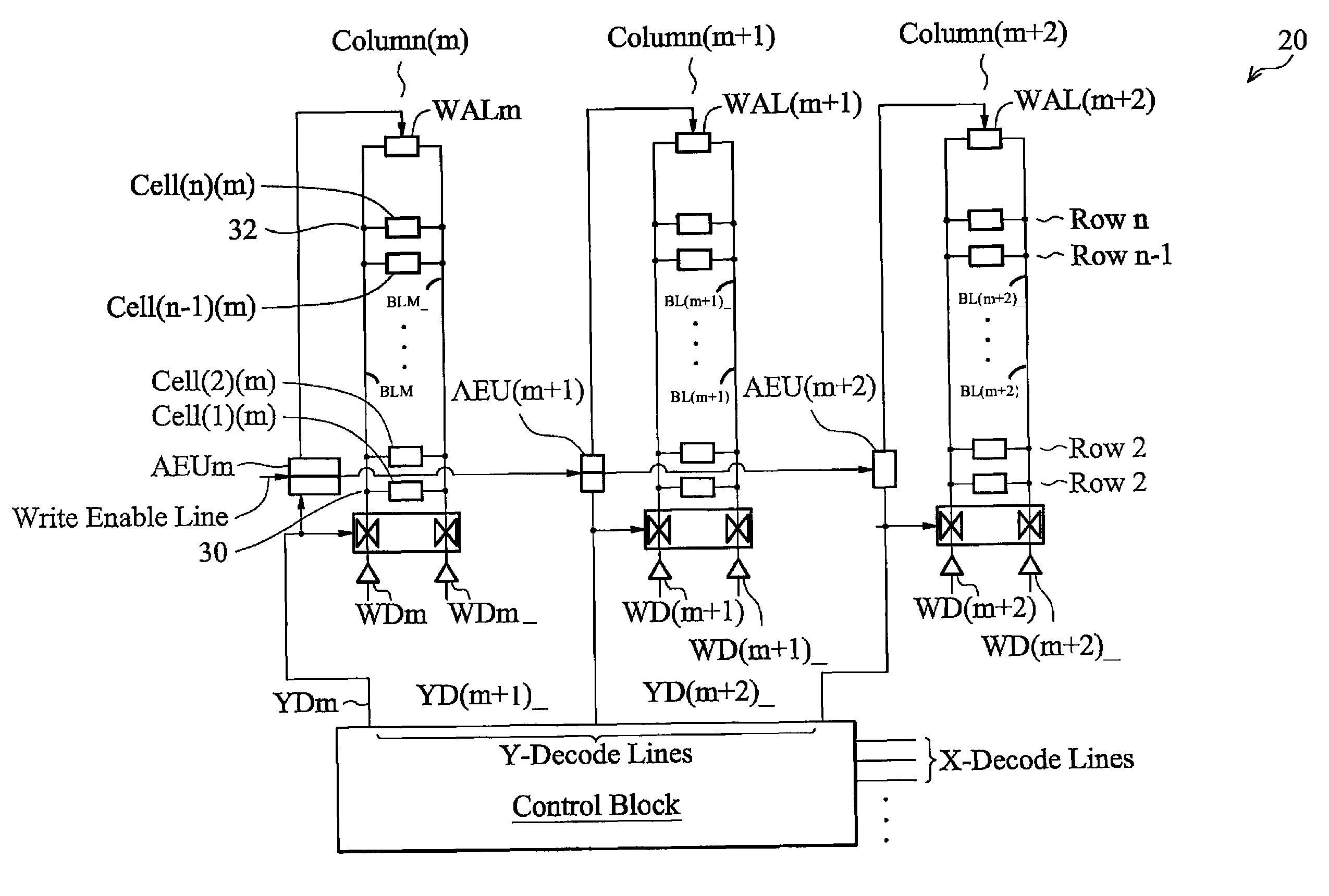
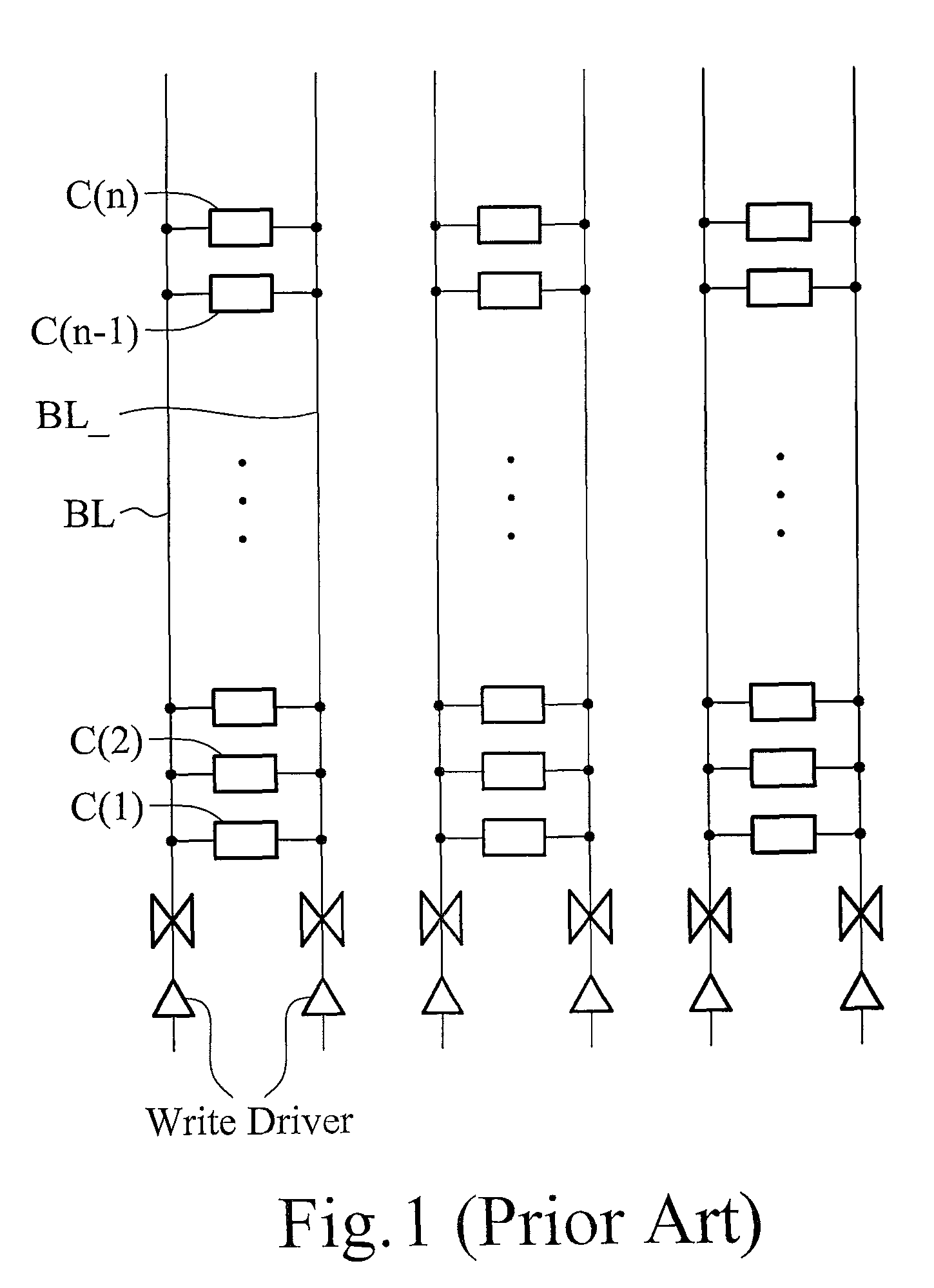
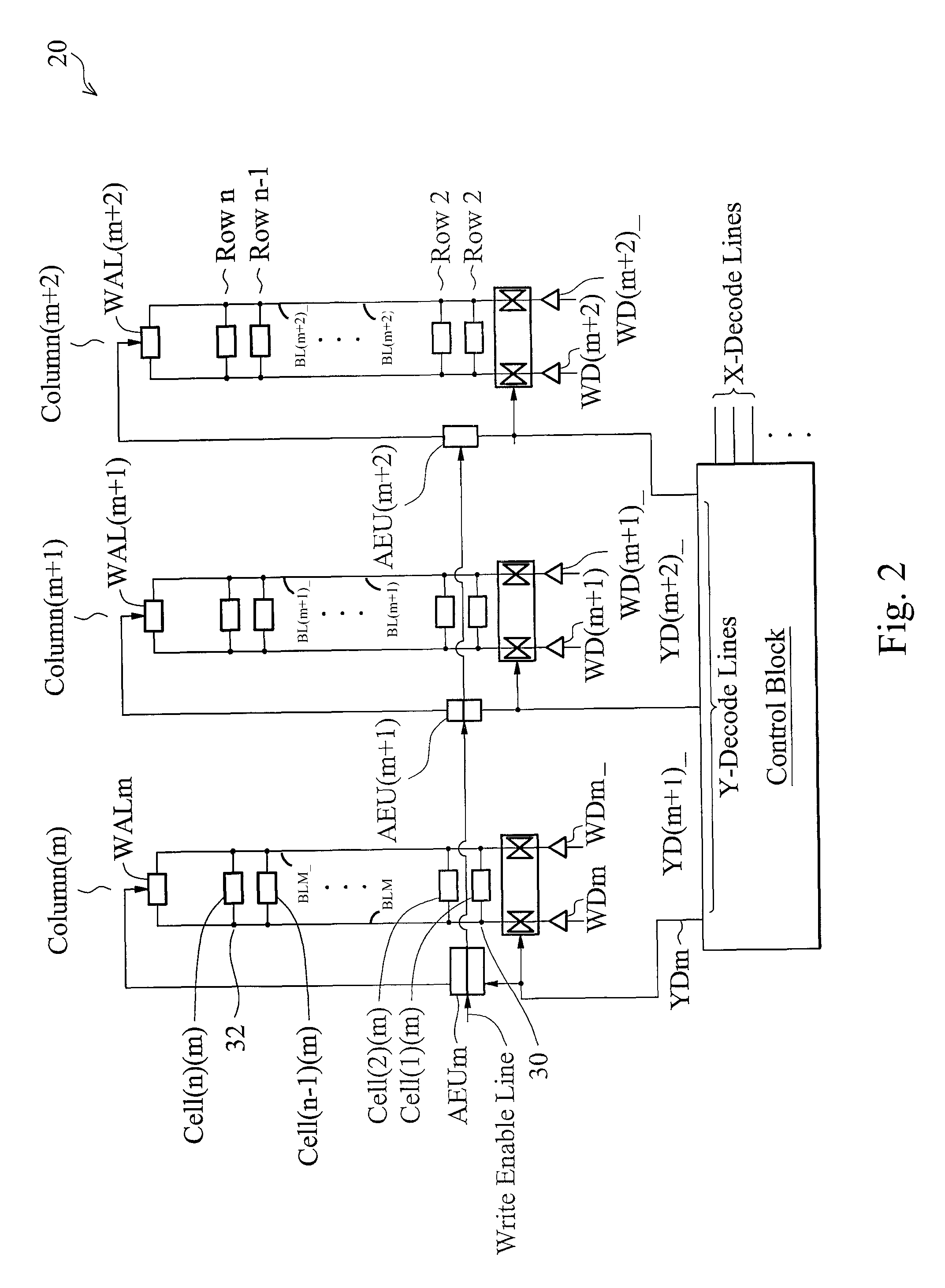
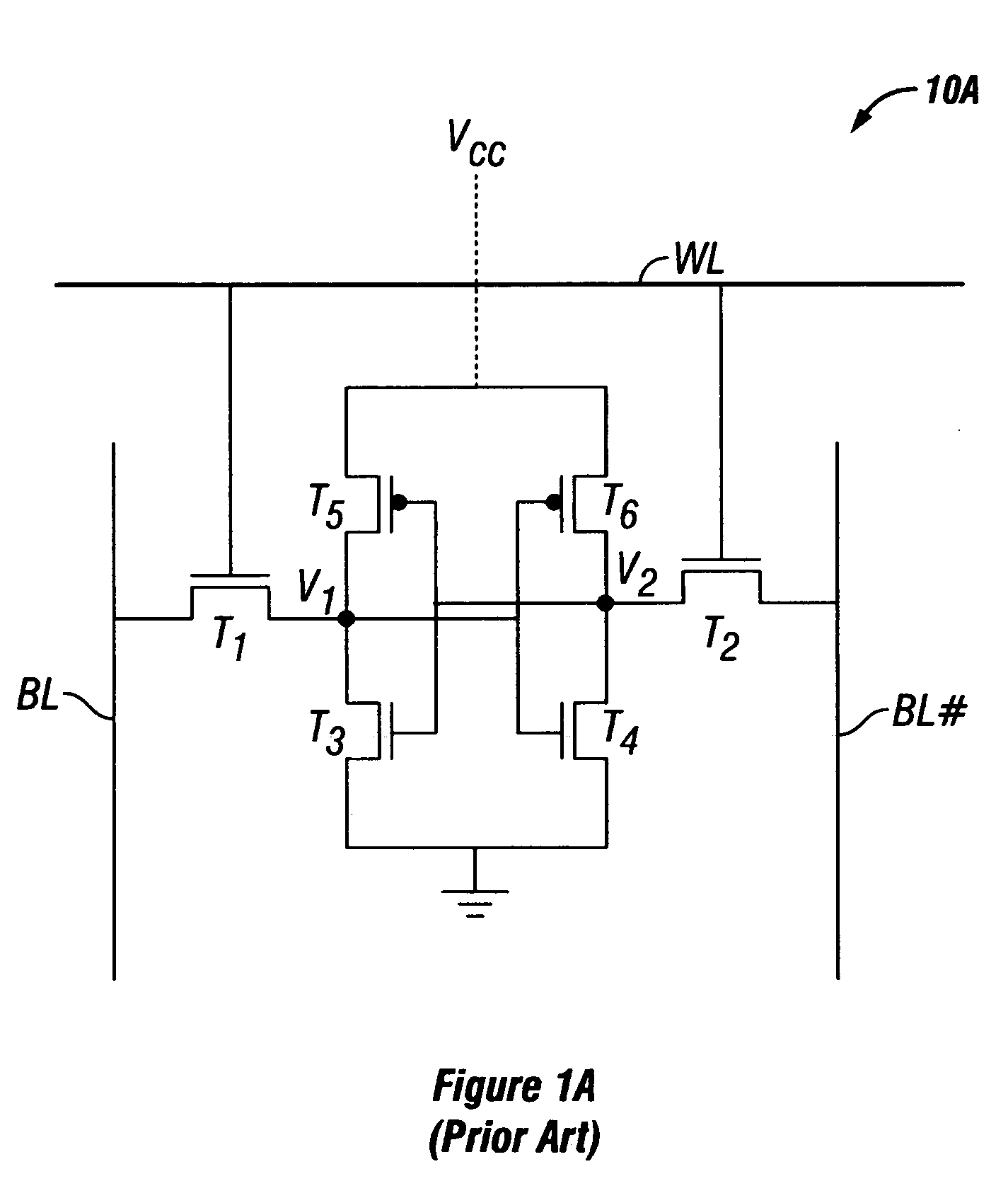
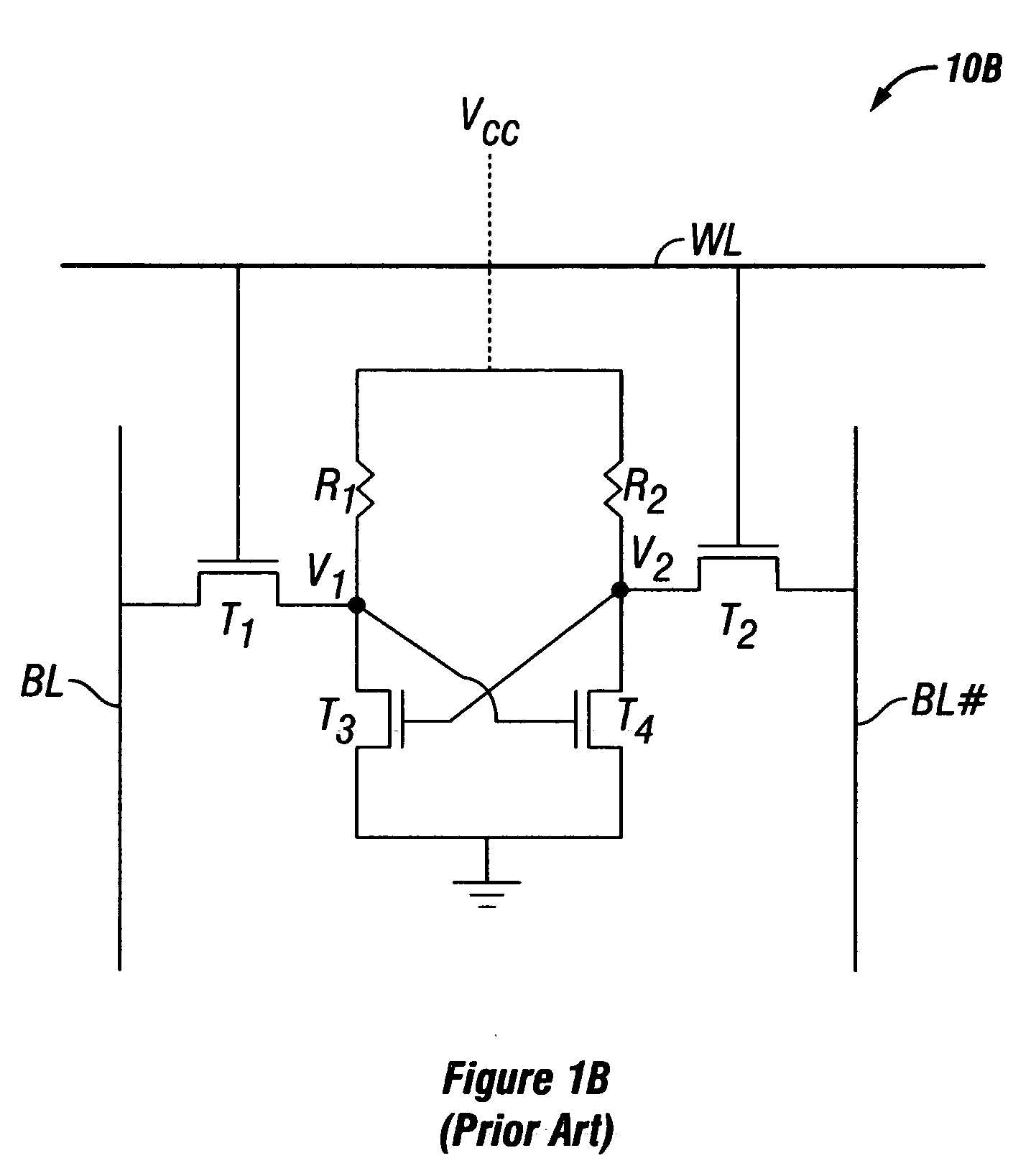
Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
118 results about "Write margin" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Writing in the Margins is a cognitive reading strategy that makes transparent six ways competent readers process and react to ideas in texts. The work that readers do in the margins depends on what the text says and what the text does. Mostly used as a reading comprehension strategy, Writing in the Margins will teach students how to think about...
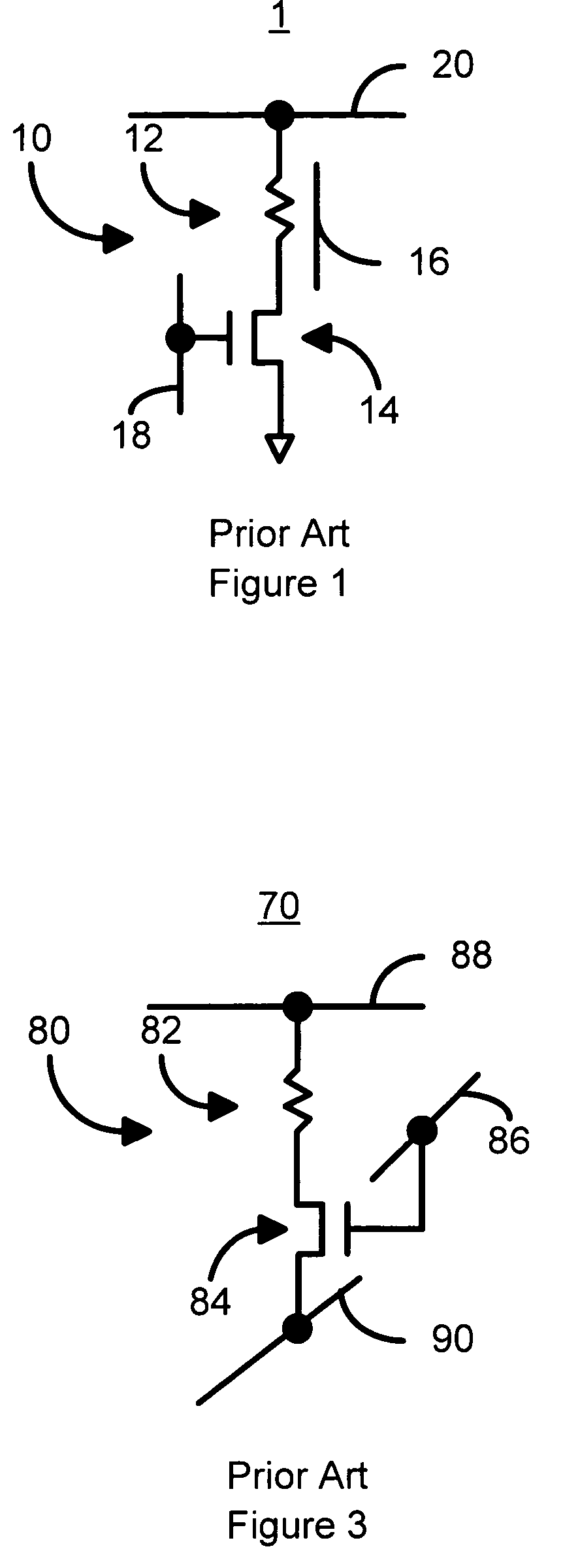
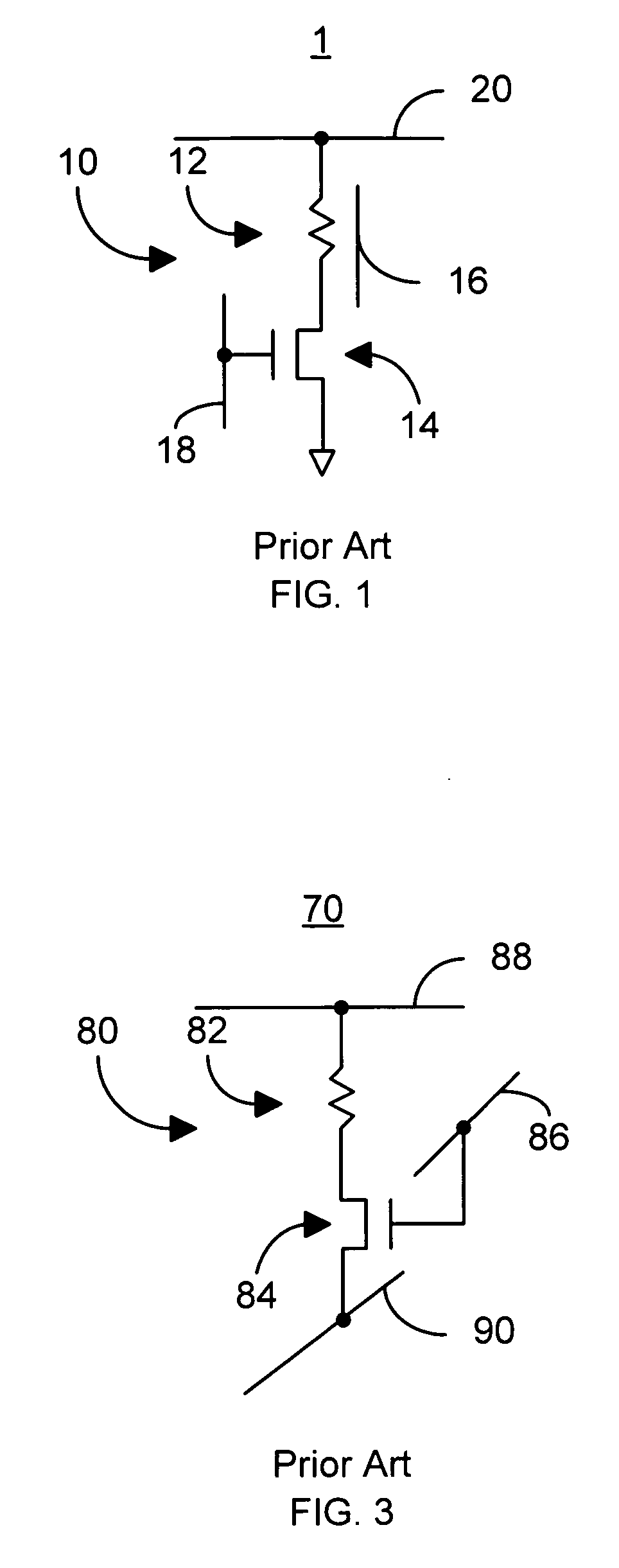
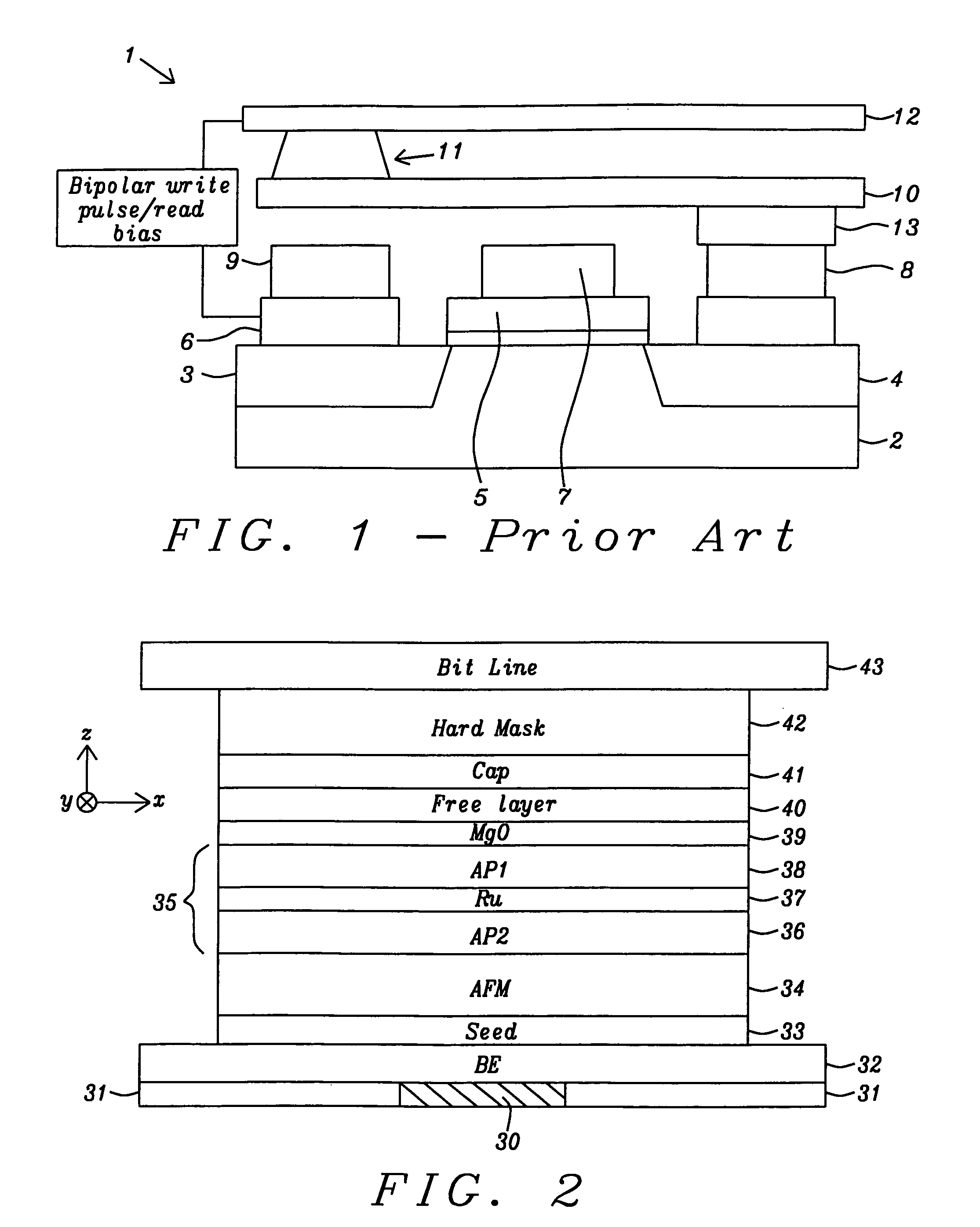
Current driven switching of magnetic storage cells utilizing spin transfer and magnetic memories using such cells having enhanced read and write margins
ActiveUS7379327B2Higher read and write marginDigital storageHigh resistanceElectrical resistance and conductance
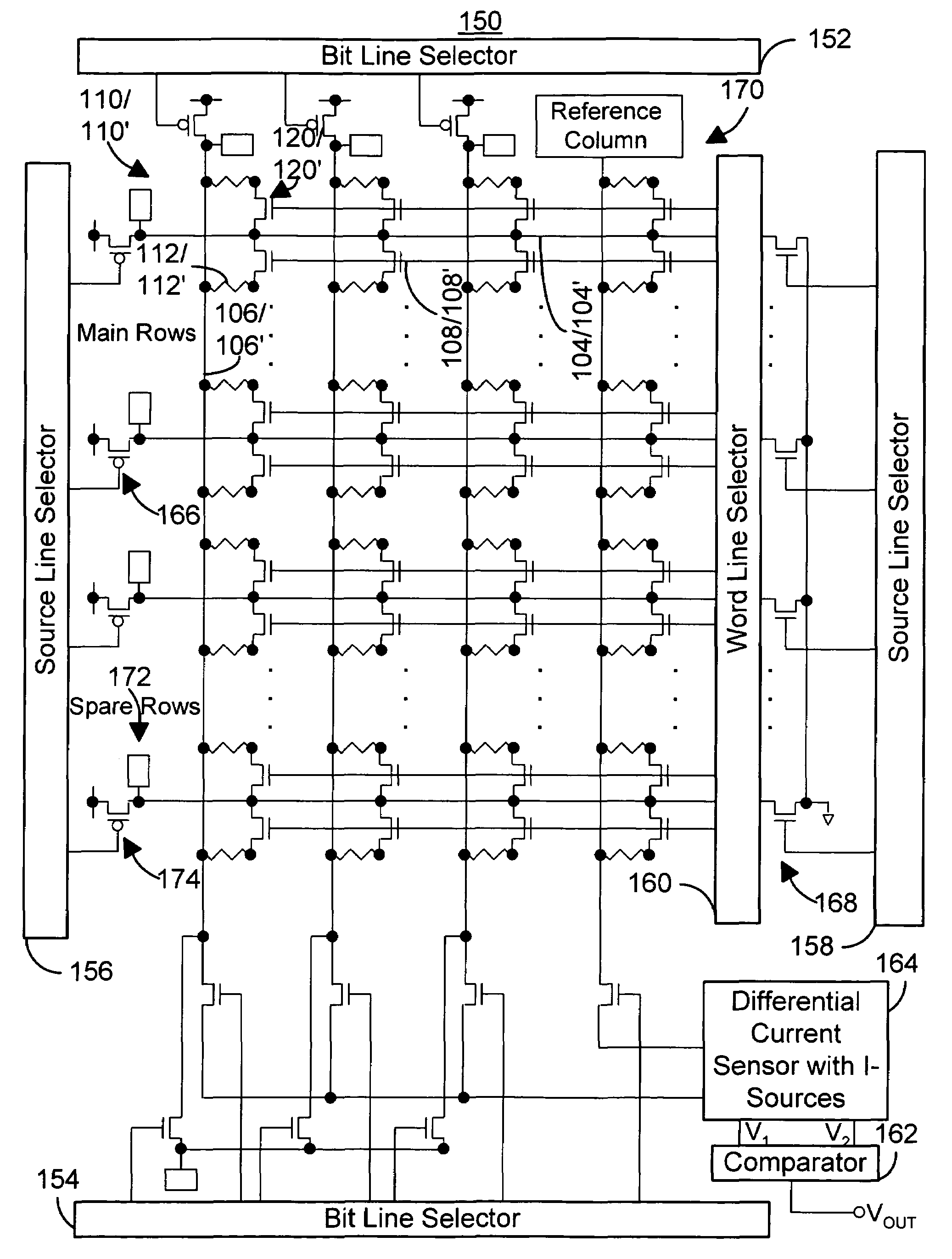
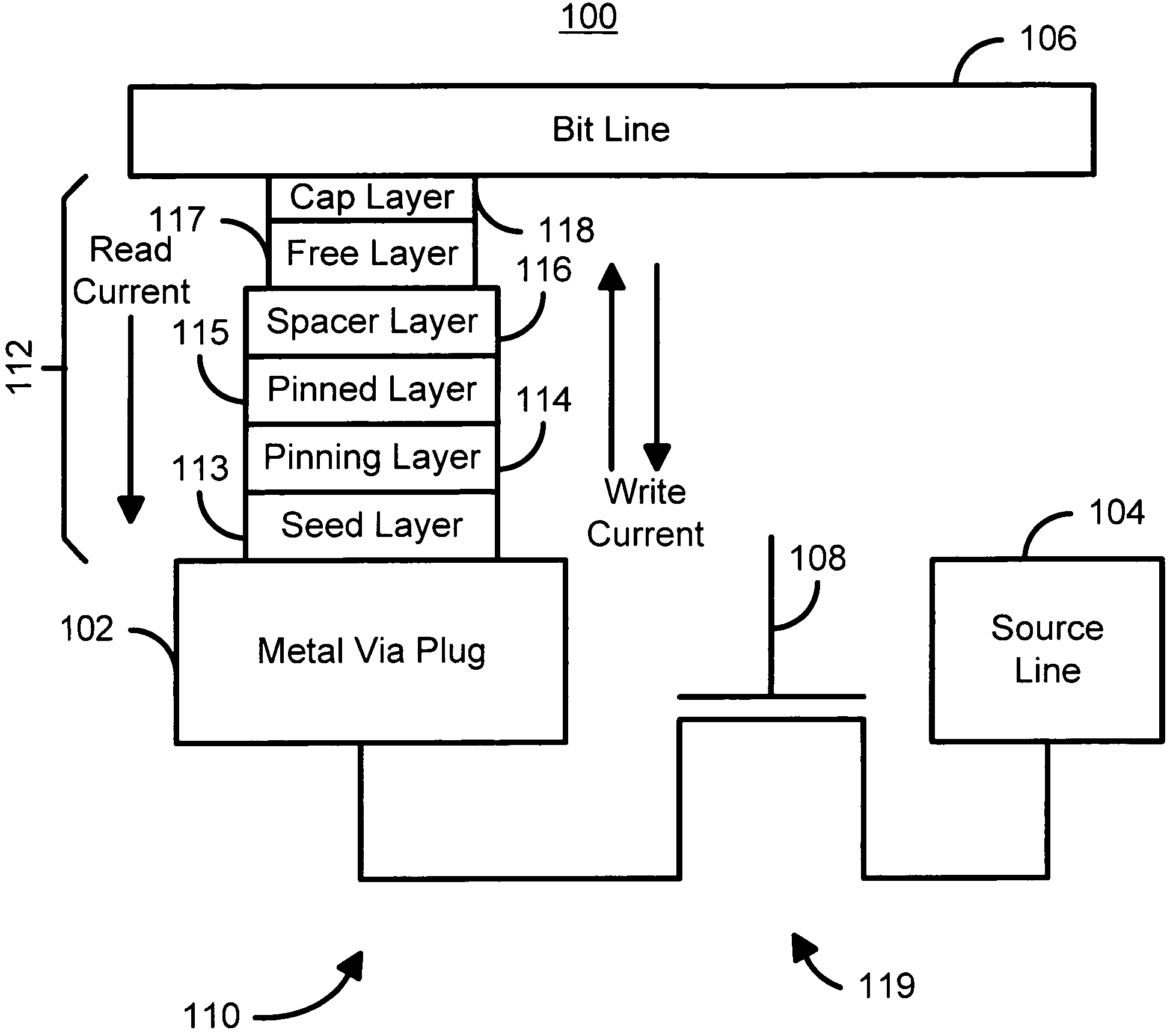
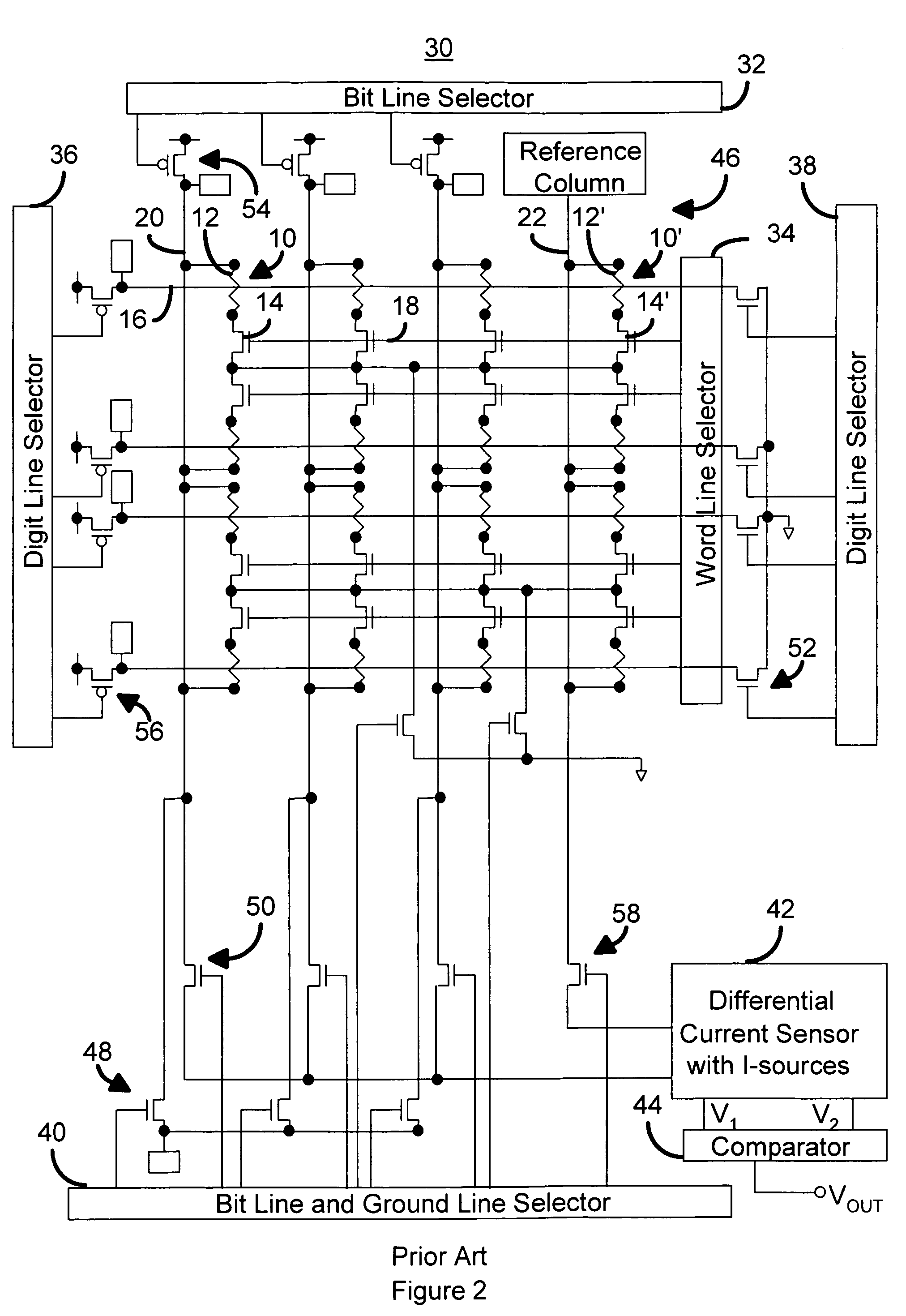
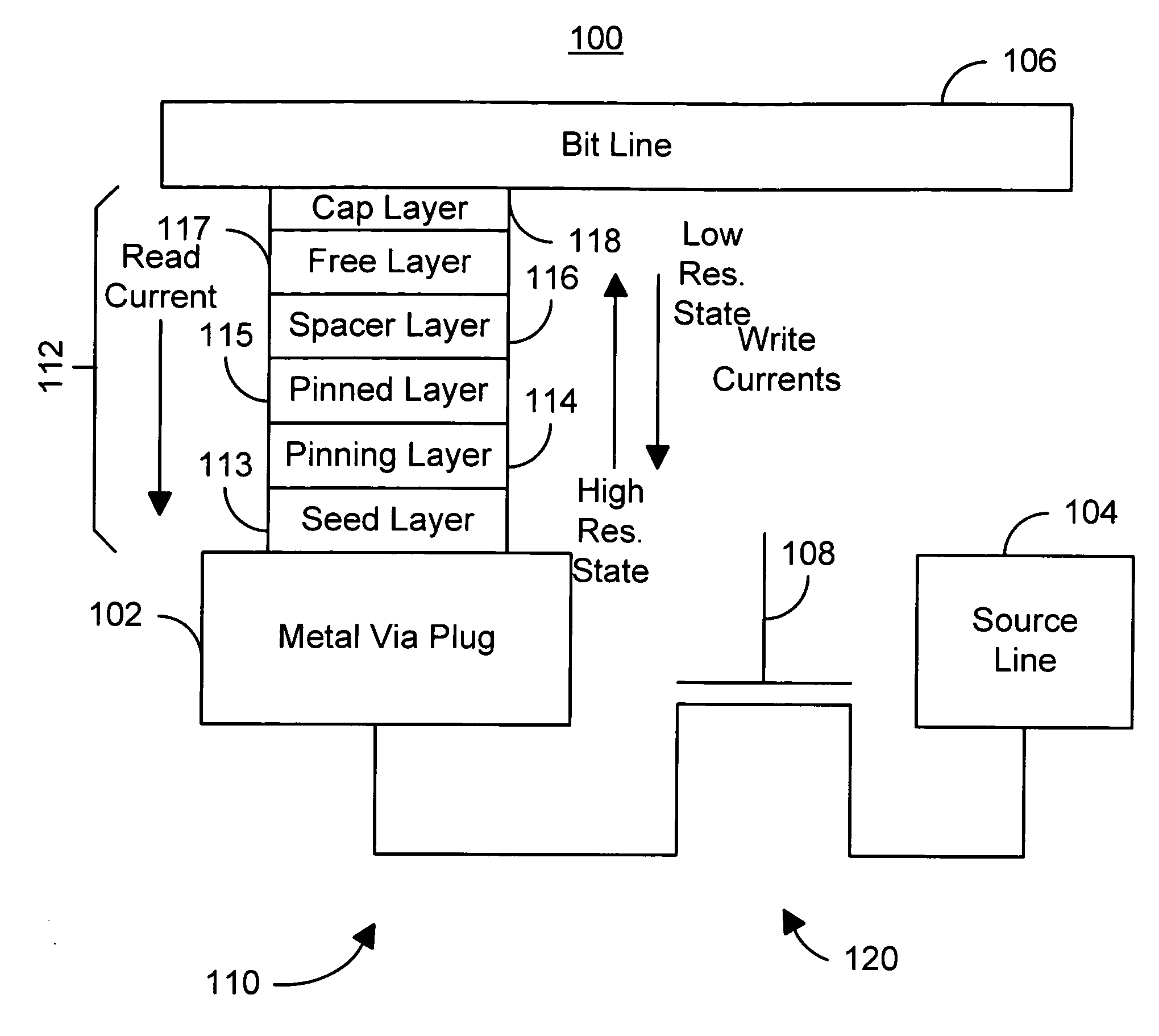
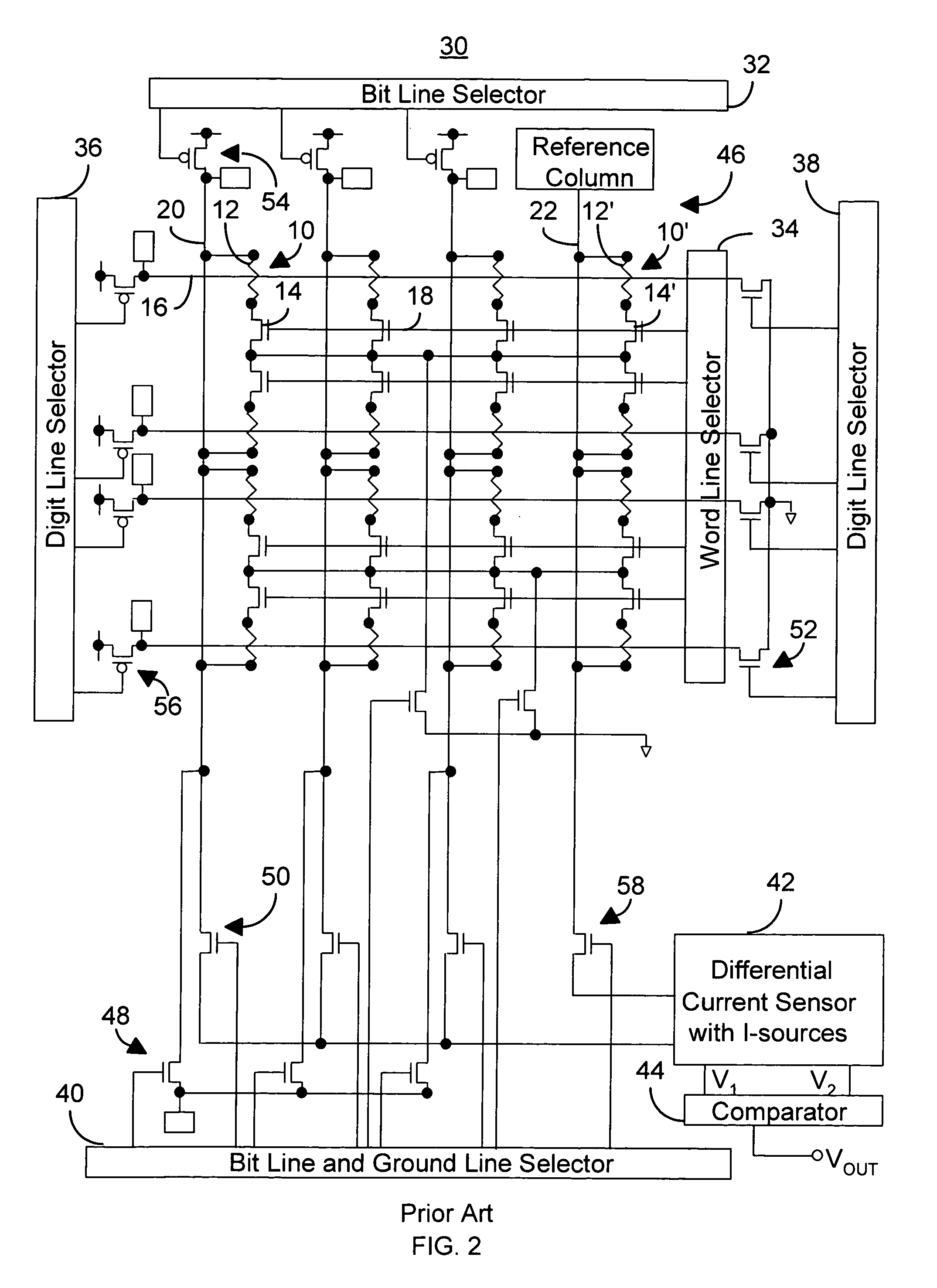
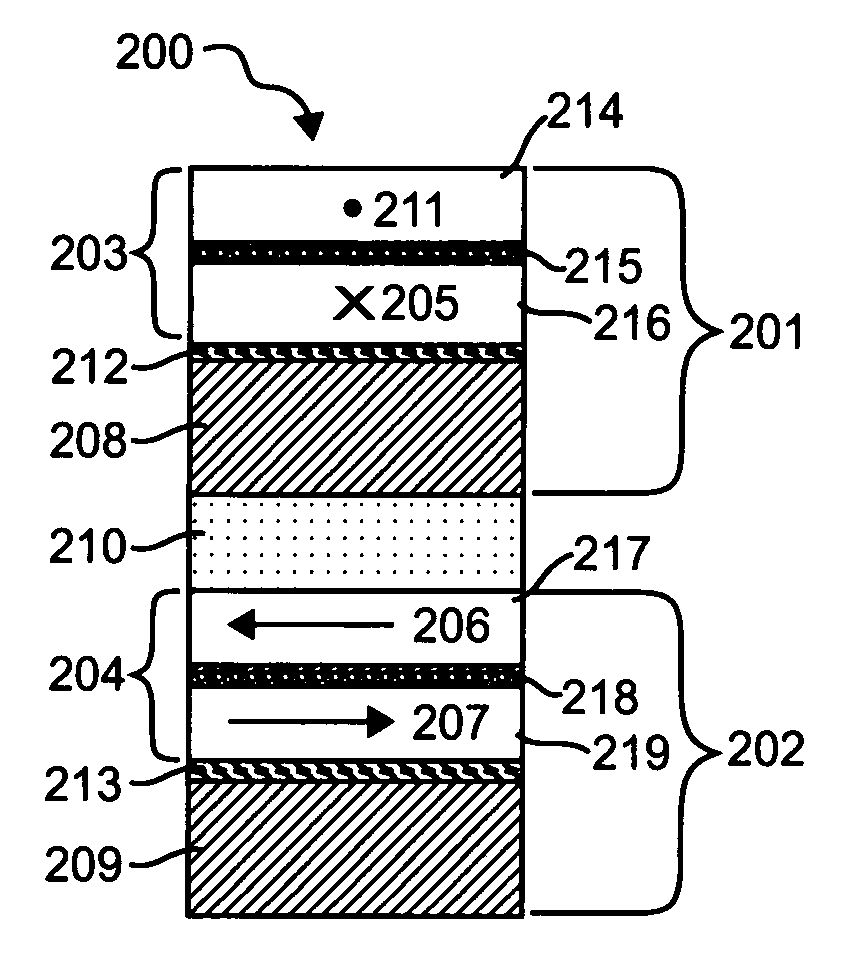
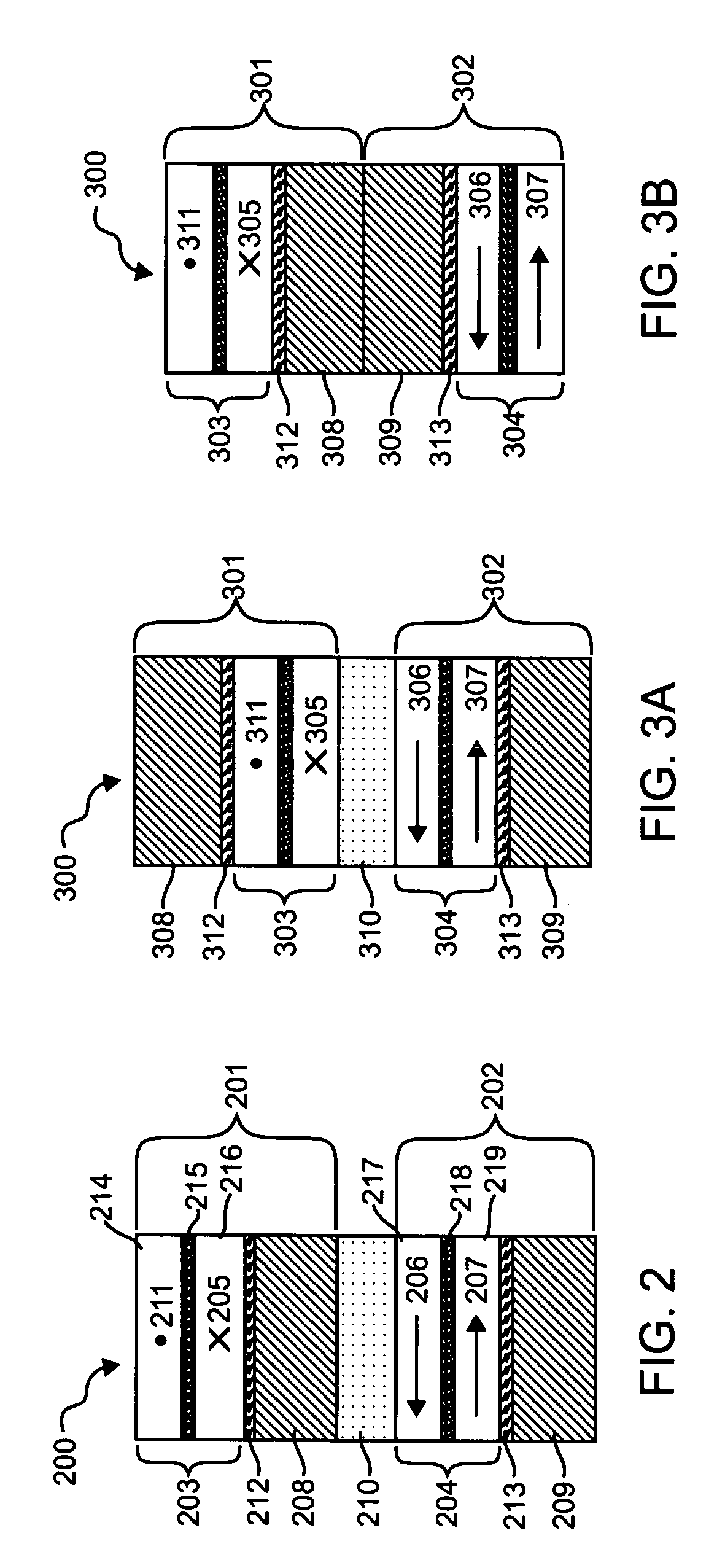
A method and system for providing a magnetic memory. The magnetic memory includes magnetic storage cells in an array, bit lines, and source lines. Each magnetic storage cell includes at least one magnetic element. The magnetic element(s) are programmable by write currents driven through the magnetic element(s). Each magnetic element has free and pinned layer(s) and a dominant spacer. The magnetic memory is configured such that either the read current(s) flow from the free layer(s) to the dominant spacer if the maximum low resistance state read current divided by the minimum low resistance state write current is greater than the maximum high resistance state read current divided by the minimum high resistance state write current or the read current(s) flow from the dominant spacer to the free layer(s) if the maximum low resistance state read current divided by the minimum low resistance state write current is less than the maximum high resistance state read current divided by the minimum high resistance state write current.
Owner:SAMSUNG SEMICON +1
Current driven switched magnetic storage cells having improved read and write margins and magnetic memories using such cells
