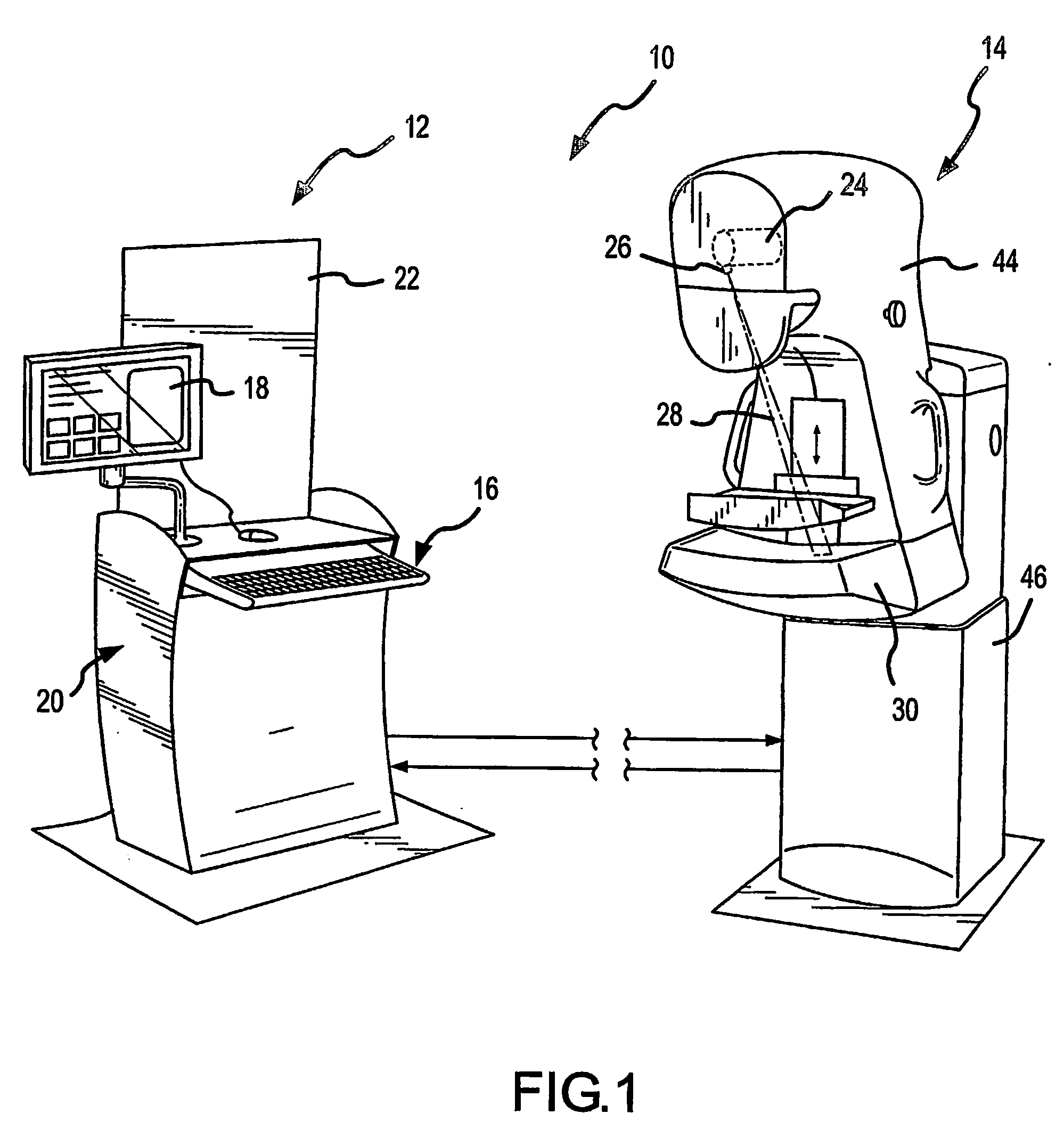
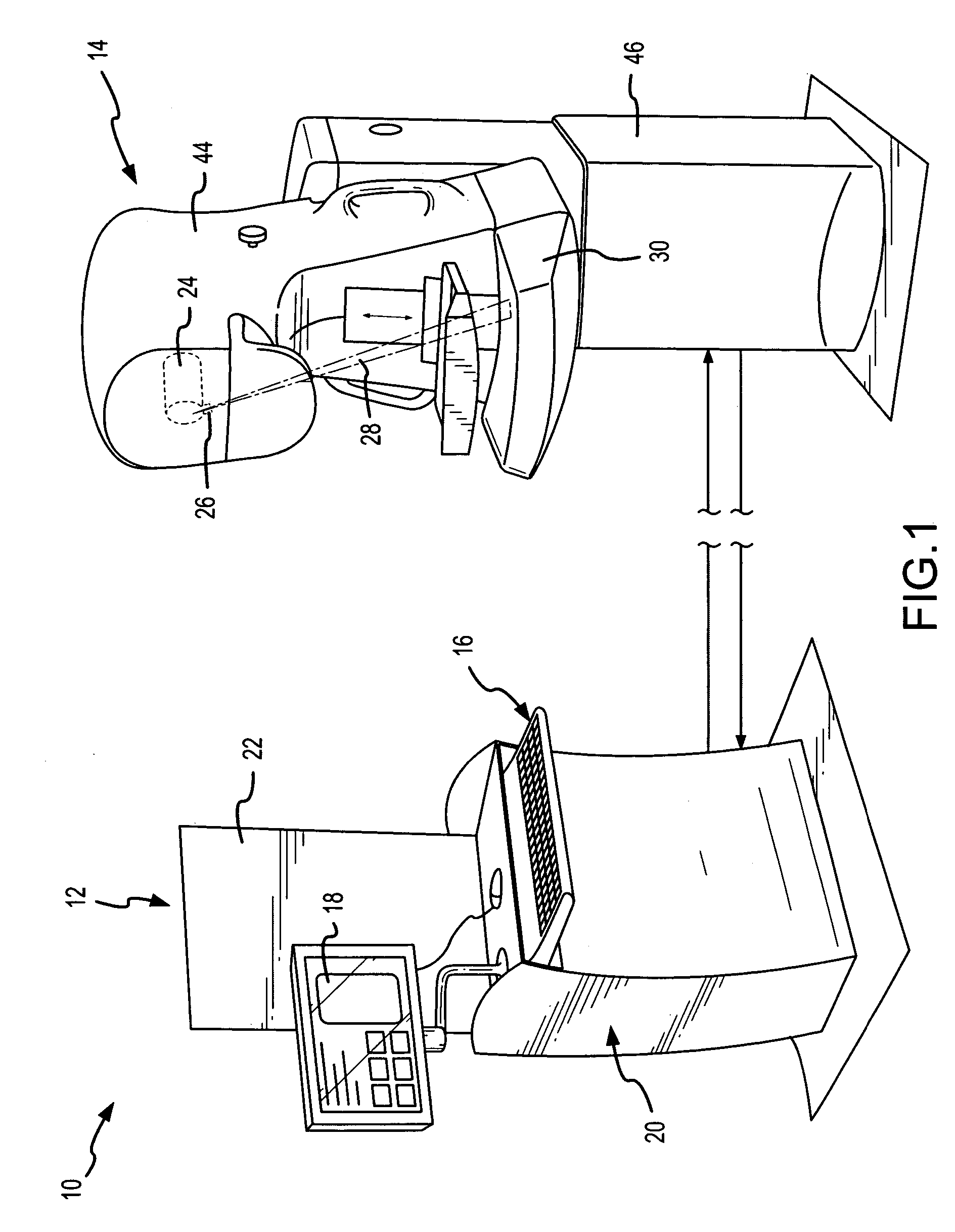
Signal profiling for medical imaging systems
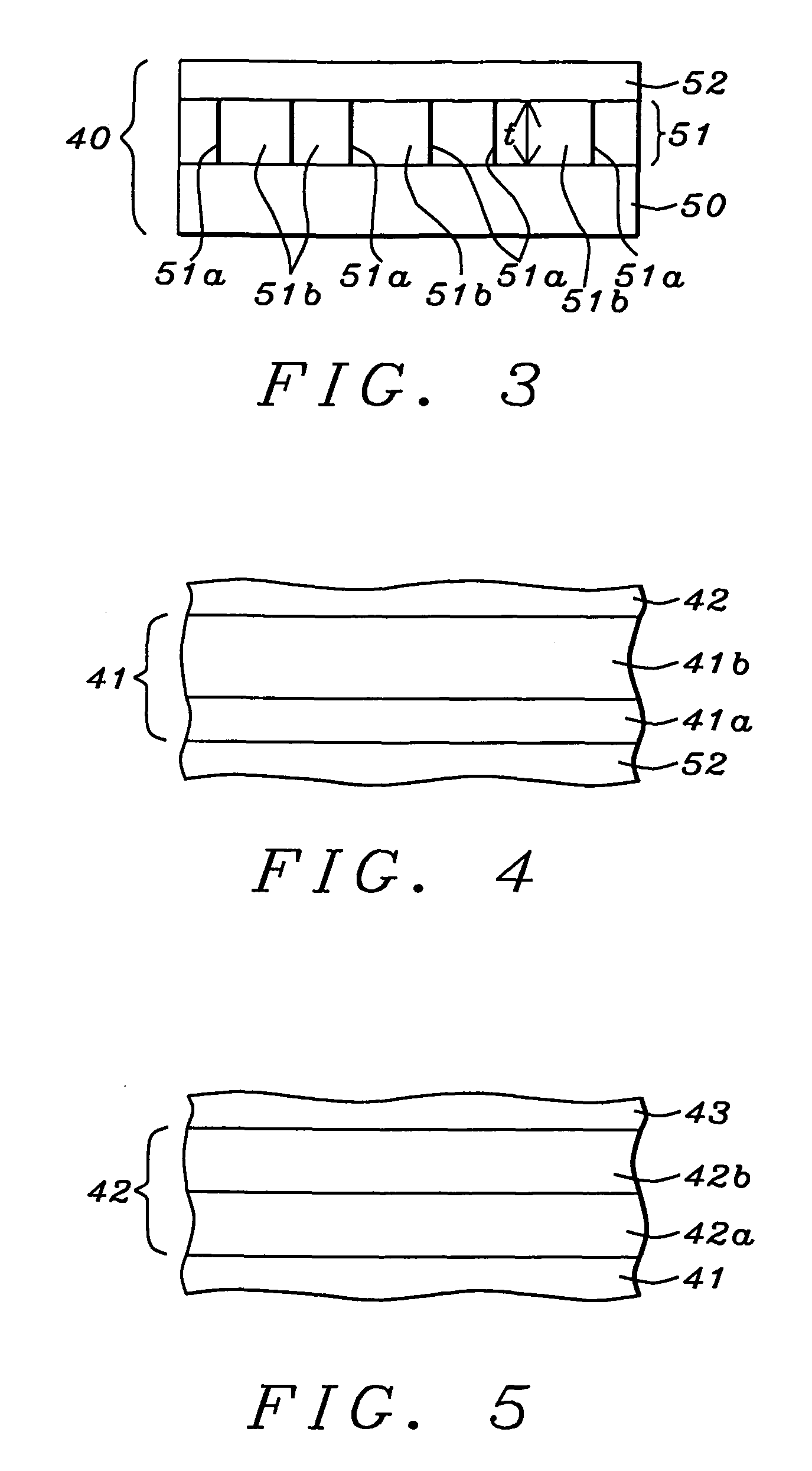
InactiveUS7092482B2Improved scatter compensationReduced scatter composite imaging informationMaterial analysis using wave/particle radiationPatient positioning for diagnosticsRayleigh scatteringScattering effect
Scatter effects are reduced in a radiographic imaging device, such as a digital slot scan mammographic imaging device, by reducing detected scatter and processing detector information to compensate for scatter effects. Spatial intensity profile information together with other imaging signal and patient dependent parameters can be used in image processing to estimate and compensate for various scatter effects including single and multiple scatters and Compton and Rayleigh scatter.
