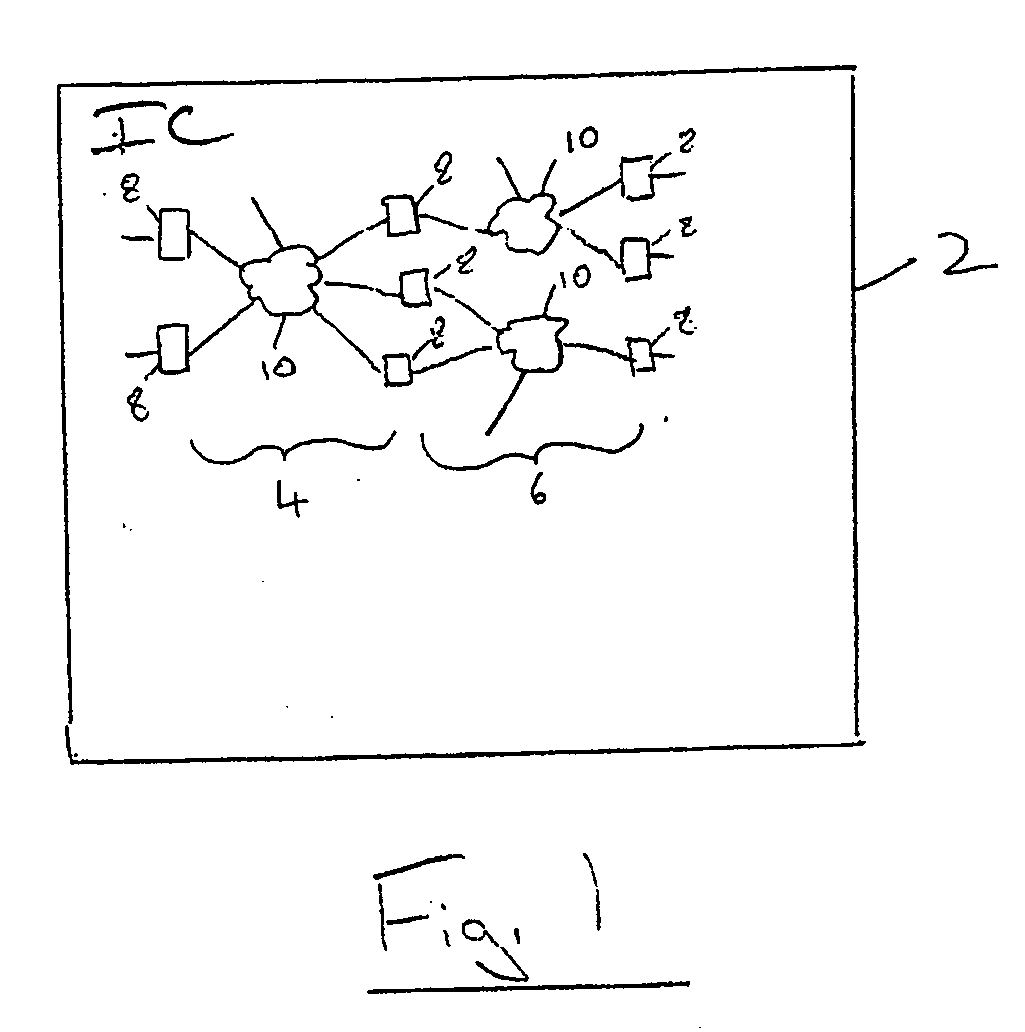
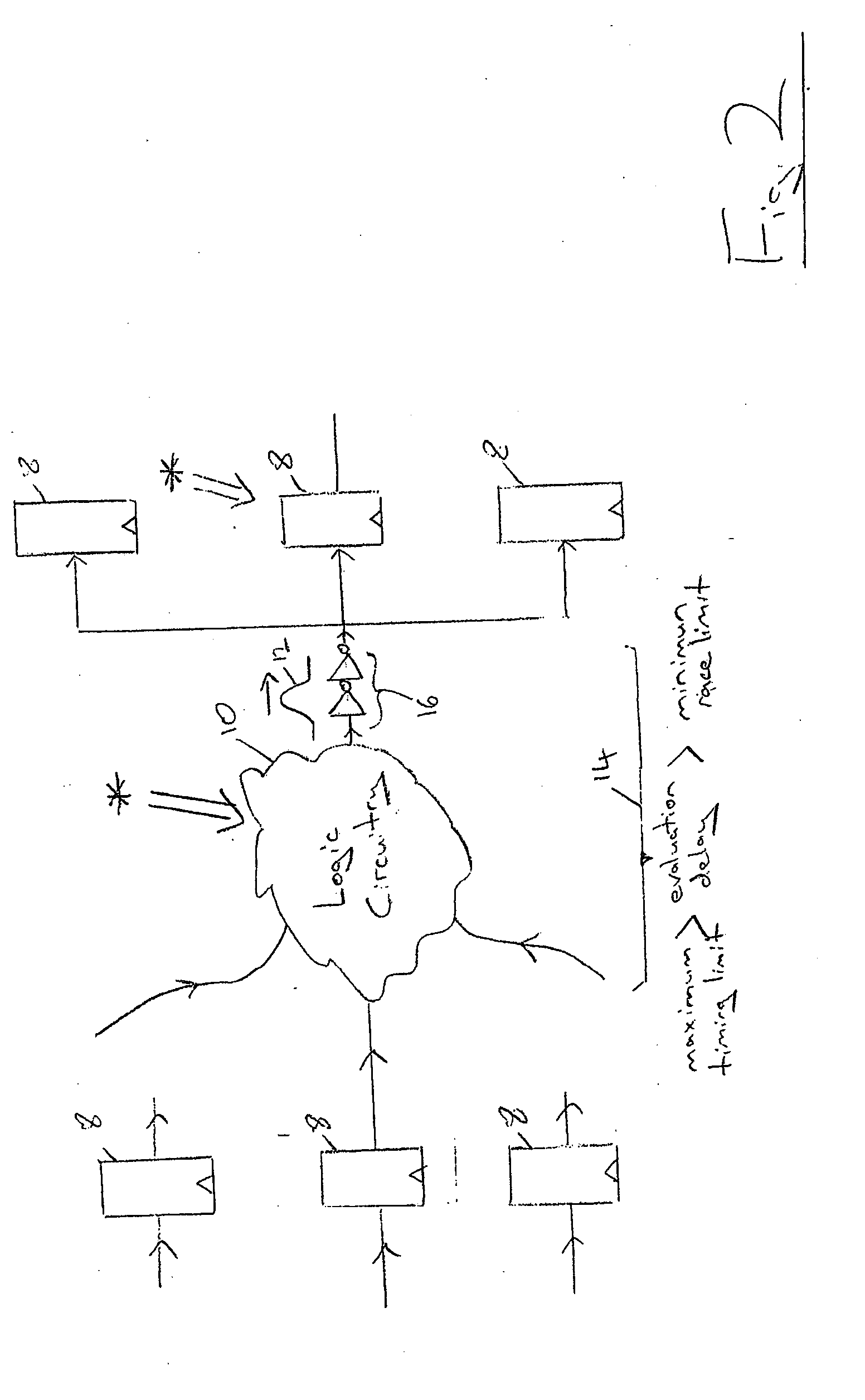
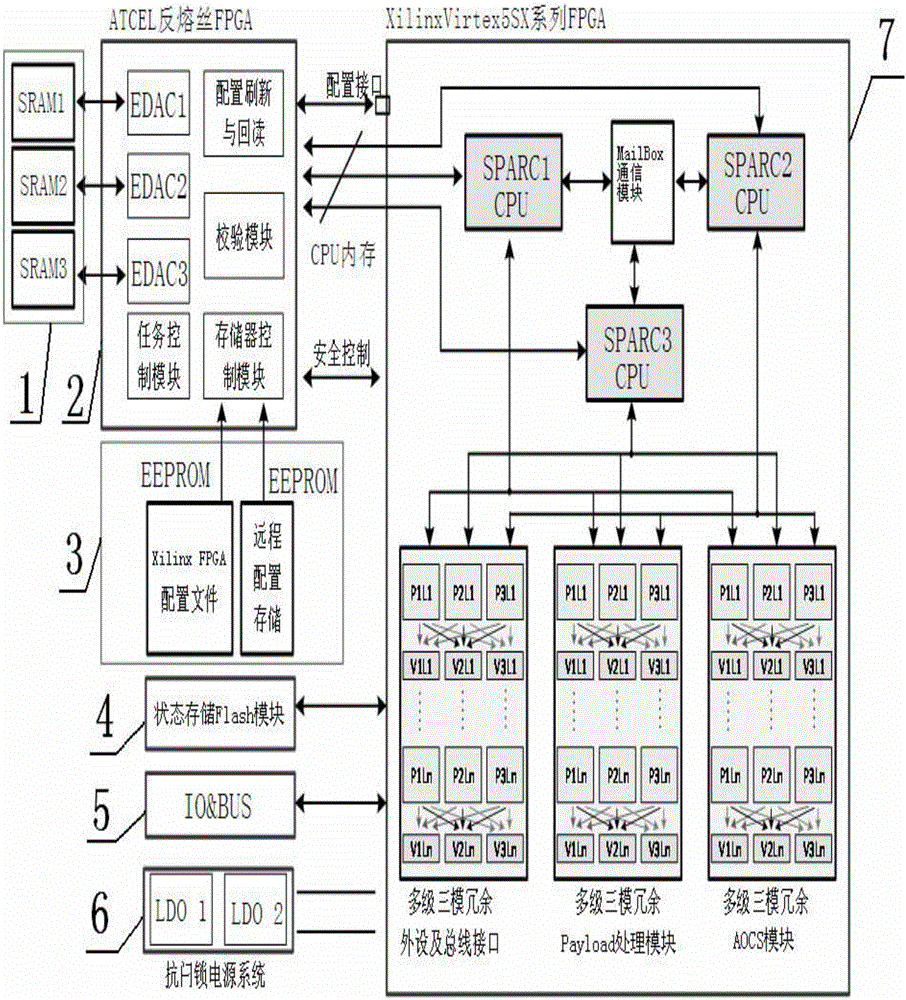
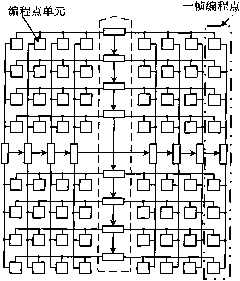
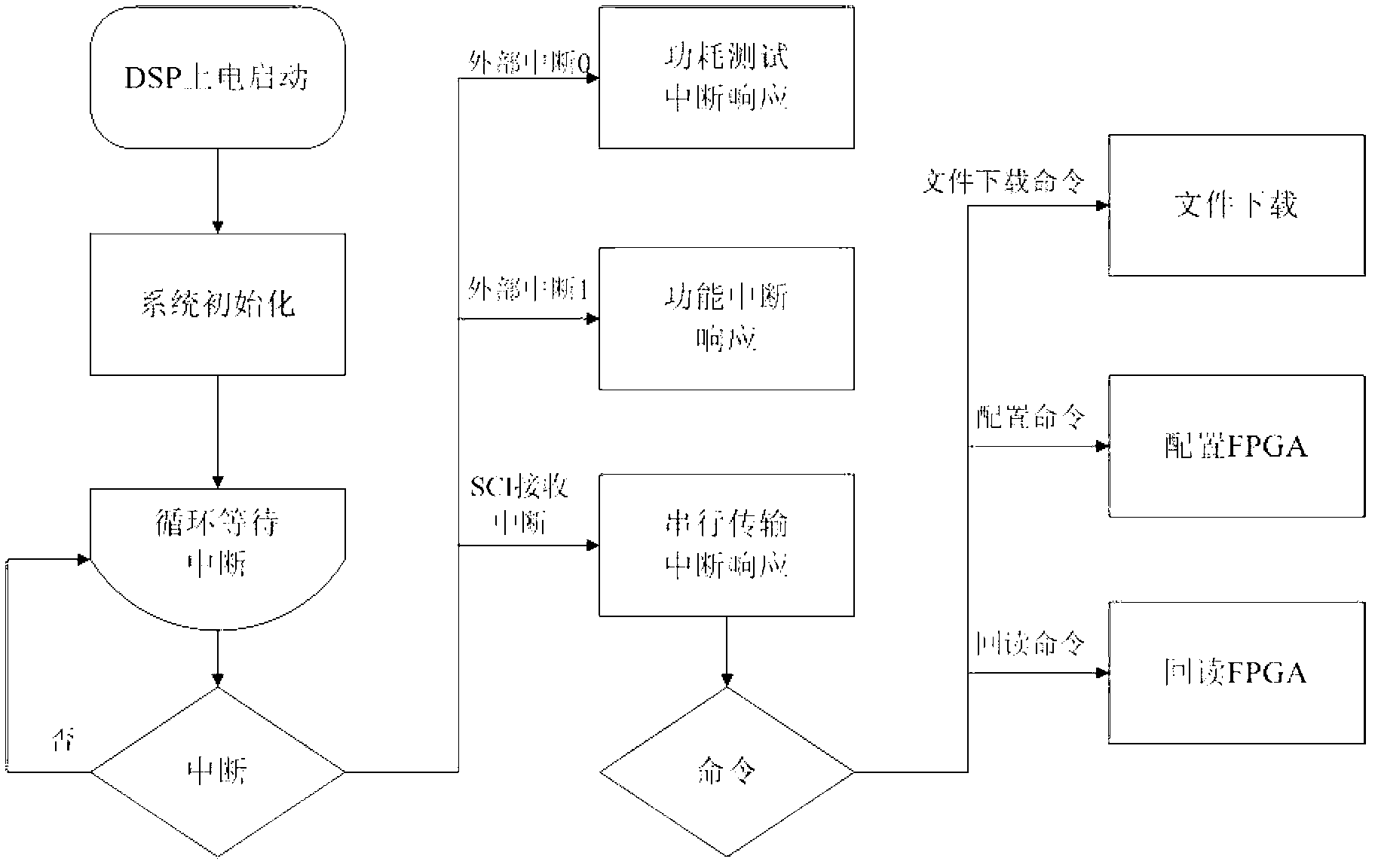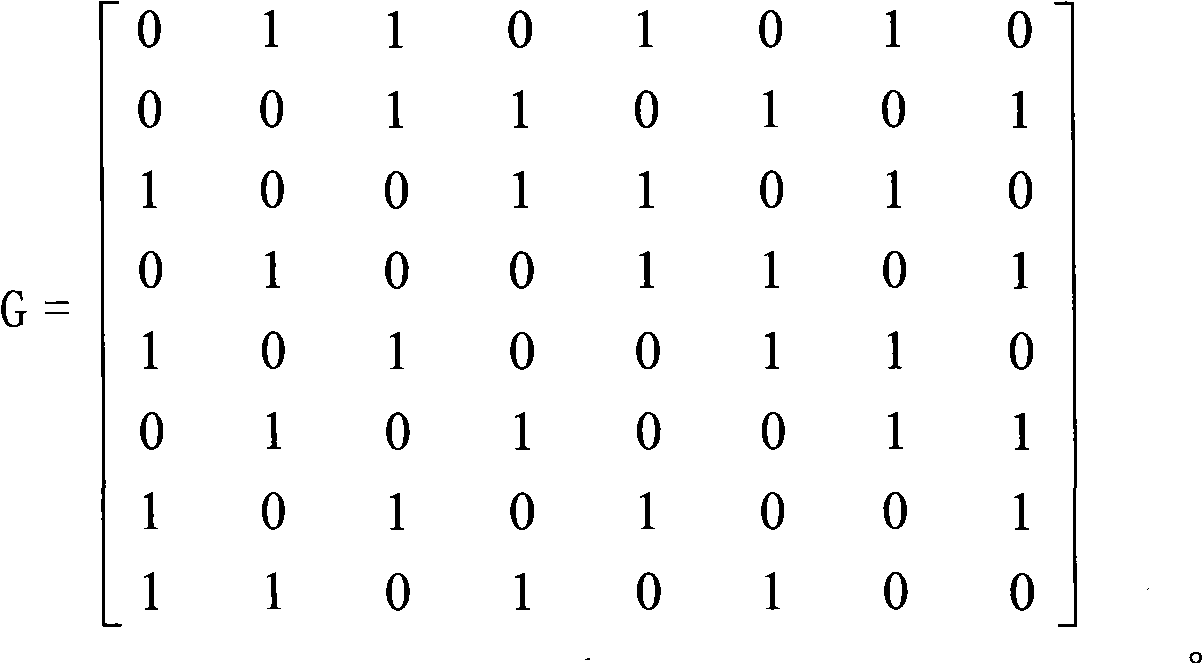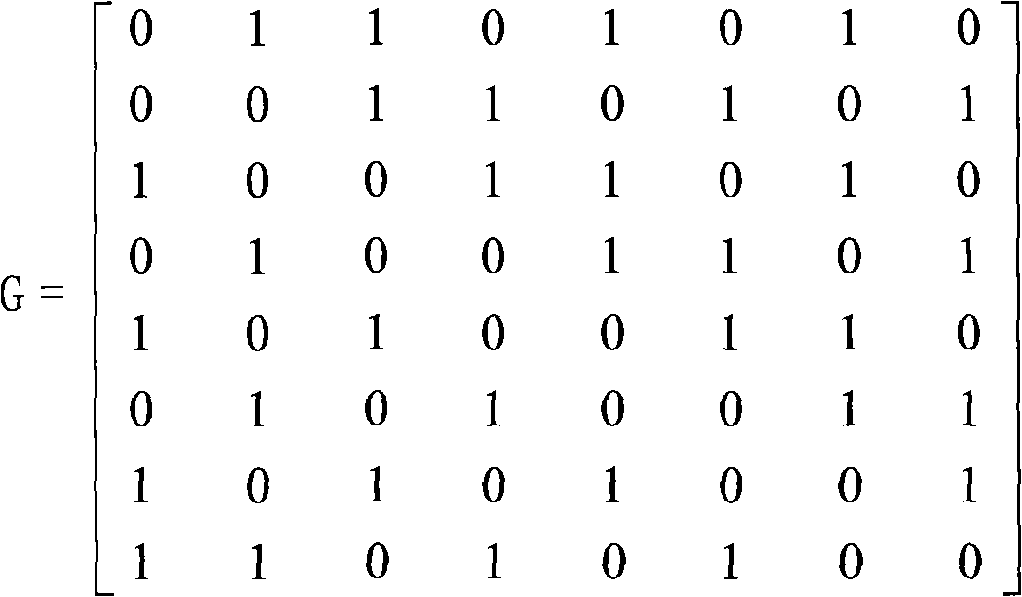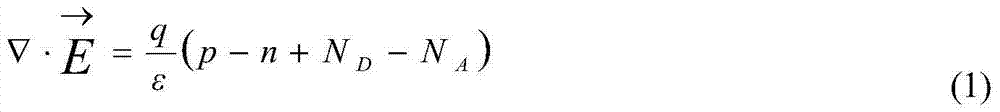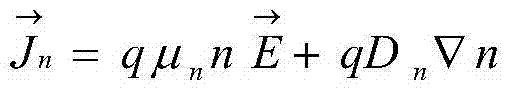Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
611 results about "Single event upset" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
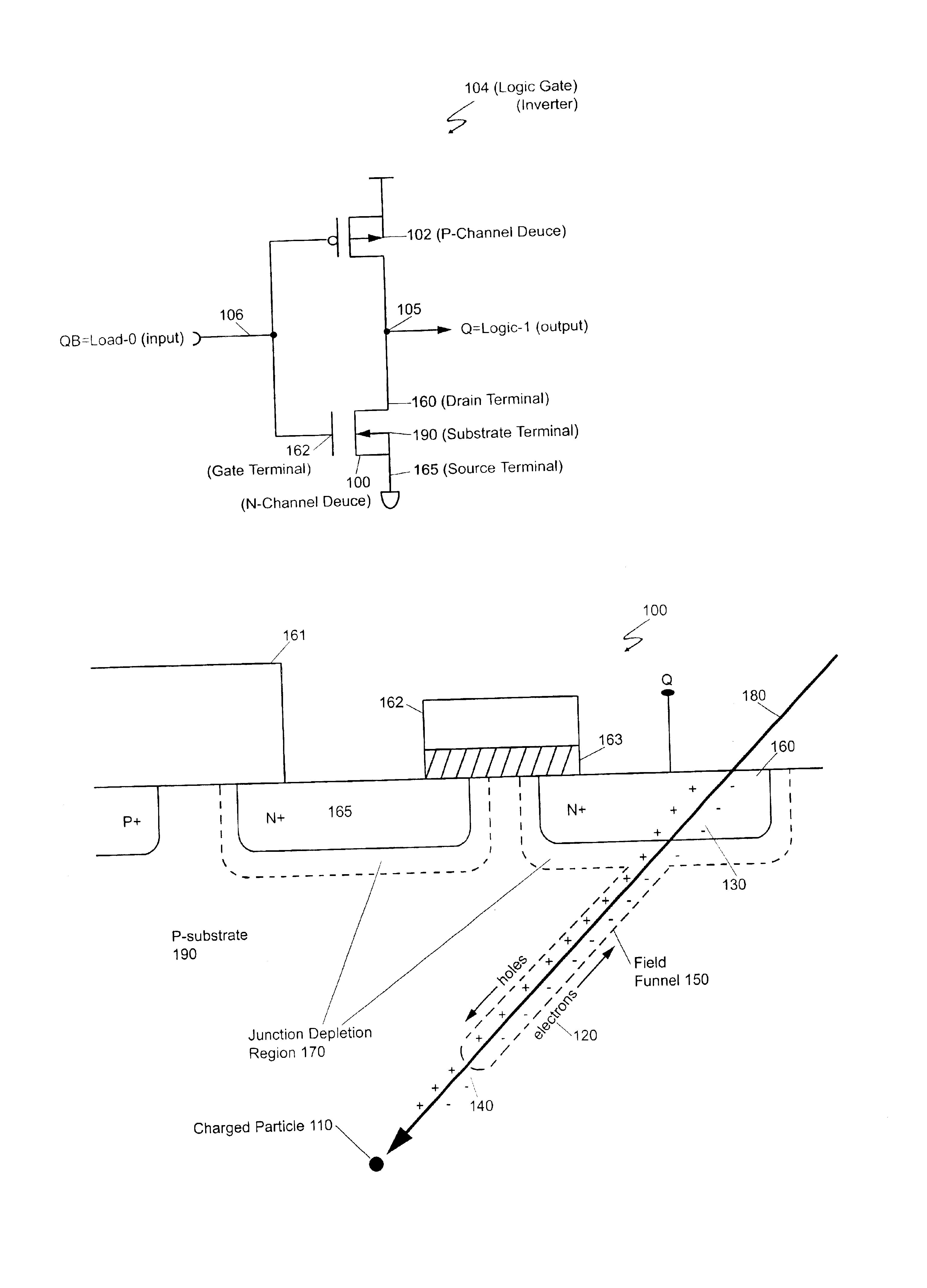
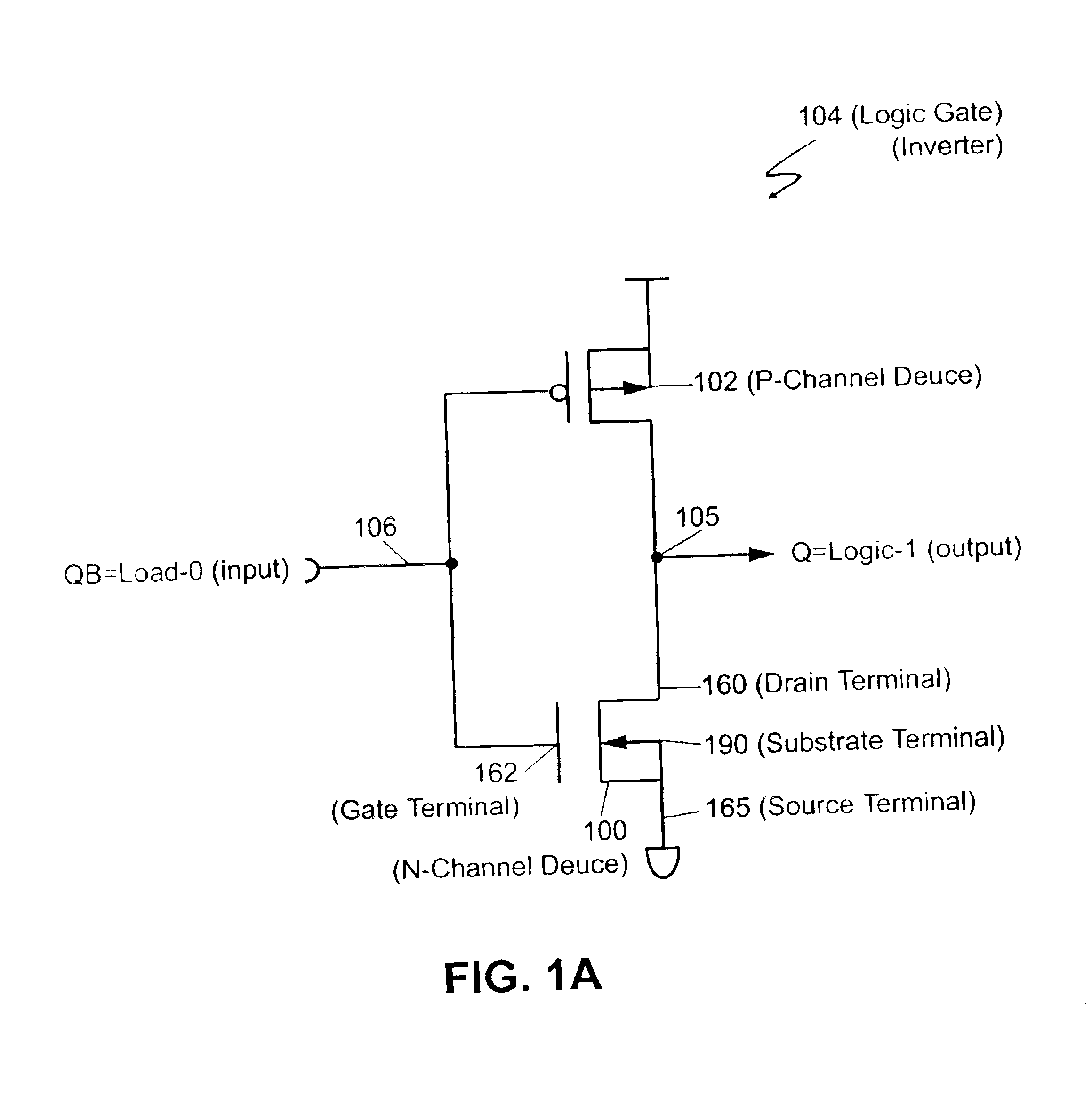
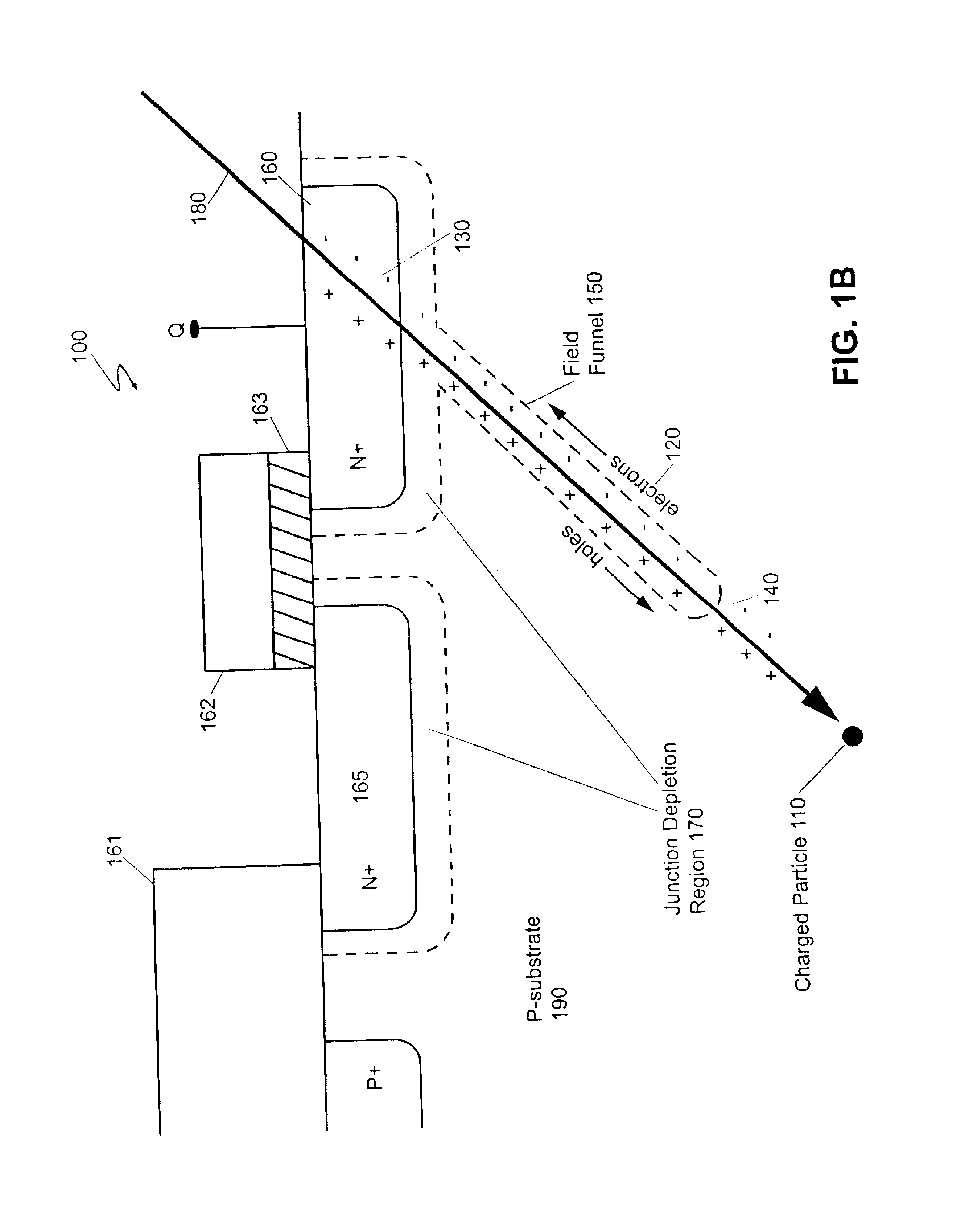
A single-event upset (SEU) is a change of state caused by one single ionizing particle (ions, electrons, photons...) striking a sensitive node in a micro-electronic device, such as in a microprocessor, semiconductor memory, or power transistors. The state change is a result of the free charge created by ionization in or close to an important node of a logic element (e.g. memory "bit"). The error in device output or operation caused as a result of the strike is called an SEU or a soft error.
