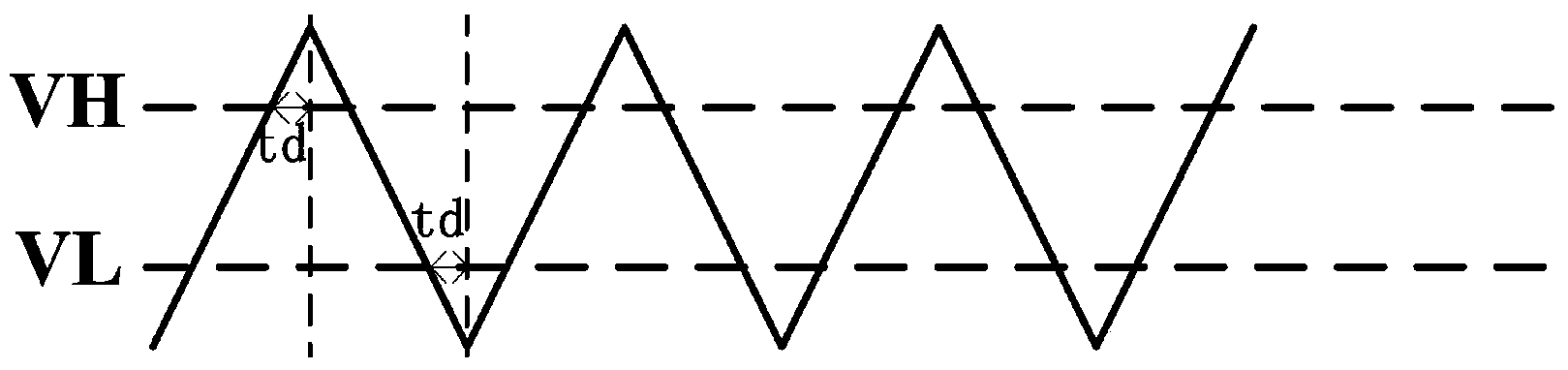Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
1088 results about "Transmission gate" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
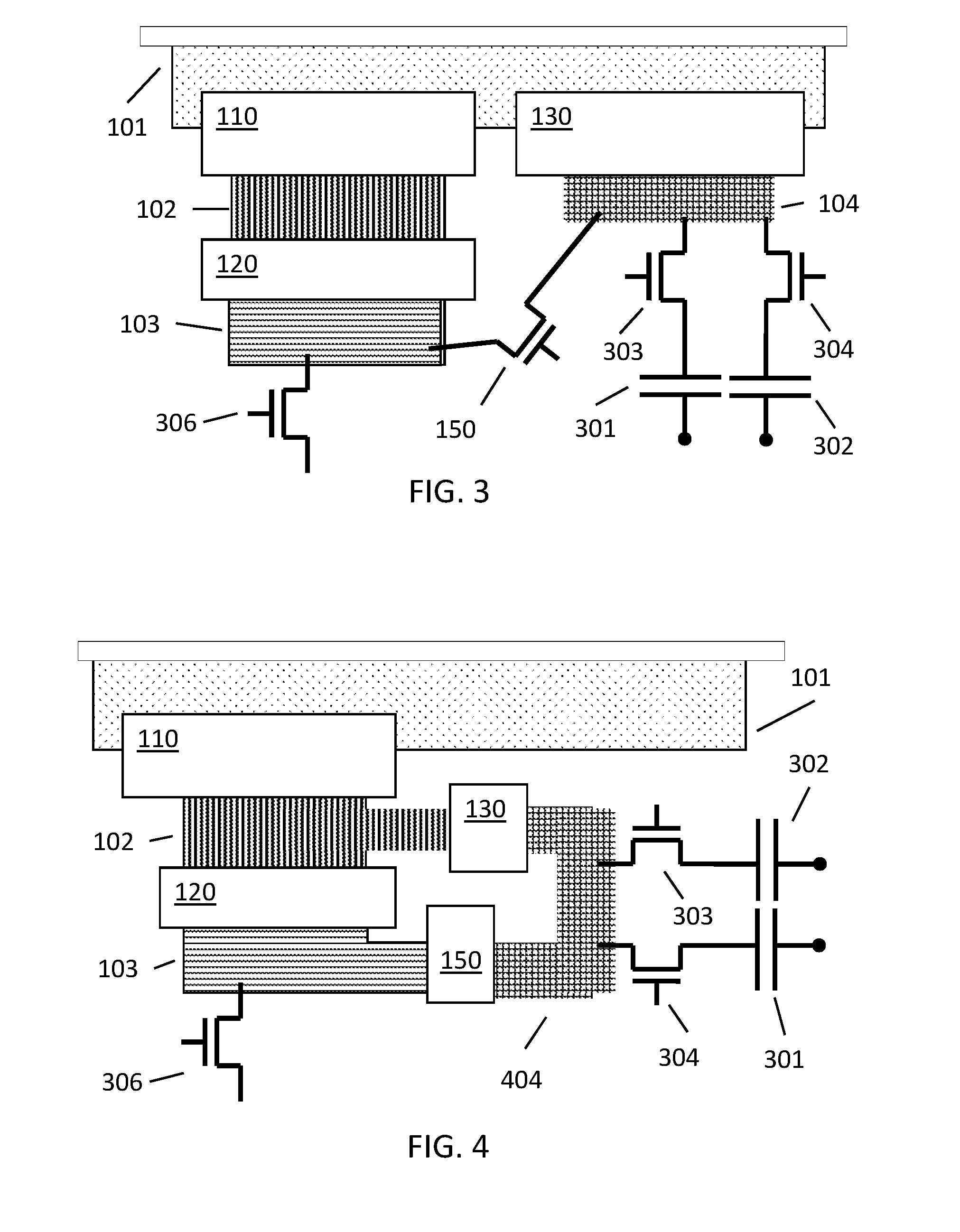
A transmission gate (TG) is an analog gate similar to a relay that can conduct in both directions or block by a control signal with almost any voltage potential. It is a CMOS-based switch, in which PMOS passes a strong 1 but poor 0, and NMOS passes strong 0 but poor 1. Both PMOS and NMOS work simultaneously.
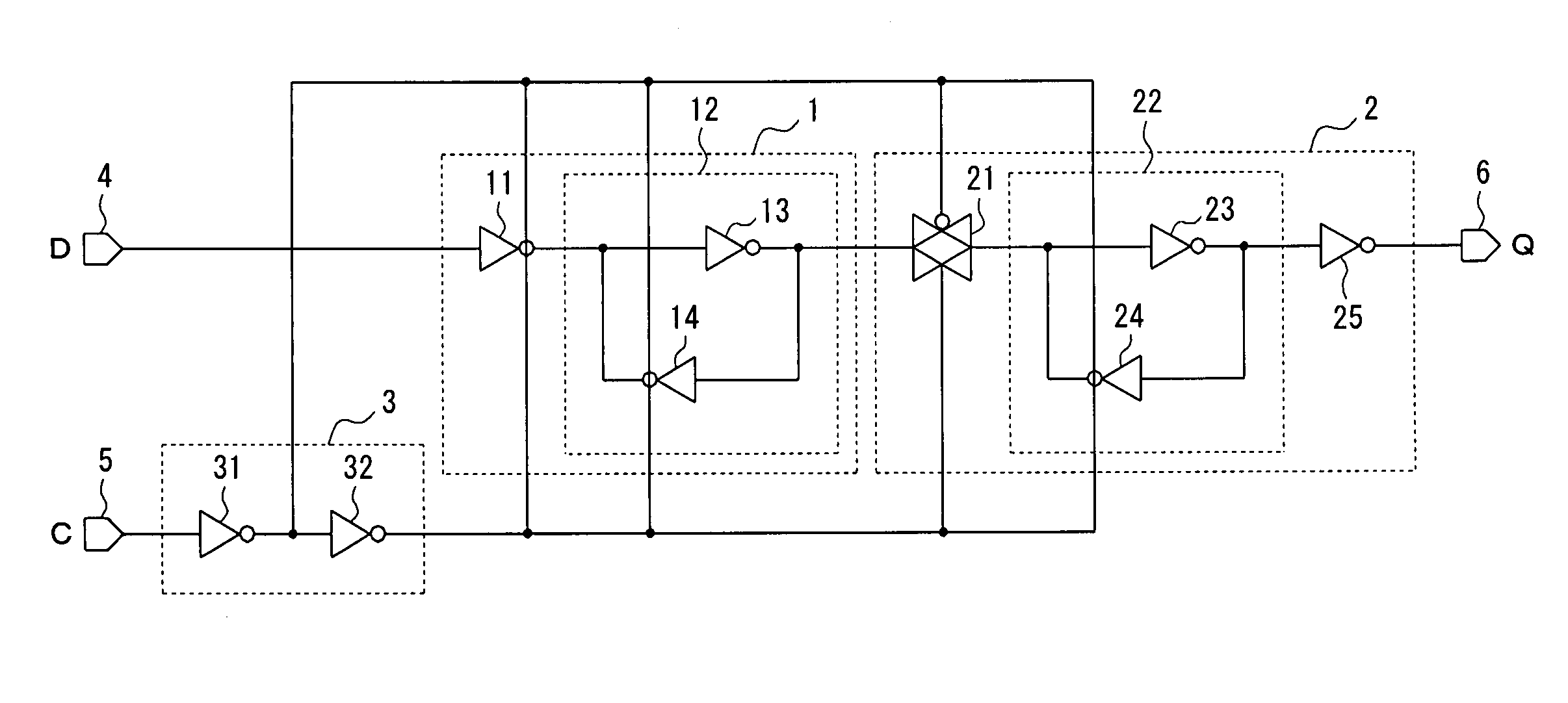
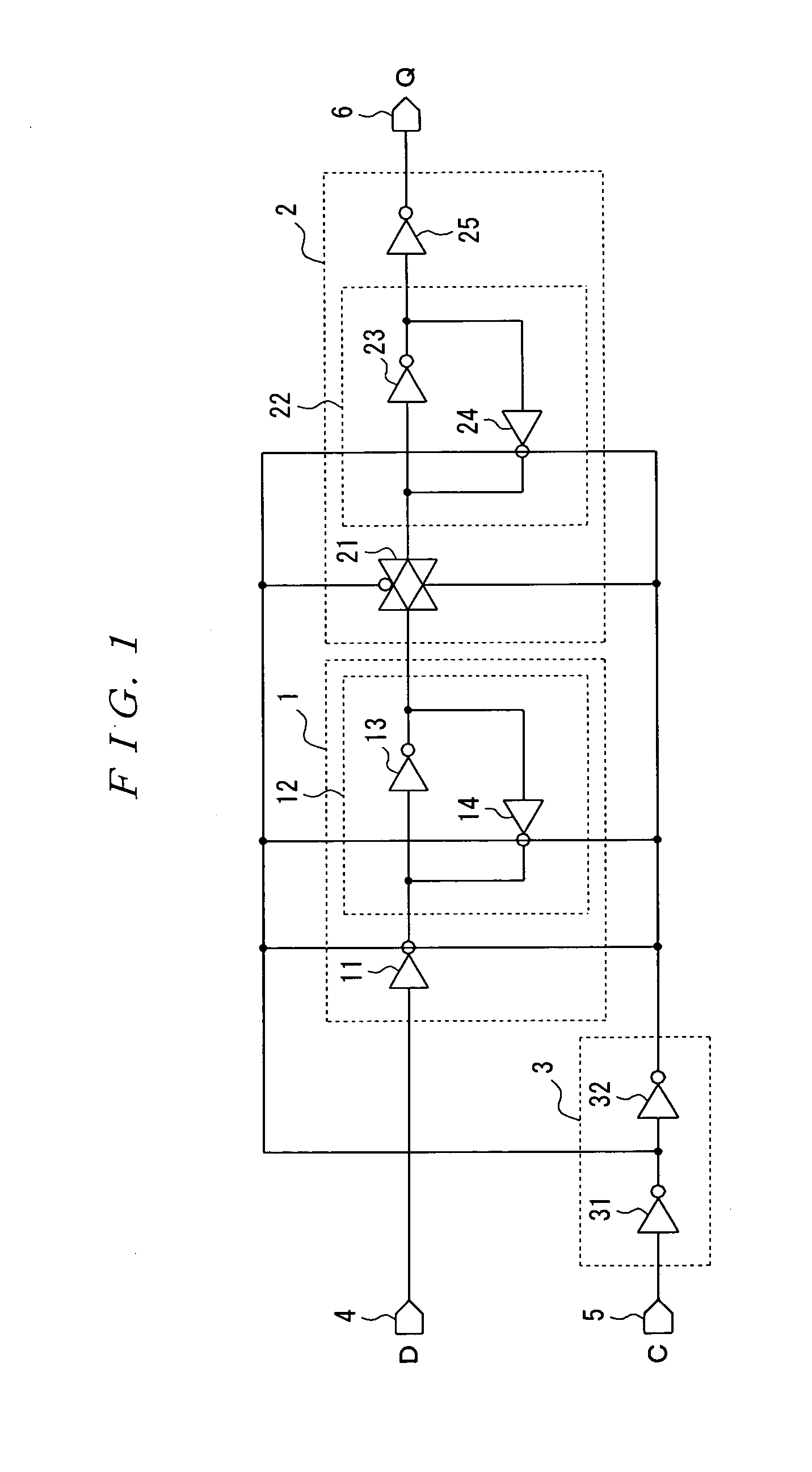
Chain-connected shift register and programmable logic circuit whose logic function is changeable in real time
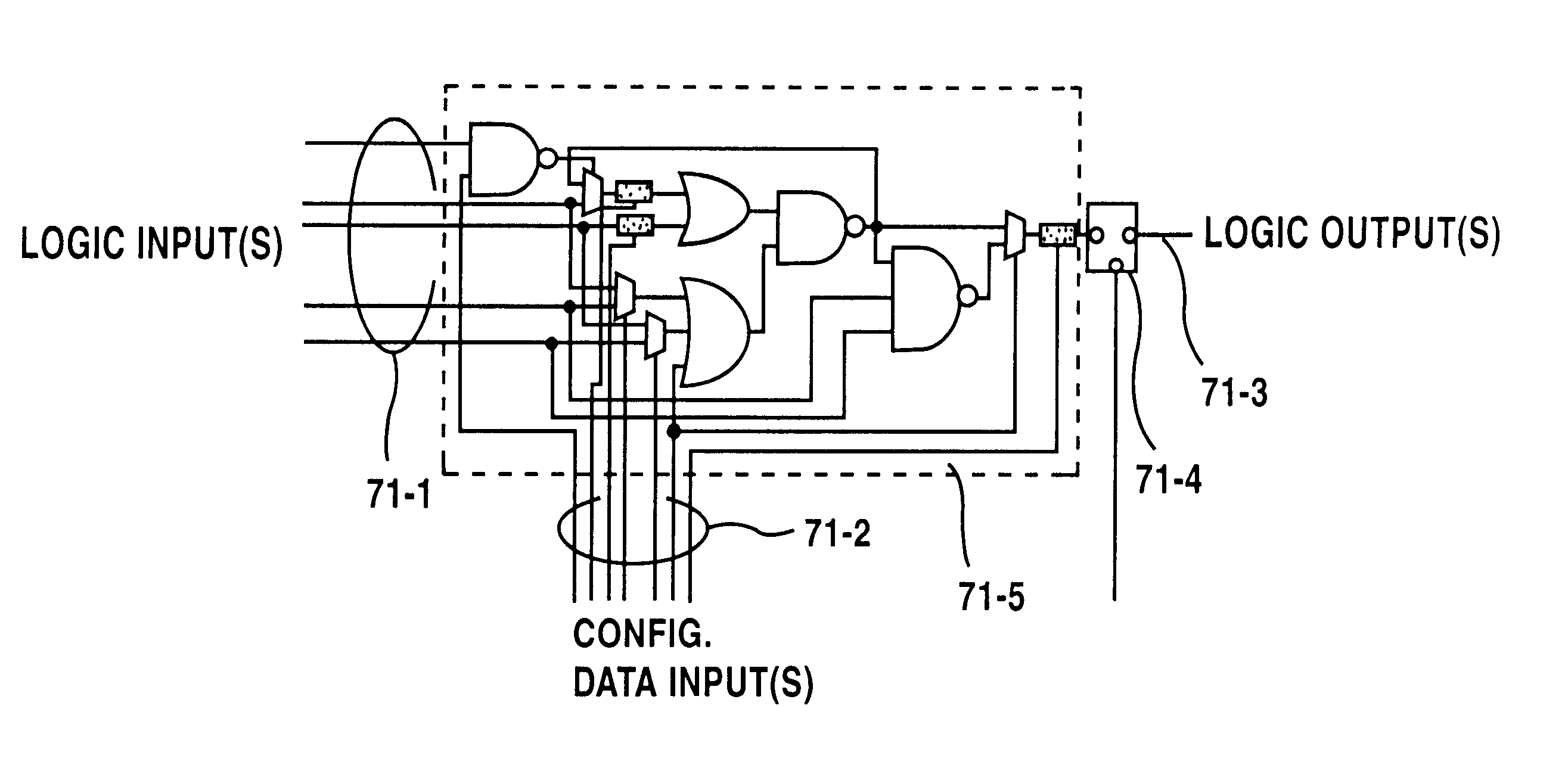
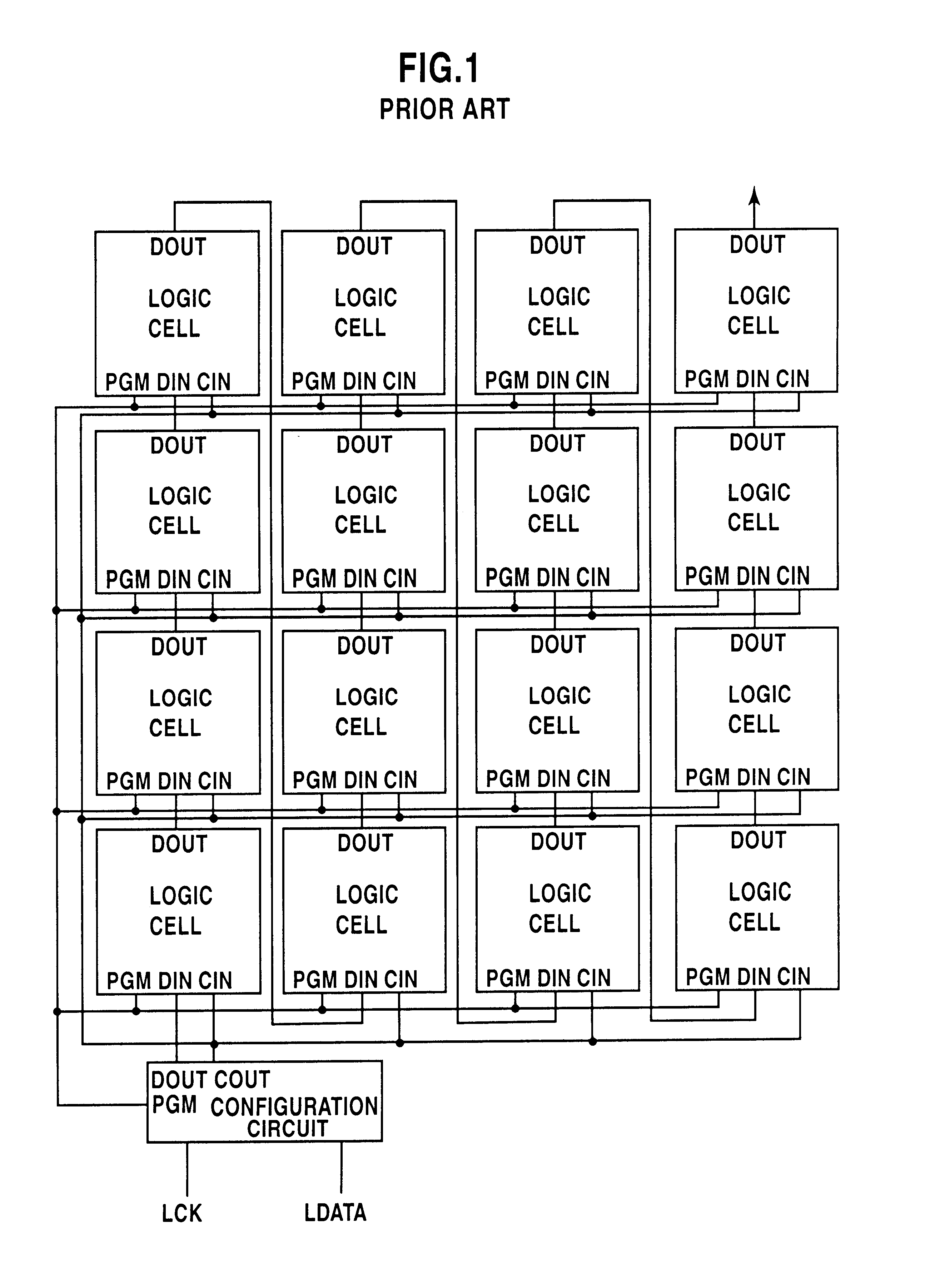
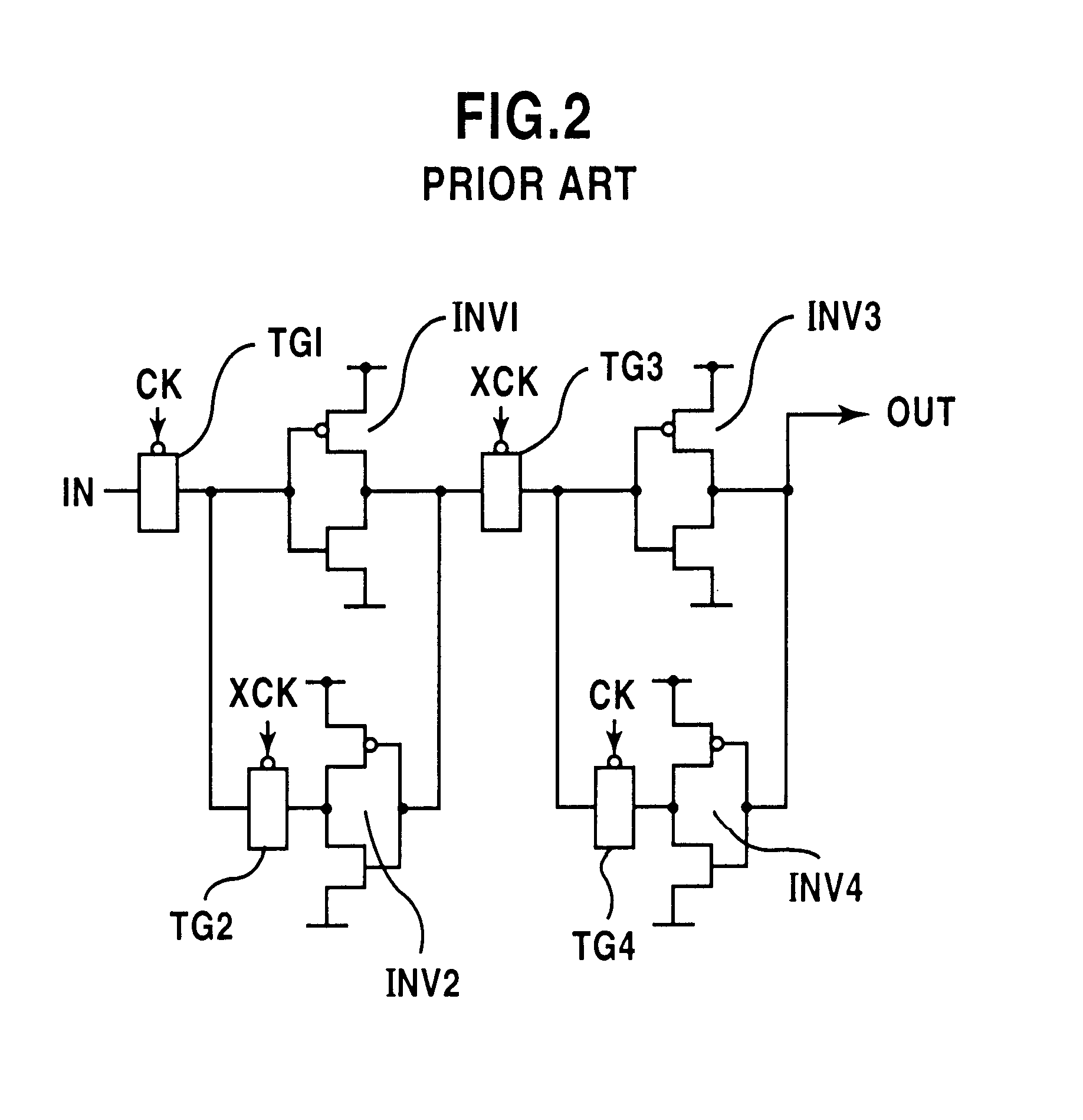
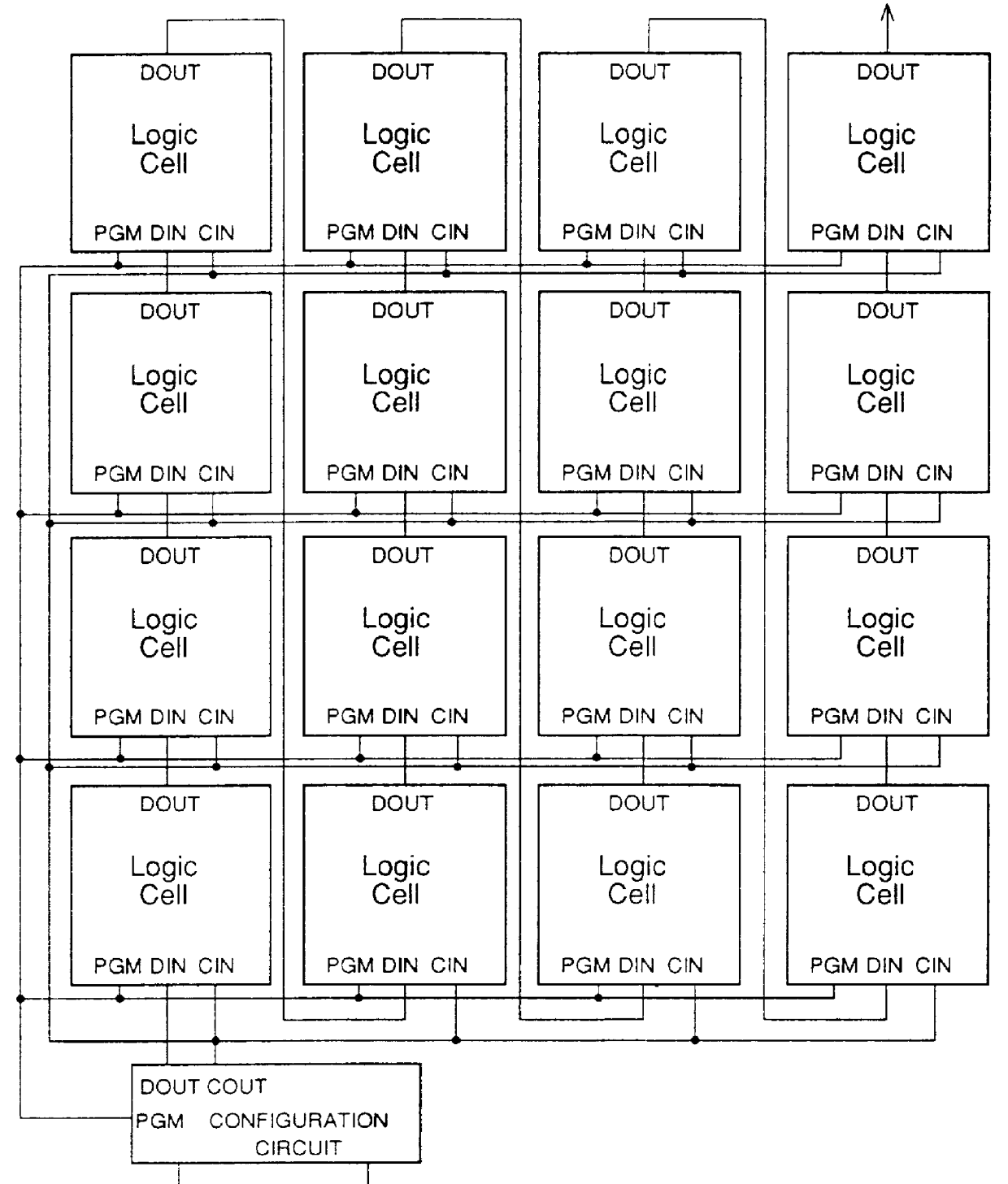
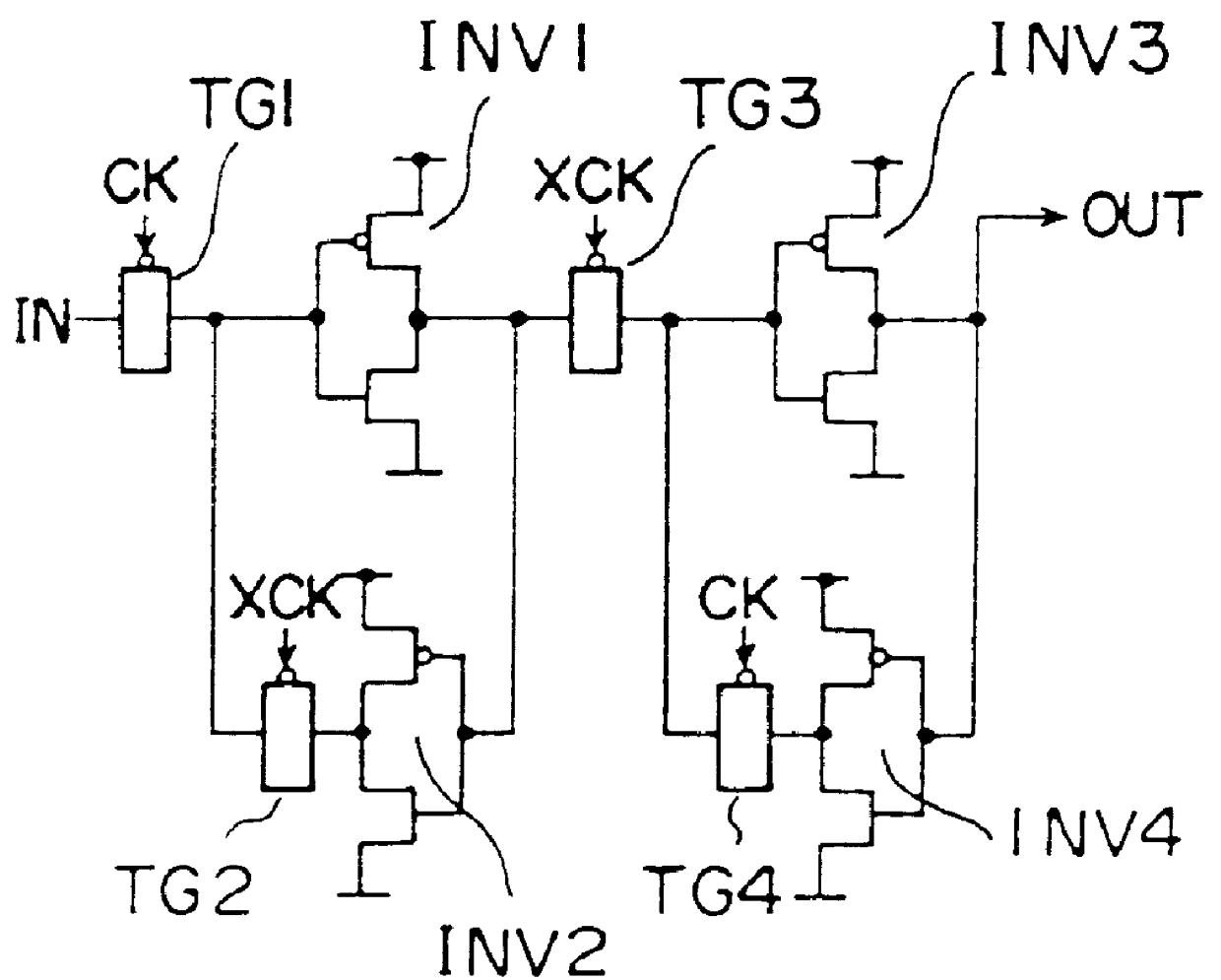
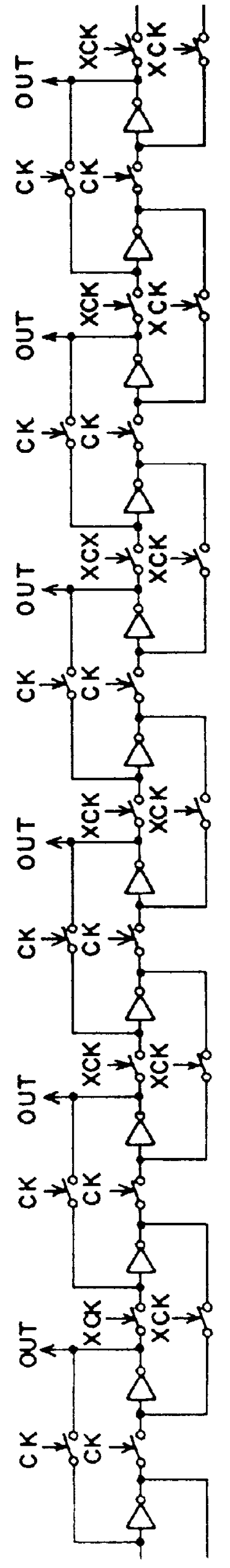
A shift register having a plurality of circuit cells successively connected in a chain formation is proposed. Each of the circuit cells includes a first inversion gate, a first transmission gate, connected to an output of the first inversion gate, being switched by a clock, and a second inversion gate connected to an output of the first transmission gate. The circuit cell further includes a first P-channel transistor, connected between an output of the second inversion gate and an input of the first inversion gate, being switched by the clock, a second transmission gate, connected to the output of the second inversion gate, being switched by an inversion clock, and a second P-channel transistor, connected to the output of the first transmission gate, being switched by the inversion clock. In the shift register, the plurality of circuit cells are successively connected such that the input of the first inversion gate of the circuit cell is connected to an output of a second transmission gate of a former-stage circuit cell, and the output of the first inversion gate of the circuit cell is connected to an output of a second P-channel transistor of the former-stage circuit cell.