A method and system for providing a magnetic memory is described. The magnetic memory includes a plurality of magnetic storage cell and at least one bit line and a plurality of source lines corresponding to the plurality of magnetic storage cells. Each magnetic storage cell includes a magnetic element that is programmed to a high resistance state by a first write current driven through the magnetic element in a first direction and to a low resistance state by a second write current driven through the magnetic element in a second direction. The bit line(s) and the source lines are configured to drive the first write current through the magnetic element in the first direction, to drive the second write current through the magnetic element in the second direction, and to drive at least one read current through the magnetic element in a third direction that does not destabilize the low resistance state.
Owner:SAMSUNG SEMICON
Current driven switching of magnetic storage cells utilizing spin transfer and magnetic memories using such cells having enhanced read and write margins
ActiveUS20070297223A1High readHigh write marginDigital storageHigh resistanceElectrical resistance and conductance
A method and system for providing a magnetic memory is described. The magnetic memory includes magnetic storage cells in an array, bit lines, and source lines. Each magnetic storage cell includes at least one magnetic element. The magnetic element(s) are programmable by write currents driven through the magnetic element(s). Each magnetic element has free and pinned layer(s) and a dominant spacer. The magnetic memory is configured such that either the read current(s) flow from the free layer(s) to the dominant spacer if the maximum low resistance state read current divided by the minimum low resistance state write current is greater than the maximum high resistance state read current divided by the minimum high resistance state write current or the read current(s) flow from the dominant spacer to the free layer(s) if the maximum low resistance state read current divided by the minimum low resistance state write current is less than the maximum high resistance state read current divided by the minimum high resistance state write current.
Owner:SAMSUNG SEMICON +1
Semiconductor integrated circuit device
Owner:RENESAS ELECTRONICS CORP
Multiple-bit magnetic random access memory cell employing adiabatic switching
InactiveUS7109539B2Improve storage densityReducing a write margin of the memory cellSolid-state devicesElectric analogue storesBit lineComputer architecture
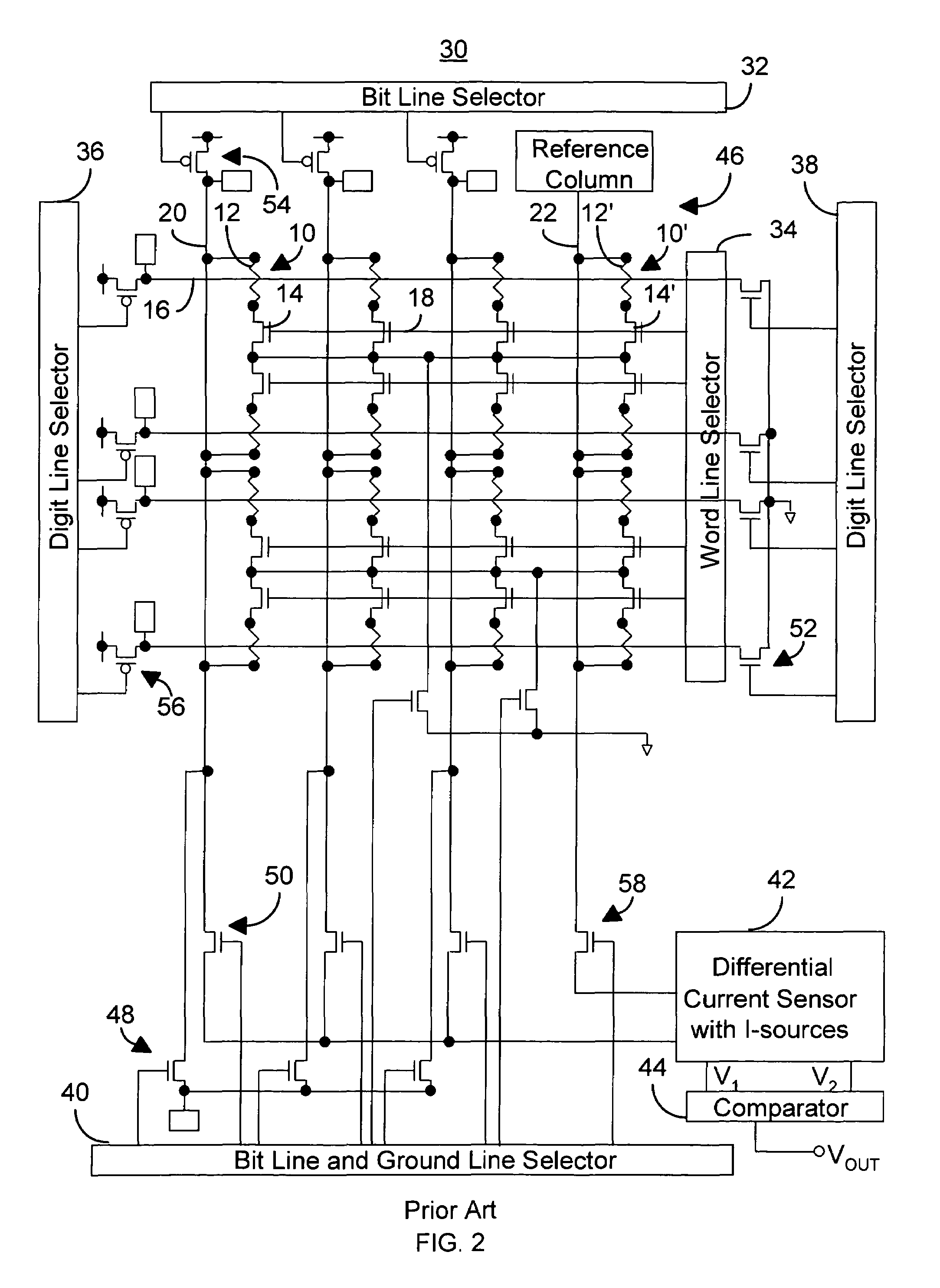
A multiple-bit memory cell for use in a magnetic random access memory circuit includes a first adiabatic switching storage element having a first anisotropy axis associated therewith and a second adiabatic switching storage element having a second anisotropy axis associated therewith. The first and second anisotropy axes are oriented at a substantially non-zero angle relative to at least one bit line and at least one word line corresponding to the memory cell. The memory cell is configured such that two quadrants of a write plane not used for writing one of the storage elements can be beneficially utilized to write the other storage element so that there is essentially no loss of write margin in the memory cell.