Owner:HOLOGIC INC
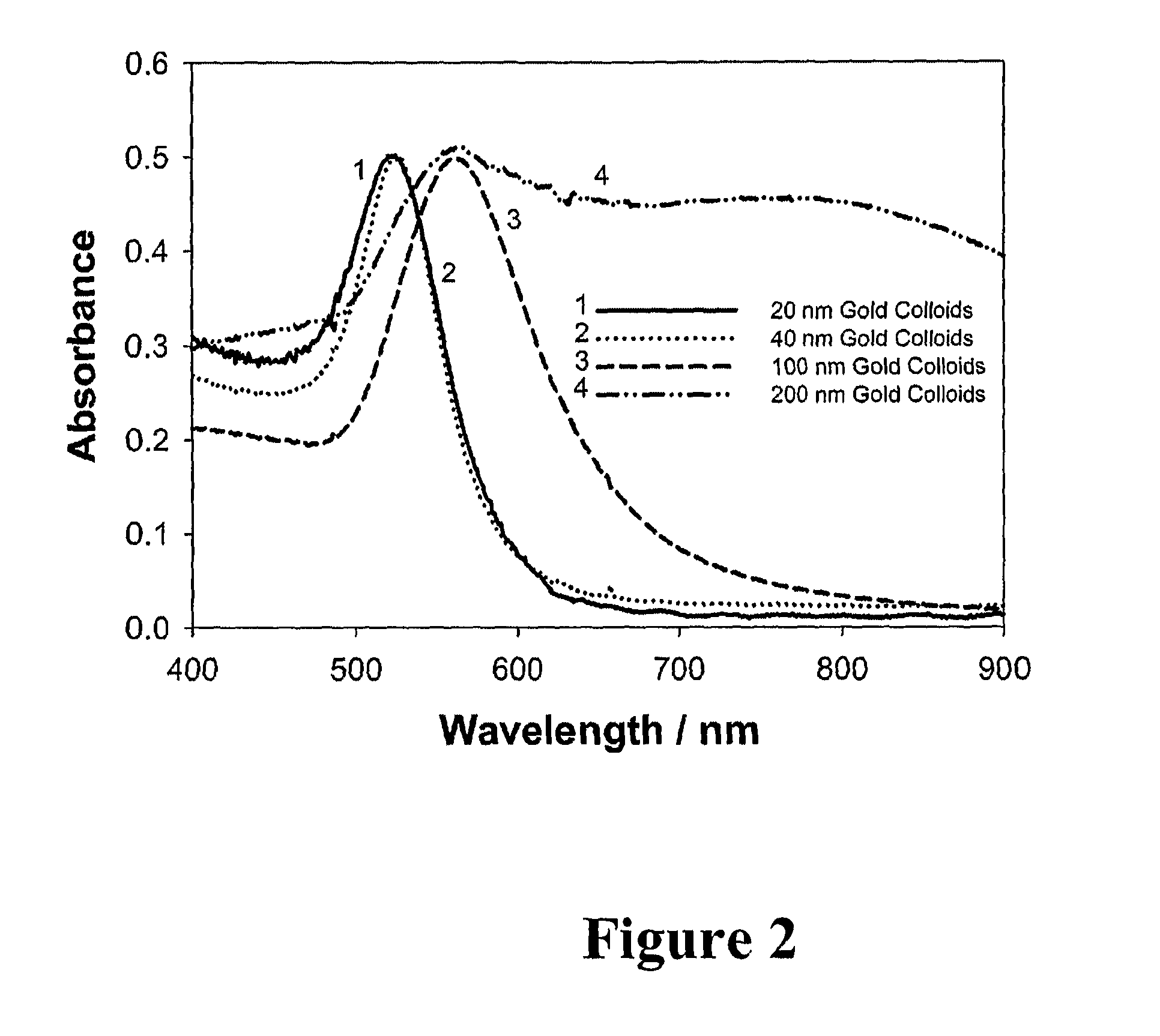
Bioassays using plasmonic scattering from noble metal nanostructures
ActiveUS20100062545A1Reduce couplingExcellent fluorophoresPreparing sample for investigationVacuum evaporation coatingScattering effectLength wave
The present invention relates to detecting and / or measuring scattering effects due to the aggregating metallic nanostructures or the interaction of plasmonic emissions from approaching metallic nanoparticles. The scattering effects may be measured at different angles, different wavelengths, changes in absorption and / or changes in polarization relative to changes in the distances between nanoparticles.
Owner:UNIV OF MARYLAND BALTIMORE COUNTY
Laser scanning method for laser melting in selected area
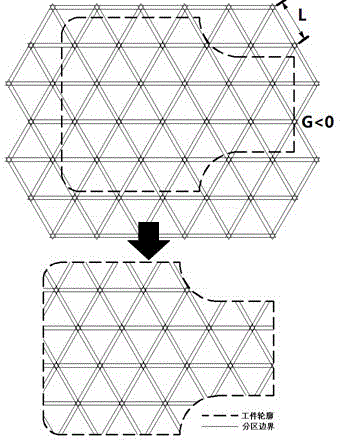
ActiveCN104550950AGuaranteed compactnessGuaranteed accuracyIncreasing energy efficiencyGraphicsLaser scanning
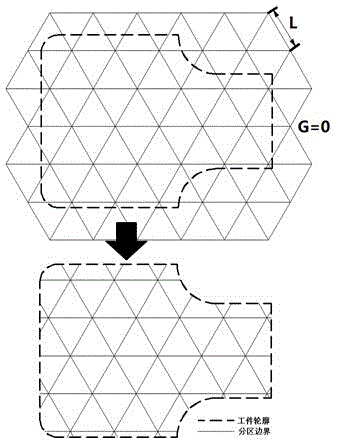
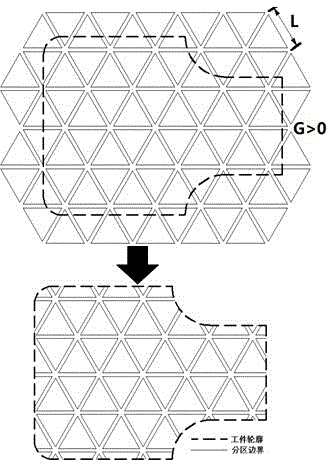
The invention discloses a laser scanning method for laser melting in a selected area. The laser scanning method comprises the following steps: dividing a workpiece area into a plurality of latticed regular triangles with side length being 1mm-10mm and a plurality of irregular figures at borders according to the cross section information of a workpiece, taking a gap G between the adjacent figures from -1mm to 1mm; scanning the irregular figures at the borders as the zoning regular triangles and adopting an equidistant scanning line for successively finishing the zoning figure scanning; according to the zoning direction, adopting the equidistant scanning line for successively finishing the gap scanning; scanning along a practical outline of the workpiece or the outline deviating within 1mm inward or outward to the practical outline of the workpiece according to the requirement, or repeatedly scanning along a plurality of outlines deviating from the practical outline of the workpiece within 1mm, thereby finishing the cross section canning for the workpiece. According to the scanning method provided by the invention, the scattering effect of residual stress in the workpiece during a laser scanning process is improved, the laser scanning direction during the scanning process does not need to be repeatedly changed, the scanning efficiency is high, the technique control is simple, and the compactness and the precision of the workpiece are ensured.
Owner:HUNAN FARSOON HIGH TECH CO LTD
Single-fiber bidirectional transmission system based on mode division multiplexing
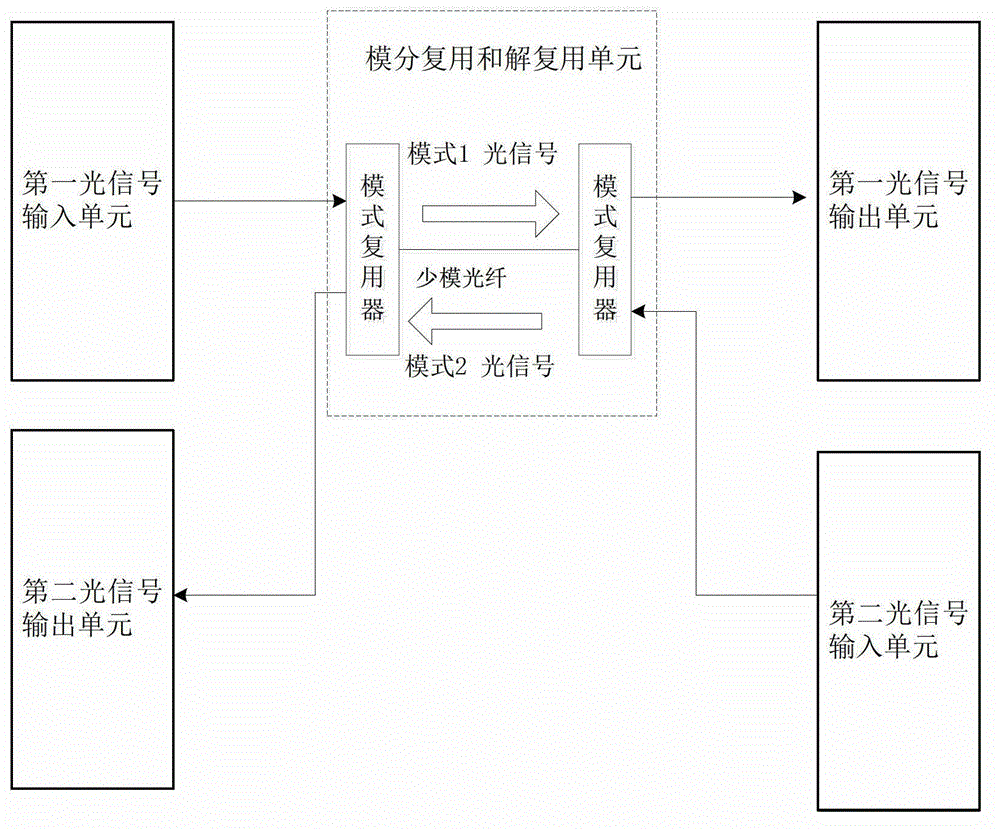
ActiveCN103152099AOvercome backscatterImprove spectrum utilizationDistortion/dispersion eliminationPolarization diversityPolarization multiplexed
The invention discloses a single-fiber bidirectional transmission system based on mode division multiplexing. The single-fiber bidirectional transmission system based on the division multiplexing mainly comprises two optical signal input units, two optical signal output units and a mode division multiplexing and demultiplexing unit, wherein the mode division multiplexing and demultiplexing unit comprises two mode-type multiplexers which are connected through few-mode fiber. Polarization multiplexing optical signals are generated by the signal input units, the polarization multiplexing optical signals are enabled to be coupled into a mode field of the few-mode fiber by the mode-type multiplexer to finish the mode division multiplexing, the polarization multiplexing optical signals carried by the mode field are sent to the other mode-type multiplexer through the few-mode fiber, the received polarization multiplexing optical signals are enabled to be coupled into single-mode fiber by the other mode-type multiplexer and sent to the optical signal output units through the single-mode fiber, polarization diversity, mixing and balance detection are carried out on the received optical signals by the signal output units, then the received optical signals are changed into electric signals and then changed into digital signals. According to the single-fiber bidirectional transmission system based on the mode division multiplexing, the few-mode fiber is used for overcoming Rayleigh backward scattering effect, single-fiber bidirectional transmission is achieved, and use efficiency of optical fiber and wavelength resources is improved.
Owner:HUAZHONG UNIV OF SCI & TECH
Optical recording medium using scattering bodies to enhance modulation
InactiveUS6848115B2Convenient ArrangementLight generatedLayered productsNanoinformaticsScattering effectOptical recording
Owner:PIONEER CORP
Method and apparatus for monitoring biological substance
InactiveUS20050219526A1Scattering properties measurementsColor/spectral properties measurementsTurbidityEngineering
A disclosed apparatus and method provide a wide range, real-time and on-line continuous detection for a biological substance concentration by monitoring the turbidity of the biological fluid medium in a transparent container with techniques that suppressing ambient light, non-uniform concentration distribution, bubble and interface scattering effects in a dynamic environment.
Owner:PENG HONG
Electron beam proximity correction method for hierarchical design data
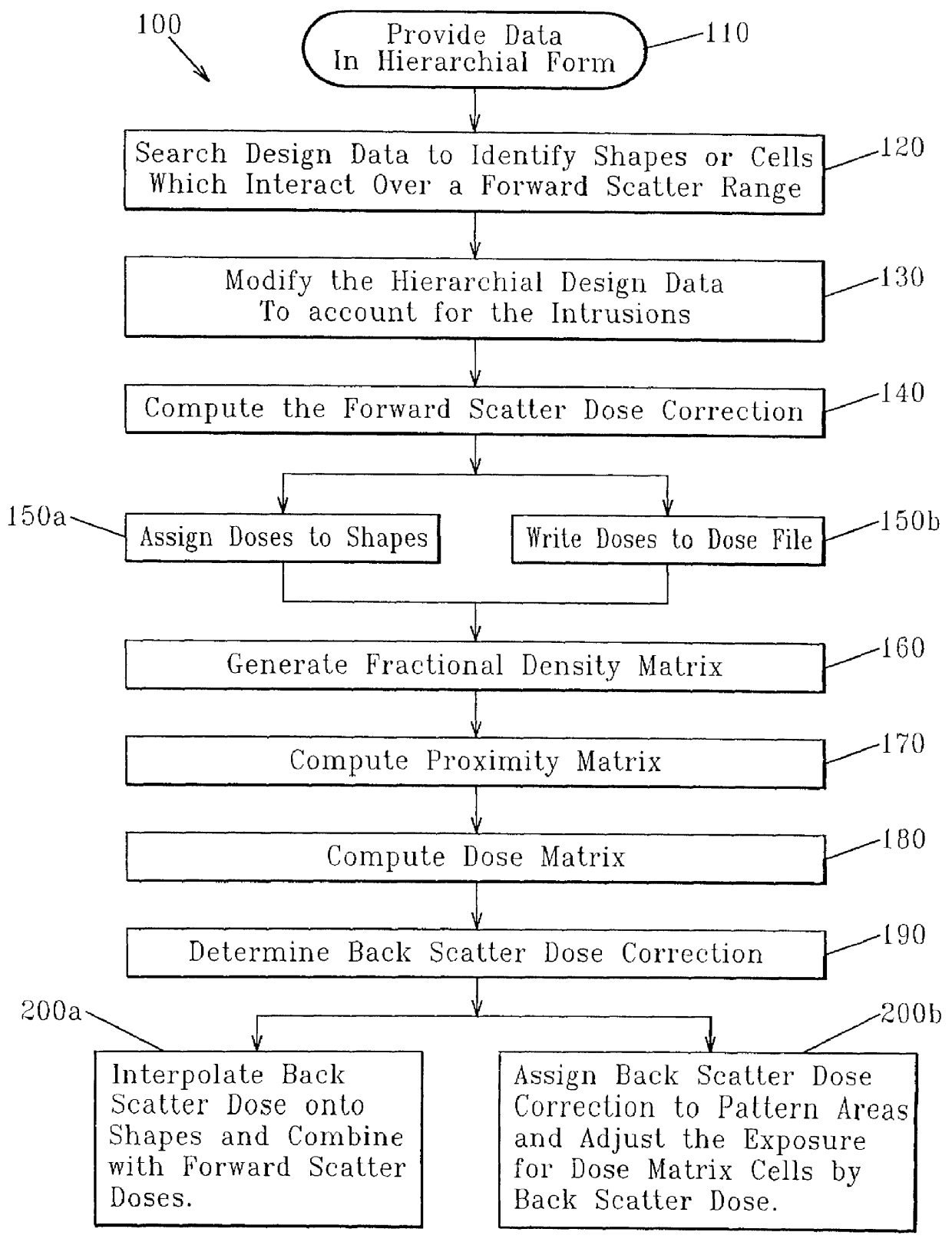
InactiveUS6035113AReduce proximity effectImprove computing efficiencyElectric discharge tubesSpecial data processing applicationsForward scatterResist
A method for formulating an exposure dose for an electron beam on a resist film for a pattern of geometric shapes which compensates for electron scattering effects utilizing hierarchial design data which is preserved to as great as an extent as possible in the computation of the exposure dose. The exposure dose is corrected for both the forward scatter and backscatter effects of the electron beam in which the design data is modified for interactions of shapes which are affected only over the forward scatter range. In another version of the method, a multiple Gaussian approximation is used where the short term Gaussian terms are treated as the forward scatter terms and the long term Gaussian terms are treated as the back scatter terms.