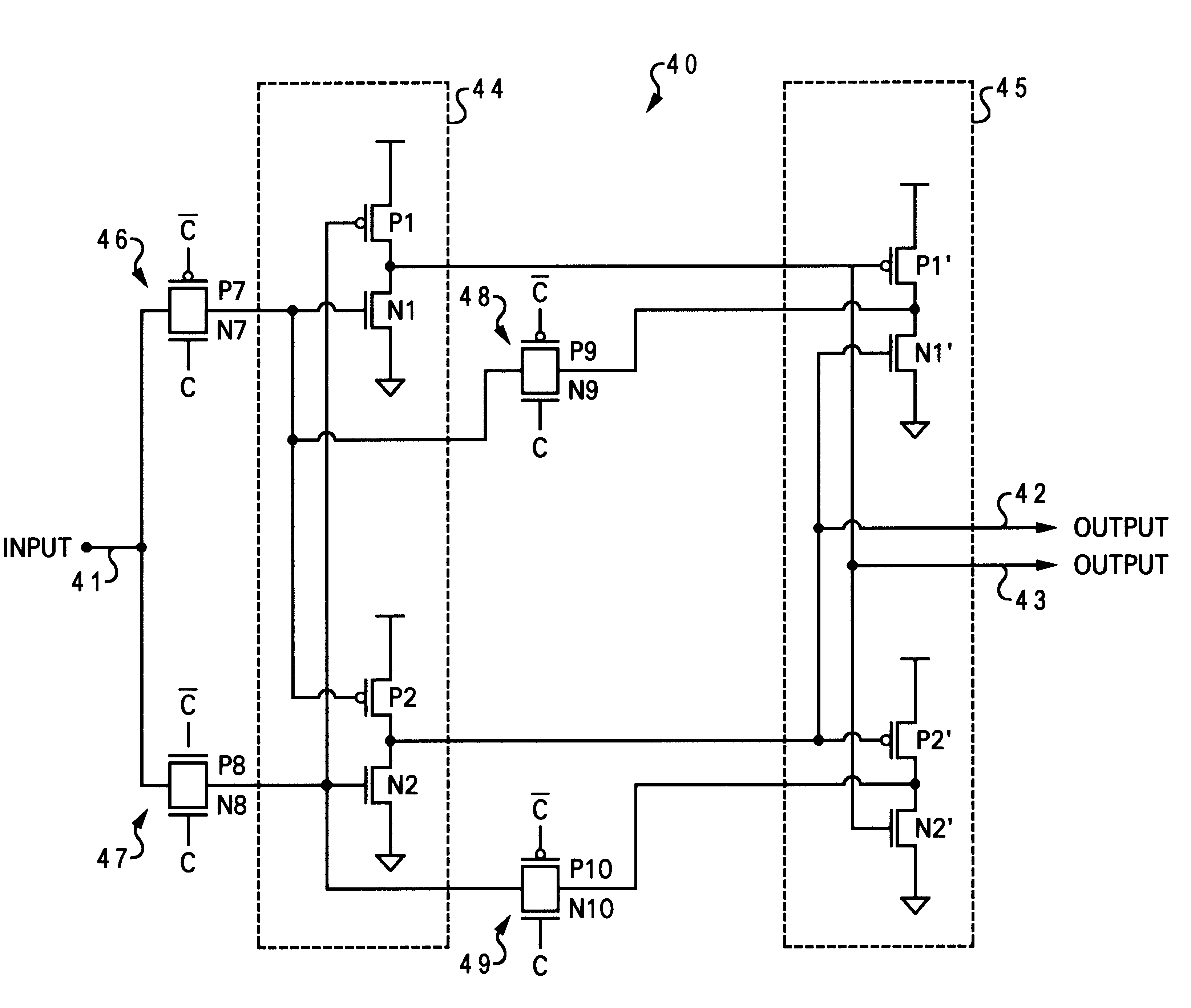
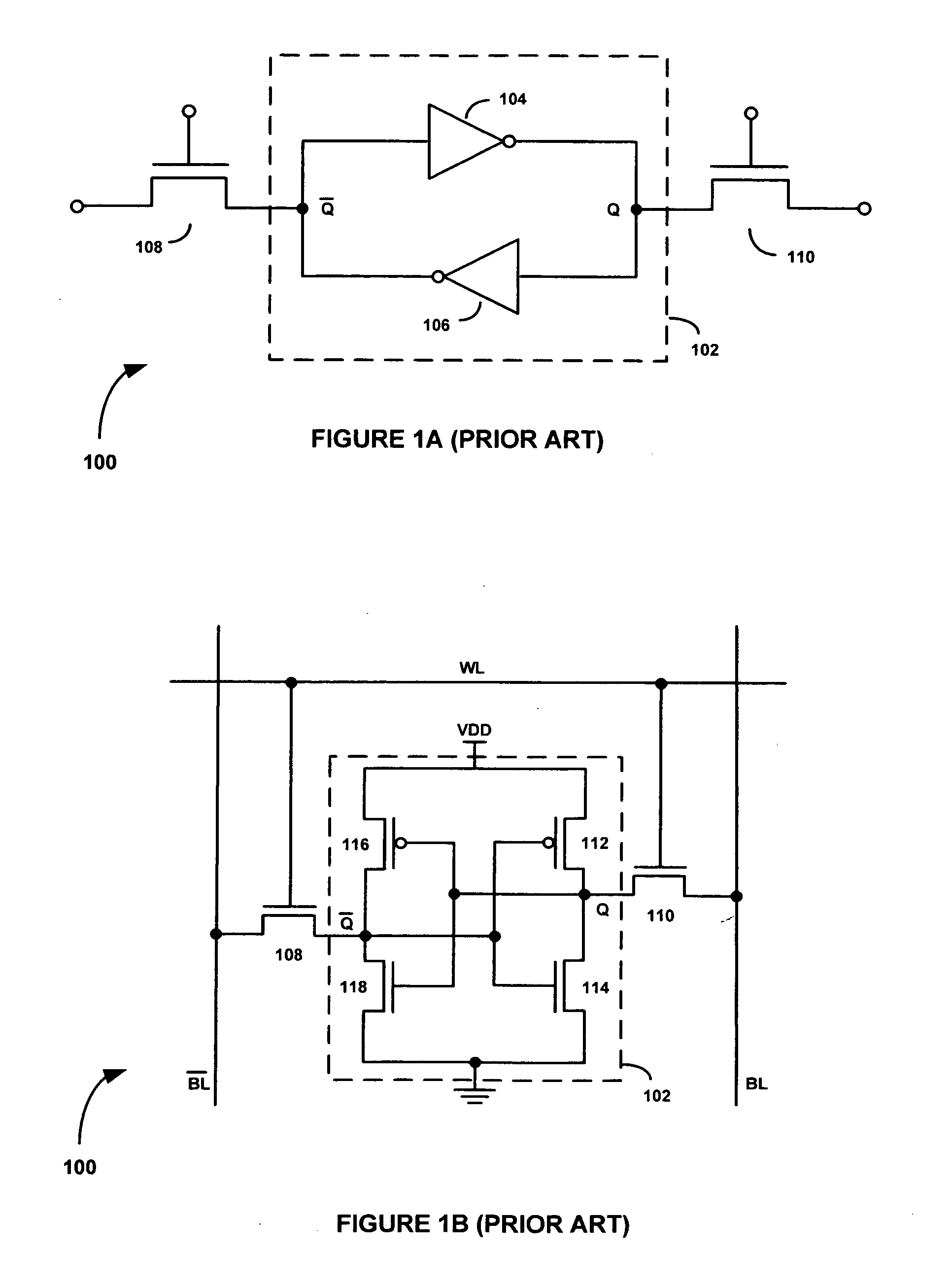
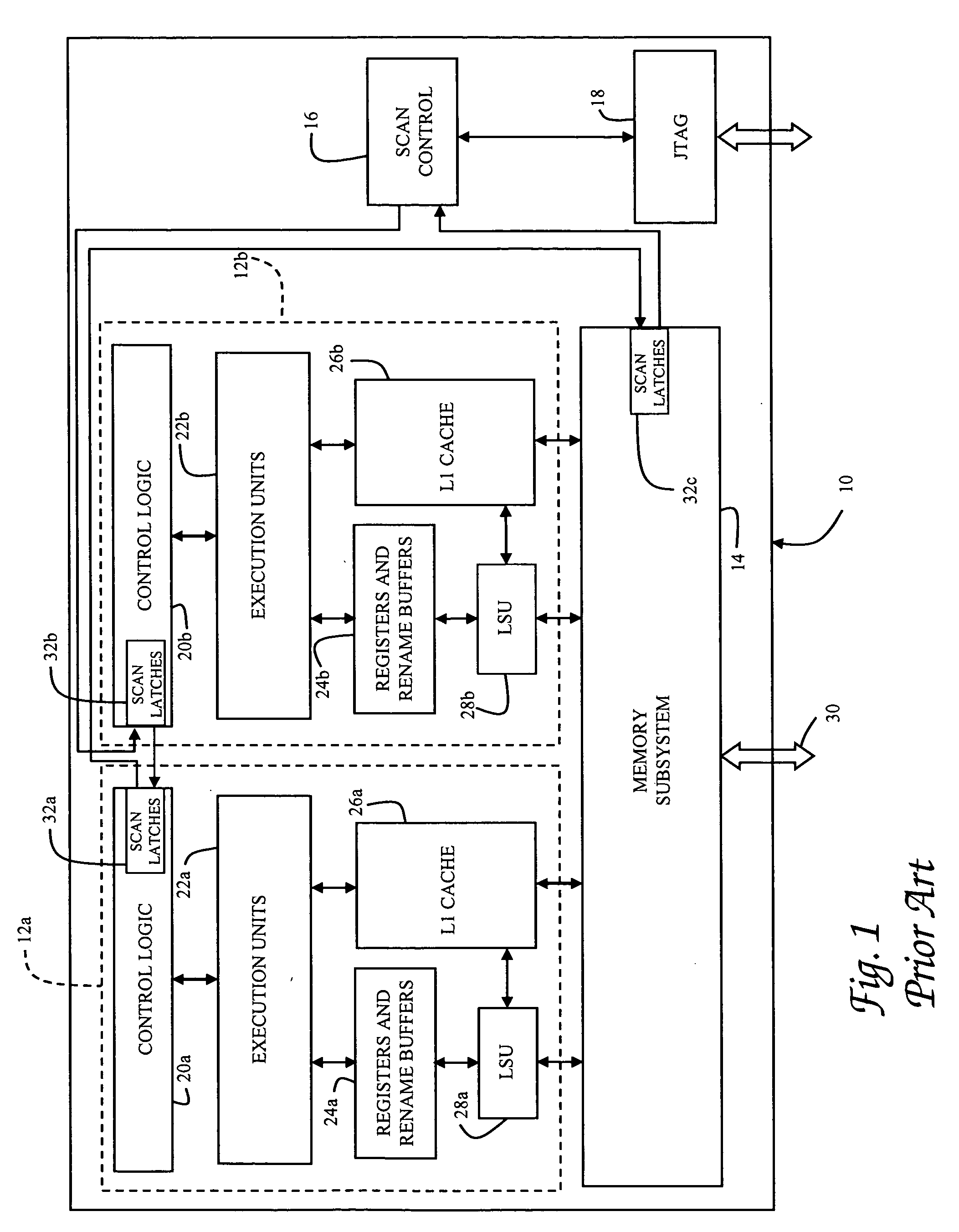
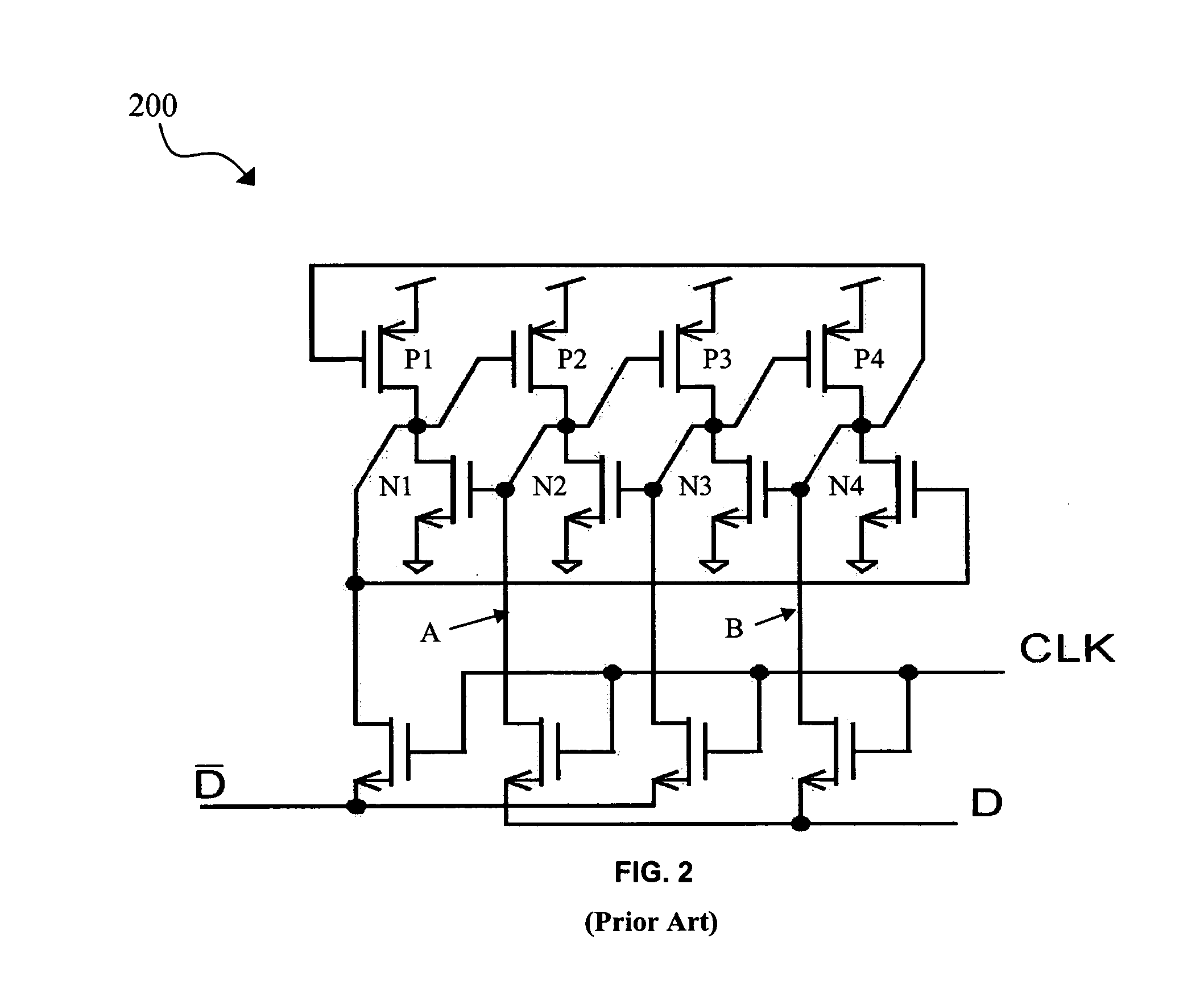
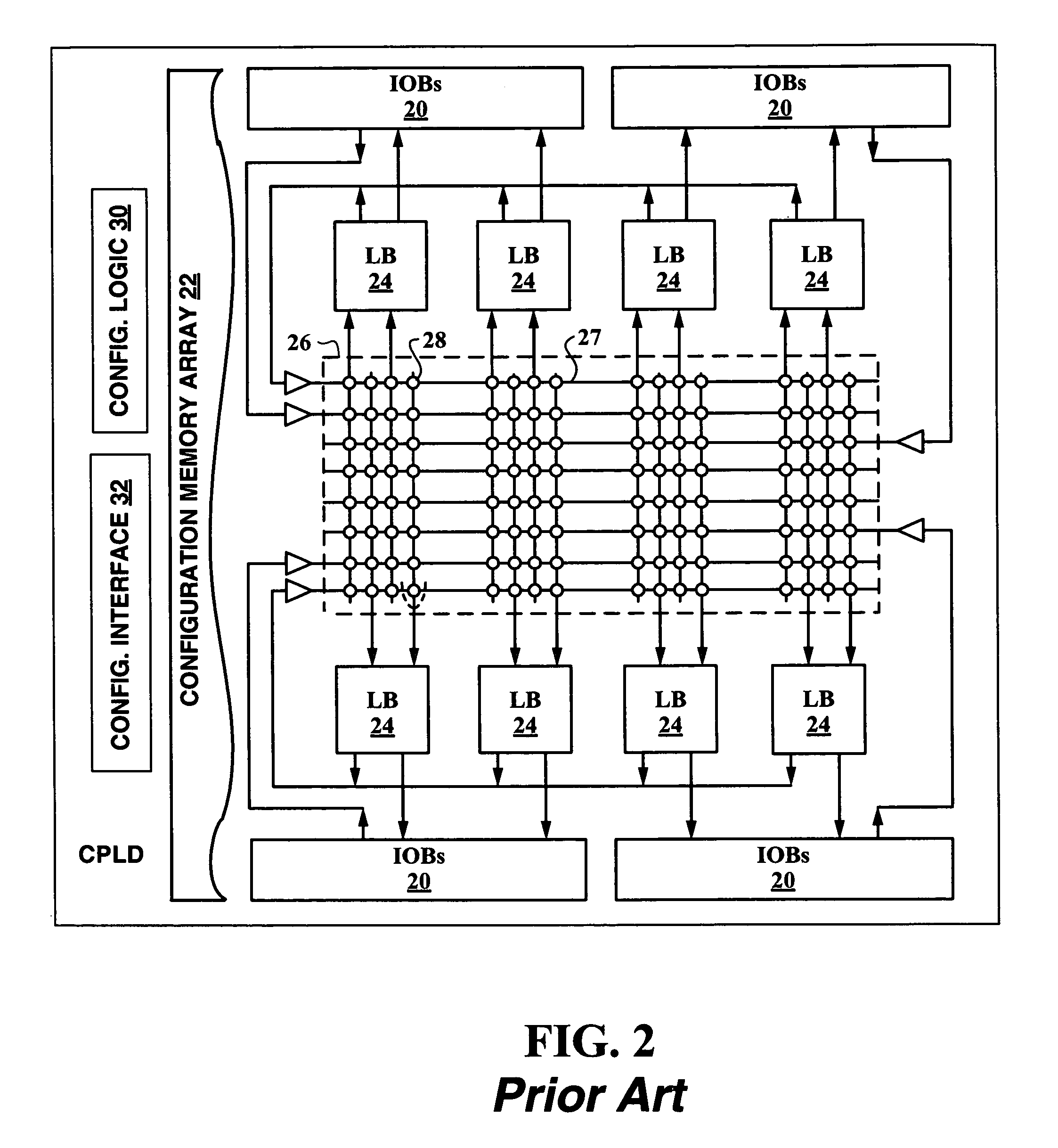
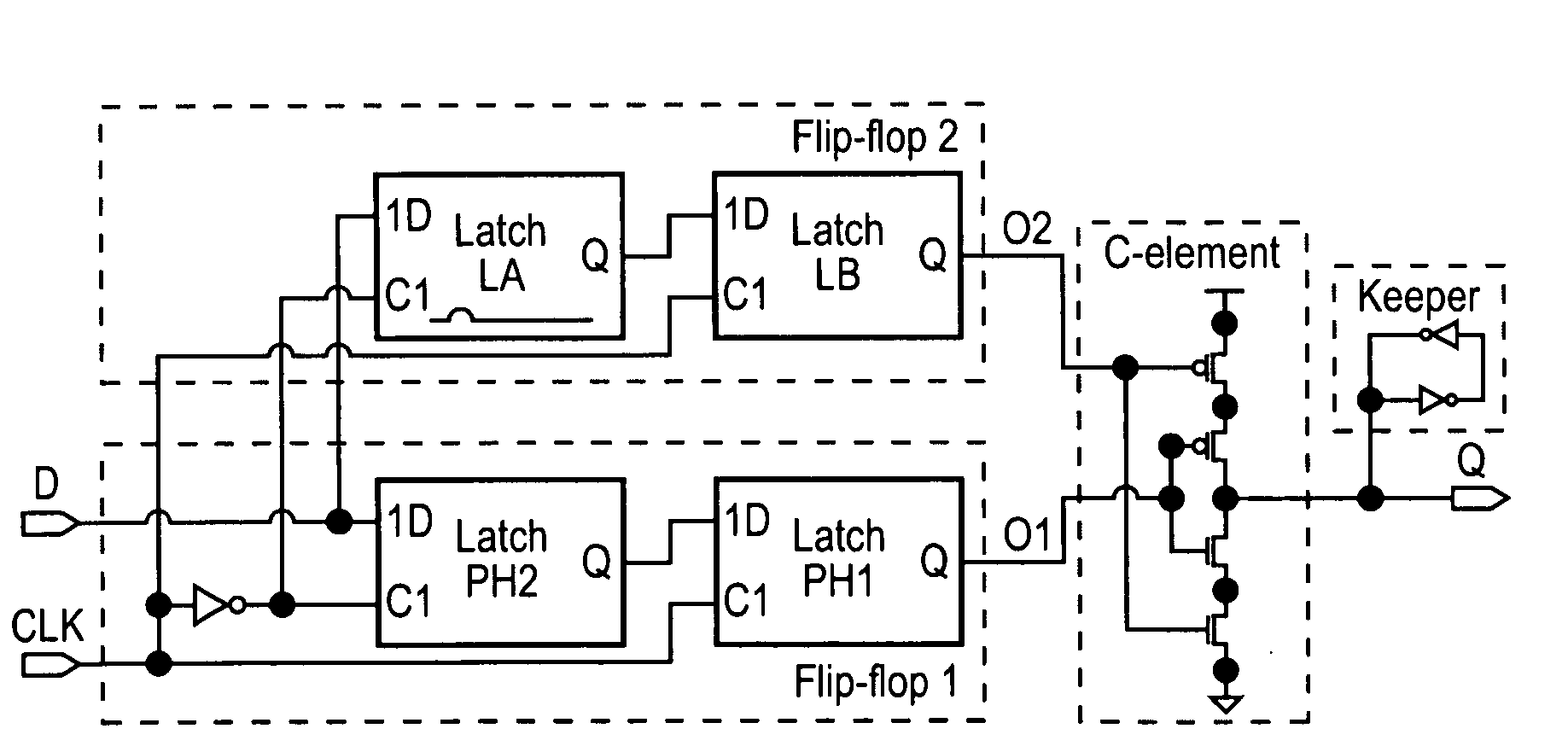
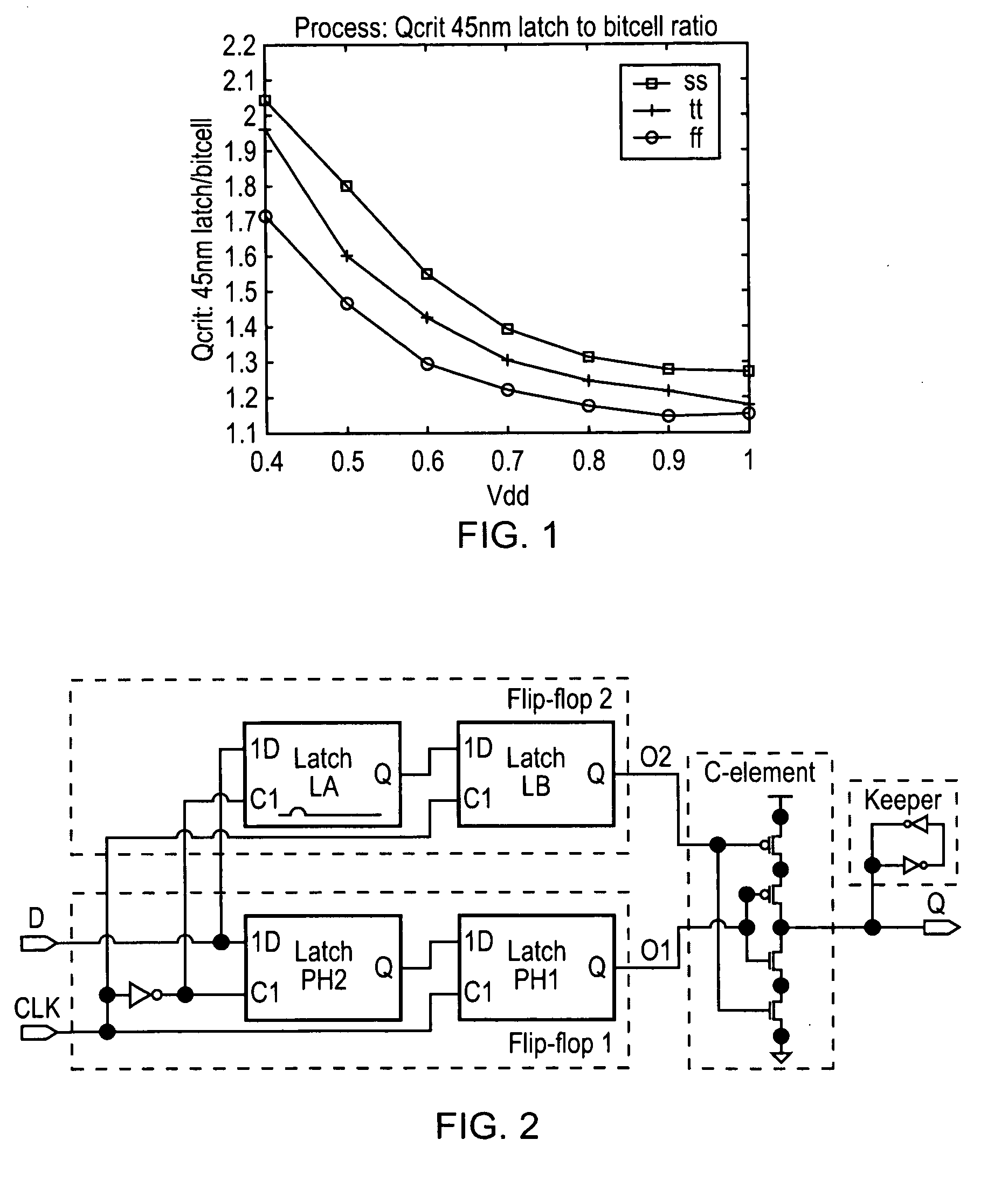
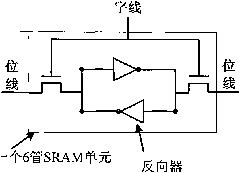
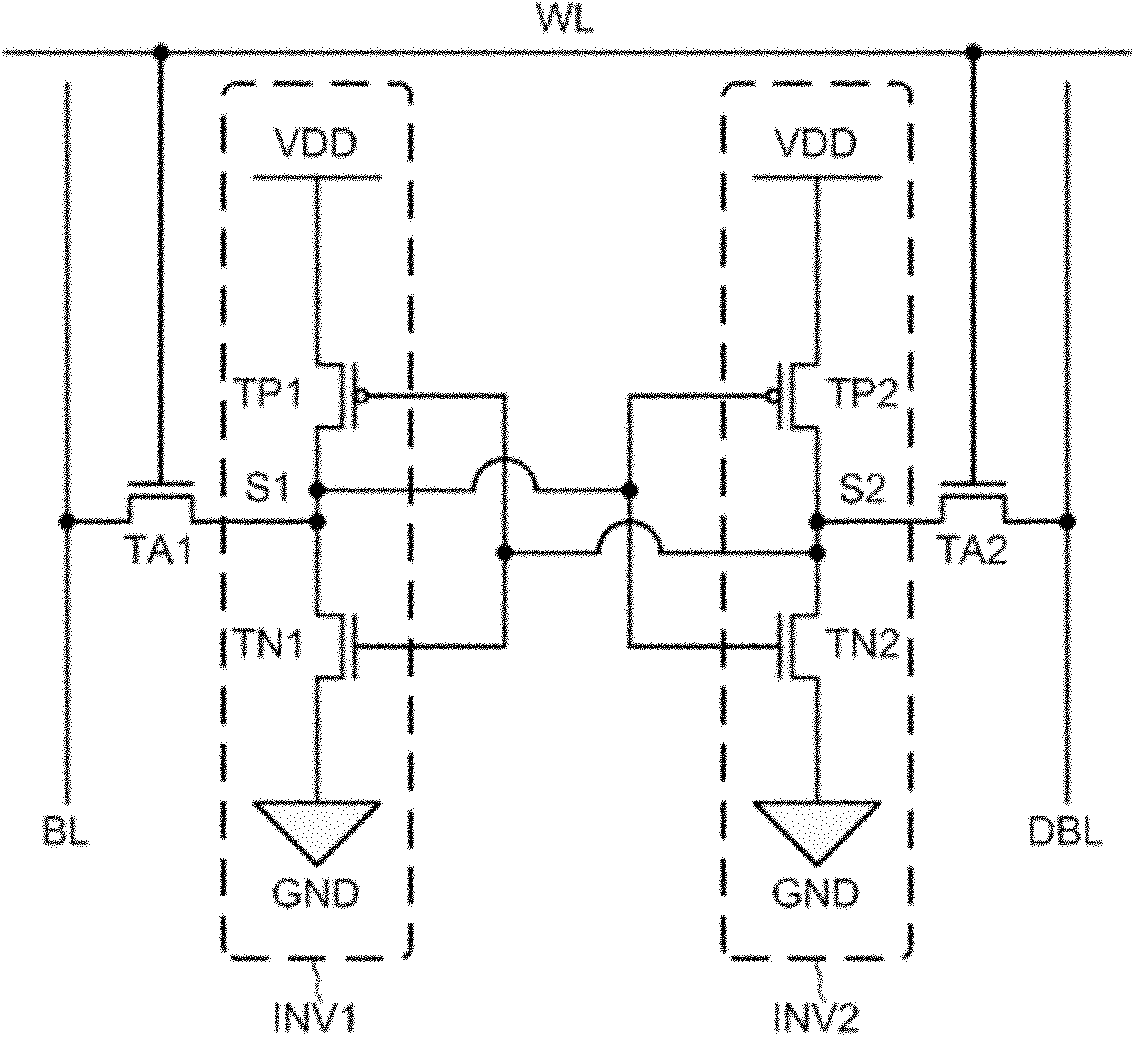
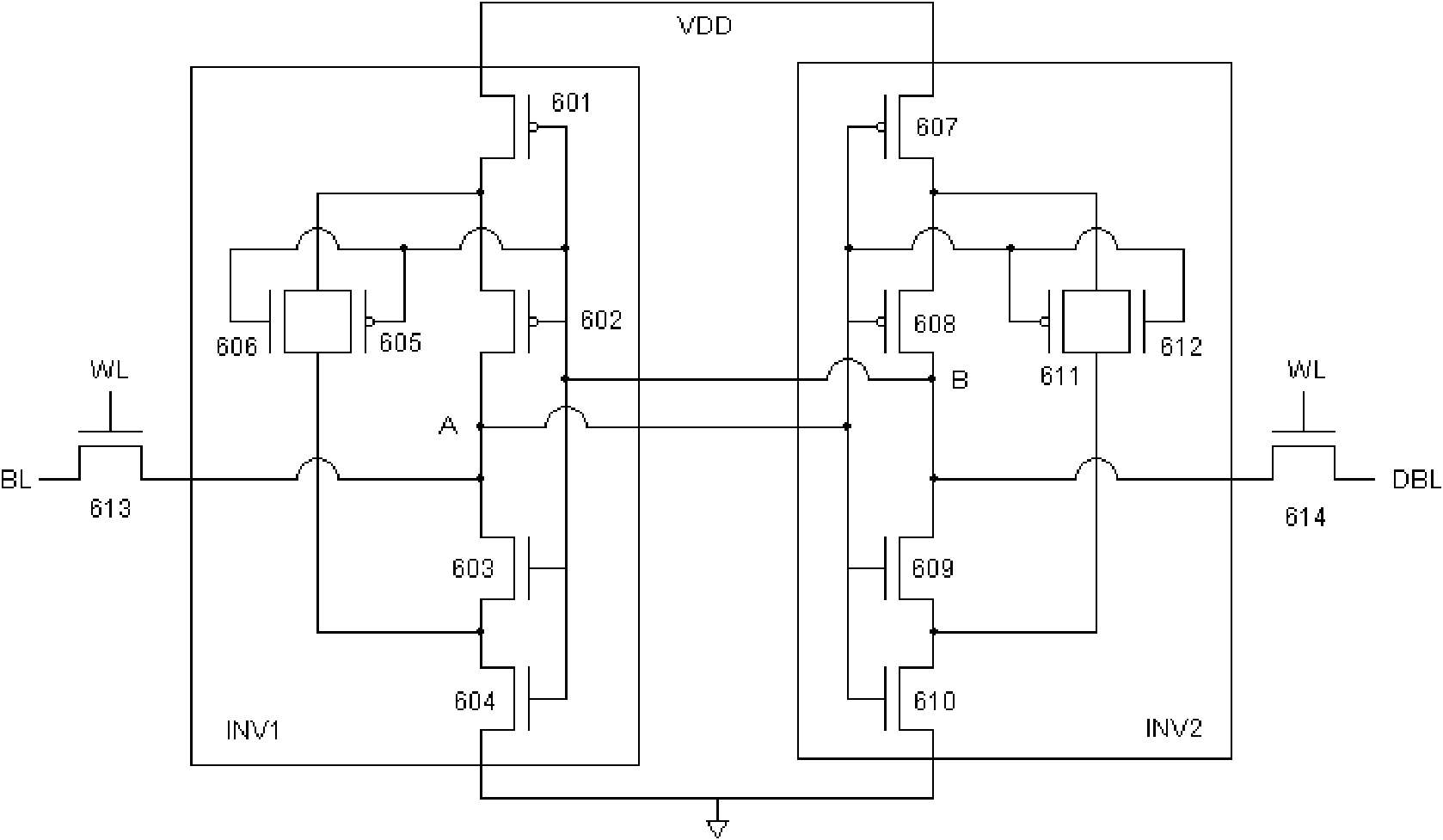
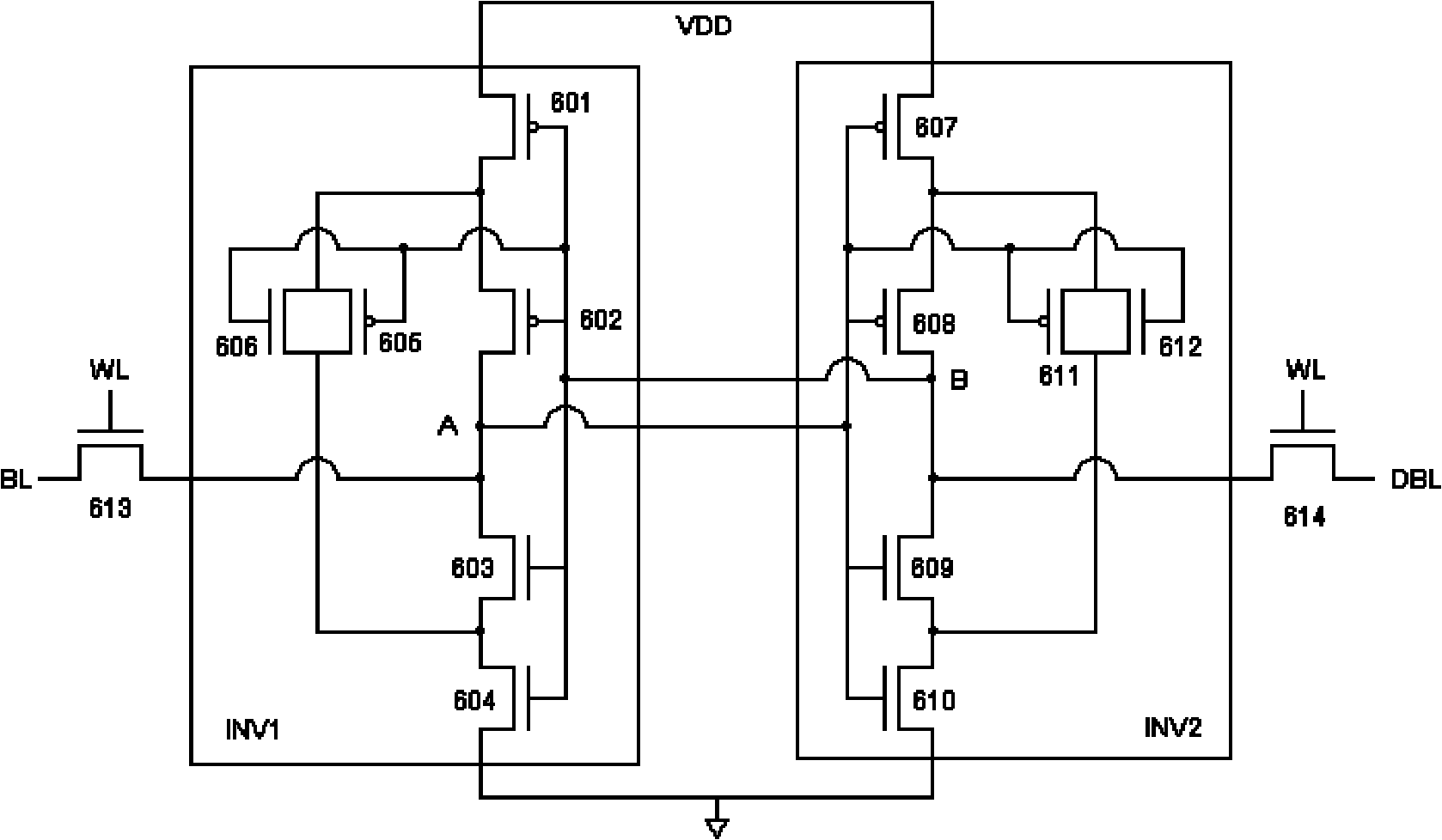
Single event upset (SEU) hardened latch circuit
A single event upset hardened latch circuit is disclosed. The single event hardened latch circuit includes a first dual-port inverter and a second dual-port inverter. An input is coupled to the first dual-port inverter via a first set of pass gates. The first dual-port inverter is coupled to the second dual-port inverter via a second set of pass gates. The output is connected to the first and second dual-port inverters.
Owner:BAE SYST INFORMATION & ELECTRONICS SYST INTERGRATION INC
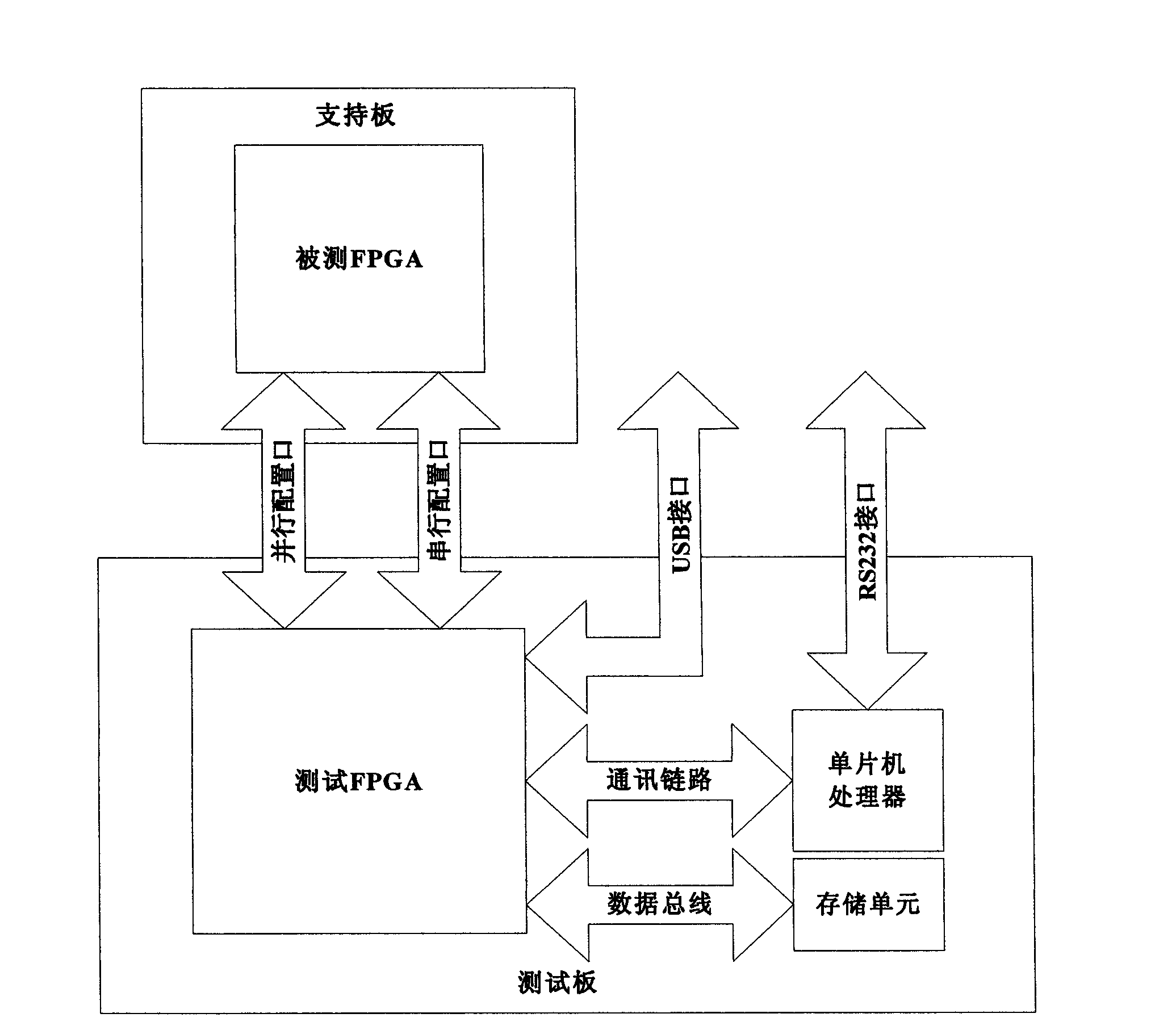
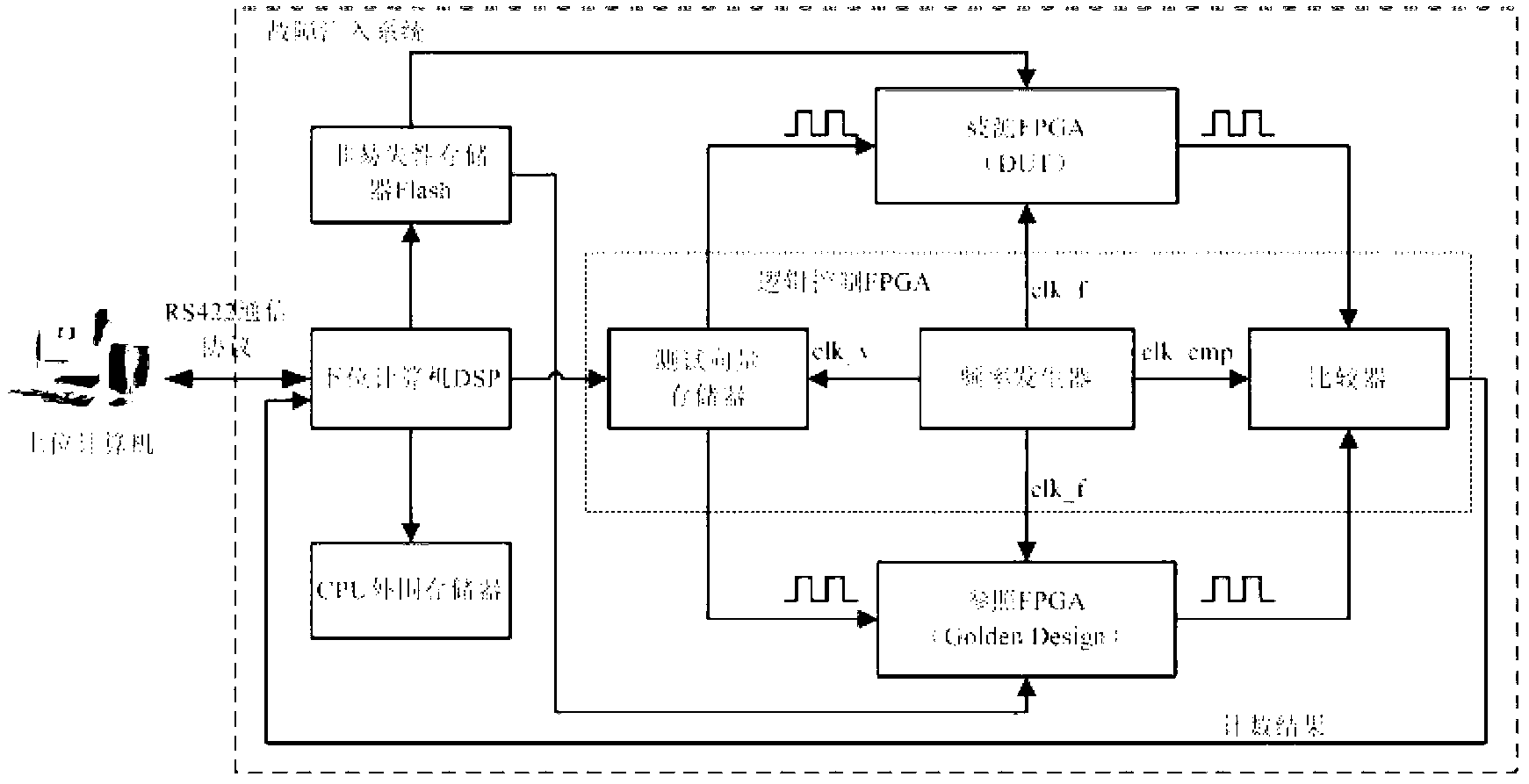
Test system and method for single event effect of SRAM (System Random Access Memory) type FPGA (Field Programmable Gate Array)
ActiveCN102332307AEasy to operateImplement rollover detectionStatic storagePilot systemRandom access memory
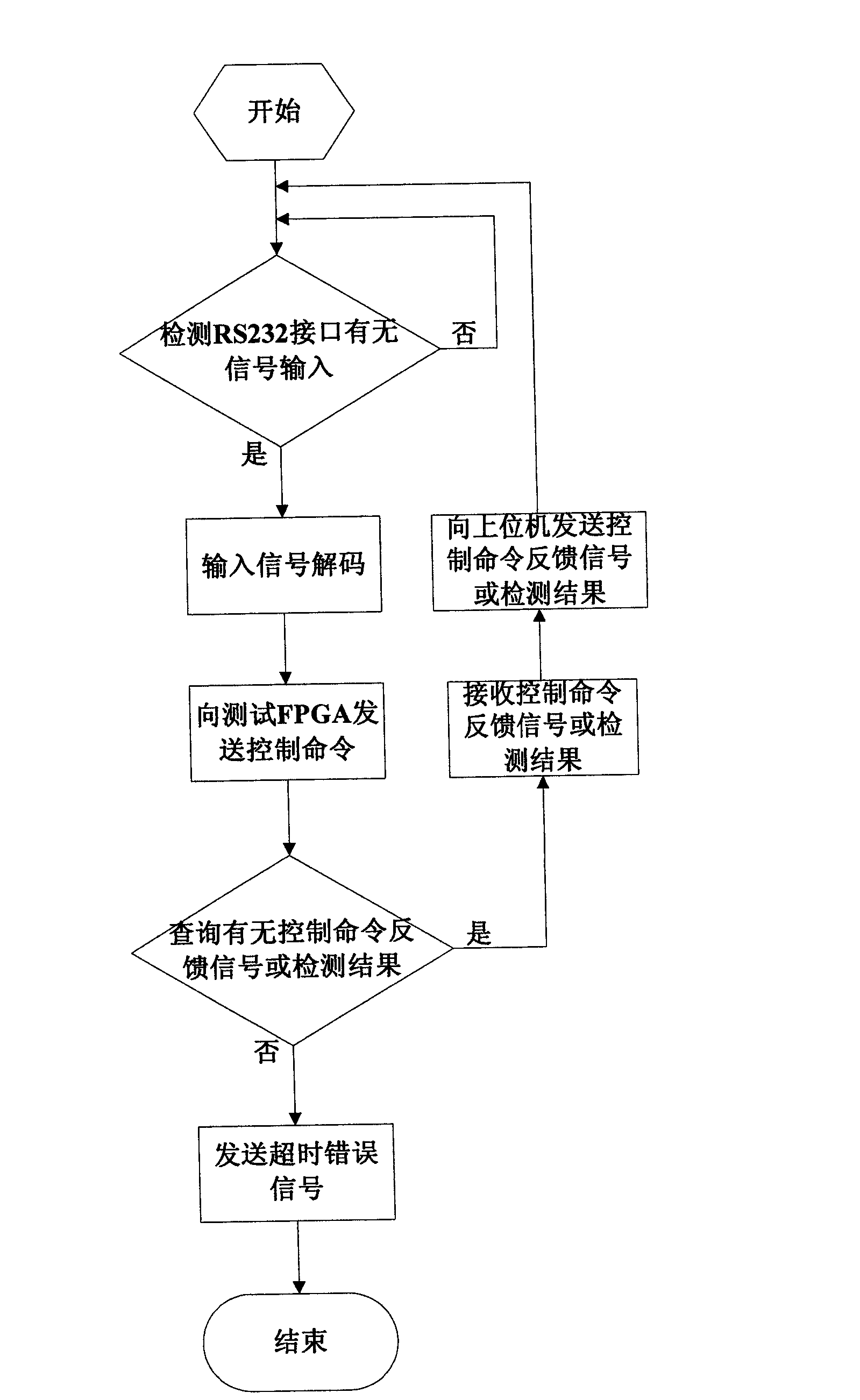
The invention provides a test system and method for a single event effect of an SRAM (System Random Access Memory) type FPGA (Field Programmable Gate Array). The test system comprises a single chip microcomputer processor, an RS232 interface circuit, a USB (Universal Serial Bus) interface circuit, a test FPGA and a storage unit. The test system and method can be used for fault injection tests of a configuration memory and a BRAM (Battery Random Access Memory) of the SRAM type FPGA, and single event function interrupting detection, single event locking detection and single event turning detection including single event turning detection for a configuration storage region, the BRAM and a trigger of the SRAM type FPGA are realized. The invention has the advantages of simplicity in operation, entirety in detection, high accuracy, good real-time property and strong universality.