Owner:IBM CORP
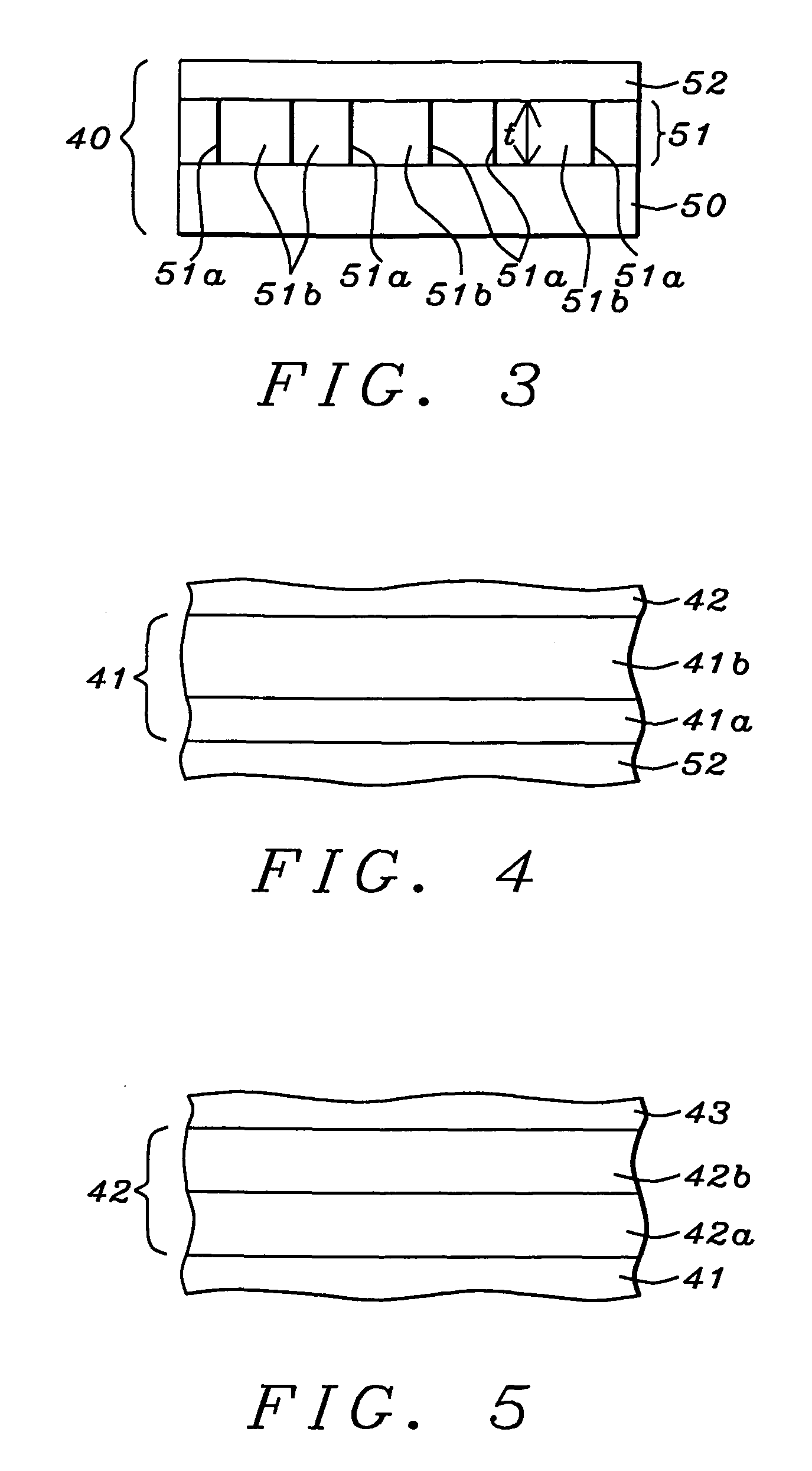
Structure and method to fabricate high performance MTJ devices for spin-transfer torque (STT)-RAM
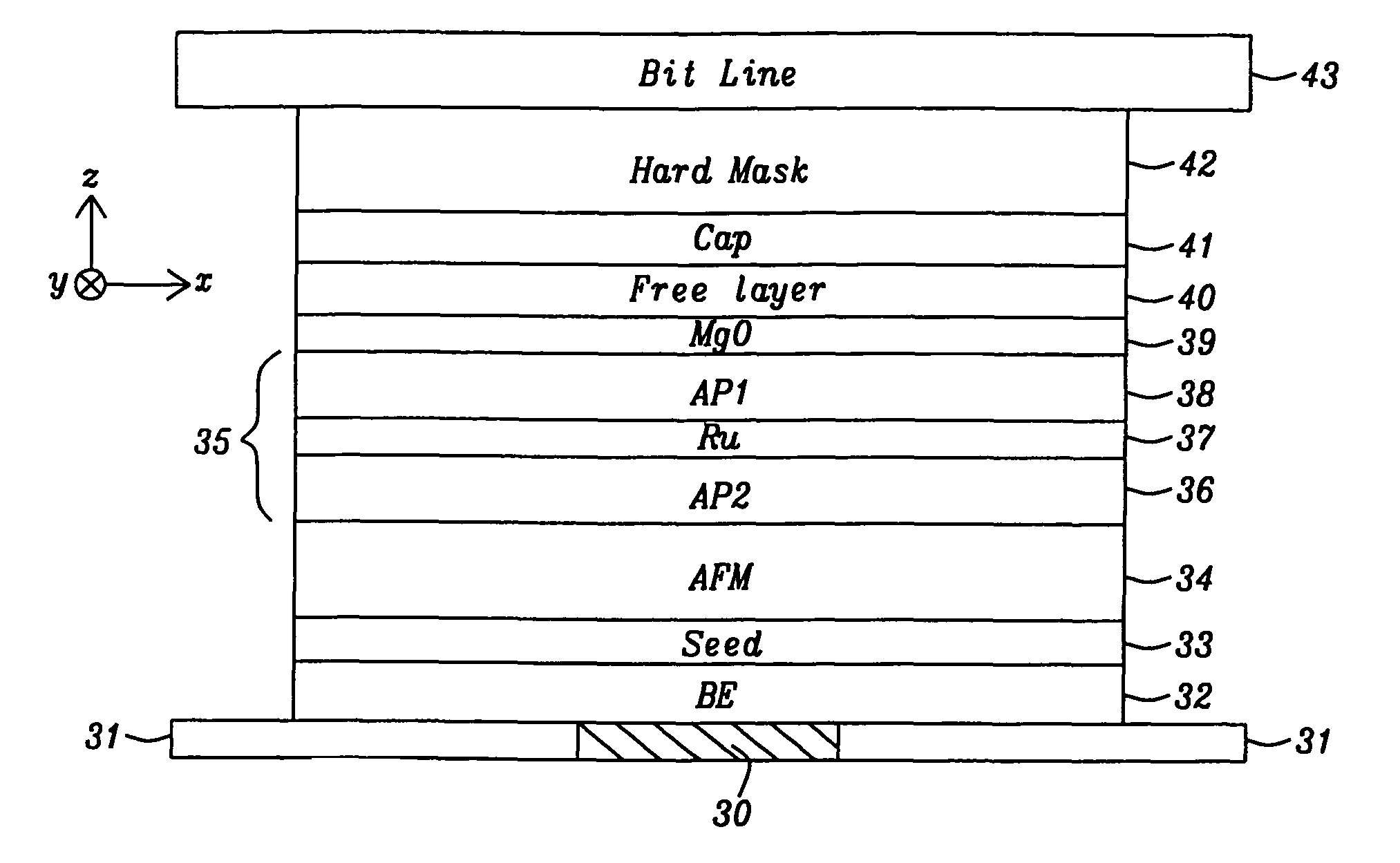
A STT-RAM MTJ is disclosed with a MgO tunnel barrier formed by a NOX process, a CoFeB / FeSiO / CoFeB composite free layer with a middle nanocurrent channel layer to minimize Jc0, and a Ru capping layer to enhance the spin scattering effect and increase dR / R. Good write margin is achieved by modifying the NOX process to afford a RA less than 10 ohm-μm2 and good read margin is realized with a dR / R of >100% by annealing at 330° C. or higher to form crystalline CoFeB free layers. The NCC thickness is maintained in the 6 to 10 Angstrom range to reduce Rp and avoid Fe(Si) granules from not having sufficient diameter to bridge the distance between upper and lower CoFeB layers. A FeSiO layer may be inserted below the Ru layer in the capping layer to prevent the Ru from causing a high damping constant in the upper CoFeB free layer.
Owner:TAIWAN SEMICON MFG CO LTD
Asymmetrical memory cells and memories using the cells
ActiveUS7362606B2Improve stabilityImprove write performanceTransistorDigital storageBit lineNon symmetric
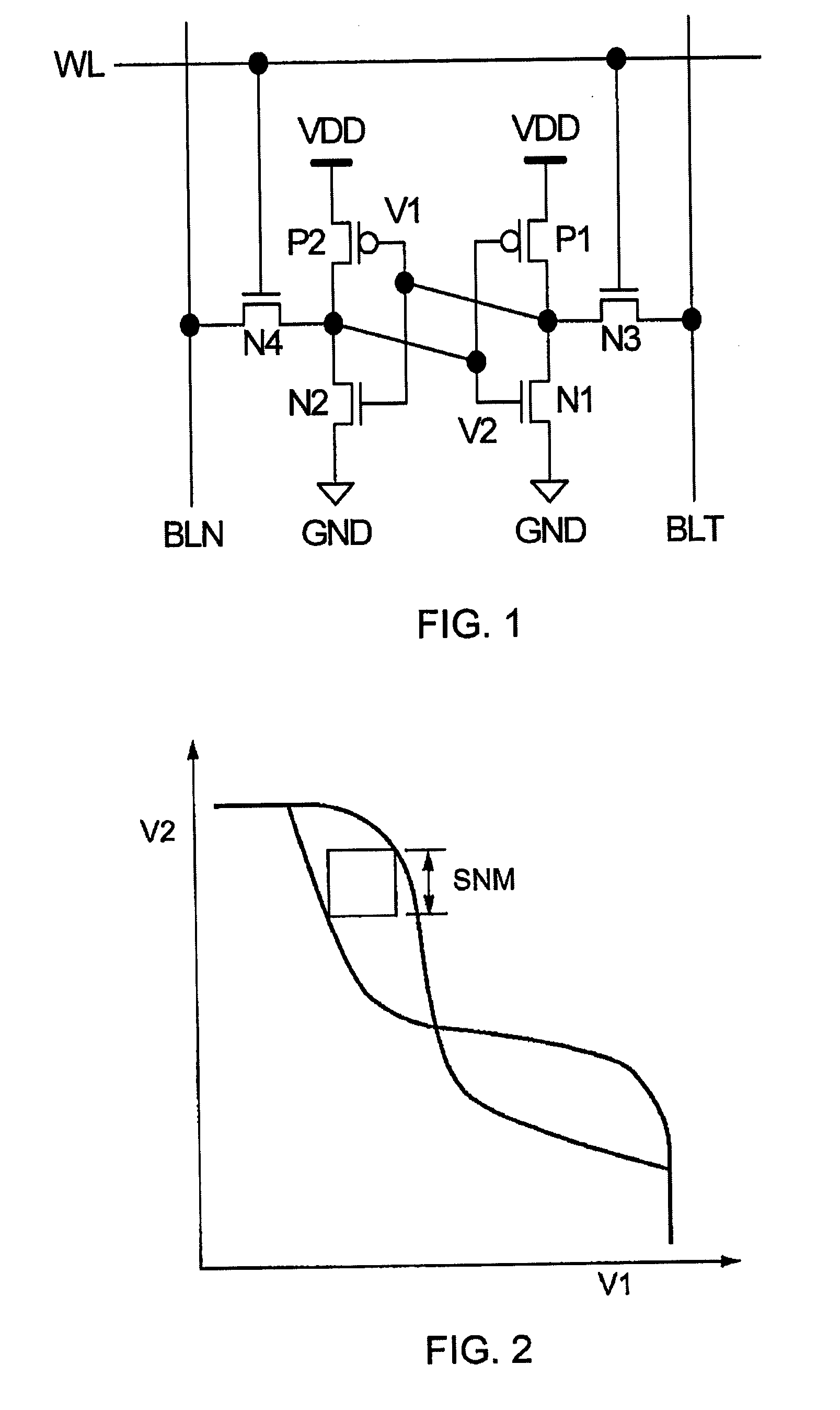
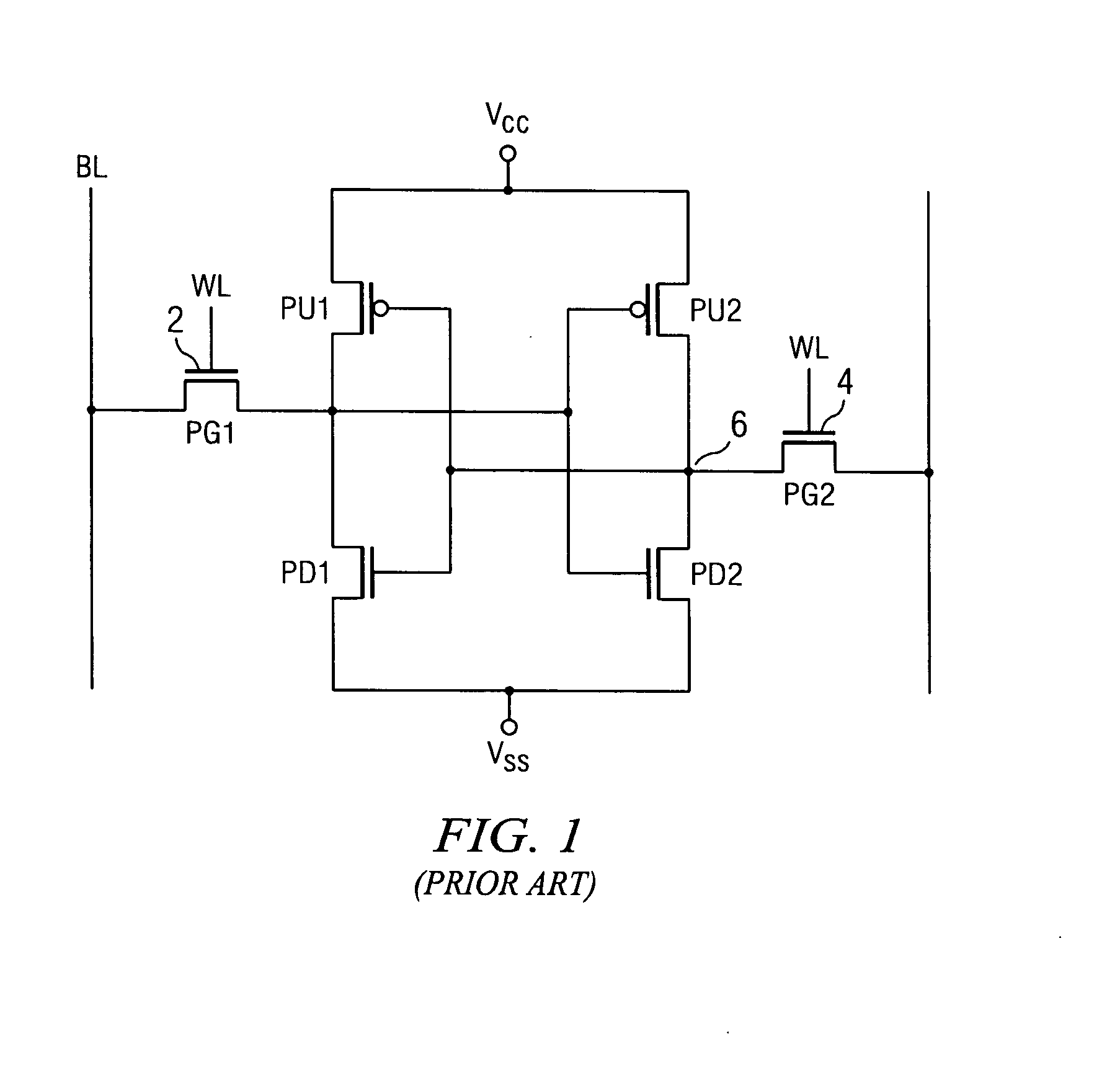
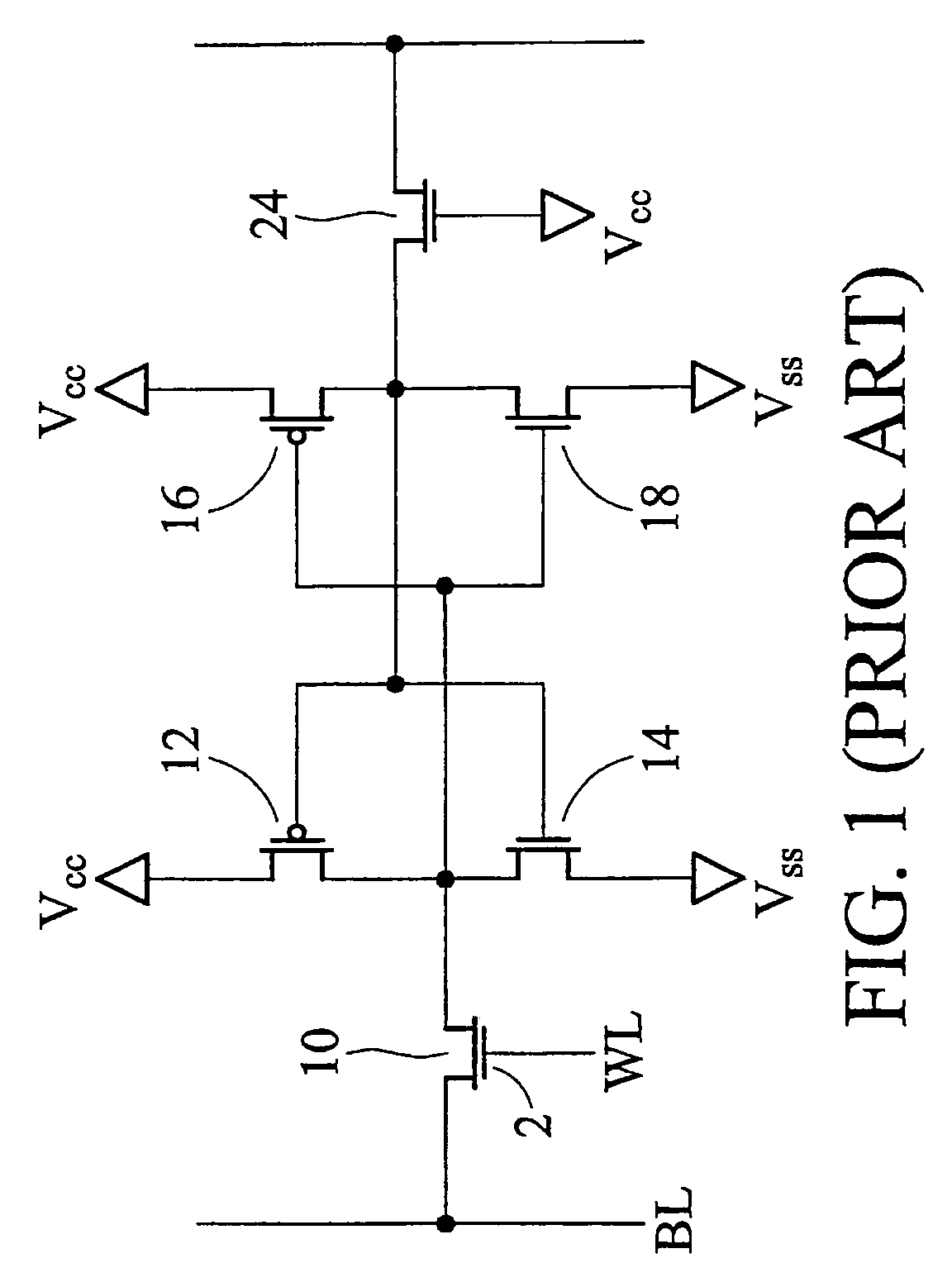
Techniques are provided for asymmetrical SRAM cells which can be improved, for example, by providing one or more of improved read stability and improved write performance and margin. A first inverter and a second inverter are cross-coupled and configured for selective coupling to true and complementary bit lines under control of read and write word lines. The first inverter is formed by a first, n-type, FET (NFET) and a second, p-type, FET (PFET). Process and / or technology approaches can be employed to adjust the relative strength of the FETS to obtain, for example, read margin, write margin, and / or write performance improvements.