Owner:GLOBALFOUNDRIES INC
High-fog-degree and high-transparency LED lamp tube material and preparation method thereof
The invention discloses a high-fog-degree and high-transparency LED lamp tube material and a preparation method thereof. The LED lamp tube material comprises the following components by weight ratio (%): 97-99% of engineering plastic, 0.3-1% of light-scattering agent; 0.3-1% of dispersant; 0.2-0.6% of color protection agent and 0.1-3% of other additives. The invention uses the engineering plastic PC as a main body, and adds the organic bead resin light-scattering agent, the color protection agent and other additives to carry out extrusion granulation by melt blending. The polycarbonate engineering plastic prepared by the invention can be used for extrusion molding of the LED lamp tube material, not only has good scattering effect but also has high luminousness, and has excellent physical and mechanical performances and simple process. The preparation method of the LED lamp tube material comprises the following process steps: firstly, mixing raw materials in proportion; then sending into a plastic extrusion machine, and controlling the temperature between 250 DEG C and 300 DEG C; and finally, carrying out granulation.
Owner:SHENZHEN KEJU NEW MATERIAL
Modified Powder and Cosmetic Composition Using the Same
ActiveUS20070253989A1Water resistance and cleansabilityUltraviolet protection effect of cosmetic compositions could also be improvedCosmetic preparationsPowder deliveryMass ratioUltraviolet
The present invention provides a modified powder that is obtainable by coating the surface of a base powder with a hydrophobizing agent and a cationic surfactant. In the modified powder described above, it is preferable that the amount of coated hydrophobizing agent and the amount of coated cationic surfactant are 3 to 90% by mass and 0.5 to 10% by mass, respectively, relative to the self weight of the base powder. In the modified powder described above, it is preferable that the mass ratio of the coated hydrophobizing agent and the coated cationic surfactant is from 1:1 to 9:1. In addition, the present invention provides a cosmetic composition comprising the above modified powder wherein the modified powder and the base powder have an ultraviolet scattering effect. In the cosmetic composition described above, it is preferable that the blended amount of the modified powder is from 0.5 to 100% by mass. Furthermore, the present invention provides a sunscreen cosmetic composition comprising the above modified powder with an ultraviolet scattering effect. In the sunscreen cosmetic composition described above, it is preferable that the base powder is one or more selected from the group consisting of titanium oxide, zinc oxide, iron oxide, cerium oxide, bismuth oxide, zirconium oxide, chromium oxide, and tungstic acid. In the sunscreen cosmetic composition described above, it is preferable that the blended amount of the modified powder is from 1 to 40% by mass.
Owner:SHISEIDO CO LTD
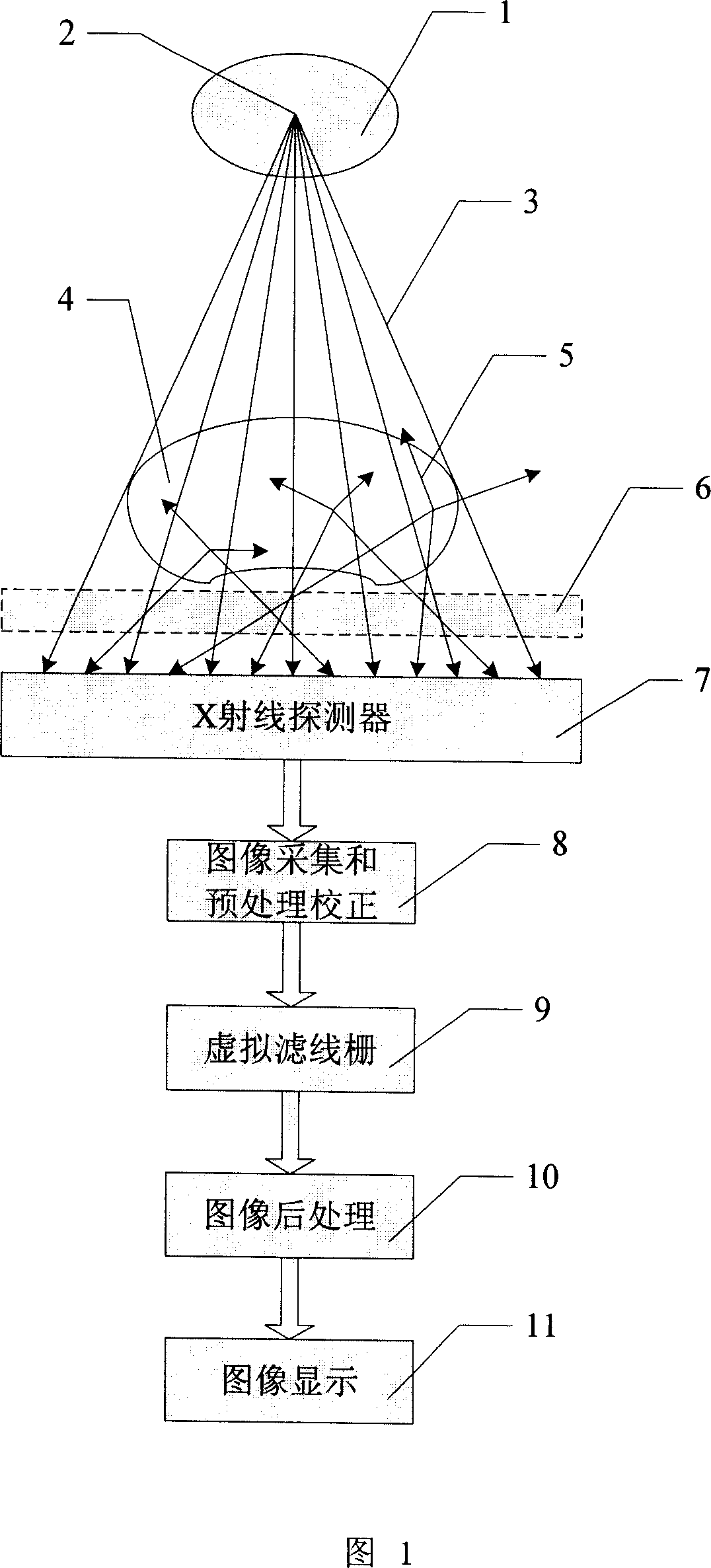
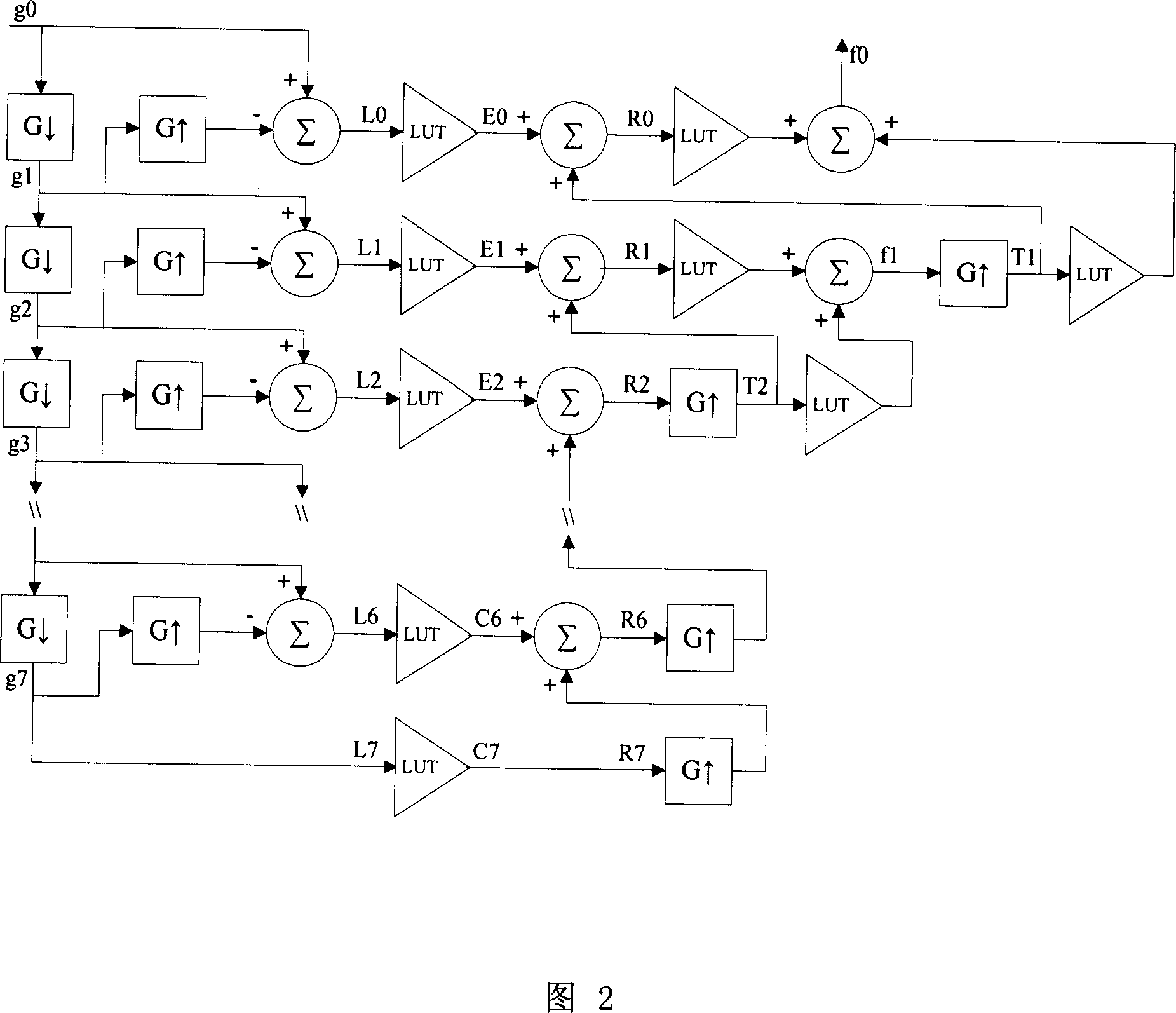
Virtual grid imaging method and system used for eliminating influence of scattered radiation
ActiveCN101109718AEliminate the effects ofIncrease contrastImage enhancementImage analysisVirtual screenRadiology
The invention discloses an imaging method and system for a virtual screen grid that can remove any radiation and scattering effect. The method is essentially used in a high-energy ray imaging. The scattering rays arriving at the detector surface are not filtered first, all the scattering rays and direct-emitting rays are sampled, then the sampled data go through separation and suppression of the components of scattering rays, so as to remove the components of scattering rays in the images. The procedures are: (1) a digital image is discomposed into a multi-frequency image from high to low frequency; (2) the low-frequency images are de-scattered; (3) the contrast of the hi-frequency images are enhanced; (4) images of different frequencies got by (2) and (3) are combined, and output images are formed. According to experiments, in digital X-ray imaging, the invention can obviously remove the radiation and scattering effect, and can greatly reduce the dosage of rays, which is 1 / 3 of ordinary screen grid with a given image brightness.
Owner:TCL HEALTHCARE EQUIP SHANGHAI CO LTD
Preparation method of anode slurry of lithium ion battery
ActiveCN102683644AImprove electrochemical performanceEasy to operateCell electrodesAdhesiveSodium-ion battery
The invention belongs to the technical field of manufacturing of lithium ion batteries and especially relates to a preparation method of anode slurry of a lithium ion battery. The preparation method comprises the following steps: 1) respectively weighting anode active materials, adhesives and conductive additive CNT powder in proportion; 2) mixing a part of anode active materials with all the conductive additive CNT powder, thereby obtaining mixed powder; 3) adding the adhesives and a part of solvent into the mixed powder; 4) kneading and stirring the mixture obtained in the step 3), thereby obtaining primary slurry; and 5) adding the remained solvent, the remained anode active materials and the remained adhesives into the primary slurry, and uniformly stirring, thereby obtaining the anode slurry. Compared with the prior art, the preparation method provided by the invention has the advantages that: the primary slurry is high in solid content in the kneading process, so that a huge mechanical force can be applied to the primary slurry by a stirring paddle; and meanwhile, the added anode active materials have a function of an abrasive material; and the force applied by a stirrer is finally applied to CNT aggregates, so that a better CNT scattering effect is obtained.