Owner:FUJITSU LTD
Chain-connected shift register and programmable logic circuit whose logic function is changeable in real time
InactiveUS6018559ADigital storageLogic circuits using elementary logic circuit componentsShift registerTransmission gate
A shift register having a plurality of circuit cells successively connected in a chain formation is proposed. Each of the circuit cells includes a first inversion gate, a first transmission gate, connected to an output of the first inversion gate, being switched by a clock, and a second inversion gate connected to an output of the first transmission gate. The circuit cell further includes a first P-channel transistor, connected between an output of the second inversion gate and an input of the first inversion gate, being switched by the clock, a second transmission gate, connected to the output of the second inversion gate, being switched by an inversion clock, and a second P-channel transistor, connected to the output of the first transmission gate, being switched by the inversion clock. In the shift register, the plurality of circuit cells are successively connected such that the input of the first inversion gate of the circuit cell is connected to an output of a second transmission gate of a former-stage circuit cell, and the output of the first inversion gate of the circuit cell is connected to an output of a second P-channel transistor of the former-stage circuit cell.
Owner:FUJITSU LTD
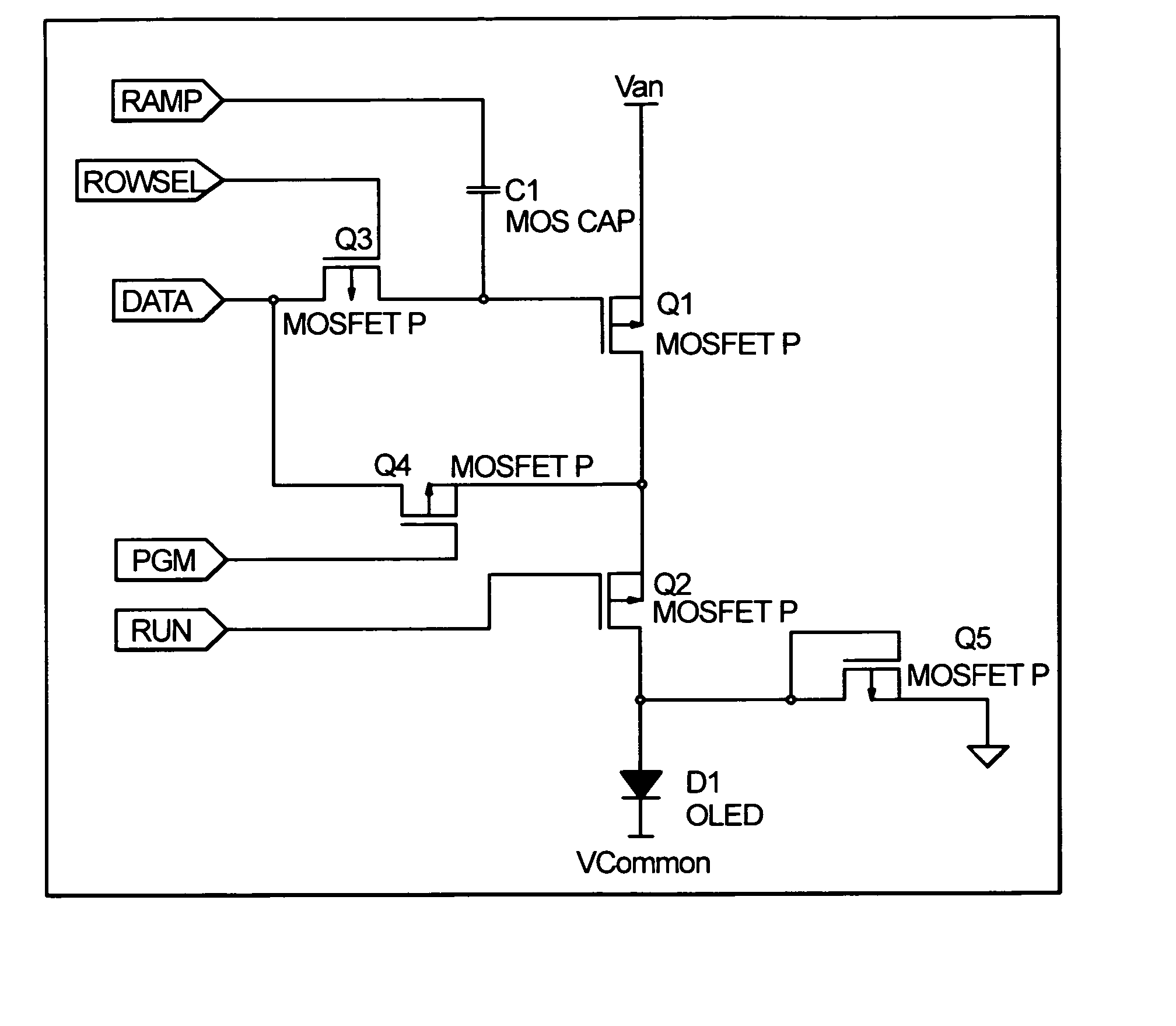
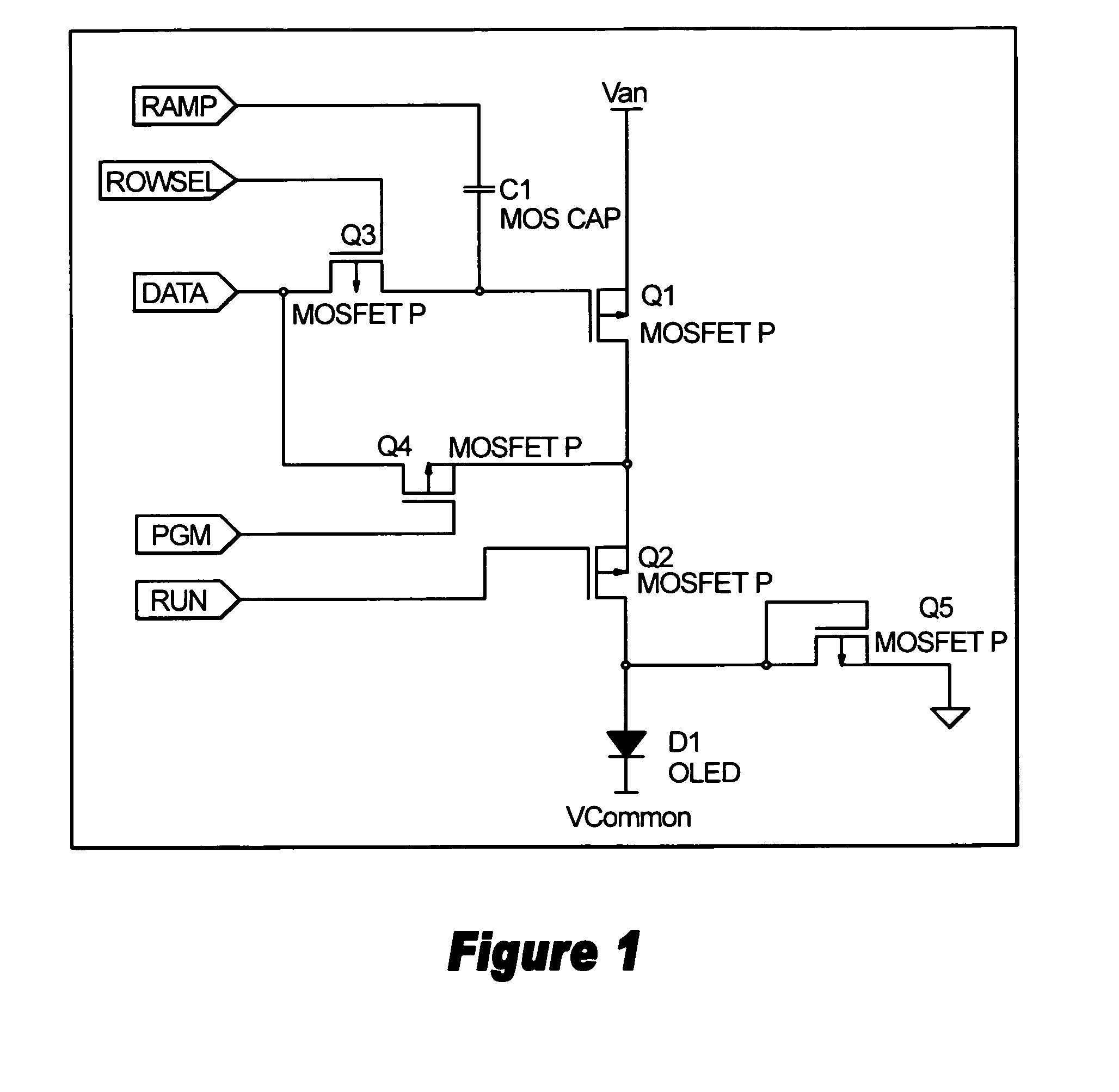
OLED active matrix cell designed for optimal uniformity
Owner:EMAGIN CORP
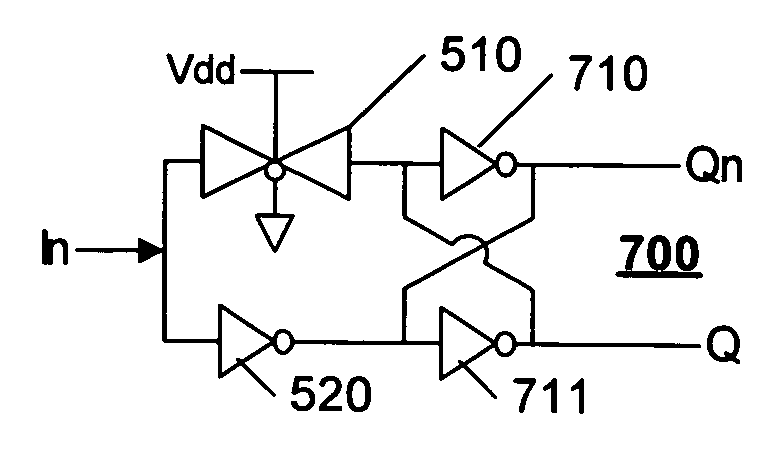
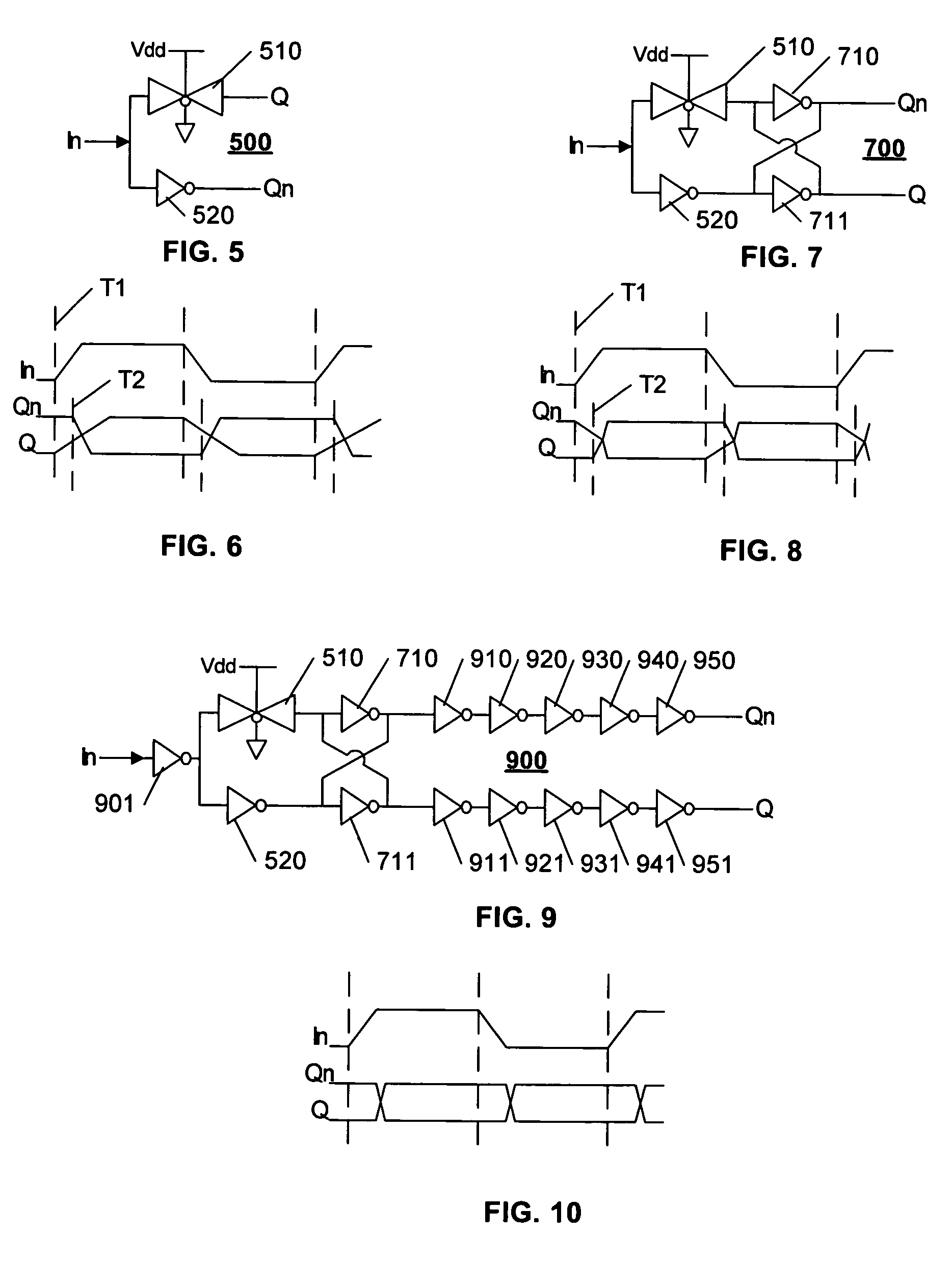
Low-skew single-ended to differential converter
InactiveUS7119602B2Reduce offsetReduce static power consumptionTransistorSingle output arrangementsTransmission gateEngineering
A single-ended to differential converter uses a cross-coupled latch that maximizes the output zero-crossing symmetry and is self compensating over PVT variations. An in-phase driving signal is provided by an always-on transmission gate coupled to the input. An out-of-phase driving signal is provided by an inverter coupled to the input. The in-phase and out-of-phase driving signals each drive an input of the cross-coupled latch. The in-phase driving signal from the always-on transmission gate starts to bring the cross-coupled latch into conduction, and when the out-of-phase driving signal arrives, the simultaneous driving of the cross-coupled latch causes a rapid and symmetric transition of both outputs of the cross-coupled latch.
Owner:TELEFON AB LM ERICSSON (PUBL)
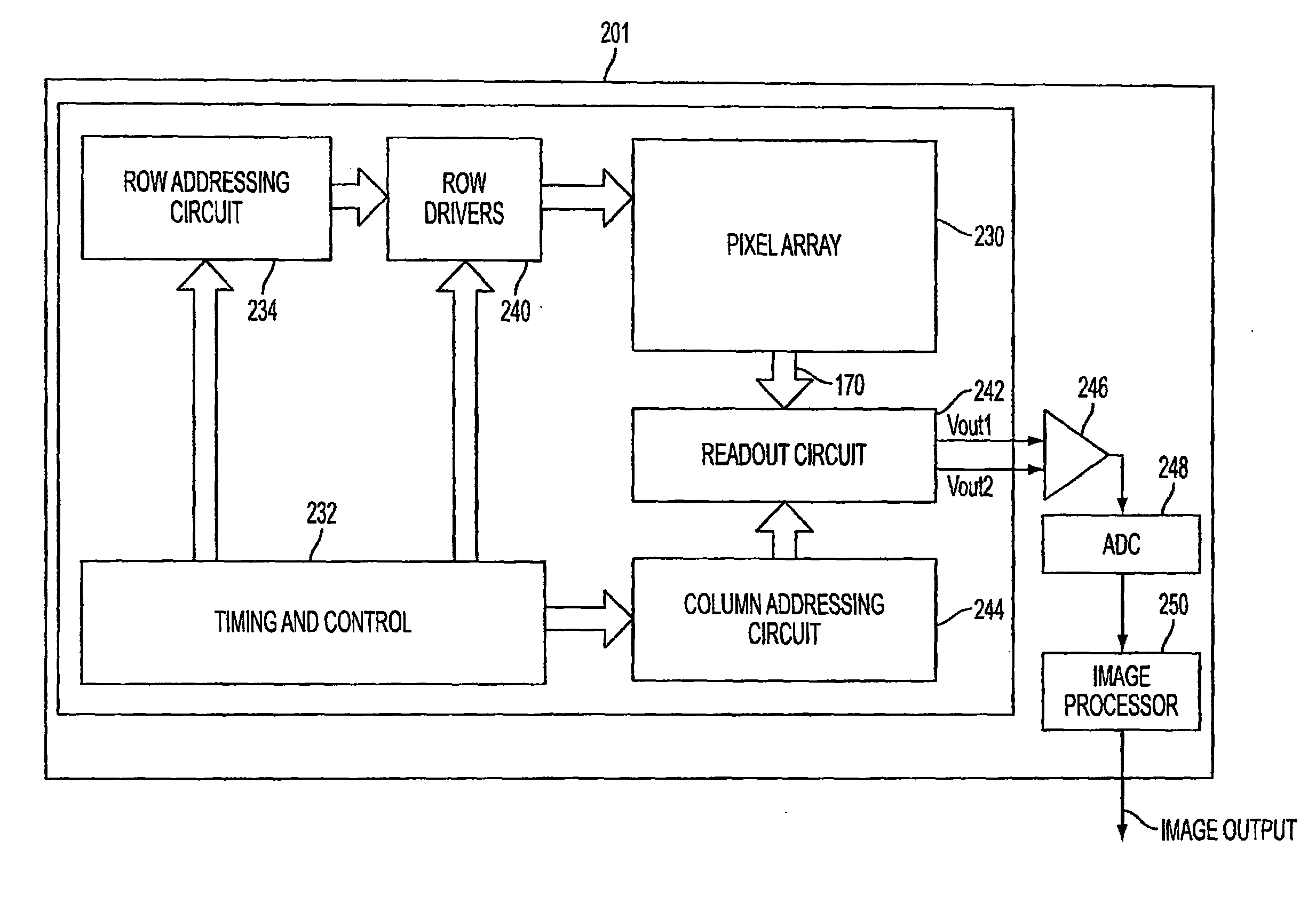
High dynamic range image sensor
ActiveUS20060071254A1Improve dynamic rangeImprove the level ofTelevision system detailsSolid-state devicesDual purposeGate oxide
A pixel cell with controlled leakage is formed by modifying the location and gate profile of a high dynamic range (HDR) transistor. The HDR transistor may have a dual purpose, acting as both a leaking transistor and either a transfer gate or a reset gate. Alternatively, the HDR transistor may be a separate and individual transistor having the gate profile of a transfer gate or a reset gate. The leakage through the HDR transistor may be controlled by modifying the photodiode implants around the transistor, adjusting the channel length of the transistor, or thinning the gate oxide on the transistor. The leakage through the HDR transistor may also be controlled by applying a voltage across the transistor.
Owner:APTINA IMAGING CORP
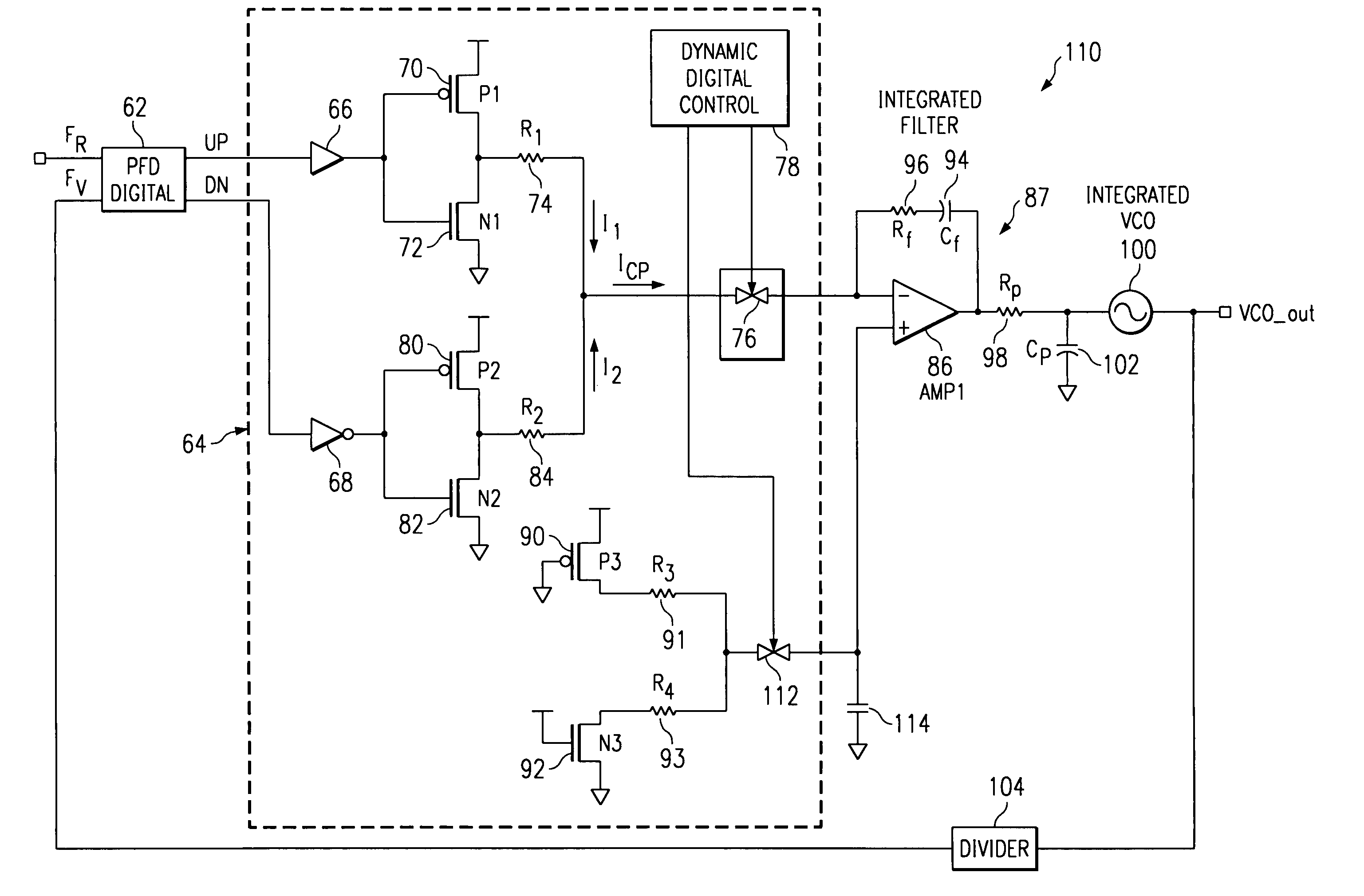
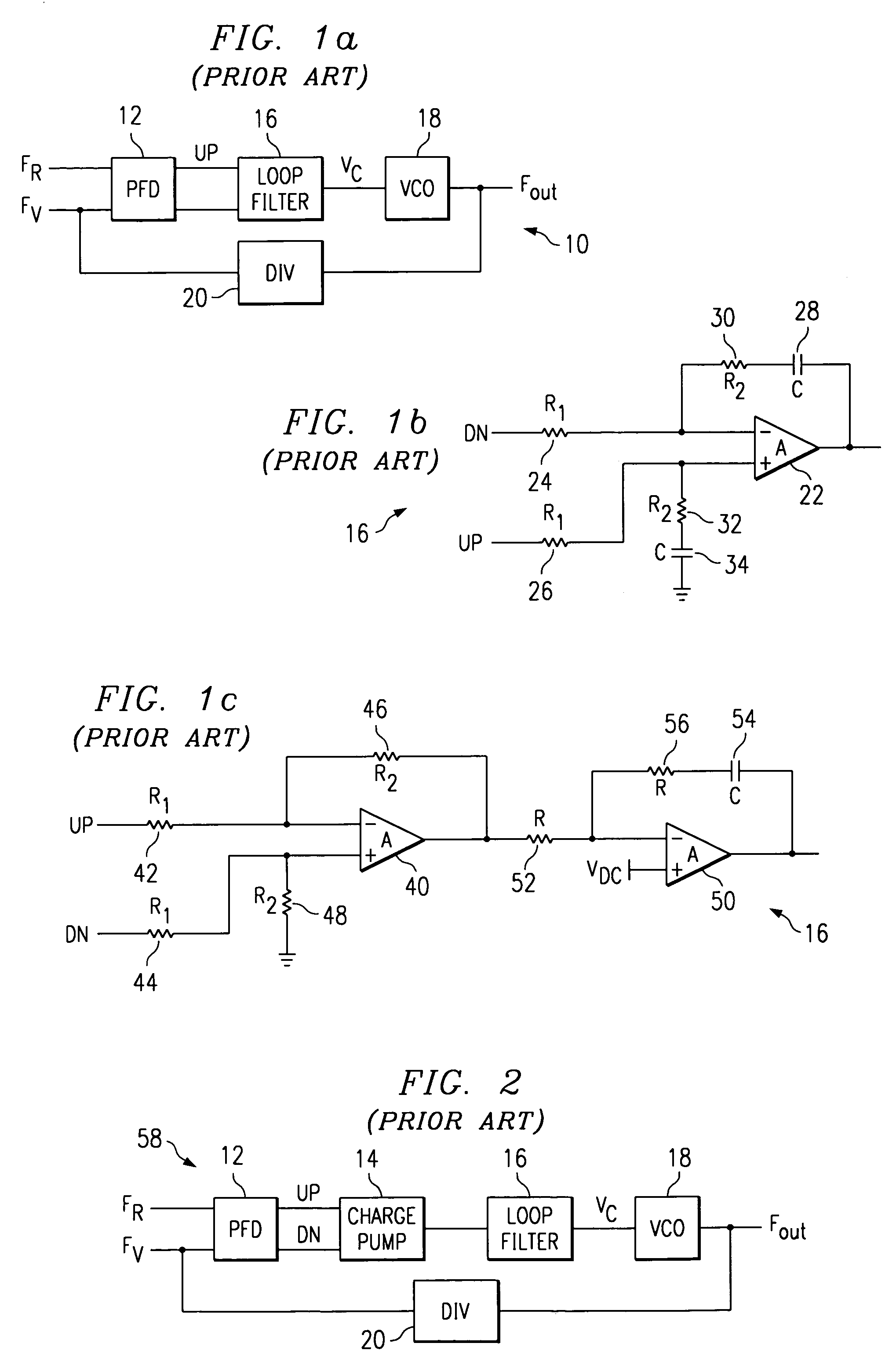
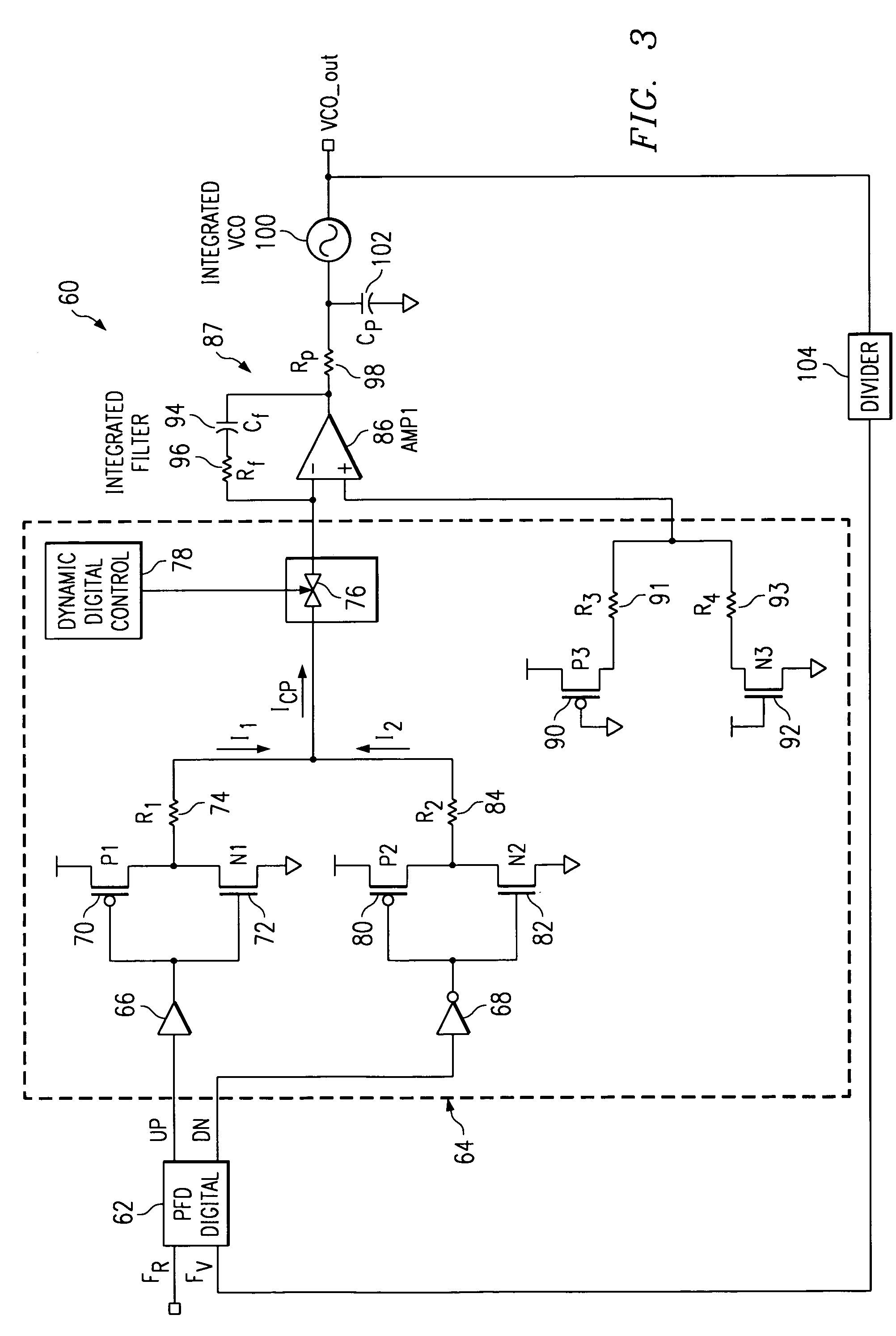
Charge pump phase locked loop with improved power supply rejection
ActiveUS6963233B2Improve power supply rejection ratioVoltage variationPulse automatic controlElectric variable regulationPhase detectorElectricity
A phase lock loop circuit (60) has a phase frequency detector (62), a charge pump (64), an active filter (87) and a voltage-controlled oscillator (100). The phase detector generates signals responsive to reference signal FR and VCO output signal FV. A charge pump generates a voltage at the input of a first transmission gate (76) according to the values of the phase detector signals. A predetermined voltage is generated at the input of a second transmission gate (112). When the transmission gates (76, 110) are closed (low impedance) the charge pump may sink or source current to the inverting input of the operational amplifier (86) of the active filter 86 and the predetermined voltage is applied to the non-inverting input. When the transmission gates are open (high impedance state) the inverting input is electrically isolated from the node and the non-inverting output is isolated from the power supply.