Owner:GLOBALFOUNDRIES U S INC
Semiconductor integrated circuite device
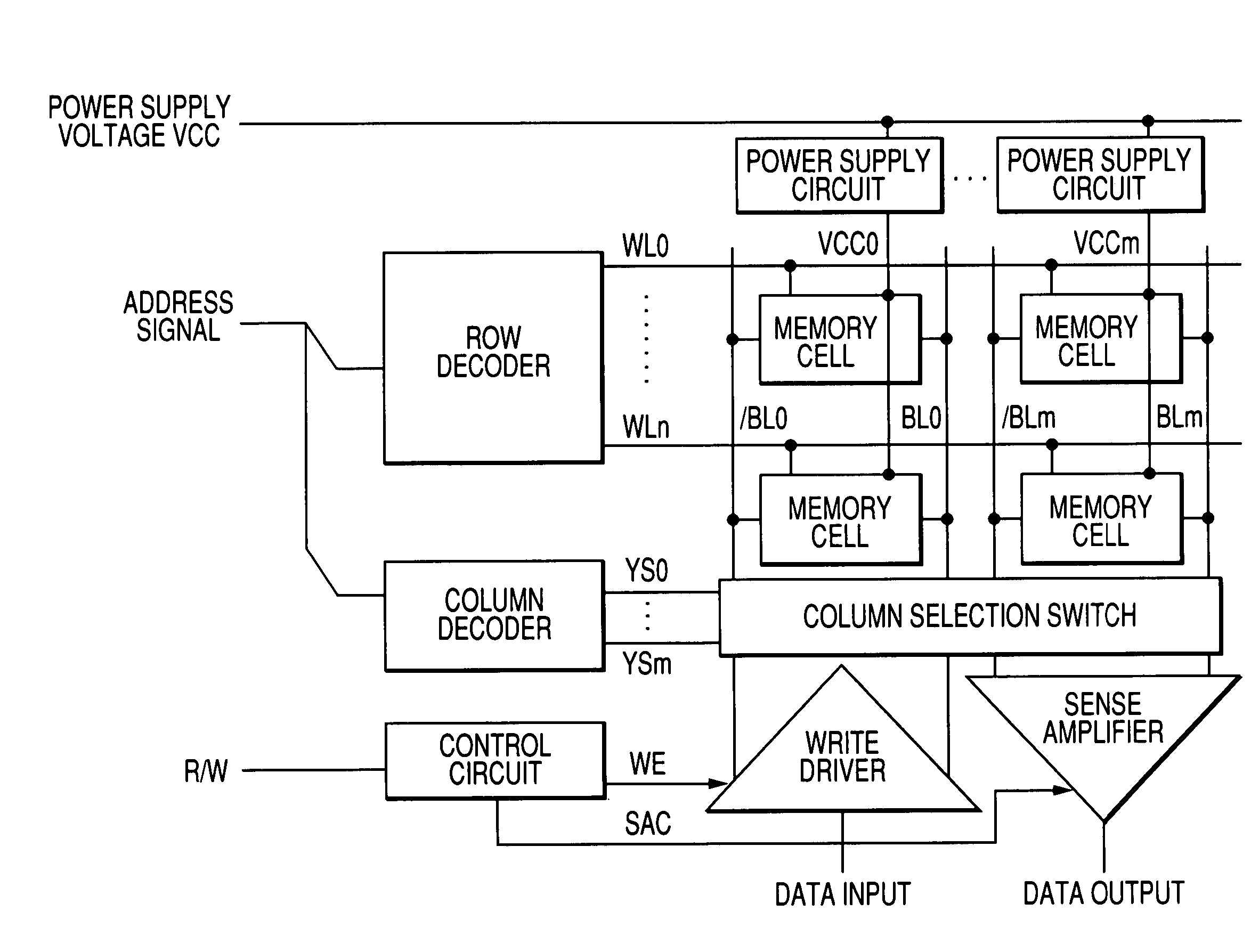
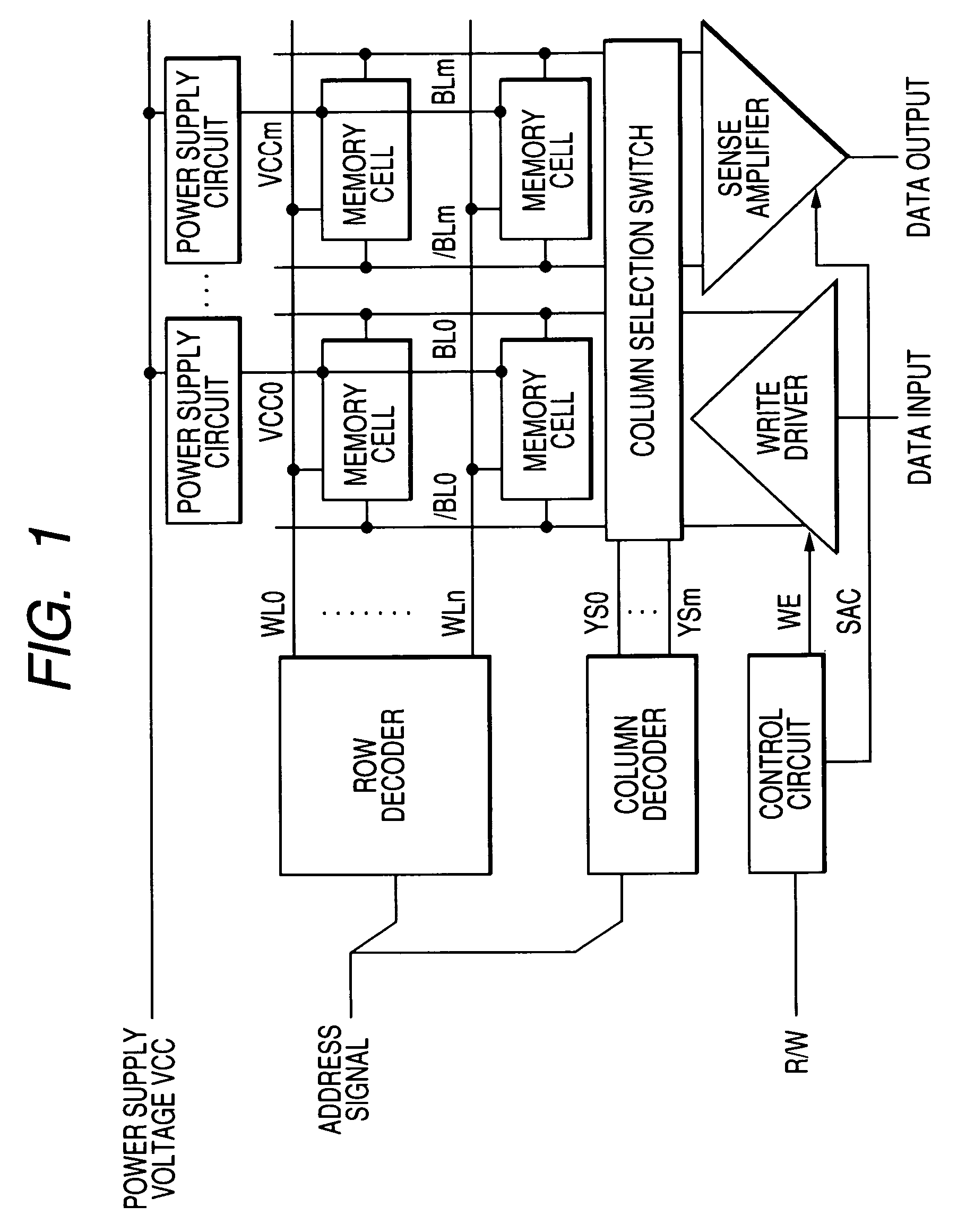
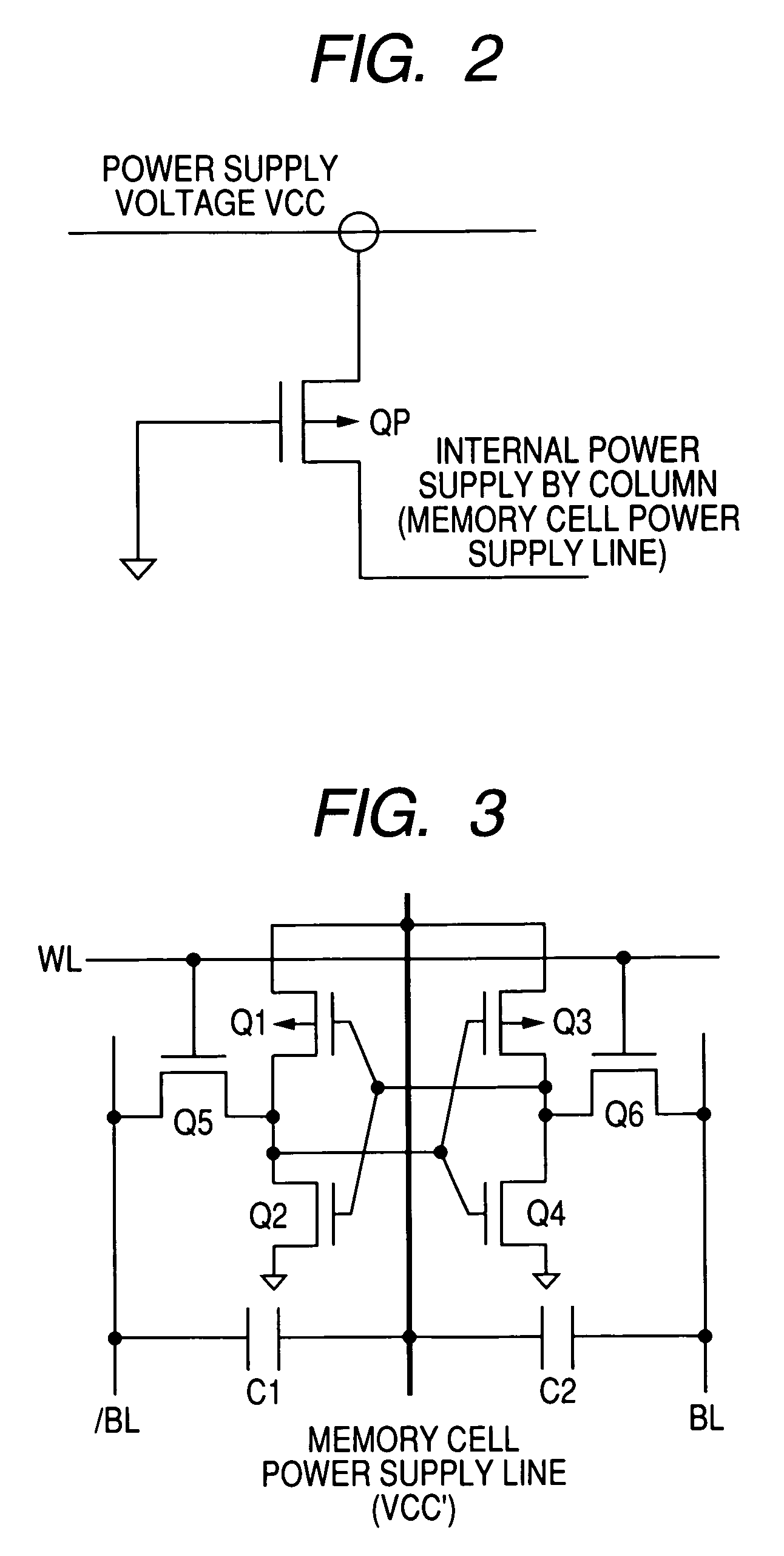
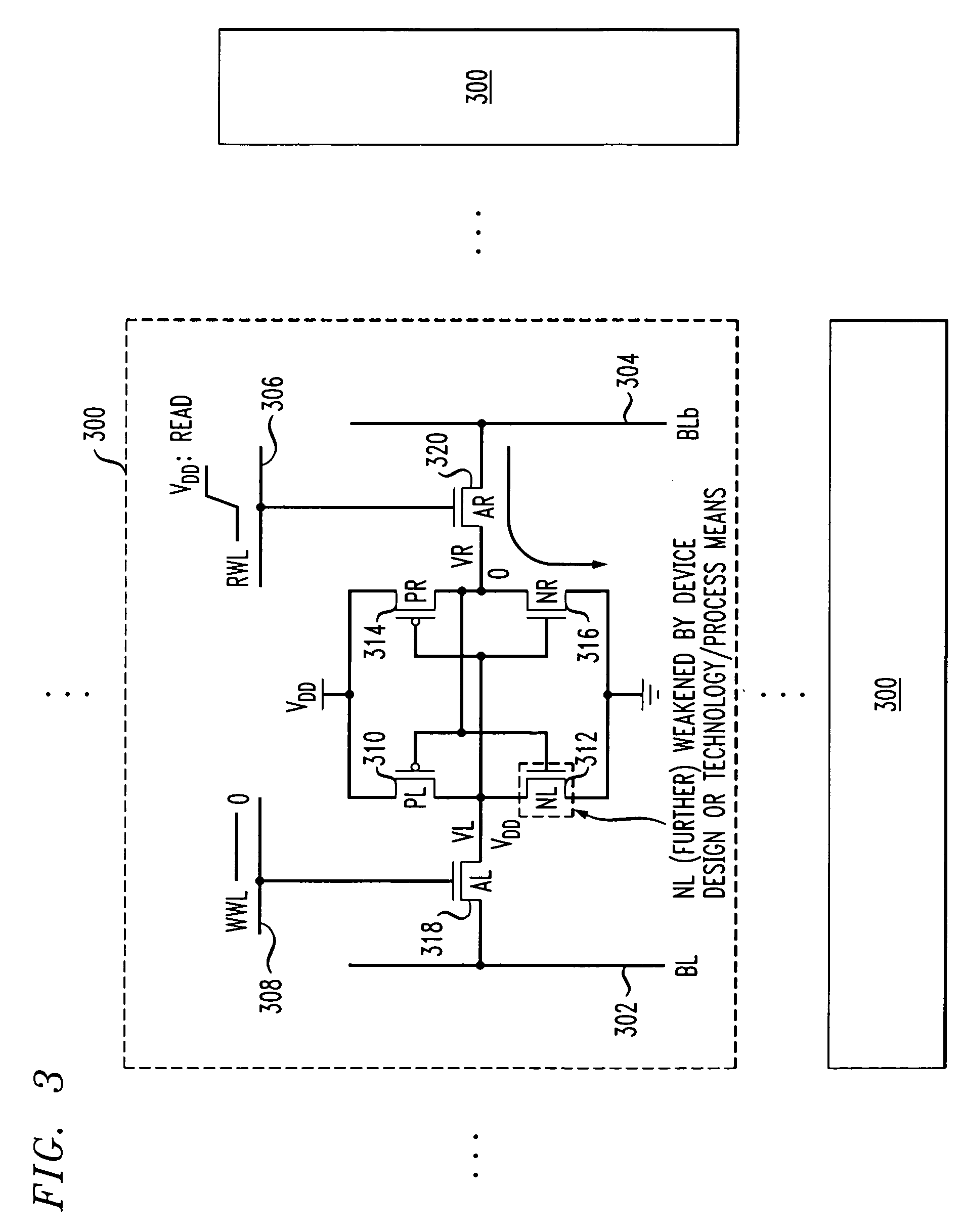
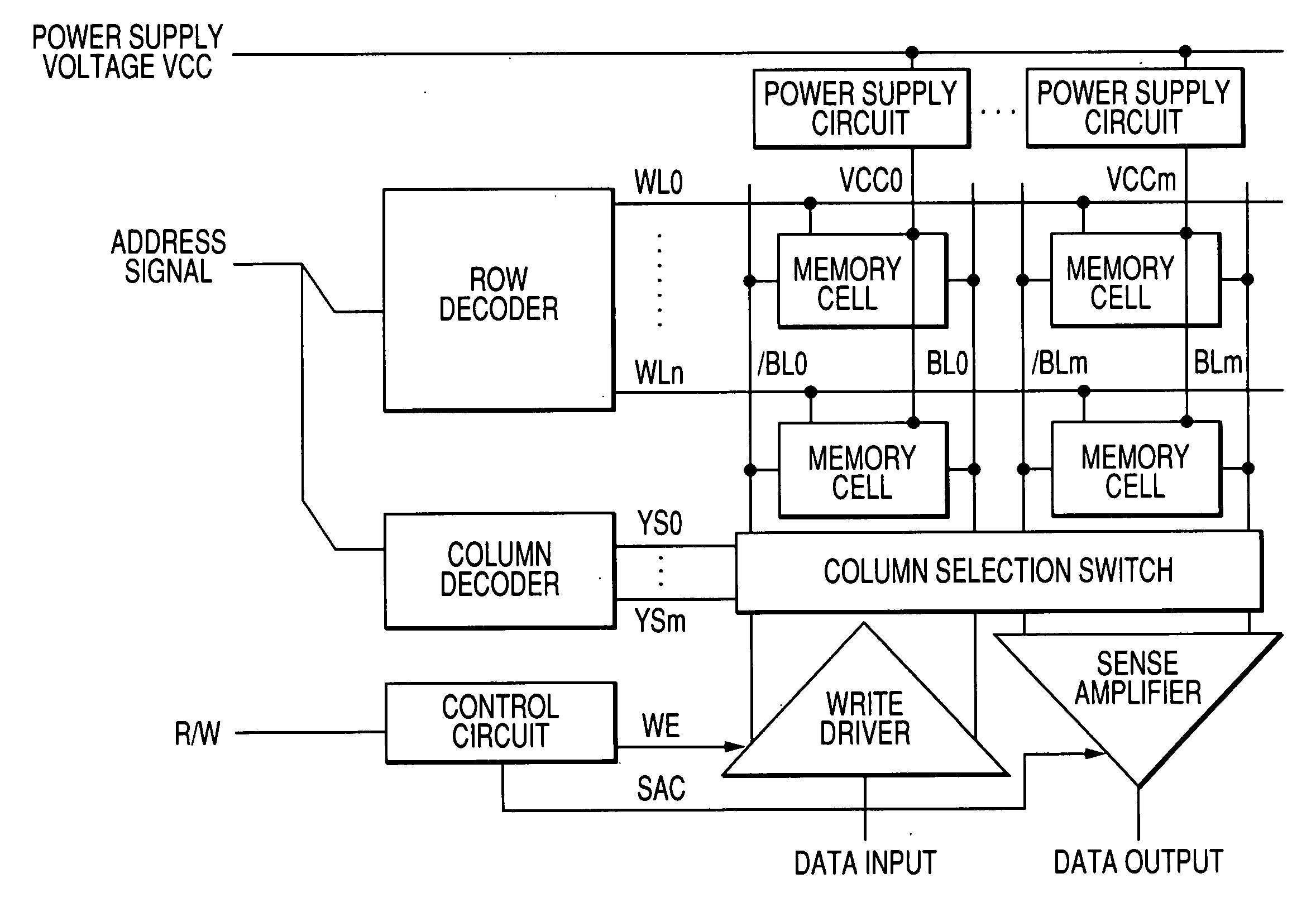
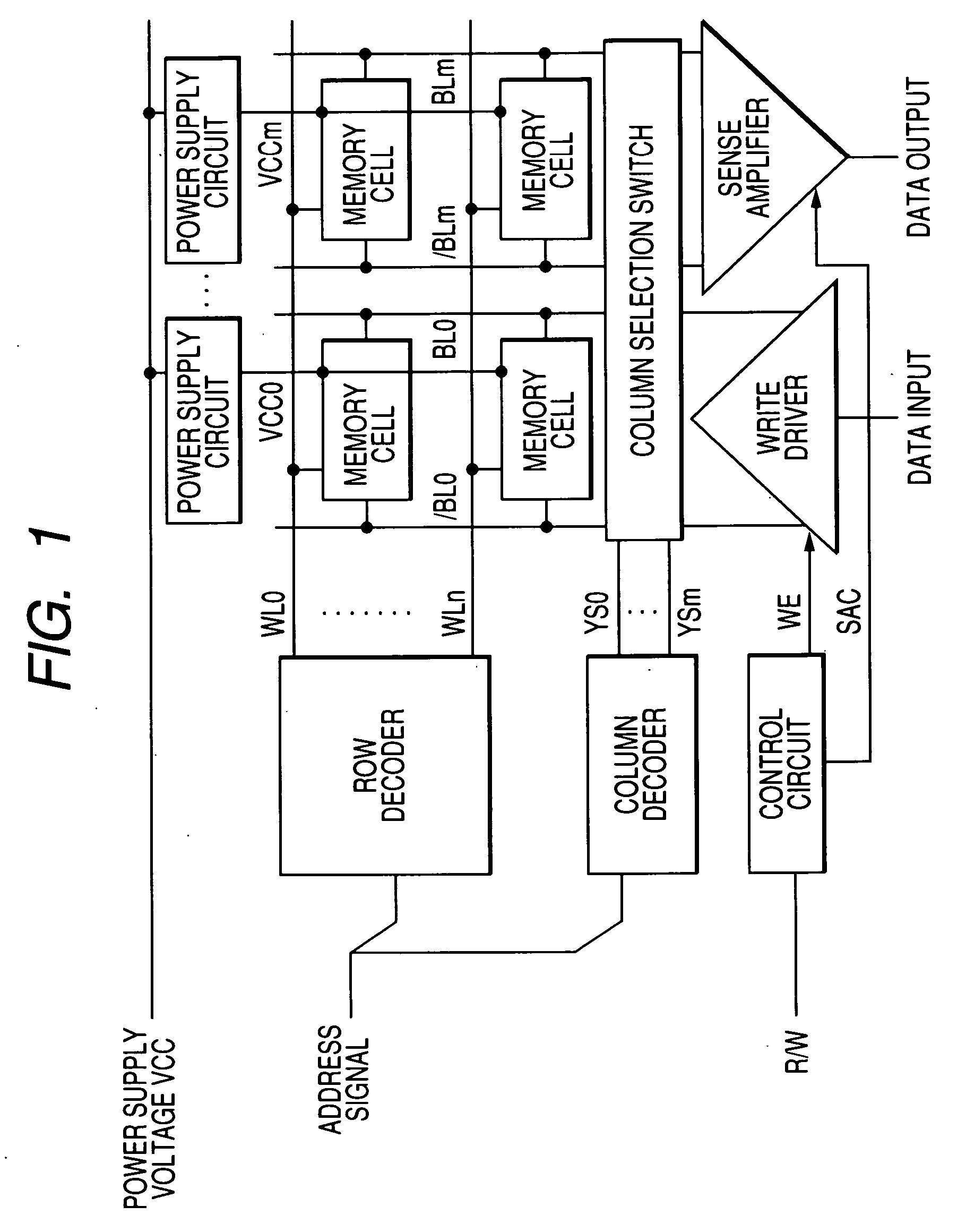
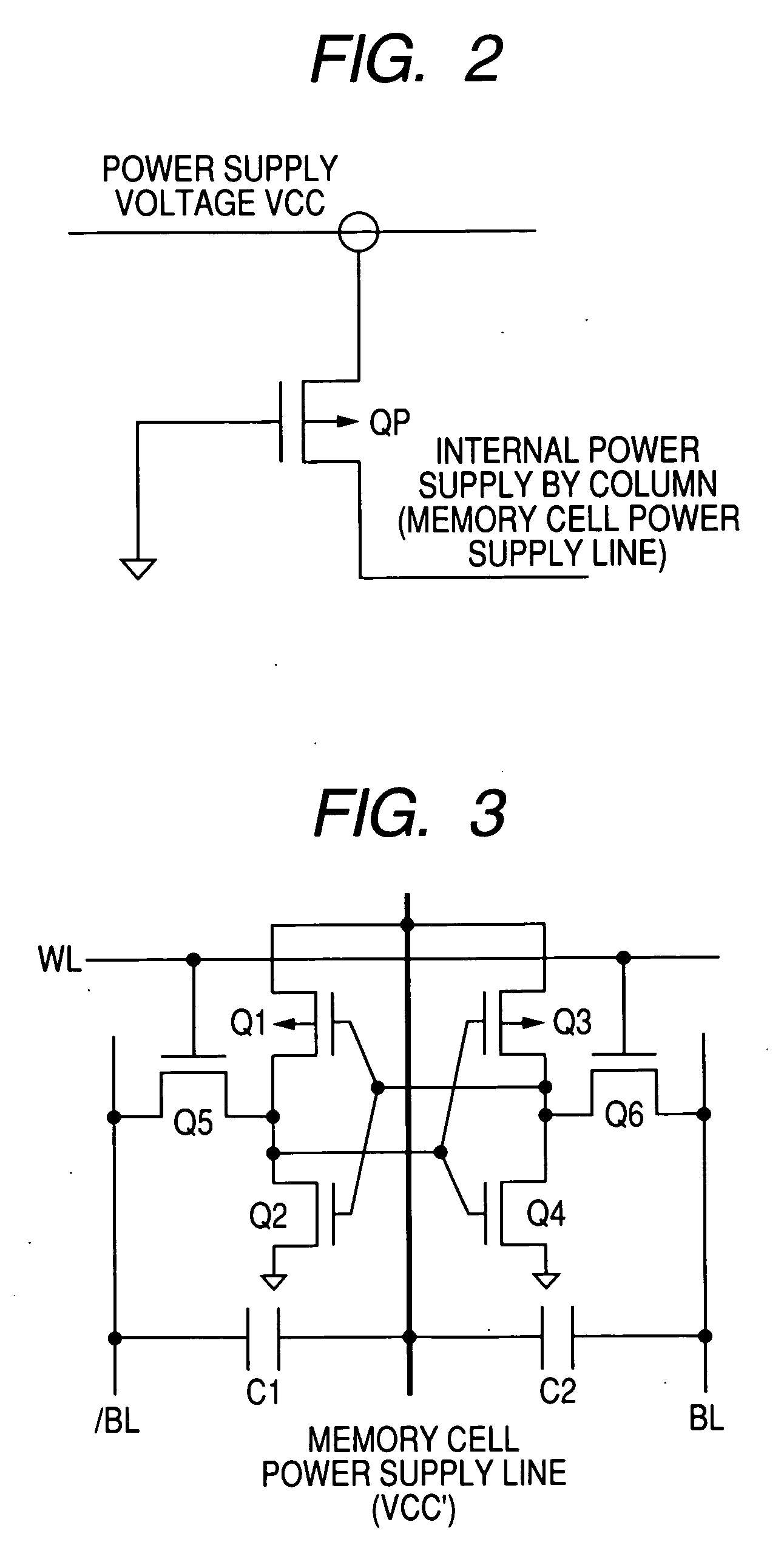
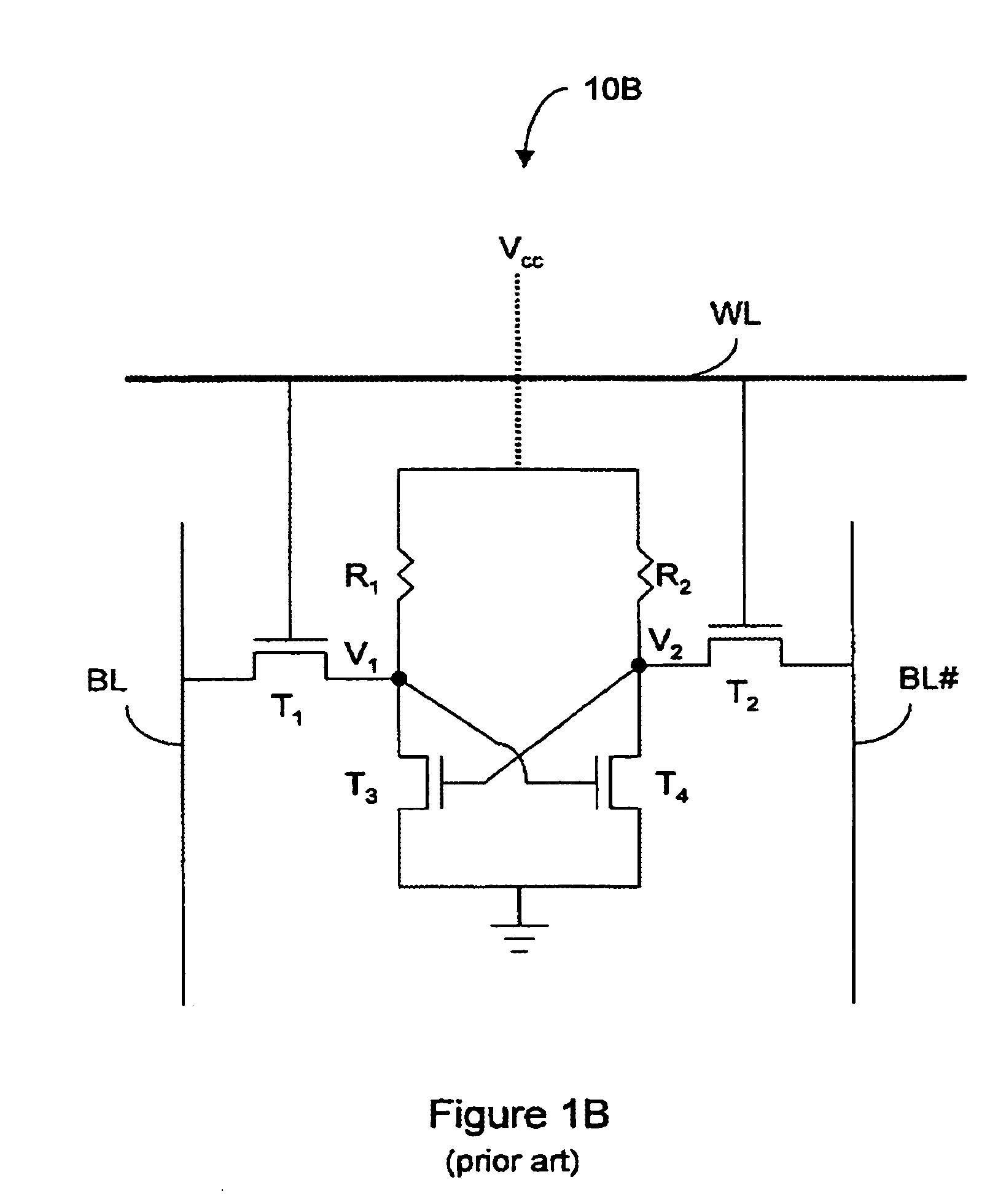
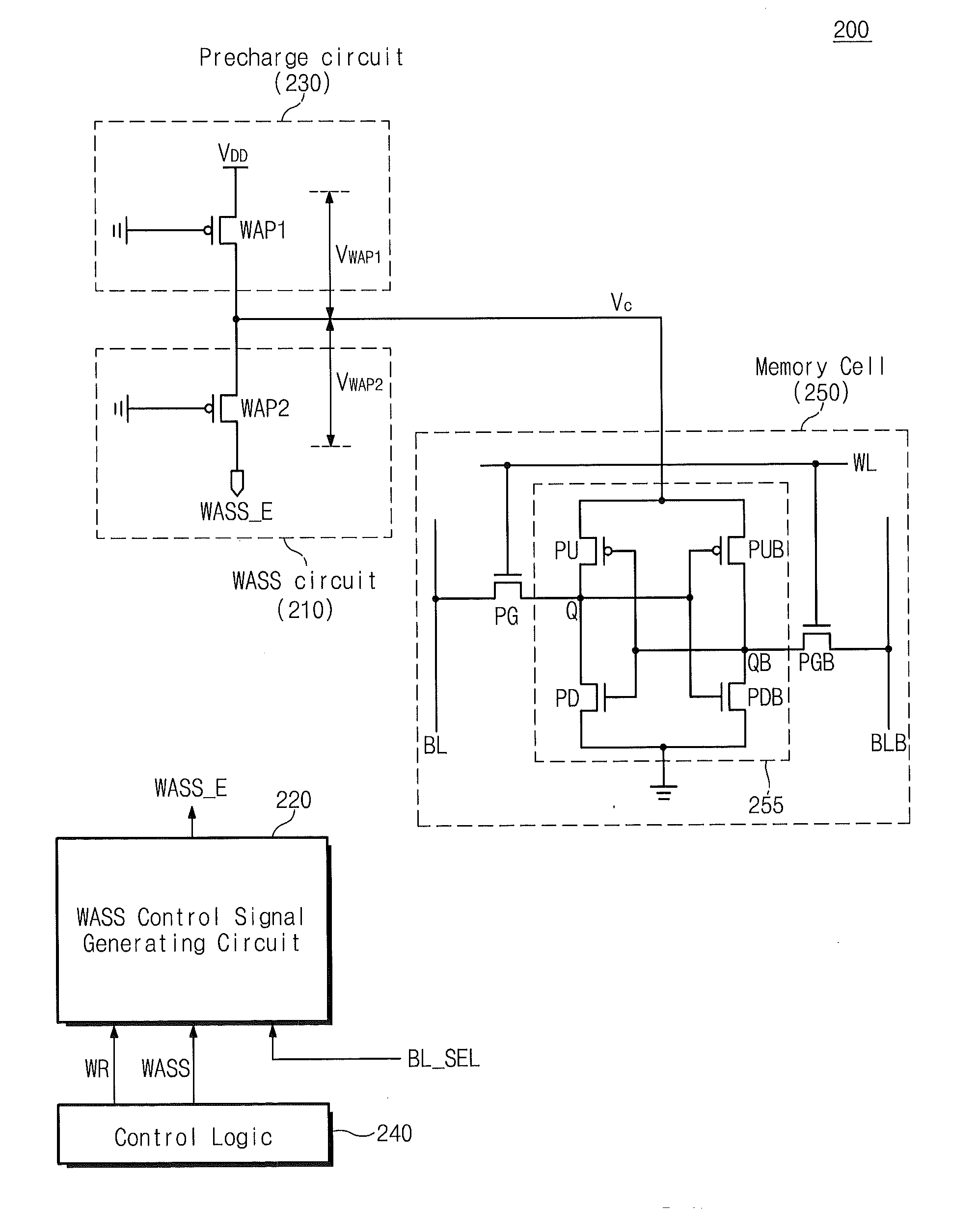
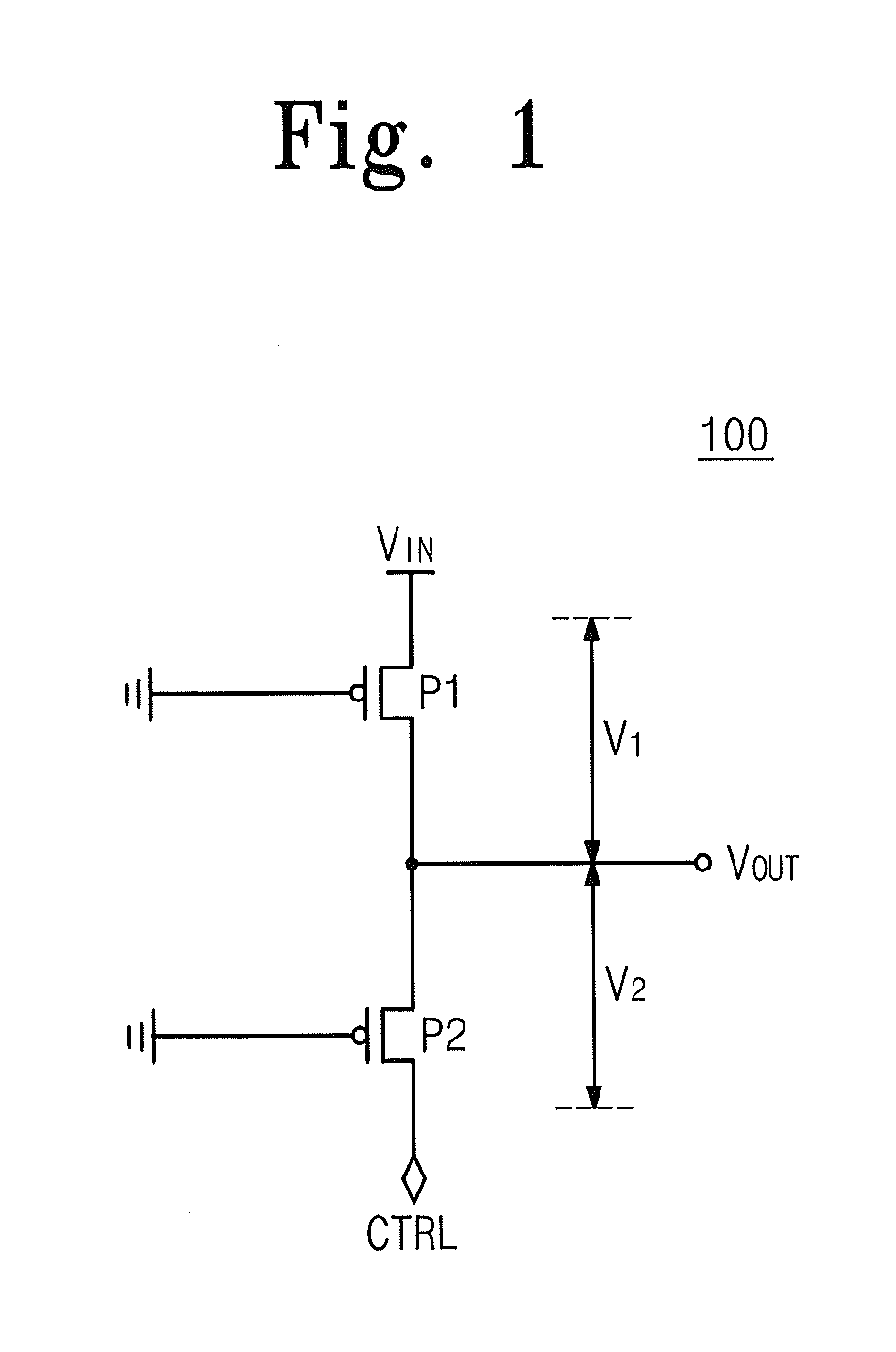
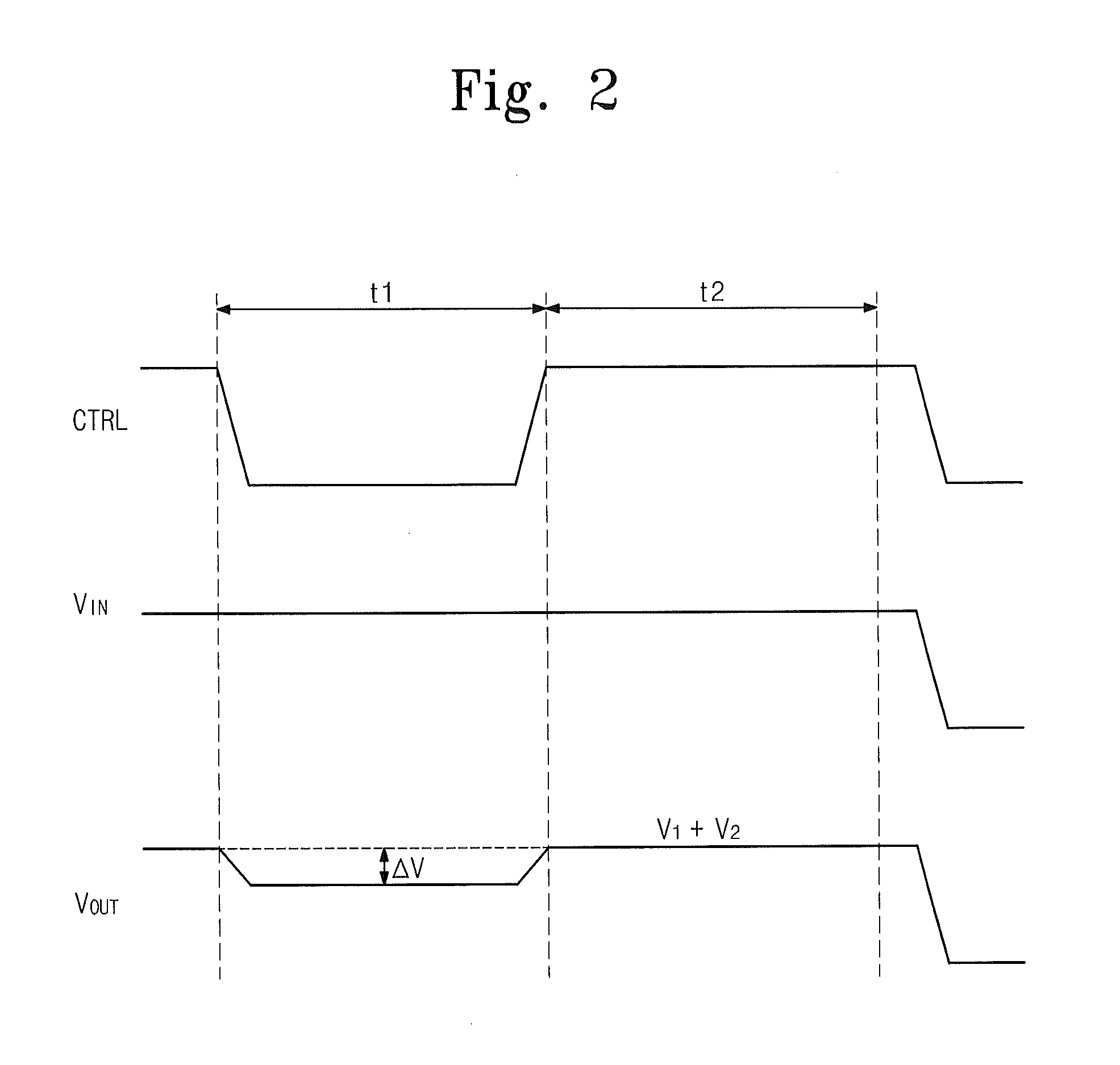
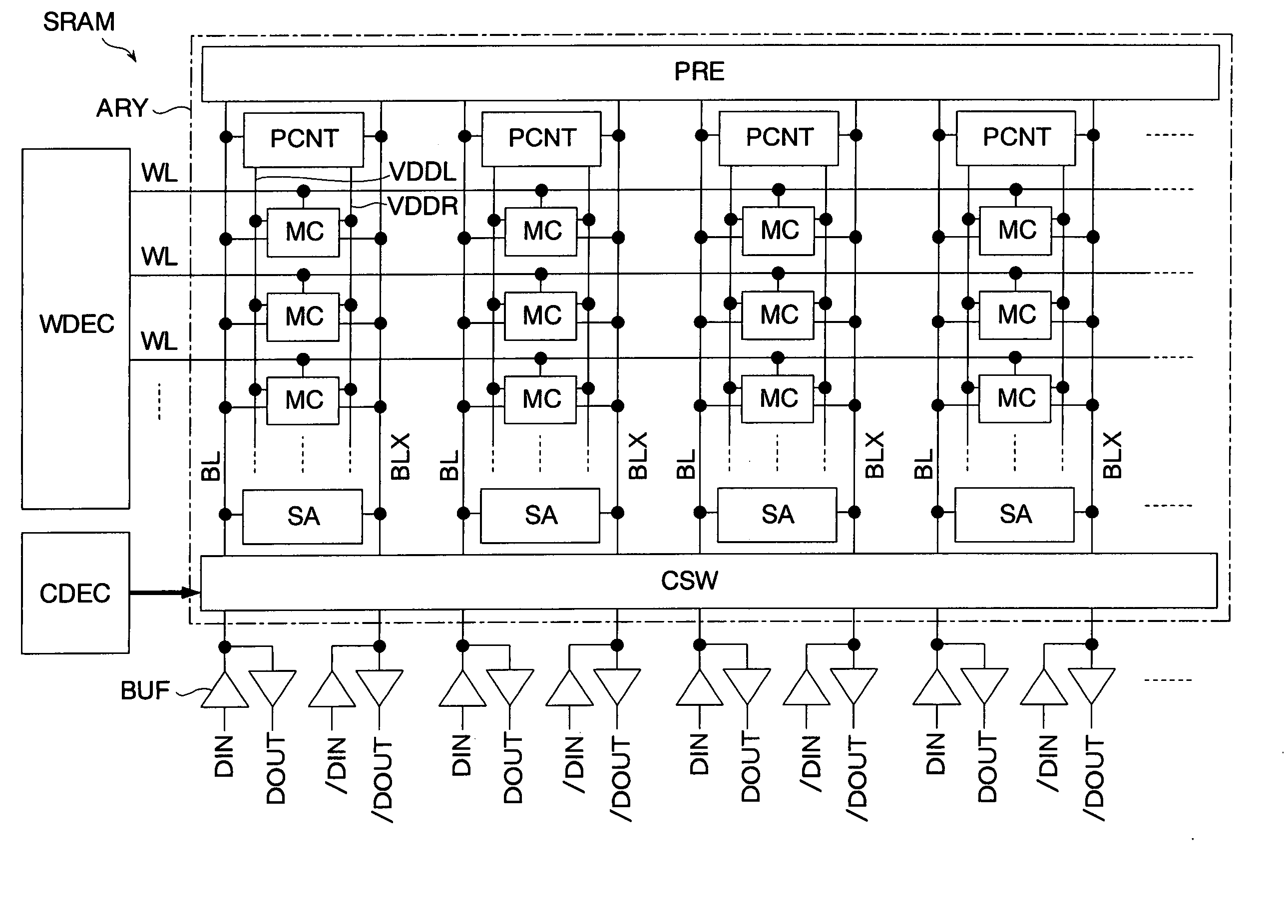
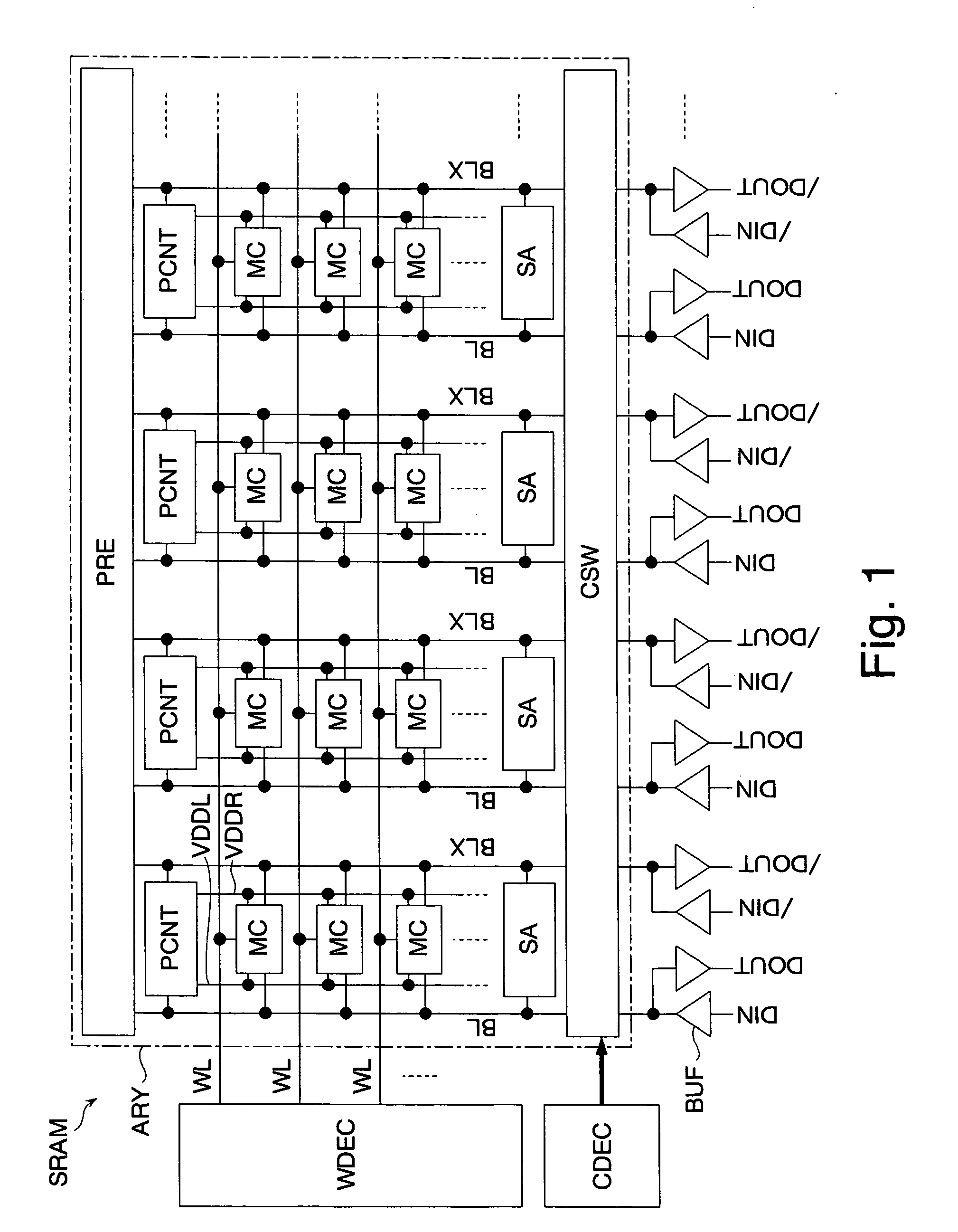
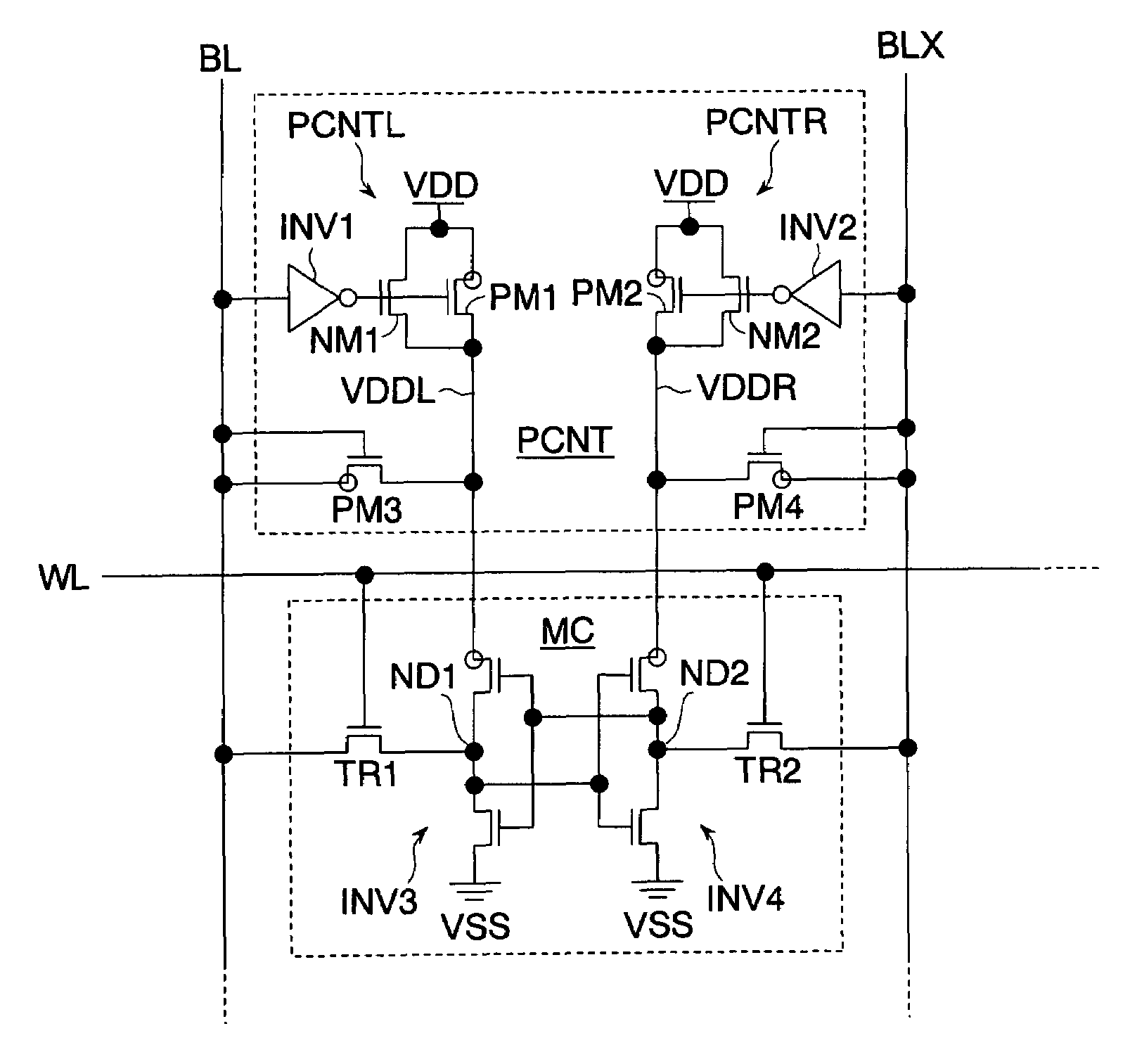
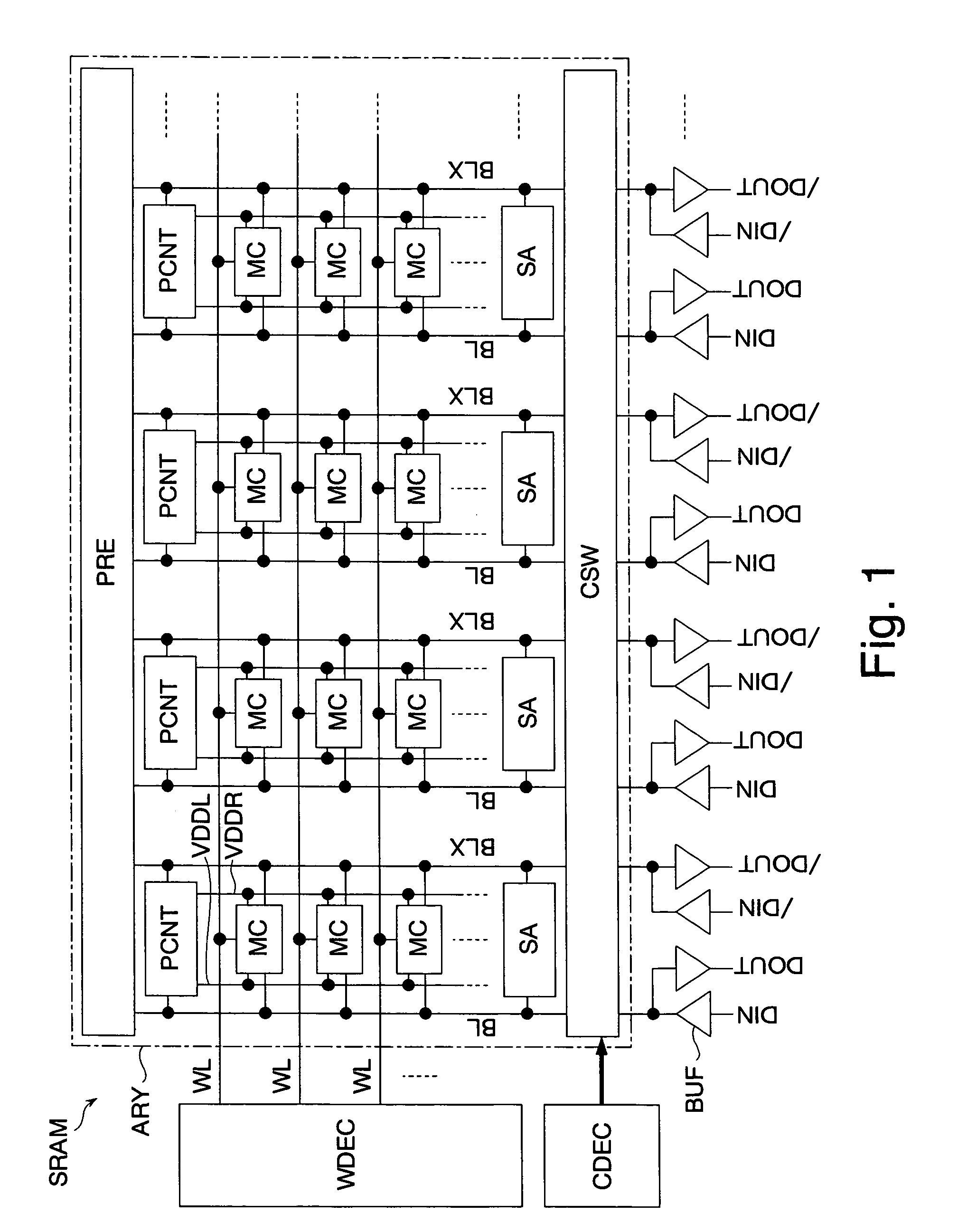
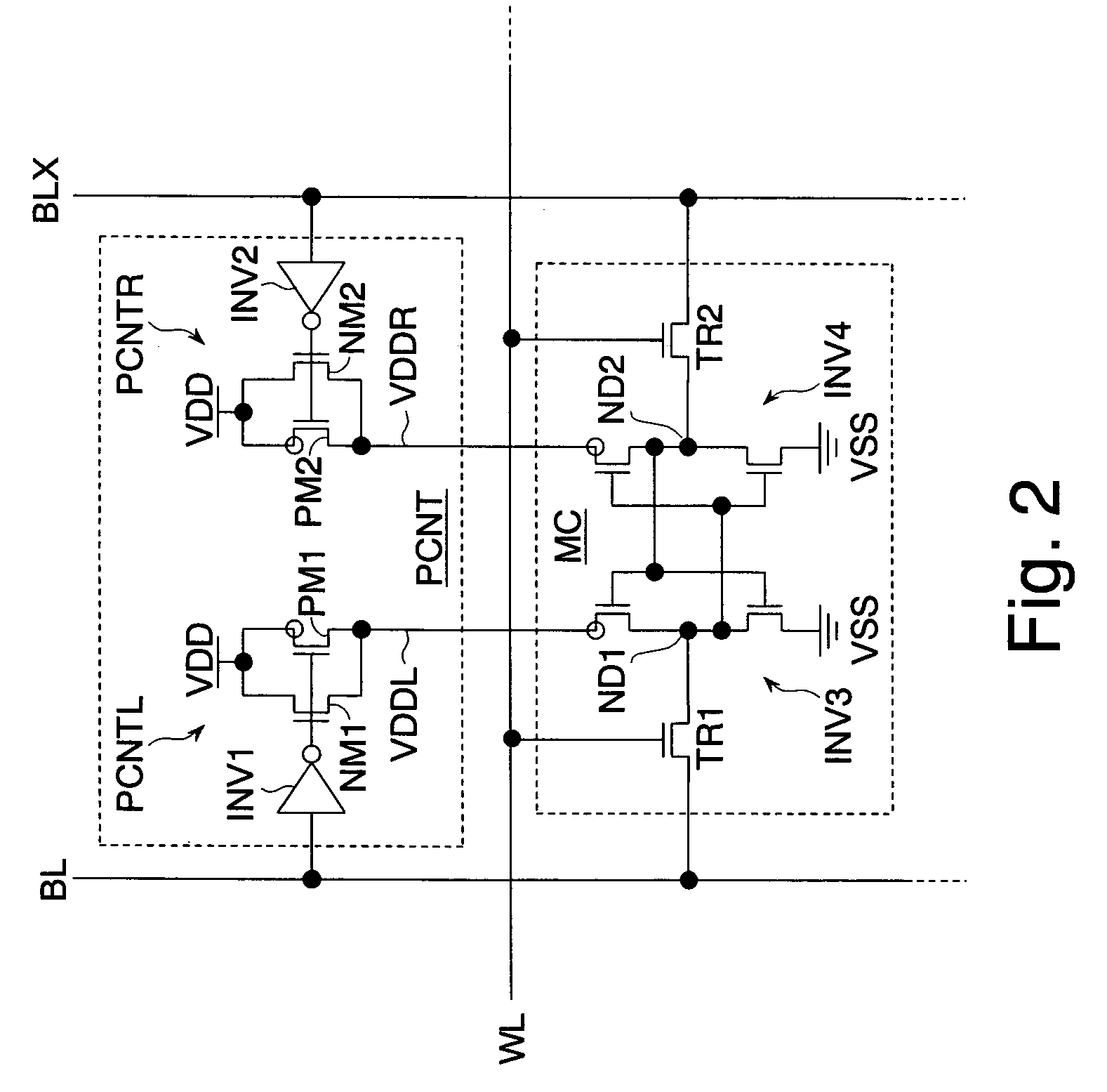
The invention provides a semiconductor integrated circuit device provided with an SRAM that satisfies the requirements for both the SNM and the write margin with a low supply voltage. The semiconductor integrated circuit device include: multiple static memory cells provided in correspondence with multiple word lines and multiple complimentary bit lines; multiple memory cell power supply lines that each supply an operational voltage to each of the multiple memory cells connected to the multiple complimentary bit lines each; multiple power supply circuits comprised of resistive units that each supply a power supply voltage to the memory cell power supply lines each; and a pre-charge circuit that supplies a pre-charge voltage corresponding to the power supply voltage to the complimentary bit lines, wherein the memory cell power supply lines are made to have coupling capacitances to thereby transmit a write signal on corresponding complimentary bit lines.