Owner:CHINA ACADEMY OF SPACE TECHNOLOGY
SRAM type FPGA single particle irradiation test system and method
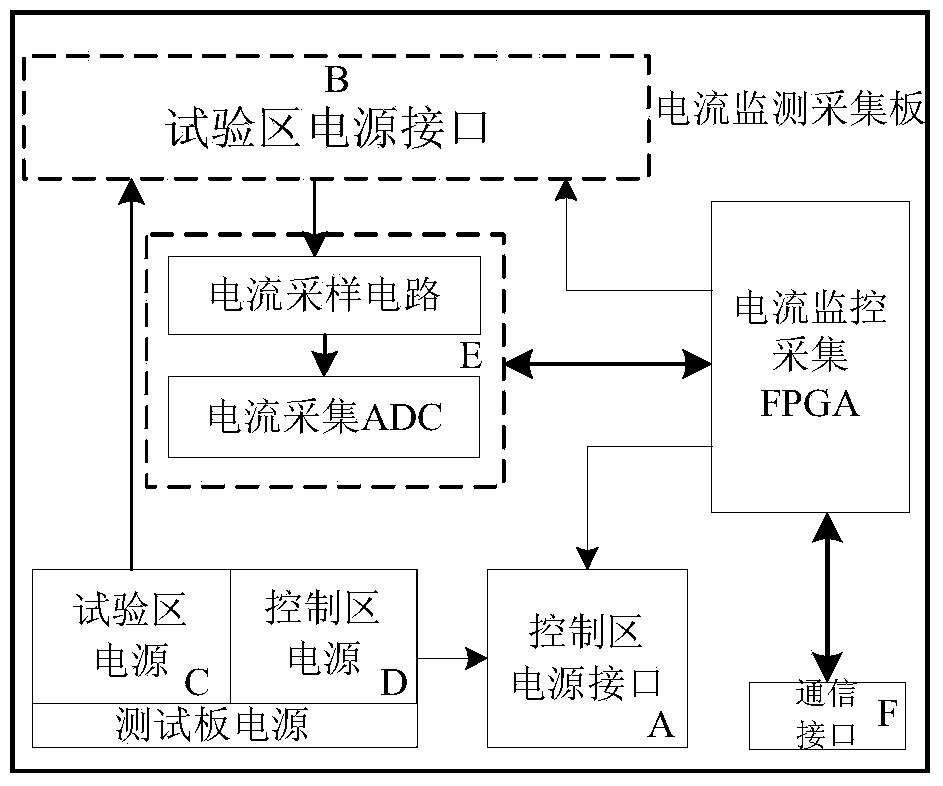
ActiveCN103744014ARefresh is convenient and reliableReliably flip dataElectrical testingCommunication interfacePower flow
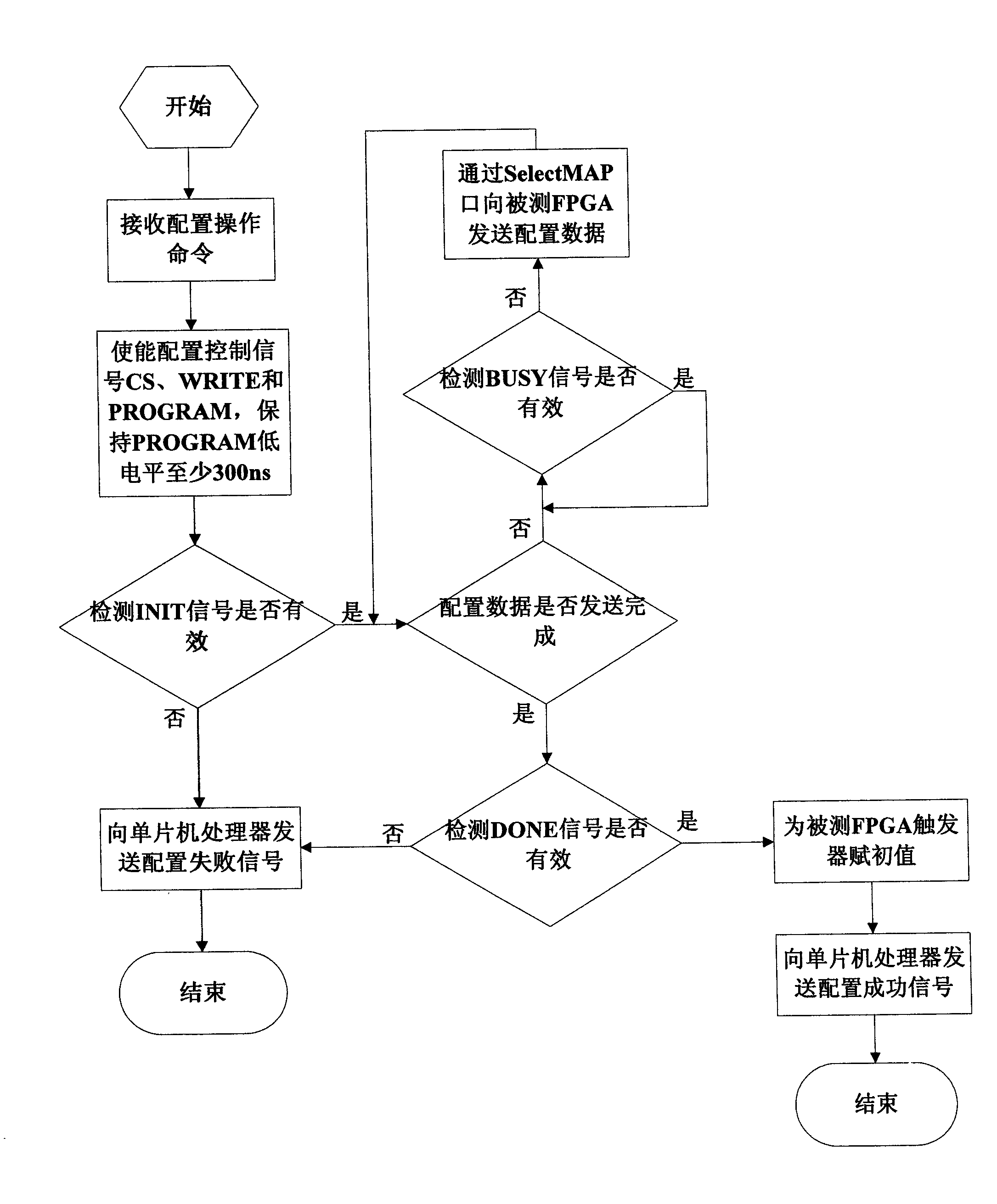
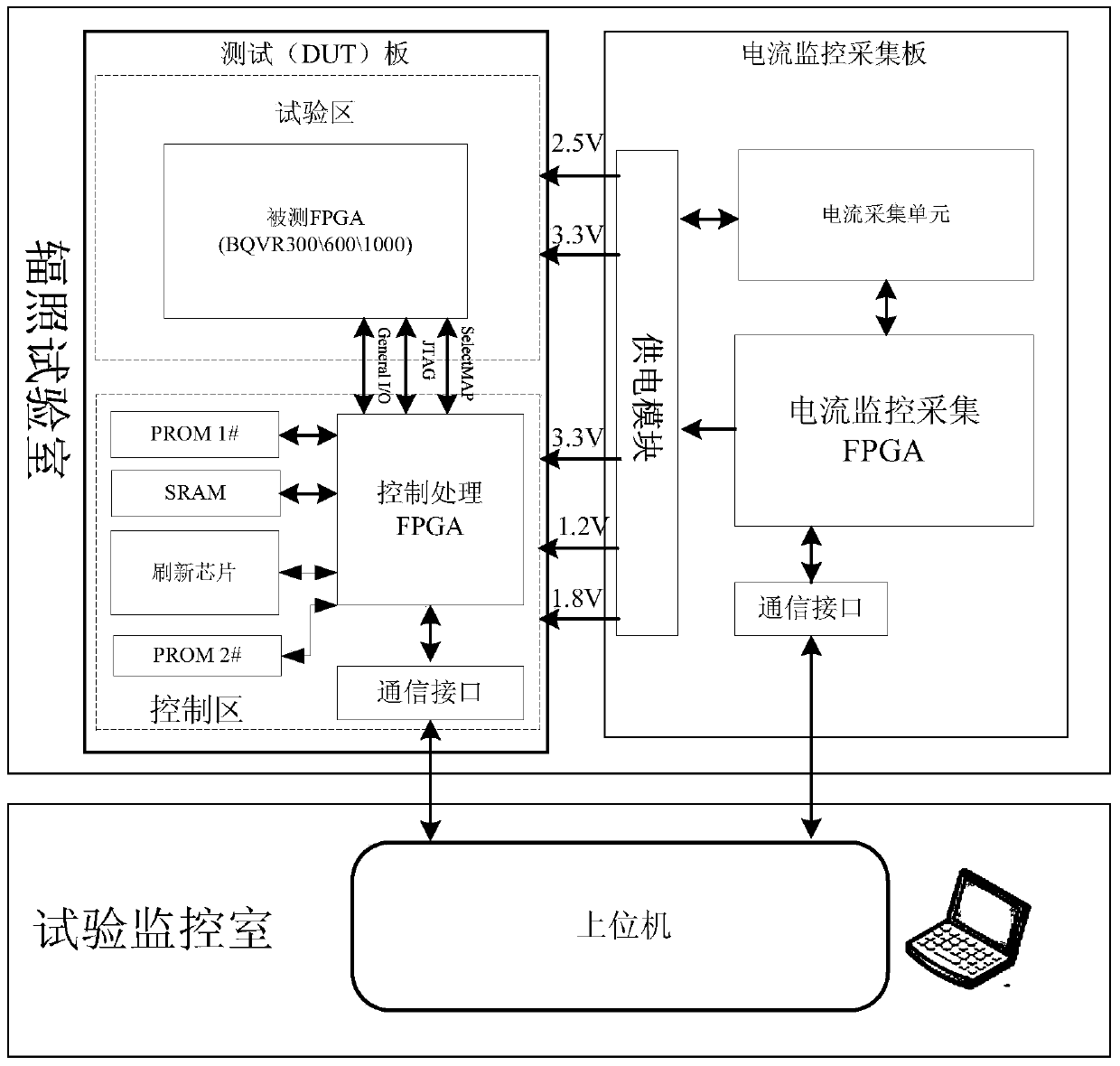
The invention provides an SRAM type FPGA single particle irradiation test system and method. The test system comprises a host computer, a current monitoring acquisition plate and a test plate. The current monitoring acquisition plate comprises a current monitoring acquisition FPGA, a current acquisition unit, a power supply module and a first communication interface; the test plate comprises a control processing FPGA, a refreshing chip, an SRAM, a configuration PROM, a storage PROM, a second communication interface and a detected FPGA; the host computer is in charge of flow control and data processing; the current monitoring acquisition plate is in charge of power-on and power-off of the test plate and monitoring and testing of FPGA currents; and the test plate is in charge of processing a command sent by the host computer and performing work such as single particle overturning, single particle function interruption detection and the like. According to the invention, the refreshing chip is utilized to replace some of the reconfiguration modules in a conventional irradiation test system so that a detected chip can be more conveniently and reliably refreshed; and the system and method provided by the invention can realize static and dynamic overturning testing on a trigger, and more reliable trigger overturning data can be obtained by combing the two methods.