Owner:TEXAS INSTR INC
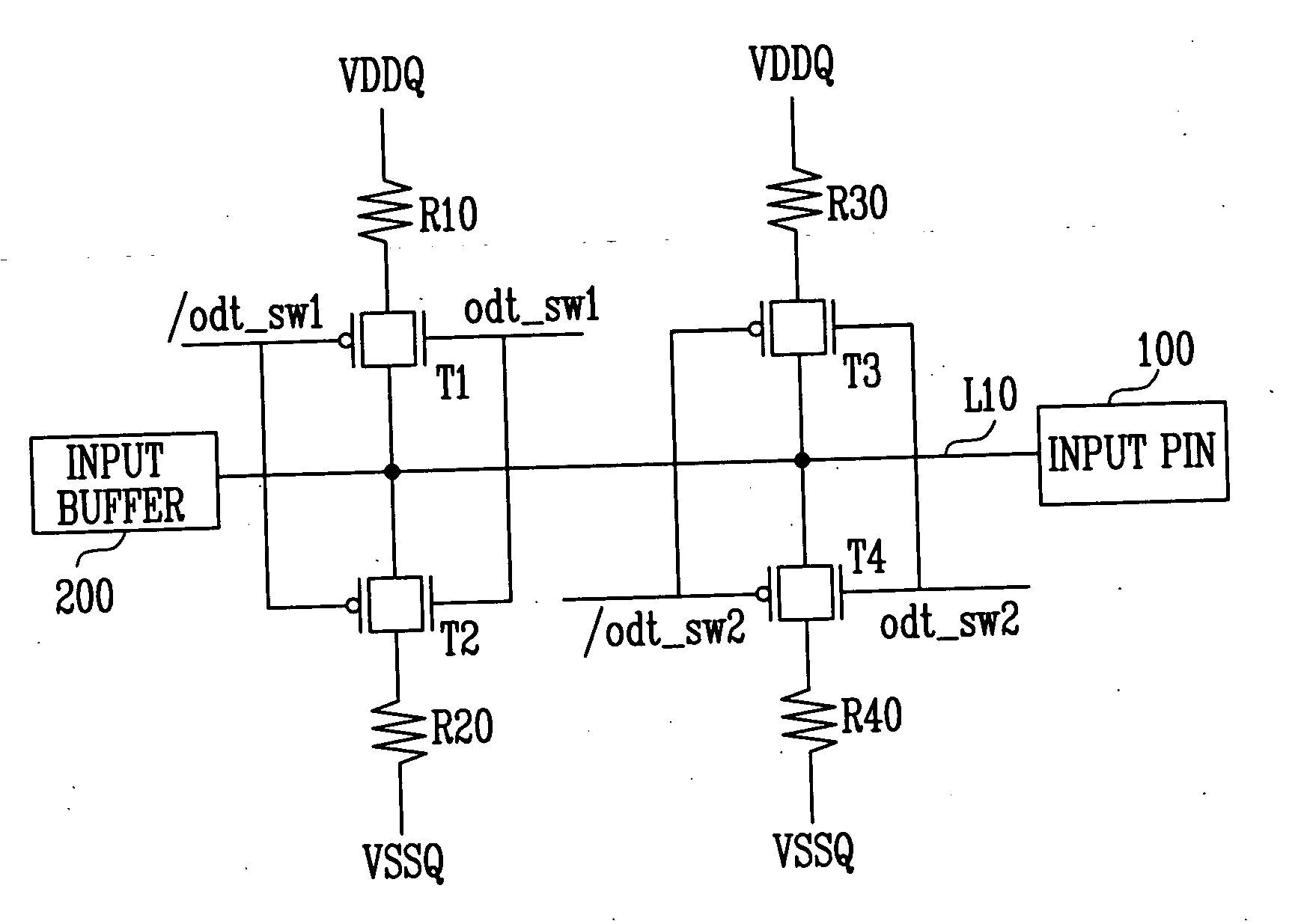
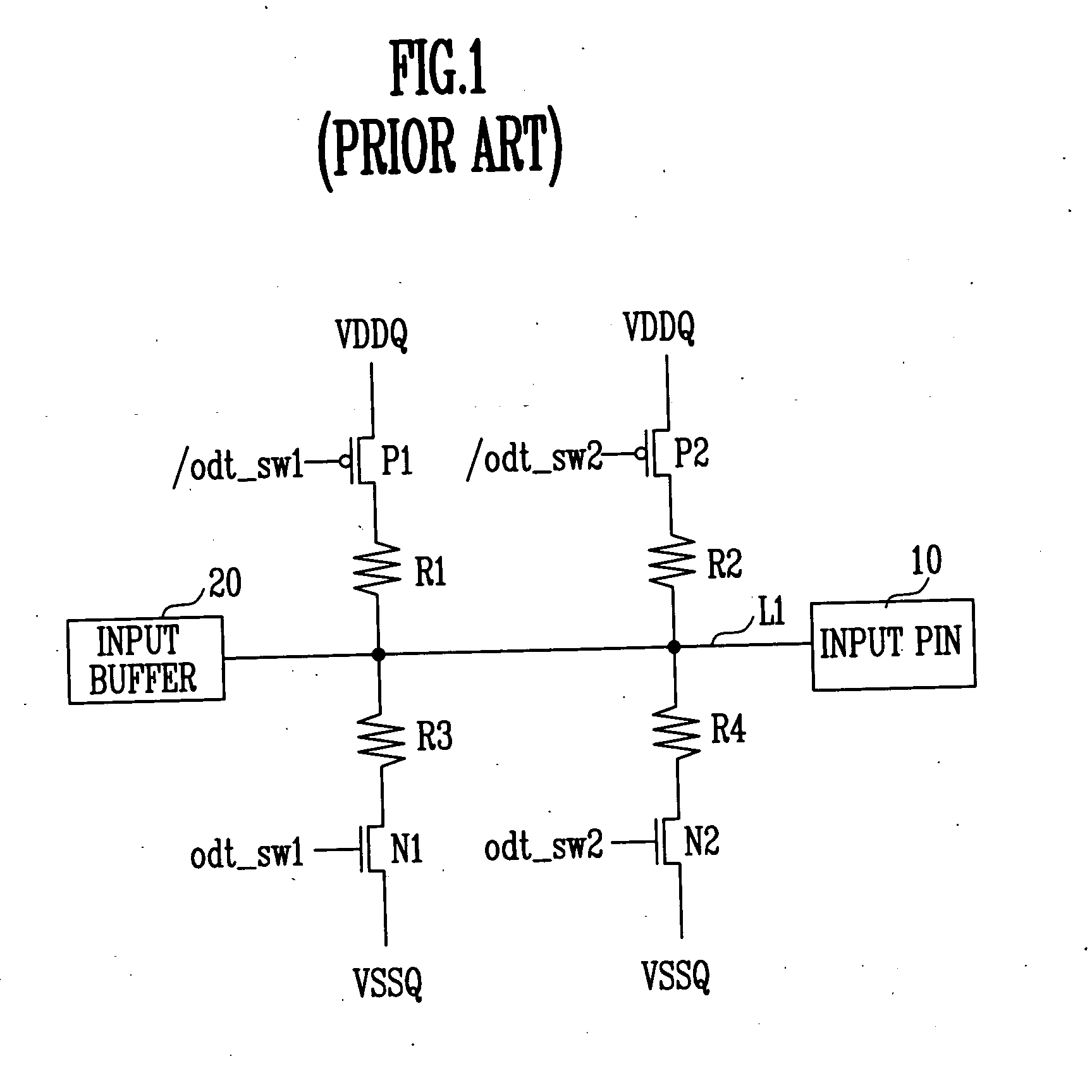
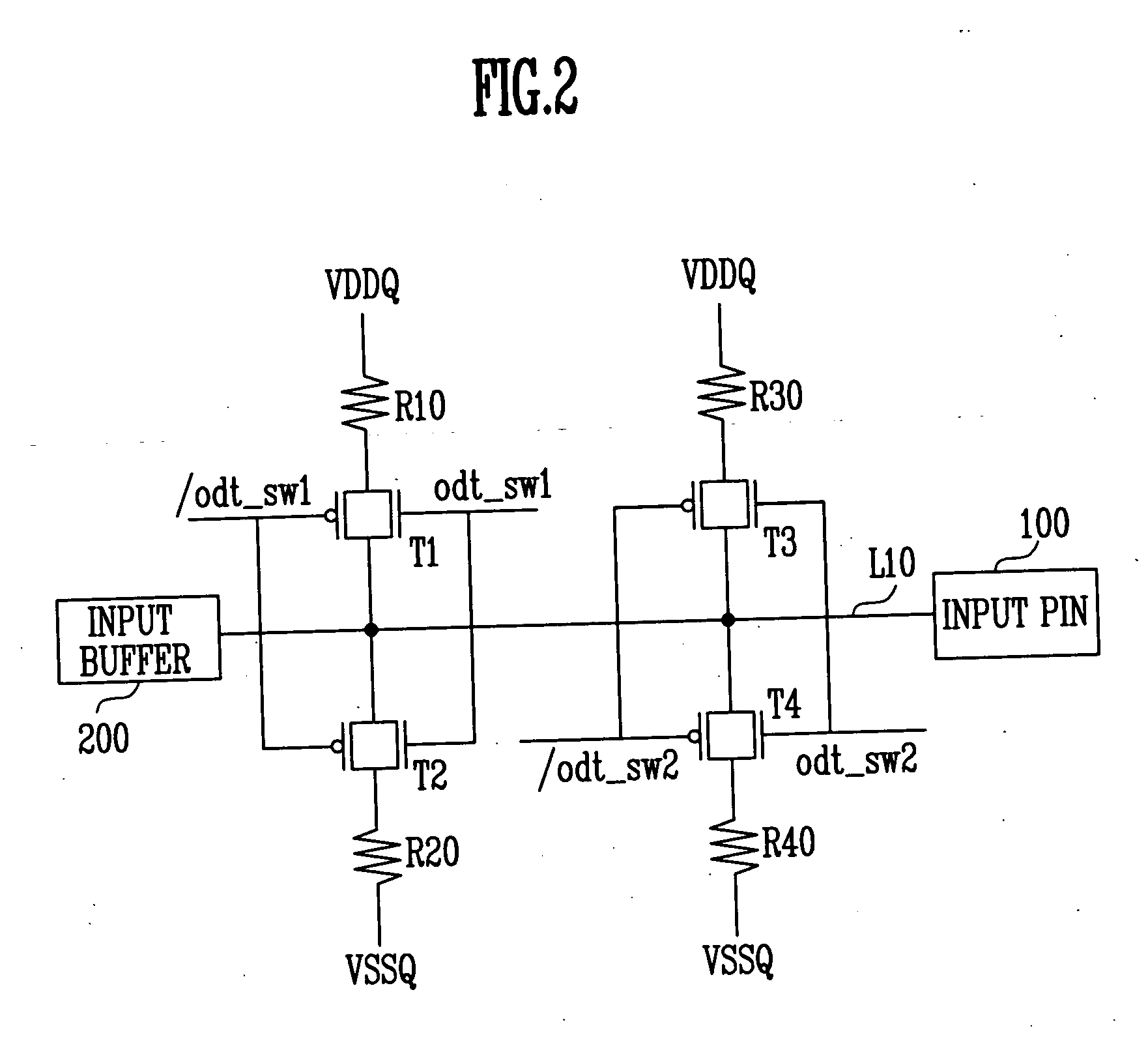
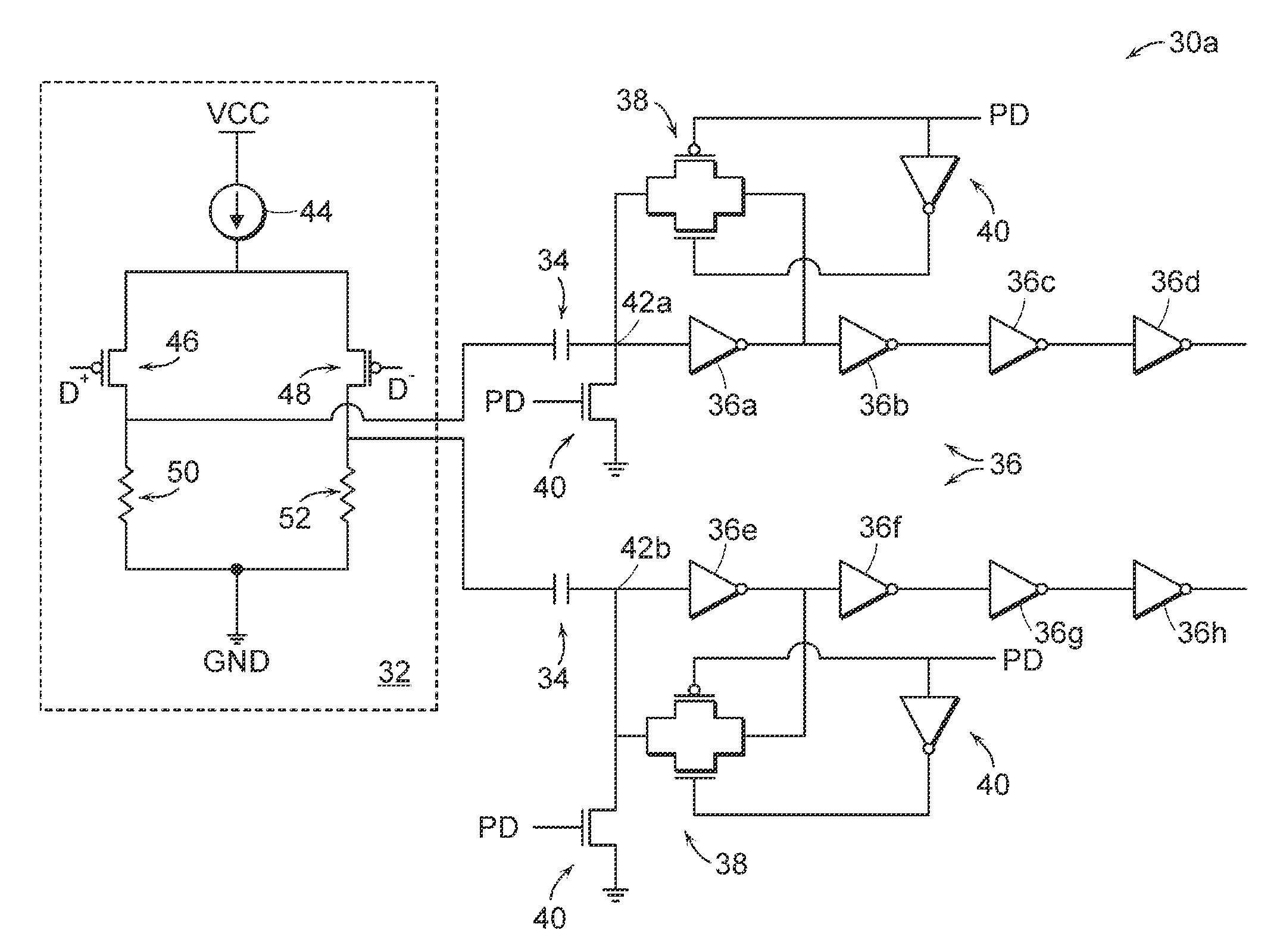
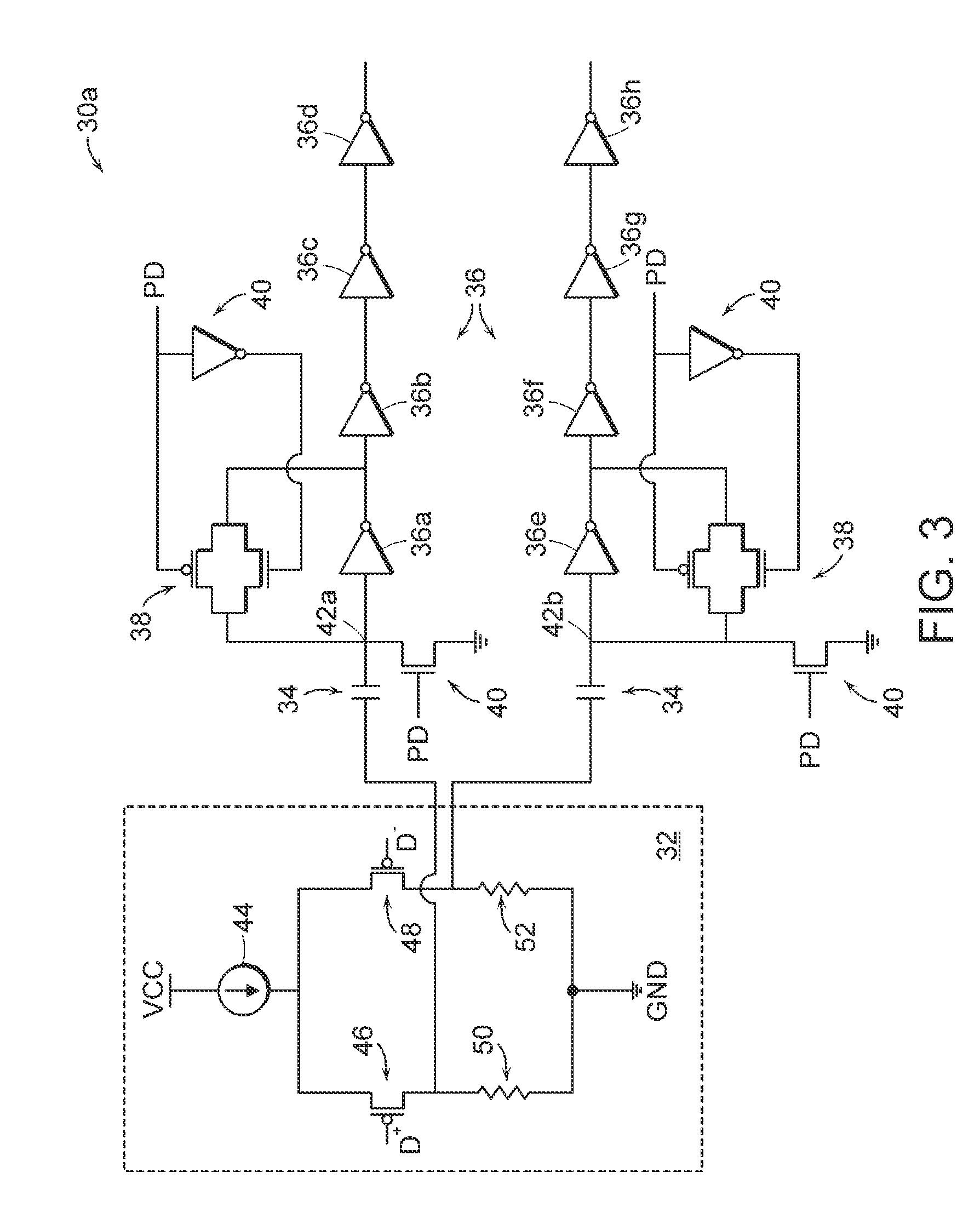
On die termination circuit
ActiveUS20050225353A1Constant voltage of an input pinEasy to operateReliability increasing modificationsLogic circuits characterised by logic functionTransmission gateOn-die termination
The present invention discloses an on die termination circuit. The on die termination circuit used in a DDR2 employs transmission gates as pull-up and pull-down switches, equalizes pull-up and pull-down resistance values by changing connection relations between switches and resistors, and maintains a constant voltage of an input pin.
Owner:SK HYNIX INC
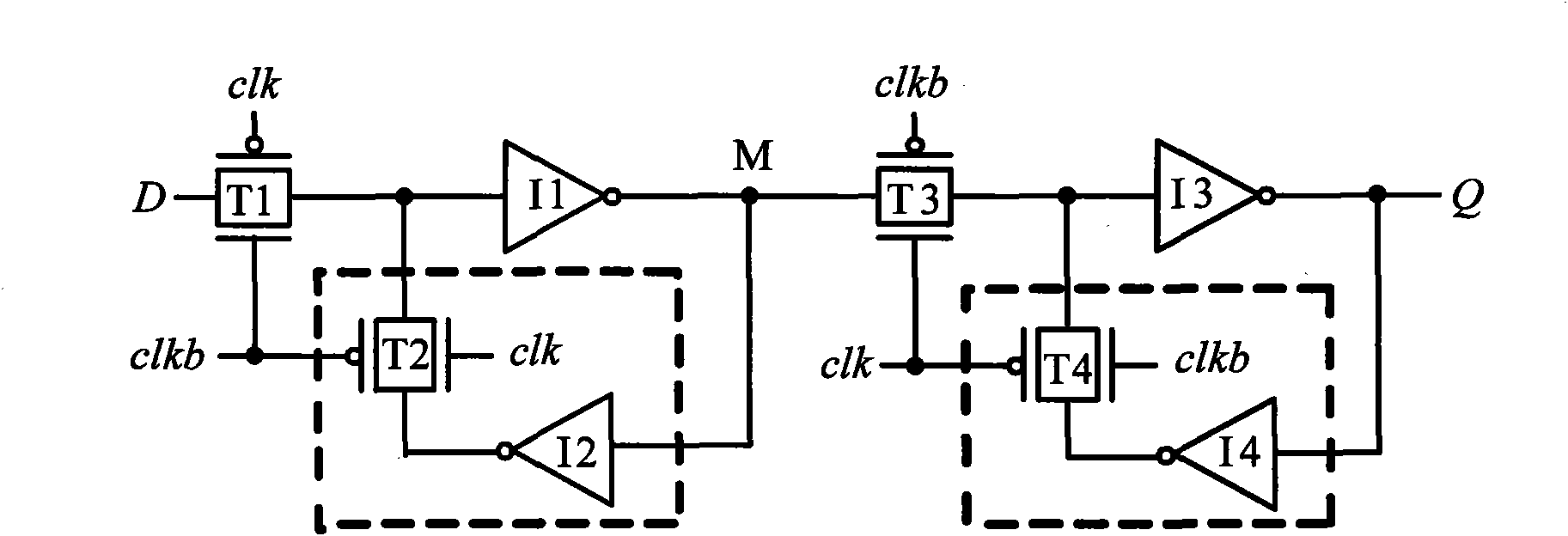
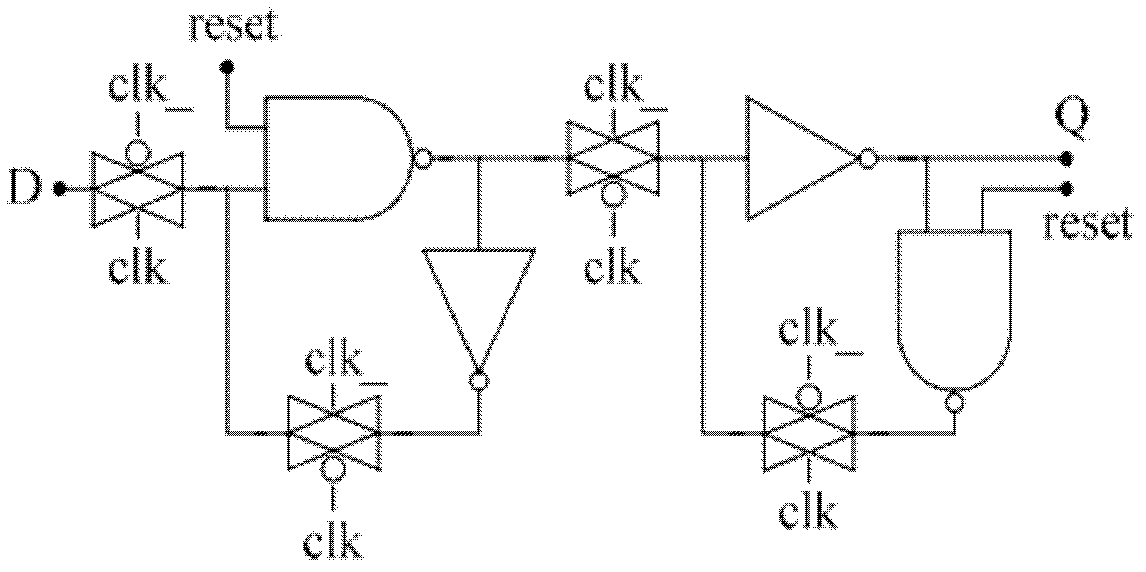
Low-power dissipation RS latch unit and low-power dissipation master-slave D flip-flop
InactiveCN101777907ASimple and completely symmetrical structureGood leakage power suppression performanceElectric pulse generatorLogic circuitsHemt circuitsControl theory
The invention discloses a low-power dissipation RS latch unit and a low-power dissipation master-slave D flip-flop, which is characterized in that the low-power dissipation RS latch unit comprises an input driving and synchronizing circuit, a pull-down circuit, a function control circuit, a first phase inverter and a second phase inverter, wherein the first phase inverter and the second phase inverter are mutually overlapped and coupled. The low power dissipation master-slave D flip-flop is composed of an input phase inverter, a clock phase inverter, a first low-power dissipation RS latch unit and a second low-power dissipation RS latch unit, wherein the first low power dissipation RS latch unit and the second low power dissipation RS latch unit have the same inner structure and are cascaded. The low power dissipation master-slave D flip-flop has the advantages that the low-power dissipation RS latch units use three kinds of leaked power consumption lowering technology, i.e. P-type logic technology, function control technology and double-threshold technology, so that the low-power dissipation RS latch units have better leaked power consumption inhibiting performance. The low-power dissipation master-slave D flip-flop has simple and totally symmetrical circuit structure. Compared with the traditional single-threshold transmission gate D trigger circuit, the invention can save 80% of leaked power consumption and 40% of total power consumption in the 90 nm process, so that the invention is suitable to serve as a digital circuit unit to the design of low-power consumption integrated circuits in the deep sub-micron CMOS process.
Owner:NINGBO UNIV
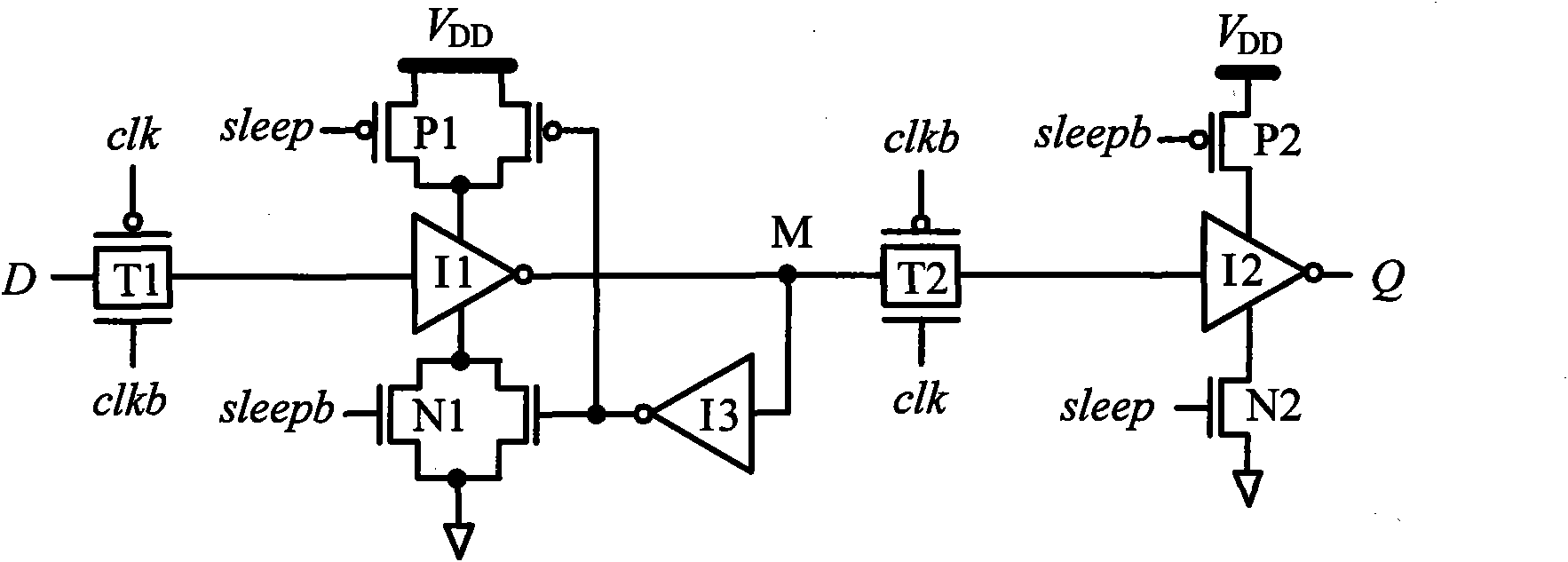
Master-slave type flip-flop circuit
InactiveUS20090002044A1Reduce power consumptionReduce EMISolid-state devicesElectric pulse generatorTransmission gateGate array
A master-slave type flip-flop circuit consisting of a master latch and a slave latch, wherein the master latch comprises: a first clocked inverter to which data are input and a first latch circuit configuring a closed circuit with a first inverter and a second clocked inverter so that an output of the first clocked inverter is input to the first inverter and; the slave latch comprises: a transmission gate to which an output from the first latch circuit is input and a second latch circuit configuring a closed circuit with a second inverter and a third clocked inverter so that an output of the transmission gate is input to the second inverter, respective components configuring the master latch and the slave latch are configured with Sea Of Gate (hereinafter to be referred to as SOG) configuring a gate array, a basic cell of the SOG consists of triplely arrayed N-type transistors and corresponding triplely arrayed P-type transistors, the triplely arrayed N-type transistors consist of double-arrayed normally sized main transistors and one auxiliary transistor sized smaller than in a normal size and the triplely arrayed P-type transistors consist of double-arrayed normally sized main transistors and one auxiliary transistor sized smaller than in a normal size.