Owner:RENESAS ELECTRONICS CORP
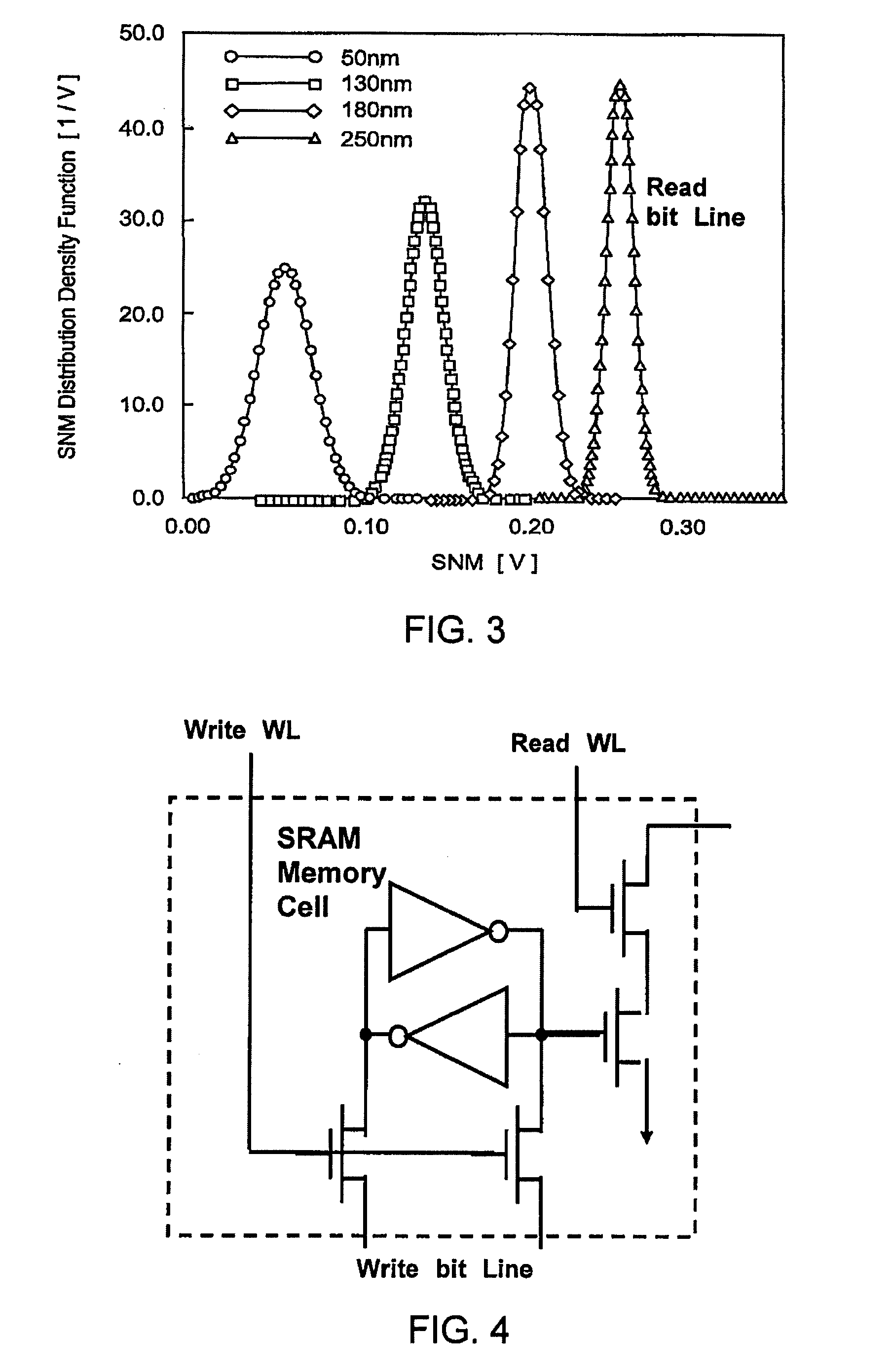
Semiconductor memory device and driving method thereof
ActiveUS20090027947A1Reduce leakage currentPrevent corruptionTransistorDigital storageWrite marginEngineering
In a reading operation, an off time and a reading time of a holding control transistor is controlled by a replica circuit, so that a read margin is enlarged. Furthermore, a high power source potential and a low power source potential of an SRAM memory cell are switched in reading and writing operations of the memory cell and in a data holding state by a power source potential switching portion. As a result, a write margin is enlarged, and a leakage current is reduced.
Owner:NEC CORP
Dynamic multi-Vcc scheme for SRAM cell stability control
A dynamic multi-voltage memory array features SRAM cells that are subjected to different biasing conditions, depending on the operating mode of the cells. The selected SRAM cell receives a first voltage when a read operation is performed, and receives a second voltage when a write operation is performed. By biasing the cell differently for the two distinct operations, a total decoupling of the read and write operations is achieved. The disclosed memory array, as well as future SRAM designs incorporating the multi-voltage capability thus avoid the conflicting requirements of read and write operations. Random single-bit failures of the memory array are reduced, due to the improvement in read stability and write margin.