Owner:BEIJING MICROELECTRONICS TECH INST +1
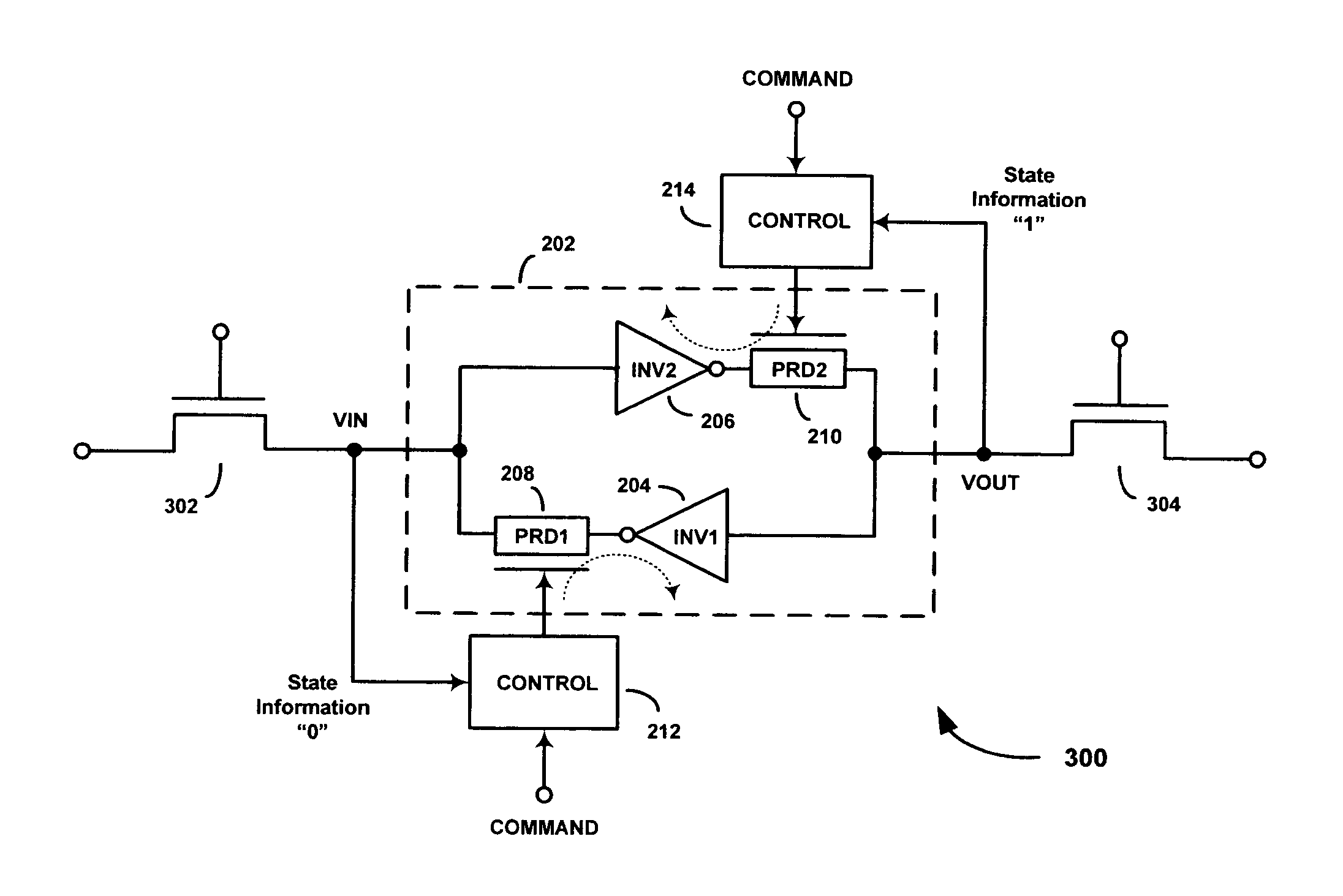
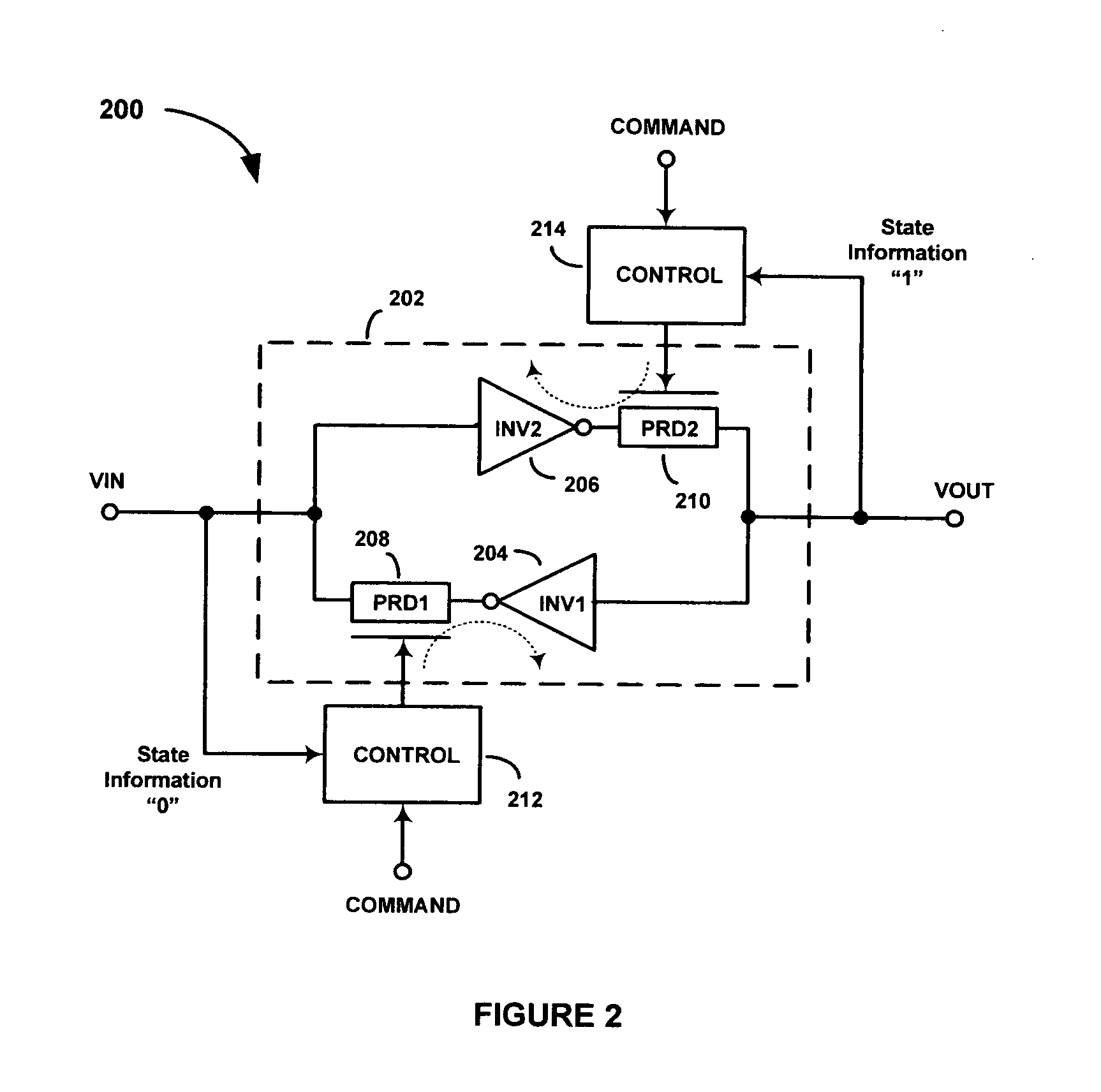
SEU hardened latches and memory cells using progrmmable resistance devices
Apparatus and methods for reducing single-event upsets (SEUs) in latch-based circuitry (e.g., static random access memory (SRAM) cells) and other digital circuitry. According to an exemplary embodiment, a latch-based circuit includes a radiation-hardened latch having first and second cross-coupled inverters and first and second programmable resistance devices (PRDs). The first PRD is coupled between the output of the first inverter and the input of the second inverter. The second PRD is coupled between the output of the second inverter and the input of the first inverter. The PRDs may be programmed to low or high-resistance states. When SET to a low-resistance state, the latch of the latch-based circuitry may be accessed to read the current logic state stored by the latch or to write a new logic state into the latch. When RESET to a high-resistance state, the latch is in a radiation-hard state, thereby preventing the latch from generating SEUs.
Owner:AGATE LOGIC BEIJING
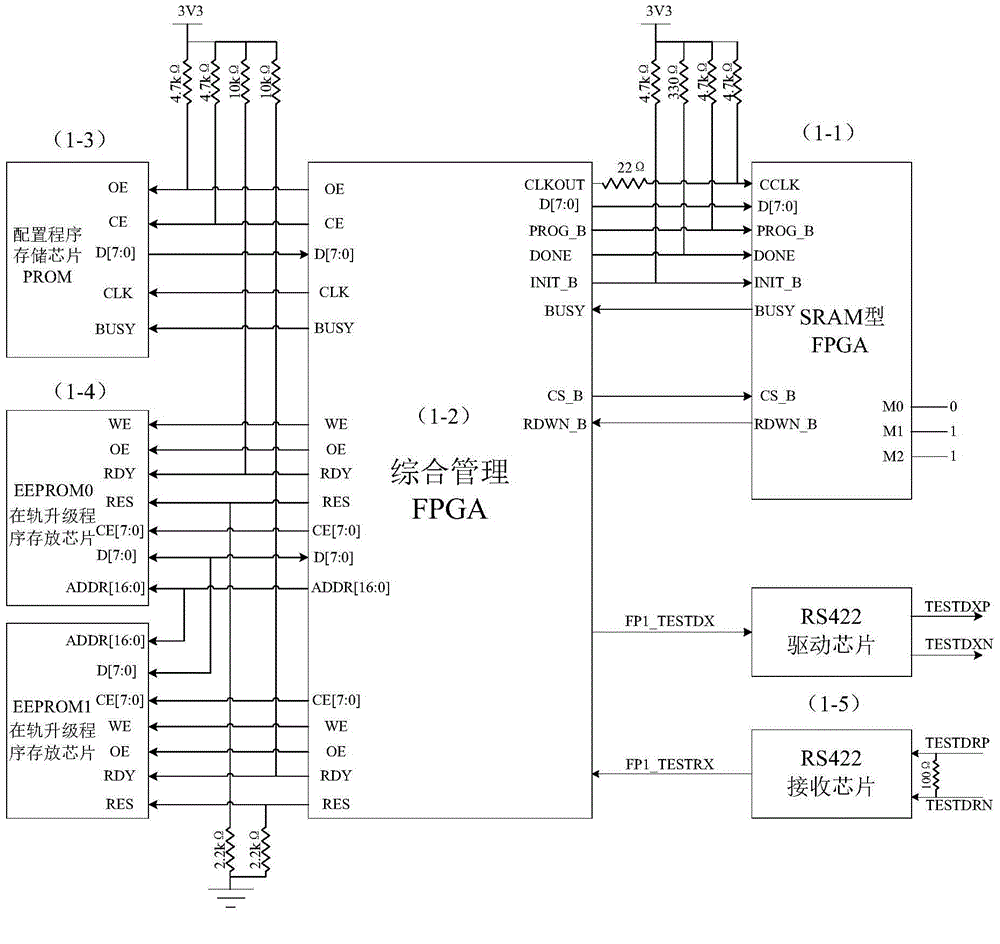
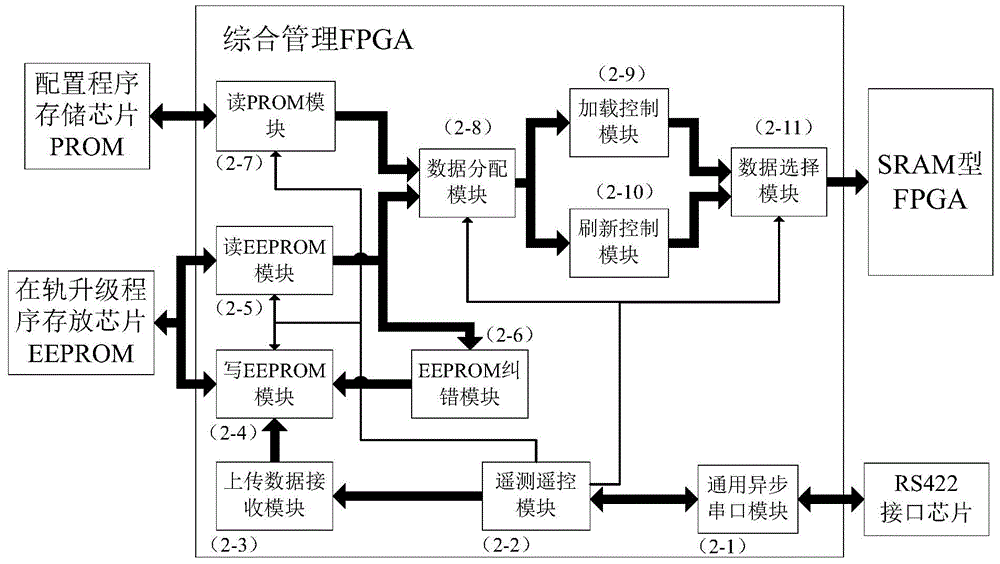
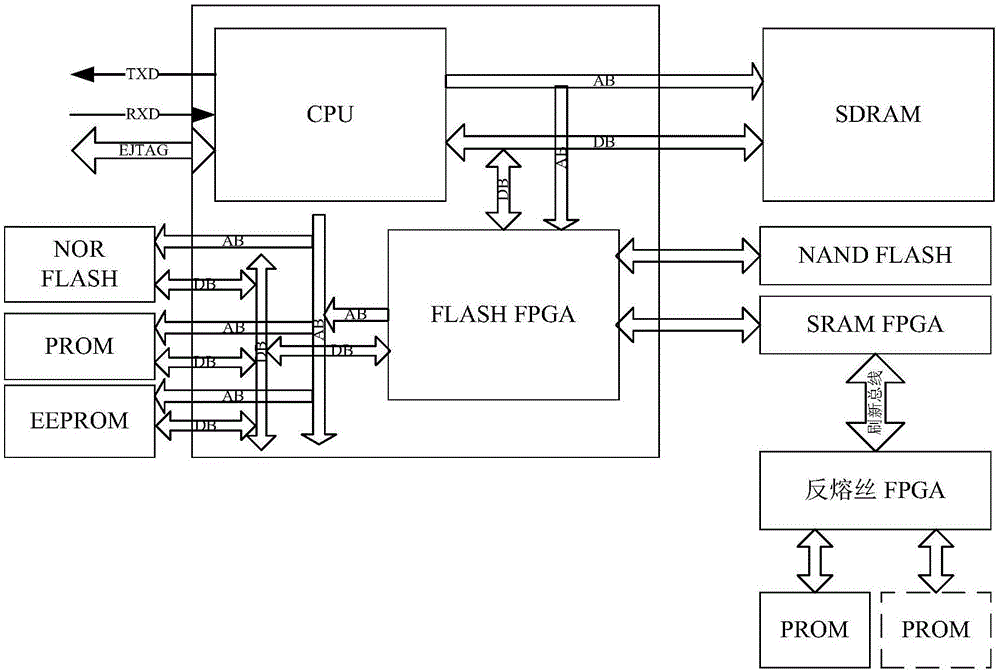
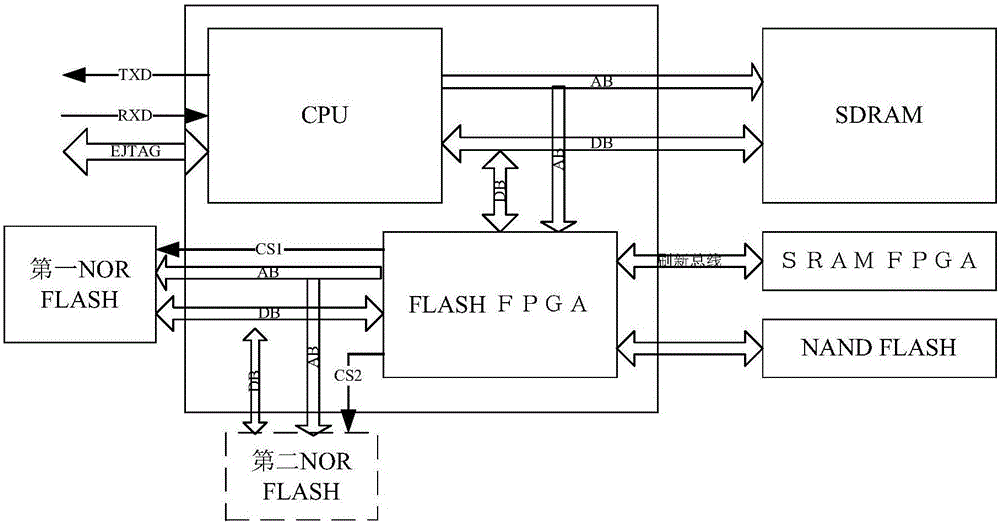
Configuration, refreshing and program upgrading integrated system for SRAM (Static Random Access Memory) type FPGA (Field Programmable Gate Array)
ActiveCN104484214AIncrease flexibilityImprove versatilityProgram loading/initiatingProgrammable read-only memoryLogic gate
The invention discloses a configuration, refreshing and program upgrading integrated system for an SRAM (Static Random Access Memory) type FPGA (Field Programmable Gate Array), belongs to the technical field of aerospace and aims to solve the problem of SEU (Single Event Upset) of the SRAM type FPGA in a spatial irradiation environment. The configuration, refreshing and program upgrading integrated system has a capability of performing program upgrading on the SRAM type FPGA which is in on-orbit work for a long time. The configuration, refreshing and program upgrading integrated system comprises an on-site programmable logic gate array SRAM type FPGA, a comprehensive management anti-fuse FPGA, a configuration program storage chip PROM (Programmable Read-Only Memory), an on-orbit upgrading program storage chip EEPORM (Electrically-Erasable Programmable Read-Only Memory) and an RS422 interface chip. The configuration, refreshing and program upgrading integrated system disclosed by the invention can be used for effectively solving the problem of the SEU of the SRAM type FPGA which is in on-orbit work for a long time and correcting the SEU and single event accumulation inside the SRAM type FPGA without being shut down, also has the function of on-orbit program upgrading of the SRAM type FPGA, and has the characteristics of instantaneity, reliability, flexibility, universality and low cost.
Owner:HUAZHONG UNIV OF SCI & TECH
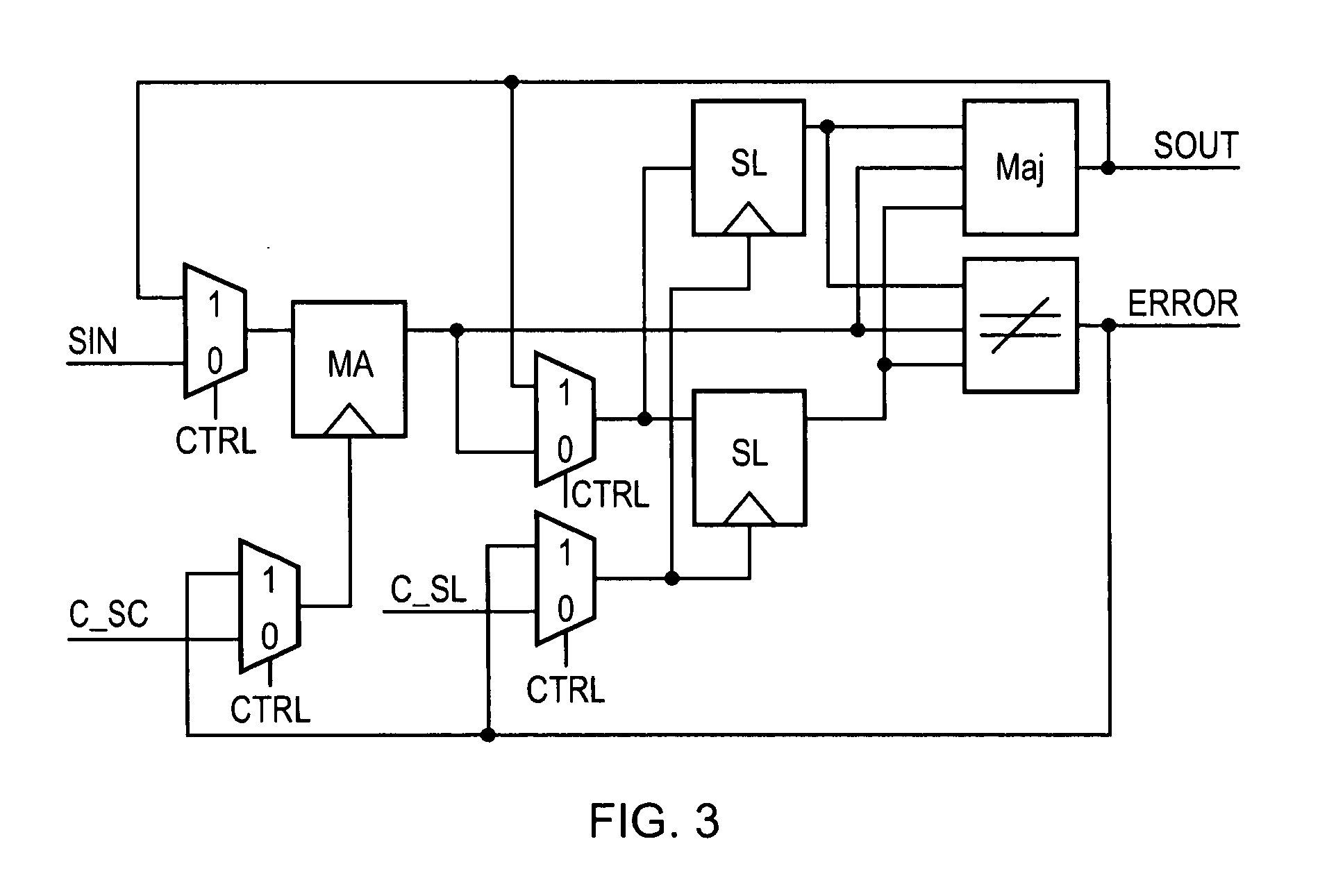
Self-resetting, self-correcting latches
ActiveUS20070028157A1Efficient designElectronic circuit testingRedundant data error correctionControl systemMultiplexer
A latch circuit having three latch stages generates a majority output value from the stages, senses when the latch stage outputs are not all equal, and feeds the majority output value back to inputs of the latch stages to reload the latch stages. The latch circuit uses a not-equal gate whose output is an error signal that can be monitored to determine when a single-event upset has occurred. A master stage is controlled by a first multiplexer which receives one system clock signal, while a slave stage is controlled by a second multiplexer which receives another system clock signal, and the latch stage outputs are connected to respective inputs of the not-equal gate, whose output is connected to second inputs of the multiplexers. The latch circuit is part of a latch control system, and reloading of the latch stages takes less than one cycle of the system clock (less than 500 picoseconds).
Owner:IBM CORP
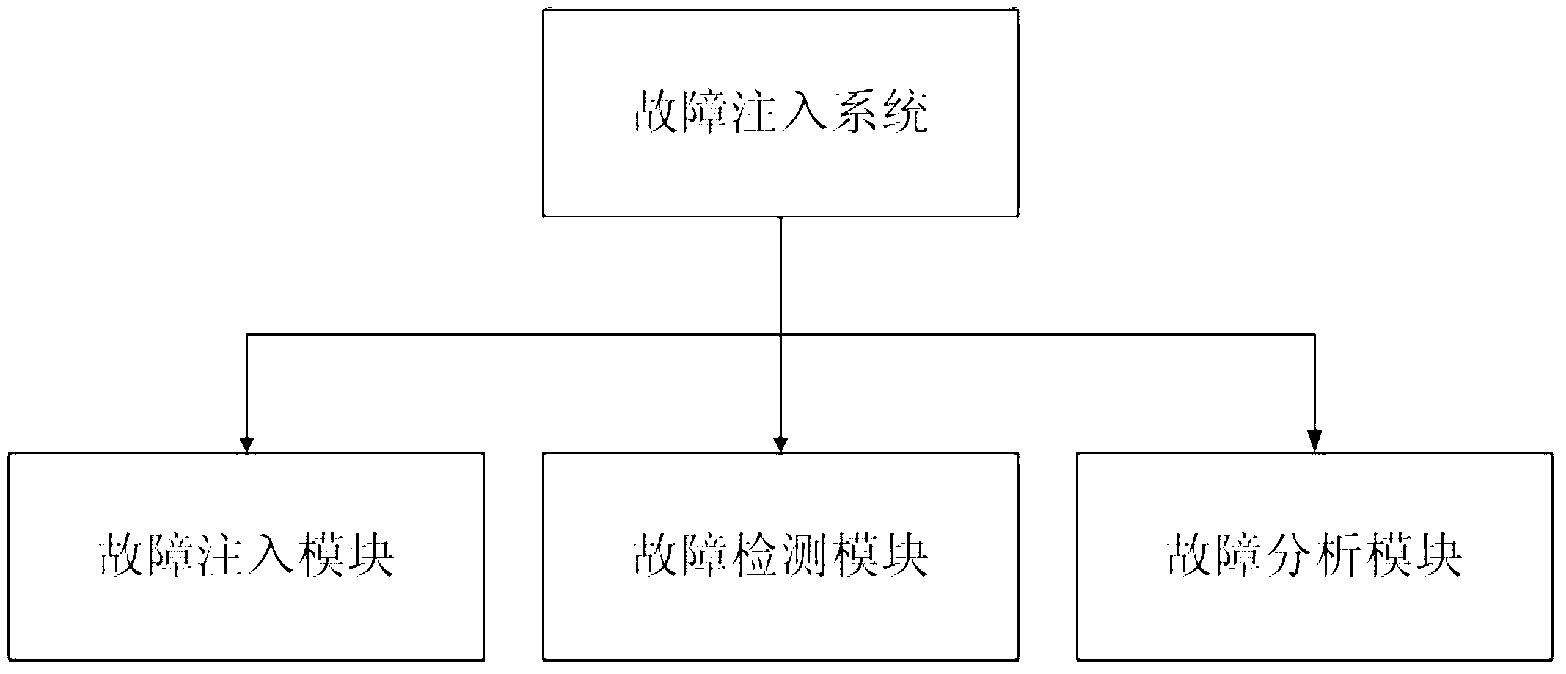
Fault simulation system and fault analysis method for single event upset
InactiveCN103198868ANo damageThrottling flow timeStatic storageSpecial data processing applicationsComputer moduleFault analysis
The invention relates to a fault simulation system and a fault analysis method for single event upset in a large scale integrated circuit SRAM-type FPGA (Field Programmable Gate Array). The fault simulation system comprises a host computer and a control board, wherein the control board comprises a fault injection module, a fault detecting module and a fault analyzing module. The fault simulation system and the fault analysis method provided by the invention are flexible to use, low in cost, high in simulation precision, fast in simulation speed and free from any physical damage to a chip.