Owner:DONGGUAN AMPEREX TECH +1
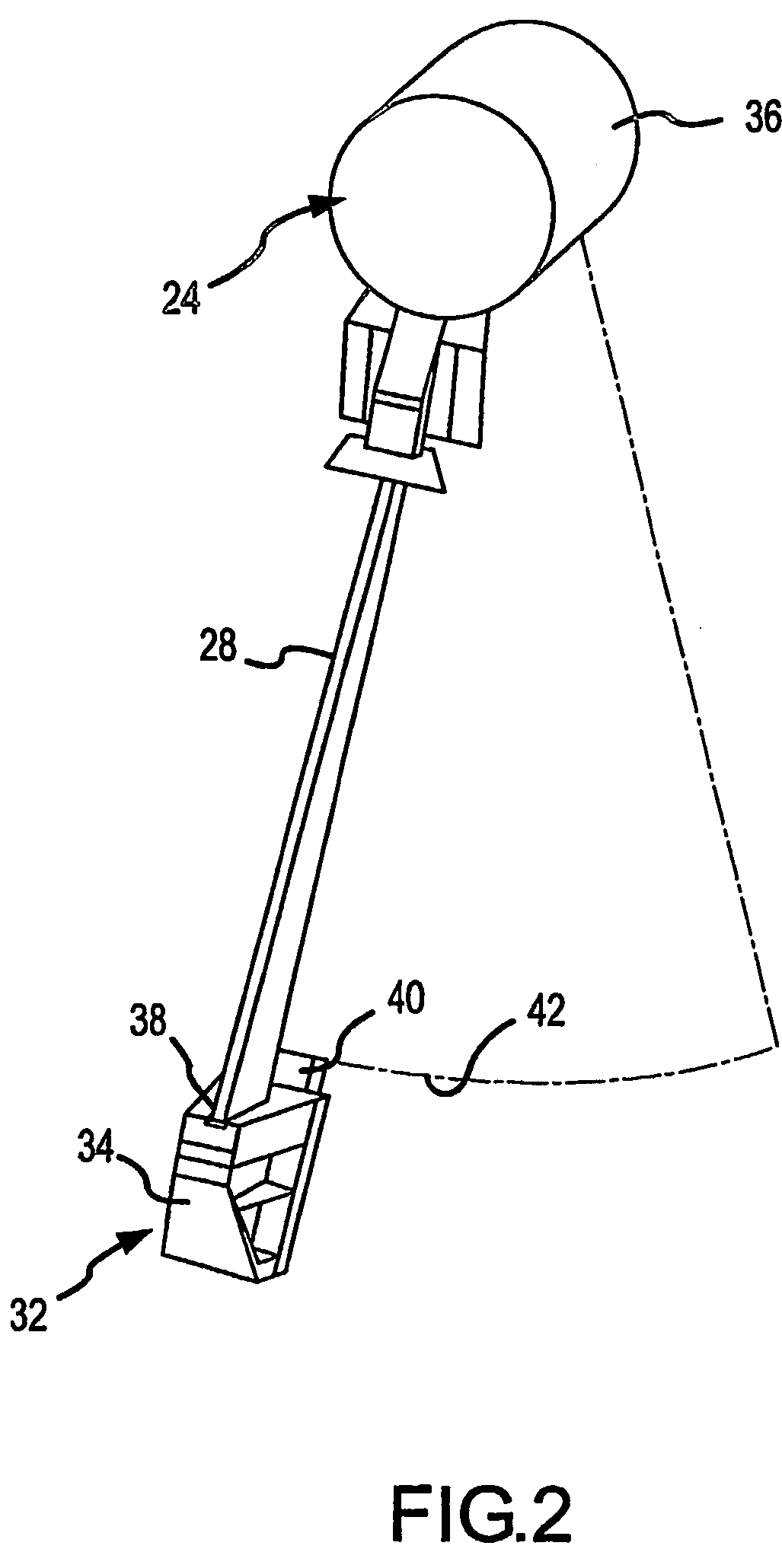
Scatter rejection for composite medical imaging systems
ActiveUS20070104313A1Improved scatter compensationReduced scatter composite imaging informationImage enhancementMaterial analysis using wave/particle radiationRayleigh scatteringDetector array
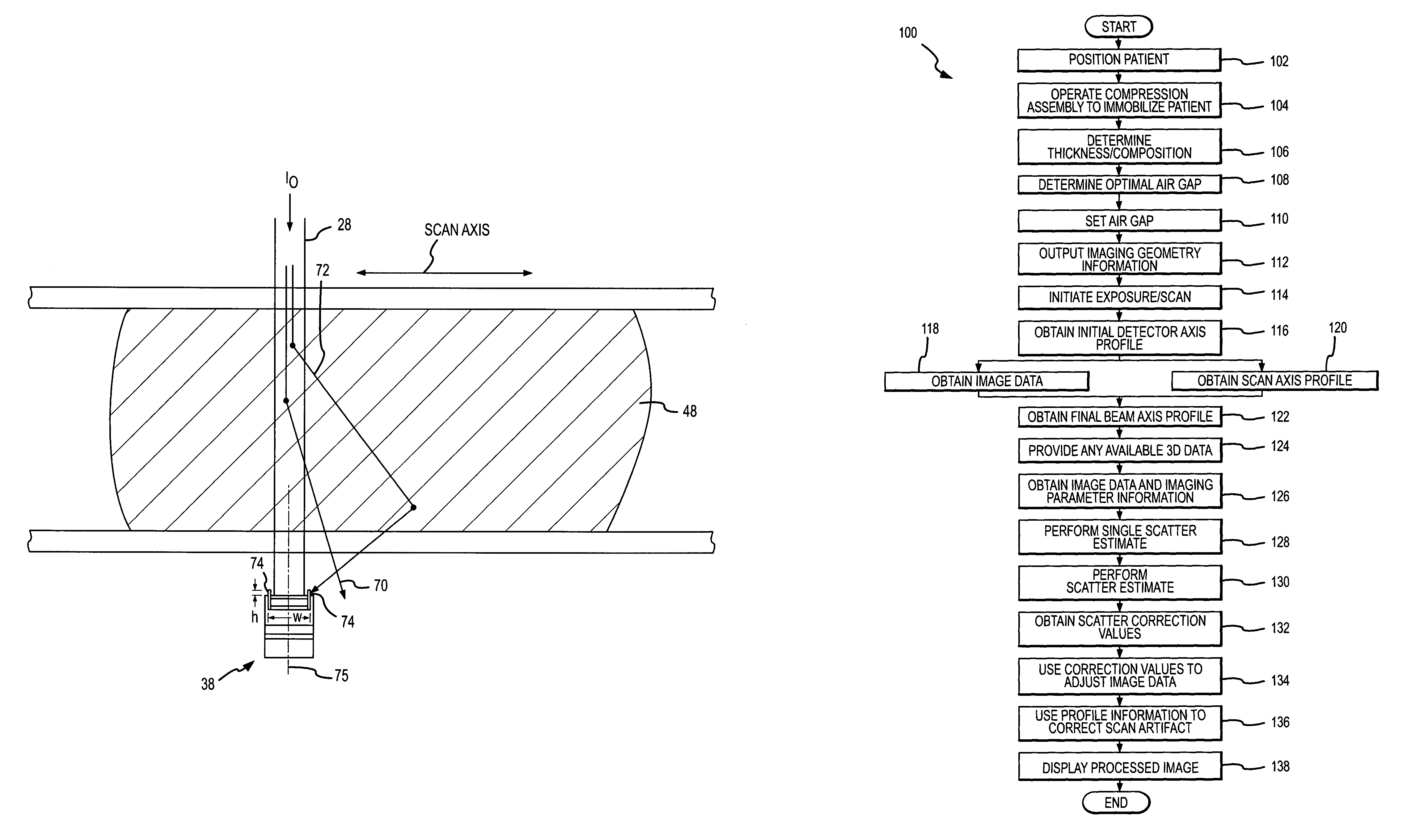
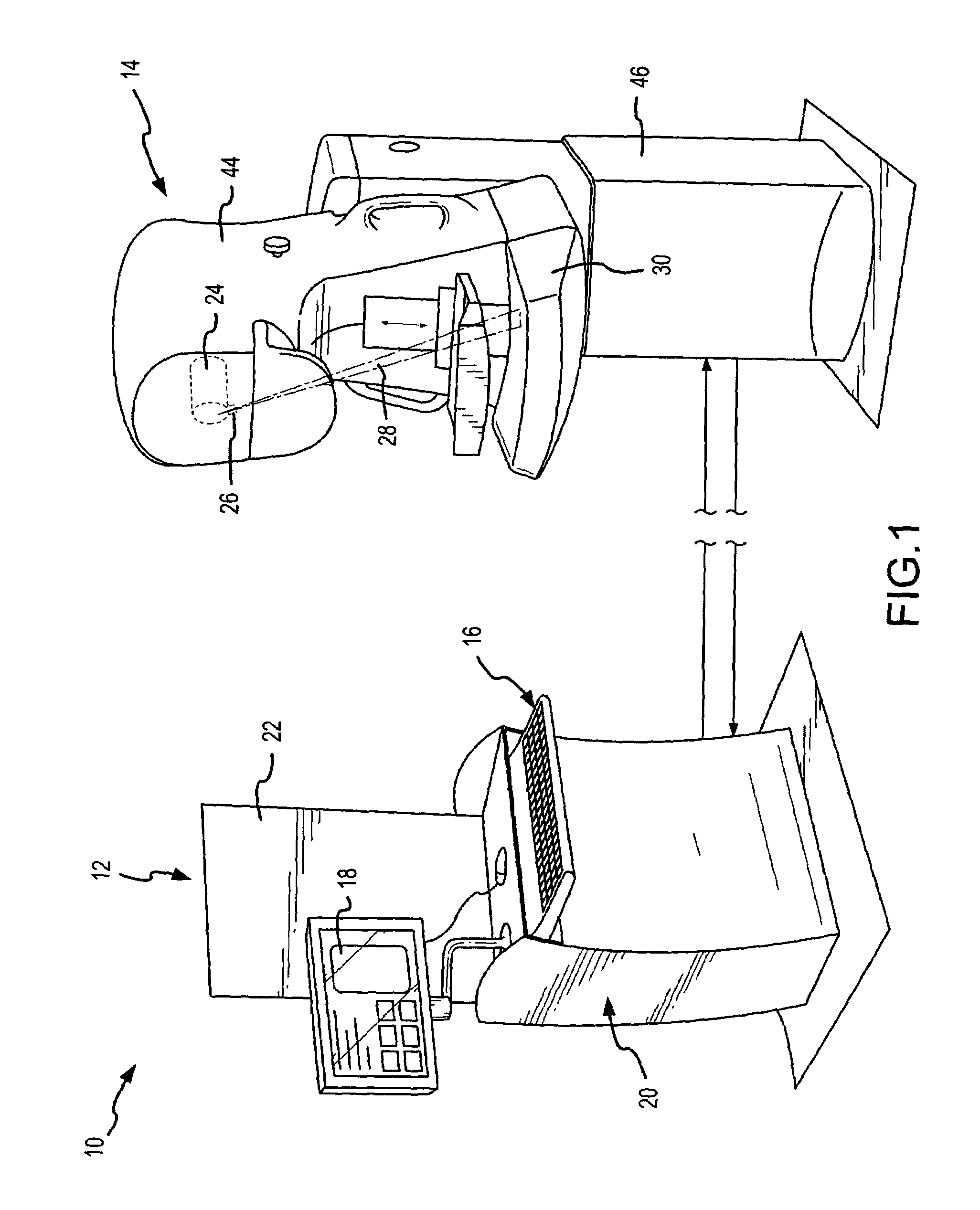
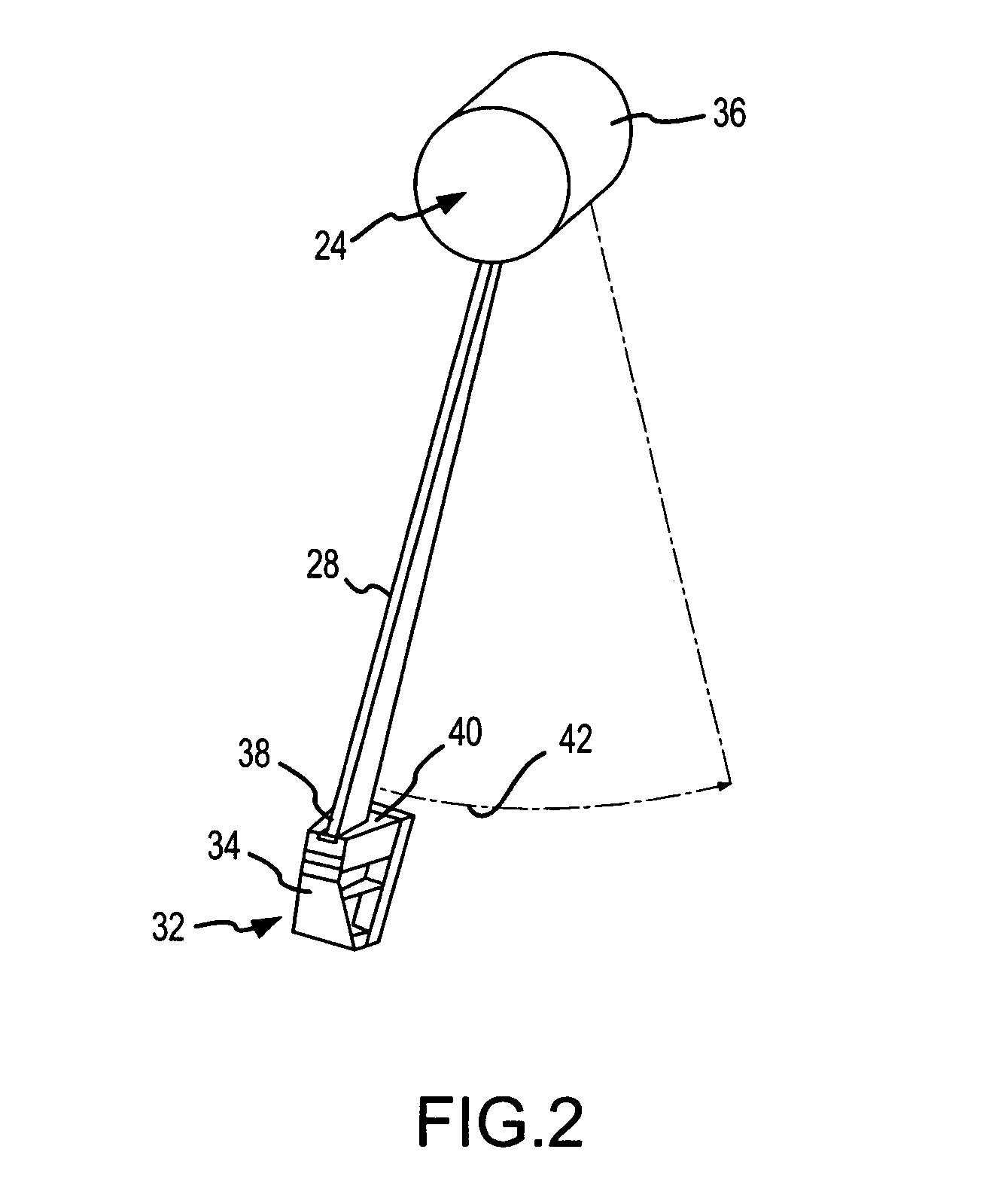
Scatter effects are reduced in a radiographic imaging device, such as a digital slot scan mammographic imaging device, by reducing detected scatter and processing detector information to compensate for scatter effects. In one embodiment, a digital mammographic imaging system (10) includes a source (24) for transmitting a narrow beam (28) and a detector assembly (32) for detecting the beam (28). The beam (28) and the detector assembly (32) are synchronously scanned across the patient's breast (48) to obtain an image. Collimator slats (74) are provided at the leading and trailing edges of the detector to reduce detected scatter. Additionally, attenuators (76 and 92) are provided at the ends of the scanned motion and at the anterior edge of the detector array to assist in determining a spatial intensity profile. The spatial intensity profile information together with other imaging signal and patient dependent parameters are used in image processing to estimate and compensate for various scatter effects including single and multiple scatters and Compton and Rayleigh scatter.