Owner:SEIKO EPSON CORP
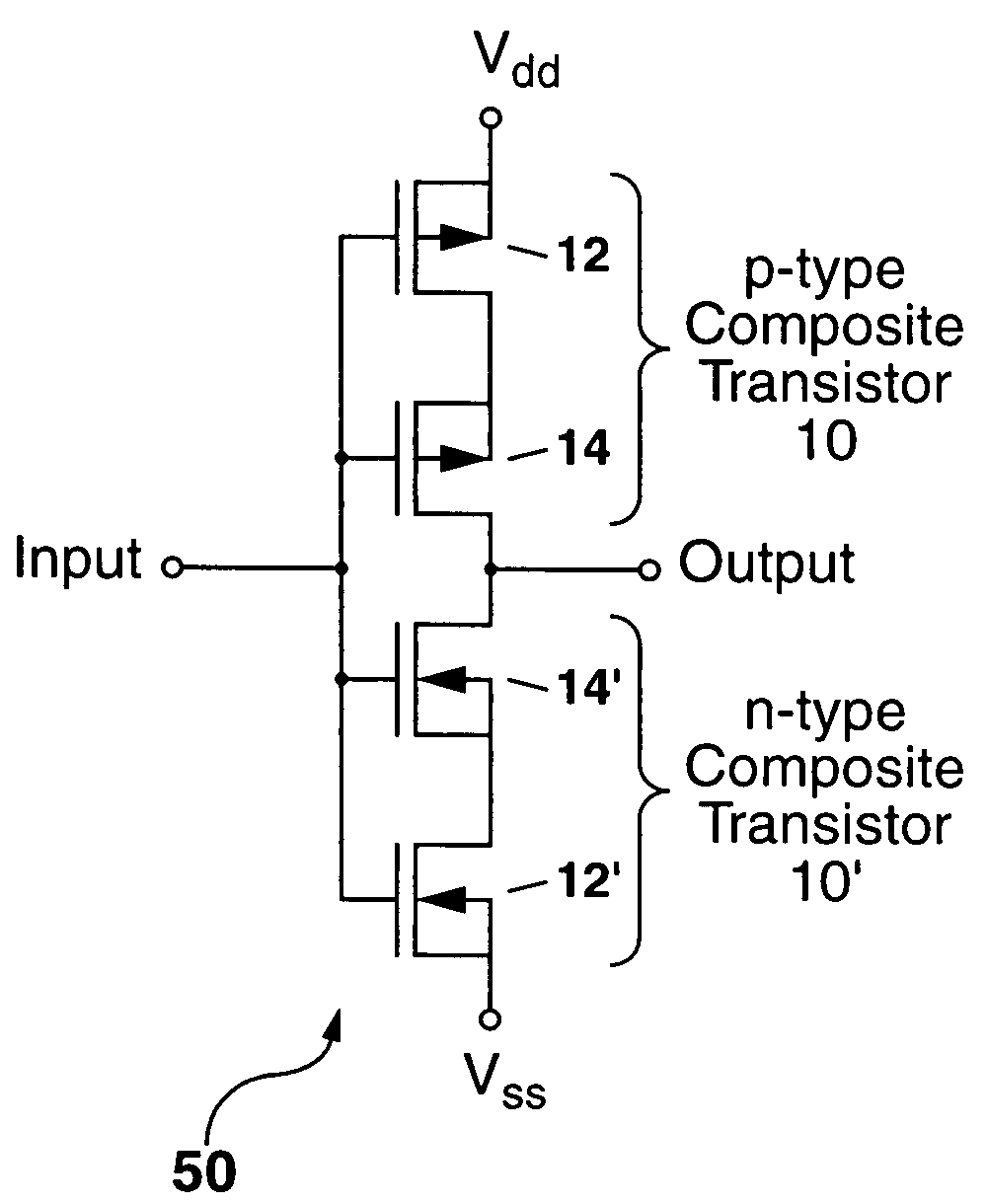
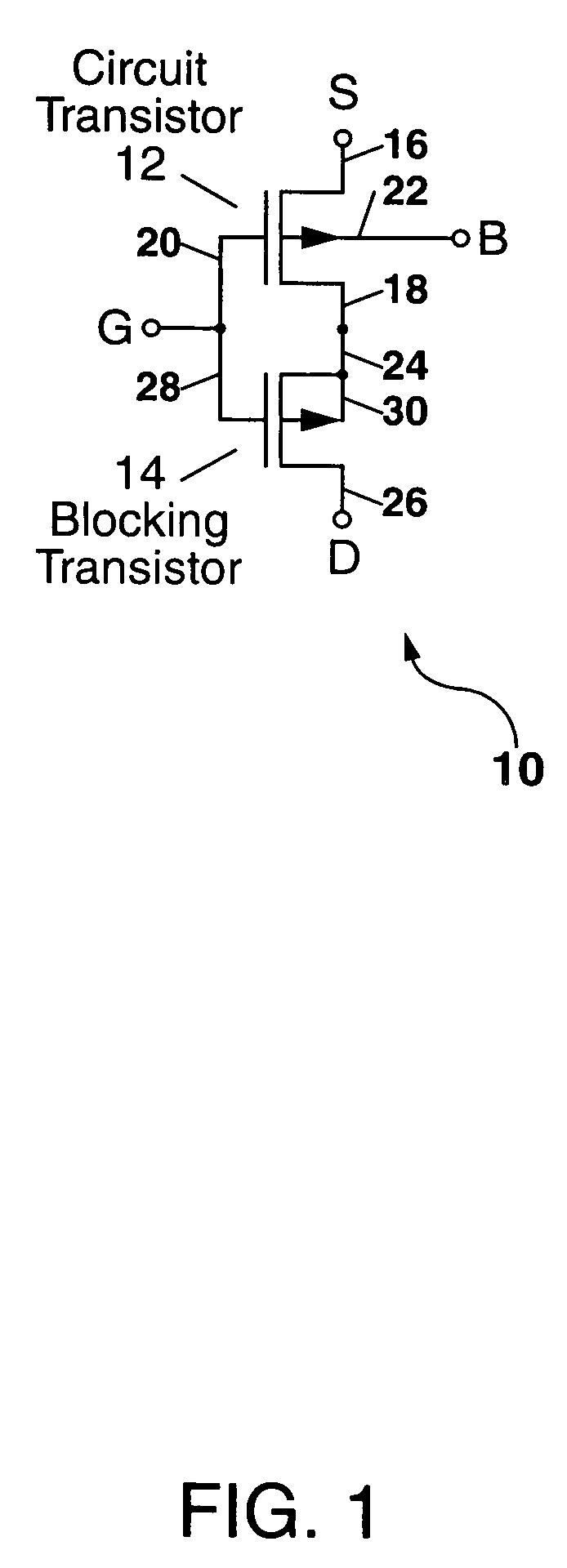
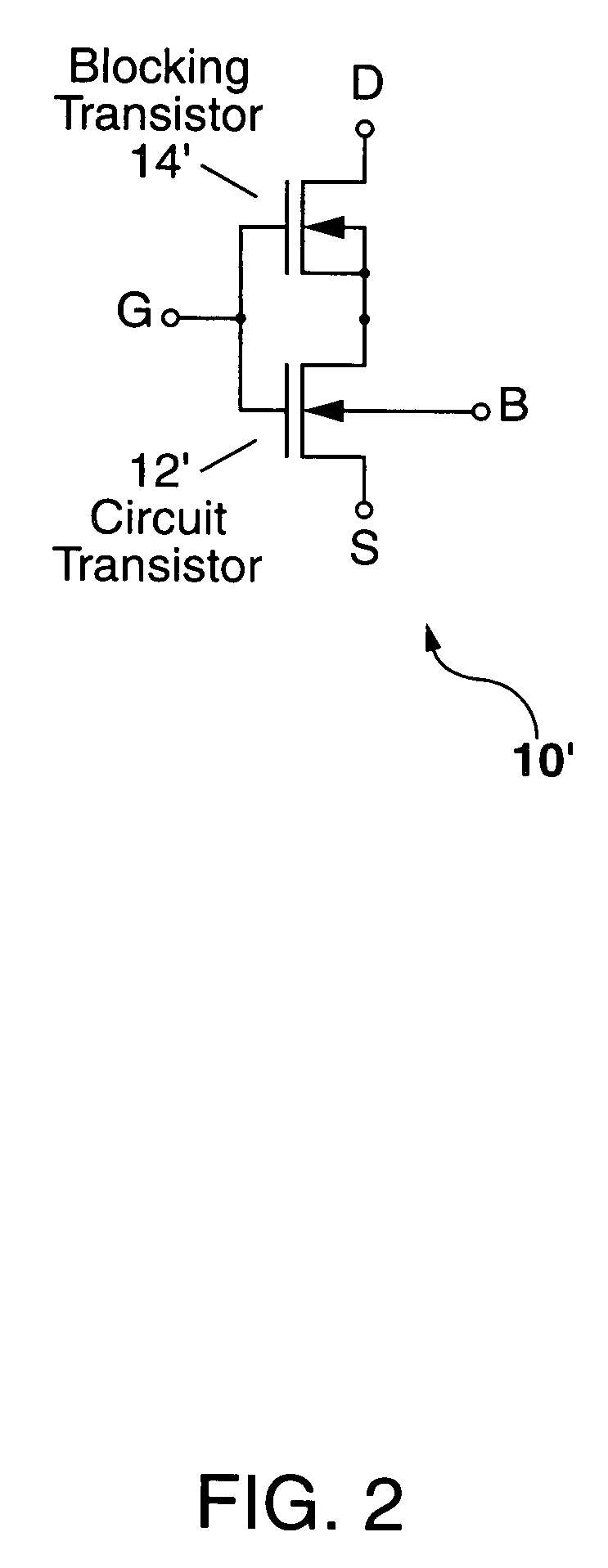
Radiation-hardened transistor and integrated circuit
A composite transistor is disclosed for use in radiation hardening a CMOS IC formed on an SOI or bulk semiconductor substrate. The composite transistor has a circuit transistor and a blocking transistor connected in series with a common gate connection. A body terminal of the blocking transistor is connected only to a source terminal thereof, and to no other connection point. The blocking transistor acts to prevent a single-event transient (SET) occurring in the circuit transistor from being coupled outside the composite transistor. Similarly, when a SET occurs in the blocking transistor, the circuit transistor prevents the SET from being coupled outside the composite transistor. N-type and P-type composite transistors can be used for each and every transistor in the CMOS IC to radiation harden the IC, and can be used to form inverters and transmission gates which are the building blocks of CMOS ICs.
Owner:NAT TECH & ENG SOLUTIONS OF SANDIA LLC
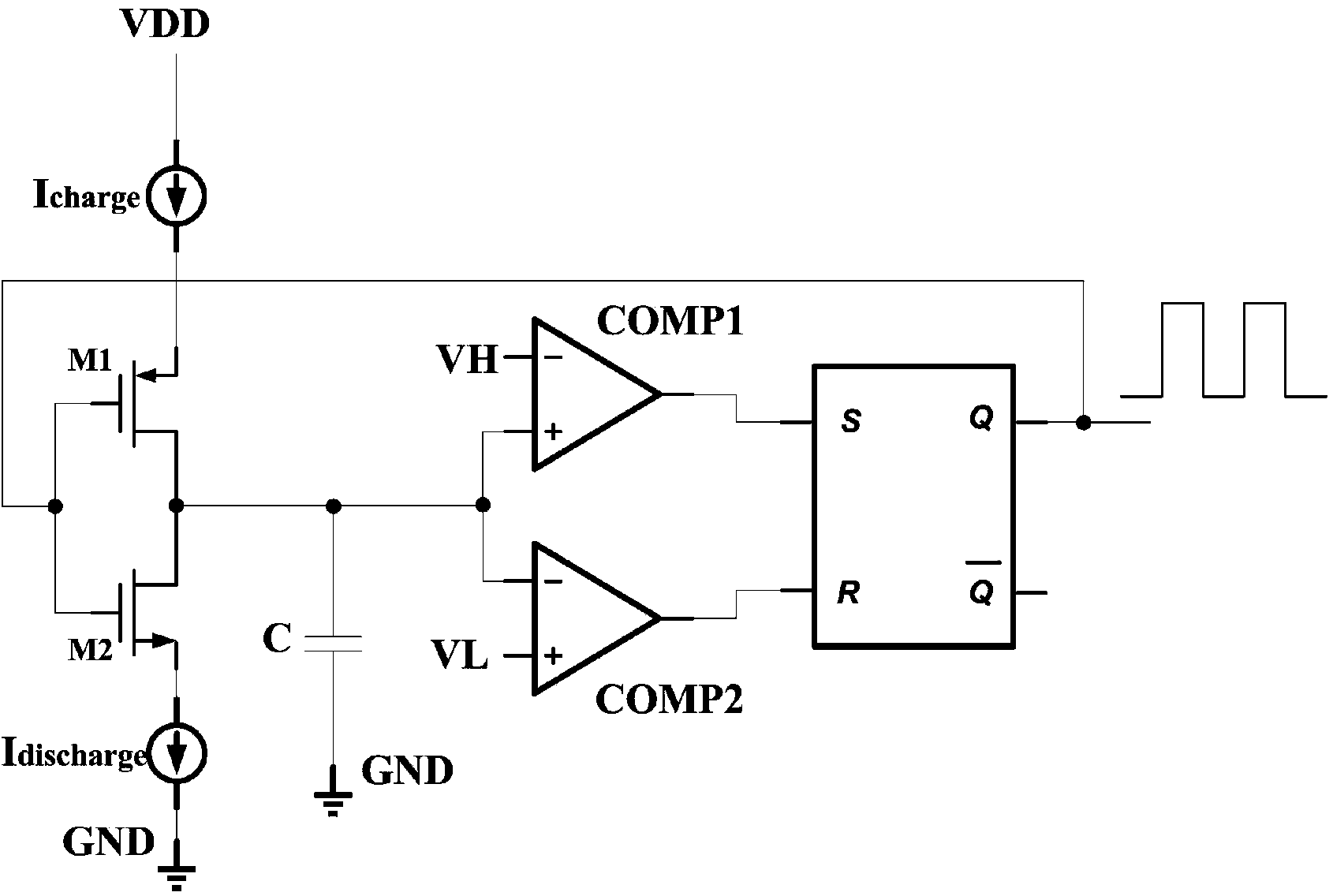
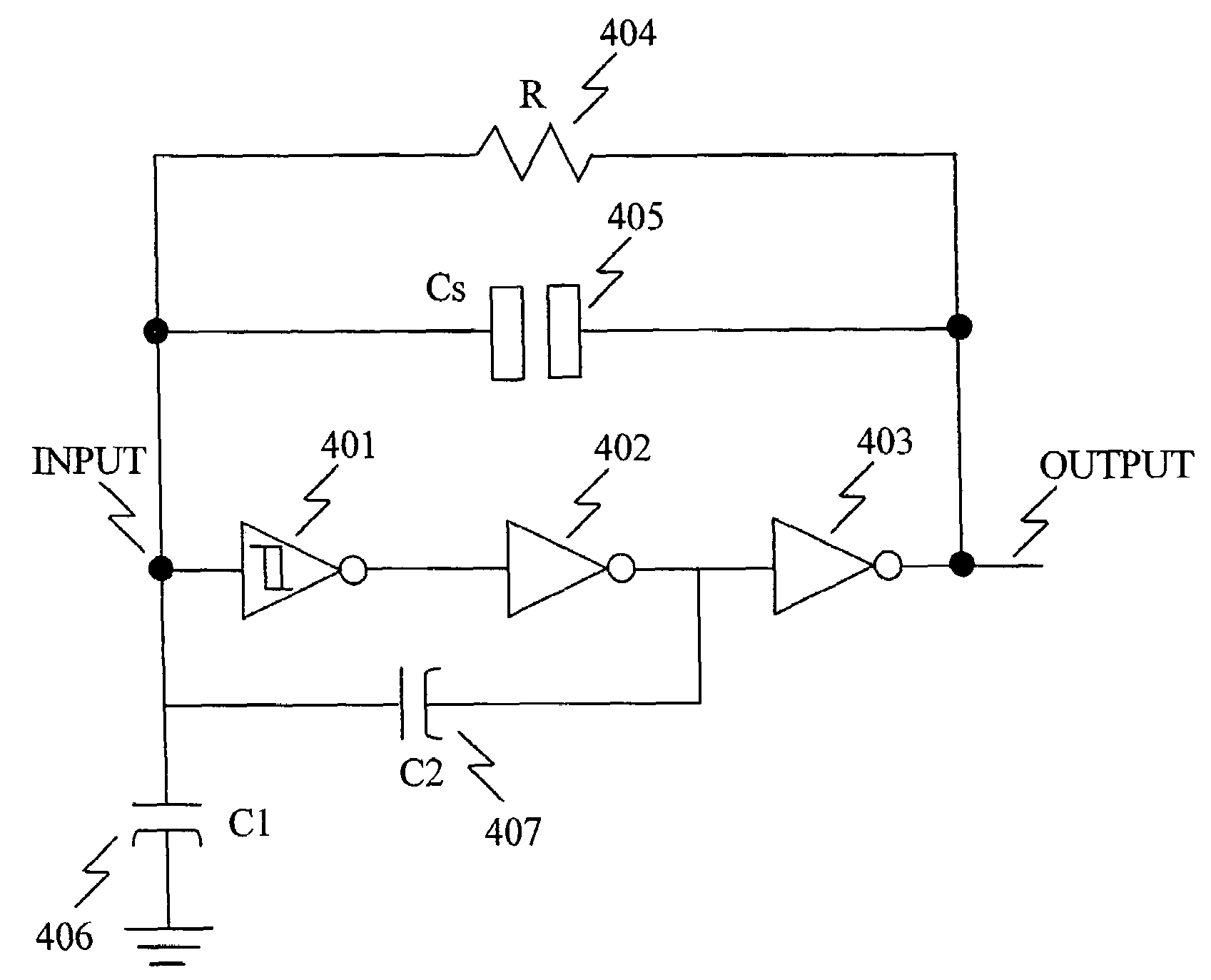
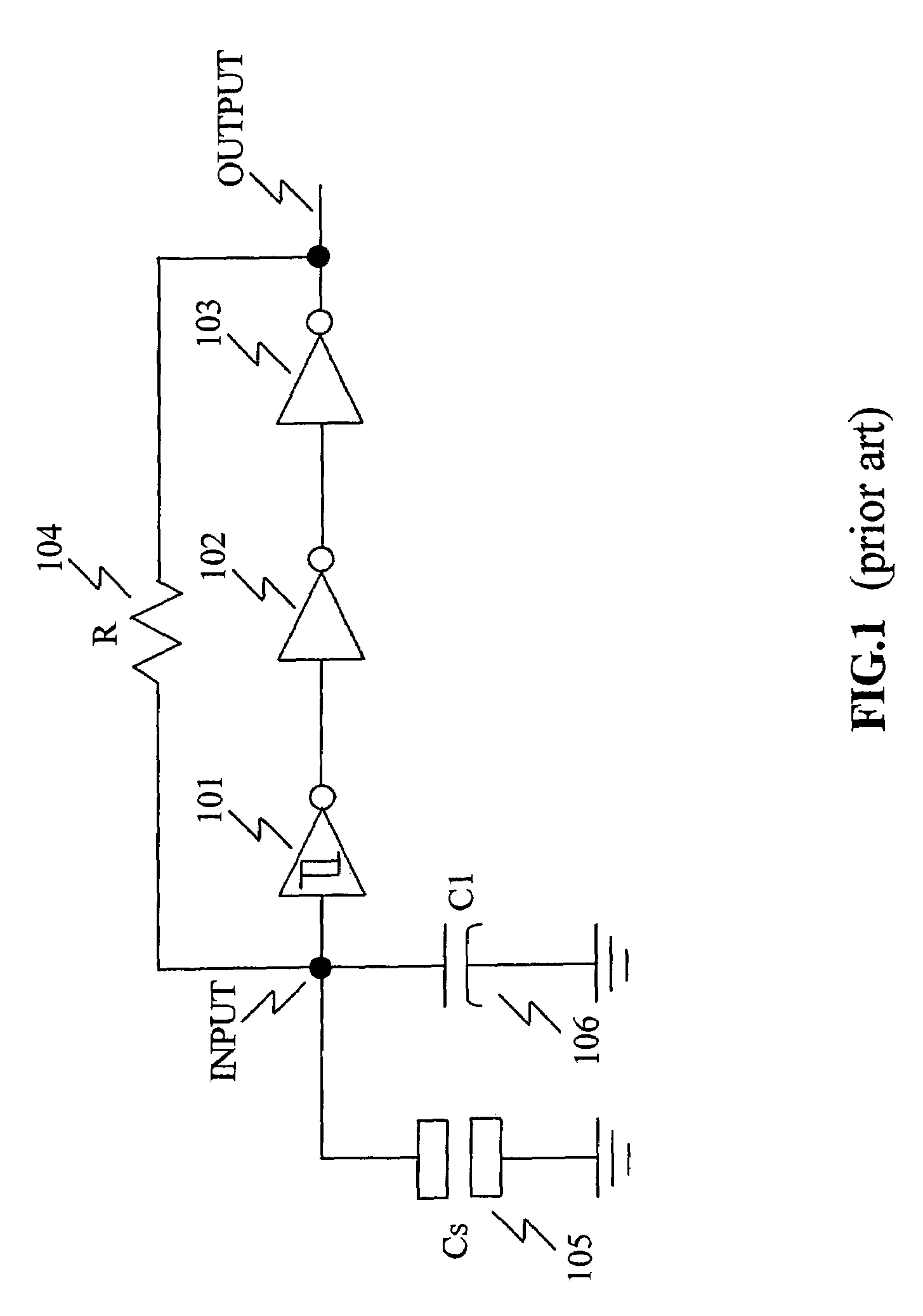
High-linearity relaxation oscillator
ActiveCN103546123AImprove linearityLong cyclePulse generation by differential amplifiersTransmission gateCapacitor voltage
The invention provides a relaxation oscillator of which the linearity is significantly improved. The relaxation oscillator comprises an oscillating circuit, a reference level self-regulating circuit and a transmission gate selective signal generating circuit. Capacitor voltage overshoot caused by delay of a control circuit is worked out by detecting the voltage peak of charge and discharge capacitors in the oscillating circuit, and accordingly the reference level of comparators in the oscillating circuit is reduced by a corresponding quantity to serve as a new reference level so that the oscillation amplitude of the charge and discharge capacitors can be just a theoretical value. According to the high-linearity relaxation oscillator, when the new reference level is larger than zero, influence, brought by the capacitor voltage overshoot caused by delay of the control circuit, of the charge and discharge capacitors on output frequency is eliminated, and the linearity of a frequency-control circuit of the relaxation oscillator is significantly improved. The transmission gate selective signal generating circuit provides the initial reference level for the comparators by controlling transmission gates and transmits the new reference level to the reverse phase ends of the comparators when the new reference level is generated, and therefore the initial reference level can be isolated from the reverse phase ends of the comparators.
Owner:SOUTHEAST UNIV
Memory module with dynamic termination using bus switches timed by memory clock and chip select
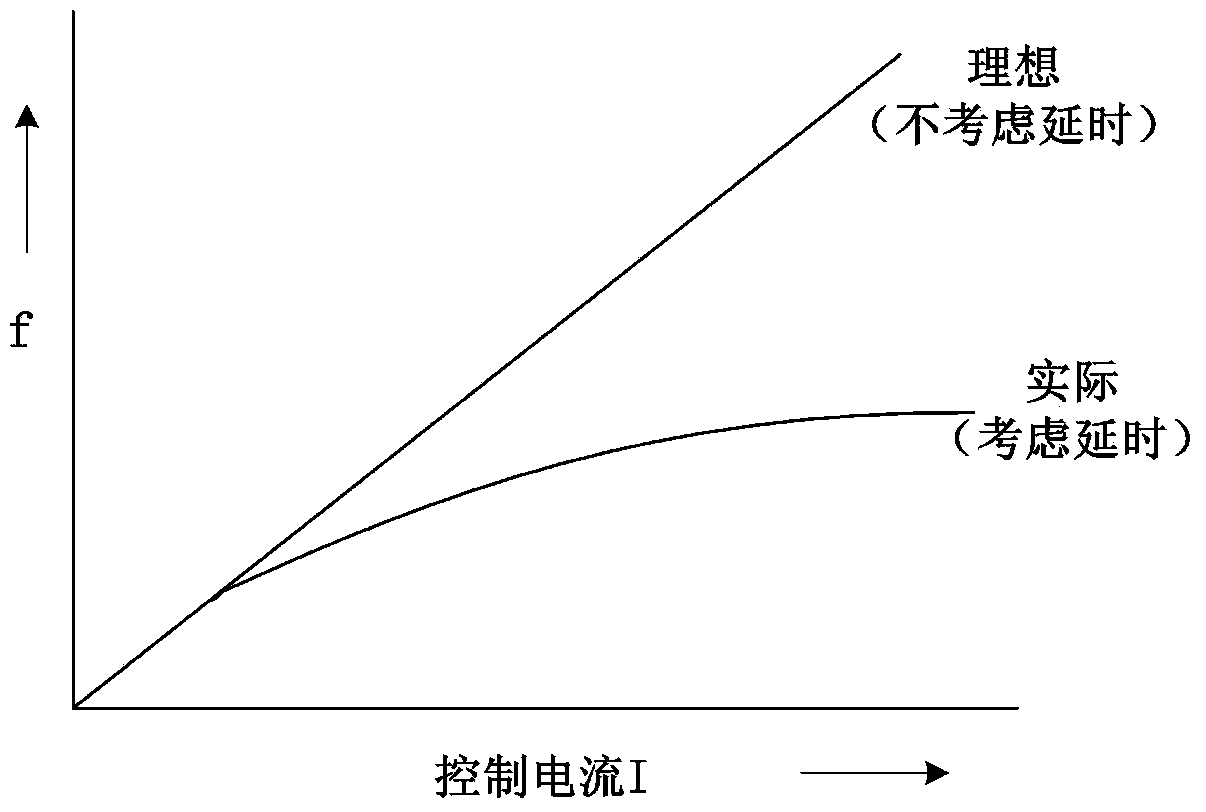
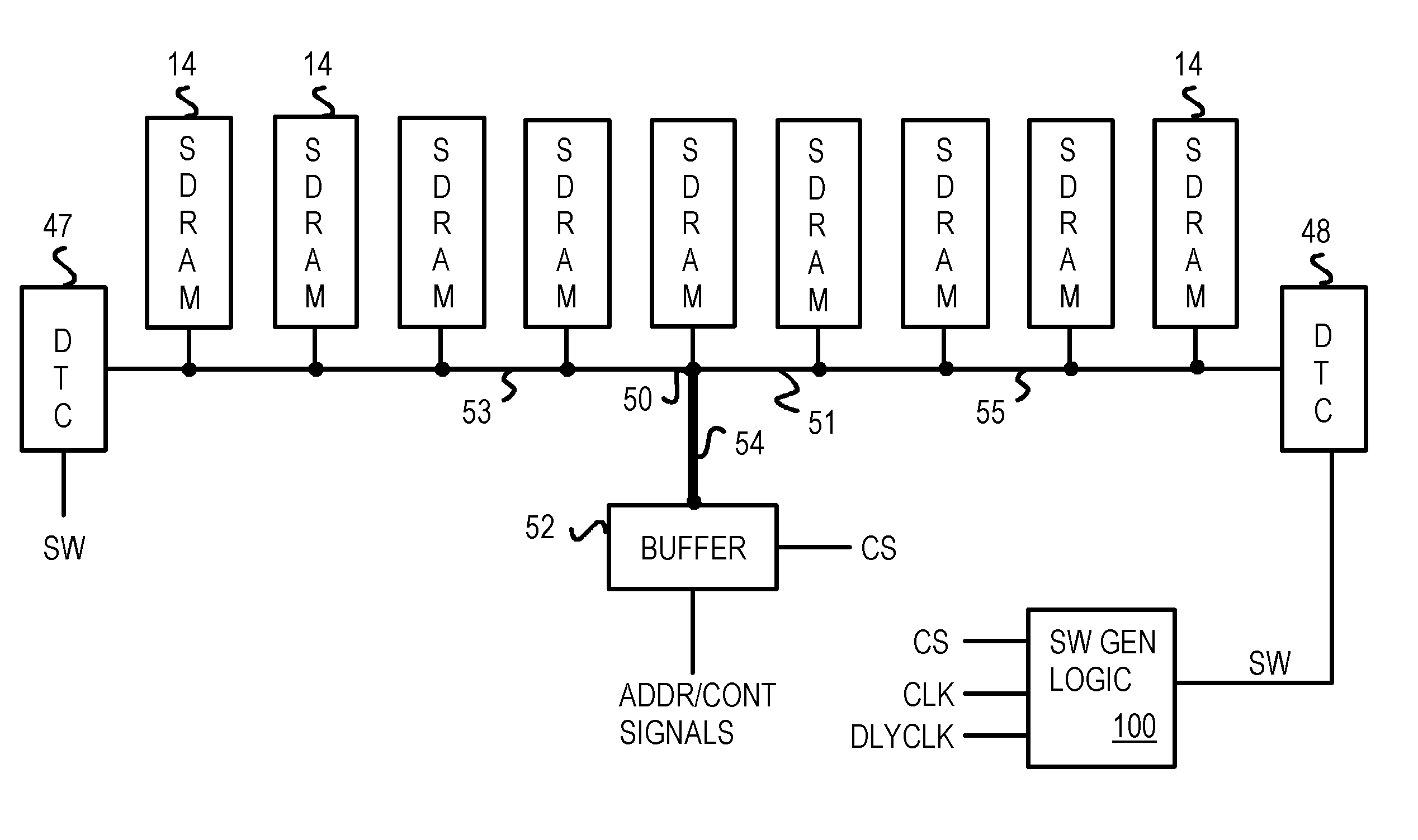
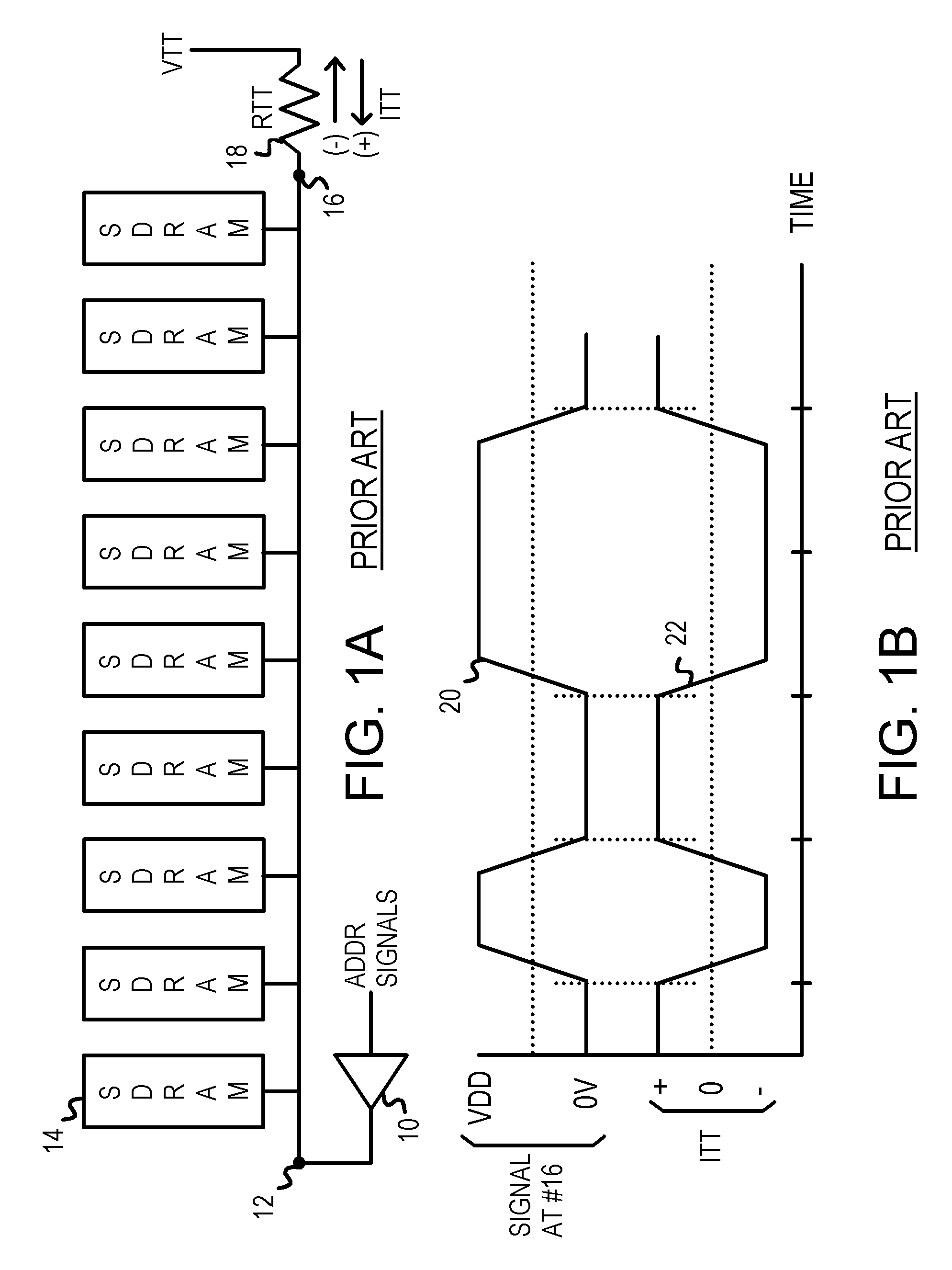
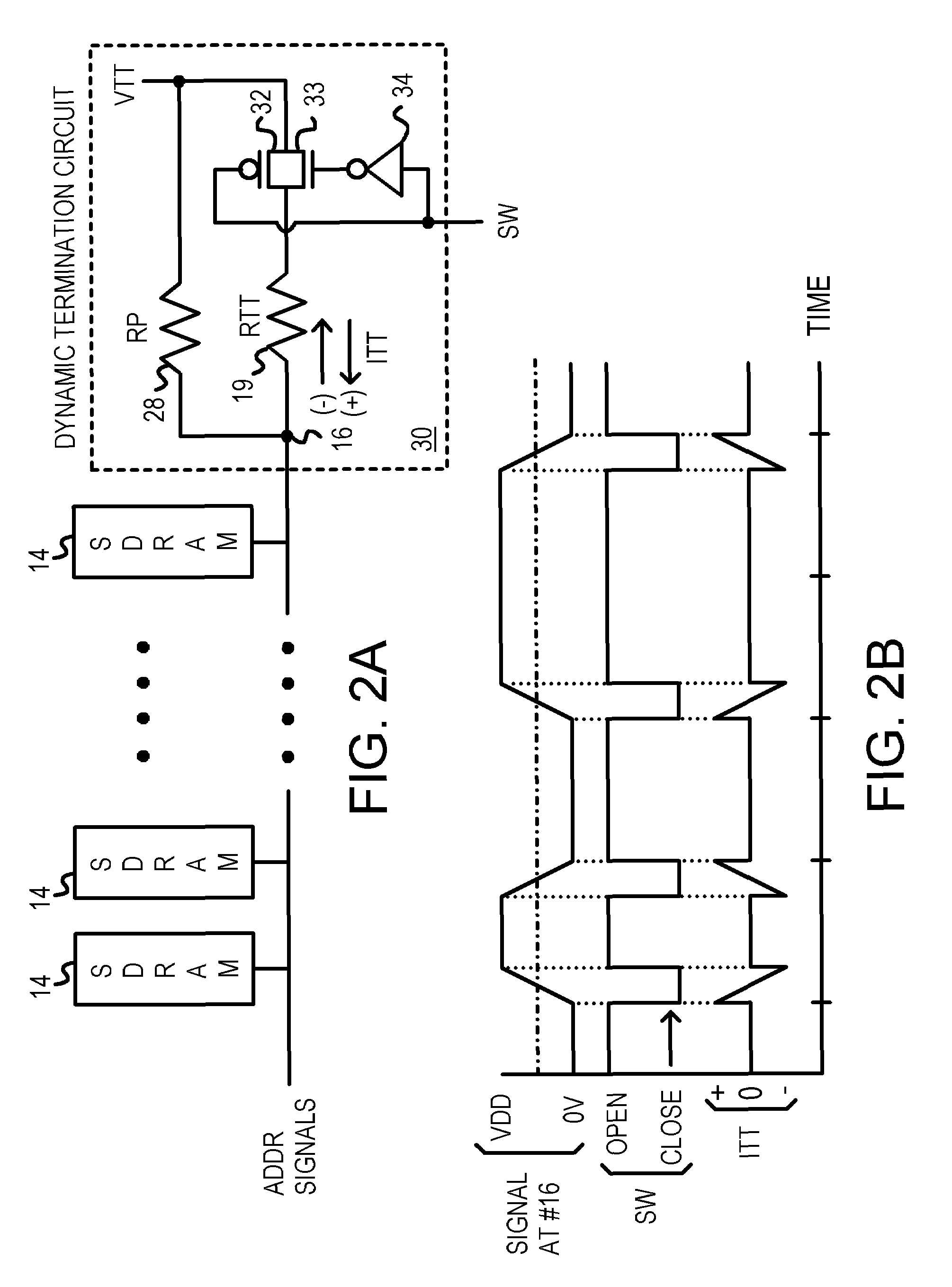
InactiveUS7068064B1Energy efficient ICTReliability increasing modificationsTransmission gateChip select
A low-power memory module has an active termination circuit at each end of critical signal traces. The dynamic termination circuit has a low-value resistor that is connected to a termination voltage by a transmission gate that is turned on by a switch signal. The switch signal is activated when the memory module is selected by a chip-select signal, and when a time window is open. The time window is generated from the clock to synchronous DRAMs on the memory module. The time window can be one-quarter of the clock period by ANDing the clock and a delayed clock that is delayed by one-quarter of a cycle. A static terminating resistor in parallel with the low-value resistor provides a much smaller terminating current that is not switched on and off. Traces can be impedance-matched at junctions to branches that each has a dynamic termination circuit at the far end.