Owner:NORTHWEST INST OF NUCLEAR TECH
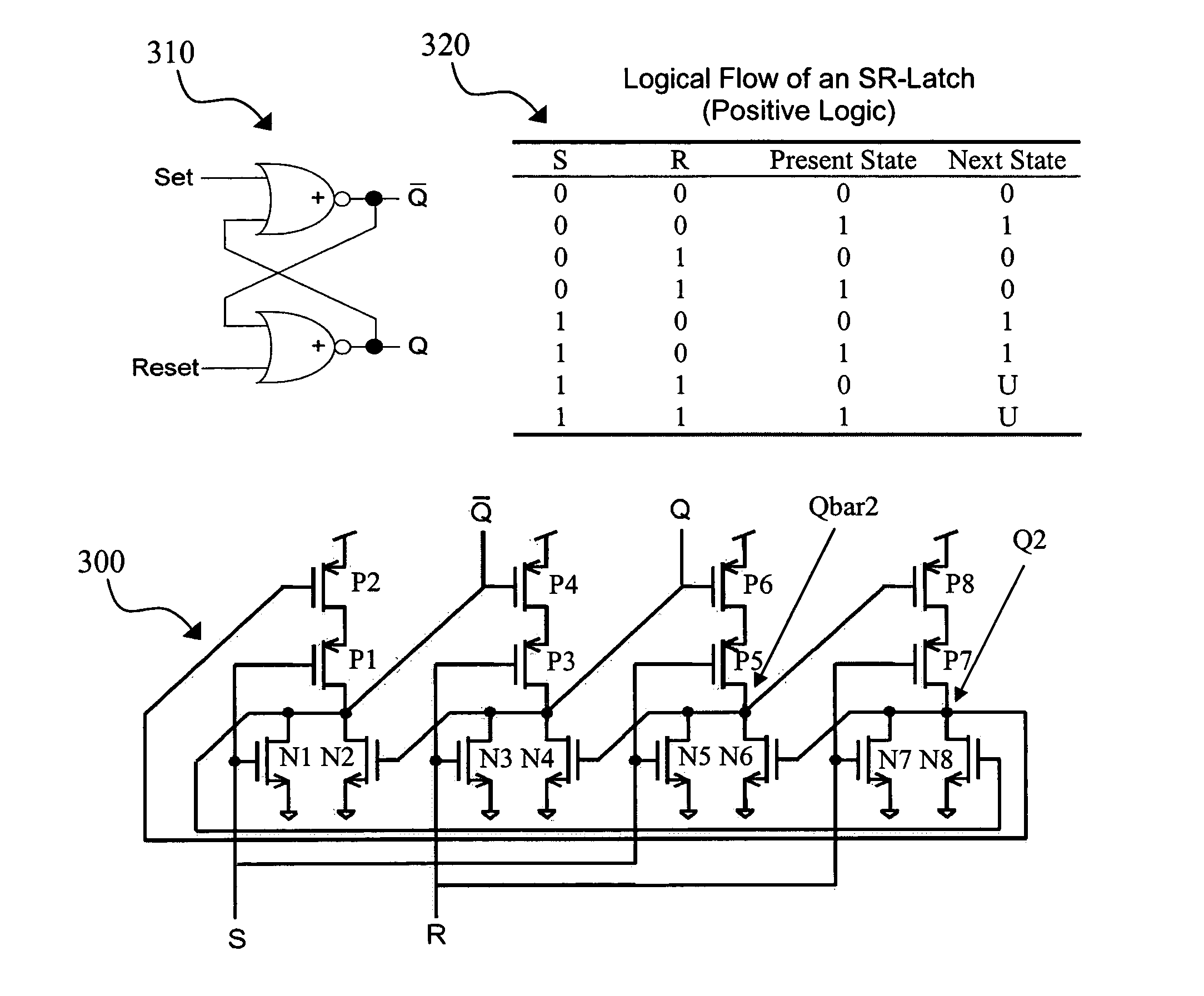
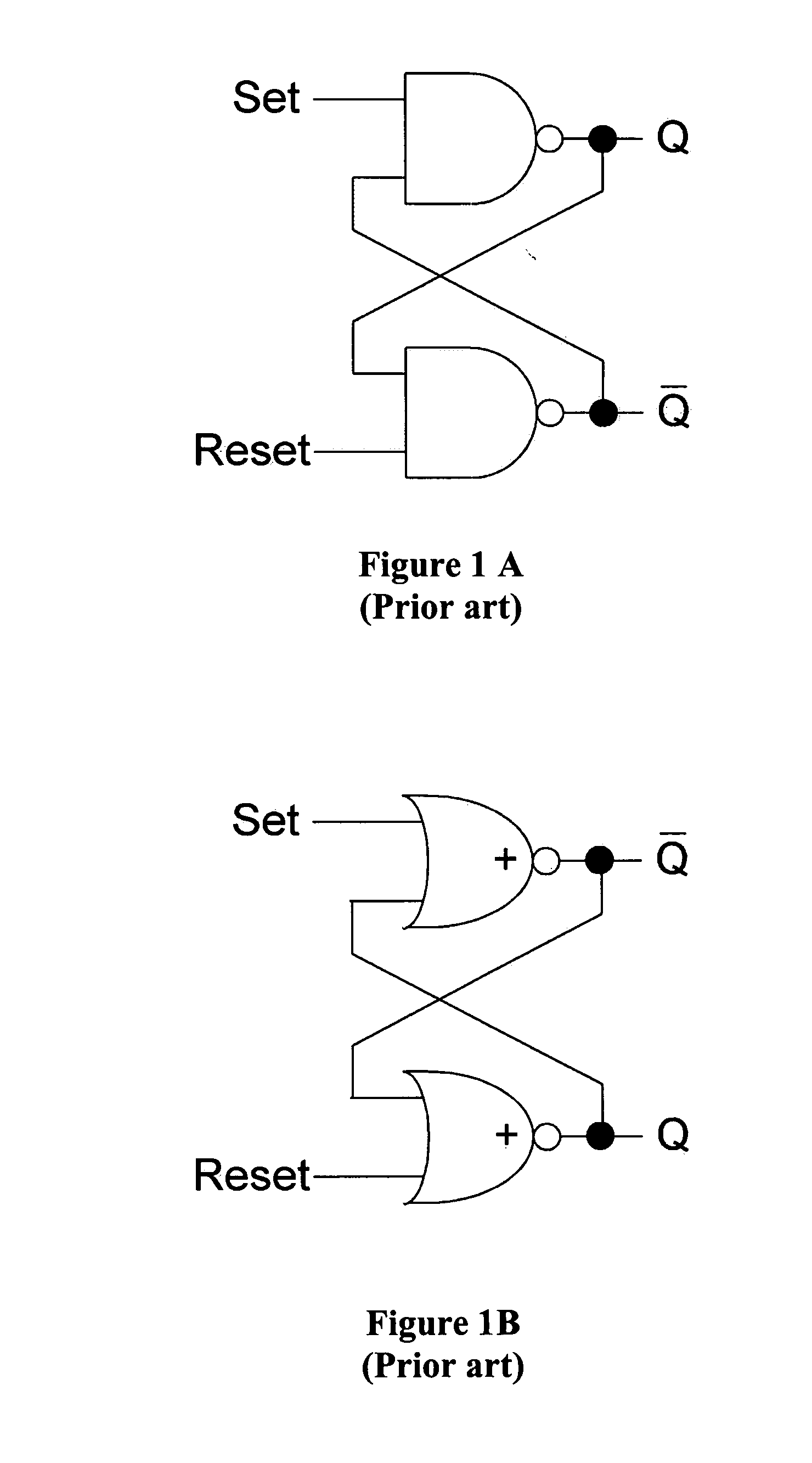
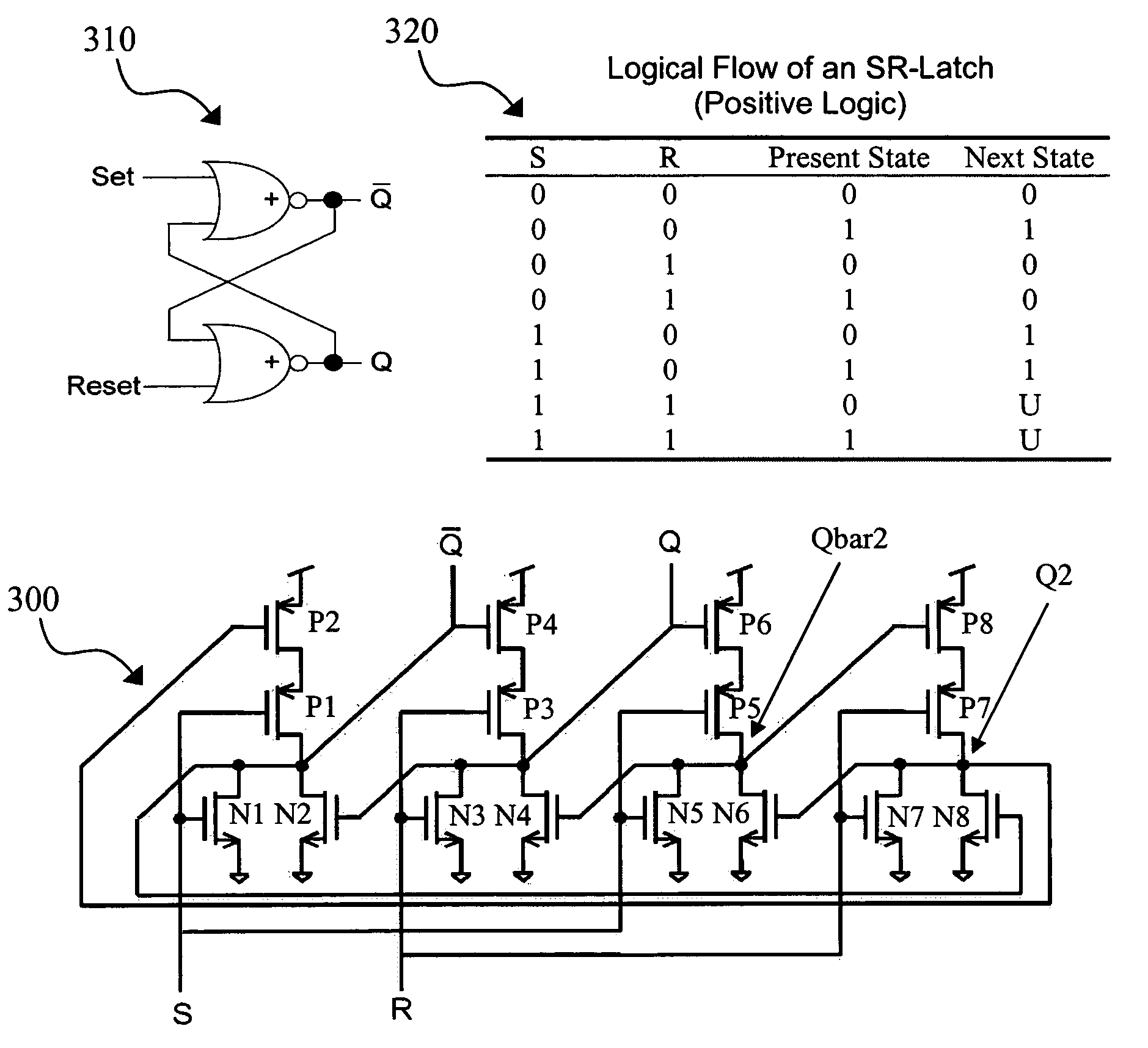
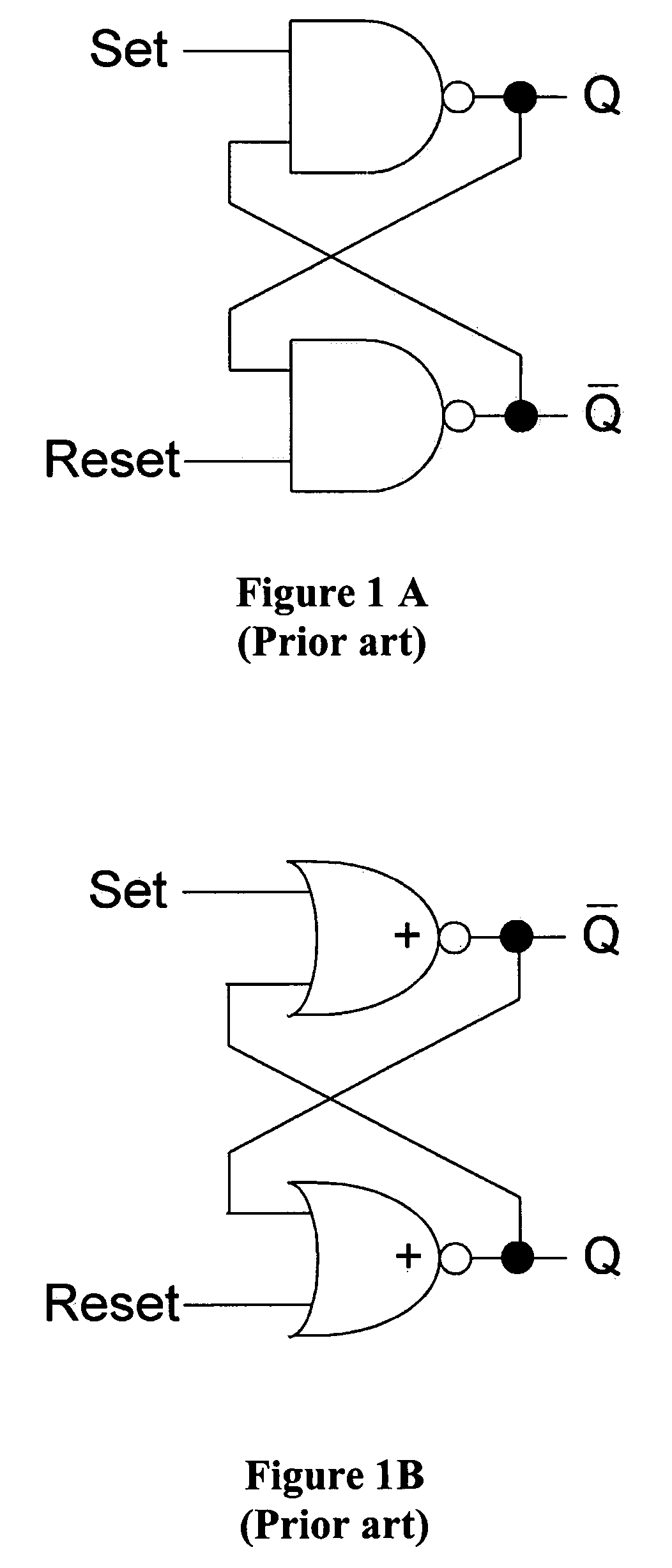
Redundant single event upset supression system
CMOS transistors are configured to operate as either a redundant, SEU-tolerant, positive-logic, cross-coupled Nor Gate SR-flip flop or a redundant, SEU-tolerant, negative-logic, cross-coupled Nand Gate SR-flip flop. The register can operate as a memory, and further as a memory that can overcome the effects of radiation. As an SR-flip flop, the invention can be altered into any known type of latch or flip-flop by the application of external logic, thereby extending radiation tolerance to devices previously incapable of radiation tolerance. Numerous registers can be logically connected and replicated thereby being electronically configured to operate as a redundant circuit.
Owner:FERMI RESEARCH ALLIANCE LLC
Real-time adaptive SRAM array for high SEU immunity
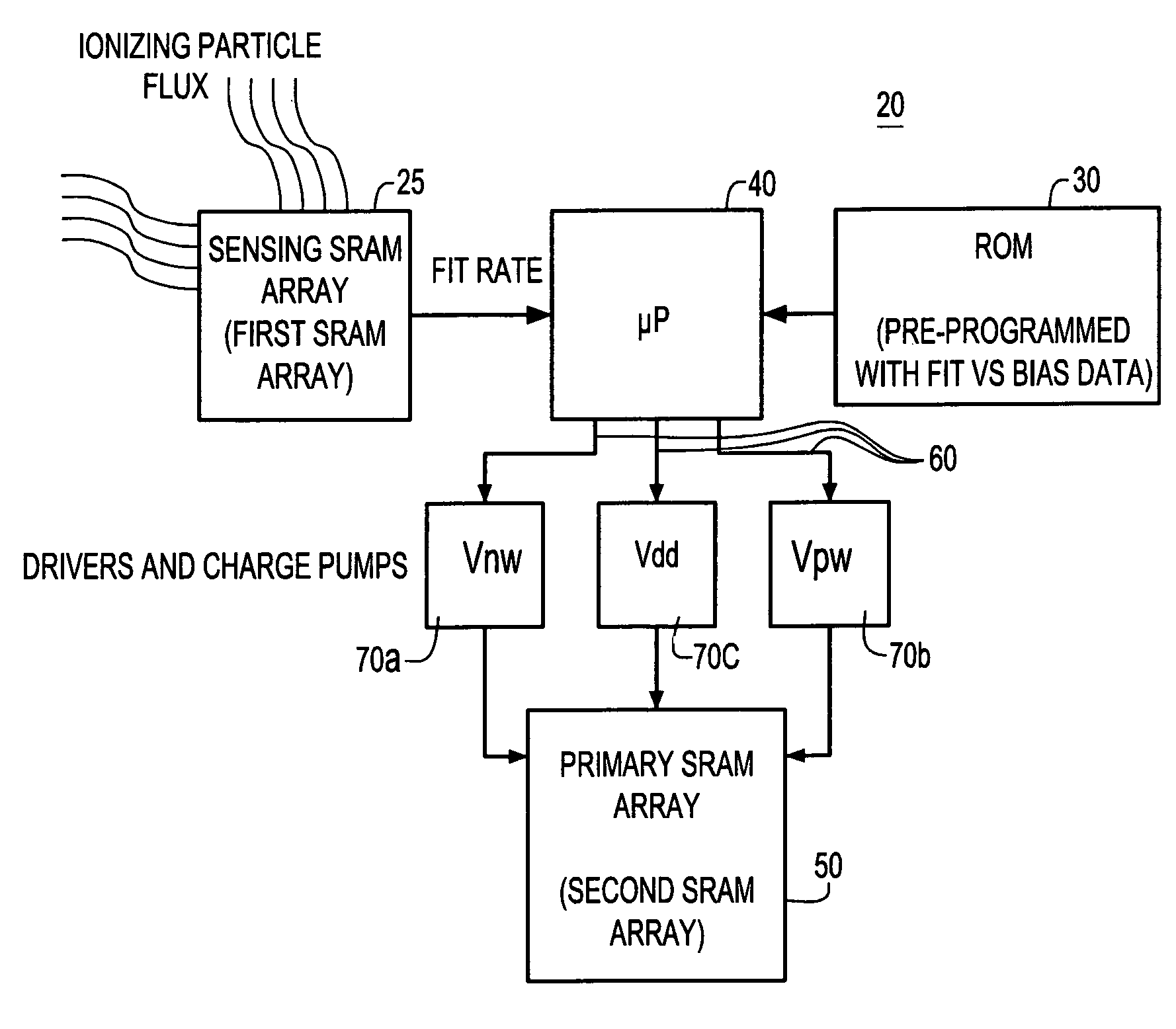
InactiveUS7283410B2Performance maximizationRead-only memoriesDigital storageElectricityOperating point
A system and method for automatically adjusting one or more electrical parameters in a memory device, e.g., SRAM arrays. The system and method implements an SRAM sensing sub-array for accelerated collection of fail rate data for use in determining the operating point for optimum tradeoff between single event upset immunity and performance of a primary SRAM array. The accelerated fail rate data is input to an algorithm implemented for setting the SEU sensitivity of a primary SRAM memory array to a predetermined fail rate in an ionizing particle environment. The predetermined fail rate is maintained on a real-time basis in order to provide immunity to SEU consistent with optimum performance.
Owner:GOOGLE LLC
Redundant single event upset supression system
CMOS transistors are configured to operate as either a redundant, SEU-tolerant, positive-logic, cross-coupled Nor Gate SR-flip flop or a redundant, SEU-tolerant, negative-logic, cross-coupled Nand Gate SR-flip flop. The register can operate as a memory, and further as a memory that can overcome the effects of radiation. As an SR-flip flop, the invention can be altered into any known type of latch or flip-flop by the application of external logic, thereby extending radiation tolerance to devices previously incapable of radiation tolerance. Numerous registers can be logically connected and replicated thereby being electronically configured to operate as a redundant circuit.
Owner:FERMI RESEARCH ALLIANCE LLC
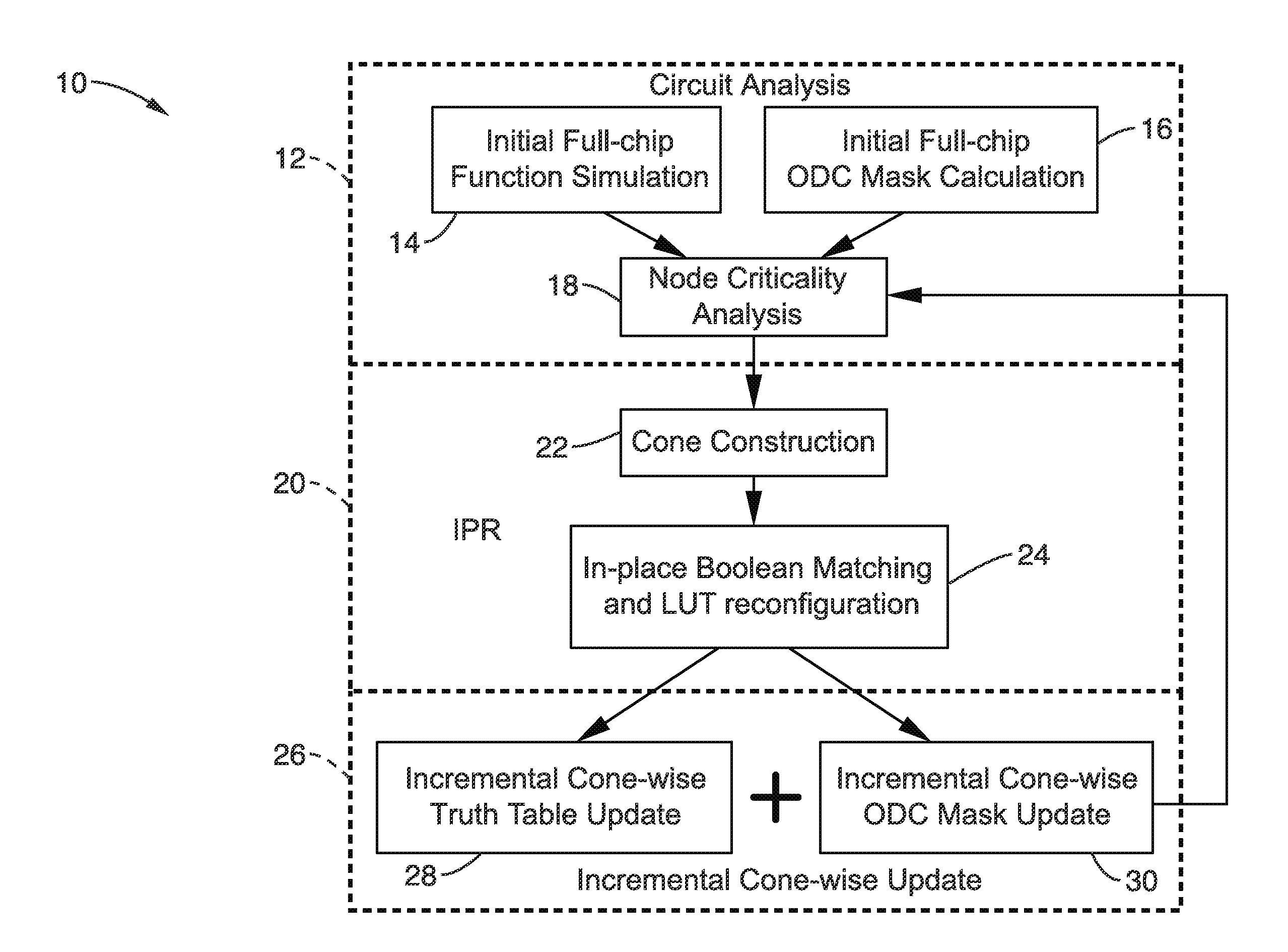
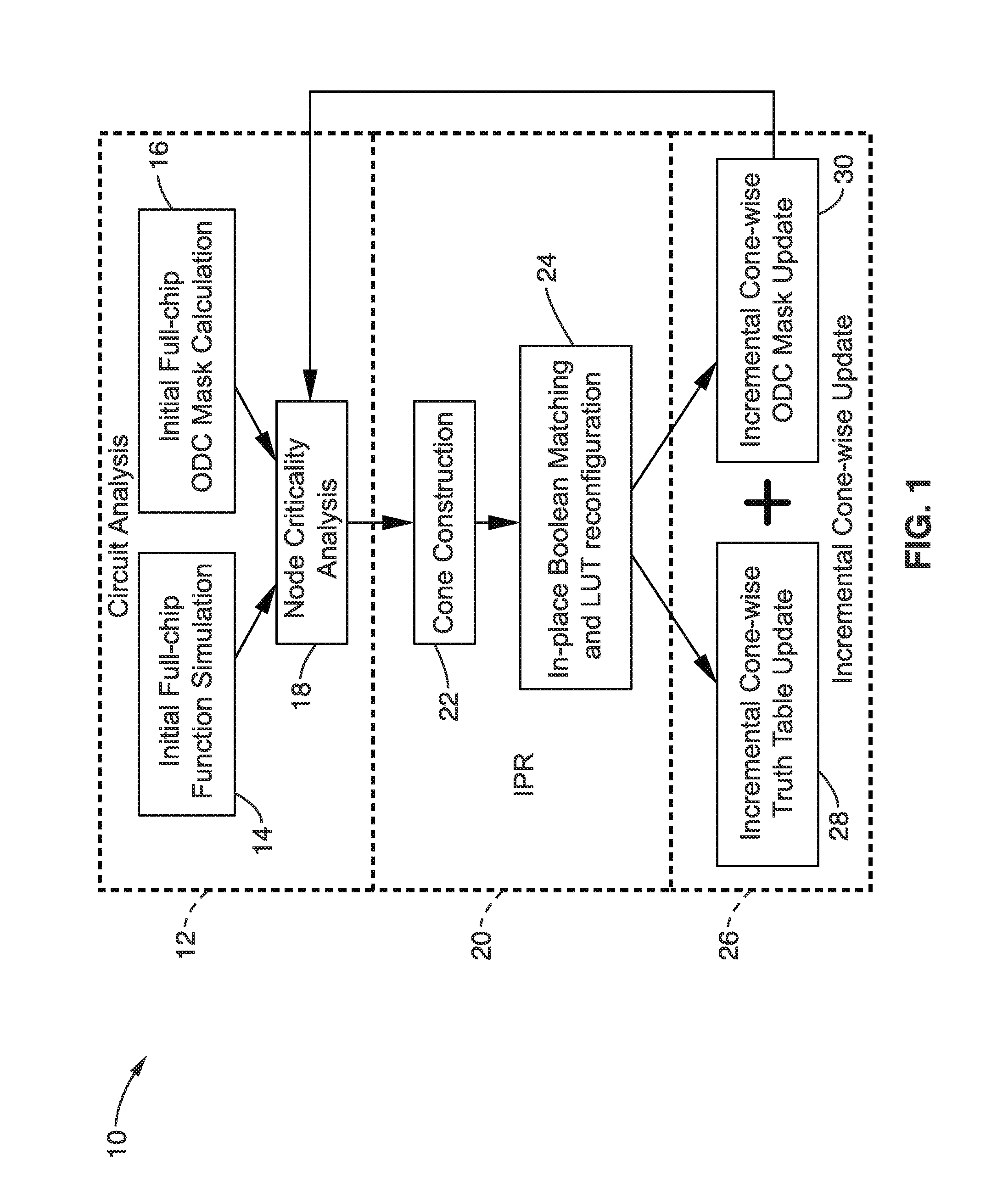
In-place resynthesis and remapping techniques for soft error mitigation in FPGA
InactiveUS20130305199A1Efficient and accurateImprove fault toleranceCAD circuit designRadiation hardeningFpga architectureDecomposition
In-place resynthesis for static memory (SRAM) based Field Programmable Gate Arrays (FPGAs) toward reducing sensitivity to single event upsets (SEUs). Resynthesis and remapping are described which have a low overheard and improve FPGA designs without the need of rerouting LUTs of the FPGA. These methods include in-place reconfiguration (IPR), in-place X-filling (IPF), and in-place inversion (IPV), which reconfigure LUT functions only, and can be applied to any FPGA architecture. In addition, for FPGAs with a decomposable LUT architecture (e.g., dual-output LUTs) an in-place decomposition (IPD) method is described for remapping a LUT function into multiple smaller functions leveraging the unused outputs of the LUT, and making use of built-in hard macros in programmable-logic blocks (PLBs) such as carry chain or adder. Methods are applied in-place to mapped circuits before or after routing without affecting placement, routing, and design closure.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA
Apparatus and method of error detection and correction in a radiation-hardened static random access memory field-programmable gate array
InactiveUS6838899B2Reliability increasing modificationsSolid-state devicesProgrammable logic deviceComputer module
The present system comprises a radiation tolerant programmable logic device having logic modules and routing resources coupling together the logic modules. Configuration data lines providing configuration data control the programming of the logic modules and the routing resources. Error correction circuitry coupled to the configuration data lines analyzes and corrects any errors in the configuration data that may occur due to a single event upset (SEU).The present system also comprises a method for correcting errors in a programmable logic device having configuration data to program the programmable logic device. The method comprises a background reading of the configuration data. Next, the configuration data is analyzed for errors. Finally, the configuration data is then corrected and the configuration data is rewritten if errors are located.