Owner:HOLOGIC INC
Bioassays using plasmonic scattering from noble metal nanostructures
ActiveUS8101424B2Excellent fluorophoresEasy dischargePreparing sample for investigationVacuum evaporation coatingScattering effectWavelength
The present invention relates to detecting and / or measuring scattering effects due to the aggregating metallic nanostructures or the interaction of plasmonic emissions from approaching metallic nanoparticles. The scattering effects may be measured at different angles, different wavelengths, changes in absorption and / or changes in polarization relative to changes in the distances between nanoparticles.
Owner:UNIV OF MARYLAND BALTIMORE COUNTY
Random-distribution feedback optical fiber laser
InactiveCN102354900AShorten the lengthIncrease output powerOptical resonator shape and constructionActive medium shape and constructionRayleigh scatteringGrating
The invention relates to a random-distribution feedback optical fiber laser which can realize stable, space-irrelevant and continuous laser output, and belongs to the technical field of the optical fiber laser. The random-distribution feedback optical fiber laser comprises a pump laser, a wavelength division multiplexer, a fiber bragg grating, an Er-doped optical fiber, an optical fiber Raman laser and a long monomode optical fiber. The reflection effect of the fiber bragg grating is combined with the distributed Rayleigh scattering effect of the optical fiber to form a distributed random feedback optical resonant cavity; and the light is subjected to gain amplification by an Er-doped optical fiber and the stimulated Raman scattering effect. Compared with the random-distribution feedback optical fiber laser reported before, the threshold value of the pump laser and the length of the monomode optical fiber can be reduced, and the limitation on stimulated emission wavelength and the wavelength number by a Rayleigh gain peak is broken through, thereby realizing the purpose of tuning the laser wavelength. The random-distribution feedback optical fiber laser is suitable for fields, such as remote optical fiber sensing, remote communication and the like.
Owner:唐山市神州科贸有限公司
High-bandwidth microwave photon filter based on stimulated Brillouin scattering effect and binary system phase shift keying technology
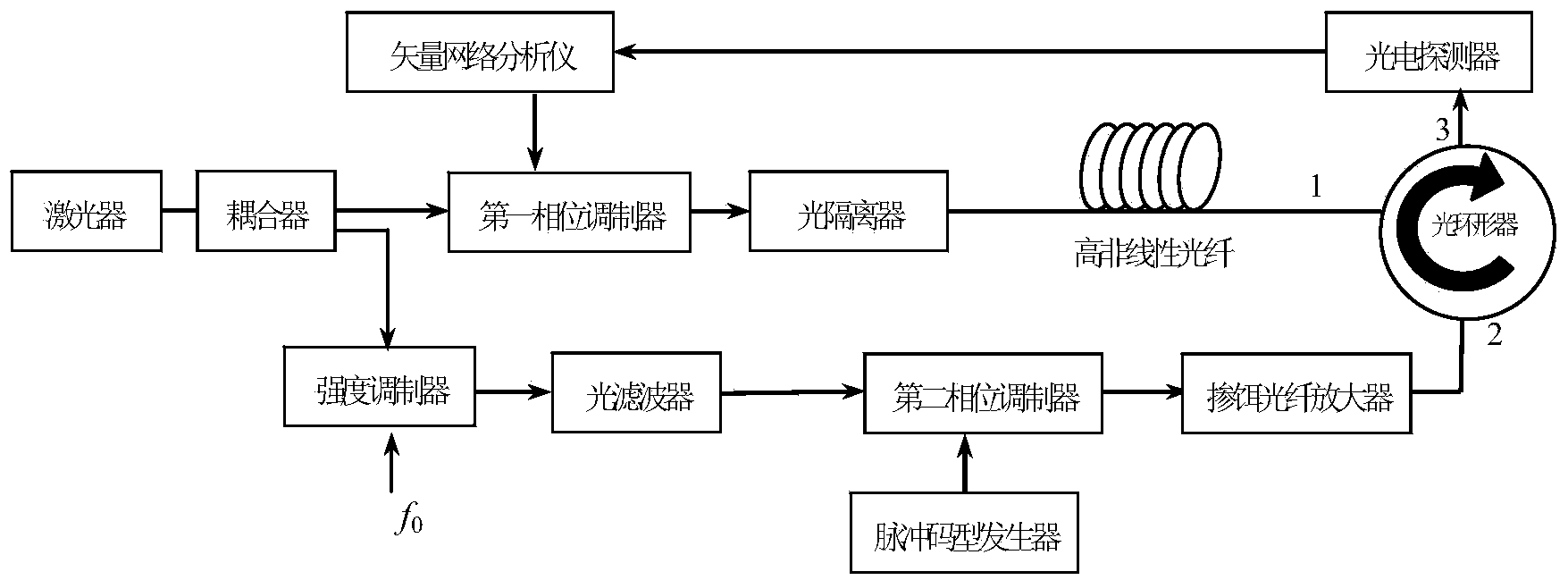
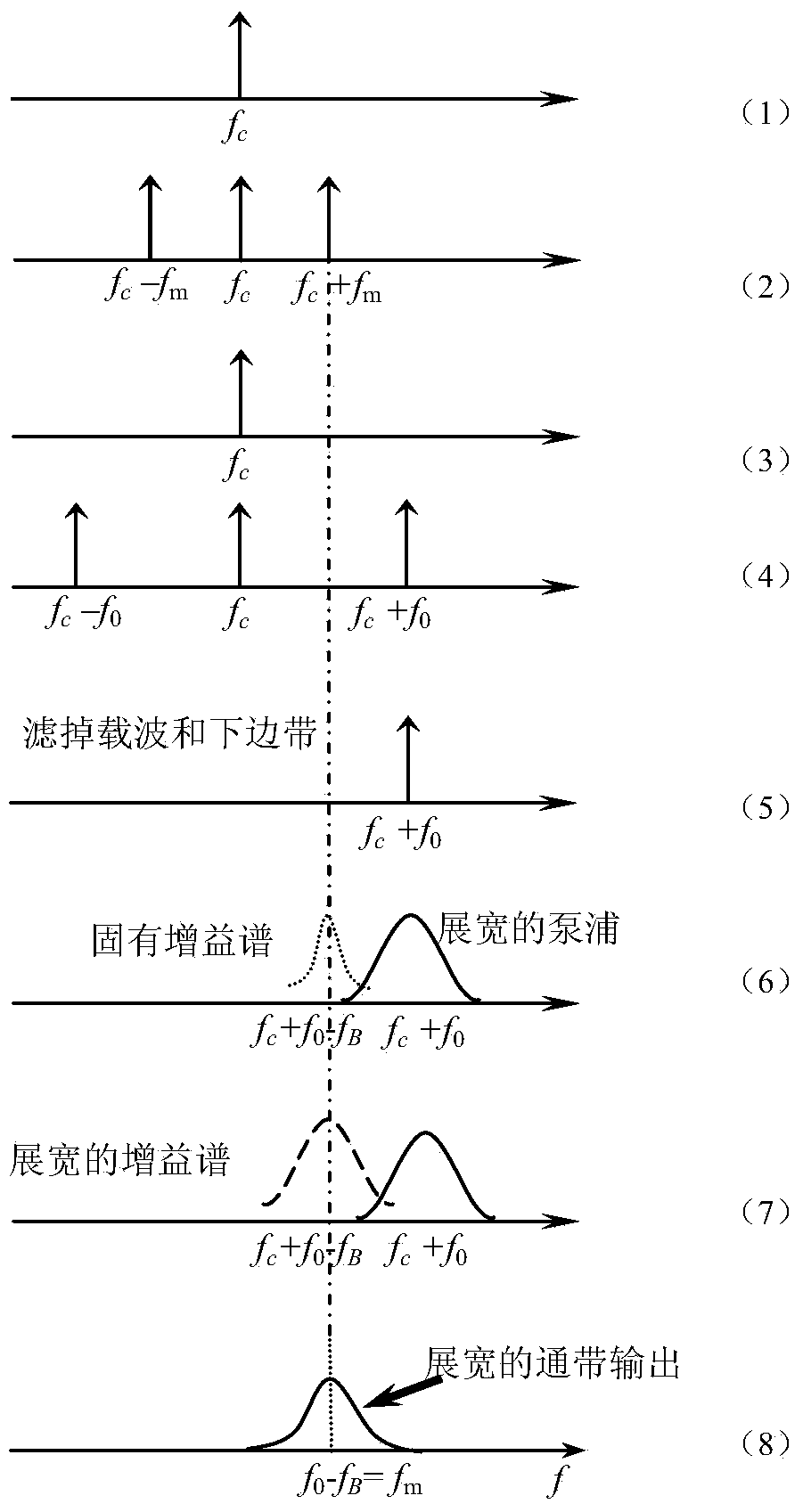
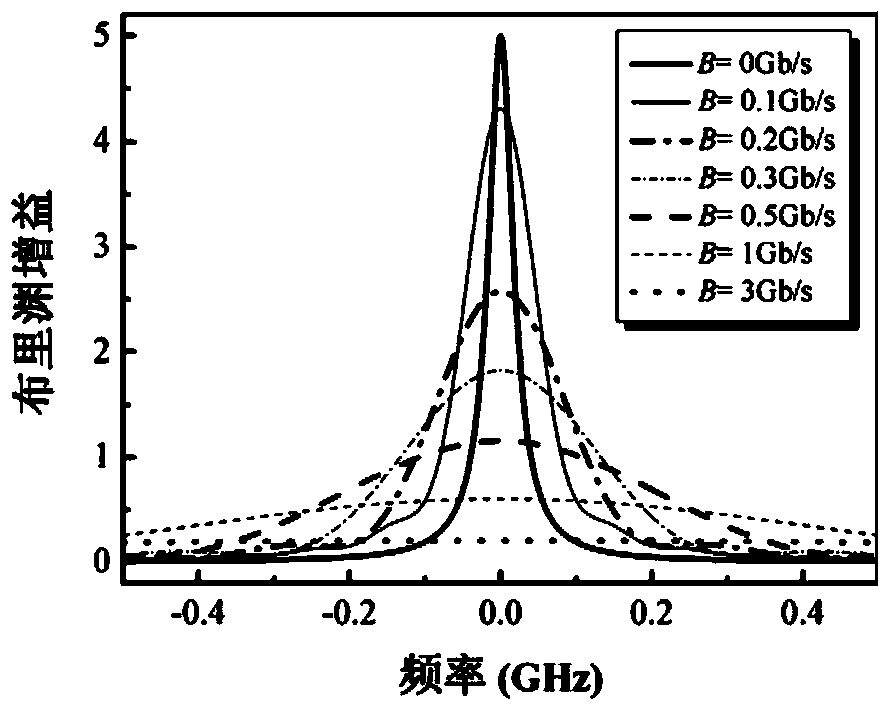
The invention provides a high-bandwidth microwave photon filter based on a stimulated Brillouin scattering effect and a binary system phase shift keying technology, and belongs to the technical field of microwave photonics. The high-bandwidth microwave photon filter is composed of a laser, a coupler, a first phase modulator, an optical isolator, a vector network analysis meter, a high non-linear optical fiber, a strength modulator, an optical filter, a second phase modulator, an impulse code type generator, an Er-doped fiber amplifier, an optimal circulator and a photoelectric detector. The bandwidth of pumping signals is broadened through the binary system phase shift keying technology, the broadened pumping signals will generate a broadened stimulated Brillouin gain spectrum, and therefore the single-passband response microwave photon filter system with the broadened and adjustable bandwidth is obtained.