Owner:DIODES INC
Low lag transfer gate device
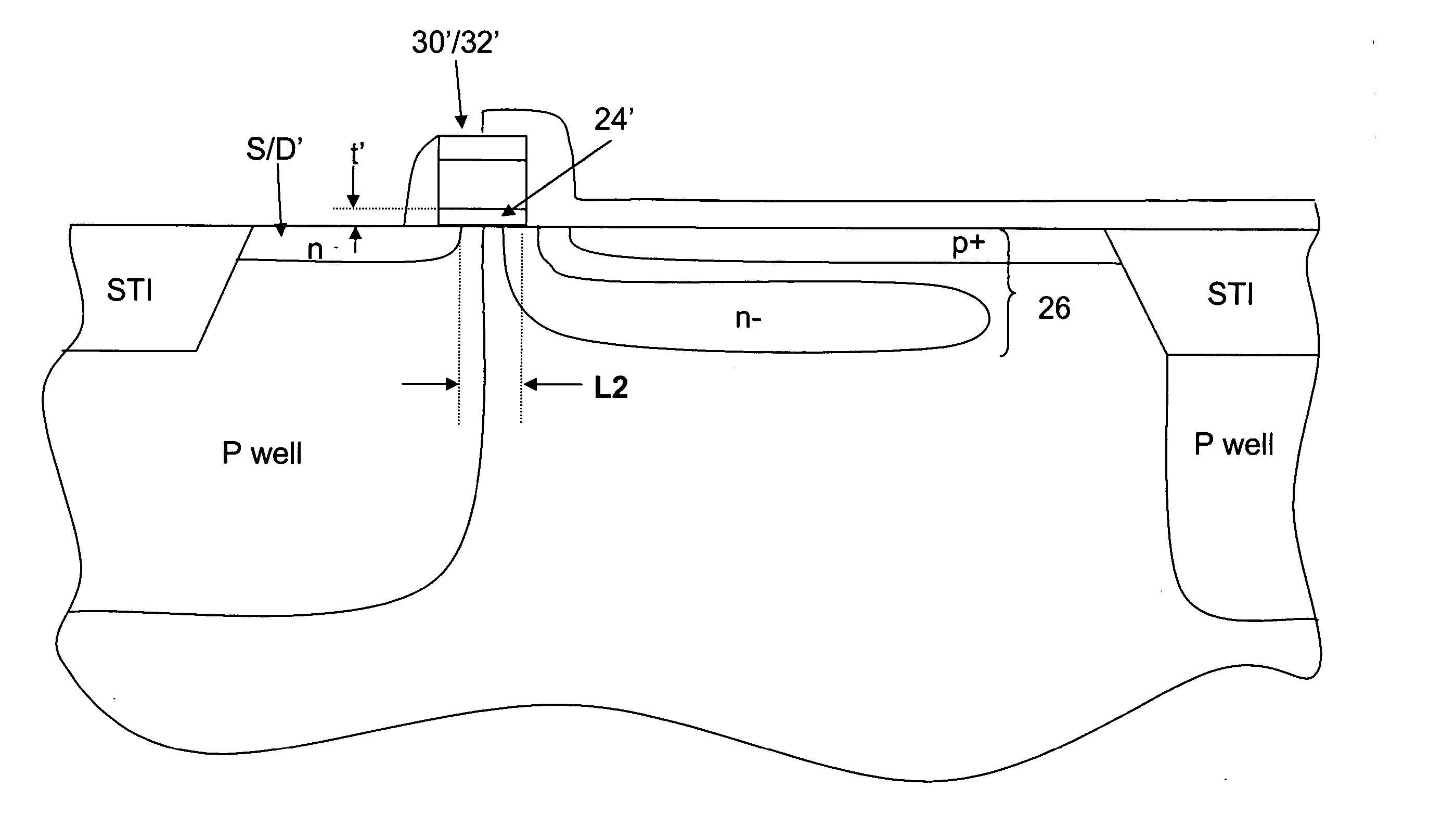
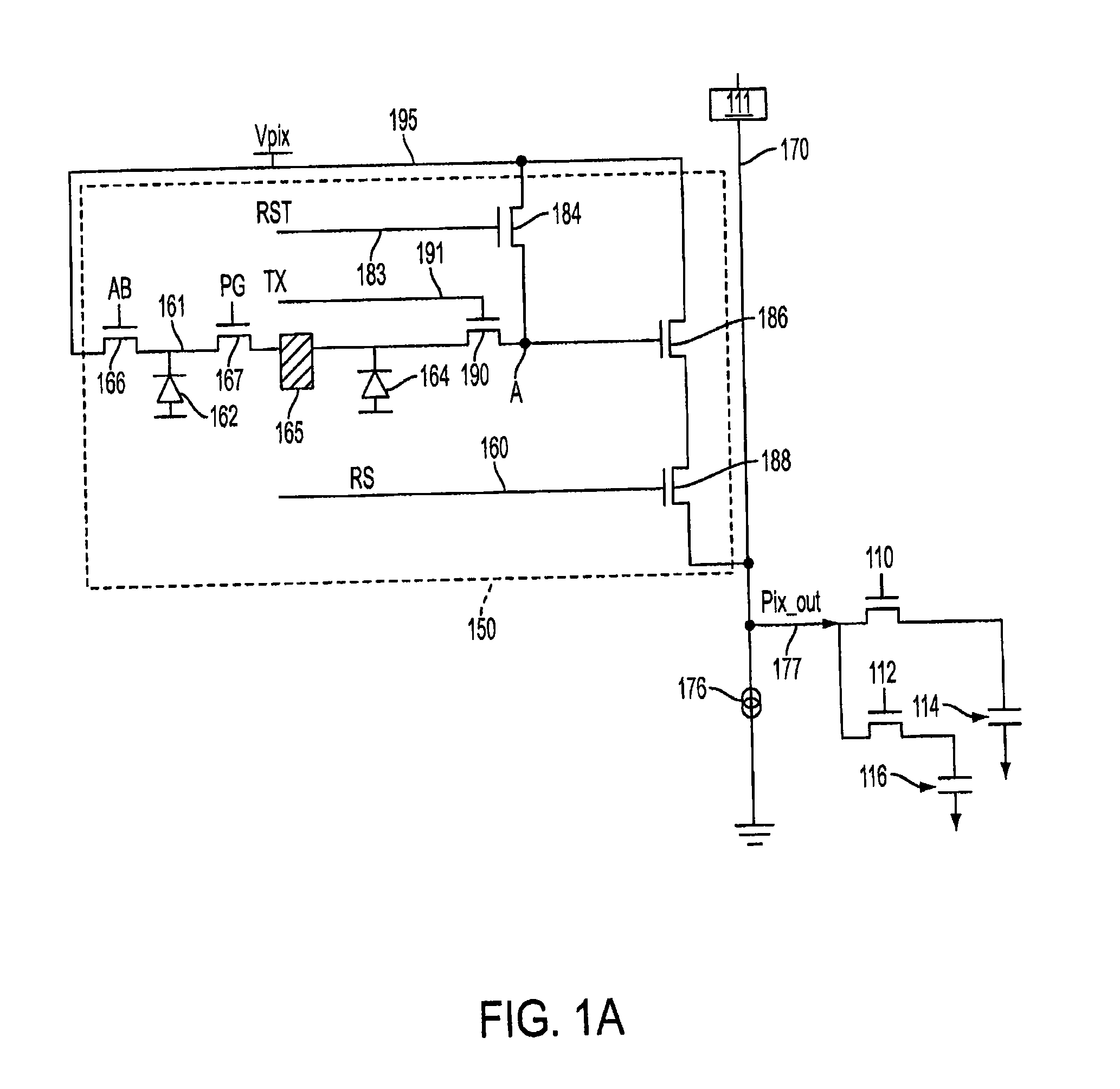
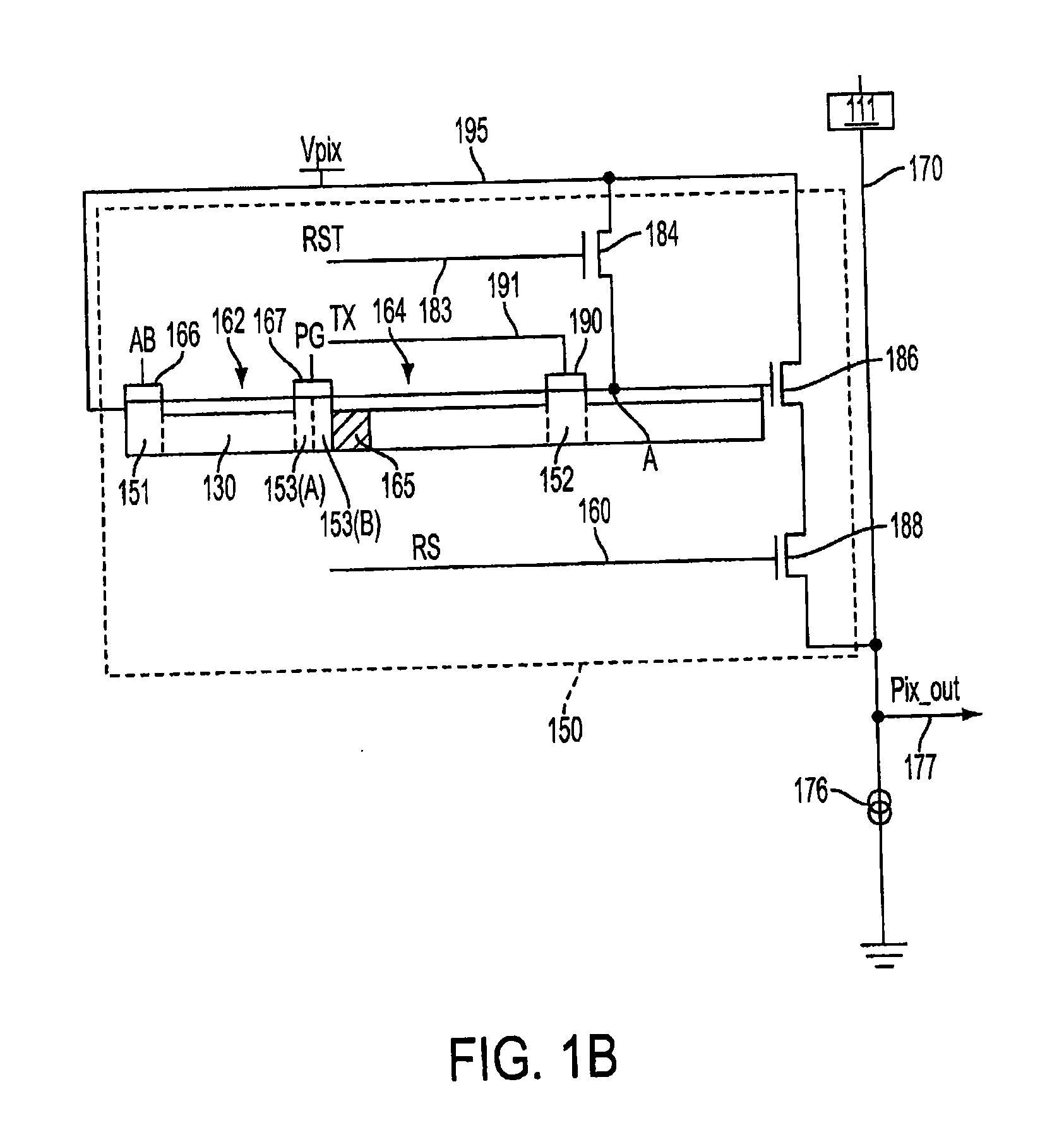
ActiveUS20090180010A1Prevent overflowTelevision system detailsTelevision system scanning detailsElectrical conductorEngineering
A method of forming a CMOS active pixel sensor (APS) cell structure having at least one transfer gate device and method of operation. A first transfer gate device comprises a diodic or split transfer gate conductor structure having a first doped region of first conductivity type material and a second doped region of a second conductivity type material. A photosensing device is formed adjacent the first doped region for collecting charge carriers in response to light incident thereto, and, a diffusion region of a second conductivity type material is formed at or below the substrate surface adjacent the second doped region of the transfer gate device for receiving charges transferred from the photosensing device while preventing spillback of charges to the photosensing device upon timed voltage bias to the diodic or split transfer gate conductor structure. Alternately, an intermediate charge storage device and second transfer gate device may be provided which may first temporarily receive charge carriers from the photosensing device, and, upon activating the second transfer gate device in a further timed fashion, read out the charge stored at the intermediate charge storage device for transfer to the second transfer gate device while preventing spillback of charges to the photosensing device. The APS cell structure is further adapted for a global shutter mode of operation, and further comprises a light shield element is further provided to ensure no light reaches the photosensing and charge storage devices during charge transfer operation.
Owner:GLOBALFOUNDRIES US INC
Low Power Nanoelectronics
ActiveUS20150333534A1Improve power efficiencyReduce channel resistanceTransformersCircuit arrangementsLow voltageElectric power system
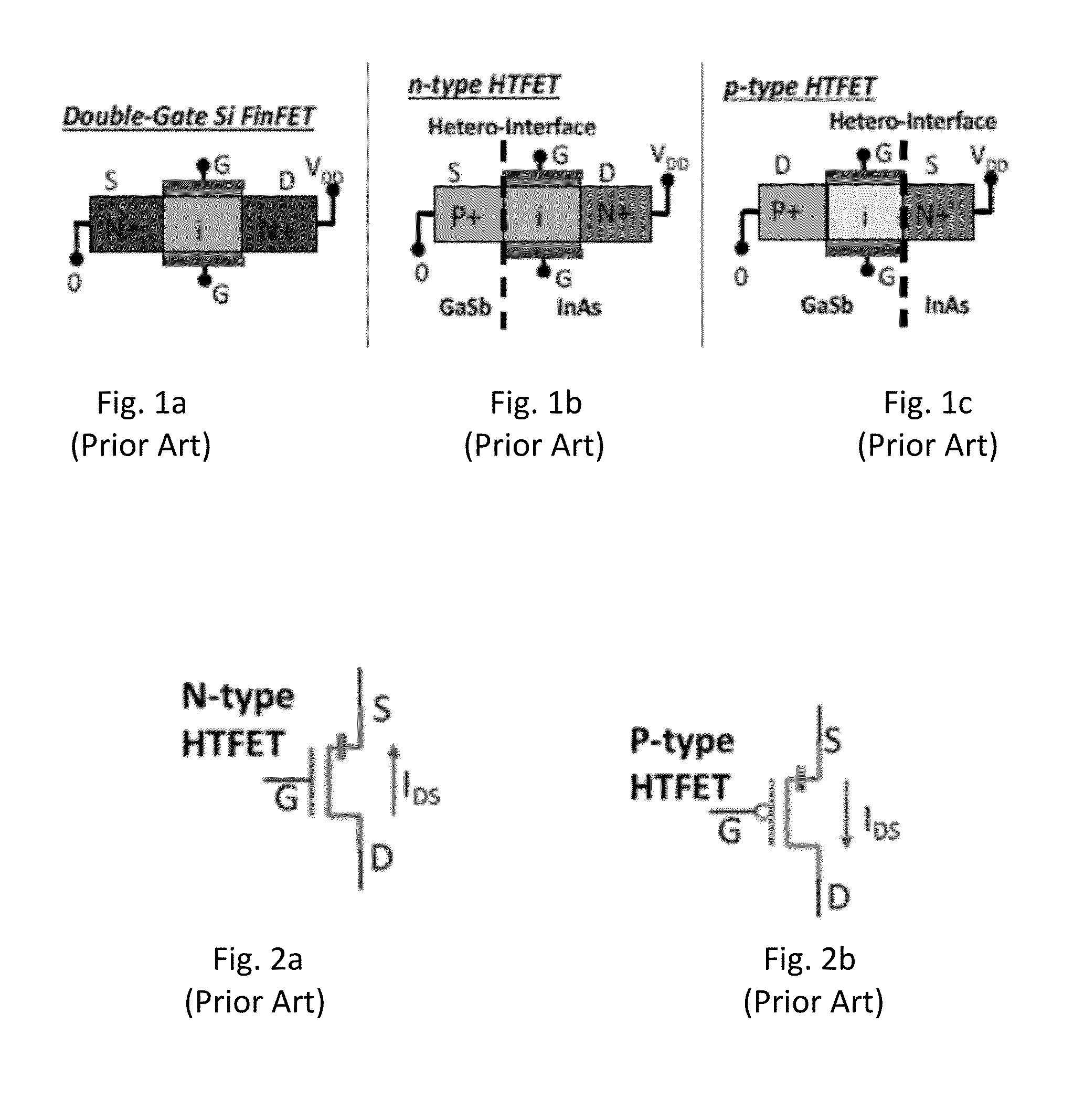
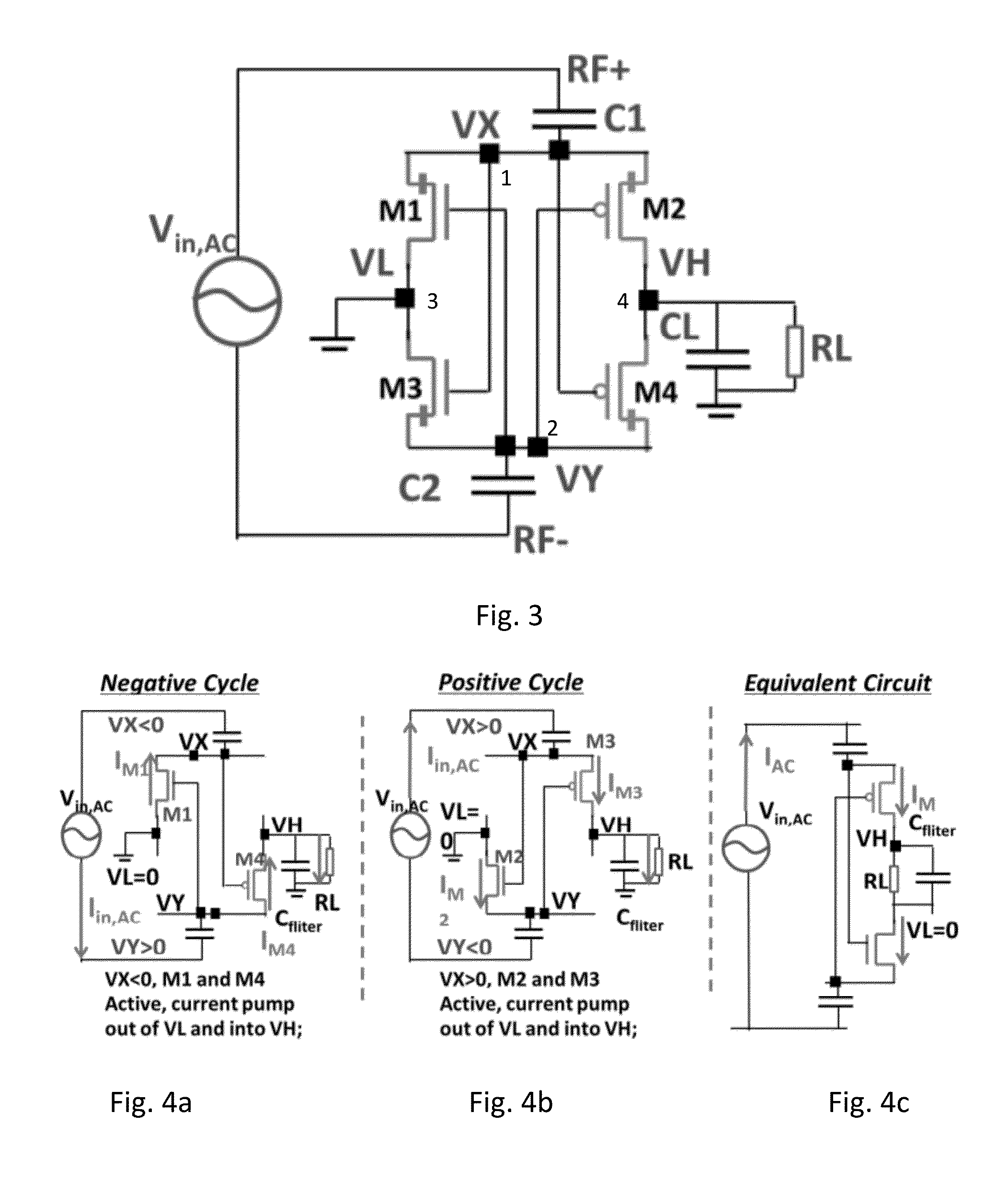
Disclosed are low power electronic devices configured to exploit the sub-threshold swing, unidirectional tunneling, and low-voltage operation of steep slope-tunnel tunnel field-effect transistors (TFET) to improve power-conversion efficiency and power-efficiency of electrical systems incorporating the TFET as an electrical component to perform energy harvesting, signal processing, and related operations. The devices include a HTFET-based rectifier having various topologies, a HTFET-based DC-DC charge pump converter, a HTFET-based amplifier having an amplifier circuit including a telescopic operational transconductance amplifier, and a HTFET-based SAR A / D converter having a HTFET-based transmission gate DFF. Any one of the devices may be used to generate a RF-powered system with improved power conversion efficiencies of power harvesters and power efficiencies of processing components within the system.
Owner:PENN STATE RES FOUND
Global shutter high dynamic range sensor
ActiveUS20160360127A1Quality improvementGood quality pixelsTelevision system detailsSolid-state devicesTransmission gateShutter
The present invention provides a pixel circuit comprising a pinned photodiode, at least one first transfer gate for electrically connecting the pinned photodiode to at least one storage node and at least one further transfer gate. The at least one further gate can connect the at least one storage node with at least one floating diffusion node. At least one merging switch is included for allowing connection between the at least one floating diffusion node with one or more capacitor nodes, which can accept charge that exceeds the maximum storage capacity of the storage node.
Owner:CAELESTE CVBA
Vertically stacked image sensor
A vertically stacked image sensor having a photodiode chip and a transistor array chip. The photodiode chip includes at least one photodiode and a transfer gate extends vertically from a top surface of the photodiode chip. The image sensor further includes a transistor array chip stacked on top of the photodiode chip. The transistor array chip includes the control circuitry and storage nodes. The image sensor further includes a logic chip vertically stacked on the transistor array chip. The transfer gate communicates data from the at least one photodiode to the transistor array chip and the logic chip selectively activates the vertical transfer gate, the reset gate, the source follower gate, and the row select gate.