Owner:MICROSEMI SOC
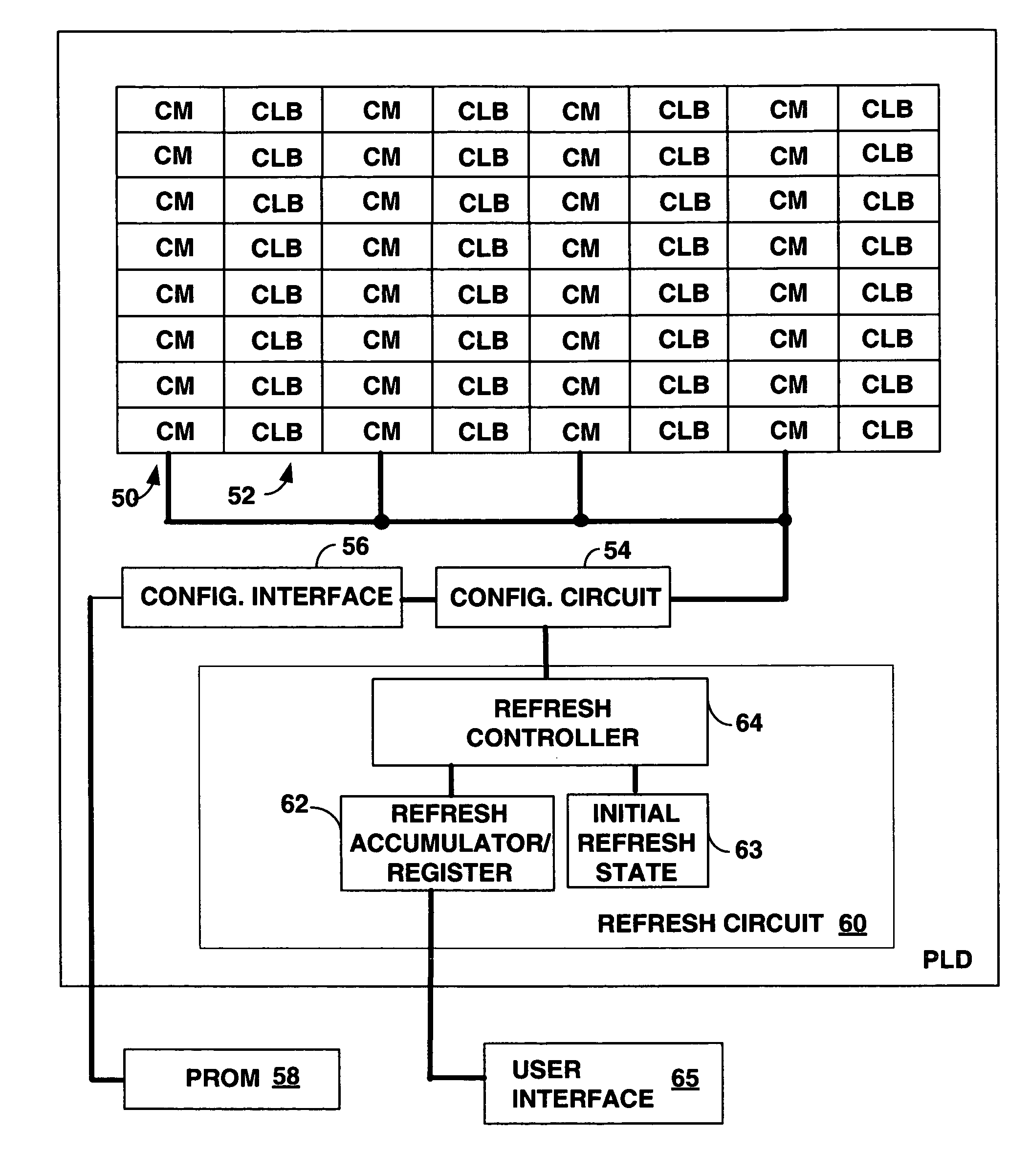
Programmable logic device (PLD) with memory refresh based on single event upset (SEU) occurrence to maintain soft error immunity
ActiveUS7764081B1Reduce memory cell densityMinimized circuitReliability increasing modificationsFail-safe circuitsProgrammable logic deviceSingle event upset
A Programmable Logic Device (PLD) is provided with configuration memory cells displaying a superior soft error immunity by combating single event upsets (SEUs) as the configuration memory cells are regularly refreshed from non-volatile storage depending on the rate SEUs may occur. Circuitry on the PLD uses a programmable timer to set a refresh rate for the configuration memory cells. Because an SEU which erases the state of a small sized memory cell due to collisions with cosmic particles may take some time to cause a functional failure, periodic refreshing will prevent the functional failure. The configuration cells can be DRAM cells which occupy significantly less space than the SRAM cells. Refresh circuitry typically provided for DRAM cells is reduced by using the programming circuitry of the PLD. Data in the configuration cells of the PLD are reloaded from either external or internal soft-error immune non-volatile memory.
Owner:XILINX INC
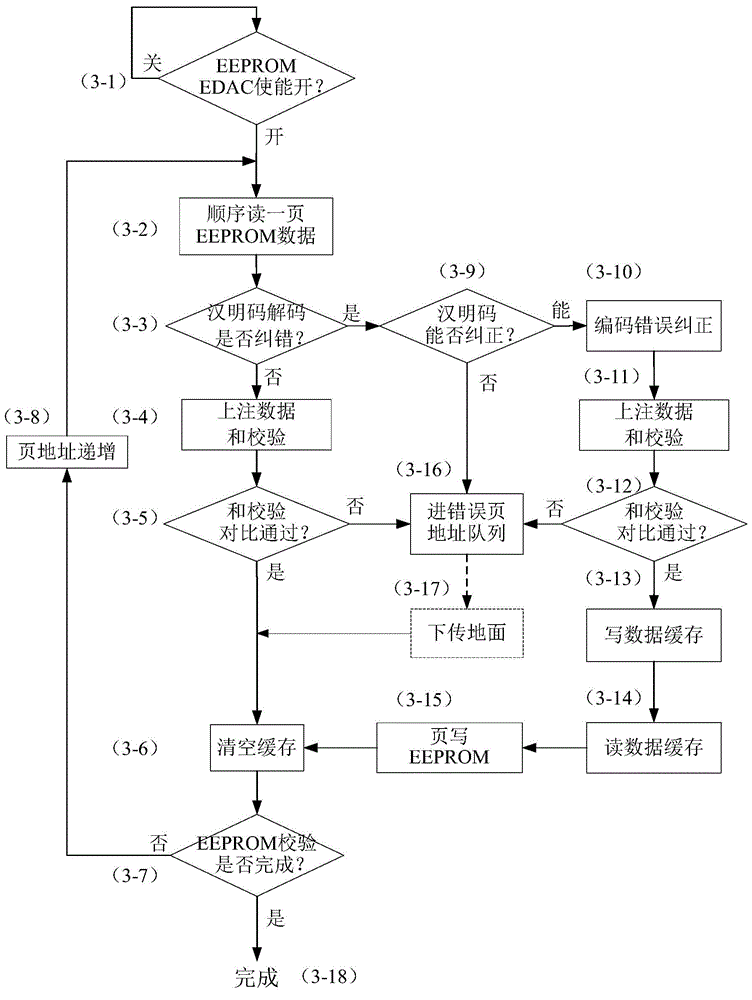
Method for error correcting and detecting for memory anti-single particle overturn
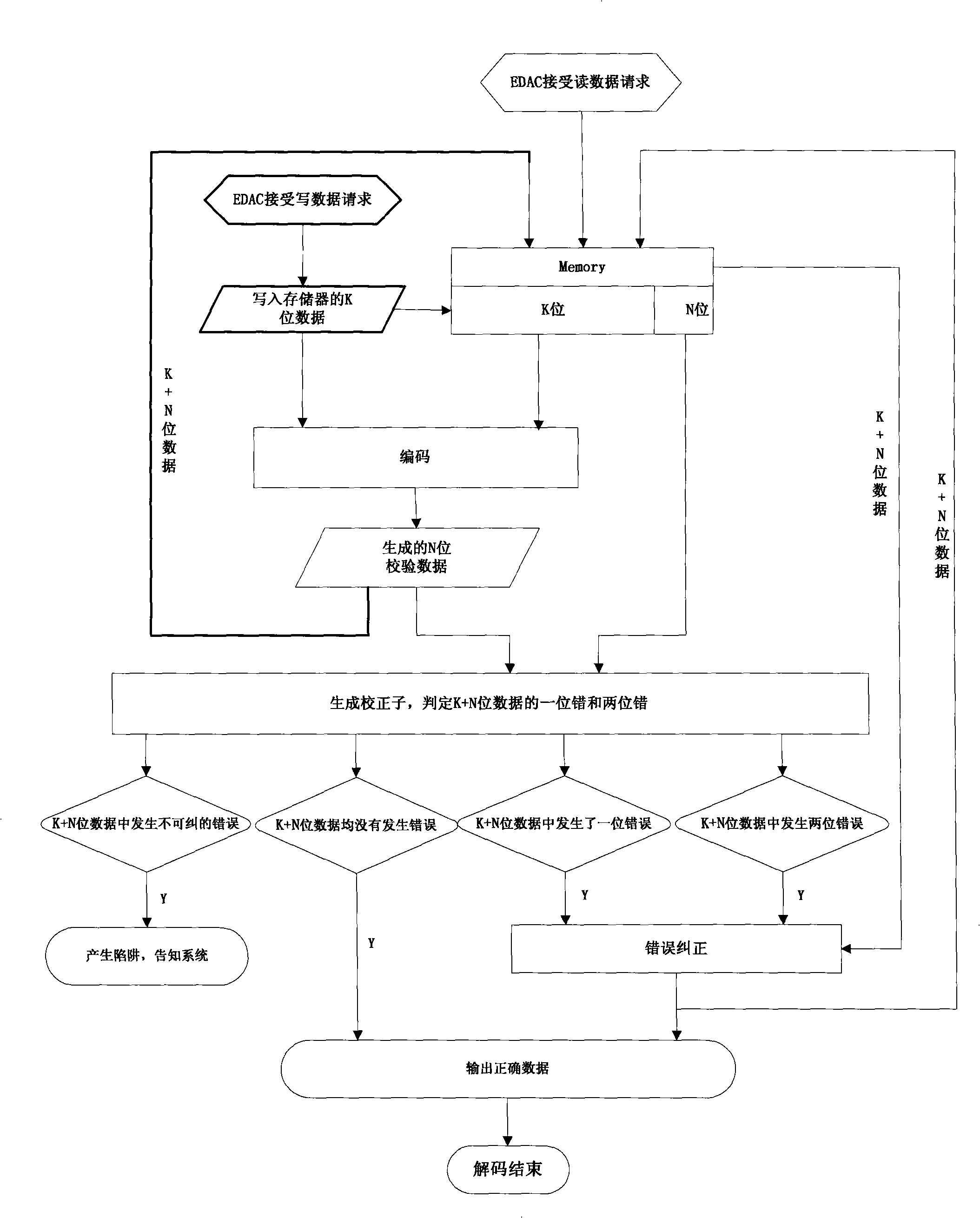
InactiveCN101281481ACorrect oneCorrect two digit data errorsRedundant data error correctionError checkingData error
The invention provides an anti-single-event-upset error checking and correction method for memory, which comprises: (1) receiving K-bit information data from CPU; (2) generating N-bit check data A corresponding to the K-bit information data; (3) storing the K-bit information data and the N-bit check data A to a memory; (4) reading the K-bit information data from the memory and regenerating a N-bit check data B corresponding to the K-bit information data; (5) performing XOR operation on the check data A and the check data B to obtain a corrector; and (6) locating error in the information data and the check data A by the corrector. If one or two bits of data error occurs, the data error is corrected and correct data is outputted; if two bits or testable more than three bits of data error occurs, the information that non-correctable error occurs is prompted. The method has strong error correction ability, simple operation, and one-bit or two-bit error of memory caused by single event effect is effectively corrected.
Owner:BEIJING MXTRONICS CORP +1
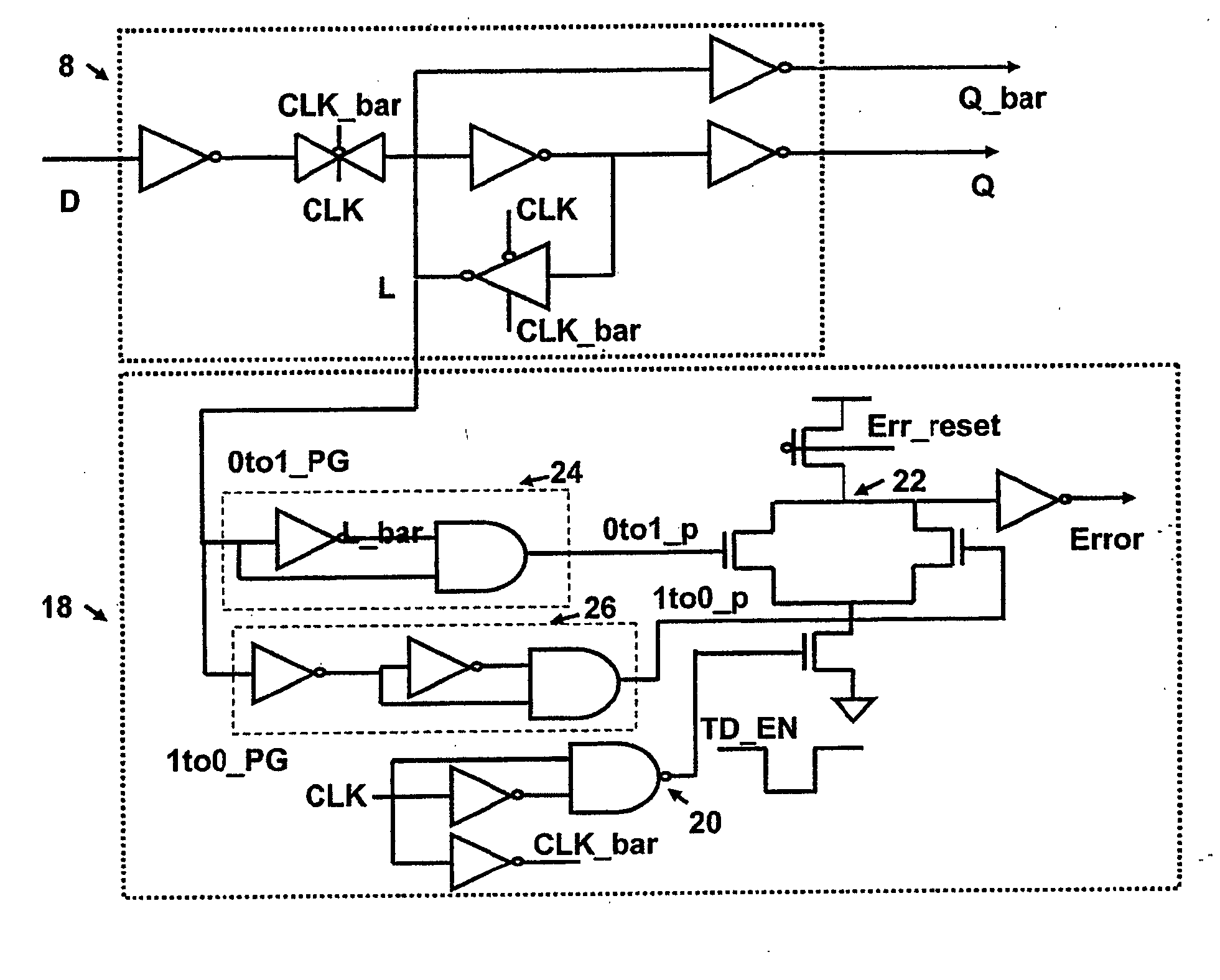
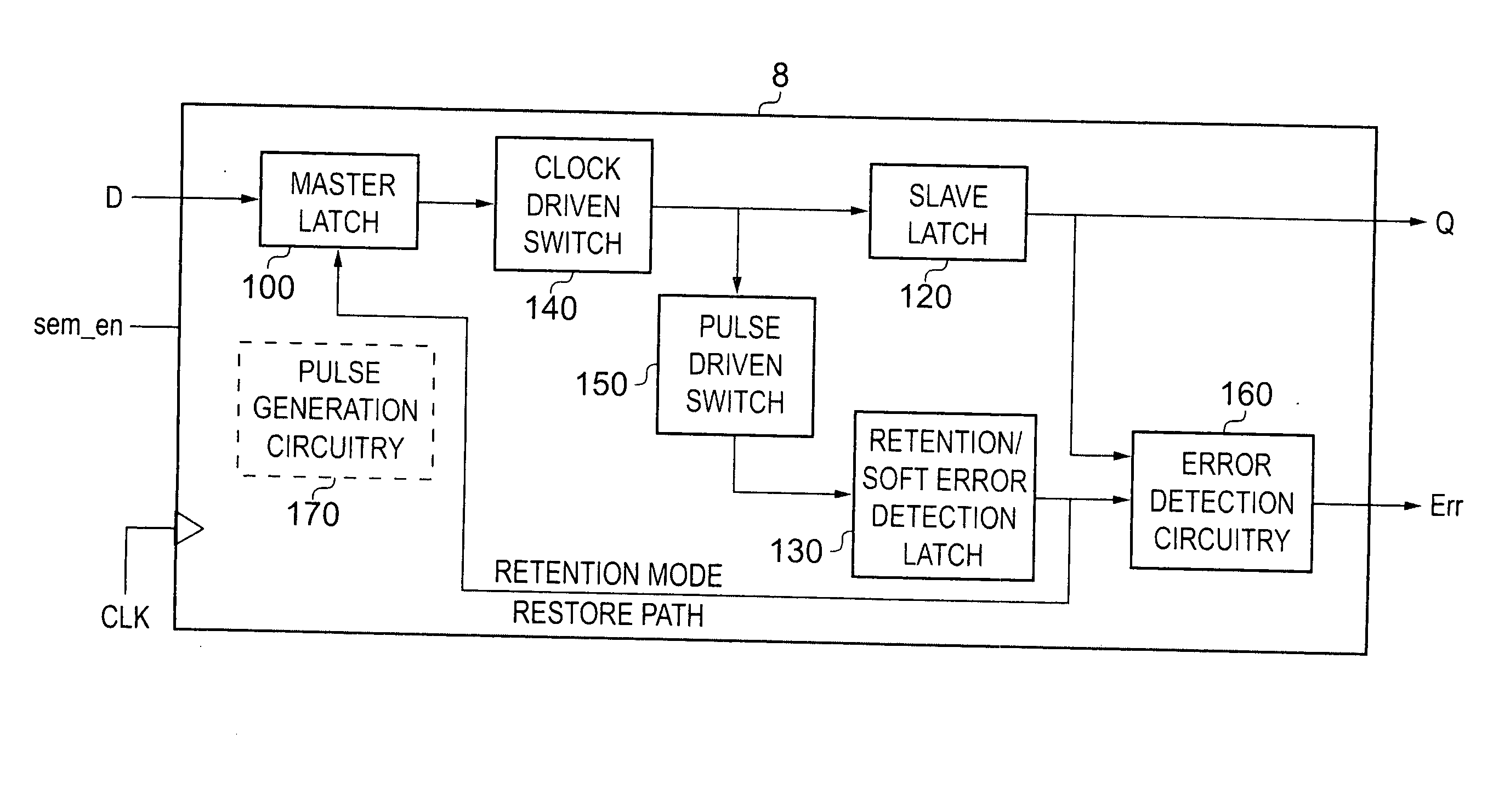
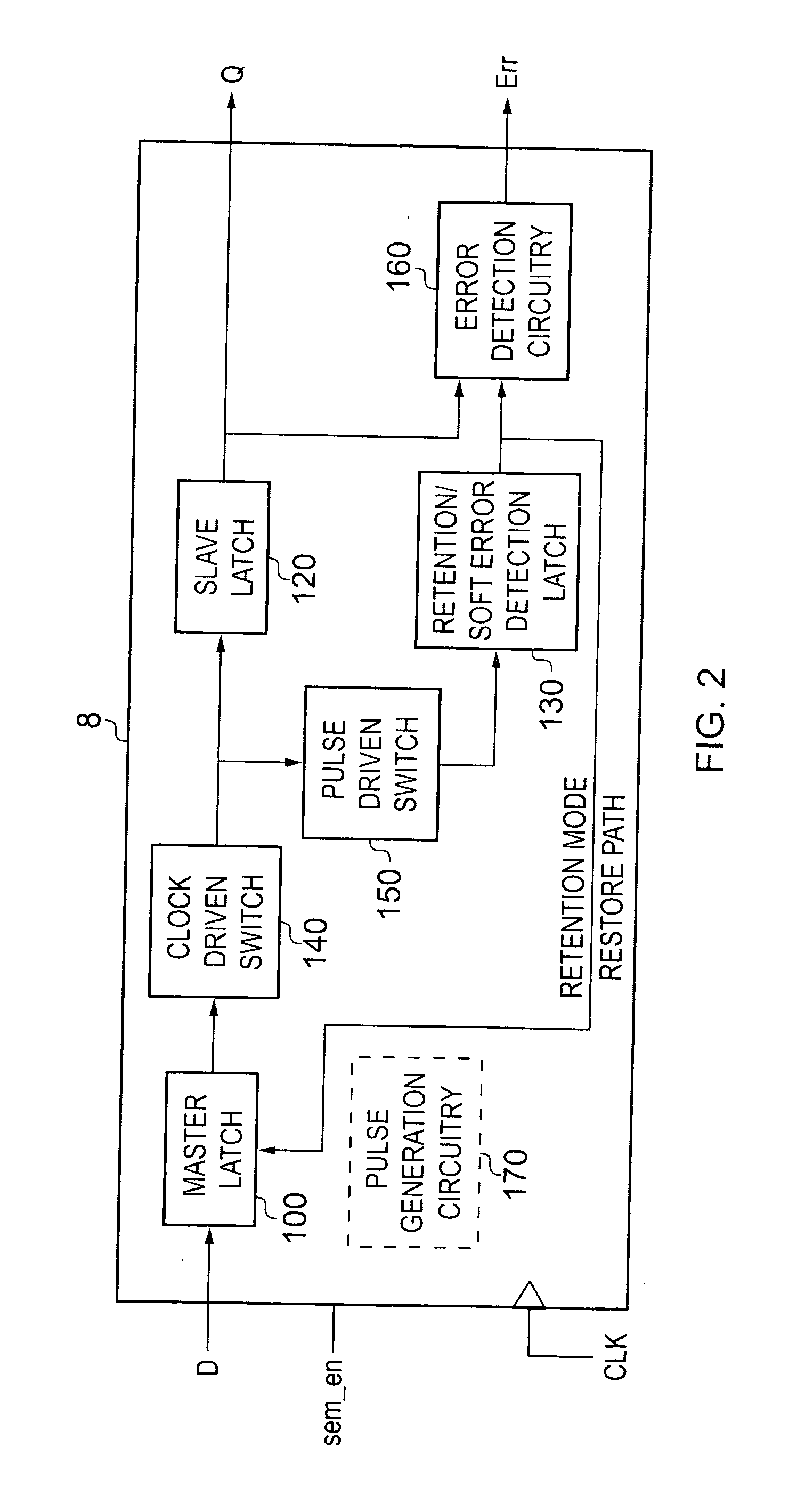
Correction of single event upset error within sequential storage circuitry of an integrated circuit
ActiveUS20100088565A1False errorRapid responseError preventionTransmission systemsSingle event upsetData value
Sequential storage circuitry for an integrated circuit is disclosed that comprises storage circuitry comprising: a first storage element for storing, during a first phase of a clock signal, a first indication of an input data value received by said sequential storage circuitry; a second storage element coupled to an output of said first storage element, for storing a second indication of said input data value during a second phase of said clock signal; and error detection circuitry for detecting a single event upset error in any of said first and second storage elements comprising: two additional storage elements for storing third and fourth indications of said input data value respectively in response to a pulse signal derived from said clock signal; comparison circuitry for comparing said third and fourth indications of said input data value; and further comparison circuitry for comparing during a first phase of said clock signal said first indication and at least one of said third and fourth indications, and for comparing during a second phase of said clock signal said second indication and at least one of said third and fourth indications; and output circuitry for correcting any detected errors in said storage circuitry and for outputting an output value; said output circuitry being responsive to no match by said comparison circuitry to output said first indication during a first phase of said clock signal and said second indication during said second phase of said clock signal, and said output circuitry being responsive to a match by said comparison circuitry to output a value in dependence upon comparisons performed by said further comparison circuitry; said output circuitry being responsive to a match by said further comparison circuitry during a first phase of said clock signal to output said first indication during said first clock cycle and to a no match to output an inverted value of said first indication; and said output circuitry being responsive to a match by said further comparison circuitry during a second phase of said clock signal to output said second indication during said second phase of said clock signal and to a no match to output an inverted value of said second indication.
Owner:ARM LTD
Single event upset error detection within an integrated circuit
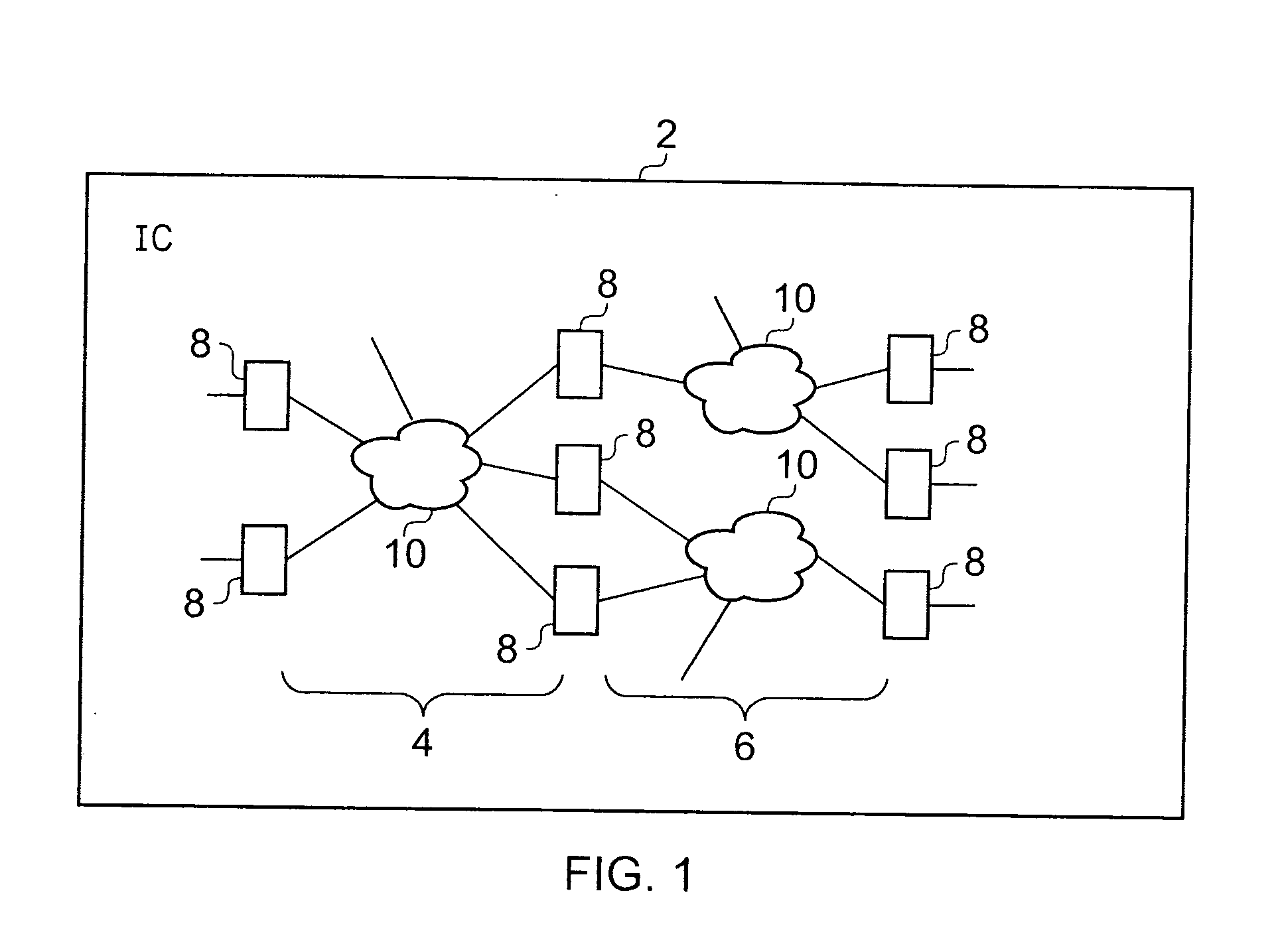
ActiveUS20070162798A1Increase probabilityShort time windowRecording carrier detailsElectronic circuit testingSingle event upsetLogic circuitry
An integrated circuit 2 includes logic circuitry 10 and sequential storage elements 8 . Both the logic circuit 10 and sequential storage elements 8 can be subject to particle strikes giving rise to single event upset errors. These single event upset errors can be detected by detecting a transition in the stored value stored by the sequential storage elements 8 occurring outside of a valid transition period associated with that sequential storage element 8.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF MICHIGAN +1
Multilevel fault tolerance reinforcement satellite information processing system based on SRAM FPGA
ActiveCN105045672AImprove performanceAchieve protectionFault responseArtificial satellitesInformation processingFault tolerance
The invention provides a multilevel fault tolerance reinforcement satellite information processing system based on an SRAM (Static Random Access Memory) FPGA (Field Programmable Gate Array), and relates to satellite information processing. The invention aims at solving the problems that when the SRAM FPGA is used as a satellite information processing system, the system reliability is influenced by single event upset and latch-up effects and the like, and a satellite practical task is not combined with a protection measure. The system is realized through the following modules including a memory module, a checking and control module, a memory configuration module, a state storage Flash module, an IO / BUS module, an anti-latch power supply module and a main processing module, wherein the memory module is used for data storage and program loading of a main processing module; the checking and control module is used for single event upset effect immunization; the memory configuration module is used for storing initial configuration files and remote updating configuration files; the state storage Flash module is used for realizing the data access state; the IO / BUS module is used for realizing communication and control; the anti-latch power supply module is used for system single event latch-up effect protection and power supplying to each module; and the main processing module is used for data processing and satellite event management. The multilevel fault tolerance reinforcement satellite information processing system based on the SRAM FPGA is applied to the technical field of satellites.