Owner:JILIN UNIV
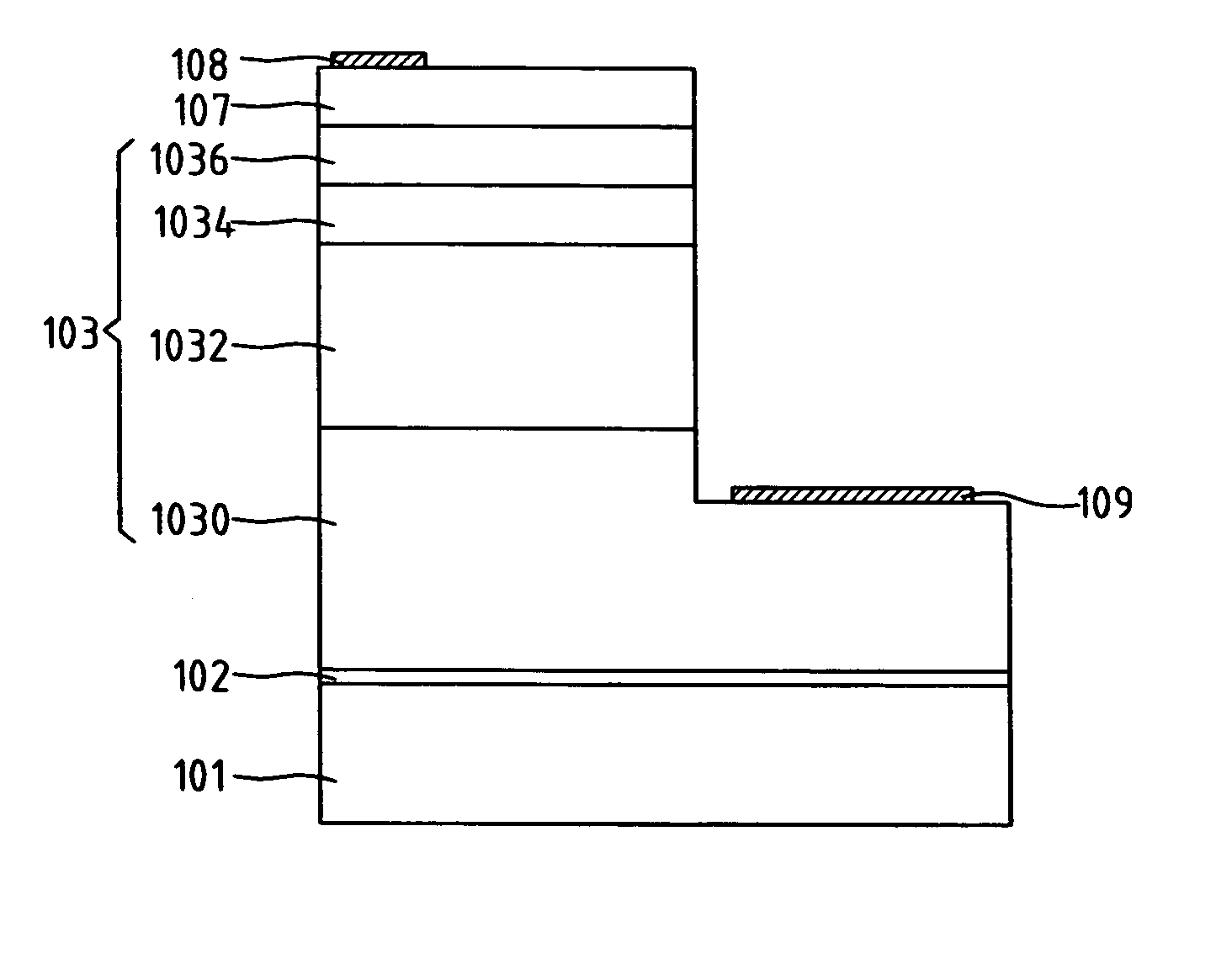
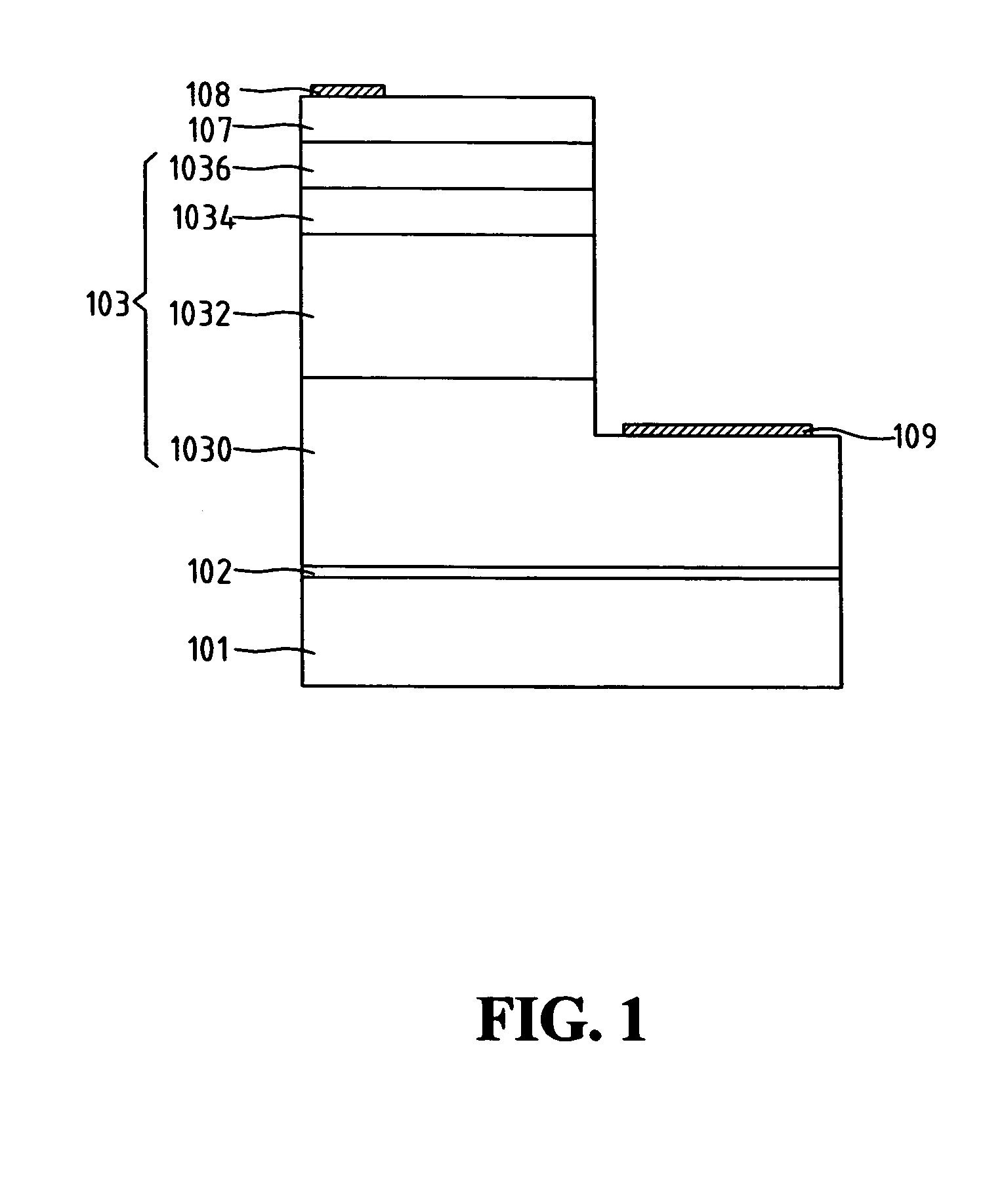
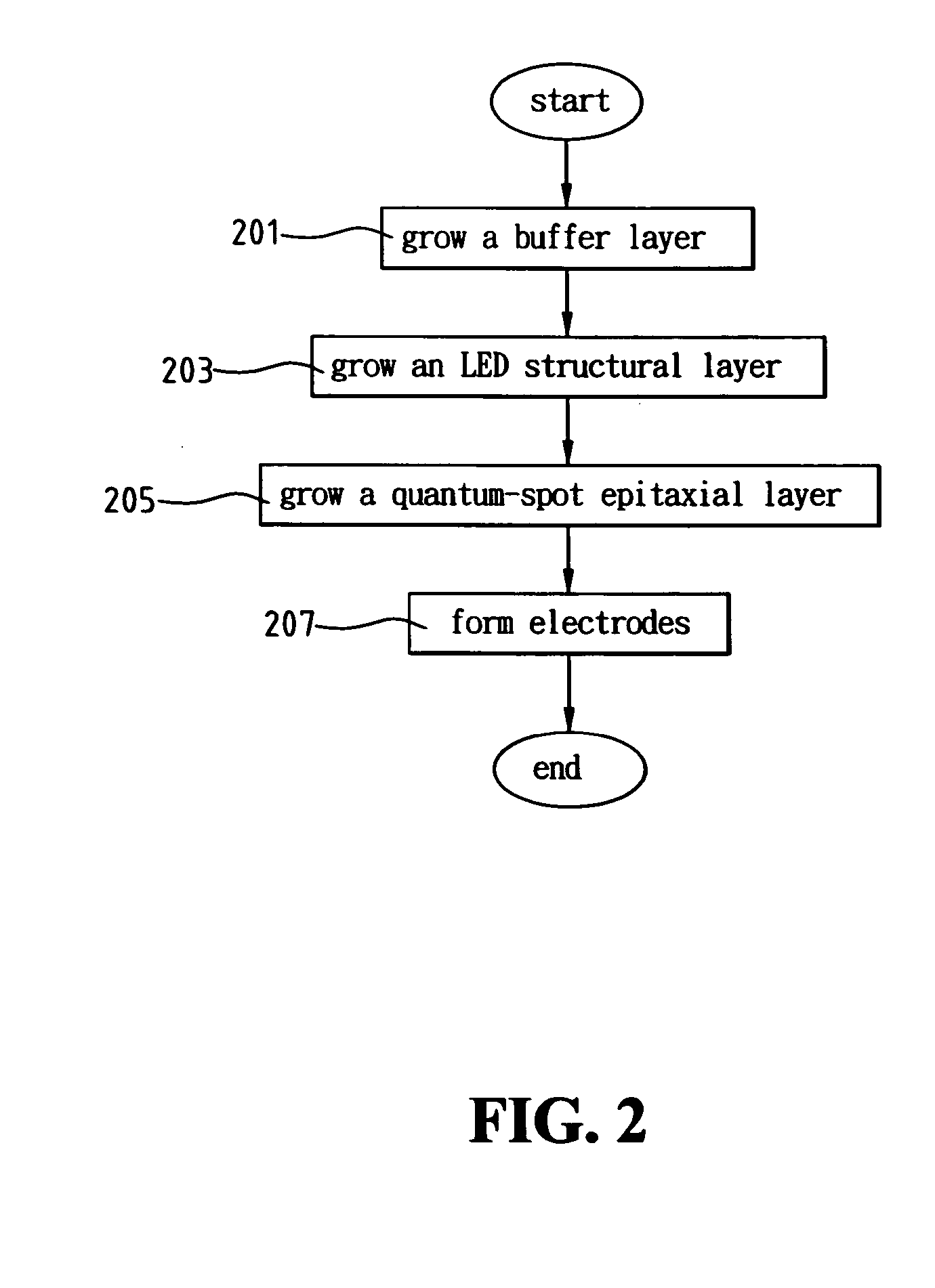
Light emitting diode structure and manufacture method thereof
InactiveUS20050026399A1Improve efficiencyReduce probabilityMaterial nanotechnologyFrom solid stateQuantum dotScattering effect
A light emitting diode (LED) structure and manufacture method thereof are disclosed, wherein a buffer layer is grown on a substrate and then an LED structural layer is grown on the buffer layer. The LED structural layer comprises a p-type quantum-dot epitaxial layer on a p-type GaN layer. As the p-type quantum-dot epitaxial layer has a coarsening and scattering effect, the path of light emitted from an INGaN multiple-quantum-well structural layer is changed. Therefore, it is possible to lessen the probability of total reflection and thereby heighten the light-emitting efficiency of LED.