Owner:TAHOE RES LTD
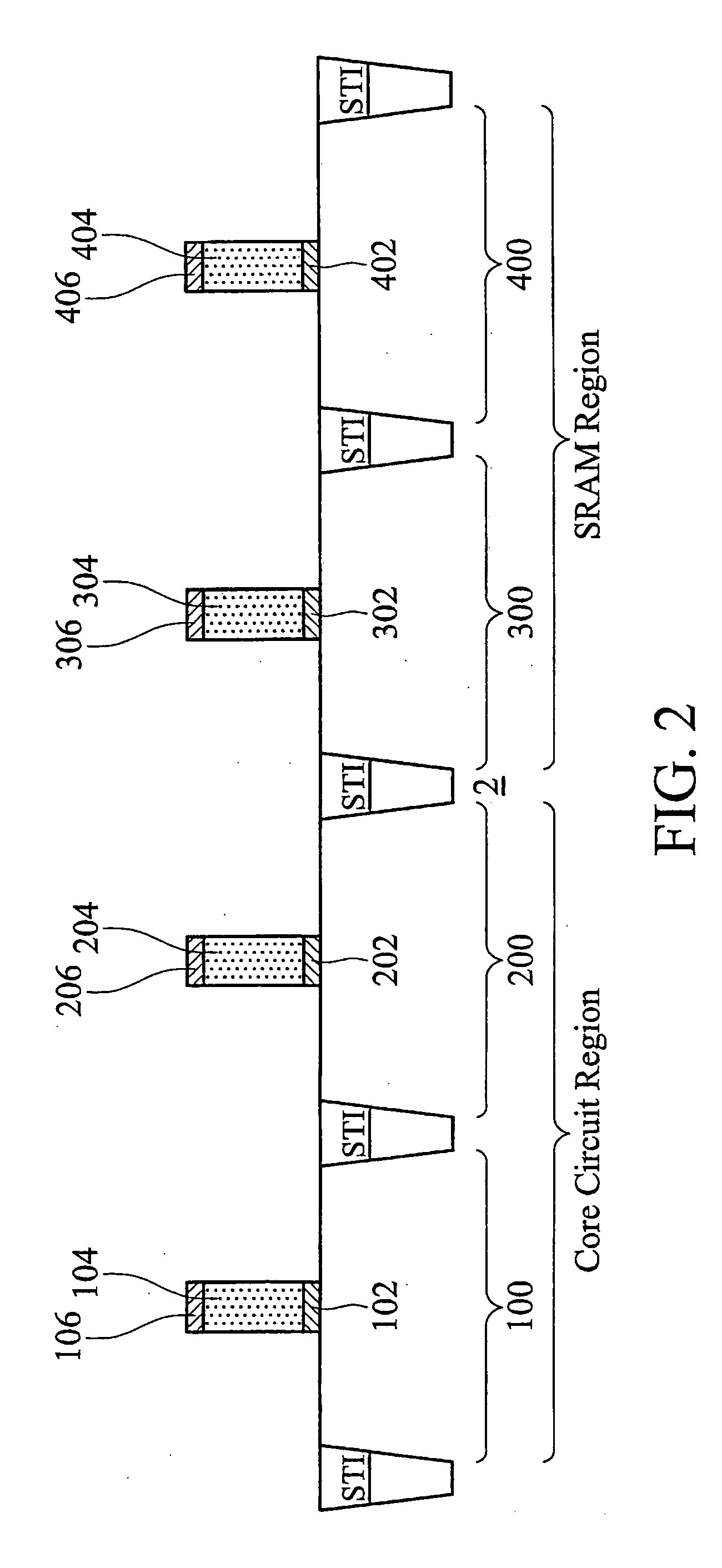
Write margin improvement for SRAM cells with SiGe stressors
ActiveUS20070235817A1Total current dropWrite margins of SRAM cells are improvedTransistorSolid-state devicesWrite marginSemiconductor structure
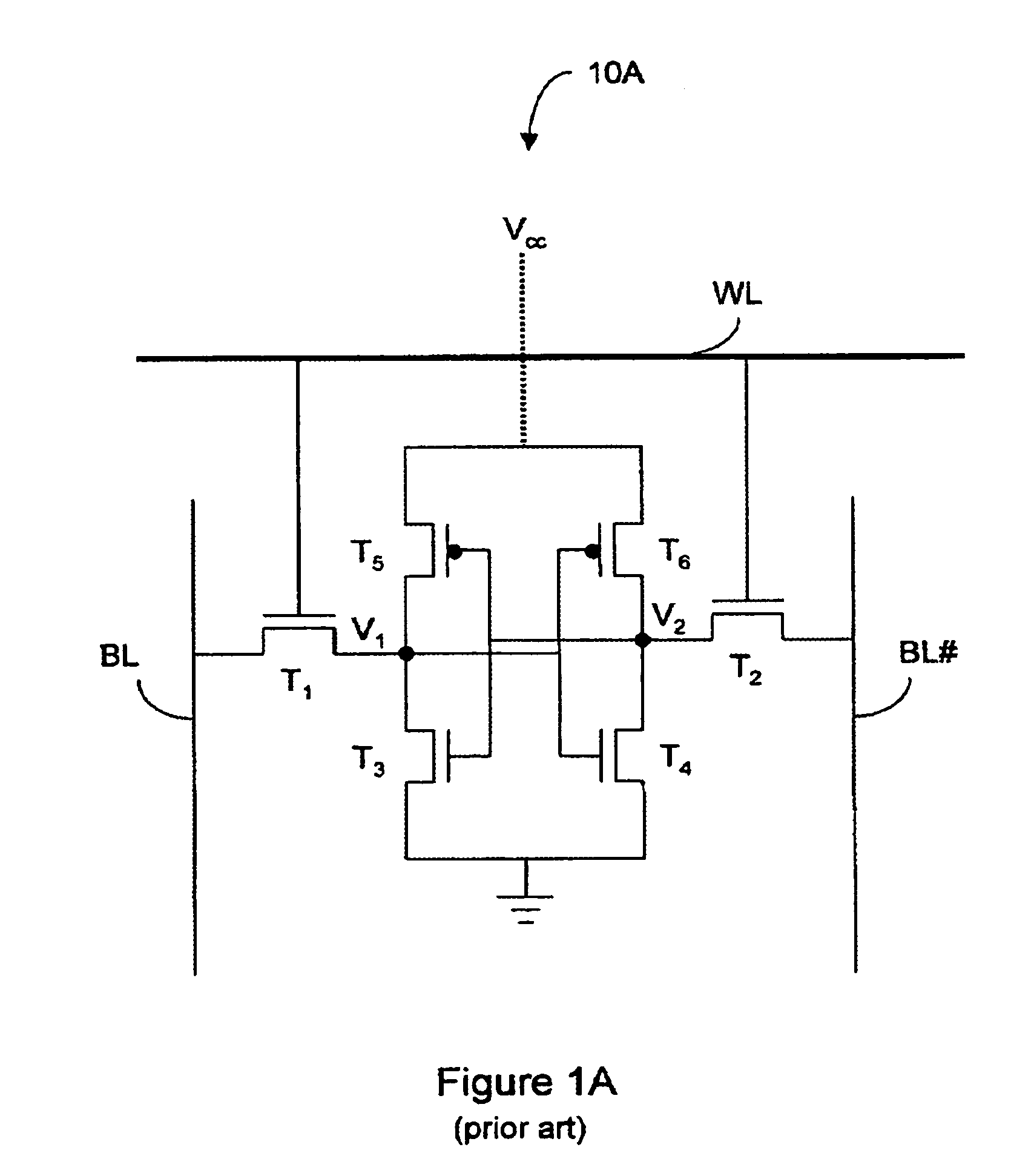
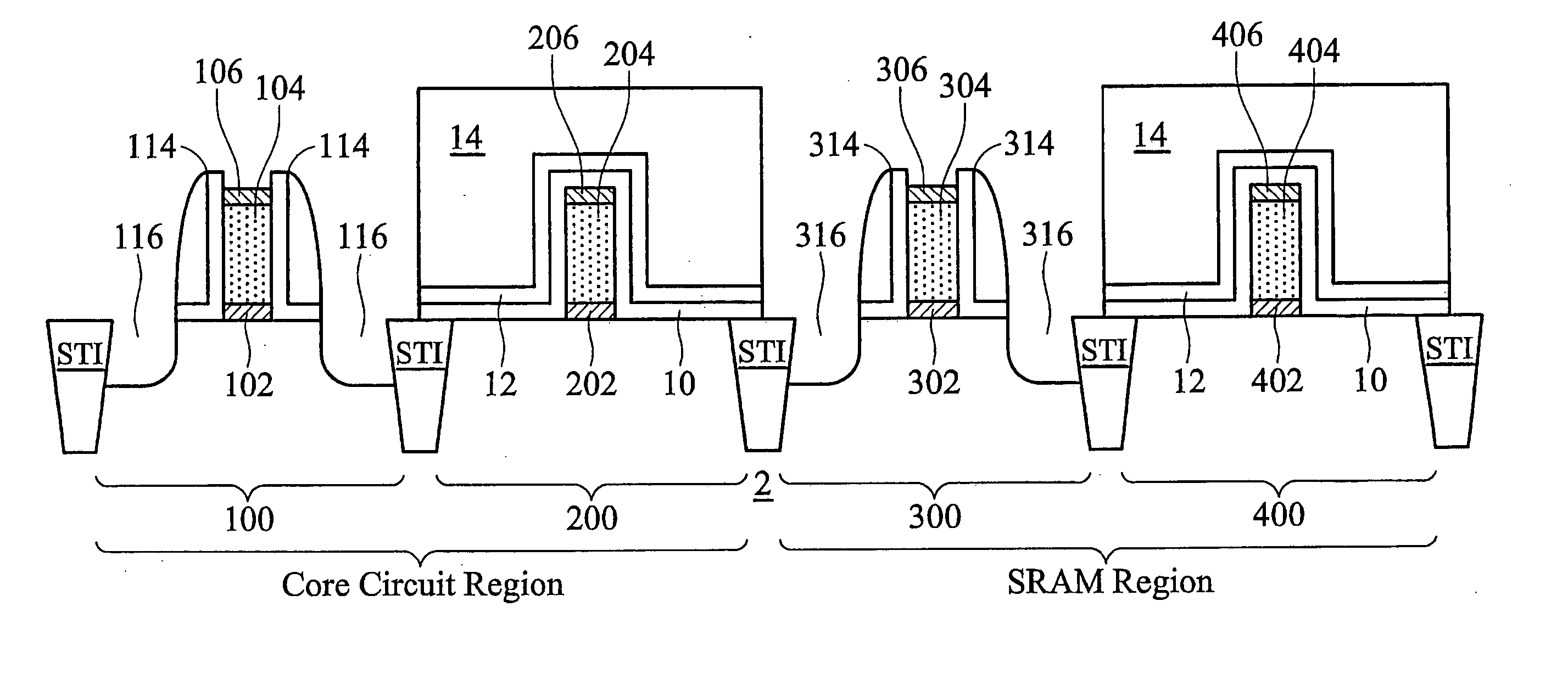
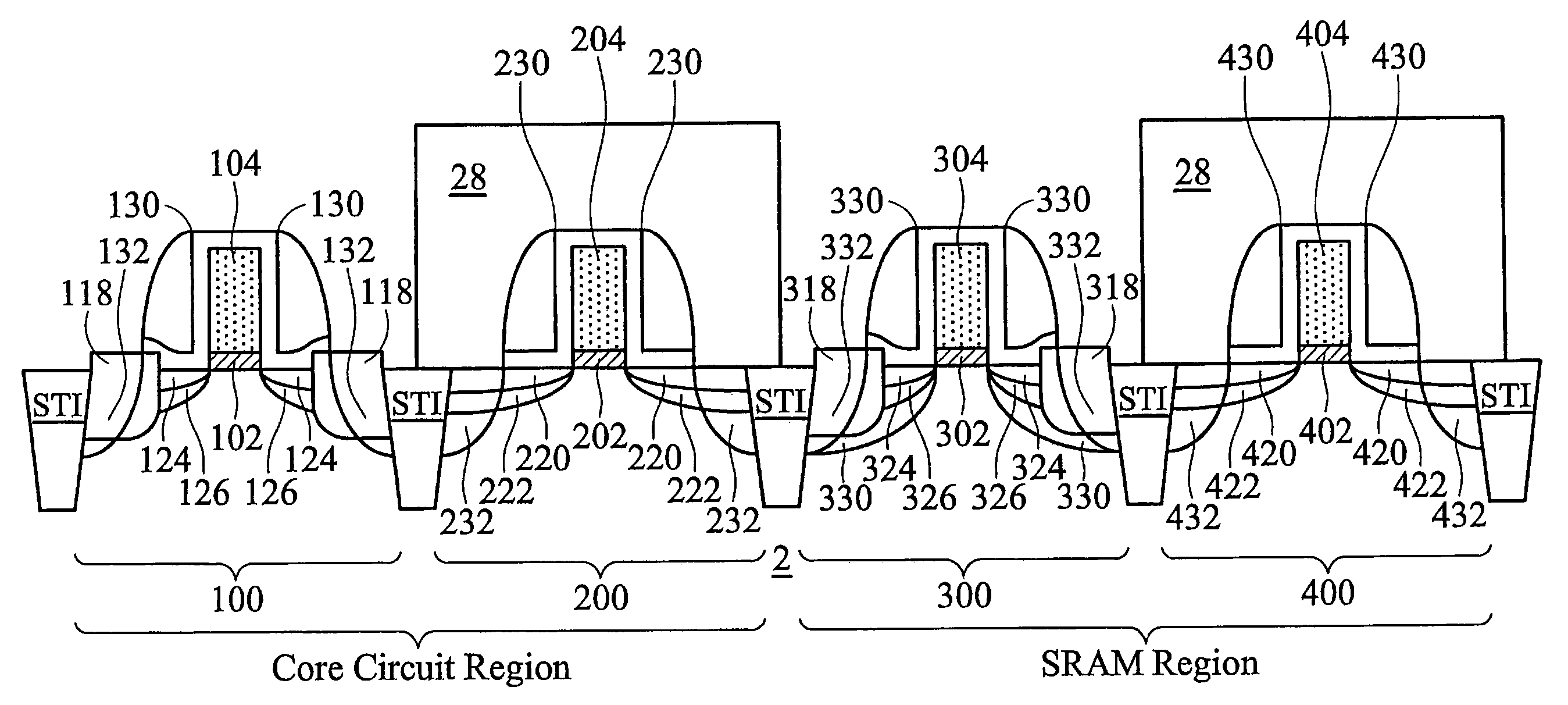
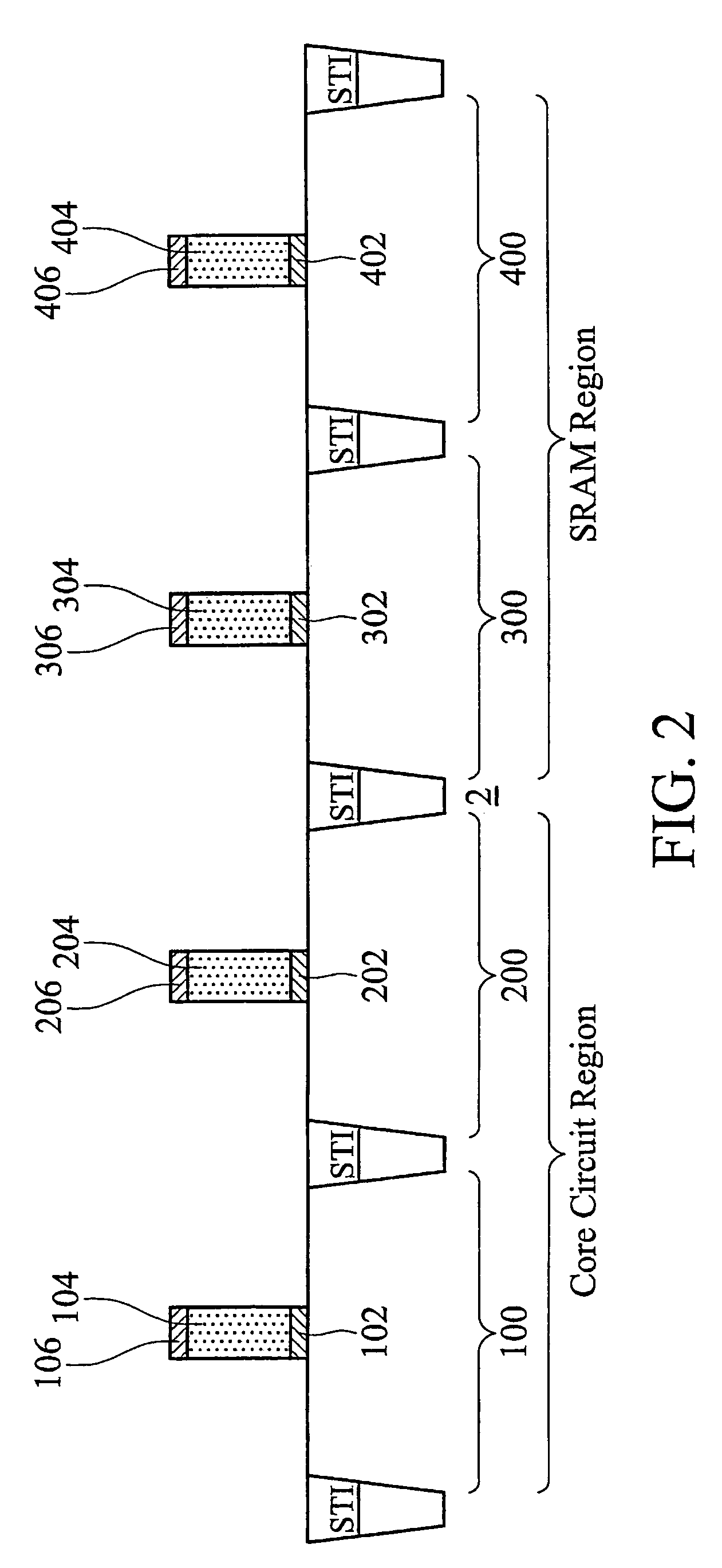
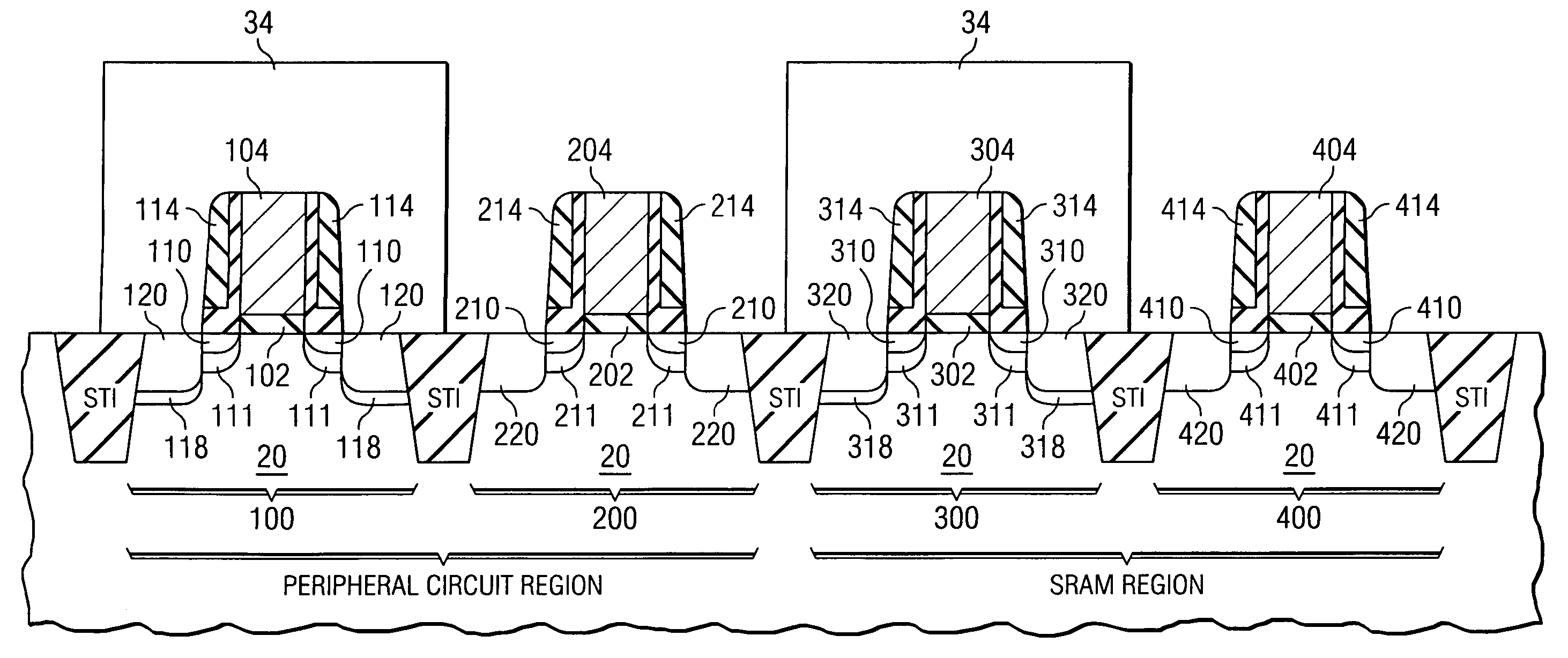
A semiconductor structure including SRAM cells with improved write margins and a method for forming the same are provided. The semiconductor structure comprises a substrate including a core circuit and an SRAM cell. The SRAM cell includes a pull-up PMOS device that comprises a first source / drain region in the substrate, a first SiGe stressor having a portion overlapping at least a portion of the first source / drain region, and a first current-tuning region having a portion overlapping at least a portion of the first source / drain region. The core circuit comprises a core PMOS device that comprises a second source / drain region in the substrate, and a second SiGe stressor having a portion overlapping at least a portion of the second source / drain region. The core PMOS device is free of current-tuning regions.
Owner:TAIWAN SEMICON MFG CO LTD
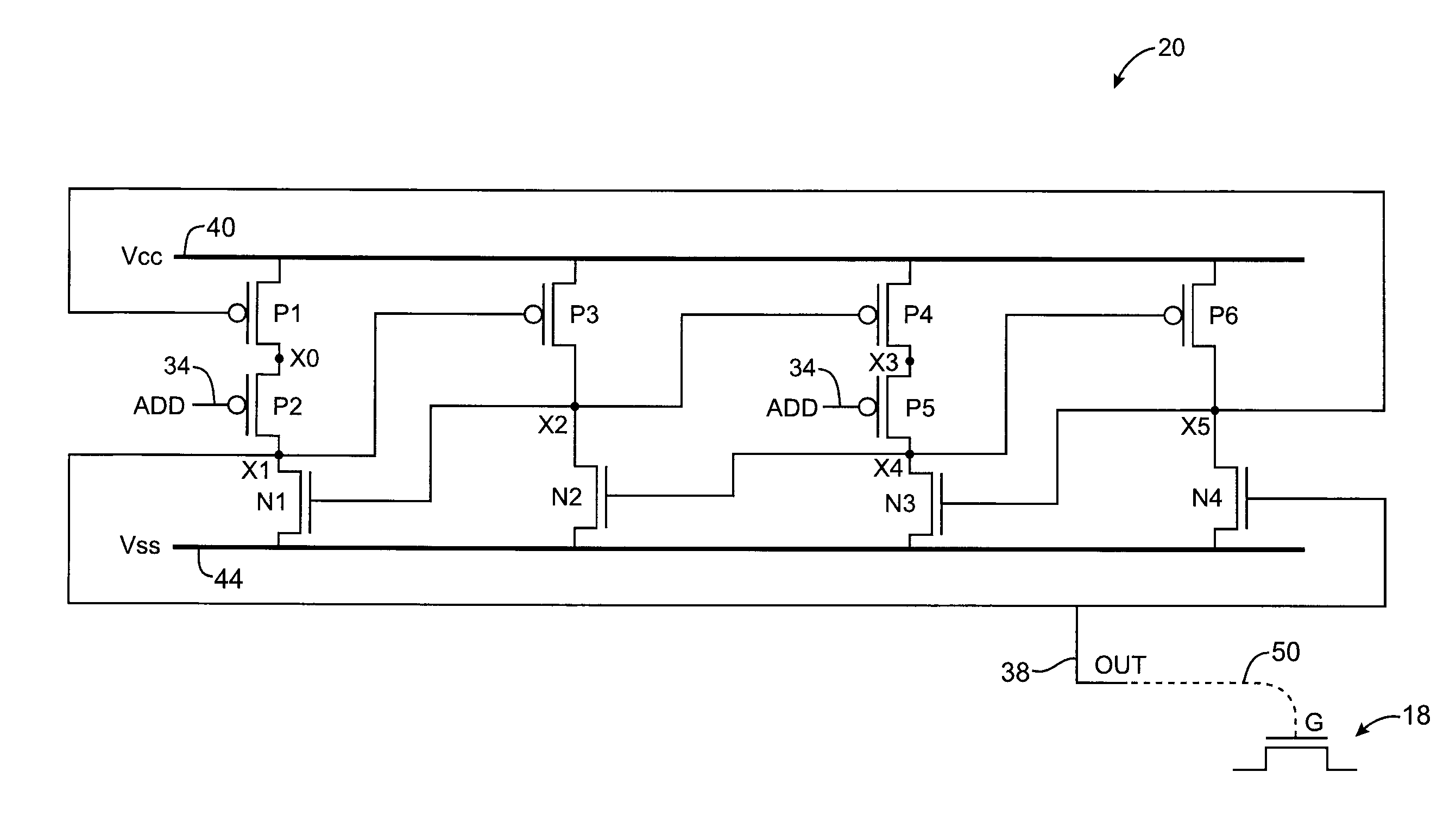
Memory elements with increased write margin and soft error upset immunity
Memory elements are provided that exhibit immunity to soft error upset events when subjected to radiation strikes such as high-energy atomic particle strikes. The memory elements may each have four inverter-like transistor pairs that form a bistable element and a pair of address transistors. There may be four nodes in the transistor each of which is associated with a respective one of the four inverter-like transistor pairs. There may be two control transistors each of which is coupled between the transistors in a respective one of the inverter-like transistor pairs. During data writing operations, the two control transistors may be turned off to temporarily decouple the transistors in two of the four inverter-like transistor pairs.