Owner:HARBIN INST OF TECH
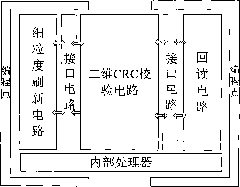
Circuit and method for resisting SEU of SRAM FPGA device
ActiveCN101826038AImprove mean time between failuresLong trouble-free timeRedundant data error correctionMachine controlFpga chip
The invention belongs to the technical field of field programmable gate array (FPGA), and particularly relates to a circuit and a method having the function of resisting the single event upset (SEU) effect for an SRAM FPGA device. The SEU-resisting circuit comprises a read-back circuit, a fine-grained refresh circuit and a two-dimensional CRC calibration circuit. A bus state machine controls the read-back circuit to read information stored in a programming point in a read-back register in the read-back circuit, and then, the two-dimensional CRC calibration circuit calibrates the information and writes the address of the programming point generating the SEU effect in an SEU register; and an internal processor generates a fine-grained refreshing bit stream via the fine-grained refresh circuit based on the output of the SEU register, and the refreshing bit stream is written in an internal programming point of the FPGA chip via a self-configuration interface. The programming point generating the SEU error in the FPGA is refreshed again, thereby realizing the SEU-resistant function. Meanwhile, the invention also reduces the time and power consumption for reconstructing the FPGA after the SEU generation.
Owner:FUDAN UNIV
Single event upset-resistant satellite-borne data processing system and method
ActiveCN106557346AReduce areaLow costProgram loading/initiatingRedundant data error correctionData processing systemData treatment
Owner:NAT SPACE SCI CENT CAS
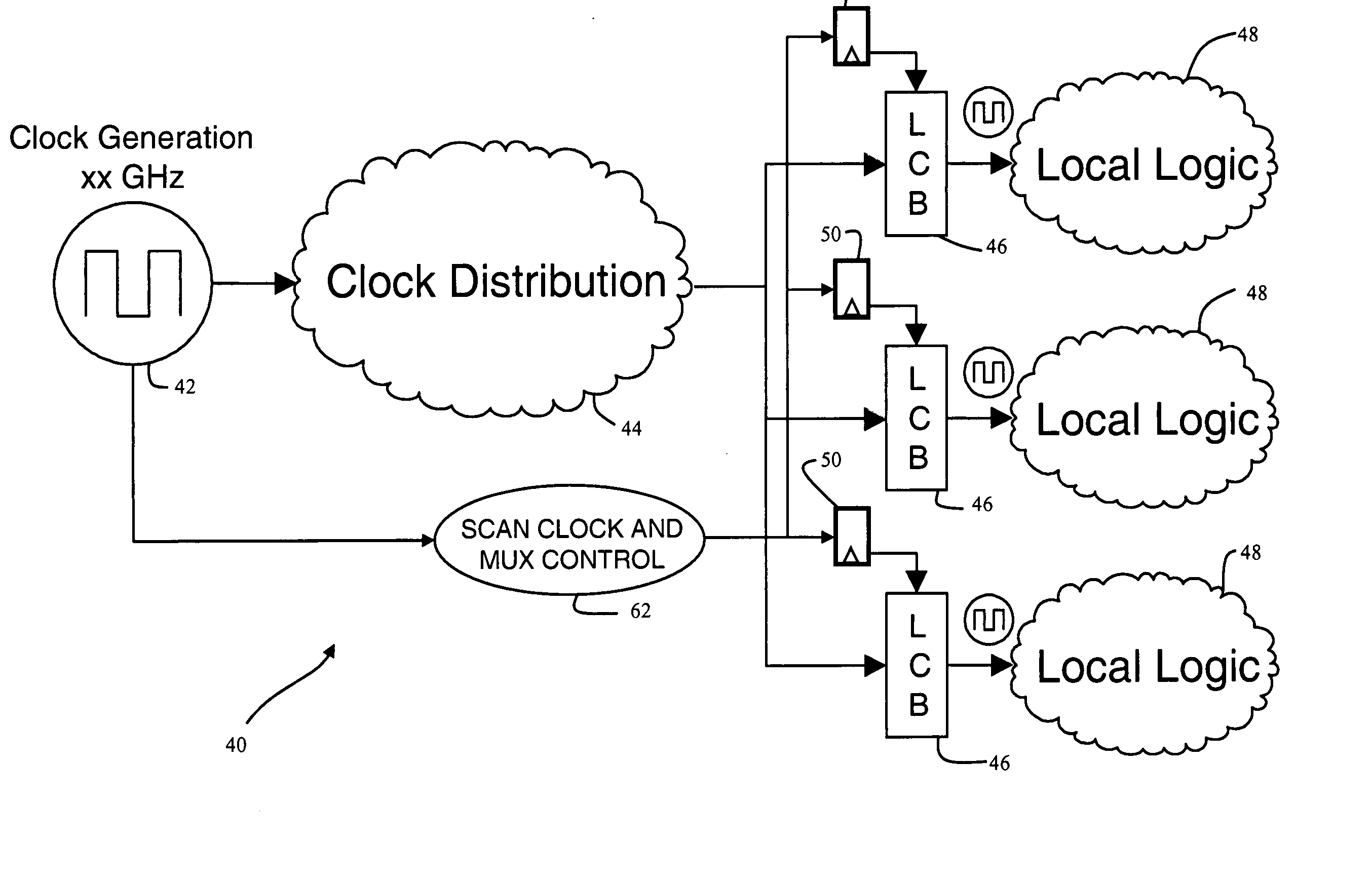
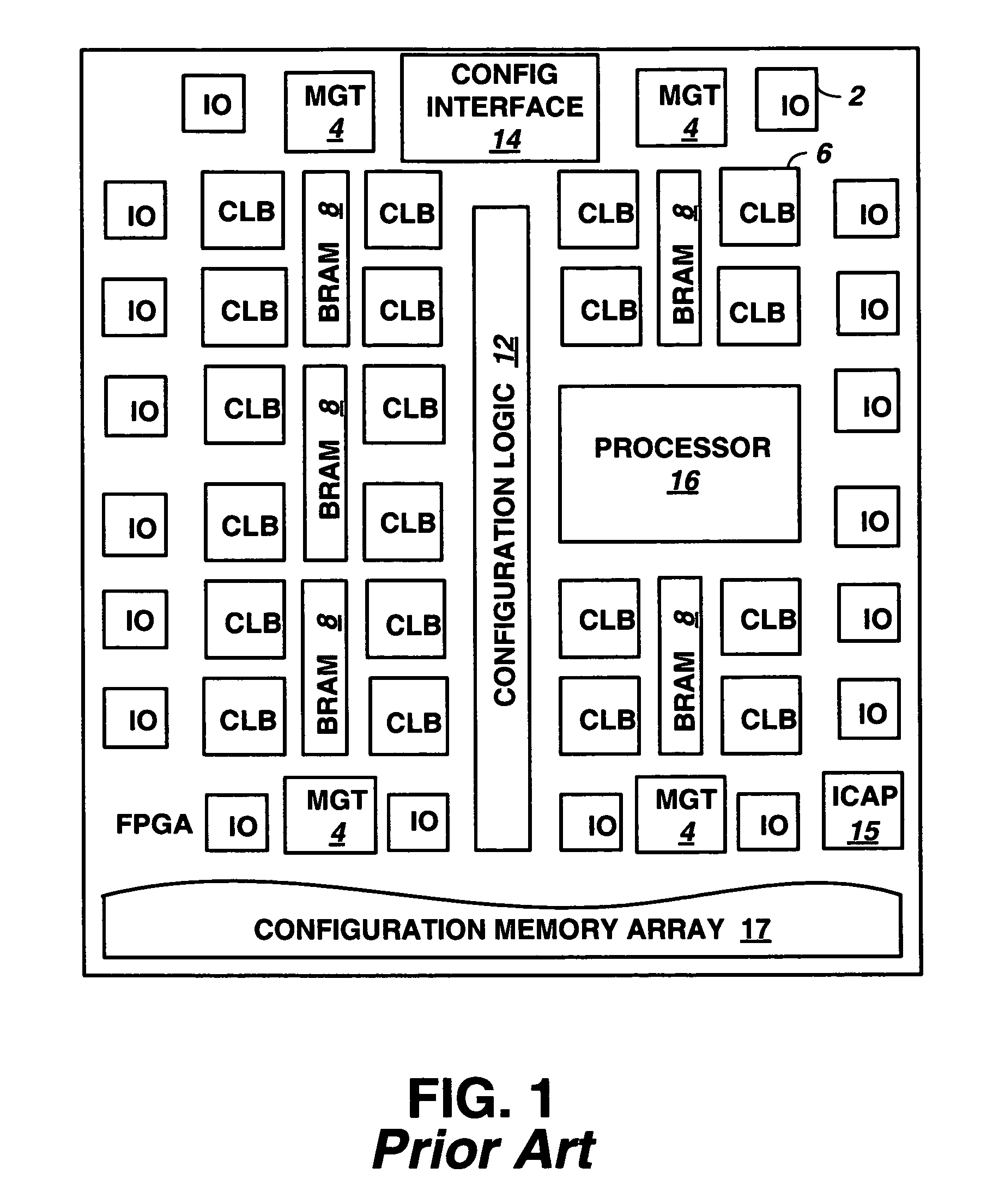
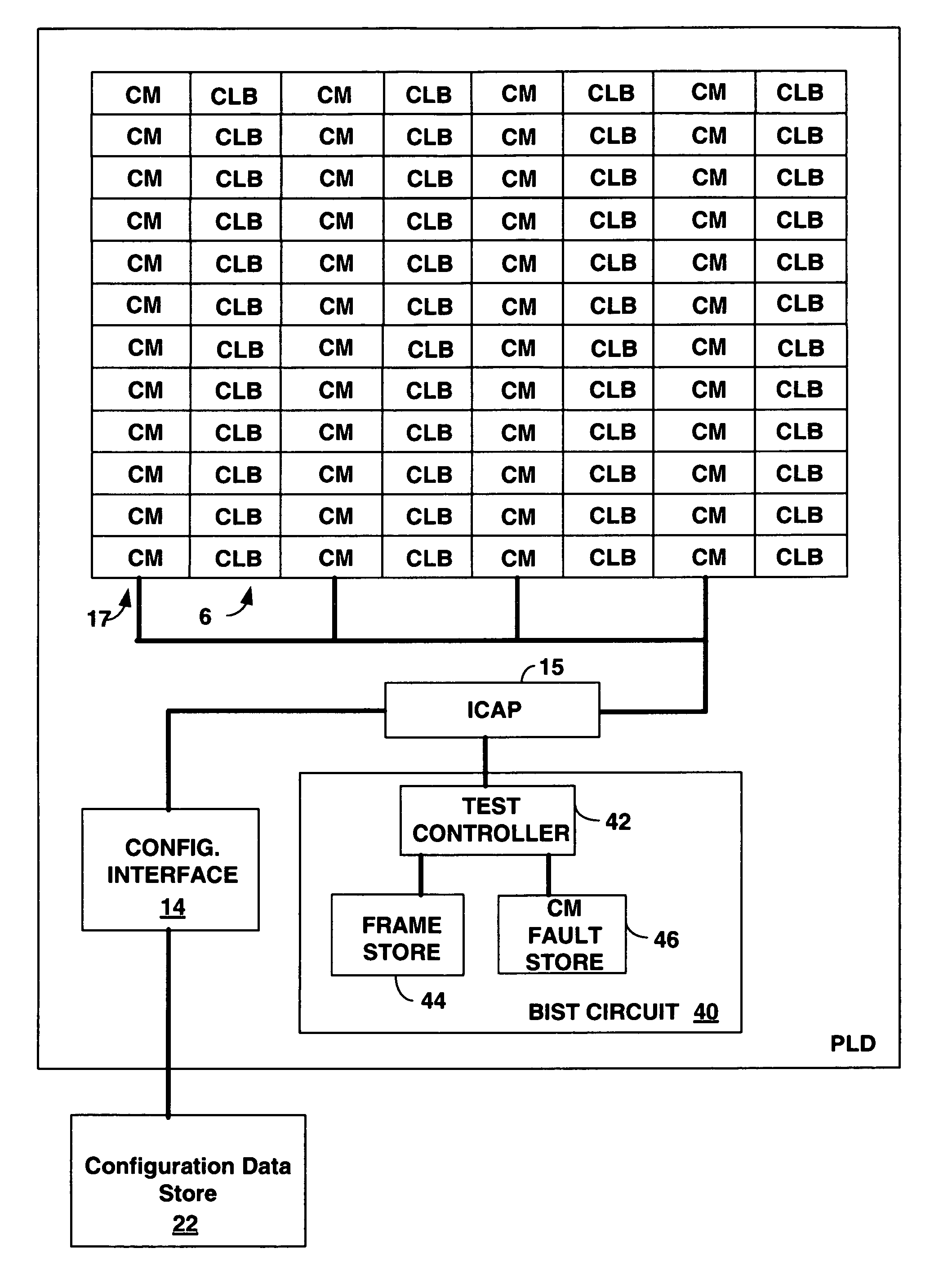
Total configuration memory cell validation built in self test (BIST) circuit
ActiveUS7409610B1Minimal circuitryElectronic circuit testingDigital storageElectricityProgrammable logic device
A built in self test (BIST) circuit is provided for a programmable logic device (PLD) constructed from fixed or hard core logic that includes circuitry to write recurring patterns of bits in the configuration memory in a frame by frame manner and read the cell state to enable the validation of every configuration bit at power up. The BIST circuitry can further be used to program the recurring patterns into the configuration memory, and then read frames of the configuration memory to detect the occurrence of single event upsets (SEU) that corrupt data in the configuration memory. The recurring patterns programmed do not require time consuming functional configuration of the PLD, and can be done in a production environment after power up without knowledge of how the PLD will later be configured. No soft logic is needed to form the BIST circuit, enabling 100% test coverage of the programmable configuration memory cells.
Owner:XILINX INC
SRAM type FPGA single event upset effect simulation method
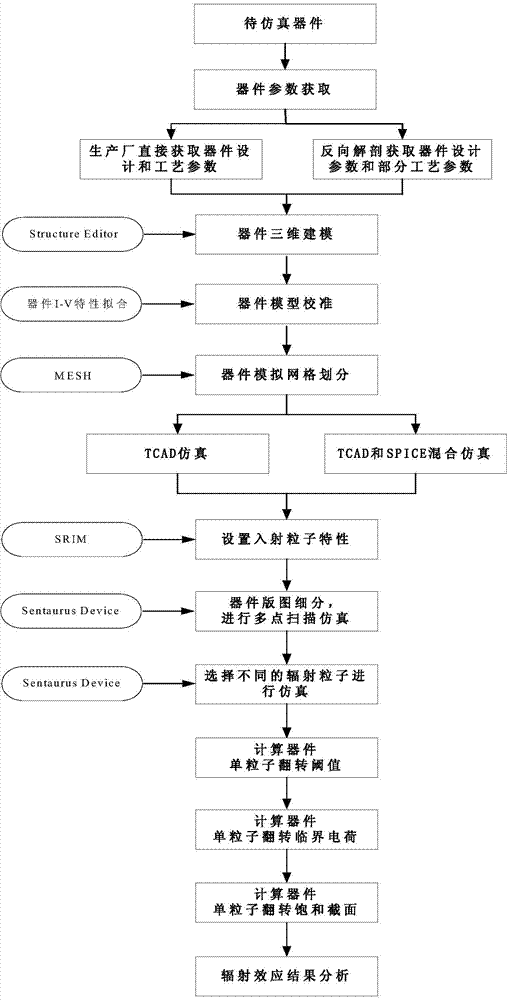
ActiveCN103577643ATime-consuming to solveSolve the resultSpecial data processing applicationsPhysical modelAnalysis tools
Disclosed is an SRAM type FPGA single event upset effect simulation method. The method includes the steps that firstly, design and process parameters of a device to be simulated are acquired; secondly, a three-dimensional geometrical shape of the device is constructed through a modeling tool, and doped areas, doping concentration, discretization strategies and the like of the device are set; thirdly, the design and process parameters of the device are calibrated according to an I-V characteristic curve of the device; fourthly, a meshed device structure is generated, and the mesh is refined on a channel, the light doped area and a PN junction border; fifthly, a device-level TCAD simulation method or a device-level TCAD and circuit-level Spice hybrid simulation method is selected according to the circuit scale and practical conditions of the device; sixthly, characteristics of incident heavy ions are acquired by using a radiating particle characteristic tool to conduct calculation; seventhly, physical model parameters, simulation time, boundary conditions and the like are set, and single event effect simulation of the device is carried out through a TCAD tool; eighthly, particles different in energy are selected to be simulated again according to simulation results; ninthly, the simulation results are acquired through a simulation data analysis tool.
Owner:CHINA ACADEMY OF SPACE TECHNOLOGY
Anti-single event effect static random access memory unit
InactiveCN102097123AImprove Flip EffectSuppress key node voltage changesDigital storageRadiation resistantTransmission gate
The invention discloses an anti-single event effect static random access memory unit, which can effectively improve the single event upset resistance of a static random access memory (SRAM) unit and remarkably increase an upset threshold of an SRAM. The SRAM unit is a 14-transistor memory unit, and comprises two access N-channel metal oxide semiconductor (NMOS) transistors and two phase inverters, wherein each phase inverter consists of six metal oxide semiconductor (MOS) transistors. Different from the phase inverters forming the most basic six-transistor unit, the inverter structure of the anti-single event effect SRAM unit regulates a level by the two NMOS transistors as drive transistors, two P-channel metal oxide semiconductor (PMOS) transistors as load transistors and a transmission gate consisting of the PMOS transistor and the NMOS transistor so as to realize the anti-single event upset of the memory unit. The SRAM unit has a relatively simpler structure, and is easy to realize in the designing of a radiation resistant SRAM chip.
Owner:INST OF SEMICONDUCTORS - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
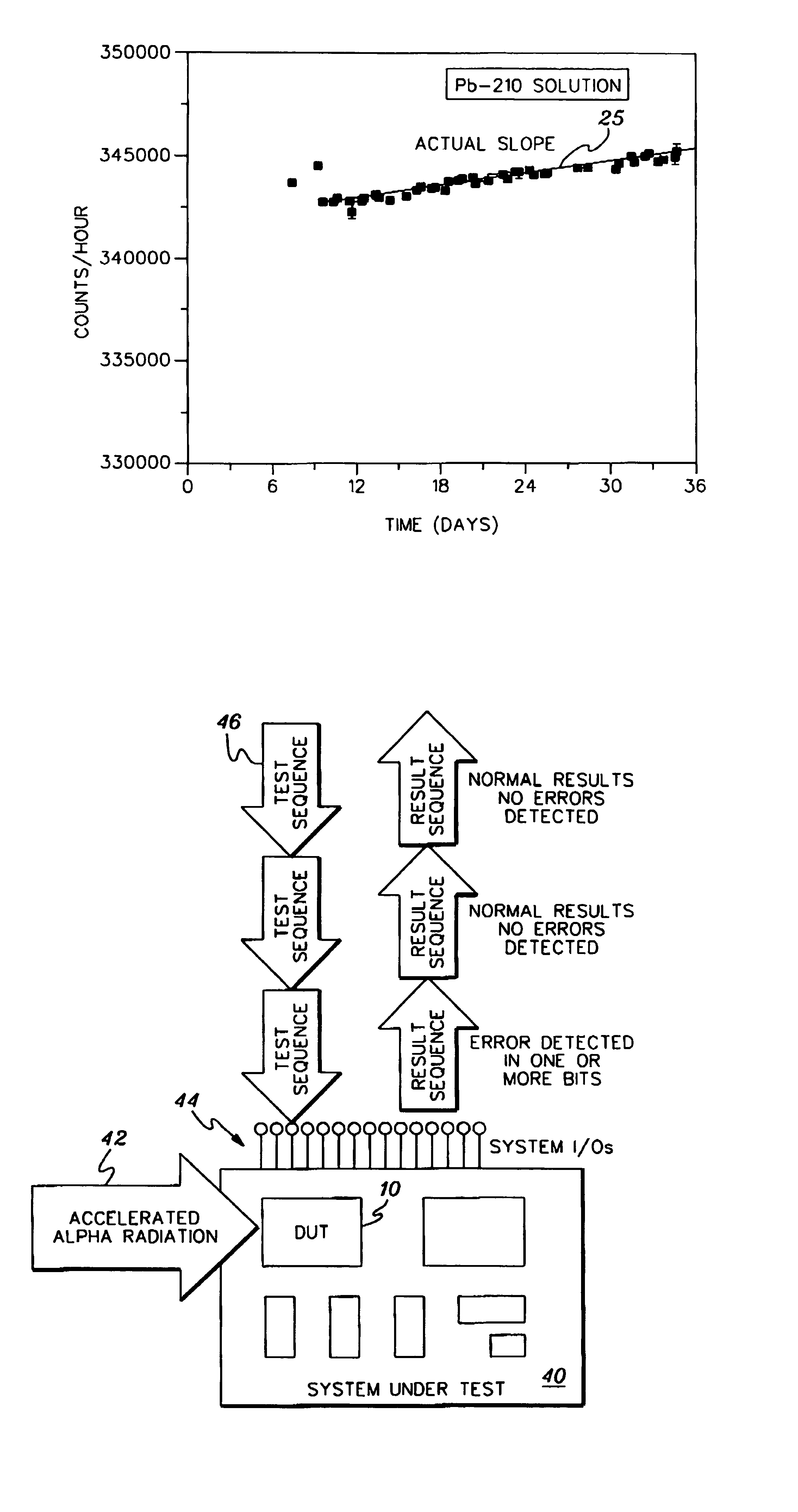
System and method for accelerated detection of transient particle induced soft error rates in integrated circuits
InactiveUS7084660B1Overcomes shortcomingEnhanced advantageSemiconductor/solid-state device testing/measurementSemiconductor/solid-state device detailsEmissivityTime segment
A method and system are provided for accelerated detection of soft error rates (SER) in integrated circuits (IC's) due to transient particle emission. An integrated circuit is packaged for accelerated transient particle emission by doping the underfill thereof with a transient-particle-emitting material having a predetermined emission rate. The emission rate is substantially constant over a predetermined period of time for testing. Accelerated transient-particle-emission testing is performed on the integrated circuit. Single-event upsets due to soft errors are detected, and a quantitative measurement of SER is determined.
Owner:IBM CORP
Single Event Upset error detection within sequential storage circuitry of an integrated circuit
ActiveUS20090249175A1Reduces instanceReduce the possibilityError preventionFault responseSingle event upsetData value
Sequential storage circuitry for a integrated circuit is provided, comprising a first storage element, a second storage element and an additional storage element. The first storage element stores, during a first phase of a clock signal, a first indication of an input data value received by the sequential storage circuitry. The second storage element is coupled to an output of the first storage element, and stores a second indication of the input data value during a second phase of the clock signal. The additional storage element is driven by a pulse signal derived from the clock signal, and is arranged on occurrence of that pulse signal to store a third indication of the input data value. Error detection circuitry is then provided for detecting a single event upset error in either the first storage element or the second storage element. In particular, during the first phase of the clock signal, the error detection circuitry detects the single event upset error in the first storage element if there is a difference in the input data value as indicated by the first indication and the third indication. Further, during the second phase of the clock signal, the error detection circuitry detects a single event upset error in the second storage element if there is a difference in the input data value as indicated by the second indication and the third indication. Such an arrangement provides a simple mechanism for detecting soft errors in both the first storage element and the second storage element using only one additional storage element.
Owner:ARM LTD
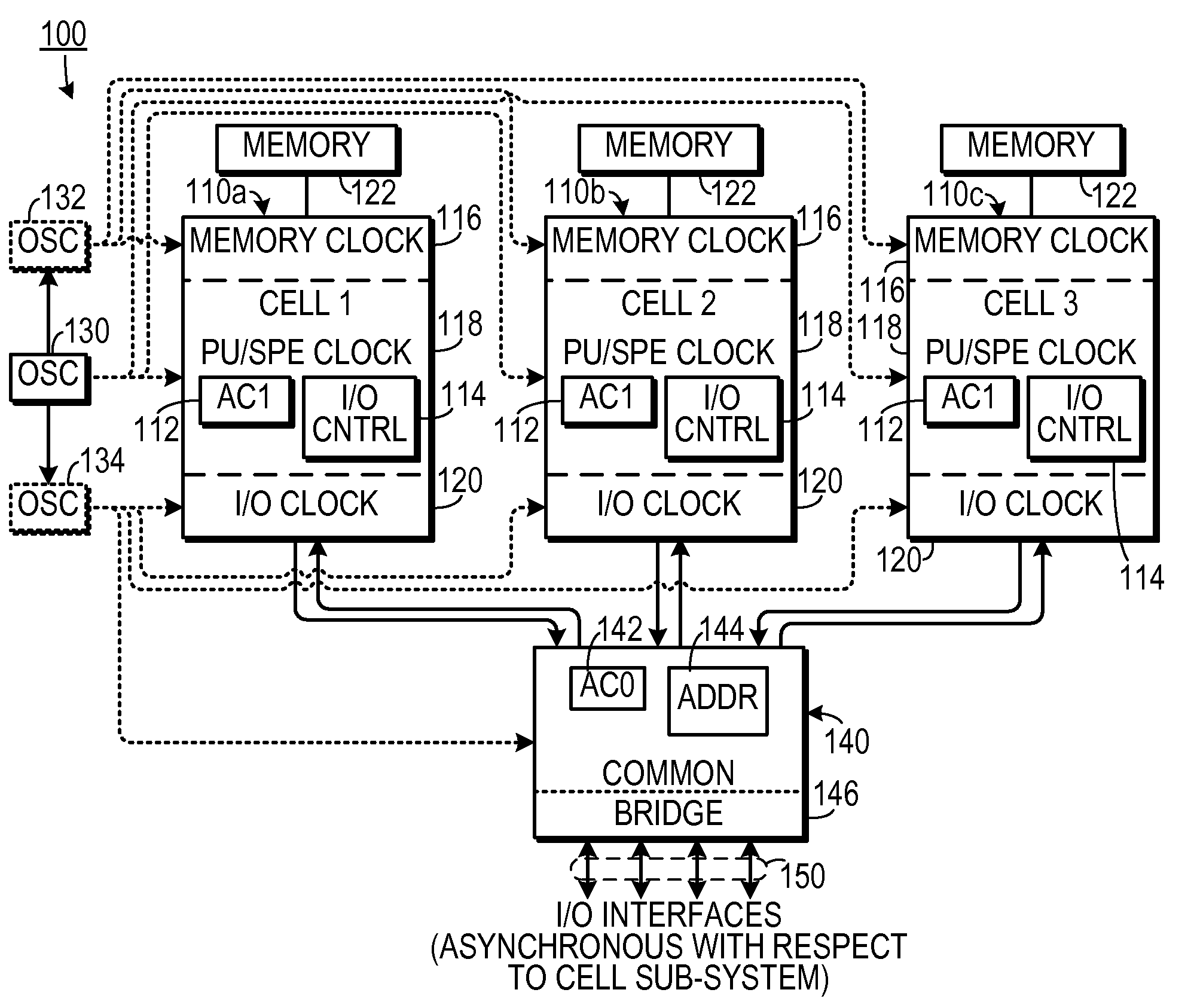
Triple voting cell processors for single event upset protection
InactiveUS7797575B2Overcome disadvantagesError detection/correctionGenerating/distributing signalsSingle event upsetError correcting
In a system for operating three address concentrating processors, a common clock signal is transmitted to each of the three address concentrating processors. A common data unit is transmitted simultaneously to each of the three address concentrating processors. A received data unit is received simultaneously from each of the three address concentrating processors. Each of the received data units are compared to each other. An error correcting routine is activated when the data units received from the three address concentrating processors are not all identical.