Owner:FORMOSA EPITAXY INCORPORATION +1
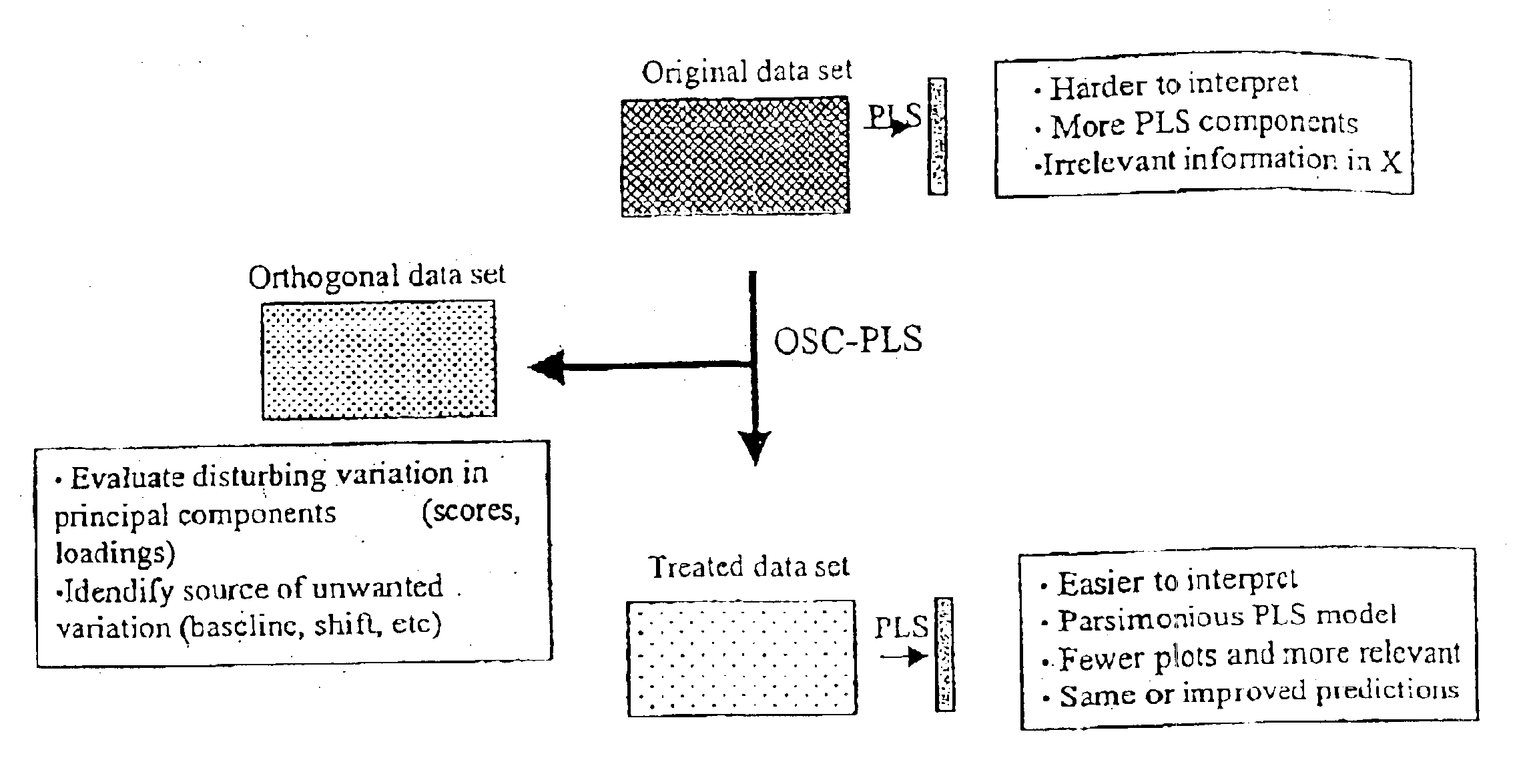
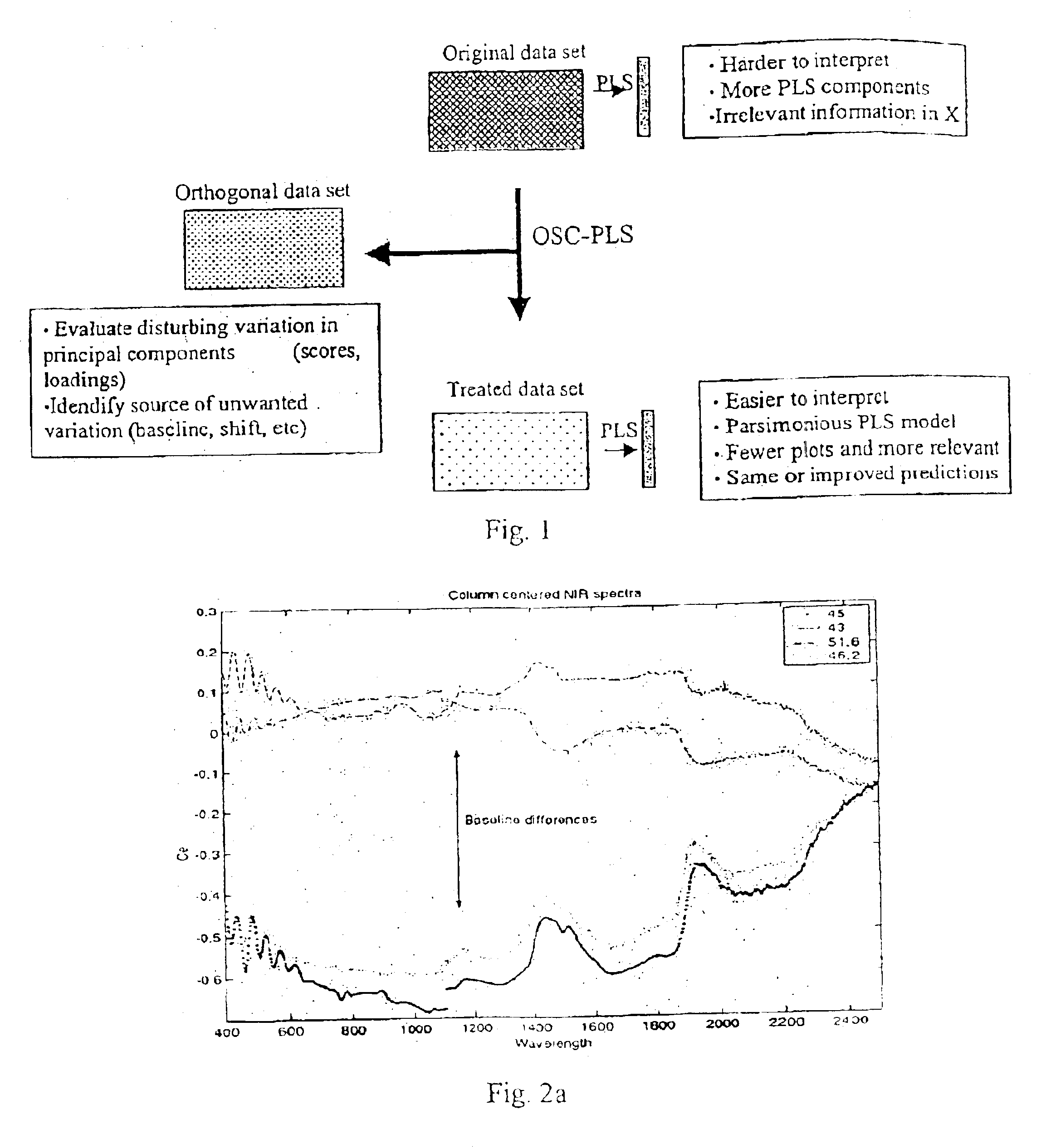
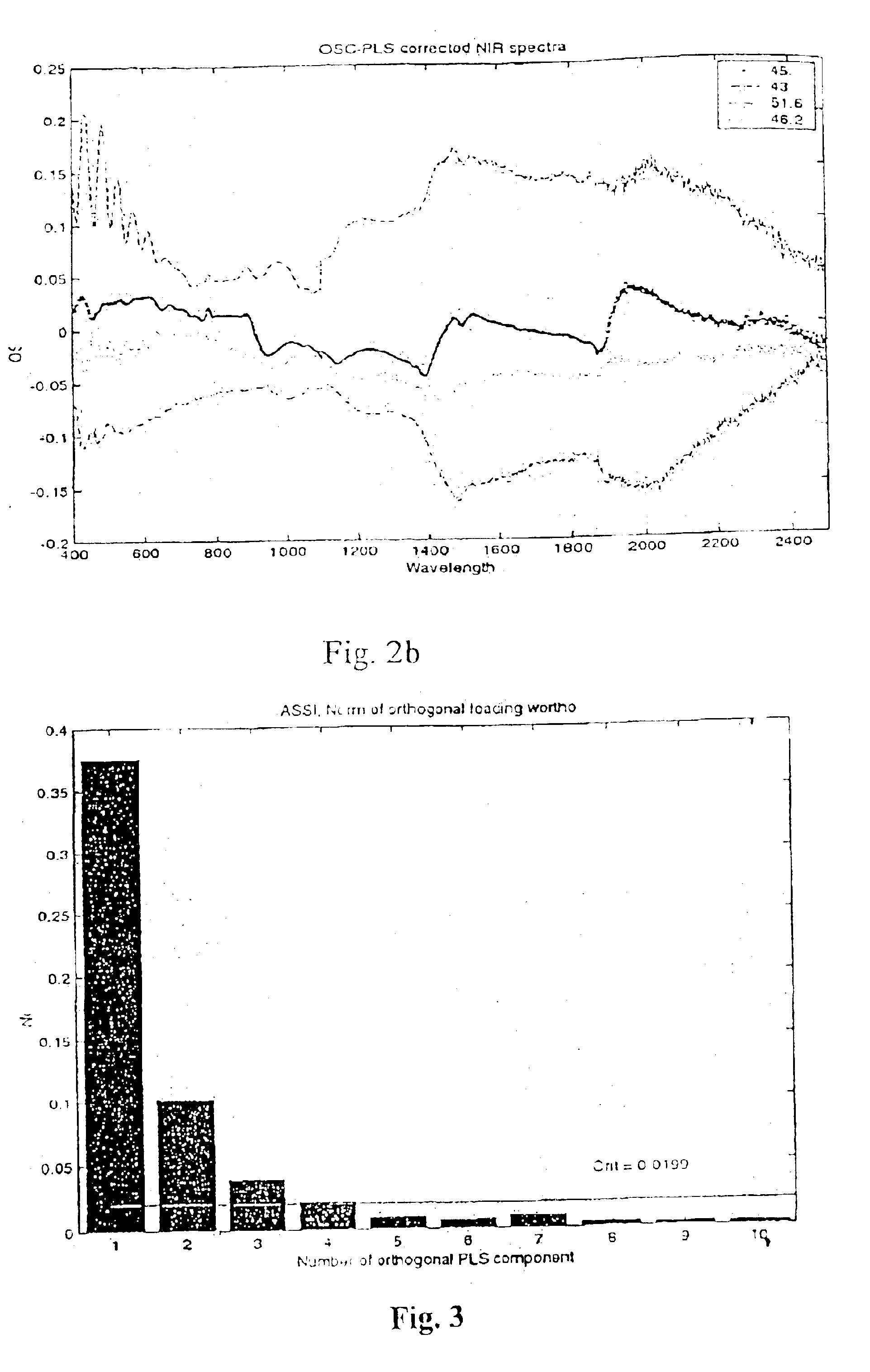
Orthogonal signal projection
InactiveUS6853923B2Overcome problemsImprove interpretationAnalogue computers for chemical processesElectrical measurementsSignal correctionScattering effect
The invention provides a method and an arrangement for filtering or pre-processing most any type of multivariate data exemplified by NIR or NMR spectra measured on samples in order to remove systematic noise such as base-line variation and multiplicative scatter effects. This is accomplished by differentiating the spectra to first or second derivatives, by Multiplicative Signal Correction (MSC), or by similar filtering methods. The pre-processing may, however, also remove information from the spectra, as well as other multiple measurement arrays, regarding (Y) (the response variables). Provided is a variant of PLS that can be used to achieve a signal correction that is as close to orthogonal as possible to a given (y) vector or (Y) matrix. Hence, ensuring that the signal correction removes as little information as possible regarding (Y). A filter according to the present invention is named Orthogonal Partial Least Squares (OPLS).
Owner:UMETRICS
Wrap around antenna
ActiveUS20160365624A1Particular array feeding systemsSimultaneous aerial operationsCommunications systemScattering effect
Aspects of the present disclosure may be directed to a wrap-around antenna capable of being wrapped around a support structure to provide antenna patterns for a communication system. Such an assembly may be aesthetically pleasing and, because the antenna assembly allows for radiation away from the support structure, scattering effects due to interference from the support structure may be eliminated.
Owner:COMMSCOPE TECH LLC
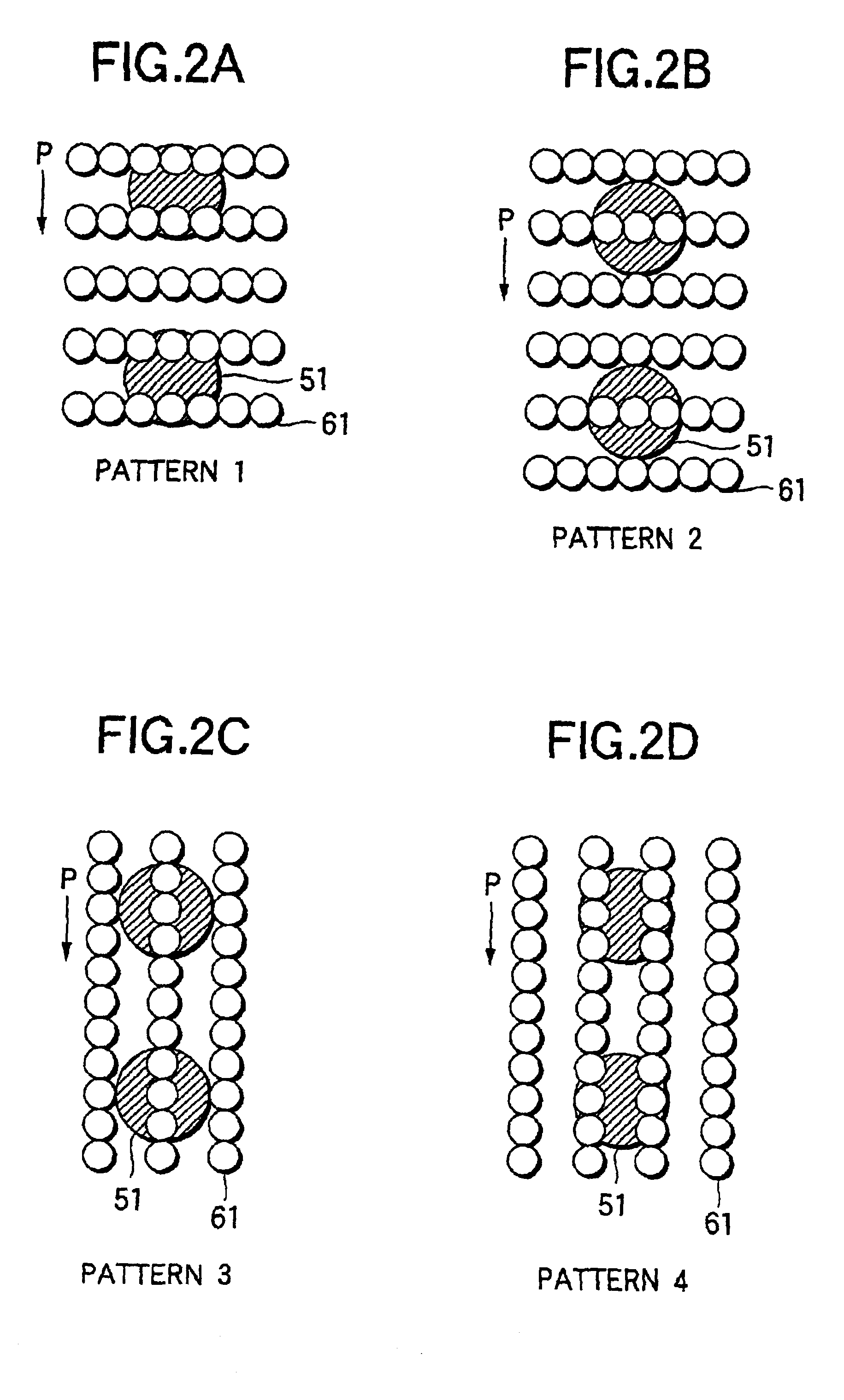
Tracking system with scattering effect utilization, in particular with star effect and/or cross effect utilization
InactiveUS8446473B2High resolutionPointing accuratelyUltrasonic/sonic/infrasonic diagnosticsTelevision system detailsCross effectScattering effect
An image generating device for an optical, in particular medical tracking system, for determining the position of a recorded image point, includes a light scattering effect generating device, in particular a star and / or cross effect generating device. The invention further provides a tracking system including such an image generating device and to a method for determining the position of a recorded image point using an optical, in particular medical tracking system, in which: an image is generated using an image generating device; a light scattering effect, in particular a star and / or cross effect, is generated on the image for predetermined image points; and in which the position of an image point is ascertained on the basis of the light scattering pattern projected on the image, in particular on the basis of the star and / or cross effect lines and / or their intersection points.