Owner:APPLE INC
Anti-single event effect static random access memory unit
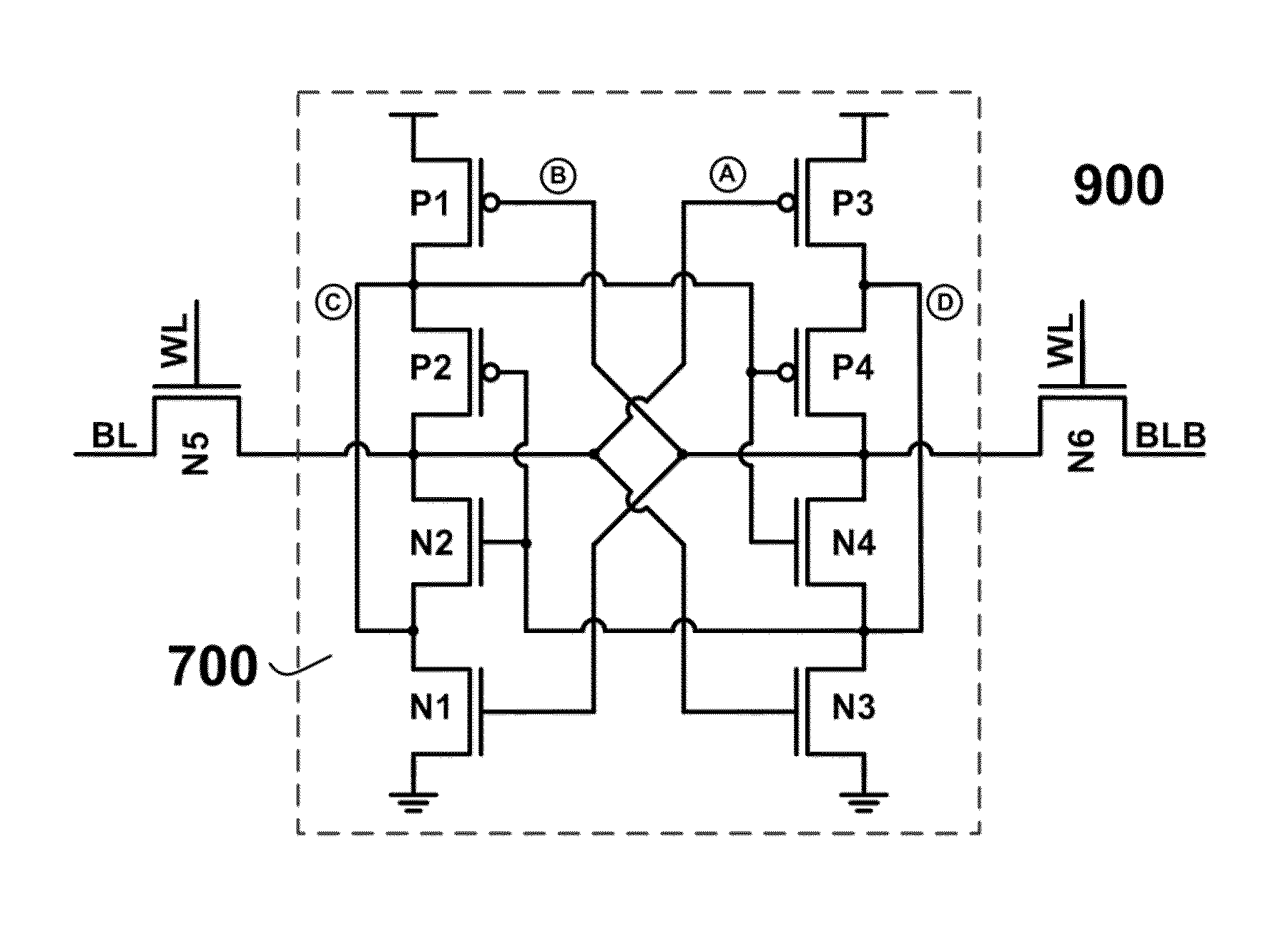
InactiveCN102097123AImprove Flip EffectSuppress key node voltage changesDigital storageRadiation resistantTransmission gate
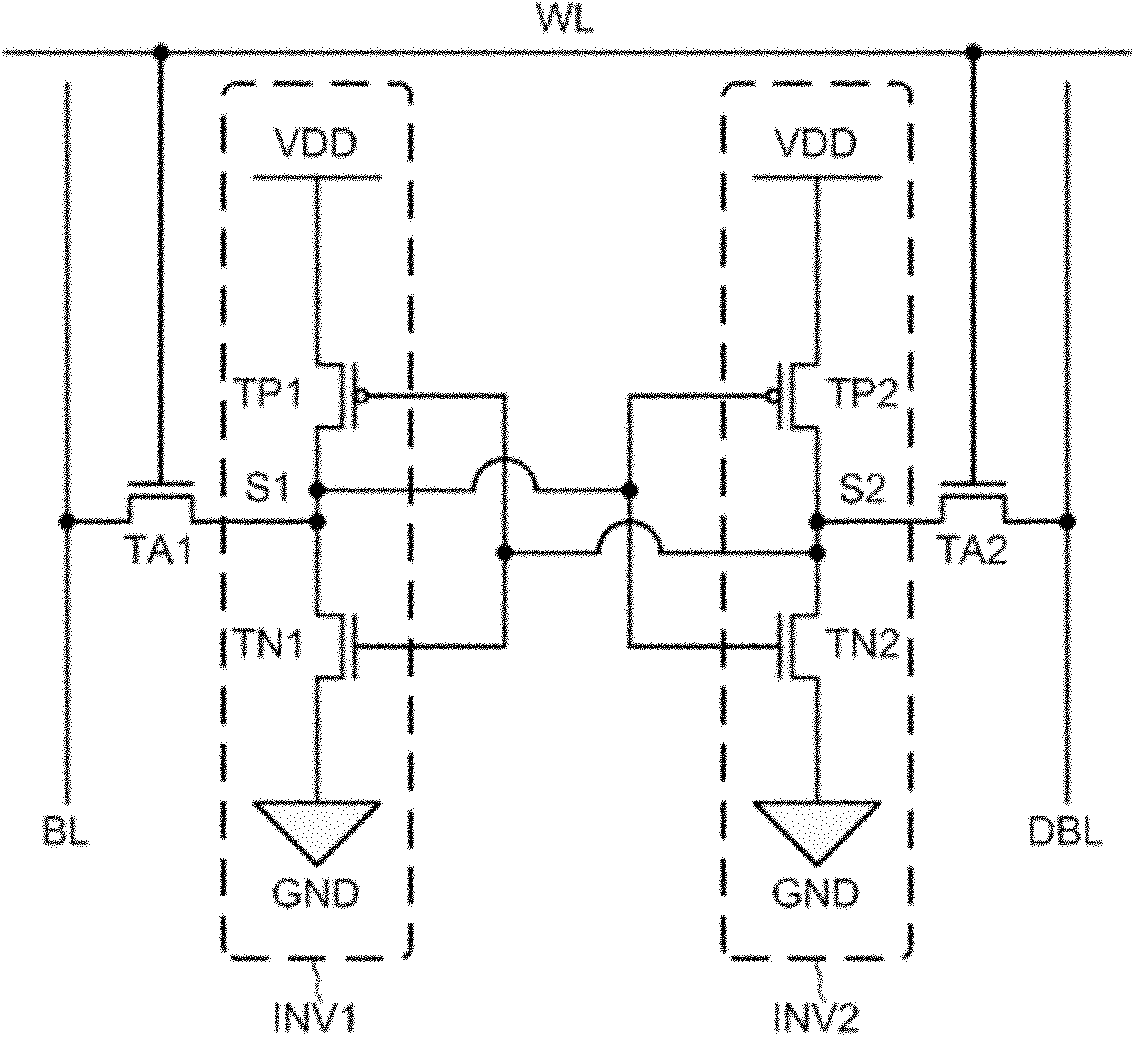
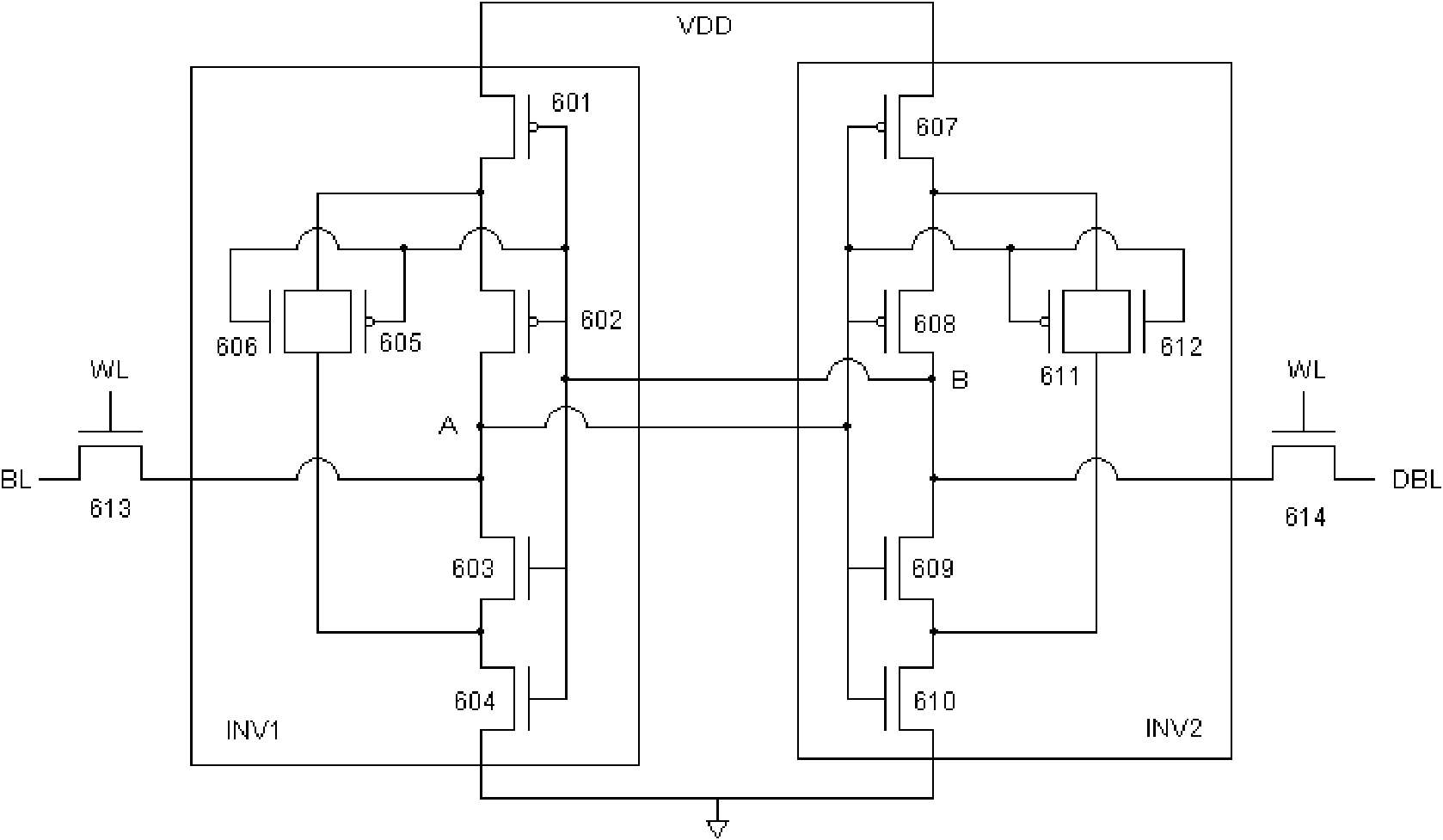
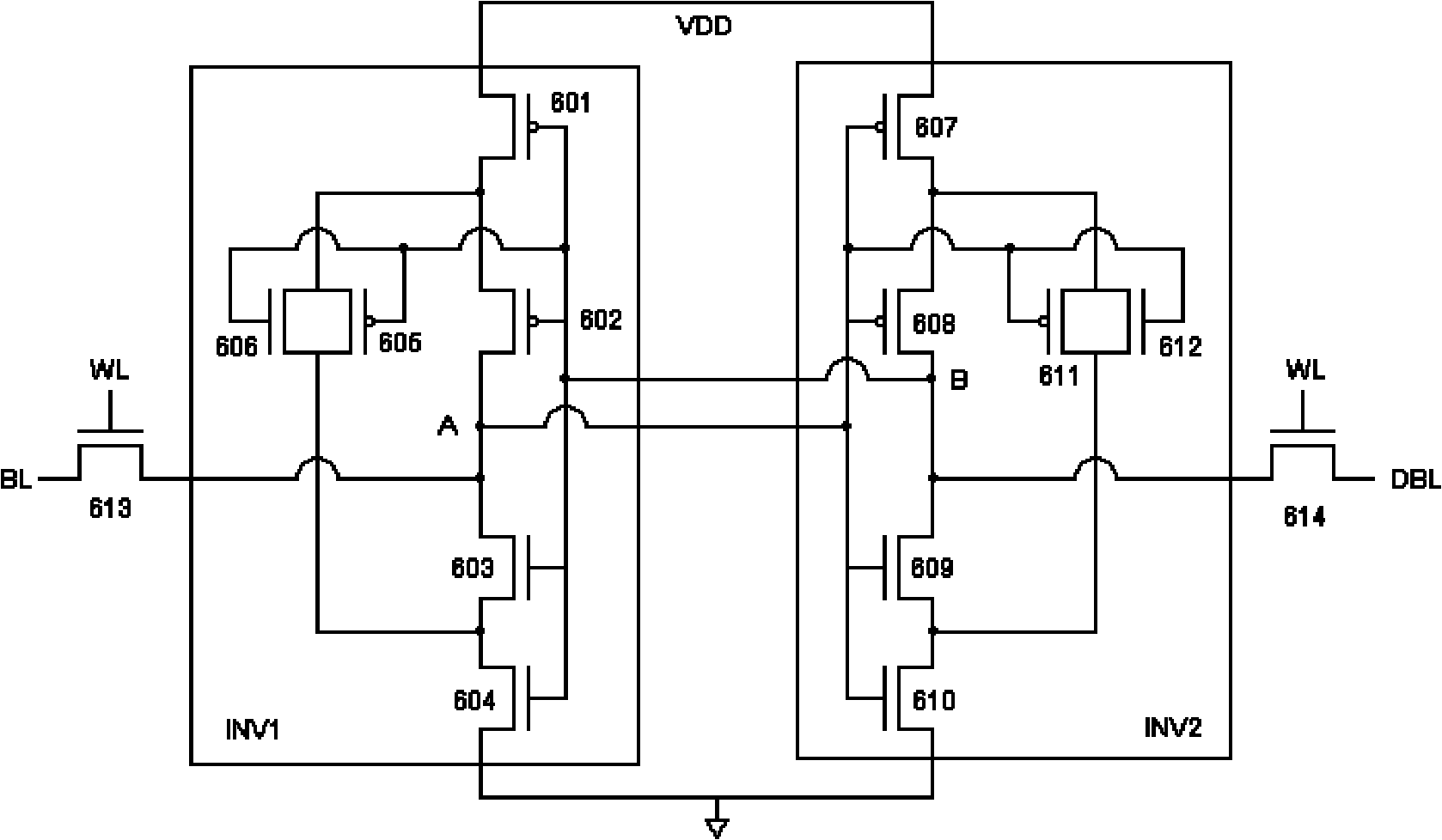
The invention discloses an anti-single event effect static random access memory unit, which can effectively improve the single event upset resistance of a static random access memory (SRAM) unit and remarkably increase an upset threshold of an SRAM. The SRAM unit is a 14-transistor memory unit, and comprises two access N-channel metal oxide semiconductor (NMOS) transistors and two phase inverters, wherein each phase inverter consists of six metal oxide semiconductor (MOS) transistors. Different from the phase inverters forming the most basic six-transistor unit, the inverter structure of the anti-single event effect SRAM unit regulates a level by the two NMOS transistors as drive transistors, two P-channel metal oxide semiconductor (PMOS) transistors as load transistors and a transmission gate consisting of the PMOS transistor and the NMOS transistor so as to realize the anti-single event upset of the memory unit. The SRAM unit has a relatively simpler structure, and is easy to realize in the designing of a radiation resistant SRAM chip.
Owner:INST OF SEMICONDUCTORS - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Pumped pinned photodiode pixel array
The present invention relates to a pumped pixel that includes a first photo-diode accumulating charge in response to impinging photons, a second photo-diode and a floating diffusion positioned on a substrate of the pixel. The pixel also includes a charge barrier positioned on the substrate between the first photo-diode and the second photo-diode, where the charge barrier temporarily blocks charge transfer between the first photo-diode and the second photo-diode. Also included is a pump gate positioned on the substrate adjacent to the charge barrier. The pump gate pumps the accumulated charge from the first photo-diode to the second photo-diode through the charge barrier in response to a pump voltage applied by a controller. Also included is a transfer gate positioned on the substrate between the second photo-diode and the floating diffusion. The transfer gate transfers the pumped charge from the second photo-diode to the floating diffusion in response to a transfer voltage applied by a controller.
Owner:SEMICON COMPONENTS IND LLC
Six-input look-up table for use in a field programmable gate array
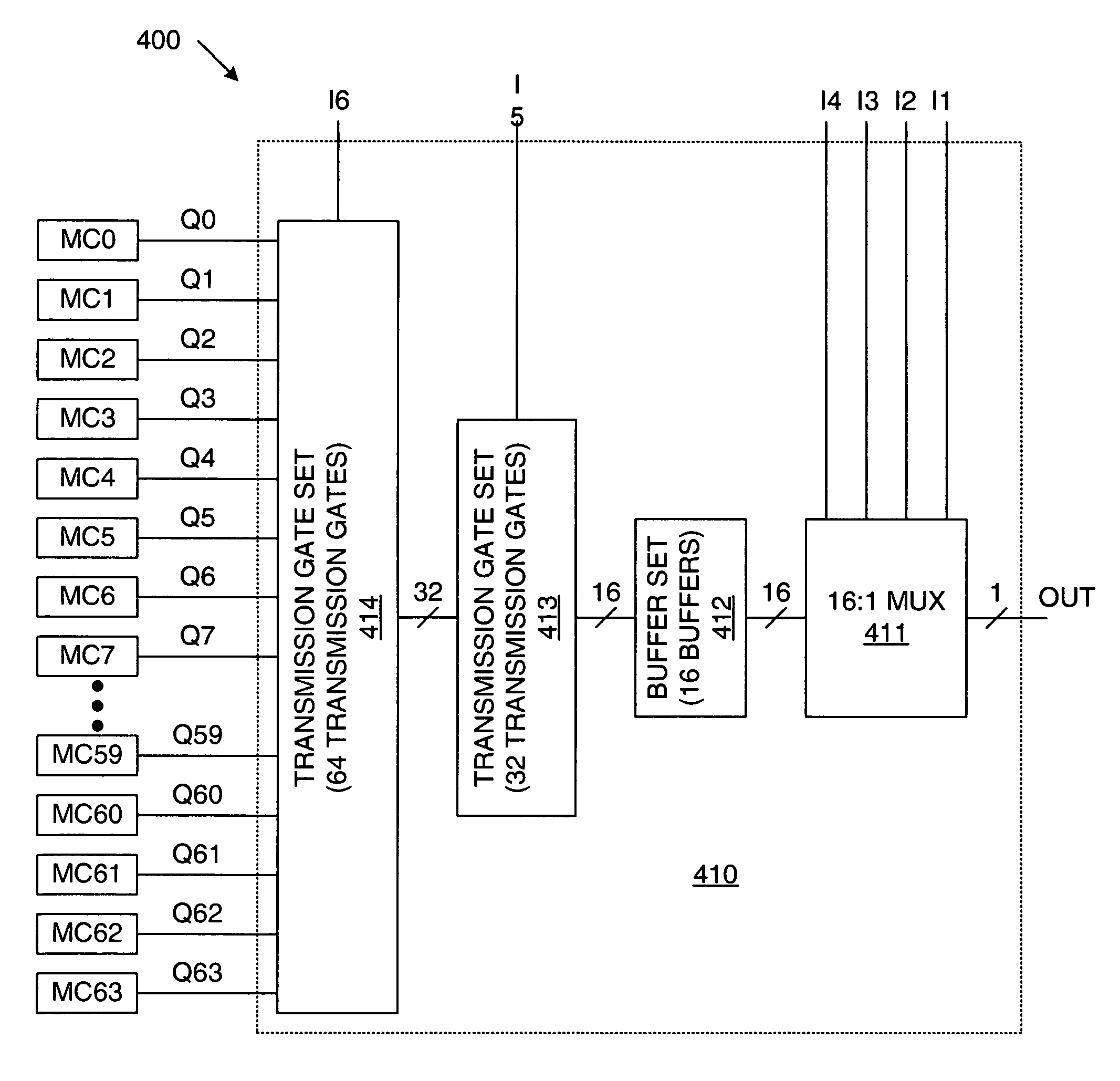
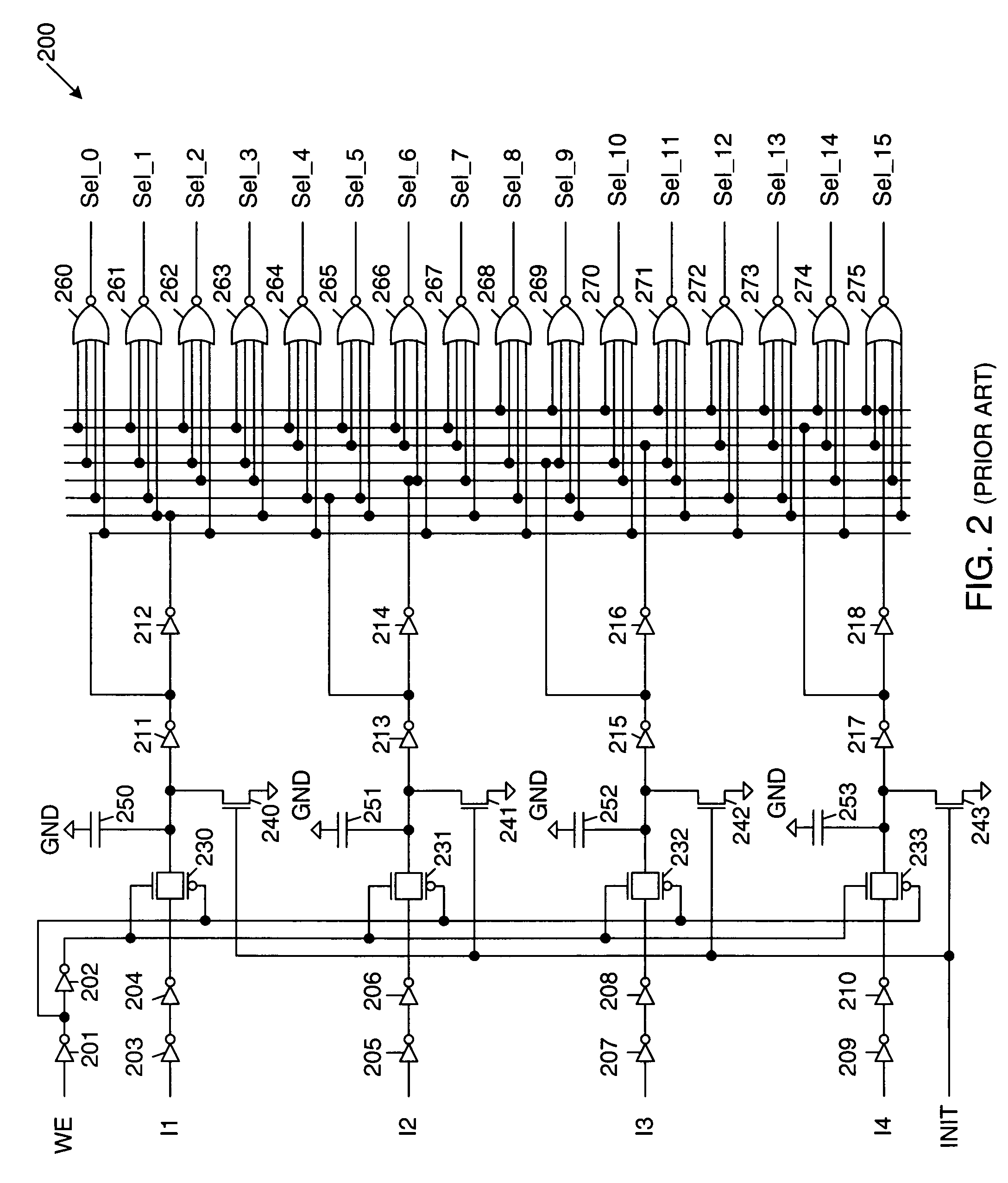
ActiveUS7061271B1Minimizes layout areaArea minimizationSolid-state devicesCAD circuit designTransmission gateMultiplexer
A 6-input LUT architecture includes 64 memory cells, which store 64 corresponding data values. A set of 64 transmission gates is configured to receive the 64 four data values. A first input signal is applied to the set of 64 transmission gates, thereby routing 32 of the 64 data values. A set of 32 transmission gates is coupled to receive the 32 data values routed by the set of 64 transmission gates. A second input signal is applied to the set of 32 transmission gates, thereby routing 16 of the 32 data values. A 16:1 multiplexer receives the sixteen data values routed by the set of 32 transmission gates. Third, fourth, fifth and sixth input signals are applied to the 16:1 multiplexer, thereby routing one of the 16 data values as the output of the LUT.
Owner:XILINX INC
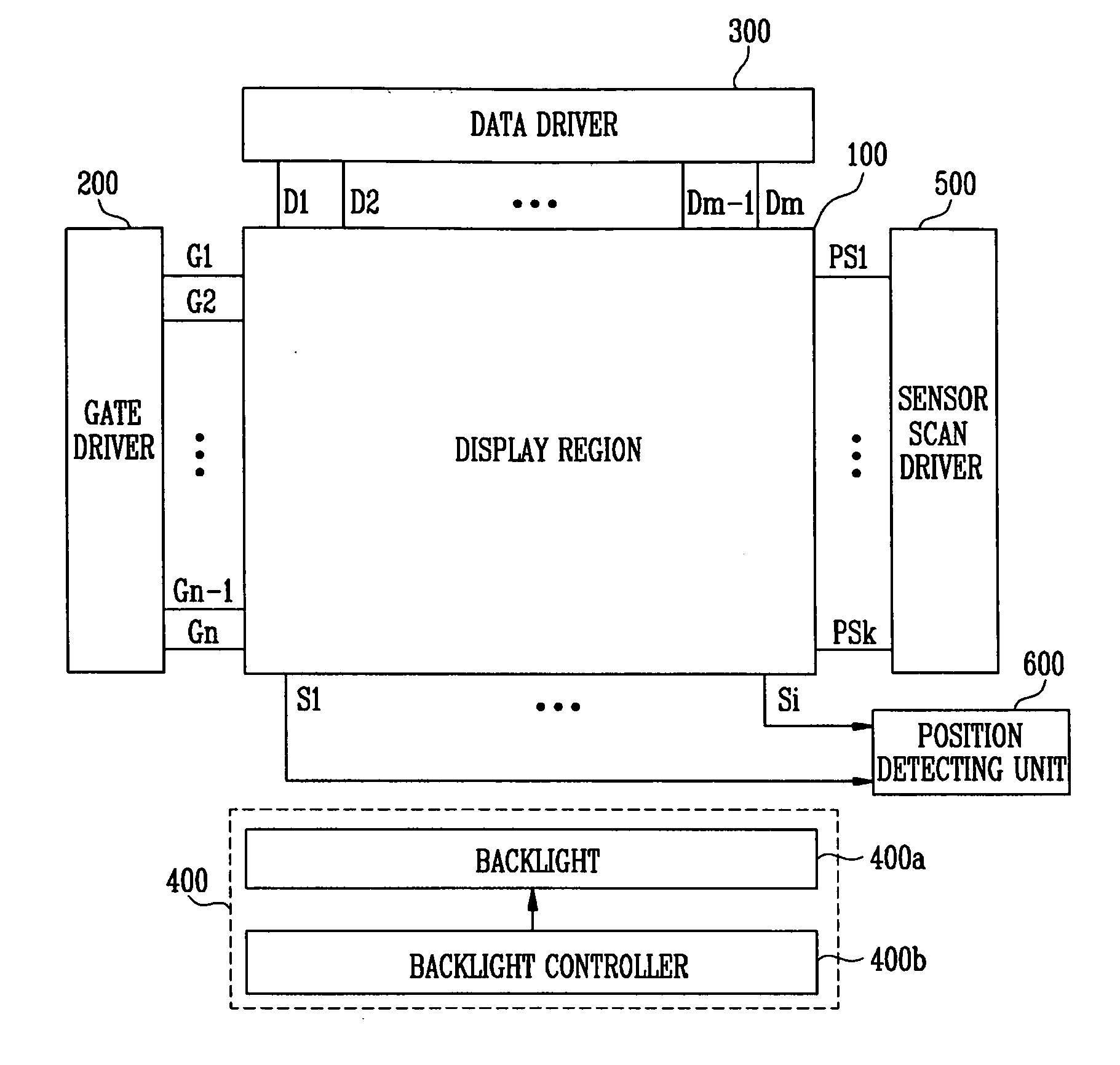
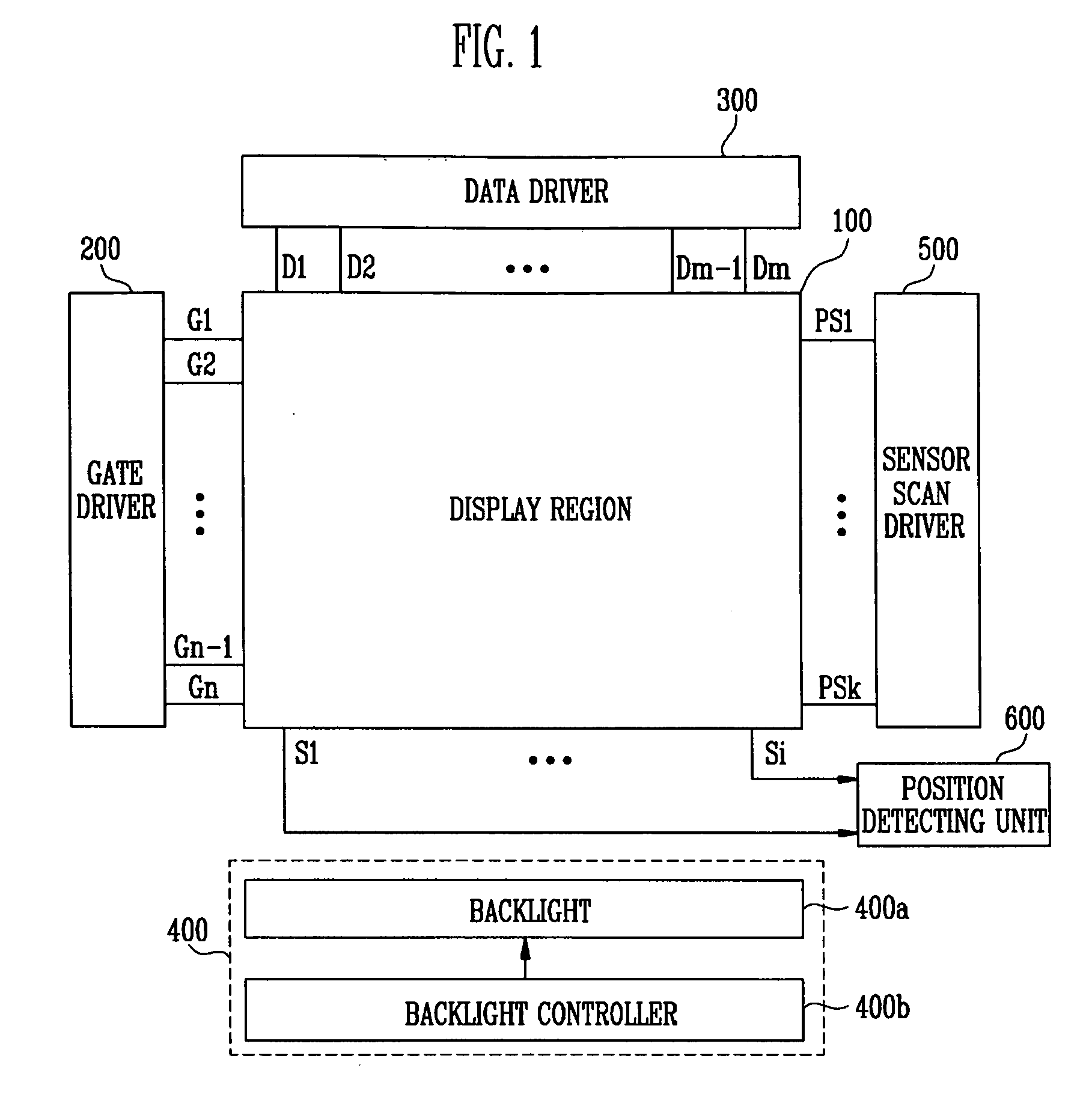
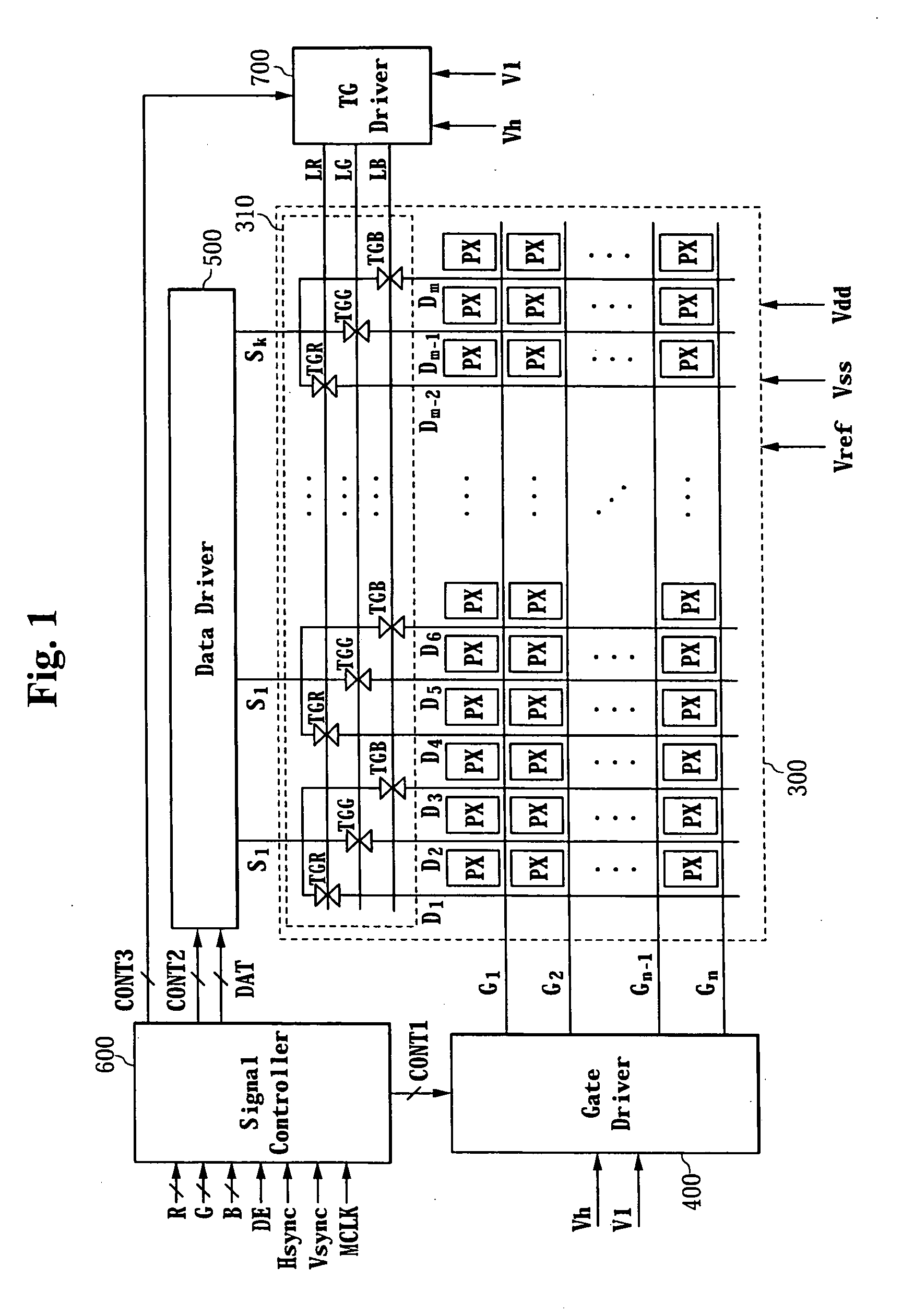
Sensor scan drivers, flat panel displays with built-in touch screen including such a sensor scan driver, and methods of driving such flat panel displays
ActiveUS20110096027A1Improved optical sensitivityImprove featuresCathode-ray tube indicatorsDigital storageShift registerTransmission gate
A sensor scan driver may include a shift register unit for driving photodiodes, a transmission gate unit for changing a voltage range of sensor scan signals generated by the shift register unit, and a buffer unit for supplying the sensor scan signals supplied from the transmission gate unit to the photodiodes, wherein the transmission gate unit includes first and second transmission gates, each including an electrode adapted to receive an output signal of the shift register unit, another electrode adapted to receive the inverted output signal of the shift register unit, an input terminal coupled to first and second power sources, respectively, and an output terminal coupled to an output terminal of the transmission gate unit.