Owner:IBM CORP
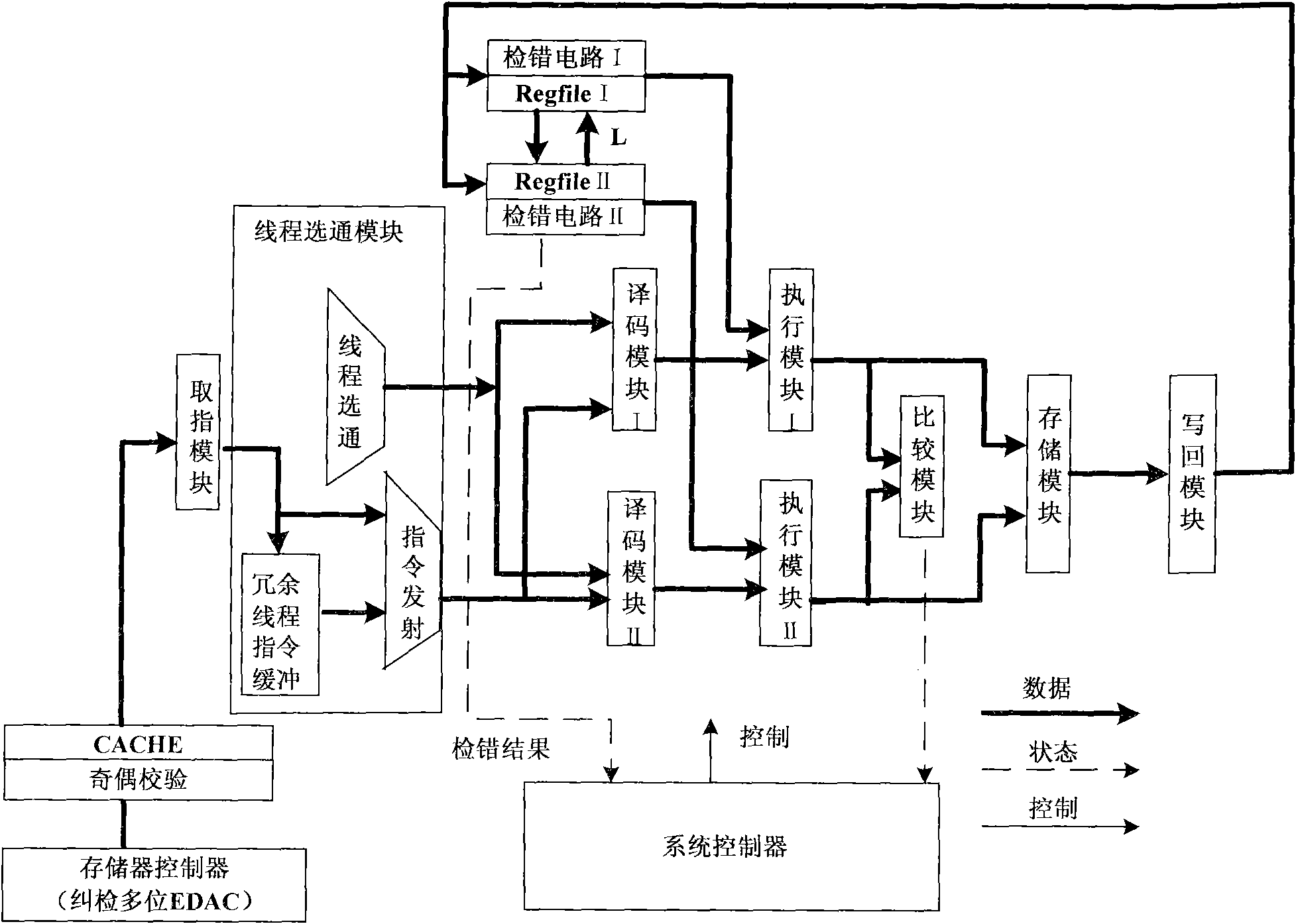
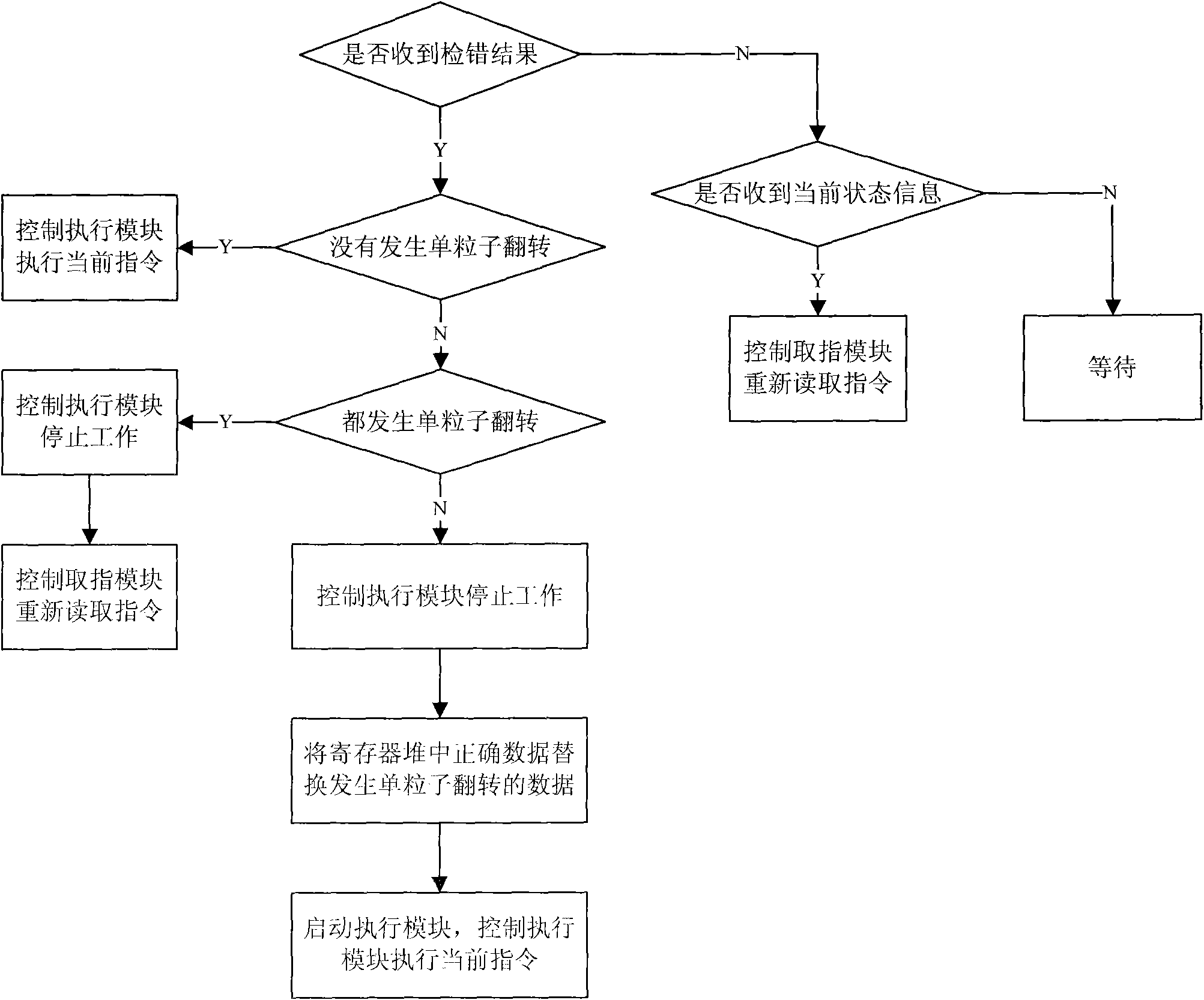
An anti-SEE system and method based on synchronizing redundant threads and coding technique
InactiveCN101551764AAvoid complex processingIndependent executionConcurrent instruction executionRedundant operation error correctionProcessor registerSingle event upset
Through the research and improvement of error-correcting codes and error-detecting codes, the anti-SEE system and method based on synchronizing redundant threads and coding technique enables this coding technique to quickly detect the SEU (single event upset) occurring in register file and meanwhile design the both-threaded mechanism of the processor into a redundant both-threaded mechanism. When the register file of a thread is found with SEU, the register data with upset error will be corrected through replacing this register file with the register file of the other redundant thread; through the comparison mechanism of synchronous execution results in the layer of redundant both-threaded instructions, the pipelined circuit is judged whether there is SET (single-event transient) error. If such error occurs, it will be quickly eliminated from the pipeline through the designed redundant thread pipeline restart mechanism. This method satisfactorily solves the two frequent and difficult problems: SMU of register file in processor and pipeline SET.
Owner:BEIJING MXTRONICS CORP +1
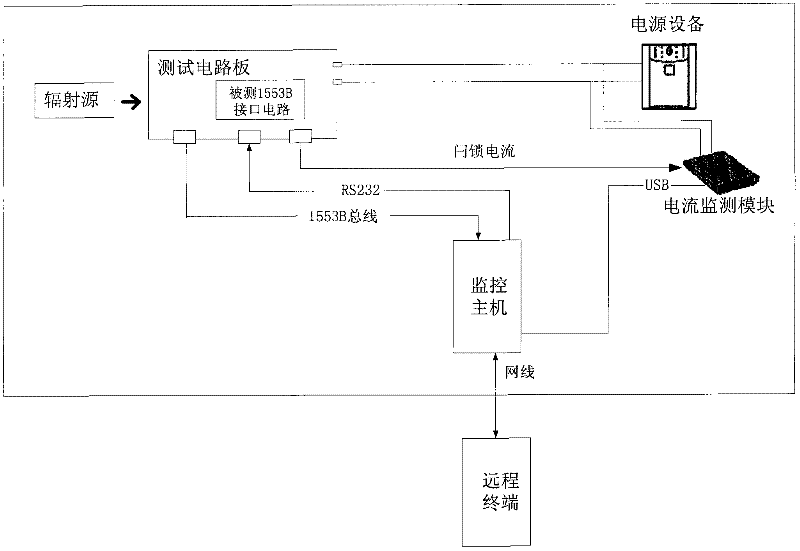
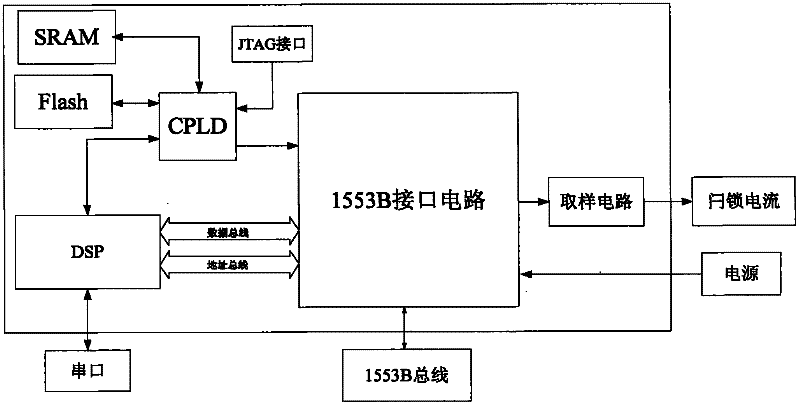
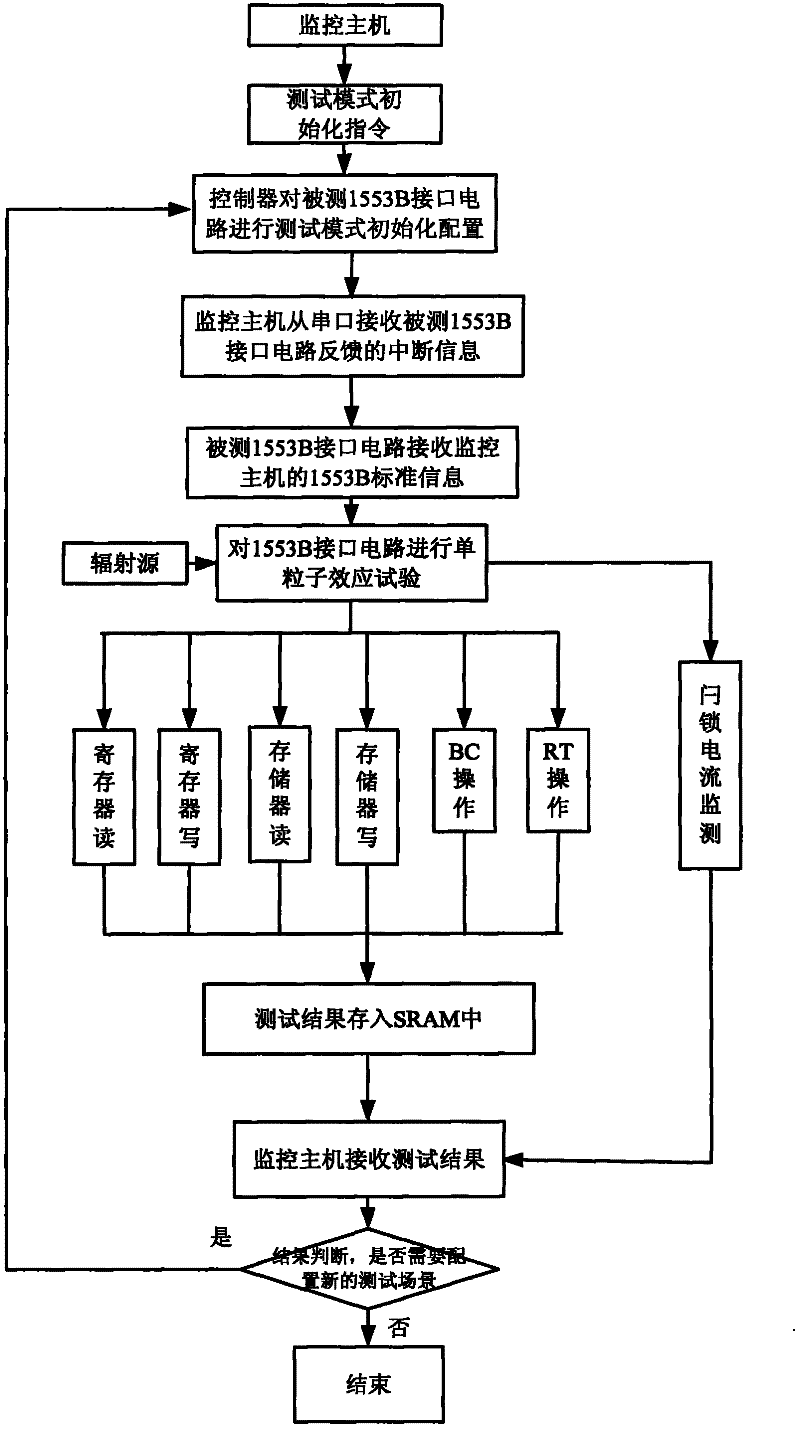
Device for detecting single event effect of 1553B interface circuit
InactiveCN102183723AImprove reliabilityConfidenceElectrical testingBus networksTransceiverDependability
The invention discloses a device for detecting the single event effect of a 1553B interface circuit. The device is connected with a monitoring host through a 1553B bus; in a real 1553B bus communication environment, a tester controls a digital signal processor (DSP) through the monitoring host to transmit various test modes to the tested 1553B interface circuit and execute a multi-scene, multi-vector and multi-round single event effect test; various single event effects such as single event turning, single event latching, single event function interruption and the like of the tested 1553B interface circuit under irradiation of a radiation source can be detected by the DSP; and trial tests under different environmental conditions of high temperature, low temperature, vacuum and the like can be implemented, and reliable and effective test data can be acquired, so the reliability and the credibility of the test data are improved. In the device, a plurality of currents of a protocol logiccircuit, a transceiver and the like in the 1553B circuit can be monitored and controlled by a sampling circuit; and correct and effective feedback control can be provided for data receiving and result analysis.
Owner:BEIJING MXTRONICS CORP +1
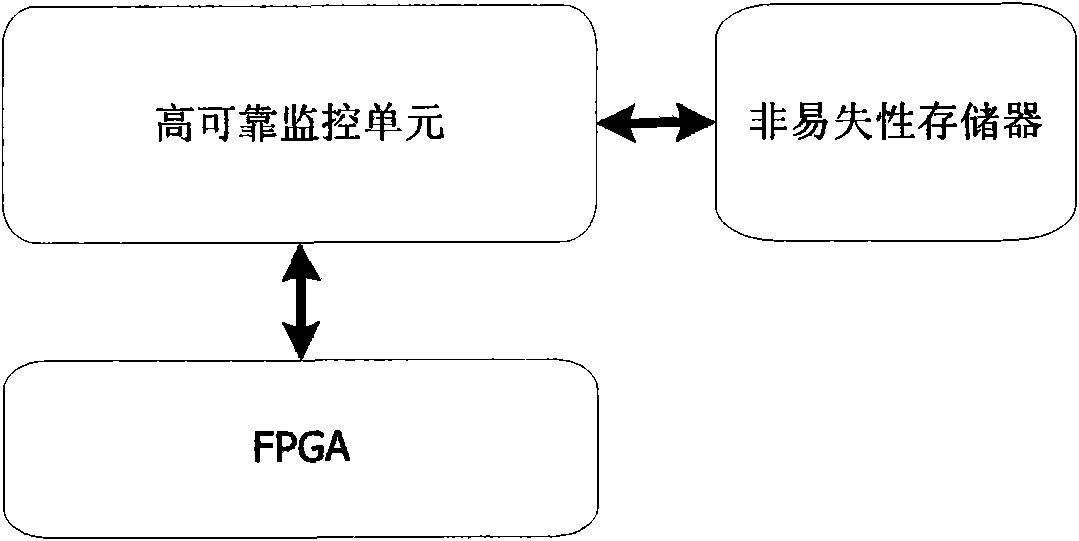
Method and device for testing single event upset in in-field programmable logic gate array
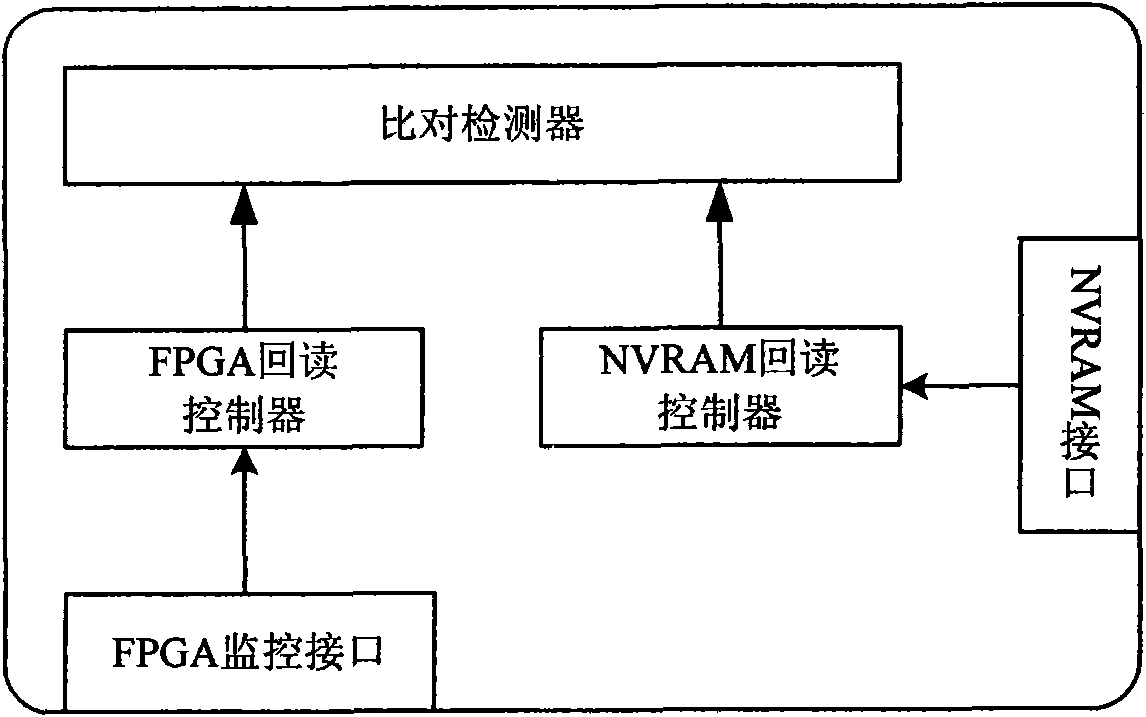
The invention discloses a method and a device for testing single event upset in in in-field programmable logic gate array, comprising the following steps: a highly reliable monitor unit which is connected with the field programmable logic gate array and used for realizing the testing flow of the single event upset is arranged; the highly reliable monitor unit executes the read back flow of the configuration memory of the field programmable logic gate array, reads the configuration frame of the field programmable logic gate array, and executes an original configuration frame which is read from a nonvolatile memory by a standard NVRAM interface; and the highly reliable monitor unit compares the read back configuration frame of the field programmable logic gate array with the original configuration frame by means of byte, when the configuration frame is wrong in comparing, namely, the configuration memory of the field programmable gate array is judged to have the single event upset. The device comprises the highly reliable monitor unit which is connected with the nonvolatile memory by a bus. The invention has the advantages of simple structural principle, high reliability, good stability, etc.
Owner:NAT UNIV OF DEFENSE TECH
Method and system for monitoring single event upset effect of FPGA (field programmable gate array) and correcting reloading
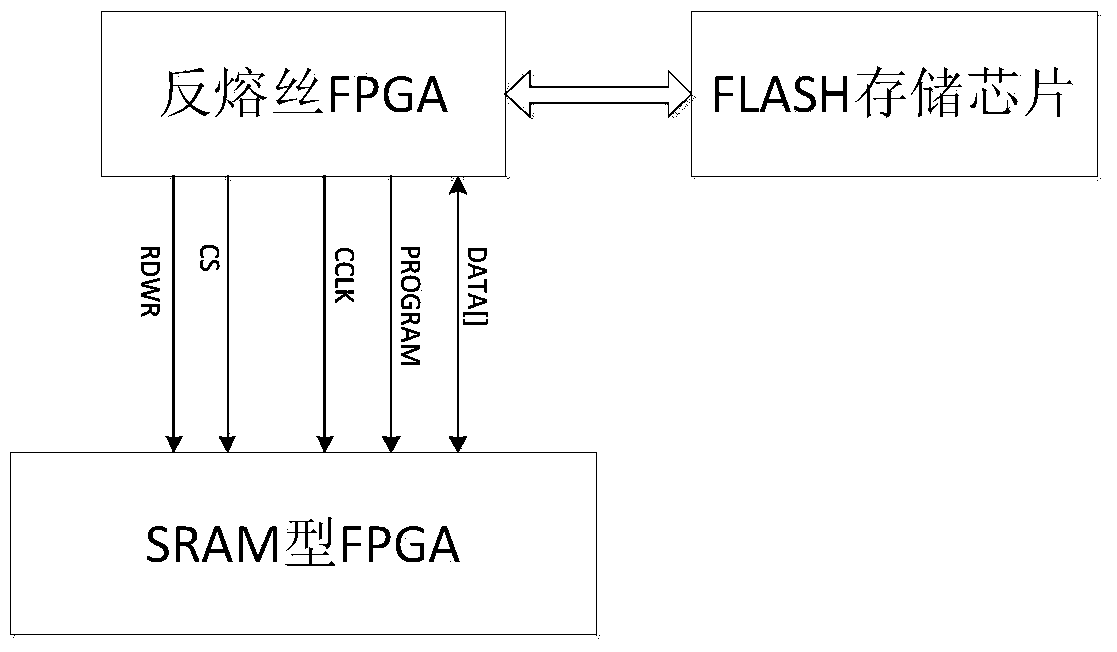
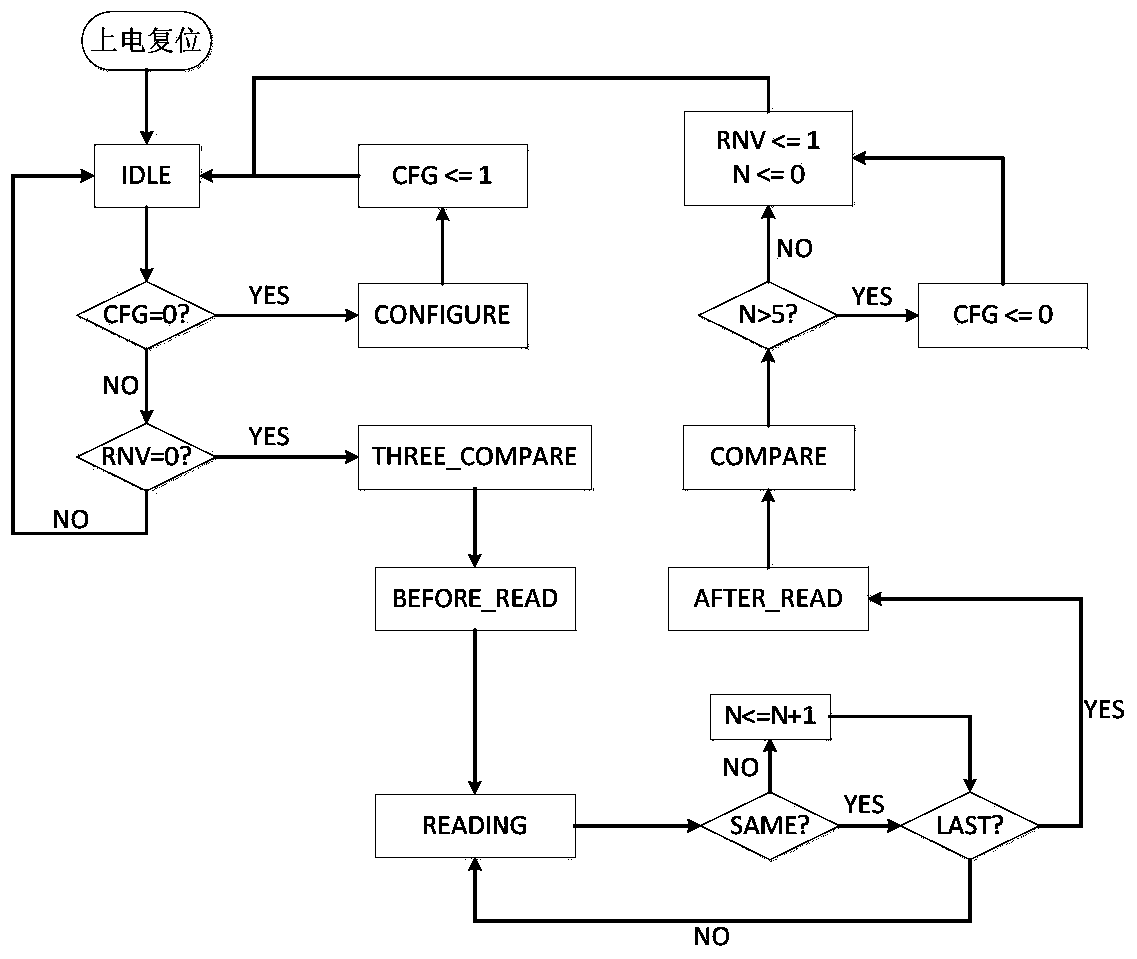
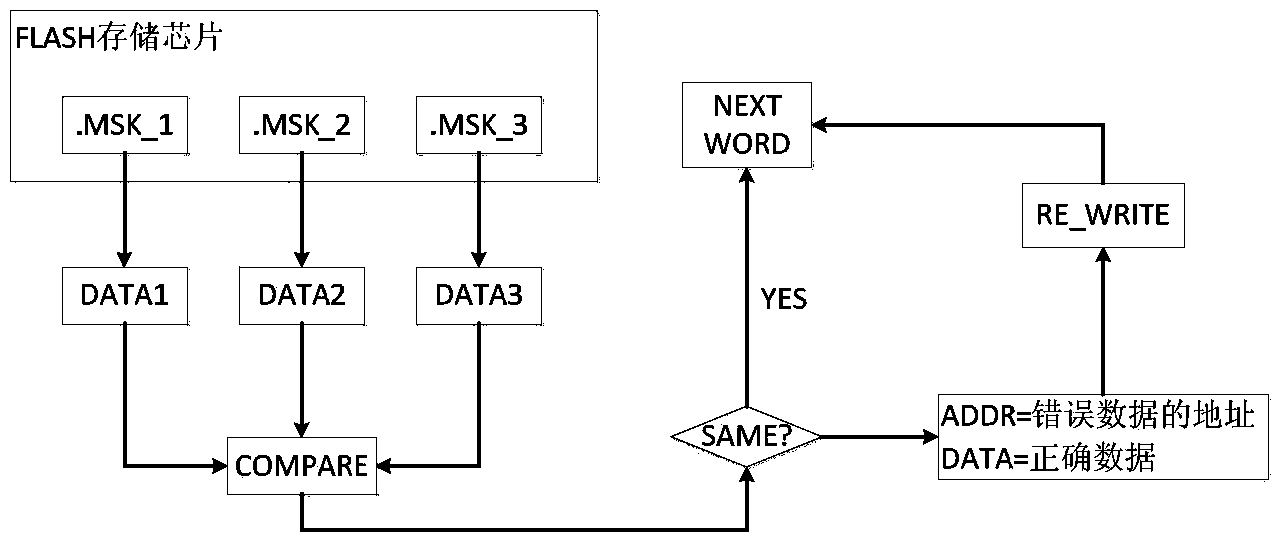
InactiveCN103971732AReduce areaImproved ability to resist single event effectsDigital storageFpga field programmable gate arrayProgrammable read-only memory
The invention discloses a method for monitoring a single event upset effect of an FPGA (field programmable gate array) and correcting reloading. The method comprises the steps: an antifuse FPGA reads back a configuration word through a configuration word readback function of an SRAM (static random access memory) type FPGA, compares the configuration word with a correct configuration word pre-stored in an FLASH storage chip, checks whether the SRAM type FPGA generates single event upset or not, and performs reloading through a loading program pre-stored in the FLASH storage chip if the SRAM type FPGA generates the single event upset. The invention also discloses a system for monitoring the single event upset effect of the FPGA and correcting the reloading. The system comprises the FLASH storage chip, the antifuse FPGA and the SRAM type FPGA which are connected in sequence. The method and the system which are disclosed by the invention simulate a time sequence of a PROM (programmable read-only memory) to load the SRAM type FPGA through a loading file pre-stored in the FLASH storage chip; compared with the system adopting a preliminary writing PROM, the system disclosed by the invention has the advantages that the distribution area of a PCB (printed circuit board) is reduced, and equipment minimization is facilitated.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV
Experiment method for pulsed laser single event upset cross section
InactiveCN102169022AEstimated realizationFlip capability estimationContactless circuit testingClassical mechanicsIrradiation
The invention provides an experiment method for a pulsed laser single event upset cross section. The method comprises the steps of scanning and irradiating an inside of a device according to pulsed laser E of a certain value; obtaining a laser single event upset cross section value under the E according to single event upset frequency, irradiation frequency (stationing number of scanning) of the monitored device; and obtaining a Sigma~E curve of the laser single event upset cross section through changing the pulsed laser with different energy for scanning and irradiating. The invention provides technical support for pre-estimating single event upset resistance of a to-be-tested device and enables easier and more practical research on ground pulsed laser simulation of single event effects in the future.
Owner:NO 510 INST THE FIFTH RES INST OFCHINA AEROSPAE SCI & TECH
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com