Owner:BRAINLAB
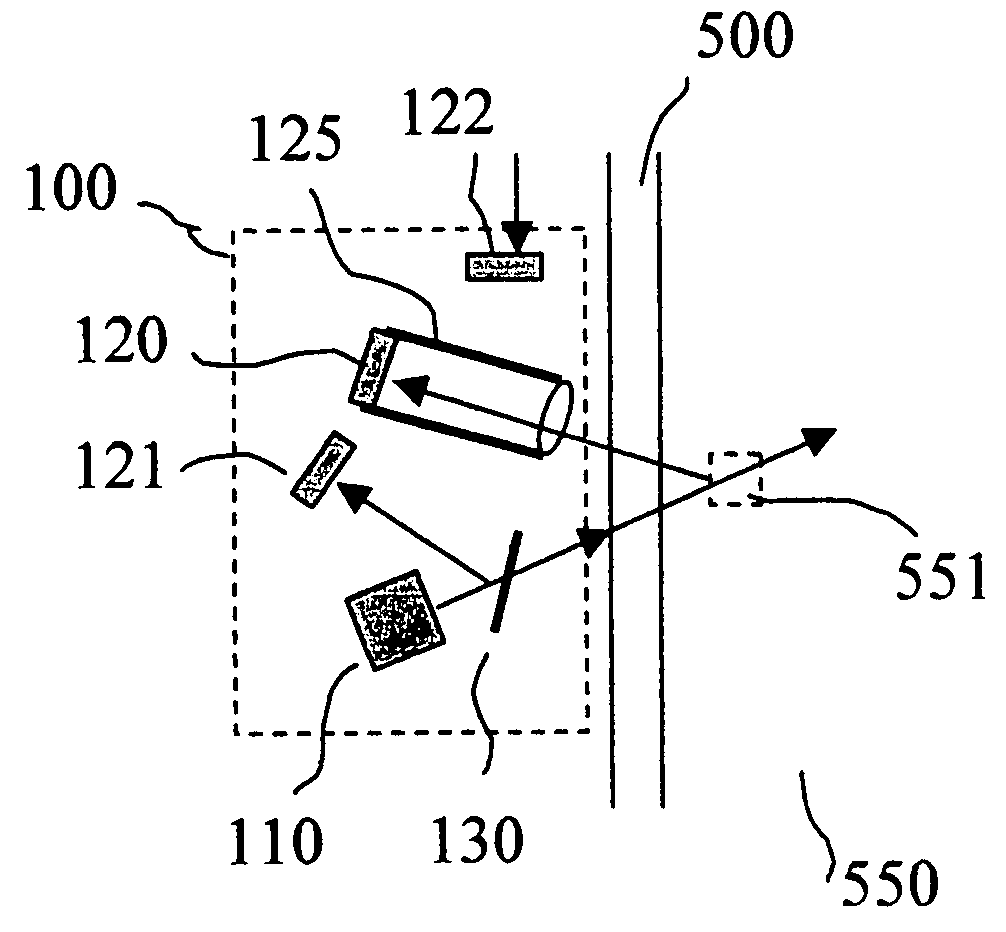
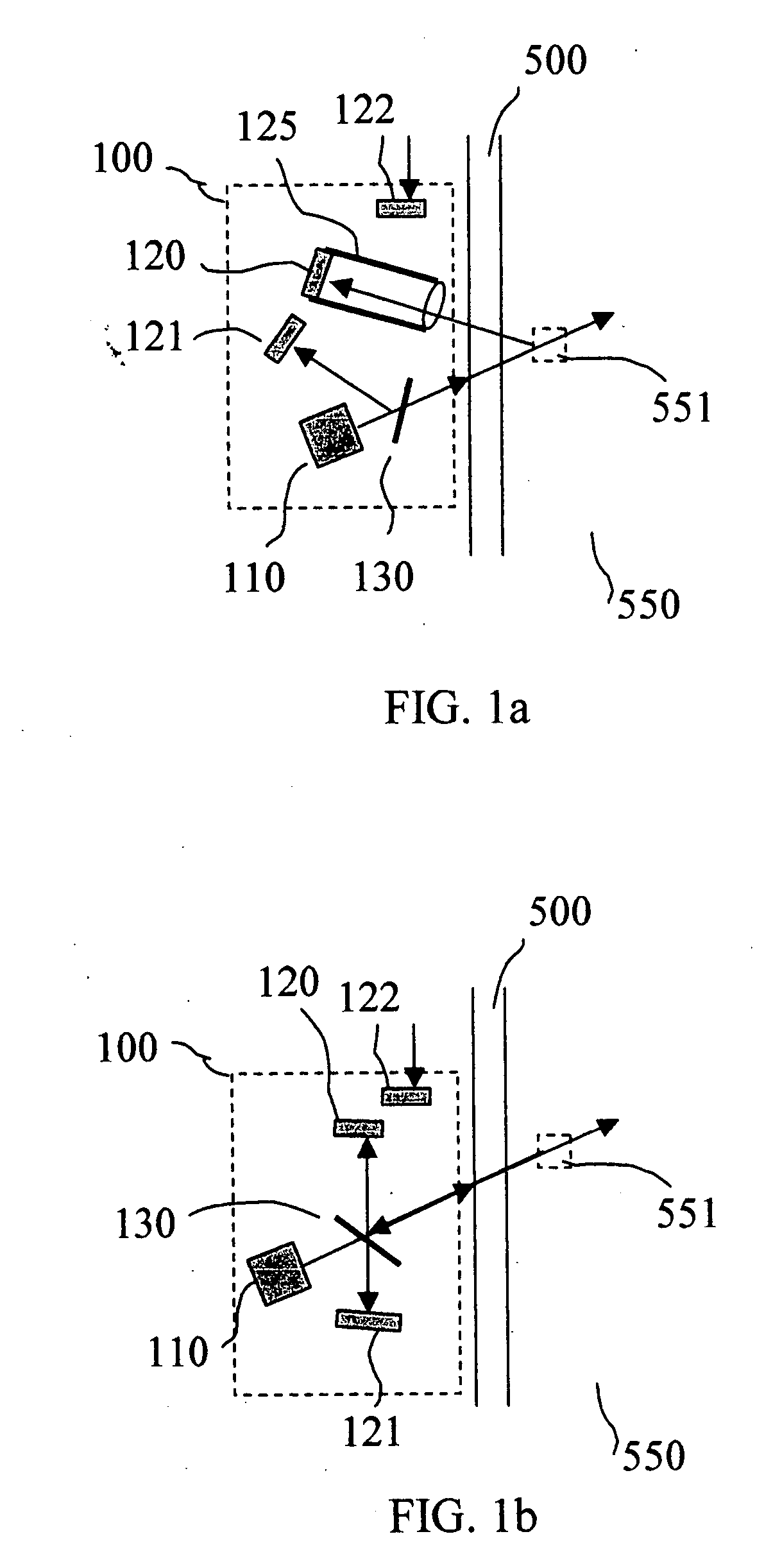
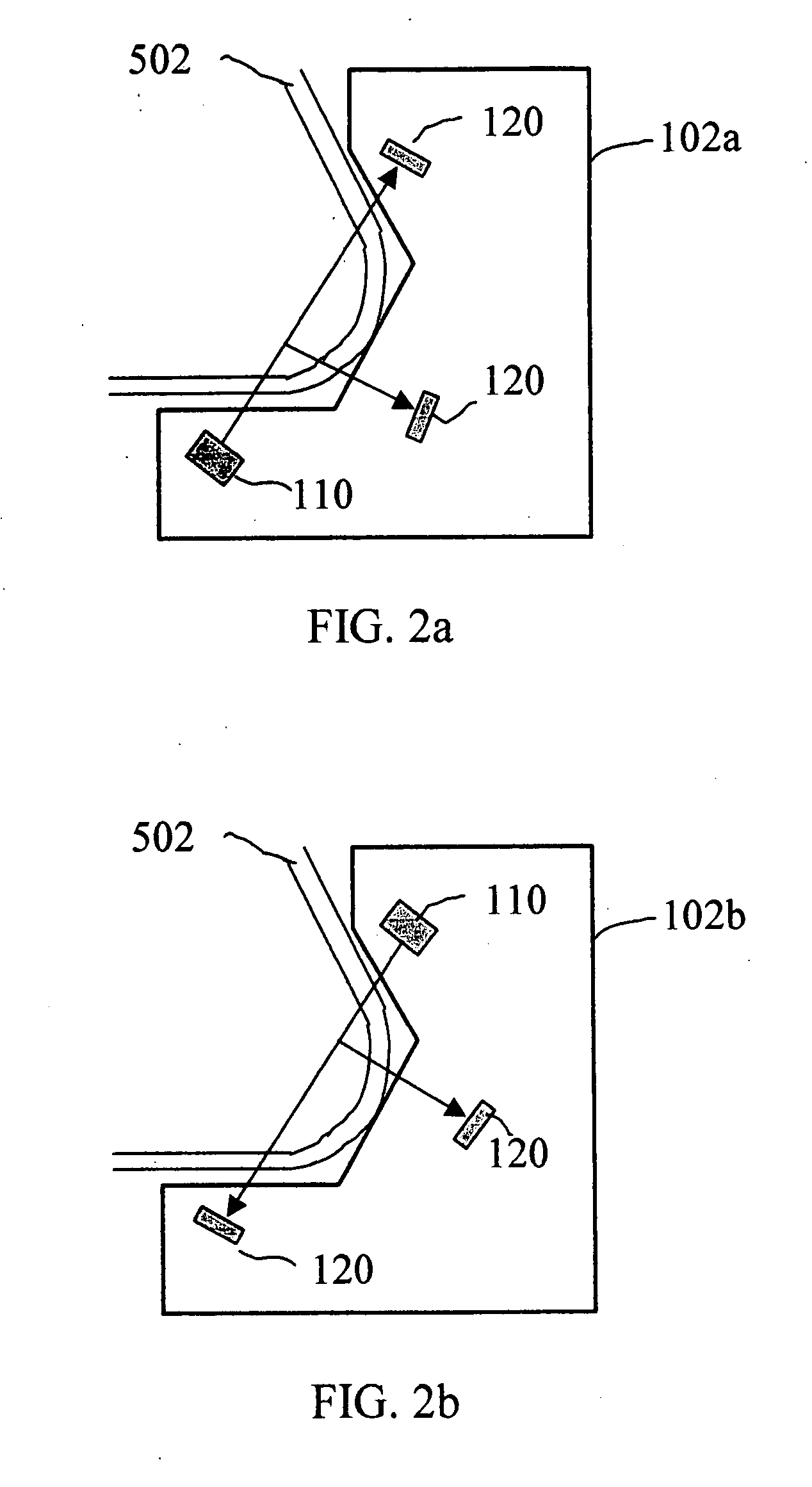
Method and apparatus for blocking radiographic scatter
InactiveUS7319734B2Reduce impactReduce artifactsRadiation/particle handlingPatient positioning for diagnosticsDetector arrayScattering effect
Scatter effects are reduced in a radiographic imaging device, such as a digital slot scan mammographic imaging device, by reducing detected scatter and processing detector information to compensate for scatter effects. A digital mammographic imaging system (10) may include a source (24) for transmitting a narrow beam (28) and a detector assembly (32) for detecting the beam (28). The beam (28) and the detector assembly (32) may synchronously scann across the patient's breast (48) to obtain an image. Collimator slats (74) at the leading and trailing edges of the detector may reduce detected scatter. Attenuators (76 and 92) at the ends of the scanned motion and at the anterior edge of the detector array may assist in determining a spatial intensity profile. The spatial intensity profile information together with other imaging signal and patient dependent parameters may be used to estimate and compensate for various scatter effects.
Owner:HOLOGIC INC
Lighting device with lens, and manufacturing process for making the same
InactiveUS20050254254A1Simple and cost-effective manufactureVehicle headlampsGlass pressing apparatusEffect lightScattering effect
A lens is disclosed for lighting purposes suited in particular as a lens for a poly-ellipsoid reflector headlamp for imaging the light emitted by a light source and reflected by a poly-ellipsoid reflector for the purpose of producing a predetermined lighting pattern. At least one of the two lens surfaces comprises areas having different optical scattering effects which areas are configured as zones that are transferred from a mold to the surface by a hot-pressing process.
Owner:SCHOTT AG
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com