Owner:TAHOE RES LTD
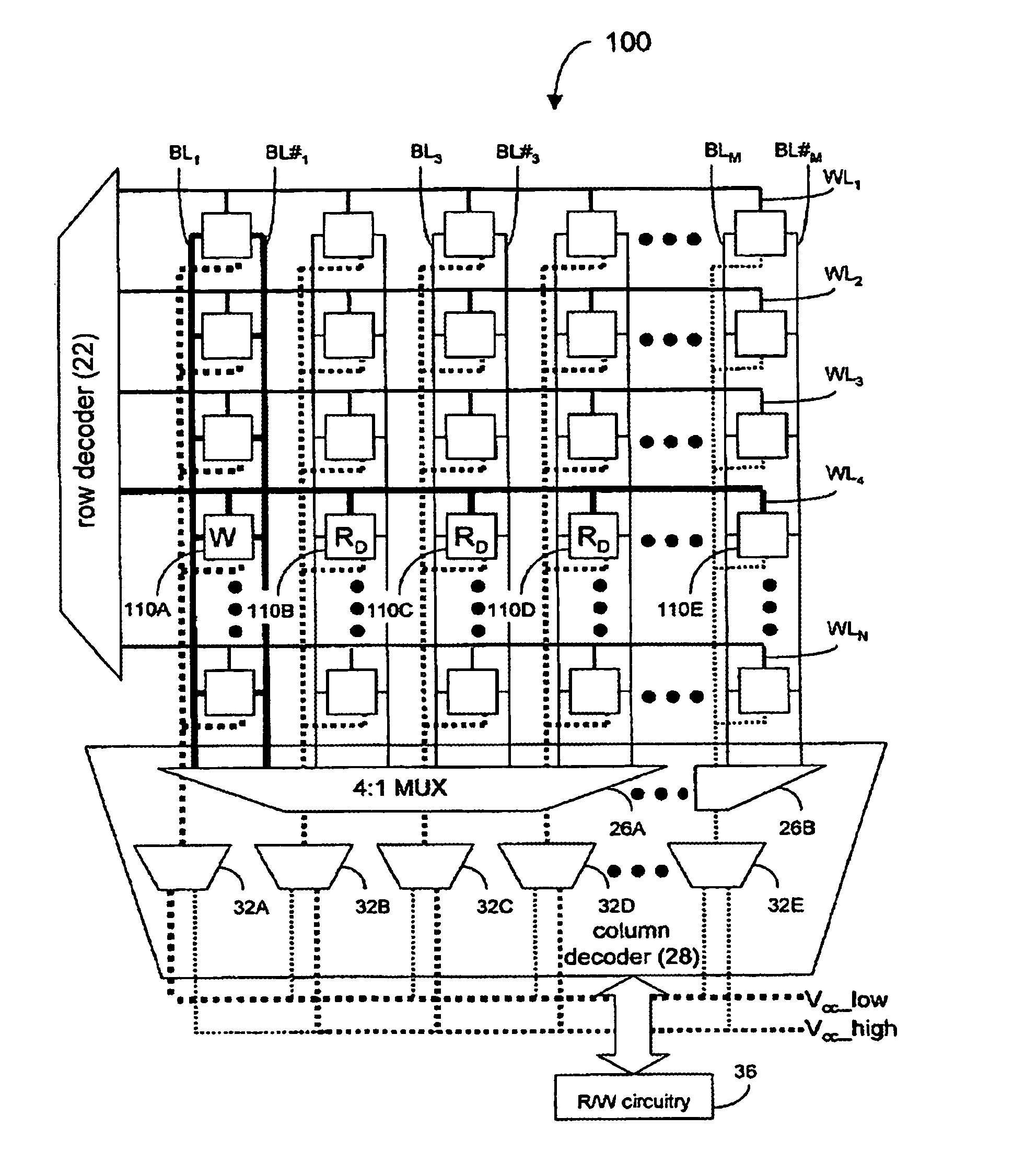
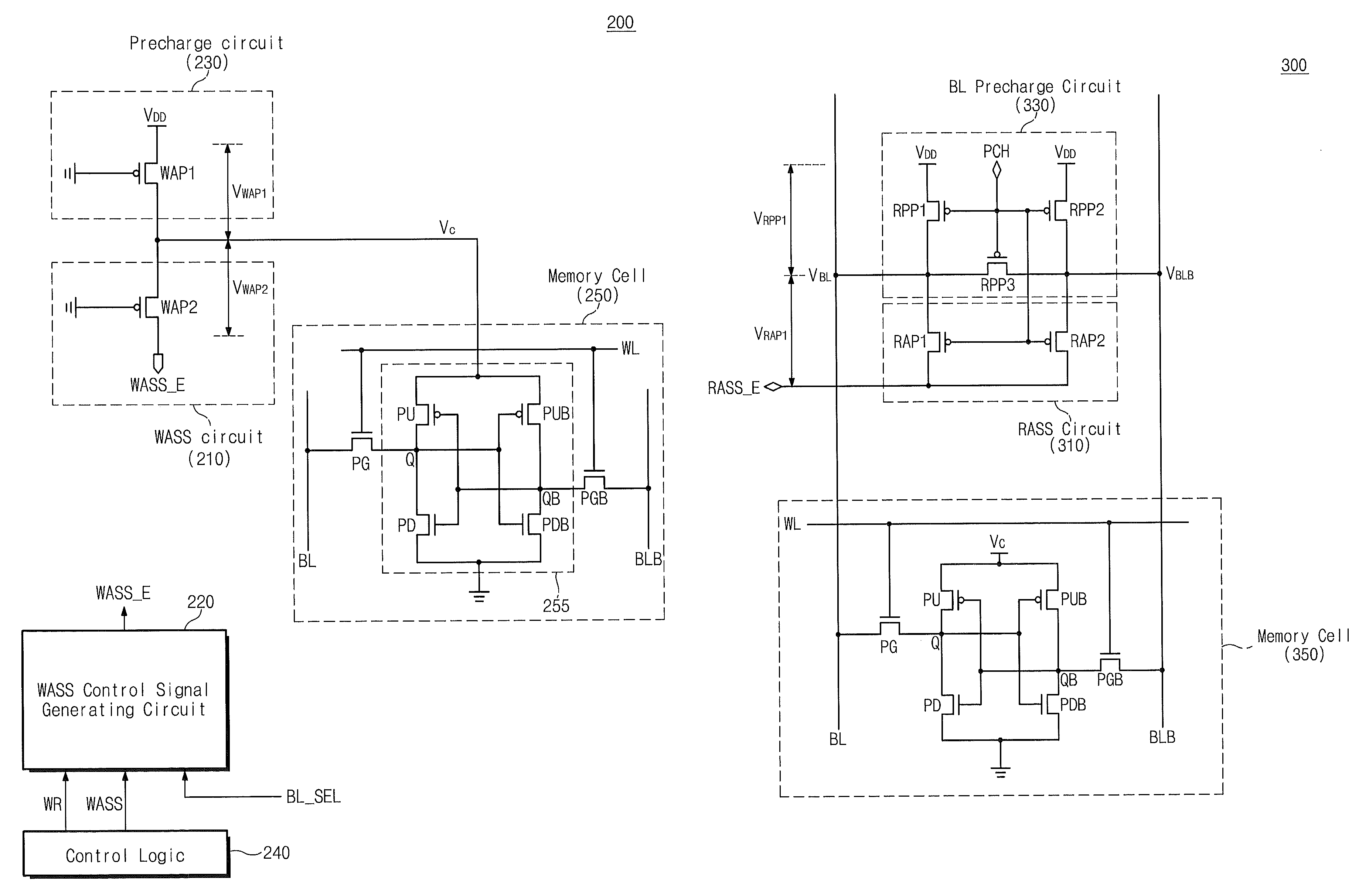
Static Random Access Memory Devices Having Read And Write Assist Circuits Therein That Improve Read And Write Reliability
Integrated circuit memory devices include a memory cell configured to receive a power supply signal and a write assist circuit. The. write assist circuit is configured to improve write margins by reducing a magnitude of the power supply signal supplied to the memory cell from a first voltage level to a lower second voltage level during an operation to write data into the memory cell. The memory device further includes at least one bit line electrically coupled to the memory cell and a read assist circuit. The read assist circuit may be configured to improve read reliability by partially discharging the at least one bit line from an already precharged voltage level to a lower third voltage level in preparation to read data from the memory cell.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
Semiconductor memory
InactiveUS20070081407A1Improve write marginIncrease in circuit scaleDigital storageWrite marginEngineering
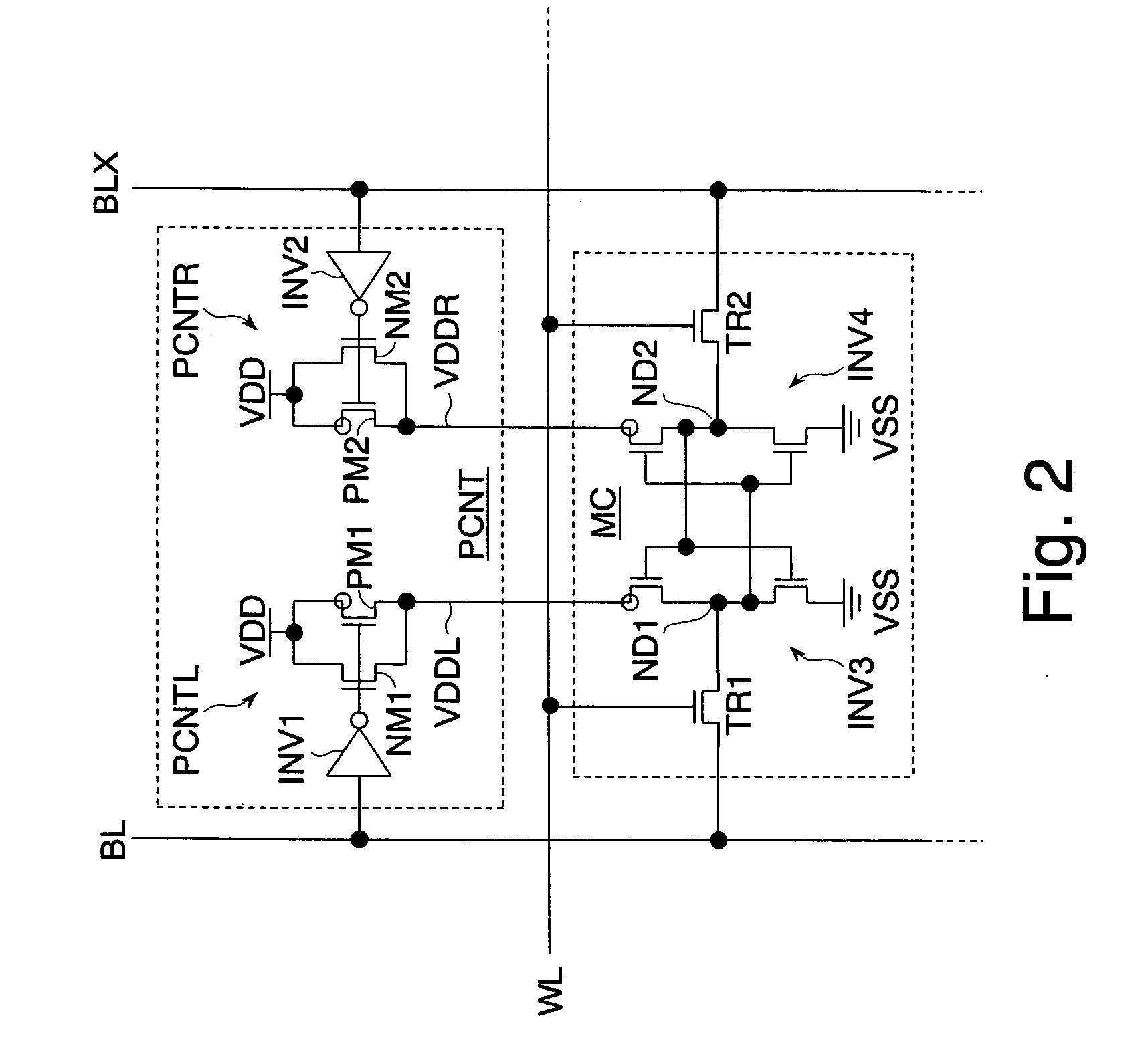
Each memory cell has a pair of inverters whose inputs and outputs are connected to each other and holds complementary data respectively in storage nodes which are outputs of the inverters. In a write operation during which the complementary data are written to the storage nodes respectively, the power control circuit sets a power supply voltage of the inverter having the storage node to which low level is written lower than a power supply voltage of the inverter having the storage node to which high level is written. Since power supply capability to the inverter having the storage node to which the low level is written lowers, the voltage of the storage node easily changes to the low level. That is, a write margin of a memory cell can be improved.
Owner:SOCIONEXT INC
Static memory cell and SRAM device
Owner:TEXAS INSTR INC
Modifying work function in PMOS devices by counter-doping
InactiveUS20070257308A1Increased write marginsImprove reliabilityTransistorSolid-state devicesDriving currentGate dielectric
A semiconductor structure comprising an SRAM / inverter cell and a method for forming the same are provided, wherein the SRAM / inverter cell has an improved write margin. The SRAM / inverter cell includes a pull-up PMOS device comprising a gate dielectric over the semiconductor substrate, a gate electrode on the gate dielectric wherein the gate electrode comprises a p-type impurity and an n-type impurity, and a stressor formed in a source / drain region. The device drive current of the pull-up PMOS device is reduced due to the counter-doping of the gate electrode.
Owner:TAIWAN SEMICON MFG CO LTD
Write margin of SRAM cells improved by controlling power supply voltages to the inverters via corresponding bit lines
Owner:SOCIONEXT INC
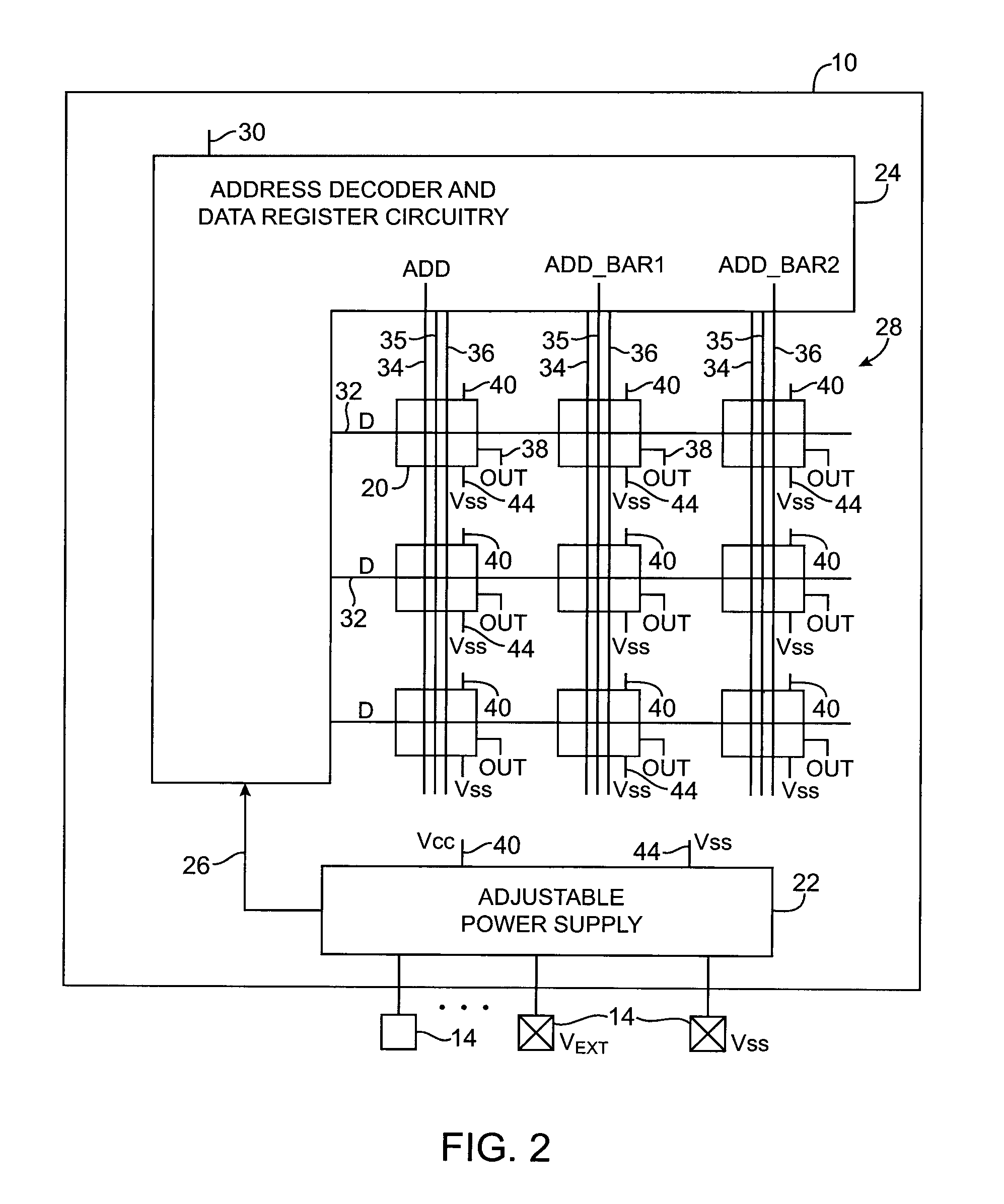
Volatile memory elements with boosted output voltages for programmable logic device integrated circuits
ActiveUS20070113106A1Increases write marginReduce power supply voltageVolume/mass flow measurementPower supply for data processingWrite marginProgrammable logic device
Integrated circuits are provided that have memory elements. The memory elements produce output signals. The integrated circuits may be programmable logic device integrated circuits containing programmable logic including transistors with gates. When loaded with configuration data, the memory elements produce output signals that are applied to the gates of the transistors in the programmable logic device to customize the programmable logic. To ensure that the transistors in the programmable logic are turned on properly, the memory elements are powered with an elevated power supply level during normal device operation. During data loading operations, the power supply level for the memory elements is reduced. Reducing the memory element power supply level during loading increases the write margin for the memory elements.
Owner:ALTERA CORP
Dual-port static random access memory having improved cell stability and write margin
A dual-port memory includes a plurality of memory cells coupled to a row decoder and column logic. Each memory cell includes two storage nodes, where each storage node is coupled to a bit line via an access transistor. Each memory cell also includes a logic gate for logically combining a word line signal with a column address signal and providing the resulting output signal to the gates of the access transistors. In one embodiment, the logic gate is a NOR logic gate and in another embodiment, the logic gate is a transmission gate. This prevents a potential read disturb problem with unselected memory cells of a row. This also reduces power consumption in the memory.
Owner:NORTH STAR INNOVATIONS
Multiport semiconductor memory device capable of sufficiently steadily holding data and providing a sufficient write margin
InactiveUS7161868B2Reduced current driving force ratioHold data significantly steadilyDigital storageBit lineWrite margin
Owner:RENESAS TECH CORP
Write assist circuit for improving write margins of SRAM cells
ActiveUS7898875B2Increased VccminIncrease write speedRead-only memoriesDigital storageBit lineWrite margin
A memory circuit includes a memory array, which further includes a plurality of memory cells arranged in rows and columns; a plurality of first bit-lines, each connected to a column of the memory array; and a plurality of write-assist latches, each connected to one of the plurality of first bit-lines. Each of the plurality of write-assist latches is configured to increase a voltage on a connecting one of the plurality of first bit-lines.
Owner:TAIWAN SEMICON MFG CO LTD
Semiconductor device
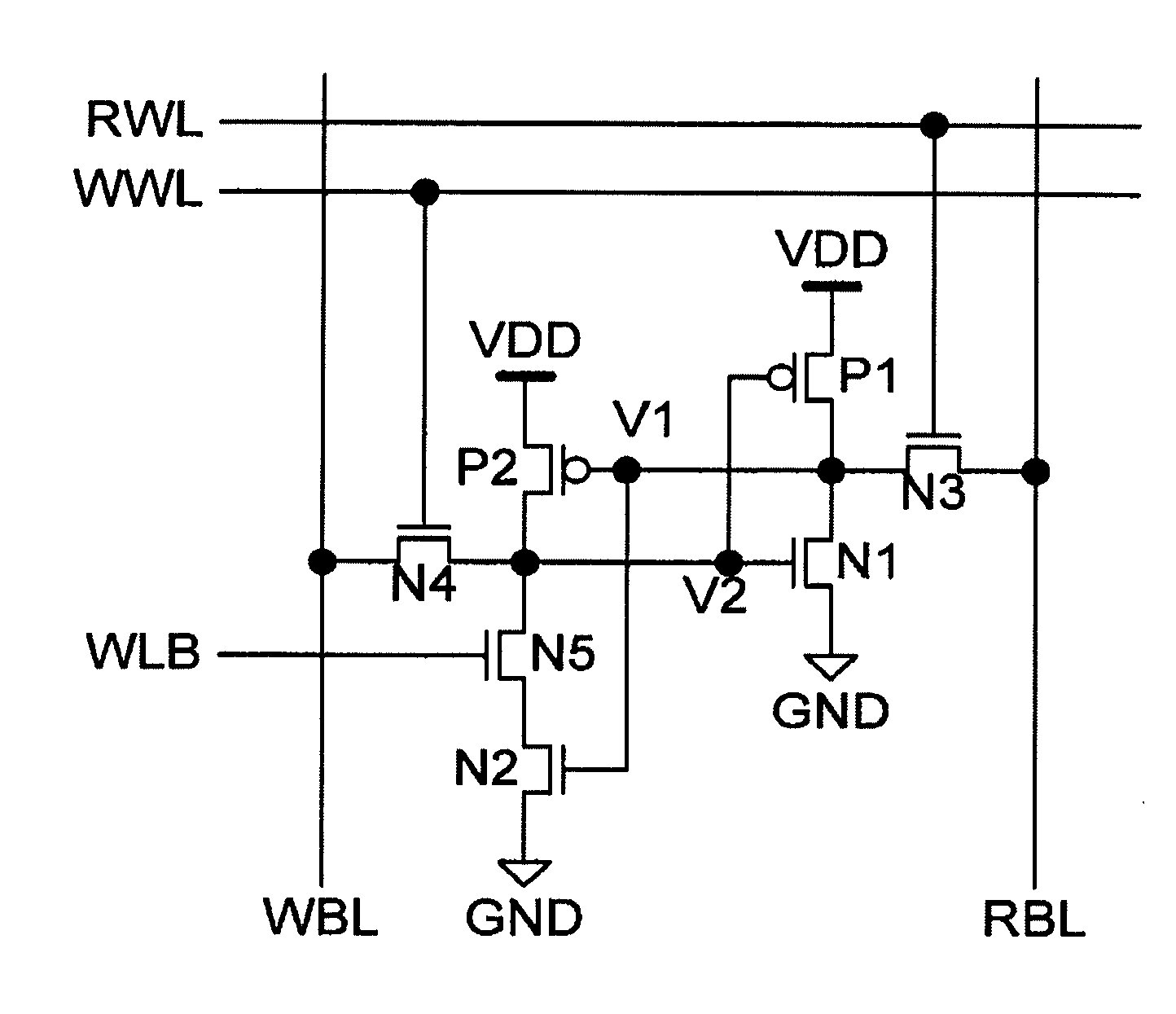
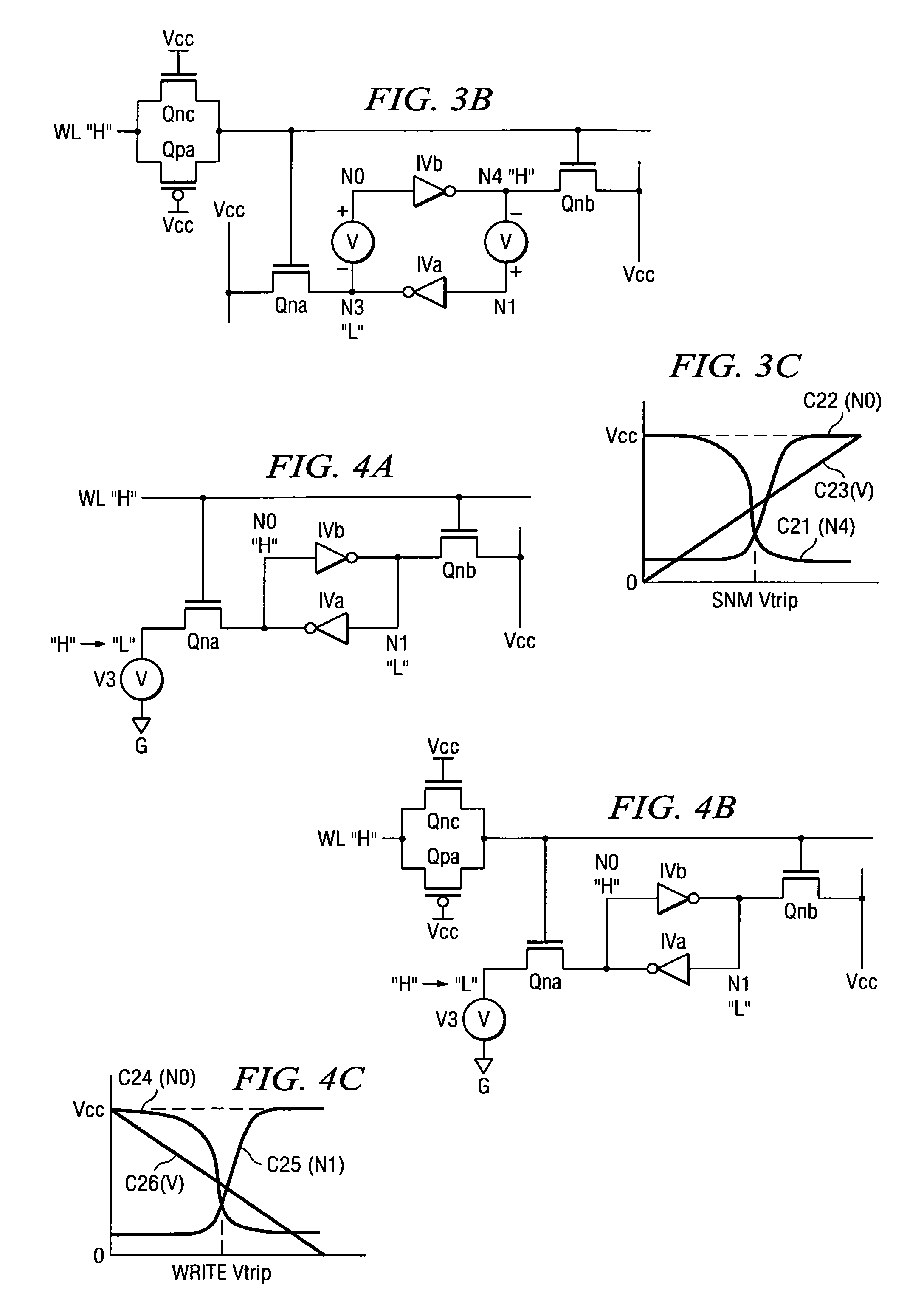
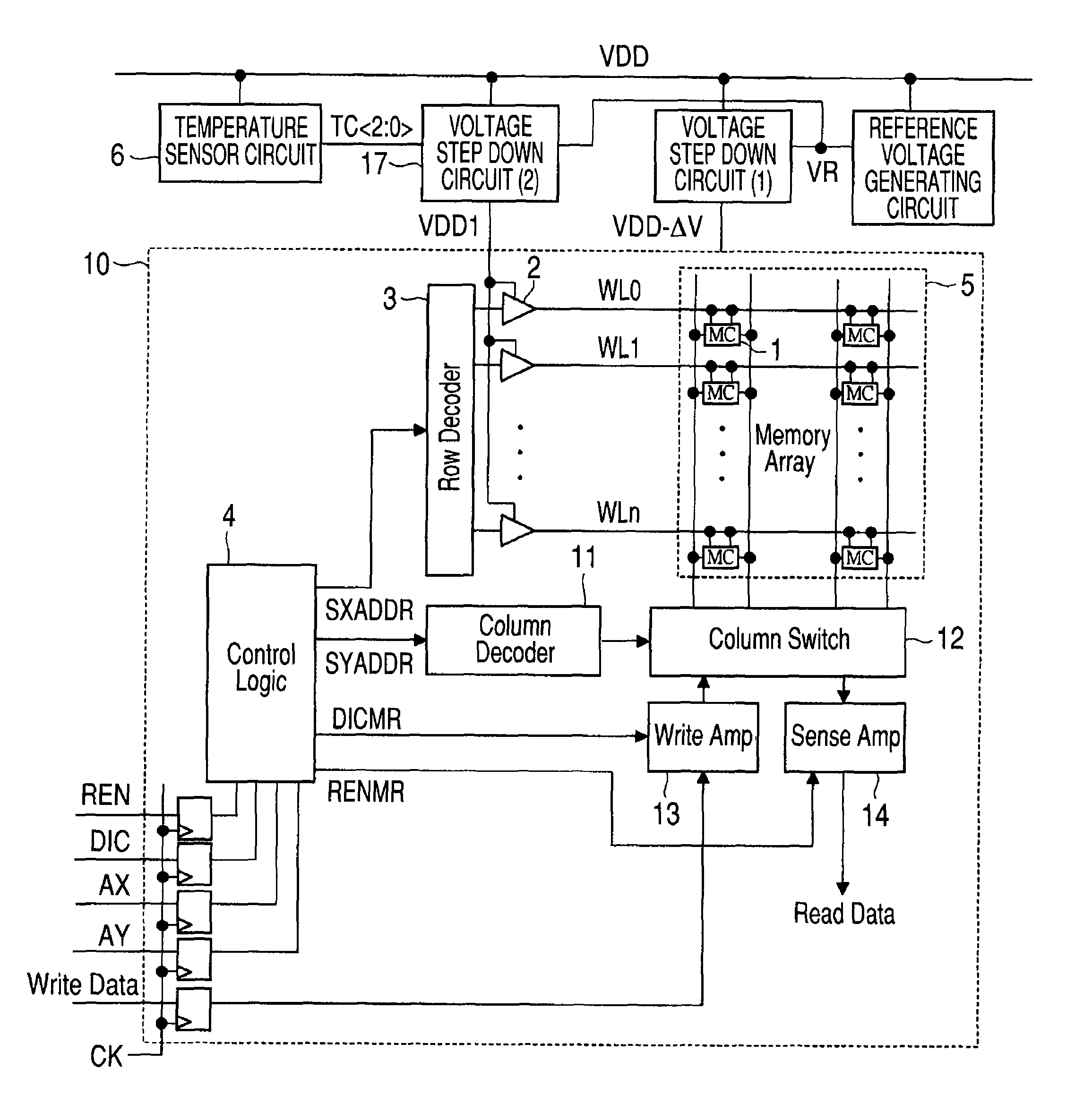
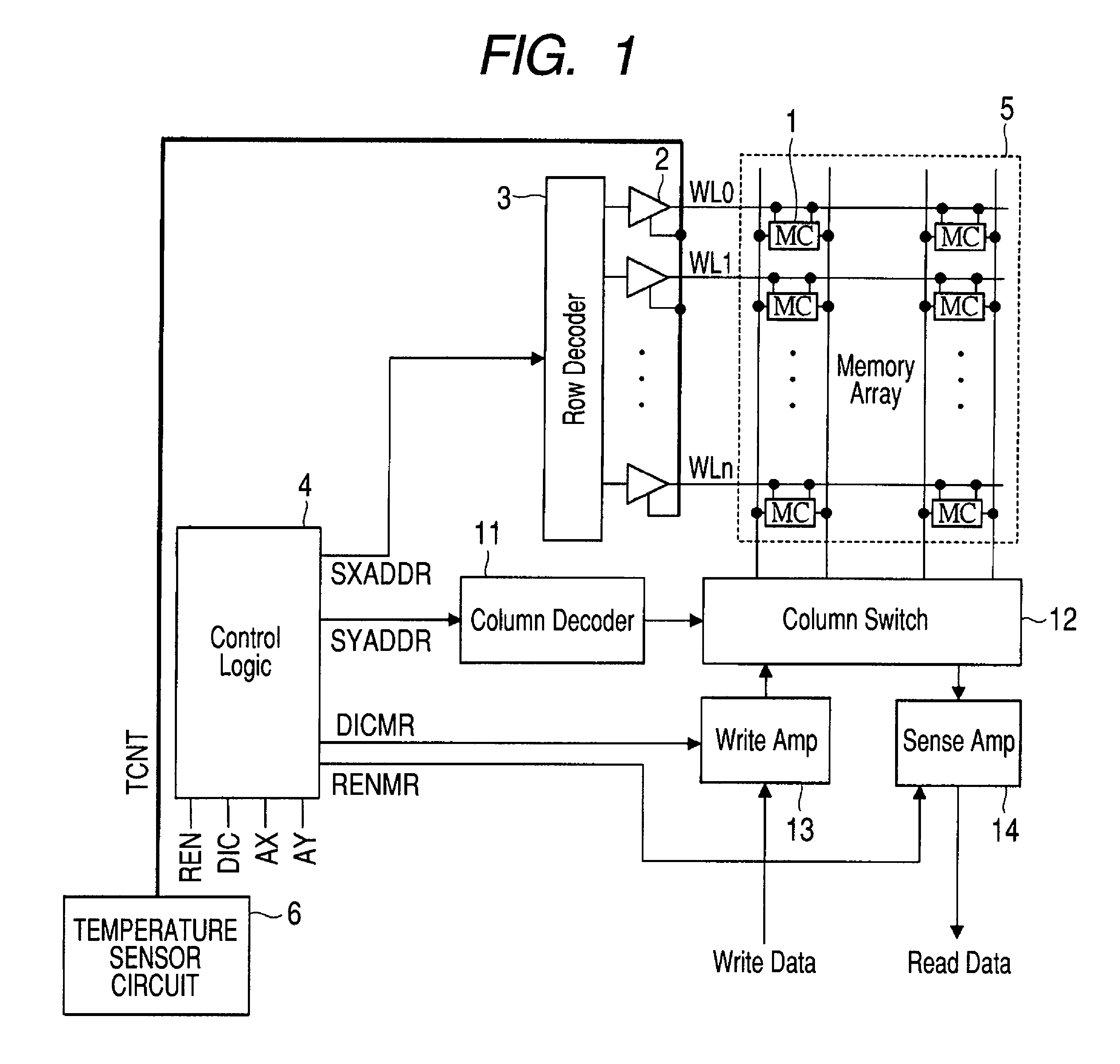
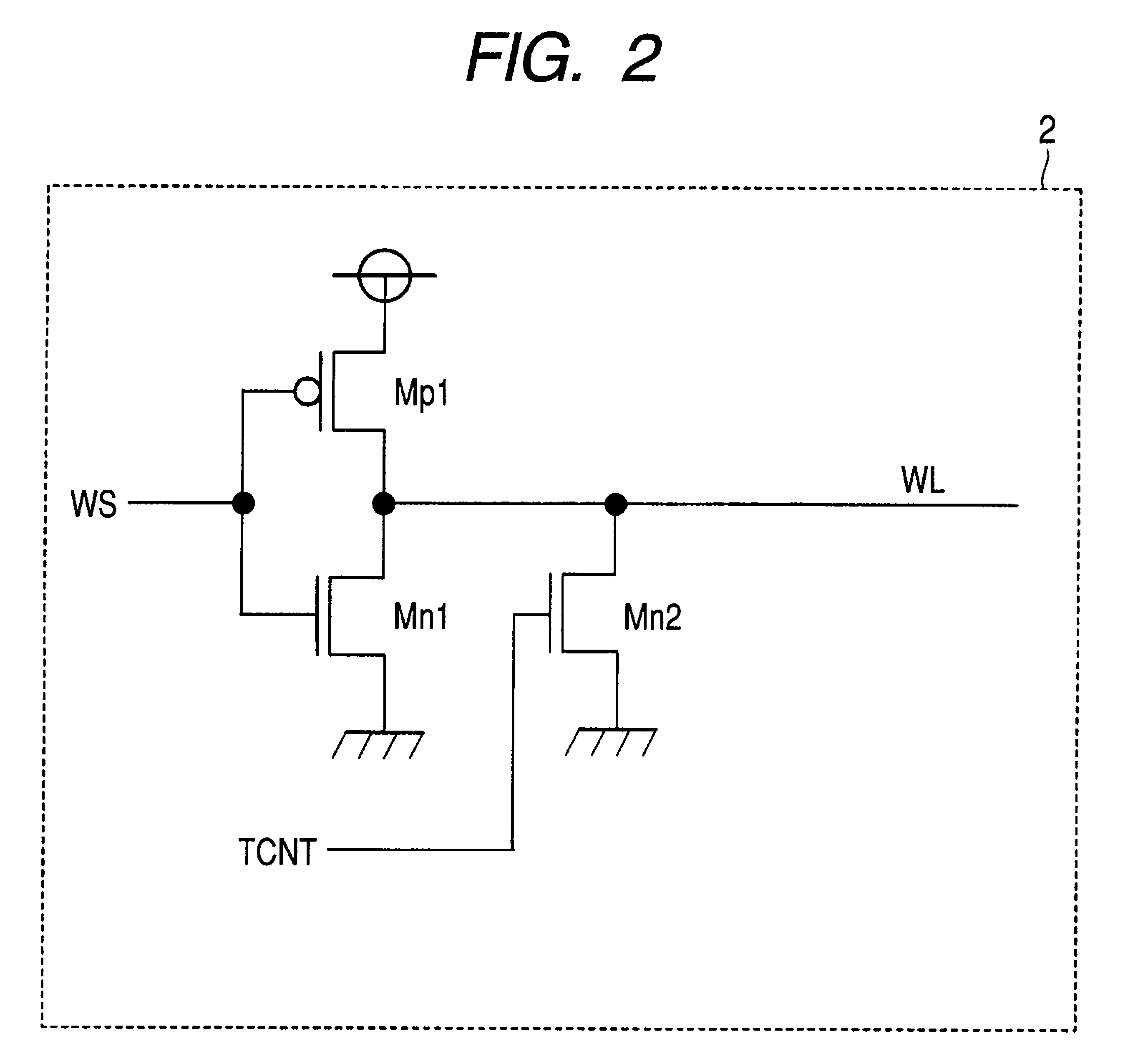
There is provided a technique for ensuring both an SNM and a write margin simultaneously in a semiconductor device having static memory cells. A semiconductor device has a plurality of static memory cells. The semiconductor device includes a memory cell array having the static memory cells arranged in a matrix, a temperature sensor circuit for sensing a temperature in the semiconductor device, and a word driver for controlling a voltage supplied to a word line of the memory cell array based on an output of the temperature sensor circuit at the time of writing to or reading from a memory cell.