Owner:SAMSUNG DISPLAY CO LTD
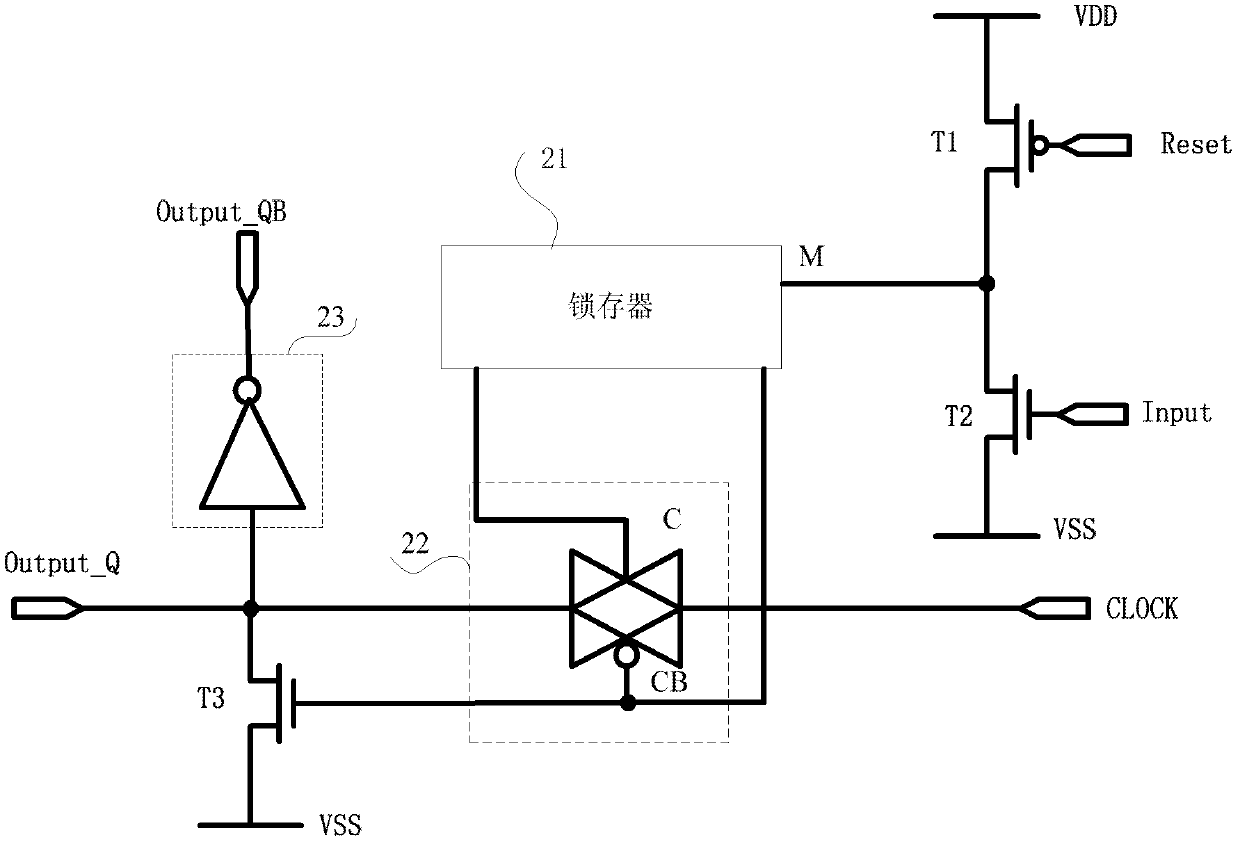
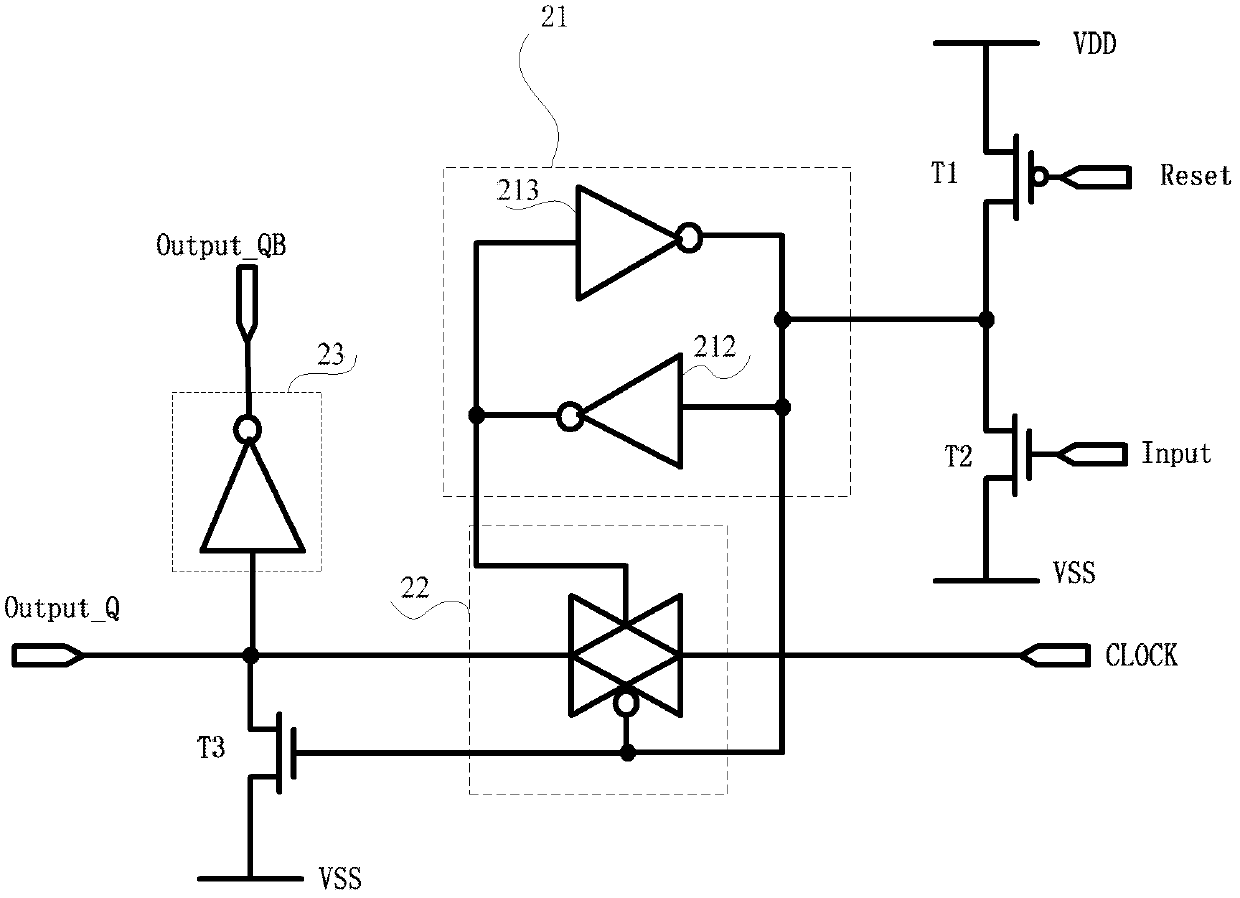
Semiconductor device having a data latching or storing function
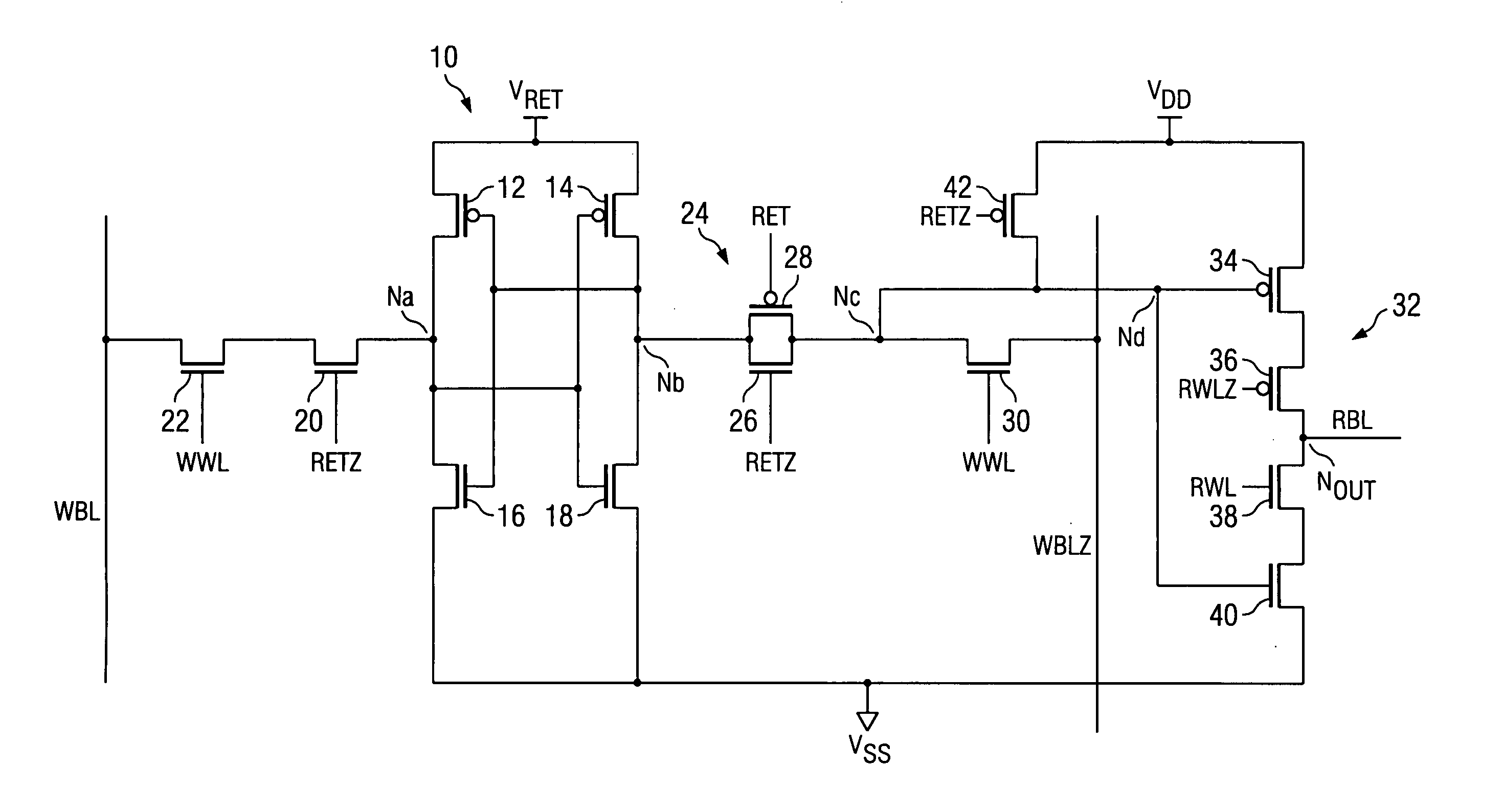
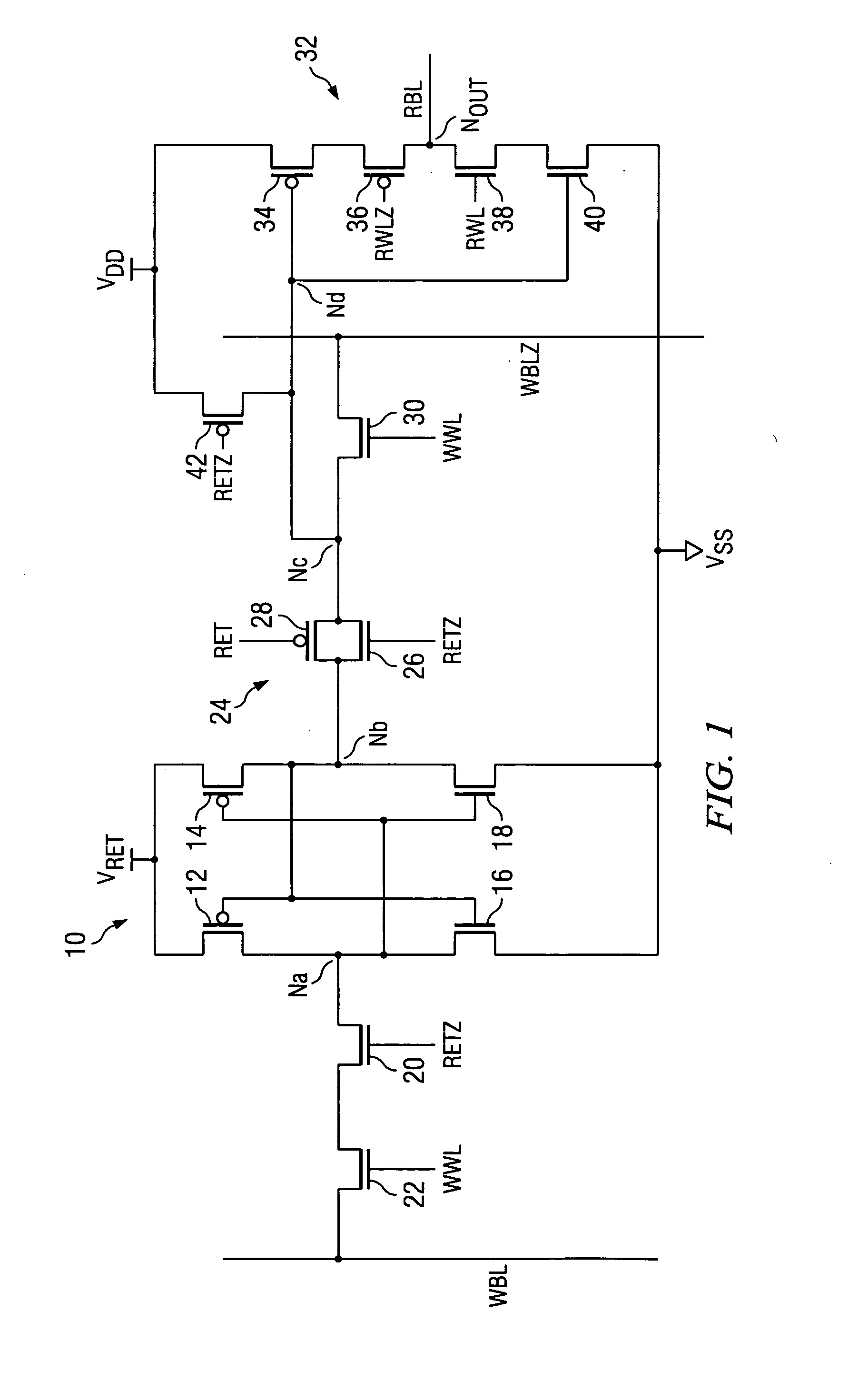
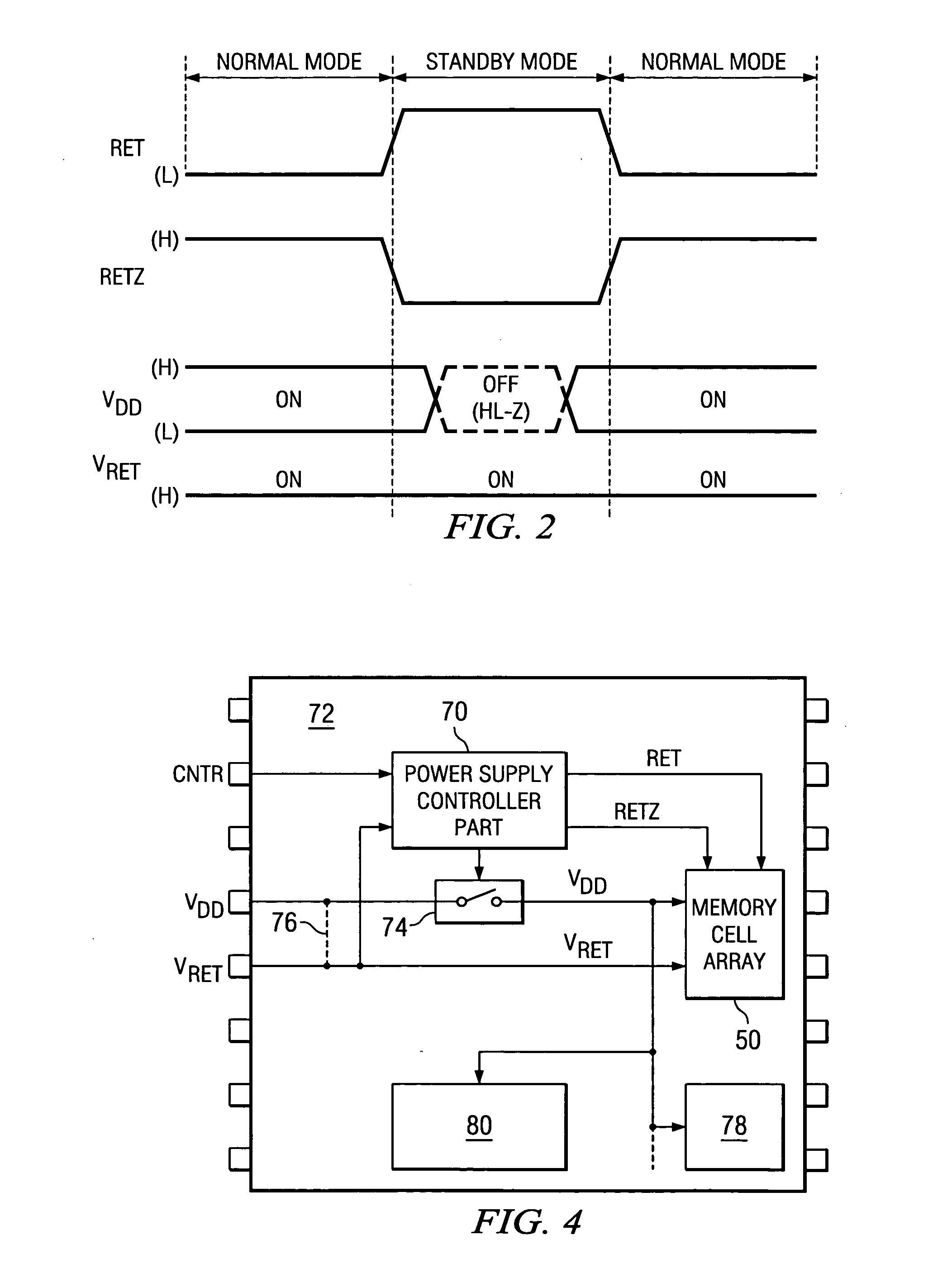
The current consumed by latching data and during standby are significantly decreased in order to realize reduced power consumption. In this memory cell, source voltages VRET and VDD are supplied to latch circuit 10 and output circuit 32 from different systems. Latch circuit 10 can be separated from a peripheral circuit by NMOS transistor 20 and transmission gate 24. MOS transistors 12, 14, 16, and 18, which constitute latch circuit 10 and MOS transistors 20, 26, and 28, which constitute the switch circuit, are configured using low-leakage MOS transistors with leakage current significantly lower than those of standard MOS transistors used to configure the peripheral circuit including output circuit 32.
Owner:TEXAS INSTR INC
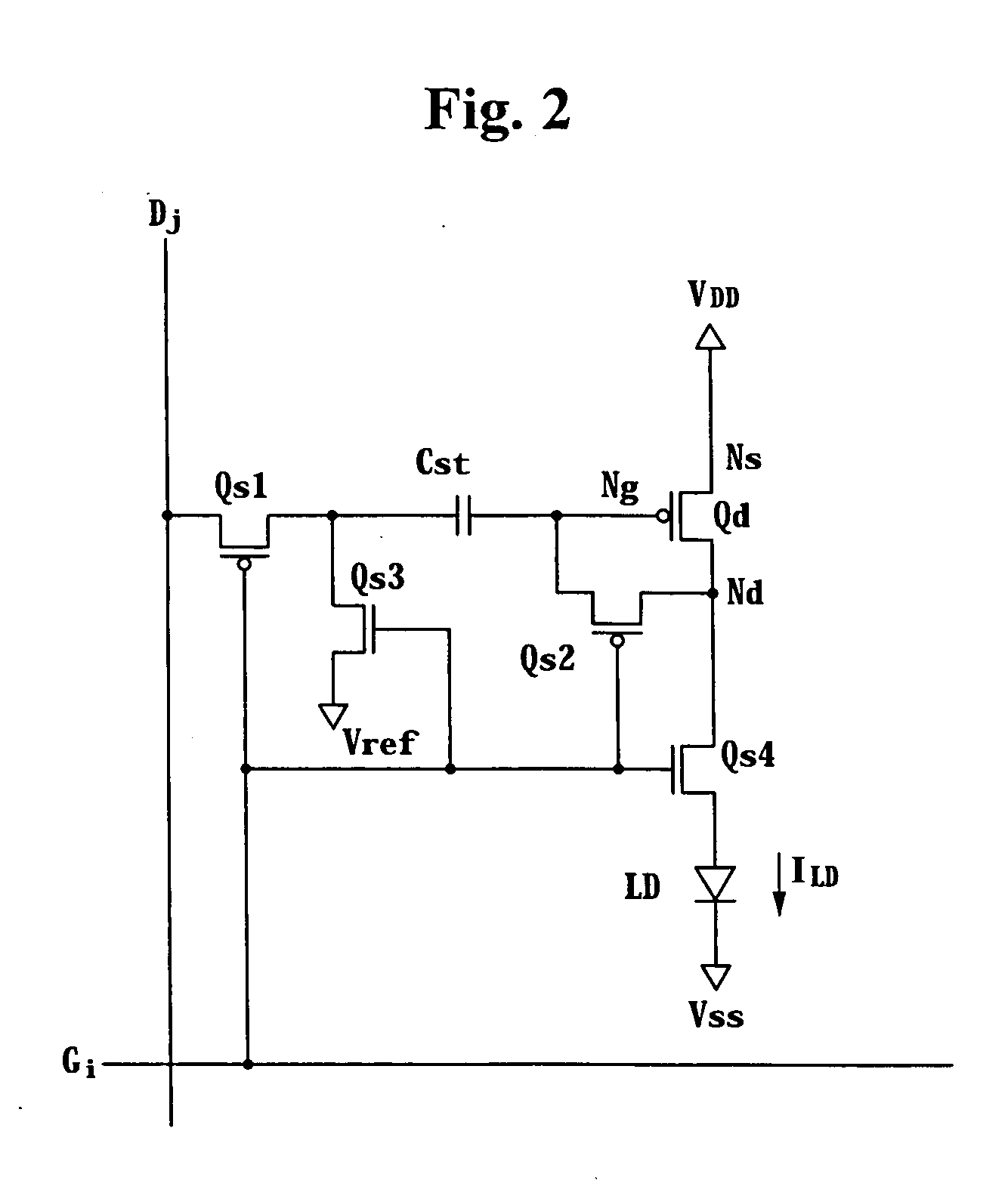
Display device and driving method thereof
ActiveUS20060176251A1Static indicating devicesMechanical energy handlingDriving currentTransmission gate
A display device includes a plurality of data lines, a transmission gate element connected to the data lines, wherein the transmission gate supplies precharge voltages and data voltages to the data lines in response to transmission gate signals, and a plurality of pixels connected to the data lines. Each of the pixels includes: a light emitting element; a capacitor; a driving transistor having a control terminal connected to the capacitor, an input terminal, and an output terminal, wherein the driving transistor supplies a driving current to the light emitting element; a first switch, wherein the first switch diode-connects the driving transistor in response to a gate signal and connects one of the data lines to the capacitor; and a second switch, wherein the second switch supplies a reference voltage to the capacitor in response to the gate signal and connects the driving transistor to the light emitting element, wherein the precharge voltage, the data voltage, and the reference voltage are applied to the capacitor, and wherein the capacitor stores a charging voltage based on the applied data voltage and a threshold voltage of the driving transistor.
Owner:SAMSUNG DISPLAY CO LTD
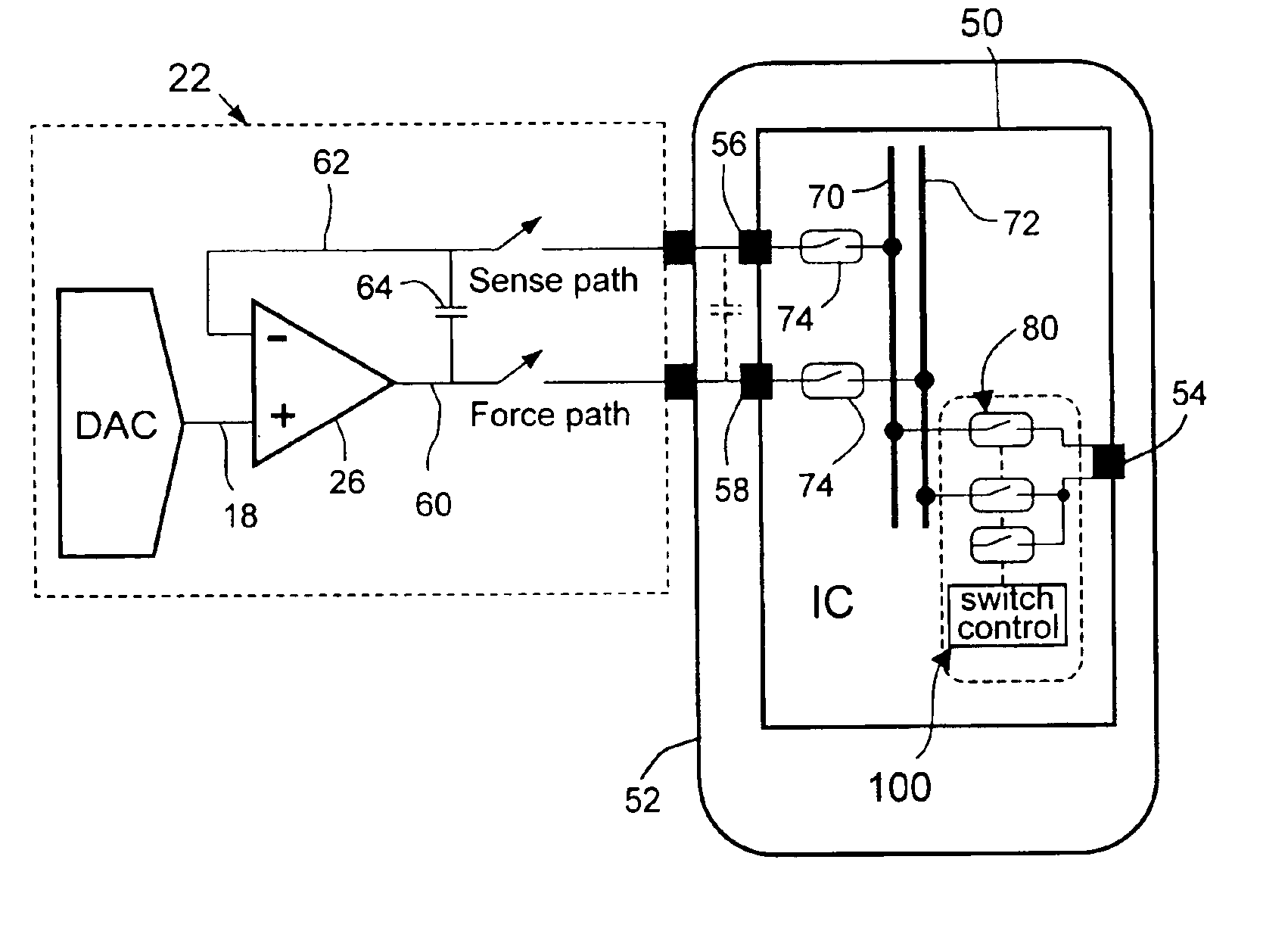
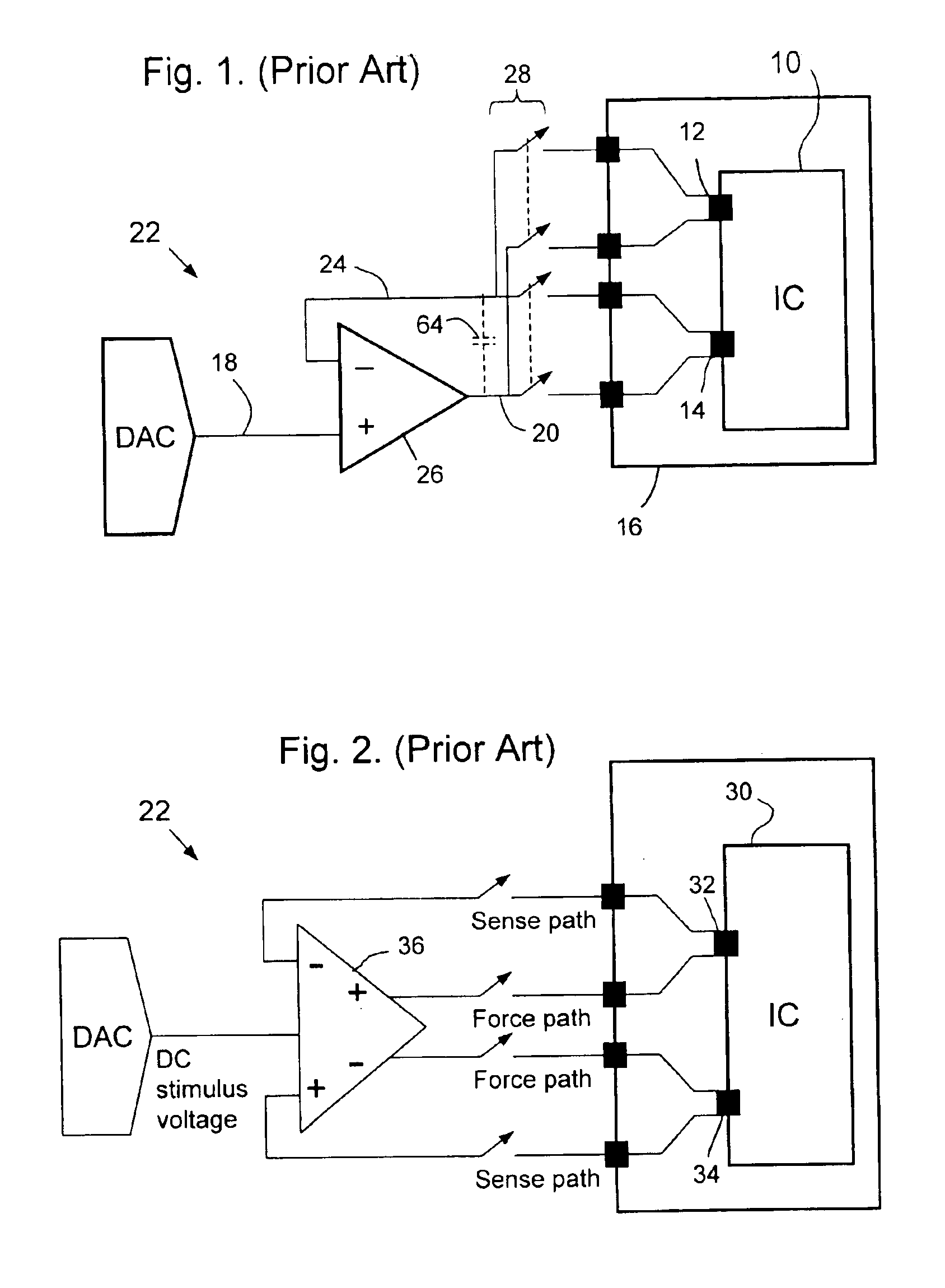
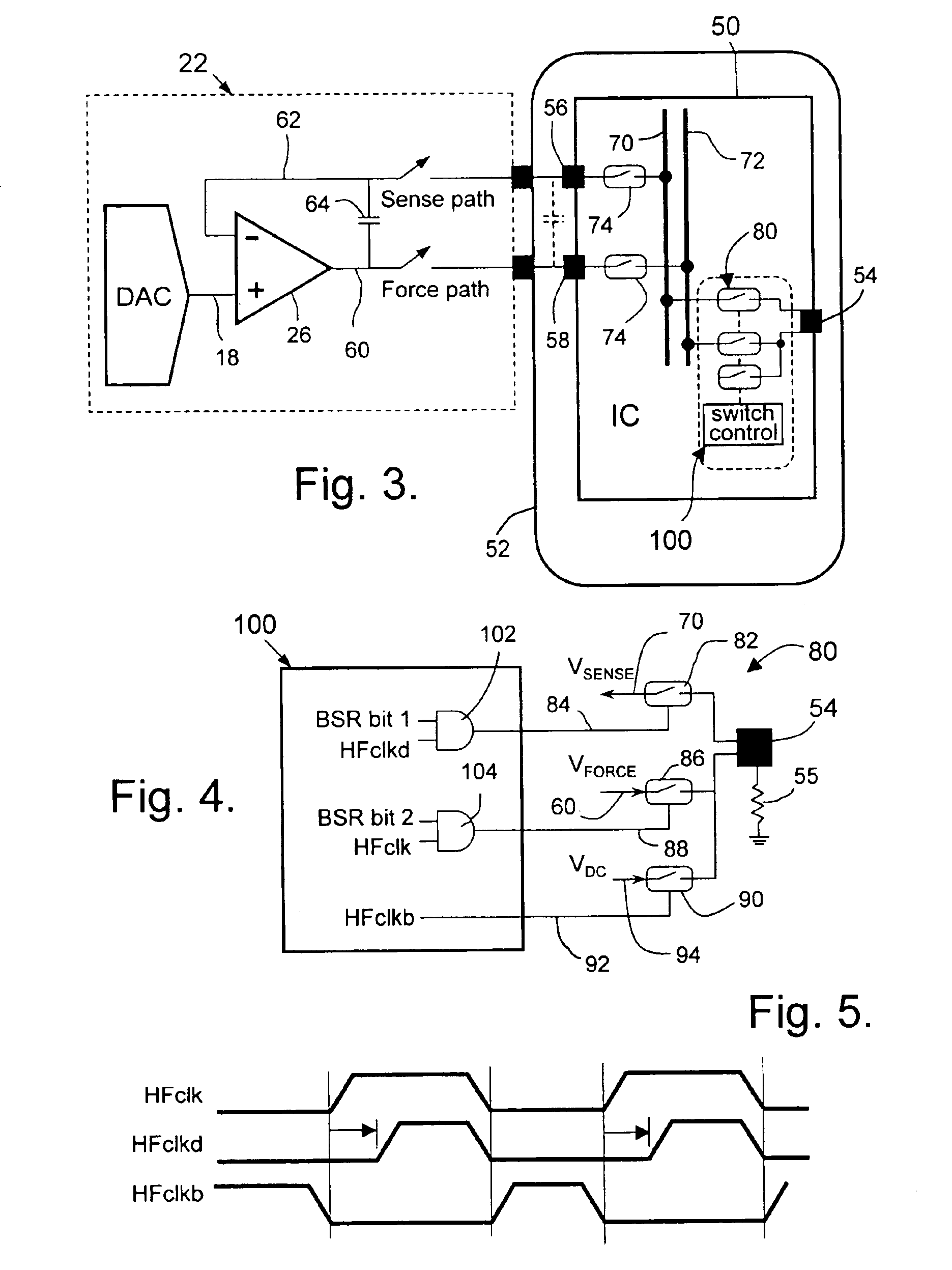
Circuit and method for accurately applying a voltage to a node of an integrated circuit
InactiveUS6885213B2Precise deliveryVoltage is accurateElectronic circuit testingIndividual semiconductor device testingTransmission gateStimulus voltage
A method for accurately delivering a voltage to a circuit node of an integrated circuit having analog buses and transmission gates selectively connecting the circuit node to the buses, comprises sensing the voltage on the circuit node via a first of the buses under control of a first periodic signal; applying a first stimulus voltage to the circuit node via a second bus under control of a second periodic signal; and applying a second stimulus voltage to the circuit node under control of a third periodic signal which is inverted with respect to the second periodic signal so that the circuit node is driven alternately to the first stimulus voltage and to the second stimulus voltage.
Owner:SIEMENS PROD LIFECYCLE MANAGEMENT SOFTWARE INC
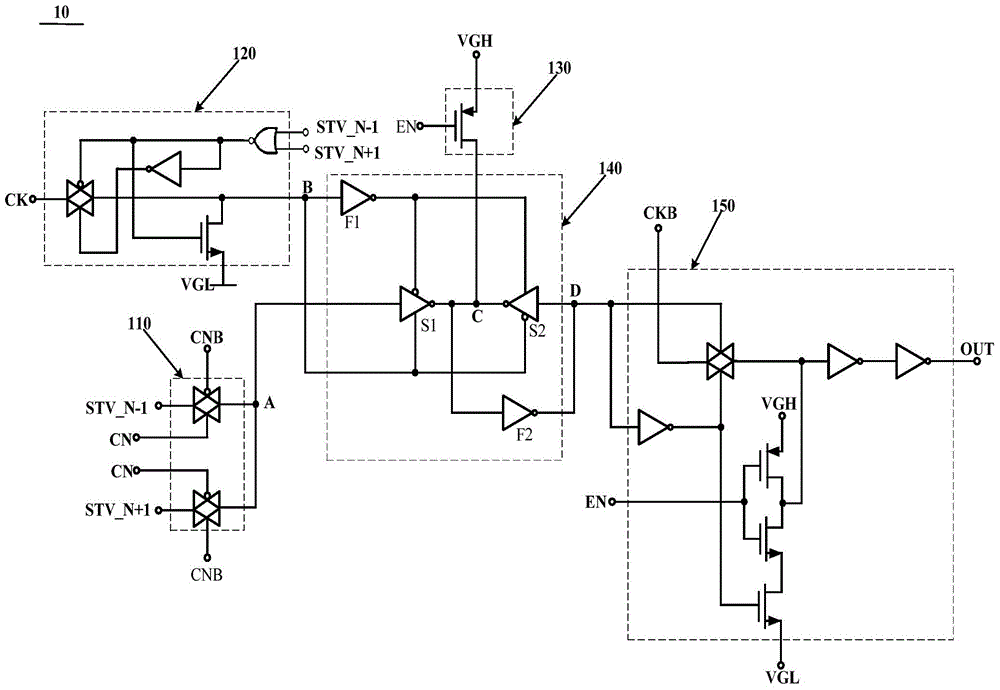
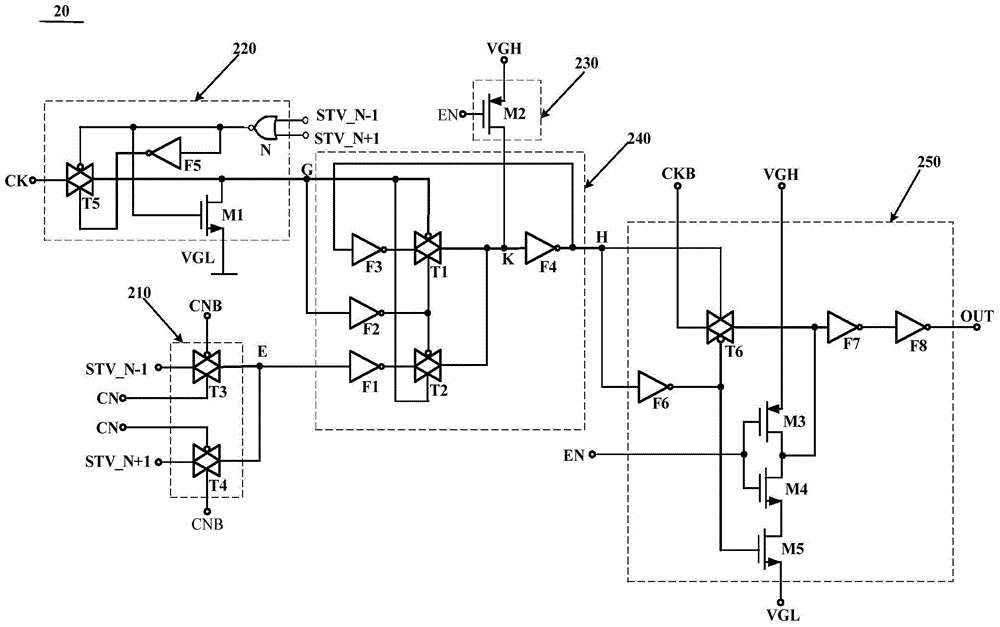
Shift register, grid driving device and display device
ActiveCN102708816AAchieve shiftStatic indicating devicesDigital storageShift registerTransmission gate
The invention provides a shift register, a grid driving device and a display device. The shift register comprises a latch, a transmission gate, a first thin film transistor, a second thin film transistor, a third thin film transistor and a first inverter, wherein a grid of the first thin film transistor is connected with a reset terminal of the shift register, a drain of the first thin film transistor is respectively connected with a drain of the second thin film transistor and an input terminal of the latch, a grid of the second thin film transistor is connected with an input terminal of theshift register, a grid of the third thin film transistor is connected with an inverted output terminal of the latch, a drain of the third thin film transistor is connected with an input terminal of the first inverter, an output terminal of the transmission gate is connected with the drain of the third thin film transistor, an input terminal of the transmission gate is connected with a clock signal input terminal, the drain of the third thin film transistor is connected with a normal phase output terminal of the shift register, and an output terminal of the first inverter is connected with an inverted output terminal of the shift register. The shift register can realize signal shift by the aid of one latch.
Owner:BOE TECH GRP CO LTD +1
Eight transistor soft error robust storage cell
Owner:NYTELL SOFTWARE LLC
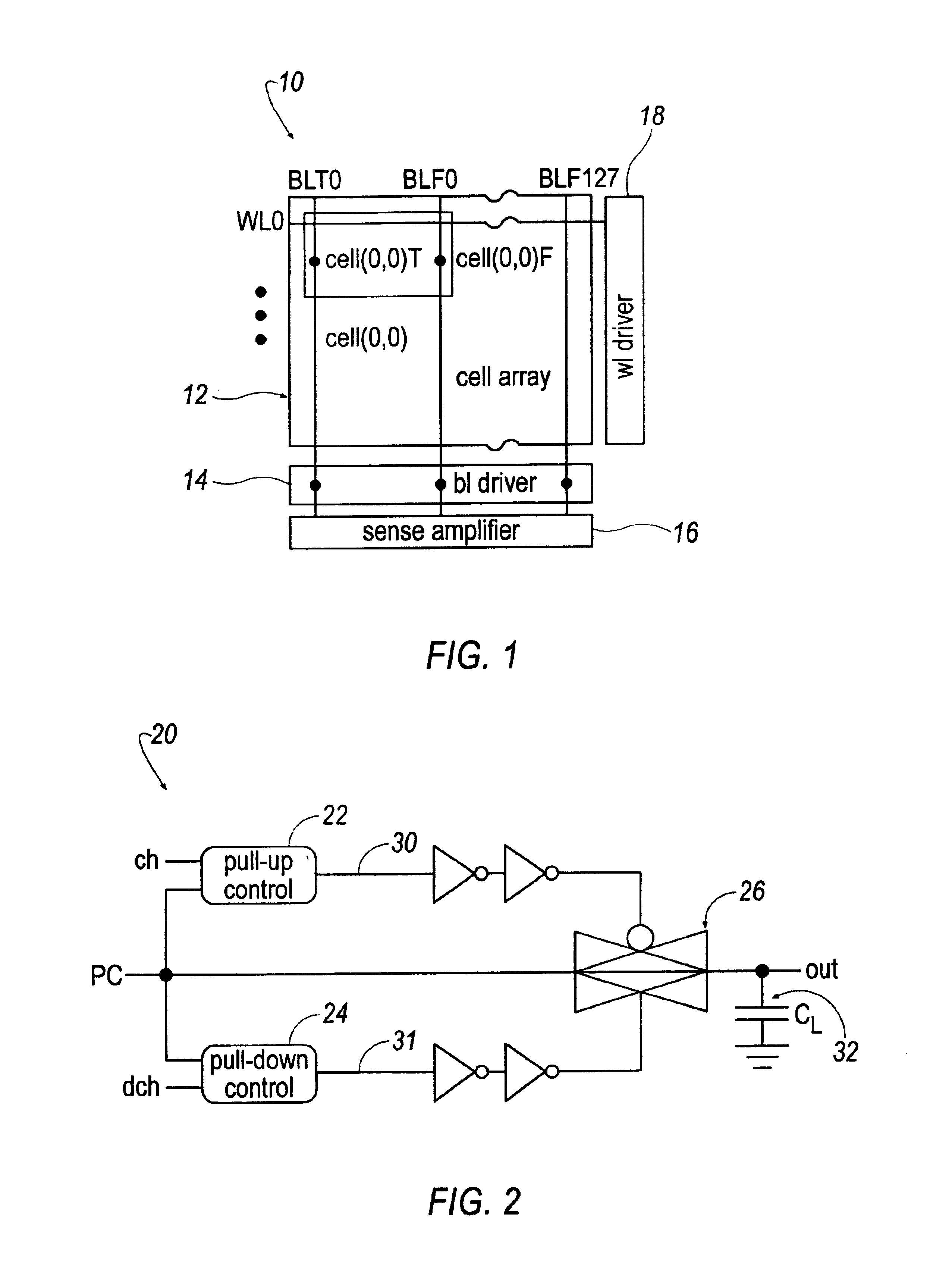
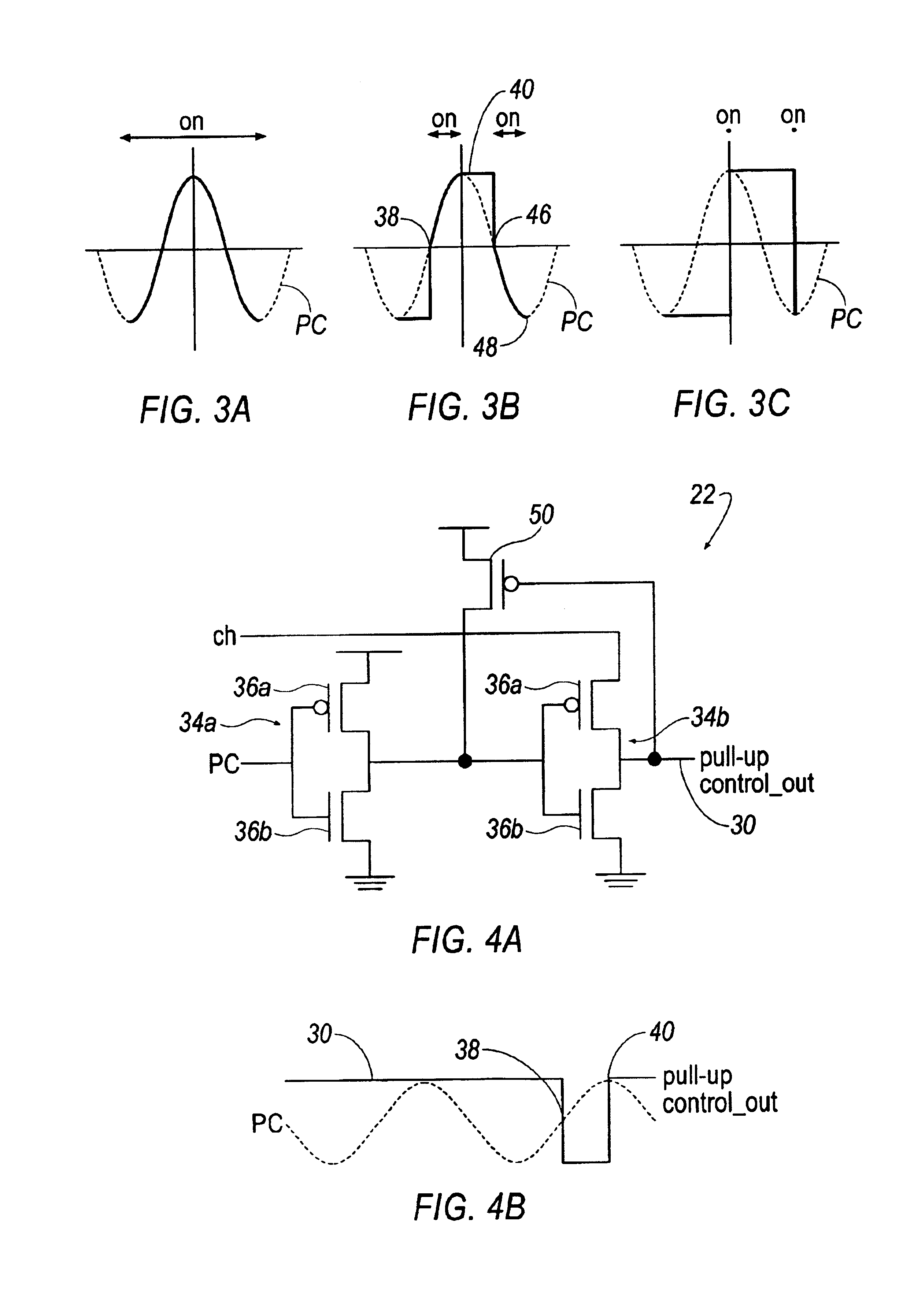
Low-power driver with energy recovery
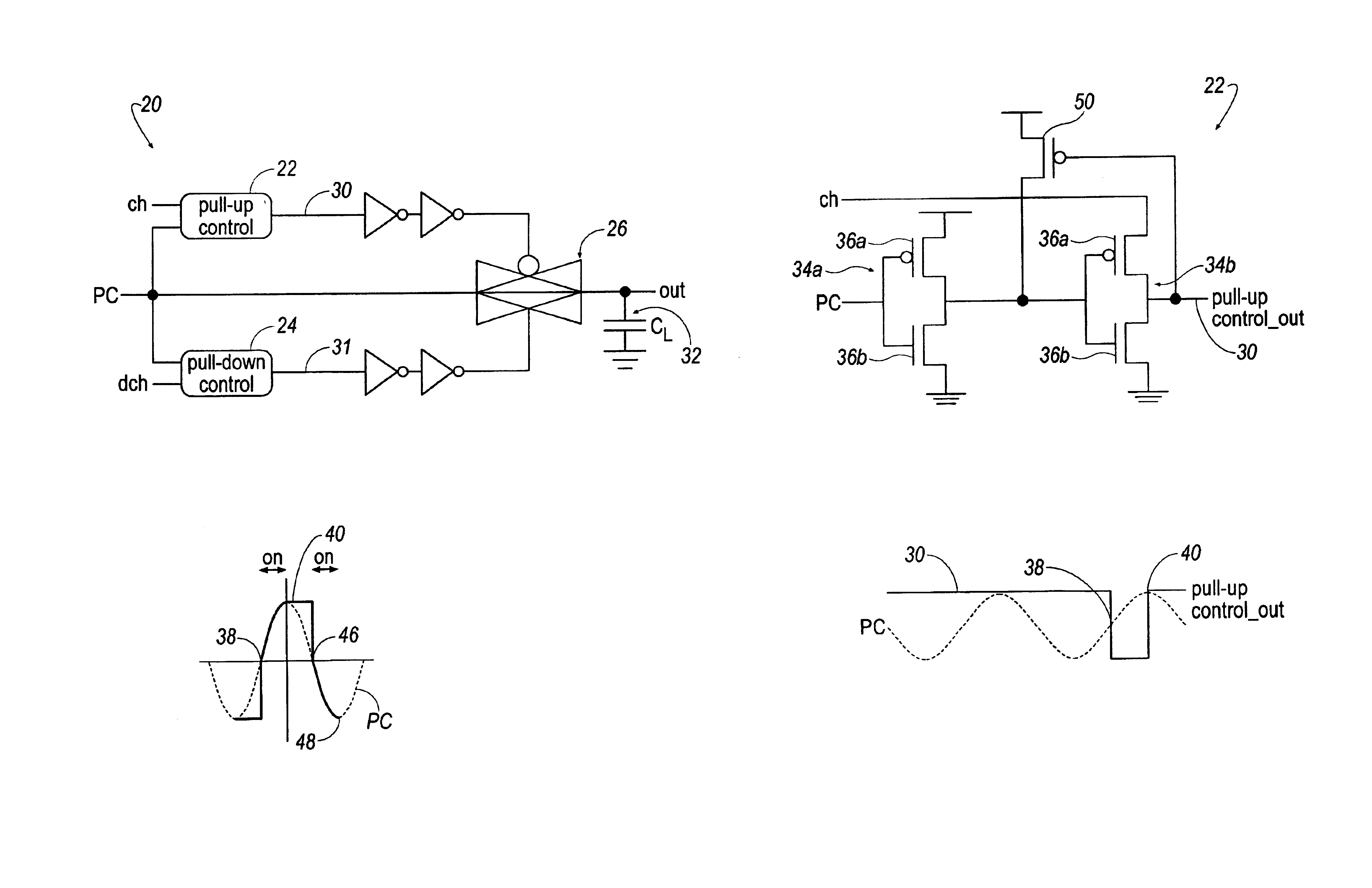
The present invention provides an energy recovering driver that includes a pull-up control, a pull-down control and a transmission gate. The pull up control is responsive to a pull-up control signal and a clock signal to turn the transmission gate ON and OFF and predetermined positions of the clock signal. The pull-down control is responsive to a pull-down control signal and the clock signal to turn the transmission gate ON and OFF at other predetermined locations of the clock signal. The transmission gate transmits the clock signal when at an ON condition and does not transmit the clock signal when in an OFF condition.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF MICHIGAN
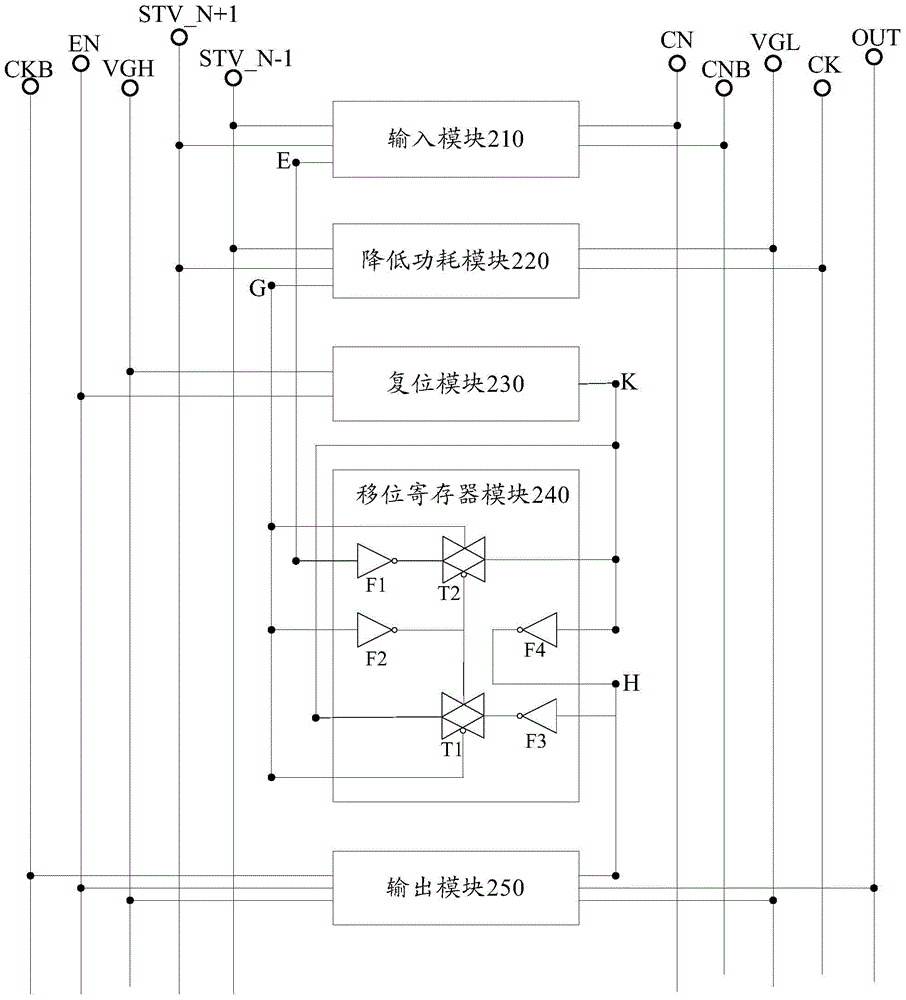
GOA (Gate Driver On Array) unit, driving method of GOA unit, GOA circuit and display device
ActiveCN104992662AReduce power consumptionReduce power lossStatic indicating devicesShift registerTransmission gate
The invention discloses a GOA (Gate Driver On Array) unit, a driving method of the GOA unit, a GOA circuit and a display device, and belongs to the field of display technologies. The GOA unit comprises an input module, a power consumption reduction module, a reset module, a shifting register module and an output module, wherein the input module is connected with an input signal end, a first node and a control signal end; the power consumption reduction module is connected with the input signal end, a clock signal end, a power supply signal end and a second node; the reset module is connected with the power supply signal end, the control signal end and a third node; the shifting register module is connected with the first node, the second node, the third node and a fourth node; the output module is connected with the fourth node, the clock signal end, the power supply signal end, the control signal end and the output signal end; and the shifting register module comprises an inverter and a transmission gate. According to the invention, problems that the power loss of the GOA unit is high and that the electric potential of output signals cannot be determined are solved, and effects of reducing the power loss and improving the accuracy of the output signals are achieved.
Owner:BOE TECH GRP CO LTD +1
Structure of object proximity and position detector
InactiveUS7023221B1Maintain stabilitySensitivity of sensor is importantResistance/reactance/impedenceElectronic switchingTransmission gateCapacitor
The present invention offers an object proximity detector and an object position detector. The variation of frequency of an oscillator is used to detect the proximity of an object to the sensor plates. The dependence of frequency on process parameter is minimized by a compensation capacitor. It is not need to calibrate the product during the manufacture. In order to magnify the sensitivity, the sensor plates are placed in the feedback loop of the oscillator, instead of at the input of the oscillator. The independence of the process parameter and increasing of the sensitivity can be achieved by adding the compensation capacitor and place the sensor plates in the feedback loop at the same time. Multiple transmission gates are connected to the input and the output of the oscillator, and the sensor plates are connected to the transmission gates to form an object position detector.
Owner:HOLYLITE MICROELECTRONICS
Low duty cycle distortion differential to CMOS translator
ActiveUS7176720B1Easy to implementReduce dependencePulse generation by non-linear magnetic/dielectric devicesDifferential amplifiersCMOSTransmission gate
Disclosed is a circuit comprising a differential input amplifier stage, a capacitor stage, an inverter chain stage, and a biasing circuit. The inverter chain stage may be formed with or without feedback depending on whether a clock signal or data signal is to be translated using the disclosed circuit. The biasing circuit can be formed using either inverters or transmission gates. Moreover, the biasing circuit, the inverter chain stage, and the amplifier stage can be connected to a power down circuit which, when the translator is not being used, will ensure various circuitry of the translator will not consume extensive power. The inverter chain stage, biasing circuit, and capacitor stage are formed on both an upper and lower section to produce true and complementary outputs that have a consistent and equal delay from the transitions of the incoming differential input signal so as to minimize jitter and associated duty cycle of the translated output.
Owner:CYPRESS SEMICON CORP
Solid state imaging device, method of producing solid state imaging device, and electronic apparatus
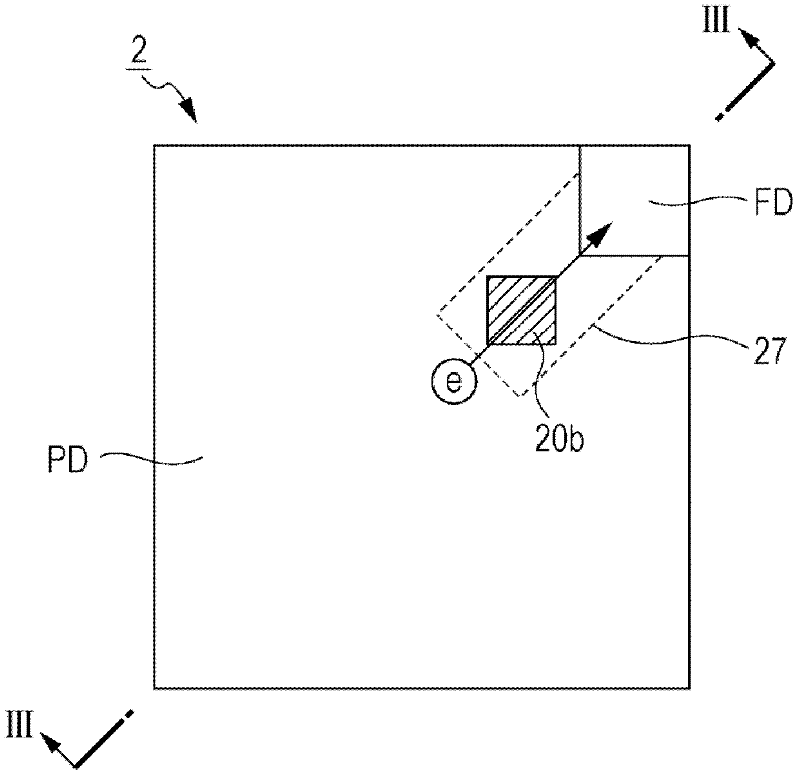
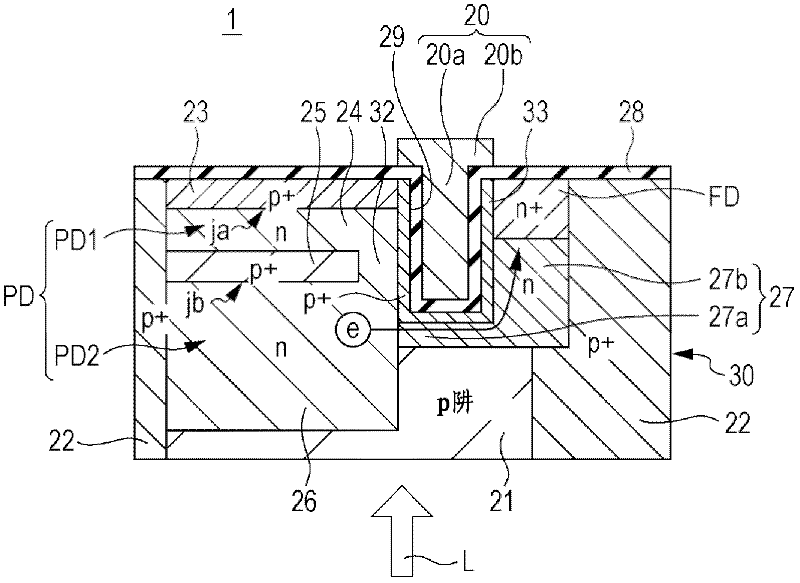
ActiveCN102693989AMinimizes changes in saturation chargeIncrease productionTransistorSolid-state devicesTransmission gateEngineering
The invention discloses a solid state imaging device, a method of producing solid state imaging device, and an electronic apparatus. A solid state imaging device includes: a substrate; a photoelectric conversion unit that is formed on the substrate to generate and accumulate signal charges according to light quantity of incident light; a vertical transmission gate electrode that is formed to be embedded in a groove portion formed in a depth direction from one side face of the substrate according to a depth of the photoelectric conversion unit; and an overflow path that is formed on a bottom portion of the transmission gate to overflow the signal charges accumulated in the photoelectric conversion unit.
Owner:SONY CORP
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com