Owner:RENESAS ELECTRONICS CORP
Static random access memory devices having read and write assist circuits therein that improve read and write reliability
Integrated circuit memory devices include a memory cell configured to receive a power supply signal and a write assist circuit. The write assist circuit is configured to improve write margins by reducing a magnitude of the power supply signal supplied to the memory cell from a first voltage level to a lower second voltage level during an operation to write data into the memory cell. The memory device further includes at least one bit line electrically coupled to the memory cell and a read assist circuit. The read assist circuit may be configured to improve read reliability by partially discharging the at least one bit line from an already precharged voltage level to a lower third voltage level in preparation to read data from the memory cell.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
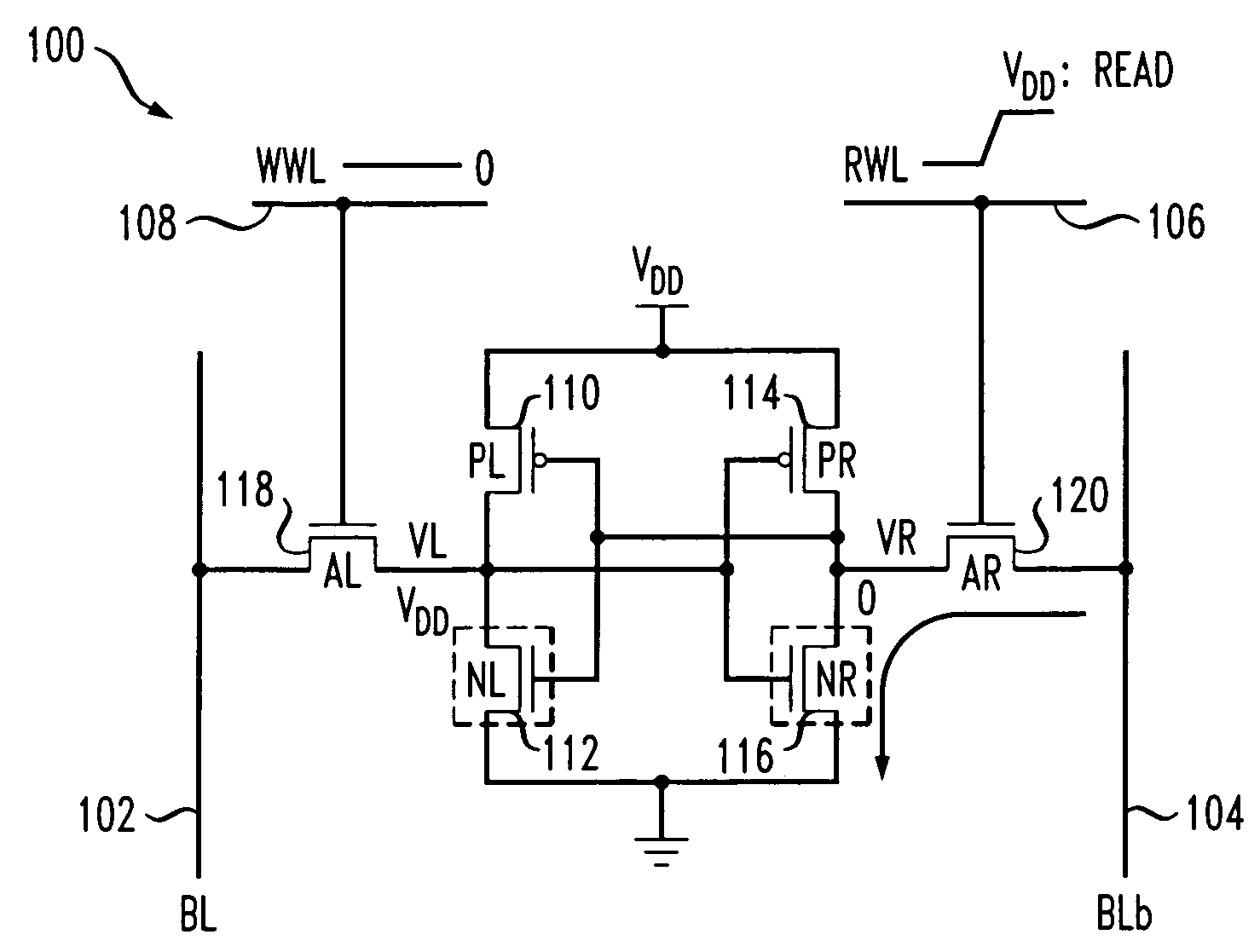
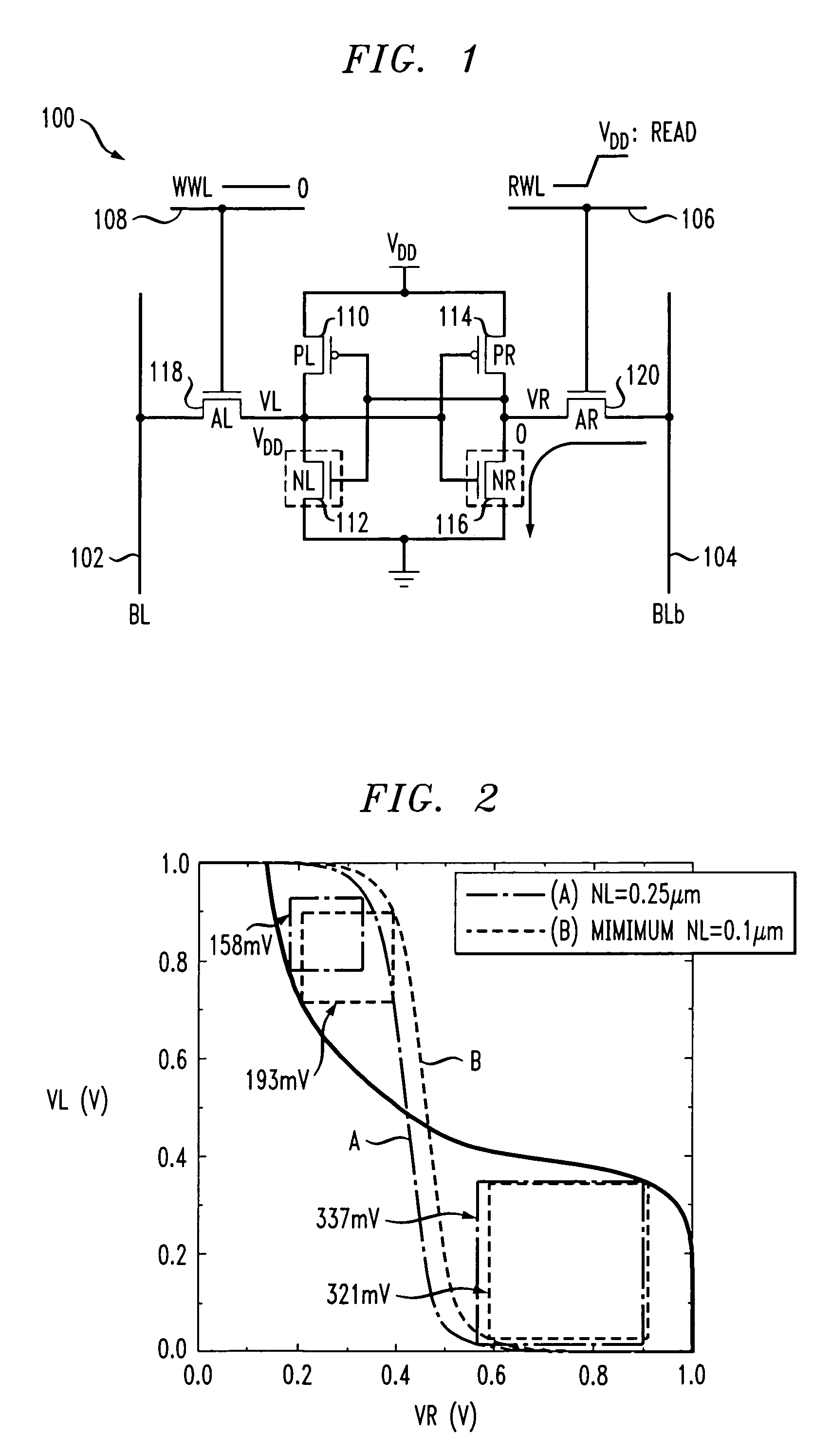
Memory with increased write margin bitcells
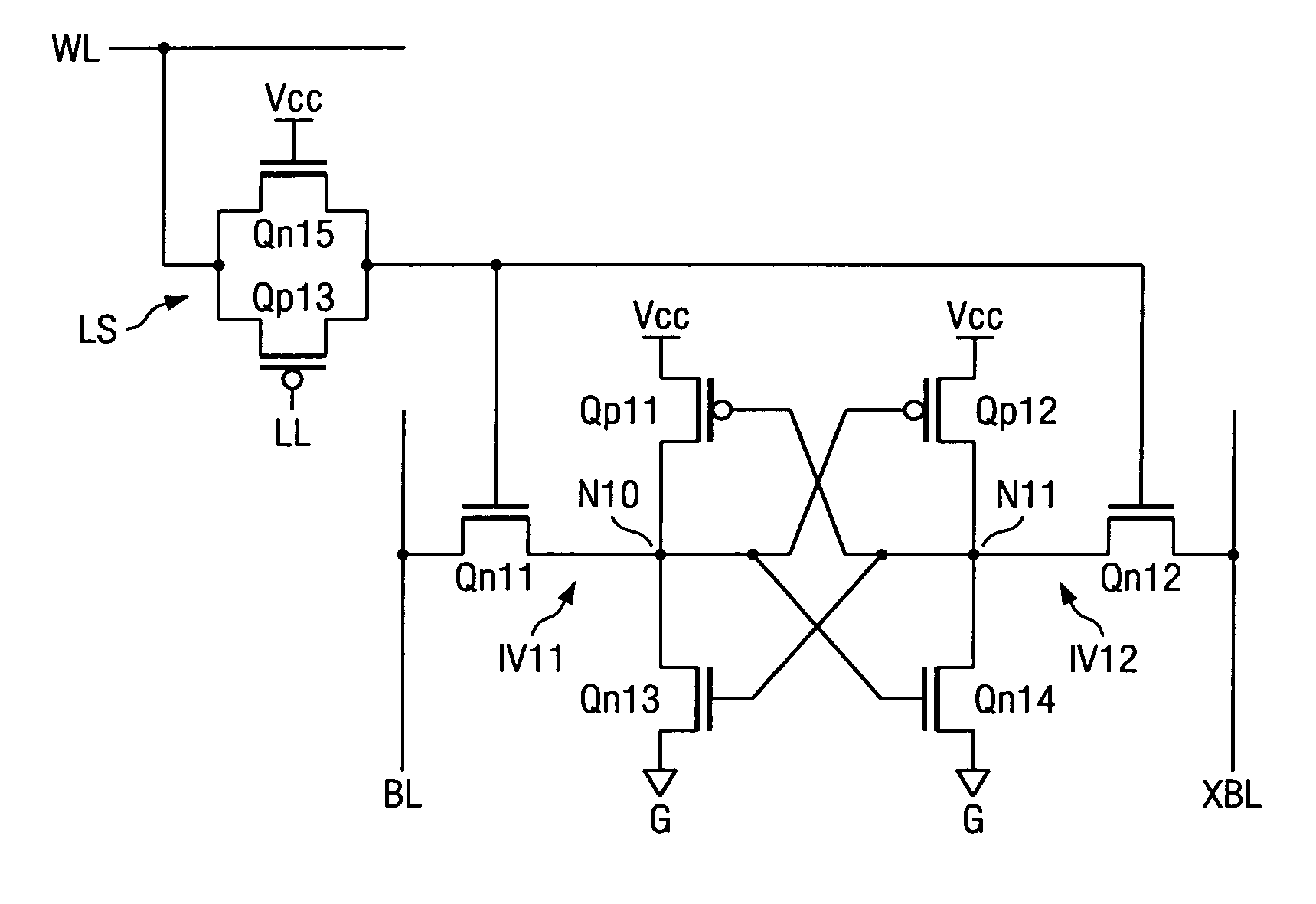
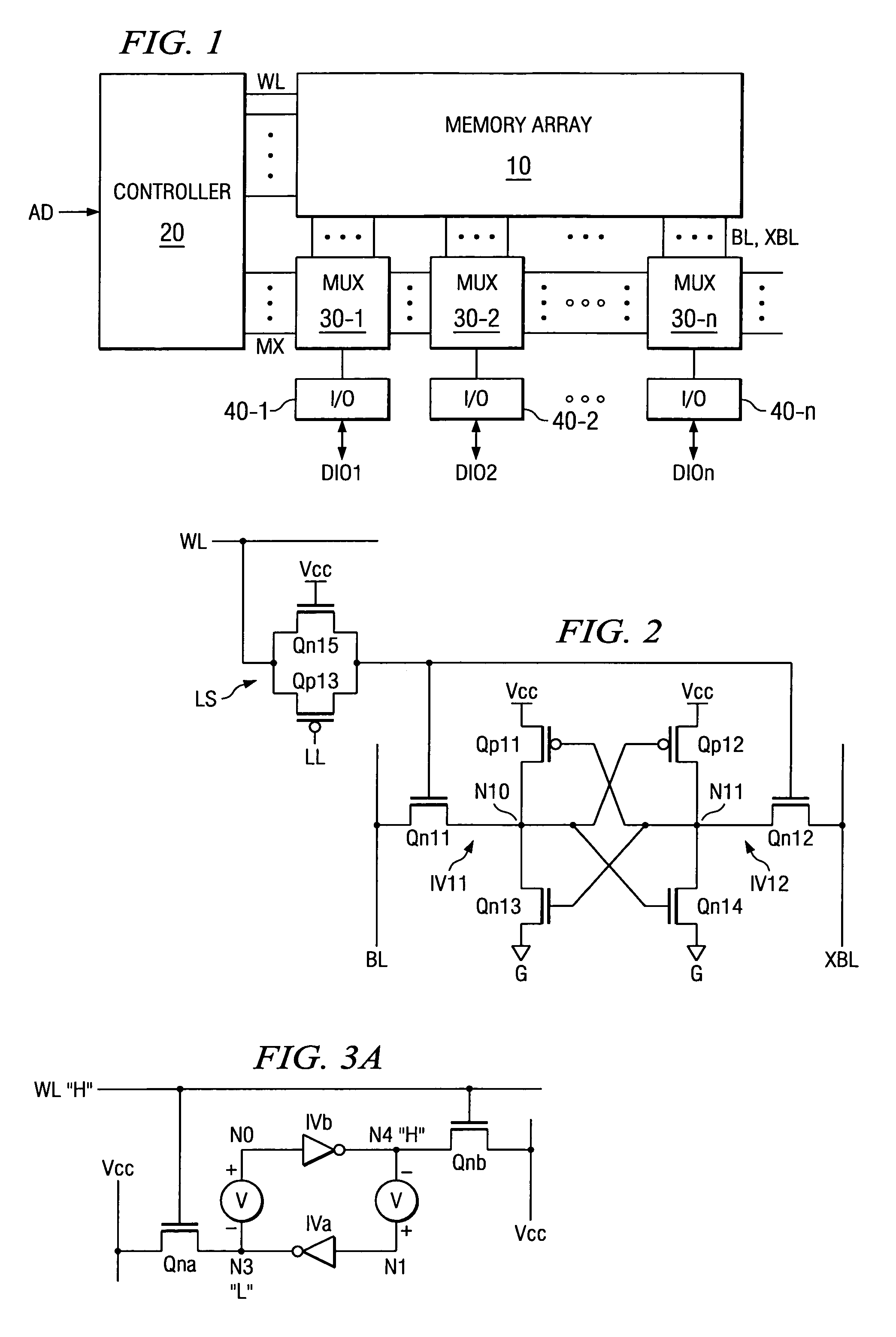
A memory comprising a first bit line, a second bit line, a word line, a first pair of cross-coupled inverters having a first input / output node and a second input / output node, a first power supply node and a second power supply node, wherein the first power supply node is coupled to a first power supply terminal, is provided. The memory further comprises a first gating transistor coupled between a second power supply terminal and the second power supply node, the first gating transistor receiving a first write enable signal that gates the gating transistor to a non-conductive condition during a write of the first pair of cross-coupled inverters. The memory further comprises a first pass transistor coupled to the first word line, the first input / output node, and the first bit line and a second pass transistor coupled to the first word line, the second input / output node, and the second bit line.
Owner:HUAWEI TECH CO LTD
Write margin improvement for SRAM cells with SiGe stressors
ActiveUS7449753B2Total current dropWrite margins of SRAM cells are improvedTransistorSolid-state devicesSemiconductor structureWrite margin
A semiconductor structure including SRAM cells with improved write margins and a method for forming the same are provided. The semiconductor structure comprises a substrate including a core circuit and an SRAM cell. The SRAM cell includes a pull-up PMOS device that comprises a first source / drain region in the substrate, a first SiGe stressor having a portion overlapping at least a portion of the first source / drain region, and a first current-tuning region having a portion overlapping at least a portion of the first source / drain region. The core circuit comprises a core PMOS device that comprises a second source / drain region in the substrate, and a second SiGe stressor having a portion overlapping at least a portion of the second source / drain region. The core PMOS device is free of current-tuning regions.
Owner:TAIWAN SEMICON MFG CO LTD
Modifying work function in PMOS devices by counter-doping
InactiveUS7750416B2Increased write marginImprove reliabilityTransistorSolid-state devicesDriving currentGate dielectric
A semiconductor structure comprising an SRAM / inverter cell and a method for forming the same are provided, wherein the SRAM / inverter cell has an improved write margin. The SRAM / inverter cell includes a pull-up PMOS device comprising a gate dielectric over the semiconductor substrate, a gate electrode on the gate dielectric wherein the gate electrode comprises a p-type impurity and an n-type impurity, and a stressor formed in a source / drain region. The device drive current of the pull-up PMOS device is reduced due to the counter-doping of the gate electrode.
Owner:TAIWAN SEMICON MFG CO LTD
SRAM memory cell with double gate transistors provided with means to improve the write margin
InactiveUS20100315889A1Improve reading stabilityEasy dischargeDigital storageBit lineRandom access memory
A random access memory cell including: two double-gate access transistors respectively arranged between a first bit line and a first storage node and between a second bit line and a second storage node, a word line, a first double-gate load transistor and a second double-gate load transistor, a first double-gate driver transistor and a second double-gate driver transistor, a mechanism to apply a given potential to at least one electrode of each of the load or driver transistors, and a mechanism to cause the given potential to vary.
Owner:COMMISSARIAT A LENERGIE ATOMIQUE ET AUX ENERGIES ALTERNATIVES
Multiple-bit magnetic random access memory cell employing adiabatic switching
InactiveUS20050199927A1Improve storage densityReducing a write margin of the memory cellSolid-state devicesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingBit lineRandom access memory
A multiple-bit memory cell for use in a magnetic random access memory circuit includes a first adiabatic switching storage element having a first anisotropy axis associated therewith and a second adiabatic switching storage element having a second anisotropy axis associated therewith. The first and second anisotropy axes are oriented at a substantially non-zero angle relative to at least one bit line and at least one word line corresponding to the memory cell. The memory cell is configured such that two quadrants of a write plane not used for writing one of the storage elements can be beneficially utilized to write the other storage element so that there is essentially no loss of write margin in the memory cell.
Owner:IBM CORP
Design and fabrication methods of partial cladded write line to enhance write margin for magnetic random access memory
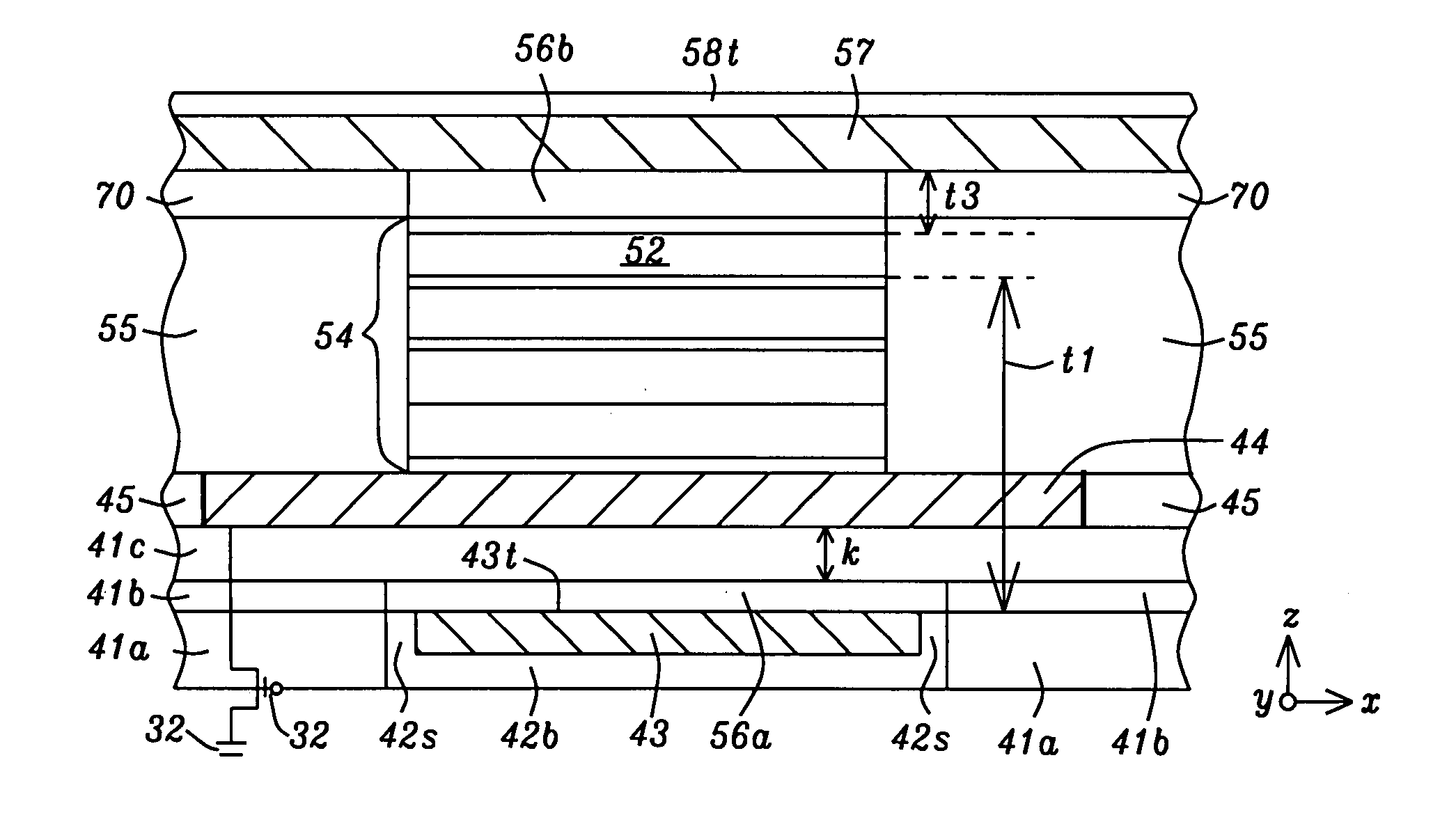
ActiveUS20110062536A1Disturb problemSacrificing writing power of writeNanomagnetismMagnetic-field-controlled resistorsStatic random-access memoryControl layer
A cladding structure for a conductive line used to switch a free layer in a MTJ is disclosed and includes two cladding sidewalls on two sides of the conductive line, a top cladding portion on a side of the conductive line facing away from the MTJ, and a highly conductive, non-magnetic spacing control layer formed between the MTJ and conductive line. The spacing control layer has a thickness of 0.02 to 0.12 microns to maintain the distance separating free layer and conductive line between 0.03 and 0.15 microns. The spacing control layer is aligned parallel to the conductive line and contacts a plurality of MTJ elements in a row of MRAM cells. Half-select error problems are avoided while maintaining high write efficiency. A spacing control layer may be formed between a word line and a bottom electrode in a top pinned layer or dual pinned layer configuration.
Owner:TAIWAN SEMICON MFG CO LTD
Dynamic multi-Vcc scheme for SRAM cell stability control
A dynamic multi-voltage memory array features SRAM cells that are subjected to different biasing conditions, depending on the operating mode of the cells. The selected SRAM cell receives a first voltage when a read operation is performed, and receives a second voltage when a write operation is performed. By biasing the cell differently for the two distinct operations, a total decoupling of the read and write operations is achieved. The disclosed memory array, as well as future SRAM designs incorporating the multi-voltage capability thus avoid the conflicting requirements of read and write operations. Random single-bit failures of the memory array are reduced, due to the improvement in read stability and write margin.
Owner:TAHOE RES LTD
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com